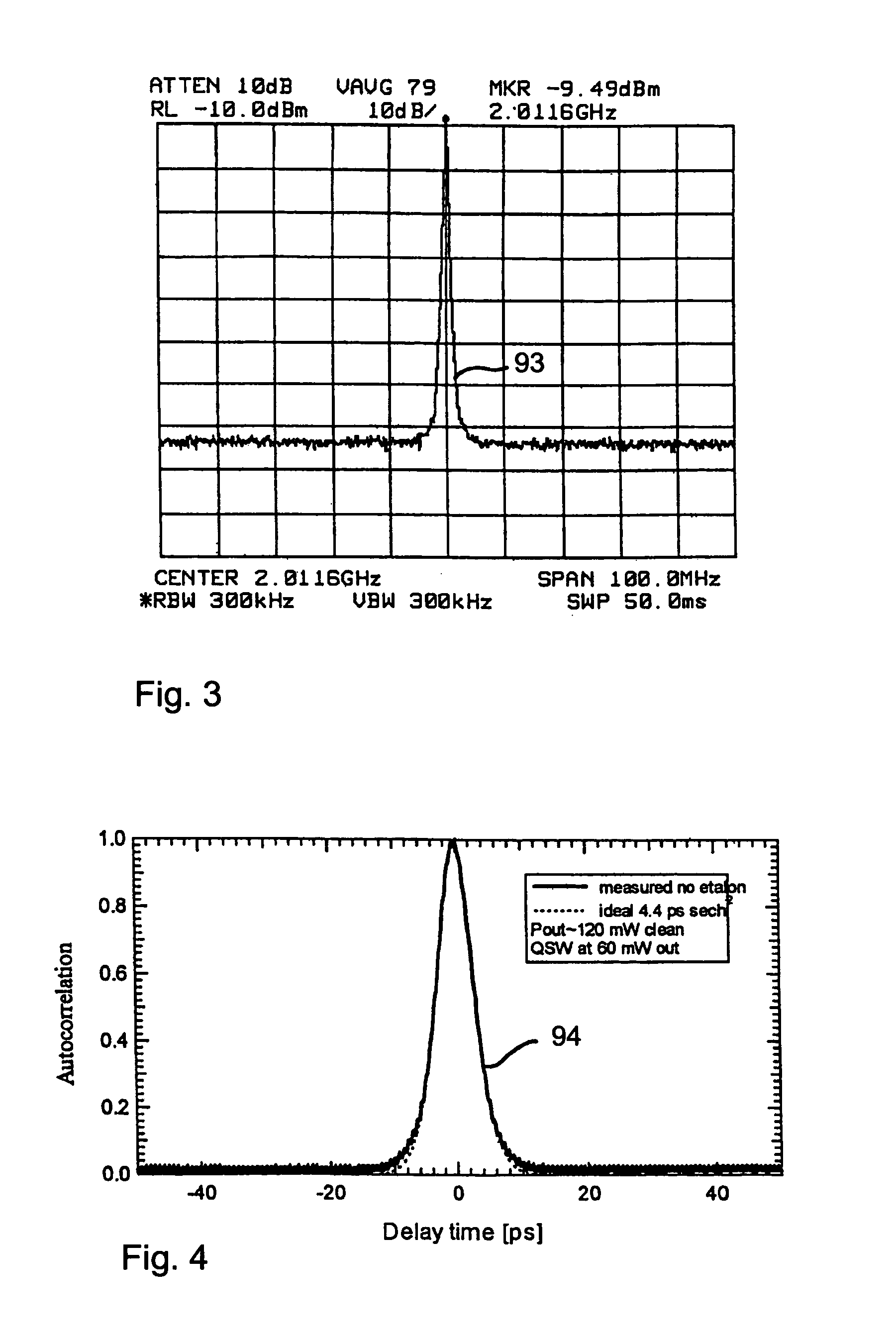
Patents
Literature
446 results about "Stimulated emission" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Stimulated emission is the process by which an incoming photon of a specific frequency can interact with an excited atomic electron (or other excited molecular state), causing it to drop to a lower energy level. The liberated energy transfers to the electromagnetic field, creating a new photon with a phase, frequency, polarization, and direction of travel that are all identical to the photons of the incident wave. This is in contrast to spontaneous emission, which occurs at random intervals without regard to the ambient electromagnetic field.
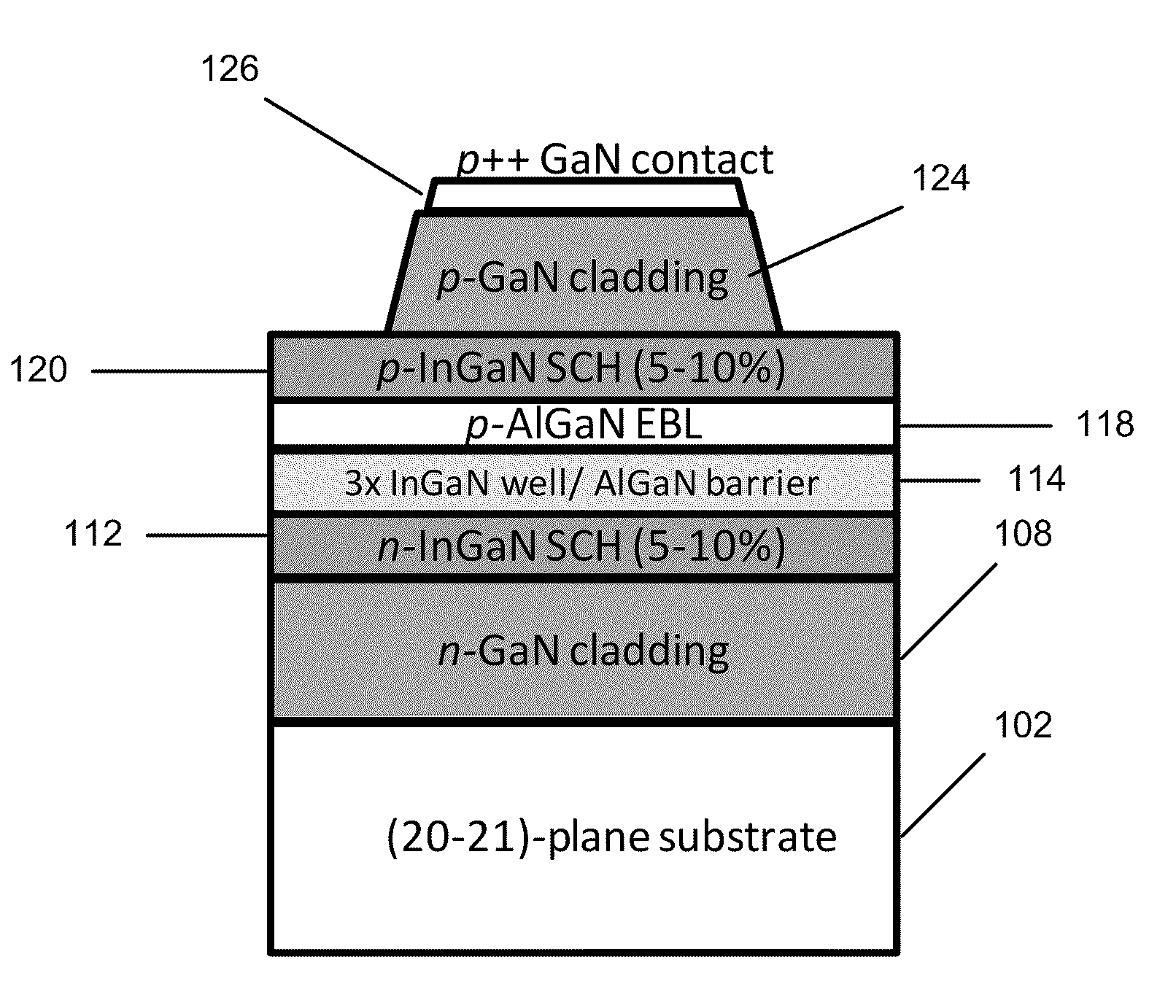
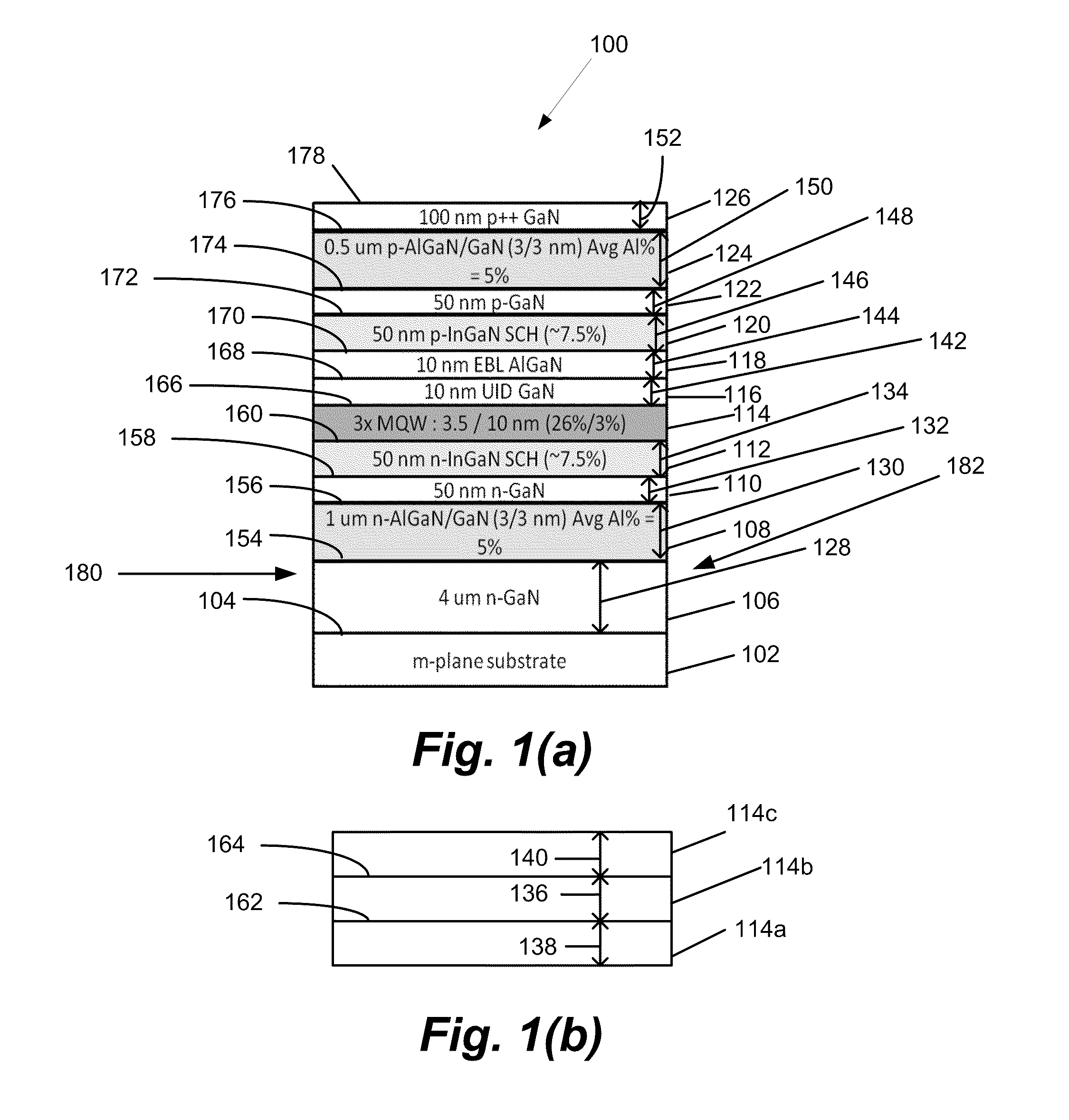
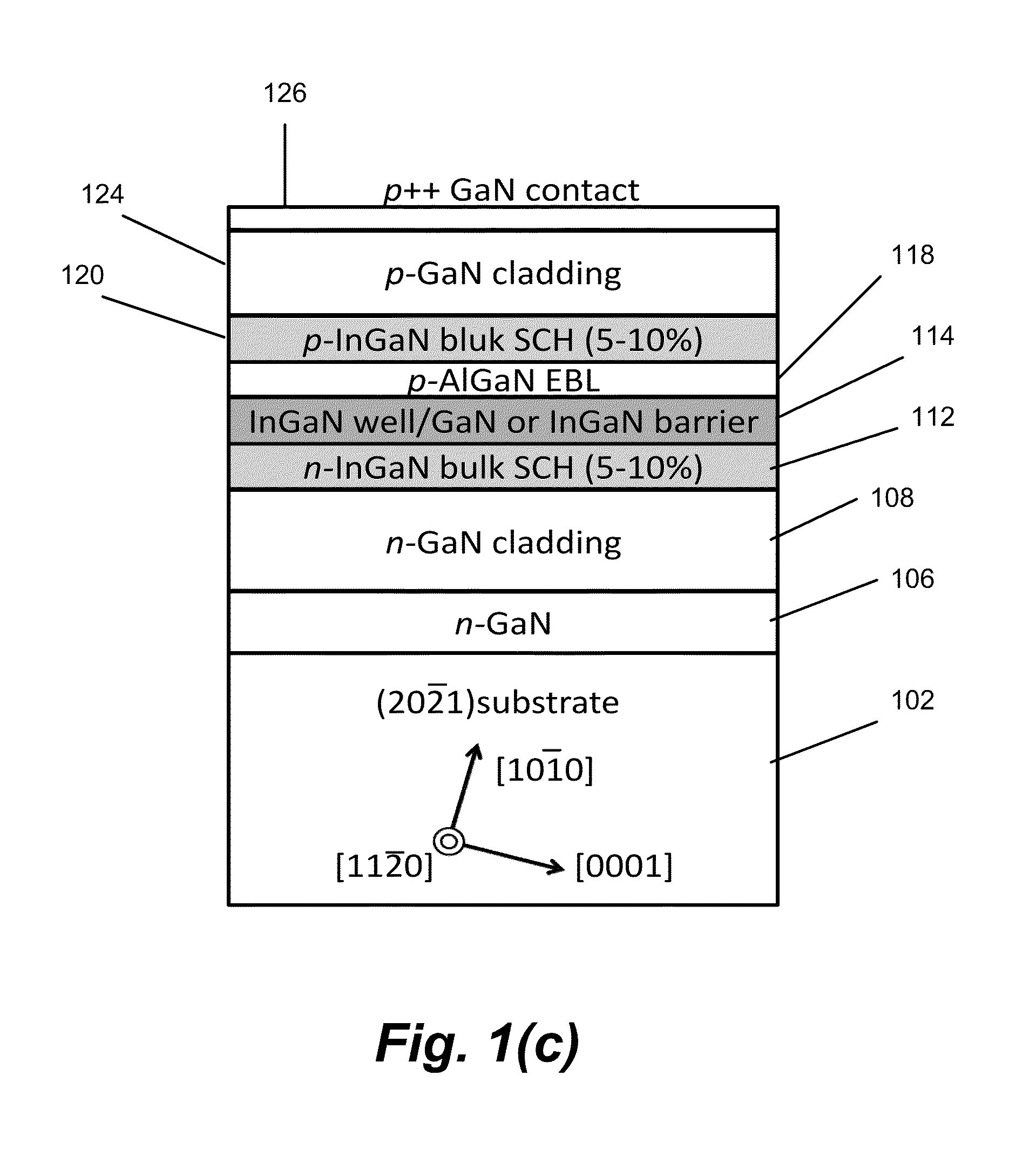
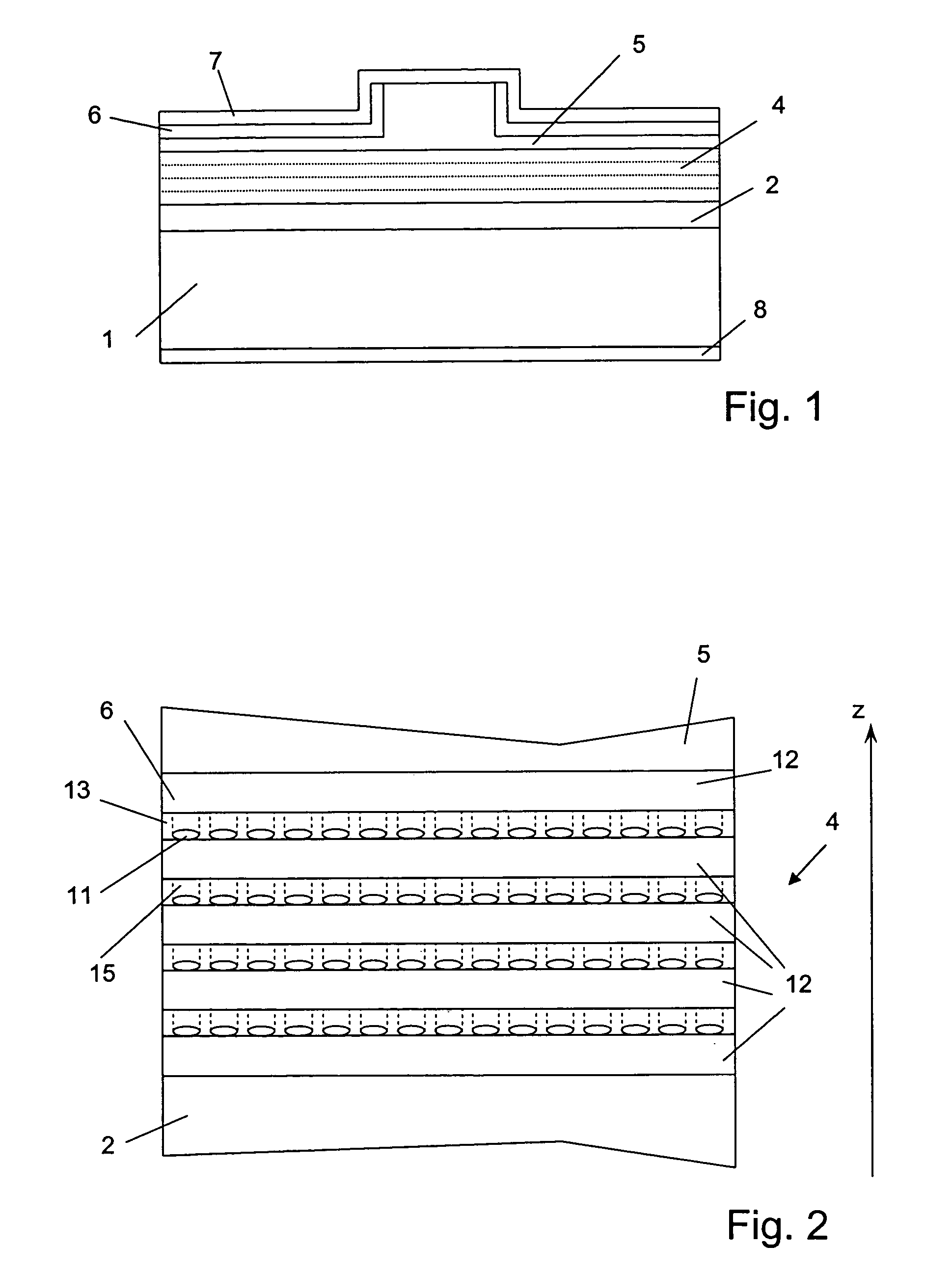
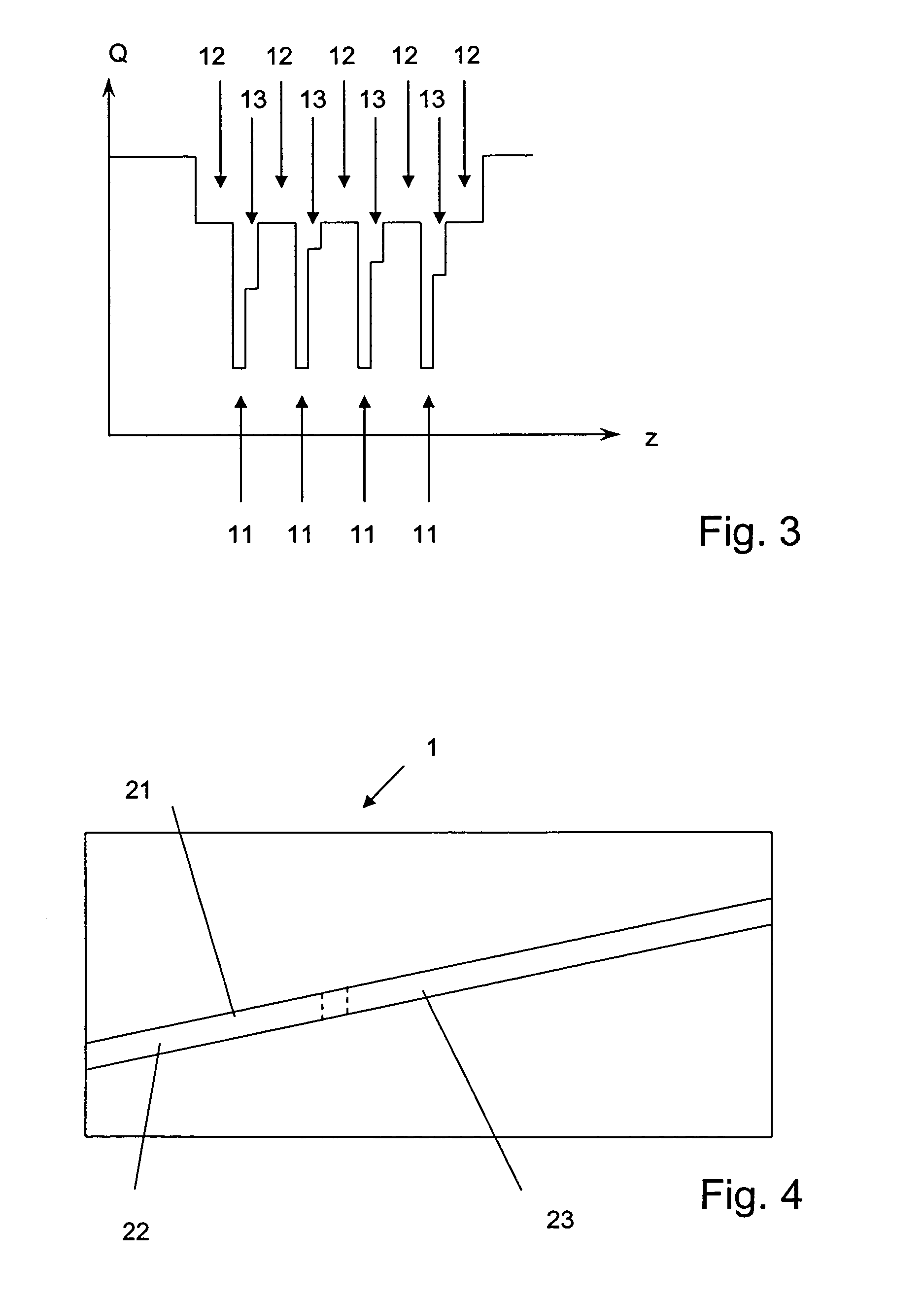
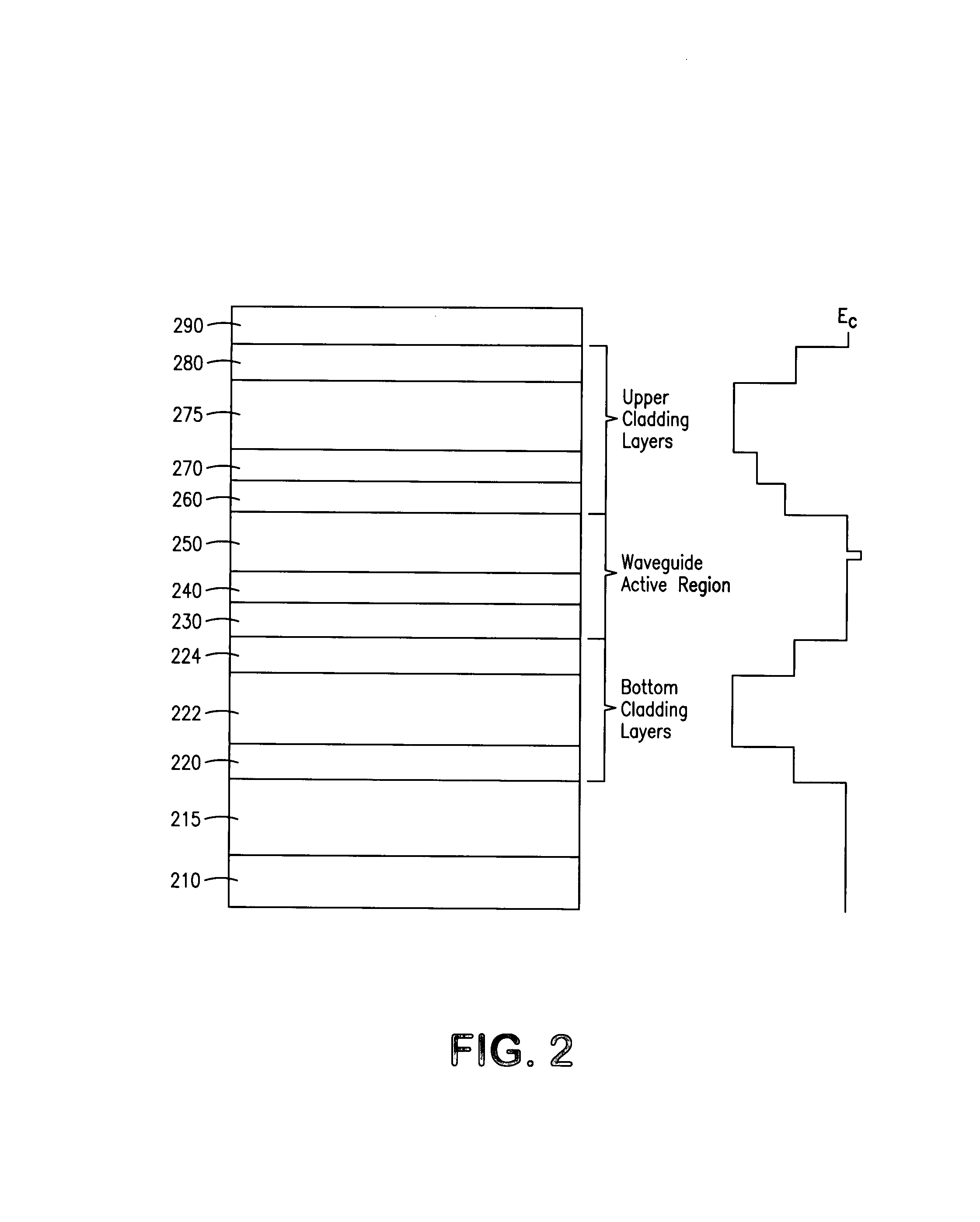
LONG WAVELENGTH NONPOLAR AND SEMIPOLAR (Al,Ga,In)N BASED LASER DIODES
InactiveUS20100309943A1Simple structureImprove electricityOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsContact layerStimulated emission
A laser diode, grown on a miscut nonpolar or semipolar substrate, with lower threshold current density and longer stimulated emission wavelength, compared to conventional laser diode structures, wherein the laser diode's (1) n-type layers are grown in a nitrogen carrier gas, (2) quantum well layers and barrier layers are grown at a slower growth rate as compared to other device layers (enabling growth of the p-type layers at higher temperature), (3) high Al content electron blocking layer enables growth of layers above the active region at a higher temperature, and (4) asymmetric AlGaN SPSLS allowed growth of high Al containing p-AlGaN layers. Various other techniques were used to improve the conductivity of the p-type layers and minimize the contact resistance of the contact layer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Broadband light emitting device
ActiveUS7019325B2Increase heightBroad emission spectrumLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionStimulated emissionP–n junction
The invention concerns a superluminescent light emitting diode (SLED) comprising a semiconductor heterostructure forming a PN junction and a waveguide. The semiconductor heterostructure includes a gain region with a contact means for biasing the PN junction so as to produce light emission including stimulated emission from an active zone of the gain region, and in the active zone a plurality of quantum dot layers, each quantum dot layer made up of a plurality of quantum dots and a plurality of adjoining layers, each adjoining layer adjacent to one of said quantum dot layers. The material composition or a deposition parameter of at least two adjoining layers is different. This ensures an enhanced emission spectral width.
Owner:EXALOS
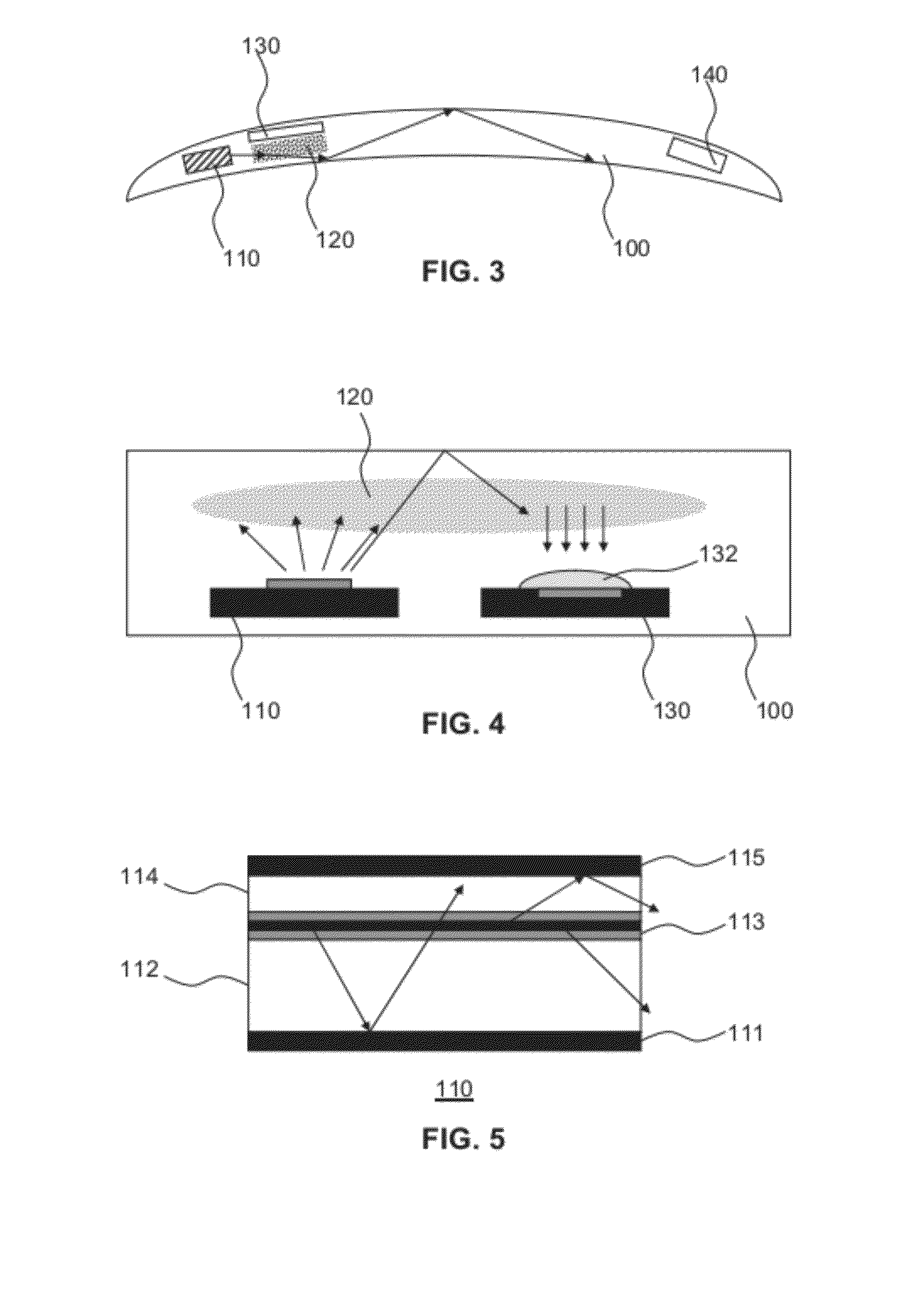
Flexible Eye Insert and Glucose Measuring System
ActiveUS20120259188A1Improve accuracyReduce exposureSolid-state devicesEye treatmentPhotodetectorStimulated emission
