Patents
Literature
1549results about "Semiconductor laser optical device" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Resonator-enhanced optoelectronic devices and methods of making same
Optical resonators that are enhanced with photoluminescent phosphors and are designed and configured to output light at one or more wavelengths based on input / pump light, and systems and devices made with such resonators. In some embodiments, the resonators contain multiple optical resonator cavities in combination with one or more photoluminescent phosphor layers or other structures. In other embodiments, the resonators are designed to simultaneously resonate at the input / pump and output wavelengths. The photoluminescent phosphors can be any suitable photoluminescent material, including semiconductor and other materials in quantum-confining structures, such as quantum wells and quantum dots, among others.
Owner:VERLASE TECH
2-D Planar VCSEL Source for 3-D Imaging
InactiveUS20150260830A1Accurate proximityImprove accuracyLaser detailsSolid-state devicesOperation modeUltimate tensile strength
An apparatus and a method are provided for 3-D proximity sensing, imaging and scanning using a 2-D planar VCSEL array source using reflected radiation from an object being detected. An important aspect of the apparatus is a compact high power optical source and in particular, an optical source comprising a plurality of VCSELs to illuminate the object. VCSELs in the optical source are configured in different 2-D planar arrangements, such that the optical source may be used in many different modes to adapt to different sensing, imaging and scanning requirement suited for different environments including one where shape, size and illumination mode require to be altered dynamically. When used in different modes of operation the apparatus provides a comprehensive set of measured distance and intensity profile of the object to compute a 3-D image.
Owner:PRINCETON OPTRONICS
Quantum dot-wavelength converter, manufacturing method of the same and light emitting device including the same
InactiveUS20100051898A1Improve emission effectSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingQuantum dotLength wave
There is provided a quantum dot wavelength converter including a quantum dot, which is optically stable without any change in an emission wavelength and improved in emission capability. The quantum dot wavelength converter includes: a wavelength converting part including a quantum dot wavelength-converting excitation light and generating a wavelength-converted light and a dispersive medium dispersing the quantum dot; and a sealer sealing the wavelength converting part.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Use of volume Bragg gratings for the conditioning of laser emission characteristics
ActiveUS20050018743A1High damage thresholdLarge clear apertureLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsGratingLight emitting device
Apparatus and methods for altering one or more spectral, spatial, or temporal characteristics of a light-emitting device are disclosed. Generally, such apparatus may include a volume Bragg grating (VBG) element that receives input light generated by a light-emitting device, conditions one or more characteristics of the input light, and causes the light-emitting device to generate light having the one or more characteristics of the conditioned light.
Owner:NECSEL INTPROP
Synchronization of projected illumination with rolling shutter of image sensor
Imaging apparatus includes an illumination assembly, including a plurality of radiation sources and projection optics, which are configured to project radiation from the radiation sources onto different, respective regions of a scene. An imaging assembly includes an image sensor and objective optics configured to form an optical image of the scene on the image sensor, which includes an array of sensor elements arranged in multiple groups, which are triggered by a rolling shutter to capture the radiation from the scene in successive, respective exposure periods from different, respective areas of the scene so as to form an electronic image of the scene. A controller is coupled to actuate the radiation sources sequentially in a pulsed mode so that the illumination assembly illuminates the different, respective areas of the scene in synchronization with the rolling shutter.
Owner:APPLE INC
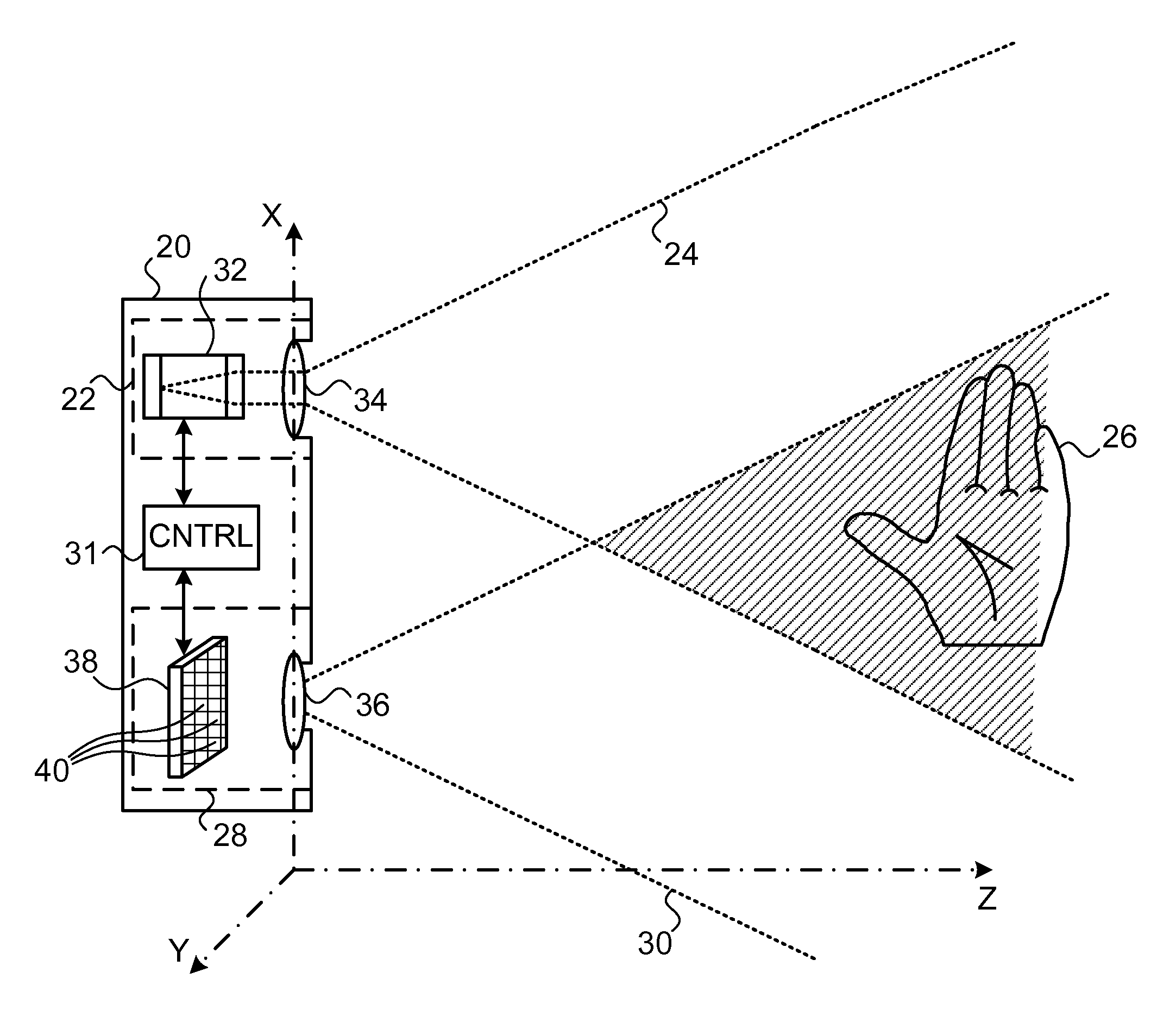
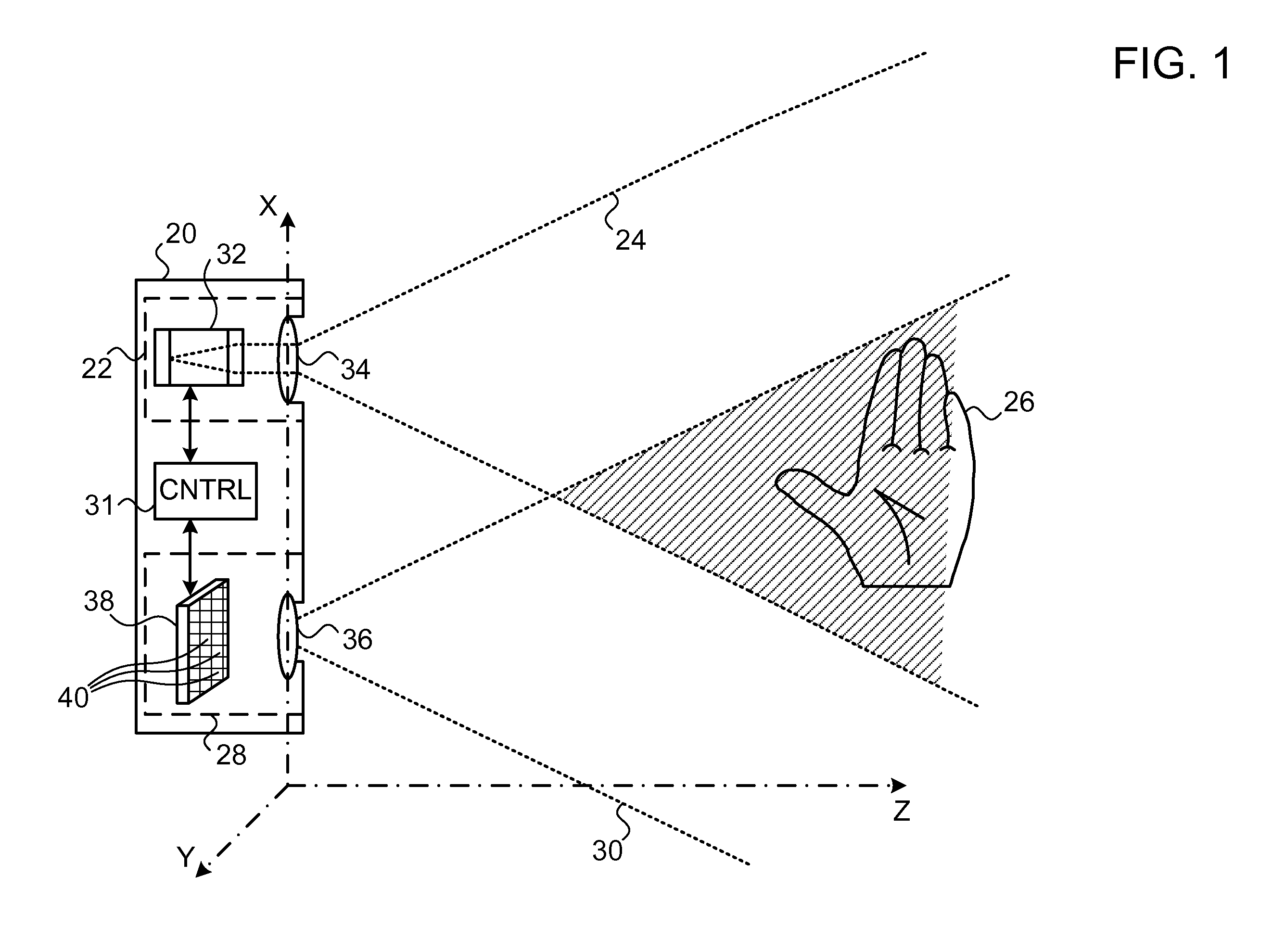
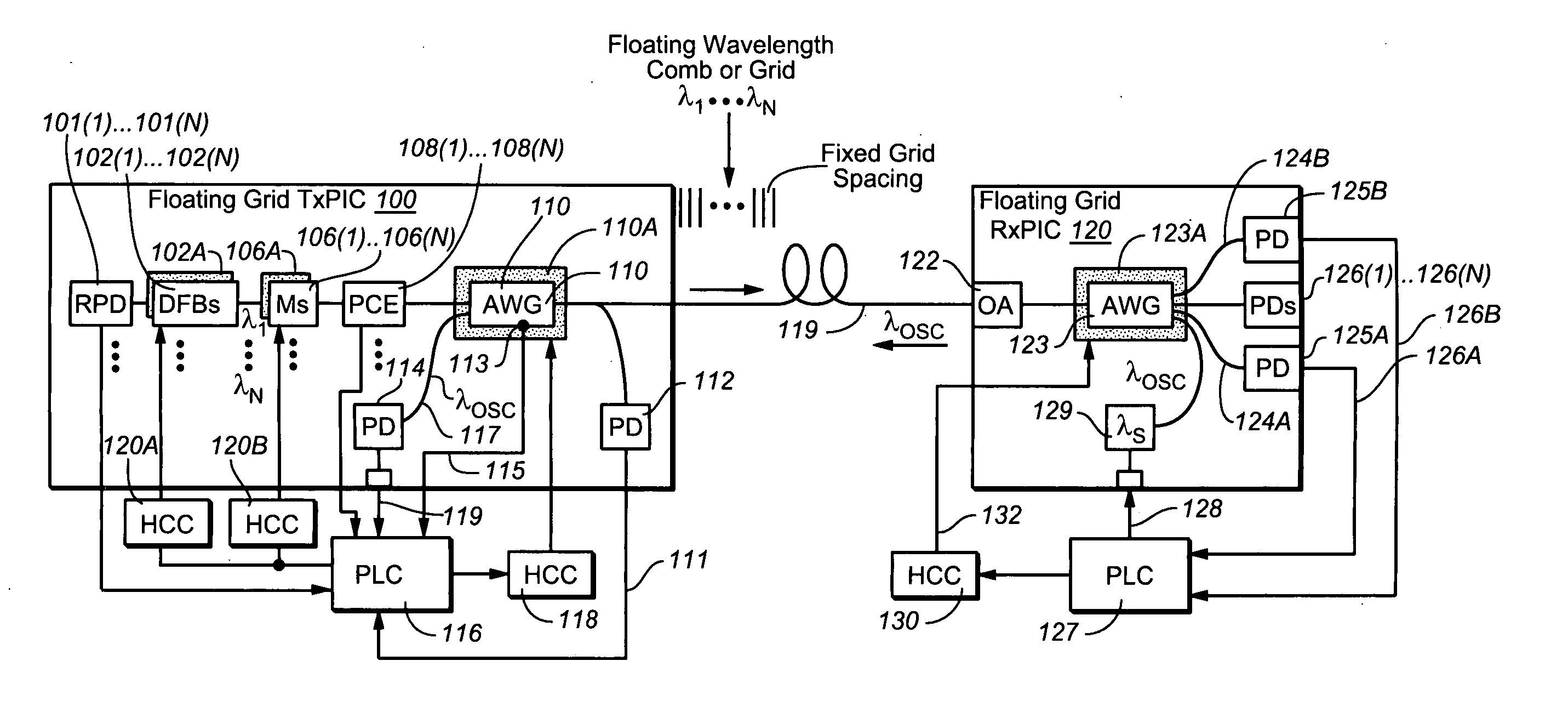
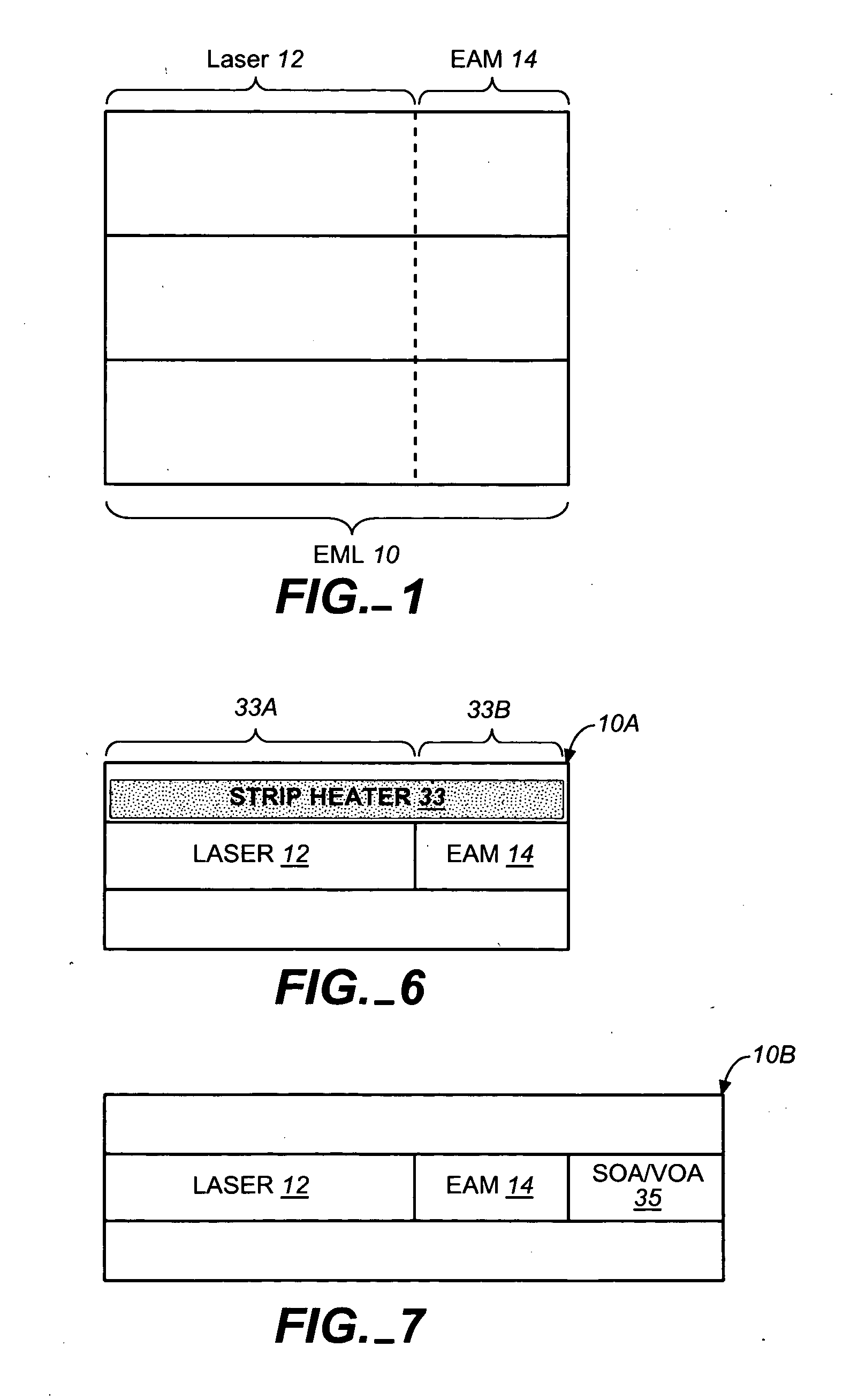
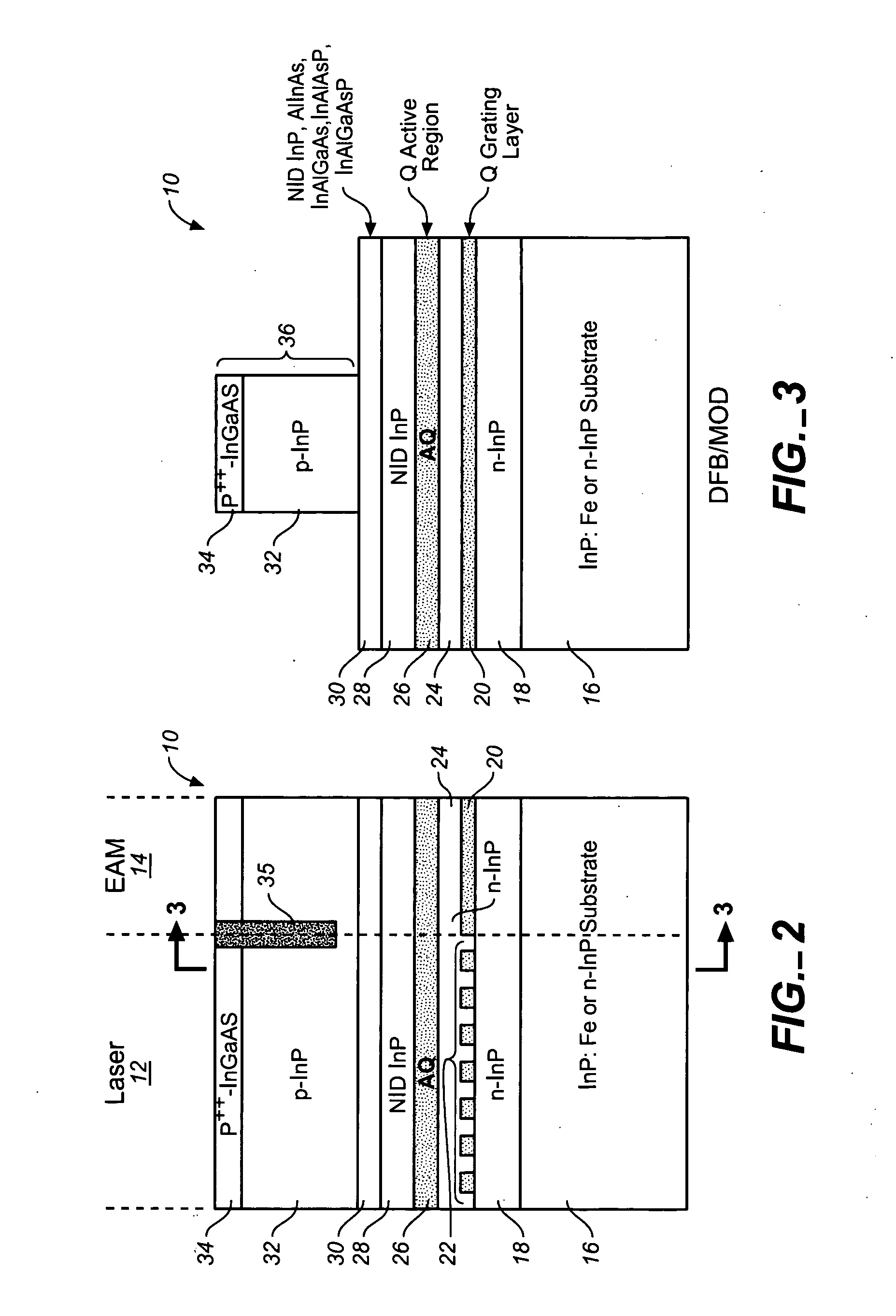
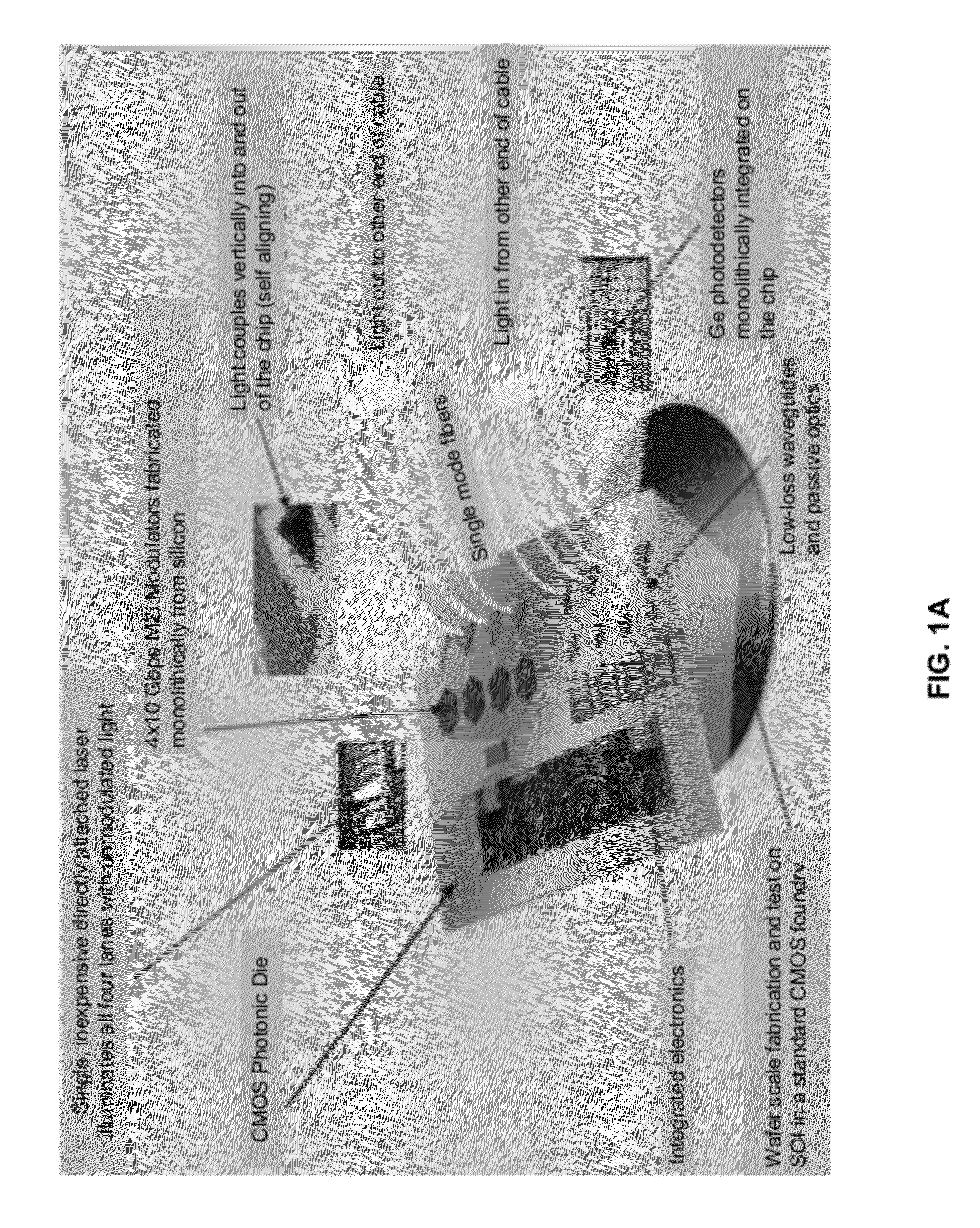
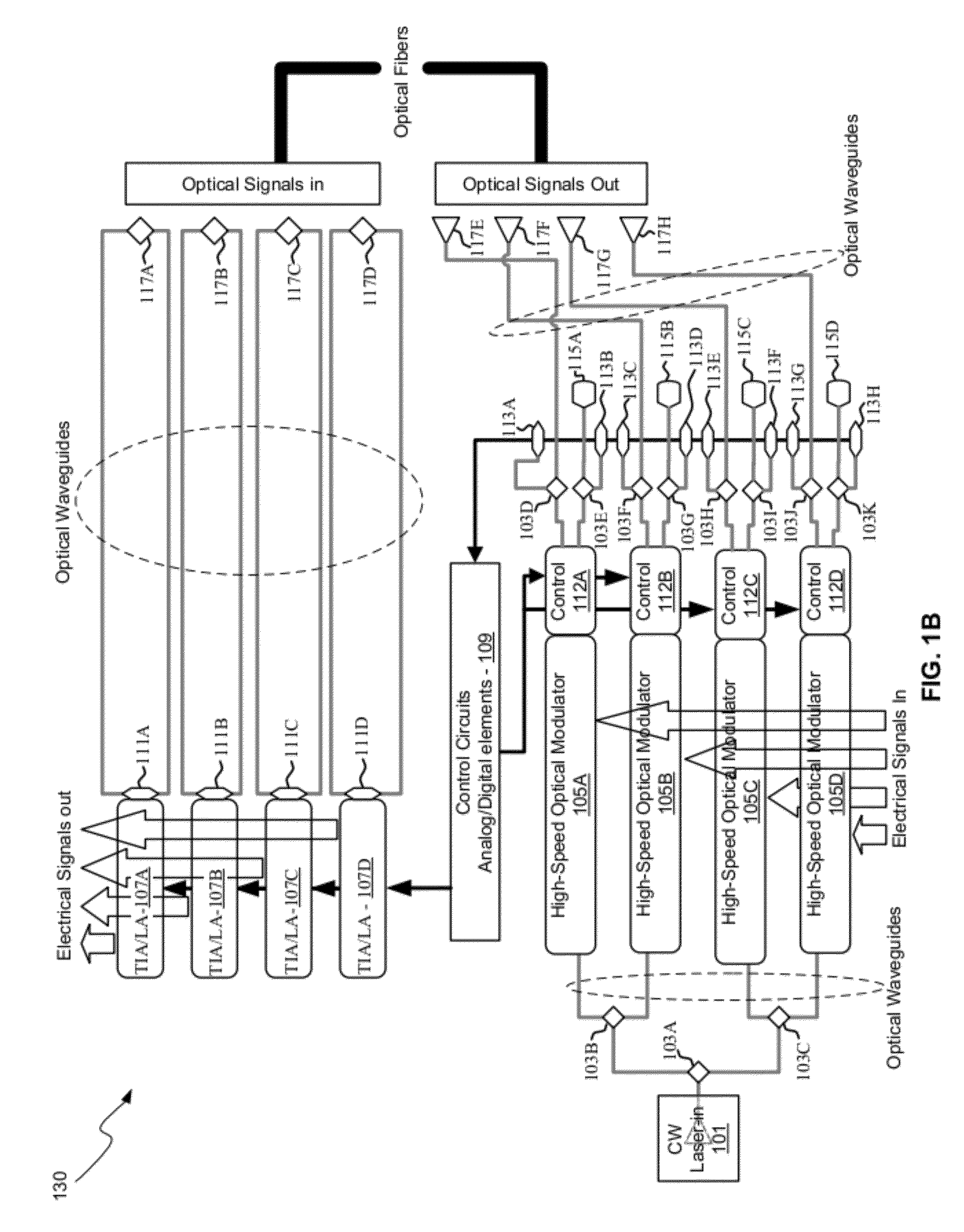
Coolerless photonic integrated circuits (PICs) for WDM transmission networks and PICs operable with a floating signal channel grid changing with temperature but with fixed channel spacing in the floating grid
ActiveUS20050249509A1Requirements for a hermetically sealed package are substantially relievedEasy to controlLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsElectro-absorption modulatorHermetic packaging
