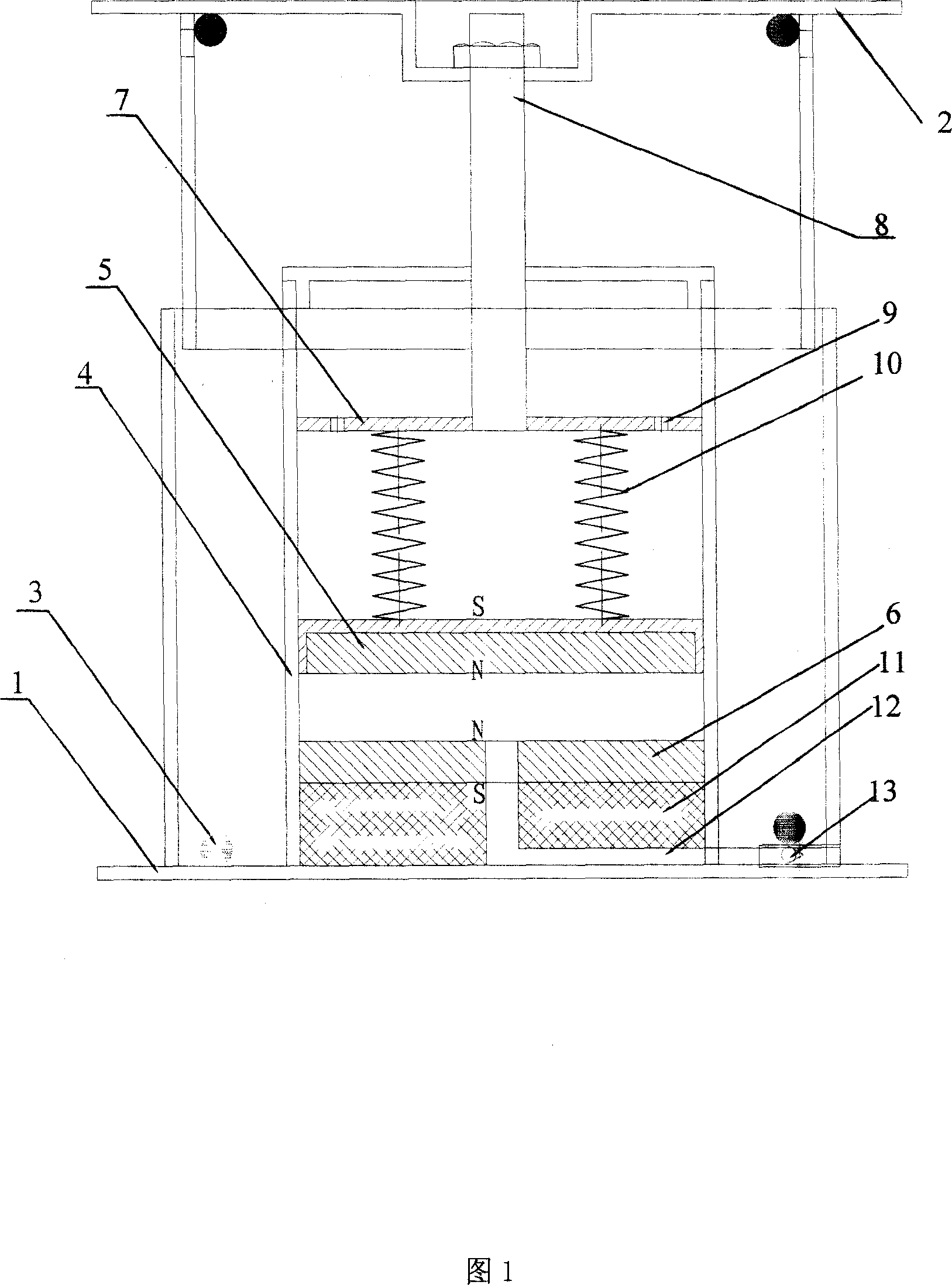
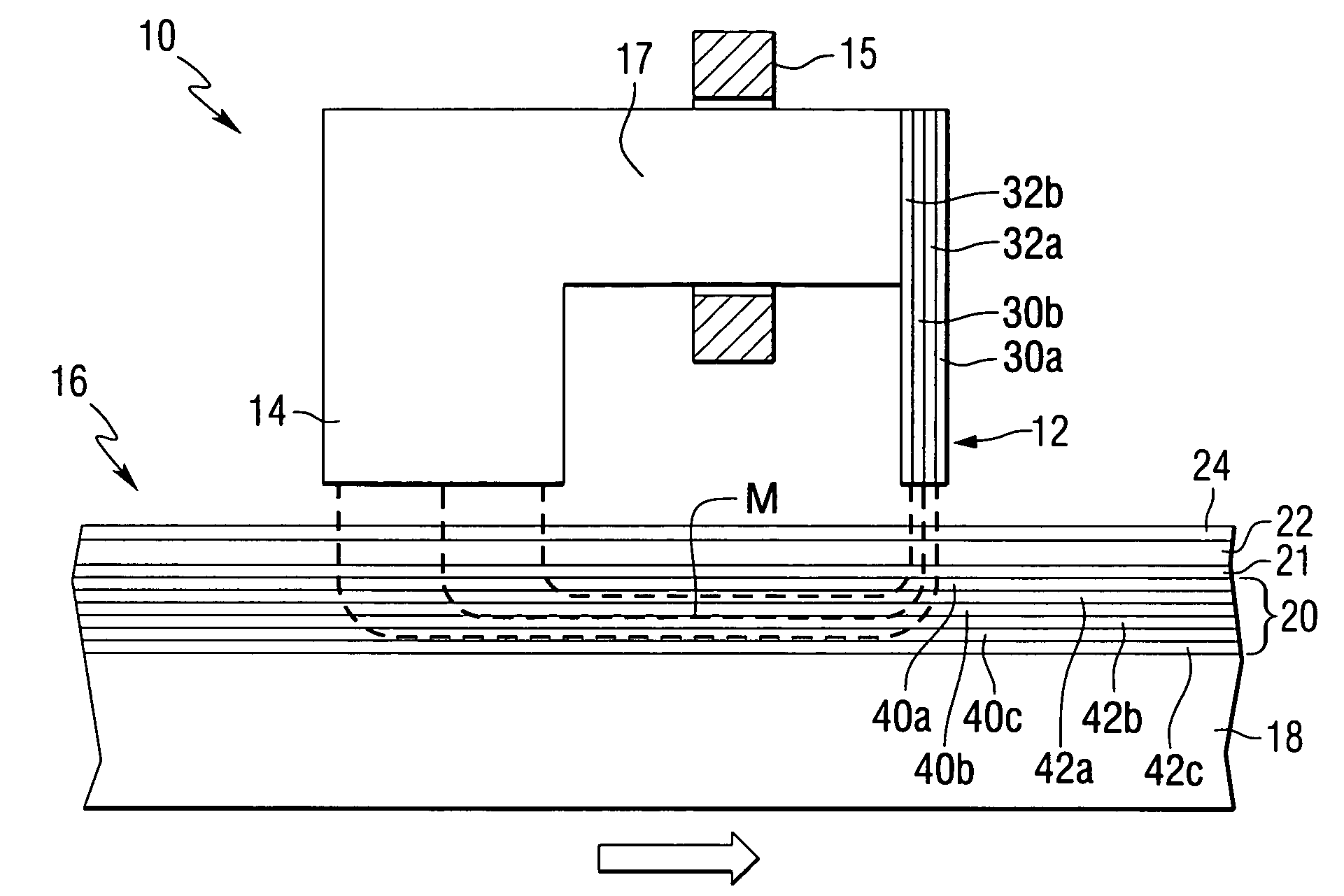
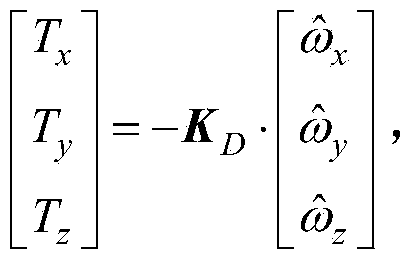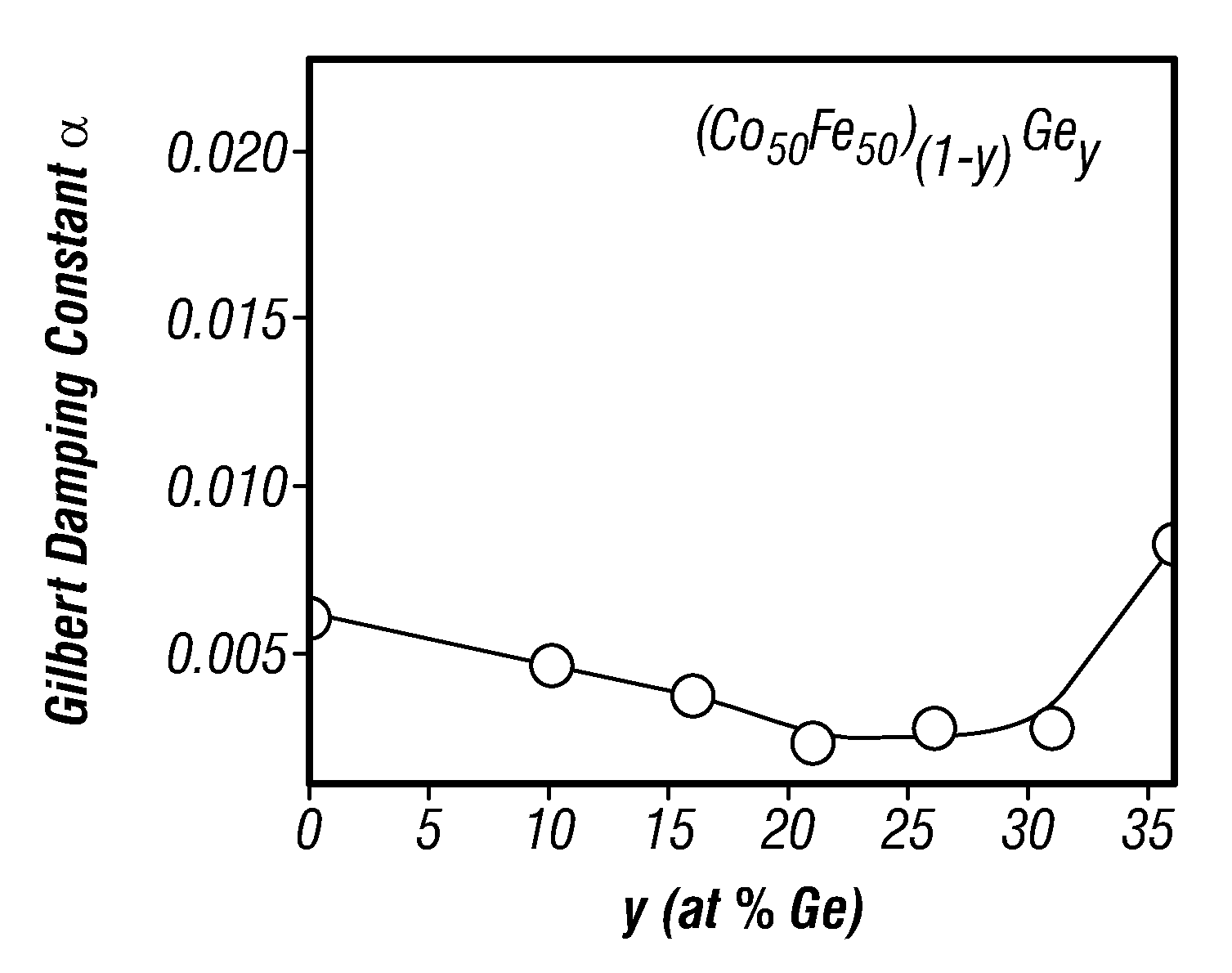Patents
Literature
341 results about "Magnetic damping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
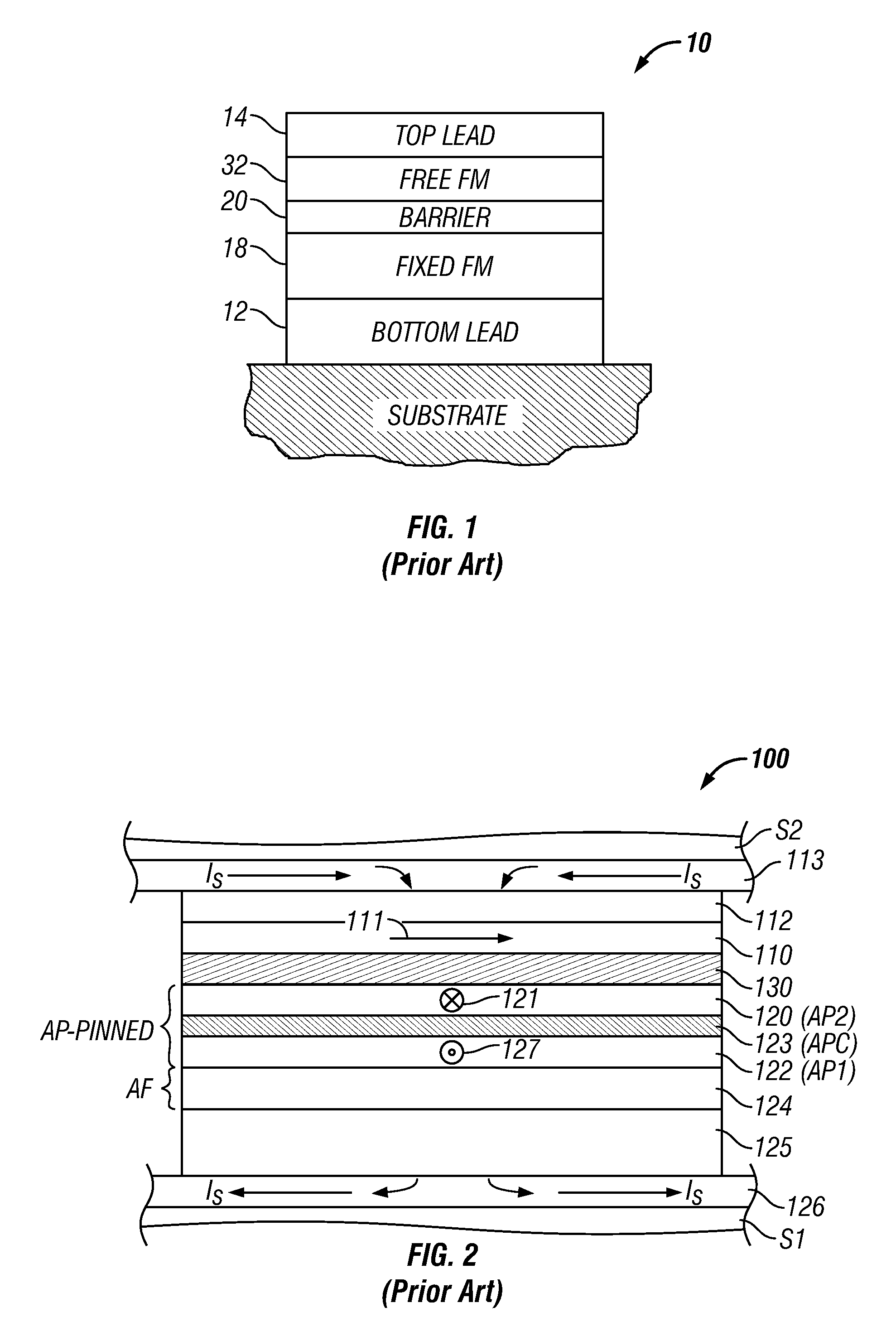
Magnetic damping is a form of damping that occurs when a magnetic field (i.e. a magnet) travels some distance through or past an electrical conductor (or vice versa).
