Patents
Literature
1247 results about "Linear arrays" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
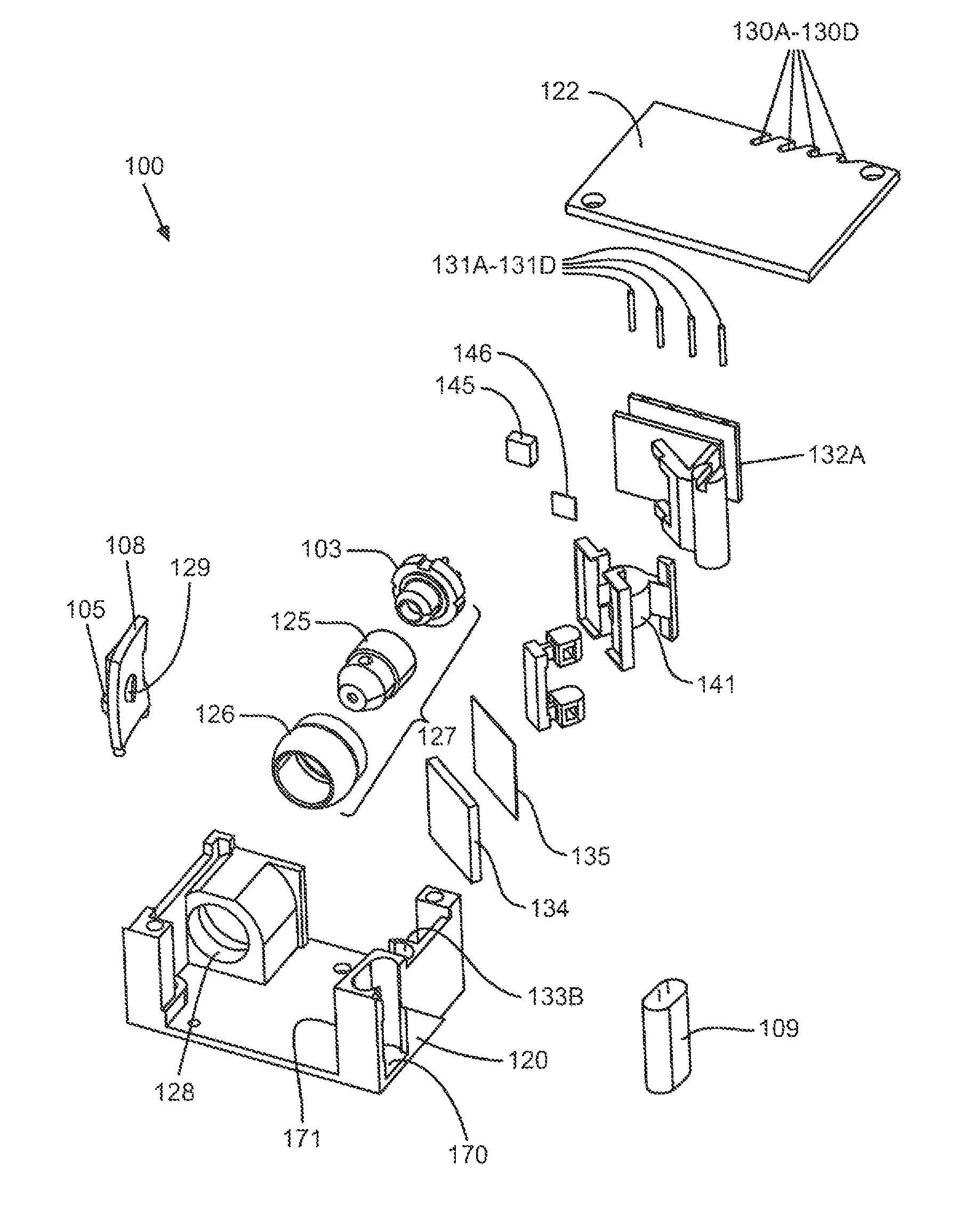
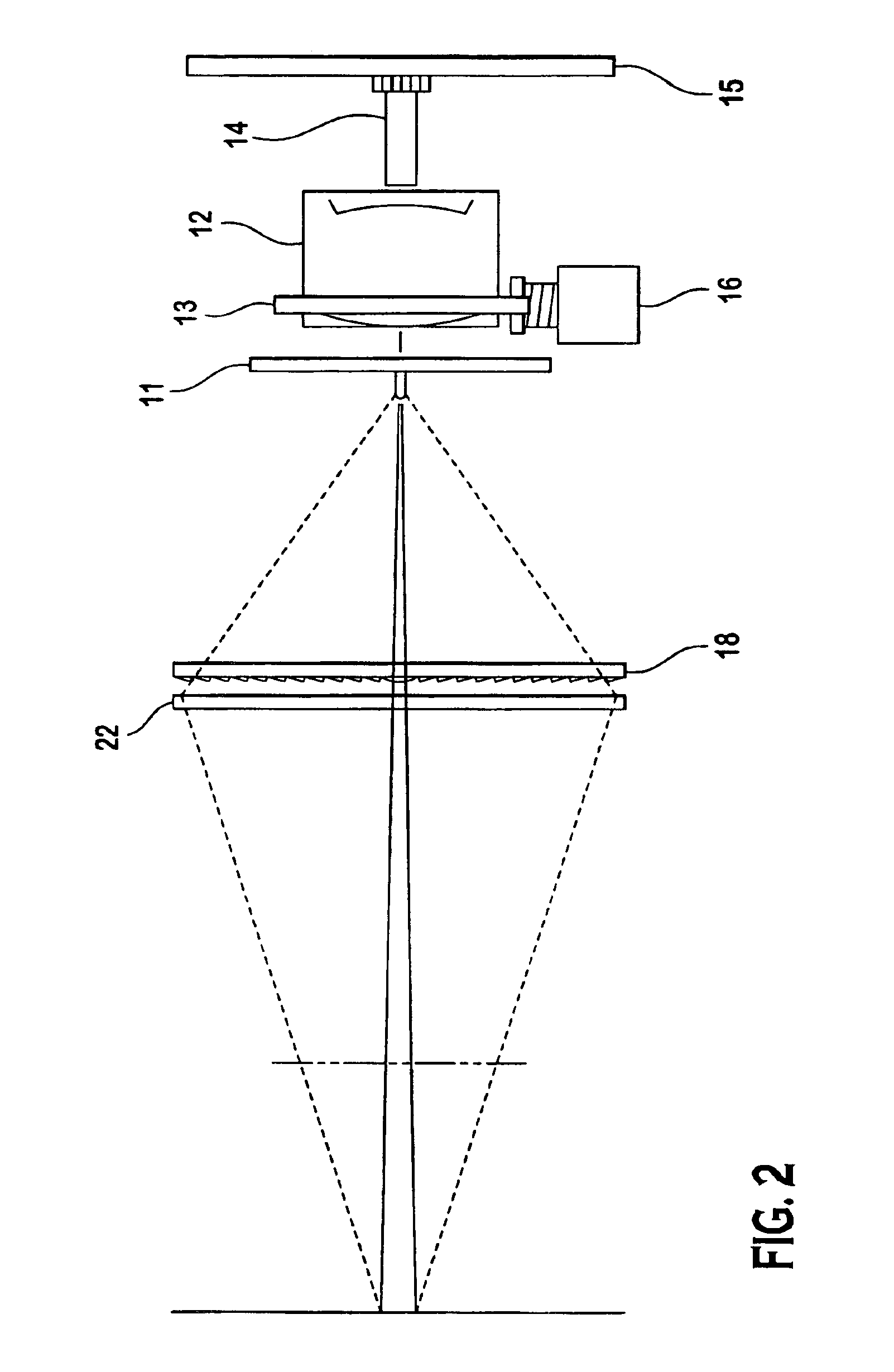
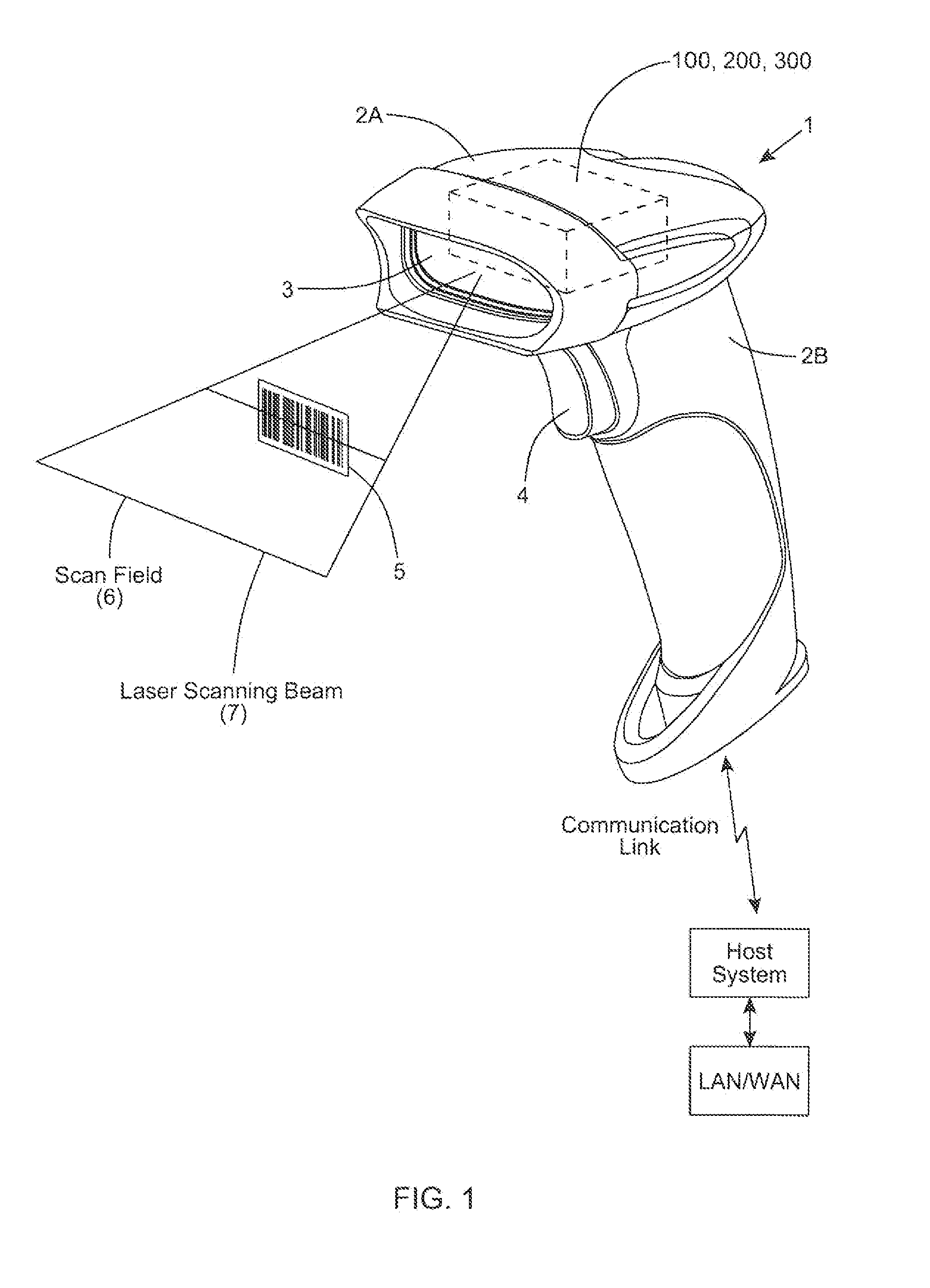
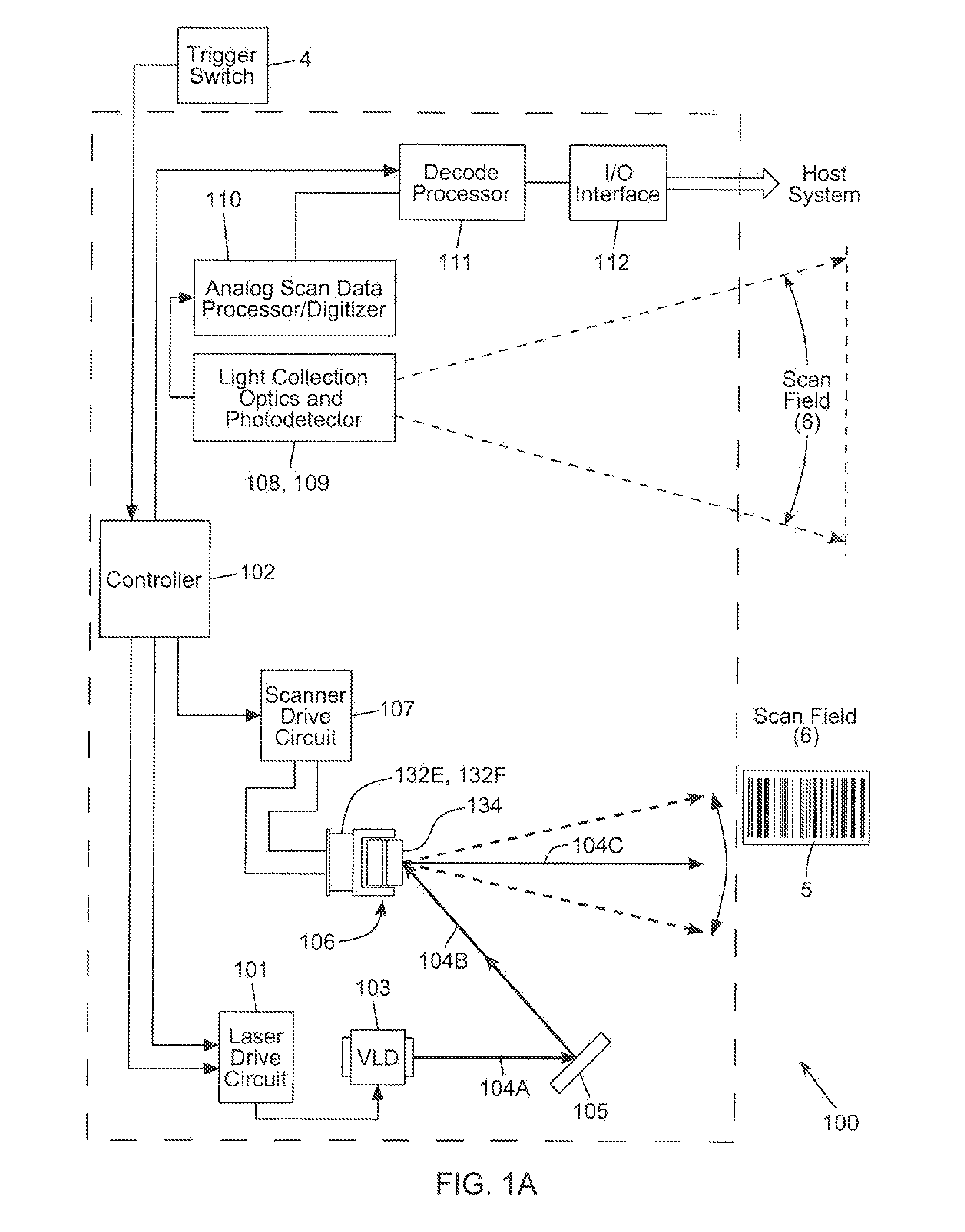
Laser scanning module with rotatably adjustable laser scanning assembly
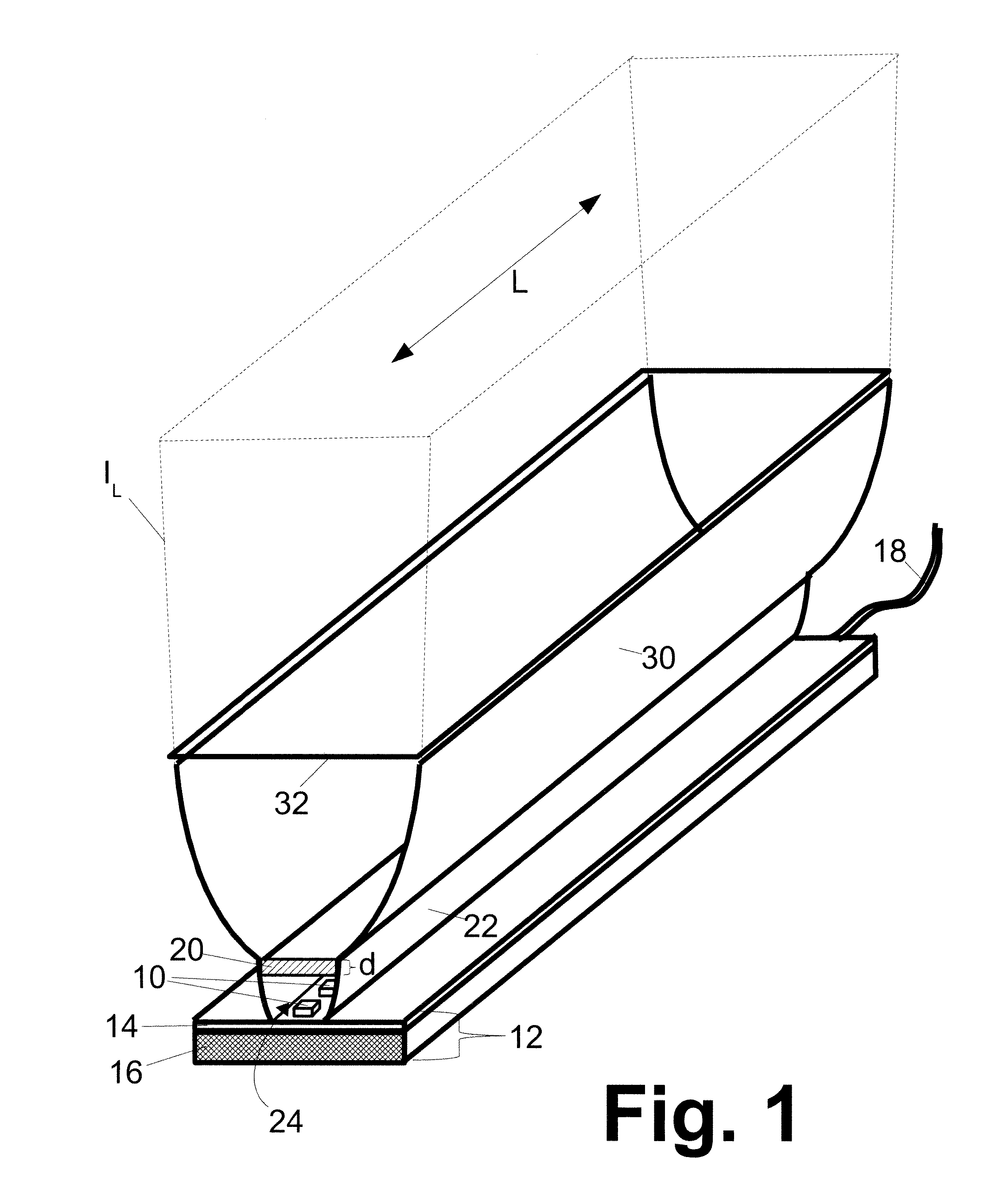
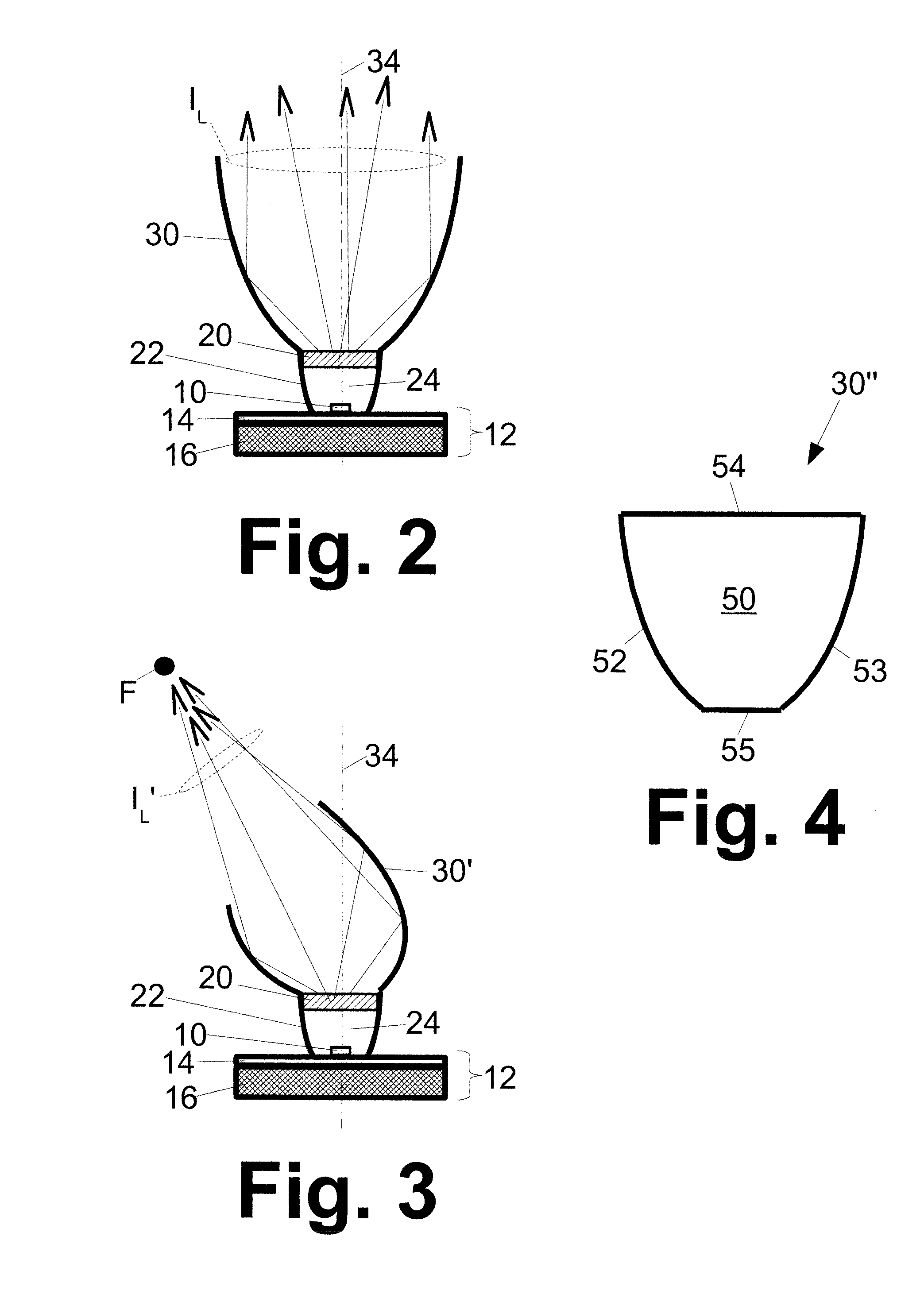
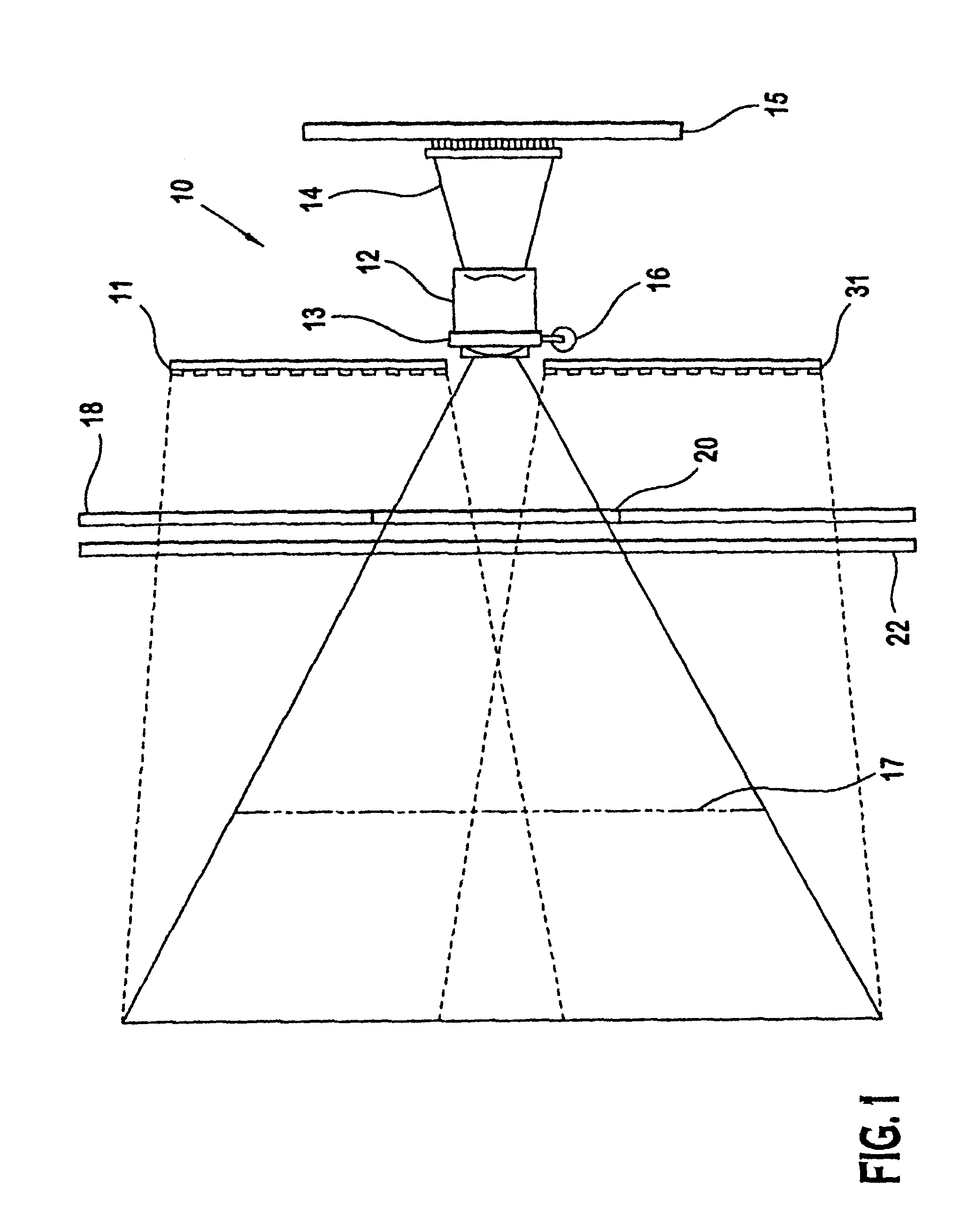
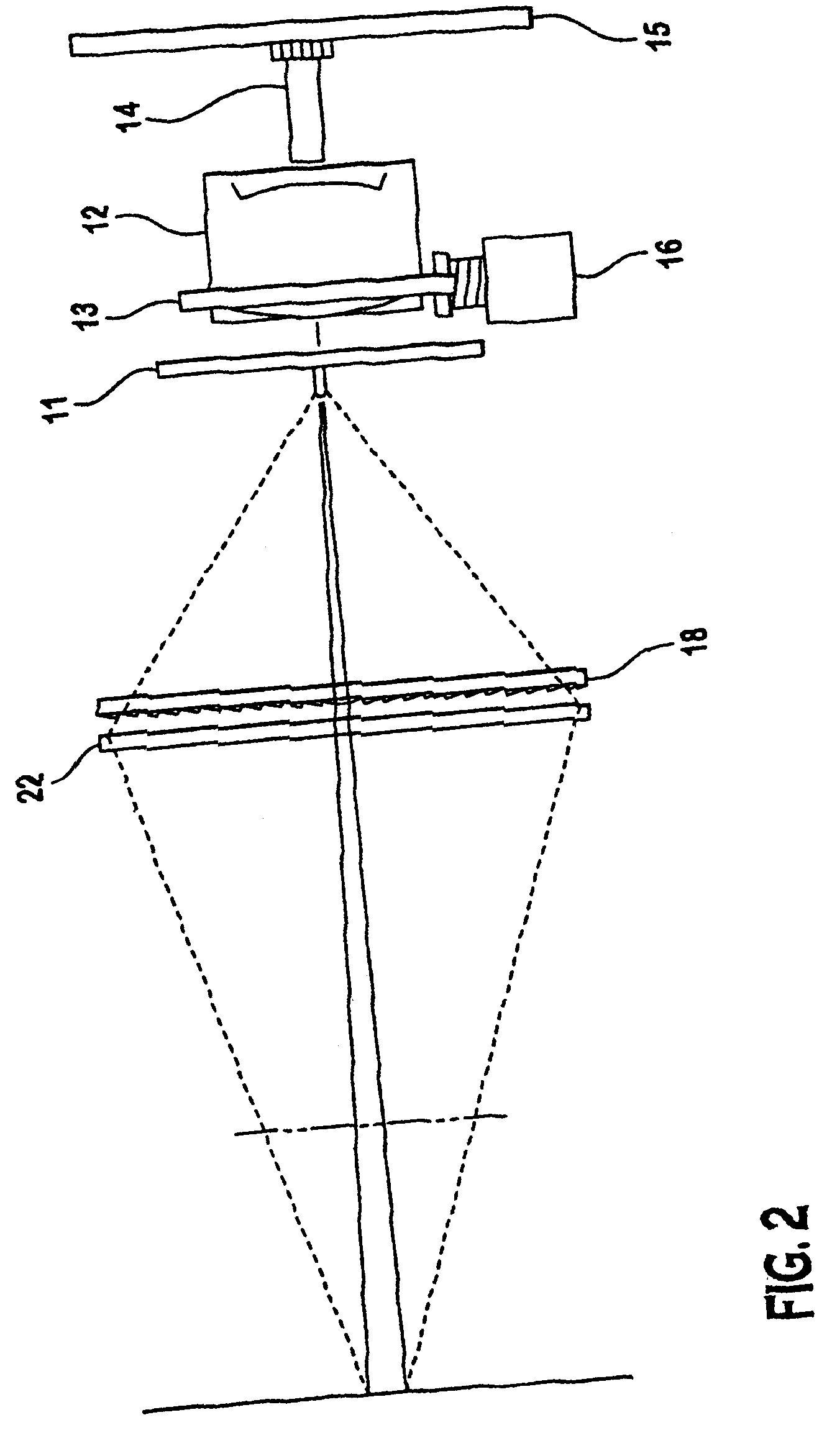
A laser scanning module employing a laser scanning assembly mounted within a module housing using a mechanism that allows the laser scanning assembly to be rotated to an angular position within the engine housing so that light collection, beam folding and light collection mirrors in the module housing are optically aligned. A PC board is mounted on a side of the housing and has a configuration of elongated apertures of open-ended and / or closed geometry, arranged in a non-parallel manner. An electromagnetic coil structure, associated with the laser scanning assembly, has a linear array of electrically-conductive pins that project through the configuration of elongated holes, at locations along the elongated holes that are determined by the angular rotation of the laser scanning assembly attained during optical alignment conditions during manufacture.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
Low-cost one-dimensional electromagnetic band gap waveguide phase shifter based ESA horn antenna
A one-dimensional electromagnetic band gap (EBG) waveguide phase shifter electronically scanned array (ESA) horn antenna utilizes a linear array of EBG waveguide phase shifters for scanning and radiating a beam. A linear array feed feeds the linear array of EBG waveguide phase shifters. A horn directs radiation from the linear array of EBG waveguide phase shifters. Each of the EBG waveguide phase shifters is a waveguide with vertical and horizontal sidewalls. EBG devices are located on the vertical waveguide walls to shift phase to scan the beam.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
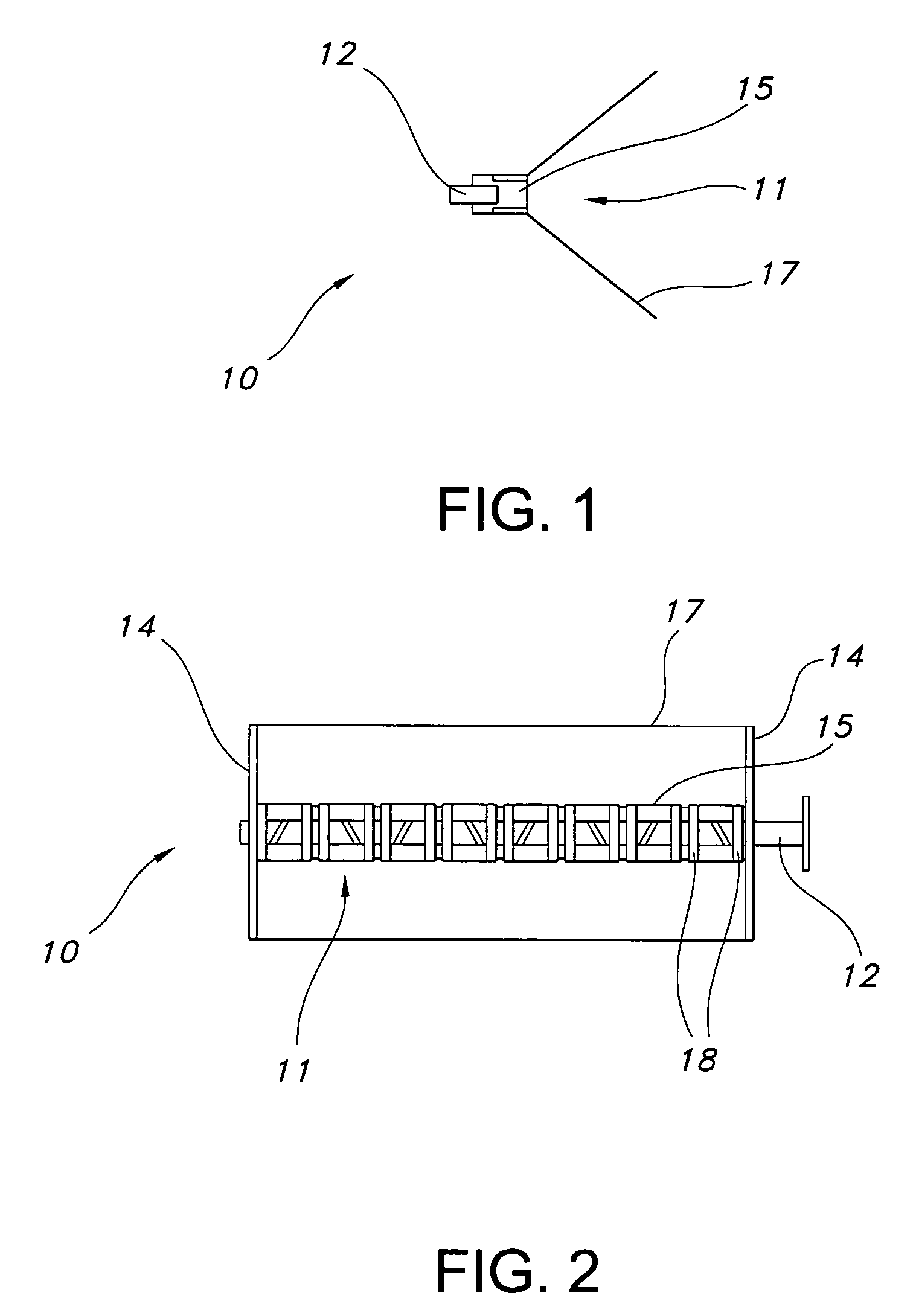
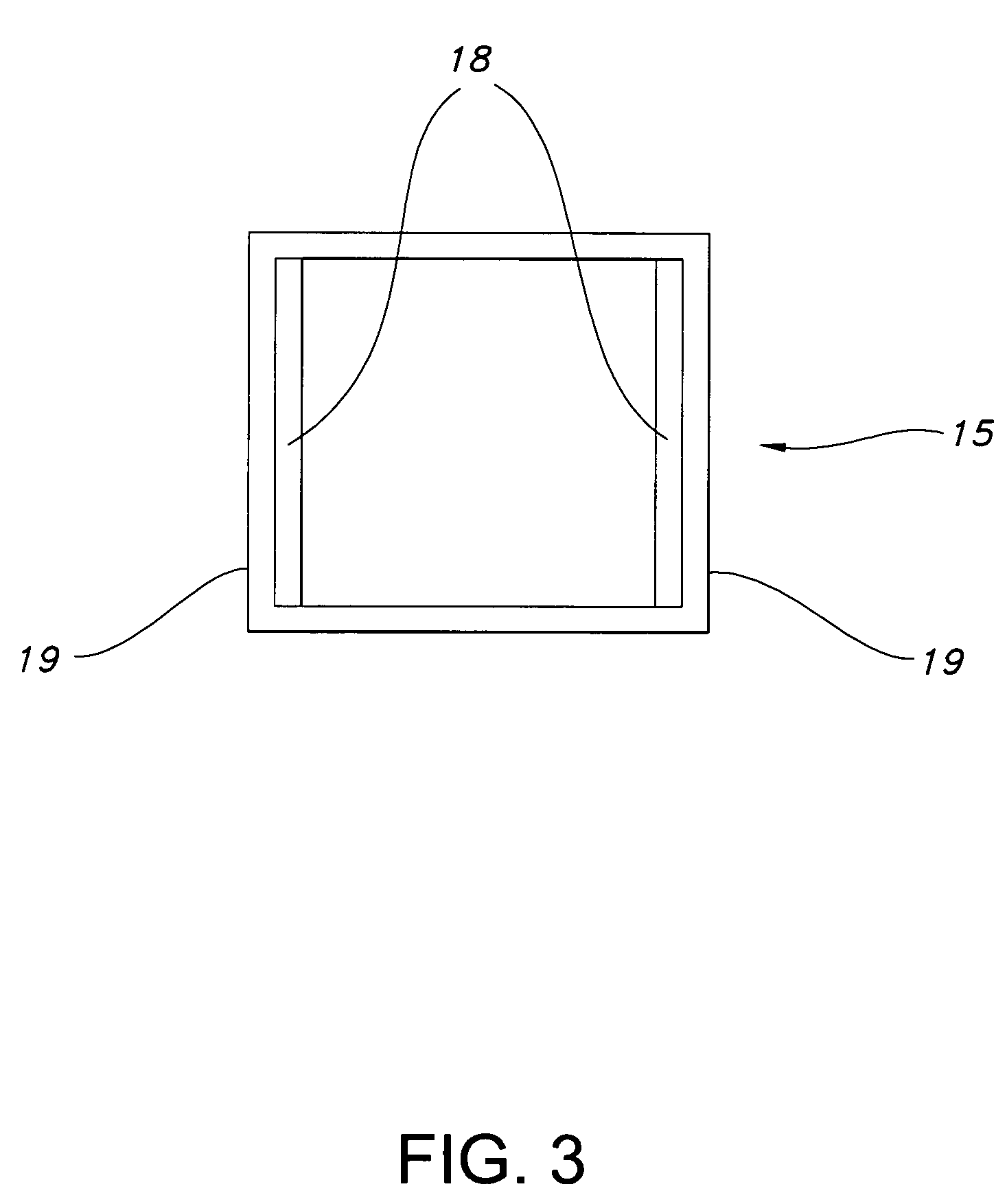
Orthogonal linear transmit receive array radar
ActiveUS20100141527A1High resolution imagingHigh resolution imageIndividually energised antenna arraysPolarised antenna unit combinationsRadar systemsLight beam
