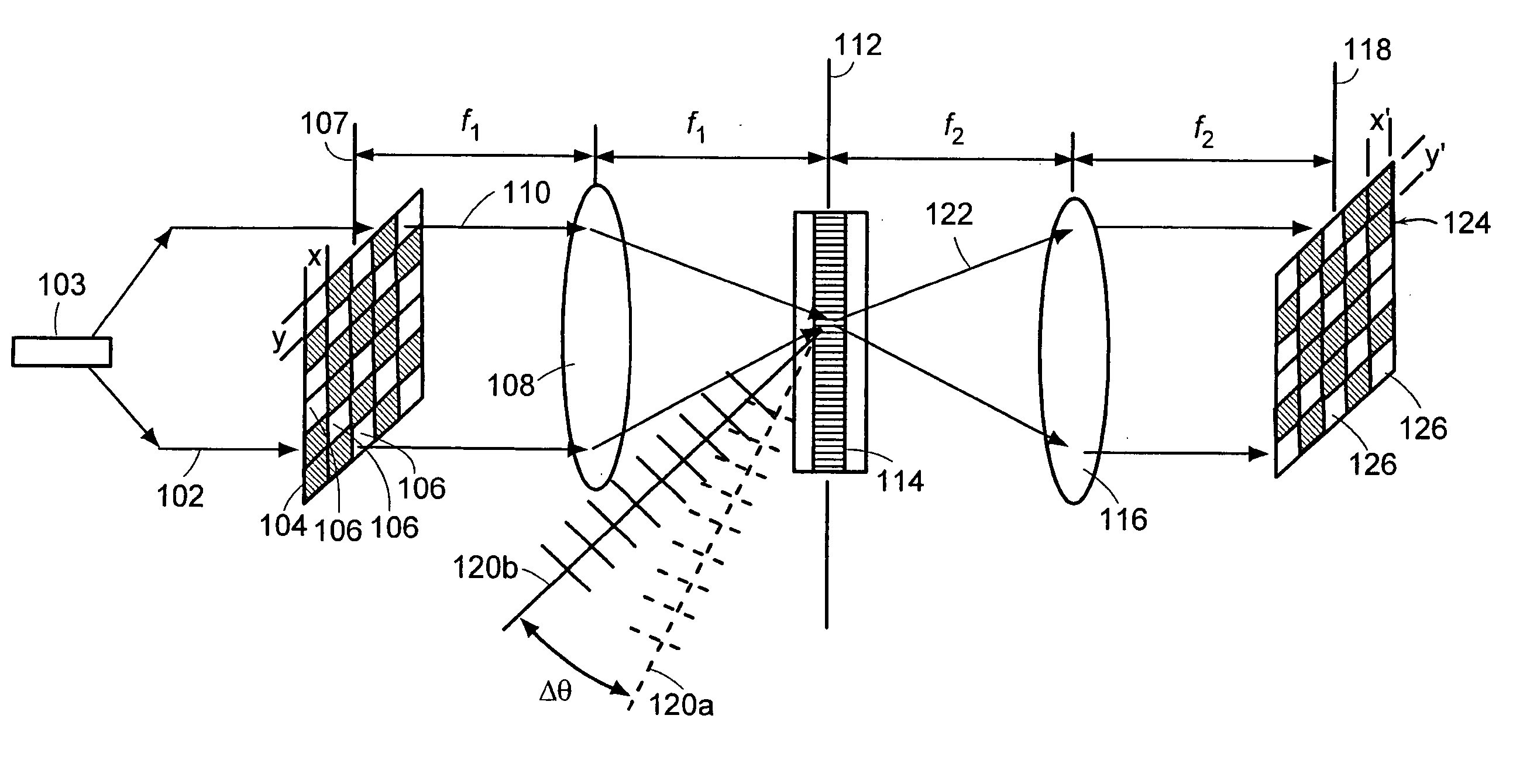
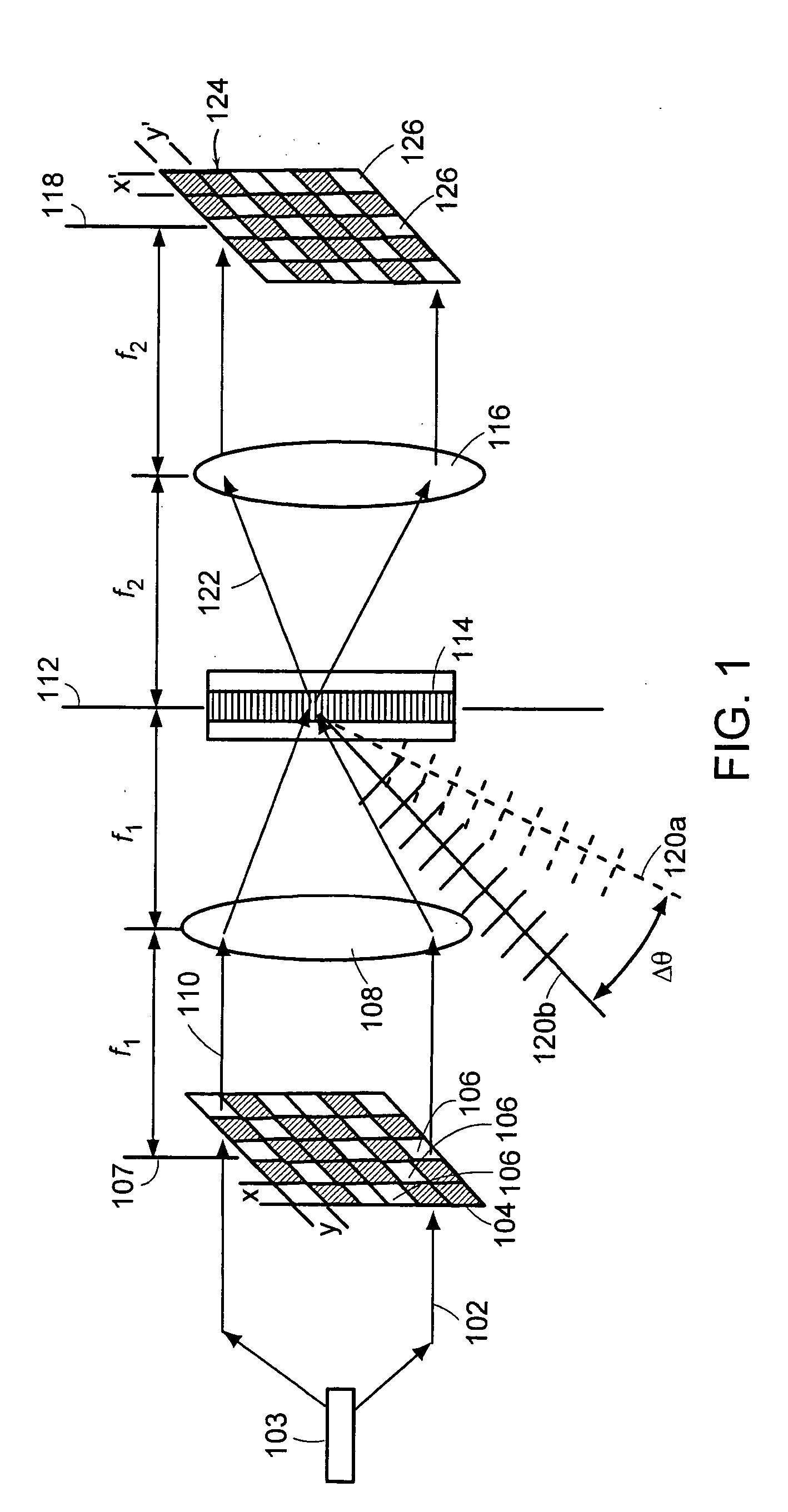
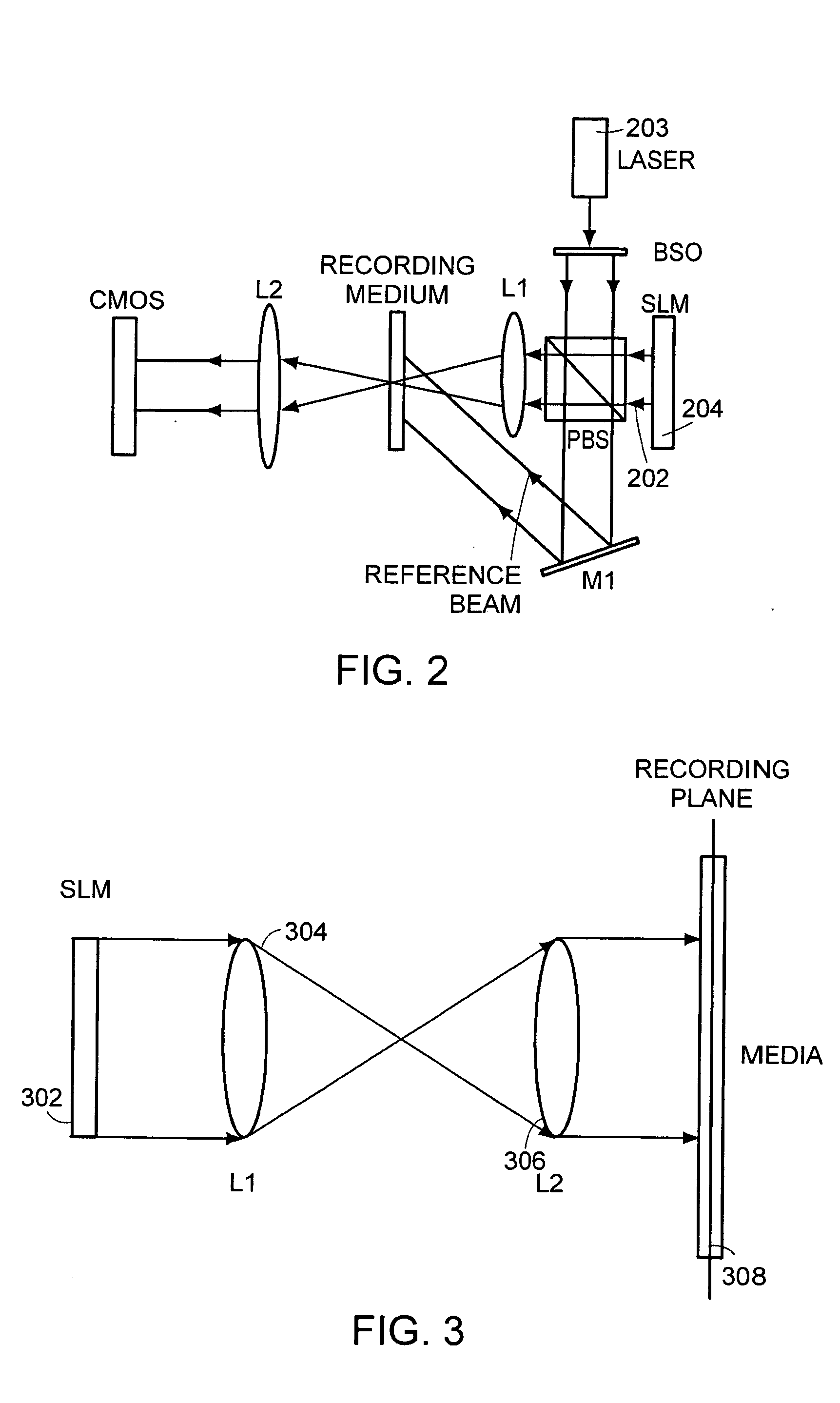
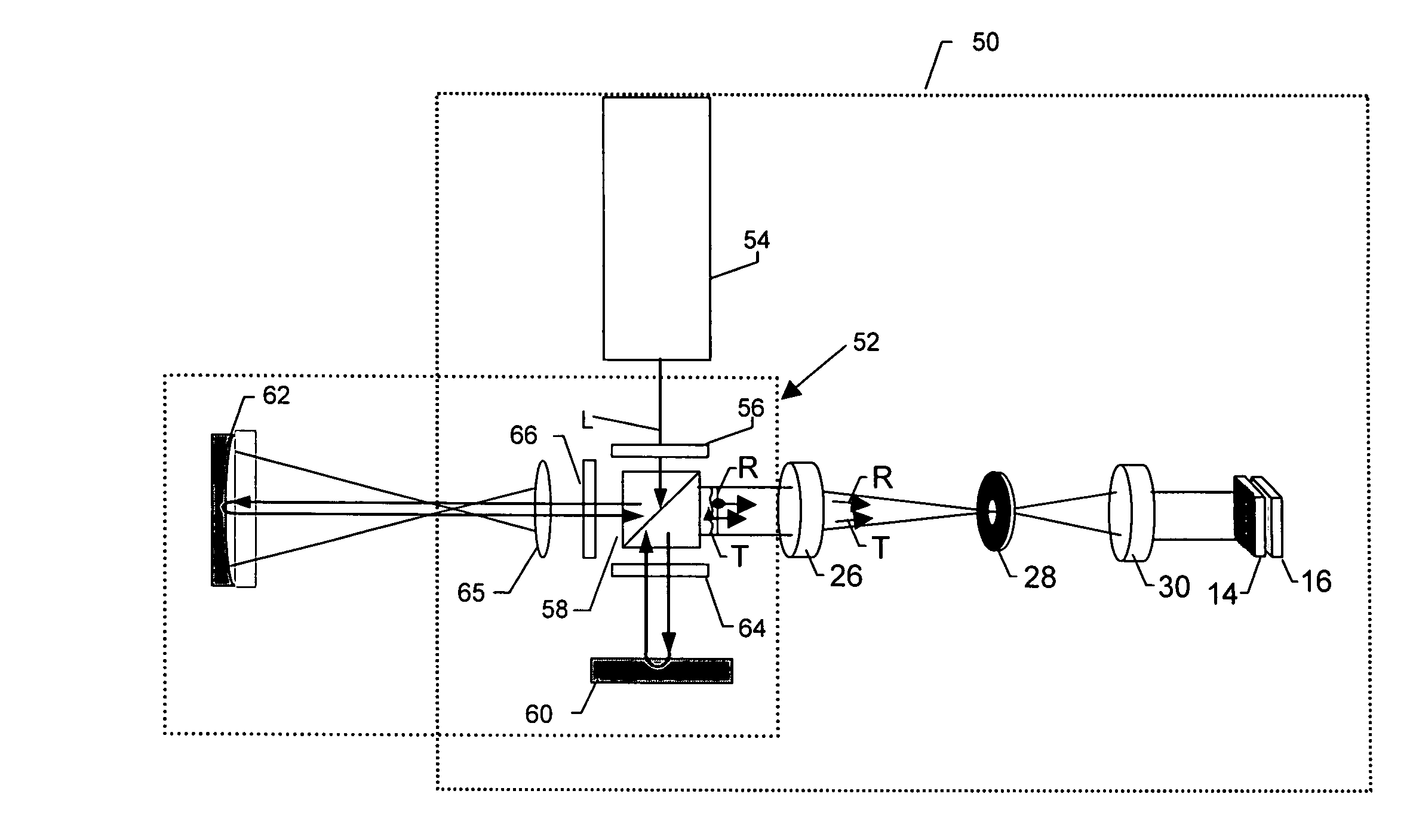
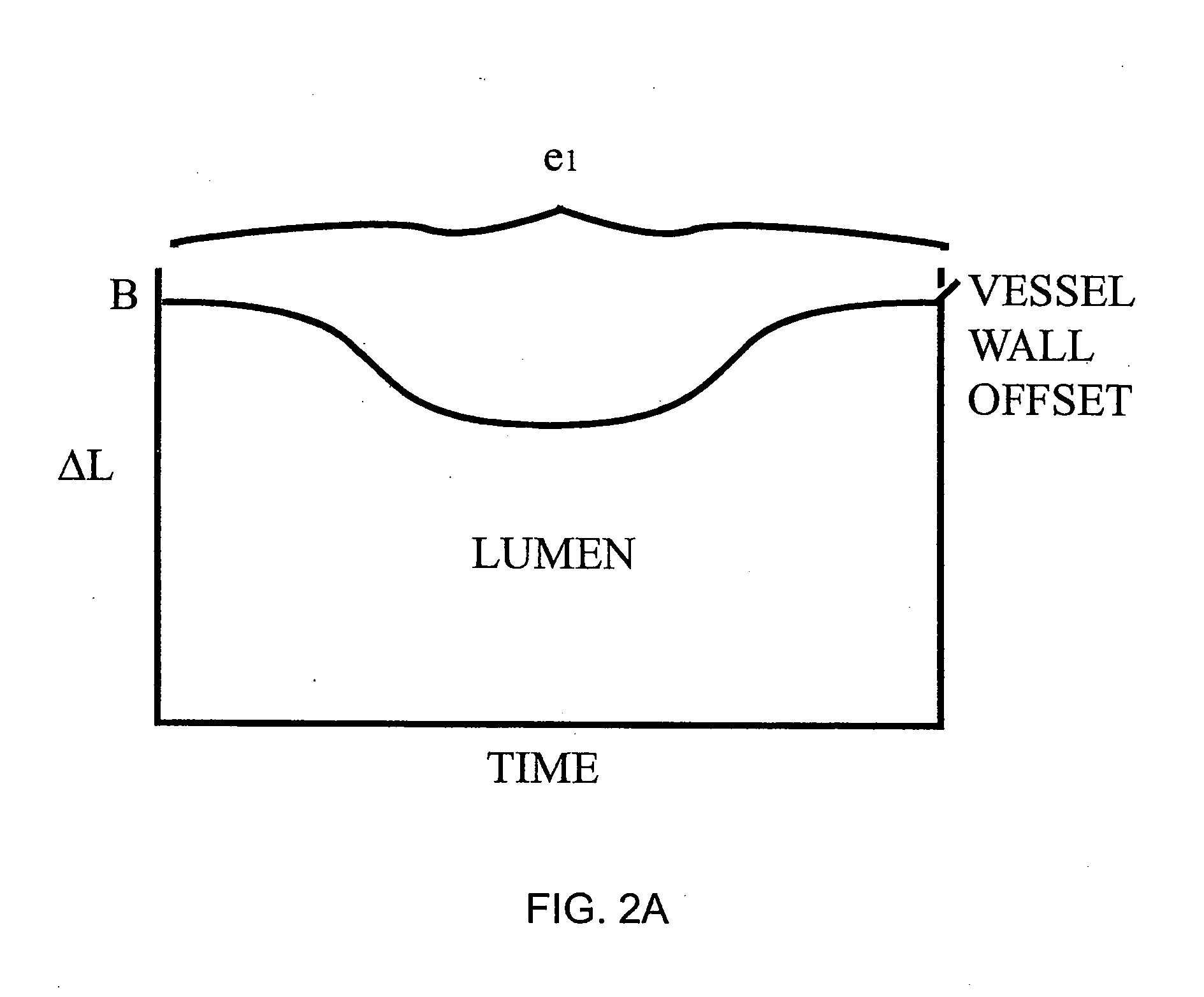
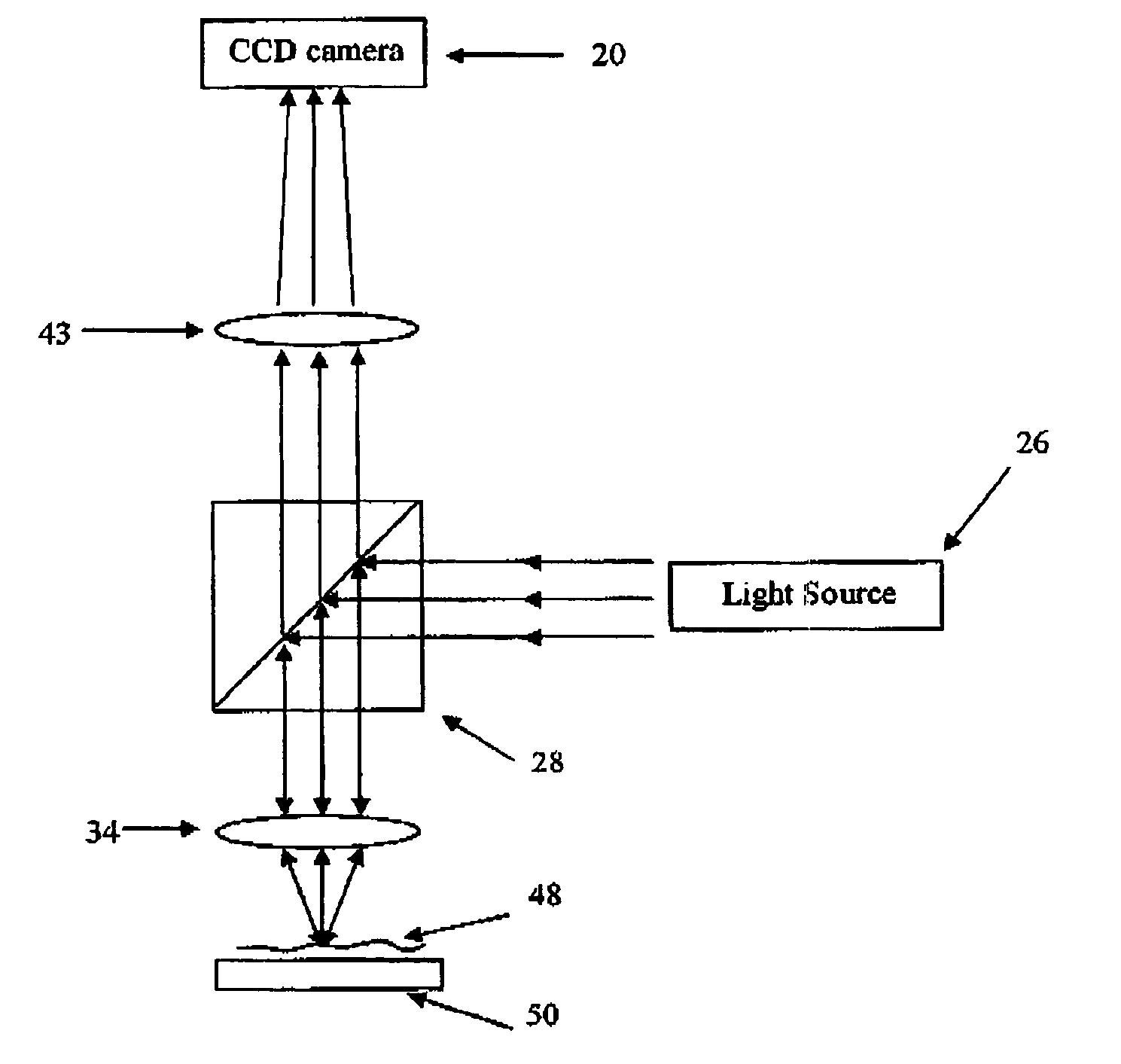
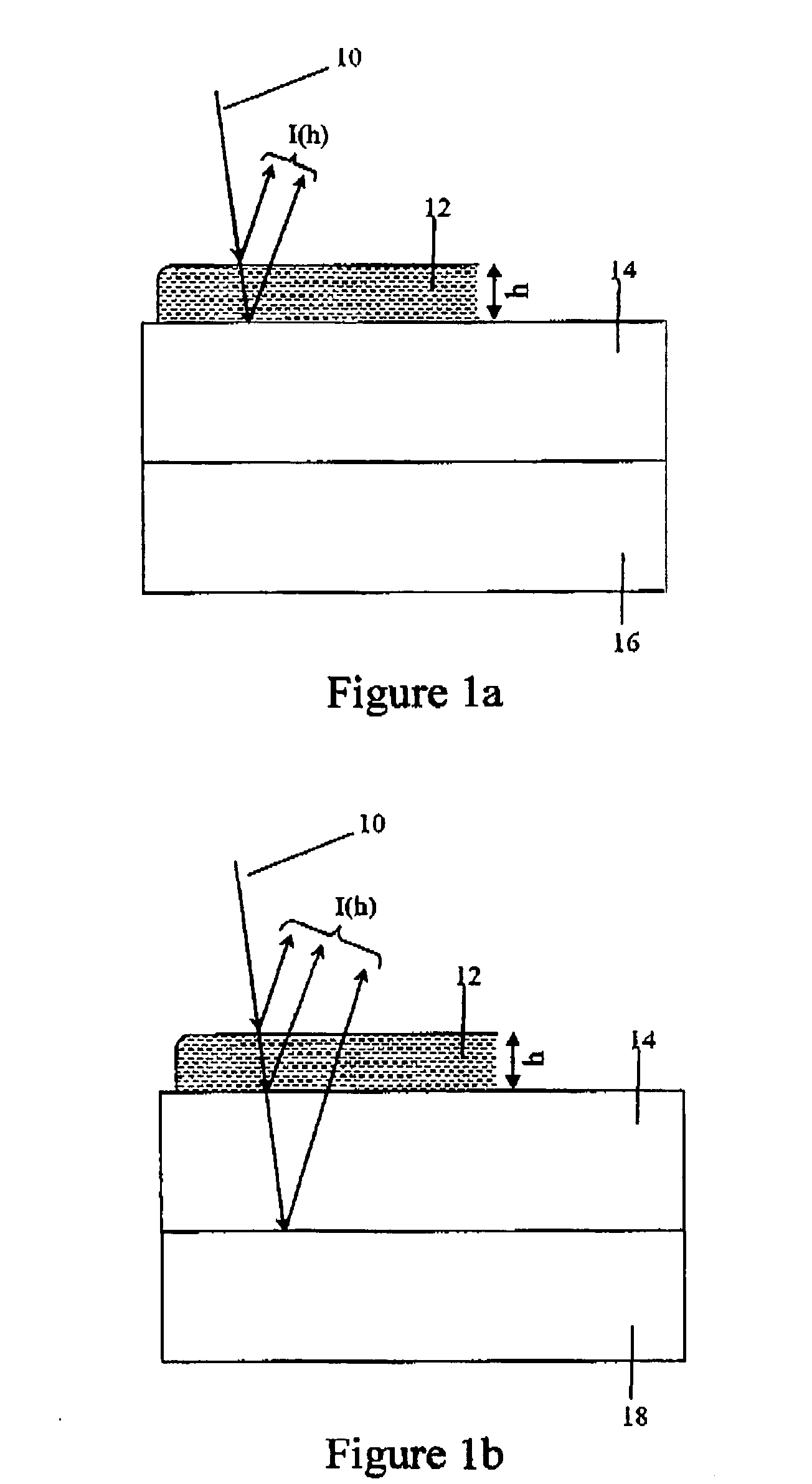
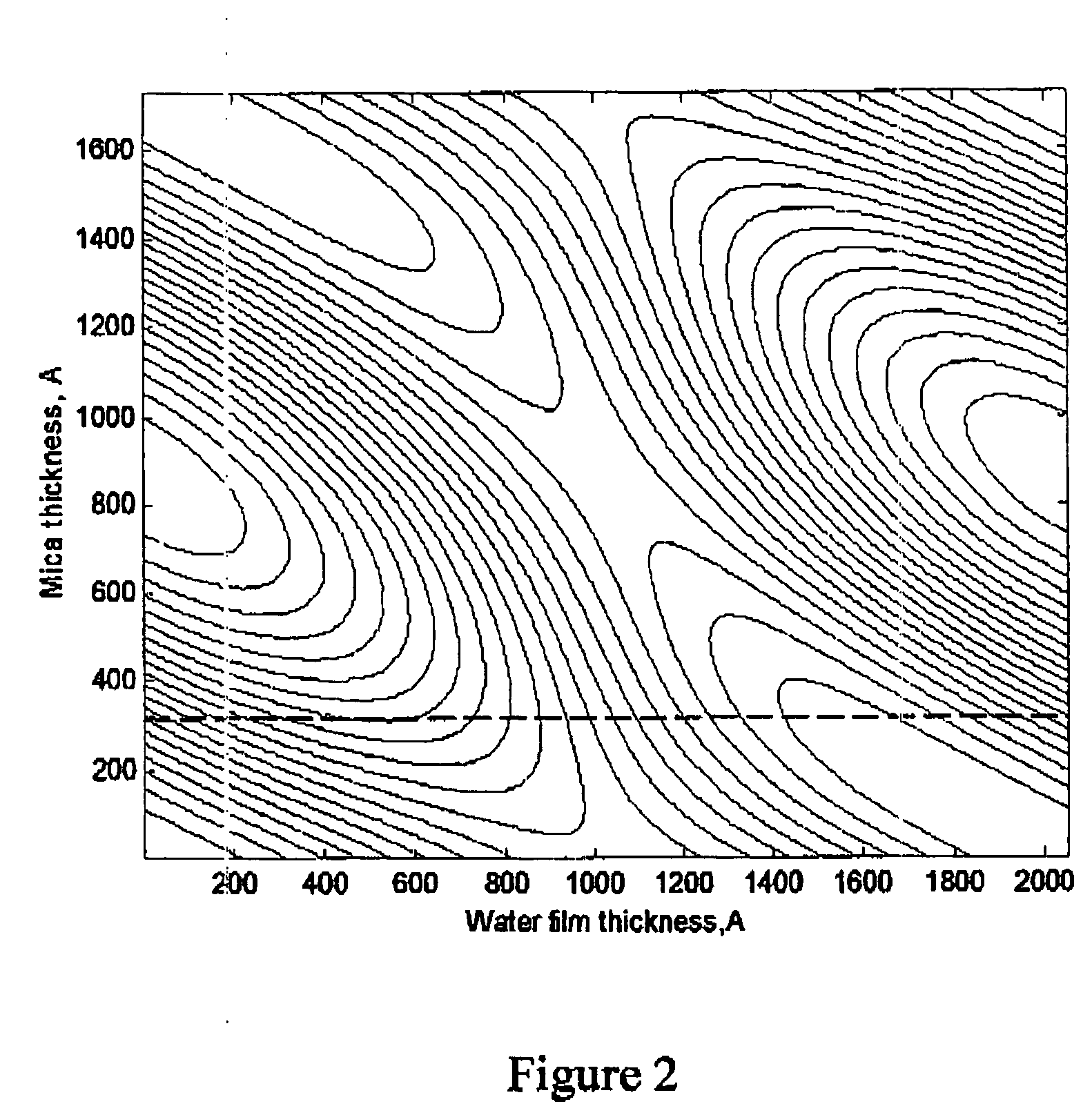
Patents
Literature
1991 results about "Reference beam" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
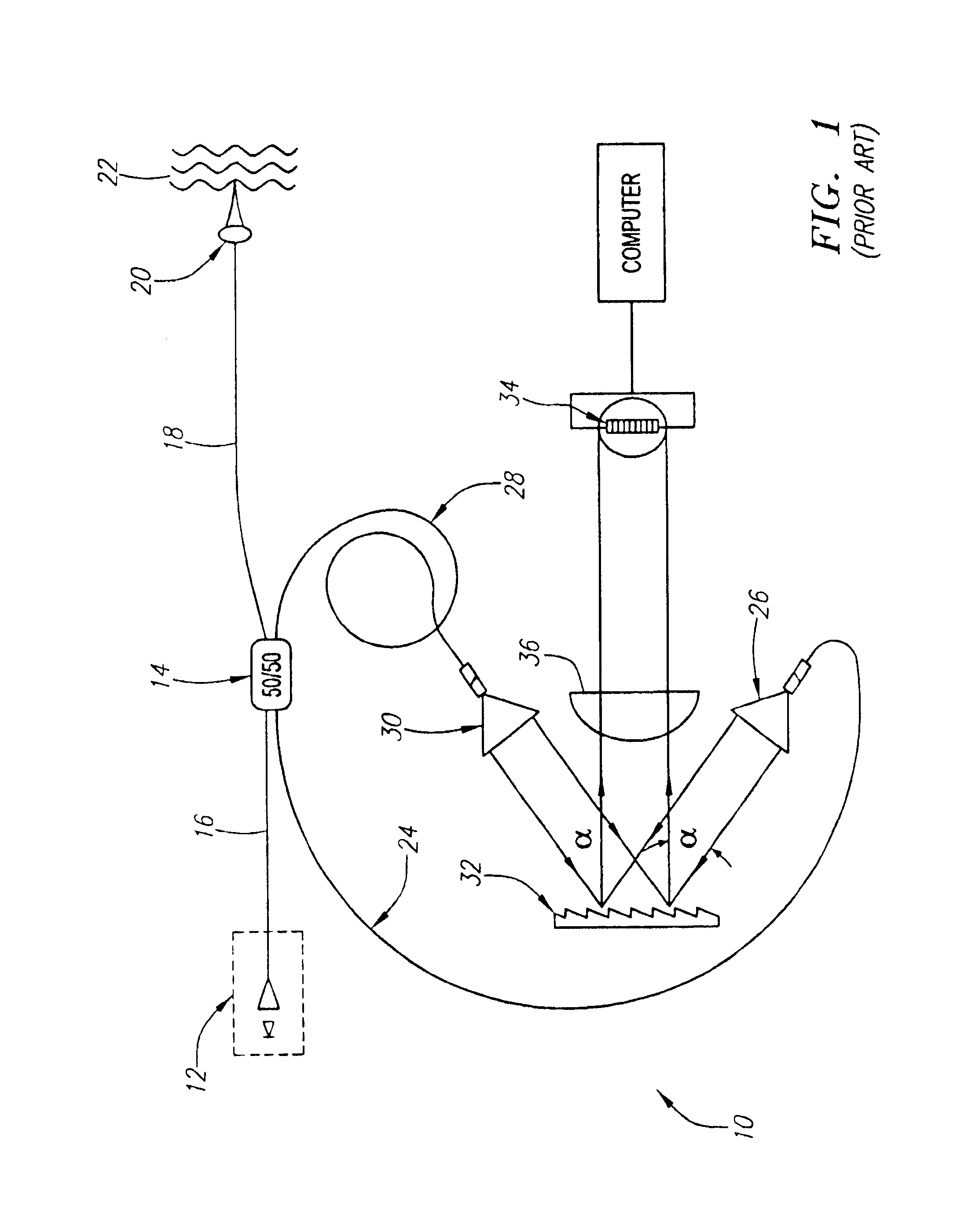
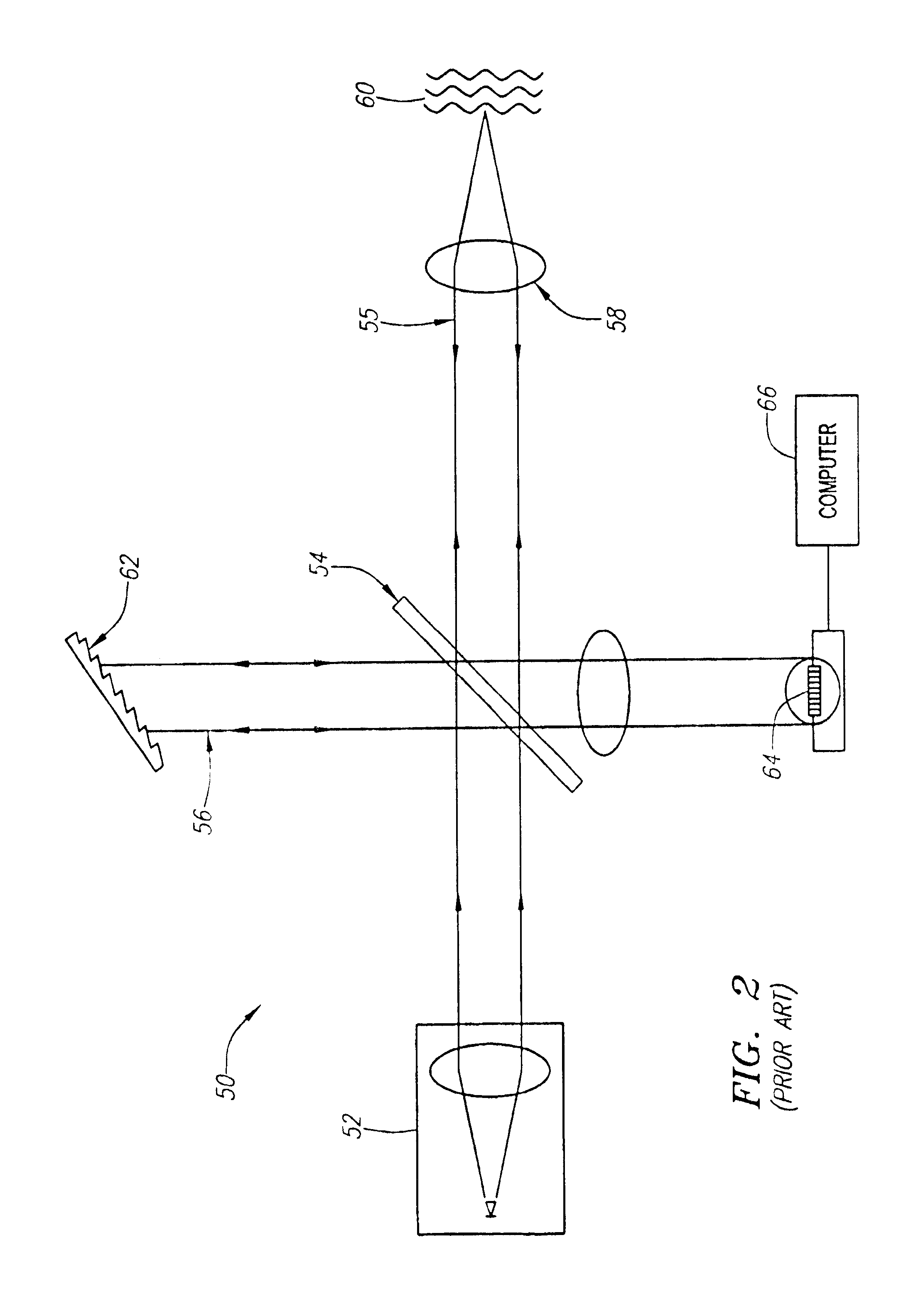
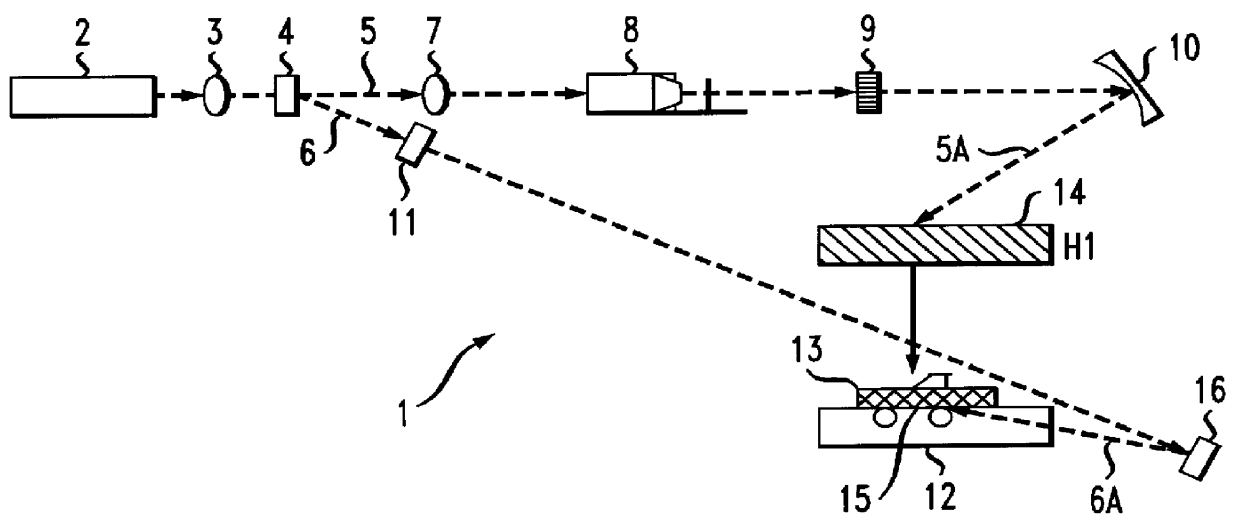
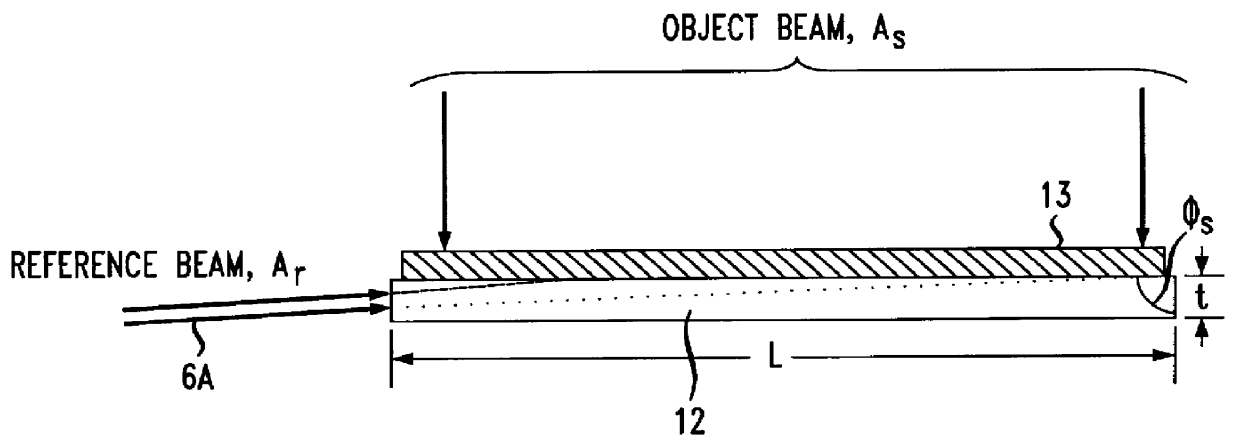
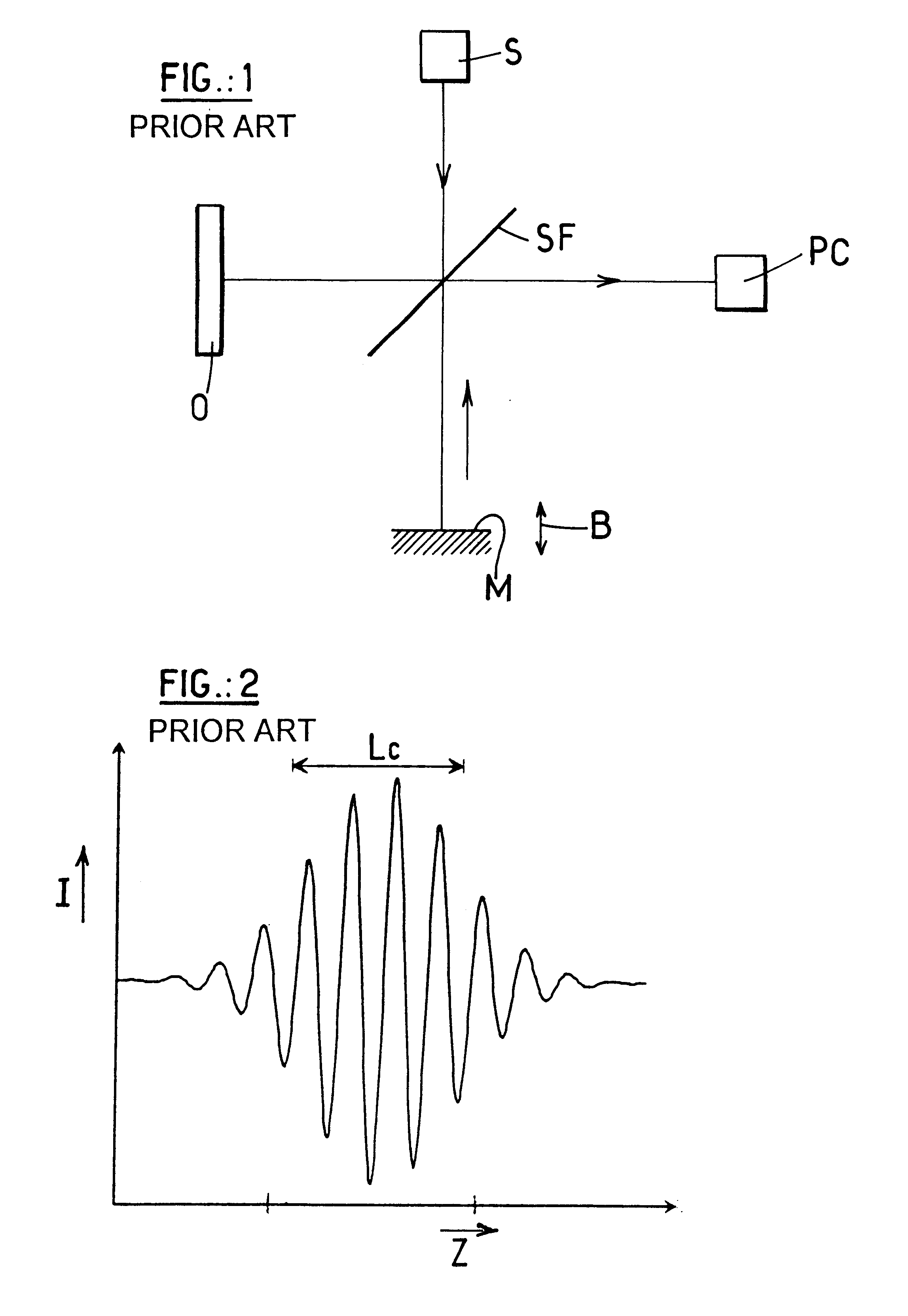
A reference beam is a laser beam used to read and write holograms. It is one of two laser beams used to create a hologram. In order to read a hologram out, some aspects of the reference beam (namely its angle of incidence, beam profile and wavelength) must be reproduced exactly as when it was used to write the hologram. As a result, usually reference beams are Gaussian beams or spherical wave beams (beams that radiate from a single point) which are fairly easy to reproduce.
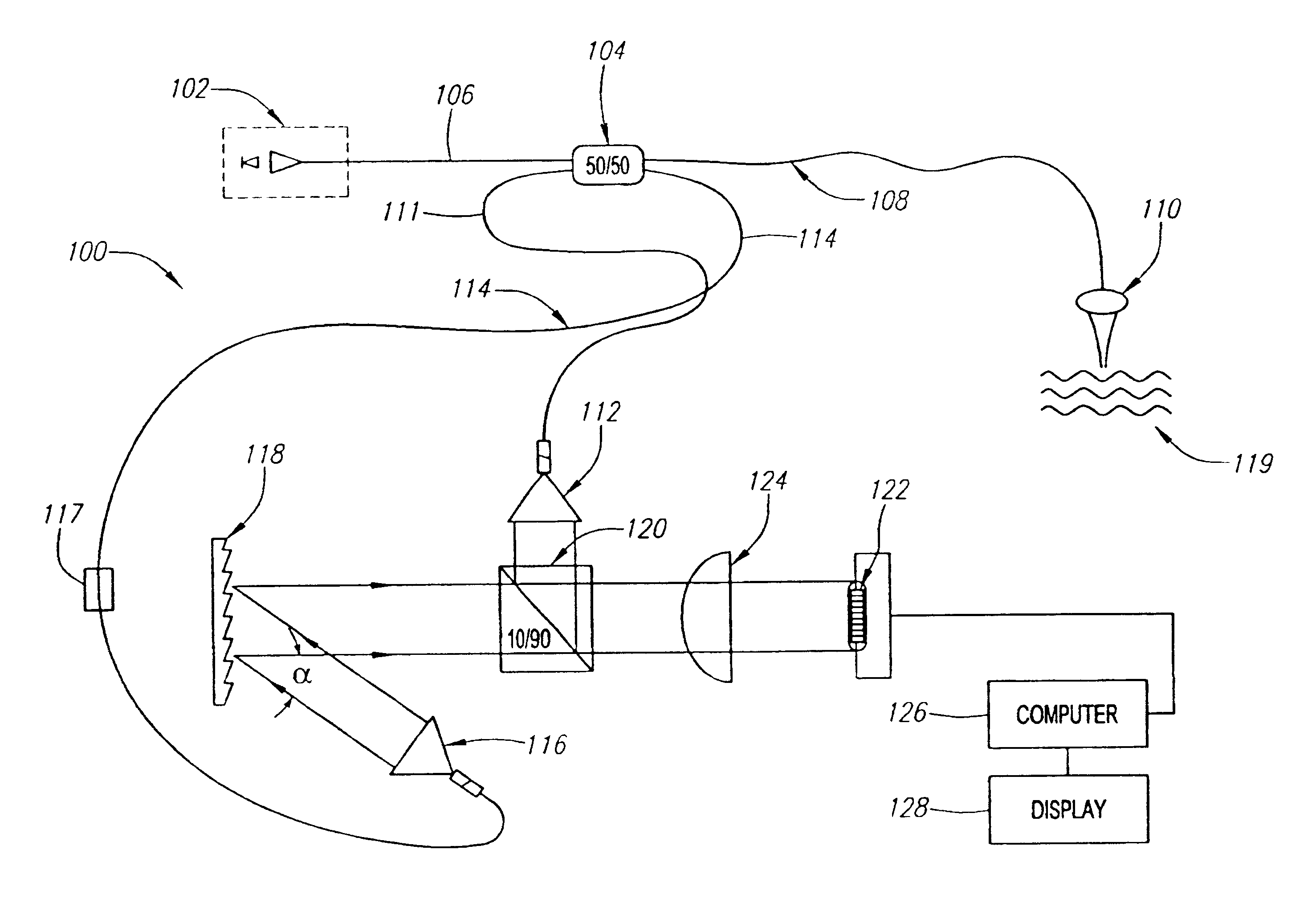
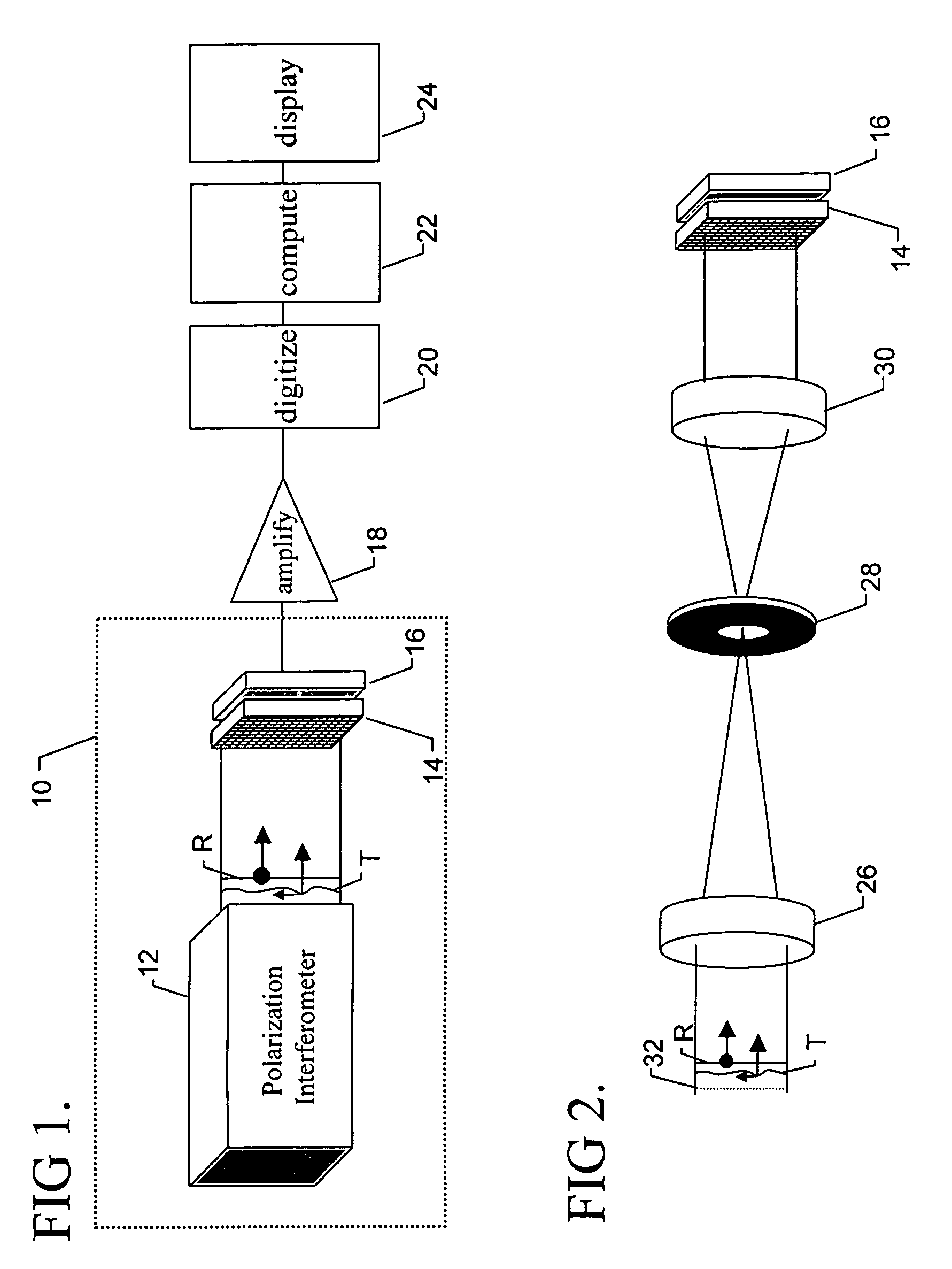
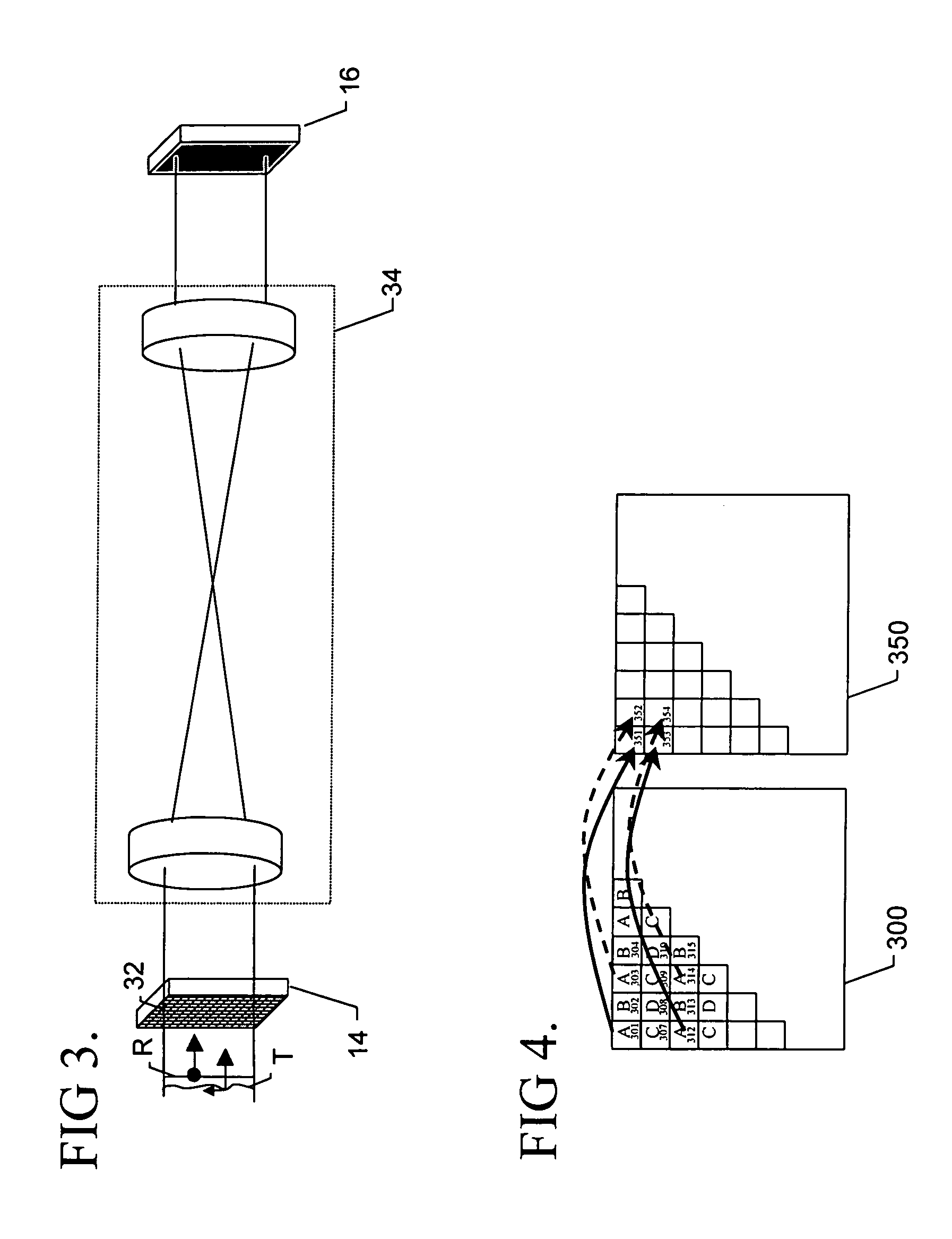
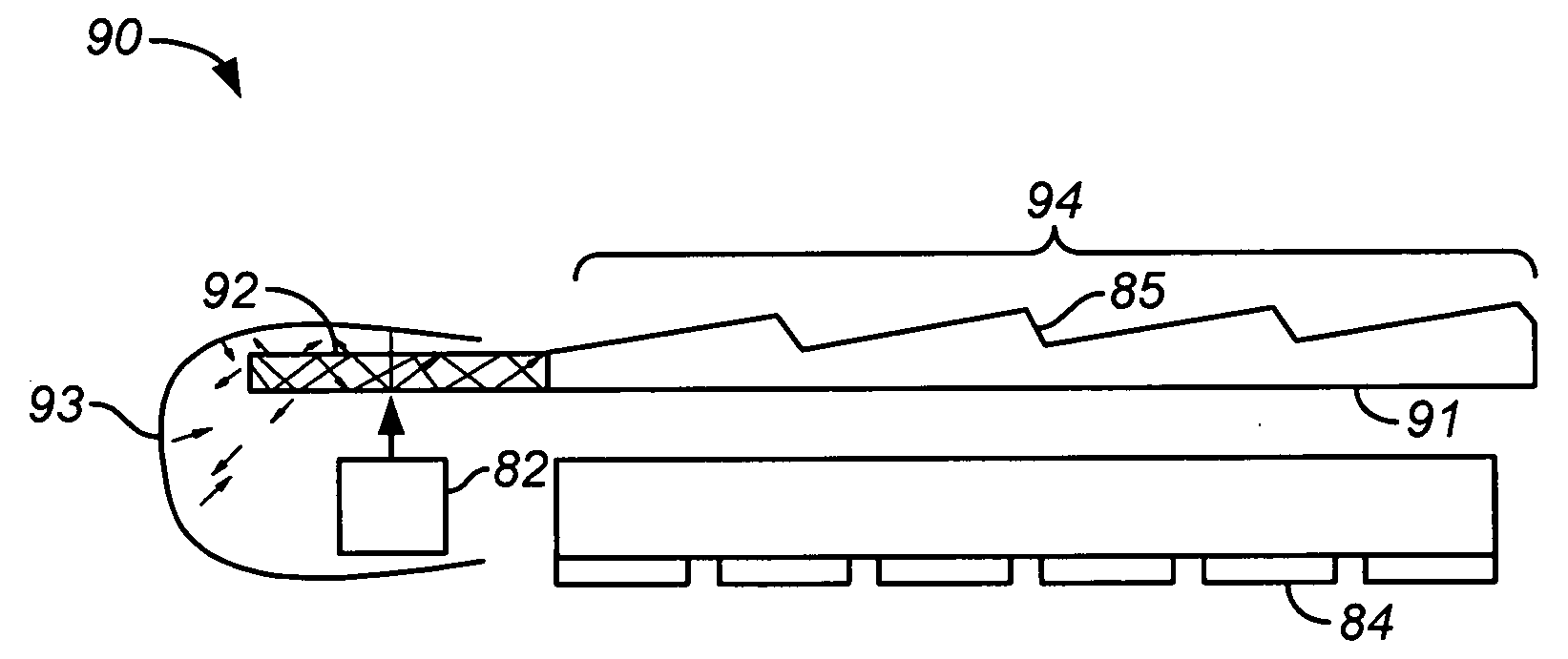
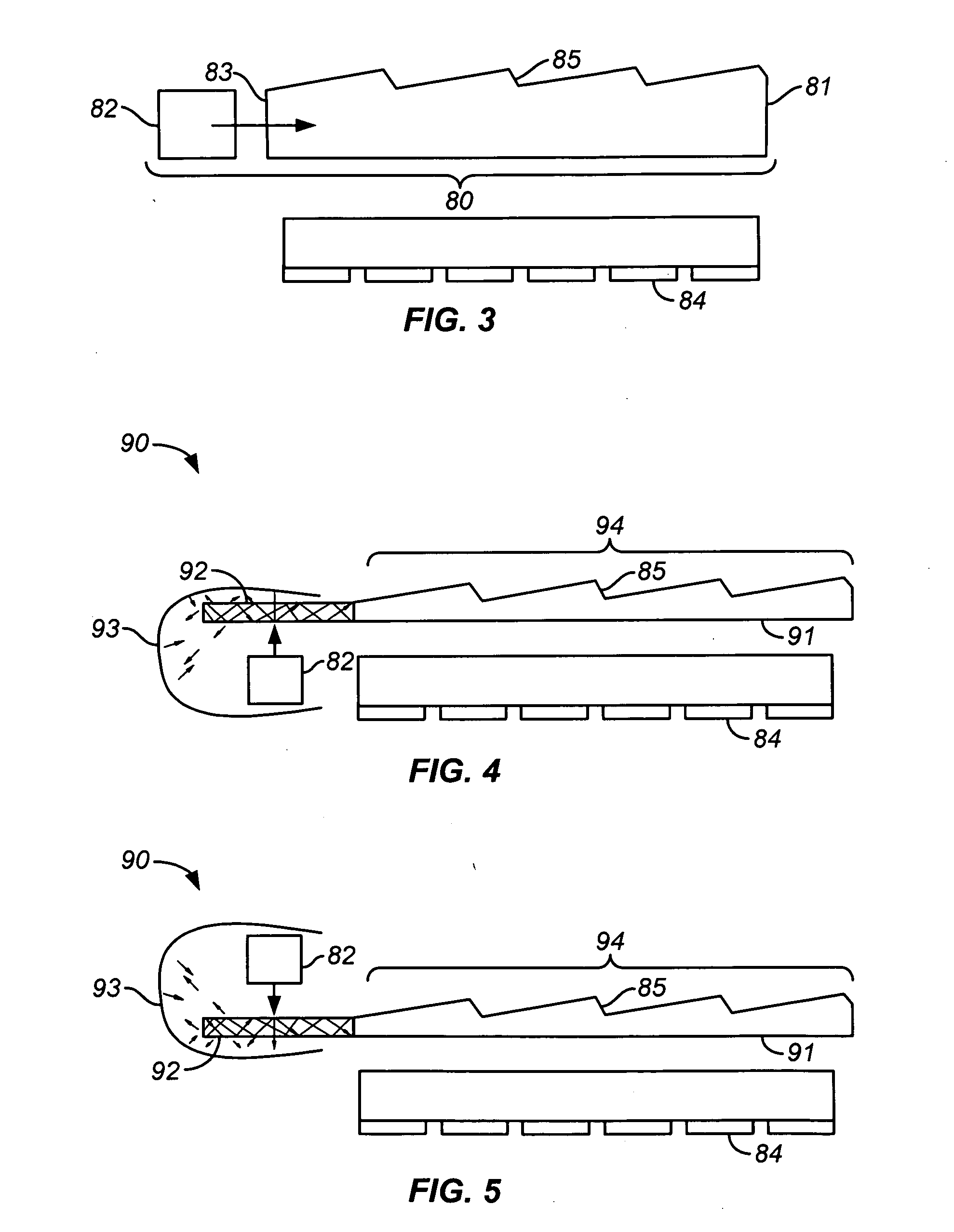
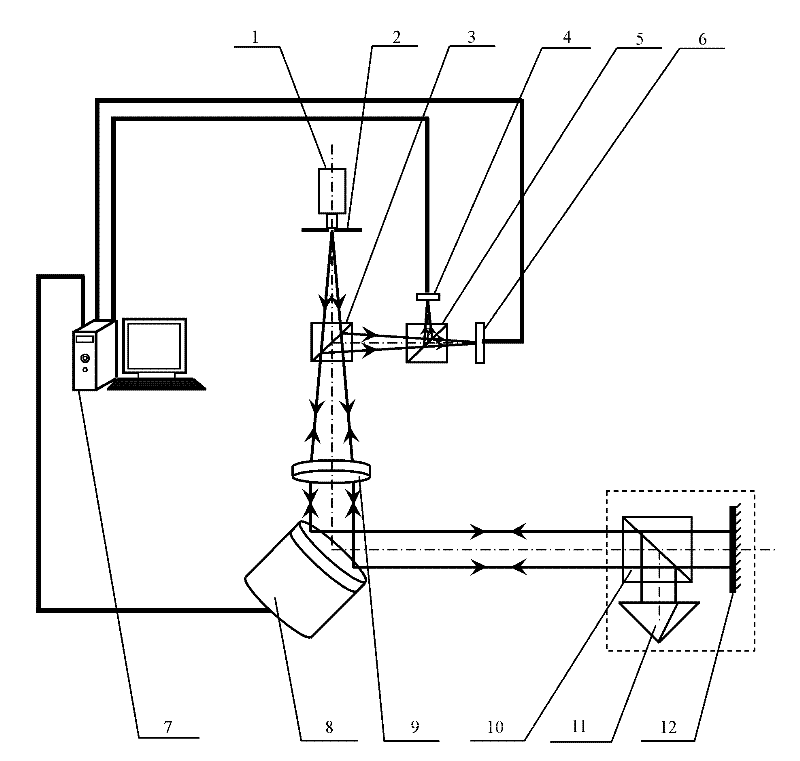
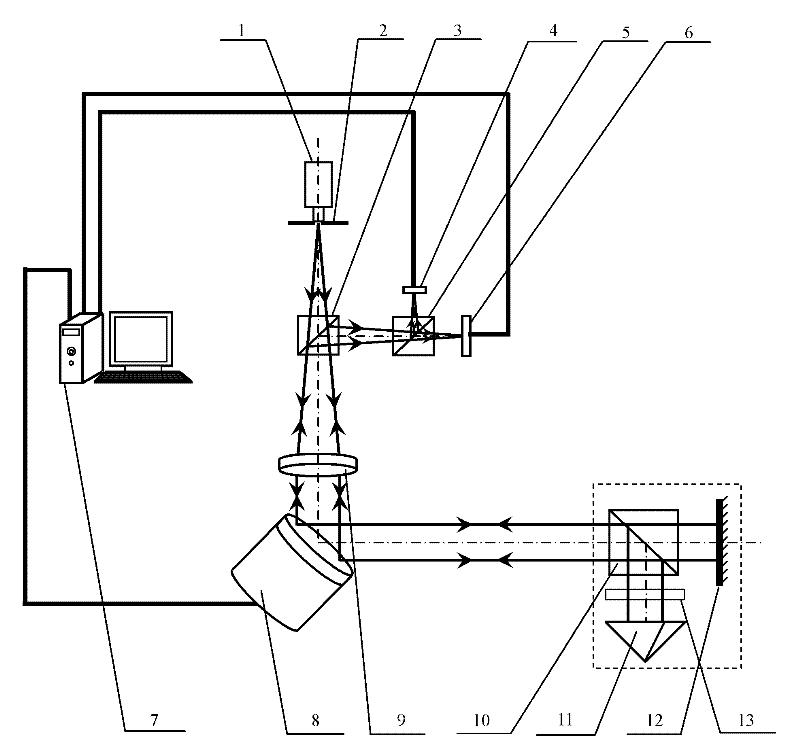
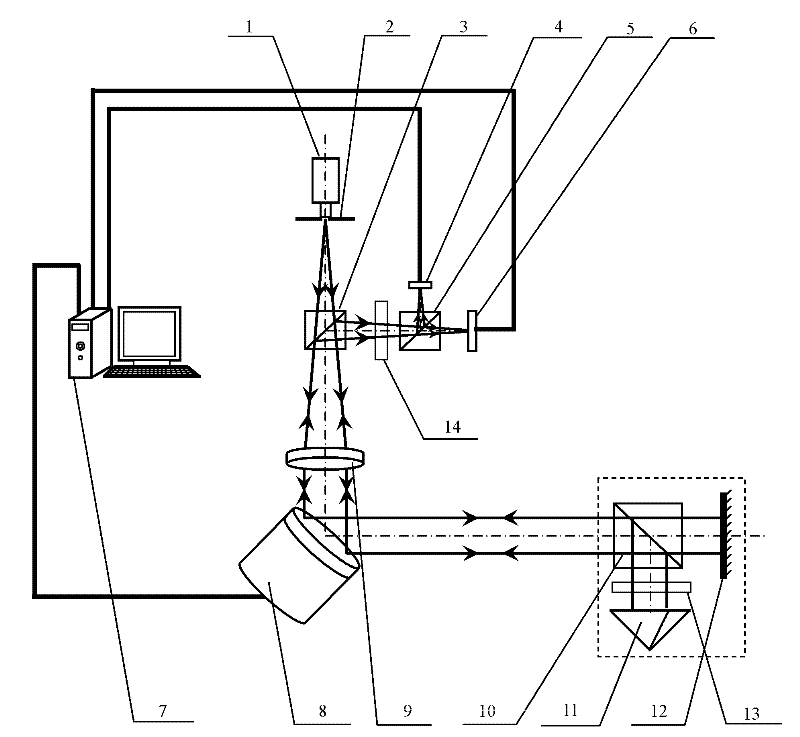
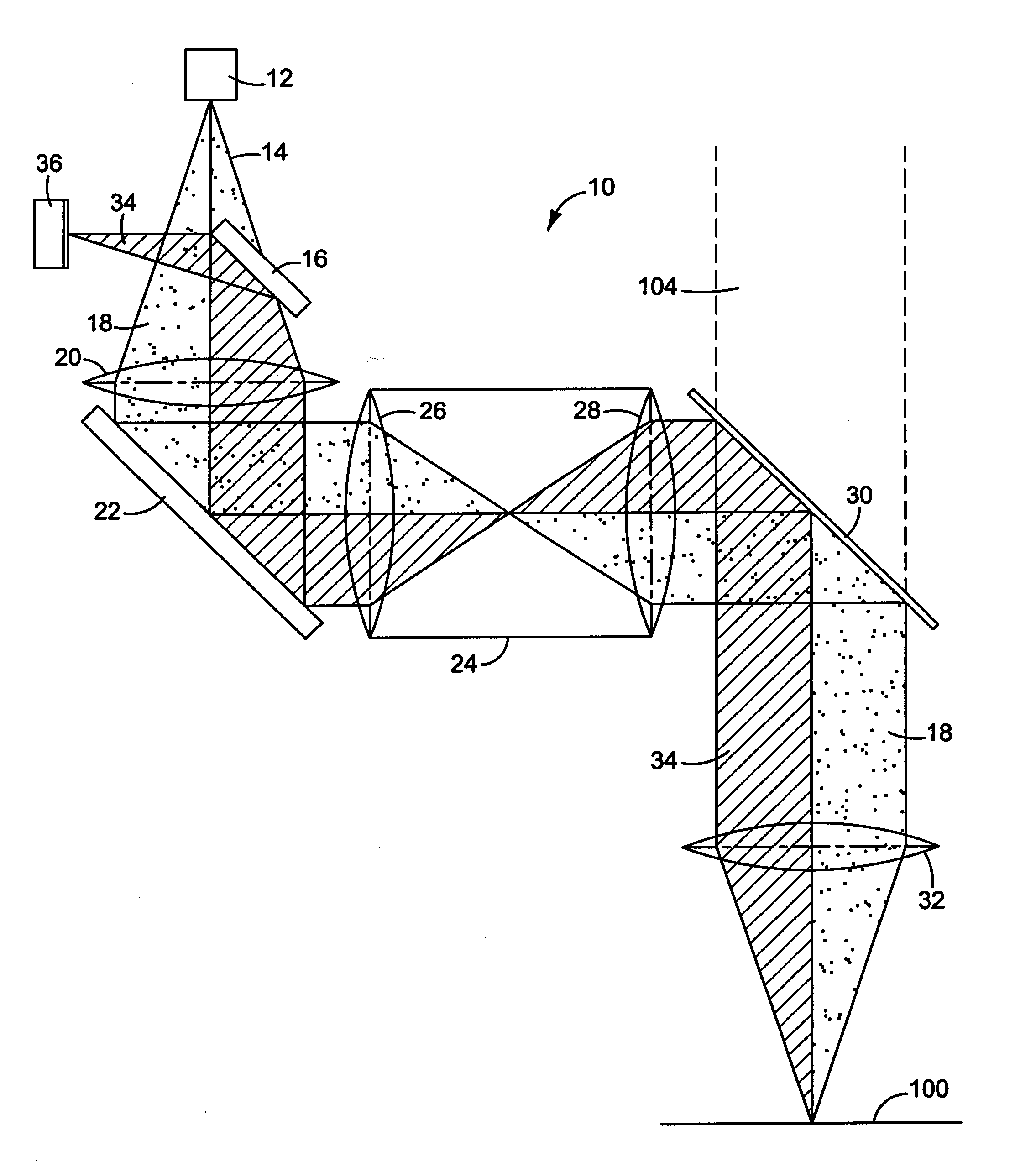
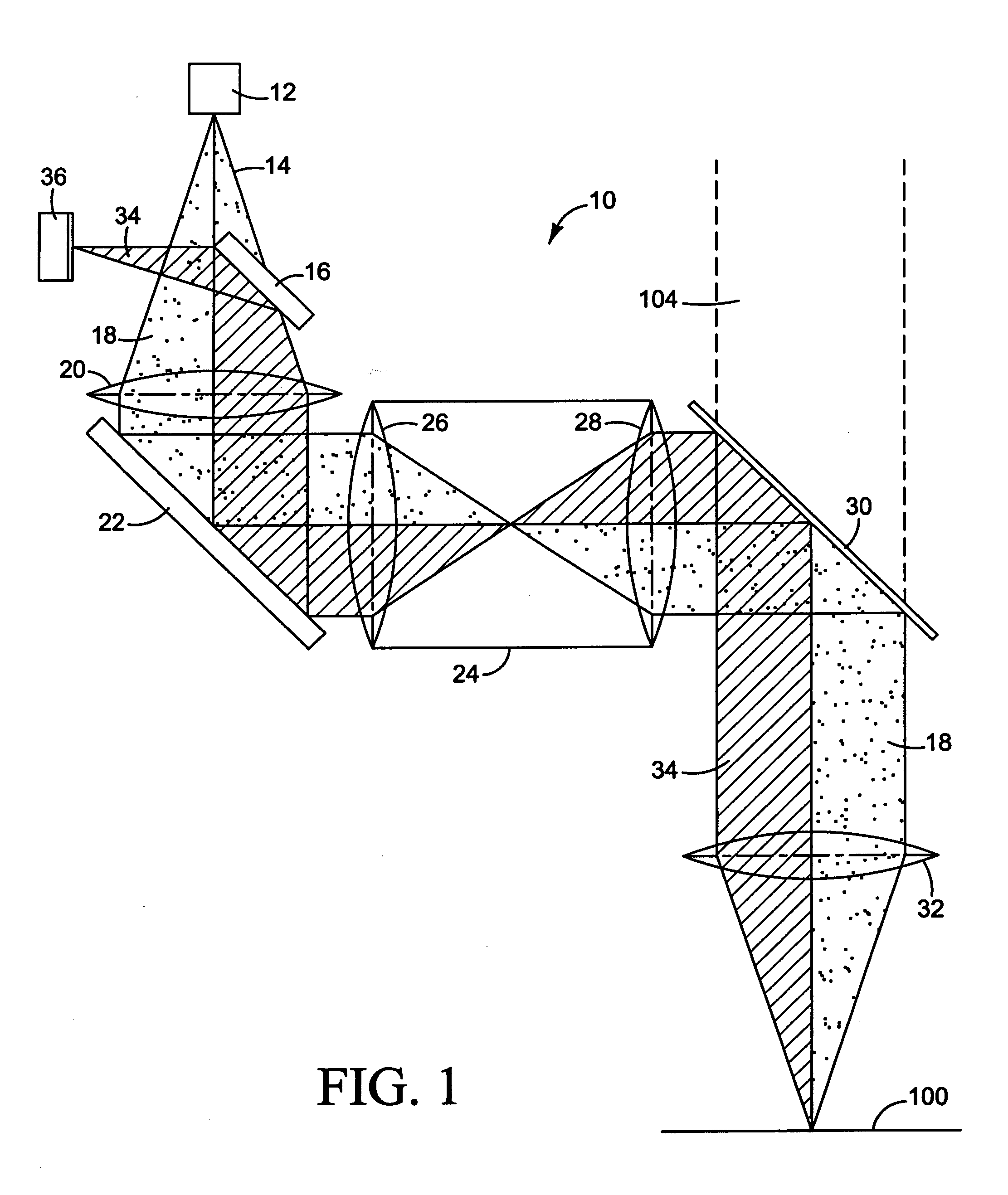
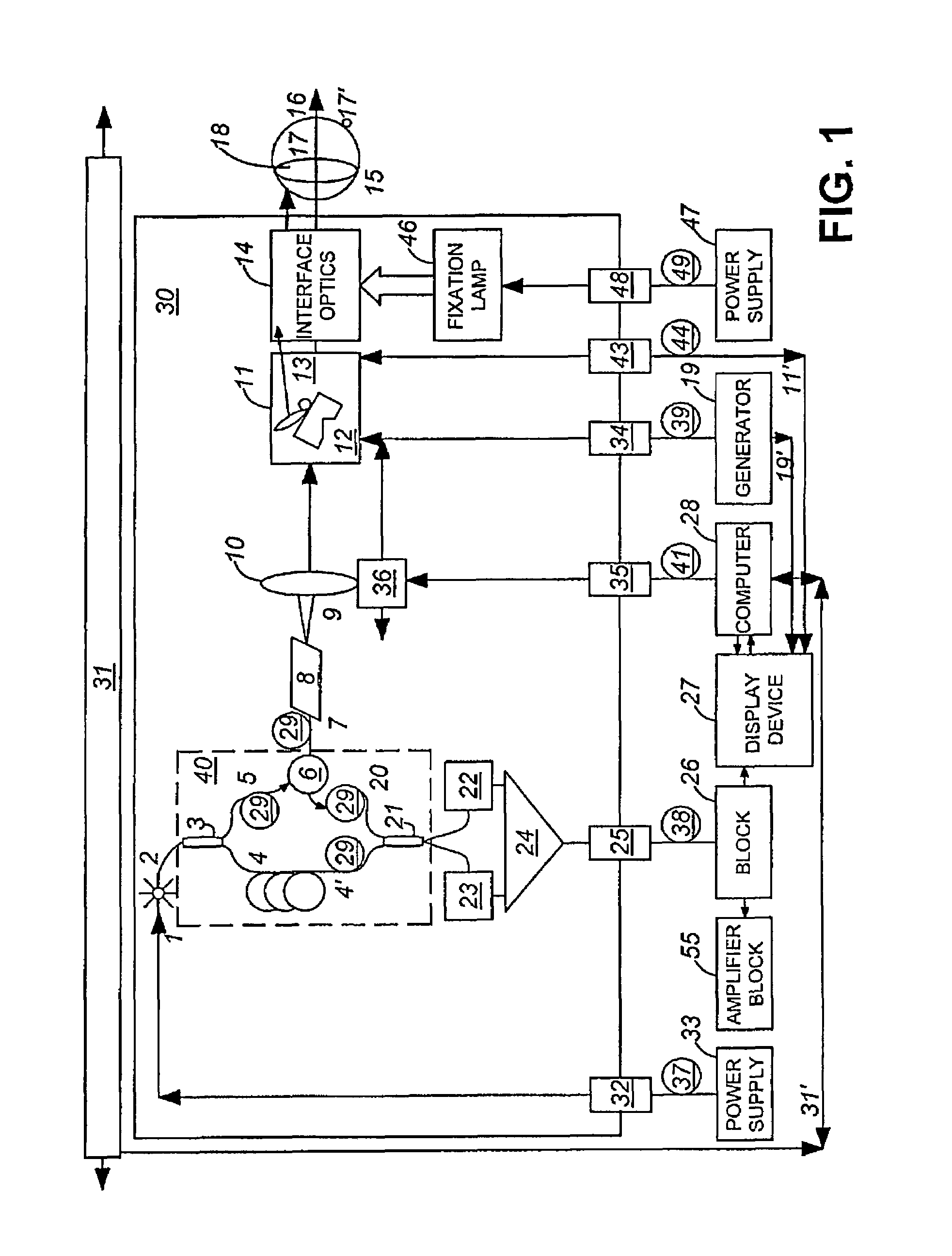
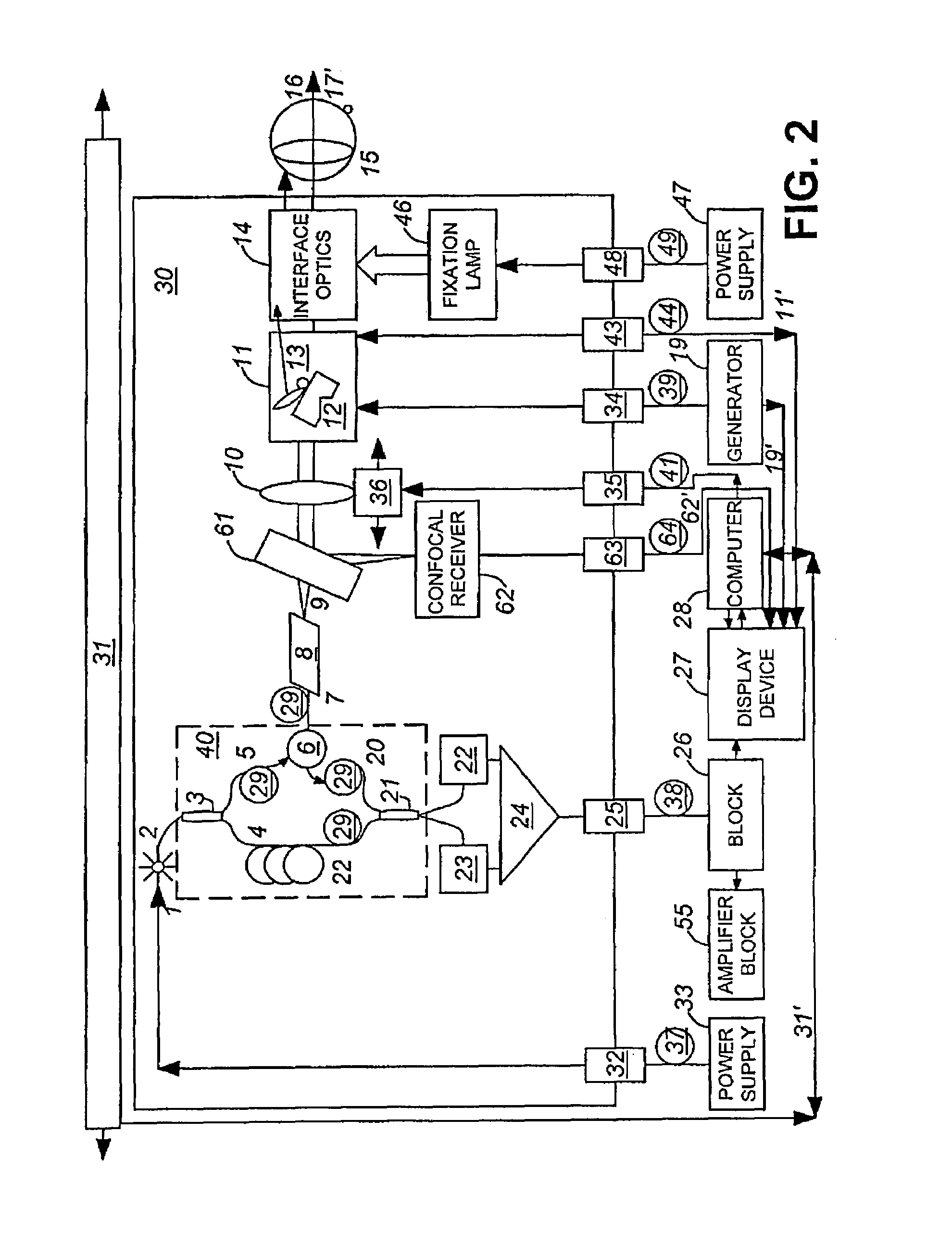
Diffraction grating based interferometric systems and methods
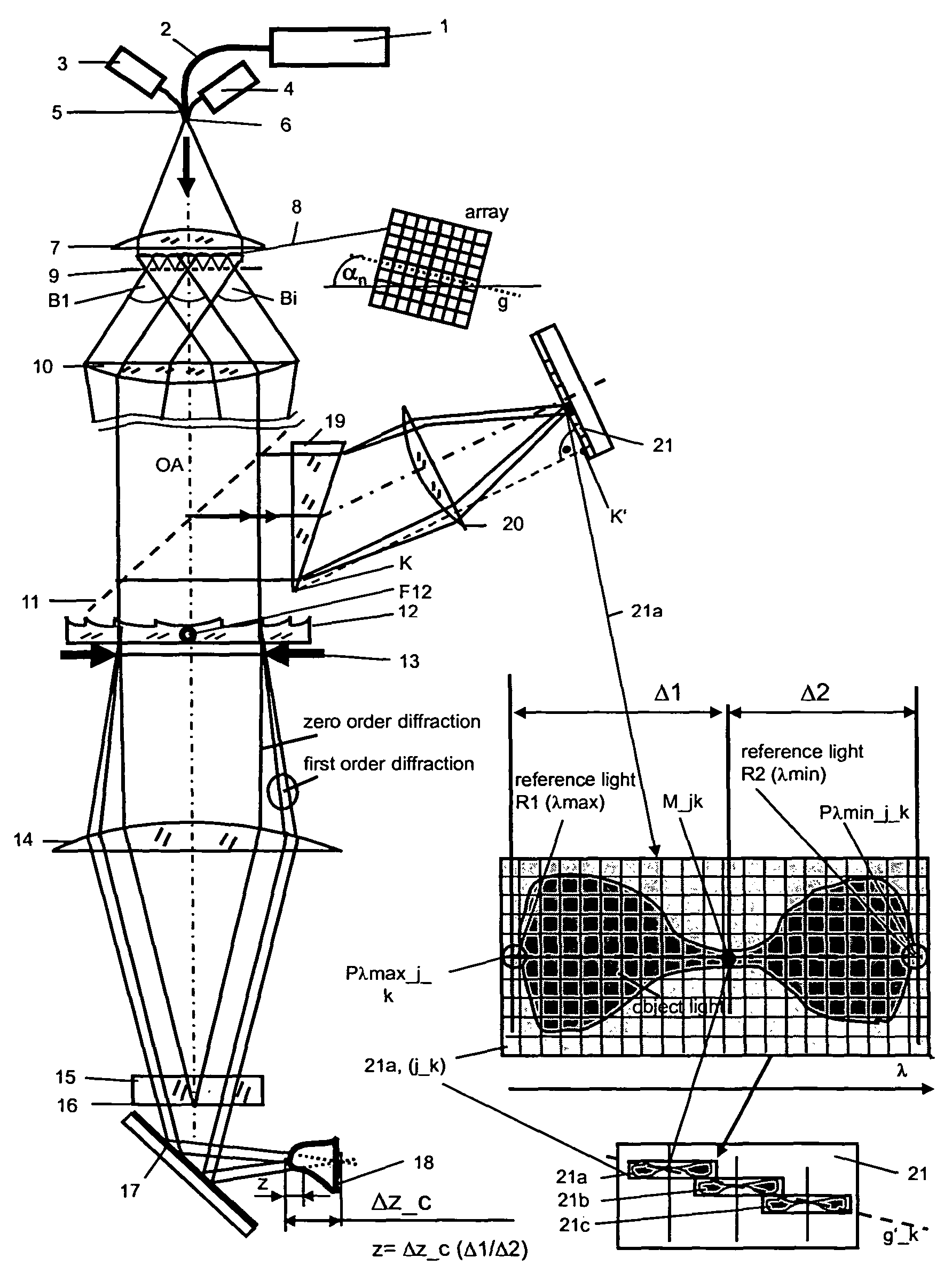
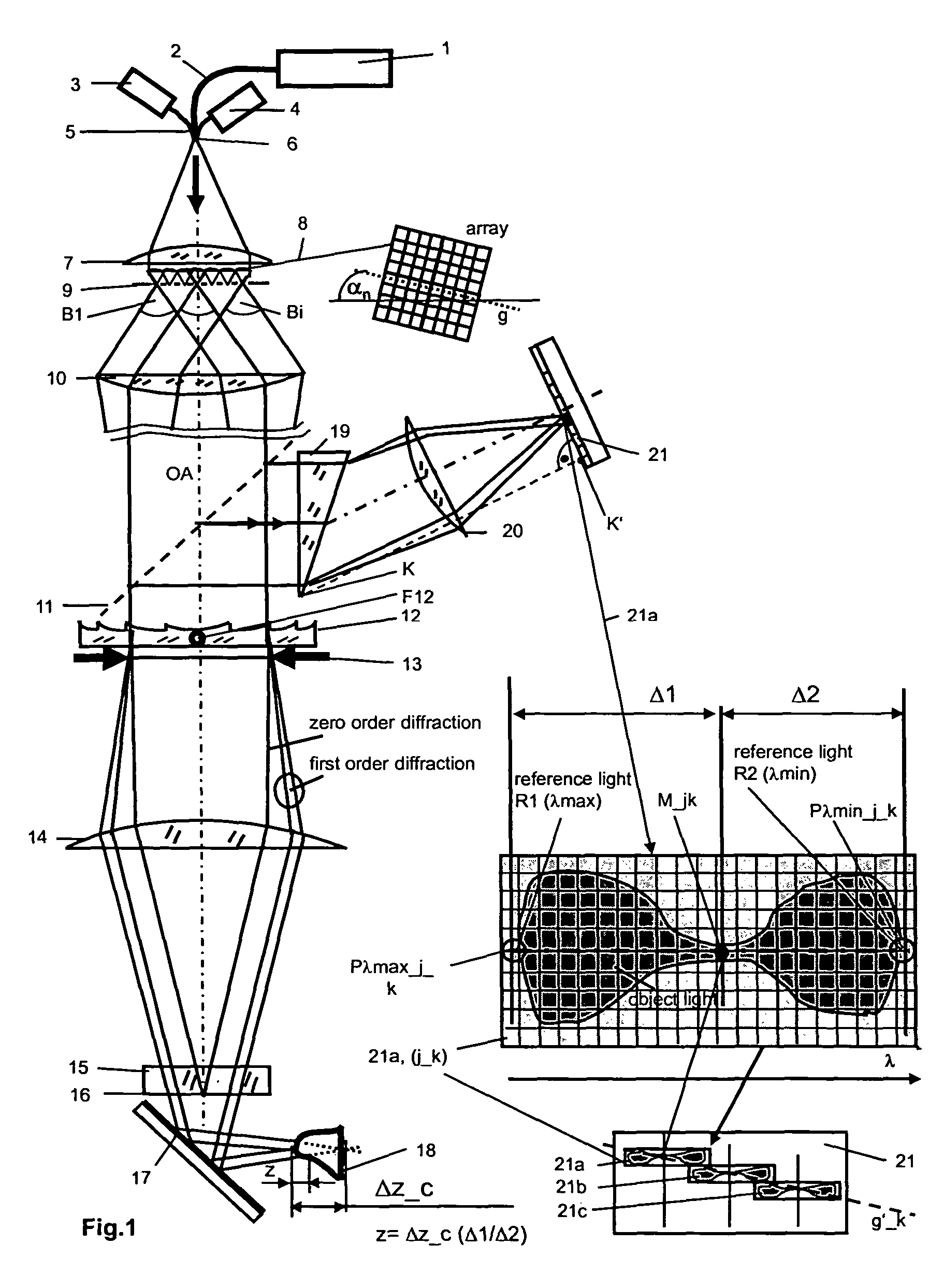