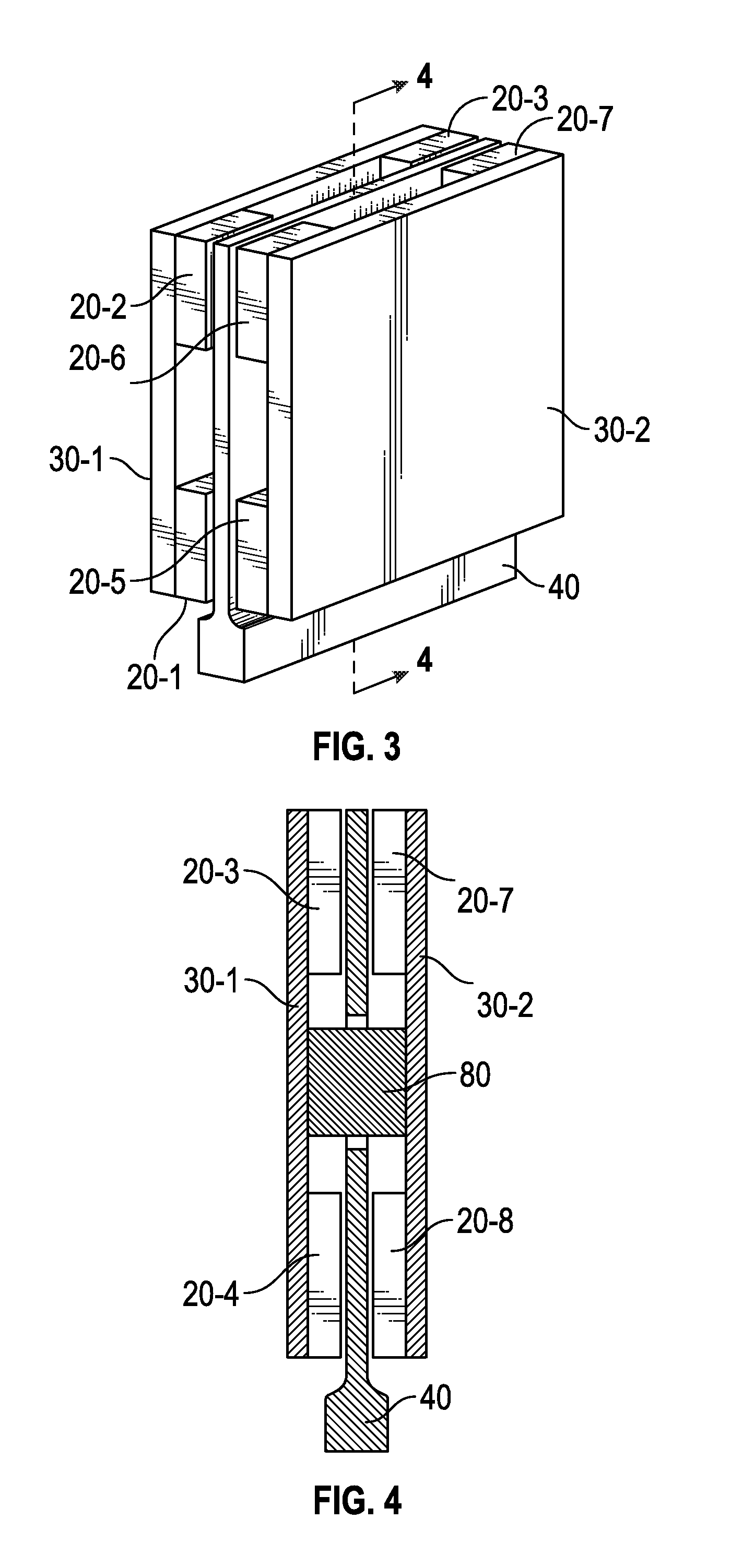
Thin seeded Co/Ni multilayer film with perpendicular anisotropy for spintronic device applications
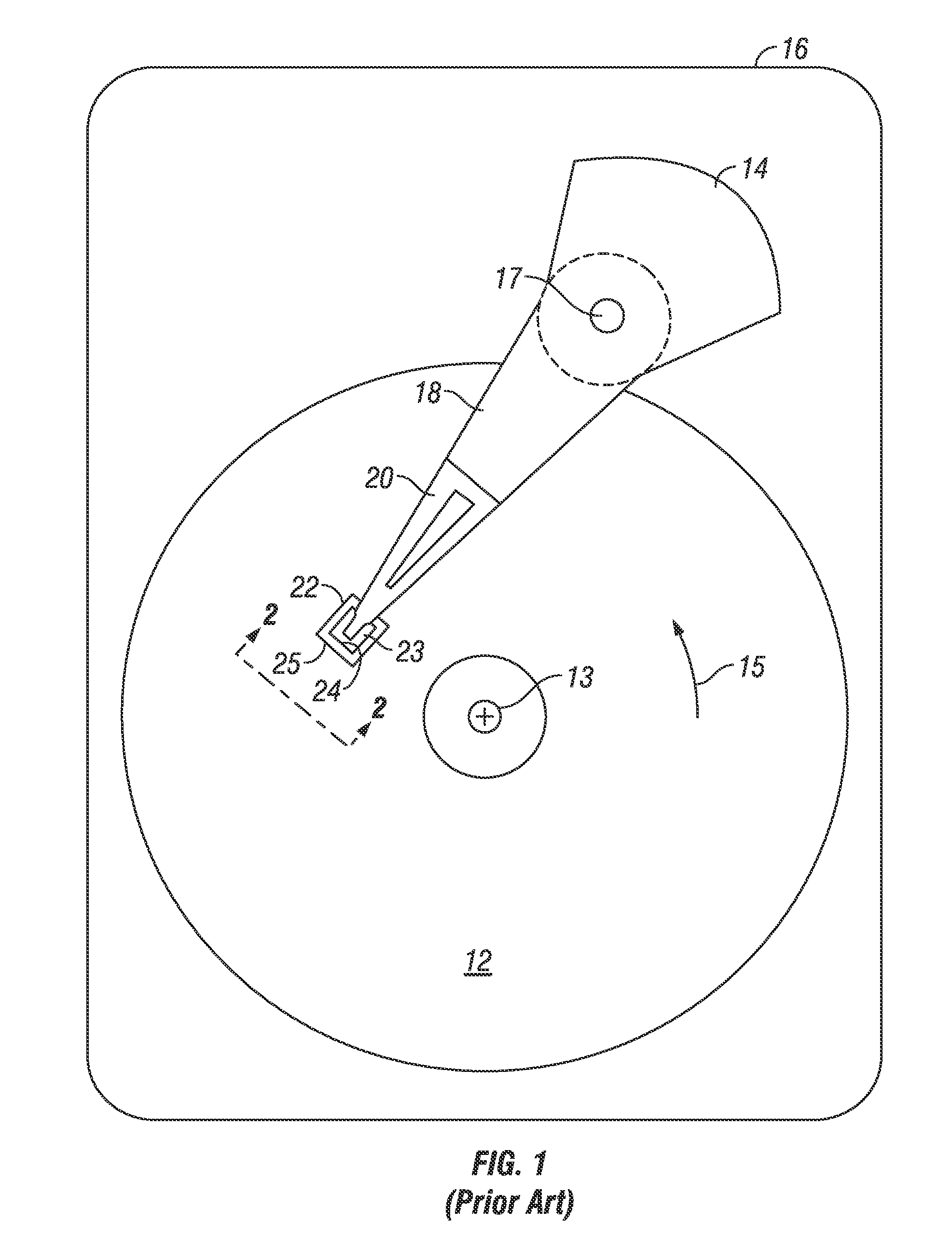
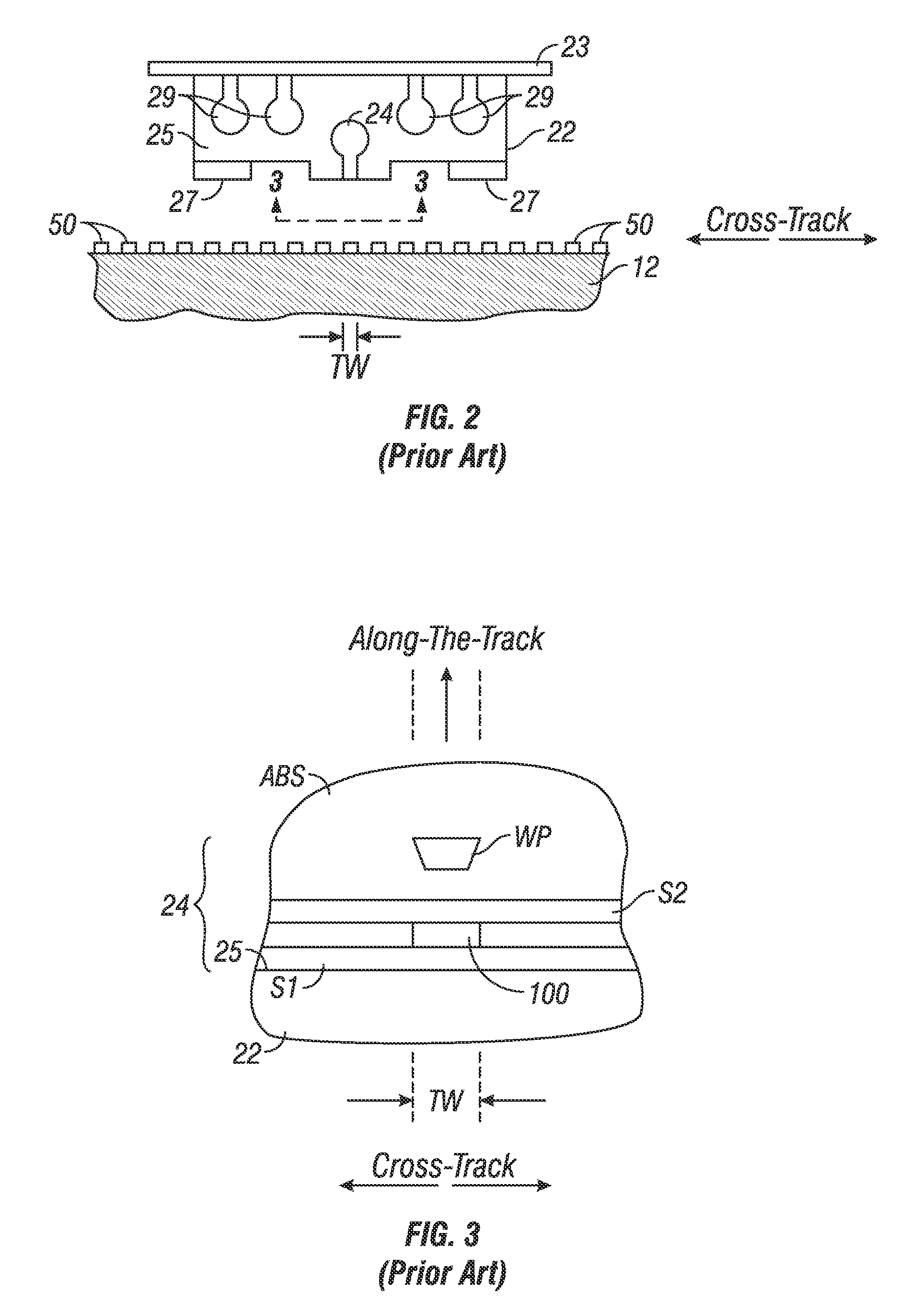
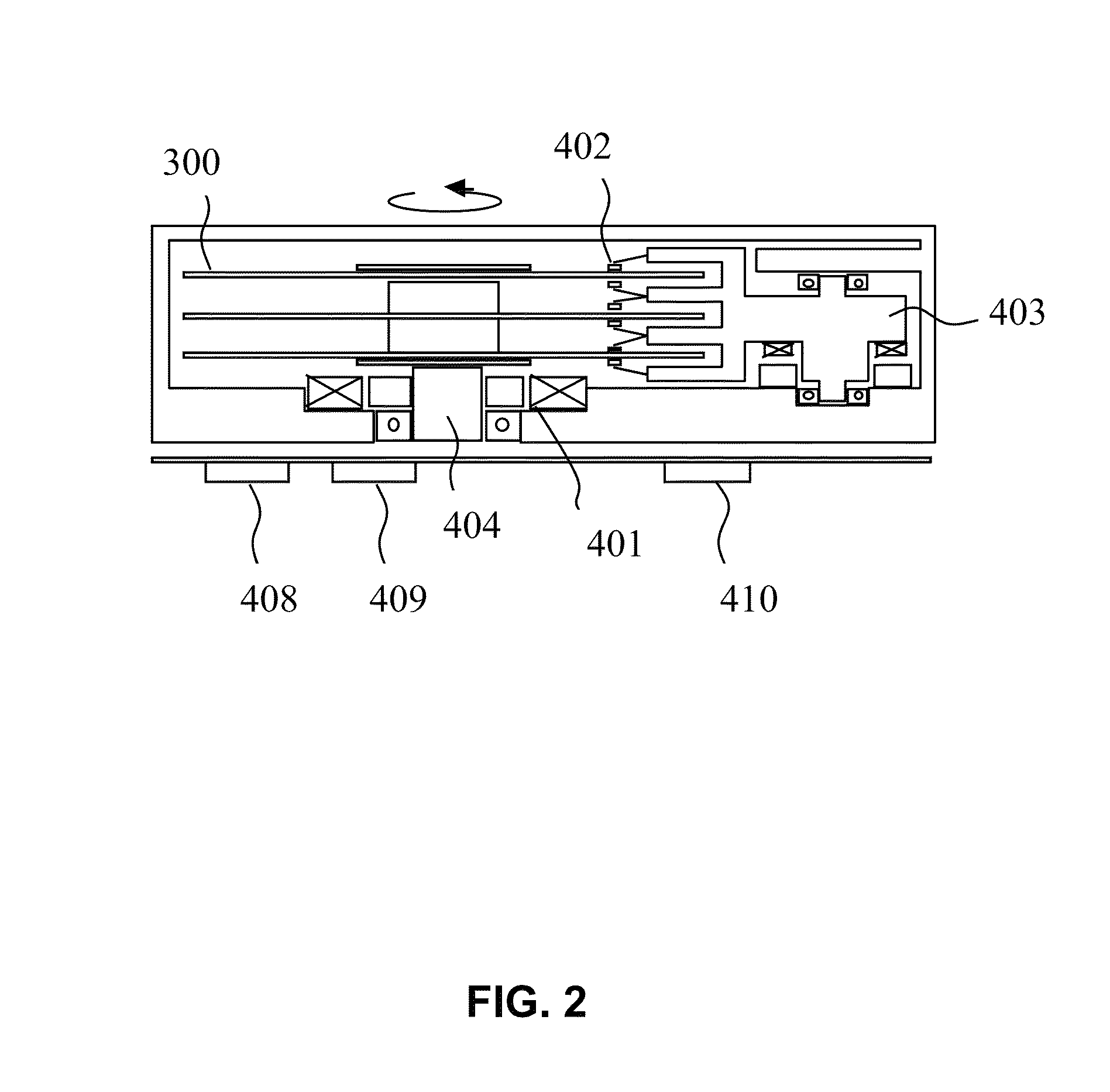
ActiveUS20090257151A1Raise the ratioNot to damageMagnetic measurementsVacuum evaporation coatingPerpendicular anisotropySpins
A spin valve structure for a spintronic device is disclosed and includes a composite seed layer made of at least Ta and a metal layer having a fcc(111) or hcp(001) texture to enhance perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA) in an overlying (Co / Ni)x multilayer. The (Co / Ni)x multilayer is deposited by a low power and high Ar pressure process to avoid damaging Co / Ni interfaces and thereby preserving PMA. As a result, only a thin seed layer is required. PMA is maintained even after annealing at 220° C. for 10 hours. Examples of GMR and TMR spin valves are described and may be incorporated in spin transfer oscillators and spin transfer MRAMs. The free layer is preferably made of a FeCo alloy including at least one of Al, Ge, Si, Ga, B, C, Se, Sn, or a Heusler alloy, or a half Heusler alloy to provide high spin polarization and a low magnetic damping coefficient.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION +1
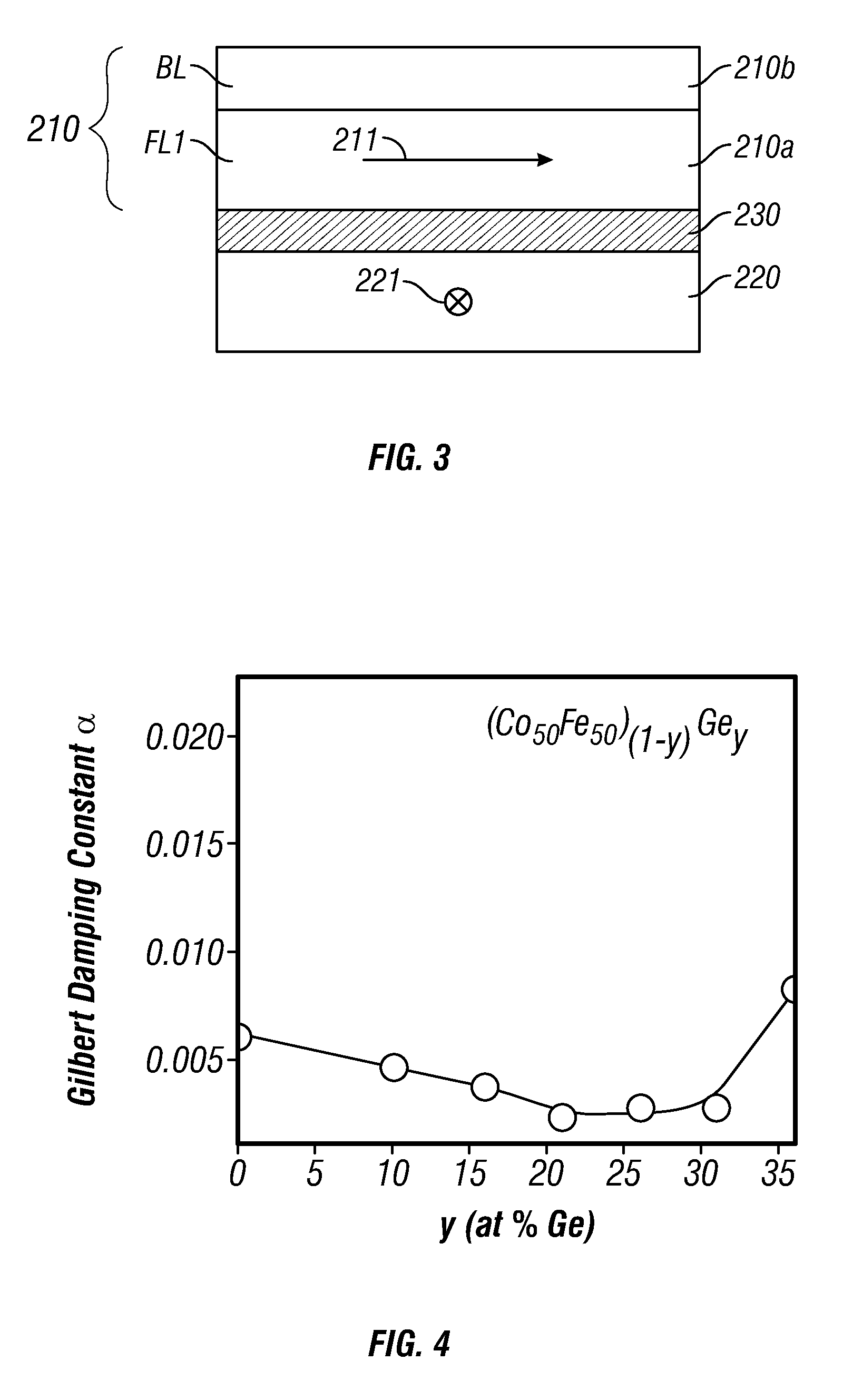
Spin-torque oscillator (STO) with magnetically damped free layer