Disclosed is a flexible insert (100) for placement on the human eye, comprising a light source (110) in said insert such that light emitted from the light source is shielded from the human eye upon correct placement of the insert on the human eye, a light-responsive material (120) placed in the light path of the light source, said light-responsive material emitting light upon stimulation by the light from said light source, the intensity of said stimulated emission being sensitive to a chemical interaction of the light-sensitive material with an analyte of interest, a photodetector (130) for detecting the light emitted by the light-responsive material; and a transmitter (140) coupled to the photodetector for transmitting a photodetector reading. The insert may be used in conjunction with a reader for automated monitoring of an analyte of interest such as glucose in the tear fluid of its wearer.
Owner:NXP BV
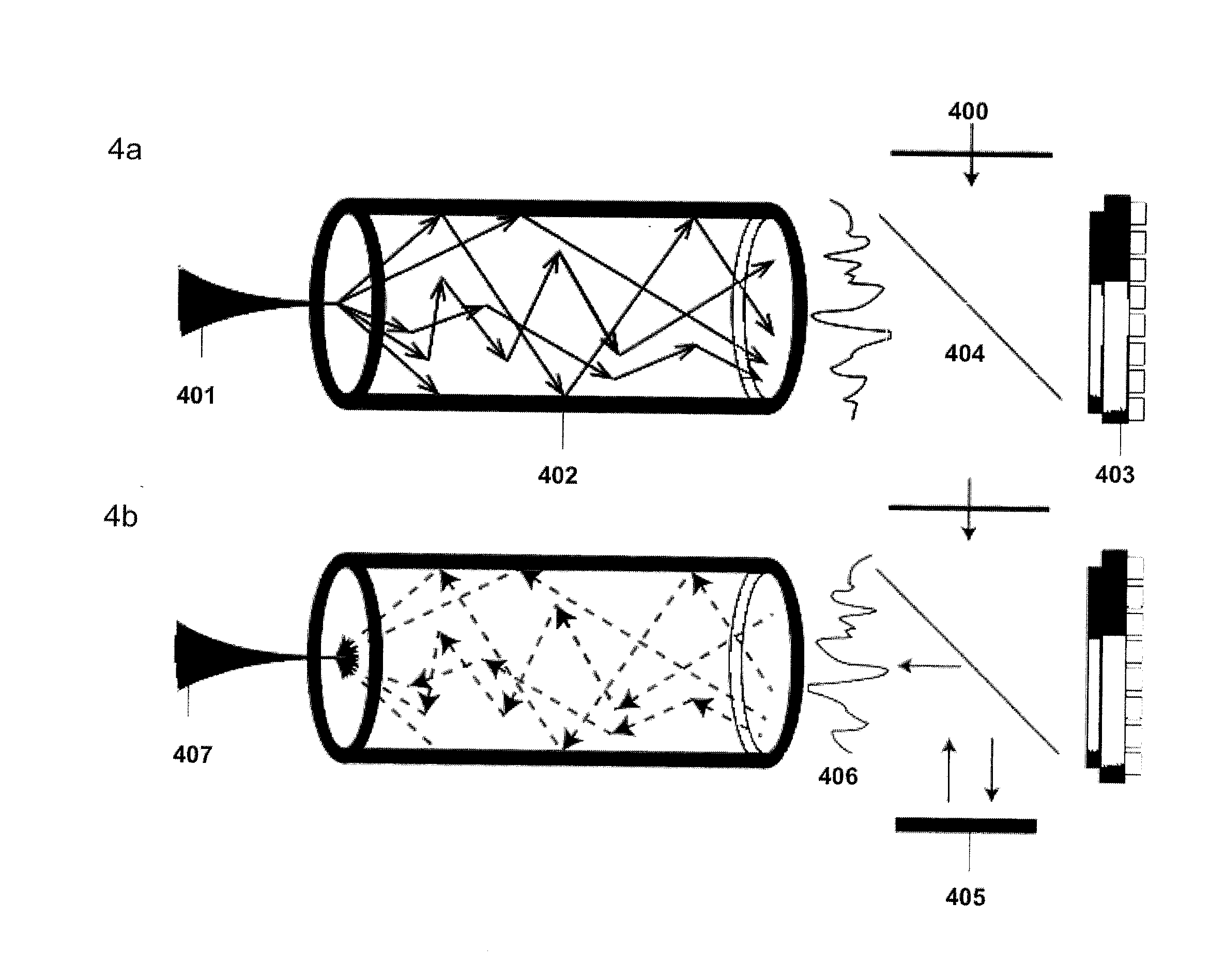
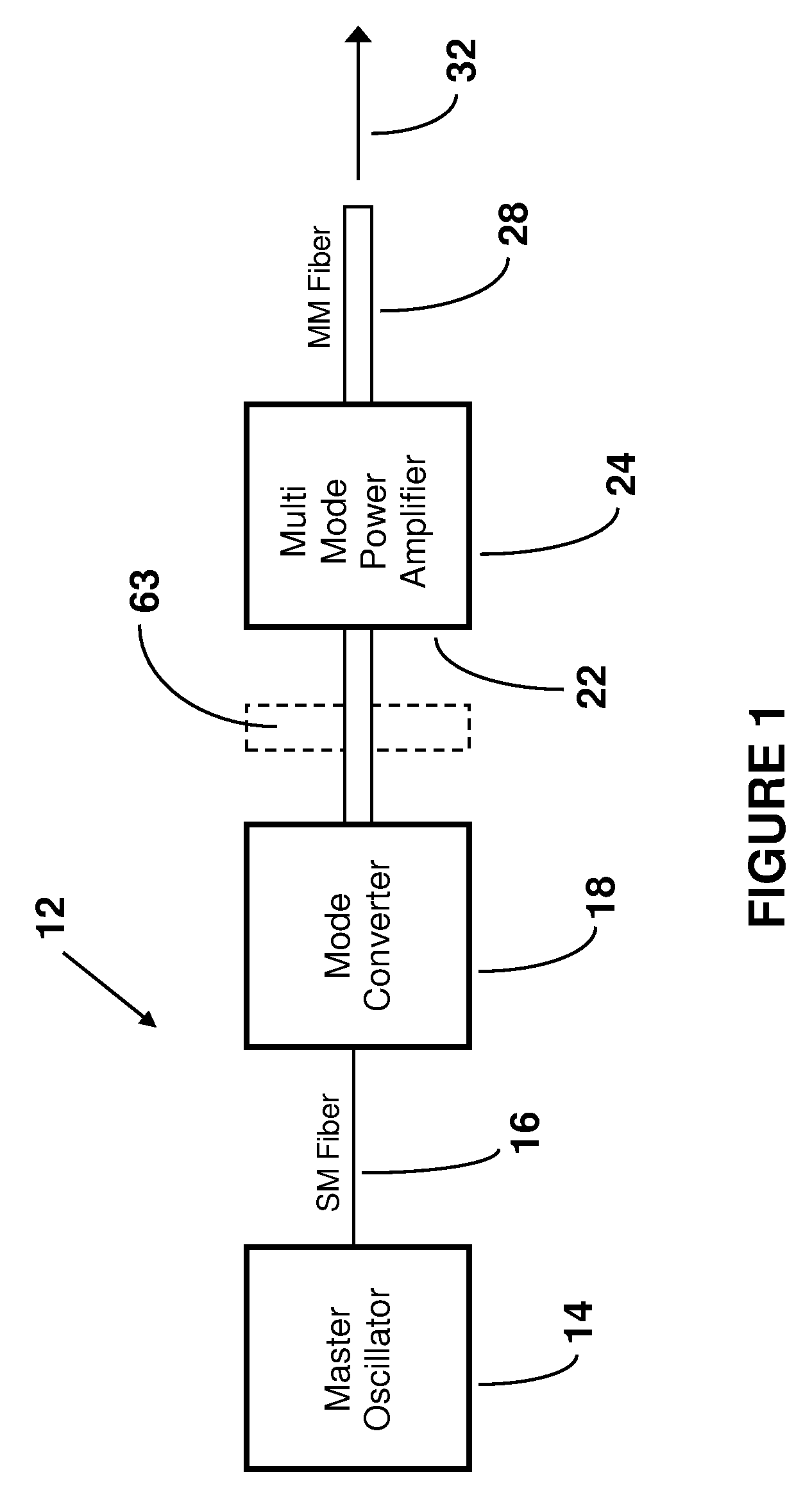
Methods and apparatus for imaging with multimode optical fibers
ActiveUS20150015879A1Radiation pyrometryOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingLight dispersionImage resolution
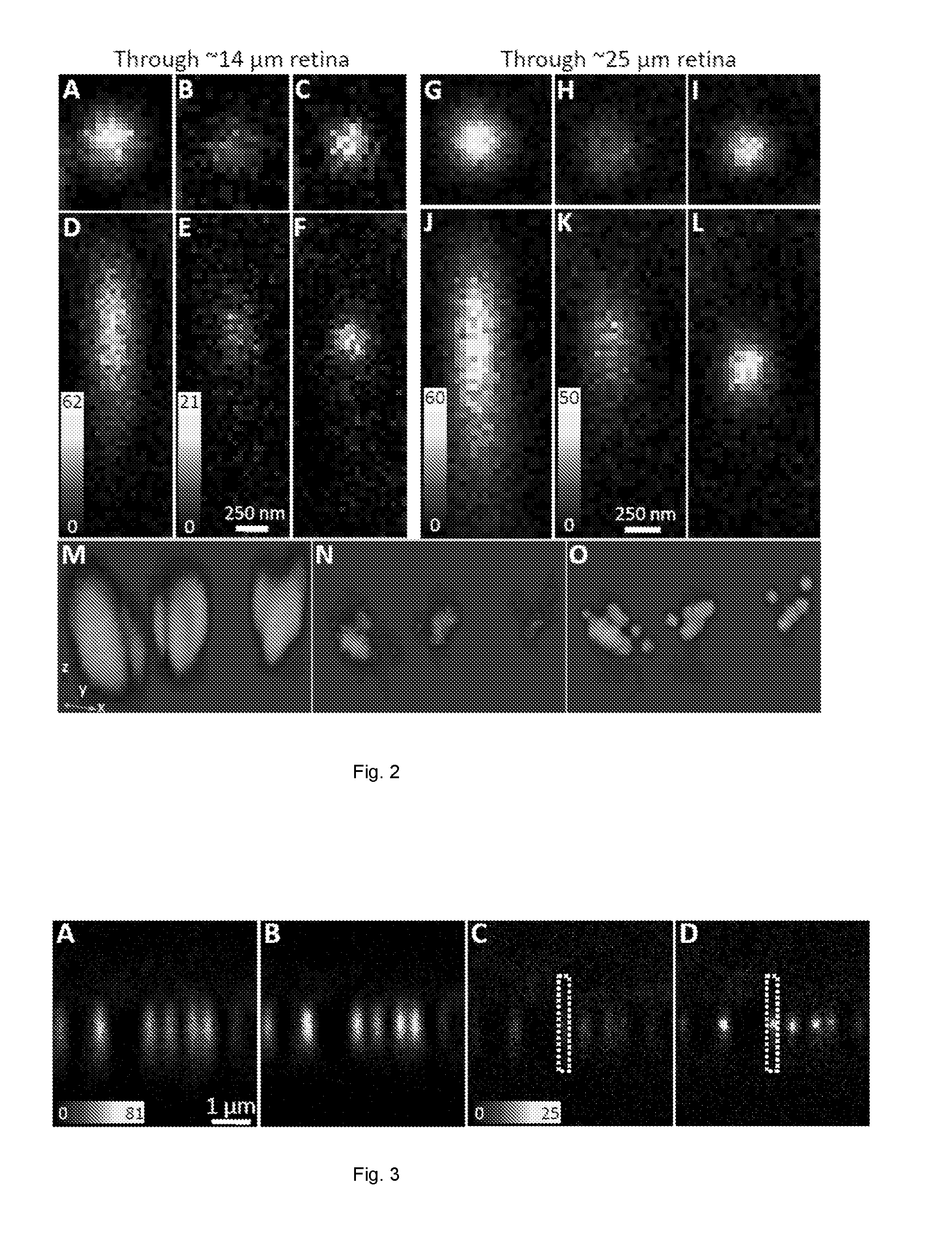
A multimode waveguide illuminator and imager relies on a wave front shaping system that acts to compensate for modal scrambling and light dispersion by the multimode waveguide. A first step consists of calibrating the multimode waveguide and a second step consists in projecting a specific pattern on the waveguide proximal end in order to produce the desire light pattern at its distal end. The illumination pattern can be scanned or changed dynamically only by changing the phase pattern projected at the proximal end of the waveguide. The third and last step consists in collecting the optical information, generated by the sample, through the same waveguide in order to form an image. Known free space microscopy technique can be adapted to endoscopy with multimode waveguide, such as, but not limited to, fluorescence imaging or Raman spectroscopy or imaging, 3D linear scattering imaging or two-photon imaging. Super-resolution, i.e., resolution below the diffraction limit, is achieved for example but not limited to, using the STimulated Emission Depletion microscopy (STED) technique or the Structured Illumination Microscopy (SIM) technique or a stochastic illumination based method (PALM, STORM) in combination with the multimode waveguide imaging method.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Light source apparatus and optical communication module comprising it
ActiveUS20050226636A1Small sizeLow costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor laser optical deviceHigh densityMagnifying glass
A light source device for radiating a stimulated emission from a semiconductor laser to outside via a multiple scattering optical system, which system has a first region located adjacent to the semiconductor laser and a second region that abuts on the first region and reaches the outside. The first region contains scatterers at a higher density than the second region does. The light source device has an amount of near-field pattern speckles σPAR of 3×10−3 or more. The second region may have a lens portion as a magnifier for at least a principle part of a secondary planar light source formed at an interface between the first and second regions.