A radar system having orthogonal antenna apertures is disclosed. The invention further relates to an antenna system wherein the orthogonal apertures comprise at least one transmit aperture and at least one receive aperture. The cross-product of the transmit and receive apertures provides a narrow spot beam and resulting high resolution image. An embodiment of the invention discloses orthogonal linear arrays, comprising at least one electronically scanned transmit linear array and at least one electronically scanned receive linear array. The design of this orthogonal linear array system produces comparable performance, clutter and sidelobe structure at a fraction of the cost of conventional 2D filled array antenna systems.
Owner:FIRST RF CORP
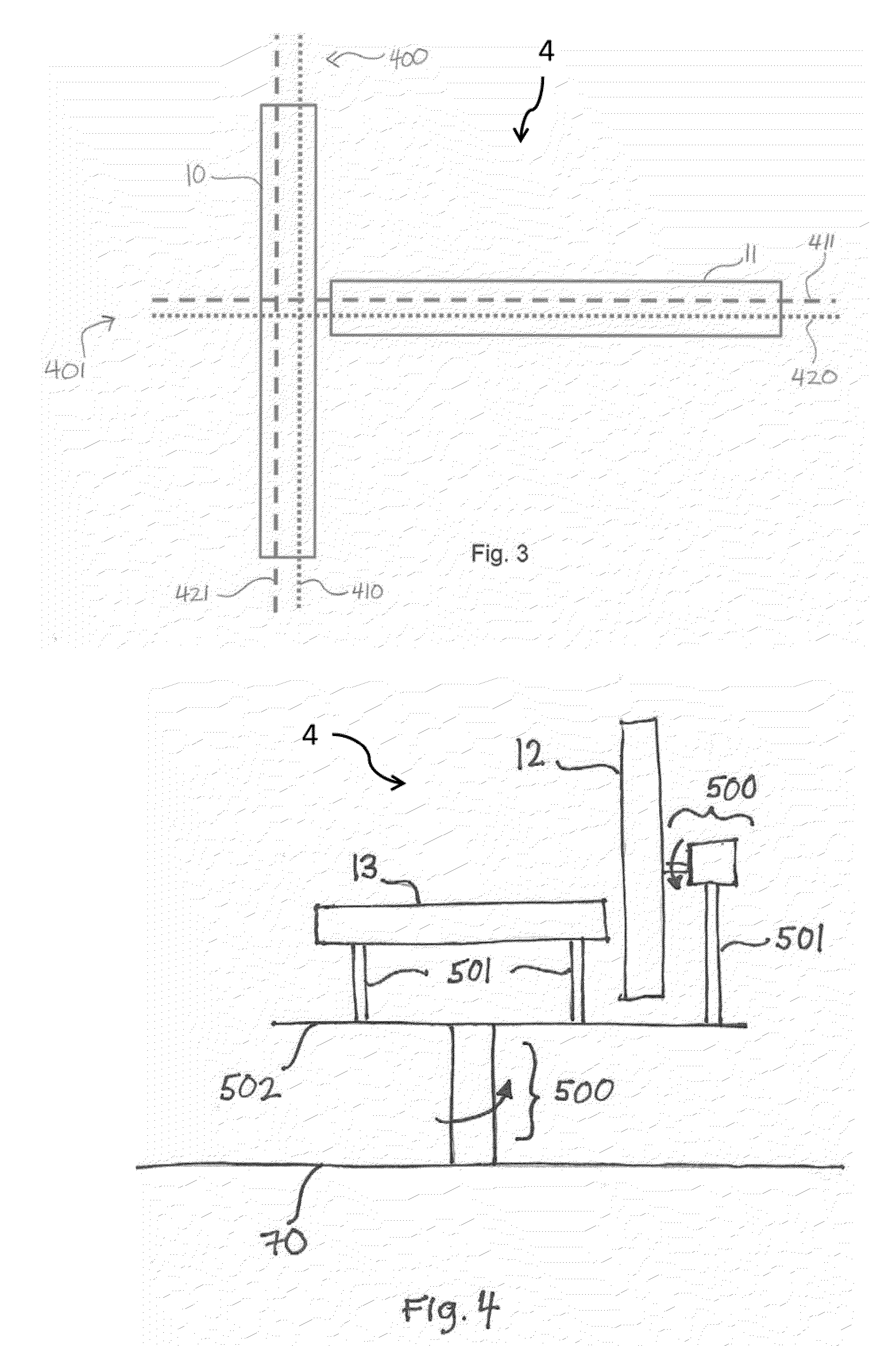
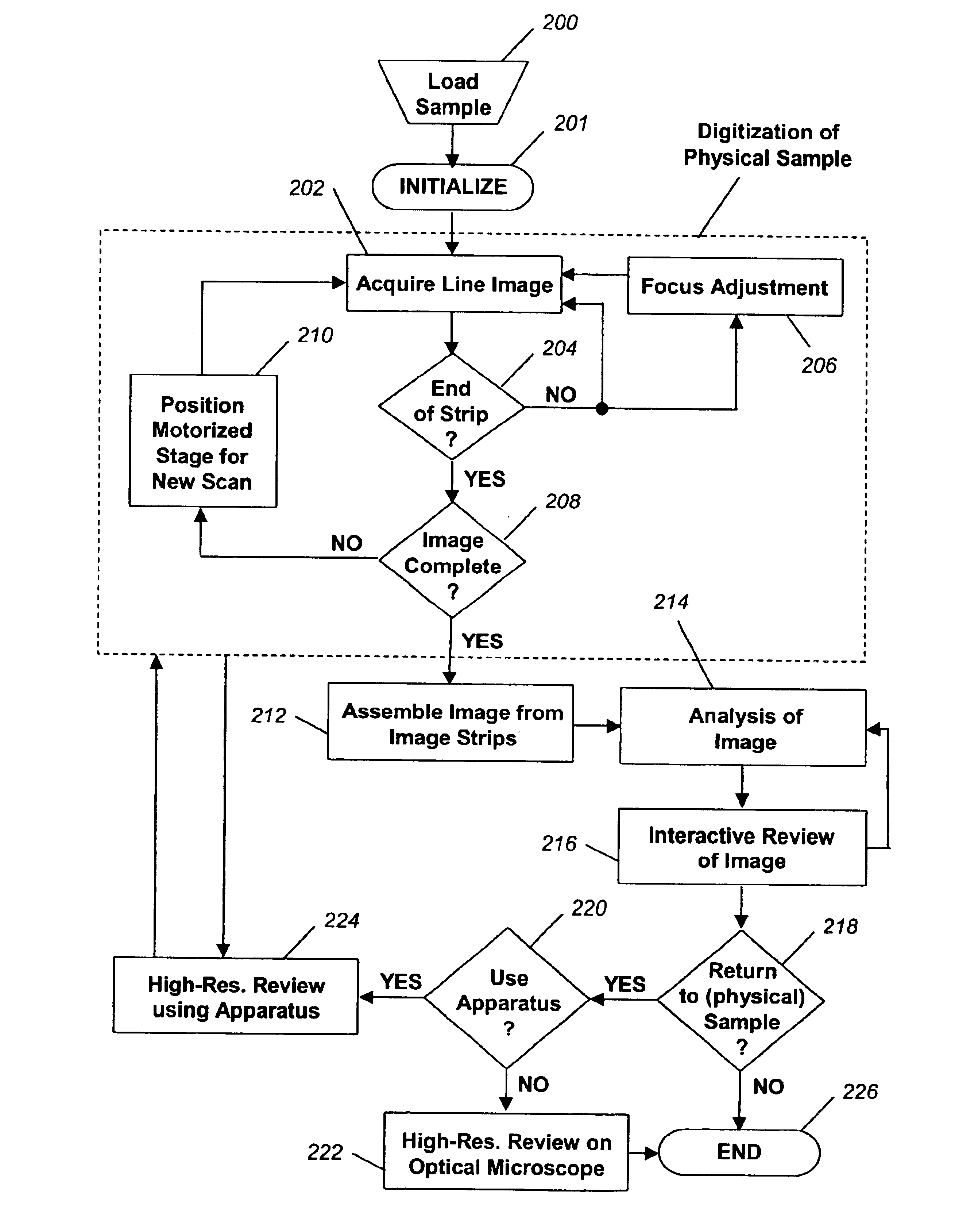
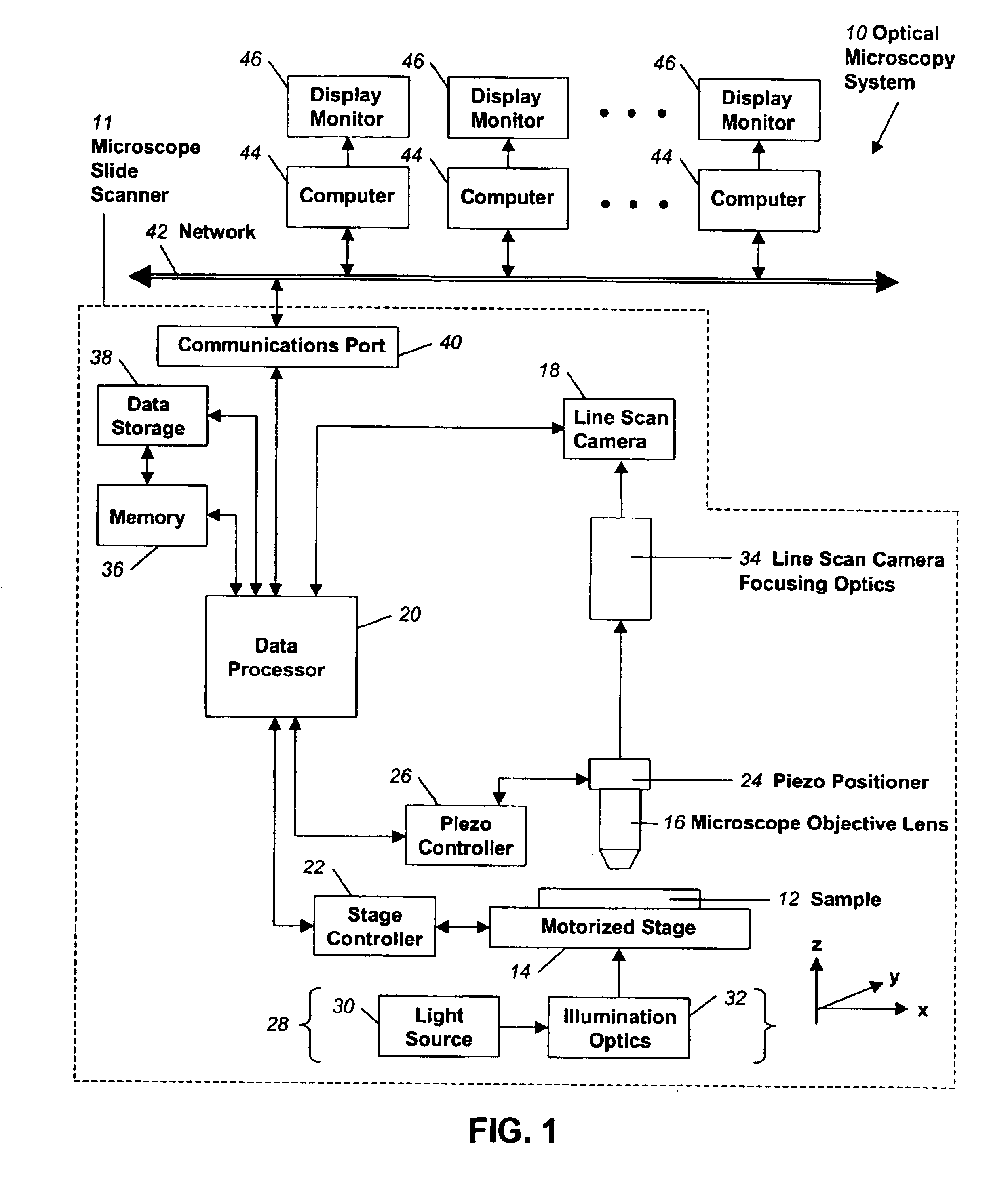
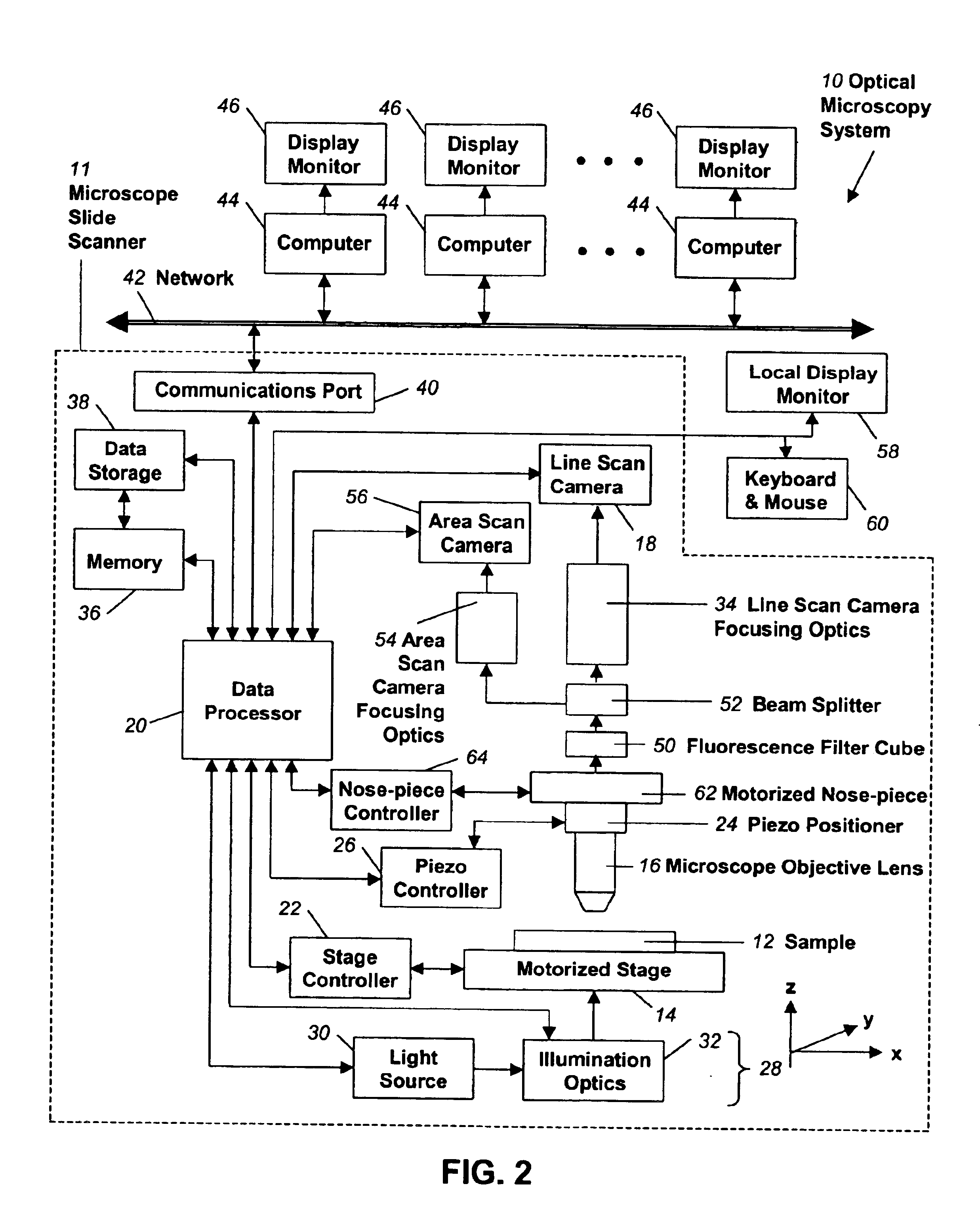
Fully automatic rapid microscope slide scanner
InactiveUS6917696B2Television system detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscope slideContinuous scanning
Apparatus for and method of fully automatic rapid scanning and digitizing of an entire microscope sample, or a substantially large portion of a microscope sample, using a linear array detector synchronized with a positioning stage that is part of a computer controlled microscope slide scanner. The invention provides a method for composing the image strips obtained from successive scans of the sample into a single contiguous digital image. The invention also provides a method for statically displaying sub-regions of this large digital image at different magnifications, together with a reduced magnification macro-image of the entire sample. The invention further provides a method for dynamically displaying, with or without operator interaction, portions of the contiguous digital image. In one preferred embodiment of the invention, all elements of the scanner are part of a single-enclosure that has a primary connection to the Internet or to a local intranet. In this embodiment, the preferred sample type is a microscope slide and the illumination and imaging optics are consistent with transmission mode optics optimized for diffraction-limited digital imaging.