A spin-torque oscillator (STO) has increased magnetic damping of the oscillating free ferromagnetic layer. The Gilbert magnetic damping parameter (α) is at least 0.05, and preferably greater than 0.05. The free layer may be a any type of conventional ferromagnetic material, but contains one or more damping elements as a dopant. The damping element is selected from the group consisting of Pt, Pd and the 15 lanthanide elements. The free layer damping may also be increased by a damping layer adjacent the free layer. One type of damping layer may be an antiferromagnetic material, like a Mn alloy. As a modification to the antiferromagnetic damping layer, a bilayer damping layer may be formed of the antiferromagnetic layer and a nonmagnetic metal electrically conductive separation layer between the free layer and the antiferromagnetic layer. Another type of damping layer may be one formed of one or more of the elements selected from Pt, Pd and the lanthanides.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
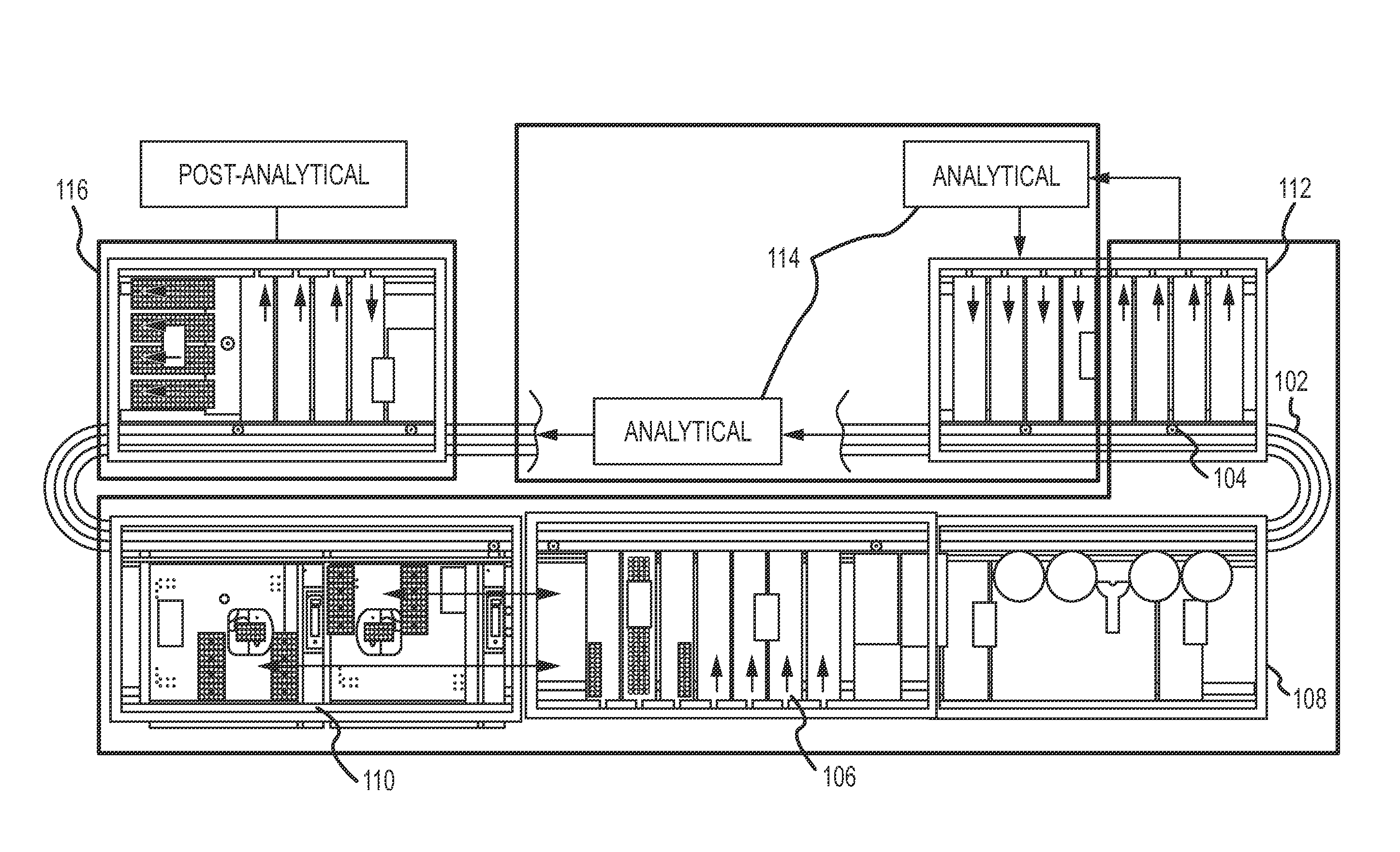
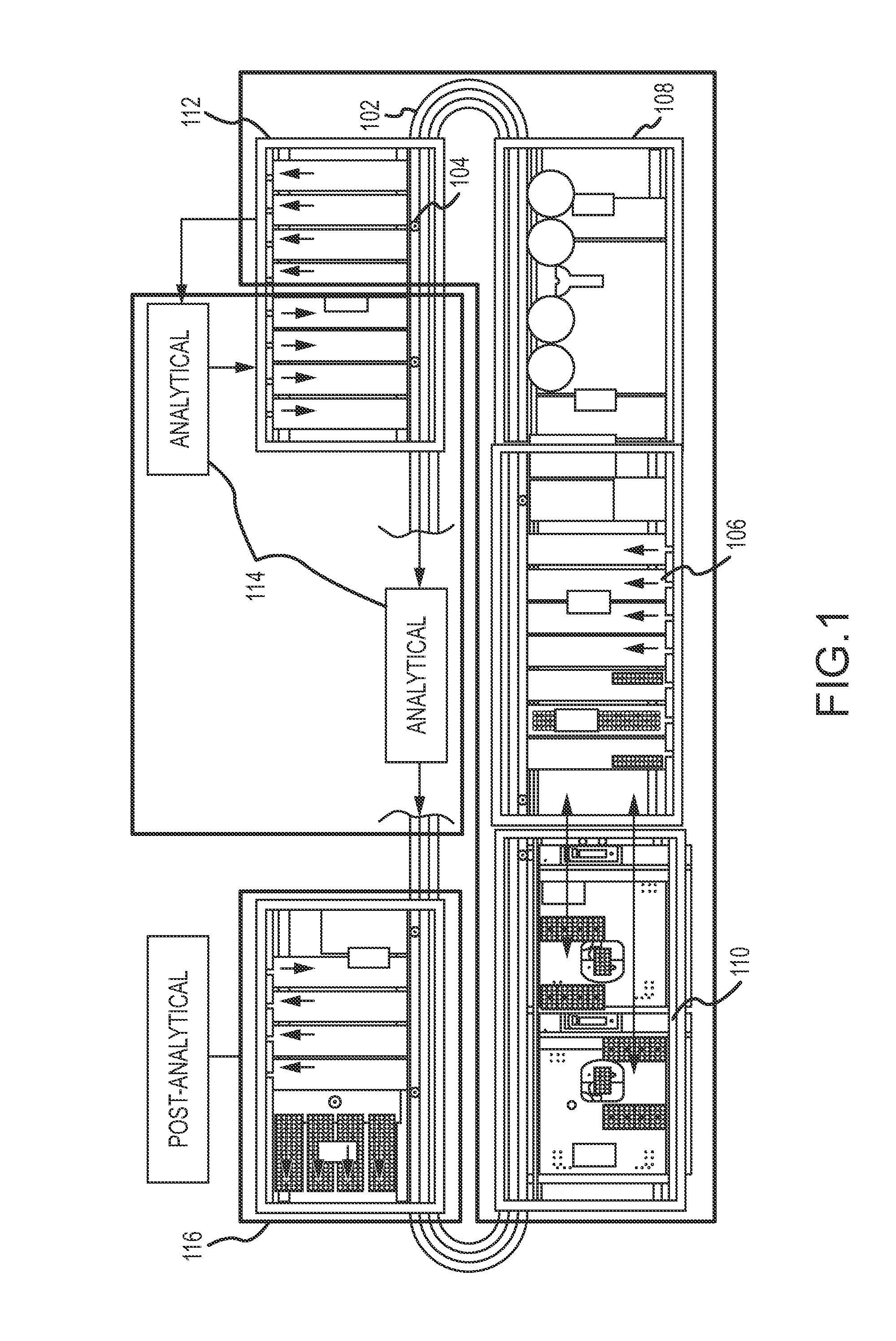
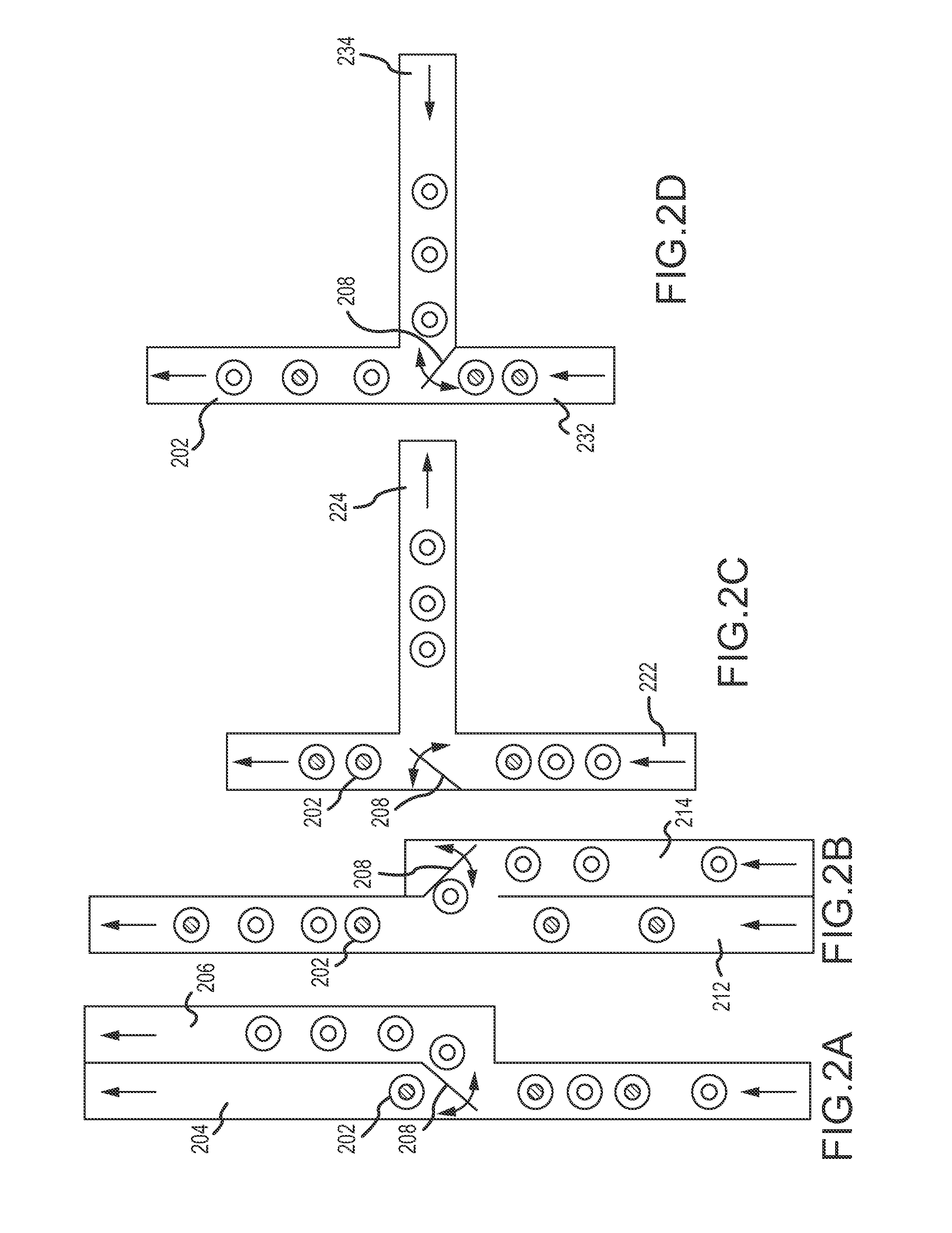
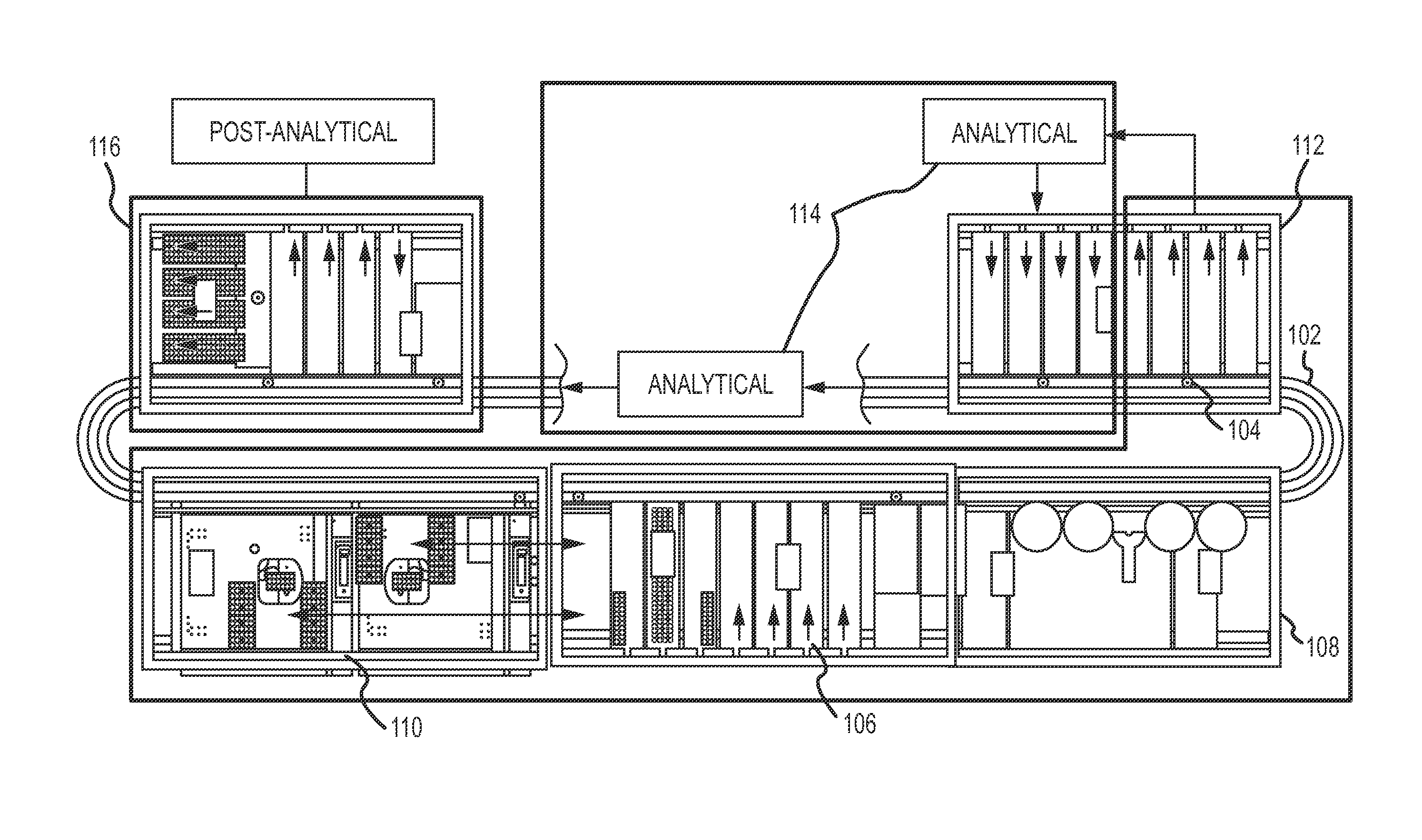
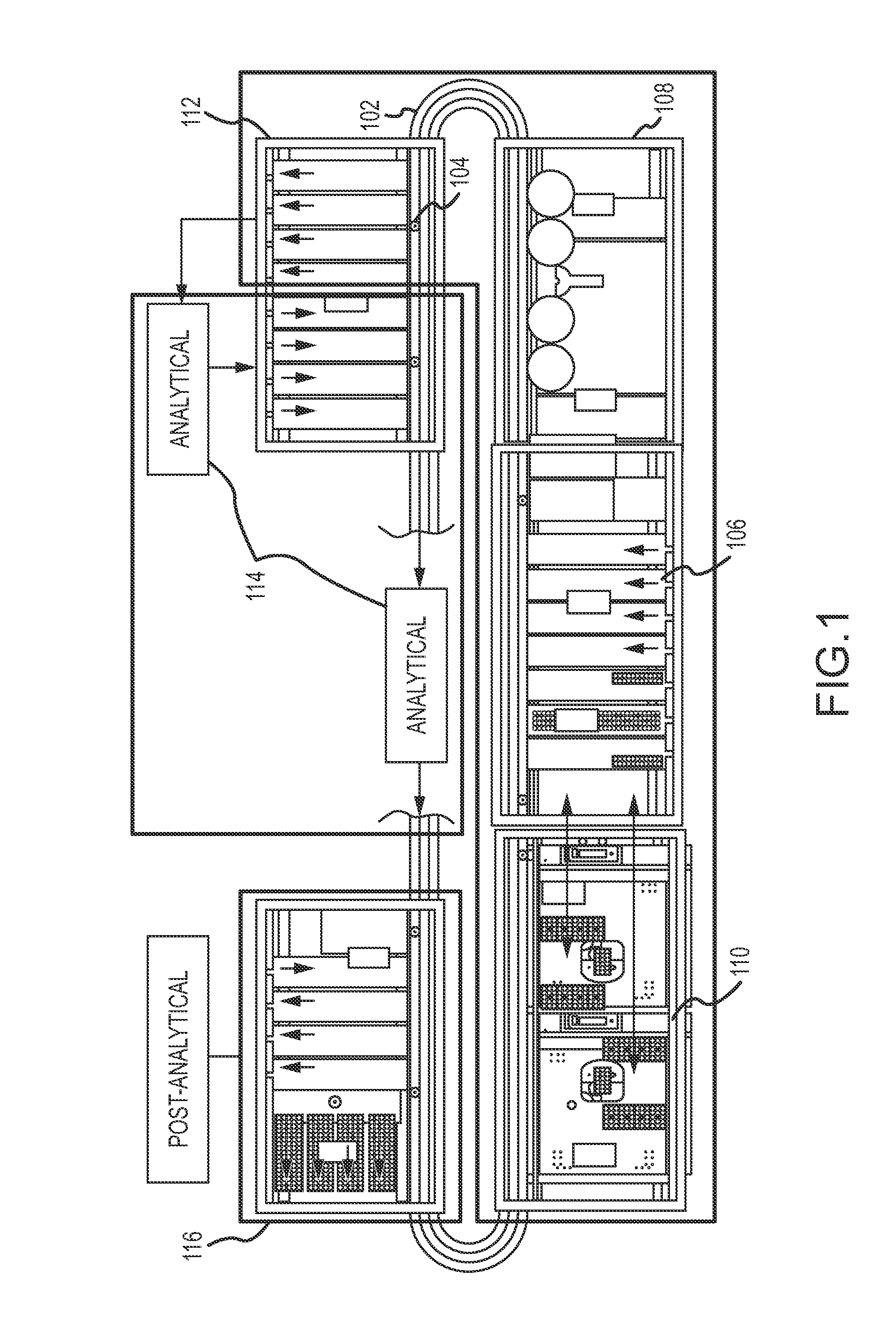
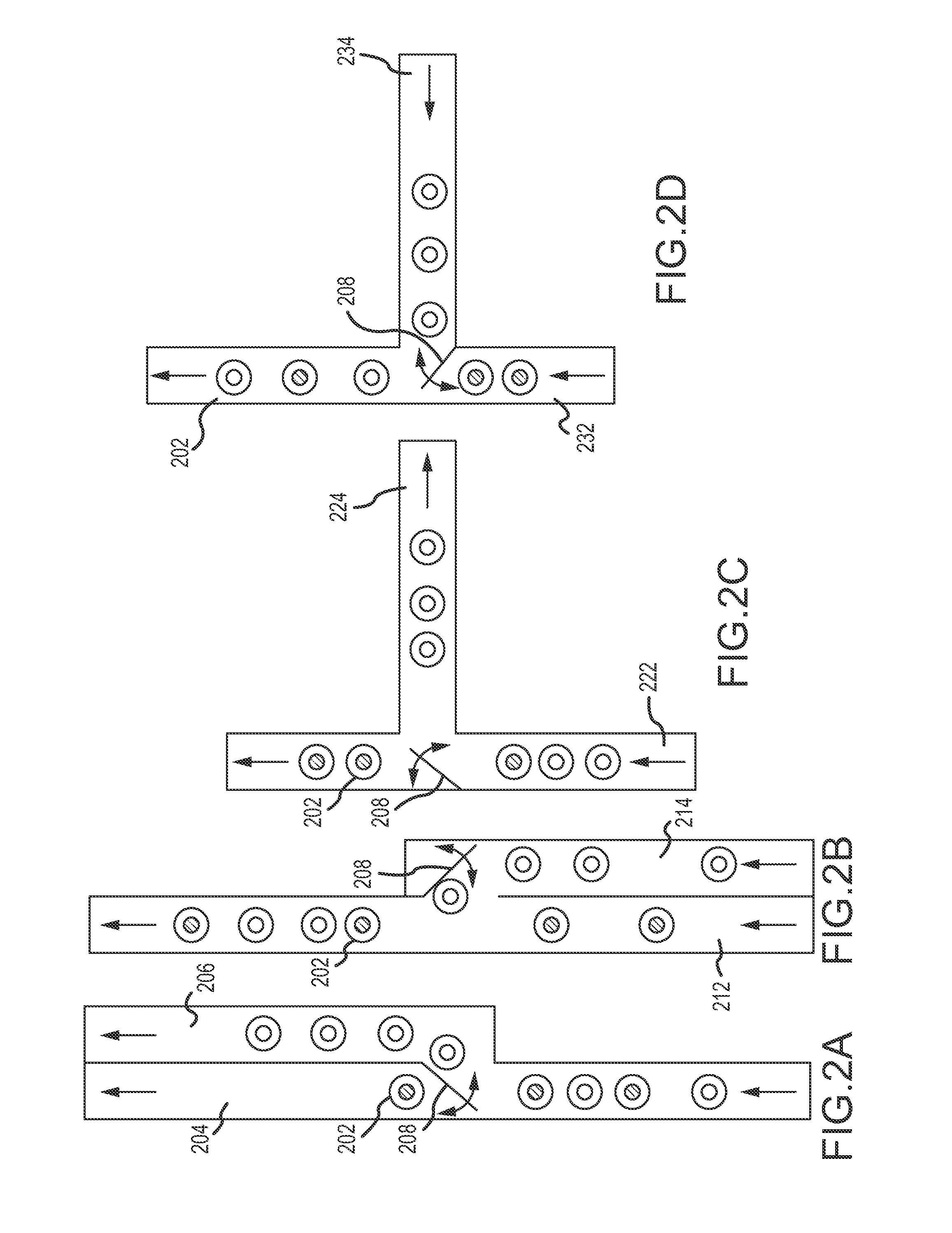
Magnetic damping for specimen transport system
ActiveUS20130126302A1Efficient processingClosure with auxillary devicesStatic/dynamic balance measurementTransport systemMagnetic damping
