Patents
Literature
1058 results about "Laser interferometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
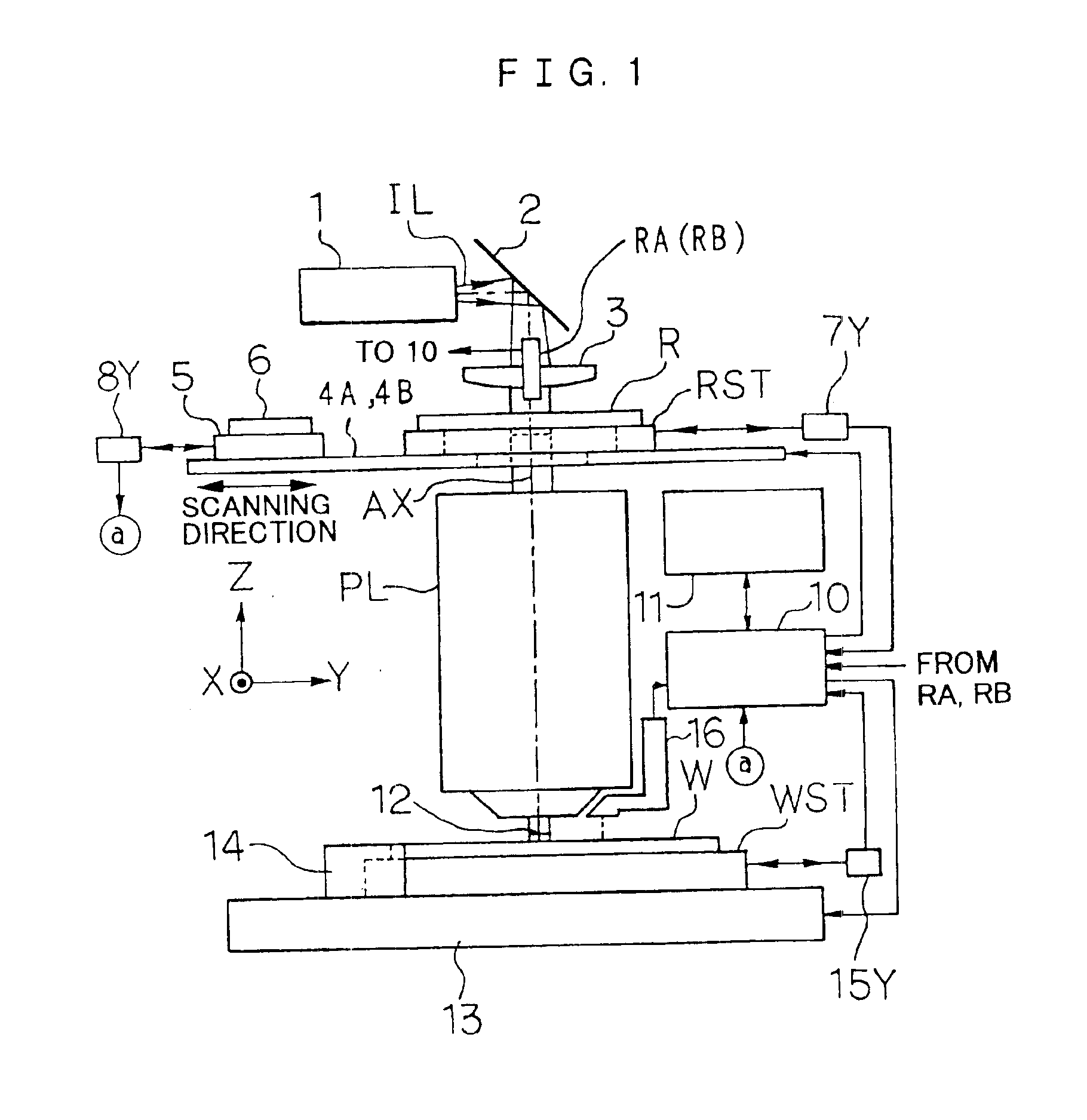
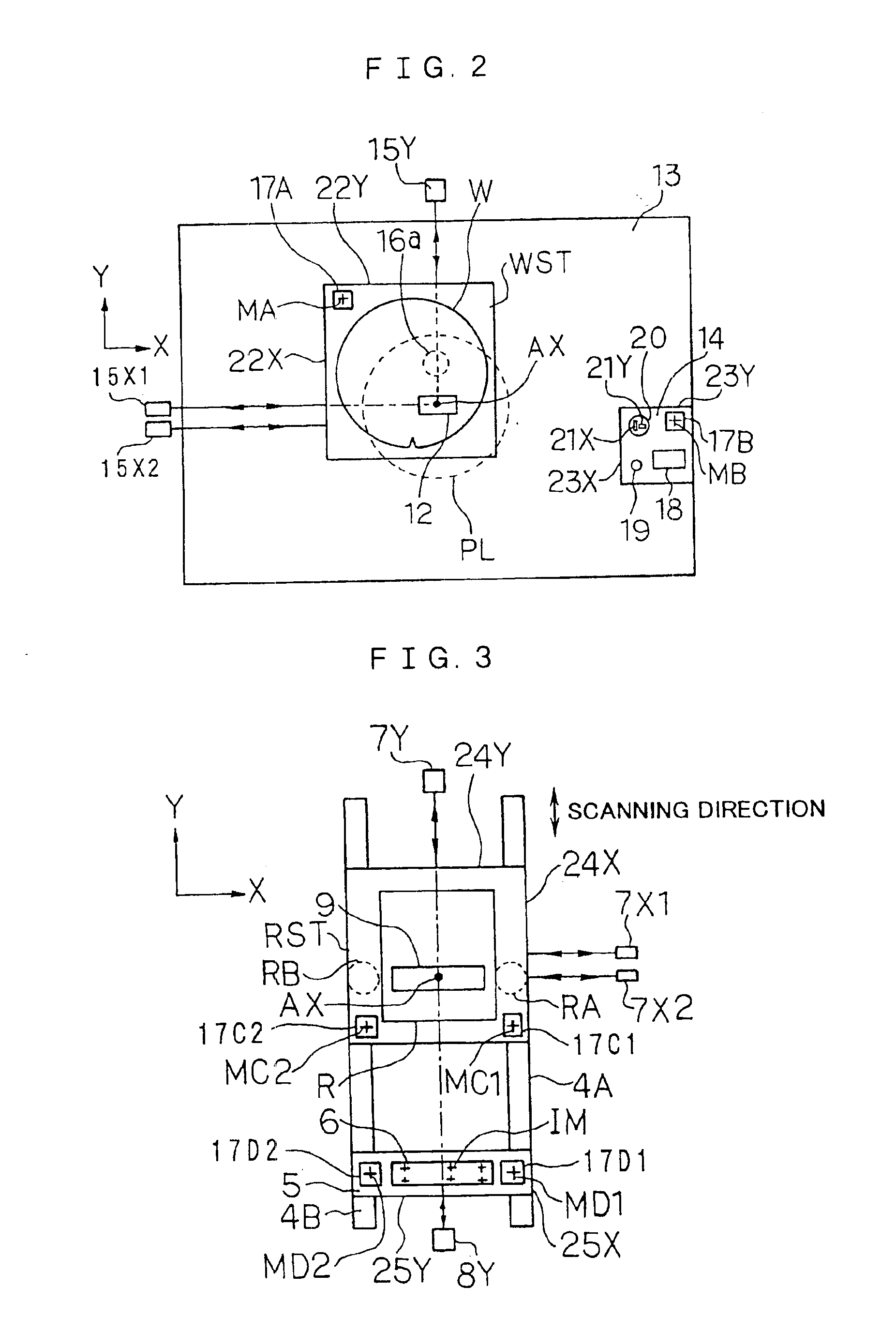
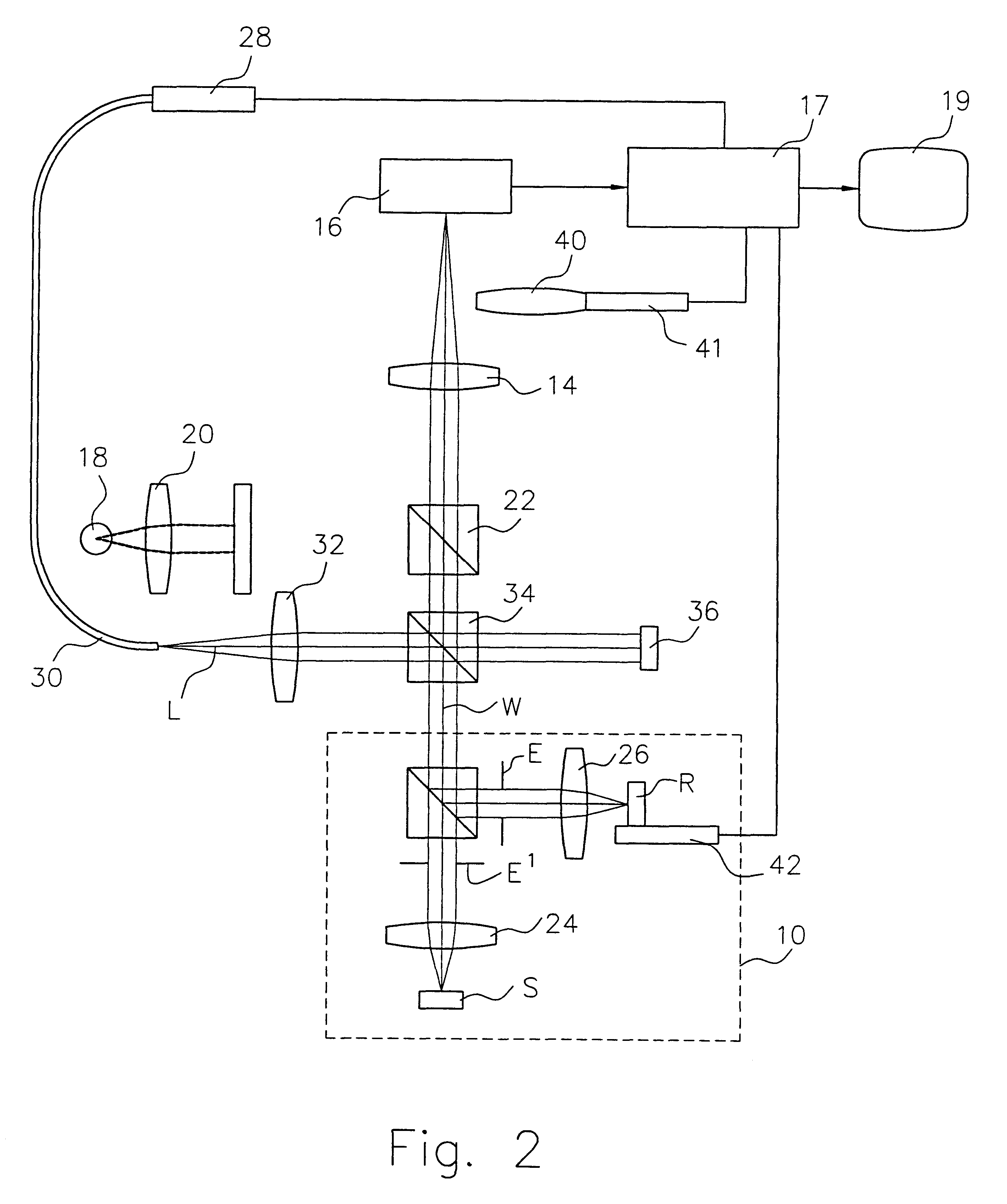
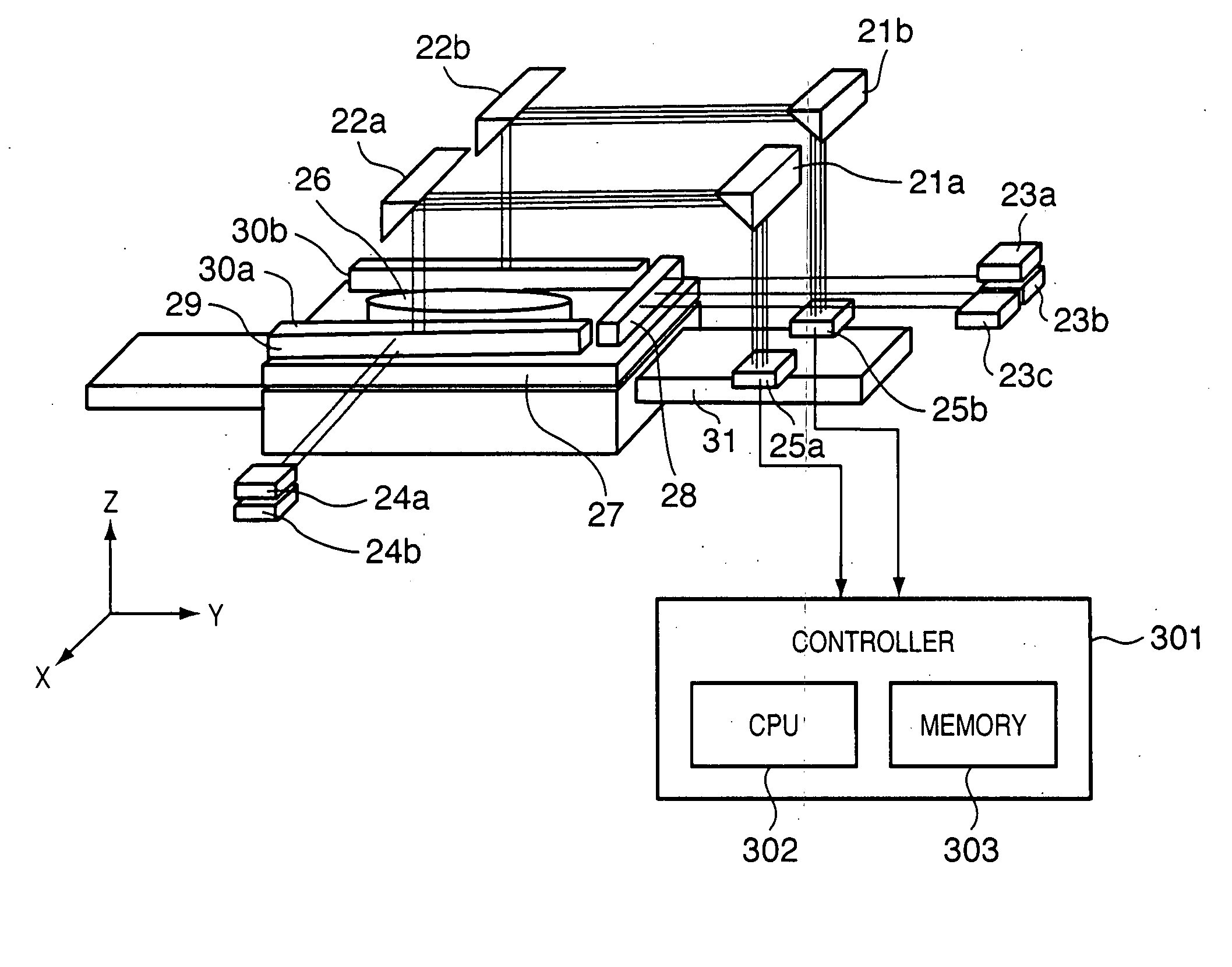
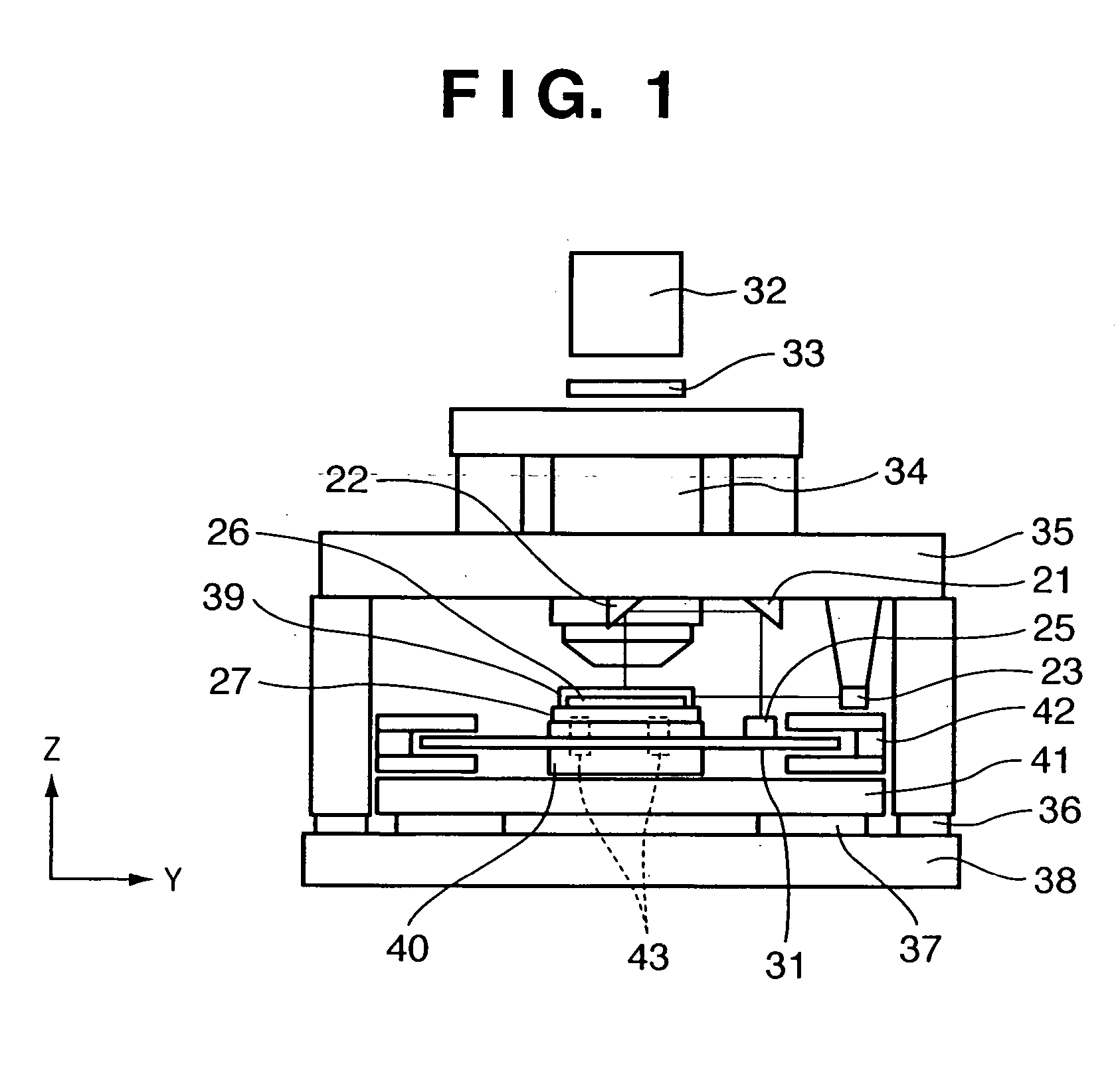
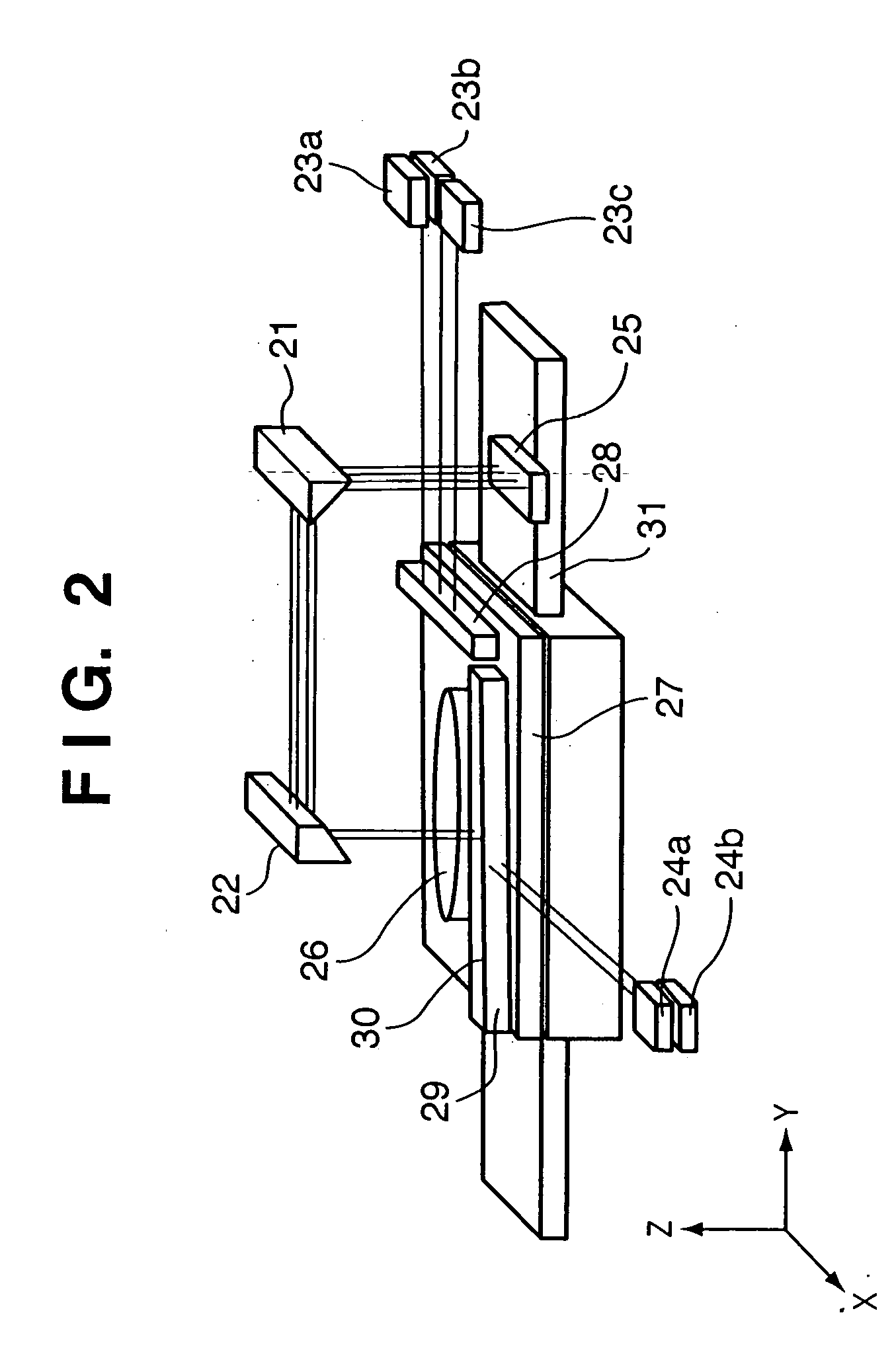
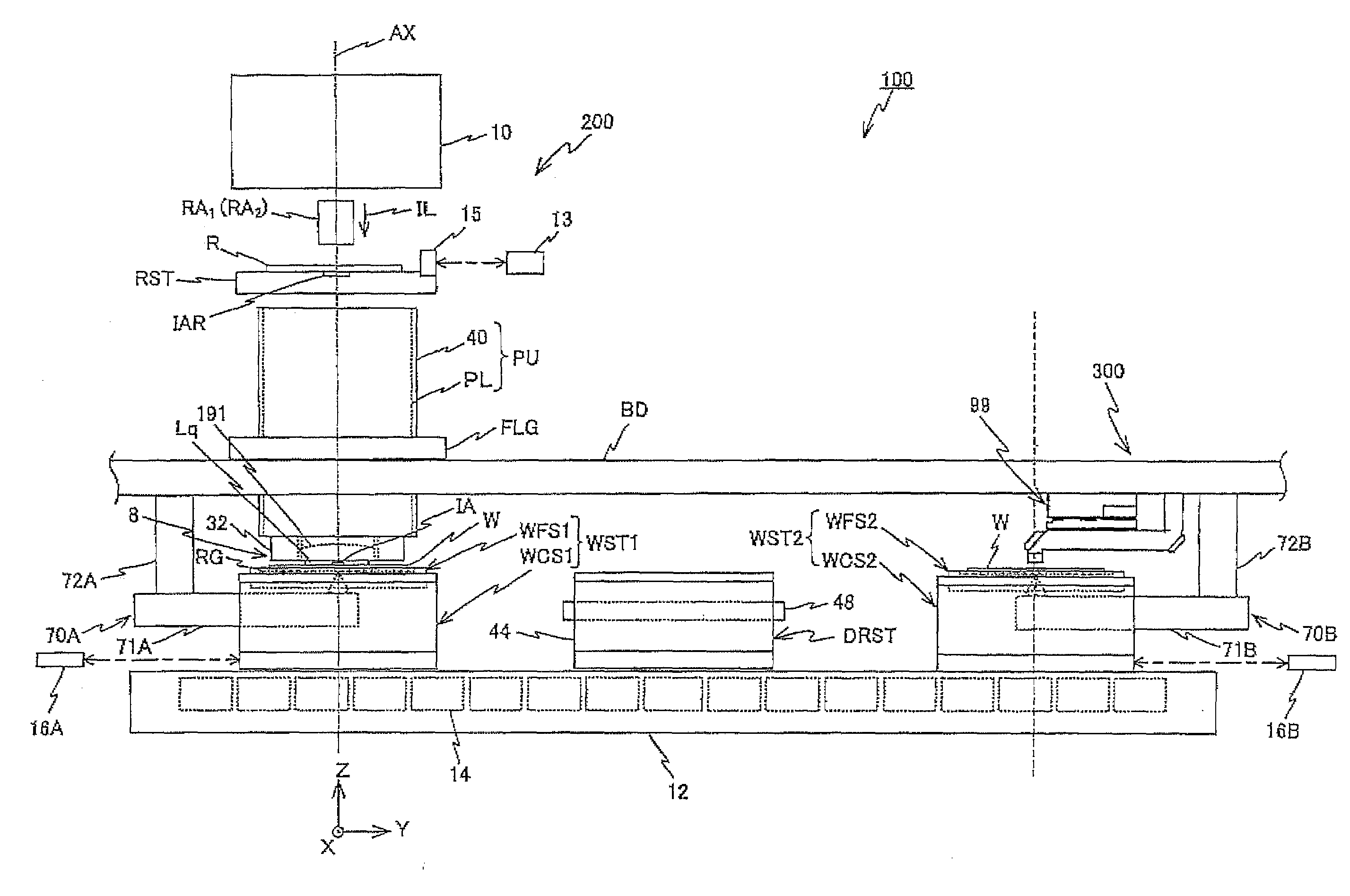
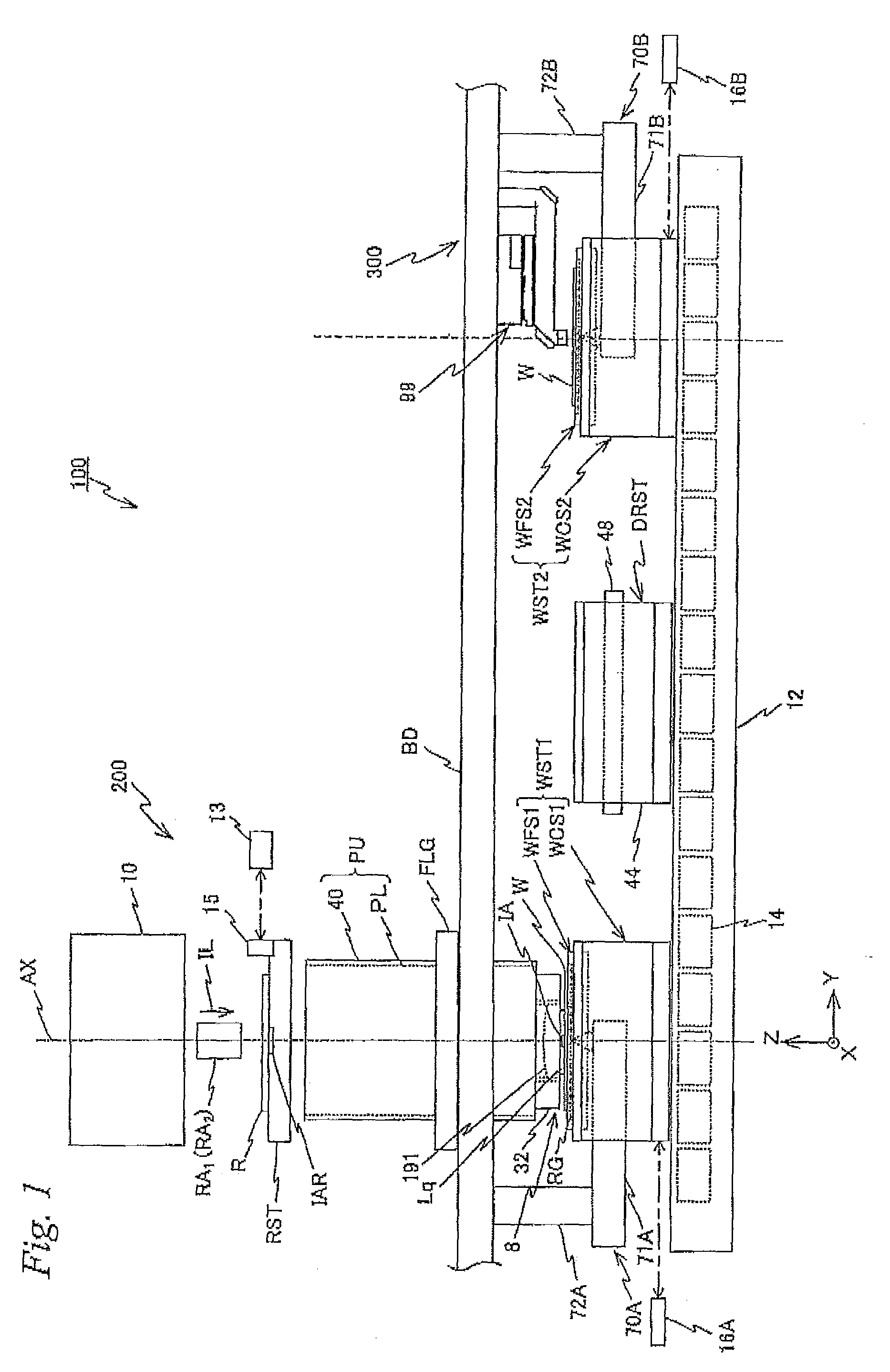
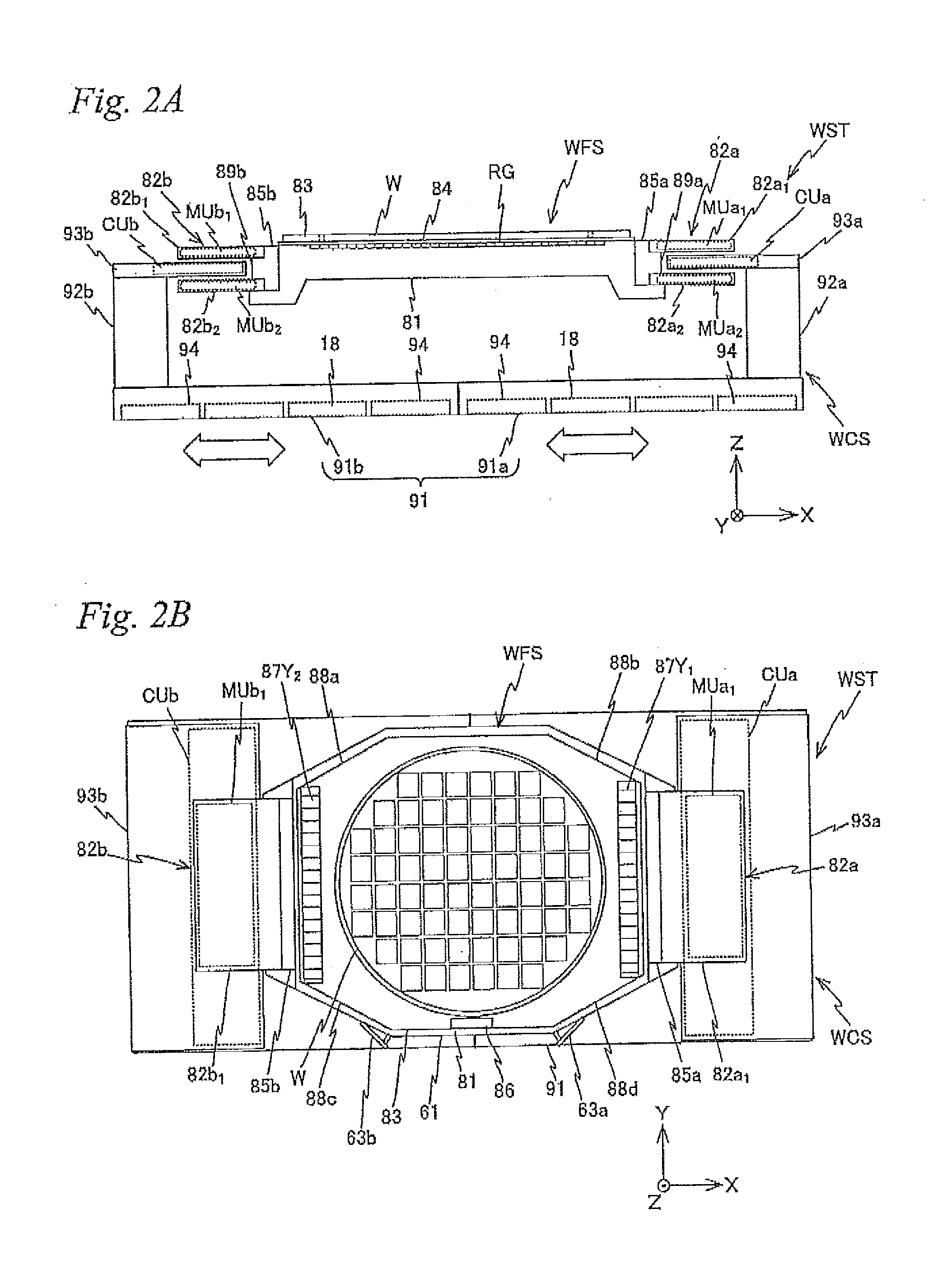
Stage device and exposure apparatus
InactiveUS6897963B1Increase speedImprove throughputSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingUsing optical meansLaser beamsSemiconductor
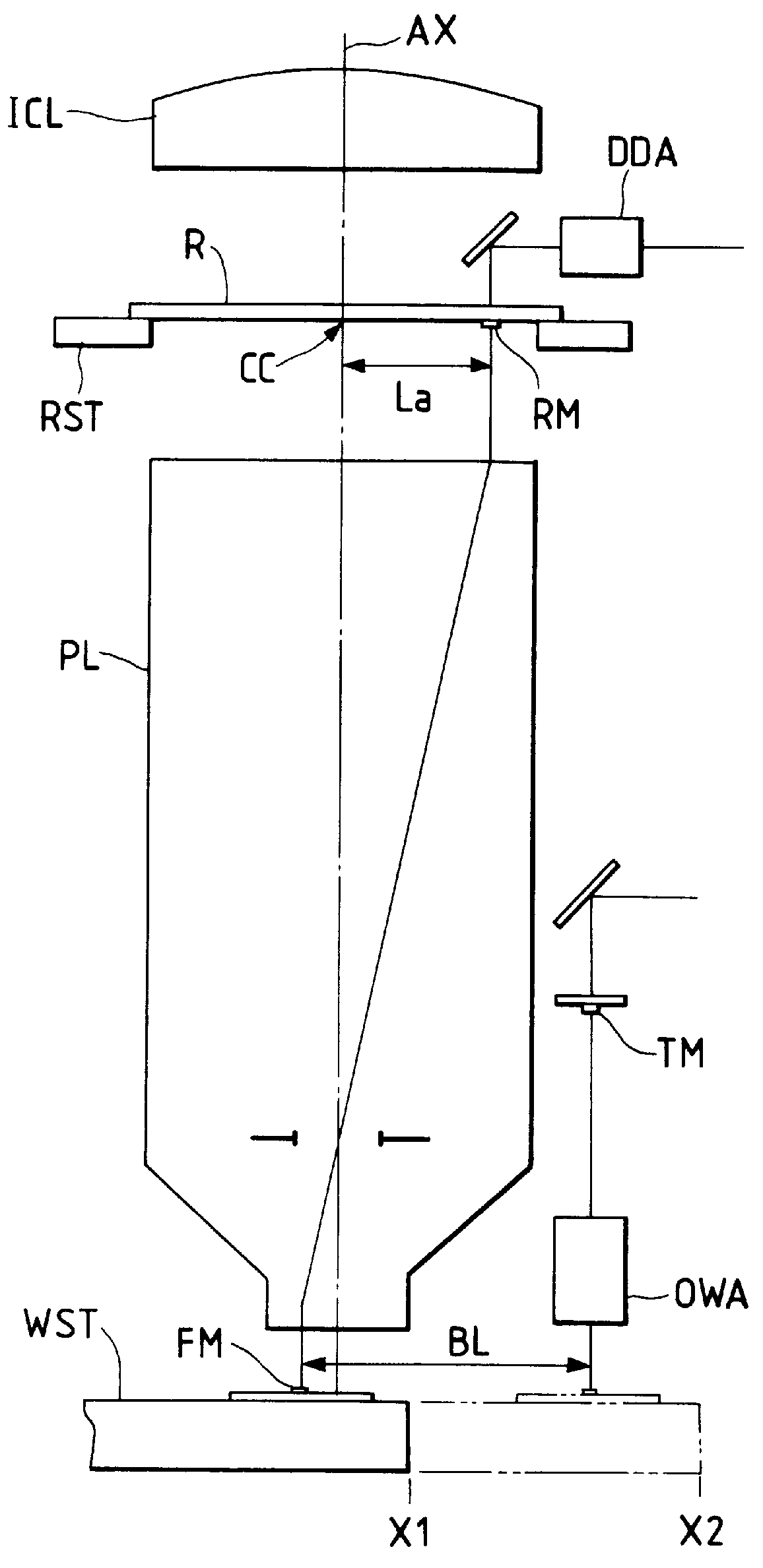
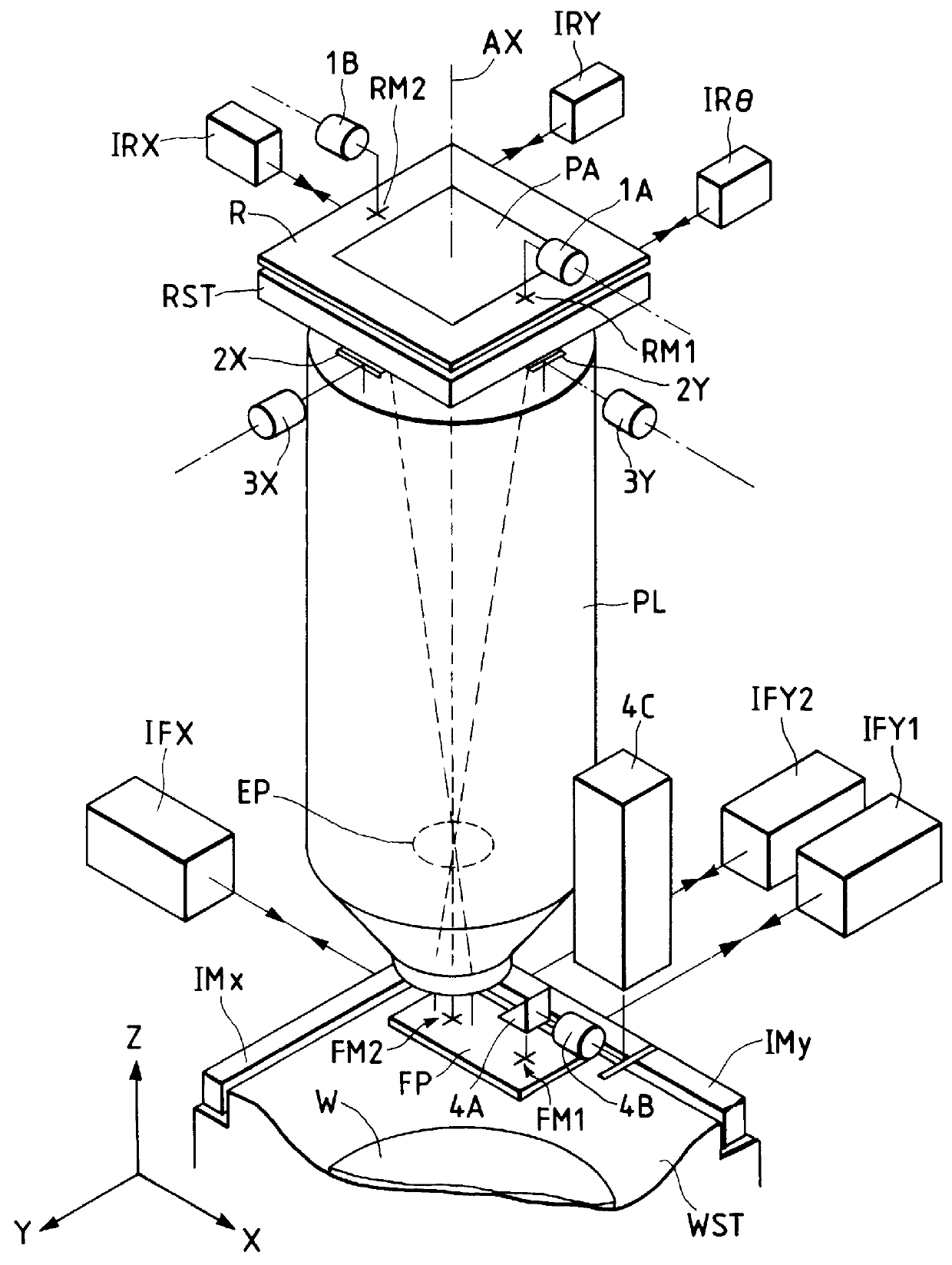
A stage device suitable for exposure apparatus used to produce semiconductor devices, is movable in an area wider than the measurement area of interferometer for position measurement, and is capable of measuring the position with high precision. When a movable stage moves from the position where the laser beams from laser interferometers are not applied into the measurement area of the laser interferometer, the position of reference mark is measured by a wafer alignment sensor, and the measurement value measured by the laser interferometer is corrected based on the results of the measurement by the wafer alignment sensor. When another movable stage enters the measurement area of the laser interferometer, the position of the reference mark is similarly measured by a wafer alignment sensor, and the measurement value measured by the laser interferometer is corrected based on the results of the measurement by the wafer alignment sensor.