A coolerless photonic integrated circuit (PIC), such as a semiconductor electro-absorption modulator / laser (EML) or a coolerless optical transmitter photonic integrated circuit (TxPIC), may be operated over a wide temperature range at temperatures higher then room temperature without the need for ambient cooling or hermetic packaging. Since there is large scale integration of N optical transmission signal WDM channels on a TxPIC chip, a new DWDM system approach with novel sensing schemes and adaptive algorithms provides intelligent control of the PIC to optimize its performance and to allow optical transmitter and receiver modules in DWDM systems to operate uncooled. Moreover, the wavelength grid of the on-chip channel laser sources may thermally float within a WDM wavelength band where the individual emission wavelengths of the laser sources are not fixed to wavelength peaks along a standardized wavelength grid but rather may move about with changes in ambient temperature. However, control is maintained such that the channel spectral spacing between channels across multiple signal channels, whether such spacing is periodic or aperiodic, between adjacent laser sources in the thermally floating wavelength grid are maintained in a fixed relationship. Means are then provided at an optical receiver to discover and lock onto floating wavelength grid of transmitted WDM signals and thereafter demultiplex the transmitted WDM signals for OE conversion.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
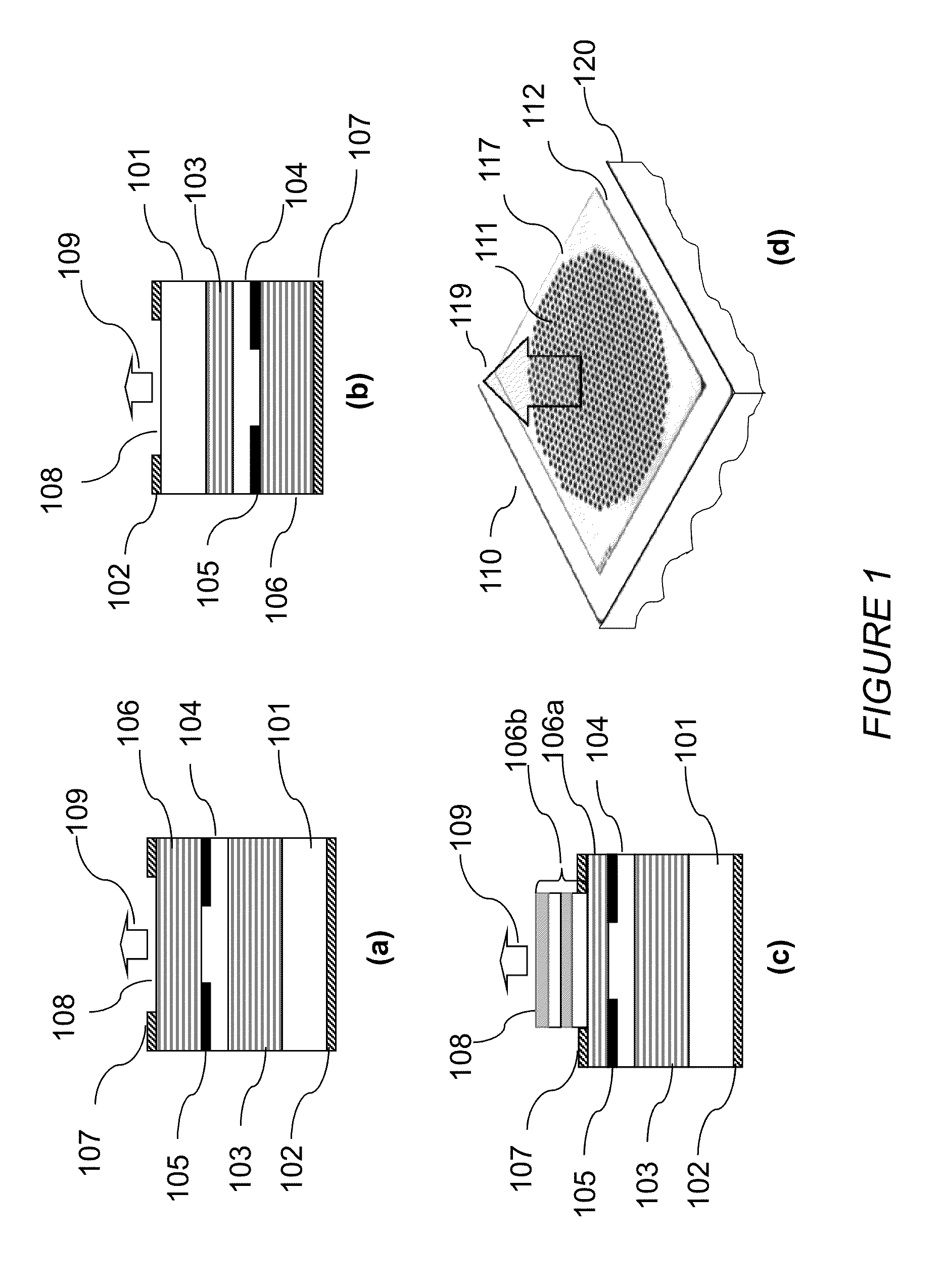
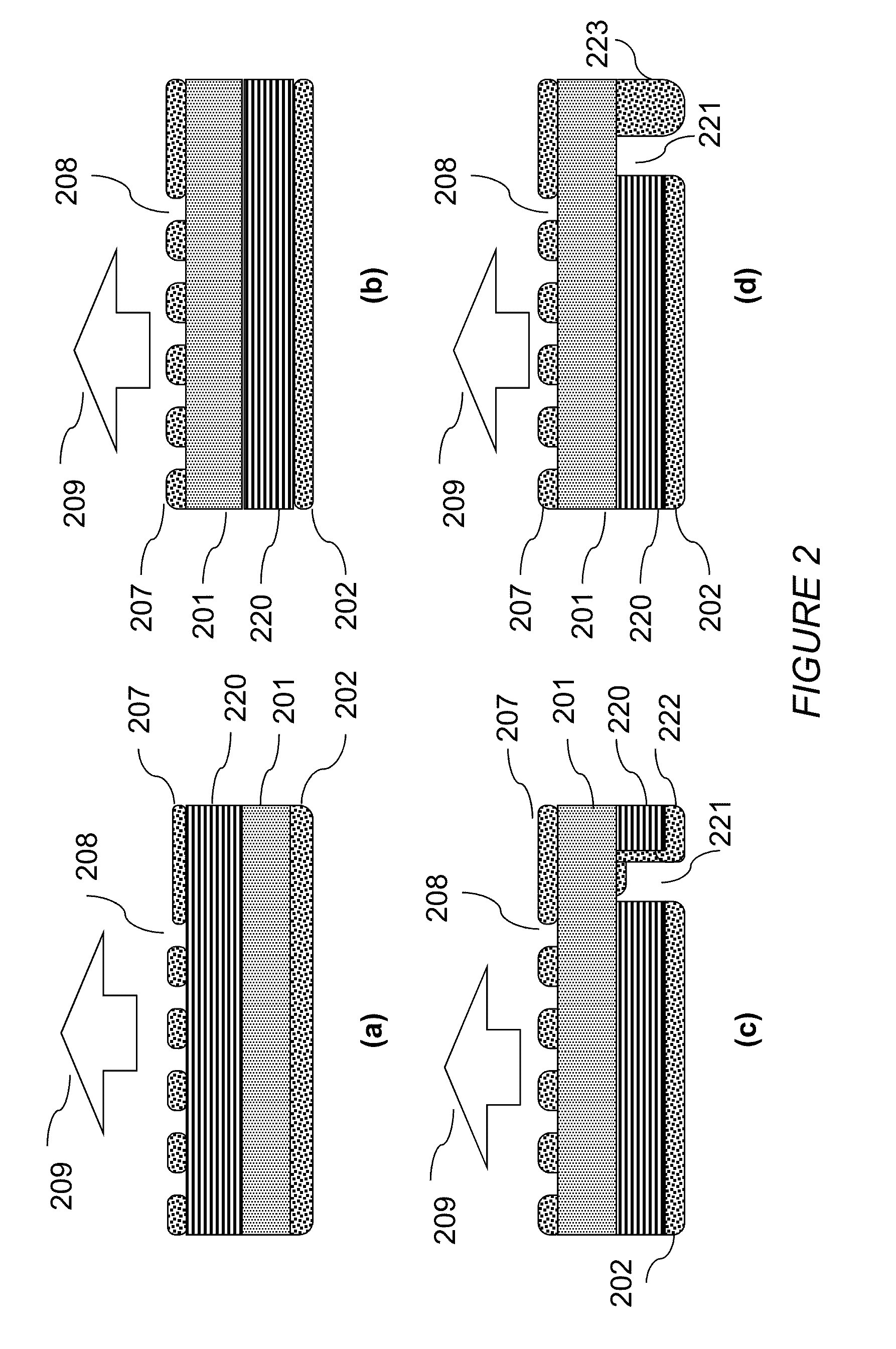
Laser Package Having Multiple Emitters Configured on a Substrate Member
ActiveUS20130022064A1Simple and cost-effectiveCost-effectiveLaser detailsSolid-state devicesLaser transmitterOptoelectronics
A method and device for emitting electromagnetic radiation at high power using nonpolar or semipolar gallium containing substrates such as GaN, AN, InN, InGaN, AlGaN, and AlInGaN, is provided. In various embodiments, the laser device includes plural laser emitters emitting green or blue laser light, integrated a substrate.
Owner:KYOCERA SLD LASER INC
Semiconductor Lasers in Optical Phase-Locked Loops
InactiveUS20060239312A1Increase optical powerHigh beam qualityLaser detailsSemiconductor laser optical devicePhase noiseLaser array
This invention relates to opto-electronic systems using semiconductor lasers driven by feedback control circuits that control the laser's optical phase and frequency. Feedback control provides a means for coherent phased laser array operation and reduced phase noise. Systems and methods to coherently combine a multiplicity of lasers driven to provide high power coherent outputs with tailored spectral and wavefront characteristics are disclosed. Systems of improving the phase noise characteristics of one or more semiconductor lasers are further disclosed.
Owner:TELARIS
Optical System and Method for Use in Projection Systems
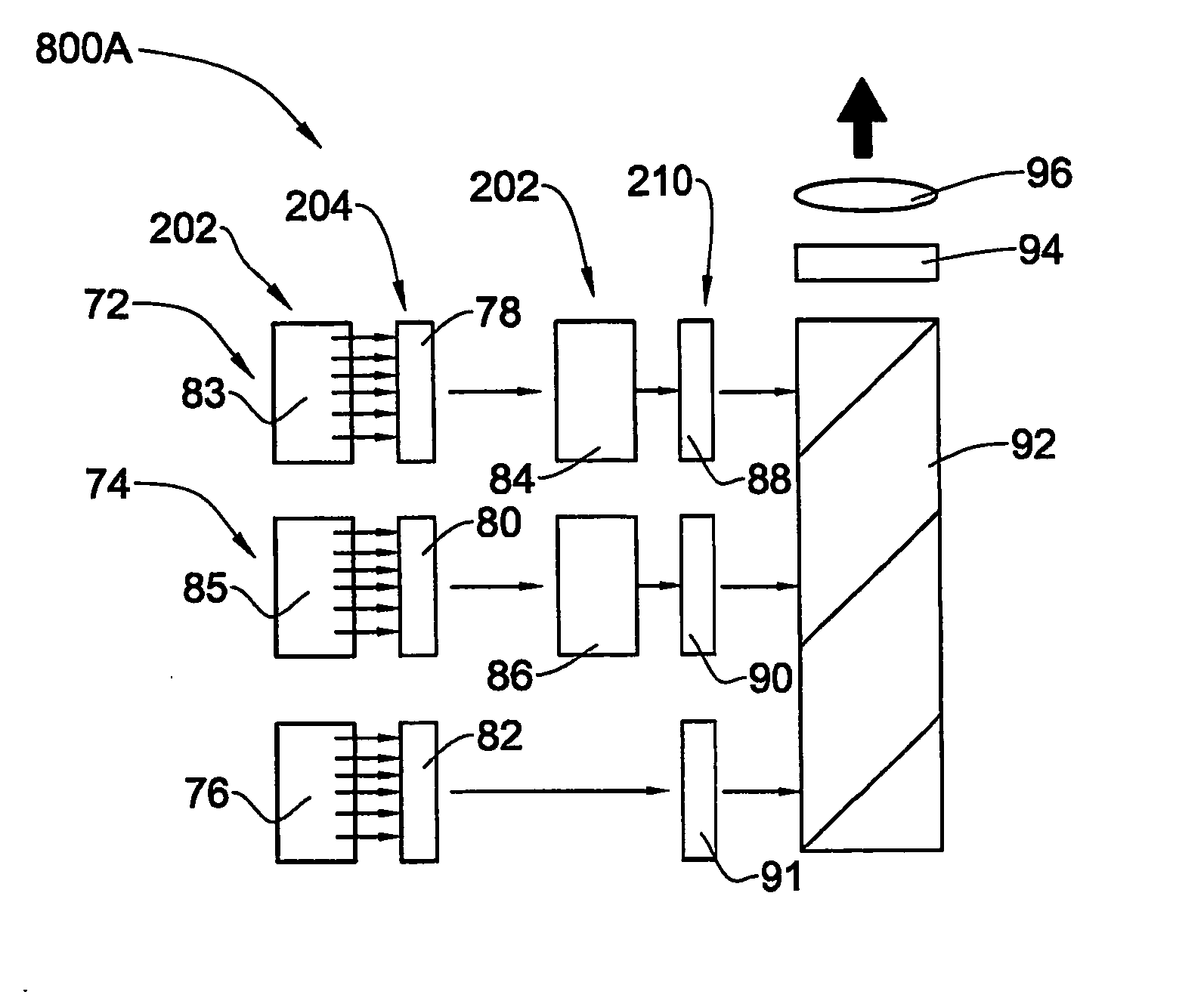
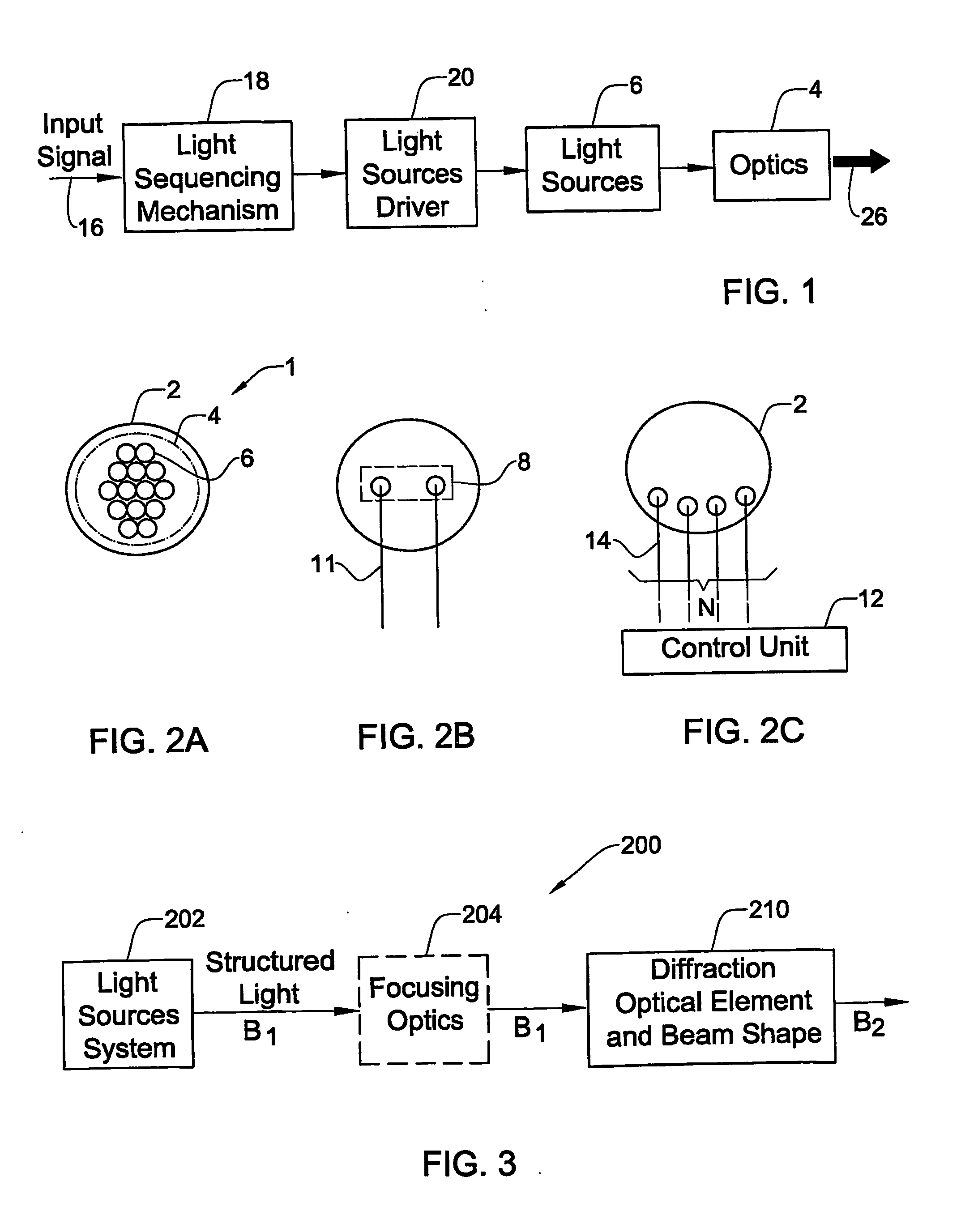
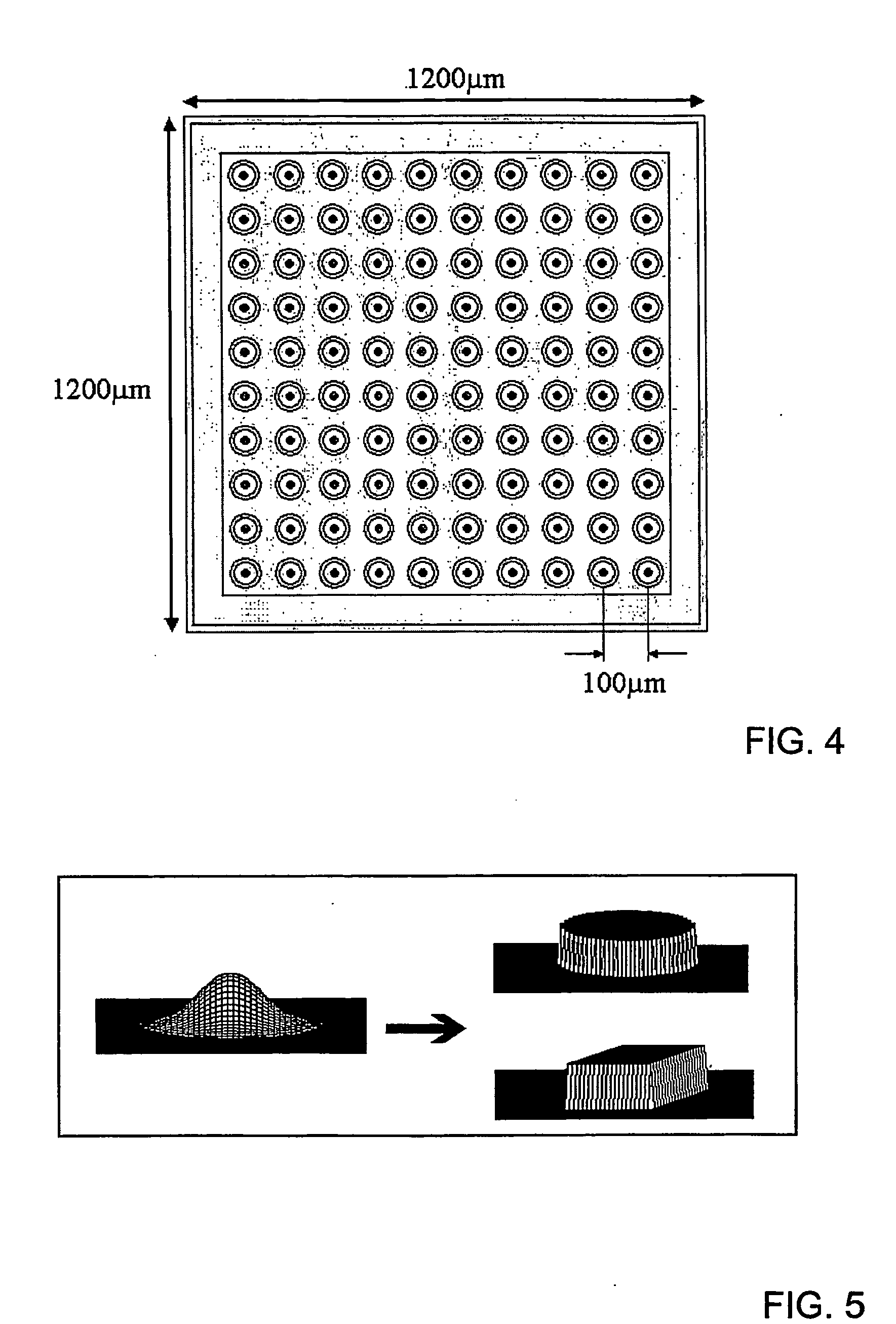
InactiveUS20070273957A1Reduce physical sizeImprove and optimize projection systemSemiconductor laser optical deviceDiffraction gratingsLight beamProjection system
An optical system and method are presented to produce a desired illuminating light pattern. The system comprises a light source system configured and operable to produce structured light in the form of a plurality of spatially separated light beams; and a beam shaping arrangement. The beam shaping arrangement is configured as a diffractive optical unit configured and operable to carry out at least one of the following: (i) combining an array of the spatially separated light beams into a single light beam thereby significantly increasing intensity of the illuminating light; (ii) affecting intensity profile of the light beam to provide the illuminating light of a substantially rectangular uniform intensity profile.
Owner:EXPLAY
Optical illuminator
ActiveUS8675706B2Eliminate needIncrease the areaLighting heating/cooling arrangementsSolid-state devicesSurface mountingCurrent driver
Illuminator module comprising VCSEL arrays with planar electrical contacts, readily adaptable for surface mounting, is provided. Monolithic VCSEL arrays are configured in array patterns on two and three-dimensional surfaces. Illuminator modules are easily expandable by increasing the array size or by modularly arranging more arrays with or without a transparent substrate. Different shapes of illuminator modules may be configured by tiling array modules monolithically on a common substrate, or by tiling small modules. The surface mountable illuminator modules are easily assembled on a thermally conductive surface that may be air or liquid cooled for efficient heat dissipation. Array modules may be integrated with other electronic circuits such as current drivers, sensors, controllers, processors, etc. on a common platform, for example, a single or multiple layer printed circuit boards (PCB) to assemble illumination systems for different applications including a gesture recognition apparatus and a battery operated portable illuminator devices.