A specimen transport system with magnetic damping and method for transporting specimens with magnetic damping are disclosed. A conveyance device transports sample carriers configured to carry specimen containers. One or more of the sample carriers include magnets. The system may also include a diverting arm having a magnet. When a first sample carrier is transported toward a second sample carrier, a first sample carrier magnet coupled to the first sample carrier repels a second sample carrier magnet coupled to the second sample carrier. When a sample carrier is transported toward a diverting arm, a diverting arm magnet of the diverting arm repels a sample carrier magnet of the sample carrier.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Magnetic damping for specimen transport system
ActiveUS8973736B2Closure with auxillary devicesStatic/dynamic balance measurementTransport systemMagnetic damping
A specimen transport system with magnetic damping and method for transporting specimens with magnetic damping are disclosed. A conveyance device transports sample carriers configured to carry specimen containers. One or more of the sample carriers include magnets. The system may also include a diverting arm having a magnet. When a first sample carrier is transported toward a second sample carrier, a first sample carrier magnet coupled to the first sample carrier repels a second sample carrier magnet coupled to the second sample carrier. When a sample carrier is transported toward a diverting arm, a diverting arm magnet of the diverting arm repels a sample carrier magnet of the sample carrier.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Preparation method of iron strontium oxide magnetic nanoparticles and magnetic damping rubber thereof
