Patents
Literature
17871 results about "Magnetism" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
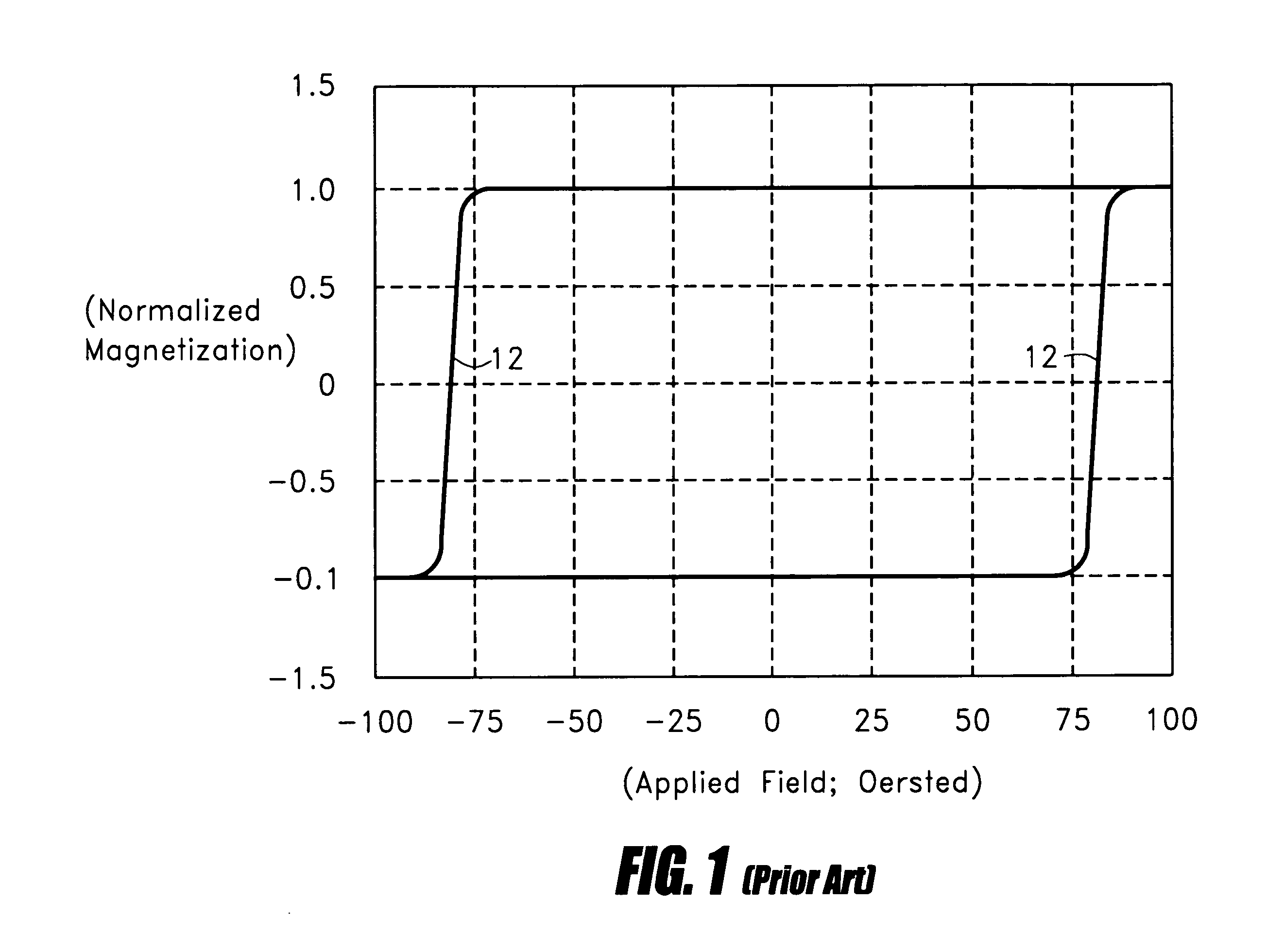
Magnetism is a class of physical phenomena that are mediated by magnetic fields. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, which acts on other currents and magnetic moments. The most familiar effects occur in ferromagnetic materials, which are strongly attracted by magnetic fields and can be magnetized to become permanent magnets, producing magnetic fields themselves. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic; the most common ones are iron, cobalt and nickel and their alloys. The prefix ferro- refers to iron, because permanent magnetism was first observed in lodestone, a form of natural iron ore called magnetite, Fe₃O₄.
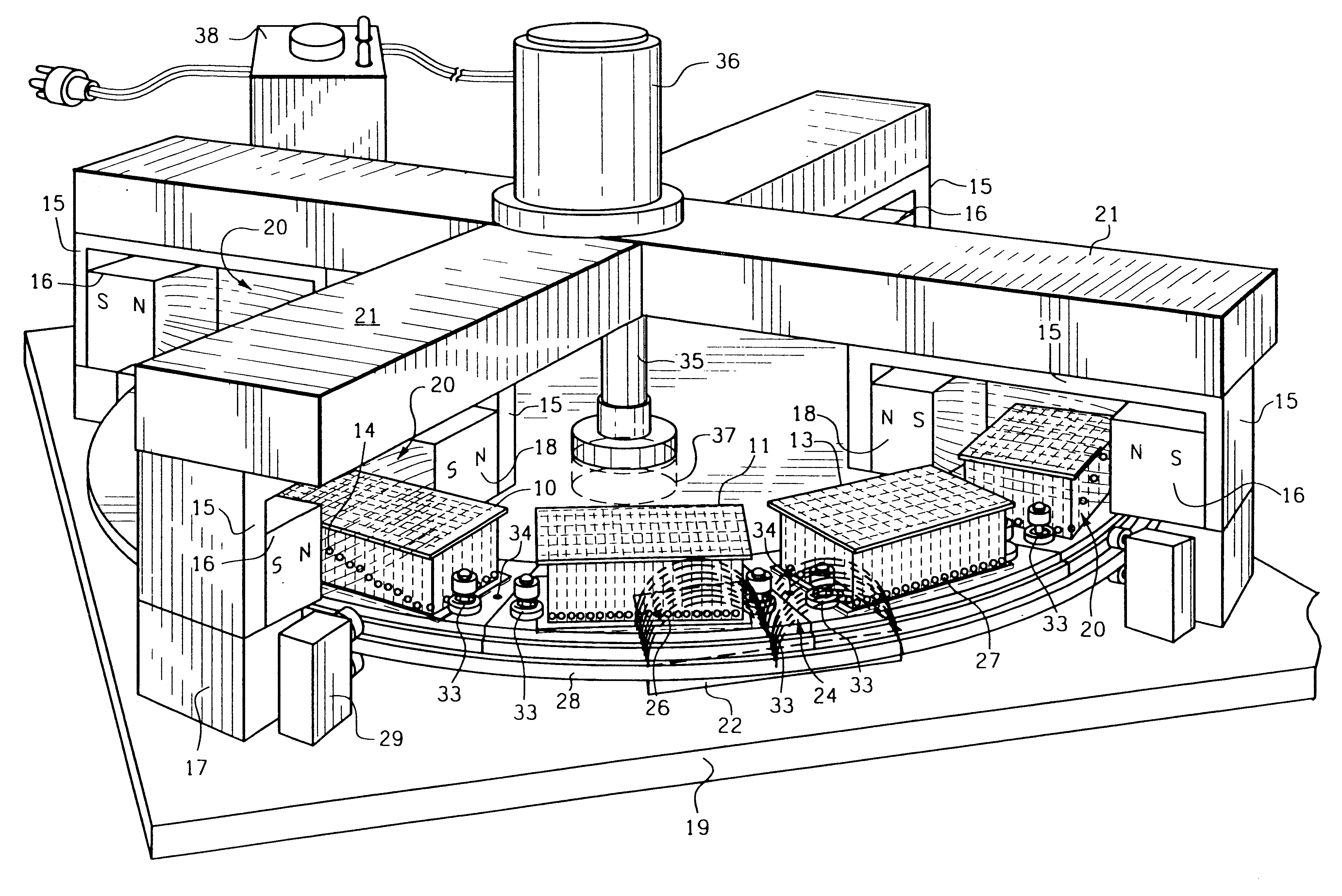
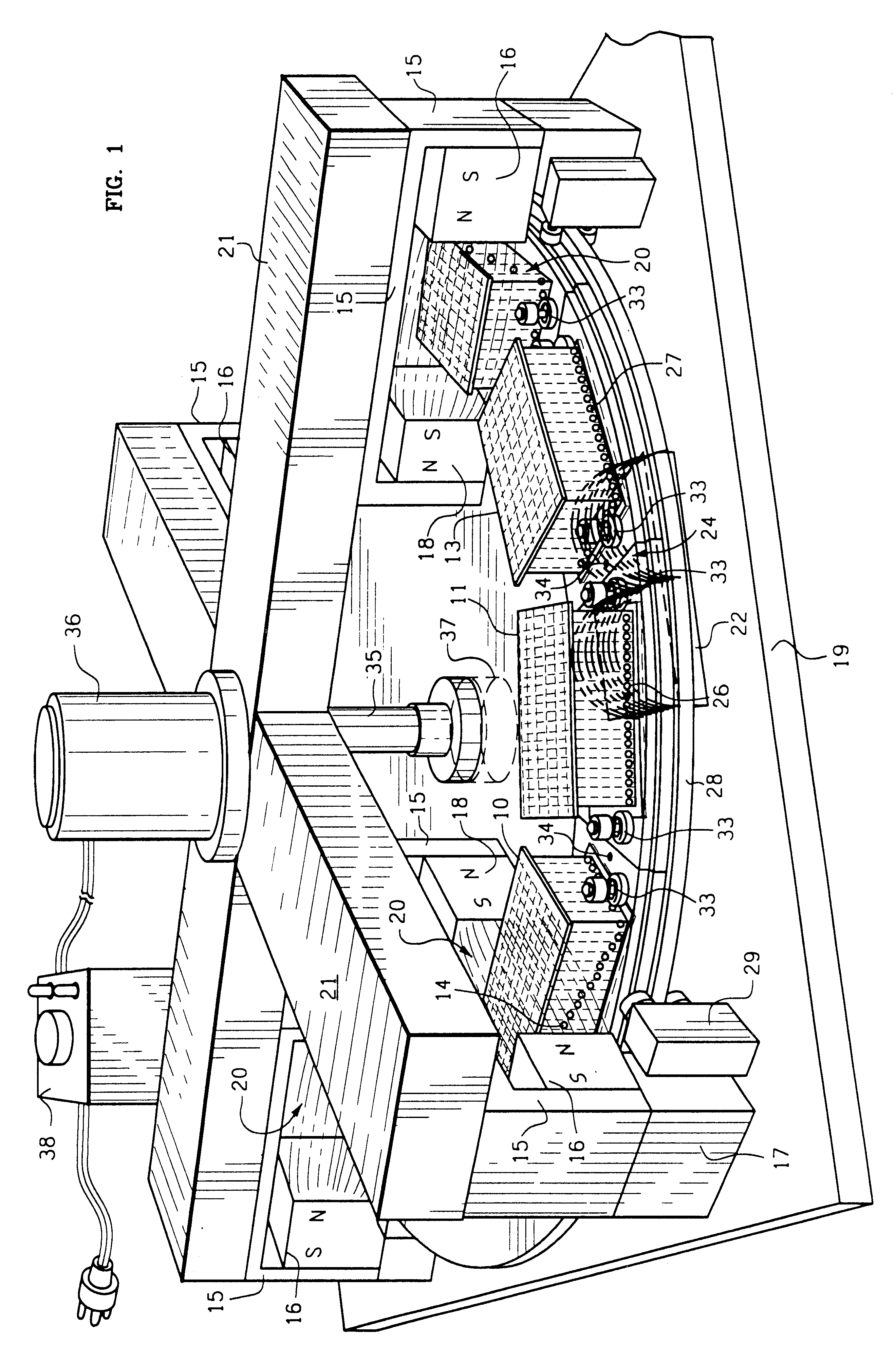
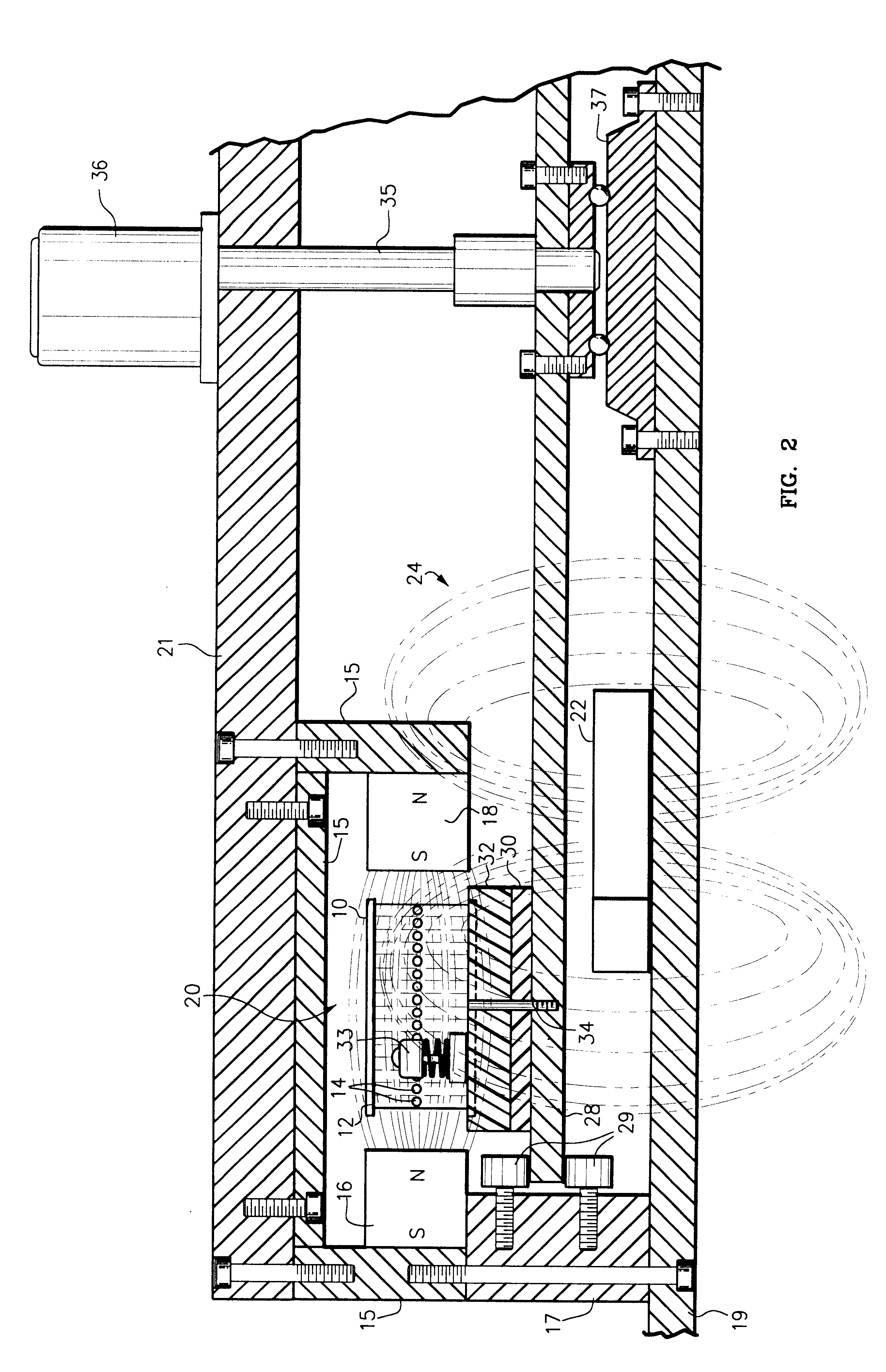
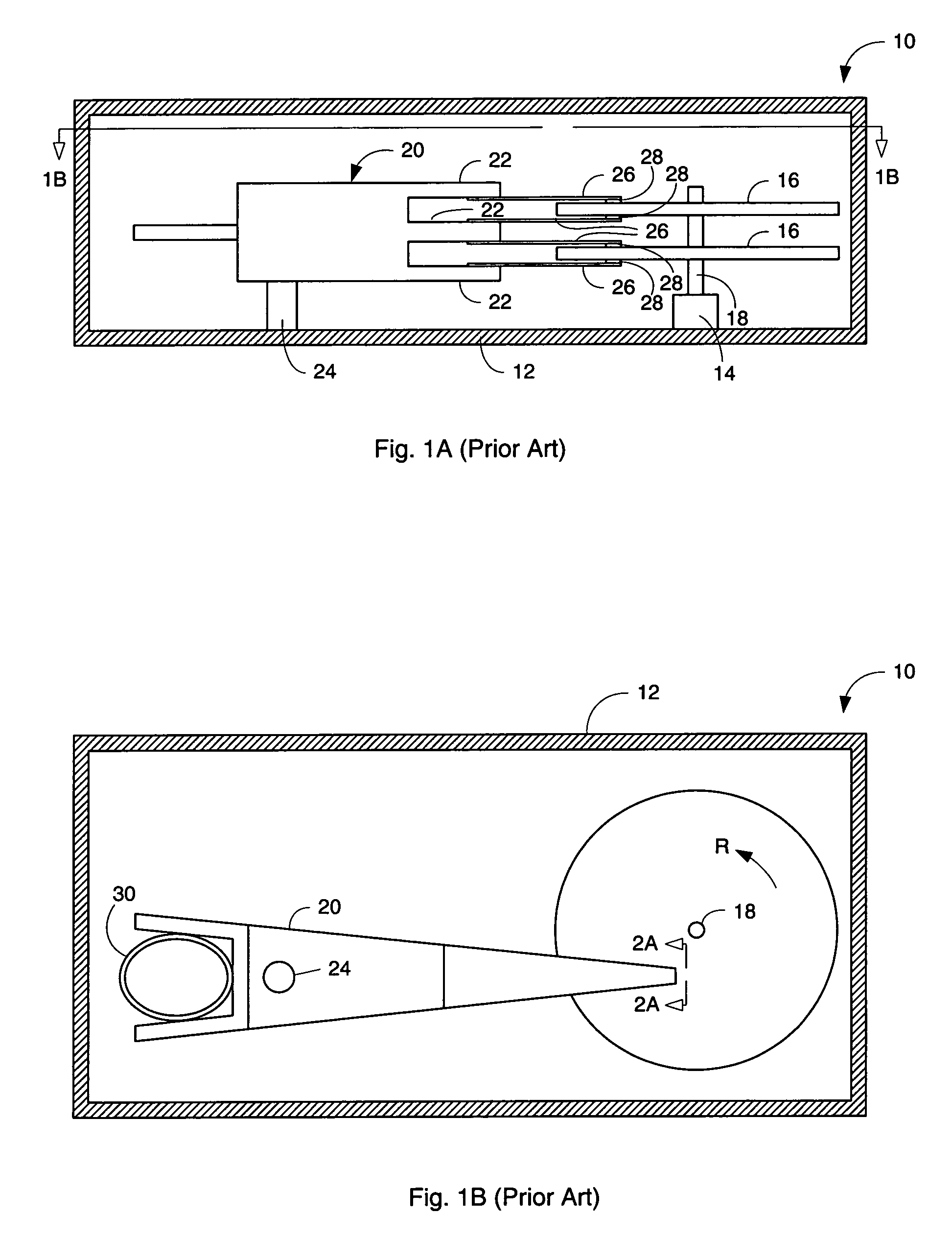
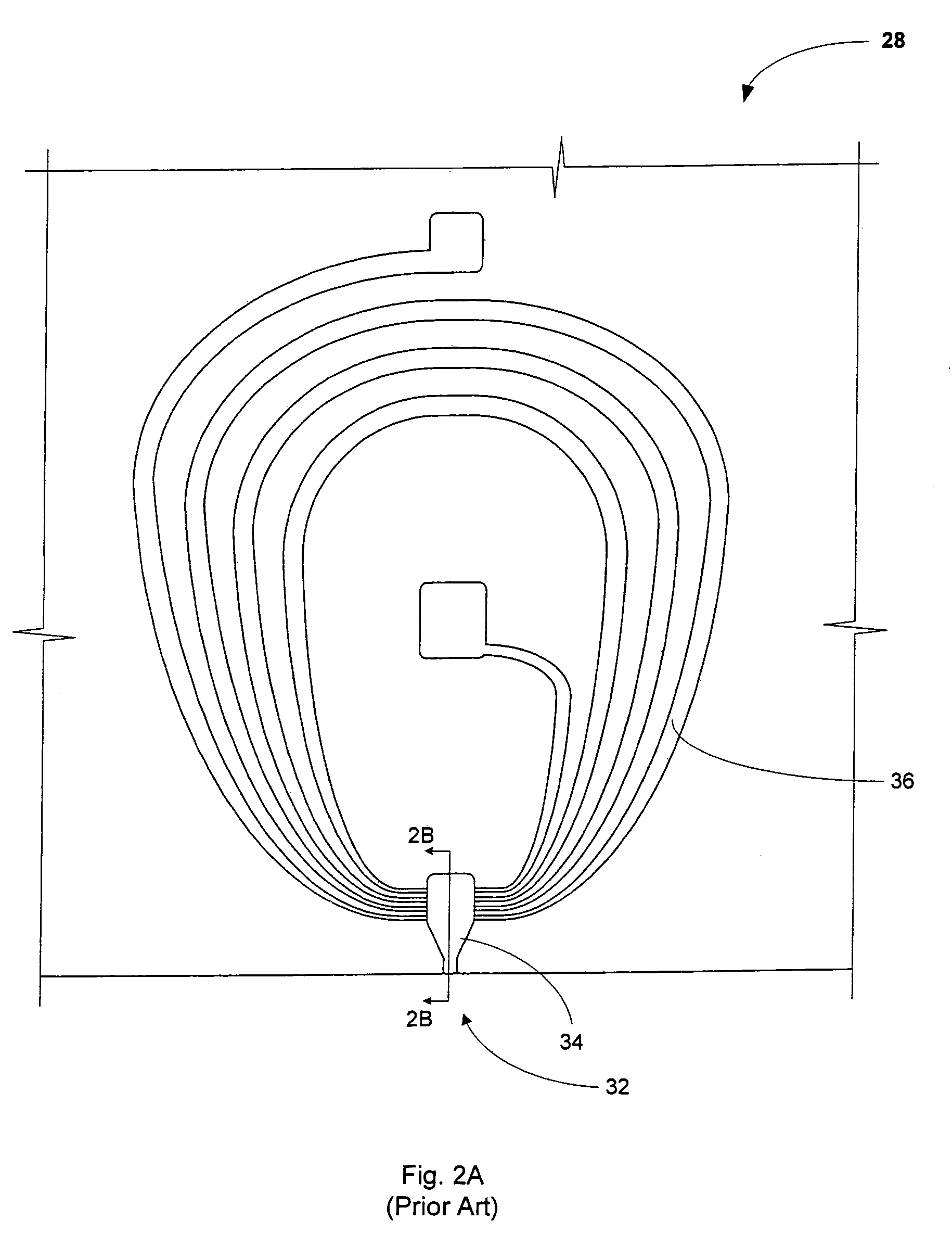
Magnetic field permeable barrier for magnetic position measurement system
InactiveUS6246231B1SurgeryElectric/magnetic position measurementsOrientation measurementMetallic Object
A magnetic field position and orientation measurement system contains, confines and re-directs the magnetic field from one or more transmitters such that the fields are attenuated in areas outside of the operating volume in areas where metallic objects are commonly found. A thin barrier made of a highly permeable material such as ferrite or mumetal is placed on top of a conductive plate. The thickness of the permeable layer is from 0.01 inches to 0.25 inches while the conductive plate, preferably made of an aluminum alloy, may preferably be from {fraction (3 / 16)} of an inch to ¼ inch in thickness. On top of the permeable barrier, a rhombic three axis transmitter is placed. In the preferred embodiment, the transmitter consists of a PC board carrying the transmitter. PC boards having thicknesses varying from 0.03125-0.125 inches may be employed. Thus, the entire "stack" including the transmitter, the permeable barrier and the conductive plate may only be from ½ inch to ⅝ of an inch in thickness. The permeable barrier may have a flat, planar configuration. Alternatively, it may be made to resemble, in cross-section, a cake pan having a flat central region with uplifted peripheral edges. Alternatively, the permeable barrier may have a generally flat configuration with peripheral edges that taper outwardly from the top surface thereof to the bottom surface thereof with the taper making an angle with the bottom surface in the range of, preferably, 30° to 85°.
Owner:ASCENSION TECH
Magnetic data recording device
Owner:FITBIT INC
Analytic methods of tissue evaluation
InactiveUS20110301441A1Simple conditionsFacilitates effectivenessImage enhancementImage analysisWater basedElectromagnetic radiation
The present invention generally relates to methods and systems for (i) skin assessment based on the utilization of bioimpedance and fractional calculus and implementation of methods for skin hydration assessment based on the utilization of bioimpedance and fractional calculus and systems thereof, (ii) an Opto-Magnetic method based on RGB and gray images data as “cone-rods” principles with enhanced qualitative and quantitative parameters for analyzing water based on Opto-Magnetic properties of light-matter interaction and systems thereof, and (iii) imaging and analyzing skin based on the interaction between matter and electromagnetic radiation and implementation of an Opto-Magnetic method with enhanced qualitative and quantitative parameters for imaging and analyzing skin based on Opto-Magnetic properties of light-matter interaction and systems thereof.
