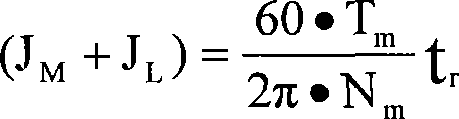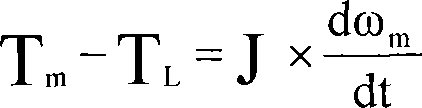Patents
Literature
882 results about "Servomechanism" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In control engineering a servomechanism, sometimes shortened to servo, is an automatic device that uses error-sensing negative feedback to correct the action of a mechanism. It usually includes a built-in encoder or other position feedback mechanism to ensure the output is achieving the desired effect.
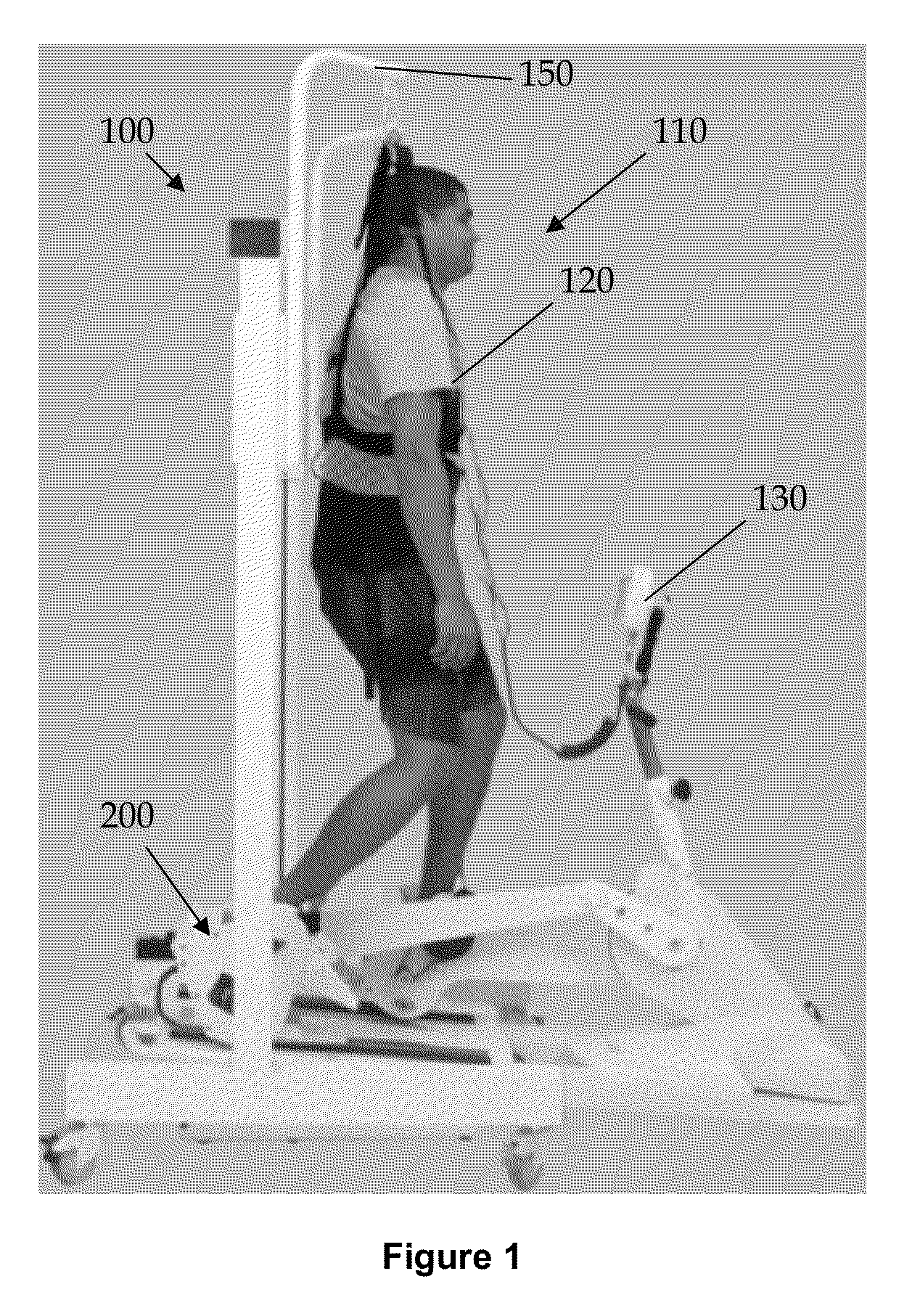
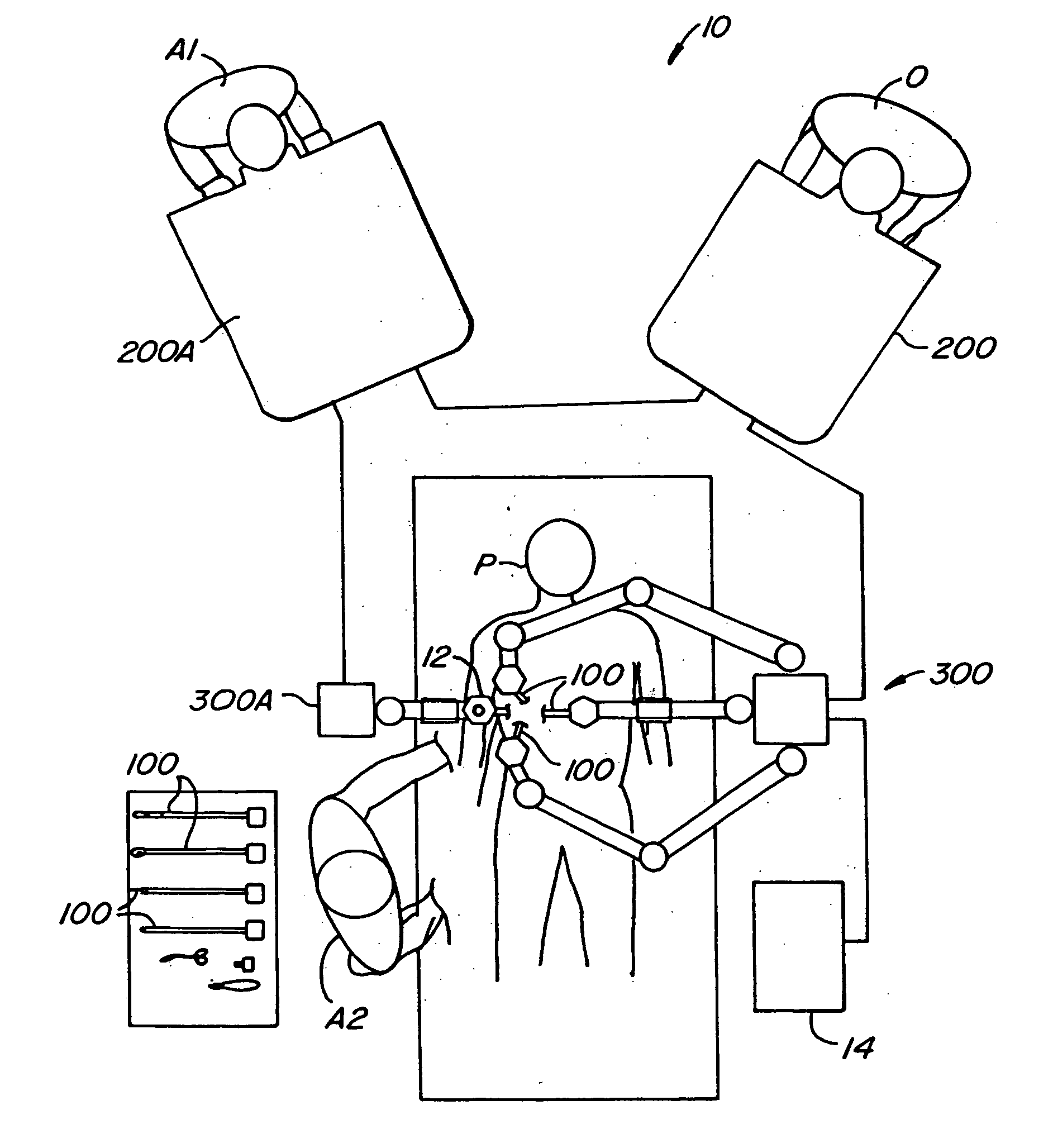
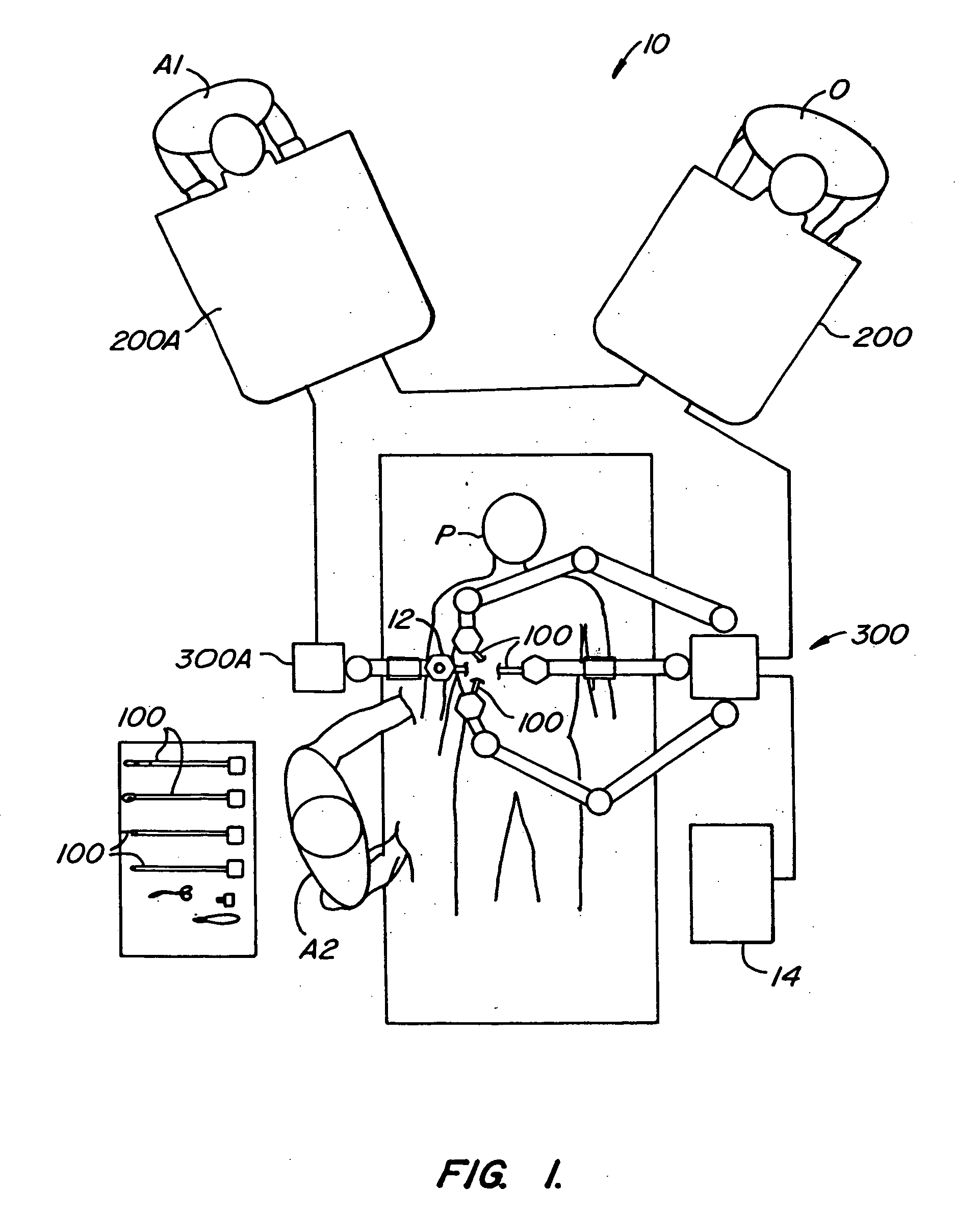
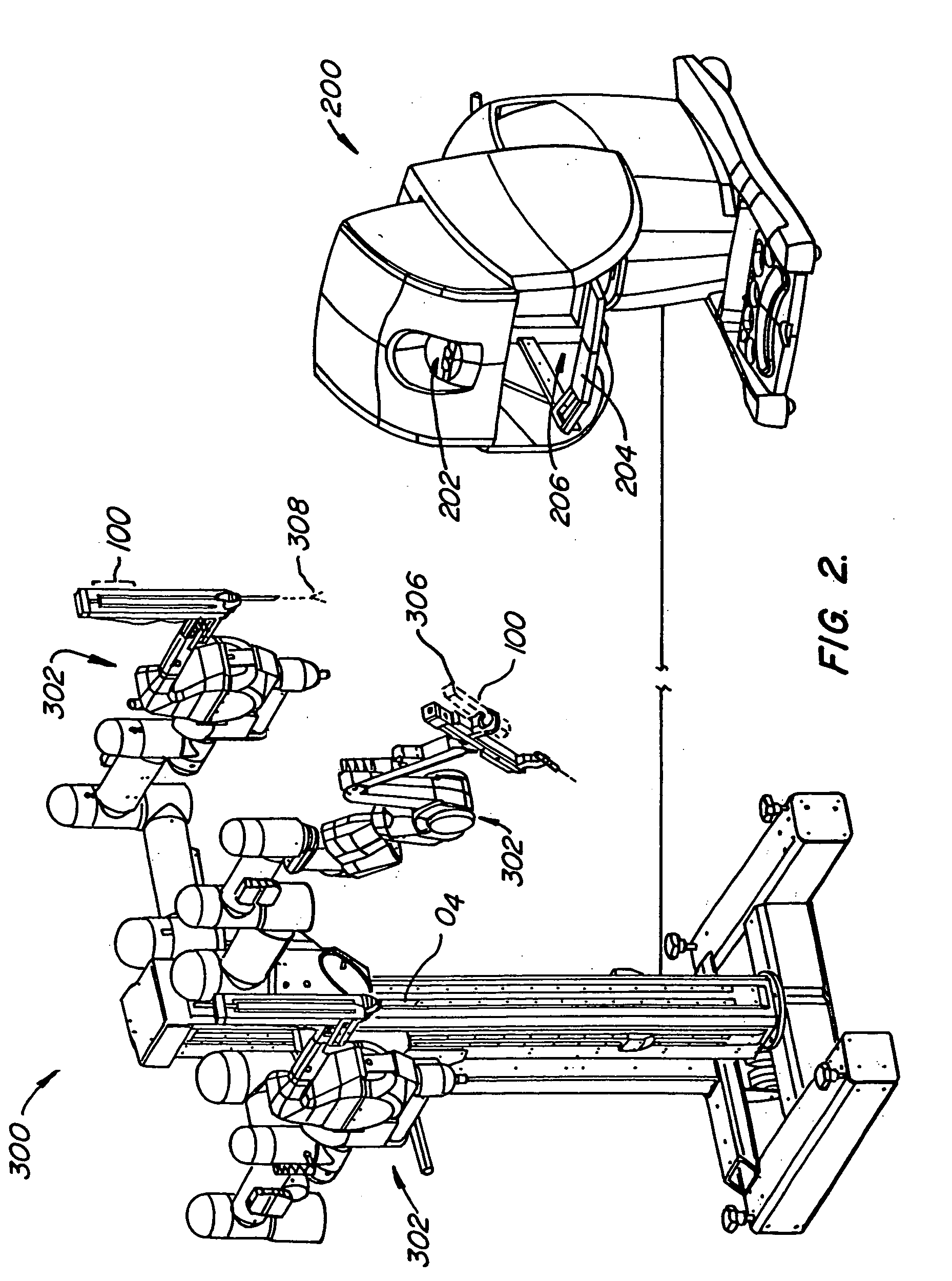
System and method for remote endoscopic surgery
InactiveUS6731988B1Improve satisfactionStrong sense of satisfactionComputer controlSimulator controlControl armDisplay device
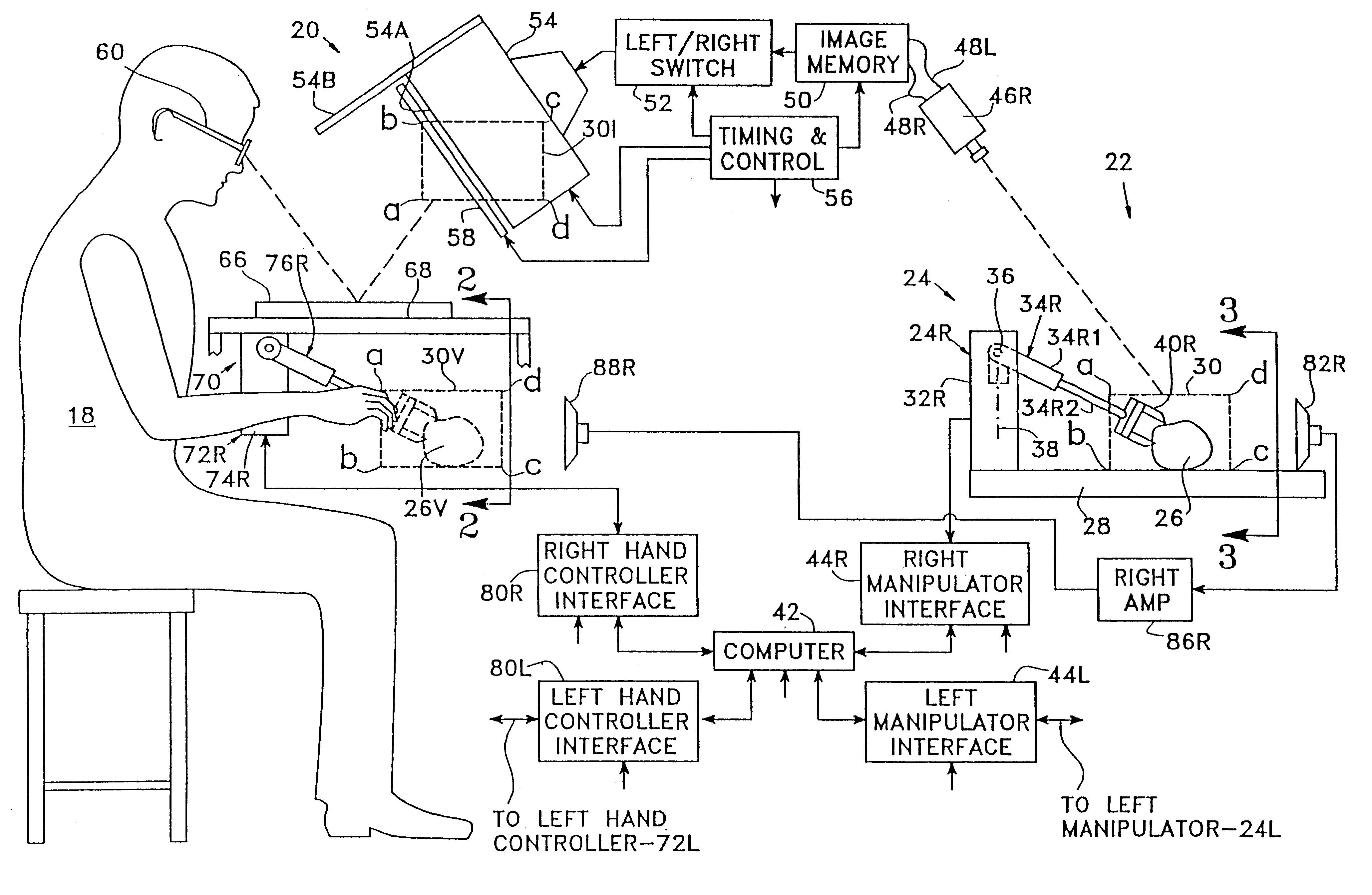
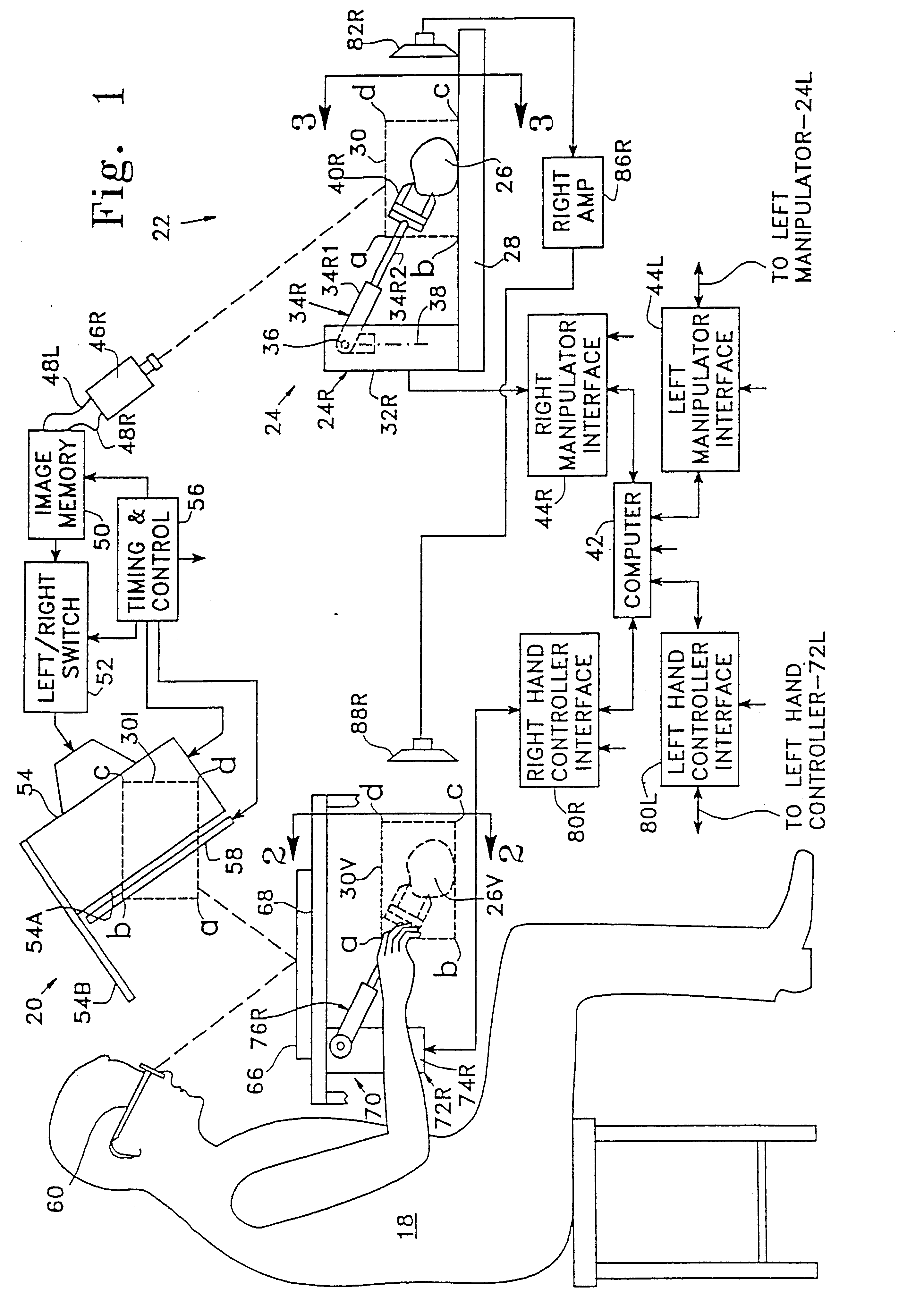
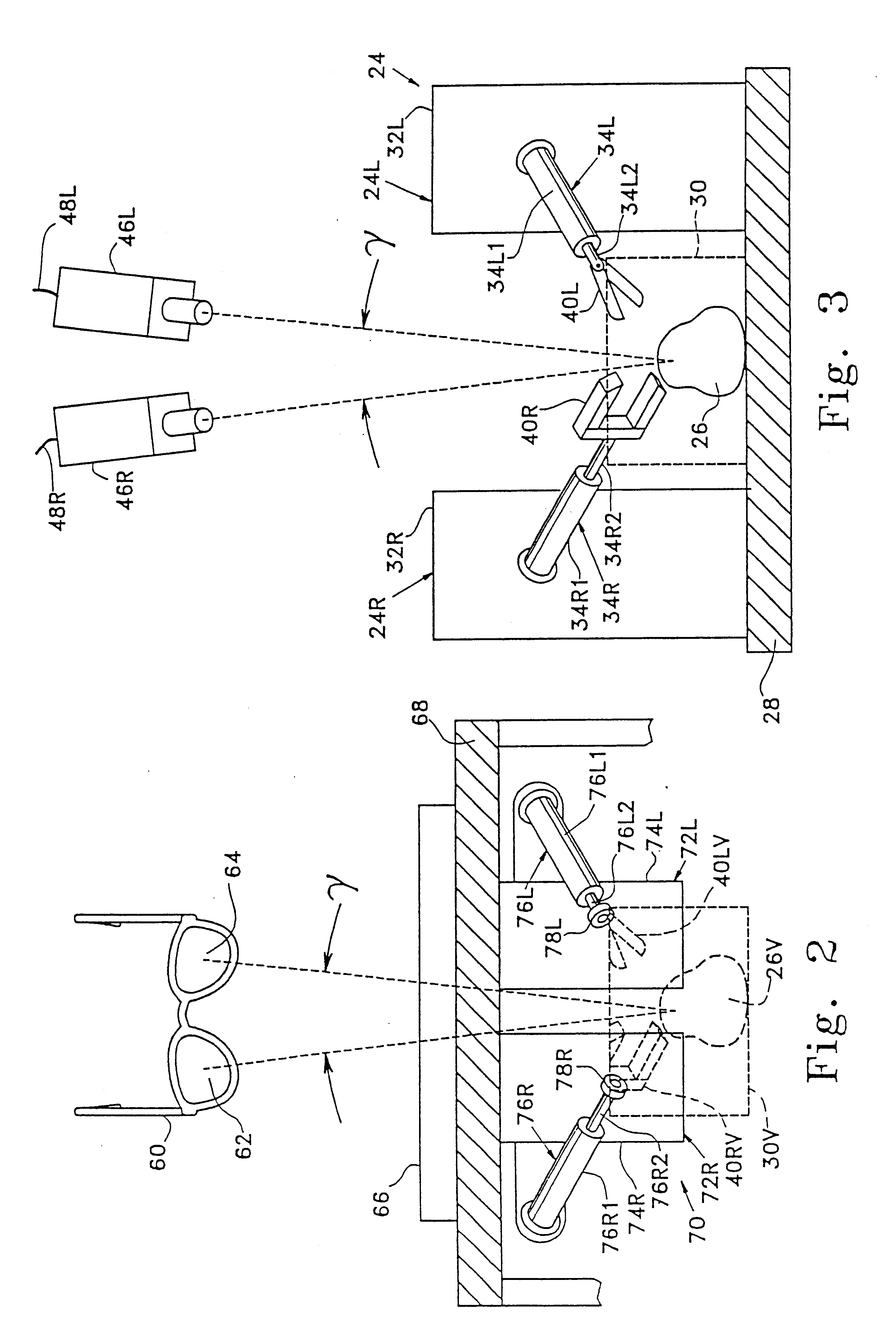
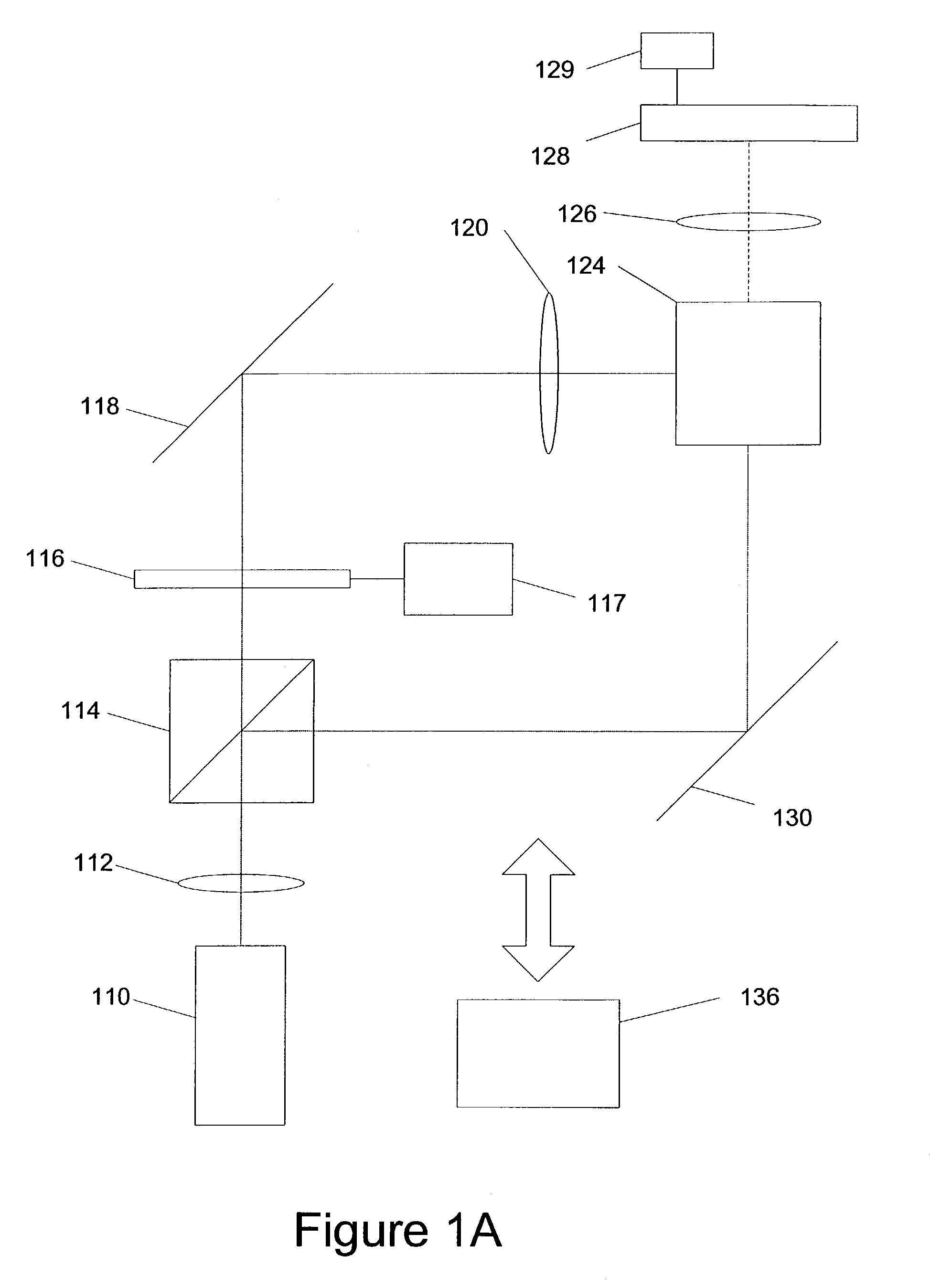
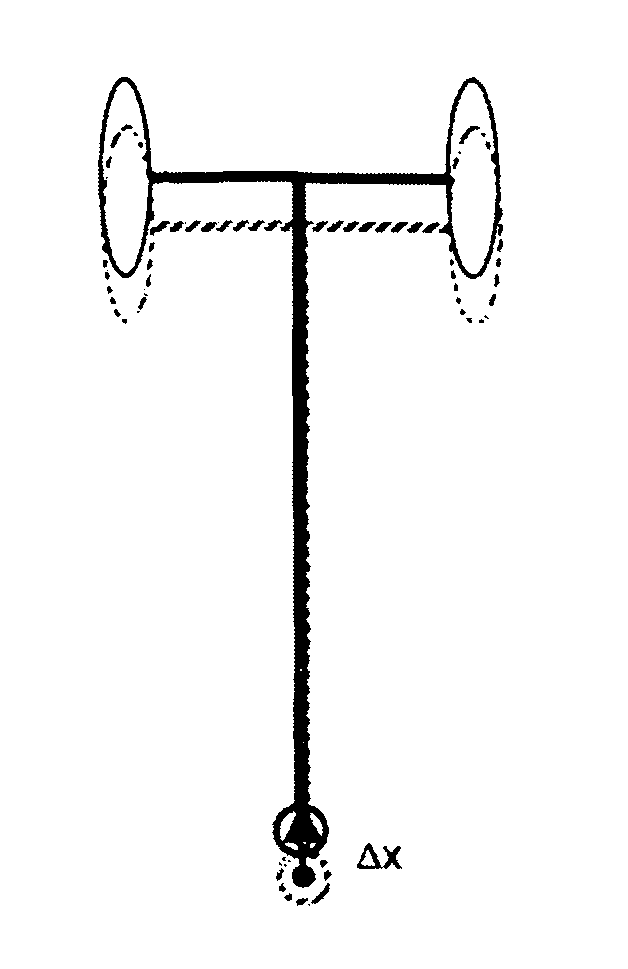
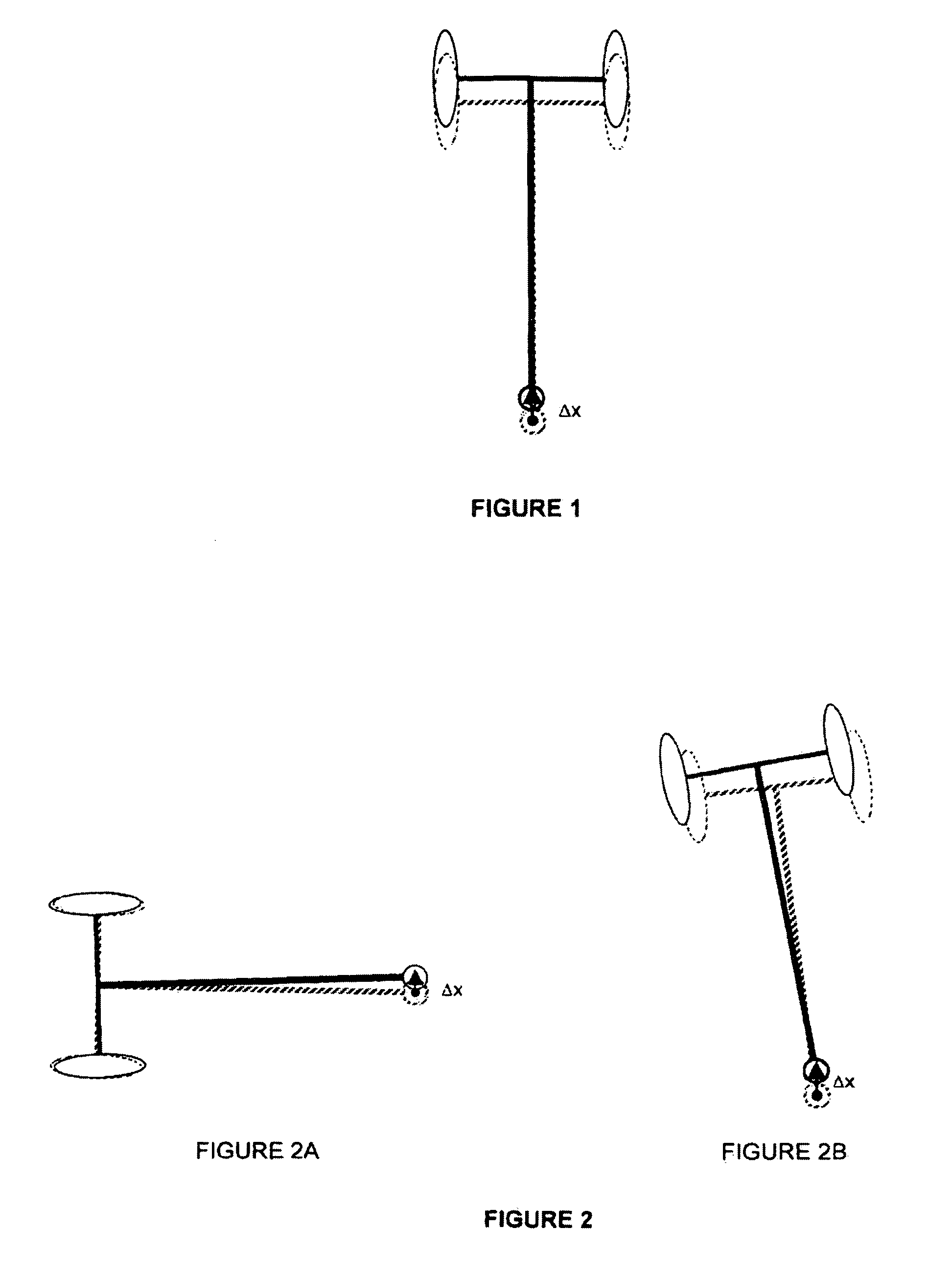
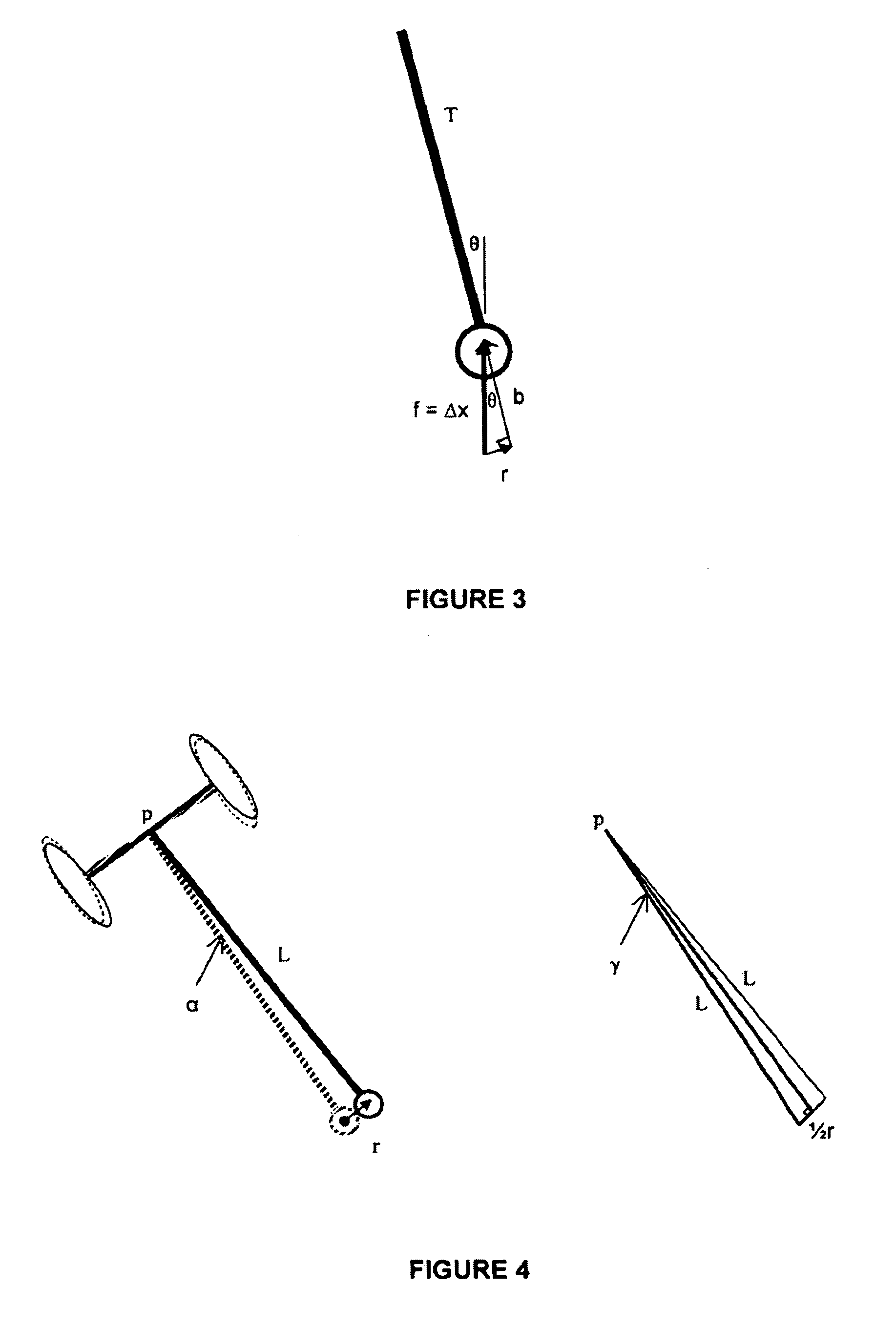
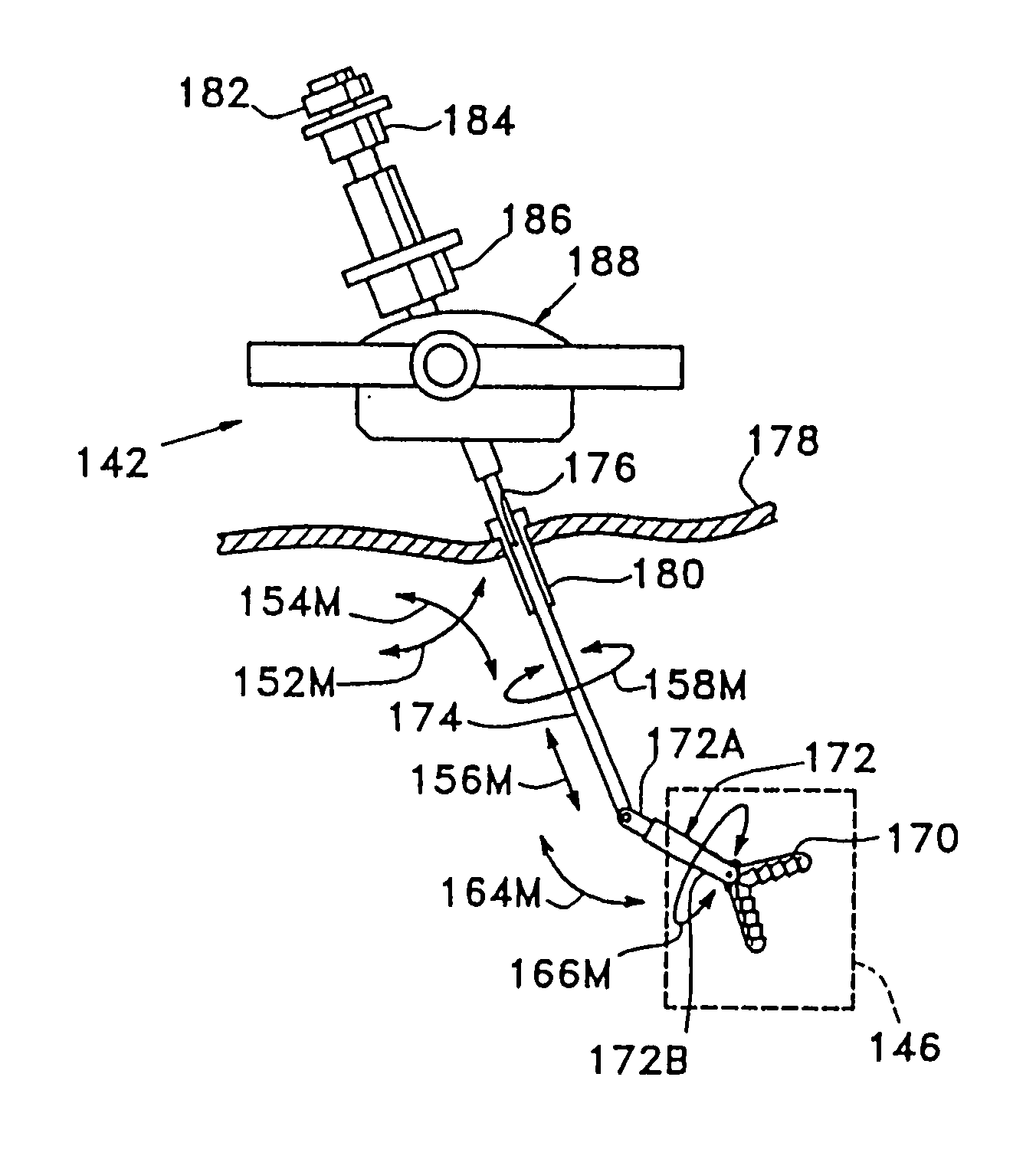
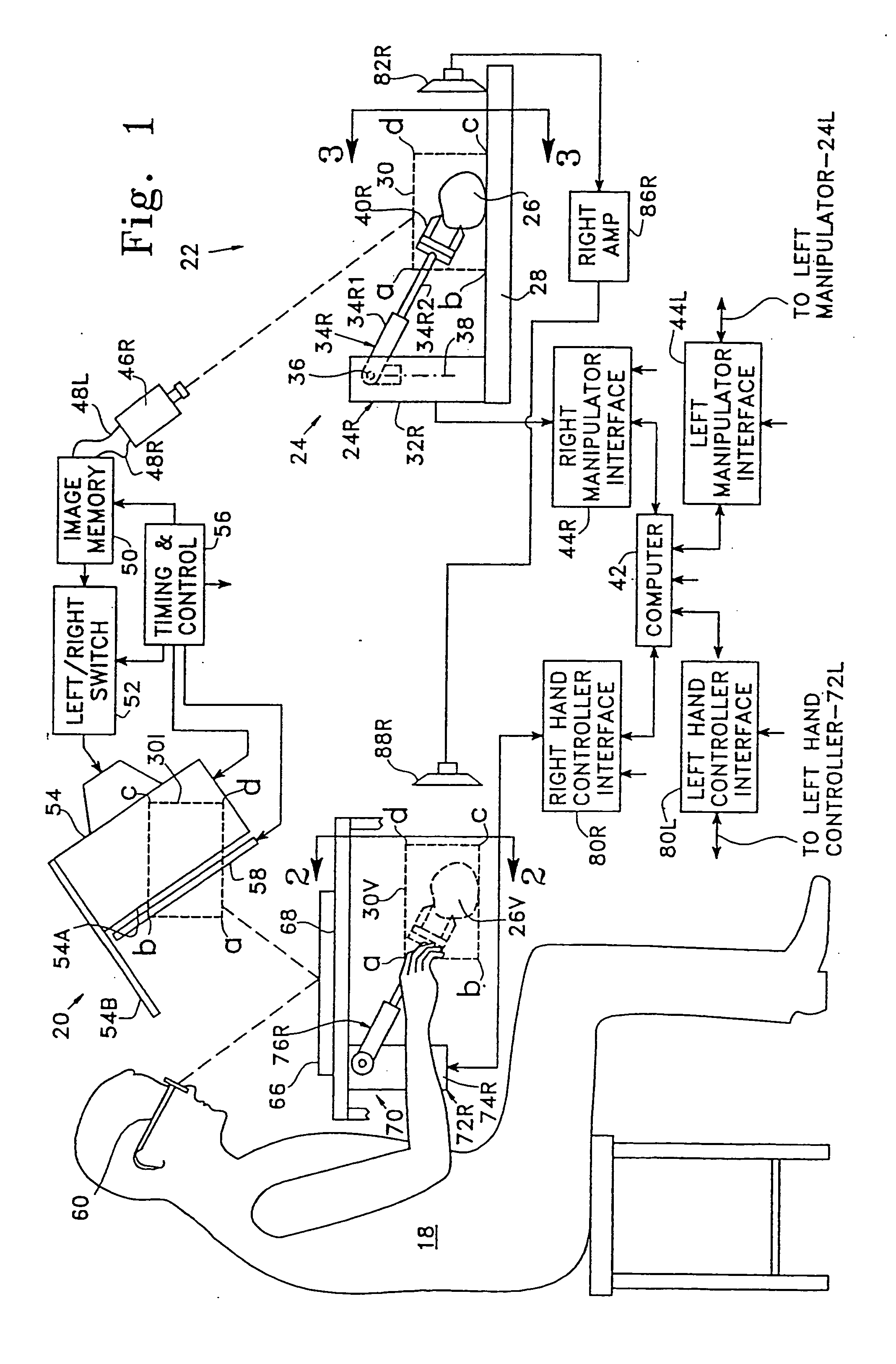
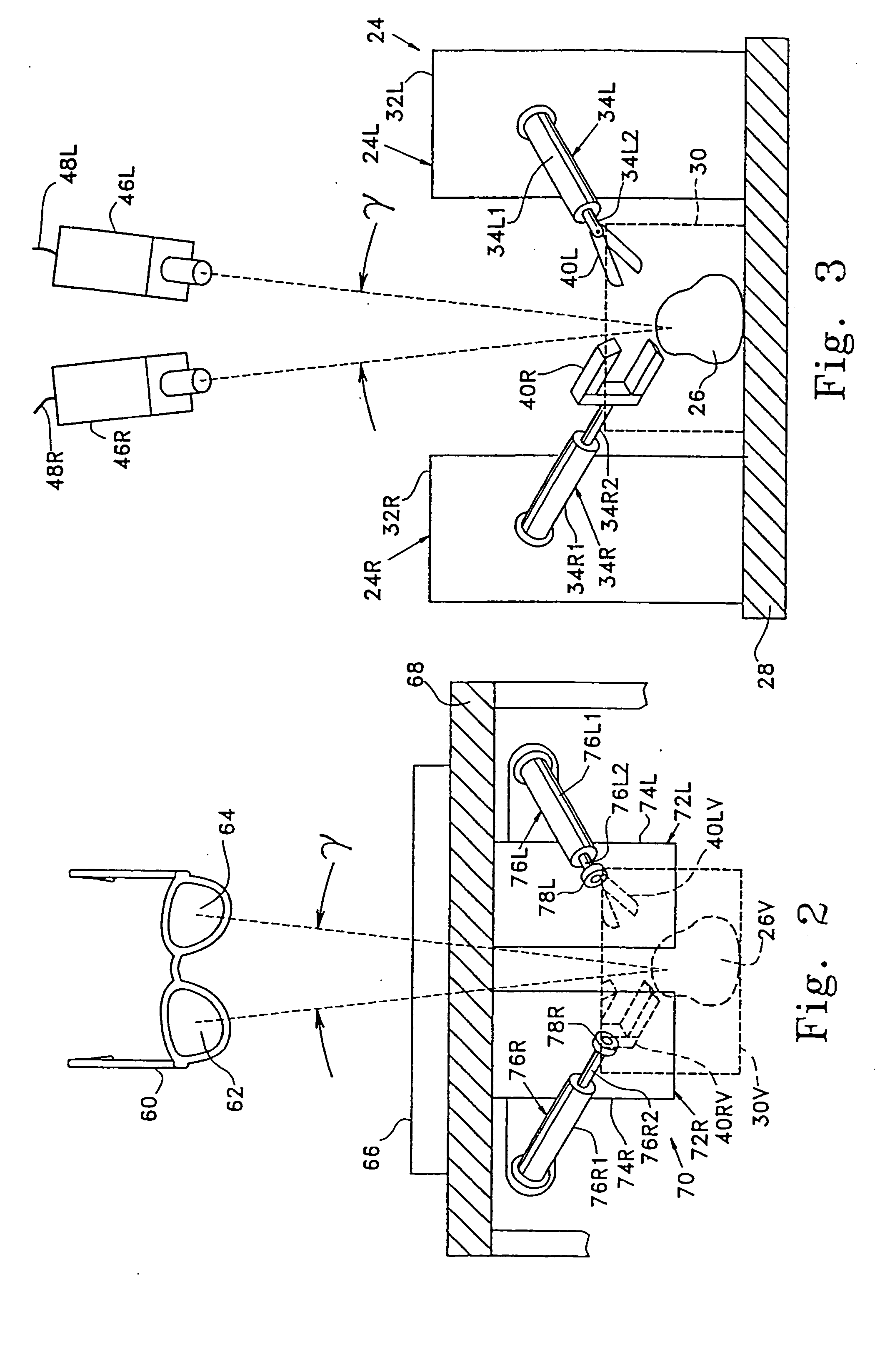
A teleoperator system with telepresence is shown which includes right and left hand controllers (72R and 72L) for control of right and left manipulators (24R and 24L) through use of a servomechanism that includes computer (42). Cameras (46R and 46L) view workspace (30) from different angles for production of stereoscopic signal outputs at lines (48R and 48L). In response to the camera outputs a 3-dimensional top-to-bottom inverted image (30I) is produced which, is reflected by mirror (66) toward the eyes of operator (18). A virtual image (30V) is produced adjacent control arms (76R and 76L) which is viewed by operator (18) looking in the direction of the control arms. By locating the workspace image (30V) adjacent the control arms (76R and 76L) the operator is provided with a sense that end effectors (40R and 40L) carried by manipulator arms (34R and 34L) and control arms (76R and 76L) are substantially integral. This sense of connection between the control arms (76R and 76L) and end effectors (40R and 40L) provide the operator with the sensation of directly controlling the end effectors by hand. By locating visual display (246) adjacent control arms (244R and 244L) image (240I) of the workspace is directly viewable by the operator (FIGS. 12 and 13). Use of the teleoperator system for surgical procedures is also disclosed (FIGS. 7-9 and 13).
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Micro-positioning movement of holographic data storage system components
InactiveUS7116626B1Control positionRecord information storageRecording/reproducing/erasing using optical interference patternsSpatial light modulatorMicro actuator
According to one aspect, a holographic storage system including micro-actuators is presented. In one example of one aspect of the invention, the device includes a spatial light modulator, a detector, a storage medium, and at least one micro-actuator configured to move at least one of the spatial light modulator, the detector, and the storage medium. The micro-actuators may include a servomechanism or the like to control the positioning of a component based on feedback associated with a misalignment of a detected image. According to another aspect of the invention, various methods for determining component misalignments of a holographic storage system are presented.
