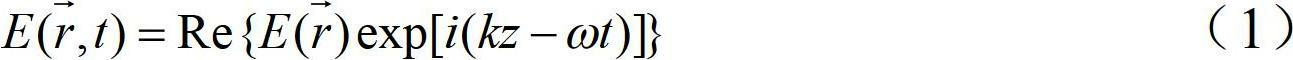Patents
Literature
49 results about "Optical phase conjugation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
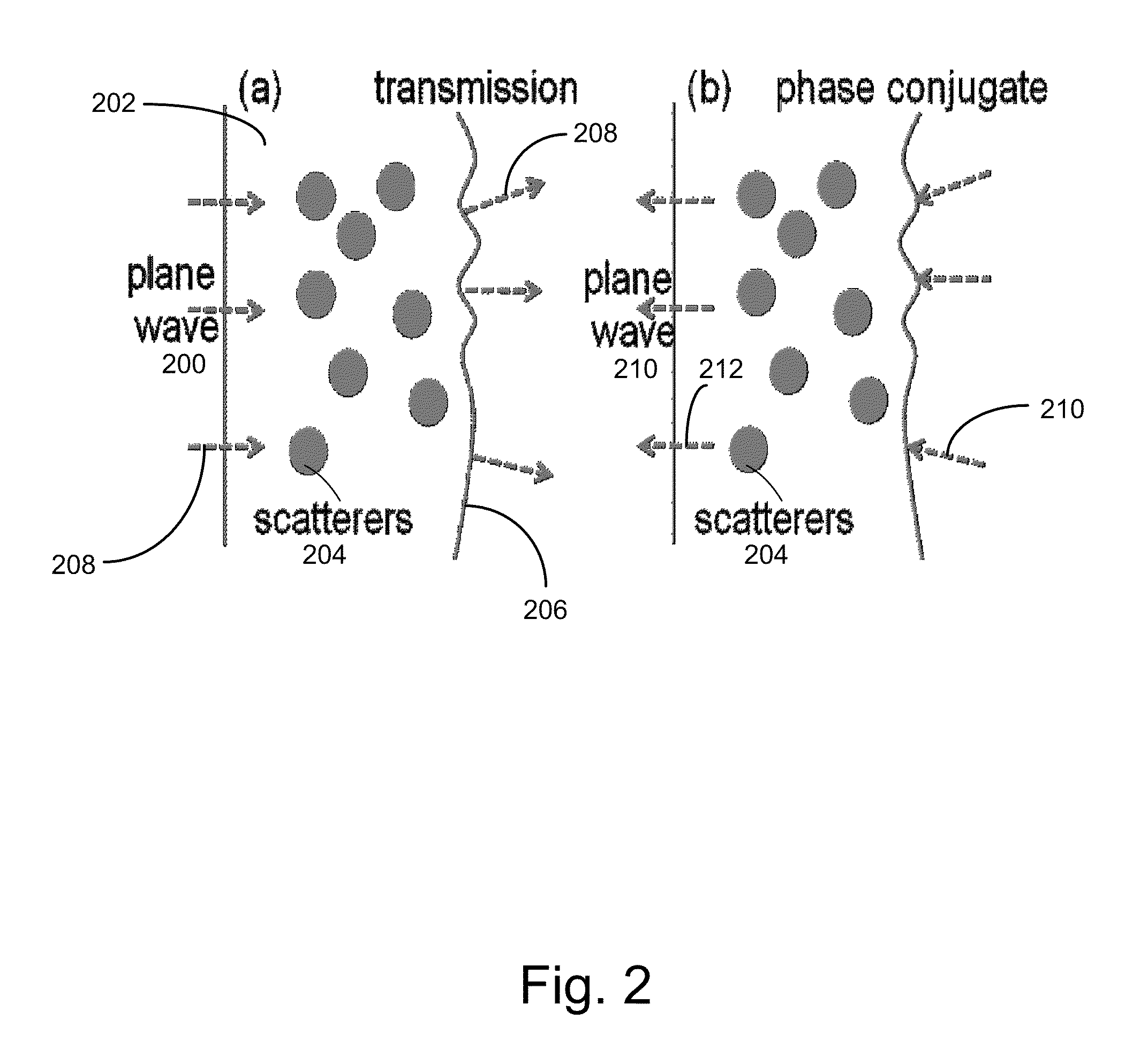
The most common way of producing optical phase conjugation is to use a four-wave mixing technique, though it is also possible to use processes such as stimulated Brillouin scattering. A device producing the phase-conjugation effect is known as a phase-conjugate mirror (PCM).
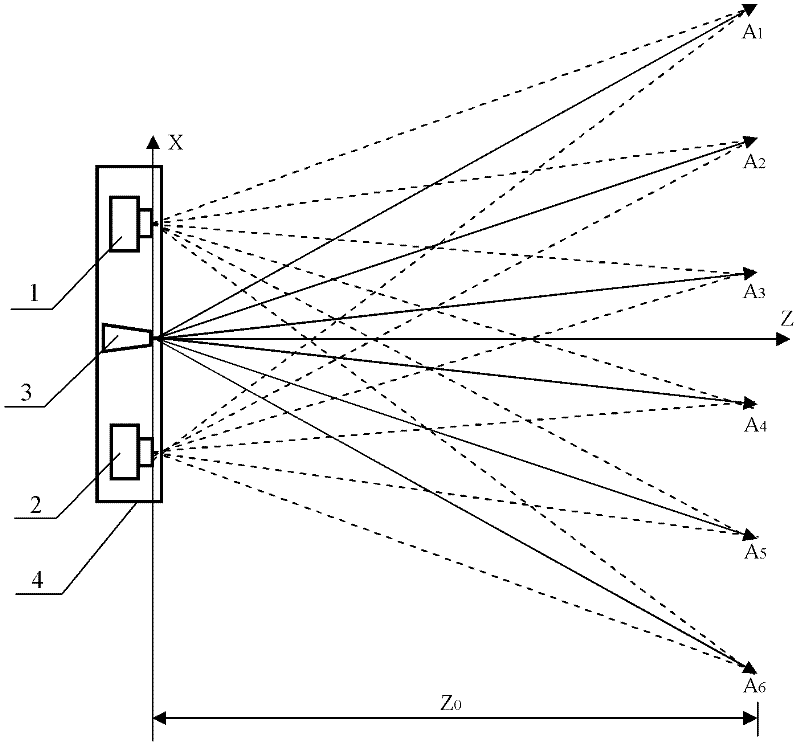
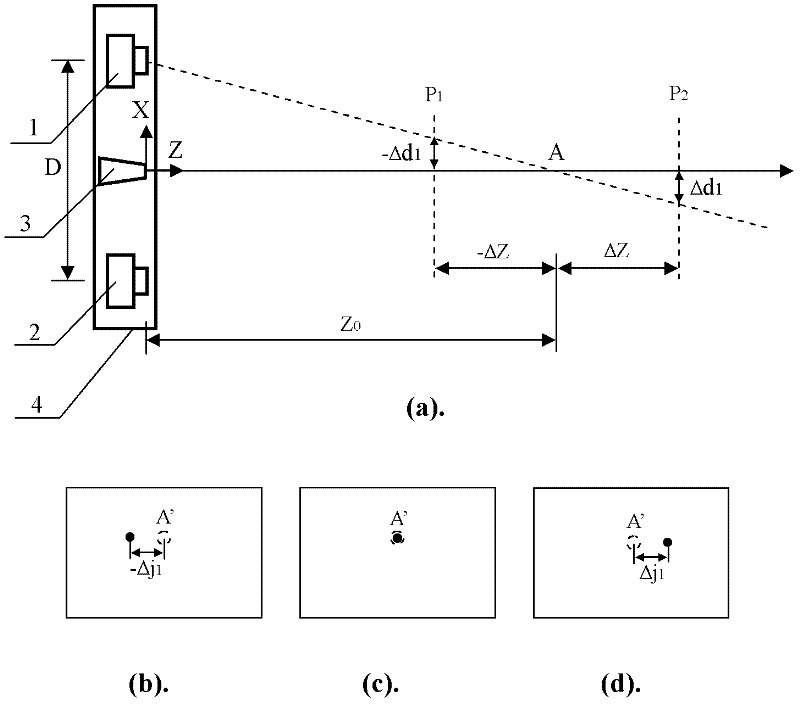
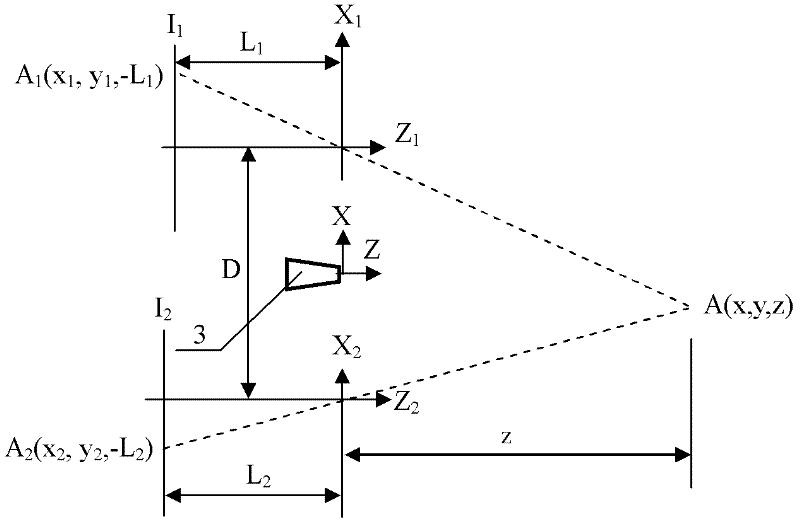
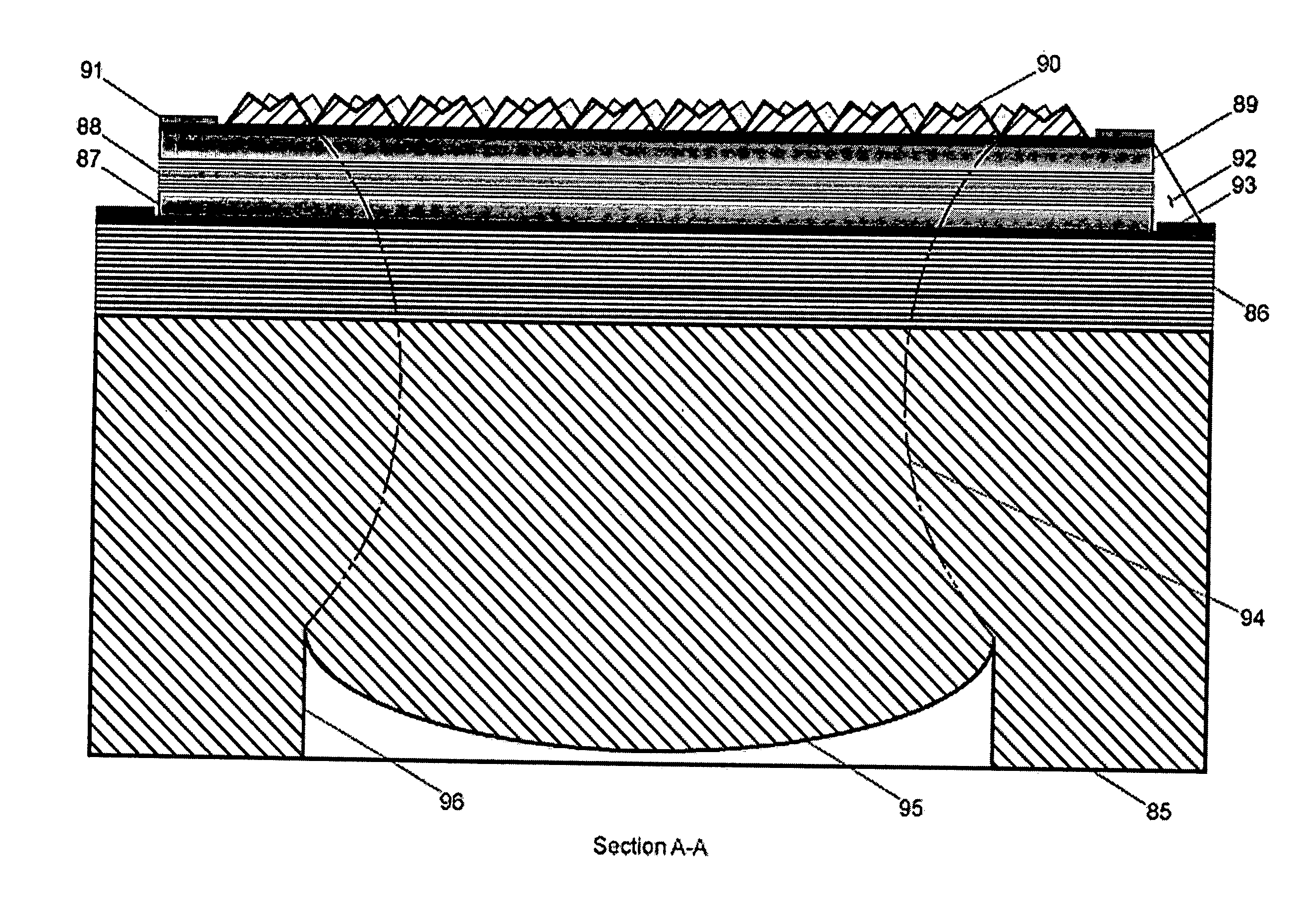
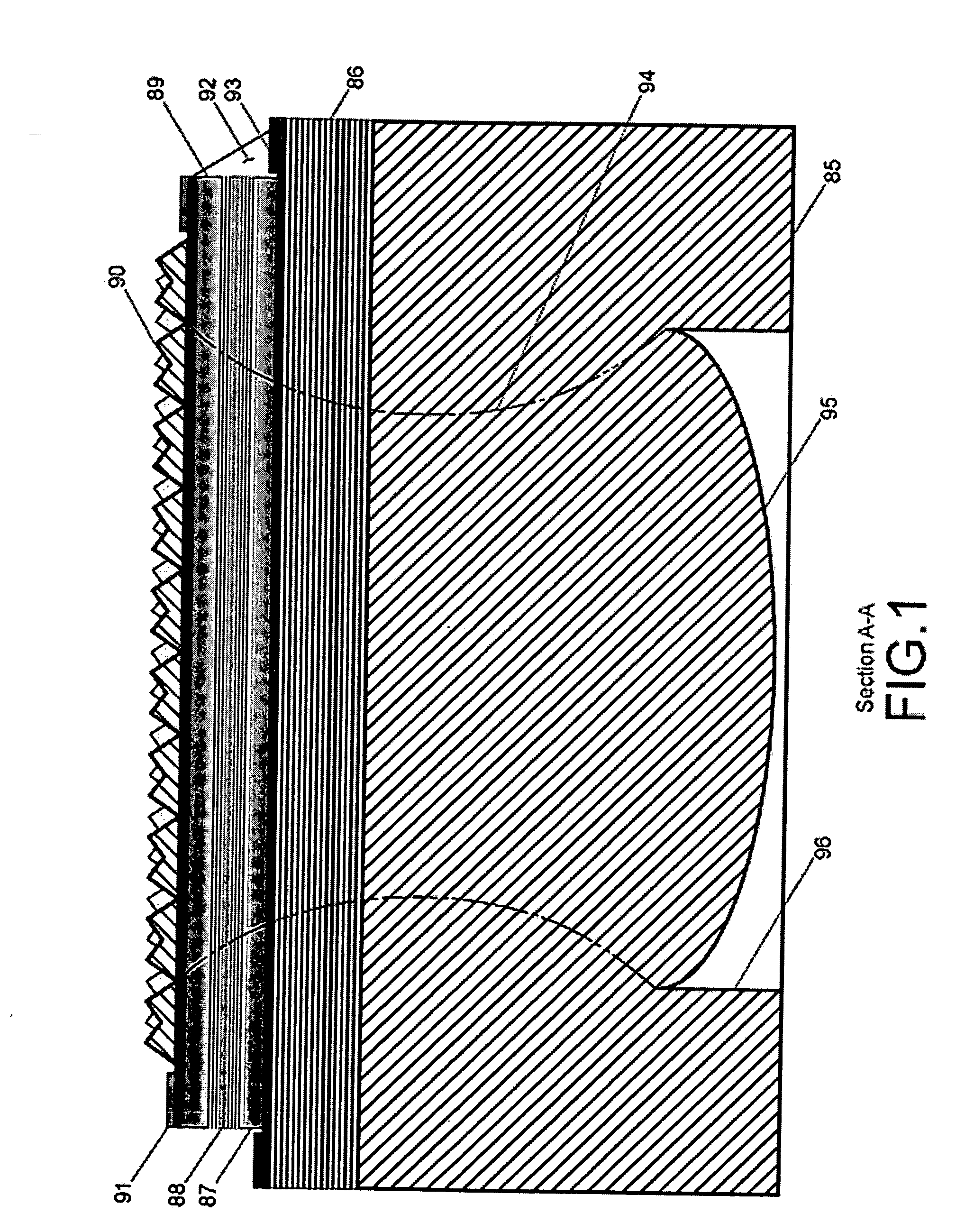
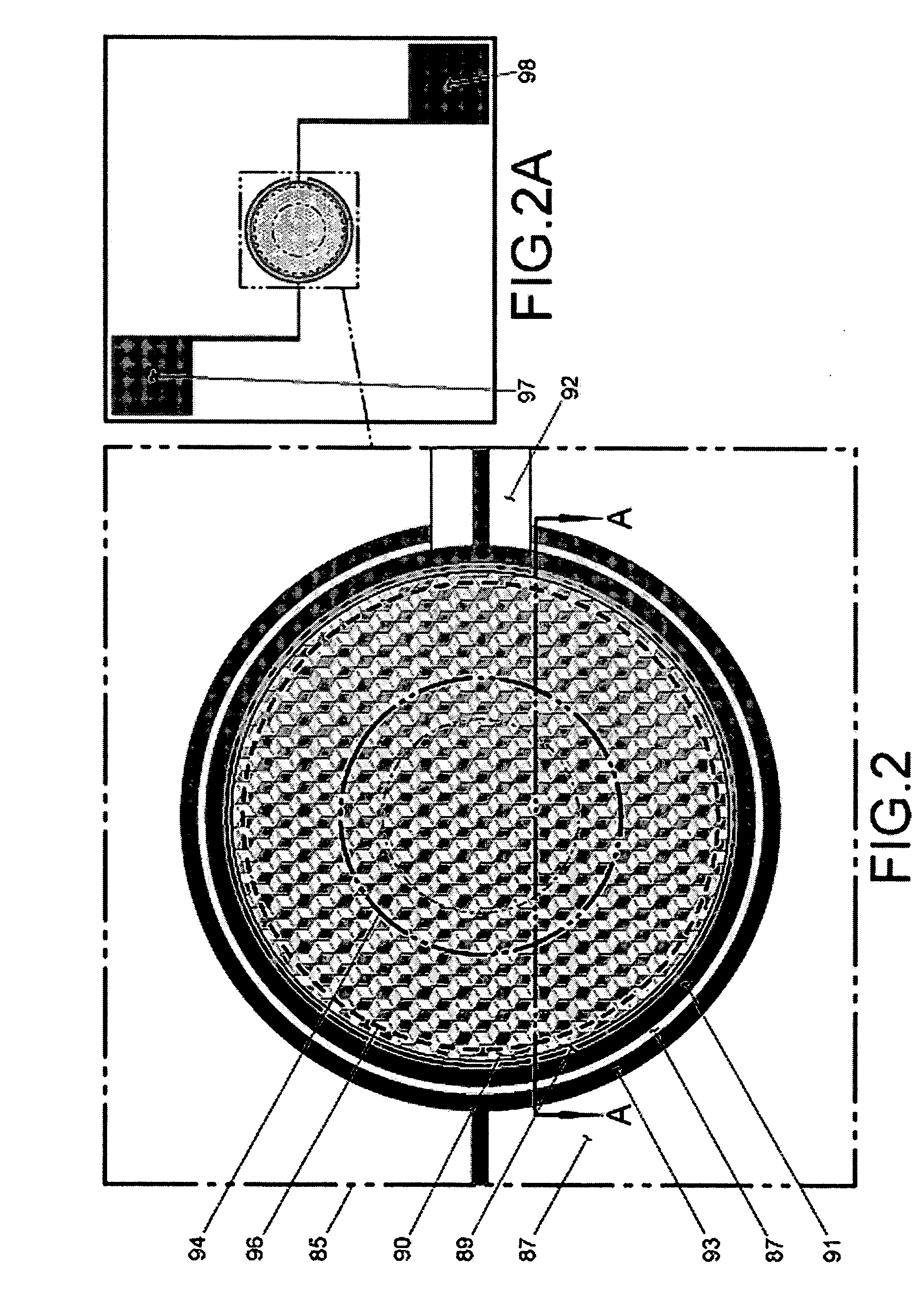
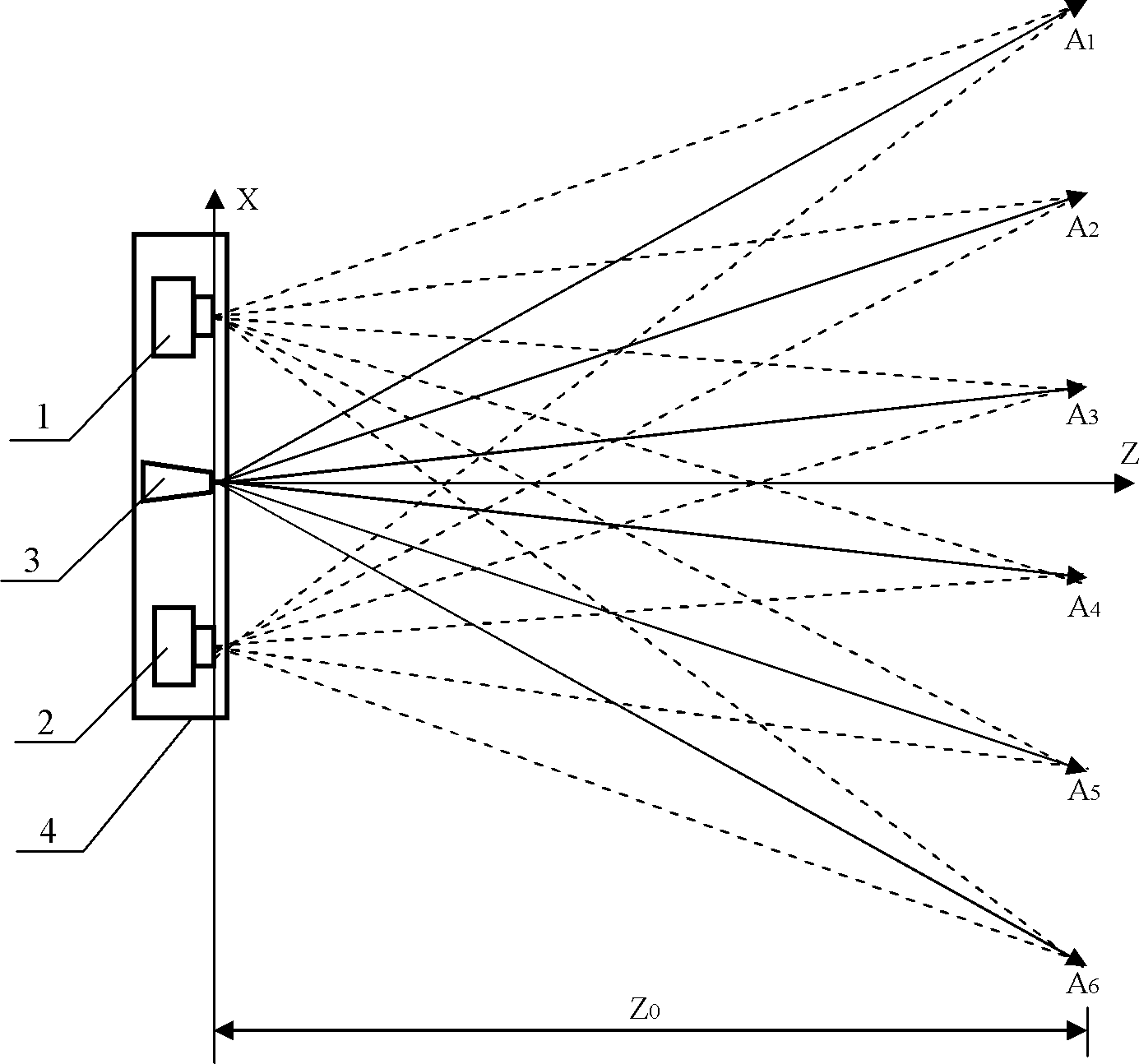
Three-dimensional photographing process based on laser probe array and device utilizing same
InactiveCN102494609AAvoid damageAvoid submersionUsing optical meansStereoscopic photographyMatch treatmentStereo matching
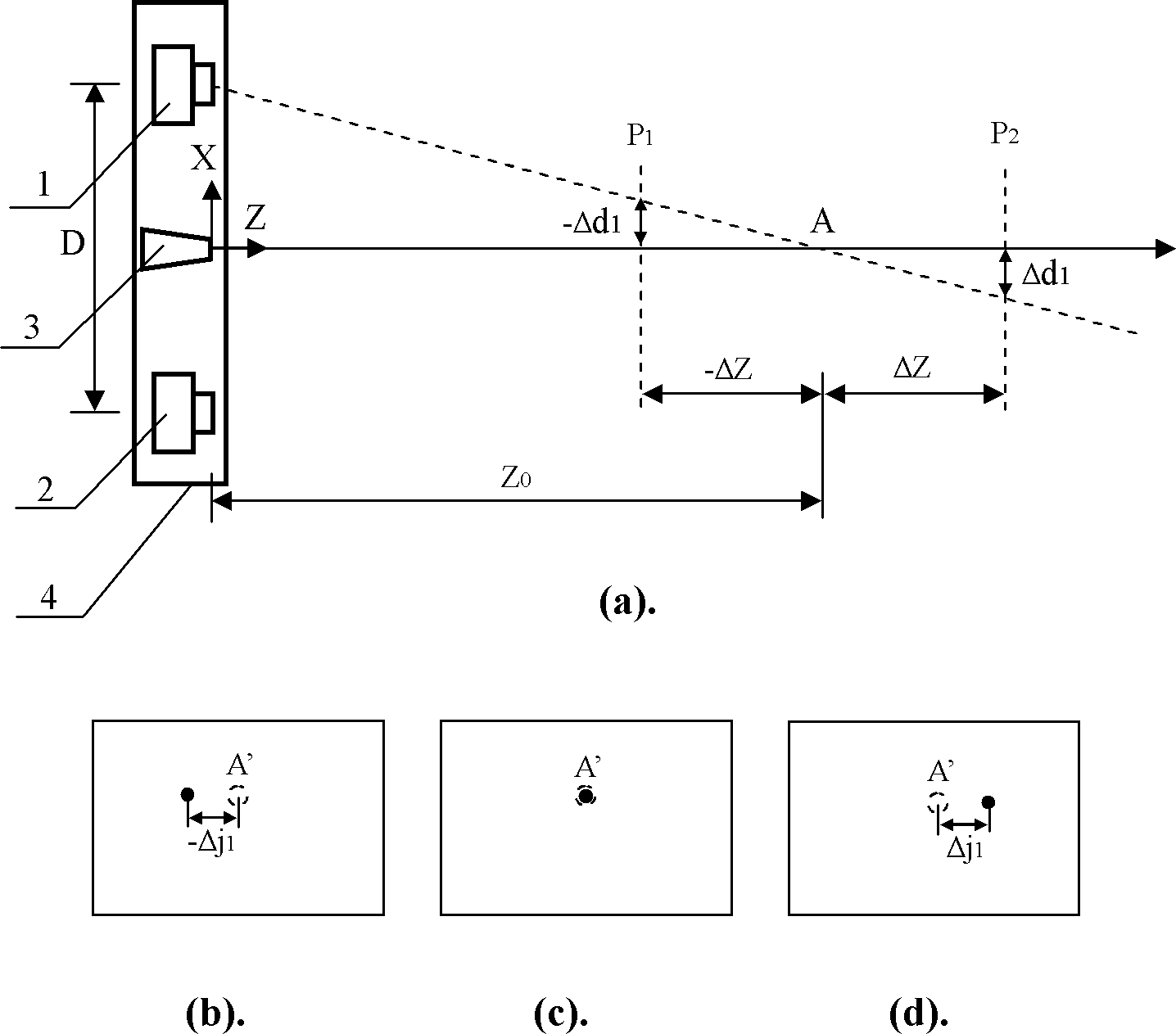
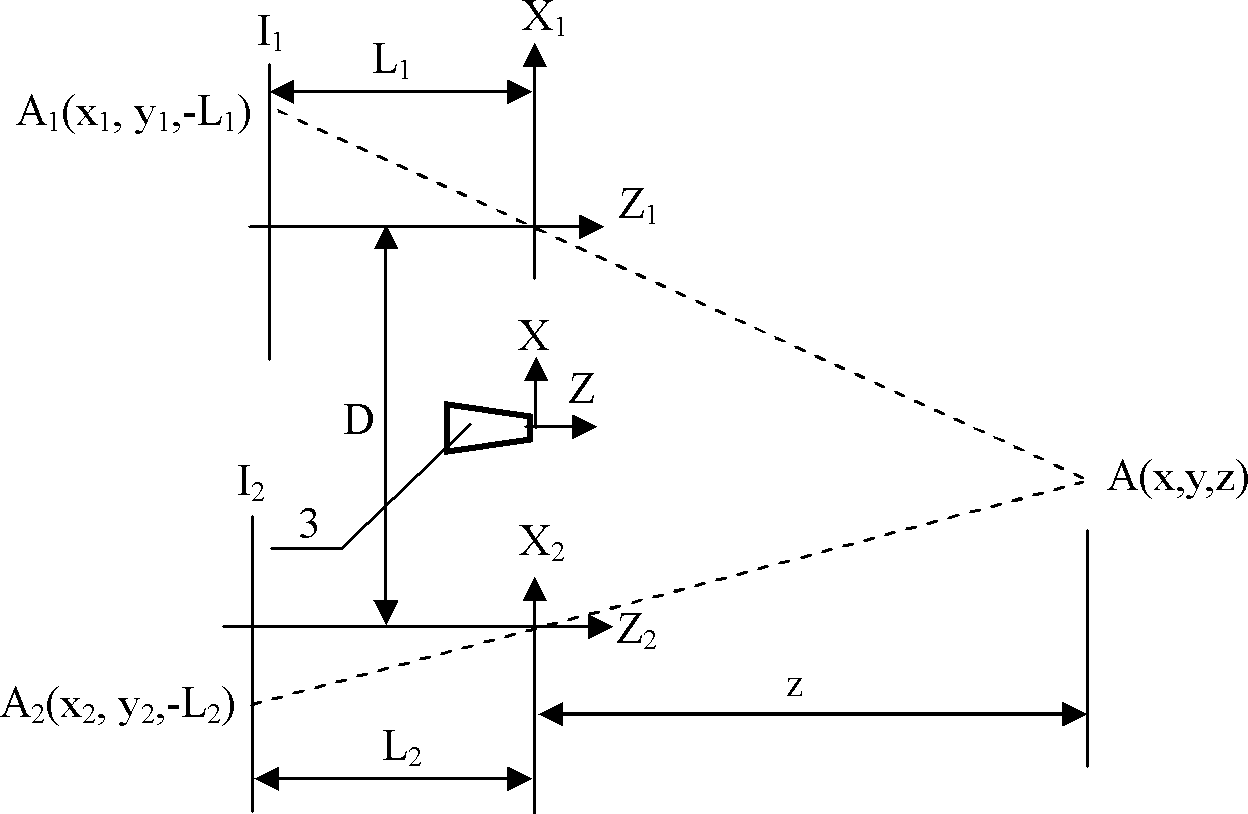
The invention discloses a three-dimensional photographing process based on a laser probe array and a device utilizing the same, and belongs to the field of three-dimensional photographing and measuring. Thousands of laser probes are projected to preset space positions according to the digital optical phase conjugation principle, reflection of the laser probes on surfaces of articles is monitored by a general two-dimensional camera, and then three-dimensional coordinate measurement is realized. Meanwhile, since the laser probe array is combined with a pair of three-dimensional cameras, more three-dimensional coordinates can be acquired by means of three-dimensional reconstruction, and accurate and compact three-dimensional coordinate measurement for large sites can be realized. Accordingly, three-dimensional matching treatment accuracy of three-dimensional images in the three-dimensional reconstruction process can be improved, matching treatment time is shortened, images picked up by the three-dimensional cameras can be compensated at the post stage, error in focal length and installation of the two cameras is eliminated, and requirements for the previous stage installation and synchronization of the focal length in the actual photographing process of the three-dimensional cameras are lowered. The three-dimensional photographing process based on the laser probe array and the device utilizing the same are applicable to fields of three-dimensional films, robots, intelligent driving, quick detection for obstacles, automatic measurement for industrial parts, and the like.