Owner:NIKON CORP
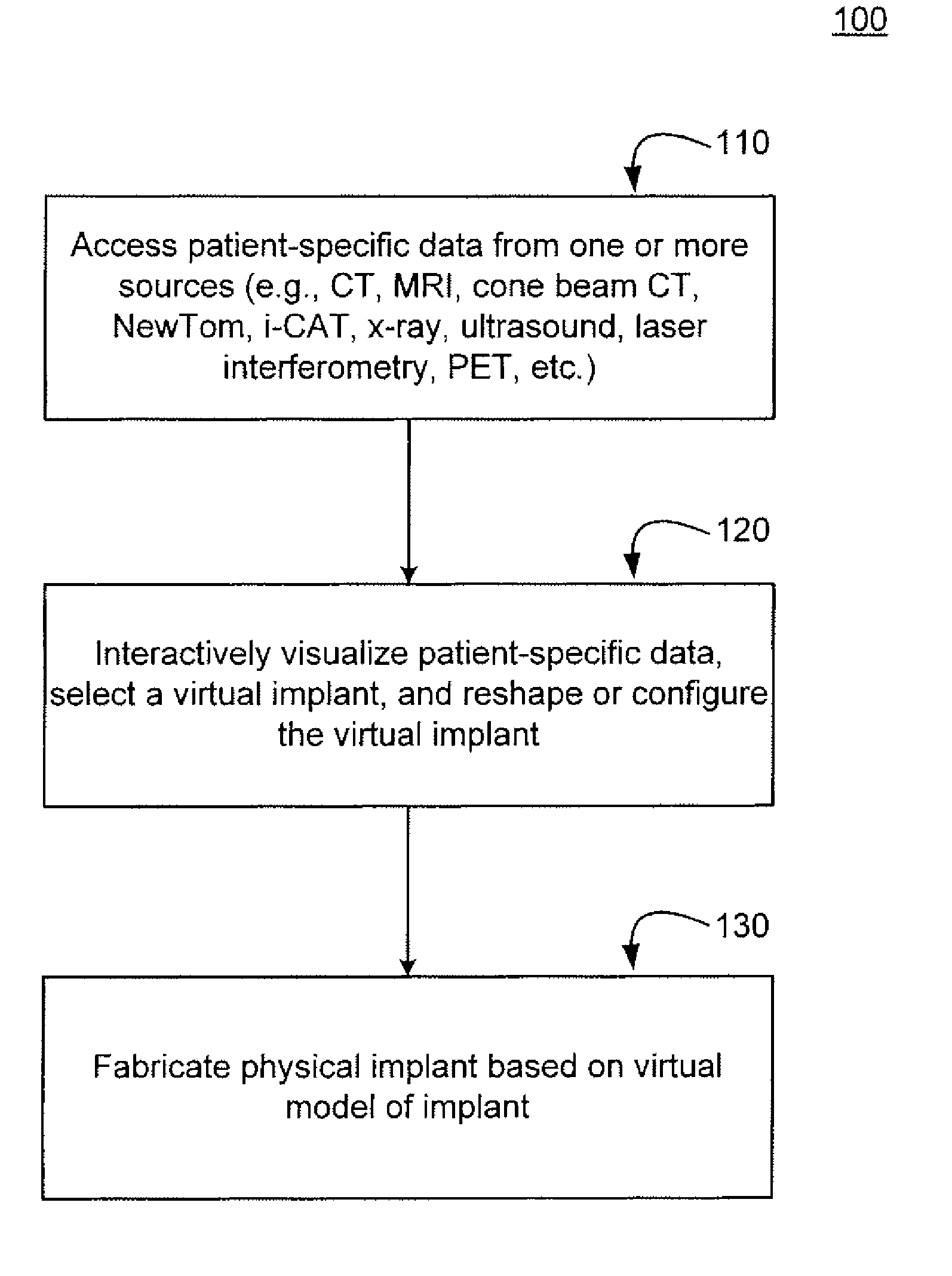
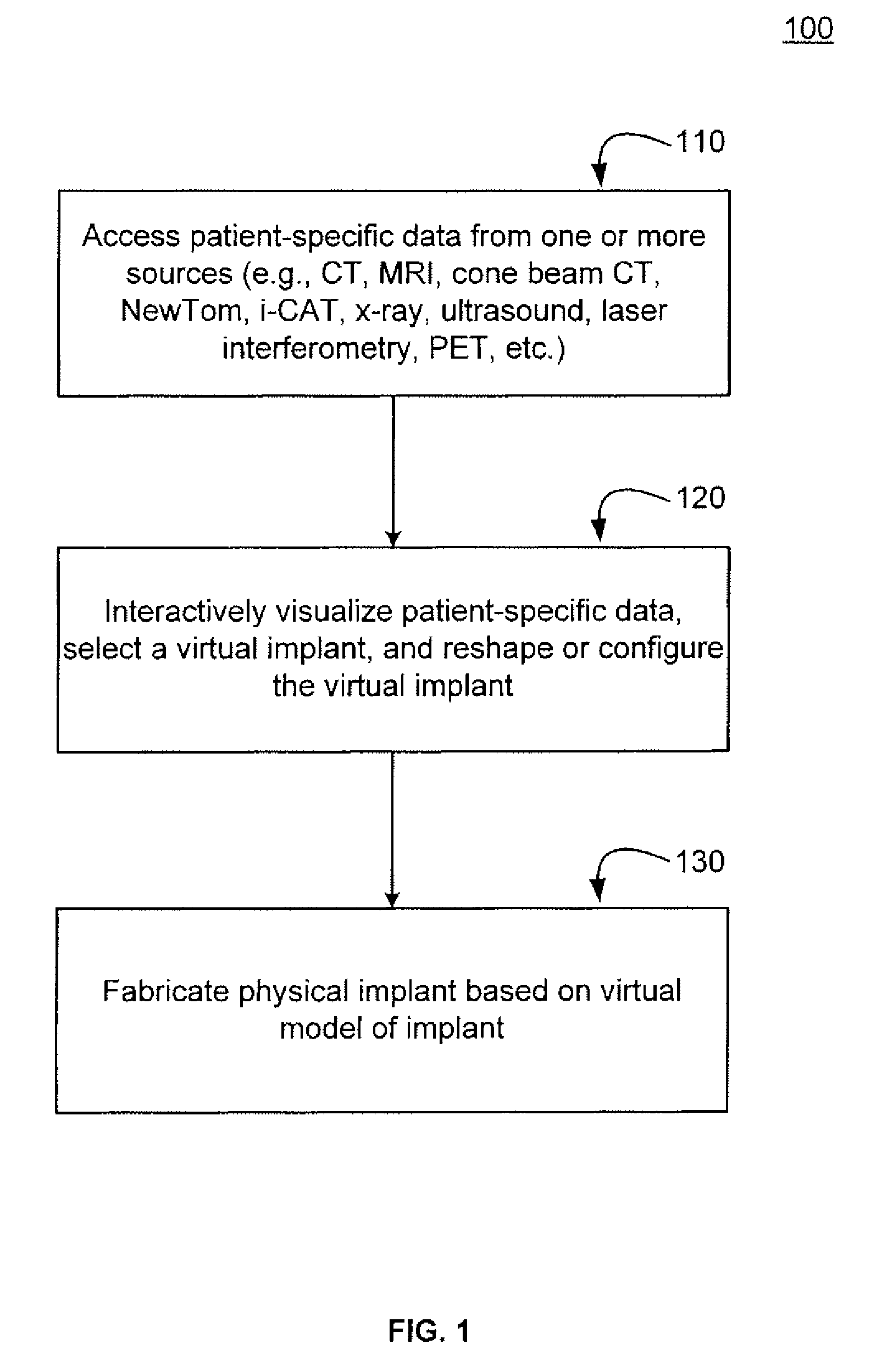
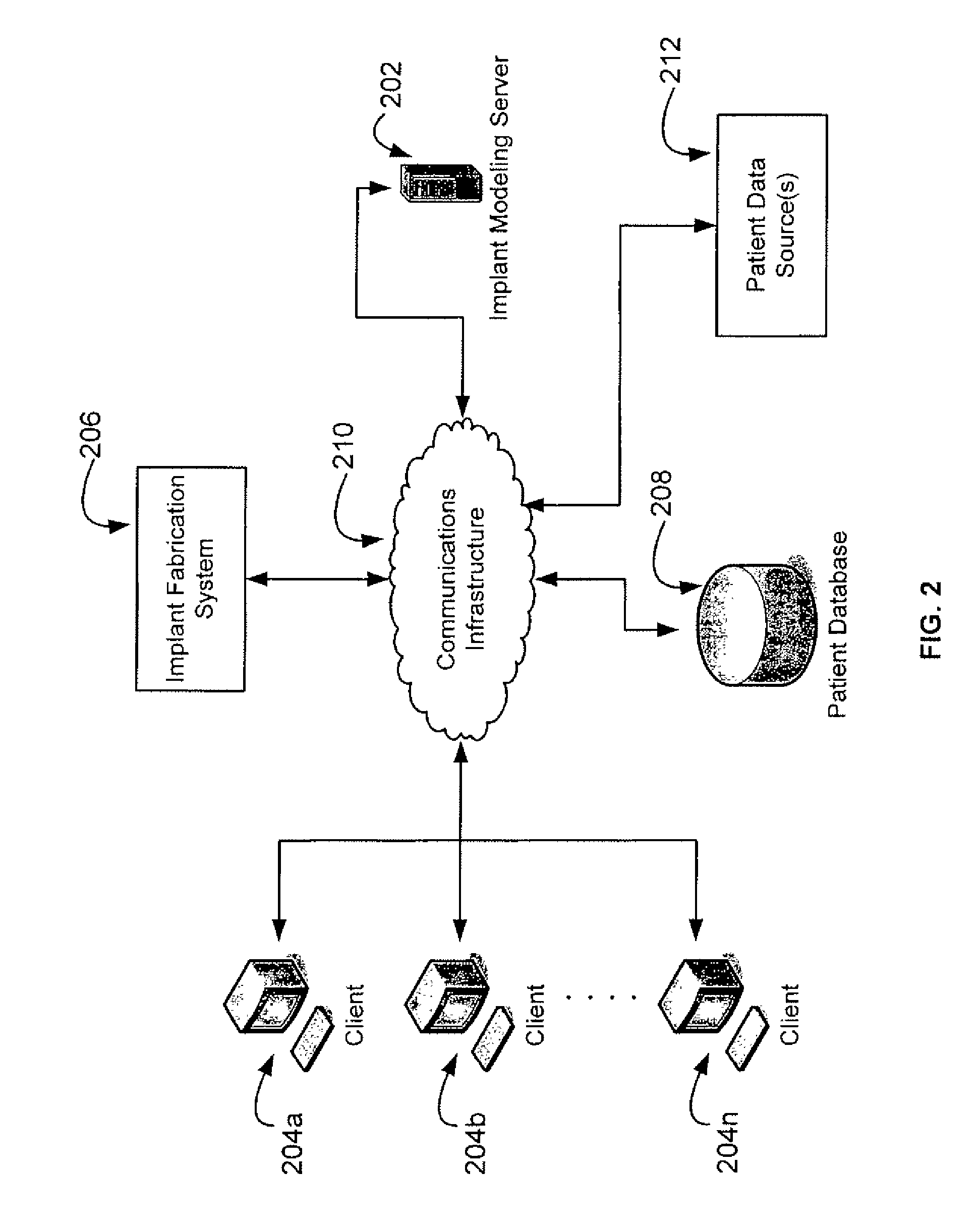
Methods, systems, and computer program products for shaping medical implants directly from virtual reality models
InactiveUS20090149977A1Improve aestheticsReduce probabilityMedical simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAnatomical structuresX-ray
A virtual interactive environment enables a surgeon or other medical professional to manipulate implants, prostheses, or other instruments using patient-specific data from virtual reality models. The patient data includes a combination of volumetric data, surface data, and fused images from various sources (e.g., CT, MRI, x-ray, ultrasound, laser interferometry, PET, etc.). The patient data is visualized to permit a surgeon to manipulate a virtual image of the patient's anatomy, the implant, or both, until the implant is ideally positioned within the virtual model as the surgeon would position a physical implant in actual surgery. Thus, the interactive tools can simulate changes in an anatomical structure (e.g., bones or soft tissue), and their effects on the external, visual appearance of the patient. CAM software is executed to fabricate the implant, such that it is customized for the patient without having to modify the structures during surgery or to produce a better fit.
Owner:SCHENDEL STEPHEN A
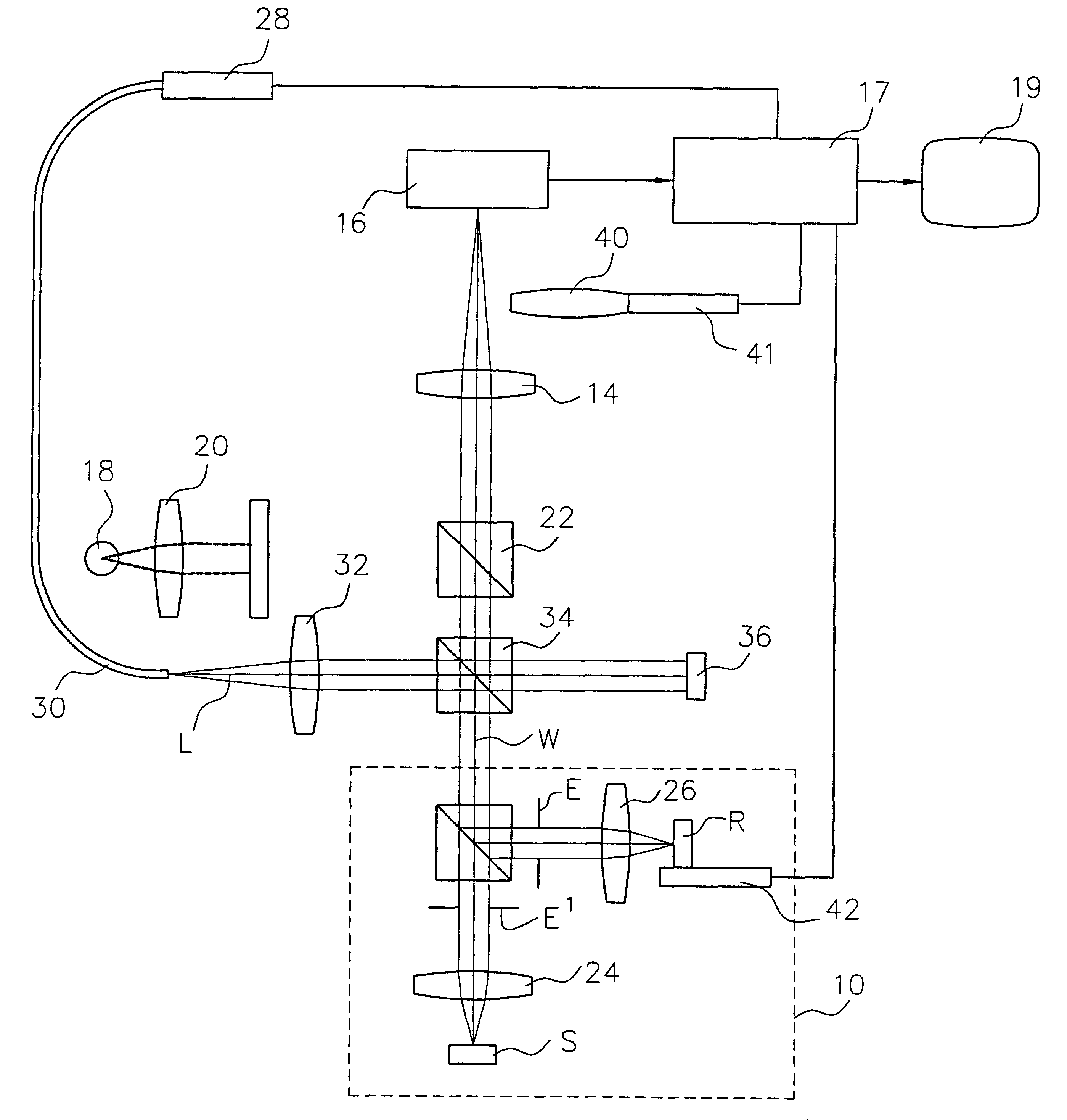
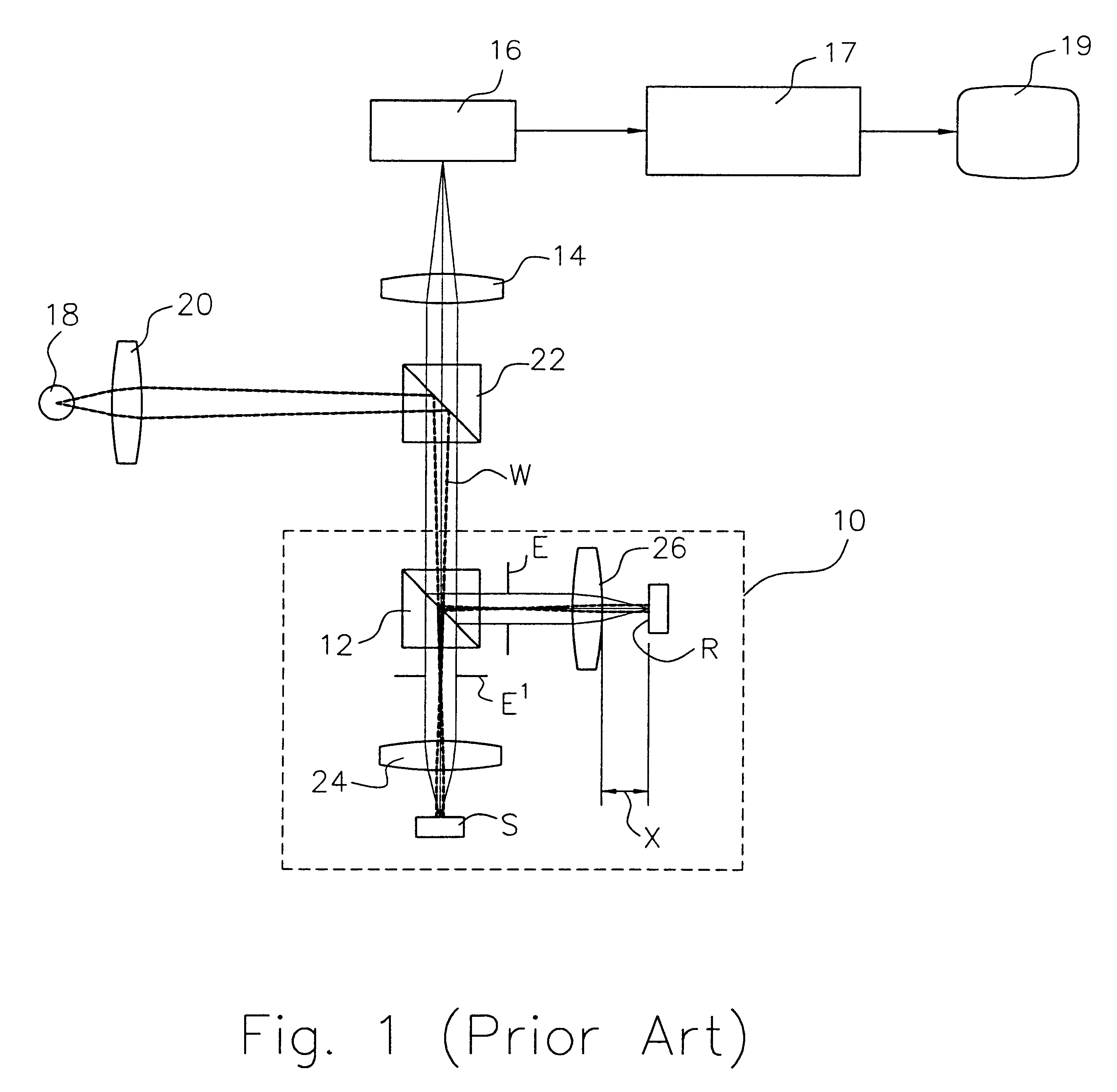
Embedded interferometer for reference-mirror calibration of interferometric microscope
InactiveUS6545761B1Implemented easily and economicallyAccurately determineInterferometersUsing optical meansClosed loopOptoelectronics
A laser interferometer is embedded into an interference microscope to precisely determine the in-focus position of the microscope objective's reference mirror. A collimated laser beam is introduced into the microscope system and split into two beams directed toward a calibration reference surface and the interference objective. The light reflected from the calibration reference surface is returned to the camera. The light into the interference objective is focused onto the reference mirror and returned to the camera. For the purpose of calibration, the two beams are combined at the camera to produce interference fringes. When the reference mirror is in focus, the returned beam is collimated; if the mirror is on either side of focus, the beam is either converging or diverging. Accordingly, the interferogram produced at the camera reflects the in-focus or out-of-focus condition of the reference mirror. The curvature of the wavefront returned from the reference mirror is determined electronically by analyzing the interference fringes produced with the beam returned from the calibration reference surface. By minimizing the curvature of the reference-mirror wavefront as the mirror is translated along the optical path, the reference mirror can be focused with an accuracy greater than possible by visual observation. Furthermore, by automating the focusing system with a precise translation mechanism driven by closed-loop control, operator-to-operator variations are completely eliminated.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
Magnetic recording medium
ActiveUS7014927B2Reduce noiseImprove tribological propertiesRecord information storageMagnetic recordingMaximum differenceMagnetic layer
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
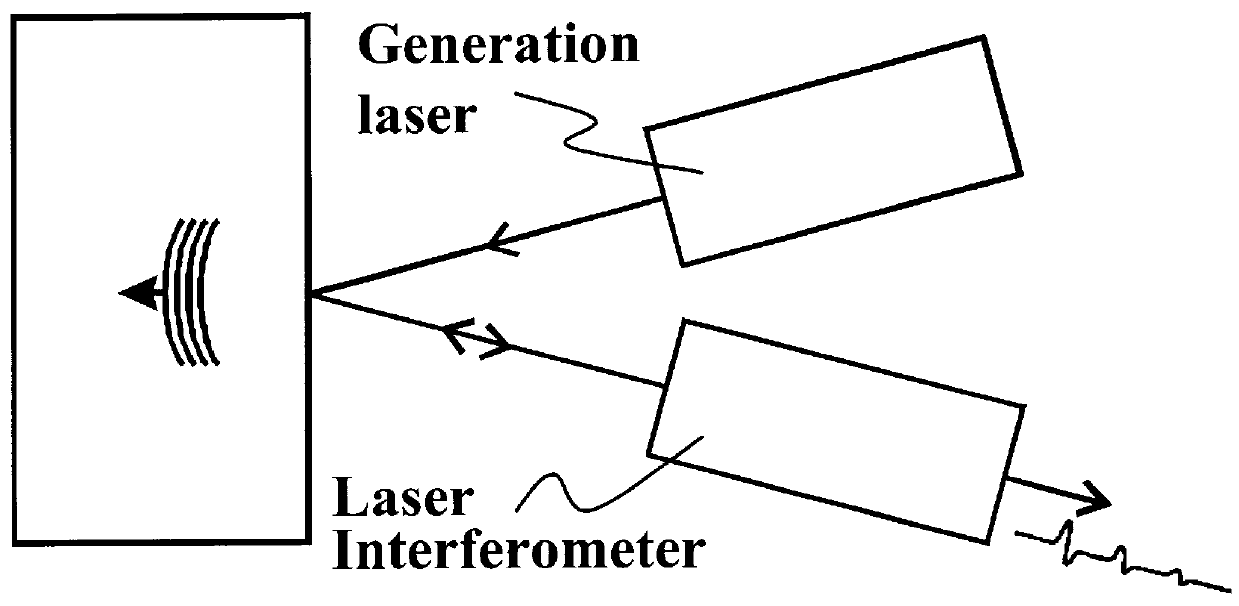
Method and system for high resolution ultrasonic imaging of small defects or anomalies.