Owner:SHARP FUKUYAMA LASER CO LTD
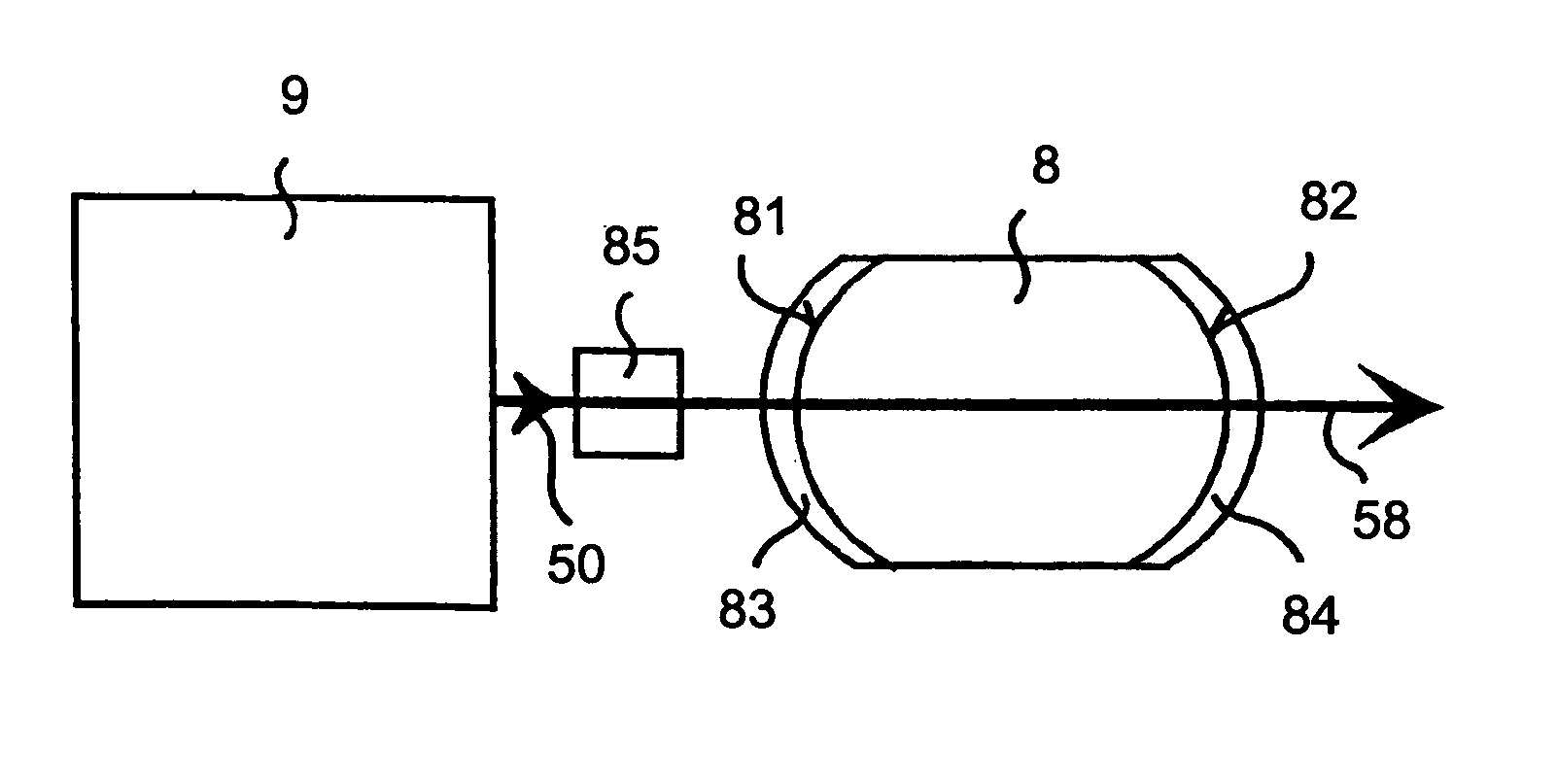
Optical fiber laser, and components for an optical fiber laser, having reduced susceptibility to catastrophic failure under high power operation
ActiveUS20090080835A1Avoid damageReduce susceptibilityLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingStimulated emissionInterconnection
Optical fiber lasers and components for optical fiber laser. An optical fiber laser can comprise a fiber laser cavity having a wavelength of operation at which the cavity provides output light, the cavity including optical fiber that guides light having the wavelength of operation, the fiber having first and second lengths, the first length having a core having a V-number at the wavelength of operation and a numerical aperture, the second length having a core that is multimode at the wavelength of operation and that has a V-number that is greater than the V-number of the core of the first length optical fiber at the wavelength of operation and a numerical aperture that is less than the numerical aperture of the core of the first length of optical fiber. At least one of the lengths comprises an active material that can provide light having the wavelength of operation via stimulated emission responsive to the optical fiber receiving pump light. Components include a mode field adapter and optical fiber interconnection apparatus, which can be used to couple the first and second lengths of optical fiber, or can couple the fiber laser to an optical fiber power amplifier, which can be a multimode or single mode amplifier.
Owner:NUFERN
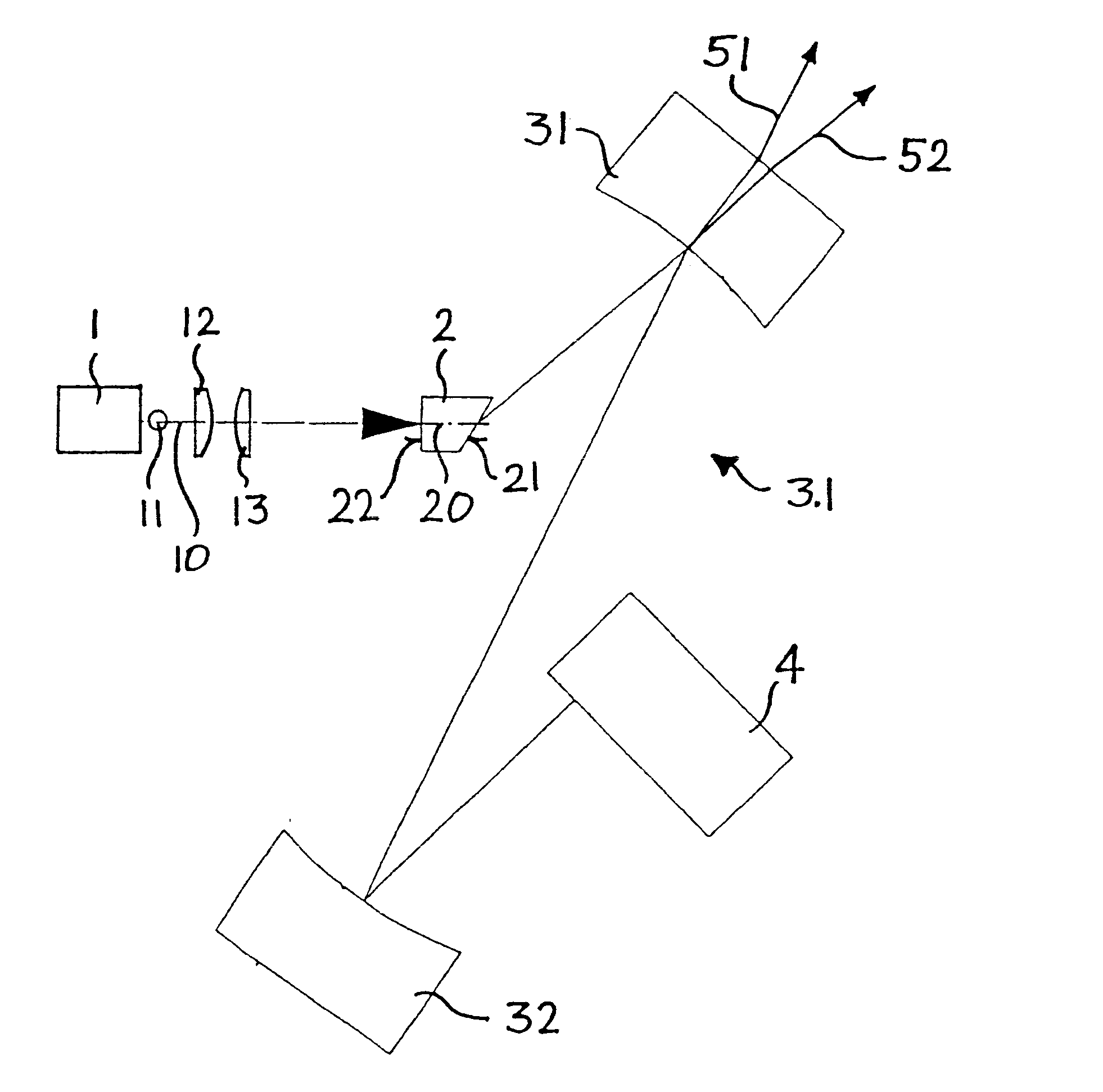
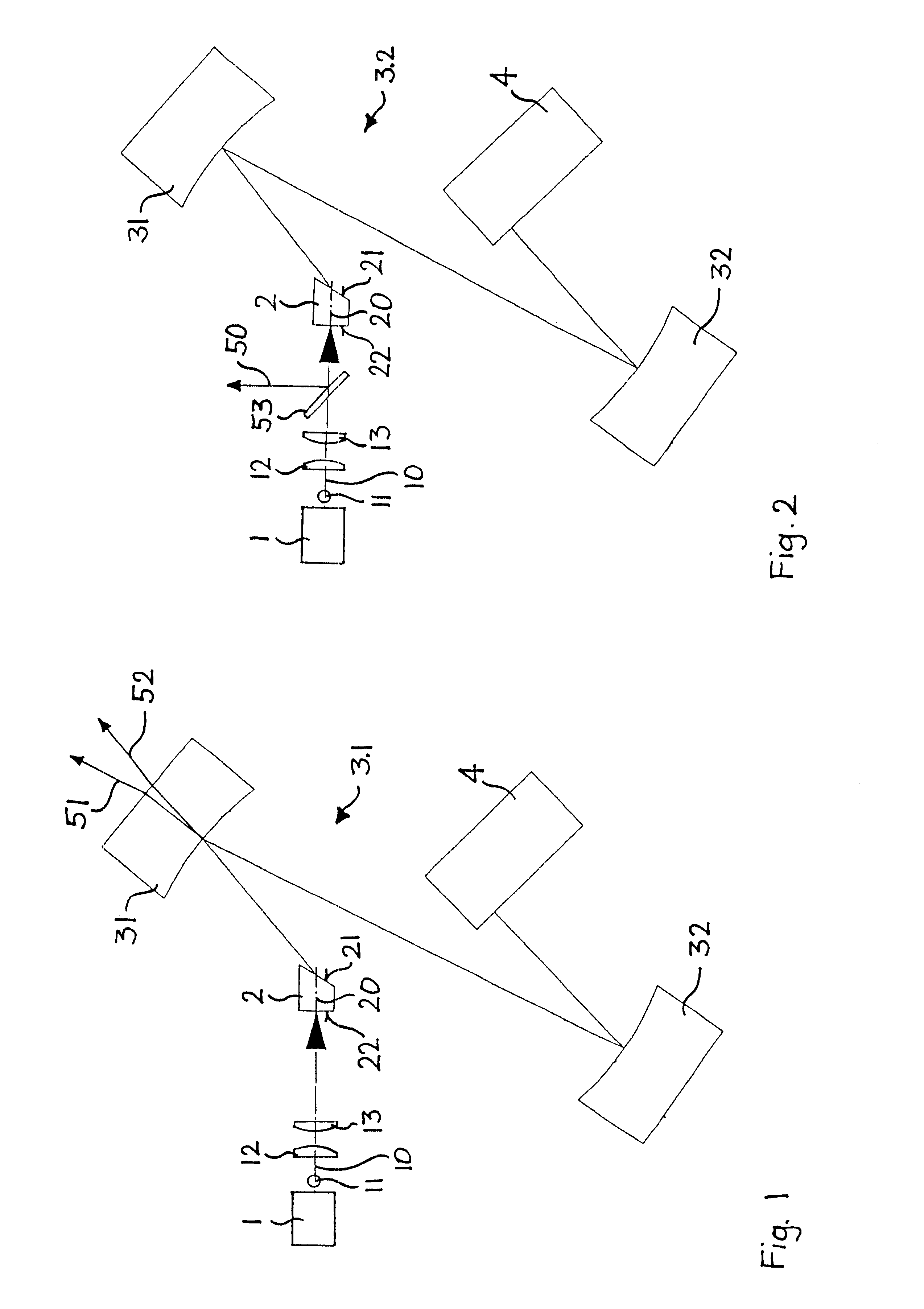
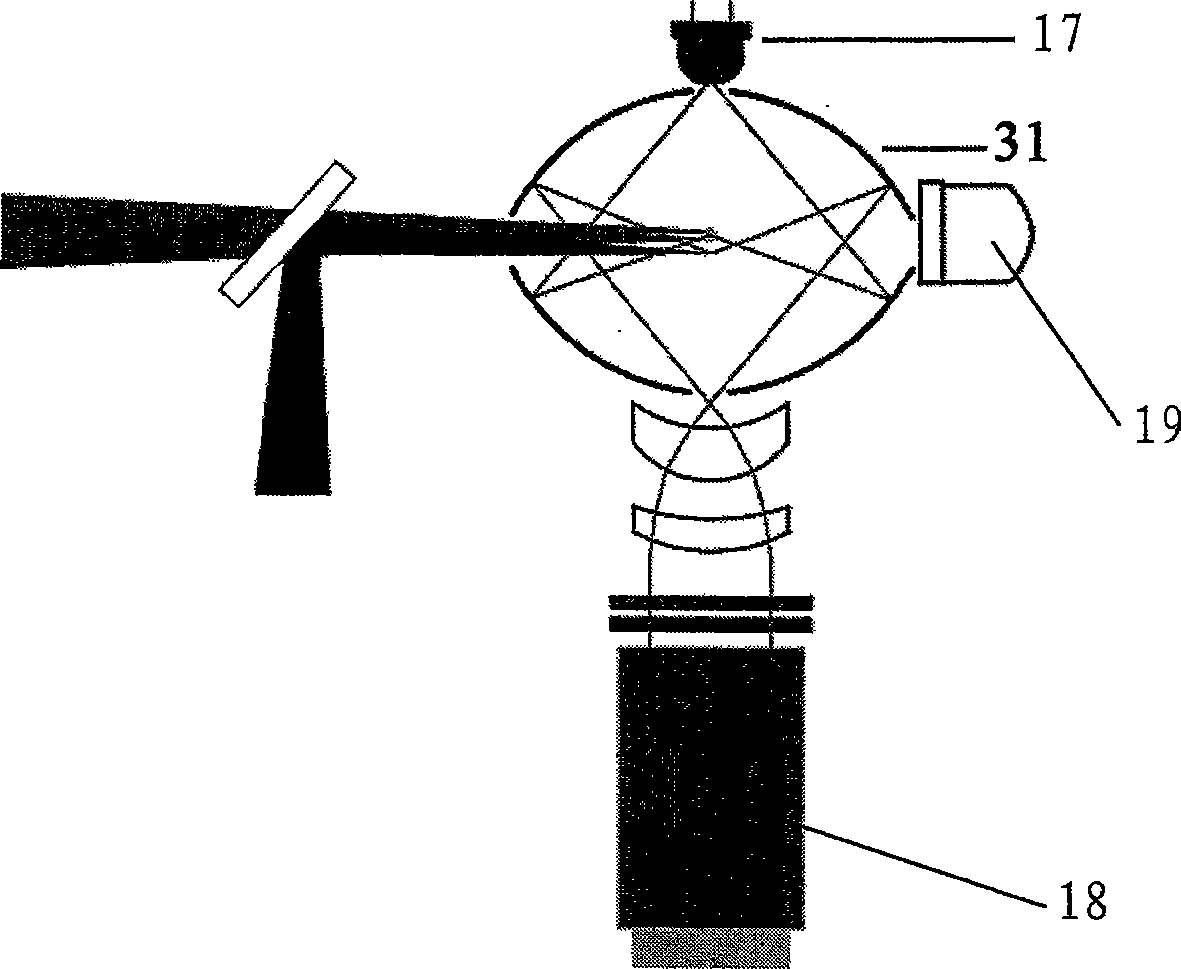
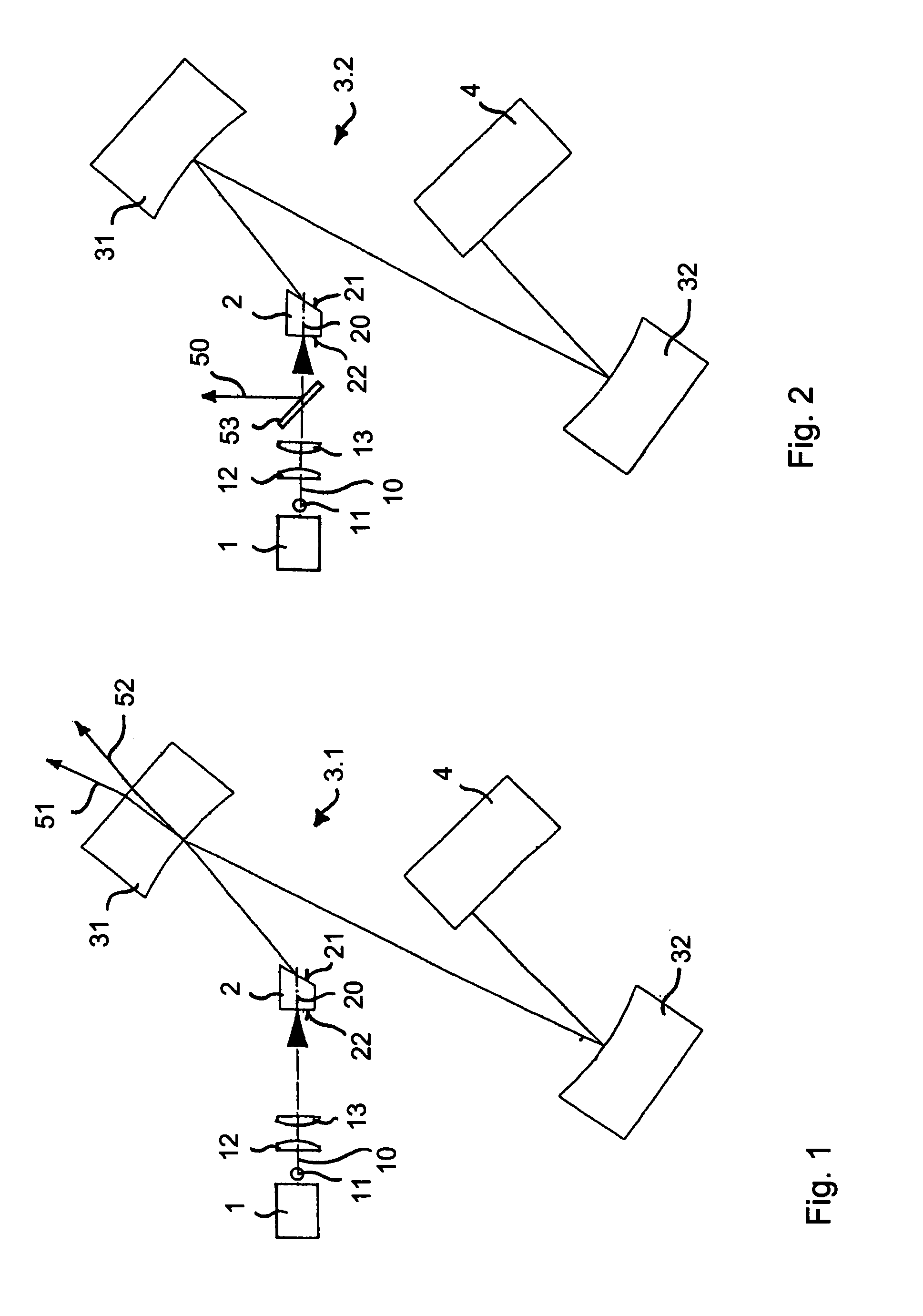
High-repetition rate passively mode-locked solid-state laser
InactiveUS6393035B1Simple designOptical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersOptical probingMode-locking
A passively mode-locked solid-state laser for emitting a continuous-wave train of electromagnetic-radiation pulses, the fundamental repetition rate of the emitted pulses exceeding 1 GHz, without Q-switching has an optical resonator, a solid-state laser gain element placed inside the optical resonator, an exciter for exciting said laser gain element to emit electromagnetic radiation having the effective wavelength, and a saturable absorber for passive mode locking. The laser gain element preferably consists of a laser material with a stimulated emission cross section exceeding 0.8x10-18 cm-2 at the effective wavelength. Typically, the laser gain element is made of Nd:vanadate. The saturable absorber is preferably a semiconductor saturable absorber mirror device. The laser is simple, robust, compact, efficient, and low-cost. It generates a relatively large average power of 100 mW and higher, which is useful for a number of optical probing and detection applications, in a beam which is substantially a fundamental spatial mode.
