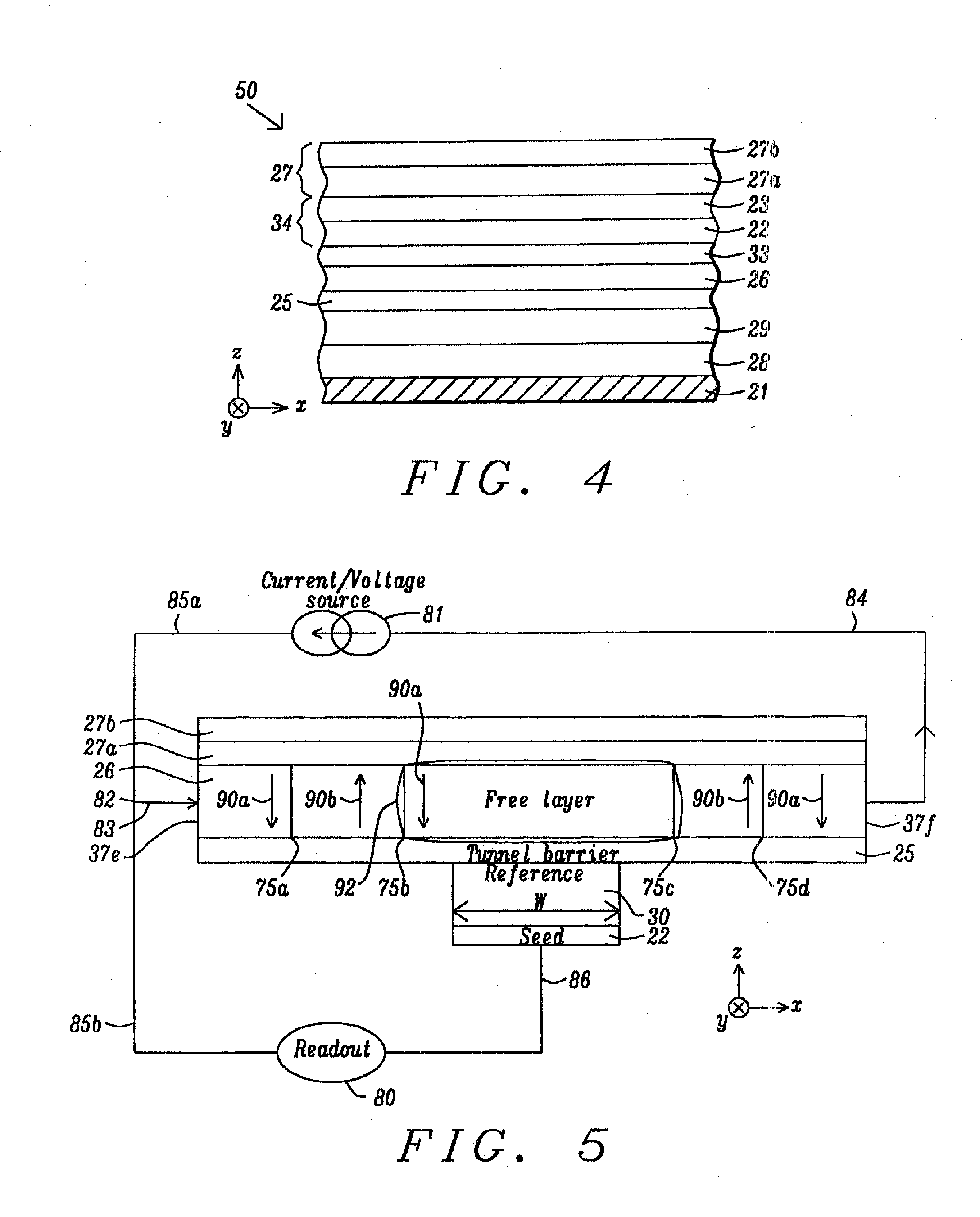
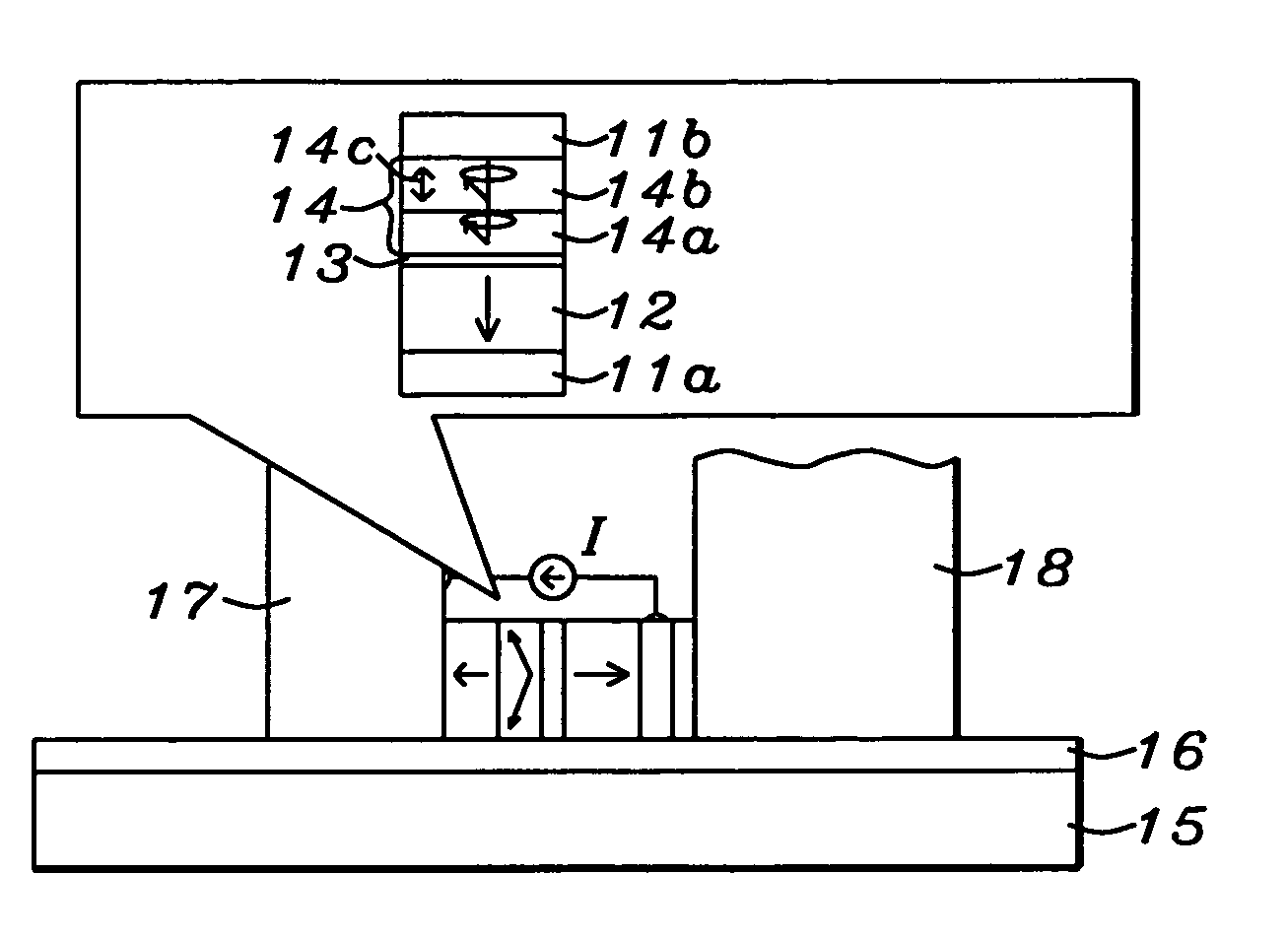
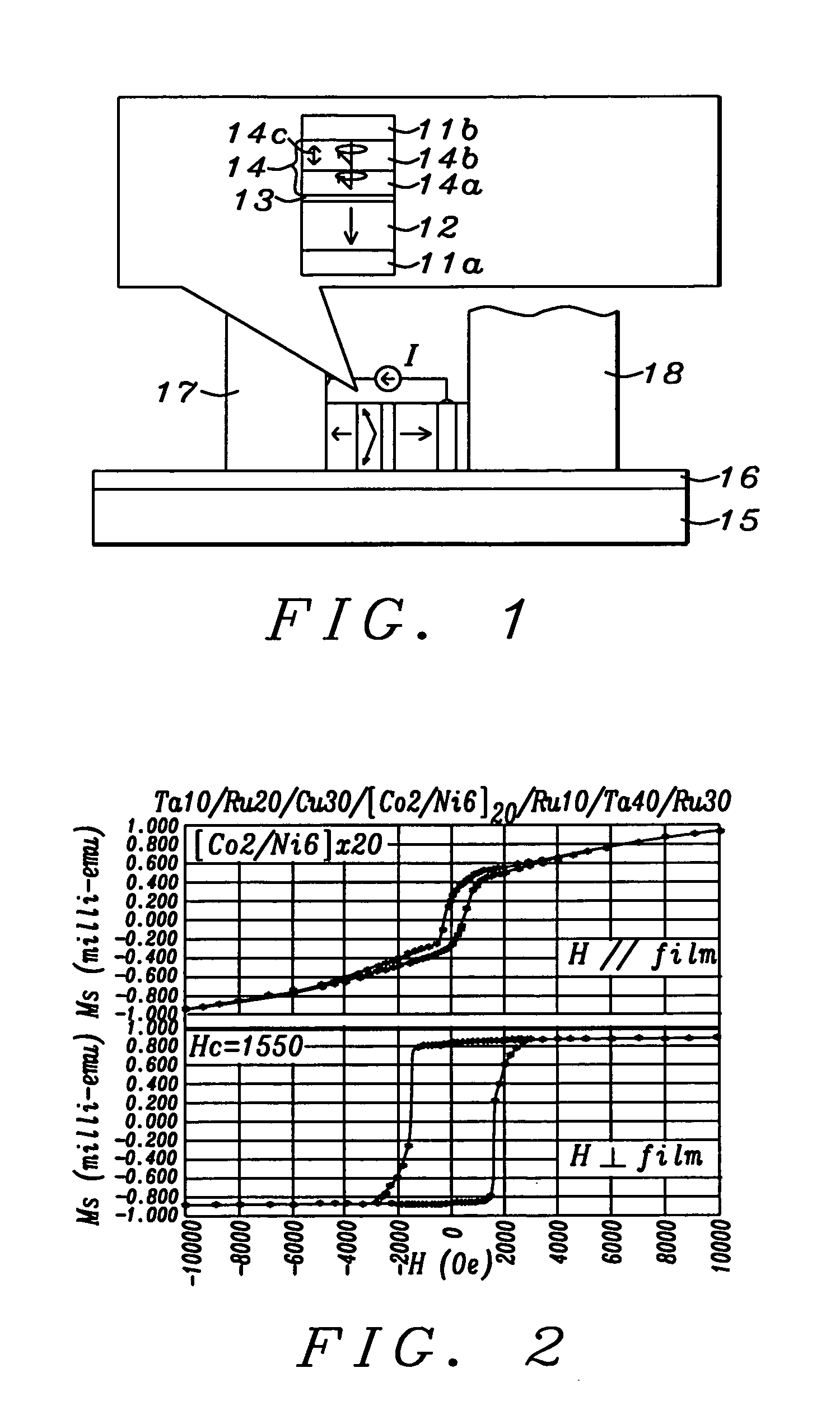
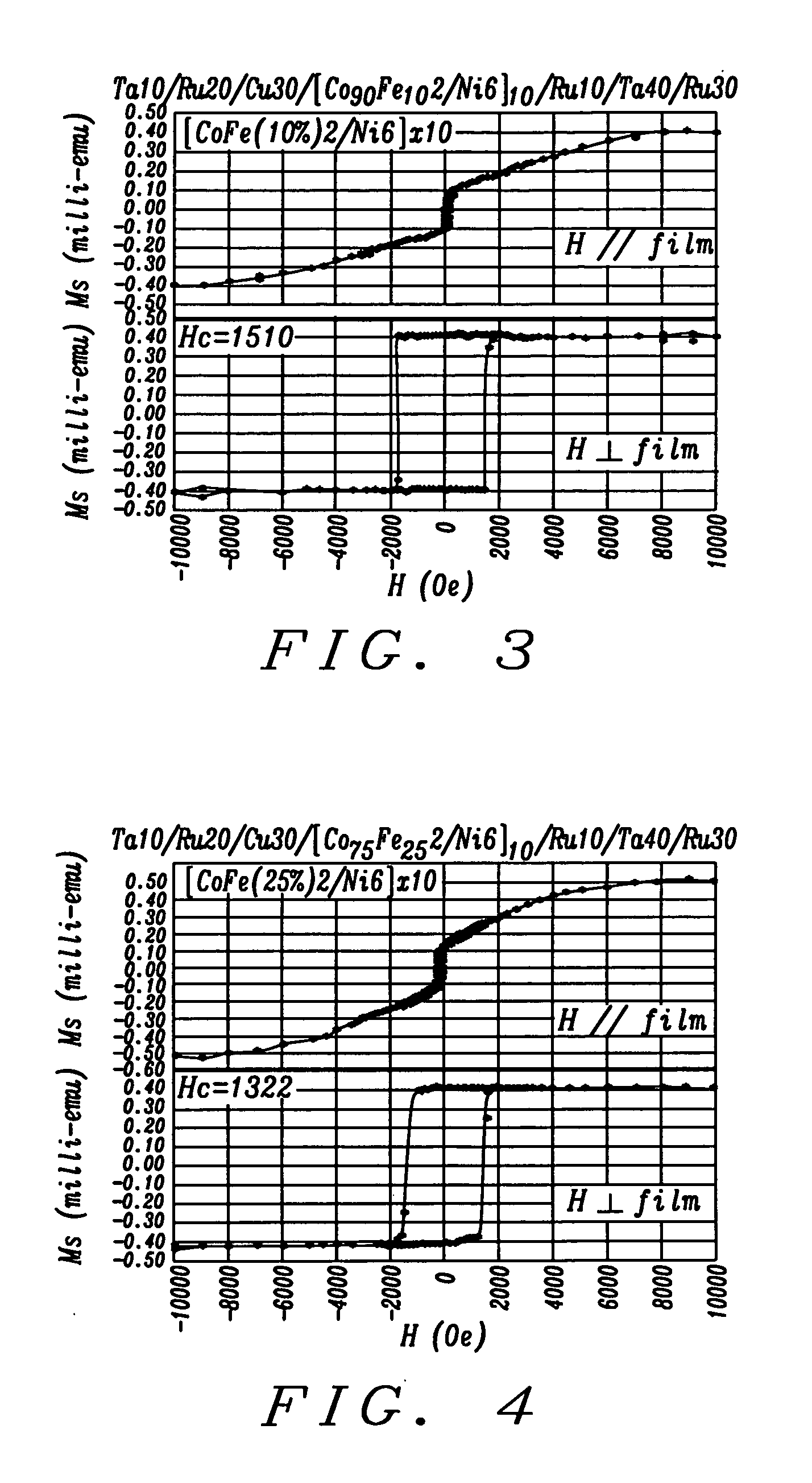
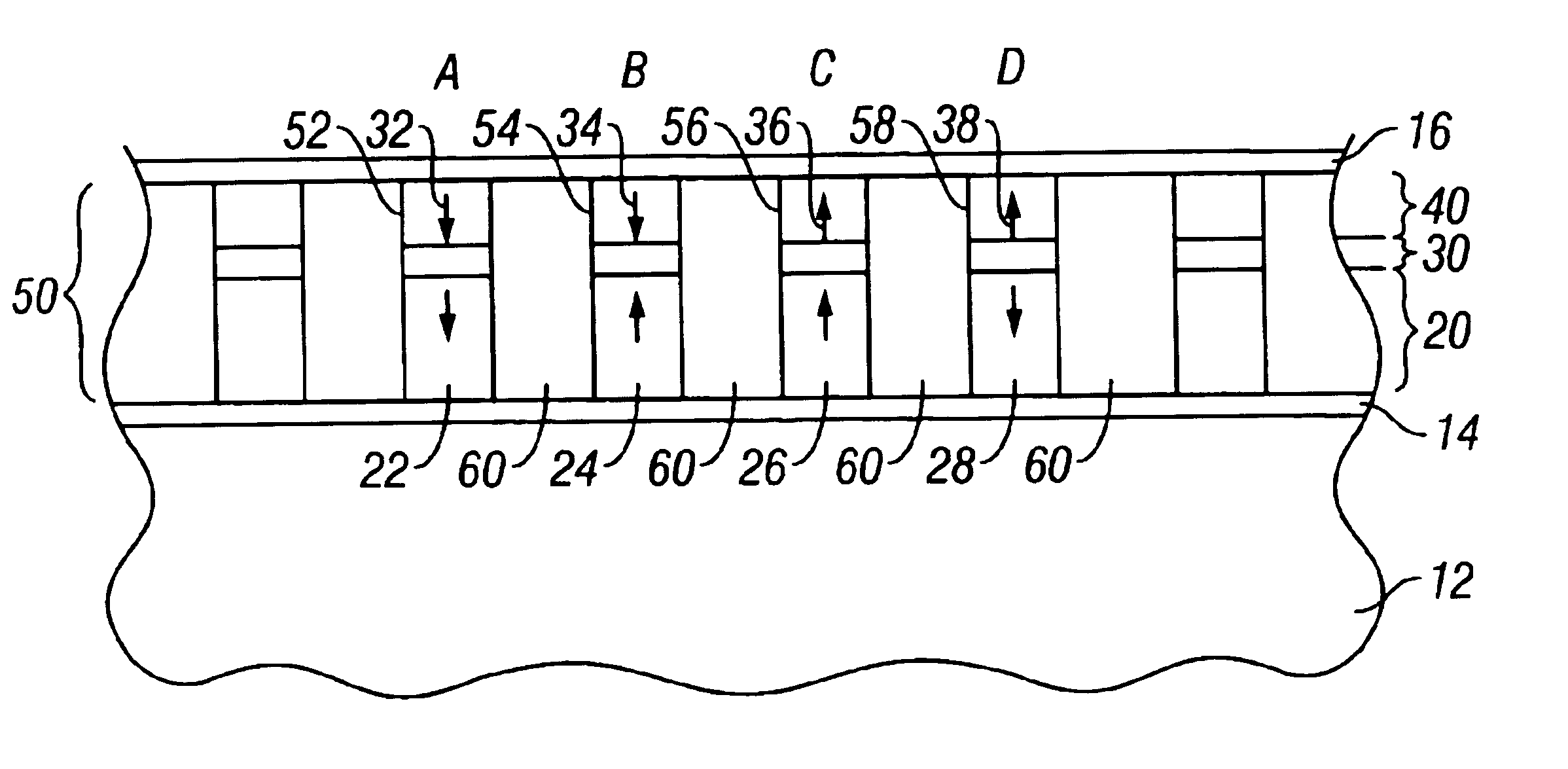
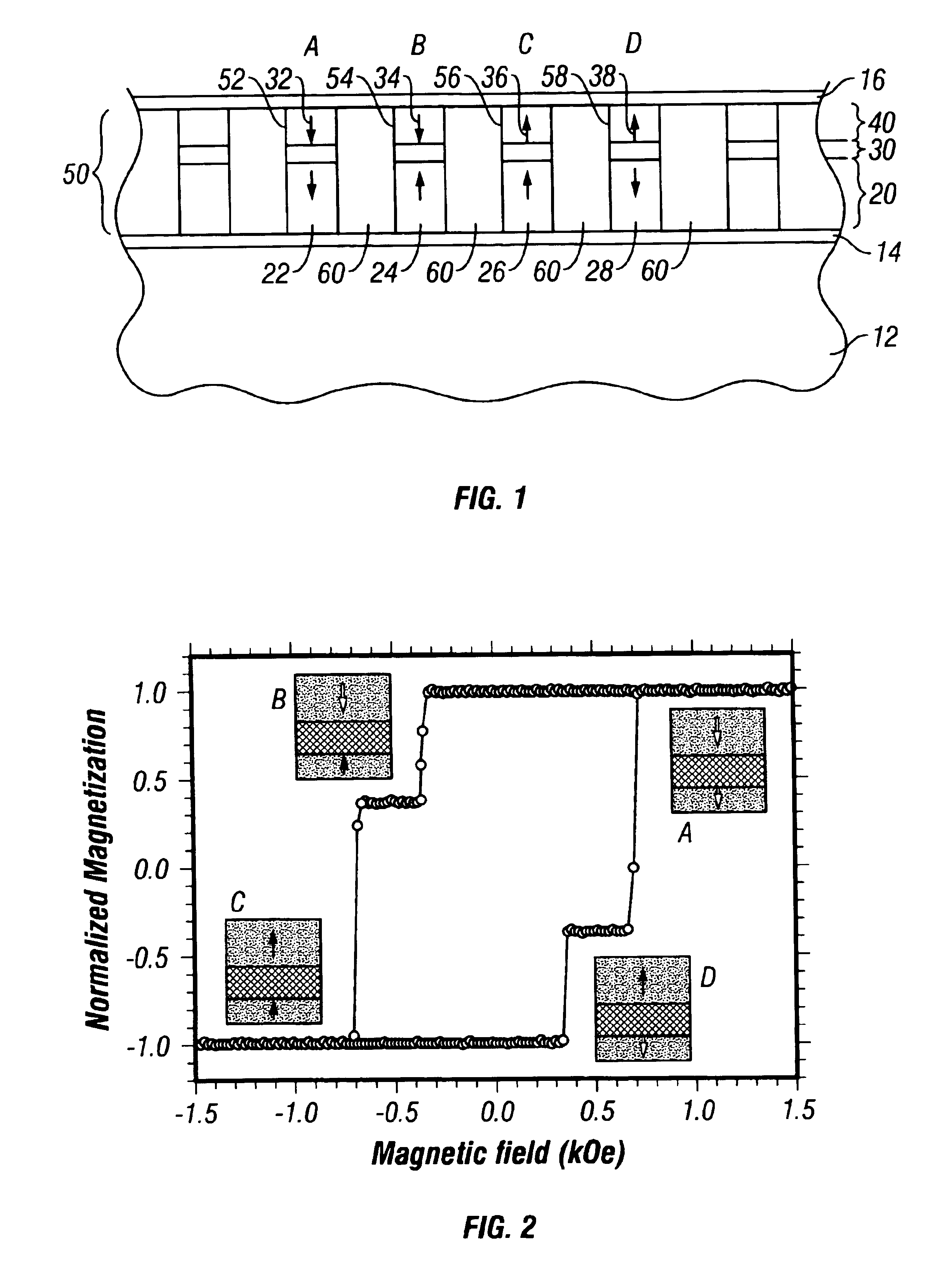
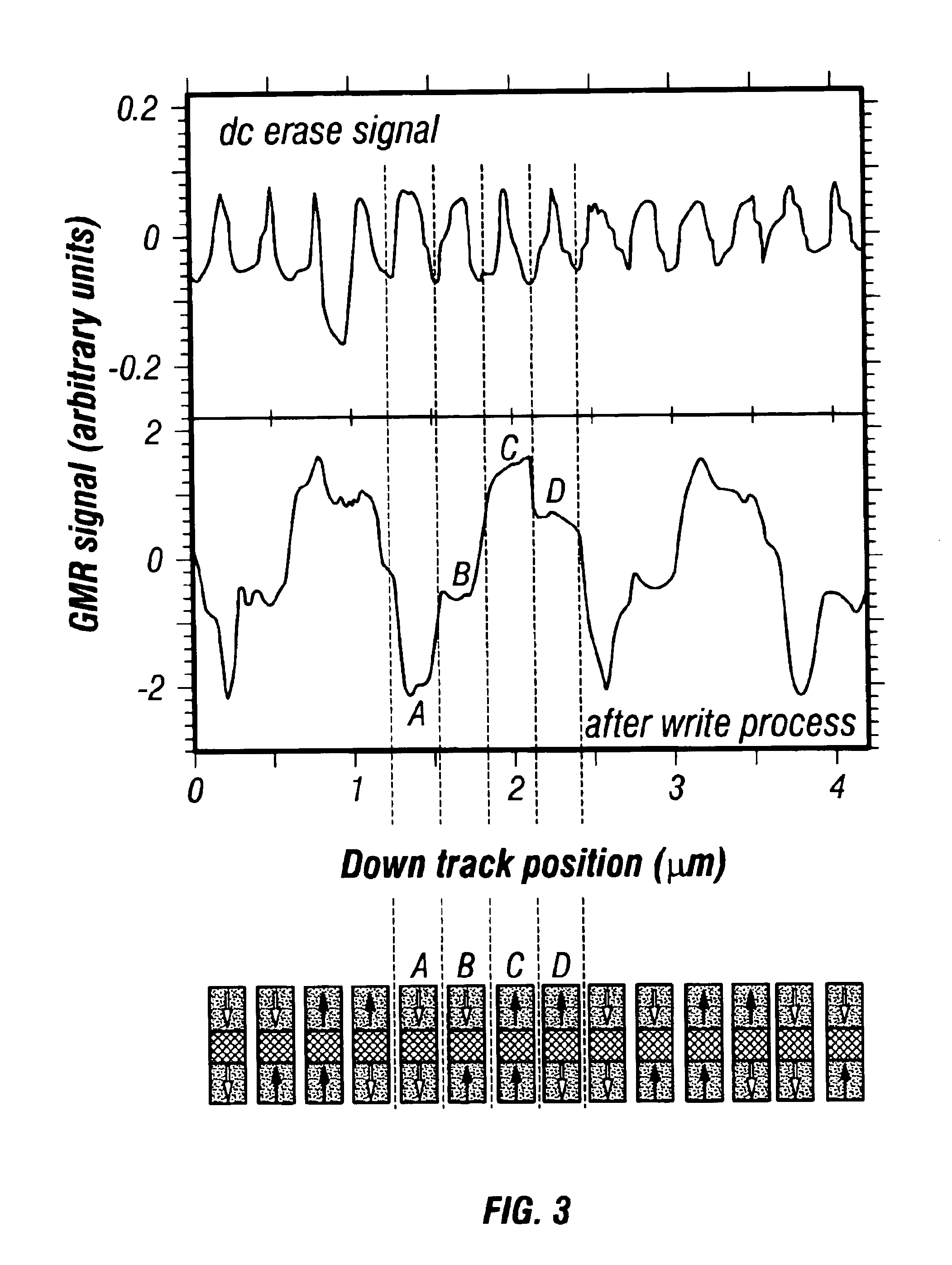
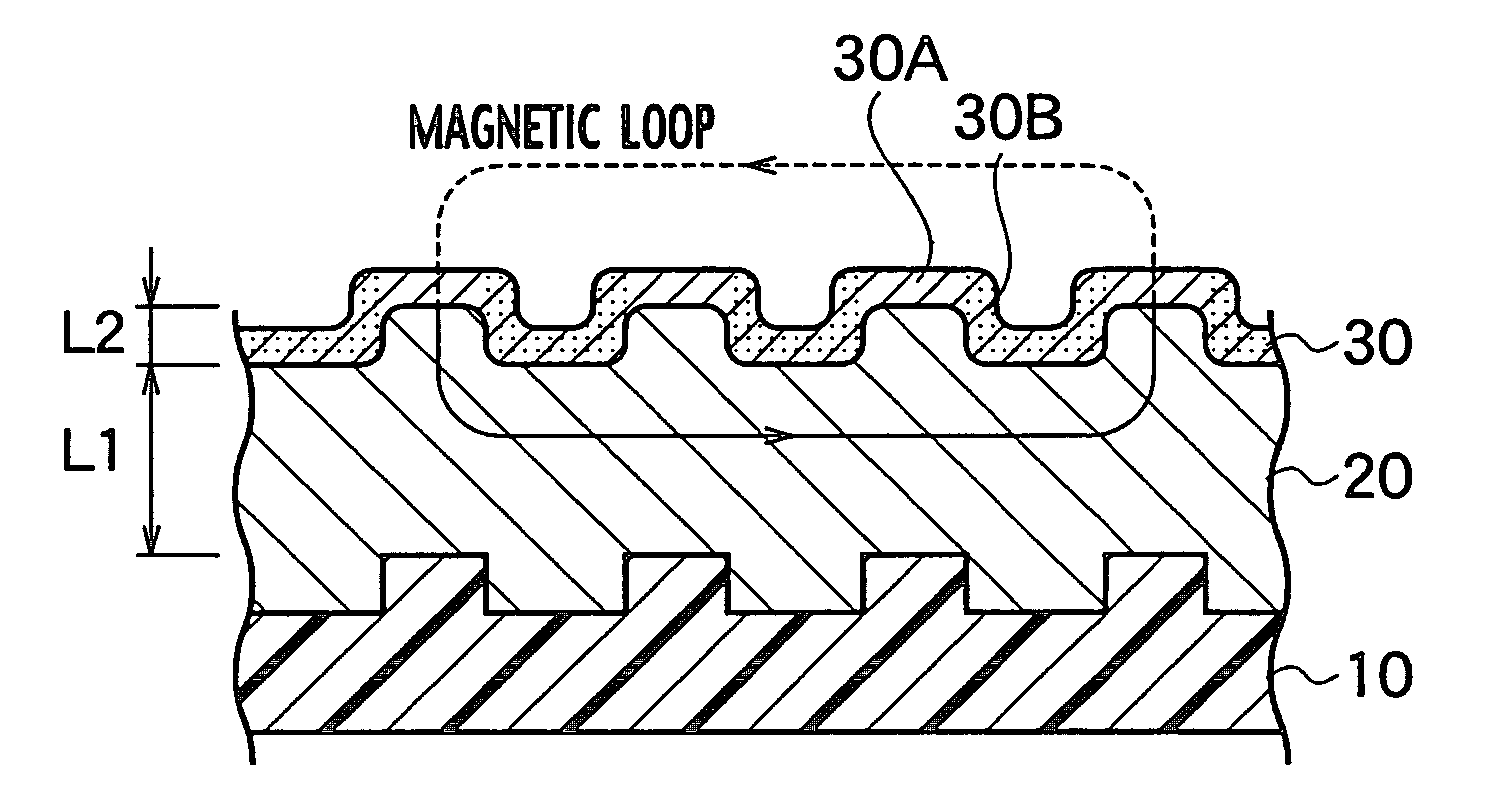
Patents
Literature
447 results about "Perpendicular magnetic anisotropy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
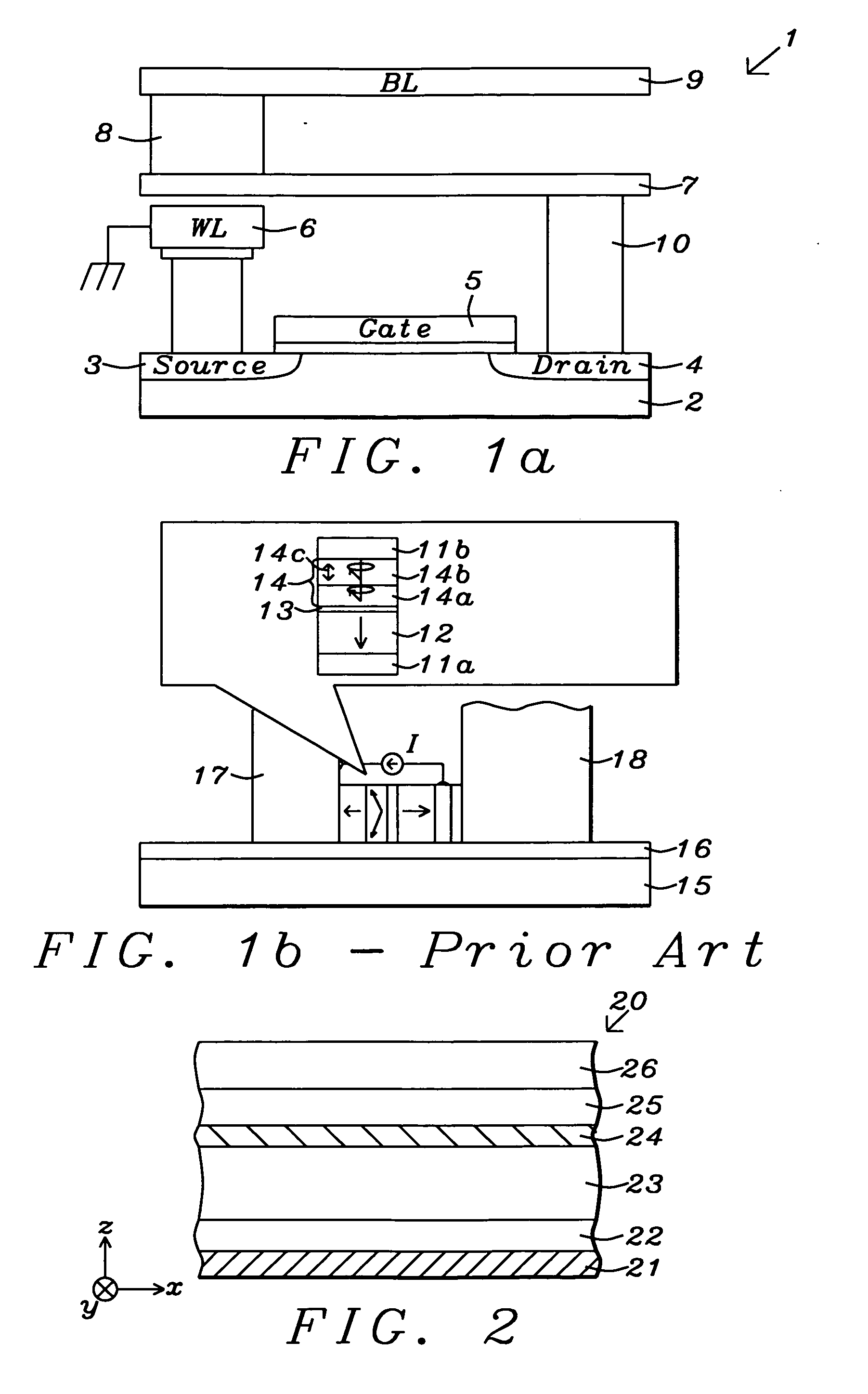
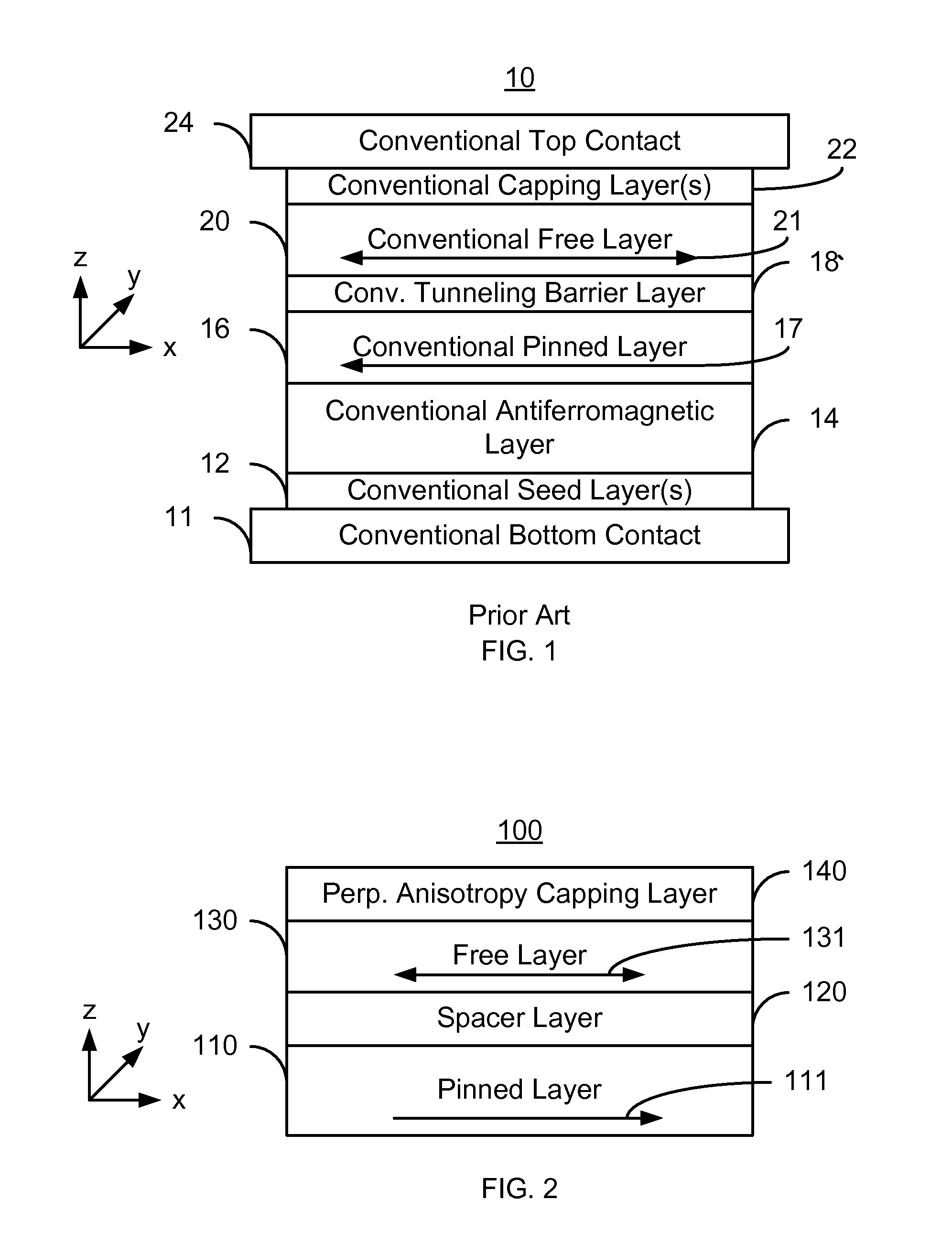
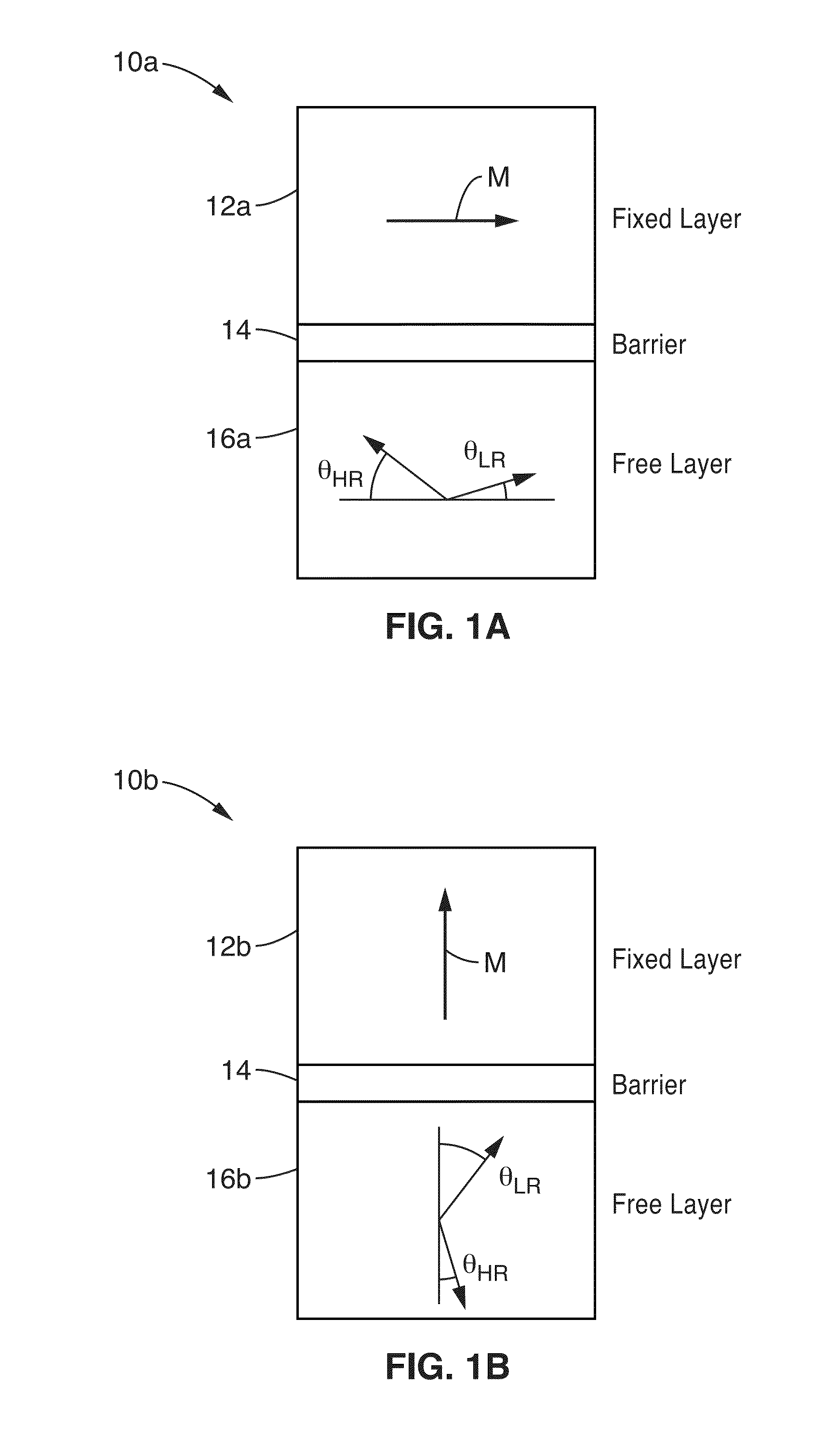
Abstract Perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA) is an essential condition for CoFe thin films used in magnetic random access memories. Until recently, interfacial PMA was mainly known to occur in materials stacks with MgO\CoFe(B) interfaces or using an adjacent crystalline heavy metal film.
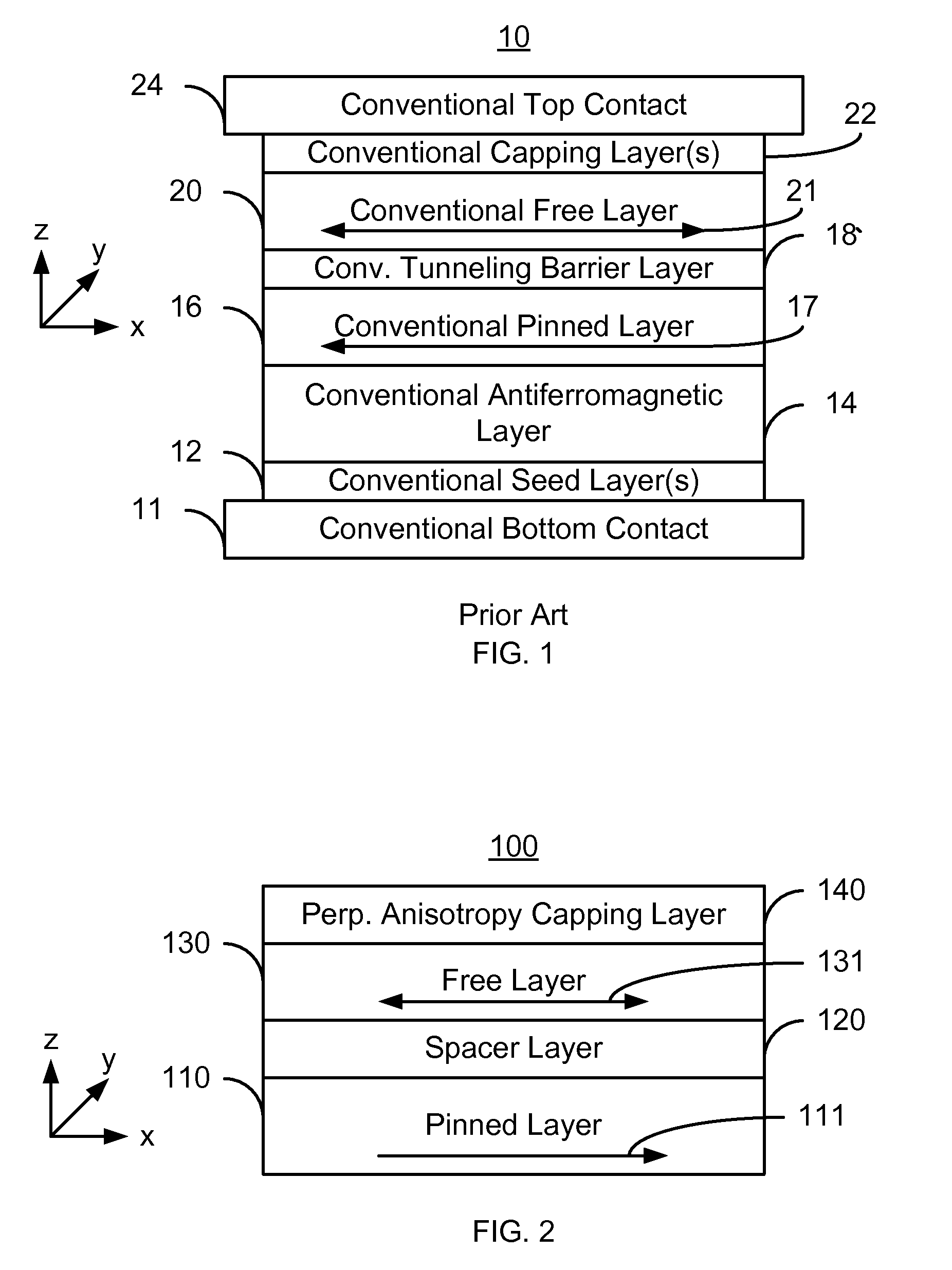
Spin-transfer torque magnetic random access memory having magnetic tunnel junction with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy
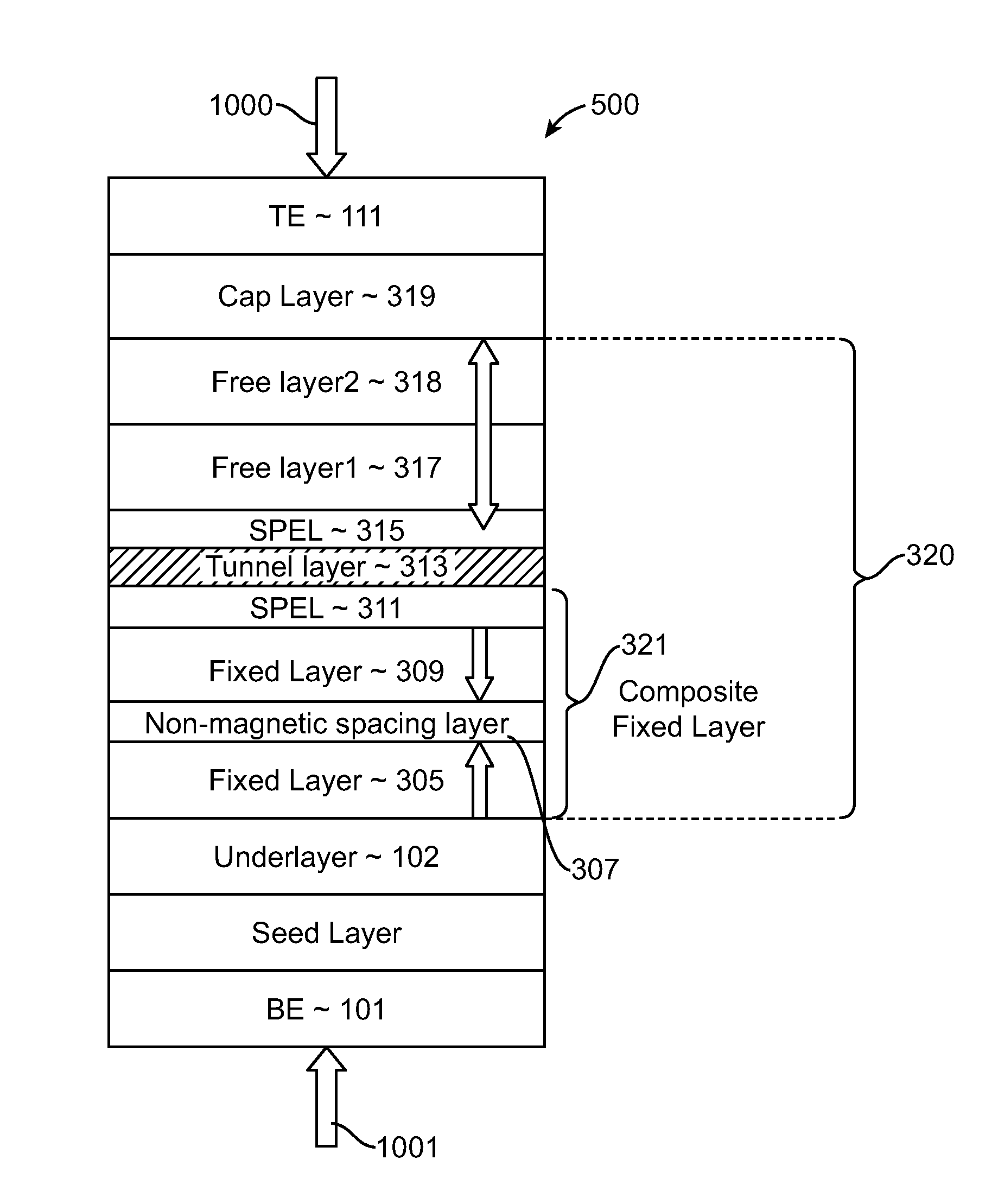
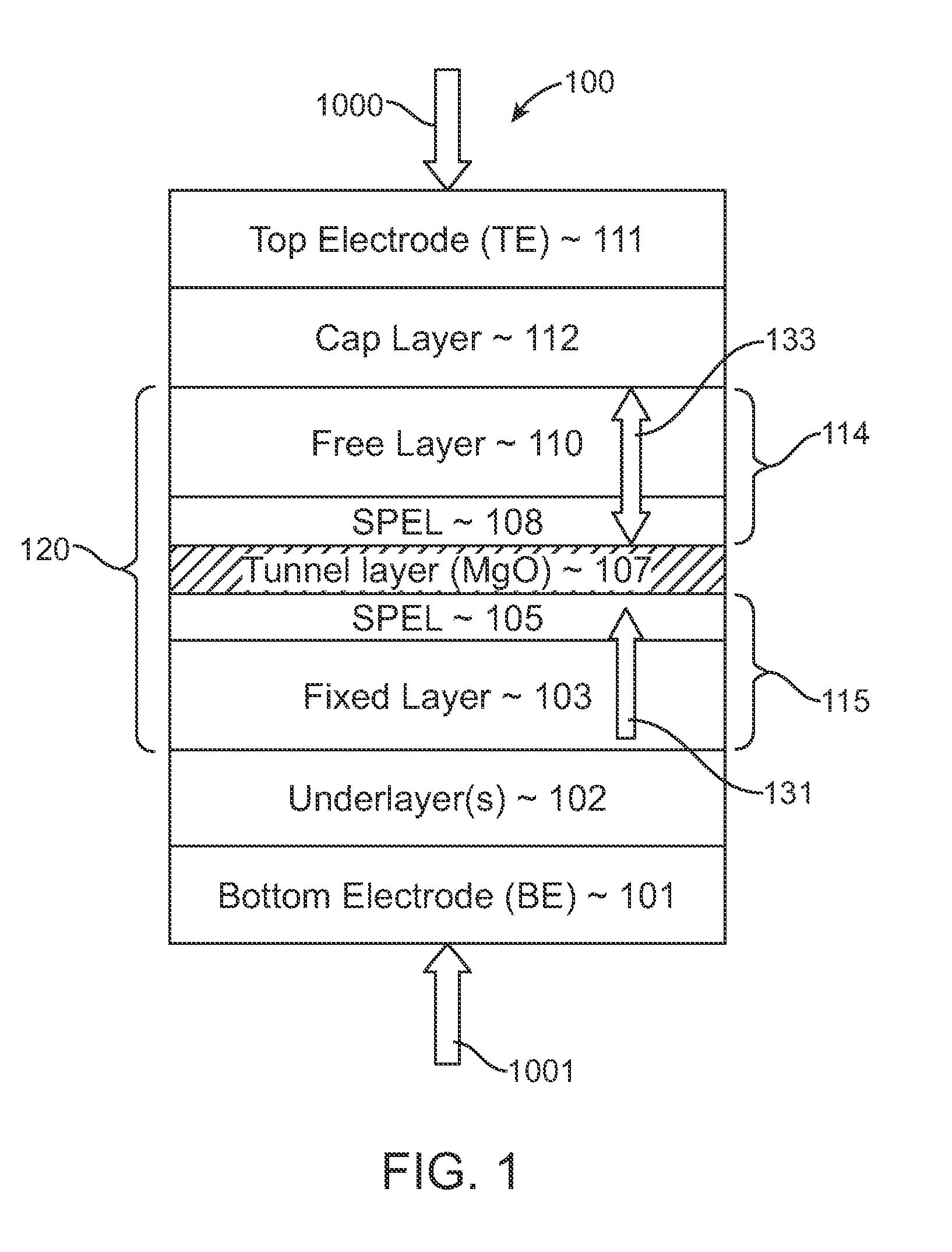
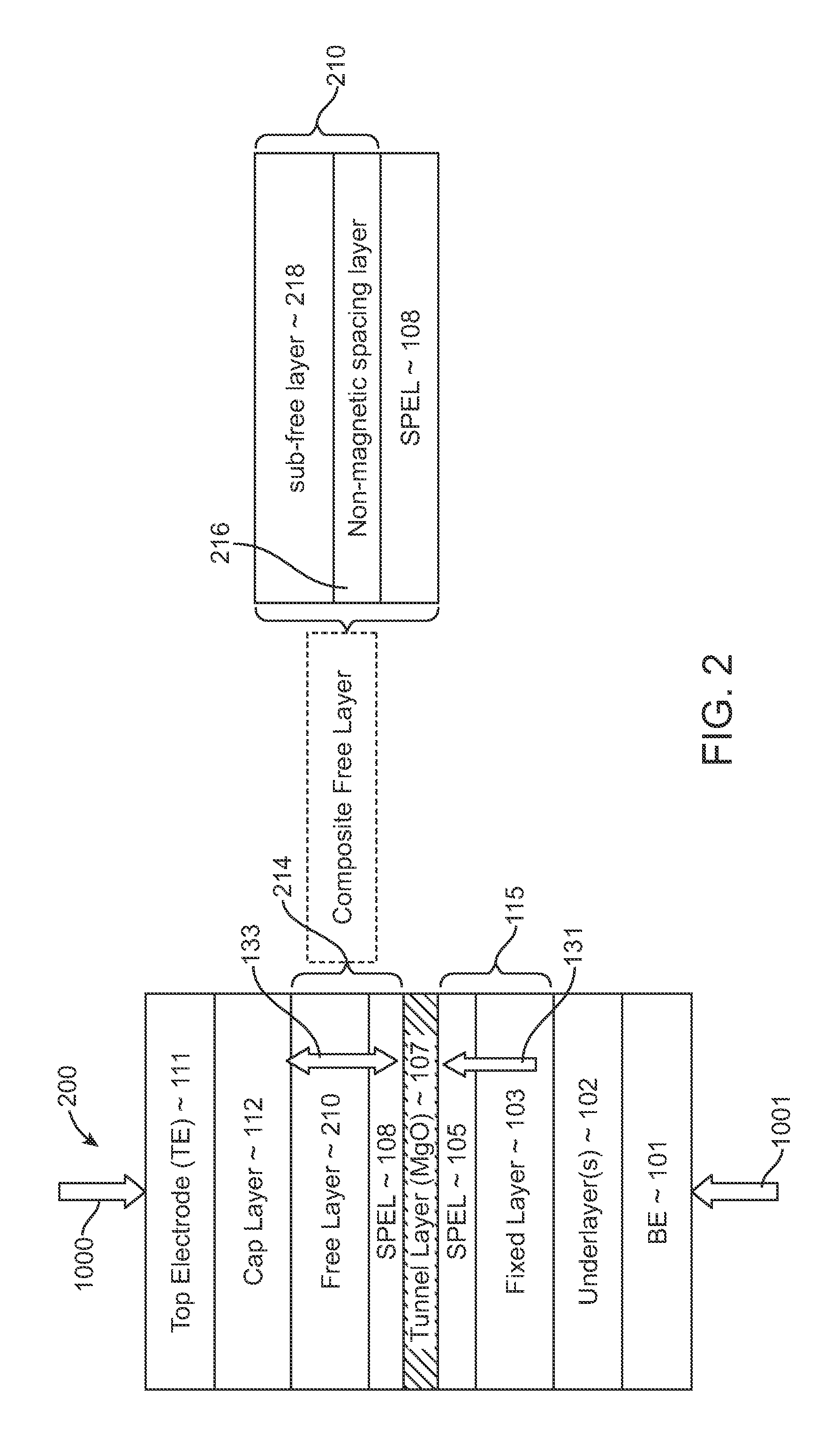
A spin-torque transfer memory random access memory (STTMRAM) element includes a fixed layer formed on top of a substrate and a a tunnel layer formed upon the fixed layer and a composite free layer formed upon the tunnel barrier layer and made of an iron platinum alloy with at least one of X or Y material, X being from a group consisting of: boron (B), phosphorous (P), carbon (C), and nitride (N) and Y being from a group consisting of: tantalum (Ta), titanium (Ti), niobium (Nb), zirconium (Zr), tungsten (W), silicon (Si), copper (Cu), silver (Ag), aluminum (Al), chromium (Cr), tin (Sn), lead (Pb), antimony (Sb), hafnium (Hf) and bismuth (Bi), molybdenum (Mo) or rhodium (Ru), the magnetization direction of each of the composite free layer and fixed layer being substantially perpendicular to the plane of the substrate.
