Three-dimensional photographing process based on laser probe array and device utilizing same
A laser probe and array technology, applied in the direction of optical devices, photography, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problems of small measurement area, shadow blocking, and inability to quickly provide dense three-dimensional coordinates
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
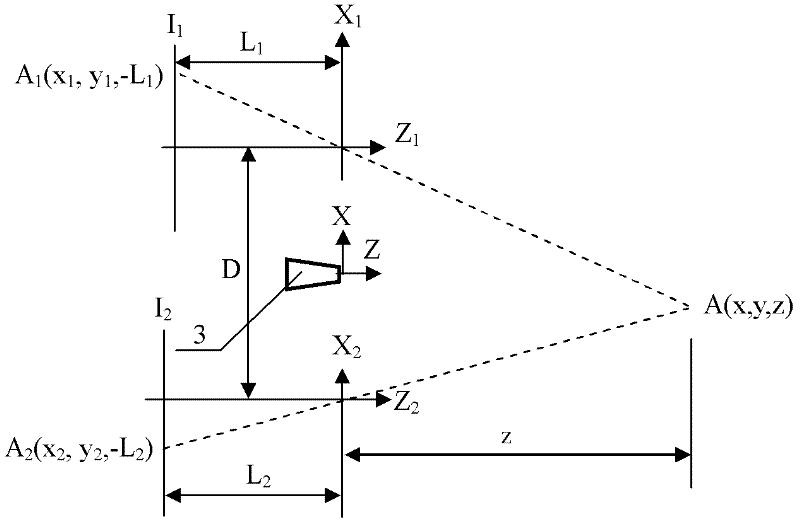
[0040] Step 1. Set the optical center of the laser probe generator as the coordinate origin, the optical axis of the laser probe generator is the Z axis, the X axis is perpendicular to the Z axis, the X axis Z axis plane is the horizontal plane, and the Y axis is perpendicular to the X axis Z axis plane; the first two-dimensional camera and the second two-dimensional camera are arranged symmetrically on both sides of the origin on the X axis, and the optical axes of the first two-dimensional camera and the second two-dimensional camera are parallel to the Z axis, so that the first two-dimensional camera and the second two-dimensional camera are The second two-dimensional camera constitutes a pair of stereoscopic cameras, while the first two-dimensional camera and the second two-dimensional camera respectively form a three-dimensional measurement device based on the laser probe array with the laser probe generator;
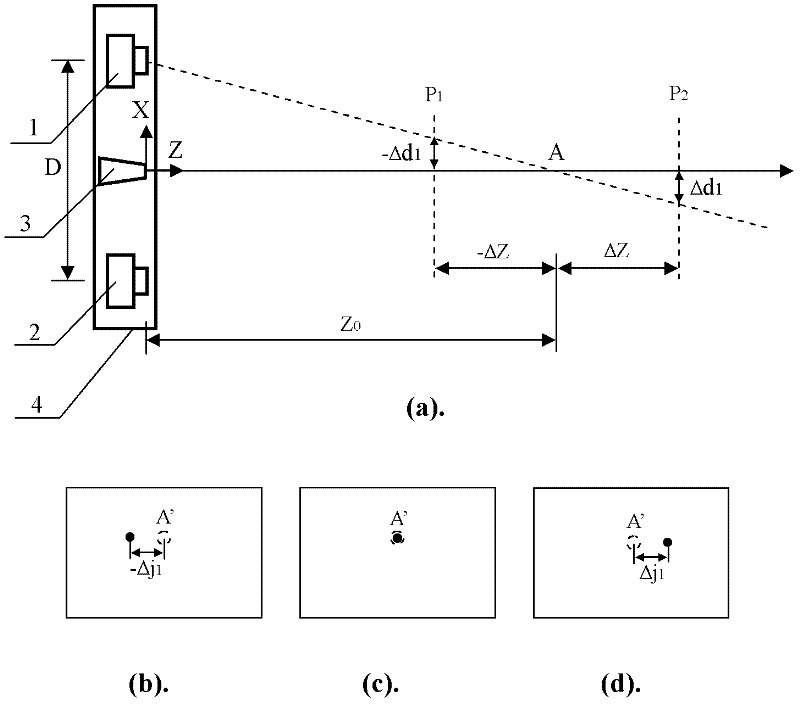
[0041] Step 2, setting the predetermined focus point of the la...