InactiveUS6128092ARadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometrySonificationSynthetic aperture focusing
A method and system is provided for enhanced ultrasonic detection and imaging of small defects inside or at the surface of an object. The Synthetic Aperture Focusing Technique (SAFT) has been used to improve the detectability and to enhance images in conventional ultrasonics and this method has recently been adapted to laser-ultrasonics. In the present invention, an improved version of the frequency-domain SAFT (F-SAFT) based on the angular spectrum approach is described. The method proposed includes temporal deconvolution of the waveform data to enhance both axial and lateral resolutions, control of the aperture and of the frequency bandwidth to improve signal-to-noise ratio, as well as spatial interpolation of the subsurface images. All the above operations are well adapted to the frequency domain calculations and embedded in the F-SAFT data processing. The aperture control and the spatial interpolation allow also a reduction of sampling requirements to further decrease both inspection and processing times. This method is of particular interest when ultrasound is generated by a laser and detected by either a contact ultrasonic transducer or a laser interferometer.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
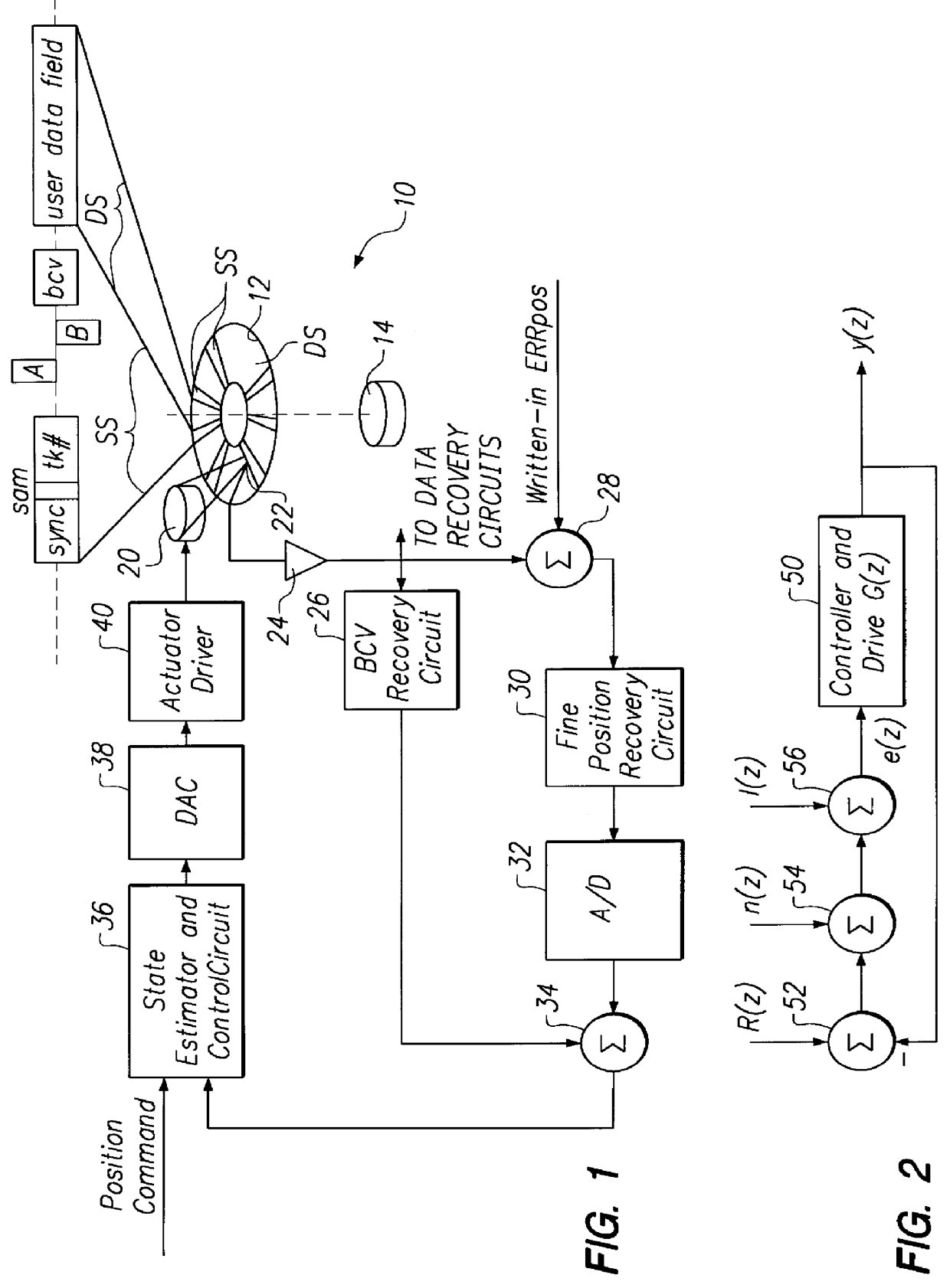
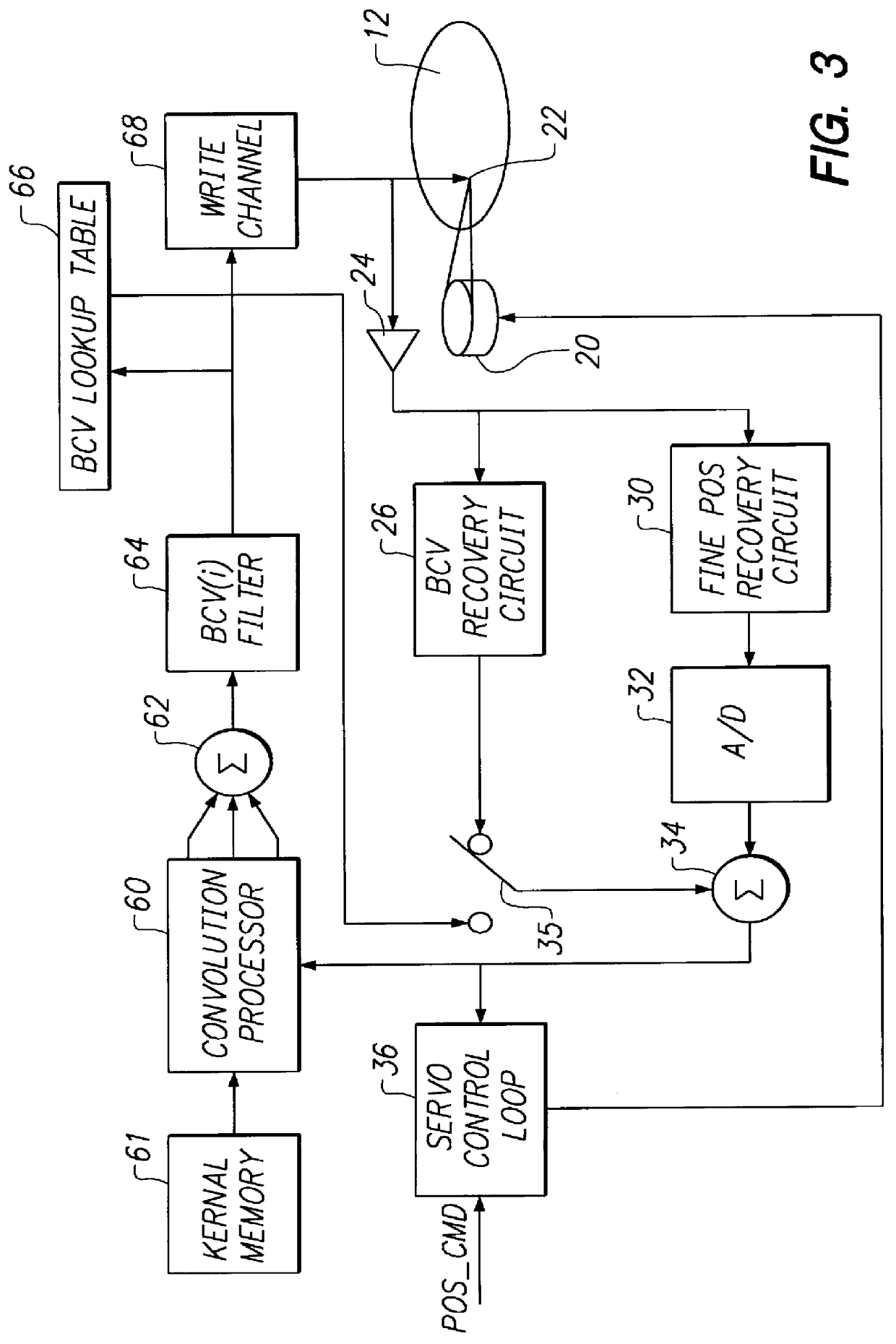
In-drive correction of servo pattern errors
InactiveUS6061200AImprove RRO correction valueTrack finding/aligningRecord information storageHard disc driveClosed loop
Embedded servo sectors within a data track of a hard disk drive including a rotating data storage disk and a closed loop rotary actuator structure for positioning a data transducer head relative to the data track are written by a method including the steps of positioning the rotary actuator structure relative to the data track with a laser-interferometer-based servo writer and writing a pattern of circumferentially sequential, radially offset fine position bursts within each servo sector with the data transducer head, this step including writing-in undetermined position errors within each pattern being written, moving the disk drive to a self scan environment away from the servo writer, operating the rotary actuator structure in closed loop for following the data track by reference to the servo burst pattern, extracting the undetermined position error from each pattern thereby to iteratively determine written-in position errors, generating burst correction values from the determined written-in position errors, and writing the burst correction values to the data track for later use by the closed loop rotary actuator structure during following of the data track to remove the written-in position errors.
Owner:MATSUSHITA KOTOBUKI ELECTRONICS IND LTD
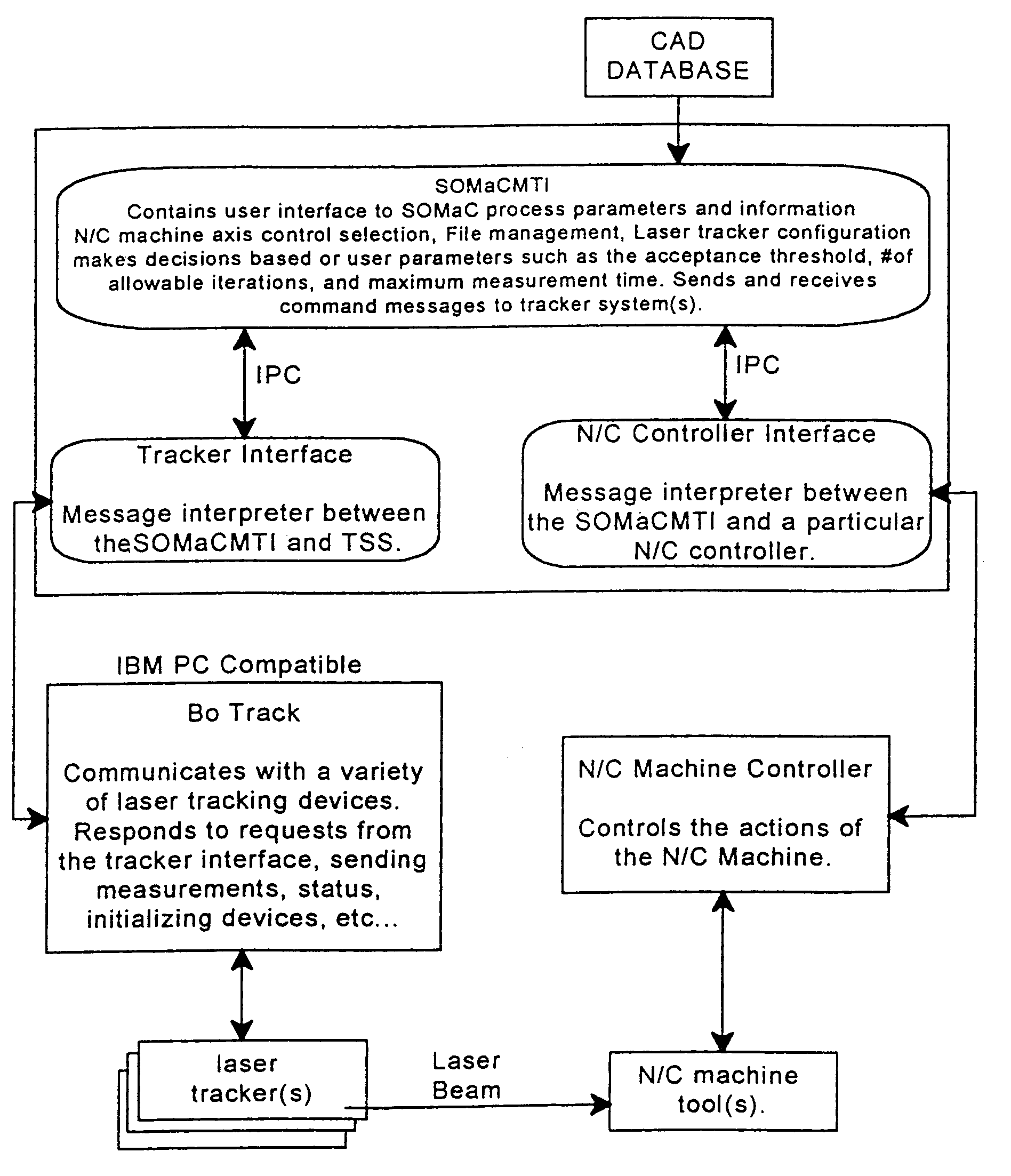
Software for improving the accuracy of machines
InactiveUS6980881B2Overcome mistakesEliminate the effects ofProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlThermal expansionActuator
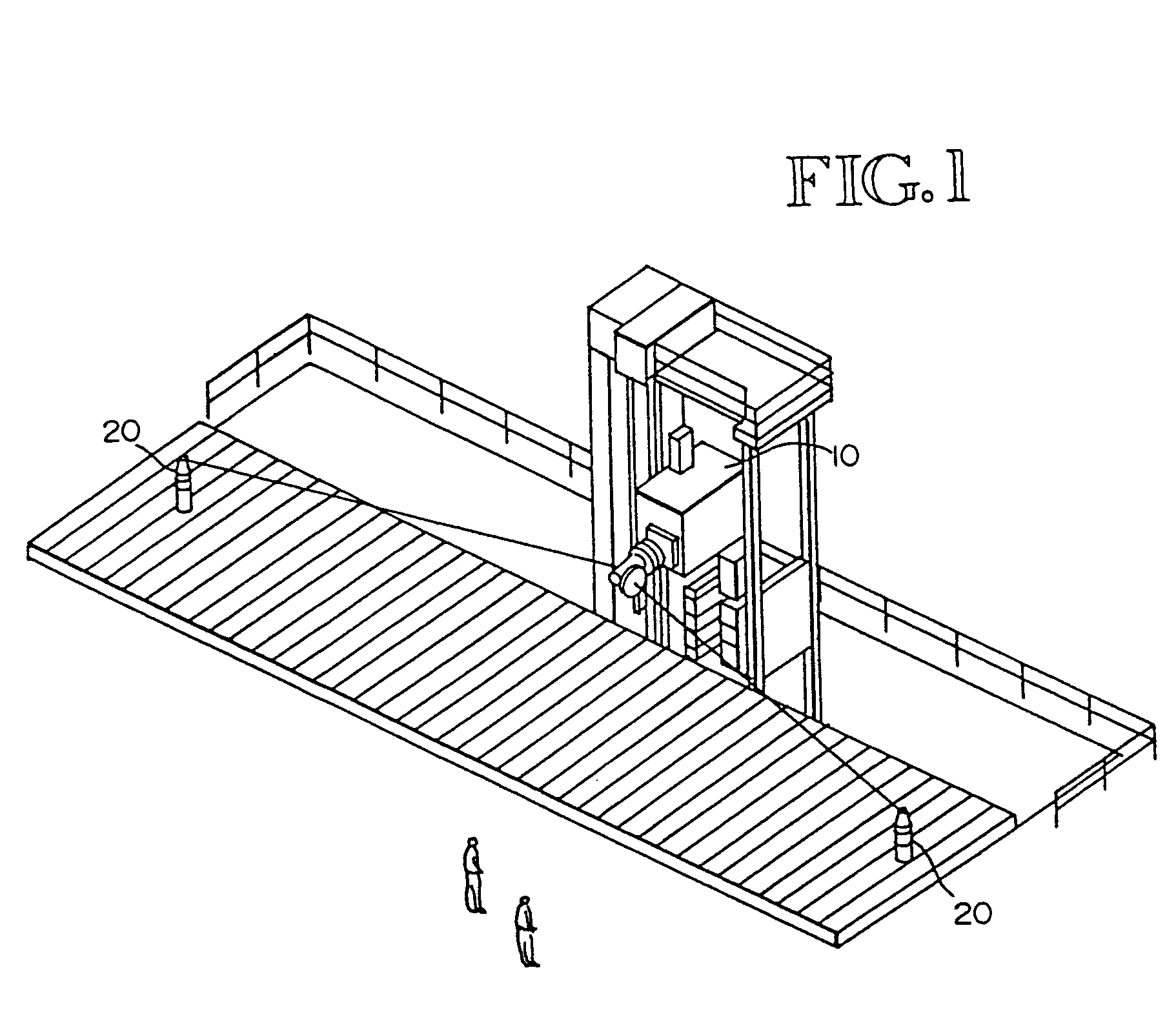
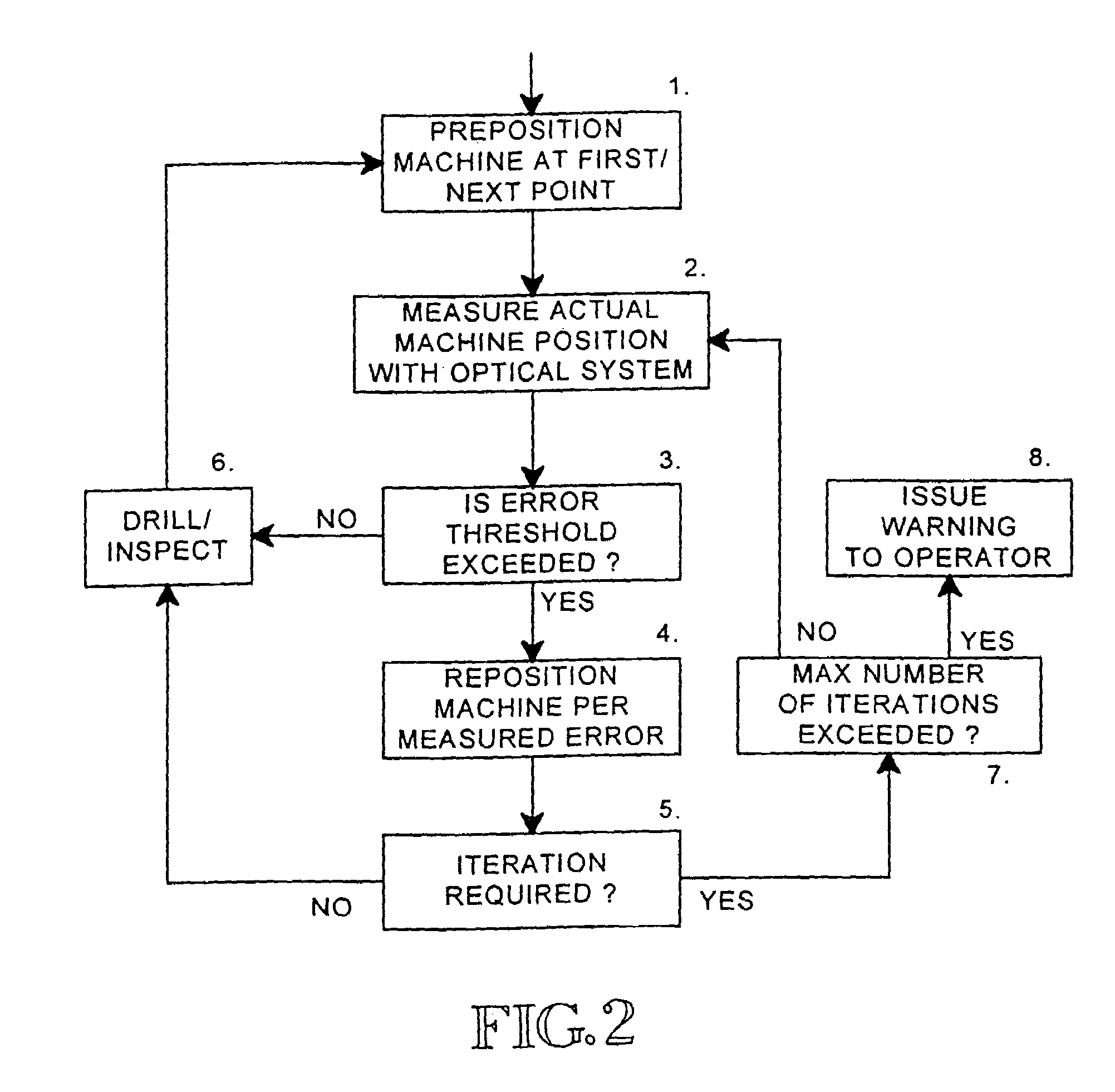
Large machines, especially those having working envelopes in excess of fifteen feet, exhibit unacceptable errors because of thermal expansion and mechanical misalignments between the axes. The errors have traditionally been minimized by enclosing the machine in a thermal enclosure, by careful calibration, or by mounting a laser interferometer on each axis. These solutions are costly, may require frequent recalibration, and do not correct for small rotations of one axis relative to another axis due to wear etc. The present invention uses an interferometric laser tracker or a comparable 3D position sensor to measure the position of a retroreflector attached to the end effector, e.g. a machine head when the machine comes to rest. A computer compares the measured position to the desired position according to the machine media, and adds the appropriate correction with trickle feed media statements to move the machine to the correct position prior to further machining.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Projection exposure apparatus having an off-axis alignment system and method of alignment therefor
InactiveUSRE36730E1Unnecessary to provideIncrease speedInvestigating moving sheetsUsing optical meansOptoelectronicsProjection lens
An exposure apparatus for exposing mask patterns on a sensitive plate comprises a set (for X and Y direction) of a laser interferometer for measuring a position of a wafer stage and satisfying Abbe's condition with respect to a projection lens and a set (for X and Y direction) of the laser interferometer and satisfying Abbe's condition with respect to off-axis alignment system. When a fiducial mark on the wafer stage is positioned directly under the projection lens, a presetting is performed so that measuring values by the two sets of laser interferometers are equal to each other.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Stage apparatus and control method therefor
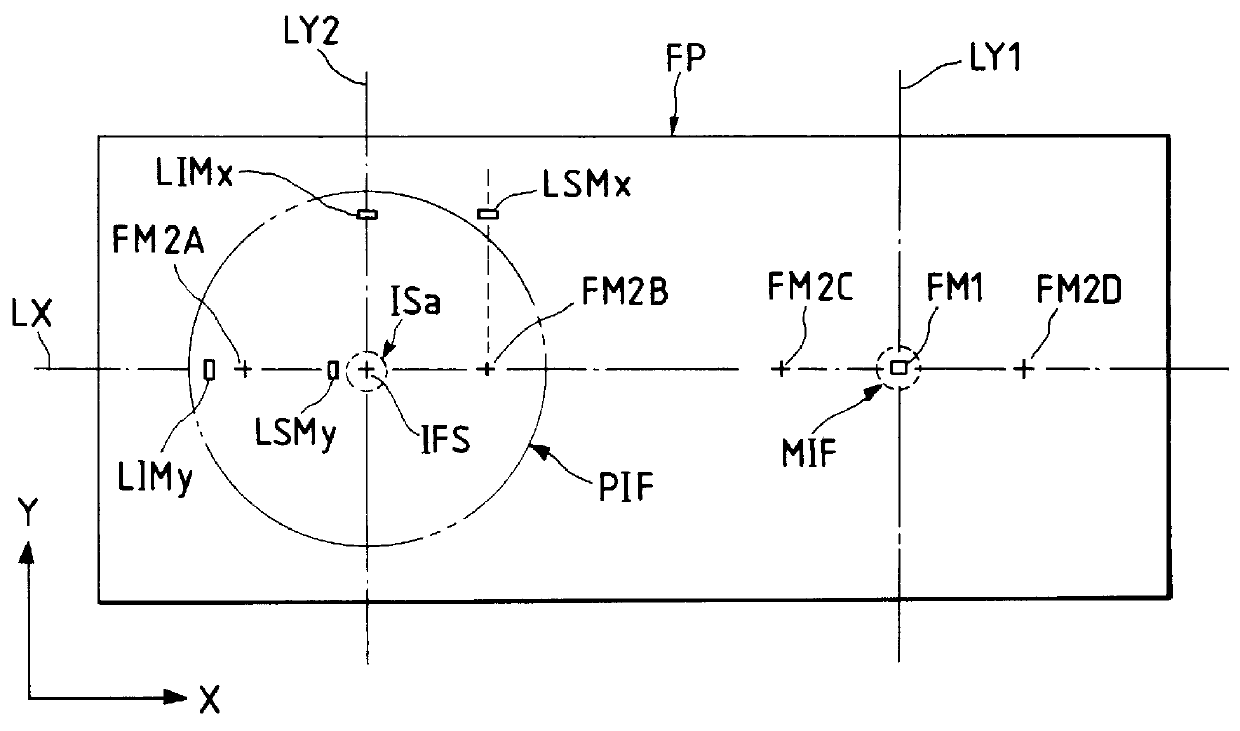
ActiveUS20050190375A1Reduce misalignmentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingUsing optical meansOverlap zonePhysics
A stage apparatus has a stage movable in a first direction and first and second measurement systems measuring a position of the stage in a predetermined direction. The first and second measurement systems each has a laser interferometer and a mirror system including a first reflecting mirror elongated in the first direction. A measurement value is transferred from one measurement system in use to the other measurement system and the measurement system in use is switched between the first and second measurement systems within a overlapping zone where said first and second measurement system can simultaneously measure the position of the stage. In the switch, the measurement value to be transferred is corrected based on a difference in the lengths of the light paths due to a shape of a surface of the first reflecting mirror of the first and second measurement systems.