Owner:PRINCETON OPTRONICS
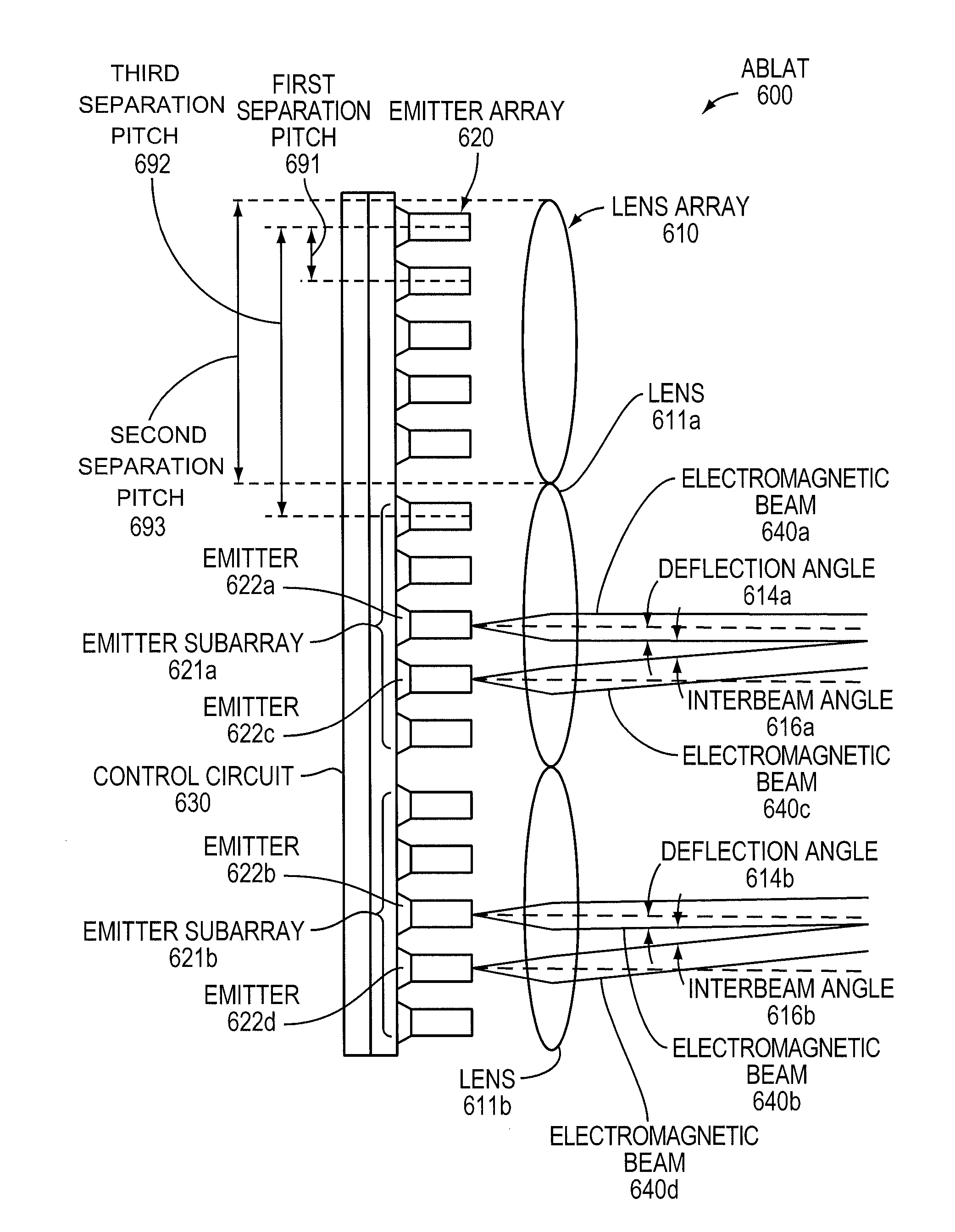
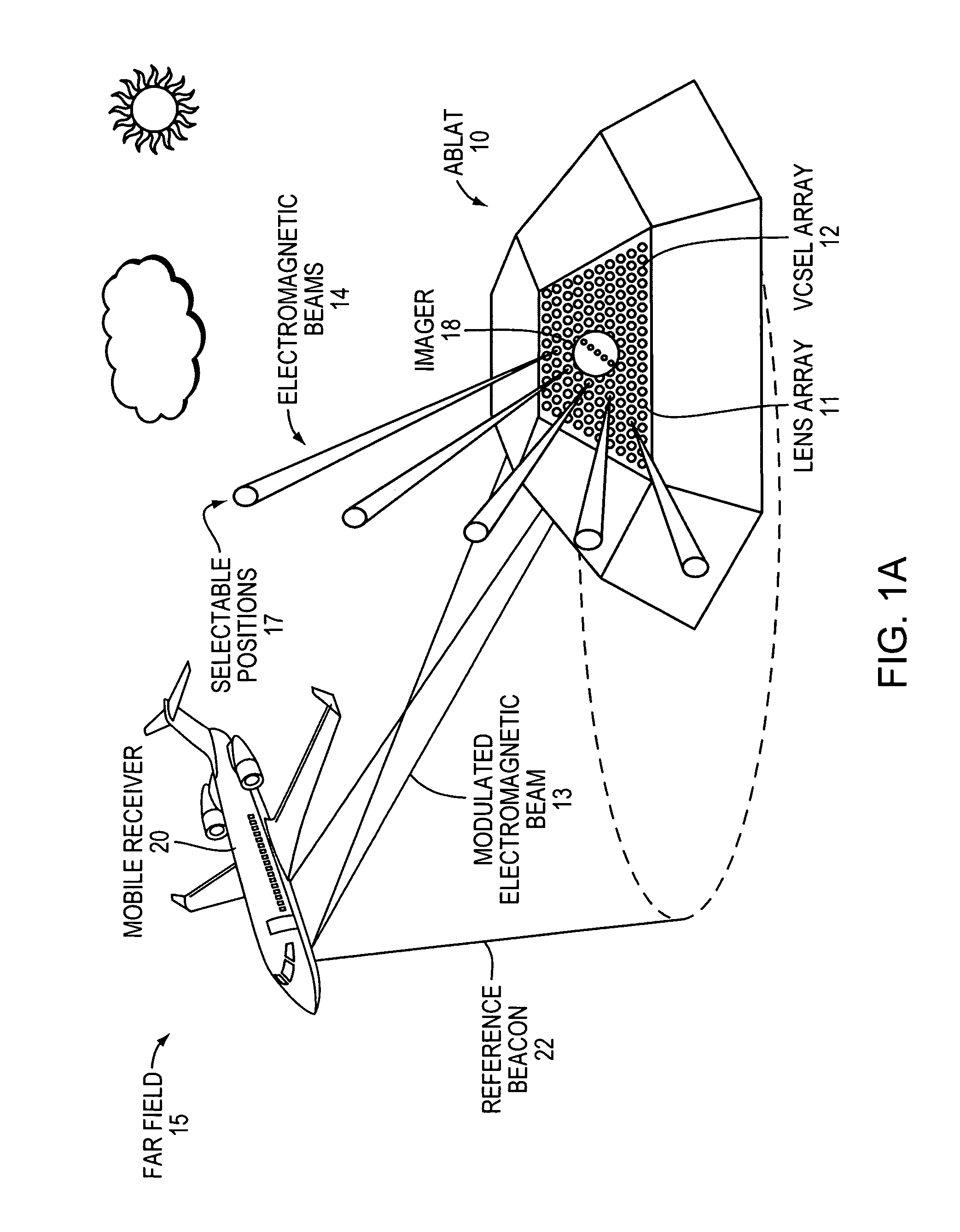
Agile-beam laser array transmitter
ActiveUS8301027B2Turn fasterWave based measurement systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsLaser arrayBeam steering
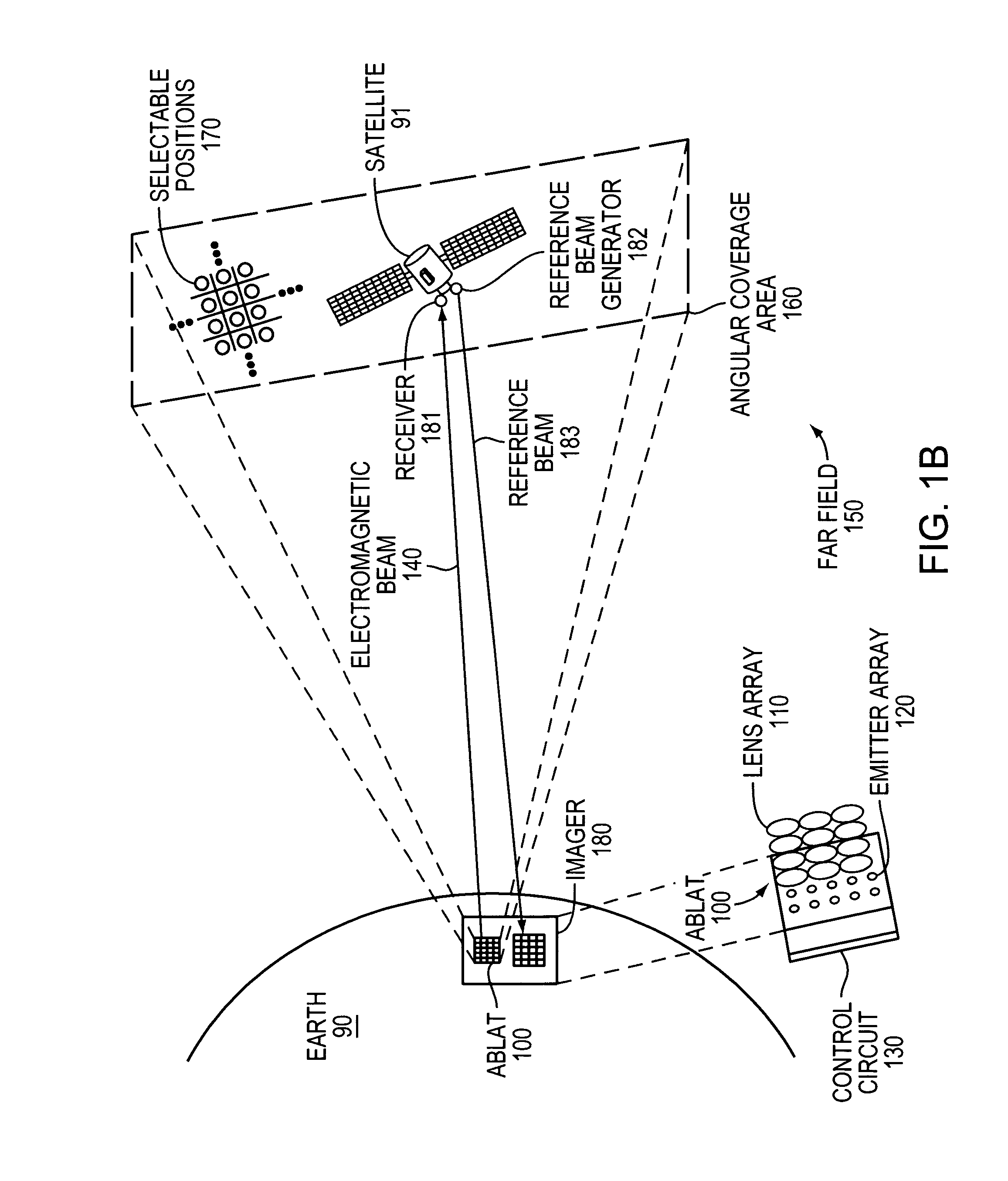
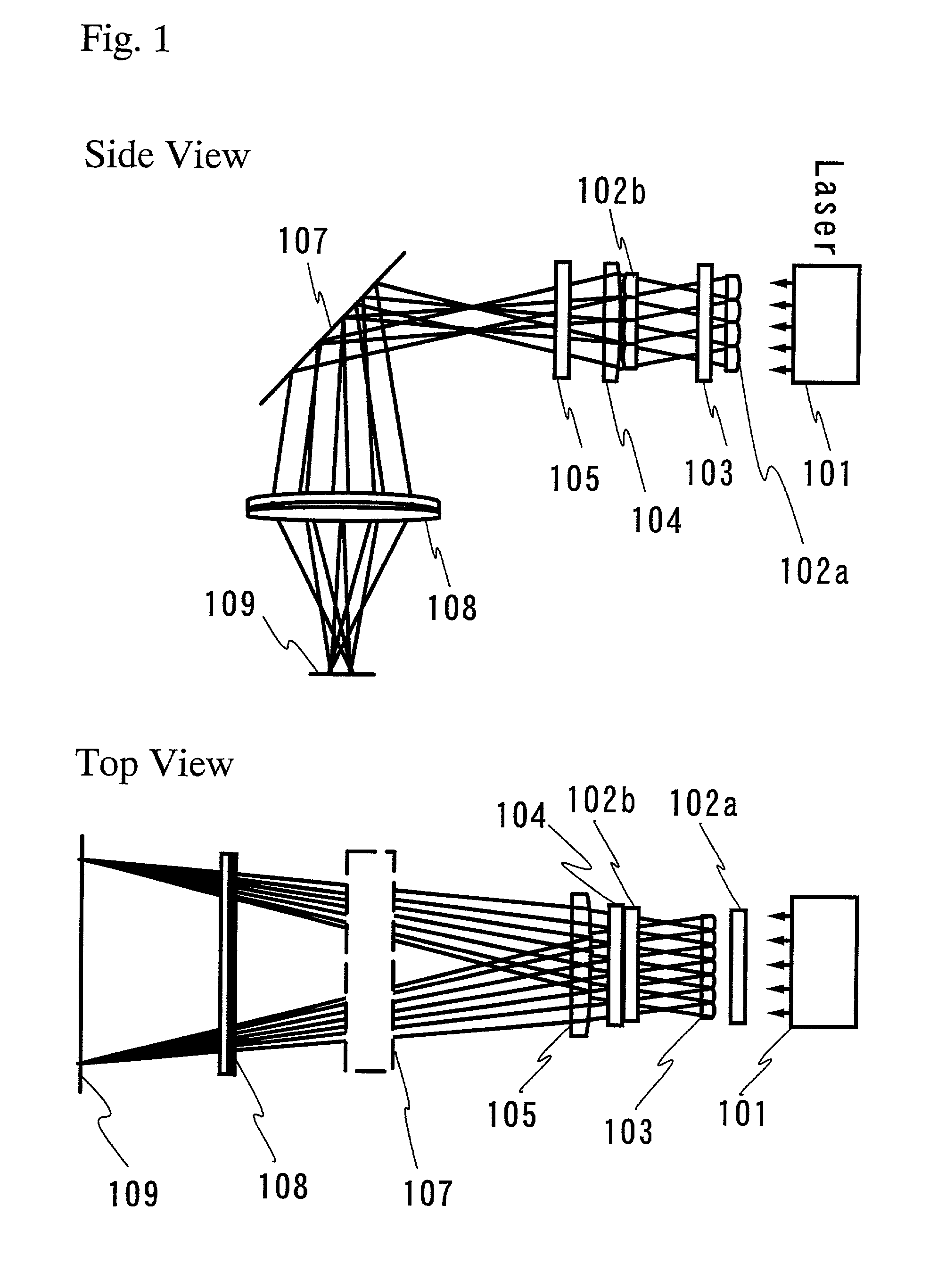
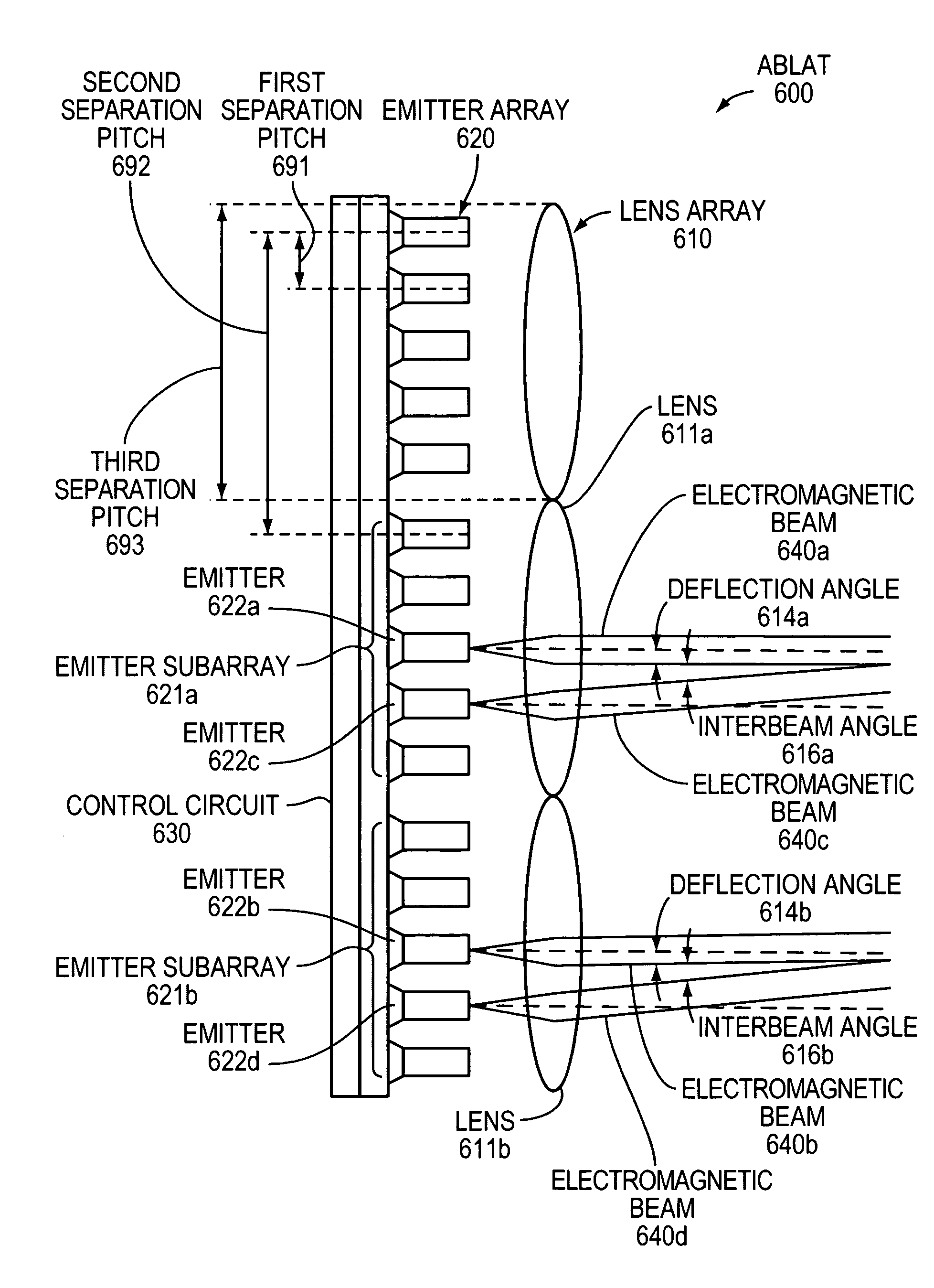
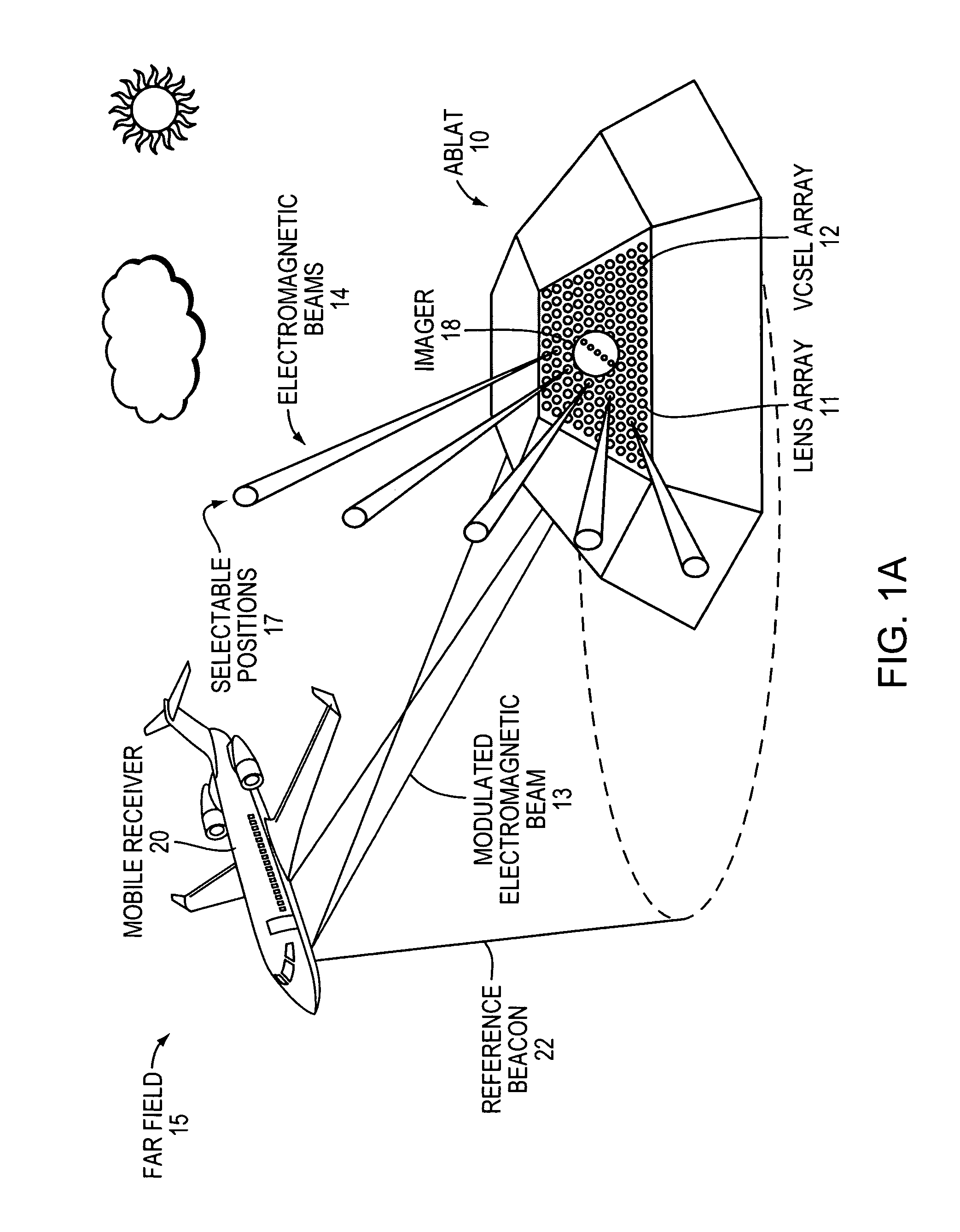
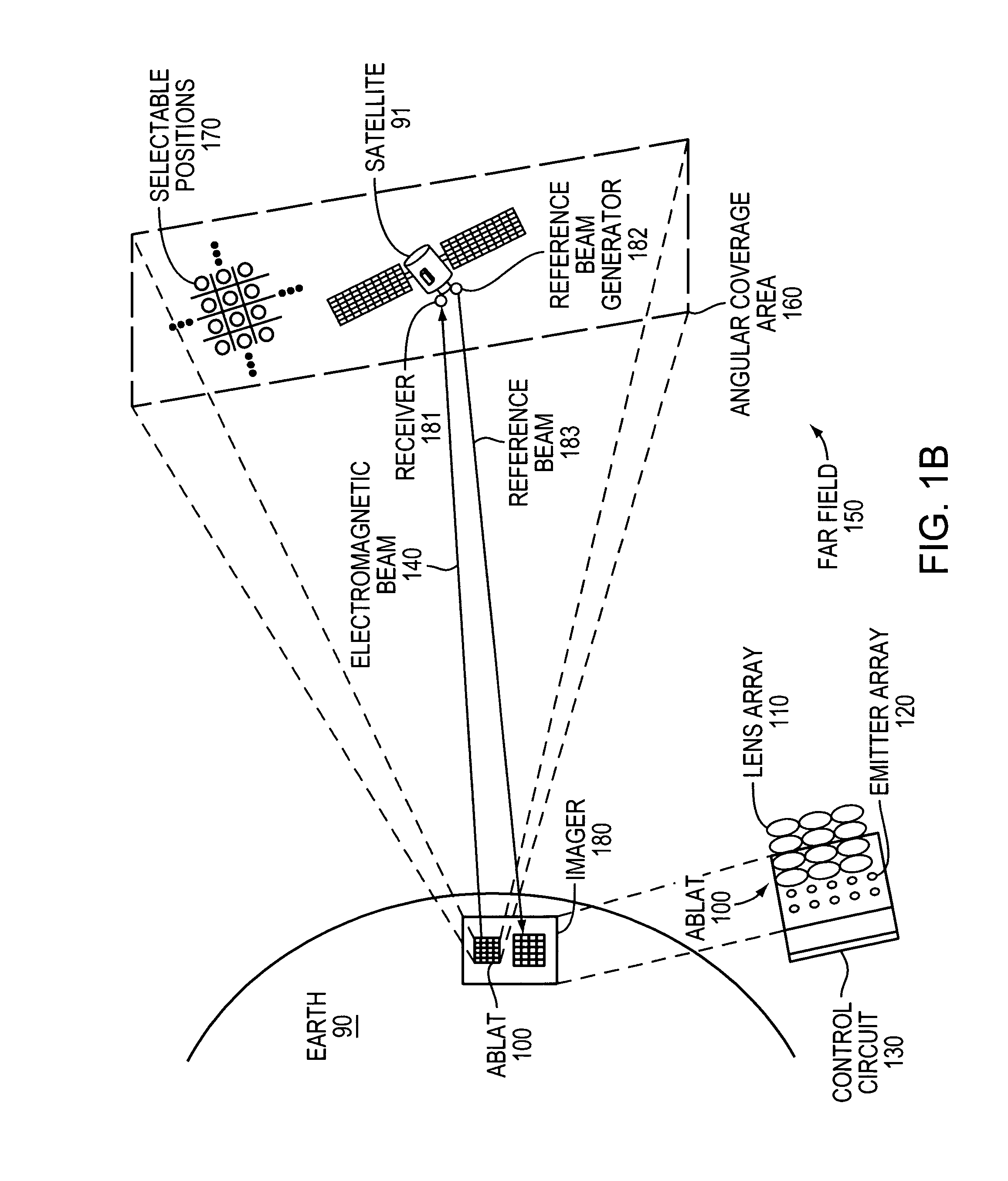
An Agile-Beam Laser Array Transmitter (ABLAT) uses an array of emitters and an array of lenses to project electromagnetic beams over a wide angular coverage area in the far field. Differences in the separation pitches of the two arrays allows the ABLAT to project beams to contiguous and / or overlapping positions, depending on the ratio of the separation pitches and the lens focal length. Compared to other beam steering technology, the ABLAT is a smaller, lighter, and more efficient means of projecting beams over wider angular coverage areas. Various embodiments can be used in any beam steering application, including, but not limited to: free-space optical communications; light detection and ranging (lidar); optical scanning (e.g., retinal or bar-code scanning); display projection; image capture; optical character recognition; scanning laser microscopy; non-destructive testing; printing; facsimiles; map making; web inspection; color print processing; phototypesetting and platemaking; laser marking; material processing; DNA analysis; and drug discovery.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
