Patents
Literature
2448 results about "Cylindrical lens" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
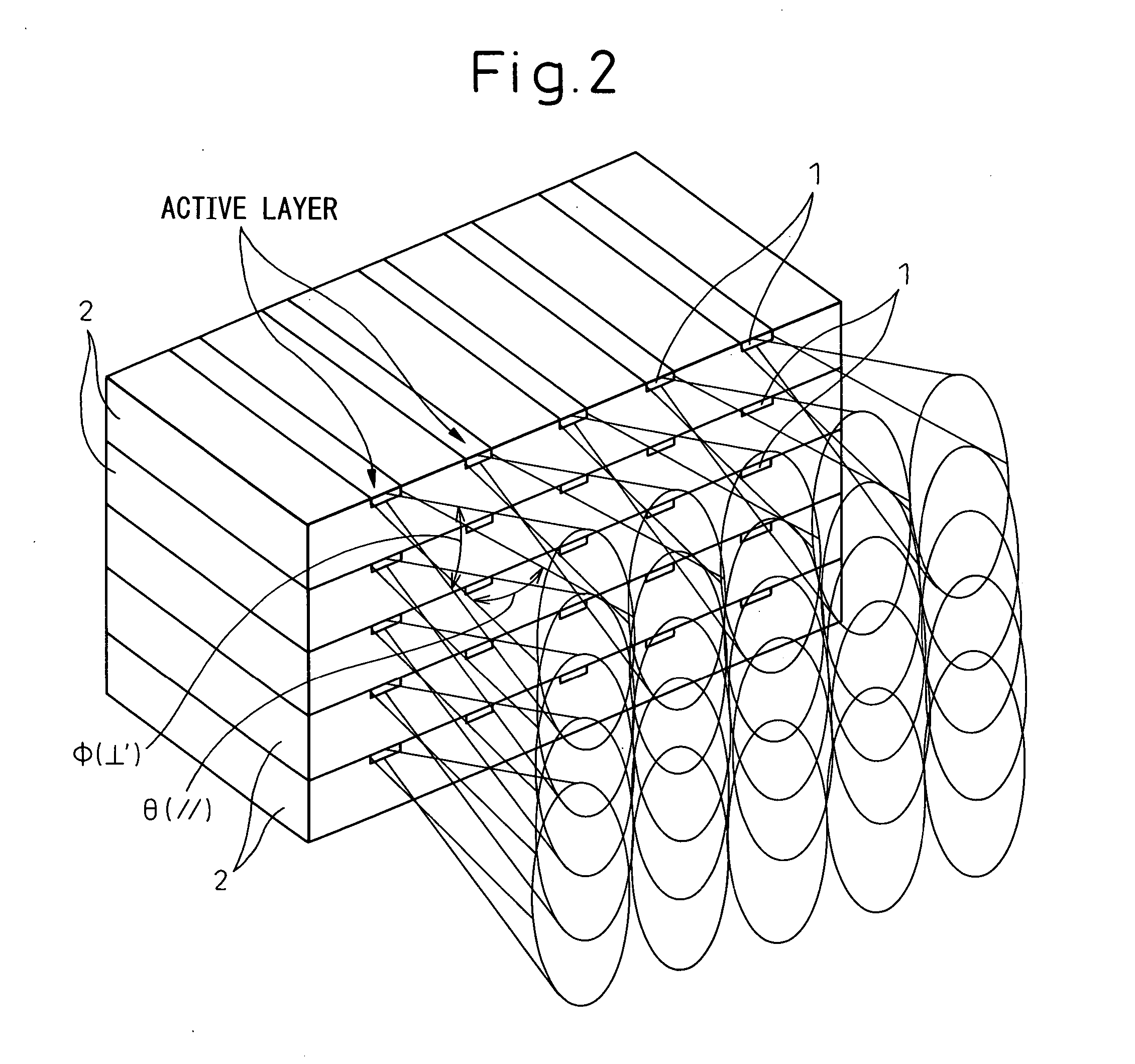
A cylindrical lens is a lens which focuses light into a line instead of a point, as a spherical lens would. The curved face or faces of a cylindrical lens are sections of a cylinder, and focus the image passing through it into a line parallel to the intersection of the surface of the lens and a plane tangent to it. The lens compresses the image in the direction perpendicular to this line, and leaves it unaltered in the direction parallel to it (in the tangent plane). In a light sheet microscope, a cylindrical lens is placed in front of the illumination objective to create the light sheet used for imaging.
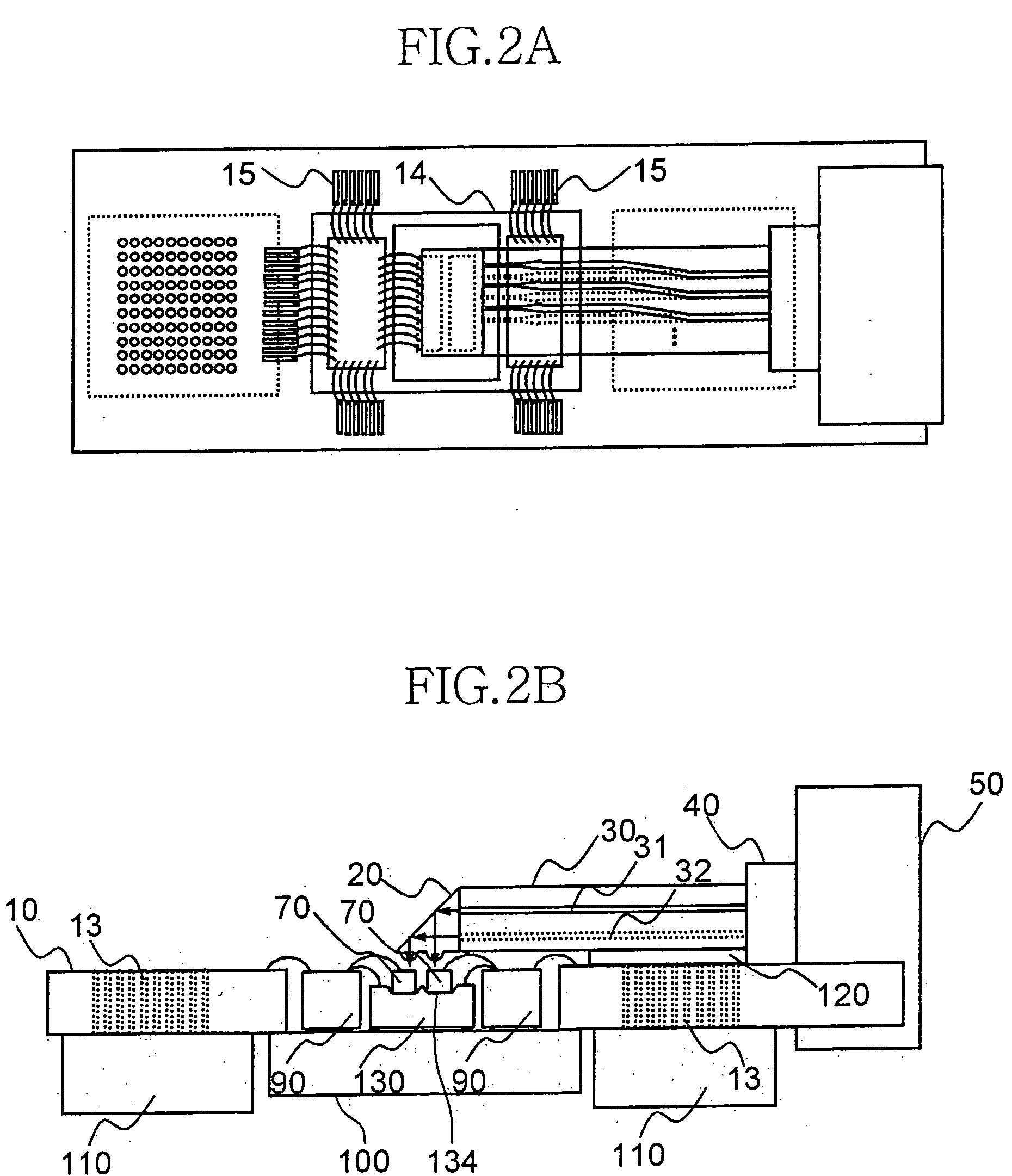
Helical radial spacing of contacts on a cylindrical lead
ActiveUS20110238129A1Head electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringBiomedical engineeringCylindrical lens
A device for brain stimulation includes a lead having a longitudinal surface, a proximal end and a distal end; and a plurality of electrodes disposed along the longitudinal surface of the lead near the distal end of the lead. The plurality of electrodes includes at least four segmented electrodes having exposed surfaces where each exposed surface has a center point. The center points of the at least four segmented electrodes are disposed on a substantially helical path about the longitudinal surface of the lead.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Beam homogenizer and laser irradiation apparatus
InactiveUS6393042B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical resonator shape and constructionLight beamOptoelectronics
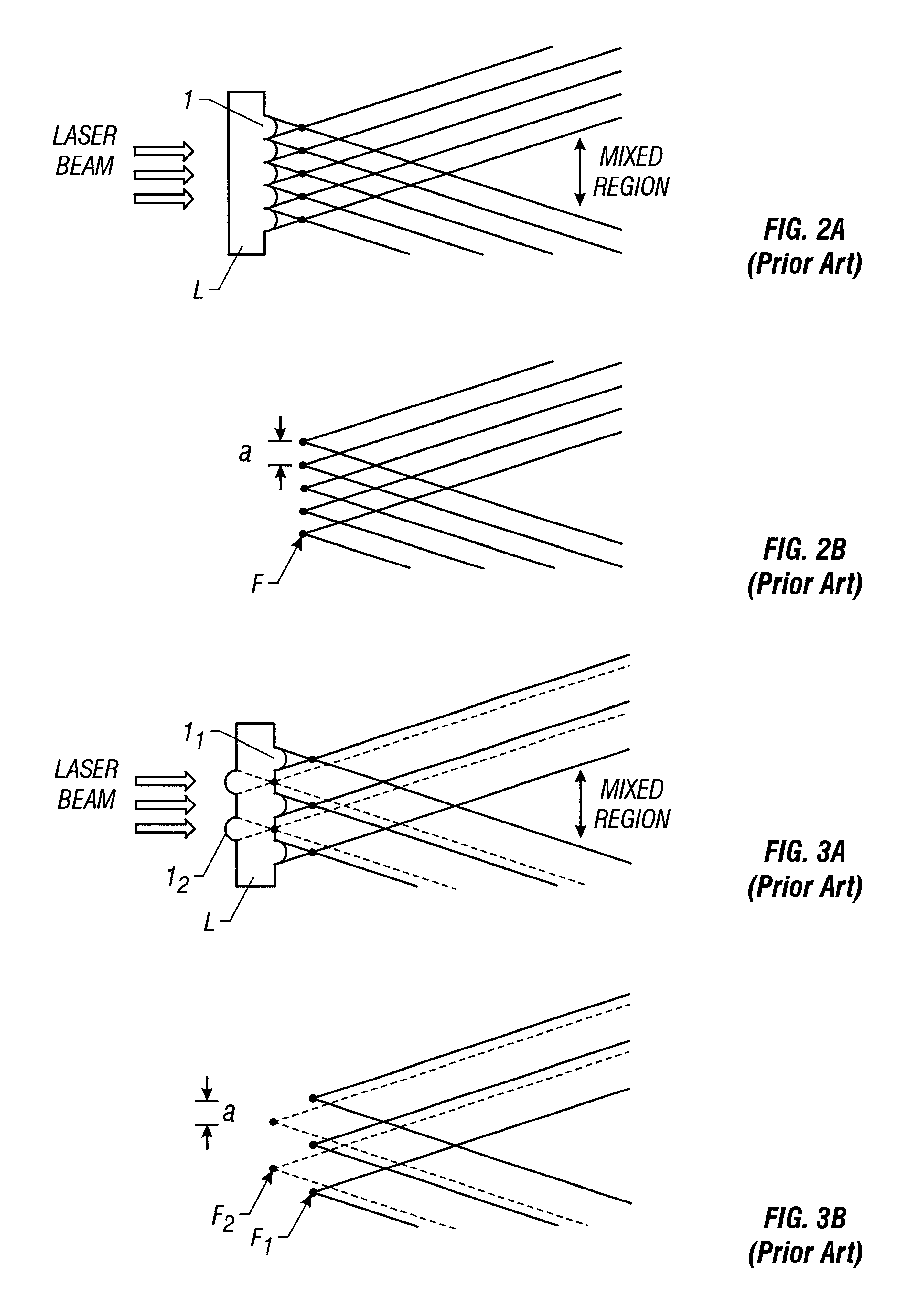
There is provided a beam homogenizer which can unify the energy distribution of a linear laser beam in a longitudinal direction. In the beam homogenizer including cylindrical lens groups for dividing a beam, and a cylindrical lens and a cylindrical lens group for condensing the divided beams, the phases, in the longitudinal direction, of linear beams passing through individual cylindrical lenses of the cylindrical lens group for condensing the divided beams are shifted, and then, the beams are synthesized, so that the intensity of interference fringes of the linear beam on a surface to be irradiated is made uniform.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
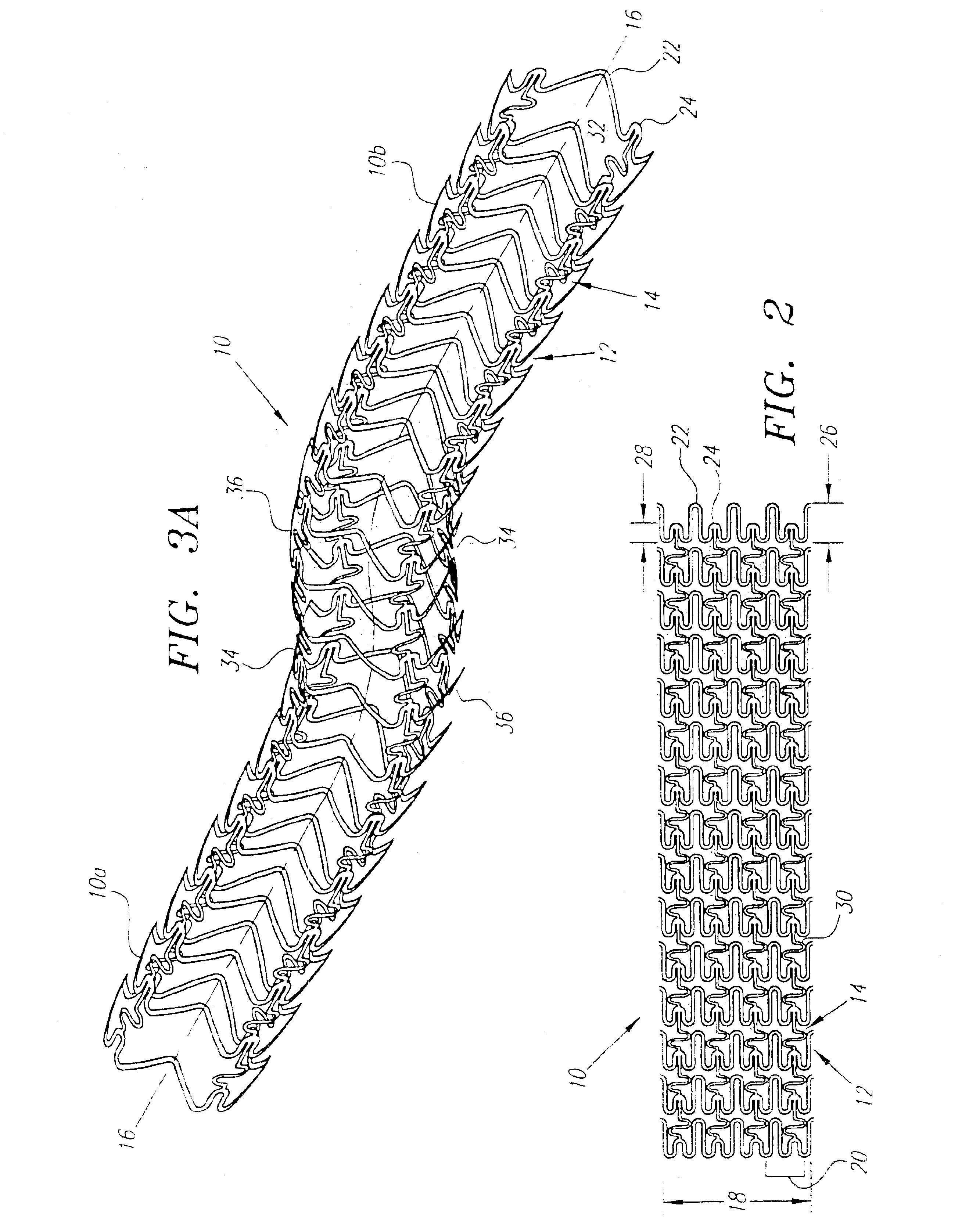
Deformable scaffolding multicellular stent
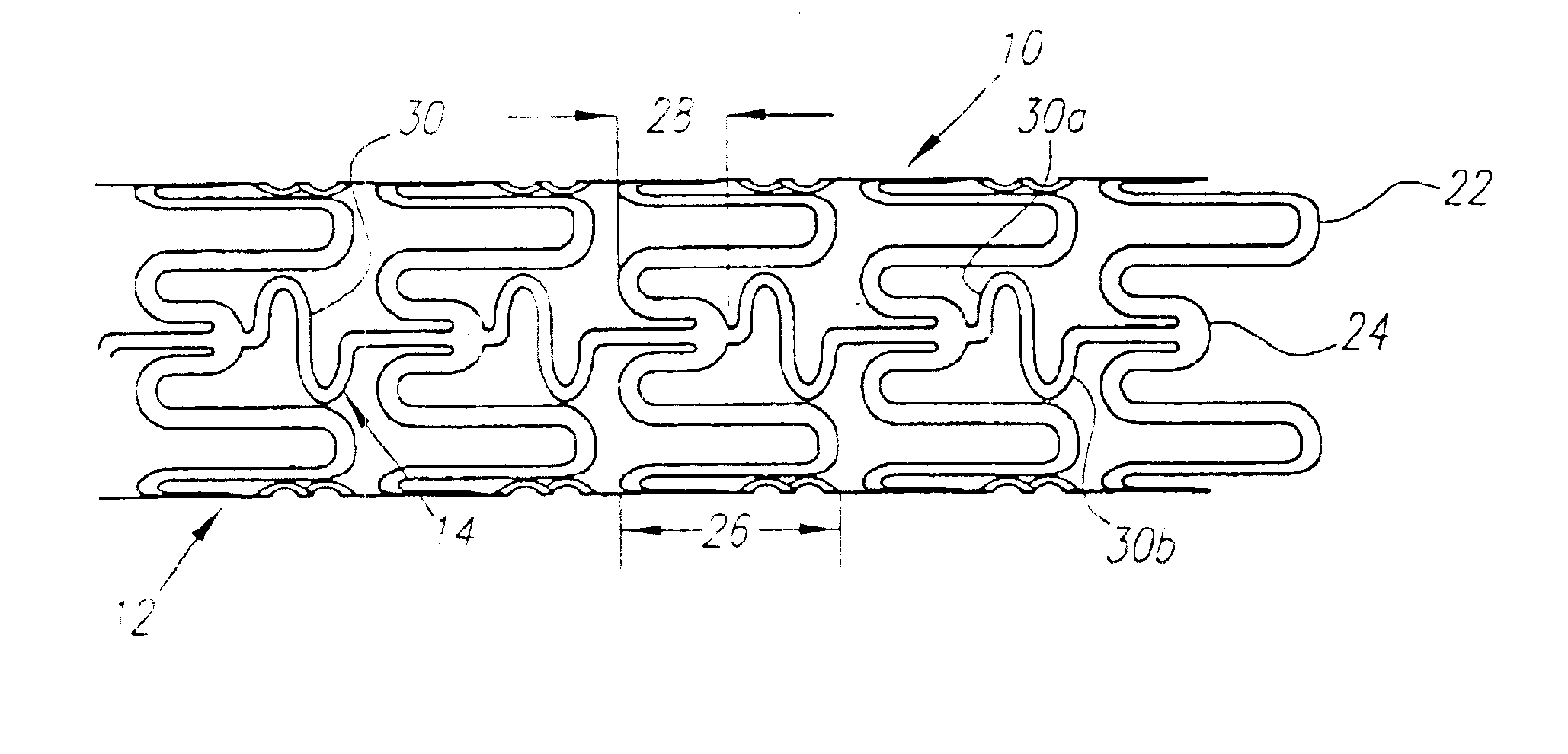
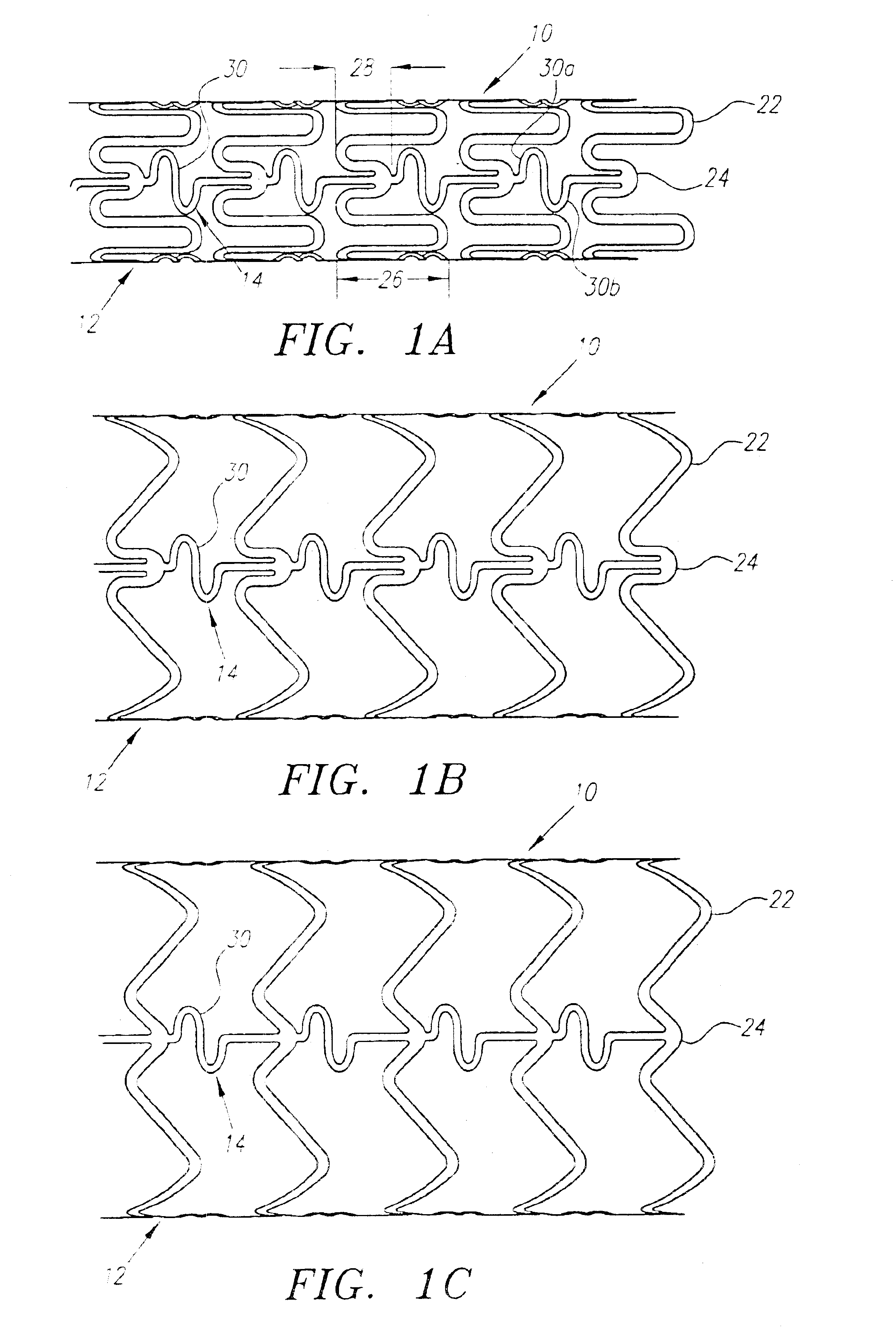
A plastically deformable stent for implantation within a body passage includes a plurality of cylindrical segments, and a plurality of connectors extending between adjacent segments. Each segment has an alternating pattern of curvilinear elements extending about its circumference, including first and second sets of curvilinear elements having different resistances to expansion, and preferably defining “U” shapes with alternating lengths that are connected to one another to define a substantially sinusoidal pattern. The connectors define a sinusoidal shape adapted to extend and compress axially substantially evenly when the adjacent segments are subjected to bending. The stent may be delivered on a device including an elongate member with a nose cone, an expandable member, and a proximal shoulder thereon, and an outer sheath for slidably receiving the elongate member therein. The outer sheath and / or nose cone may have perfusion holes for allowing continued perfusion of fluid during stent delivery. The device may be used in a method for implanting a stent within a curved region of a body passage, particularly for creating and / or maintaining a channel connecting a vein to an adjacent artery, preferably in the coronary system.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