Owner:CANON KK
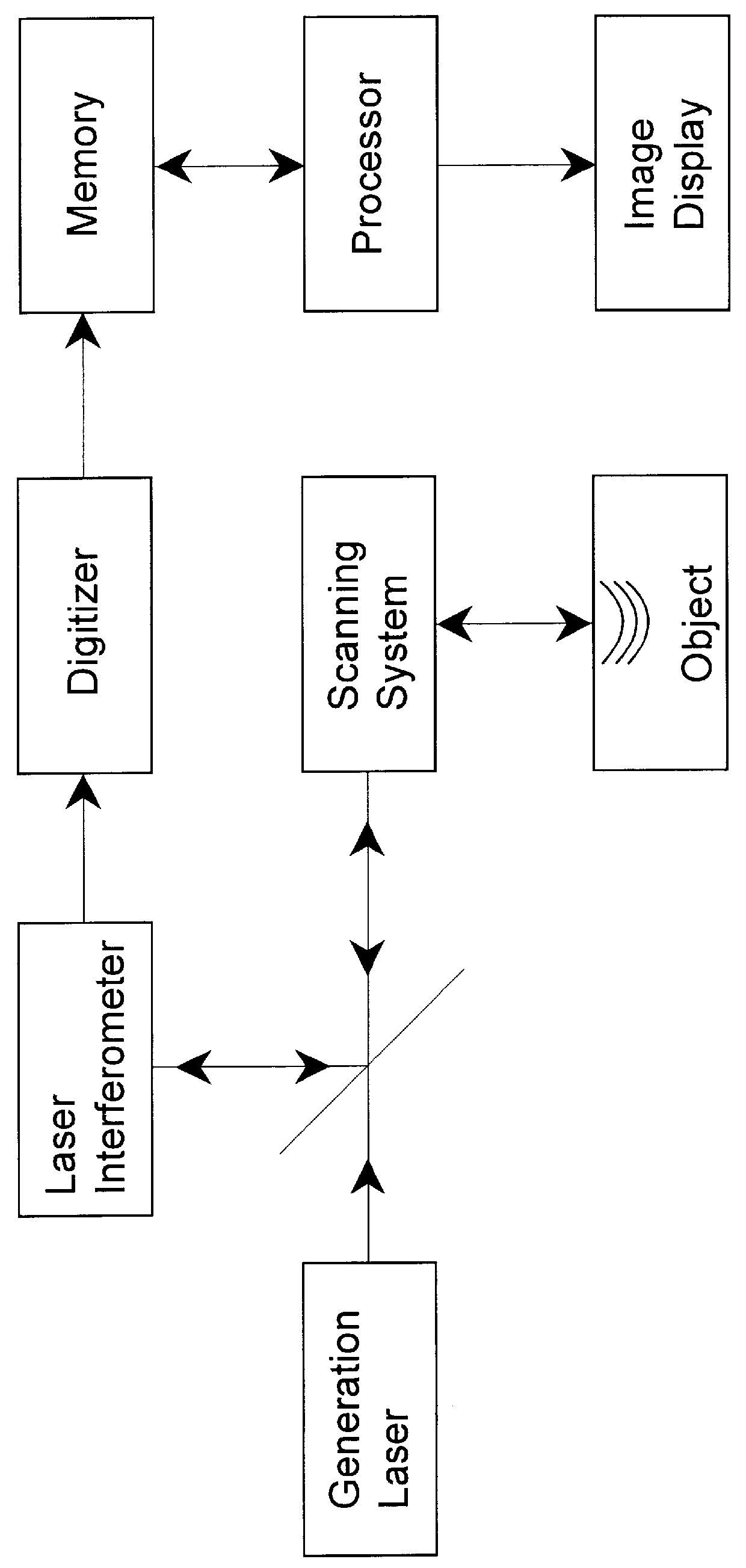
Tracking type laser interferometer and method for resetting the same
InactiveUS20080316497A1Adjustment workAccurate and stable measurementInterferometersActive open surveying meansOptical axisOptoelectronics
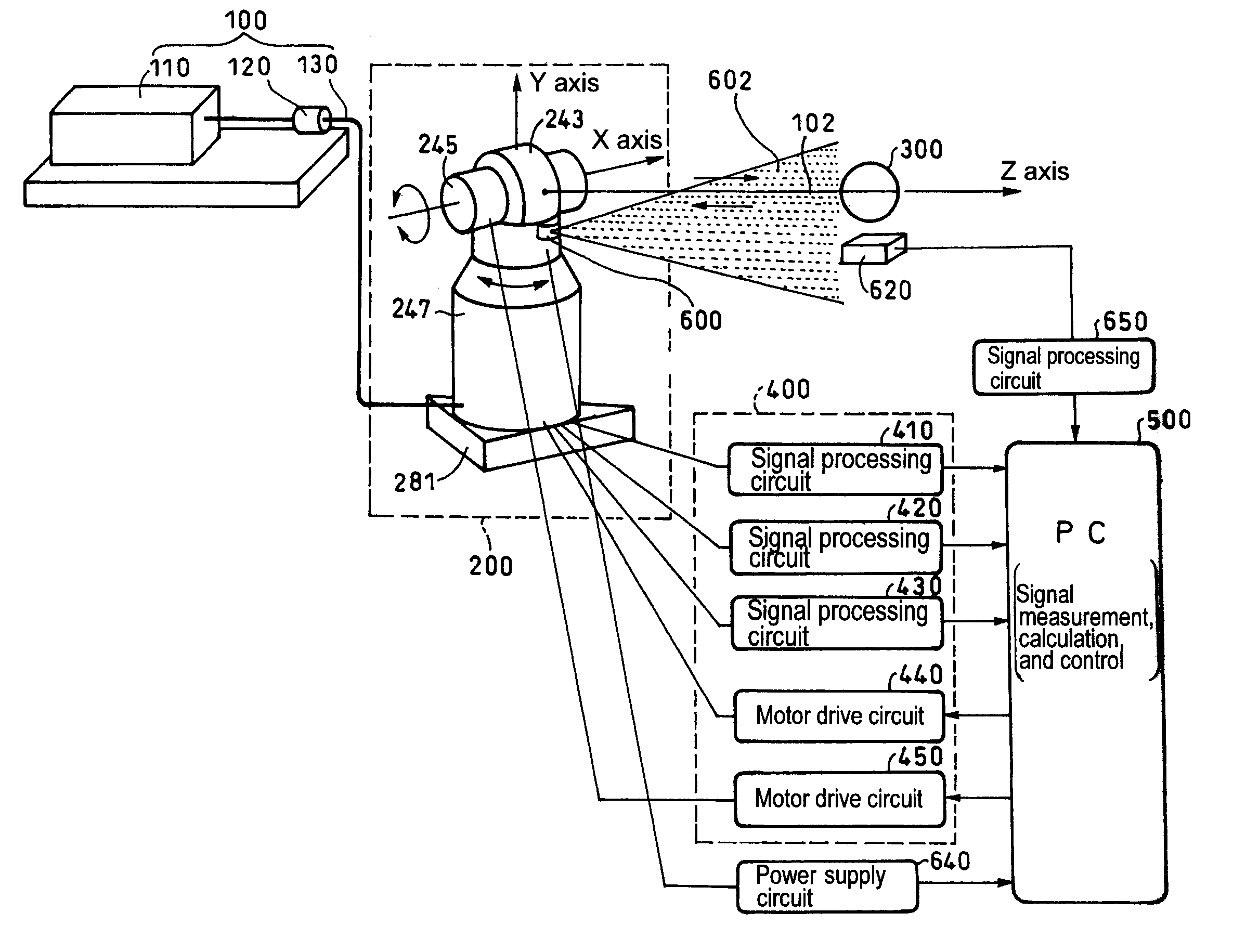
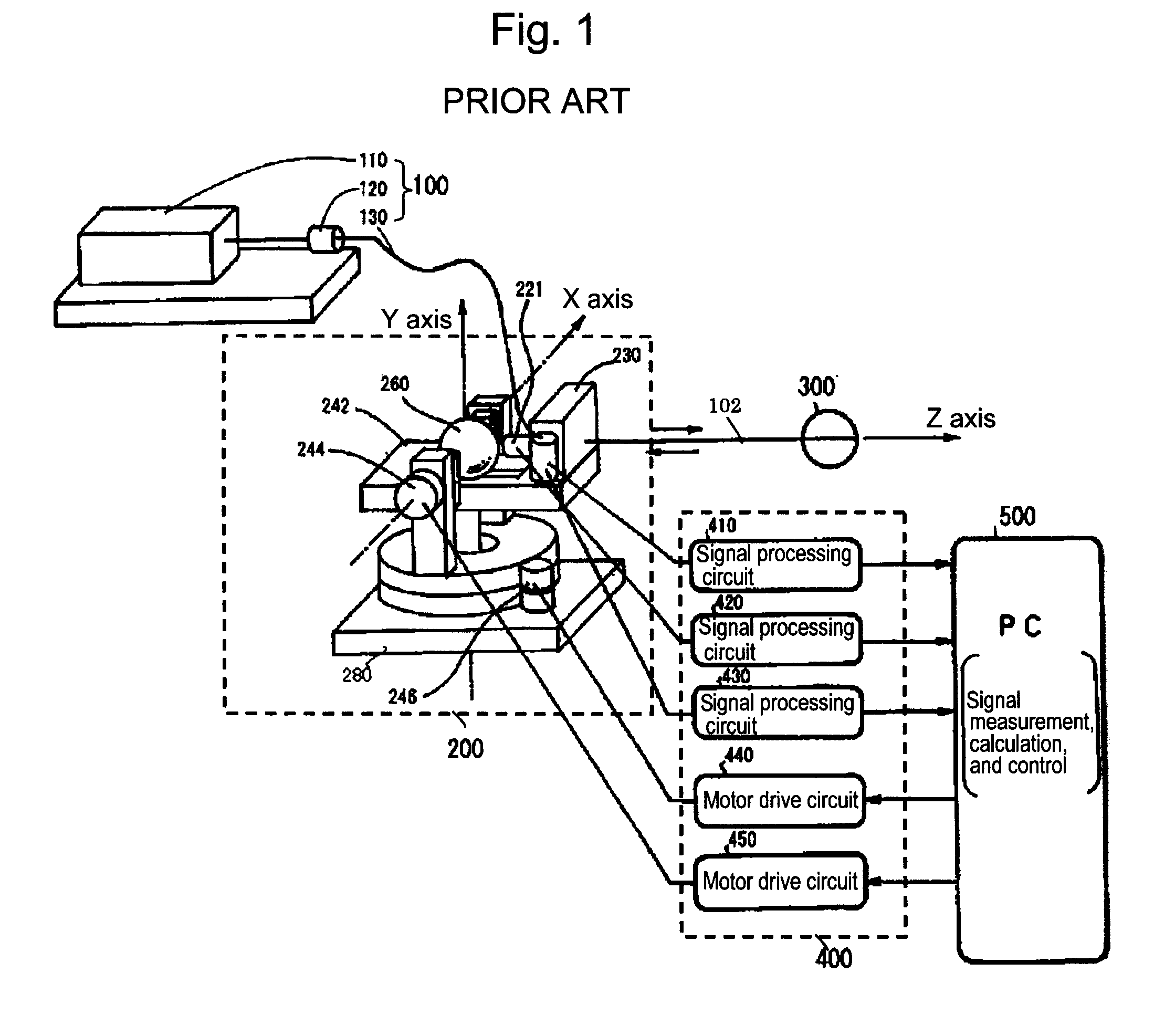
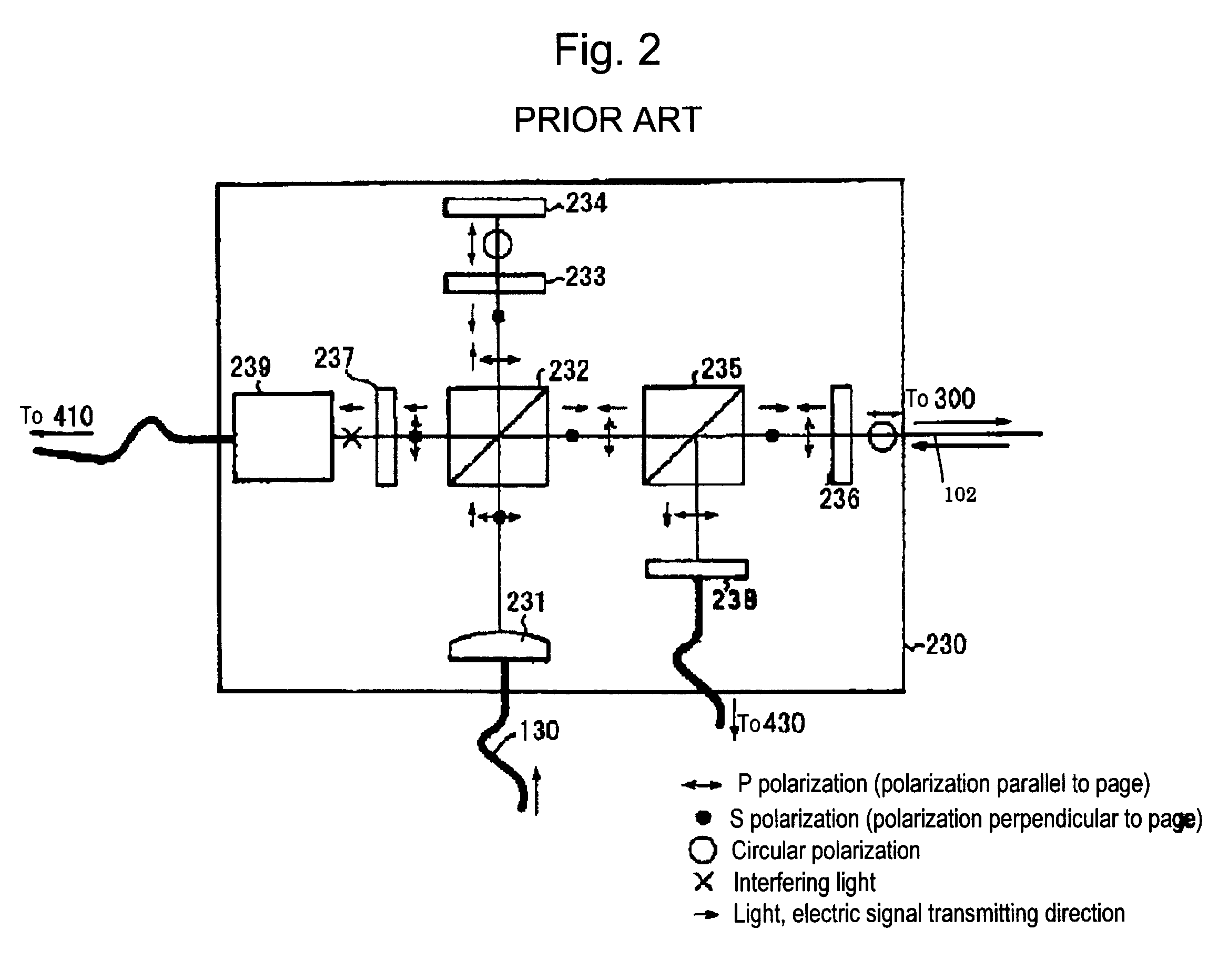
A tracking type laser interferometer that detects displacement of a retroreflector 300 being an object to be measured by utilizing interference of a laser beam 102 irradiated onto the retroreflector 300 and reflected by the retroreflector 300 in the returning direction, and carries out tracking by means of a two-axis turning mechanism 240 using displacement in the position of the optical axis of the laser beam 102; the same tracking type laser interferometer, includes; a light irradiator 600 that emits a fan-shaped laser light 602 that is fan-shaped including the optical axis of the laser beam 102, is interlocked with turning movements of the two-axis turning mechanism 240 around an axis orthogonal to the center axis of the corresponding fan shape; and a light receptor 620 that has a specific positional relationship with the retroreflector 300 or the light irradiator 600 and receives the fan-shaped laser light. Thereby, tracking can be automatically reset when the tracking is disabled due to a reason such as interruption of laser light or initial adjustment work can be automated when commencing measurement.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Digital controlled lathe thermal error measuring compensation system and method
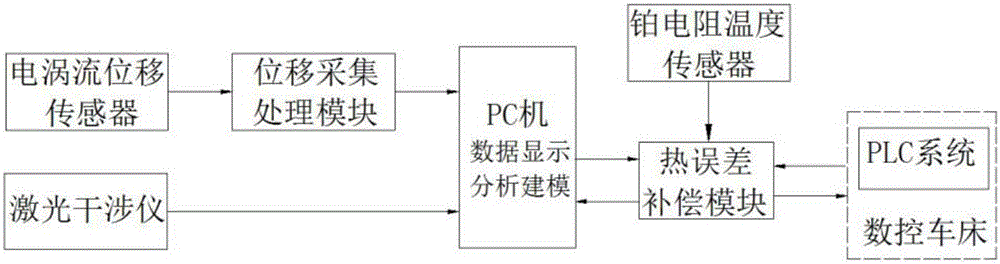
ActiveCN106736848AImprove machining accuracyRealize intelligenceAutomatic control devicesMeasurement/indication equipmentsNumerical controlElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention discloses a digital controlled lathe thermal error measuring compensation system and method. The system comprises an eddy current displacement sensor, a platinum resistor temperature sensor, a laser interferometer, a displacement collecting and processing module, a thermal error compensation module and a PC. The platinum resistor temperature sensor measures the temperature of a lathe body heat sensitive point, the eddy current displacement sensor measures heat deformation of a spindle, the laser interferometer measures the locating error of a feeding system, and the spindle and a feeding shaft system are subjected to real-time thermal error comprehensive modeling. The thermal error compensation module compensates for axial heat expansion and radial heat inclination of a spindle workpiece in real time according to the temperature of the heat sensitive point and the coordinate value of a tool. The coupling problem of the digital controlled lathe spindle and the feeding shaft thermal error is solved, the thermal error can be compensated for in real time, and the machining precision of a digital controlled lathe is improved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Laser multiple degree-of-freedom measuring system and method
InactiveCN1439864AEasy to adjustReduce usageUsing optical meansLight polarisation measurementLaser transmitterLight beam
A multi-freedom laser measuring system is composed of laser emitter, polarizing-splitting unit, 4-freedom error sensing unit, photoelectric receiver unit and signal processing unit. Said 4-freedom error sensing unit consists of quater-wavelength wave plate, optical splitter and optical reflector. The laser beam is splitted into the perpendicular mutually linear polarized light beams in two polarizing directions. The light beam received by said 4-freedom error sensing unit is splitted to two beans received by two photoelectric receiver. The linearity error of an object in two directions and the pitch angle error can be obtained after signal processing.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Image input apparatus and inspection apparatus
InactiveUS20050196059A1Enter exactlySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDiode testingElectricityControl circuit
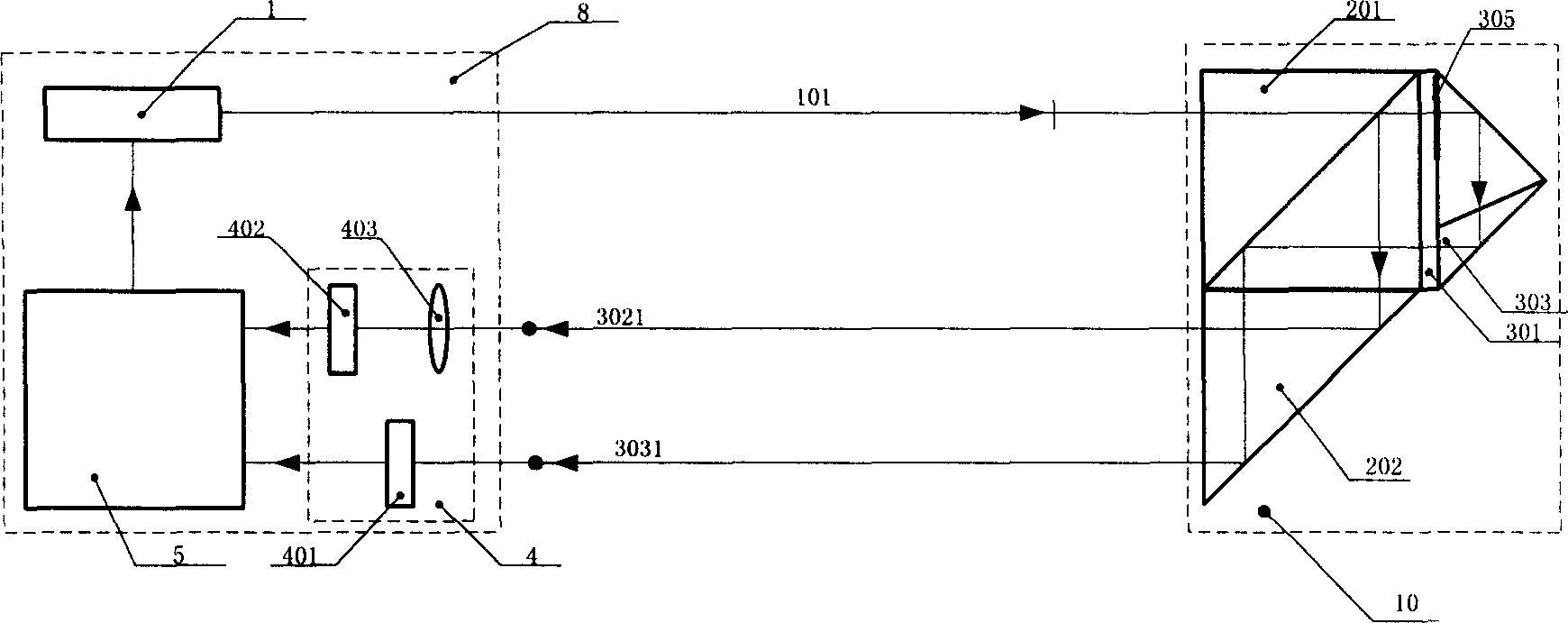
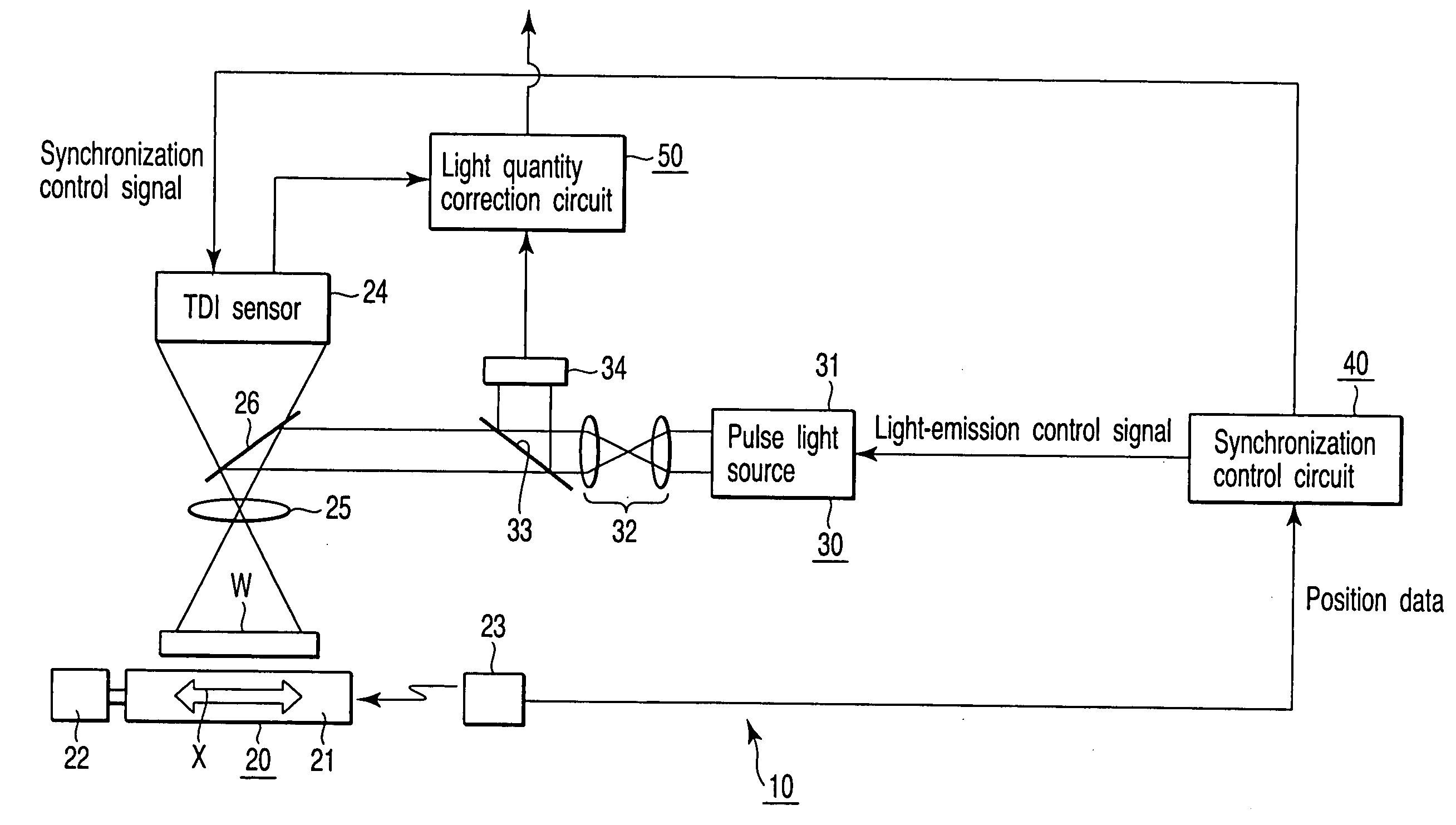
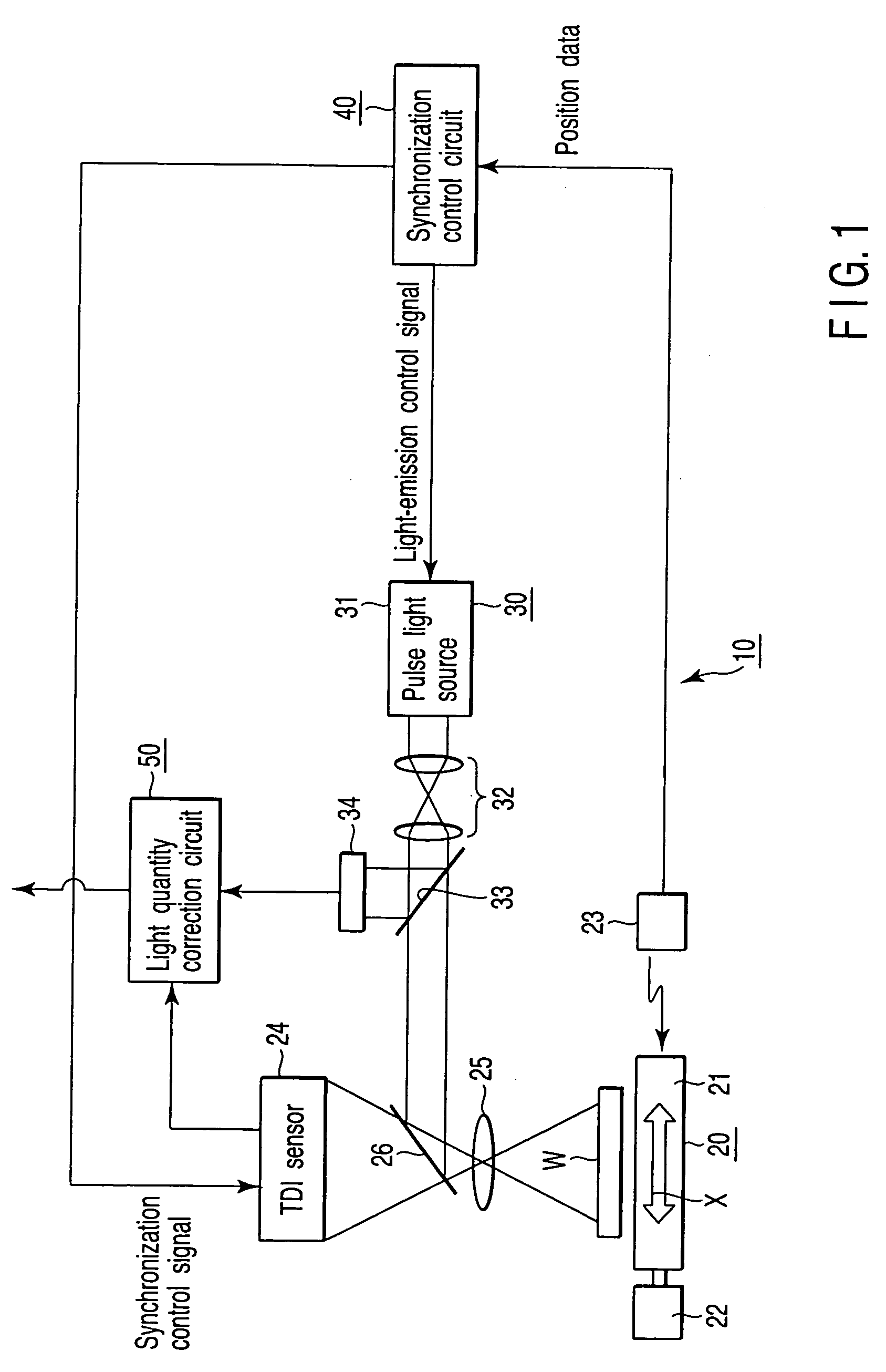
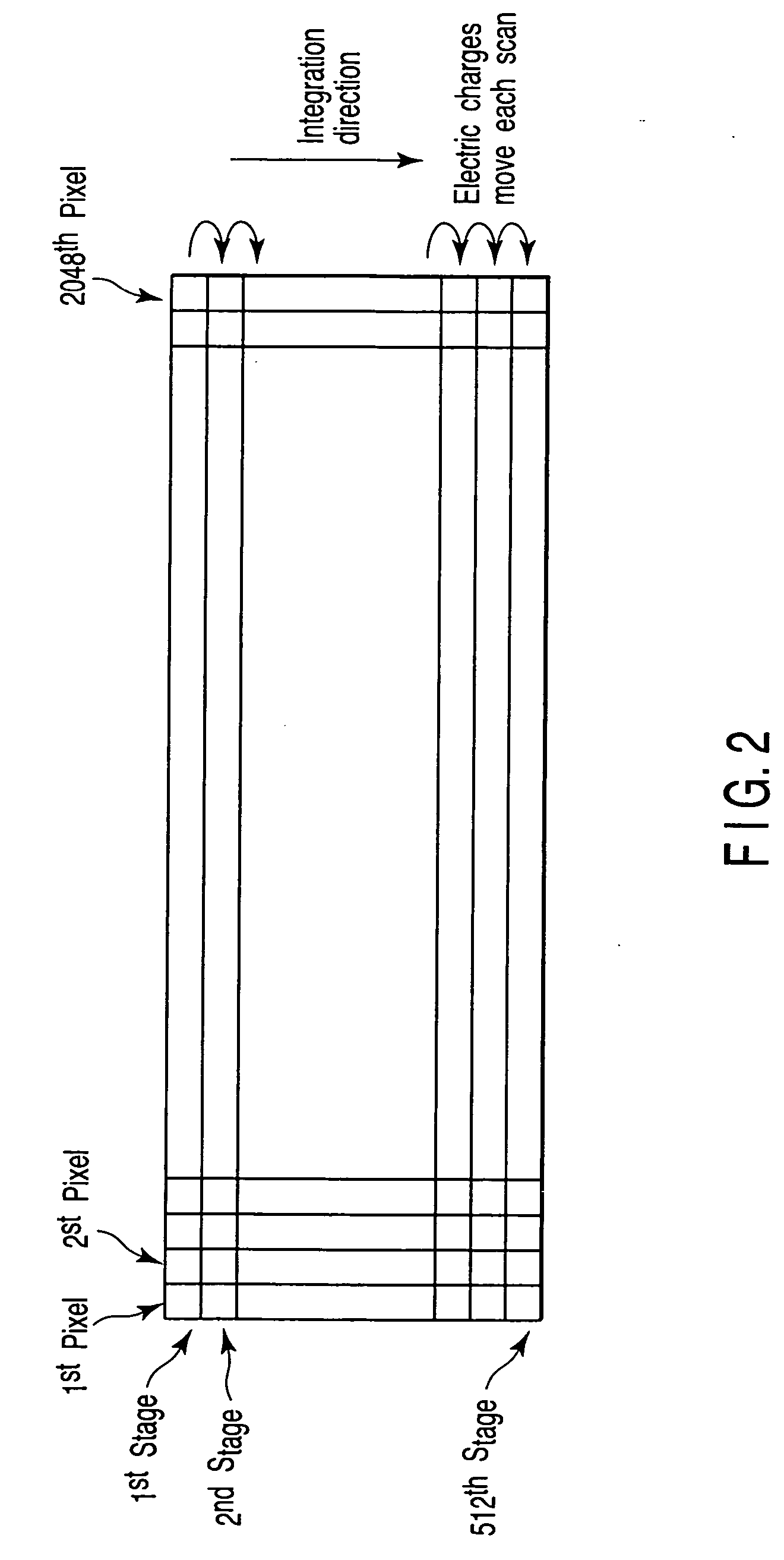
An image input apparatus for inputting an image of an object and outputting the image as an electric signal, the image input apparatus comprises a stage which supports the object, a laser interferometer which measures a position of the stage, a light source which emits a pulse light, an illumination optical system which irradiates the object with an illuminating light, a sensor which converts an image-formed optical image into an electric image signal, an imaging optical system which forms an image of the object on the sensor, a synchronization control circuit which controls a light-emission interval of the light source and synchronization of the sensor on the basis of position information of the laser interferometer, a light quantity monitor which measures a quantity of light, and a light quantity correction circuit which corrects the electric image signal on the basis of an output of the light quantity monitor.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