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST IMAGING
Optical system for batwing distribution
A radiation distribution system designed to produce a batwing distribution. The system may be used with radiative sources emitting in the visible spectrum or in other spectra. The system comprises a specially shaped lens disposed over a radiative source, such as an LED, for example. The lens and source are arranged between two reflector bodies, both of which have an elongated reflective surface that faces the source. The reflector bodies each have two different reflective surfaces that face outward and away from each other. The lens and both reflective surfaces work in concert to redirect a portion of the emitted radiation to create the desired batwing distribution. Several sources may be arranged linearly between a single pair of reflector bodies on a common surface to create a linear array of sources. Likewise, multiple linear arrays may be combined to form a two-dimensional array. In the two-dimensional configuration, linear arrays of sources are disposed on both sides of a reflector body, so that both of the reflective surfaces are utilized.
Owner:IDEAL IND LIGHTING LLC
Directional linear light source
ActiveUS20090168395A1Light couplingPoint-like light sourceElongate light sourcesPhosphorLinear arrays
An illumination apparatus includes a linear array of light emitting diode (LED) chips disposed on a support. A linear reflector assembly has a light coupling reflector portion and a one dimensional light collimation or focusing portion. The linear reflector assembly is secured to the support parallel with the linear array of LED chips. An encapsulant is disposed in the light coupling reflector portion of the linear reflector assembly and pots the LED chips. An elongate phosphor element is disposed over the encapsulant such that the light coupling reflector portion and the encapsulant enhance light coupling between the LED chips and the elongate phosphor element, and the one-dimensional light collimation or focusing portion one-dimensionally collimates or focuses light emitted by the combination of the LED chips and the elongate phosphor element.
Owner:GE LIGHTING SOLUTIONS LLC
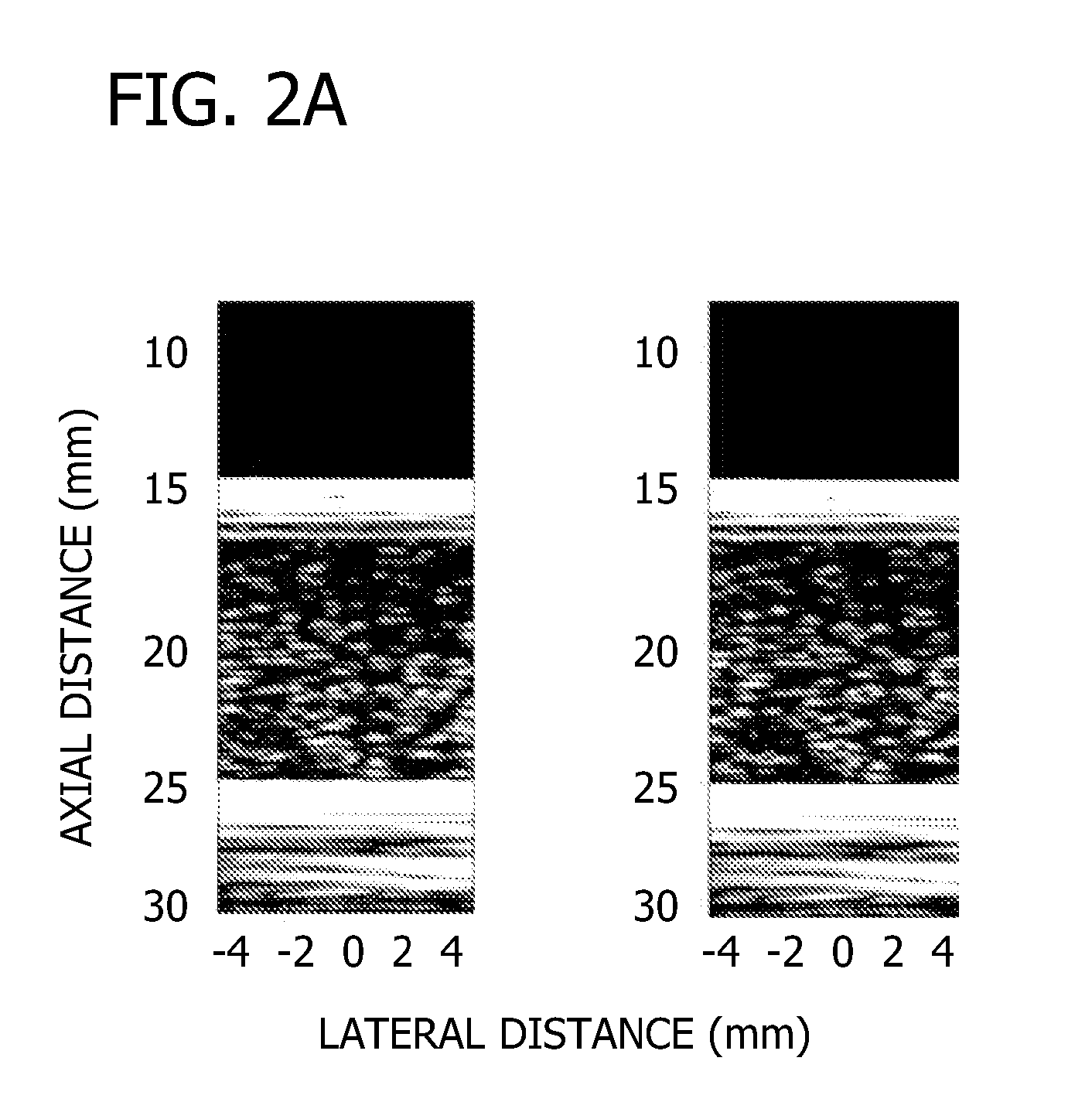
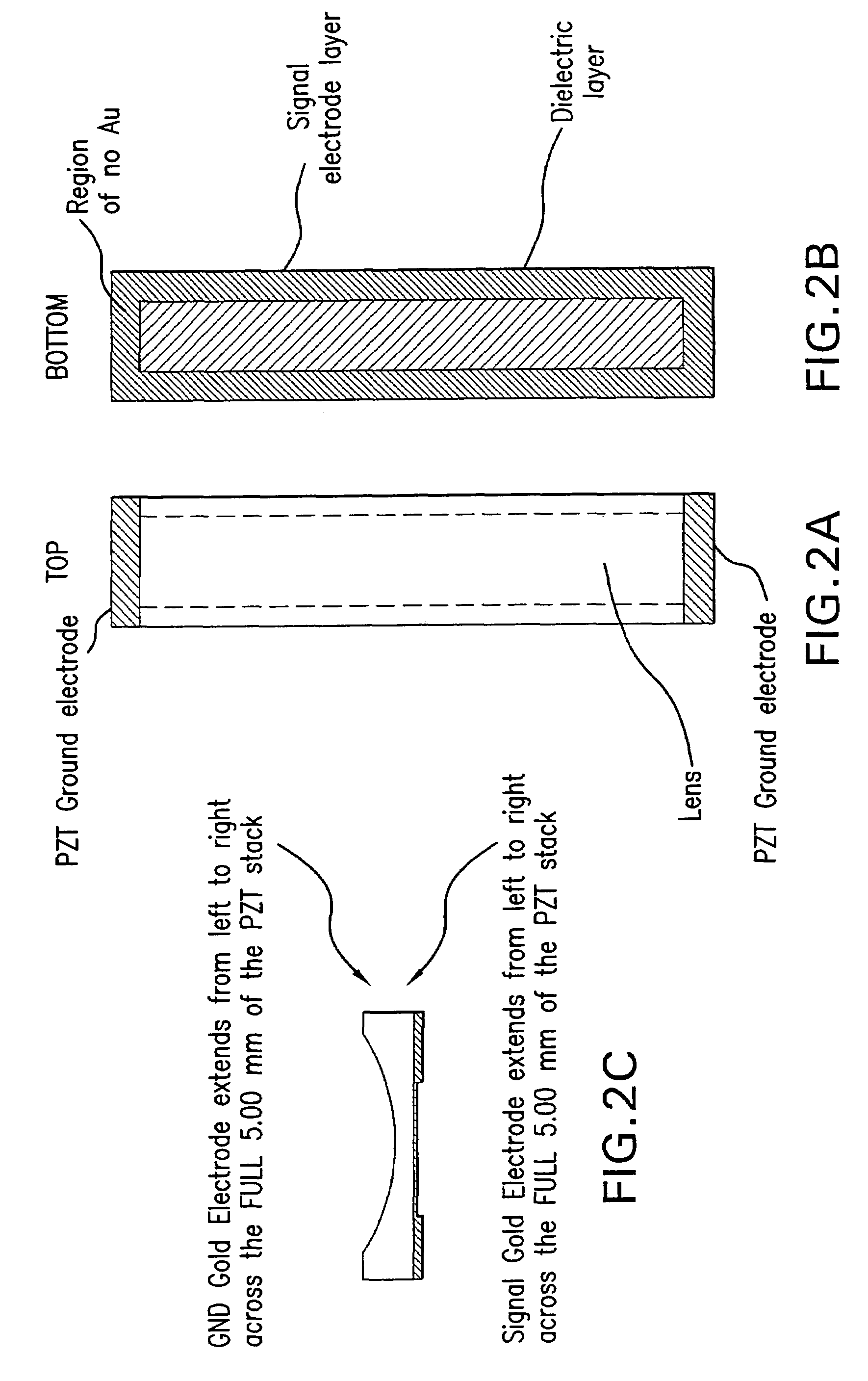
High frequency array ultrasound system
ActiveUS20070239001A1Time indicationSynchronous motors for clocksPhased array transducerLinear arrays
A system for acquiring an ultrasound signal comprises a signal processing unit adapted for acquiring a received ultrasound signal from an ultrasound transducer having a plurality of elements. The system is adapted to receive ultrasound signals having a frequency of at least 20 megahertz (MHz) with a transducer having a field of view of at least 5.0 millimeters (mm) at a frame rate of at least 20 frames per second (fps). The signal processing can further produce an ultrasound image from the acquired ultrasound signal. The transducer can be a linear array transducer, a phased array transducer, a two-dimensional (2-D) array transducer, or a curved array transducer.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCI CENT +1
High repetition rate laser produced plasma EUV light source