Owner:AKONIA HOLOGRAPHICS
Robotic surgical system
ActiveUS20070185486A1Reduce exposureShorten the timeSurgical navigation systemsSurgical instrument detailsServomechanismCatheter device
A robotic surgical system includes a track, a catheter holding device including a catheter receiving portion translatably associated with the track, a translation servo mechanism to control translation of the catheter holding device relative to the track, a catheter deflection control mechanism, a deflection servo mechanism to control the catheter deflection control mechanism, and a controller to control at least one of the servo mechanisms. The catheter receiving portion is adapted for quick installation and removal of a catheter. The catheter receiving portion may be rotatable, with a rotation servo mechanism to control the rotatable catheter receiving portion. The controller controls at least one of the deflection and rotation servo mechanisms to maintain a substantially constant catheter deflection as the catheter rotates. An introducer, which may be steerable, and an expandable, collapsible sterile tube may also be provided.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Combining information from parallel servo channels
InactiveUS7839599B2Driving/moving recording headsAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic tapeEngineering
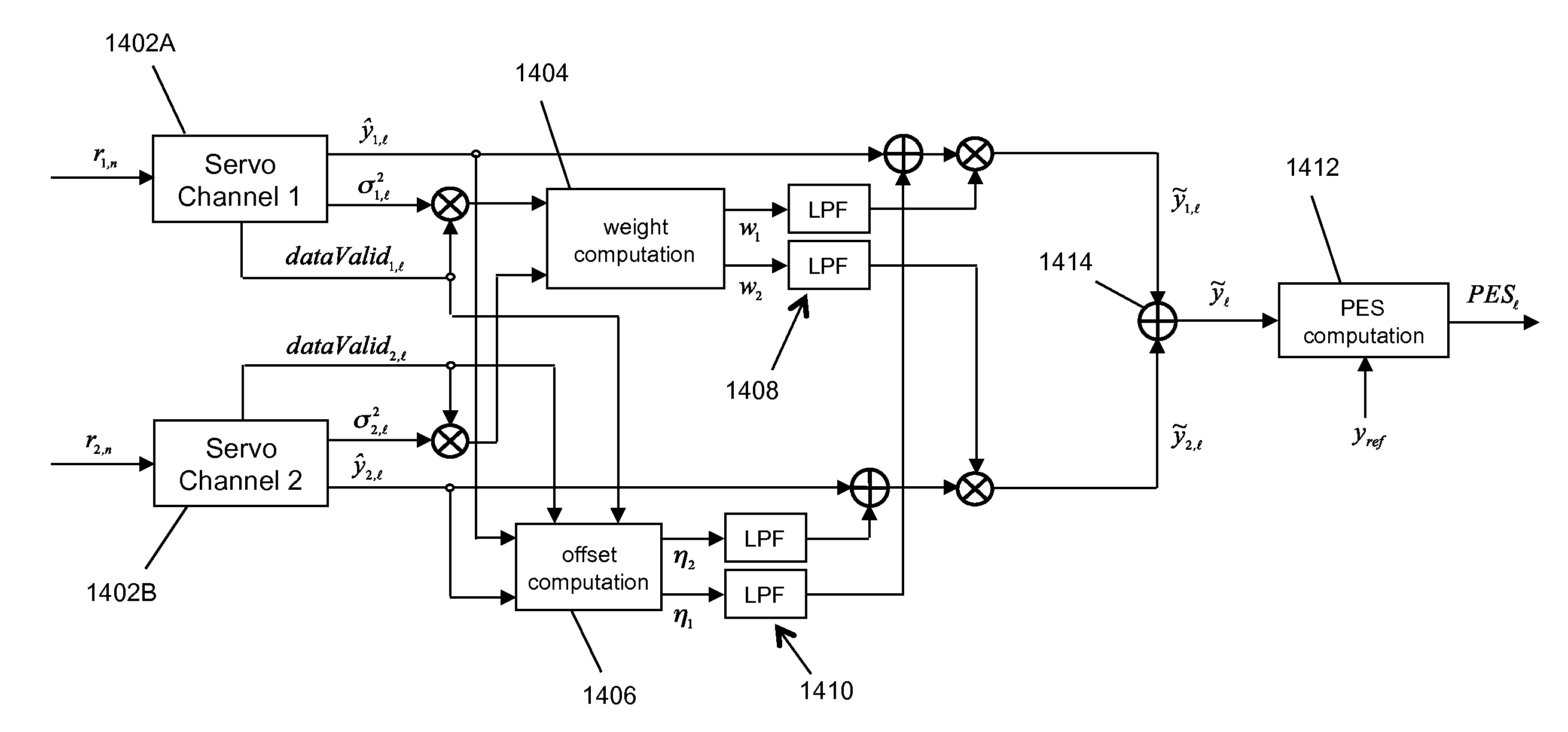
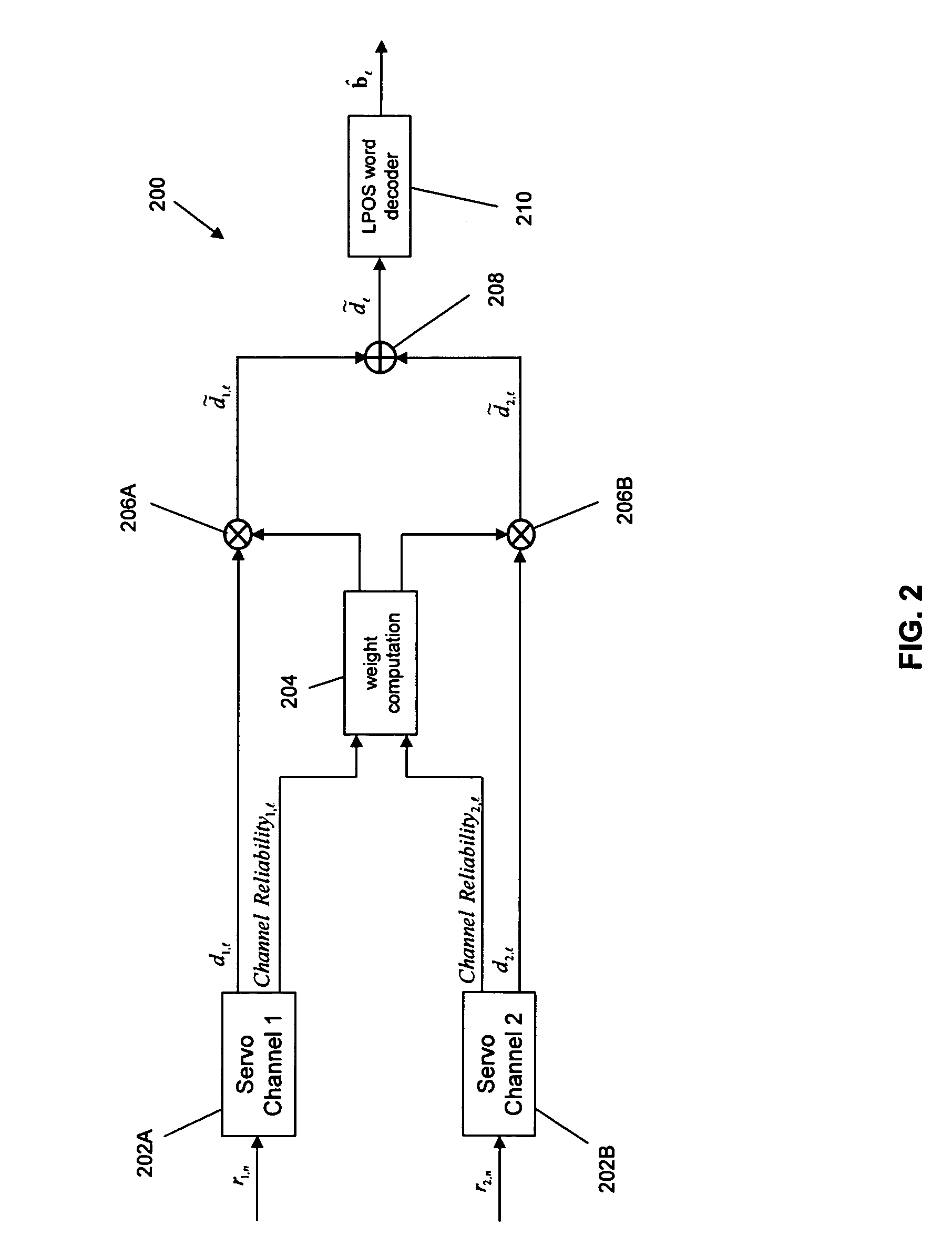
A weighted combining scheme exploits information from two servo channels operating in parallel. A timing-based servo module comprises two synchronous servo channels coupled respectively to receive two digital servo signals read from a data tape. Both channels have outputs for an unweighted parameter estimate and for a measure of the channel reliability. A weight computation module provides first and second weight signals using the measures of channel reliability from the servo channels. An offset computation module provides first and second offset terms which are summed with the unweighted parameter estimates. Multiplying nodes receive the unweighted parameter estimates and the weight signals and outputs offset weighted parameter estimates. A summing node receives the offset weighted parameter estimates and outputs a combined offset weighted parameter estimate to a servomechanism.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Trailer backing up device and table based method
InactiveUS20130024064A1Easy to operateSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsSteering wheelDriver/operator
The present invention, when used to backed-up a trailer, indicates which direction and how much to steer to steer. The present invention is a method for rapidly determining the predicted direction where the vehicle and trailer become generally in-line. Servomechanisms can be incorporated to enable the vehicle to steer itself while the driver indicates the direction travel desired for the trailer, otherwise a pointer would indicate, for the current position of the vehicle's steering wheel, the predicted direction of the trailer. To back-up the trailer, the driver would turn the vehicle's wheel such that the pointer is kept pointing in the direction of the intended trailer destination. Furthermore, the present invention will indicated the projected directions of the left and right limits to control the direction of the trailer, particularly when maneuvering complex paths.