Diffraction grating based fiber optic interferometric systems for use in optical coherence tomography, wherein sample and reference light beams are formed by a first beam splitter and the sample light beam received from a sample and a reference light beam are combined on a second beam splitter. In one embodiment, the first beam splitter is an approximately 50 / 50 beam splitter, and the second beam splitter is a non 50 / 50 beam splitter. More than half of the energy of the sample light beam is directed into the combined beam and less than half of the energy of the reference light beam are directed into the combined beam by the second beam splitter. In another embodiment, the first beam splitter is a non 50 / 50 beam splitter and the second beam splitter is an approximately 50 / 50 beam splitter. An optical circulator is provided to enable the sample light beam to bypass the first beam splitter after interaction with a sample. Two combined beams are formed by the second beam splitter for detection by two respective detectors. More than half of the energy of the light source provided to the first beam splitter is directed into the sample light beam and less than half of the energy is directed into the reference light beam. The energy distribution between the sample and reference light beams can be controlled by selection of the characteristics of the beam splitters.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
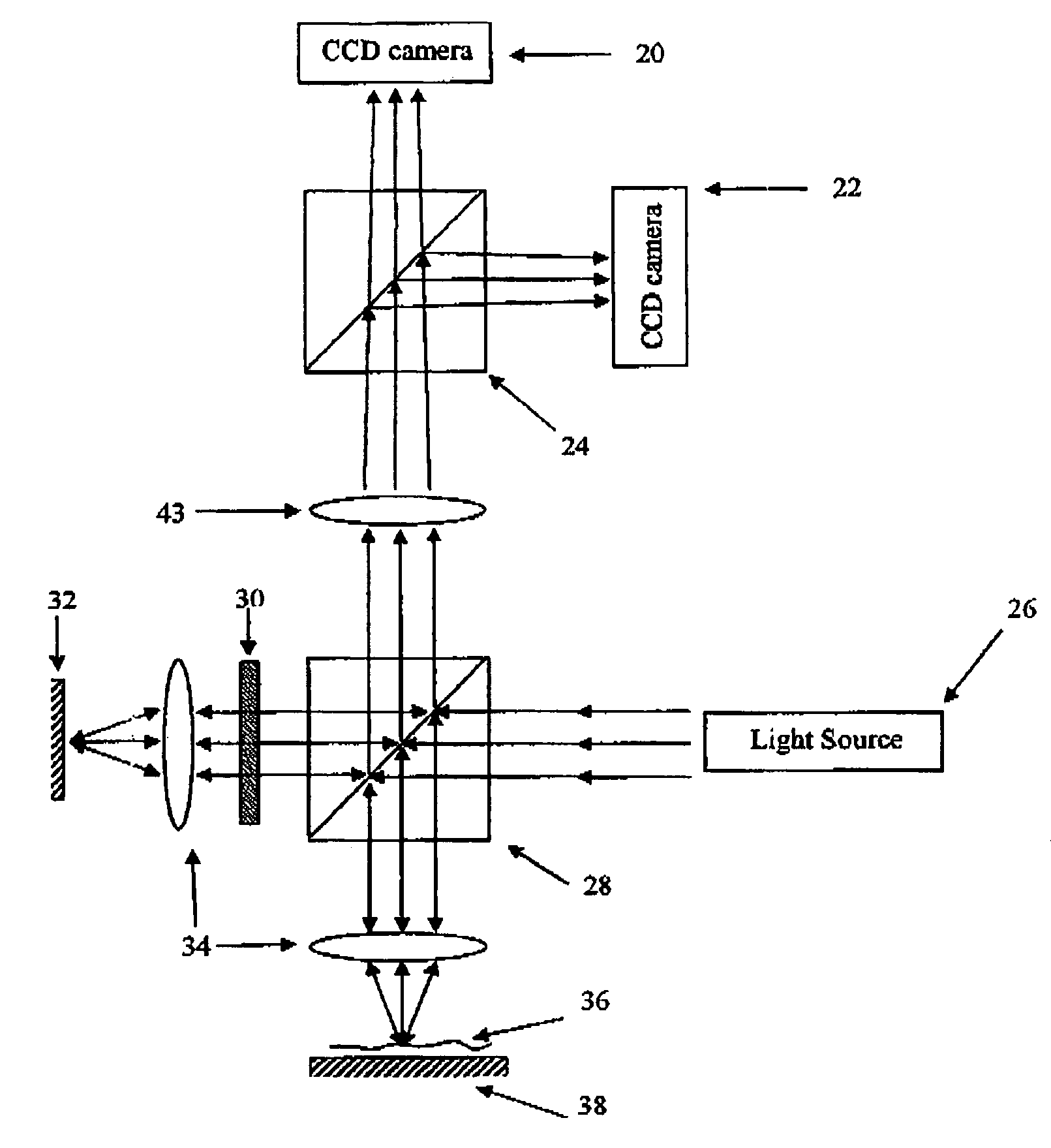
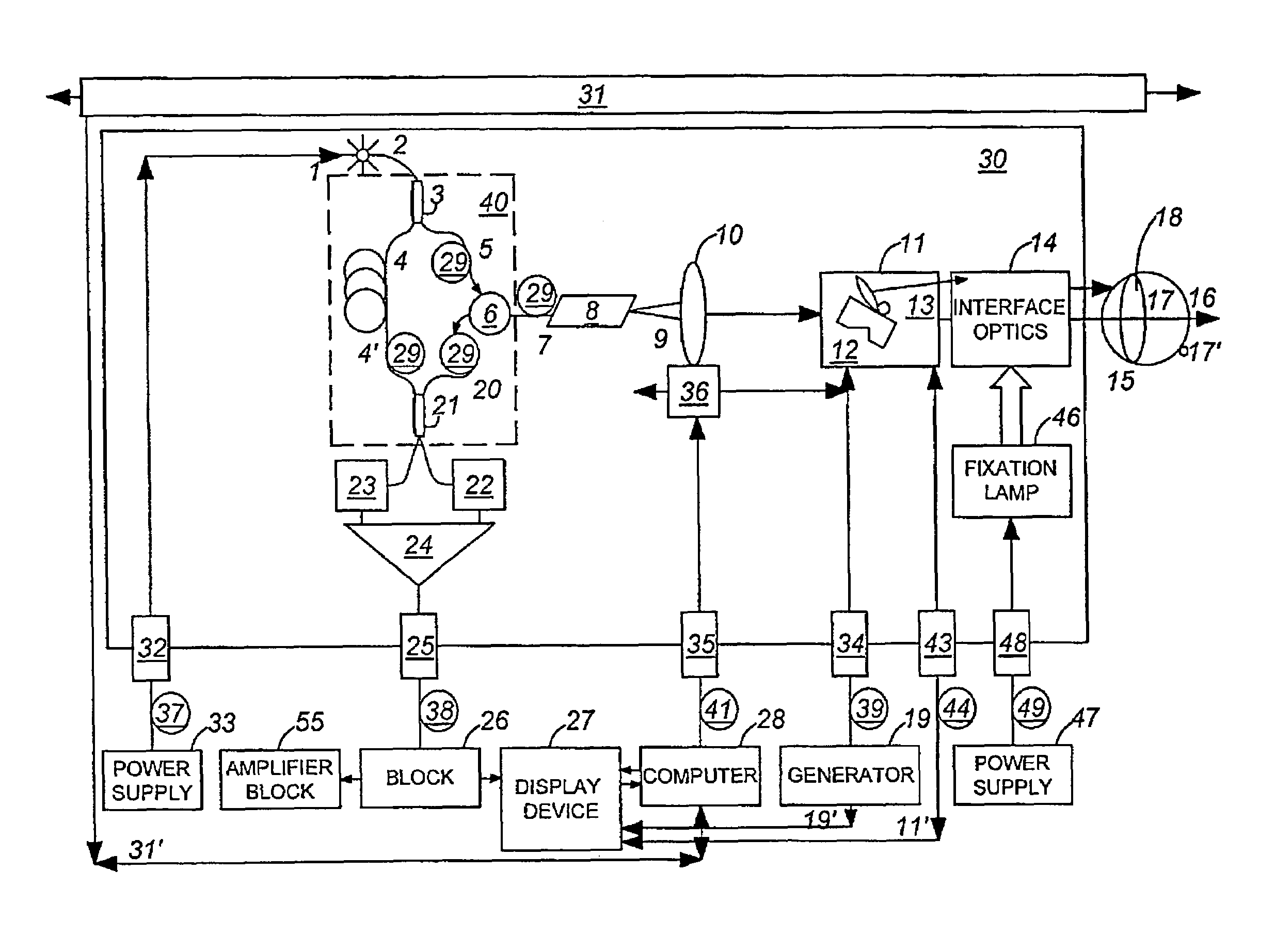
Optical tomography apparatus
ActiveUS20070019208A1High resolutionMaintain good propertiesMaterial analysis by optical meansCatheterMultiplexingDiffusion
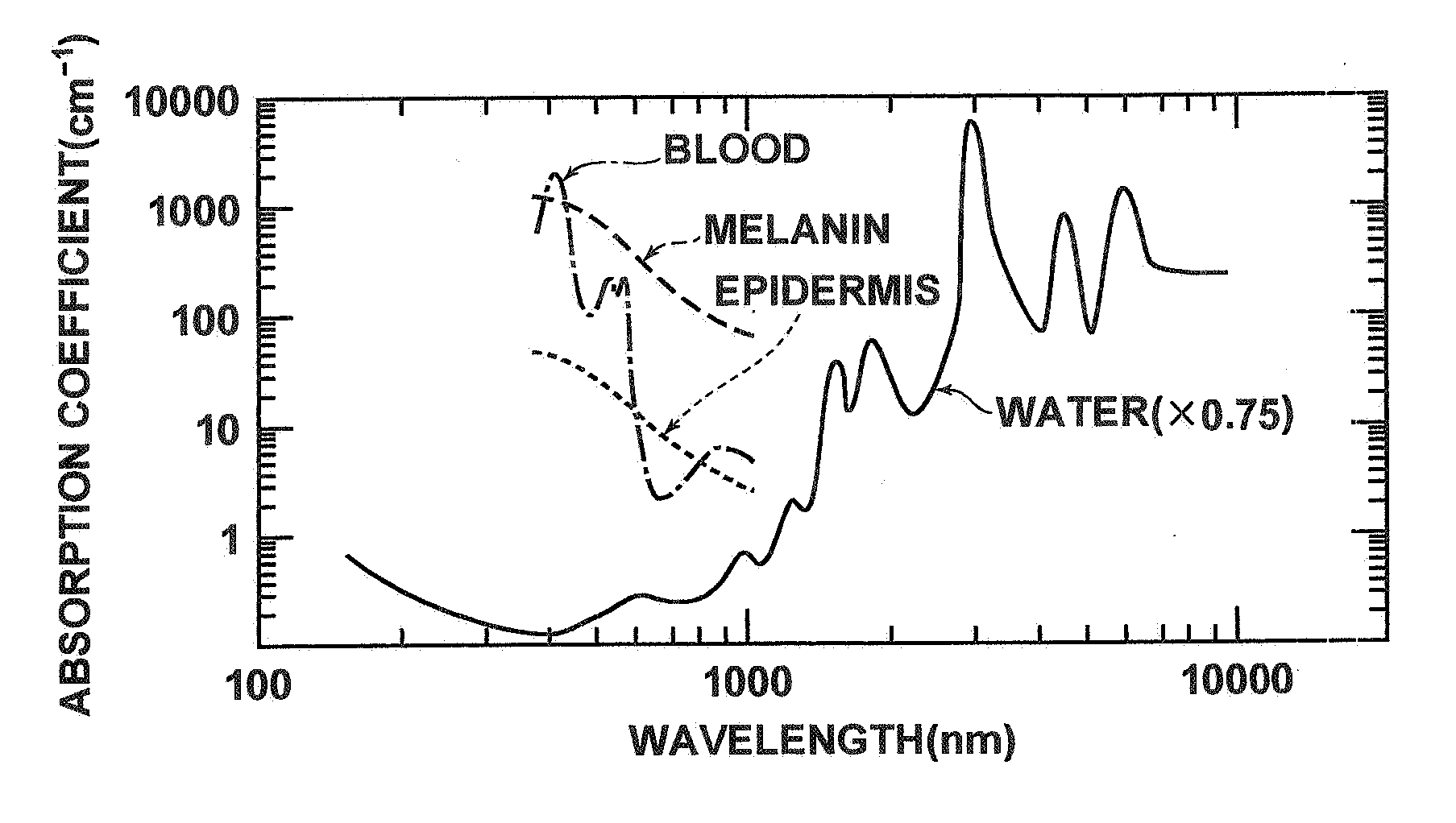
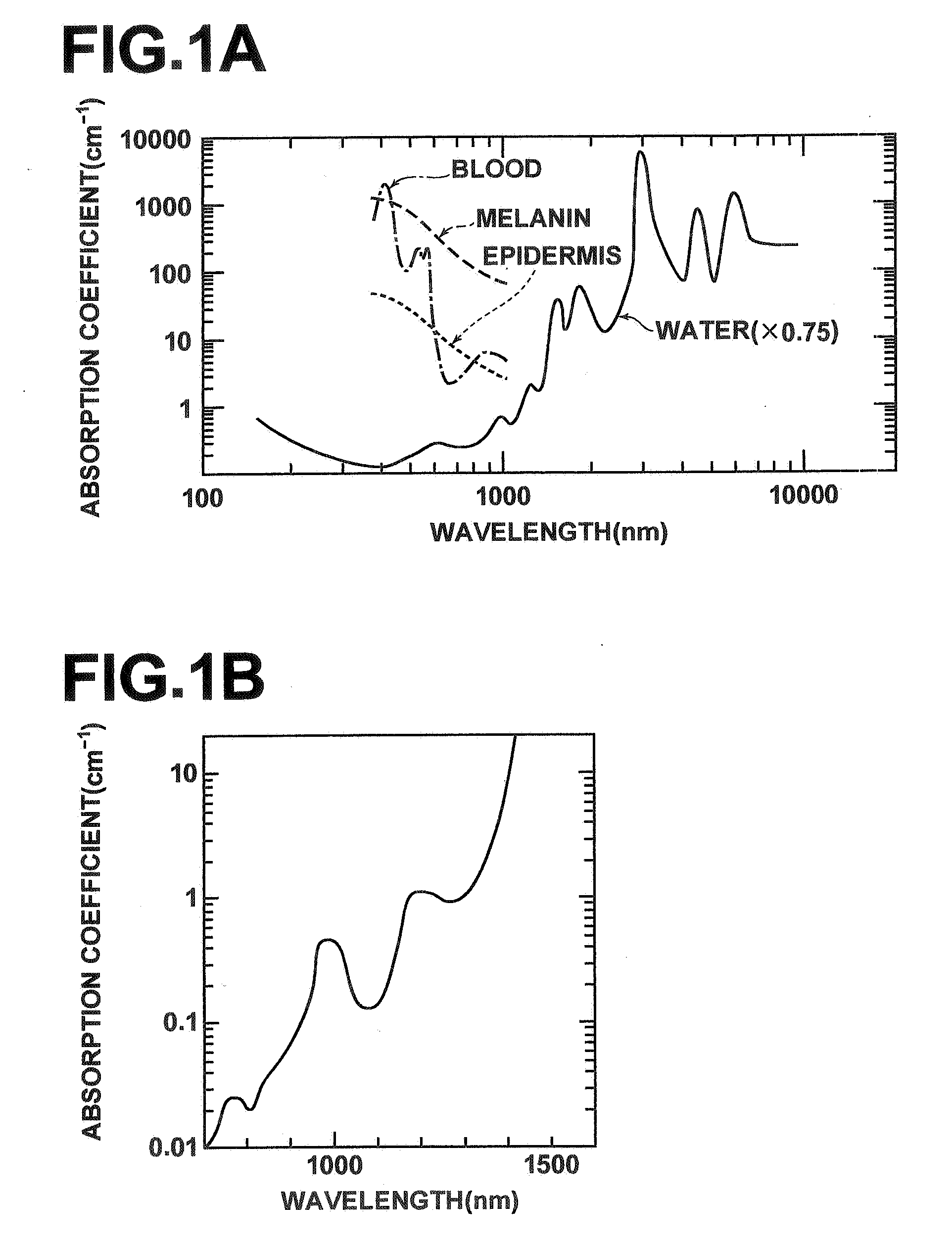
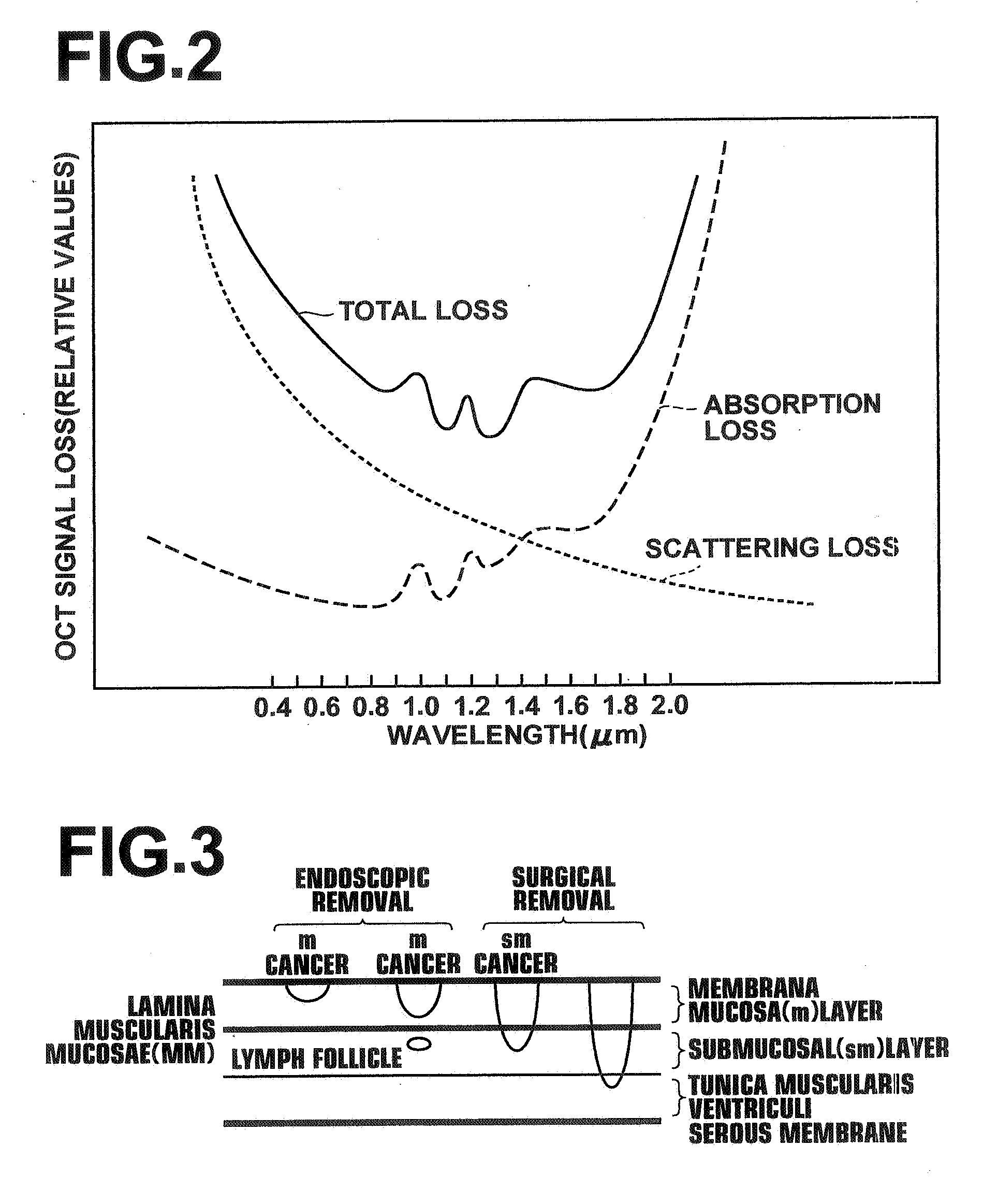
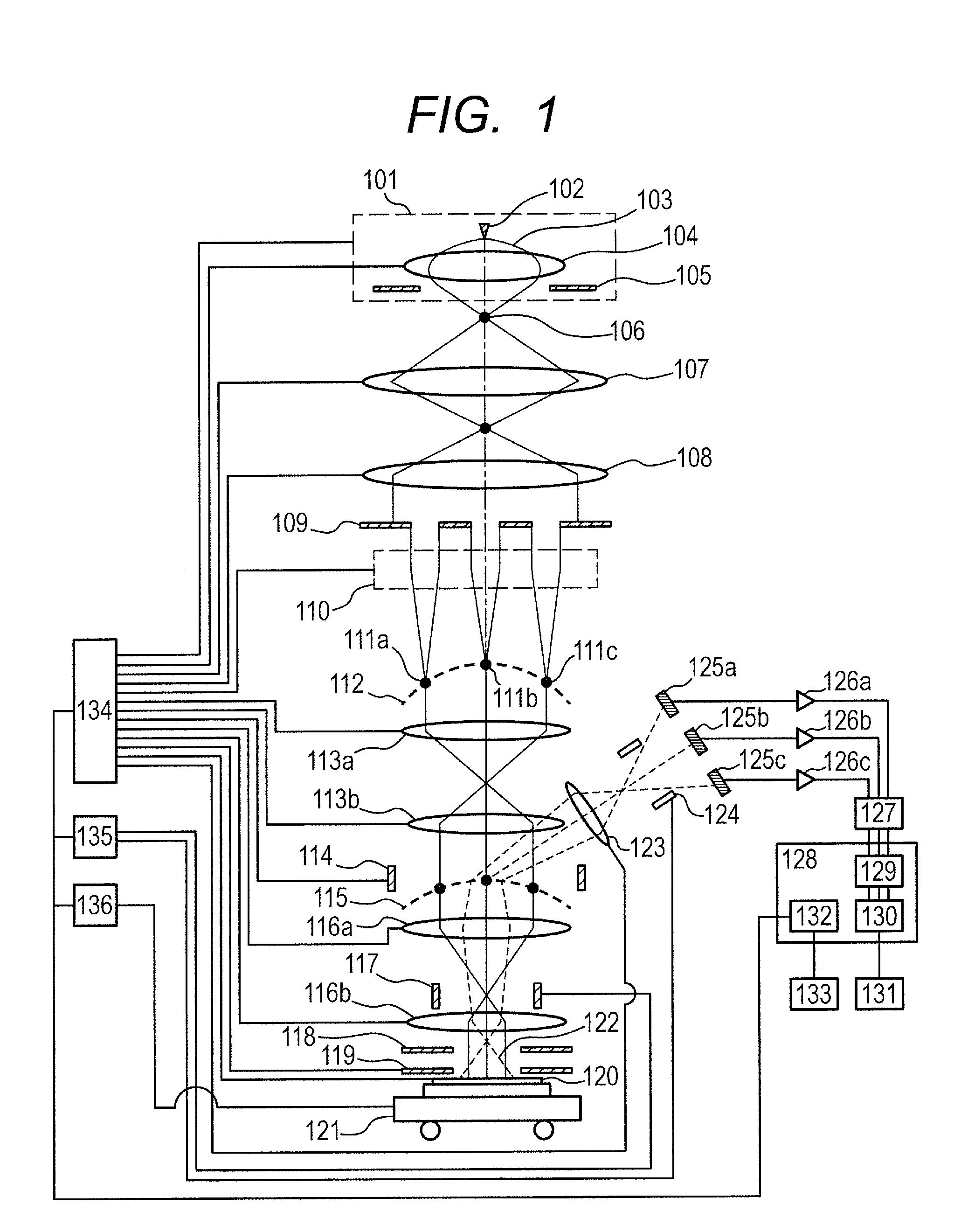
