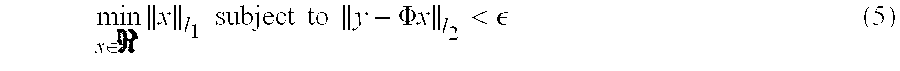Patents
Literature
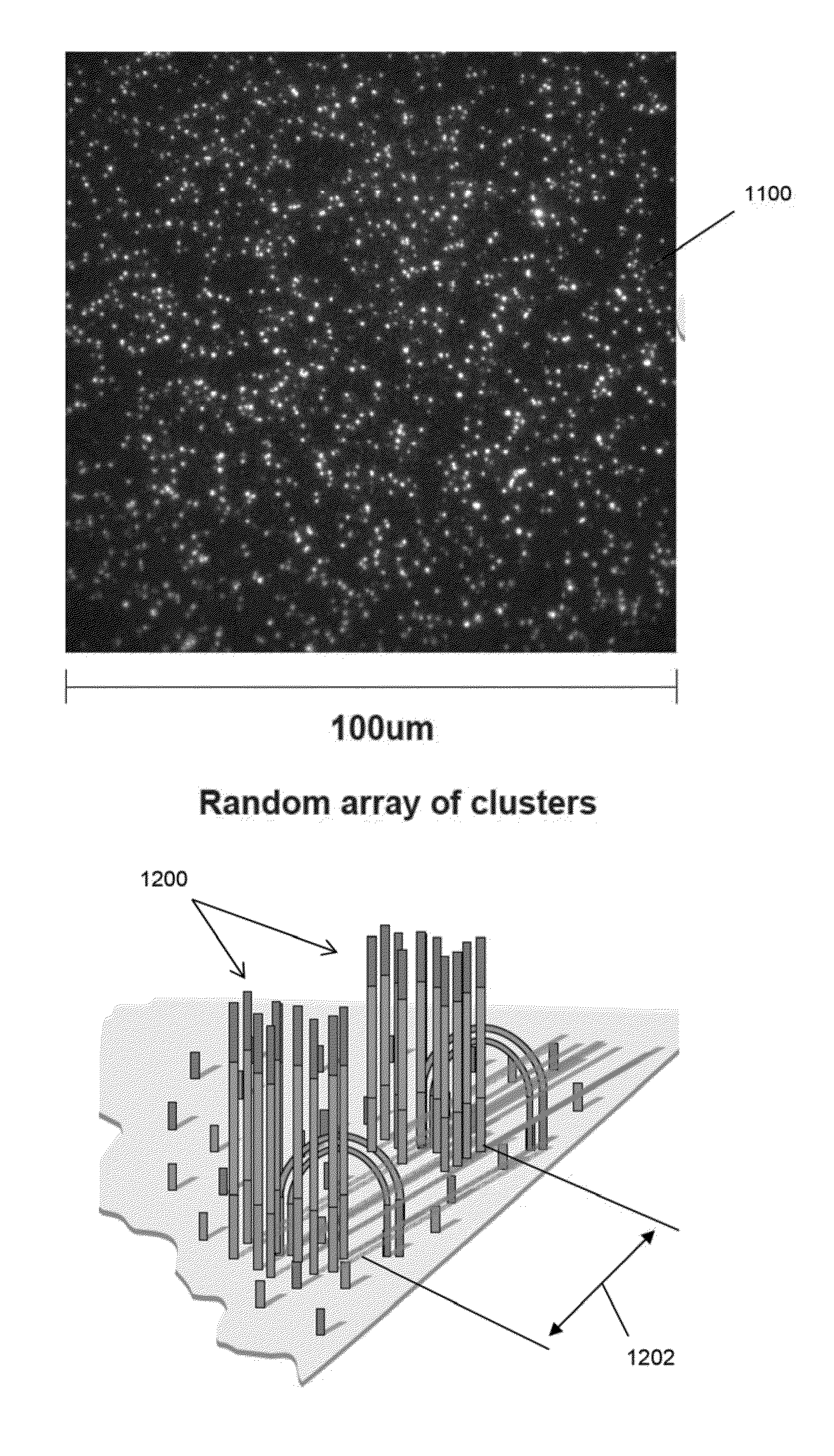
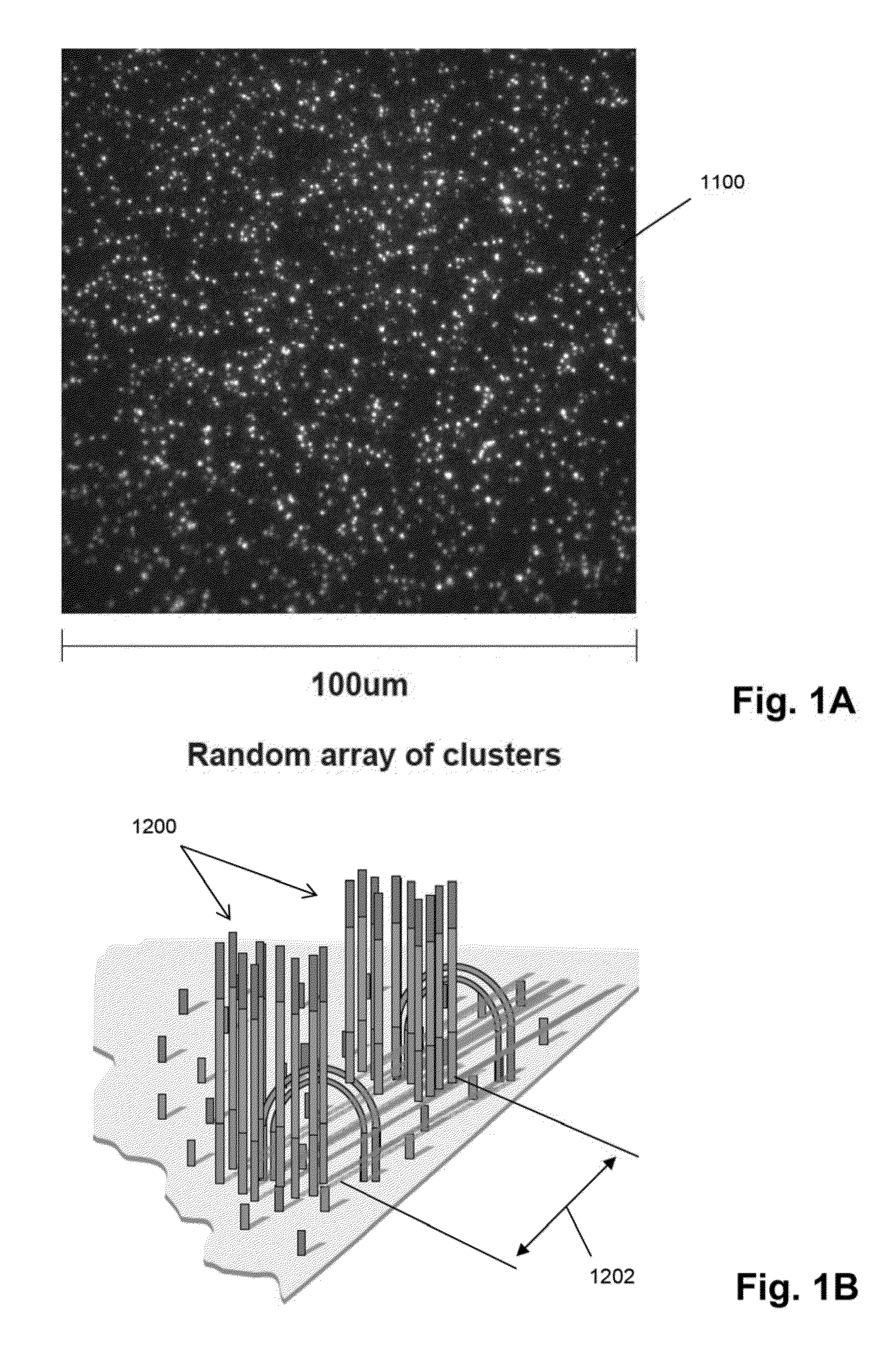
187 results about "Random array" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
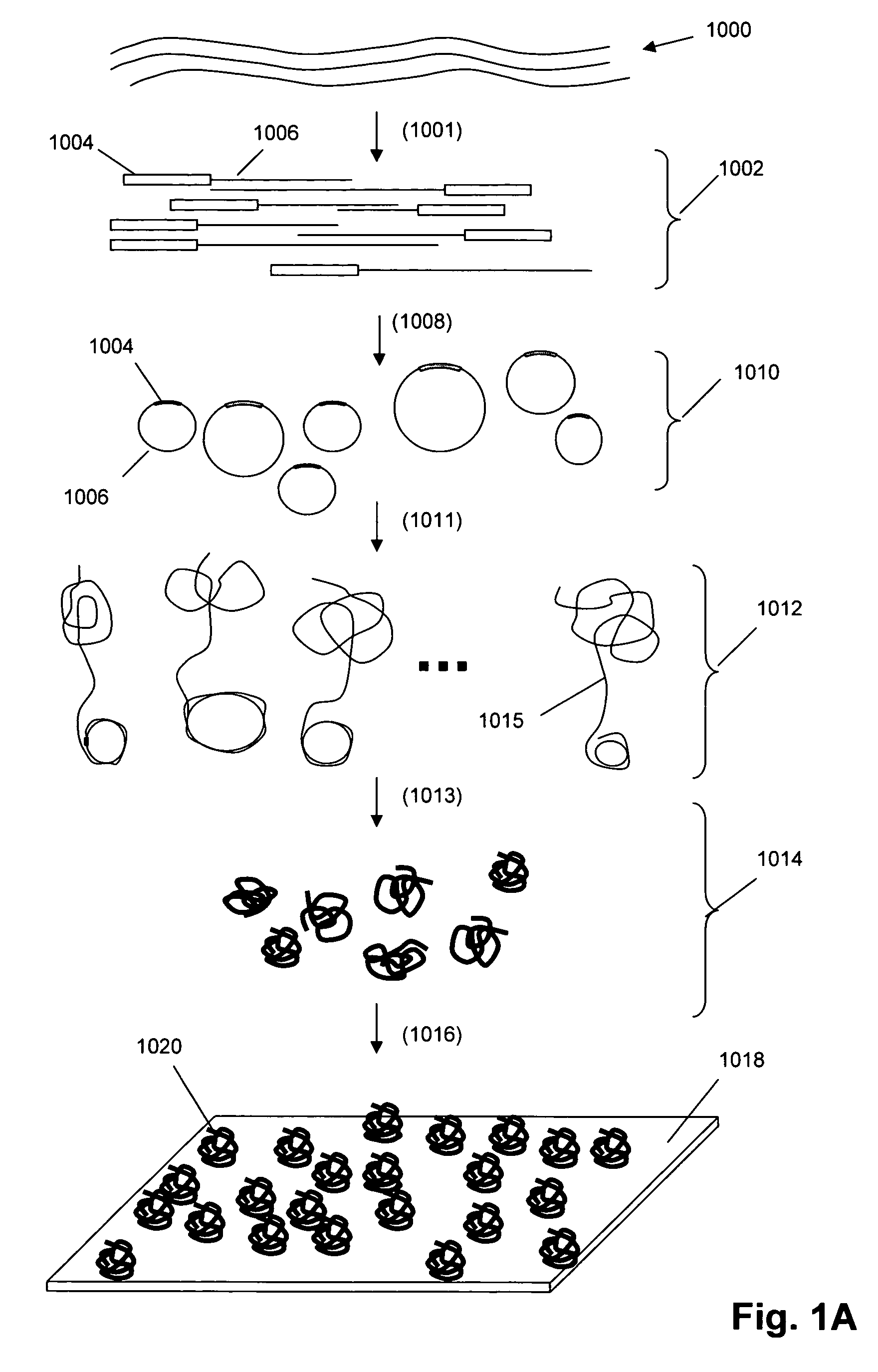
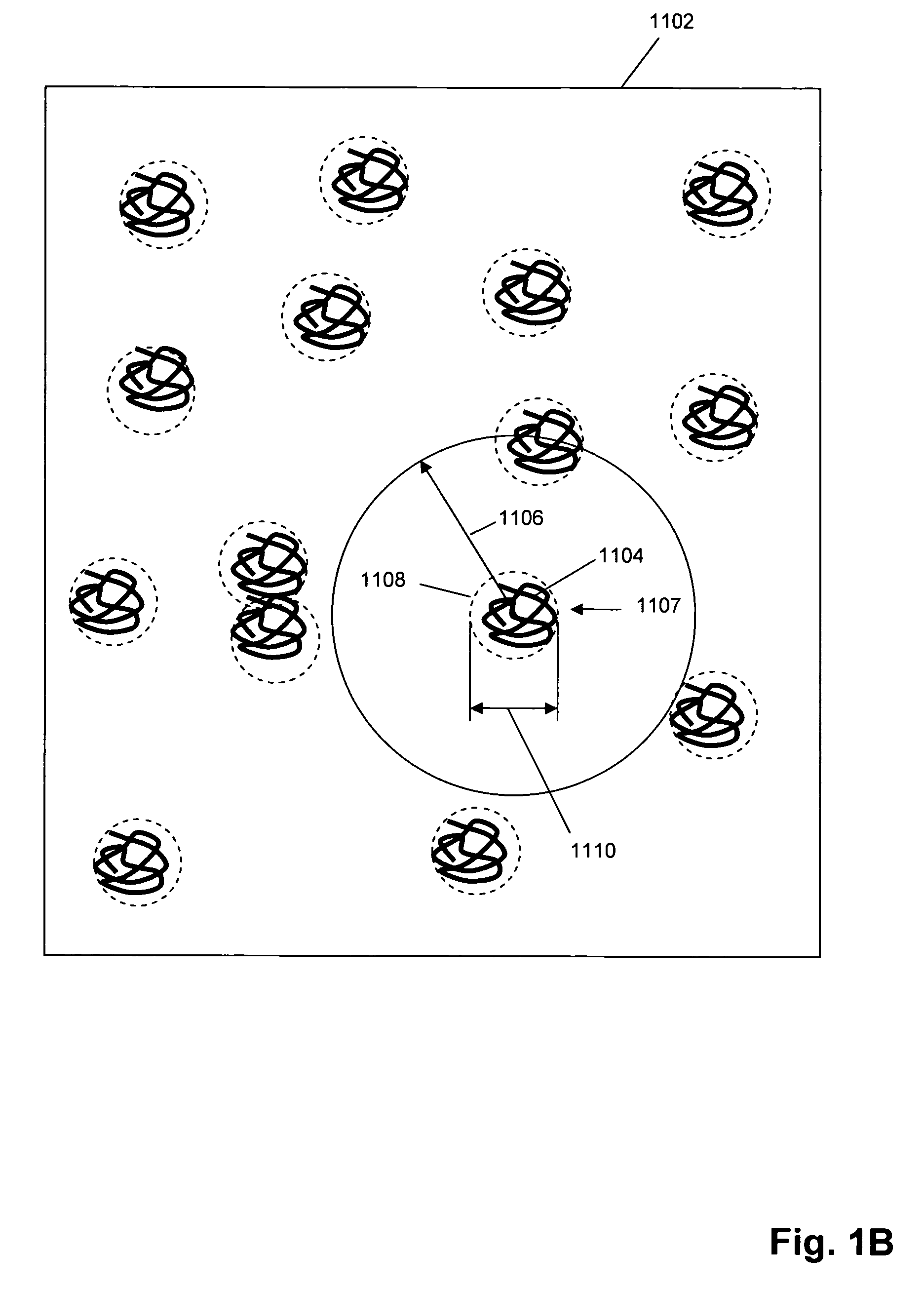
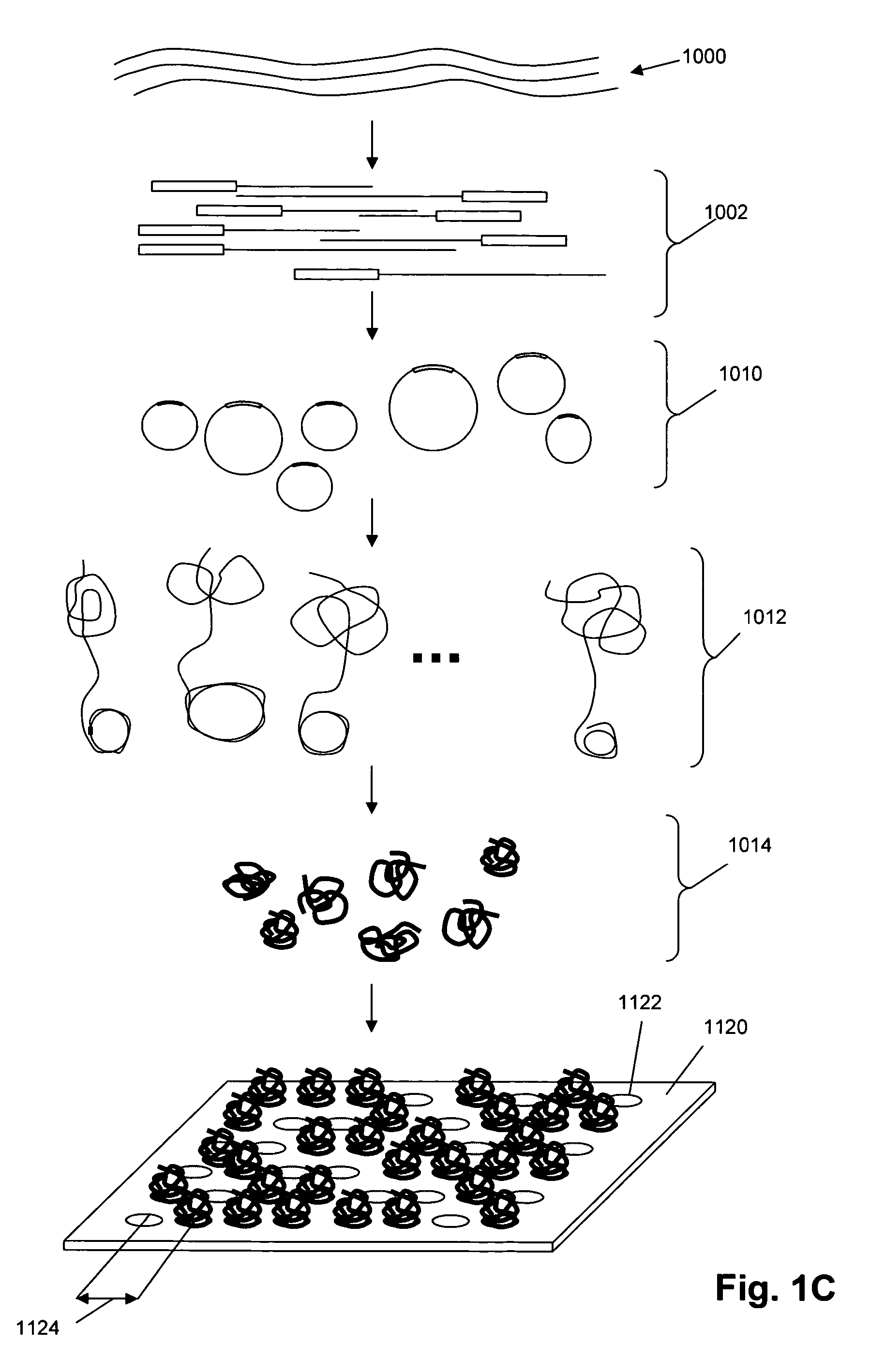
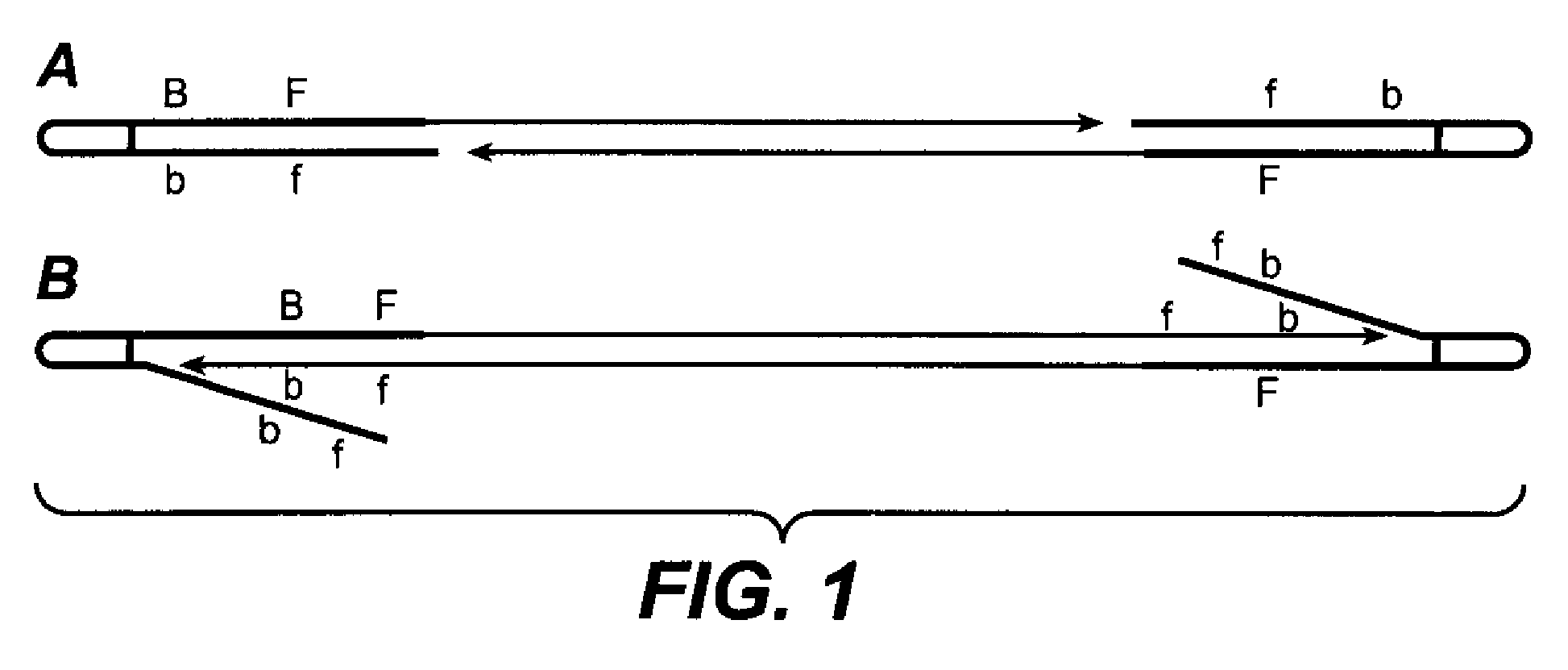
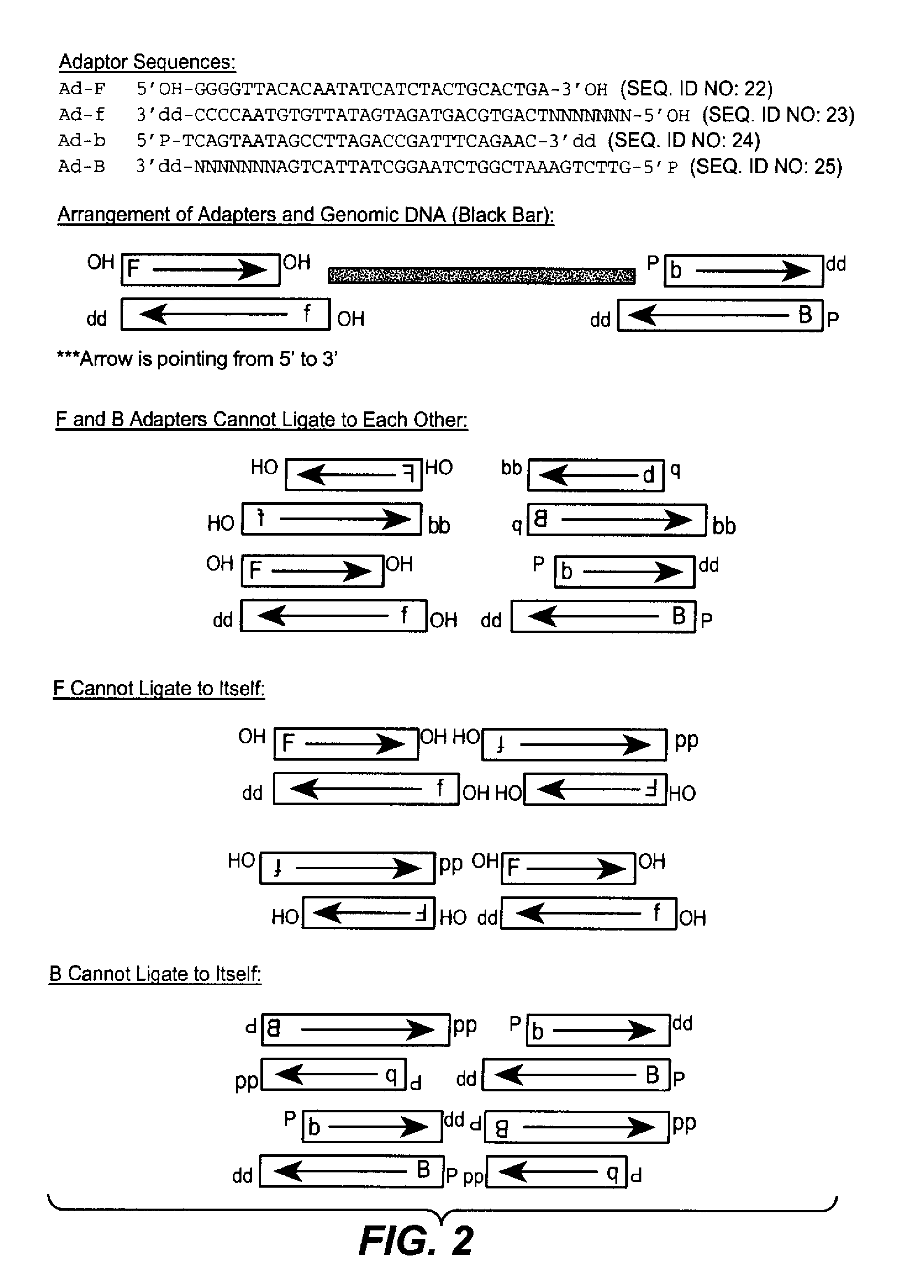
Single molecule arrays for genetic and chemical analysis
ActiveUS20070099208A1Efficient high resolution analysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanotechImage resolutionRandom array
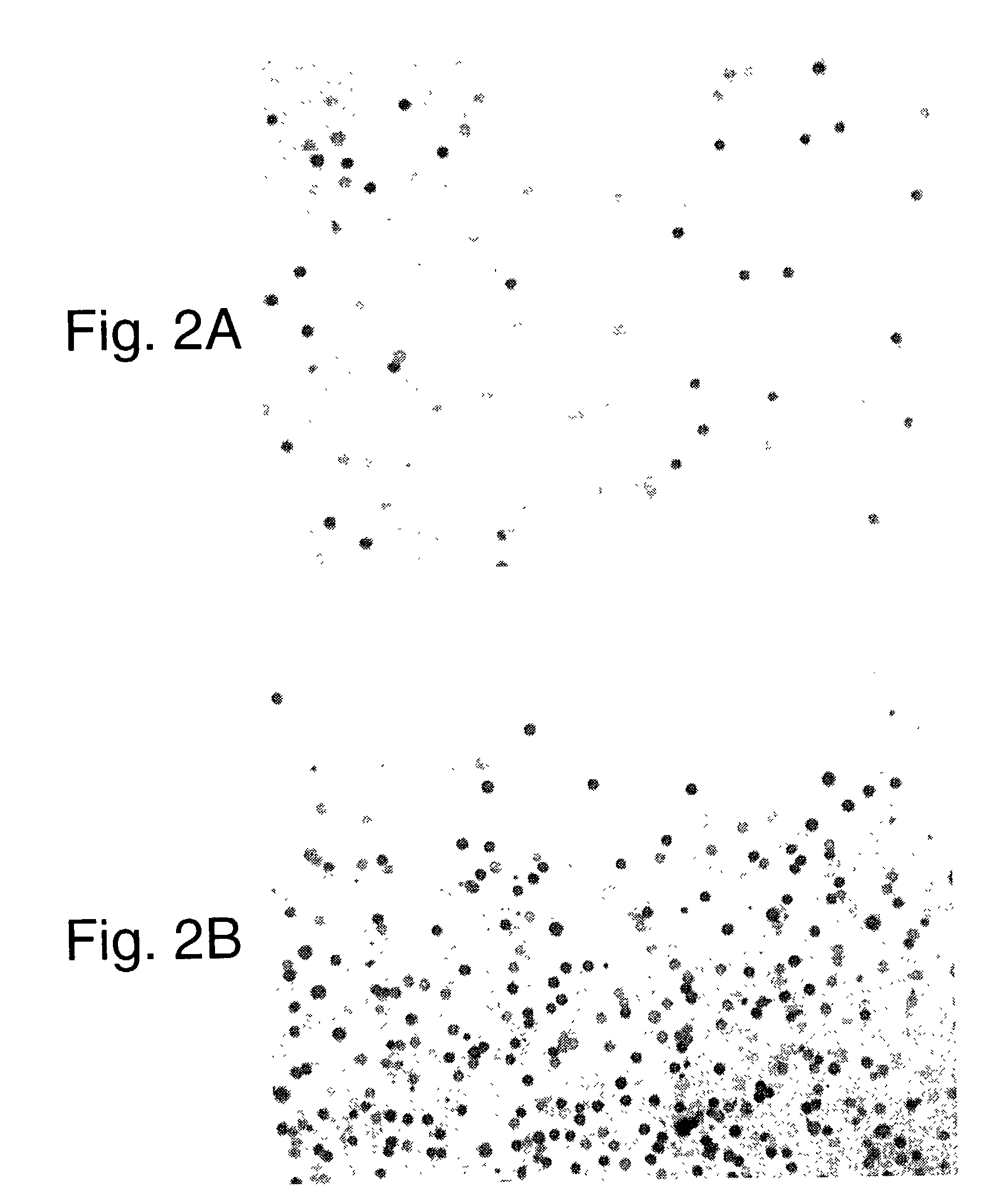
Random arrays of single molecules are provided for carrying out large scale analyses, particularly of biomolecules, such as genomic DNA, cDNAs, proteins, and the like. In one aspect, arrays of the invention comprise concatemers of DNA fragments that are randomly disposed on a regular array of discrete spaced apart regions, such that substantially all such regions contain no more than a single concatemer. Preferably, such regions have areas substantially less than 1 μm2 and have nearest neighbor distances that permit optical resolution of on the order of 109 single molecules per cm2. Many analytical chemistries can be applied to random arrays of the invention, including sequencing by hybridization chemistries, sequencing by synthesis chemistries, SNP detection chemistries, and the like, to greatly expand the scale and potential applications of such techniques.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
Random array of micro-spheres for the analysis of nucleic acids
InactiveUS7011945B2Easy to analyzeMore cost-effectivelyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsRandom arrayBarcode
A method of identifying nucleic acid samples comprising: providing a mircoarray including a substrate coated with a composition including a population of micro-spheres dispersed in a fluid containing a gelling agent or a precursor to a gelling agent and immobilized at random positions on the substrate, at least one sub-population of said population micro-spheres containing an optical barcode generated from at least one colorant associated with the micro-spheres and including a nucleic acid probe sequence; contacting said array with a target nucleic acid sequence; and detecting the color barcode of said sub-population of micro-spheres due to the interaction of said probe nucleic acid sequence and said target nucleic acid sequence.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Random array DNA analysis by hybridization
ActiveUS20090005259A1Sufficient amountMaterial nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsRandom arrayNucleic acid sequencing
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
Random array dna analysis by hybridization
ActiveUS20070037152A1Reliable measurementSufficient amountMaterial nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsRandom arrayNucleic acid sequencing