Owner:SHEPARD DANIEL ROBERT
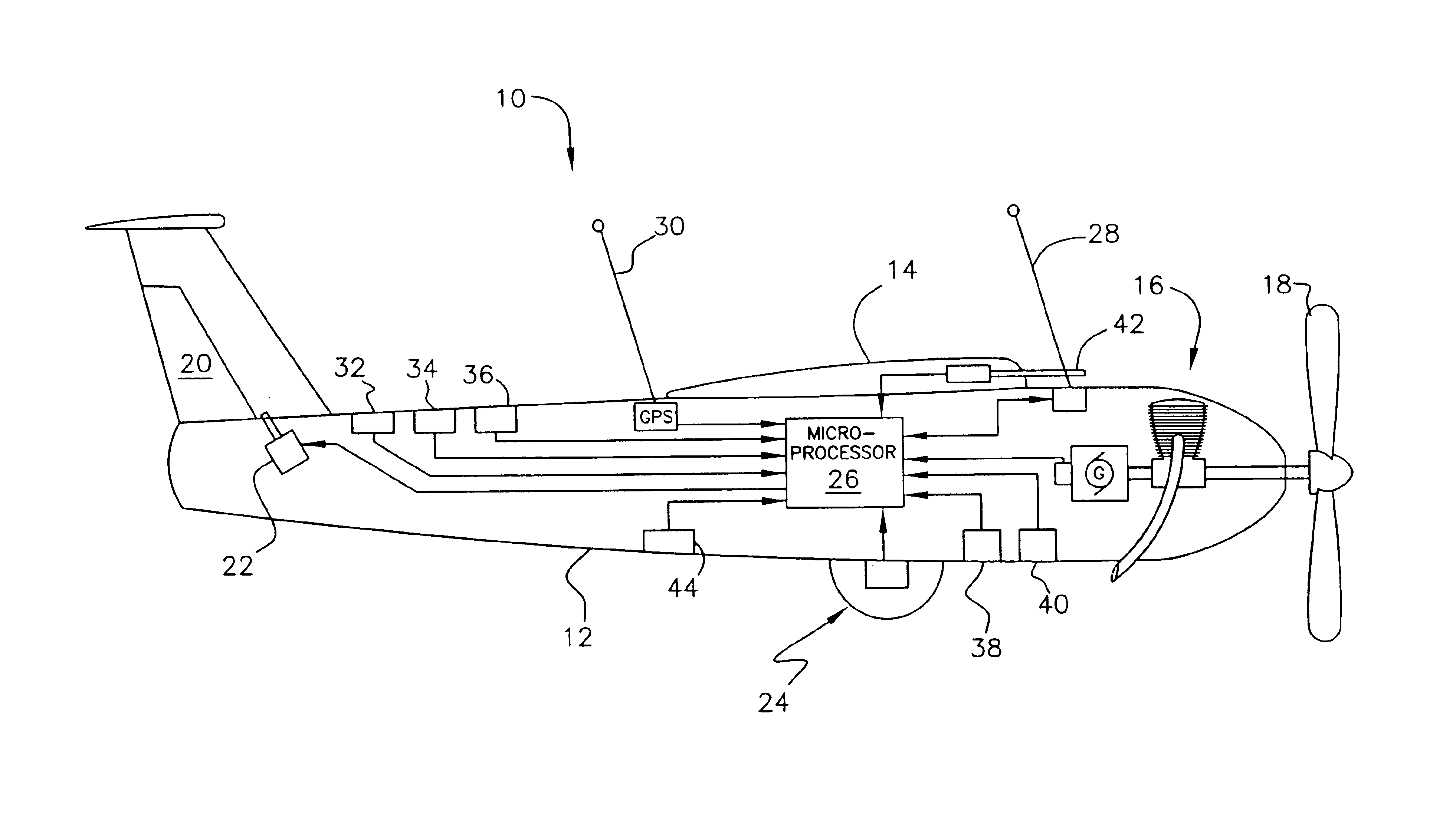
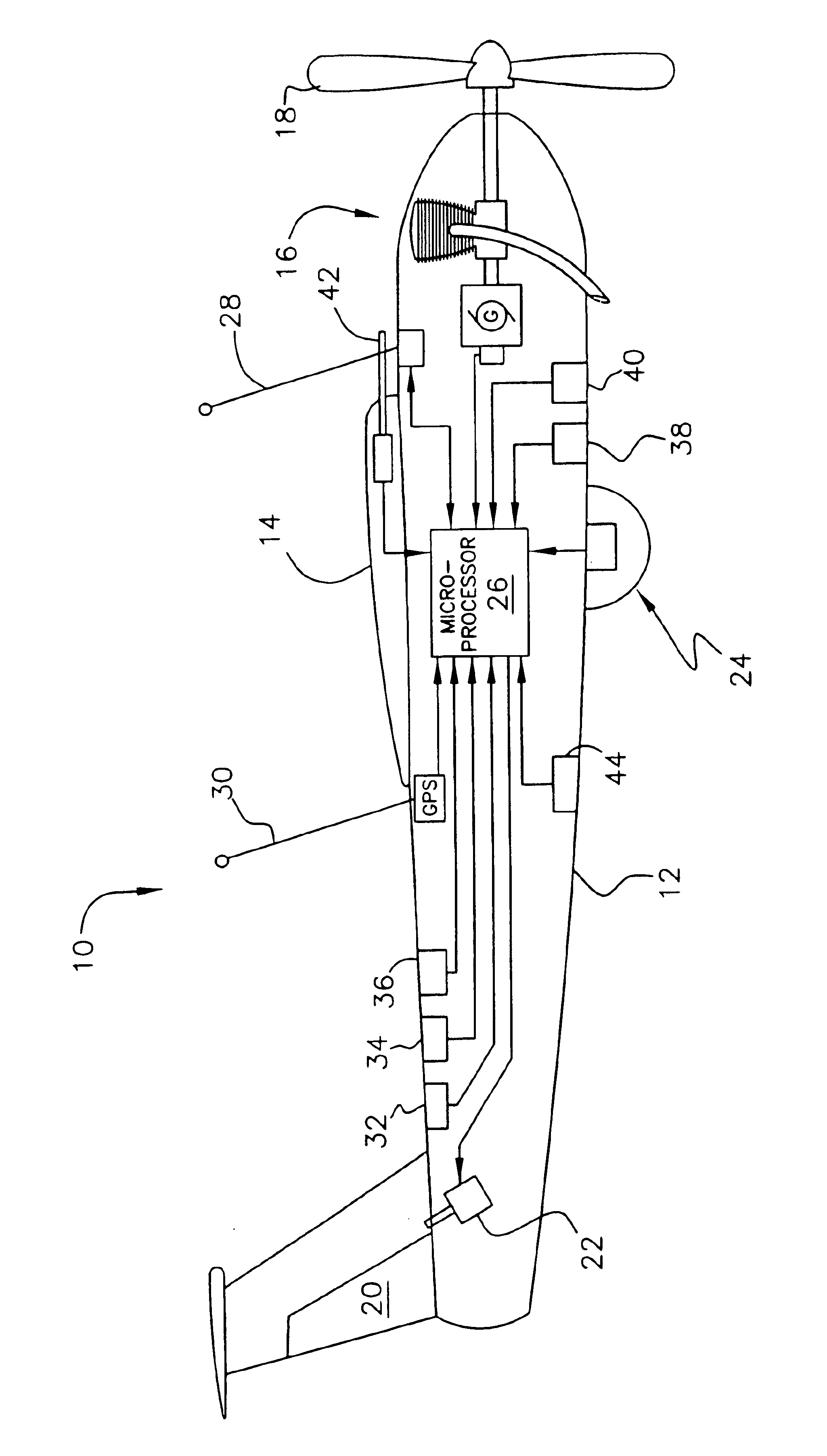
Miniature, unmanned aircraft with onboard stabilization and automated ground control of flight path
InactiveUS6847865B2Maintain flight stabilityMinimizing any typeElectrical controlDigital data processing detailsFlight directionTransceiver
A miniature, unmanned aircraft for acquiring and / or transmitting data, capable of automatically maintaining desired airframe stability while operating by remote directional commands. The aircraft comprises a fuselage and a wing, a piston engine and propeller, a fuel supply, at least one data sensor and / or radio transceiver, a microprocessor disposed to manage flight, a radio transceiver for receiving remotely generated flight direction commands, a GPS receiver, a plurality of control surfaces and associated servomechanisms, for controlling flight stabilization and direction, roll, pitch, yaw, velocity, and altitude sensors. The microprocessor uses roll, pitch, yaw, and altitude data to control attitude and altitude of the aircraft automatically, but controls flight direction solely based on external commands. The aircraft does not exceed fifty-five pounds.
Owner:CARROLL ERNEST A
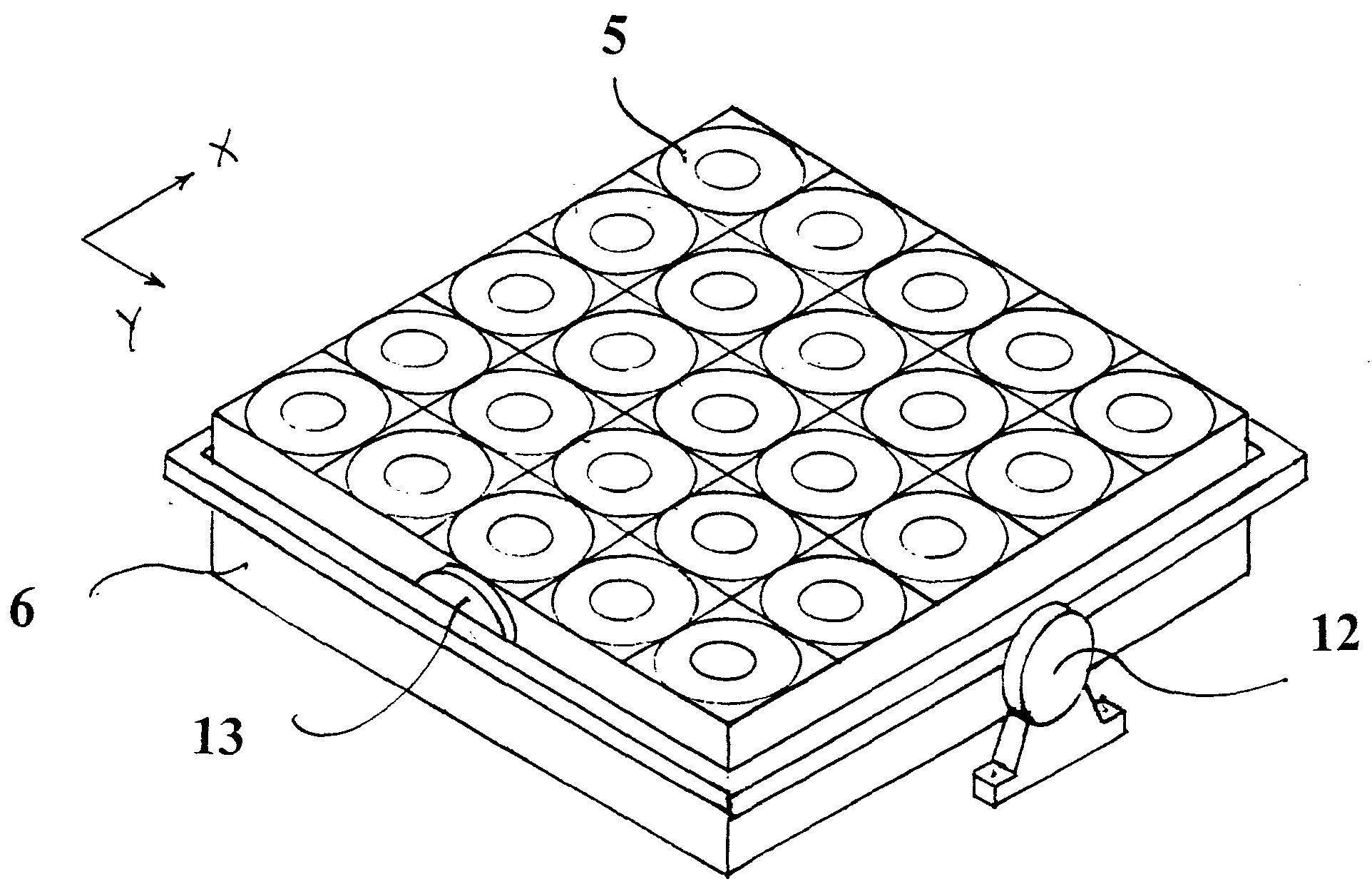
Photovoltaic array for concentrated solar energy generator
InactiveUS20080087321A1Dissipate excessive heatImprove cooling effectPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyEngineeringServomechanism
An extensive photovoltaic array for generating electric power from concentrated solar radiation, formed of an extensive planar structural grid wherein a multitude of power generating modules are installed, said structural grid being positioned by a primary servomechanism to keep incident solar radiation perpendicular to the plane of the array at all times.
Owner:SCHWARTZMAN ZALMAN
Trailer backing up device and table based method
InactiveUS9132856B2Easy to operateSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsMicrocomputerSteering wheel
The present invention is a guidance computing system used by the driver of a vehicle towing a trailer while backing-up that rapidly calculates and predicts the direction in which the tow vehicle and trailer will become generally in-line for a given position of the steering wheel, thereby enabling the use of slower, lower cost microcomputers. This is accomplished by using a predetermined table, based on a baseline trailer of known length, having a measure of turning as one of its axes; such an axis is necessary to facilitate ratiometric scaling to convert table values to correspond to any length trailer. In a specially equipped vehicle incorporating servomechanisms to enable the vehicle to steer itself, the driver indicates the direction desired for the trailer to travel. The present invention also predicts left and right path limits for controlling the direction of the trailer when maneuvering complex paths.
Owner:SHEPARD DANIEL ROBERT
Roll-pitch-roll wrist methods for minimally invasive robotic surgery
InactiveUS20050102062A1Improve satisfactionStrong sense of satisfactionEndoscopesSurgical manipulatorsServomechanismManipulator
A teleoperator system with telepresence is shown which includes right and left hand controllers (72R and 72L) for control of right and left manipulators (24R and 24L) through use of a servomechanism that includes computer (42). Cameras (46R and 46L) view workspace (30) from different angles for production of stereoscopic signal outputs at lines (48R and 48L). In response to the camera outputs a 3-dimensional top-to-bottom inverted image (30I) is produced which, is reflected by mirror (66) toward the eyes of operator (18). A virtual image (30V) is produced adjacent control arms (76R and 76L) which is viewed by operator (18) looking in the direction of the control arms. Use of the teleoperator system for surgical procedures also is disclosed.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Distance measuring system
ActiveUS20070138371A1Improve propertiesMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesTarget surfacePhotovoltaic detectors
A distance measuring device capable of being used in microscopes or other optical systems. Embodiments of the invention employ one or more scanning mirrors to scan a reference beam over a target to be inspected. The reference beam is returned and detected by a photodetector. The reference beam may be created by using a knife-edge element which allows the outgoing reference beam and incoming reference beam to follow the same path so that the apparent motion of the spot on the target surface is not detected by the photodetector. The photodetector generates an electronic signal corresponding to the displacement of the target away from the ideal focal point. The electrical signal may be used to drive a servomechanism to displace either the target or the microscope objective lens to bring the target in focus.
Owner:MARSHALL DANIEL R
High-precision autonomous obstacle-avoiding flying method for unmanned plane
ActiveCN104850134AHigh positioning accuracySpatial location is accuratePosition/course control in three dimensionsAircraft navigation/guiding aidsTerrainControl signal
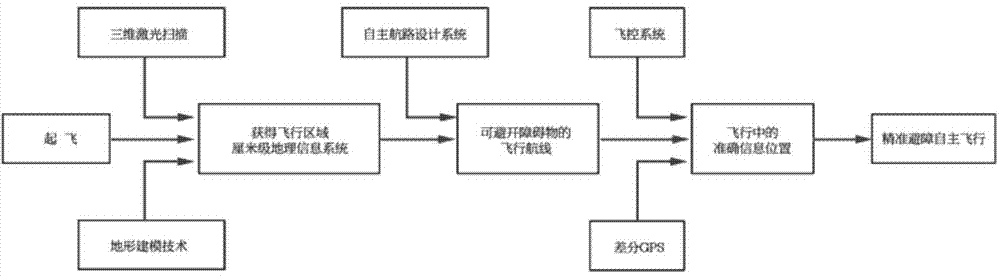
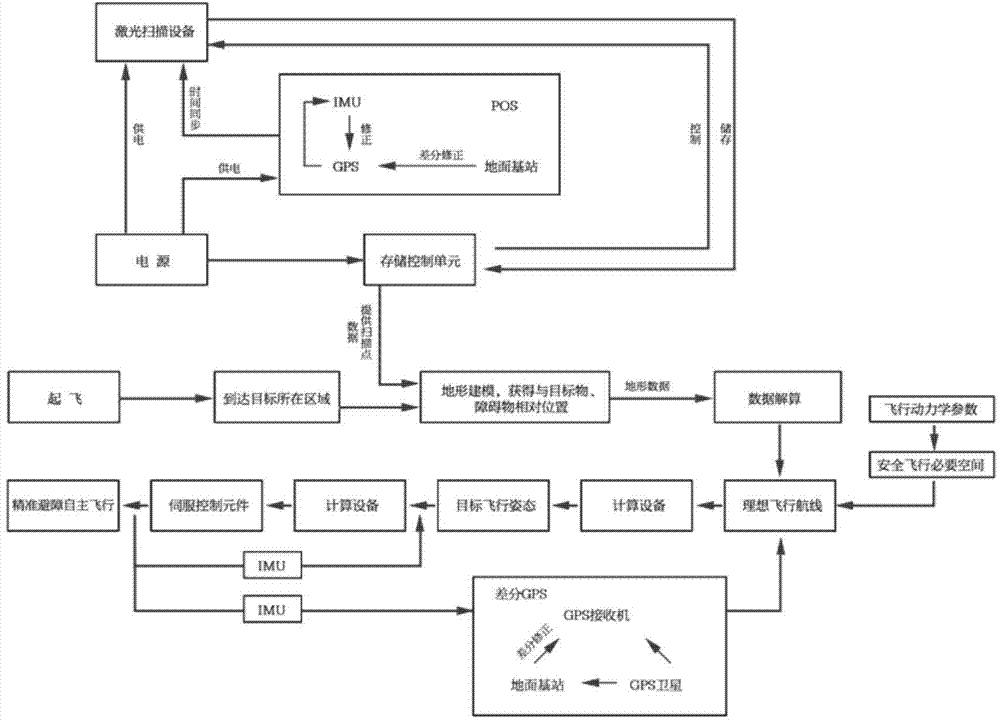
The invention relates to a high-precision autonomous obstacle-avoiding flying method for an unmanned plane, and the method comprises the following steps: (1) building a high-precision map model; (2) planning flight control for a three-dimensional airline; (3) transmitting a flight control signal at step (2) to a steering engine of an unmanned plane servo mechanism, thereby achieving the control purpose through the changing of the position of the steering engine. The advantages of the method lie in that the space coordinates of the terrain environment of a region through the combination of the technology of laser scanning and the technology of differential GPS, thereby providing support for the autonomous obstacle-avoiding line planning; the position control error of the whole flight process is controlled at a centimeter level, thereby guaranteeing that the unmanned plane can fly along a planned path, achieving an effect of automatically avoiding obstacles, and finally enabling the unmanned plane to arrive at a destination for operation.
Owner:BEIJING ZHONGFEIAIWEI AERO SCI & TECH
Motorized Functional Electrical Stimulation Step and Stand Trainer
A functional electrical stimulation step and stand system comprising two footplates (left and right) connected to a primary drive motor that cause the footplates to move in a reciprocal motion. The footplates are further connected to corresponding servos, which allow for control of the movement of the footplate with respect to an axis. system comprises an electrical stimulation control unit. The stimulation step and stand system further comprises a control unit that has electrical stimulation leads connected to electrodes that deliver an electrical impulse to a patient's muscles. In a further embodiment, the control unit has one or more wireless stimulators.
Owner:RESTORATIVE THERAPIES
Stabilizer for robotic beating-heart surgery
InactiveUS20050033270A1Physiological motion of stabilizedAvoid relative motionSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsRobotic systemsChest surgery
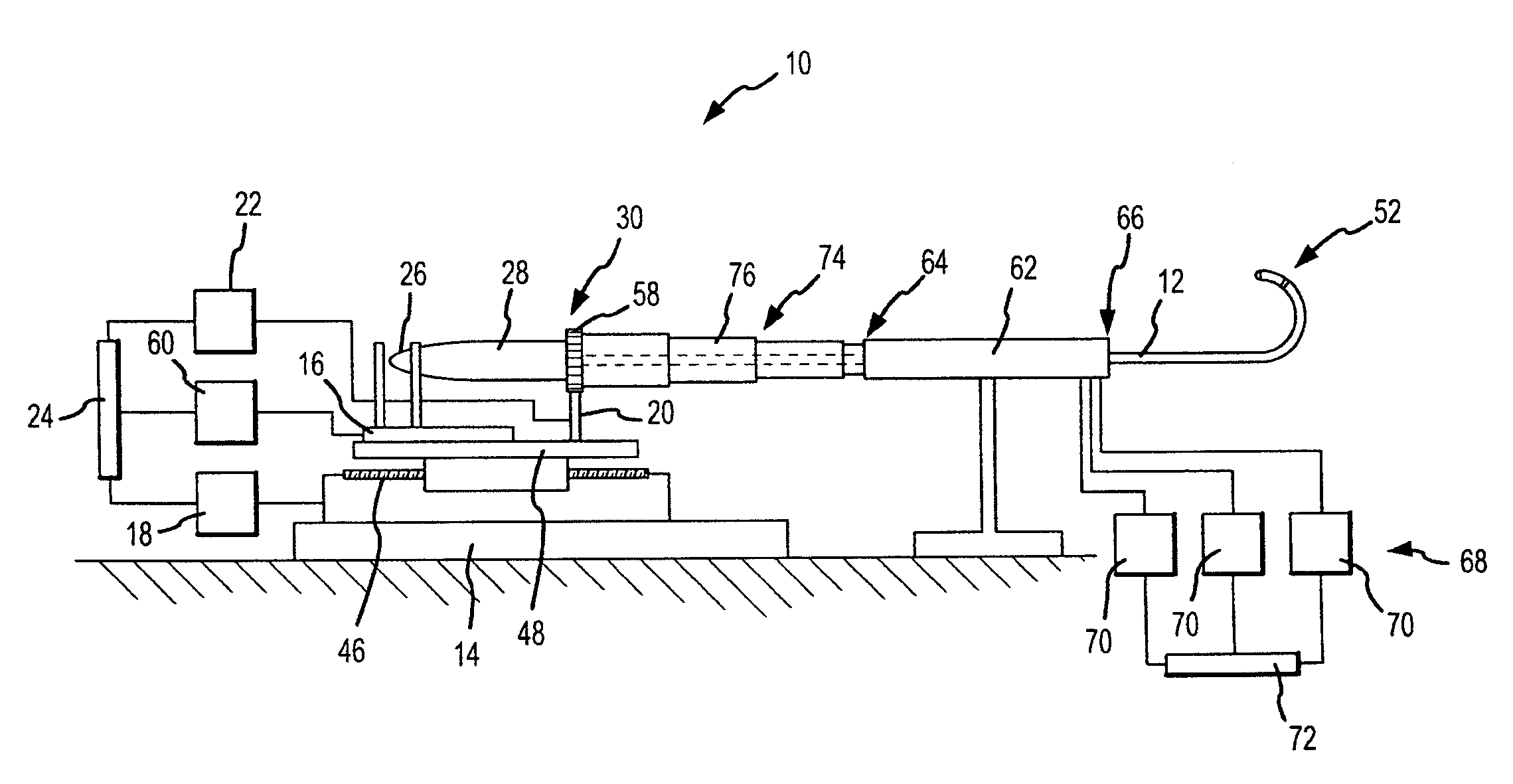
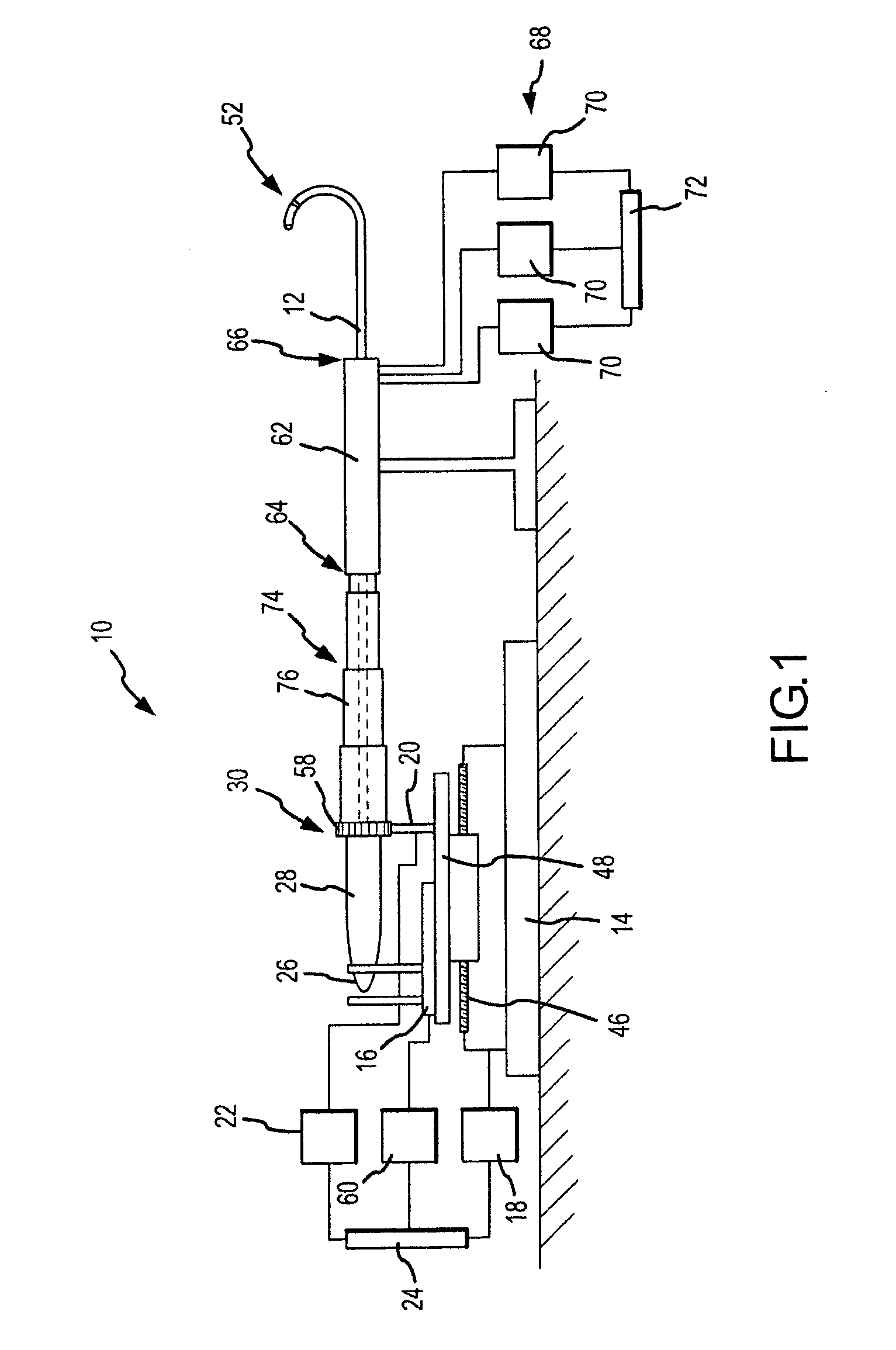
Surgical methods and devices allow closed-chest surgery to be performed on a heart of a patient while the heart is beating. A region of the heart is stabilized by engaging a surface of the heart with a stabilizer without having to stop the heart. Motion of the target tissues is inhibited sufficiently to treat the target tissues with robotic surgical tools which move in response to inputs of a robotic system operator. A stabilizing surface of the stabilizer is coupled to a drive system to position the surface from outside the patient, preferably by actuators of the robotic servomechanism. Exemplary stabilizers includes a suture or other flexible tension member spanning between a pair of jointed bodies, allowing the member to occlude a coronary blood vessel and / or help stabilize the target region between the stabilizing surfaces.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
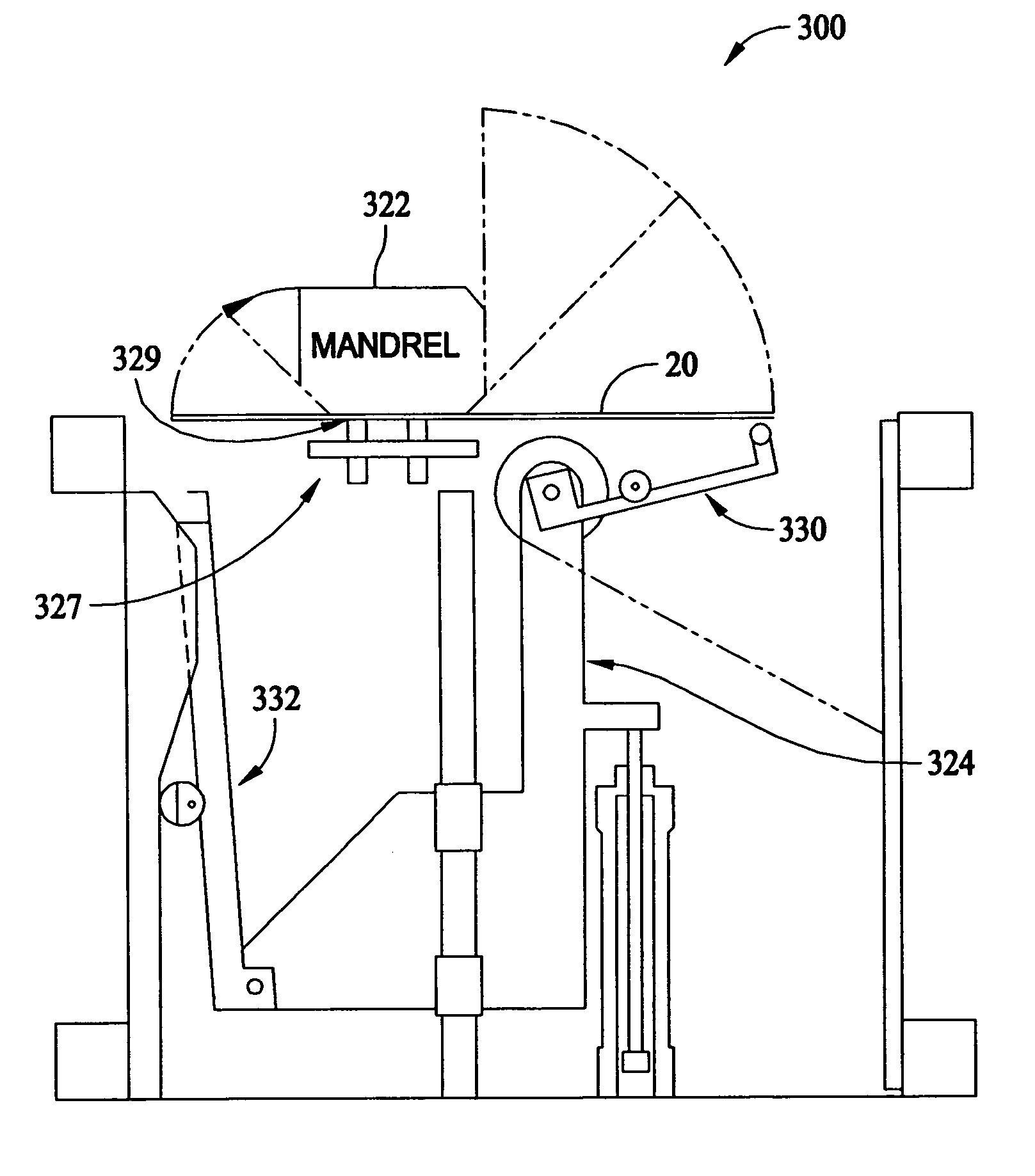
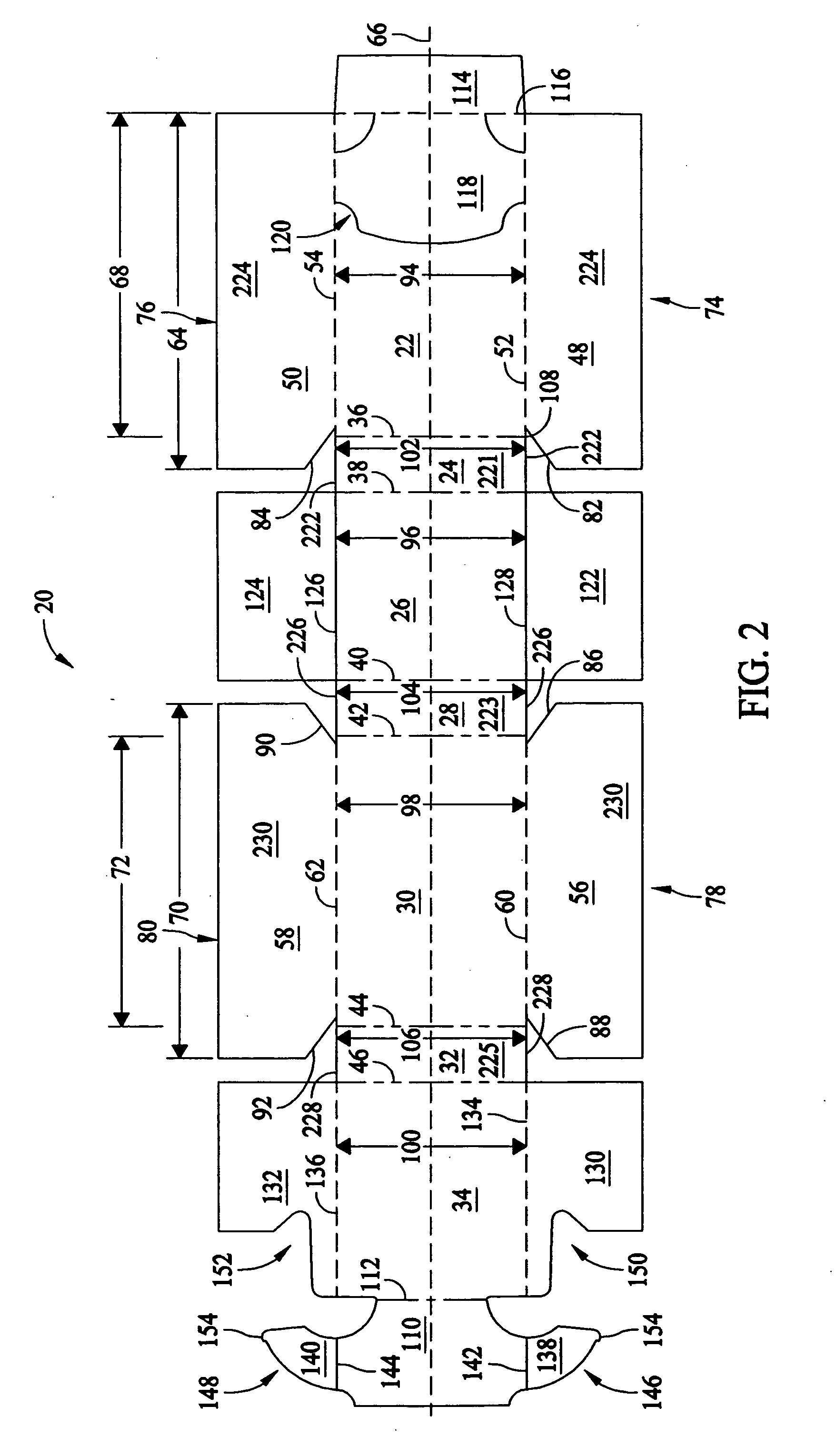
Blank and methods and apparatus for forming a dispenser case from the blank
A machine for forming a case from a blank of sheet material includes a body, a mandrel mounted on the body and having an external shape complimentary to an internal shape of at least a portion of the case, a member mounted on the body adjacent the mandrel for applying a force to the blank for at least one of folding a portion of the blank around the mandrel, moving the blank, and securing portions of the blank together, and a servomechanism operatively connected to the member for driving and controlling movement of the member to apply the force to the blank.