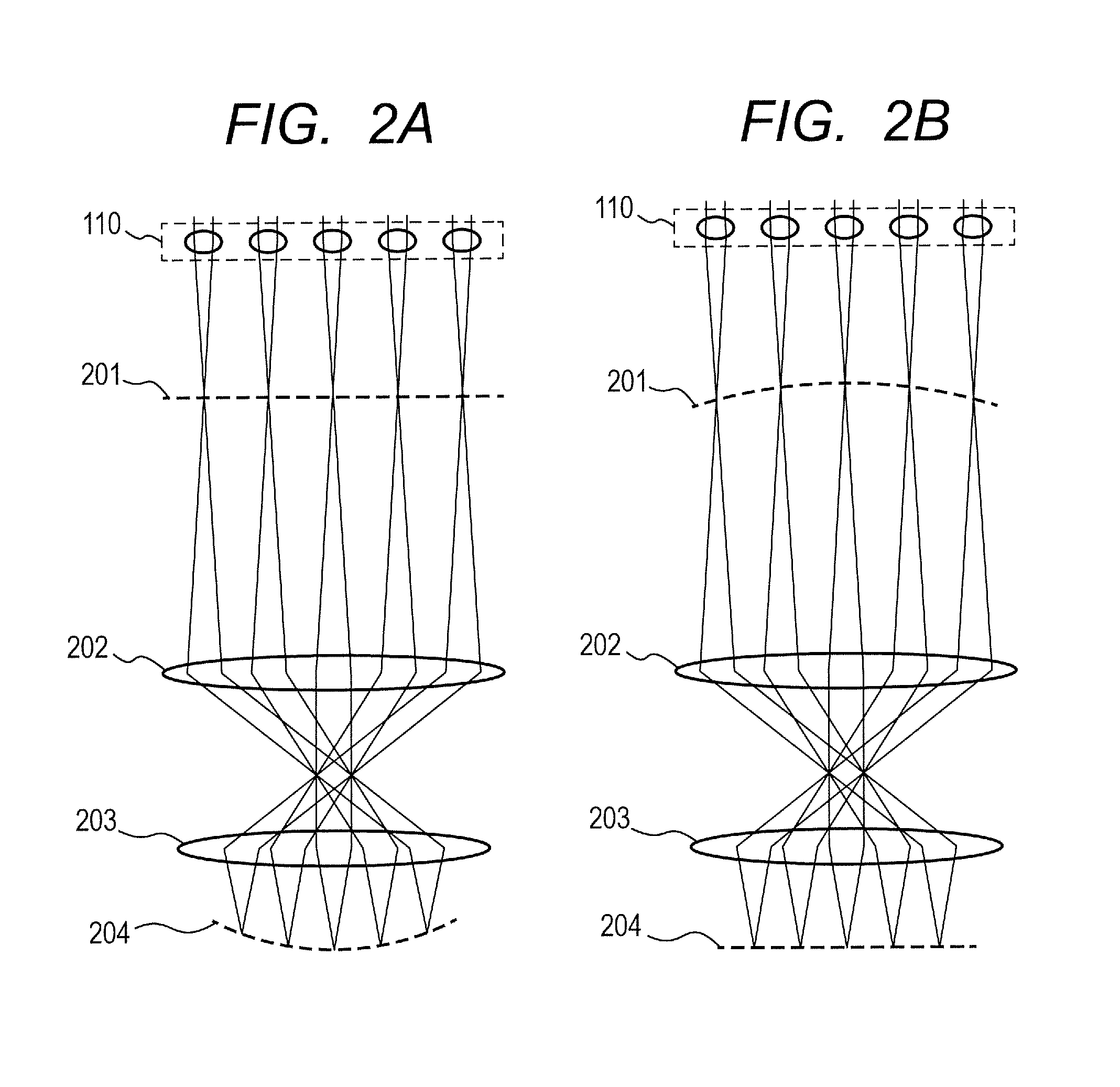
Low coherence light having a central wavelength λc of 1.1 μm and a full width at half maximum spectrum Δλ of 90 nm is emitted. The low coherence light has wavelength properties suited for the light absorbing properties, the diffusion properties, and the dispersion properties of living tissue. A light dividing means divides the low coherence light into a measuring light beam, which is irradiated onto a measurement target via an optical probe, and a reference light beam that propagates toward an optical path length adjusting means. A multiplexing means multiplexes a reflected light beam, which is the measuring light beam reflected at a predetermined depth of the measurement target, and the reference light beam, to form coherent light. A coherent light detecting means detects the optical intensity of the multiplexed coherent light. An image obtaining means performs image processes, and displays an optical tomographic image on a display apparatus.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
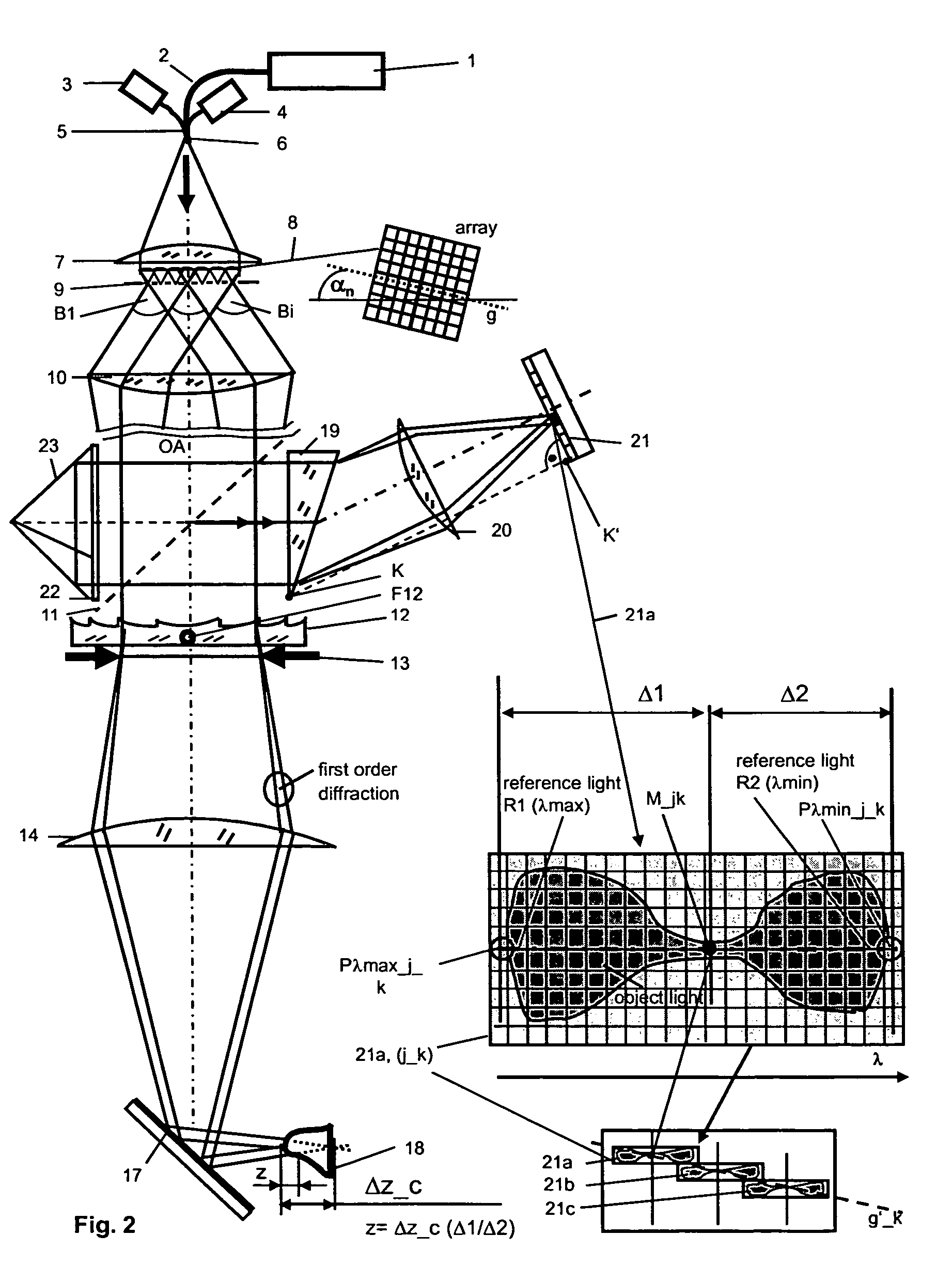
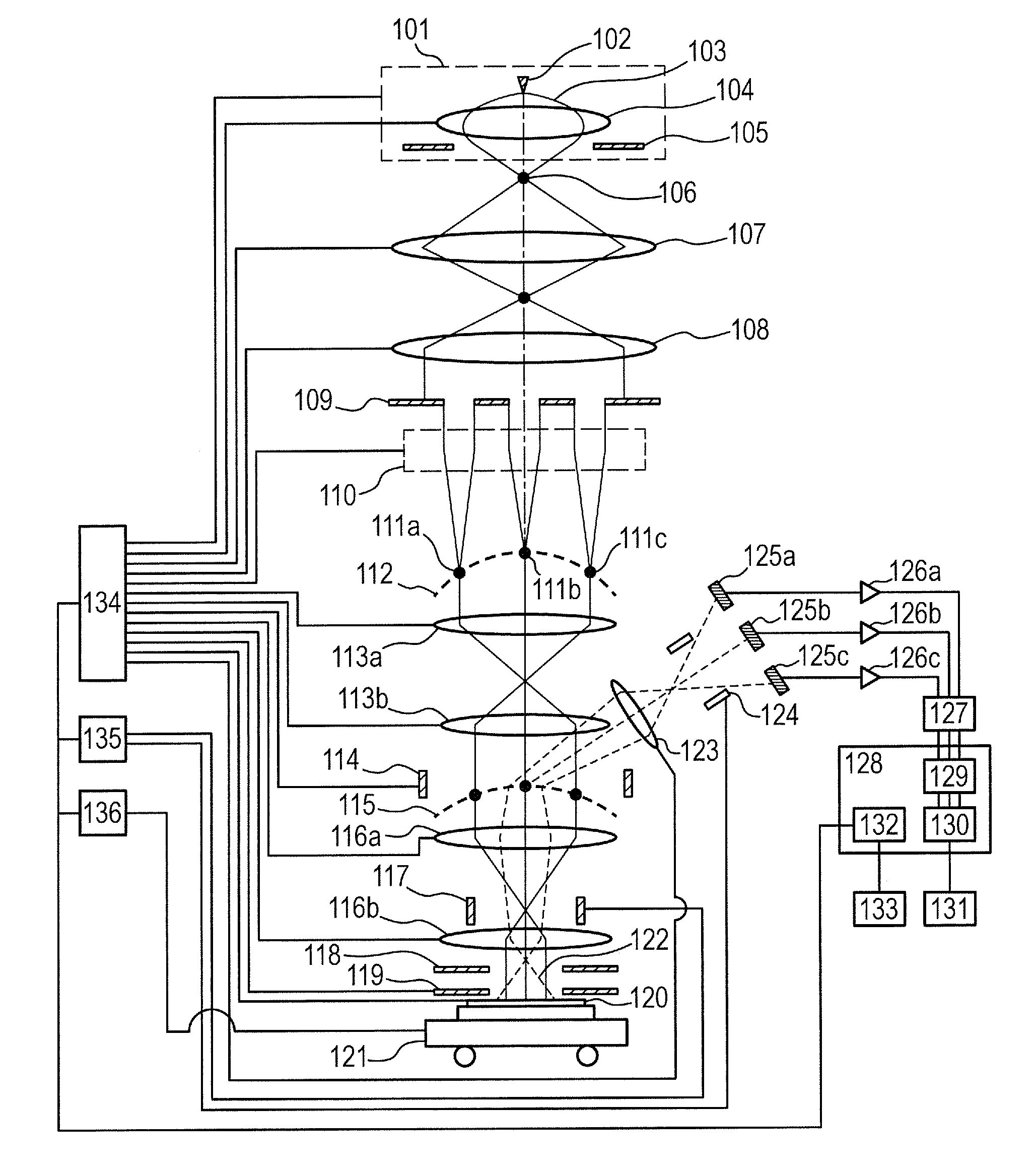
Method and arrangement for a rapid and robust chromatic confocal 3D measurement technique
ActiveUS7787132B2Quick measurementImprove robustnessImage analysisUsing optical meansPoint lightBeam splitter
A chromatic confocal technique and apparatus for the rapid three-dimensional measurement of an object shape, particularly of a tooth in a patient's jaw, using an array of polychromatic point light sources, a planar detector matrix, a beam splitter for lateral spectral separation, and an objective for illuminating and recording the object. Spectral defined reference light bundles are generated, injected into the detection beam path via