Owner:MYSKIN
Manipulation of displayed objects by virtual magnetism
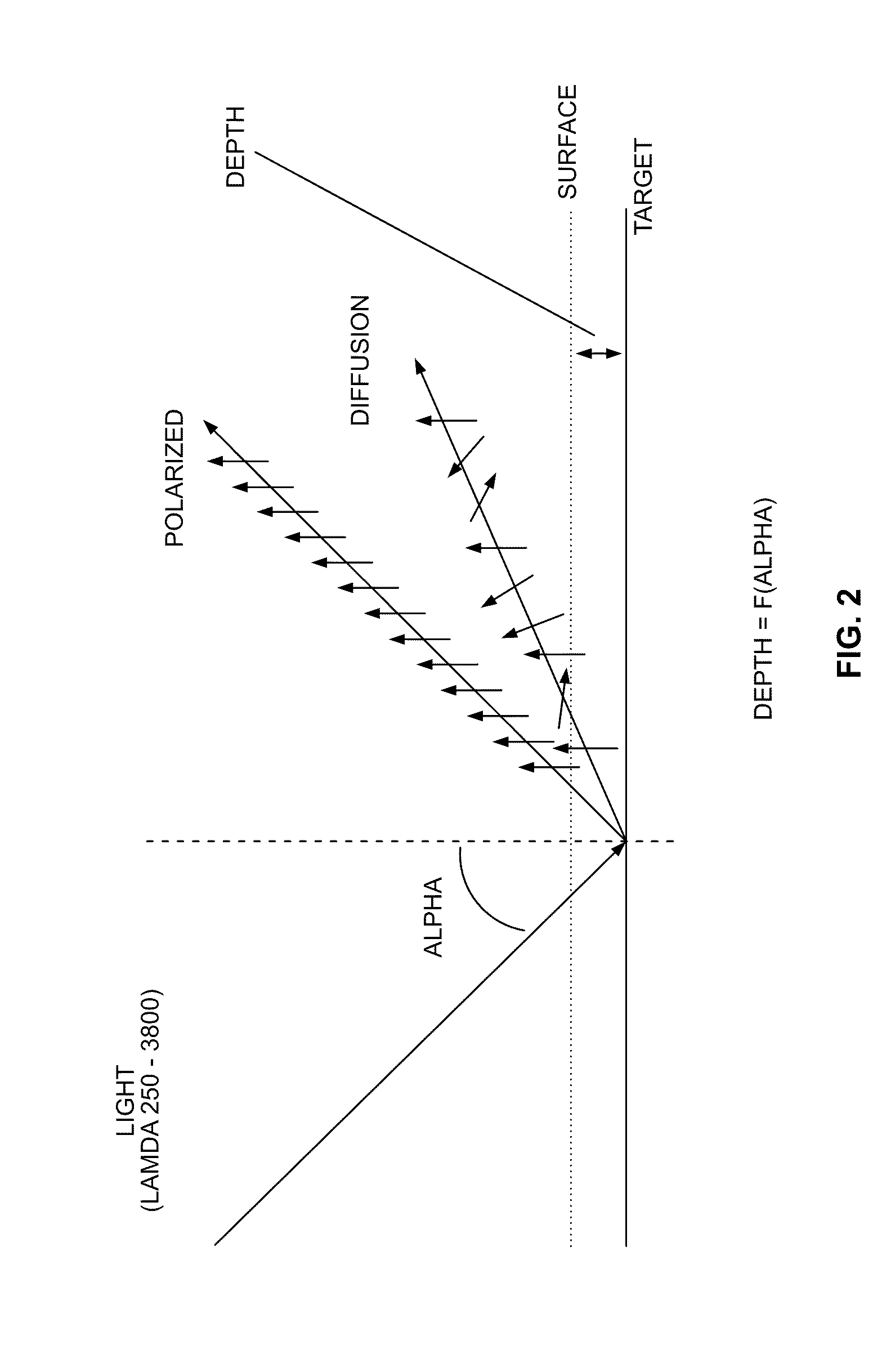
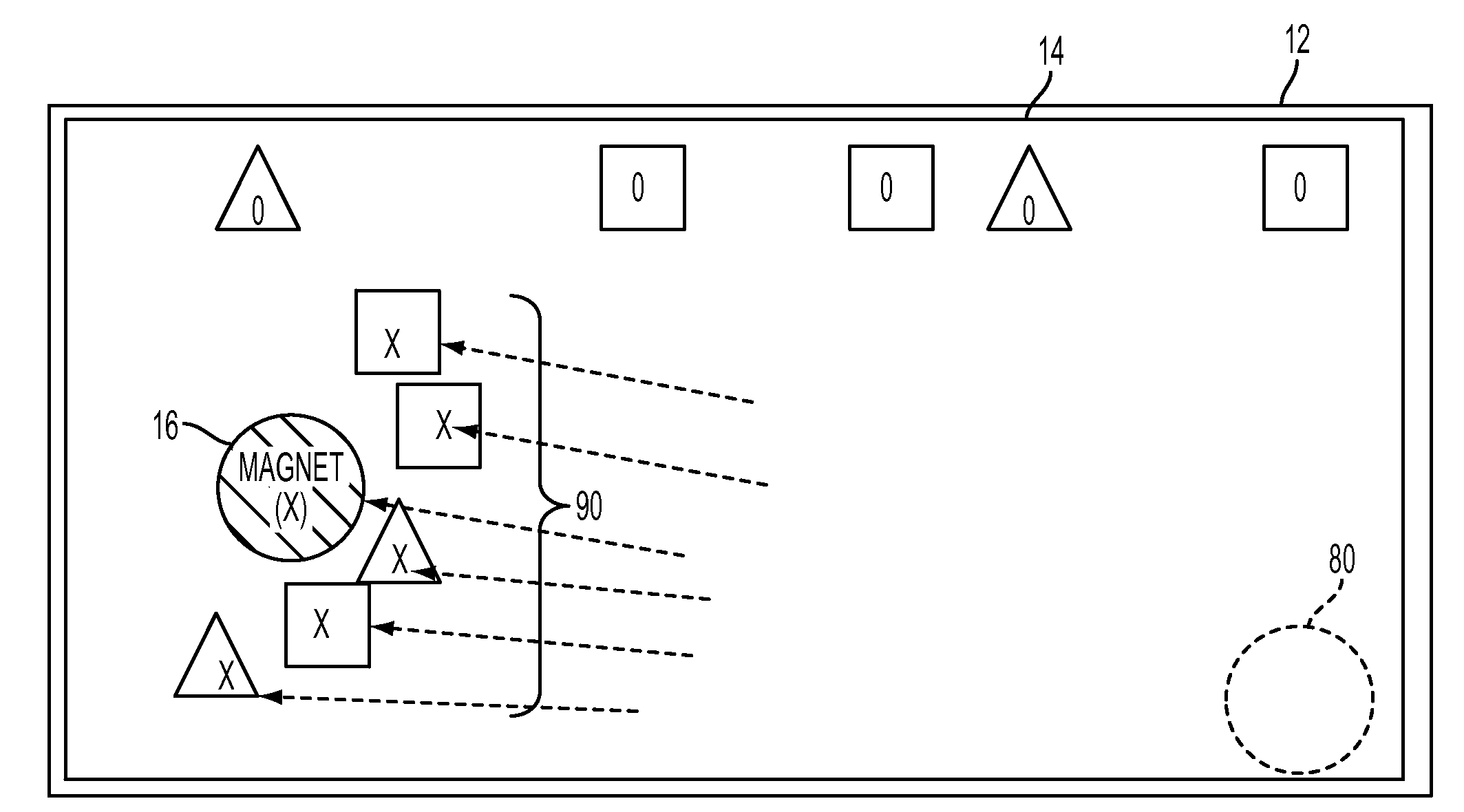
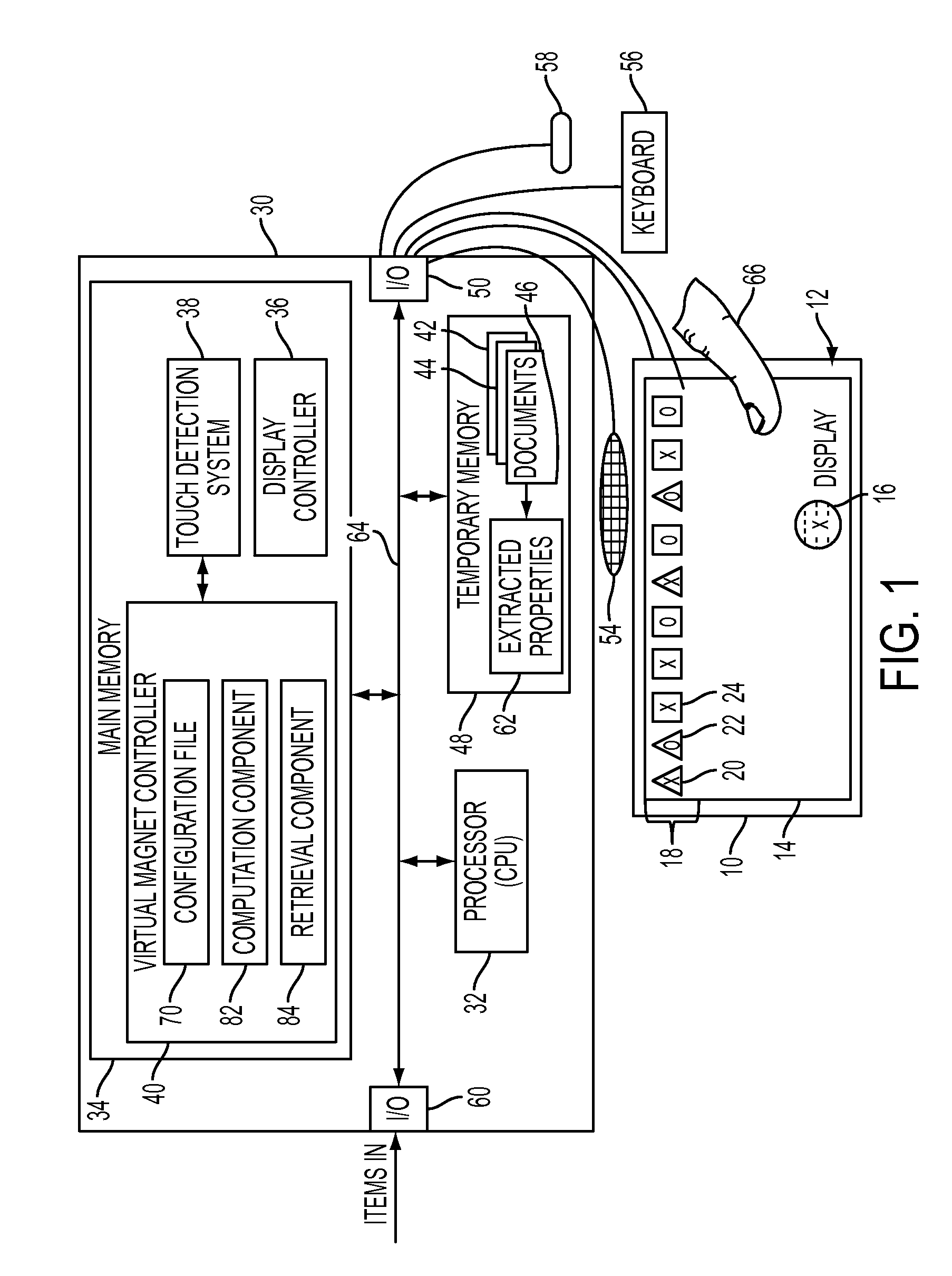
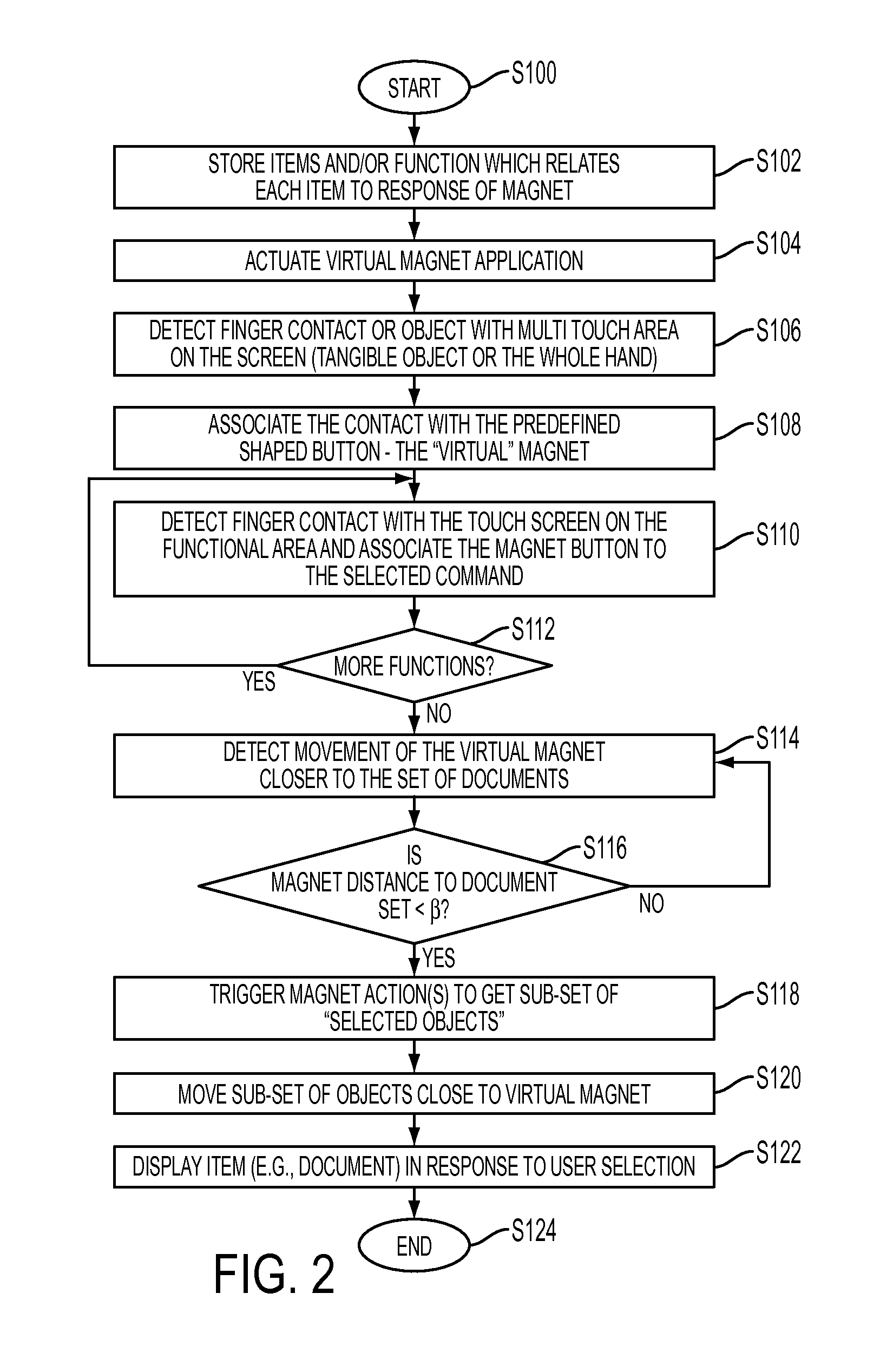
A computer implemented tactile user interface (TUI) and a method of manipulating objects with a virtual magnet are provided. The TUI includes a display comprising a touch-screen. The display is configured for displaying a set of graphic objects, each graphic object representing a respective one of a set of items, such as documents, e.g., text documents or images. A virtual magnet is caused to move on the display, in response to touching on the touch-screen, e.g., by dragging a finger or other implement across. The magnet is associated with a particular function command such that a subset of the graphic objects exhibits a response to the virtual magnet (e.g., is caused to move, relative to the virtual magnet or exhibits another visible response), each graphic object in the subset moving or otherwise responding as a function of an attribute of the underlying item represented by the graphic object.
Owner:XEROX CORP
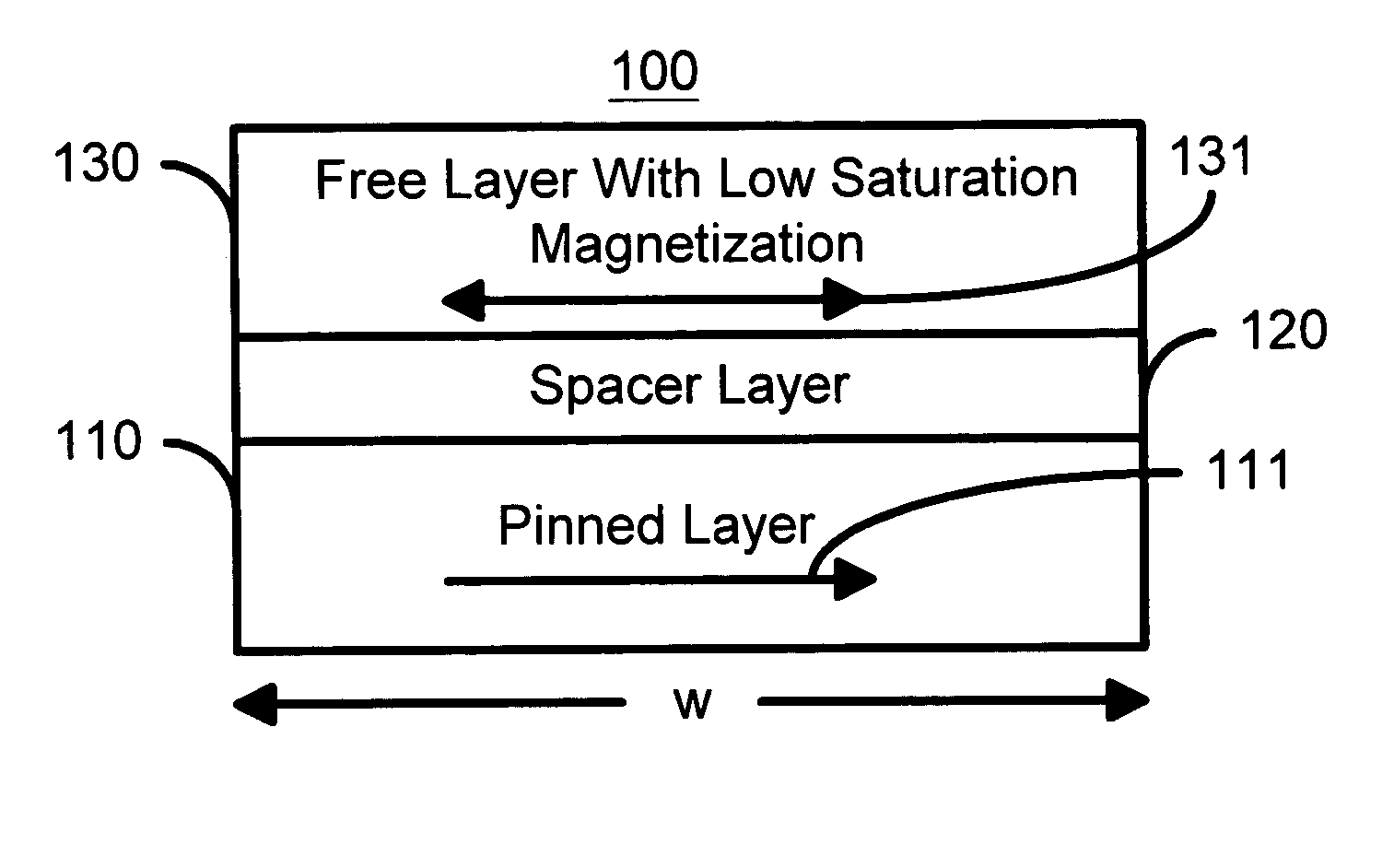
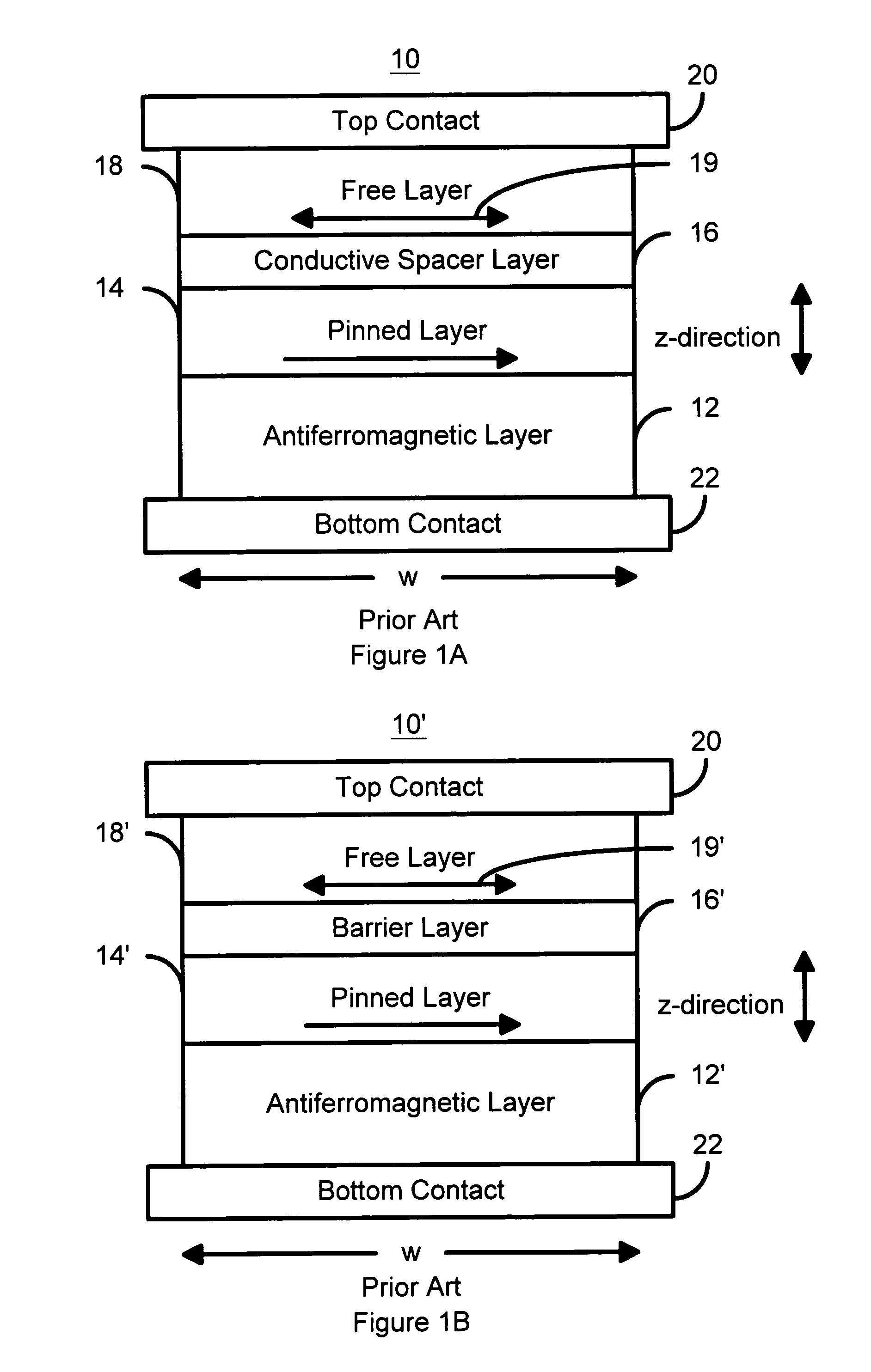
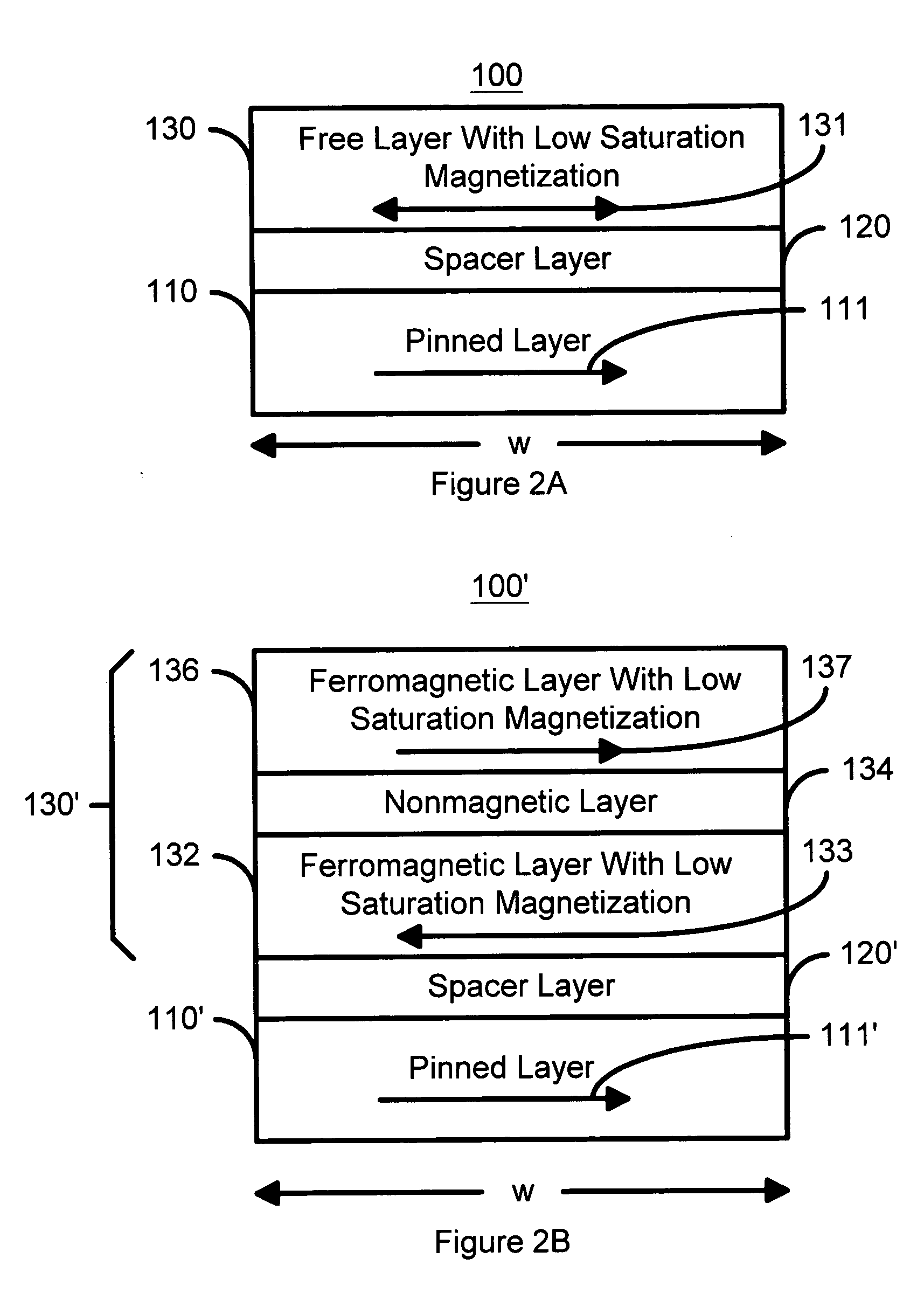
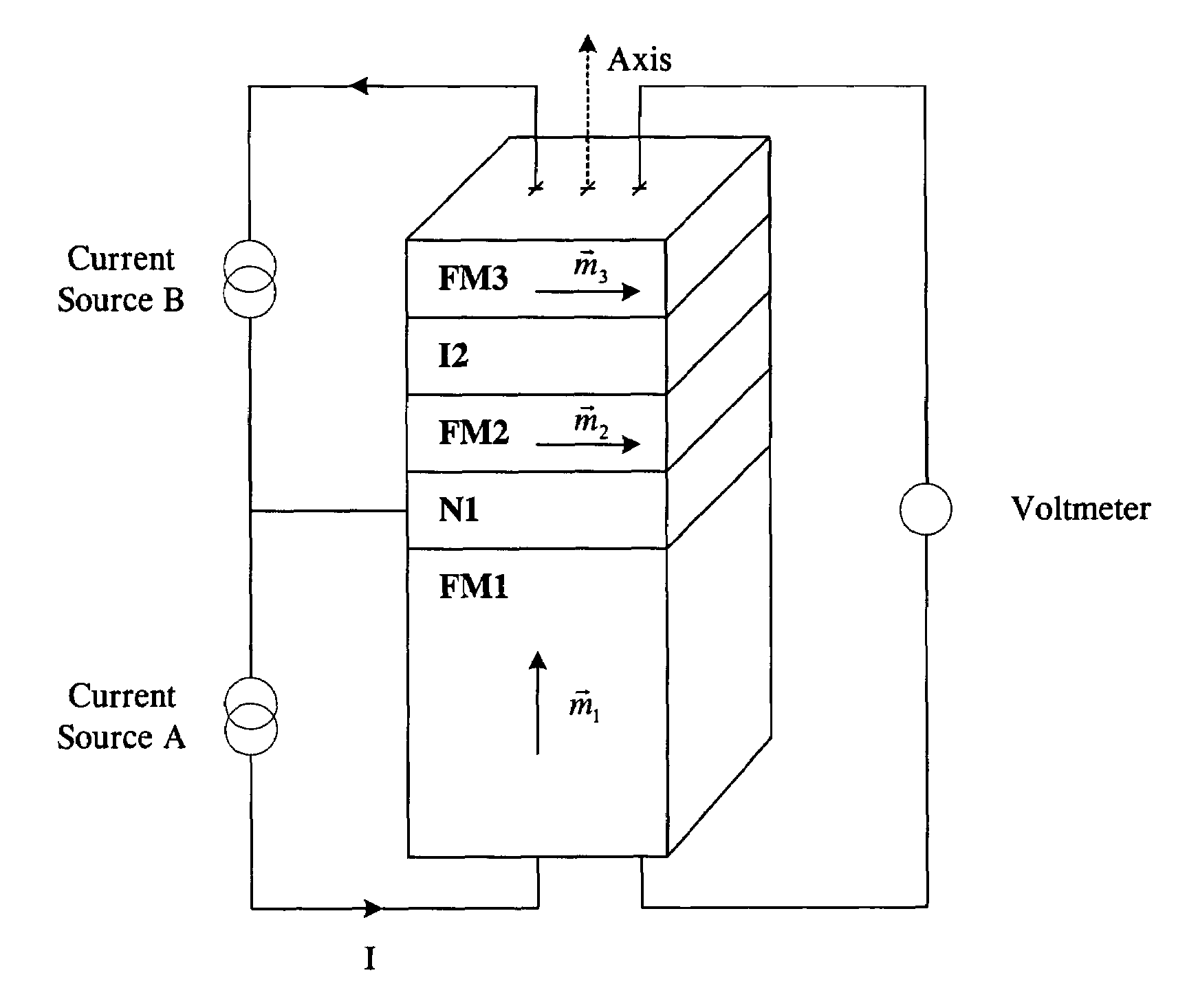
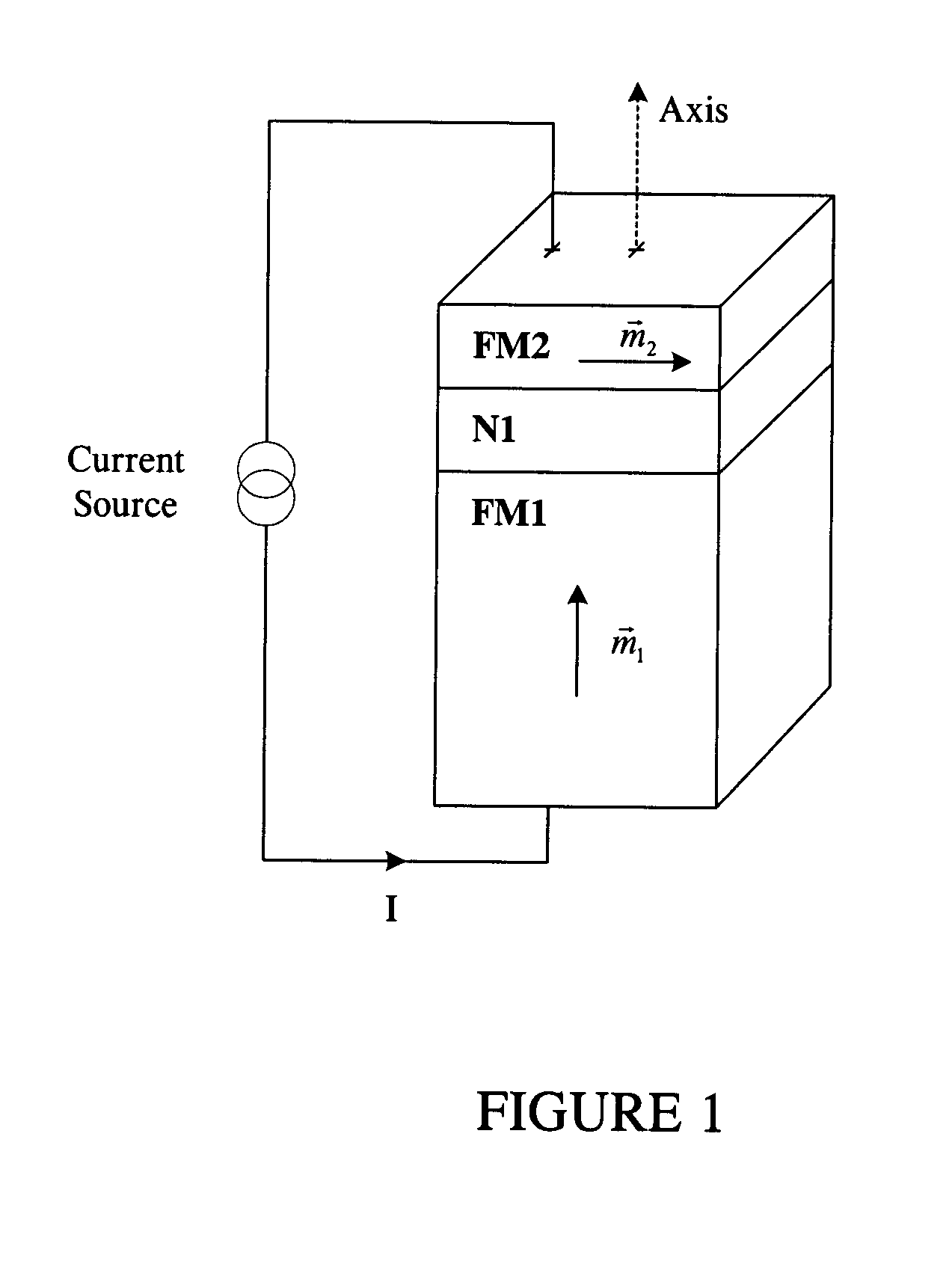
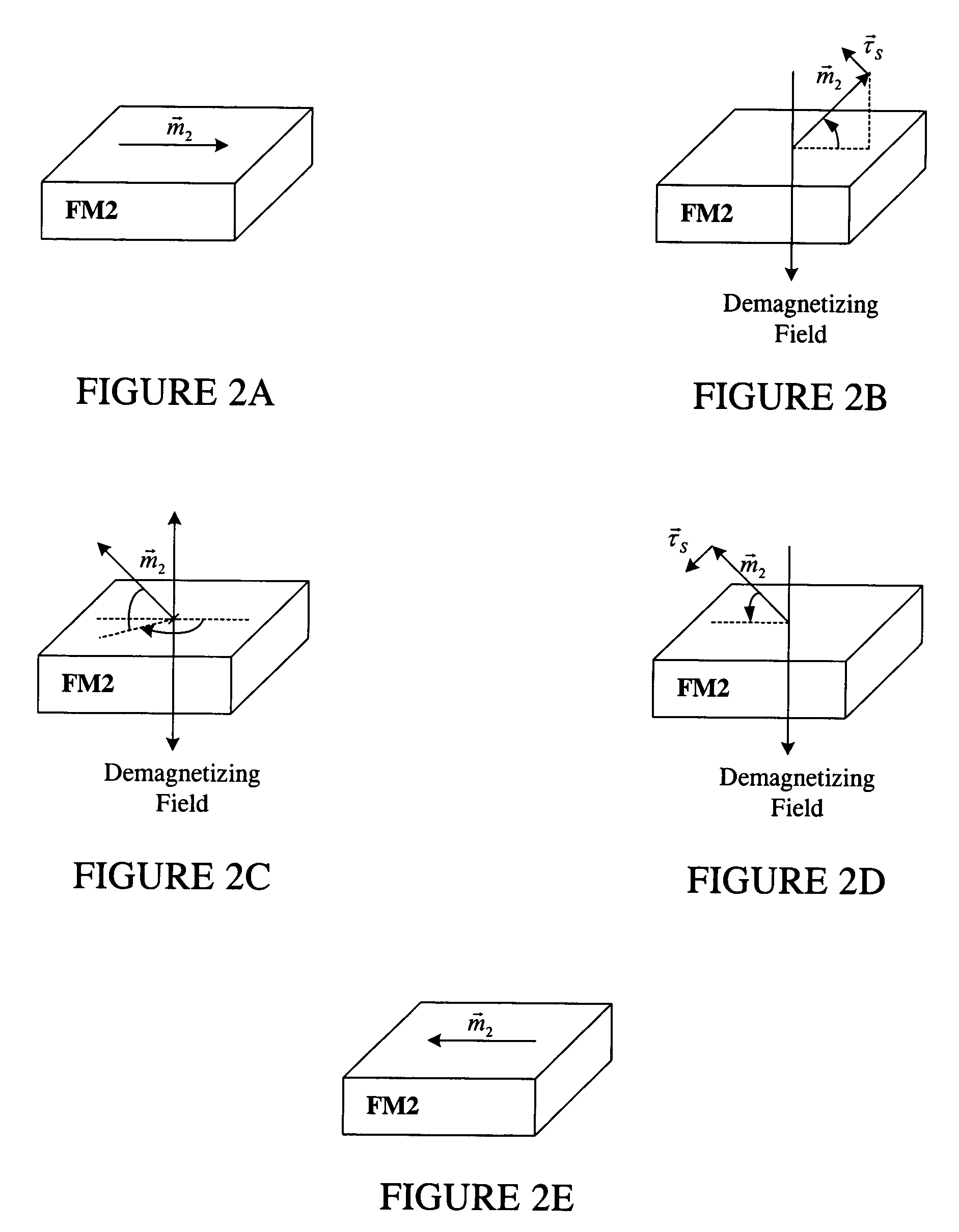
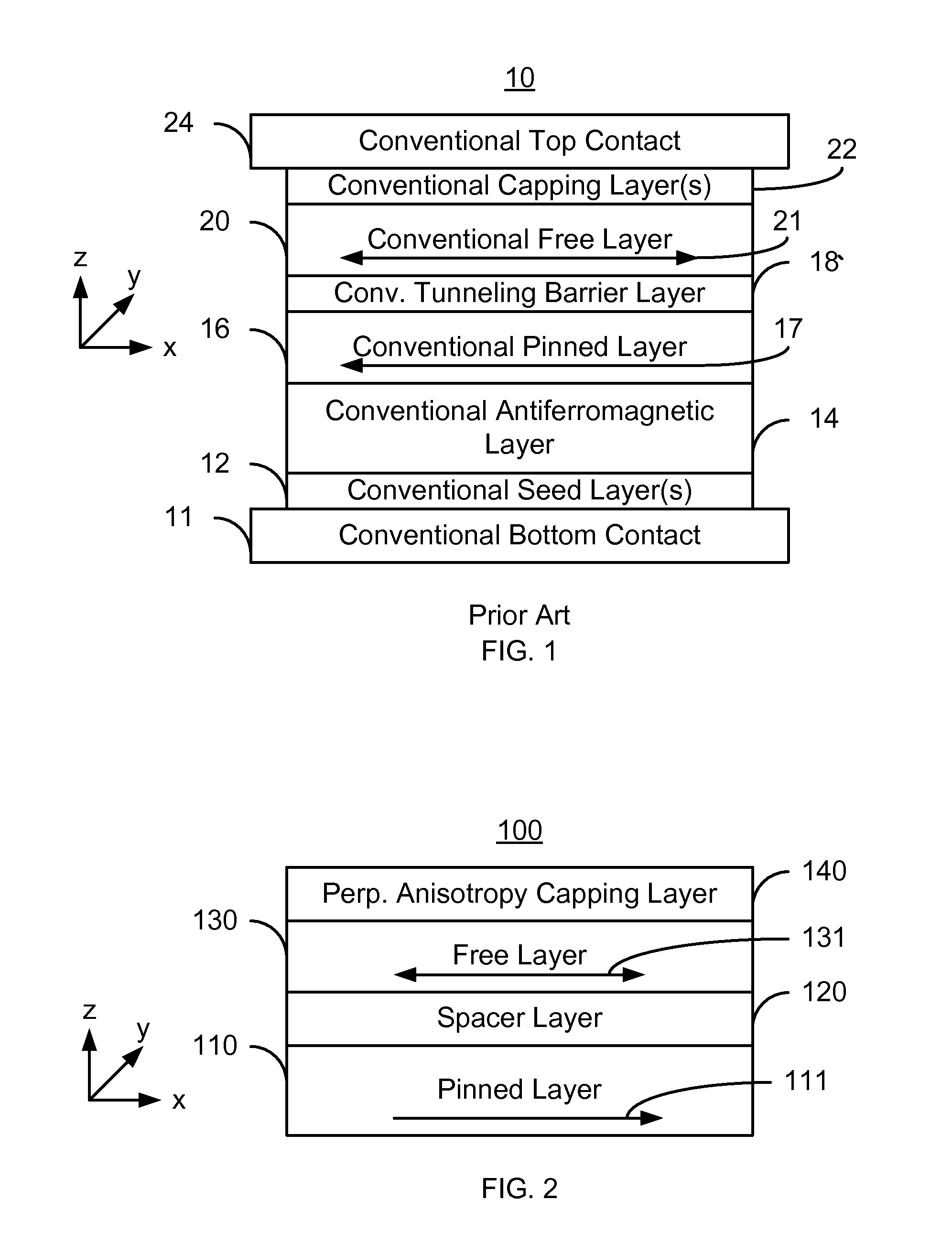
Spin transfer magnetic element having low saturation magnetization free layers
ActiveUS20050184839A1Current densityNanostructure applicationNanomagnetismMagnetic memoryNon magnetic
A method and system for providing a magnetic element that can be used in a magnetic memory is disclosed. The magnetic element includes pinned, nonmagnetic spacer, and free layers. The spacer layer resides between the pinned and free layers. The free layer can be switched using spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element. The magnetic element may also include a barrier layer, a second pinned layer. Alternatively, second pinned and second spacer layers and a second free layer magnetostatically coupled to the free layer are included. In one aspect, the free layer(s) include ferromagnetic material(s) diluted with nonmagnetic material(s) and / or ferrimagnetically doped to provide low saturation magnetization(s).