Owner:WESTROCK SHARED SERVICES LLC
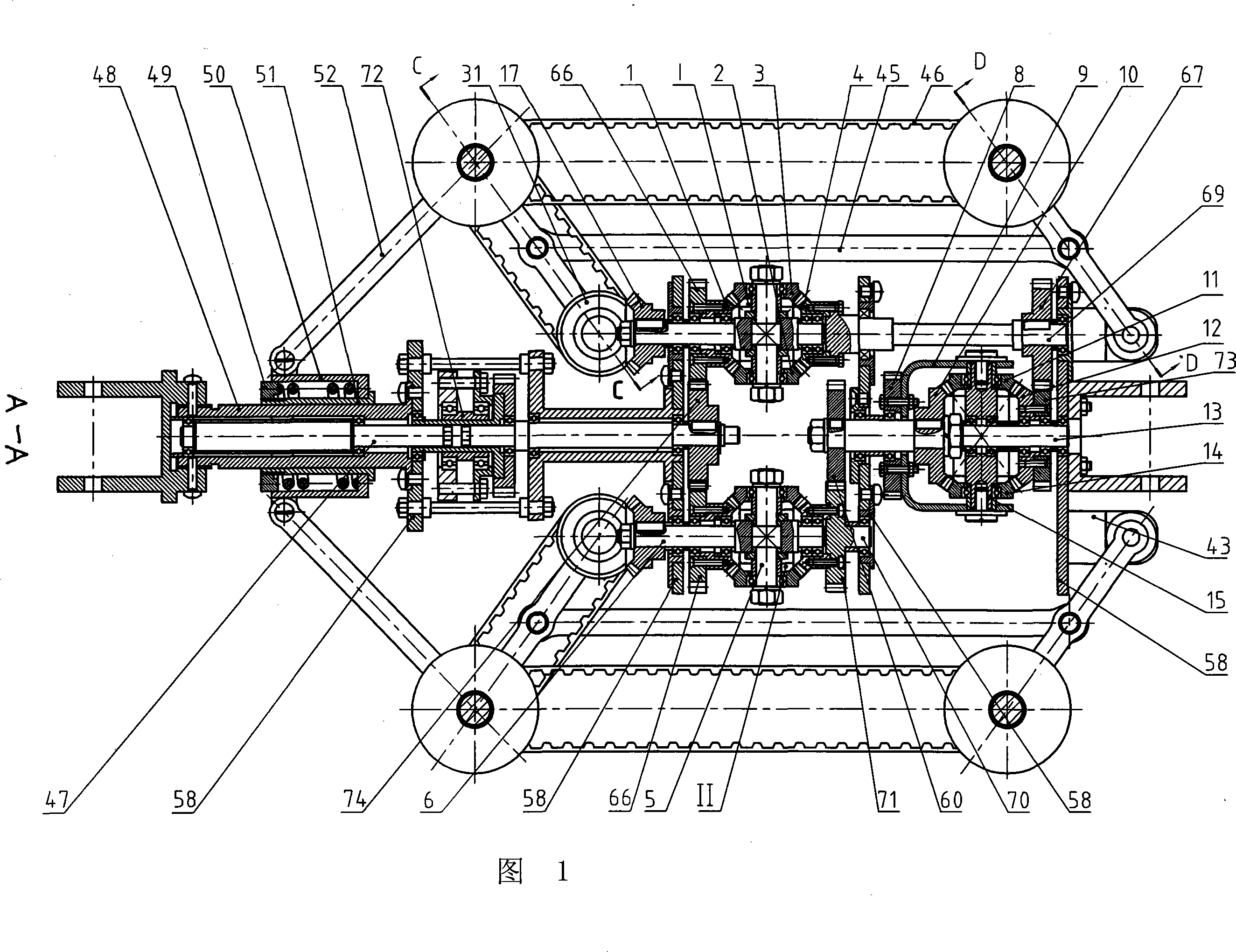
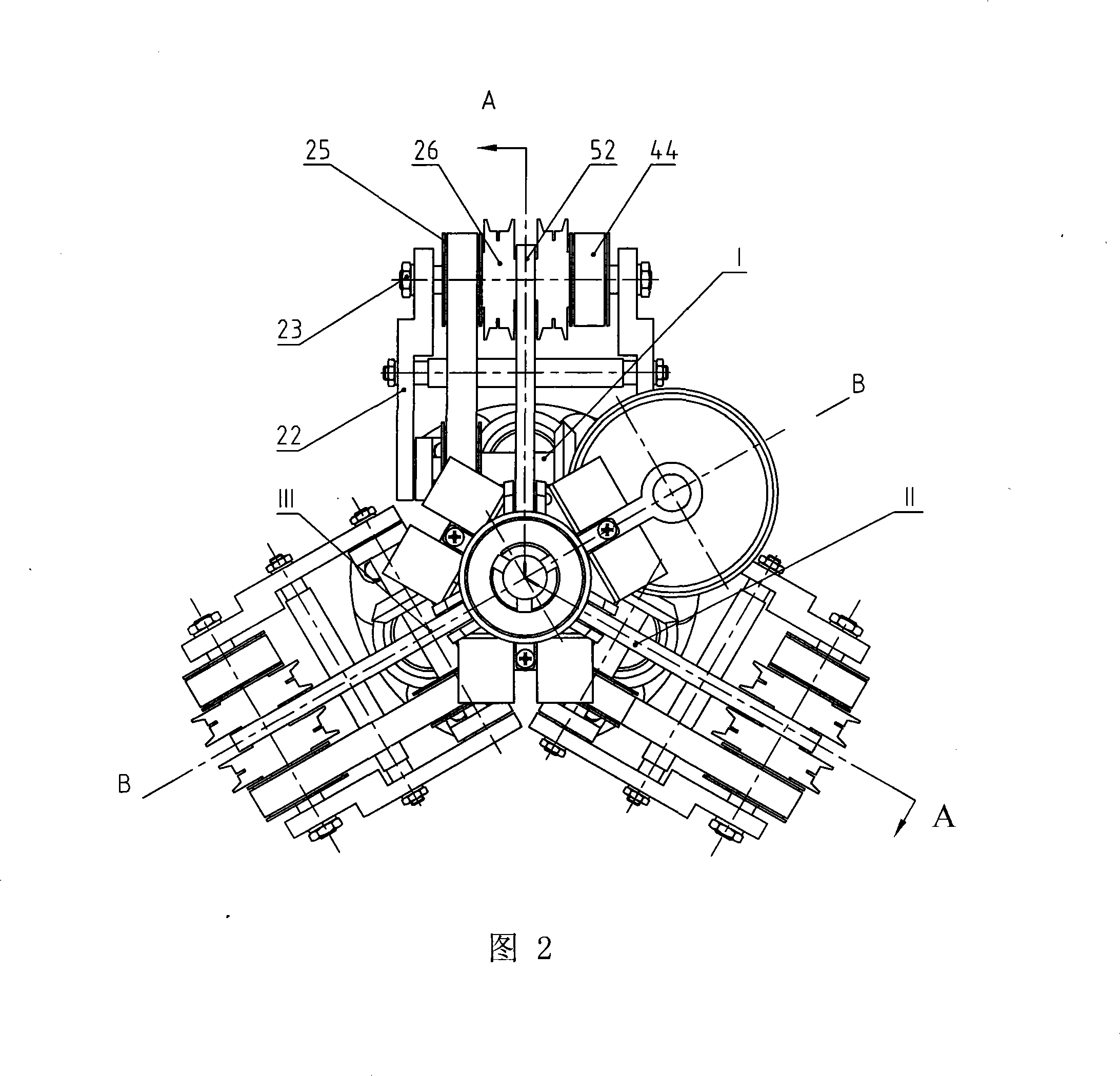
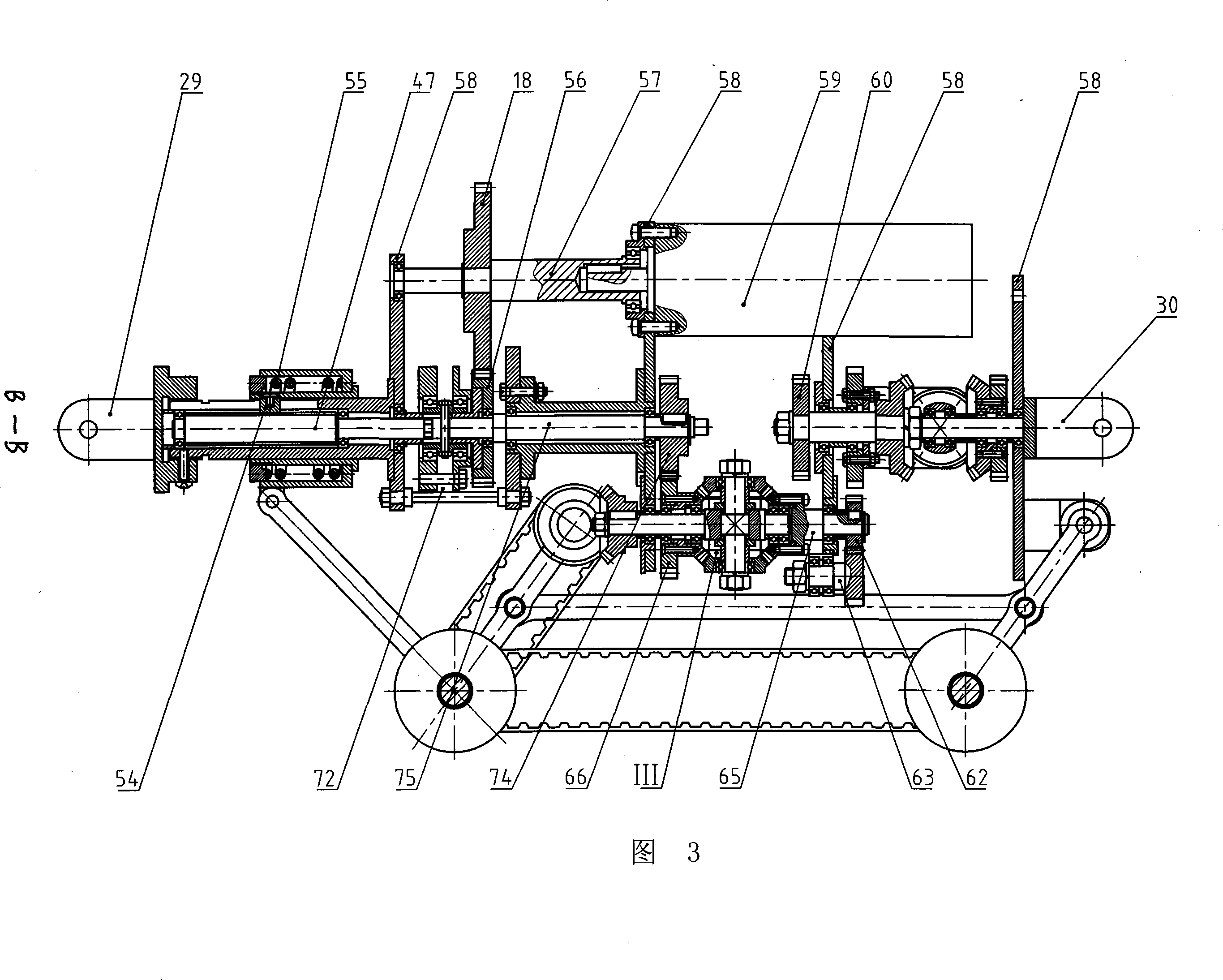
Triaxial differential type pipe creeping device
The invention relates to a three- shaft differential type pipe creeper, which is characterized in that the invention comprises three differential gears with same structure I, II, III, a transfer gear, three creeping wheel servomechanisms with same structure, a preloaded reducing mechanism, and a driving mechanism, the invention can connect with various pipe operation devices which are matched with the invention to proceed creeping operation along to the inner walls of the pipe, the creep speed of each creeping wheel is real-time regulated according to the self-attitude and pipe environment condition in order to realize self-regulation, and to avoid the phenomenon of motion interference which is generated at the moment that the current wheel type pipe creeper passes through the pipe or passes through the pipe whose inner physical dimension is changed, thereby increasing driving efficiency and traction ability, and reducing input power and the friction and abrasion of the a driving pair in the process of motion. The creeping wheel can realize the total main drive through a driving mechanism of a motor, and the invention has the advantages of simple structure, high driving efficiency, small power volume, low cost, long service life, spreading application range, etc.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH +1
Platform shield door intelligent control system
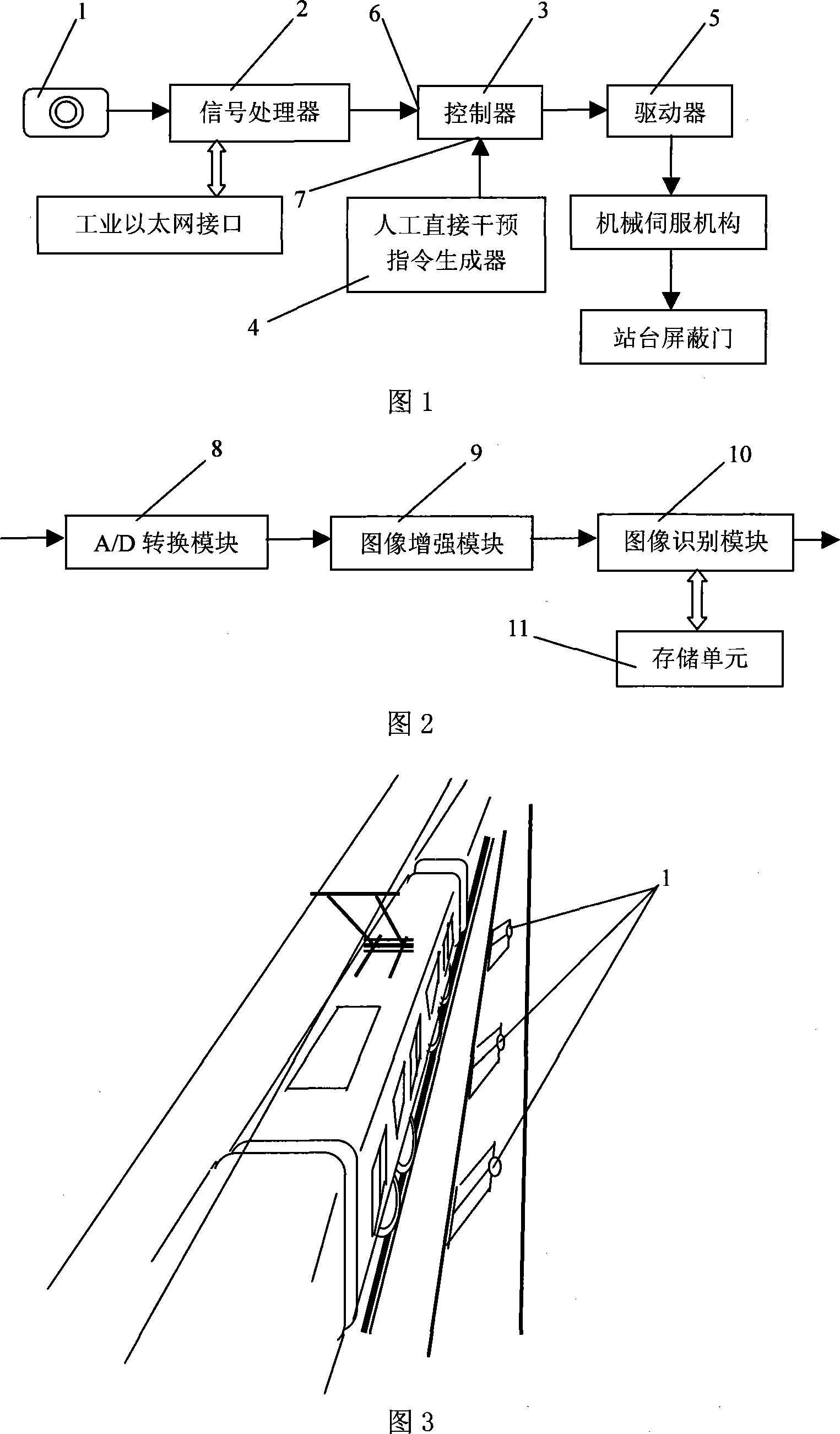
InactiveCN101105096ASafe and on timeEnsure comfort and safetyRailway componentsCharacter and pattern recognitionCMOSAutomatic control
An intelligent control system for platform screen doors is provided, which belongs to the field of automatic control technology and comprises a CMOS camera, a signal processor, a controller, and a driver. The CMOS camera collects and outputs images to the signal processor. The signal processor is used for the A / D conversion, enchantment processing and information recognition of the images, and converts the recognition results to a control command and outputs the command to the controller. The controller converts the digital control command and emergency control command to an analog control signal and outputs the analog control signal to the driver. The driver drives a mechanical servomechanism after amplification of the analog control signal, thereby controlling the opening / closing operation of the screen door. The inventive system has simple structure and high operational reliability, and can ensure the comfortable travel for passengers and safe and on-time operation of the train.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
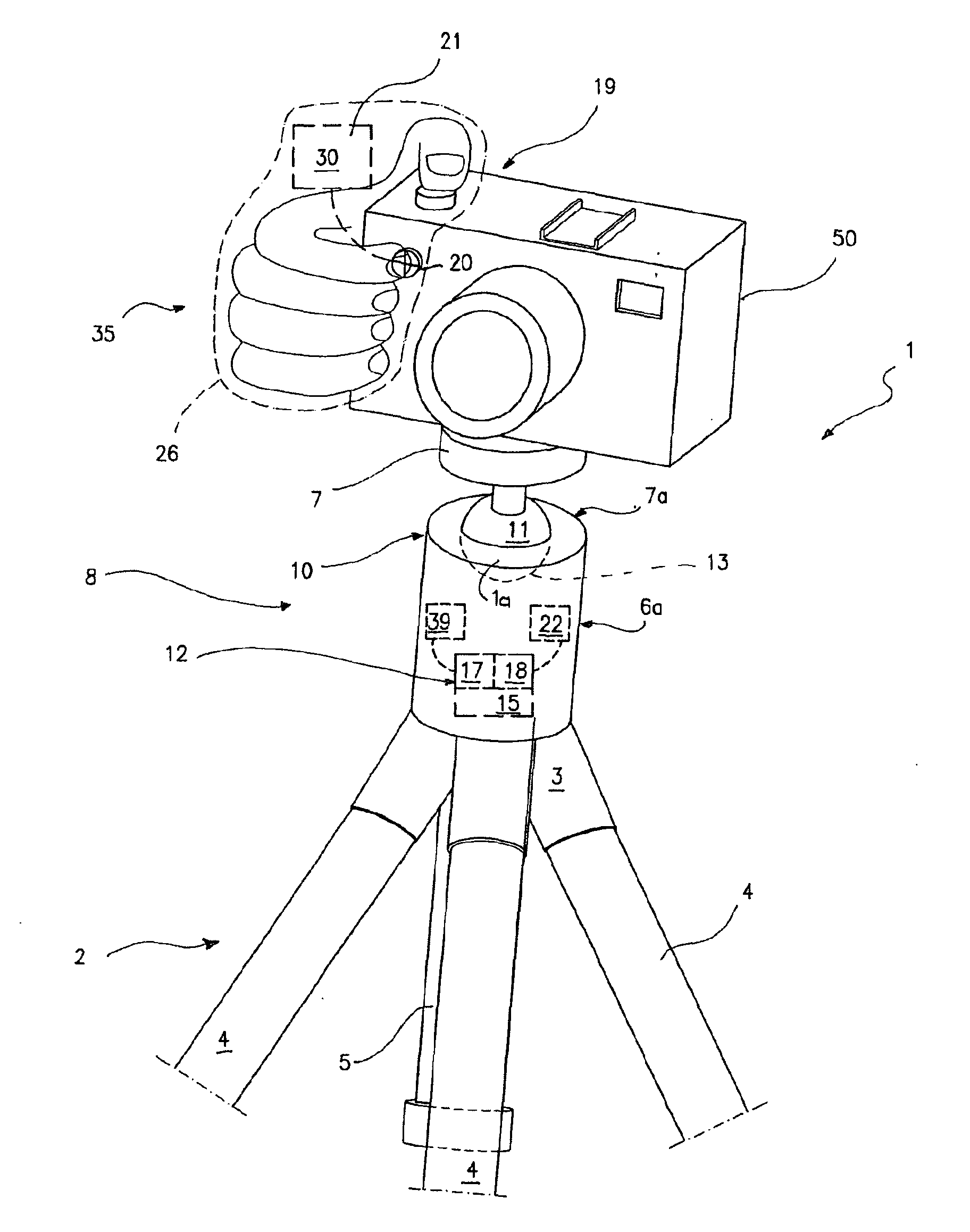
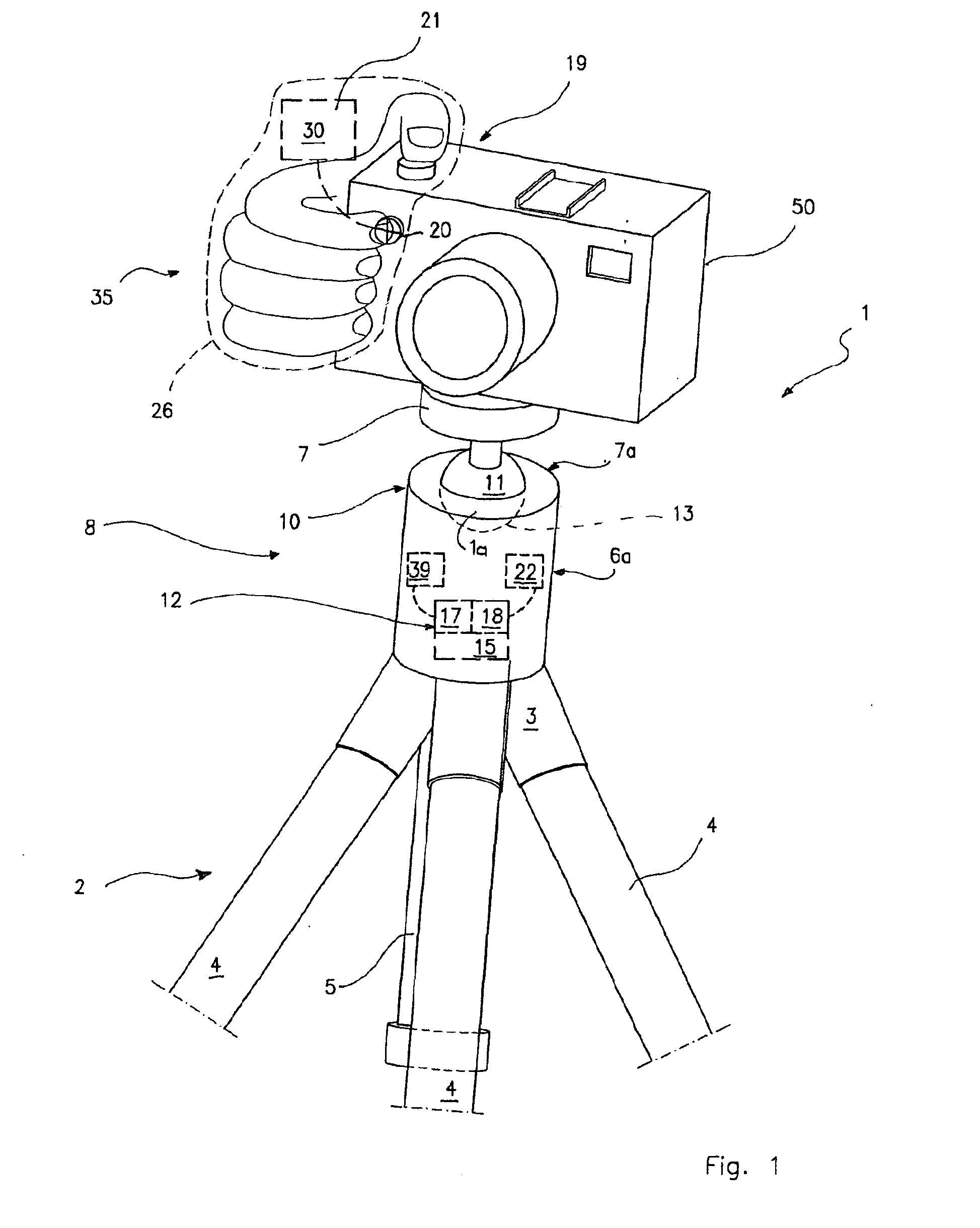
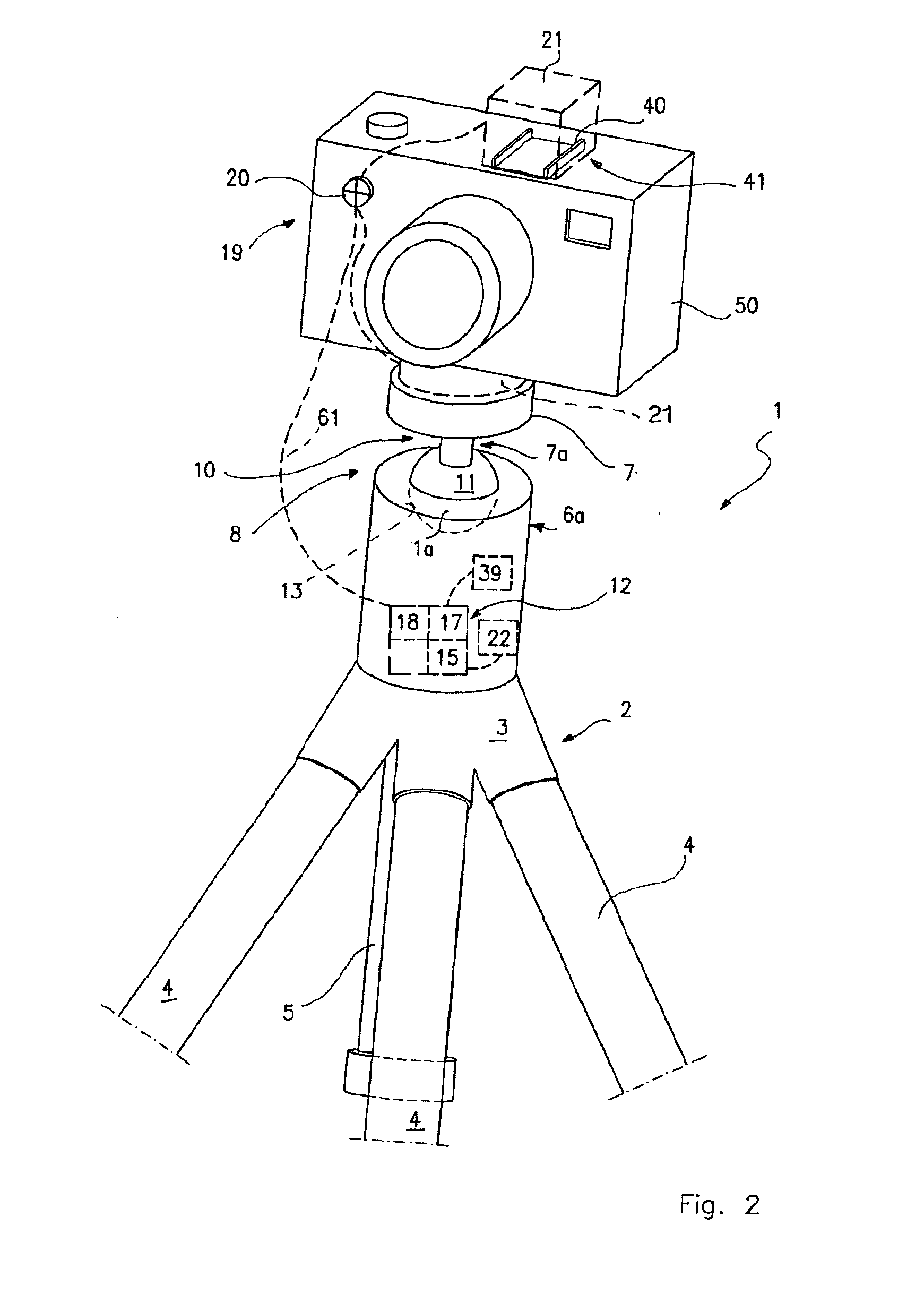
System for the Remote Control of Setting Up a Supporting Head for Optical and/or Photo-Cinematographic Equipment
InactiveUS20090317071A1Overcome limitationsStands/trestlesCamera body detailsRemote controlControl system
This invention describes a system for the remote control of setting up an adjustable head for optical and / or photo-cinematographic equipment comprising an adjustable head for mounting by adjustable setting-up of optical and / or photo-cinematographic equipment, at least one servomechanism for locking and / or unlocking and / or setting up a movable part of the head in relation to a fixed part thereof, as well as remote control means of said servomechanism for setting up the head comprising at least one pushbutton control, remote in relation to the servomechanism, that can be operated by the user while he is holding said equipment.