Owner:李志扬
Iteration of optical time reversal by ultrasonic encoding in biological tissue
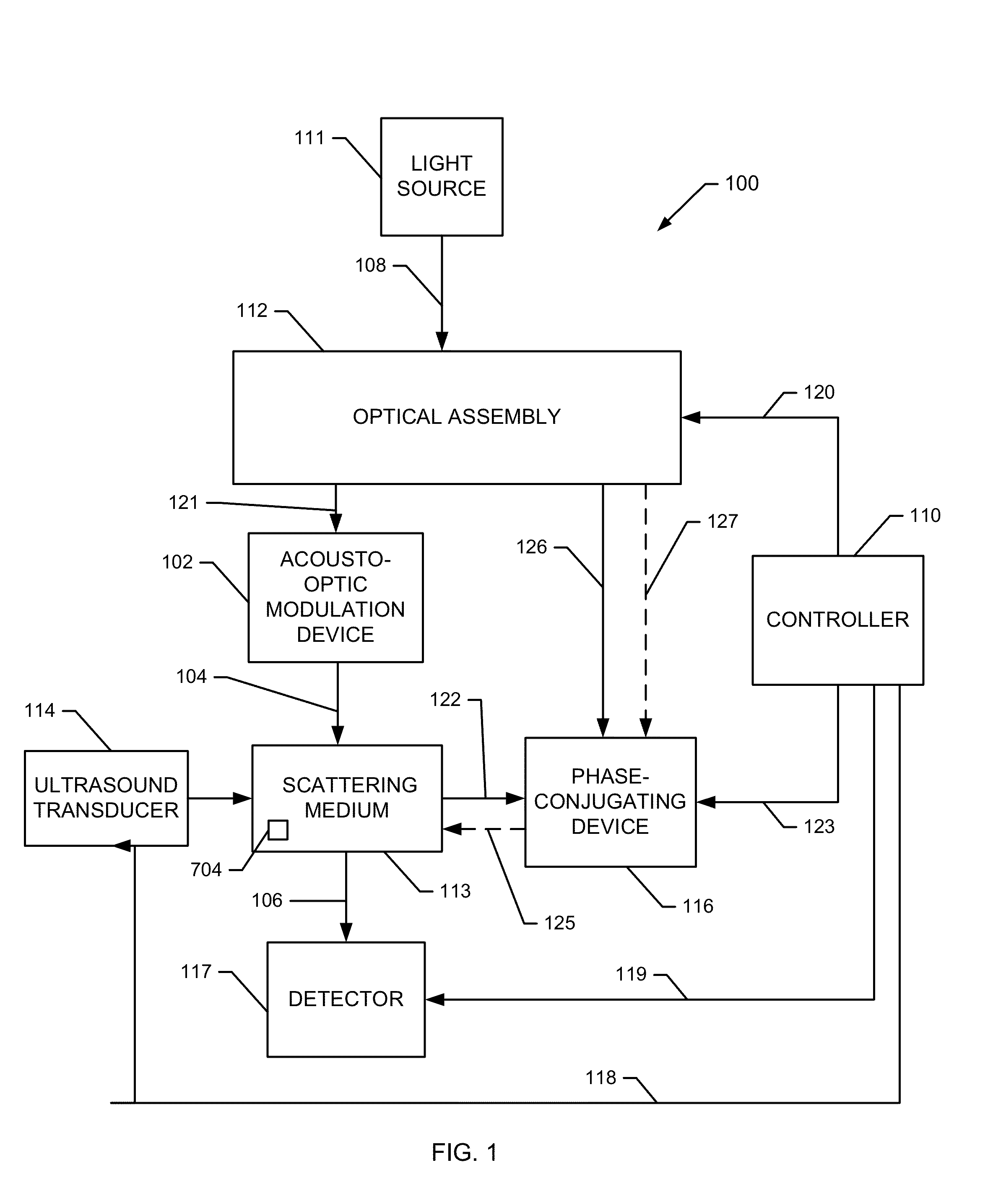
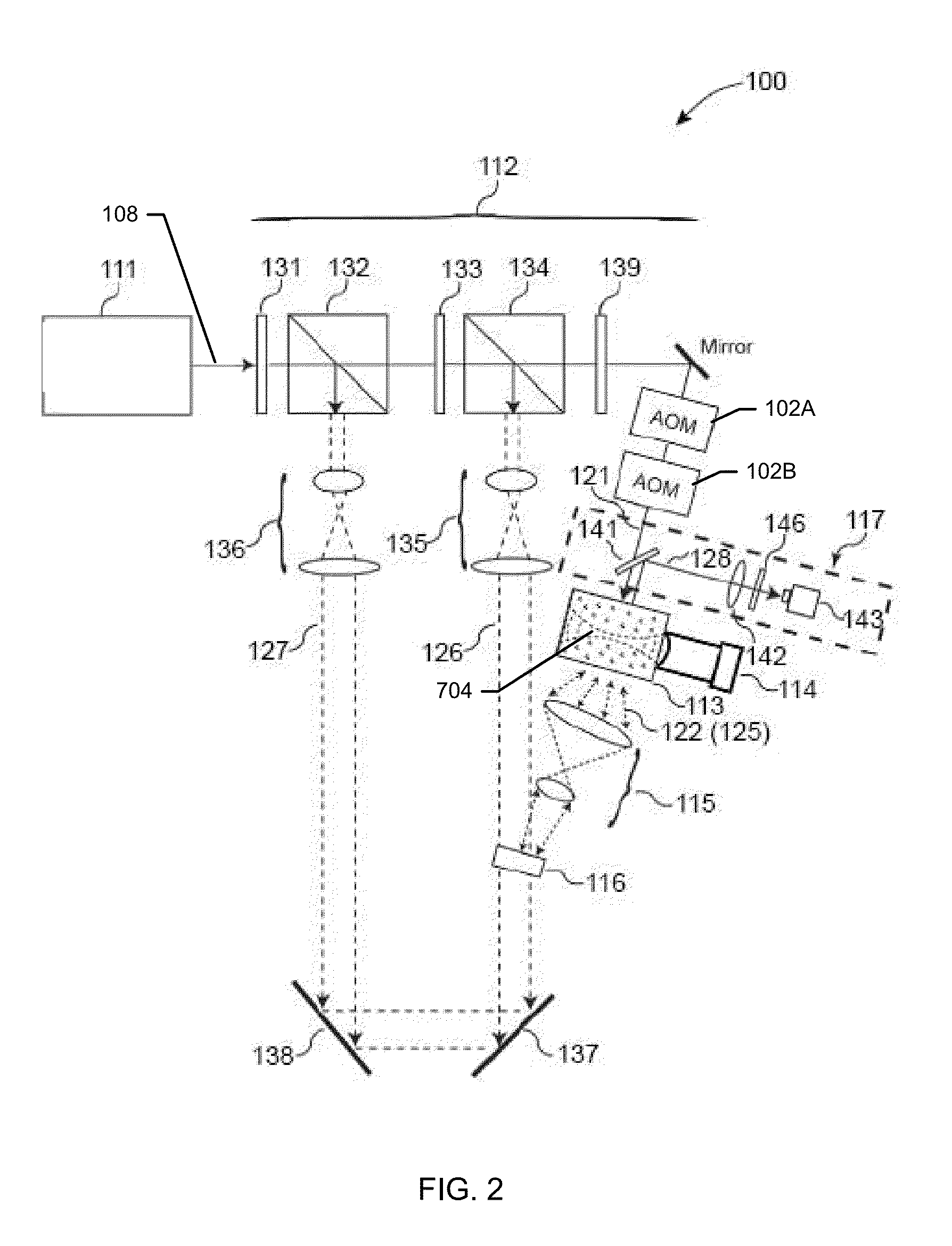
ActiveUS20140009808A1Beam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansSonificationOptical phase conjugation
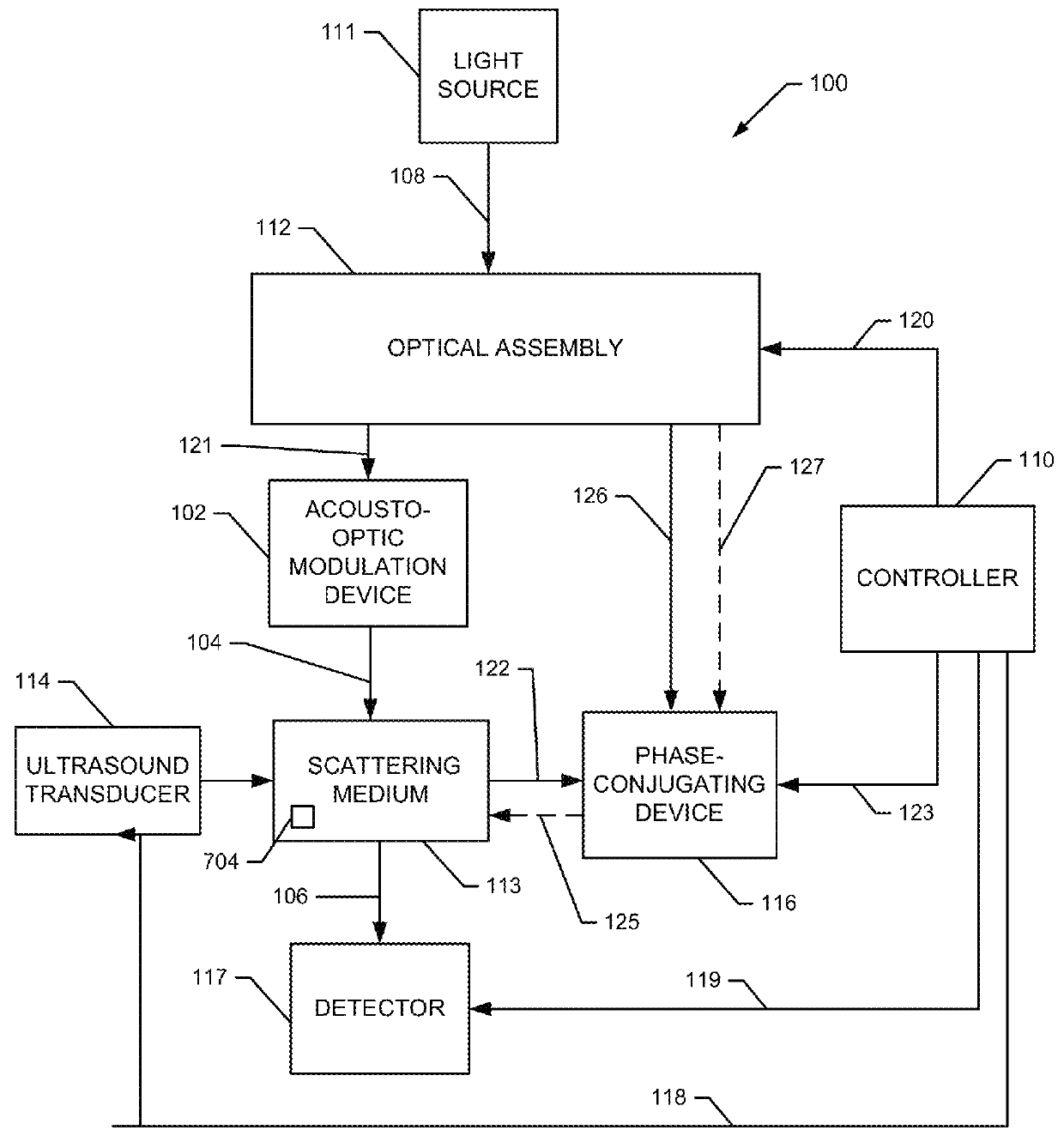
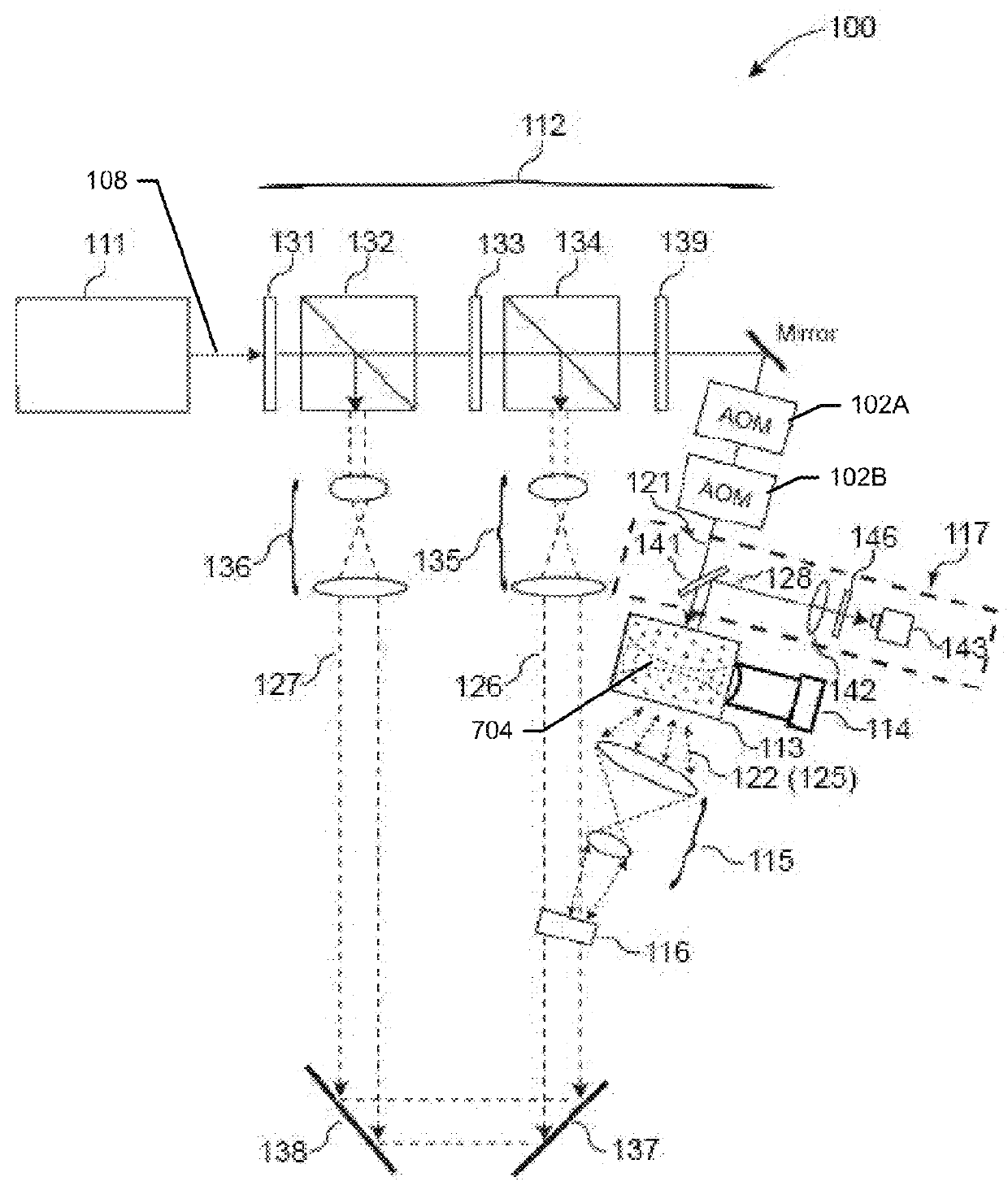
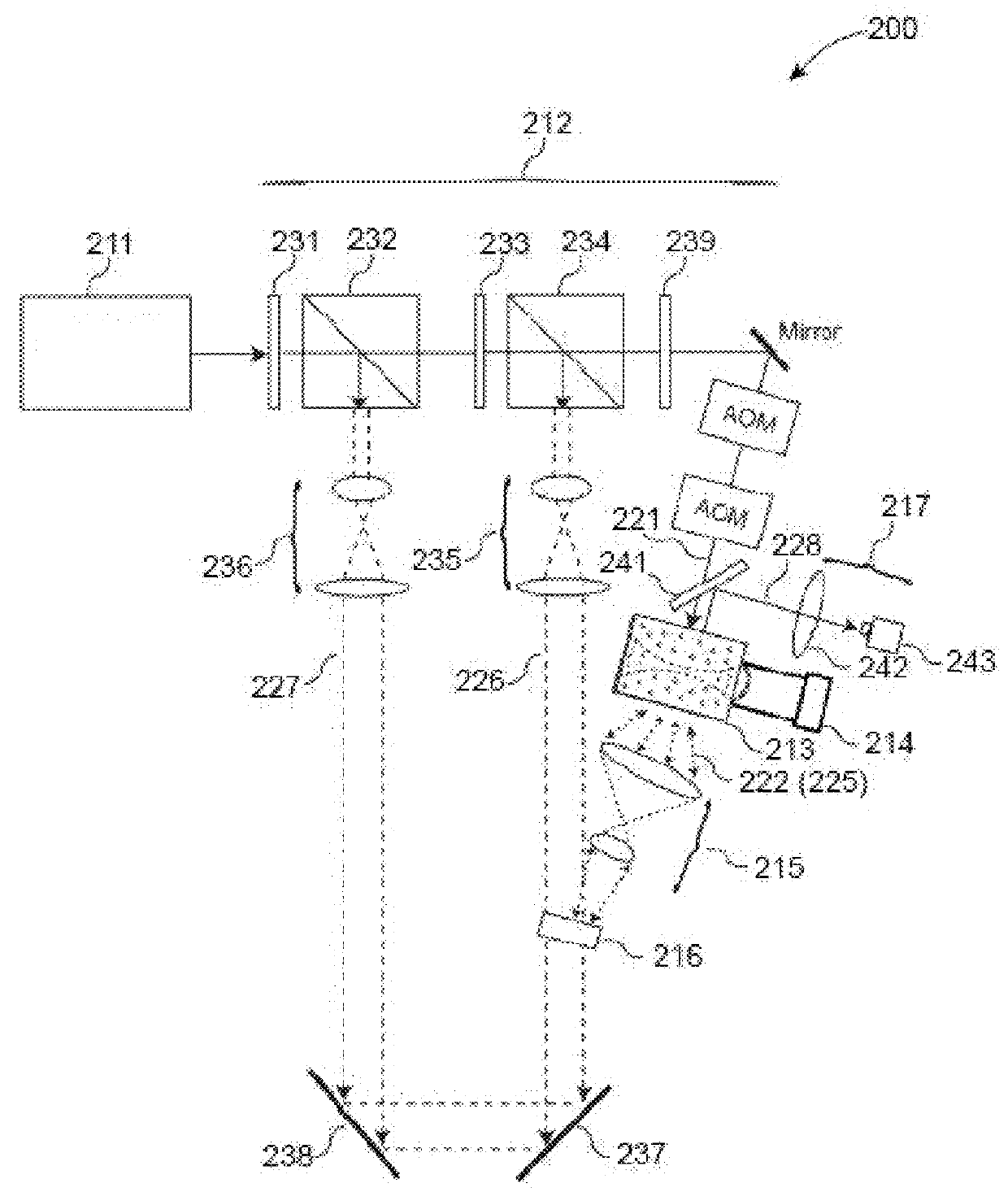
Iterating an optical phase conjugation of ultrasonically-modulated diffuse light emitted by a scattering medium includes illuminating the scattering medium with a light beam from a coherent light source, modulating the diffuse light transmitted through the scattering medium with an ultrasonic wave focused on a region of interest within the scattering medium, fixing a hologram, retro-reflectively illuminating the scattering medium using a phase-conjugated copy of the diffuse light that was ultrasonically modulated, moving the ultrasonic focus, and iterating until light is focused on the final target.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
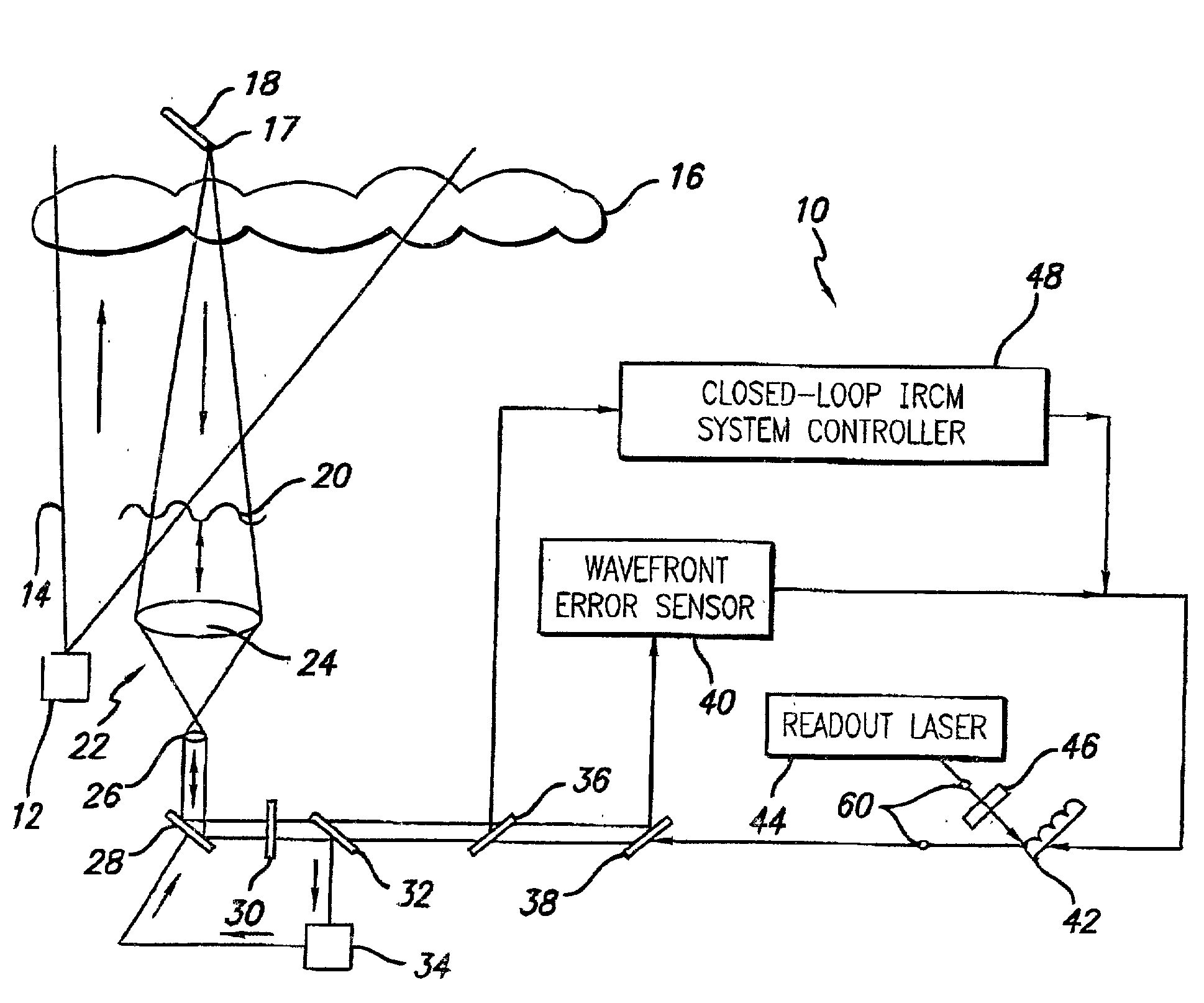
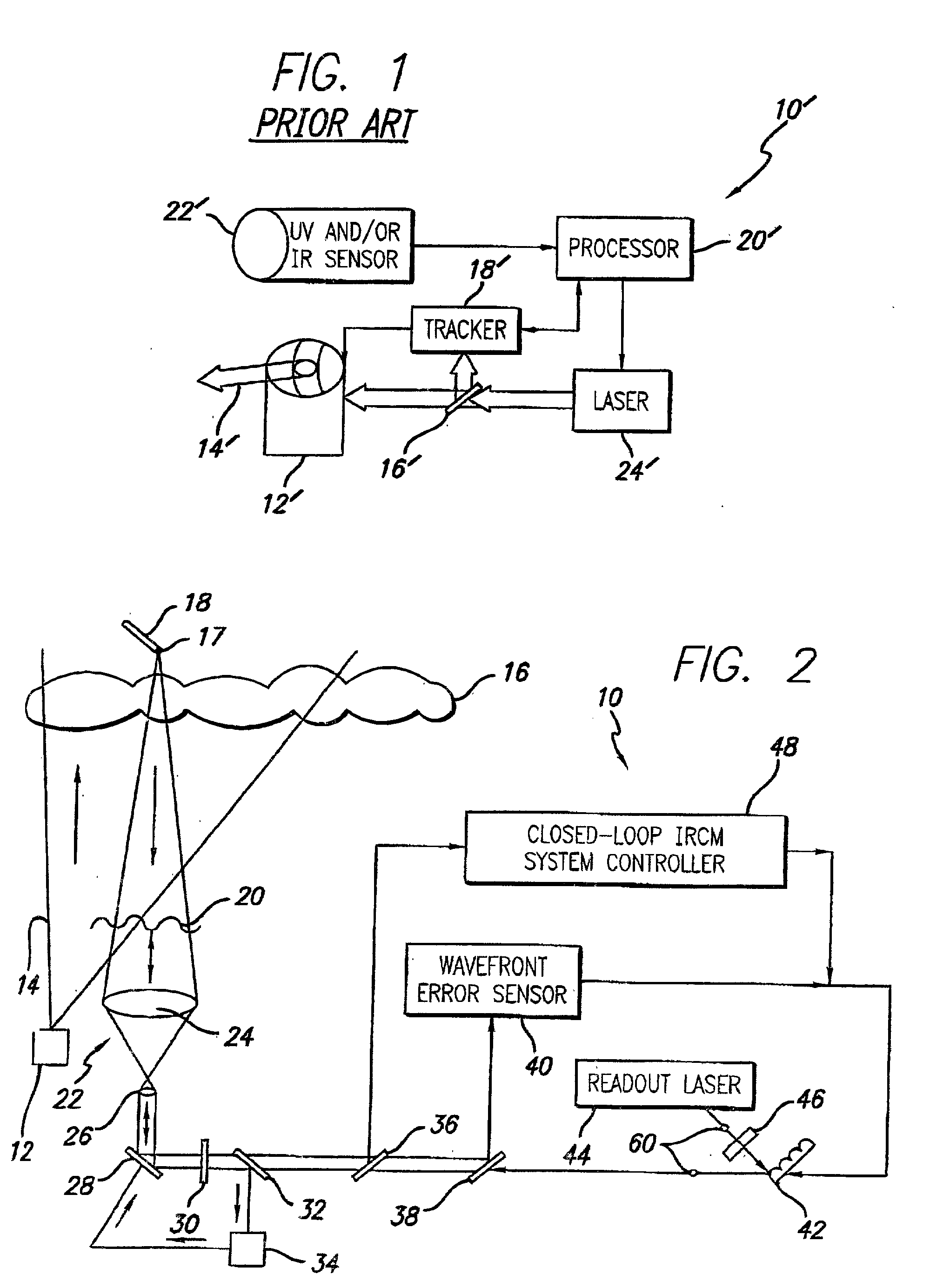
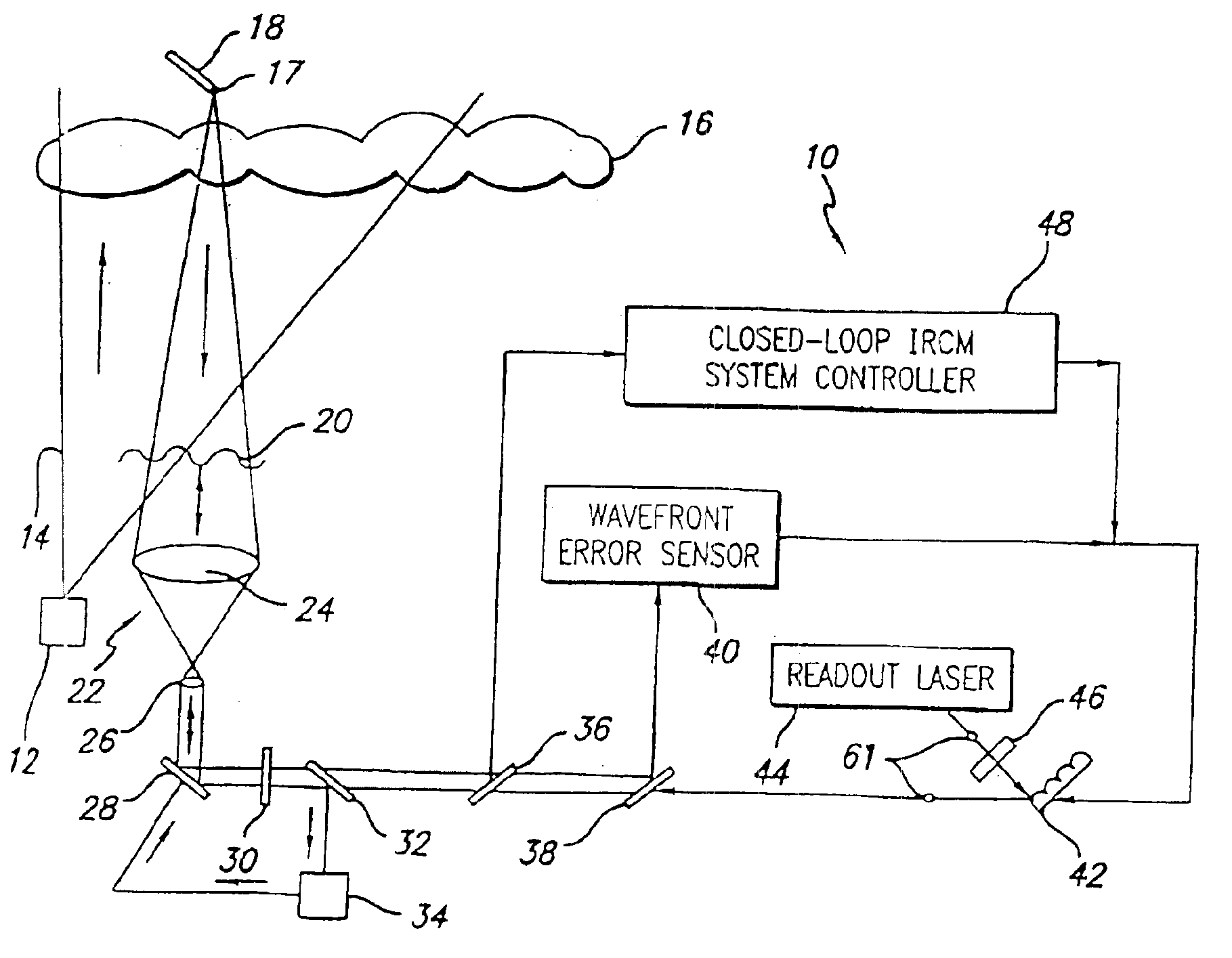
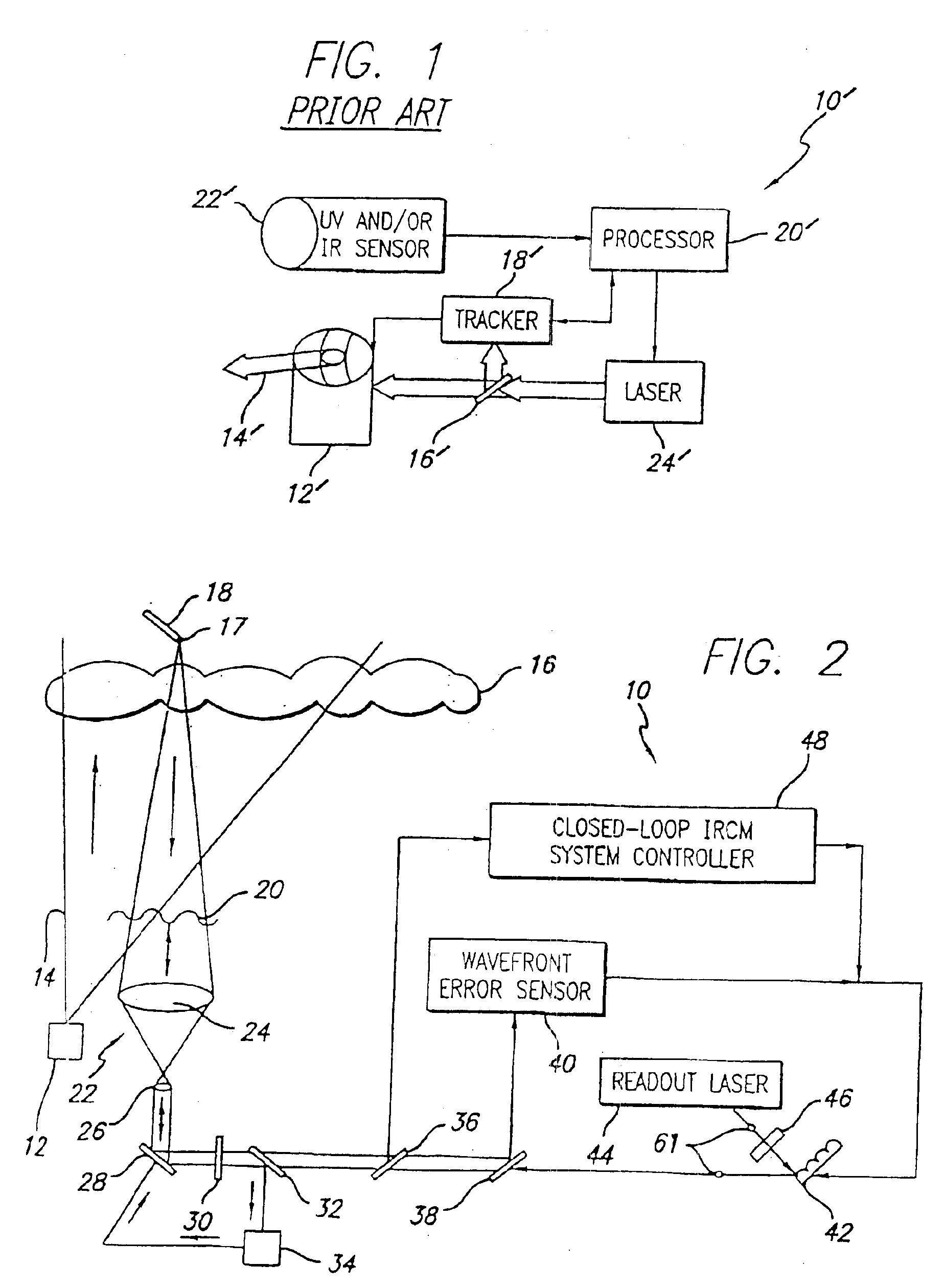
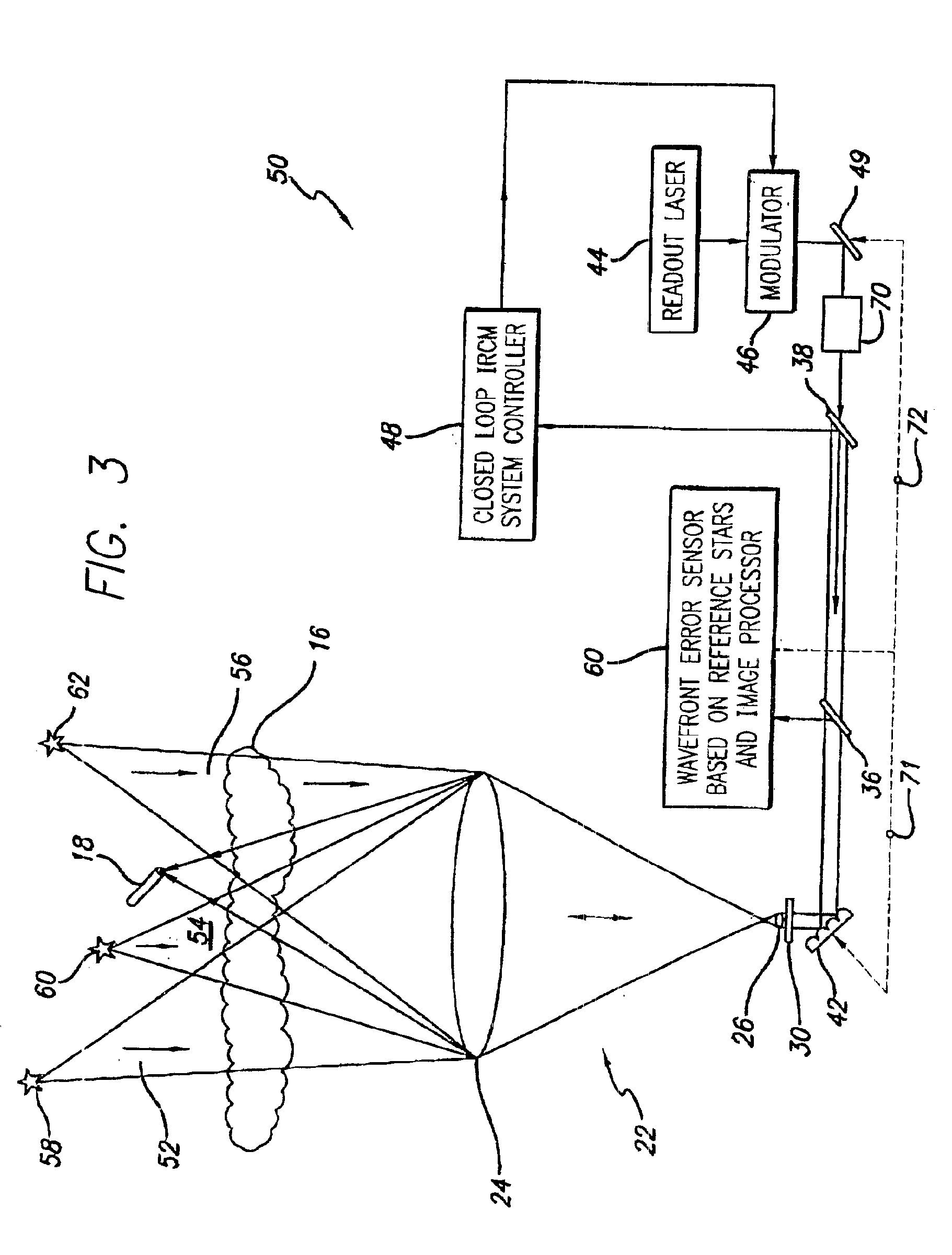
Robust infrared countermeasure system and method
InactiveUS20020153497A1Photometry using reference valueWave based measurement systemsCountermeasureOptical phase conjugation
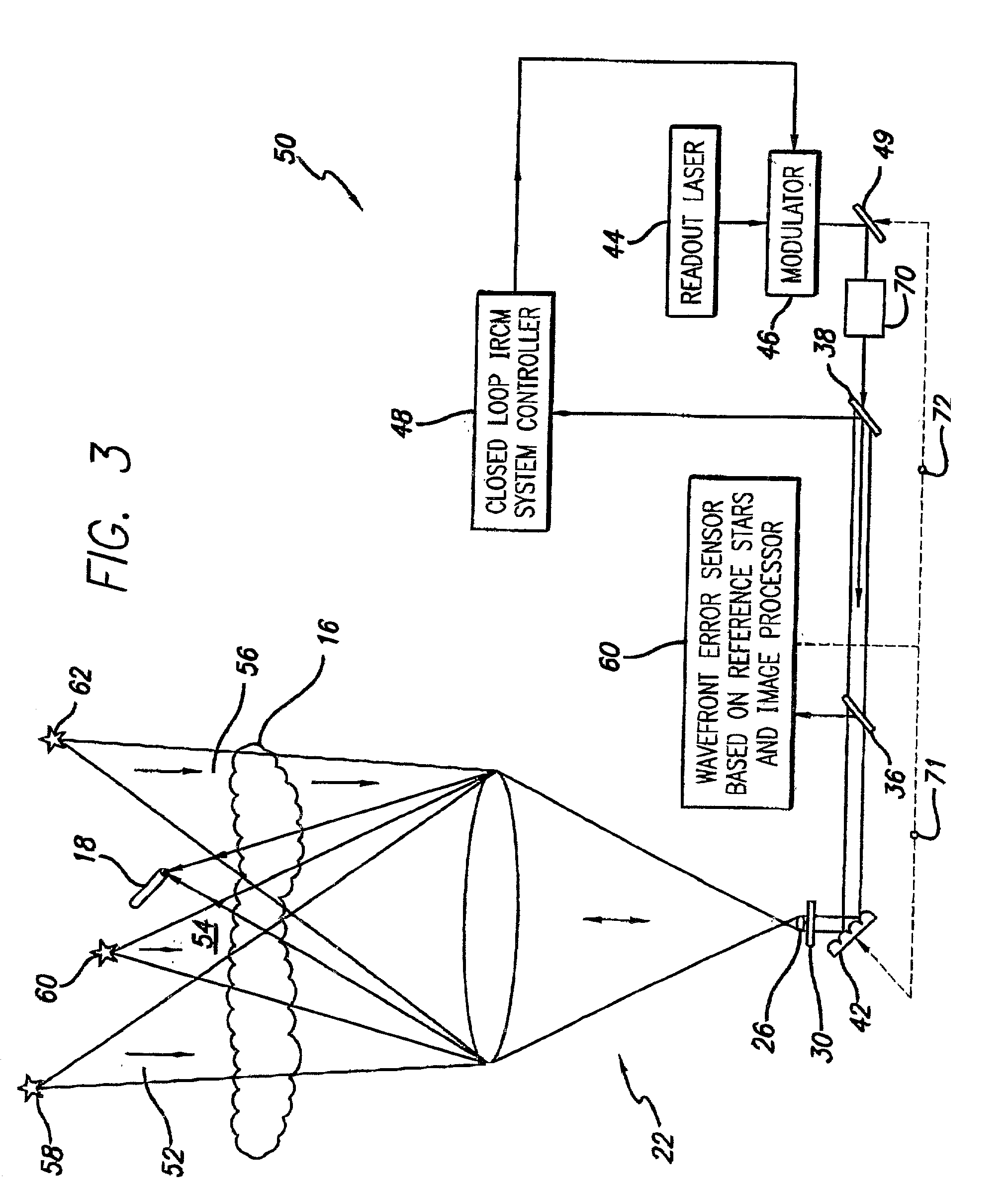
A system and method for focusing electromagnetic energy on a moving target. Generally, the inventive system sends a pilot beam to a target and analyzes a return wavefront to ascertain data with respect to any distortions and other phase and / or amplitude information in the wavefront. This information is then used to pre-distort an output beam by so that it is focused on the target by the intervening distortions. In an illustrative embodiment, the pilot beam is provided by a beacon laser mounted off-axis with respect to the output beam. The reflected wavefront is received through a gimbaled telescope. Energy received by the telescope is detected and processed to ascertain wavefront aberrations therein. This data is used to predistort a deformable mirror to create an output beam which is the phase conjugate of the received wavefront. In a first alternative embodiment, a nonlinear optical phase-conjugate mirror is employed to generate the required wavefront-reversed replica of the received wavefront. The system further includes an arrangement for modulating the output beam to confuse the target. In a second alternative embodiment, the system is adapted to examine atmospheric distortions of starlight to predistort the output beam. The alternative embodiment offers a faster response time and a lower susceptibility to detection.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Glare suppression through fog by optical phase conjugation assisted active cancellation