The invention relates to methods and devices for analyzing single molecules, i.e. nucleic acids. Such single molecules may be derived from natural samples, such as cells, tissues, soil, air and water without separating or enriching individual components. In certain aspects of the invention, the methods and devices are useful in performing nucleic acid sequence analysis by probe hybridization.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
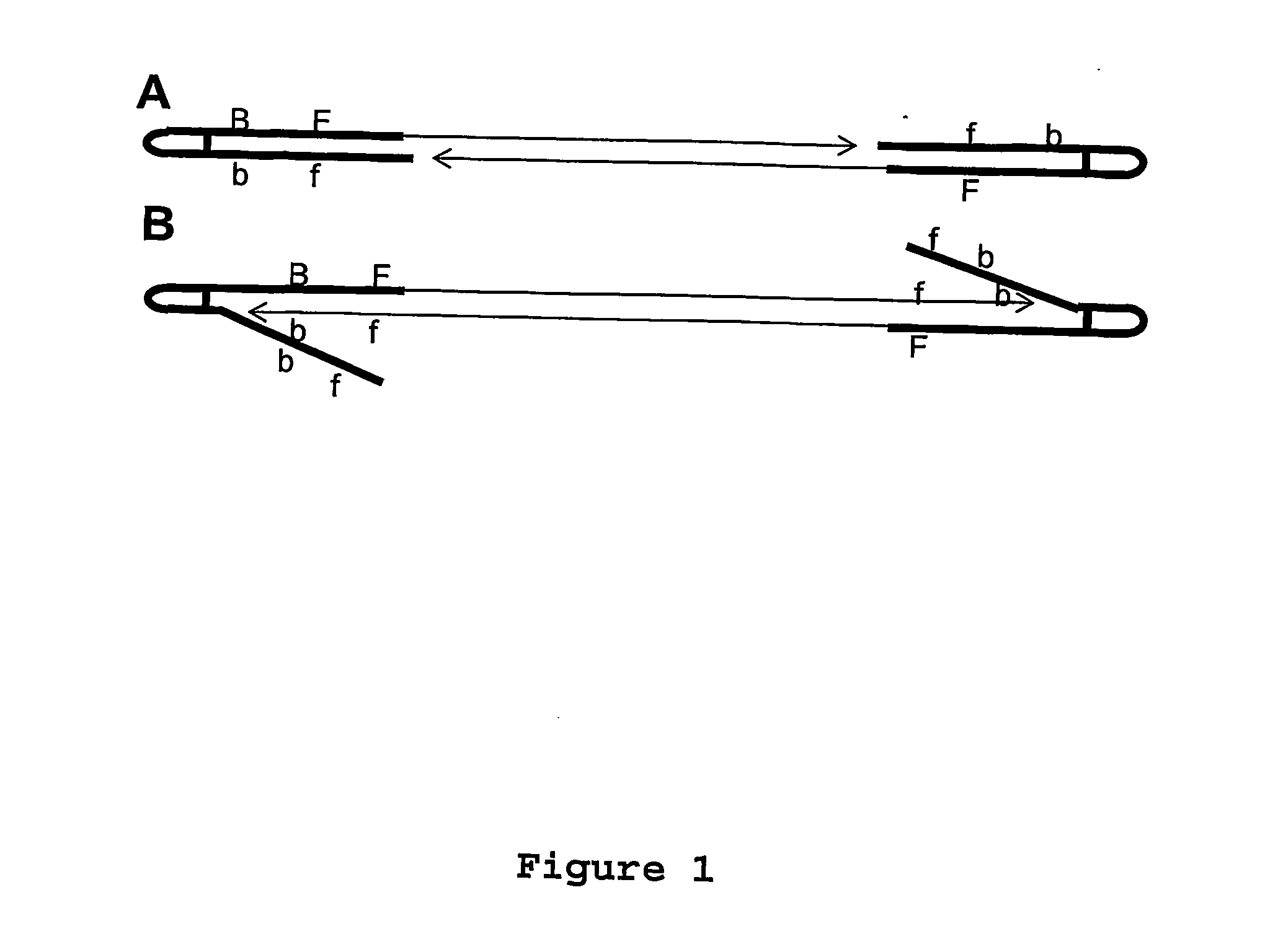
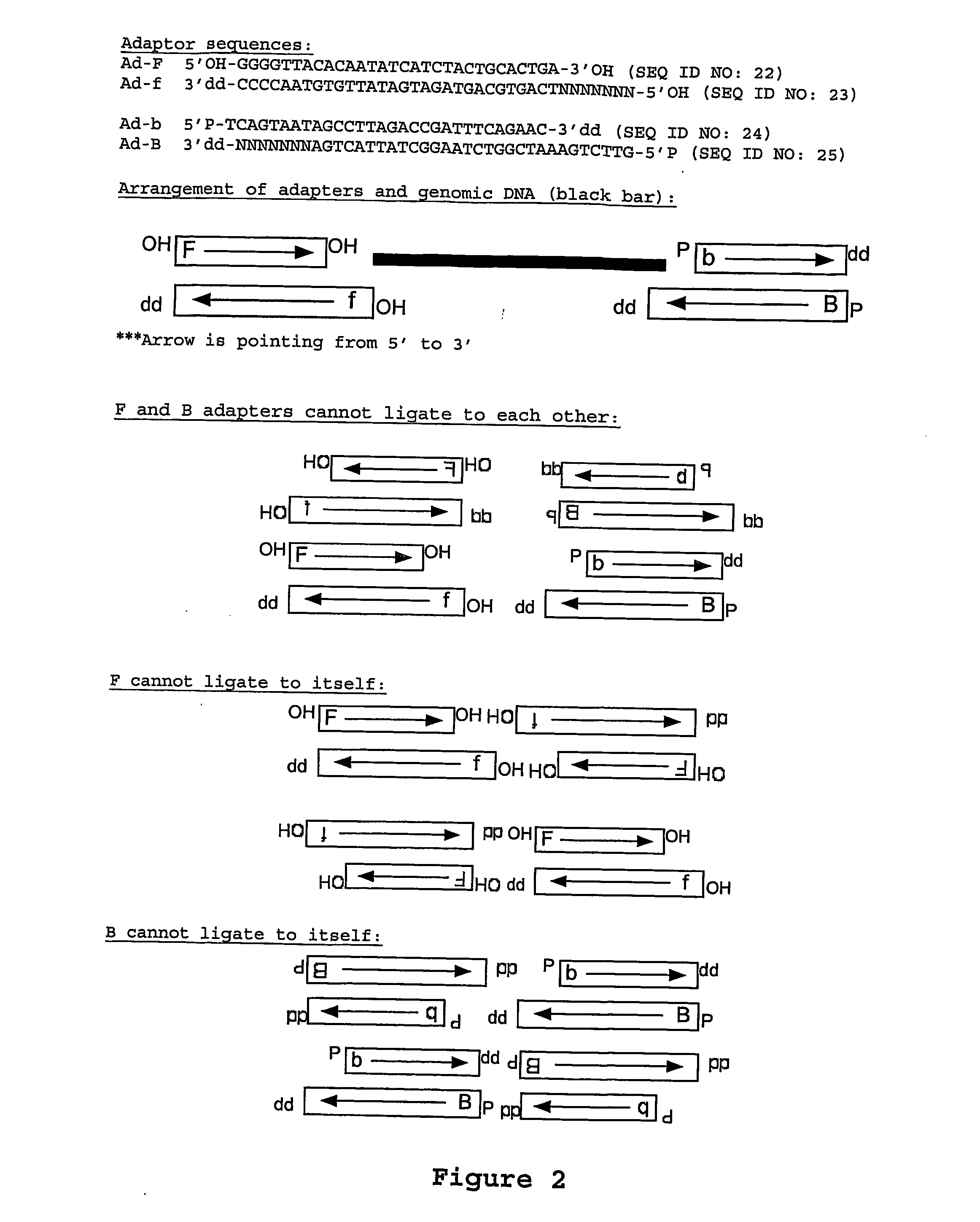
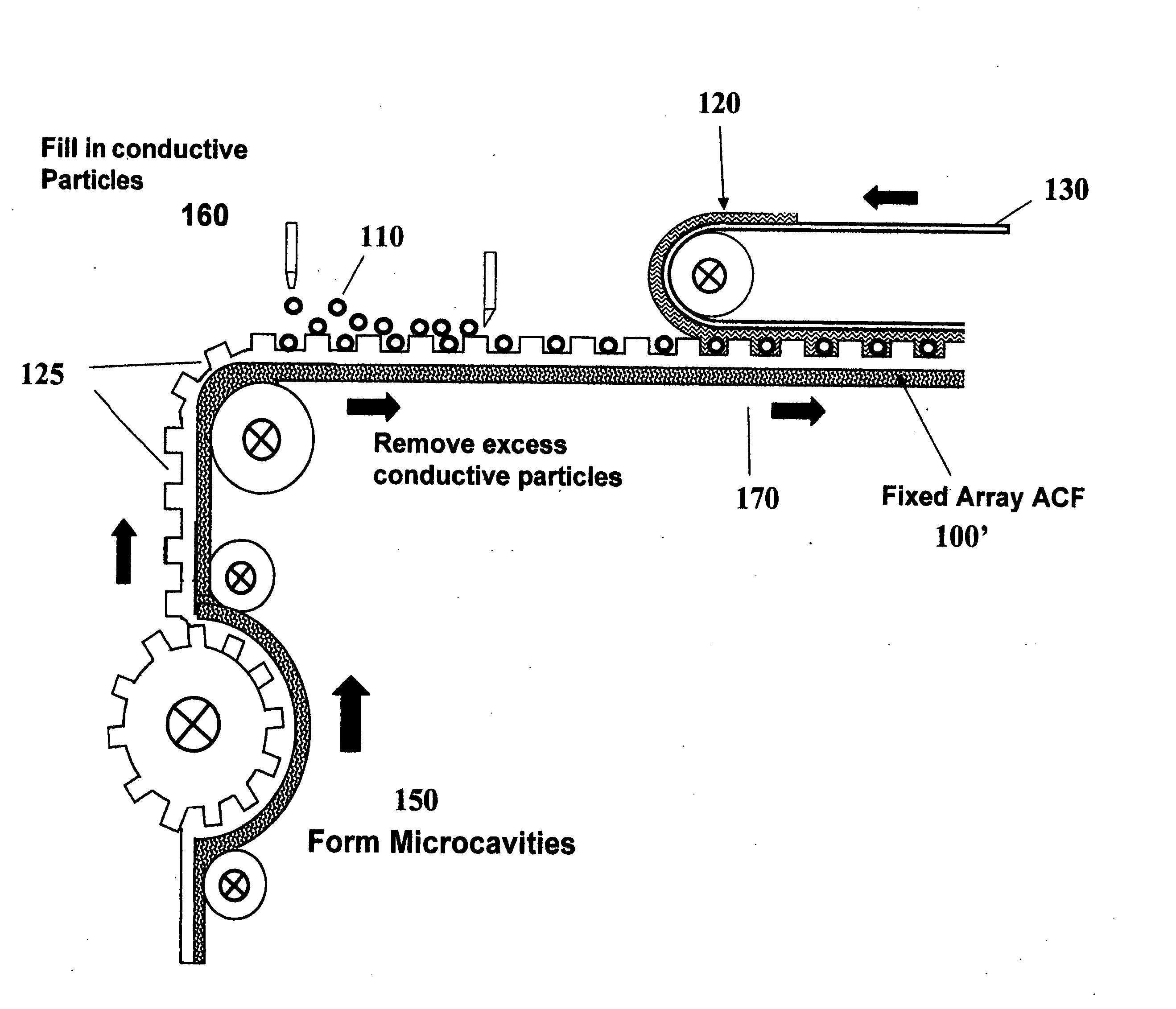
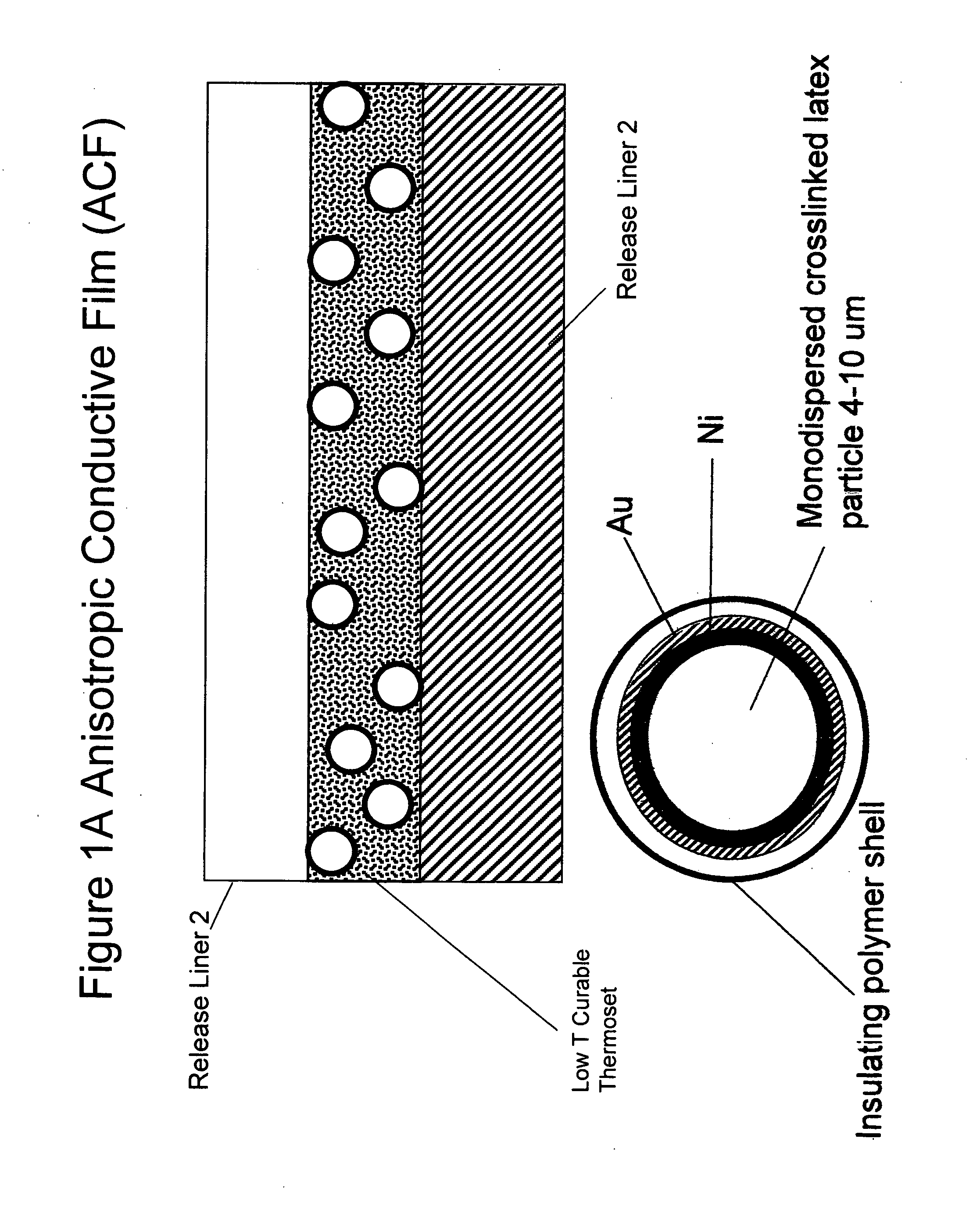
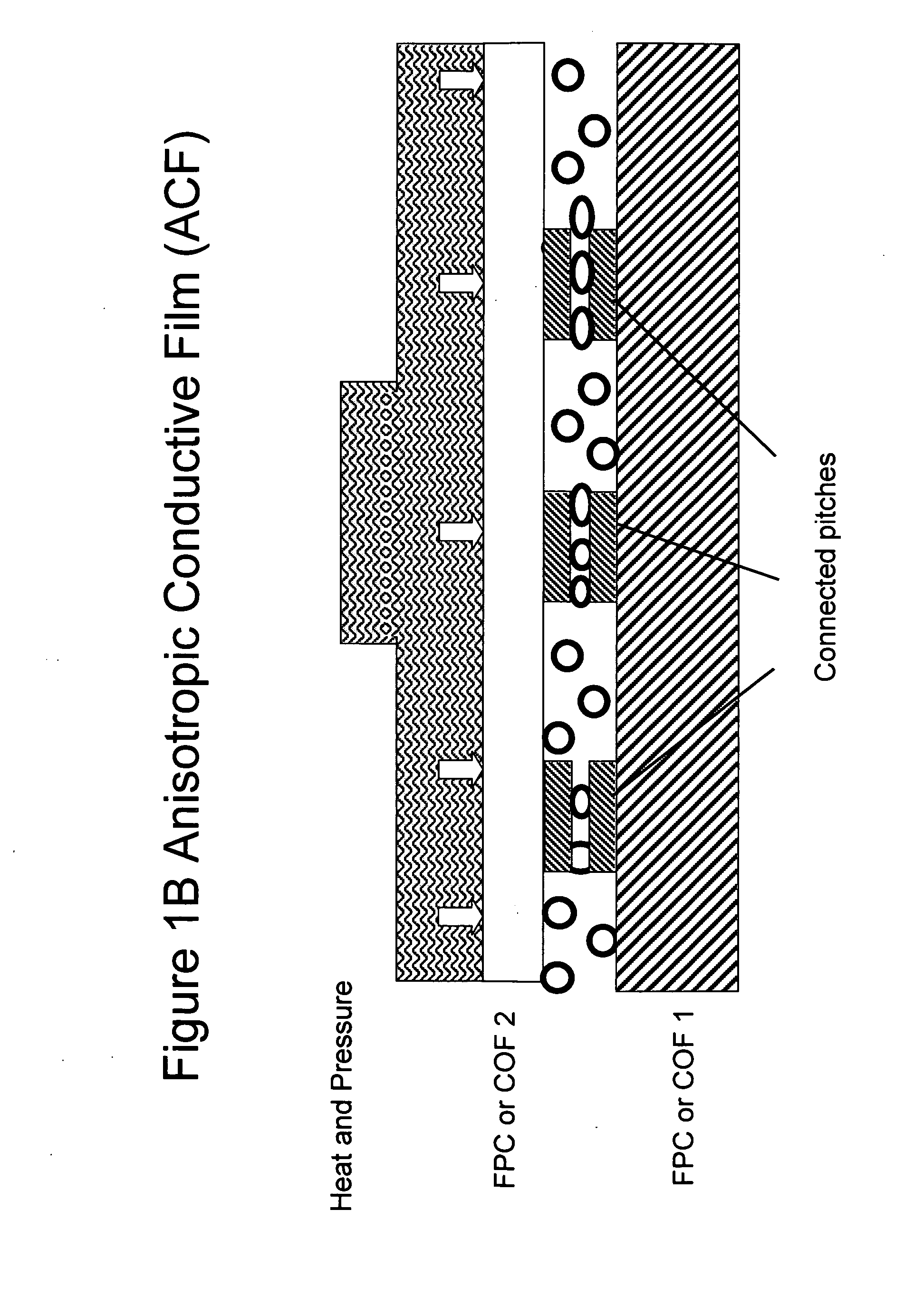
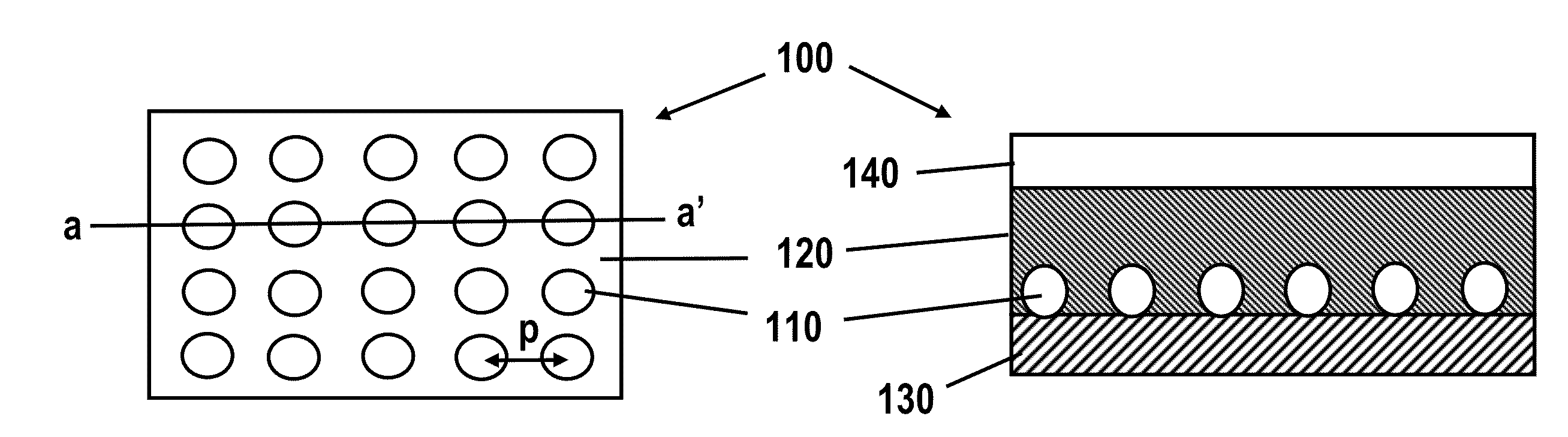
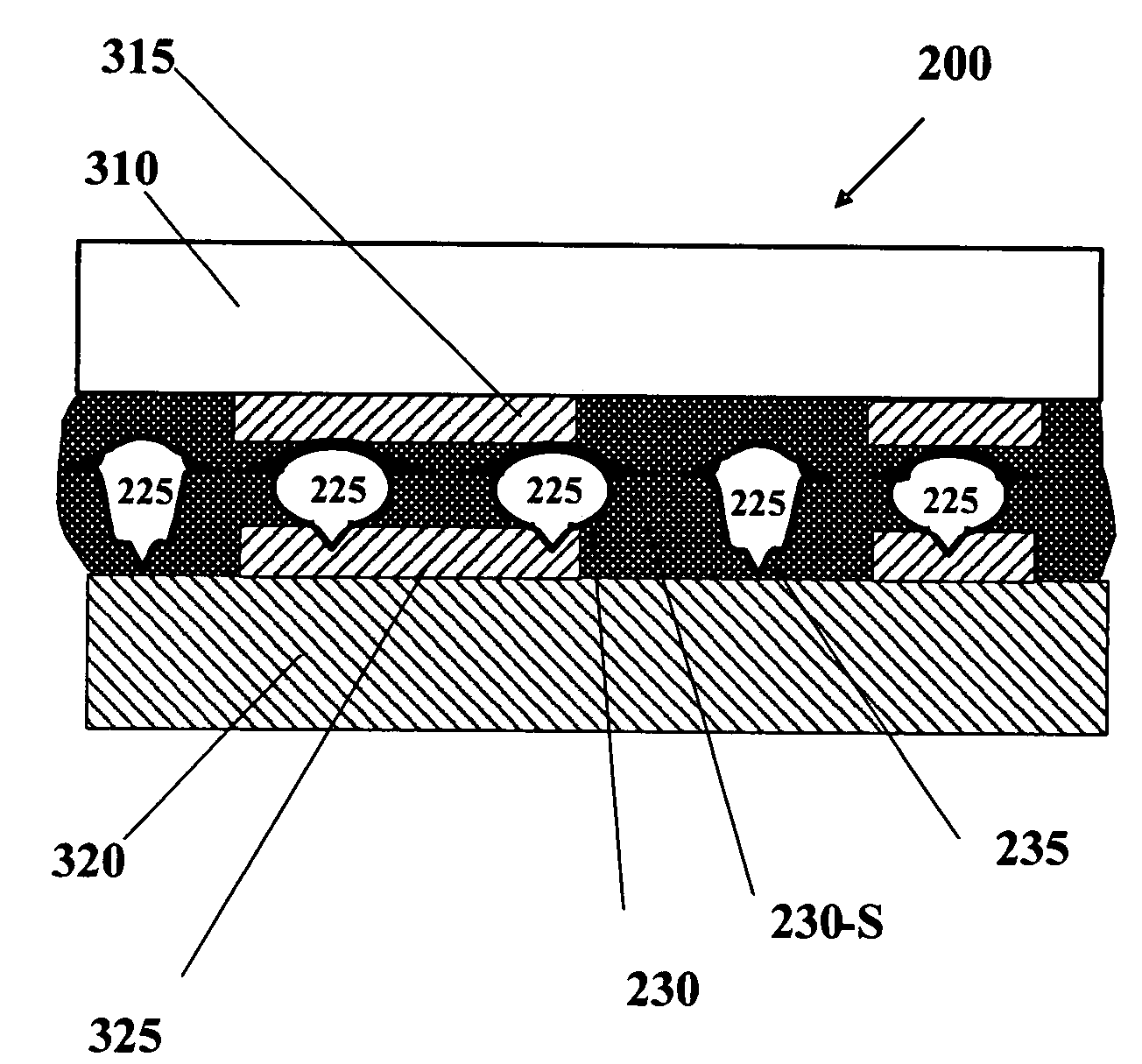
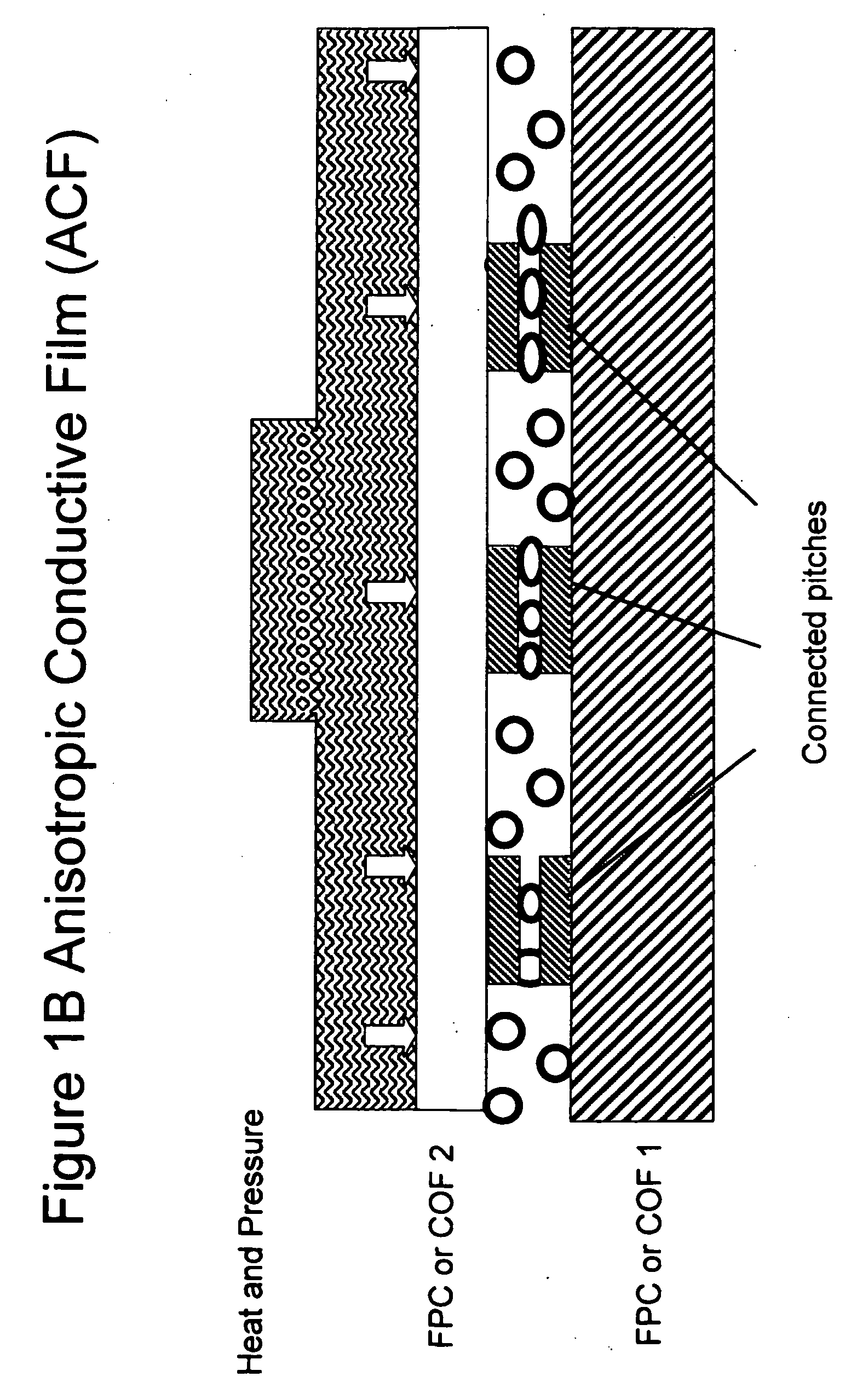
Non-random array anisotropic conductive film (ACF) and manufacturing processes
InactiveUS20060280912A1High resolutionReduce manufacturing costLayered productsCoupling device detailsAnisotropic conductive filmManufacturing technology
The present invention discloses structures and manufacturing processes of an ACF of improved resolution and reliability of electrical connection using a non-random array of microcavities of predetermined configuration, shape and dimension. The manufacturing process includes the steps of (i) fluidic filling of conductive particles onto a substrate or carrier web comprising a predetermined array of microcavities, or (ii) selective metallization of the array followed by filling the array with a filler material and a second selective metallization on the filled microcavity array. The thus prepared filled conductive microcavity array is then over-coated or laminated with an adhesive film.
Owner:TRILLION SCI INC
Random array sequencing of low-complexity libraries
ActiveUS20130065768A1Vary numberMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationHigh densityRandom array
The invention is directed to a method of sequencing low-complexity amplicons randomly arrayed at high density on a surface. Methods of the invention include preparing amplicons for sequencing by a sets of primers that ensure initial signals front different amplicons on the surface will be evenly distributed among the different nucleotides being added in a sequencing by synthesis operation.
Owner:ADAPTIVE BIOTECH
Non-random array anisotropic conductive film (ACF) and manufacturing processes
ActiveUS20100101700A1High resolutionReduce manufacturing costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAnisotropic conductive filmRandom array
Structures and manufacturing processes of an ACF array using a non-random array of microcavities of predetermined configuration, shape and dimension. The manufacturing process includes fluidic filling of conductive particles onto a substrate or carrier web comprising a predetermined array of microcavities, or selective metallization of the array followed by filling the array with a filler material and a second selective metallization on the filled microcavity array. The thus prepared filled conductive microcavity array is then over-coated or laminated with an adhesive film. Cavities in the array, and particles filling the cavities, can have a unimodal, bimodal, or multimodal distribution.