An EUV light source apparatus and method are disclosed, which may comprise a pulsed laser providing laser pulses at a selected pulse repetition rate focused at a desired target ignition site; a target formation system providing discrete targets at a selected interval coordinated with the laser pulse repetition rate; a target steering system intermediate the target formation system and the desired target ignition site; and a target tracking system providing information about the movement of target between the target formation system and the target steering system, enabling the target steering system to direct the target to the desired target ignition site. The target tracking system may provide information enabling the creation of a laser firing control signal, and may comprise a droplet detector comprising a collimated light source directed to intersect a point on a projected delivery path of the target, having a respective oppositely disposed light detector detecting the passage of the target through the respective point, or a detector comprising a linear array of a plurality of photo-sensitive elements aligned to a coordinate axis, the light from the light source intersecting a projected delivery path of the target, at least one of the which may comprise a plane-intercept detection device. The droplet detectors may comprise a plurality of droplet detectors each operating at a different light frequency, or a camera having a field of view and a two dimensional array of pixels imaging the field of view. The apparatus and method may comprise an electrostatic plasma containment apparatus providing an electric plasma confinement field at or near a target ignition site at the time of ignition, with the target tracking system providing a signal enabling control of the electrostatic plasma containment apparatus. The apparatus and method may comprise a vessel having and intermediate wall with a low pressure trap allowing passage of EUV light and maintaining a differential pressure across the low pressure trap. The apparatus and method may comprise a magnetic plasma confinement mechanism creating a magnetic field in the vicinity of the target ignition site to confine the plasma to the target ignition site, which may be pulsed and may be controlled using outputs from the target tracking system.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
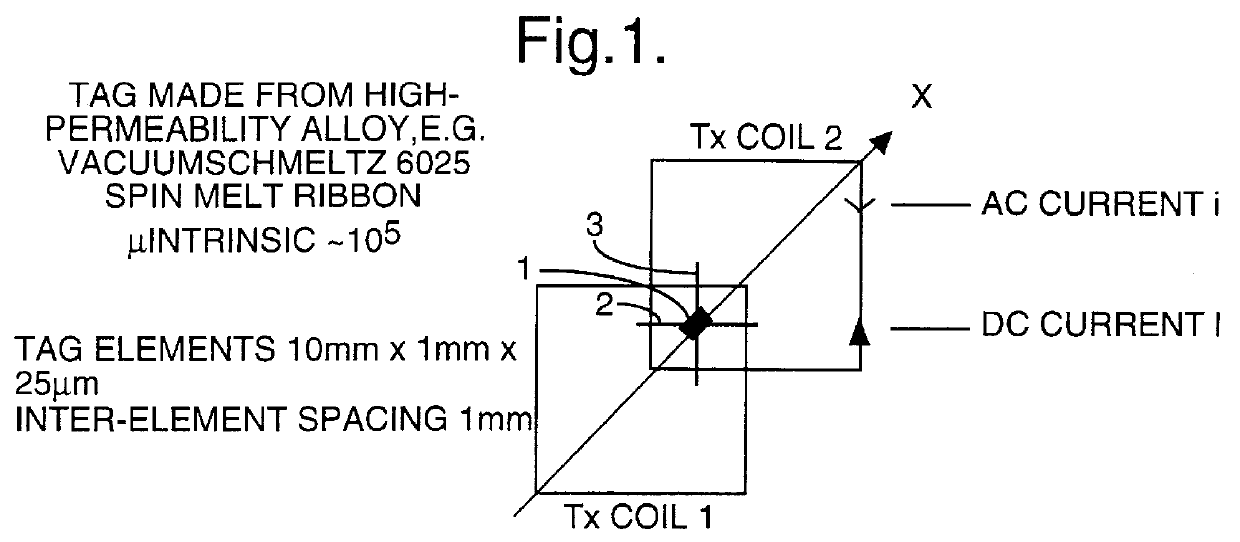
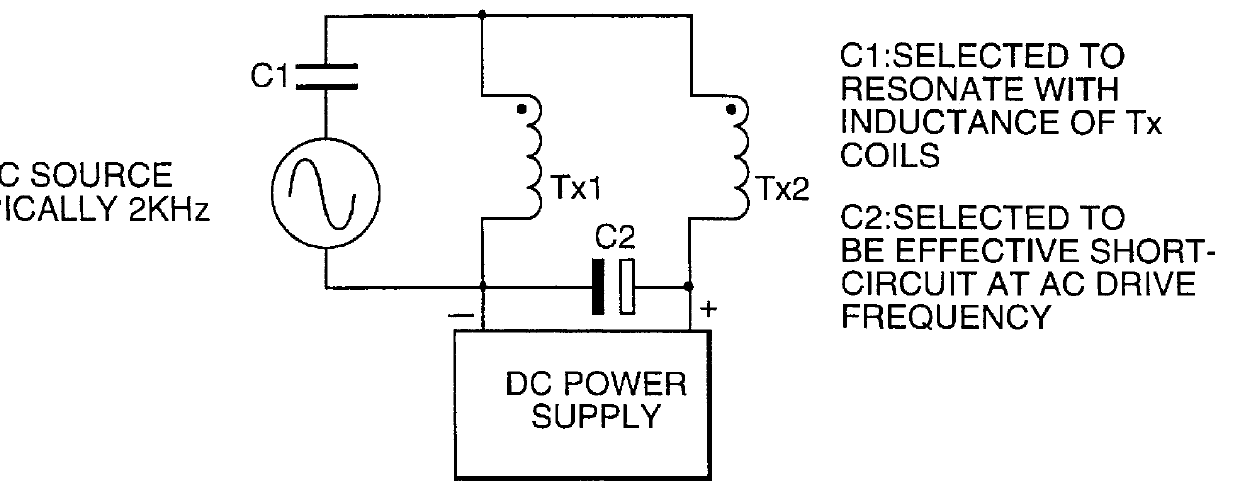
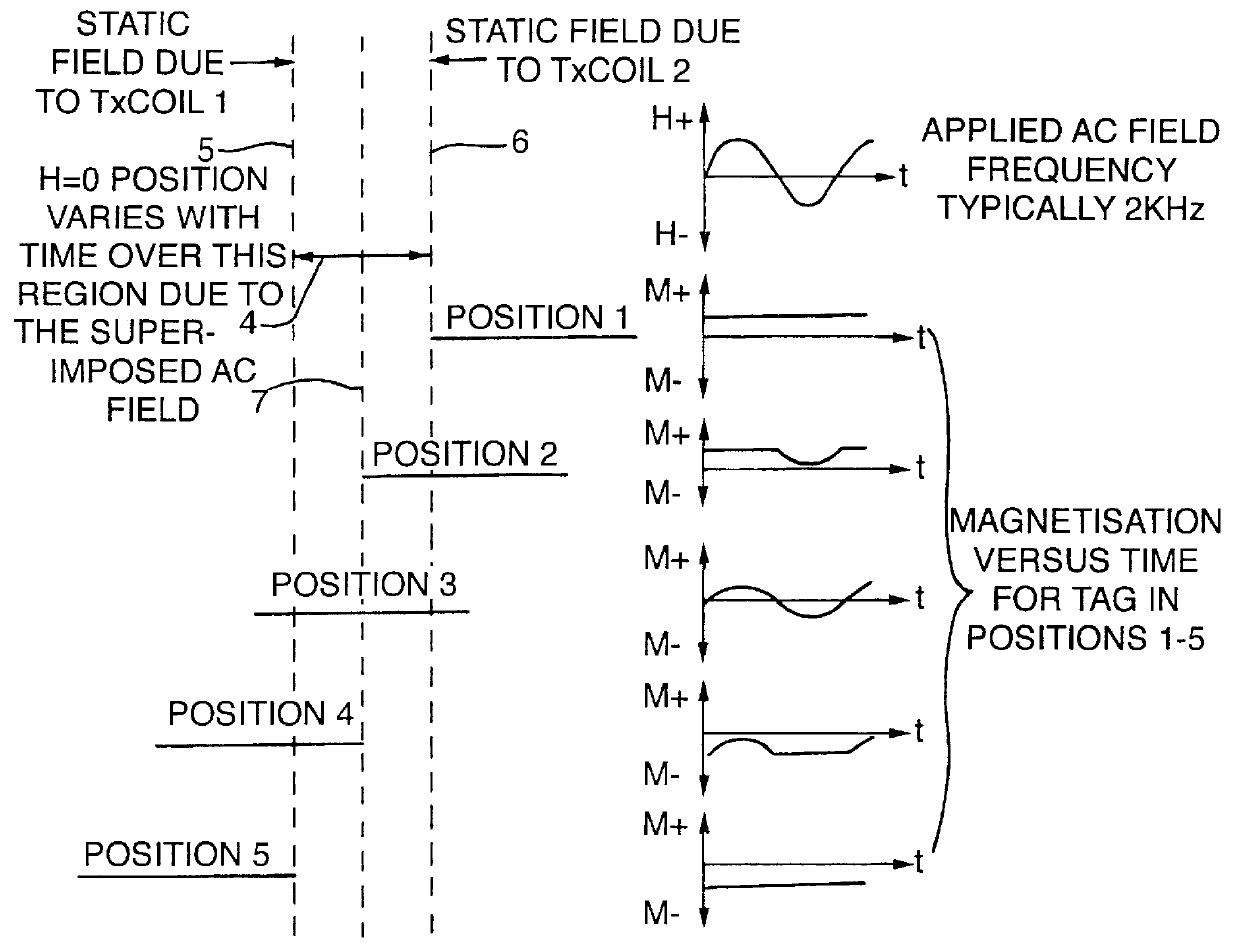
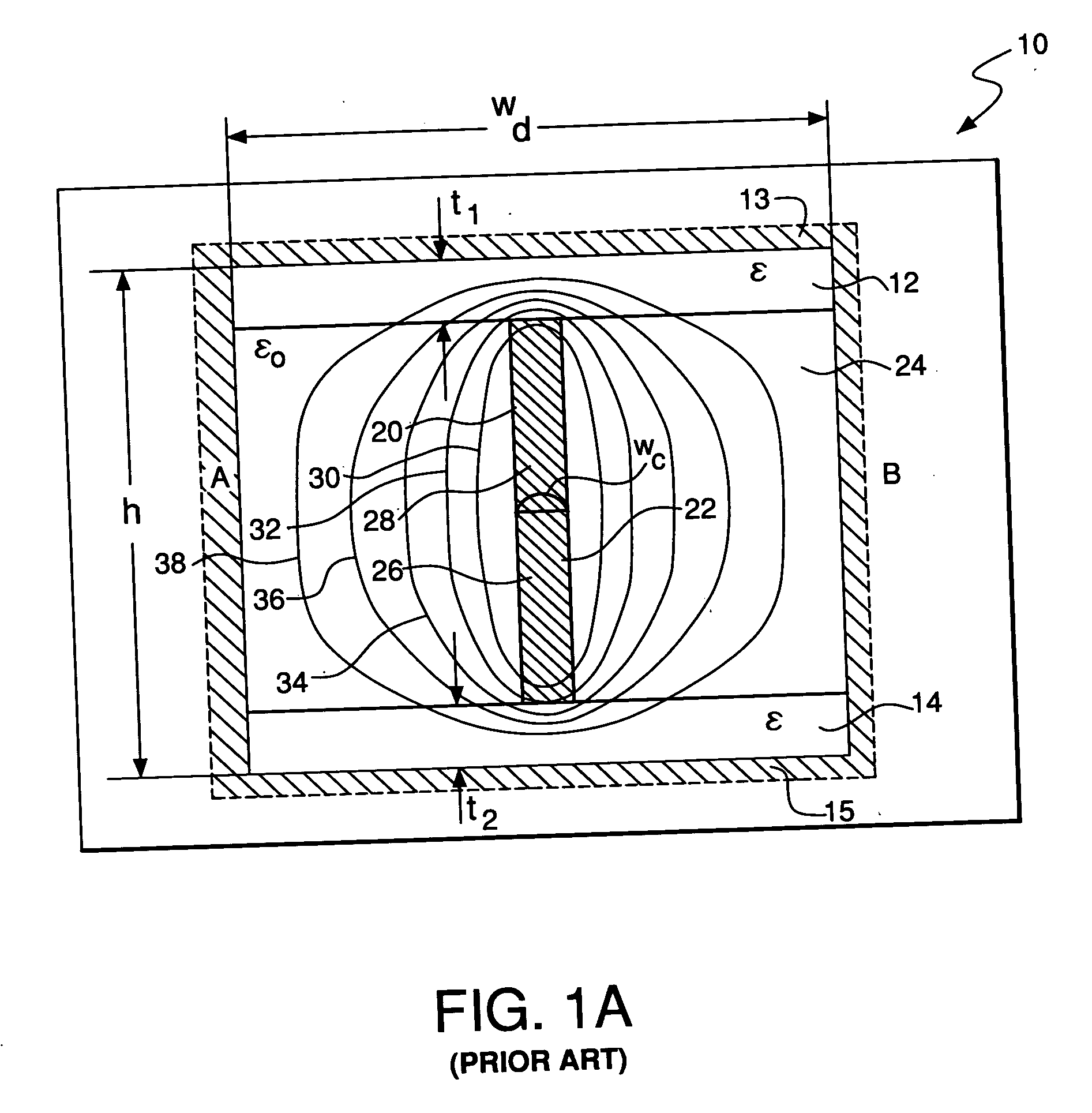
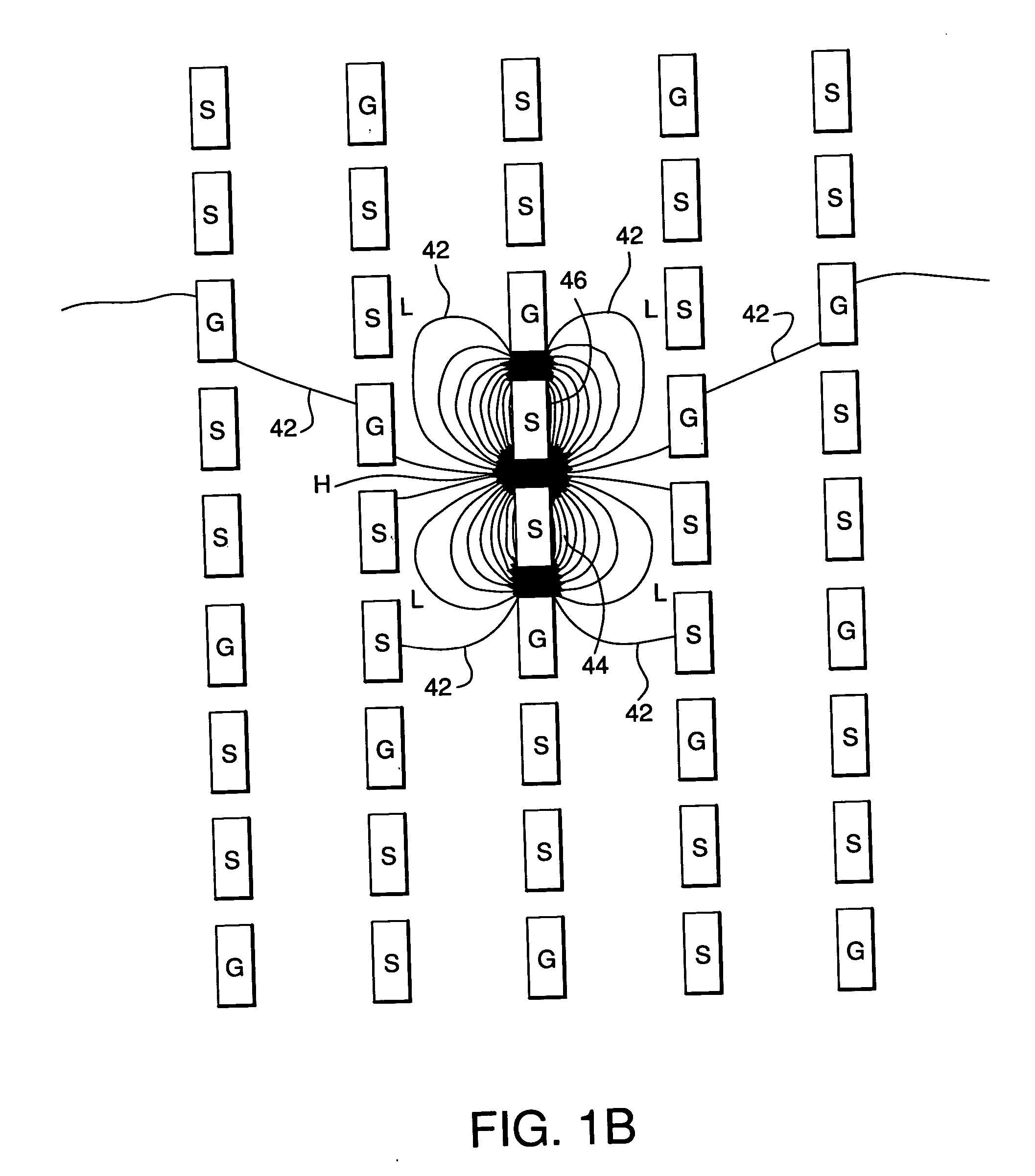
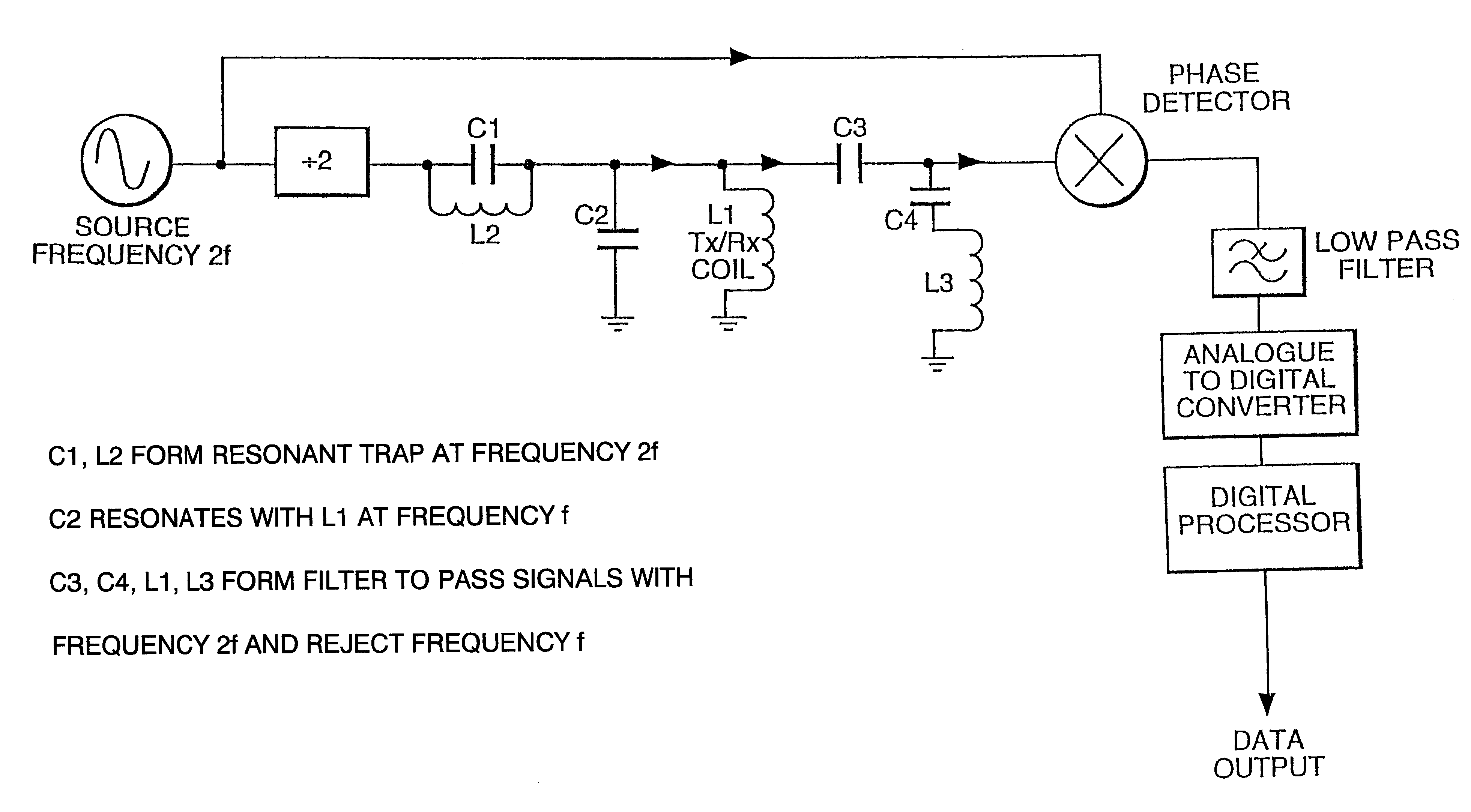
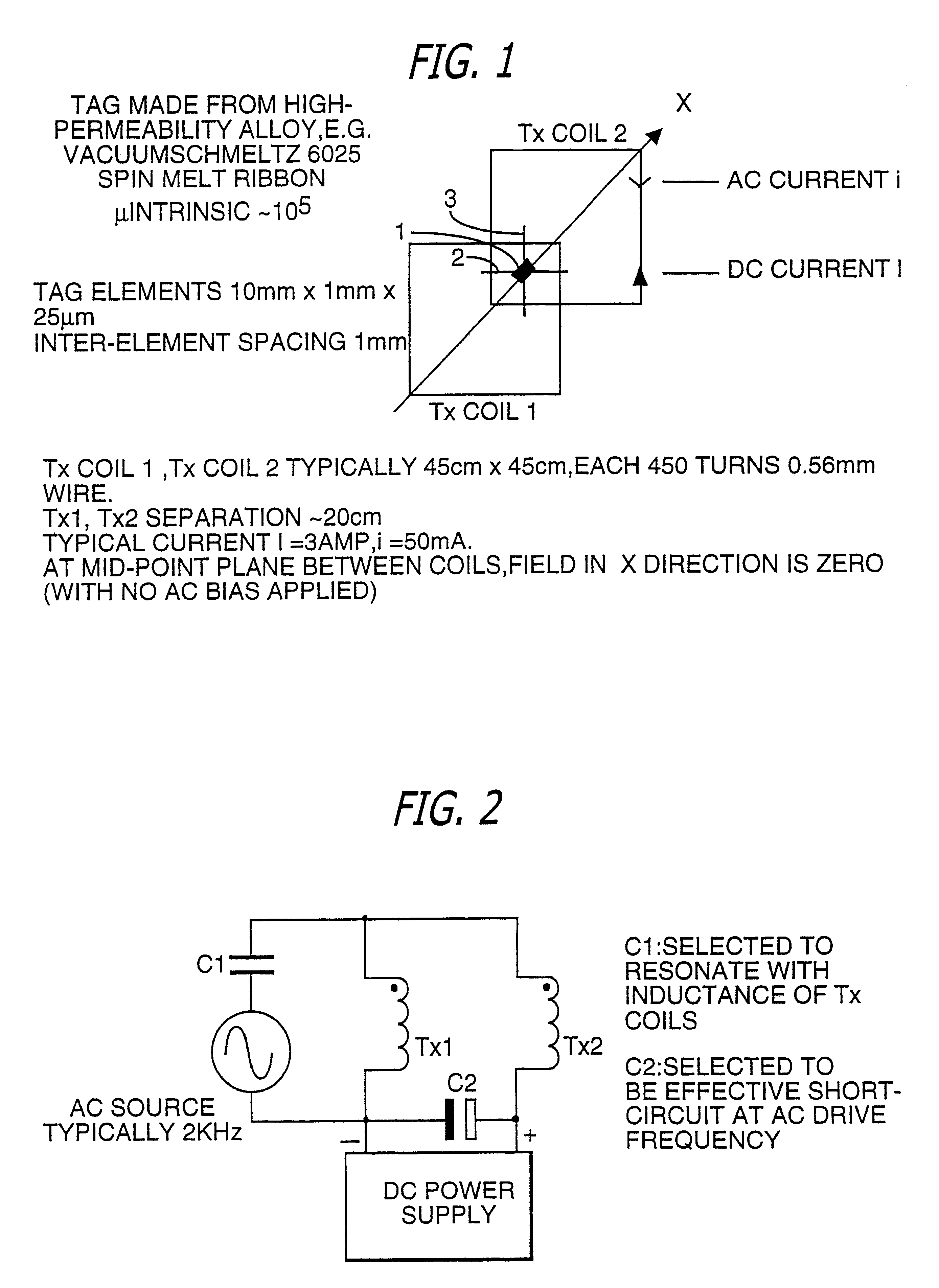
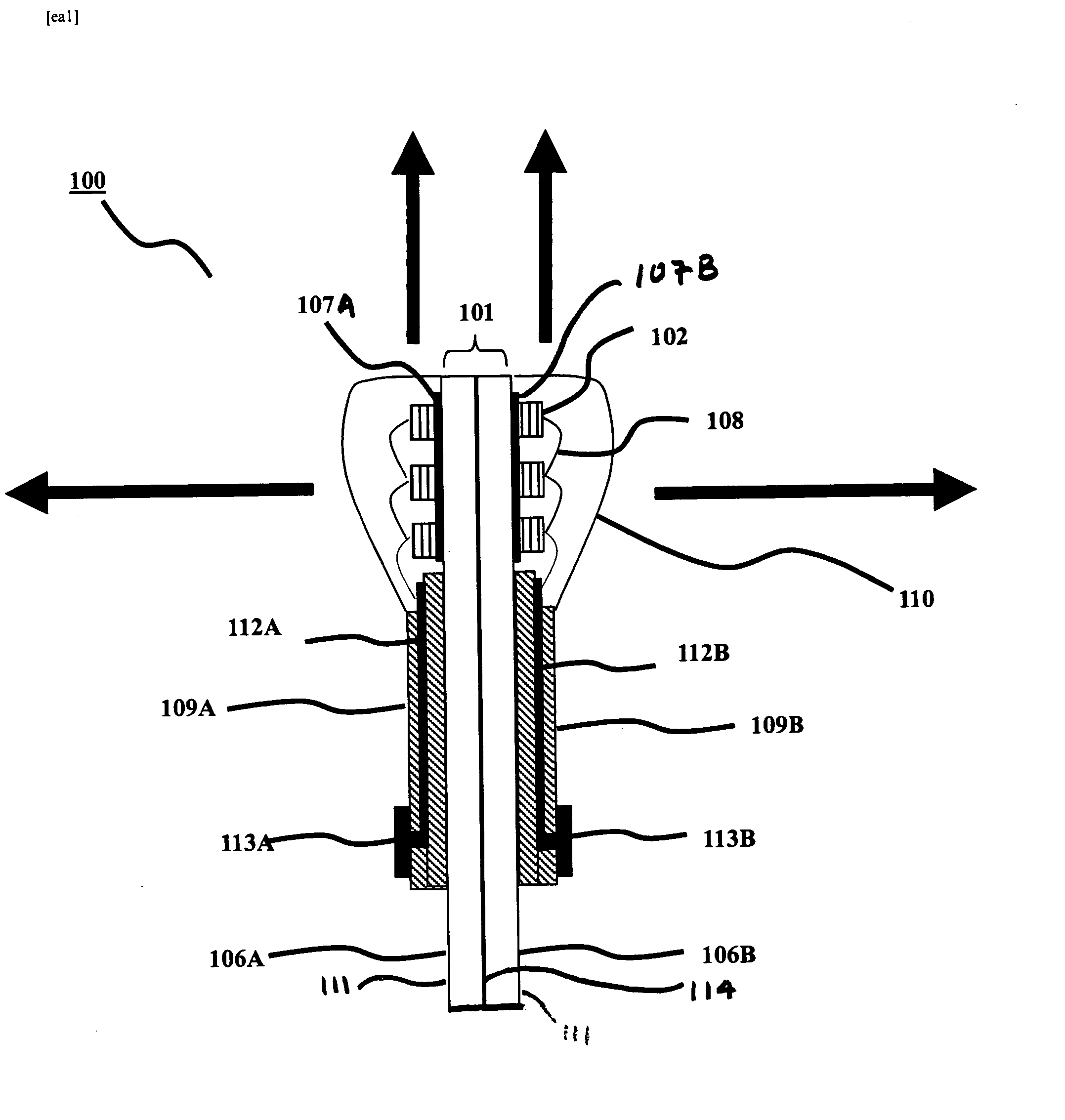
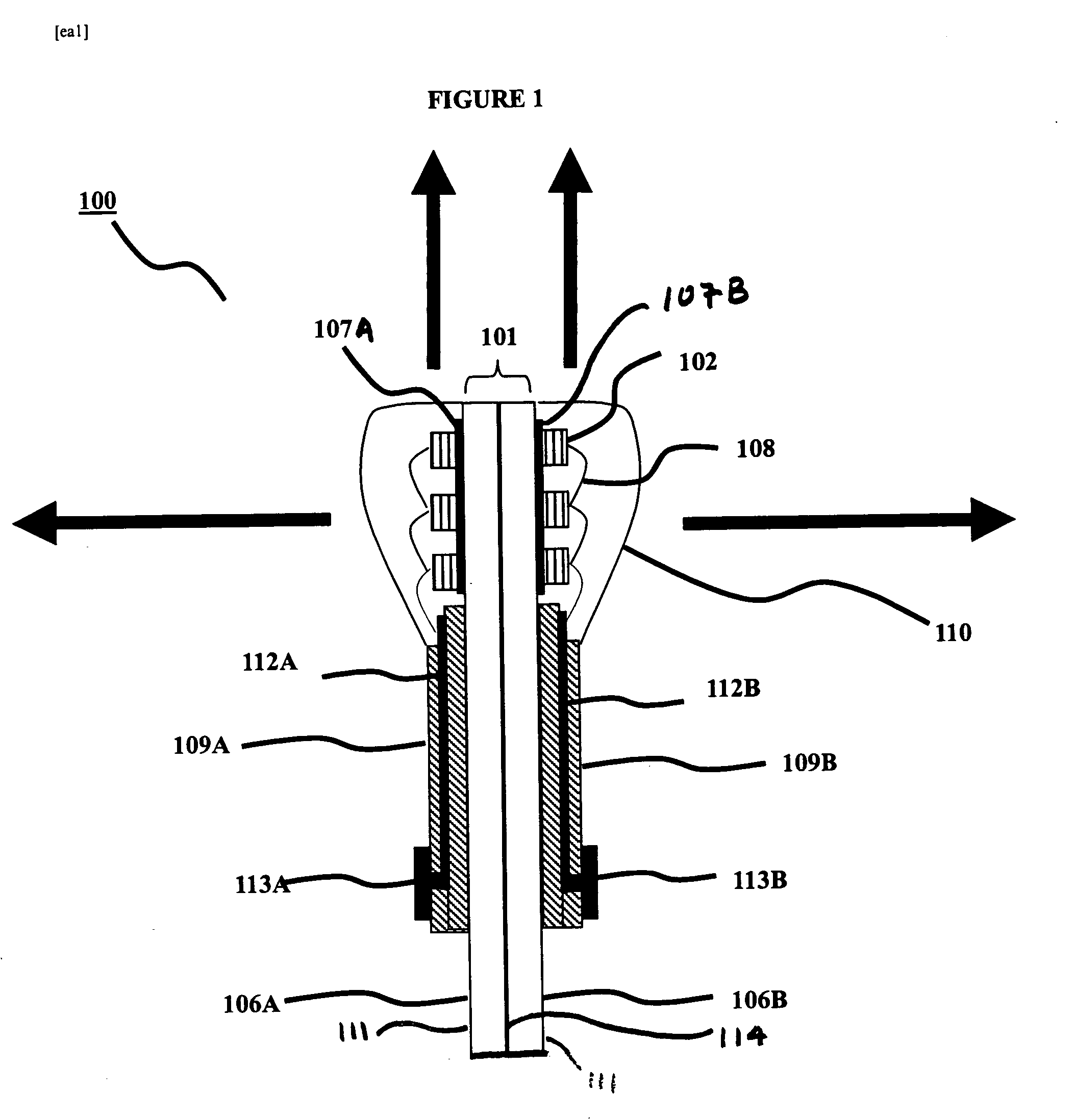
Spatial magnetic interrogation
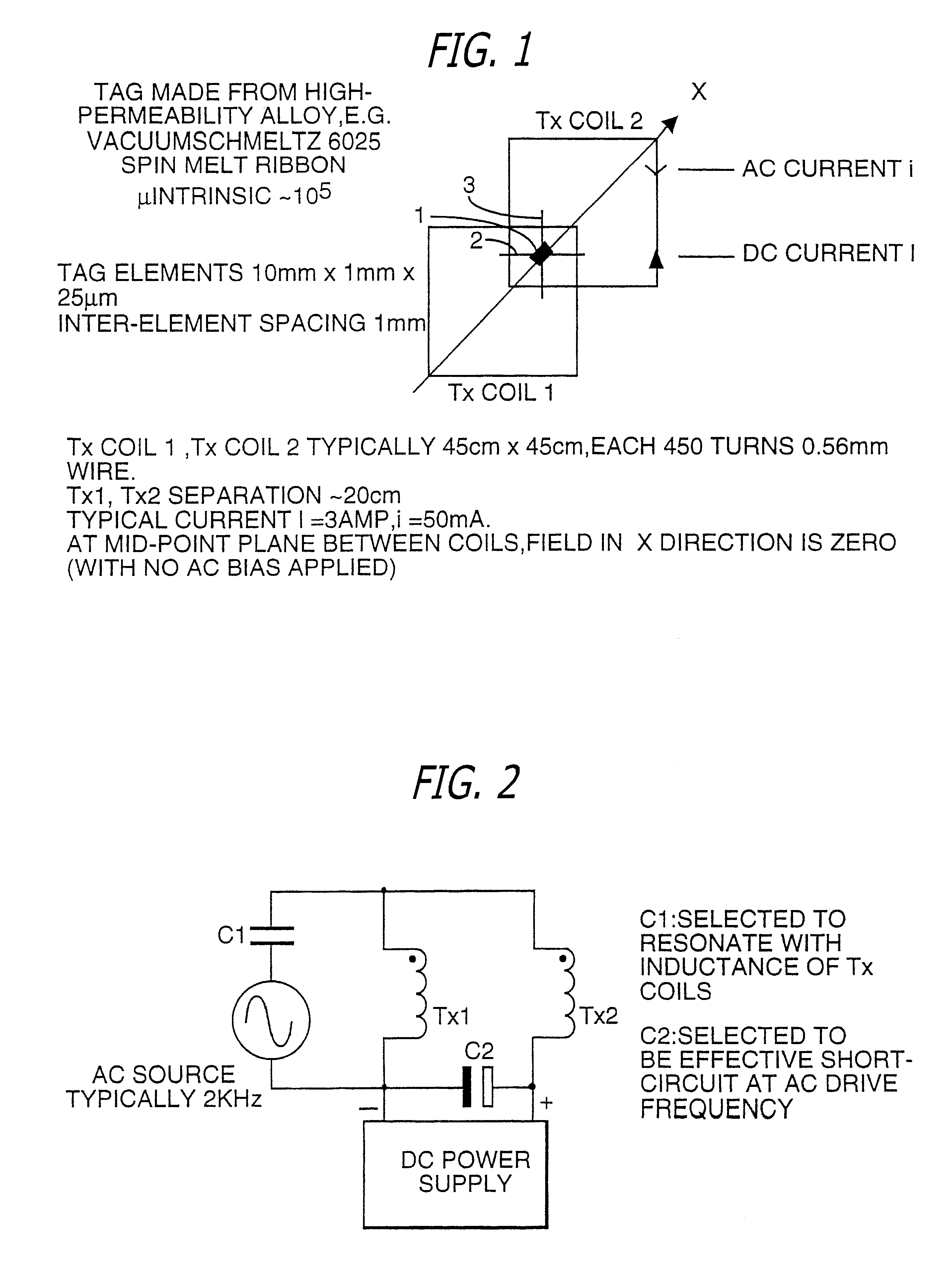
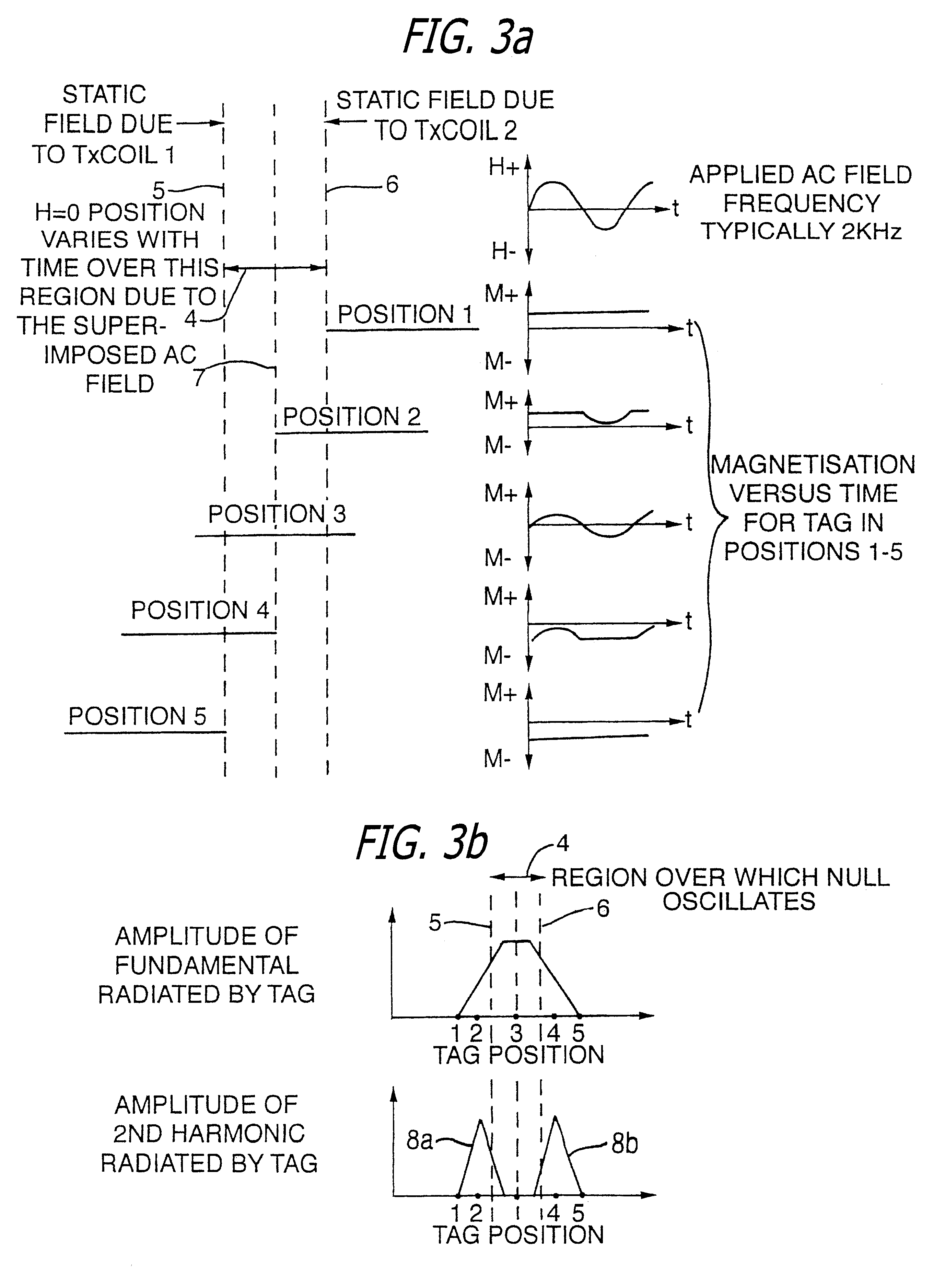
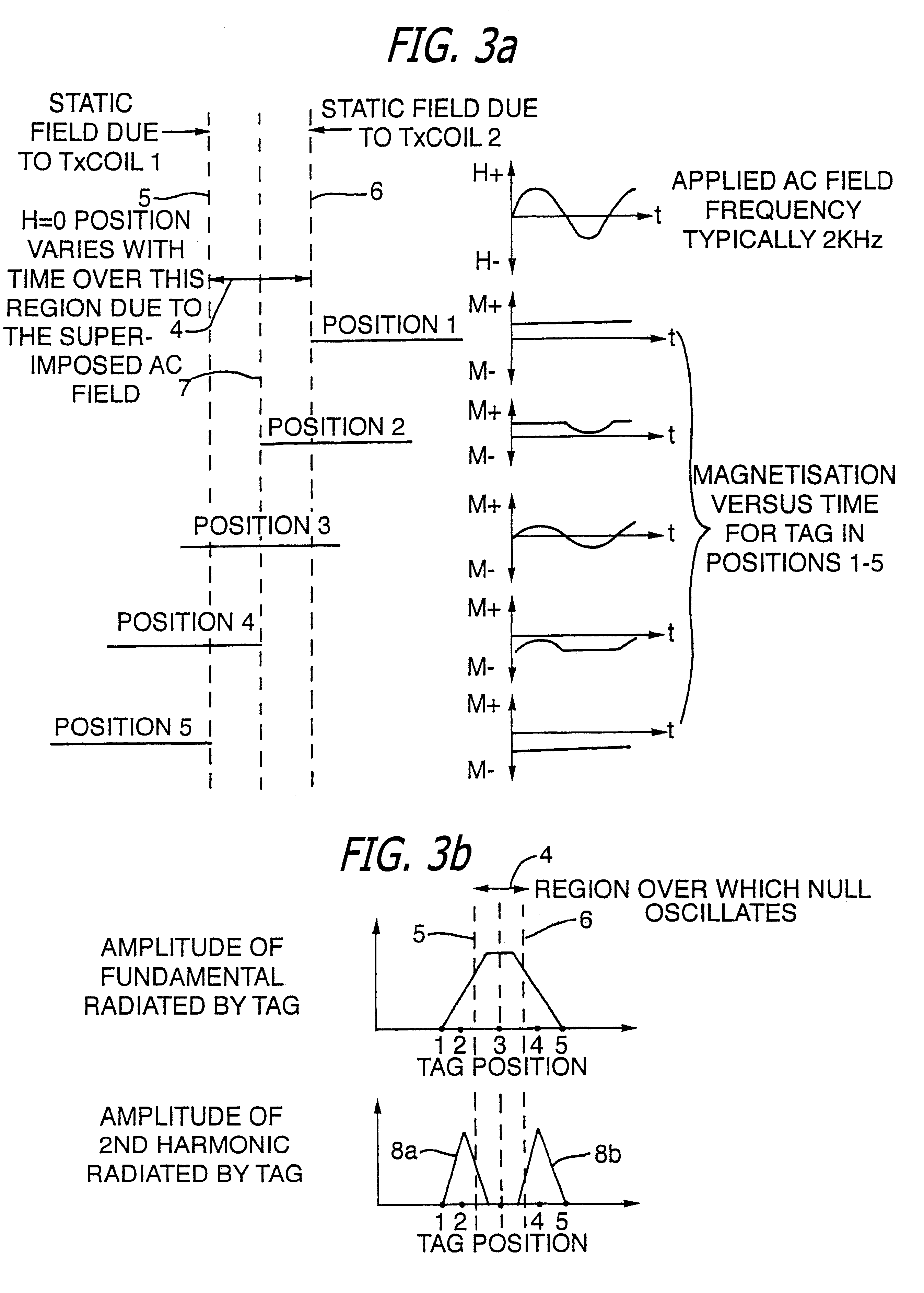
InactiveUS6144300AAvoid the needThe location information is accurateDigitally marking record carriersDiagnosticsMagnetic markerEngineering
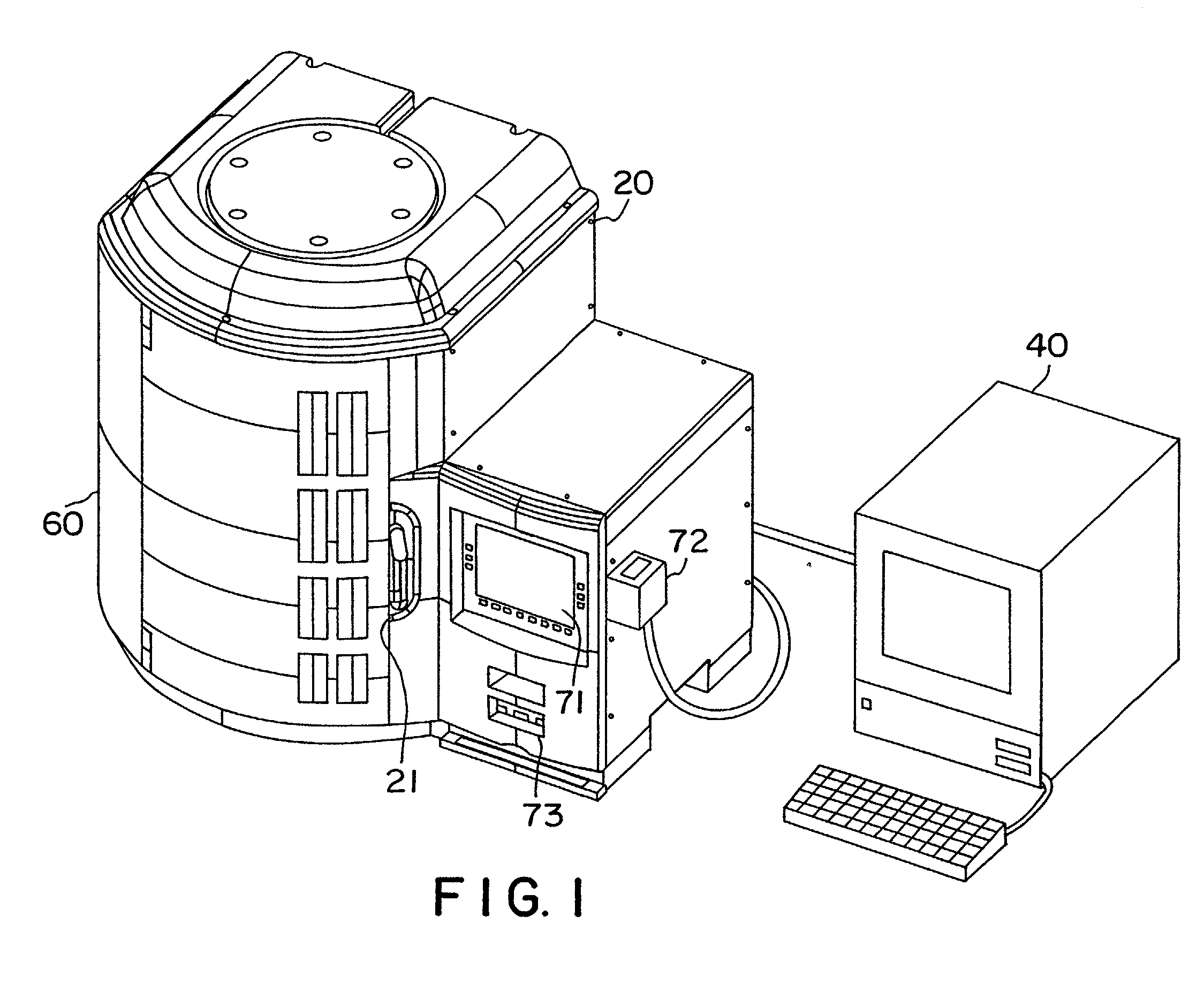
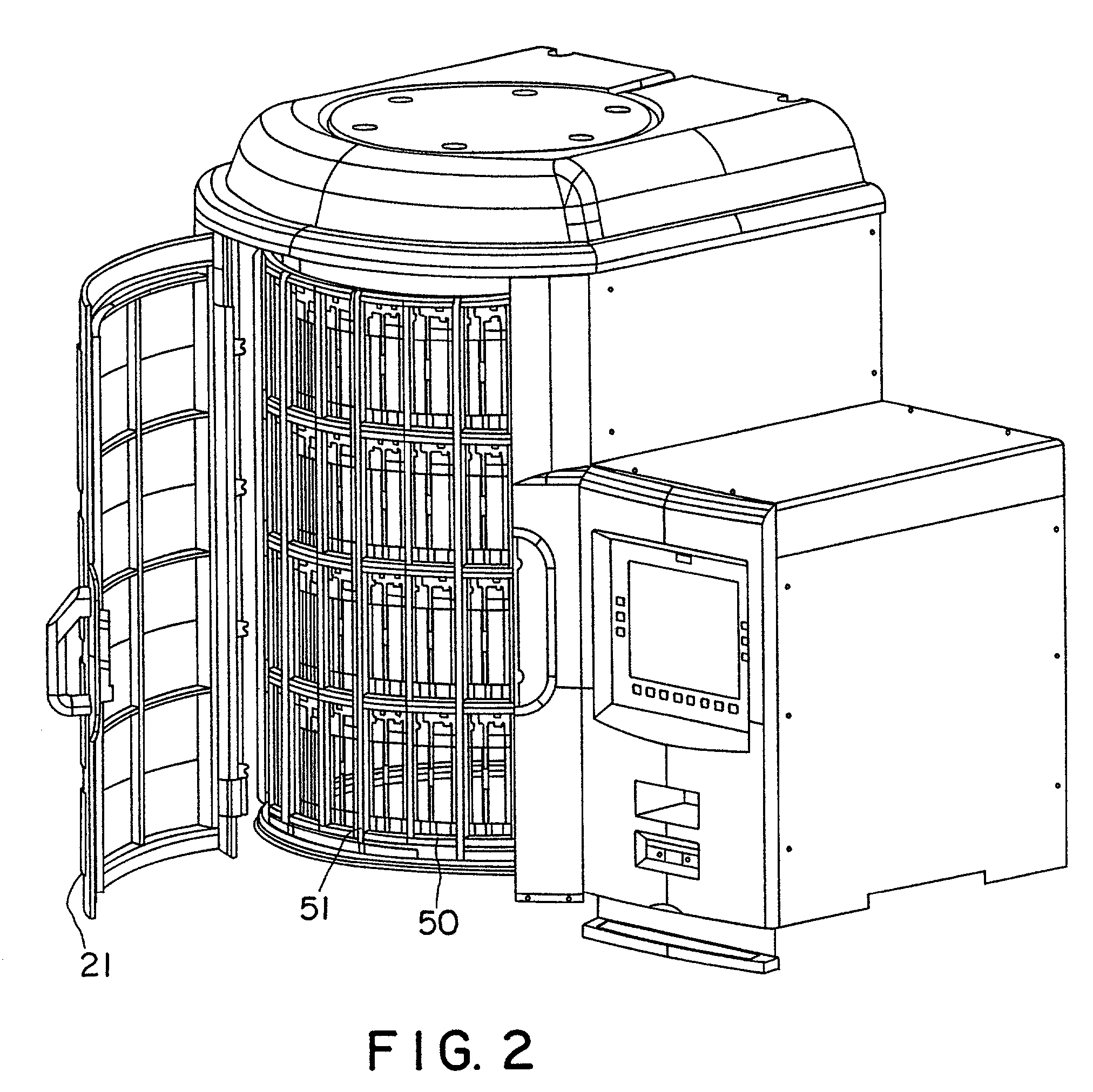
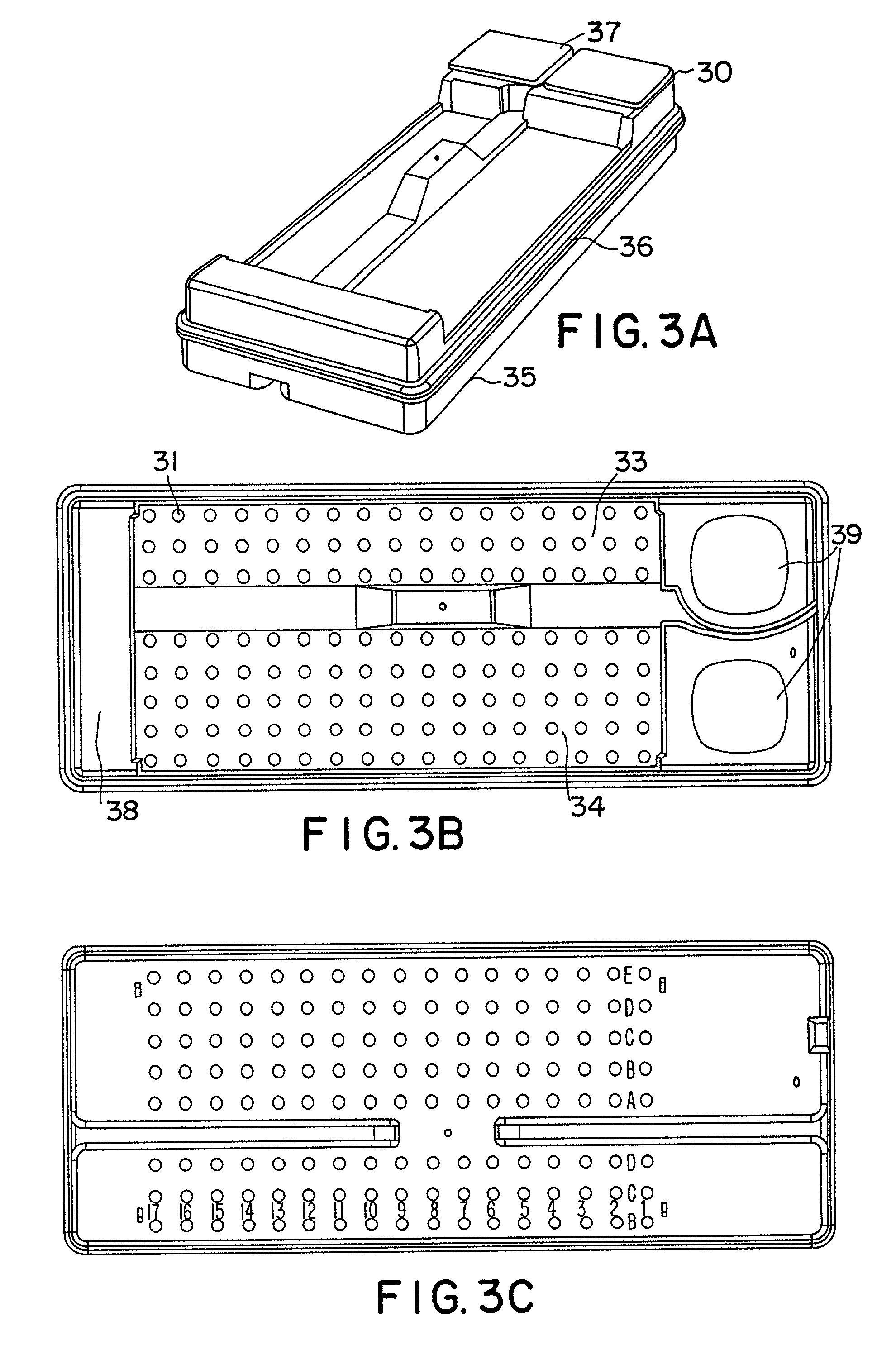
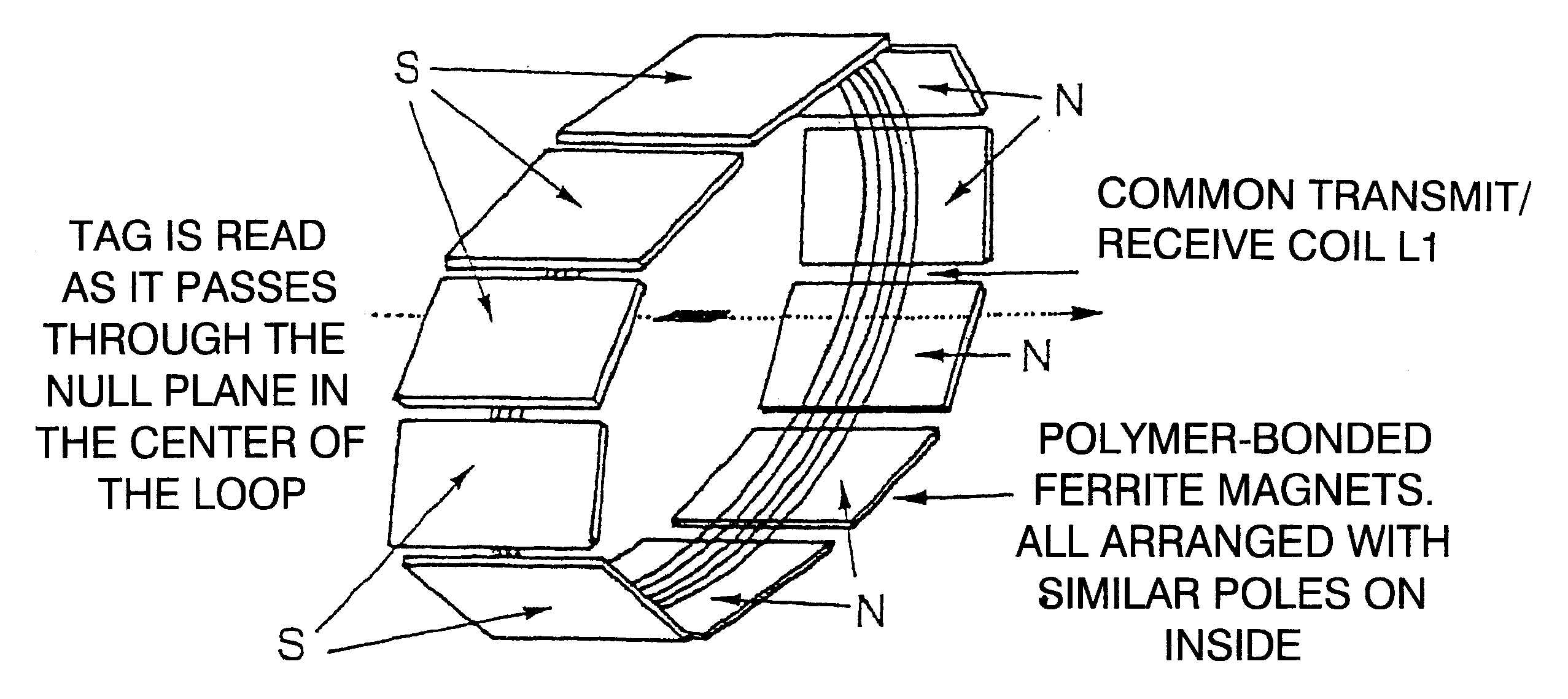