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
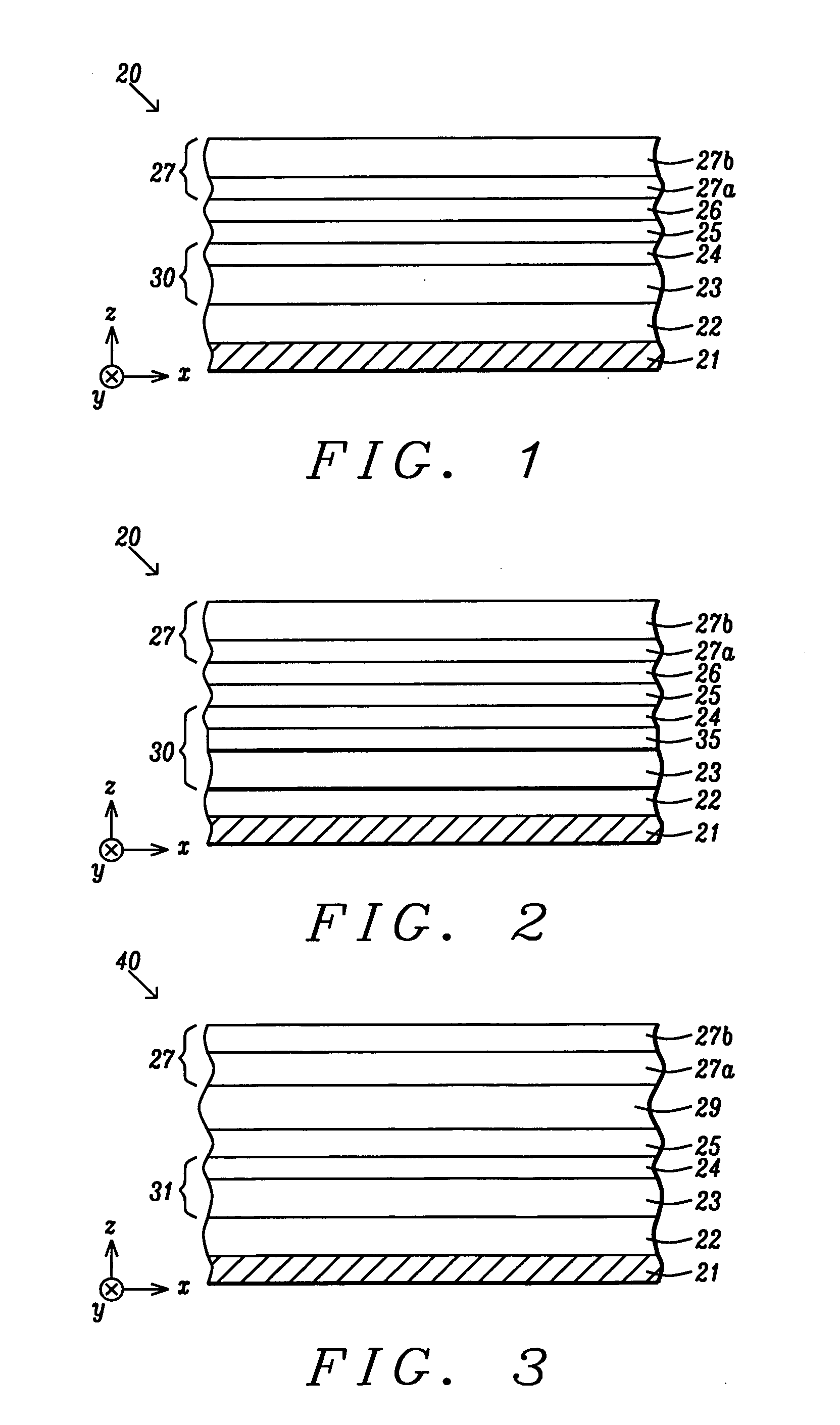
Thin seeded Co/Ni multilayer film with perpendicular anisotropy for spintronic device applications
ActiveUS20090257151A1Raise the ratioNot to damageMagnetic measurementsVacuum evaporation coatingPerpendicular anisotropySpins
A spin valve structure for a spintronic device is disclosed and includes a composite seed layer made of at least Ta and a metal layer having a fcc(111) or hcp(001) texture to enhance perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA) in an overlying (Co / Ni)x multilayer. The (Co / Ni)x multilayer is deposited by a low power and high Ar pressure process to avoid damaging Co / Ni interfaces and thereby preserving PMA. As a result, only a thin seed layer is required. PMA is maintained even after annealing at 220° C. for 10 hours. Examples of GMR and TMR spin valves are described and may be incorporated in spin transfer oscillators and spin transfer MRAMs. The free layer is preferably made of a FeCo alloy including at least one of Al, Ge, Si, Ga, B, C, Se, Sn, or a Heusler alloy, or a half Heusler alloy to provide high spin polarization and a low magnetic damping coefficient.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION +1
Spin-current switched magnetic memory element suitable for circuit integration and method of fabricating the memory element
A magnetic memory element switchable by current injection includes a plurality of magnetic layers, at least one of the plurality of magnetic layers having a perpendicular magnetic anisotropy component and including a current-switchable magnetic moment, and at least one barrier layer formed adjacent to the plurality of magnetic layers (e.g., between two of the magnetic layers). The memory element has the switching threshold current and device impedance suitable for integration with complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) integrated circuits.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
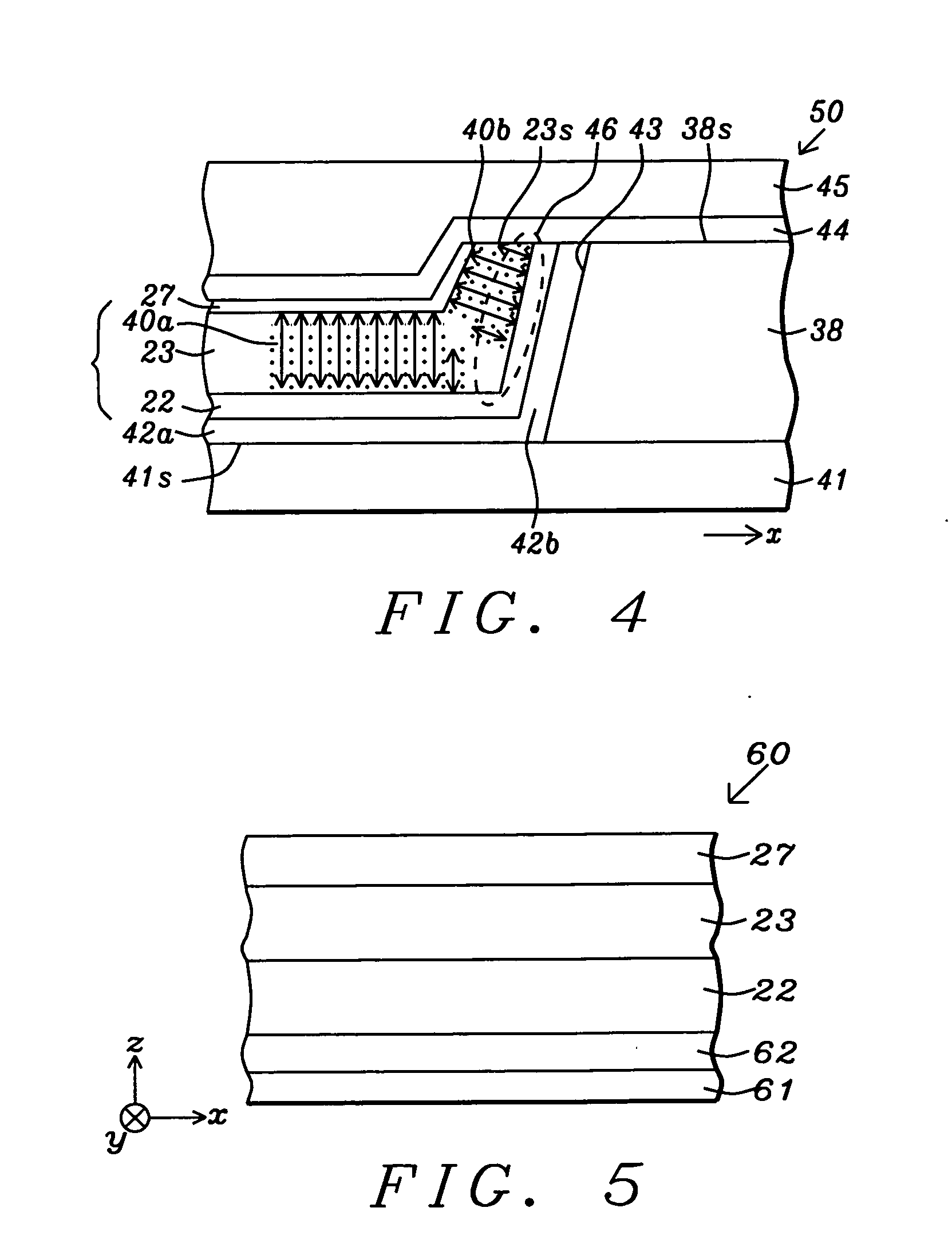
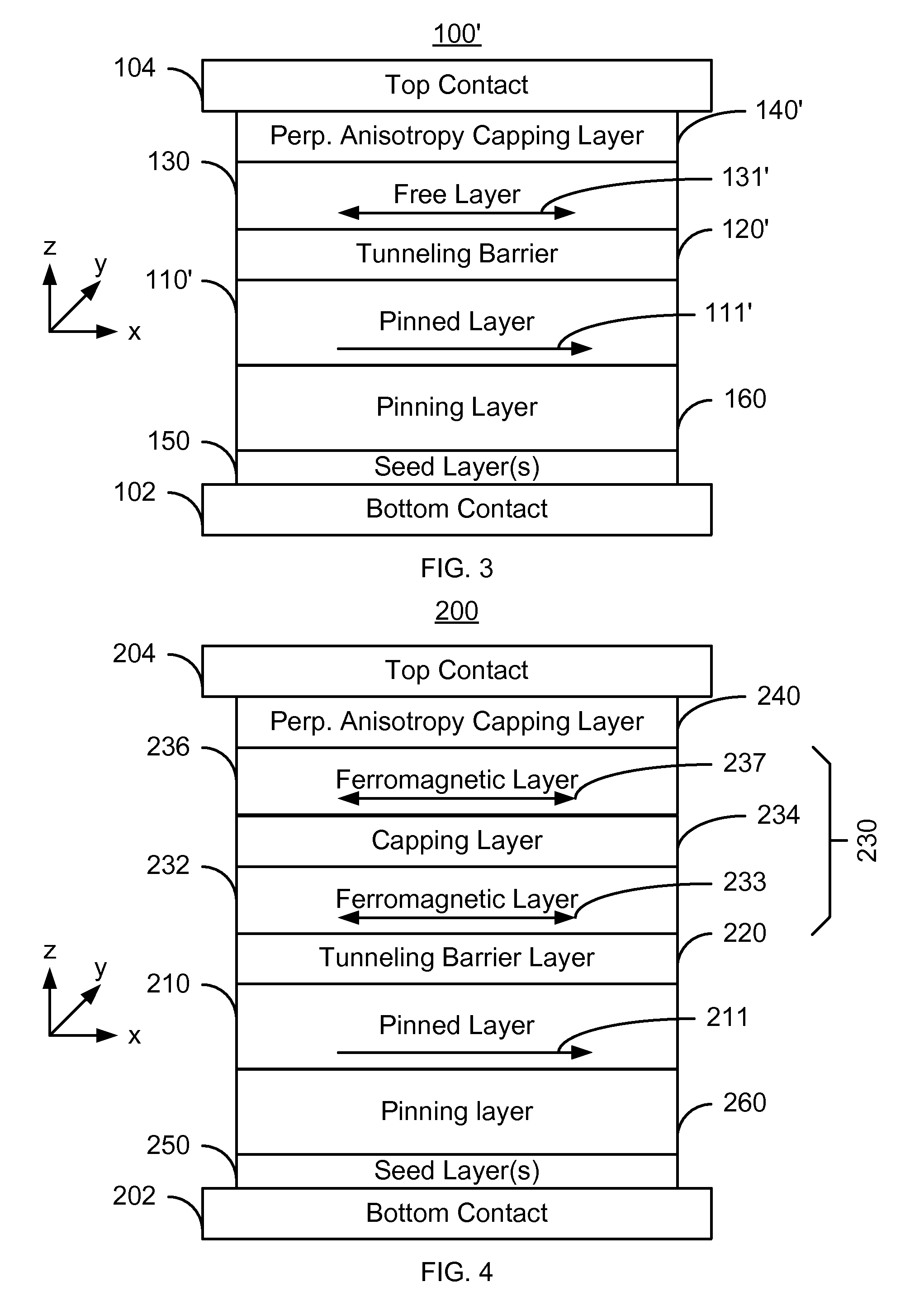
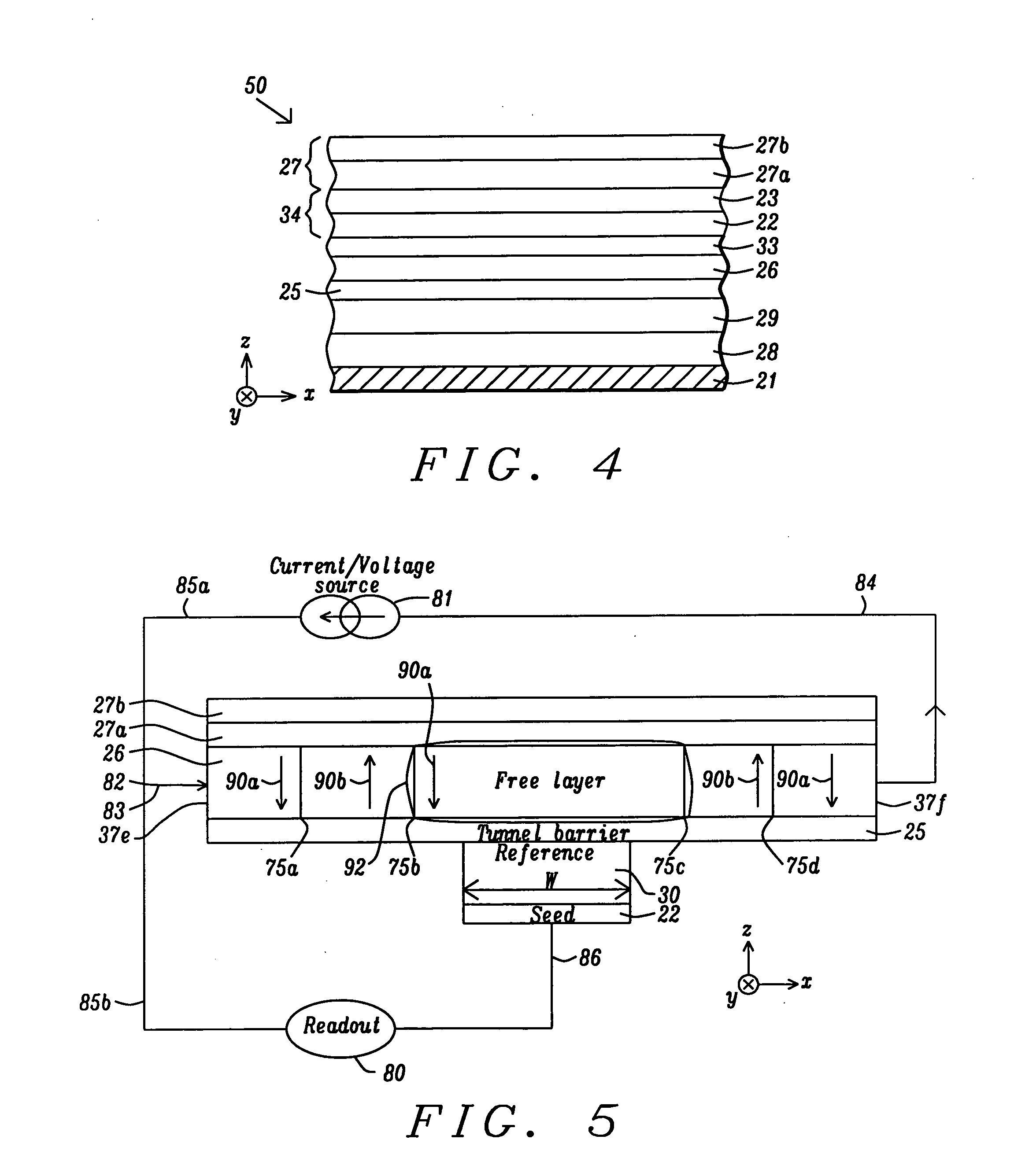
Method and system for providing magnetic tunneling junction elements having improved performance through capping layer induced perpendicular anisotropy and memories using such magnetic elements
ActiveUS20120155156A1Improve thermal stabilityNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsElectricityPower flow
A method and system for providing a magnetic element and a magnetic memory utilizing the magnetic element are described. The magnetic element is used in a magnetic device that includes a contact electrically coupled to the magnetic element. The method and system include providing pinned, nonmagnetic spacer, and free layers. The free layer has an out-of-plane demagnetization energy and a perpendicular magnetic anisotropy corresponding to a perpendicular anisotropy energy that is less than the out-of-plane demagnetization energy. The nonmagnetic spacer layer is between the pinned and free layers. The method and system also include providing a perpendicular capping layer adjoining the free layer and the contact. The perpendicular capping layer induces at least part of the perpendicular magnetic anisotropy in the free layer. The magnetic element is configured to allow the free layer to be switched between magnetic states when a write current is passed through the magnetic element.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
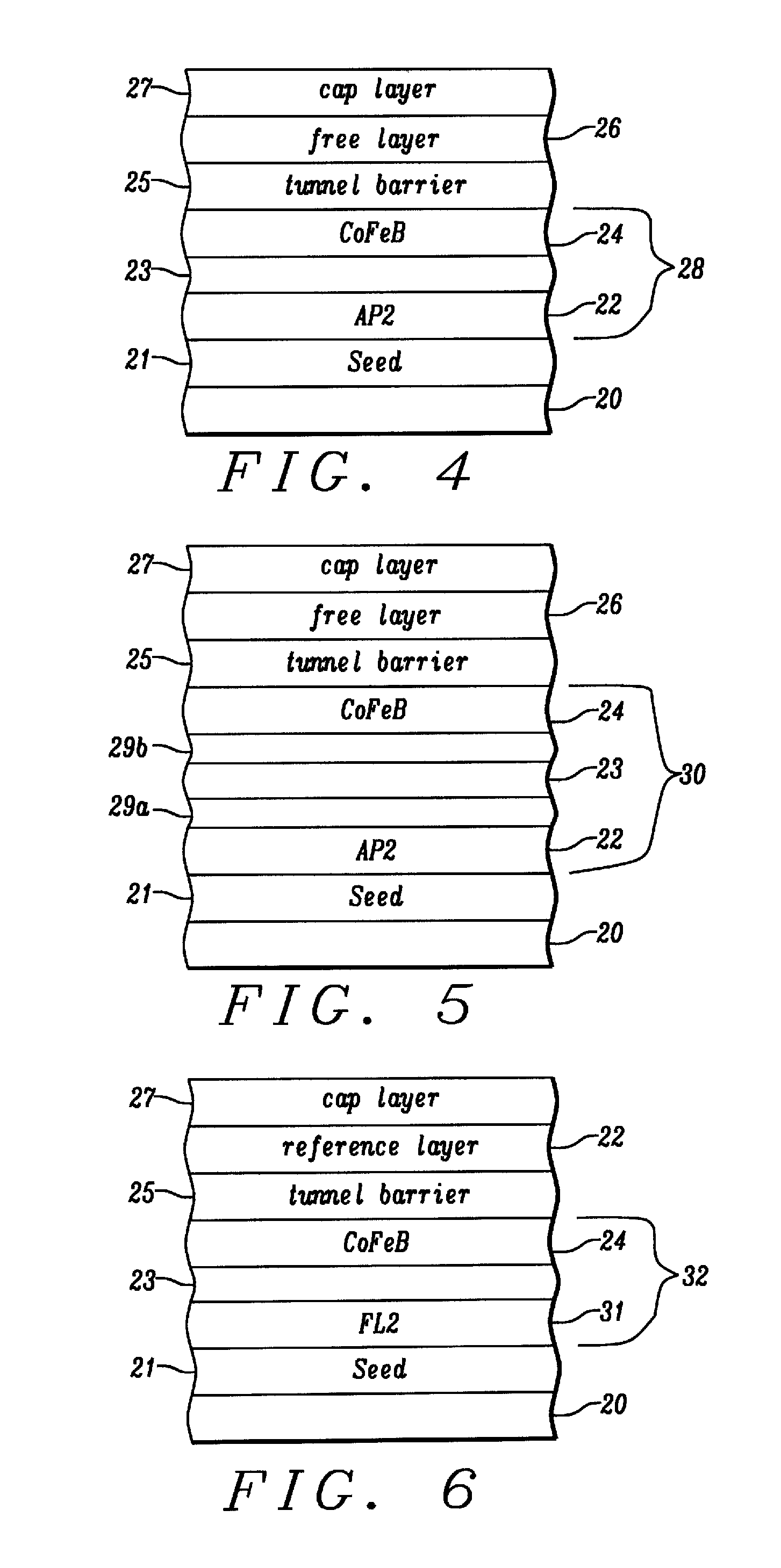
MTJ incorporating CoFe/Ni multilayer film with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy for MRAM application
ActiveUS20110096443A1Minimize impinging ion energyMaximize PMA propertyMagnetic measurementsVacuum evaporation coatingSpin transferSpin valve
A MTJ for a spintronic device is disclosed and includes a thin composite seed layer made of at least Ta and a metal layer having fcc(111) or hcp(001) texture as in Ta / Ti / Cu to enhance perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA) in an overlying laminated layer with a (CoFe / Ni)X, (Co / NiFe)X, (Co / NiCo)X, (CoFe / NiFe)X, or (CoFe / NiCo)X composition where x is from 5 to 30. In one embodiment, a CPP-TMR spin valve has one or both of a laminated free layer and laminated reference layer with the aforementioned compositions. The MTJ includes an interfacial layer made of CoFeB, CoFeB / CoFe, or CoFe / CoFeB between each laminated structure and the tunnel barrier. The laminated layers are deposited by a low power and high Ar pressure process to avoid damaging interfaces between adjoining layers. Annealing occurs at 220° C. to 400° C. A laminated layer with high PMA may also be included in one or more layers of a spin transfer oscillator.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Voltage-controlled magnetic memory element with canted magnetization
ActiveUS20140169085A1High tunneling magnetoresistance (TMRImprove adjustabilitySolid-state devicesGalvano-magnetic material selectionStable stateMagnetic memory
A memory cell including information that is stored in the state of a magnetic bit (i.e. in a free layer, FL), where the FL magnetization has two stable states that may be canted (form an angle) with respect to the horizontal and vertical directions of the device is presented. The FL magnetization may be switched between the two canted states by the application of a voltage (i.e. electric field), which modifies the perpendicular magnetic anisotropy of the free layer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
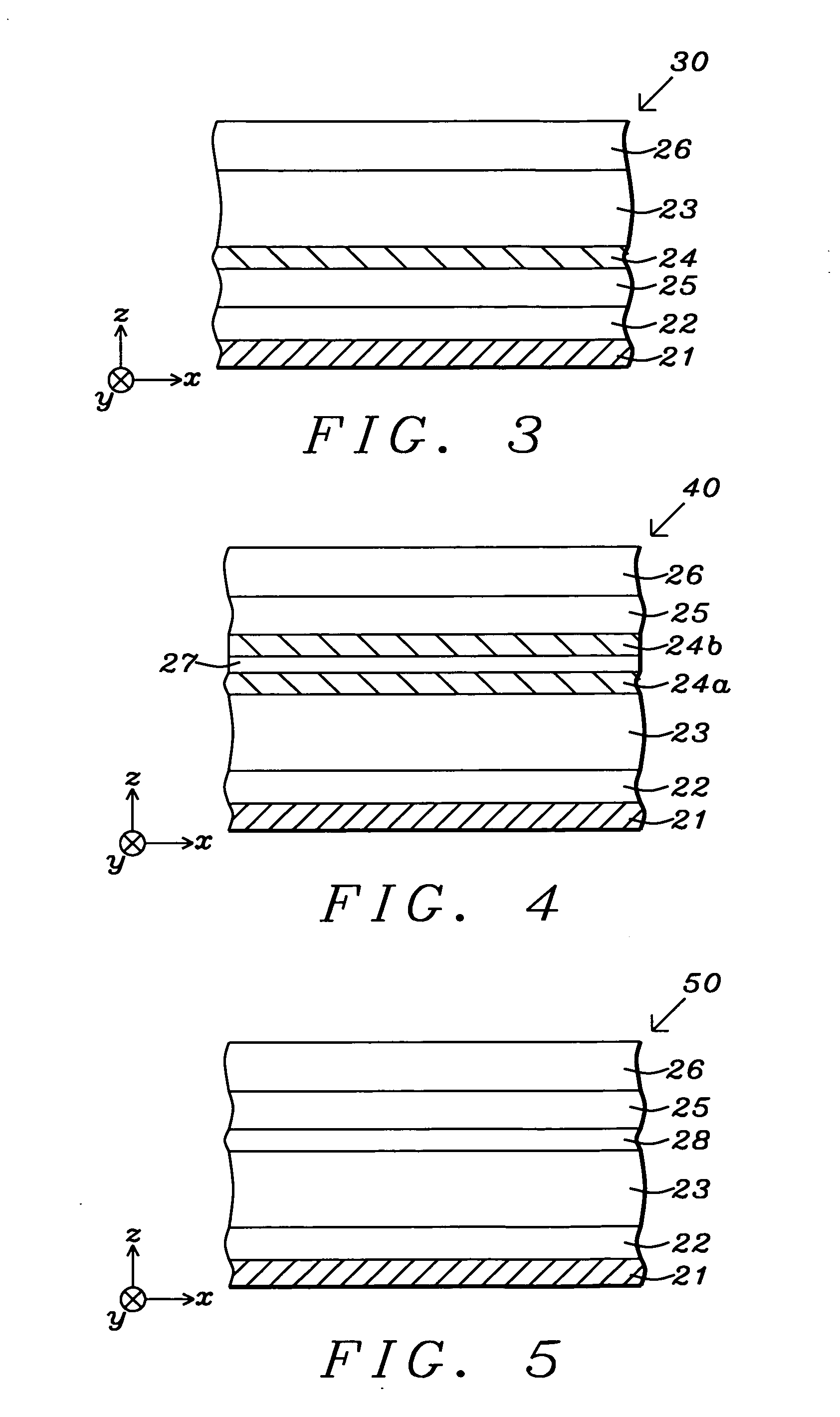
Multilayer structure with high perpendicular anisotropy for device applications
ActiveUS20110293967A1Improve performanceLow costMagnetic measurementsPretreated surfacesPerpendicular anisotropyMagnetic media
Perpendicular magnetic anisotropy and Hc are enhanced in magnetic devices with a Ta / M1 / M2 seed layer where M1 is preferably Ti, and M2 is preferably Cu, and including an overlying (Co / Ni)X multilayer (x is 5 to 50) that is deposited with ultra high Ar pressure of >100 sccm to minimize impinging energy that could damage (Co / Ni)X interfaces. In one'embodiment, the seed layer is subjected to one or both of a low power plasma treatment and natural oxidation process to form a more uniform interface with the (Co / Ni)X multilayer. Furthermore, an oxygen surfactant layer may be formed at one or more interfaces between adjoining (Co / Ni)X layers in the multilayer stack. Annealing at temperatures between 180° C. and 400° C. also increases Hc but the upper limit depends on whether the magnetic device is MAMR, MRAM, a hard bias structure, or a perpendicular magnetic medium.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Method and system for providing magnetic tunneling junction elements having improved performance through capping layer induced perpendicular anisotropy and memories using such magnetic elements
InactiveUS20110031569A1Improve thermal stabilityNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsPerpendicular anisotropyMagnetic memory
A method and system for providing a magnetic element and a magnetic memory utilizing the magnetic element are described. The magnetic element is used in a magnetic device that includes a contact electrically coupled to the magnetic element. The method and system include providing pinned, nonmagnetic spacer, and free layers. The free layer has an out-of-plane demagnetization energy and a perpendicular magnetic anisotropy corresponding to a perpendicular anisotropy energy that is less than the out-of-plane demagnetization energy. The nonmagnetic spacer layer is between the pinned and free layers. The method and system also include providing a perpendicular capping layer adjoining the free layer and the contact. The perpendicular capping layer induces at least part of the perpendicular magnetic anisotropy in the free layer. The magnetic element is configured to allow the free layer to be switched between magnetic states when a write current is passed through the magnetic element.
Owner:GRANDIS
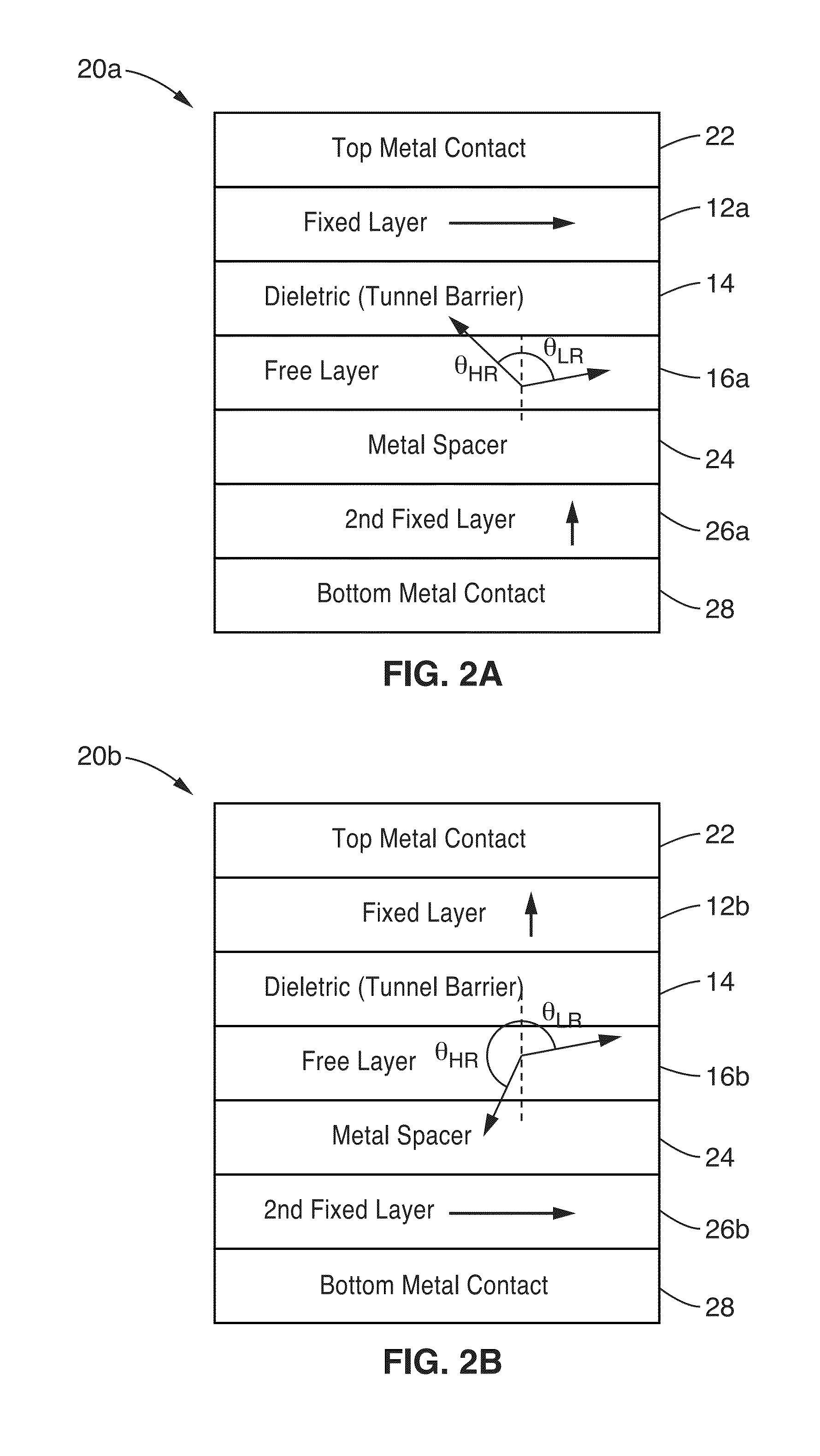
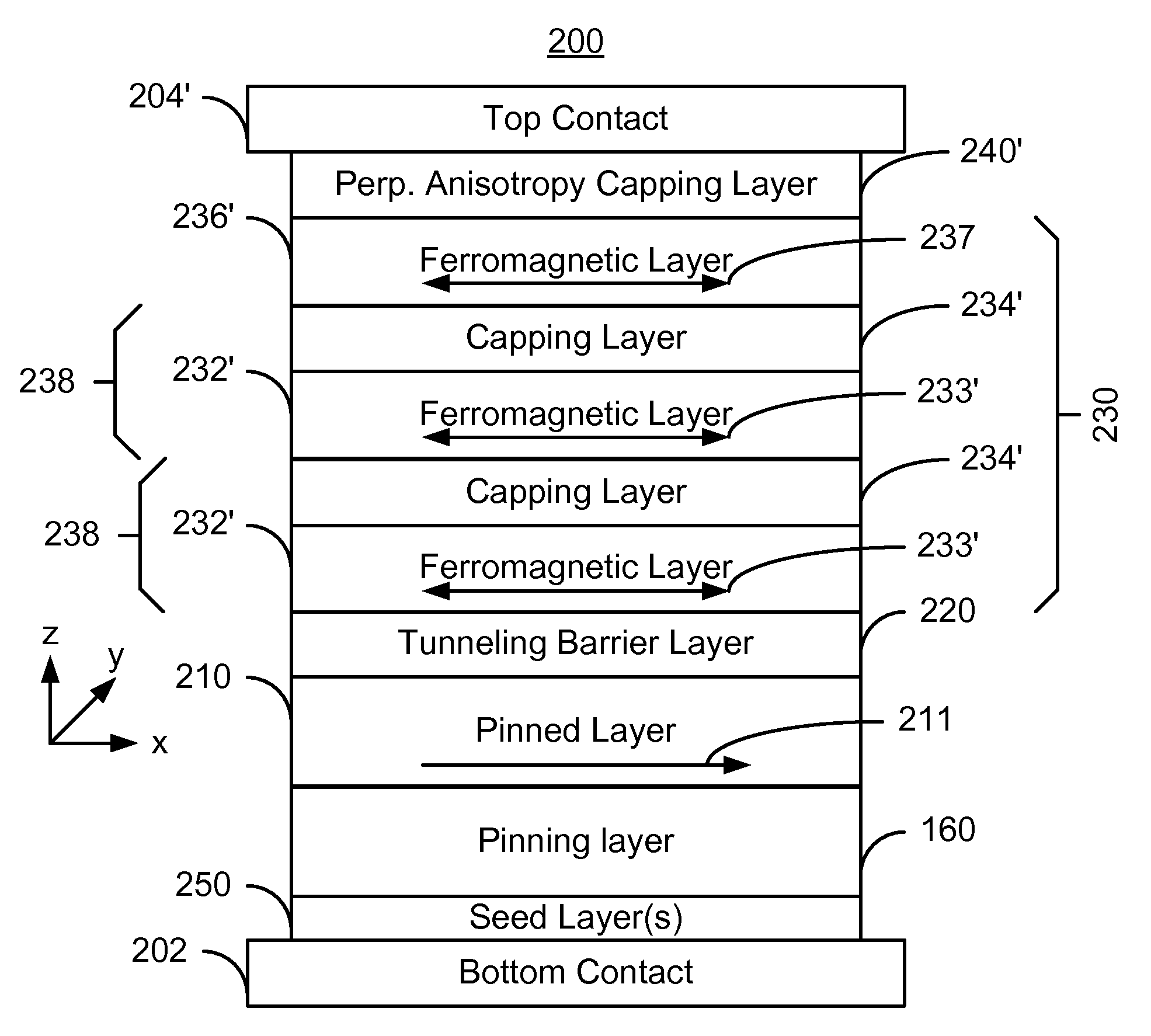
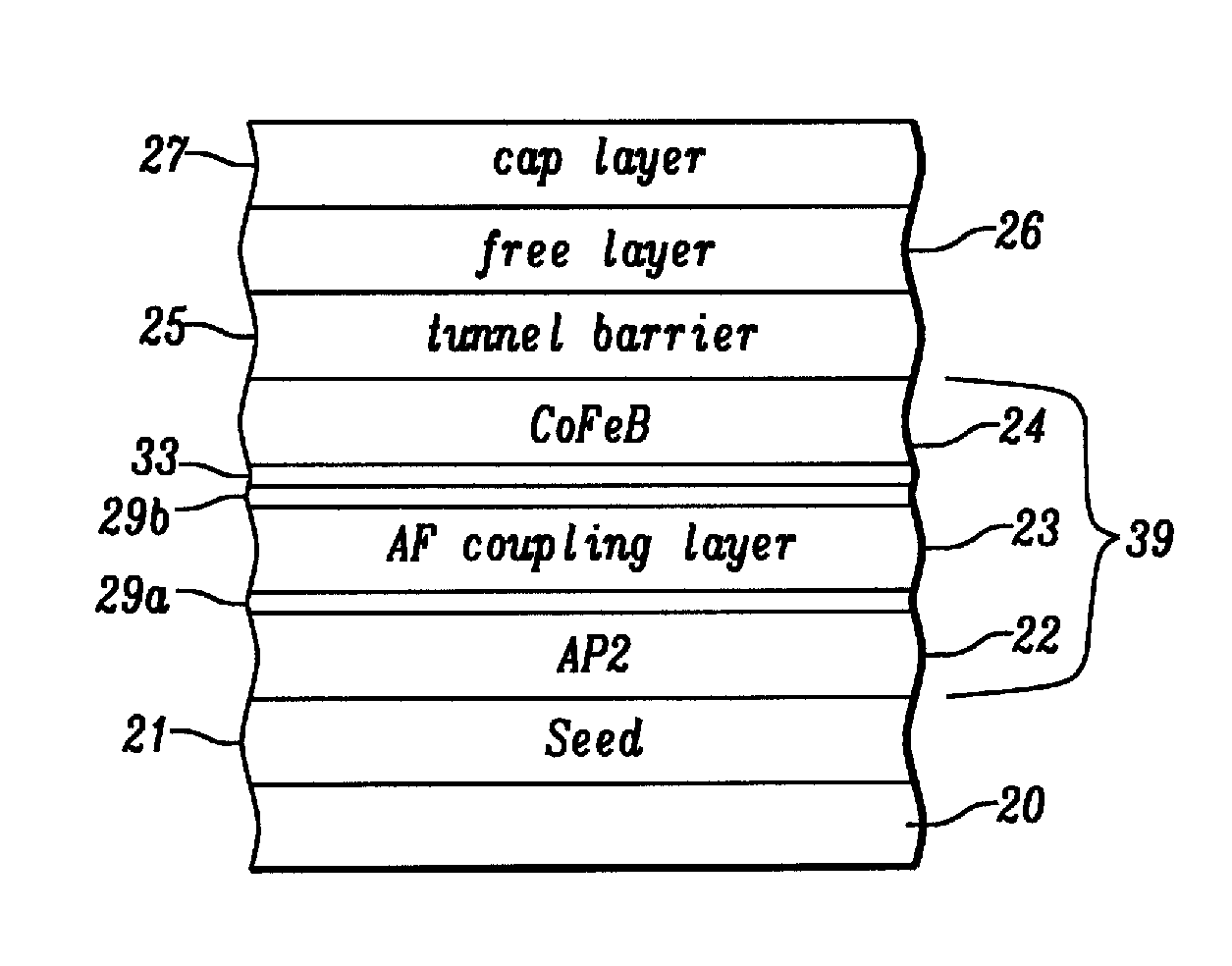
Magnetic stacks with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy for spin momentum transfer magnetoresistive random access memory
InactiveUS20120267733A1Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionMagnetic reluctanceMagnetization
A magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) includes a magnetic free layer, having a variable magnetization direction; an insulating tunnel barrier located adjacent to the free layer; a magnetic fixed layer having an invariable magnetization direction, the fixed layer disposed adjacent the tunnel barrier such that the tunnel barrier is located between the free layer and the fixed layer, wherein the free layer and the fixed layer have perpendicular magnetic anisotropy; and one or more of: a composite fixed layer, the composite fixed layer comprising a dusting layer, a spacer layer, and a reference layer; a synthetic antiferromagnetic (SAF) fixed layer structure, the SAF fixed layer structure comprising a SAF spacer located between the fixed layer and a second fixed magnetic layer; and a dipole layer, wherein the free layer is located between the dipole layer and the tunnel barrier.