Owner:LUMENTUM SWITZERLAND AG
Remote-phosphor led downlight
ActiveUS20090273918A1Low concentration of heatImprove cooling effectPoint-like light sourceLighting heating/cooling arrangementsPhosphorLight beam
Owner:SEOUL SEMICONDUCTOR
Remote-phosphor LED downlight
ActiveUS8016443B2Easy to handleAvoid high concentrationsPoint-like light sourceLighting heating/cooling arrangementsPhosphorLight beam
An embodiment of a collimating downlight has front-mounted blue LED chips facing upwards, having a heat sink on the back of the LED chips exposed in ambient air. The LED chips are mounted in a collimator that sends their blue light to a remote phosphor situated near the top of the downlight can. Surrounding the remote phosphor is a downward-facing reflector that forms a beam from its stimulated emission and reflected blue light. The phosphor thickness and composition can be adjusted to give a desired color temperature.
Owner:SEOUL SEMICONDUCTOR
Semiconductor device and mehtod
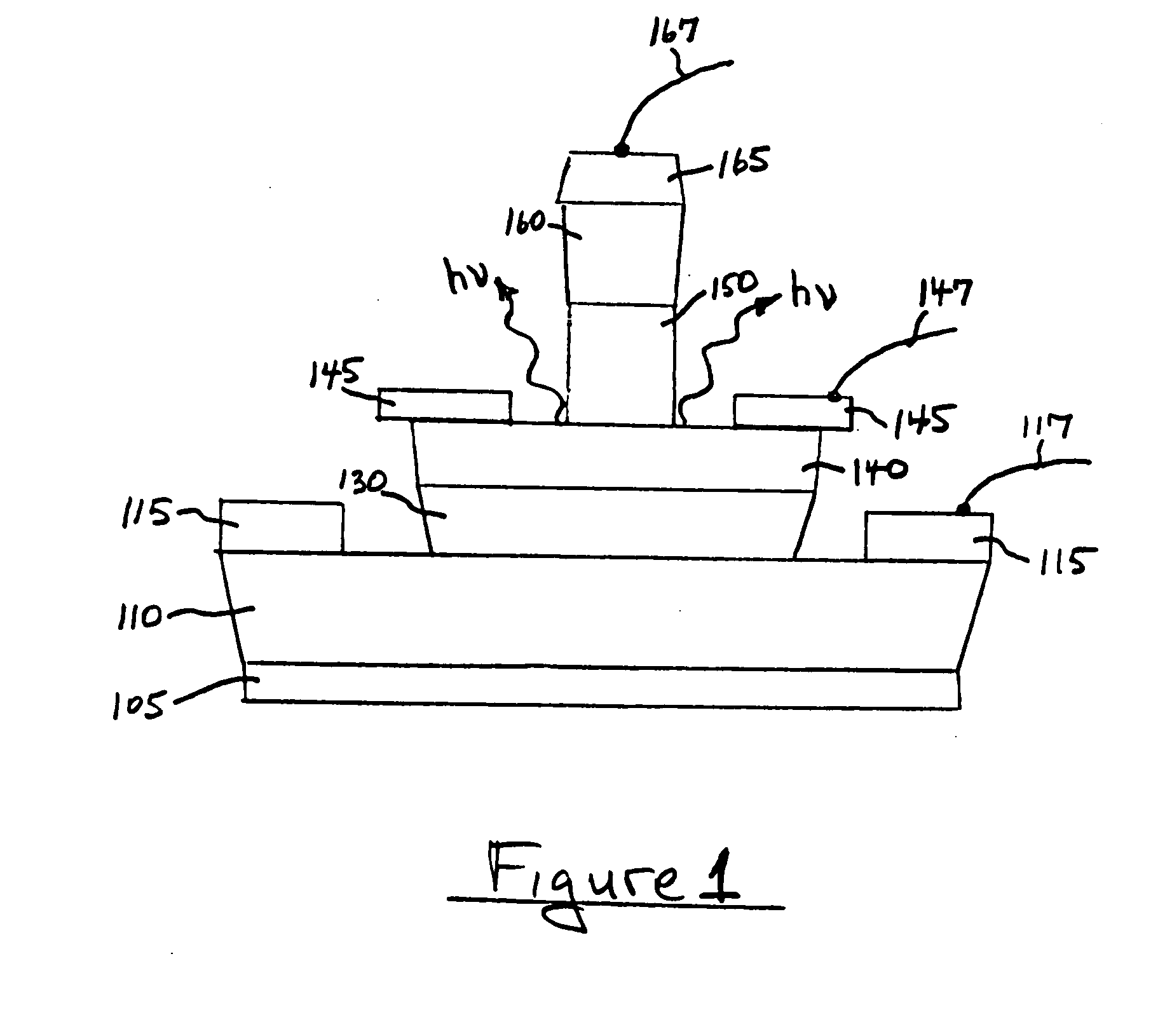
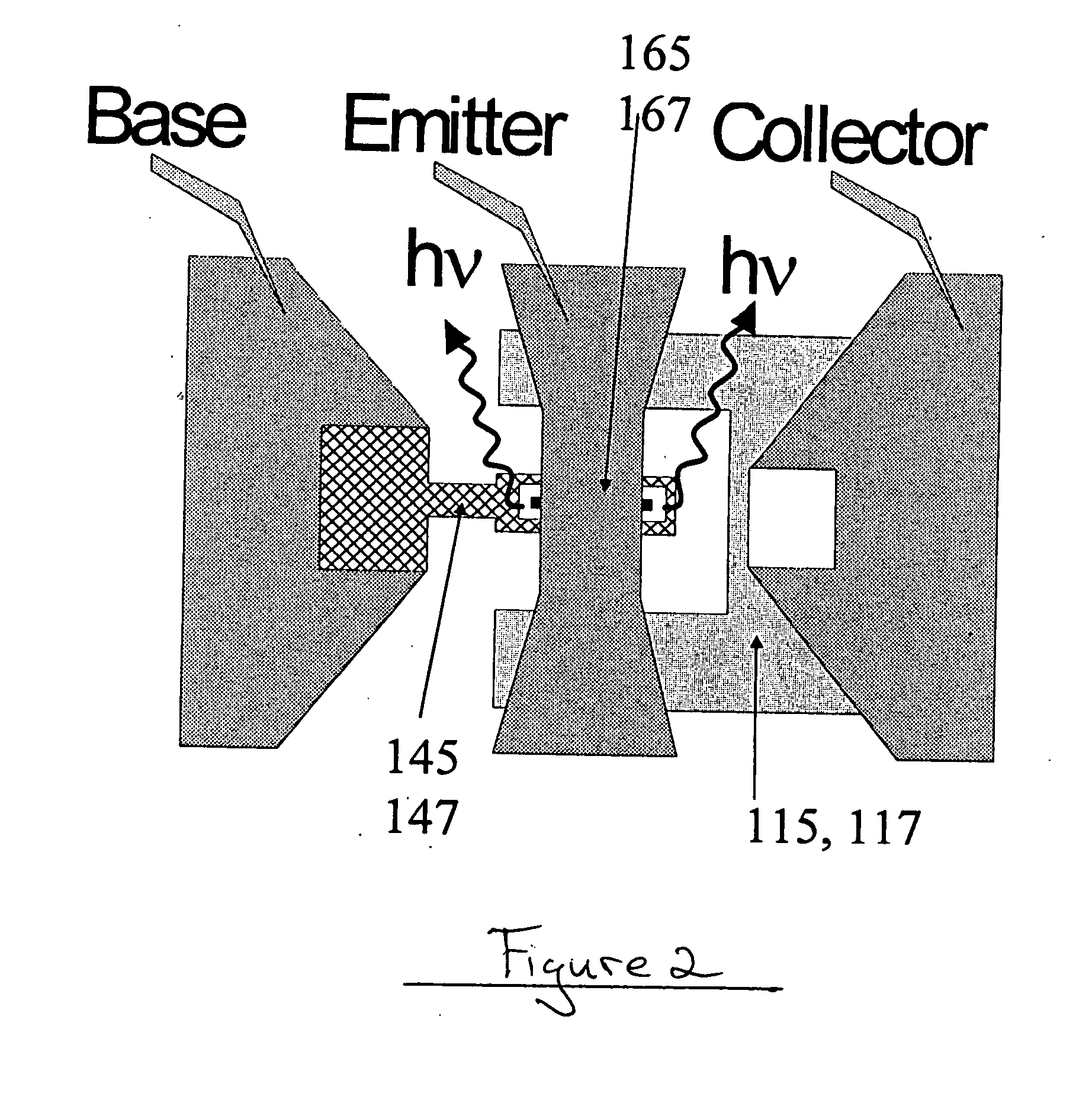
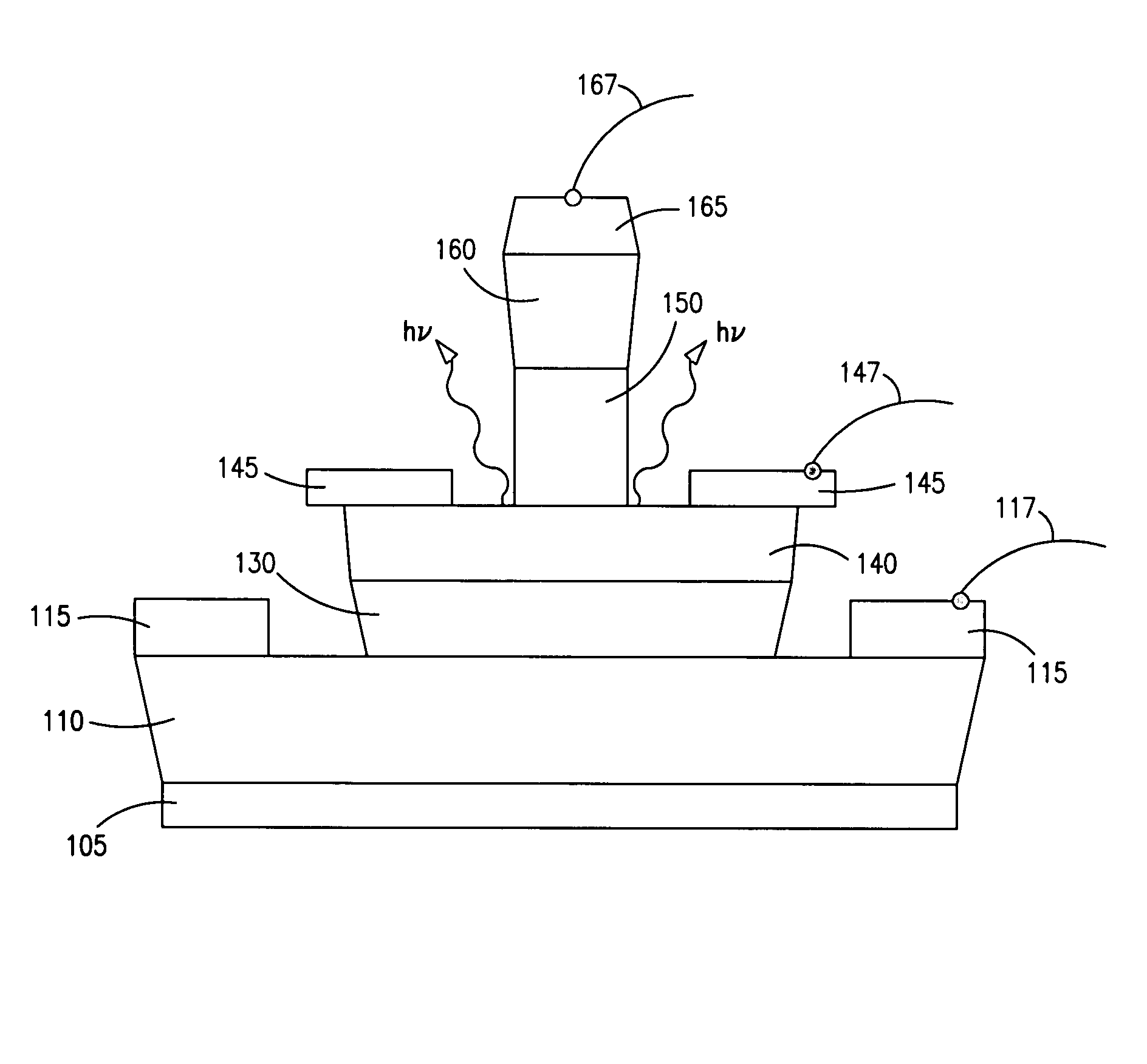
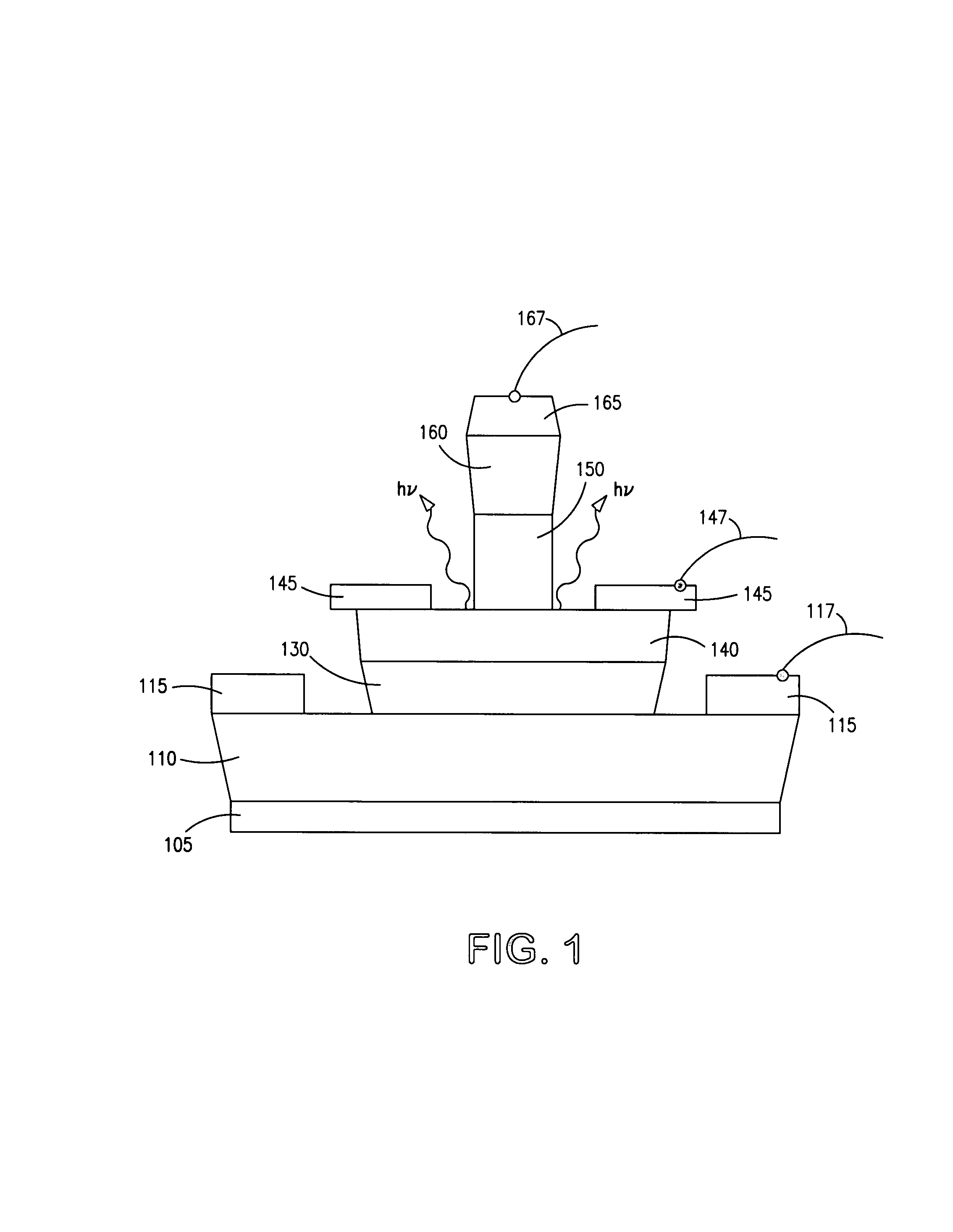
ActiveUS20050054172A1Increase speedImprove mobilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialStimulated emission
A method for increasing the speed of a bipolar transistor, includes the following steps: providing a bipolar transistor having emitter, base, and collector regions; providing electrodes for coupling electrical signals with the emitter, base, and collector regions; and adapting the base region to enhance stimulated emission to the detriment of spontaneous emission, so as to reduce carrier recombination lifetime in the base region.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Semiconductor laser devices and methods
InactiveUS7286583B2Increase speedImprove mobilityLaser detailsNanoopticsResonant cavitySemiconductor materials