a reference beam path and, following spectral splitting, are focused on the detector matrix as reference image points, wherein laterally shifted sub-matrices are numerically defined on the detector matrix for spectral analysis of the object light, which sub-matrices are implemented as spectral cells for three-dimensional measurement of the shape of the object.
Owner:SIRONA DENTAL SYSTEMS
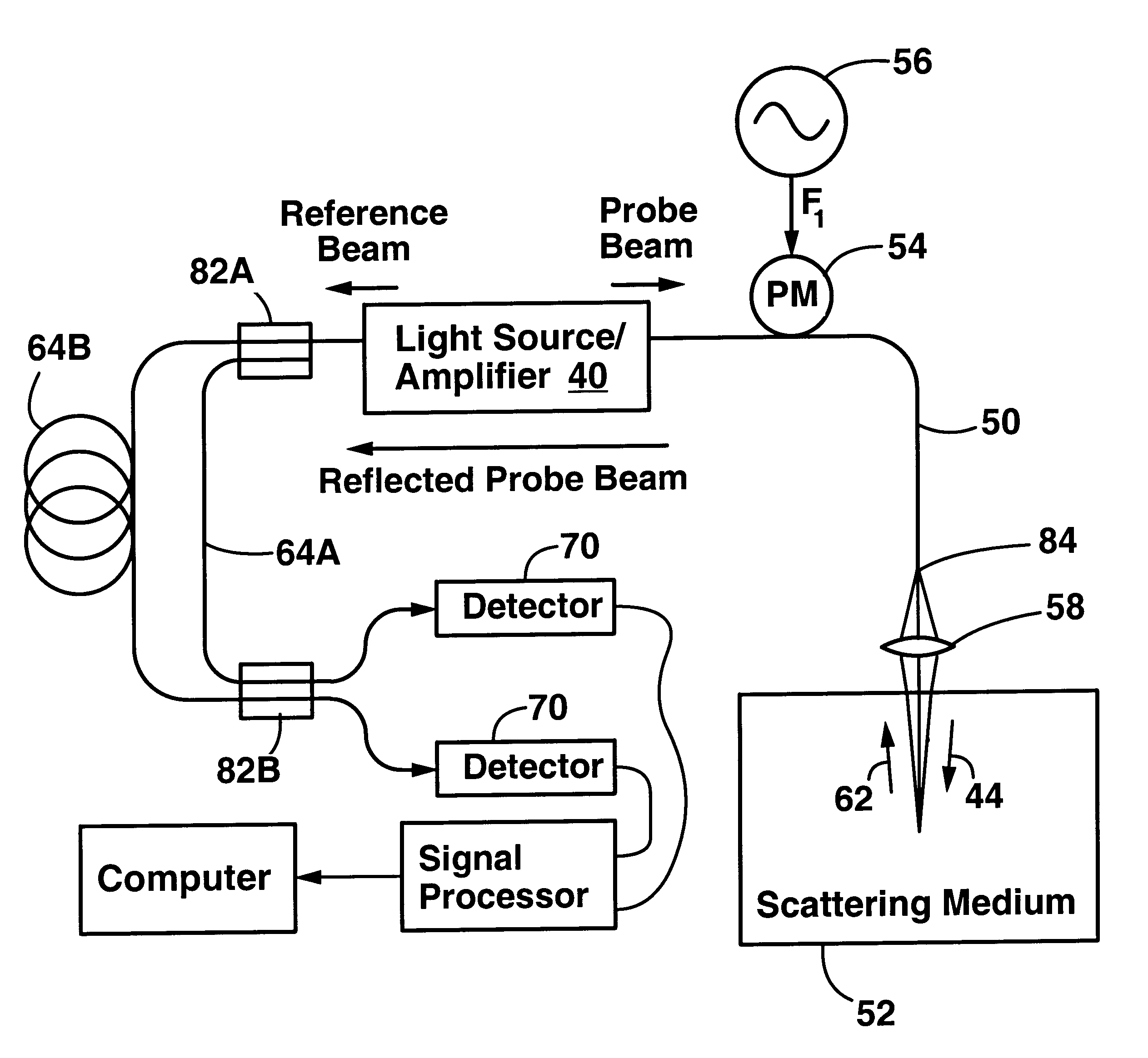
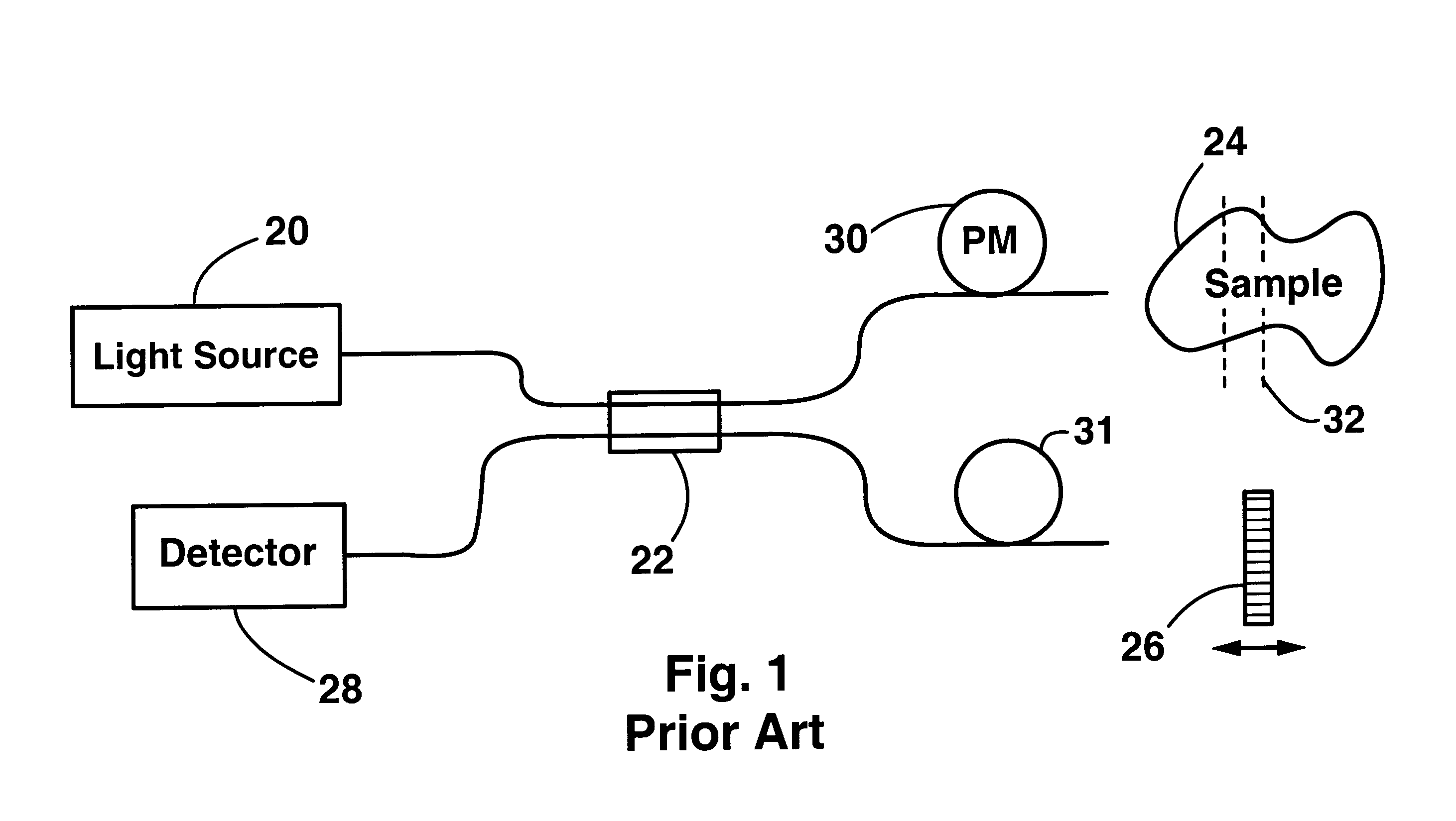
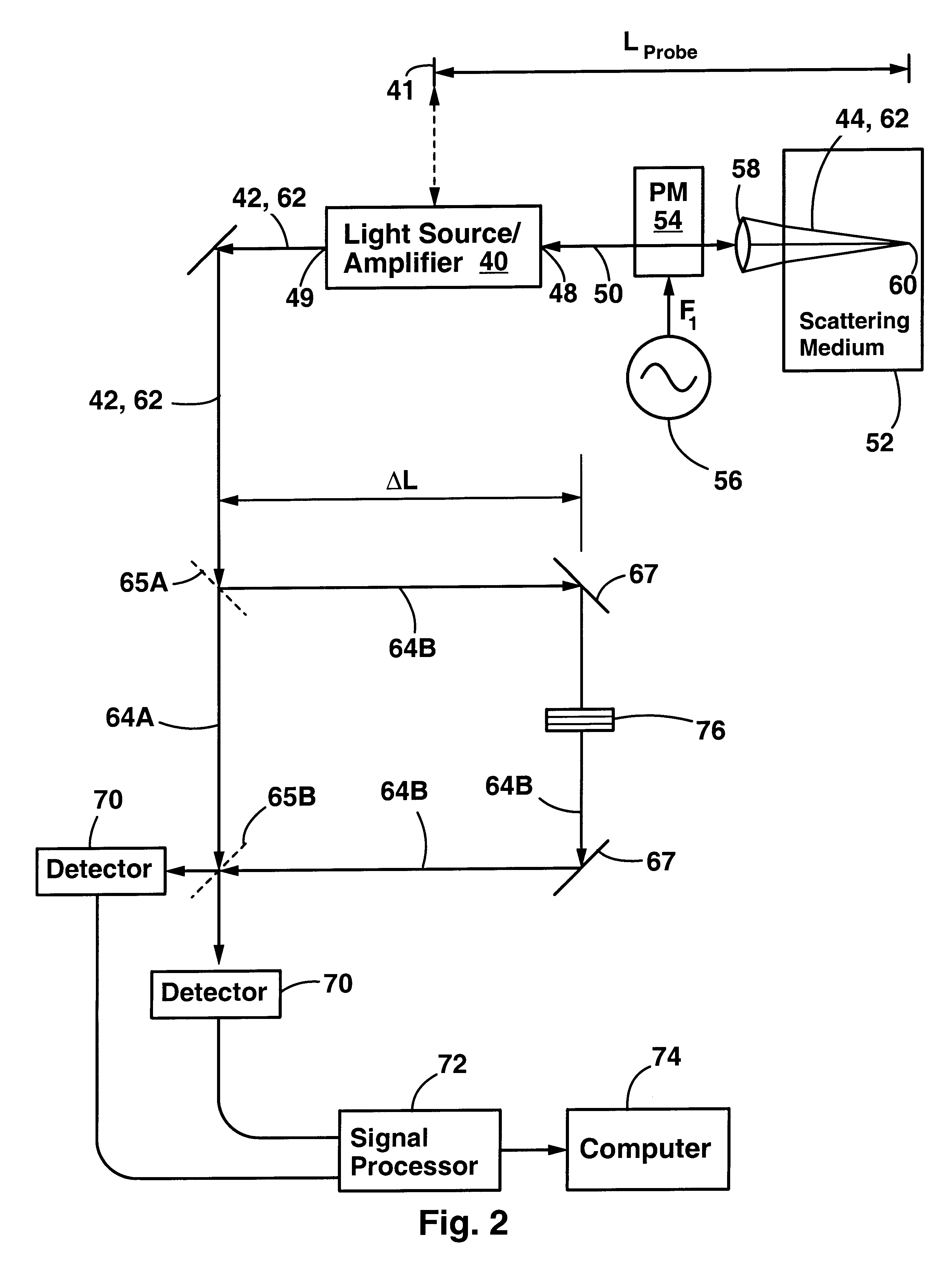
Method and apparatus for measuring optical reflectivity and imaging through a scattering medium
InactiveUS6201608B1Short data acquisition timeImprove spatial resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostic recording/measuringSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Light beam
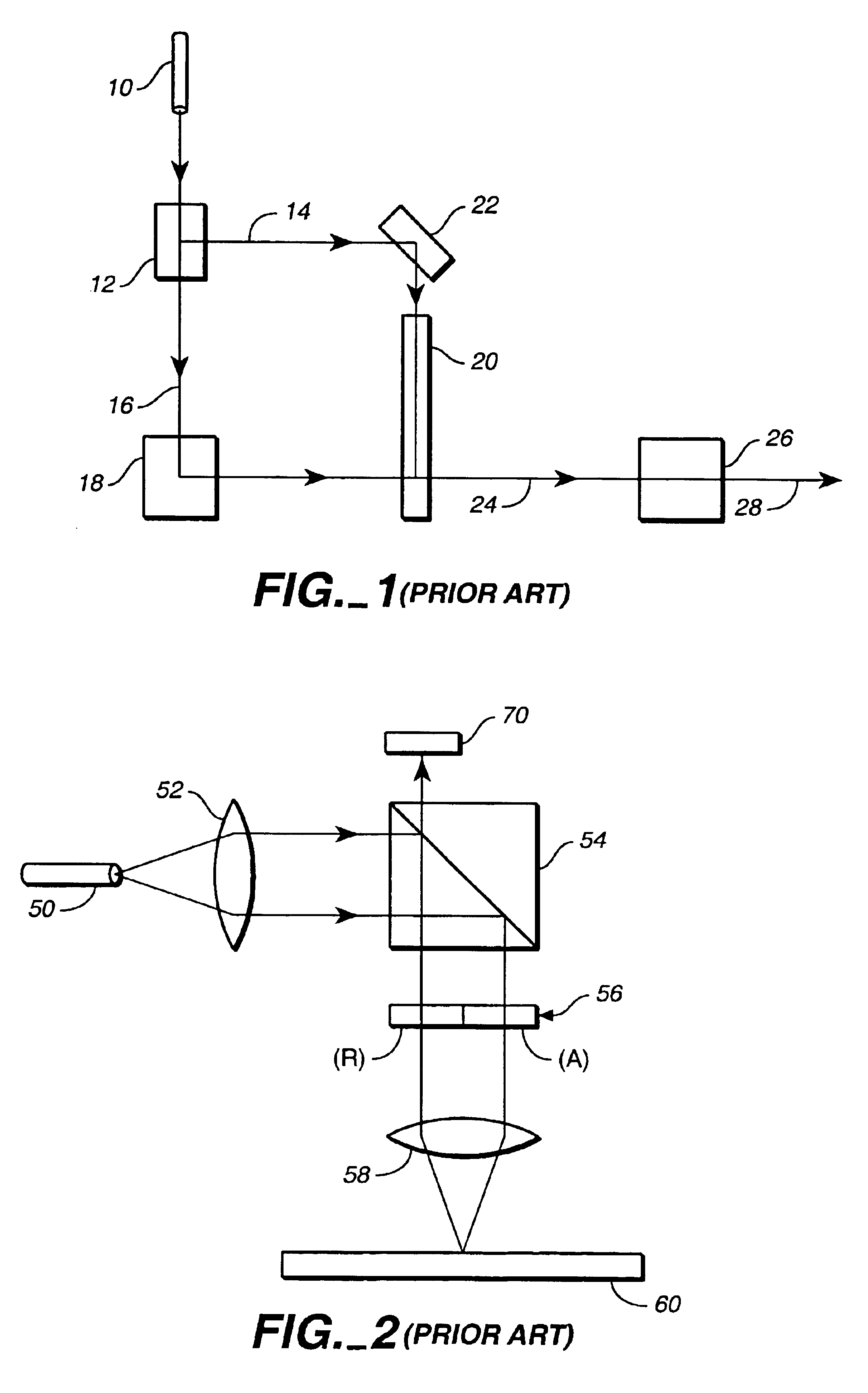
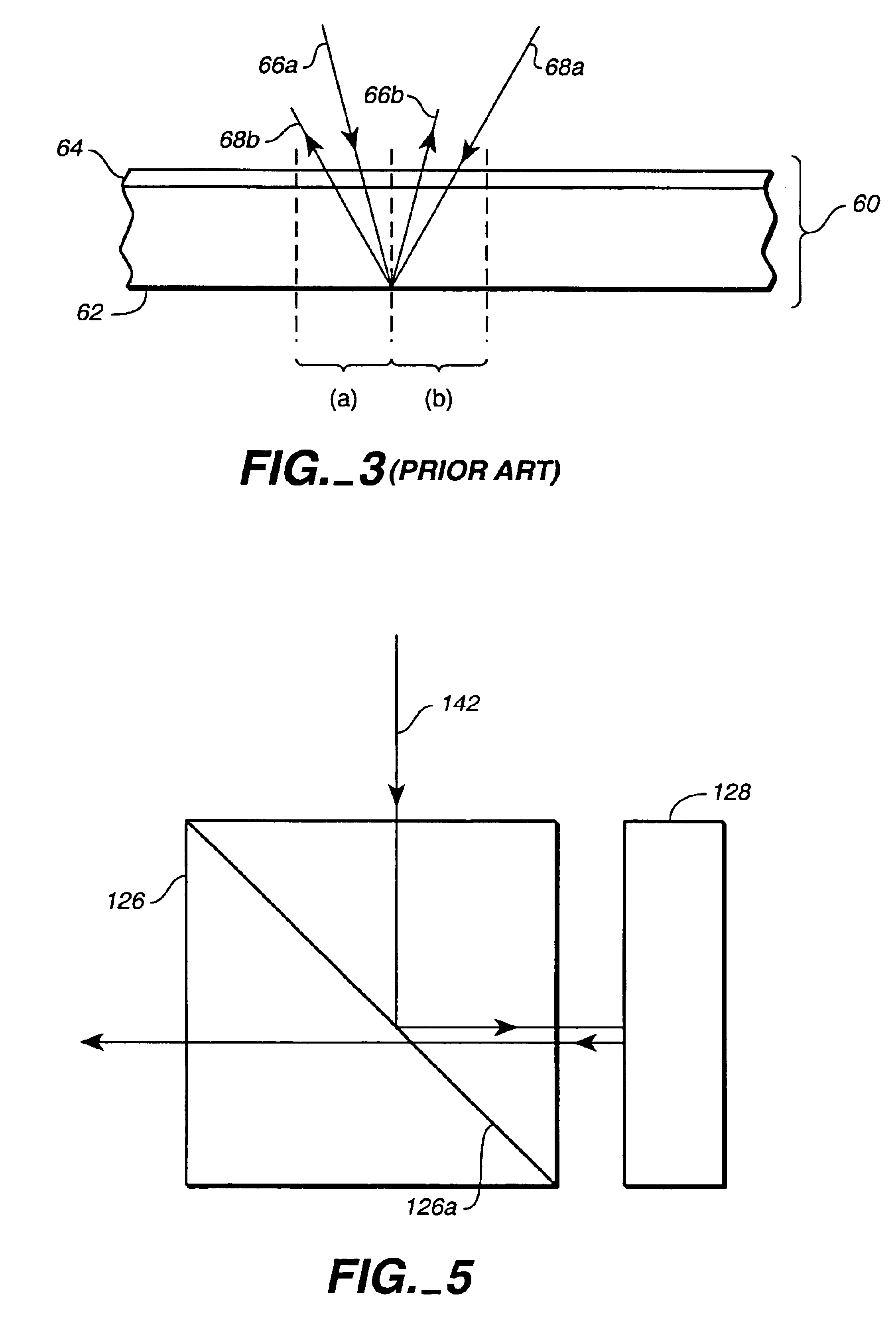
An apparatus and method for performing optical coherence domain reflectometry. The apparatus preferably includes a single output light source to illuminate a sample with a probe beam and to provide a reference beam. The reference beam is routed into a long arm of an interferometer by a polarizing beamsplitter. A reflected beam is collected from the sample. A 90.degree. double pass polarization rotation element located between the light source and the sample renders the polarizations of the probe beam and reflected beam orthogonal. The polarizing beamsplitter routes the reflected beam into a short arm of the interferometer. The interferometer combines the reference beam and the reflected beam such that coherent interference occurs between the beams. The apparatus ensures that all of the reflected beam contributes to the interference, resulting in a high signal to noise ratio.