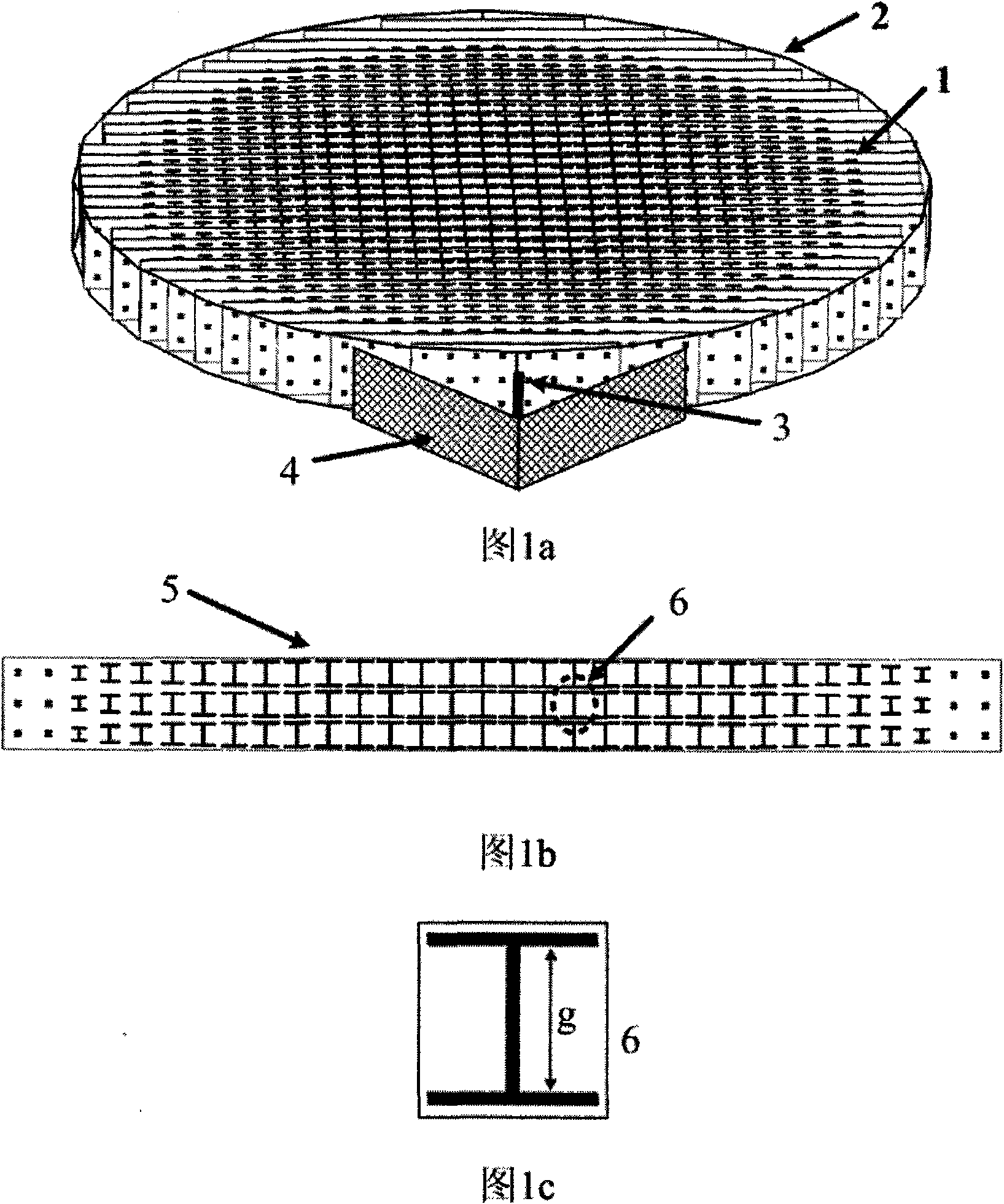
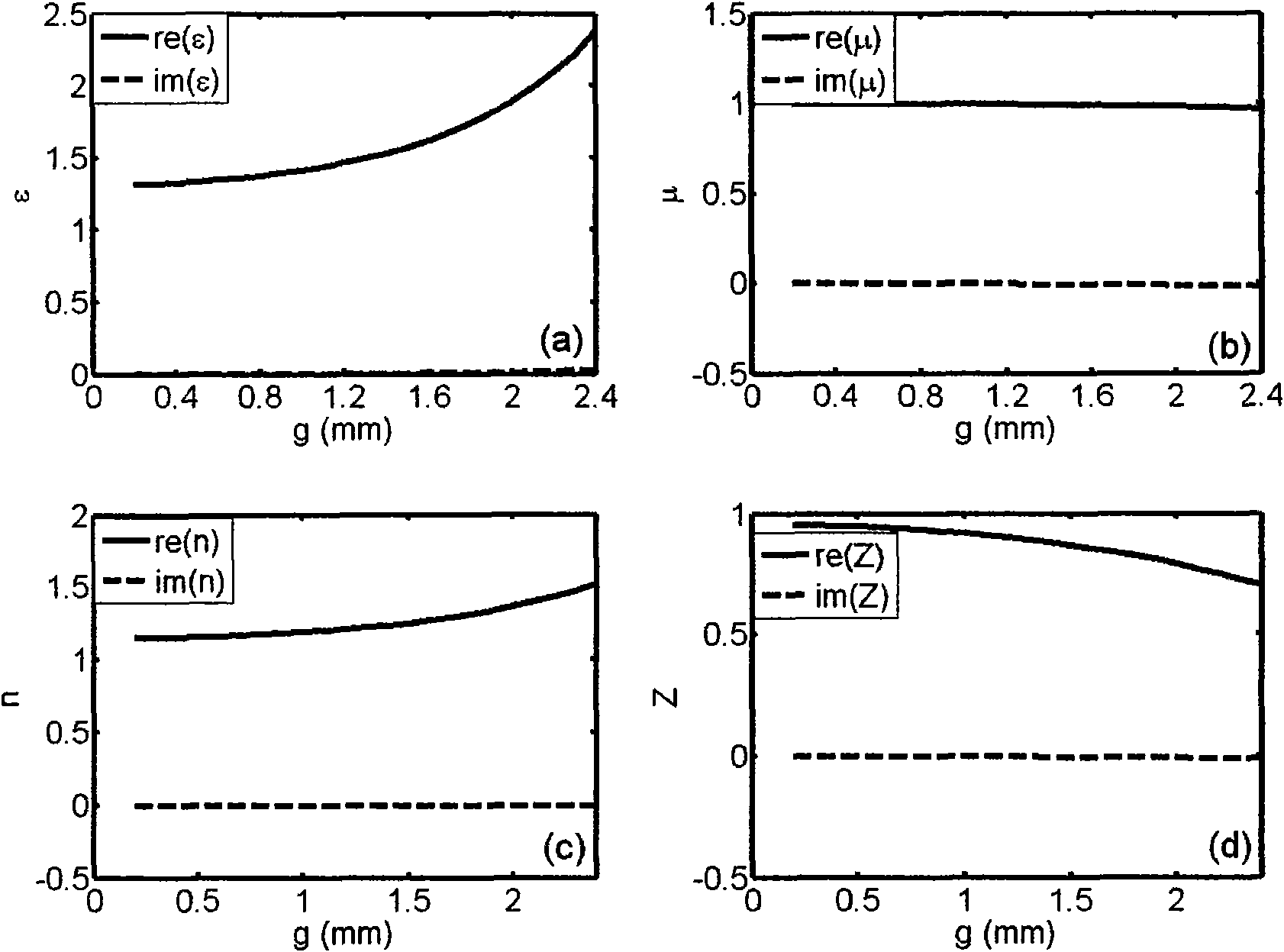
Broad band cylindrical lens antenna based on artificial electromagnetic materials
Broad band cylindrical lens antenna based on novel artificial electromagnetic materials is formed by arranging a series of novel artificial electromagnetic materials in definite regulation, composing equivalent artificial medium with gradient refractive index. The novel lens antenna includes a cylindrical lens 2 based on novel artificial electromagnetic material 1, feed source 3 used as excitation, reflector 4 for repressing backward radiation. Specific structure 5 of one printed circuit board in the novel artificial electromagnetic material 1 is a series of 'I' shaped units 6 printed on medium substrate arranged according to specific regulation. Regulating size of the 'I' shaped structure to obtain the lens needed refractive index distribution. Selecting suitable and ideal reflector 4 and disposing it back of the feed source 3 for reducing backward radiation generated by the feed source, so as to improve gain and directivity of the antenna. The invention is provided with advantages of high gain, broadband, high directivity, easy manufacture, low cost, light weight and convenient integration.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Display unit and electronic apparatus with display unit
ActiveUS20050276071A1High quality stereoscopic visionLittle crosstalkReflectorsOptical elementsParallaxLight guide
A display system includes light sources disposed at two different light input ends of a light guiding plate; a double-sided prism sheet disposed on a light emitting side of the light guiding plate, and having on a first surface facing the light guiding plate a triangular prism bank extending in a direction parallel to the light input ends of the light guiding plate, and on a second surface, opposite to the first surface, a cylindrical lens bank extending in a direction parallel to the triangular prism bank; a transmissive display panel disposed on a light emitting side of the double-sided prism sheet; and a synchronization driving section causing the transmissive display panel to display two different images in synchronization with the light sources, wherein light from the light sources is emitted through the transmissive display panel at angles corresponding to right and left parallax, producing a stereoscopic display.
Owner:TRIVALE TECH
Speckle-image-based optical position transducer having improved mounting and directional sensitivities
InactiveUS6642506B1Reduce sensitivityAvoid smearingSlide gaugesMaterial analysis by optical meansImage detectionRelative motion
A speckle readhead includes a light source that outputs light towards an optically rough surface. Light scattered from this surface contains speckles. The scattered light is imaged onto an image detector, captured and stored. Subsequently, a second image is captured and stored. The two images are repeatedly compared at different offsets in a displacement direction. The comparison having the highest value indicates the amount of displacement between the readhead and the surface that occurred between taking the two images. An optical