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
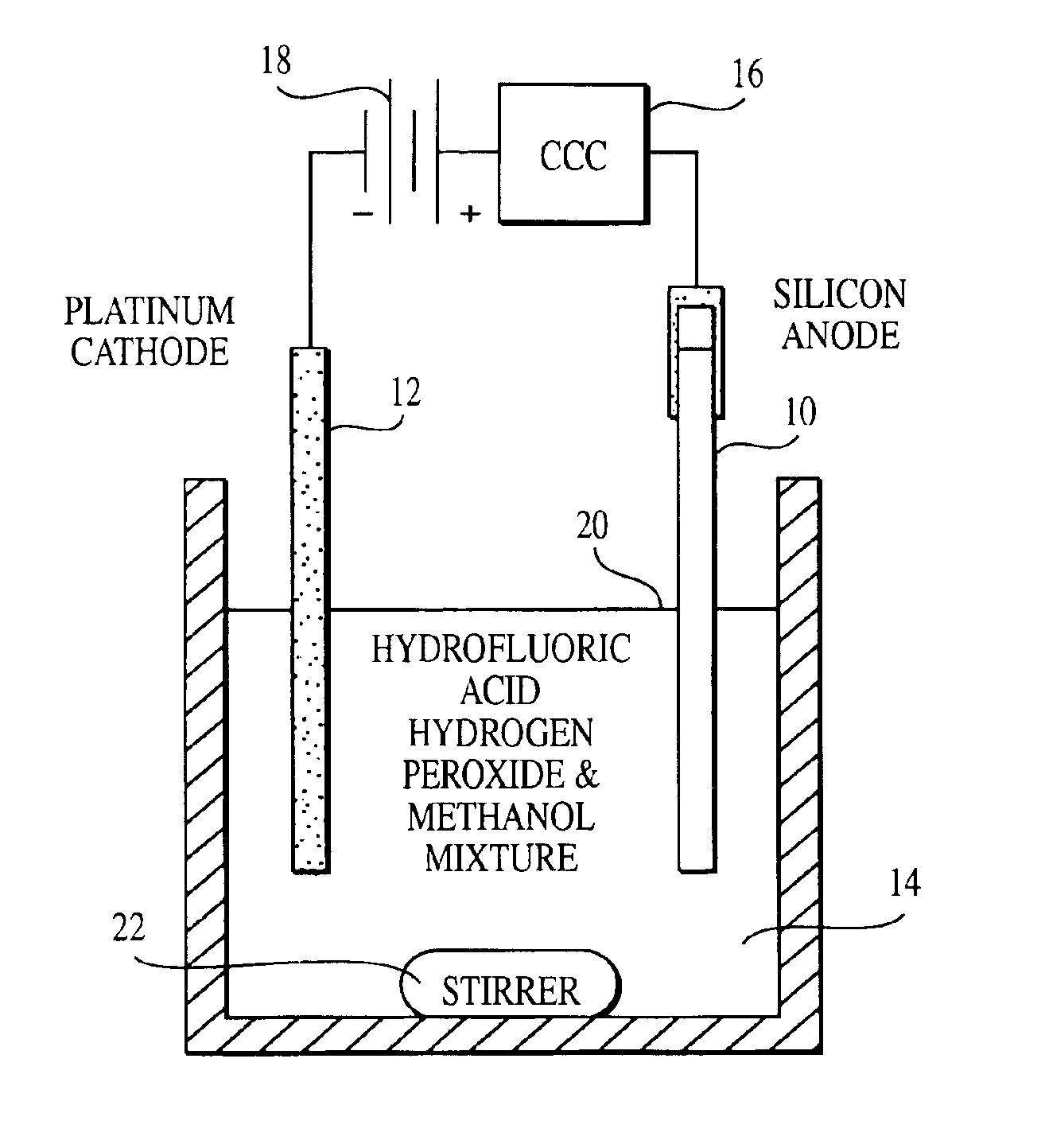
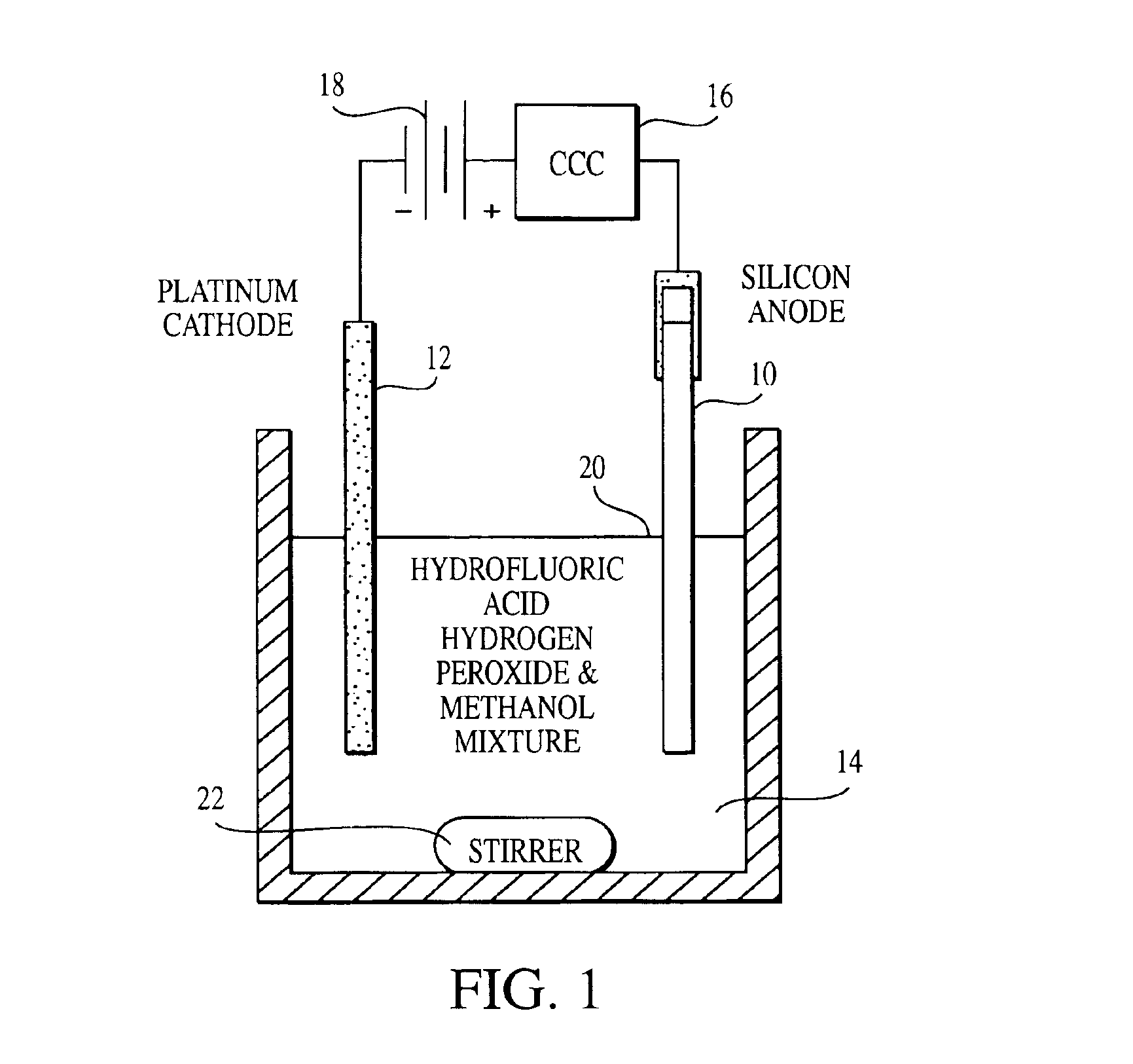
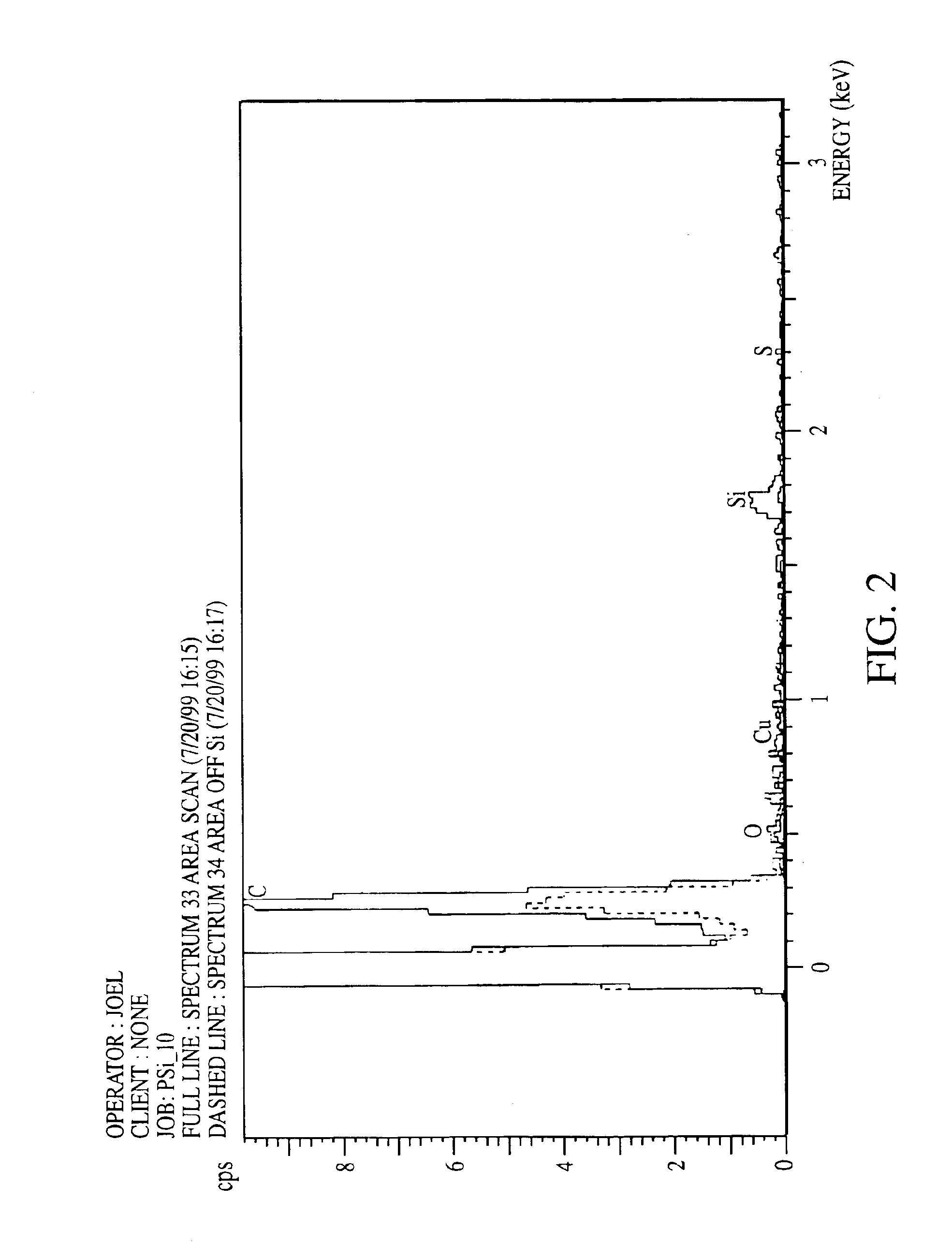
Silicon nanoparticle and method for producing the same
InactiveUS6846474B2Highly uniform in sizeEasily filtered outMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureNanoparticleColloid
Highly uniform 1 nm silicon nanoparticles are provided by the invention. The nanoparticles exhibit beneficial properties. They are a source of stimulated emissions. They may be suspended in liquids, and solids. They can be formed into crystals, colloids and films. The nanoparticles of the invention are about 1 nm having about only one part in one thousand greater than 1 nm. A method for producing the silicon nanoparticle of the invention is a gradual advancing electrochemical etch of bulk silicon. Separation of nanoparticles from the surface of the silicon may also be conducted. Once separated, various methods may be employed to form plural nanoparticles into colloids, crystals, films and other desirable forms. The particles may also be coated or doped.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
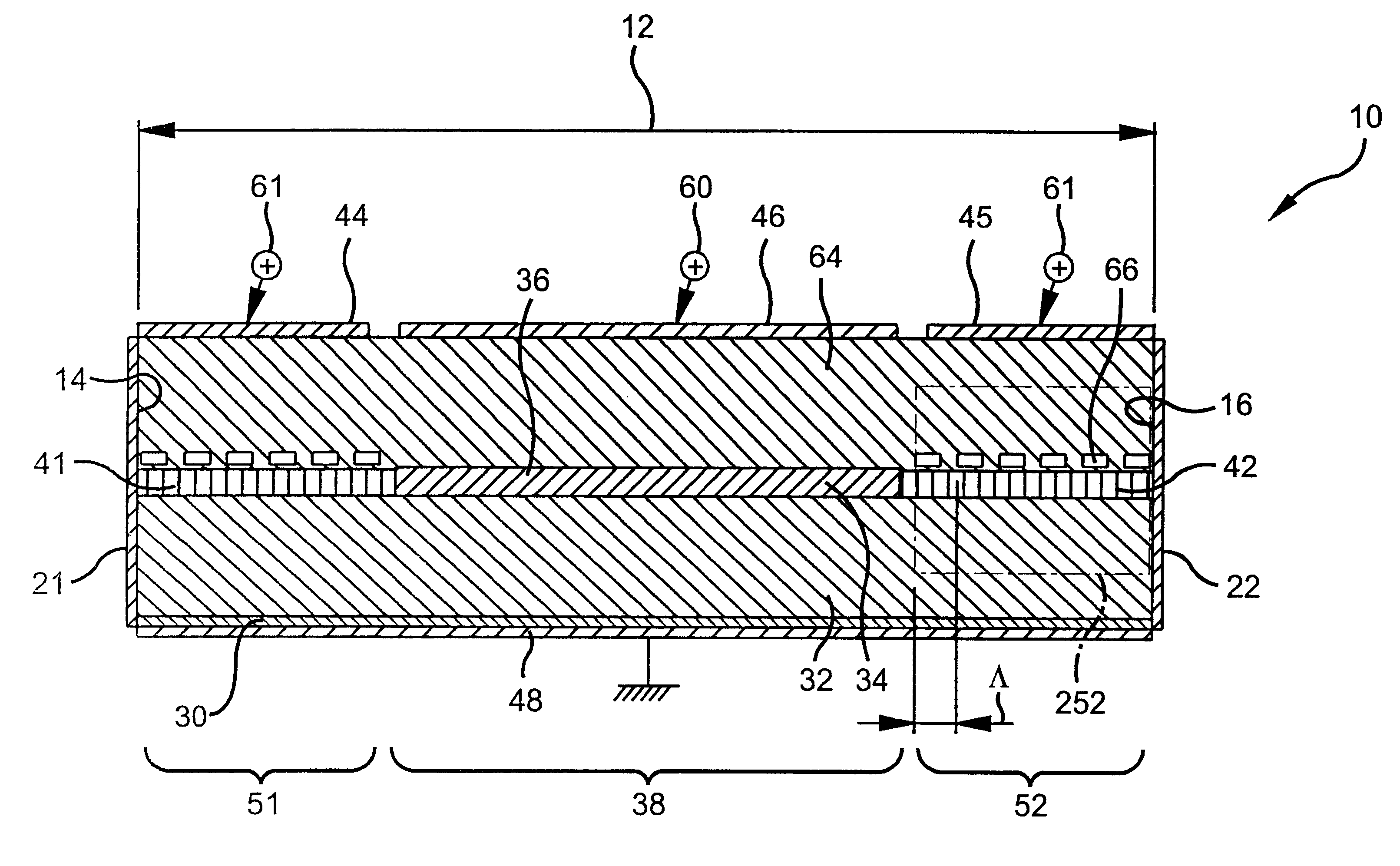
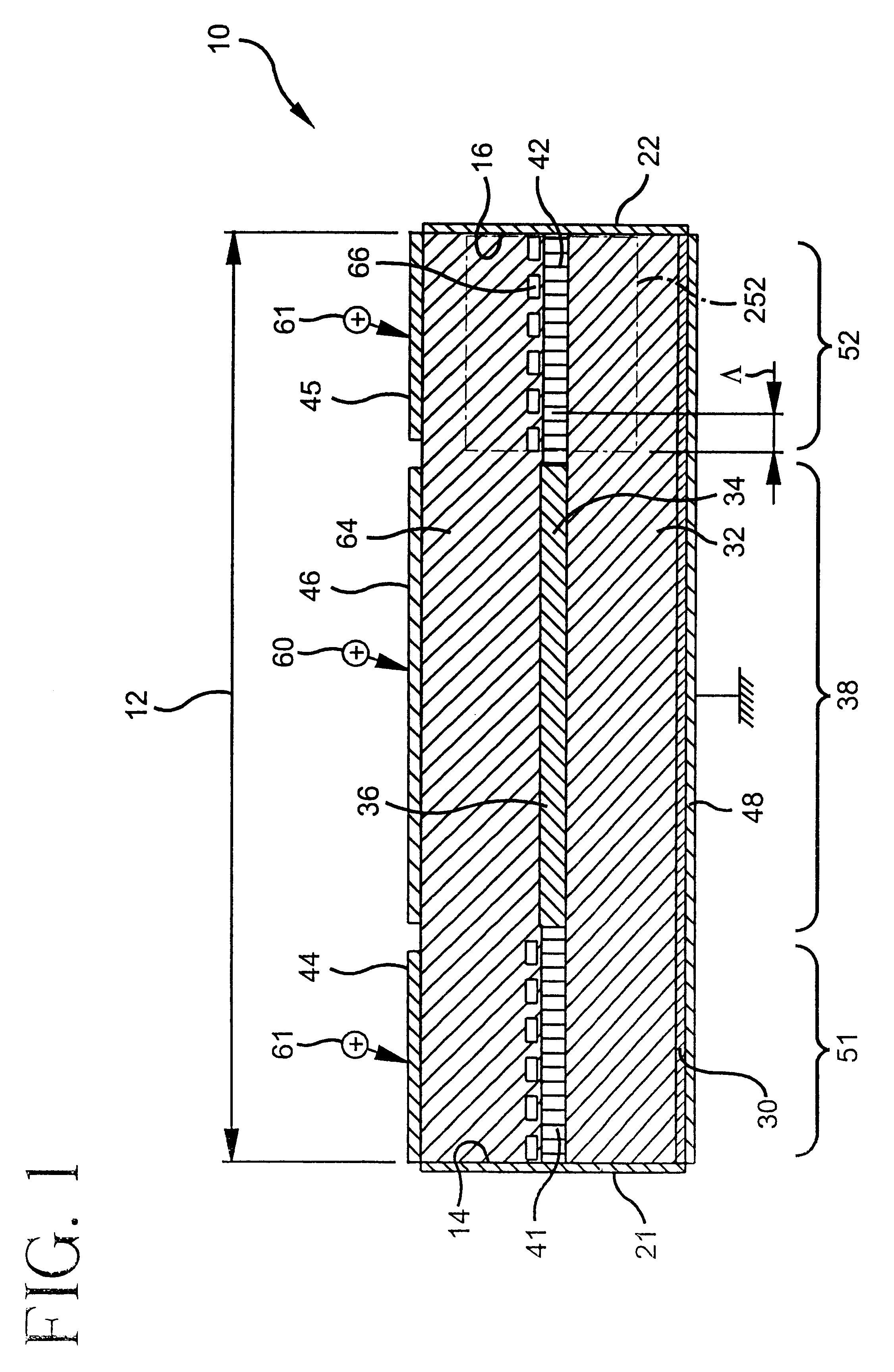
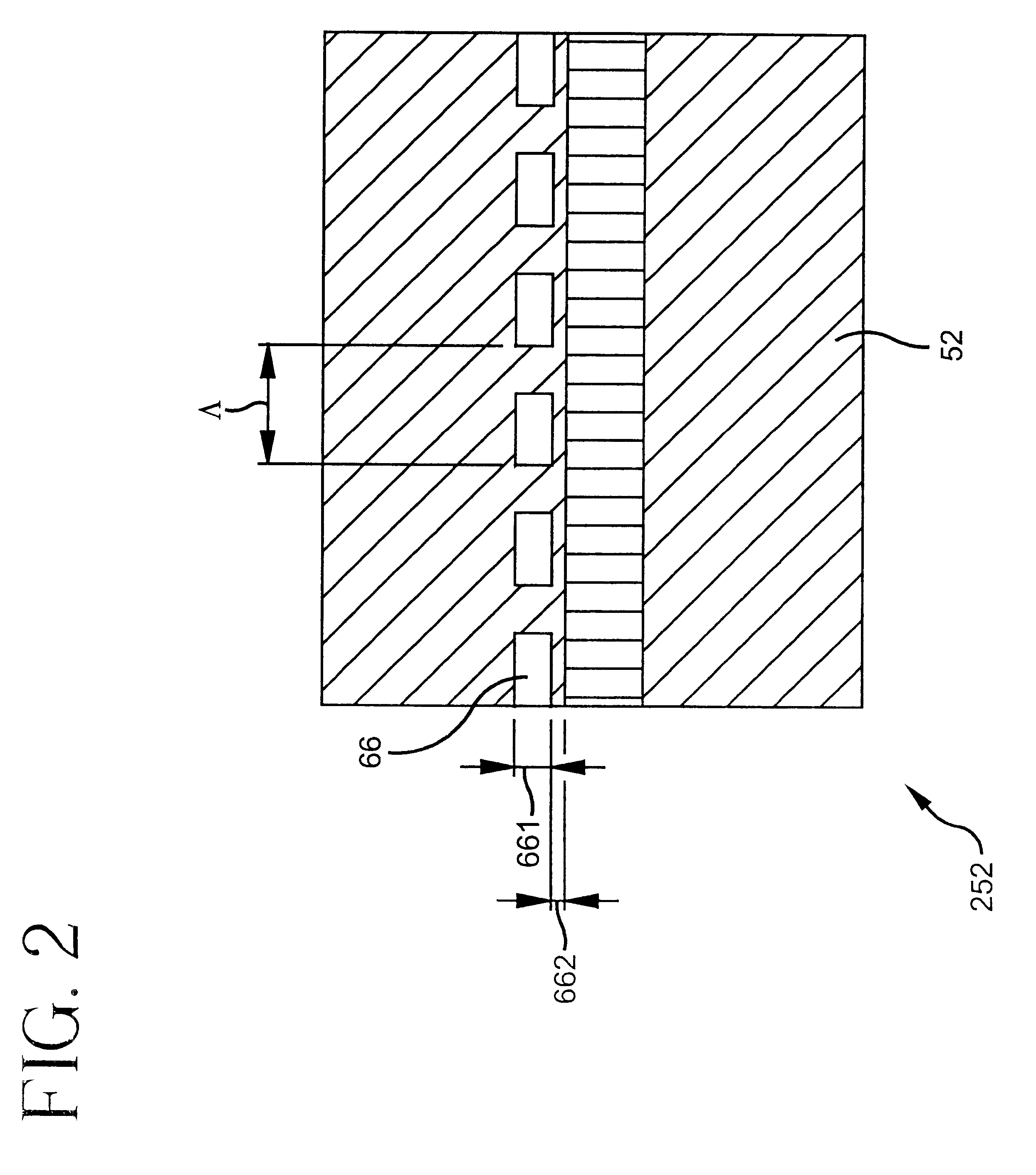
Tunable gain-clamped semiconductor optical amplifier
A gain-tunable semiconductor optical amplifier (10) includes an amplifying section (38) for amplifying an optical signal (422). A first tunable reflector section (51) and a second tunable reflector section (52) are integrated on opposed sides of the amplifying section (38) to reflect the optical signal at a clamping wavelength and to change an internal gain level to cause a stimulated emission at the clamping wavelength above the internal gain level.