Owner:POLAROID IP BV
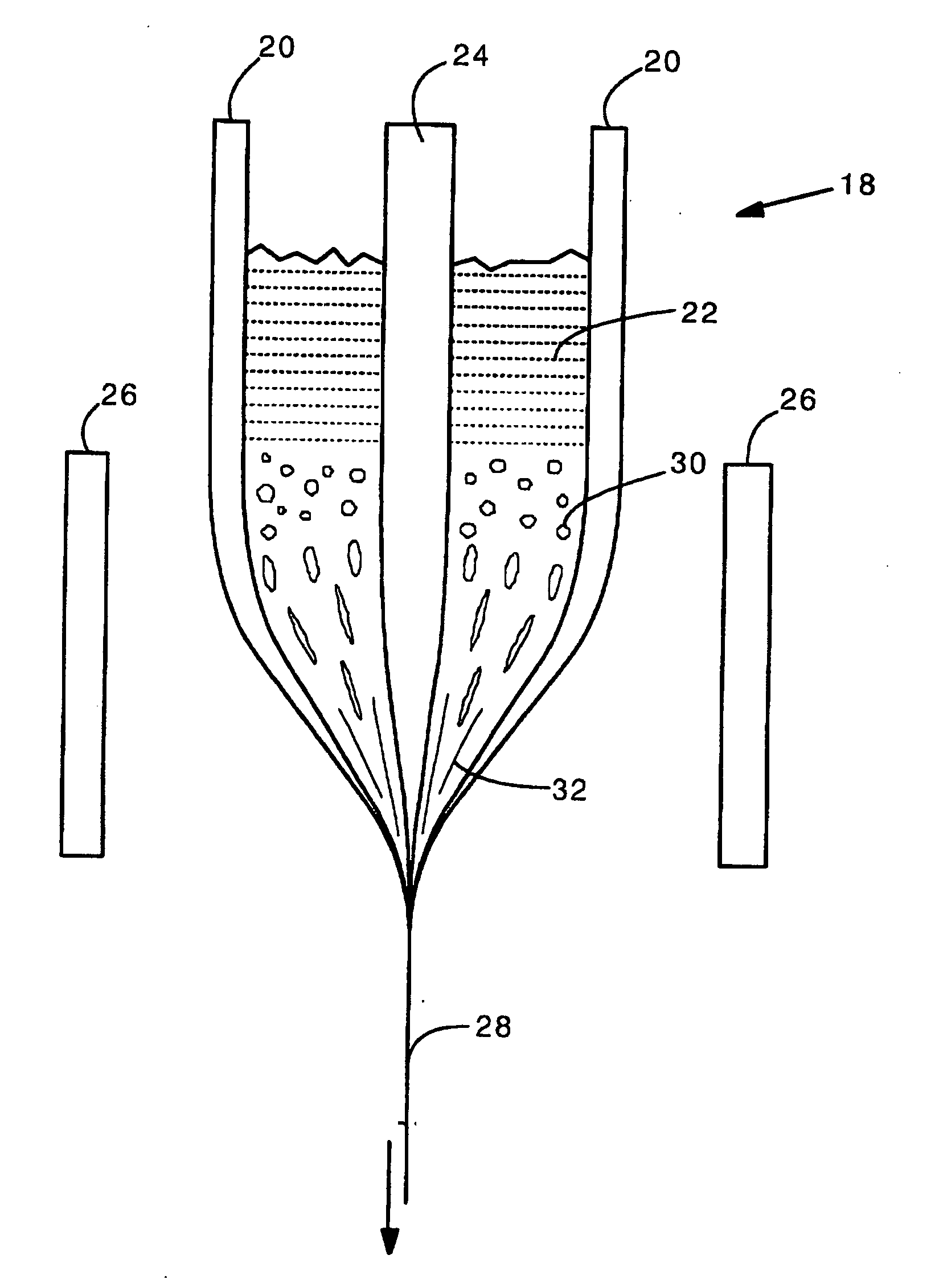
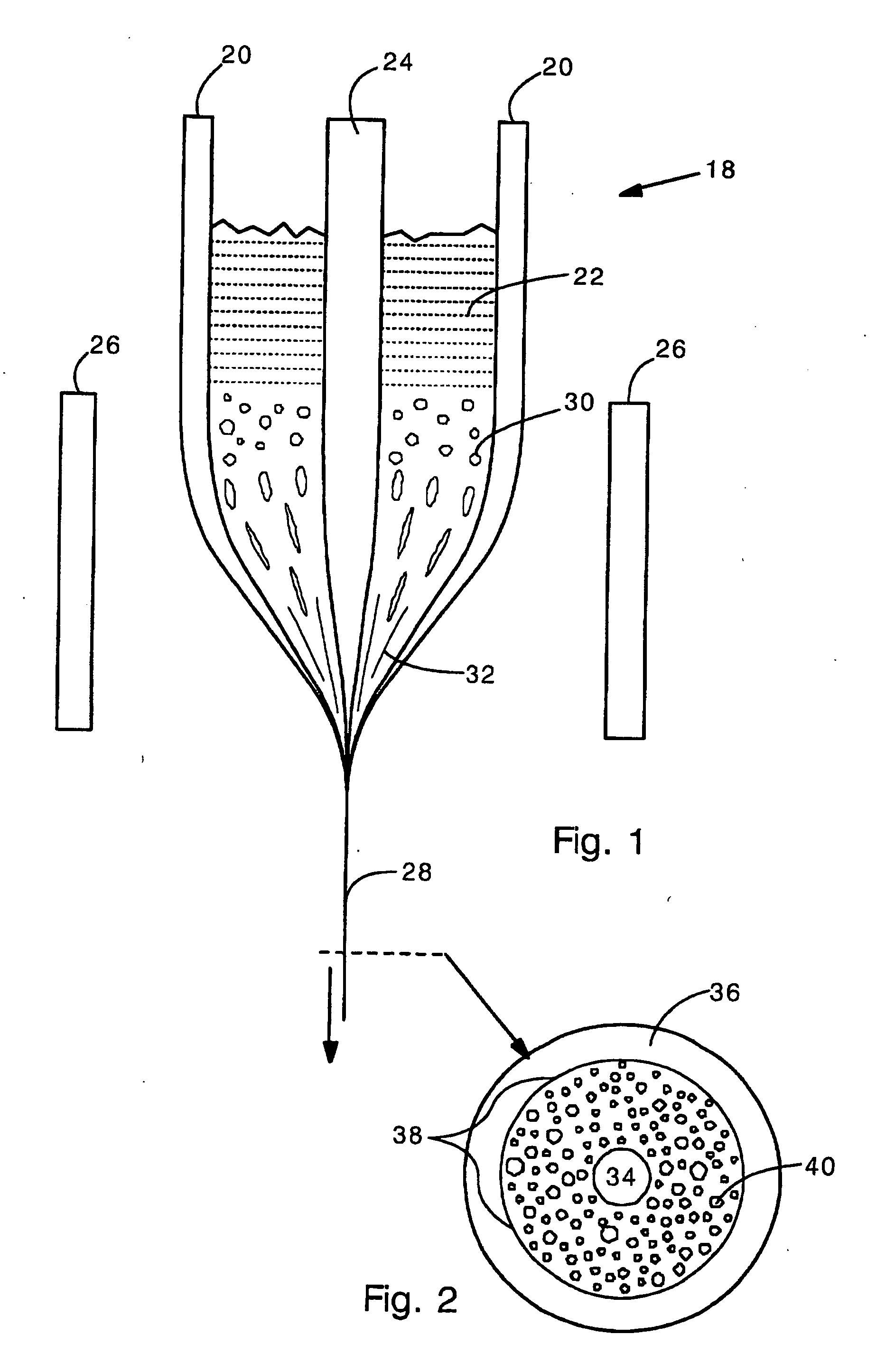
Holey optical fiber with random pattern of holes and method for making same
ActiveUS20050094954A1Glass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingSilicon dioxideAir bubble
A random array of holes is created in an optical fiber by gas generated during fiber drawing. The gas forms bubbles which are drawn into long, microscopic holes. The gas is created by a gas generating material such as silicon nitride. Silicon nitride oxidizes to produce nitrogen oxides when heated. The gas generating material can alternatively be silicon carbide or other nitrides or carbides. The random holes can provide cladding for optical confinement when located around a fiber core. The random holes can also be present in the fiber core. The fibers can be made of silica. The present random hole fibers are particularly useful as pressure sensors since they experience a large wavelength dependant increase in optical loss when pressure or force is applied.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
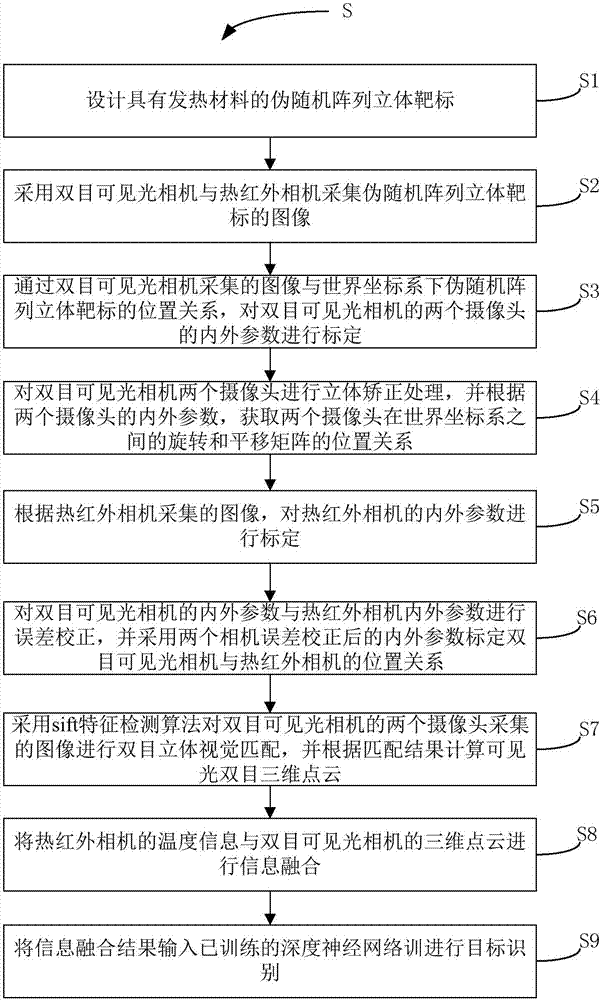
Binocular visible light camera and thermal infrared camera-based target identification method
ActiveCN108010085AImprove recognition rateDetect fasterImage enhancementImage analysisVisual matchingPoint cloud
The invention discloses a binocular visible light camera and thermal infrared camera-based target identification method. The method comprises the steps of calibrating internal and external parametersof two cameras of a binocular visible light camera through a position relationship between an image collected by the binocular visible light camera and a pseudo-random array stereoscopic target in a world coordinate system, and obtaining a rotation and translation matrix position relationship, between world coordinate systems, of the two cameras; according to an image collected by a thermal infrared camera, calibrating internal and external parameters of the thermal infrared camera; calibrating a position relationship between the binocular visible light camera and the thermal infrared camera;performing binocular stereoscopic visual matching on the images collected by the two cameras of the binocular visible light camera by adopting a sift feature detection algorithm, and calculating a visible light binocular three-dimensional point cloud according to a matching result; performing information fusion on temperature information of the thermal infrared camera and the three-dimensional point cloud of the binocular visible light camera; and inputting an information fusion result to a trained deep neural network for performing target identification.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Sensor Array Processor with Multichannel Reconstruction from Random Array Sampling
A method and system for reconstructing random samples taken across multiple sensors of a sensor array, so that each sensor's output is reconstructed. The samples are processed using a compressive sensing process. The compressive sensing process uses a time-space transform basis that represents the multi-channel data in terms of both a frequency component and an azimuthal component.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
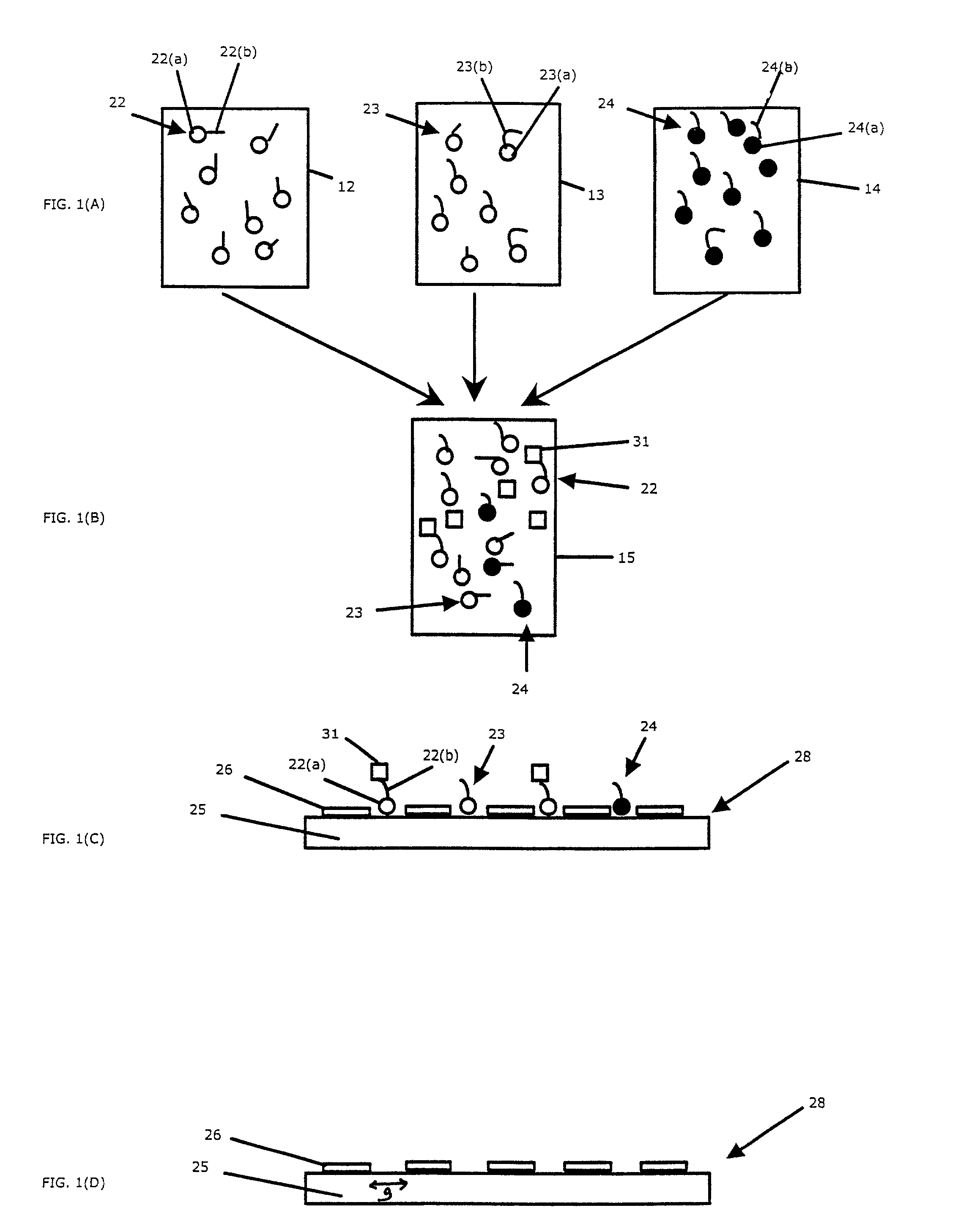
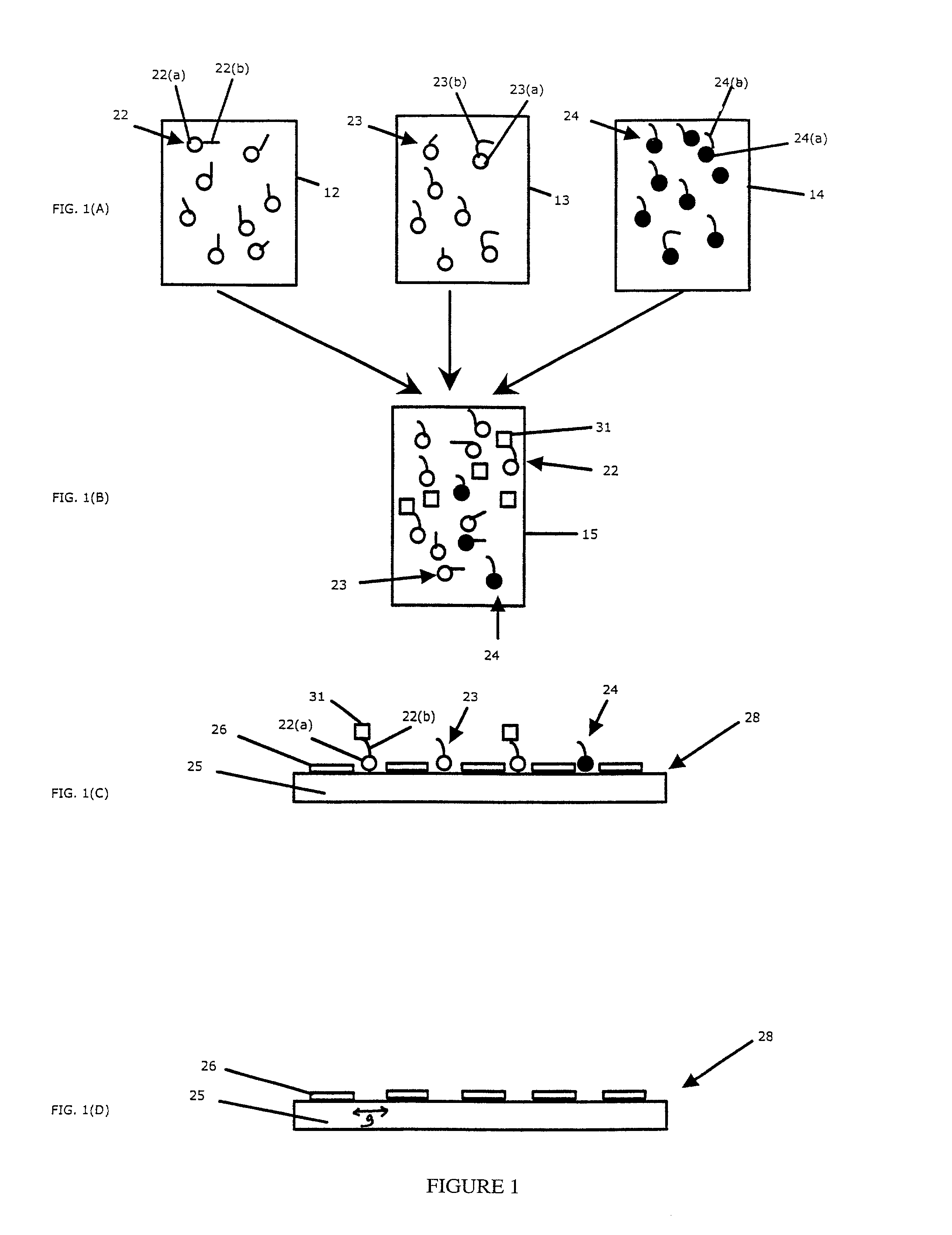
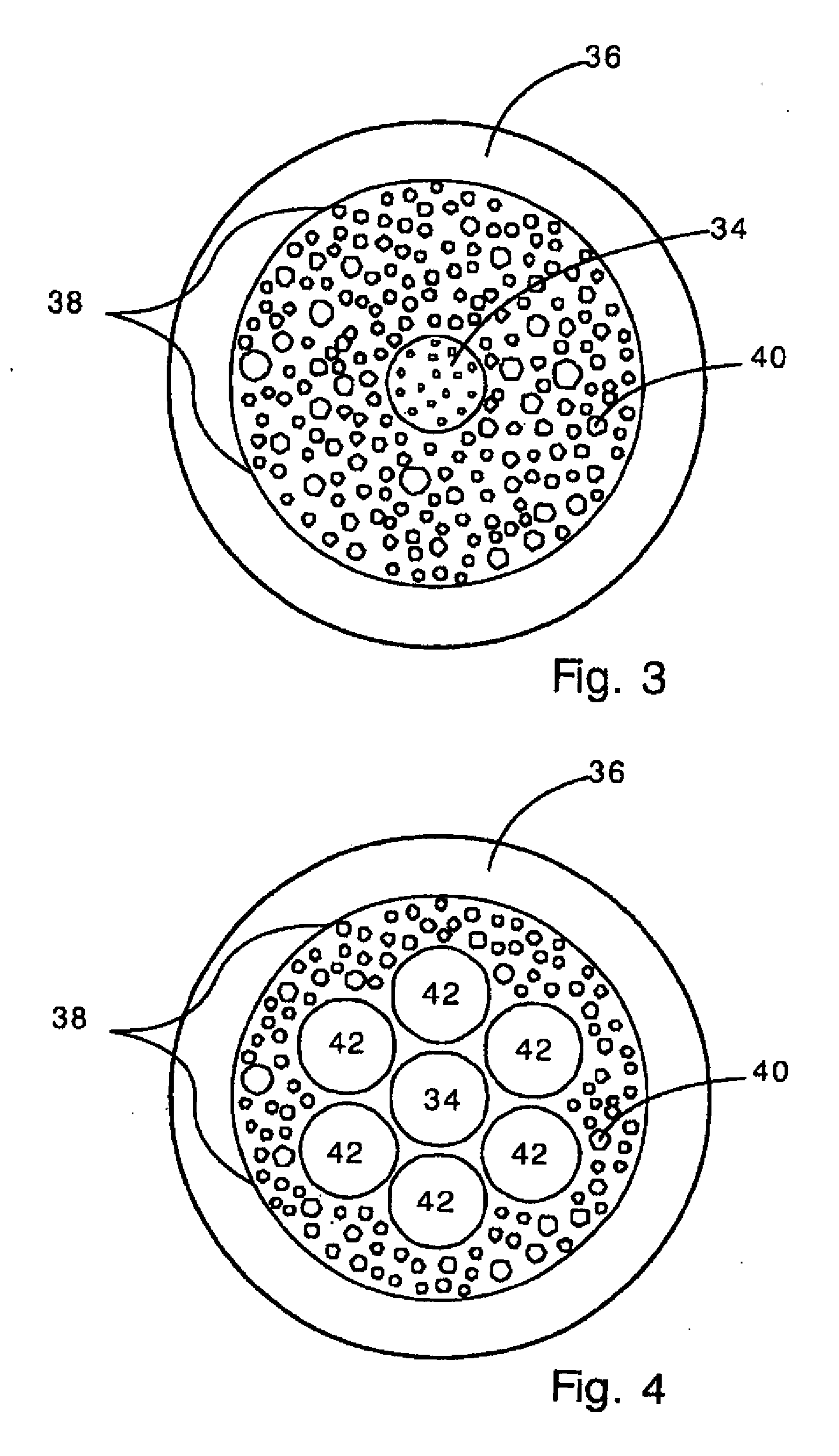
Devices and methods to form a randomly ordered array of magnetic beads and uses thereof
ActiveUS7682837B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh throughput genotypingMagnetic bead
The invention includes devices and methods for forming random arrays of magnetic particles, arrays formed using these devices and methods, and to methods of using the arrays. The invention provides an assembly (chip) with magnetic domains that produce localized magnetic fields capable of immobilizing magnetic particles such as commercially available magnetic beads. Probe or sensor molecules can be coupled to the beads, which are then dispersed on the assembly, forming a random order array. The arrays can be used for analyzing samples, targets, and / or the interaction between samples and targets. The invention finds particular use in processes such as high-throughput genotyping and other nucleic acid hybridization-based assays.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
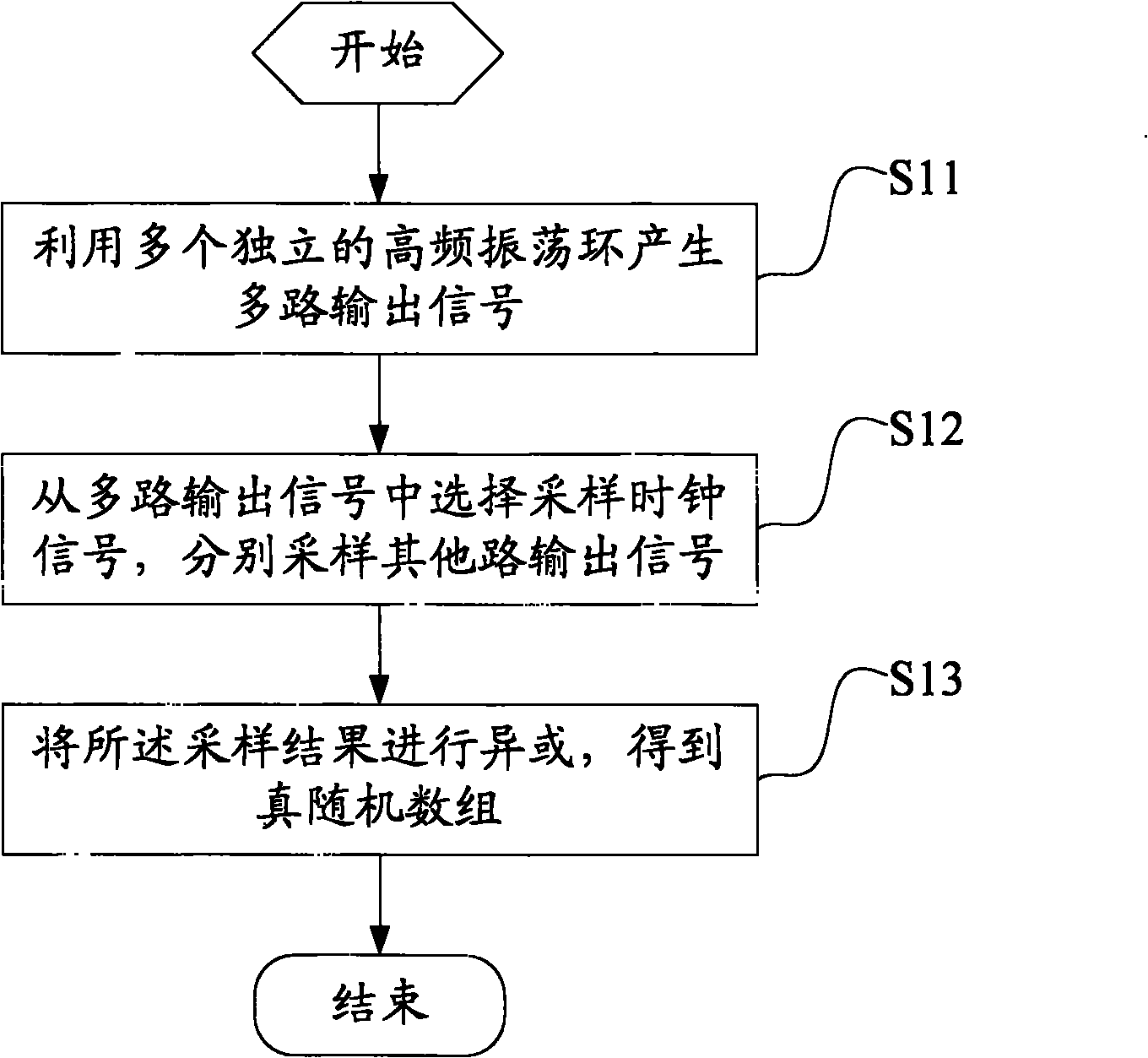
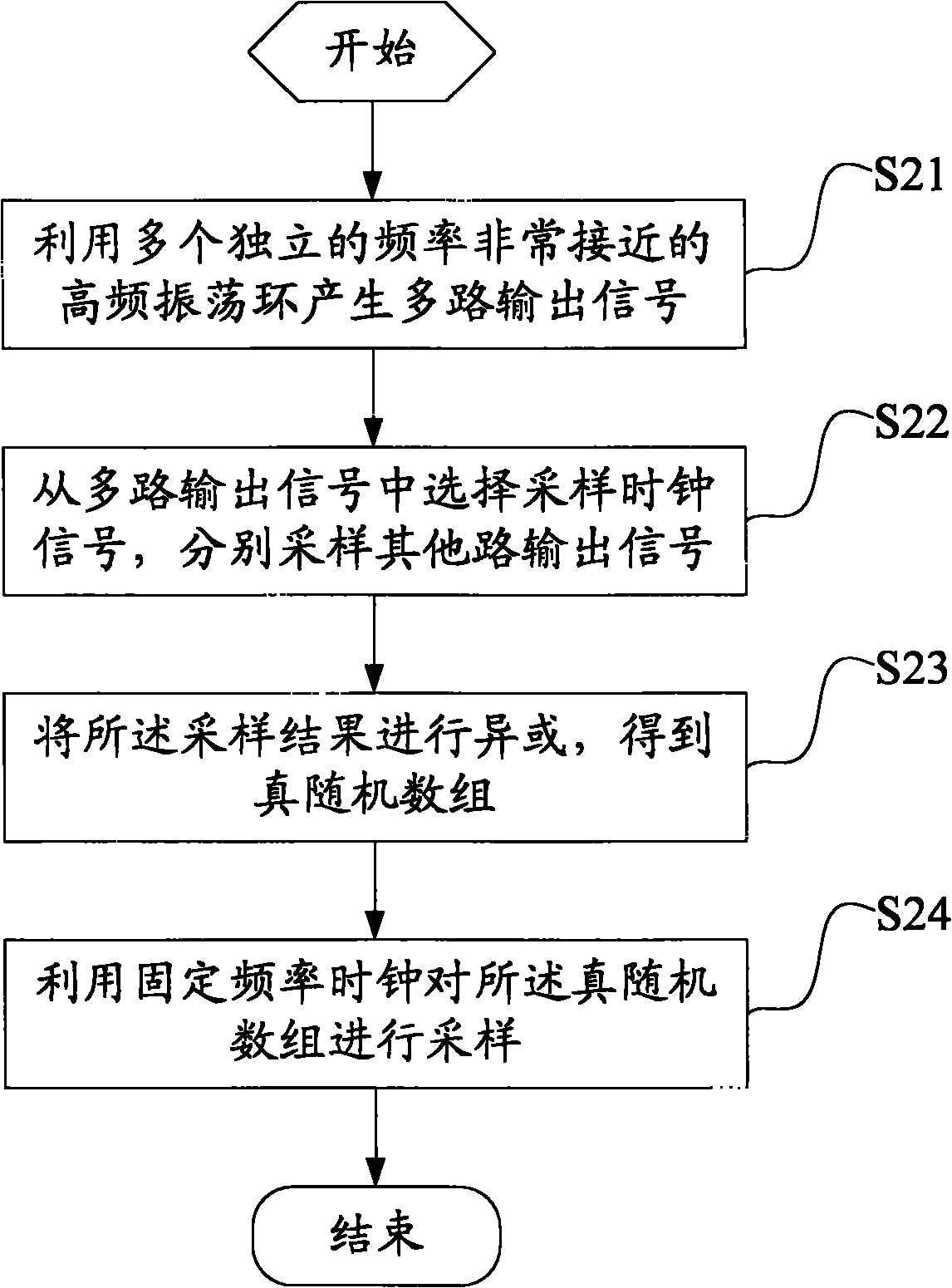
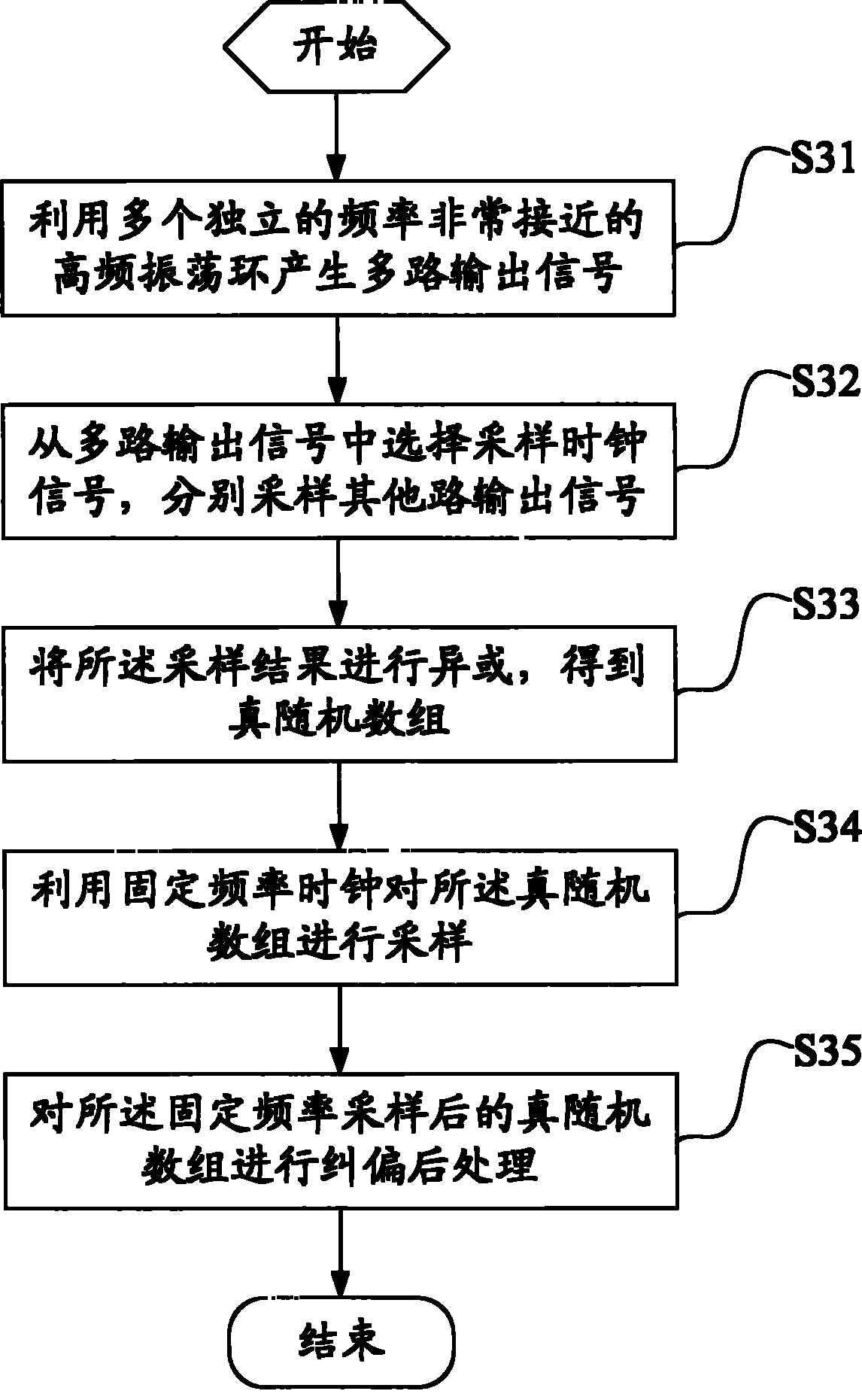
True random number generation method and generator
InactiveCN102375722AIncrease randomnessSimple structureRandom number generatorsSecuring communicationArray data structureRandom array