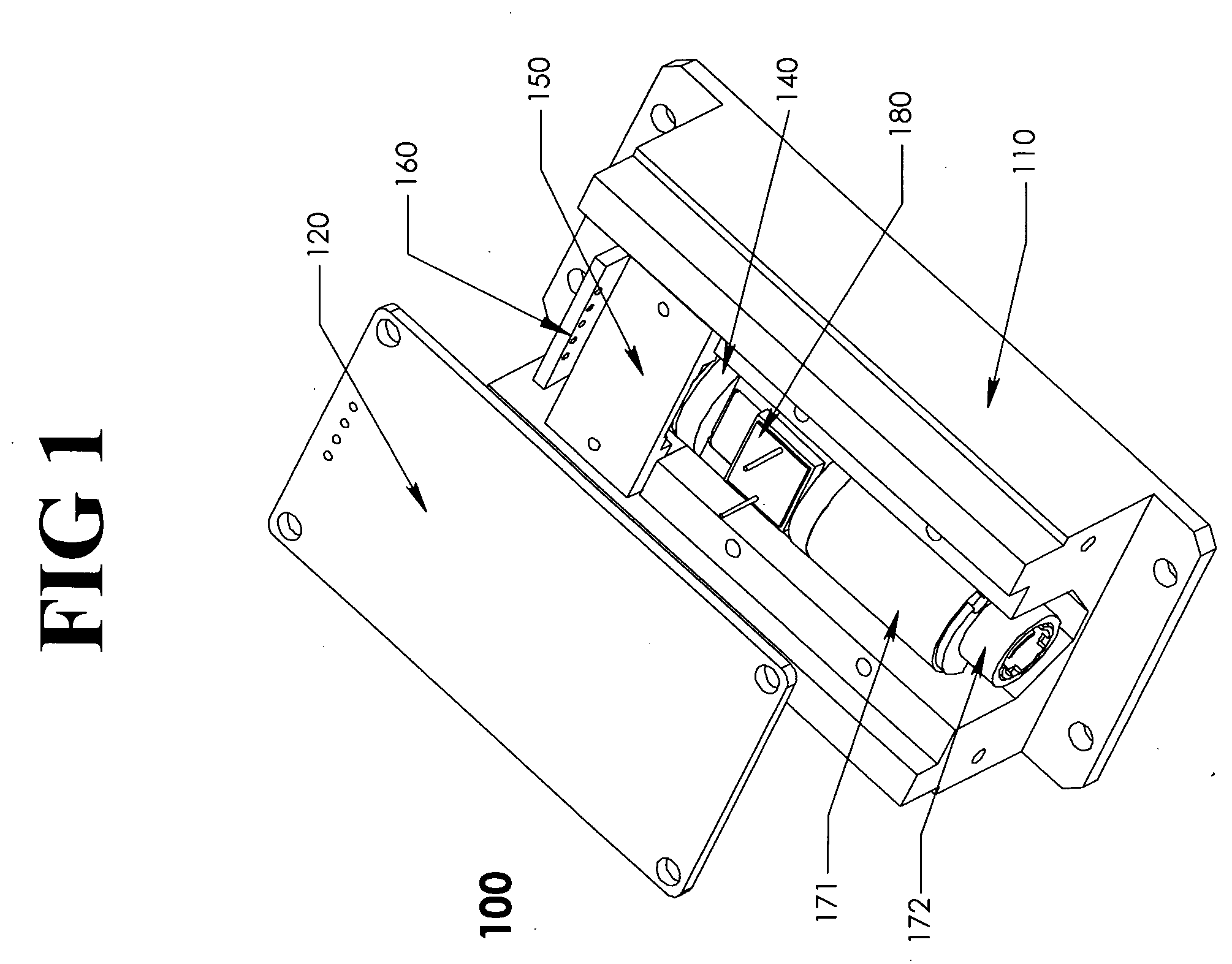
Laser diode assemblies
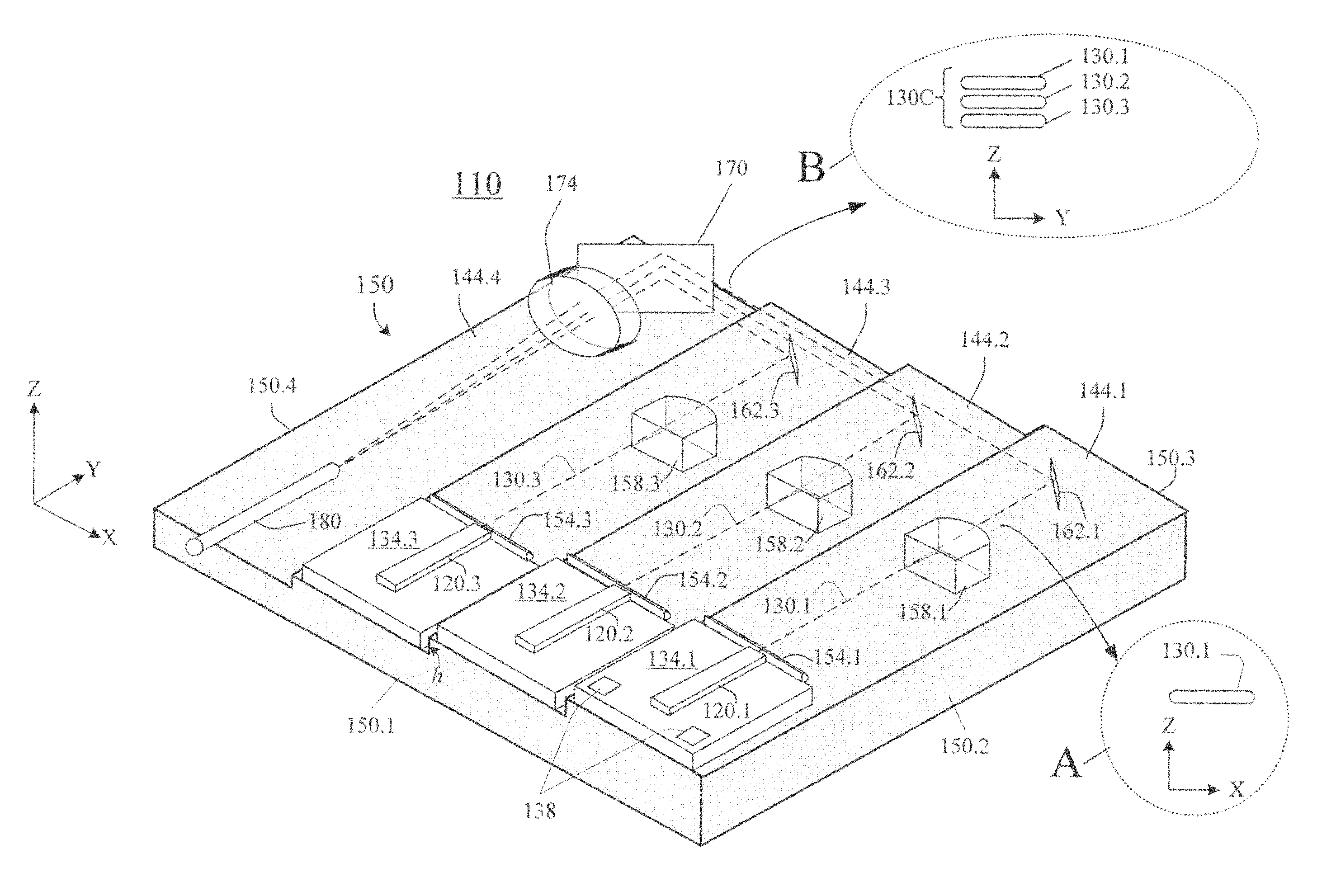
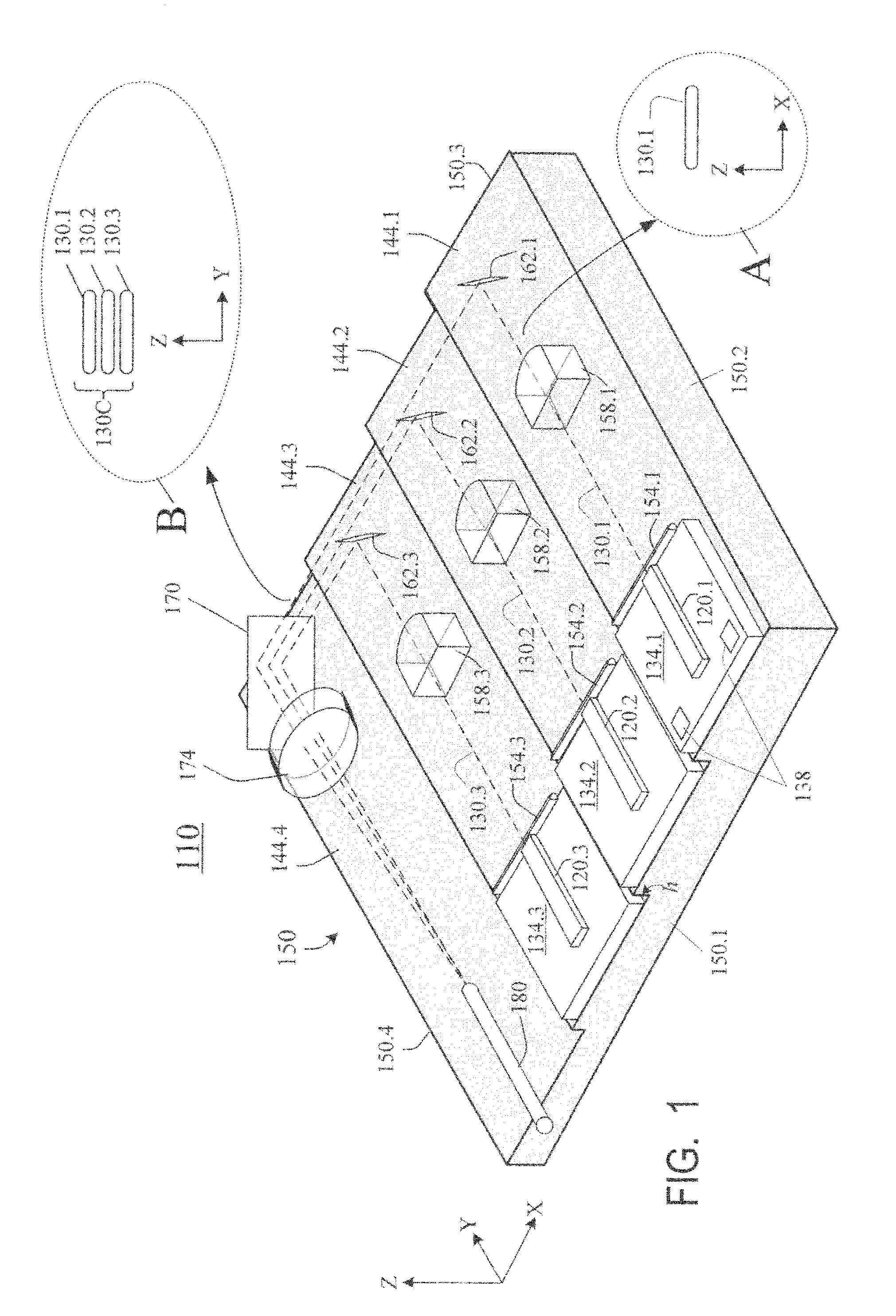
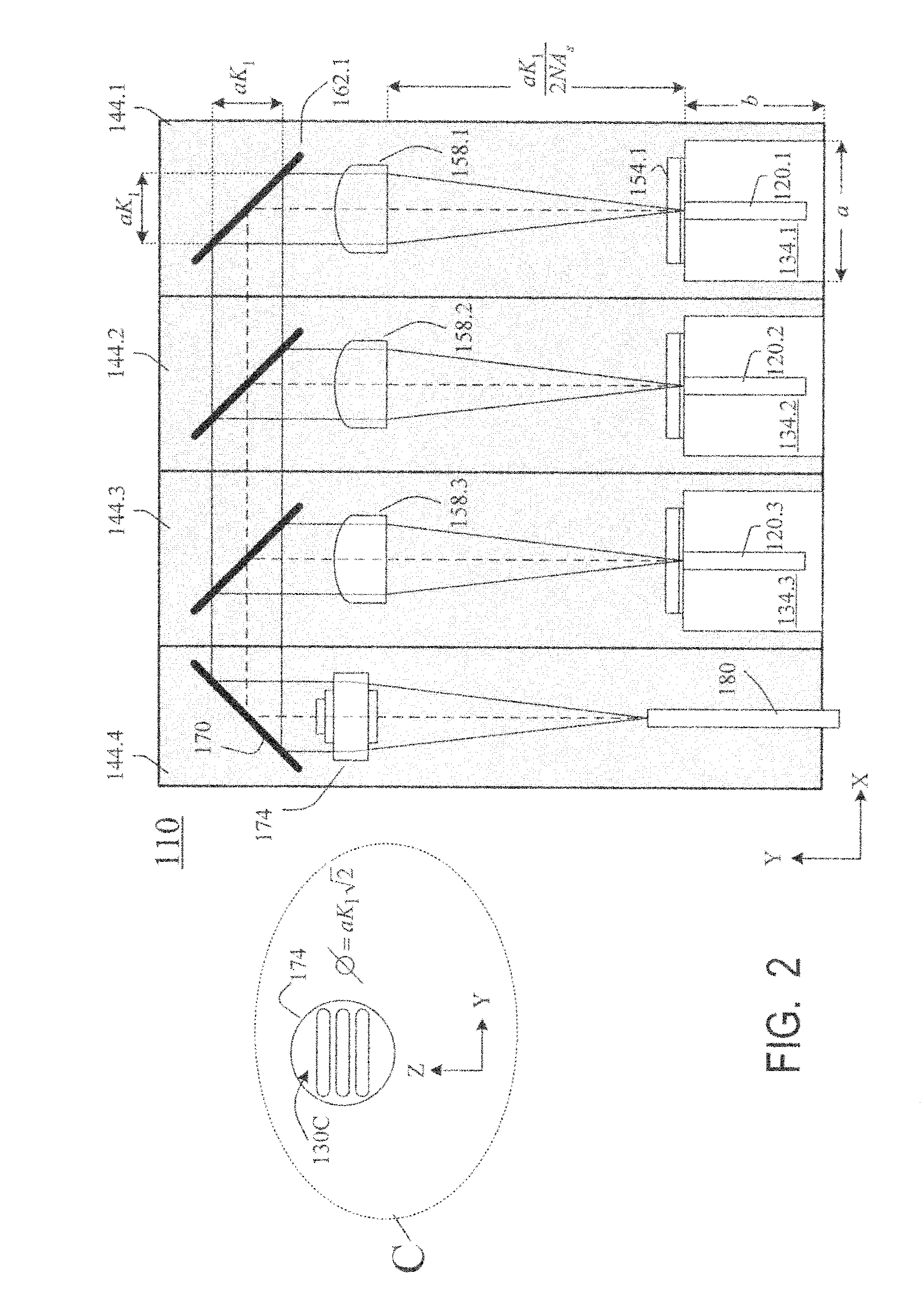
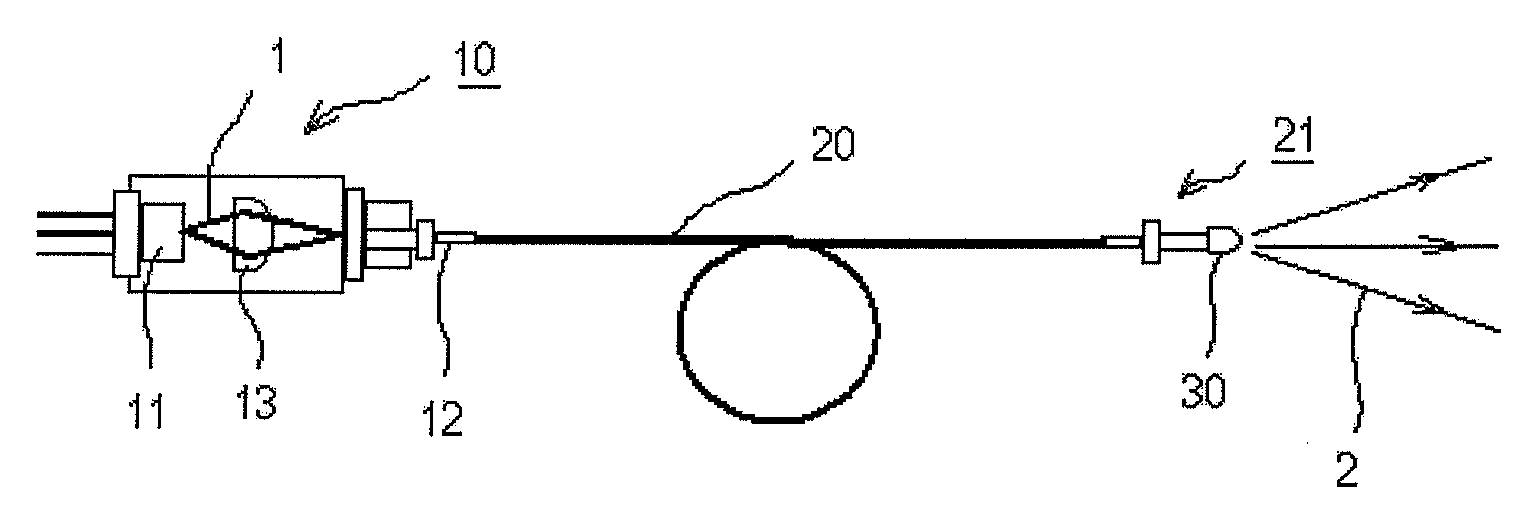
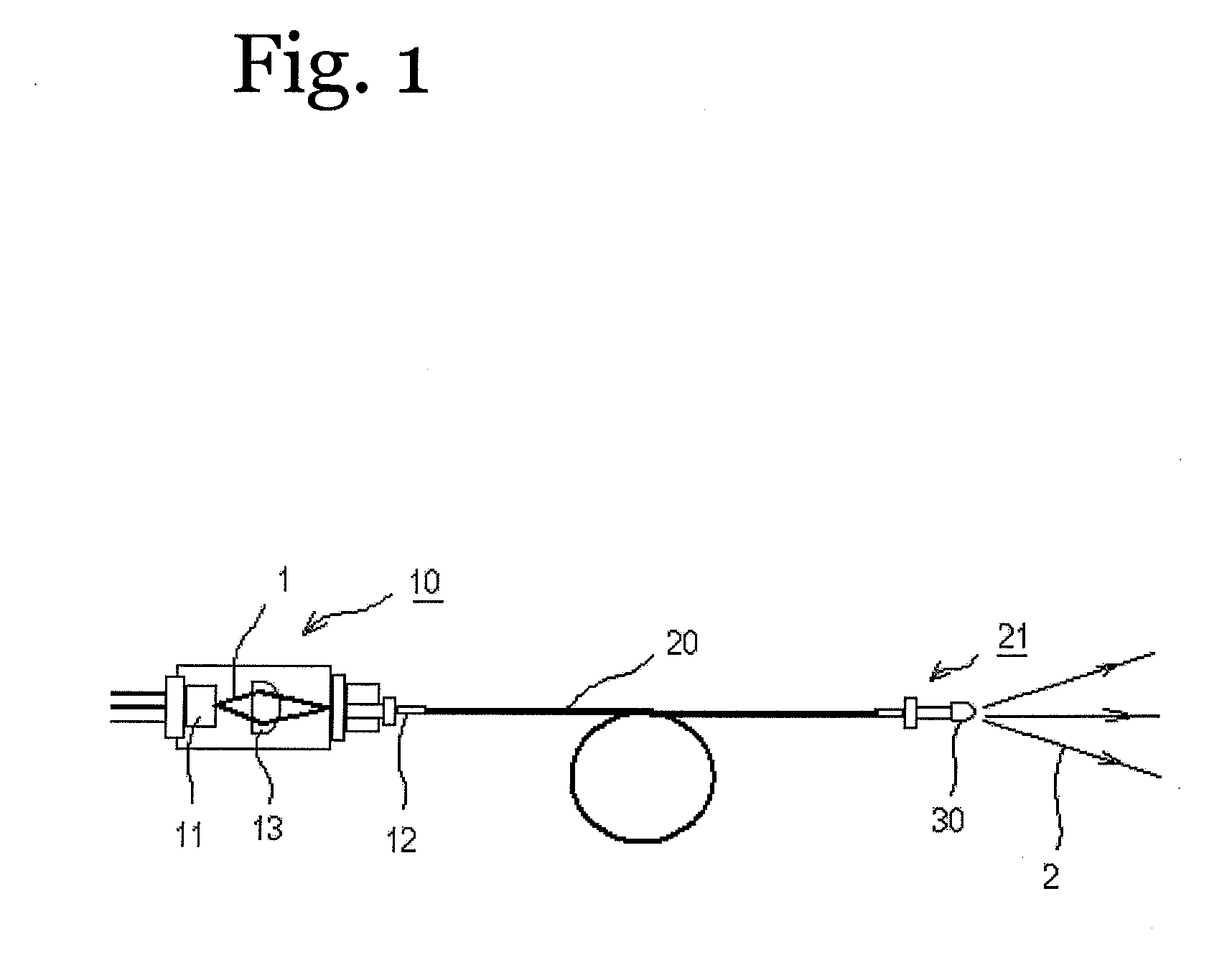
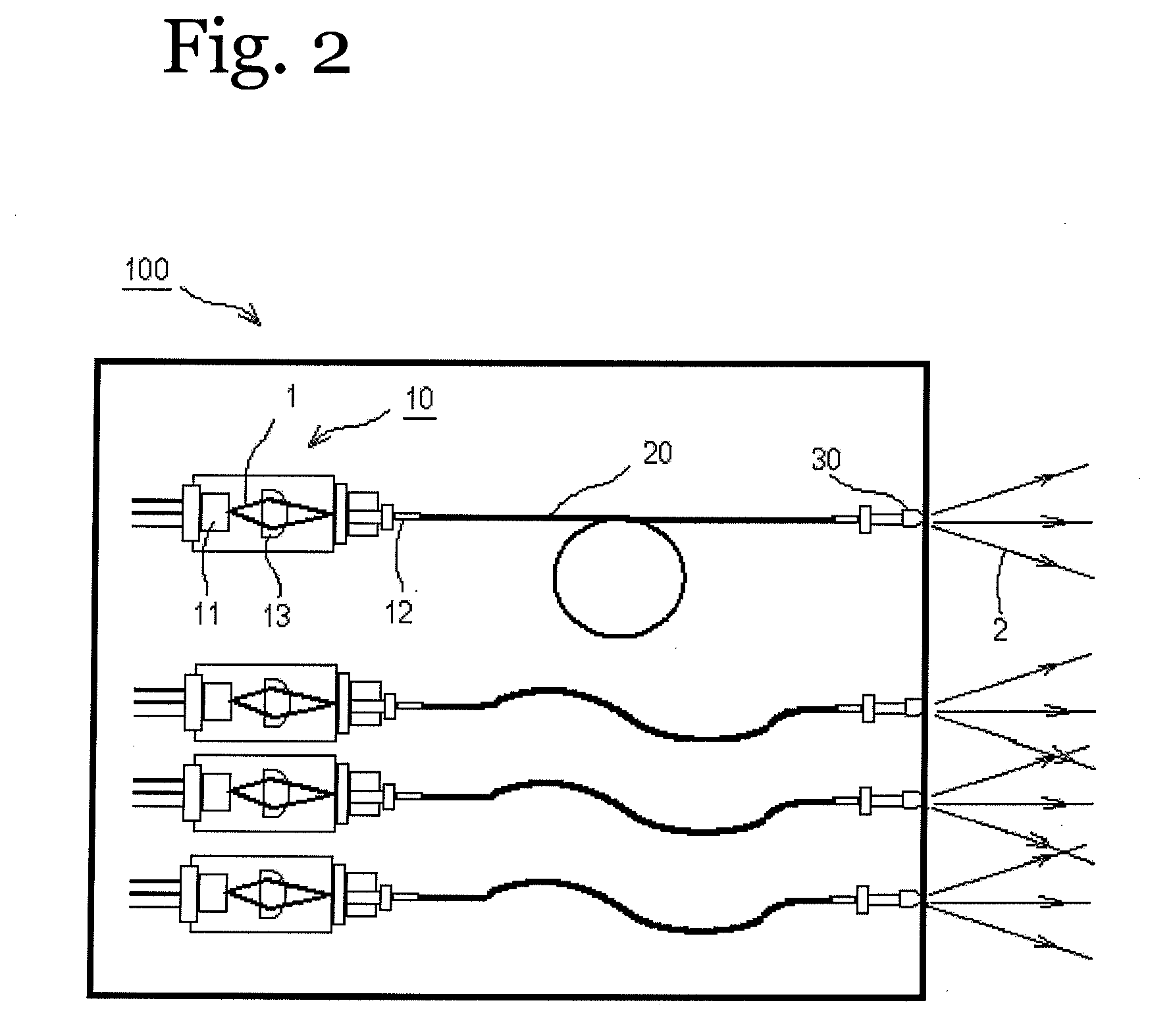
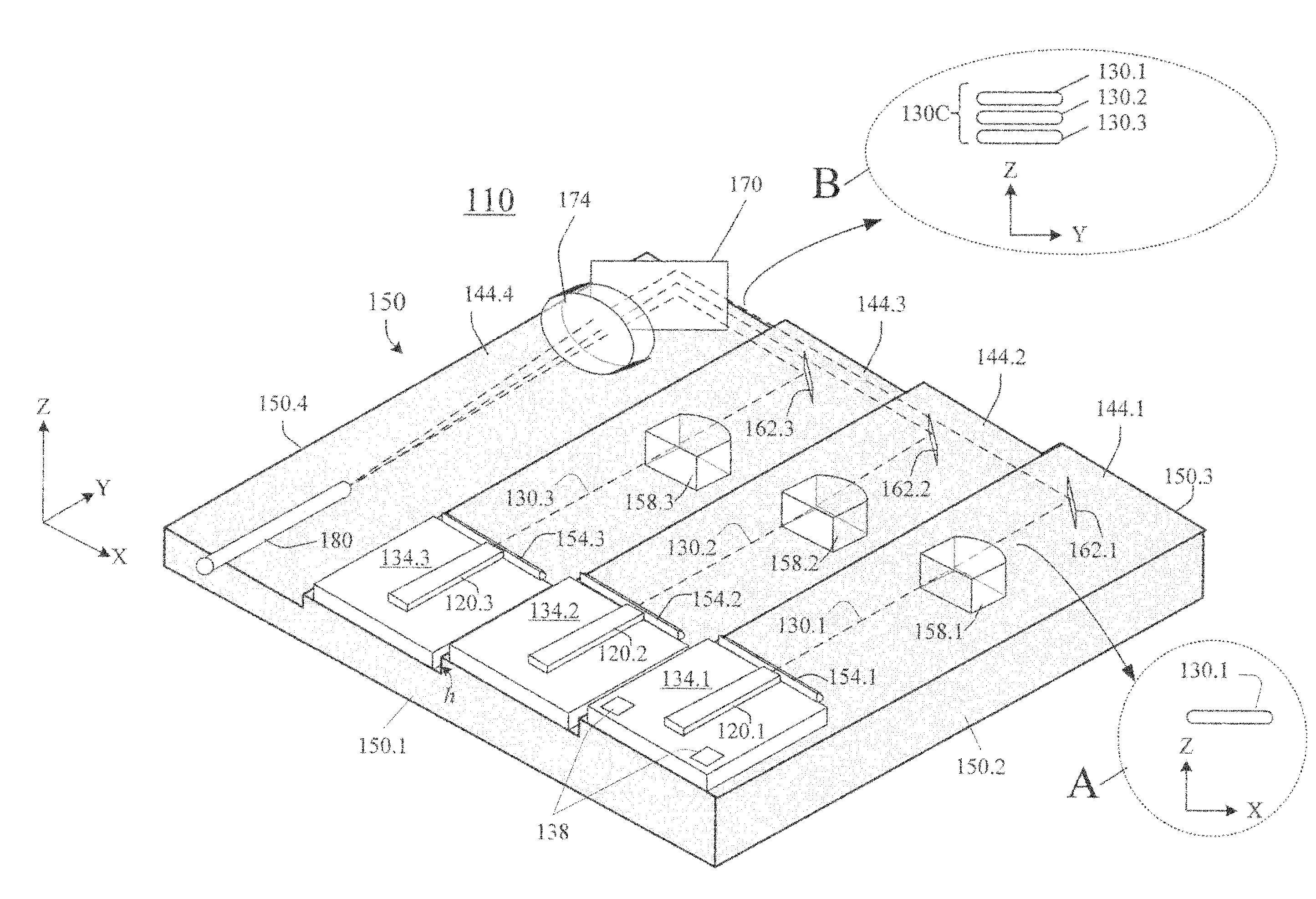
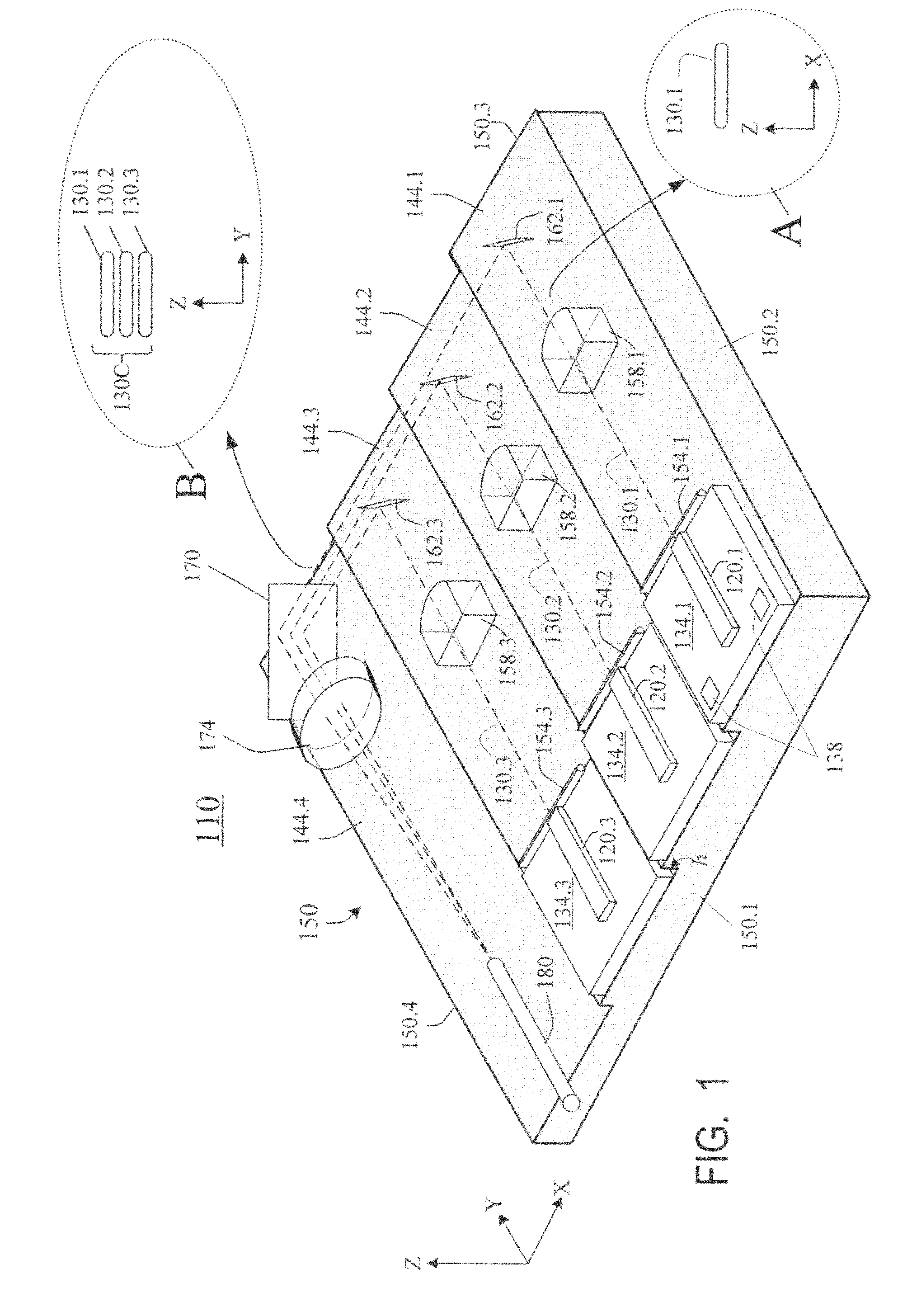
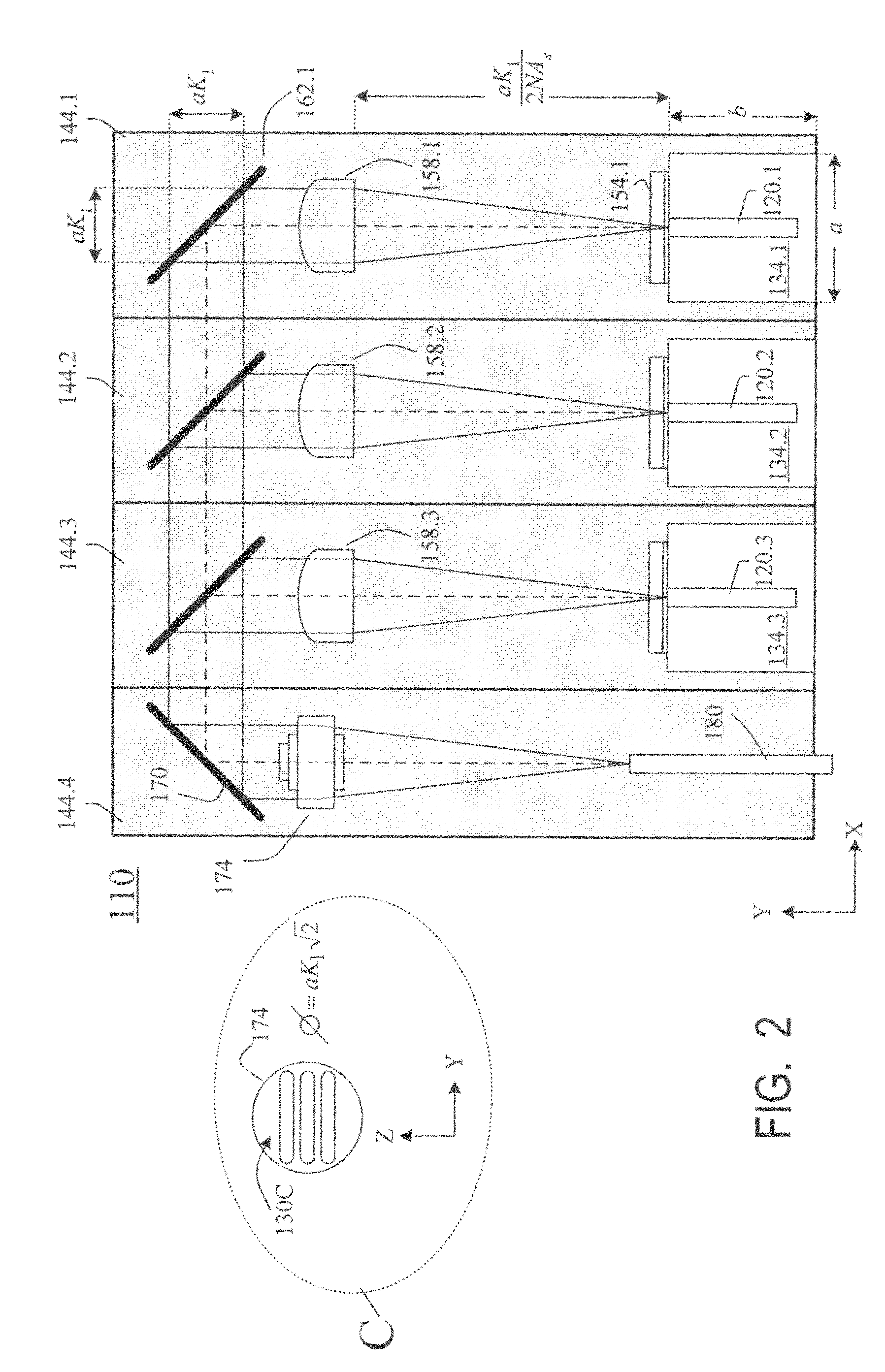
InactiveUS20090245315A1Reduce misalignmentReduce in quantitySemiconductor laser arrangementsSemiconductor laser optical deviceLight beamLaser beams
Laser diodes (120) emit laser beams along a vertical YZ plane at different distances from the YZ plane. The beams are collimated in their fast and slow axes, and are redirected by turning mirrors (162) to form a beam stack (130C) traveling along the XZ plane. The beam stack is turned by about 90°, then converged by a focusing lens (174) into an optical fiber (180). A compact assembly is thus provided. Each laser diode (120.i), its collimating optics (154.i, 158.i, i=1, 2, . . . ) and its turning mirror (162.i) are rigidly attached to a flat, heat-spreading surface (144.i) and thus remain aligned with each other in thermal cycling.