Owner:CORNING INC
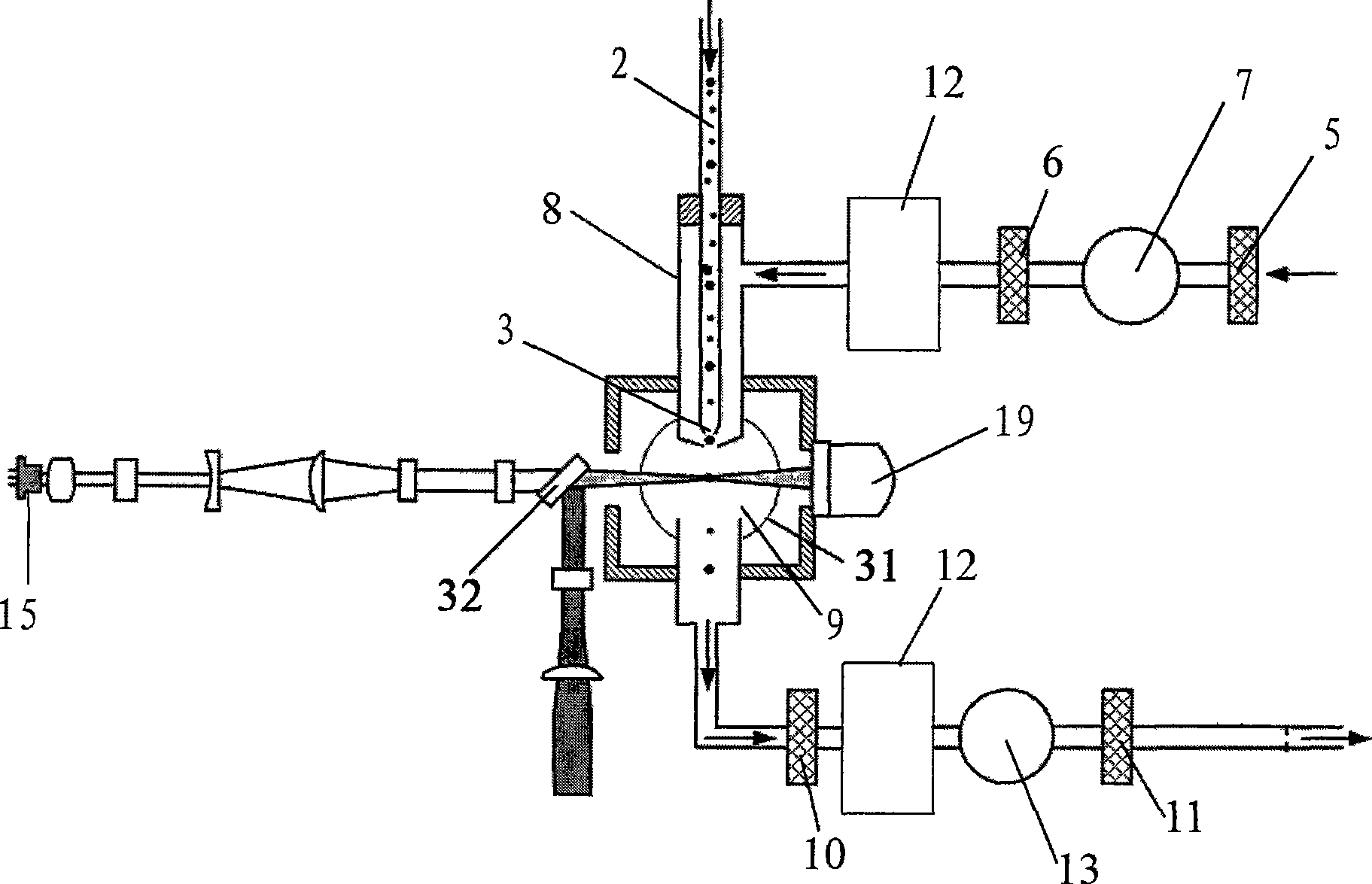
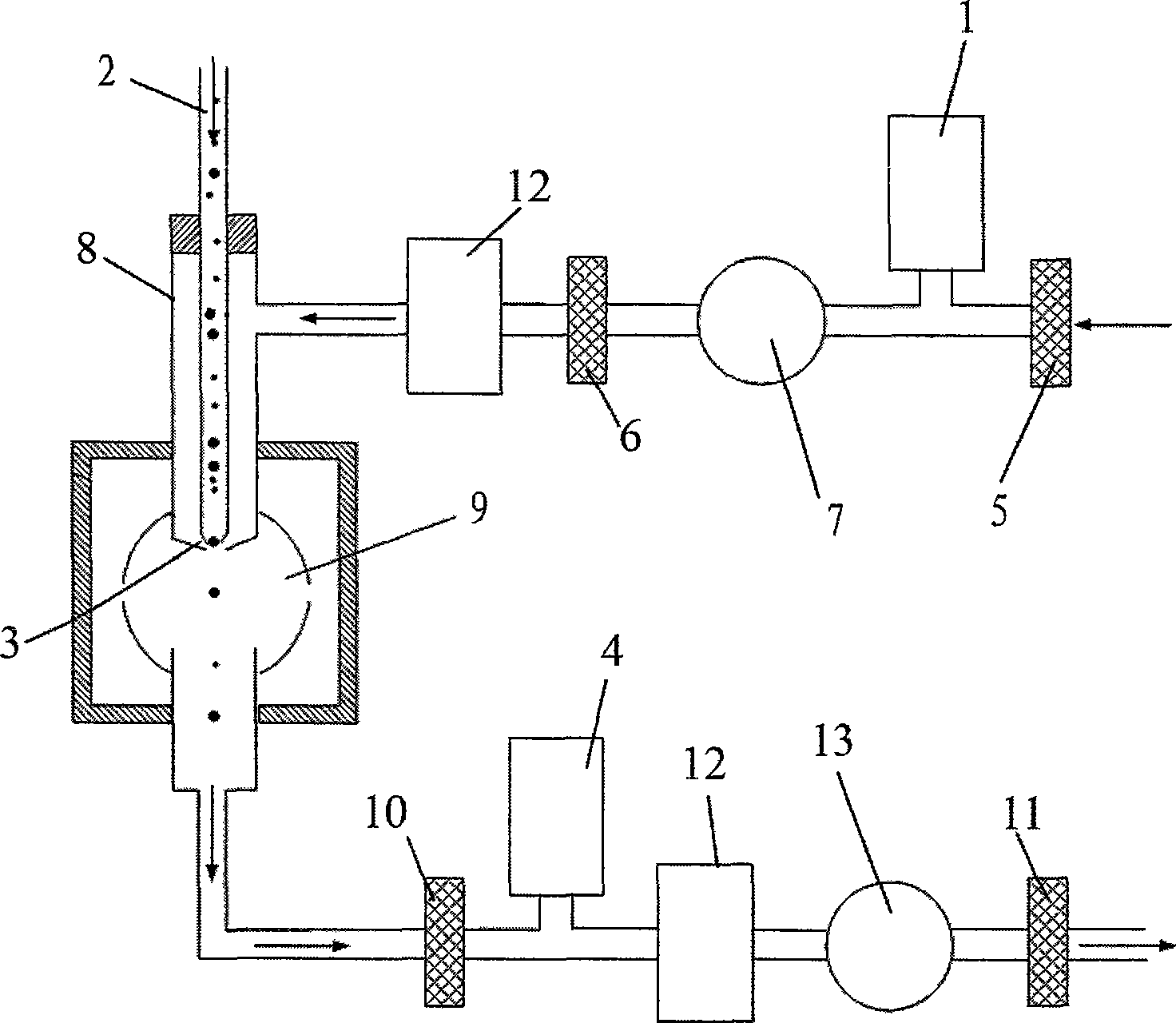
Aerated solids particle laser analyzer
ActiveCN101398367ADistinctive featuresThe test result is accurateBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceUltraviolet
The invention provides an aerosol particle laser analyzer which online and continuously detects the aerodynamic diameter and particle quantity of the aerosol particles in the air one by one in real-time and identifies whether the particles are biological particles; the aerosol particle laser analyzer comprises a particle beam queuing acceleration sampling system wrapped by shell flows, a dual-peak laser aerodynamic diameter measurement system, a biological particle fluorescent detection system induced by ultraviolet laser, an ineffective and superposed particle identification circuit, data processing, displaying and memorizing software, and a communication module. The aerosol particle laser analyzer can not only detect the physical parameters such as aerodynamic diameter, particle quantity and the like of the aerosol particles, but also can judge whether the particles are active biological particles or not according to the natural characteristic that the active biological particle emits bioluminescence when being induced and can measure the parameters of the active biological particles such as the quantity, the concentration and the like; the aerosol particle laser analyzer has exact detection results and can be used conveniently and fast for detection; and the parts have long service life and the volume of the aerosol particle laser analyzer is small, thus being convenient for movable usage.
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI +1
High-repetition-rate passively mode-locked solid-state laser
A passively mode-locked solid-state laser is designed to emit a continuous-wave train (51, 52) of electromagnetic-radiation pulses, the fundamental repetition rate of the emitted pulses exceeding 1 GHz, without Q-switching instabilities. The laser includes an optical resonator (3.1), a solid-state laser gain element (2) placed inside the optical resonator (3.1), a device (1) for exciting said laser gain element (2) to emit electromagnetic radiation having the effective wavelength, and a device (4) for passive mode locking including a saturable absorber. The laser gain element (2) is a laser material with a stimulated emission cross section exceeding 0.8×10−18 cm2 at the effective wavelength, and is made of Nd:vanadate. The saturable absorber (4) is preferably a semiconductor saturable absorber mirror (SESAM) device. Even higher repetition rates are achieved by operating the laser in the soliton regime. For use in fiber-optical telecommunication, the laser wavelength is preferably shifted to 1.5 μm by use of an optical parametric oscillator. The laser is simple, robust, compact, efficient, and low-cost. It generates a relatively large average power of 100 mW and higher, which is useful for a number of optical probing and detection applications, in a beam (51, 52) that is substantially a fundamental spatial mode.
Owner:LUMENTUM SWITZERLAND AG
Whispering gallery mode photonic device and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104253372ARealize the coupling effectSolve patterningOptical resonator shape and constructionWhispering galleryArray data structure
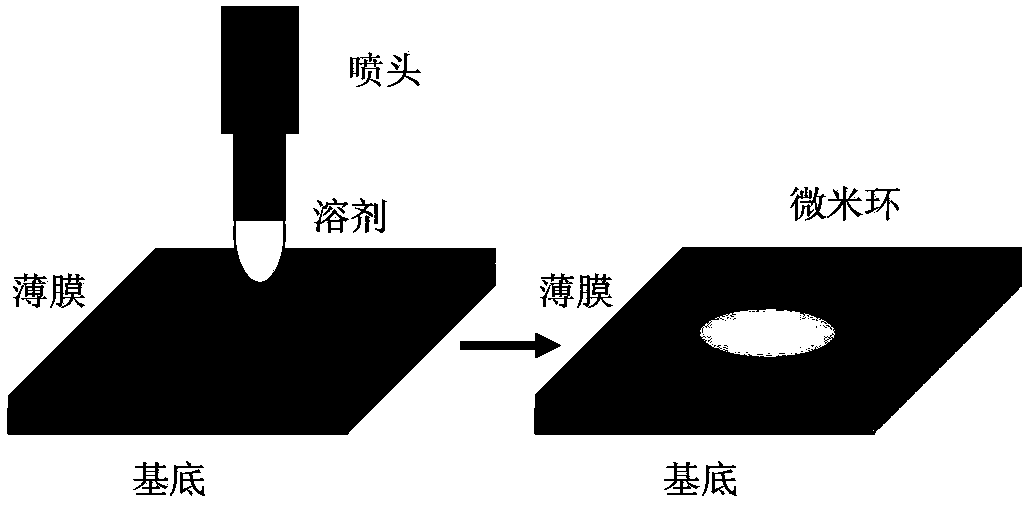
The invention provides a whispering gallery mode photonic device and a preparation method thereof. According to the preparation method of a micro ring array structure, solvent droplets are utilized to dissolve a polymer film, so that a "coffee ring effect" can be generated, and therefore, polymer can be accumulated at the periphery of liquid so as to form an annular structure of which the height is obviously different from the height of the film, and conduction and confinement of light in the polymer structure can be realized; and light signals are inputted to the micron ring structure through utilizing excitation, scattering or near field coupling modes, so that a resonance effect in a whispering gallery mode can be realized. The prepared micron ring structure can be adopted as a high-quality factor optical micro cavity, so that a modulation-mode spectrum can be obtained, the width of spectral lines of the spectrum being significantly narrowed; a whispering gallery-mode light amplification stimulated emission can be realized through optical gain; and in a multi-ring coupled array structure, light signal processing and high sensitive response to outside stimuli can be realized according to the wavelength change information of the modulated spectrum and laser modes.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical phase conjugation laser diode
A phase-conjugating resonator that includes a semiconductor laser diode apparatus that comprises a phase-conjugating array of retro-reflecting hexagon apertured hexahedral shaped corner-cube prisms, an electrically and / or optically pumped gain-region, a distributed bragg reflecting mirror-stack, a gaussian mode providing hemispherical shaped laser-emission-output metalized mirror. Wherein, optical phase conjugation is used to neutralize the phase perturbating contribution of spontaneous-emission, acoustic phonons, quantum-noise, gain-saturation, diffraction, and other intracavity aberrations and distortions that typically destabilize any stimulated-emission made to undergo amplifying oscillation within the inventions phase-conjugating resonator. Resulting in stablized high-power laser-emission-output into a single low-order fundamental transverse cavity mode and reversal of intra-cavity chirp that provides for high-speed internal modulation capable of transmitting data at around 20-Gigabits / ps.
Owner:HENRICHS JOSEPH REID
Stimulated emission depletion microscopy
ActiveUS20150226950A1Reduce optical aberrationMaximising metricPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersStimulated emissionBrightness perception
Aberrations in stimulated emission depletion microscopy are corrected using an adaptive optics approach using a metric which combines both image sharpness and brightness. Light modulators (22,32) are used to perform aberration correction in one or more of the depletion path (10), the excitation path (12), or the emission path from sample to detector.
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD
Flexible eye insert and glucose measuring system
Disclosed is a flexible insert (100) for placement on the human eye, comprising a light source (110) in said insert such that light emitted from the light source is shielded from the human eye upon correct placement of the insert on the human eye, a light-responsive material (120) placed in the light path of the light source, said light-responsive material emitting light upon stimulation by the light from said light source, the intensity of said stimulated emission being sensitive to a chemical interaction of the light-sensitive material with an analyte of interest, a photodetector (130) for detecting the light emitted by the light-responsive material; and a transmitter (140) coupled to the photodetector for transmitting a photodetector reading. The insert may be used in conjunction with a reader for automated monitoring of an analyte of interest such as glucose in the tear fluid of its wearer.