PCT No. PCT / GB96 / 00823 Sec. 371 Date Jan. 12, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jan. 12, 1998 PCT Filed Apr. 3, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 31790 PCT Pub. Date Oct. 10, 1996Magnetic tags or markers are disclosed, together with a variety of techniques by means of which such tags may be interrogated. In one aspect, the magnetic marker or tag which is characterized by carrying a plurality of discrete magnetically active regions in a linear array. In another aspect, the invention provides a method of interrogating a magnetic tag or marker within a predetermined interrogation zone, the tag comprising a high permeability magnetic material, for example to read data stored magnetically in the tag or to use the response of the tag to detect its presence and / or to determine its position within the interrogation zone, characterized in that the interrogation process includes the step of subjecting the tag sequentially to: (1) a magnetic field sufficient in field strength to sacurate the high permeability magnetic material, and (2) a magnetic null as herein defined. Applications of such techniques are describer, inter alia, in relation to (a) identifying articles to which tags are attached; (b) accurate determination of position, as in the location of surgical probes; and (c) totalisation of purchases, where cash item carries a tag coded with data representing its nature and its price.
Owner:DIGITAL MAGNETIC TECH L L C
Coplanar camera scanning system
InactiveUS6856440B2Sufficient lightingReduce intensityMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionMechanical engineeringLinear arrays
A system for scanning objects having a linear array sensor, adapted to detect light input signals, is provided. A lens is optically connected to the linear array sensor, and is adapted to receive and transmit an optical image located in a field of view along a lens axis to the linear array sensor. A light source which generates an illumination stripe in general linear alignment with the lens axis is provided. A cylindrical lens is positioned between the light source and an object to be scanned. The cylindrical lens adapted to collect, transmit and focus light from the light source to form the illumination stripe.
Owner:DATALOGIC AUTOMATION
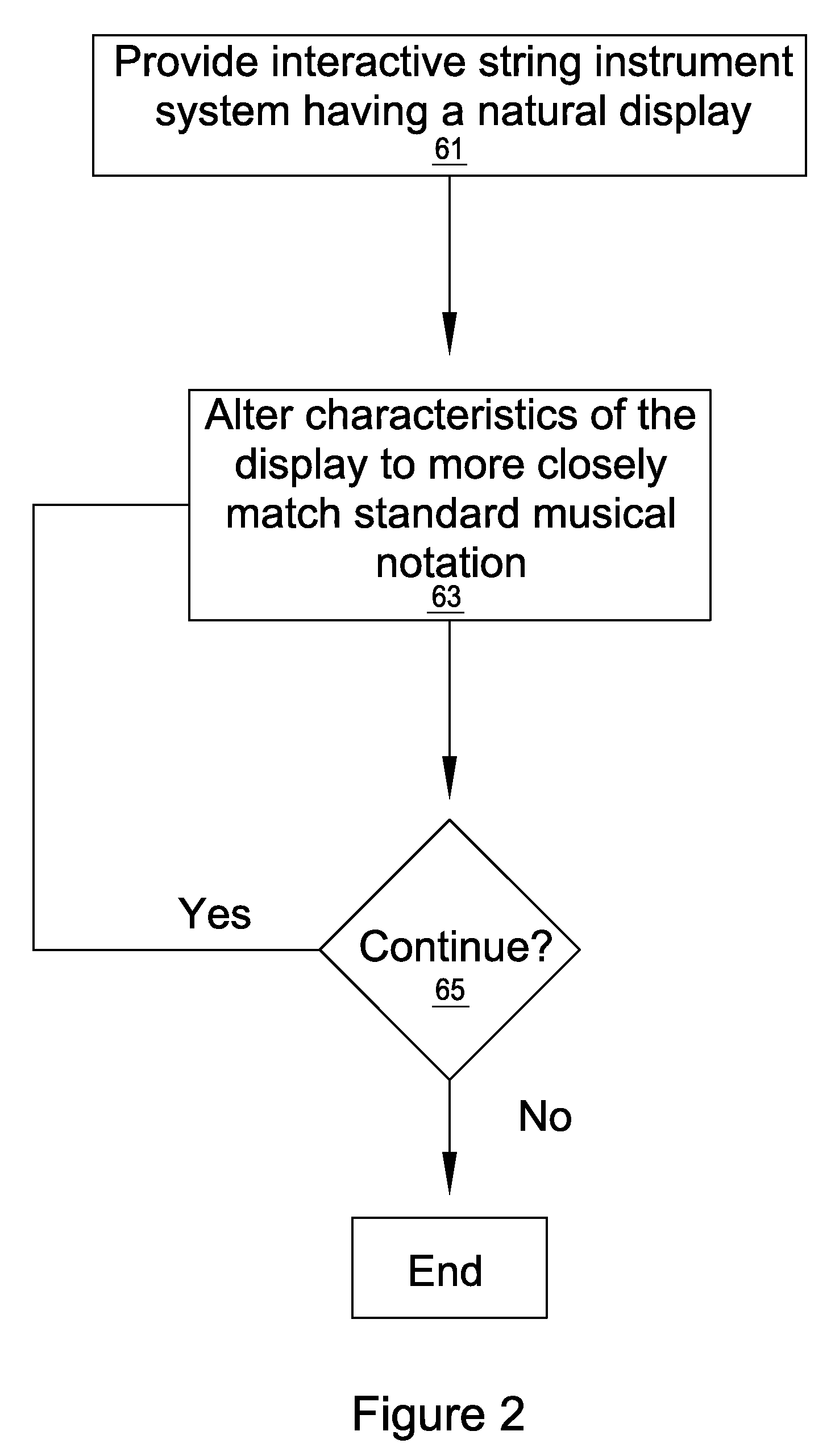
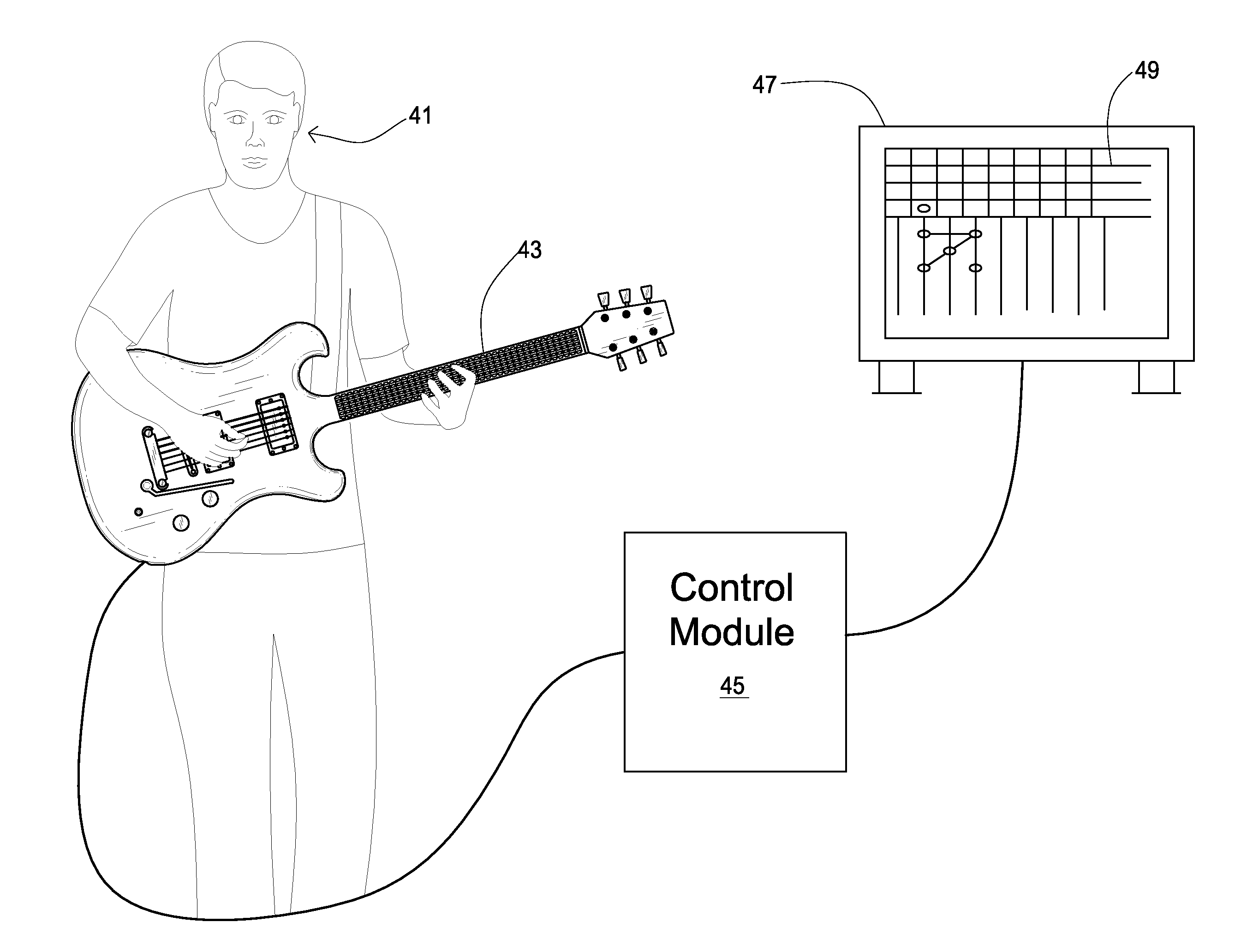
System and method of instructing musical notation for a stringed instrument
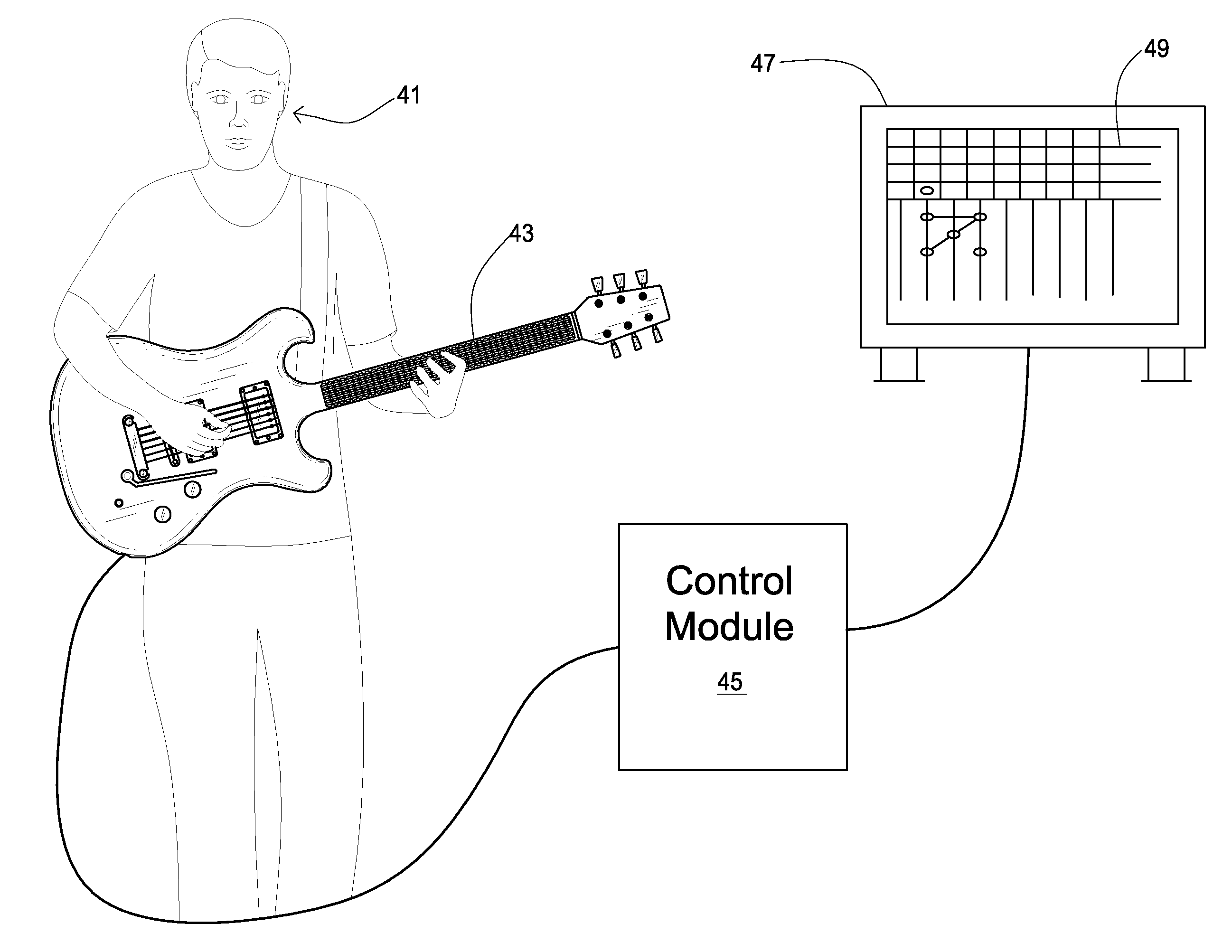
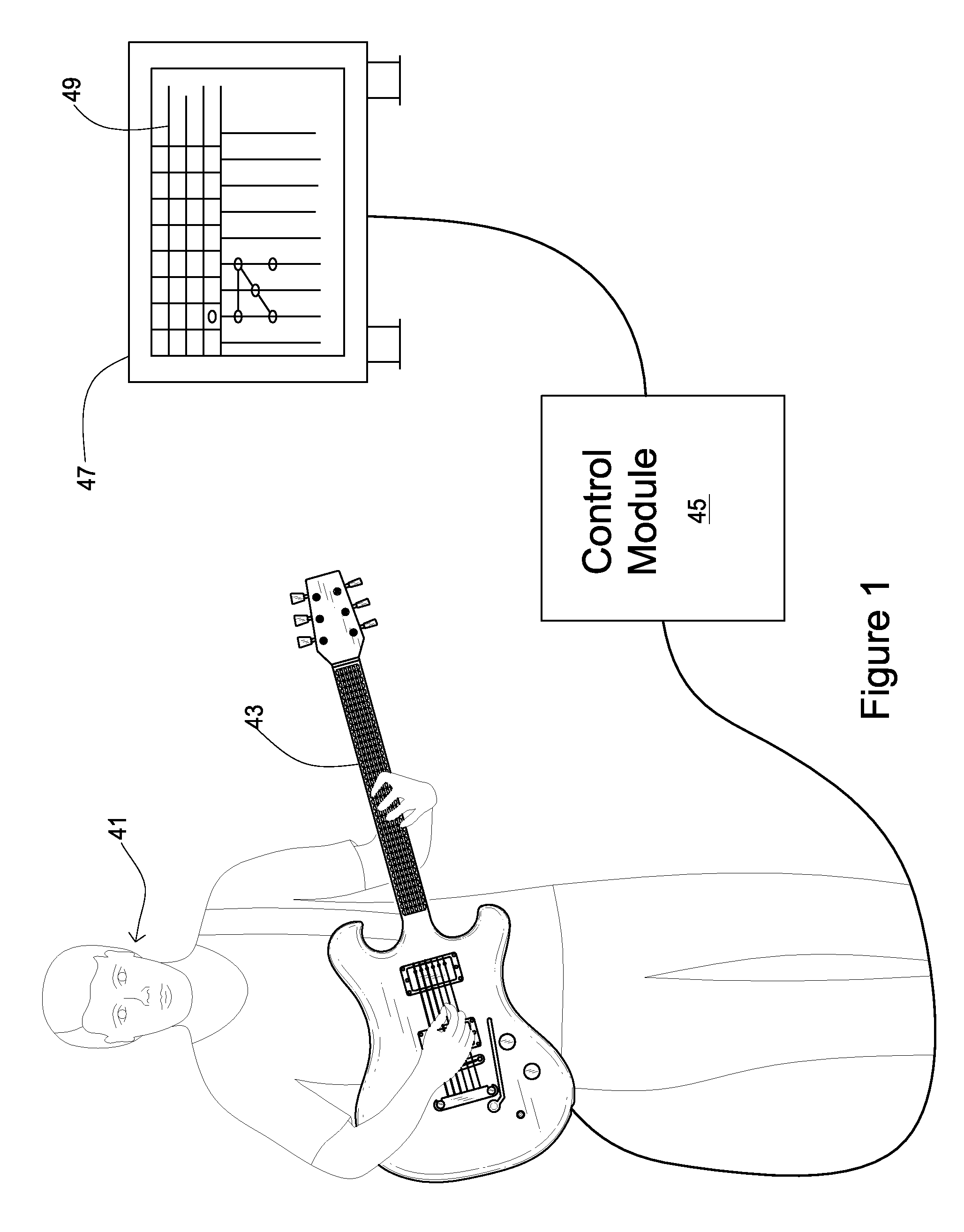
A system and method of instructing a user to read musical notation through interaction with a graphical user interface and an input instrument representative of a stringed instrument comprising a plurality of modes of instruction which progressively direct and alter characteristics of the user interface to more closely resemble standard musical notation. The graphical user interface includes a virtual fingerboard having linear arrays representing frequency ranges and note positions. The note positions and linear arrays may be coded indexed to a chromatic scale and may directly correspond to fingerboard positions on an input instrument. A game object is directed toward the virtual fingerboard in accordance with a music file is incorporated in the graphical user interface which contains data corresponding to notes in sequence that have a rhythmic pattern of arrangement coinciding with the virtual fingerboard. An evaluation of the user's performance is provided based on striking the input instrument.