Owner:OPTICAL BIOPSY TECH
Laser source comprising amplifier and adaptive wavefront/polarization driver
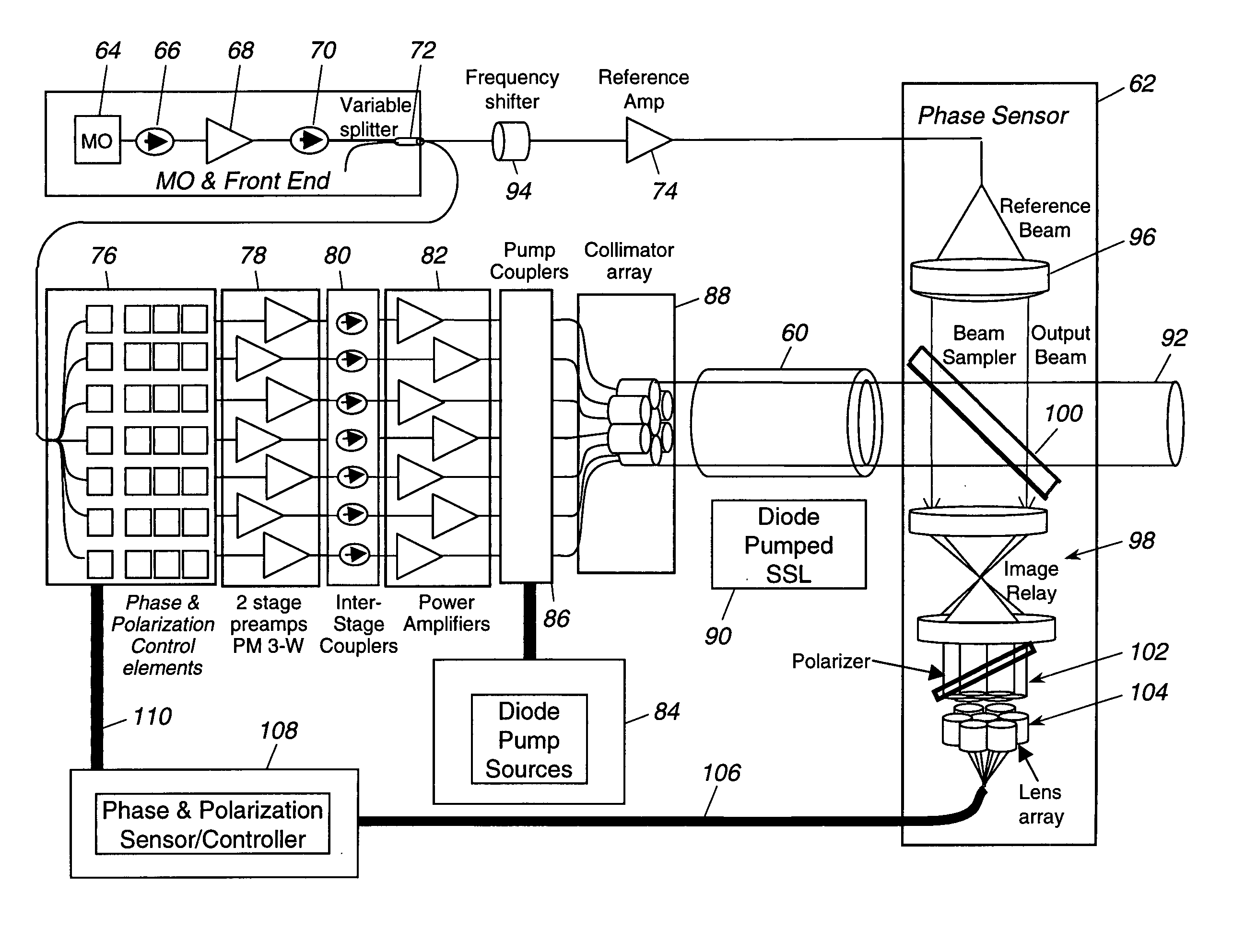
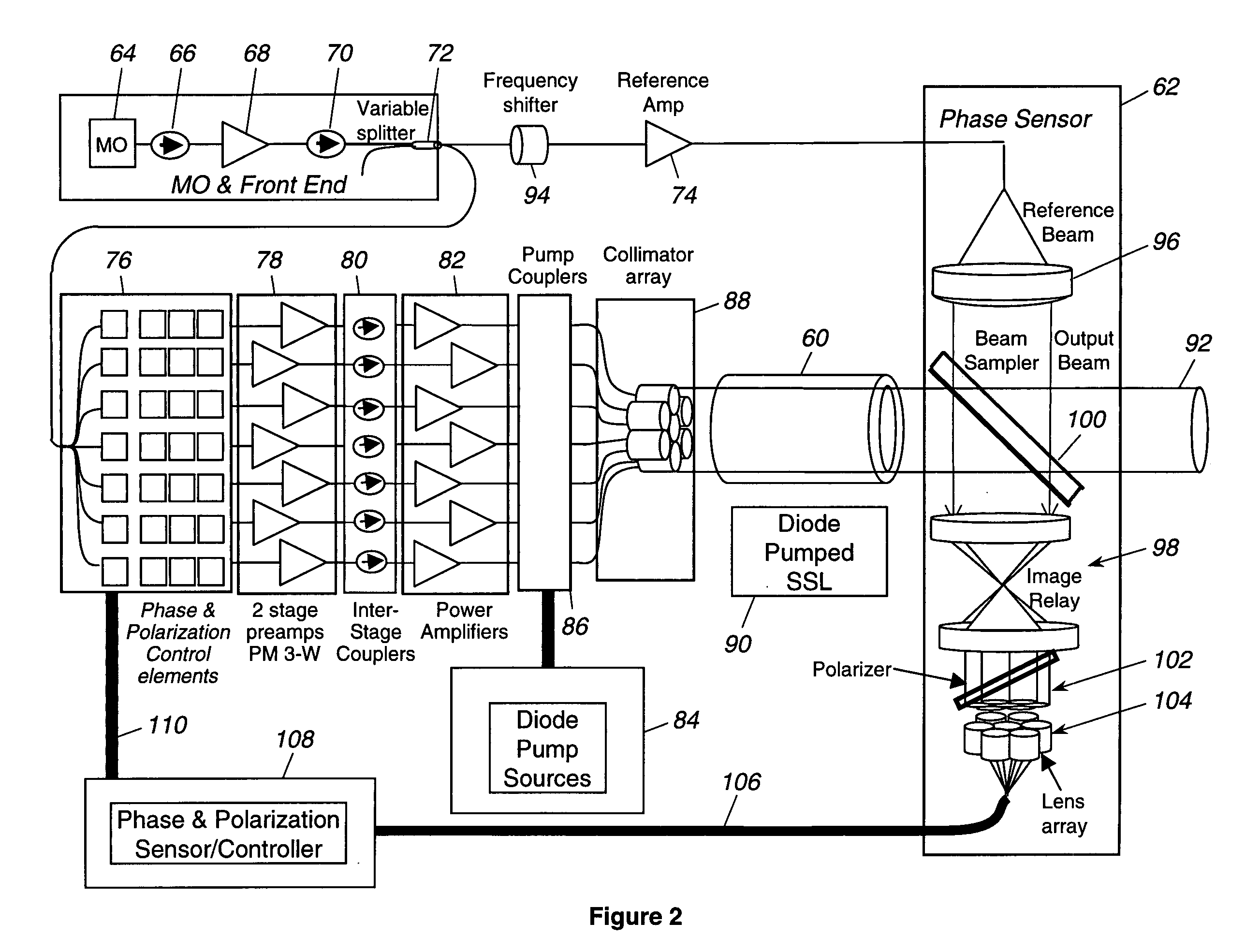
ActiveUS20050201429A1Compensation DistortionOptical measurementsLaser using scattering effectsWavefrontAudio power amplifier
A hybrid laser source including a solid state laser driven by an array of fiber laser amplifiers, the inputs of which are controllable in phase and polarization, to compensate for distortions that arise in the solid state laser, or to achieve desired output beam properties relating to direction or focus. The output beam is sampled and compared with a reference beam to obtain phase and polarization difference signals across the output beam cross section, at spatial positions corresponding with the positions of the fiber laser amplifiers providing input to the solid state laser. Therefore, phase and polarization properties of the output beam may be independently controlled by predistortion of these properties in the fiber laser amplifier inputs.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Grazing incidence holograms and system and method for producing the same
InactiveUS6151142AThin geometryUltra-compact overall geometryMechanical apparatusHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesCouplingLight diffraction
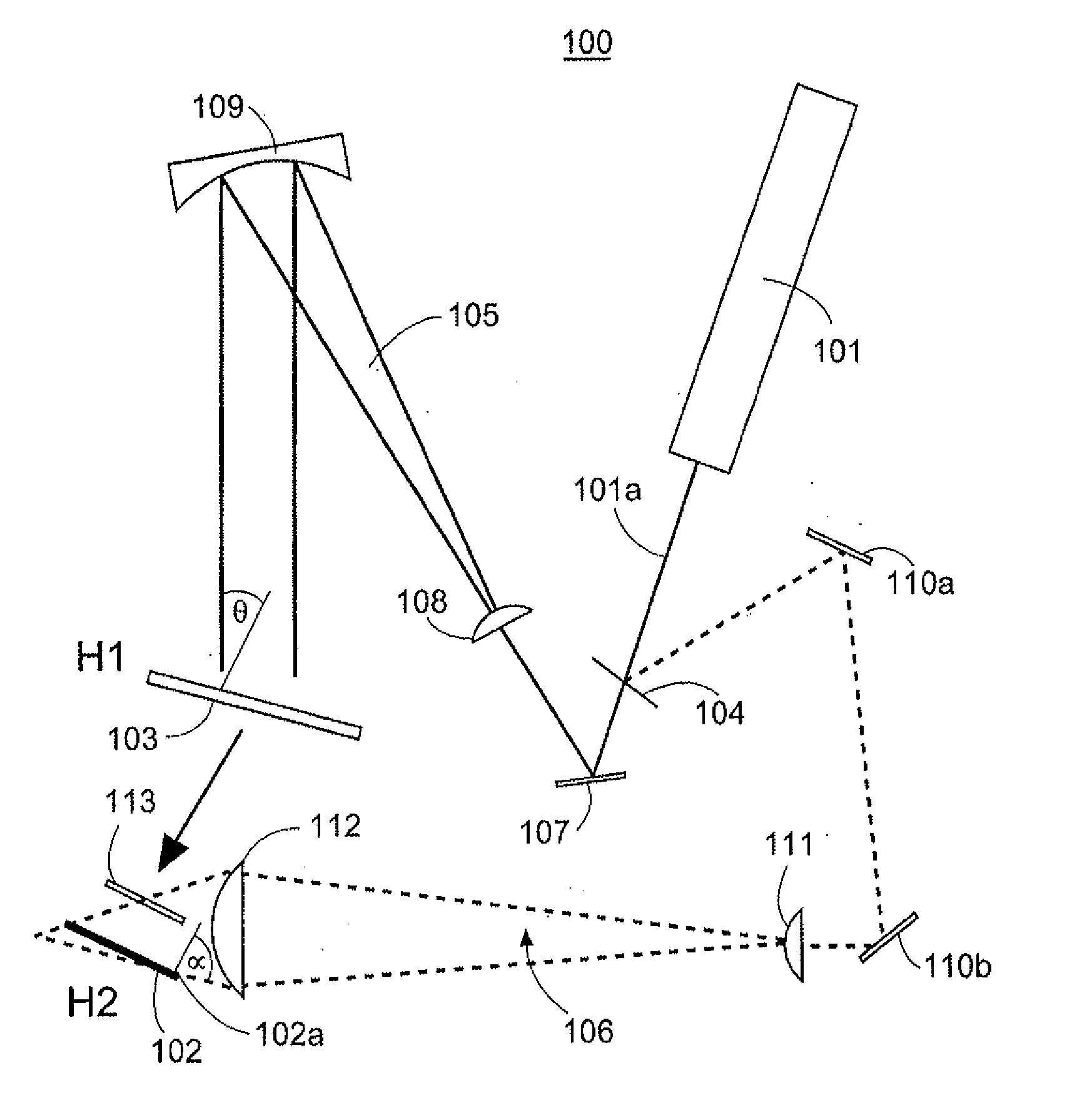
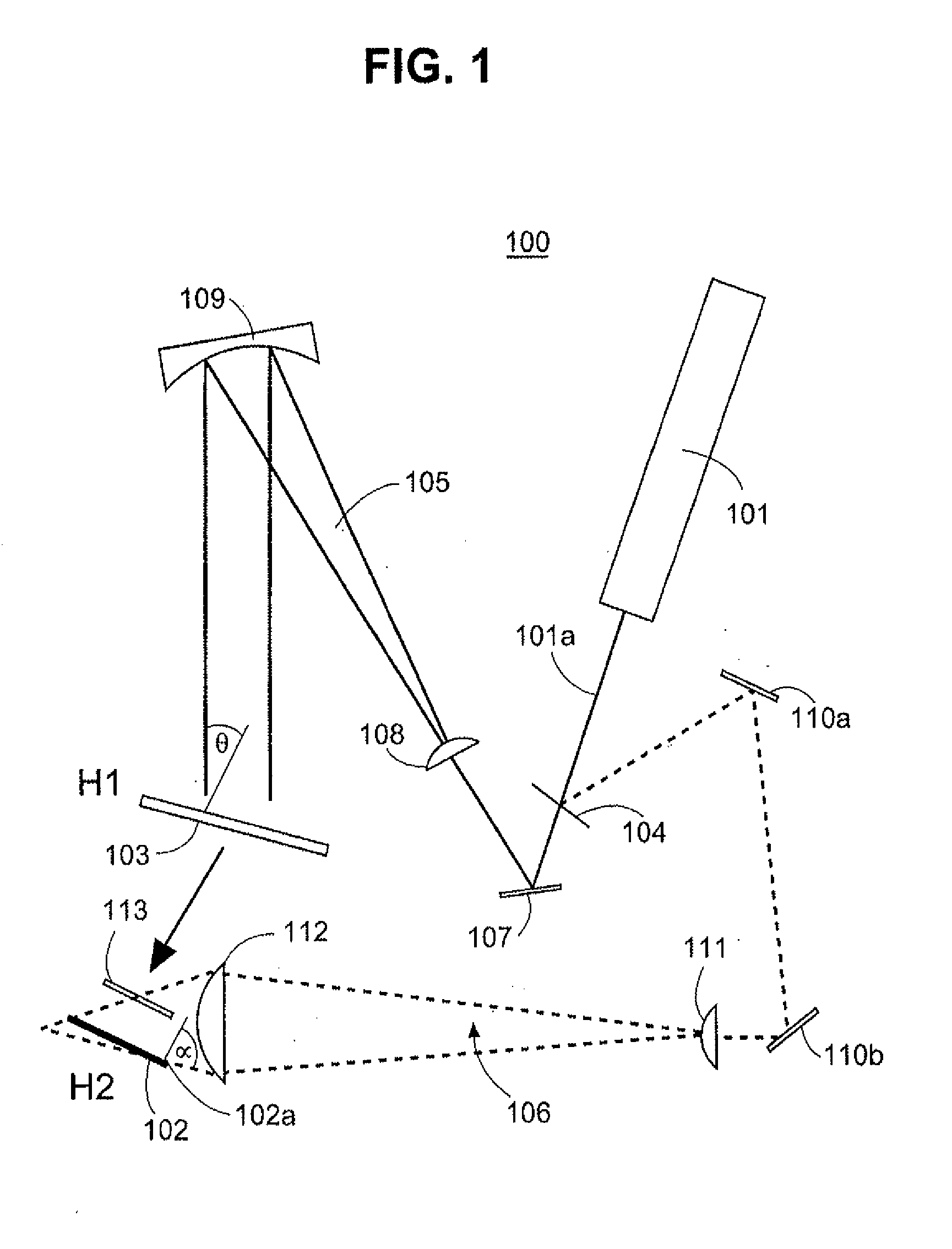
A method and system are disclosed for recording and displaying grazing-incidence (i.e., steep reference beam angle) holograms supported on a substrate having thin edge-illuminatable geometry. The system and process use thin edge-illuminated substrates that facilitate optimal coupling of the reference light beam at steep angles approaching grazing incidence, while maximizing the contrast of the slanted fringe structures thereof. Different recording techniques are employed when the index of refraction of the substrate is greater than that of the recording medium, than when the index of refraction of the substrate is less than that of the recording medium. A recording and playback system of complementary design is provided for recording slanted-fringe volume holograms under relaxed conditions, without compromising the light diffraction efficiency of the holograms under different playback conditions.