The invention discloses a true random number generation method and generator. The generation method comprises the following steps of: generating multiple paths of output signals by using a plurality of independent high-frequency oscillating rings; selecting a sampling clock signal from the multiple paths of output signals, and respectively sampling the other paths of output signals; and carrying out exclusive-OR operation on the obtained sampling results so as to obtain a true random array. In the true random number generation method disclosed by the embodiment of the invention, true random numbers are obtained by way of generating multiple paths of output signals by using a plurality of independent high-frequency oscillating rings, selecting a sampling clock signal from the output signals, and then sampling the other output signals, therefore, the randomness of the random number is increased; and because hundreds of sets of oscillators in the prior art are not required to be used, the system structure and complexity are simplified, and the method is easy to implement.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
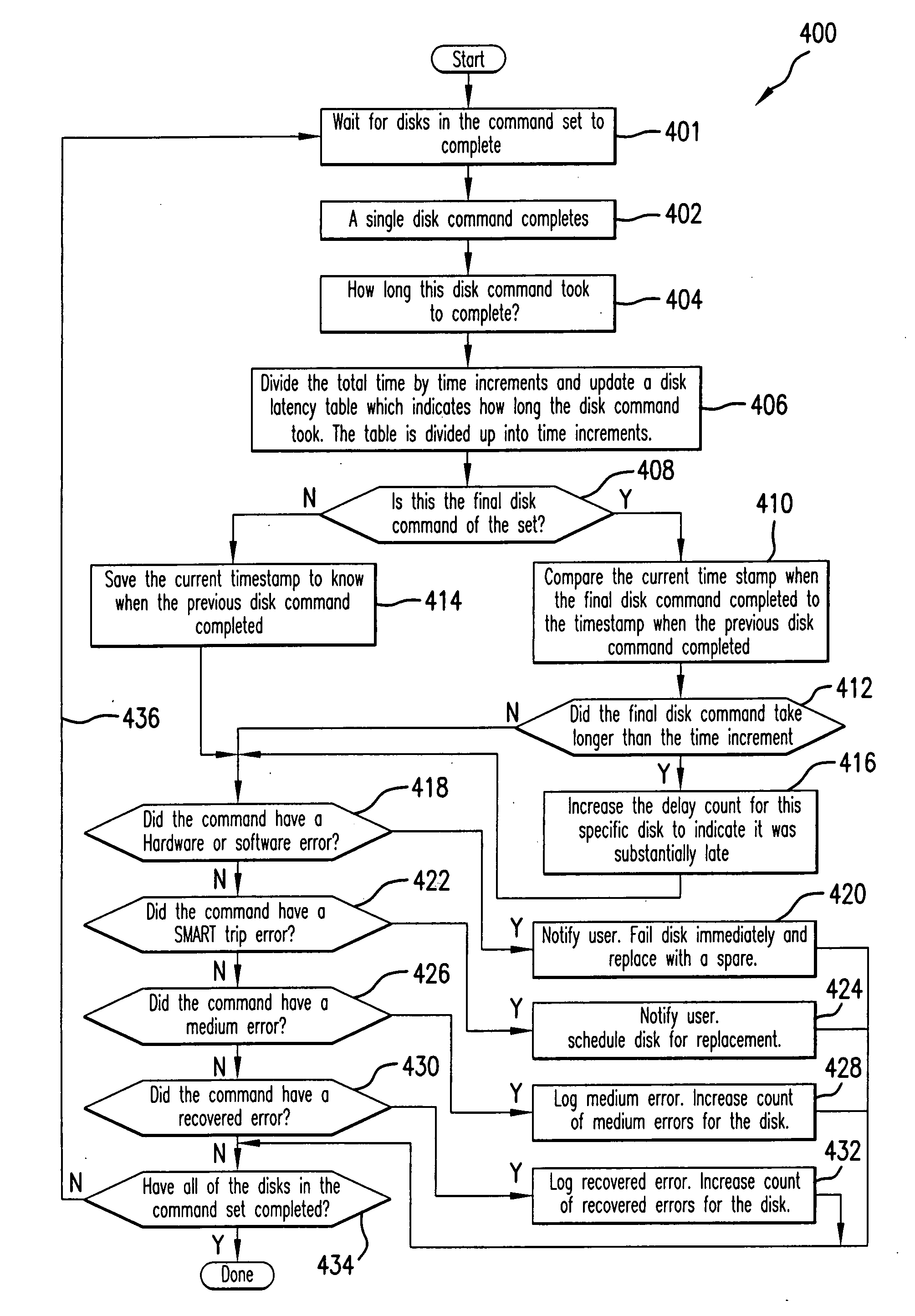
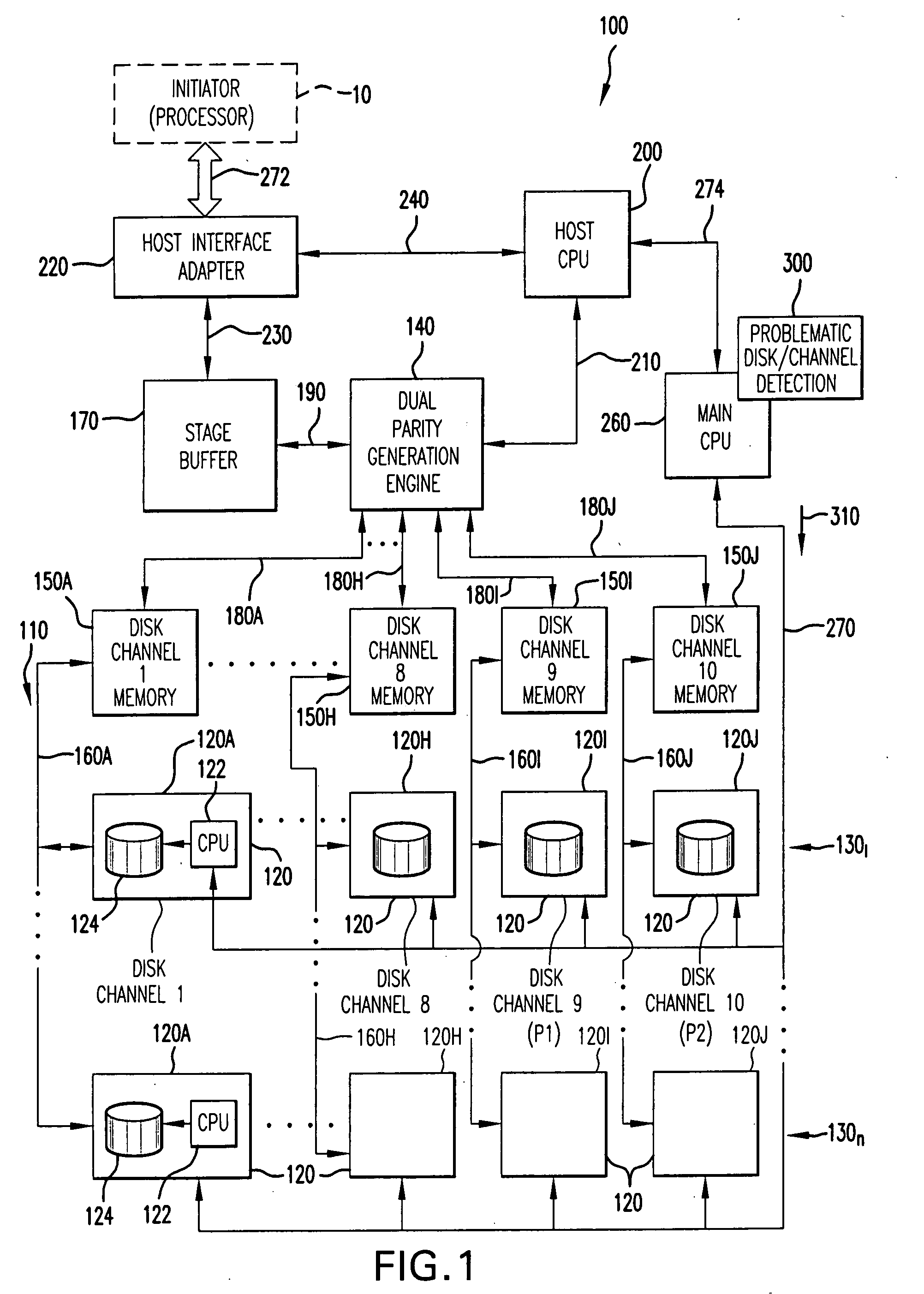
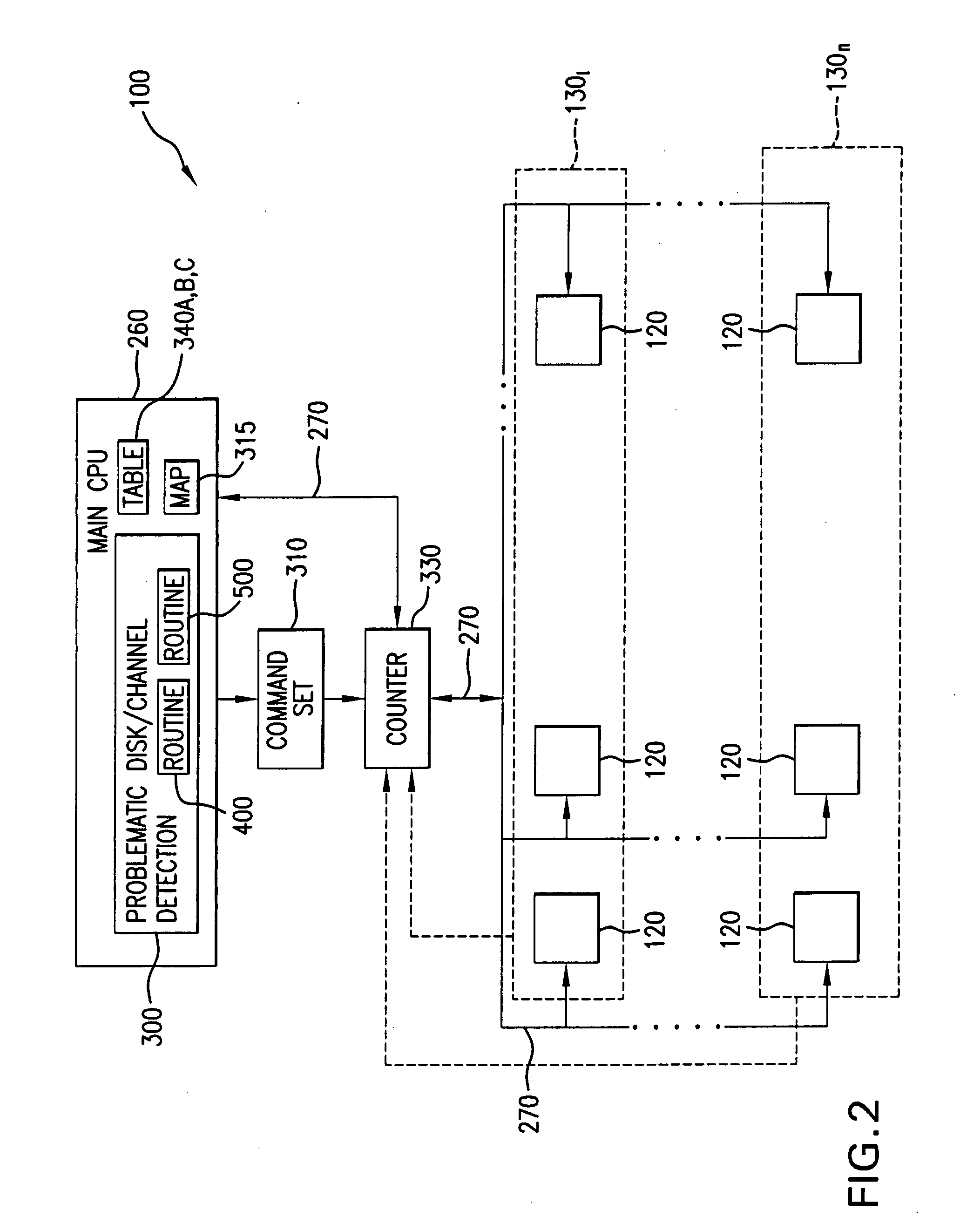
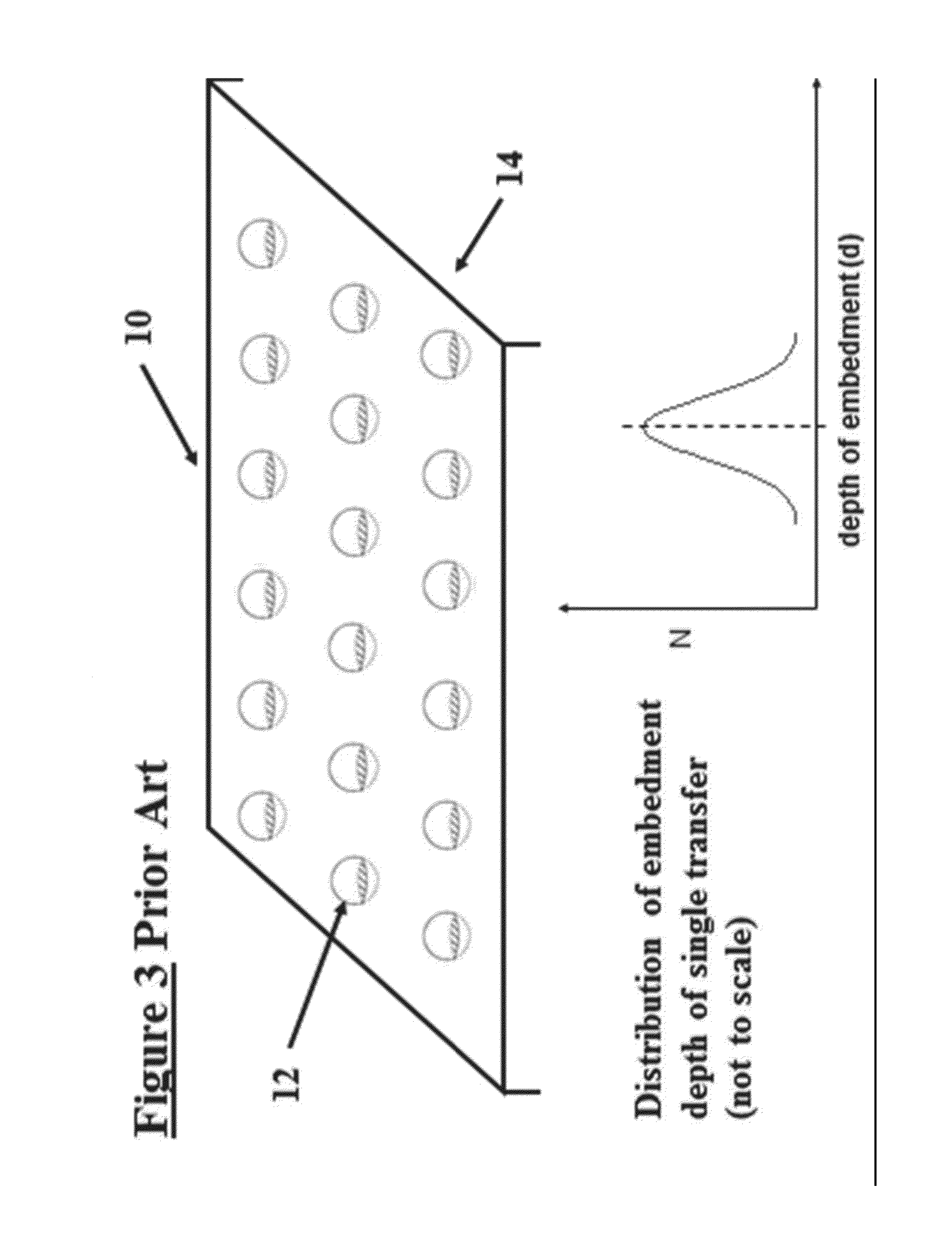
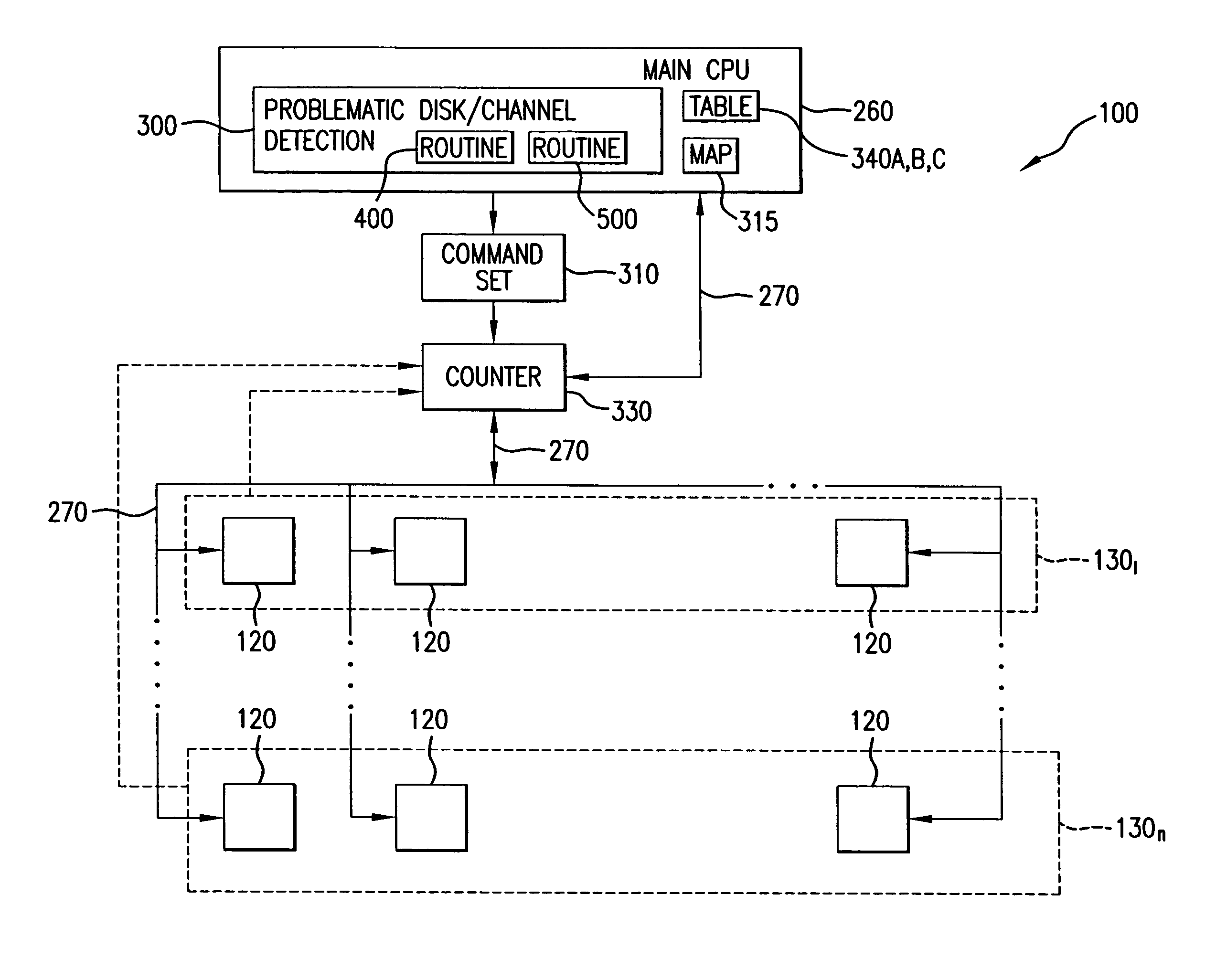
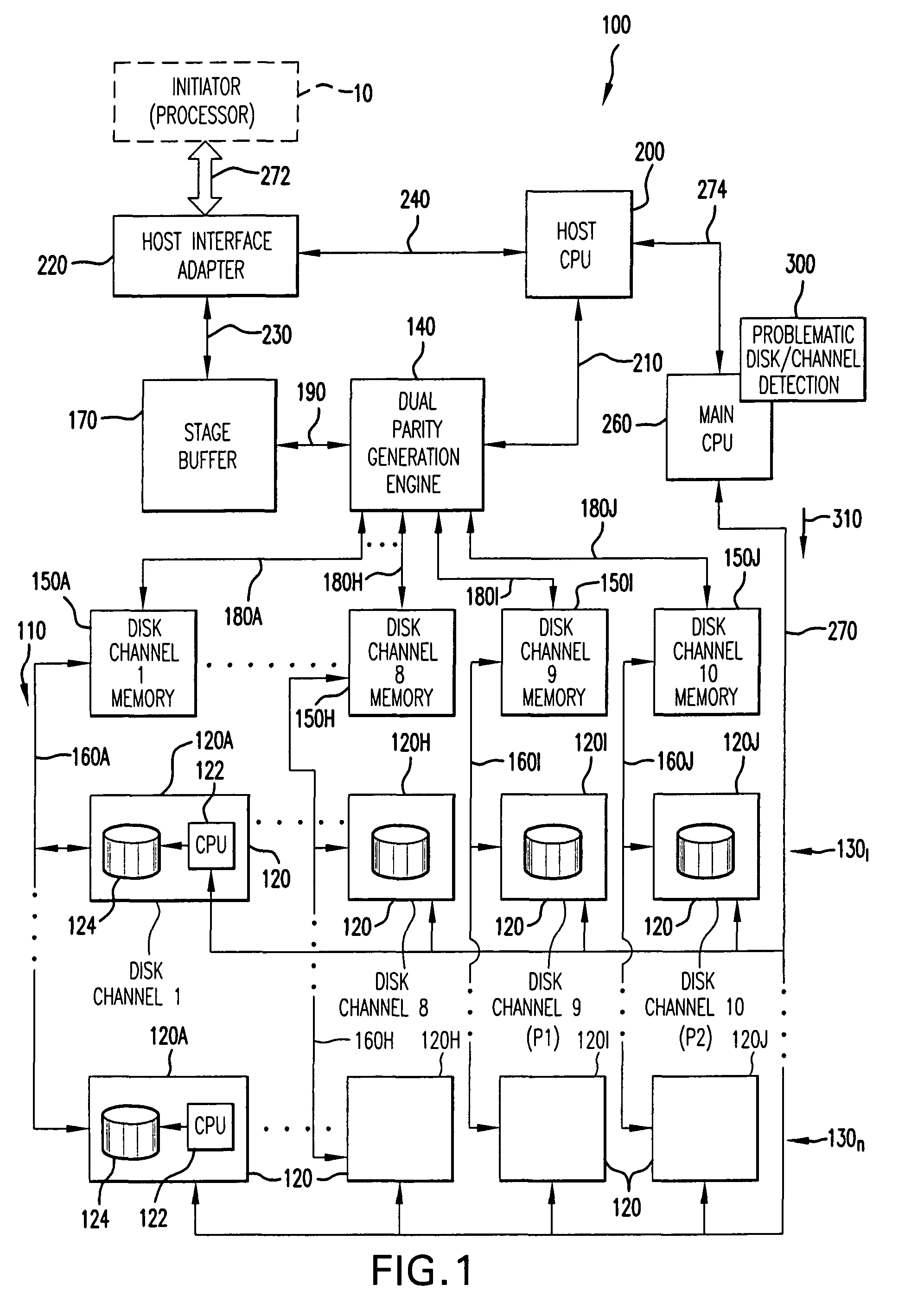
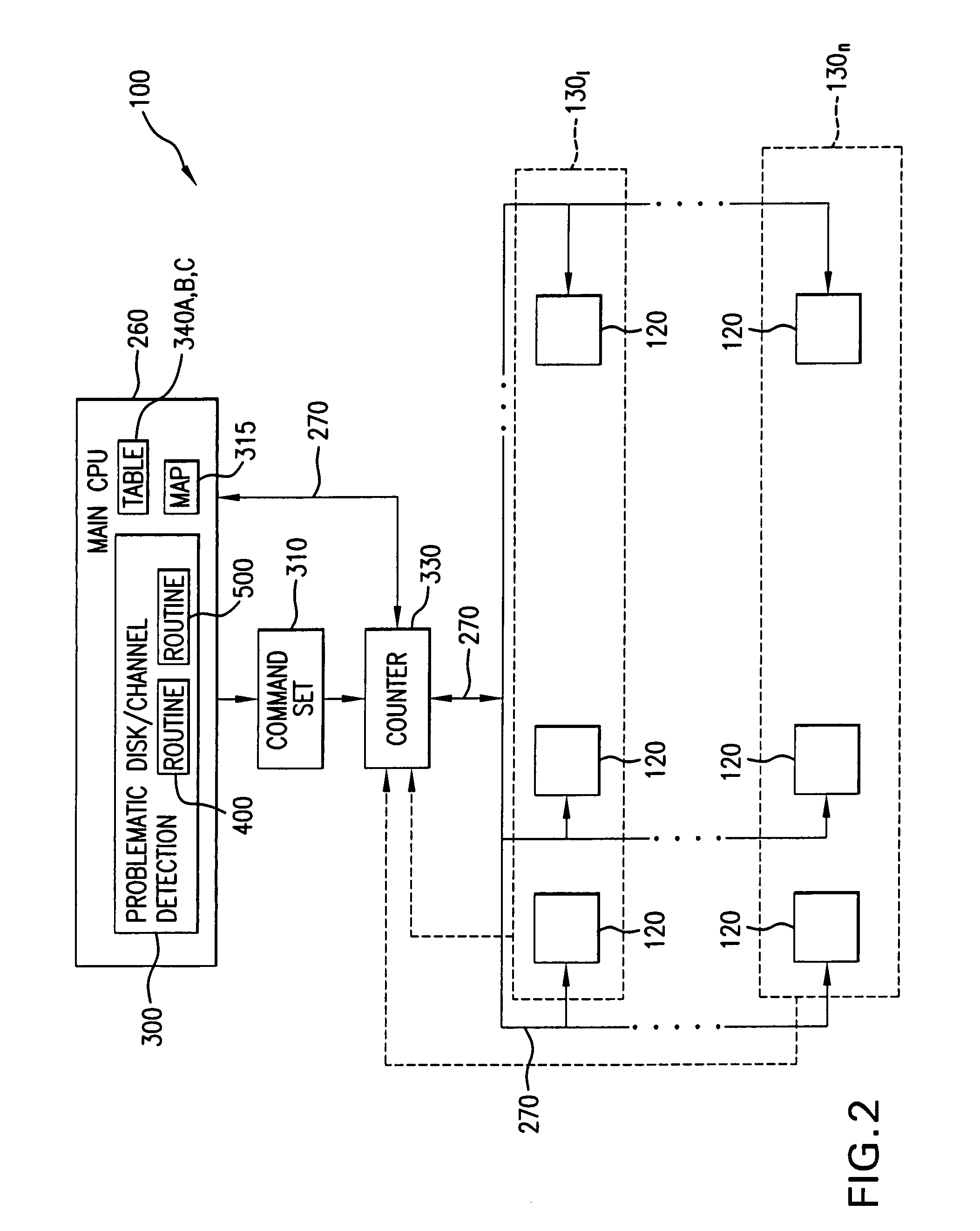
Method for detecting problematic disk drives and disk channels in a RAID memory system based on command processing latency
ActiveUS20090106602A1Early detectionImprove abilitiesReliability/availability analysisFunctional testingRAIDRandom array
In order to detect problematic drives in random arrays of independent disks, the system measures the latency of executing command sets which are broadcast to all disks in the data storage system and the results are compared to identify which disks take substantially longer to complete the requests. Disks that take longer to complete requests are likely to be problematic and are candidates for further examination and replacement. The disks in each tier group are compared to determine if any disk in that group exhibits problems. Also, counters for each tier group are compared to determine if the problem is with the disk or with the channel of the tier group. The latency of each disk in the tier group is saved in a table to provide a histogram of the latency of the disks in the tier group. Histograms of the disks in a single tier group are compared to determine if a specific disk is problematic. Histograms of each tier group are compared to determine if a specific disk is problematic or all the disks on the same channel exhibit problems.
Owner:DATADIRECT NETWORKS
Non-random array anisotropic conductive film (ACF) and manufacturing process
InactiveUS20090053859A1High resolutionReduce manufacturing costLayered productsCoupling device detailsAnisotropic conductive filmImage resolution
The present invention discloses structures and manufacturing processes of an ACF of improved resolution and reliability of electrical connection using a non-random array of microcavities of predetermined configuration, shape and dimension. The manufacturing process includes the steps of (i) fluidic filling of conductive particles onto a substrate or carrier web comprising a predetermined array of microcavities, or (ii) selective metallization of the array followed by filling the array with a filler material and a second selective metallization on the filled microcavity array. The thus prepared filled conductive microcavity array is then over-coated or laminated with an adhesive film.
Owner:TRILLION SCI INC
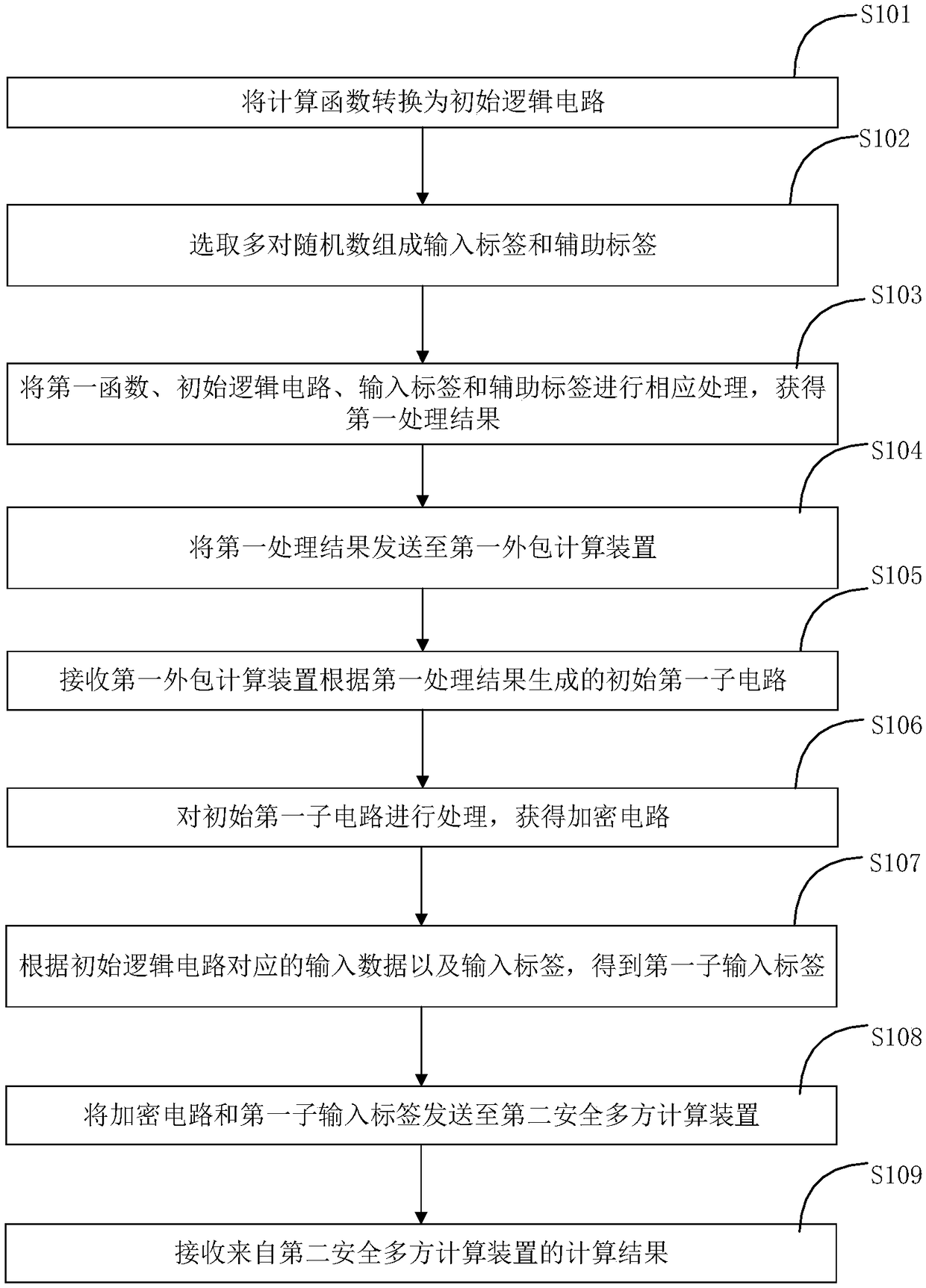
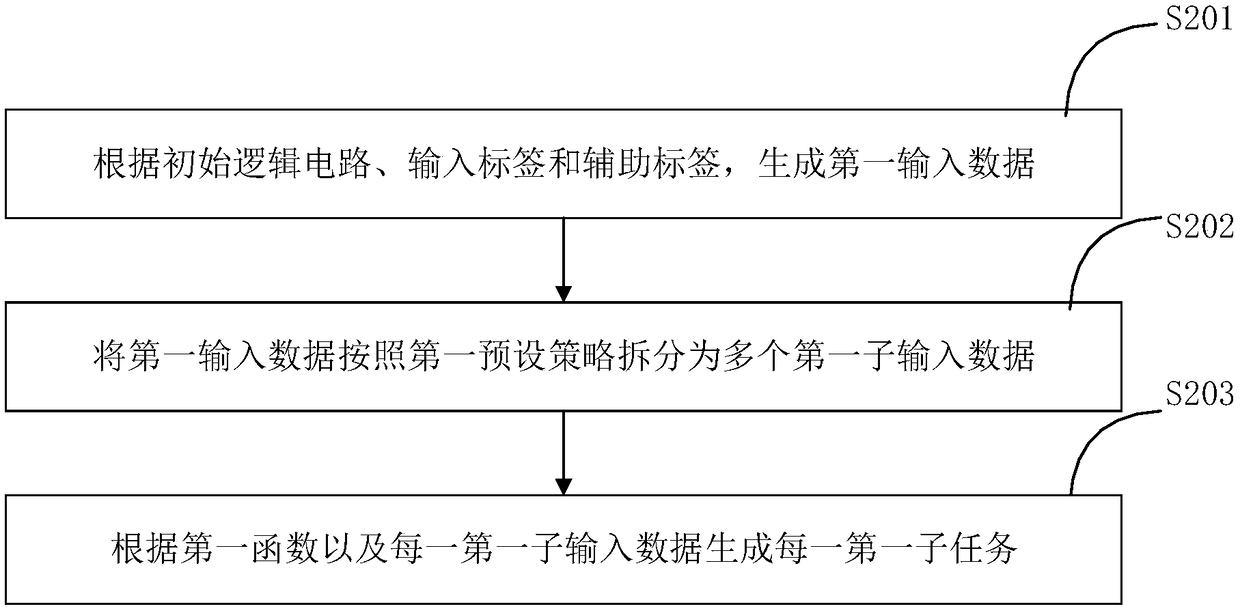
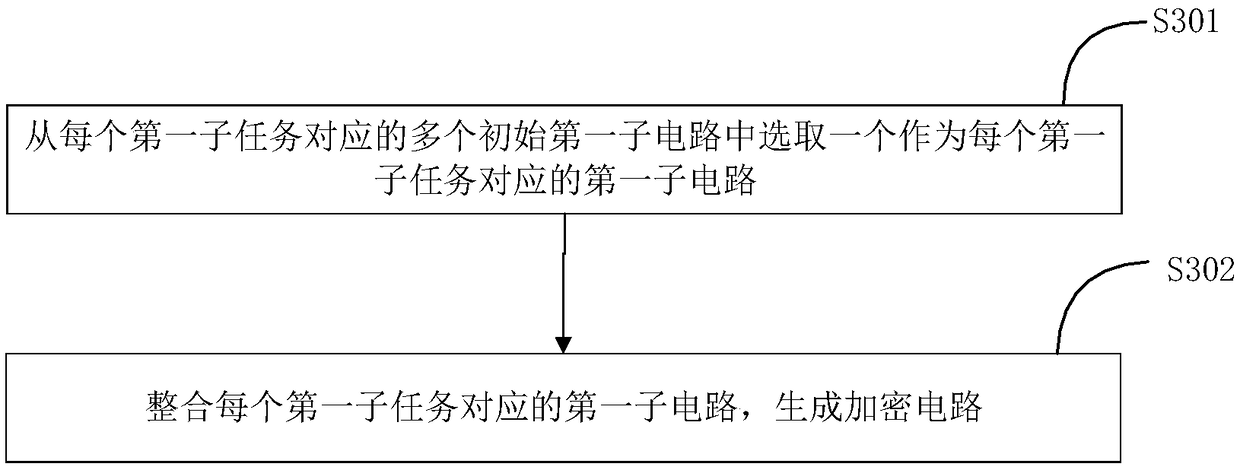
Secure multiparty computing method, device and system
ActiveCN108809623AReduce occupancyImprove computing efficiencySecuring communicationTheoretical computer scienceSecure multi-party computation
The invention provides a secure multiparty computing method, device and system. The secure multiparty computing method comprises the steps of converting a computing function into an initial logic circuit; selecting multiple pairs of random number so as to form an input label and an auxiliary label; processing a first function, the initial logic circuit, the input label and the auxiliary label correspondingly, so as to obtain a first processing result; sending the first processing result to a first outsourced computing device; receiving an initial first sub-circuit generated by the first outsourced computing device according to the first processing result; processing the initial first sub-circuit so as to acquire an encrypted circuit; obtaining a first sub-input label according to input data corresponding to the initial logic circuit and the input label; sending the encrypted circuit and the first sub-input label to a second secure multiparty computing device; and receiving a computingresult from the second secure multiparty computing device. Fewer local resources are used, computing efficiency is improved, and the performance of the secure multiparty computing technology is improved.