Owner:IBM CORP
Co/Ni Multilayers with Improved Out-of-Plane Anisotropy for Magnetic Device Applications
ActiveUS20120299134A1Raise the ratioStrong textureMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionAlloyElectron
A MTJ for a spintronic device is disclosed and includes a thin seed layer that enhances perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA) in an overlying laminated layer with a (Co / X)n or (CoX)n composition where n is from 2 to 30, X is one of V, Rh, Ir, Os, Ru, Au, Cr, Mo, Cu, Ti, Re, Mg, or Si, and CoX is a disordered alloy. A CoFeB layer may be formed between the laminated layer and a tunnel barrier layer to serve as a transitional layer between a (111) laminate and (100) MgO tunnel barrier. The laminated layer may be used as a reference layer, dipole layer, or free layer in a MTJ. Annealing between 300° C. and 400° C. may be used to further enhance PMA in the laminated layer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
CoFe/Ni Multilayer film with perpendicular anisotropy for microwave assisted magnetic recording
ActiveUS20110279921A1Improve vibrationImprove robustnessNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsPerpendicular anisotropySpin transfer
A spin transfer oscillator with a seed / SIL / spacer / FGL / capping configuration is disclosed with a composite seed layer made of Ta and a metal layer having a fcc(111) or hcp(001) texture to enhance perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA) in an overlying (A1 / A2)X laminated spin injection layer (SIL). Field generation layer (FGL) is made of a high Bs material such FeCo. Alternatively, the STO has a seed / FGL / spacer / SIL / capping configuration. The SIL may include a FeCo layer that is exchanged coupled with the (A1 / A2)X laminate (x is 5 to 50) to improve robustness. The FGL may include an (A1 / A2)Y laminate (y=5 to 30) exchange coupled with the high Bs layer to enable easier oscillations. A1 may be one of Co, CoFe, or CoFeR where R is a metal, and A2 is one of Ni, NiCo, or NiFe. The STO may be formed between a main pole and trailing shield in a write head.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
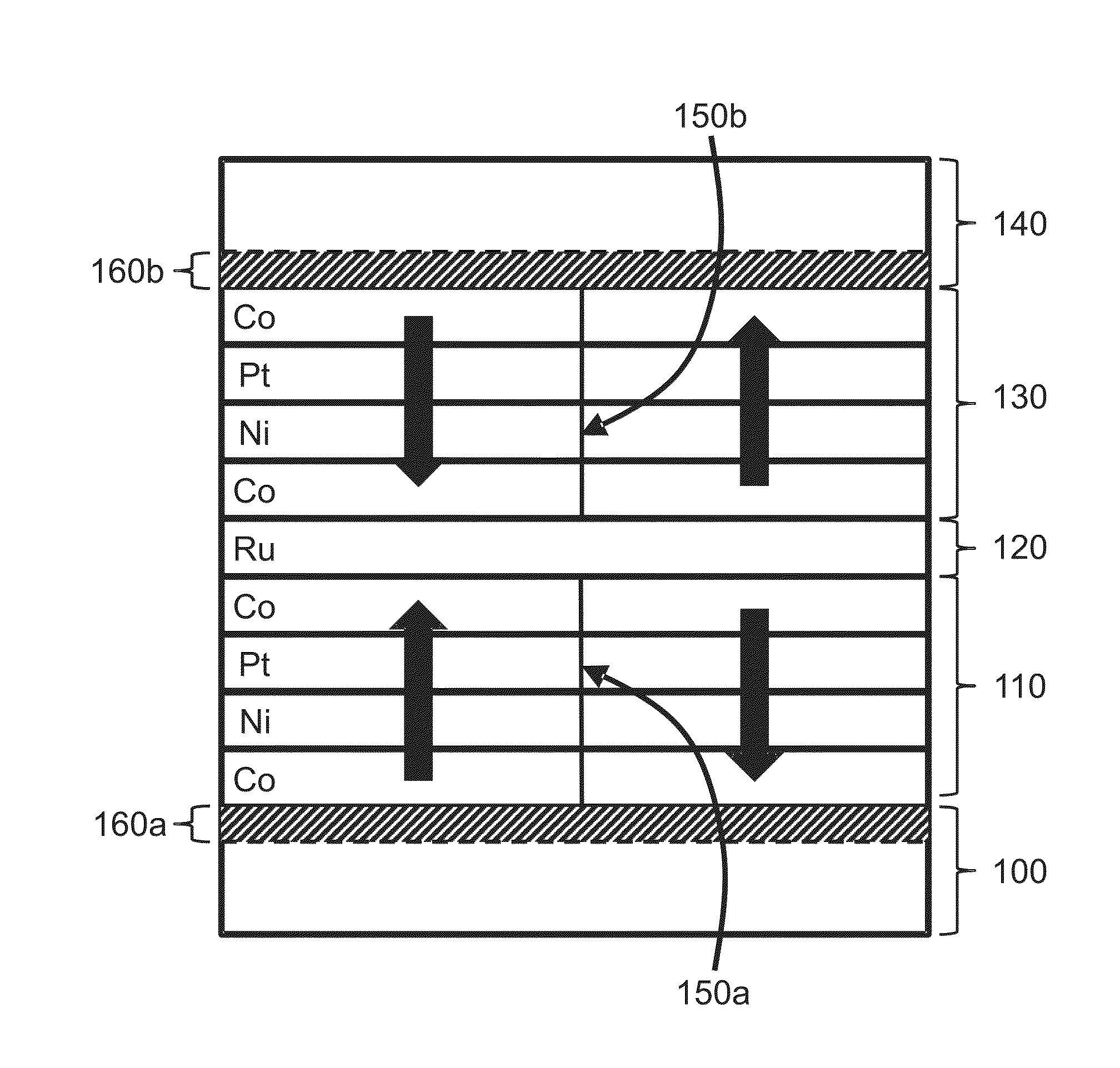
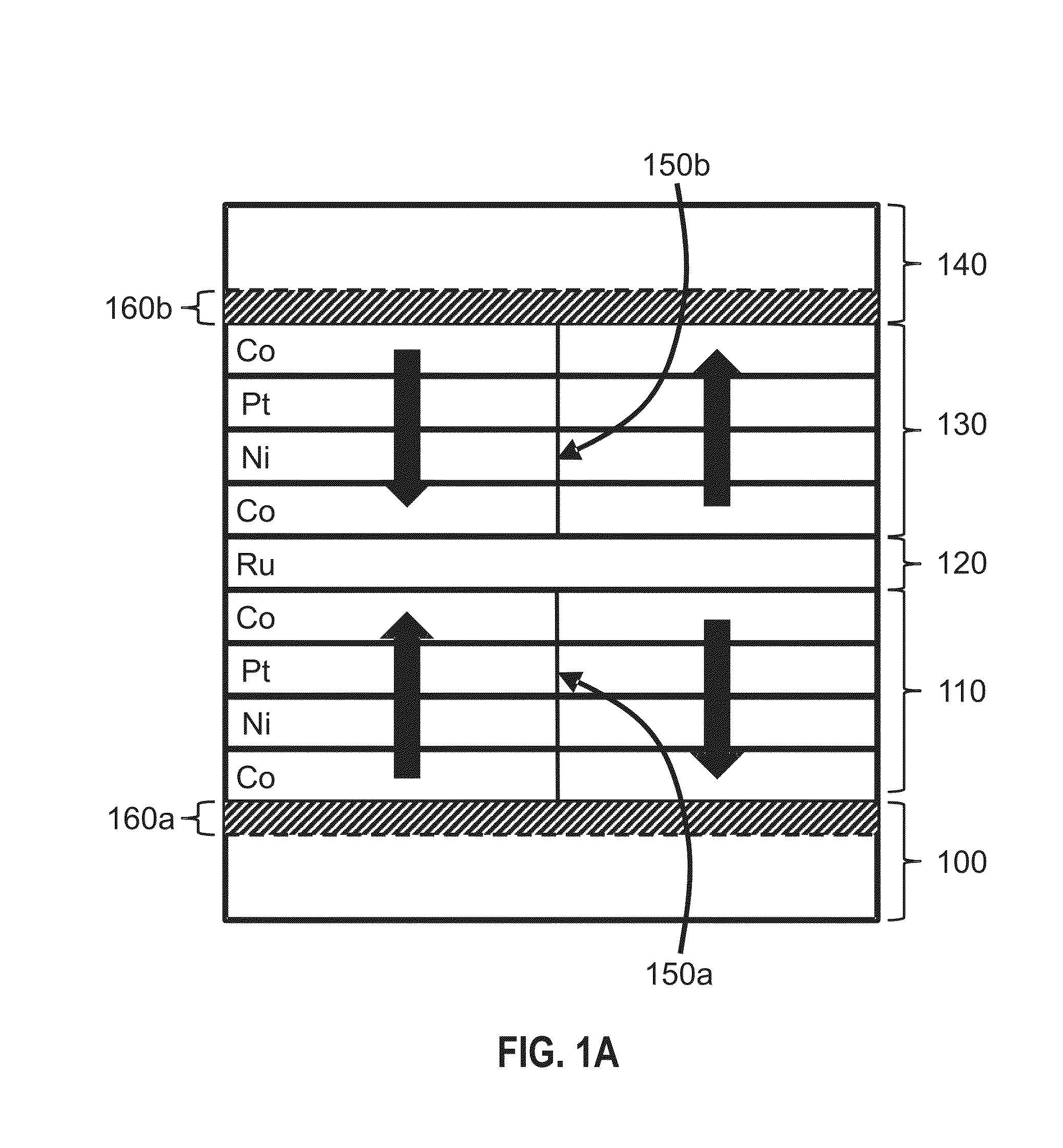
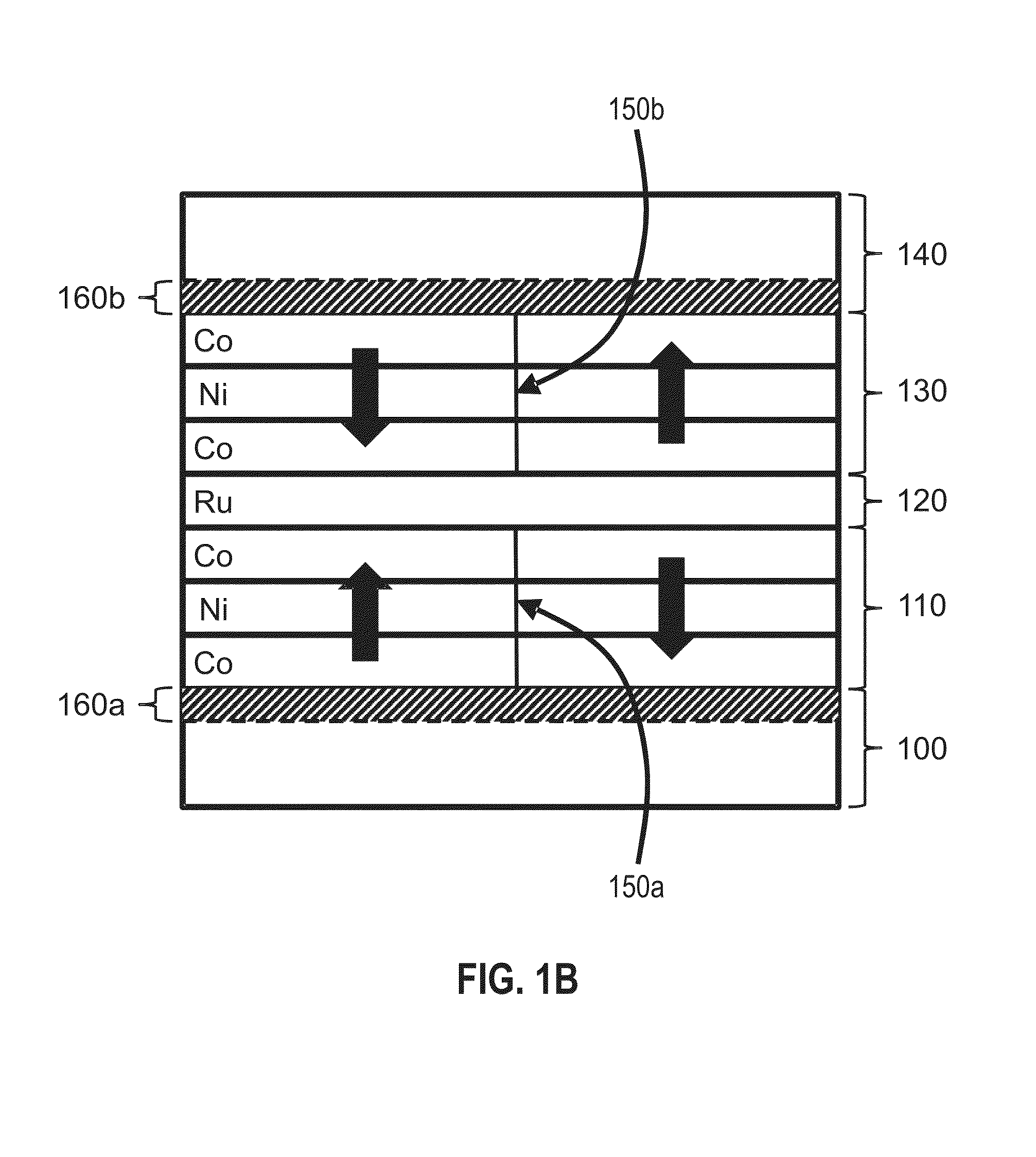
Domain wall motion in perpendicularly magnetized wires having artificial antiferromagnetically coupled multilayers with engineered interfaces
ActiveUS20140009994A1Digital storageThin magnetic filmsPerpendicular magnetizationAntiferromagnetic coupling
Magnetic wires that include two antiferromagnetically coupled magnetic regions show improved domain wall motion properties, when the domain walls are driven by pulses of electrical current. The magnetic regions preferably include Co, Ni, and Pt and exhibit perpendicular magnetic anisotropy, thereby supporting the propagation of narrow domain walls. The direction of motion of the domain walls can be influenced by the order in which the wire's layers are arranged.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Co/Ni multilayers with improved out-of-plane anisotropy for magnetic device applications
ActiveUS20120286382A1Raise the ratioStrong textureMagnetic measurementsMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsOptoelectronicsMagnetic layer
A MTJ for a spintronic device is disclosed and includes a thin seed layer that enhances perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA) in an overlying laminated layer with a (Co / Ni)n composition or the like where n is from 2 to 30. The seed layer is preferably NiCr, NiFeCr, Hf, or a composite thereof with a thickness from 10 to 100 Angstroms. Furthermore, a magnetic layer such as CoFeB may be formed between the laminated layer and a tunnel barrier layer to serve as a transitional layer between a (111) laminate and (100) MgO tunnel barrier. There may be a Ta insertion layer between the CoFeB layer and laminated layer to promote (100) crystallization in the CoFeB layer. The laminated layer may be used as a reference layer, dipole layer, or free layer in a MTJ. Annealing between 300° C. and 400° C. may be used to further enhance PMA in the laminated layer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Minimal thickness synthetic antiferromagnetic (SAF) structure with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy for STT-MRAM