system of the readhead includes a lens and an aperture. The aperture can be round, with a diameter chosen so that the average size of the speckles is approximately equal to, or larger than, the dimensions of the elements of the image detector. The dimension of the aperture in a direction perpendicular to the direction of displacement can be reduced. Thus, the imaged speckles in that direction will be greater than the dimension of the image detector elements in that direction. Such a readhead is relatively insensitive to lateral offsets. The lens can be a cylindrical lens that magnifies the relative motion along the direction of displacement but does not magnify relative motions in the direction perpendicular to the direction of displacement. The optical system can also be telecentric. Thus, the readhead is relatively insensitive to both separation and relative motions between the readhead and the surface. The light source can be modulated to prevent smearing the speckles across the image detector. The light source can be strobed to freeze the image.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
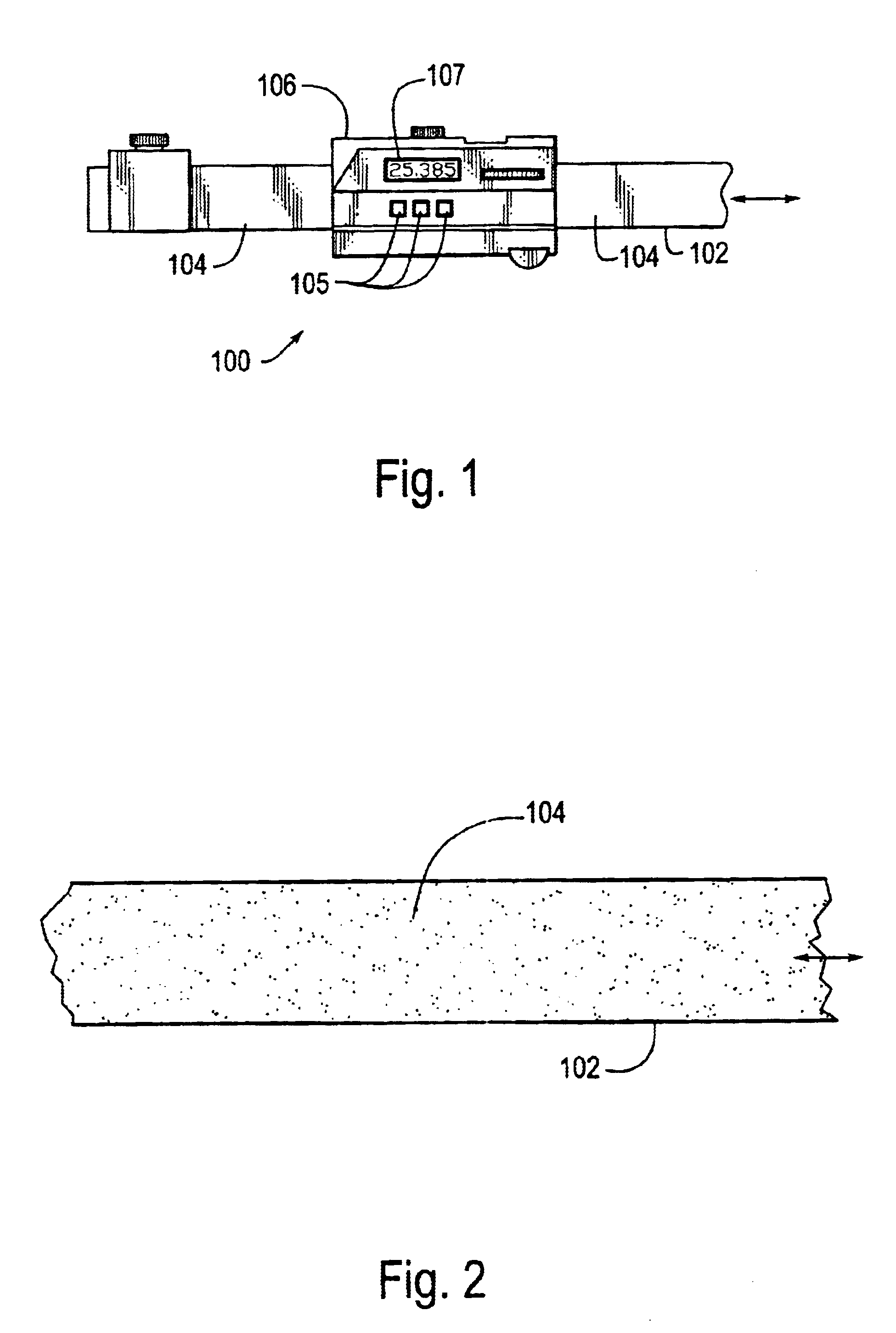
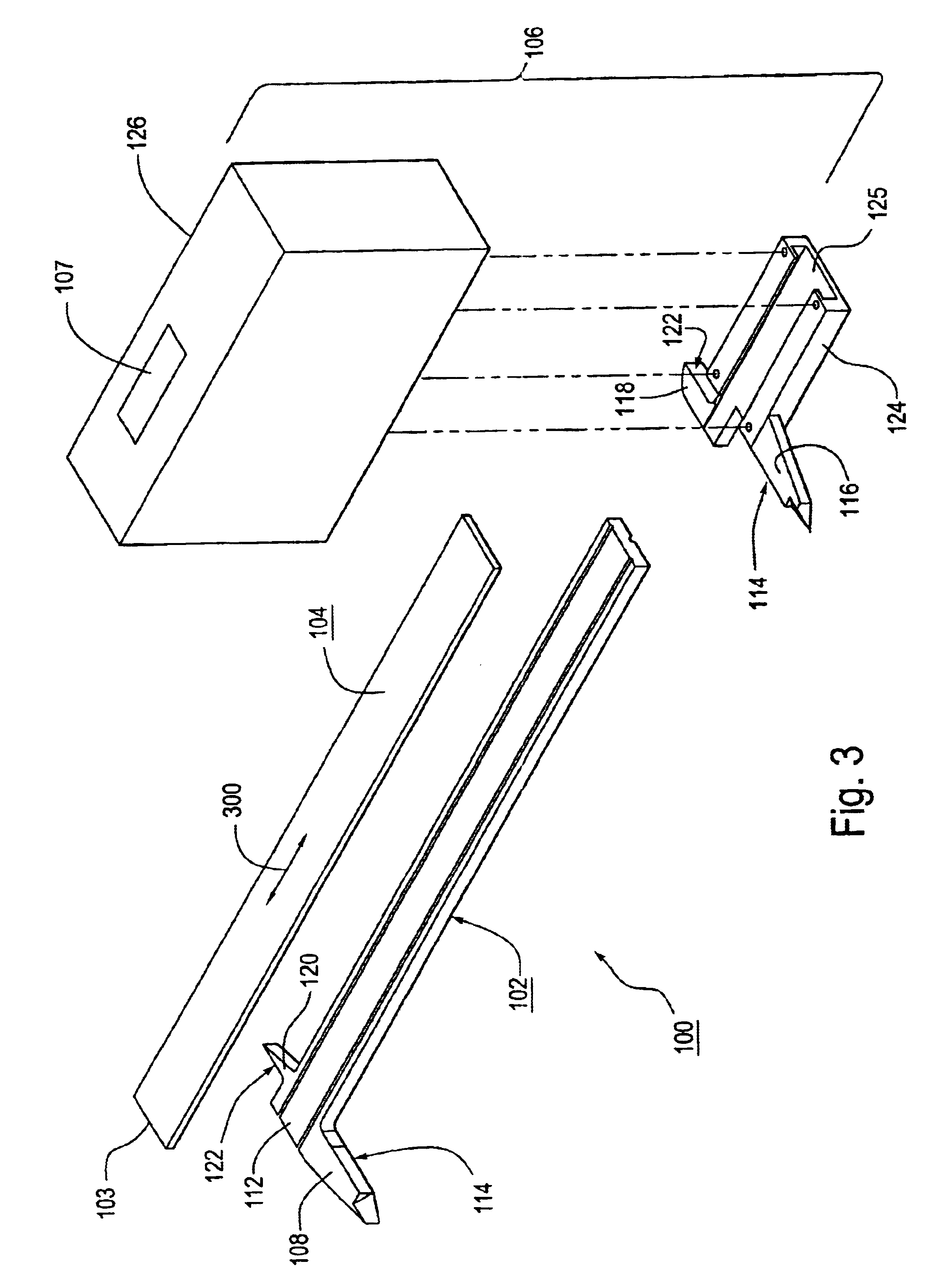
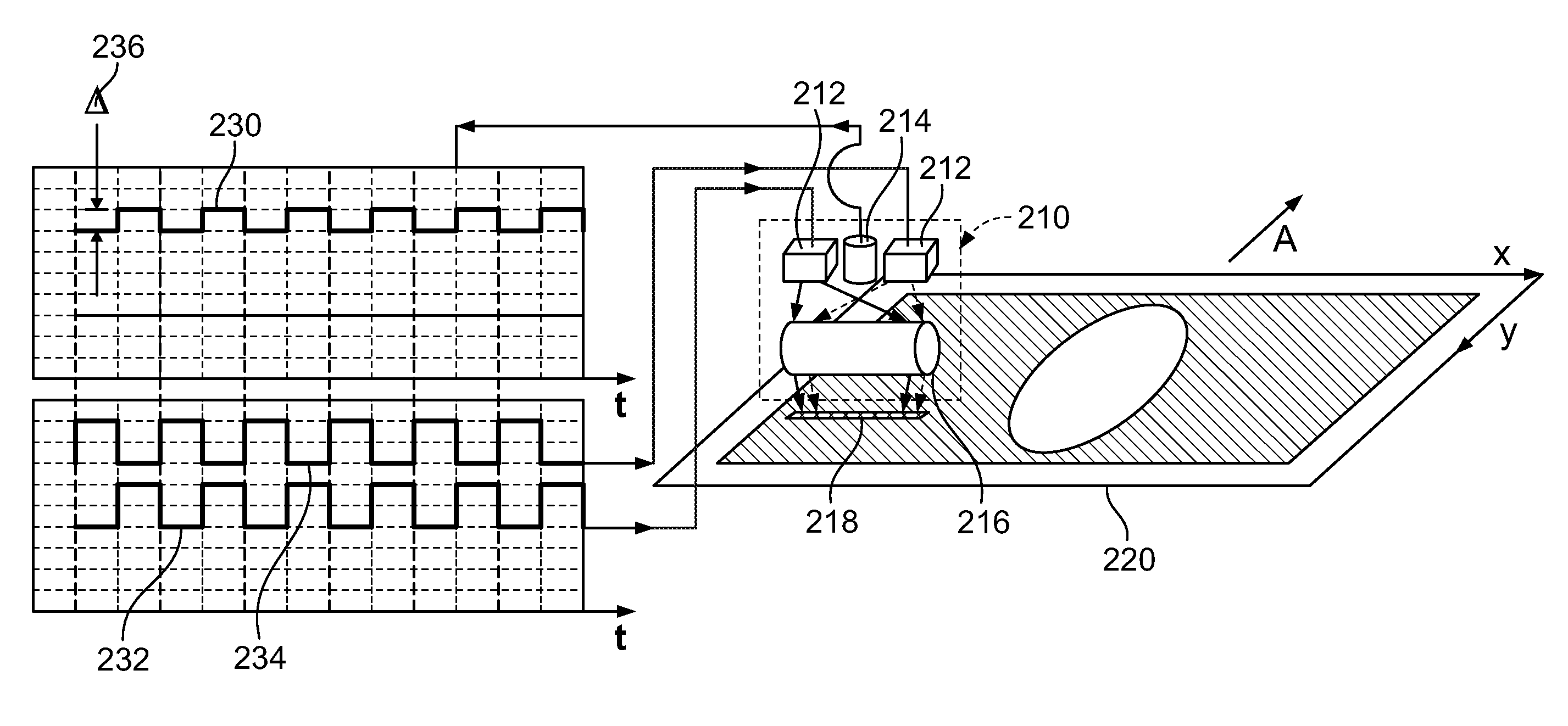
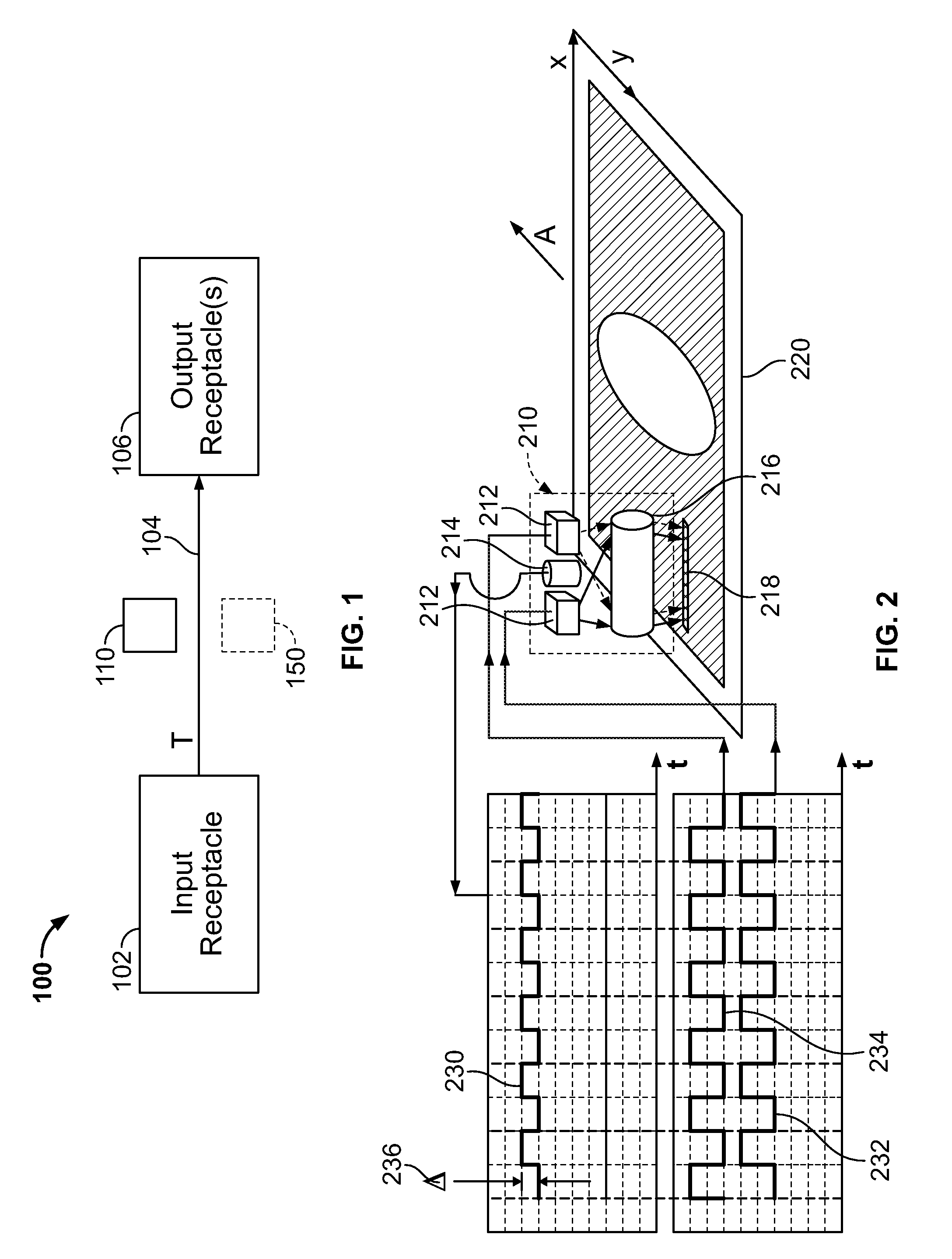
Currency bill sensor arrangement
ActiveUS20090022390A1Paper-money testing devicesCoin/currency accepting devicesPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A currency processing device for receiving a stack of U.S. currency bills and rapidly processing all the bills in the stack, the device comprising: an input receptacle adapted to receive a stack of U.S. currency bills of a plurality of denominations, the currency bills having a wide dimension and a narrow dimension; a transport mechanism positioned to transport the bills, one at a time, in a transport direction from the input receptacle along a transport path at a rate of at least about 1000 bills per minute with the narrow dimension of the bills parallel to the transport direction; a currency bill sensor arrangement positioned along the transport path, the currency bill sensor comprising: i) a multi-wavelength light source configured to emit a first wavelength of light and a second wavelength of light; ii) a cylindrical lens positioned to receive the first and second wavelengths of light from the multi-wavelength light source, the cylindrical lens illuminating an elongated strip of light on a surface of one of the plurality of currency bills, the cylindrical lens being configured to receive light reflected from the surface of the one of the plurality of currency bills; iii) a photodetector positioned to receive the reflected light, the photodetector generating an electrical signal in response to the received reflected light; iv) a processor configured to receive the electrical signal generated by the photodetector; wherein, the processor is configured to determine whether the surface of the one of the plurality of currency bills is a primary surface or a secondary surface based on the electrical signal.
Owner:CUMMINS-ALLISON CORP
Laser optical apparatus
InactiveUS6212012B1Diffusing elementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight beamUltimate tensile strength
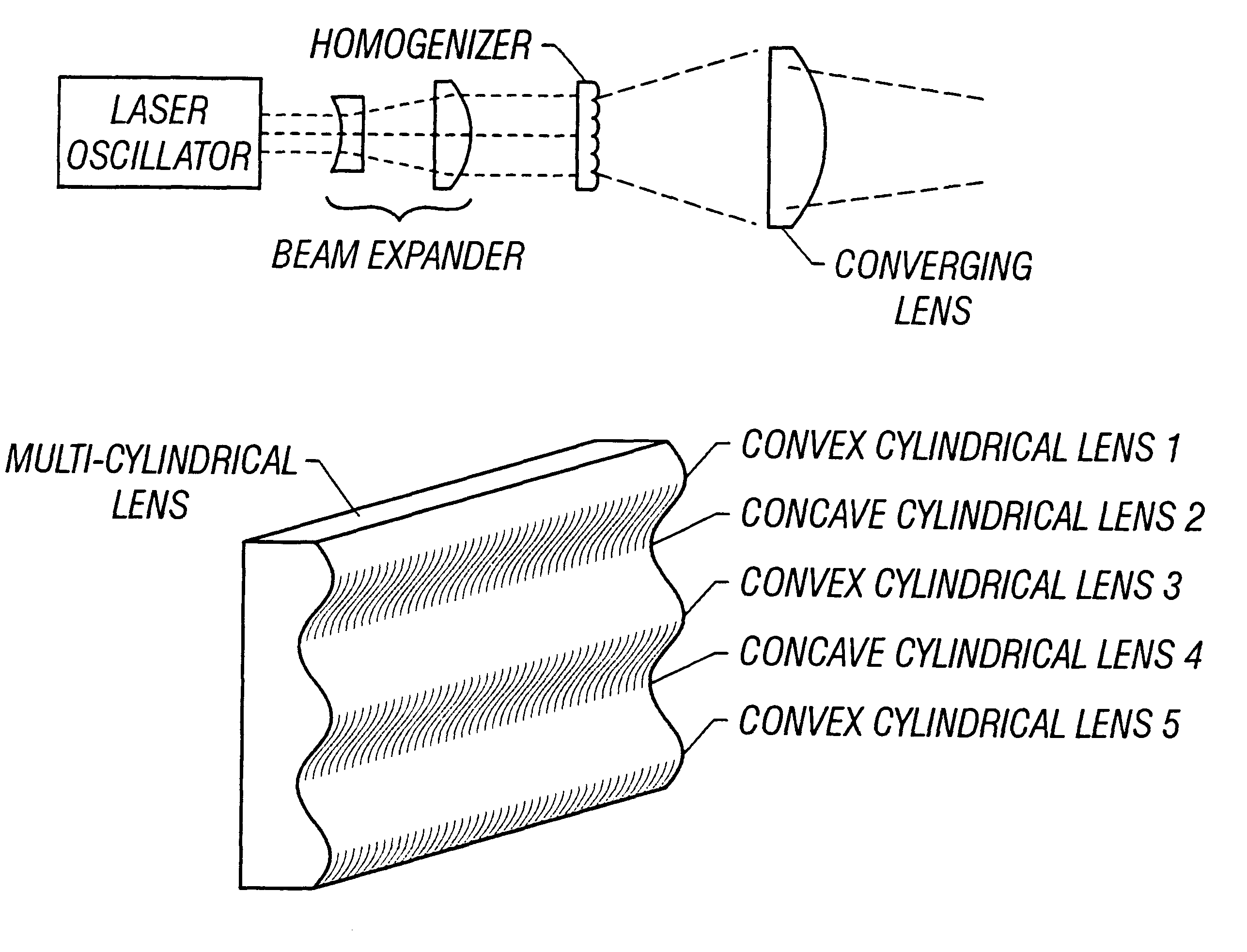
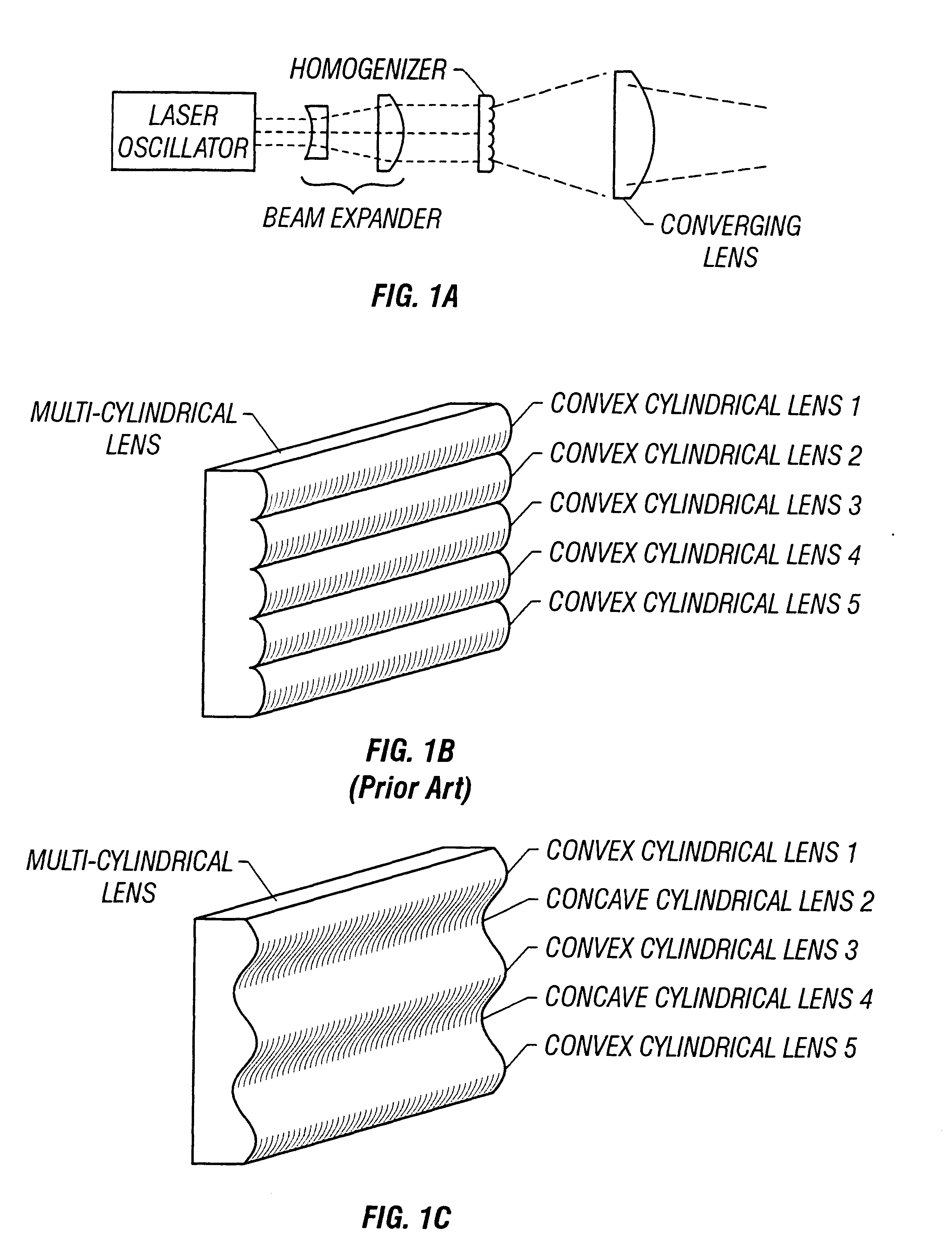
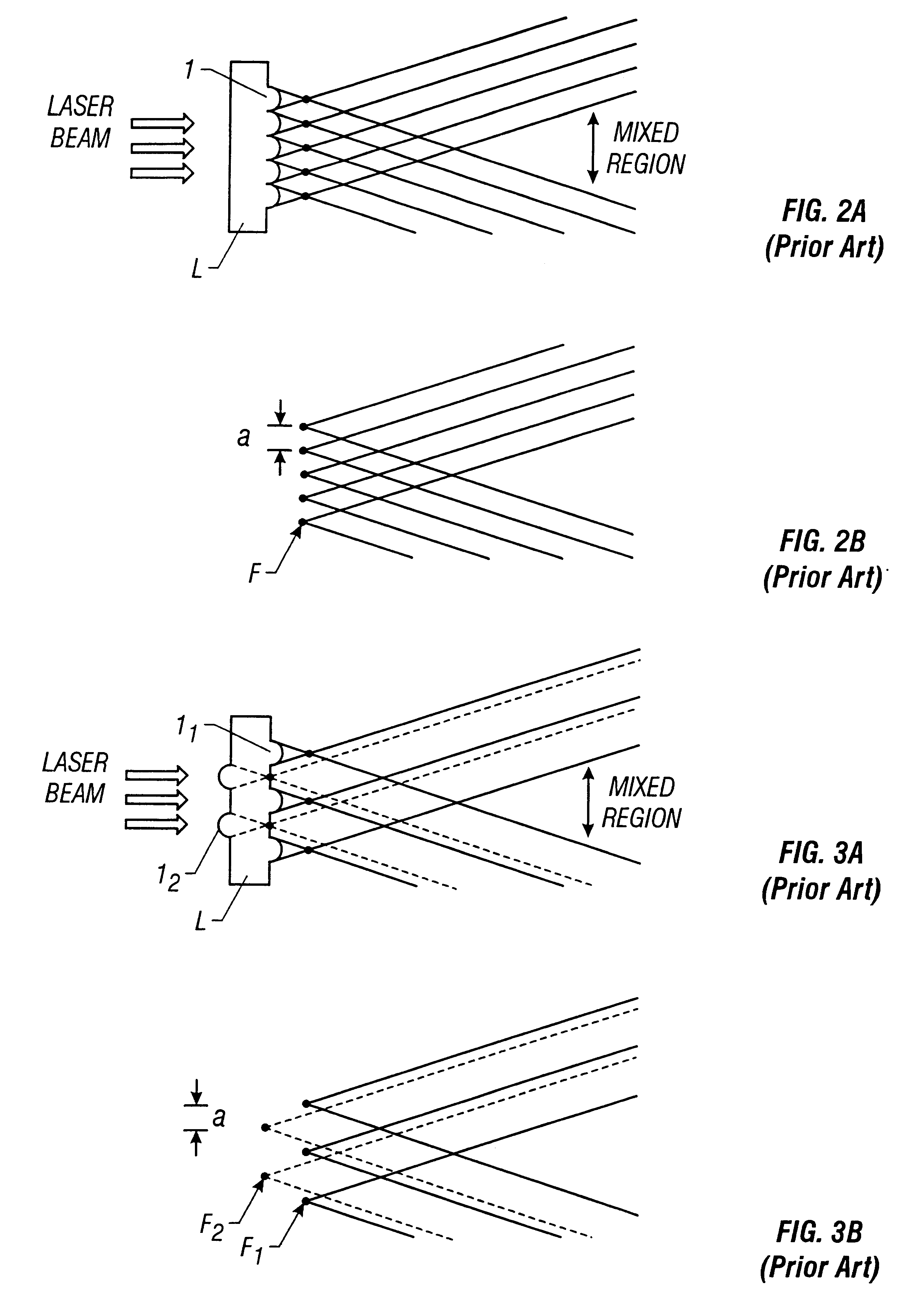
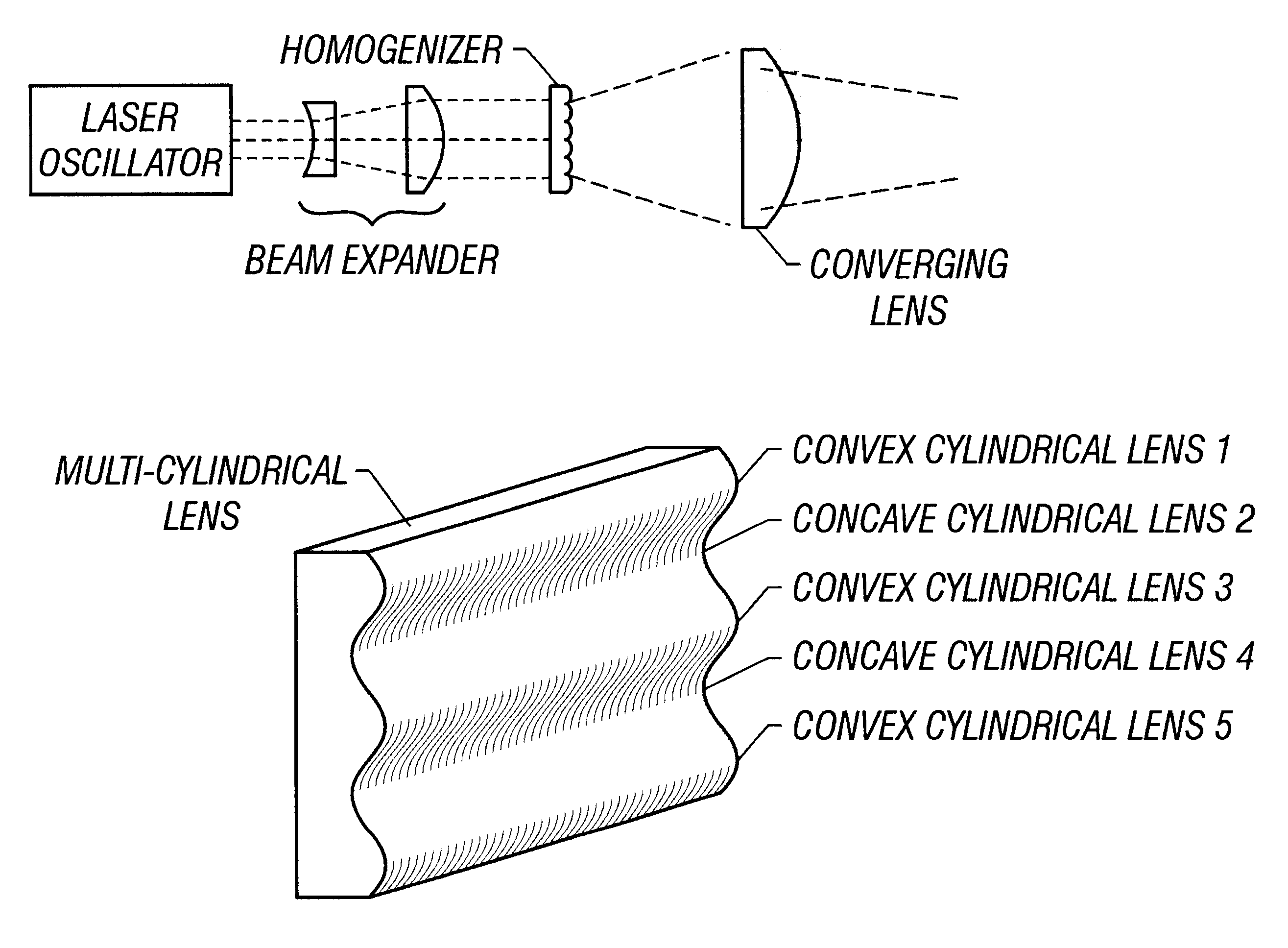
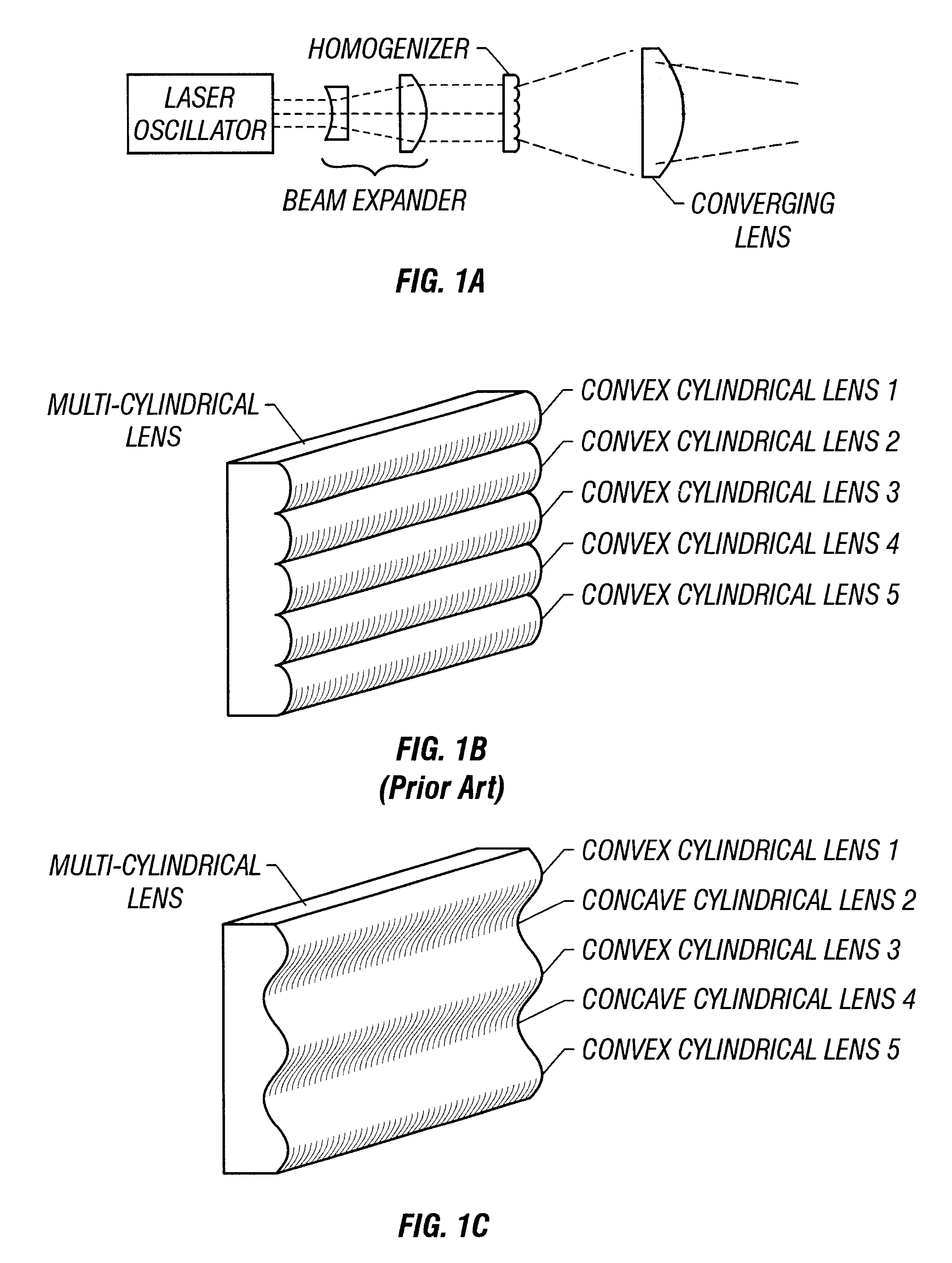