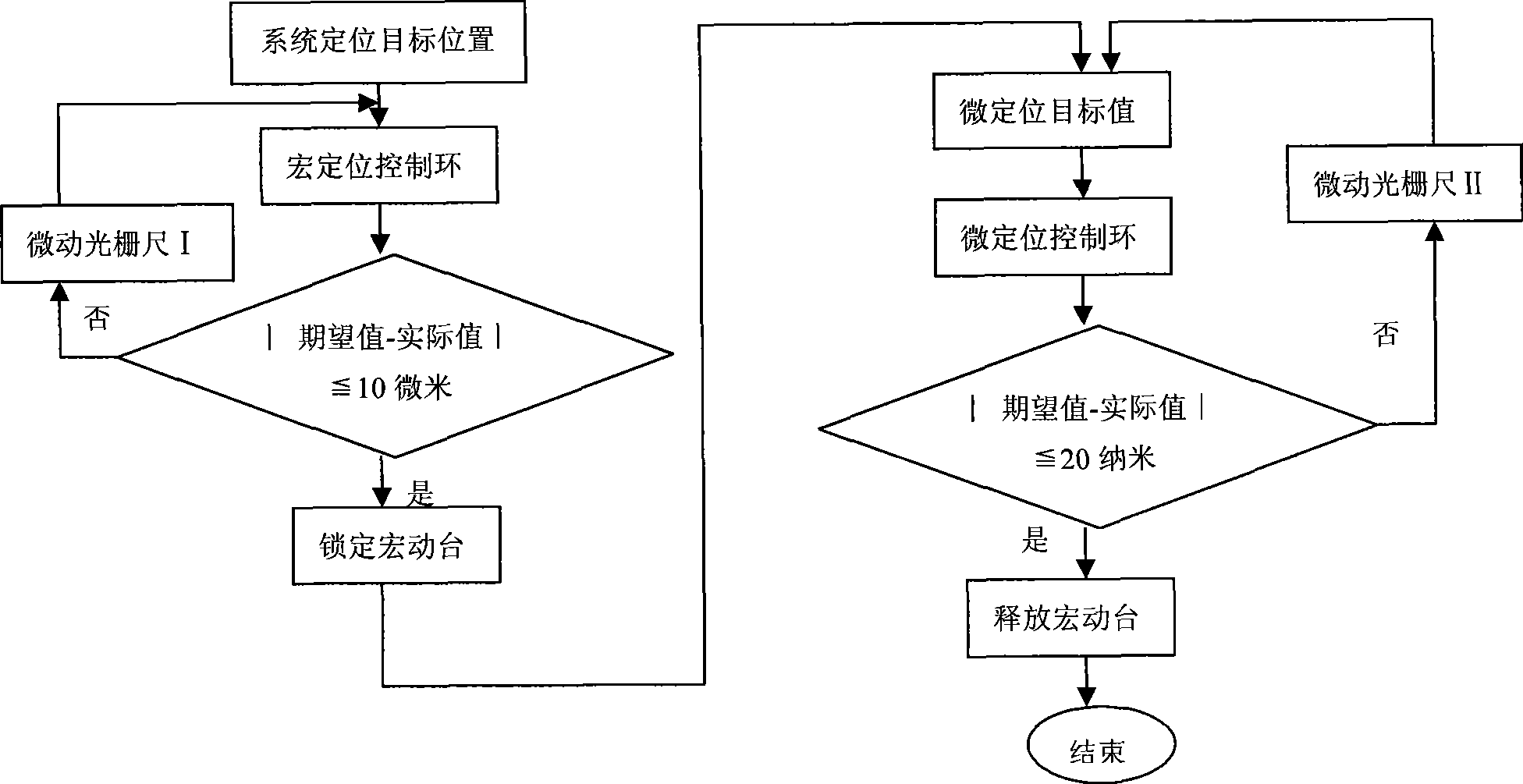
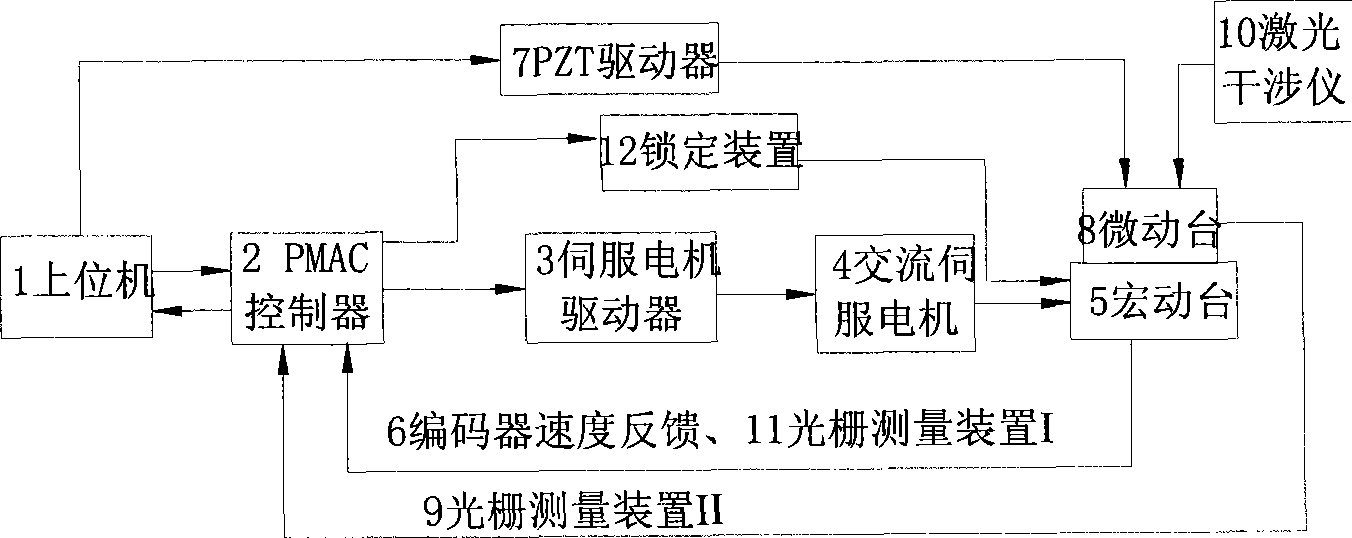
Locking control method and system of large-stroke nanometer displacement positioning macro-movement bench
InactiveCN101369155AReduce vibrationReduce positioning errorsControl using feedbackTotal factory controlHardware structureGrating
The invention relates to a locking control method of a large-travel nano-displacement and positioning macro-motion table as well as a system thereof. The method comprises the operating steps: (1) a communication interface of a computer (upper computer ) sends an instruction for controlling, firstly, a macro-positioning system is started up to drive the macro-motion table and a micro-motion worktable to move together, and the macro-positioning is finished when the detected positioning error is smaller than the switching threshold value; (2) the computer controls and locks the macro-motion worktable, and is switched to a micro-positioning system dynamically in the meanwhile; and (3) the micro-positioning system controls the micro-motion worktable to further reach the target location required by the system and complete the positioning. The system mainly comprises: the macro-motion table and the micro-motion worktable as well as corresponding driving systems; a grating feedback system; a PMAC controller; a laser interferometer calibration system; a computer system; and a vibration isolation and noise elimination device (an air floatation vibration isolation platform) and the like. The hardware structure of the existing system is configured (a piezoelectric ceramic driving device) by adopting the method as required, when the macro-motion table meets the positioning requirements and stops the movement, piezoelectric ceramics lock the table, thereby improving the positioning accuracy of the system.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
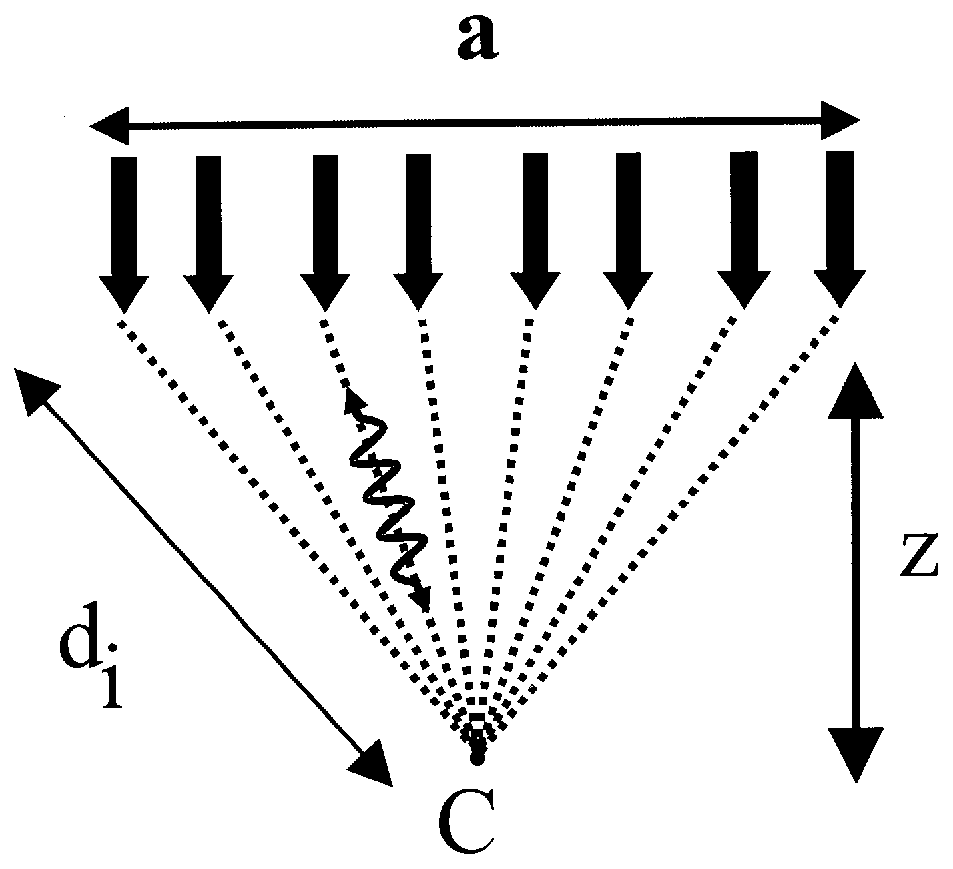
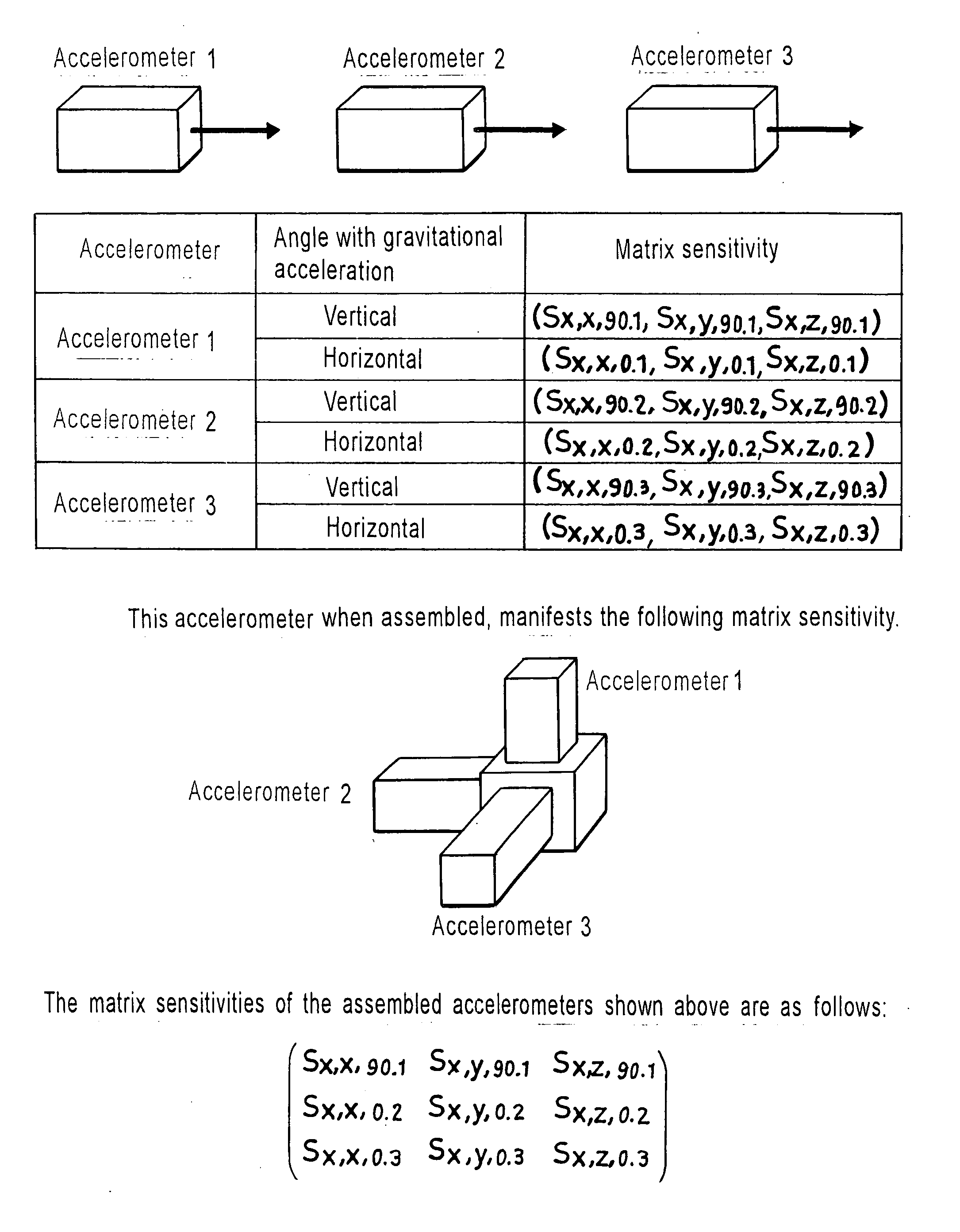
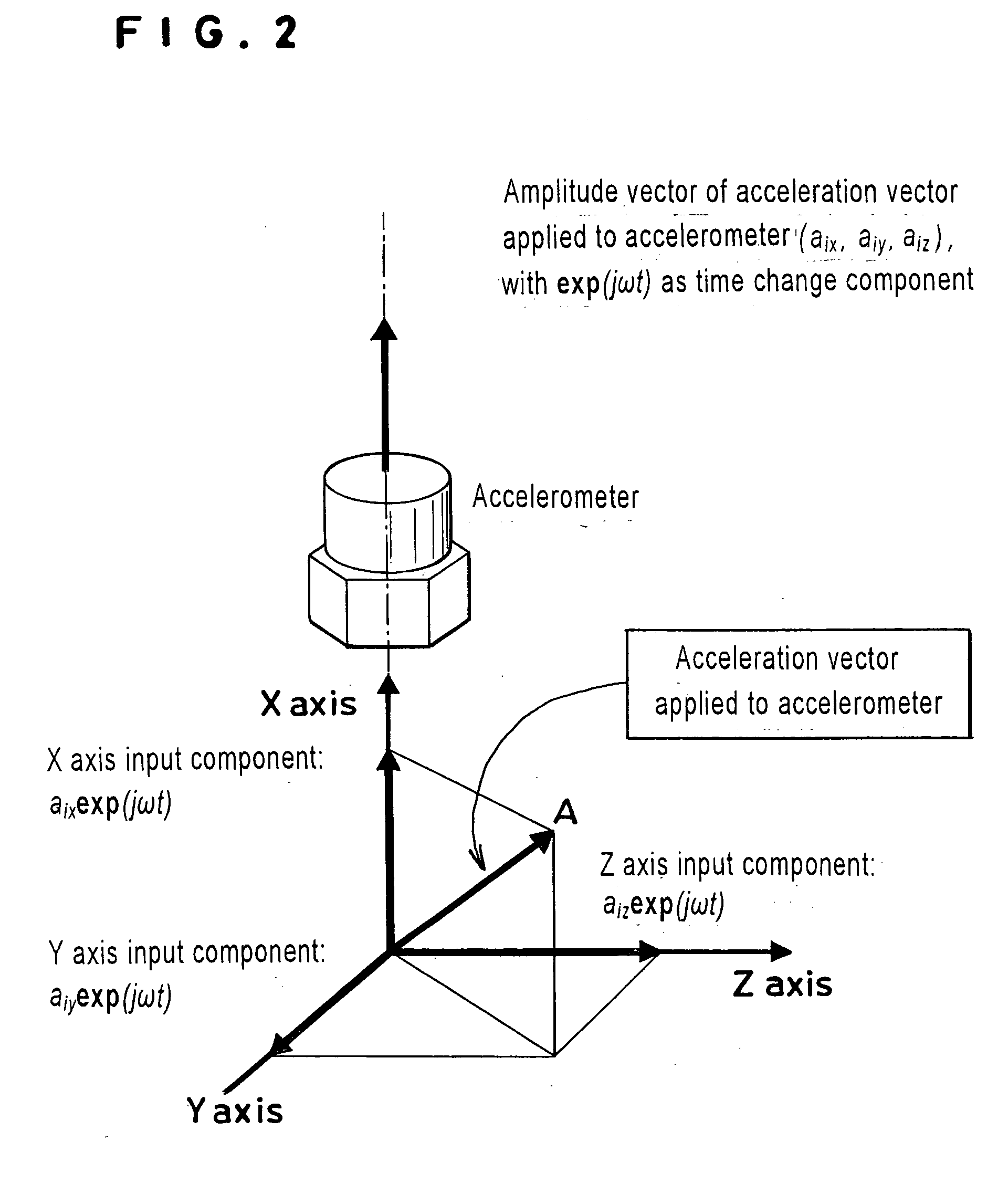
Dynamic matrix sensitivity measuring instrument for inertial sensors, and measuring method therefor
InactiveUS20070073502A1Acceleration measurement using interia forcesTesting/calibration apparatusAccelerometerMeasurement device
A device for measuring the dynamic matrix sensitivity of an inertia sensor is provided with a motion generating machine or a vibrating table for inducing a translational or rotary motion, an acceleration measuring unit, an angular velocity measuring unit or angular acceleration measuring unit, an output device for fetching an output from the unit, one or, pre light reflectors, a displacement measuring device for seizing a multidimensional motion by using a laser interferometer radiating light from a plurality of directions to the light reflectors, a data processing unit for processing a data indicating the state of motion and obtained from the displacement measuring unit, and a displaying device to display or a transmitting device to transmit the output of the data processing unit and the output of the acceleration measuring unit, angular velocity measuring unit or angular acceleration measuring unit. Since the accelerometer is exposed to acceleration in every conceivable direction and possibly fails to find a correct value of acceleration as encountered by the conventional one-dimensional calibration, it is actually calibrated by applying acceleration from all possible directions thereto.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
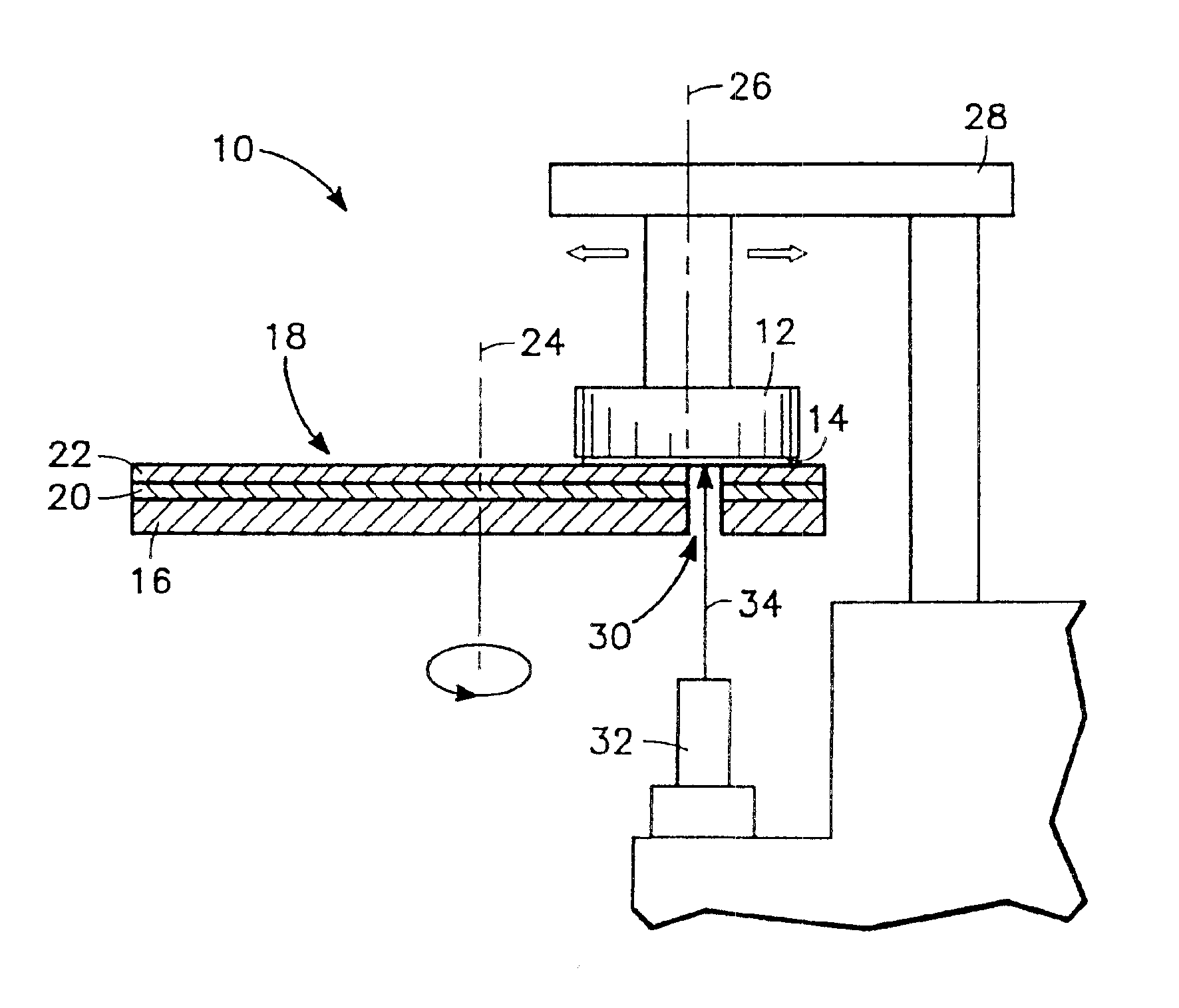
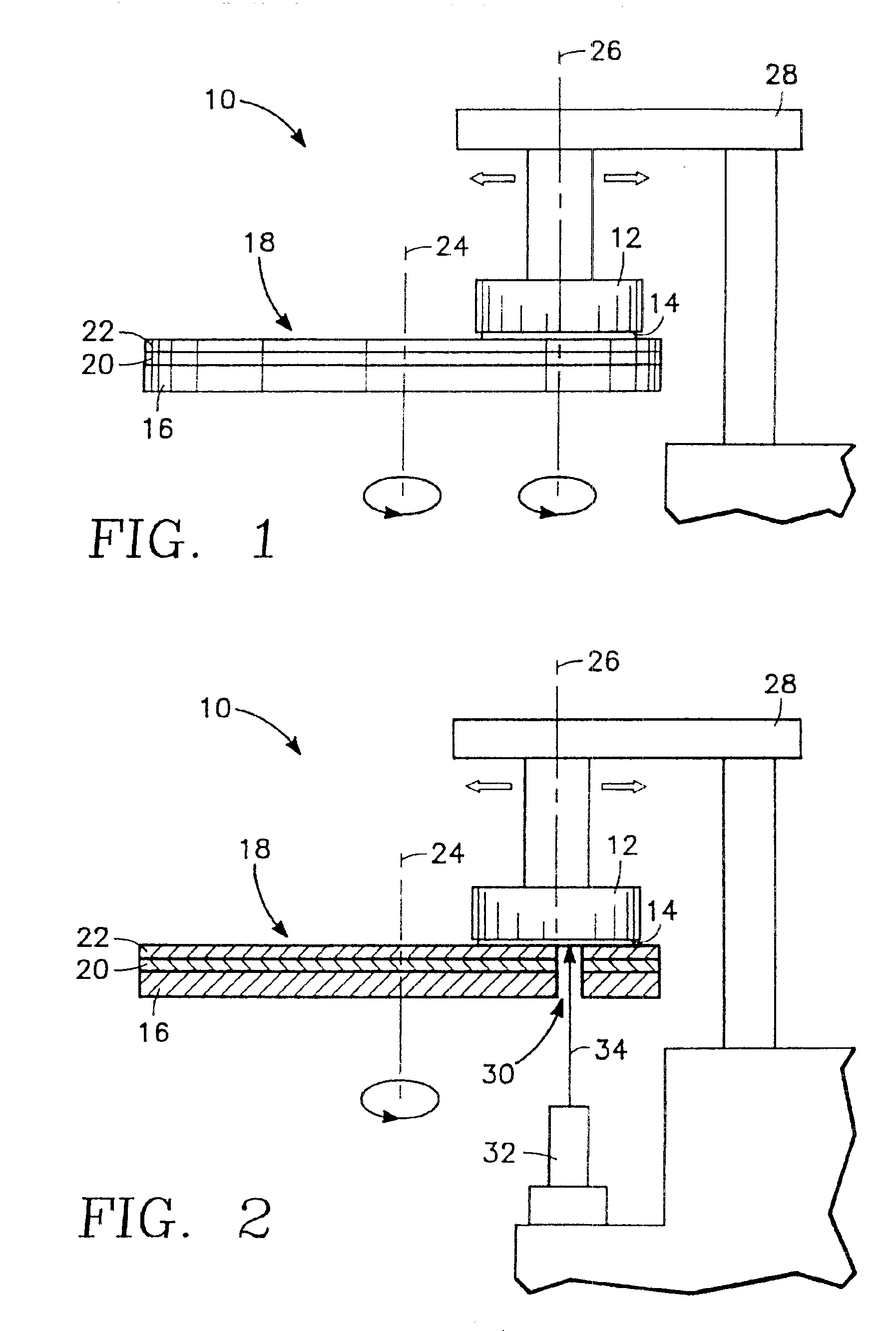
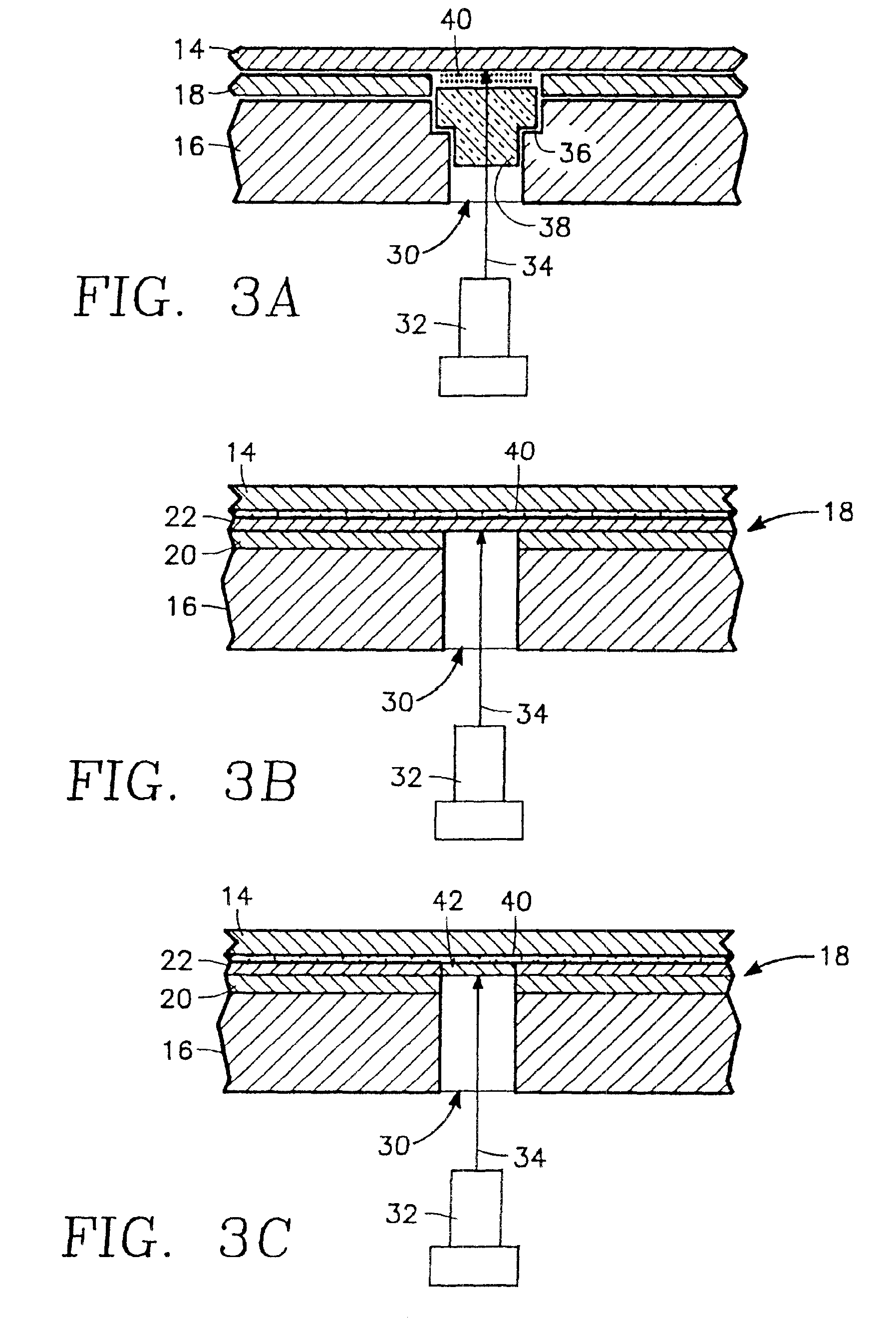
Apparatus and method for in-situ endpoint detection for chemical mechanical polishing operations
InactiveUS6876454B1Improve accuracySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementGrinding drivesWaferingEngineering
An apparatus and method of chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) of a wafer employing a device for determining, in-situ, during the CMP process, an endpoint where the process is to be terminated. This device includes a laser interferometer capable of generating a laser beam directed towards the wafer and detecting light reflected from the wafer, and a window disposed adjacent to a hole formed through a platen. The window provides a pathway for the laser beam during at least part of the time the wafer overlies the window.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Laser sensor based system for status detection of tires
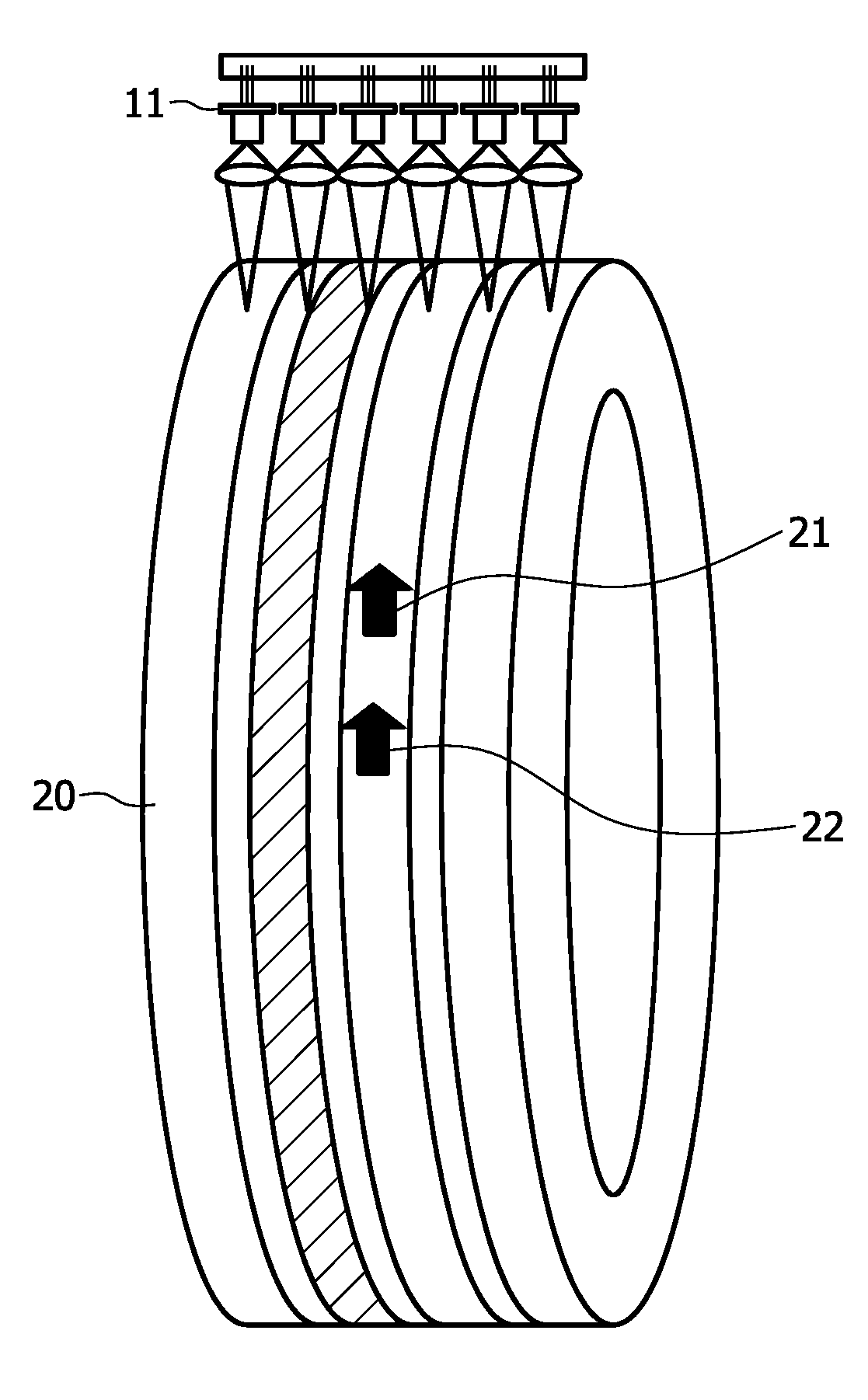
InactiveUS20110126617A1Simple and cost-effectiveUsing optical meansTyre measurementsEngineeringLaser sensor
A system is described which enables parameters of a tire (20) to be measured by means of self-mixing laser interferometry. Laser sensors (1) using self-mixing laser interferometry can measure distances and / or speed of surface elements of a tire (20). Consequently, a system comprising such a laser sensor (1) can for example be used to measure and indicate tire tread wear, tire load or speed. In comparison with laser sensor based systems using the well-known time of flight method, the described system is simple, cost effective and, due to the small size of the laser sensor (1), can easily be integrated in cars.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