Owner:FAYBISHENKO VICTOR
Systems, devices, and methods for focusing laser projectors
ActiveUS20170299956A1Reduce disagreementSemiconductor laser arrangementsNon-optical adjunctsHead-up displayLaser light
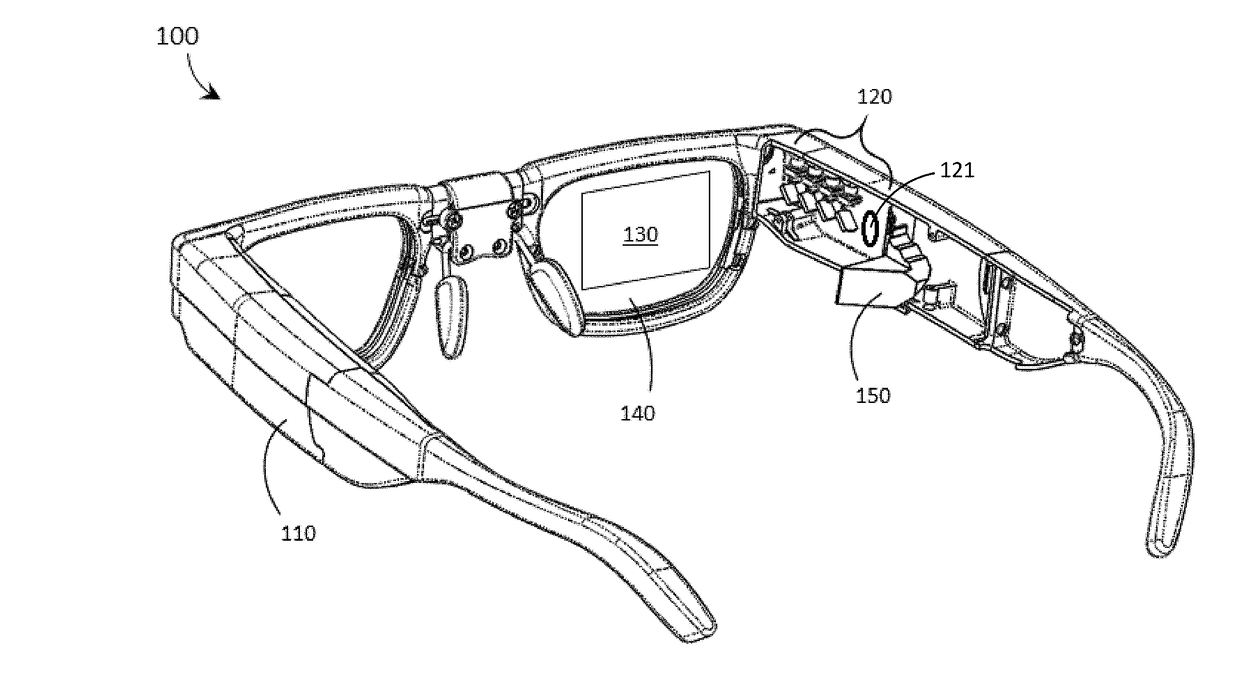
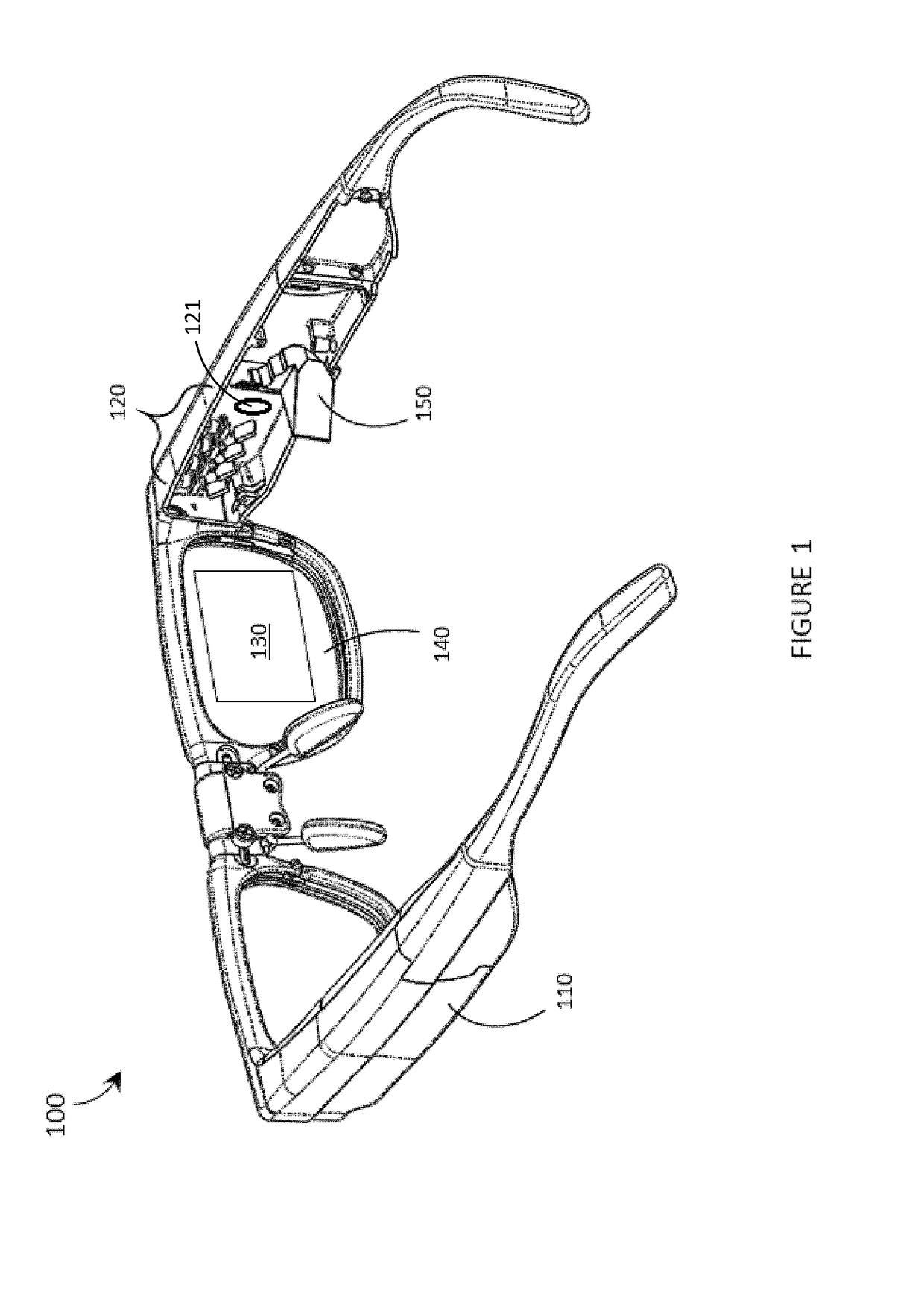
Systems, devices, and methods for focusing laser projectors are described. A laser projector includes N≧1 laser diodes, each of which emits laser light having a divergence. Each laser diode is paired with a respective primary or collimation lens to at least reduce a divergence of the laser light that the laser diode produces. Downstream from the primary lens(es) in the optical path(s) of the laser light, a single dedicated secondary or convergence lens converges the laser light to a focus. By initiating the convergence of the laser light at the secondary or convergence lens as opposed to at the primary or collimation lens(es), numerous benefits that are particularly advantageous in laser projection-based wearable heads-up displays are realized.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
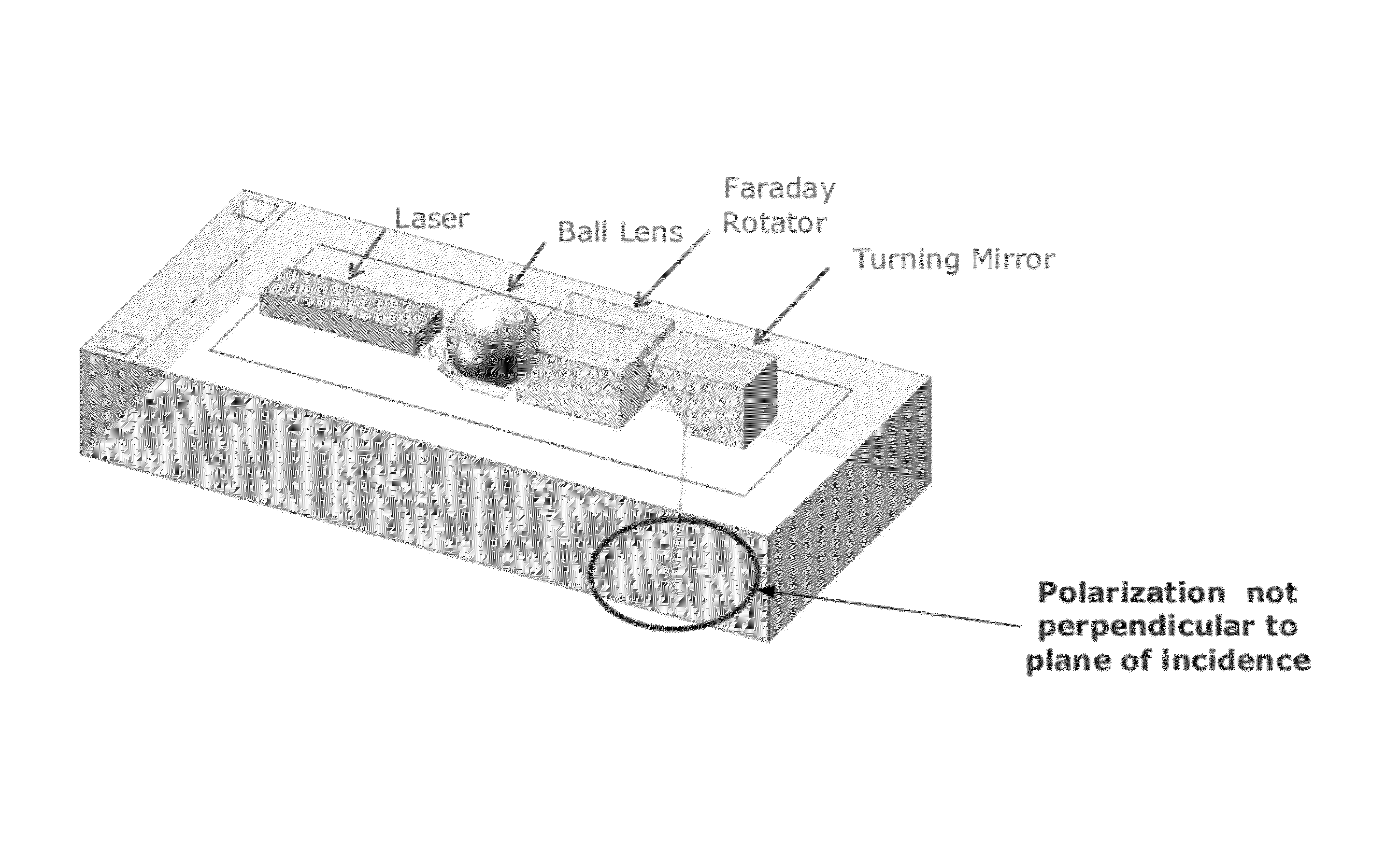
Laser irradiation apparatus and method of fabricating a semiconductor device
There is provided an optical system for reducing faint interference observed when laser annealing is performed to a semiconductor film. The faint interference conventionally observed can be reduced by irradiating the semiconductor film with a laser beam by the use of an optical system using a mirror of the present invention. The optical system for transforming the shape of the laser beam on an irradiation surface into a linear or rectangular shape is used. The optical system may include an optical system serving to convert the laser beam into a parallel light with respect to a traveling direction of the laser beam. When the laser beam having passed through the optical system is irradiated to the semiconductor film through the mirror of the present invention, the conventionally observed faint interference can be reduced. Besides, the optical system which has been difficult to adjust can be simplified.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
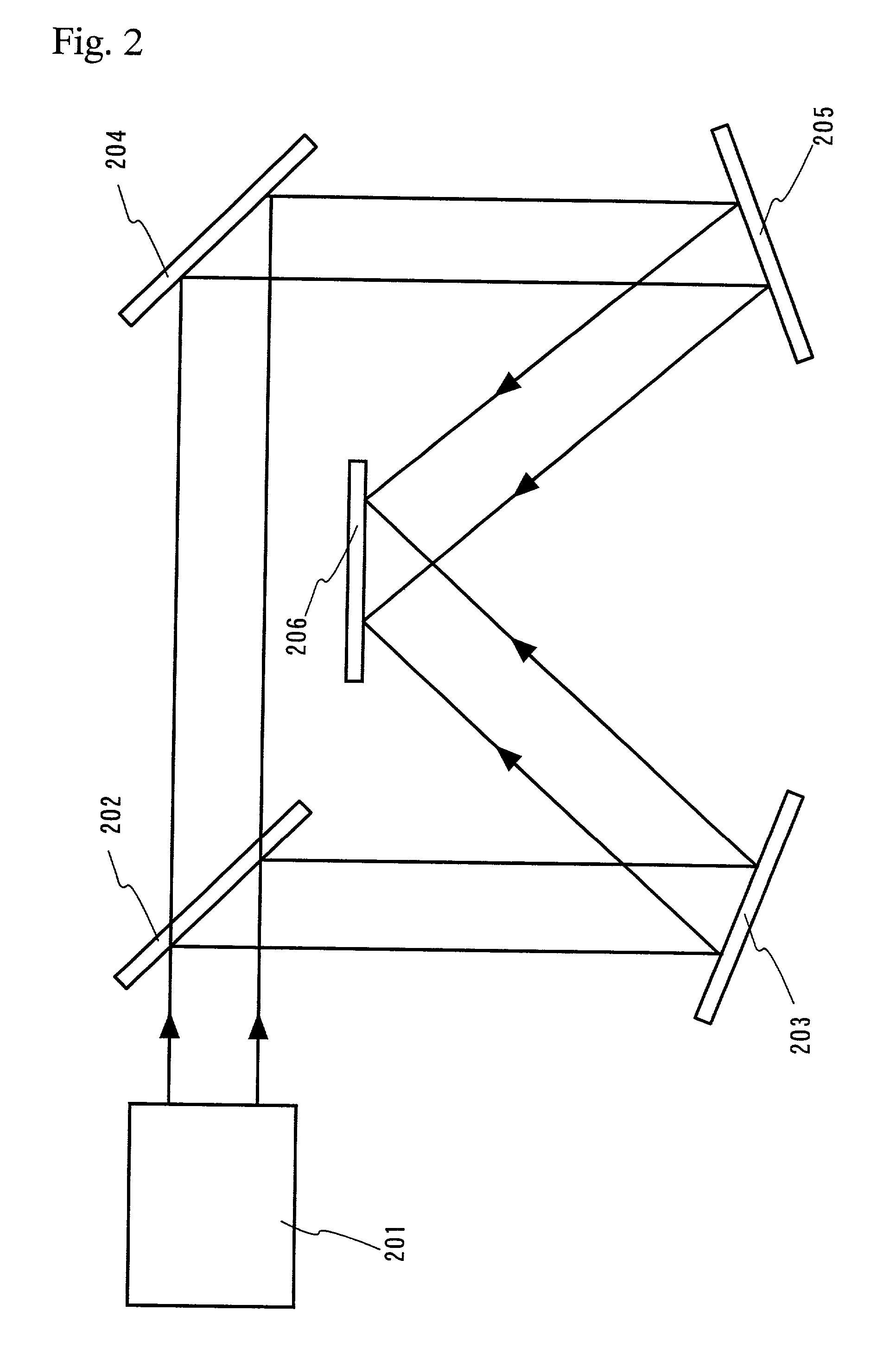
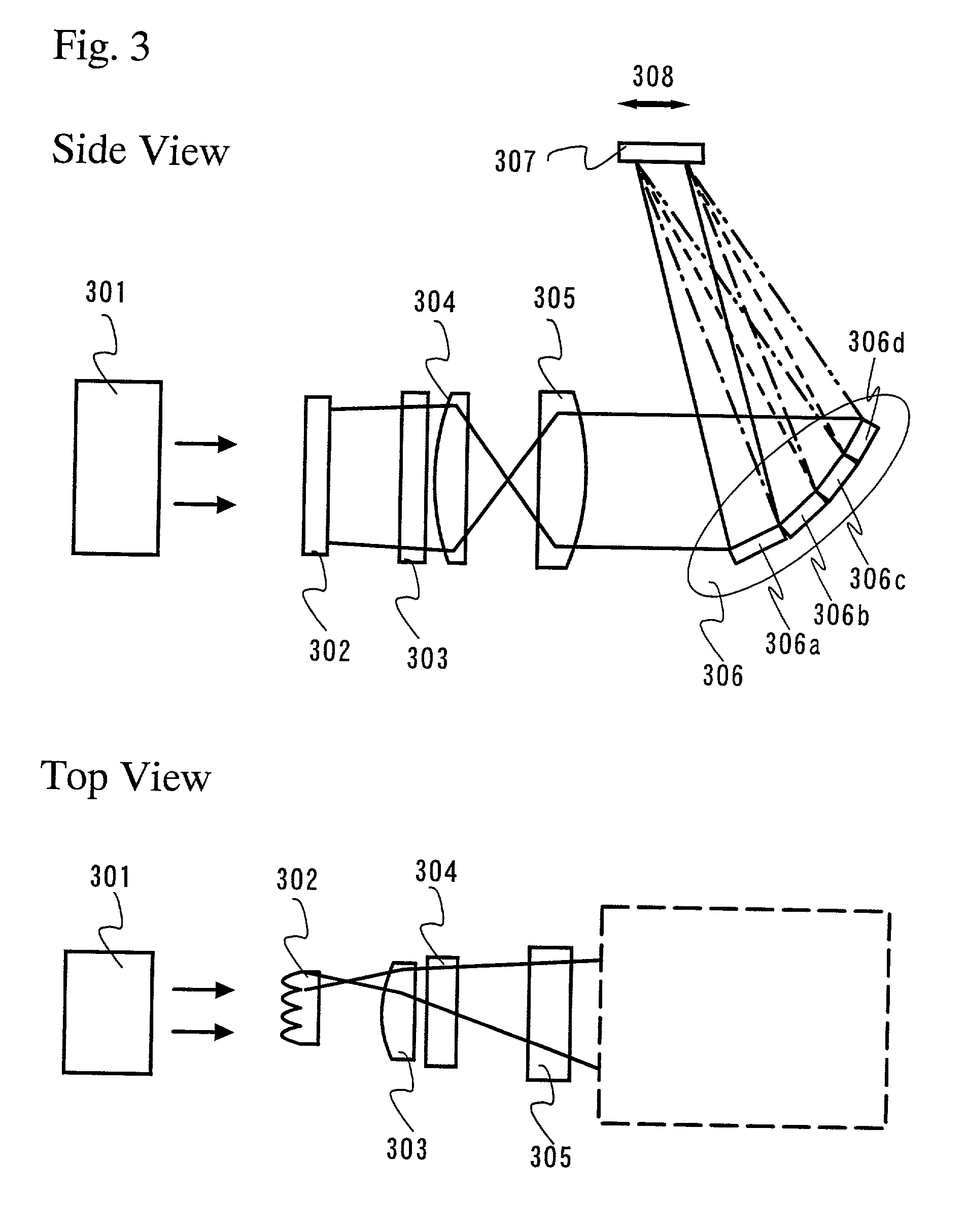
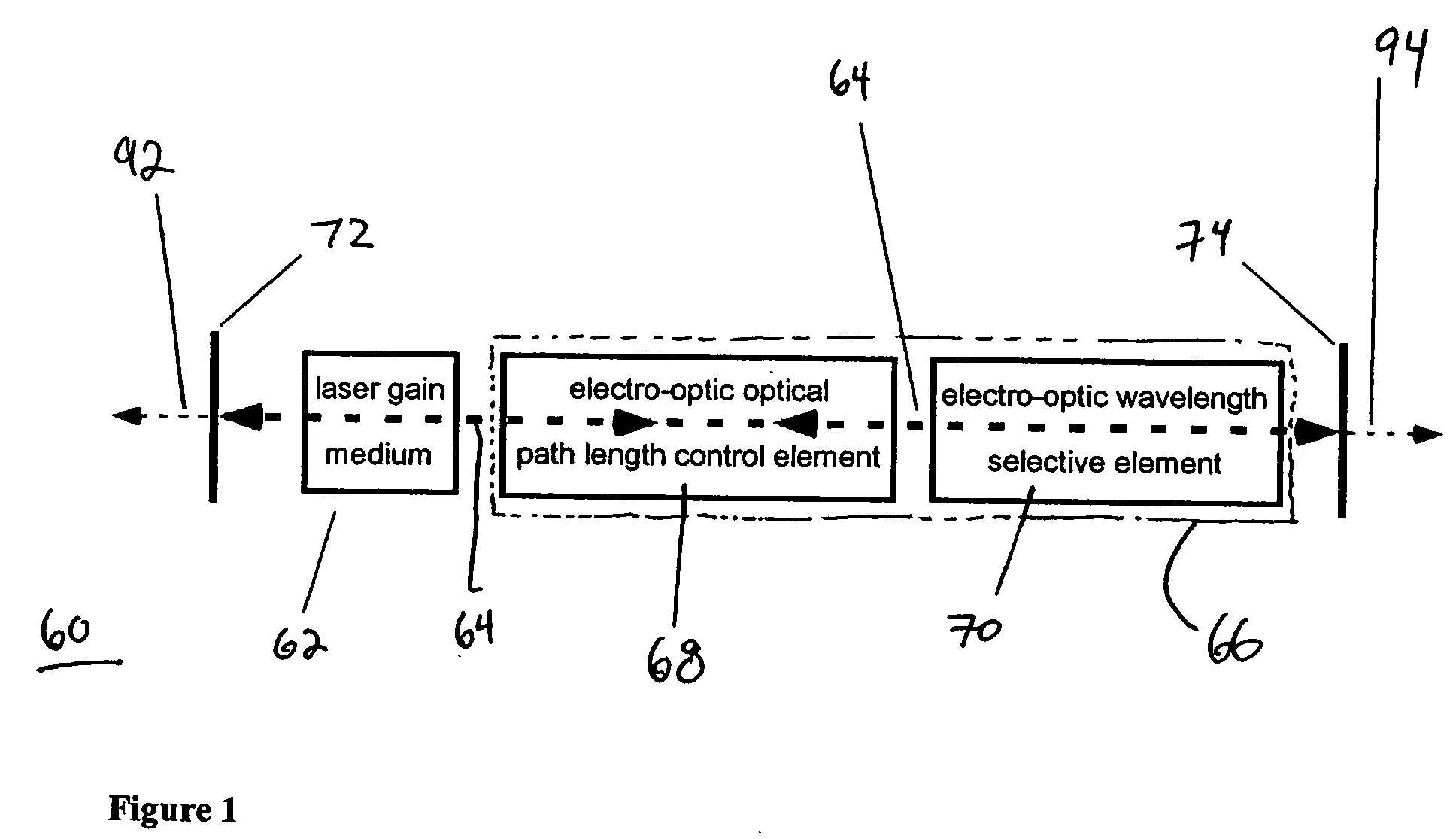
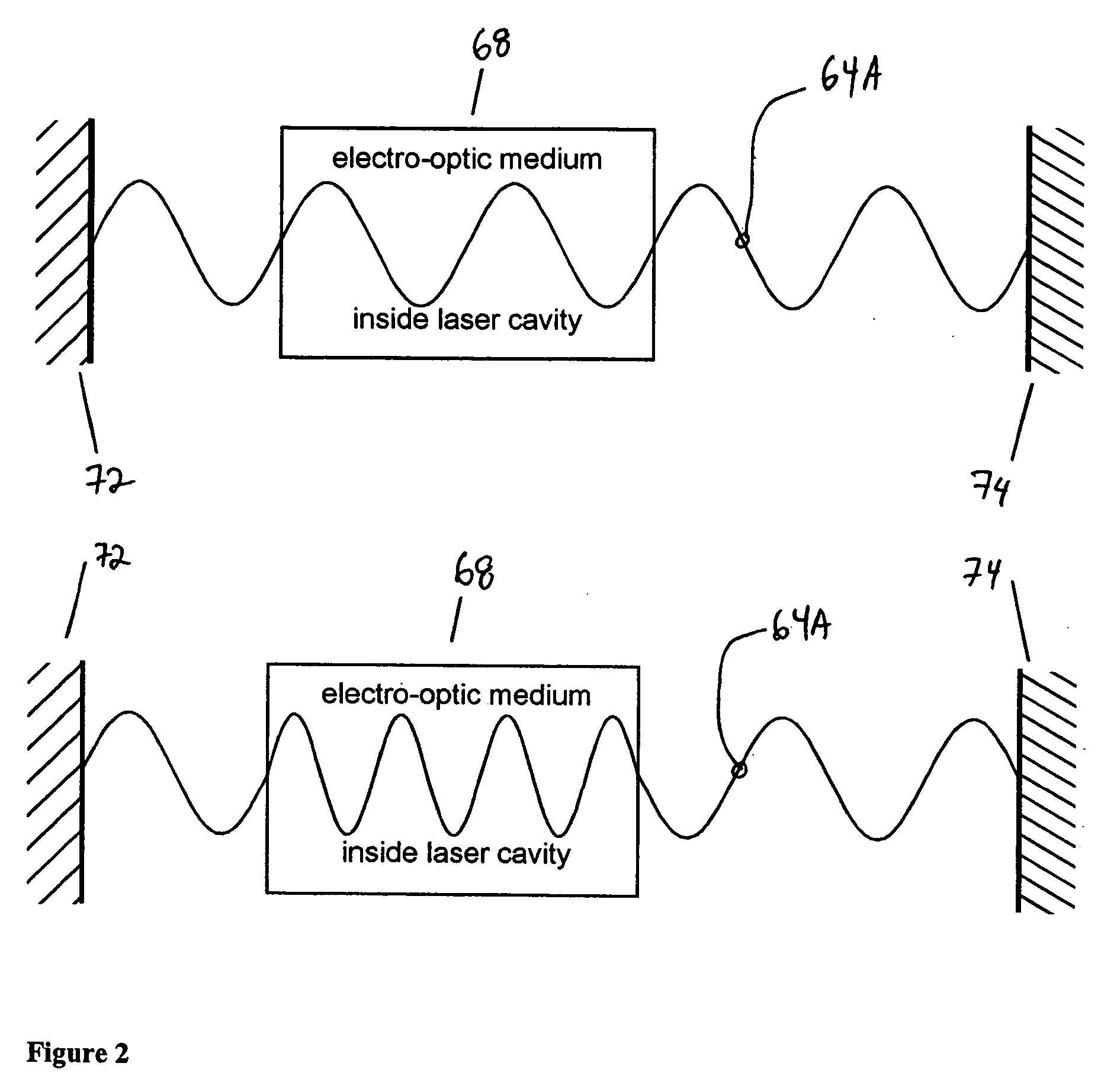
Tunable laser having liquid crystal waveguide
A tunable laser for providing a laser beam with a selectable wavelength. In one example, the tunable laser includes a gain medium for generating the laser beam; a waveguide for processing the laser beam, the waveguide having liquid crystal material or other electro-optic material disposed therein; an optical path length control element disposed within said waveguide for controlling an effective optical path length of the laser cavity; and a wavelength selective element for controlling the wavelength of the laser beam. The tunable laser may be designed without any moving mechanical parts if desired.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Laser ranging with large-format VCSEL array
InactiveUS20070071056A1Economical and reliableLaser detailsSemiconductor laser optical deviceLaser rangingBeam angle
The present invention relates to laser ranging and detection by sequentially emitting a plurality of beams from a vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL) structure, re-directing the beams through optical elements such that they are fanned out over the region of view, and detecting any beams that may be reflected by objects in the region of view. The range and bearing of such objects can be determined from the beam time-of-flight and beam angle.