ActiveUS20170118423A1Small impactGlare suppressionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptical phase conjugationMethod of images
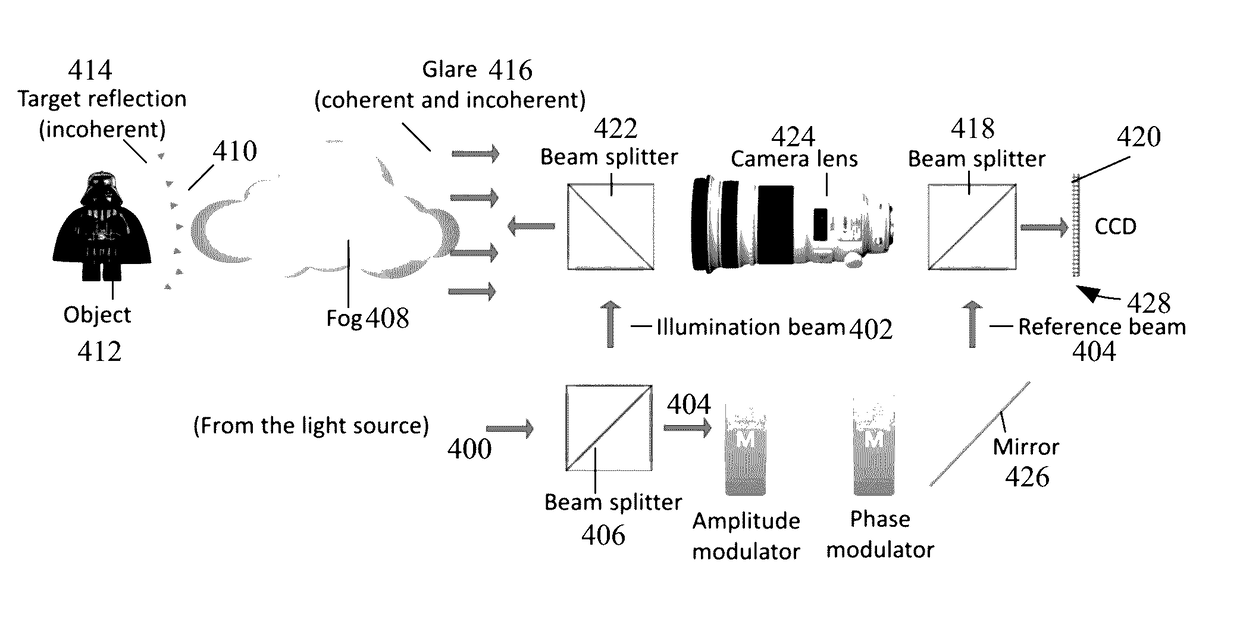
A method of imaging an object on one or more sensor pixels and with reduced glare. The method includes irradiating a scattering medium and the object behind the scattering medium, creating backscattered radiation and imaging radiation that are received on the one or more pixels. The method includes digitally adjusting a phase, an amplitude, or a phase and amplitude, of reference radiation transmitted onto the one or more sensor pixels, wherein the reference radiation destructively interferes with the backscattered radiation (glare) on the one or more sensor pixels while the object is imaged on the one or more sensor pixels using the imaging radiation.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Optical phase conjugation laser diode
A phase-conjugating resonator that includes a semiconductor laser diode apparatus that comprises a phase-conjugating array of retro-reflecting hexagon apertured hexahedral shaped corner-cube prisms, an electrically and / or optically pumped gain-region, a distributed bragg reflecting mirror-stack, a gaussian mode providing hemispherical shaped laser-emission-output metalized mirror. Wherein, optical phase conjugation is used to neutralize the phase perturbating contribution of spontaneous-emission, acoustic phonons, quantum-noise, gain-saturation, diffraction, and other intracavity aberrations and distortions that typically destabilize any stimulated-emission made to undergo amplifying oscillation within the inventions phase-conjugating resonator. Resulting in stablized high-power laser-emission-output into a single low-order fundamental transverse cavity mode and reversal of intra-cavity chirp that provides for high-speed internal modulation capable of transmitting data at around 20-Gigabits / ps.
Owner:HENRICHS JOSEPH REID
Acoustic assisted phase conjugate optical tomography
ActiveUS20110108707A1Improve efficiencySufficient powerOptical radiation measurementSolid-state devicesSpatial light modulatorOptical tomography
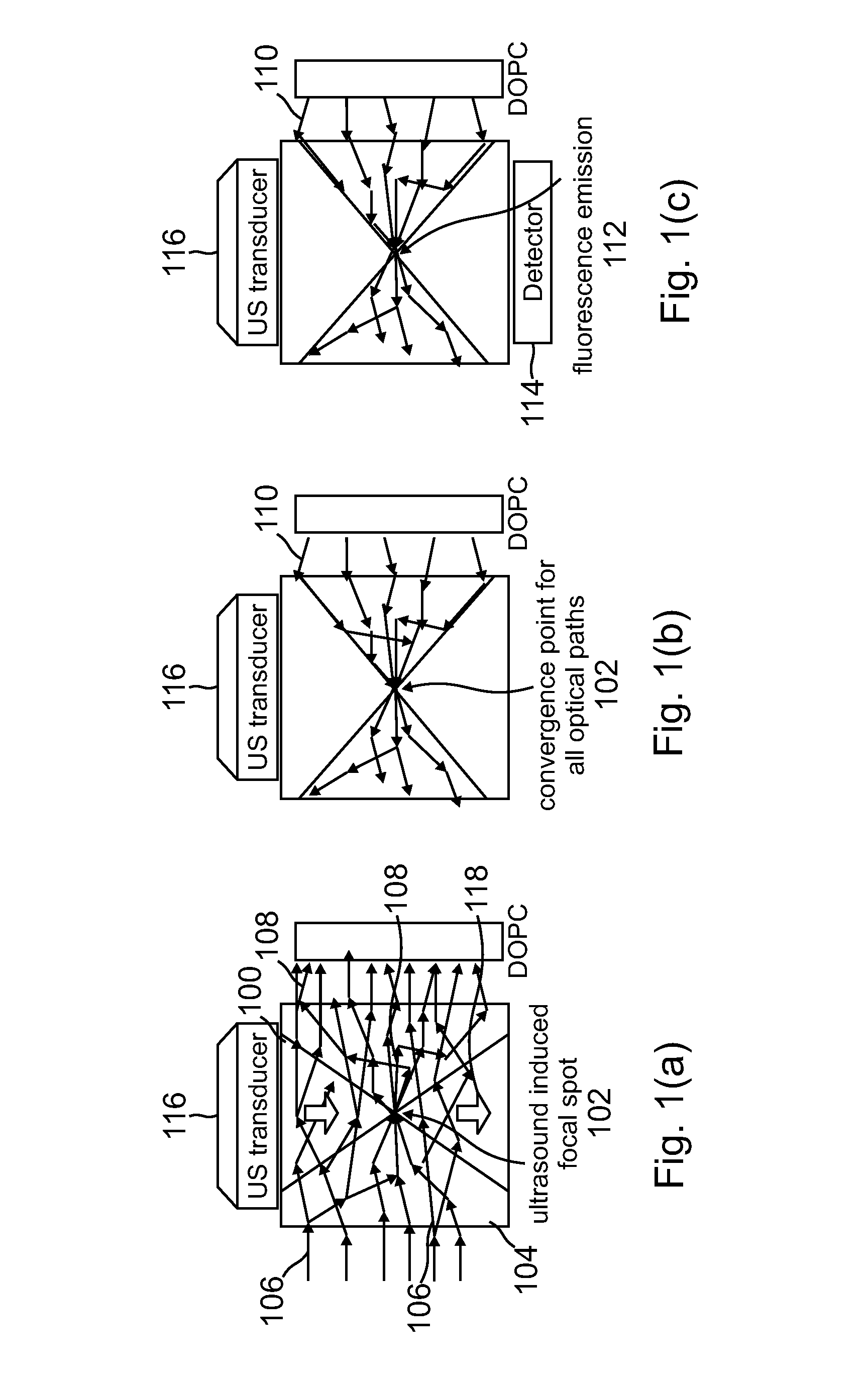
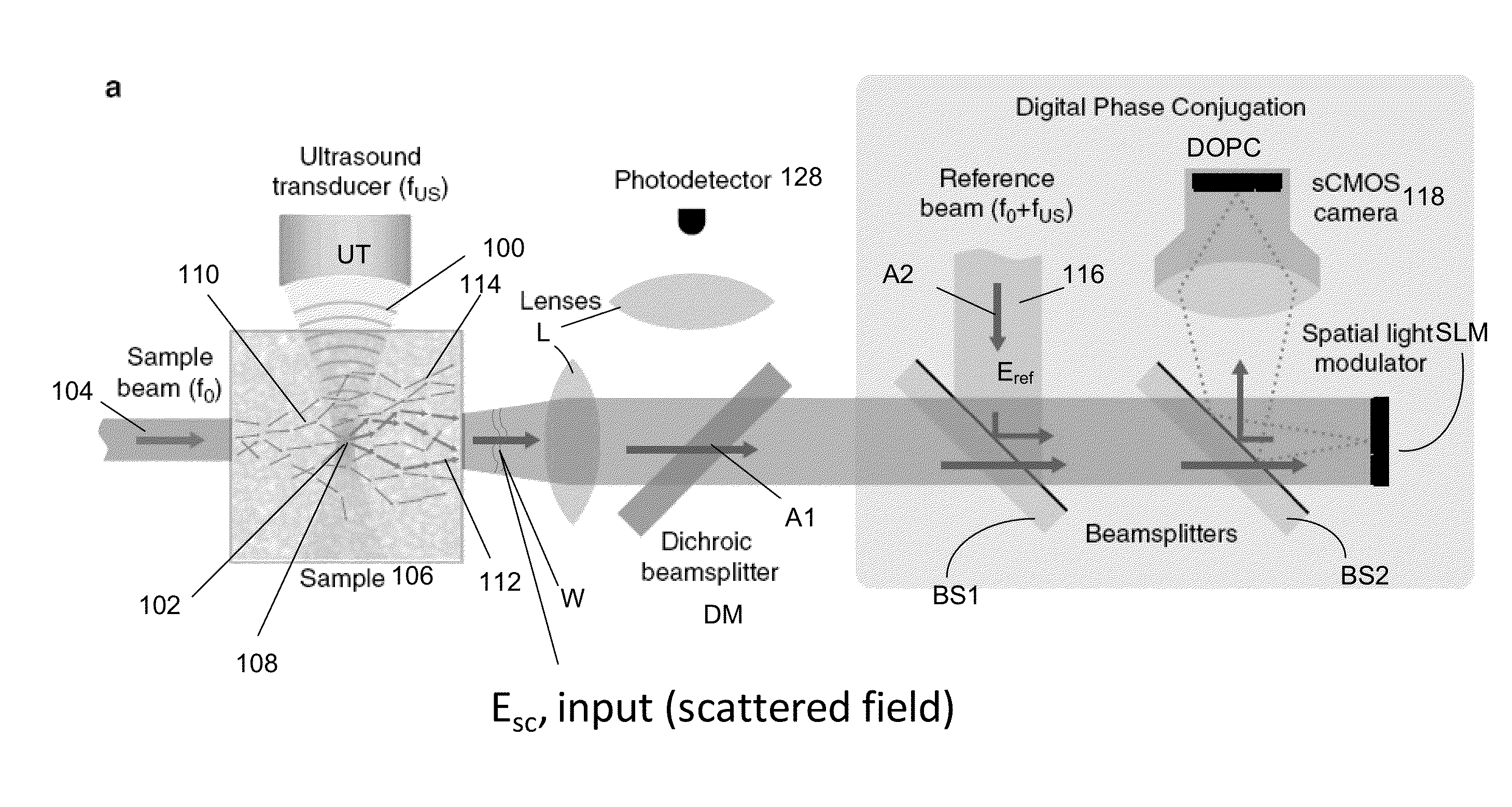
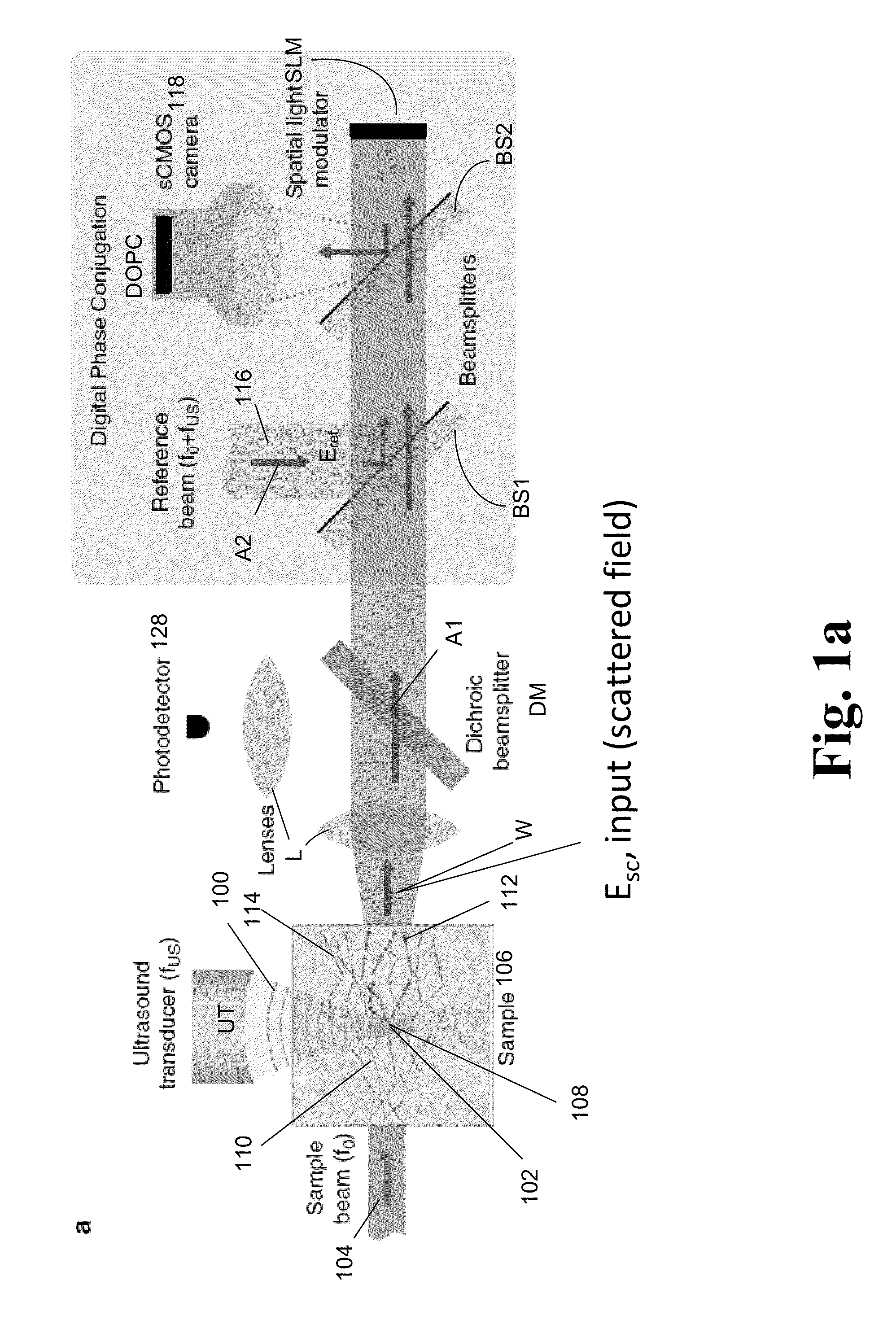
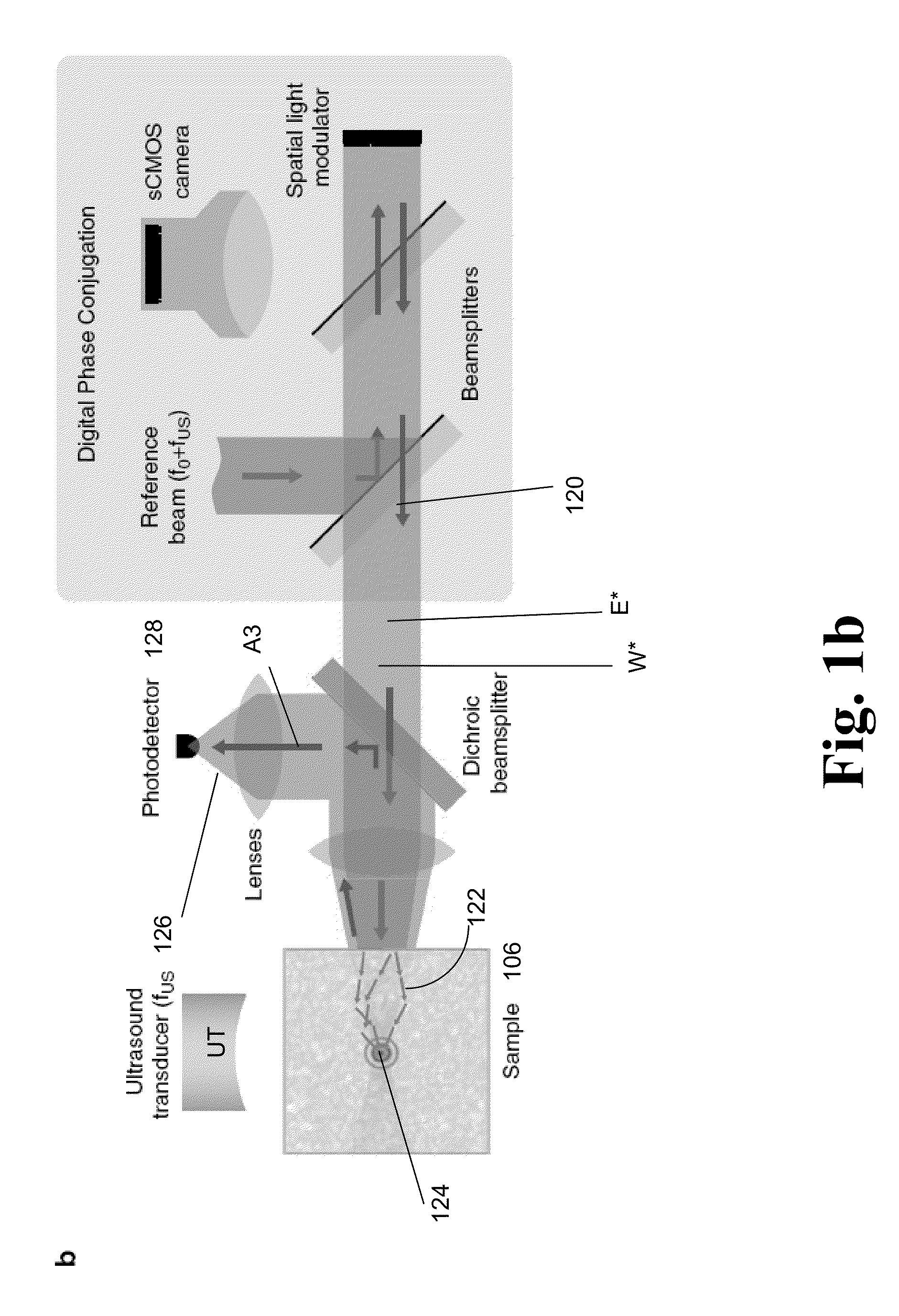
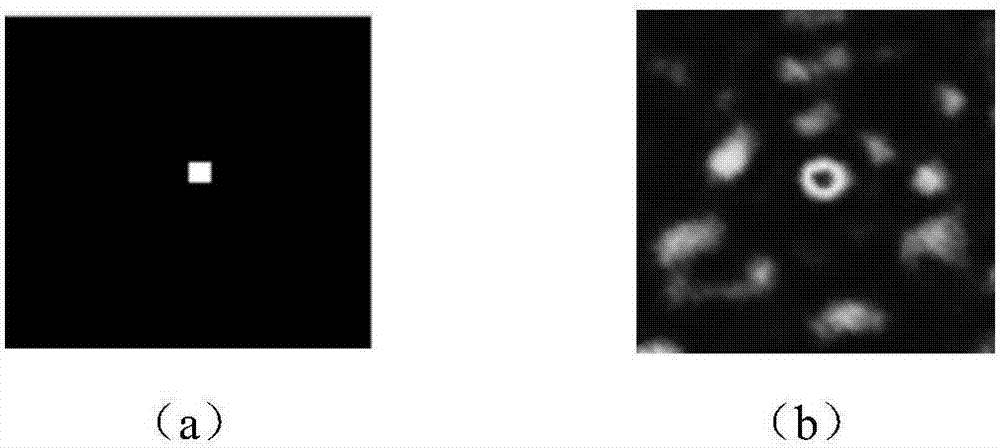
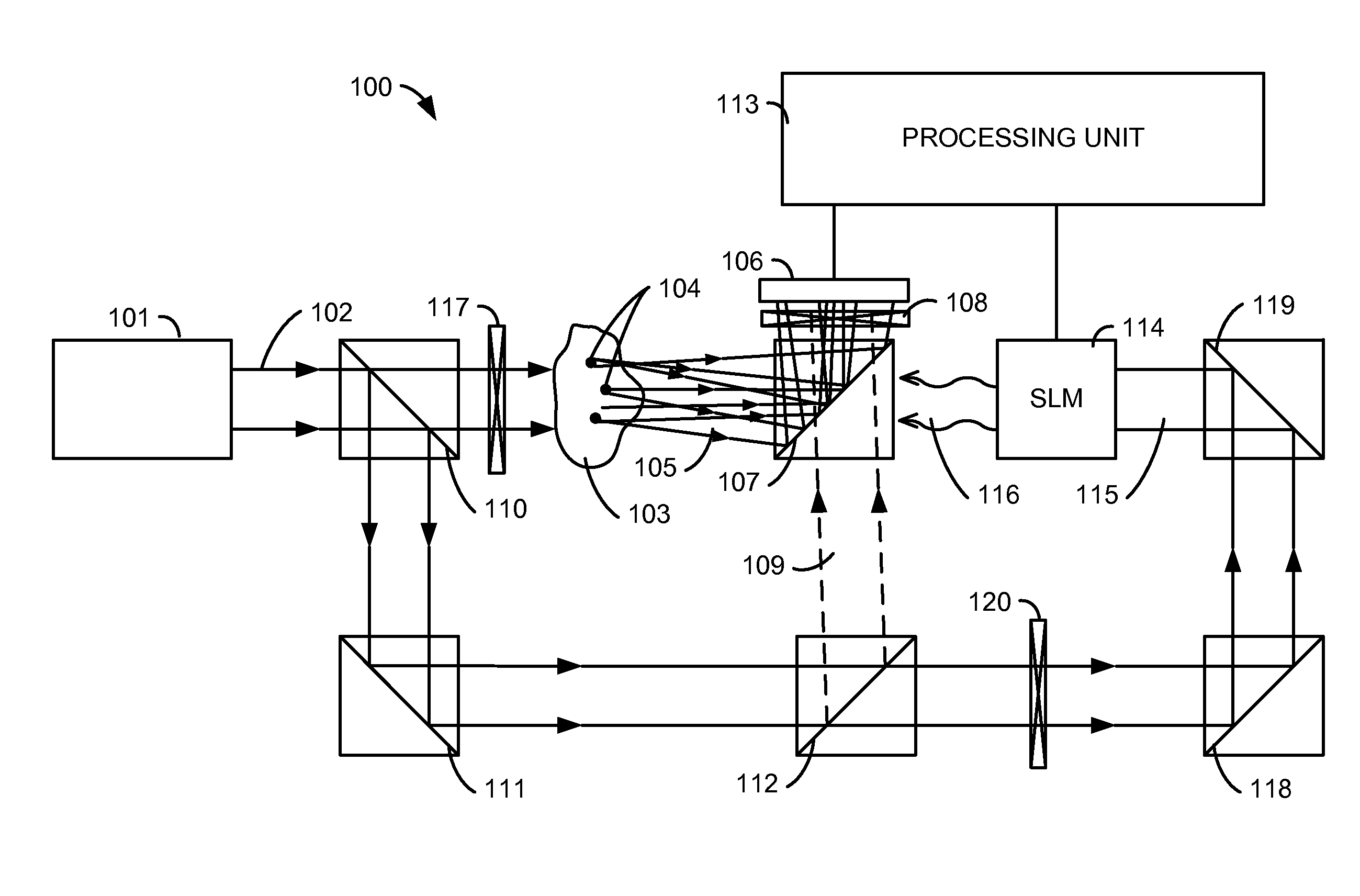
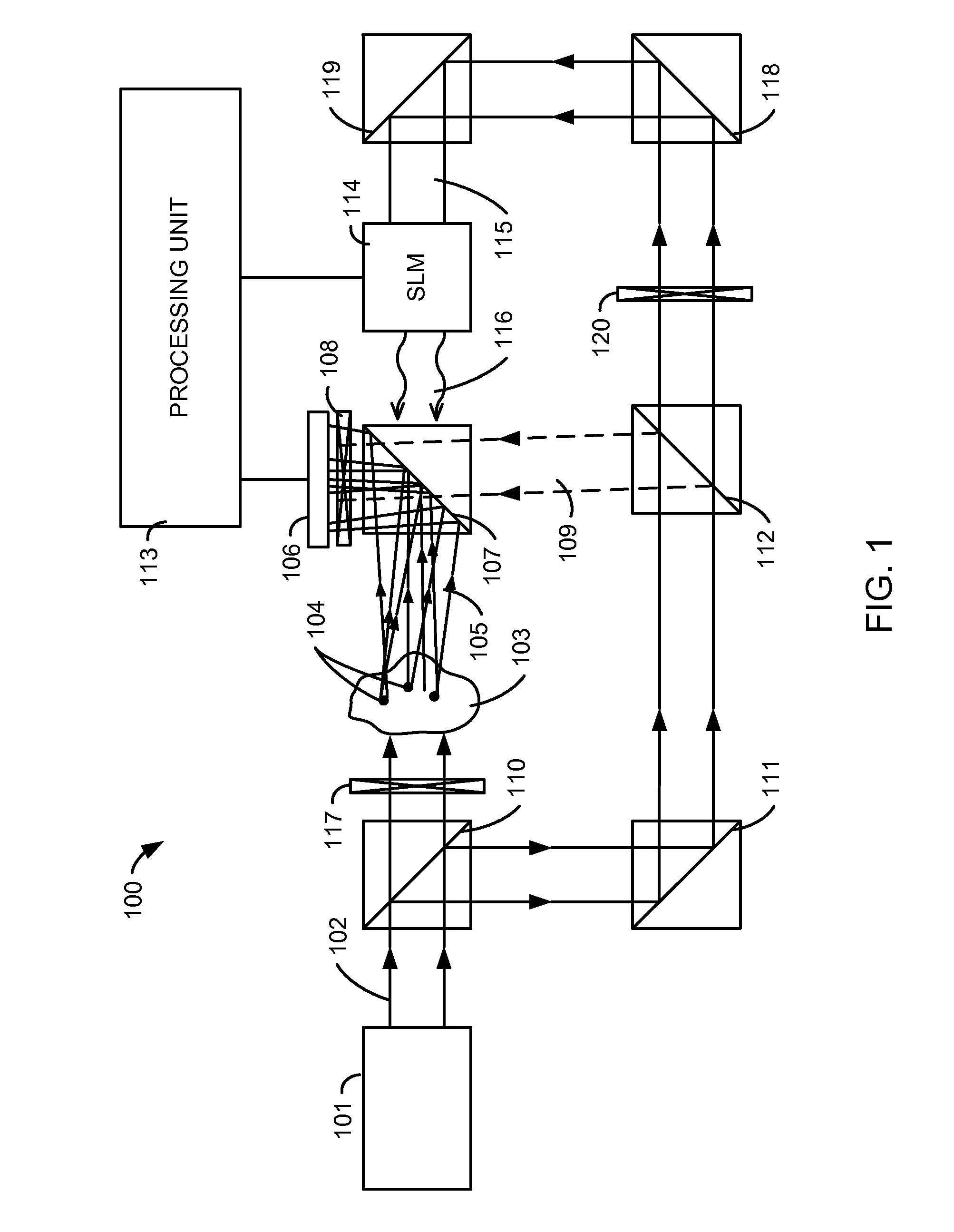
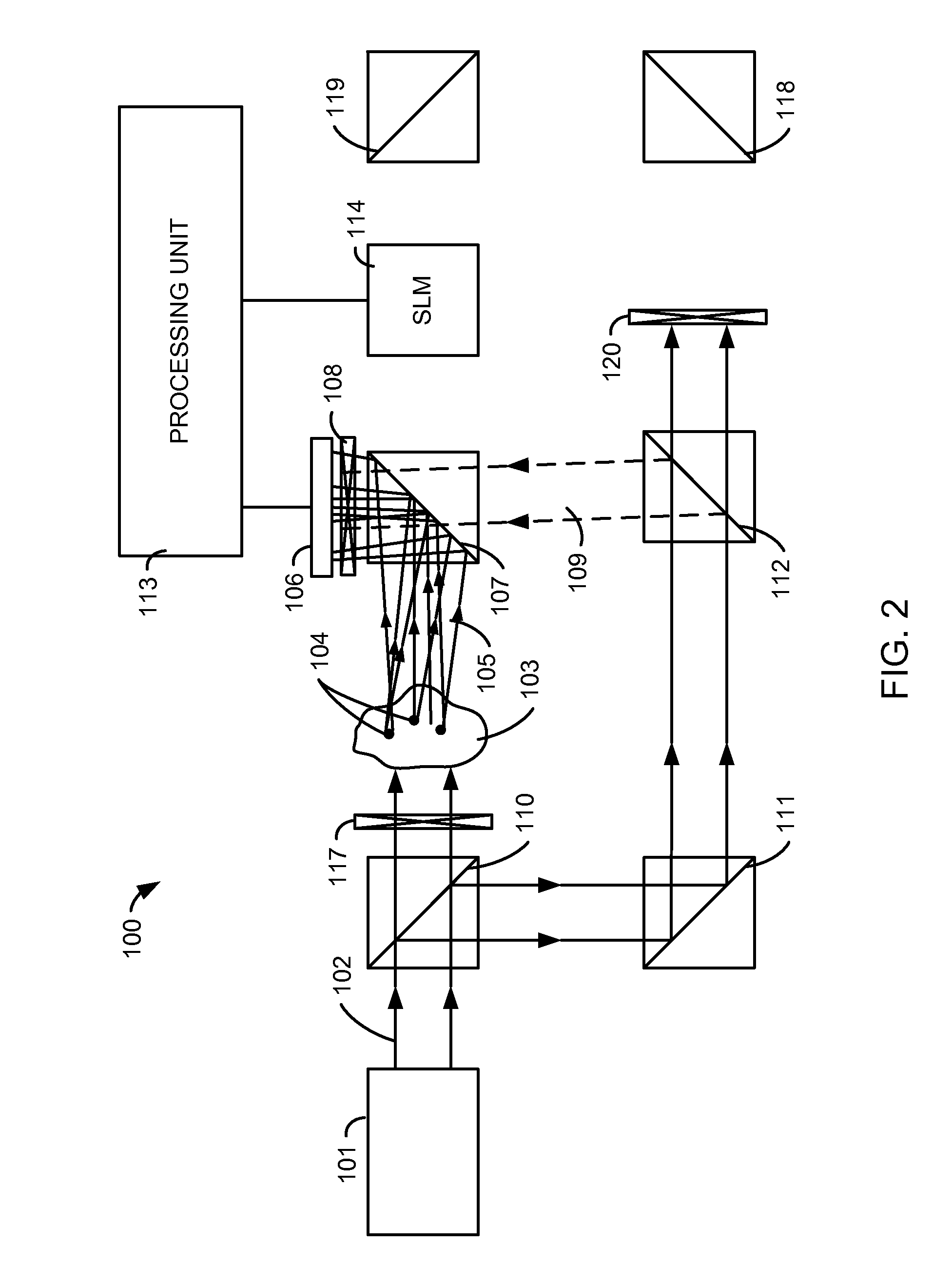
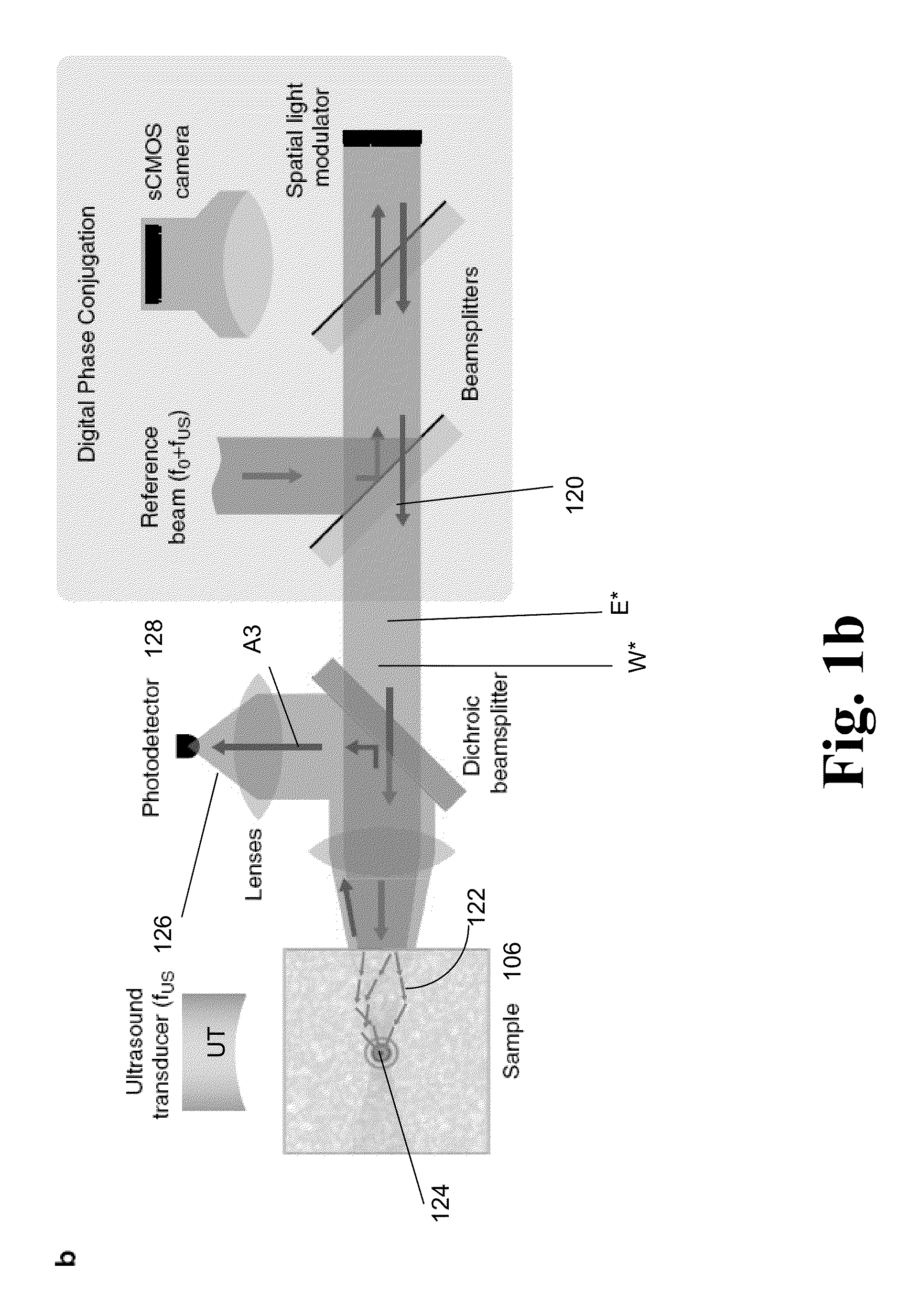