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
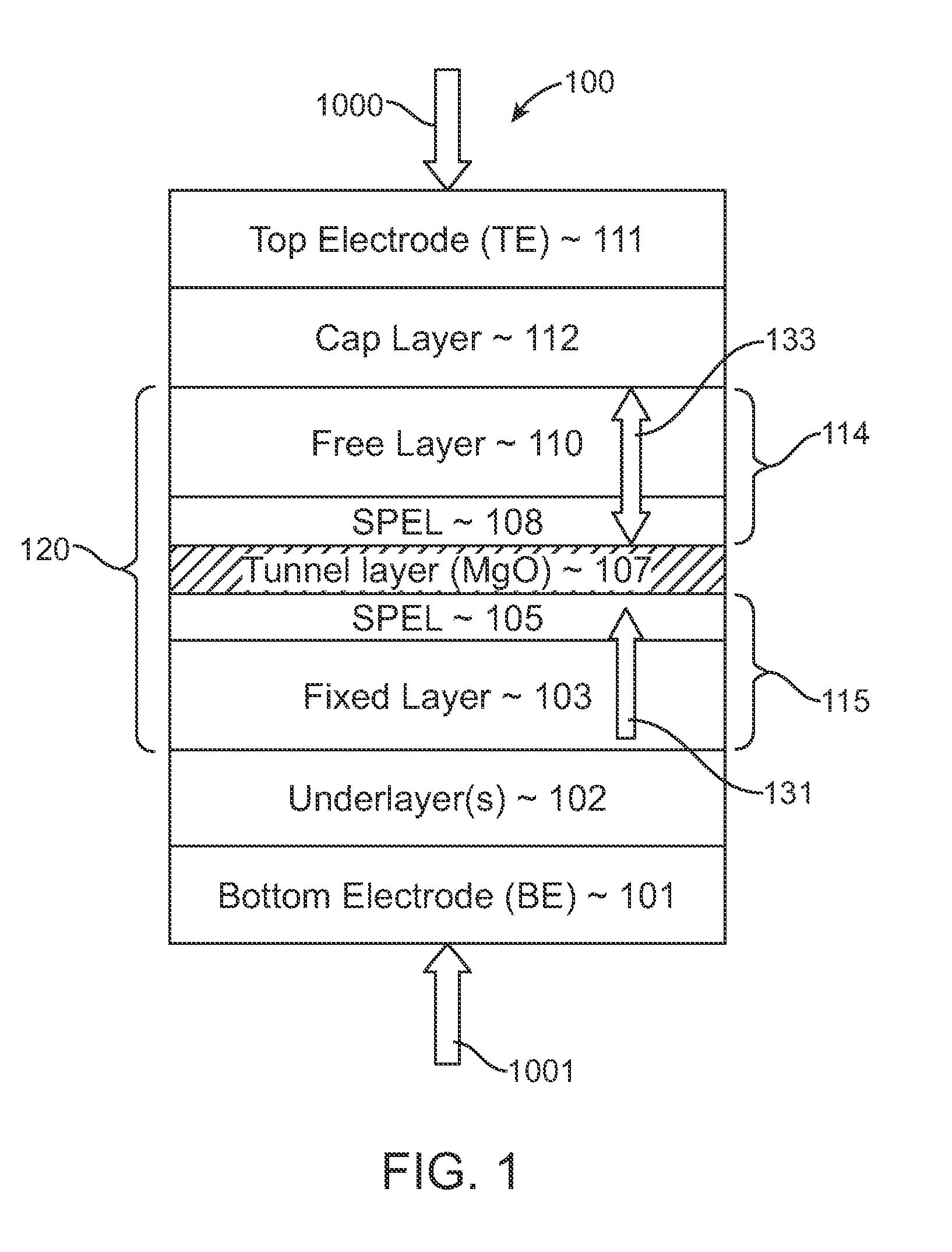
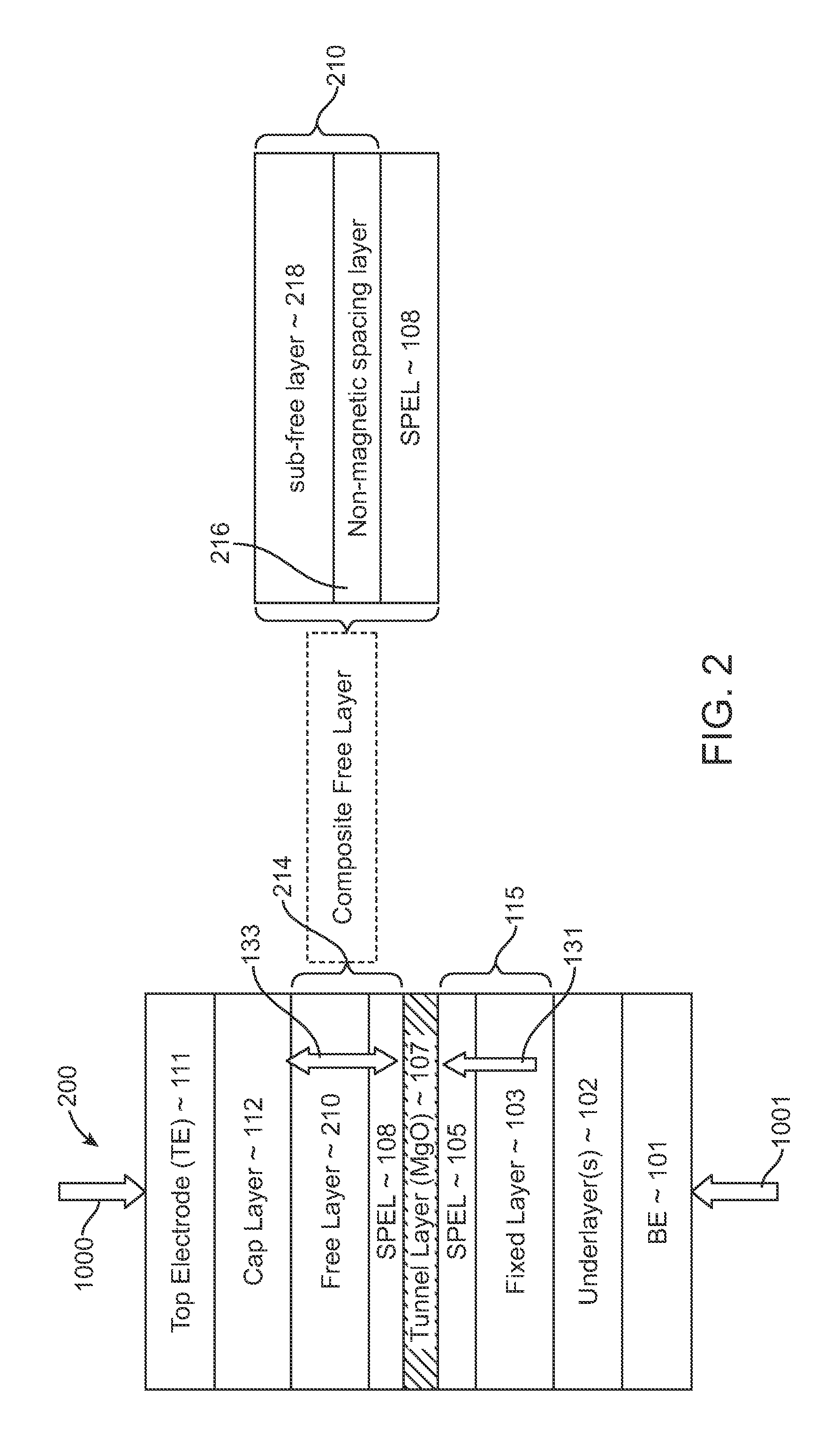
Spin-transfer torque magnetic random access memory having magnetic tunnel junction with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy
A spin-torque transfer memory random access memory (STTMRAM) element includes a fixed layer formed on top of a substrate and a a tunnel layer formed upon the fixed layer and a composite free layer formed upon the tunnel barrier layer and made of an iron platinum alloy with at least one of X or Y material, X being from a group consisting of: boron (B), phosphorous (P), carbon (C), and nitride (N) and Y being from a group consisting of: tantalum (Ta), titanium (Ti), niobium (Nb), zirconium (Zr), tungsten (W), silicon (Si), copper (Cu), silver (Ag), aluminum (Al), chromium (Cr), tin (Sn), lead (Pb), antimony (Sb), hafnium (Hf) and bismuth (Bi), molybdenum (Mo) or rhodium (Ru), the magnetization direction of each of the composite free layer and fixed layer being substantially perpendicular to the plane of the substrate.
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
High speed low power magnetic devices based on current induced spin-momentum transfer
InactiveUS6980469B2Operational advantageReduce the required powerNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsMagnetic memoryMagnetization
The present invention generally relates to the field of magnetic devices for memory cells that can serve as non-volatile memory. More specifically, the present invention describes a high speed and low power method by which a spin polarized electrical current can be used to control and switch the magnetization direction of a magnetic region in such a device. The magnetic device comprises a pinned magnetic layer with a fixed magnetization direction, a free magnetic layer with a free magnetization direction, and a read-out magnetic layer with a fixed magnetization direction. The pinned magnetic layer and the free magnetic layer are separated by a non-magnetic layer, and the free magnetic layer and the read-out magnetic layer are separated by another non-magnetic layer. The magnetization directions of the pinned and free layers generally do not point along the same axis. The non-magnetic layers minimize the magnetic interaction between the magnetic layers. A current is applied to the device to induce a torque that alters the magnetic state of the device so that it can act as a magnetic memory for writing information. The resistance, which depends on the magnetic state of the device, is measured to thereby read out the information stored in the device.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
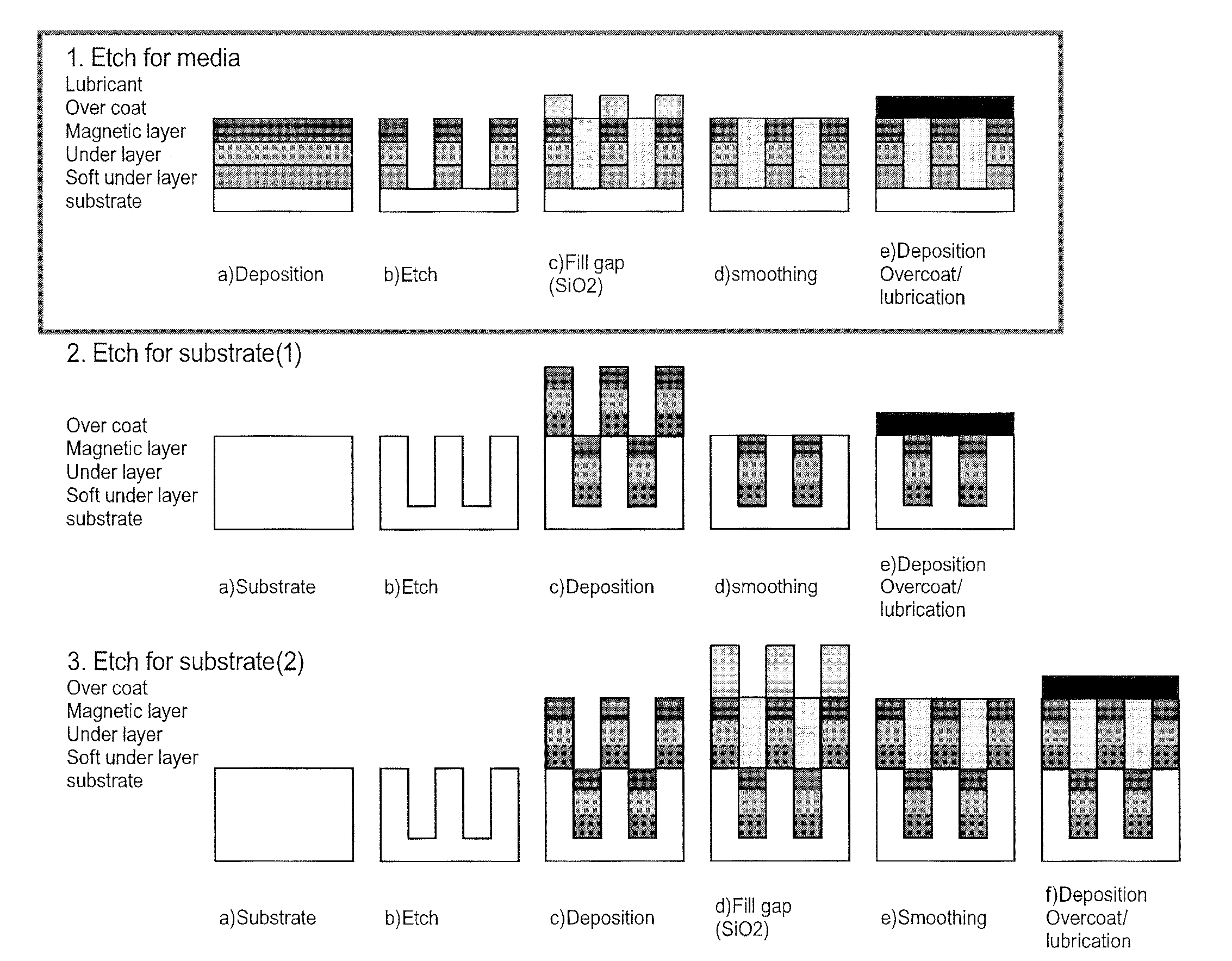
System for Fabricating a Pattern on Magnetic Recording Media
InactiveUS20120223048A1Easy to useReduce system footprintLiquid surface applicatorsDecorative surface effectsHard disc driveMagnetic media
An inline processing system for patterning magnetic recording layers on hard discs for use in a hard disc drive. Discs are processed on both sides simultaneously in a vertical orientation, in round plate-like holders called MDCs. A plurality (as many as 10) discs are held in a dial carrier of the MDC, and transferred from one process station to another. The dial carrier of the MDC may be rotated and / or angled at up to 70° from normal in each process station, so that one or a plurality of process sources may treat the discs simultaneously. This configuration provides time savings and a reduction in the number and size of process sources needed. A mask enhancement process for patterning of magnetic media, and a filling and planarizing process used therewith, are also disclosed.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
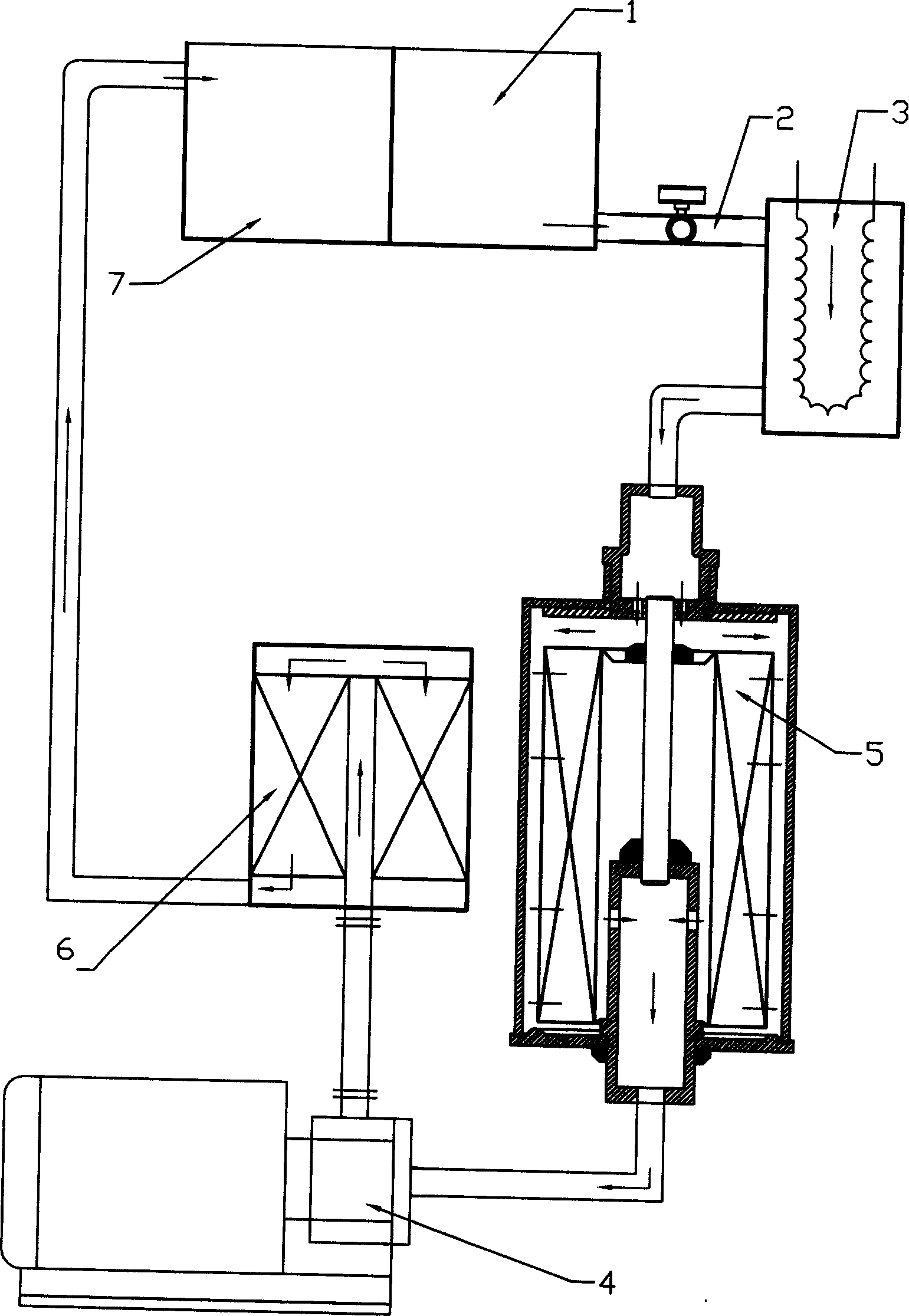
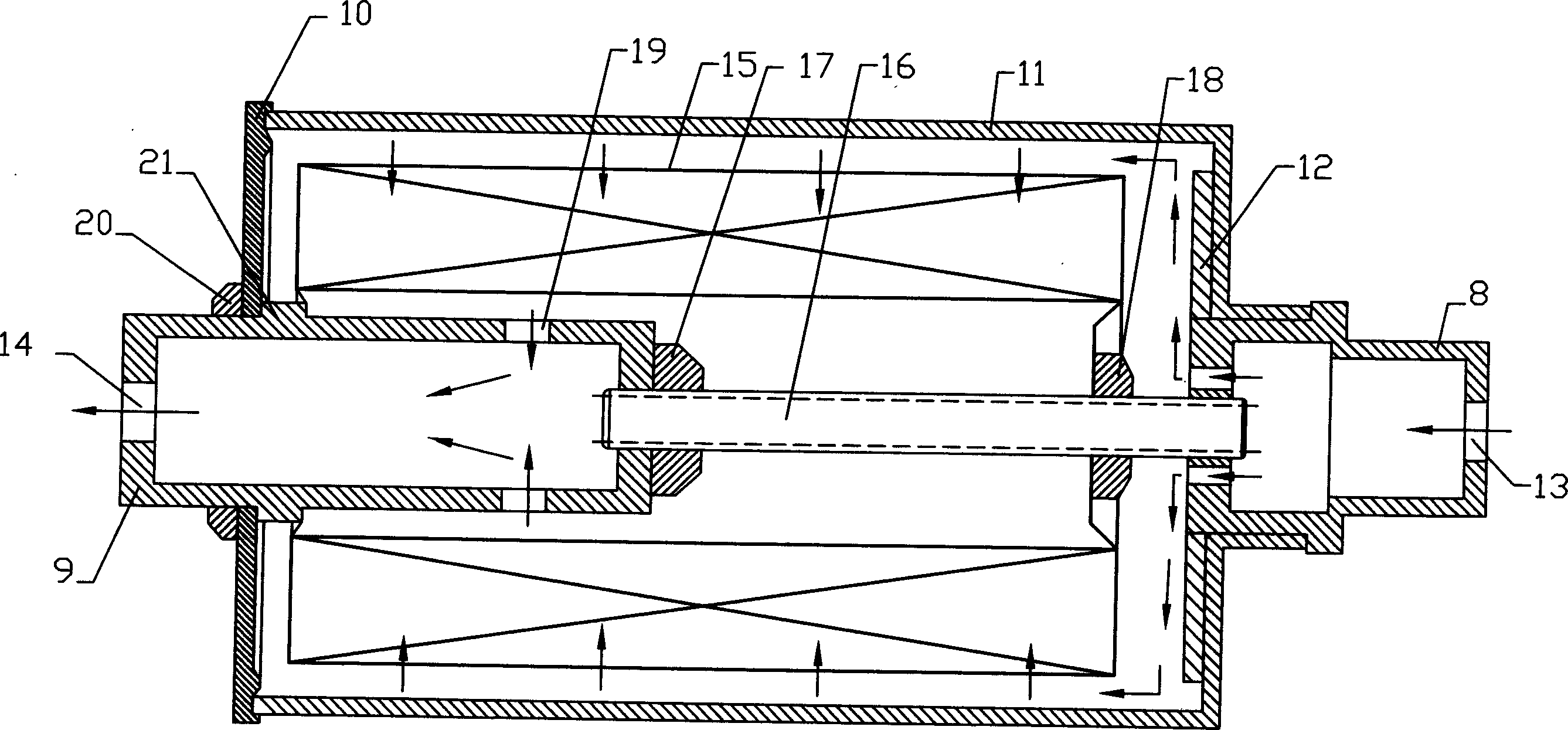
Method and system for purifying hydraulic-oil
InactiveCN1546198AEasy to installEasy to operateFiltration circuitsLubricant compositionControl systemFuel tank
The invention refers to a method and system for purifying the hydraulic pressure oil in hydraulic pressure machine. The method includes magnetism absorbing step which absorbs the metal particles in the hydraulic oil through magnetism structure onto the magnetism structure and a filter step blocking the impurities in the sift filter core, and finishes the first grade filter, and the second filter step with a sorption filter; the system includes: forward oil boxes connected in series, oil heater, magnetism filter, oil pump, sorption filter, backwards oil boxes and electric control system. Each device is connected through oil pipes and valves, all of which are set in a mobile machine box, moves the box, the purification to hydraulic pressure oil of different locations can be carried on conveniently.