Owner:KREMEN MR STANLEY H
Scatterometry by phase sensitive reflectometer
A phase-sensitive interferometeric broadband reflectometer includes an illumination source for generating an optical beam. A beam splitter or other optical element splits the optical beam into probe beam and reference beam portions. The probe beam is reflected by a subject under test and then rejoined with the reference beam. The combination of the two beams creates an interference pattern that may be modulated by changing the length of the path traveled by the probe or reference beams. The combined beam is received and analyzed by a spectrometer.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
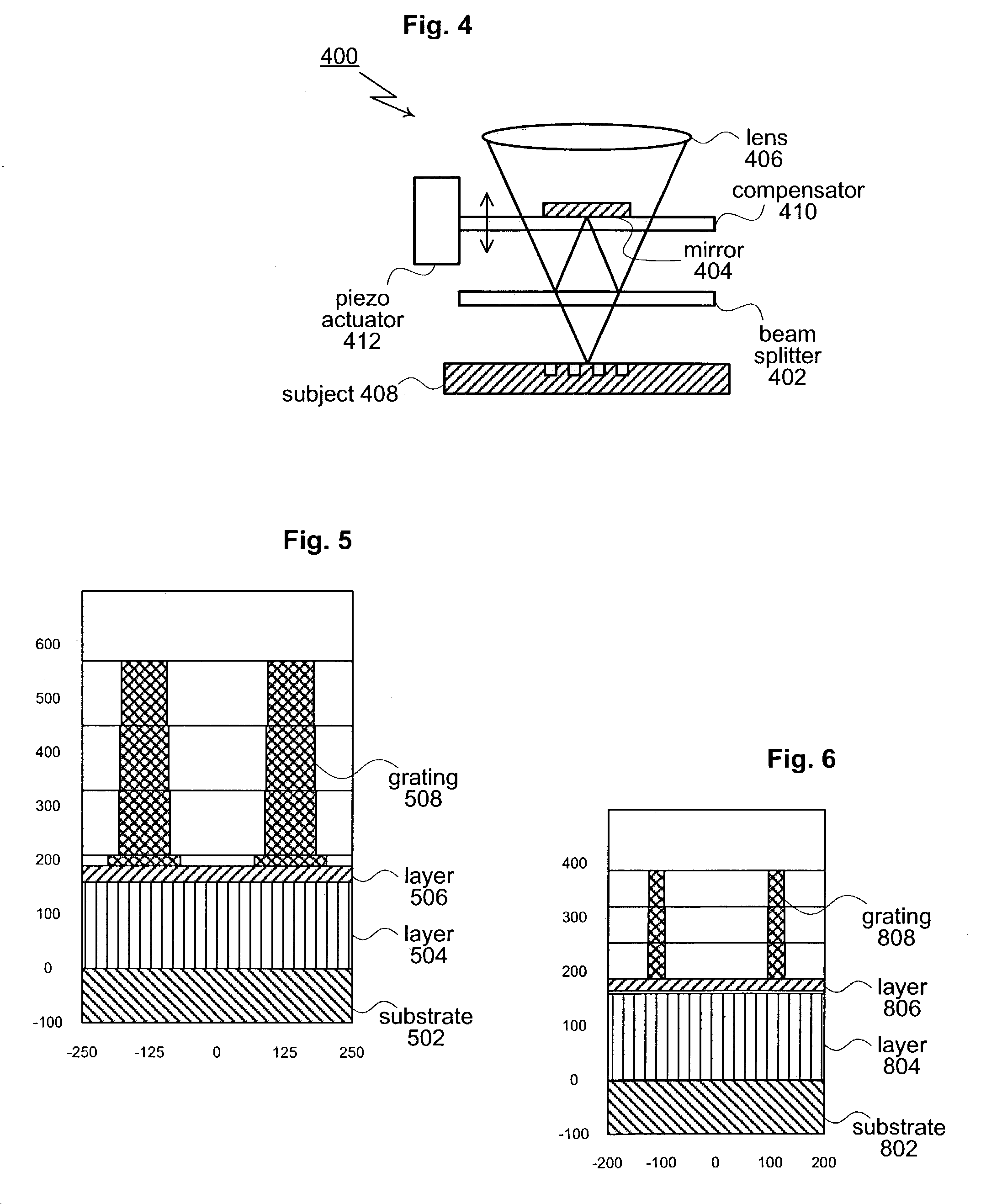
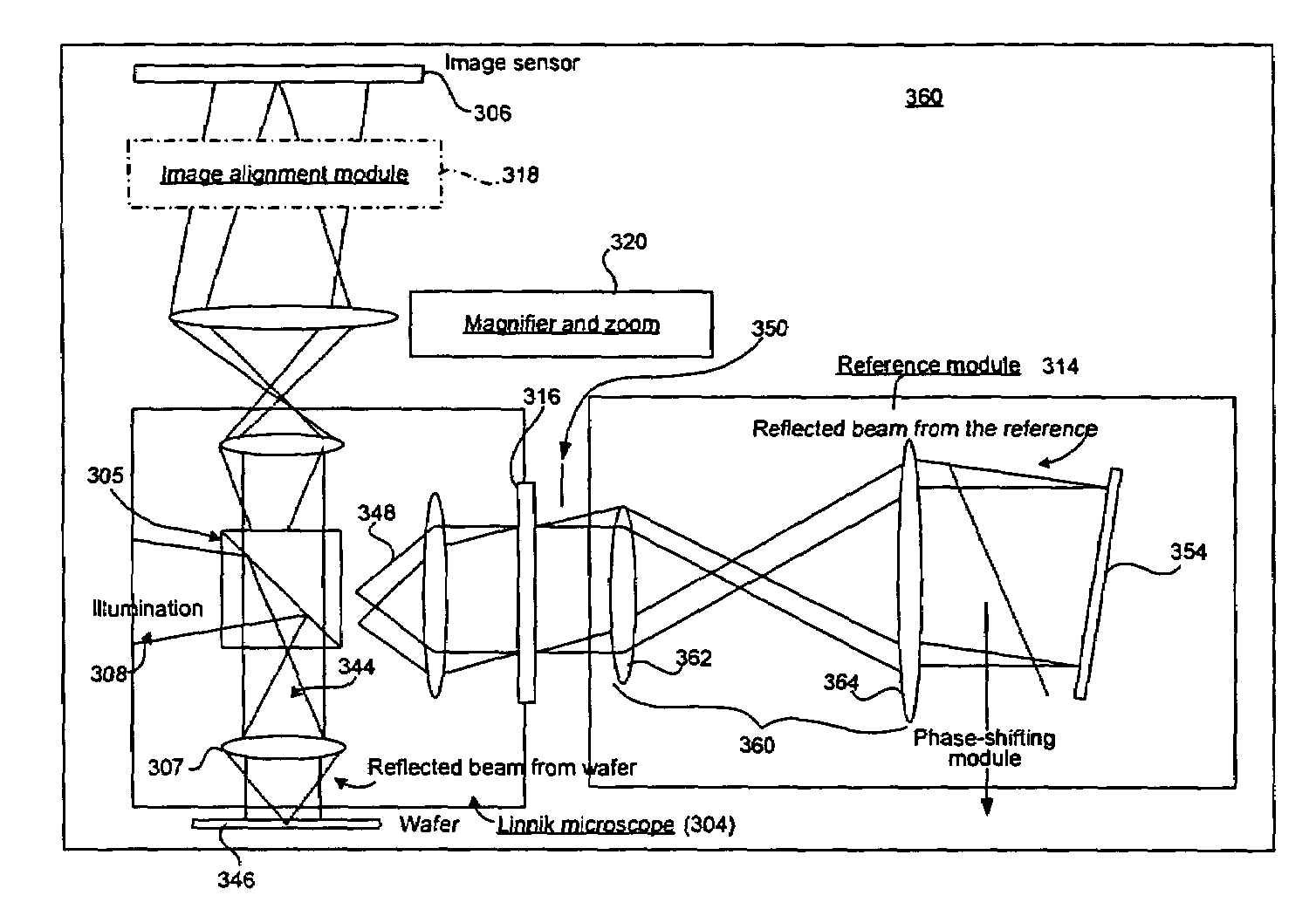
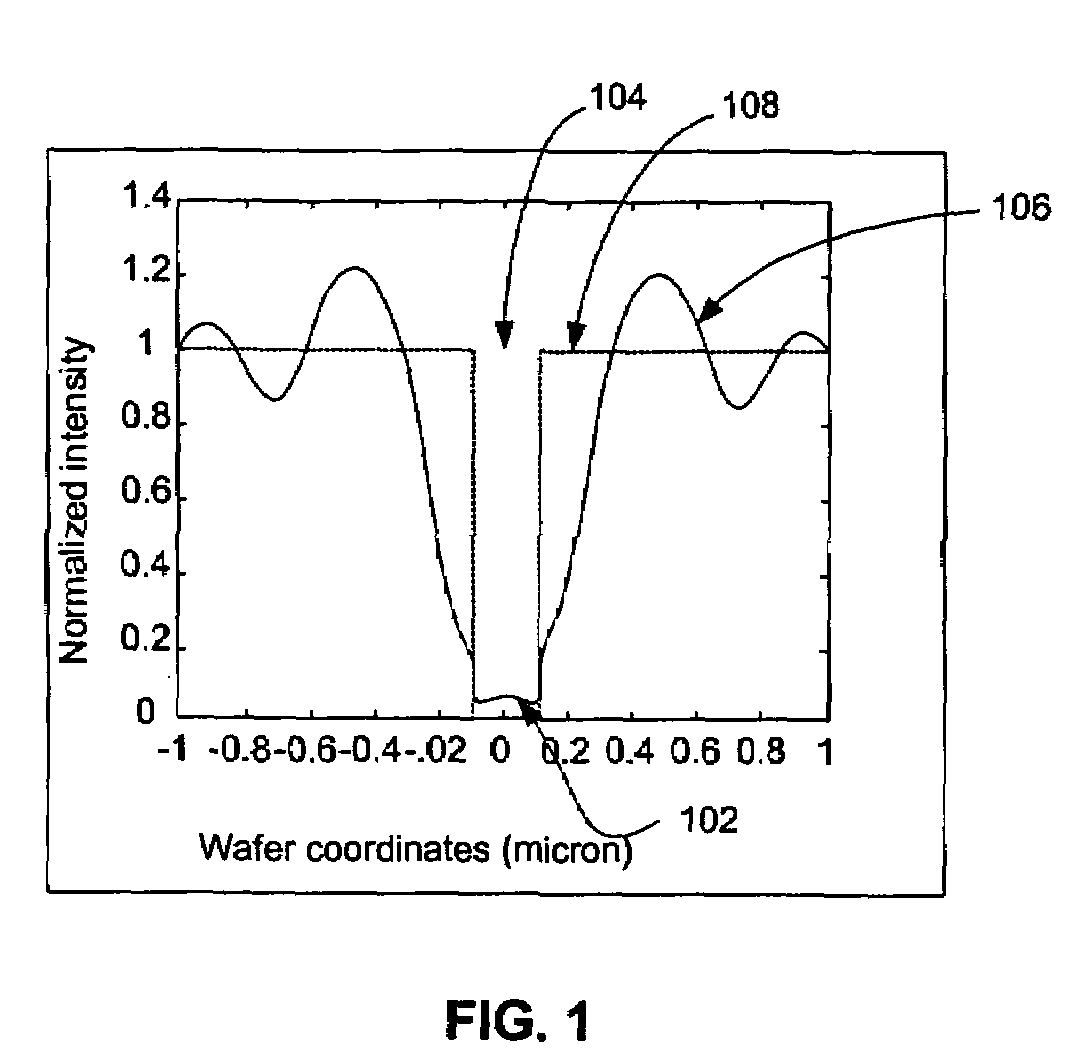
Method and apparatus using interferometric metrology for high aspect ratio inspection
ActiveUS7061625B1Easy alignmentMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansMetrologyOptical path
In one embodiment, the present invention provides an interferometric inspection system for inspecting semiconductor samples. The system includes at least one illumination source for generating an illumination beam and an interferometric microscope module for splitting the illumination beam into a test beam directed to the semiconductor sample and a reference beam directed to a tilted reference mirror. The beams are combined to generate an interference image at an image sensor. The tilted reference mirror is tilted at a non-normal angle with respect to the reference beam that is incident on the mirror to thereby generate fringes in the interference image. The system also includes an image sensor for acquiring the interference image from the interferometric microscope module and generates an inherence signal. The system further includes a processing module configured to generate complex field information corresponding to the sample from the interference image signal and an alignment module located in the optical path between the interferometric module and the image sensor. In another embodiment, the processing module is configured to generate complex field information from either spatial fringe analysis or temporal fringe analysis performed on the interference image signal.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
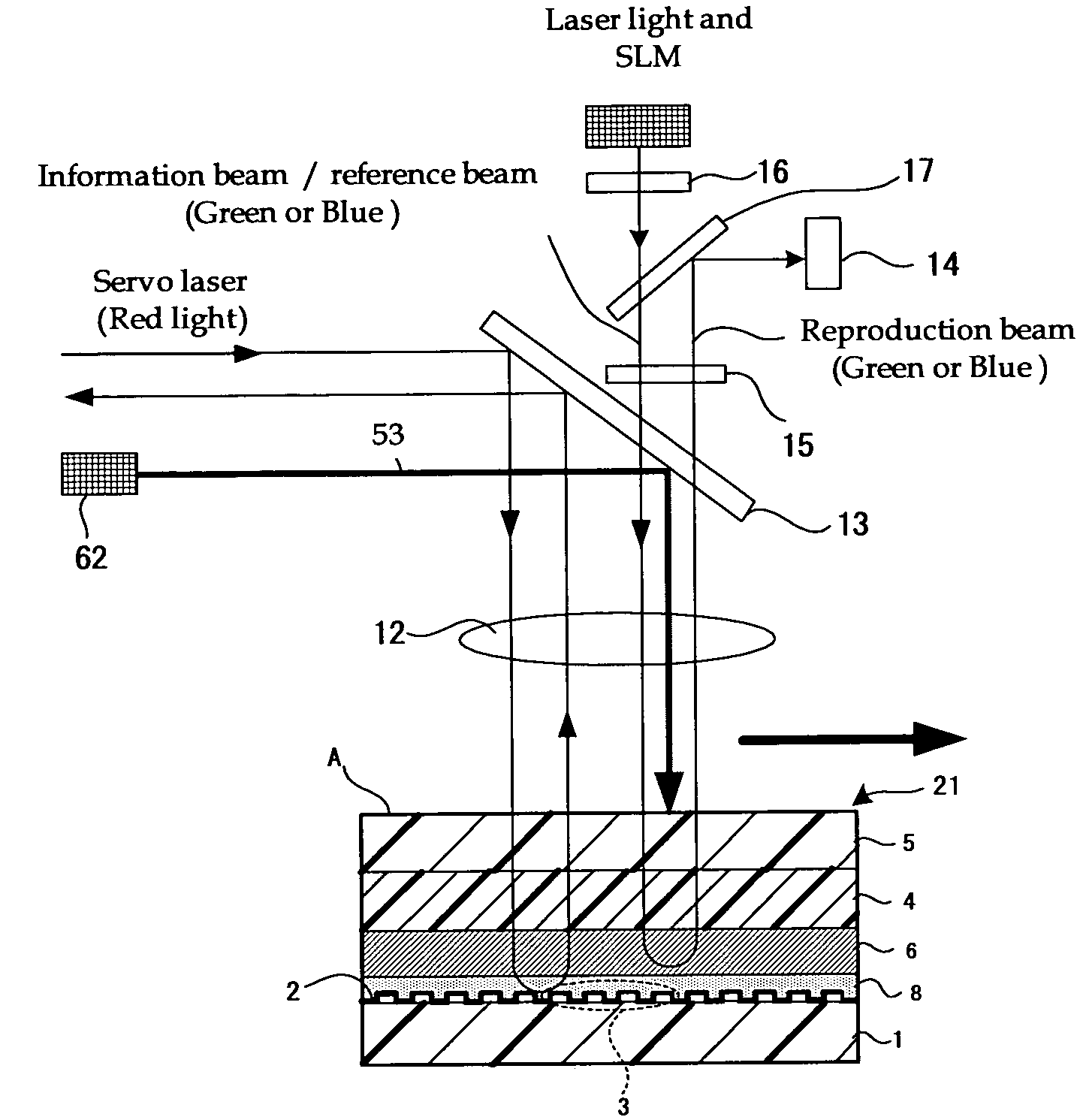
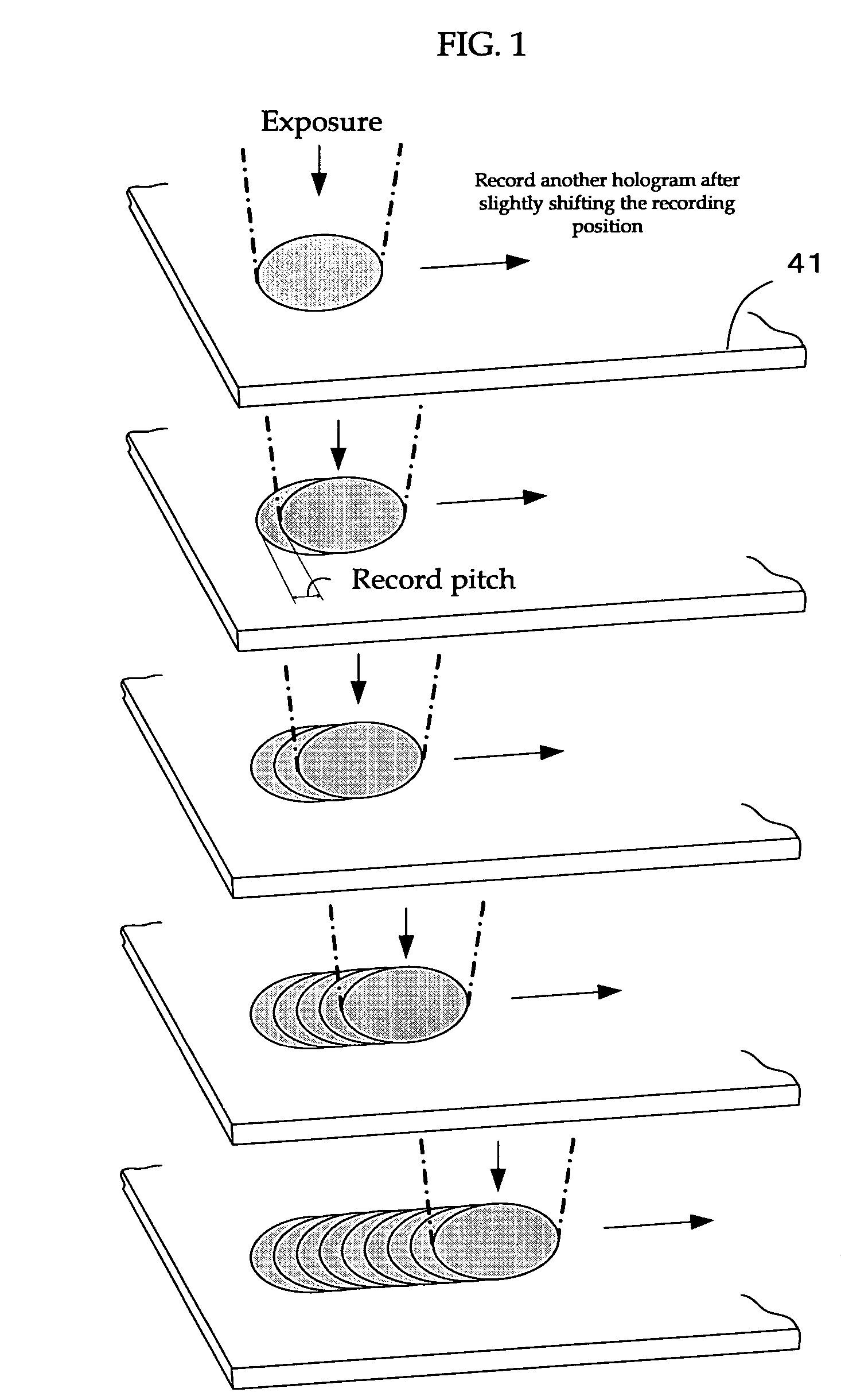
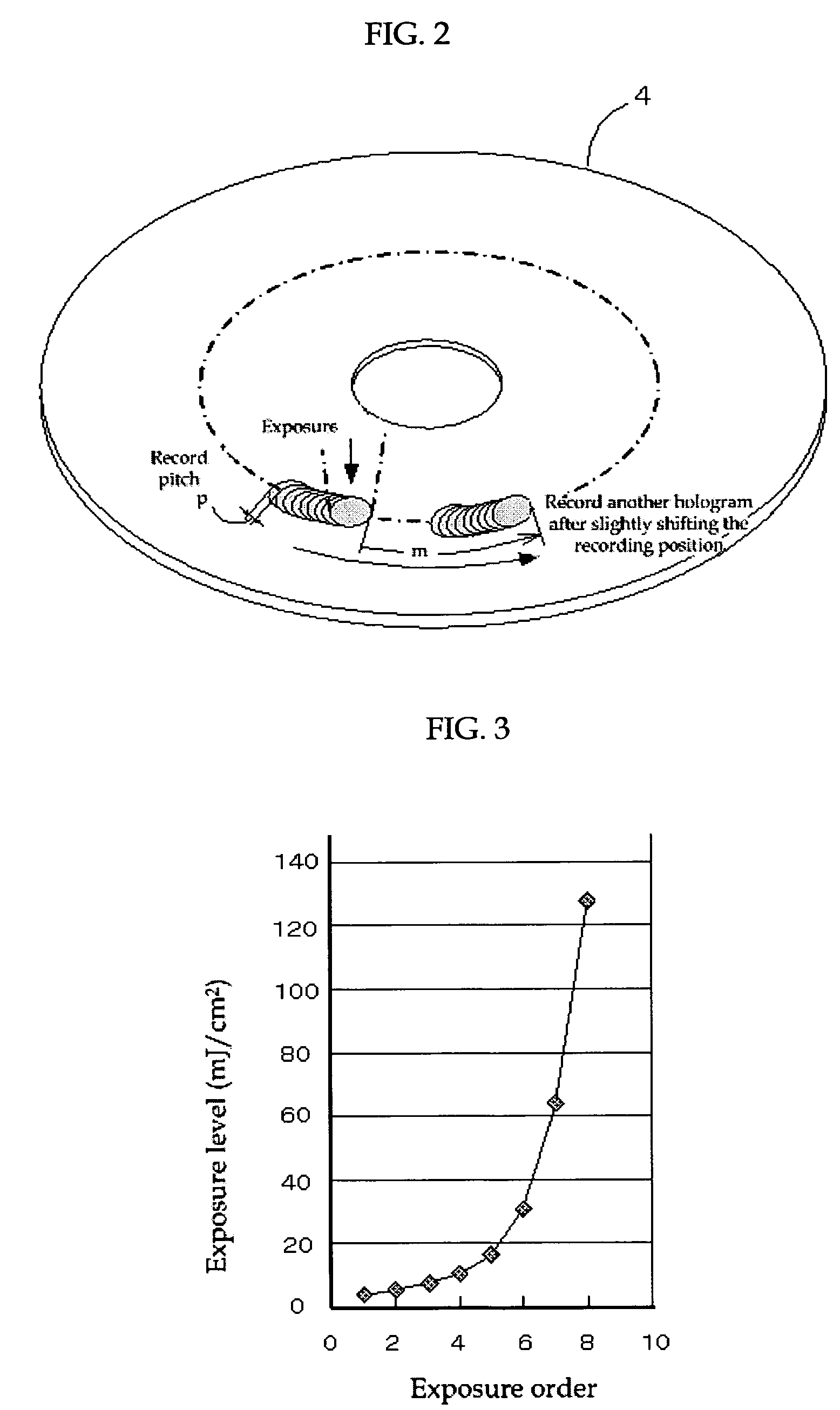
Optical information recording method, optical information recording apparatus and optical information recording medium
InactiveUS7626913B2Reduce sensitivitySufficient informationRecord information storageInstrumental componentsLight beamRecording layer
To provide an excellent optical information recording method, optical information recording medium and optical information recording apparatus both of which use the method. The method generates no excessively-exposed region, can sufficiently fix recorded information, and never reduce the sensitivity of non-recorded regions. This is achieved because the method applies a fixing beam onto at least a portion of an exposed region of a recording layer of the optical information recording medium, the recording layer recording information by holography, at an exposure level T (mJ / cm2) that satisfies the condition H<(S+T)<2H (where S is an integrated exposure level (mJ / cm2), which is the total of the exposure level in each predetermined region that constitutes the exposed region where an interference image has been recorded by irradiating the recording layer with an information beam and a reference beam, and H is a minimum fixing exposure level (mJ / cm2) required to fix the interference image).
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP
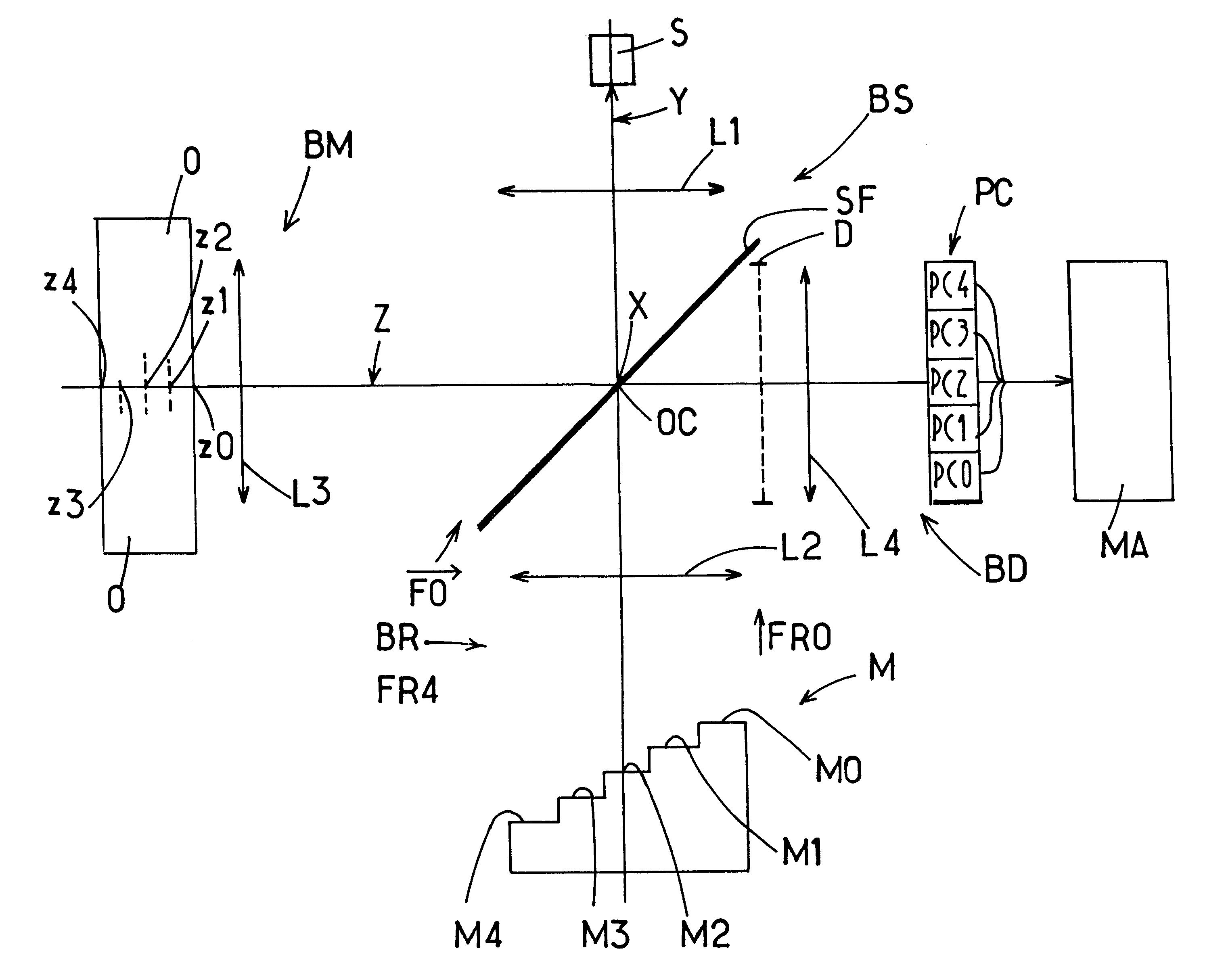
Interferometric device for recording the depth optical reflection and/or transmission characteristics of an object
InactiveUS6268921B1InterferometersColor/spectral properties measurementsOptical reflectionPath length
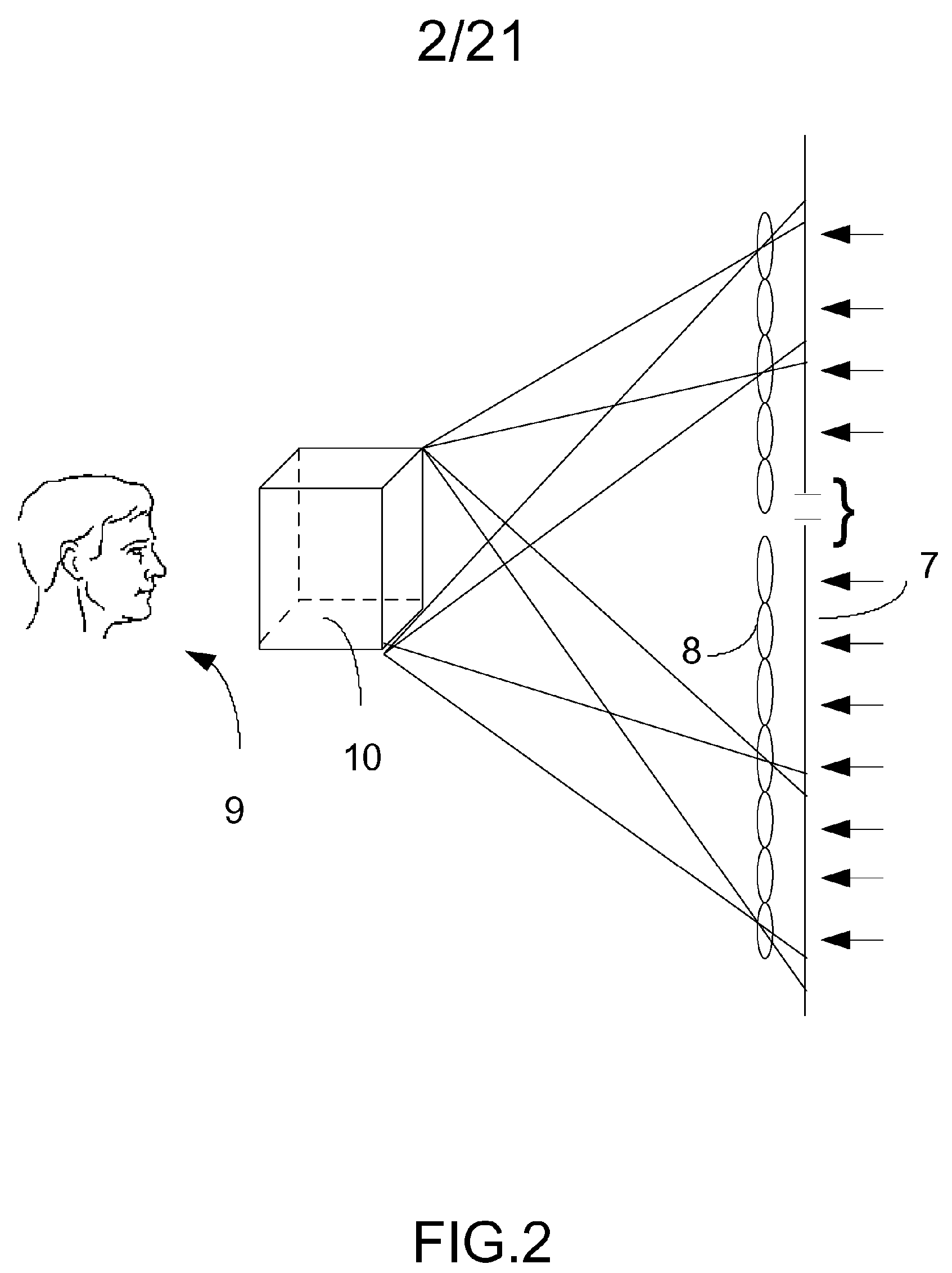
A tomographic interferometer device in which a spectral light source lights an object to create an object beam originating from that object. A stepped optical block is also exposed to the source to create a plurality of individual reference beams having different path lengths. The object beam and reference beams are made to interfere and the resulting light is sent to an array of side by side photodetectors. A plurality of lenses steer the light generated by the interference of each of the individual reference beams with the object beam to different photodetector cells of the array for generating a tomographic image of the object
Owner:CSEM CENT SUISSE DELECTRONIQUE & DE MICROTECHNIQUE SA RECH & DEV
Apparatus and method for interferometric measurement of a sample
ActiveUS7982881B2Quick measurementRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryLight beamWavelength
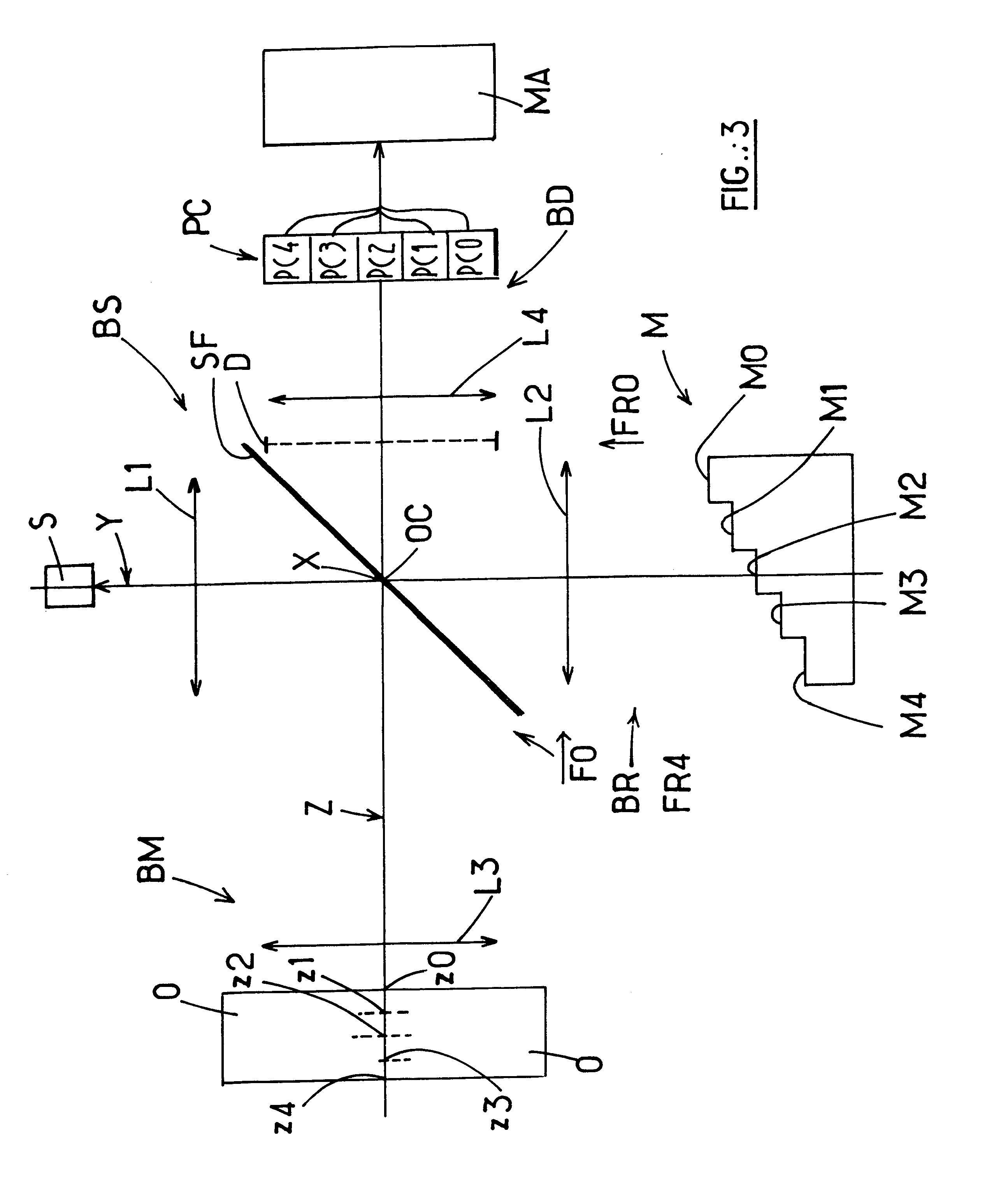
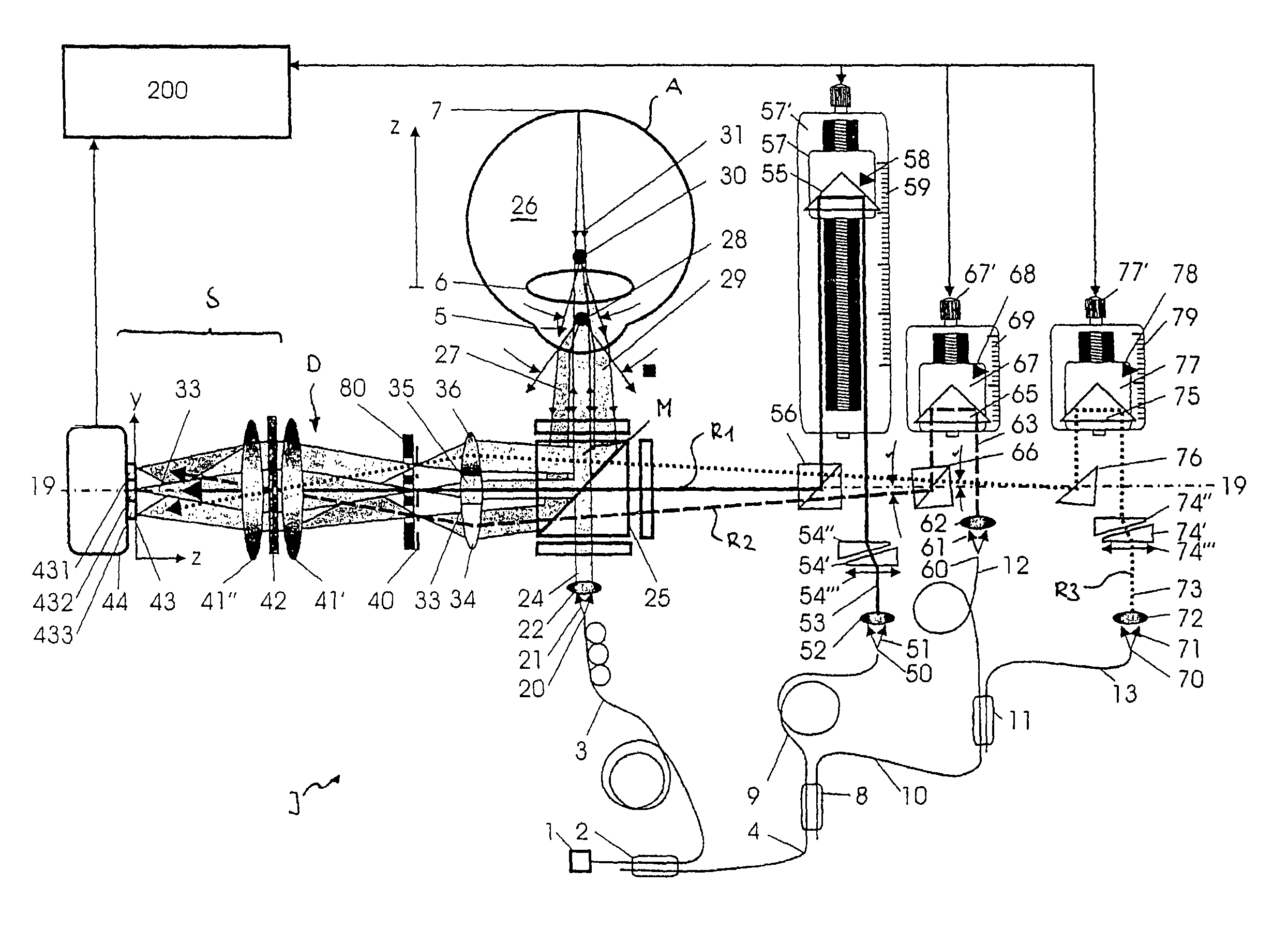
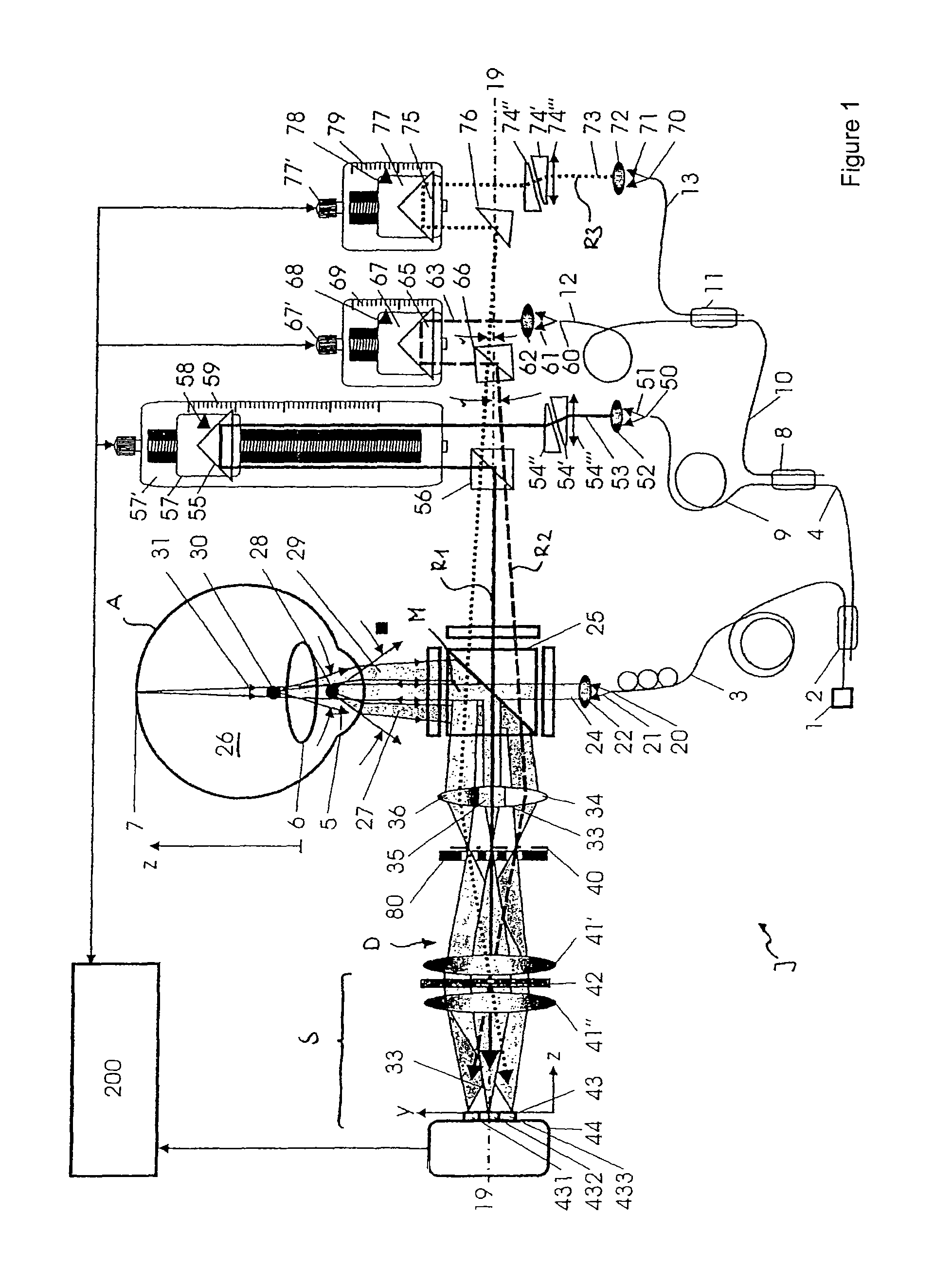
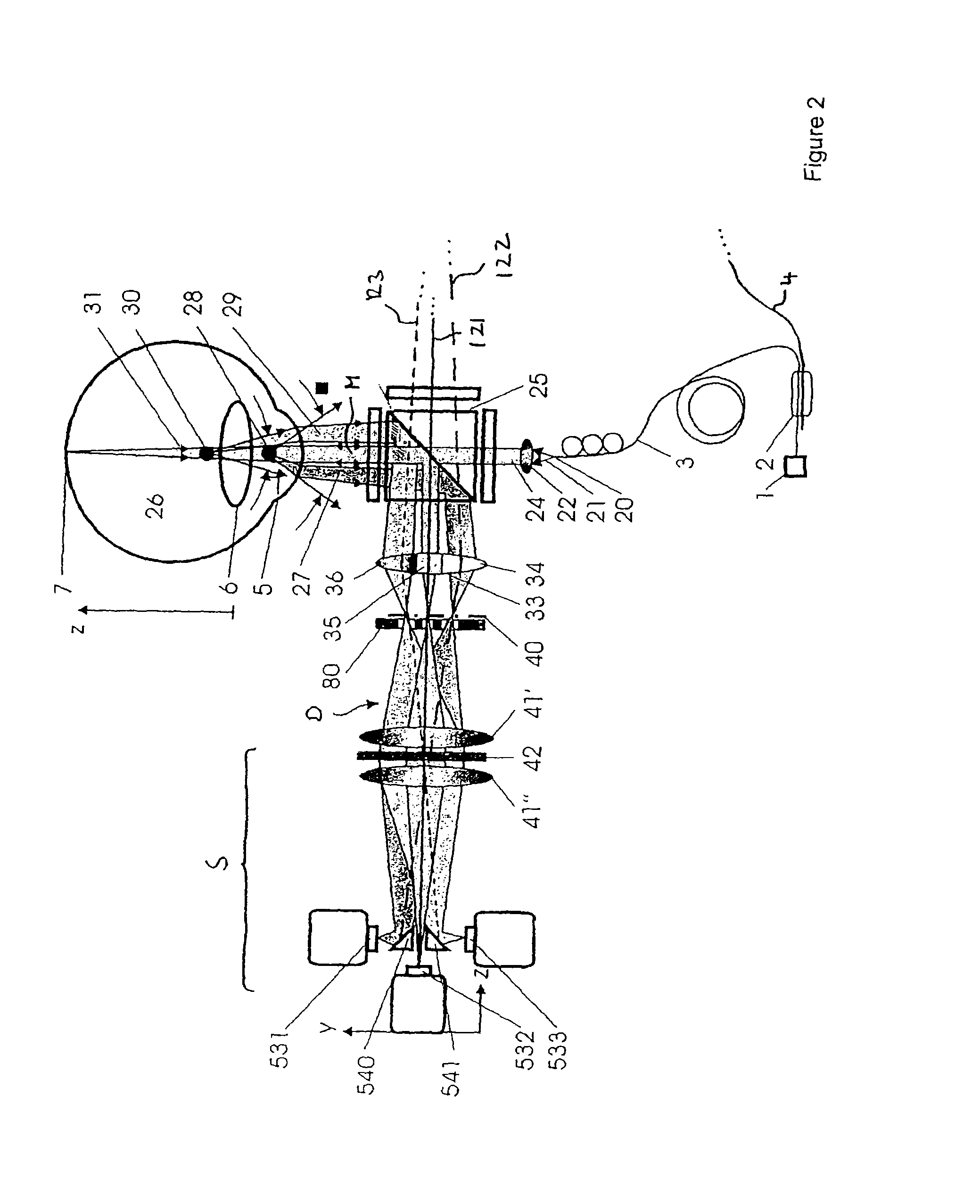
A device for the interferometric measurement of a sample, in particular the eye, including an interferometer arrangement with a first measurement beam path, through which a measurement beam falls onto the sample, and a first reference beam path, through which a reference beam runs, which is applied to the measuring beam for interference. The interferometer arrangement includes a second measuring beam path and / or second reference beam path. The optical path lengths of the second measuring beam path and / or second reference beam path are different from one of the first beam paths. The wave length difference is selected according to a distance of two measuring areas which are arranged at a distance in the depth direction of the sample.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Synthetic aperture ladar system and method using real-time holography
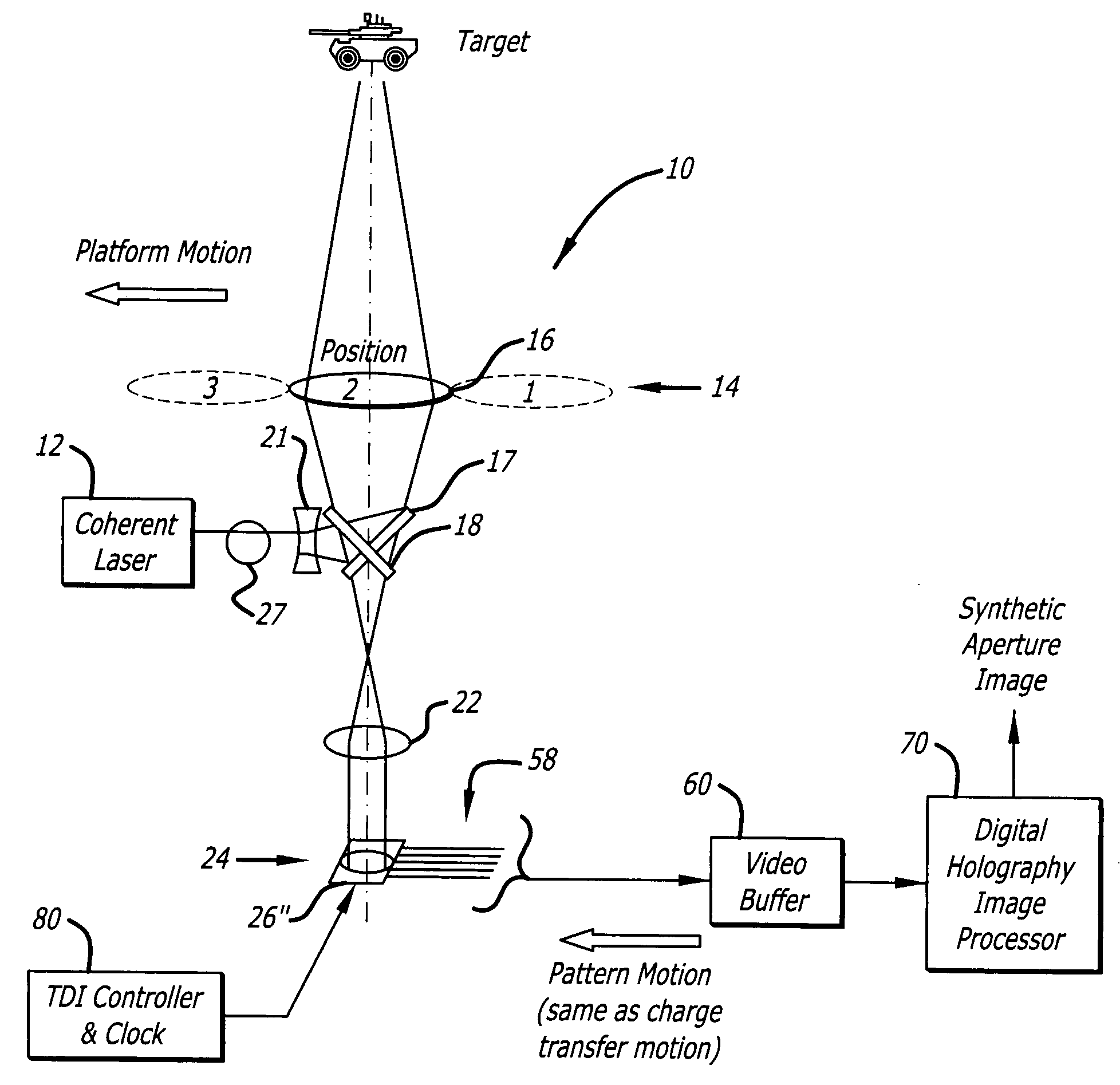
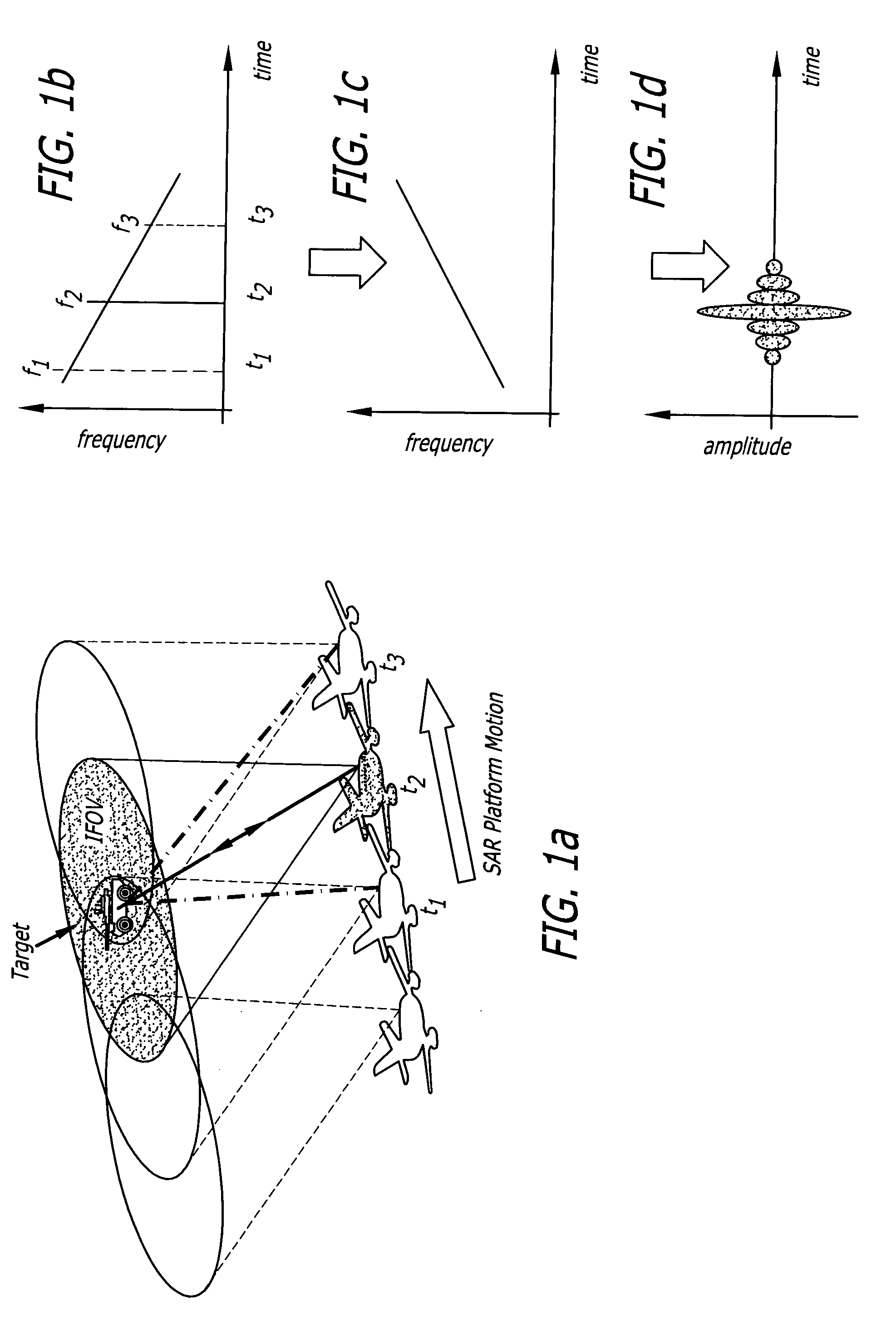
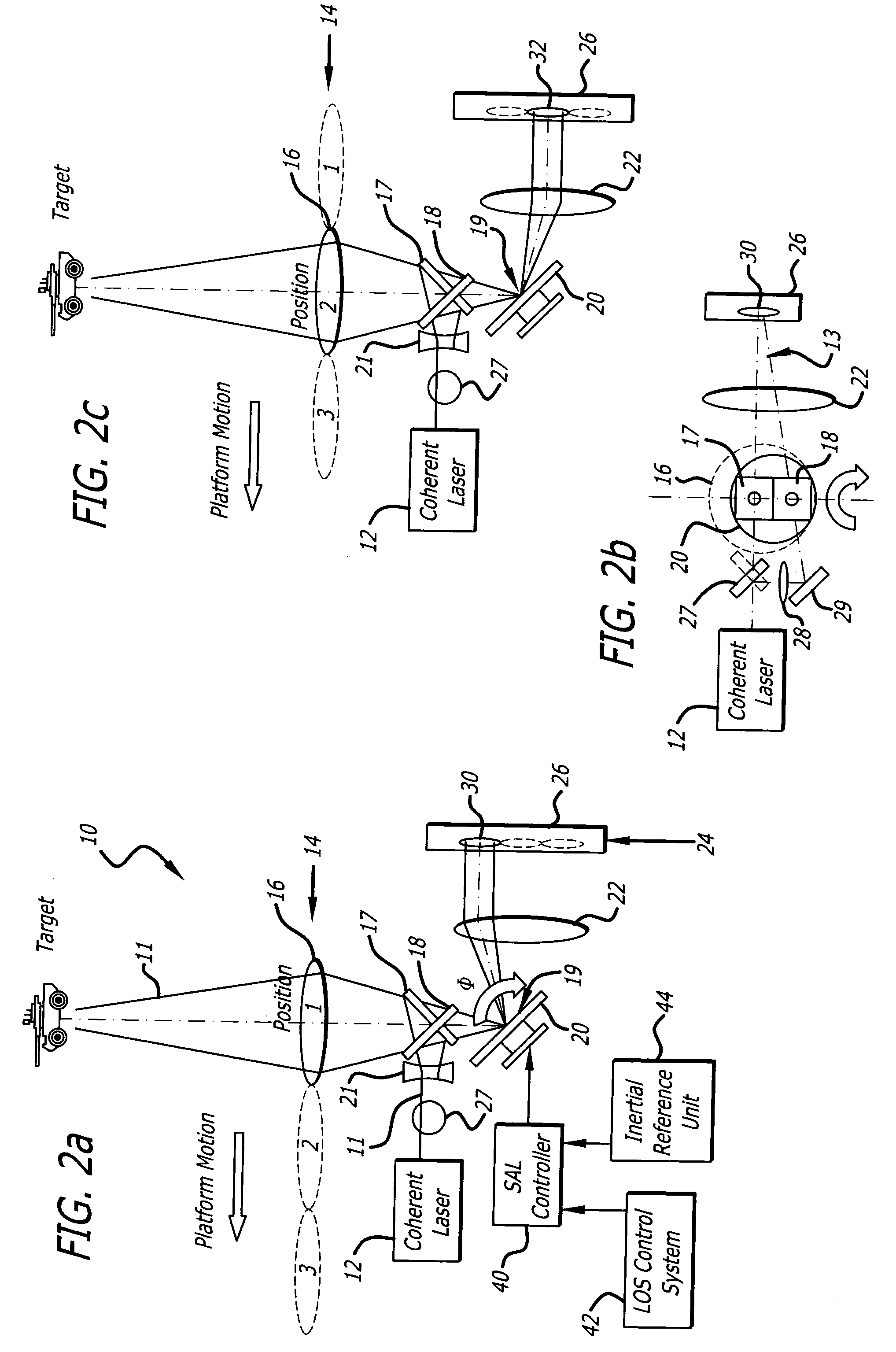
ActiveUS20050057654A1Motion compensationTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersSynthetic aperture radarReal time holography