A light microscope for imaging a sample containing one or more fluorescent agents, comprising a source for generating acoustic waves that are focused at a focus in the sample, wherein the acoustic waves frequency shift a frequency of light passing through the focus, thereby creating a frequency shifted light beam; at least one spatial light modulator (SLM) positioned to illuminate the sample with an output beam that is an optical phase conjugate of the frequency shifted light beam, wherein the output beam is a reflection of a first reference beam off one or more pixels of the SLM, and the pixels are for modulating the first reference beam to create the output beam; and a detector positioned to detect fluorescence generated by the output beam exciting the fluorescent agents at the focus in the sample, thereby imaging the sample.
Owner:LONDON SCHOOL OF HYGIENE & TROPICAL MEDICINE +1
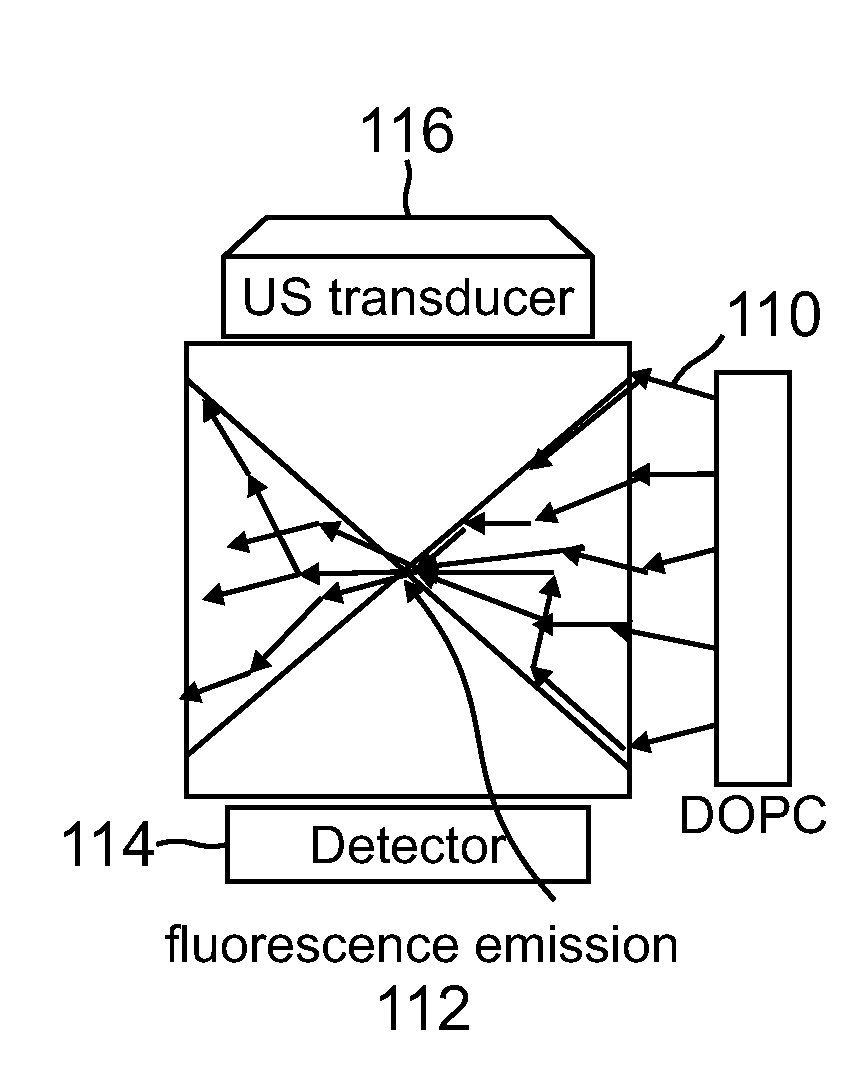
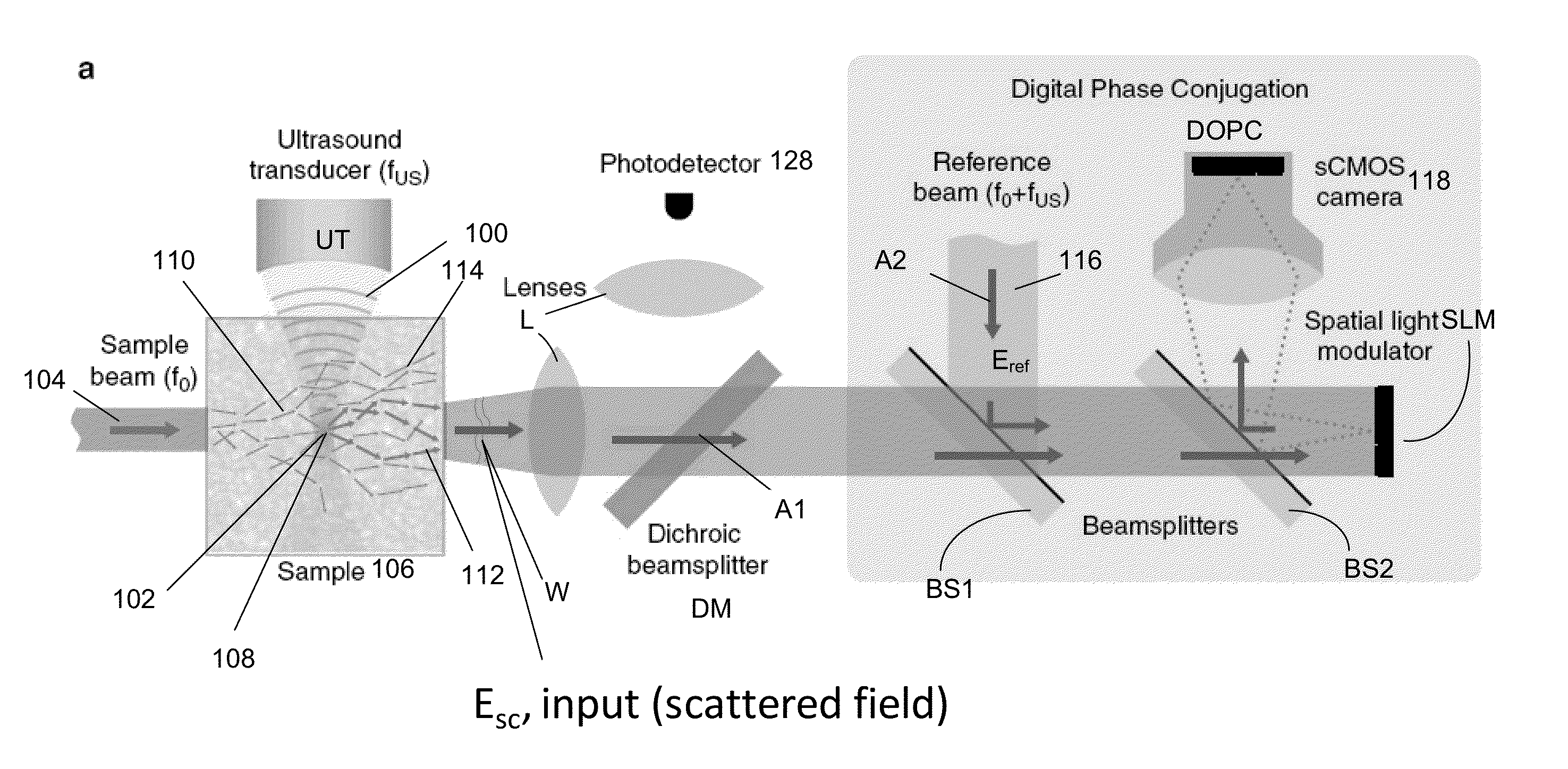
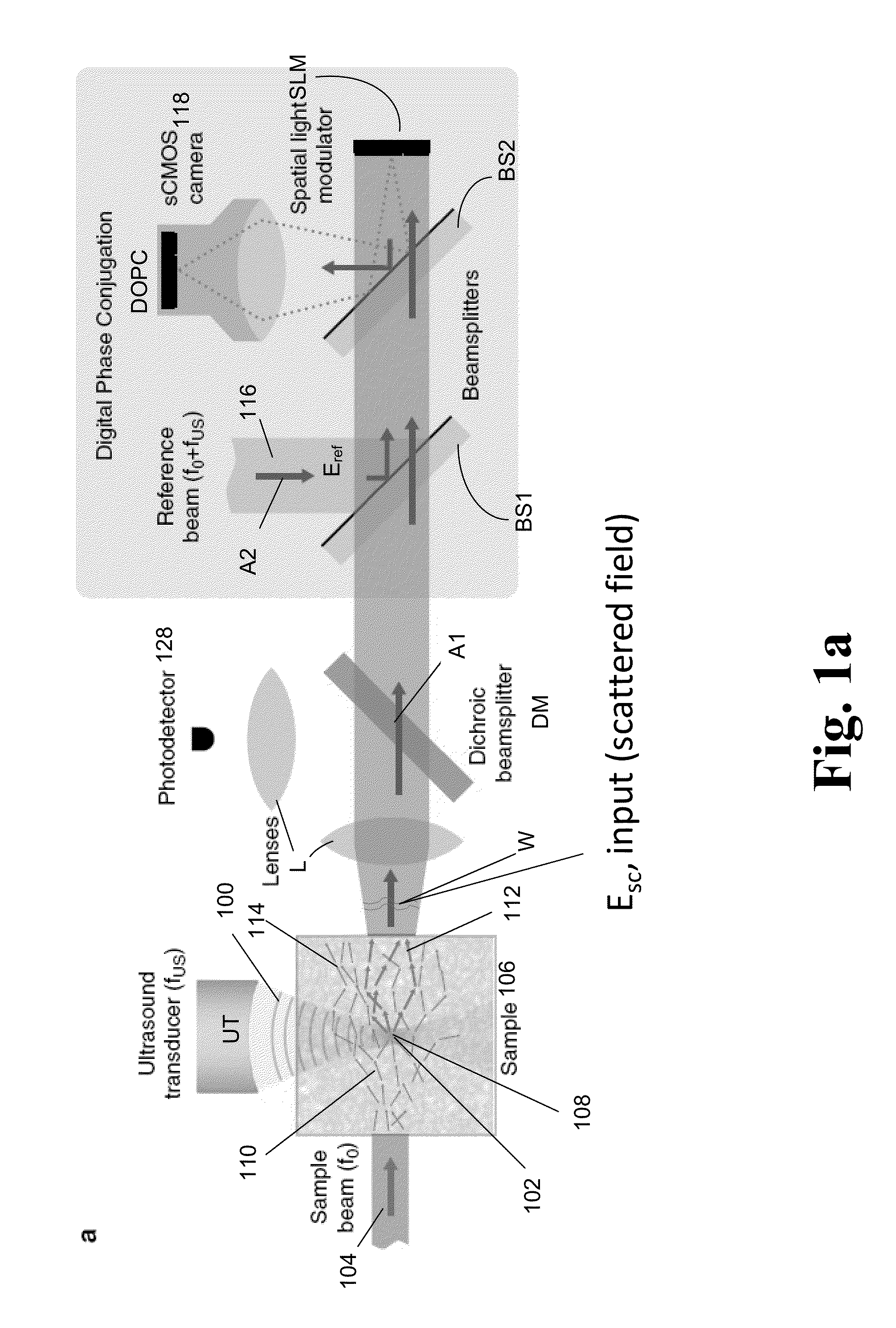
Deep tissue focal fluorescence imaging with digitally time-reversed ultrasound-encoded light
ActiveUS9313423B2Television system detailsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSpatial light modulatorSonification
A device and method for performing fluorescence imaging with digitally time reversed ultrasound encoded light, using a source of ultrasound waves, a coherent light source, a digital optical phase conjugation (DOPC) device comprising a camera and a spatial light modulator (SLM), a detector of fluorescence, and one or more computers, to obtain an output that at least approximates an interaction between a complete time reversed field, of all of the encoded light's fields, and the scattering medium.
Owner:LONDON SCHOOL OF HYGIENE & TROPICAL MEDICINE +1
Iteration of optical time reversal by ultrasonic encoding in biological tissue
ActiveUS9335605B2Holographic object characteristicsUsing optical meansSonificationOptical phase conjugation
Iterating an optical phase conjugation of ultrasonically-modulated diffuse light emitted by a scattering medium includes illuminating the scattering medium with a light beam from a coherent light source, modulating the diffuse light transmitted through the scattering medium with an ultrasonic wave focused on a region of interest within the scattering medium, fixing a hologram, retro-reflectively illuminating the scattering medium using a phase-conjugated copy of the diffuse light that was ultrasonically modulated, moving the ultrasonic focus, and iterating until light is focused on the final target.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
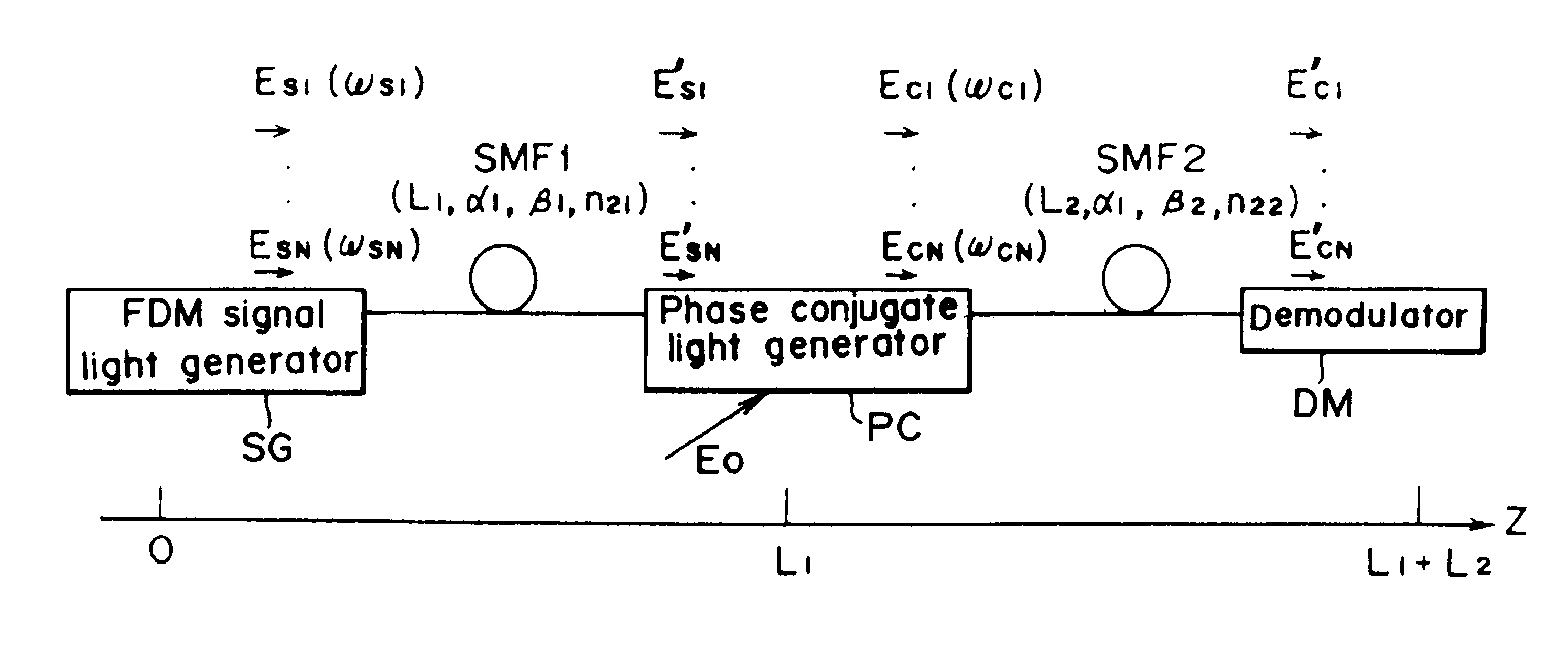
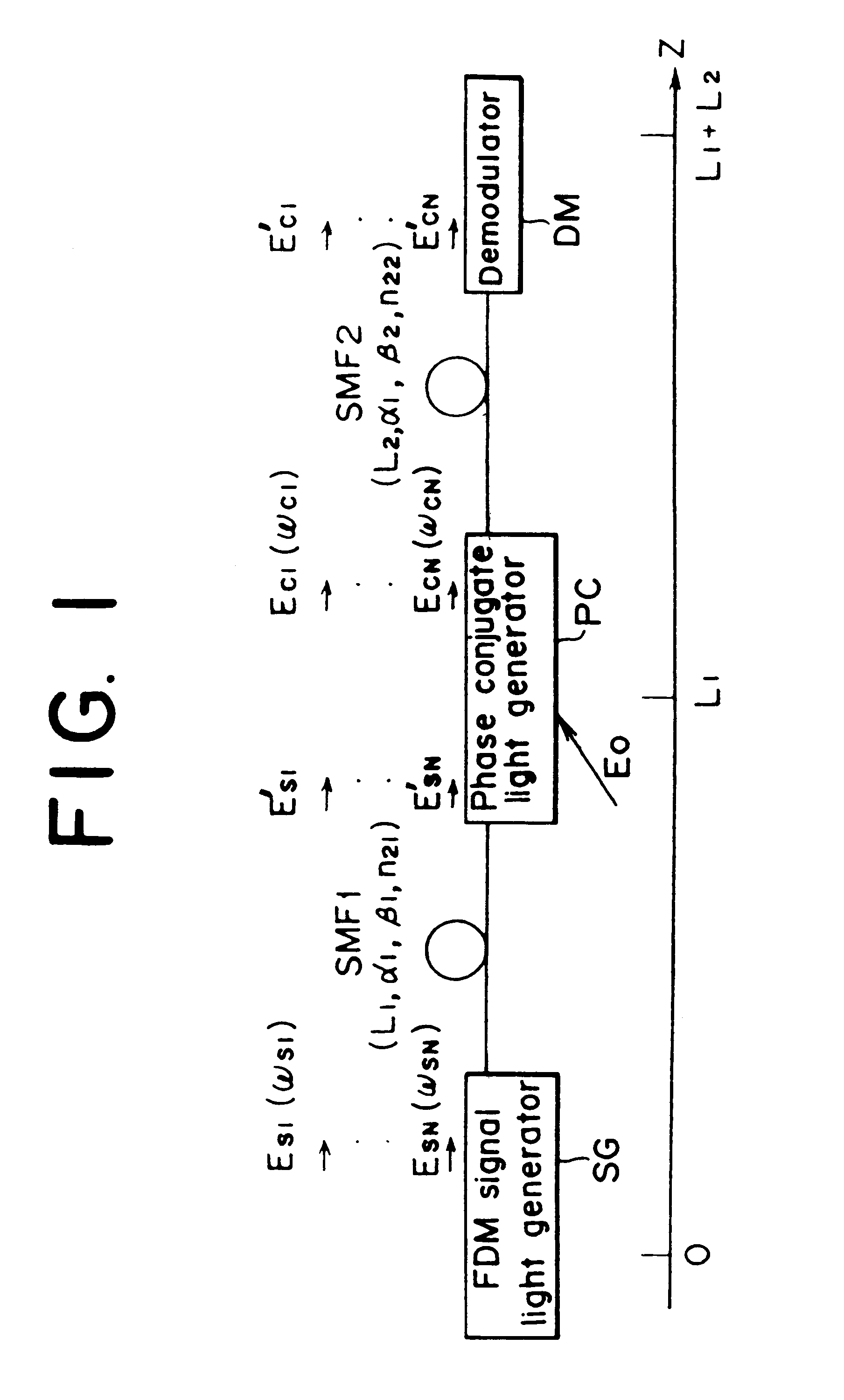
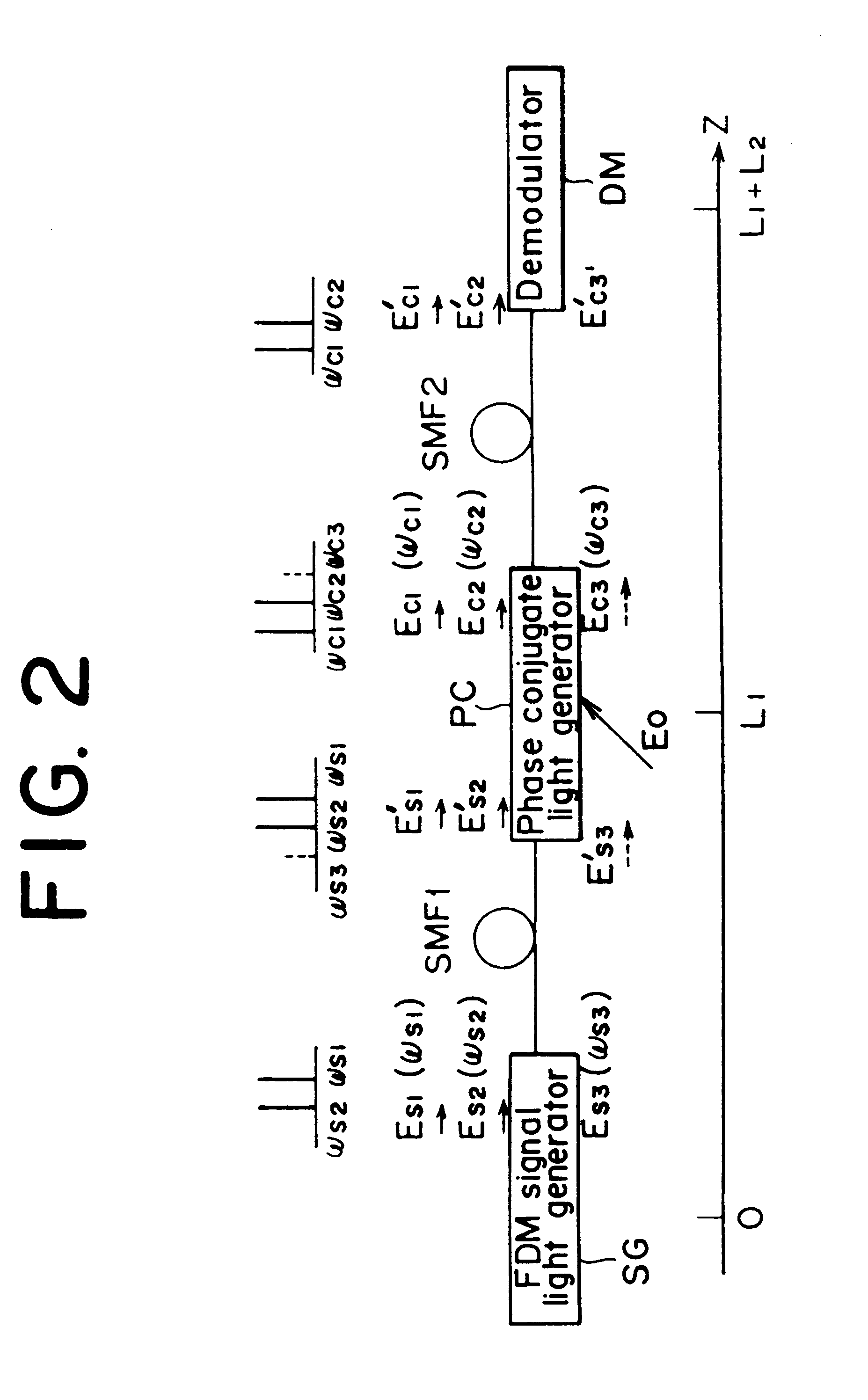
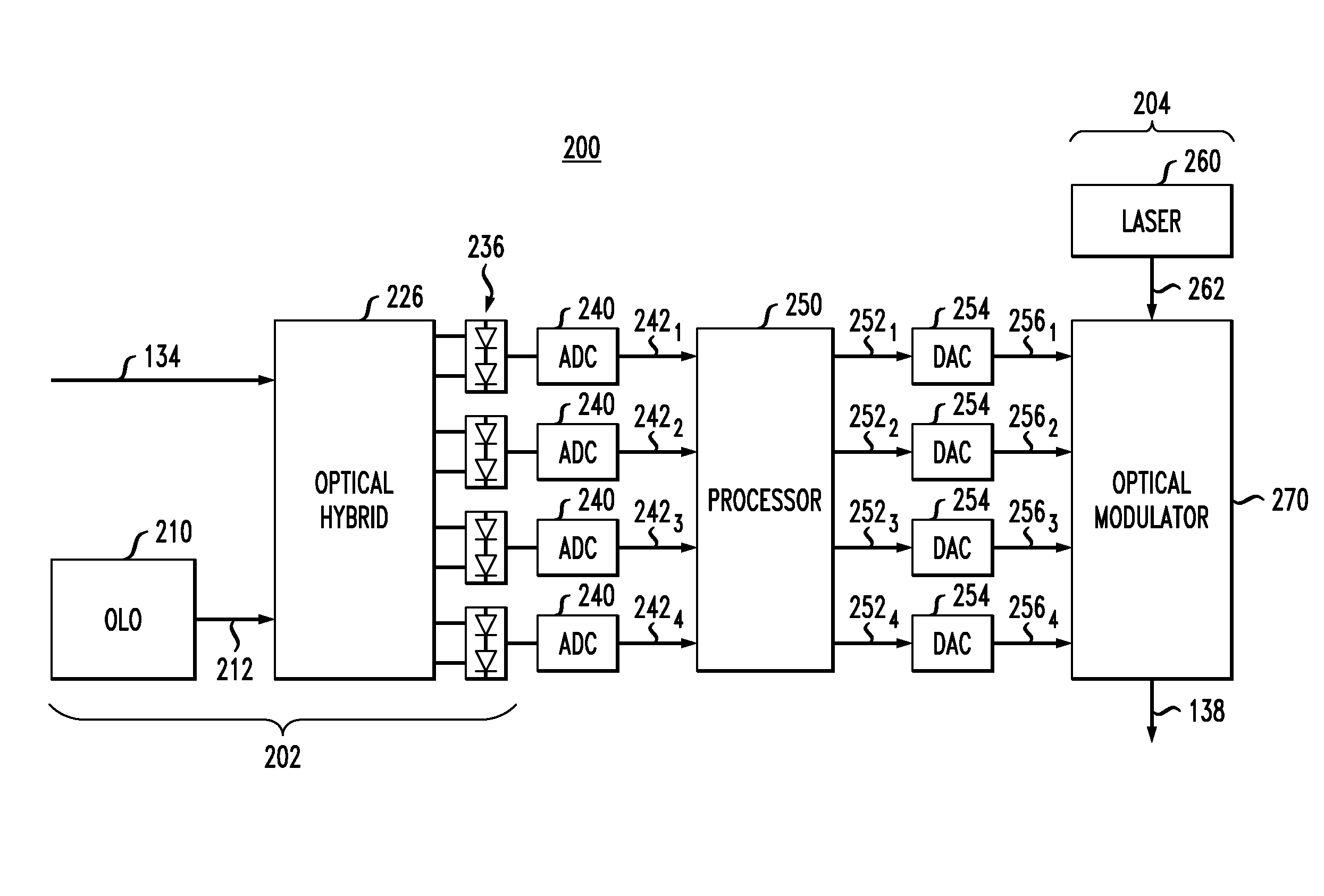
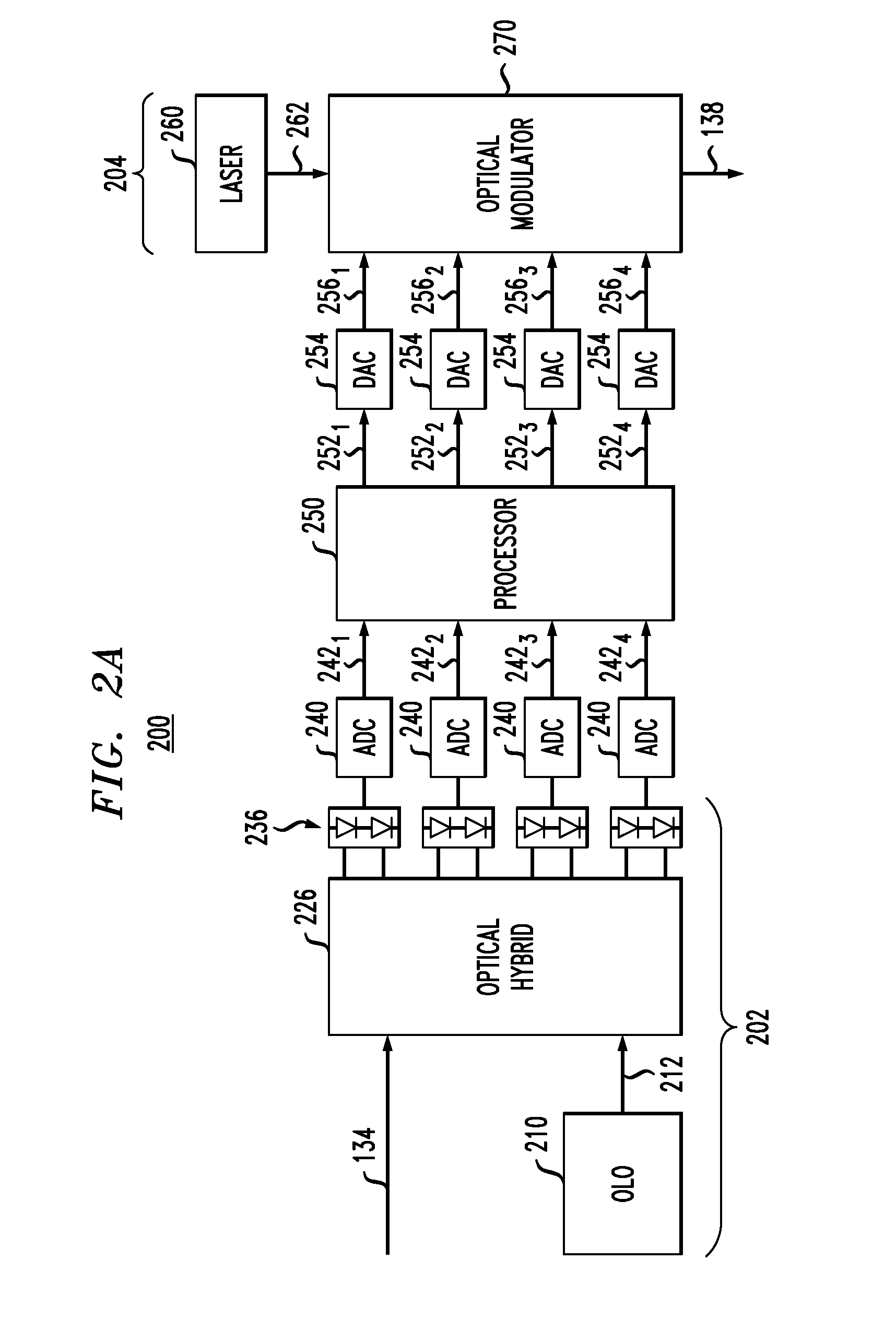
Optical communication method and optical communication system based on optical phase conjugation
InactiveUS6304348B1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringCommunications systemOptical phase conjugation