Owner:邝念曾
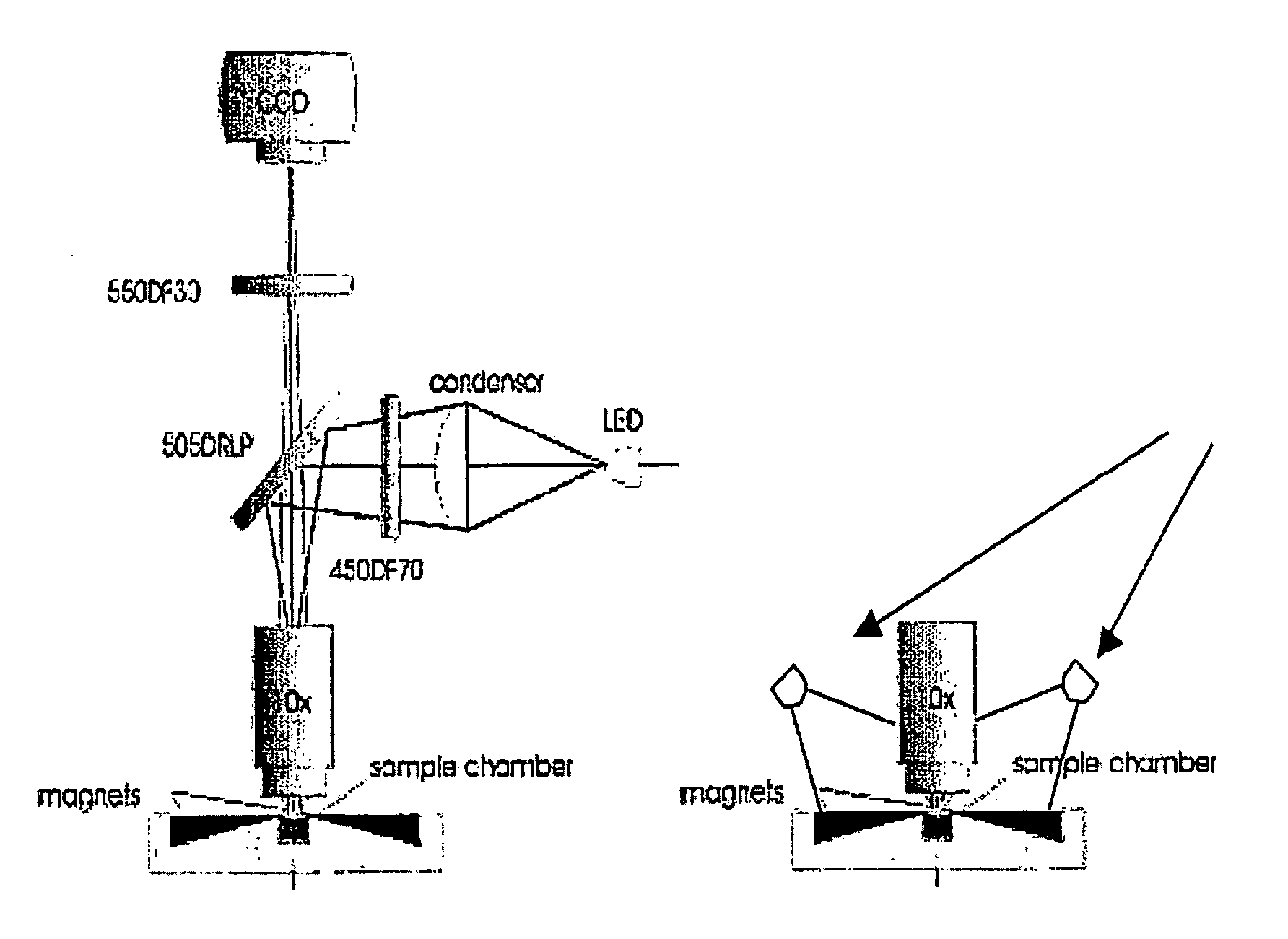
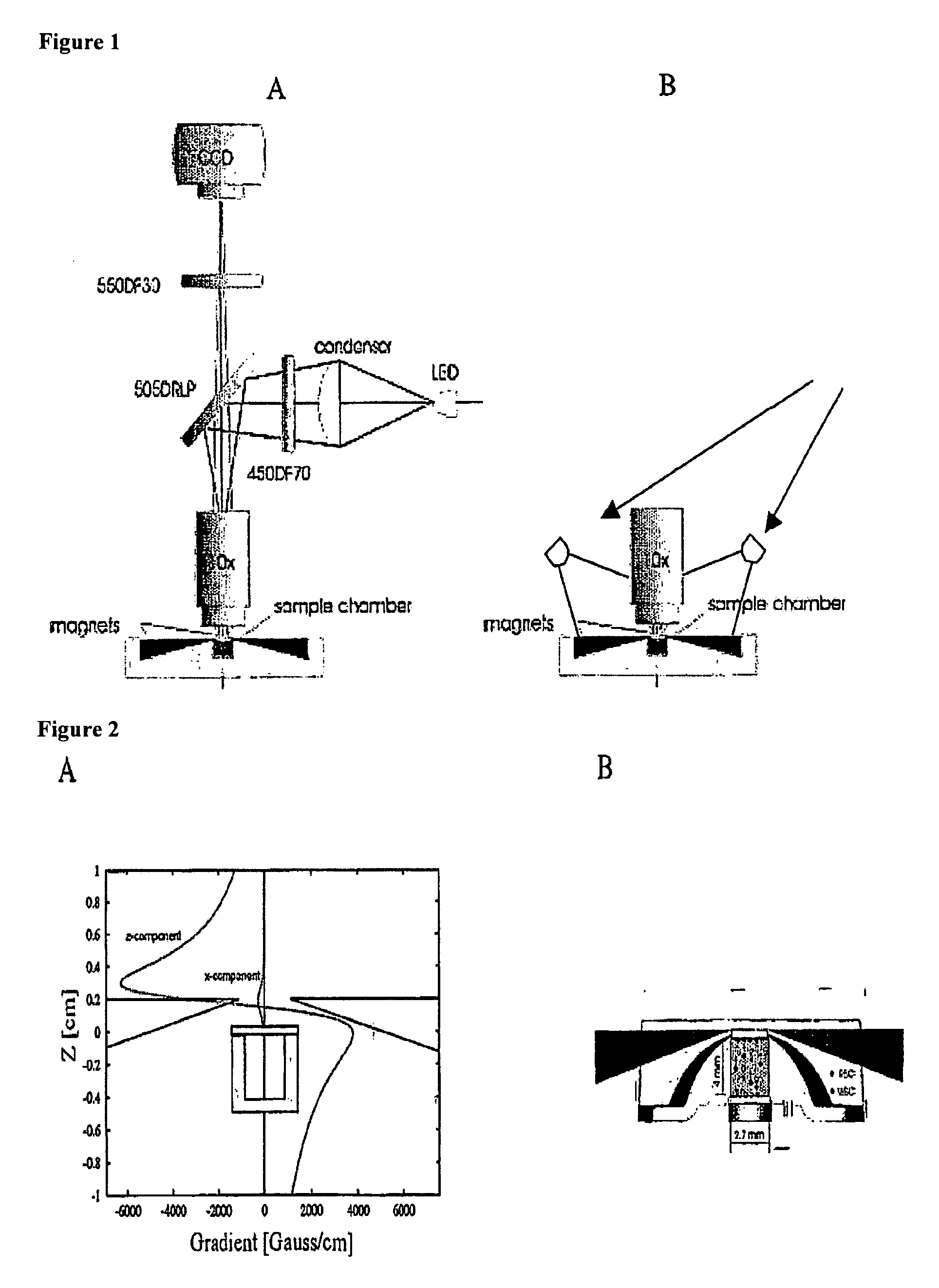
Methods and algorithms for cell enumeration in low-cost cytometer
InactiveUS20060024756A1Simple designReduce operating costsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWhite blood cellCcd camera
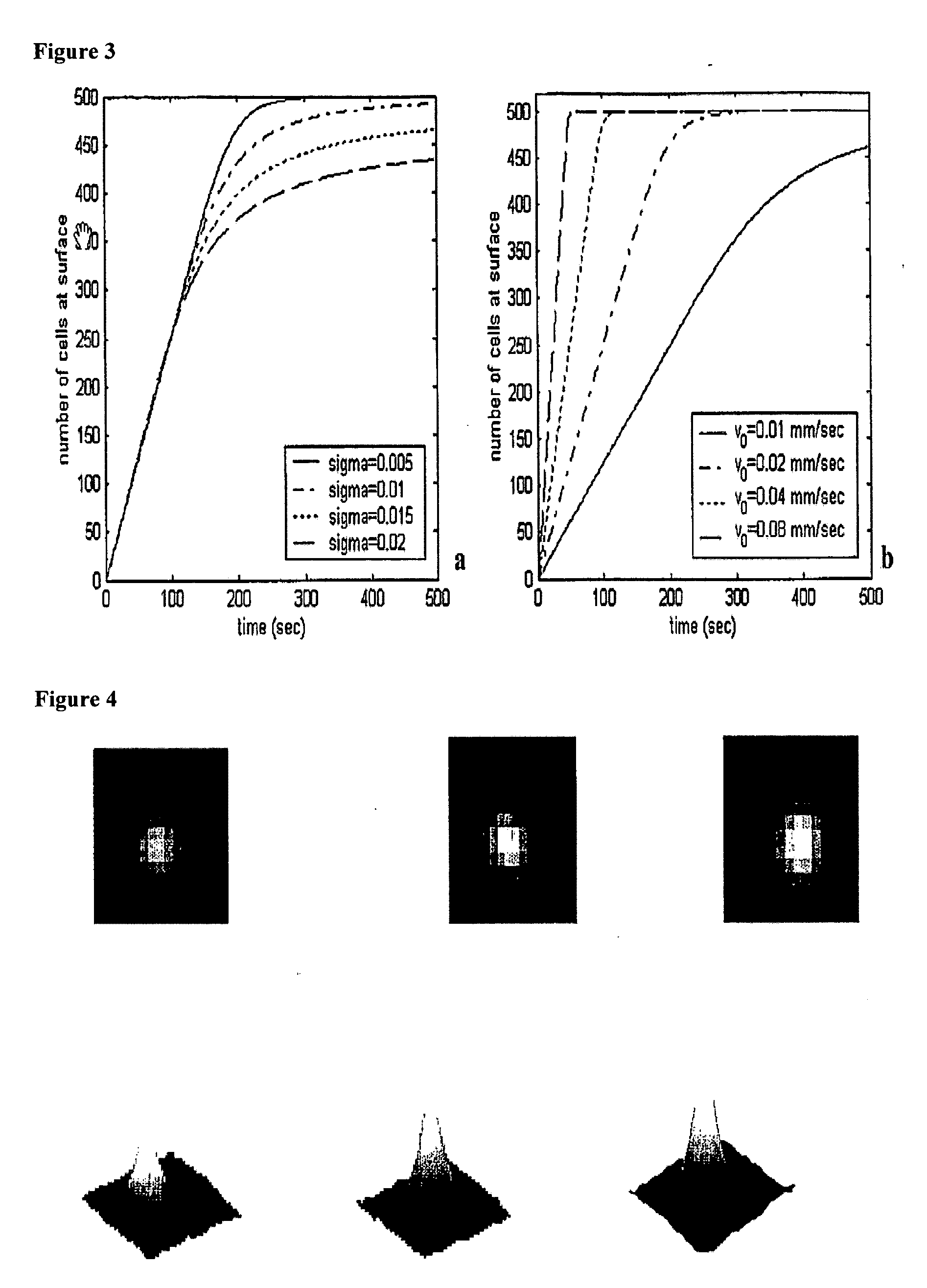
The enumeration of cells in fluids by flow cytometry is widely used across many disciplines such as assessment of leukocyte subsets in different bodily fluids or of bacterial contamination in environmental samples, food products and bodily fluids. For many applications the cost, size and complexity of the instruments prevents wider use, for example, CD4 analysis in HIV monitoring in resource-poor countries. The novel device, methods and algorithms disclosed herein largely overcome these limitations. Briefly, all cells in a biological sample are fluorescently labeled, but only the target cells are also magnetically labeled. The labeled sample, in a chamber or cuvet, is placed between two wedge-shaped magnets to selectively move the magnetically labeled cells to the observation surface of the cuvet. An LED illuminates the cells and a CCD camera captures the images of the fluorescent light emitted by the target cells. Image analysis performed with a novel algorithm provides a count of the cells on the surface that can be related to the target cell concentration of the original sample. The compact cytometer system provides a rugged, affordable and easy-to-use technique, which can be used in remote locations.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TWENTE
Magnetic element with improved out-of-plane anisotropy for spintronic applications
ActiveUS20120205758A1Without degrading thermal stability and MR ratioEnhanced interfacial perpendicular anisotropyMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionPerpendicular anisotropyAlloy
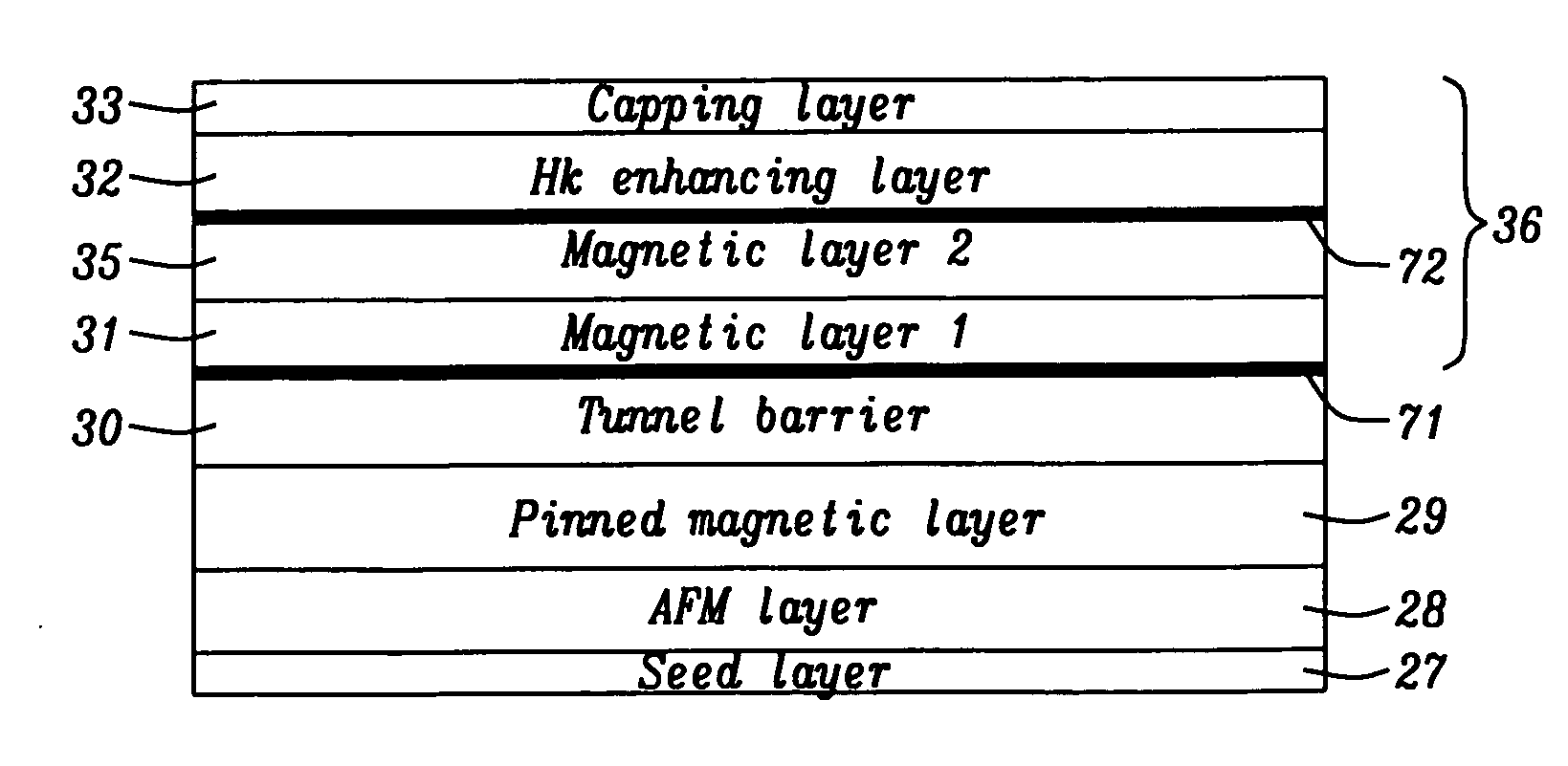
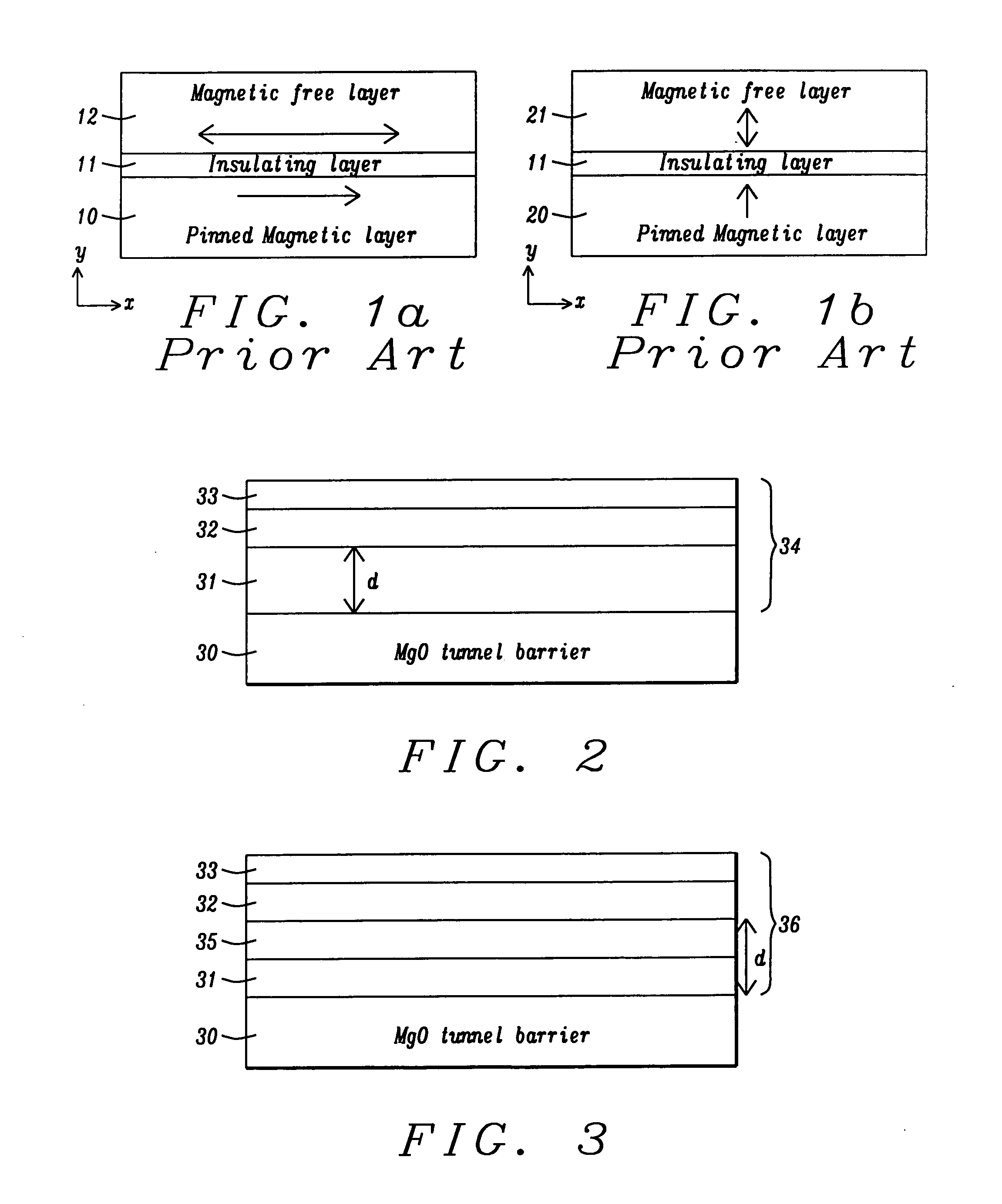
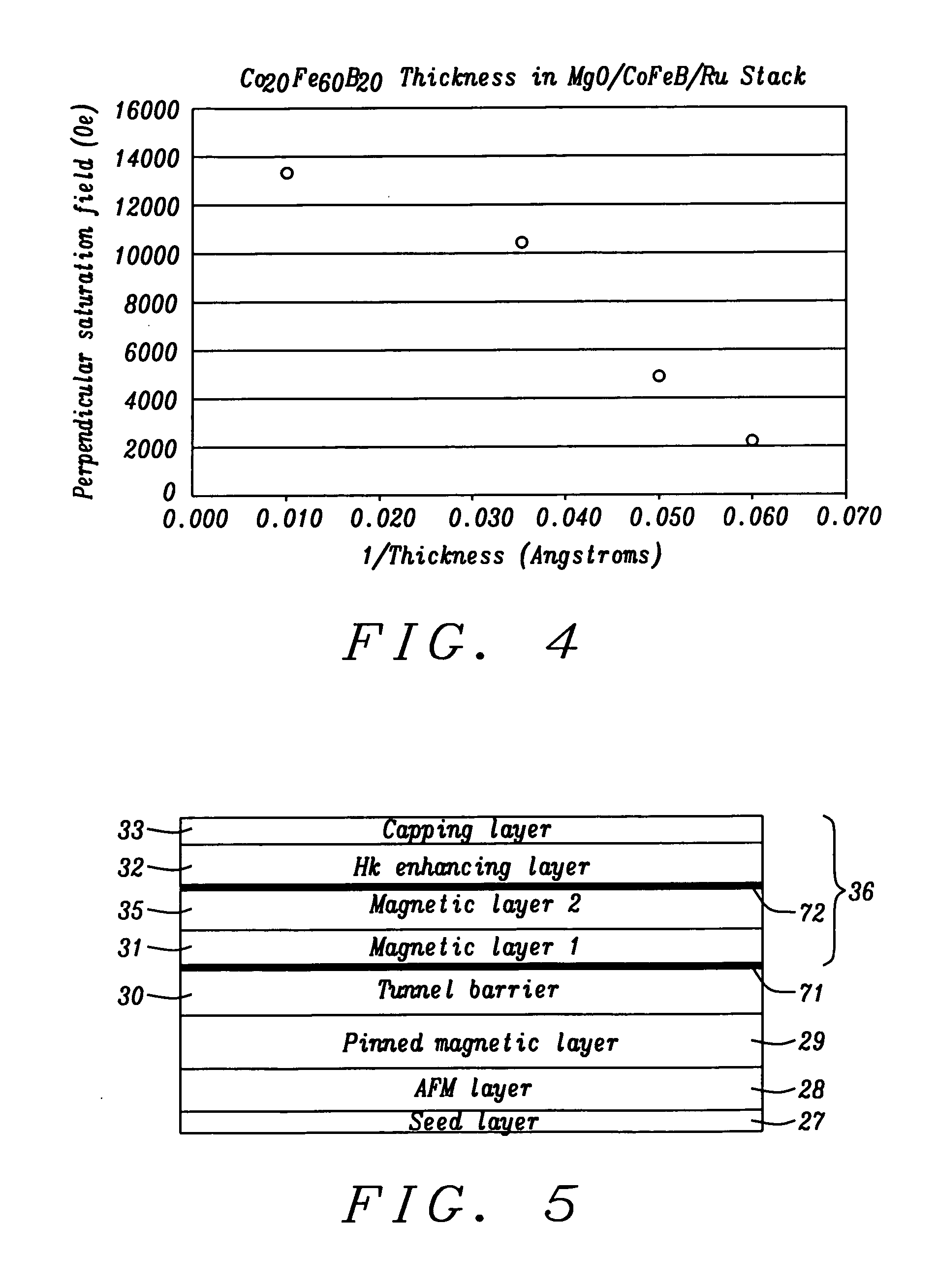
A magnetic element is disclosed wherein first and second interfaces of a free layer with a Hk enhancing layer and tunnel barrier, respectively, produce enhanced surface perpendicular anisotropy to lower switching current or increase thermal stability in a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ). In a MTJ with a bottom spin valve configuration where the Hk enhancing layer is an oxide, the capping layer contacting the Hk enhancing layer is selected to have a free energy of oxide formation substantially greater than that of the oxide. The free layer may be a single layer or composite comprised of an Fe rich alloy such as Co20Fe60B20. With a thin free layer, the interfacial perpendicular anisotropy may dominate the shape anisotropy to generate a magnetization perpendicular to the planes of the layers. The magnetic element may be part of a spintronic device or serve as a propagation medium in a domain wall motion device.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Magnetic levitation stirring devices and machines for mixing in vessels
InactiveUS6357907B1Increase surface areaIncrease aerationTransportation and packagingMaterial analysis by optical meansMagnetic polesMagnetic stirrer
The invention provides a simple method, devices and several machines for simultaneously stirring and aerating thousands of vessels or wells of microplates in a robust manner and with economy. This method uses the simple principle of magnetic stirrers being levitated vertically when passed laterally or vertically through a strong horizontal dipole magnetic field. The dipole magnetic fields may be produced by using permanent magnets, electromagnets or a modulating / reversing electro-magnetic field. Each vessel contains a magnetic ball, disc, bar, dowel or other shape (stirrers) which in their magnetic attraction to the dipole magnetic field will cause the stirrers to levitate up in the vessel as the stirrer's magnetic poles attempt to align with the center of the dipole's magnetic field. The stirrers will fall to the bottom of the vessel by gravity or by changing the relative position of the levitating magnetic field to pull them down, or by passing the vessel laterally over another magnetic field. The up and down movement of the stirrers provides a vigorous mixing of the contents of many vessels at same time. If the level of the vessel's meniscus is situated so the stirrers pass through it on their way up and down, the air / liquid interface is significantly increased thereby significantly increasing aeration of the liquid.