Owner:LINO MANFROTTO & CO SPA
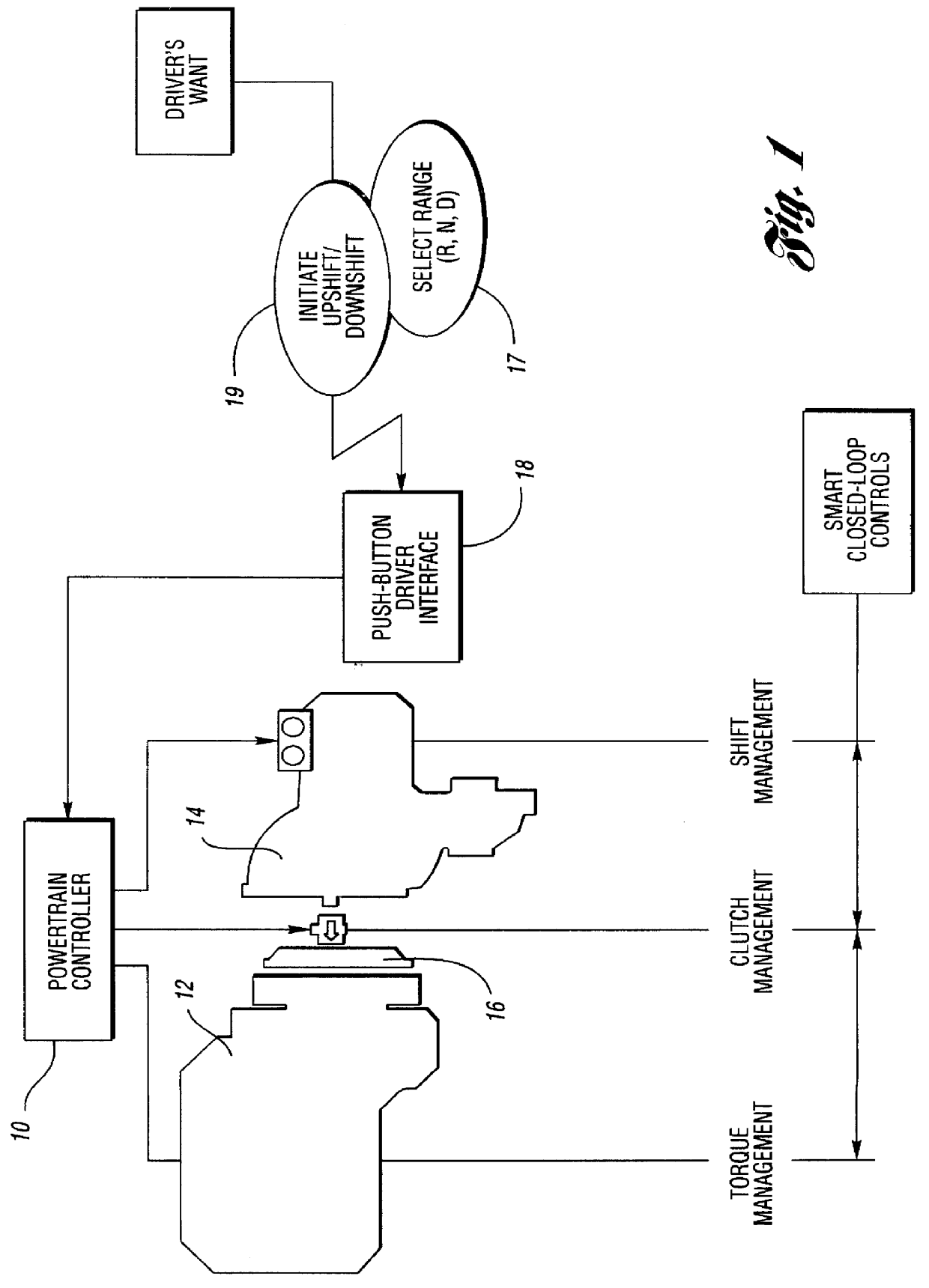
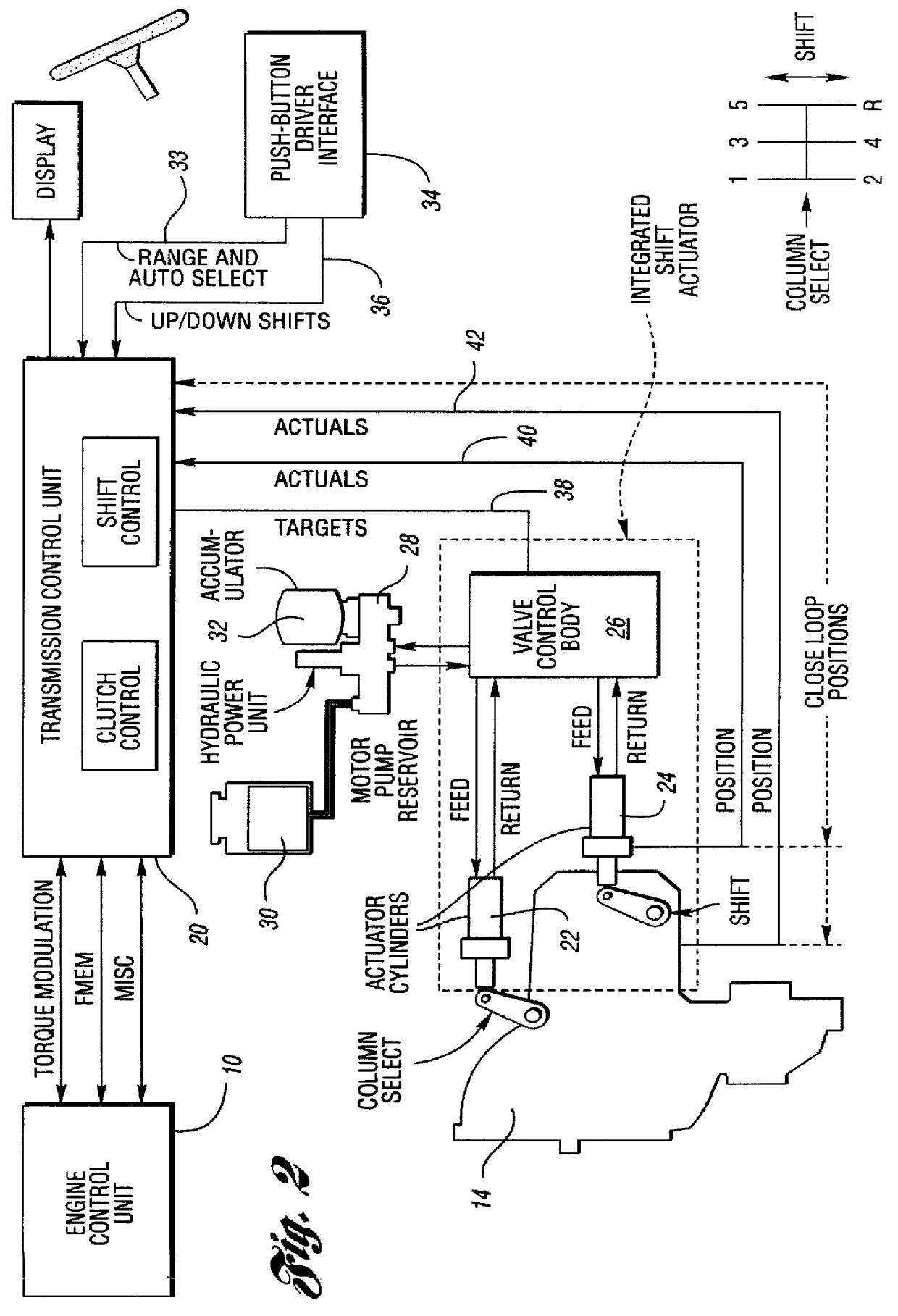
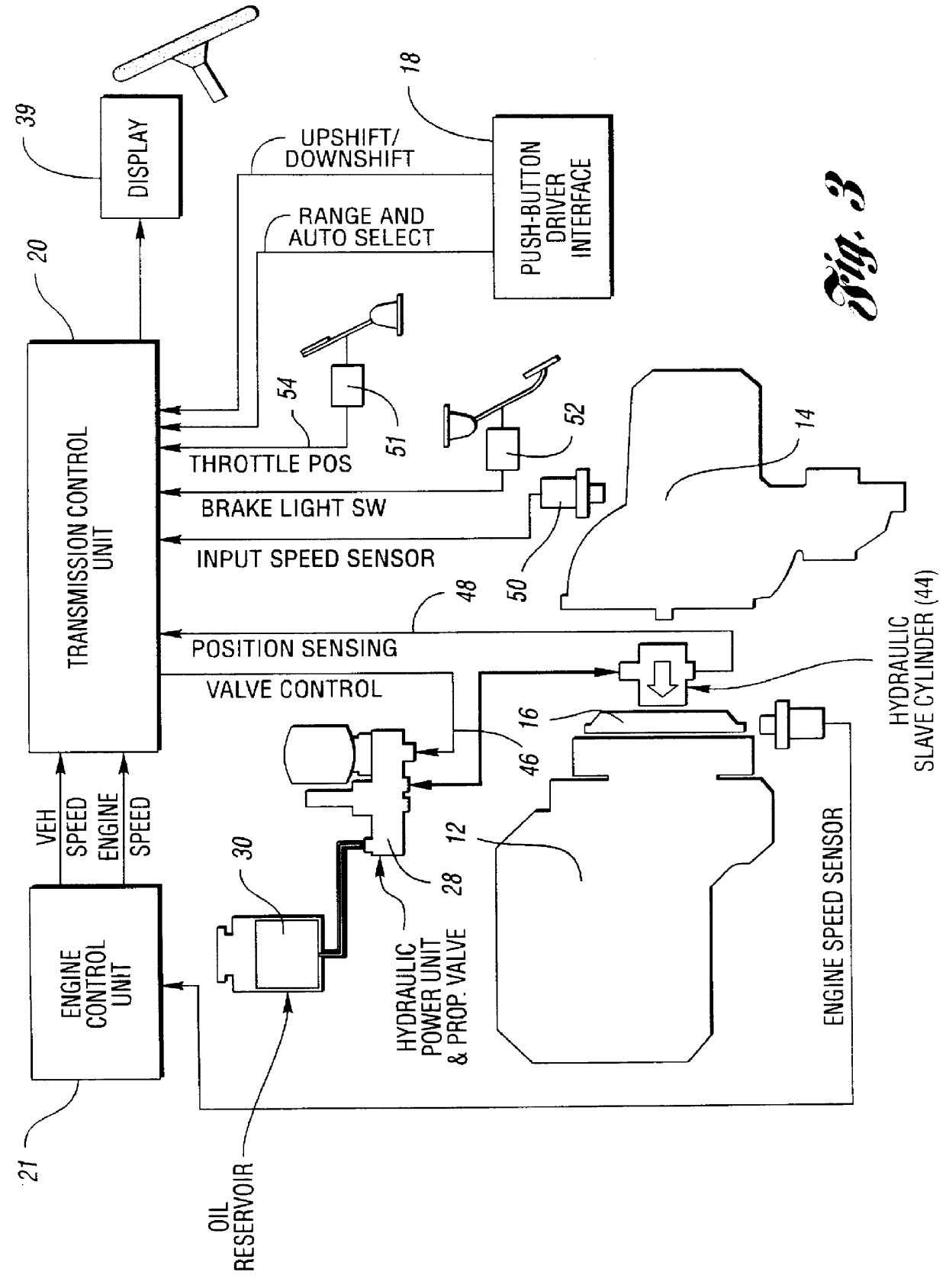
Shift controls for automated shifting manual transmissions with range sensing redundancy
InactiveUS6056669AImprove protectionGuaranteed uptimeGearing controlEngine controllersDriver/operatorControl system
An automated shifting system for a manual transmission having a neutral clutch connecting an engine to a multiple ratio transmission, the transmission having servo operated gear shift mechanism. A driver-controlled gear shift switching mechanism is used to activate the servos that effect ratio range changes. A gear shift switching mechanism includes multiple switches for triggering operation of the servos that control the ratio range changes. A range sensing redundancy strategy for the ratio range switches provide improved protection against an unintended change in direction due to three-bit separation between bits of the valid codes and to a range sensing switch failure strategy by identifying when a range change commanded by the driver exhibits a single-point fault condition. A fault condition due to a single-point sensing switch failure is identified even in those instances when a range change commanded by the driver allows continued normal control system operation, although the driver is notified of the failure by a system warning device.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
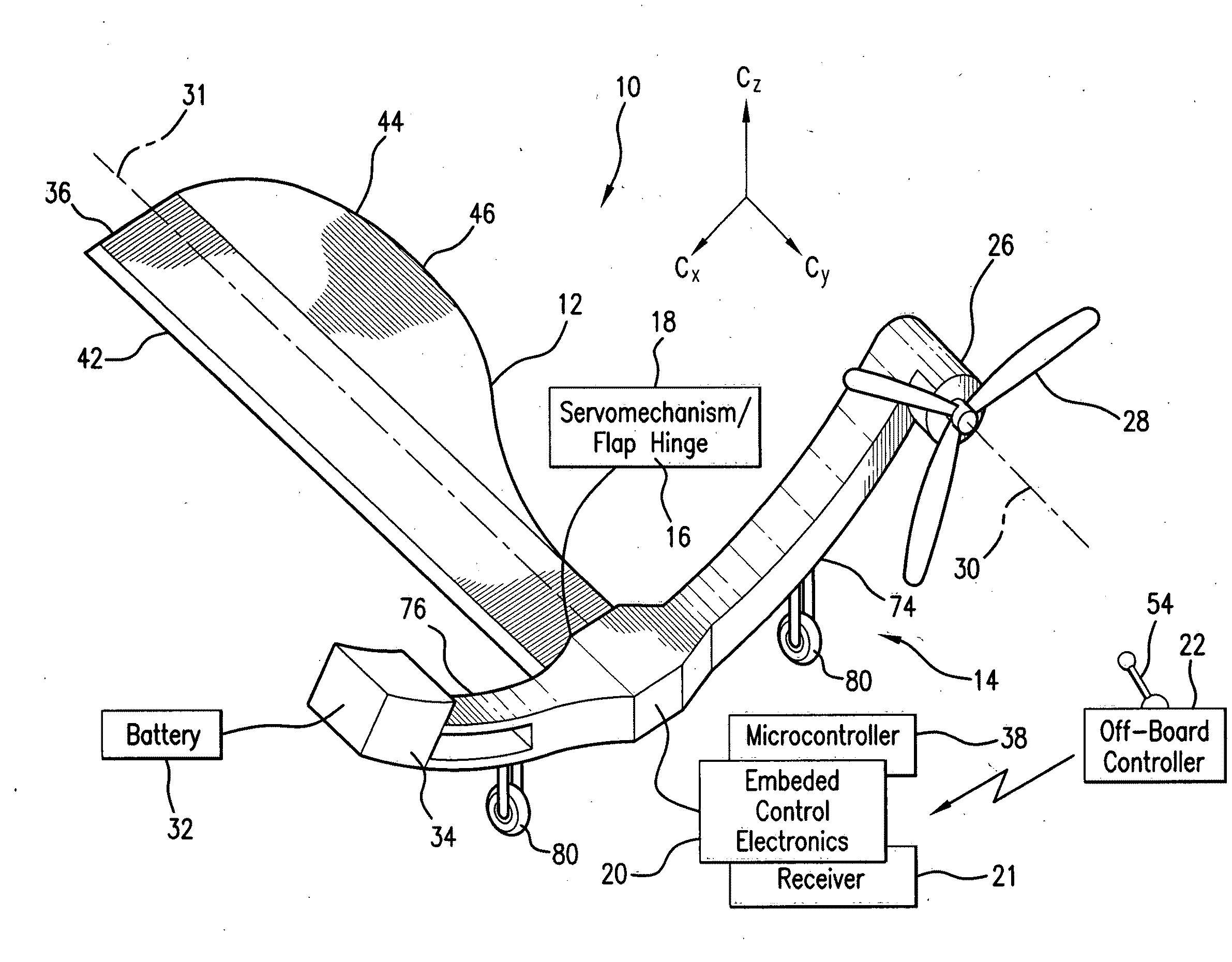
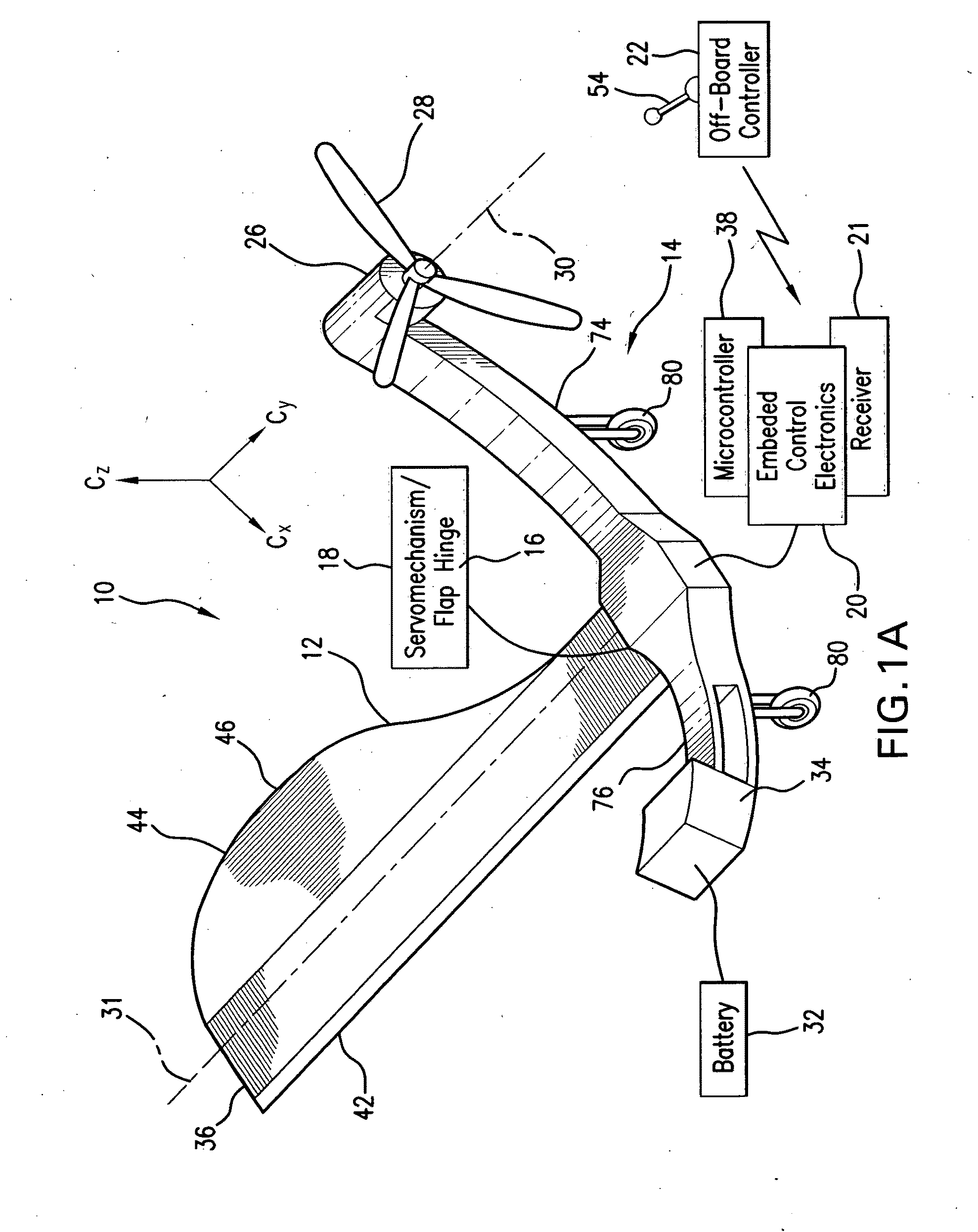
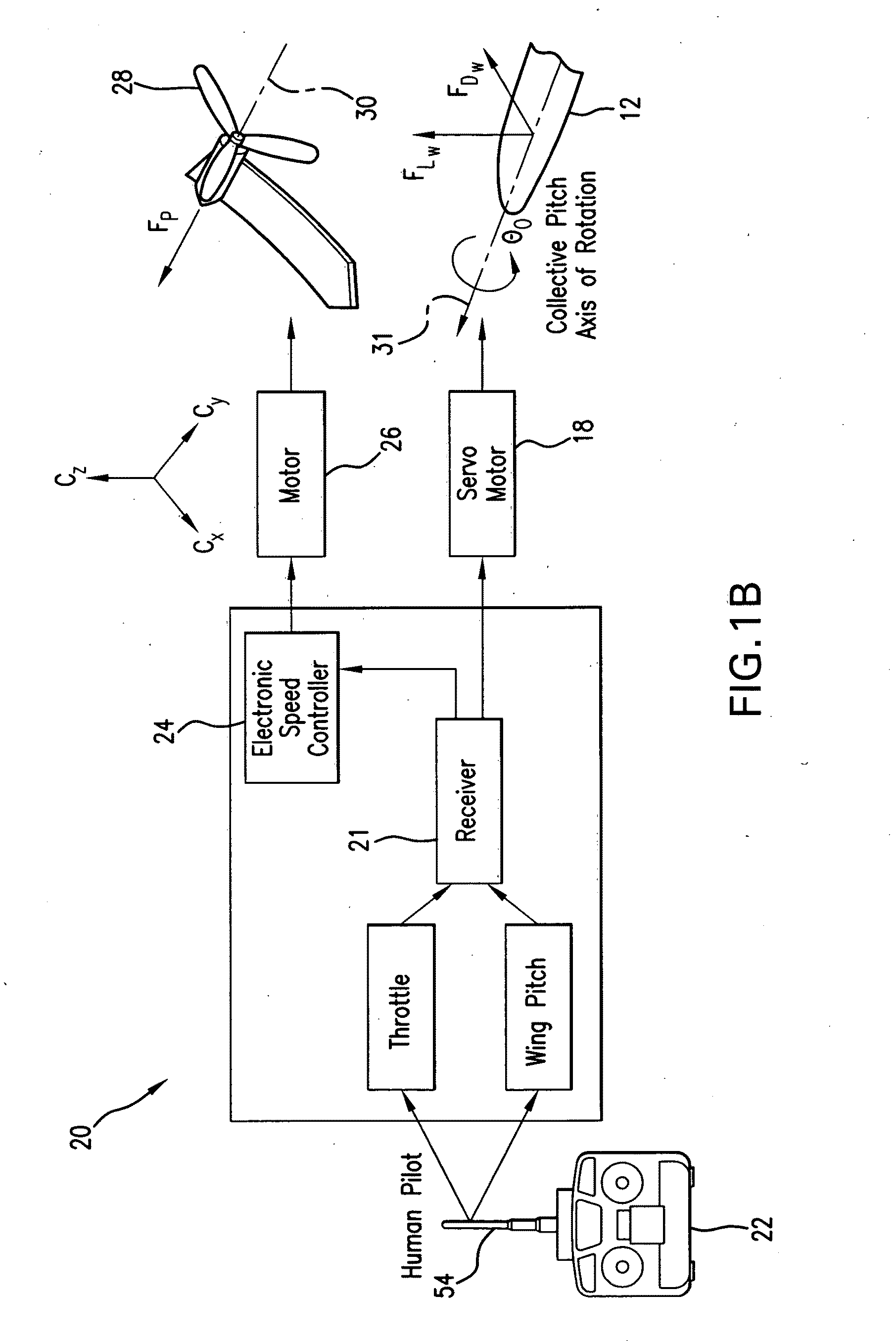
Controllable miniature mono-wing aircraft
ActiveUS20110062278A1Improve the level ofReduce power consumptionPropellersPump componentsJet aeroplaneLinear control
Micro / nano mono-wing aircraft with the wing configured as a winged seed (Samara) is uniquely suited for autonomous or remotely controlled operation in confined environments for surrounding images acquisition. The aircraft is capable of effective autorotation and steady hovering. The wing is flexibly connected to a fuselage via a servo-mechanism which is controlled to change the wing's orientation to control the flight trajectory and characteristics. A propeller on the fuselage rotates about the axis oriented to oppose a torque created about the longitudinal axis of the fuselage and is controlled to contribute in the aircraft maneuvers. A controller, either ON-board or OFF-board, creates input command signals to control the operation of the aircraft based on a linear control model identified as a result of extensive experimentations with a number of models.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
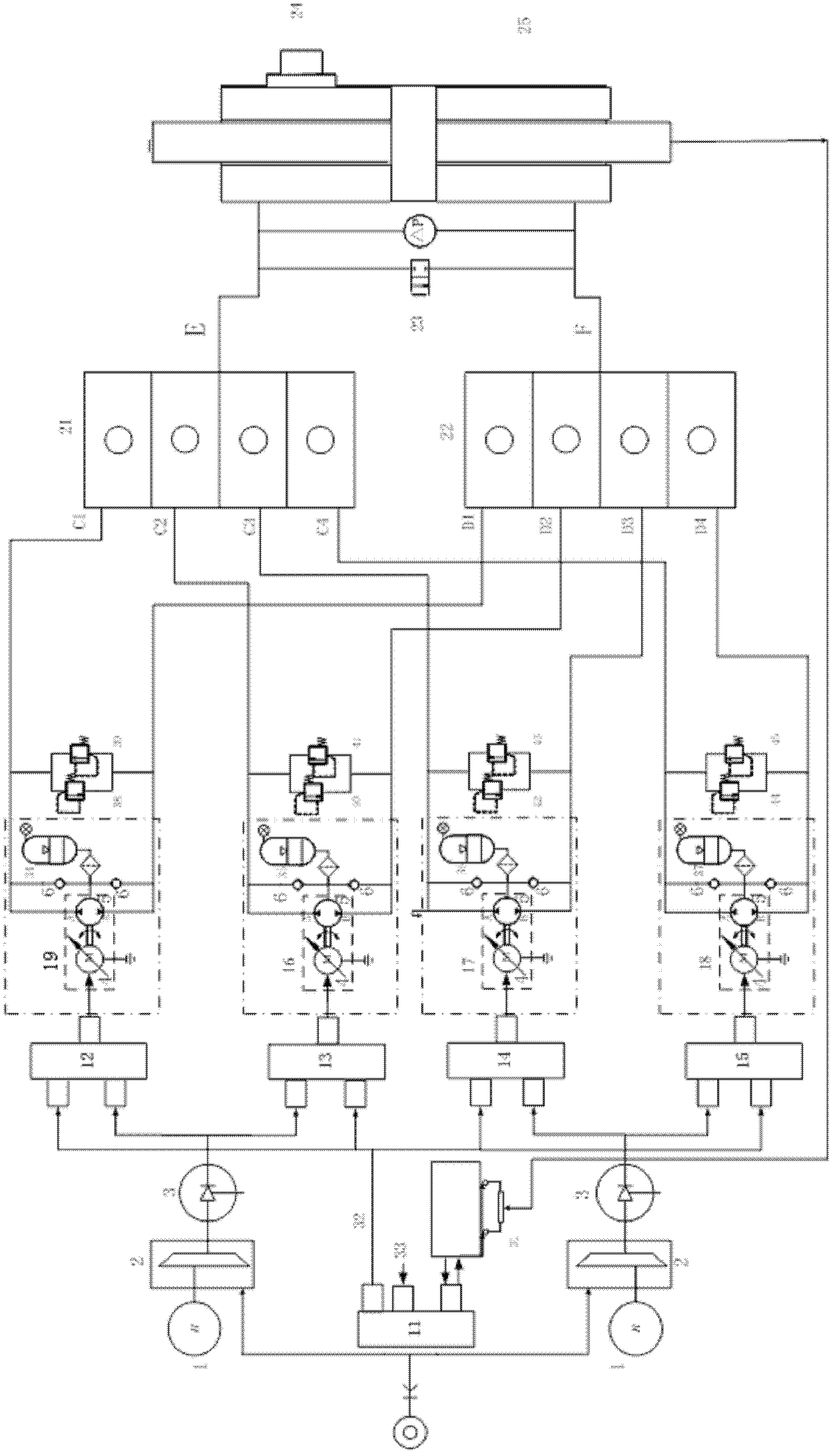
Novel multi-redundancy electromechanical hydrostatic servo mechanism
InactiveCN103075393AOvercoming the defect of easy cloggingAdapt to high reliability requirementsFluid-pressure actuator componentsControl vectorElectric machine
The invention belongs to a thrust vector control servo system for a manned space carrier rocket or missile which has a demand for high reliability to provide thrust for an engine or a steering engine on the rocket or the missile, and particularly relates to a novel multi-redundancy electromechanical hydrostatic servo mechanism. The novel multi-redundancy electromechanical hydrostatic servo mechanism has the advantages that since a servo motor is directly used for driving a bidirectional rotating constant plunger pump, the defect that a valve-controlled electro-hydraulic servo system is apt to be blocked is overcome and the requirement of high reliability is satisfied; since a controller, a motor driver, a servo electric pump and a displacement sensor adopt multi-redundancy configuration, under the situation of at most two-redundancy faults, the system can still work normally and the feasibility of high reliability is guaranteed from structural design; since peak power is provided for a load through the maximum overload of an alternating-current permanent magnet motor and the alternating-current permanent magnet motor is designed according to load average power, compared with an alternating-current permanent magnet motor which is designed according to load maximum power, the size is small, the weight is light and the requirements on long-term use, light weight and small size are better satisfied.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF PRECISE MECHATRONICS CONTROLS +1
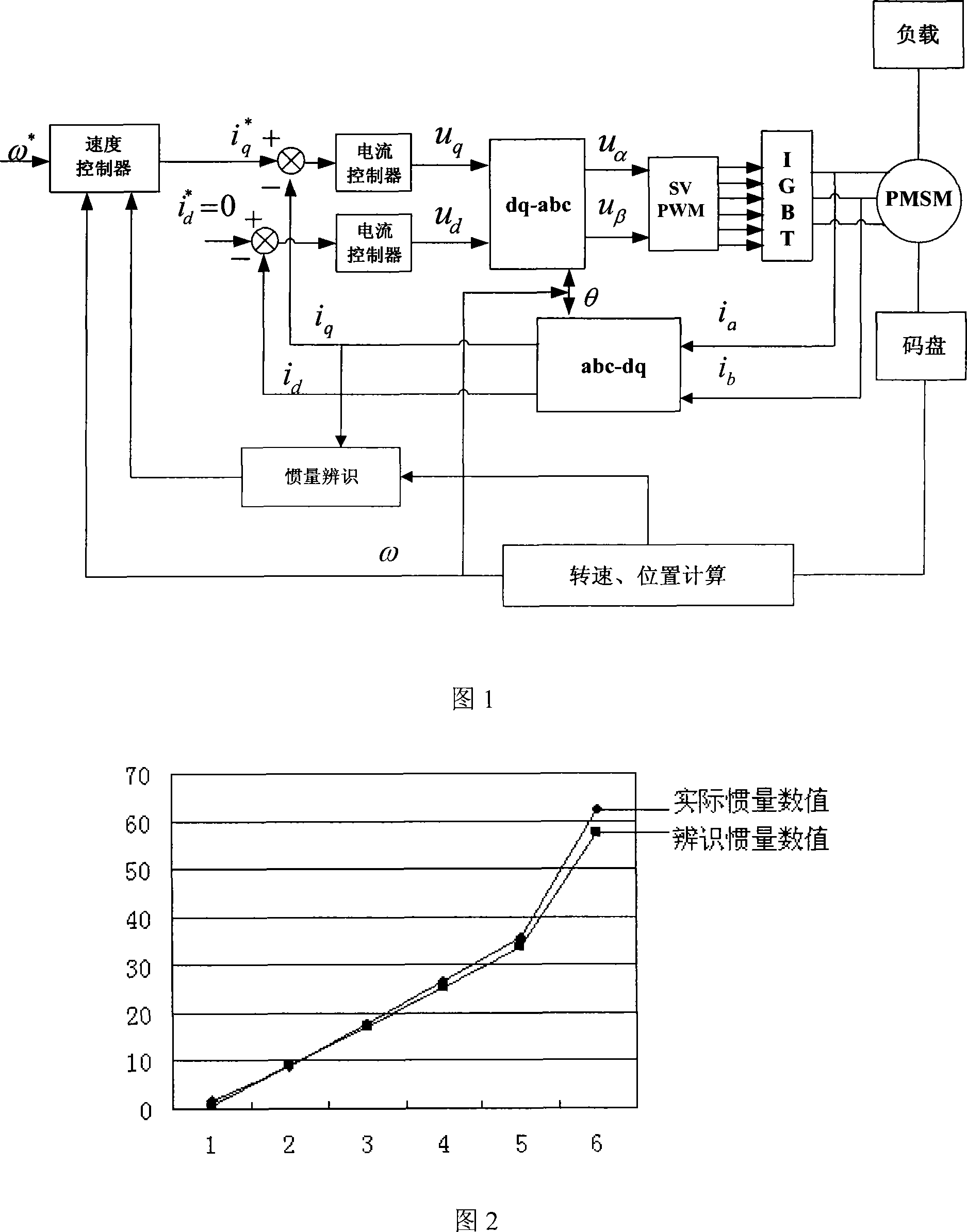
Method for identification of rotational inertia of AC servo
InactiveCN101231207AImprove torque performanceGood dynamic responseStatic/dynamic balance measurementElectric controllersServo actuatorLoad torque
The invention relates to a rotary inertia identification method of an alternating-current servomechanism, the load inertia and the rotor inertia of a motor are regarded as a whole inertia, a servo system does an accelerated motion and a decelerated motion, so as to obtain the system output torque and the motor average rotate speed for a period of time. The average torque of the servo system can be obtained by the system output torque, the value of the whole inertia can be obtained according to the motor average rotate speed, the average torque of the servo system, and the total operation time of the accelerated motion and the decelerated motion of the system, that is, the rotary inertia of the alternating-current servomechanism can be identified. The invention does not need to singly identify the load inertia or the load torque for identifying the system rotary inertia, but causes the load inertia and the motor rotary inertia to be regarded as an inertia, and the identification of the system rotary inertia can be realized by combining the system output torque. The implementation of the method is simple, the use is convenient, the identified inertia precision is higher, and the method can be applied to the servo system inertia detection of a permanent magnetism synchronous servo-actuator.