Embodiment 2
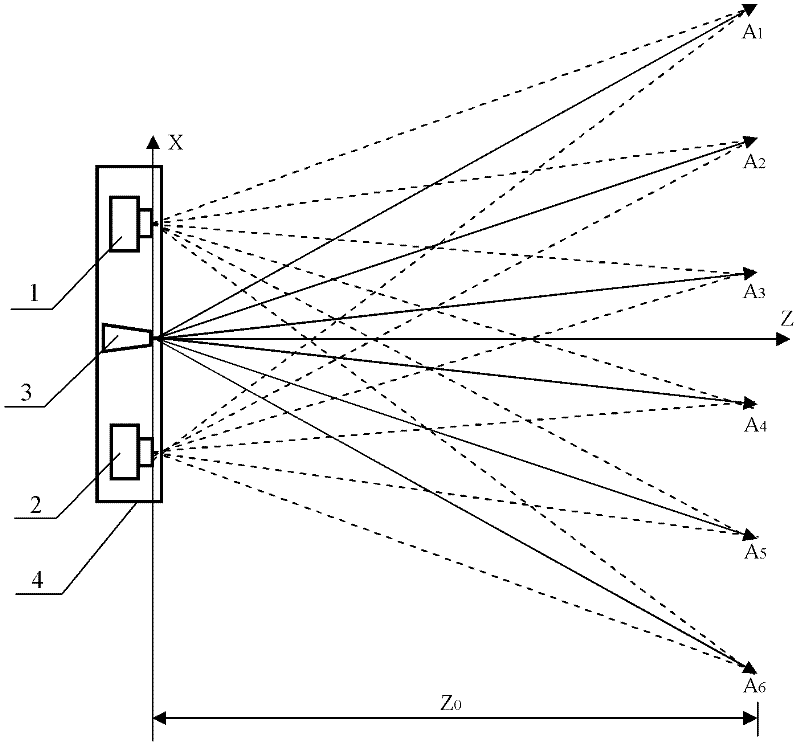
[0054] figure 1 A three-dimensional imaging device based on a laser probe array is provided, which includes a first two-dimensional camera 1, a second two-dimensional camera 2, a laser probe generator 3 and a support 4, the first two-dimensional camera 1, the laser probe The needle generator 3 and the second two-dimensional camera 2 are fixed on the support 4 at equal intervals in turn, and the optical axis of the first two-dimensional camera 1, the optical axis of the laser probe generator 3 and the optical axis of the second two-dimensional camera 2 are mutually Parallel and on the same plane, the line connecting the optical center of the optical lens of the first two-dimensional camera 1 and the optical center of the optical lens of the second two-dimensional camera 2 is perpendicular to their optical axis, and the optical center of the laser probe generator 3 Located on the line connecting the optical center of the optical lens of the first two-dimensional camera 1 and the...
Embodiment 3
[0090] Figure 5 A schematic diagram of the structure of a dual-band two-dimensional camera is given, which is composed of a first image sensor 7, a second image sensor 8, an optical lens 5 and a wavelength selective beam splitter 6, the reflective surface of the wavelength selective beam splitter 6 and the optical lens 5 The optical axis is 45 degrees, and the first image sensor 7 and the second image sensor 8 are symmetrically placed on the two image planes of the optical lens 5, respectively, so that the incident infrared light is reflected by the wavelength selection beam splitter 6 and imaged to the first image sensor 7, while the incident visible light is transmitted through the wavelength selective beam splitter 6 and imaged to the second image sensor 8 . In addition, the dual-band two-dimensional camera also includes a narrow-band infrared filter 9 , which is placed in front of the first image sensor 7 .
[0091] exist figure 1 In the 3D imaging device based on the l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com