Owner:V & P SCI
Magnetic write head with high moment magnetic thin film formed over seed layer
A magnetic write head includes a seed layer and a magnetic layer on the seed layer. The seed layer includes seed-layer grains having either a face-centered cubic (fcc) crystalline structure with a surface plane substantially oriented in a [111] direction or a hexagonal-close-packed (hcp) crystalline structure with a surface plane substantially oriented in a [0001] direction. The magnetic layer includes magnetic-layer grains having a body-centered-cubic (bcc) crystalline structure with a surface plane substantially oriented in a [110] direction.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Magnetic recording medium and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS8535817B2Excellent characteristicsIncreased durabilityMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageMetallurgyNon magnetic
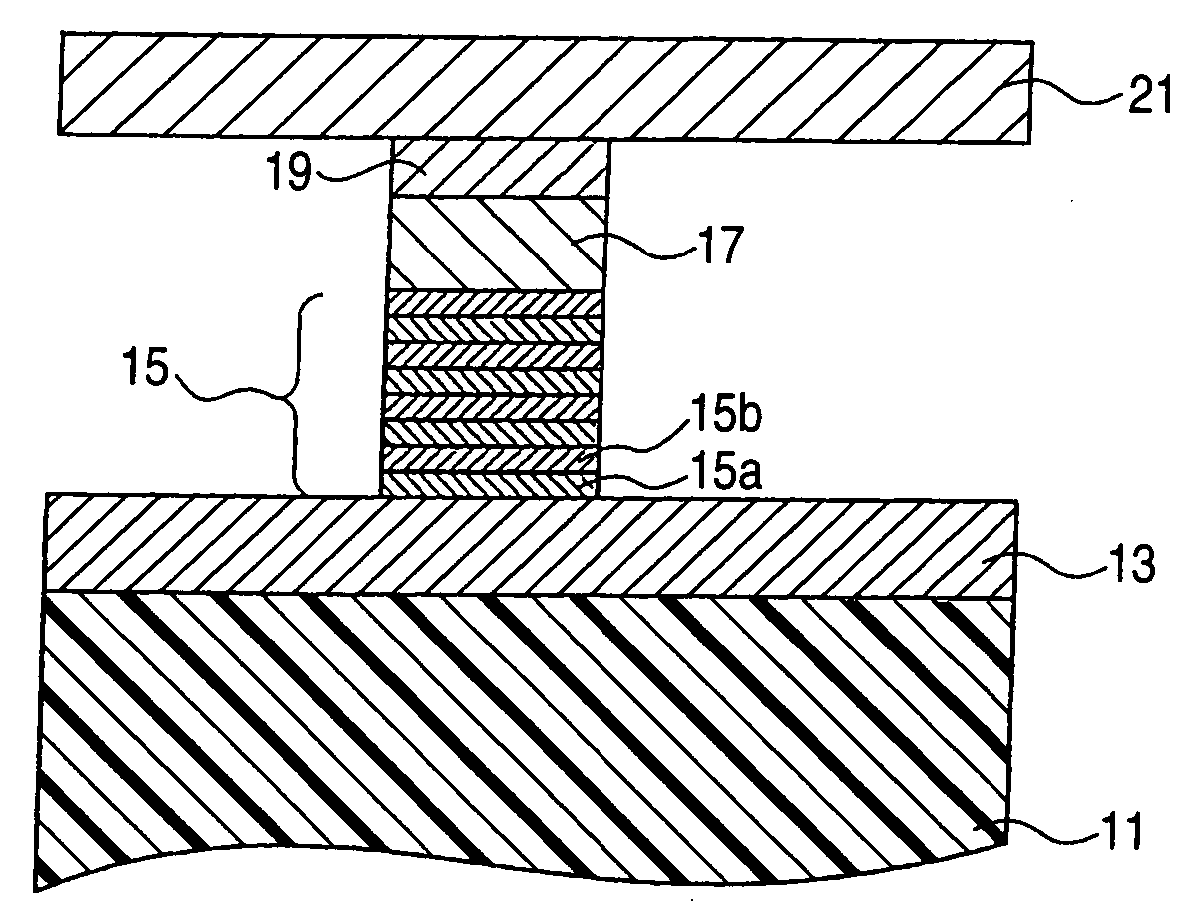
An aspect of the present invention relates to a magnetic recording medium comprising a nonmagnetic layer containing a nonmagnetic powder and a binder and a magnetic layer containing a ferromagnetic powder and a binder in this order on a nonmagnetic support, whereinthe magnetic layer comprises a nonmagnetic powder of which coefficient of variation CV of a particle size distribution as denoted by the following formula (1):CV(%)=σ / φ×100 (1)is less than 20 percent, andthe magnetic layer has a thickness being equal to or less than 0.1 μm and falling within a range of 1.1≦φ / t≦8.0, wherein σ denotes a standard deviation of a particle diameter, φ denotes an average particle diameter of the nonmagnetic powder comprised in the magnetic layer being expressed in μm, and t denotes a thickness of the magnetic layer being expressed in μm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
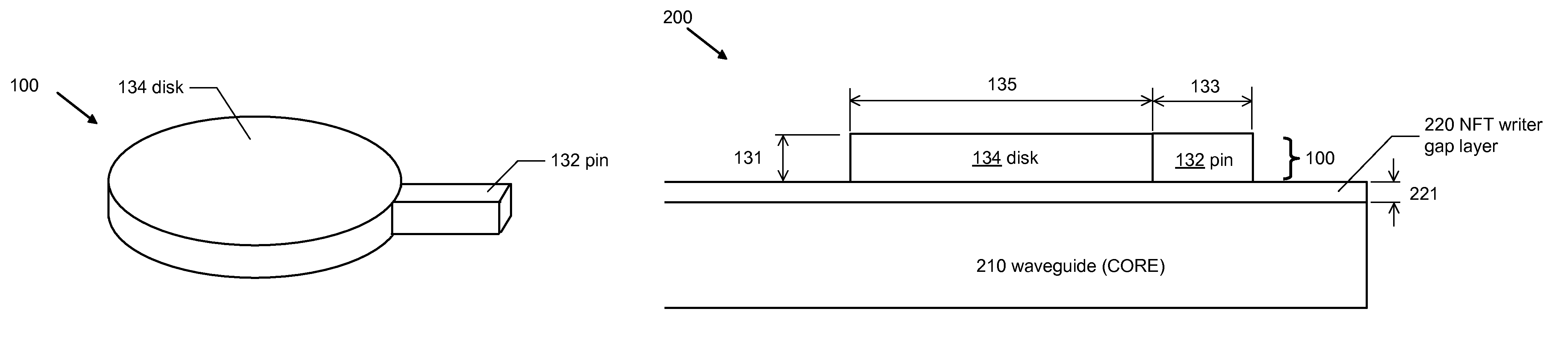
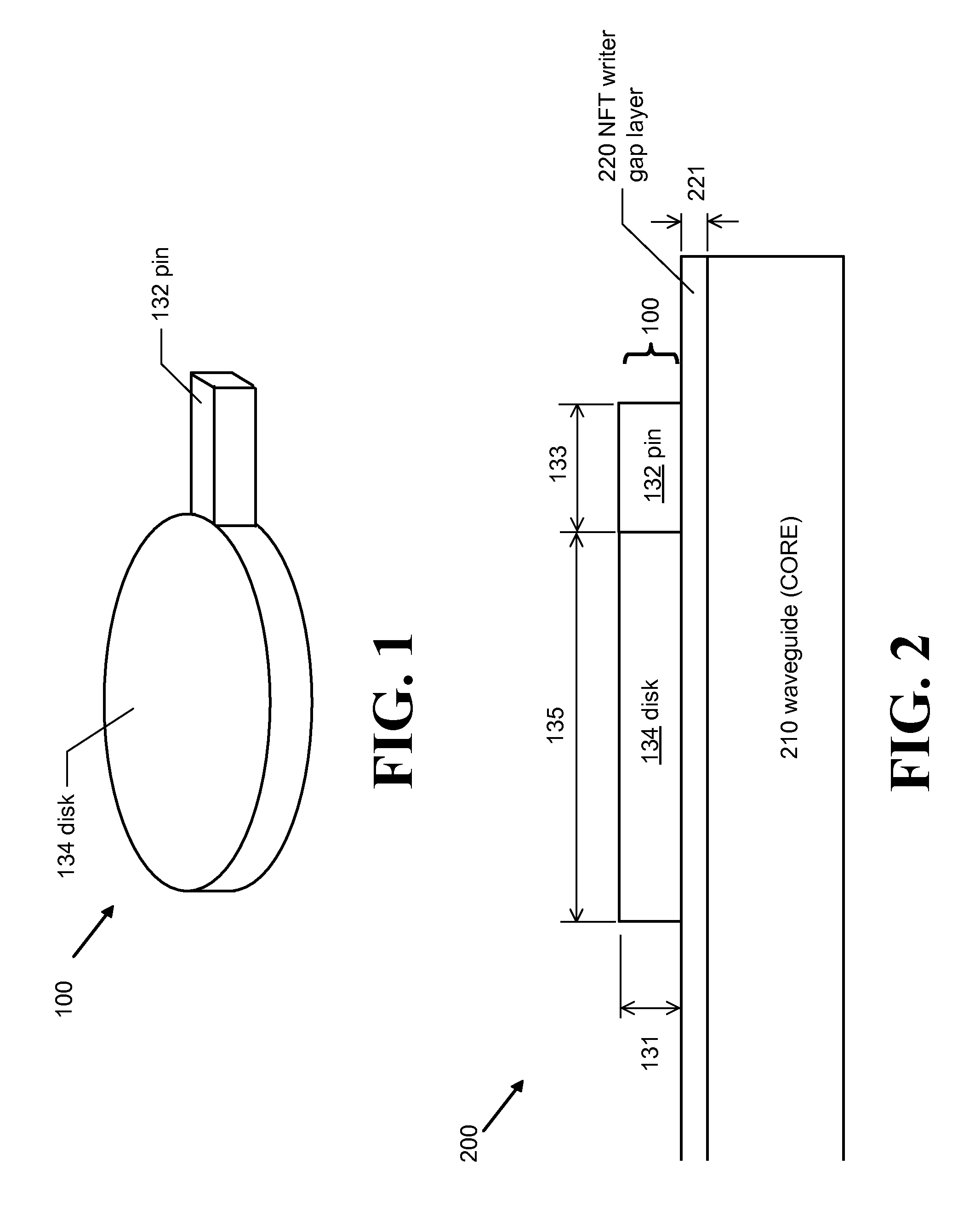
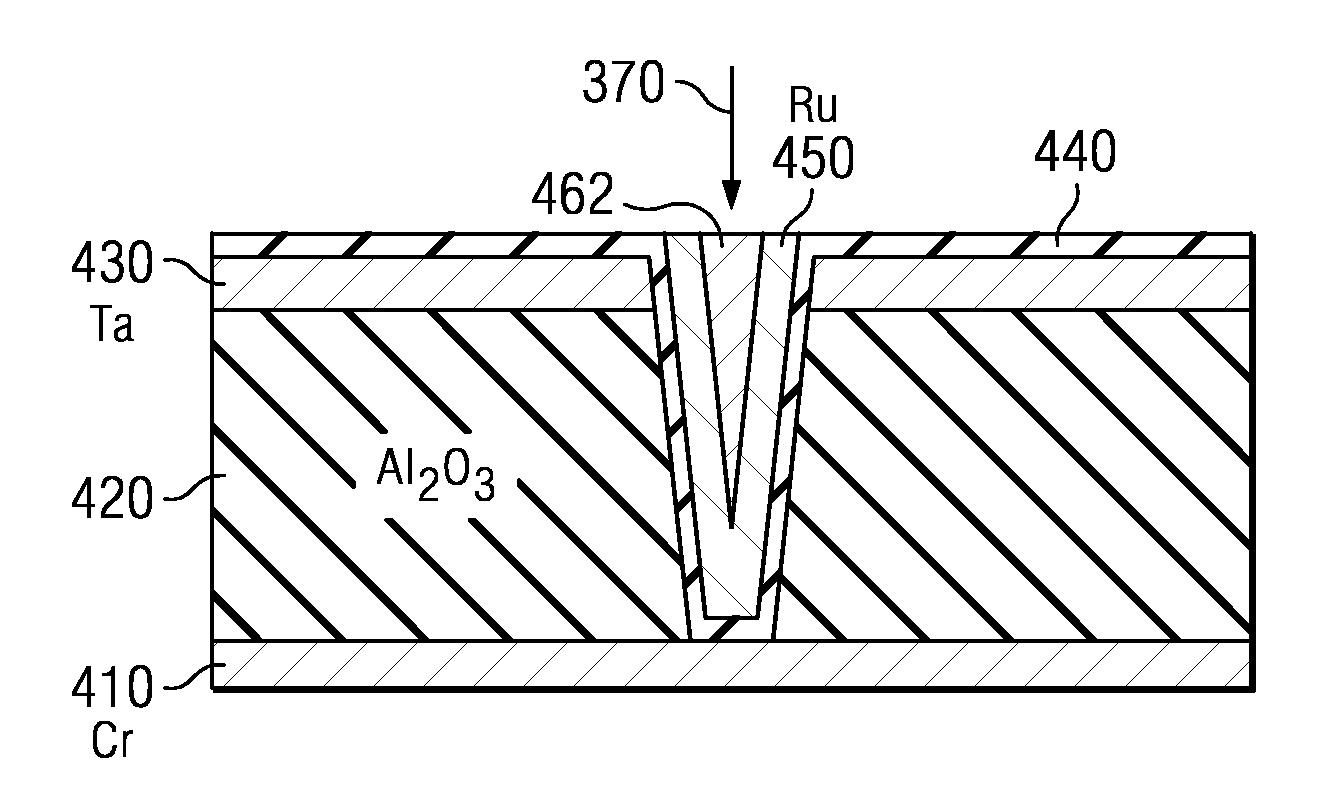
Double hard-mask mill back method of fabricating a near field transducer for energy assisted magnetic recording
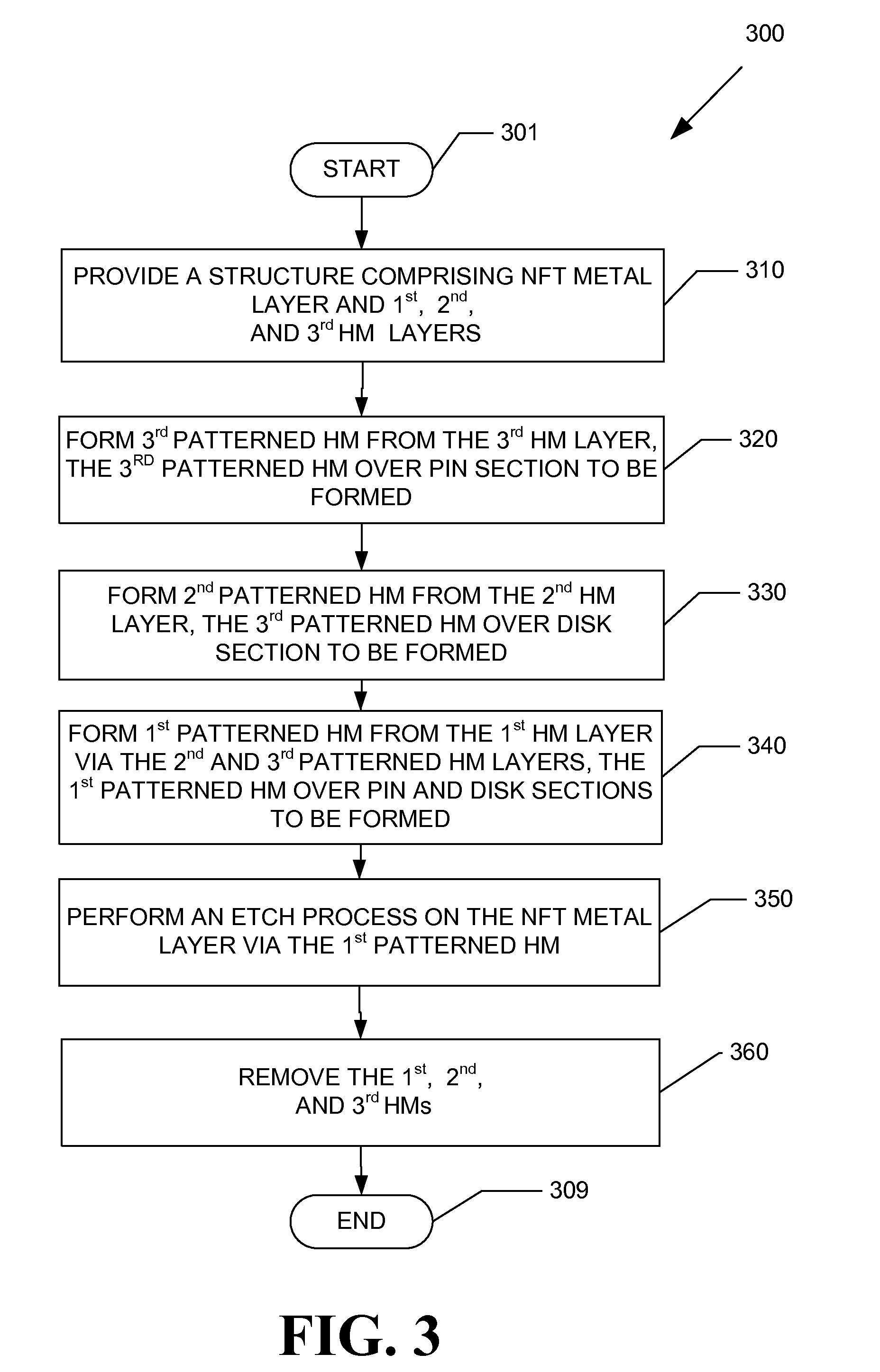
A method of forming a near field transducer (NFT) for energy assisted magnetic recording is disclosed. A structure comprising an NFT metal layer and a first hardmask layer over the NFT metal layer is provided A first patterned hardmask is formed from the first hardmask layer, the first patterned hardmask disposed over a disk section and a pin section of the NFT to be formed. An etch process is performed on the NFT metal layer via the first patterned hardmask, the etch process forming the NFT having the disk section and the pin section.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
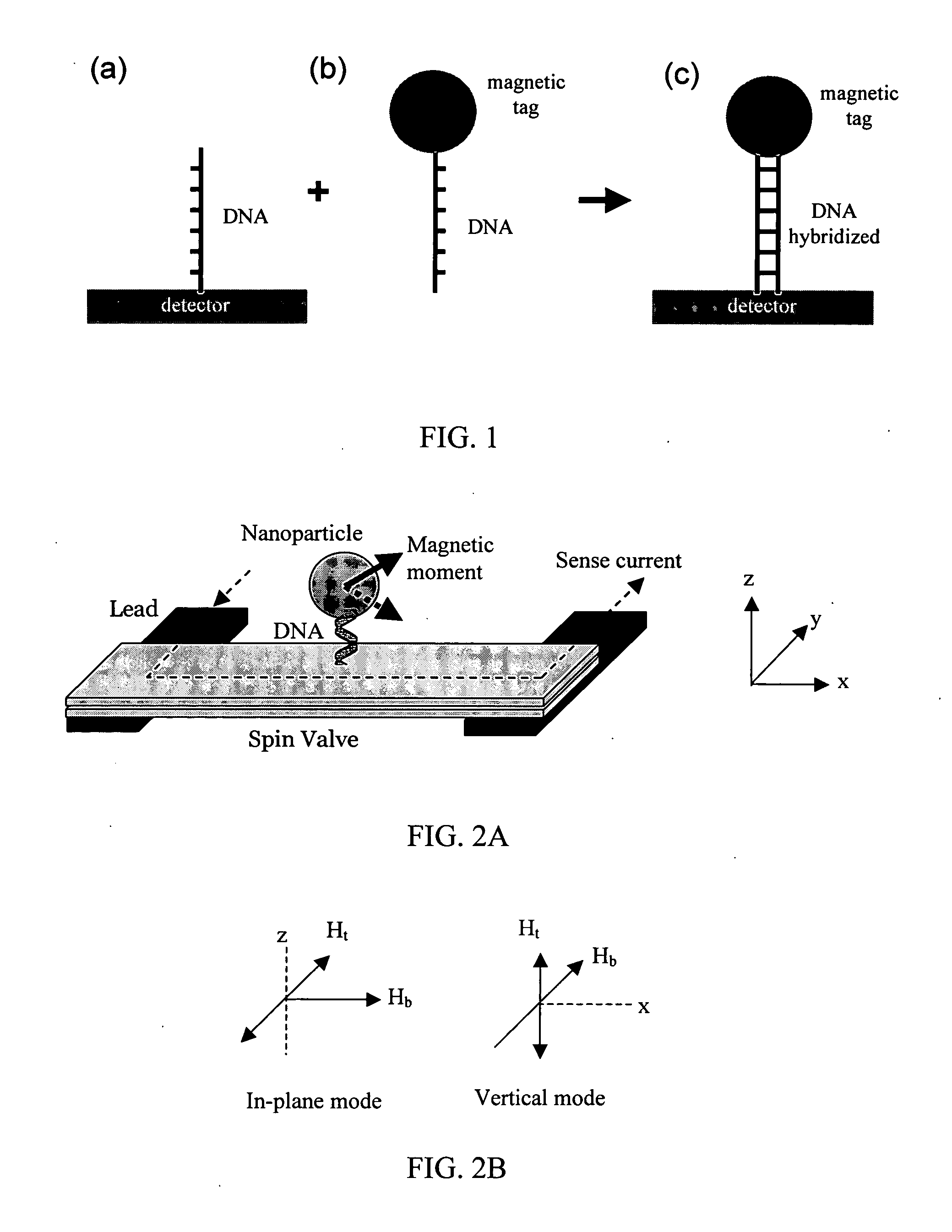
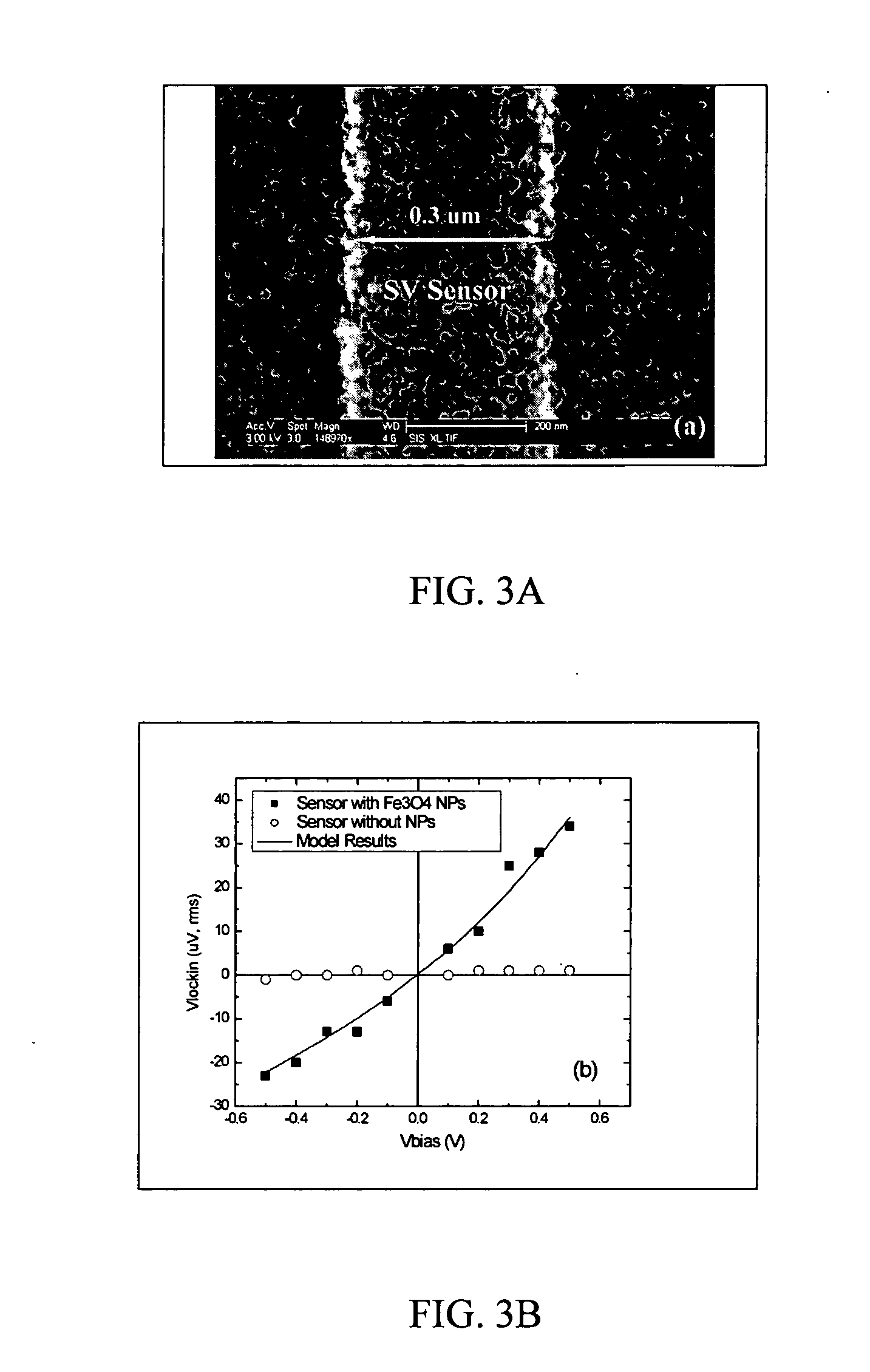
Magnetic nanoparticles, magnetic detector arrays, and methods for their use in detecting biological molecules
Magnetic nanoparticles and methods for their use in detecting biological molecules are disclosed. The magnetic nanoparticles can be attached to nucleic acid molecules, which are then captured by a complementary sequence attached to a detector, such as a spin valve detector or a magnetic tunnel junction detector. The detection of the bound magnetic nanoparticle can be achieved with high specificity and sensitivity.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
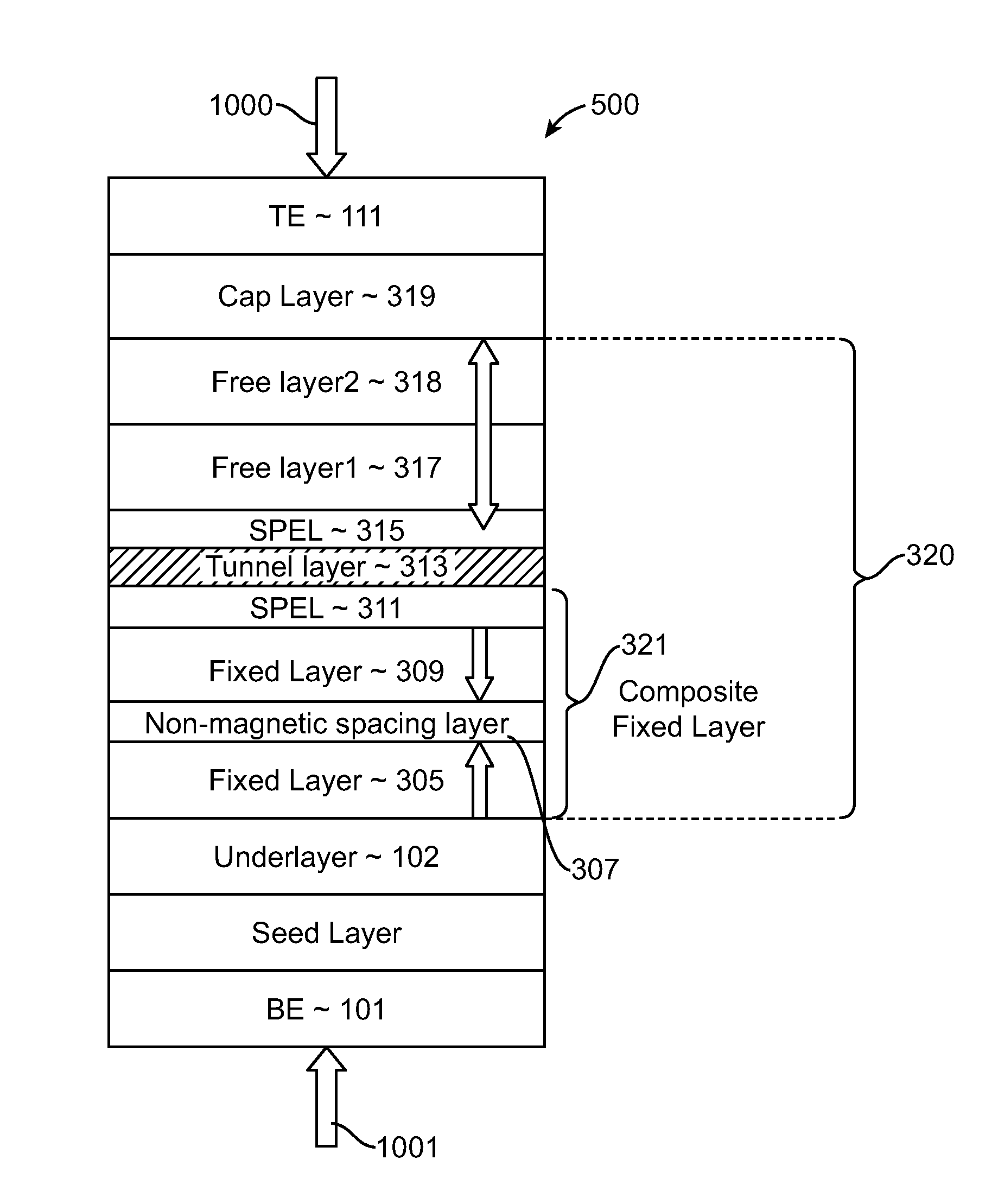
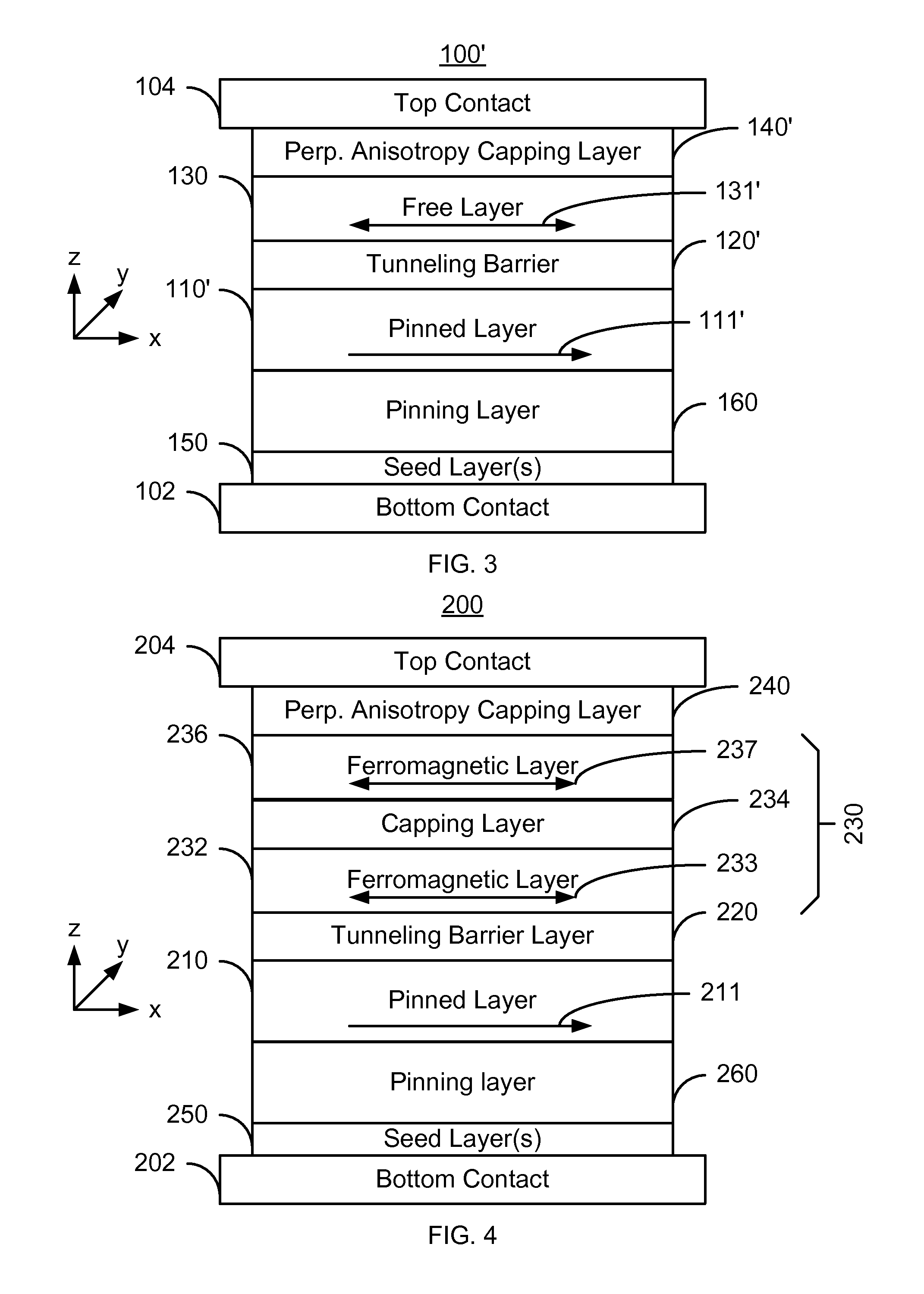
Method and system for providing magnetic tunneling junction elements having improved performance through capping layer induced perpendicular anisotropy and memories using such magnetic elements
ActiveUS20120155156A1Improve thermal stabilityNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsElectricityPower flow
A method and system for providing a magnetic element and a magnetic memory utilizing the magnetic element are described. The magnetic element is used in a magnetic device that includes a contact electrically coupled to the magnetic element. The method and system include providing pinned, nonmagnetic spacer, and free layers. The free layer has an out-of-plane demagnetization energy and a perpendicular magnetic anisotropy corresponding to a perpendicular anisotropy energy that is less than the out-of-plane demagnetization energy. The nonmagnetic spacer layer is between the pinned and free layers. The method and system also include providing a perpendicular capping layer adjoining the free layer and the contact. The perpendicular capping layer induces at least part of the perpendicular magnetic anisotropy in the free layer. The magnetic element is configured to allow the free layer to be switched between magnetic states when a write current is passed through the magnetic element.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
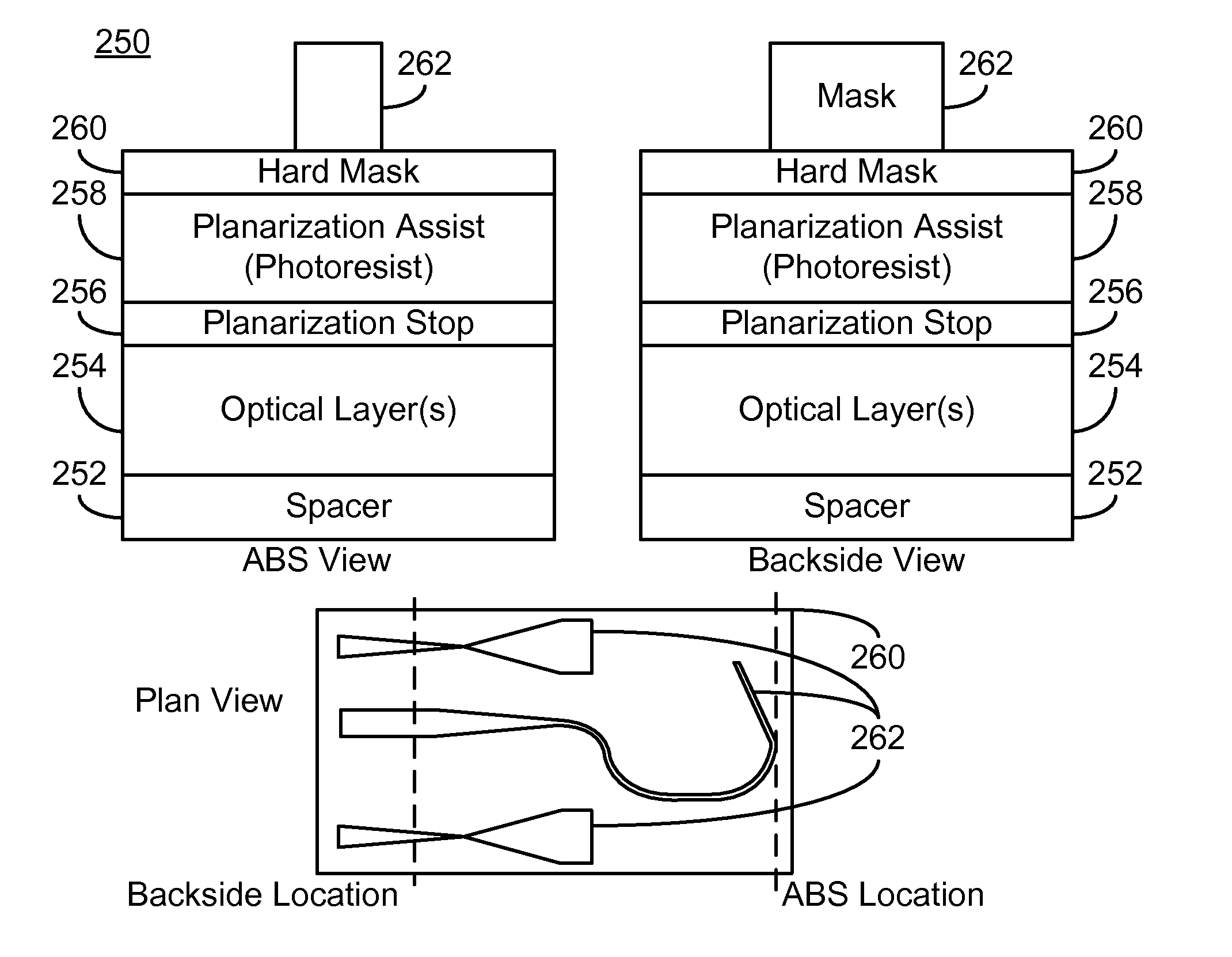
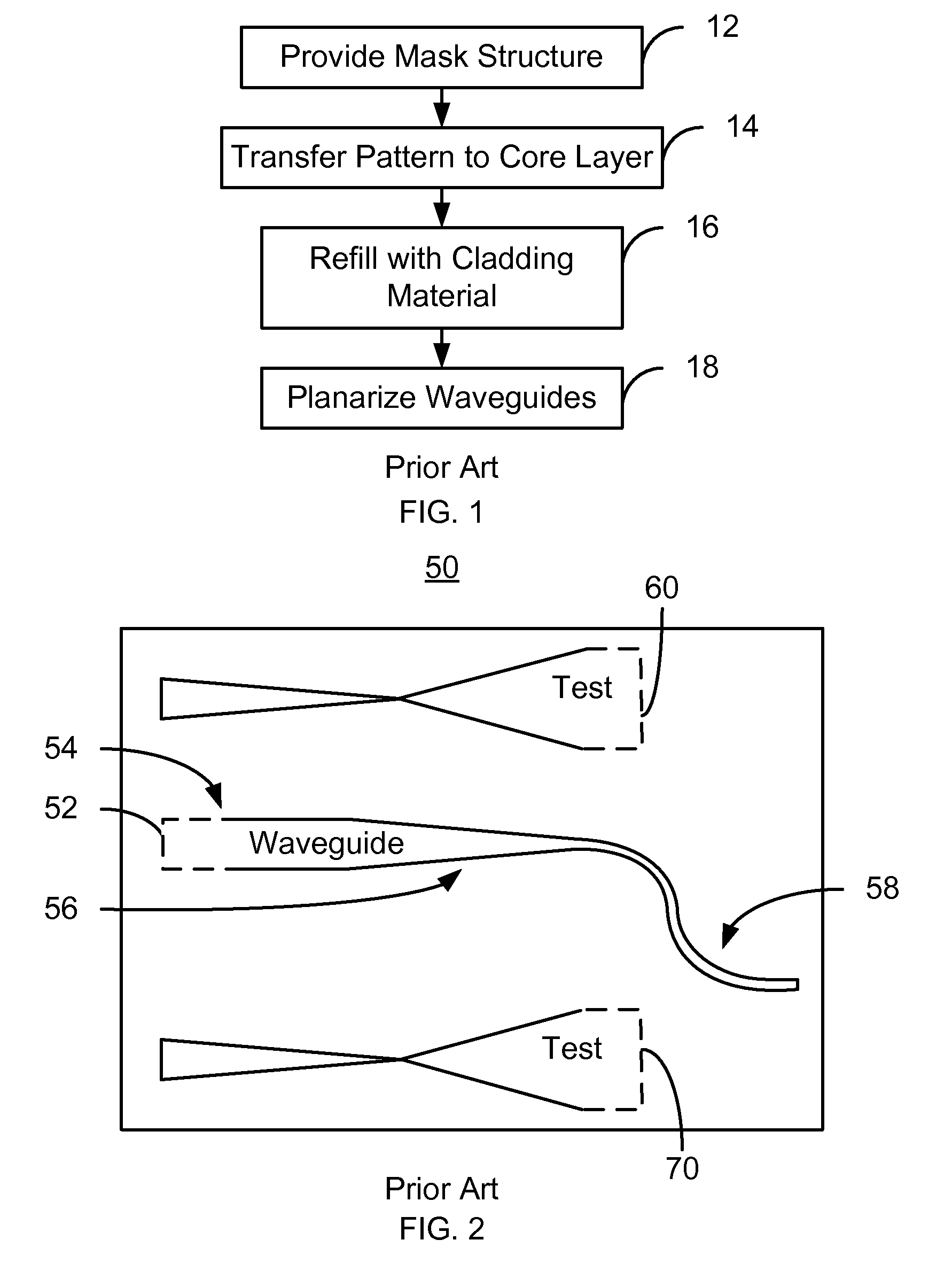
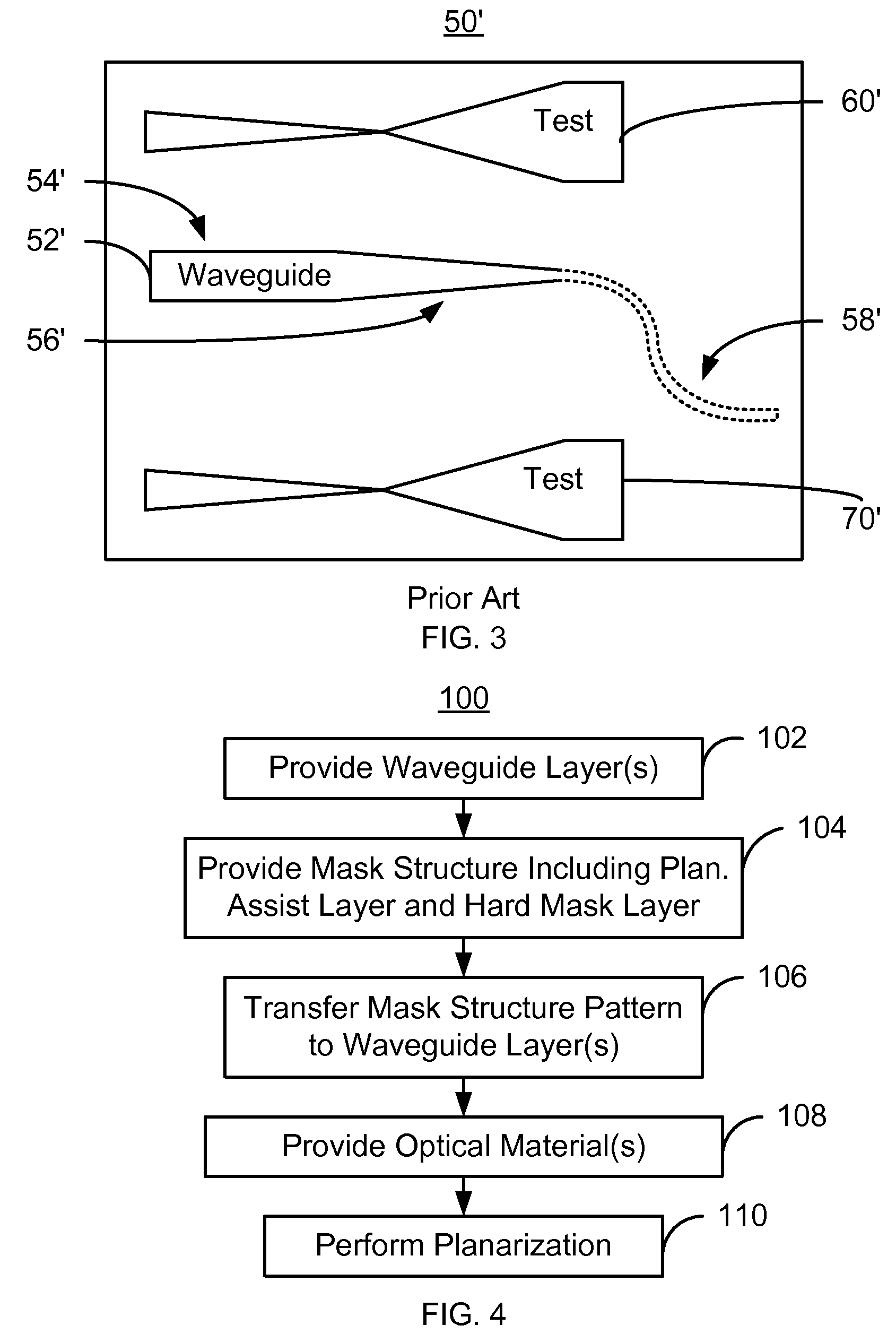
Method and system for manufacturing tapered waveguide structures in an energy assisted magnetic recording head
A method for providing waveguide structures for an energy assisted magnetic recording (EAMR) transducer is described. The waveguide structures have a plurality of widths. At least one waveguide layer is provided. Mask structure(s) corresponding to the waveguide structures and having a pattern are provided on the waveguide layer(s). The mask structure(s) include a planarization stop layer, a planarization assist layer on the planarization stop layer, and a hard mask layer on the planarization assist layer. The planarization assist layer has a low density. The pattern of the mask structure(s) is transferred to the waveguide layer(s). Optical material(s) that cover the waveguide layer(s) and a remaining portion of the mask structure(s) are provided. The optical material(s) have a density that is at least twice the low density of the planarization assist layer. The method also includes performing a planarization configured to remove at least a portion of the optical material(s).