An optical communication system comprising means for modulating a plurality of light carriers and then performing frequency division multiplexing on the modulated light carriers to generate a frequency division multiplexed light, a first single-mode fiber for transmitting the frequency division multiplexed signal light, means for generating a frequency division multiplexed signal light corresponding to a phase conjugate wave of the transmitted frequency division multiplexed signal light, and a second single-mode fiber for transmitting the frequency division multiplexed phase conjugate light. In the disclosed optical communication system, appropriate setting of parameters such as a mean light intensity of each fiber permits to eliminate an effect of channel-to-channel crosstalk.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
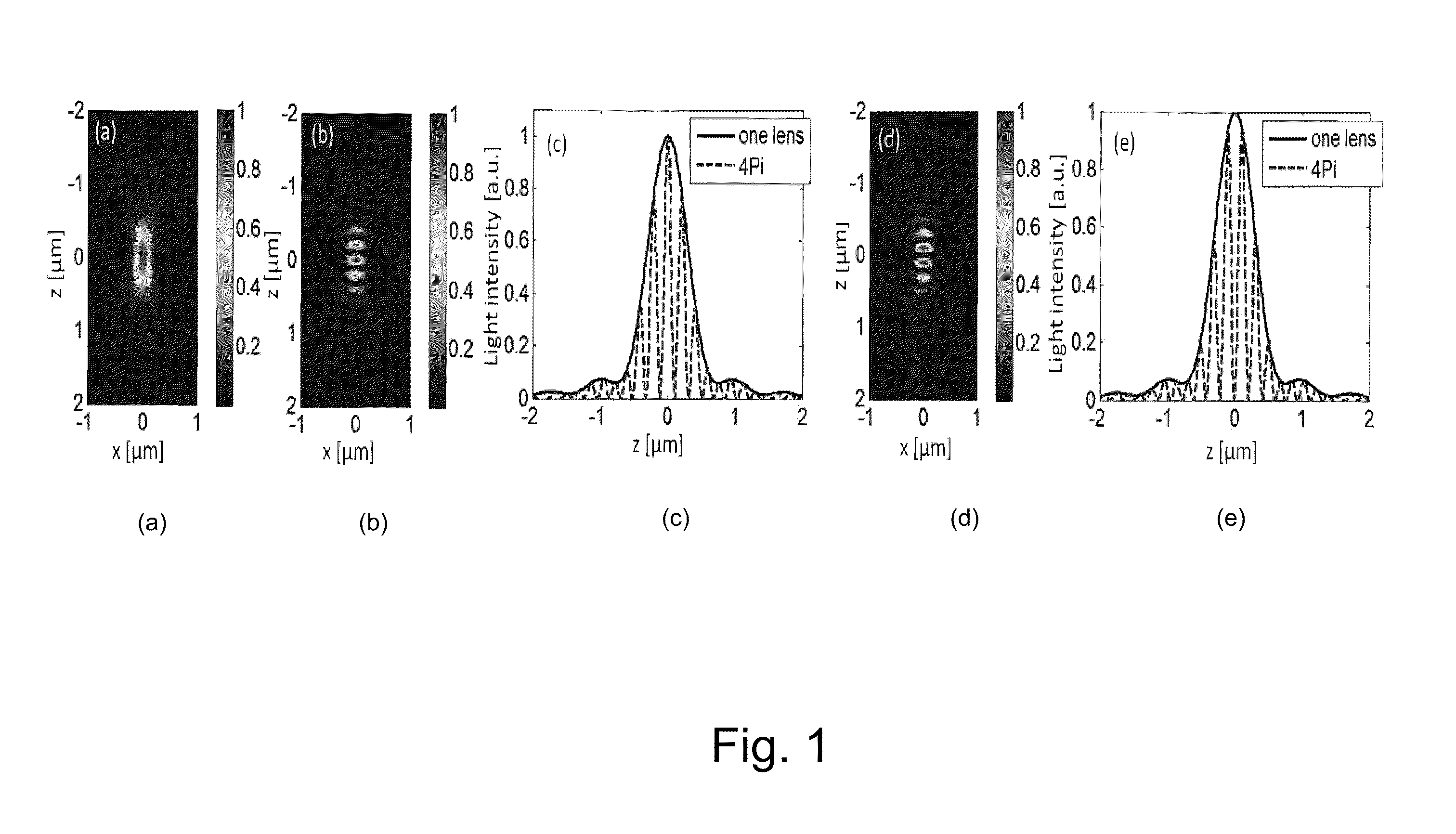
Optical phase conjugation 4 pi microscope
ActiveUS20110109962A1Improve rendering capabilitiesOptimizing fluorescenceDiagnostics using lightMaterial analysis by optical meansSpatial light modulatorOptical phase conjugation
A 4-Pi microscope for imaging a sample, comprising a first objective for focusing a first light beam on the sample at a spatial point one or more Digital Optical Phase Conjugation (DOPC) devices, wherein the DOPC devices include a sensor for detecting the first light beam that has been transmitted through the sample and inputted on the sensor; and a spatial light modulator (SLM) for outputting, in response to the first light beam detected by the sensor, a second light beam that is an optical phase conjugate of the first light beam; and a second objective positioned to transmit the first light beam to the sensor and focus the second light beam on the sample at the spatial point, so that the first light beam and the second light beam are counter-propagating and both focused to the spatial point.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
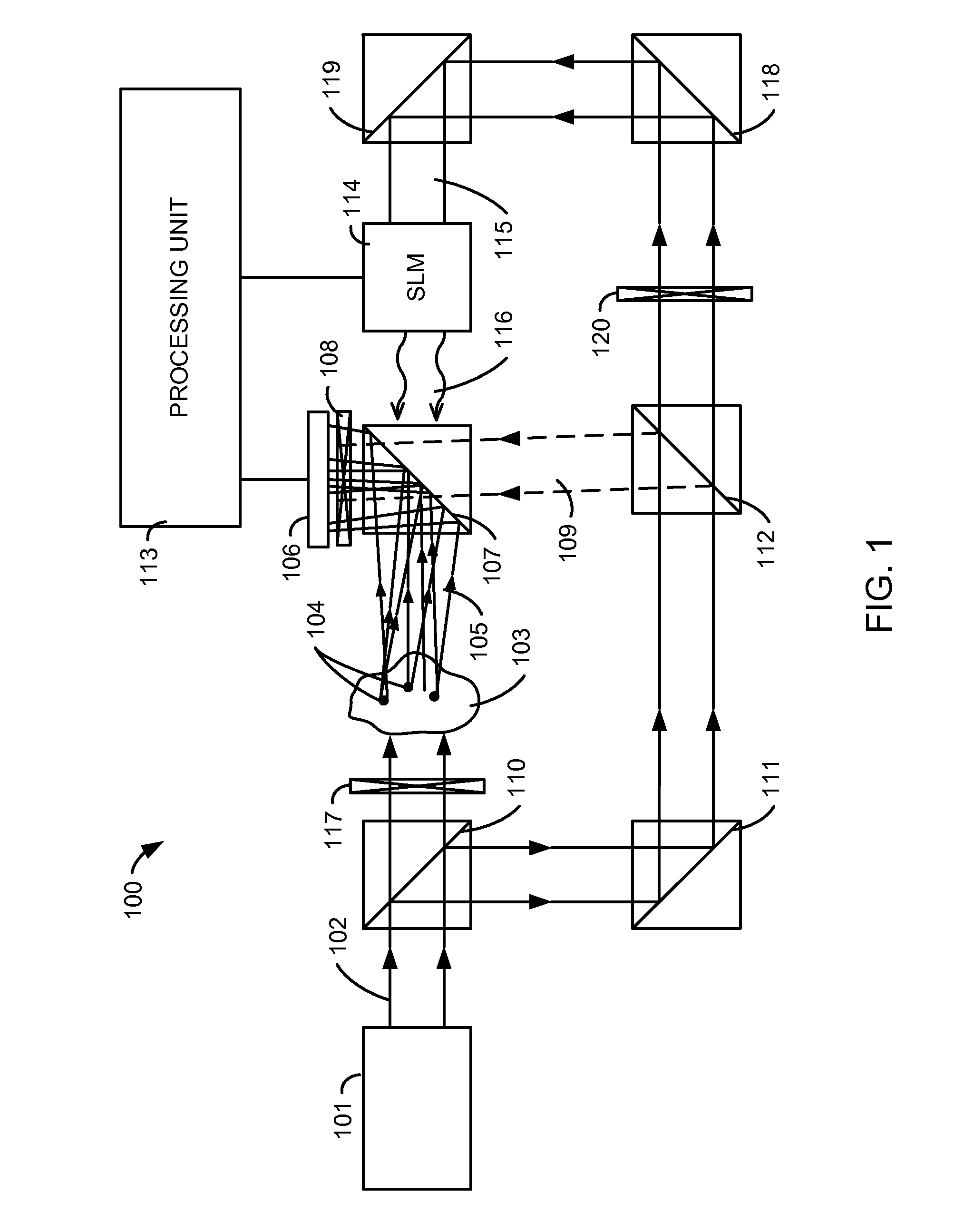
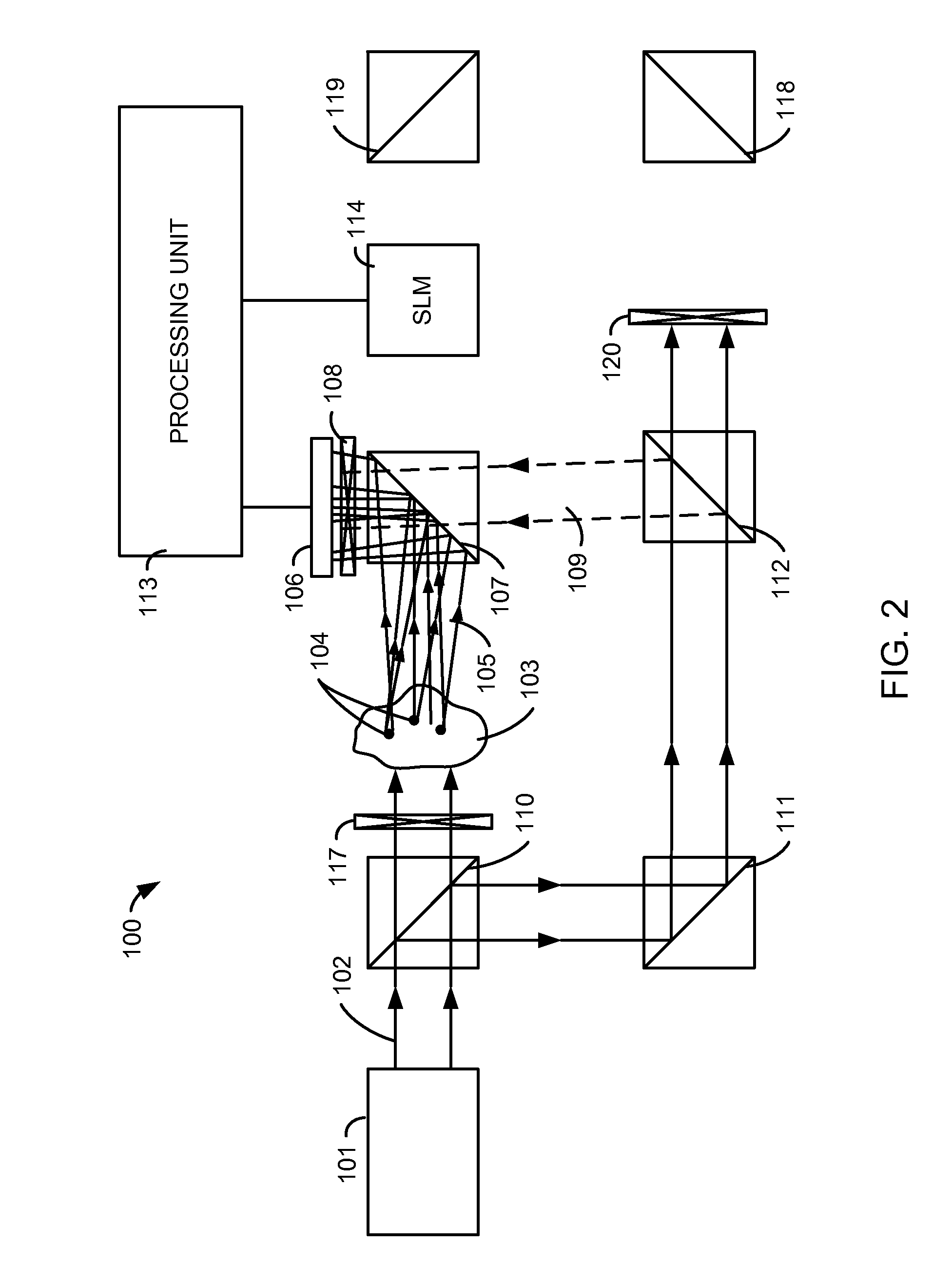
Programmable optical component based on scattering medium, optical field regulation system, and optical field regulation method
ActiveCN106950195ASimple structureVersatileScattering properties measurementsSpatial light modulatorPhotonics
The invention provides a programmable optical component based on a scattering medium, an optical field regulation system, and an optical field regulation method, and solves technical problems that a conventional optical component has single function, is high in optical wave modulation cost, has complex apparatus and low integration degree. The system in the invention is successively provided with a light source beam expanding module, a modulation module, a scattering medium microscopic module and a detection module, a data processing module arranged between the modulation module and the detection module. A computer circularly