Owner:JUZIX TECH SHENZHEN CO LTD
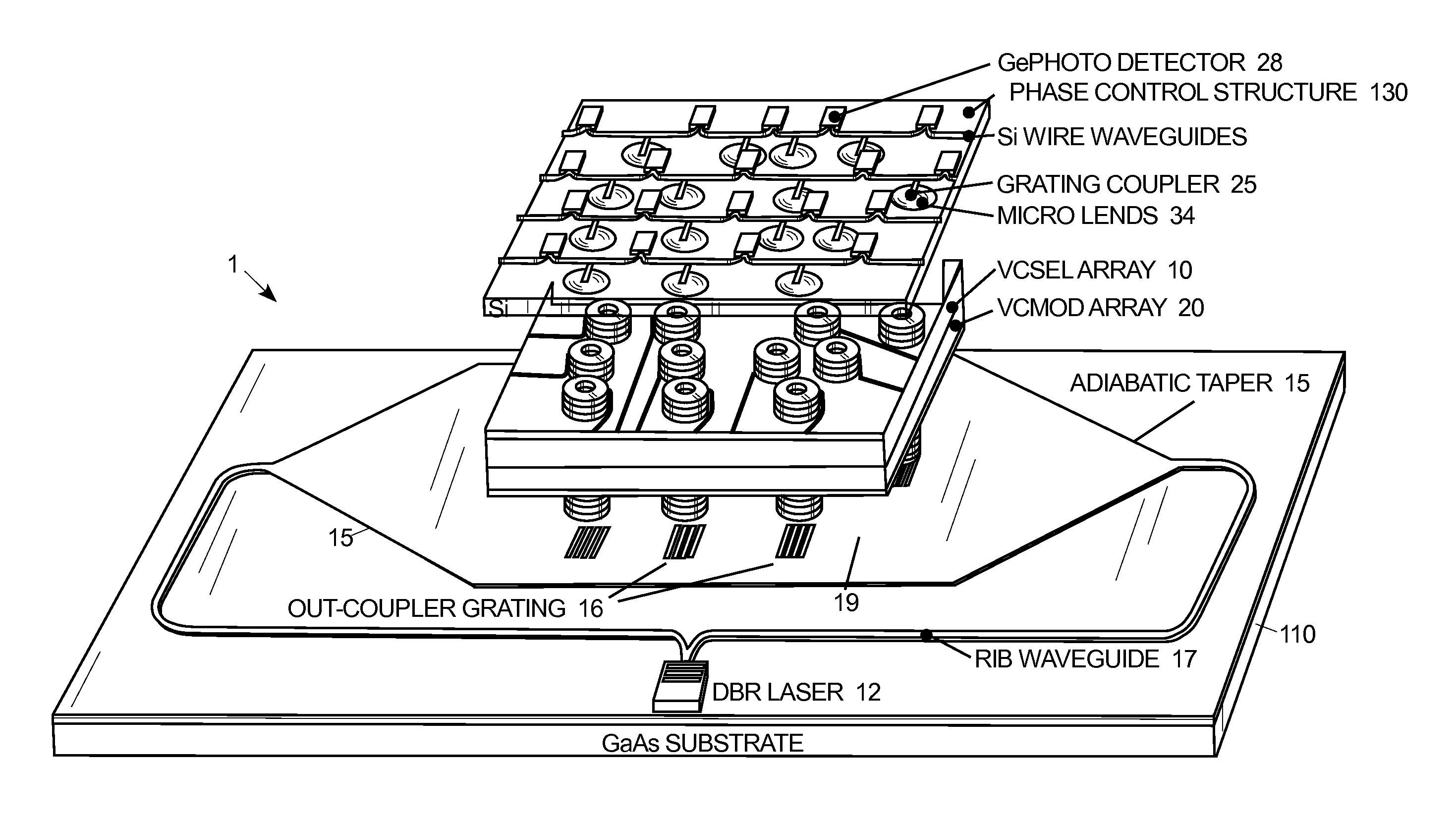
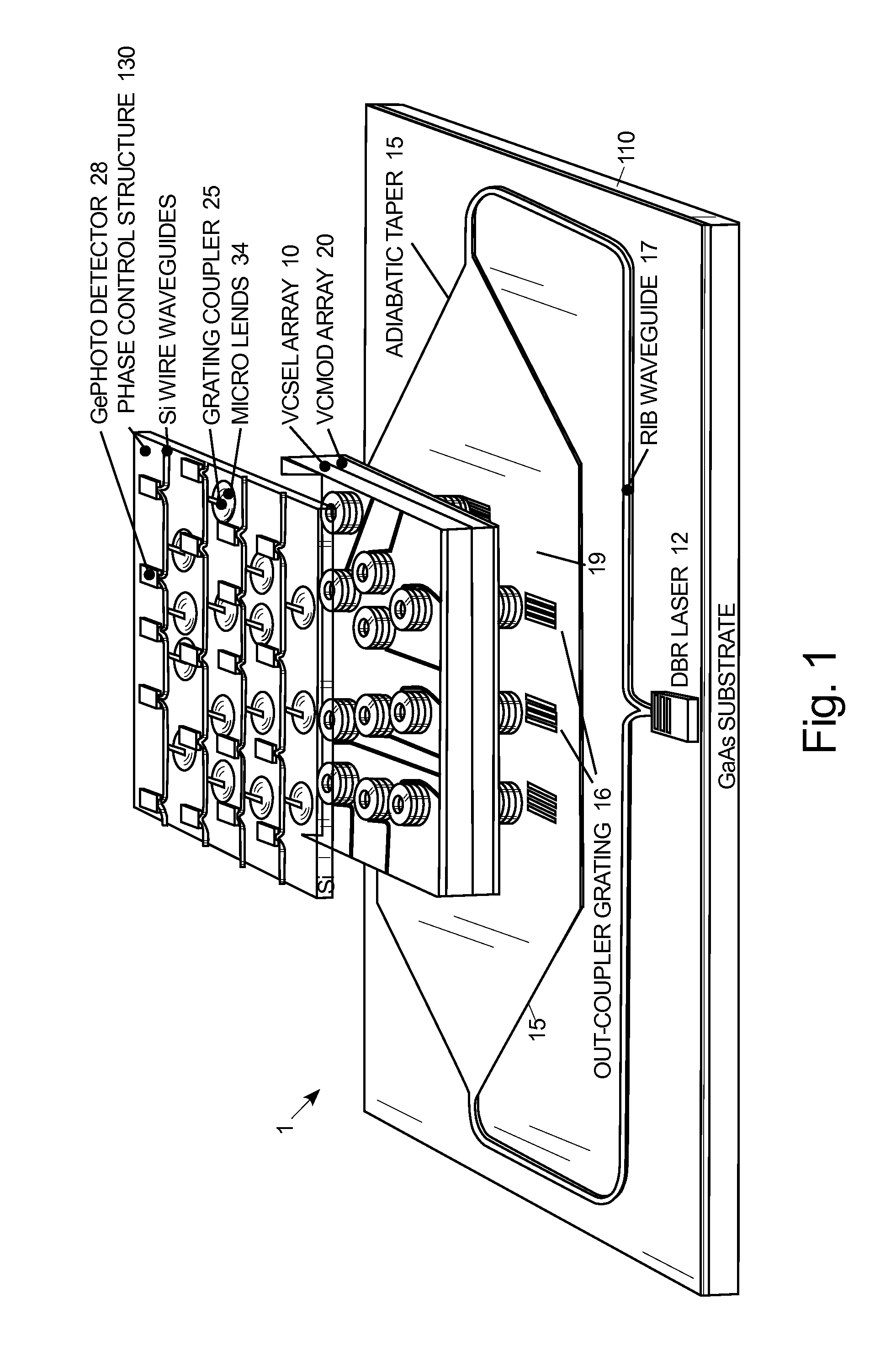
Vertically integrated optical phased array with pseudo-random array architecture
ActiveUS8615028B1Reducing grating lobeLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersInjection lockedVertical-cavity surface-emitting laser
A vertically integrated optical phased array has an array of a plurality of vertical cavity surface emitting lasers disposed in an aperiodic arrangement thereof, the plurality of vertical cavity surface emitting lasers having light emitting ports disposed parallel to one another. An array of a plurality of vertical cavity phase modulators disposed in the same aperiodic arrangement as the array of the plurality of vertical cavity surface emitting lasers, with individual modulators of said array of a plurality of vertical cavity phase modulators each being disposed in optical alignment with an injection port of a corresponding one of said plurality of vertical cavity surface emitting lasers. An array of a plurality of laser ports, fed by a master laser, are disposed in the same aperiodic arrangement as the array of the plurality of vertical cavity surface emitting lasers, the master laser providing, in use, injection beamlets, each injection beamlet, in use, injection locking a corresponding one of said plurality of vertical cavity surface emitting lasers via a corresponding one of said plurality of vertical cavity phase modulators.
Owner:HRL LAB
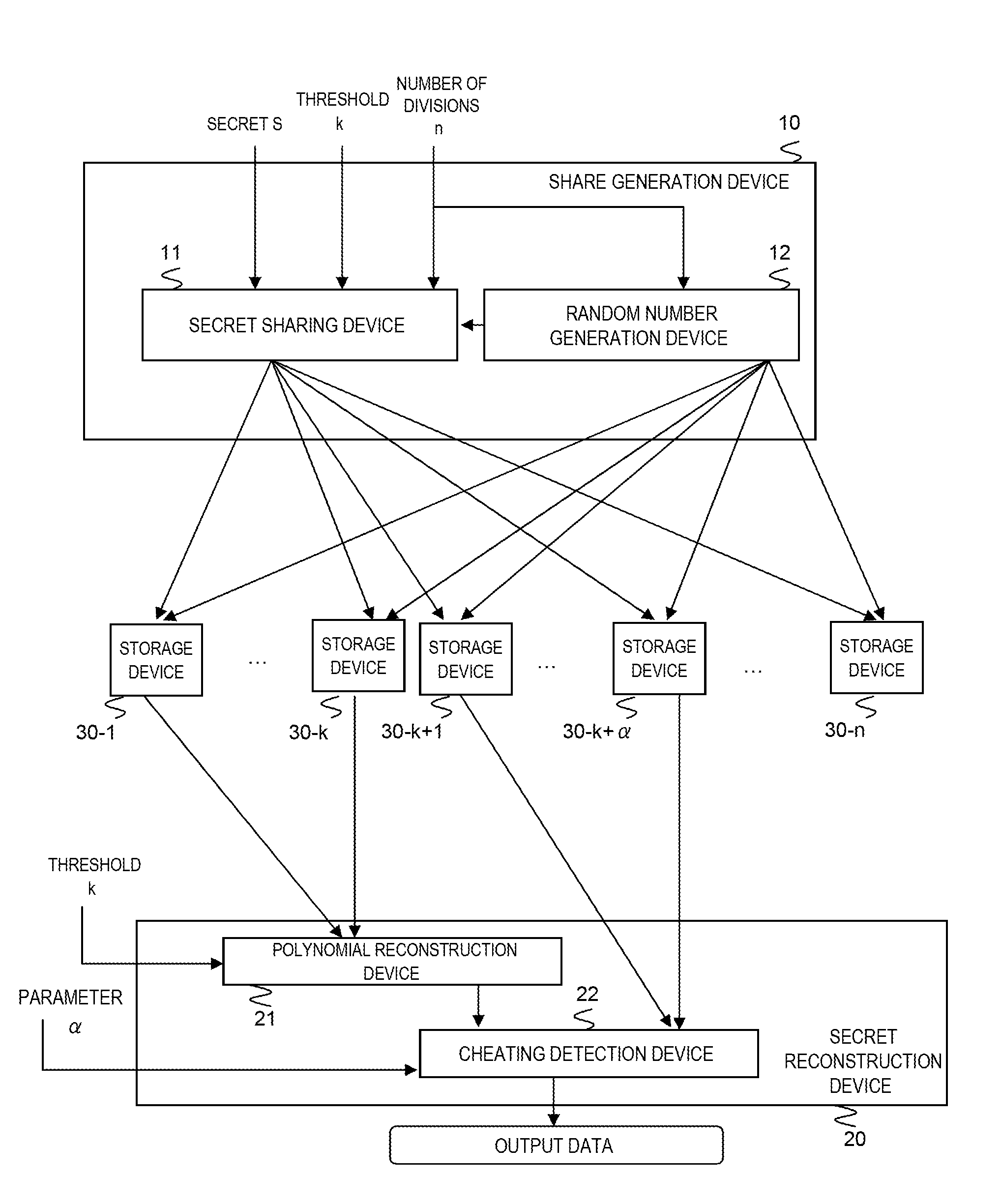
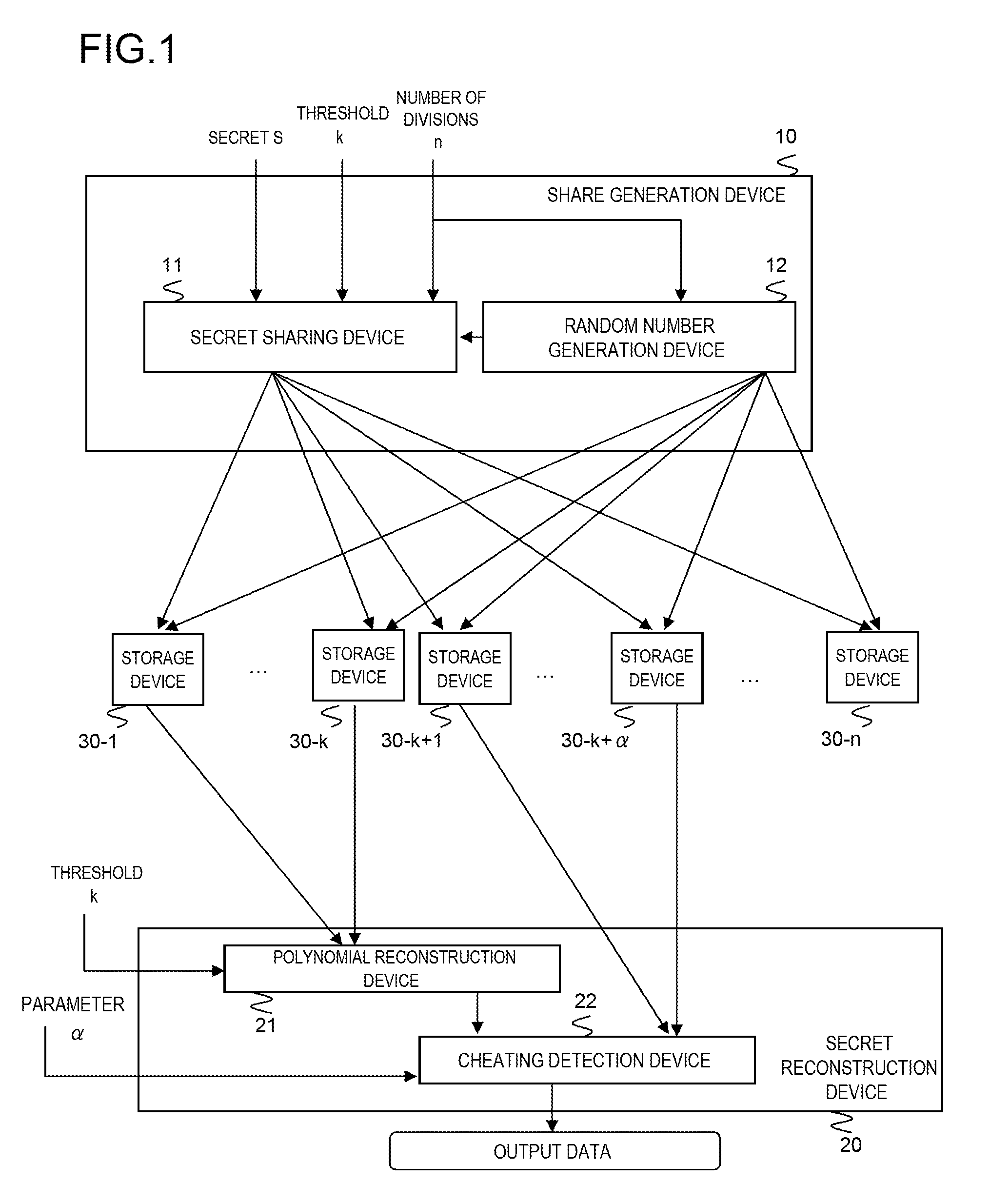
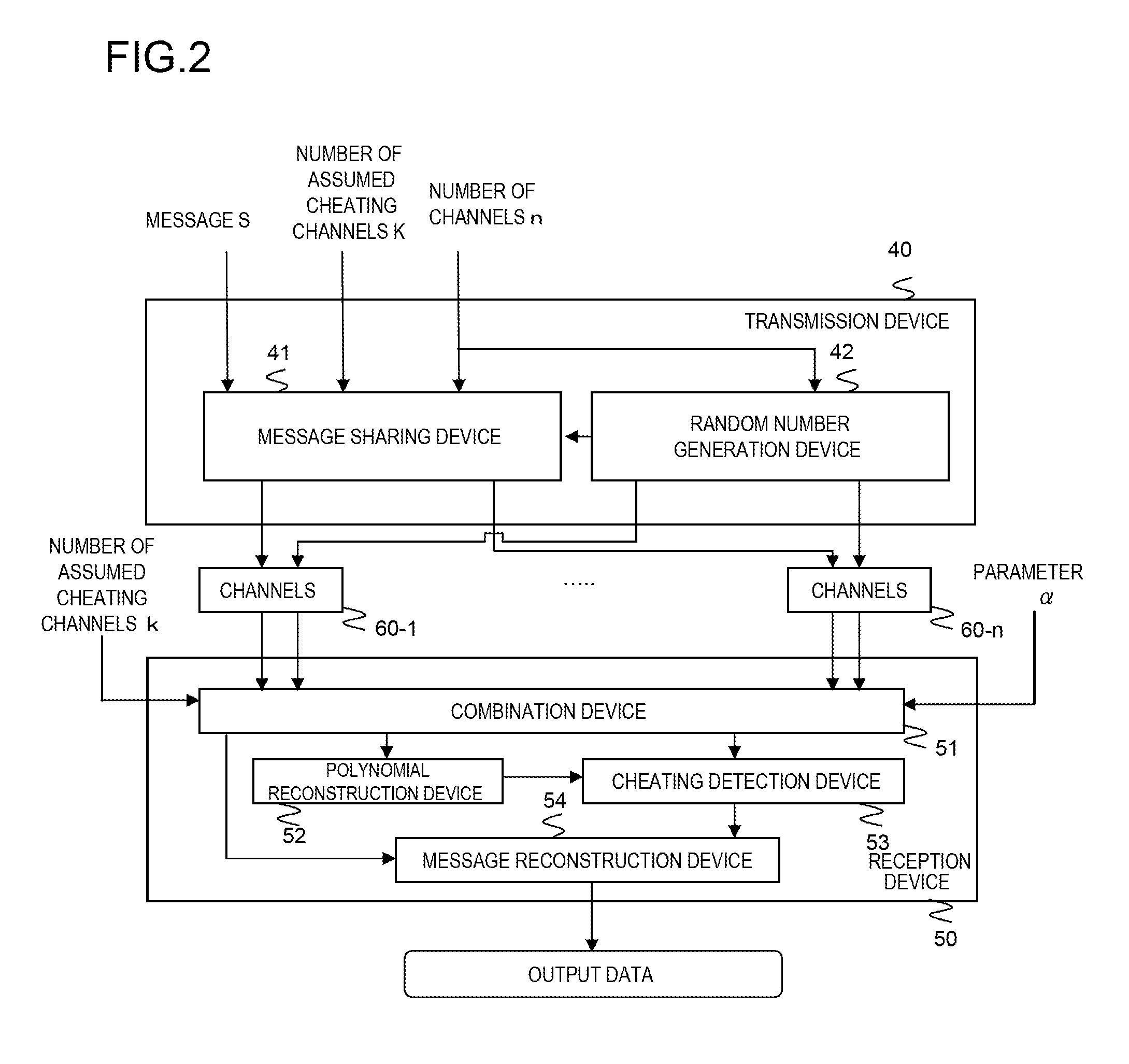
Secret information distribution system, method, program, and transmission system
ActiveUS20110126291A1Efficient detectionDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsAlgorithmRandom array
A secret reconstruction method comprises: receiving (k+α) pairs out of n pairs (ri, fi) each composed of a random number ri and a share fi where α is a natural number (steps B1-B5); determining if a (k−1) degree polynomial g(x) is reconstructed that satisfies fi=g(ri) for all received pairs (steps B5 and B6); and outputting g(0) as the secret if the polynomial is reconstructed and otherwise outputting a signal indicating that at least one of the received pairs is forged (steps B7 and B8).