ActiveUS8860156B2Raise the ratioTransformersGalvano-magnetic material selectionCouplingMagnetization
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
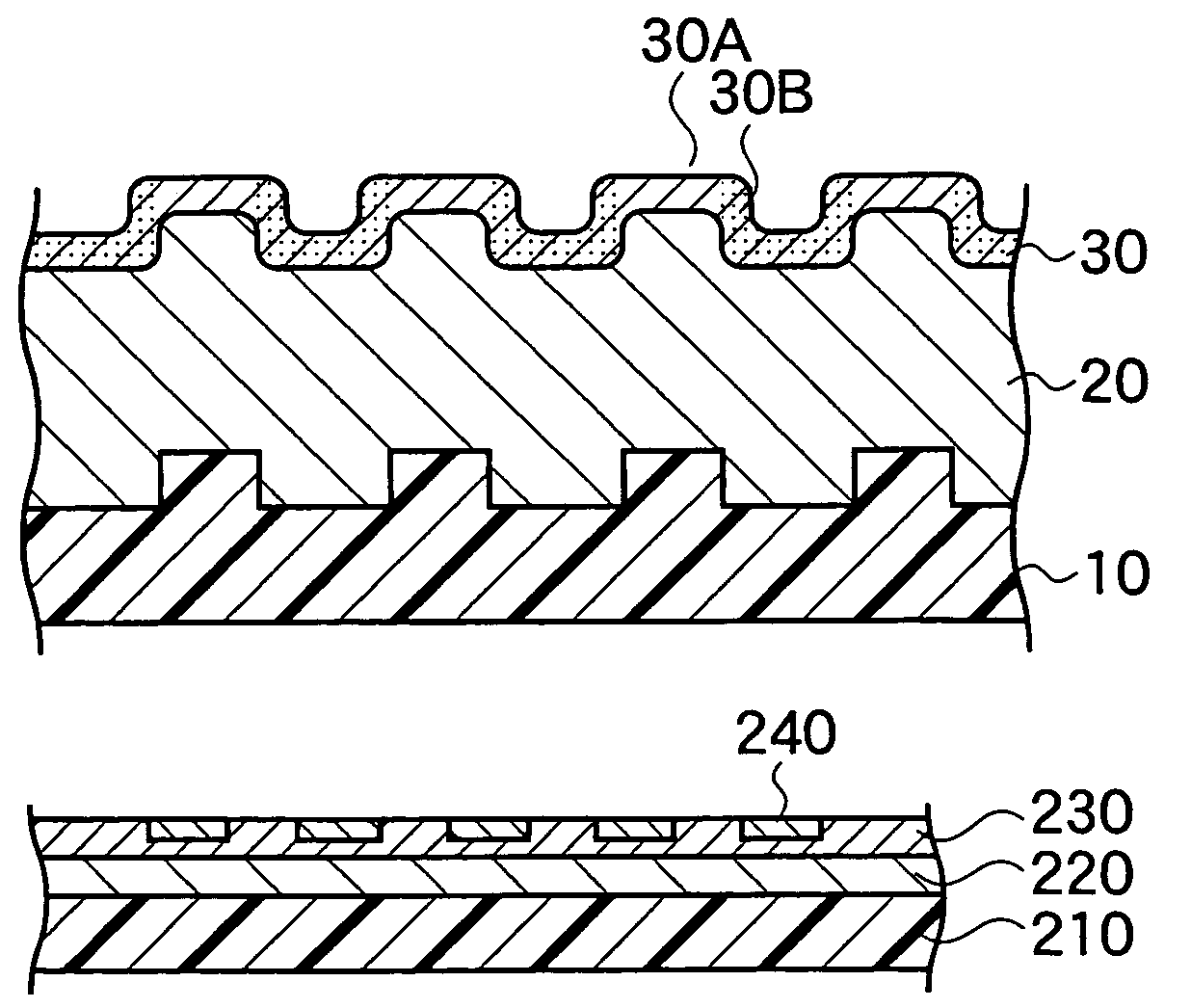
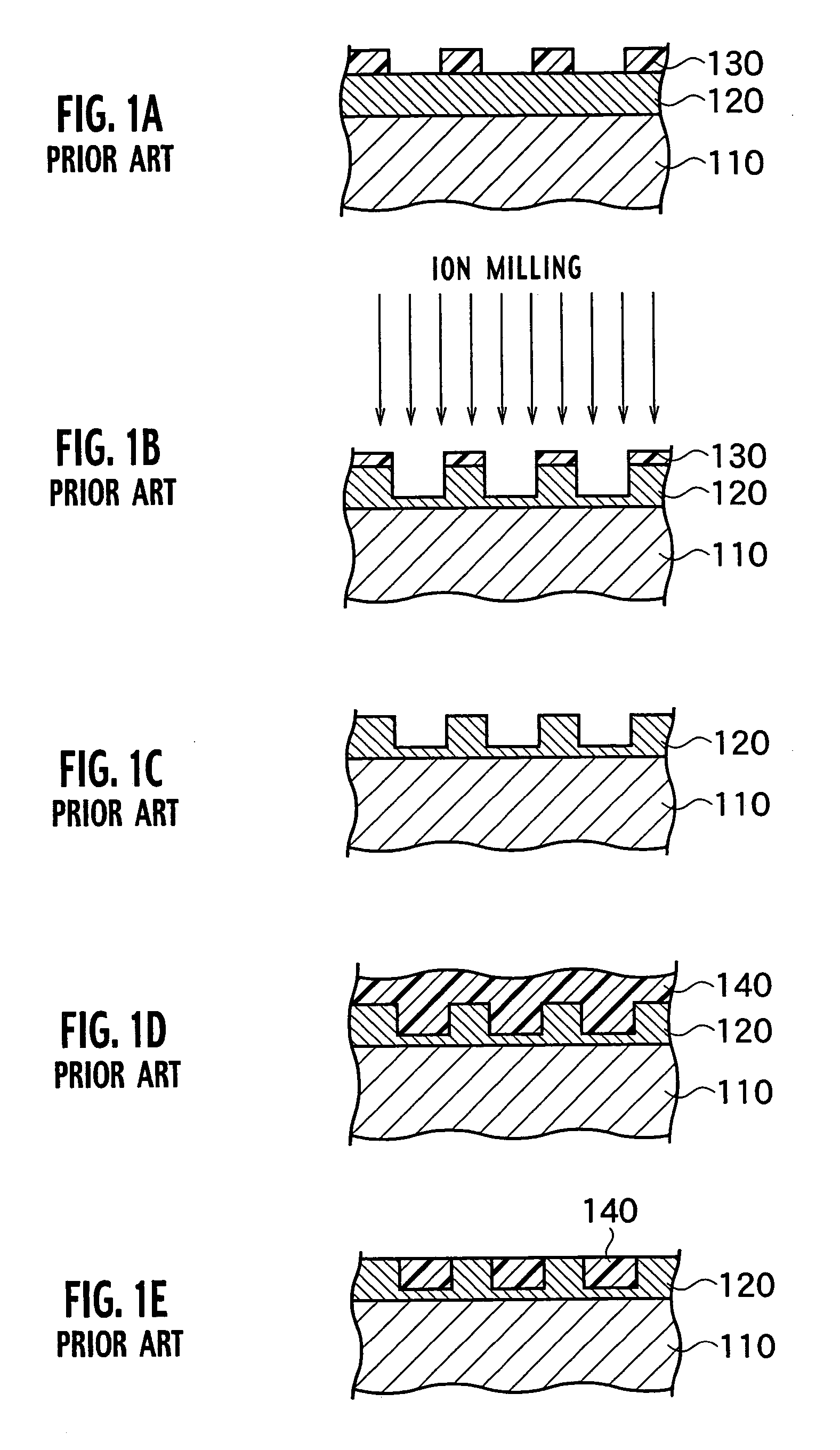
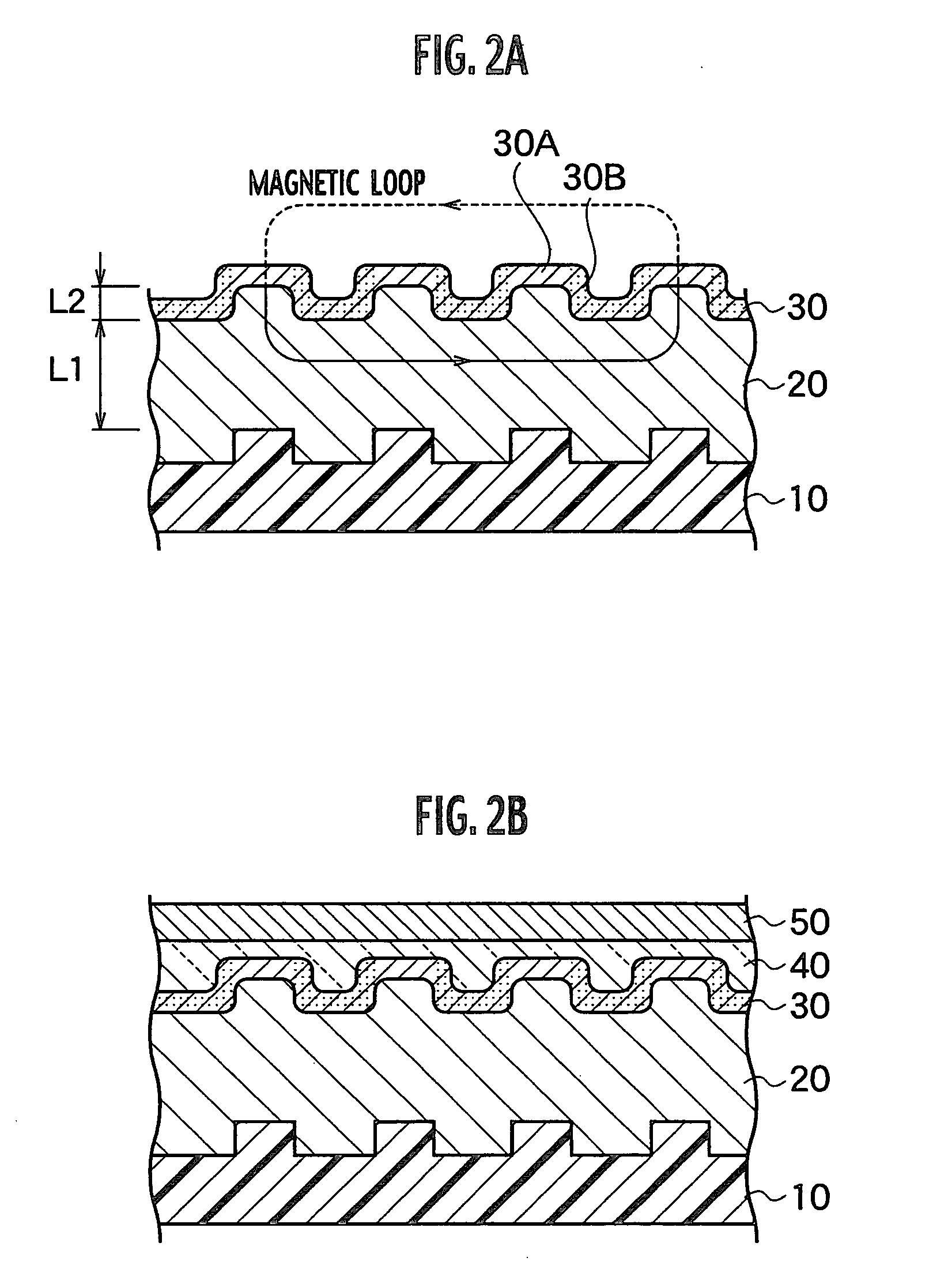
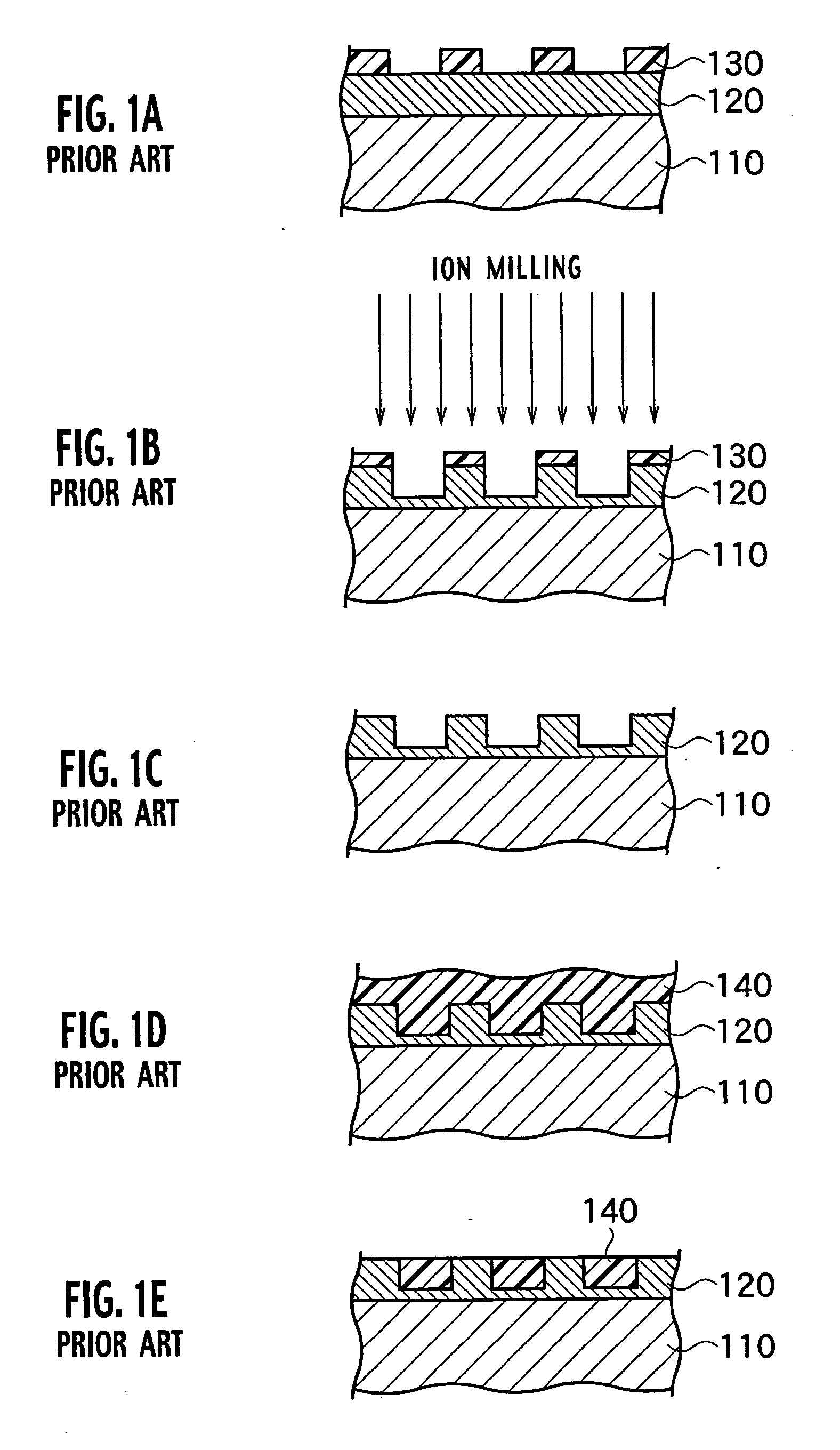
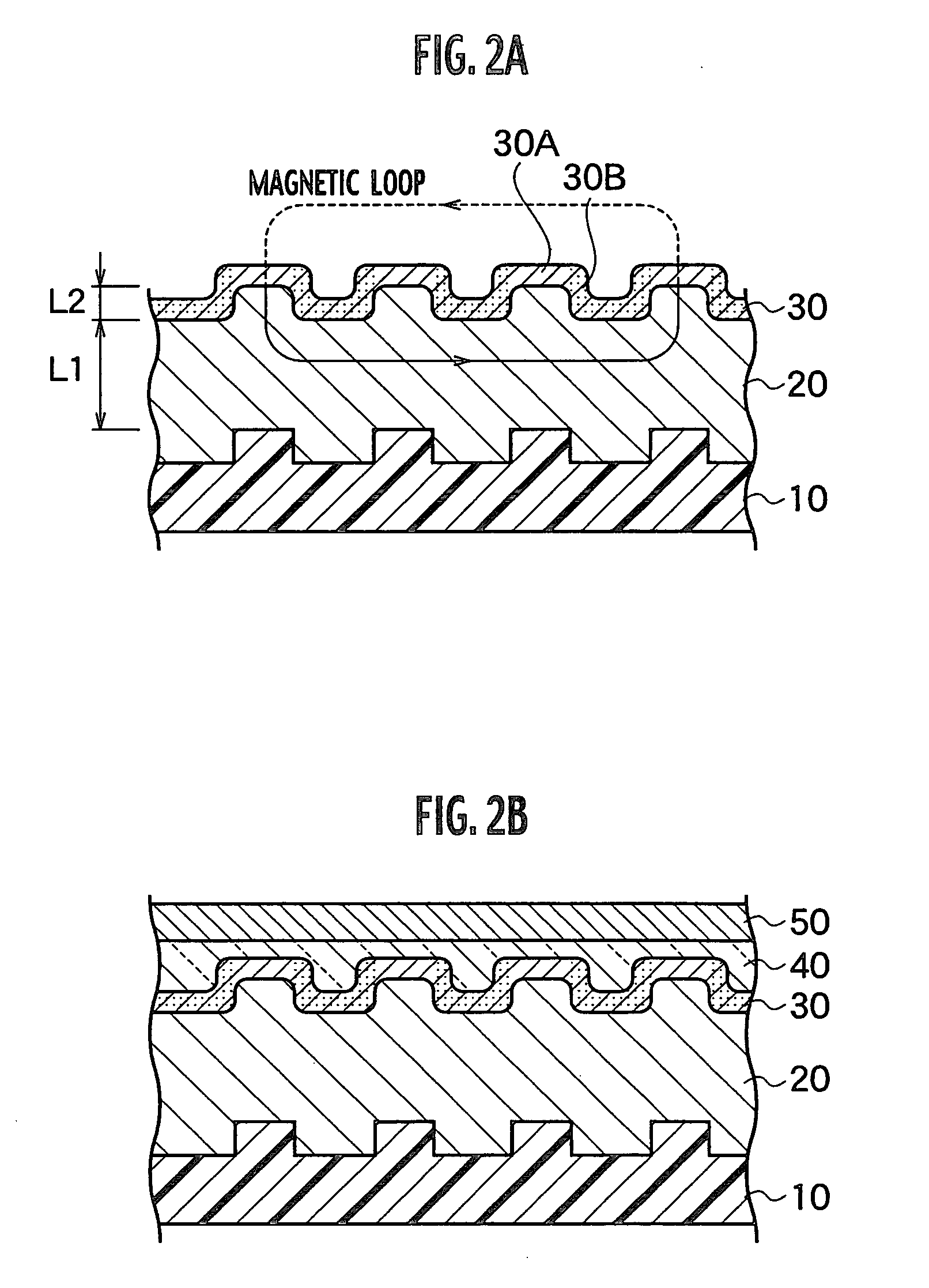
Magnetic recording medium having a patterned soft magnetic layer
InactiveUS7067207B2Reduce noiseMagnetic materials for record carriersBase layers for recording layersNon magneticFerromagnetism
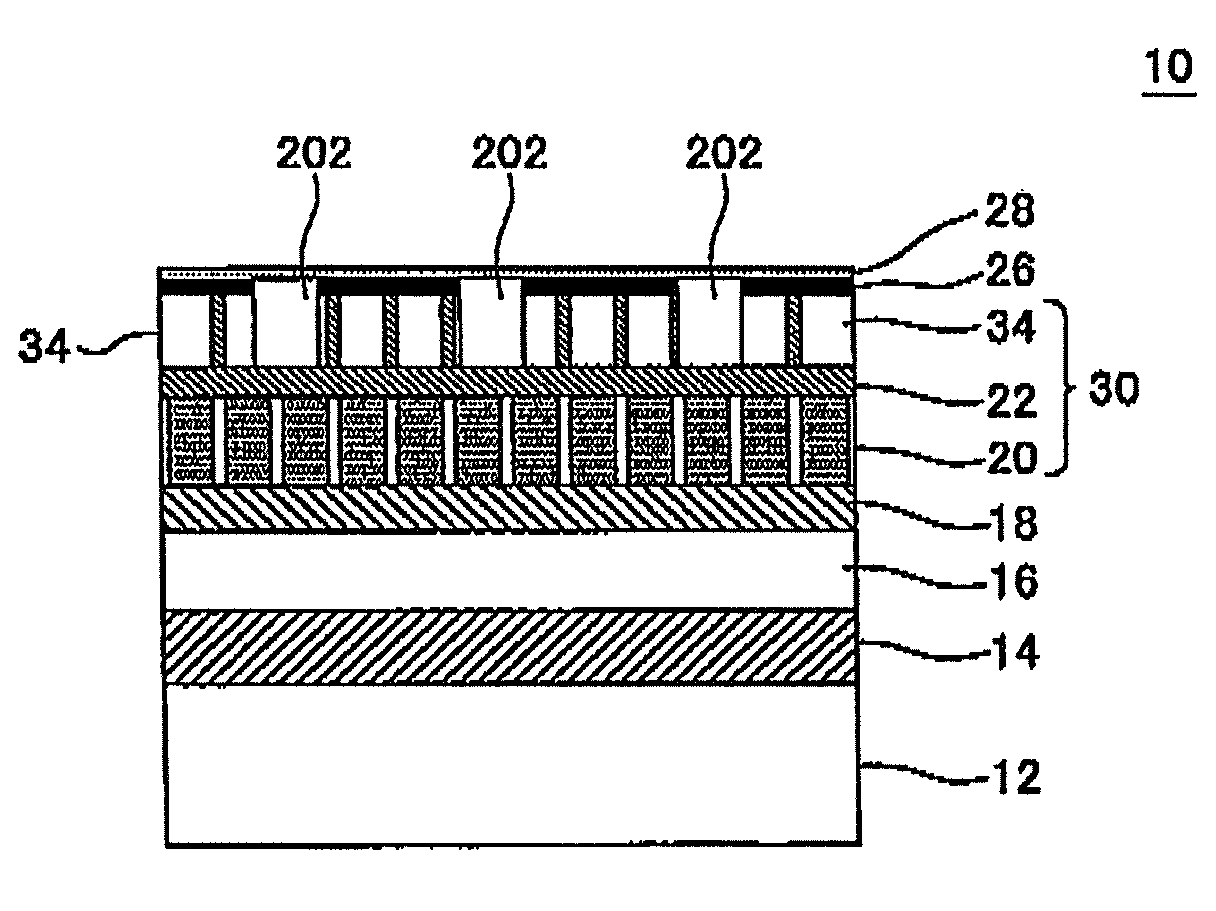
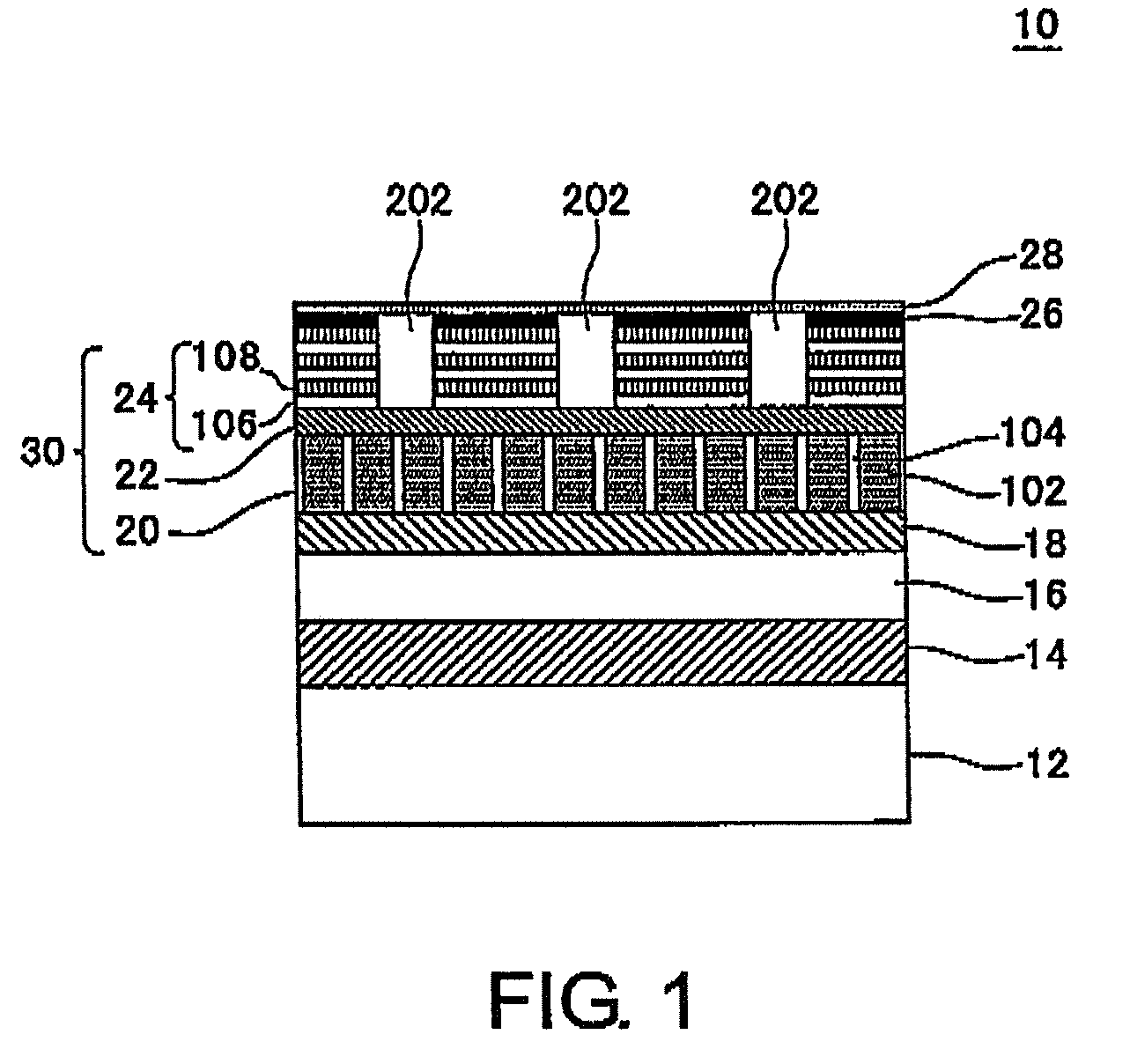
A magnetic recording medium includes a non-magnetic substrate; a soft magnetic layer which is formed on the non-magnetic substrate and which includes projected parts arranged on the surface thereof and recessed parts surrounding each of the projected part; and a ferromagnetic layer which is formed on the soft magnetic layer and which includes projected parts and recessed parts reflecting the projected parts and the recessed parts of the soft magnetic layer. Further the magnetic recording medium includes recording areas which have perpendicular magnetic anisotropy and ferromagnetism, and which are formed of the projected parts of the ferromagnetic layer and separated magnetically from their surroundings. A method for manufacture of the magnetic recording medium includes forming a soft magnetic layer including of projected parts arranged regularly on the surface thereof and recessed parts surrounding each projected part; and forming a ferromagnetic layer having perpendicular magnetic anisotropy on the soft magnetic layer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Patterned multilevel perpendicular magnetic recording media
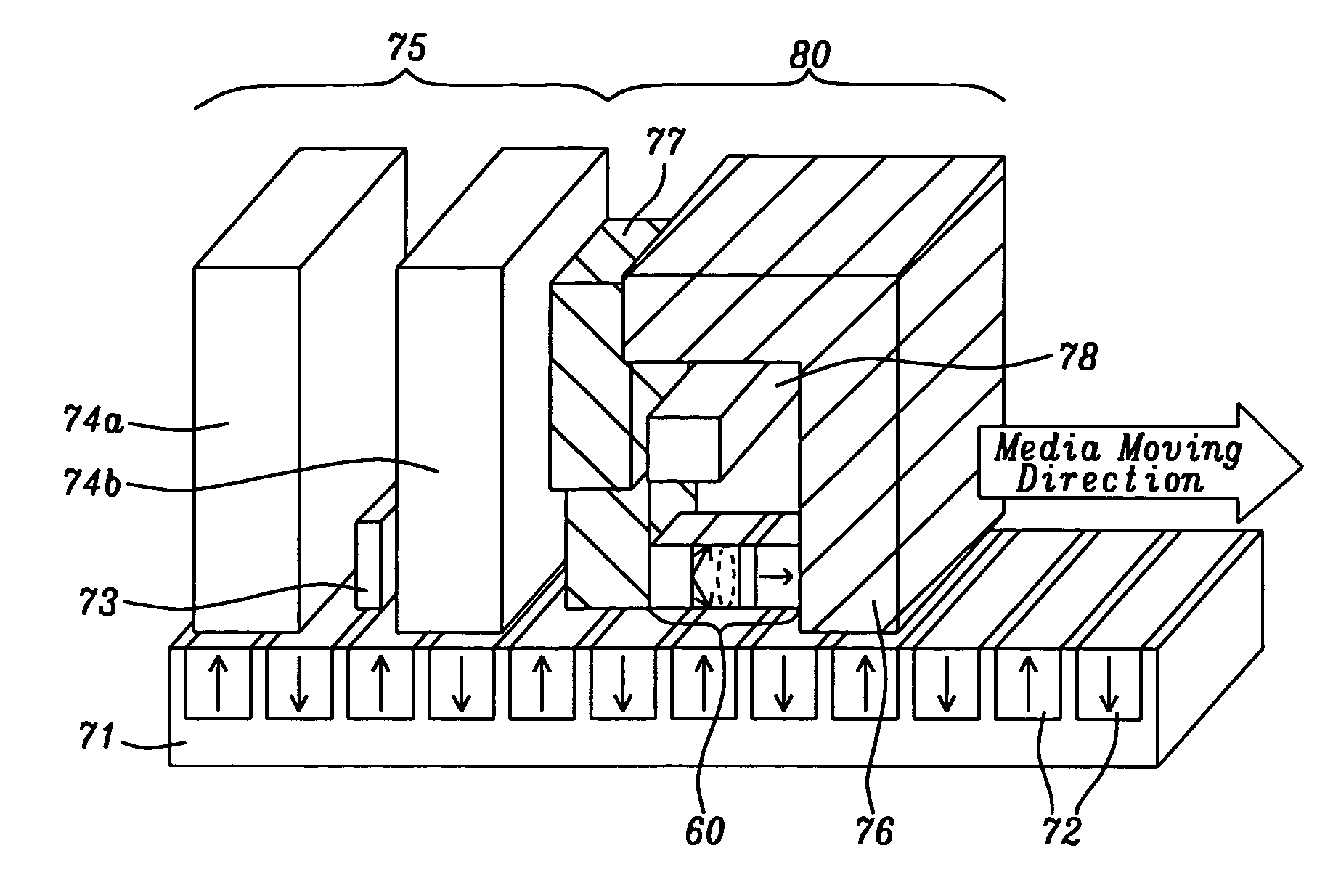
InactiveUS6947235B2Improve noiseImprove recording densityBase layers for recording layersPatterned record carriersMaterials scienceMagnetic moment
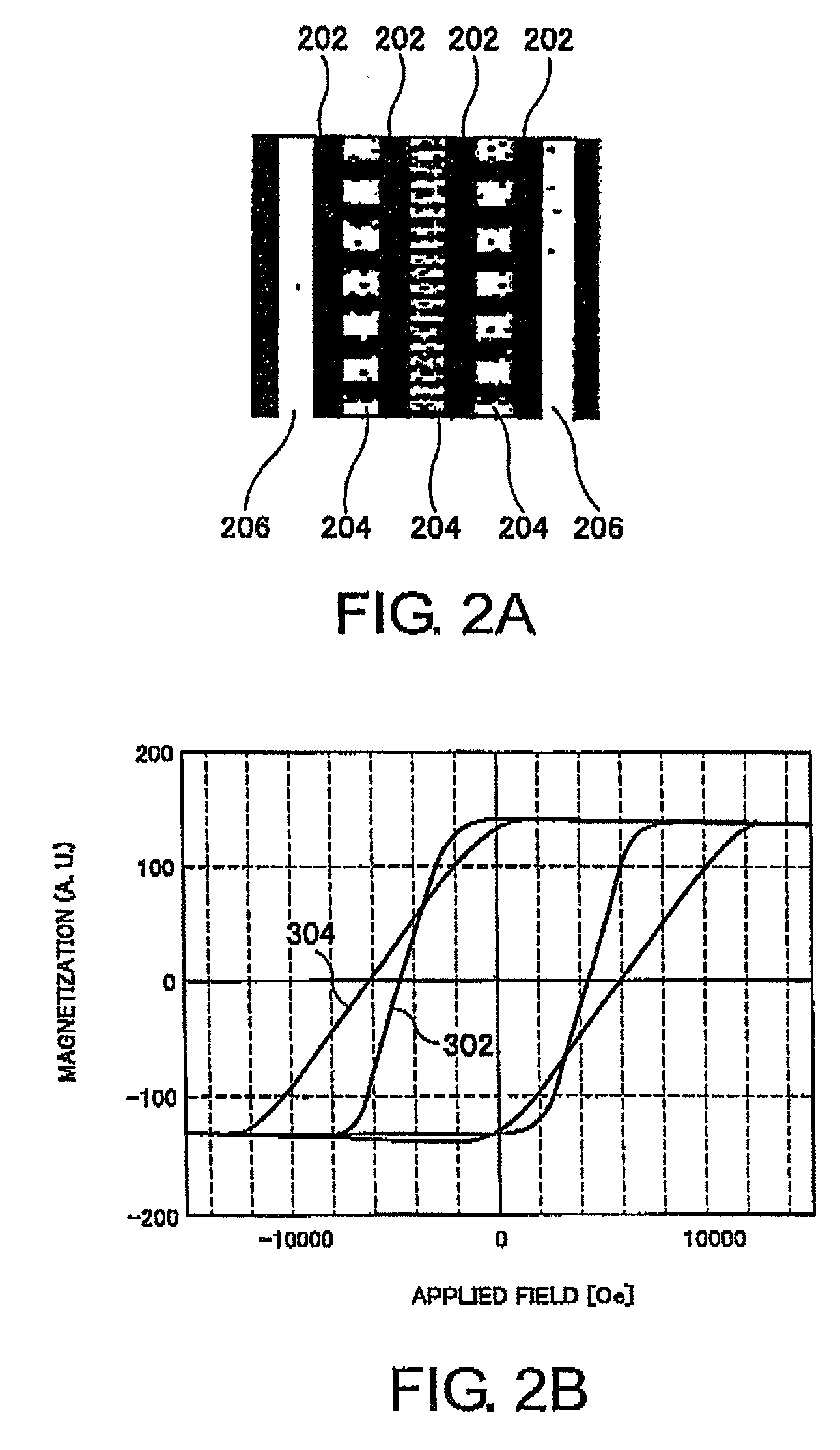
A patterned perpendicular magnetic recording medium has magnetic islands that contain stacks of individual magnetic cells to provide multilevel recording. Each cell in an island is formed of a material or set of materials to provide the cell with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy and is a single magnetic domain. Each cell is magnetically decoupled from the other cells in its island by nonmagnetic spacer layers. Thus each cell can have a magnetization (magnetic moment) in one of two directions (into or out of the plane of the layer making up the cell), and this magnetization is independent of the magnetization of the other cells in its island. This permits multiple magnetic levels or states to be recorded in each magnetic island.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Magnetic recording medium and method for manufacture thereof
InactiveUS20040091748A1Magnetic materials for record carriersBase layers for recording layersEngineeringNon magnetic
A magnetic recording medium includes a non-magnetic substrate; a soft magnetic layer which is formed on the non-magnetic substrate and which includes projected parts arranged on the surface thereof and recessed parts surrounding each of the projected part; and a ferromagnetic layer which is formed on the soft magnetic layer and which includes projected parts and recessed parts reflecting the projected parts and the recessed parts of the soft magnetic layer. Further the magnetic recording medium includes recording areas which have perpendicular magnetic anisotropy and ferromagnetism, and which are formed of the projected parts of the ferromagnetic layer and separated magnetically from their surroundings. A method for manufacture of the magnetic recording medium includes forming a soft magnetic layer including of projected parts arranged regularly on the surface thereof and recessed parts surrounding each projected part; and forming a ferromagnetic layer having perpendicular magnetic anisotropy on the soft magnetic layer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
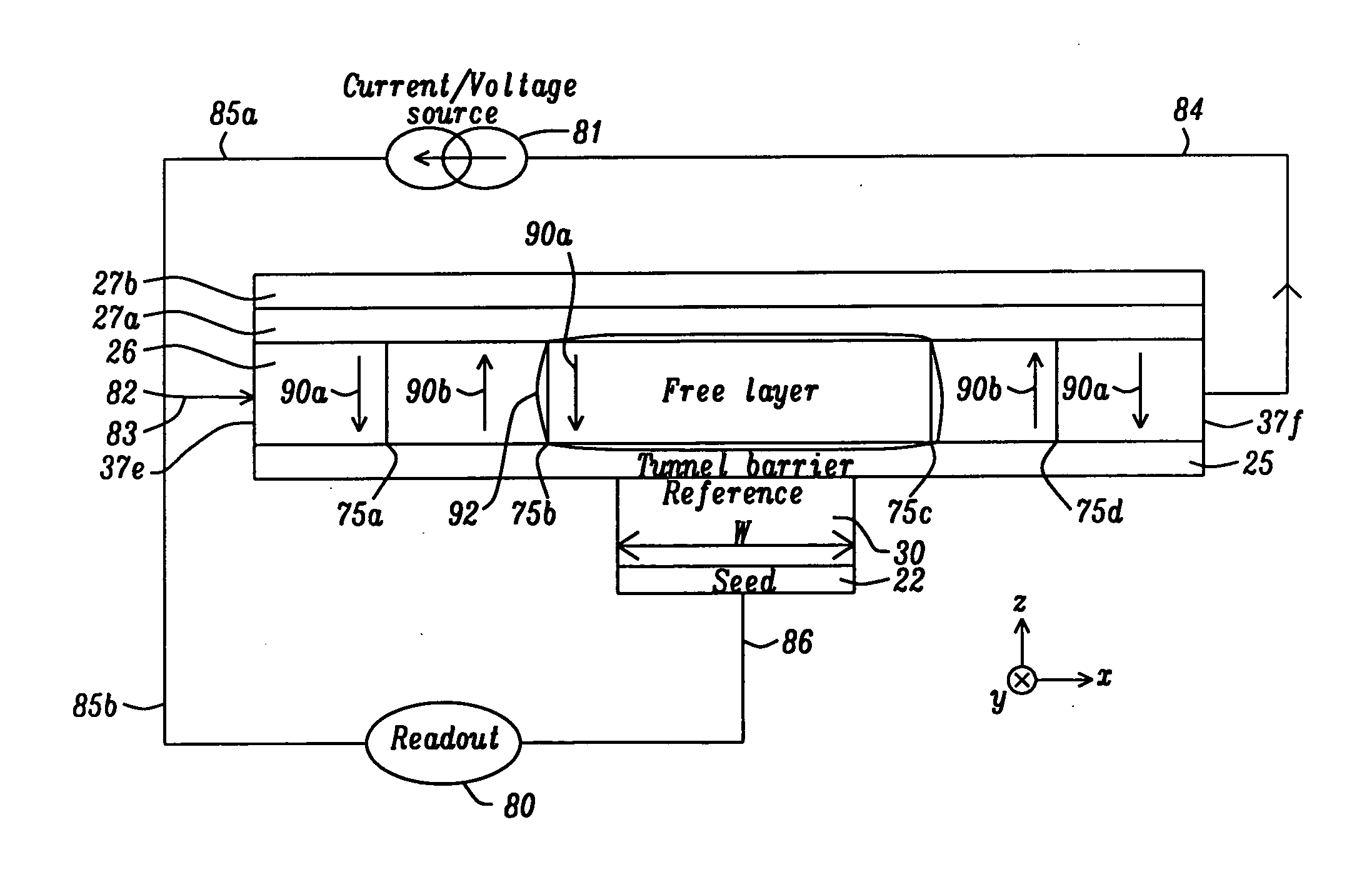
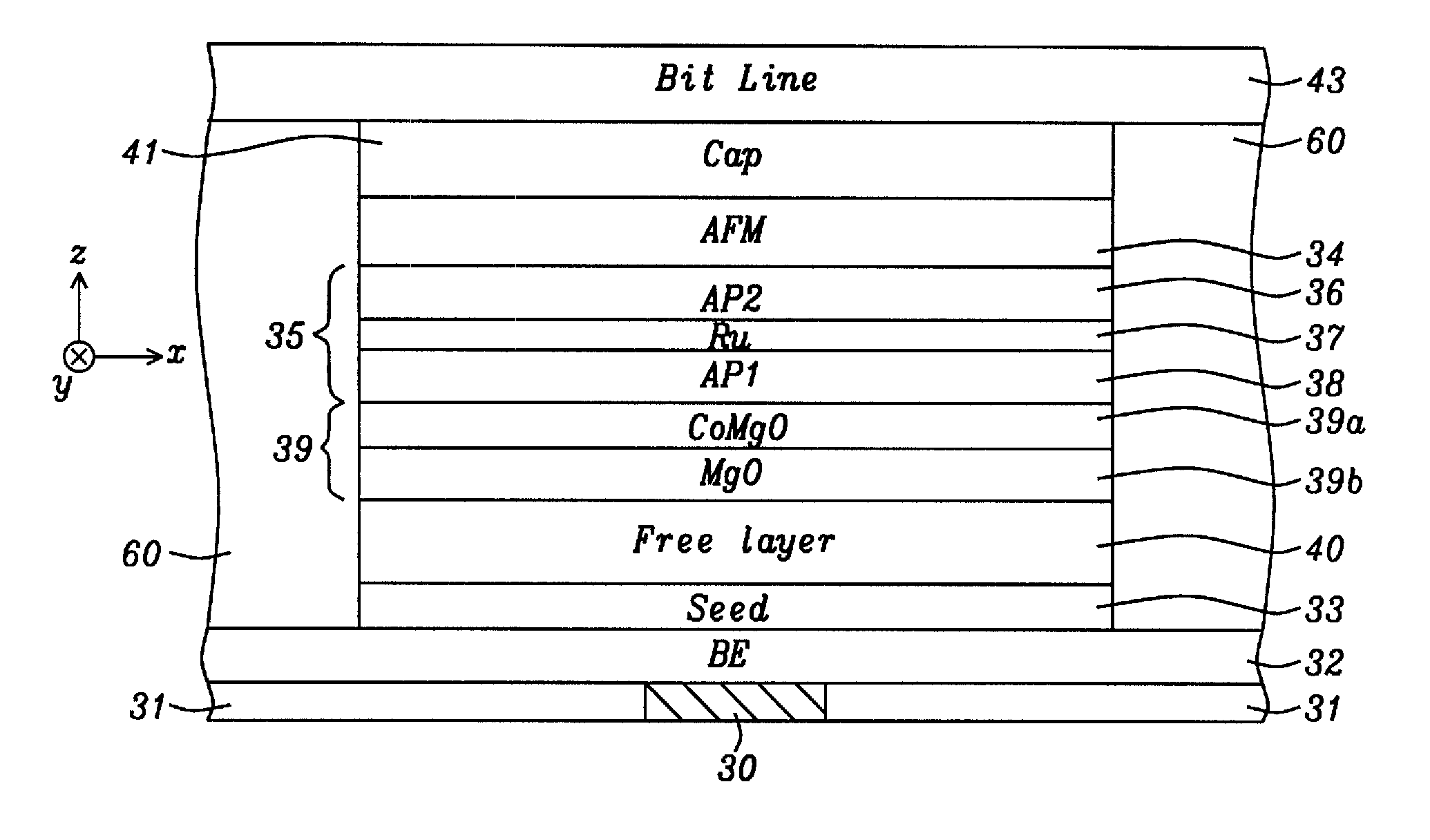
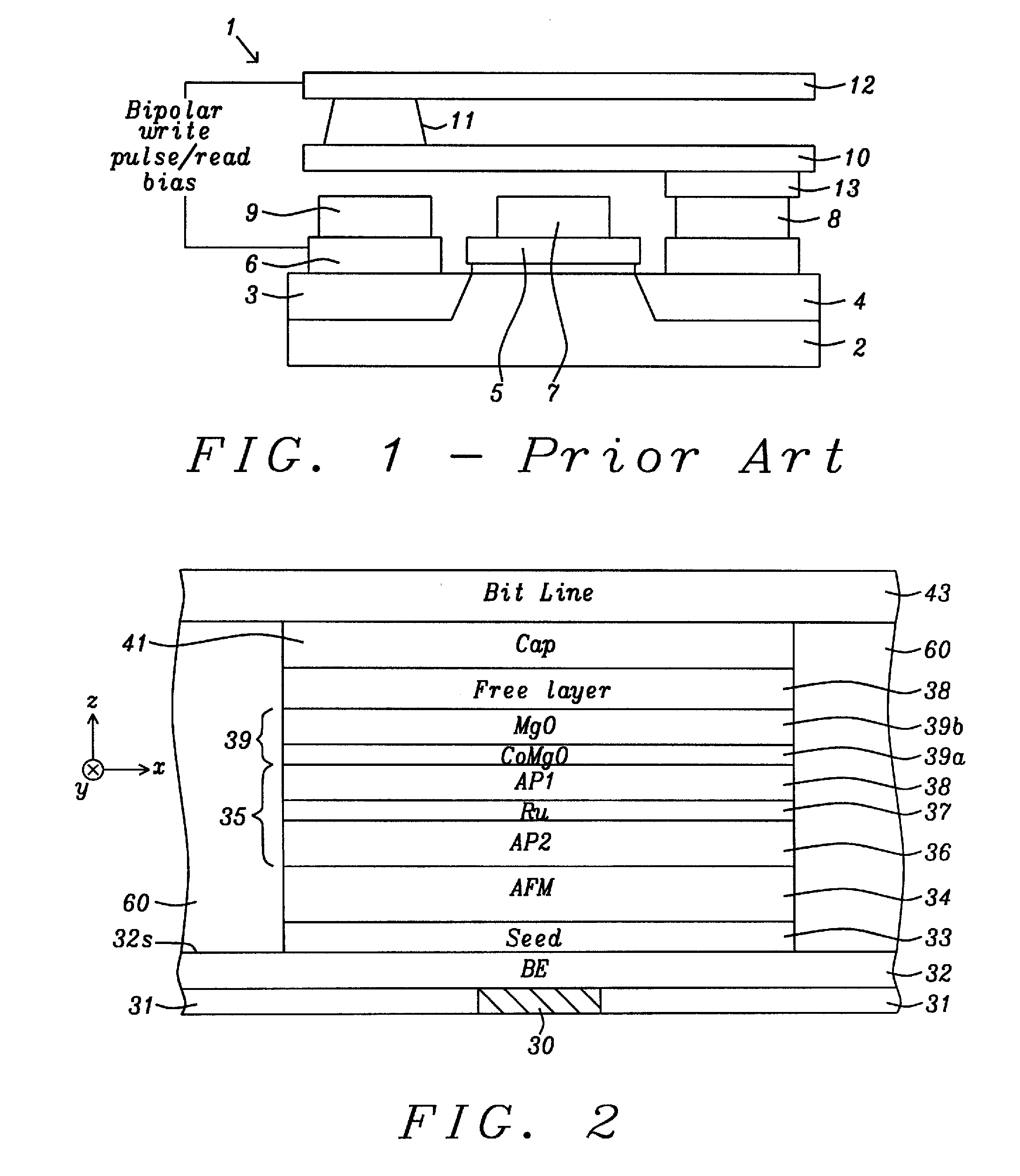
Spin torque transfer magnetic tunnel junction fabricated with a composite tunneling barrier layer