controls a space light modulator to modulate an input optical field, and a detector detects an output optical field; then data shaping is carried out and an optical transmission matrix of the scattering medium is detected; and then a programmable optical component is constructed so as to achieve optical field regulation with methods such as optical phase conjugation, phase retrieval, speckle reconstruction and the like, wherein the optical field regulation includes imaging, chromatic dispersion, abnormal chromatic dispersion, focusing, shaping, etc. The programmable optical component and the system are intelligent, multi-functional, low-cost, easy to operate, highly integrated and strong in operability, and can be applied to the scientific research fields such as military science, bio-medicines, integrated optic, nano photonics, etc.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
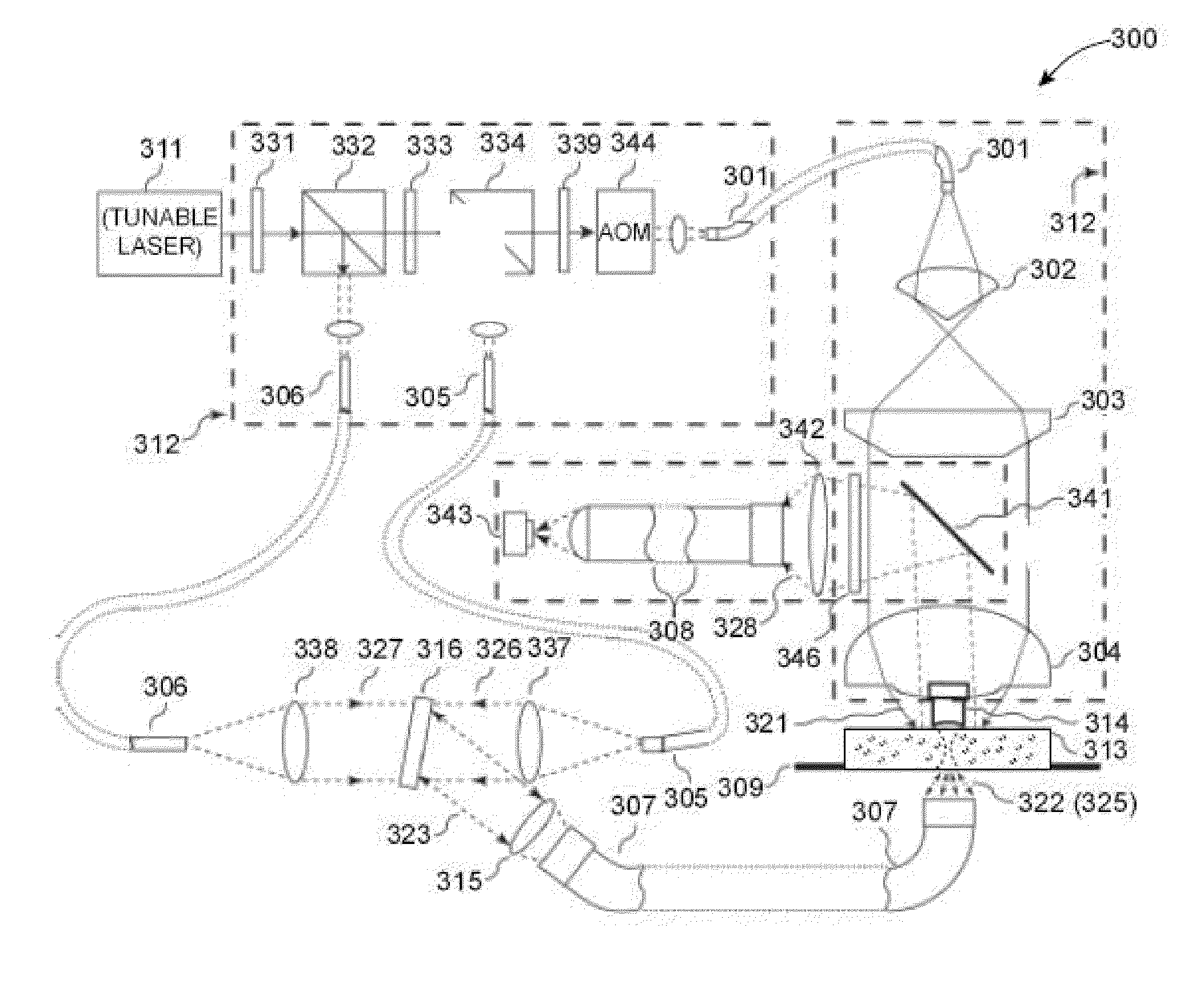
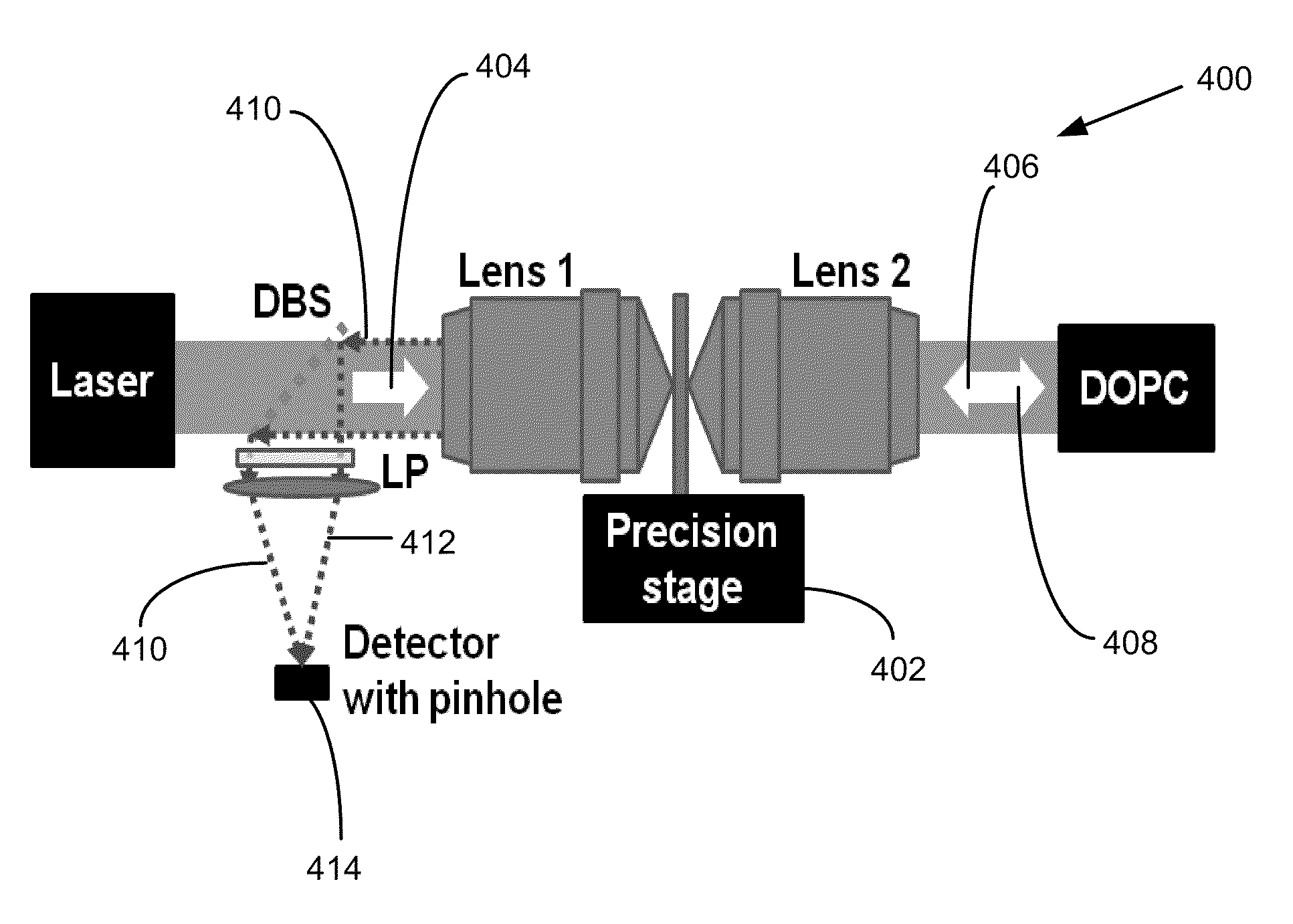
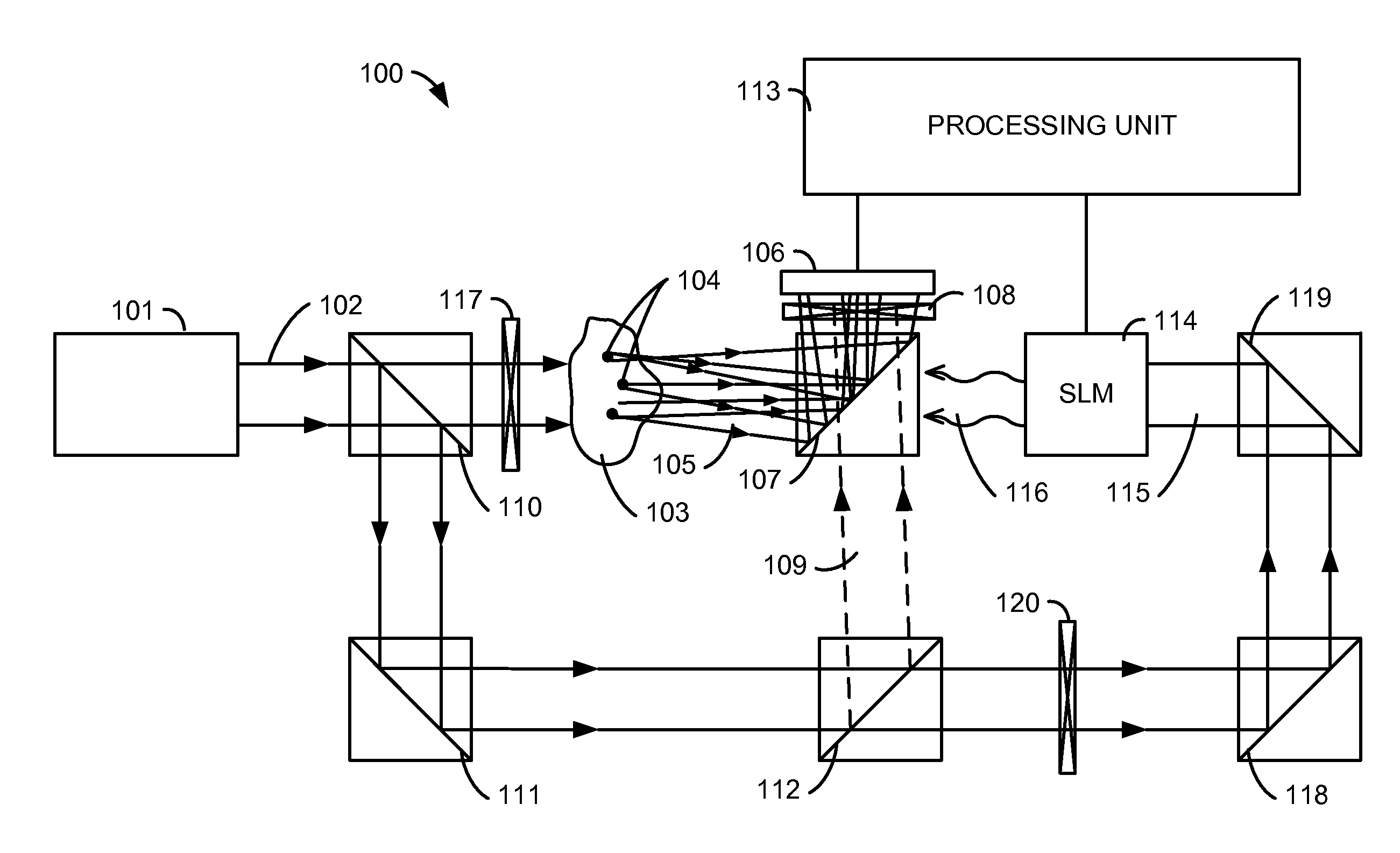
Near real time optical phase conjugation
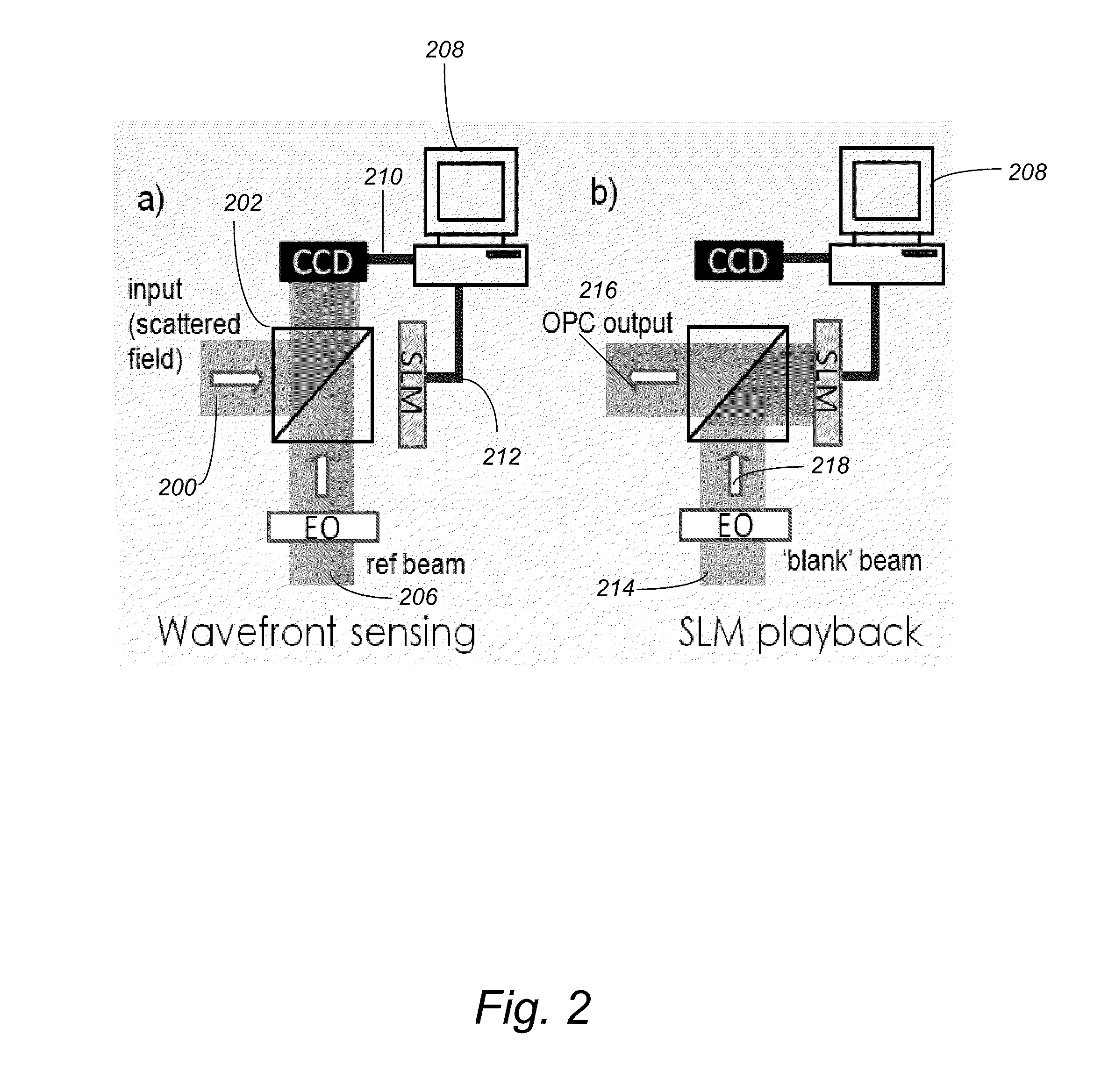
ActiveUS8451450B2Material analysis by optical meansSurgical instrument detailsSpatial light modulatorOptical phase conjugation
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
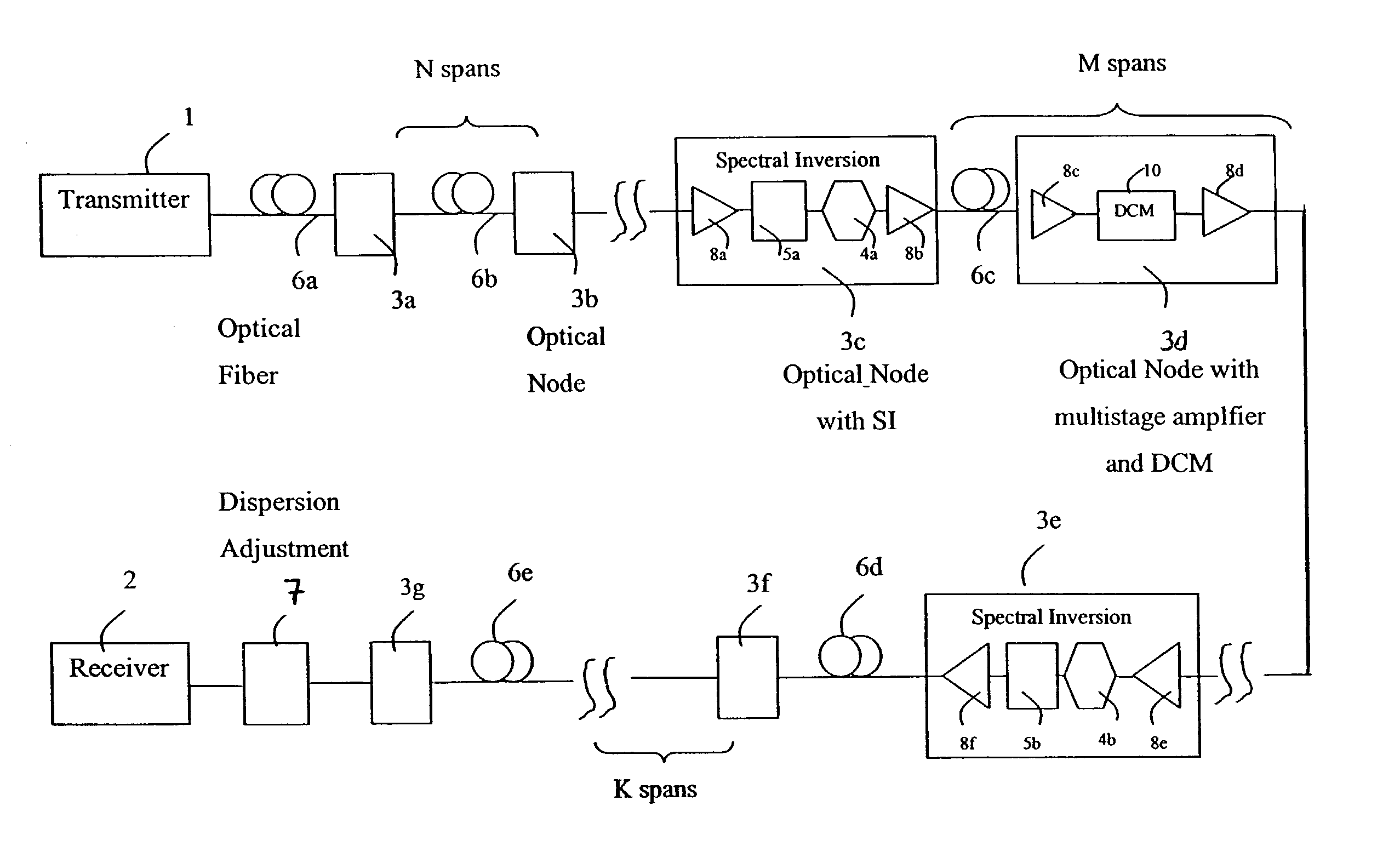
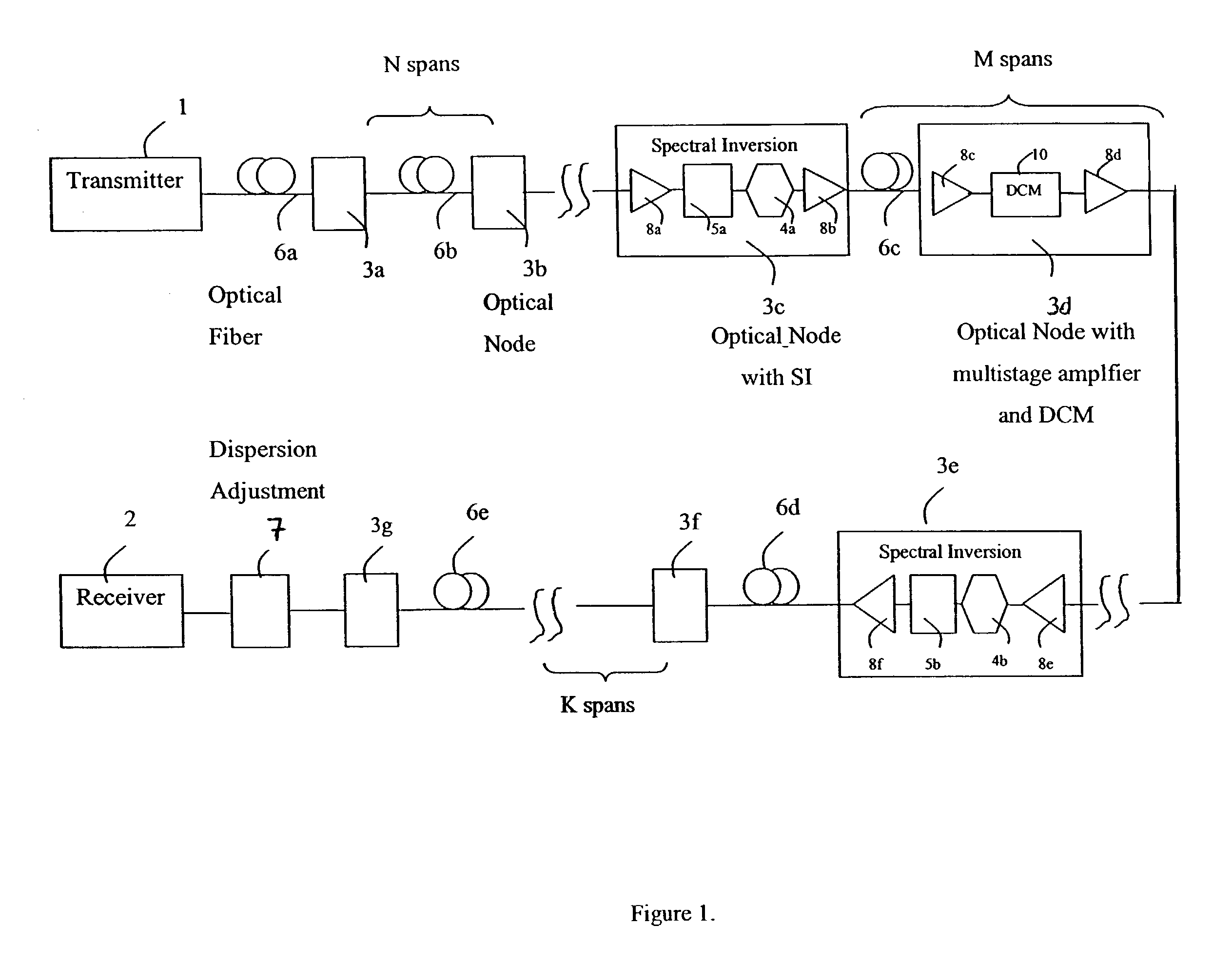
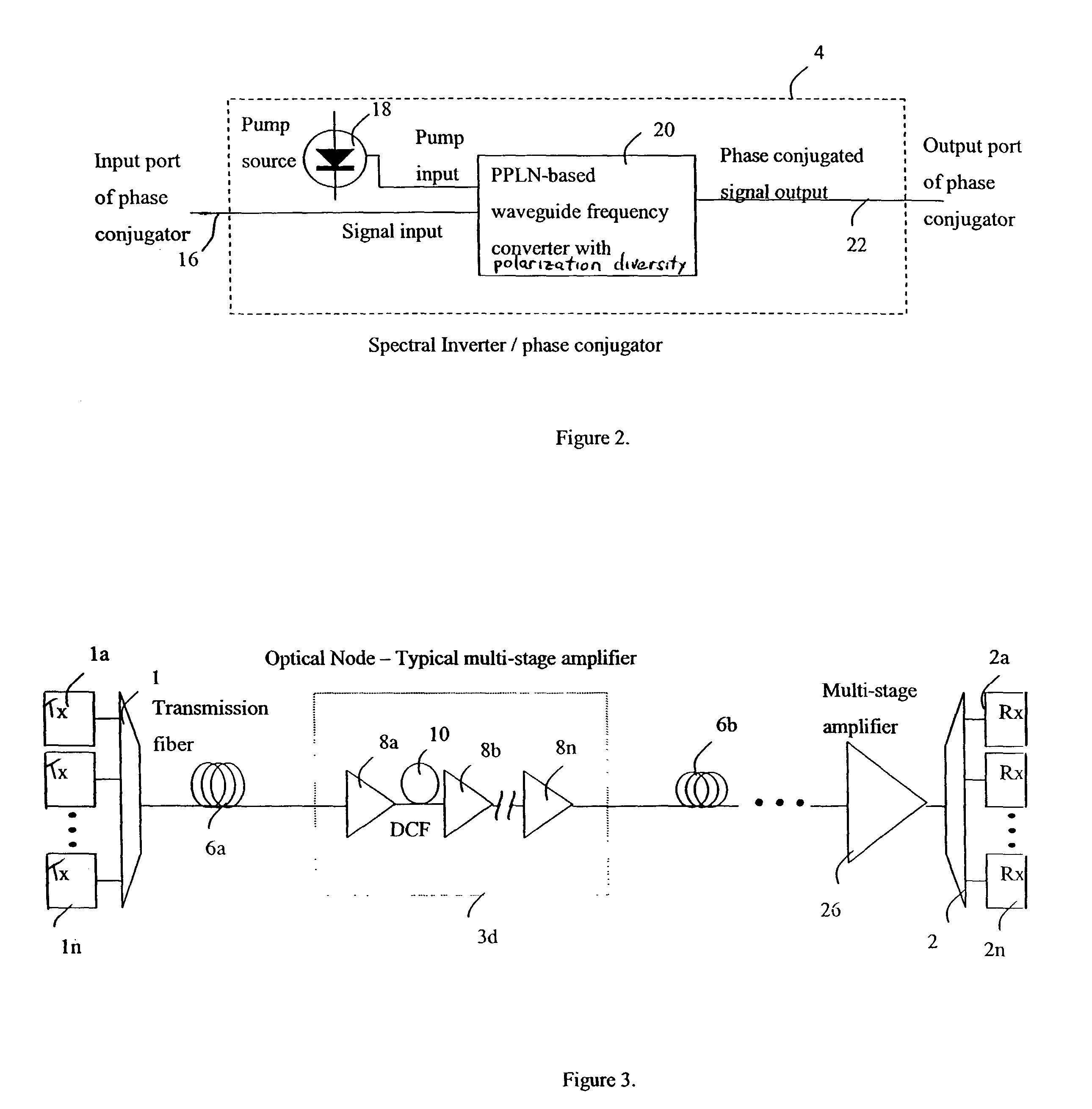
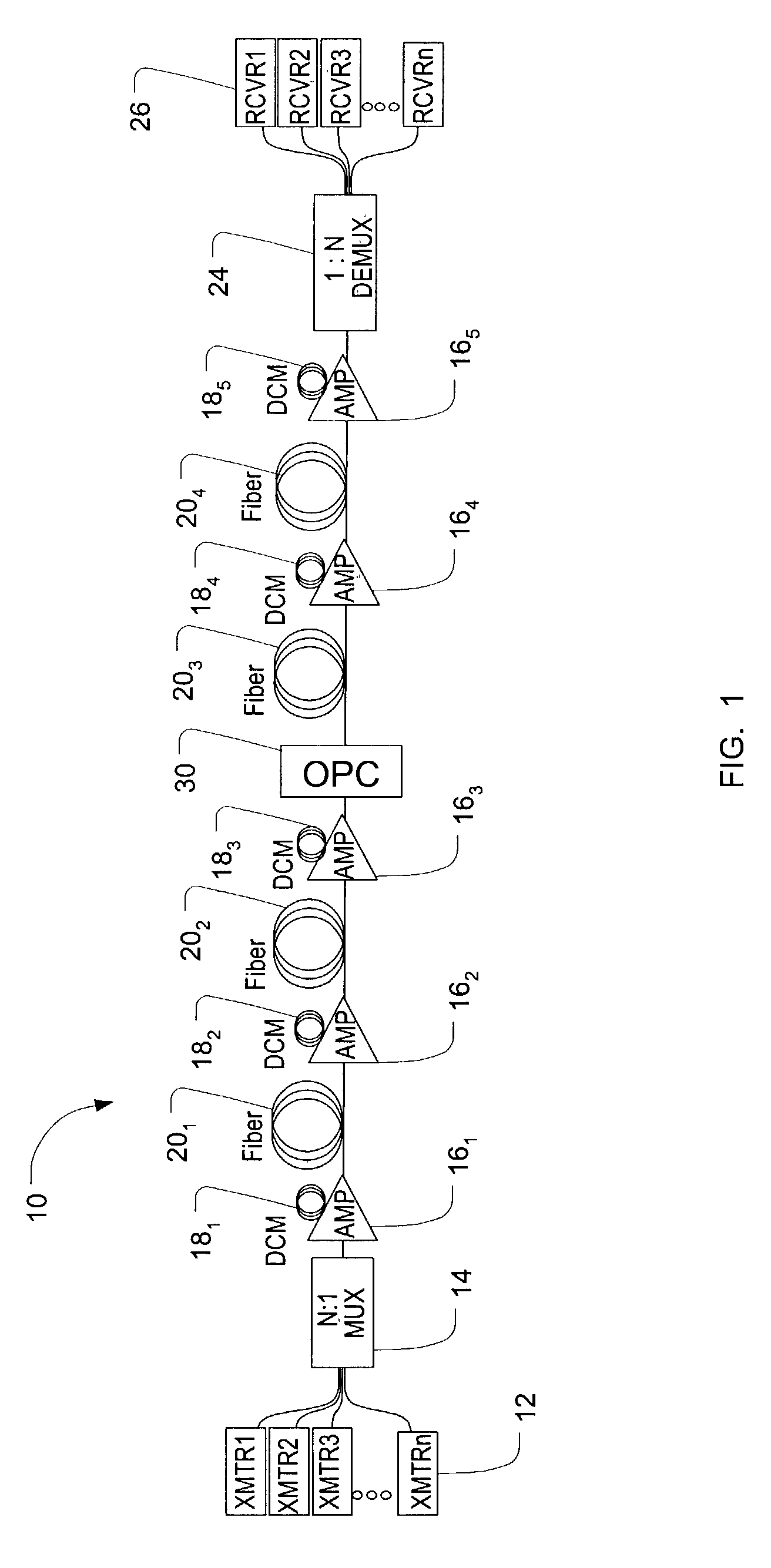
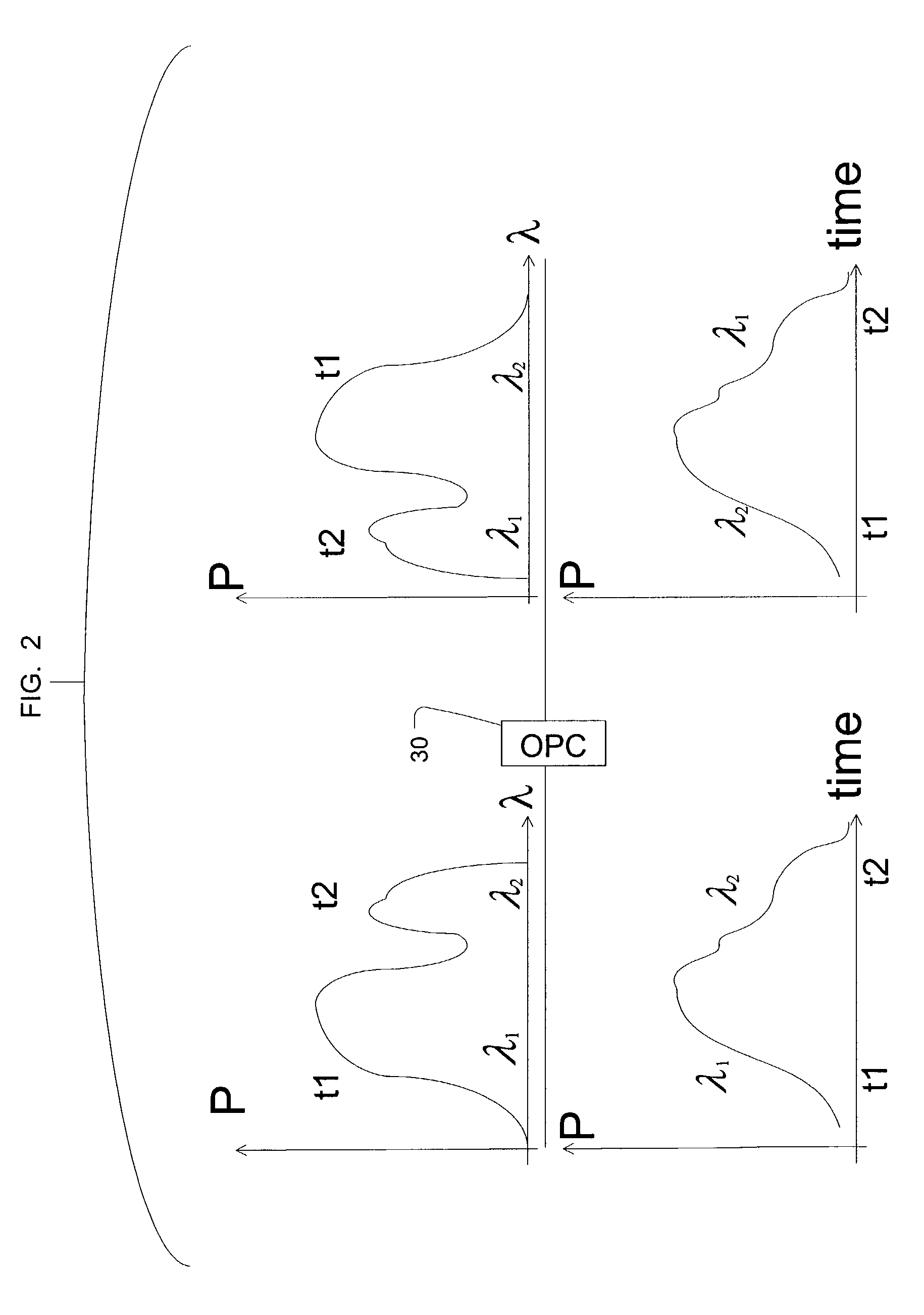
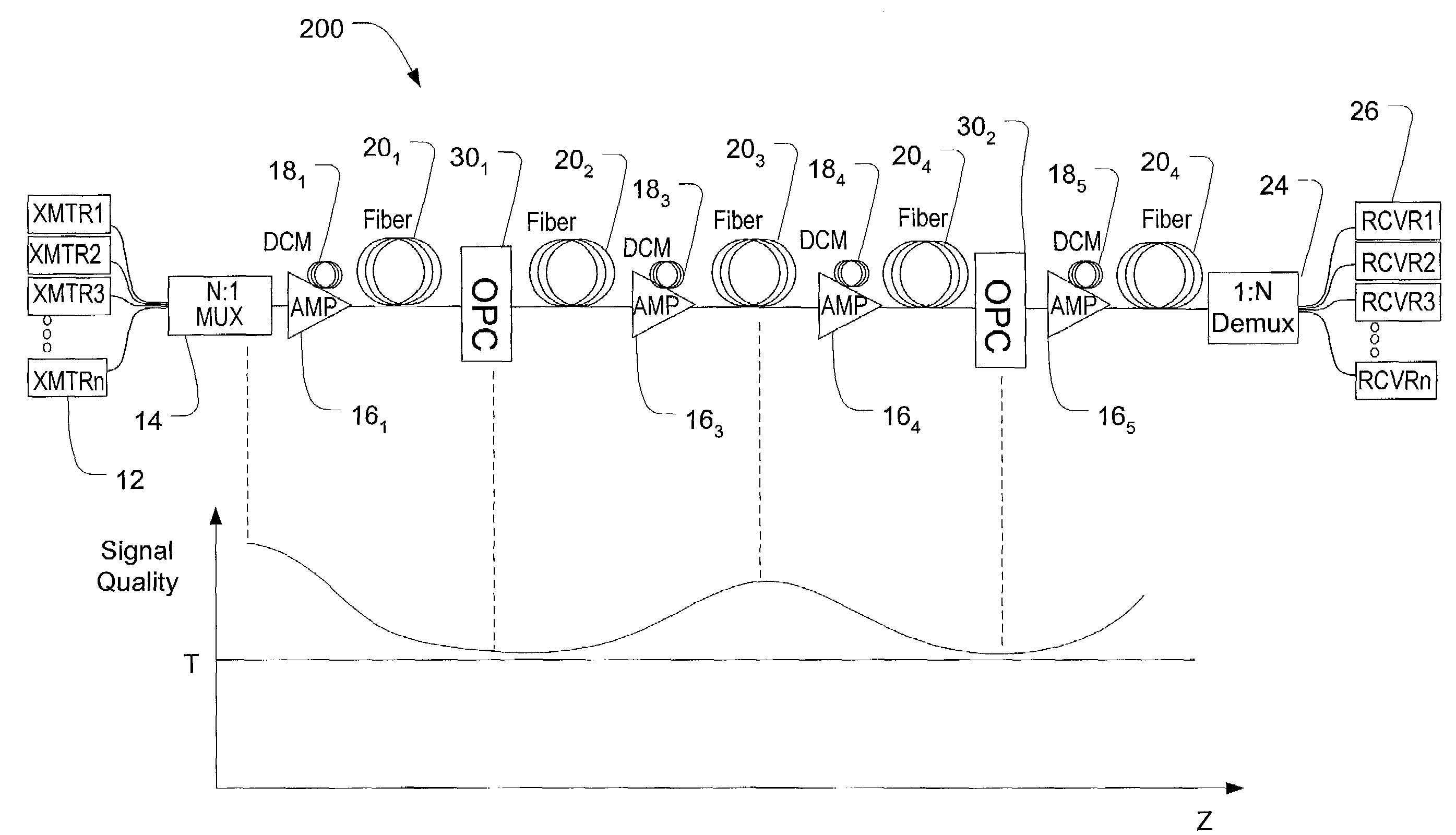
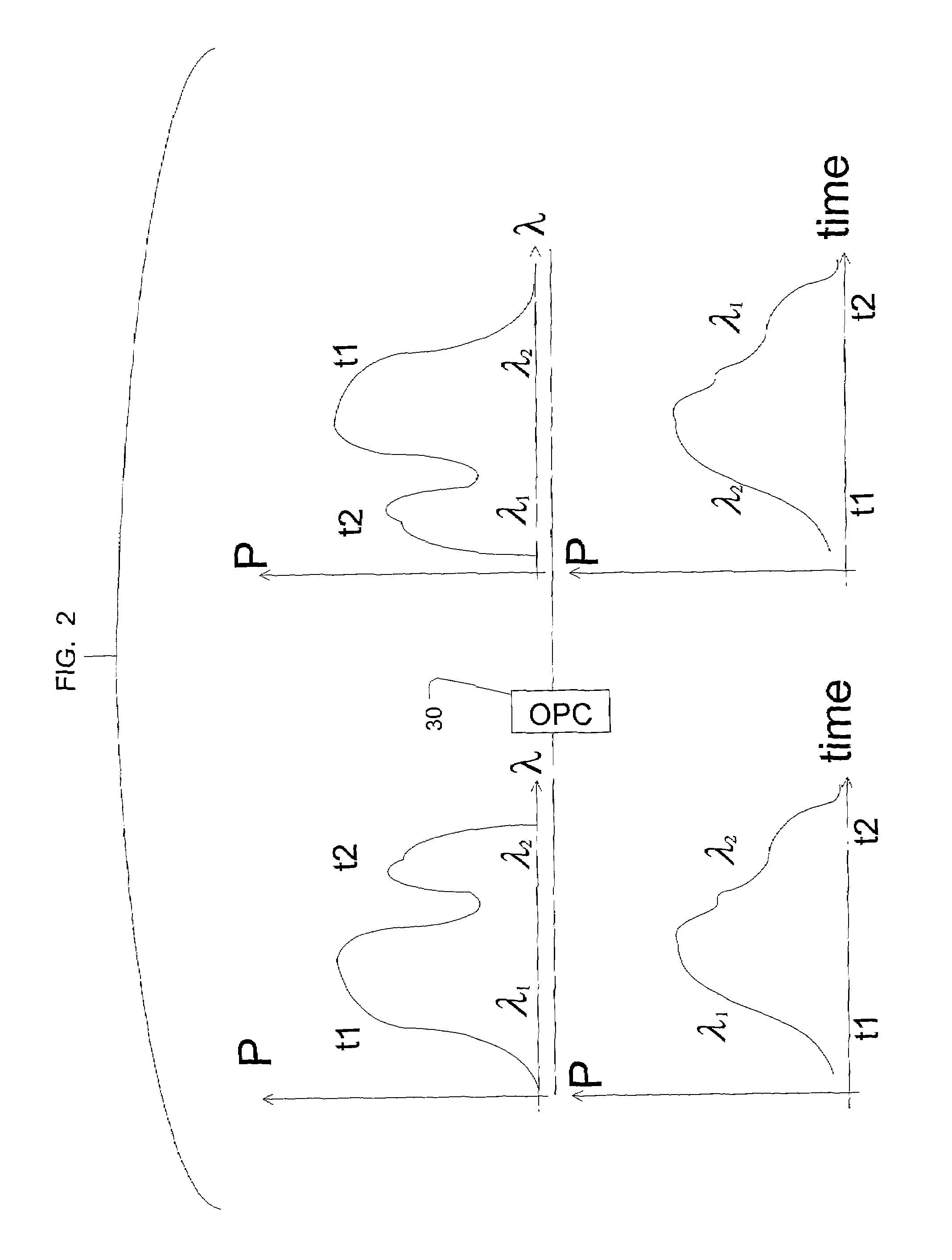
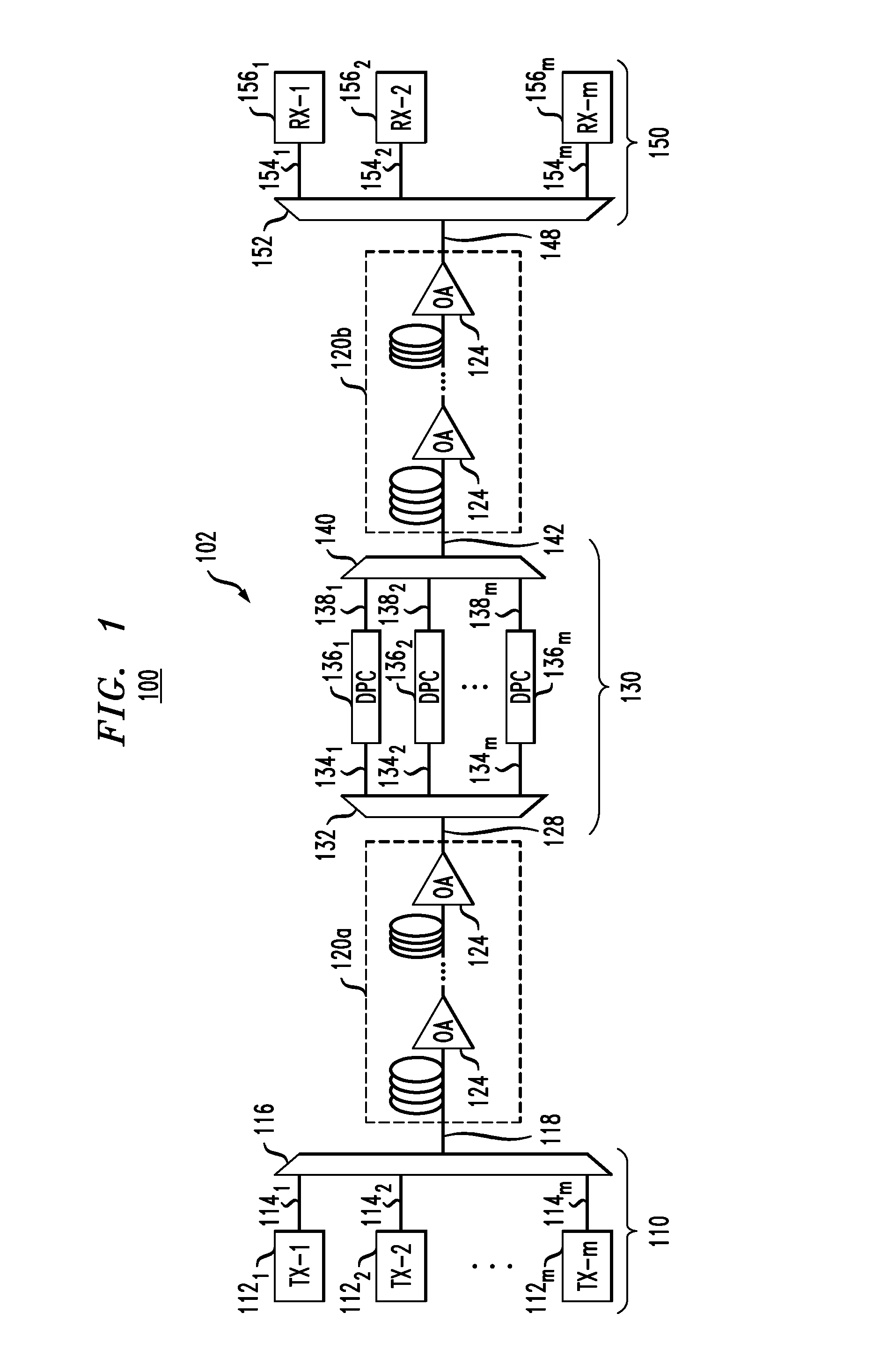
Spectral inversion and chromatic dispersion management in optical transmission systems
InactiveUS20030118347A1Adequate cancellationImprove performanceElectromagnetic transmissionFrequency spectrumAudio power amplifier
A system and method for improving performance of optical fiber networks. The combination of optical spectral inversion and dispersion management enhances performance in optical fiber transmission by controlling the effect of fiber nonlinearities. An optical fiber link, which includes a number of segments or spans, each with a length of fiber and an optical node (typically consisting of at least an amplifier), is provided with at least one spectral inverter, or an optical phase conjugator, connected in the link. Additionally, each span is provided with an amount of dispersion compensation, such as a length of appropriately chosen fiber, to compensate for dispersion as well as other distortion from dispersion's interplay with fiber nonlinear effects. Additional dispersion adjustment is provided in association with the spectral inverter. The location of the spectral inverter (or inverters) and the amount of appropriate dispersion compensation are designed along with other transmission parameters for optimized system performance.