Owner:NEC CORP
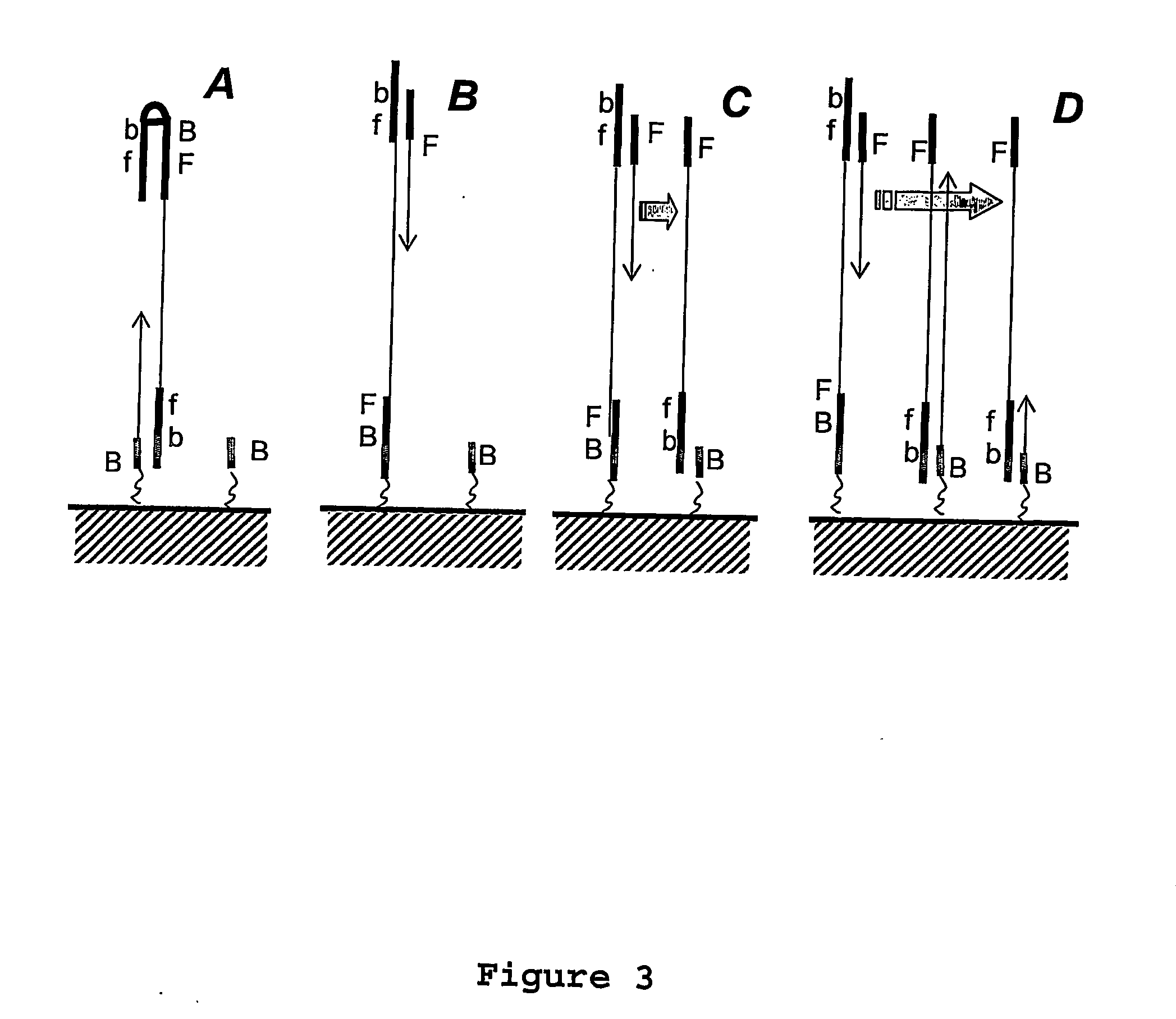
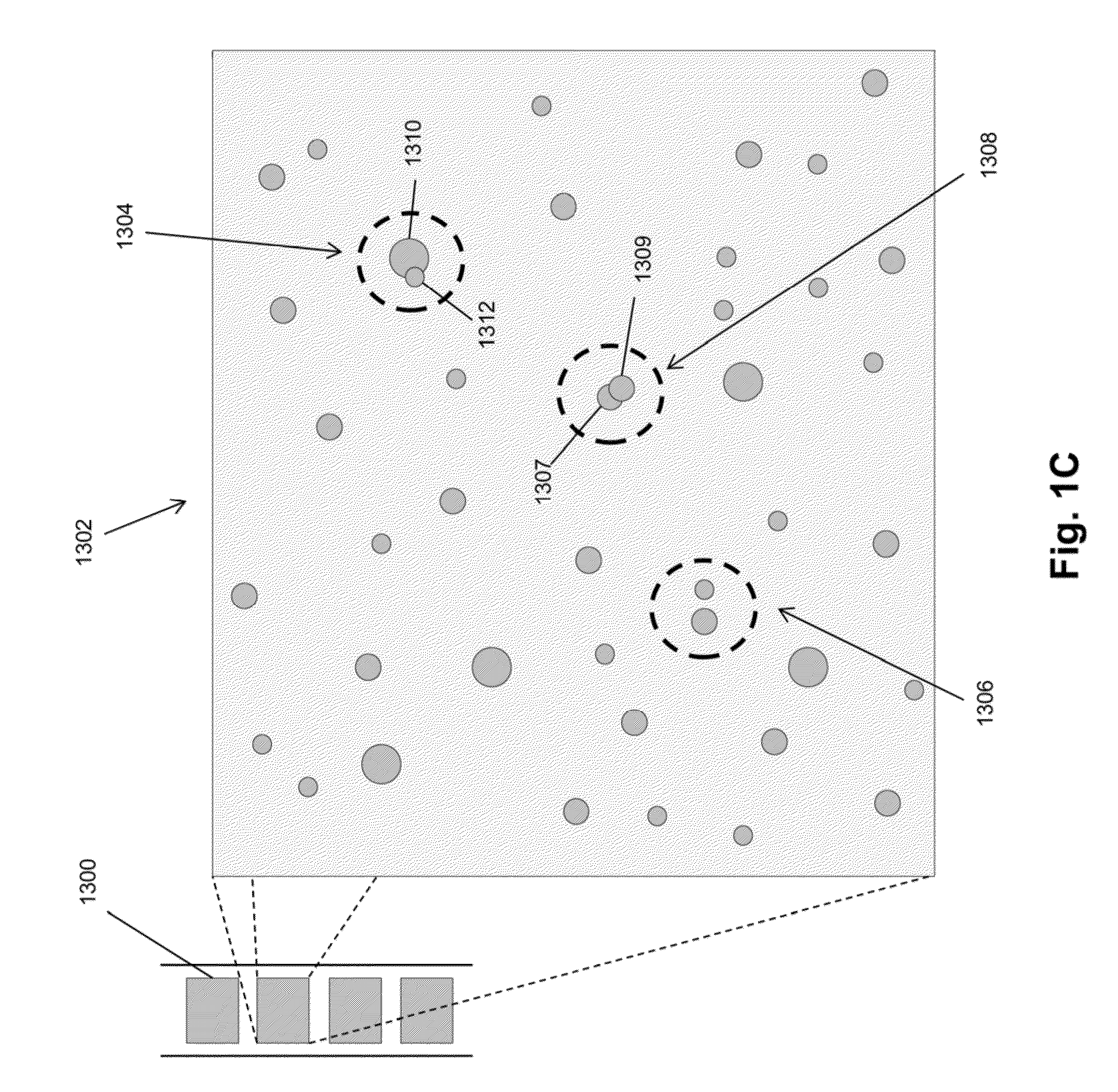
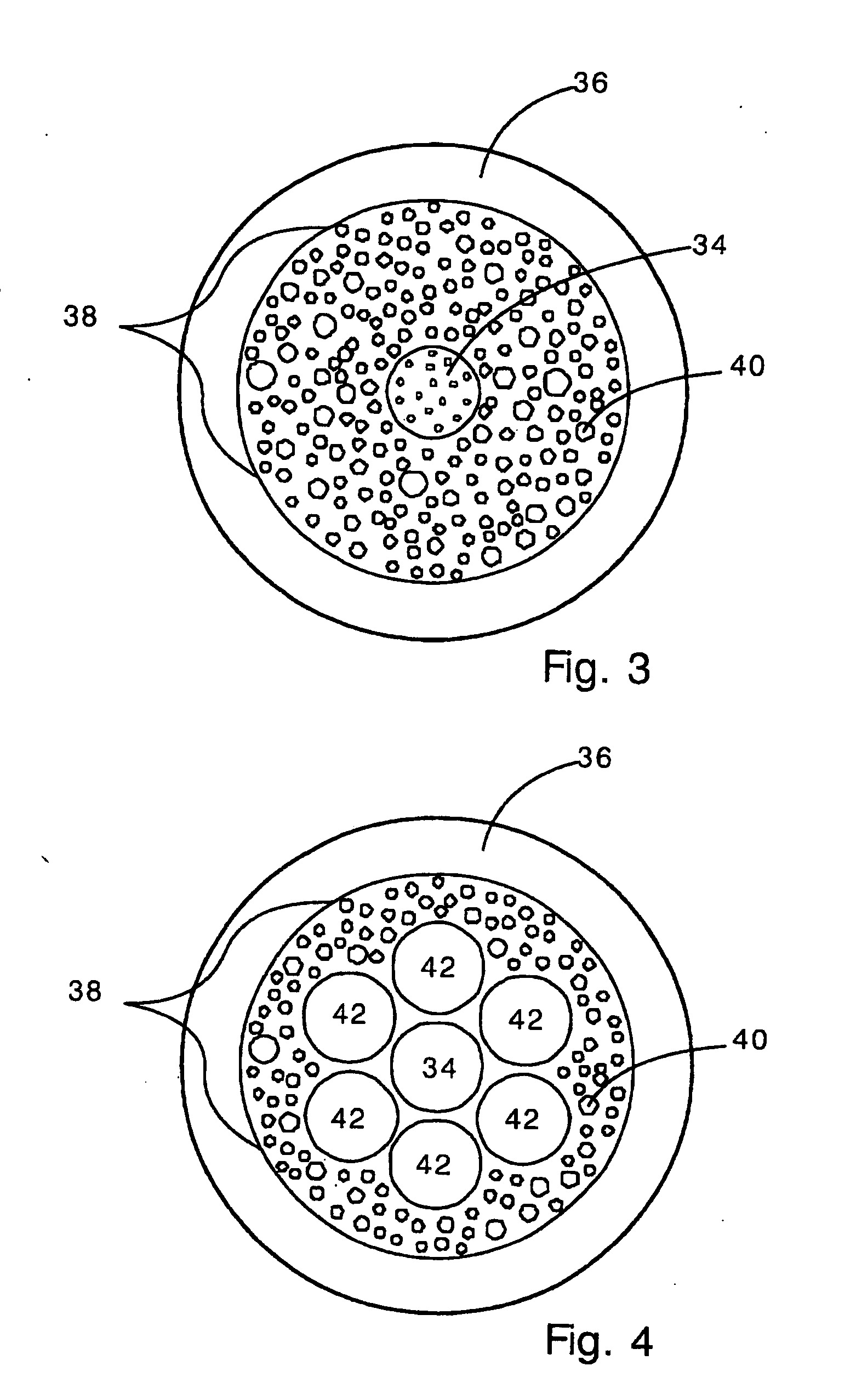
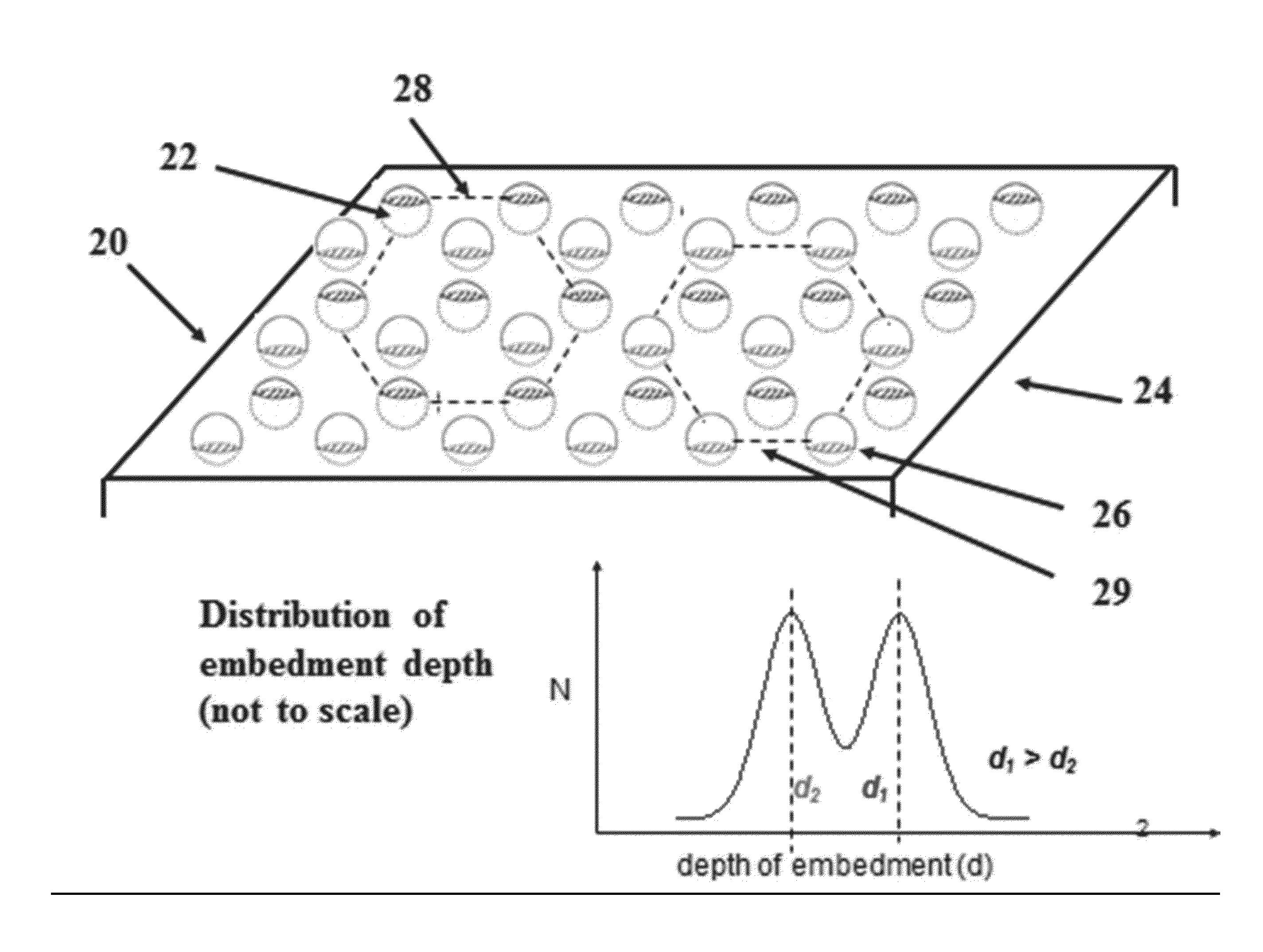
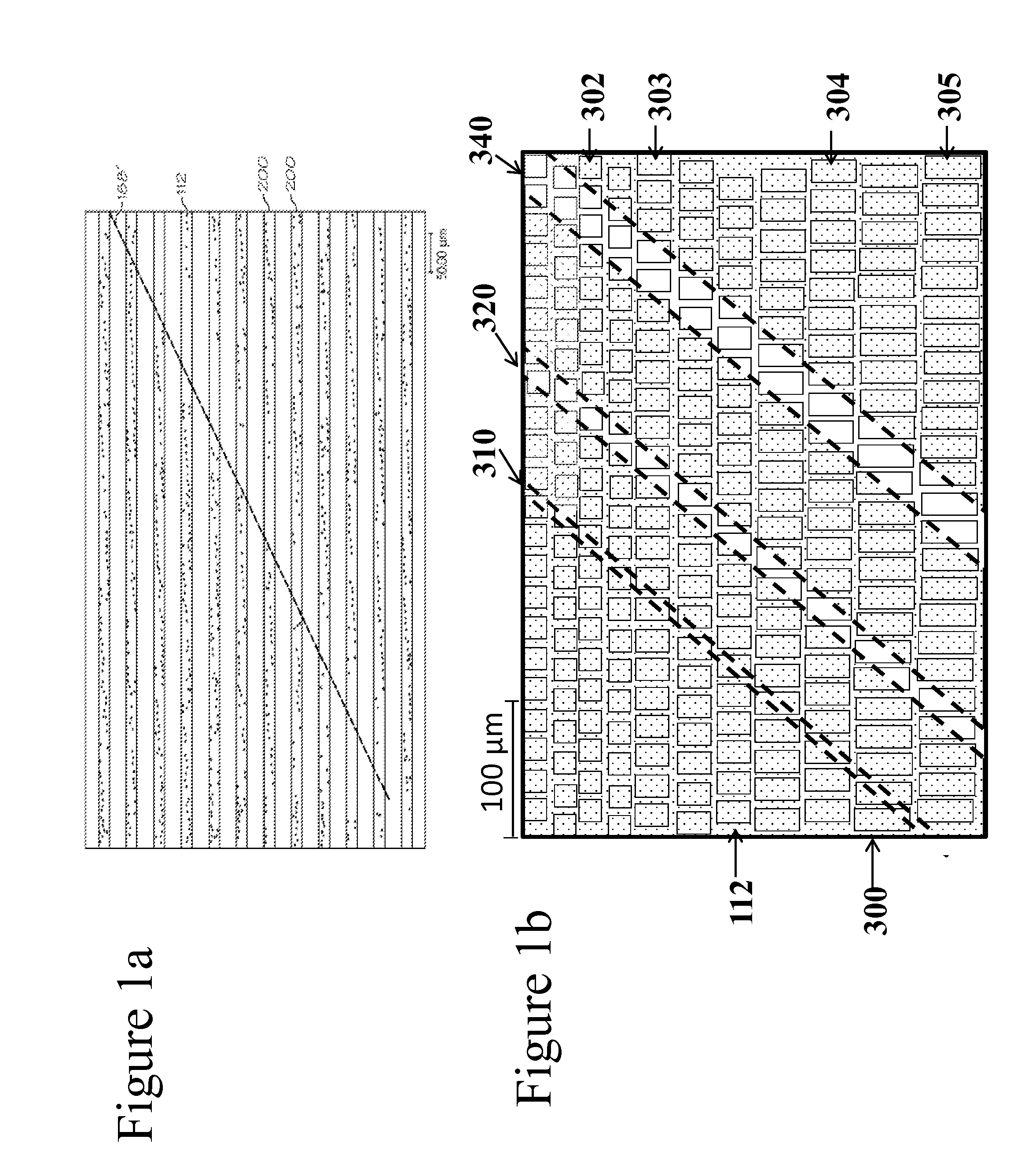
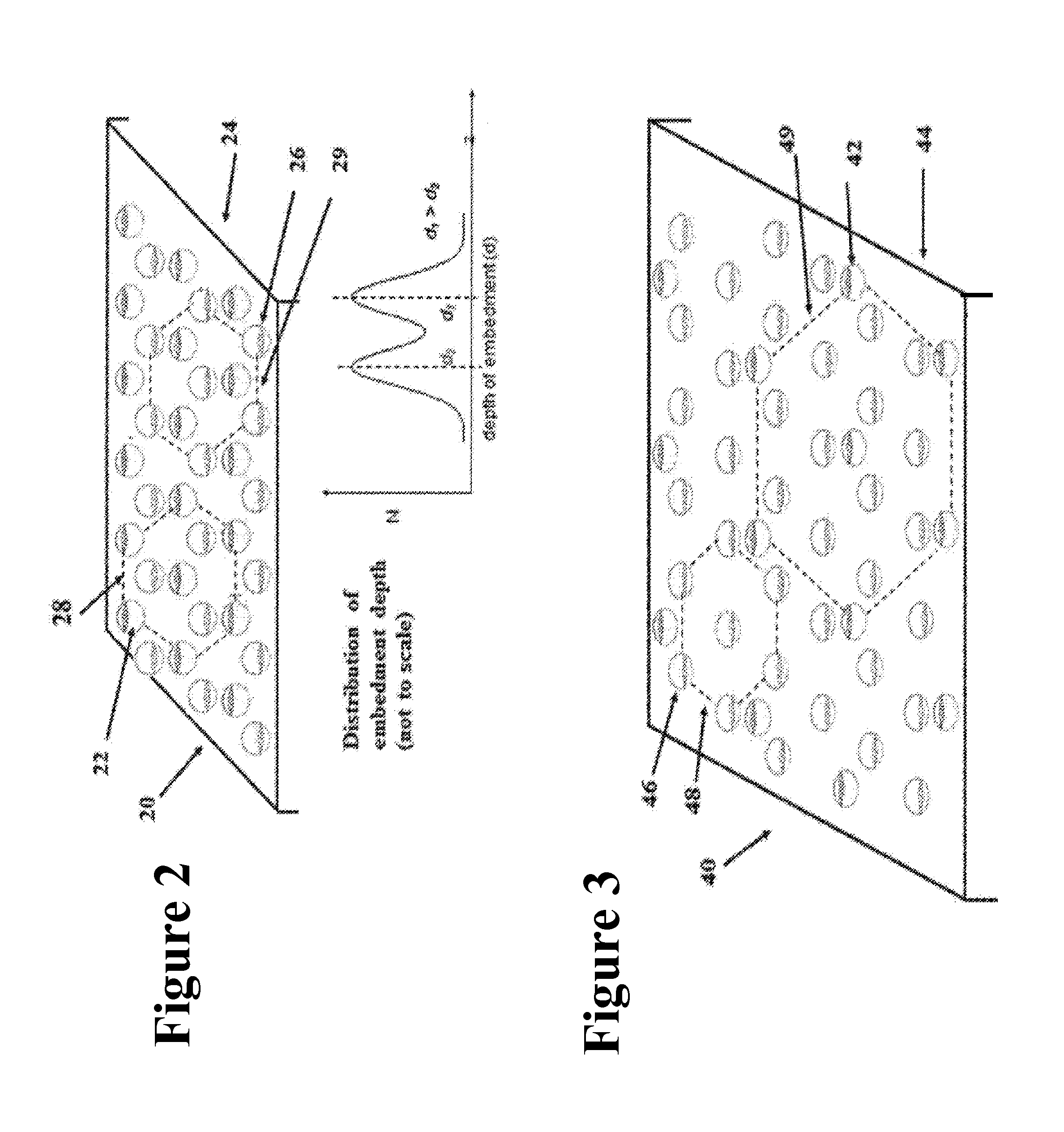
FIXED ARRAY ACFs WITH MULTI-TIER PARTIALLY EMBEDDED PARTICLE MORPHOLOGY AND THEIR MANUFACTURING PROCESSES
InactiveUS20140141195A1Increase catch rateIncrease contact resistanceFilm/foil adhesivesLayered productsAnisotropic conductive filmRandom array
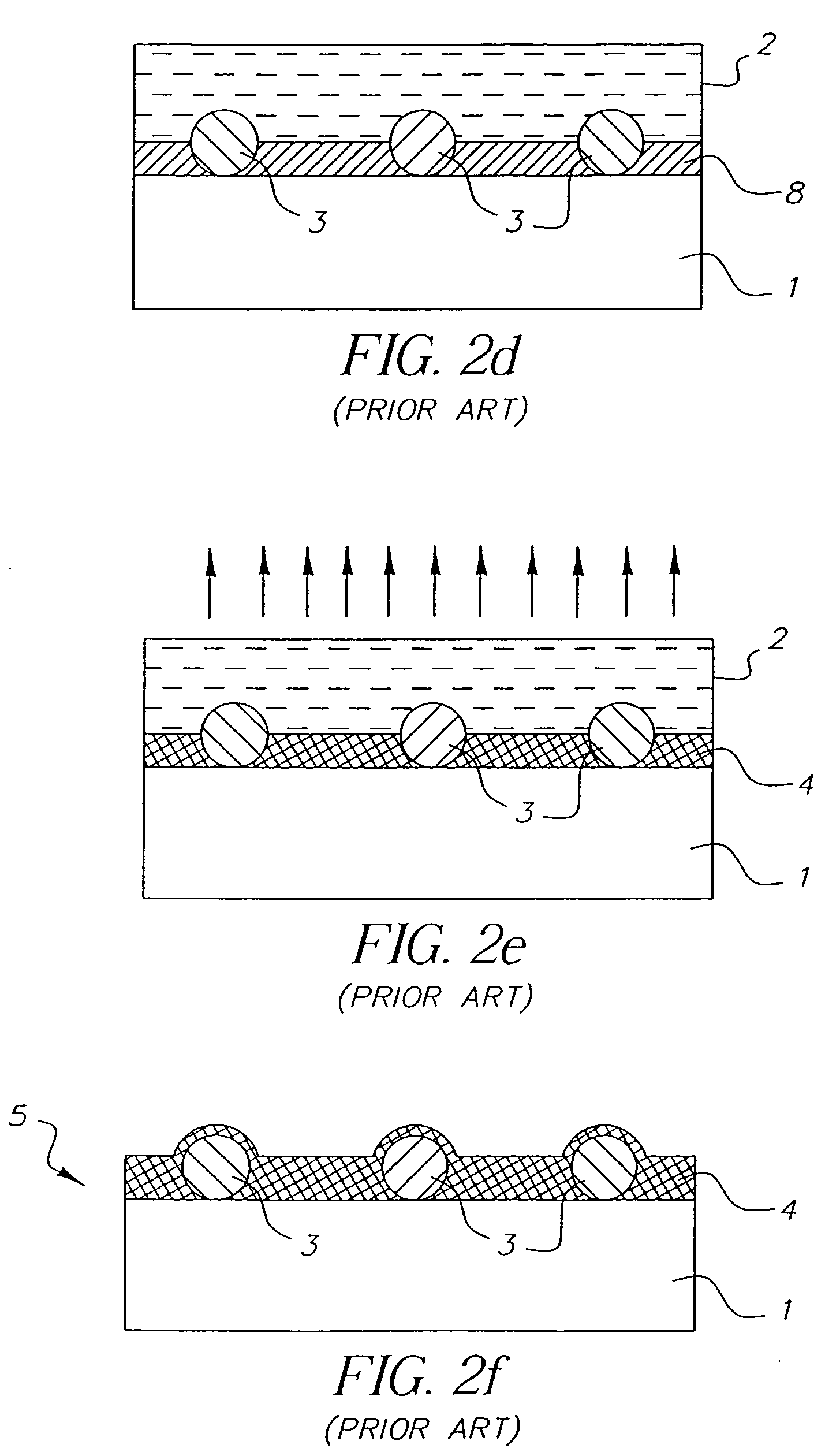
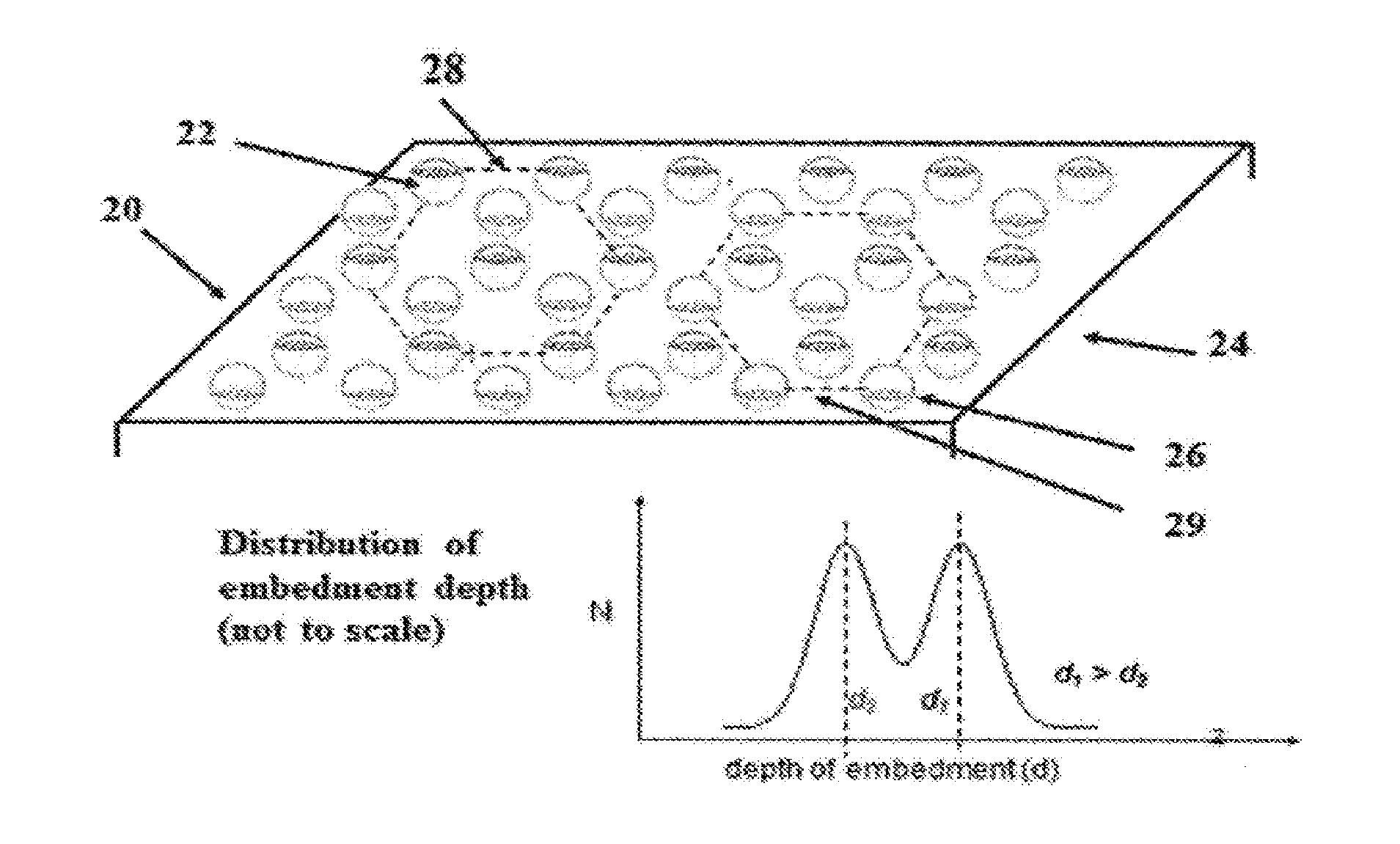
An anisotropic conductive film (ACF) comprising: (a) an adhesive layer having a substantially uniform thickness; and (b) a plurality of conductive particles individually adhered to the adhesive layer, wherein the conductive particles include a first non-random array of particle sites partially embedded at a first depth within the adhesive layer and a second fixed non-random array or dispersion of conductive particles partially embedded at a second depth or a dispersion of conductive particles fully embedded within the adhesive layer, wherein the first depth and the second depth are distinctly different. The ACF may be supplied as a sheet, a continuous film or as a roll and the multi-tier morphology may be present throughout the length of the product or in select areas.
Owner:TRILLION SCI INC
Method for detecting problematic disk drives and disk channels in a RAID memory system based on command processing latency
In order to detect problematic drives in random arrays of independent disks, the system measures the latency of executing command sets which are broadcast to all disks in the data storage system and the results are compared to identify which disks take substantially longer to complete the requests. Disks that take longer to complete requests are likely to be problematic and are candidates for further examination and replacement. The disks in each tier group are compared to determine if any disk in that group exhibits problems. Also, counters for each tier group are compared to determine if the problem is with the disk or with the channel of the tier group. The latency of each disk in the tier group is saved in a table to provide a histogram of the latency of the disks in the tier group. Histograms of the disks in a single tier group are compared to determine if a specific disk is problematic. Histograms of each tier group are compared to determine if a specific disk is problematic or all the disks on the same channel exhibit problems.
Owner:DATADIRECT NETWORKS
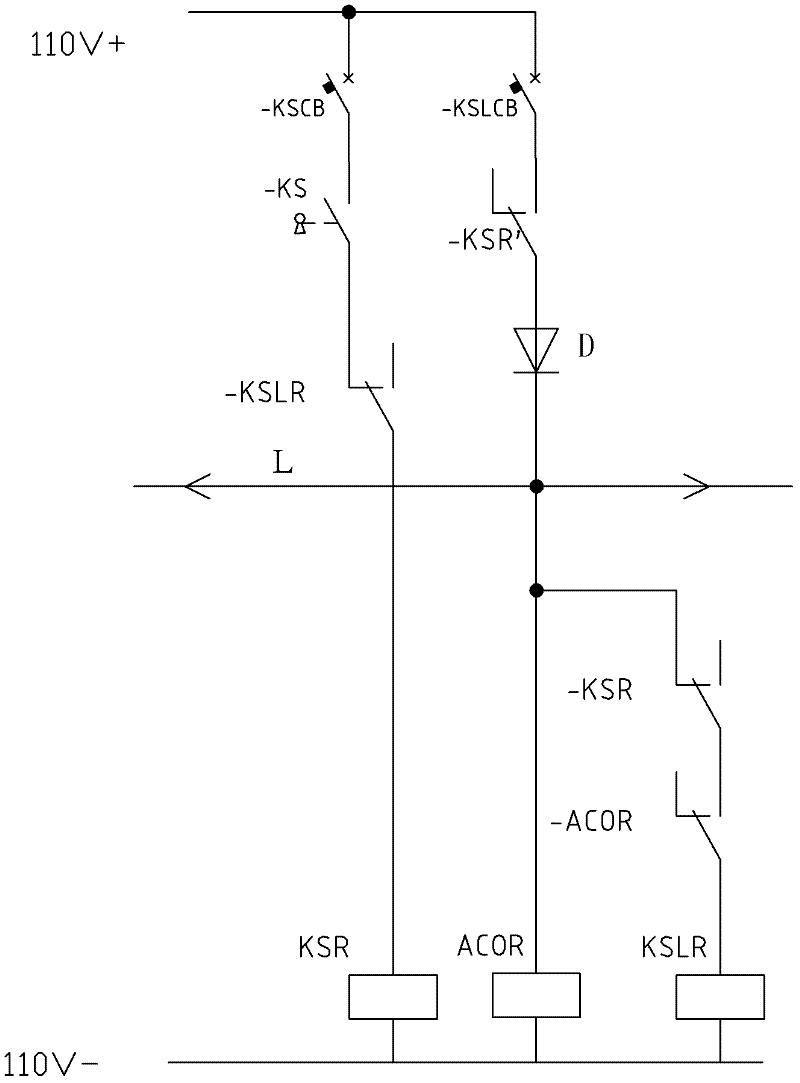
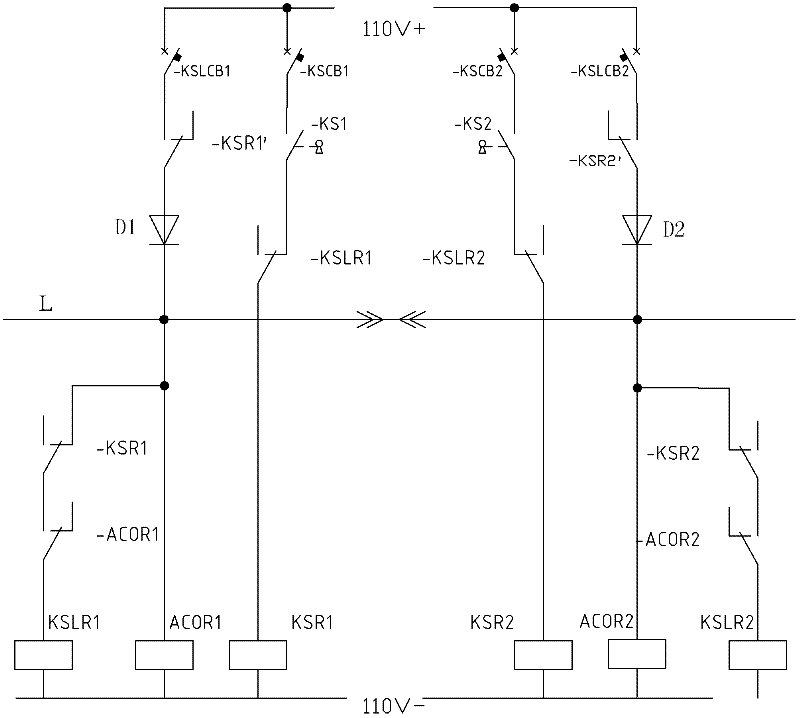
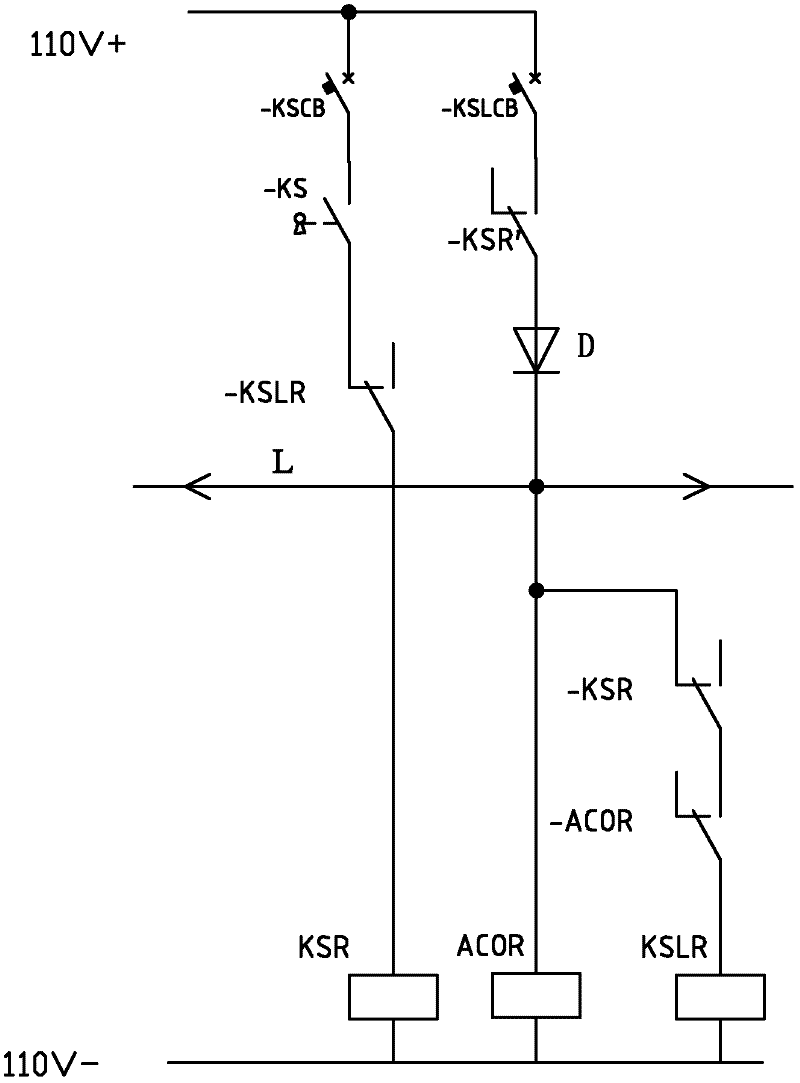
Train cab interlocking and mutual-controlling system based on train line
The invention provides a train cab interlocking and mutual-controlling system based on a train line. The system comprises one train line which penetrates through a train; a cab is internally provided with a key switch, a key relay, a key interlocking relay and an occupation relay, wherein the key switch, a normally-closed contact of the key interlocking relay and the key relay are connected in series and then are switched into a train power grid; the key switch, a normally-opened contact of the occupation relay and the normally-closed contact of the key relay are connected in series and then are connected with the relay in parallel, all of the members are connected with the normally-opened contact of the key relay in series and then are switched into the train power grid; and the train line is connected with a lead wire between the occupation relay and the normally-opened contact of the key relay. The system provided by the invention has an ingenious concept and the interlocking and the mutual-controlling of the cab can be realized by only using one train line, so that the system is beneficial to simplifying design and construction and improving the reliability; according to the system provided by the invention, not only the interlocking and the mutual-controlling of keys of the two cabs in the train are realized, but also the interlocking and the mutual-controlling of the keys of any two cabs can be realized when random arrays of the trains are coupled.