Owner:NXP BV
Method and device for two-photon fluorescence stimulated emission differential super-resolution microscopy
InactiveCN104062750AReduce scatterImprove signal-to-noise ratioMicroscopesOptoelectronicsStimulated emission
The invention discloses a method for two-photon fluorescence stimulated emission differential super-resolution microscopy. The method includes the steps that (1) after being collimated, pulsed laser beams are converted into linear polarized light and polarization modulation is conducted on the linear polarized light, so that radial polarized light is obtained; (2) the radial polarized light is converted into circular polarized light and projected onto a sample to be tested, two-photon stimulated emission is conducted, fluorescence is collected, and therefore first signal light intensity I1 is obtained; (3) polarization modulation is conducted on the linear polarized light obtained in the step (1) and the linear polarized light is converted into tangential polarized light; (4) the tangential polarized light is converted into circular polarized light and projected onto the sample to be tested, two-photon stimulated emission is conducted, fluorescence is collected, and therefore second signal light intensity I2 is obtained; (5) effective signal light intensity I is calculated according to a formula I=I1-gammaI2 , so that super-resolution imaging is achieved. The invention further discloses a device for two-photon fluorescence stimulated emission differential super-resolution microscopy. The device is simple, free of light division, low in light power, capable of weakening the photobleaching effect, higher in resolution and larger in imaging depth.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
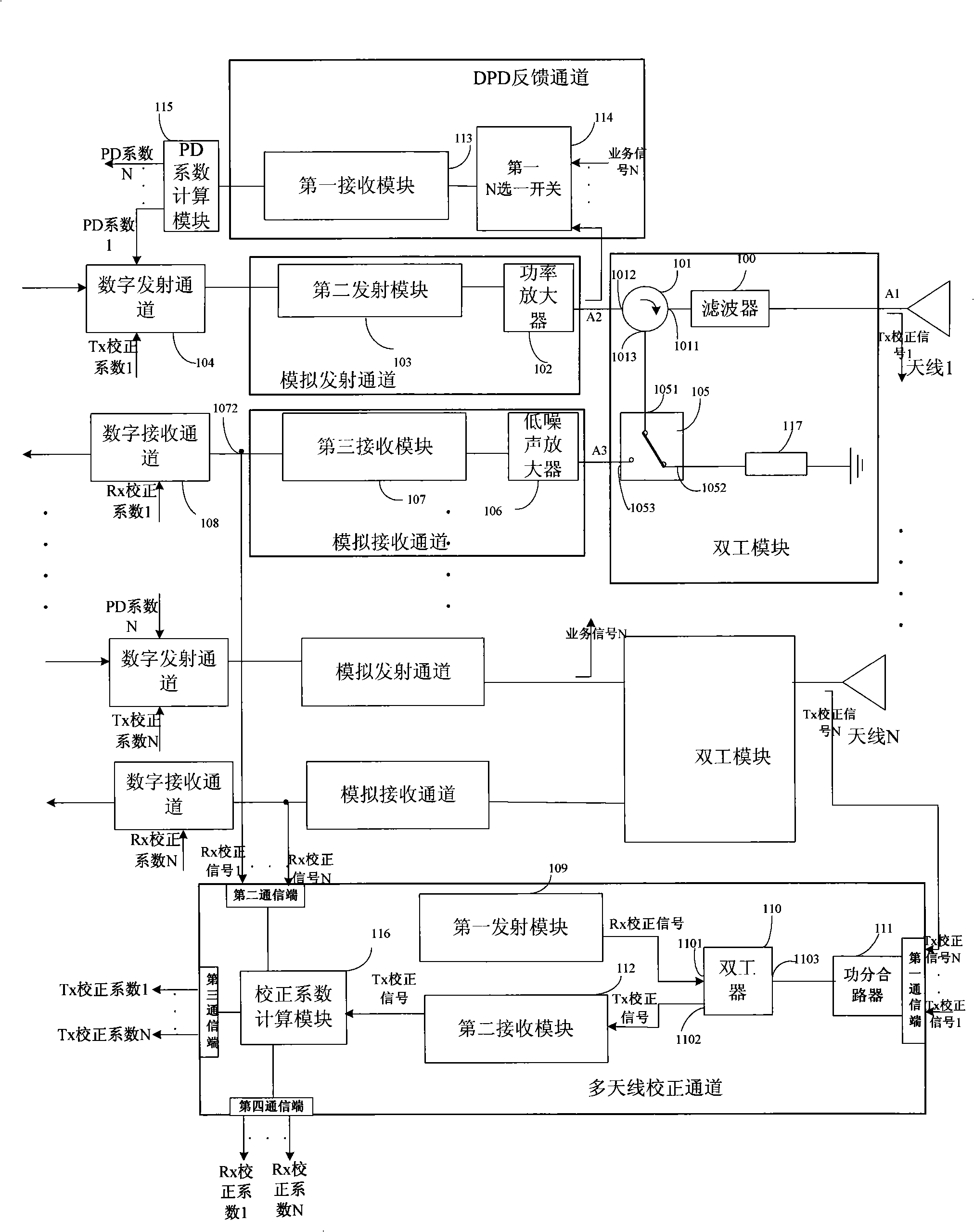
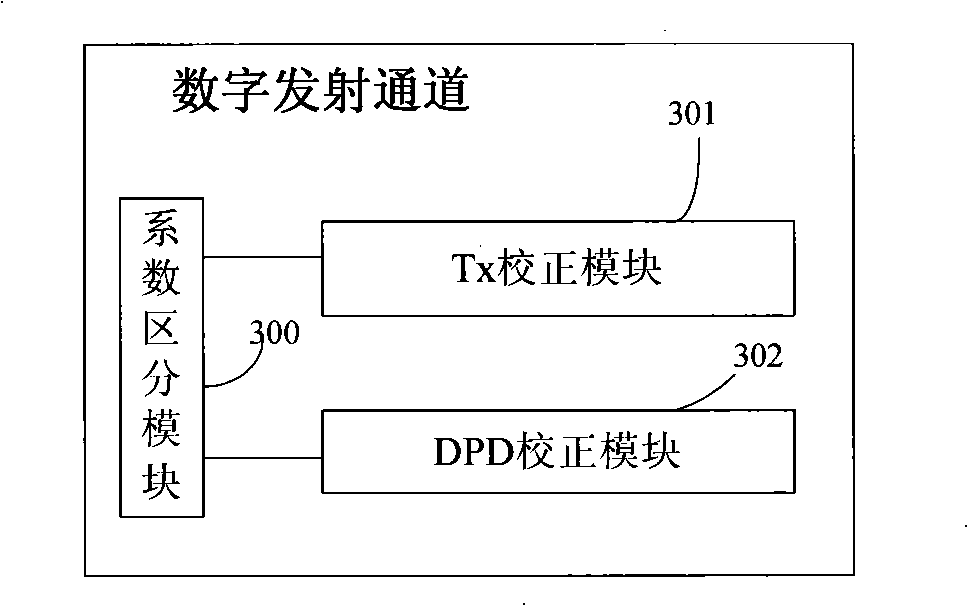
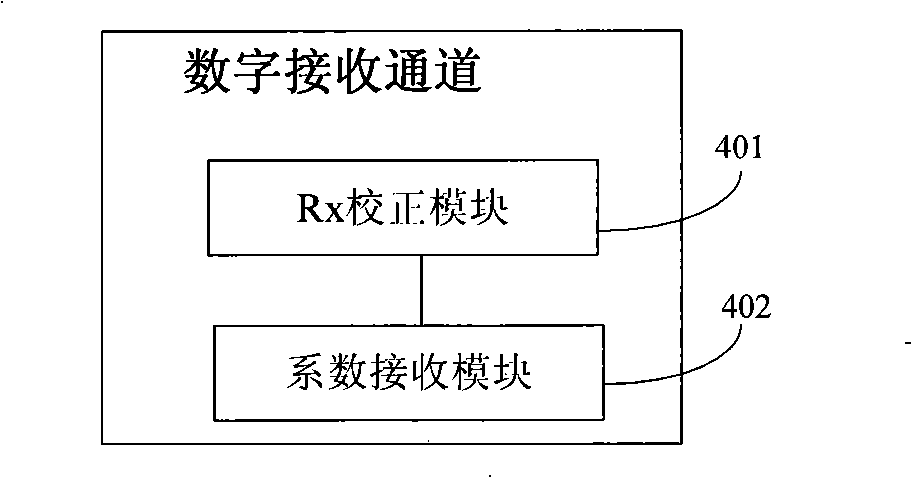
Multi-antenna correcting method, multi-antenna transceiving device and base station system
ActiveCN101335966AImprove performanceSpatial transmit diversityRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsEmission channelingEngineering
The invention discloses a multi-antenna correction method, a multi-antenna transmitter and a base station system, wherein the device includes at least one antenna, at least a duplex module, at least a stimulated emission channel and a digital emission channel, at least a stimulated receiving channel and a digital receiving channel, a DPD feedback channel, and a multi-antenna correction channel, wherein, the DPD feedback channel is used for receiving the operation signals output by the stimulated emission channel, and transmitting to the PD coefficient computing module to compute the obtained PD coefficient, and outputting to the digital emission channel to perform DPD correction; the multi-antenna correction channel computes the Tx correction coefficient according to the Tx correction signal and transmits to the digital emission channel to transmit the correction, or obtains the Rx correction coefficient according to the Rx correction signal, transmits to the digital receiving channel for receiving correction. According to the invention, the multi-antenna correction and DPD correction are combined, thereby advancing system performance.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Optical fiber laser, and components for an optical fiber laser, having reduced susceptibility to catastrophic failure under high power operation
InactiveUS8027557B2Avoid damageReduce susceptibilityLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingStimulated emissionInterconnection
Owner:NUFERN
Partial discharge detecting system for all-fiber power transformer and detecting method thereof
The invention relates to a partial discharge detecting system for all-fiber power transformer and a detecting method thereof. The system comprises a controller, a transmission device and a detecting device. The detecting device comprises four groups of fiber bragg grating F-P ultrasonic sensors, optical fiber delayers are arranged between every two fiber bragg gratings, and the four groups of fiber bragg grating F-P ultrasonic sensors and a fluorescent probe are in serial connection on an optical fiber. The transmission device is connected with the detecting device through a through part. The controller is connected with the transmission device. In the calculation processing end, the partial discharge position can be calculated and determined through the time difference for the four groups of sensors to receive sound wave and by taking time division multiplexing time error into consideration. According to the strength of stimulated emission light signals of the fluorescent probe, the apparent discharge magnitude of the partial discharge is calculated. Through the comparison between the ultrasonic sensors and the signals of the fluorescent probe, whether the system is interfered by external environment to cause error judgment is judged. Furthermore, false alarm of the system is avoided. The partial discharge detecting system has the advantages of being simple in structure, facilitating networking, resisting to electromagnetic interference and the like.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
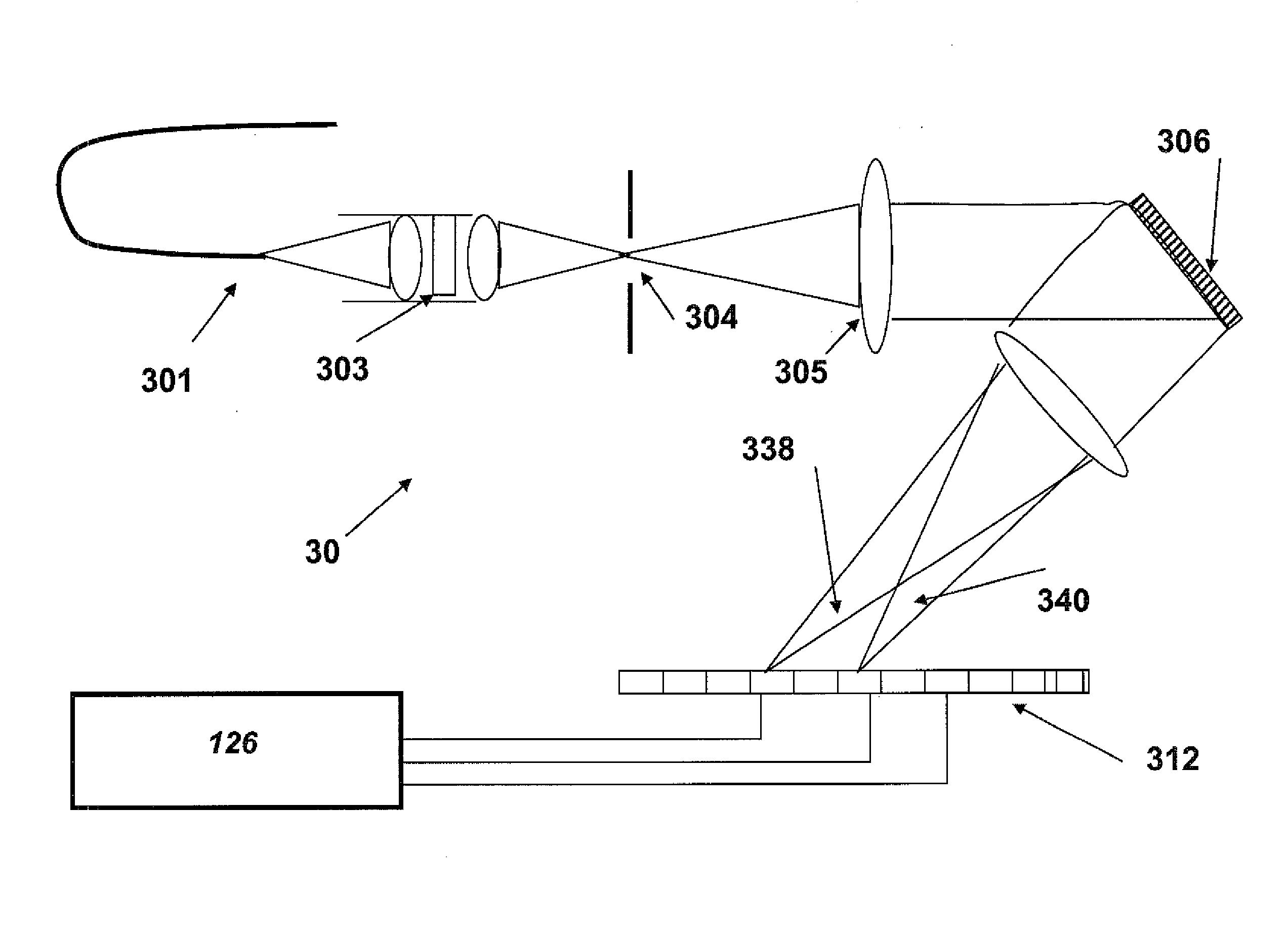
Scanning microscope with a detector and light source for exciting an energy state in a specimen and module for a scanning microscope
InactiveUS6958470B2Improve spatial resolutionEasy to implementBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansImage resolutionHigh spatial resolution
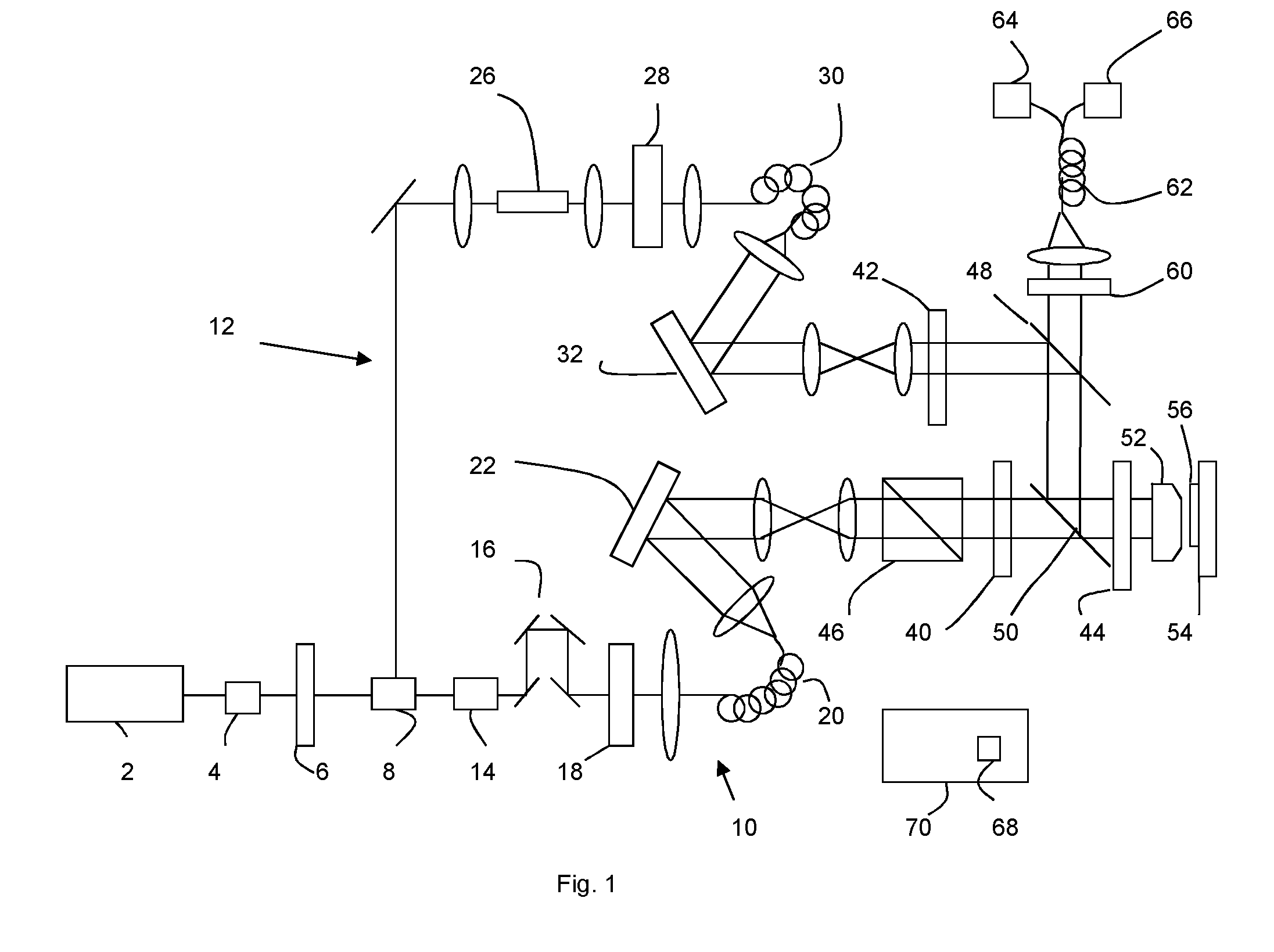
The invention discloses a scanning microscope for optical measurement with high spatial resolution of a specimen point of a specimen, having a light source for emitting an exciting light beam suitable for exciting an energy state of the specimen; a detector for detection of the emitted light; and a stimulating light beam, coming from the light source, for generating stimulated emission of the specimen excited by the exciting light beam at the specimen point, the exciting light beam and the stimulating light beam being arranged in such a way that their intensity distributions in the focal region partially overlap, wherein optical elements which shape the stimulating light beam are combined into at least one module that is positionable in the beam path of the scanning microscope.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Broadband light emitting device
ActiveUS20050279989A1Increase heightBroad emission spectrumLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionStimulated emissionP–n junction
The invention concerns a superluminescent light emitting diode (SLED) comprising a semiconductor heterostructure forming a PN junction and a waveguide. The semiconductor heterostructure includes a gain region with a contact means for biasing the PN junction so as to produce light emission including stimulated emission from an active zone of the gain region, and in the active zone a plurality of quantum dot layers, each quantum dot layer made up of a plurality of quantum dots and a plurality of adjoining layers, each adjoining layer adjacent to one of said quantum dot layers. The material composition or a deposition parameter of at least two adjoining layers is different. This ensures an enhanced emission spectral width.
Owner:EXALOS
Display panel and display device
InactiveCN109471300AEasily damagedEliminate moiréSolid-state devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayGrating
The invention discloses a display panel and a display device. The display panel comprises a first display module and a second display module which is located at the light emission side of the first display module; the second display module is a liquid crystal display module, and the first display module is used for modulating light rays entering the second display module; the first display modulecomprises multiple first pixel units which are distributed in an array; the second display module comprises multiple second pixel units which are distributed in an array; the display panel further comprises quantum dot layers between the first pixel units and the second pixel units. By adopting a mode that emergent light of the first pixel units excites quantum dots, mixed-color light is generated, and backlight is provided for the second display module. Quantum dot materials in the quantum dot layers are emitted to the periphery at all angles through the light rays emitted by stimulation, theoriginal propagation direction of the ray lights is changed, the generated light rays can better damage a pattern generated by a periodicity grating structure, and accordingly the moire fringe is removed.
Owner:HISENSE VISUAL TECH CO LTD
Tunable gain-clamped semiconductor optical amplifier
A gain-tunable semiconductor optical amplifier (10) includes an amplifying section (38) for amplifying an optical signal (422). A first tunable reflector section (51) and a second tunable reflector section (52) are integrated on opposed sides of the amplifying section (38) to reflect the optical signal at a clamping wavelength and to change an internal gain level to cause a stimulated emission at the clamping wavelength above the internal gain level.
Owner:CORNING INC
Semiconductor light emitting device
ActiveUS20080251794A1Reduce spontaneous emissionEasy to detectLaser detailsSolid-state devicesPhotodetectorRefractive index
The present invention provides a semiconductor light emitting device realizing lower detection level of spontaneous emission light by a semiconductor photodetector and improvement in light detection precision by selectively reflecting spontaneous emission light. The semiconductor light emitting device includes a semiconductor light emitting element for generating light including stimulated emission light having a wavelength λo and spontaneous emission light having a wavelength band including the wavelength λo, a multilayer filter having a stack structure in which a low-refractive-index layer having a thickness of λ1 / (4×na) (λ1<λo and na denotes refractive index) and a high-refractive-index layer having a thickness of λ1 / (4×nb) (nb>na and nb denotes refractive index) are alternately stacked, and a semiconductor photodetector having a light absorption layer that absorbs a part of light passed through the multilayer filter.