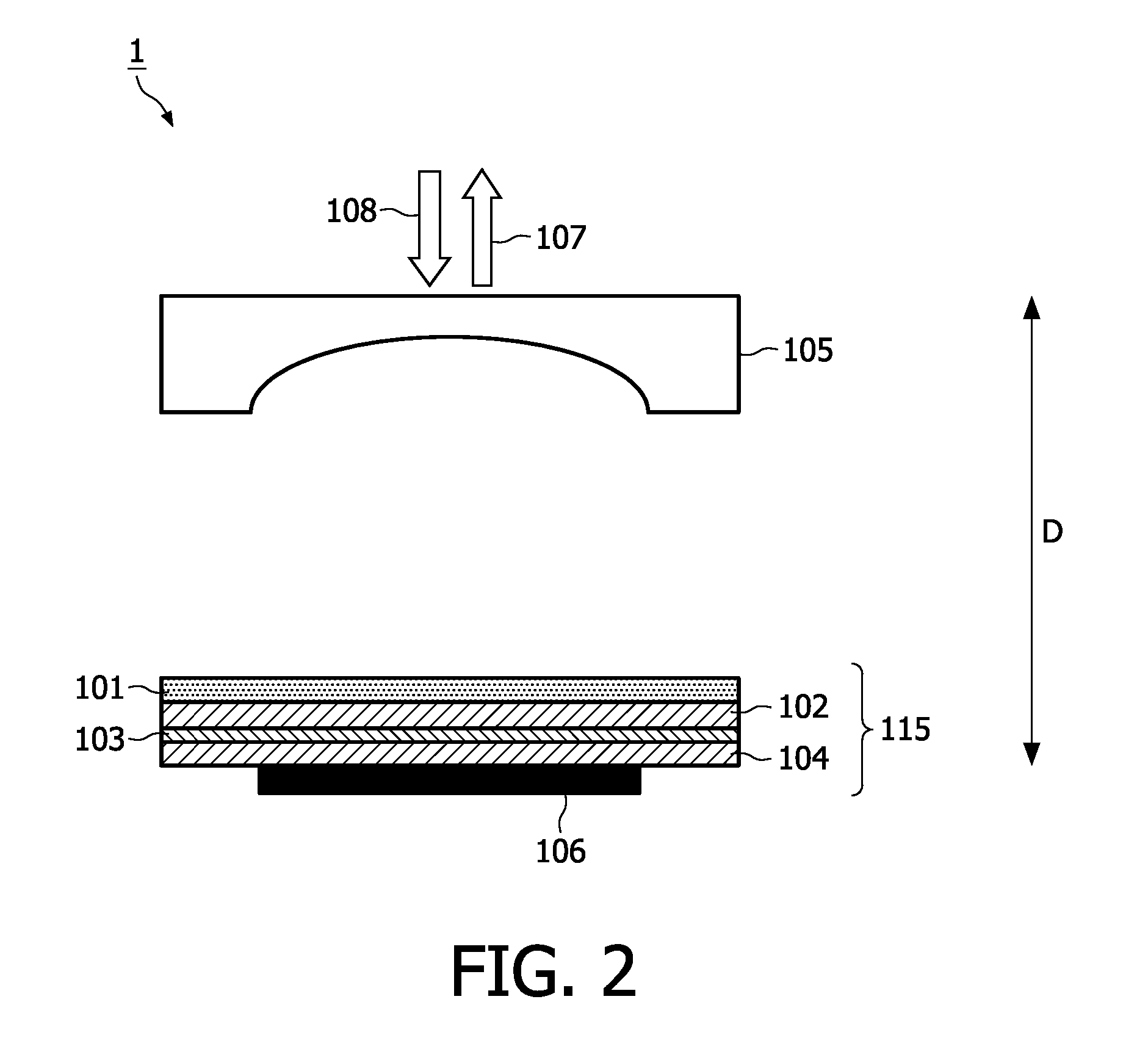
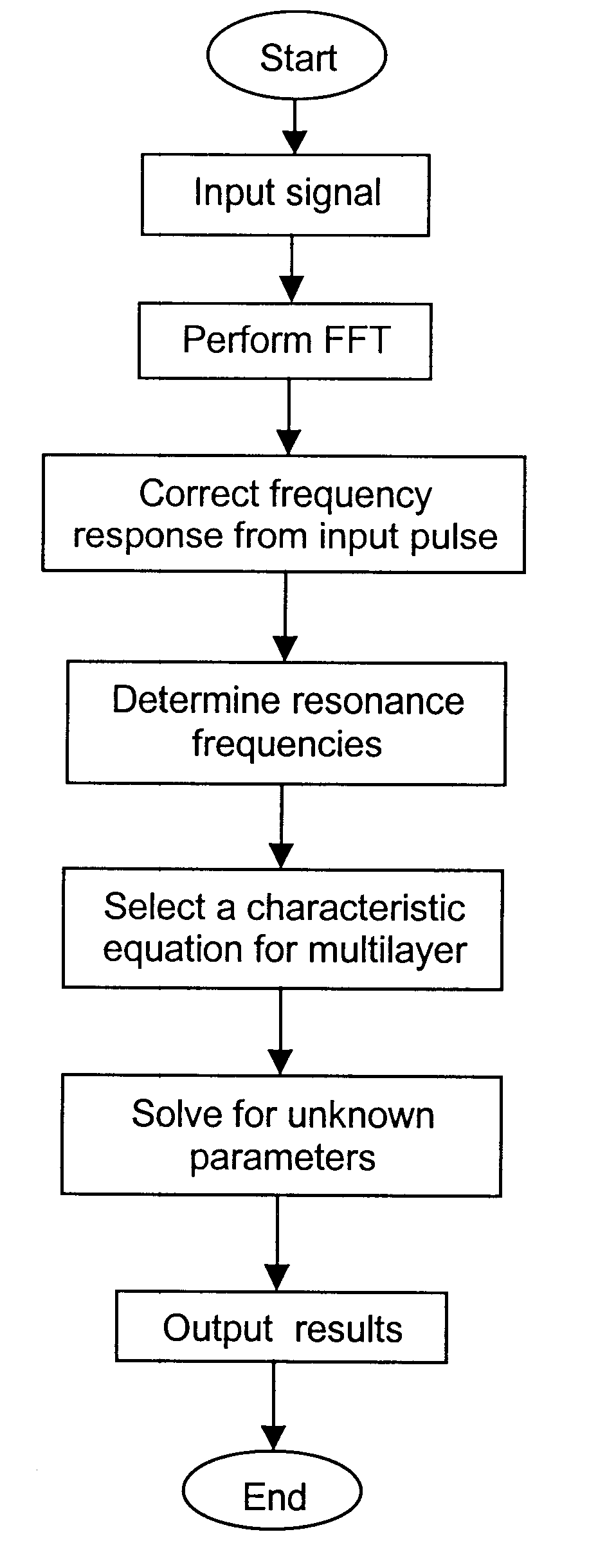
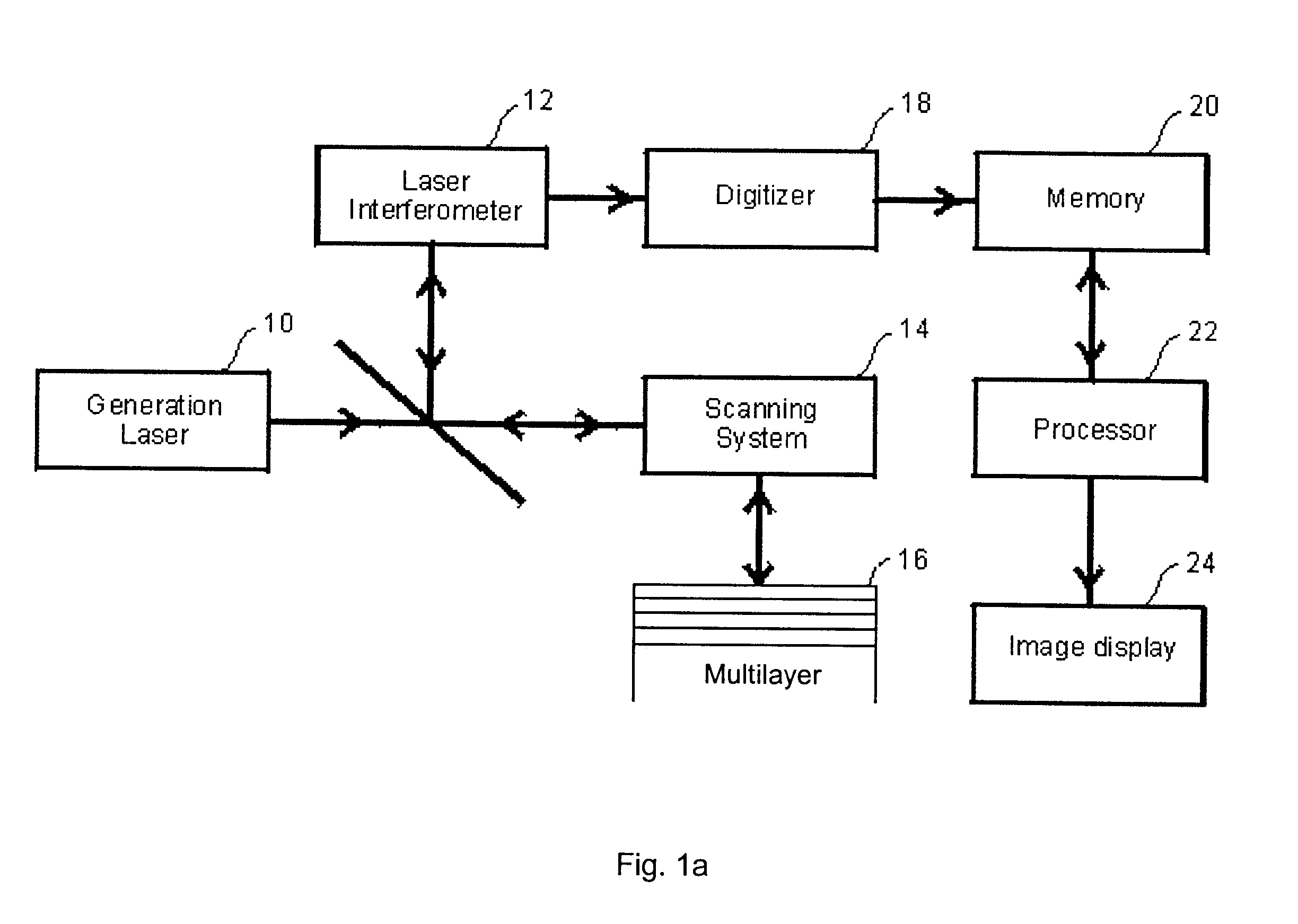
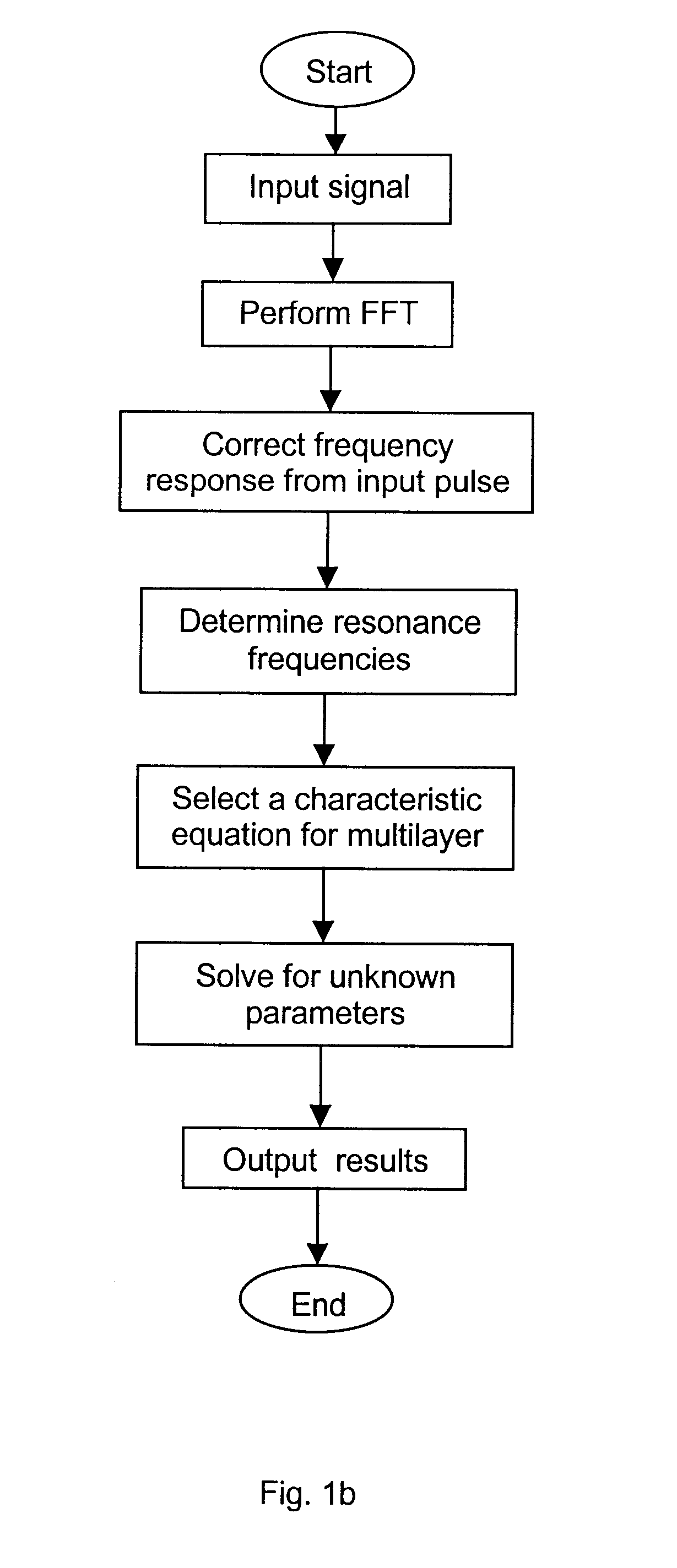
Ultrasonic spectroscopy apparatus for determining thickness and other properties of multilayer structures
InactiveUS6397680B1Reduce processing timeEasy to useVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasound deviceSonification
An ultrasonic apparatus and method based on location of resonance frequencies is provided for determining unknown parameters in a multilayer structure, such as thickness, elastic properties of individual layers, or bonding strength between layers. Predicted resonance frequencies are obtained from the roots of a characteristic equation describing the multilayer structure. The predicted resonance frequencies are compared using a best-fit technique with the measured resonance frequencies to obtain the desired parameter. The method is of particular interest when ultrasound is generated by a laser and detected by either a contact ultrasonic transducer or a laser interferometer.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
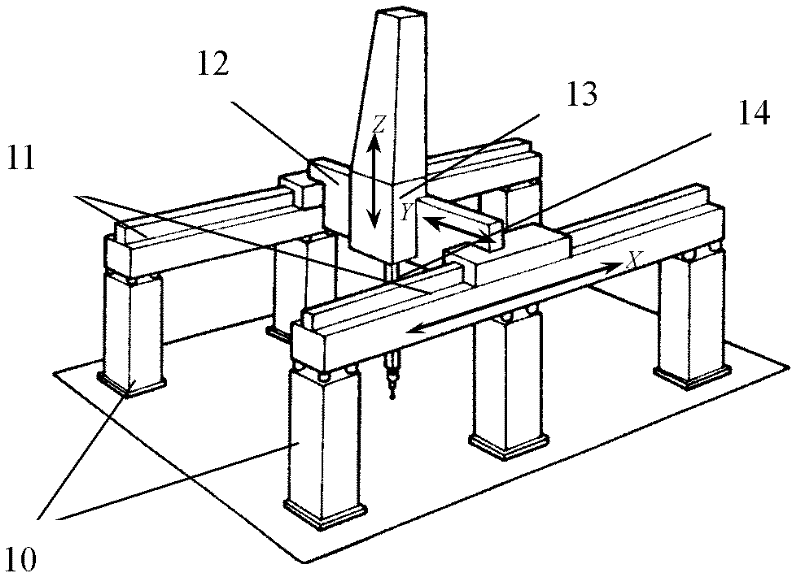
Large three-dimensional coordinate measuring method with laser tracking and device
InactiveCN102506702AMeasuring outsideMeasurement characteristicsUsing optical meansMechanical measuring arrangementsMeasurement deviceControl system
The invention relates to space coordinate measurement of large engineering and large machines and workpieces, and provides a large three-dimensional coordinate measuring system, which can be used on an engineering or production site, has high measurement accuracy, safe and reliable working and large measurement range, can detect the internal and external characteristics of a detected object and can meet the requirement for large size measurement in various engineering and production. The technical scheme adopted by the invention is as follows: the large three-dimensional coordinate measuring device with laser tracking comprises a measuring machine, a laser tracker and a calculation control system as well as a laser interferometer for measuring linear displacement, wherein the measuring machine is provided with a horizontal arm capable of doing x-direction movement and a main shaft capable of doing z-direction movement; the other end of the horizontal arm is provided with a corner prism; one end of the main shaft is provided with a measuring head rotating body which is provided with a measuring head; the other end of the main shaft is provided with a target and an angle measuring device; and a temperature measuring element which is used for carrying out temperature compensation is stuck on the main shaft. The invention is mainly applied in three-dimensional coordinate measurement.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
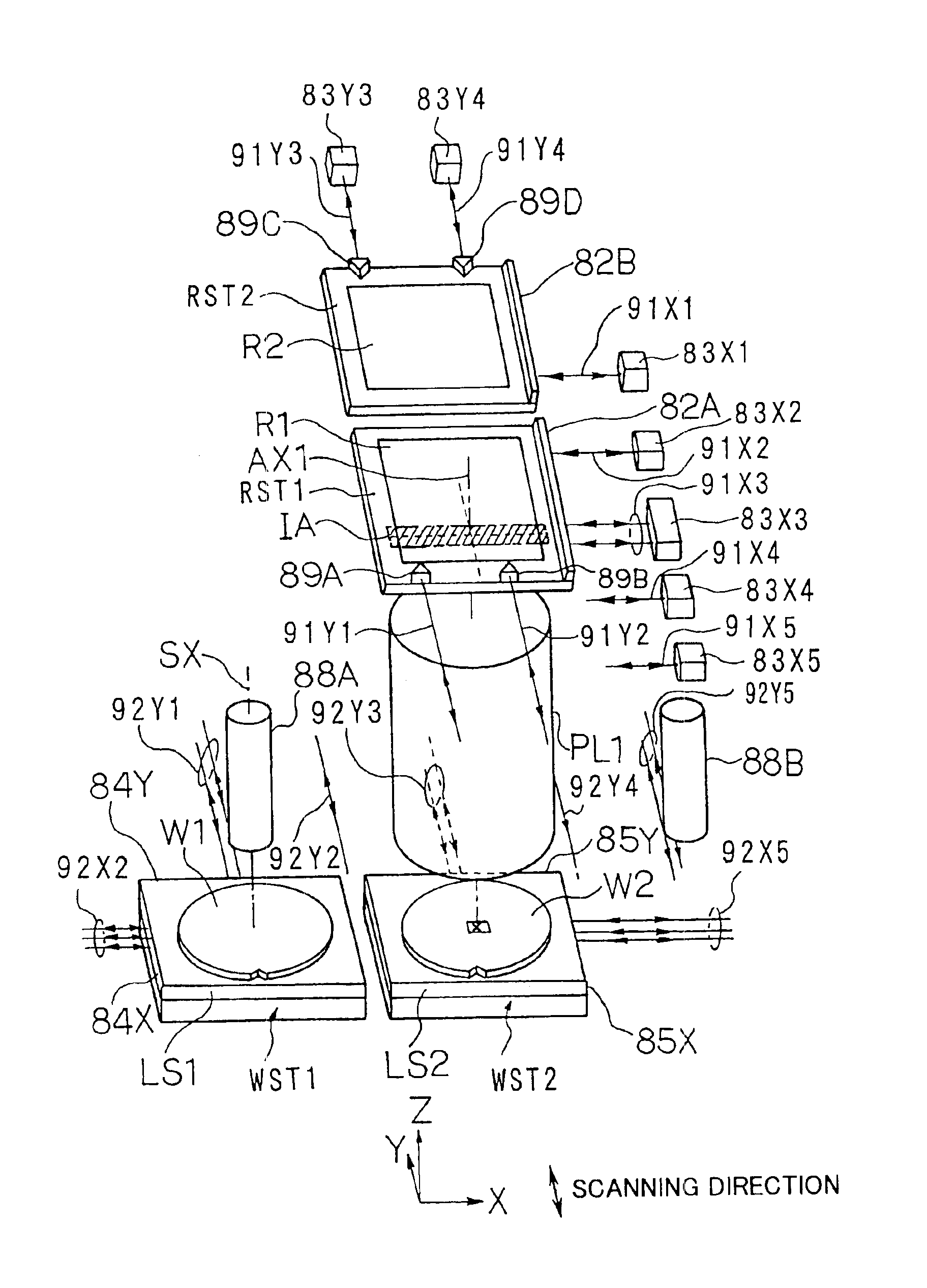
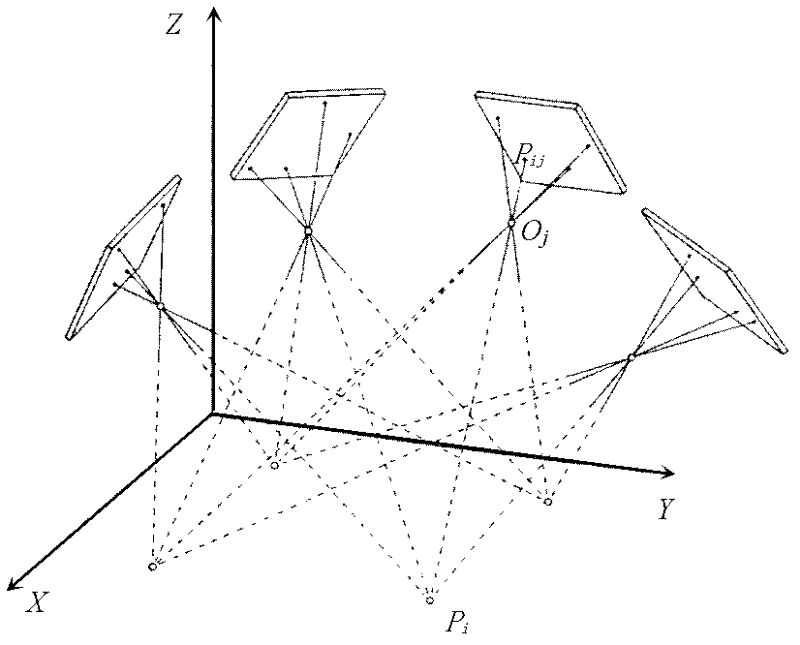
Movable body apparatus, exposure apparatus, exposure method, and device manufacturing method
ActiveUS20100159403A1Possible to measureImprove accuracySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingUsing optical meansEngineeringMeasurement station
In an exposure station, positional information of a stage holding a wafer is measured by a first fine movement stage position measurement system including a measurement arm, and in a measurement station, positional information of a stage holding a wafer is measured by a second fine movement stage position measurement system including another measurement arm. An exposure apparatus has a third fine movement stage position measurement system which can measure positional information of a stage when the stage is carried from the measurement station to the exposure station. The third fine movement stage measurement system includes an encoder system including a plurality of Y heads and a laser interferometer system including a laser interferometer.
Owner:NIKON CORP
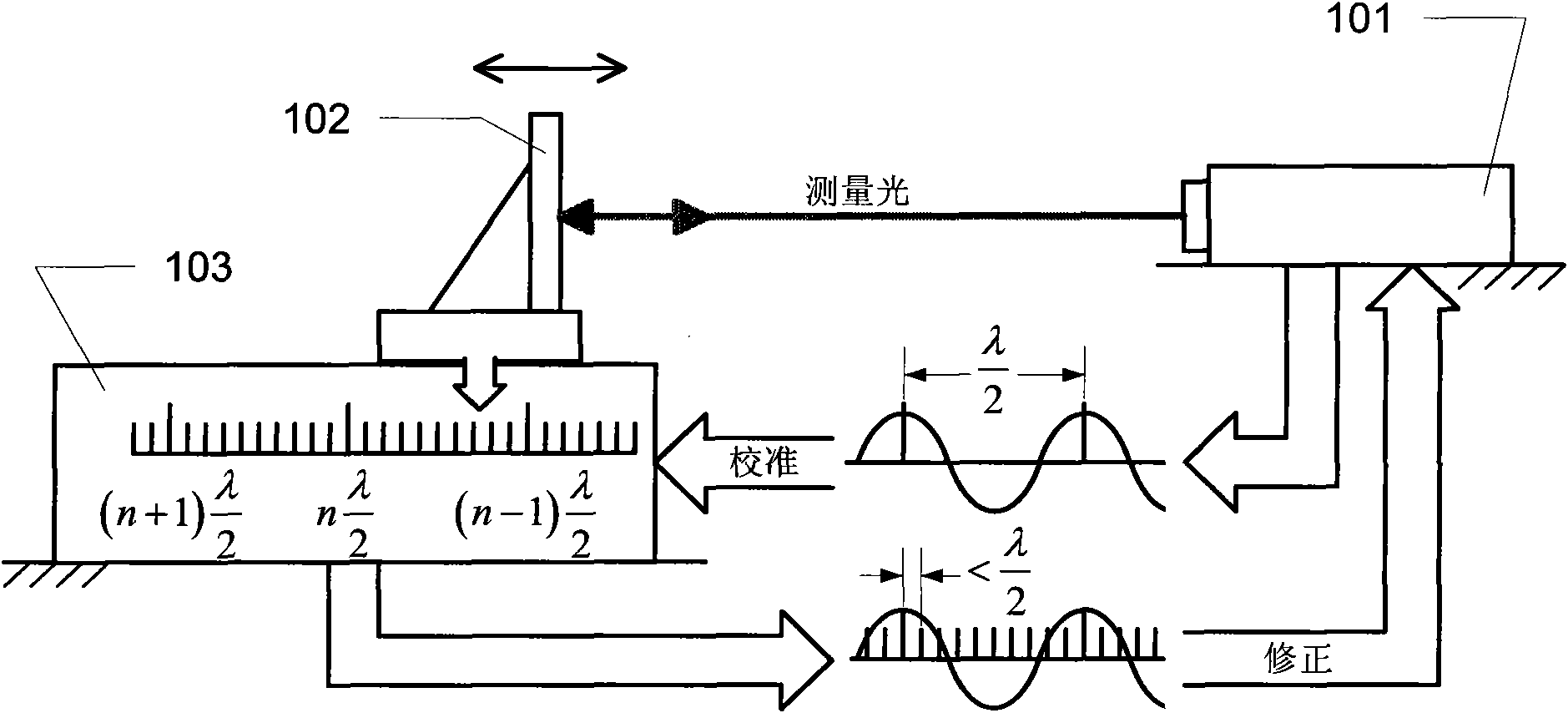
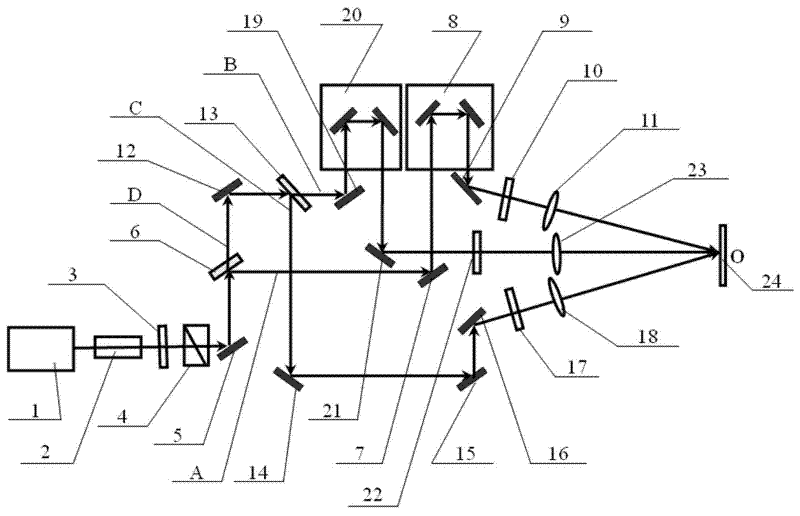
Single-frequency laser interferometer non-linear error compensation device
ActiveCN106225667ACompensate for phase non-orthogonality errorCompensate for non-linear errorsUsing optical meansGrismPlane mirror