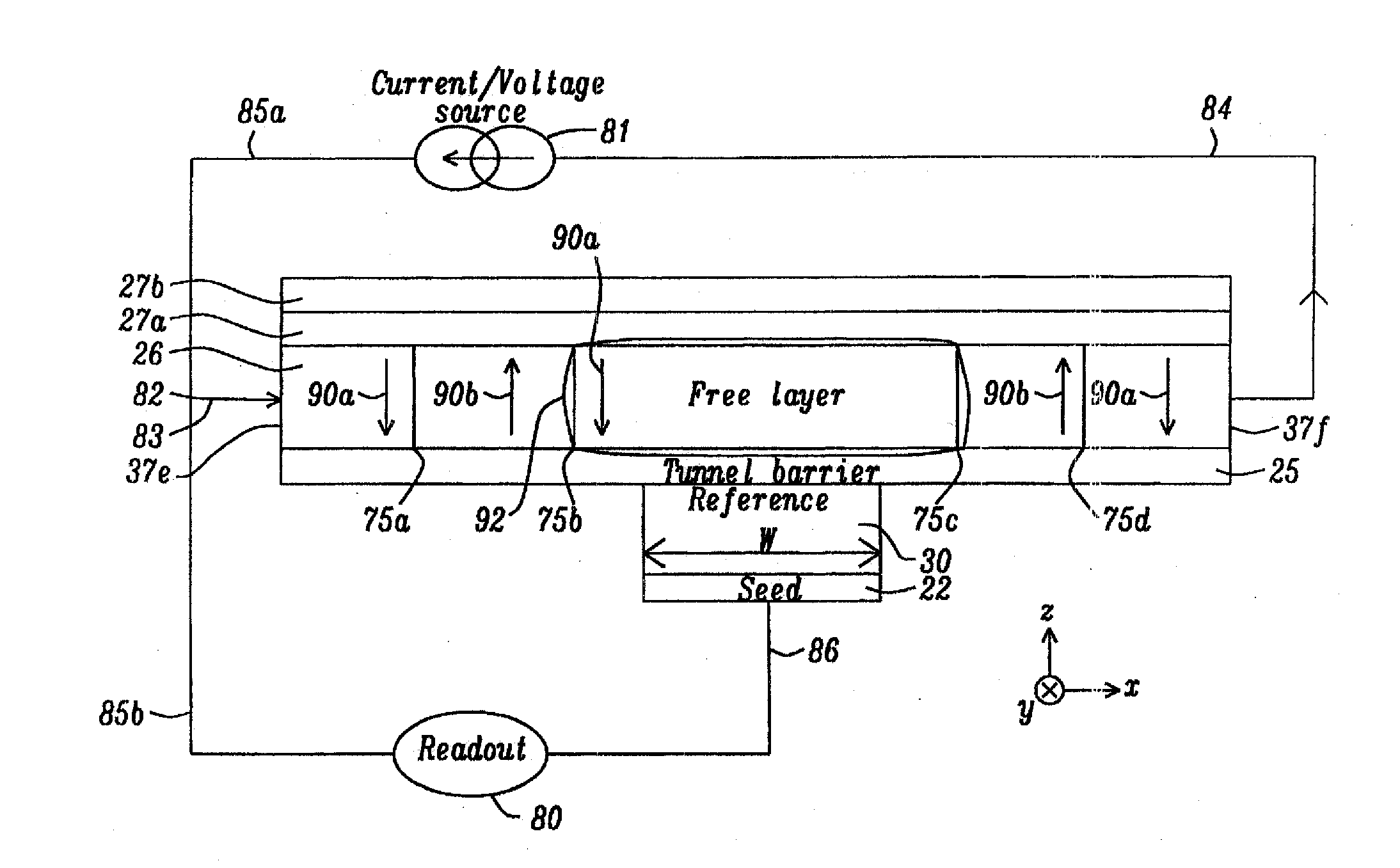
ActiveUS8823118B2Improve performanceHigh densityMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesIn planeSpins
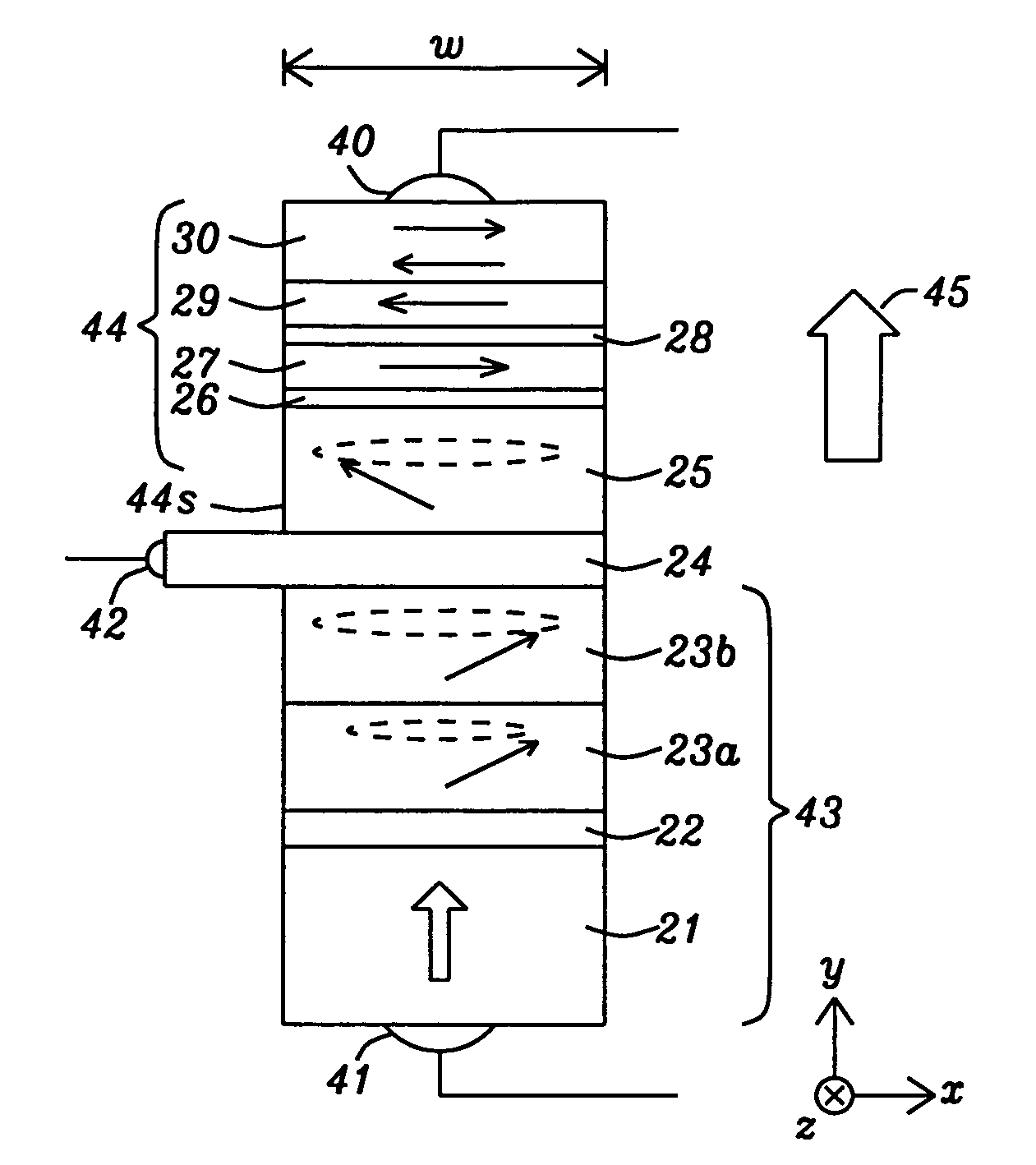
A STT-RAM MTJ is disclosed with a composite tunnel barrier comprised of a CoMgO layer that contacts a pinned layer and a MgO layer which contacts a free layer. A CoMg layer with a Co content between 20 and 40 atomic % is deposited on the pinned layer and is then oxidized to produce Co nanoconstrictions within a MgO insulator matrix. The nanoconstrictions control electromigration of Co into an adjoining MgO layer. The free layer may comprise a nanocurrent channel (NCC) layer such as FeSiO or a moment dilution layer such as Ta between two ferromagnetic layers. Furthermore, a second CoMgO layer or a CoMgO / MgO composite may serve as a perpendicular Hk enhancing layer formed between the free layer and a cap layer. One or both of the pinned layer and free layer may exhibit in-plane anisotropy or perpendicular magnetic anisotropy.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Perpendicular magnetic tunnel junctions, magnetic devices including the same and method of manufacturing a perpendicular magnetic tunnel junction
InactiveUS20110149647A1NanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSpin polarizationTunnel junction
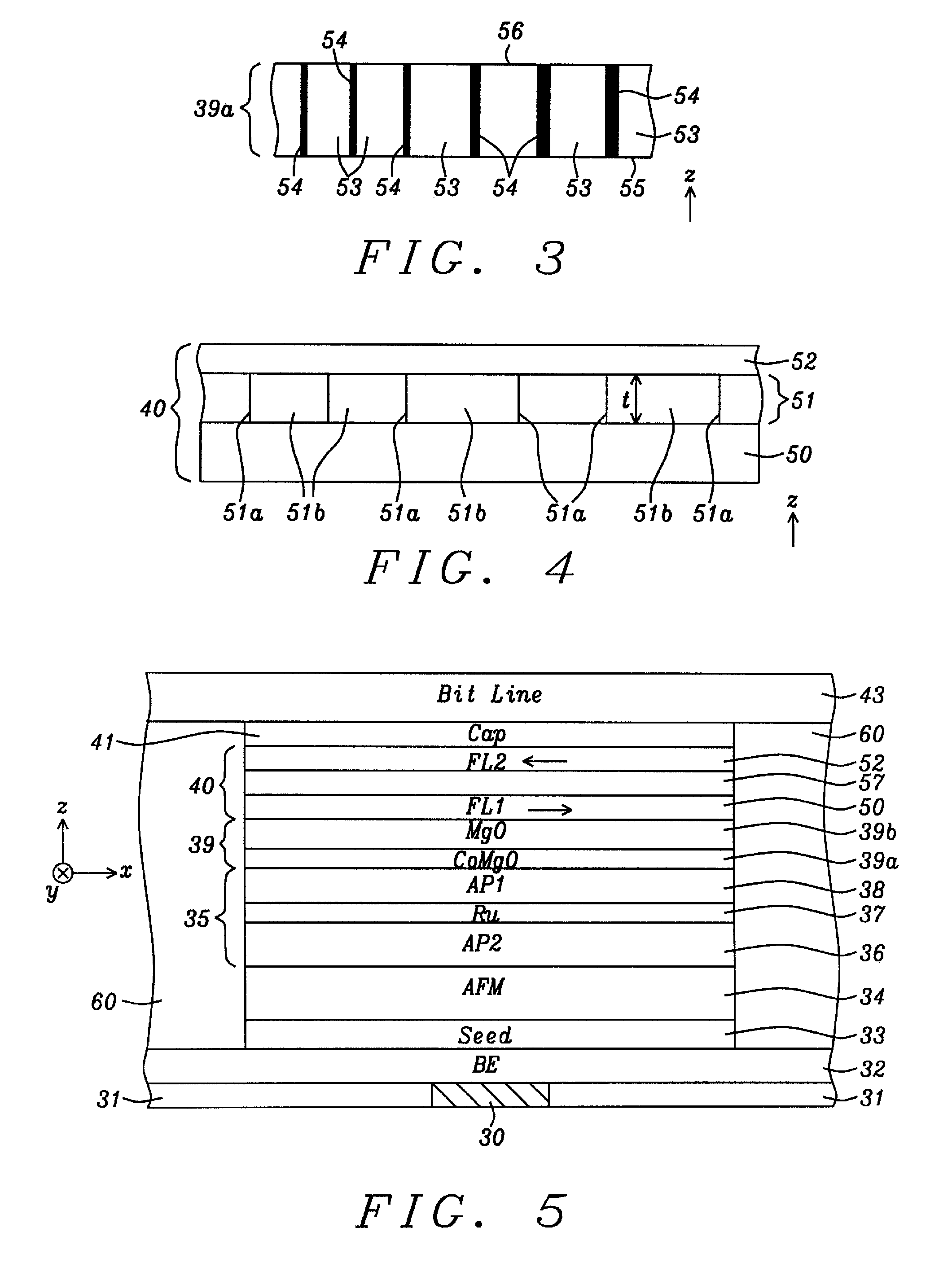
Provided are a perpendicular magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ), a magnetic device including the same, and a method of manufacturing the MTJ, the perpendicular MTJ includes a lower magnetic layer; a tunnelling layer on the lower magnetic layer; and an upper magnetic layer on the tunnelling layer. One of the upper and lower magnetic layers includes a free magnetic layer that exhibits perpendicular magnetic anisotropy, wherein the magnetizing direction of the free magnetic layer is changed by a spin polarization current. A polarization enhancing layer (PEL) and an exchange blocking layer (EBL) are stacked between the tunnelling layer and the free magnetic layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Magnetic recording medium and method for manufacturing magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS7833639B2Delay transitionImprove thermal stabilityPatterned record carriersNanoinformaticsGrain boundaryCrystallite
Owner:WD MEDIA SINGAPORE PTE
Field tunable spin torque oscillator for RF signal generation
ActiveUS8203389B1Promote efficient magnetostatic couplingInduce oscillationPulse automatic controlRecord information storageHigh densitySpin torque oscillators
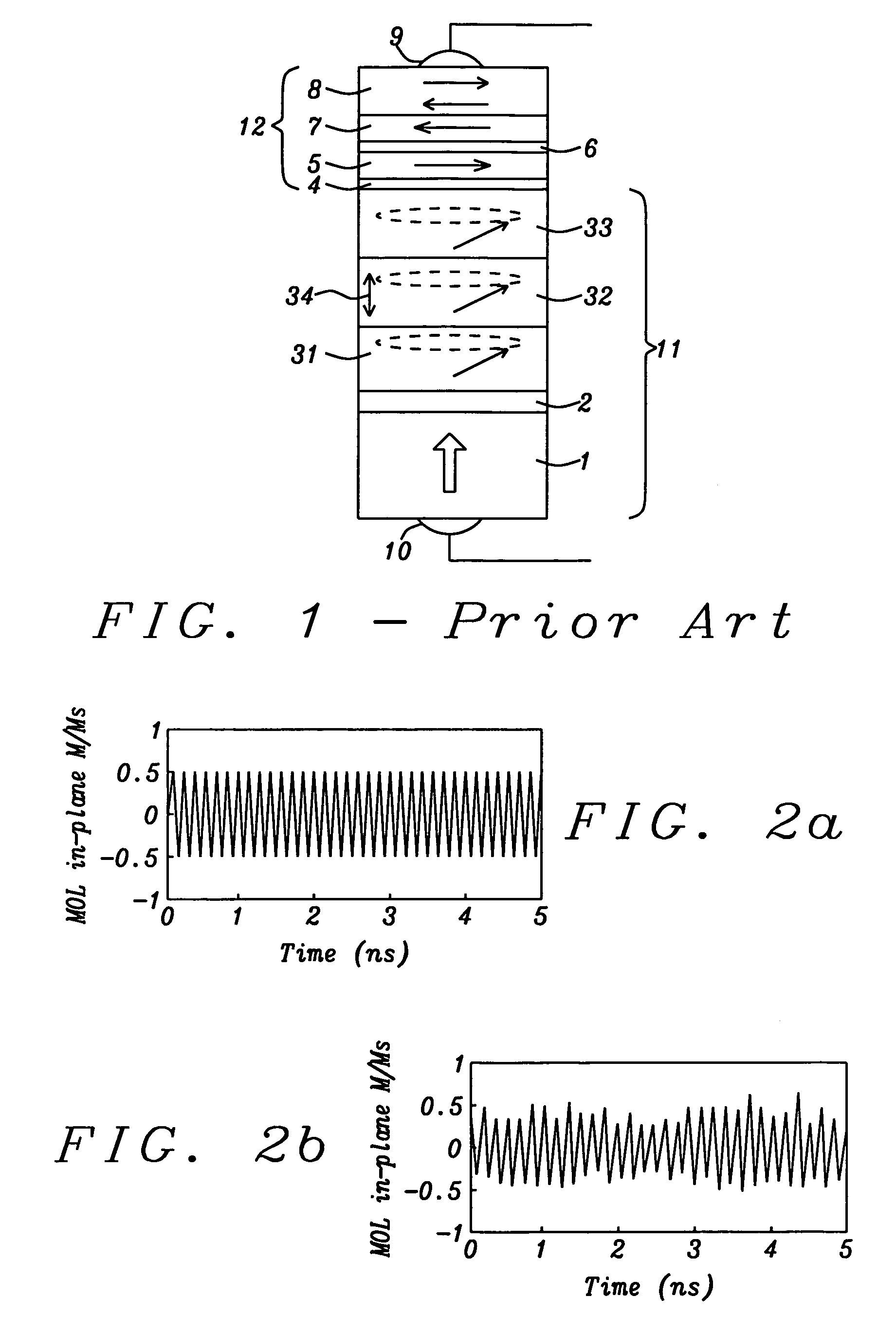
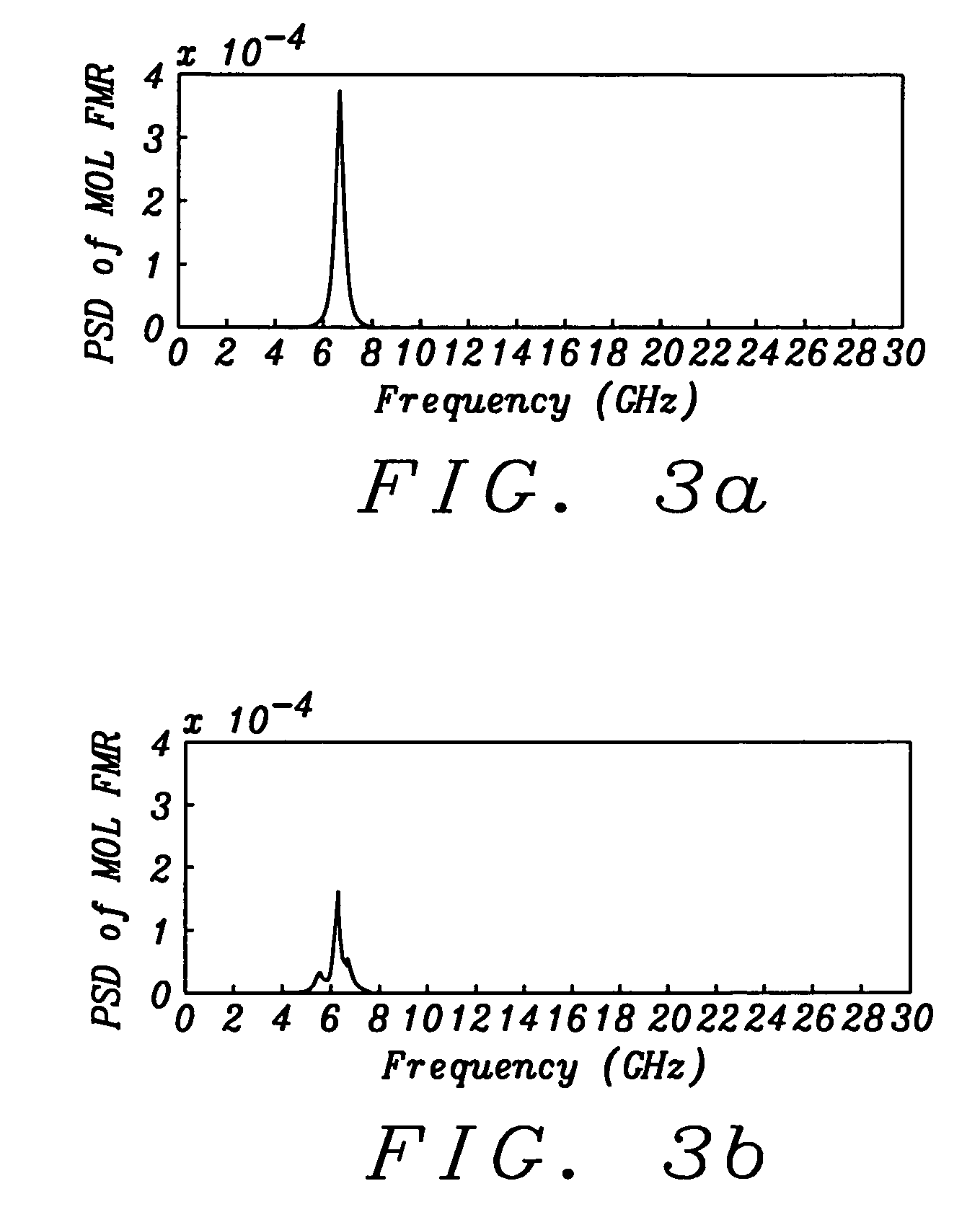
A spin transfer oscillator (STO) device is disclosed with a giant magnetoresistive (GMR) junction comprising a magnetic resistance layer (MRL) / spacer / magnetic oscillation layer (MOL) configuration, and a MR sensor including a sensing layer / junction layer / reference layer configuration. MOL and sensing layer are magnetostatically coupled and separated by a conductive spacer. MRL has perpendicular magnetic anisotropy while MOL and sensing layer have a Mst (saturation magnetization×thickness) value within ±50% of each other. When a magnetic field is applied perpendicular to the planes of the MOL and a high density current flows from the conductive spacer to the MRL, a MOL oscillation state with a certain frequency is induced. Consequently, the sensing layer oscillates with a similar RF frequency and when a low density current flows across the MR sensor, an AC voltage signal is generated to determine the sensing layer frequency that can be varied by adjusting the applied field.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Perpendicular magnetic recording disk and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20090311557A1Low noise characteristicsSignificant changeRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsRecording layerNon magnetic
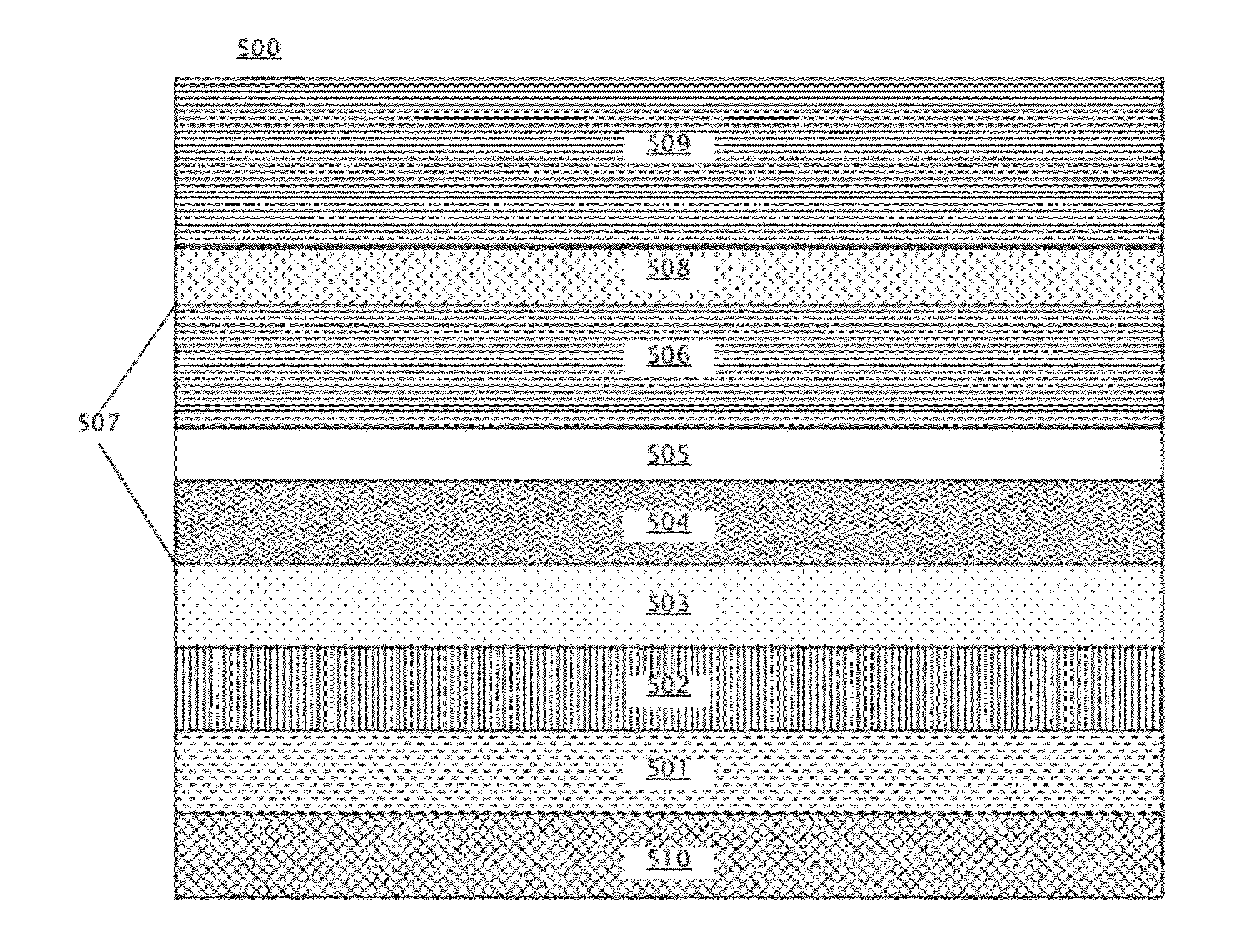
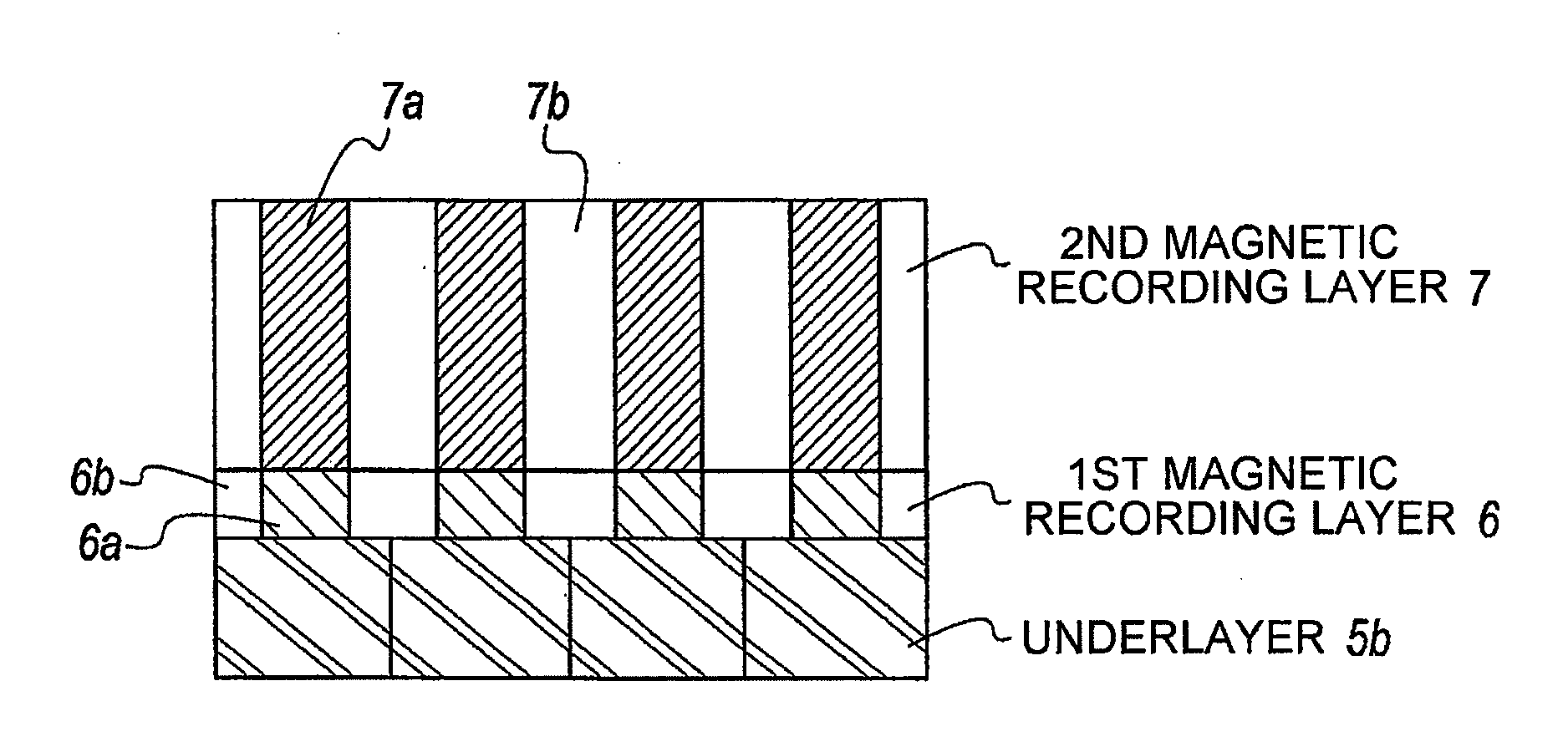
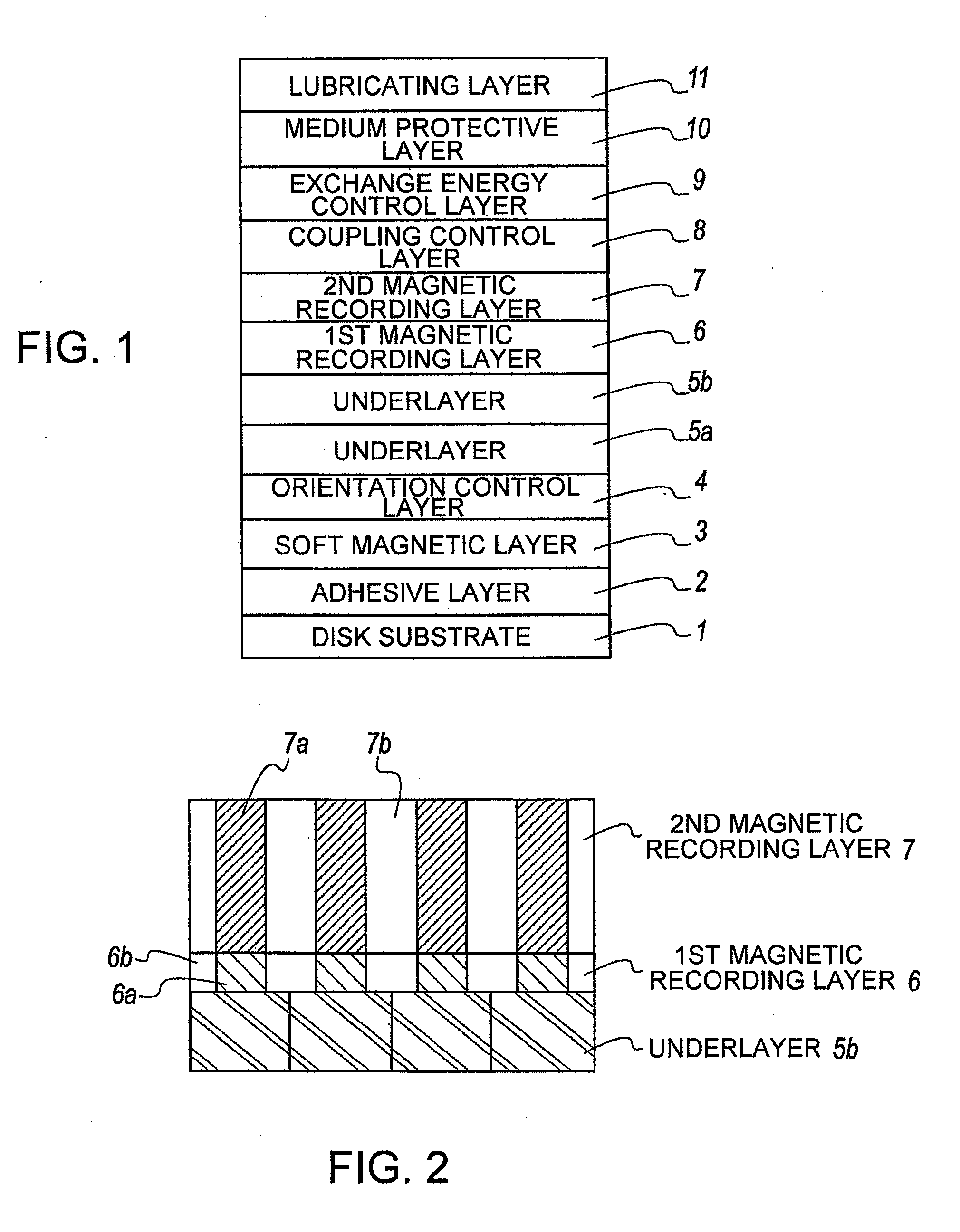
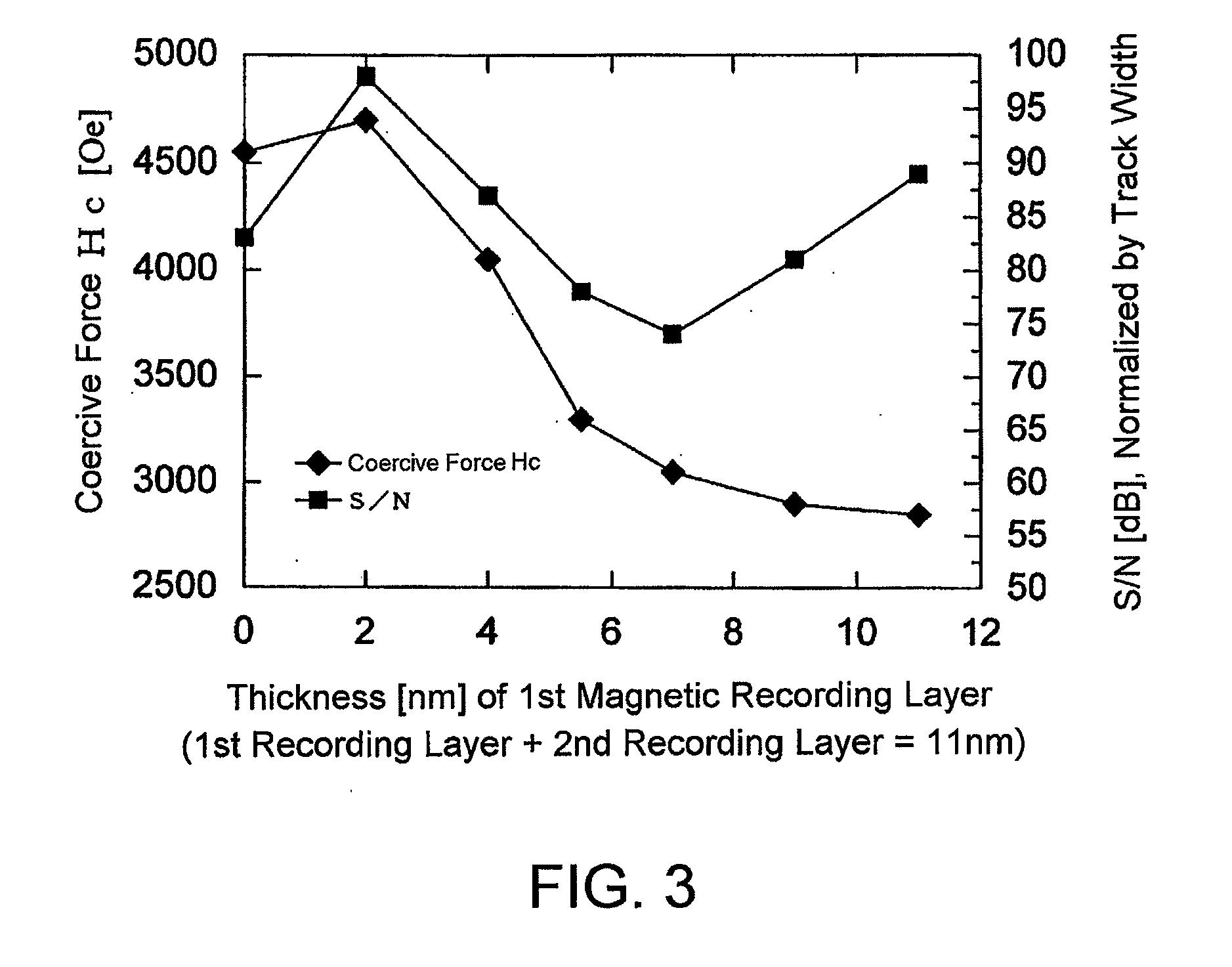
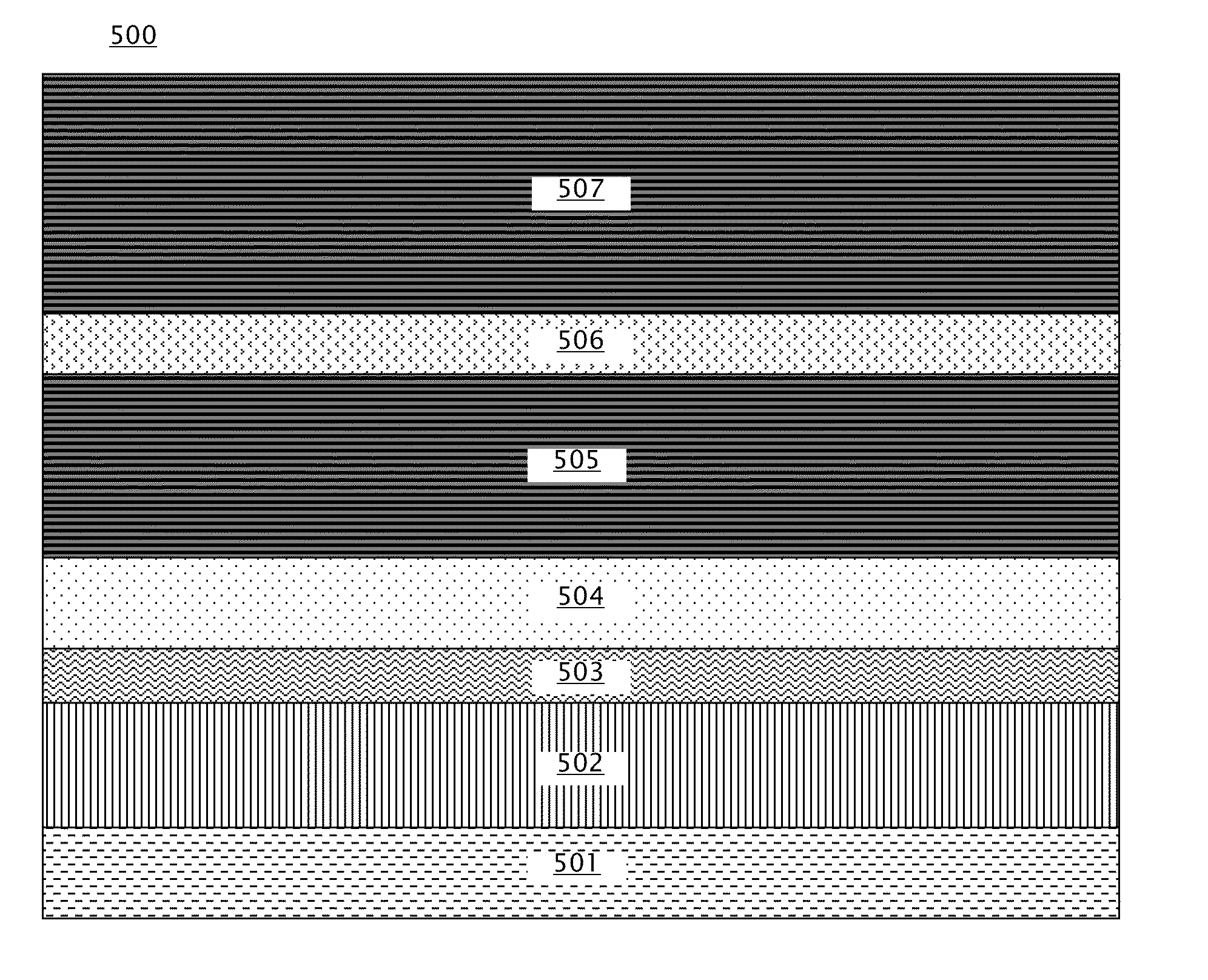