This invention uses a real-time holographic medium to record the amplitude and phase information collected from a moving platform at the aperture plane of a side-looking optical sensor over the collection time. A back-scan mirror is used to compensate platform motion during the synthetic aperture integration time. Phase errors caused by a nonlinear platform motion are compensated by controlling the phase offset between the illumination beam and the reference beam used to write the hologram based on inertial measurements of the flight path and the sensor line-of-sight pointing angles. In the illustrative embodiment, a synthetic aperture ladar (SAL) imaging system is mounted on a mobile platform. The system is adapted to receive a beam of electromagnetic energy; record the intensity and phase pattern carried by the beam; and store the pattern to compensate for motion of the platform relative to an external reference. In the illustrative embodiment, the image is stored as a holographic image. The system includes a back-scan mirror, which compensates the stored holographic pattern for motion of the platform. The medium and back-scan mirror may be replaced with a digital camera and one-dimensional and two-dimensional arrays may be used. In a specific embodiment, a two-dimensional array is used with a time delay and integration (TDI) scheme, which compensates for motion of the platform in the storage of the optical signals. In an alternative embodiment, a back-scanning mirror is used to compensate for motion of the platform. Consequently, the interference pattern between a relayed image of the aperture plane and a reference beam is continuously stored. In this embodiment, the instantaneous location of the received beam on the recording medium is controlled to compensate for motion of the platform.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Match filters for a real time fingerprint sensor and verification system
InactiveUS6111671AAcquiring/reconising fingerprints/palmprintsOptical elementsPhase correlationSpatial light modulator
A real time fingerprint verification system includes a recording device and a verification device each having a fingerprint scanner for generating a flat, dimensionally undistorted, high contrast, fingerprint image, and an intensity sensitive, spatial light modulator (SLM) for receiving and transforming the flat fingerprint image into a planar, coherent light image. In the recording device, the planar coherent light image beam of the fingerprint from the SLM is Fourier transformed, and input into a microscope objective lens system which expands the Fourier transformed beam image sufficiently to allow mechanical blocking of its central portion or order, whereupon it is directed to interact as an object beam with a reference beam from the particular coherent light source to record a holographic matched filter. In the verification device, the planar coherent light image beam of the fingerprint is Fourier transformed and input into a microscope objective lens system to allow similar mechanical blocking of its central portion or order whereupon it is directed to interrogates a previously recorded holographic matched filter of a fingerprint image as an object beam for determining a match or not between the respective recorded and interrogating images. The spatial light modulator (SLM) in both the respective recording and verification devices enables phase correlation (optical path length determination) of one device to another device. X-Y alignment and rotational orinentation of the respective real time image and holographic matched filter image is accomplished by jittering (orbiting and angularly oscillating) either the interrogating object beam, real time, relative to the matched filter or visa versa.
Owner:ADVANCED PRECISION TECH
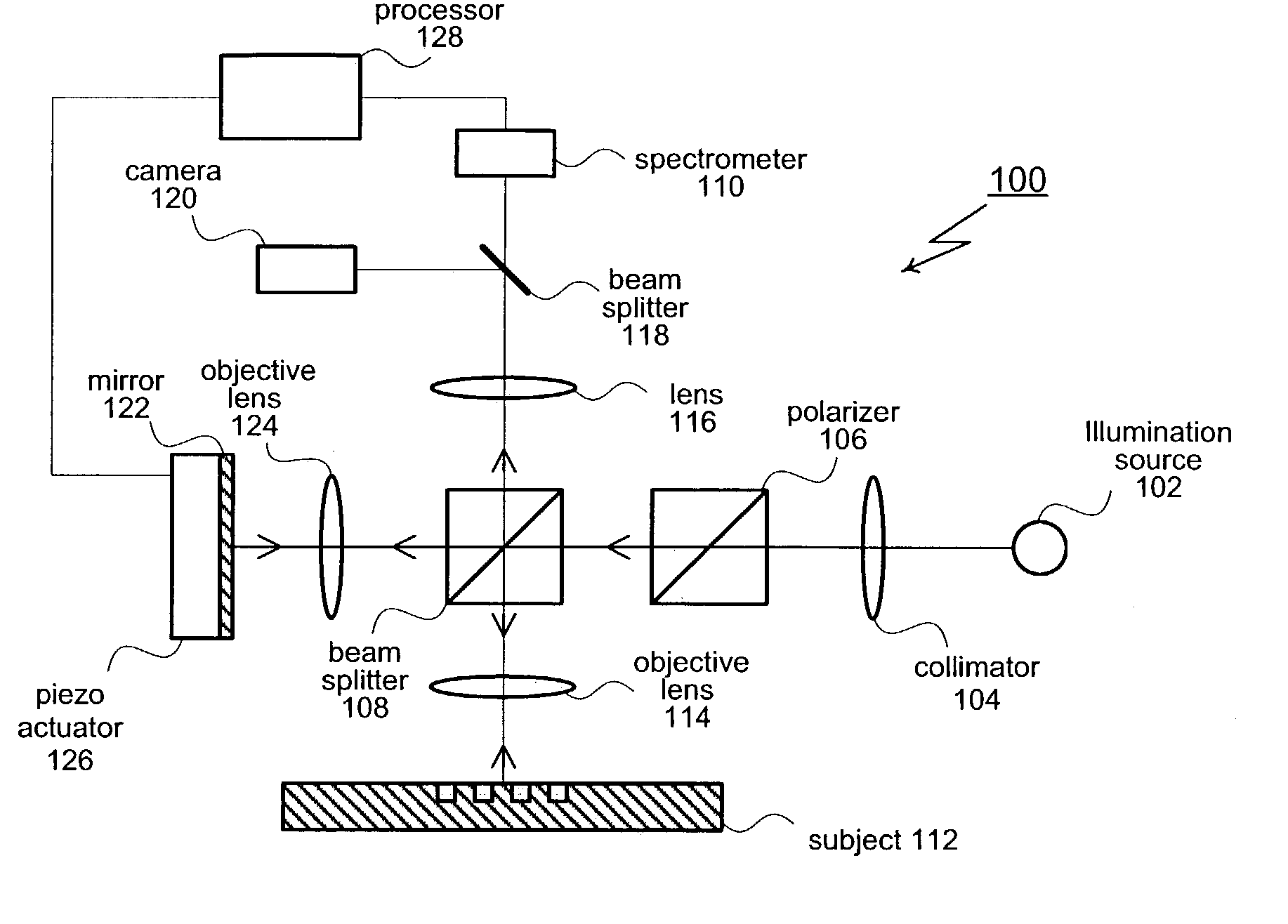
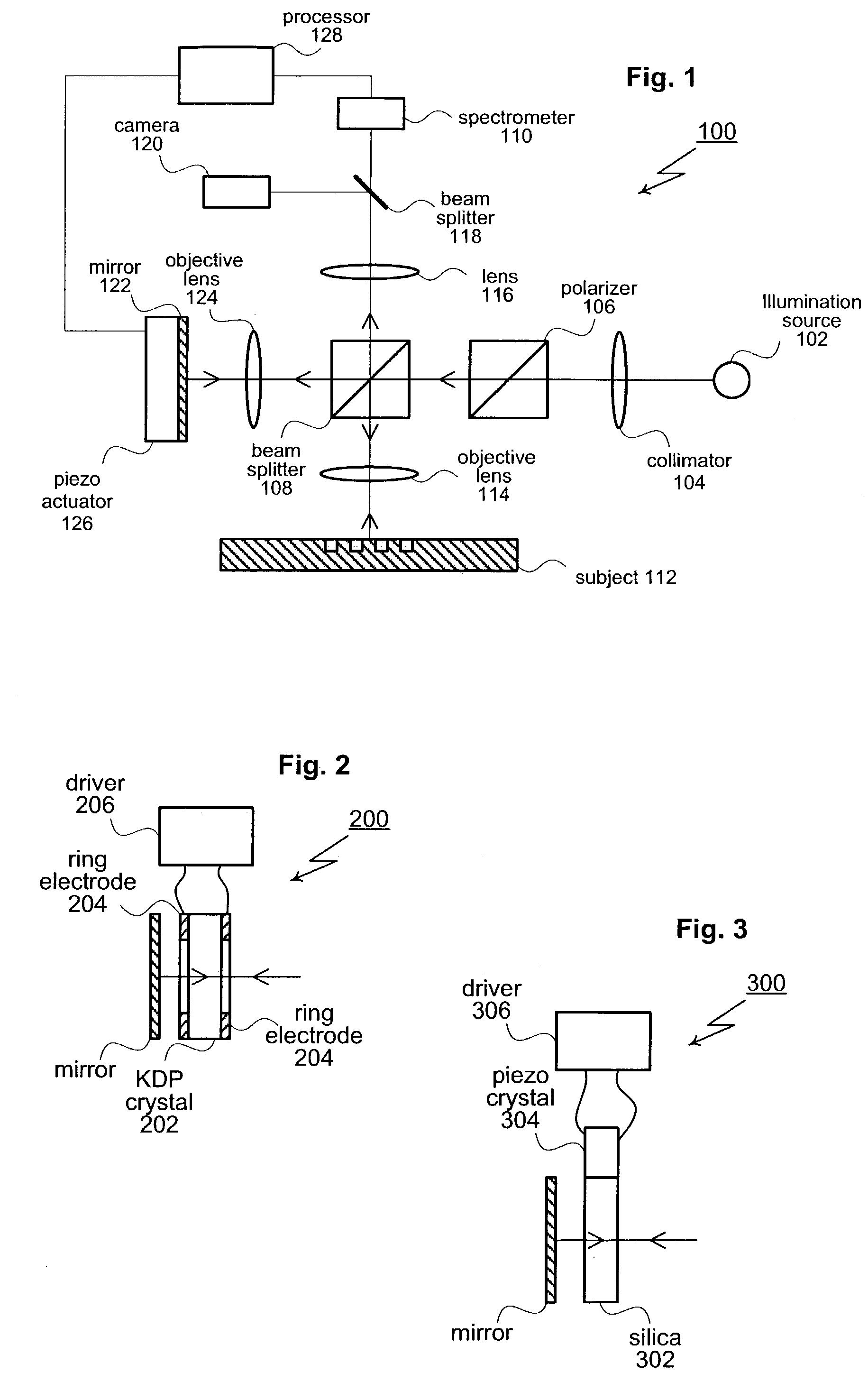
High resolution, multispectral, wide field of view retinal imager
An ophthalmic instrument (for obtaining high resolution, wide field of area multi-spectral retinal images) including a fundus retinal imager, (which includes optics for illuminating and imaging the retina of the eye); apparatus for generating a reference beam coupled to the fundus optics to form a reference area on the retina; a wavefront sensor optically coupled to the fundus optics for measuring the wavefront produced by optical aberrations within the eye and the imager optics; wavefront compensation optics coupled to the fundus optics for correcting large, low order aberrations in the wavefront; a high resolution detector optically coupled to the imager optics and the wavefront compensation optics; and a computer (which is connected to the wavefront sensor, the wavefront compensation optics, and the high resolution camera) including an algorithm for correcting, small, high order aberrations on the wavefront and residual low order aberrations.
Owner:KESTREL CORP
Confocal microscopy
InactiveUS7333213B2Improves confocal microscopyMicroscopesUsing optical meansPhotodetectorDisplay device
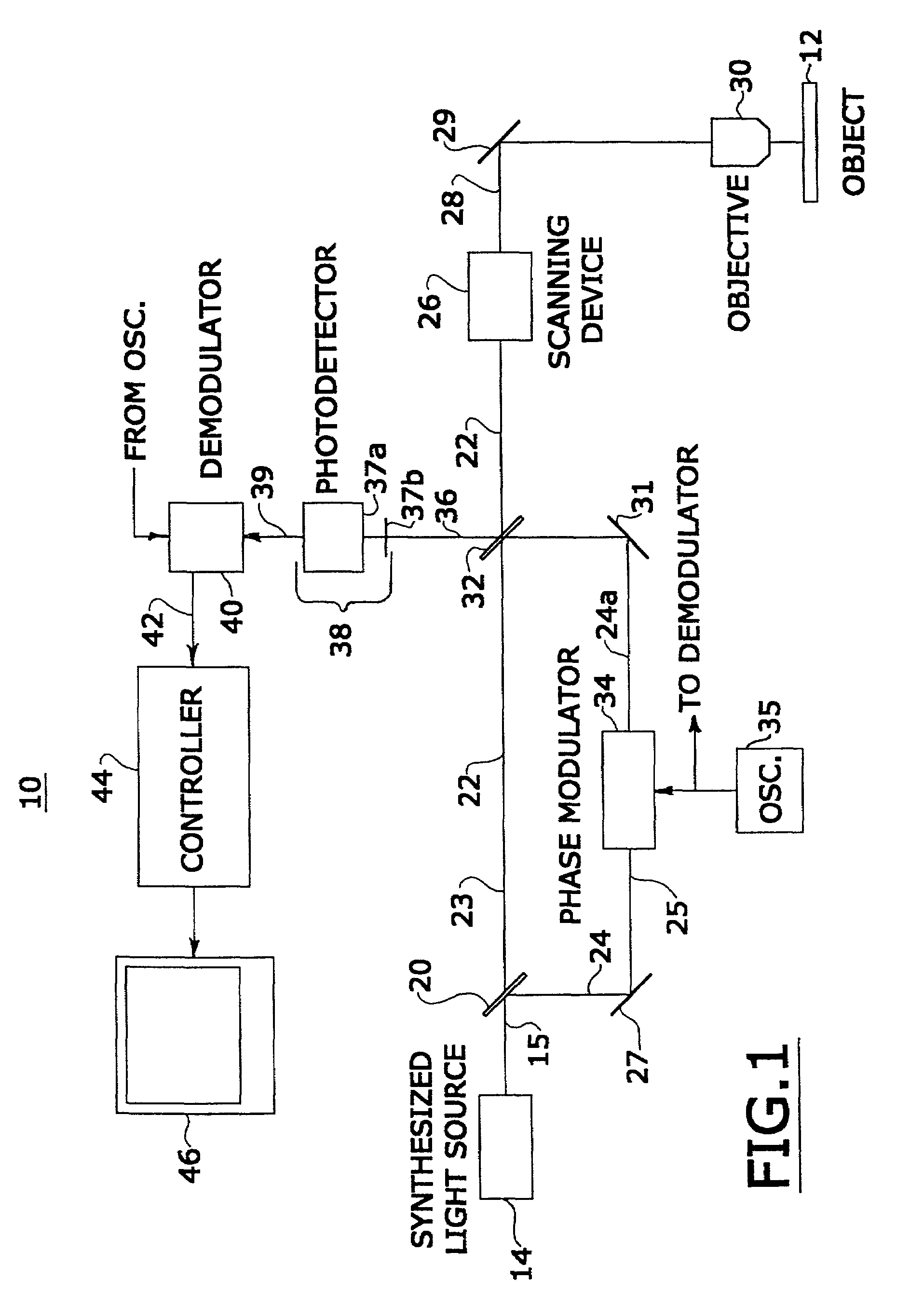
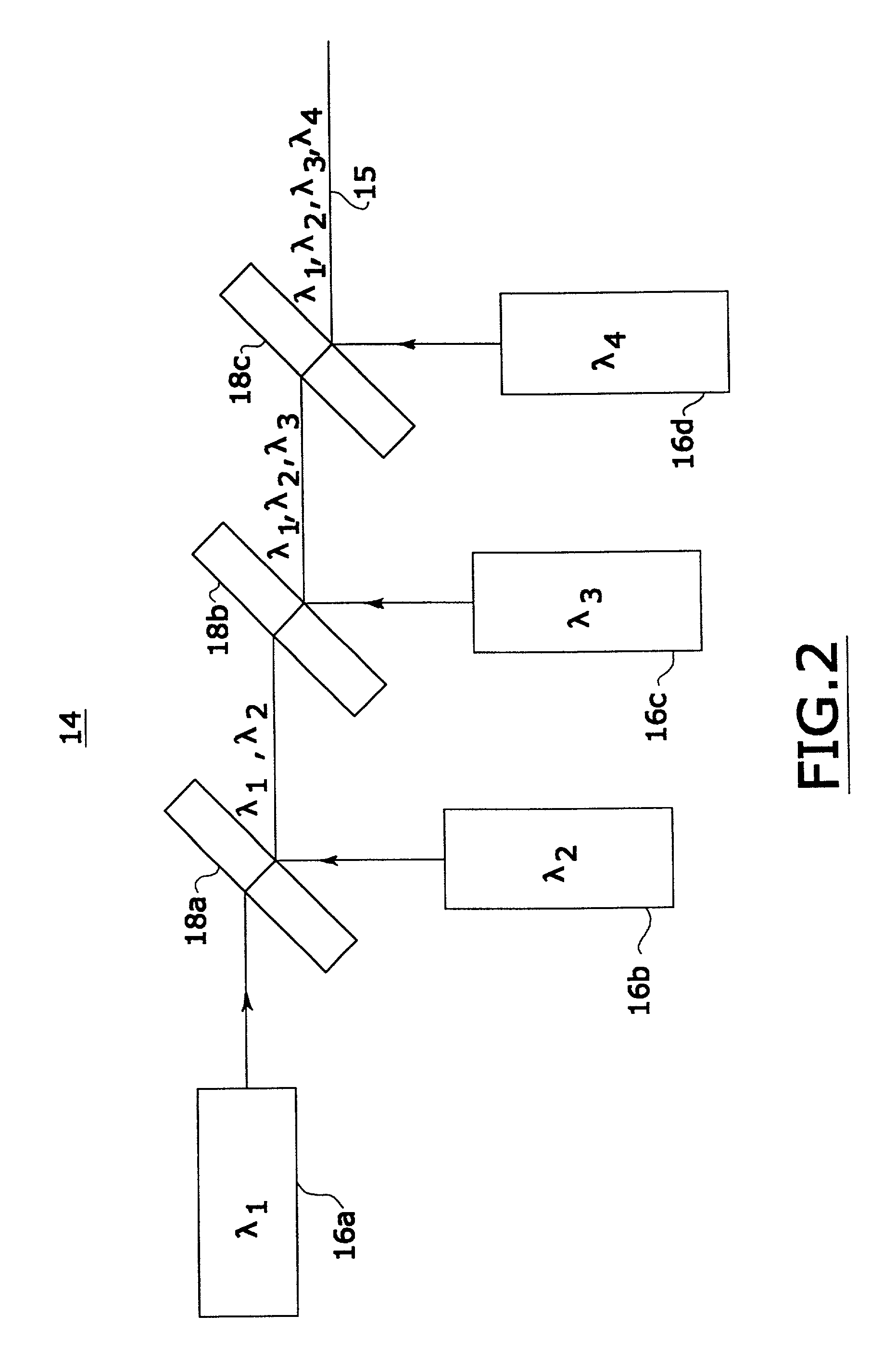
An improved confocal microscope system is provided which images sections of tissue utilizing heterodyne detection. The system has a synthesized light source for producing a single beam of light of multiple, different wavelengths using multiple laser sources. The beam from the synthesized light source is split into an imaging beam and a reference beam. The phase of the reference beam is then modulated, while confocal optics scan and focus the imaging beam below the surface of the tissue and collect from the tissue returned light of the imaging beam. The returned light of the imaging beam and the modulated reference beam are combined into a return beam, such that they spatially overlap and interact to produce heterodyne components. The return beam is detected by a photodetector which converts the amplitude of the return beam into electrical signals in accordance with the heterodyne components. The signals are demodulated and processed to produce an image of the tissue section on a display. The system enables the numerical aperture of the confocal optics to be reduced without degrading the performance of the system.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Method for creating a holographic screen that reconstructs uniformly magnified three-dimensional images from projected integral photographs
A method of producing a holographic screen for reconstruction of uniformly magnified three-dimensional images from projected integral photographs. The screen is produced as an array of holographic imaging elements whose center distances and focal lengths have been scaled-up uniformly by the magnification factor. In the preferred embodiment, when illuminated with a white light reference beam, the screen reconstructs a linear array comprising an alternating series of red, green, and blue vertical lines. However, when an enlarged integral photograph representative of a three-dimensional scene is correctly projected onto the screen, a uniformly magnified three-dimensional image of that scene is reconstructed. The screen may be manufactured as rectangular tiles that are assembled to form the entire screen.