Owner:ALLEGRO MULTIMEDIA
Linear solid-state lighting with broad viewing angle
ActiveUS20110176297A1Energy lossLighting support devicesPoint-like light sourceSmart lightingSurface mounting
A linear light-emitting diode (LED)-based solid-state device comprising a curved surface to hold a flexible printed circuit board with multiple linear arrays of surface mount LEDs provides lighting applications with a broad viewing angle over 180° along the radial direction. On each of the two lamp bases of the lamp, a shock-protection switch is mounted to prevent shock hazard during re-lamping.
Owner:ALEDDRA INC
Extended, ultrasound real time 3D image probe for insertion into the body
InactiveUS20050203396A1Minimize the numberReduce in quantityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryUltrasound imagingMinimal invasive surgery
An ultrasound imaging probe for real time 3D ultrasound imaging from the tip of the probe that can be inserted into the body. The ultrasound beam is electronically scanned within a 2D azimuth plane with a linear array, and scanning in the elevation direction at right angle to the azimuth plane is obtained by mechanical movement of the array. The mechanical movement is either achieved by rotation of the array through a flexible wire, or through wobbling of the array, for example through hydraulic actuation. The probe can be made both flexible and stiff, where the flexible embodiment is particularly interesting for catheter imaging in the heart and vessels, and the stiff embodiment has applications in minimal invasive surgery and other procedures. The probe design allows for low cost manufacturing which allows factory sterilized probes to be disposed after use.
Owner:ANGELSEN BJORN A J +1
Rigging system for supporting and pointing solar concentrator arrays
InactiveUS20080168981A1Reduce bending forceConvenient and reliable cable-tension adjustmentPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyTerrainRotational axis
Embodiments in accordance with the present invention relate to the design of inexpensive mounting and pointing apparatuses for linear arrays of solar energy collectors and converters. Particular embodiments in accordance with the present invention disclose a rigging system comprising at least one, and preferably a plurality of, tensile cables onto which a plurality of solar modules are fastened. Such an arrangement provides a way of suspending solar modules over land, vegetation, bodies of water, and other geographic features without substantial perturbation of the underlying terrain. Certain embodiments comprise additional tensile cables fastened to the solar modules, such that differential axial motion of the cables produces a rotational motion component of the individual solar modules of the array. This rotational motion component effects an orientation control along one rotational axis.
Owner:COOLEARTH SOLAR
Coplanar camera scanning system
InactiveUS6912076B2Reduce intensityUniform resolutionSensing by electromagnetic radiationPictoral communicationImage resolutionLinear arrays
A system for scanning objects having at least two linear array sensors, adapted to detect light input signals, is provided. A lens is optically connected to each of the linear array sensors, and are adapted to receive and transmit an optical image located in a respective lens field of view along a respective lens axis to the respective one of the at least two linear array sensor. A light source which generates an illumination stripe in general linear alignment with the lens axis across a depth of the field of view is provided. A cylindrical lens is positioned between the light source and an object to be scanned. The cylindrical lens adapted to collect, transmit and focus light from the light source to form the illumination stripe. This arrangement provides a wider system field of view with generally more uniform resolution.
Owner:DATALOGIC AUTOMATION
Telecommunications patch panel with angled connector modules
A telecommunications patch panel is provided having a plurality of connector modules rotatably mounted to a frame member. Each connector module has a front face and an opposite facing rear face, and each front face includes a plurality of connector jacks. Each rear face includes a plurality of wire termination blocks. The wire termination blocks are electrically connected to the connector jacks. Each connector module is rotatable about a rotation axis relative to the frame member. A lock selectively locks each connector module to the frame member as desired. The connector jacks and the connector modules are arranged in linear arrays perpendicular to the axis of rotation.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Automated microbiological testing apparatus and method therefor
InactiveUS7115384B2Quick analysisAccurate identificationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiotechnologyFluorescence
A diagnostic microbiological testing system and method for microorganism identification (ID) and antimicrobial susceptibility determinations (AST). The system includes multiple-well test panels capable of performing ID and AST testing on the same test panel. Each test panel is inoculated with reagents, broth-suspended organisms, and placed into the instrument system. The instrument system includes a rotating carousel for incubation and indexing, multiple light sources each emitting different wavelength light, precision calorimetric and fluorometric detection, barcode test panel tracking and a control processor for making determinations based on measured test data. One light source includes a plurality of LEDs arranged in a linear array. Each of the LEDs' junction currents are controllable to produce a predetermined illumination profile.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Apparatus for interrogating a magnetically coded tag
InactiveUS6323770B1Improve accuracyDigitally marking record carriersDiagnosticsMagnetic markerMagnetic tension force
Magnetic tags or markers are disclosed, together with a variety of techniques by means of which such tags may be interrogated. In one aspect, the magnetic marker or tag which is characterized by carrying a plurality of discrete magnetically active regions in a linear array. In another aspect, the invention provides a method of interrogating a magnetic tag or marker within a predetermined interrogation zone, the tag comprising a high permeability magnetic material, for example to read data stored magnetically in the tag or to use the response of the tag to detect its presence and / or to determine its position within the interrogation zone, characterized in that the interrogation process includes the step of subjecting the tag sequentially to: (1) a magnetic field sufficient in field strength to saturate the high permeability magnetic material, and (2) a magnetic mill as herein defined. Applications of such techniques are described, inter alia, in relation to (a) identifying articles to which tags are attached; (b) accurate determination of position, as in location of surgical probes, and (c) totalization of purchases, where each item carries a tag coded with data representing its nature and its price.
Owner:DIGITAL MAGNETIC TECH L L C
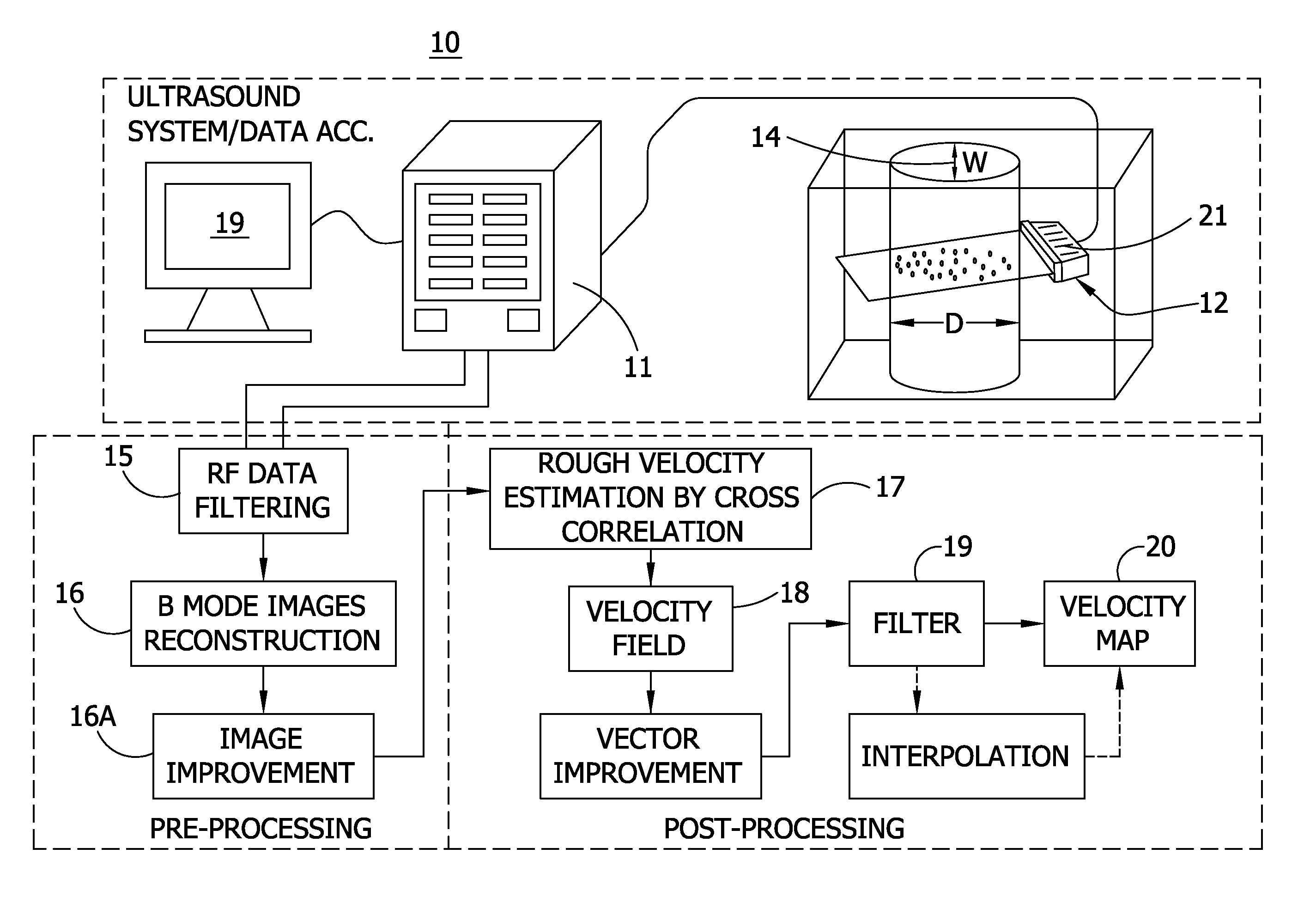
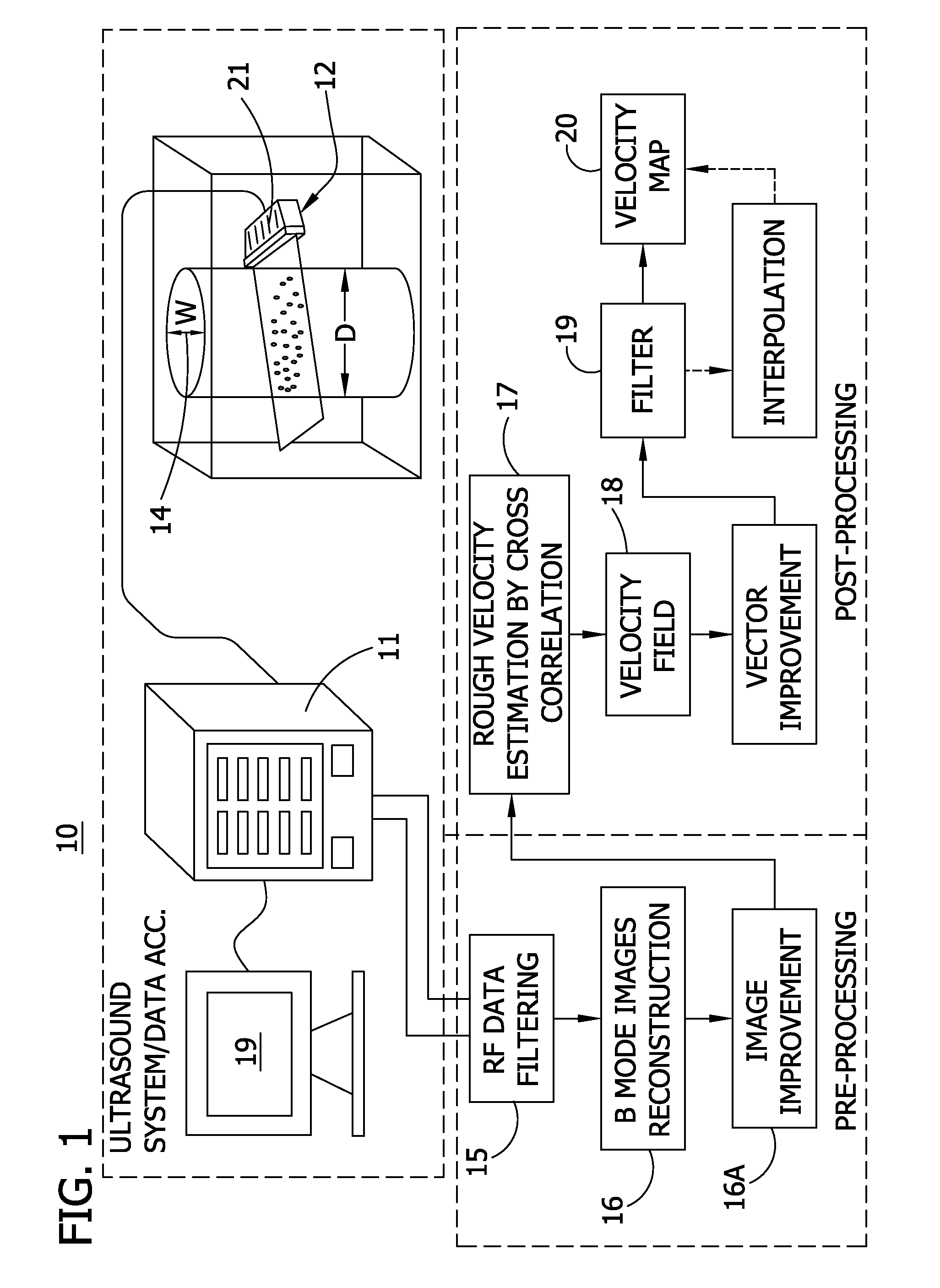
Echo particle image velocity (EPIV) and echo particle tracking velocimetry (EPTV) system and method
A system and method for detecting fluid flow. An ultrasound system comprises a signal generator providing ultrasound firing sequences applied to a linear array transducer. The transducer generating ultrasound energy applied to the fluid flow. A pre-processor comprises a digital RF data acquisition component receiving an RF signal from the transducer of back-scattered ultrasound energy and a B-mode image generation component for reconstructing images form the RF data. A post-processor executes particle image velocity (PIV) algorithms for generating velocity vectors indicative of the fluid flow. The sequences may have triangular waveforms.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
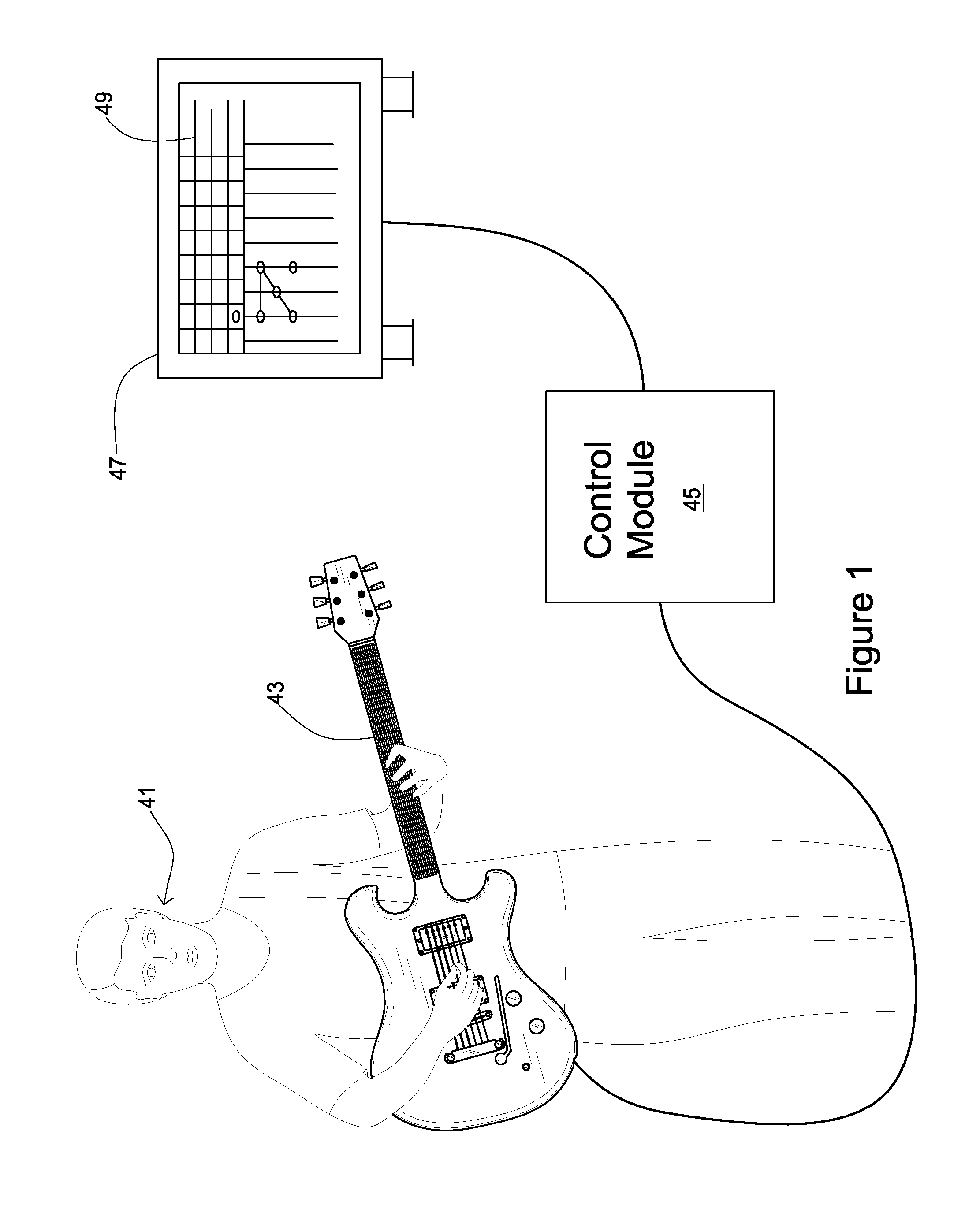
System and Method of Instructing Musical Notation for a Stringed Instrument
A system and method of instructing a user to read musical notation through interaction with a graphical user interface and an input instrument representative of a stringed instrument comprising a plurality of modes of instruction which progressively direct and alter characteristics of the user interface to more closely resemble standard musical notation. The graphical user interface includes a virtual fingerboard having linear arrays representing frequency ranges and note positions. The note positions and linear arrays may be coded indexed to a chromatic scale and may directly correspond to fingerboard positions on an input instrument. A game object is directed toward the virtual fingerboard in accordance with a music file is incorporated in the graphical user interface which contains data corresponding to notes in sequence that have a rhythmic pattern of arrangement coinciding with the virtual fingerboard. An evaluation of the user's performance is provided based on striking the input instrument.