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
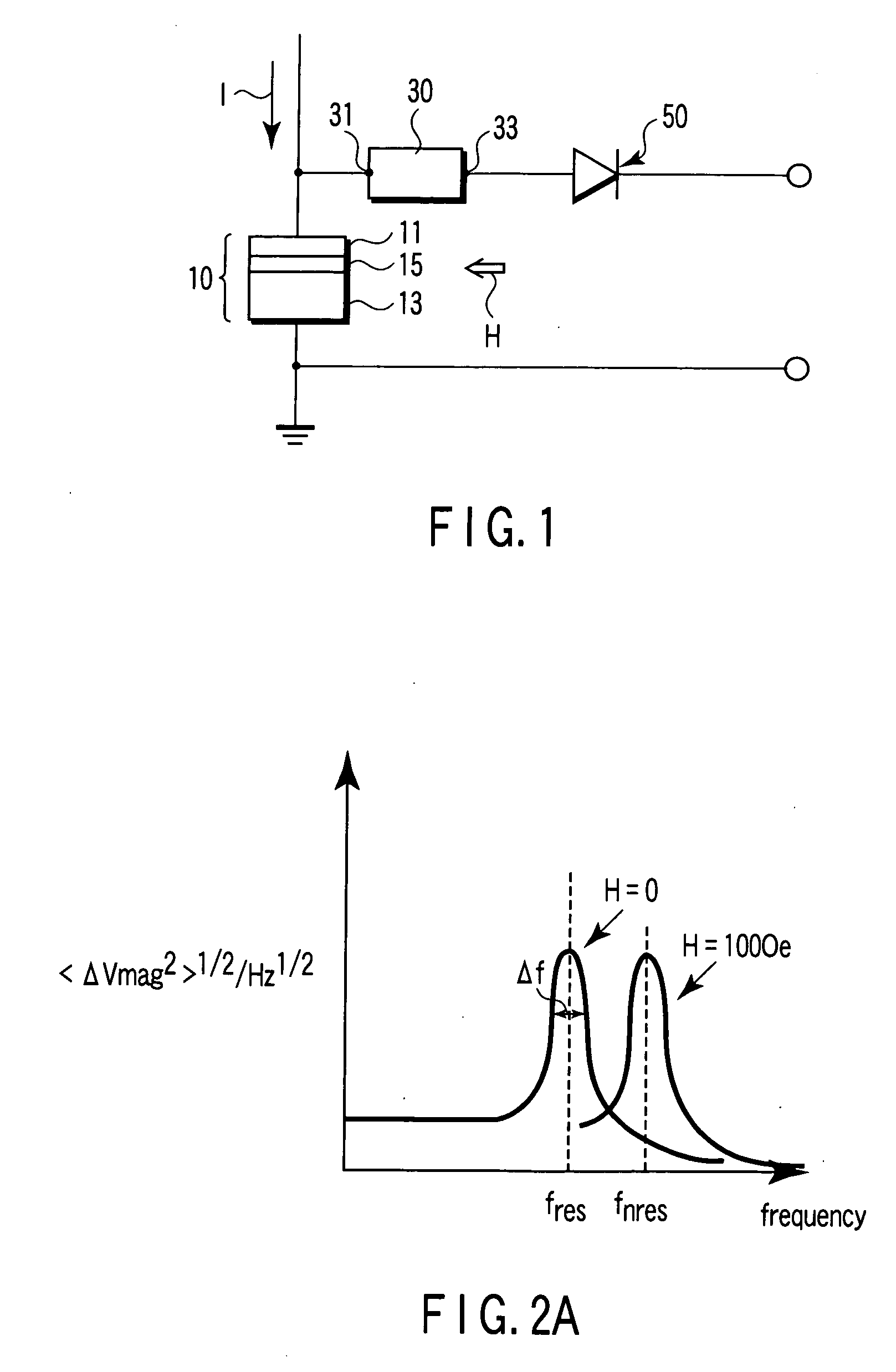
Magnetic sensor, magnetic field sensing method, semagnetic recording head, and magnetic memory device
ActiveUS20050219771A1Modification of read/write signalsNanomagnetismFrequency filteringMagnetization
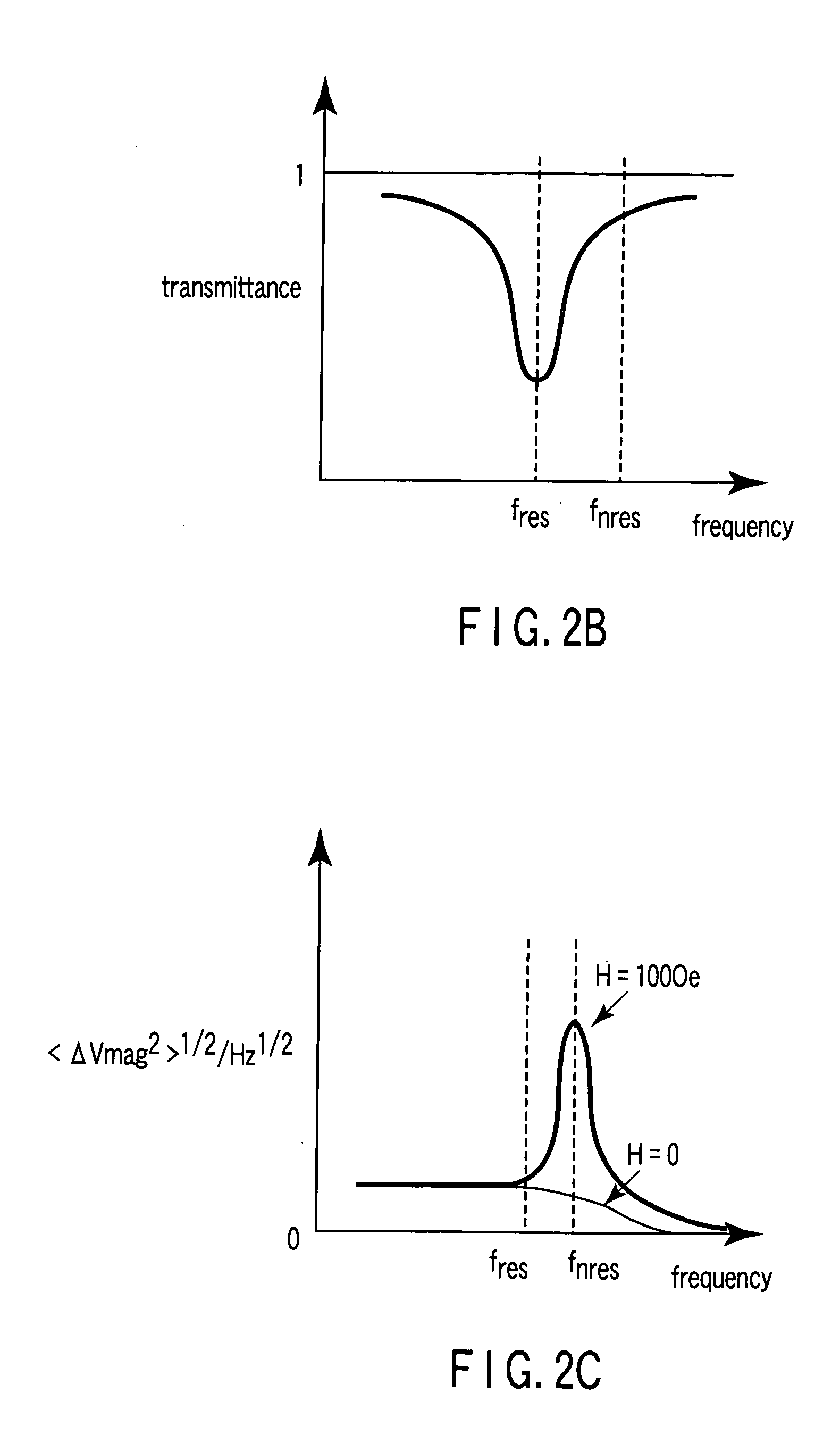
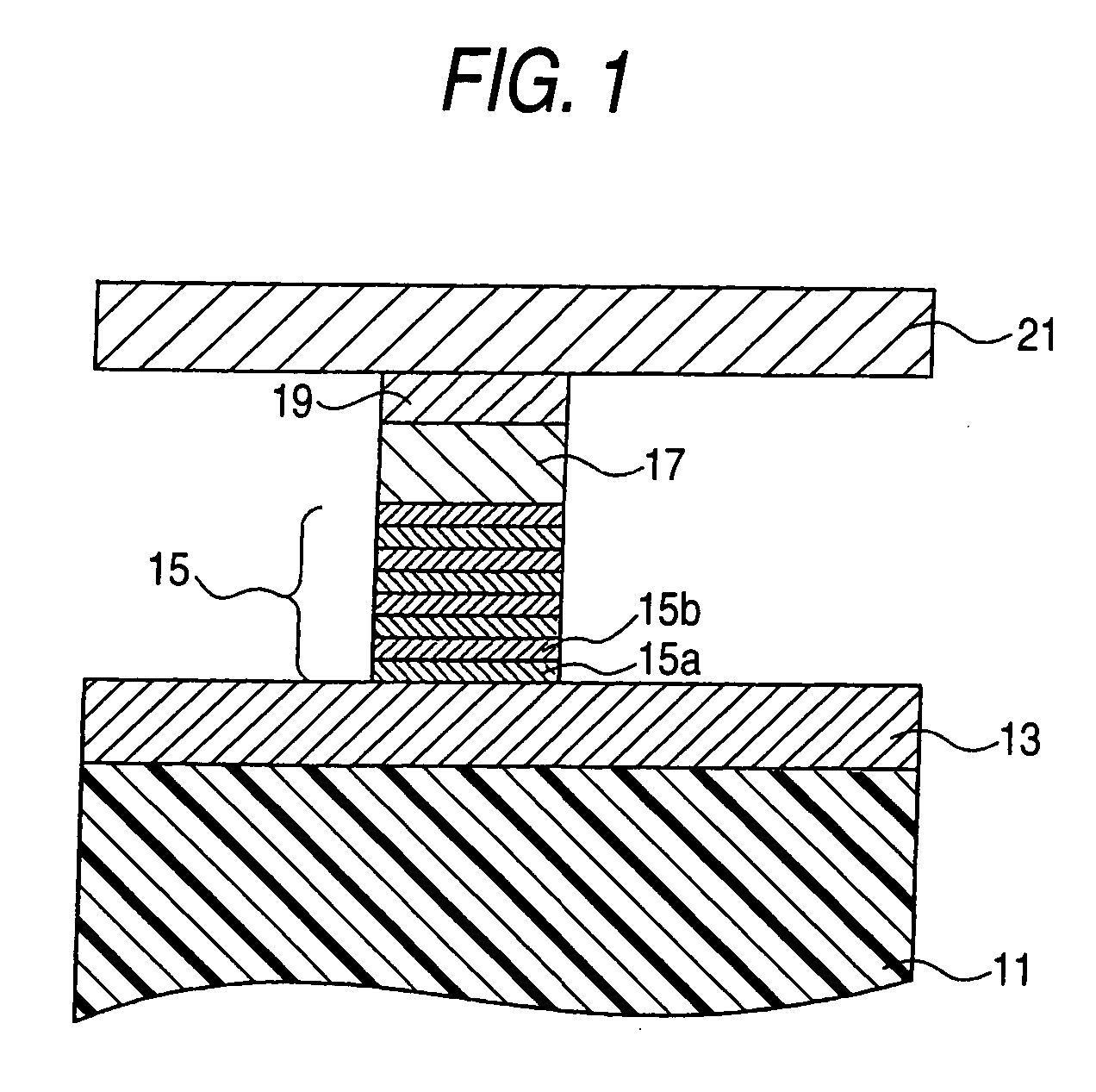
A magnetic sensor includes a magnetoresistance element having a peak of a thermal fluctuation strength of magnetization under a magnetic field having a certain frequency, a frequency filter connected to the magnetoresistance element and having its transmittance decreased or increased in substantially the frequency of the magnetic field to output a signal corresponding substantially to the peak of the thermal fluctuation strength of magnetization, and a detector connected to the frequency filter to detect the magnetic field based on the signal of the frequency filter.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
High speed low power annular magnetic devices based on current induced spin-momentum transfer
InactiveUS20080112094A1Operational advantageReduce the required powerRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsElectrical resistance and conductanceMagnetization
A high speed and low power method to control and switch the magnetization direction and / or helicity of a magnetic region in a magnetic device for memory cells using spin polarized electrical current. The magnetic device comprises a reference magnetic layer with a fixed magnetic helicity and / or magnetization direction and a free magnetic layer with a changeable magnetic helicity. The fixed magnetic layer and the free magnetic layer are preferably separated by a non-magnetic layer, and the reference layer includes an easy axis perpendicular to the reference layer. A current can be applied to the device to induce a torque that alters the magnetic state of the device so that it can act as a magnetic memory for writing information. The resistance, which depends on the magnetic state of the device, is measured to thereby read out the information stored in the device.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
High-frequency oscillation element, magnetic information recording head, and magnetic storage device
ActiveUS20050023938A1Increase temperatureIncrease speedPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSolid-state devicesMagnetic storageResonance
A high-frequency oscillation element has a ferromagnetic material which exhibits thermal fluctuation of magnetization and generates spin fluctuations in conduction electrons, a nonmagnetic conductive material which is laminated on the first magnetic material and transfers the conduction electrons, a magnetic material which is laminated on the nonmagnetic conductive material, generates magnetic resonance upon injection of the conduction electrons, and imparts magnetic dipole interaction to magnetization of a neighboring magnetic area by means of magnetic vibration stemming from the magnetic resonance, a first electrode electrically coupled with the first magnetic material, and a second electrode electrically coupled with the second magnetic material.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
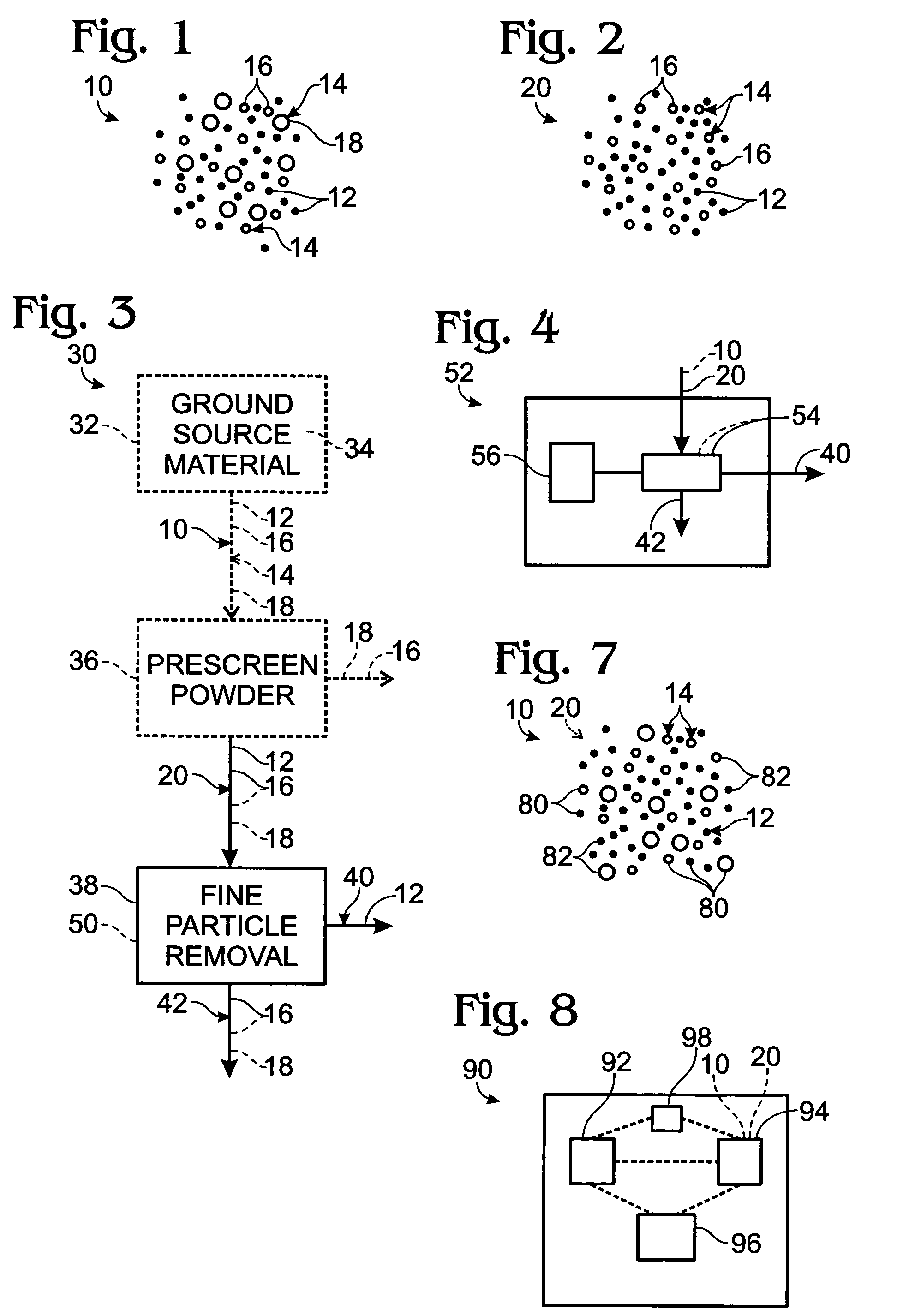
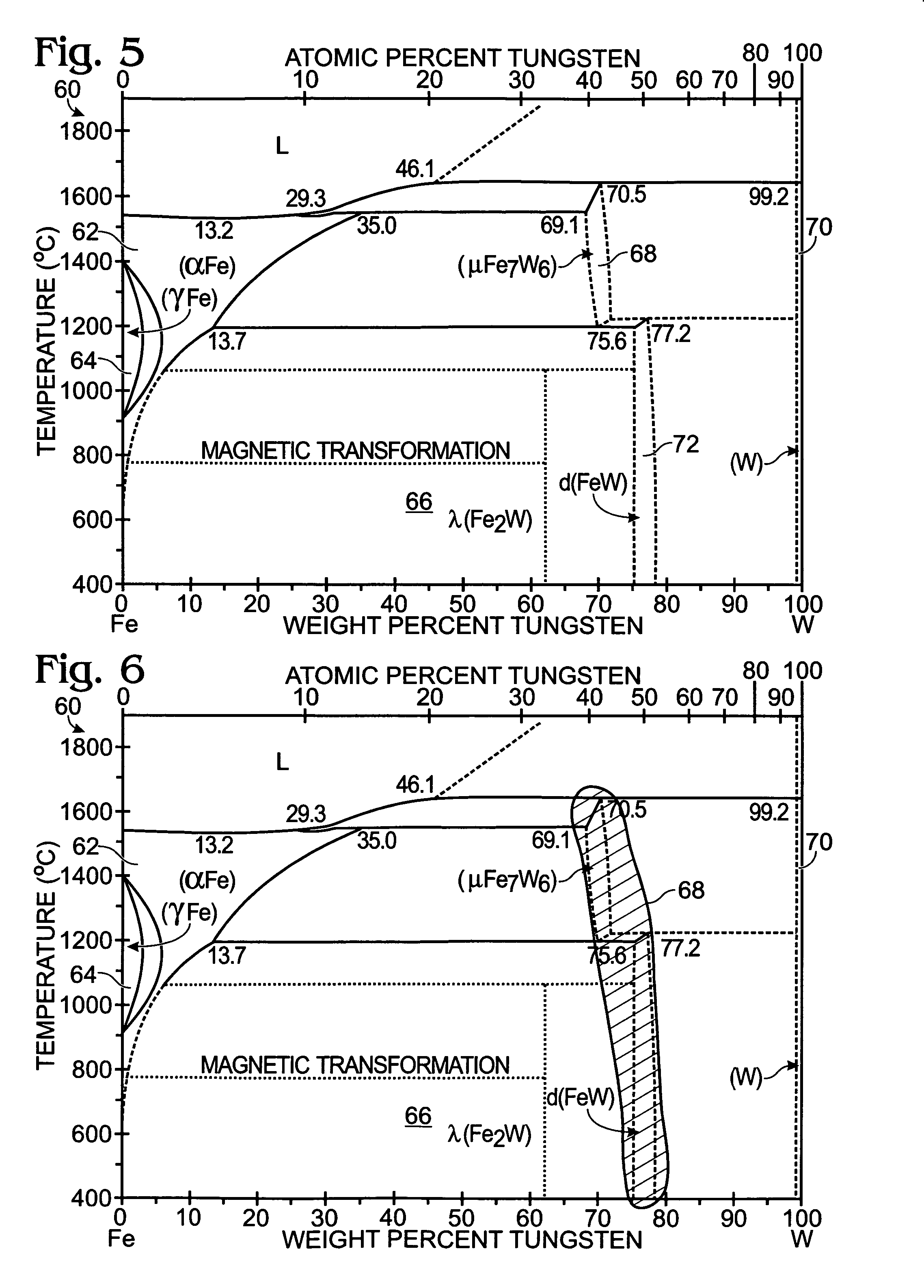
System and method for processing ferrotungsten and other tungsten alloys, articles formed therefrom and methods for detecting the same
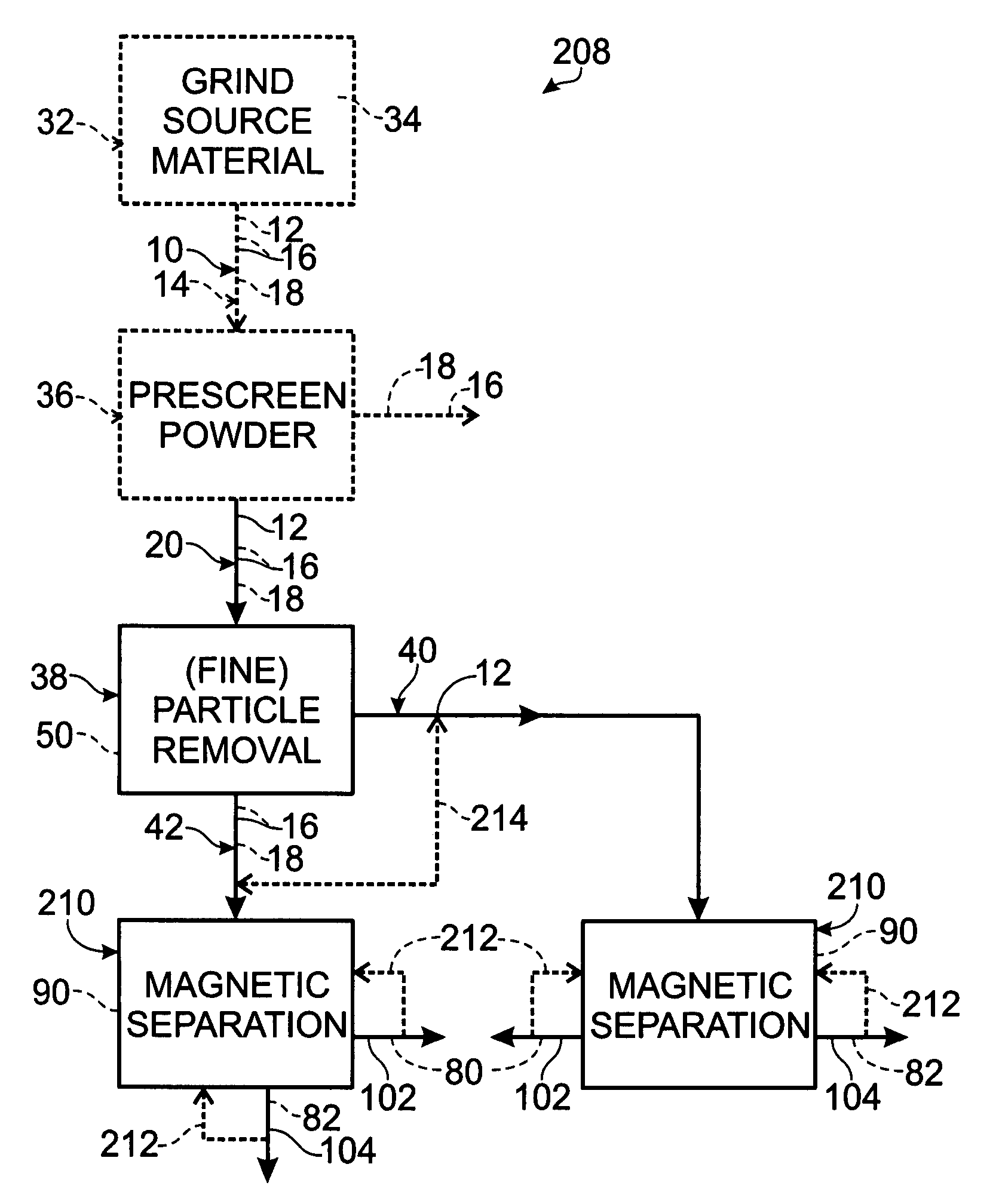
Systems and methods for refining or otherwise processing tungsten alloys, including ferrotungsten powder and articles formed therefrom, and methods for detecting the presence of the same. The methods include at least one of magnetically-separating and particle-size-separating ferrotungsten or ferrotungsten-containing powder. In some embodiments, powder may be separated to remove fine particles, and optionally to separate the remaining particles into fractions containing selected particle size distributions. The powder additionally or alternatively may be separated into at least magnetic and non-magnetic fractions. In some embodiments, portions of two or more size and / or magnetism fractions are mixed to provide a ferrotungsten-containing feedstock. Selected fractions resulting from the size and magnetism separation steps may be utilized to provide a ferrotungsten-containing feedstock from which articles are produced and which may include additional components.