Owner:KREMEN STANLEY H
Method and apparatus for phase correlation holographic drive
InactiveUS6909529B2Record information storageSystems characterised by carrier structurePhase correlationHolographic storage
A holographic storage apparatus for recording data in a holographic medium includes at least one light source for generating a reference beam and a signal beam. The reference beam is preferably a phase beam of unchanging phase content. The apparatus also includes a holographic medium placed in a path of the reference beam and a path of the signal beam. The holographic medium has a first face and both the reference beam and the signal beam enter the holographic medium through the first face. The holographic medium also includes a data reflective surface. The reference beam and the signal beam interfere in the holographic medium to create a hologram only after at least one of the reference beam and the signal beam have reflected off of the data reflective surface.
Owner:AKONIA HOLOGRAPHICS
Fourier transform spectrometer apparatus using multi-element mems
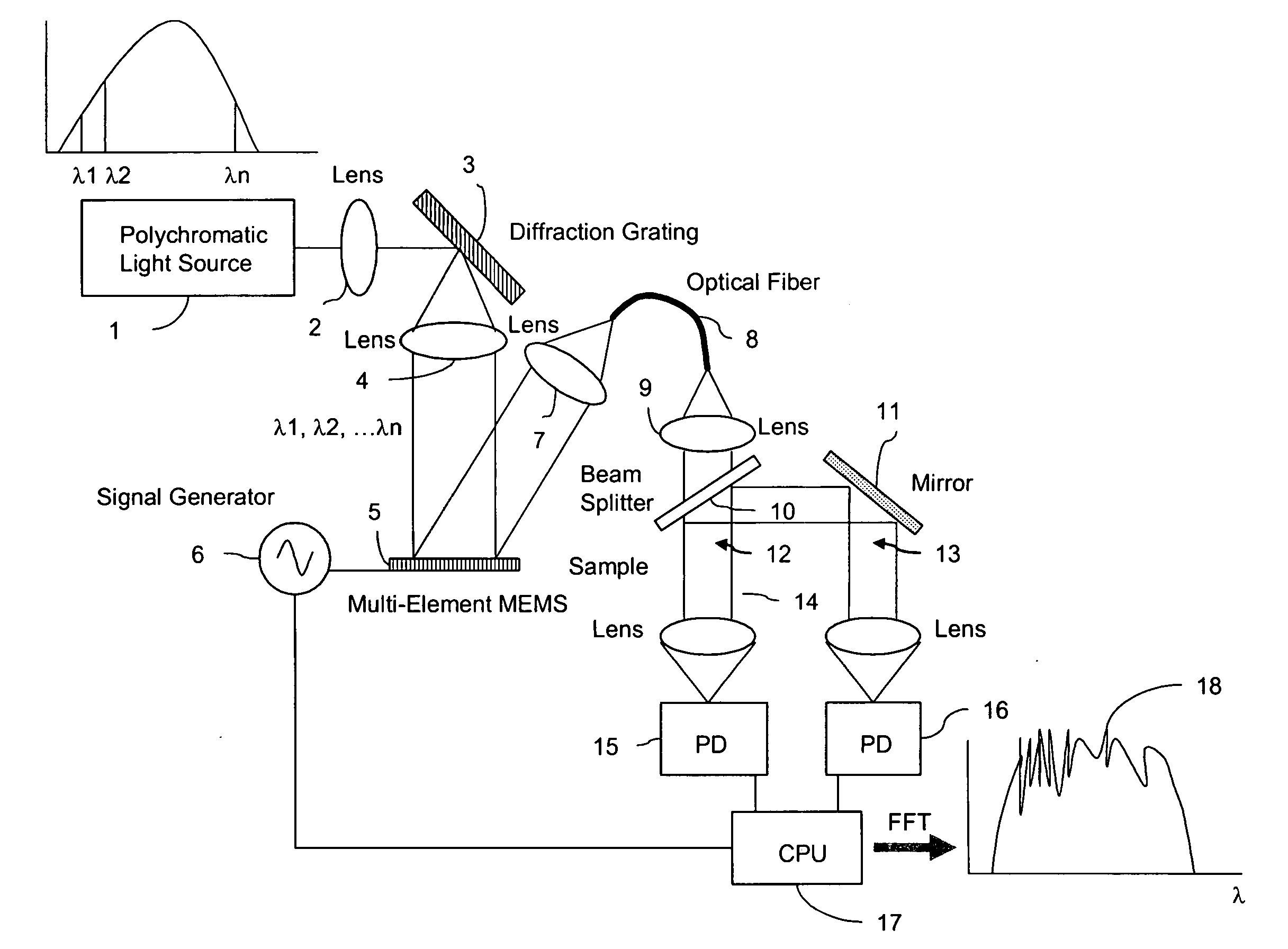
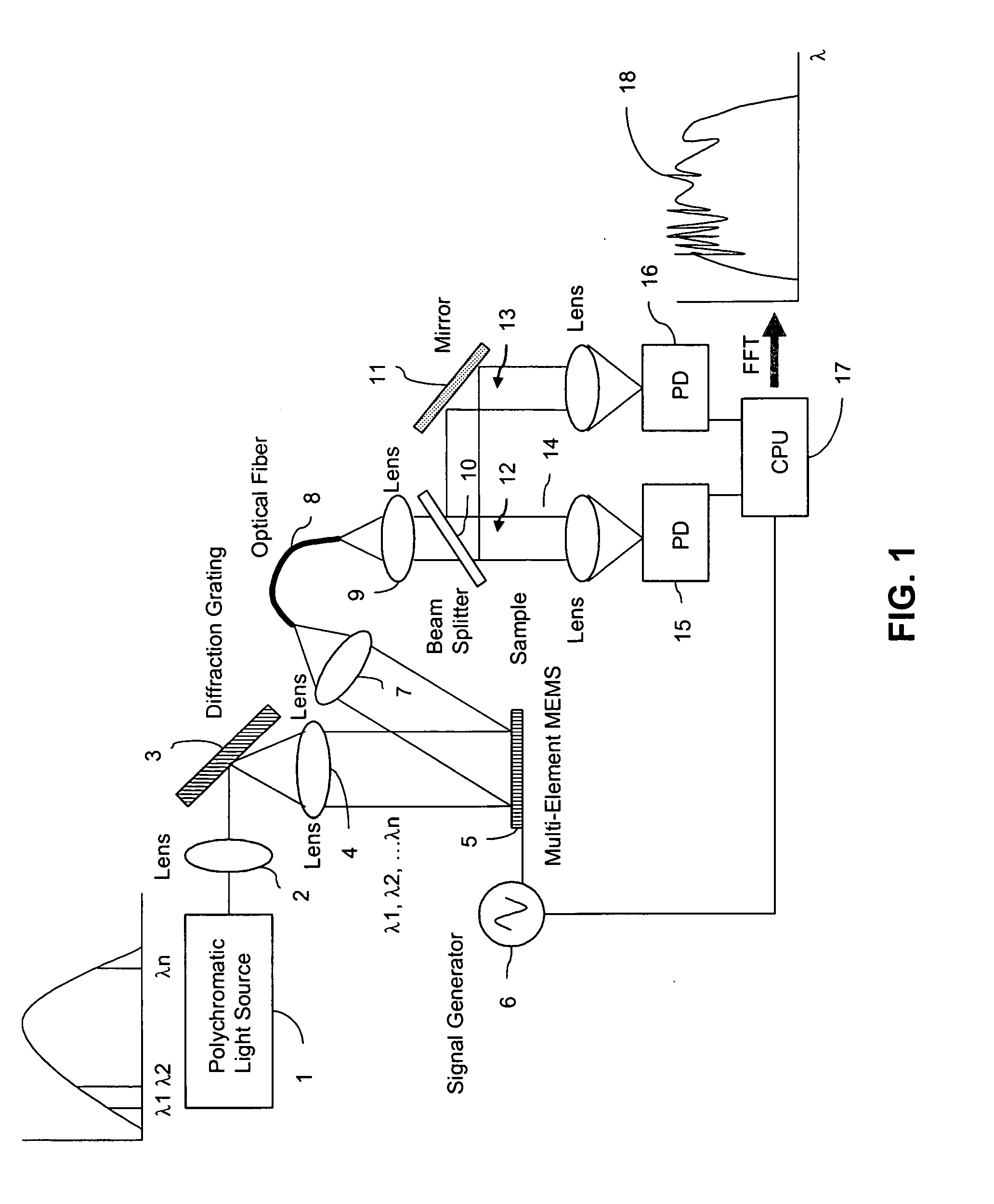
InactiveUS20050185179A1Low costHigh enough speedRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationGratingPhotovoltaic detectors
A Fourier Transform (FT) spectrometer apparatus uses multi-element MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical-Systems) or D-MEMS (Diffractive Micro-Electro-Mechanical-Systems) devices. A polychromatic light source is first diffracted or refracted by a dispersive component such as a grating or prism. The dispersed beam is intersected by a multi-element MEMS apparatus. The MEMS apparatus encodes each spectral component thereof with different time varying modulation through corresponding MEMS element. The light radiation is then spectrally recombined as a single beam. The beam is further split into to a reference beam and a probe beam. The probe light is directed to a sample and then the transmitted or reflected light is collected. Both the reference beam and probe beam are detected by a photo-detector. The detected time varying signal is analyzed by Fourier transformation to resolve the spectral components of the sample under measurement.
Owner:METROHM SPECTRO INC
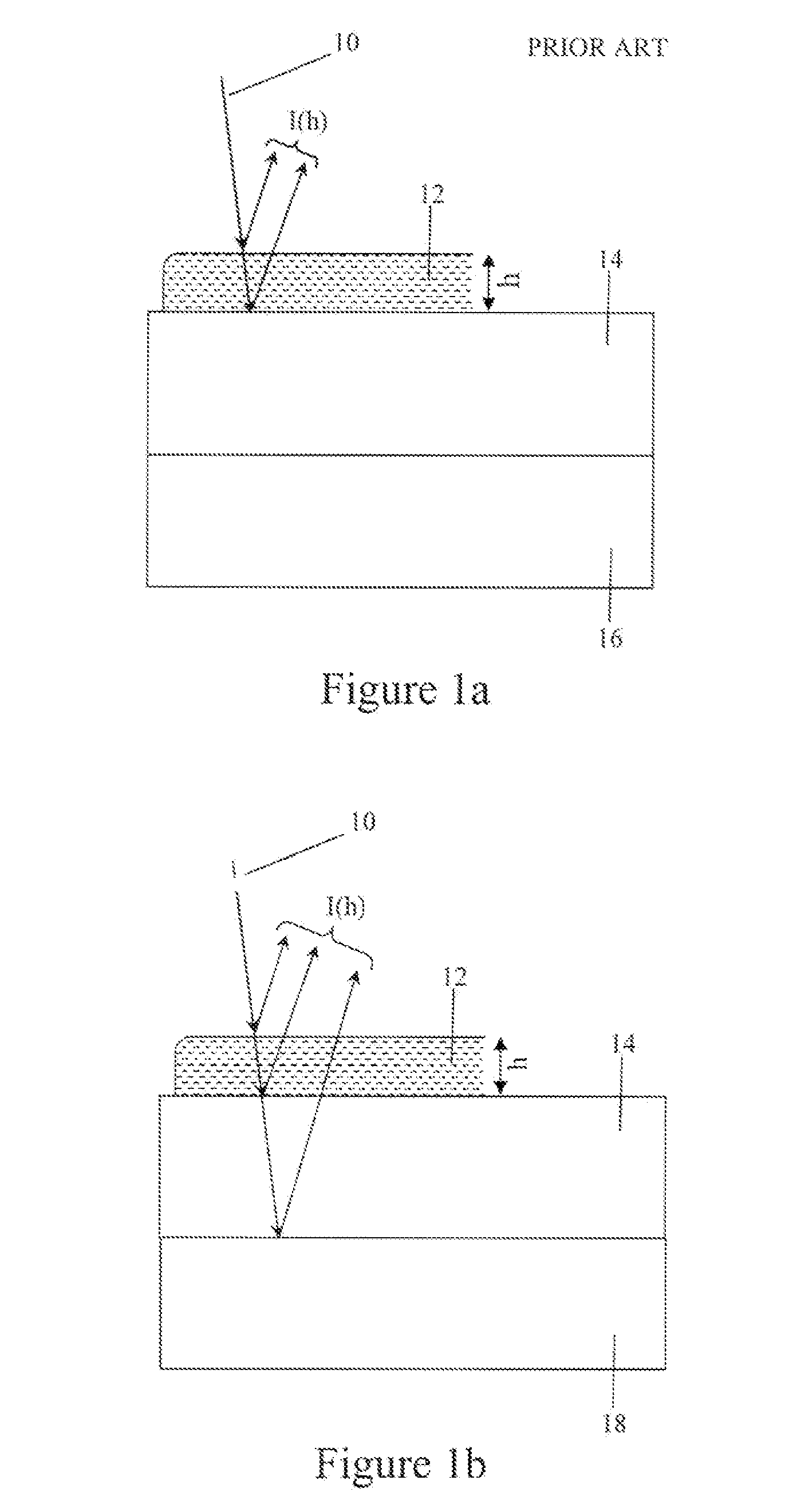
Determination of thin film topography
A method and device for determining the topography of a thin film having a front surface and a back surface. The method comprises: irradiating the film with an incident coherent or partially coherent light beam so as to get two reflected beams, the first reflected beam being reflected from the front surface of the film, and the second beam being reflected from the back surface of the film; creating an interferometric image from a united beam comprising the two reflected beams and a reference beam, the reference beam originating from the incident beam, and made to be substantially parallel to the two reflected beams. The reference beam acquires a phase shift. The interferometric image is created the interference between a combined beam comprising the reference beam and the second reflected beam, and the first reflected beam, thus acquiring information on the topography of the film, that cannot be acquired using the two reflected beams alone.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Correlation of concurrent non-invasively acquired signals
A non-invasive imaging and analysis system suitable for measuring attributes of a target, such as the blood glucose concentration of tissue, includes an optical processing system which provides a probe and reference beam. It also includes a means that applies the probe beam to the target to be analyzed, combines the probe and reference beams interferometrically, detects concurrent interferometric signals and correlates the detected signals with previously stored electronic data to determine the attribute of the target.
Owner:COMPACT IMAGING
Method and apparatus for phase-encoded homogenized Fourier transform holographic data storage and recovery
InactiveUS20050134948A1Improves fidelity and efficiencyReduce cross-correlationRecord information storageActive addressable light modulatorSpatial light modulatorLight beam
An apparatus for writing and reading holograms, comprising a spatial light modulator (SLM) operable in phase mode, having a plurality of pixels for generating an object beam that overlaps with a reference beam; a holographic recording medium (HRM) in the path of the object beam; and a first lens element disposed in the path of the object beam between the SLM and the HRM; wherein the HRM is disposed at or near the Fourier transform plane of the first lens element.
Owner:POSTECH CO LTD
Pixelated phase-mask interferometer
ActiveUS7230717B2Increase rangeReduce complexityInterferometersUsing optical meansPhase differenceDetector array
A phase-difference sensor measures the spatially resolved difference in phase between orthogonally polarized reference and test wavefronts. The sensor is constructed as a pixelated phase-mask aligned to and imaged on a pixelated detector array. Each adjacent pixel of the phase-mask measures a predetermined relative phase shift between the orthogonally polarized reference and test beams. Thus, multiple phase-shifted interferograms can be synthesized at the same time by combining pixels with identical phase-shifts. The multiple phase-shifted interferograms can be combined to calculate standard parameters such as modulation index or average phase step. Any configuration of interferometer that produces orthogonally polarized reference and object beams may be combined with the phase-difference sensor of the invention to provide, single-shot, simultaneous phase-shifting measurements.
Owner:ONTO INNOVATION INC
Method and Apparatus for Improving Image Clarity and Sensitivity in Optical Tomography Using Dynamic Feedback to Control Focal Properties and Coherence Gating
InactiveUS20110201924A1Accurately determineMoved much faster and more accuratelyInterferometersScattering properties measurementsOptical tomographyFeedback control
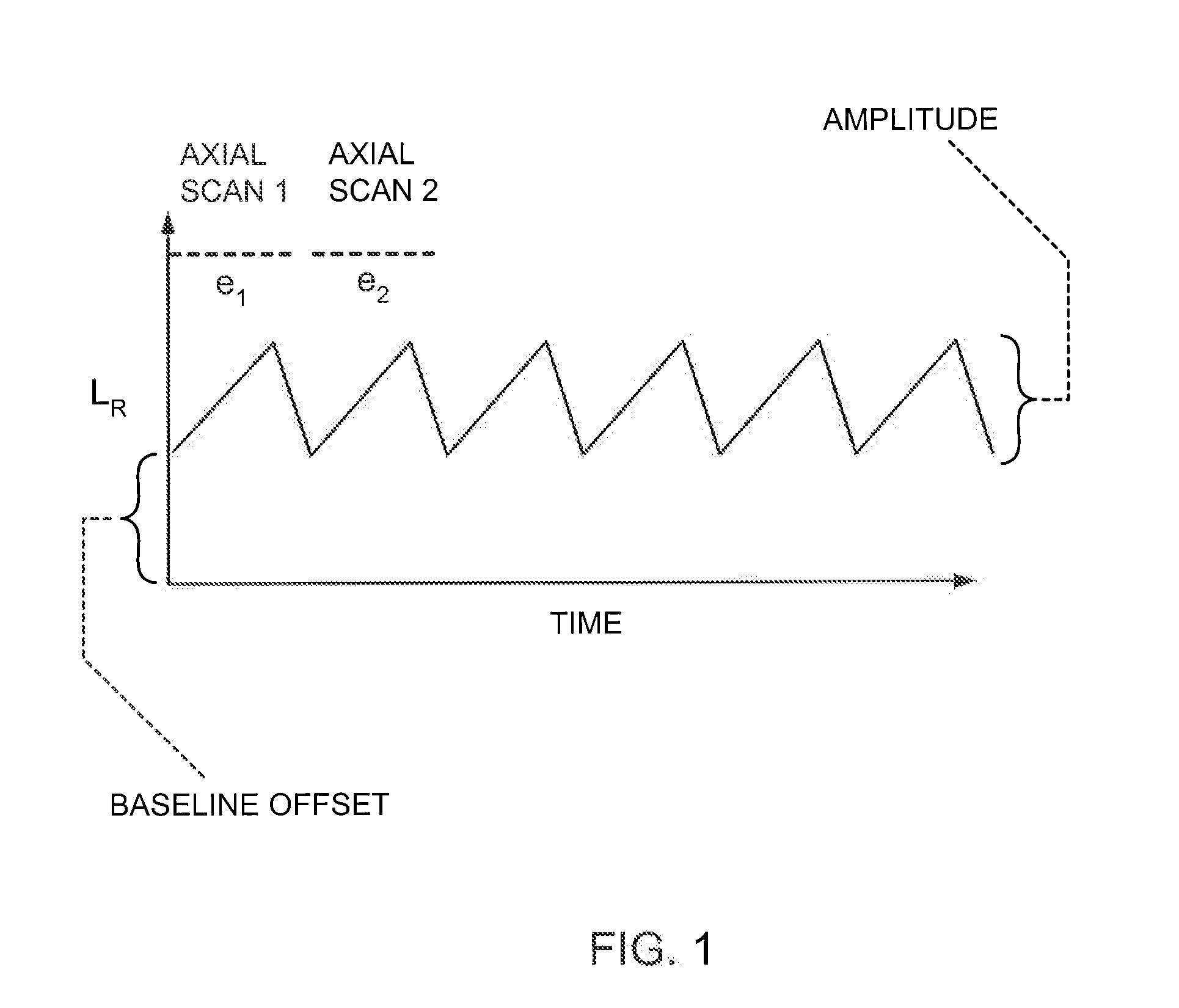
Methods for optical imaging, particularly with optical coherence tomography, using a low coherence light beam reflected from a sample surface and compared to a reference light beam, wherein real time dynamic optical feedback is used to detect the surface position of a tissue sample with respect to a reference point and the necessary delay scan range. The delay is provided by a tilting / rotating mirror actuated by a voltage adjustable galvanometer. An imaging probe apparatus for implementing the method is provided. The probe initially scans along one line until it finds the tissue surface, identifiable as a sharp transition from no signal to a stronger signal. The next time the probe scans the next line it adjusts the waveform depending on the previous scan. An algorithm is disclosed for determining the optimal scan range.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Determination of thin film topograhpy
A method and apparatus for determining the topography of a thin film having a front surface and a back surface. The method comprises: irradiating the film with an incident coherent or partially coherent beam so as to get two reflected beams, the first reflected from the front surface, and the second from the back surface; and using a third reference beam originating from the incident beam, and substantially parallel to the two reflected beams, wherein the third reference beam acquires a controlled phase shift. The three said beams are used to create an interferometric image of the film, whereby the interference of the three beams allows acquisition of information on the topography of the film that cannot be acquired using the two reflected beams alone.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Dithered holographic frontlight
InactiveUS20100238529A1Less efficientUniform lightMechanical apparatusLight guides for lighting systemsLight beamWaveguide
A reflective or transmissive hologram may be used to extract light from a waveguide. The hologram may be formed by separately exposing each of a plurality of areas of a holographic medium with object beams and / or reference beams having attributes (e.g., illumination angles) that vary randomly or pseudorandomly over the entire hologram. The areas may be contiguous (e.g., in a tiled pattern) or overlapping. In some embodiments, the spacing and / or orientation of the diffraction gratings may vary from area to area. For example, the spacing and / or orientation of the diffraction gratings may vary randomly or pseudorandomly from area to area. Some parts of the hologram may intentionally be made relatively more or relatively less efficient at extracting light from the waveguide.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Electron beam apparatus and lens array
InactiveUS20130248731A1Aberration correctionStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsLight beamElectron bunches
There is provided both an electron beam apparatus and a lens array, capable of correcting a curvature of field aberration under various optical conditions. The electron beam apparatus comprises the lens array having a plurality of electrodes, and multiple openings are formed in the respective electrodes. An opening diameter distribution with respect to the respective opening diameters of the plural openings formed in the respective electrodes are individually set, and voltages applied to the respective electrodes are independently controlled to thereby independently adjust an image forming position of a reference beam, and a curvature of the lens array image surface.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Compact holograhic human-machine interface
InactiveUS20110249309A1Minimize image distortionEasy to integrateHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesHolographic object characteristicsHuman–machine interfaceBeam source
A method of recording an object image of a first hologram as a second hologram is provided. A first hologram is recorded at a first angle of reconstruction and a holographic recording medium is provided. An object beam is directed through the first hologram at the first angle of reconstruction to reconstruct the object image on the recording medium. The recording medium is struck with a reference beam at a second angle of reconstruction to form a wave interference pattern with the object beam. The second angle of reconstruction is between 45 and 90 degrees. The wave interference pattern is recorded. A switch is provided that includes a hologram that has an angle of reconstruction between 45 and 90 degrees. A reproducing light source is positioned to direct light through the hologram at the angle of reconstruction to form a holographic image at a predetermined distance from the hologram. The switch includes a detector that detects the presence of an object proximate to the holographic image. The axis of the detector beam source is not perpendicular to the plane of the medium to which its hologram is affixed.
Owner:HOLOTOUCH
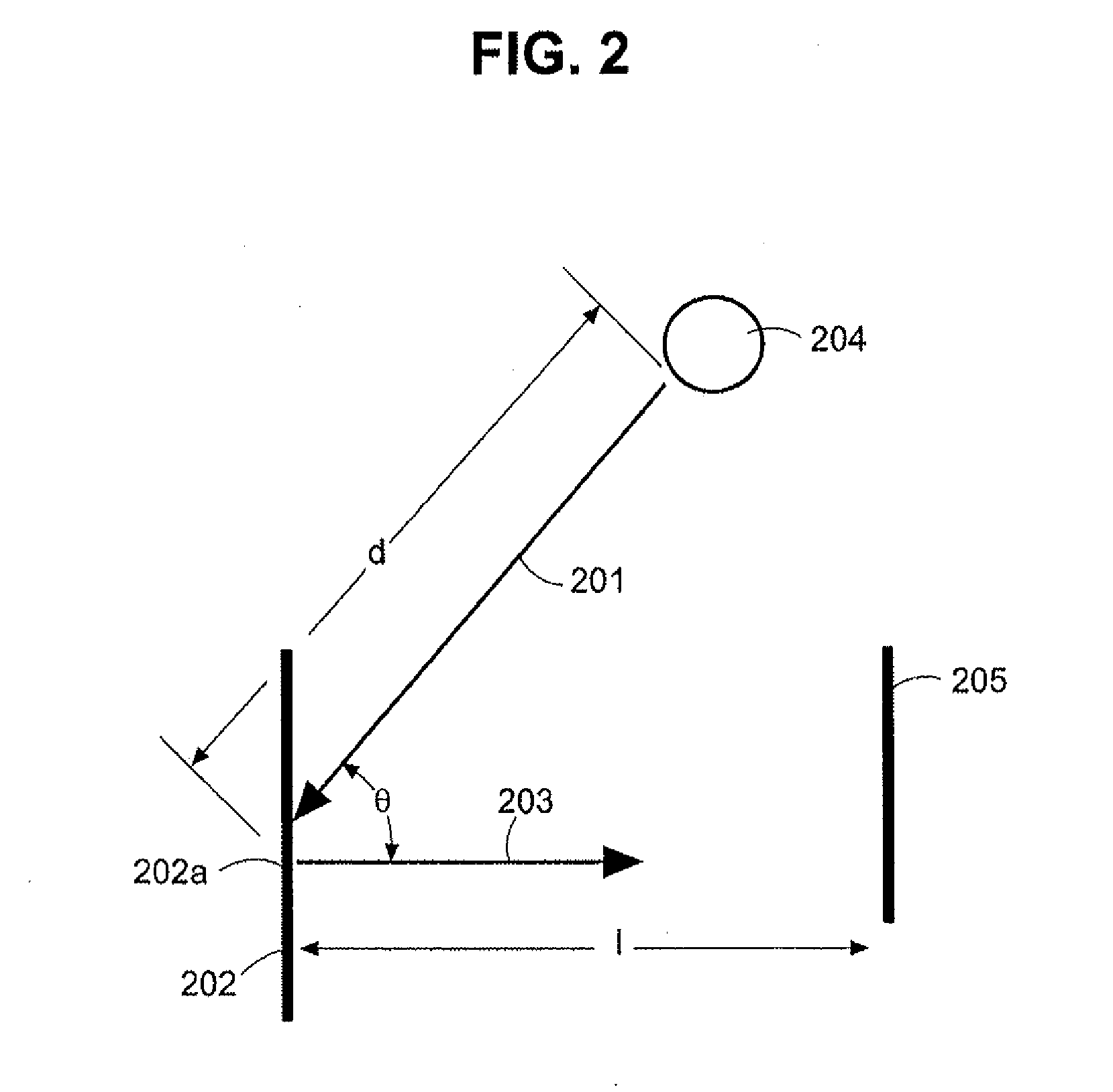
Two-dimensional photoelectric auto-collimation method and device for polarized light pyramid target common-path compensation
InactiveCN102176088AAccurately reflect the amount of driftImprove anti-interference abilityUsing optical meansOptical elementsLight beamAutocollimation
The invention discloses a two-dimensional photoelectric auto-collimation method and device for polarized light pyramid target common-path compensation, belonging to the technical field of precision instrument manufacture and precision measurement. According to the invention, high-precision photoelectric autocollimation angle measurement is realized for solving the defects in the existing method and device. The method comprises: a common-path shift quantity monitoring separating device based on a pyramid combined target can be used for curing a polarizing light splitter, a pyramid reflector and a measurement reflector to form the pyramid combined target, and separating a reference light beam which has a feature identical to that of a measurement light beam and is in common-path transmission with the measurement light beam while obtaining a two-dimensional angle variation by using the linear polarization feature of the laser; a controller is used for controlling a two-dimensional light beam deflection device in real time according to the shift quantity reflected by the reference light beam so as to inhibit the shift quantity coupled in the measurement light beam, thus the precision measurement on the two-dimensional angle variation is realized. The device for realizing the method comprises a two-dimensional photoelectric auto-collimation tube, the common-path shift quantity monitoring separating device based on the pyramid combined target, the controller and the two-dimensional light beam deflection device.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Distance measuring system
ActiveUS20070138371A1Improve propertiesMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesTarget surfacePhotovoltaic detectors
A distance measuring device capable of being used in microscopes or other optical systems. Embodiments of the invention employ one or more scanning mirrors to scan a reference beam over a target to be inspected. The reference beam is returned and detected by a photodetector. The reference beam may be created by using a knife-edge element which allows the outgoing reference beam and incoming reference beam to follow the same path so that the apparent motion of the spot on the target surface is not detected by the photodetector. The photodetector generates an electronic signal corresponding to the displacement of the target away from the ideal focal point. The electrical signal may be used to drive a servomechanism to displace either the target or the microscope objective lens to bring the target in focus.
Owner:MARSHALL DANIEL R
Compact high resolution imaging apparatus
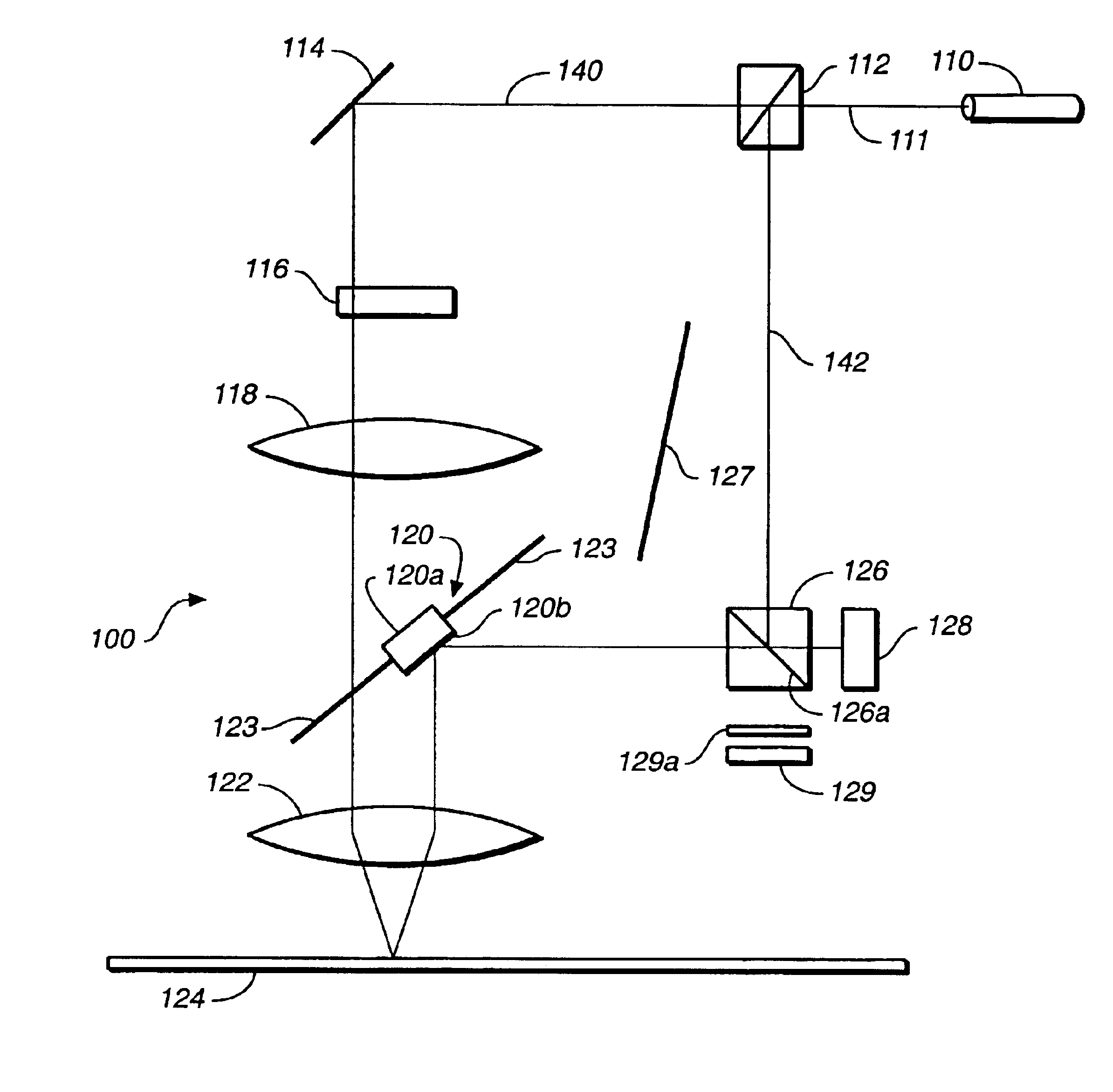
An optical coherence tomography (OCT) apparatus includes an optical source, an interferometer generating an object beam and a reference beam, a transverse scanner for scanning an object with said object beam, and a processor for generating an OCT image from an OCT signal returned by said interferometer. At least the optical source, the interferometer, and the scanner are mounted on a common translation stage displaceable towards and away from said object. A dynamic focus solution is provided when the scanner and a folded object path are placed on the translation stage.
Owner:OPTOS PLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com