There is provided a structure for reducing optical loss in an optical apparatus (homogenizer) for making the intensity distribution of a laser beam uniform.In a multi-cylindrical lens (a glass substrate having a multiplicity of cylindrical lenses formed thereon) used in a homogenizer, convex cylindrical lenses and concave cylindrical lenses are arranged alternately, and the boundaries between the cylindrical lenses have a smooth structure. This makes it possible to reduce scattering of beams that has occurred at the boundaries between the cylindrical lenses.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Laser optical apparatus
InactiveUS6239913B1Diffusing elementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight beamUltimate tensile strength
There is provided a structure for reducing optical loss in an optical apparatus (homogenizer) for making the intensity distribution of a laser beam uniform.In a multi-cylindrical lens (a glass substrate having a multiplicity of cylindrical lenses formed thereon) used in a homogenizer, convex cylindrical lenses and concave cylindrical lenses are arranged alternately, and the boundaries between the cylindrical lenses have a smooth structure. This makes it possible to reduce scattering of beams that has occurred at the boundaries between the cylindrical lenses.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Helical radial spacing of contacts on a cylindrical lead
ActiveUS8571665B2Head electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringBiomedical engineeringCylindrical lens
A device for brain stimulation includes a lead having a longitudinal surface, a proximal end and a distal end; and a plurality of electrodes disposed along the longitudinal surface of the lead near the distal end of the lead. The plurality of electrodes includes at least four segmented electrodes having exposed surfaces where each exposed surface has a center point. The center points of the at least four segmented electrodes are disposed on a substantially helical path about the longitudinal surface of the lead.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
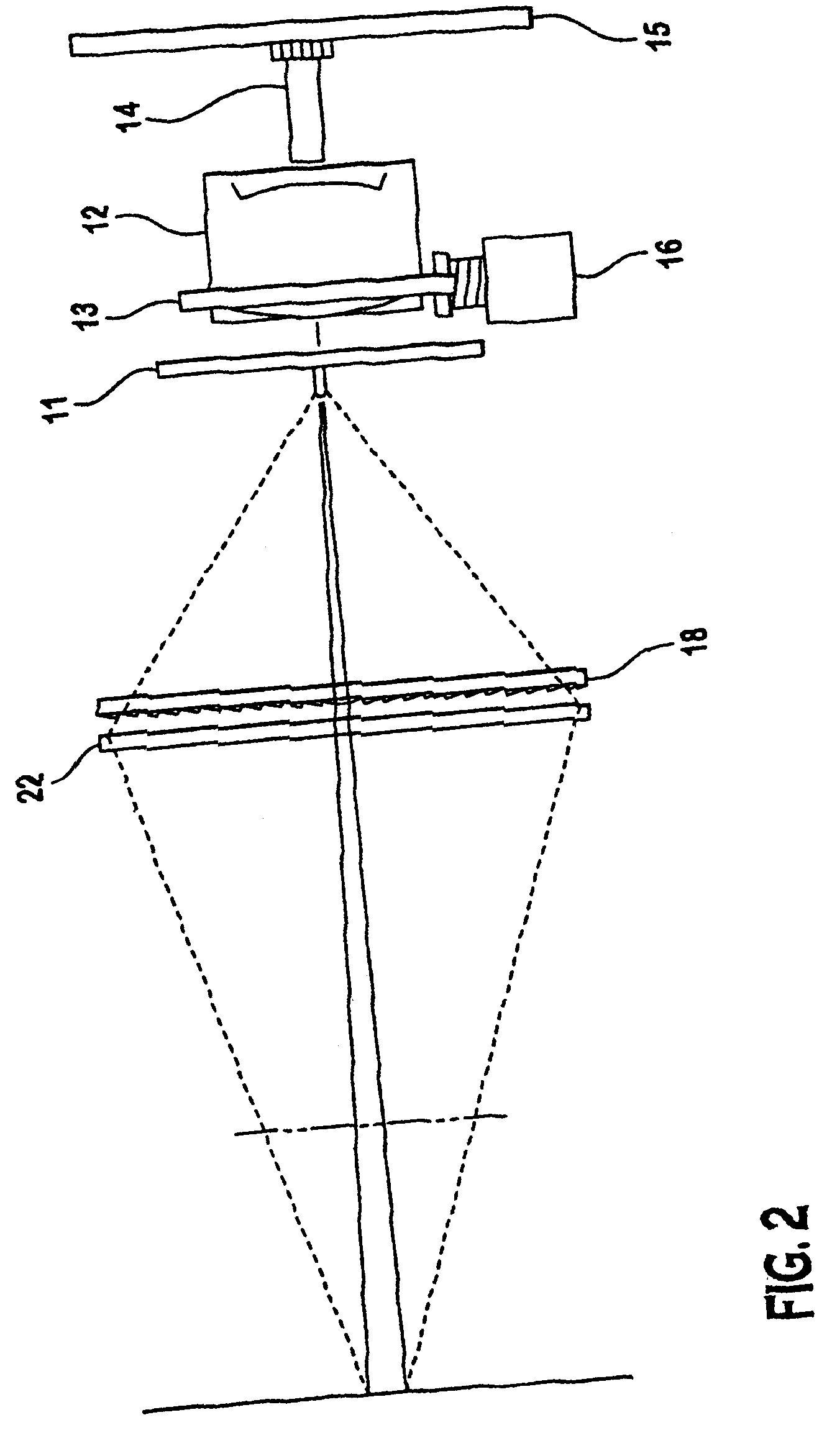
Coplanar camera scanning system
InactiveUS6856440B2Sufficient lightingReduce intensityMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionMechanical engineeringLinear arrays
A system for scanning objects having a linear array sensor, adapted to detect light input signals, is provided. A lens is optically connected to the linear array sensor, and is adapted to receive and transmit an optical image located in a field of view along a lens axis to the linear array sensor. A light source which generates an illumination stripe in general linear alignment with the lens axis is provided. A cylindrical lens is positioned between the light source and an object to be scanned. The cylindrical lens adapted to collect, transmit and focus light from the light source to form the illumination stripe.
Owner:DATALOGIC AUTOMATION
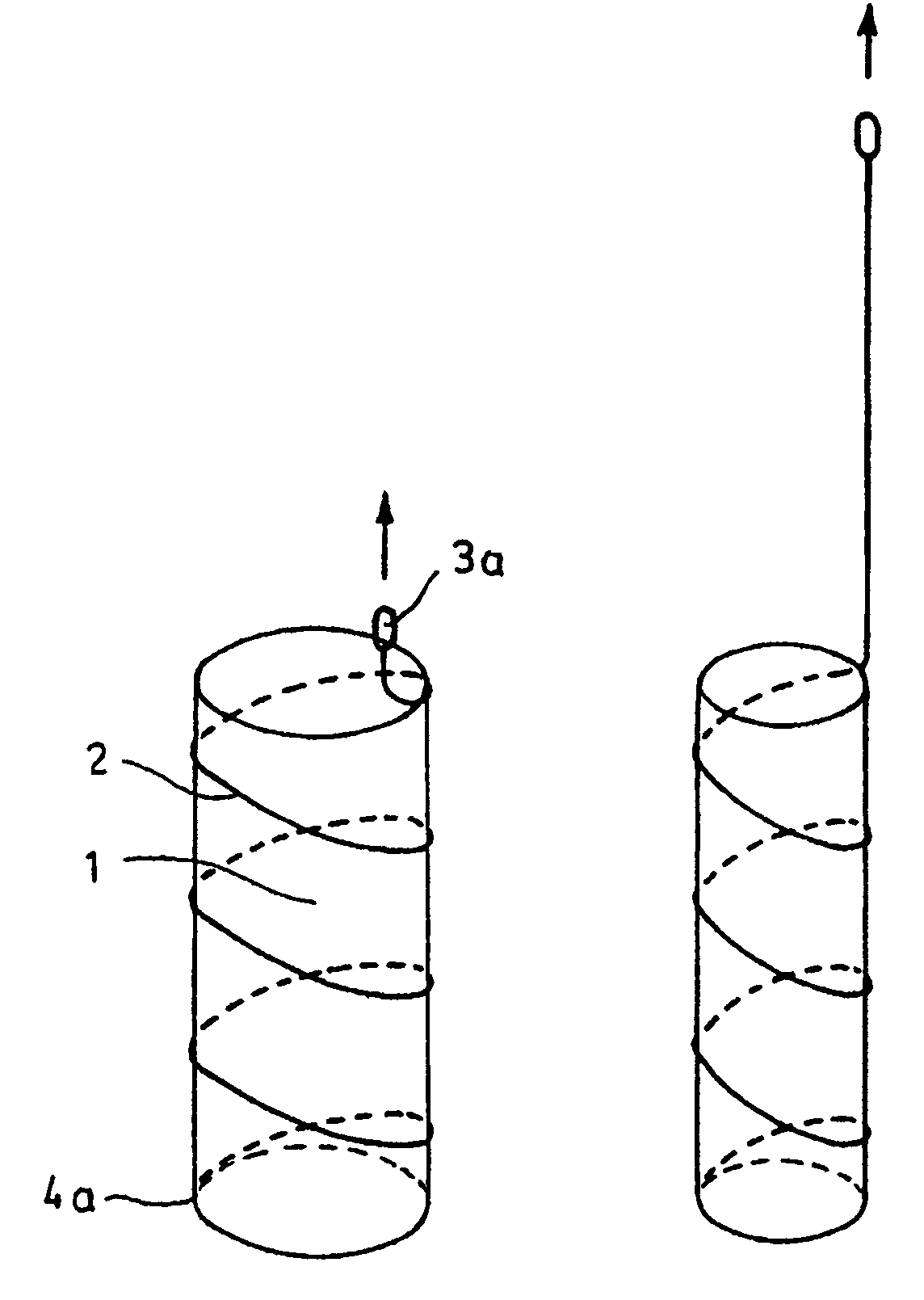
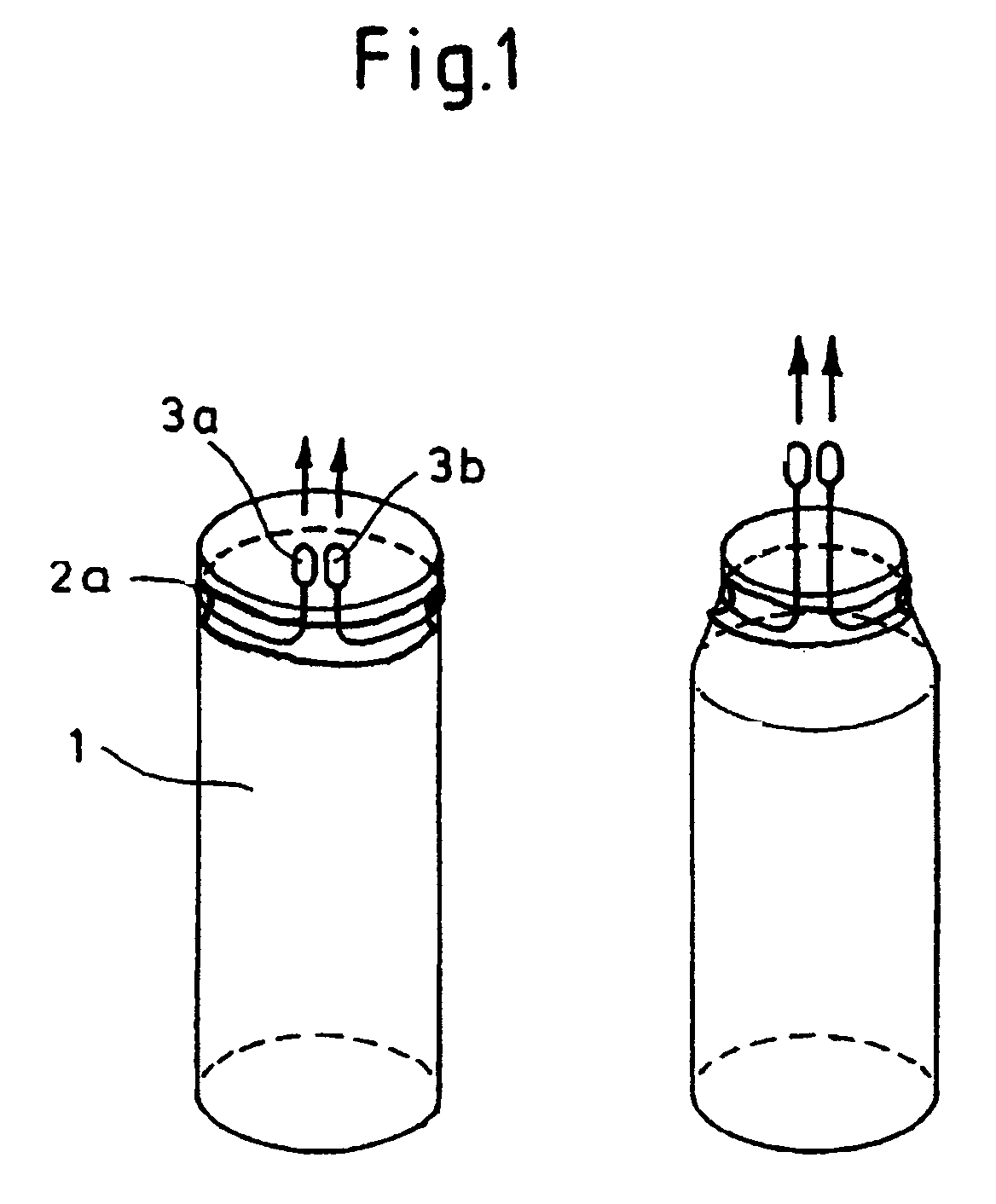
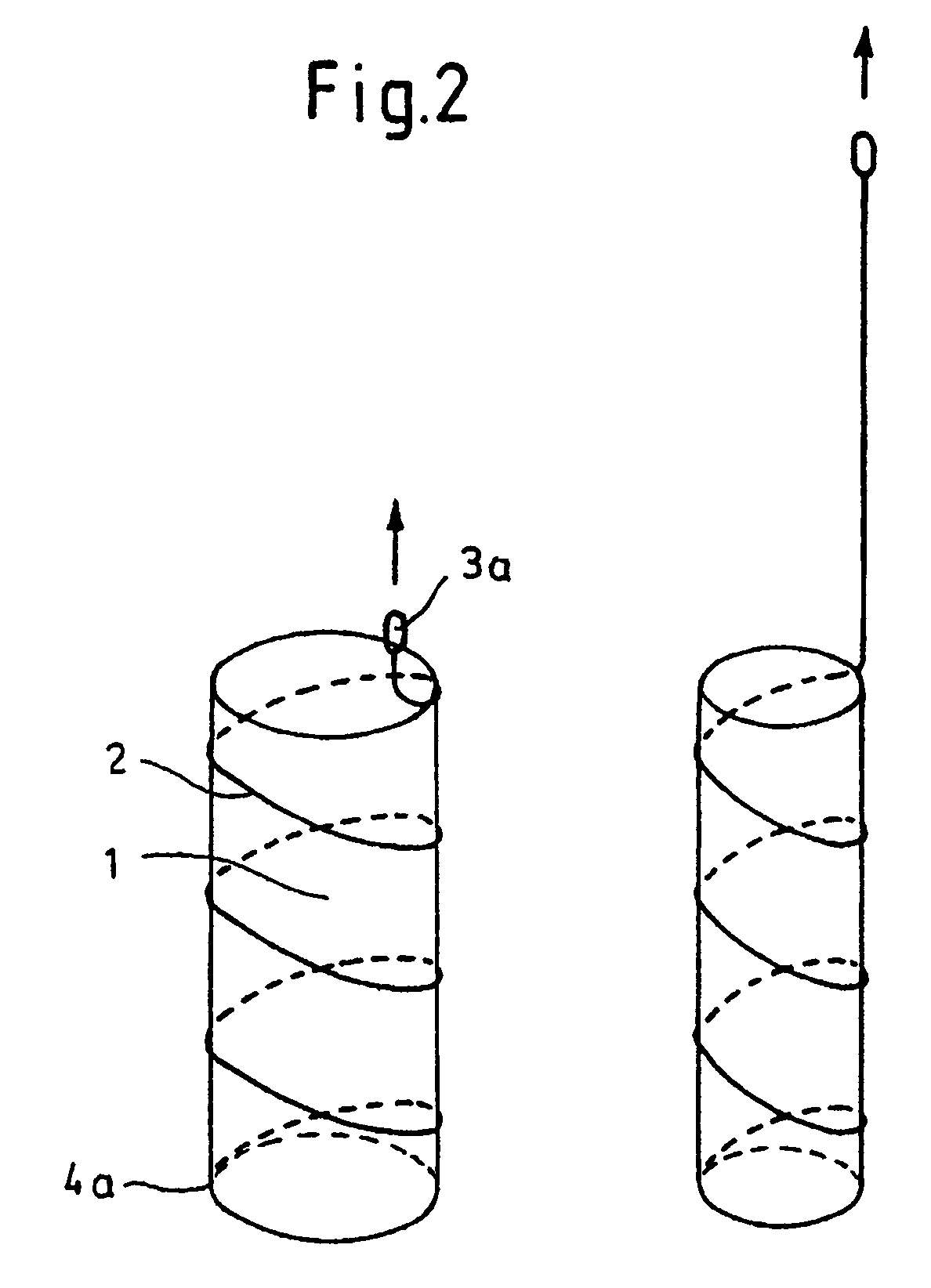
Removable essentially cylindrical implants
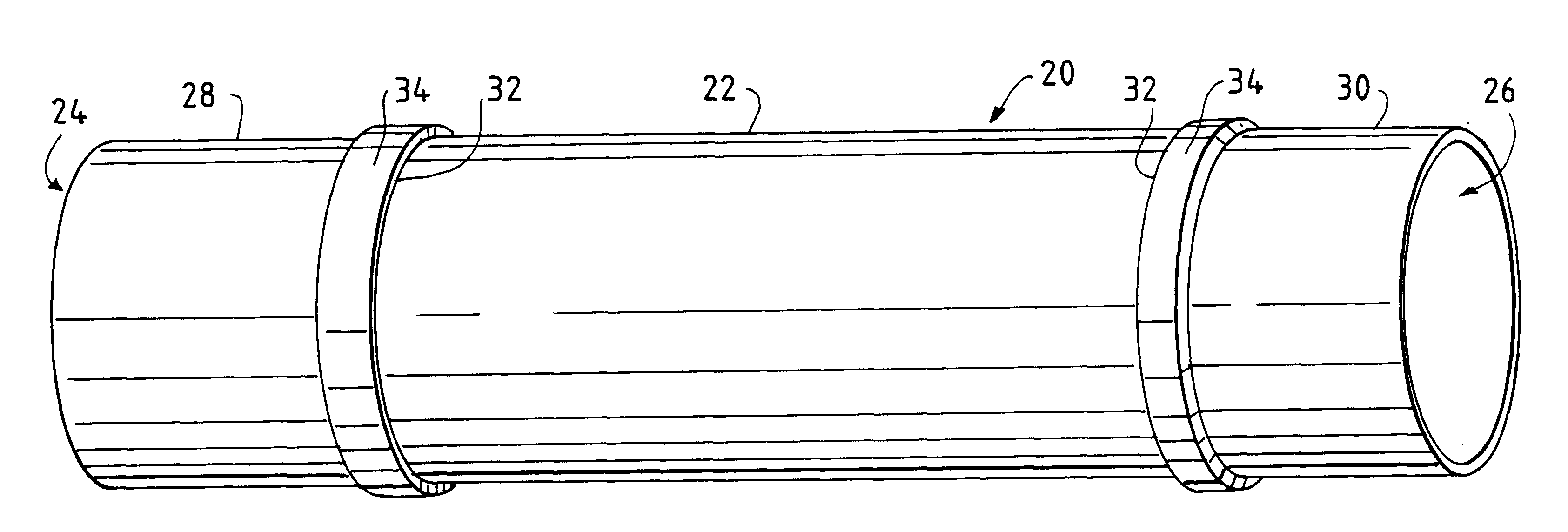
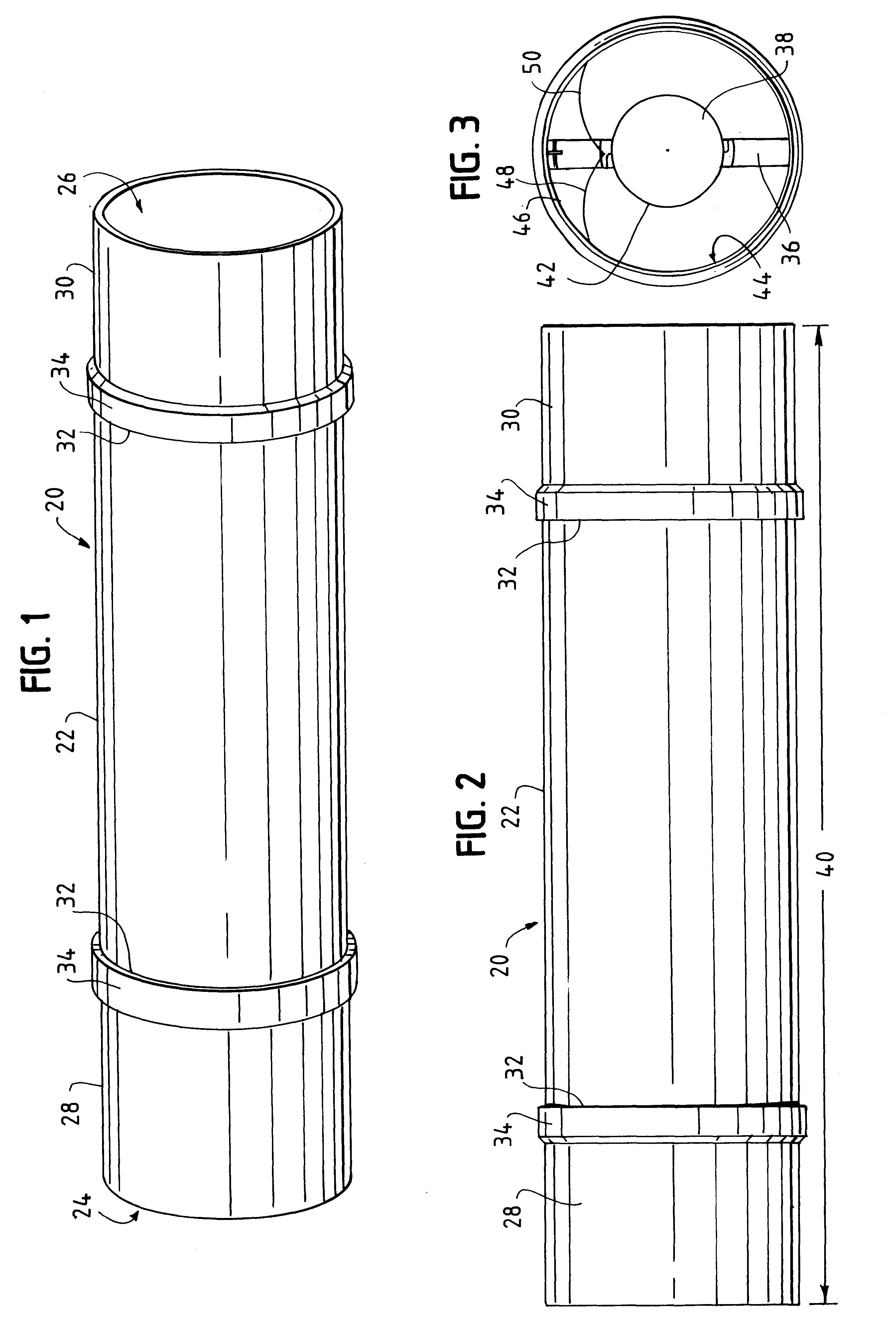
InactiveUS7252680B2Little complicationReduce the overall diameterStentsEar treatmentEngineeringCylindrical lens
The invention relates to removable, essentially cylindrical implants which are characterized in that they can be reduced in diameter and are wrapped once or several times at one or more levels by one or more elastic, thin wire-shaped structure(s) (2a, 2b) which include(s) a catch device (3a, 3b) at least on one end thereof.