Owner:SPECTRALANE
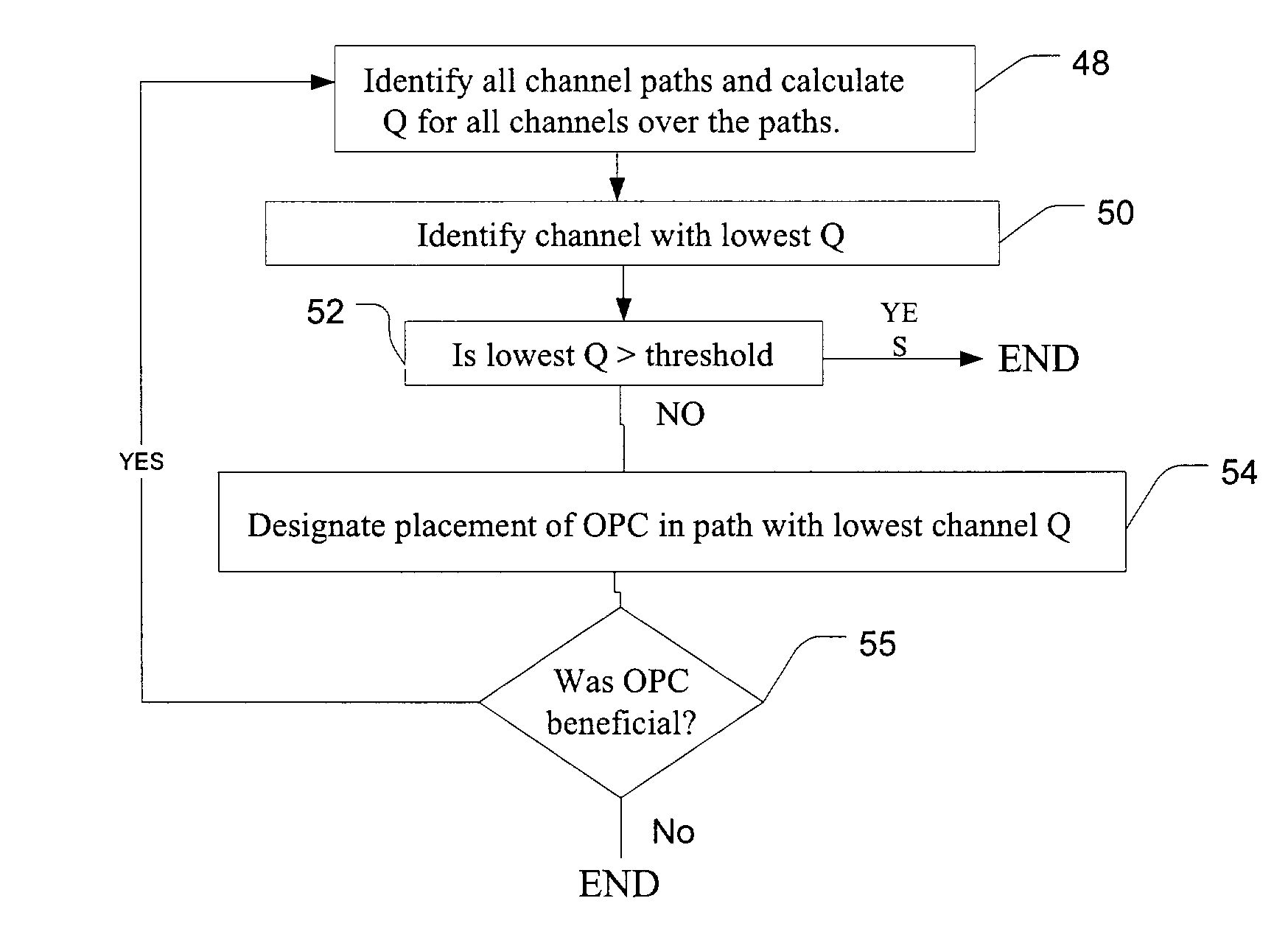
Method and system for using optical phase conjugation in an optical communications network including an add/drop multiplexer
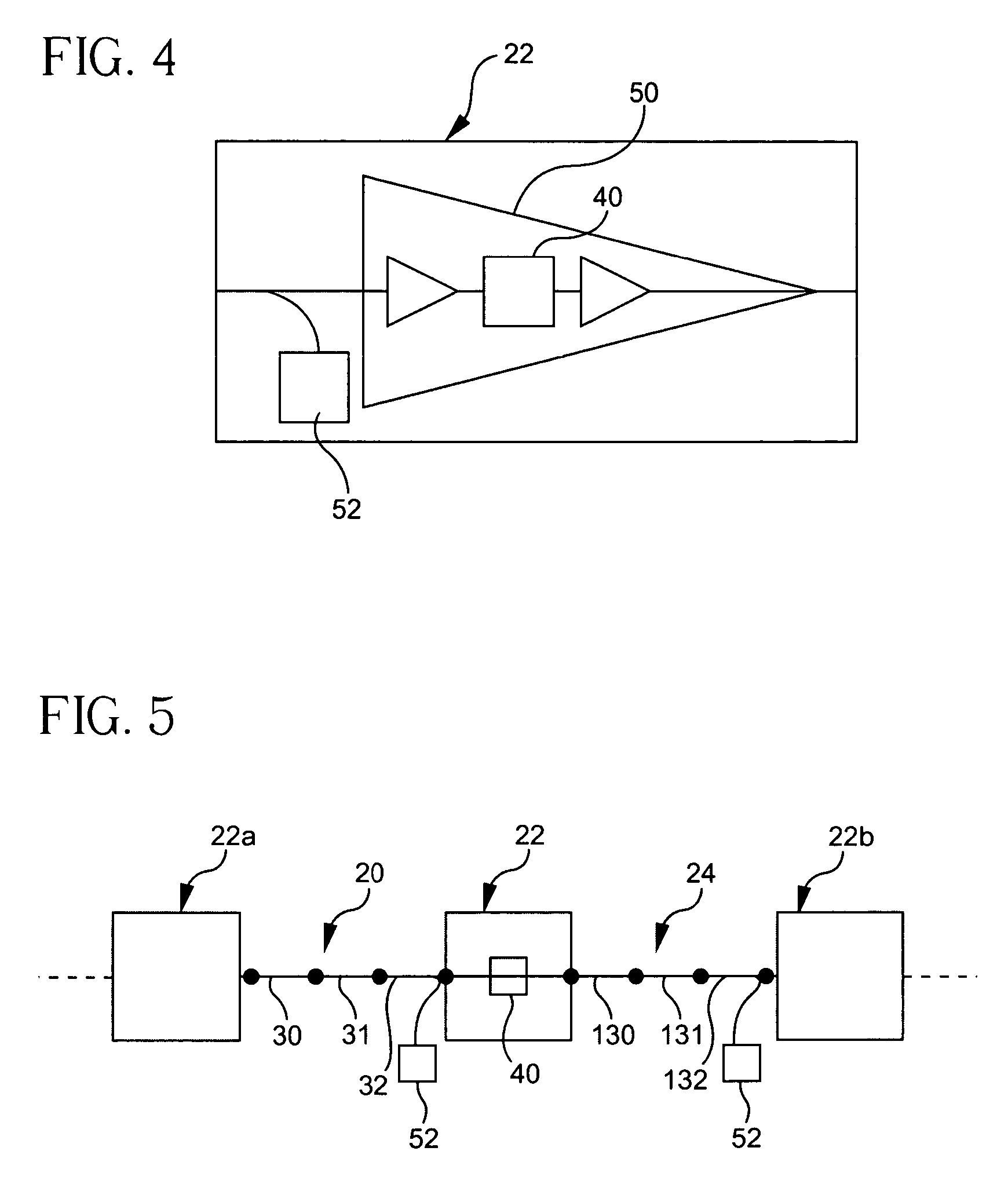
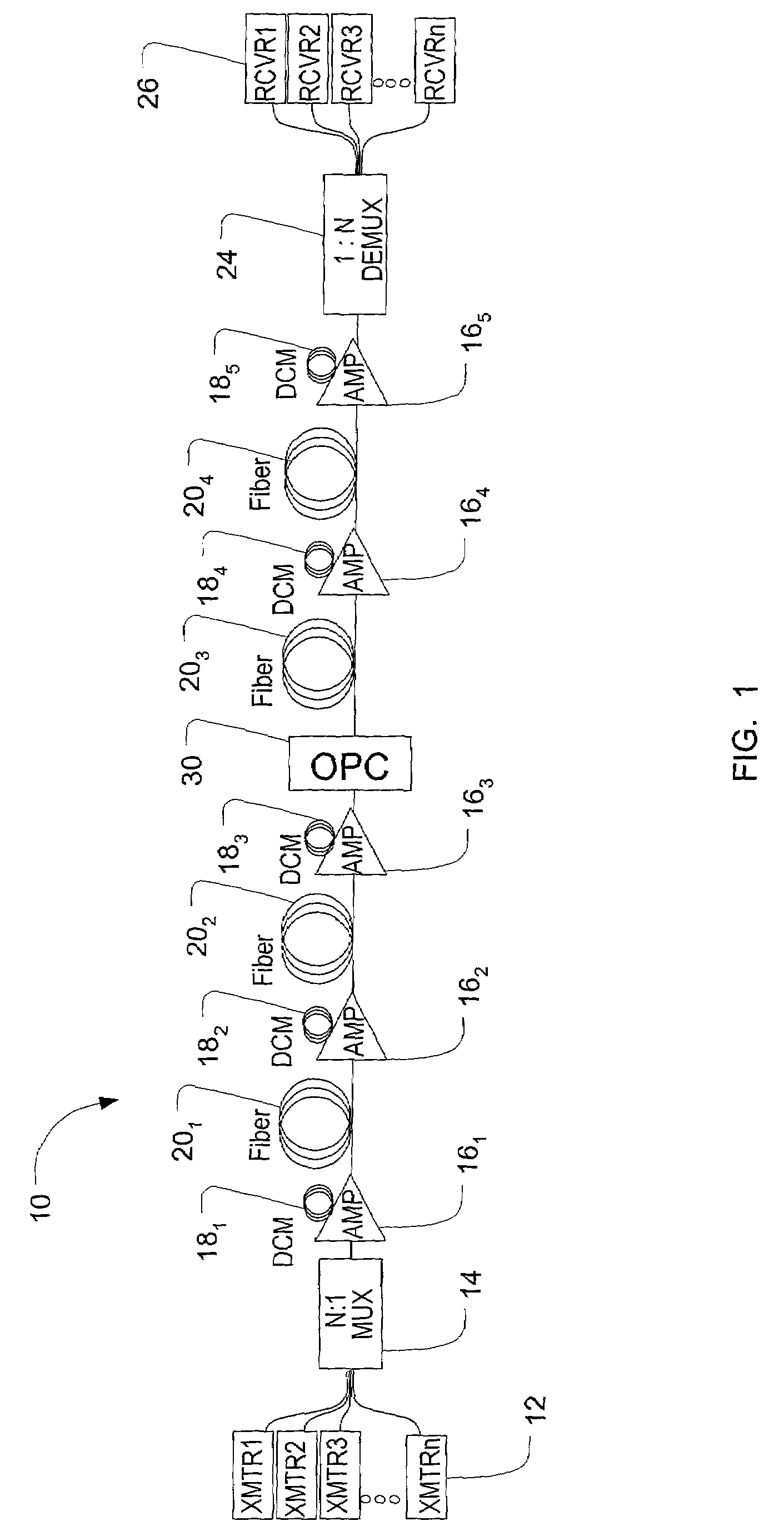
ActiveUS7184410B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsAudio power amplifierMultiplexer
A method and system for using optical phase conjugation in an optical communications network including an add-drop multiplexer. The method includes determining a position for an optical phase conjugator such that channel quality for a channel in improved above a threshold. Transmission characteristics such as amplifier launch power or dispersion features may be adjusted to compliment the optical phase conjugation. An alternate method includes positioning the optical phase conjugator to improve a weighted average channel quality for the network.
Owner:CIENA
System and method for improving laser collimation precision by utilizing optical phase conjugation principle
InactiveCN102692725AEffective compensation impactSimple structureUsing optical meansOptical elementsBeam splitterOptoelectronics
The invention provides a system for improving the laser collimation precision by utilizing an optical phase conjugation principle, comprising a laser device, wherein a polarizer, a beam expanding and collimation system, a first beam splitter, a first polarization spectroscope and a reflector are sequentially arranged along an emitting light beam of the laser device; a position detector is arranged in a beam splitting direction of the first beam splitter; reflection light of the reflector is parallel to the emitting light beam of the laser device; a second polarization spectroscope, a Faraday rotator, a second beam splitter and a space optical phase modulating device are sequentially arranged on the reflection light of the reflector; a wave-front detector is arranged in the beam splitting direction of the second beam splitter; and the space optical phase modulating device and the wave-front detector are connected to a computer. The invention further provides a method for improving the laser collimation precision by utilizing the system; the system disclosed by the invention has a simple structure and influences of uneven atmosphere on the laser collimation can be effectively compensated; and the space optical phase modulating device is used as a phase conjugation mirror so that the system has the advantages of small size, easiness for controlling and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Robust infrared countermeasure system and method
InactiveUS6872960B2Susceptibility to detectionFast response timePhotometry using reference valueInstruments for comonautical navigationCountermeasureOptical phase conjugation
A system and method for focusing electromagnetic energy on a moving target. Generally, the inventive system sends a pilot beam to a target and analyzes a return wavefront to ascertain data with respect to any distortions and other phase and / or amplitude information in the wavefront. This information is then used to pre-distort an output beam by so that it is focused on the target by the intervening distortions. In an illustrative embodiment, the pilot beam is provided by a beacon laser mounted off-axis with respect to the output beam. The reflected wavefront is received through a gimbaled telescope. Energy received by the telescope is detected and processed to ascertain wavefront aberrations therein. This data is used to predistort a deformable mirror to create an output beam which is the phase conjugate of the received wavefront. In a first alternative embodiment, a nonlinear optical phase-conjugate mirror is employed to generate the required wavefront-reversed replica of the received wavefront. The system further includes an arrangement for modulating the output beam to confuse the target. In a second alternative embodiment, the system is adapted to examine atmospheric distortions of starlight to predistort the output beam. The alternative embodiment offers a faster response time and a lower susceptibility to detection.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
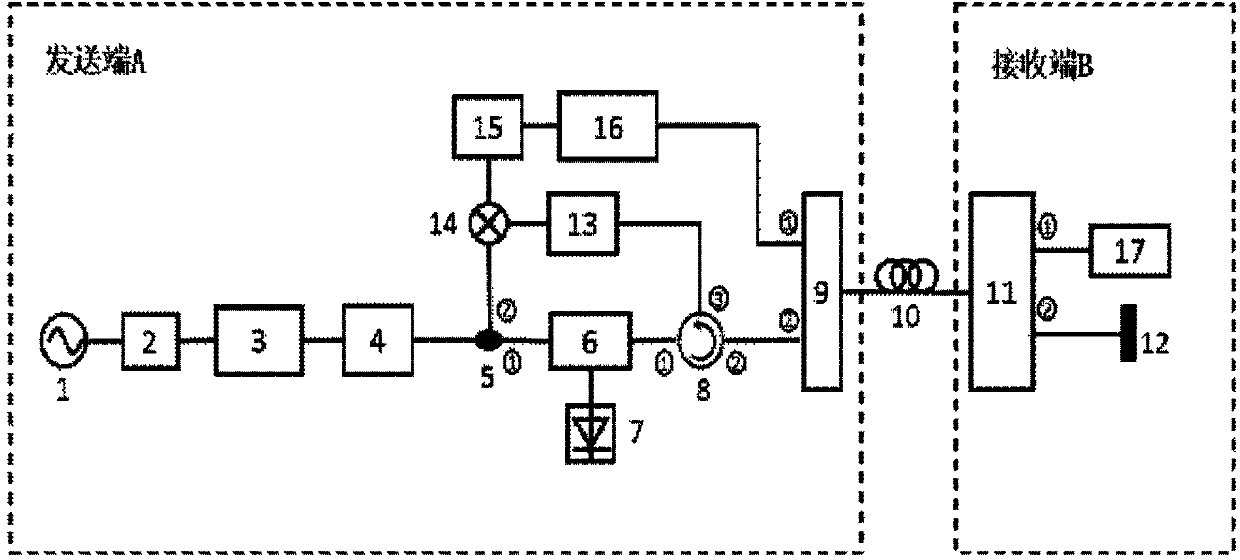
Microwave signal long distance optical fiber stationary phase transmission device based on optical phase conjugation
ActiveCN104202090AReduce usageReduce construction costsDistortion/dispersion eliminationStationary phaseFrequency mixer
Disclosed is a microwave signal long distance optical fiber stationary phase transmission device based on optical phase conjugation. The microwave signal long distance optical fiber stationary phase transmission device based on the optical phase conjugation comprises an emitting end, a receiving end and a single mode optical fiber, wherein the emitting end is connected with the receiving end through the single mode optical fiber. The microwave signal long distance optical fiber stationary phase transmission device based on the optical phase conjugation only processes a signal at the emitting end, is low in construction and maintenance cost, reduces usage frequency of a frequency mixer, performs pre-distortion of a microwave signal mainly on light, improves the bandwidth of a system, only uses a microwave source, and does not need synchronization.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
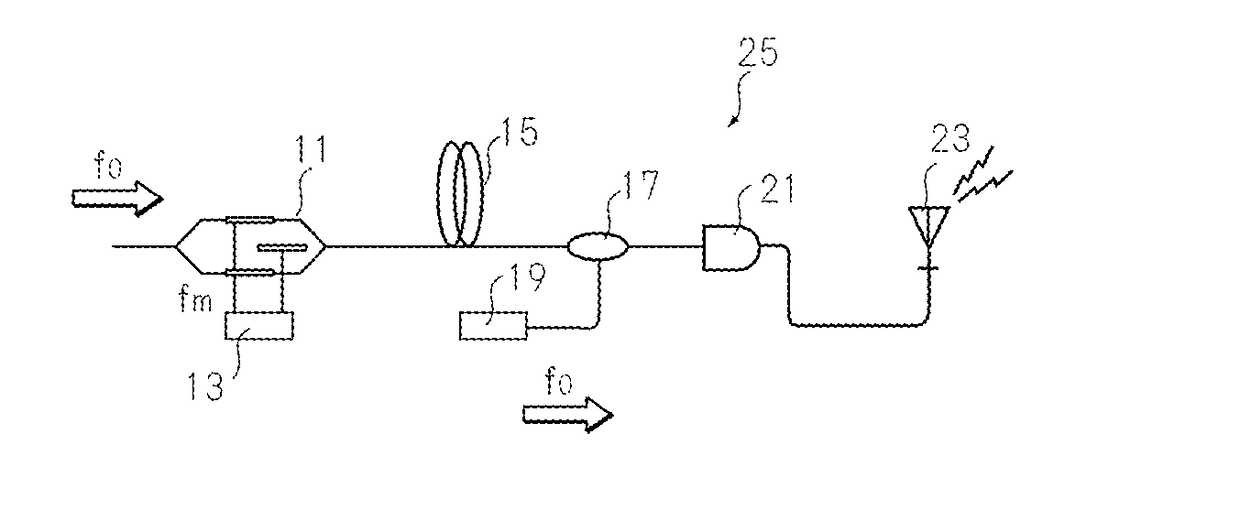
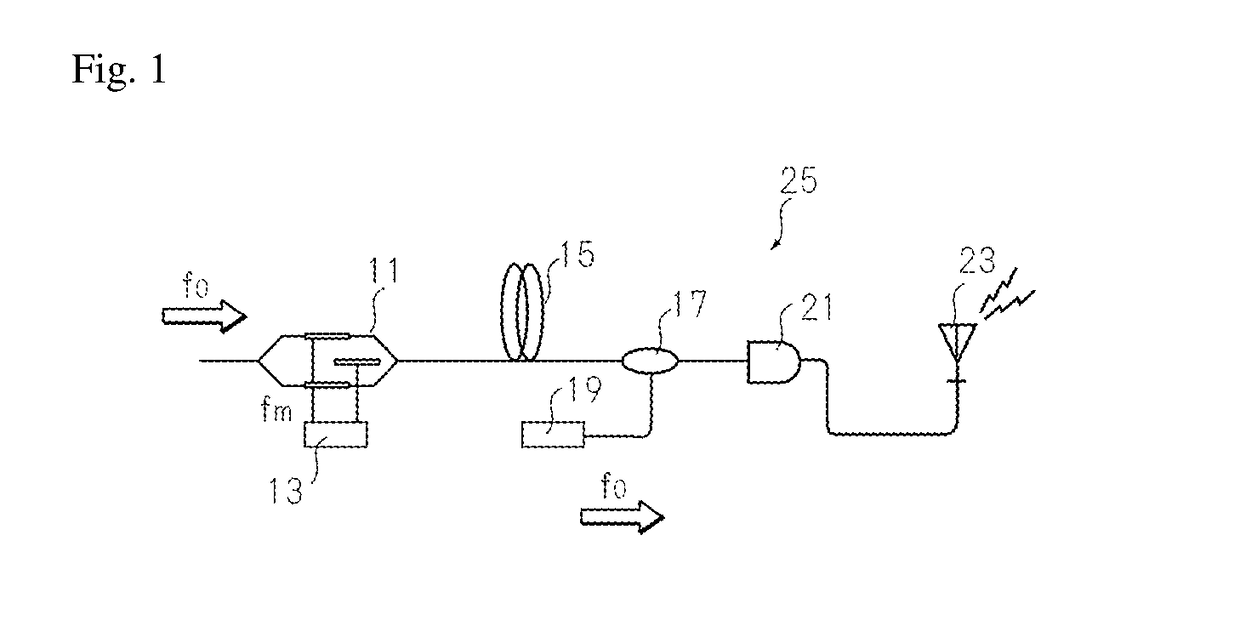
Optical up/down-conversion-type optical phase conjugate pair signal transmission/reception circuit
ActiveCN106716879ACompensation for non-linear effects ex situCompensate for nonlinear effectsDistortion/dispersion eliminationRadio-over-fibreUp conversionNon-linear effects
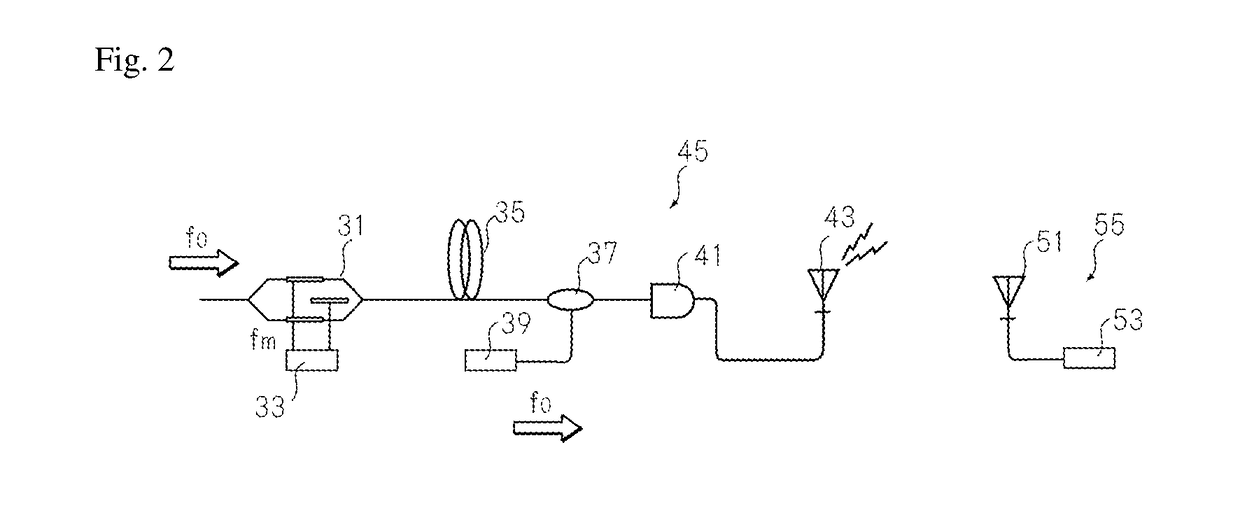
To provide a method capable of easily compensating waveform distortion due to a non-linear effect caused by a complicated electric circuit, and a device for implementing the method. Provided are a method capable of effectively compensating signal degradation such as waveform distortion due to a nonlinear effect caused by an optical fiber that is an optical transfer path using an optical phase conjugate signal pair at the time of optical up-conversion or down-conversion, and a device capable of implementing the method. This emission device (25) includes an optical modulator (11), a signal source (13), an optical fiber (15), a multiplexing unit (17), a multiplexing local signal source (19), an optical detector (21), and a transmission antenna (23).
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH
Deep tissue focal fluorescence imaging with digitally time-reversed ultrasound-encoded light
ActiveUS20130342665A1Television system detailsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSpatial light modulatorSonification
A device and method for performing fluorescence imaging with digitally time reversed ultrasound encoded light, using a source of ultrasound waves, a coherent light source, a digital optical phase conjugation (DOPC) device comprising a camera and a spatial light modulator (SLM), a detector of fluorescence, and one or more computers, to obtain an output that at least approximates an interaction between a complete time reversed field, of all of the encoded light's fields, and the scattering medium.
Owner:LONDON SCHOOL OF HYGIENE & TROPICAL MEDICINE +1
Optical fiber communication system using optical phase conjugation as well as apparatus applicable to the system and method of producing the same
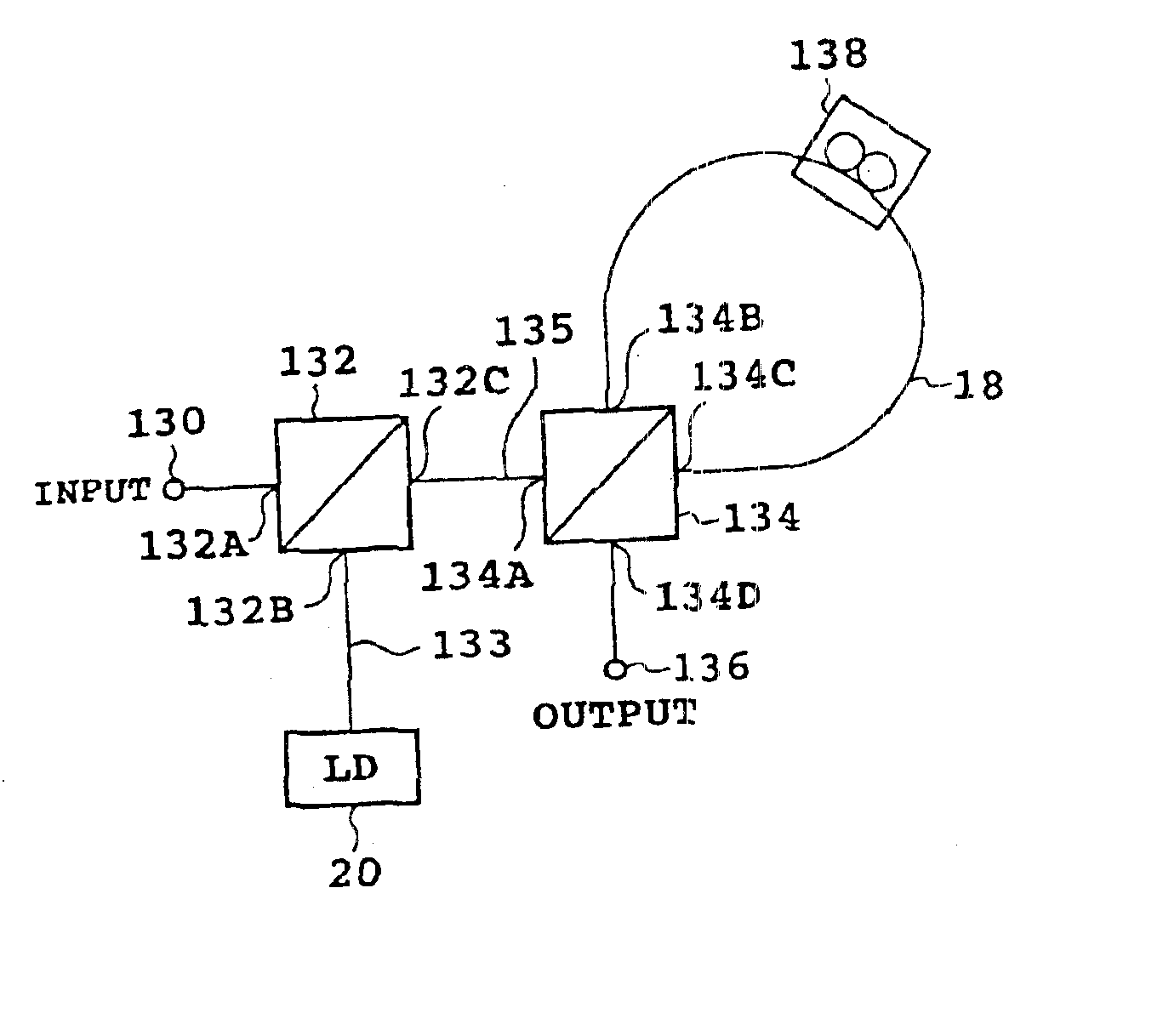
InactiveUS6870974B2Effective compensationCompensation effectRing-type electromagnetic networksBus-type electromagnetic networksOptical phase conjugationSignal beam
An optical fiber communication system according to the present invention has, for example, first and second phase conjugators. The first phase conjugator converts a signal beam from a first optical fiber into a first phase conjugate beam. The first phase conjugate beam is supplied to the second phase conjugator by a second optical fiber. The second phase conjugator converts the first phase conjugate beam into a second phase conjugate beam. The second phase conjugate beam is transmitted by a third optical fiber. The second optical fiber is composed of a first portion located between the first phase conjugator and a system midpoint and a second portion located between the system midpoint and the second phase conjugator. The total dispersion of the first optical fiber substantially coincides with the total dispersion of the first portion, and the total dispersion of the second portion substantially coincides with the total dispersion of the third optical fiber. By the construction, waveform distortion by chromatic dispersion or nonlinearity is compensated for.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
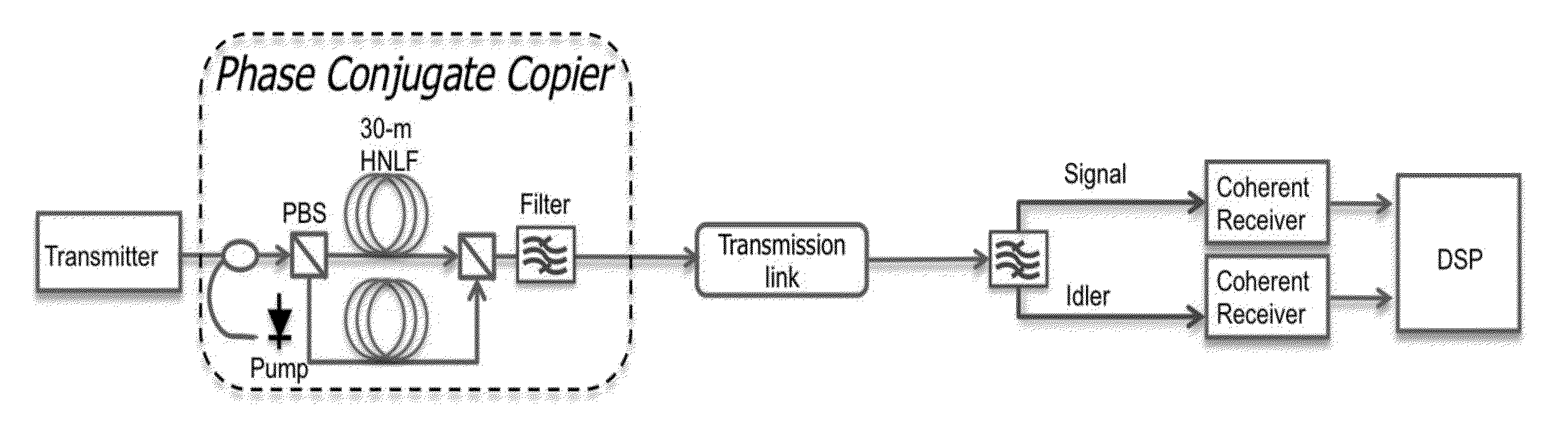
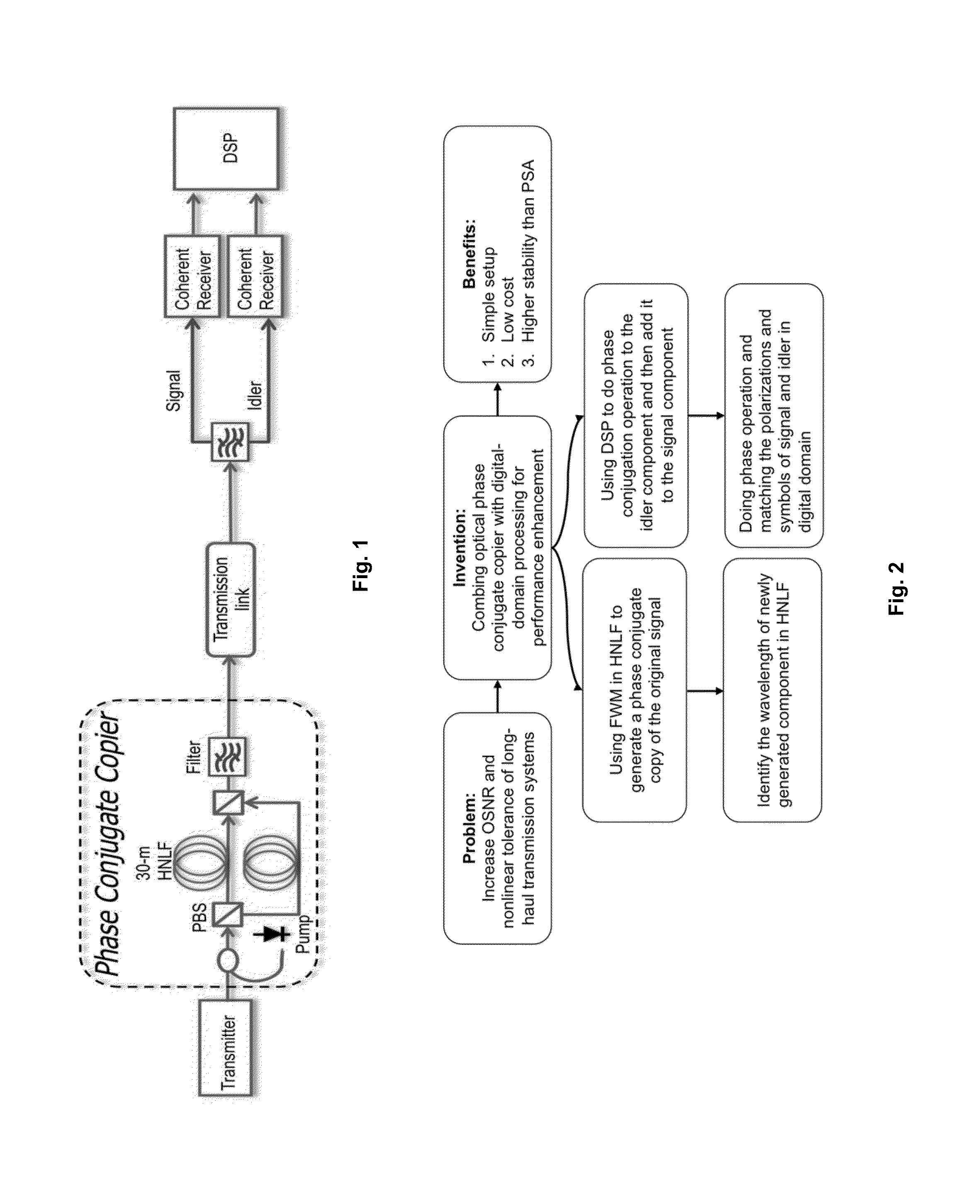
Optical Phase Conjugation Aided Long-Haul Transmission System with Enhanced Signal-to-Noise Ratio and Nonlinear Tolerance
ActiveUS20140099127A1Canceled outDistortion/dispersion eliminationElectromagnetic transmittersDigital signal processingCarrier signal
A long haul transmission system uses a digital signal processor DSP instead of an additional optical phase conjugate copier because the optical phase conjugate copier requires high quality optical carrier regeneration to recover the pump and optical PLL to maintain phase matching between signal and pump. Therefore, the use of DSP to process the signal and idler at receiver end greatly simplifies the system setup, increases the system stability and decreases the system cost.