Owner:SONY CORP
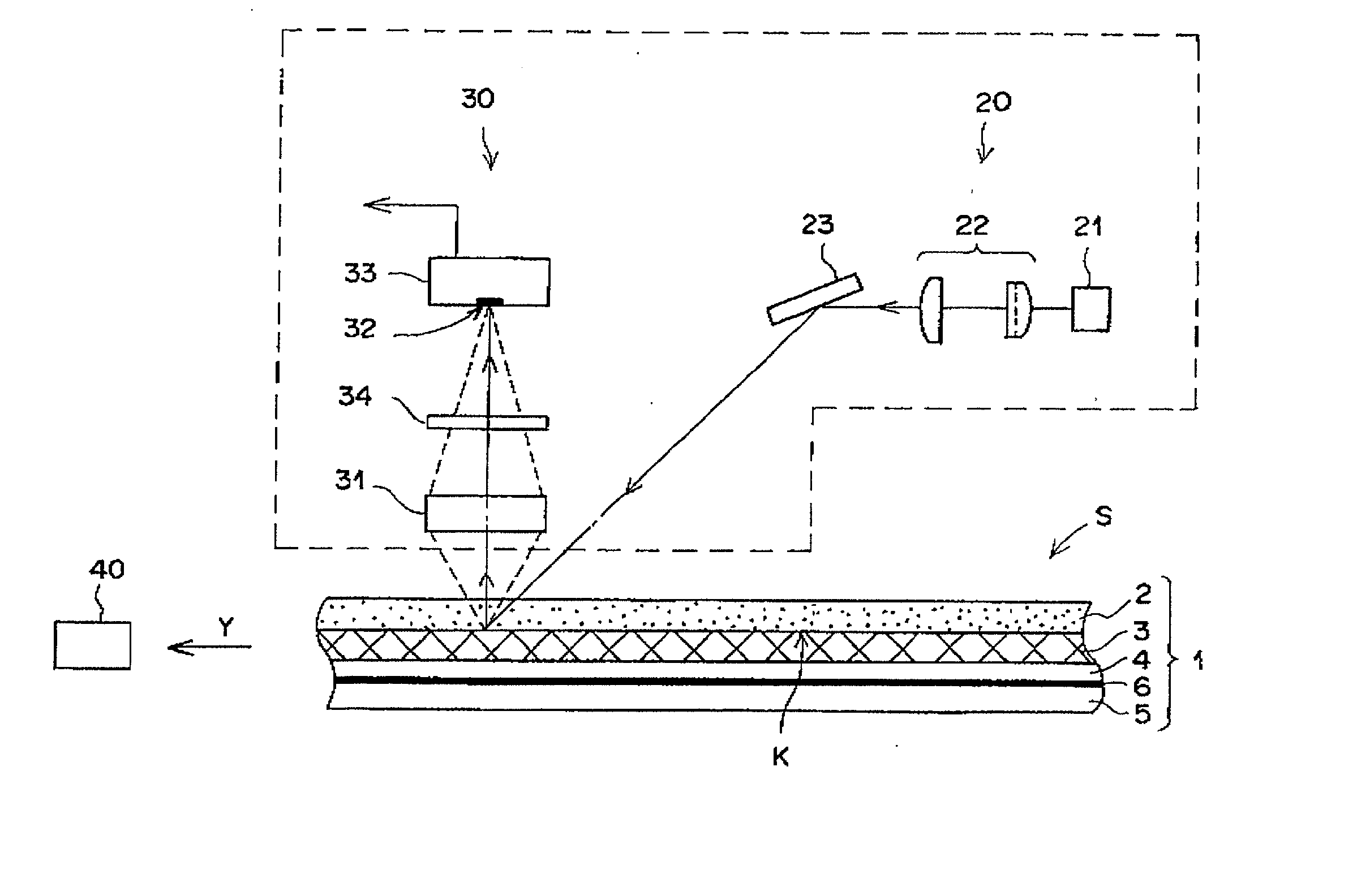
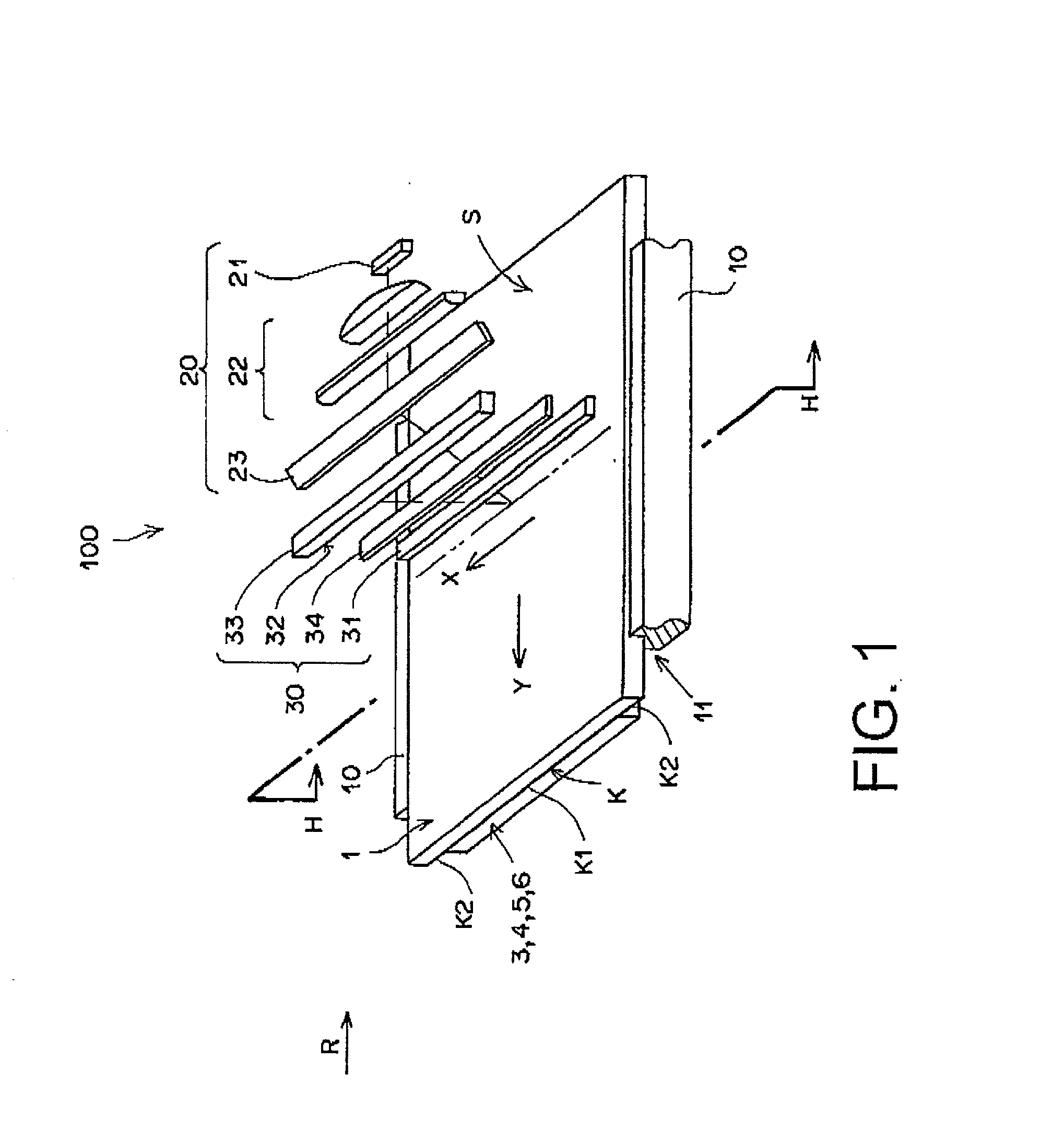
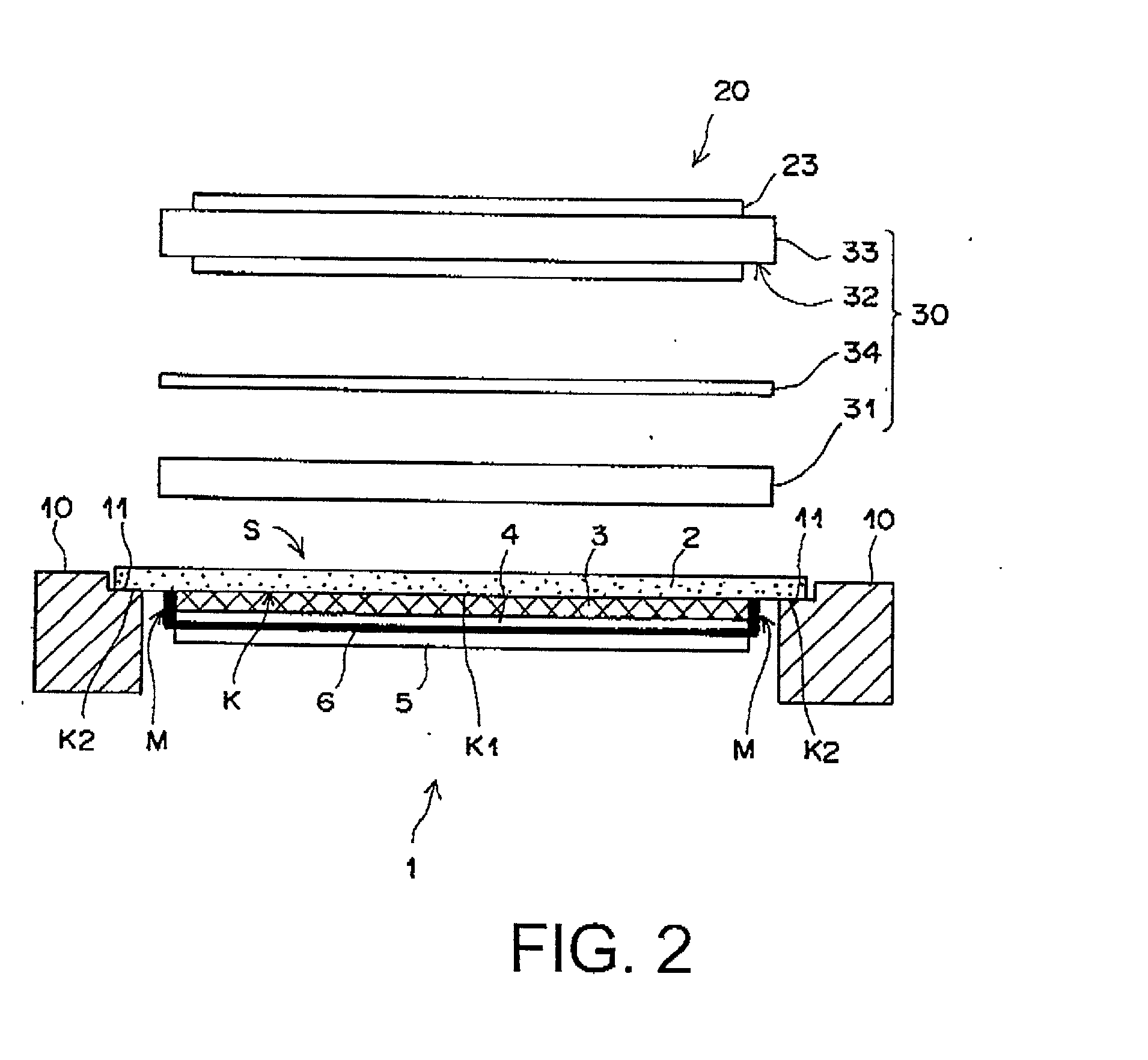
Method for reading radiation image from stimulable phosphor sheet
InactiveUS20020158216A1Easy to readImprove emission efficiencyX-ray/infra-red processesElectrical apparatusElectricityReference space
A method for reading a radiation image from a stimulable phosphor sheet composed of a substrate and a stimulable phosphor layer containing a latent radiation image by as of a radiation image-reading means having a stimulating light-applying unit and a stimulated emission-collecting unit having a lens and a stimulated emission-receiving plane, which is performed by the steps of applying a stimulating light onto the phosphor layer under the condition that the phosphor sheet moves along its sheet plane in relation to the stimulated emission-collecting unit; collecting a stimulated emission emitting from the area onto which the stimulating light is applied on the emission-receiving plane through the lens; and photoelectrically converting the collected emission into electric signals in the stimulated emission-collecting unit, is improved by moving the stimulable phosphor sheet in relation to the emission-collecting unit under the condition that the stimulating light-applied area of the stimulable phosphor layer is kept apart from the center of the emission-receiving plane with a space in the range defined by a combination of a reference space and a focal depth of the lens, in which the reference space is defined by a length at which the stimulated emission emitting from the phosphor layer focuses on the emission-receiving plane after passing through the lens.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
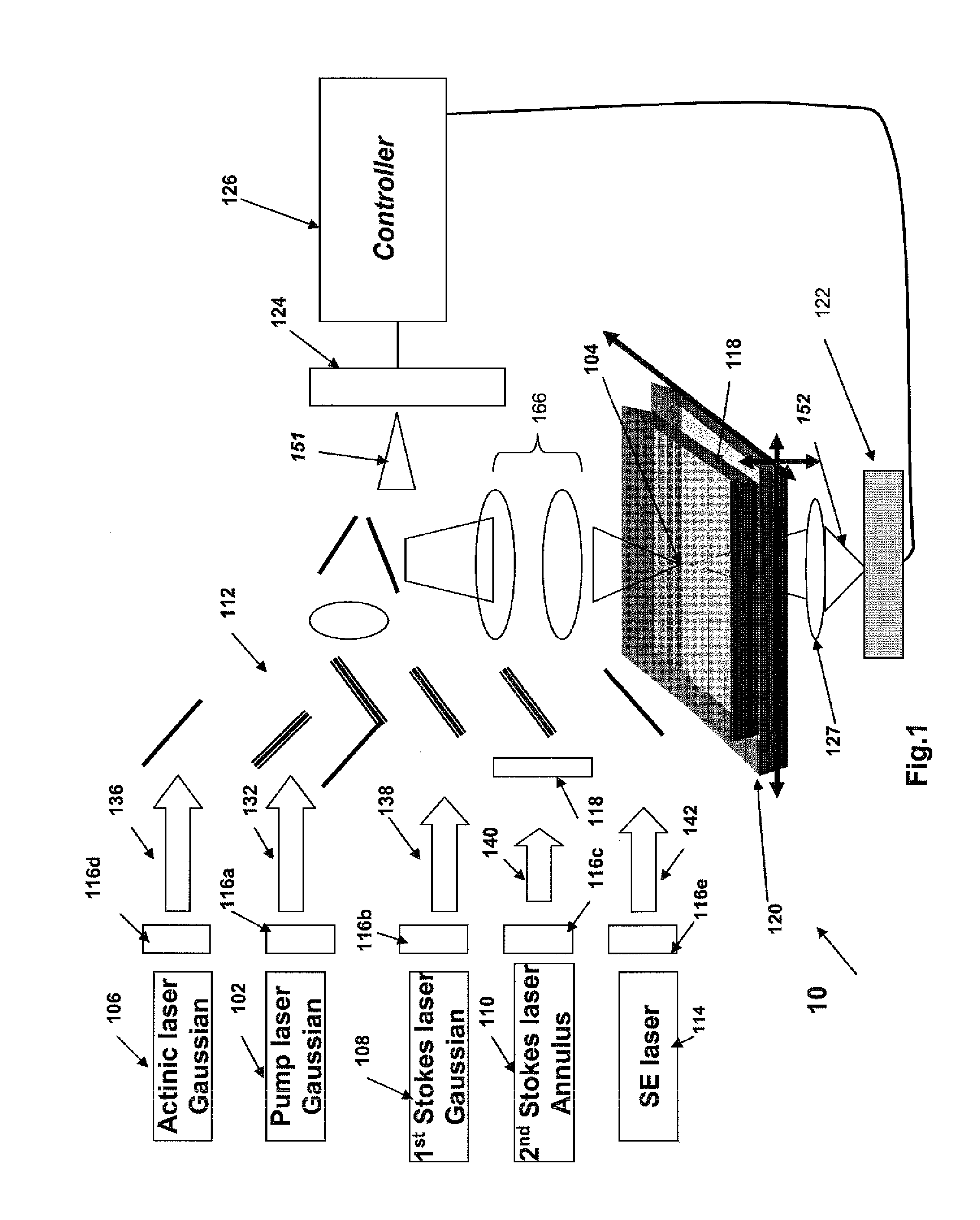
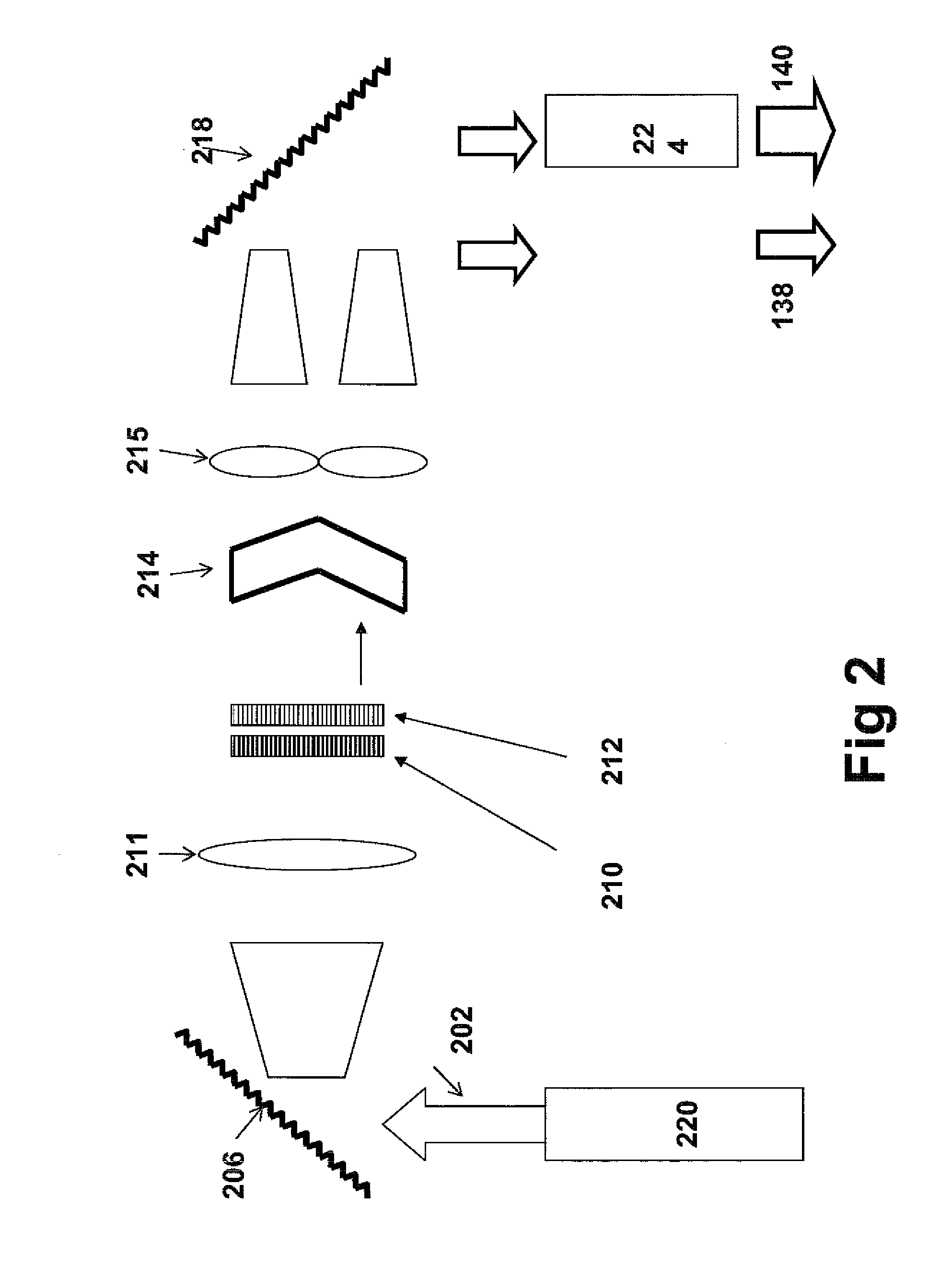
Method and system for raman, fluorescence, lithographic, stimulated emission and photochemical imaging beyond the diffraction limit
InactiveUS20120069332A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioMinimizes parasitic two-photon absorption effectsSpectrum investigationPhotomechanical apparatusResistFluorescence
Systems and methods for hyper-resolution beyond the diffraction limit of optical microscopes for applications in spectroscopy, absorption and lithographic photochemical patterning are described. These systems are based on interference of a pump pulse and a Stokes laser pulse which interfere to localize the population of an excited vibrational state in an area that is smaller than the scanning resolution of the microscope. Another (interfering) Stokes pulse has an annular shape at focus and destructively interferes with the the Stokes laser pulse. This destructive interference causes narrowing of the population distribution of the vibrational excited state well below the diffraction limit, which in turn localizes the population of the central electronic excited state by a separate actinic laser pulse having a lower energy than the ground state excitation energy of the molecule.A stepped photolithography system uses two photomasks to produce photoresist images capable of printing features smaller than 10 nm.
Owner:FREL ROBERT D
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com