Owner:MERIT MEDICAL SYST INC
Coplanar camera scanning system
InactiveUS6912076B2Reduce intensityUniform resolutionSensing by electromagnetic radiationPictoral communicationImage resolutionLinear arrays
A system for scanning objects having at least two linear array sensors, adapted to detect light input signals, is provided. A lens is optically connected to each of the linear array sensors, and are adapted to receive and transmit an optical image located in a respective lens field of view along a respective lens axis to the respective one of the at least two linear array sensor. A light source which generates an illumination stripe in general linear alignment with the lens axis across a depth of the field of view is provided. A cylindrical lens is positioned between the light source and an object to be scanned. The cylindrical lens adapted to collect, transmit and focus light from the light source to form the illumination stripe. This arrangement provides a wider system field of view with generally more uniform resolution.
Owner:DATALOGIC AUTOMATION
Autostereoscopic display
An autostereoscopic display and method of displaying multidimensional images involves a first lenticular array preferably of cylindrical lenses positioned between a viewer and a pixel array, and a second lenticular array also preferably of cylindrical lenses positioned between the first lenticular array and the viewer. The pixel array includes several pixel groups that project images through corresponding groups of first lenses within the first lenticular array. A pitch of the lenses within the second lenticular array differs from a pitch of the lenses in the first lens groups within the first lenticular array. The display can be manufactured or retrofit with the first and second lenticular arrays. By use of the first lenticular array, light from plural color pixels may be focussed to a single point so that color subpixels arranged in a direction transverse to the direction of the cylindrical lenses of the first lenticular array may be focussed to a single point on the secondary lenticular array and then as a single image to the user.
Owner:MEMS OPTICAL
Linear lenses for LEDs
InactiveUS20070058369A1Uniform lightImprove uniformityMechanical apparatusFurnace componentsIceboxLight-emitting diode
Various embodiments described herein comprise array of light emitting diodes and a cylindrical lens having front and rear curved surfaces. The cylindrical lens is disposed to receive light from the light emitting diodes and to redistribute the light. The cylindrical lens is located no more than about 8 inches distance from the front an illumination target, which may for example, comprise products on shelves in a refrigerator. The front and rear surfaces of the cylindrical lens are shaped to provide substantially uniform illumination across the target.
Owner:ANTHONY INC +1
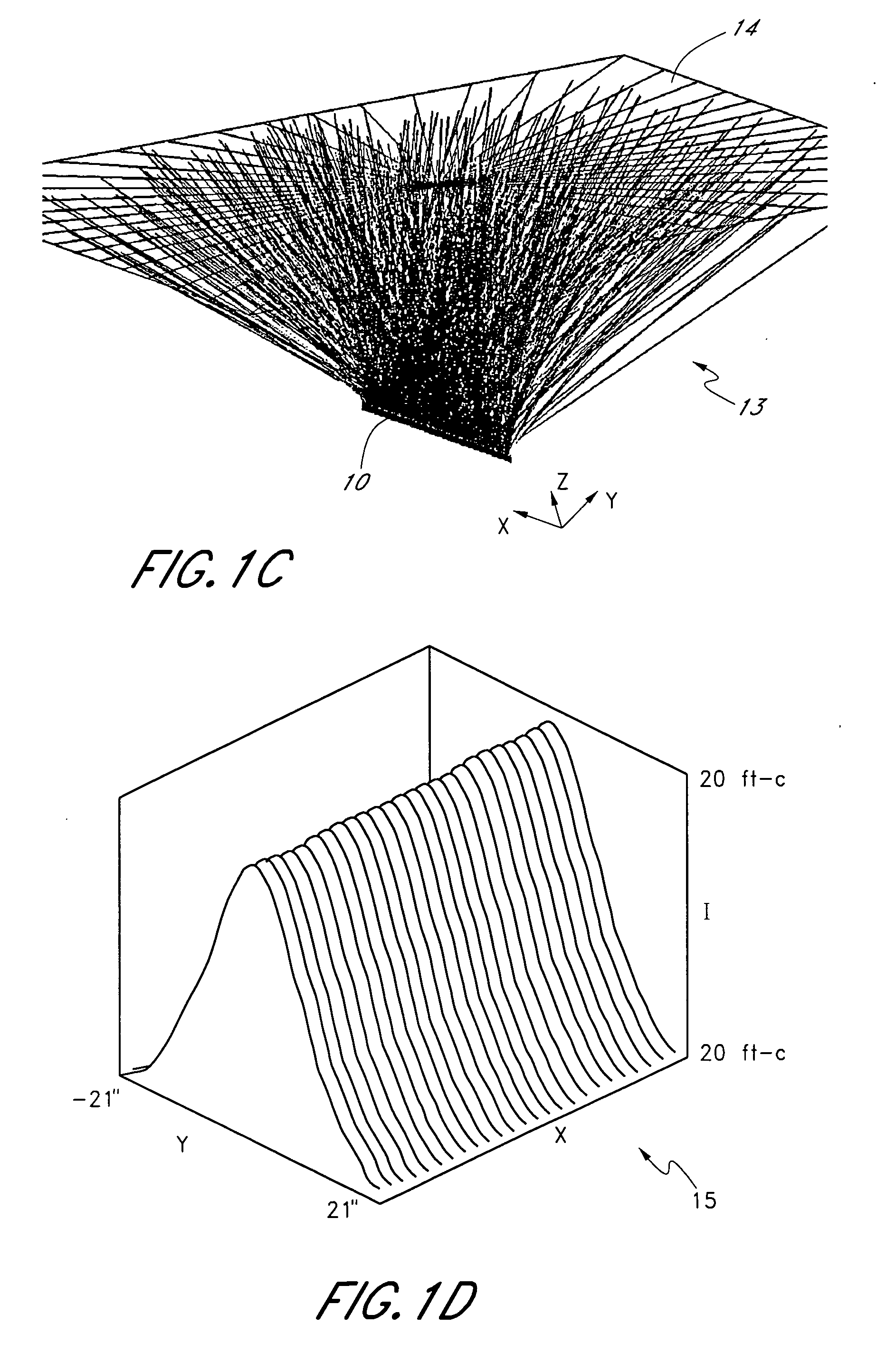
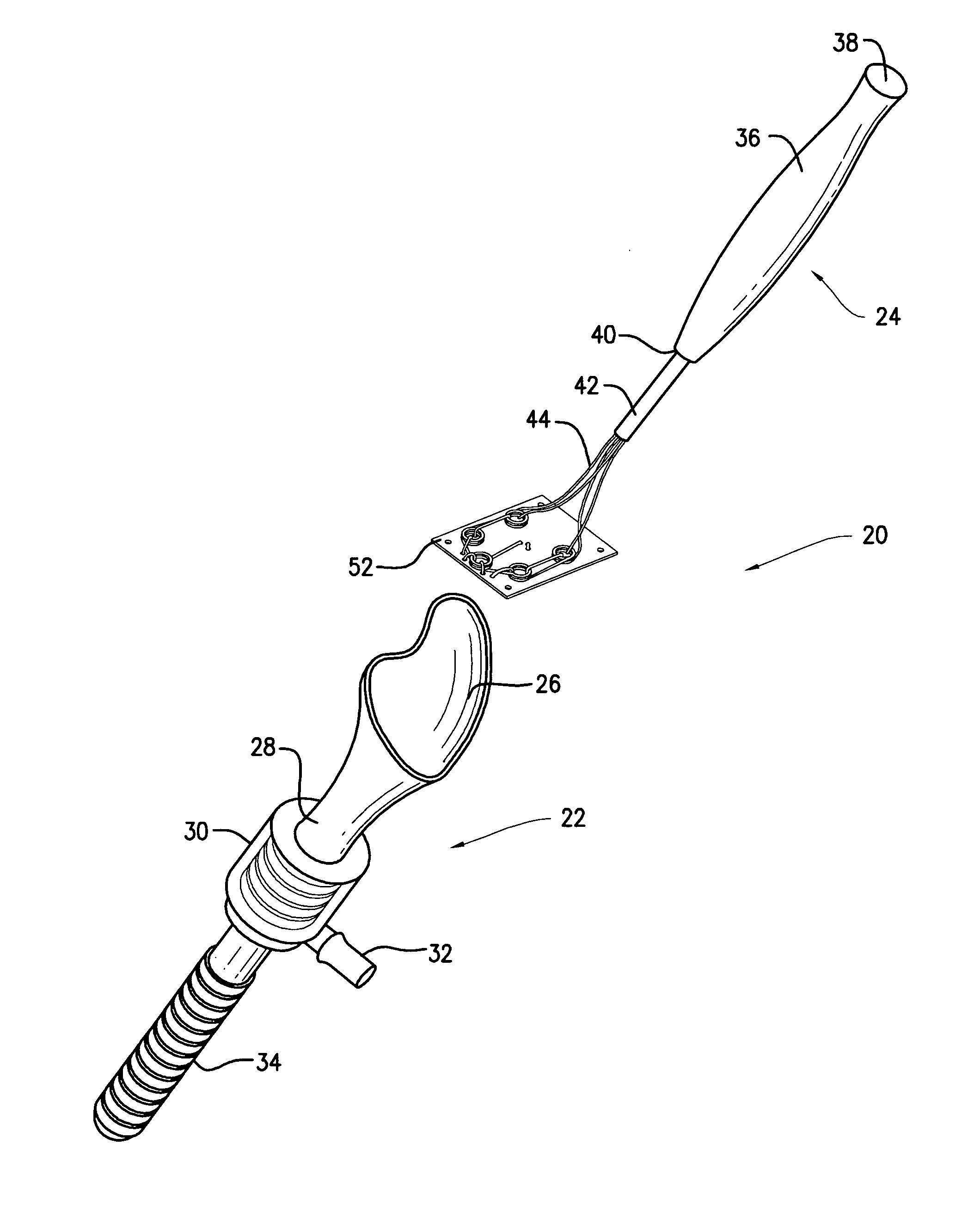
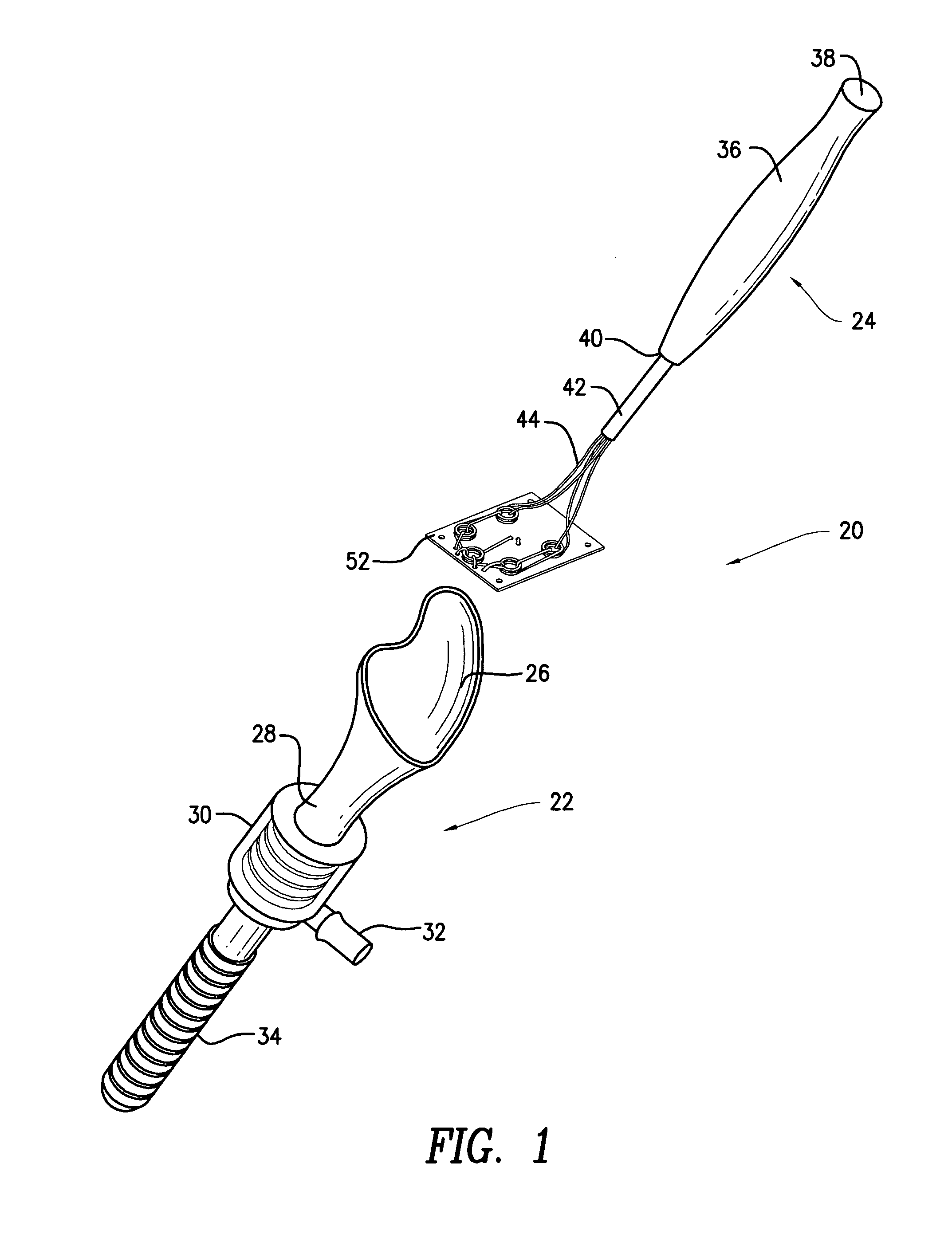
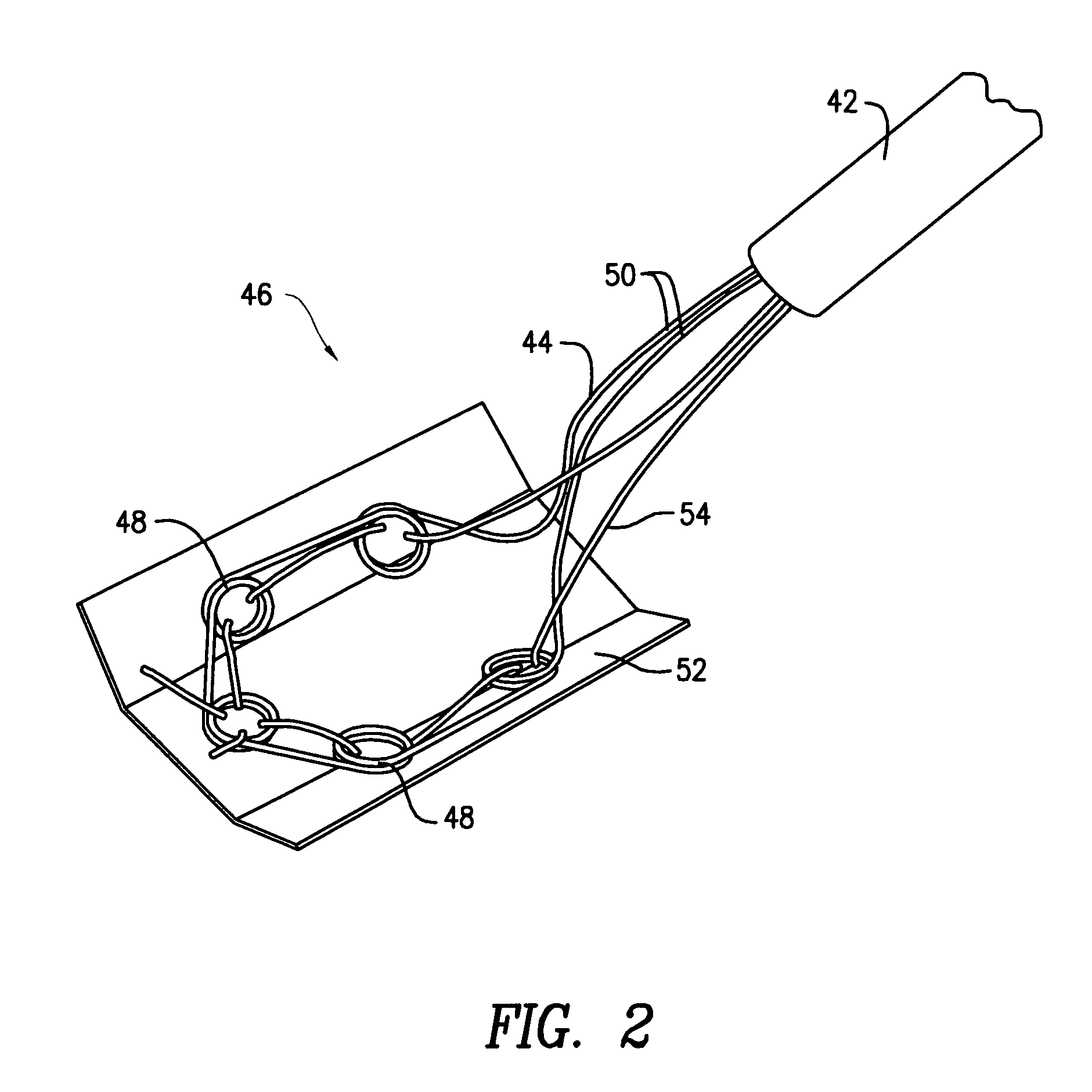
Augmentation delivery device
InactiveUS20090012521A1Held in tensionSurgical needlesLigamentsCylindrical lensBiomedical engineering
The tissue augment sheet delivery system includes a tube funnel adapter and a tissue augment sheet delivery instrument. The tube funnel adapter includes a oval / conical shaped funnel. The tissue augment sheet delivery instrument includes a handle. A cylindrical tube is connected to the handle. A wire is inserted in the tube. The wire is formed in a large loop with small loops formed in the large loop. A tissue augment sheet is attached to one side of the large loop using a monofilament. In use, the tube funnel adapter is inserted in body. The tissue augment sheet is placed in mouth of the oval / conical shaped funnel and gently moved down. While moving down, the tissue augment sheet conforms to the internal diameter of the tube funnel adapter. The handle is withdrawn to remove the large loop from the body leaving the tissue augment sheet in body.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Planar light source and planar lighting apparatus