Owner:CRRC NANJING PUZHEN CO LTD
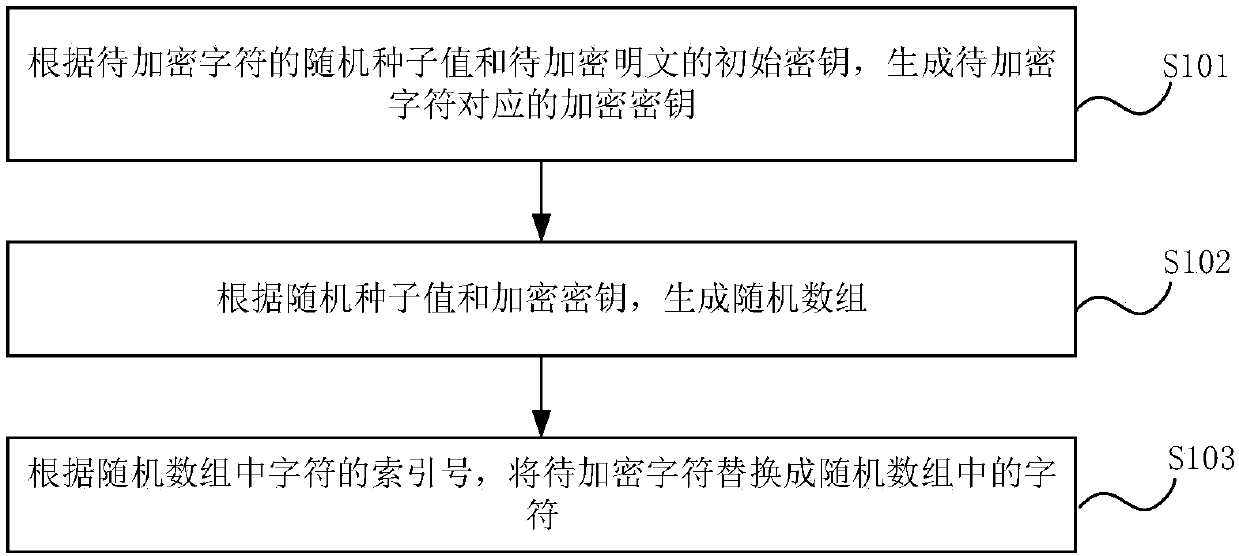
Encryption method and device, equipment and medium
ActiveCN109617680AConsistent byte lengthAvoid misuseKey distribution for secure communicationPlaintextArray data structure
The invention discloses an encryption method and device, equipment and a medium. The encryption method is carried out on each character in a to-be-encrypted plaintext. The encryption method comprisesthe steps of generating an encryption key corresponding to a to-be-encrypted character according to a random seed value of the to-be-encrypted character and an initial key of the to-be-encrypted plaintext; generating a random array according to the random seed value and the encryption key; and replacing the to-be-encrypted character by a character in the random array according to an index number of the character in the random array. According to the embodiments of the invention, byte lengths of a ciphertext and the plaintext are consistent, constraint of a data format is not broken, and when different plaintexts are encrypted, the generated ciphertexts are different, so a data operation error resulting from the same ciphertexts is avoided, and data accuracy is ensured.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GRP FUJIAN CO LTD +1
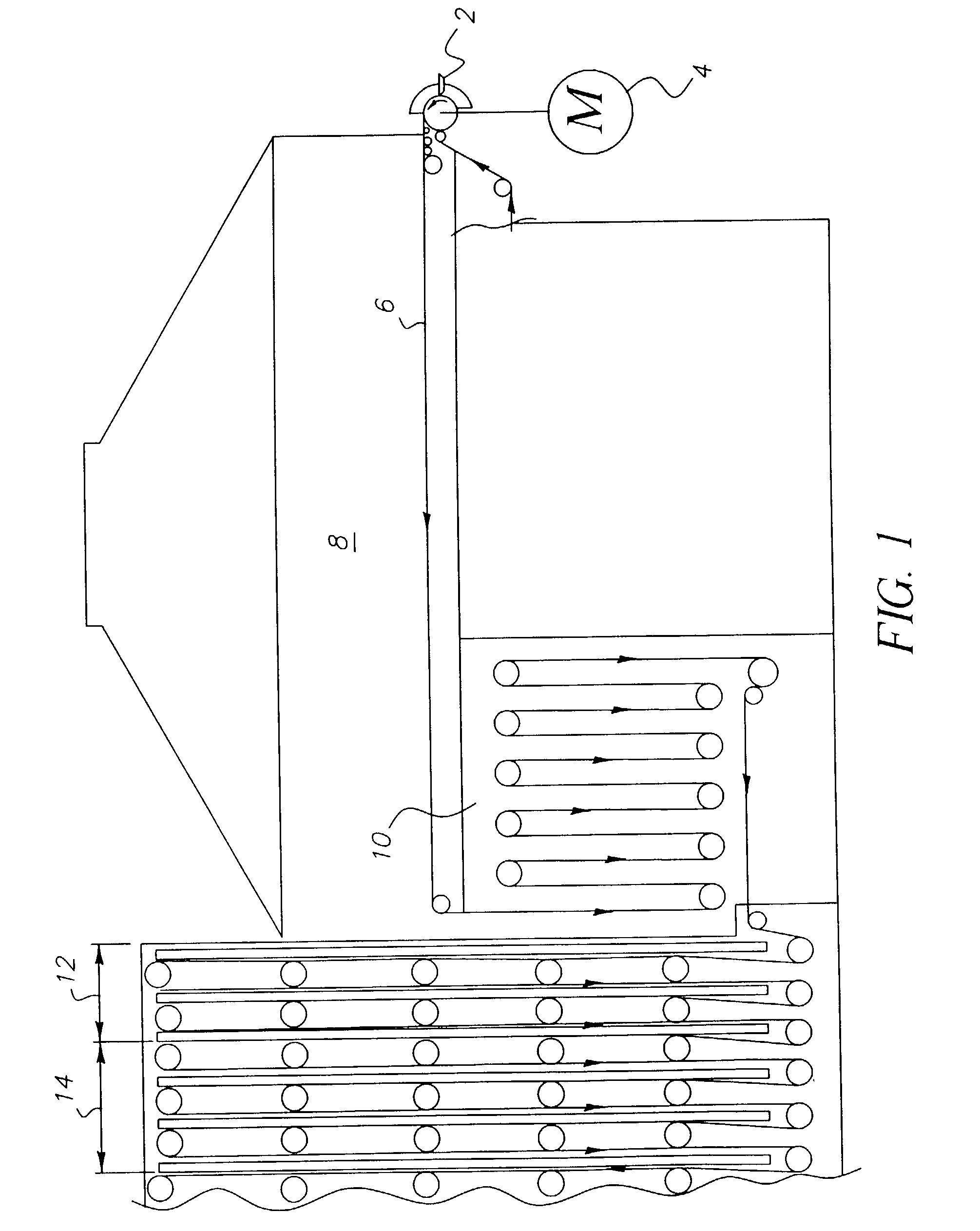
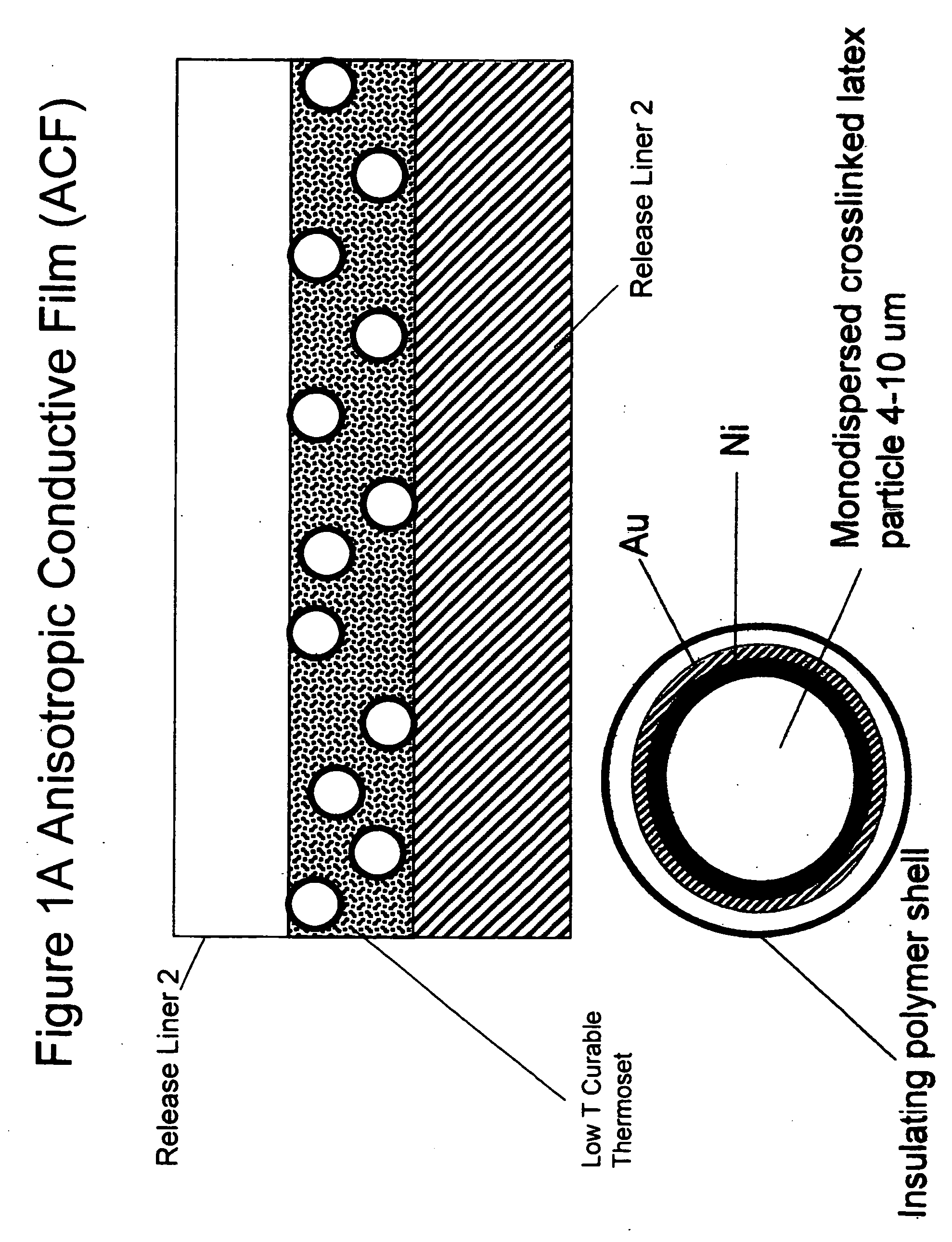
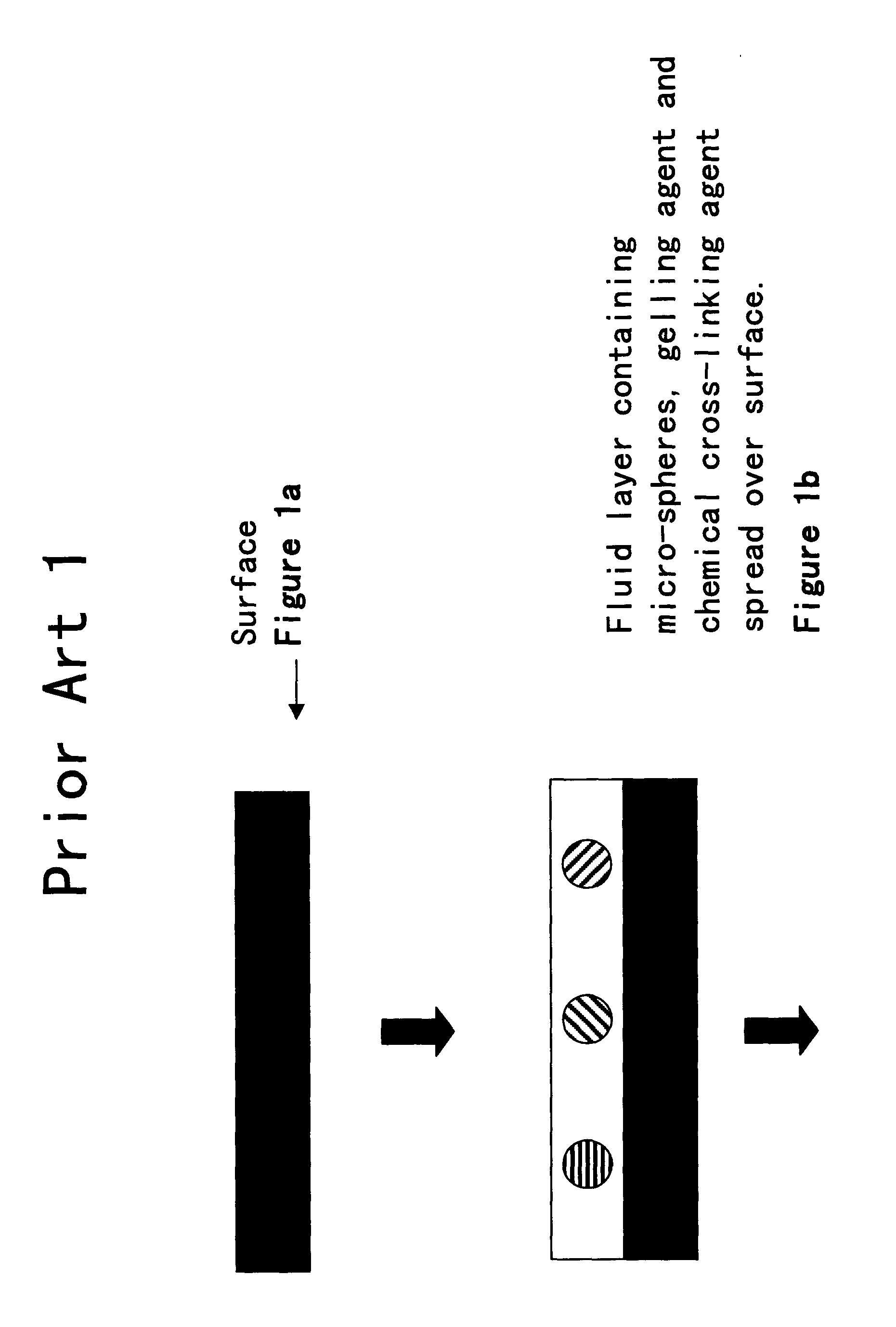
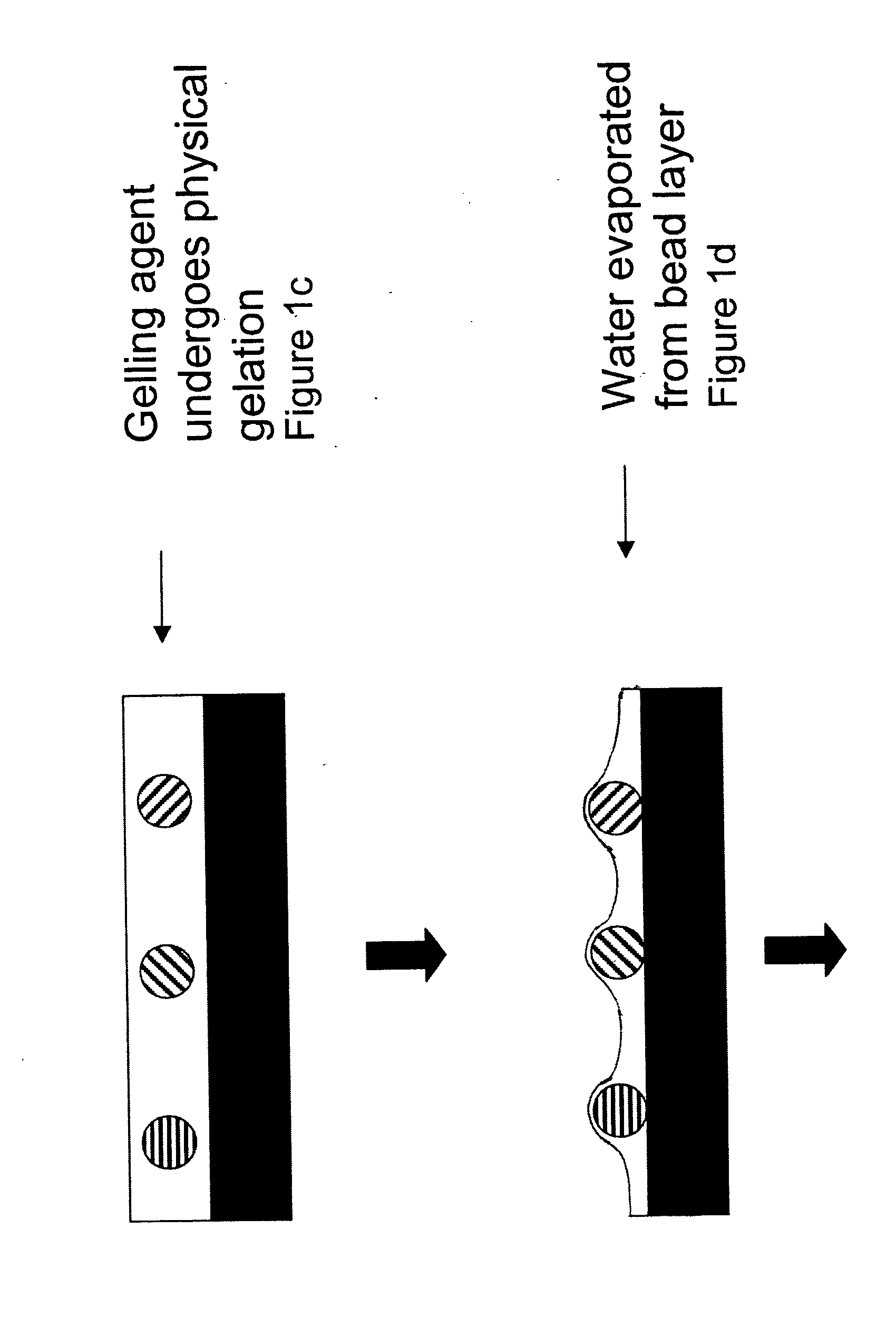
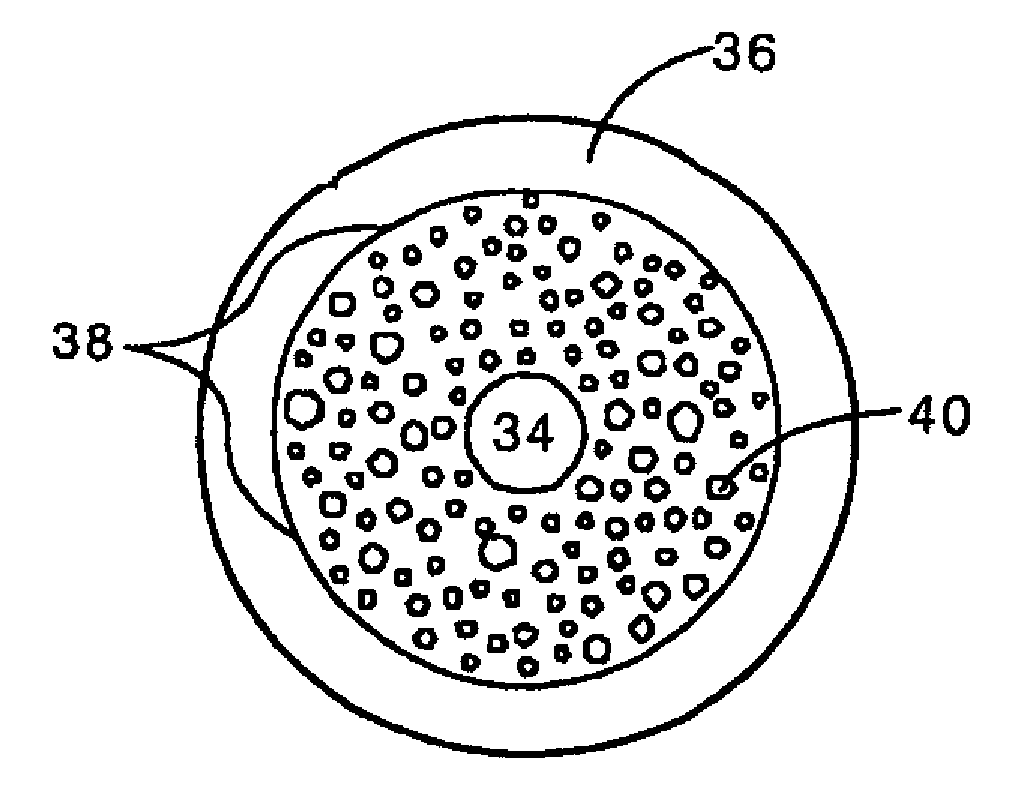
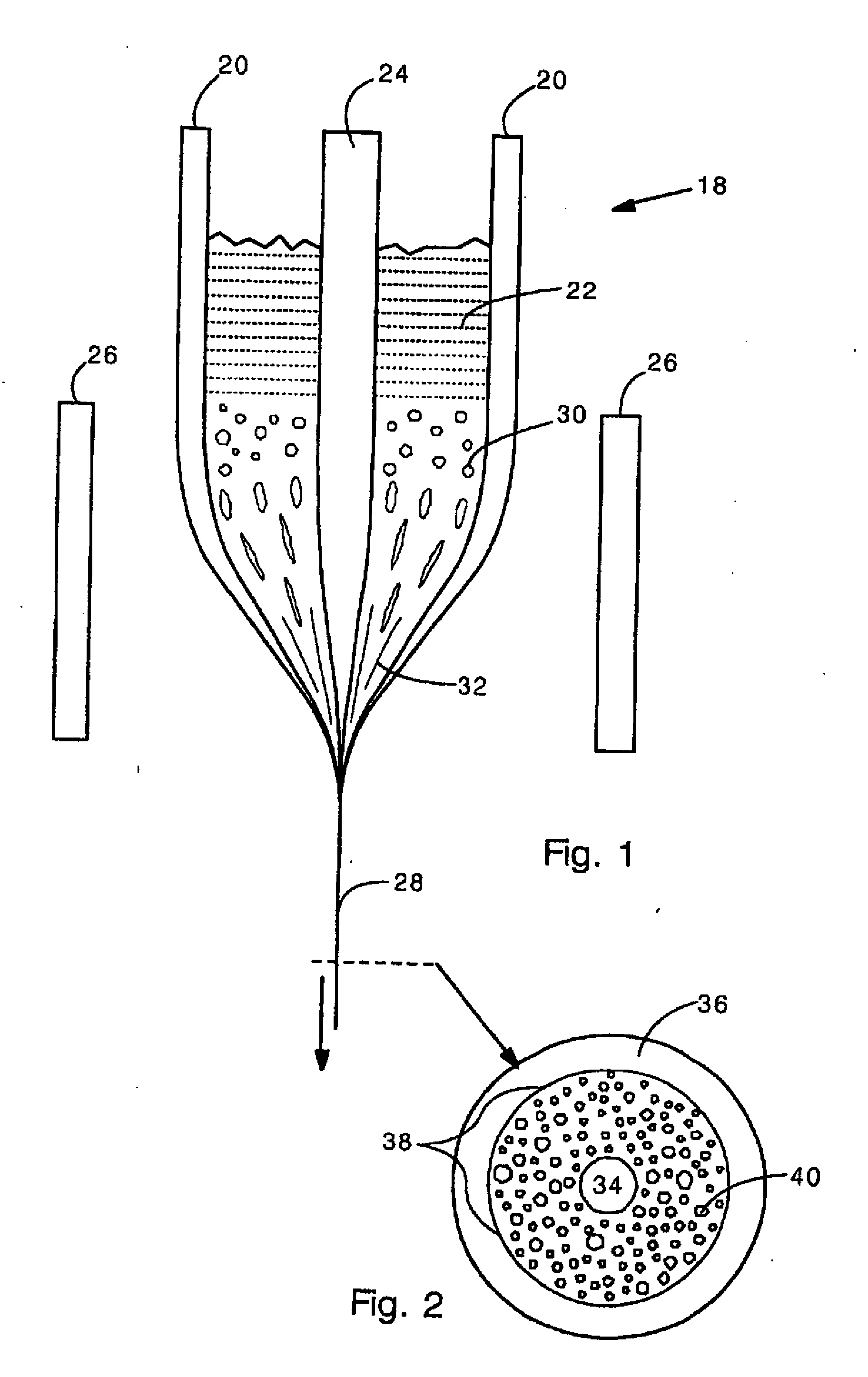
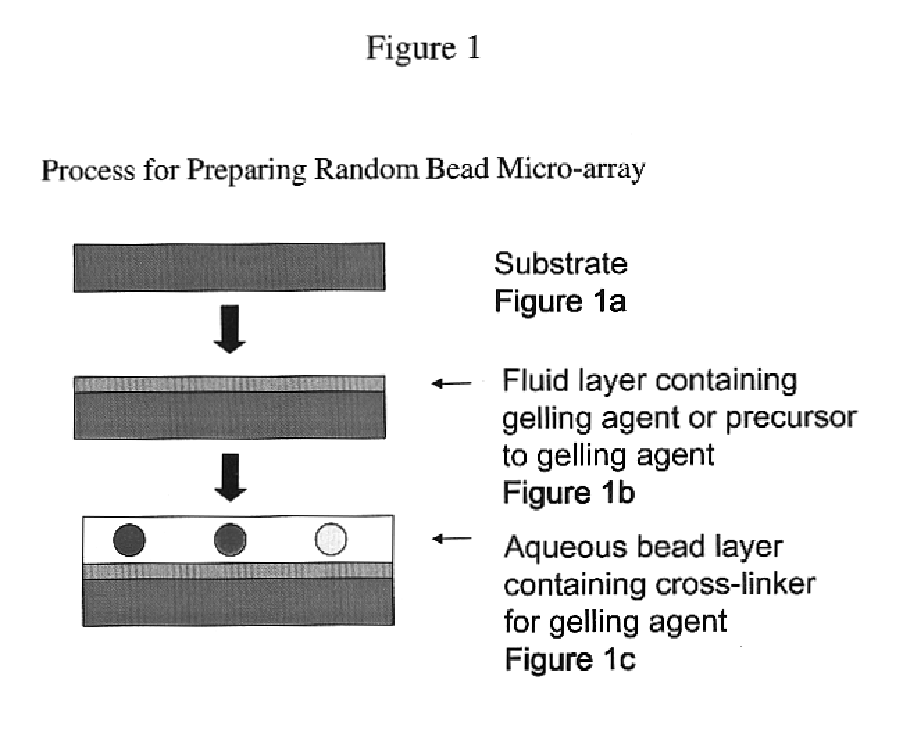
Random array of microspheres
InactiveUS20050019745A1Easy to prepareEasy accessPeptide librariesSequential/parallel process reactionsBiochemical engineeringMicrosphere
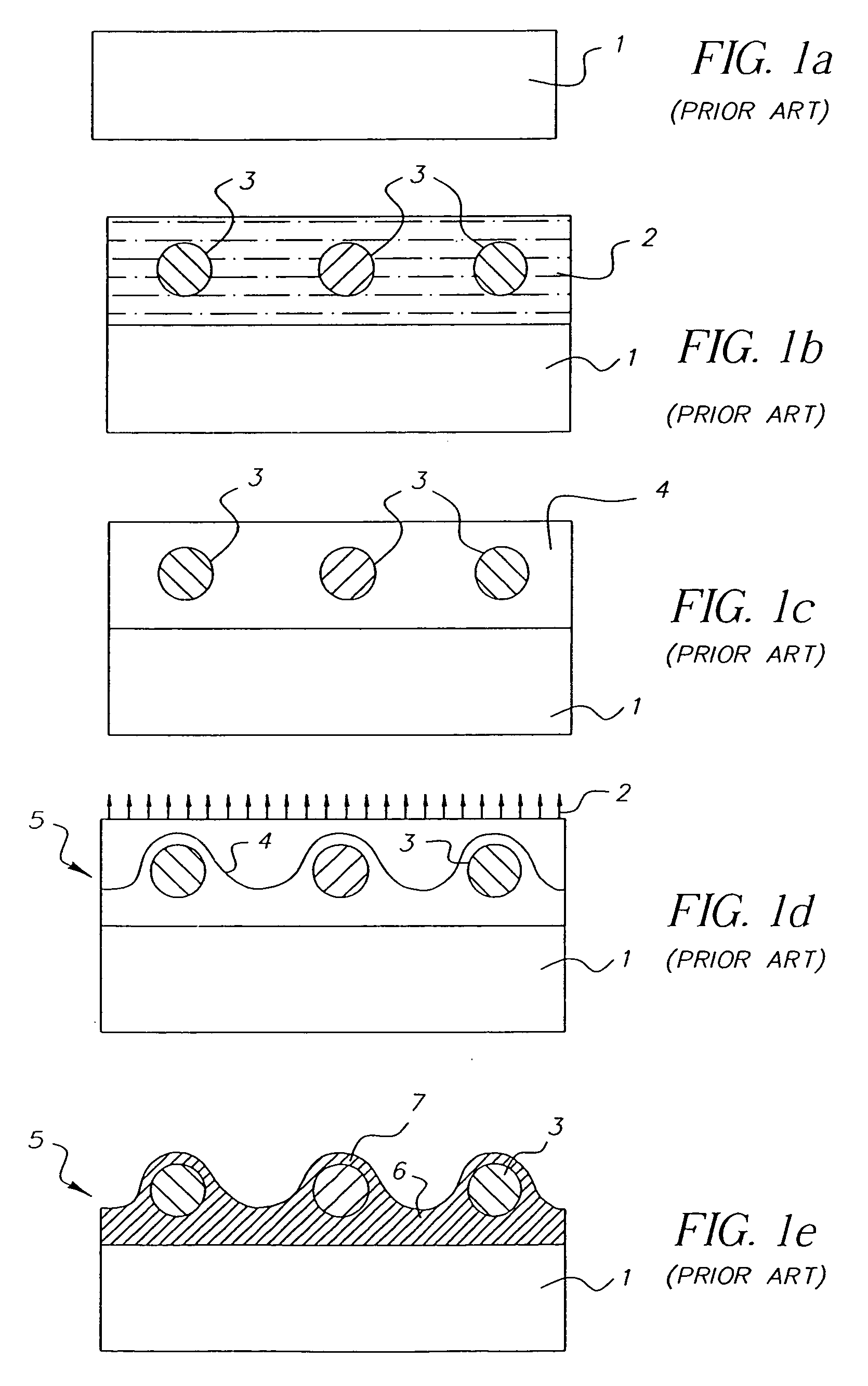
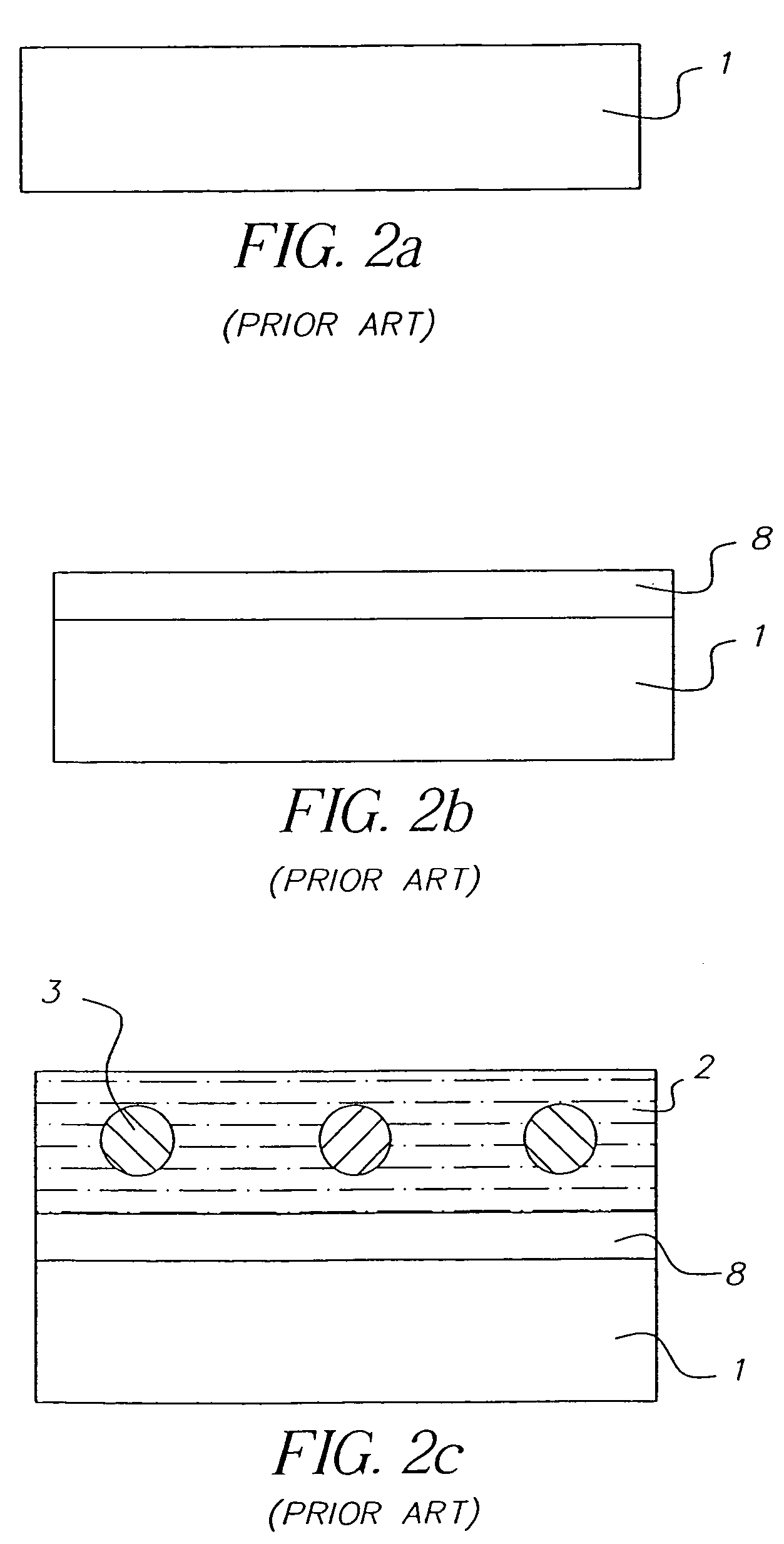
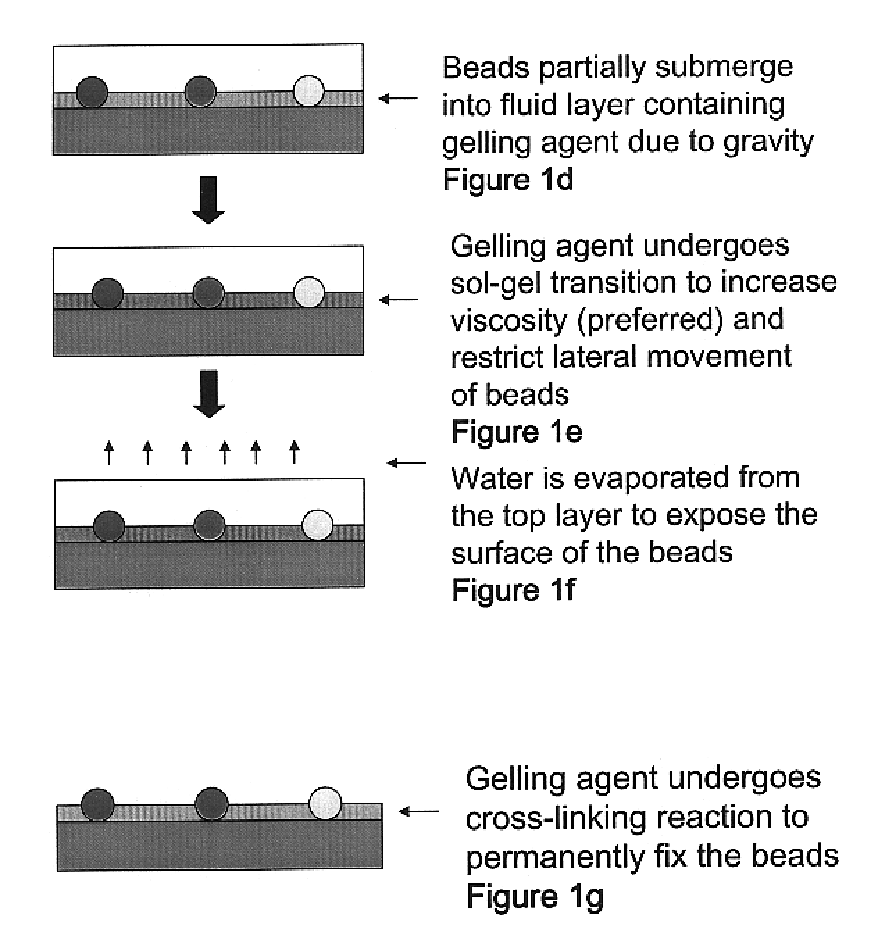
A method for making an element containing an array of microspheres on a support, the method comprising the steps of: coating a support with a coating composition to form a receiving layer with a modifiable elastic modulus; coating on the receiving layer a dispersion of microspheres in a carrier fluid; modifying the modulus to allow the microspheres to partially submerge into the intermediate layer; removing the fluid medium from the suspension of microspheres; and fixing the microspheres on the receiving layer so that the element can withstand wet processing.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Random array of microspheres
InactiveUS20050019804A1Easy to prepareEasy accessBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPeptide librariesMicrosphereRandom array
An element containing an array of microspheres on a support is described, and a method of making the element, wherein the method includes coating a support with a coating composition to form a receiving layer with a modifiable elastic modulus; coating on the receiving layer a dispersion of microspheres in a fluid suspension; modifying the modulus of the receiving layer to allow the microspheres to partially submerge into the receiving layer; removing the fluid suspension from the receiving layer; and fixing the microspheres in the receiving layer so that the element can withstand wet processing.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
FIXED ARRAY ACFs WITH MULTI-TIER PARTIALLY EMBEDDED PARTICLE MORPHOLOGY AND THEIR MANUFACTURING PROCESSES
ActiveUS20150240130A1Increase catch rateIncrease contact resistanceFilm/foil adhesivesLayered productsRandom arrayAdhesive
An ACF comprising a substrate, a layer of an adhesive on the surface of the substrate, the adhesive optionally having conductive particles dispersed therein, at least one tier of conductive particles arranged in a non-random array, the tier being formed by transfer of conductive particles from a carrier belt having a stitching line to the surface of the adhesive layer wherein the portion of the tier corresponding to the stitching line is free of conductive particles, and the adhesive layer being overcoated with a second tier of conductive particles arranged in a non-random array at least in the area of the first tier corresponding to the stitching line. The tiers may be at the same or different depths within the adhesive layer. More than two tiers of conductive particles may be present in the ACF.