ActiveCN101913855AStrong magnetismGood compatibilityPigment treatment with organosilicon compoundsMagnetic dampingMolten salt
The invention discloses a preparation method of iron strontium oxide magnetic nanoparticles and a magnetic damping rubber thereof, which solves the problem that the existing magnetic damping rubber fails to meet the requirements for excellent physical-mechanical properties and good magnetic damping effect simultaneously. In the preparation method of the iron strontium oxide magnetic nanoparticles, a chemical coprecipitation method is organically combined with a molten salt method to obtain surface-modified nano-grade iron strontium oxide in a regular shape, and then the obtained iron strontium oxide is used for preparing the magnetic damping rubber. The invention has the following advantages: the magnetic particles have nano-scale particle size and excellent magnetic property, and can be uniformly dispersed in a rubber matrix; a nitrile-butadiene rubber is taken as the matrix, thus having excellent oil resistance; and the magnetic damping rubber has excellent mechanical property.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Linear vibration motor
InactiveUS20130033128A1Mechanical vibrations separationPropulsion systemsMagnetic dampingLinear vibration
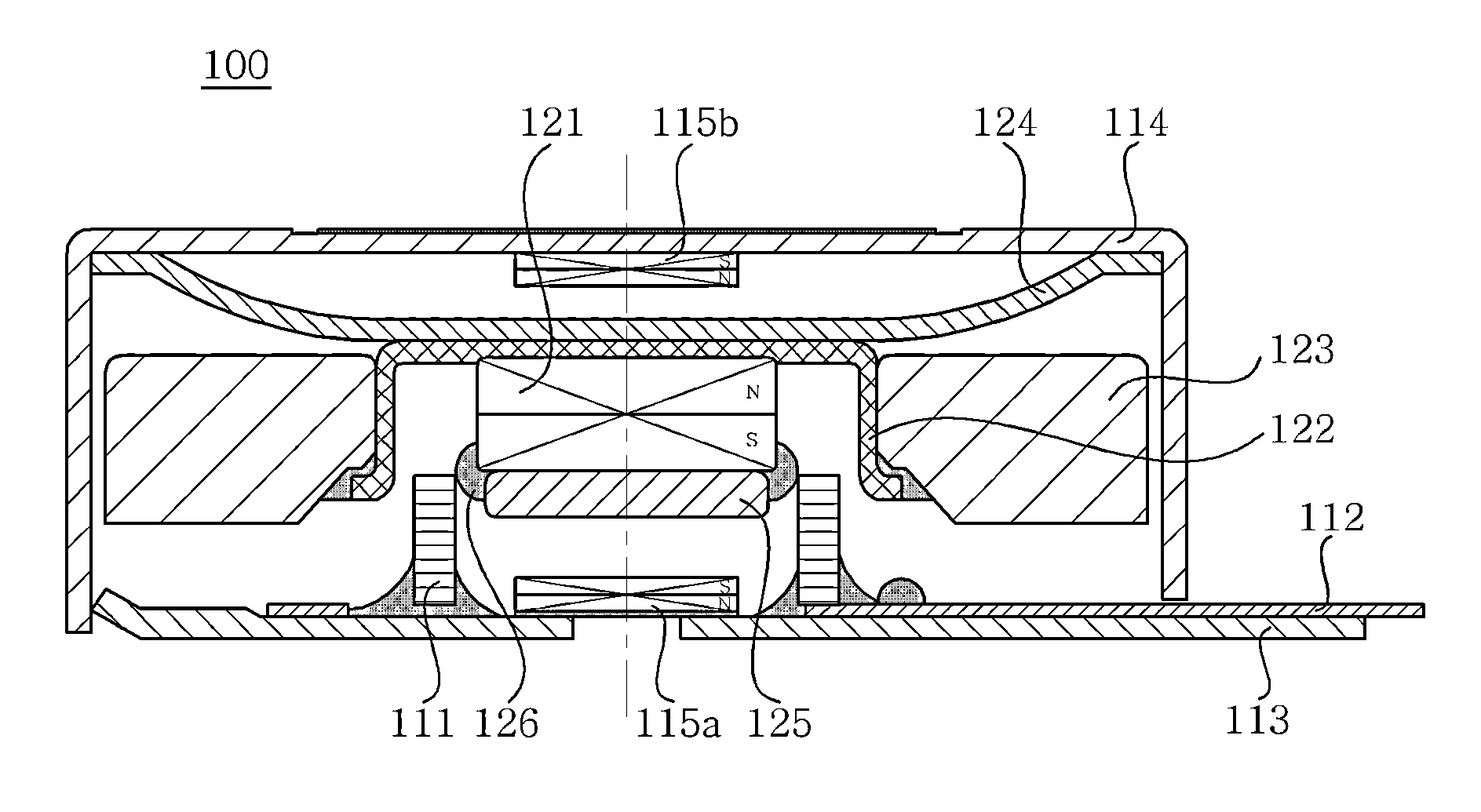
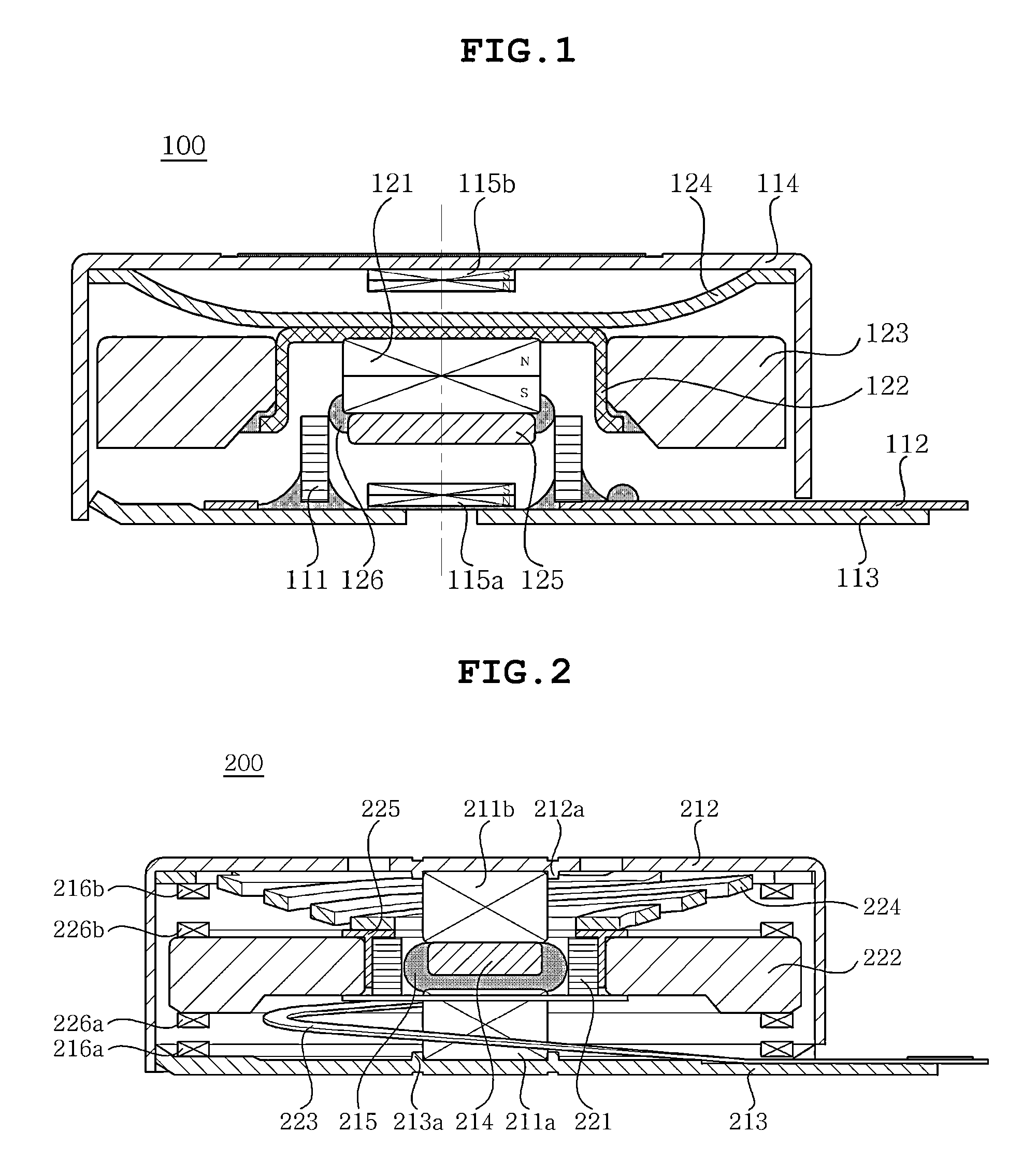
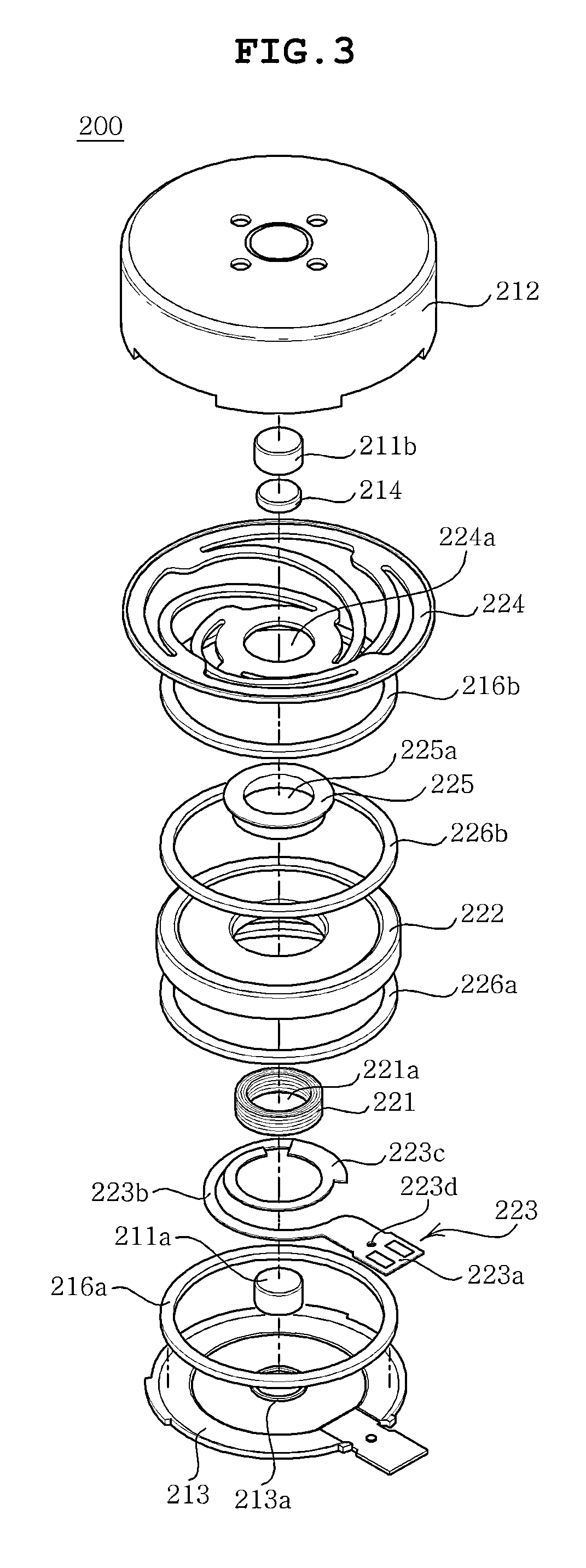
Disclosed herein is a linear vibration motor including: a stator part including a coil, a printed circuit board coupled to the coil, a bracket having the printed circuit board fixedly coupled thereto, and a case having an internal space formed therein and coupled to the bracket; and a vibrator part including a main magnet positioned to face the coil, a yoke coupled to the magnet, a weight body coupled to an outer peripheral surface of the yoke, and an elastic member having one end coupled to the case and the other end coupled to the yoke, wherein the stator part further includes sub-magnets, which are magnetic damping units, the sub-magnets being disposed to face the main magnet of the vibrator part and being mounted in the stator part so that surfaces thereof facing the main magnet have the same polarities as those of the main magnet.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
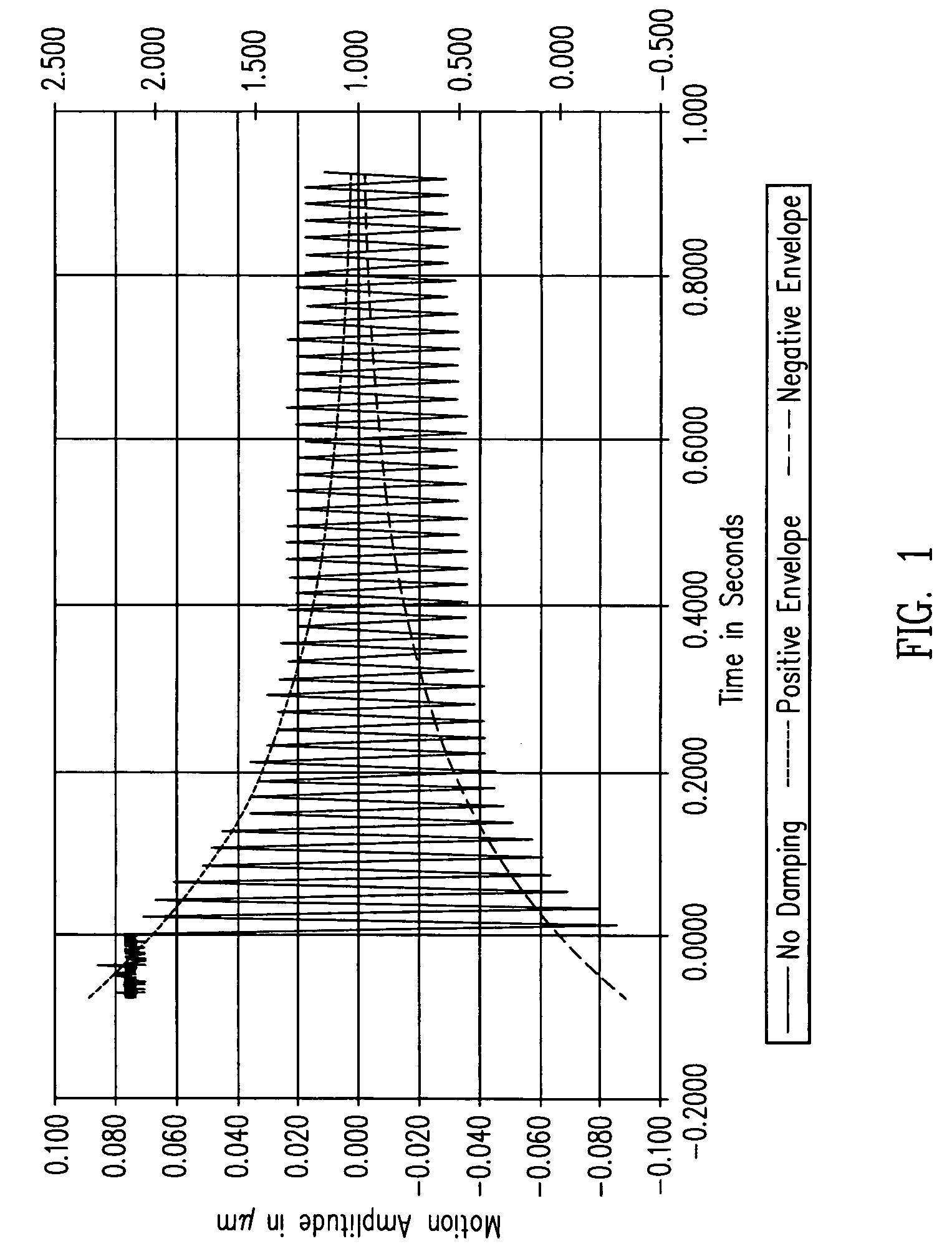
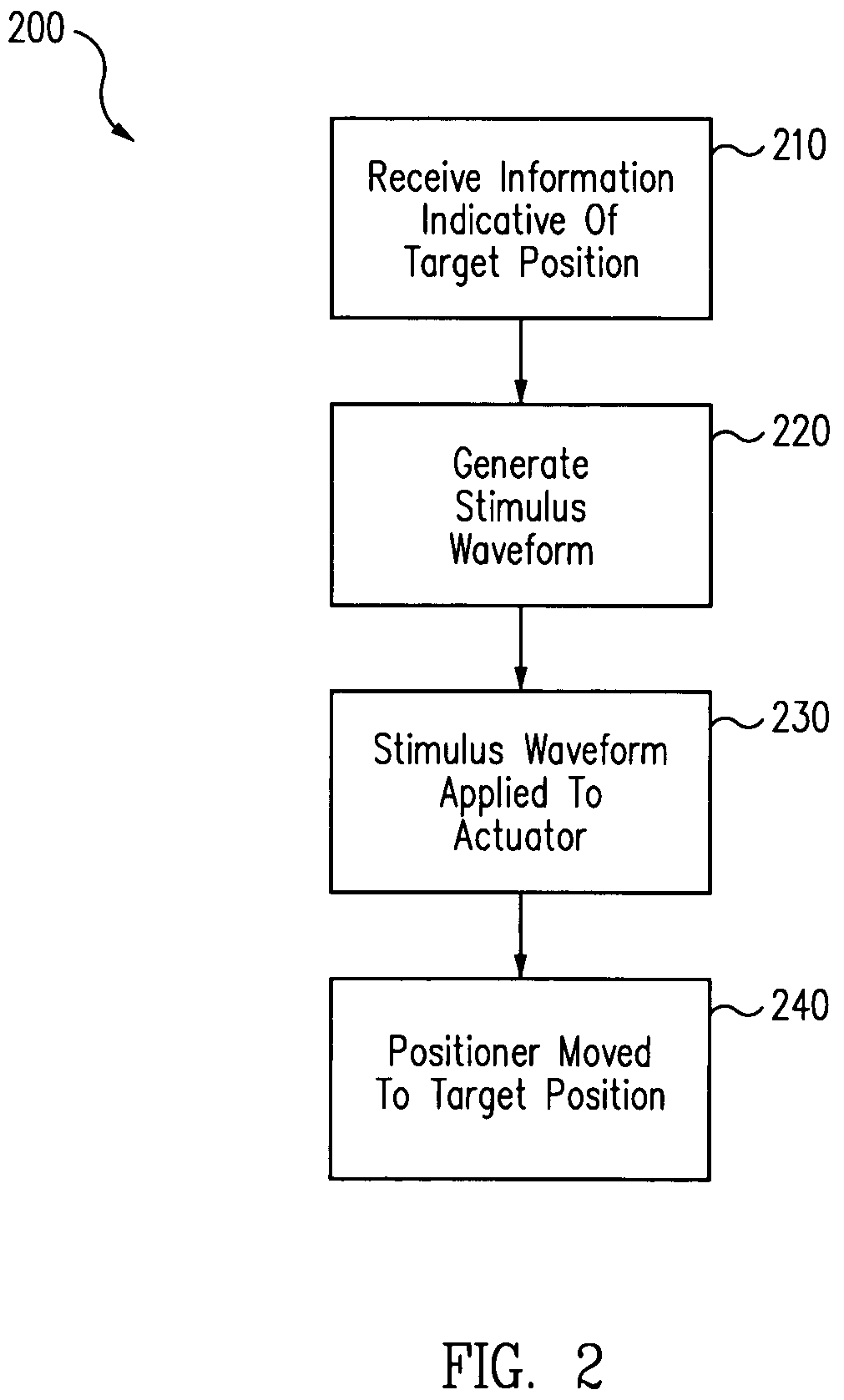
Electronic damping for stage positioning
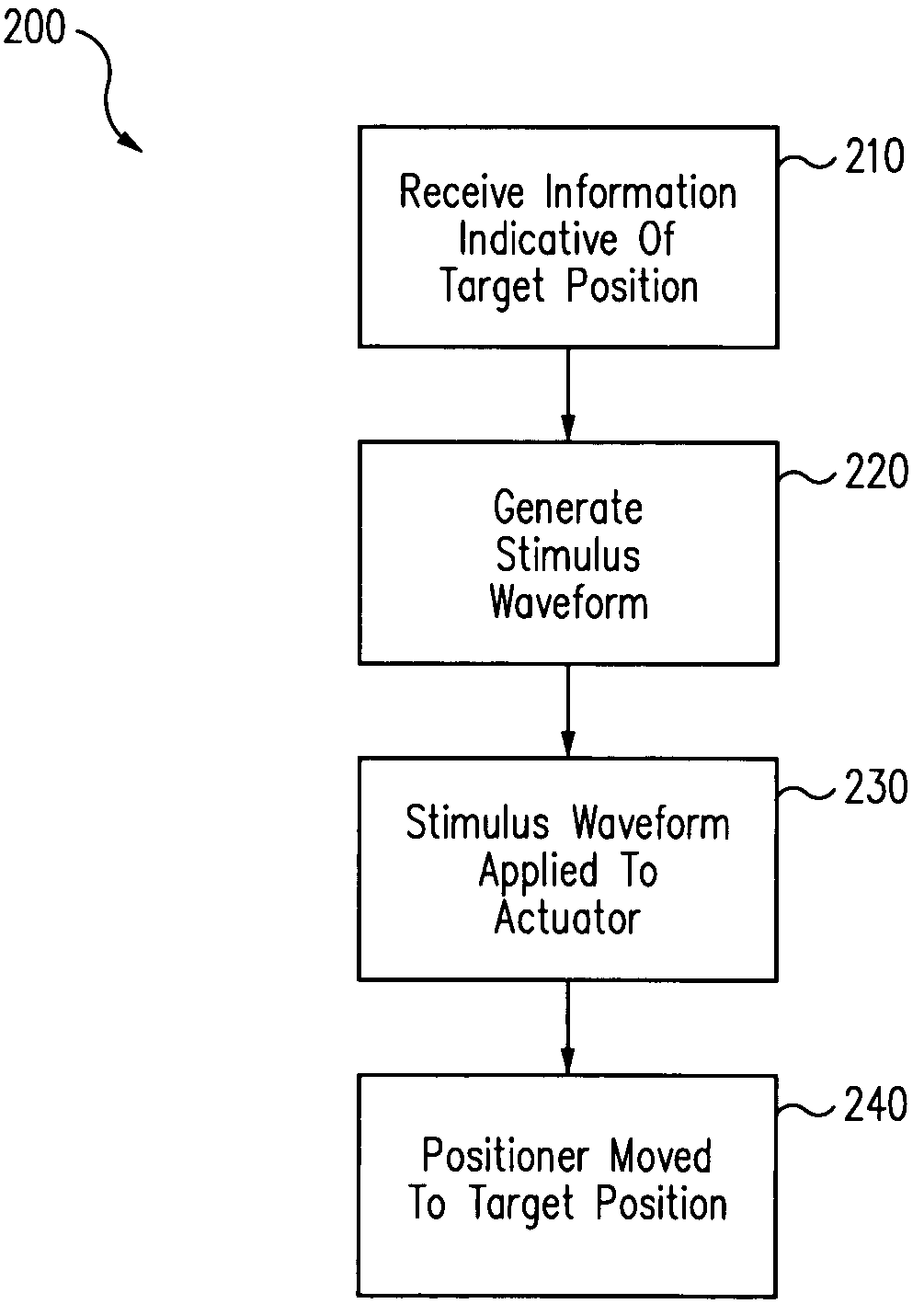
Systems and techniques for electro-magnetic damping in a stage system. An excitation waveform for one or more actuators includes one or more frequency components with associated amplitudes. Frequency components at a resonance frequency of the stage system have associated amplitudes that are substantially zero.