ActiveUS7422347B2Increase brightnessSolve the lack of balanceShow cabinetsCondensersOptoelectronicsCylindrical lens
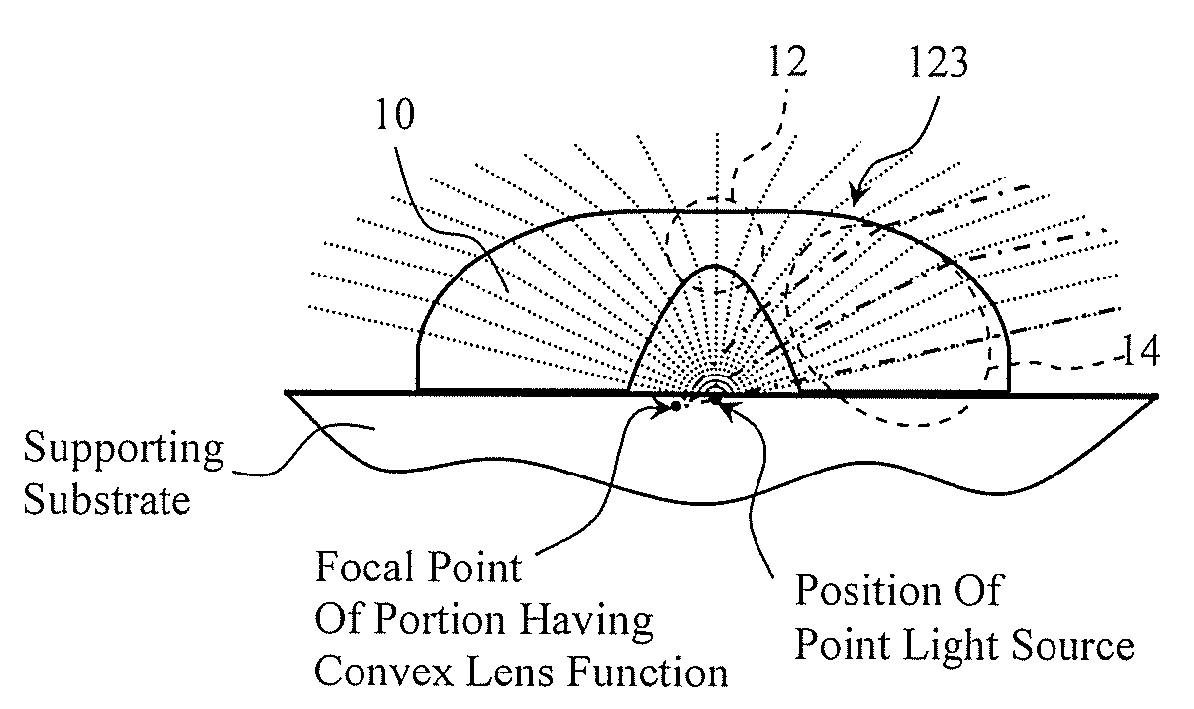
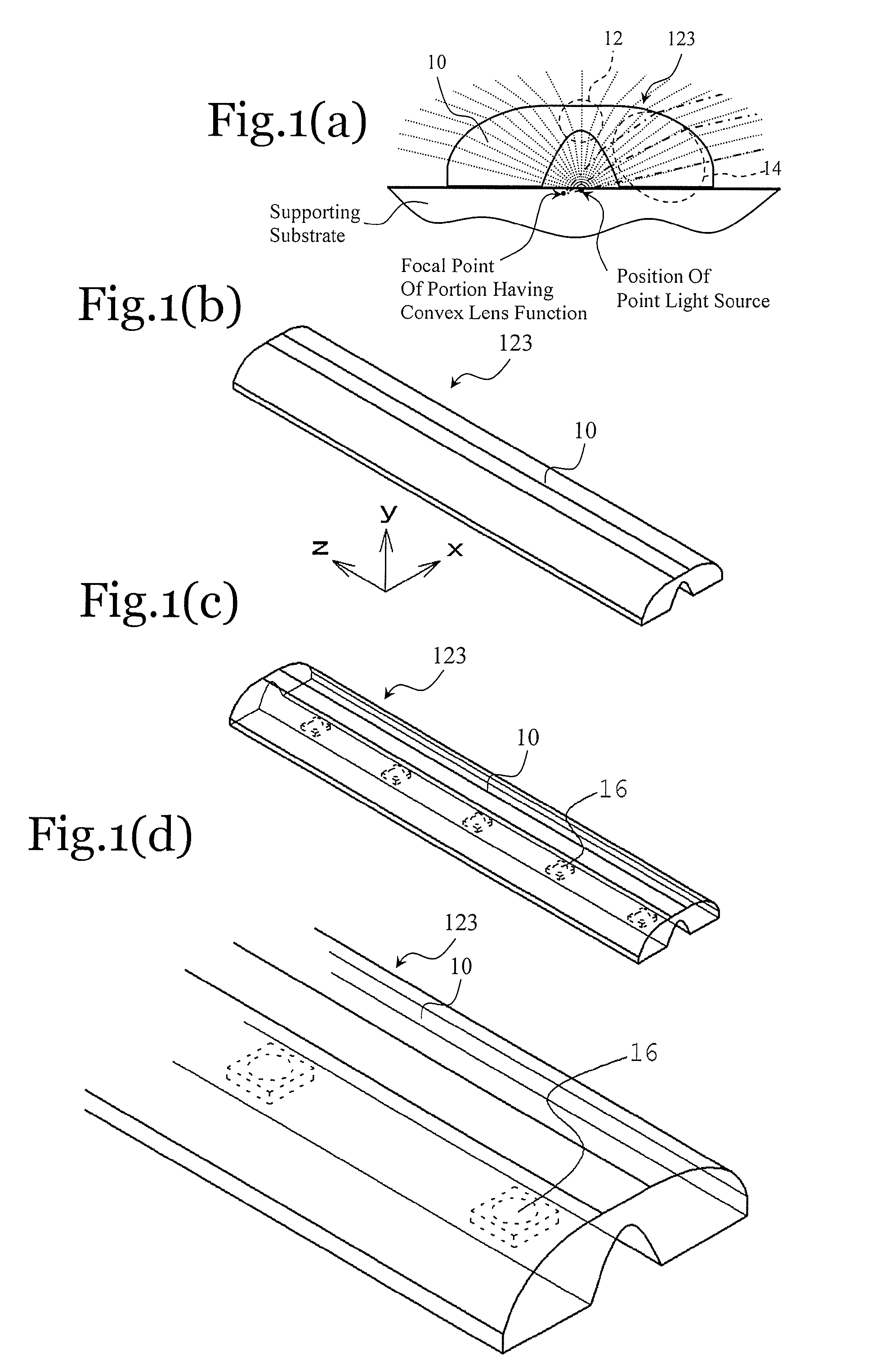
A planar light source comprises at least one point light source disposed on a supporting substrate, and a cylindrical lens that covers the light emitting observation side of the point light source, wherein the cylindrical lens has a concave lens function in the direction (y direction) perpendicular to the supporting substrate, and has a convex lens function in at least part of the horizontal direction (x direction).
Owner:NICHIA CORP
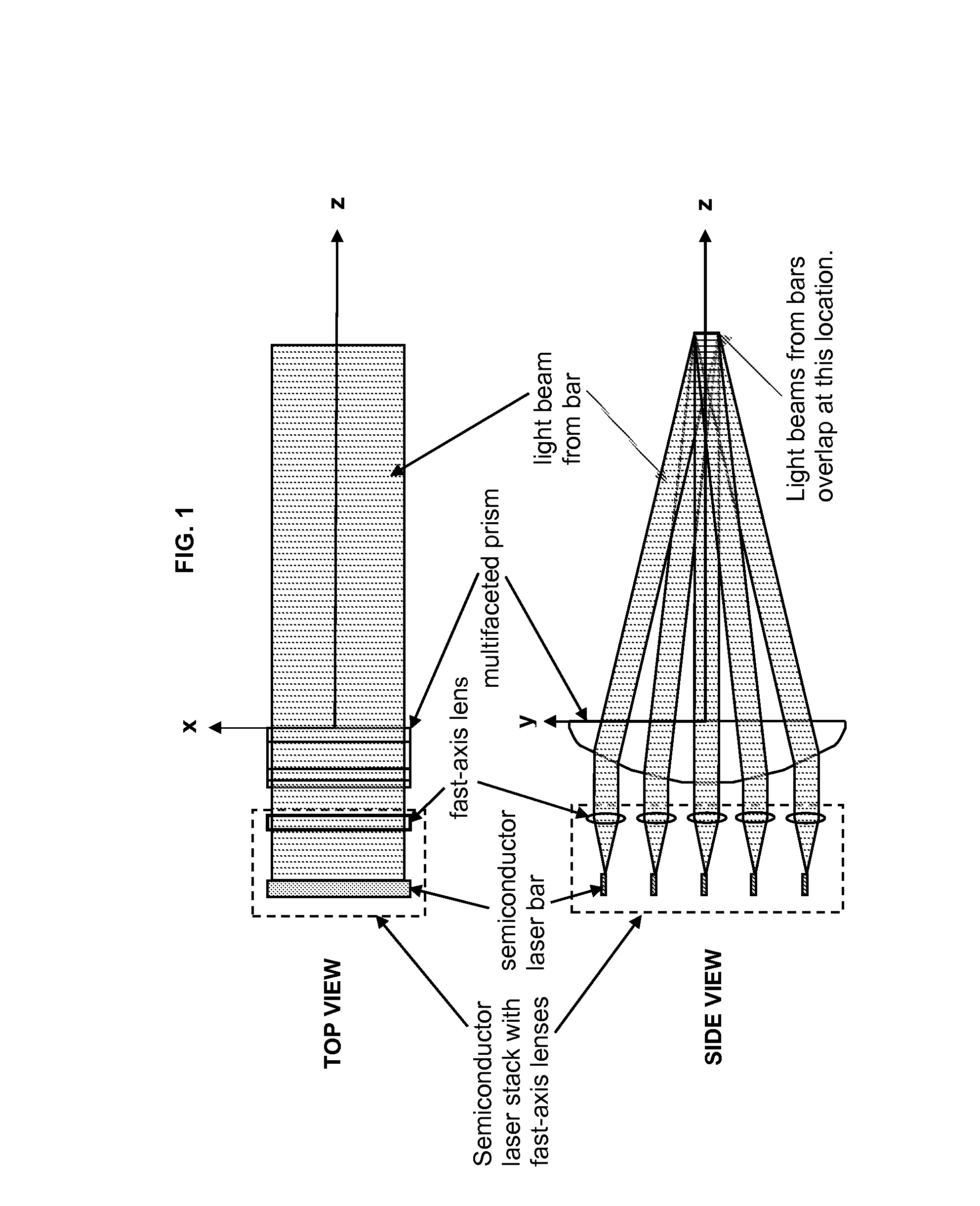
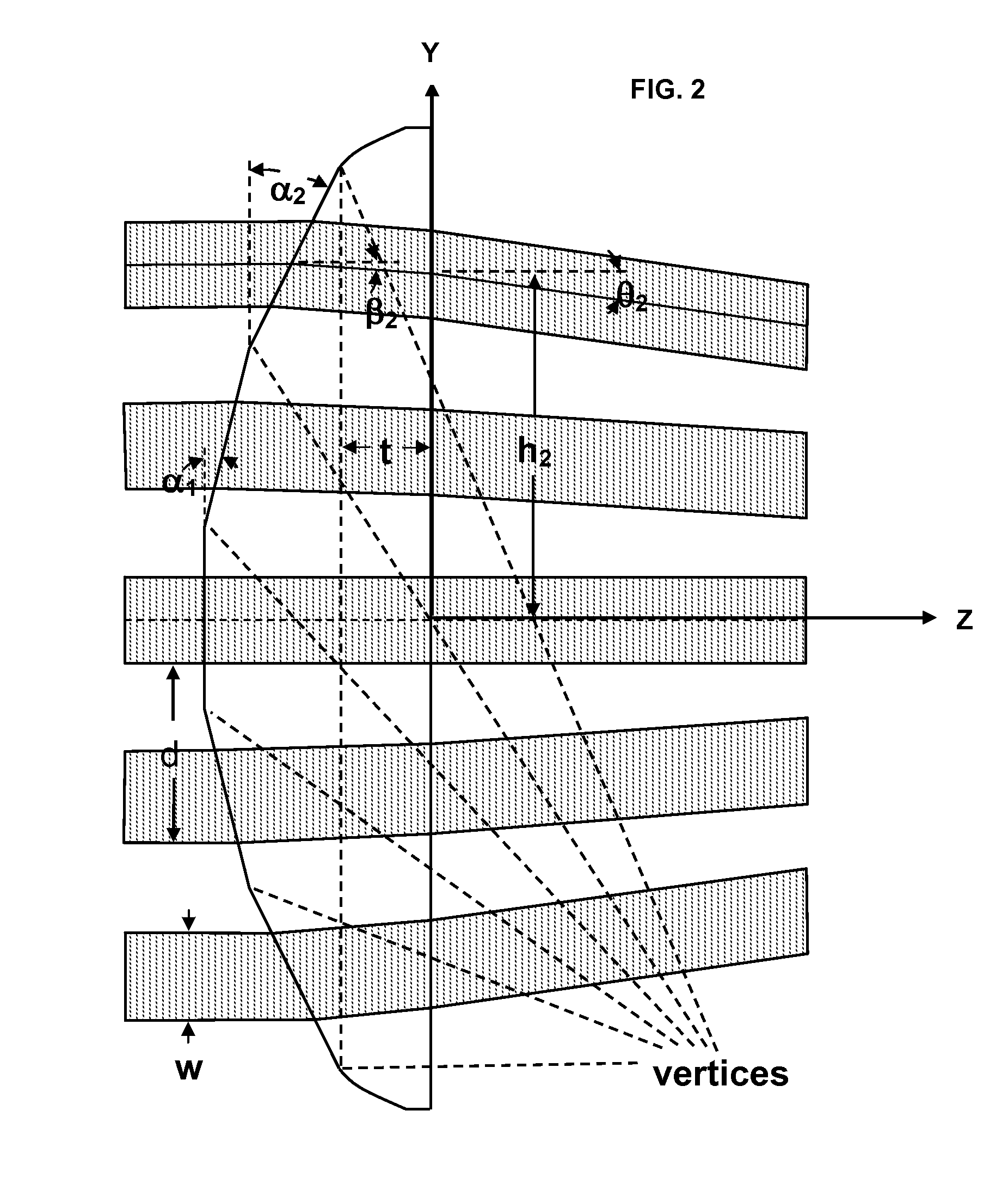
Multifaceted prism to cause the overlap of beams from a stack of diode laser bars
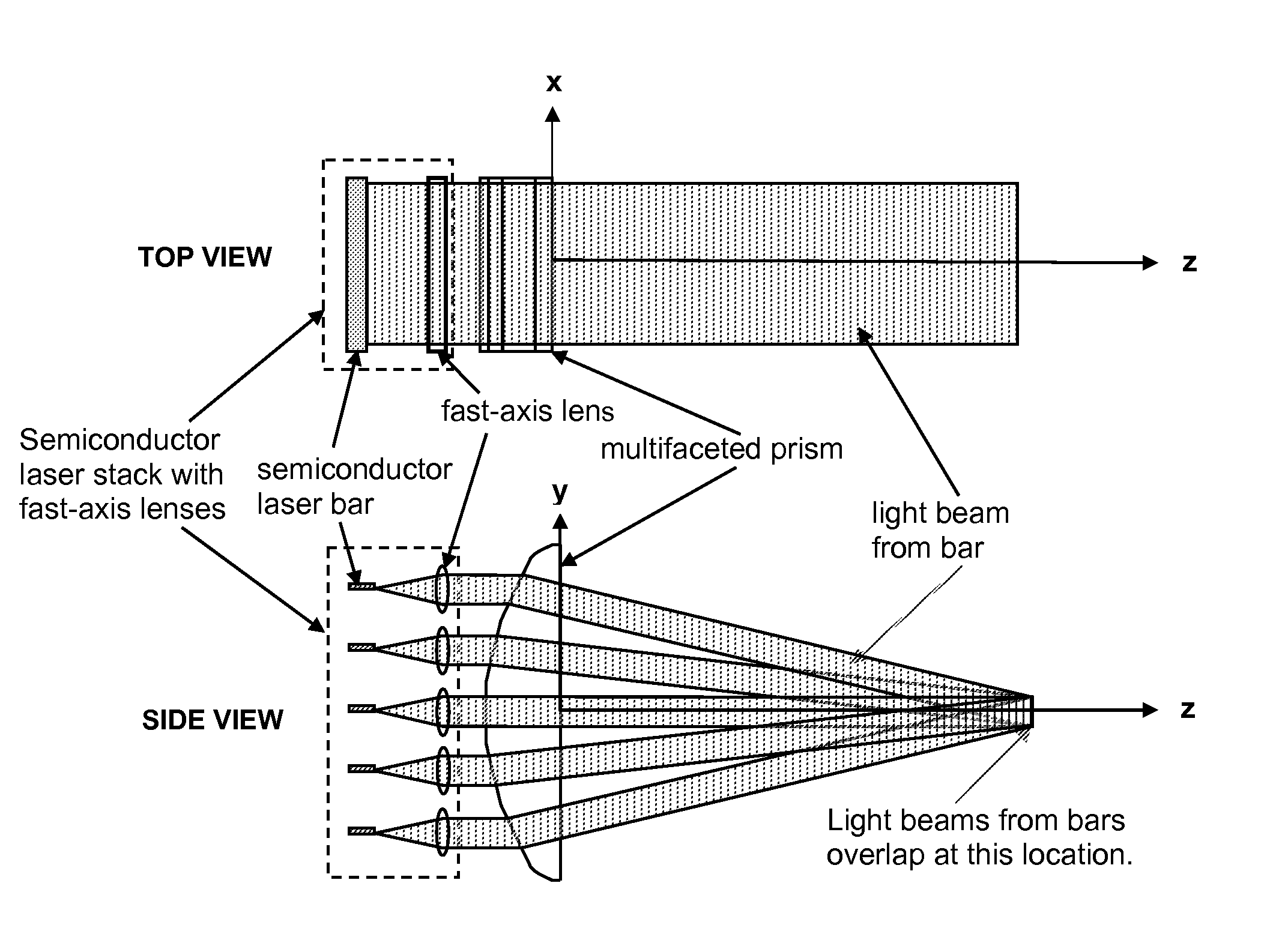
An optical element for homogenizing and, possibly, concentrating the output from high-power two-dimensional semiconductor laser arrays, which has the basic shape of a convex-flat cylindrical lens with a facet cut into the convex surface for each individual semiconductor laser bar.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES AS REPSESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE +1
Color filterless display device, optical element, and manufacture
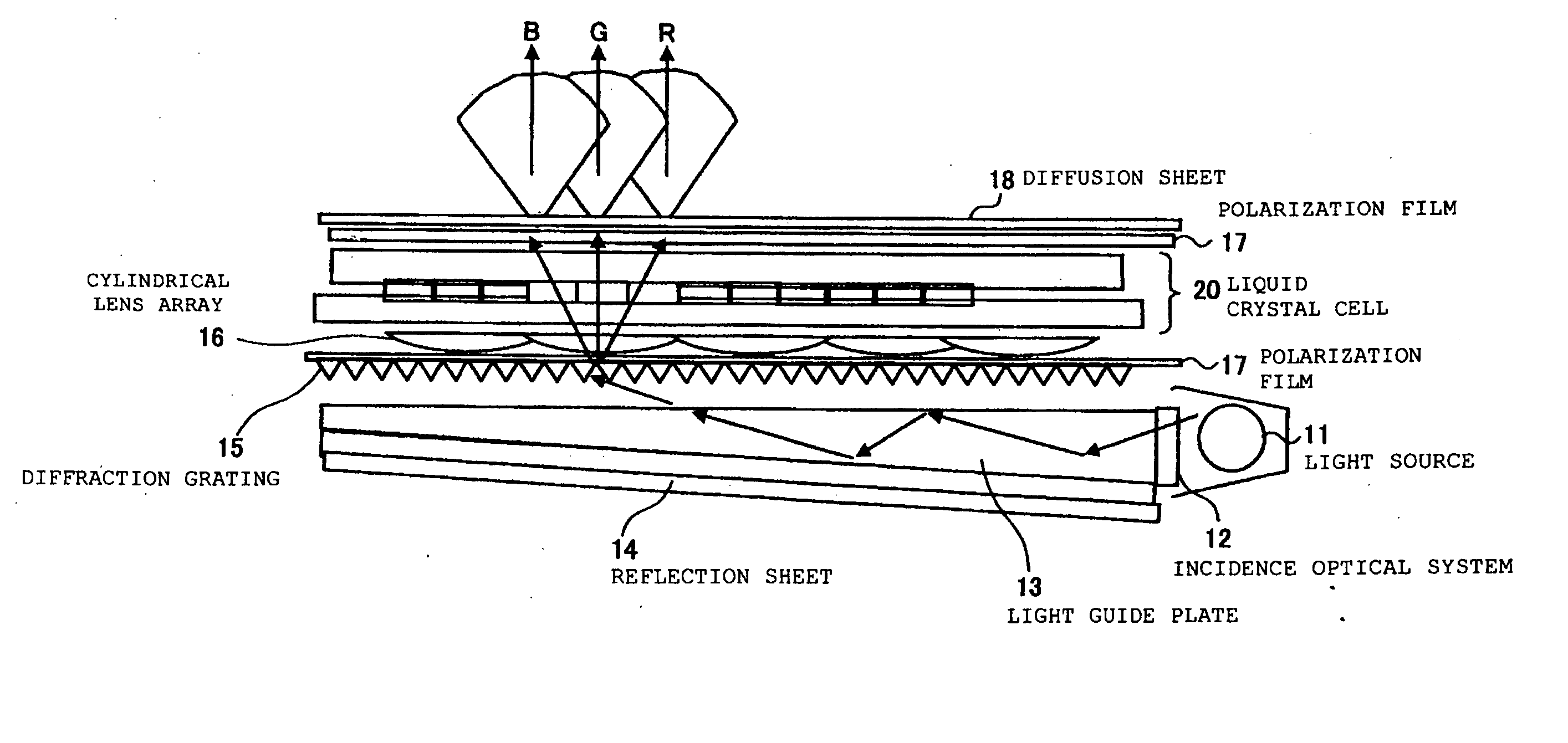
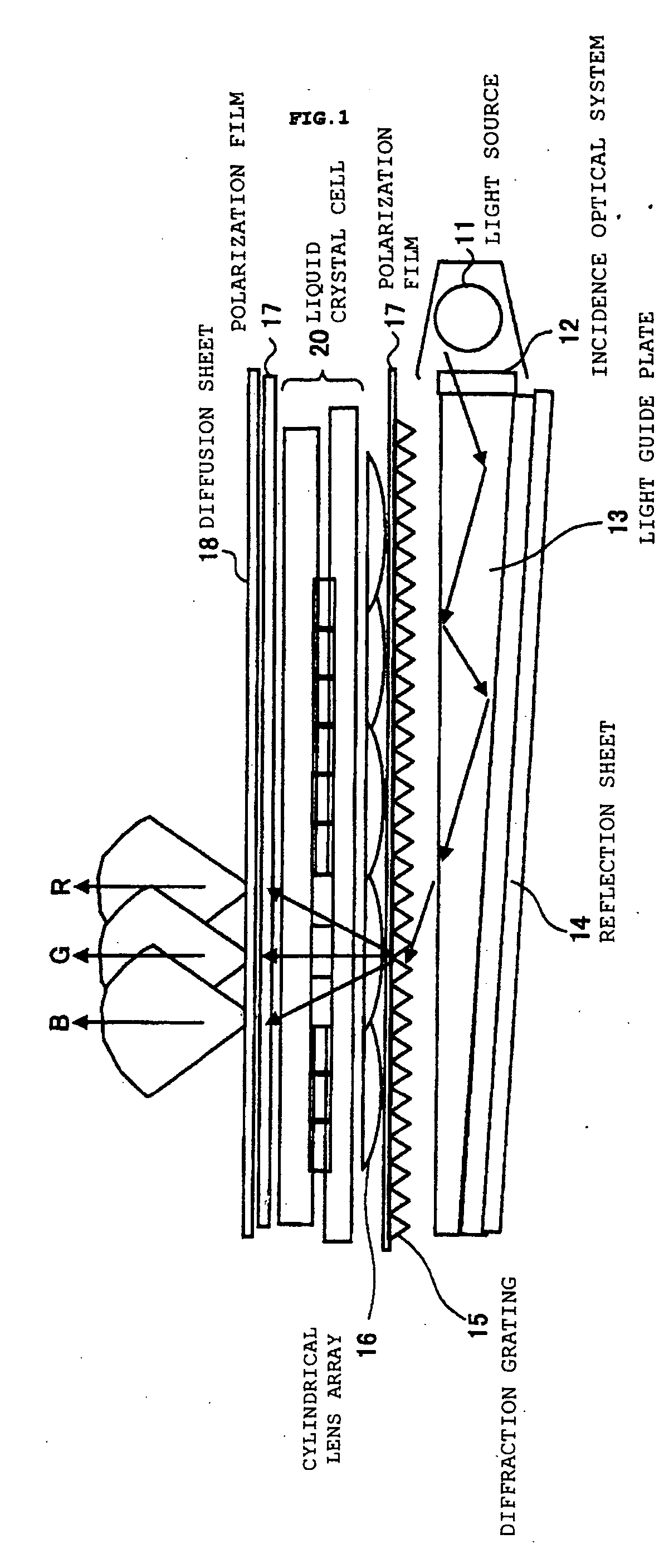
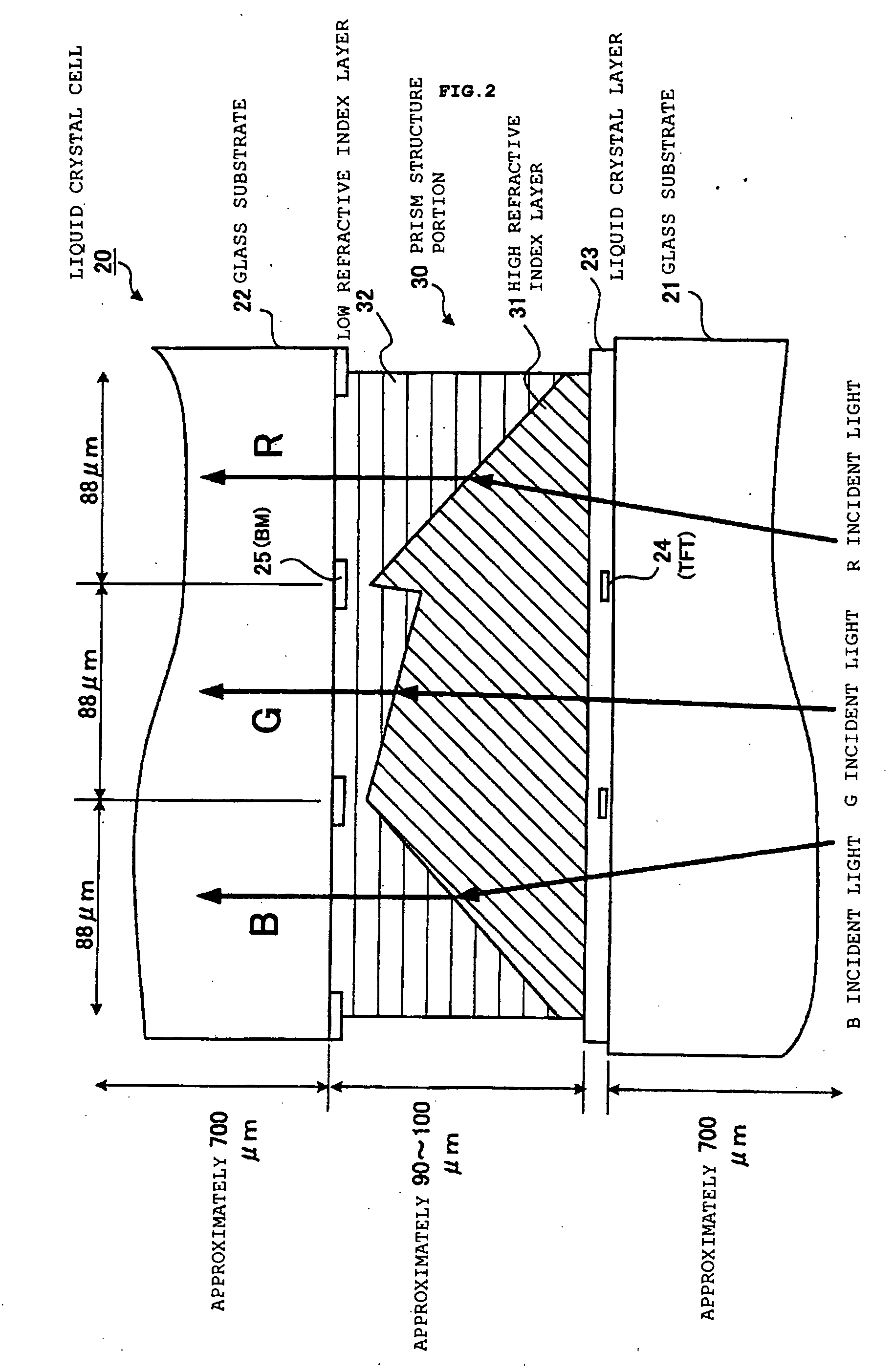
InactiveUS20050041174A1Wide color reproductivityRestricting blurPrismsMechanical apparatusRefractive indexDisplay device
A color filterless display device performing color display for expressing one pixel by three RGB sub-pixels includes: a light source; a diffraction grating for separating a light irradiated from this light source into lights of a plurality of wavelength regions; a cylindrical lens array for receiving the separated light and condensing the light while corresponding to each of the sub-pixels; and a liquid crystal cell including a structure portion for correcting an angle of the condensed light for all sub-pixels, wherein, in the structure portion of this liquid crystal cell, a side onto which a light from the cylindrical lens array is made incident is made of a high refractive index layer, an emitting side from which the light is emitted is made of a low refractive index layer, and a Fresnel-type microprism structure is formed by the high refractive index layer and the low refractive index layer.
Owner:IBM CORP
Planar light source and planar lighting apparatus
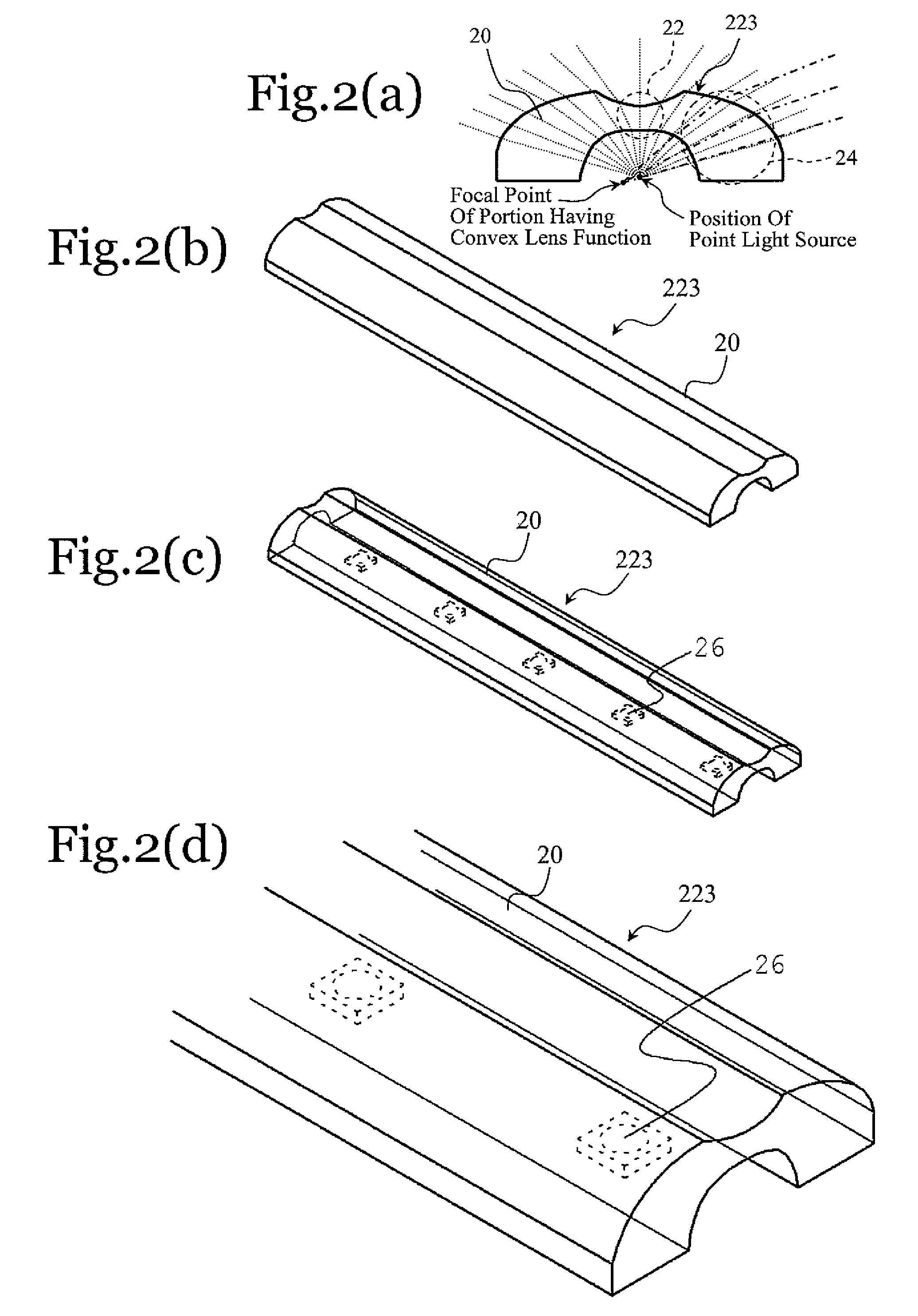
ActiveUS20060198144A1Appropriate brightnessIncrease brightnessShow cabinetsCondensersLight equipmentOptoelectronics
A planar light source comprises at least one point light source disposed on a supporting substrate, and a cylindrical lens that covers the light emitting observation side of the point light source, wherein the cylindrical lens has a concave lens function in the direction (y direction) perpendicular to the supporting substrate, and has a convex lens function in at least part of the horizontal direction (x direction).
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Longitudinally flexible expandable stent