Owner:AMICK FAMILY REVOCABLE LIVING TRUST
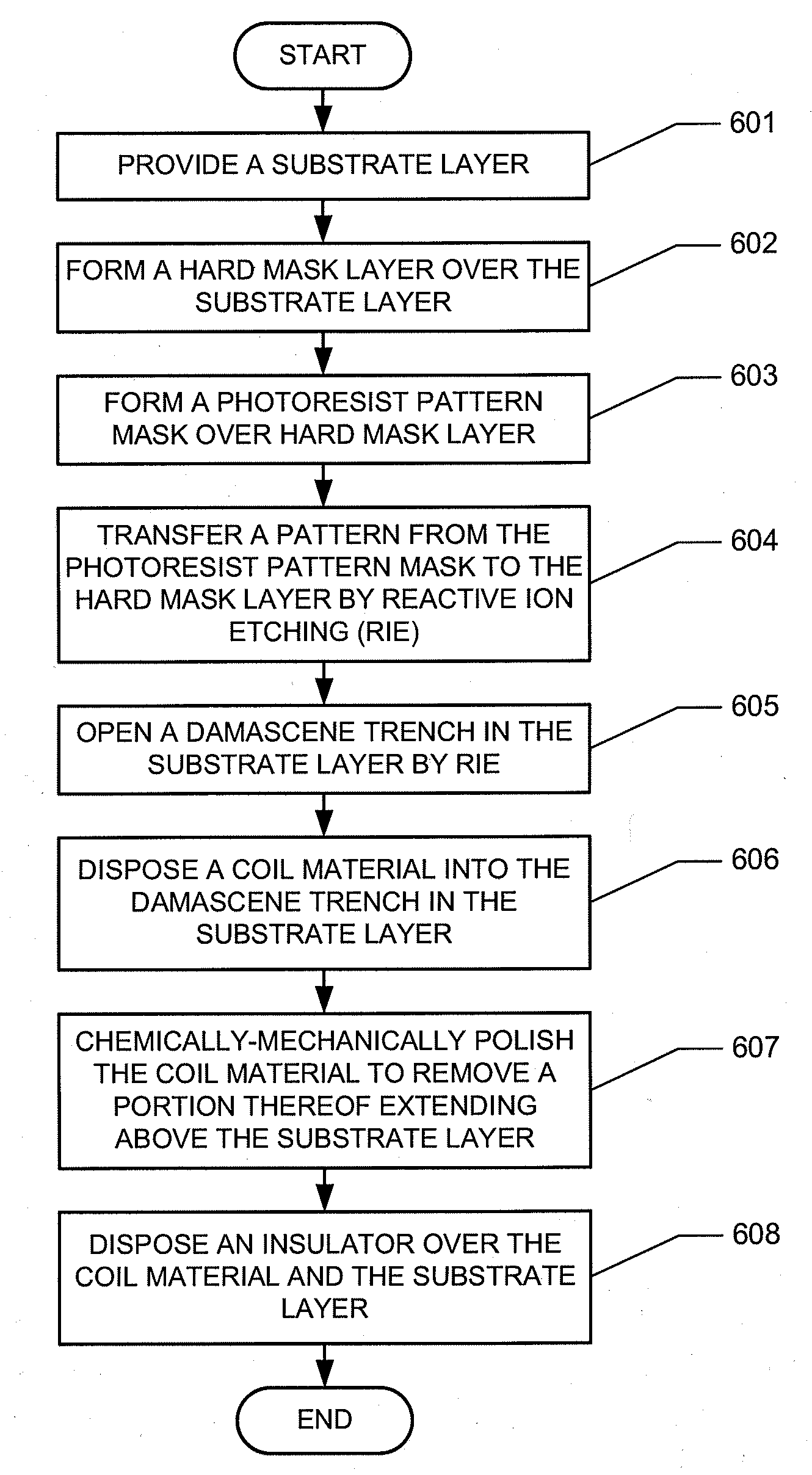
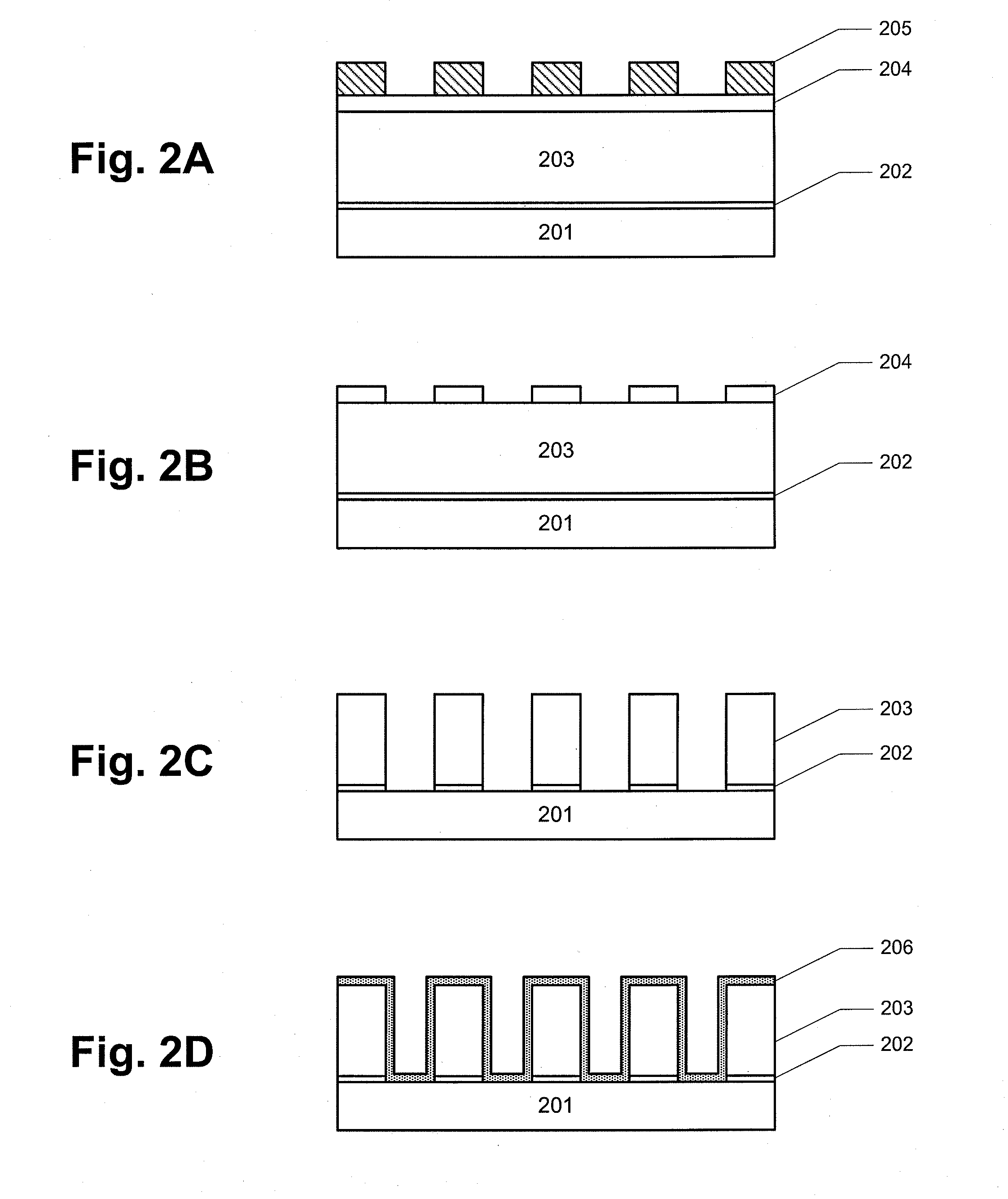
Damascene coil processes and structures
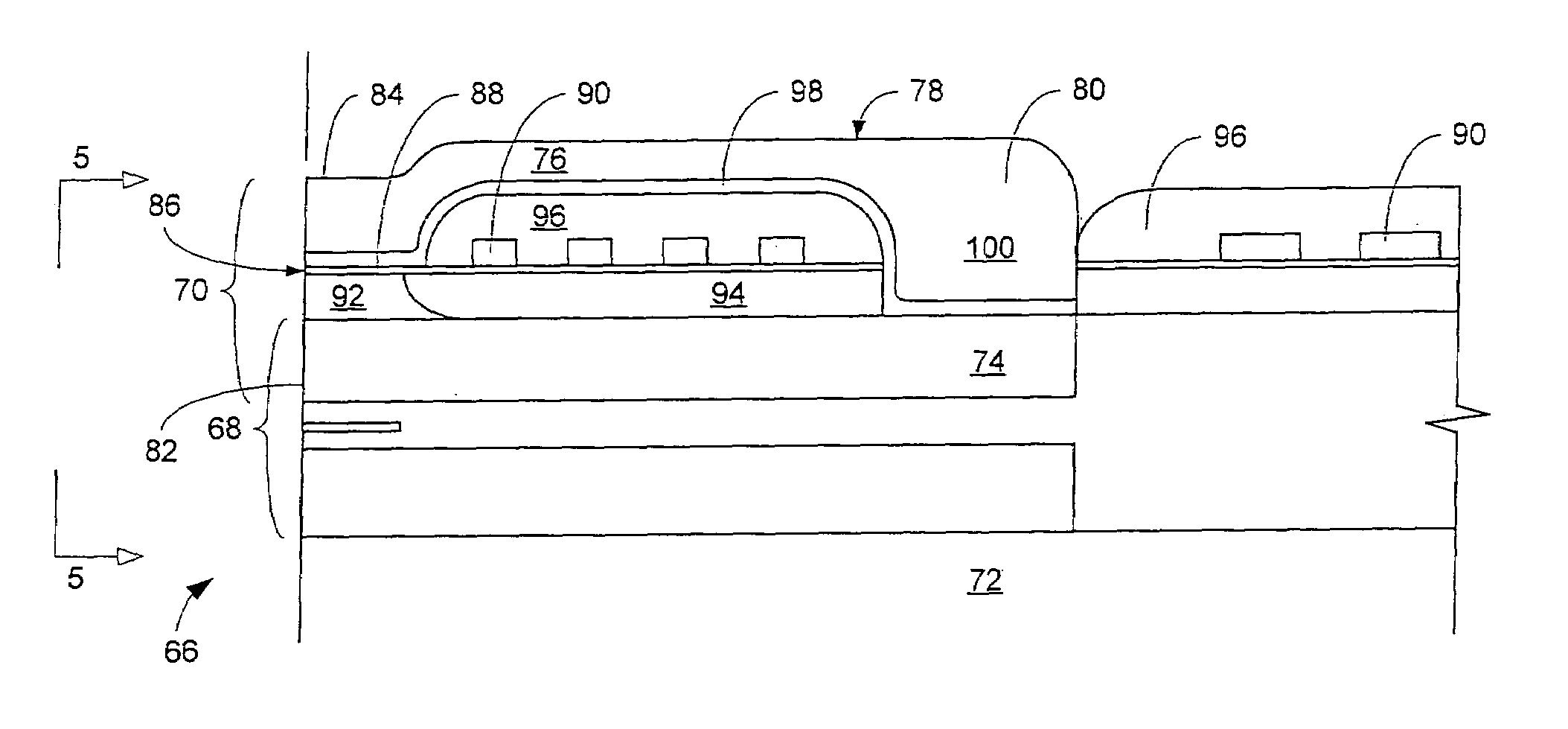
InactiveUS20100290157A1Eliminating insulation coverage problemEliminate needConstruction of head windingsDecorative surface effectsOptoelectronicsReactive-ion etching
A magnetic recording head is provided. The magnetic recording head comprises a write pole and a write coil structure configured to generate a magnetic field in the write pole. The write coil structure comprises a substrate layer and a coil material disposed within the substrate layer. The write coil structure is substantially free of photoresist. A method for forming a write coil structure is also provided. The method comprises the steps of providing a substrate layer, forming a photoresist pattern mask over the substrate layer, opening a damascene trench in the substrate layer by reactive ion etching, and disposing a coil material into the damascene trench in the substrate layer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
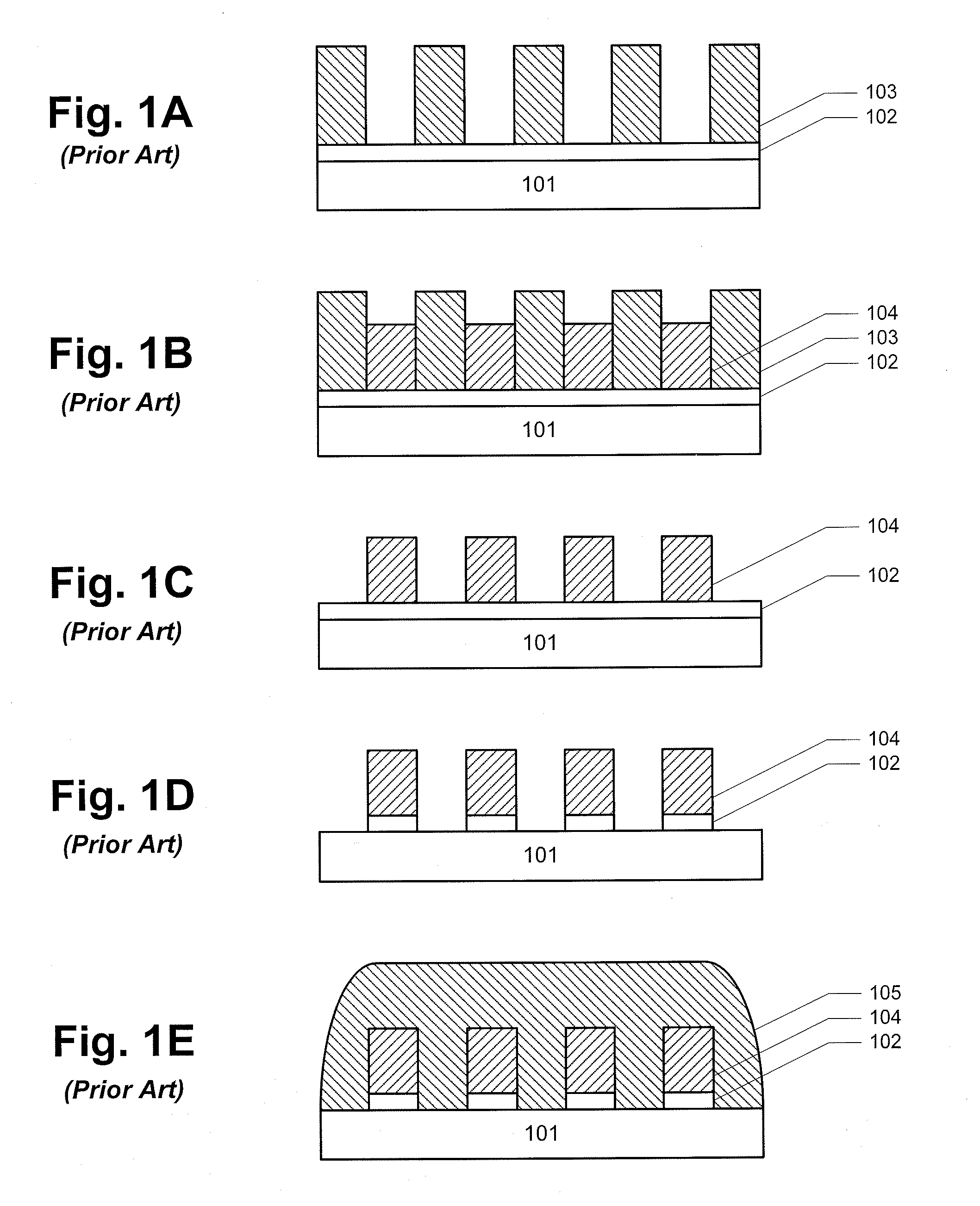
Methods of producing damascene main pole for perpendicular magnetic recording head
InactiveUS8262918B1Reduce defectsReduce complexityDecorative surface effectsRecord information storageMaterial removalEngineering
Methods of producing magnetic recording heads are disclosed. The methods can include providing a wafer comprising a substrate layer in which are disposed a plurality of damascene trenches. The method can further include depositing a pole material across the whole wafer, wherein the plurality of trenches are filled with the pole material. The methods can further include depositing a mask material over the pole material across the whole wafer. The methods can further include performing a first material removal process across the whole wafer to remove the mask material and a first portion of the pole material at a same material removal rate. The methods can further include performing a second material removal process to remove a second portion of the pole material above the substrate layer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
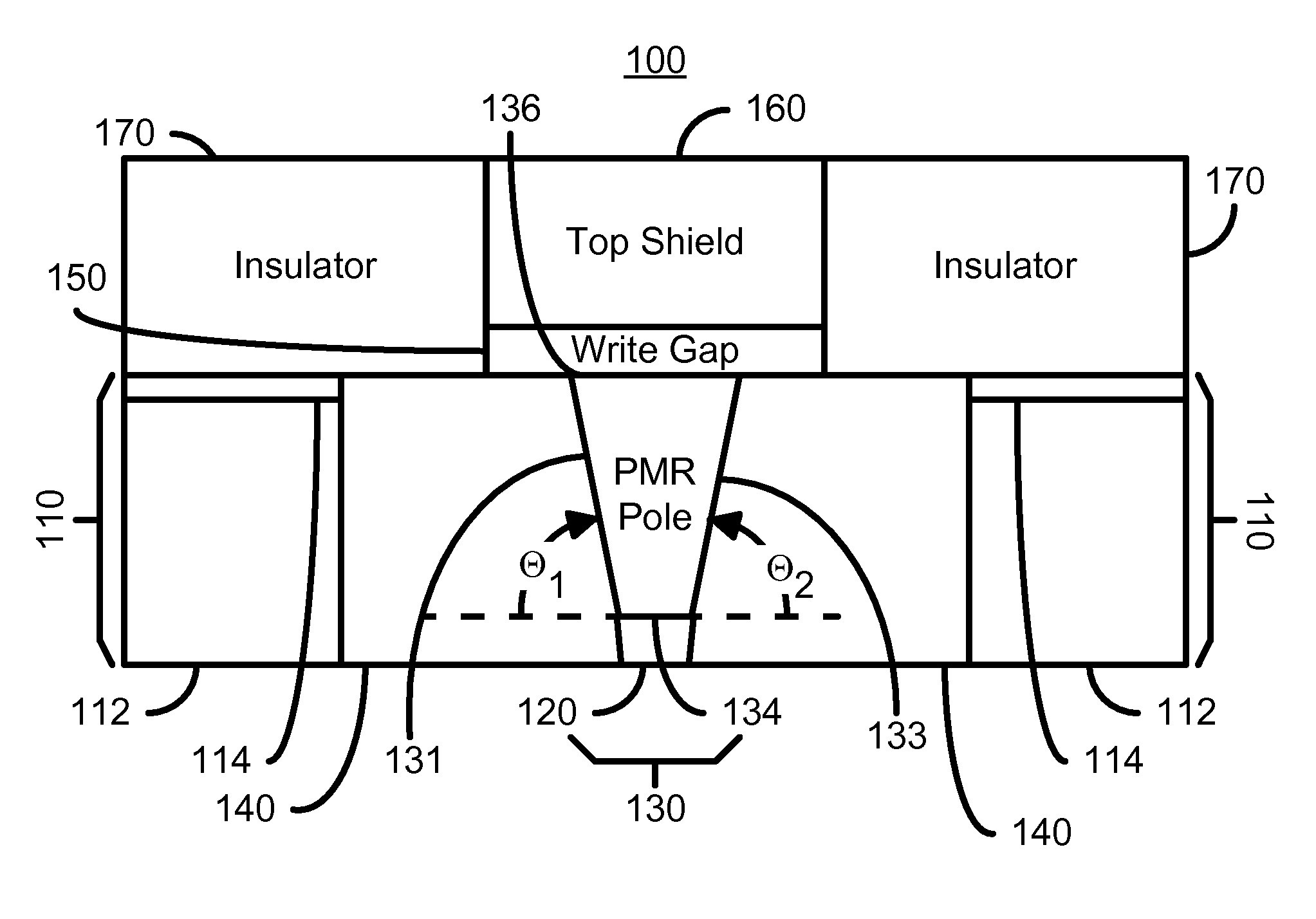
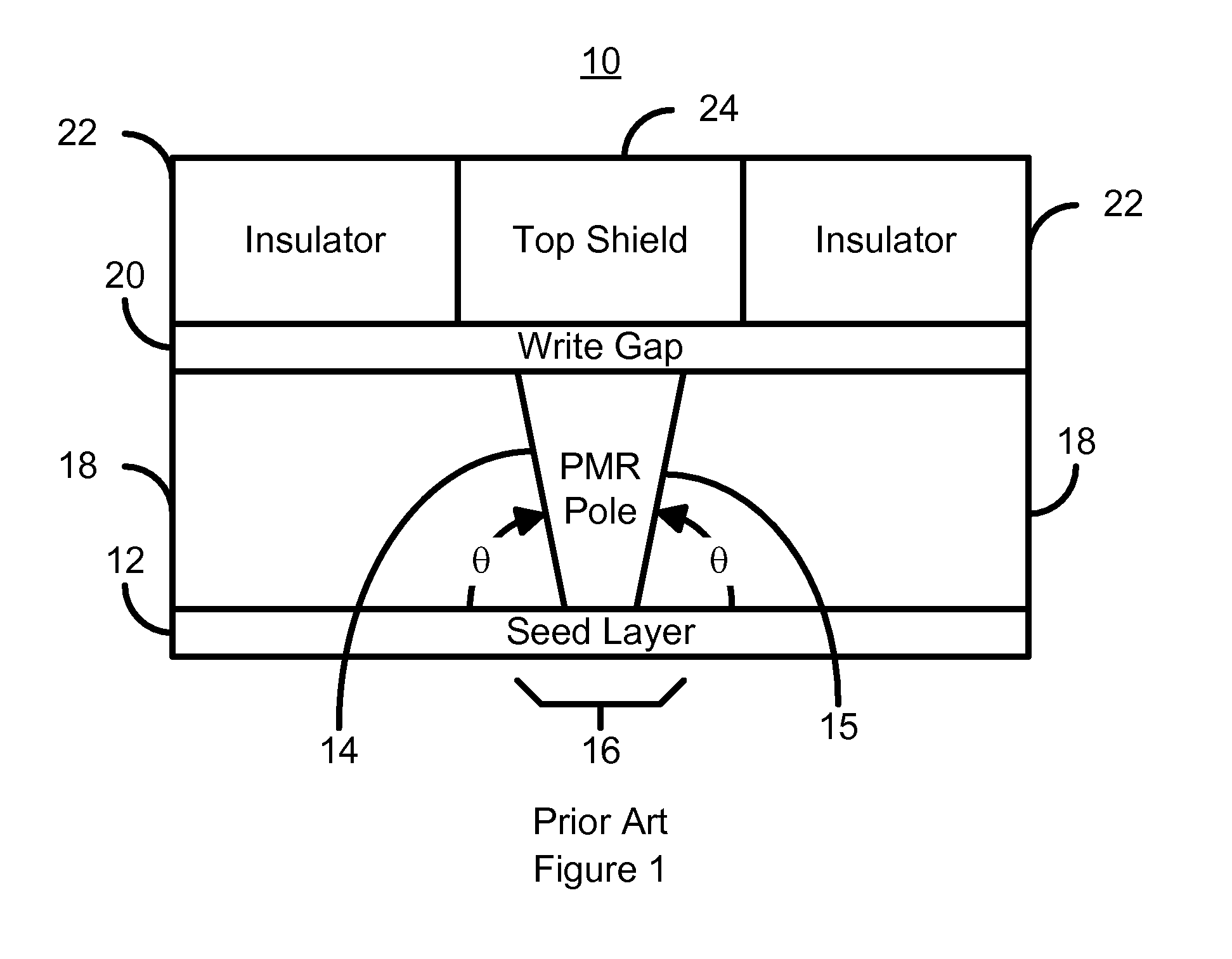
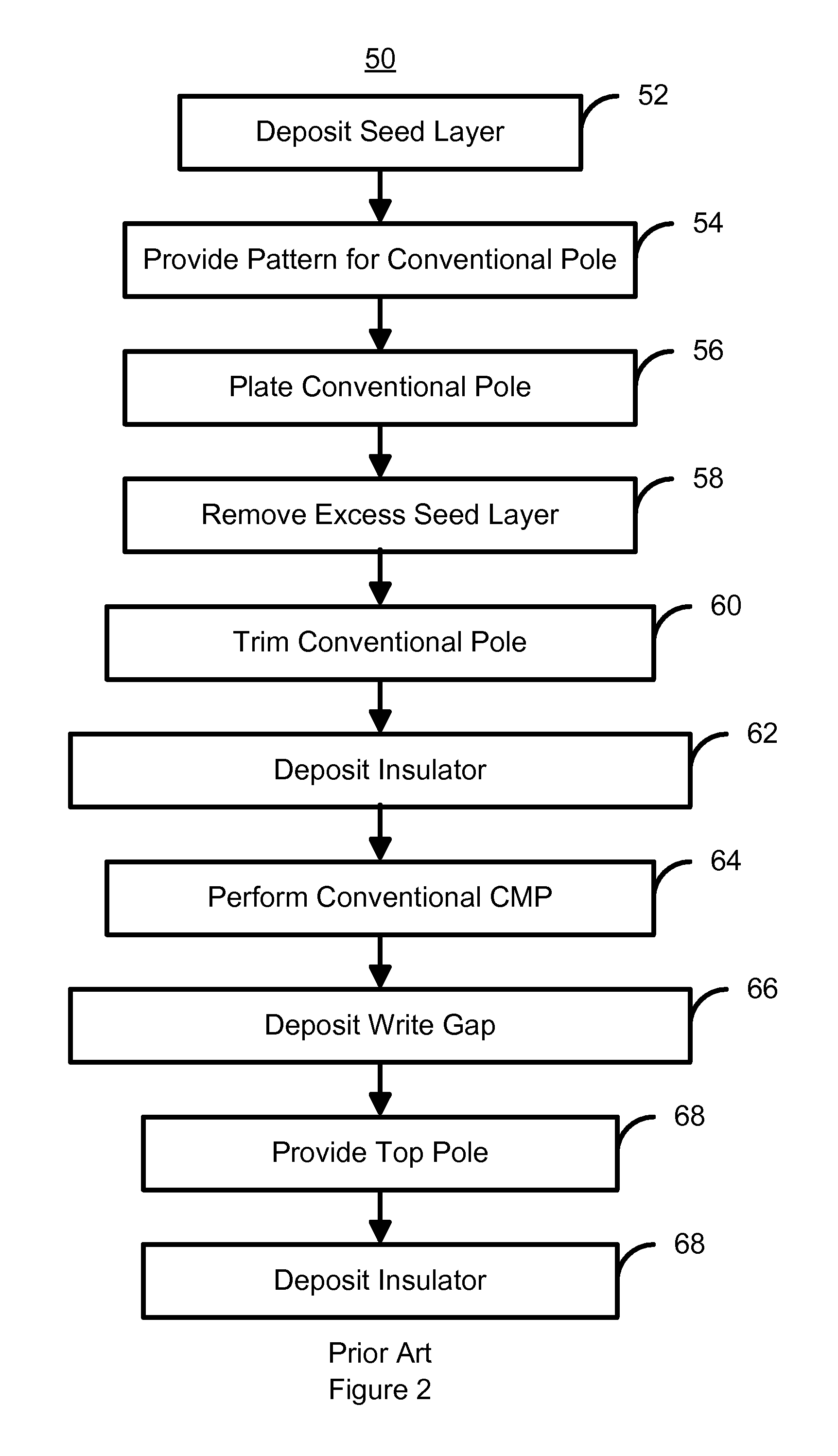
Perpendicular magnetic recording head having a pole tip formed with a CMP uniformity structure
InactiveUS8149536B1Record information storageHeads for perpendicular magnetisationsChemical-mechanical planarizationElectrical and Electronics engineering
A method and system for manufacturing a perpendicular magnetic recording head is disclosed. The method and system include providing a chemical mechanical planarization (CMP) uniformity structure having an aperture therein and forming a perpendicular magnetic recording pole within the aperture. The CMP uniformity structure may include a CMP barrier layer. The method and system further include fabricating an insulator after formation of the perpendicular magnetic recording pole and performing a CMP to remove a portion of the insulator, expose a portion of the perpendicular magnetic recording pole and planarize an exposed surface of the perpendicular magnetic recording head.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method for making high speed, high areal density inductive write structure
InactiveUS7007372B1Excellent magnetic propertiesIncrease coverageDecorative surface effectsVacuum evaporation coatingMagnetic mediaMagnetic poles
An inductive write element is disclosed for use in a magnetic data recording system. The write element provides increased data rate and data density capabilities through improved magnetic flux flow through the element. The write element includes a magnetic yoke constructed of first and second magnetic poles. The first pole includes a pedestal constructed of a high magnetic moment (high Bsat) material, which is preferably FeRhN nanocrystalline films with lamination layers of CoZrCr. The second pole includes a thin inner layer of high Bsat material (also preferably FeRhN nanocrystalline films with lamination layers of CoZrCr), the remainder being constructed of a magnetic material capable of being electroplated, such as a Ni—Fe alloy. An electrically conductive coil passes through the yoke between the first and second poles to induce a magnetic flux in the yoke when an electrical current is caused to flow through the coil. Magnetic flux in the yoke produces a fringing field at a write gap whereby a signal can be imparted onto a magnetic medium passing thereby.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
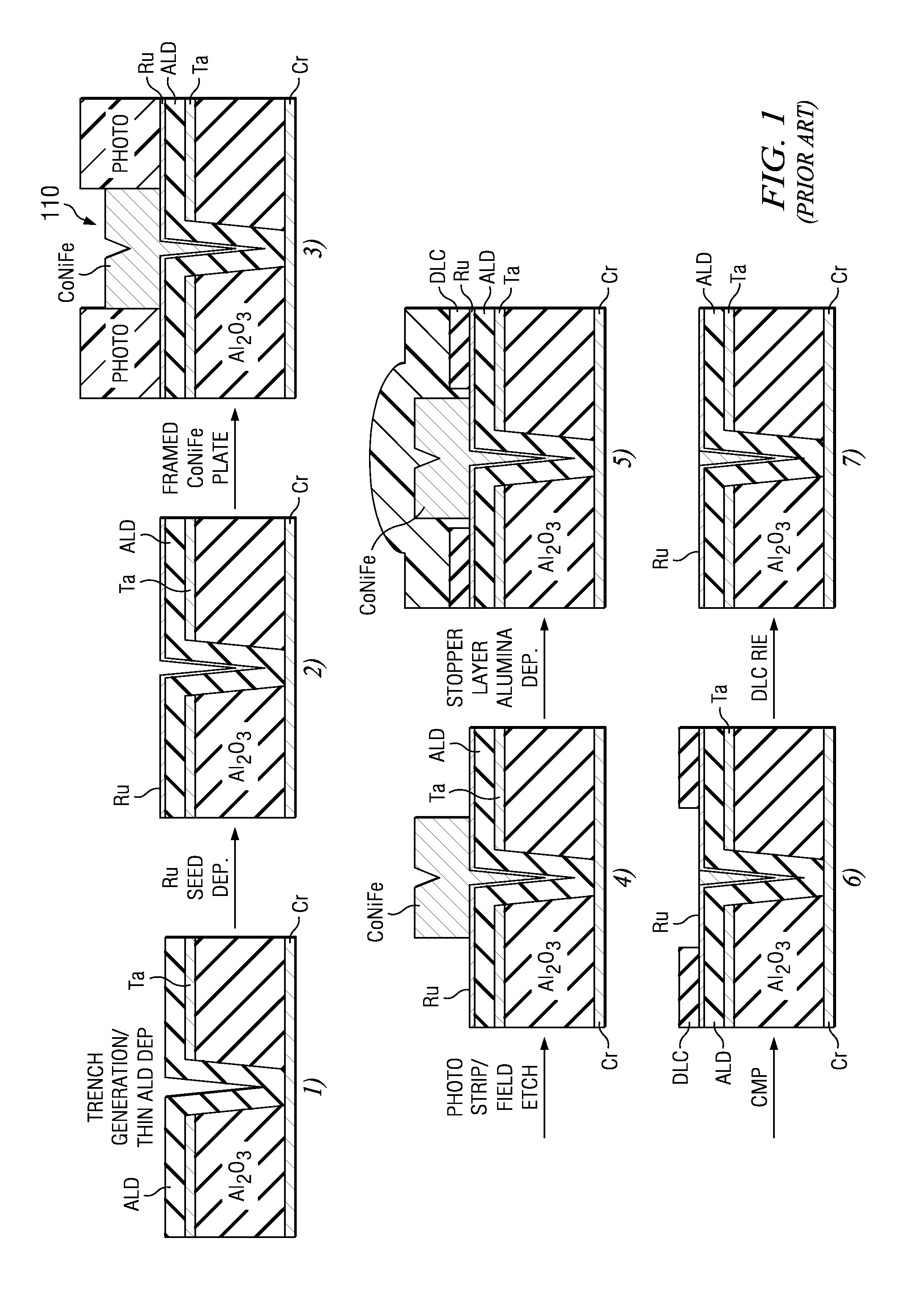
Magnetic recording head with high saturation magnetic flux density CoNiFe thin film composition
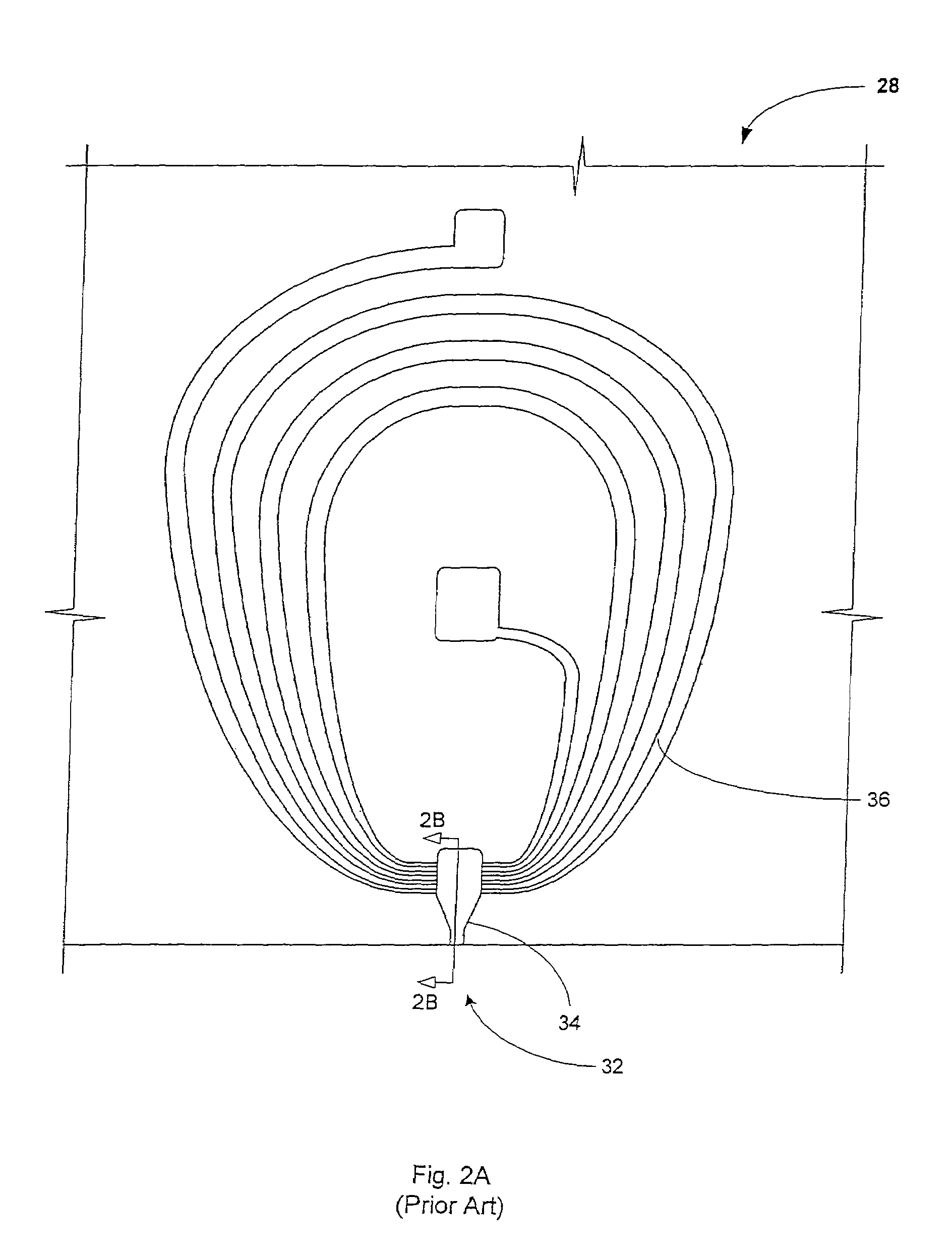
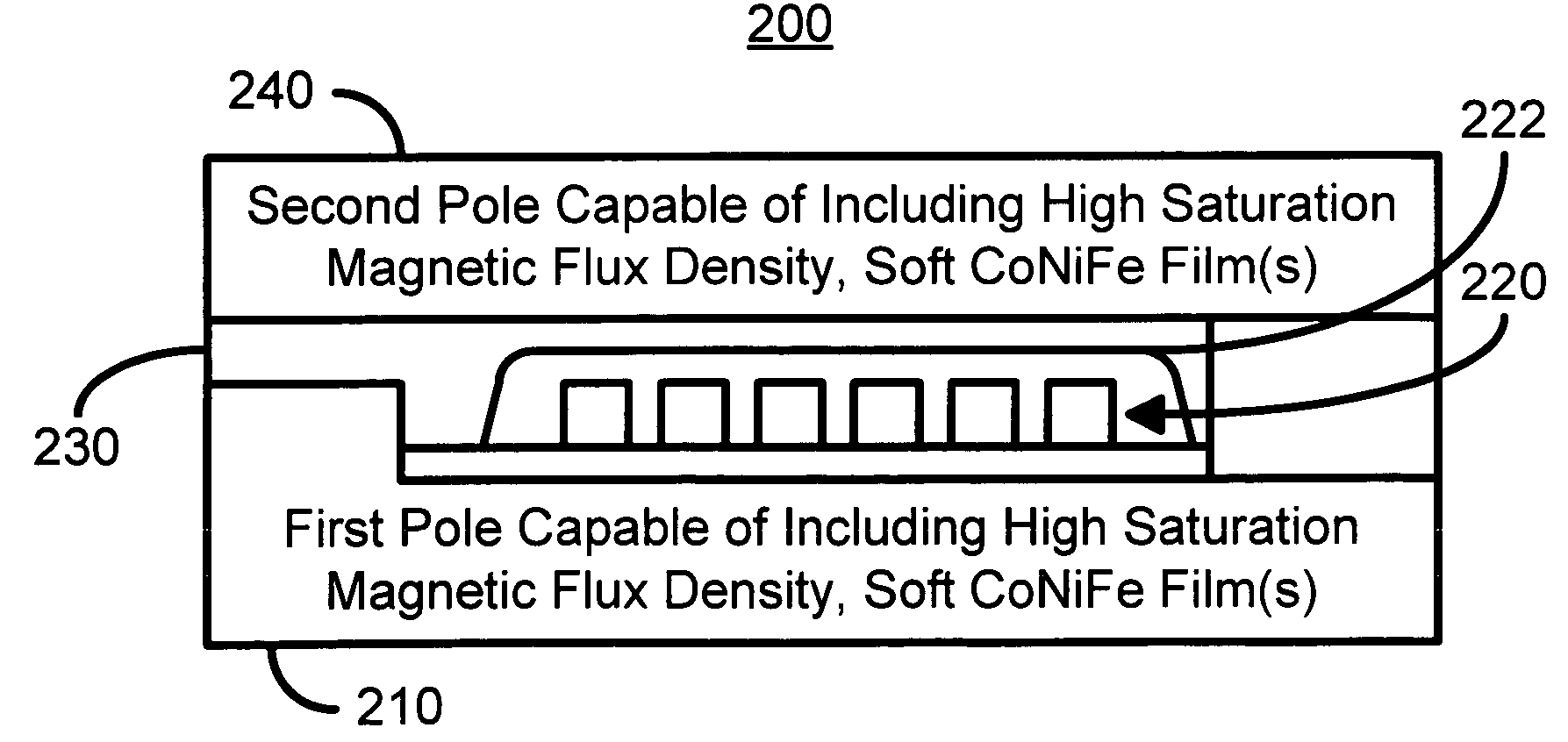
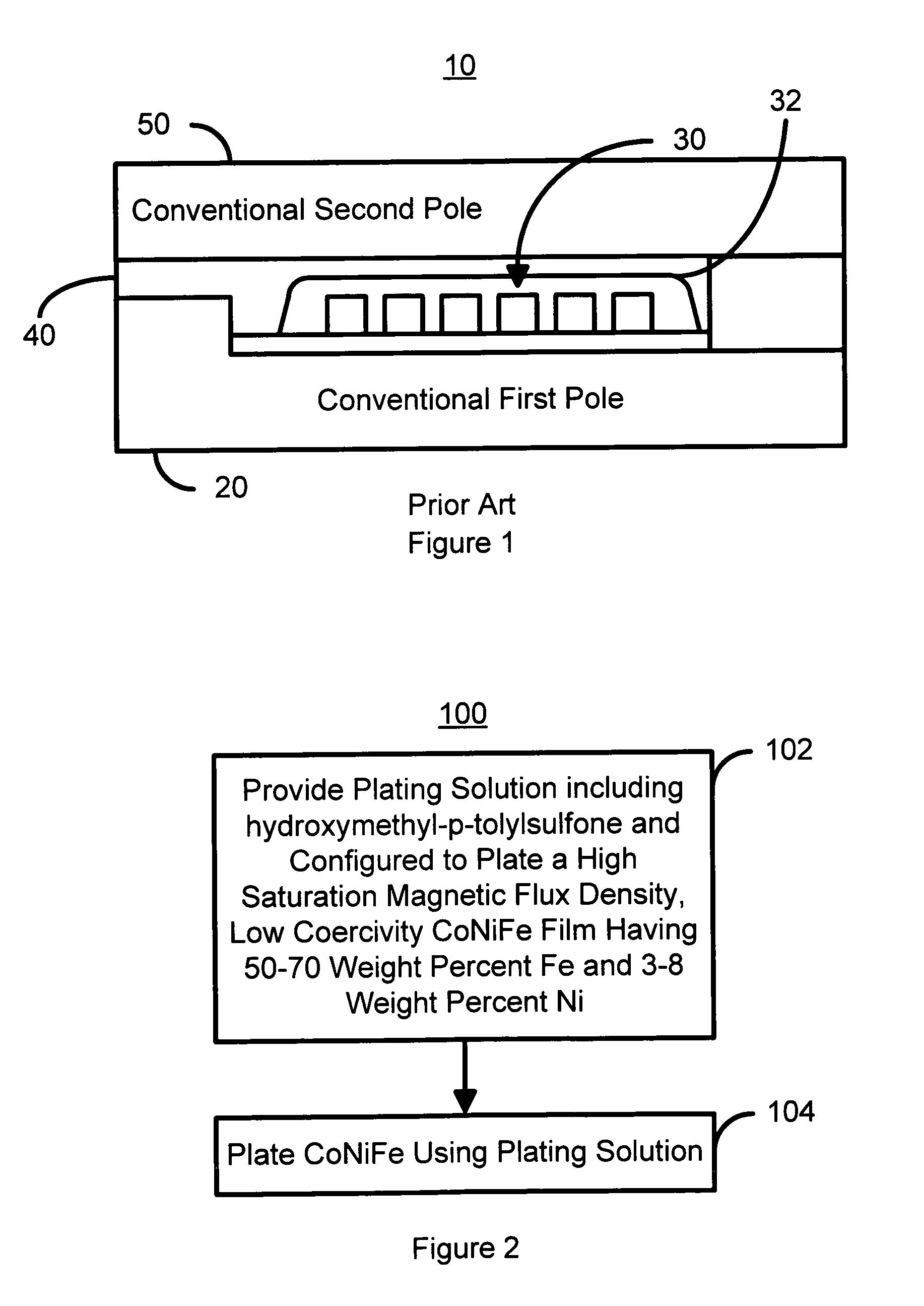
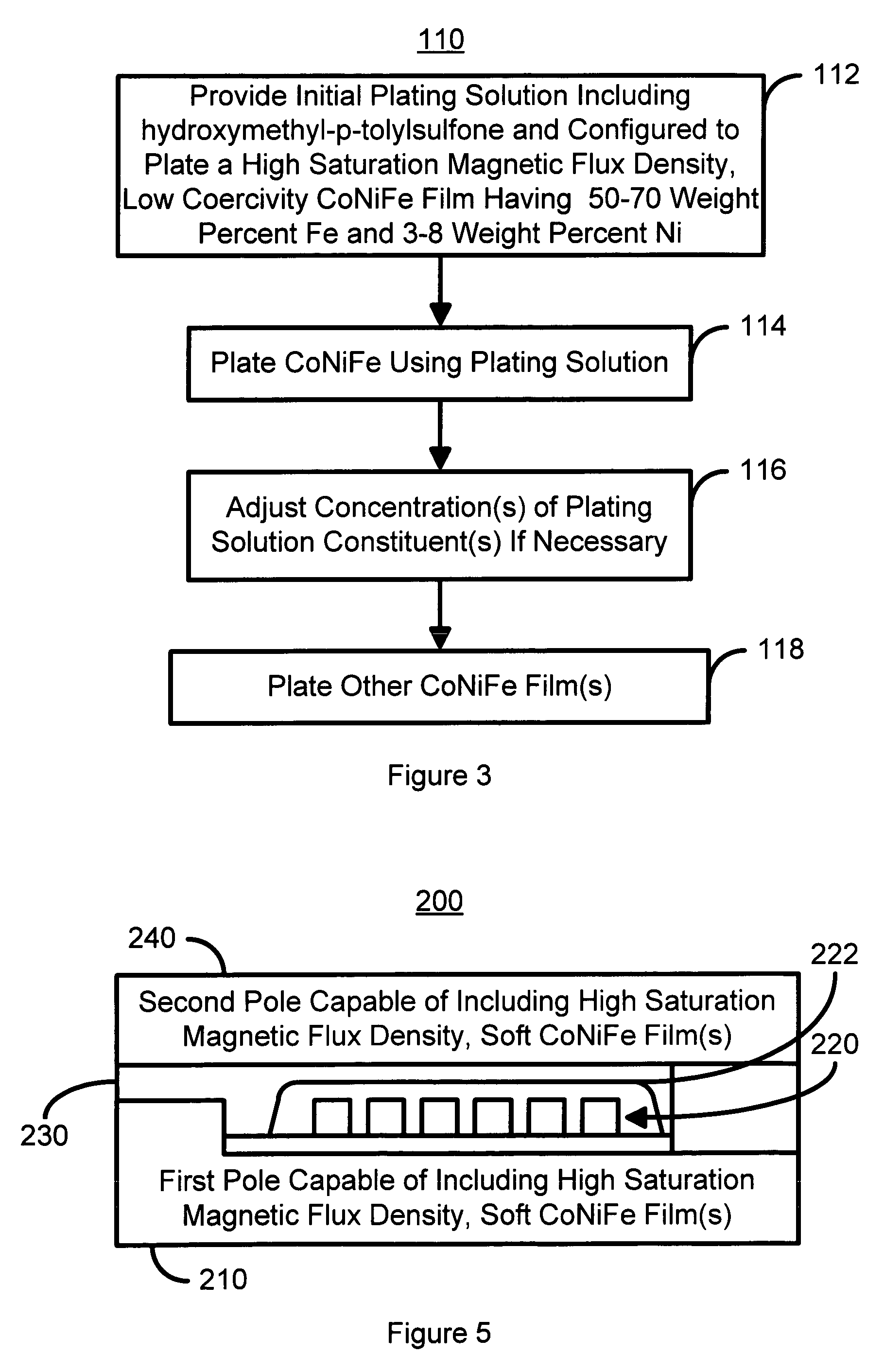