Owner:DIGITALPTICS MEMS
Spin-torque oscillator for microwave assisted magnetic recording
ActiveUS8970996B2Reduced magnetic damping constantGenerate efficientlyRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsNuclear magnetic resonancePower flow
A microwave assisted magnetic recording write head having a spin torque oscillator capable of producing high strength high frequency magnetic oscillations with reduced applied current. The spin torque oscillator uses a magnetic field generation layer with a high moment material including such as Fe and Co that is formed on an interlayer having a face centered cubic (fcc) crystal structure, that functions as an under-layer. The high moment magnetic field generation layer has also reduced magnetic damping.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Electromagnetic moldless forming method and device of pipes based on background magnetic field
The invention discloses an electromagnetic moldless forming method and device of pipes based on a background magnetic field. The device comprises a Helmholtz coil system, a support rod, upper and lower support plates, a driving rod, a pulse discharge circuit and a forming coil. The background magnetic field is combined with a pulse magnetic field to realize uniform electromagnetic bulging of the pipes (such as aluminum alloy pipes). The nonuniform flowing of corresponding plastic deformation areas of the pipes deformed at high speed is stopped by a nonuniform resistance field formed by electromagnetic damping in the background magnetic field, so that the pipes generate no local thinning or spalling, and qualified expansion pipe fittings with uniform plastic flowing are obtained. The Helmholtz coil system can accurately control the input energy of the background magnetic field, so that the final forming shapes of the pipes are precisely controlled, such defects as high size fluctuation and weak process repeatability of expansion pieces in a traditional electromagnetic free expansion process are prevented, and the batching, the mechanization and the standardization of the process are realized.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Cage twisting machine wire barrow paying out tension controlling method and apparatus
InactiveCN1933038ASmall initial pay-off tensionGood radial positioningFilament handlingCable/conductor manufactureInstabilityMagnetic poles
Strain of payoff control method and device uses for cage stranger payoff tray of electrical wire and cable equipment. Existing technology adopts strap friction to control the strain of payoff, while the strain of payoff is instability and is disaccord of some cradle payoff tray. It adopts permanent damp technology to adjust magnetic pole air-gap of damp tray and to control strain of payoff. It relates to passive damp tray, active damp tray, accommodate handle, active tray slide cover, transmission shaft, graduation direction mark, fix seat of passive damp tray, bearing, bearing cover and cradle body. Turn accommodate handle to adjust strain of payoff. Accommodate moment is extended constant and dose not change with temperature, time and opposite slide difference speed for non-friction. The whole operation keeps steady strain of payoff and realizes the coherence of strain of payoff to all cradle payoff trays by clearance graduation direction mark.