A stent comprises a plurality of adjacent cylindrical elements defining a first end section, a second end section, and a center section therebetween. Each cylindrical element has constant thickness struts formed in a generally serpentine wave pattern transverse to the longitudinal axis which contains alternating valley portions and peak portions. A plurality of interconnecting members extend between the adjacent cylindrical elements and connect the adjacent cylindrical elements to one another. The cylindrical elements are formed of a stent material, the composition of which is uniform throughout the stent. The stent material of the struts in each of the first end section and the second end section have a greater mass than the stent material of the struts of the center section.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Spinal stabilization systems with dynamic interbody devices
A stabilization system for a human spine is provided. The stabilization system may include one or more dynamic interbody devices and / or one or more dynamic posterior stabilization systems. The dynamic interbody devices may allow for coupled axial rotation and lateral bending of vertebrae adjacent to the dynamic interbody devices. In an embodiment, the dynamic interbody device includes a keel having a neck and a cylindrical base. The cylindrical base is wider than the neck. In an embodiment, portions of the dynamic interbody device that allow for flexion and / or extension of vertebra coupled to the dynamic interbody device are coupled together by ball bearings.
Owner:FLEXUSPINE INC
Display unit and electronic apparatus with display unit
A display system includes respective light sources disposed at two opposed light input ends of a light guiding plate. A double-sided prism sheet is disposed on a light-emitting side of the light guiding plate and includes, on a first surface facing the light guiding plate, a triangular prism bank extending in a direction parallel to the light input ends of the light guiding plate. The double-sided prism sheet includes, on a second surface, opposite to the first surface, a cylindrical lens bank extending in a direction parallel to the triangular prism bank. A transmissive display panel is disposed on a light-emitting side of the double-sided prism sheet. A synchronization driving section alternatively illuminates the respective light sources so the transmissive display panel displays two different images. The light from the light sources is emitted through the transmissive display panel at respective divergent angles producing two images corresponding to right and left parallax images, producing a stereoscopic display.
Owner:TRIVALE TECH
Lens array device and image display
InactiveUS20100157181A1Not easy to degradeImprove powerStatic indicating devicesSteroscopic systemsCamera lensElectricity
The lens array device includes: first and second substrates; a first electrode group formed on the first substrate to include transparent electrodes extending in a first direction; a second electrode group formed on the second substrate to include transparent electrodes extending in a second direction; and a liquid crystal layer with refractive index anisotropy arranged between the first and second substrates to produce a lens effect by changing the liquid crystal molecule alignment. The liquid crystal layer electrically changes into one of three states according to voltages applied to the first and second electrode groups. The three states include a state with no lens effect, a first lens state where a lens effect of a first cylindrical lens extending in the first direction is produced, and a second lens state where a lens effect of a second cylindrical lens extending in the second direction is produced.