Owner:ESTUN AUTOMATION TECH
Blank and methods and apparatus for forming a dispenser case from the blank
A machine for forming a case from a blank of sheet material includes a body, a mandrel mounted on the body and having an external shape complimentary to an internal shape of at least a portion of the case, a member mounted on the body adjacent the mandrel for applying a force to the blank for at least one of folding a portion of the blank around the mandrel, moving the blank, and securing portions of the blank together, and a servomechanism operatively connected to the member for driving and controlling movement of the member to apply the force to the blank.
Owner:WESTROCK SHARED SERVICES LLC
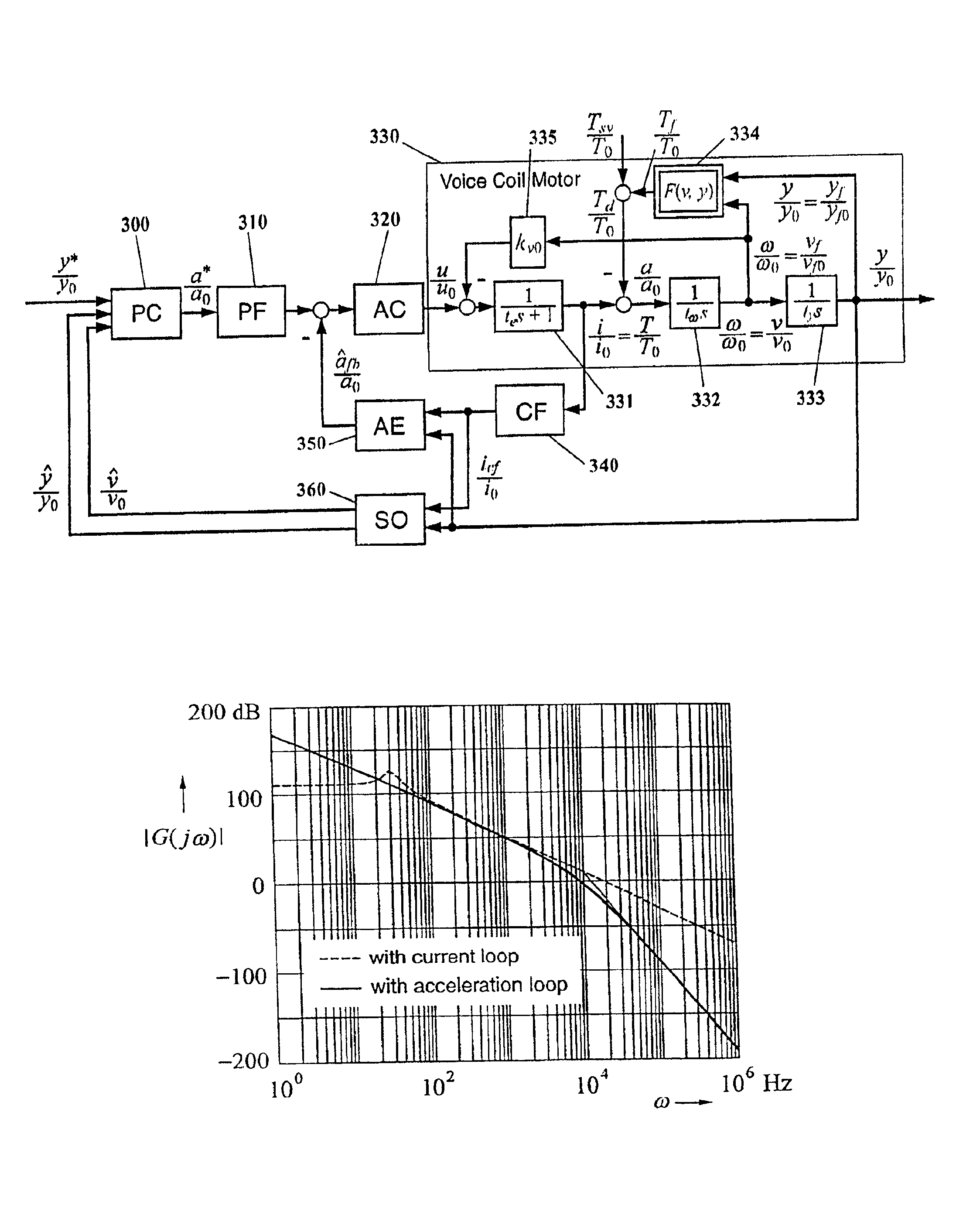
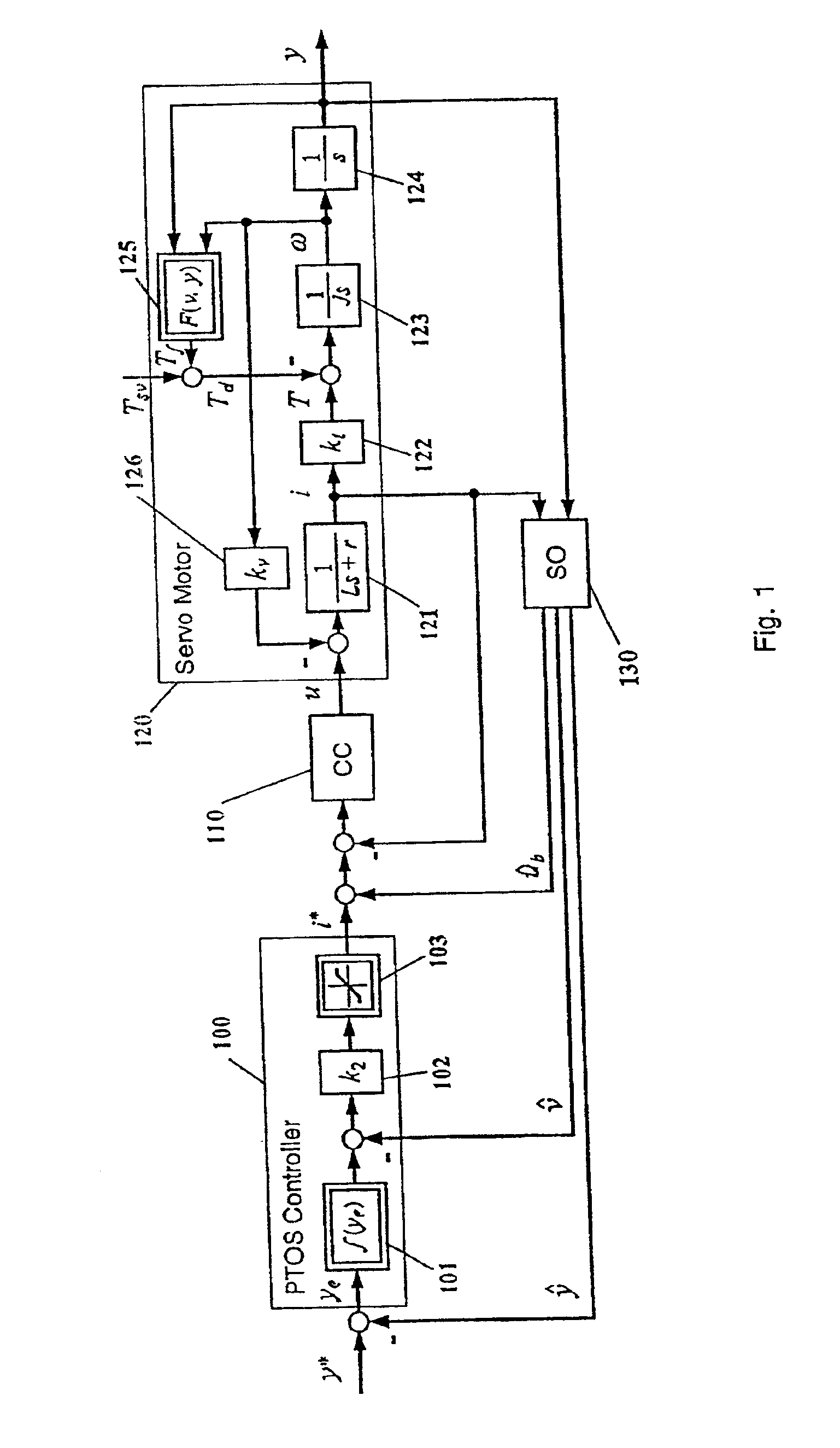
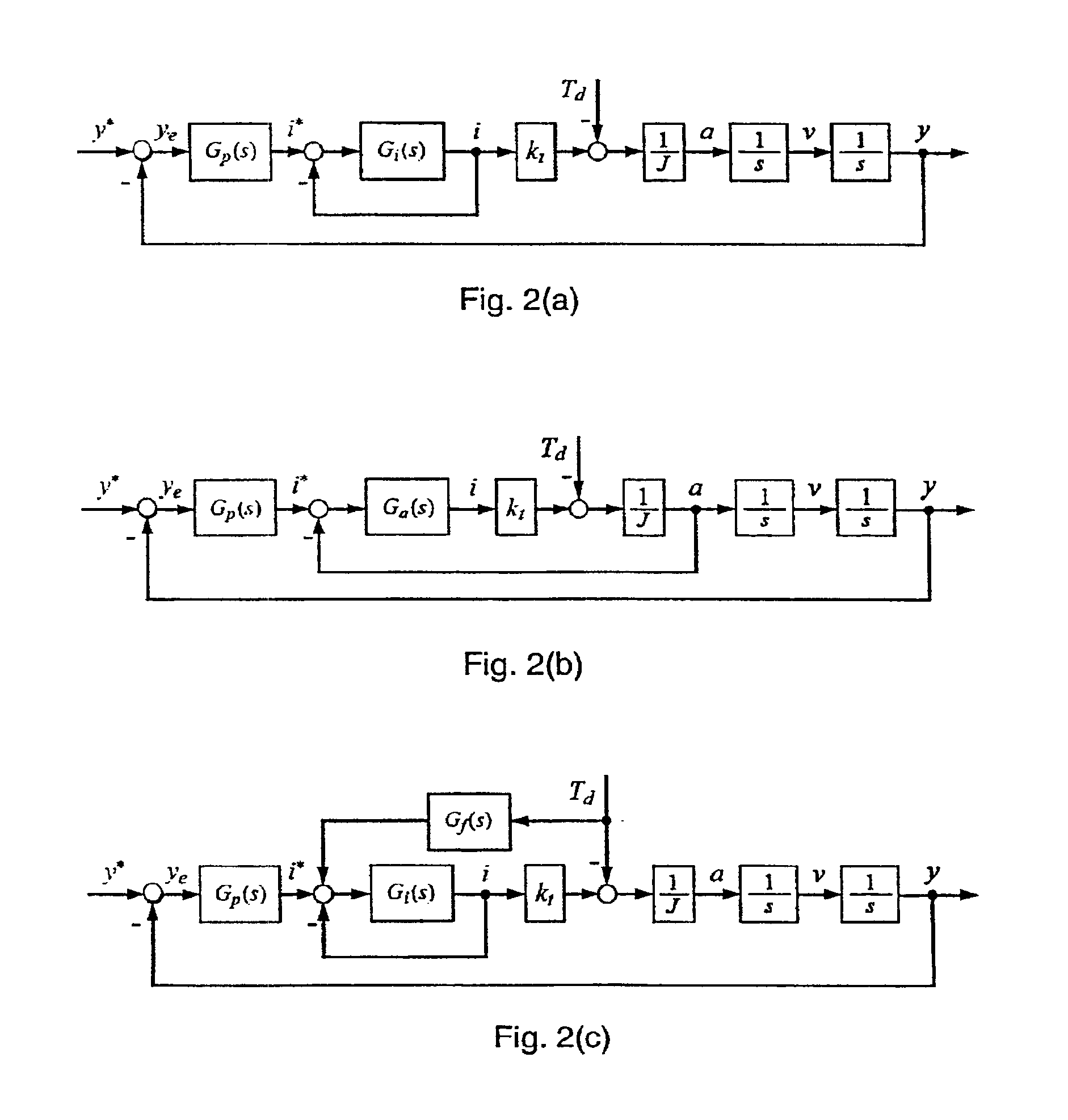
Disturbance attenuation in a precision servomechanism by a frequency-separated acceleration soft sensor
InactiveUS6876168B1Influence of disturbance can be reducedHigh positioning accuracyTrack finding/aligningComputer controlAccelerometerFeedback control
In servomechanisms, like for example used in disk drives, disturbances, for example, friction, shock and vibration, prevent the system positioning accuracy from further improvement. These disturbances occur in a relatively low-frequency range compared to the electrical dynamics. In the present invention, an acceleration feedback control loop using a frequency-separated acceleration soft sensor (350) replaces the conventionally used current control loop in the low frequency range, where the disturbances occur, so as to attenuate the influence of the disturbances enclosed in the loop. The current feedback continues to manage the electrical dynamics in the high-frequency range. Estimating the required acceleration signal by a soft sensor (350) eliminates the need for physical accelerometers, which reduce system reliability and increase system cost. The acceleration feedback control loop constructed with the obtained acceleration signal also makes the system more robust to the parameter inaccuracies and variations within the loop. This invention can be easily implemented with either software or hardware.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Disc Brake Apparatus
InactiveUS20070045061A1Small sizeLarge braking forceAxially engaging brakesBrake actuating mechanismsEngineeringCalipers
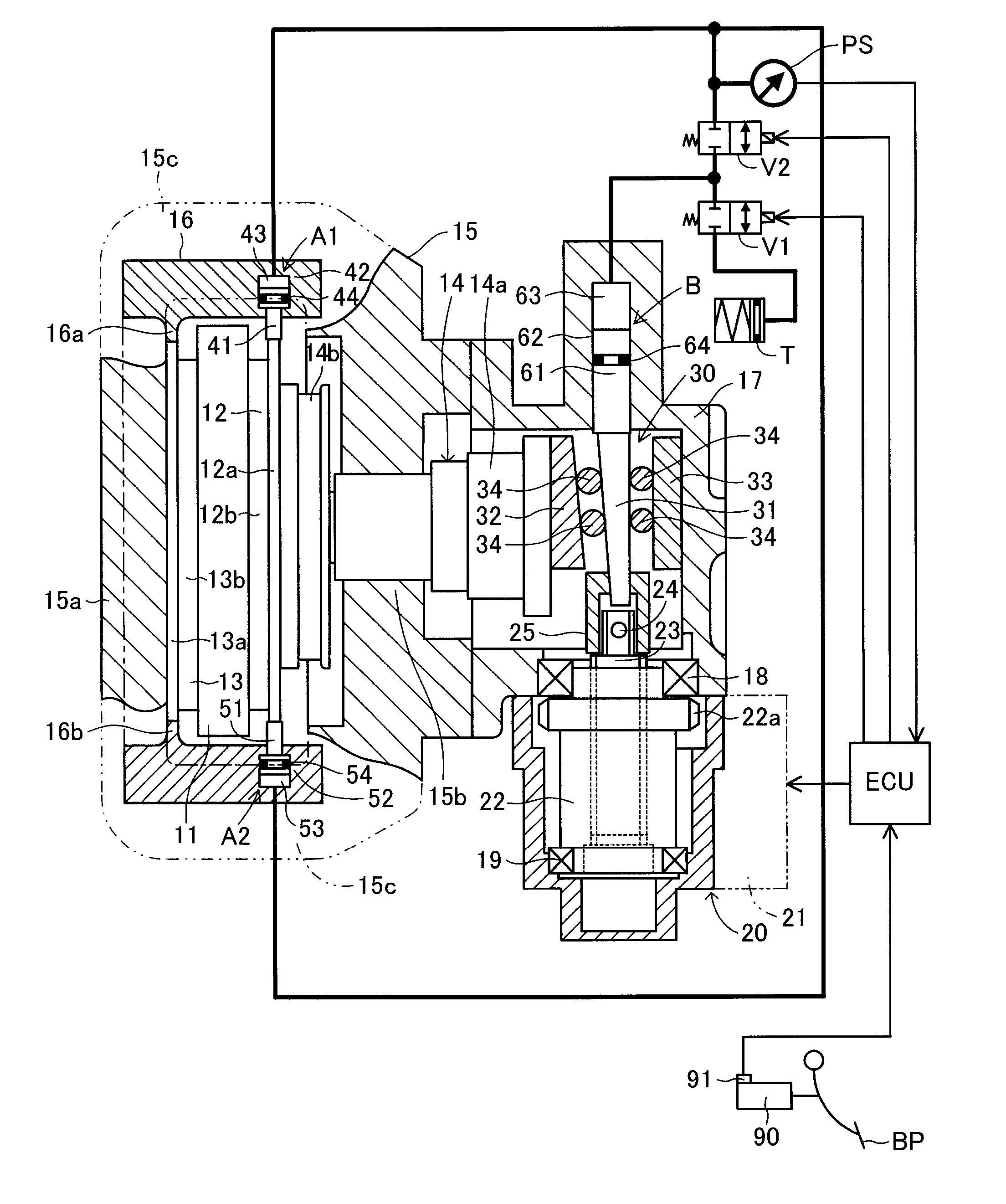
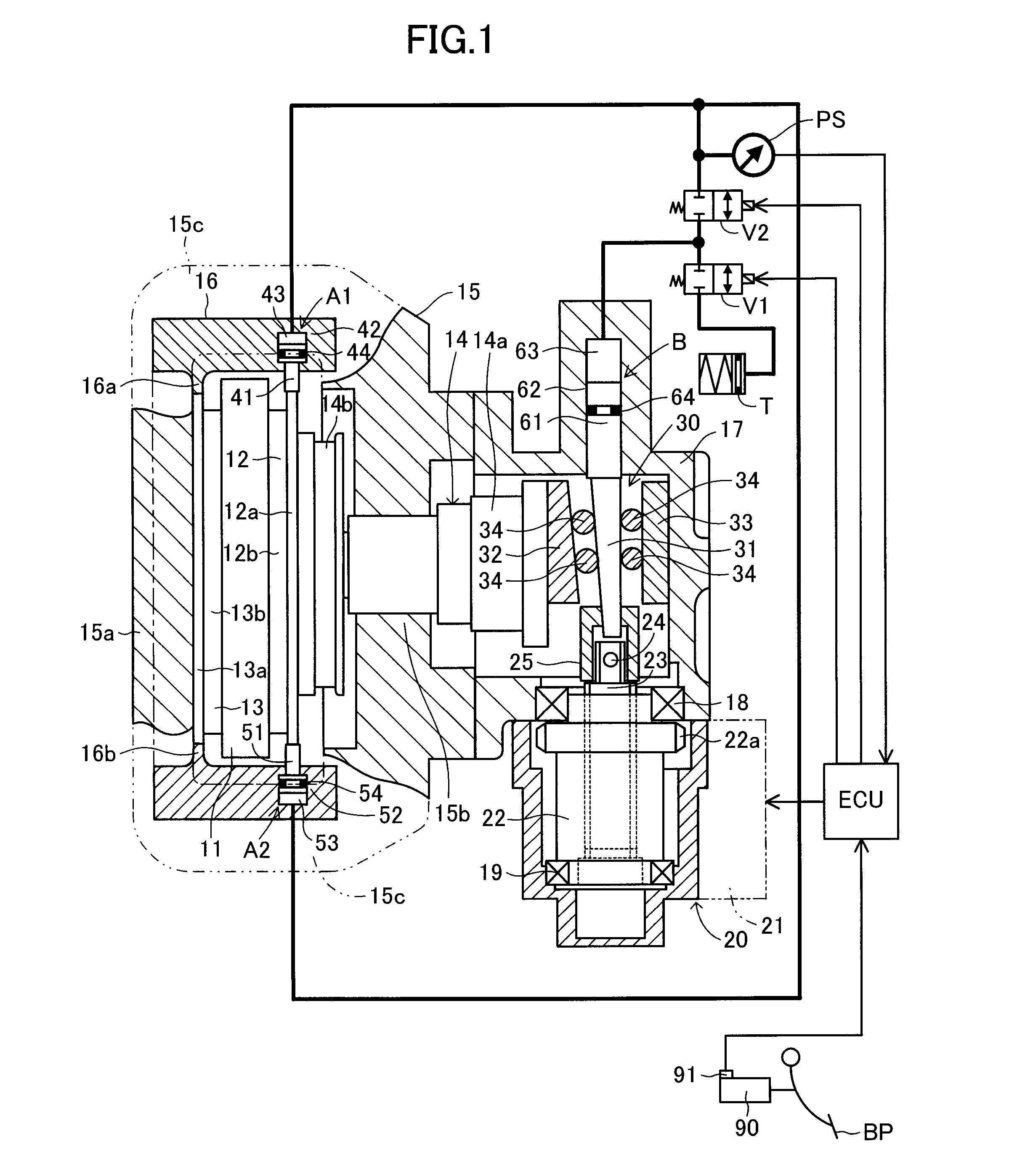
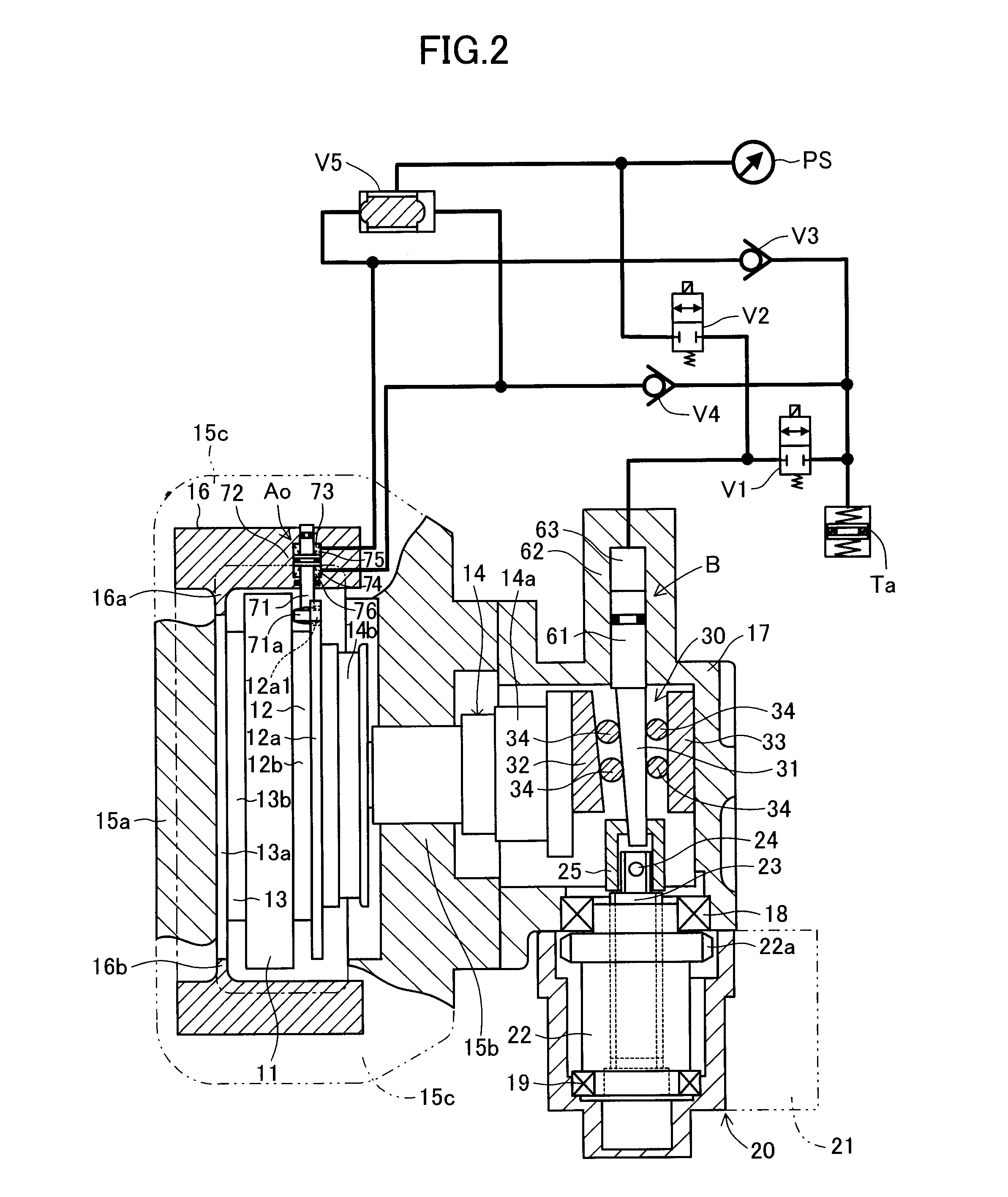
In a disc brake apparatus, by means of an actuator which operates in accordance with an operation force, a braking piston fitted into a cylinder portion of a caliper is axially driven so as to push a pad toward a disc rotor. A friction force in a circumferential direction of the disc rotor between the pad and the disc rotor is taken out as an anchor load, and is converted to a servo load by means of a servomechanism. The servo load is applied to the braking piston. The servomechanism is equipped with a hydraulic mechanism (a pressure-reducing control valve, a pressure-increasing control valve, and a reservoir tank) capable of increasing or decreasing the servo load. An electric controller controls the hydraulic mechanism in accordance with the operation force and the anchor load.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
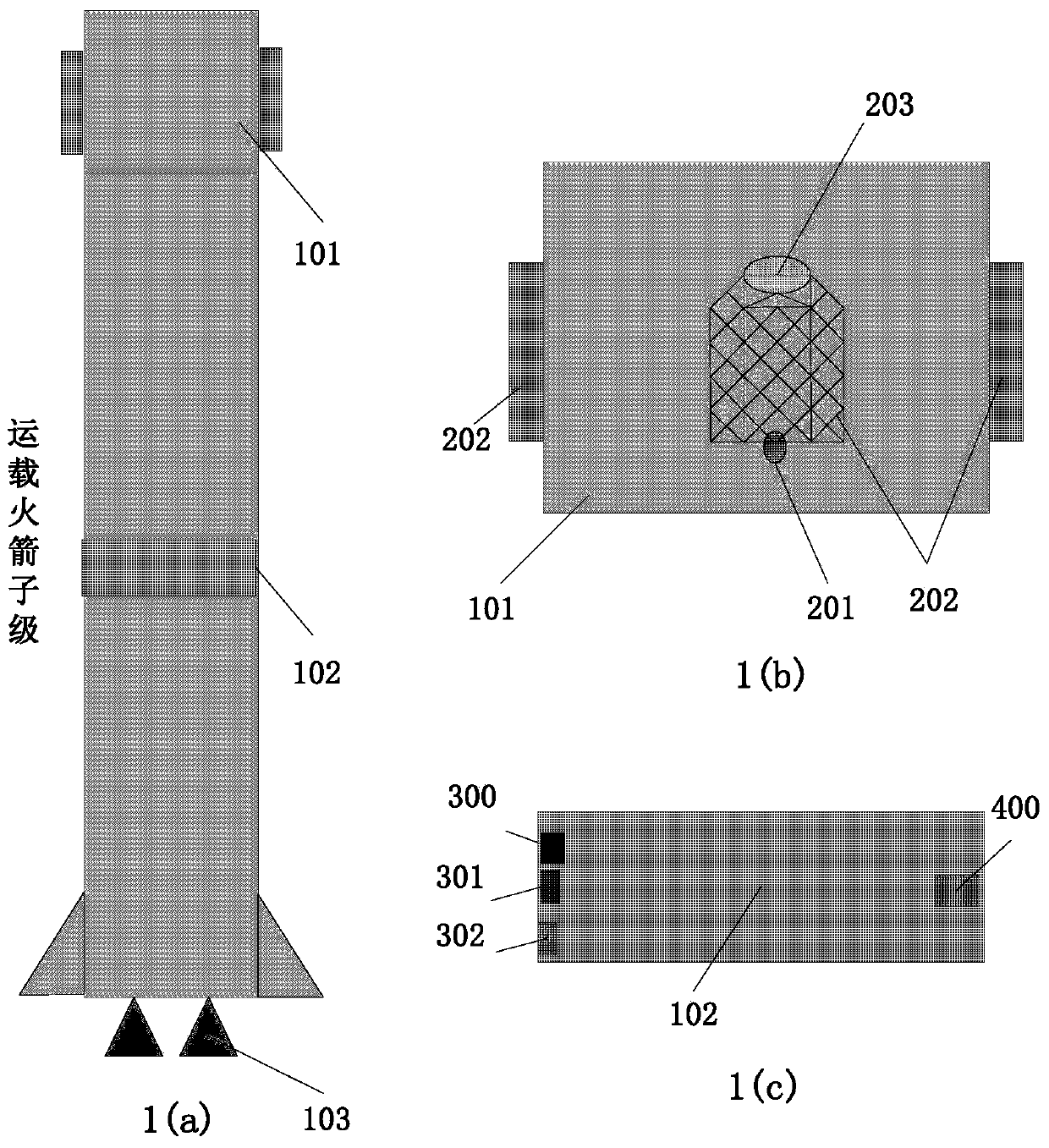
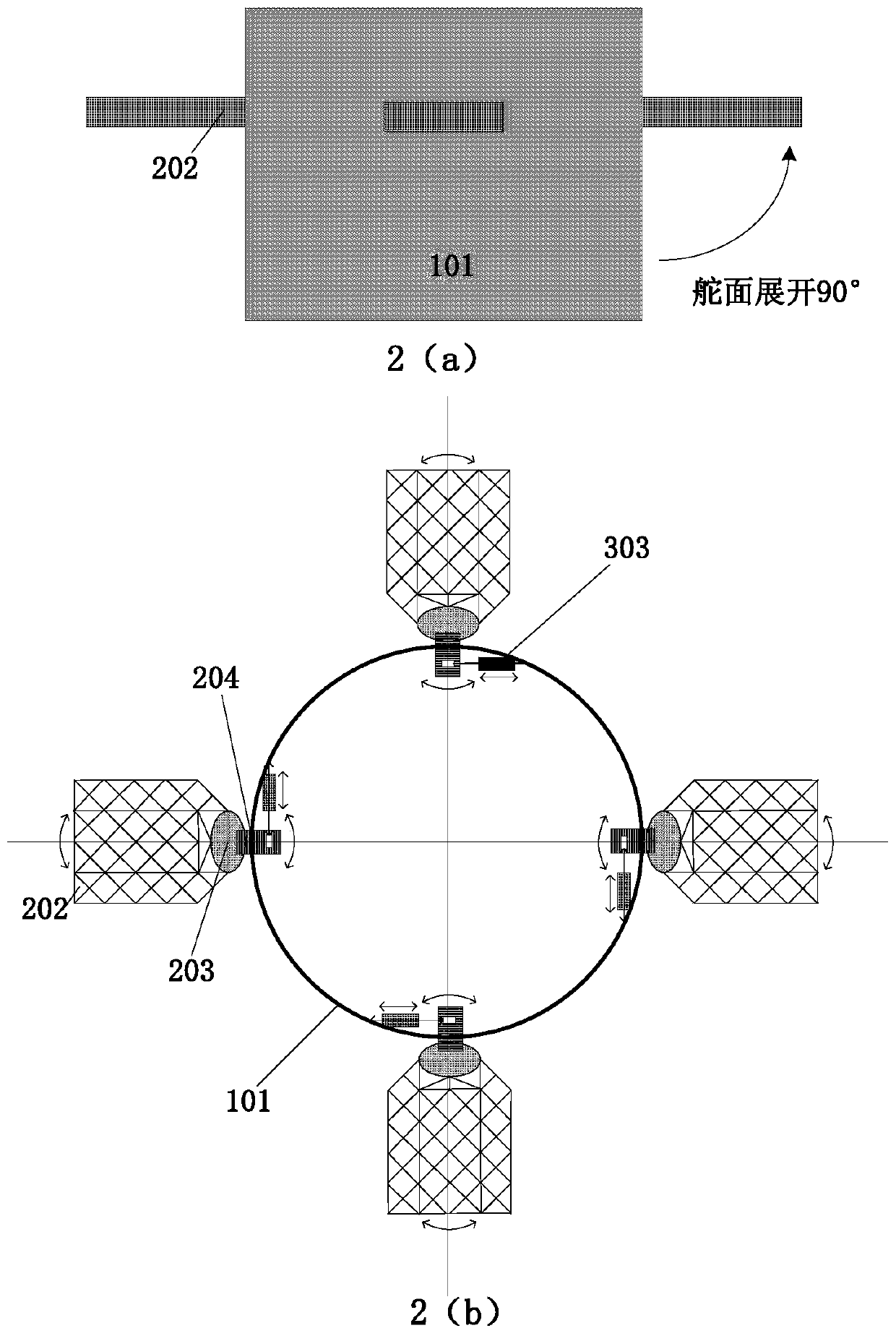
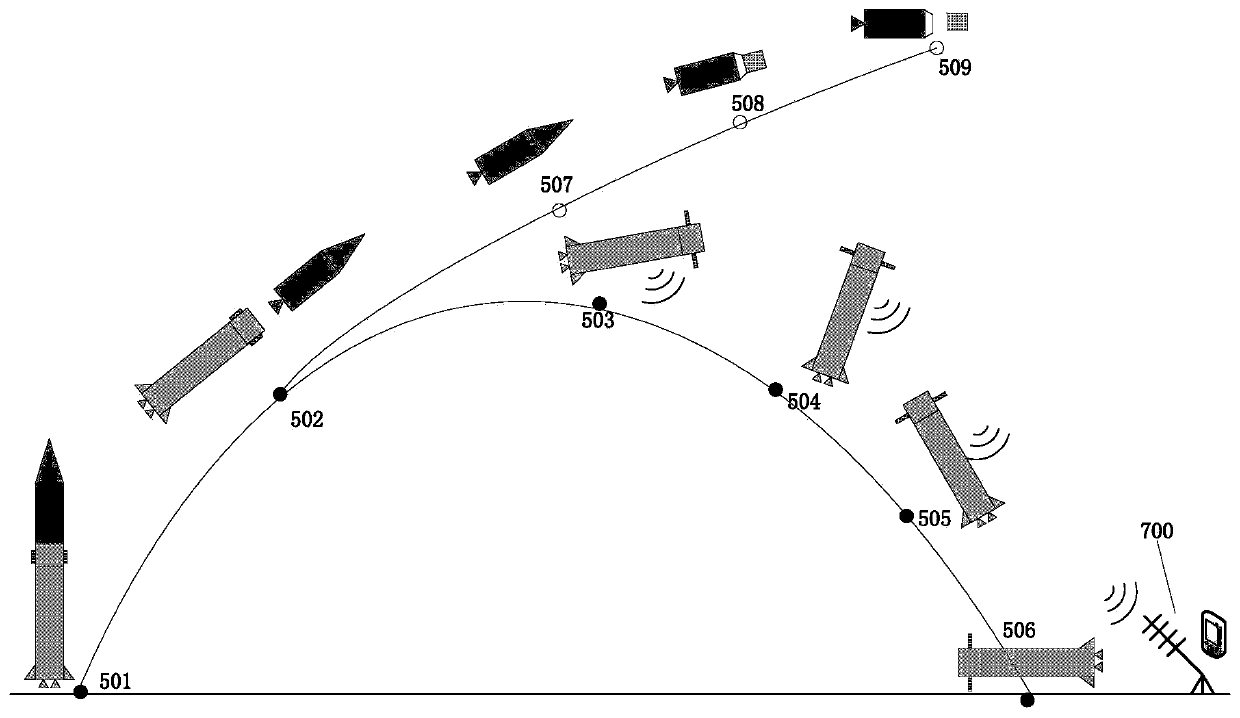
Carrier rocket sub-stage falling area range control system
ActiveCN110160407AReal-time monitoring of air positionQuick searchSelf-propelled projectilesCarrying capacityControl system