Owner:ALLEGRO MULTIMEDIA
Extended, ultrasound real time 3D image probe for insertion into the body
InactiveUS7699782B2Minimize the numberReduce in quantityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryUltrasound imagingMinimal invasive surgery
Owner:ANGELSEN BJORN A J +1
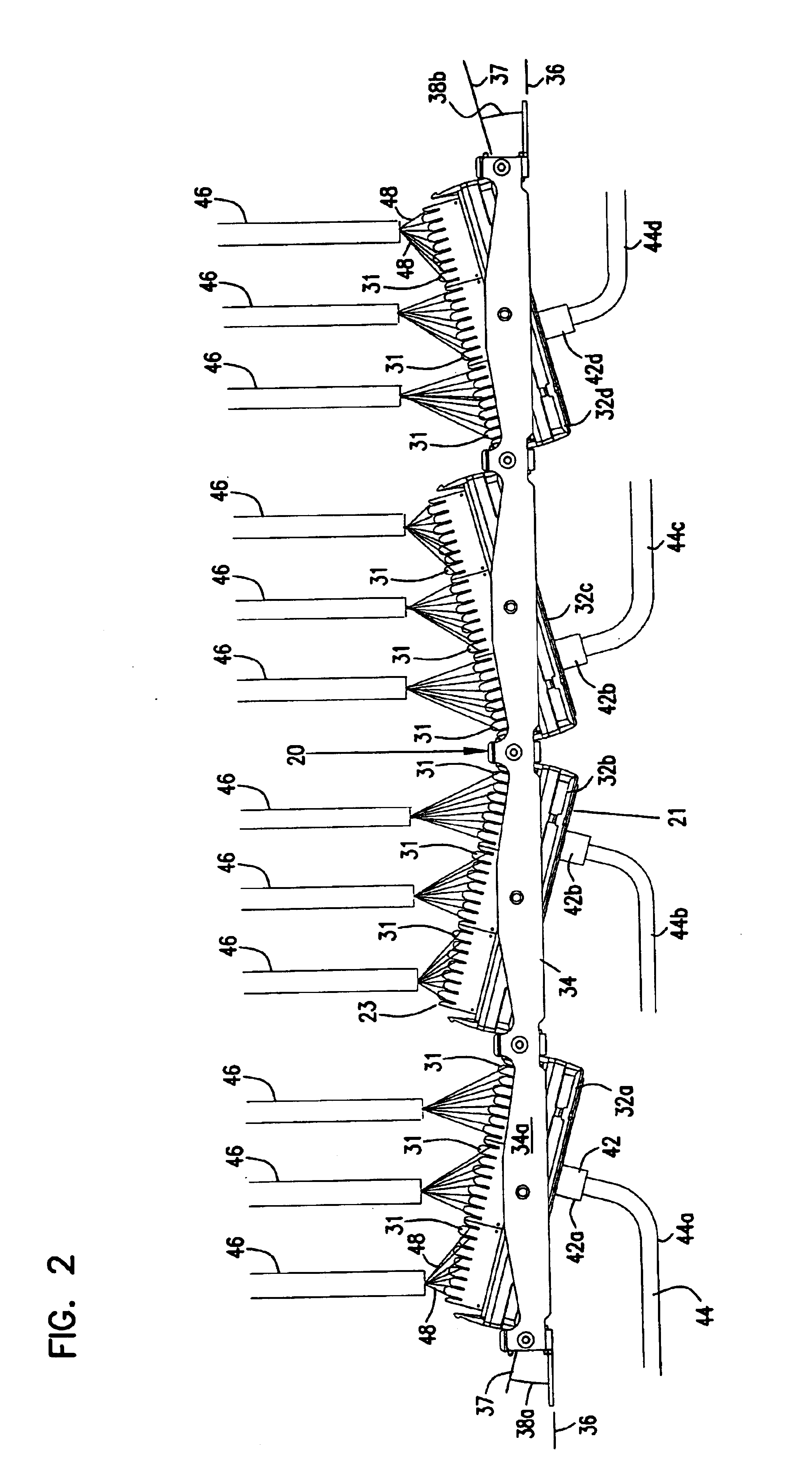
High speed electrical connector without ground contacts
InactiveUS20050170700A1Restrict levelIncrease speedCoupling protective earth/shielding arrangementsConnection contact member materialGround contactEngineering
A high speed electrical connector is disclosed. The electrical connector includes a first set of a plurality of differential signal pairs arranged in a first linear array and a second set of a plurality differential signal pairs arranged in a second linear array adjacent to the first linear array. Further, the electrical connector is devoid of a ground contact between the first linear array of differential signal pairs and the second linear array of differential signal pairs.
Owner:FCI AMERICAS TECH INC (US)
Apparatus for interrogating a magnetically coded tag
InactiveUS6323769B1Improve accuracyDigitally marking record carriersDiagnosticsMagnetic markerEngineering
Magnetic tags or markers are disclosed, together with a variety of techniques by means of which such tags may be interrogated. In one aspect, the magnetic marker or tag which is characterized by carrying a plurality of discrete magnetically active regions in a linear array. In another aspect, the invention provides a method of interrogating a magnetic tag or marker within a predetermined interrogation zone, the tag comprising a high permeability magnetic material, for example to read data stored of the tag to detect its presence and / or to determine its position within the interrogation zone, characterized in that the interrogation process includes the step of subjecting the tag sequentially to: (1) a magnetic field sufficient in field strength to saturate the high permeability magnetic material, and (2) a magnetic null as herein defined. Applications of such techniques are described, inter alia, in relation to (a) identifying articles to which tags are attached; (b) accurate determination of position, as in the location of surgical probes; and (c) totalization of purchases, where each item carries a tag coded with data representing its nature and its place.
Owner:DIGITAL MAGNETIC TECH L L C
Phased array antenna interconnect having substrate slat structures
A phased array antenna is provided having a plurality of phase shifter devices for phase shifting and beam steering a radiated beam of the phased array antenna. The plurality of phase shifter devices are interconnected with an interconnect structure comprising a plurality of linear array substrate slats. Each linear array substrate slat includes a plurality of radiating elements formed using first and second metal layers of the substrate slat, a plurality of phase shifter devices and a common RF feed conductor for the plurality of radiating elements. The common RF feed conductor is formed on a third metal layer of the substrate slat that is disposed between the first and second metal layers. The common RF feed conductor is configured to include a single location for electrical connections to receive RF signals for the plurality of radiating elements. The phased array antenna also includes bias / control conductors applied to selected areas of the third metal layer, a fourth metal layer applied over the second metal layer and a shielding metal layer applied on the fourth metal layer. The bias / control conductors are configured to include a single location for electrical connections to receive bias voltages and control signals. The fourth metal layer includes circuit connections from the bias / control circuitry to the plurality of phase shifter devices. Each phase shifter device is attached to a radiating element via a mounting location on the shielding metal layer. Accordingly, a phased array antenna interconnect structure is provided that reduces the number of electrical connections required to provide RF signals and bias / control signals to multiple radiating elements and phase shifters, respectively, of the phased array antenna and provides a cost effective phased array antenna architecture that has a single locus of electrical connection for RF and bias control signals embedded in a multi-layer linear array or slat substrate of the phased array antenna.
Owner:ADVANCED HEALTH MEDIA +1
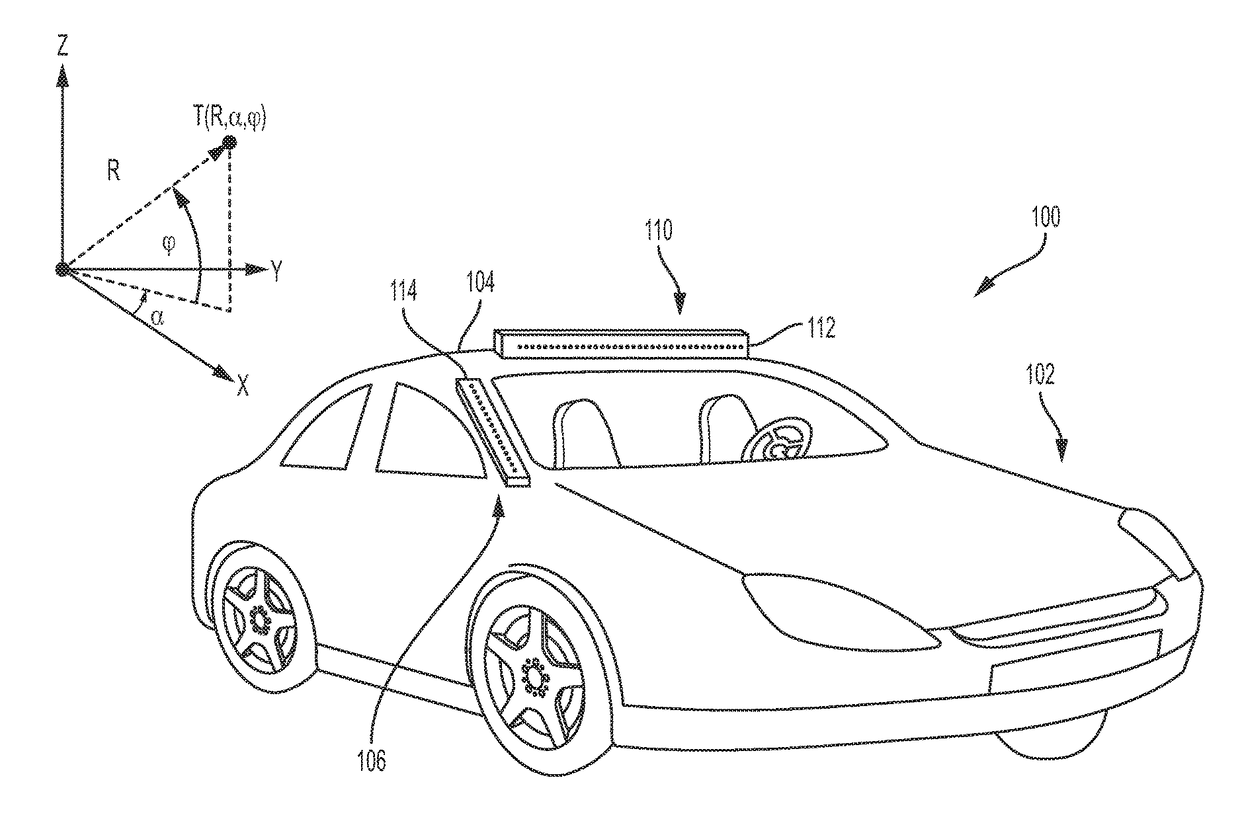
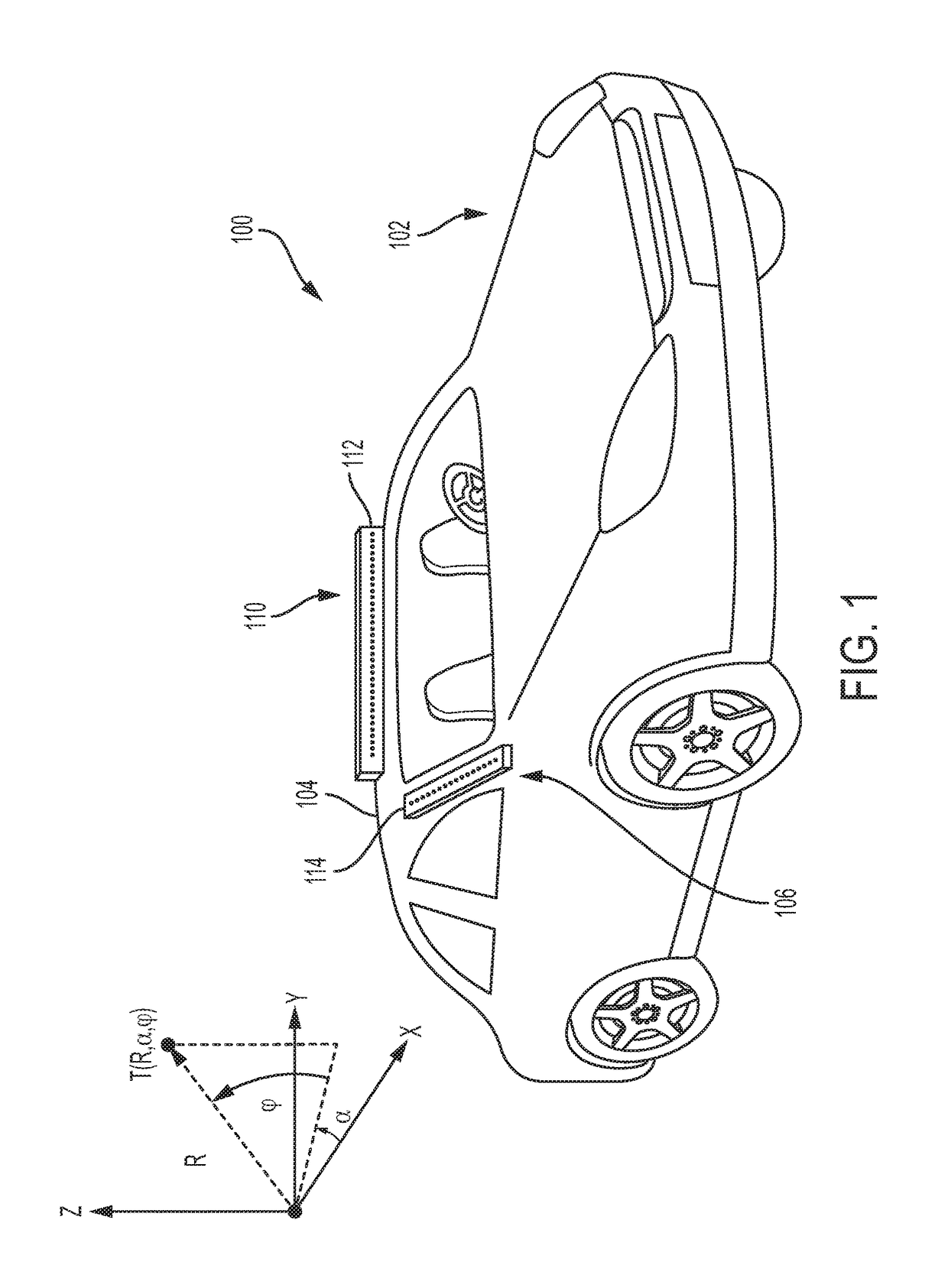
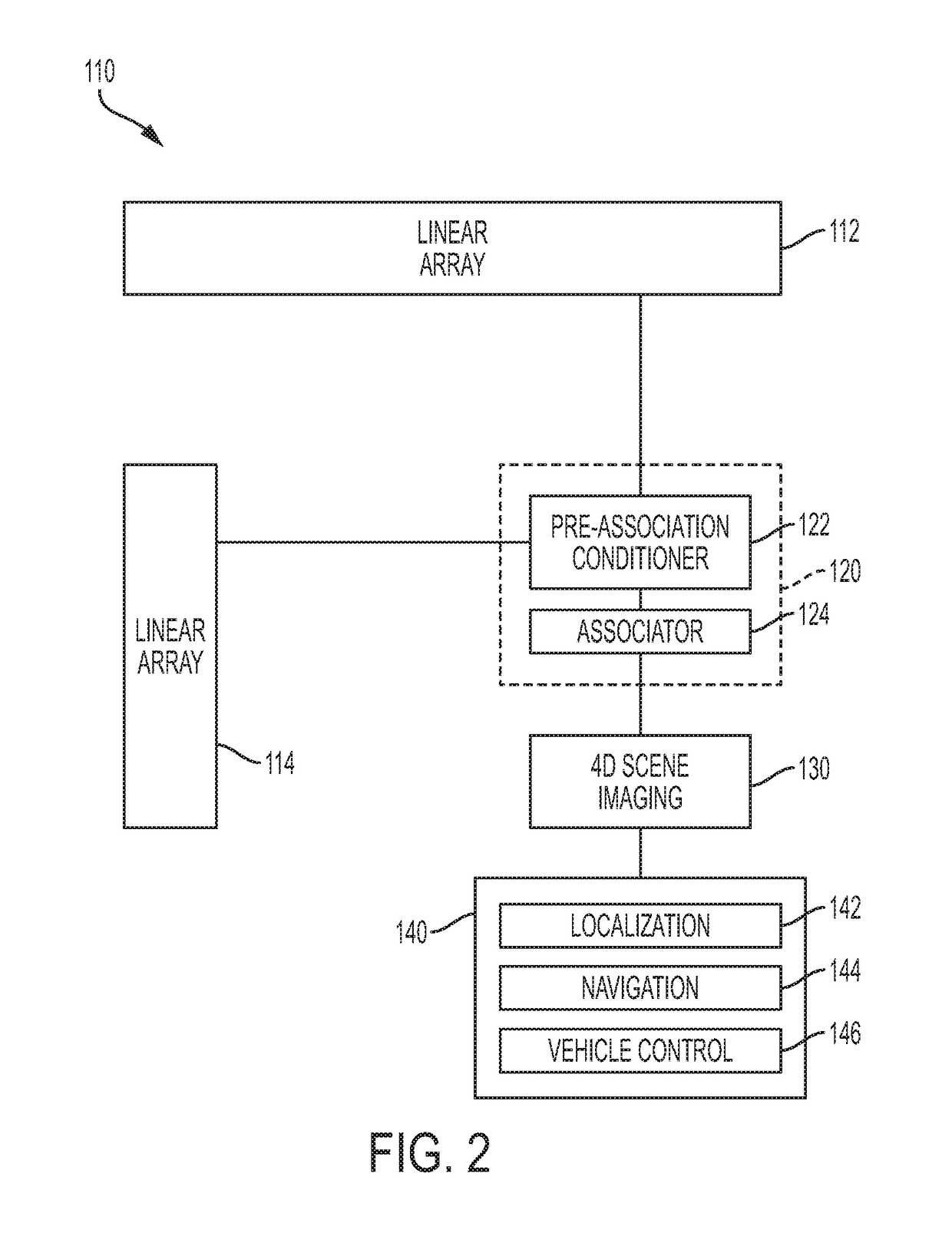
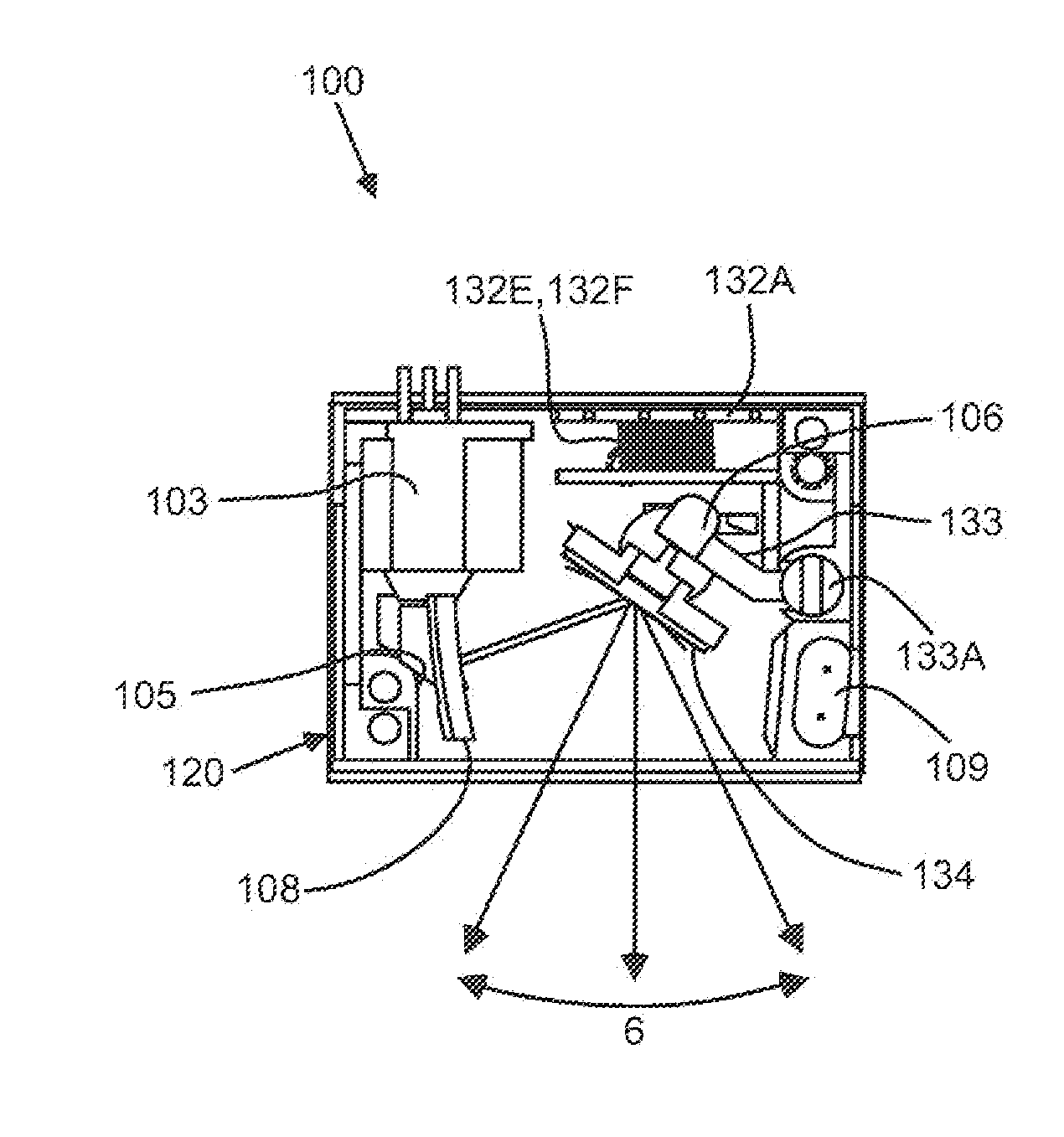
Low cost 3D radar imaging and 3D association method from low count linear arrays for all weather autonomous vehicle navigation
A low cost, all weather, high definition RF radar system for an autonomous vehicle is described. The high definition RF radar system generates true target object data suitable for imaging, scene understanding, and all weather navigation of the autonomous vehicle. The high definition RF radar system includes a pair of independent orthogonal linear arrays. Data from both linear arrays is fed to a processor that performs data association to form true target detections and target positions. A Boolean association method for determining true target detections and target positions reduces many of the ghosts or incorrect detections that can produce image artifacts. The high definition RF radar system provides near optimal imaging in any dense scene for autonomous vehicle navigation, including during visually obscured weather conditions such as fog.