Owner:SONY CORP
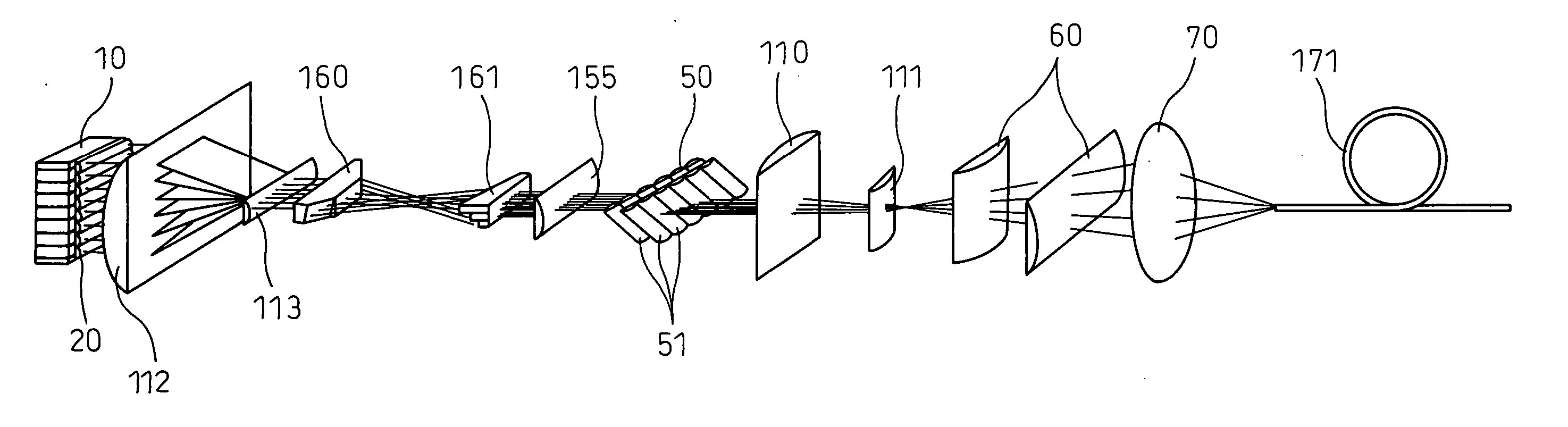
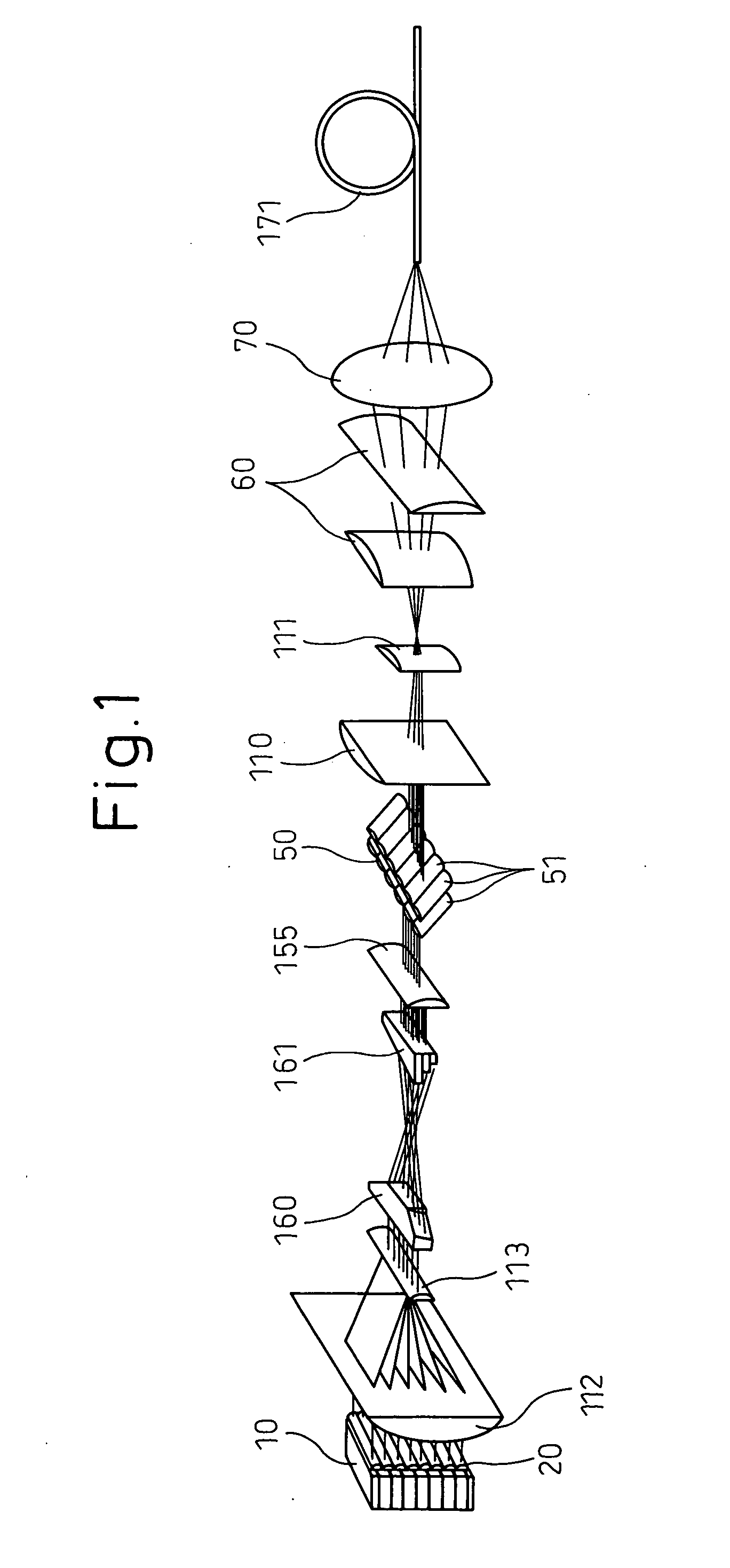
Laser irradiation device
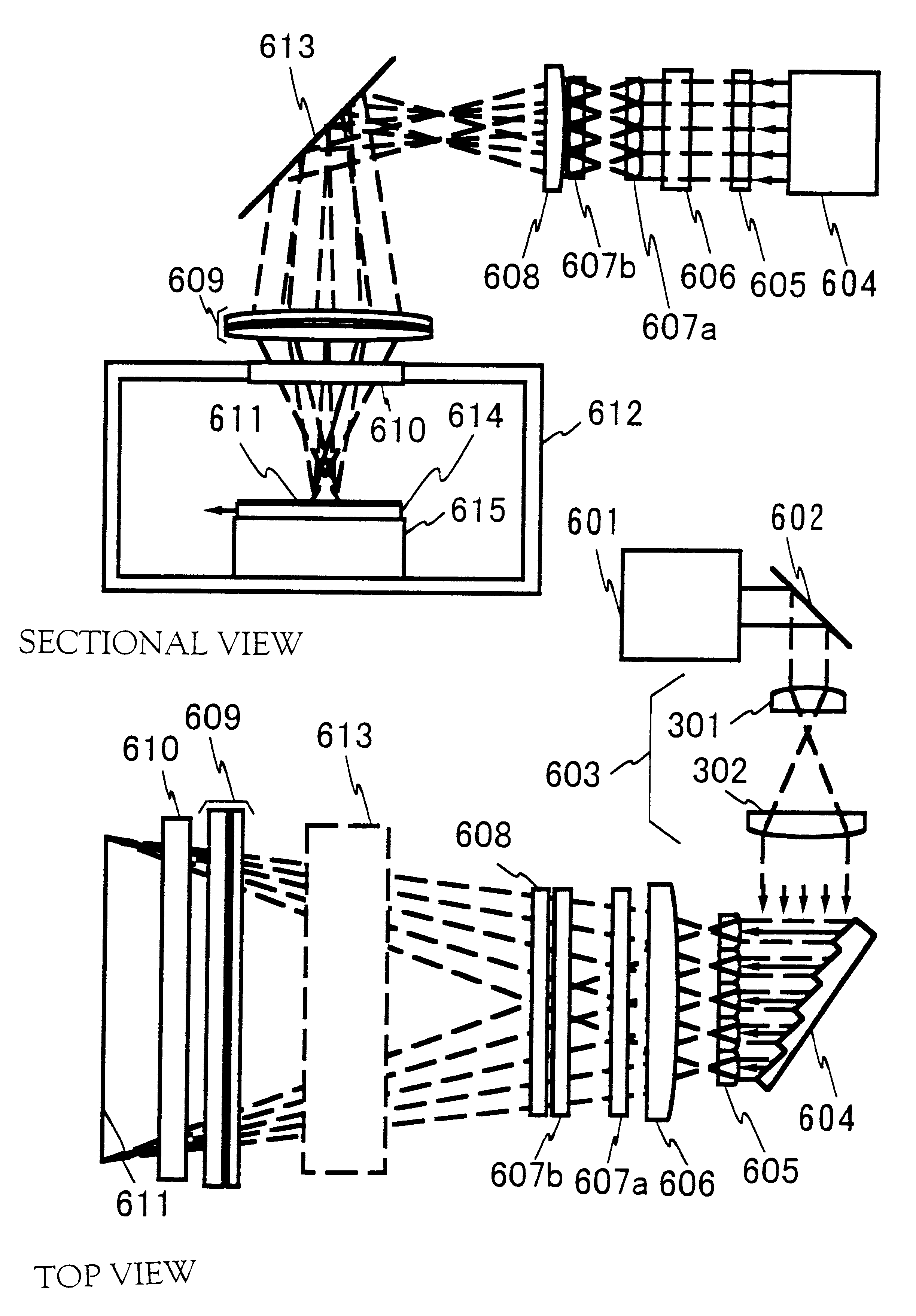
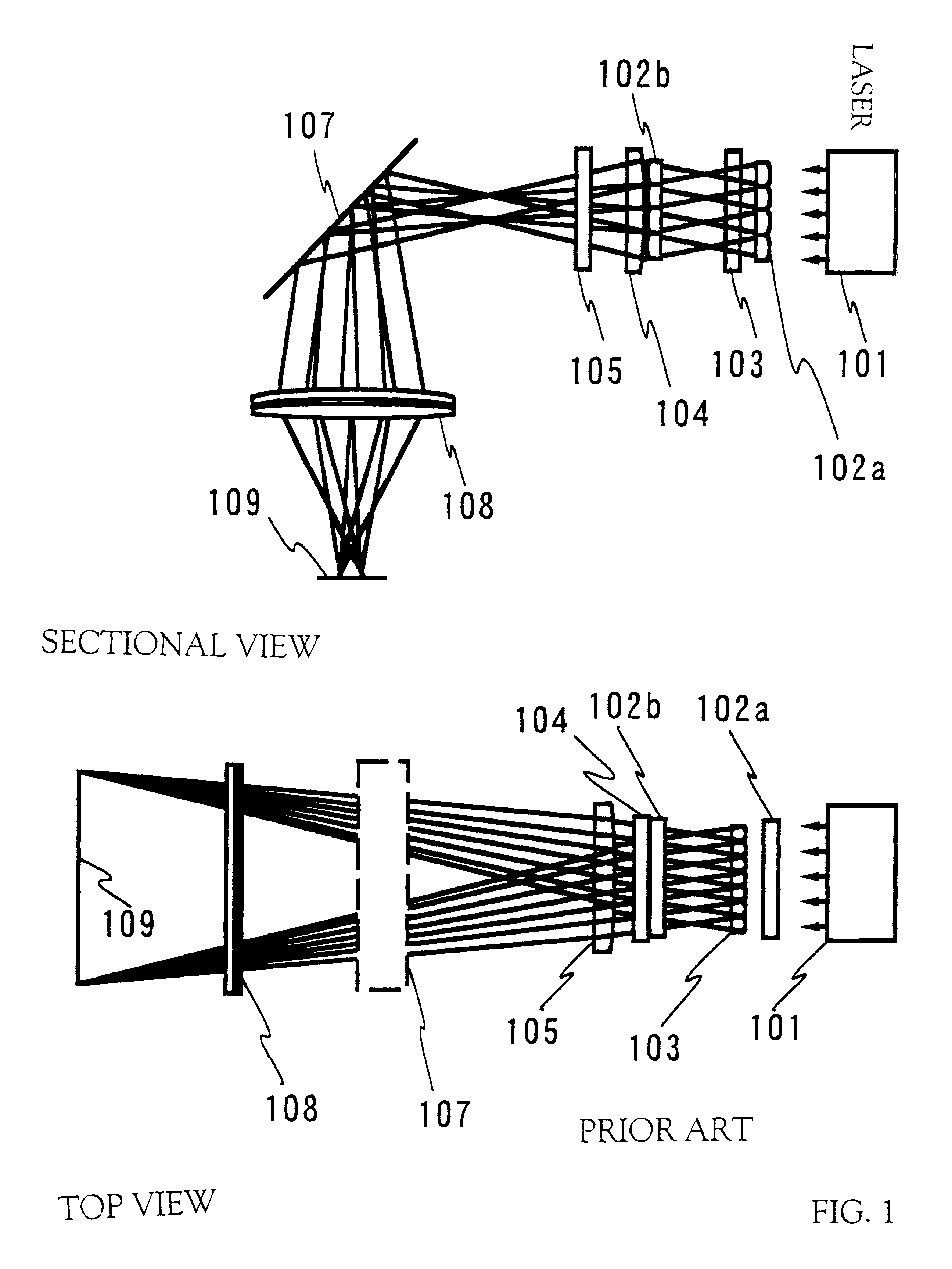
InactiveUS6563843B1Laser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight beamOptical pathlength
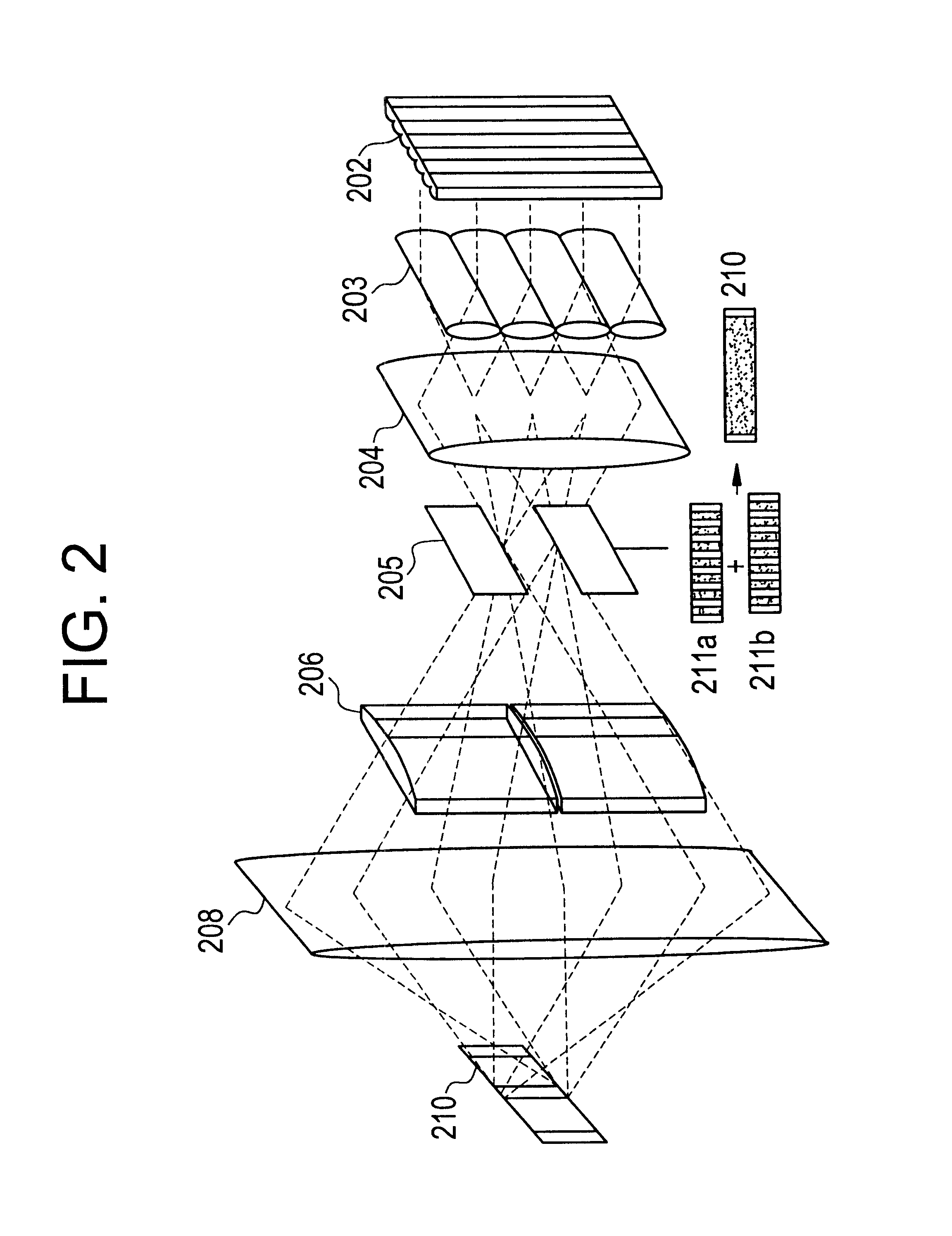
In annealing a non-single crystal silicon film through the use of a linear laser beam emitted by a YAG laser of a light source, it is the object of the present invention to prevent heterogeneity in energy caused by an optical interference produced in the linear laser beam from having an effect on the silicon film. The laser beam is divided by a mirror 604 shaped like steps into laser beams which have an optical path difference larger than the coherence length of the laser beam between them. The divided laser beams are converged on an irradiate surface 611 by the action of a cylindrical lens array 605 and a cylindrical lens 606 to homogenize the energy of the laser beam in the length direction and to determine the length of the linear laser beam. On the other hand, the laser beams divided by a cylindrical lens array 607 are converged on the irradiate surface 611 by a cylindrical lens 608 and a doublet cylindrical lens 609 to homogenize the energy in the width direction of the laser beam and to determine the width of the linear laser beam. Interference fringes parallel to the width direction of the linear laser beam disappears in the linear laser beam by the action of a mirror 604 shaped like steps. If the silicon film is annealed by the linear laser beam while the linear laser beam is being shifted in the width direction of the linear laser beam, the silicon film is remarkably homogenized as compared with a conventional silicon film.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Gridless time-of-flight mass spectrometer for orthogonal ion injection
InactiveUS20010011703A1Reduce voltageFacilitates taskMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTime-of-flight spectrometersFlight directionFlat detector
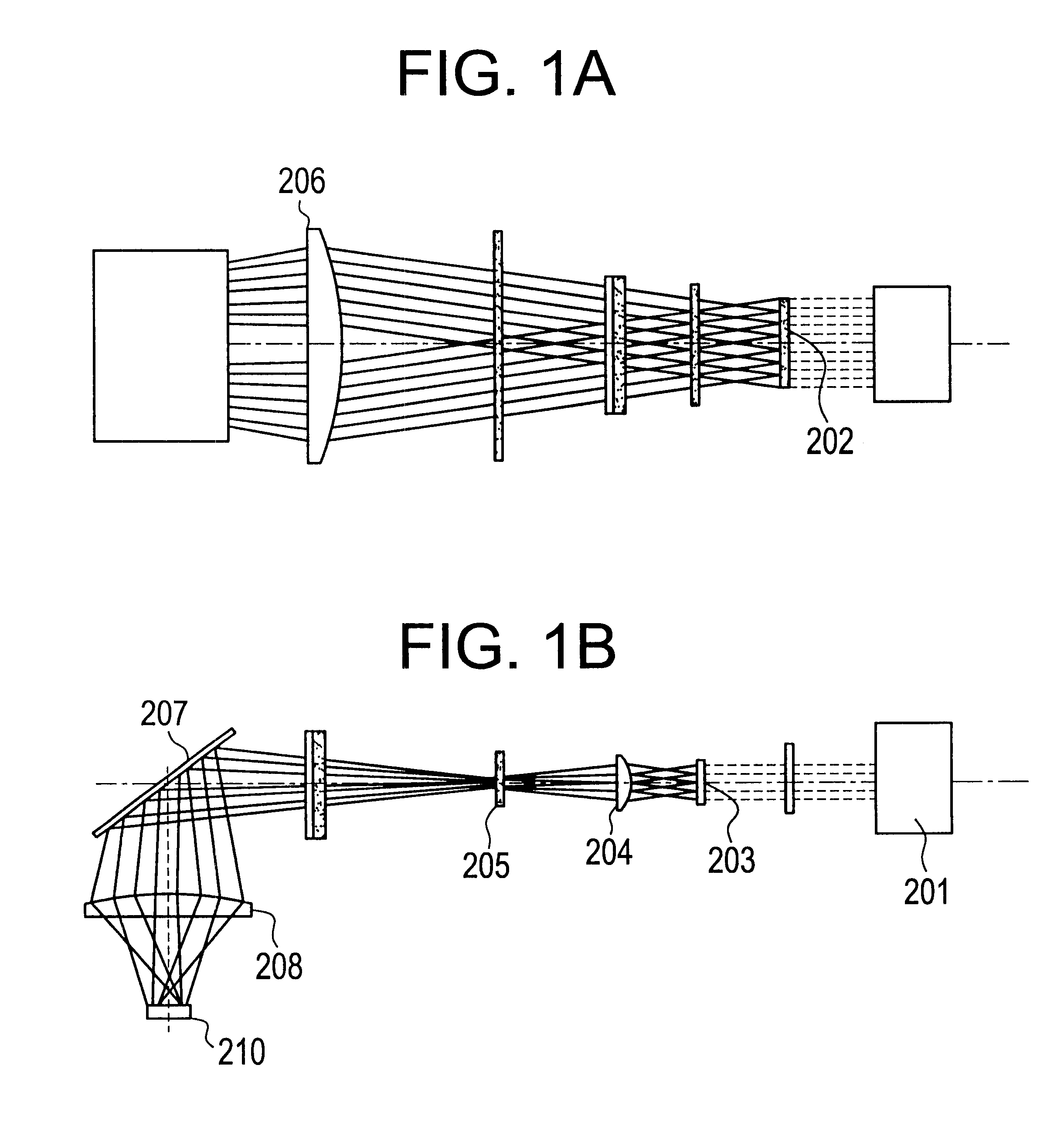
The invention relates to a time-of-flight mass spectrometer for injection of the ions orthogonally to the time-resolving axis-of-flight component, with a pulser for acceleration of the ions of the beam in the axis-of-flight direction, preferredly with a velocity-focusing reflector for reflecting the ion beam and with a flat detector at the end of the flight section. The invention consists of using, both for acceleration in the pulser and for reflection in the reflectors, a gridless optical system made up of slit diaphragms which can spatially focus the ions onto the detector in the direction vertical to the directions of injection and flight axis, but which does not have any focusing or deflecting effect on the other directions. For some reflector geometries it is essential to use an additional cylindrical lens for focusing, and for other reflector geometries the use of such a lens may be advantageous.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Laser scanning unit
InactiveUS7190499B2Reduce in quantityIncrease scan frequencyMountingsPrintingLaser scanningOptoelectronics
A laser scanning unit mainly includes a semiconductor laser, a collimator, a micro electronic mechanic system (MEMS) oscillatory mirror, and an fθ lens or an f sin θ lens. The MEMS oscillatory mirror is disposed between the collimator and the fθ lens to replace a conventional rotary polygonal mirror for controlling a direction in which laser beams are projected from the oscillatory mirror to the fθ lens. With the MEMS oscillatory mirror, the cylindrical lens may be omitted from the laser scanning unit and noises produced by the polygonal mirror rotating at high speed may be avoided. Moreover, the MEMS oscillatory mirror allows bi-directional scanning to therefore enable increased scanning frequency, simplified structure, and improved scanning efficiency.
Owner:E PIN OPTICAL IND
Low temperature horticultural light apparatus
InactiveUS6267483B1Heat generation is minimizedMinimizing heat generationElongate light sourcesElectric lighting sourcesEngineeringRadiant heat
A horticultural light apparatus that reduces heat transmitted to plants that are being illuminated is provided. The Inventive Device includes a hollow, transparent, cylindrical tube, preferably made of glass. The tube is open at both ends and adapted to receive spigot members, the spigot members also being open ended. A support bracket to mount a lightbulb is affixed to at least one of the spigots. A reflector is also installed on the interior of the tube. In use, a lightbulb is inserted into the tube and secured by the spigots. Because of the open ends, air can flow through the tube, thus eliminating over-heating of the lightbulb. The glass absorbs much of the radiant heat generated by the lightbulb while emitting substantially all of the light generated by the lightbulb. The reflector directs the light in a generally downward direction. Means for suspending the Device are also included.
Owner:HEMBERY DANIEL
Connection apparatus for parallel optical interconnect module and parallel optical interconnect module using the same
InactiveUS20050141823A1Minimize couplingSimple structureSolid-state devicesCoupling light guidesCoupling lossPrism
Provided is an optical connection apparatus for a parallel optical interconnect module and a parallel optical interconnect module using the same for reducing a coupling loss generated due to an alignment error when coupled with an optical fiber, comprising: a 2D reflector in a prism shape and having at least two rows of cylinder type lens attached thereto; a 2D optical waveguide having at least two layers of core arrays; at least two rows of 2D optical benches; and a 2D ferrule capable of loading at least two layers of optical fibers so as to facilitate the fixing of the 2D optical waveguide for optical interconnection.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Semiconductor laser apparatus capable of routing laser beams emitted from stacked-array laser diode to optical fiber with little loss
ActiveUS20060126690A1Small lossSemiconductor laser optical deviceOptical resonator shape and constructionLaser beamsSemiconductor
A semiconductor laser apparatus according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention is provided. For example, the apparatus may include a single or a plurality of stacked-array laser diodes, first beam compressors, and a separating optical device separating the group of laser beams into subgroups of laser beams in a first direction, and deflecting the subgroups of laser beams so that the subgroups of laser beams approach in the first direction and recede from one another in a second direction. In addition, a collimating optical device may be provided which is adapted to deflect the subgroups of laser beams in the first and second directions by the same angles. Further, a beam converter may be included which divides each subgroup of laser beams and turning the axis thereof, and second beam compressors and a group of cylindrical lenses can be provided that can make the angle of divergence in the first direction close to the angle of divergence in the second direction.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com