Owner:AVAGO TECHNOLOGIED FIBER IP SINGAPORE PTE LTD
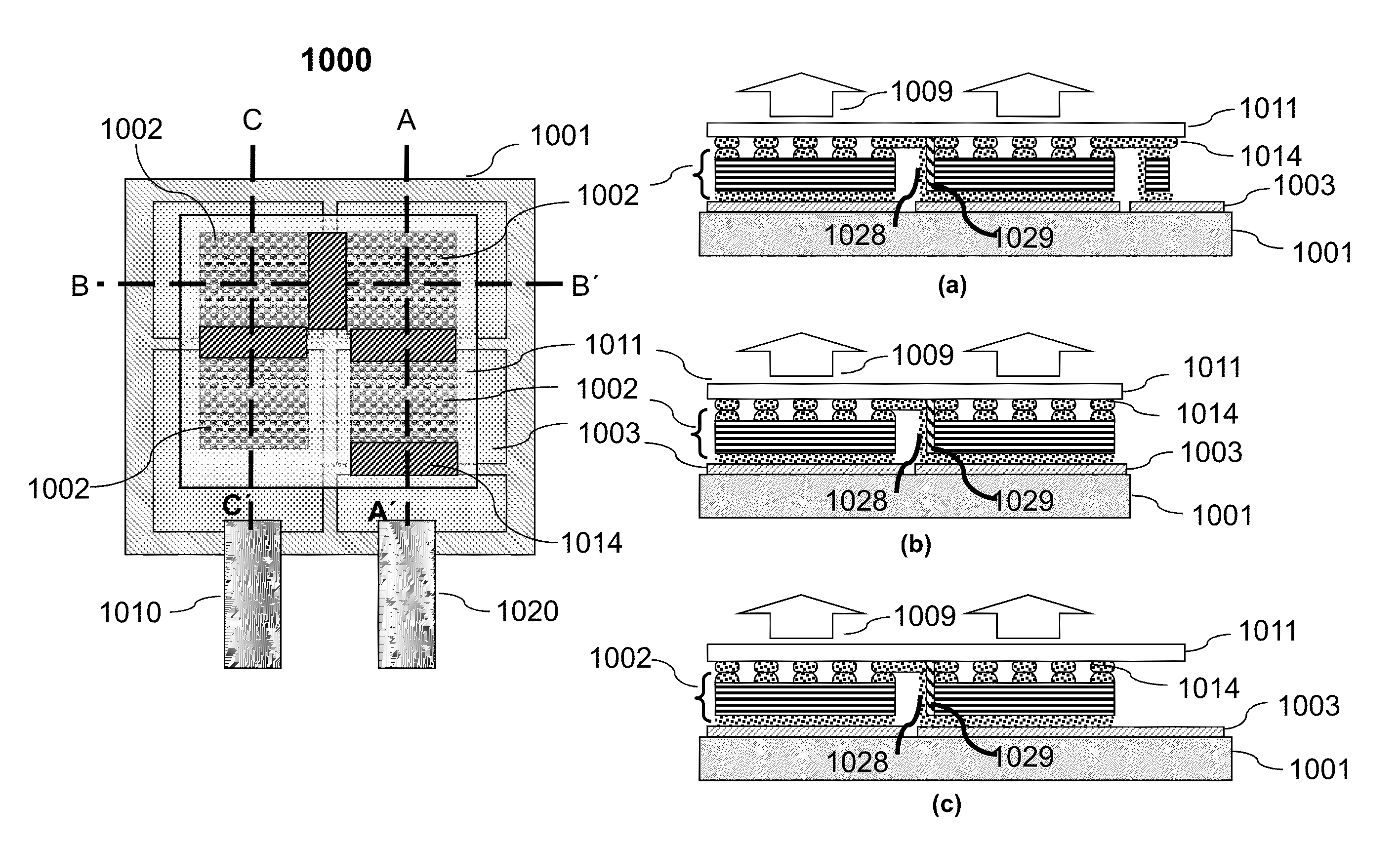
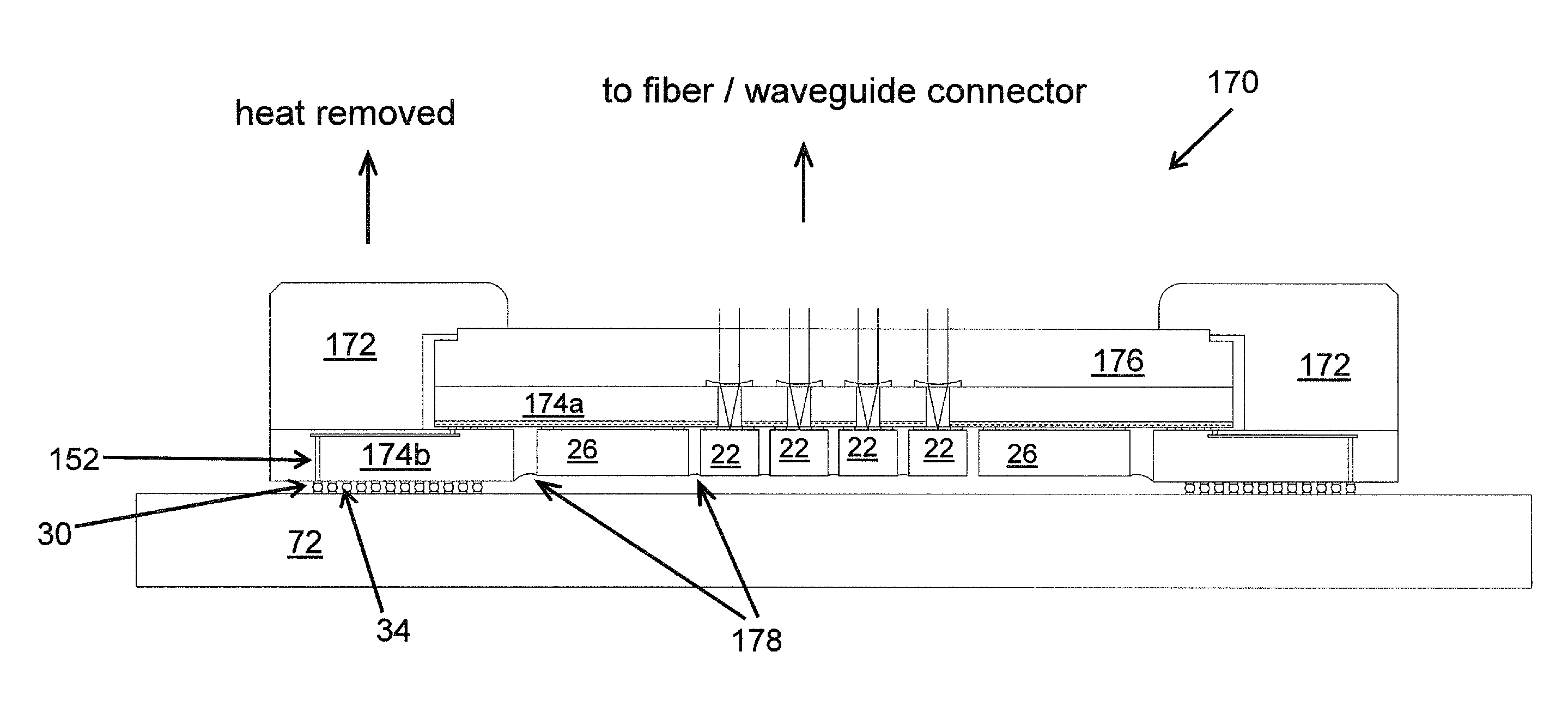
Silicon carrier optoelectronic packaging
ActiveUS20110044369A1Small sizeLow costLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsOpto electronicOptical coupling
An optoelectronic (OE) package or system and method for fabrication is disclosed which includes a silicon layer with wiring. The silicon layer has an optical via for allowing light to pass therethrough. An optical coupling layer is bonded to the silicon layer, and the optical coupling layer includes a plurality of microlenses for focusing and or collimating the light through the optical via. A plurality of OE elements are coupled to the silicon layer and electrically communicating with the wiring. At least one of the OE elements positioned in optical alignment with the optical via for receiving the light. A carrier is interposed between electrical interconnect elements. The carrier is positioned between the wiring of the silicon layer and a circuit board and the carrier is electrically connecting first interconnect elements connected to the wiring of the silicon layer and second interconnect elements connected to the circuit board.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
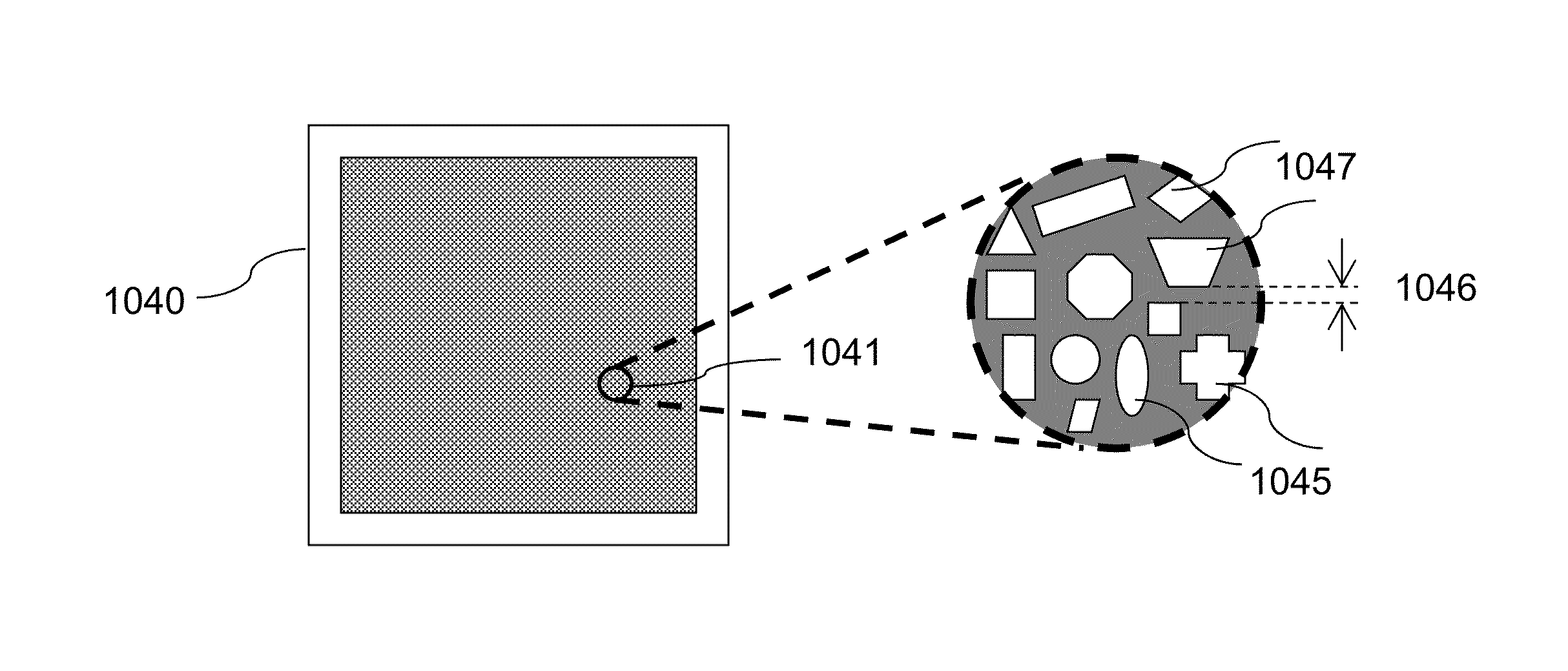
High Resolution Structured Light Source
InactiveUS20160072258A1Small and portableEasy to implementTelevision system detailsSemiconductor laser arrangementsOn boardRegular array
A structured light source comprising VCSEL arrays is configured in many different ways to project a structured illumination pattern into a region for 3 dimensional imaging and gesture recognition applications. One aspect of the invention describes methods to construct densely and ultra-densely packed VCSEL arrays with to produce high resolution structured illumination pattern. VCSEL arrays configured in many different regular and non-regular arrays together with techniques for producing addressable structured light source are extremely suited for generating structured illumination patterns in a programmed manner to combine steady state and time-dependent detection and imaging for better accuracy. Structured illumination patterns can be generated in customized shapes by incorporating differently shaped current confining apertures in VCSEL devices. Surface mounting capability of densely and ultra-densely packed VCSEL arrays are compatible for constructing compact on-board 3-D imaging and gesture recognition systems.
Owner:PRINCETON OPTRONICS
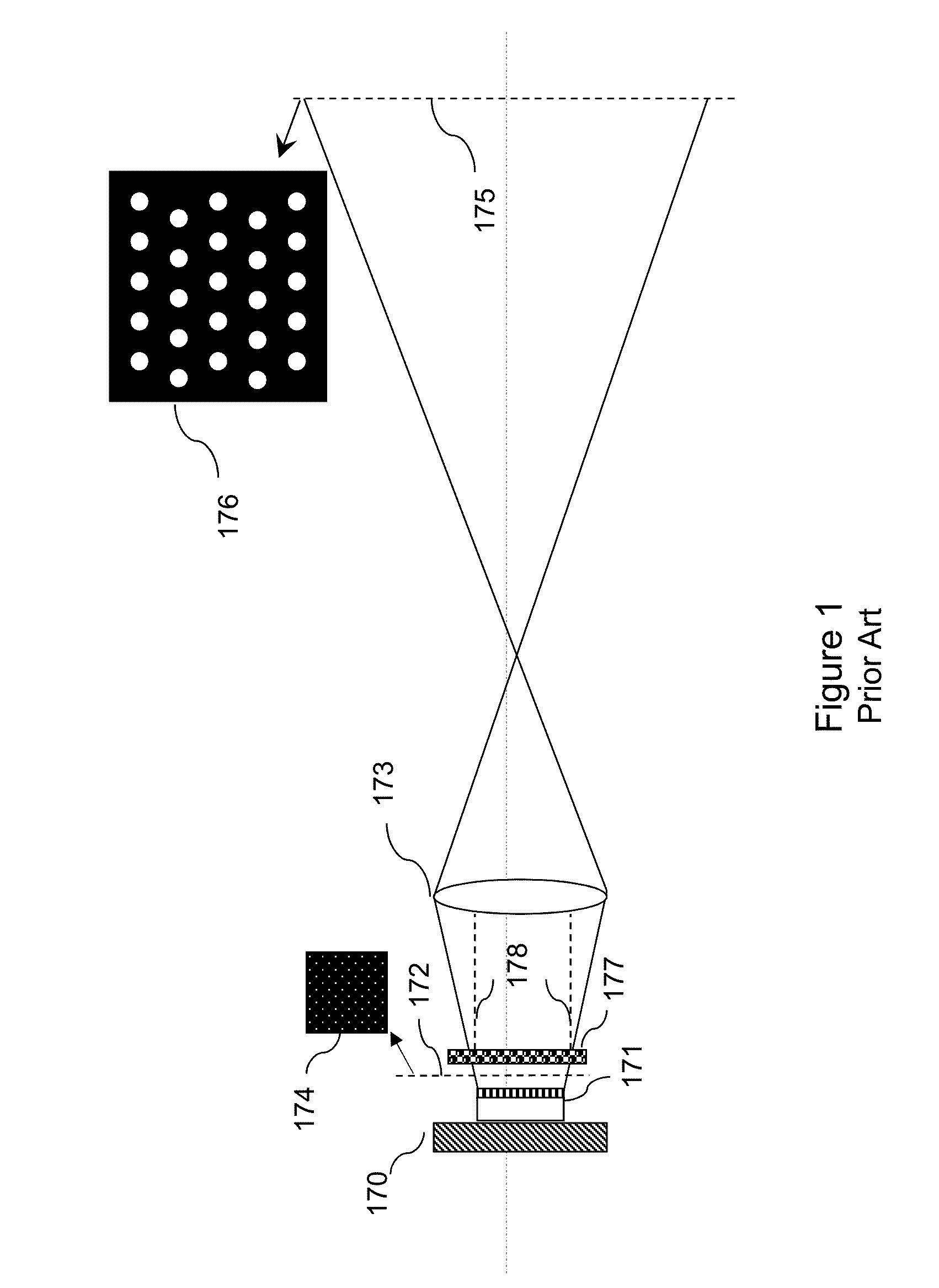
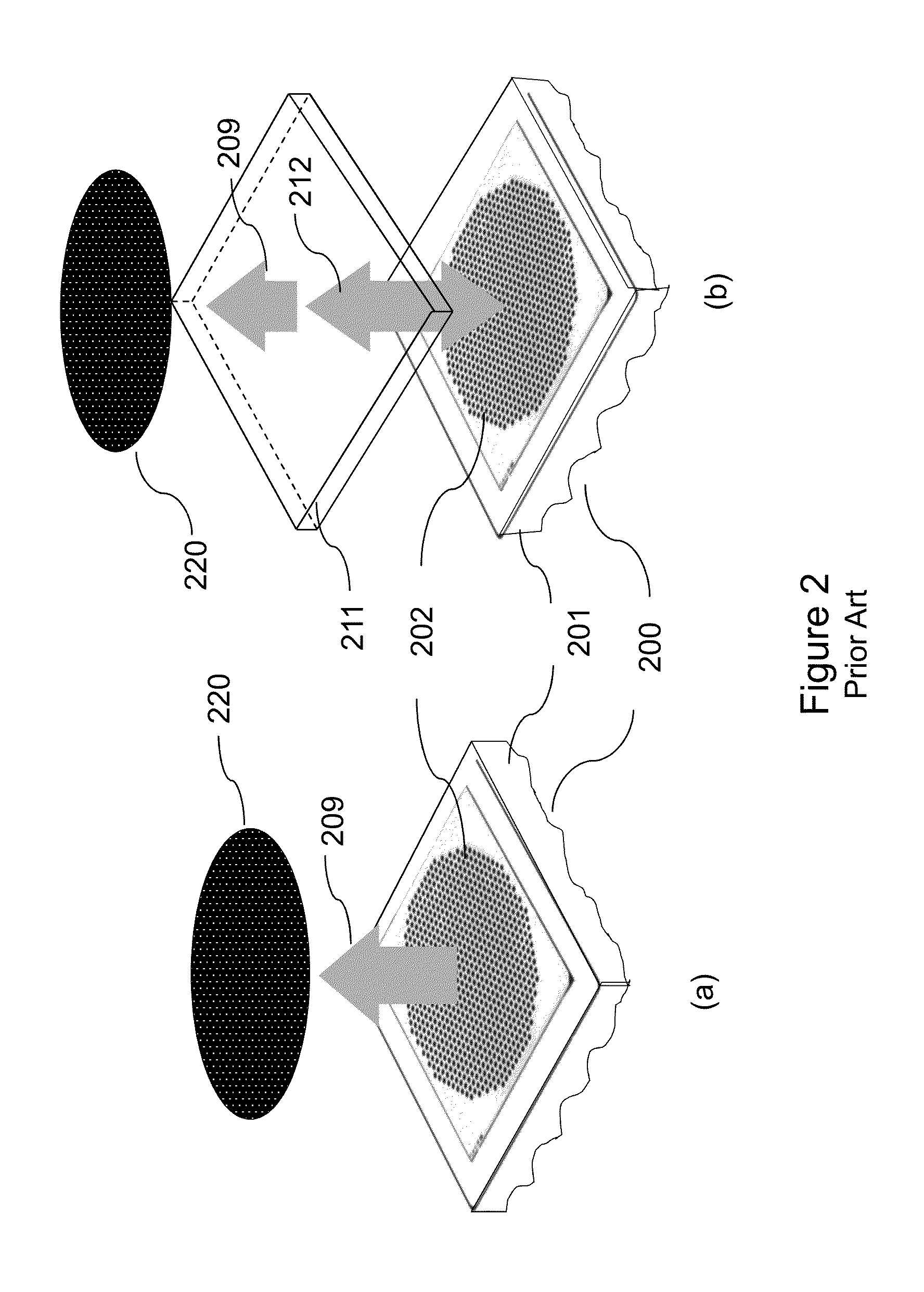
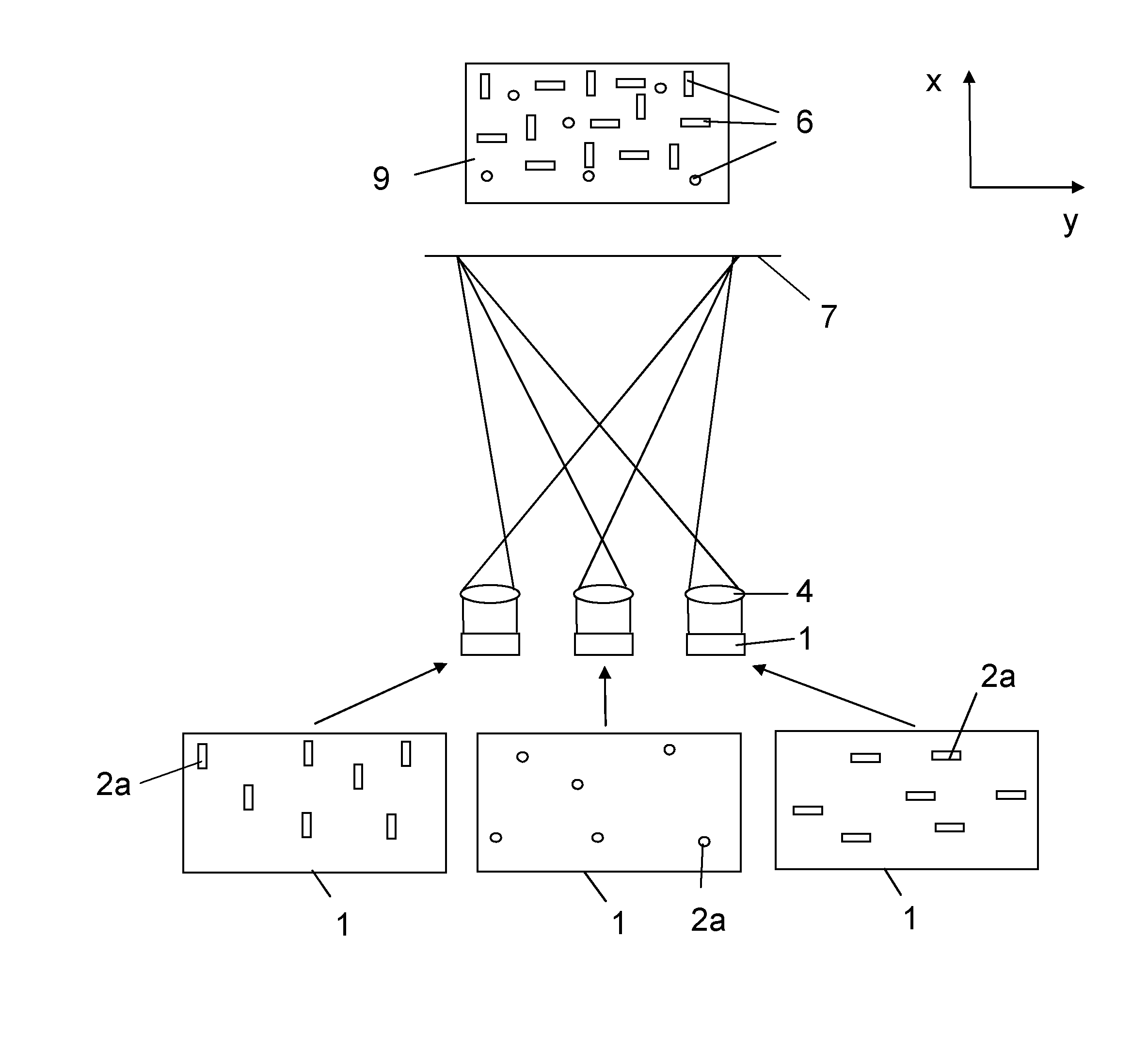
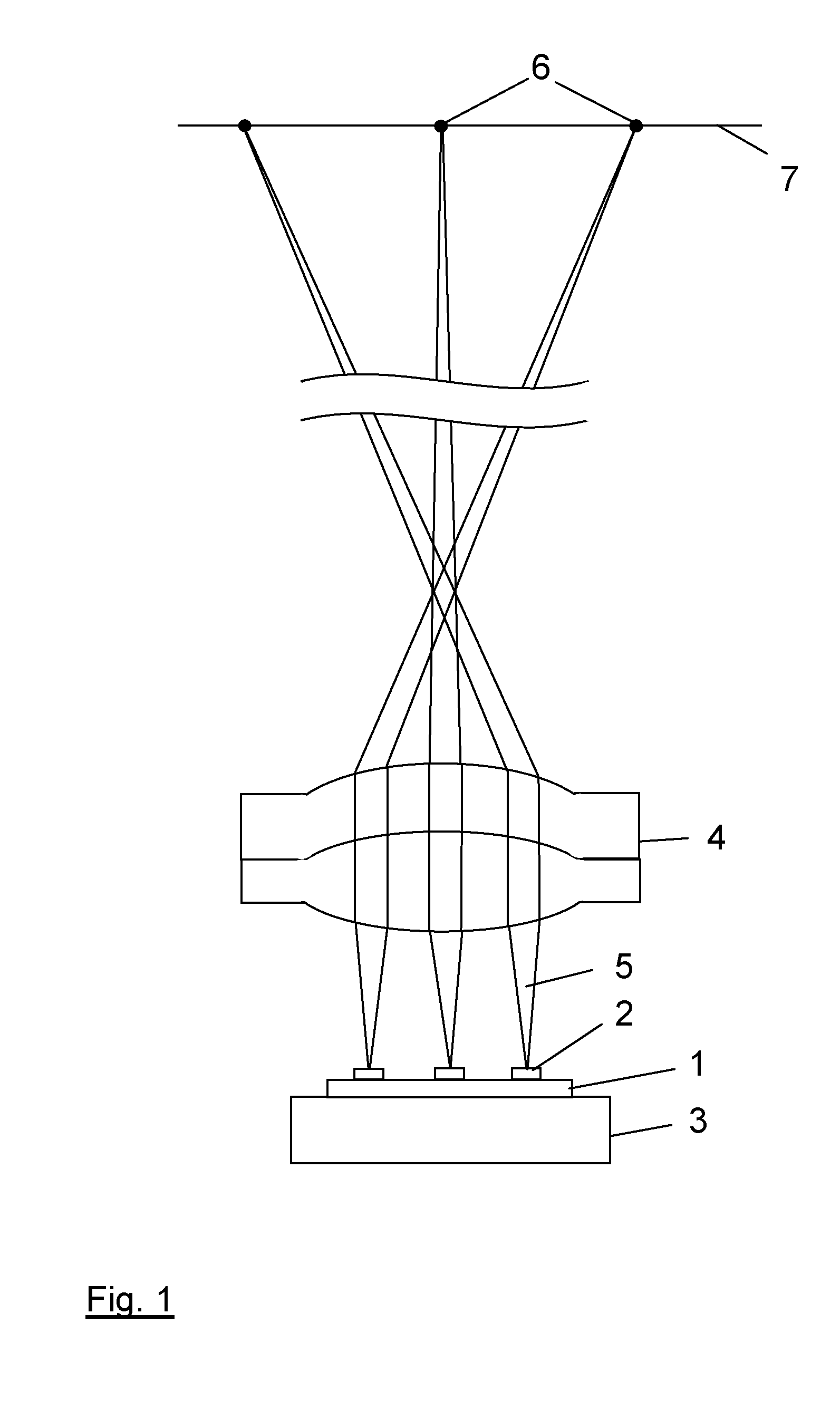
Laser device for projecting a structured light pattern onto a scene
ActiveUS20150316368A1Reduce ambiguityEasy extractionTelevision system detailsLaser detailsSemiconductorContrast ratio
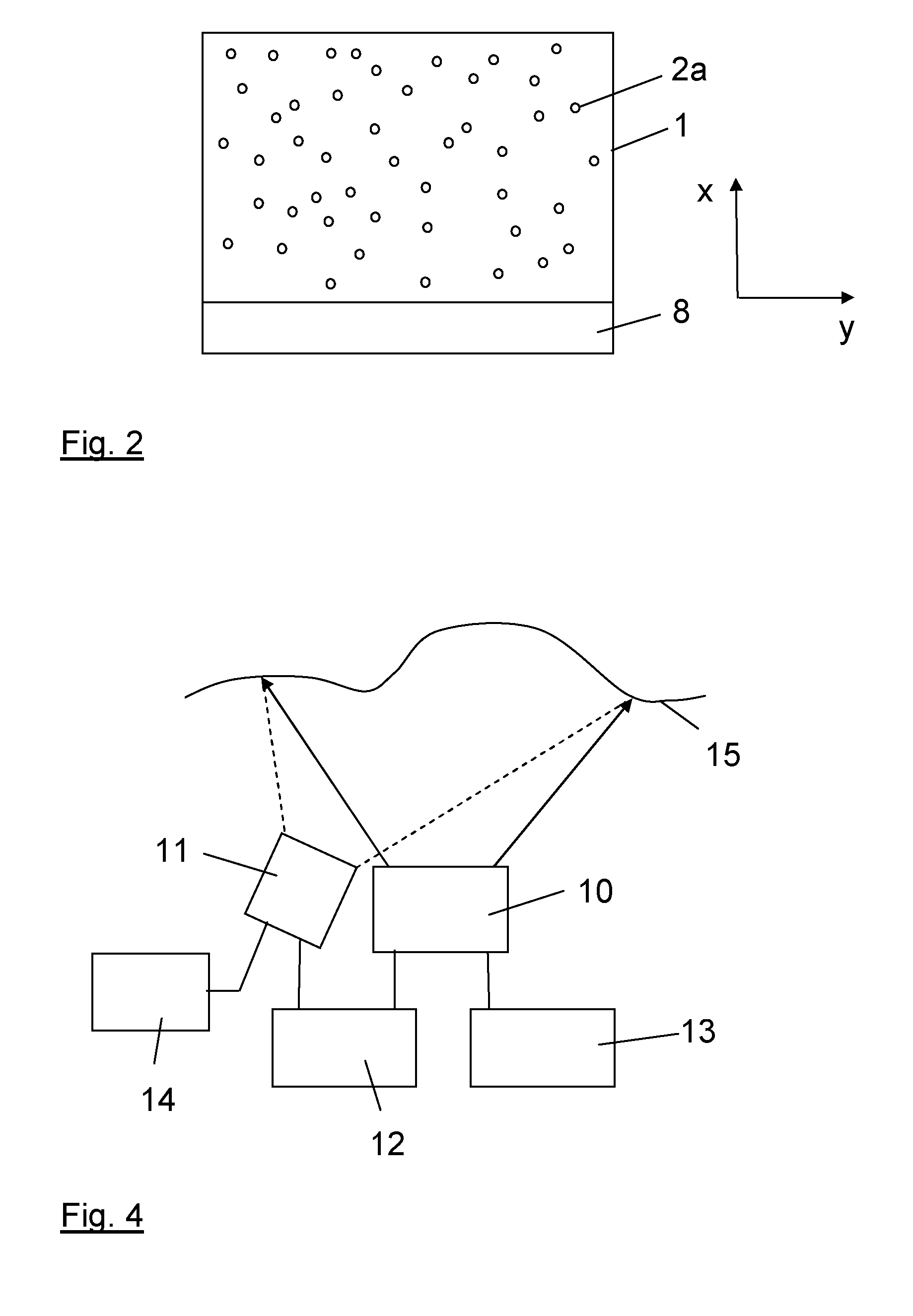