The invention discloses a carrier rocket sub-stage falling area range control system. The carrier rocket sub-stage falling area range control system comprises a grid fin structure system, a grid fin control system, a grid fin telemetering system and a ground information receiving system. Under the condition that a control unit resolves the measurement information such as the posture, the positionand the speed, a servo mechanism is controlled to deflect the fin surface by sending an instruction, so that the posture of a sub-stage of a carrier rocket is stabilized, and the sub-stage is guided to fly to the target falling area for flying landing; and the telemetering system and the ground information receiving system are used for measuring and receiving the sub-stage reentry flight information, and the sub-stage state information is monitored in real time. According to the system, the flight control time sequence and procedures are integrated, so that the sysrem has the advantages that the modification amount of the carrier rocket is small, the loss of the carrying capacity is small, the flight safety of a main task of the carrier rocket is not affected, the sub-stage falling area range of the carrier rocket can be greatly reduced, and the sub-stage return information can be monitored in real time.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE SYST ENG INST
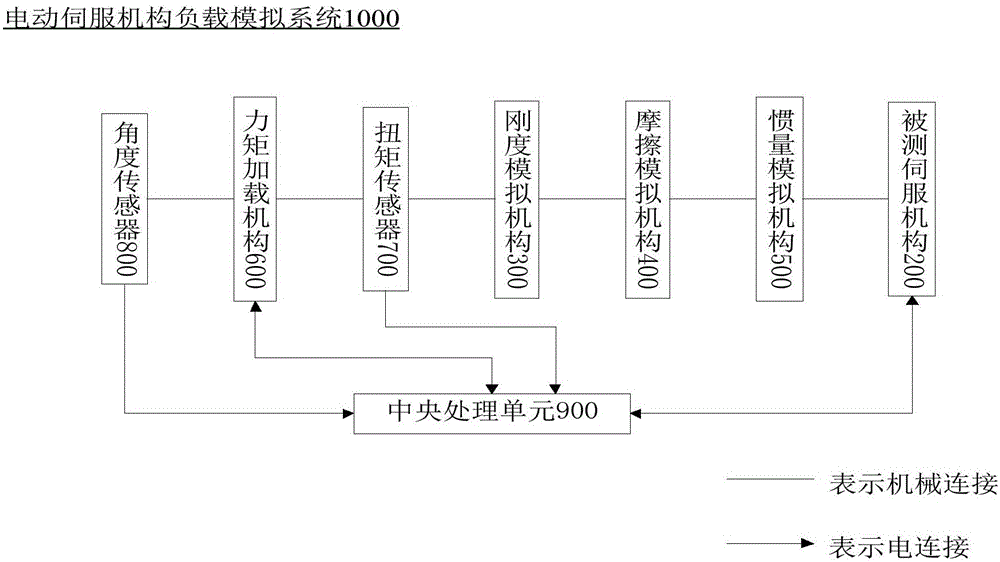
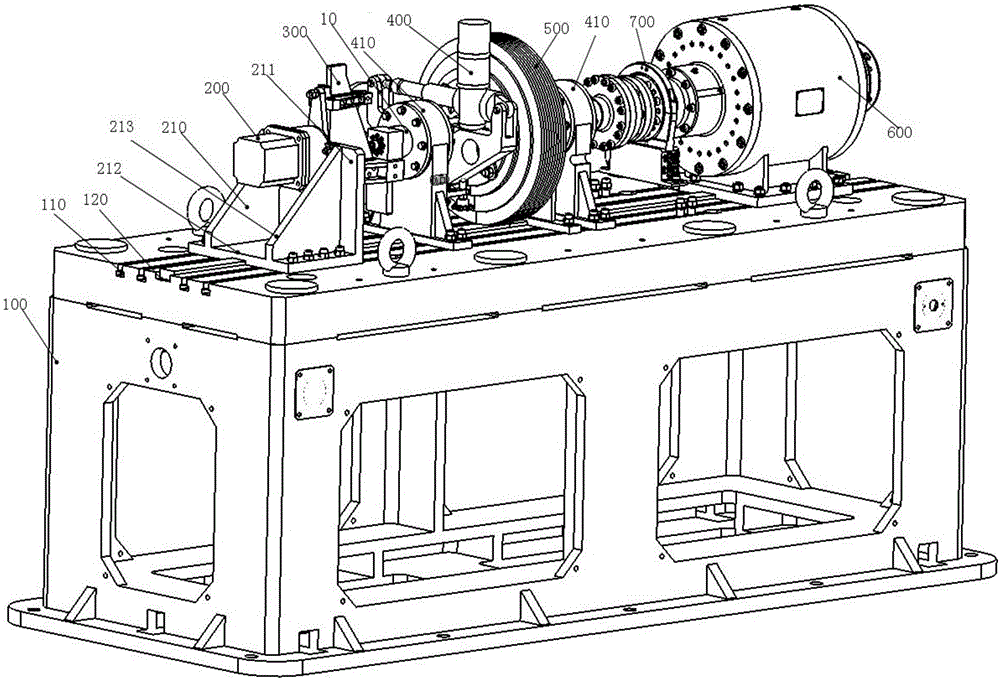
Electric servo mechanism load simulation system and simulation method thereof
The invention provides an electric servo mechanism load simulation system and a simulation method thereof. The system comprises a pedestal, a tested servo mechanism and a force moment loading mechanism which are disposed on the pedestal, a rigidness simulation mechanism, a friction simulation mechanism, an inertia simulation mechanism, a torque sensor, an angle sensor, and a central processing unit, wherein the rigidness simulation mechanism, the friction simulation mechanism, the inertia simulation mechanism and the torque sensor are disposed between the tested servo mechanism and the force moment loading mechanism, and the angle sensor is used for measuring the position and speed of the force moment loading mechanism. The rigidness simulation mechanism is connected with a rotor of the tested servo mechanism, and is driven by the rotation of the tested servo mechanism to swing. The friction simulation mechanism, the inertia simulation mechanism and the force moment loading mechanism are located in the same main axis, and are respectively used for simulating a friction load, an inertia load and an elastic load. The central processing unit receives detection signals of the torque sensor and the angle sensor, and judges whether the force moment parameter indexes of rotation inertia, rigidness, rotation speed and simulation position meet the requirements of performance testing under the condition of different loads or not.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Method and system for monitoring hard-disk damage
InactiveCN1896963AImprove detection efficiencyFully automatedDetecting faulty computer hardwareDigital signal error detection/correctionProcessor registerServomechanism
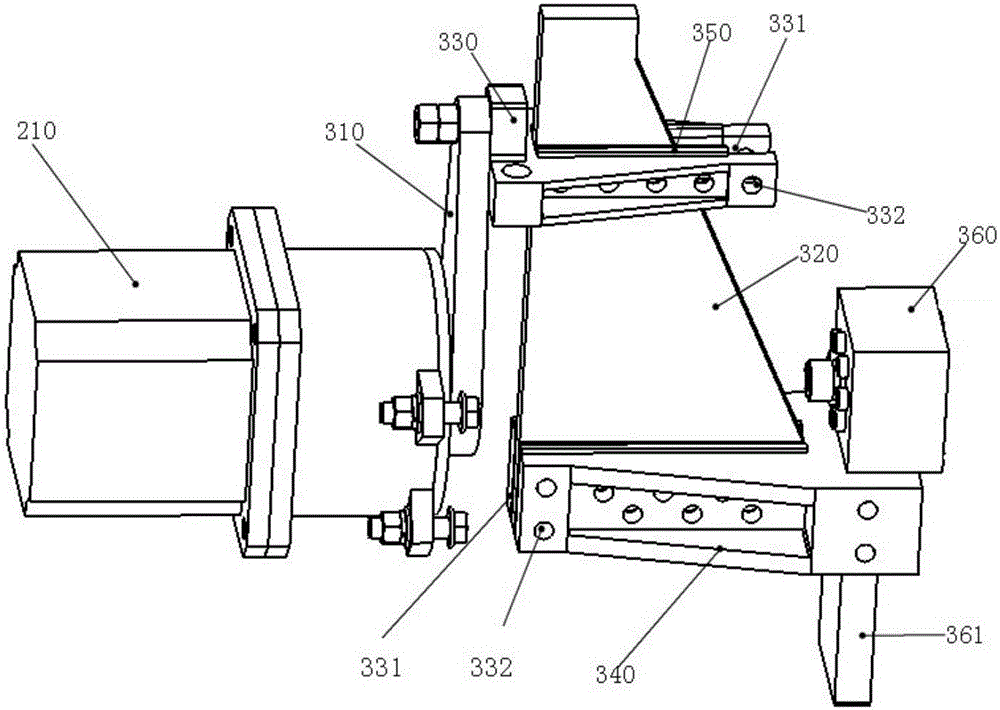
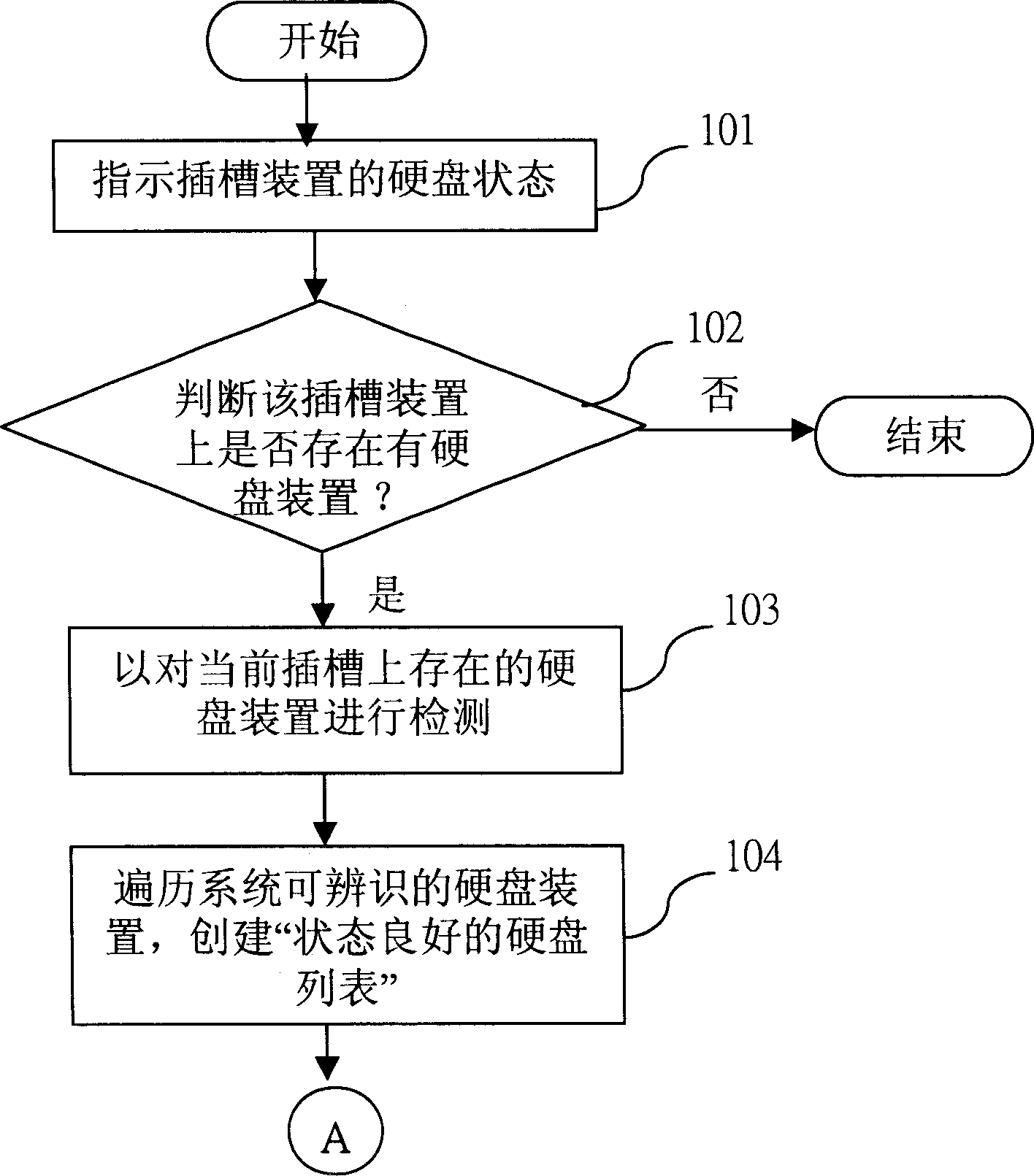
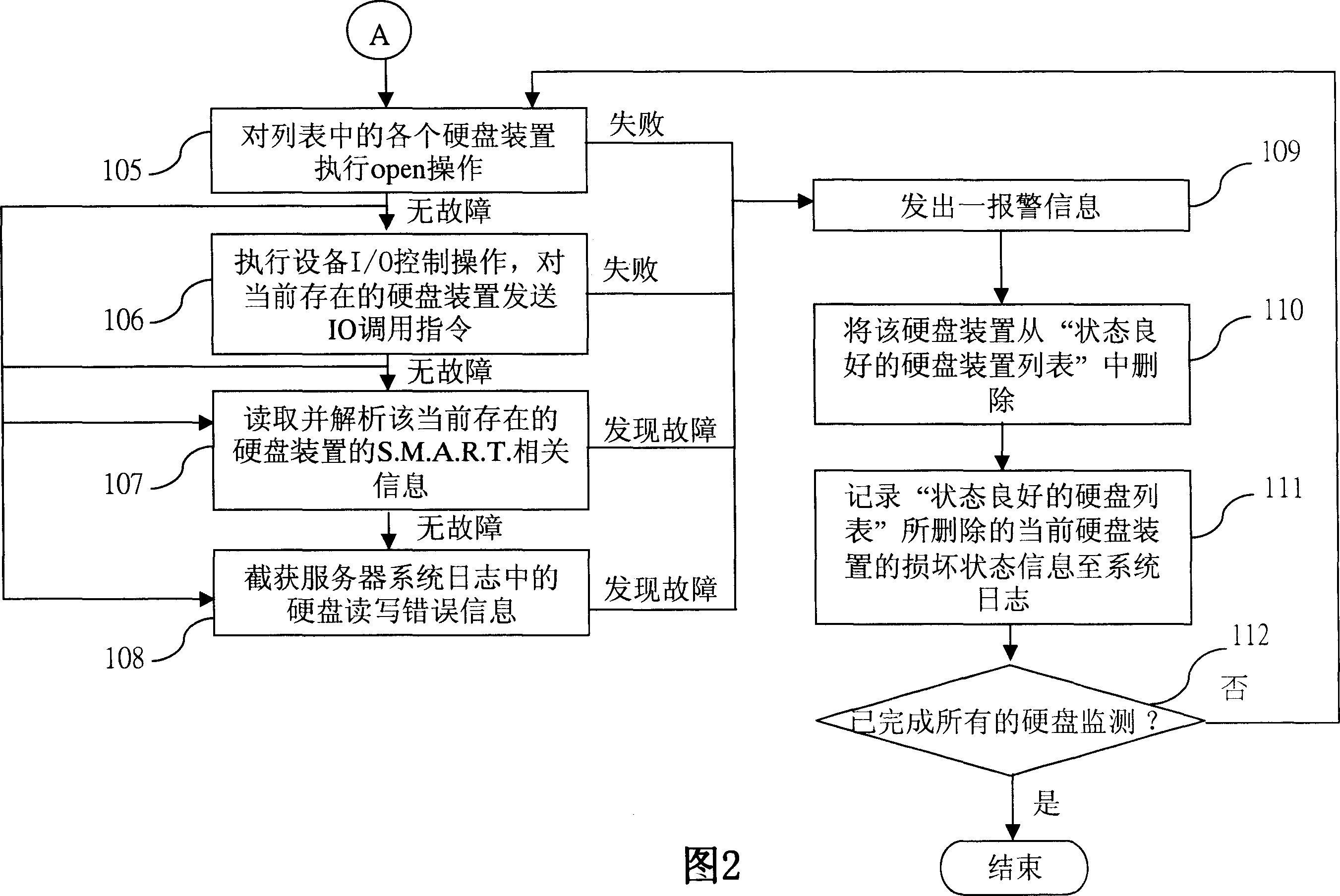
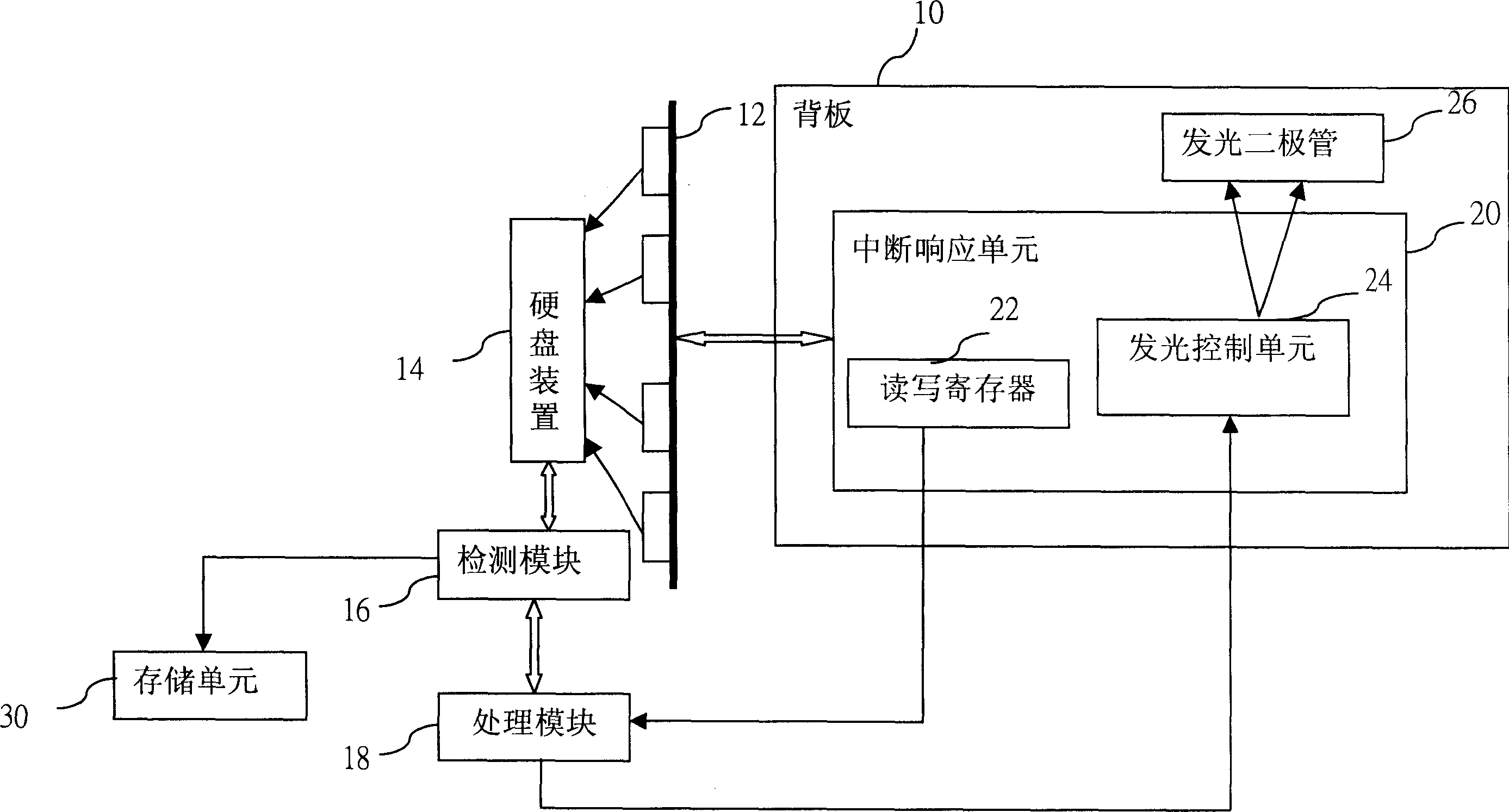
A method for monitoring damage of hard disc can be executed on a servomechanism with insertion slot unit enabling to connect on with multiple hard discs.