Owner:POLAROID IP BV
Holey optical fiber with random pattern of holes and method for making same
A random array of holes is created in an optical fiber by gas generated during fiber drawing. The gas forms bubbles which are drawn into long, microscopic holes. The gas is created by a gas generating material such as silicon nitride. Silicon nitride oxidizes to produce nitrogen oxides when heated. The gas generating material can alternatively be silicon carbide or other nitrides or carbides. The random holes can provide cladding for optical confinement when located around a fiber core. The random holes can also be present in the fiber core. The fibers can be made of silica. The present random hole fibers are particularly useful as pressure sensors since they experience a large wavelength dependant increase in optical loss when pressure or force is applied.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Feather point matching method based on colored false random coding projection
InactiveCN101763654AOvercome isolationOvercome the shortcomings that all connections will hinder decodingImage coding3D modellingShift registerTheoretical computer science
The invention belongs to the filed of image matching of coding structured light active visual sense in machine visual sense, in particular to a feather point matching method based on the colored false random coding projection. The invention is based on a false random coding principle, and designs a novel colored coding projection template by using a point and line combined method. The method comprises the following concrete steps: 1. generating a false random sequence from a0, a1 to an by a feedback network n-displacement bit register specified by a primitive polynomial h(x)=xm+hm-1xm-1+...+h1x+h0; 2. filling the false random sequence from a0, a1 to an into a matrix with the size of n=n1*n2 for generating a false random array b; and 3. using the generated array values as the discrete feather points, connecting the feather points by a feather line, and establishing a coding template. The invention introduces a morphological algorithm, and provides the extraction algorithm of the relevant feather points. In the decoding process, the invention provides the thought of mutual verification of adjacent windows, can realize the automatic extraction and matching of the feature points, and can perfectly solve the problem of shadow generation during the projection of the structural light on the surface of the complicated three-dimensional scenes and the problem of mistake feather point matching caused by that parts of coding patterns are covered because the shooting angles of a video camera are different.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Encoded random arrays and matrices
InactiveUS7156315B2Easy to disassembleProcess can be minimizedSequential/parallel process reactionsComponent separationParticulatesArray data structure
A method and apparatus for the manipulation of colloidal particulates and biomolecules at the interface between an insulating electrode such as silicon oxide and an electrolyte solution. Light-controlled electrokinetic assembly of particles near surfaces relies on the combination of three functional elements: the AC electric field-induced assembly of planar aggregates; the patterning of the electrolyte / silicon oxide / silicon interface to exert spatial control over the assembly process; and the real-time control of the assembly process via external illumination. The present invention provides a set of fundamental operations enabling interactive control over the creation and placement of planar arrays of several types of particles and biomolecules and the manipulation of array shape and size. The present invention enables sample preparation and handling for diagnostic assays and biochemical analysis in an array format, and the functional integration of these operations. In addition, the present invention provides a procedure for the creation of material surfaces with desired properties and for the fabrication of surface-mounted optical components. The invention is also for a system and method for programmable illumination pattern generation, including a novel method and apparatus to generate patterns of illumination and project them onto planar surfaces or onto planar interfaces such as the interface formed by an electrolyte-insulator-semiconductor (EIS), e.g., as described herein. This enables the creation of patterns or sequences of patterns using graphical design or drawing software on a personal computer and the projection of said patterns, or sequences of patterns (“time-varying patterns”), onto the interface using a liquid crystal display (LCD) panel and an optical design which images the LCD panel onto the surface of interest. The use of the LCD technology provides flexibility and control over spatial layout, temporal sequences and intensities (“gray scales”) of illumination patterns. The latter capability permits the creation of patterns with abruptly changing light intensities or patterns with gradually changing intensity profiles.
Owner:BIOARRAY SOLUTIONS
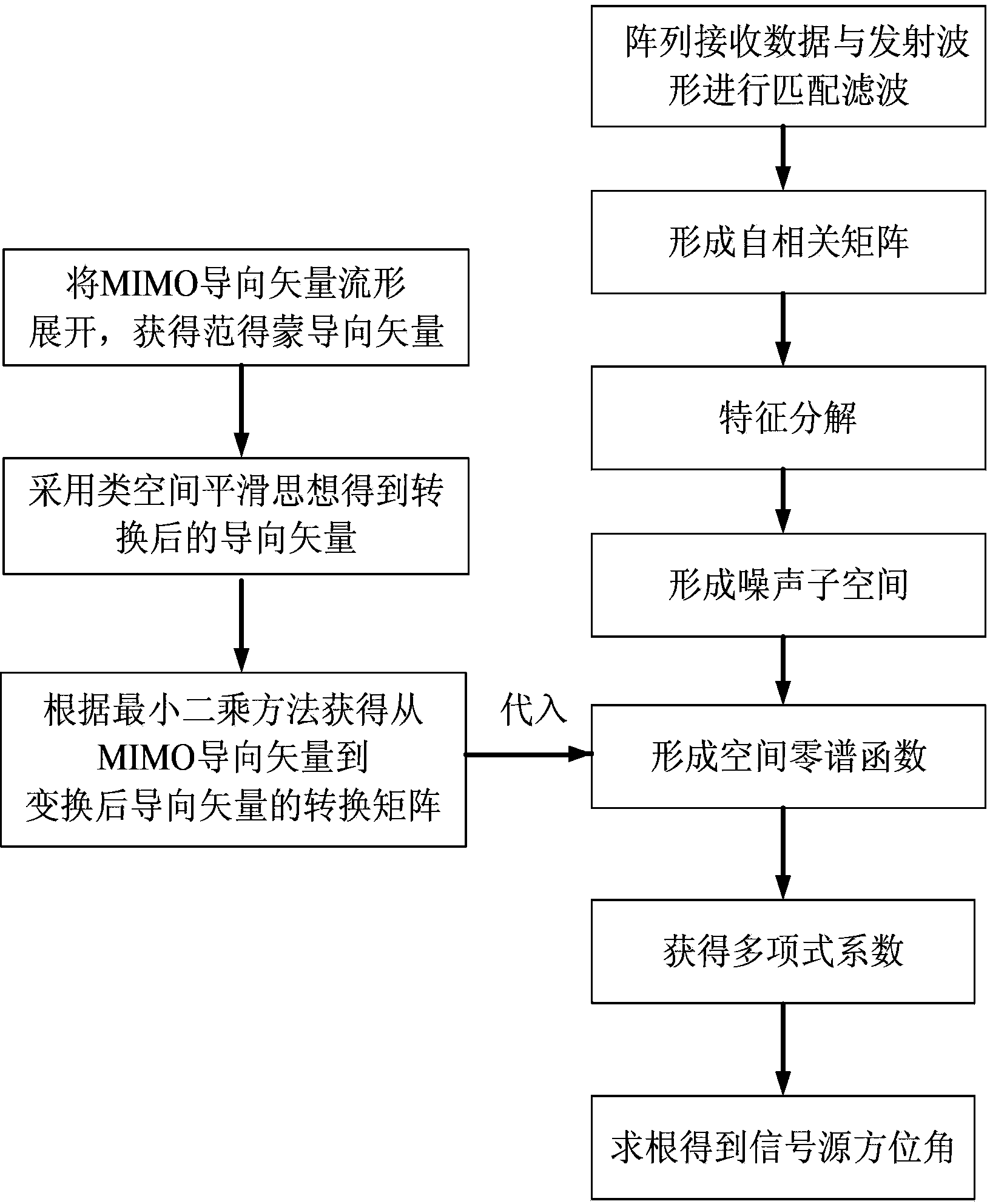
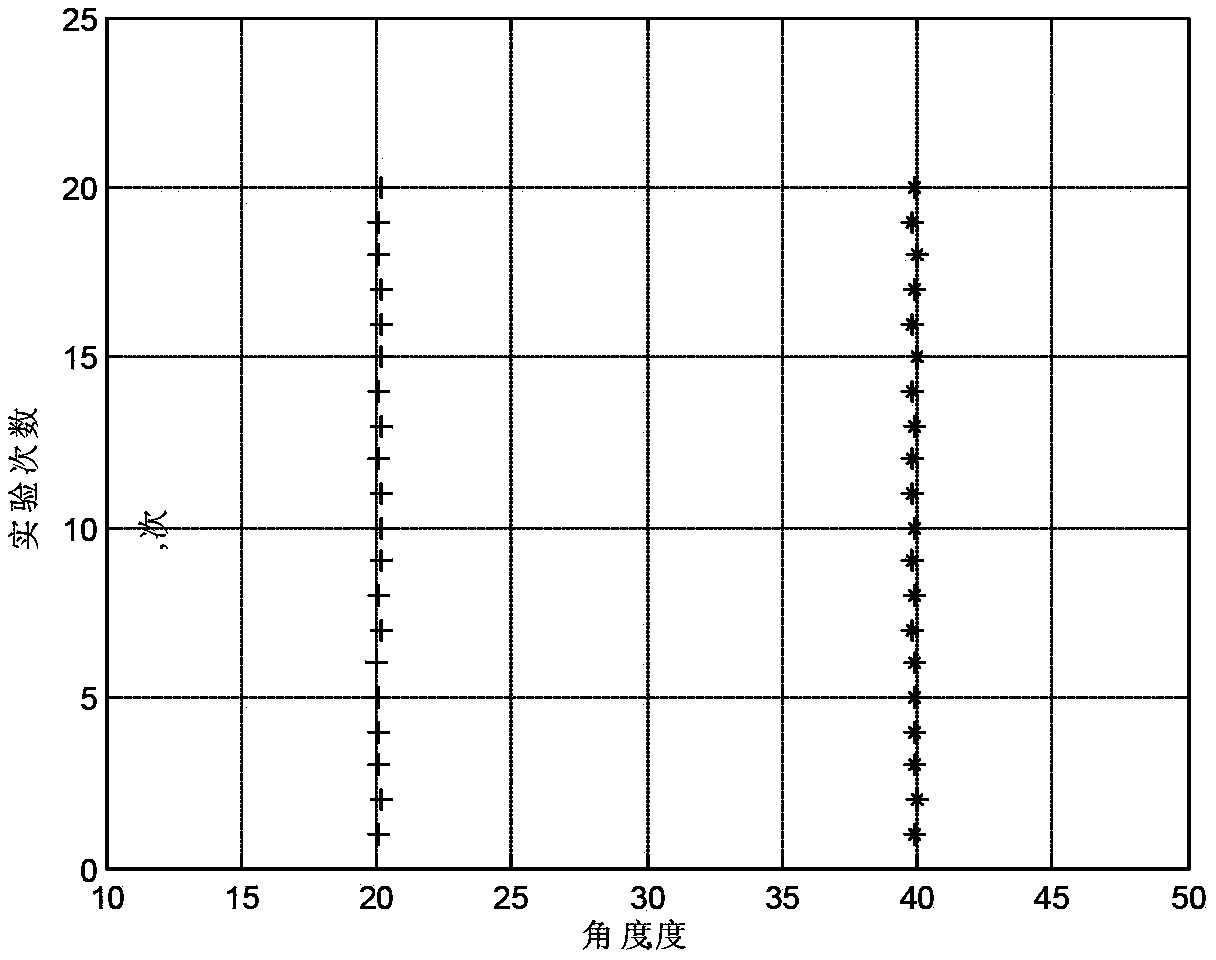
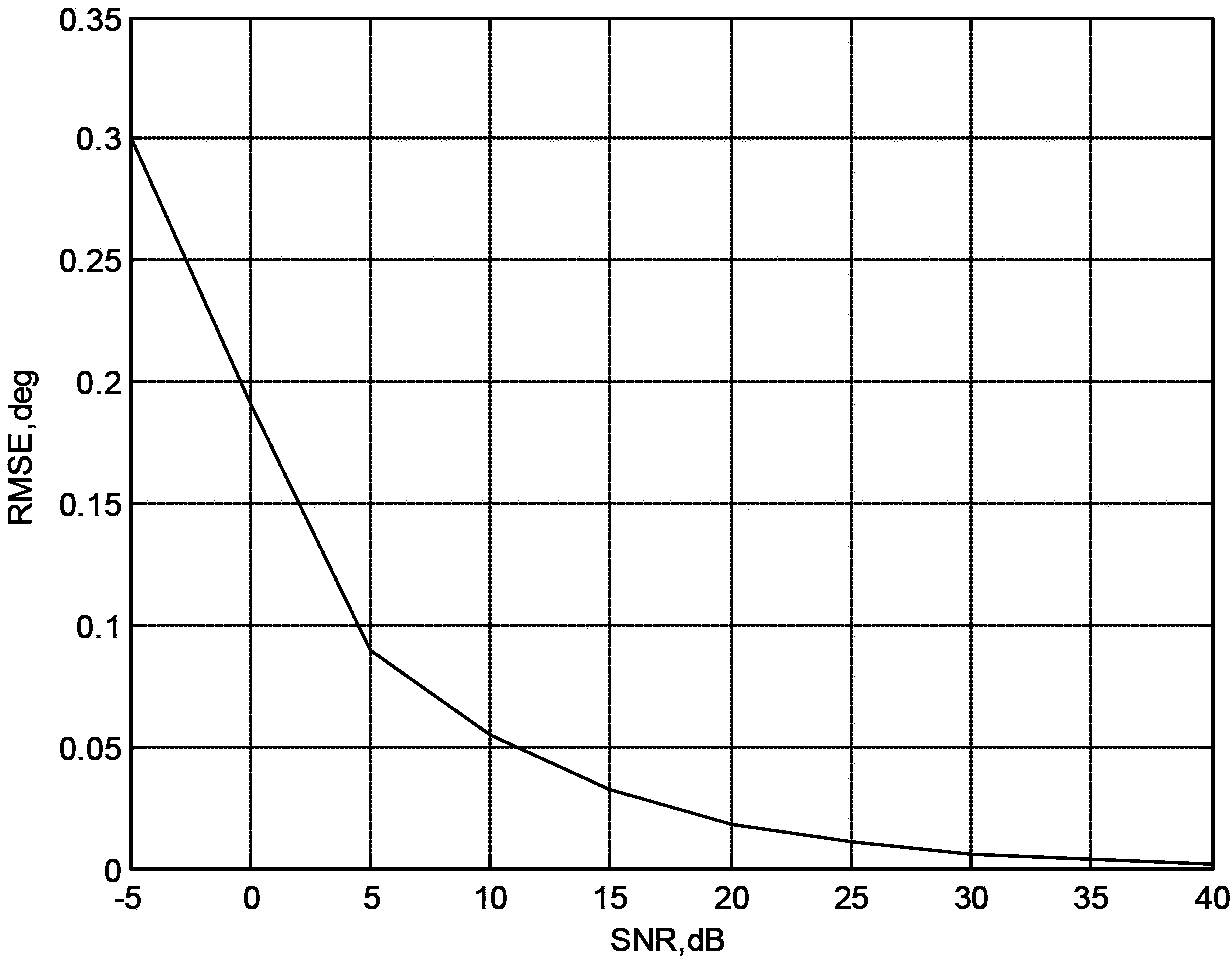
Estimation method for arriving direction of monostatic MIMO radar based on random array manifolds
The invention discloses an estimation method for the arriving direction of a monostatic MIMO radar based on random array manifolds. The method mainly solves the problems that an existing technology is only suitable for linear arrays and large in calculated quantity. The method comprises the steps that 1) the guide vector quantity of the monostatic MIMO radar is written according to the array manifolds; 2) manifold spreading is carried out on the guide vector quantity of the MIMO radar to obtain the Vandermonde guide vector quantity, guide vector quantity transfer is conducted by means of a spatial smoothing thought, and a transfer matrix from the MIMO guide vector quantity to the guide vector quantity after transfer is evaluated; 3) a receiving array and a transmitted waveform are utilized to carry out matched filtering to form an autocorrelation matrix; 4) characteristic decomposition is conducted on the autocorrelation matrix to obtain an eigenvalue and an eigenvector, and the eigenvector is selected to form a noise subspace; 5) the noise subspace is used for forming a space zero spectral function, and a polynomial rooting method is adopted to obtain an azimuth angle. The method can achieve quick estimation on the arriving direction of the monostatic MIMO radar based on the random array manifolds, is small in operation quantity, and can be used for target locating and radar tracking.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Physical unclonable function response error correcting circuit based on SRAM type memory
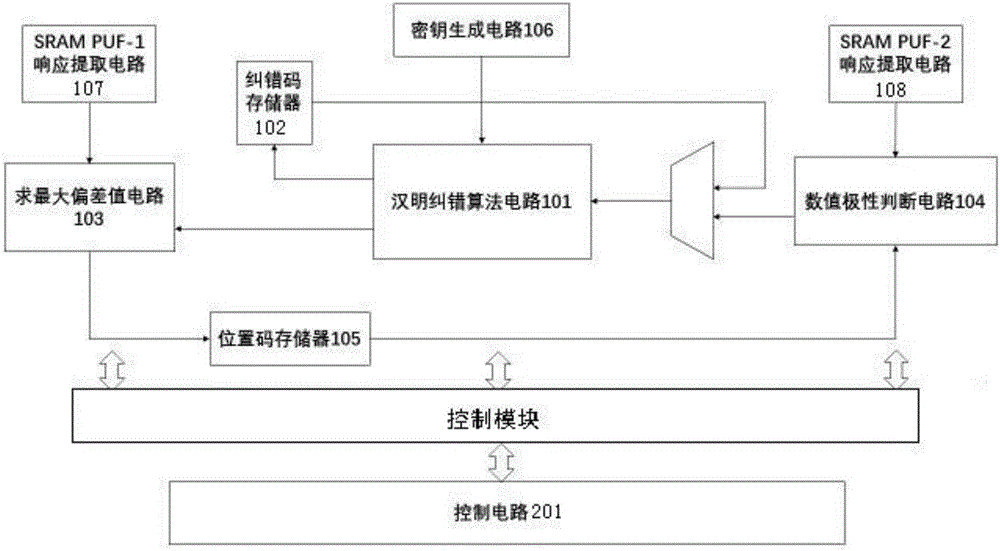
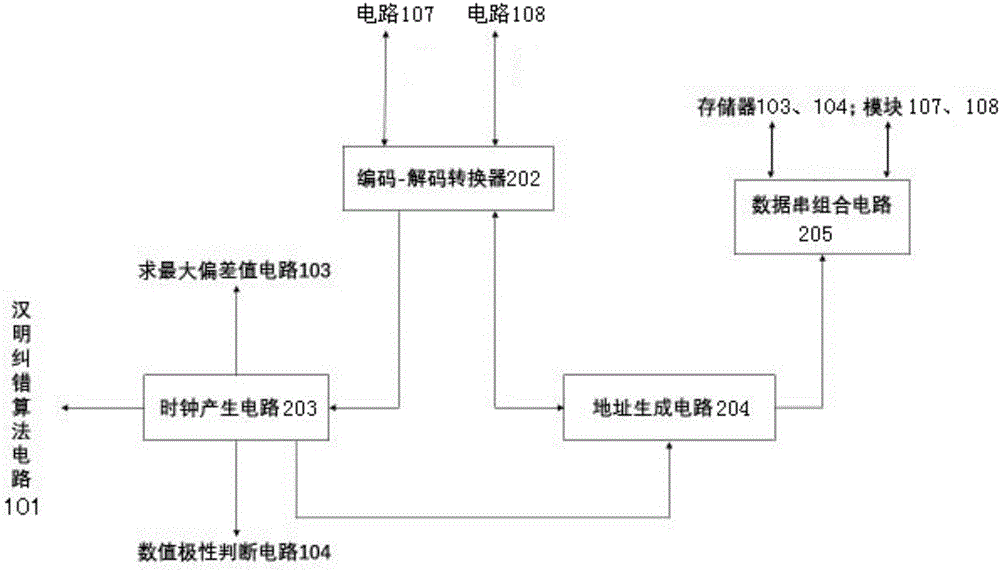
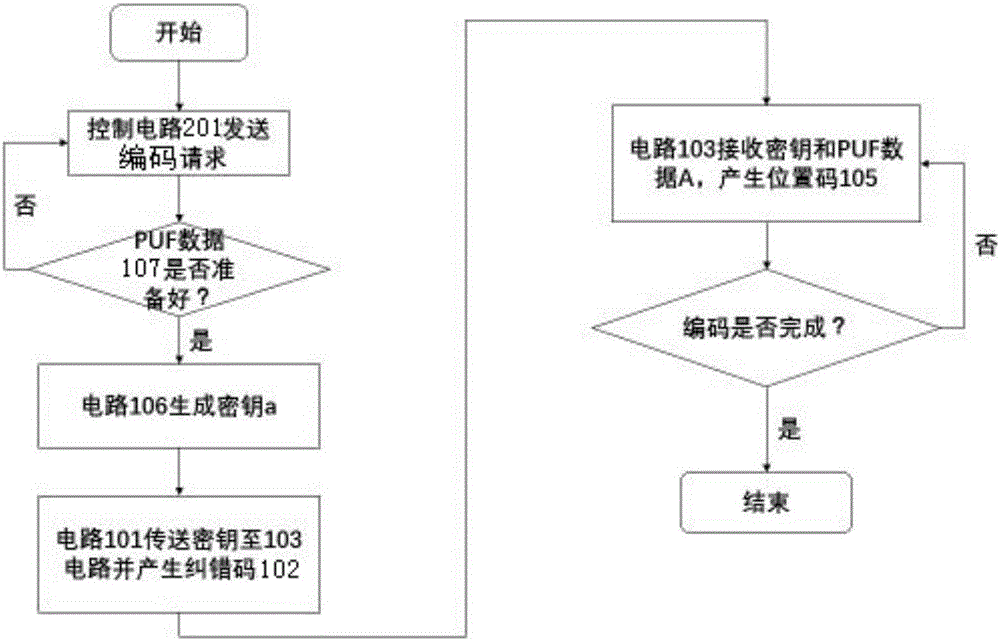
ActiveCN106301786AAchieve authenticationImprove securityUser identity/authority verificationCode moduleRandom array
The invention discloses a physical unclonable function response error correcting circuit based on an SRAM type memory. The physical unclonable function response error correcting circuit based on the SRAM type memory comprises a coding module, a decoding module and a control module, wherein the coding module is used for mapping the physical unclonable function response into a uniquely corresponding position code sequence by being combined with a key sequence formed by a random number through a specific coding rule; the decoding module is used for reversely mapping the physical unclonable function response by combining the original position code sequence for reducing the key sequence; the control module realizes the coding and decoding conversion, the time sequence and address generation, circuit control between module circuits and similarity calculation between a key before coding and a key after the coding. The physical unclonable function response error correcting circuit has the advantages that the instability of the SRAM PUF response is overcome; the unstable SRAMPUF response is output and converted into the stable mapping relationship between the key and the position code, so that the hardware identity authentication is realized; the identity authentication safety is improved; the authentication process is simplified; the authentication efficiency is improved; the hardware cost is reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
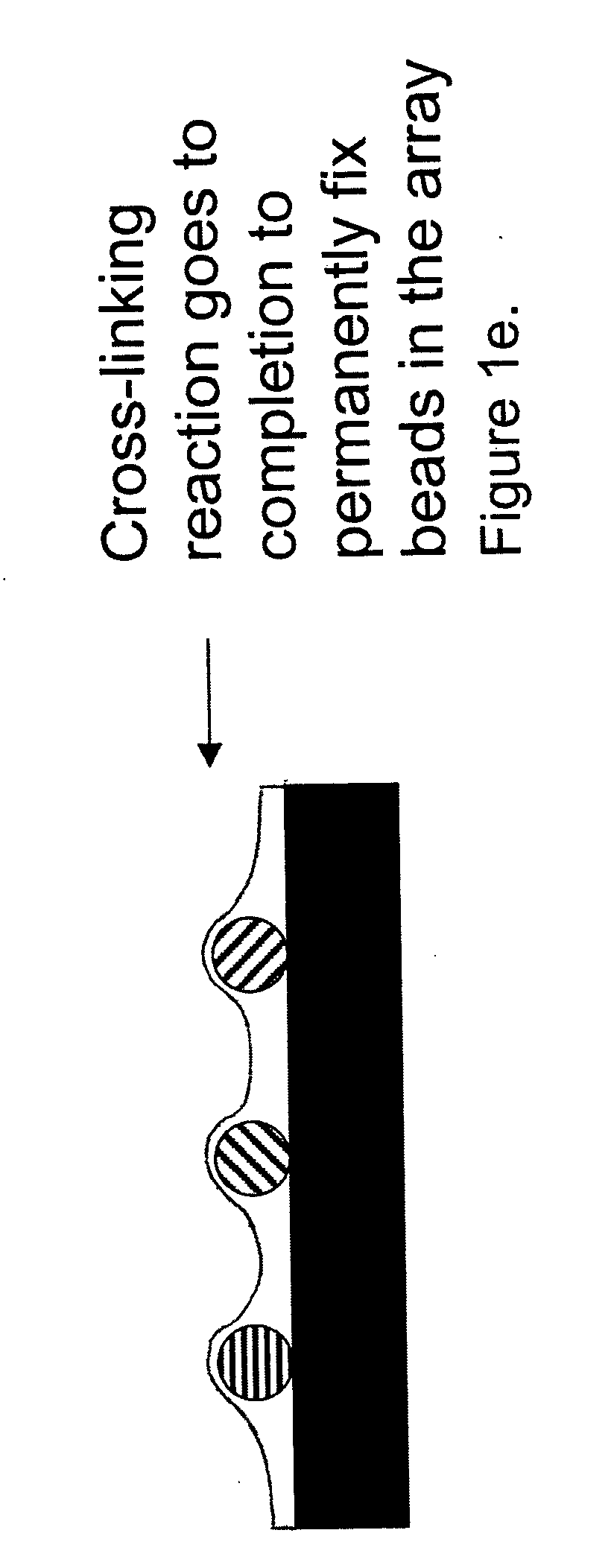
Random array of microspheres
InactiveUS7108891B2Less costlyEasy to preparePeptide librariesSequential/parallel process reactionsRandom arrayMicrosphere
A method of making a microarray comprising the steps of:providing a support;coating on the support a receiving layer to receive microspheres, the receiving layer being capable of undergoing sol / gel transition;coating on the receiving layer a dispersion of microspheres in a carrier fluid, wherein the carrier fluid contains at least one crosslinking agent and is capable of solvating the receiving layer;allowing the microspheres to partially submerge into the receiving layer;creating conditions to induce sol / gel transition in the receiving layer, thus immobilizing the microspheres;evaporating off the carrier fluid; andallowing crosslinking reaction between the receiving layer and the crosslinker in the carrier fluid.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com