Owner:RFNAV INC
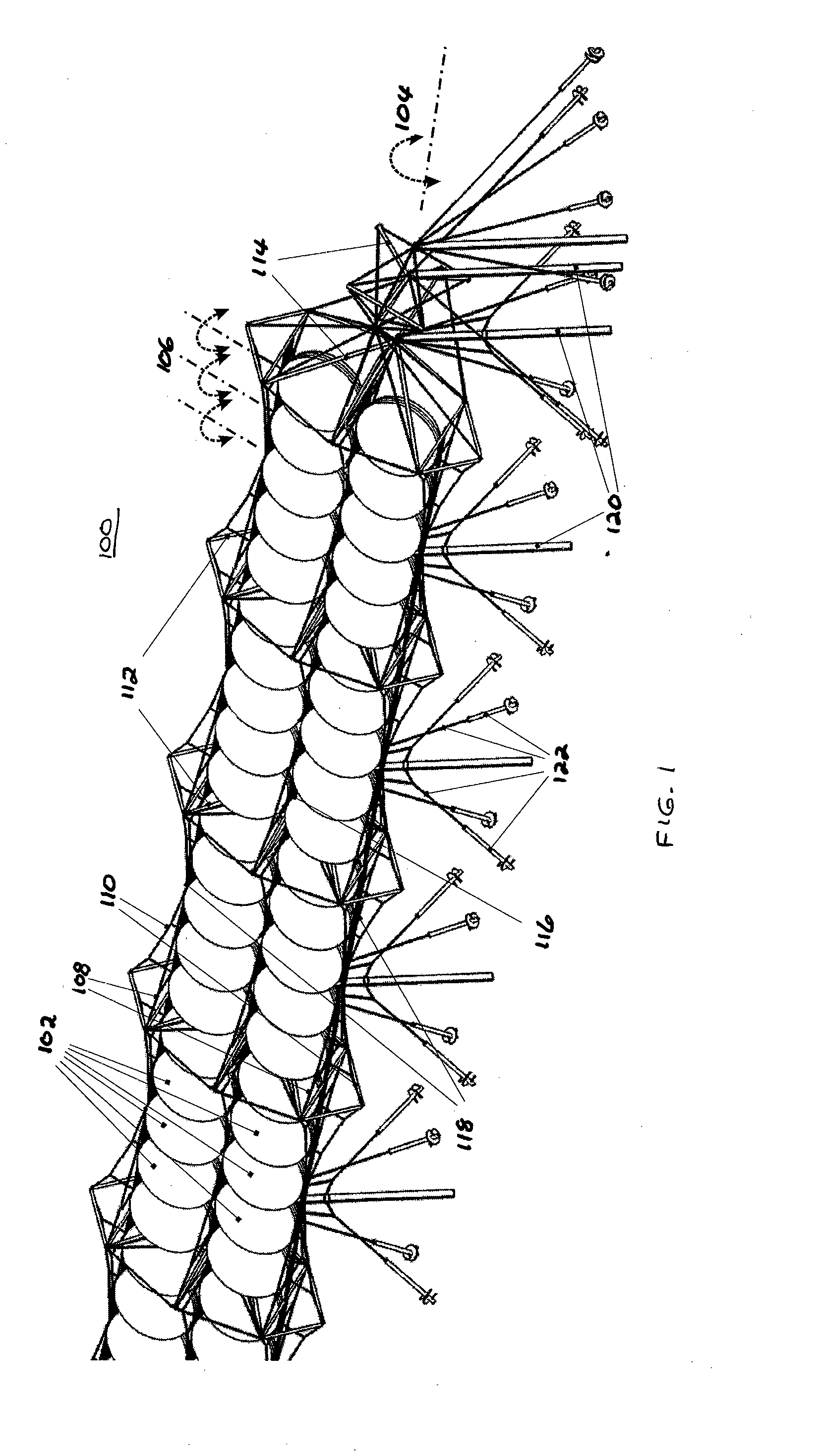
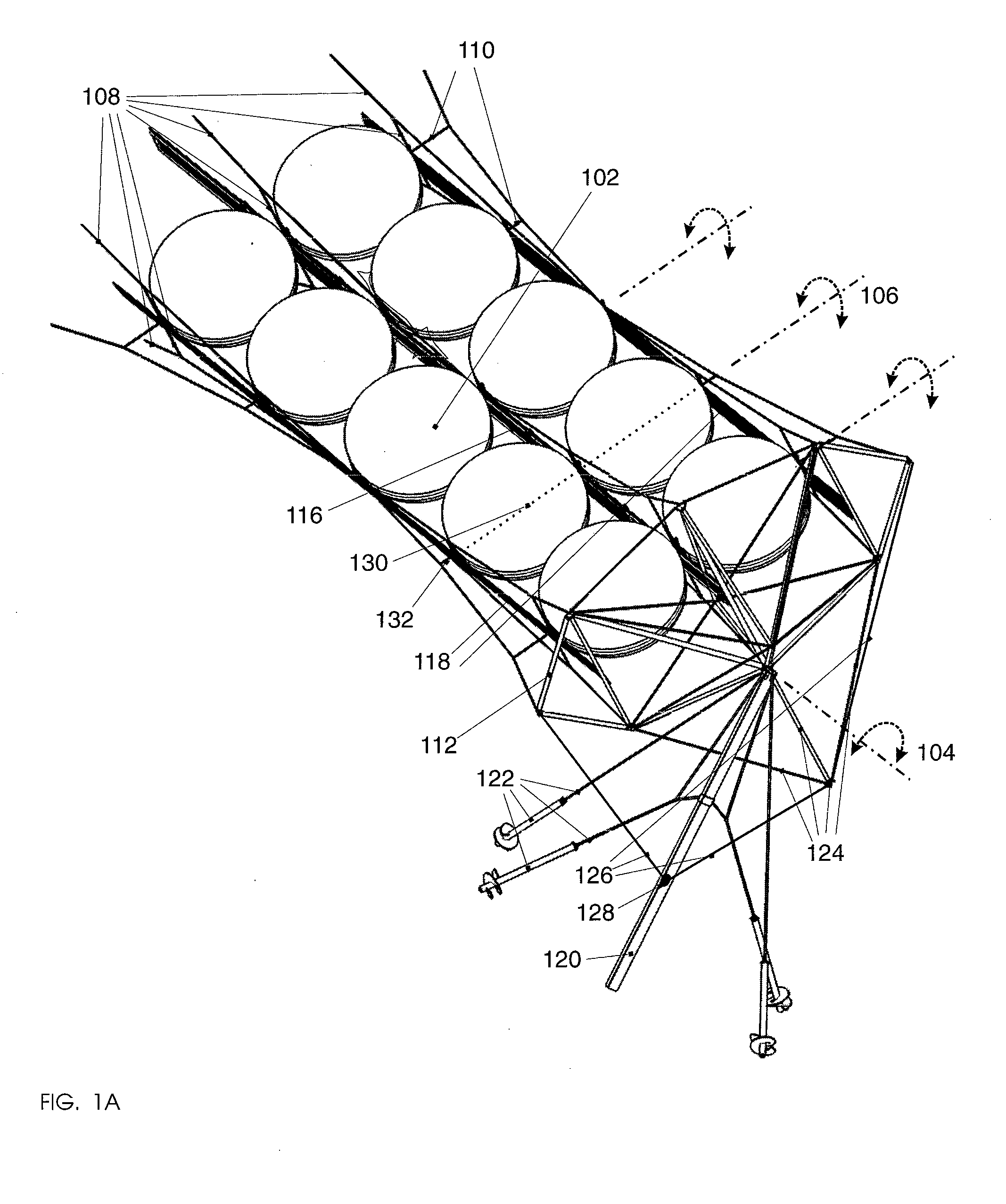
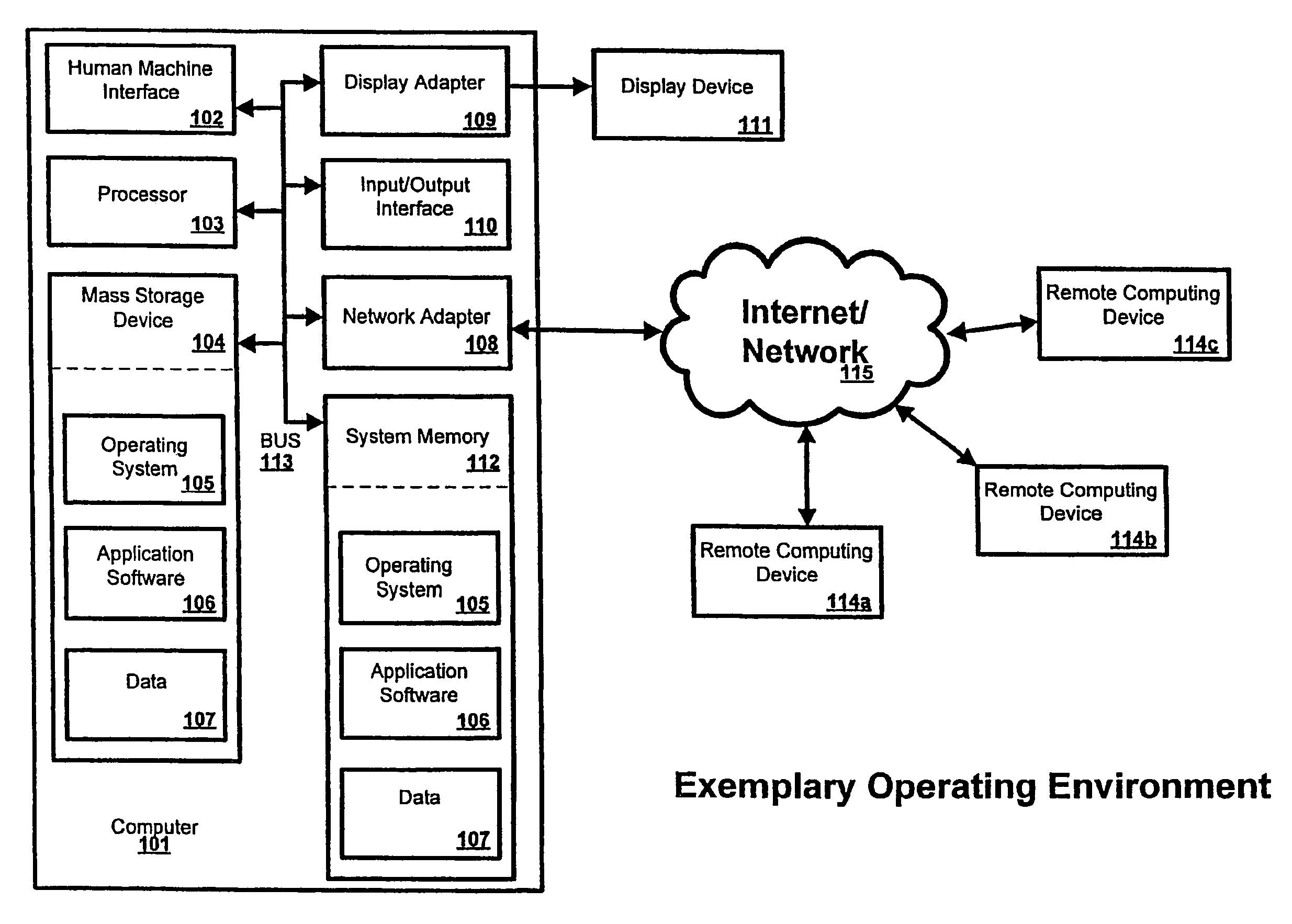
Laser scanning module with rotatably adjustable laser scanning assembly
A laser scanning module employing a laser scanning assembly mounted within a module housing using a mechanism that allows the laser scanning assembly to be rotated to an angular position within the engine housing so that light collection, beam folding and light collection mirrors in the module housing are optically aligned. A PC board is mounted on a side of the housing and has a configuration of elongated apertures of open-ended and / or closed geometry, arranged in a non-parallel manner. An electromagnetic coil structure, associated with the laser scanning assembly, has a linear array of electrically-conductive pins that project through the configuration of elongated holes, at locations along the elongated holes that are determined by the angular rotation of the laser scanning assembly attained during optical alignment conditions during manufacture.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
Light emitting diode package assembly that emulates the light pattern produced by an incandescent filament bulb
ActiveUS20050189557A1Efficient manufacturingPoint-like light sourceLighting heating/cooling arrangementsSurface layerHeat sink
In accordance with the invention, a light emitting diode package assembly is provided to emulate the pattern of light produced by an incandescent filament bulb. The package assembly is composed of a substrate for LEDs comprising a heat-sinking base having a pair of opposing major surfaces. Each major surface has an overlying of thermally conducting ceramic and an outer surface layer of light reflective material. Disposed on each surface layer is a plurality of LEDs. Advantageously, the LEDs are arranged on the surface in a configuration of low mutual obstruction. Advantageously, reflecting elements transverse to each surface layer are positioned and shaped to reflect a substantial portion of the light emitted from the LEDs that would otherwise enter neighboring LEDs. In a preferred embodiment, the LEDs are arranged in the general form of a closed curve, and a transverse reflector is disposed in the interior of the curve. Alternatively, the LEDs can be arranged in a linear array. The assembly can be efficiently fabricated by back-to-back assembly of two similar subassemblies.
Owner:LIGHTING SCI GROUP
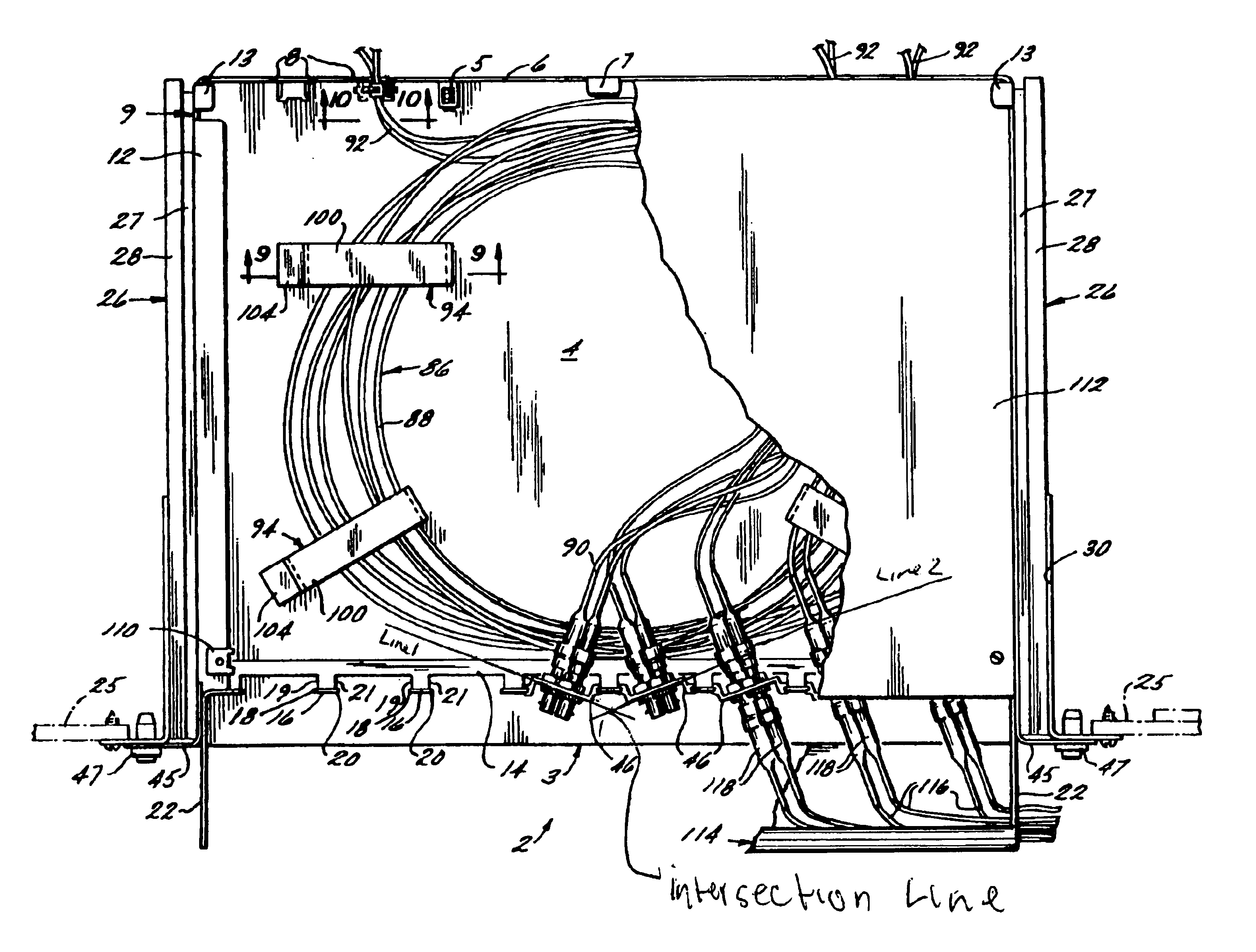
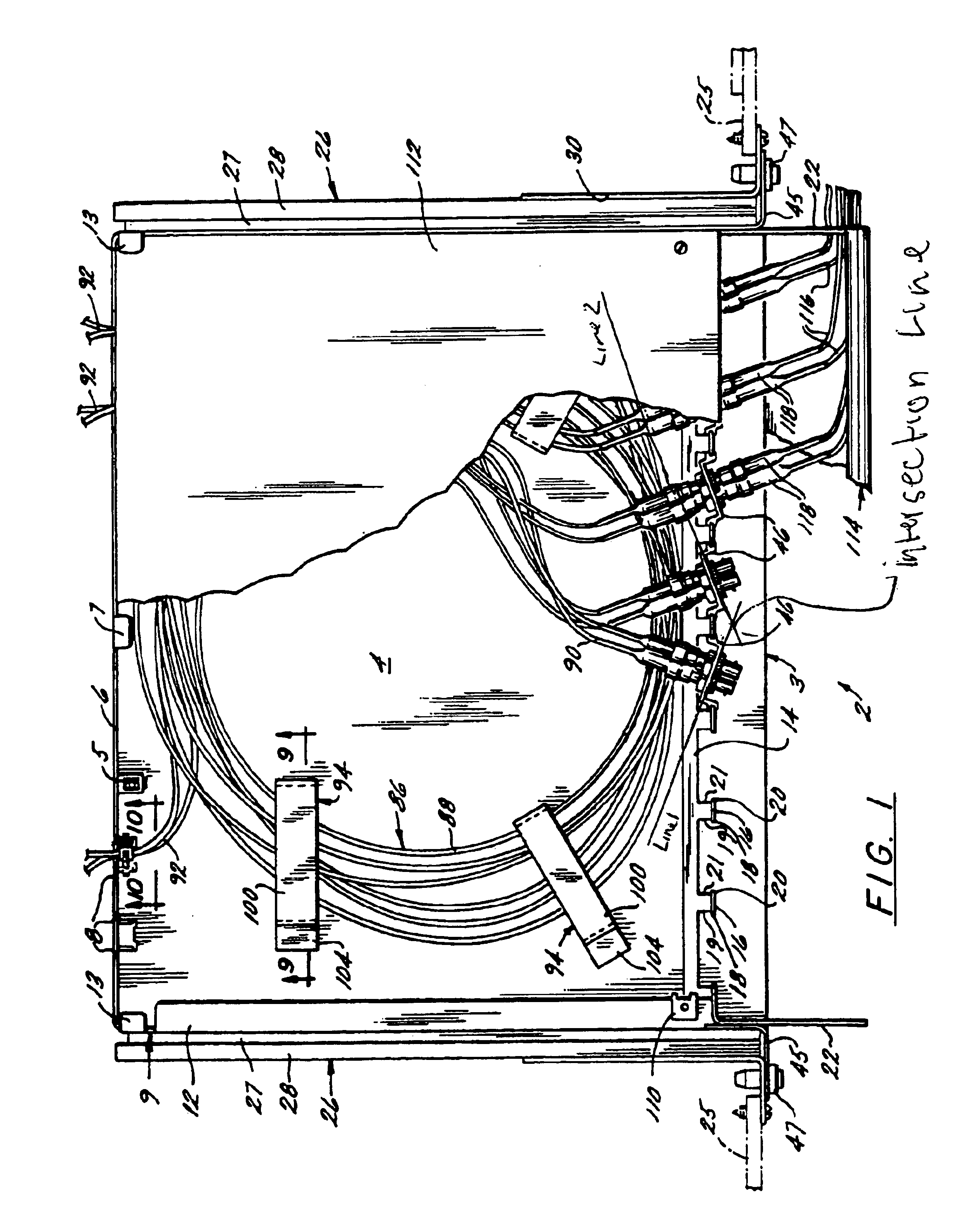
Systems and methods for detecting and analyzing polymers
InactiveUS7351538B2Easy to detectEasy to identifyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWide fieldLinear arrays
A detection system and methods for improving the ability of the detection system to recognize labels that are disposed on a polymer. Embodiments of the invention include schemes for selecting emitters and labels used within the system in a manner that allows an increase in the number of distinct labels that can be used together in a system. In other embodiments, the detection system and methods are directed to identifying portions of a detection signal that may be associated with extra labels residing within a detection zone. In other embodiments, the detection system and methods relate to using wide field imaging detectors while reducing out of focus noise contributions to detection signals of the system. Still, other embodiments relate to the use of linear array detectors to detect labels.
Owner:U S GENOMICS INC
High frequency array ultrasound system
Owner:SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCI CENT +1
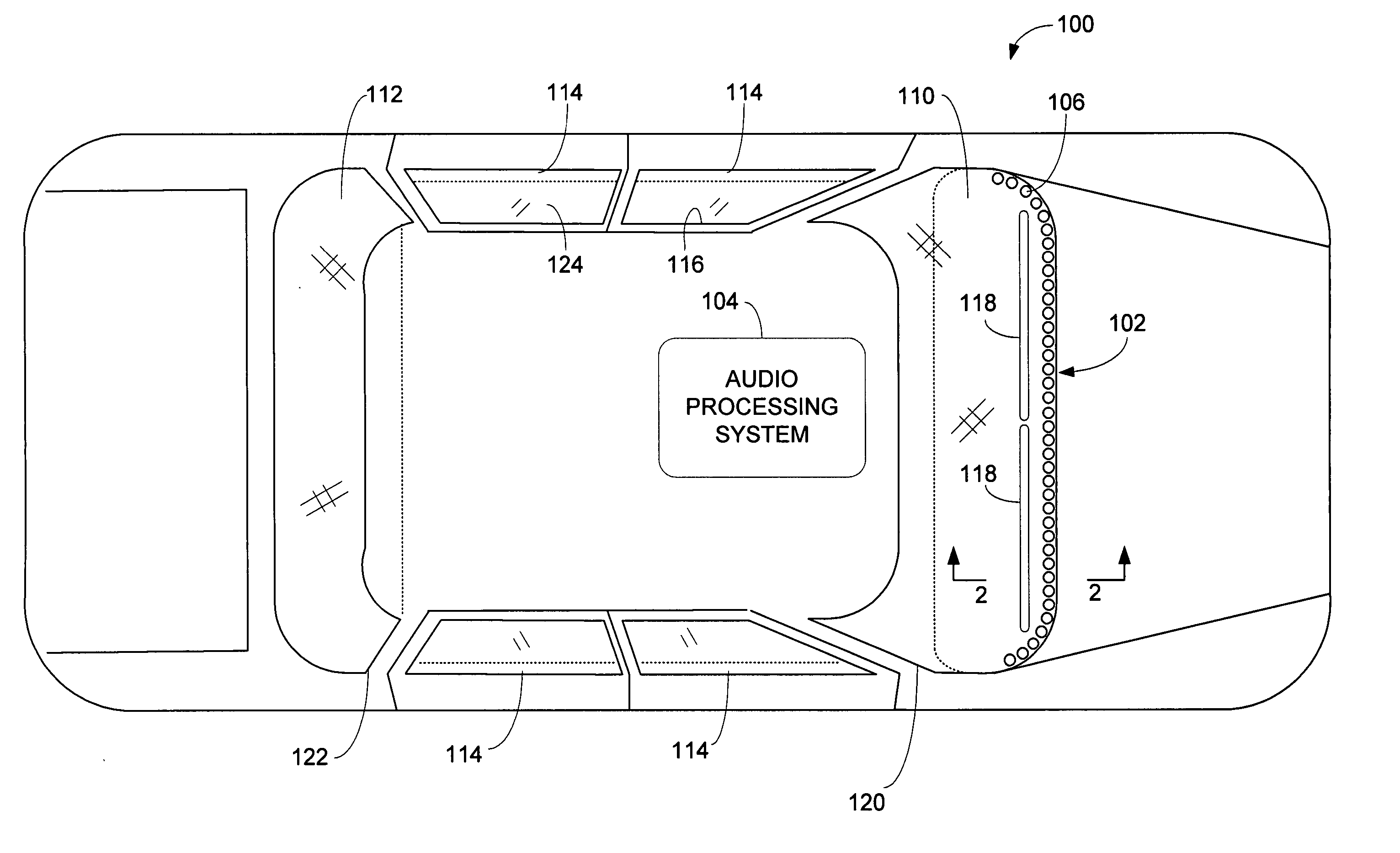
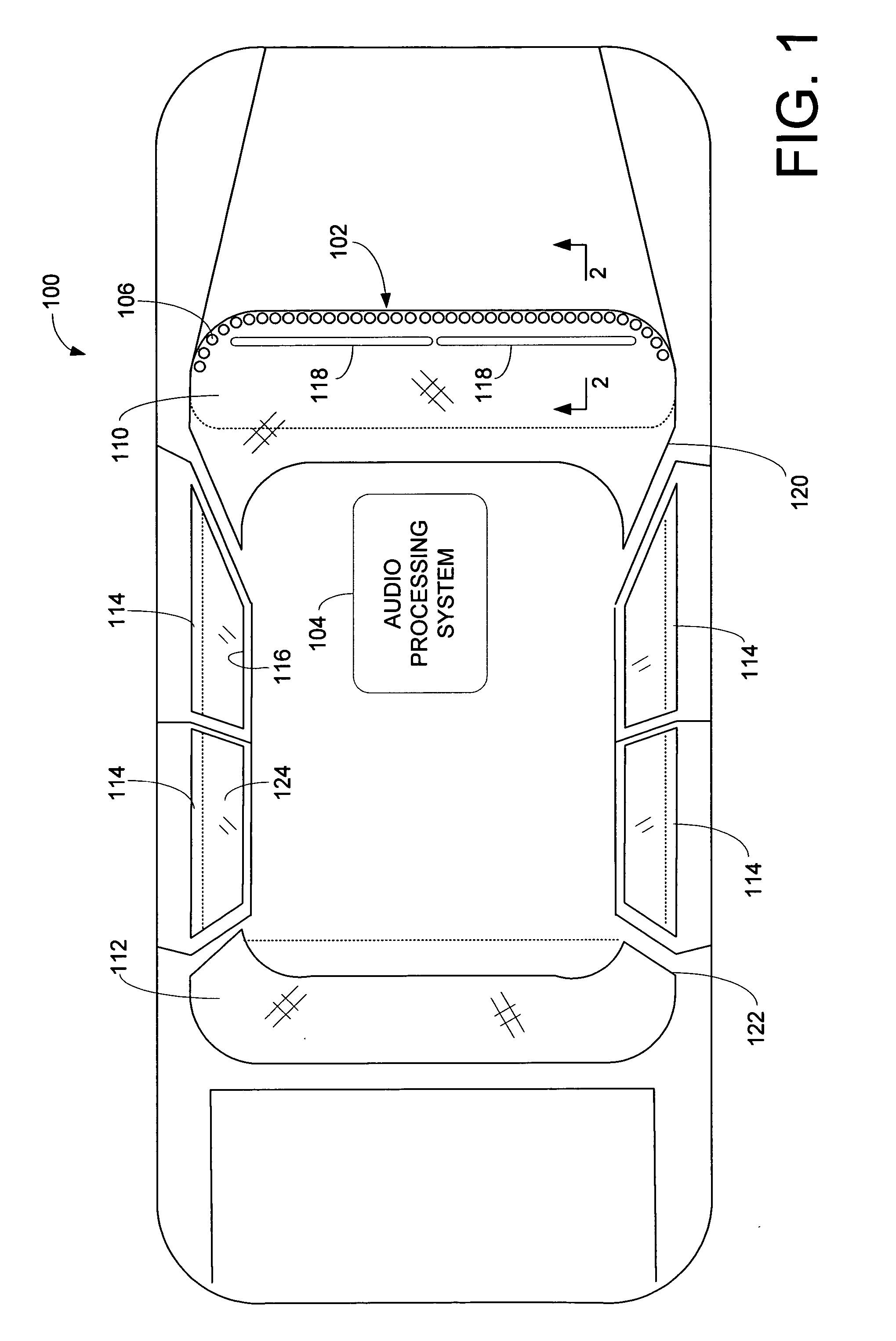
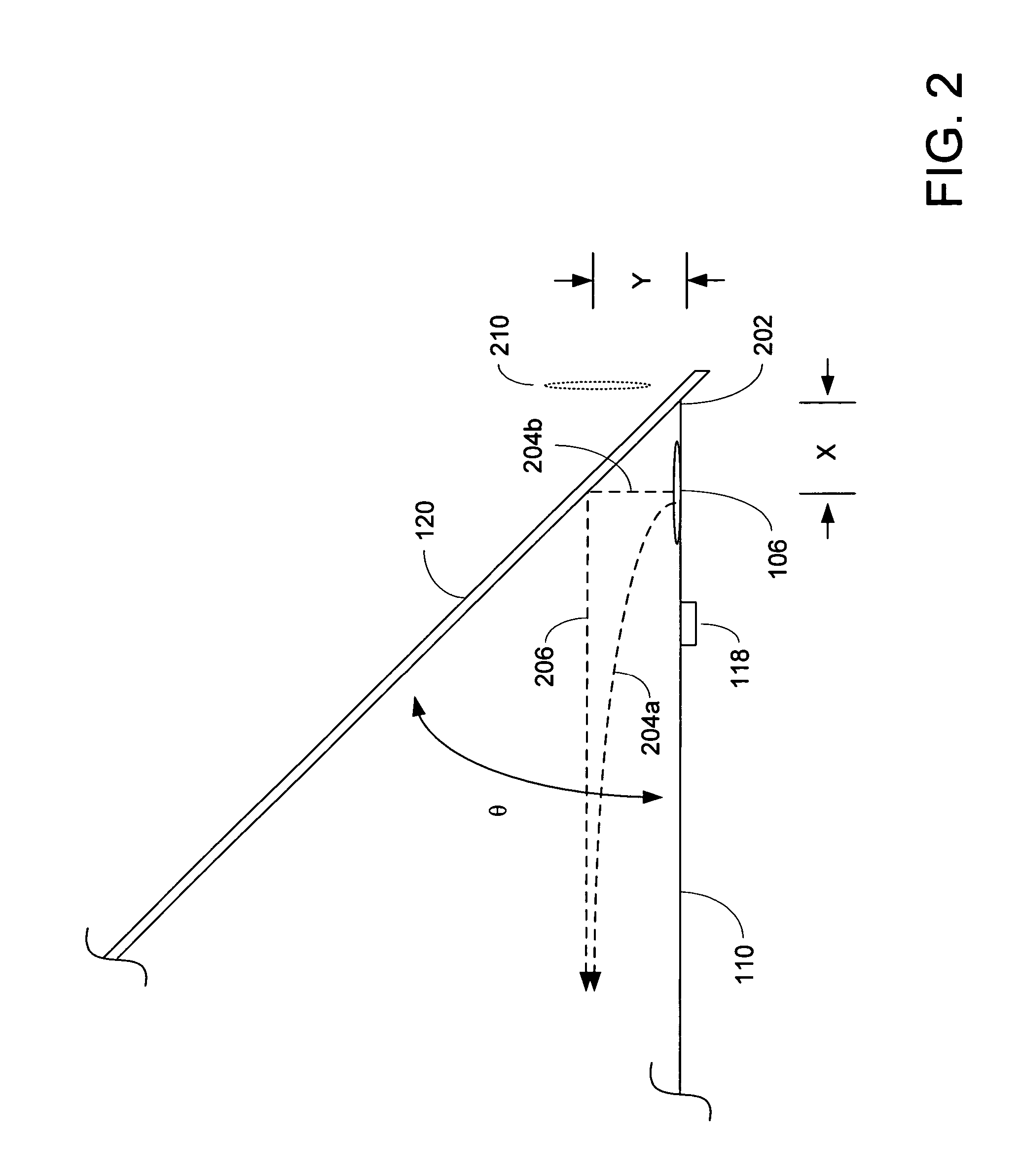
Vehicle loudspeaker array
ActiveUS20050259831A1Expand coverageImprove imaging clarityTransmissionFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsUltrasound attenuationDashboard
An audio processing system for a vehicle includes a plurality of loudspeakers positioned to form a single line array. The loudspeaker line array is positionable in a vehicle on a dashboard of the vehicle substantially at the convergence of the dashboard and a window of the vehicle. When the loudspeaker line array is driven by an audio signal, a vertically and horizontally focused and narrowed sound pattern is perceived by a listener in the vehicle. The sound pattern is the result of the constructive combination of the direct sound impulses and the reflected sound impulses produced by each loudspeaker in the array. Using delay, attenuation and phase adjustment of the audio signal, the sound pattern may be controlled, limited, and directed to one or more locations in the vehicle.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com