Owner:淮北盛大知识产权运营有限公司
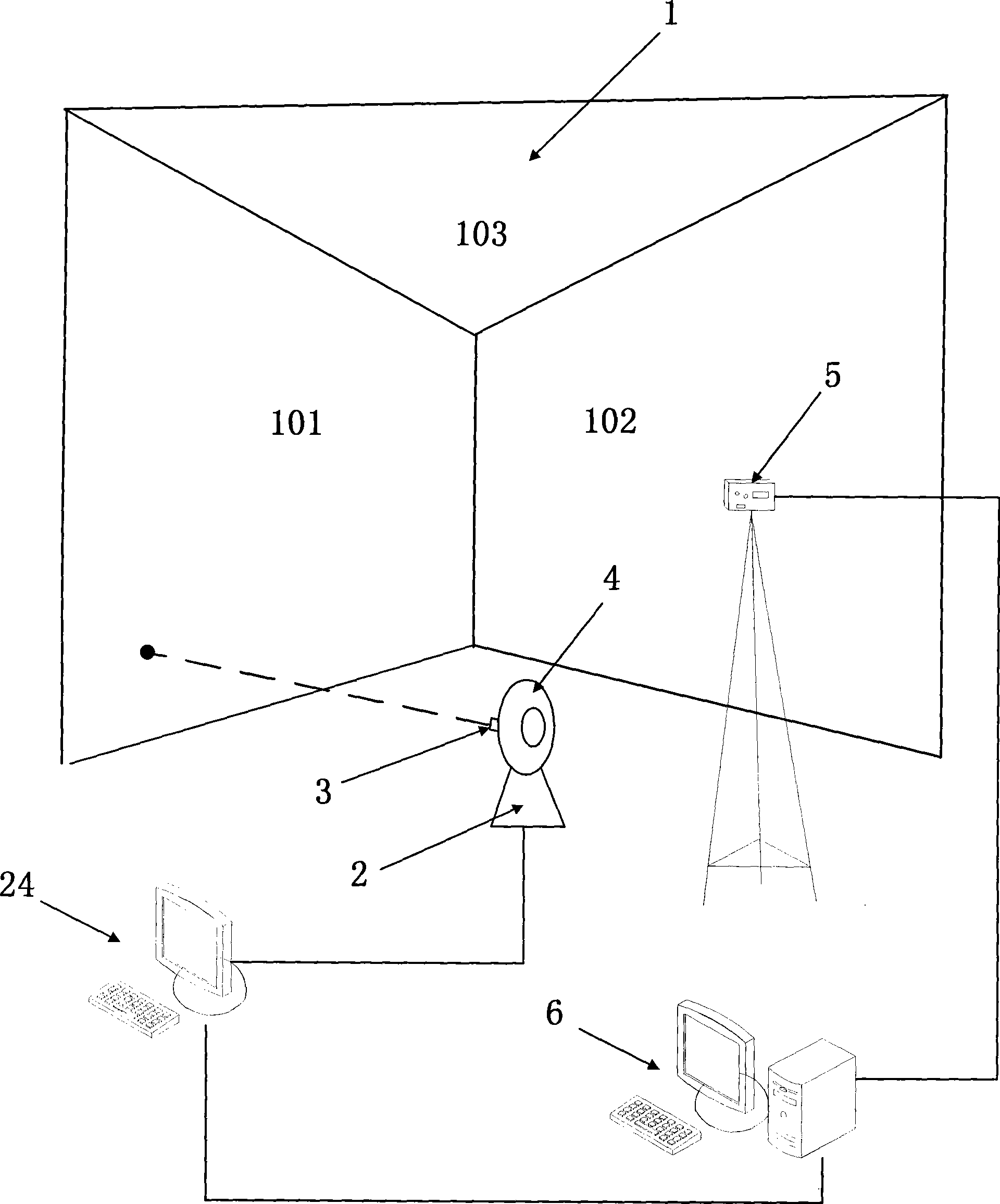
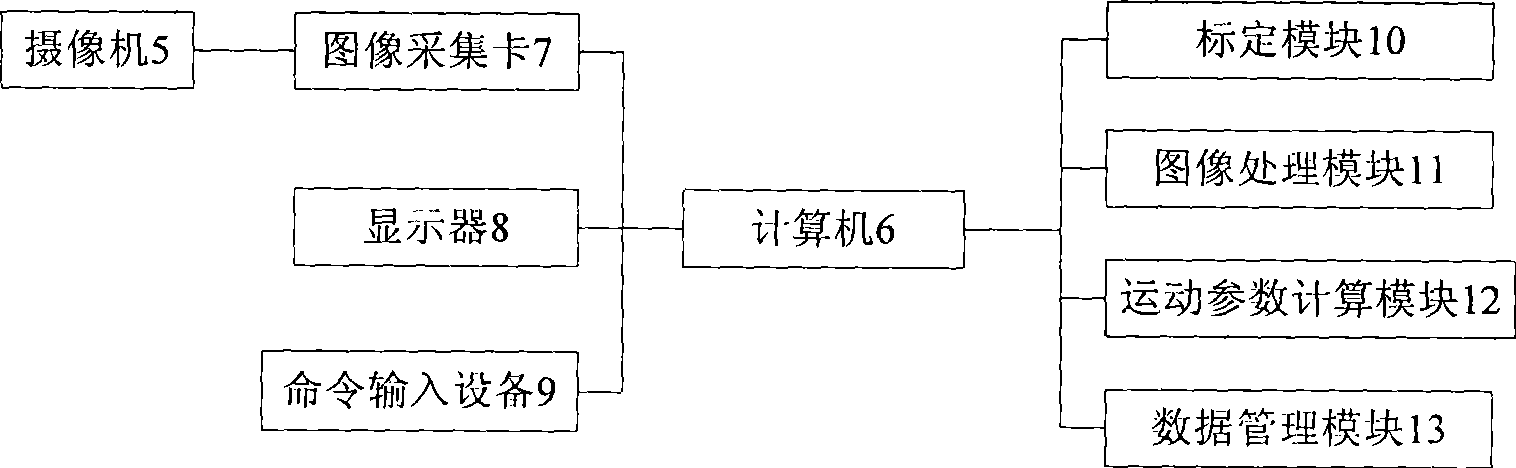
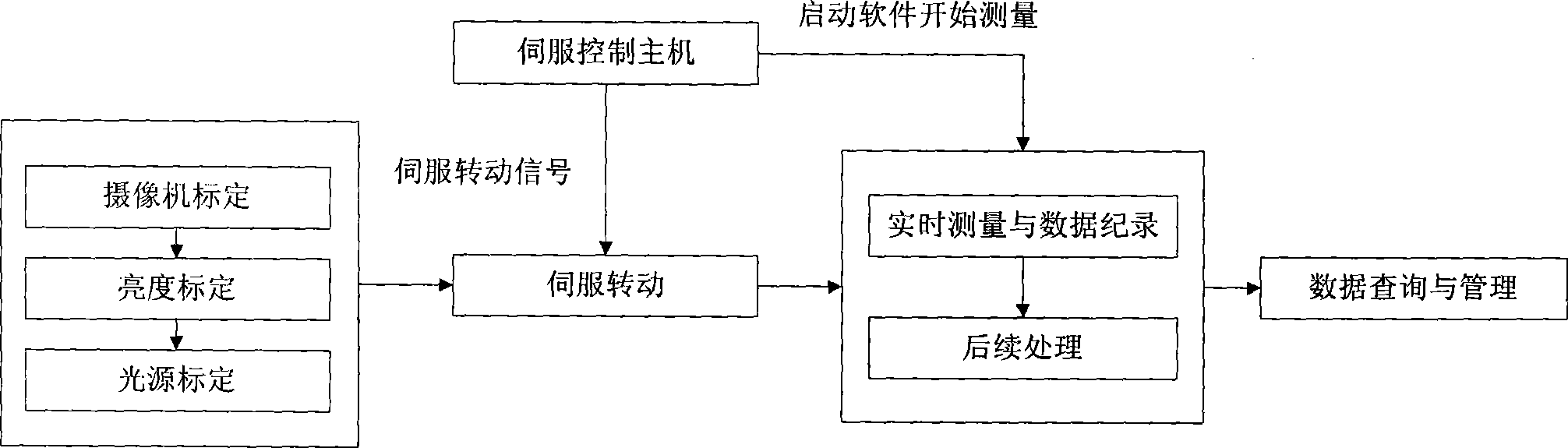
Active vision non-contact type servomechanism parameter measurement method and apparatus thereof
InactiveCN101424551AReduce difficultyAutomatically adjust shutter speedUsing optical meansMeasurement deviceAngular velocity
The invention provides an active vision non-contact servo mechanism parameter measuring device, consisting of a measuring screen, a servo mechanism mounting platform, an image acquiring and processing system, and a red light laser light source, wherein a servo mechanism to be detected is provided with the red light laser light source which is positioned on the servo mechanism mounting platform and is arranged in front of the measuring screen, a digital camera is arranged behind the measuring screen to image on the screen. Firstly, the device shoots a picture of a gridiron pattern on the measuring screen by the camera which is demarcated; secondly, the servo mechanism controls a main frame to give a command so as to control the rotation of the servo mechanism to be detected, a computer extracts laser point coordinates of the image, the rotational angle at each moment of the servo mechanism to be detected is calculated and recorded in real time, the motion parameters of the servo mechanism to be detected such as the angular velocity, the pointing accuracy, and the overshoot are calculated by the rotational angle; the measuring method is simple, convenient and flexible, and the device and the measuring method realize the measurement in real time and with high accuracy of the movement parameters of a biaxial servo mechanism through the non-contact way.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
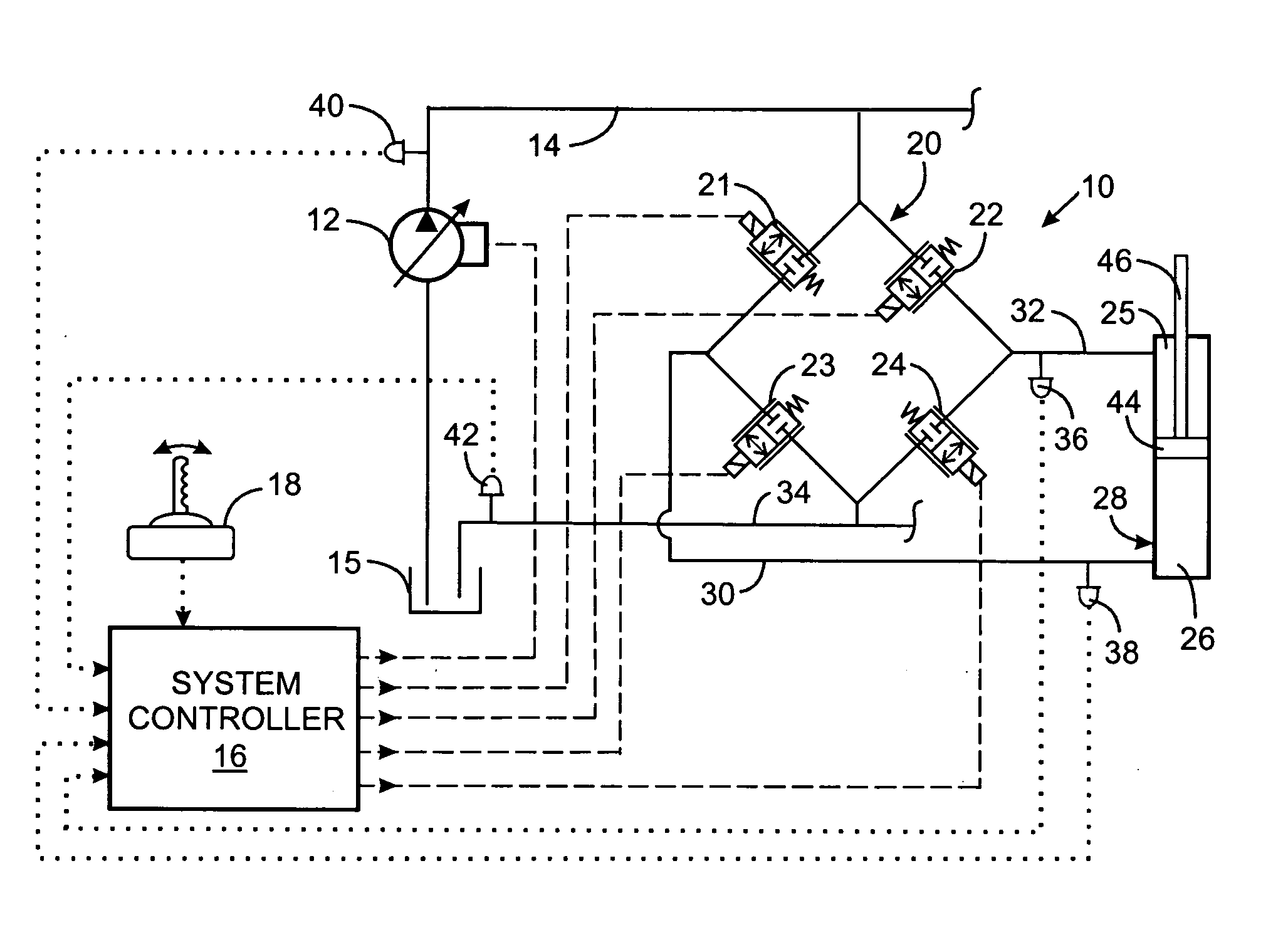
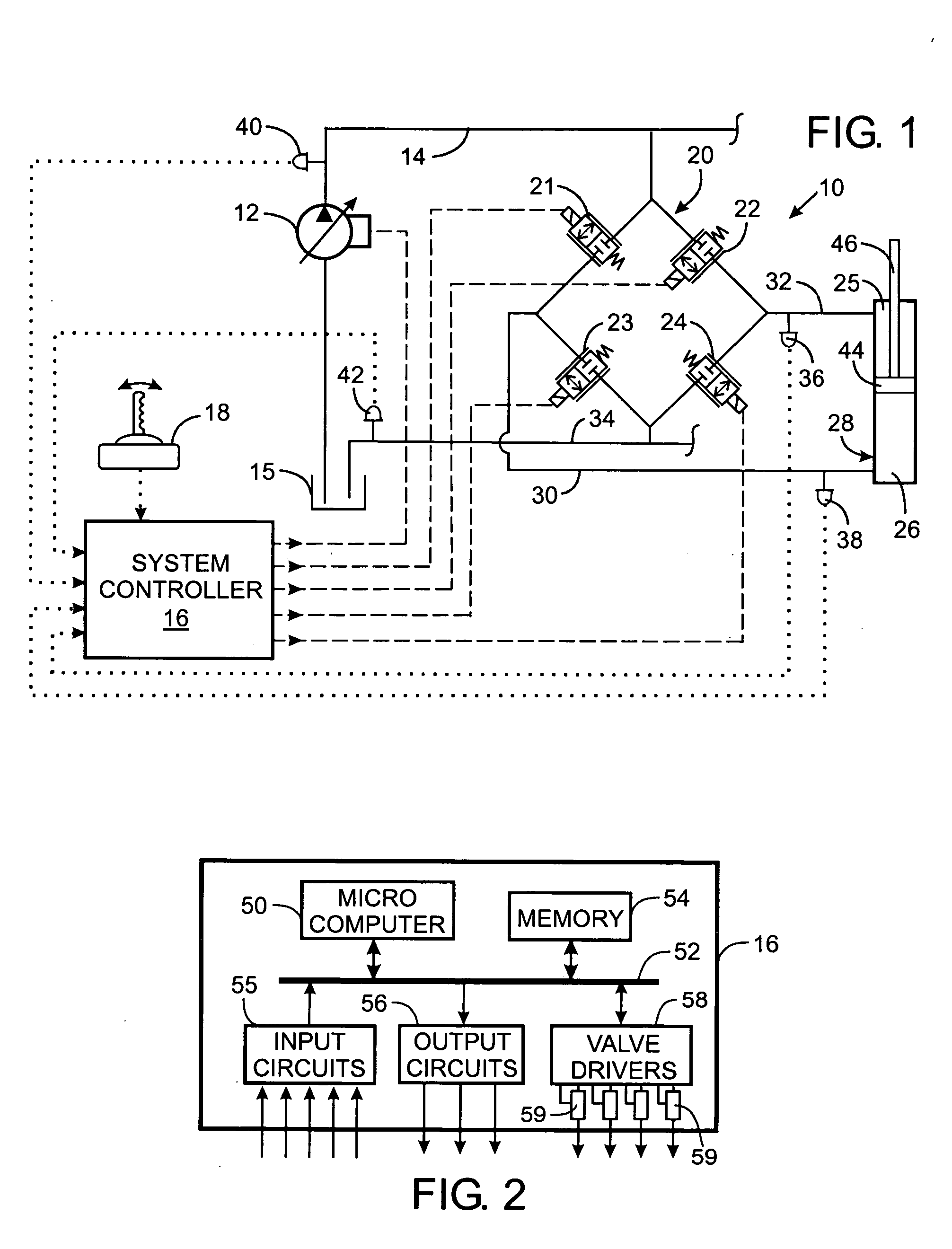
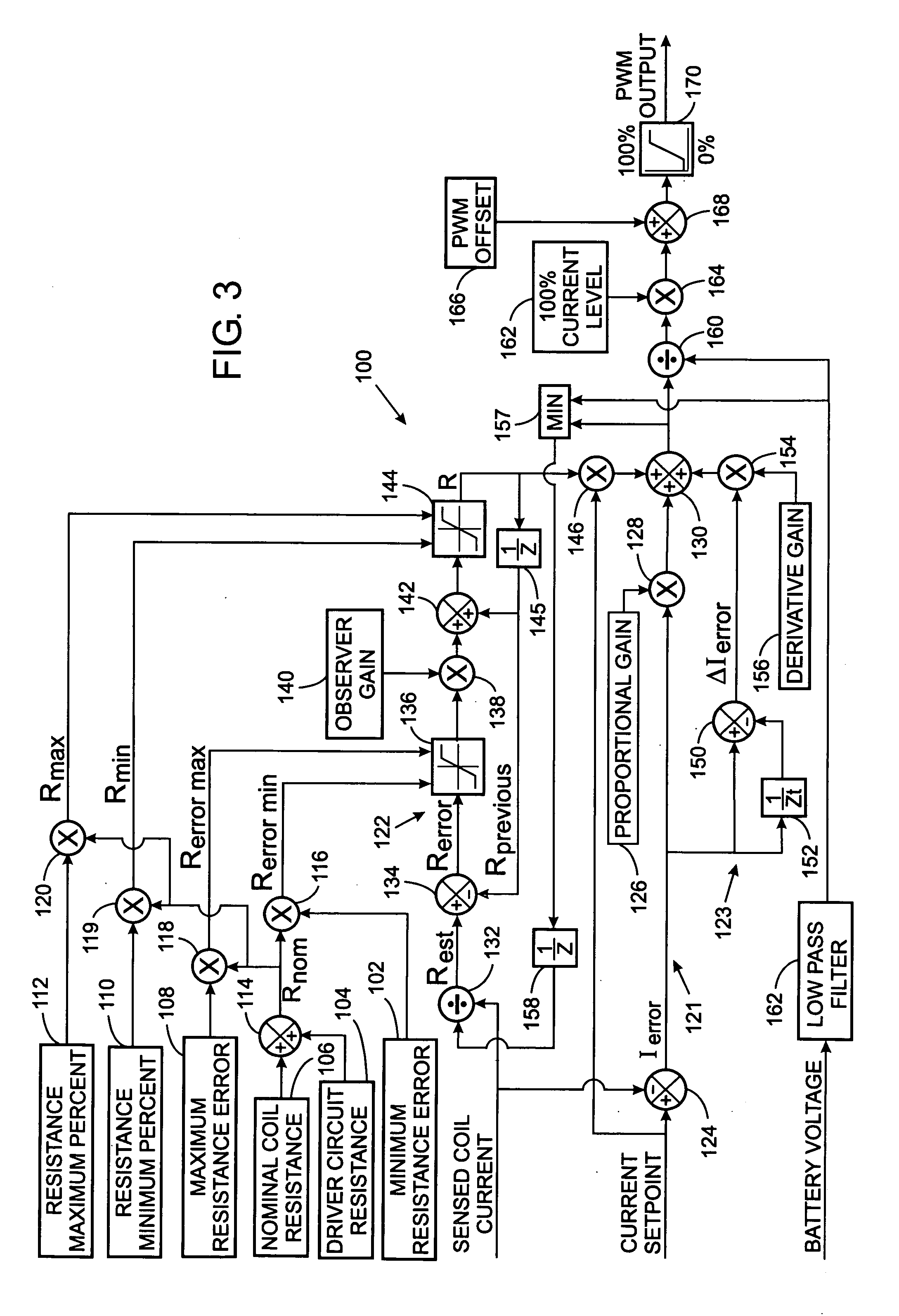
Electrohydraulic valve servomechanism with adaptive resistance estimator
InactiveUS20050211936A1Adjustable levelFluid-pressure actuator testingOperating means/releasing devices for valvesElectrical resistance and conductancePwm signals
A servomechanism includes a controller which dynamically estimates the resistance of the solenoid coil in an electrohydraulic valve as part of determining a level of electric voltage to apply to open the valve. The servomechanism receives a current setpoint designating a desired electric current level and senses the actual level of current flowing through the coil. A proportional term is derived from the current setpoint and the actual level of current. Creation of a derivative term is based on the difference between the current setpoint and the actual level of current. A feedforward term is produced by estimating the resistance of the electrohydraulic valve and limiting the feedforward term to a predefined range of acceptable values. The proportional term, derivative term, and the feedforward term are summed to define a desired voltage level, and a PWM signal for driving the electrohydraulic valve is generated based on the desired voltage level.
Owner:HUSCO INT INC
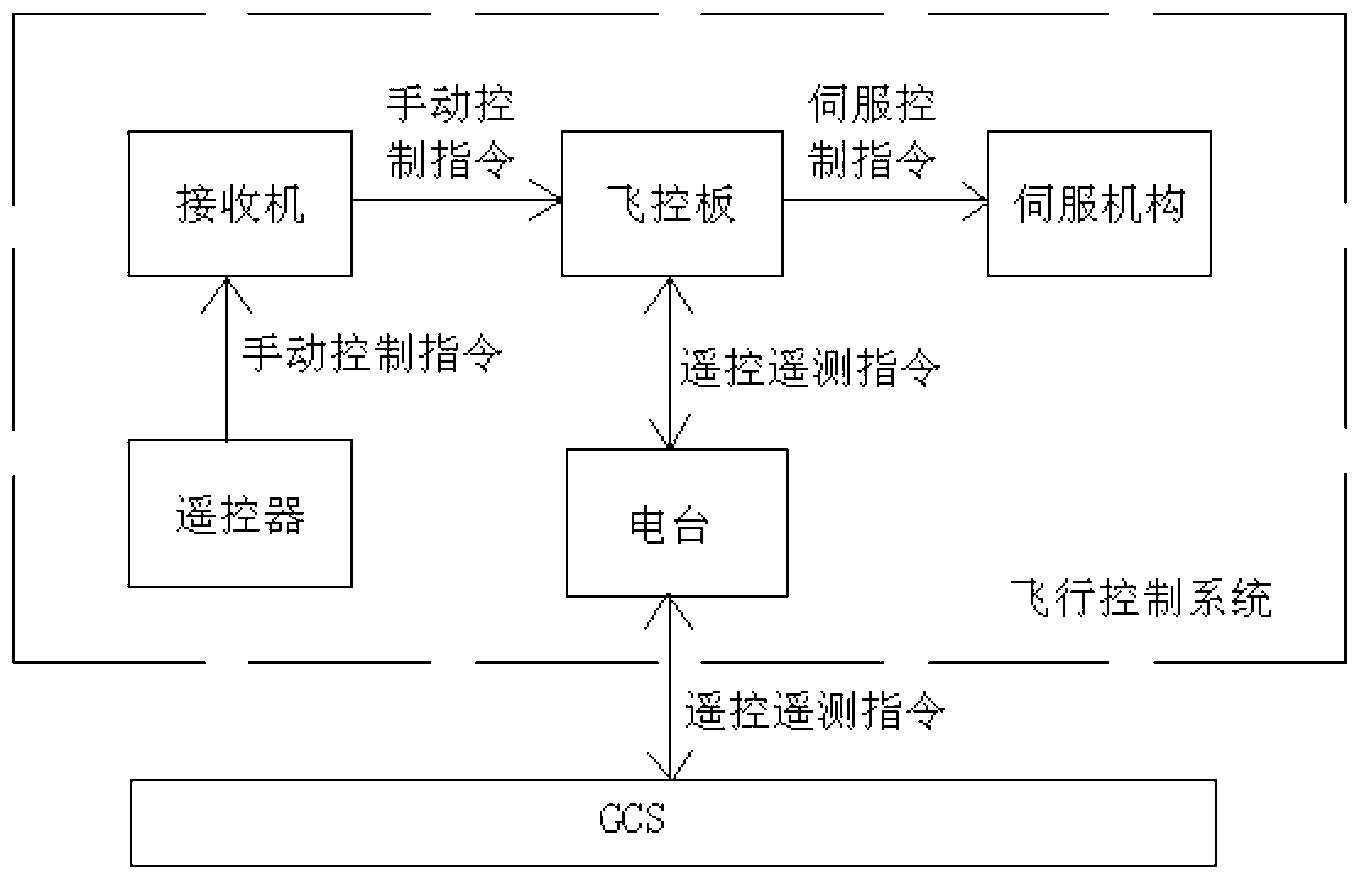
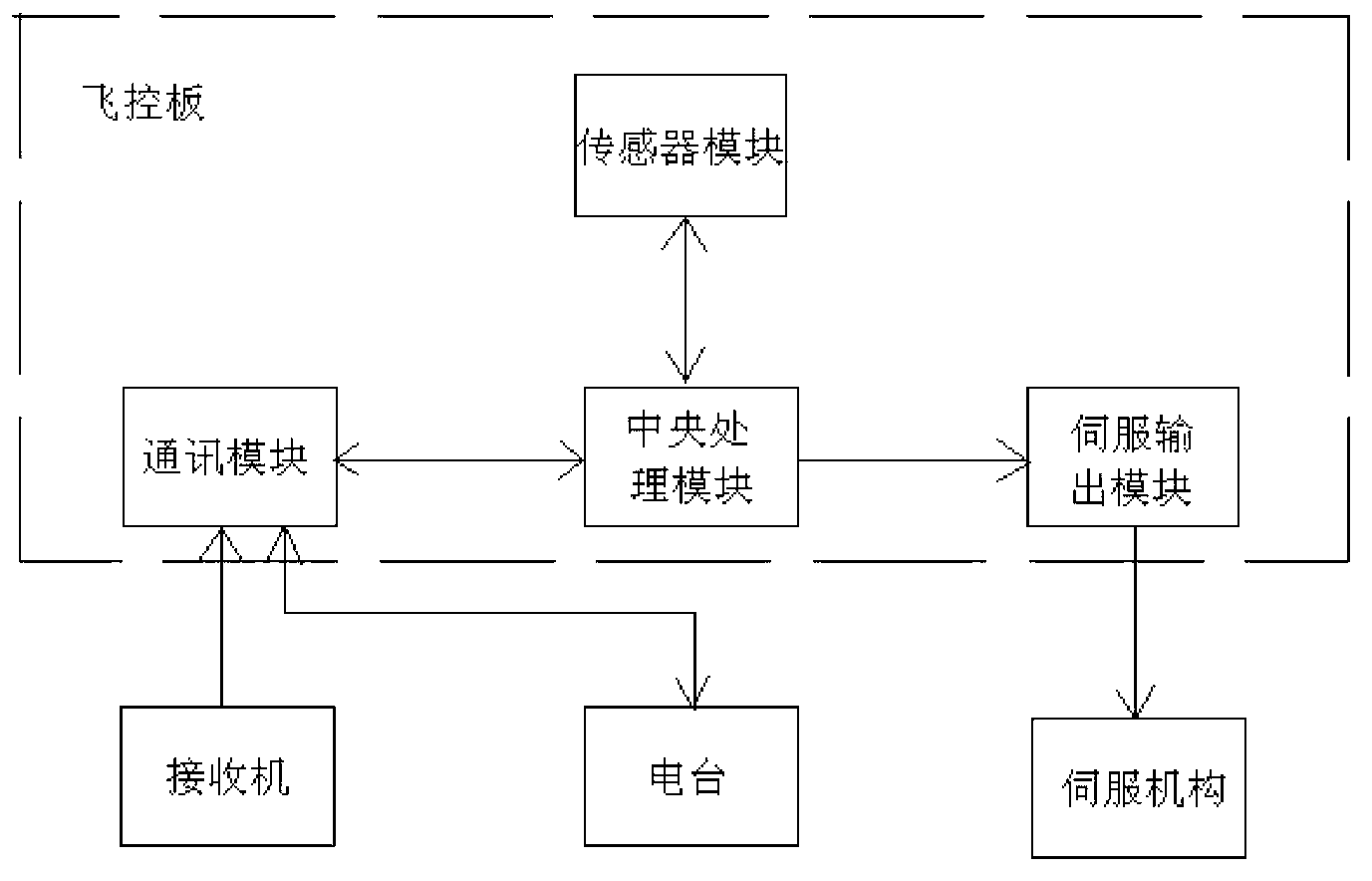
Autopilot flight control system
InactiveCN103294064ASimplify the minimum system structureSimple structurePosition/course control in three dimensionsSystems designRemote control
The invention relates to an autopilot flight control system. The autopilot flight control system comprises a flight control panel, a radio station, a servo mechanism, a receiver and a remote controller, wherein the radio station is communicated with the flight control panel in a two-way mode on remote control and telemetering, the servo mechanism receives servo control instructions of the flight control panel, the receiver transmits manual control instructions to the flight control panel, and the remote controller transmits remote manual control instructions to the receiver. The flight control panel further comprises a central processing module, a communication module which communicates with the central processing module in a two-way mode, a sensor module which communicates with the central processing module in the two-way mode, and a servo output module which receives instructions of the central processing module, wherein the communication module of the flight control panel receives instructions of the receiver and communicates with the radio station in the two-way mode. The radio station communicates in the two-way mode with a ground control system outside the autopilot flight control system. The servo output module transmits servo information to the servo mechanism. The autopilot flight control system is small in structure, simple and clear in system design, high in computation efficiency and reliability and very good in expansibility and portability.
Owner:天津全华时代航天科技发展有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com