[Object] To achieve a high coercive force (Hc) and low-noise characteristics (high S / N ratio) through realization of both segregation of SiO2 and high perpendicular magnetic anisotropy by providing a two-layer structure having magnetic recording layers with different properties.[Solution] A magnetic disk for use in perpendicular magnetic recording, having at least an underlayer 5, a first magnetic recording layer 6, and a second magnetic recording layer 7 on a substrate in this order. The first magnetic recording layer 6 and the second magnetic recording layer 7 are each a ferromagnetic layer of a granular structure containing a nonmagnetic substance forming grain boundary portions between crystal grains containing at least Co (cobalt). Given that the content of the nonmagnetic substance in the first magnetic recording layer 6 is A mol % and the content of the nonmagnetic substance in the second magnetic recording layer 7 is B mol %, A>B.
Owner:WD MEDIA SINGAPORE PTE
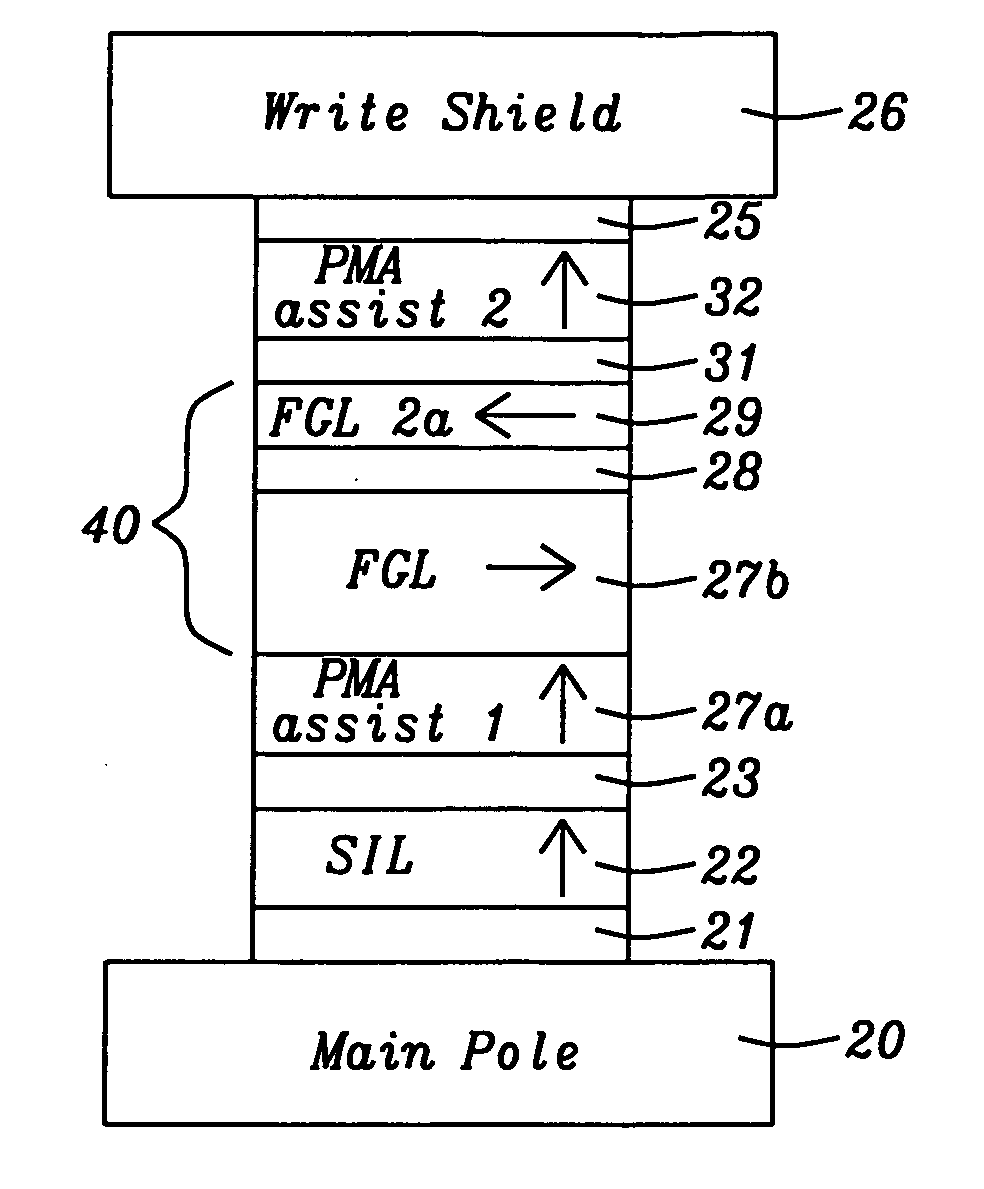
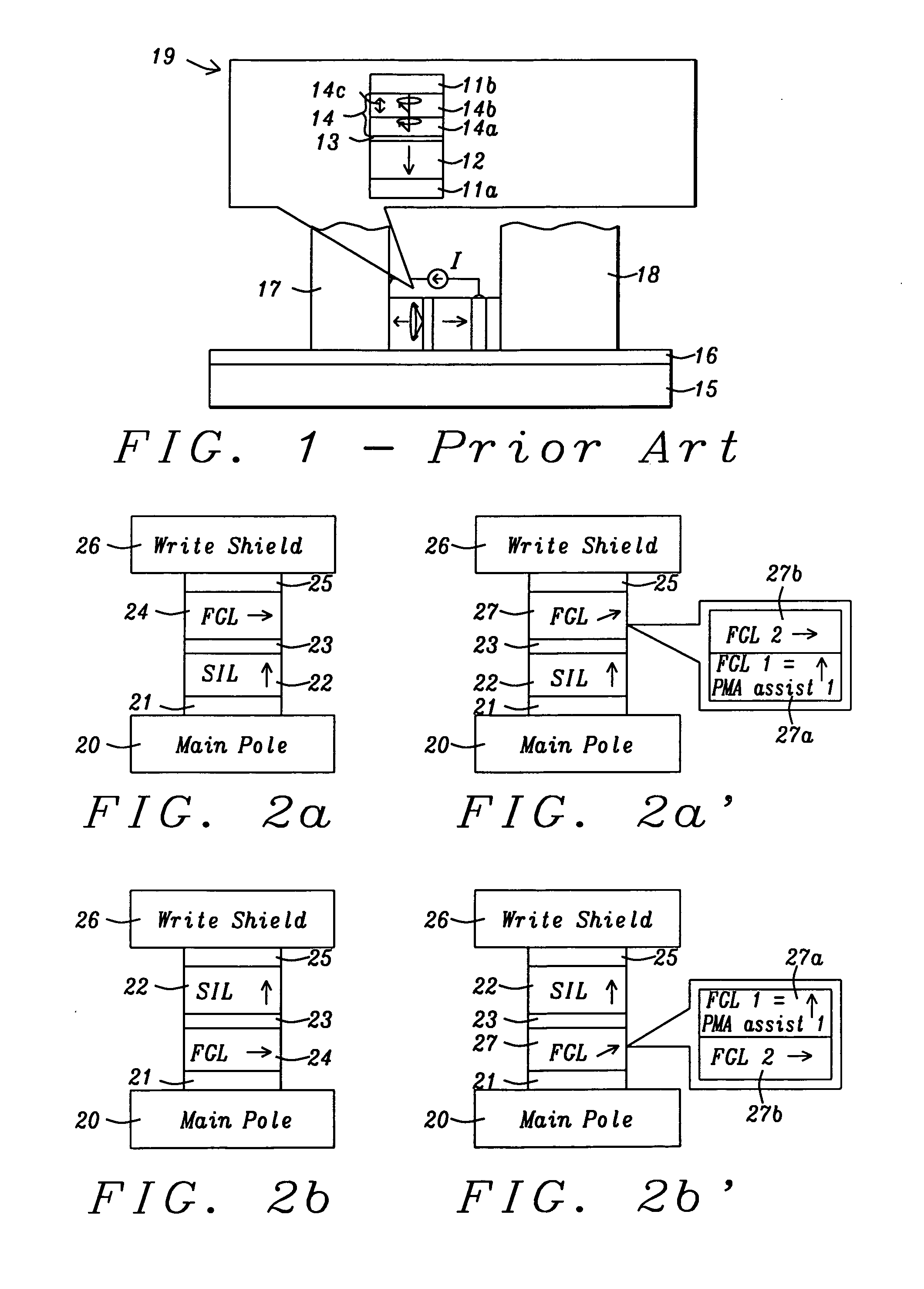
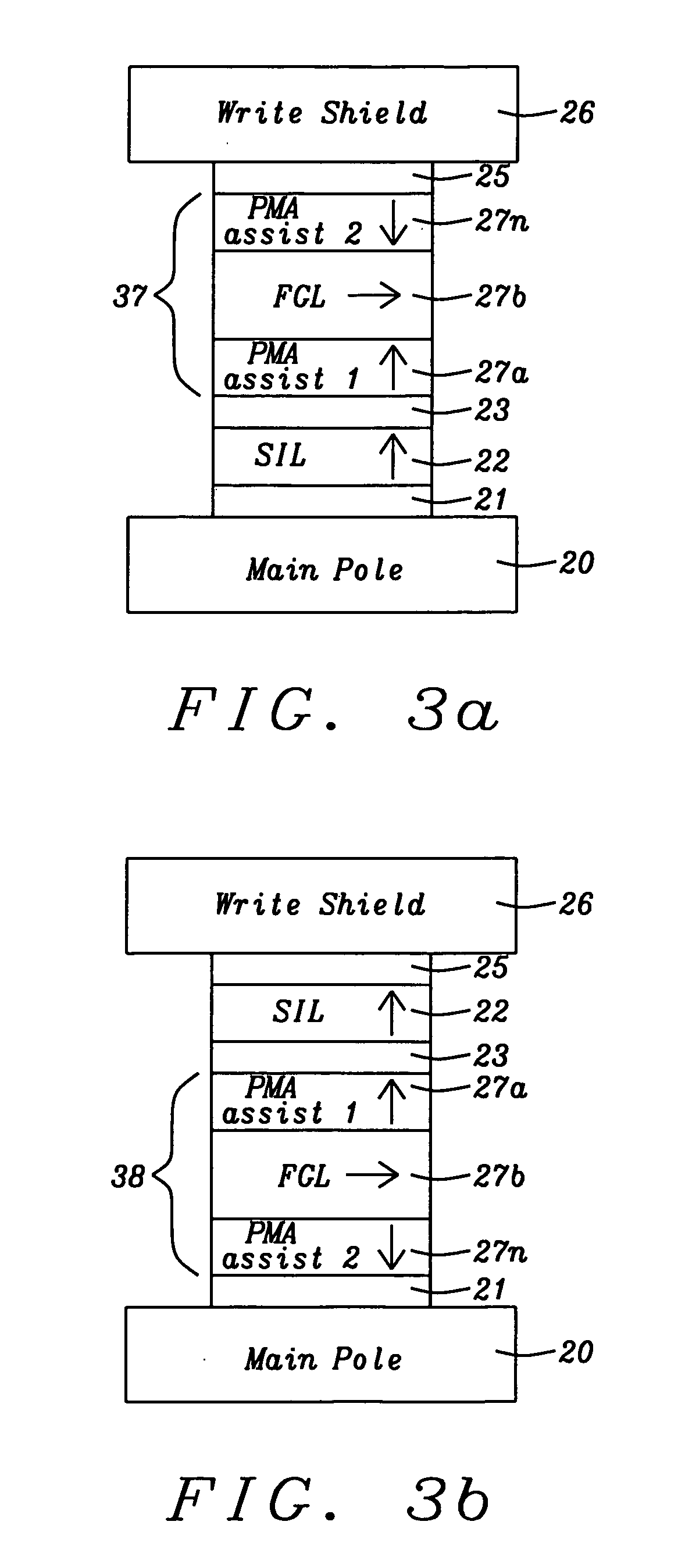
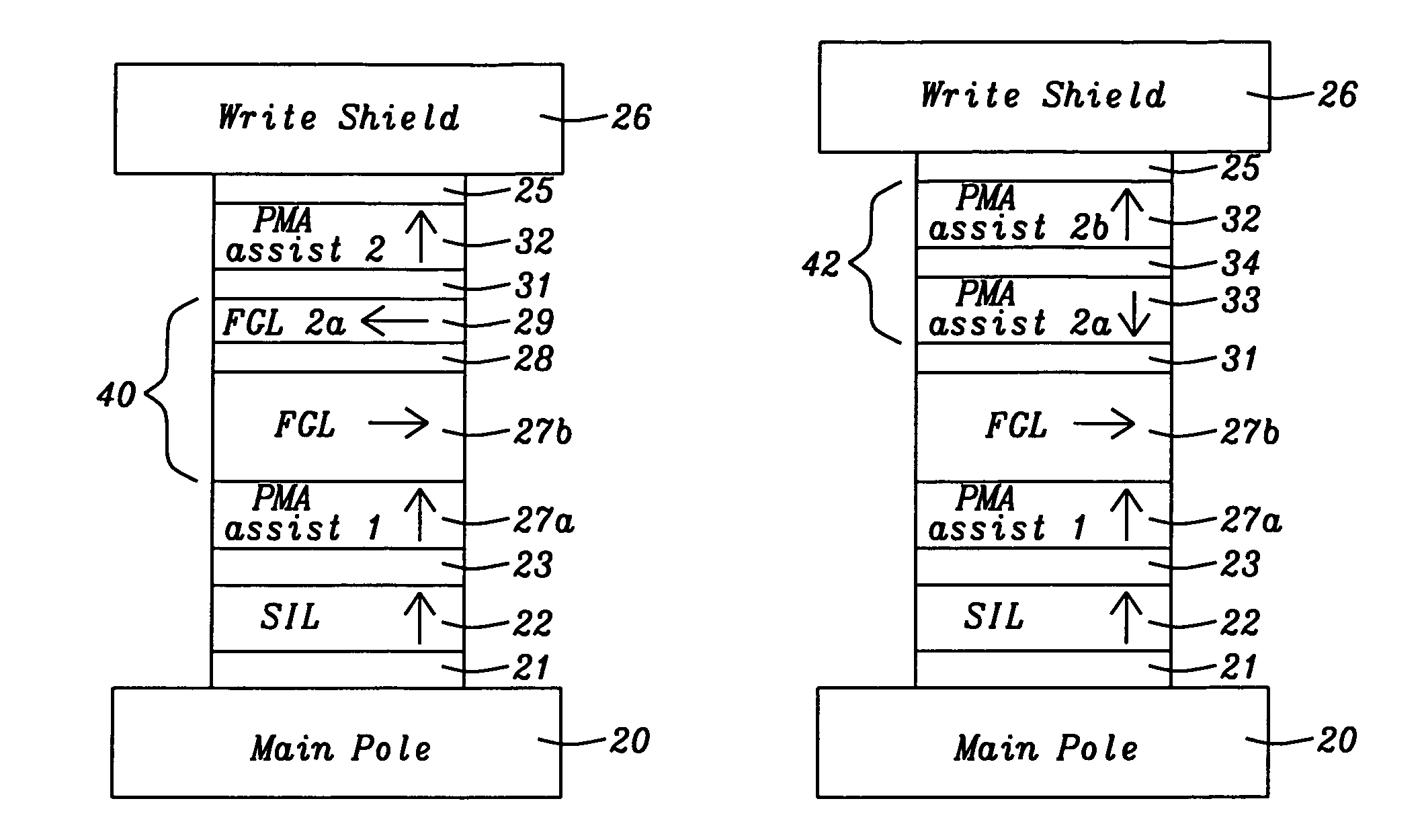
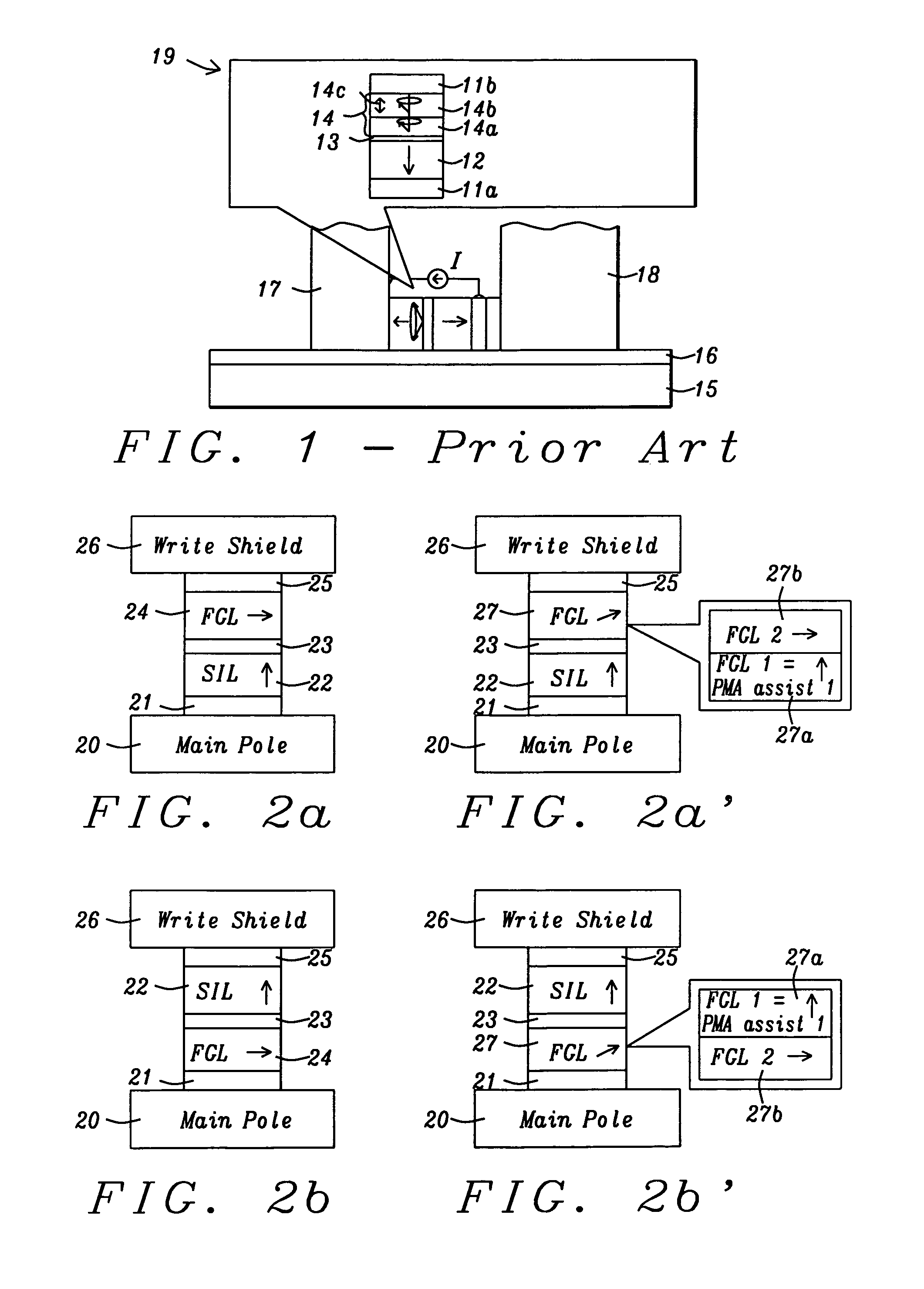
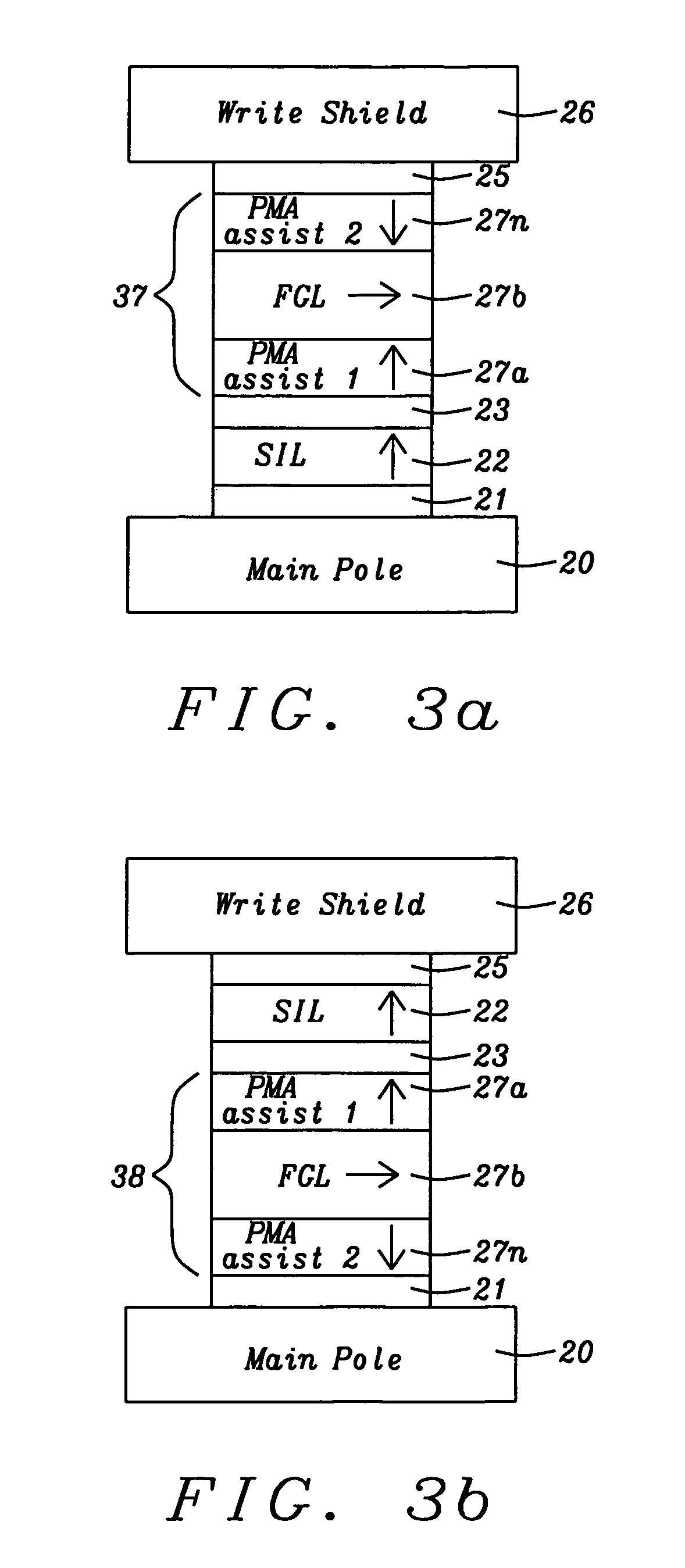
Assisting FGL oscillations with perpendicular anisotropy for MAMR
ActiveUS20120126905A1Strong oscillationLow densityRecord information storageDigital storagePower flowPerpendicular anisotropy
A spin transfer oscillator (STO) structure is disclosed that includes two assist layers with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA) to enable a field generation layer (FGL) to achieve an oscillation state at lower current density for MAMR applications. In one embodiment, the STO is formed between a main pole and write shield and the FGL has a synthetic anti-ferromagnetic structure. The STO configuration may be represented by seed layer / spin injection layer (SIL) / spacer / PMA layer 1 / FGL / spacer / PMA layer 2 / capping layer. The spacer may be Cu for giant magnetoresistive (GMR) devices or a metal oxide for tunneling magnetoresistive (TMR) devices. Alternatively, the FGL is a single ferromagnetic layer and the second PMA assist layer has a synthetic structure including two PMA layers with magnetic moment in opposite directions in a seed layer / SIL / spacer / PMA assist 1 / FGL / spacer / PMA assist 2 / capping layer configuration. SIL and PMA assist layers are laminates of (CoFe / Ni)x or the like.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Spin-orbit torque magnetic random access memory (SOT-MRAM) without external magnetic field
ActiveCN104393169AChange the state of magnetizationAddress reliabilityMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionSpin orbit torqueRandom access memory
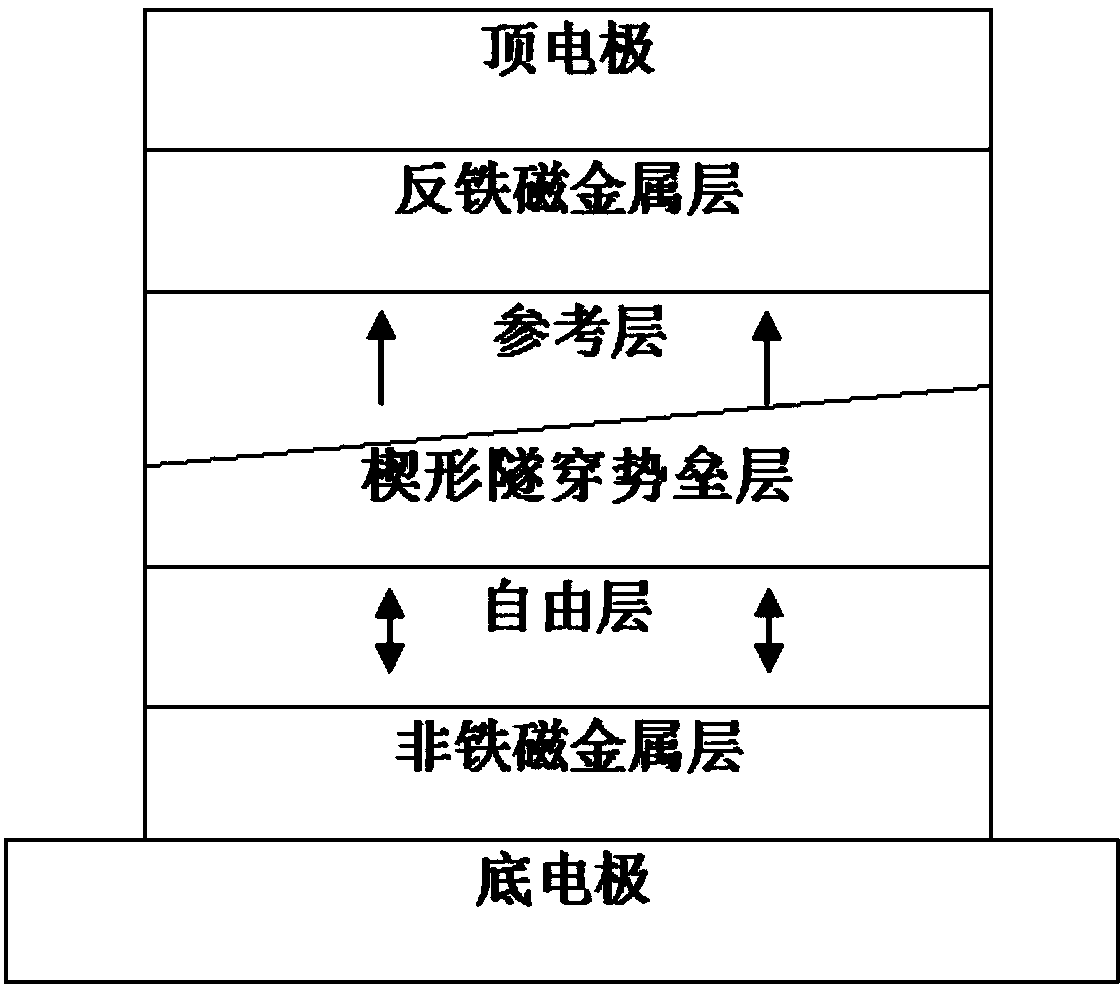
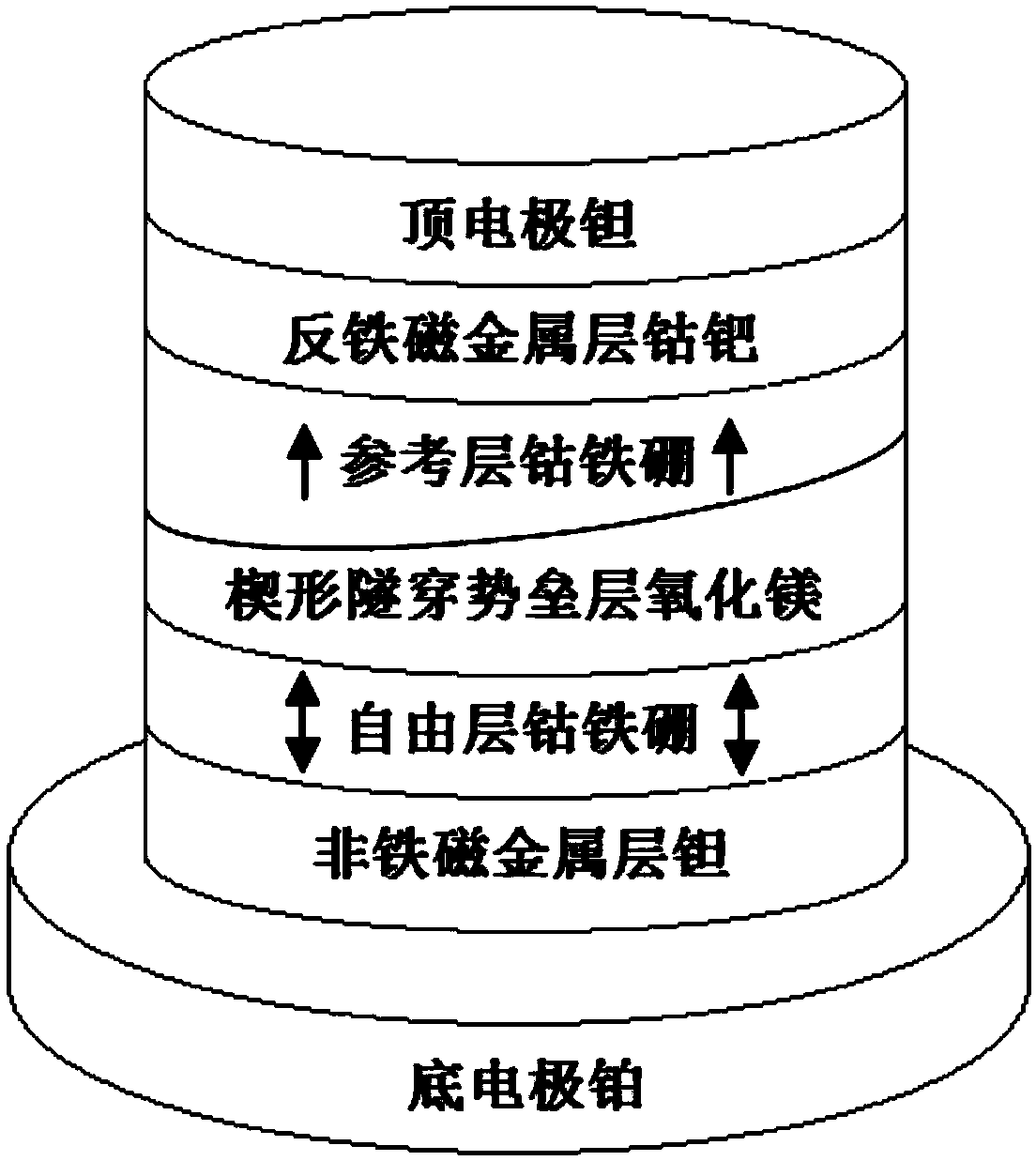
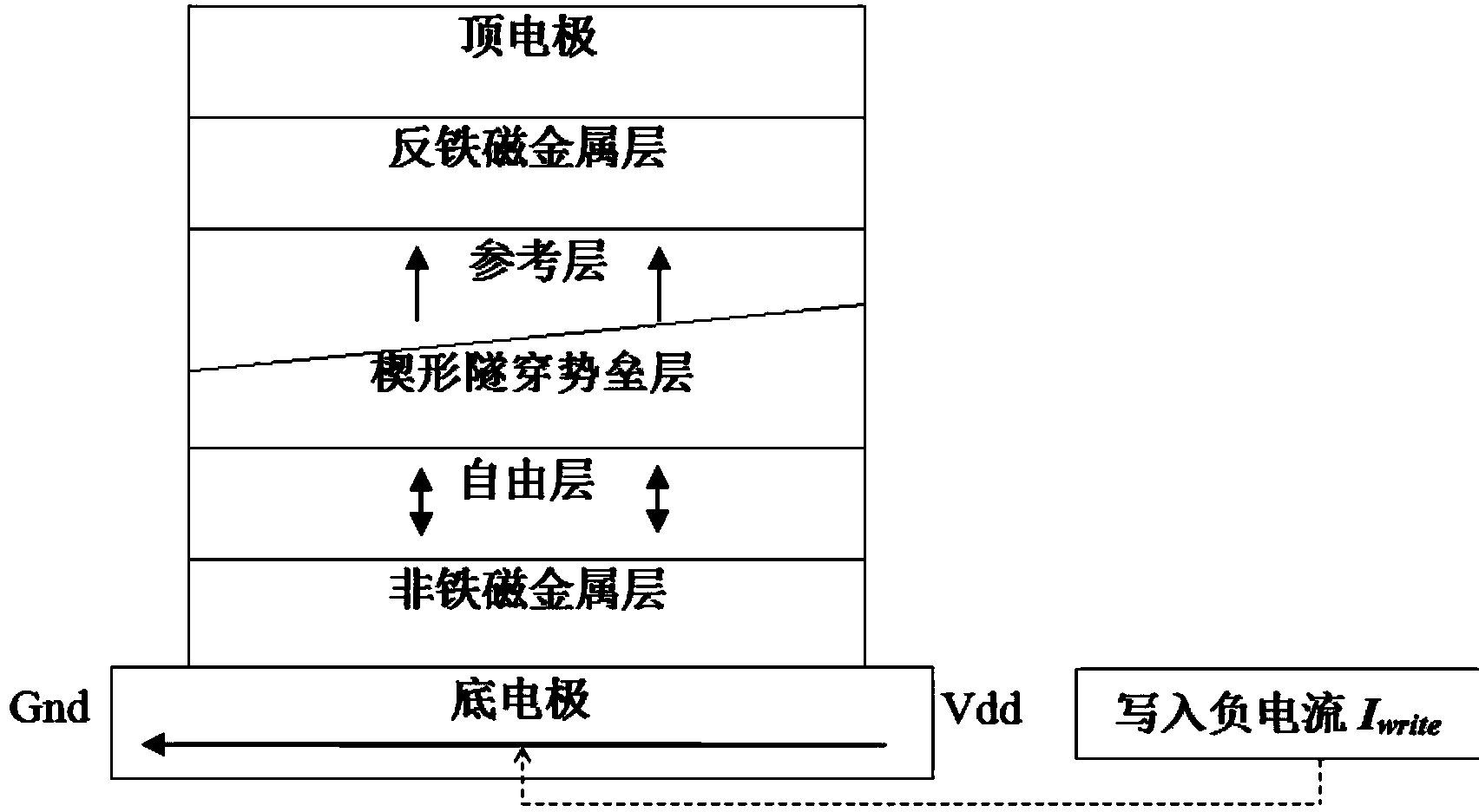
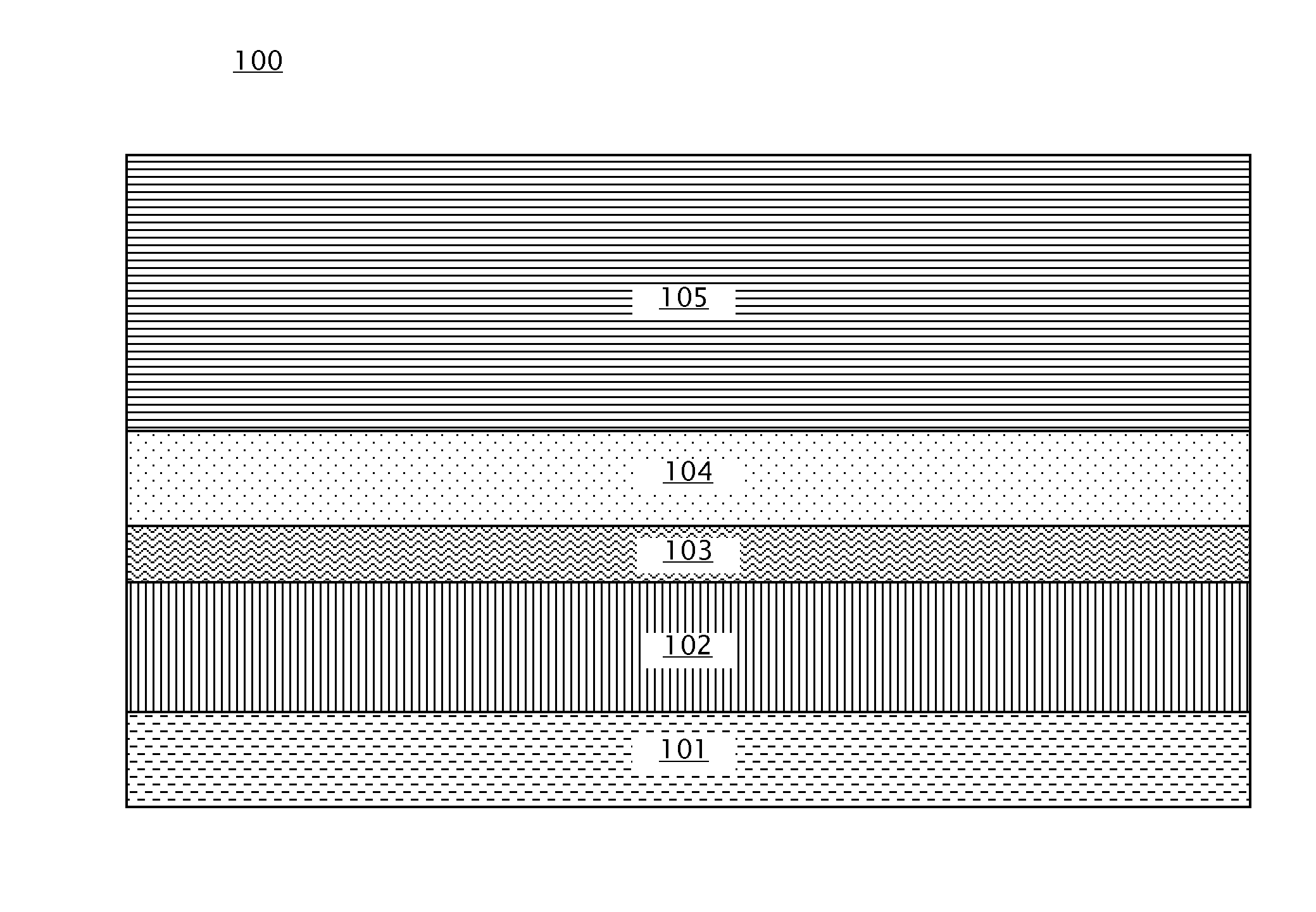
Disclosed is a spin-orbit torque magnetic random access memory (SOT-MRAM) without an external magnetic field. The spin-orbit torque magnetic tunneling junction(SOT-MTJ) of the random access memory is based on perpendicular magnetic anisotropy, apart from comprising an anti-parallel layer, a tunneling barrier layer, a reference layer and an antiferromagnetc metal layer in a conventional MTJ structure, is also additionally provided with a nonferromagnetic metal layer, optimizes the material of the antiferromagnetc metal layer and improves the shape of the tunneling barrier layer; and the SOT-MTJ structure is successively provided with seven layers which are respectively a bottom electrode, the nonferromagnetic metal layer, a first ferromagnetic metal layer, i.e., the anti-parallel layer, a wedge tunneling barrier layer, a second ferromagnetic metal layer, i.e., the reference layer, the antiferromagnetc metal layer and a top electrode from the bottom to the top. According to the invention, writing operation can be carried out without the external magnetic field. Compared to a conventional SOT-MRAM, the energy consumption is smaller, and the geometric ratio micro-shrink performance reduced along with a technical node is more excellent.
Owner:致真存储(北京)科技有限公司
Magnetic tunnel junction with iron dusting layer between free layer and tunnel barrier
InactiveUS20120241878A1Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRandom access memoryCondensed matter physics
A magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) for a magnetic random access memory (MRAM) includes a magnetic free layer having a variable magnetization direction; an iron (Fe) dusting layer formed on the free layer; an insulating tunnel barrier formed on the dusting layer; and a magnetic fixed layer having an invariable magnetization direction, disposed adjacent the tunnel barrier such that the tunnel barrier is located between the free layer and the fixed layer; wherein the free layer and the fixed layer have perpendicular magnetic anisotropy and are magnetically coupled through the tunnel barrier.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Assisting FGL oscillations with perpendicular anisotropy for MAMR
ActiveUS8274811B2Strong oscillationLow densityRecord information storageDigital storagePower flowPerpendicular anisotropy
A spin transfer oscillator (STO) structure is disclosed that includes two assist layers with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA) to enable a field generation layer (FGL) to achieve an oscillation state at lower current density for MAMR applications. In one embodiment, the STO is formed between a main pole and write shield and the FGL has a synthetic anti-ferromagnetic structure. The STO configuration may be represented by seed layer / spin injection layer (SIL) / spacer / PMA layer 1 / FGL / spacer / PMA layer 2 / capping layer. The spacer may be Cu for giant magnetoresistive (GMR) devices or a metal oxide for tunneling magnetoresistive (TMR) devices. Alternatively, the FGL is a single ferromagnetic layer and the second PMA assist layer has a synthetic structure including two PMA layers with magnetic moment in opposite directions in a seed layer / SIL / spacer / PMA assist 1 / FGL / spacer / PMA assist 2 / capping layer configuration. SIL and PMA assist layers are laminates of (CoFe / Ni)x or the like.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Spin-current switchable magnetic memory element and method of fabricating the memory element
A spin-current switchable magnetic memory element (and method of fabricating the memory element) includes a plurality of magnetic layers having a perpendicular magnetic anisotropy component, at least one of the plurality of magnetic layers including an alloy of a rare-earth metal and a transition metal, and at least one barrier layer formed adjacent to at least one of the plurality of magnetic layers.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Magnetoresistive element and magnetic memory
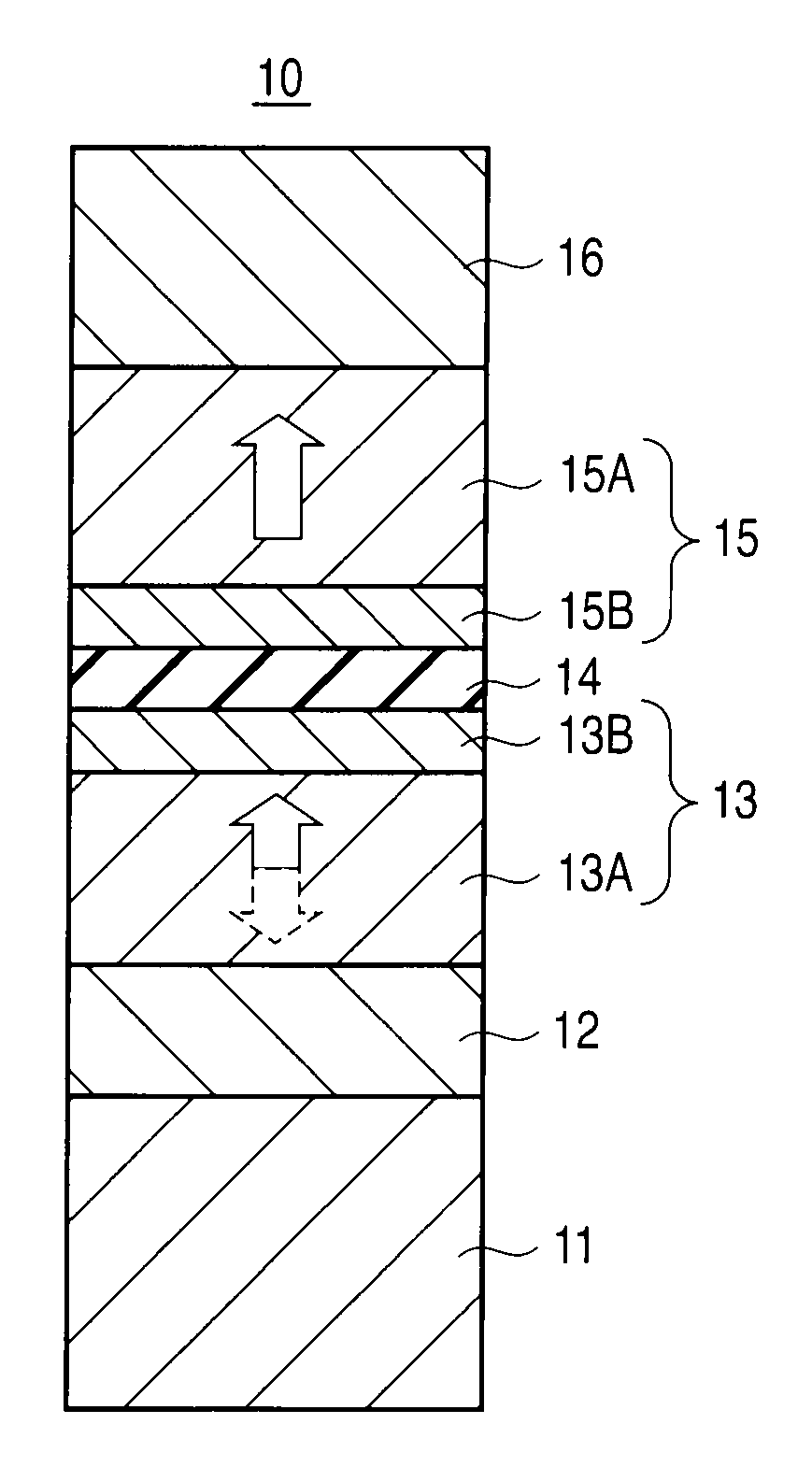
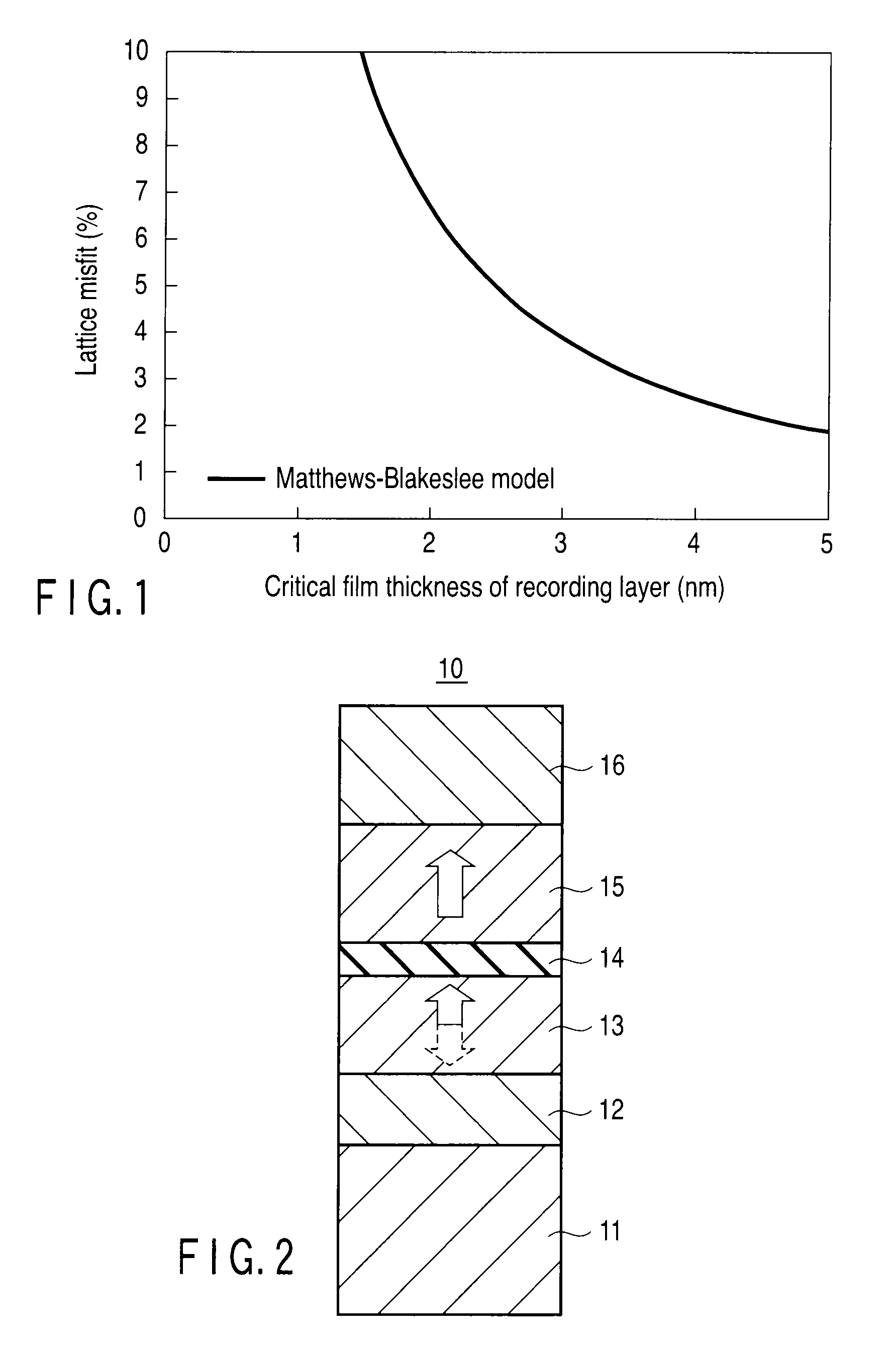
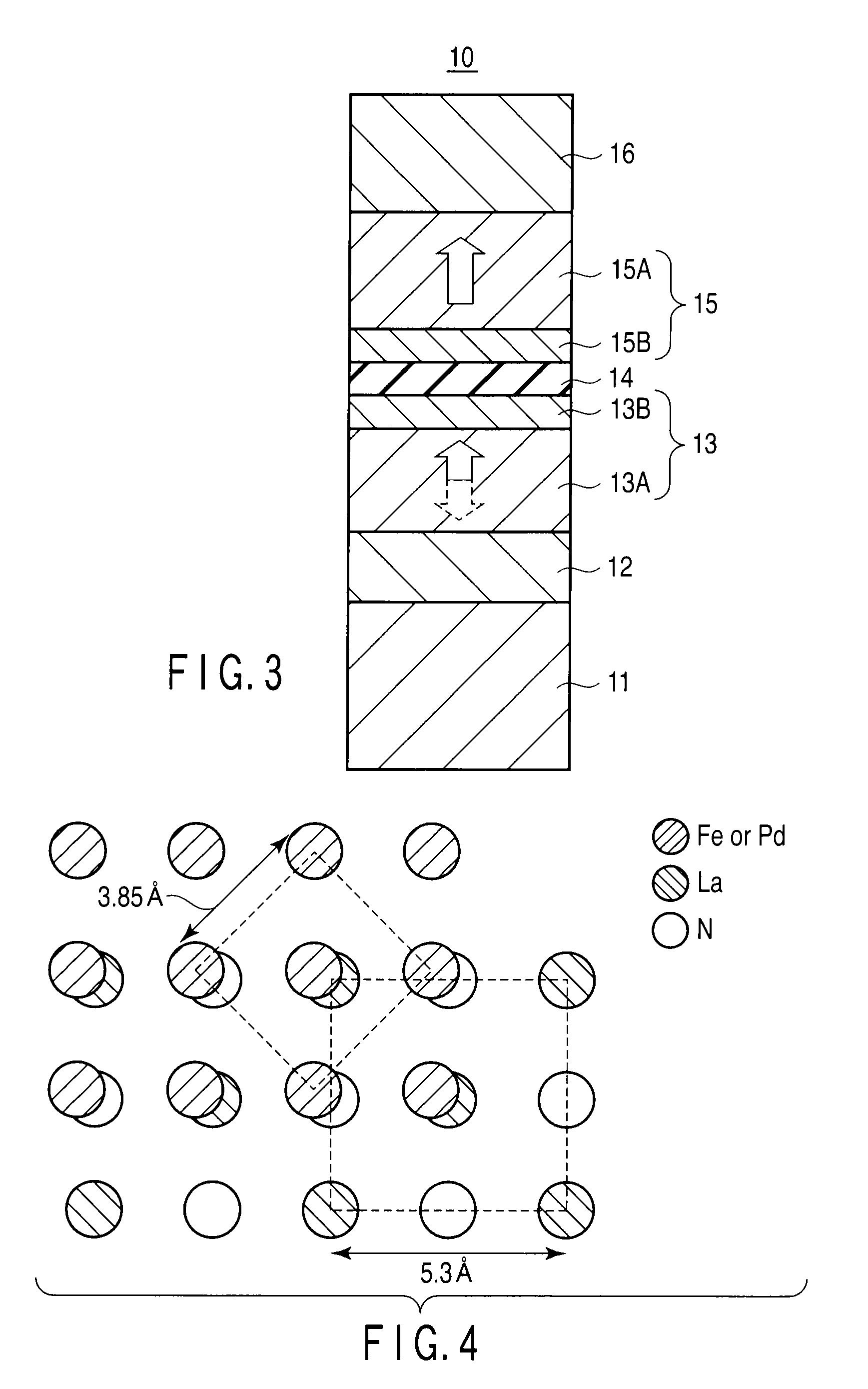
A magnetoresistive element includes an underlying layer having a cubic or tetragonal crystal structure oriented in a (001) plane, a first magnetic layer provided on the underlying layer, having perpendicular magnetic anisotropy, and having an fct structure oriented in a (001) plane, a non-magnetic layer provided on the first magnetic layer, and a second magnetic layer provided on the non-magnetic layer, and having perpendicular magnetic anisotropy. An in-plane lattice constant a1 of the underlying layer and an in-plane lattice constant a2 of the first magnetic layer satisfy the following equation in which b is a magnitude of Burgers vector of the first magnetic layer, ν is an elastic modulus of the first magnetic layer, and hc is a thickness of the first magnetic layer.|√{square root over (2)}a1 / 2−a2| / a2<b×{ln (hc / b)+1} / {2π×hc×(1+ν)}
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Magnetic tunnel junction with iron dusting layer between free layer and tunnel barrier
InactiveUS20130005052A1Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRandom access memoryCondensed matter physics
A magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) for a magnetic random access memory (MRAM) includes a magnetic free layer having a variable magnetization direction; an iron (Fe) dusting layer formed on the free layer; an insulating tunnel barrier formed on the dusting layer; and a magnetic fixed layer having an invariable magnetization direction, disposed adjacent the tunnel barrier such that the tunnel barrier is located between the free layer and the fixed layer; wherein the free layer and the fixed layer have perpendicular magnetic anisotropy and are magnetically coupled through the tunnel barrier.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com