The present invention discloses a single-frequency laser interferometer non-linear error compensation device. The single-frequency laser interferometer non-linear error compensation device is characterized in that after a light beam emitted by a laser is split by a polarization splitting prism, the transmitted light is projected to a rectangular prism and is returned to the polarization splitting prism to form the reference light S; the reflected light is projected to a plane mirror and is returned to the polarization splitting prism to form the measurement light P; a linear polaroid along an S direction is placed in a reference light path, and a linear polaroid along a P direction is arranged in a measurement light path, thereby realizing the nonorthogonal error compensation; the semi-transparent and semi-reflective mirrors are arranged in the emergent light paths of the linear polaroids, so that the reference light and the measurement light are combined and then are split by a depolarization splitting prism evenly, the transmitted light generates the interference signals I1 and I2 via a quarter-wave plate and the polarization splitting prism, the reflected light generates the interference signals I3 and I4 via the polarization splitting prism, and the mutual phase difference of the signals I1, I2, I3 and I4 is 90 degrees. According to the present invention, a non-linear error of the single-frequency laser interferometer is compensated effectively.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Rapid measuring and error compensation method for linearity error of linear guide rail
The invention provides a rapid measuring and error compensation method for linearity error of a linear guide rail, and aims at solving the problems of small measurement method, large error and complex data treatment in the prior art. The method comprises the steps of measuring and acquiring a plurality of data points on the linear guide rail through a laser interference instrument; analyzing the linearity measurement result for the data of the acquired points through a linearity data analyzing module in an XD laser measurement system so as to obtain the linearity error of the guide rail. With the adoption of the method, the mounting error, environmental error, delay error and the error caused by thermal expansion of a measured object in measuring can be analyzed; an error correcting model is built.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
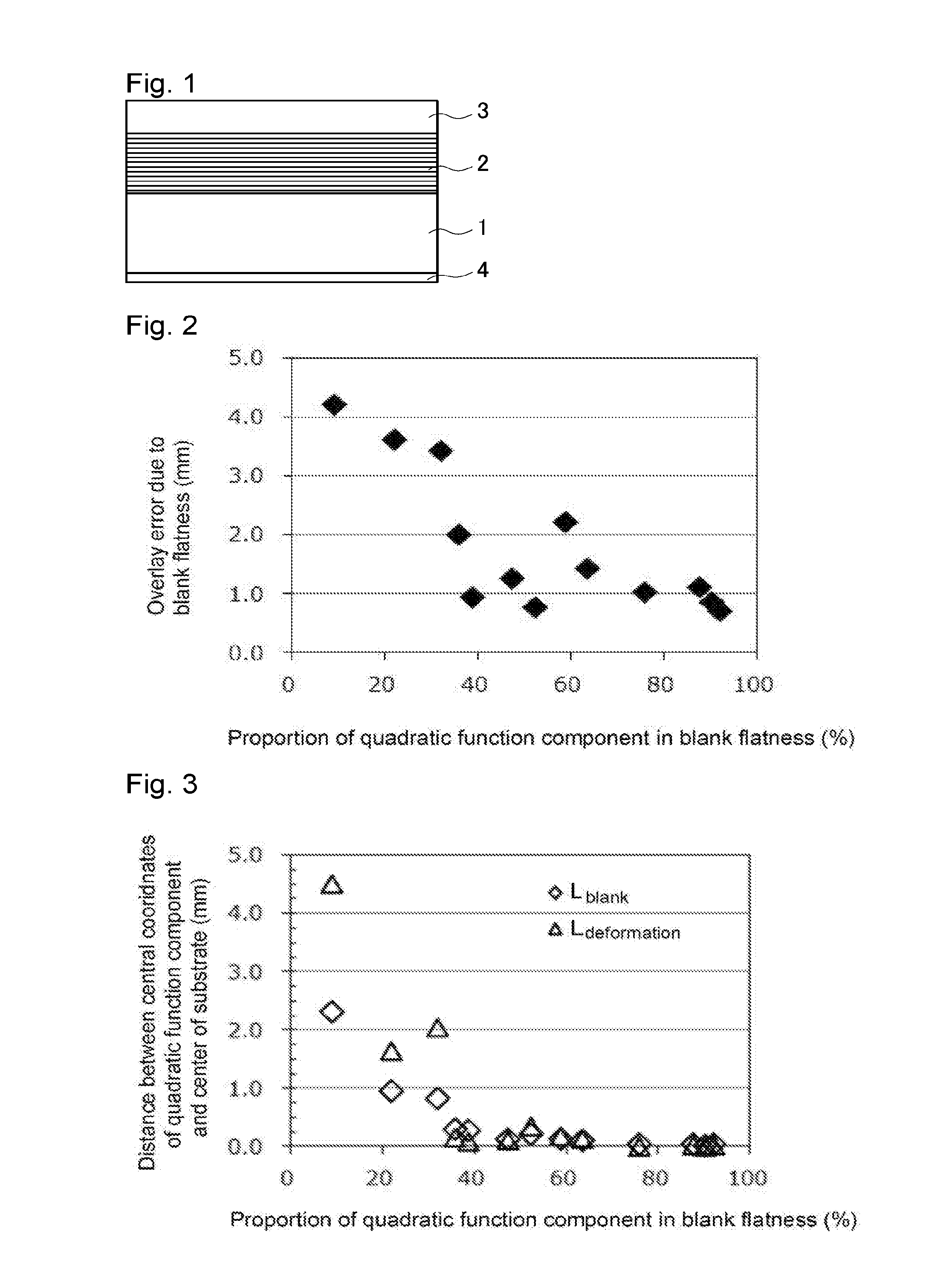
Reflective mask blank for EUV lithography
ActiveUS20160357100A1Deterioration of overlay accuracyImprove accuracyPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLithographic artistReflective layer
To provide a reflective mask blank for EUV lithography which is excellent in flatness, whereby the deterioration of the overlay accuracy at the time of pattern transfer can be relatively easily corrected, and the deterioration of the overlay accuracy due to the flatness is small.A reflective mask blank for EUVL, which is a reflective mask blank for EUV lithography having a reflective layer for reflecting EUV light and an absorber layer for absorbing EUV light formed in this order on the main surface of a substrate and having a conductive film formed on the rear surface opposite to the main surface, of the substrate, wherein when the shapes of quality-guaranteed regions of the main surface and the rear surface of the reflective mask blank for EUVL are measured by a laser interferometer, and the measured values obtained are fitted to quadratic function, the proportion of the quadratic function components is at least 35%, and the flatness at the quality-guaranteed regions of the main surface and the rear surface is at most 600 nm.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
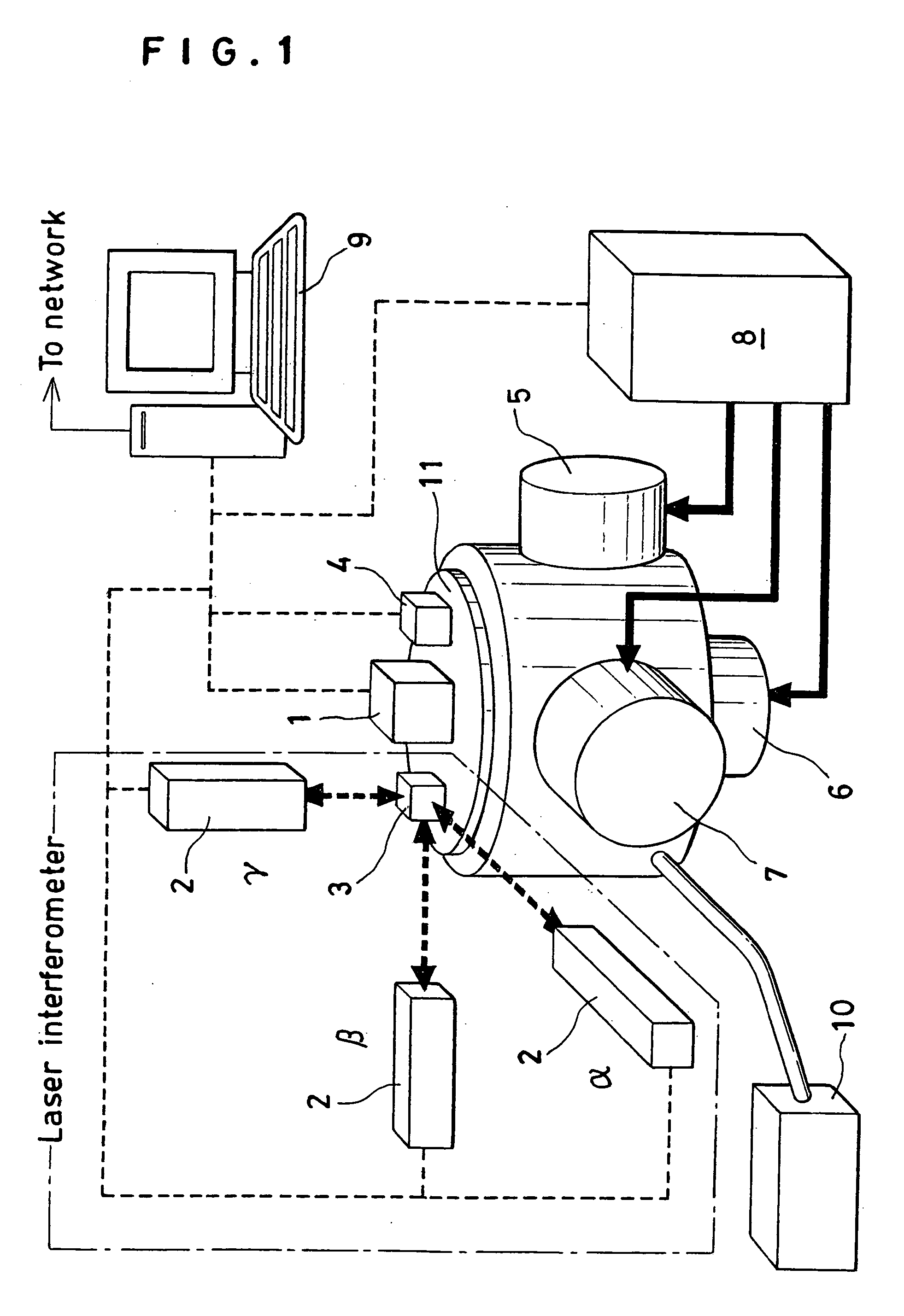
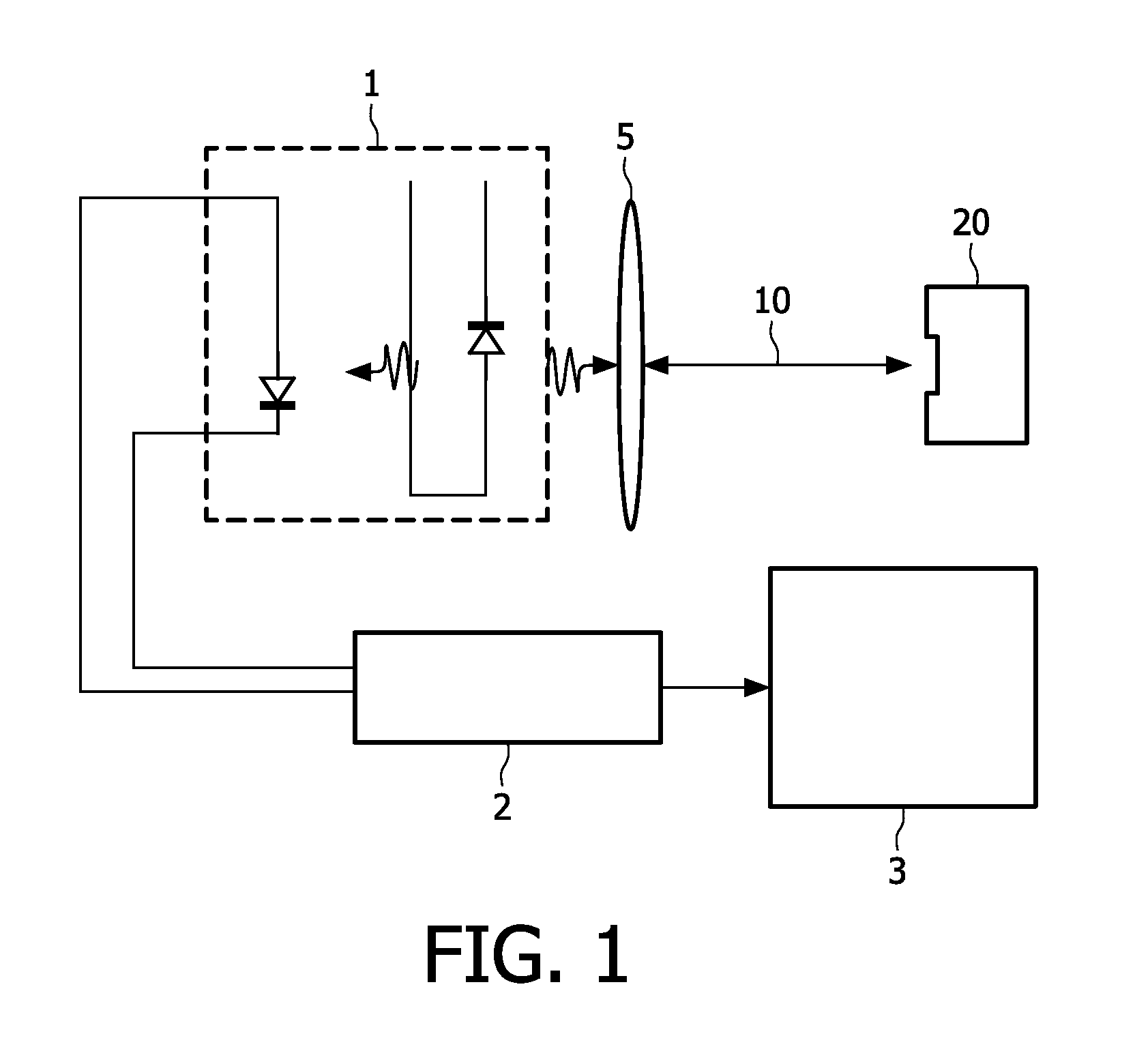
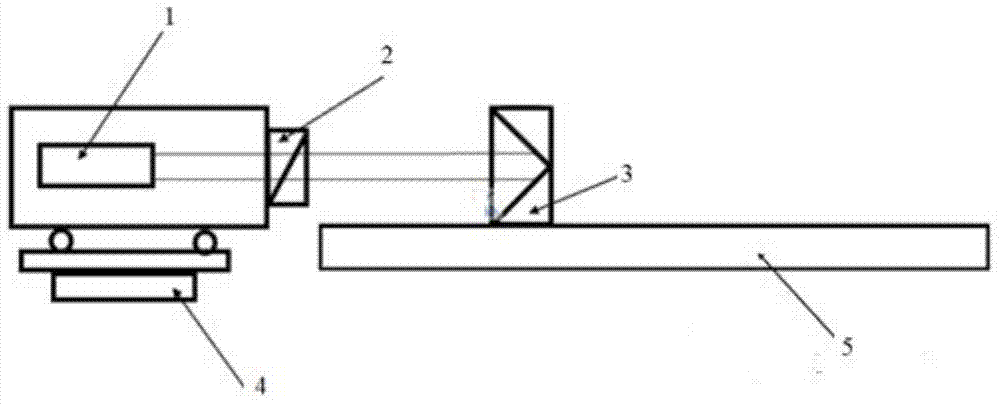
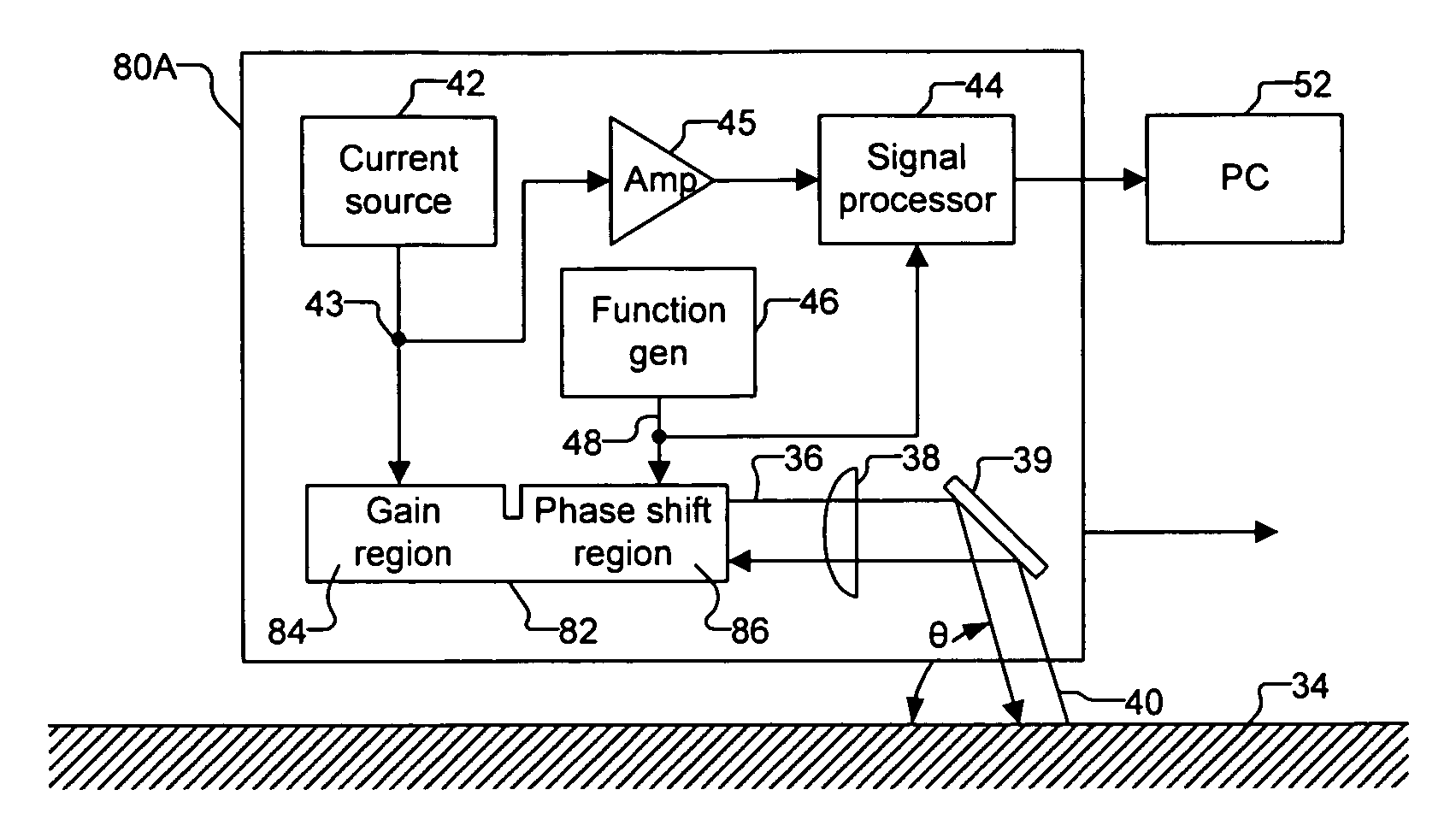
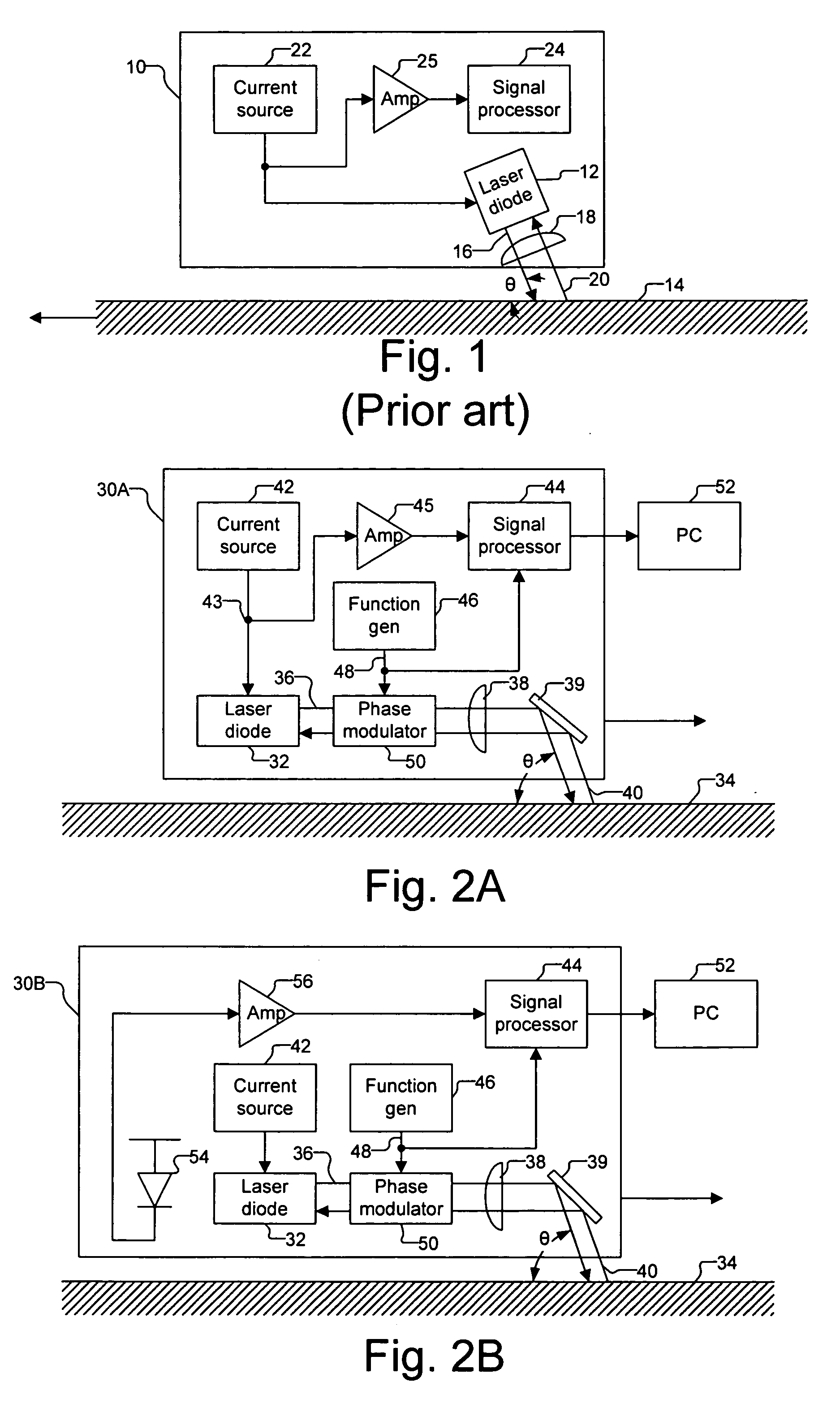
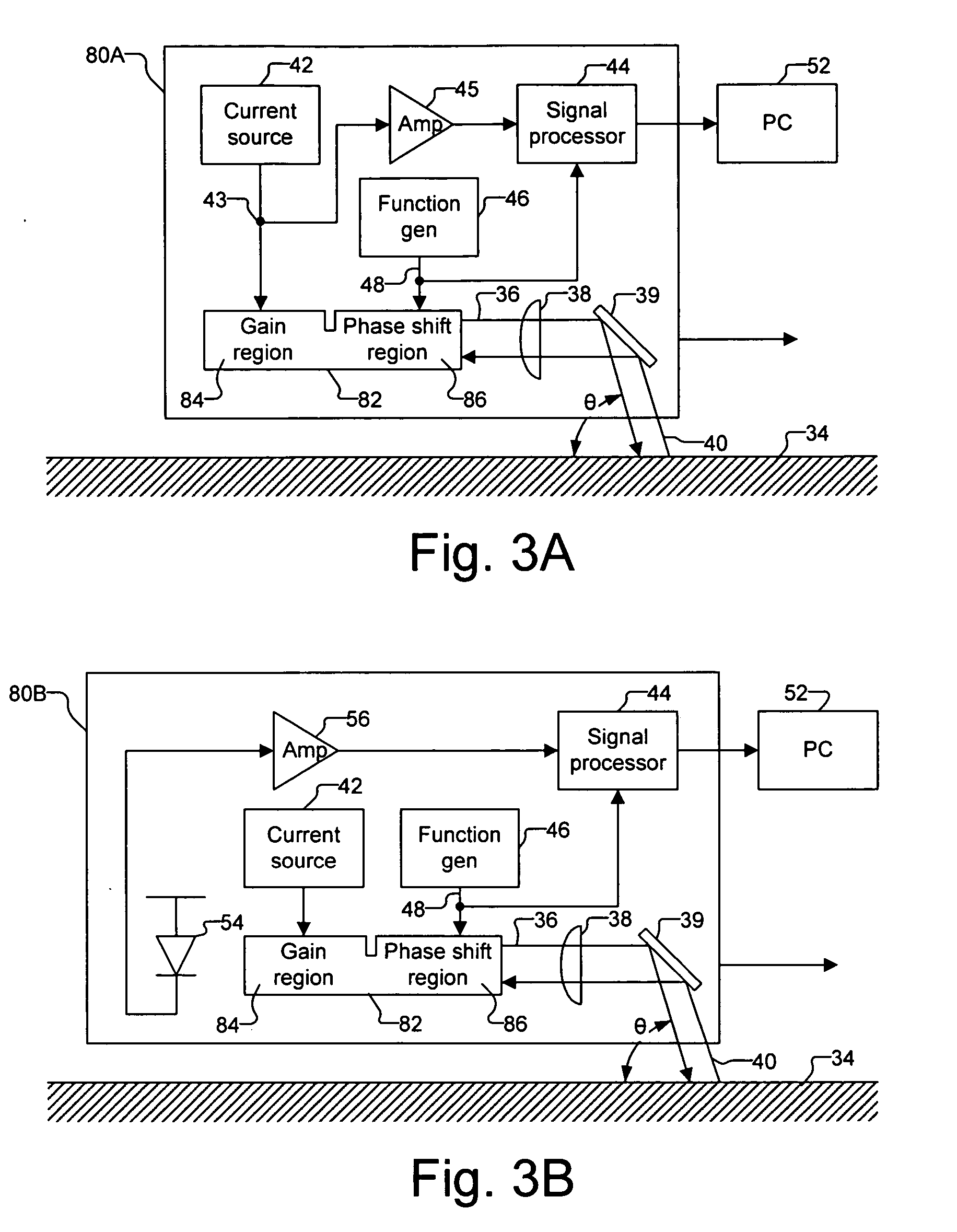
Optical navigation based on laser feedback or laser interferometry
A computer cursor control device includes (1) a light source generating light directed toward a stationary surface, (2) an optional phase modulator, (3) an optional function generator causing the phase modulator to periodically phase shift the light, and (4) a signal processor determining a direction in which the device is moving from a beat frequency or an asymmetry in the light intensity. Another computer cursor control device includes (1) an optical element combining reference and measurement beams to form a heterodyned beam, (2) a phase modulator located in an optical path of the reference beam or the measurement beam, (3) a function generator causing the phase modulator to phase shift the reference beam, and (4) a signal processor determining a direction in which the device is moving from a beat frequency of the heterodyned beam.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
System and method for positioning an object
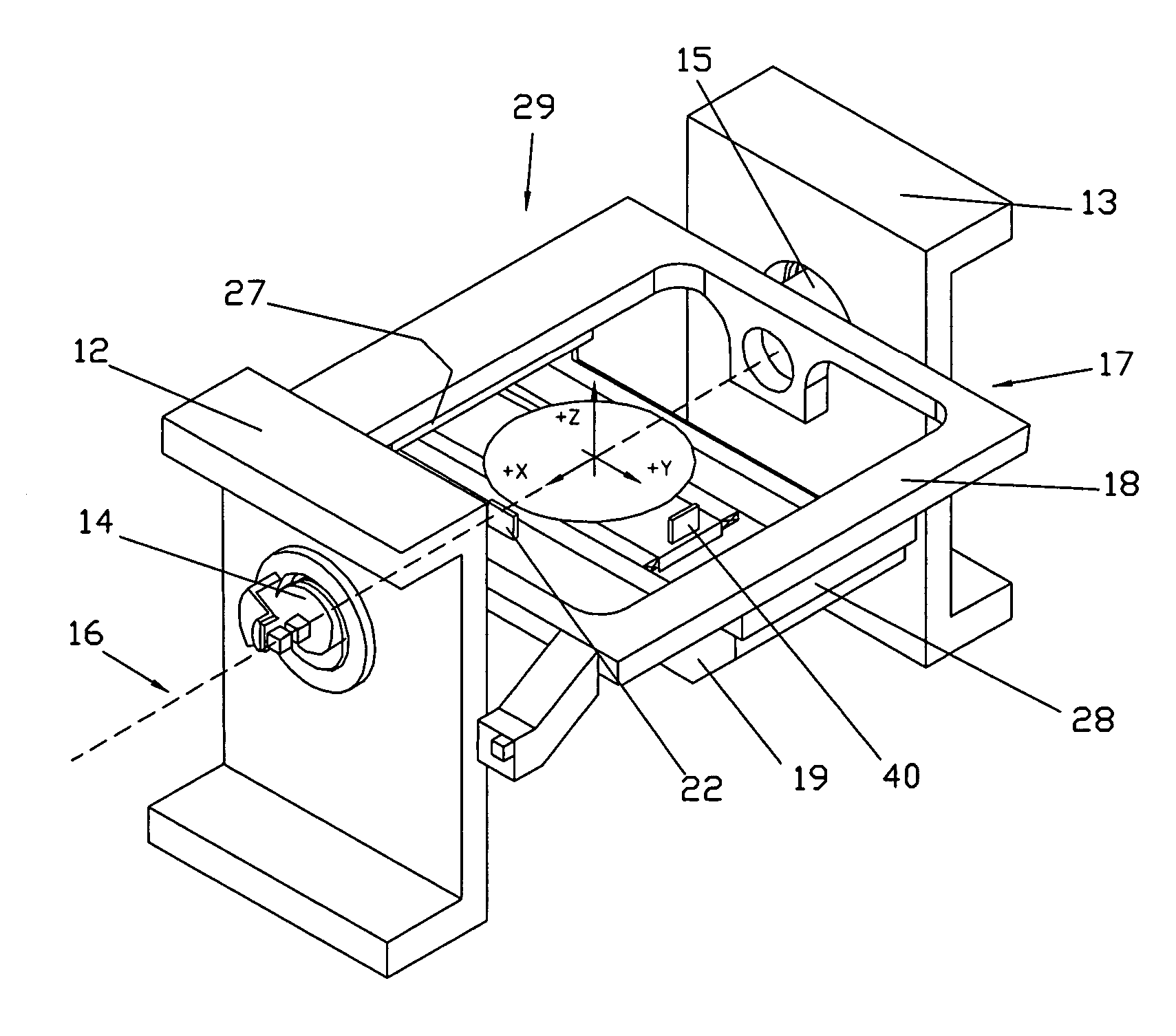
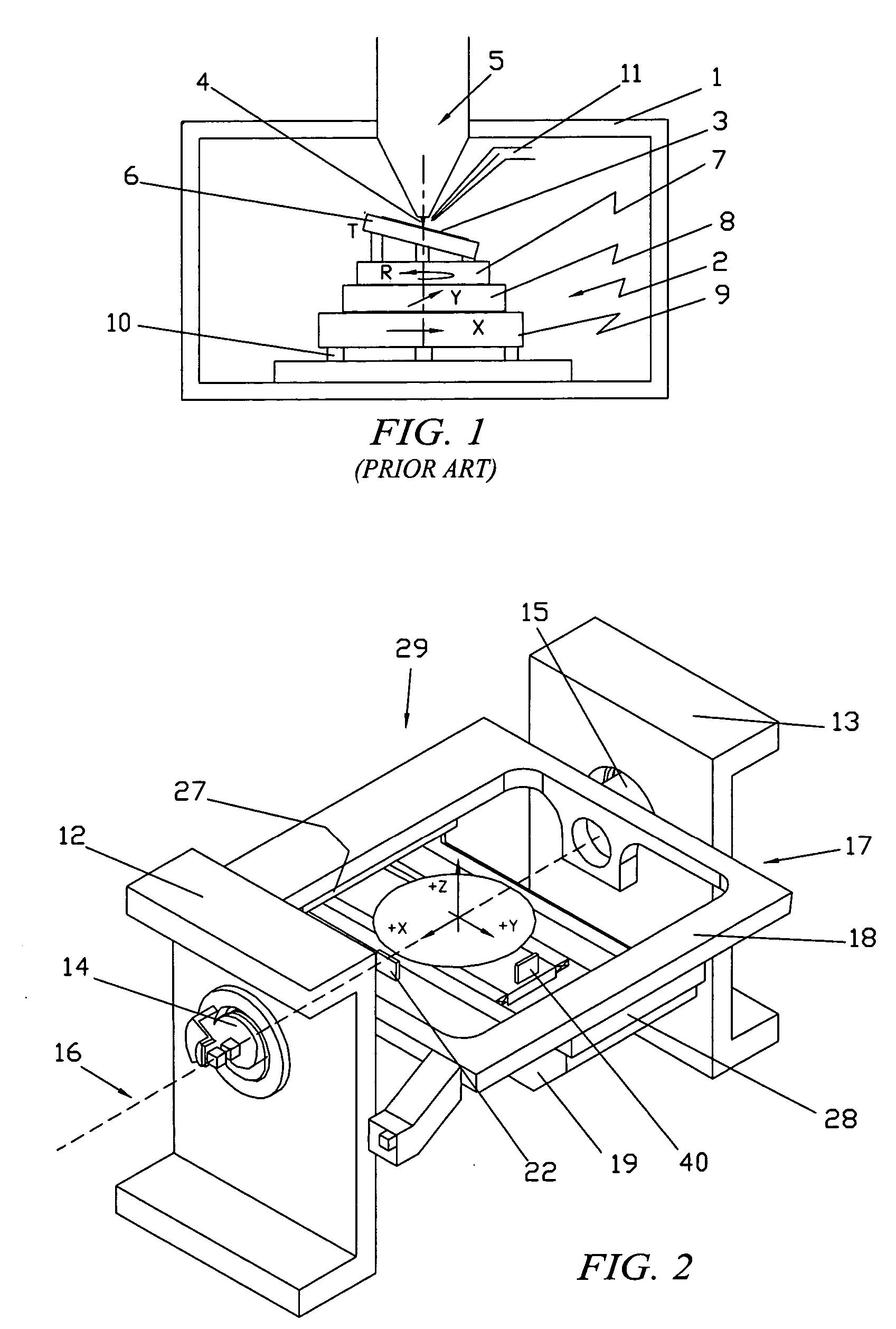
InactiveUS20070023684A1Accurate and Precise MeasurementsEasy to controlElectric discharge tubesUsing optical meansEngineeringMotion system
A motion system includes a first stage that is configured to rotate about a first axis and a second stage coupled to the first stage that includes an object carrier adapted to position an object in at least one other axis. The motion system has a novel arrangement of laser interferometer elements and axes of motion. The arrangement permits accurate and precise measurement of a position of the object carrier in up to three (or more) axes of motion even as the first stage of the motion system is tilted through relatively large angles. The novel arrangement of the axes of motion also enables very precise control of the position of the object carrier even at high tilt angles.