The present invention relates to a laser device (10) for projecting a structured light pattern (9) onto a scene (15). The device is formed of several arrays (1) of semiconductor lasers (2), each array (1) comprising an irregular distribution of emission areas (2a) of the semiconductor lasers (2). One or several imaging optics (4) image said arrays (1) to an imaging space and superpose the images of said arrays (1) in the imaging space to form said light pattern (9). The proposed laser device generates a light pattern with high contrast and efficiency which may be used for 3D imaging systems, e. g. in automotive applications.
Owner:TRUMPF PHOTONIC COMPONENTS GMBH
Organic vertical cavity laser and imaging system
InactiveUS6947459B2Semiconductor laser arrangementsLaser active region structureLaser transmitterLaser light
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Agile-beam laser array transmitter
ActiveUS20100046953A1Turn fasterWide field of viewWave based measurement systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsLaser arrayColor printing
An Agile-Beam Laser Array Transmitter (ABLAT) uses an array of emitters and an array of lenses to project electromagnetic beams over a wide angular coverage area in the far field. Differences in the separation pitches of the two arrays allows the ABLAT to project beams to contiguous and / or overlapping positions, depending on the ratio of the separation pitches and the lens focal length. Compared to other beam steering technology, the ABLAT is a smaller, lighter, and more efficient means of projecting beams over wider angular coverage areas. Various embodiments can be used in any beam steering application, including, but not limited to: free-space optical communications; light detection and ranging (lidar); optical scanning (e.g., retinal or bar-code scanning); display projection; image capture; optical character recognition; scanning laser microscopy; non-destructive testing; printing; facsimiles; map making; web inspection; color print processing; phototypesetting and platemaking; laser marking; material processing; DNA analysis; and drug discovery.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Light source apparatus and optical communication module comprising it
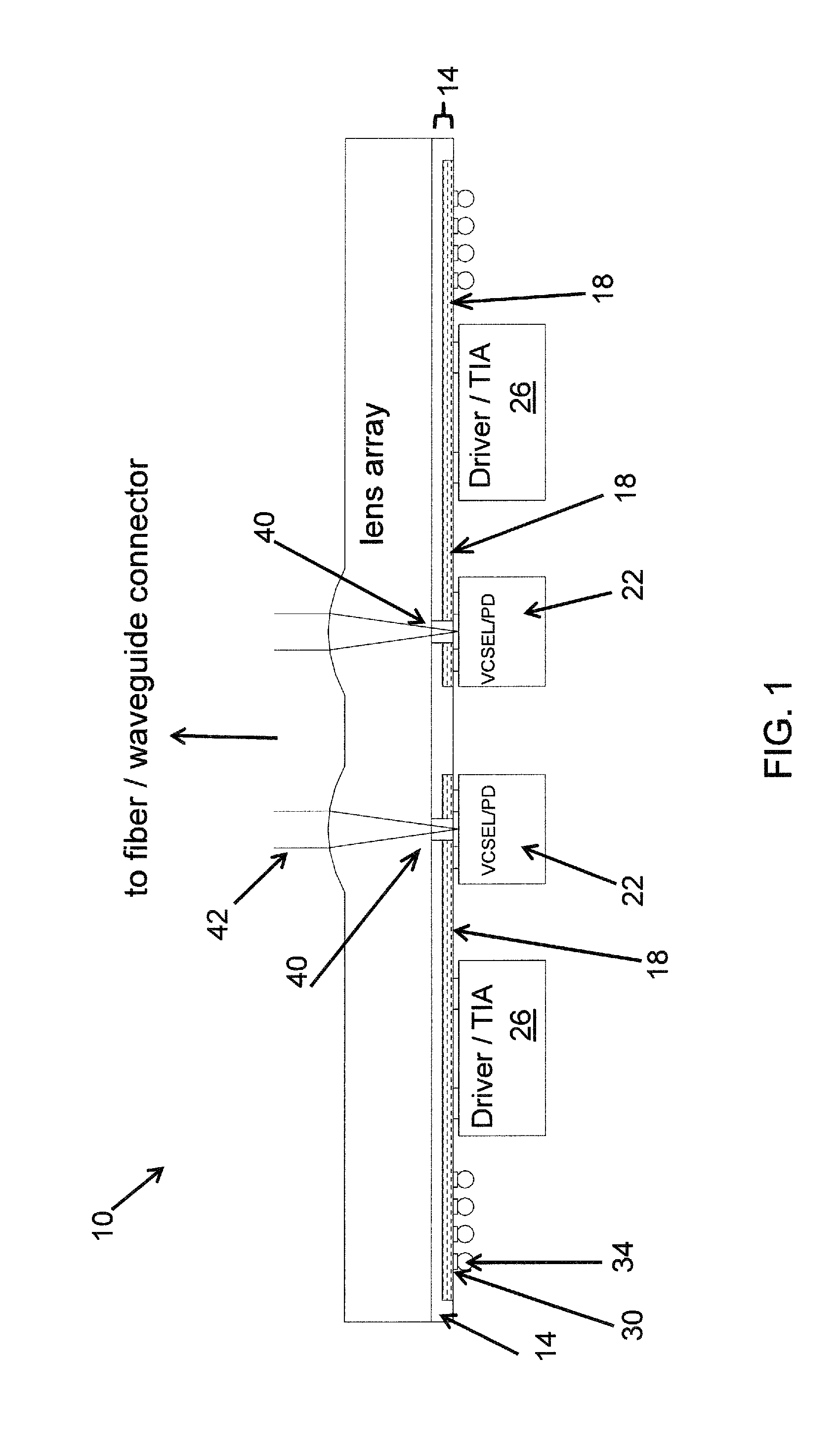
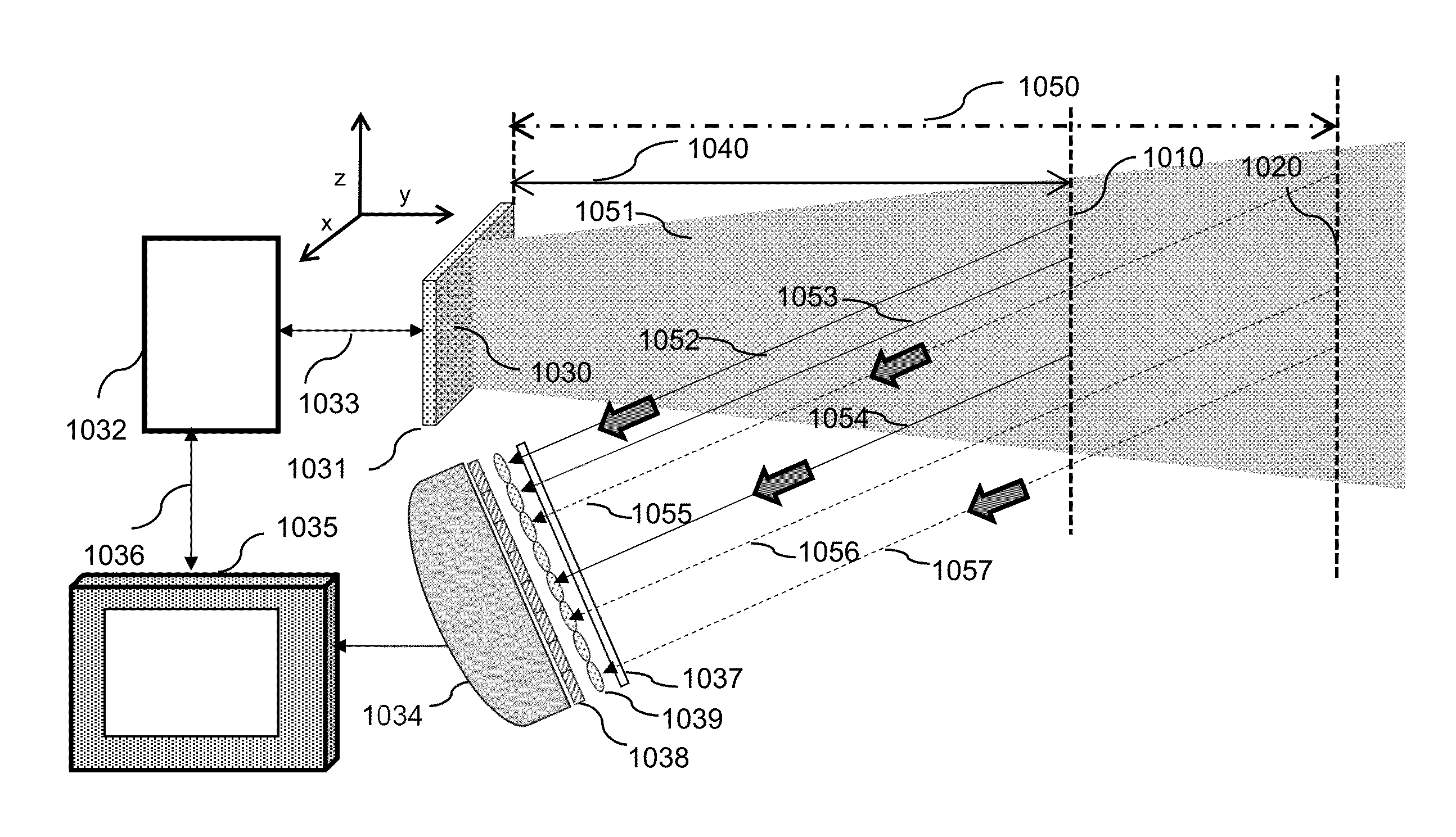
ActiveUS20050226636A1Small sizeLow costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor laser optical deviceHigh densityMagnifying glass
A light source device for radiating a stimulated emission from a semiconductor laser to outside via a multiple scattering optical system, which system has a first region located adjacent to the semiconductor laser and a second region that abuts on the first region and reaches the outside. The first region contains scatterers at a higher density than the second region does. The light source device has an amount of near-field pattern speckles σPAR of 3×10−3 or more. The second region may have a lens portion as a magnifier for at least a principle part of a secondary planar light source formed at an interface between the first and second regions.