InactiveUS7333295B1Suitable for useHigh saturationHeads using thin filmsRecord information storageElectroplatingMagnetism
A method and system for plating CoNiFe is disclosed. The method and system include providing a plating solution including hydroxymethyl-p-tolylsulfone and plating the CoNiFe film on a substrate in the plating solution. The plating solution is configured to provide a CoNiFe film having a high saturation magnetic flux density and having a composition of 50-70 weight percent of Fe and 3-8 weight percent of Ni. In another aspect, the method and system include plating at least a portion of a first and / or second pole of a write head using the plating solution including hydroxymethyl-p-tolylsulfone and configured to plate the CoNiFe film having a high saturation magnetic flux density and a composition of 50-70 weight percent of Fe and 3-8 weight percent of Ni.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
System and method for transferring data to and from a magnetic shift register with a shiftable data column
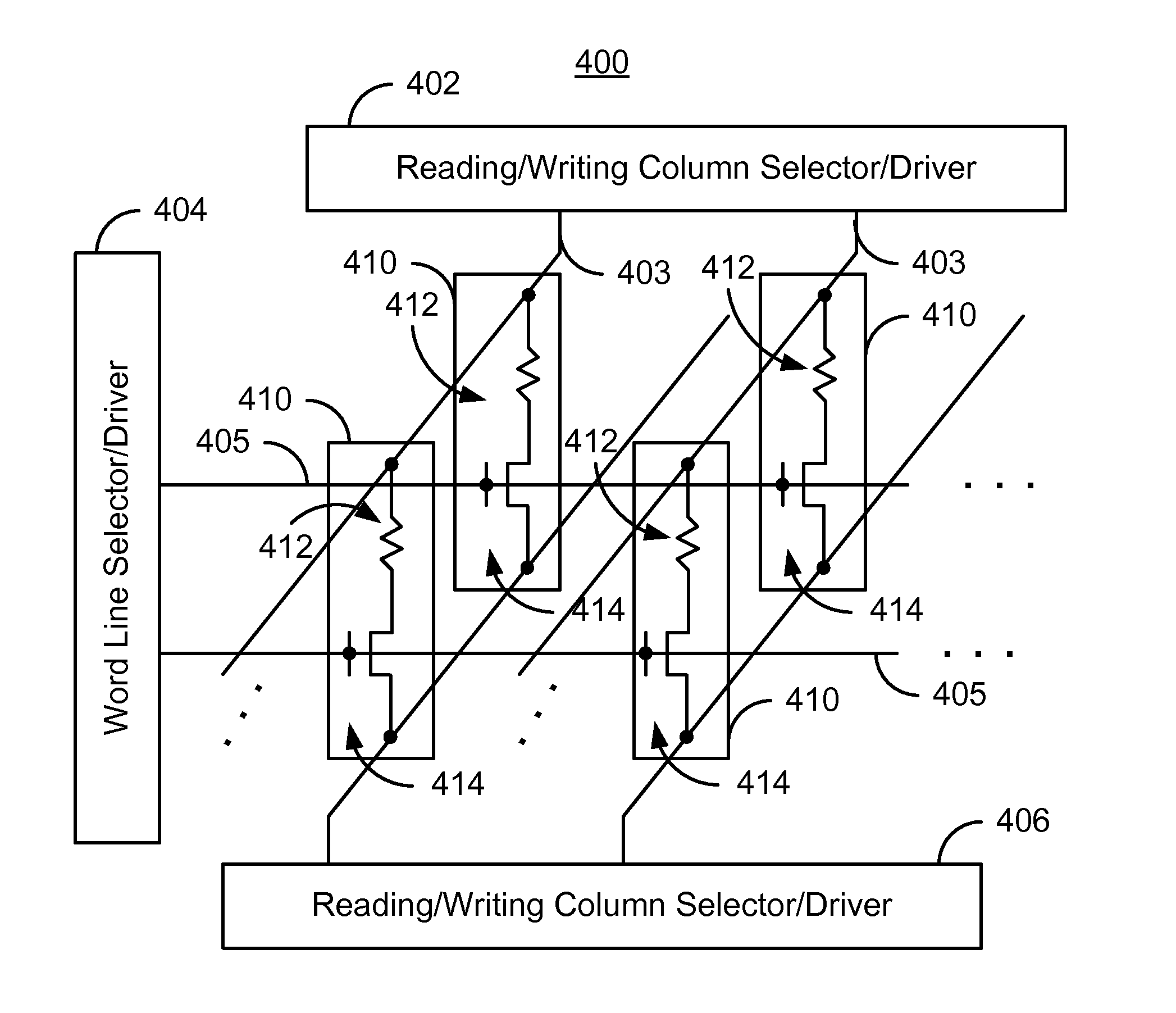
InactiveUS20060120132A1Magnitude fringing fieldEasy to operateDigital storageShift registerData storing
A magnetic shift register utilizes a data column comprising a thin wire of magnetic material. A writing element selectively changes the direction of the magnetic moment in the magnetic domains to write the data to the data column. Associated with each domain wall are large magnetic fringing fields concentrated in a very small space. These magnetic fringing fields write to and read from the magnetic shift register. When the domain wall is moved close to another magnetic material, the fringing fields change the direction of the magnetic moment in the magnetic material, effectively “writing” to the magnetic material. A reading element similar to a tunneling junction comprises a free layer and a pinned layer of magnetic material. Fringing fields change the direction of the magnetic moment in the free layer with respect to the pinned layer, changing electrical resistance of the reading element and “reading” data stored in the magnetic shift register.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Inductive write head having high magnetic moment poles and low magnetic moment thin layer in the back gap, and methods for making
InactiveUS6989962B1Avoid corrosionNegligible effectHeads using thin filmsRecord information storageMagnetic polesThin layer
The present invention provides a write element for use in magnetic data recording system such as a computer disk drive. The write head utilizes the advantageous properties of high magnetic moments while overcoming the corrosion problems engendered by such materials. The write element includes a magnetic yoke constructed of first and second magnetic poles joined to one another at a back gap. While the majority of the poles are constructed of a high magnetic moment material a layer of relatively low magnetic moment material is provided on the first pole at the back gap portion of the first pole. The relatively low magnetic moment material prevents corrosion of the first pole during subsequent manufacturing of the write head. An electrically conductive coil passes through the magnetic yoke and is insulated there from. By passing an electrical current through the electrical coil, a magnetic flux is generated in the yoke. This magnetic flux then generates a magnetic fringing field in at a write gap of the yoke. The fringing field imparts magnetic data onto a recording medium passing thereby.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
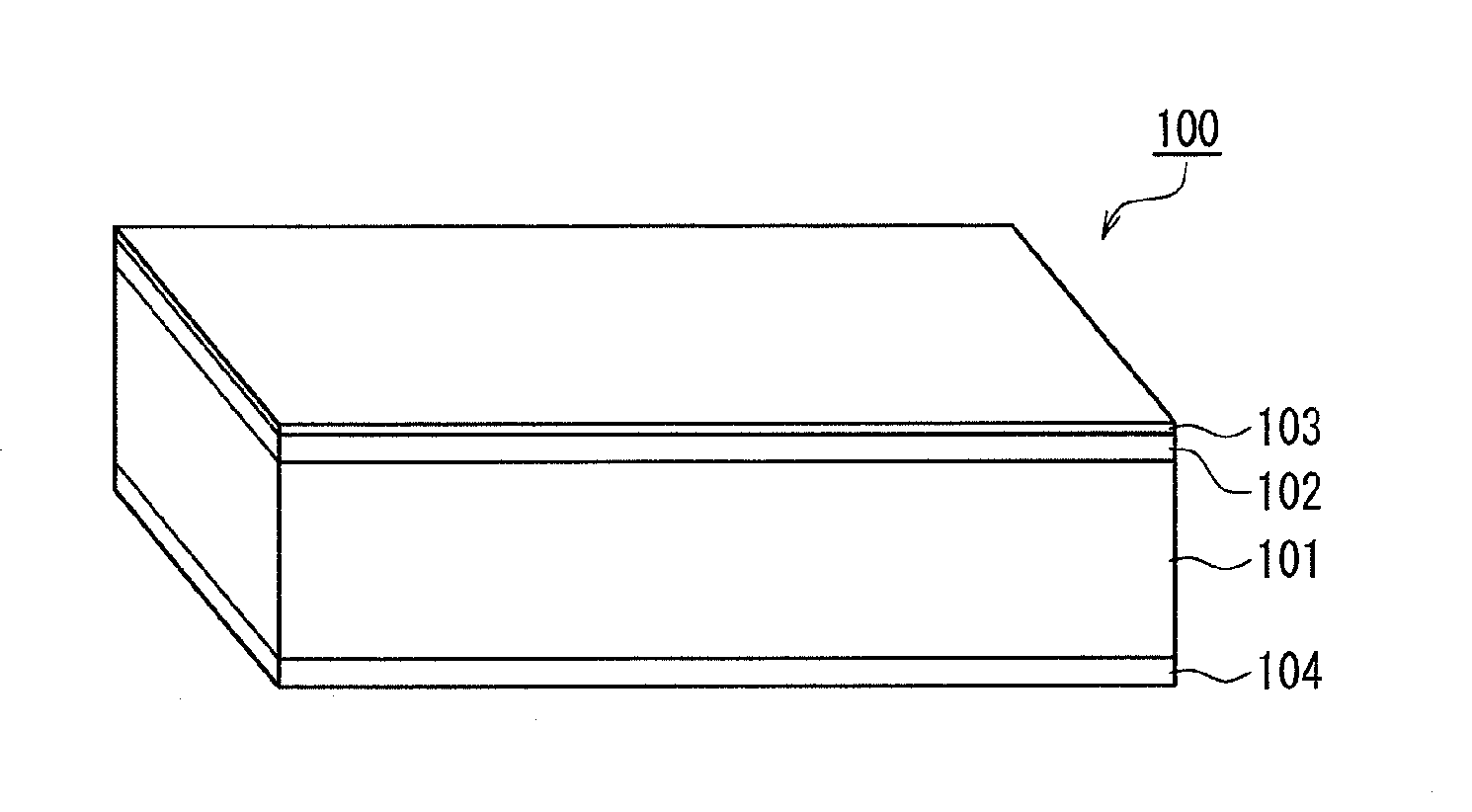
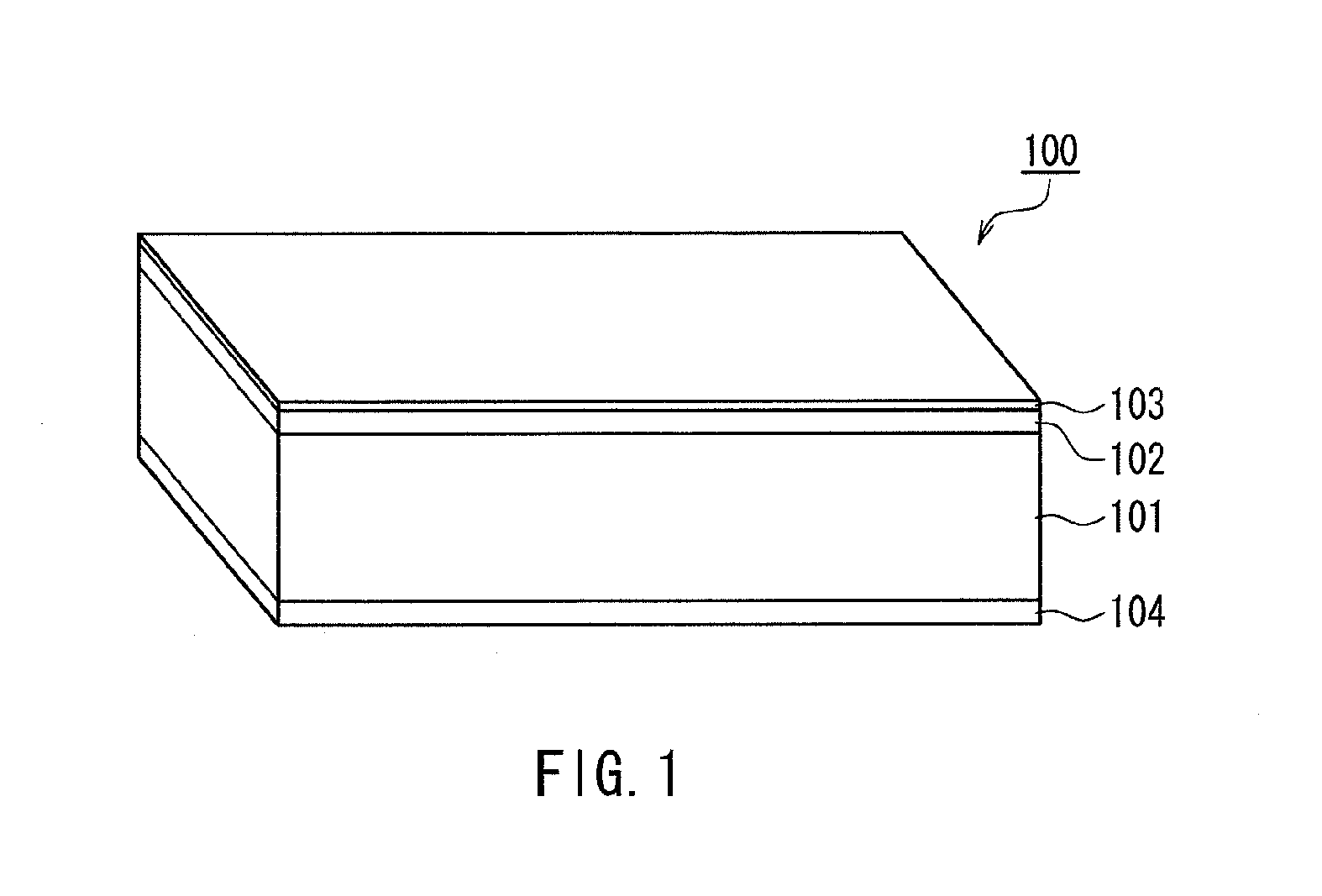
Magnetic recording medium
ActiveUS20120045664A1Superior recording/reproducing characteristicSuperior characteristic transportMaterials with ironRecord information storageNon magneticHexane
A magnetic recording medium of the present invention is a magnetic recording medium including a non-magnetic substrate; a non-magnetic layer that is formed on one of principal surfaces of the non-magnetic substrate and contains a non-magnetic powder, a binder, and a lubricant; and a magnetic layer that is formed on a principal surface of the non-magnetic layer opposite to the non-magnetic substrate and contains a magnetic powder and a binder. The magnetic powder has an average particle size between 10 inn and 35 nm inclusive. The lubricant is migratable to the magnetic layer and forms a lubricant layer on a surface of the magnetic layer when a pressure is applied to the magnetic layer. When spacing of the surface of the magnetic layer before and after washing the lubricant with n-hexane is measured with a TSA (Tape Spacing Analyzer), the value of the spacing after washing is 3 to 10 nm, and the value of the spacing before washing is 1 to 5 nm smaller than the value of the spacing after washing.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com