Owner:NEC CORP
Dispersion management with phase conjugation
InactiveUS7016583B2Minimize impactCladded optical fibreCoupling light guidesOptical phase conjugationOptical coupling
An optical transmission system is provided. The system includes first and second lines of optical fiber, each line including first, second, and third optical fiber portions, and an optical phase conjugator optically coupling the first and second lines. The first and third optical fiber portions have a local dispersion of like sign to each other, and opposite to the sign of the second optical fiber portion.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method and system for using optical phase conjugation in an optical communications network
A optical communications network including at least one optical phase conjugator for compensating for non-linear effects. The optical communications network includes at least one dispersion compensation module before the optical phase conjugator and at least one dispersion compensation module after the optical phase conjugator. The dispersion compensation modules compensate for linear effects of the transmission path such as dispersion and dispersion slope. This allows the optical phase conjugator to be designed to compensate for non-linear effects such as self-phase modulation and cross-phase modulation. The separate compensation of linear and non-linear effects provides enhanced control of these effects.
Owner:CIENA
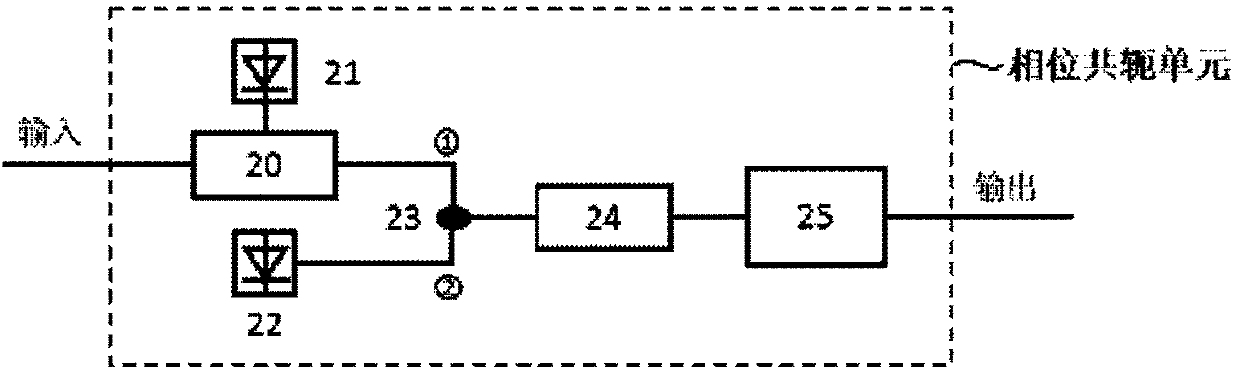
Digital phase conjugation for fiber-optic links
InactiveUS8594515B2Good effectImprove toleranceModulated-carrier systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical phase conjugationNon-linear effects
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Three-dimensional photographing process based on laser probe array and device utilizing same
InactiveCN102494609BAvoid damageAvoid submersionUsing optical meansStereoscopic photographyLaser probeOptical phase conjugation
Owner:李志扬
Processes and systems involving optical phase conjugators
InactiveUS7558485B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmissionCommunications systemOptical phase conjugation
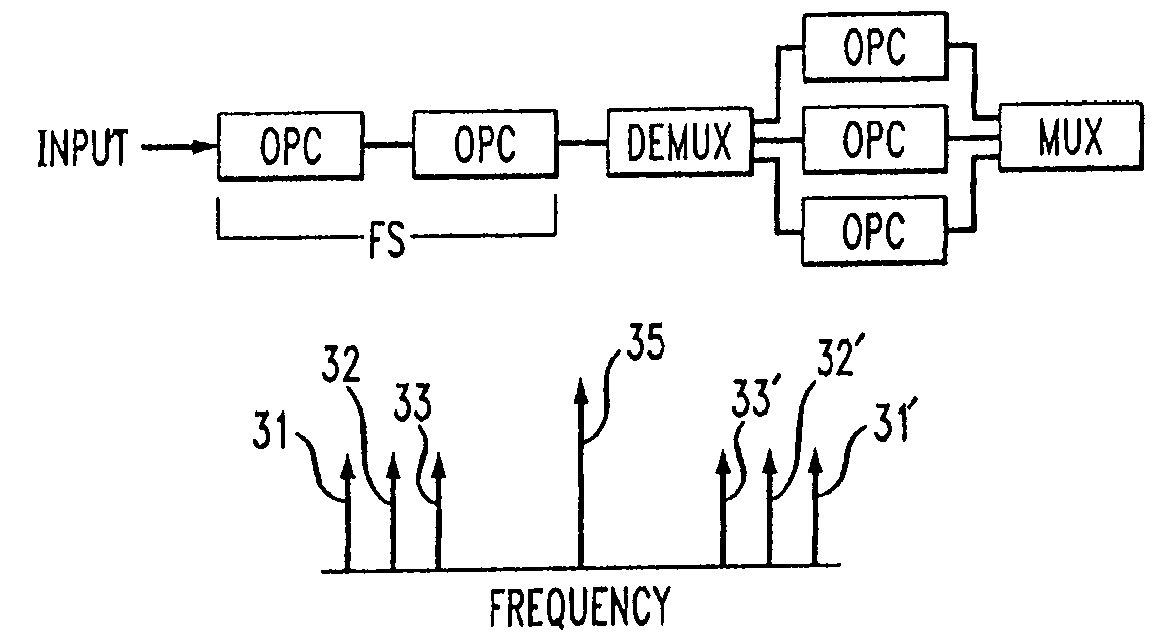
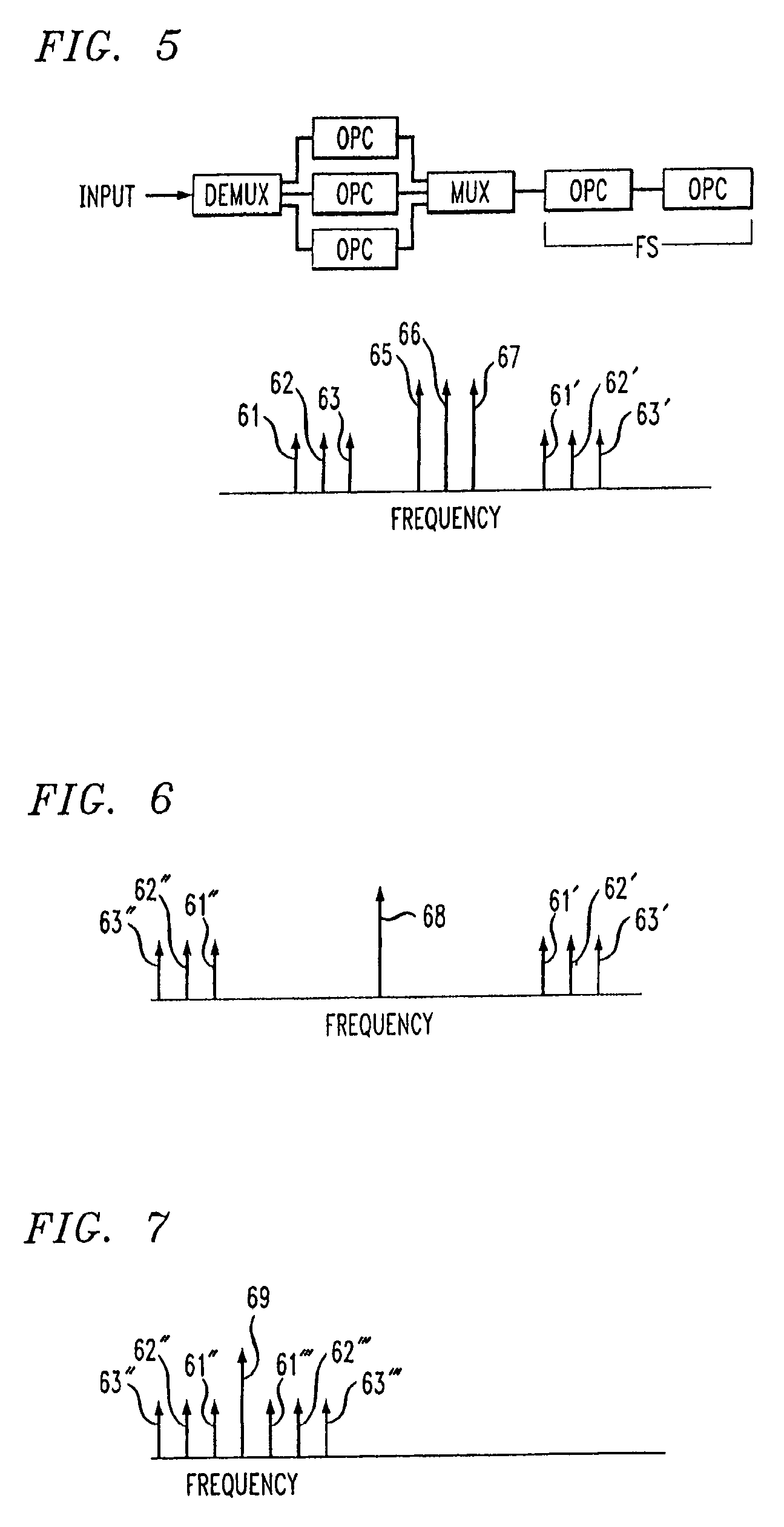
The desirable effects of an optical phase conjugator are accompanied by a frequency shift with reversal of the frequency order of channels in a multichannel optical communication system. Such effects are rectifiable by employing a sequence involving demultiplexing the multichannel signal, operating on the individual, demultiplexed channel with a corresponding optical phase conjugator or frequency shifter followed by multiplexing the signal. This sequence is combined with a complementary operation—optical phase conjugator to complement a frequency shifting sequence or frequency shifting to complement an optical phase conjugating sequence.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Silicon waveguide dispersion compensator using optical phase conjugation
InactiveUS20080240651A1Coupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmissionOptical phase conjugationWaveguide
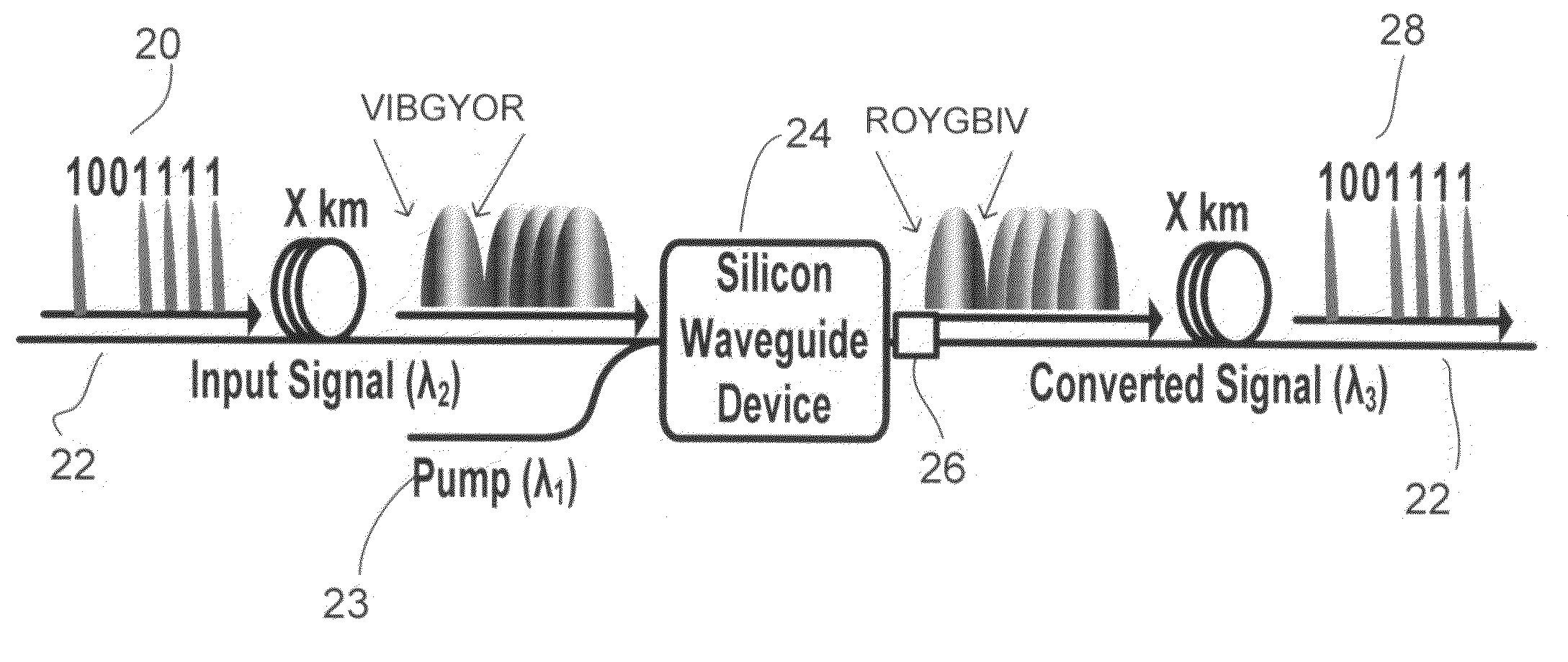
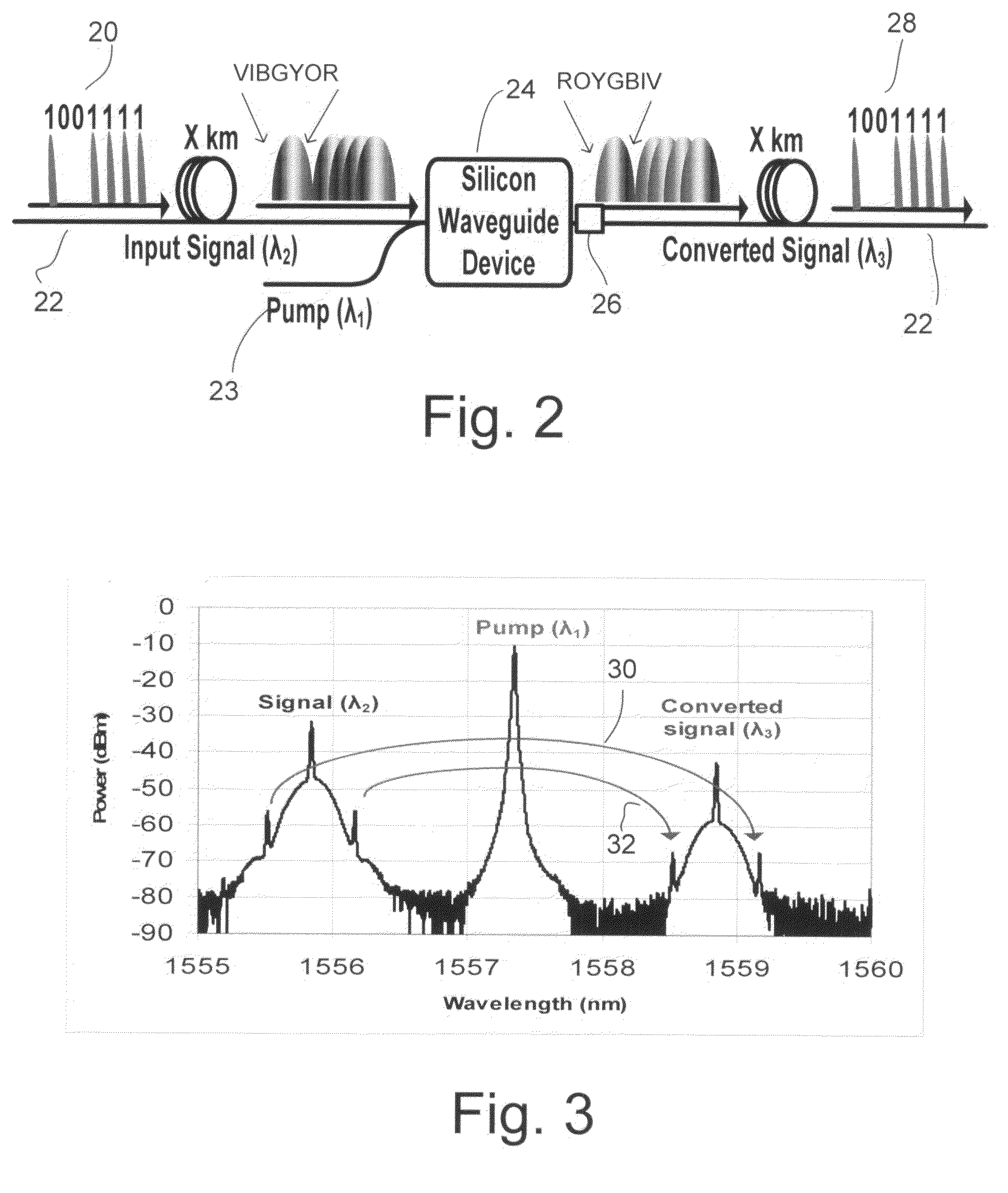
In the absence of using any chromatic dispersion compensation technique, it may be difficult to detect the transmitted data over long distances at the receiving end. Embodiments utilize the optical phase conjugation (OPC) property in silicon waveguides to compensate chromatic dispersion effect in optical fibers.
Owner:RONG HAISHENG +2
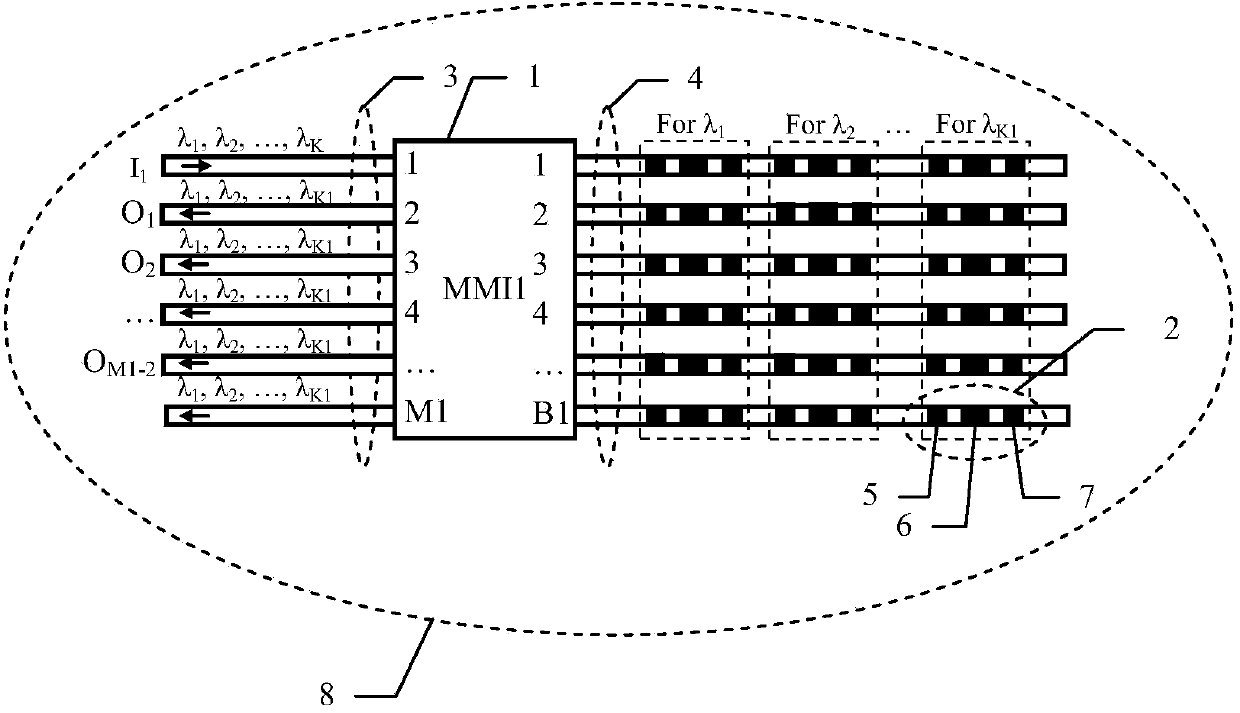
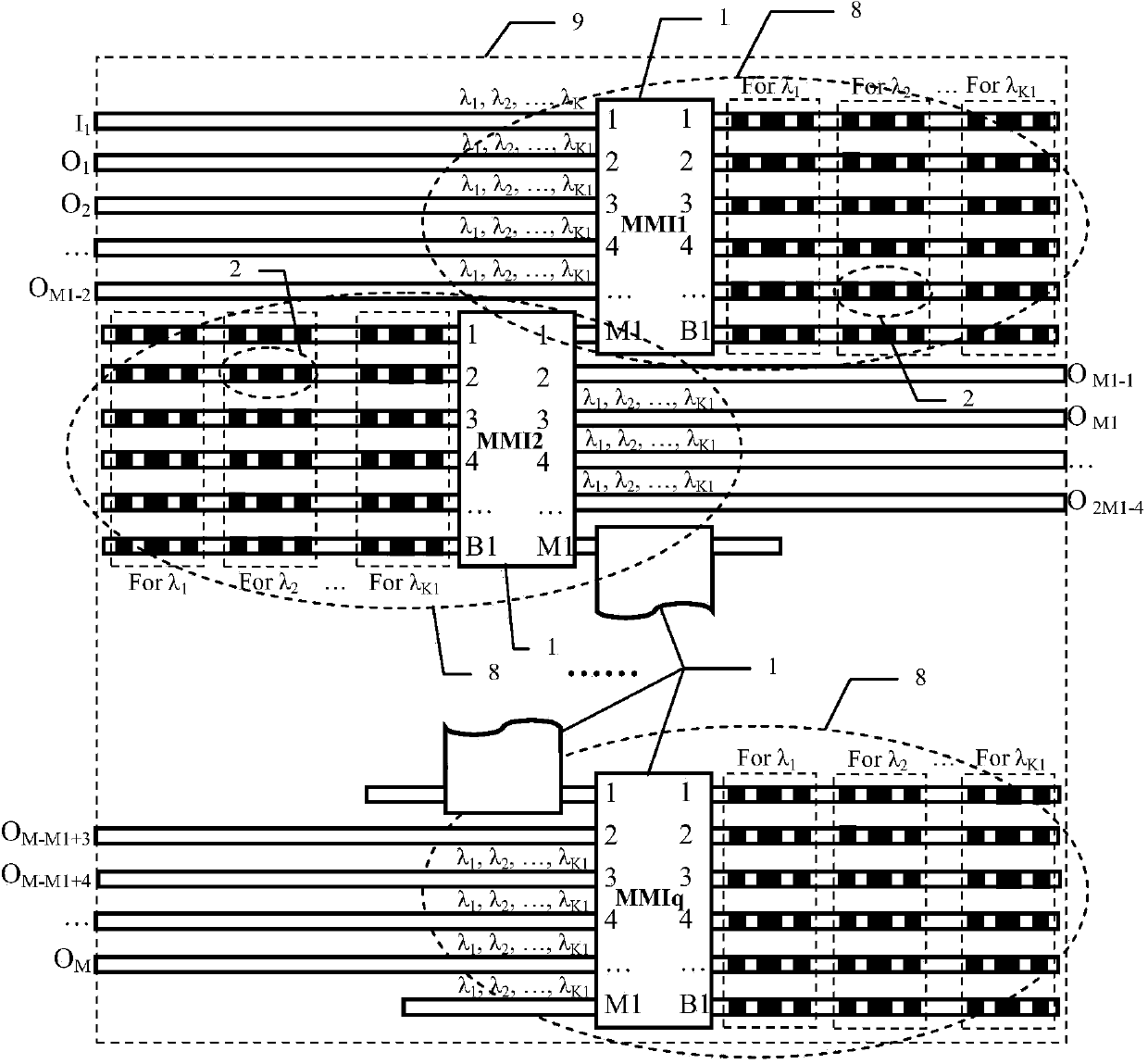
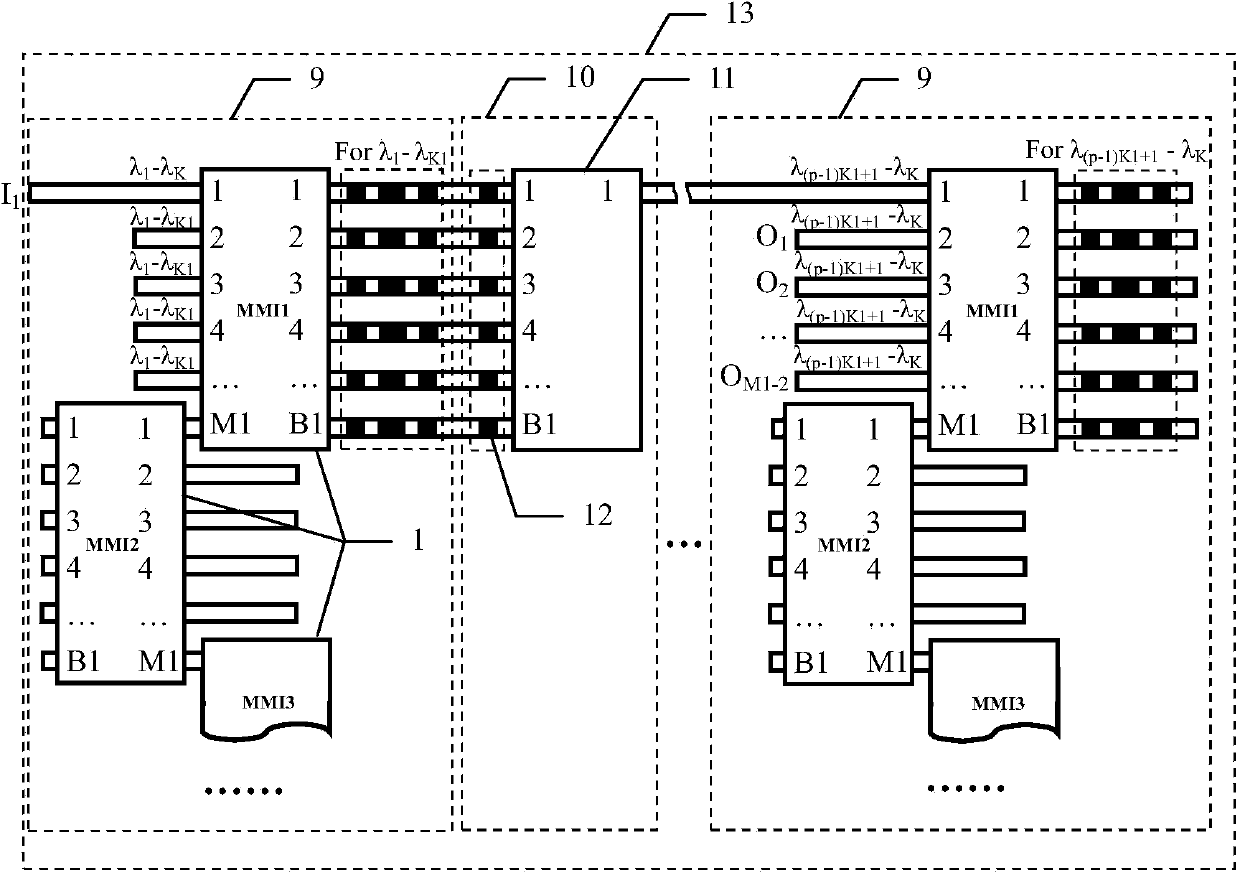
Optical switch array chip based on digital optical phase conjugation principle
ActiveCN103728693AAchieve integrationReduced passband width requirementsOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsOptical phase conjugationEngineering
The invention discloses an optical switch array chip based on a digital optical phase conjugation principle. A multi-mode interference device and a digital optical phase conjugation reflector are used for constituting a 1*(M1-2)*K1 third-level optical switch subsystem, then q 1*(M1-2)*K1 third-level optical switch subsystems are in series connection in the longitudinal direction to form a 1*M*K1 second-level optical switch subsystem, further, p 1*M*K1 second-level optical switch subsystems and p-1 connectors are in series connection in the transverse direction to form a 1*M*K first-level optical switch subsystem, and finally N 1*M*K first-level optical switch subsystems connected to N input optical waveguides share M output optical waveguides, and an N*M*K optical switch array is formed in a parallel connection mode. The digital optical phase conjugation principle is used in the optical switch array, non-blocking optical switching can be conducted on K different wave lengths, and the optical switch array chip based on the digital optical phase conjugation principle is particularly suitable for optical switching and optical intersecting interconnection of optical communication network nodes and also can be used for optical interconnection between chips and optical interconnection inside an optical computer.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
Near real time optical phase conjugation
ActiveUS20110222068A1Increase powerMaterial analysis by optical meansSurgical instrument detailsSpatial light modulatorOptical phase conjugation
An optical system and associated method enable near real time optical phase conjugation. In the method, a translucent medium is illuminated by a sample illumination beam. Light scattered by the medium is directed to an electronic image sensor while a reference beam is also directed to the electronic image sensor. The scattered light and the reference beam form an interference pattern at the electronic image sensor. A digital representation of the interference pattern is recorded using the electronic image sensor, and the characteristics of a conjugate of the sample beam are computed from the numerical representation. A conjugate beam having the computed characteristics is generated using a configurable optical element and directed back to the translucent medium. The generation of the conjugate beam may be accomplished using a spatial light modulator.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Optical up/down conversion-type optical phase conjugate pair signal transmission/reception circuit
ActiveUS20170264366A1Easily compensating non-linear effectDistortion/dispersion eliminationElectromagnetic transmittersEngineeringUp conversion
To provide a method capable of easily compensating waveform distortion due to a non-linear effect caused by a complicated electric circuit, and a device for implementing the method. Provided are a method capable of effectively compensating signal degradation such as waveform distortion due to a nonlinear effect caused by an optical fiber that is an optical transfer path using an optical phase conjugate signal pair at the time of optical up-conversion or down-conversion, and a device capable of implementing the method. This emission device 25 includes an optical modulator 11, a signal source 13, an optical fiber 15, a multiplexing unit 17, a multiplexing local signal source 19, an optical detector 12, and a transmission antenna 23.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com