Owner:LEWIS GEORGE C +1
Extreme Temperature Robust Optical Sensor Designs And Fault-Tolerant Signal Processing
InactiveUS20090296776A1Eliminates multiple unwanted optical reflectionReduce ambiguityThermometer detailsSensing radiation from gases/flamesFrequency spectrumBlack body
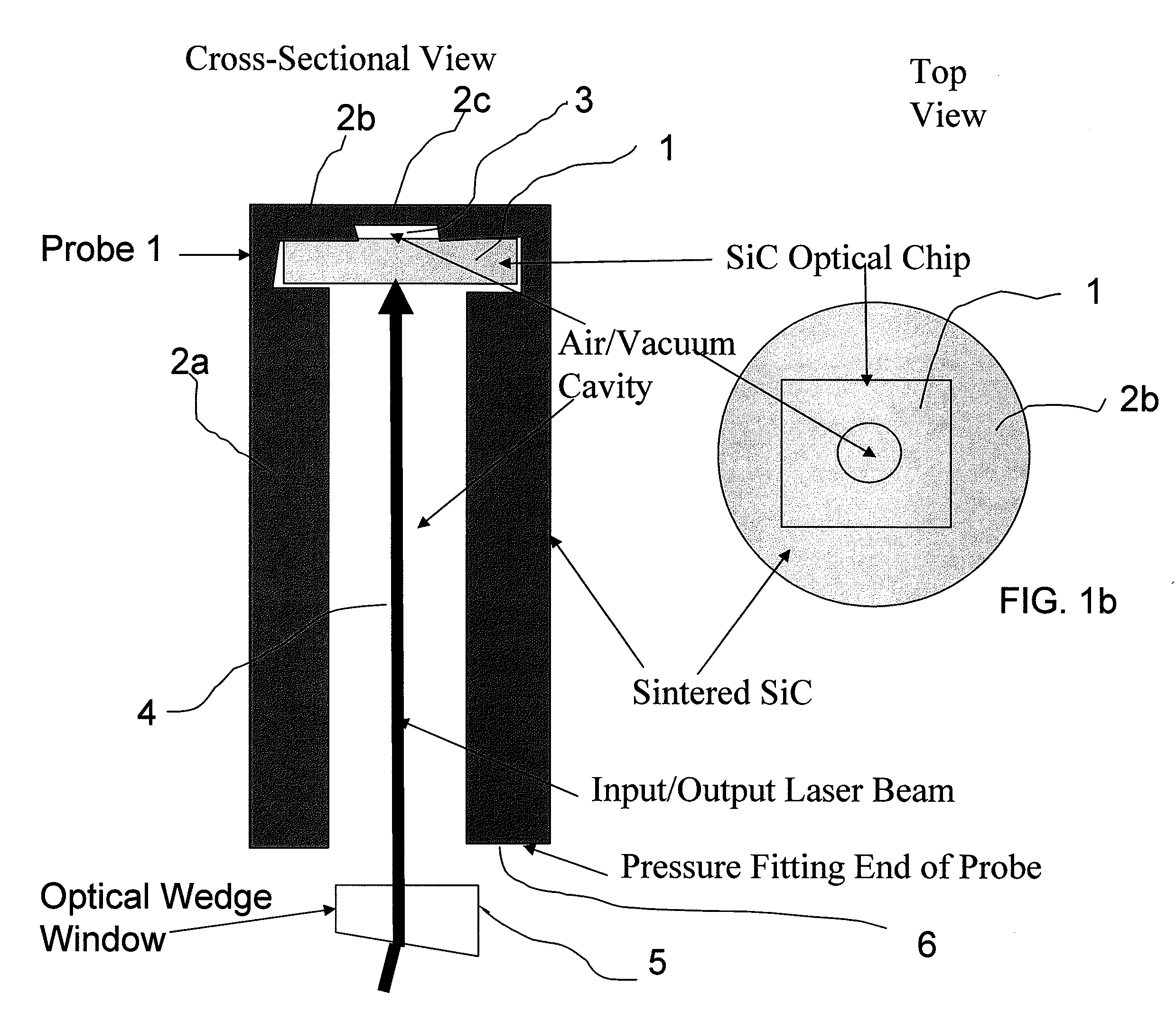
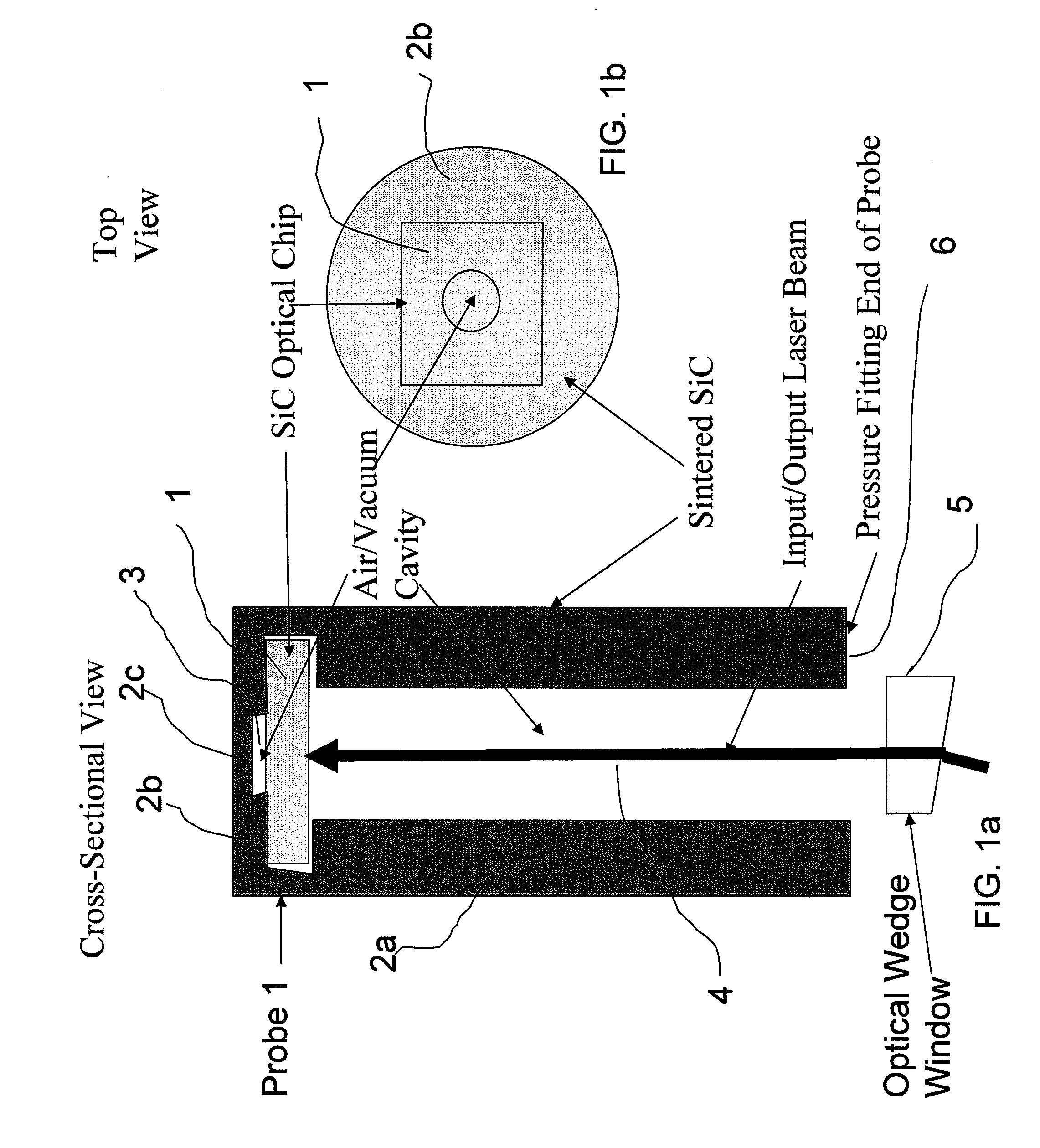
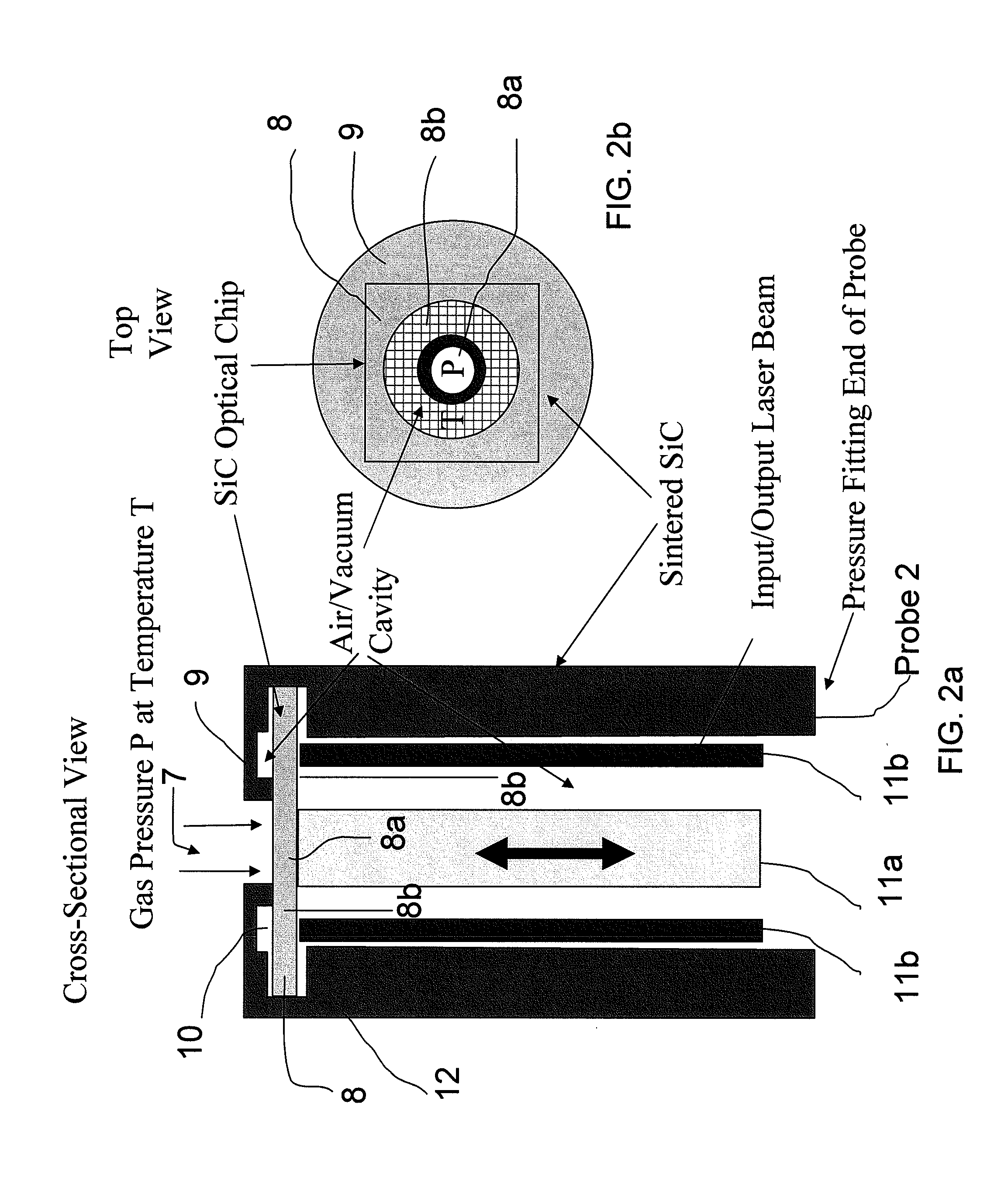
Silicon Carbide (SiC) probe designs for extreme temperature and pressure sensing uses a single crystal SiC optical chip encased in a sintered SiC material probe. The SiC chip may be protected for high temperature only use or exposed for both temperature and pressure sensing. Hybrid signal processing techniques allow fault-tolerant extreme temperature sensing. Wavelength peak-to-peak (or null-to-null) collective spectrum spread measurement to detect wavelength peak / null shift measurement forms a coarse-fine temperature measurement using broadband spectrum monitoring. The SiC probe frontend acts as a stable emissivity Black-body radiator and monitoring the shift in radiation spectrum enables a pyrometer. This application combines all-SiC pyrometry with thick SiC etalon laser interferometry within a free-spectral range to form a coarse-fine temperature measurement sensor. RF notch filtering techniques improve the sensitivity of the temperature measurement where fine spectral shift or spectrum measurements are needed to deduce temperature.
Owner:RIZA NABEEL +2
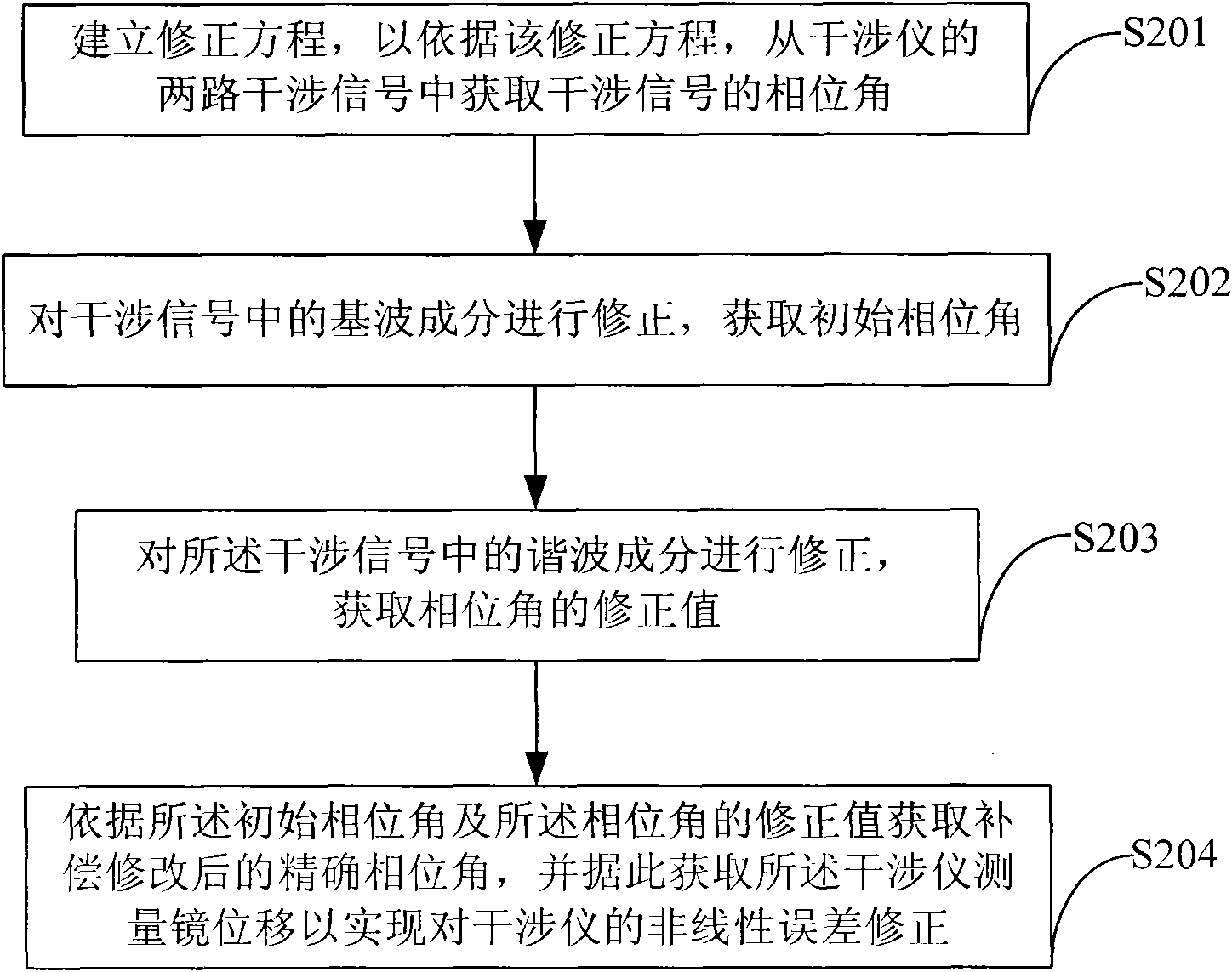
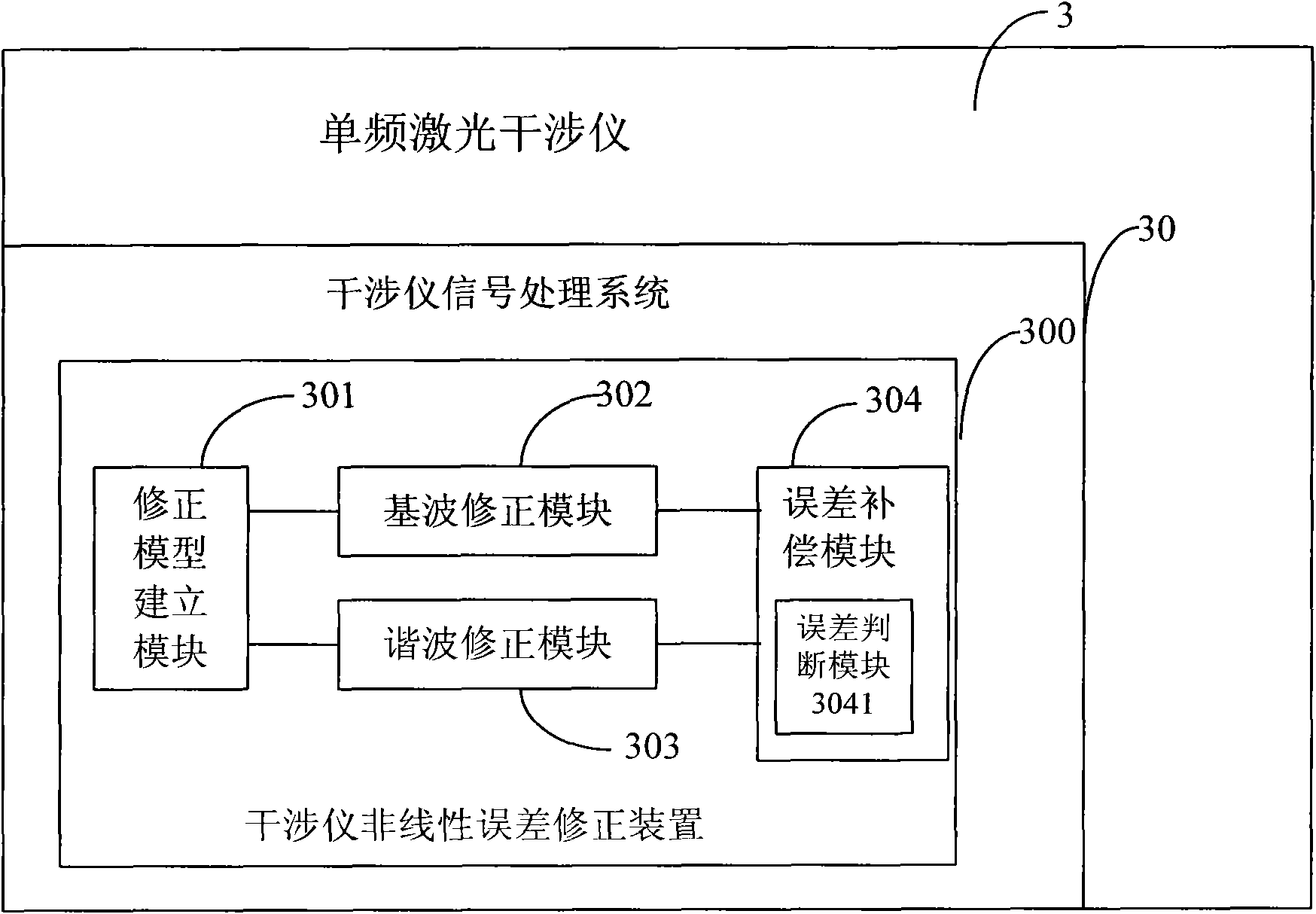
Nonlinear error correction method of laser interferometer, device and interferometer applying method and device
InactiveCN101839686ANonlinear Error Correction Compensation OptimizationUsing optical meansHarmonicLinearity error
The invention discloses a nonlinear error correction method of a single frequency laser interferometer, a device and an interferometer applying the method and the device, and the method carries out nonlinear error correction on the interferometer by utilizing the harmonic separation correction method and comprises the following steps: step 1: establishing a correction equation for obtaining a phase angle of interference signals from two lines of the interference signals of the interferometer according to the correction equation; step 2: correcting fundamental wave components in the interference signals, and obtaining the initial phase angle; step 3: correcting harmonic components in the interference signals, and obtaining the corrected value of the phase angle; and step 4: obtaining the precise phase angle after compensation modification according to the initial phase angle and the corrected value of the phase angle, accordingly obtaining the displacement of a measuring mirror of the interferometer, and further realizing the nonlinear error correction of the interferometer. The method can eliminate various harmonic components causing nonlinear errors in the interference signals, and optimize the nonlinear error correction of the single frequency laser interferometer.
Owner:NAT INST OF METROLOGY CHINA
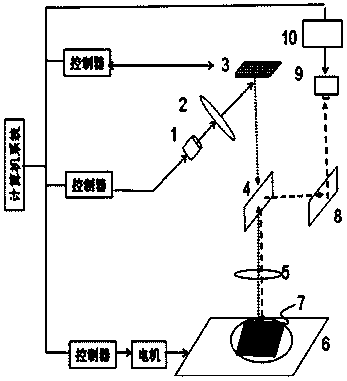
Method and device for preparing micro-nano composite periodic structure with femtosecond laser beam
InactiveCN102259826AMany tricksIncrease diversityDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingMicro nanoLight beam
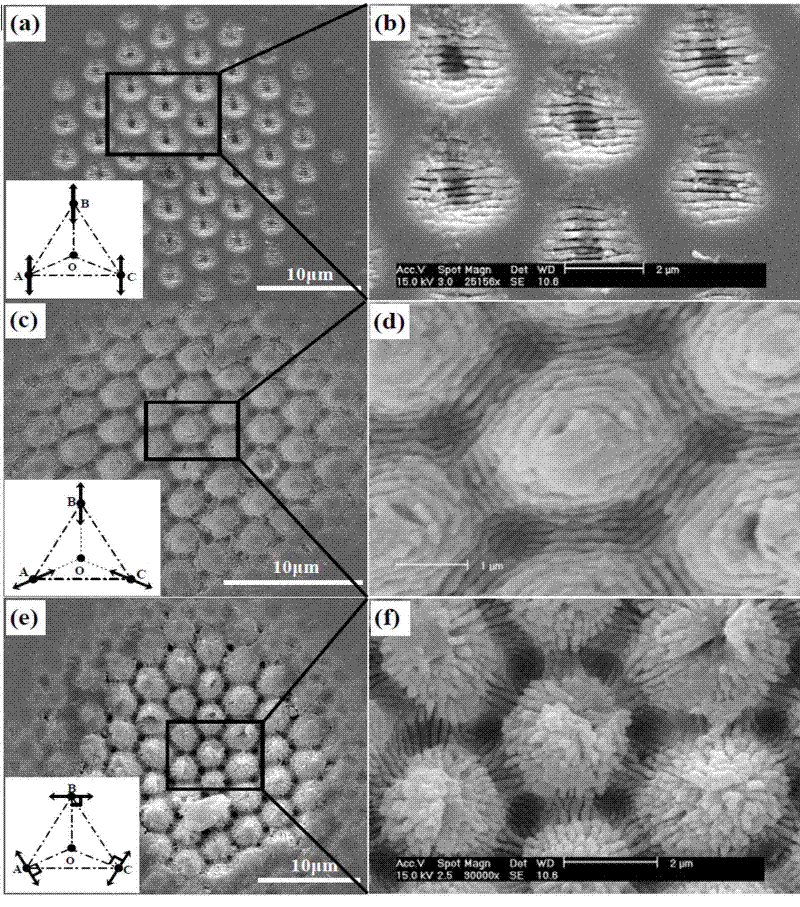
The invention discloses a method and device for preparing a micro-nano composite periodic structure with femtosecond laser beams, combining multi-beam interference technology and femtosecond laser-induced nanostructures, and developing a polarization adjustment method, using the same interference device to combine femtosecond laser The beam is divided into three beams, and by simply rotating the angle of the half-wave plate to adjust the polarization state of the three beams, a wide variety of micro-nano composite periodic structures can be prepared, which greatly enriches the patterns of surface nano-periodic structures and improves the diversity of laser interferometry. , providing new technical means for the research of laser nanoprocessing and material modification.
Owner:SHANGHAI DIANJI UNIV
Method for measuring and compensating absolute positioning accuracy of precise positioning platform
InactiveCN104199257AReduce measurementLow costPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusImage matchingMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a method for measuring and compensating absolute positioning accuracy of a precise positioning platform. The method comprises the following specific steps: putting a mask plate on a photo-etching device with high known positioning accuracy, exposing a plurality of regularly arranged Marks on the photo-etching device, measuring a positioning platform with poor accuracy by virtue of the mark plate, a CCD imaging technology and an image matching technology after etching, and compensating a measured error to a platform controller so as to improve the positioning accuracy of the platform. The method is used for measuring and compensating the error by exposing the marks on the mask plate; compared with a method of measurement and compensation with a laser interferometer in the prior art, the method is low in cost and easy to operate; when the image matching method is used for measuring and compensating, the measurement accuracy is high, and the error is 1 / 20 pixel, namely 4.65 microns / 22.3 / 20 which is about 10nm; the method is capable of effectively compensating and calibrating the two-dimensional positioning accuracy of the positioning platform.
Owner:HEFEI ADVANTOOLS SEMICON
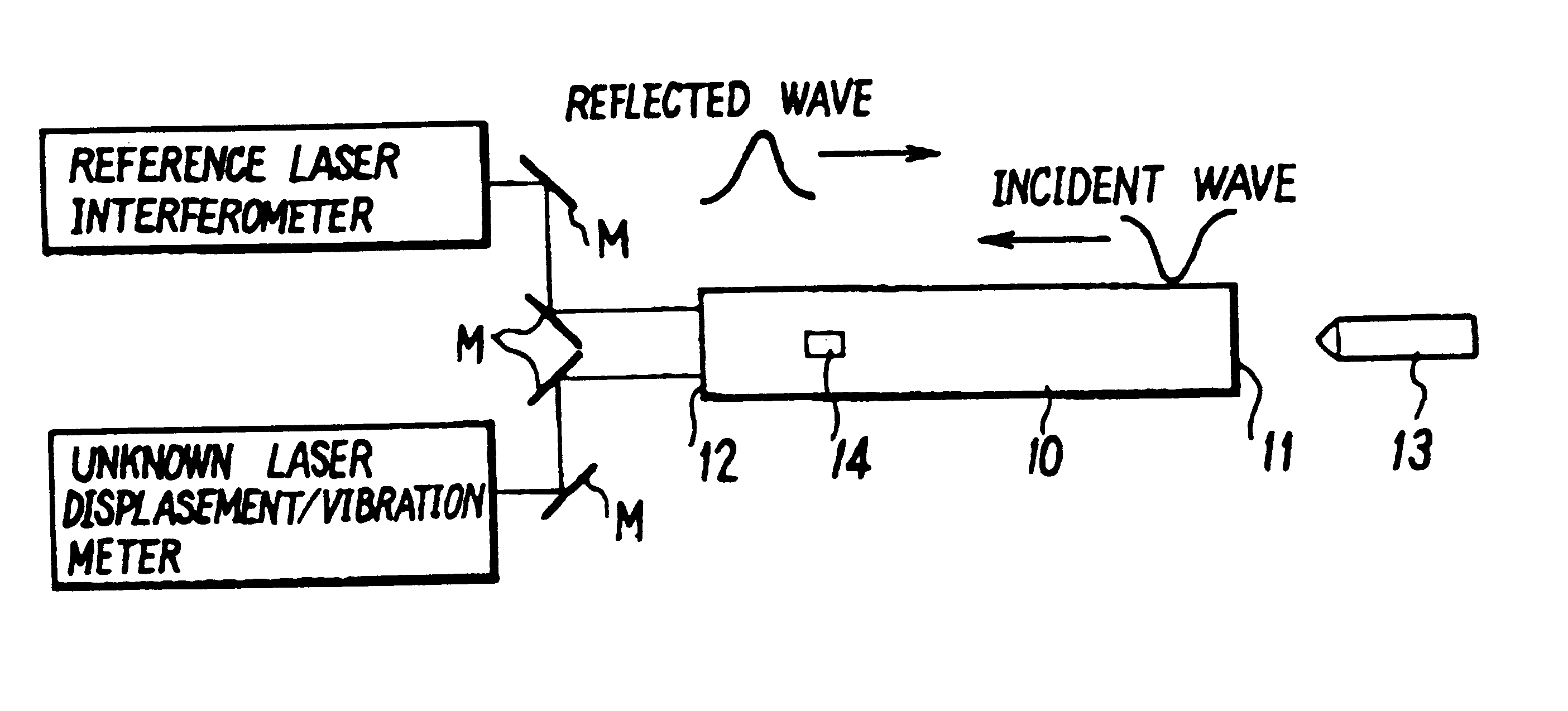
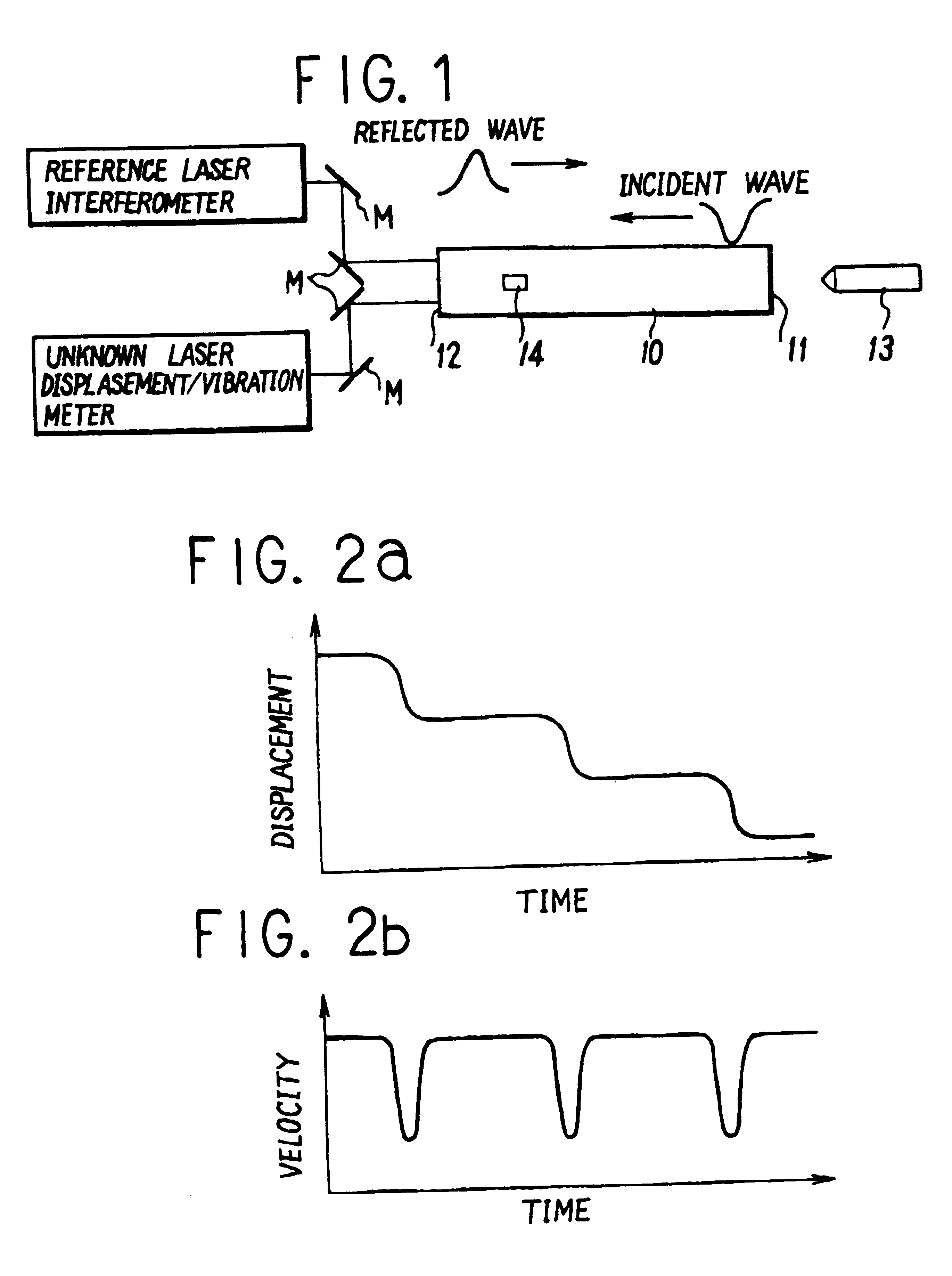
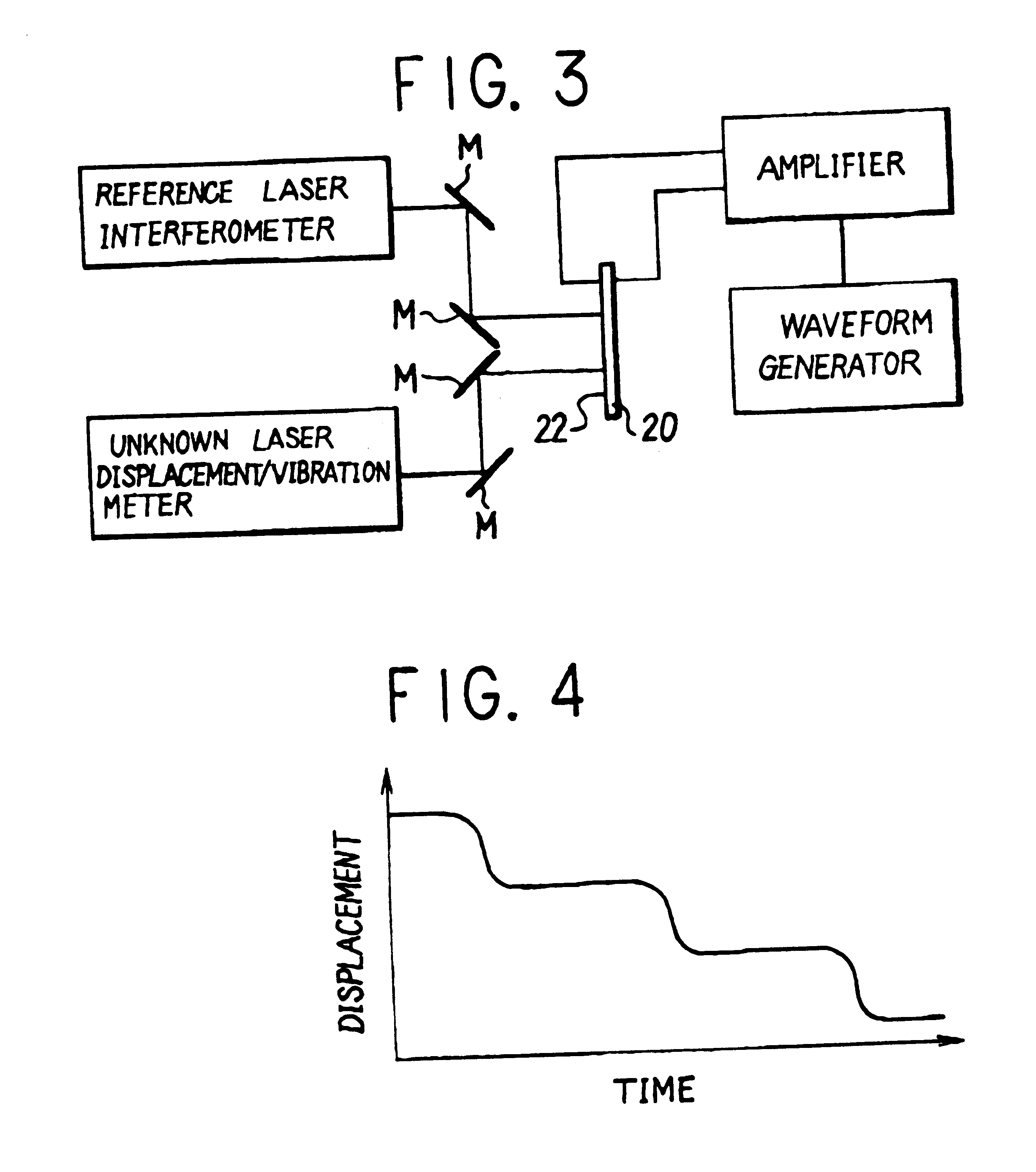
Method for testing frequency response characteristics of laser displacement/vibration meters
InactiveUS6286359B1Highly reliable measurementWide frequency rangeAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUsing mechanical meansFrequency characteristicLaser beams
A method of testing frequency characteristics of a laser displacement / vibration meter by the use of a novel which can cope with a broader frequency range and finer micro-level displacements to enhance the reliability of the displacement / vibration meter. Upon applying impact on one end face of a round metal rod, an elastic wave pulse which propagates through the metal rod generates a stepwise dynamic displacement of the other end face of the rod when reflected there. This dynamic displacement is measured simultaneously by a reference laser interferometer with a reference laser beam and a laser displacement / vibration meter with unknown frequency response characteristics, followed by comparison of measurement data over a frequency range to determine the frequency response characteristics of the unknown laser displacement / vibration meter.
Owner:DIRECTOR GENERAL OF THE AGENCY OF IND SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com