Owner:SHARP FUKUYAMA LASER CO LTD
Led lighting system with reflective board
A light emitting apparatus (8) includes one or more light emitting chips (10) that are disposed on a printed circuit board (12) and emit light predominantly in a wavelength range between about 400 nanometers and about 470 nanometers. The printed circuit board includes: (i) an electrically insulating board (14); (ii) electrically conductive printed circuitry (20); and (iii) an electrically insulating solder mask (22) having vias (24) through which the one or more light emitting chips electrically contact the printed circuitry. The solder mask (22) has a reflectance of greater than 60% at least between about 400 nanometers and about 470 nanometers.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC +1
Light-emitting device, and illumination apparatus and display apparatus using the light-emitting device
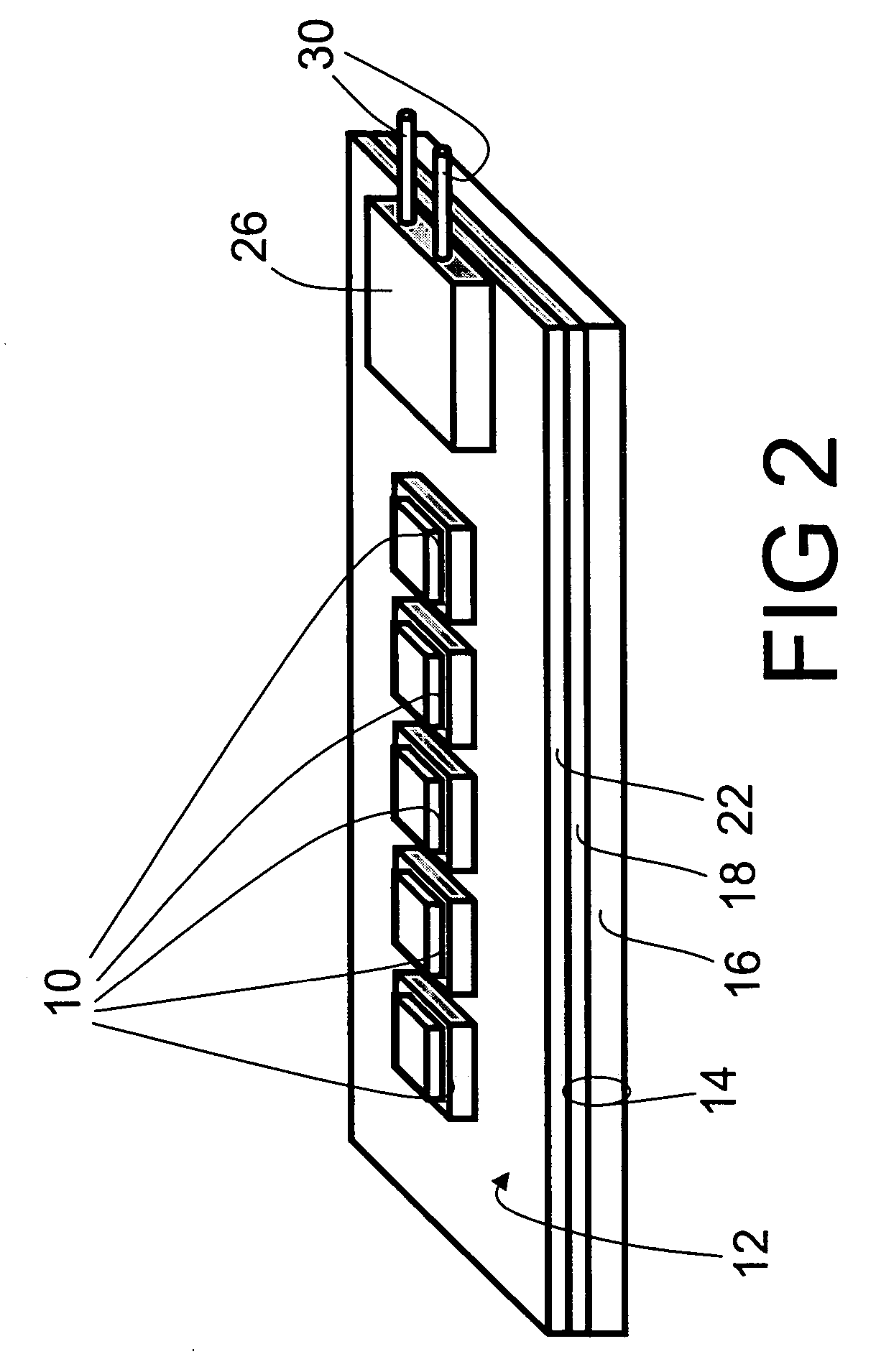
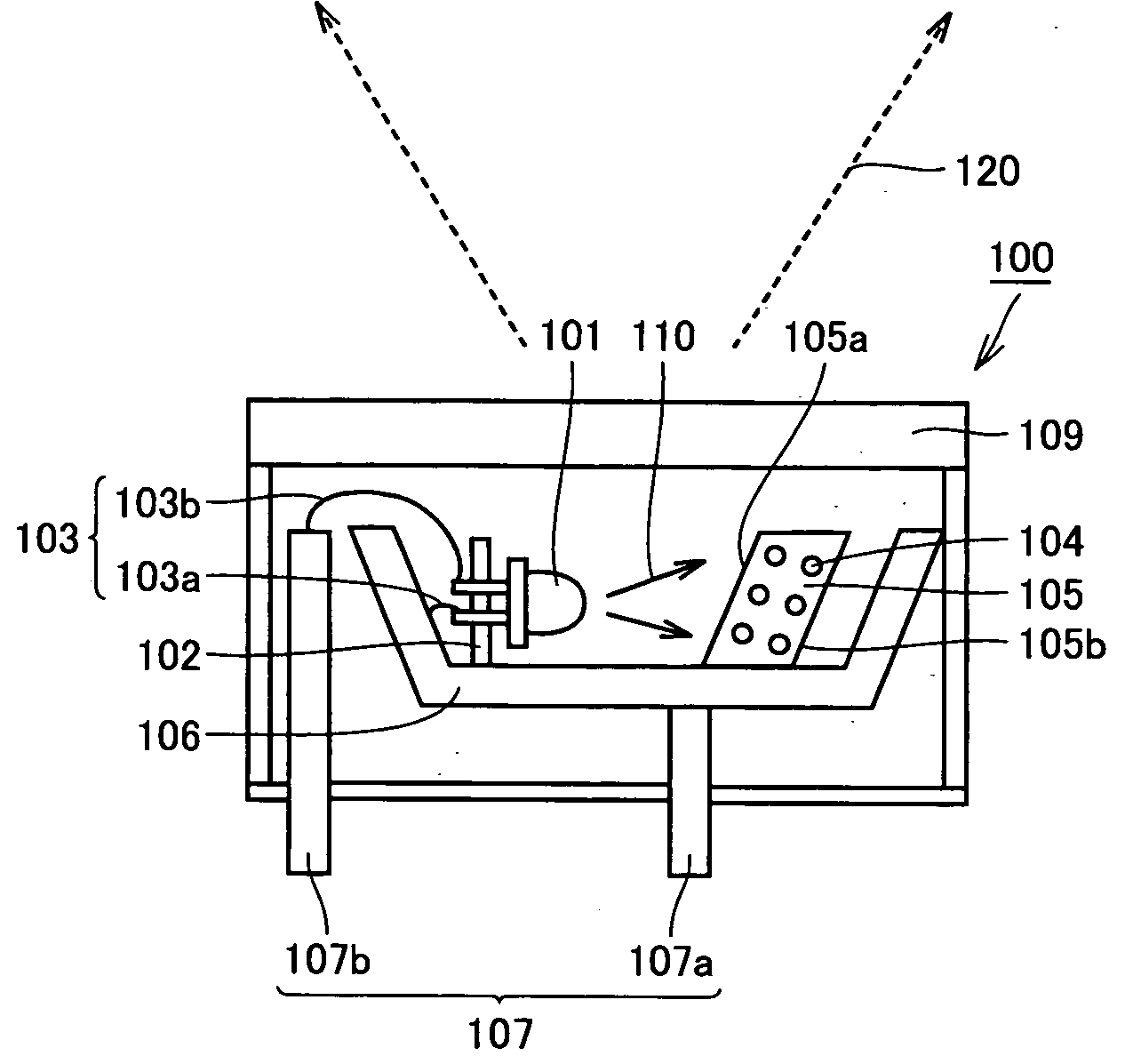
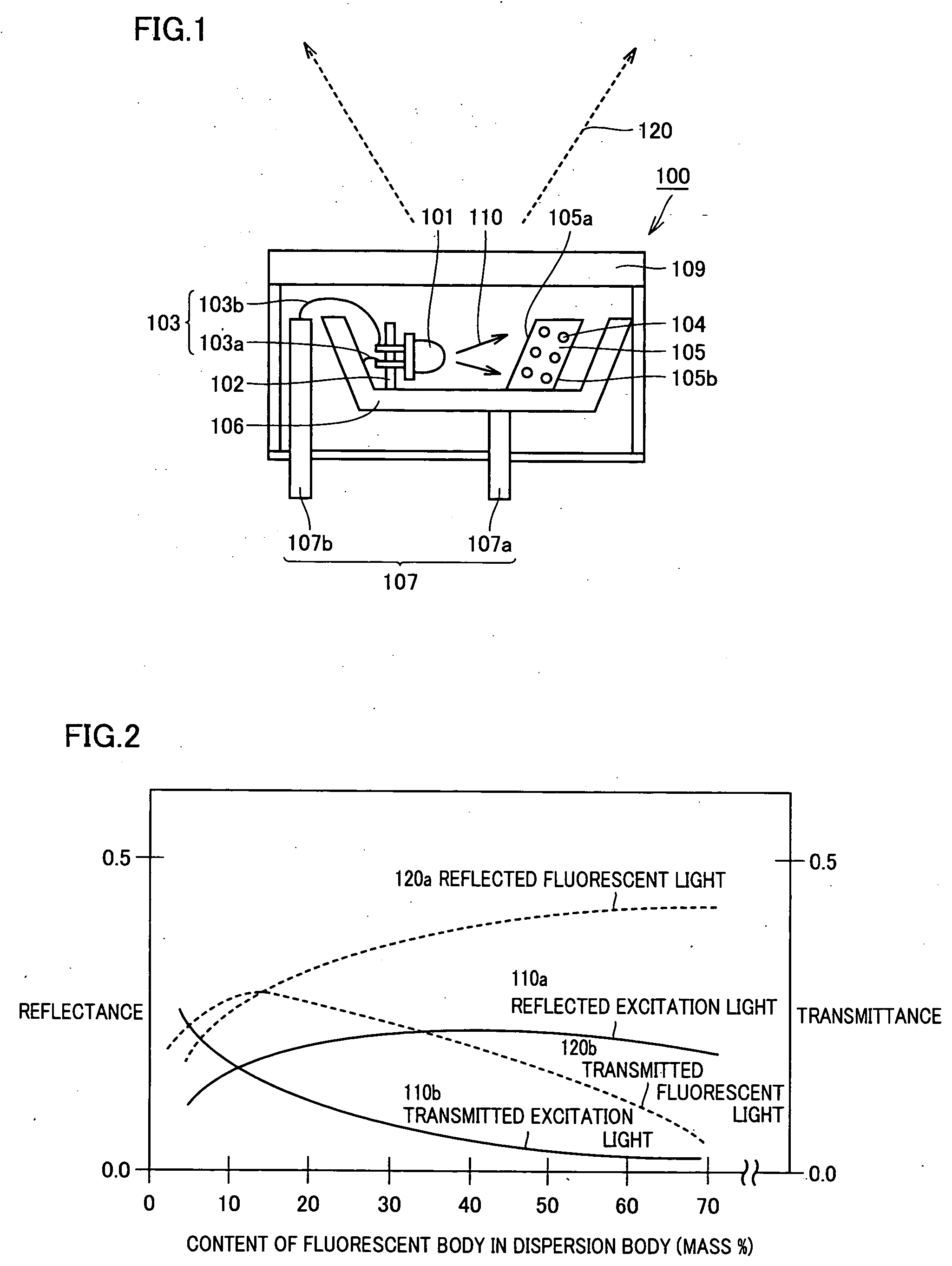
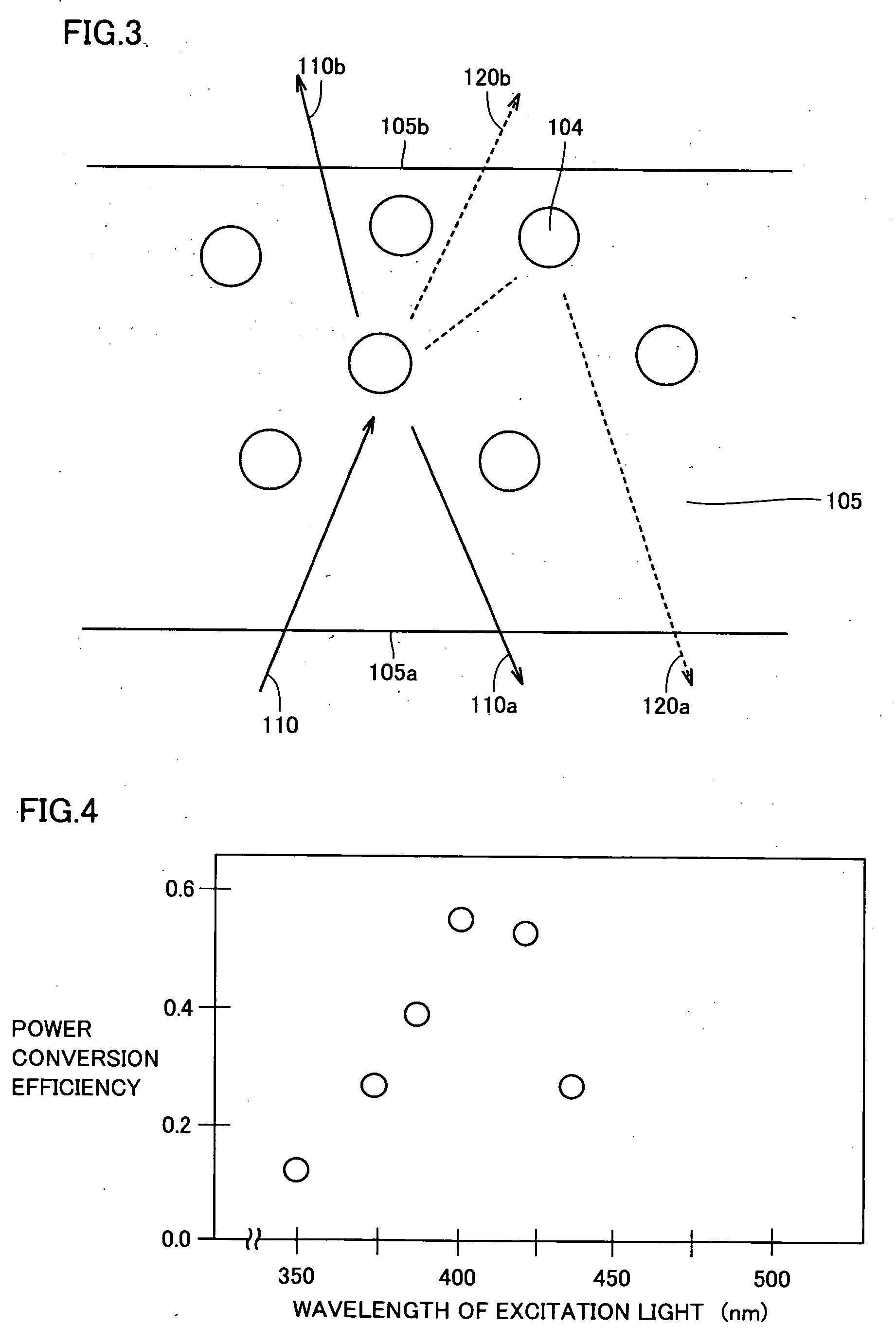
ActiveUS20060139926A1Improve light output efficiencyImprove efficiencyOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsLead frameLength wave
A light-emitting device including a light-emitting element emitting excitation light for exciting a fluorescent body, a dispersion body having the fluorescent body dispersed therein, which fluorescent body emits fluorescent light having a wavelength different from that of the excitation light, and a lead frame holding the light-emitting element and the dispersion body, wherein at least a portion of the fluorescent light emitted from the fluorescent body in the dispersion body is output to the outside from a side of the dispersion body receiving the excitation light. With this, a light-emitting device having high light output efficiency and an illumination apparatus and a display apparatus using the light-emitting device are provided.
Owner:SHARP FUKUYAMA LASER CO LTD
Light emitting device
ActiveUS20080205477A1Good color propertiesImprove luminous efficiencyEndoscopesSemiconductor laser optical deviceFiberLength wave
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Method and system for a light source assembly supporting direct coupling to an integrated circuit
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
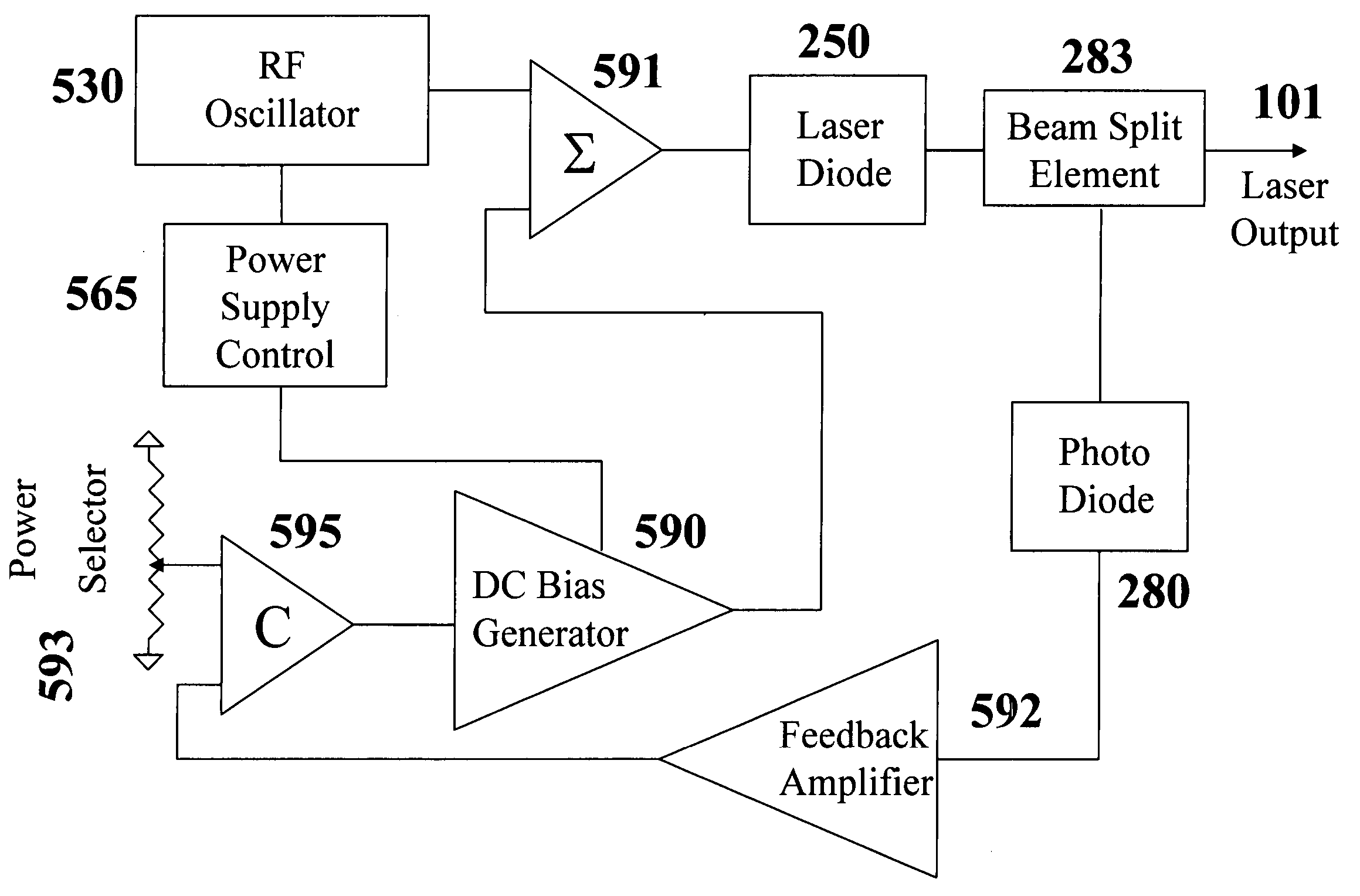
Radio frequency modulation of variable degree and automatic power control using external photodiode sensor for low-noise lasers of various wavelengths
ActiveUS20060215716A1Increase output powerWide wavelength rangeLaser detailsSemiconductor laser optical deviceLow noiseRadio frequency
A low-noise laser diode module comprises a laser diode for emitting light with a wavelength in the range from UV to IR, a drive circuit for injecting electrical current into said diode, and an automatic power control circuit for monitoring and adjusting laser output power using front-facet photodiode external to the laser assembly and a feedback loop. Said drive circuit produces injection current modulated by an RF signal with variable degrees, depending on the wavelength to be stabilized, the desired spectral bandwidths of the laser output, and / or other applications. Said RF signal can be a sine wave, a distorted sine wave, a rectified sine wave, a non-sine wave, a series of narrow pulses, or repetitive shunt. The present invention encompasses a method for producing stable, broadband, and low-coherent laser. The present invention also encompasses a method for producing stable narrowband or single longitudinal mode laser. The present invention further encompasses a compact light source applicable to DPSS lasers, fiber lasers, optical parametric oscillators, low-speckle laser display systems, and seeders, with or without nonlinear frequency conversion processes.
Owner:PAVILION INTEGRATION
Method and apparatus for modifying the spread of a laser beam
InactiveUS20070153293A1Input/output for user-computer interactionLaser detailsBeam splittingLight beam
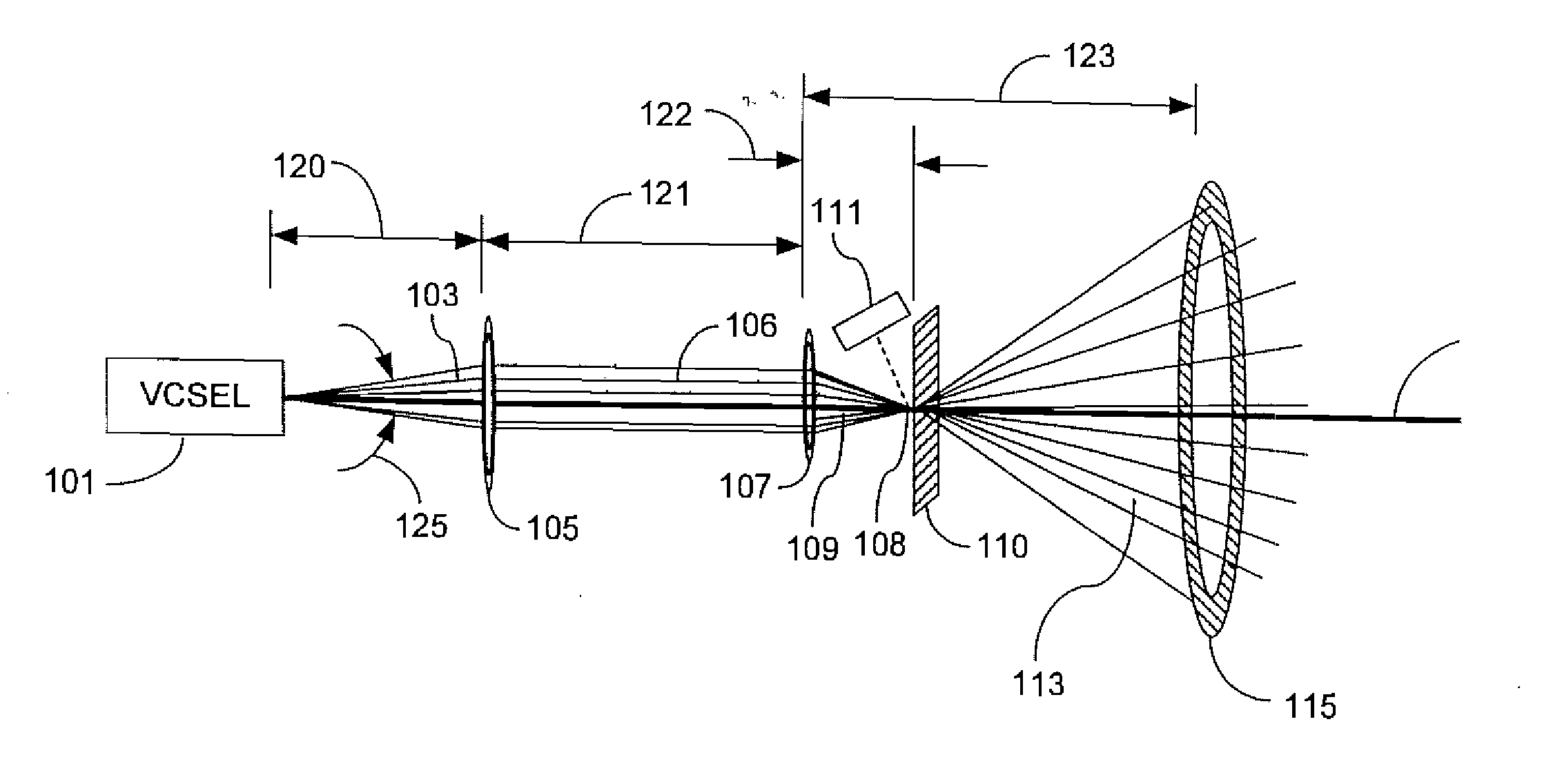
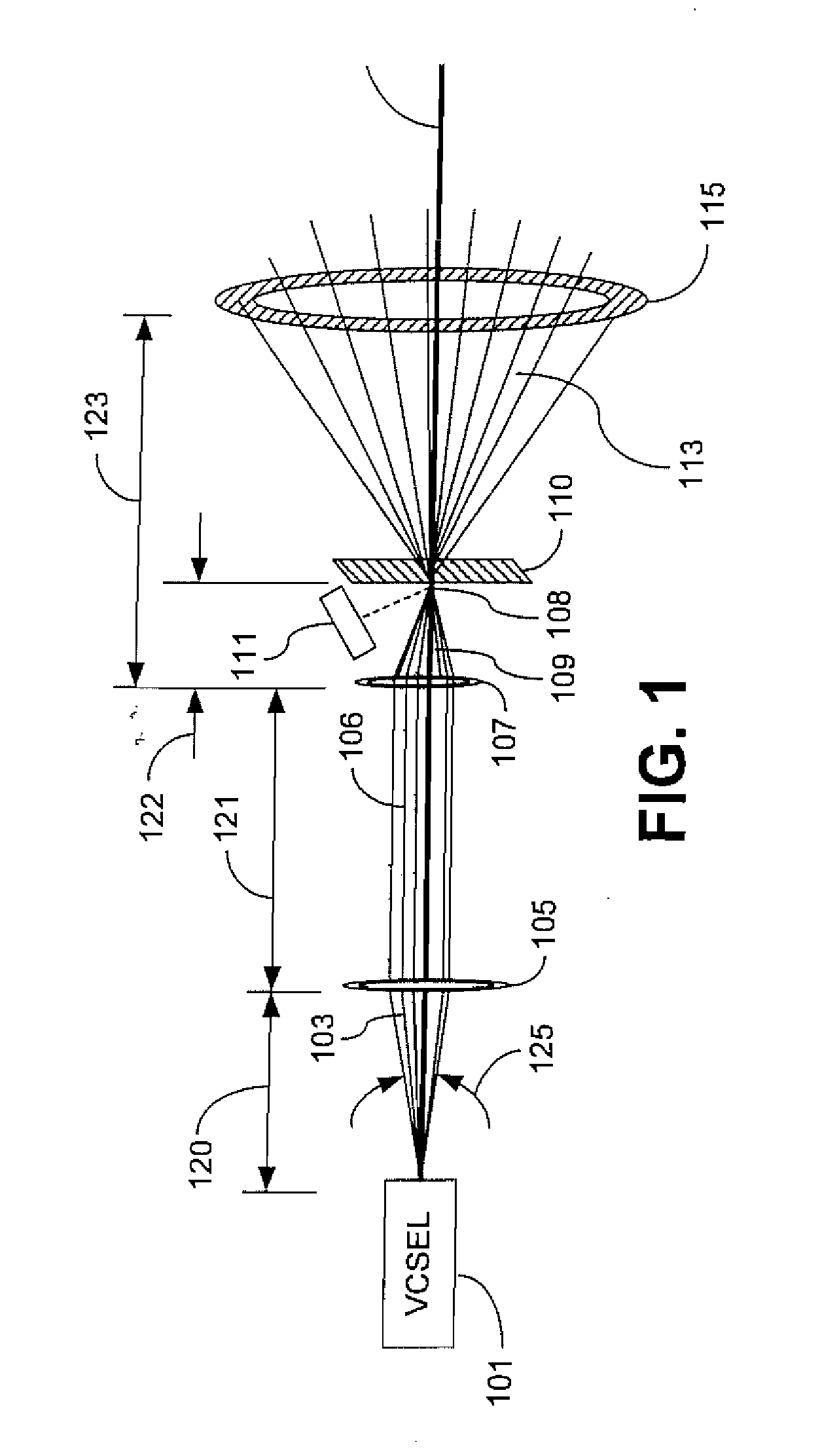
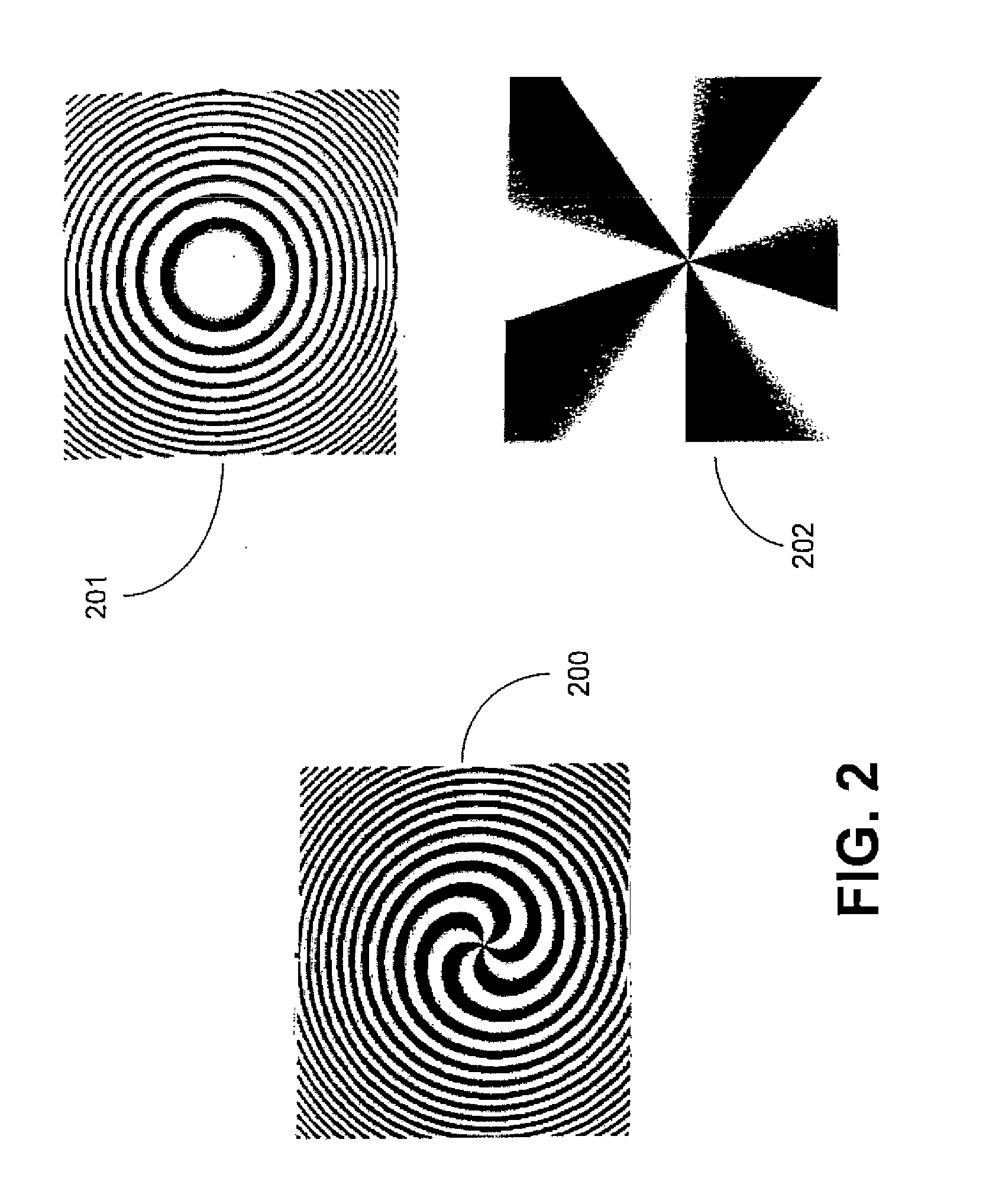
An apparatus and method for modifying the spread of a laser beam. The apparatus comprises a laser source operable to generate a laser beam having a flux that exceeds a predetermined value and an optical train operable to modify the beam such that the flux of the beam through a predetermined aperture does not exceed the predetermined value. The optical train may include a focusing lens, a diffractive focusing vortex lens, a beam splitting device, or a two-dimensional diffraction grating.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Laser diode assemblies
InactiveUS7733932B2Reduce misalignmentReduce in quantitySemiconductor laser optical deviceLaser cooling arrangementsLight beamLaser beams
Laser diodes (120) emit laser beams along a vertical YZ plane at different distances from the YZ plane. The beams are collimated in their fast and slow axes, and are redirected by turning mirrors (162) to form a beam stack (130C) traveling along the XZ plane. The beam stack is turned by about 90°, then converged by a focusing lens (174) into an optical fiber (180). A compact assembly is thus provided. Each laser diode (120.i), its collimating optics (154.i, 158.i, i=1, 2, . . . ) and its turning mirror (162.i) are rigidly attached to a flat, heat-spreading surface (144.i) and thus remain aligned with each other in thermal cycling.
Owner:FAYBISHENKO VICTOR
2-D Planar VCSEL Source for 3-D Imaging
ActiveUS20150362585A1Precise applicationAccurate proximityLaser detailsSolid-state devicesLight beamImaging lens
An apparatus and a method are provided for 3-D imaging and scanning using a 2-D planar VCSELs source configured as a lightfiled optical source. VCSELs are configured in different 2-D spatial arrangements including single VCSEL, or preferably a group, cluster, or array each to be operated effectively as an independent VCSEL array source. A set of microlens and an imaging lens positioned at a pre-determined distance collimates radiation from each VCSEL array source to a set of parallel beams. The parallel beams from different VCSEL array sources generated in a rapid pre-determined timing sequence provide scanning beams to illuminate an object. The radiation reflected from the object is analyzed for arrival time, pulse shape, and intensity to determine a comprehensive set of distance and intensity profile of the object to compute a 3-D image.
Owner:PRINCETON OPTRONICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com