Owner:百通赫思曼工业(苏州)有限公司
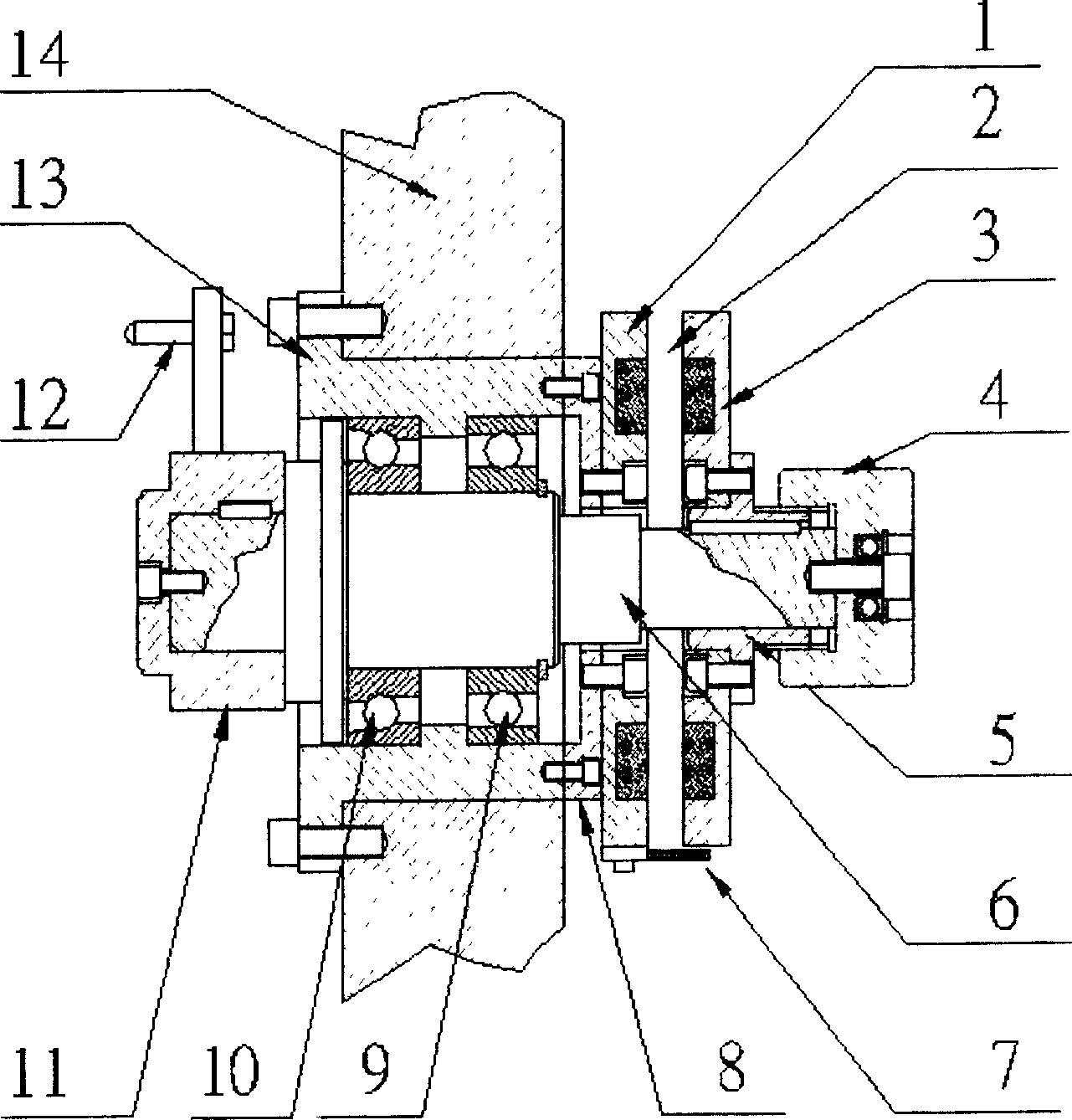
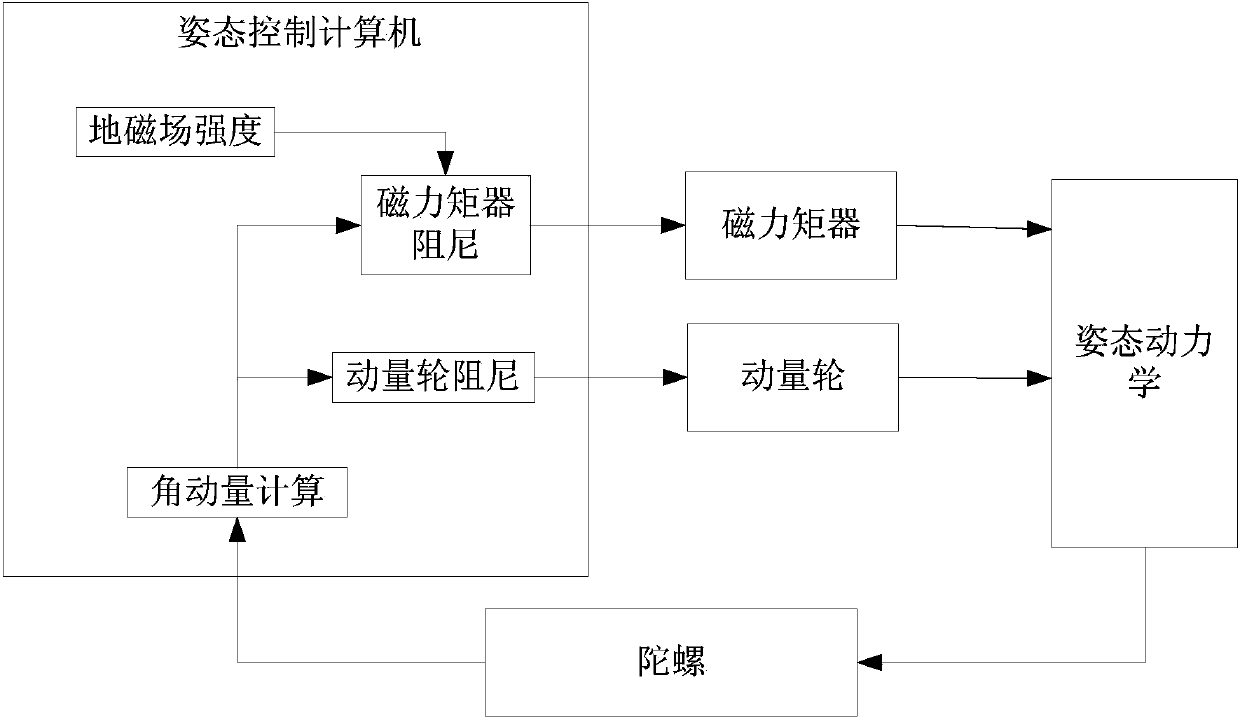
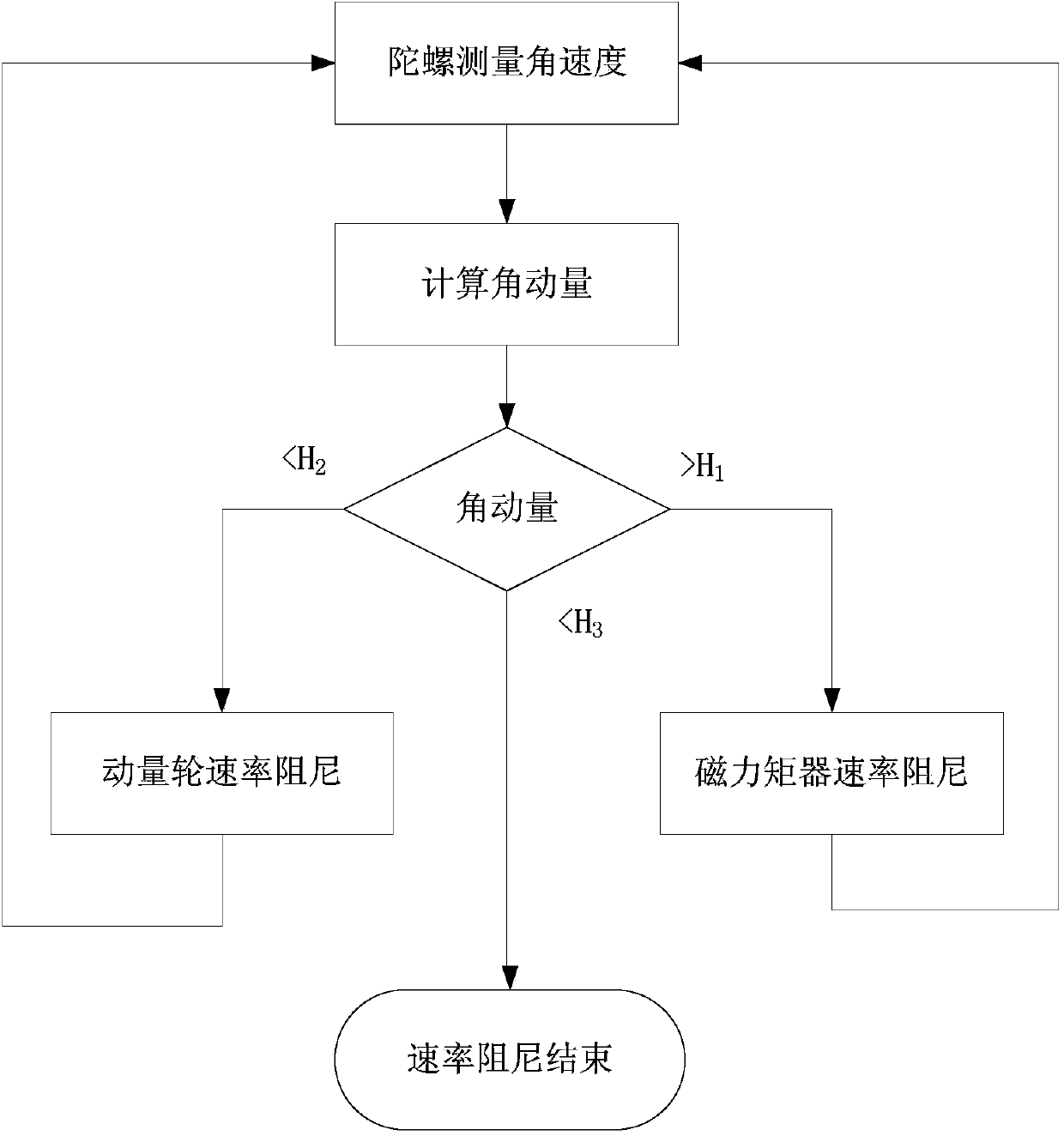
Rate damping method combining momentum wheel and magnetic torquer
The invention discloses a rate damping method combining a momentum wheel and a magnetic torquer. The total angular momentum HT of a satellite is calculated according to the angular speed measured by a gyroscope and the current angular momentum of the momentum wheel; when the angular momentum is smaller, the tri-axial momentum wheel is used for quick damping; when the angular momentum exceeds the angular momentum absorbing capacity of the momentum wheel, the tri-axial magnetic torquer is used for rate damping. During magnetic damping, once the angular momentum of the satellite is reduced to a certain range, the momentum wheel is switched for damping. According to the method, characteristics of two kinds of rate damping by the momentum wheel and the magnetic torque are combined, reasonable switching between the momentum wheel and the magnetic torquer is realized, and the time required by rate damping is shortened.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
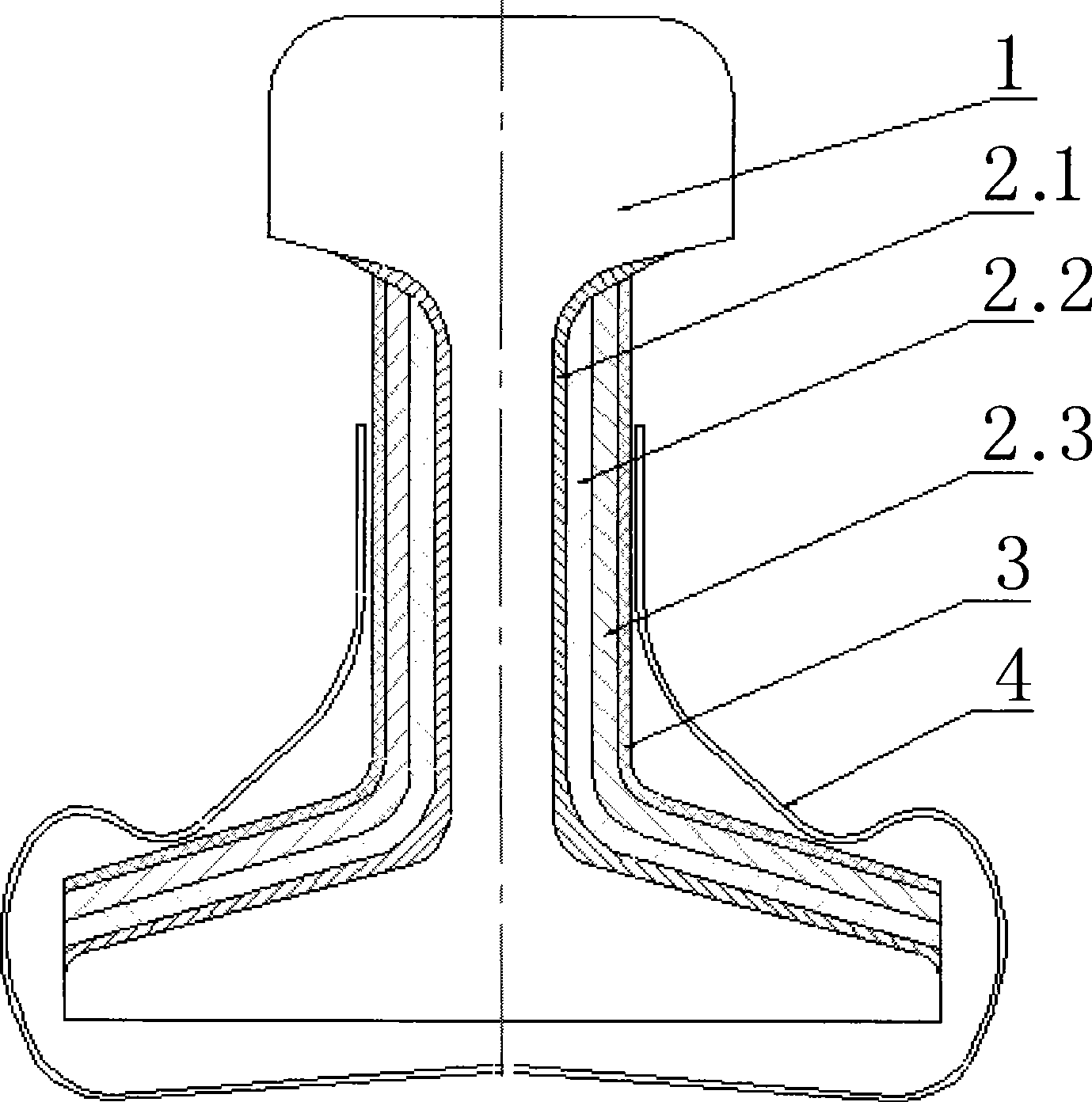
Steel rail vibration damping noise reduction method for self-absorption composite magnetic damping plate
The invention discloses a method for vibration absorption and noise reduction of steel rails by self-attraction type combined magnetic damping sheets, which comprises the following steps: a rail web and a rail foot of a steel rail (1) are symmetrically provided with the combined magnetic damping sheets (2); the outer layers of the combined magnetic damping sheets are symmetrically provided with constraint metal plates (3) which are fixed at both sides of the steel rail by a U-shaped magazine clip (4); the combined magnetic damping sheets have the magnetism and are attracted on the side surfaces of the steel rail; related interfaces inside the combined magnetic damping sheets and between the combined magnetic damping sheets and the steel rail as well as between the combined magnetic damping sheets and the constraint metal plates can cause vibration friction and slide relatively during the vibration of the steel rail; the mechanical energy of the vibration is converted into thermal energy to be dissipated to eliminate the vibration energy or the vibration amplitude of the steel rail; and the combined magnetic damping sheets and the steel rail are not adhered, so the viscoelastic damping mechanism is lost, which ensures that the range of the vibration frequency is wider, the temperature change has smaller influence, and good vibration absorption and noise reduction effects exist in a wider range of frequency domain and temperature domain. The method has convenient installation and replacement, and obvious vibration absorption and noise reduction effects, and can be widely used for vibration absorption and noise reduction engineering of track traffic.
Owner:洛阳双瑞橡塑科技有限公司
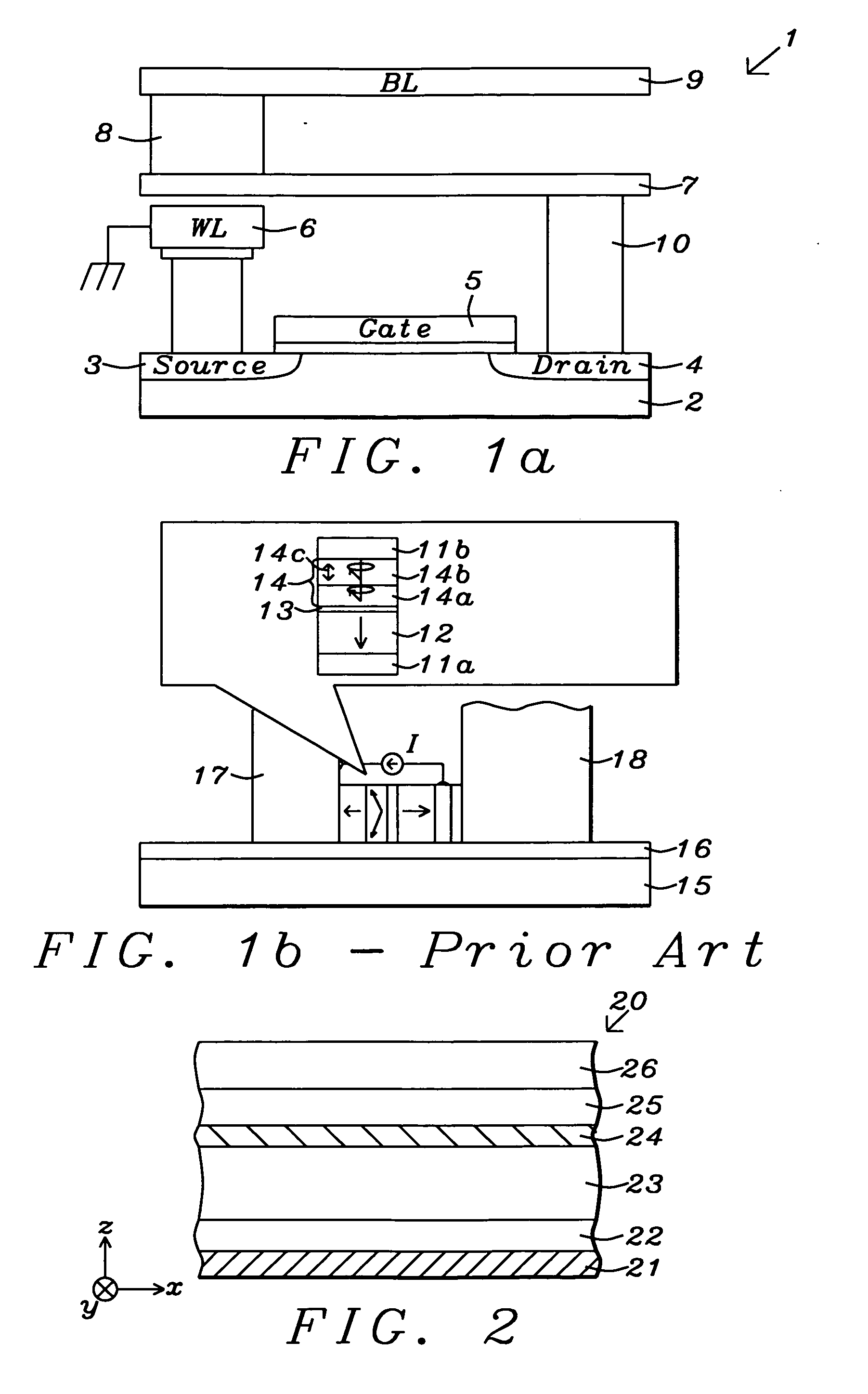
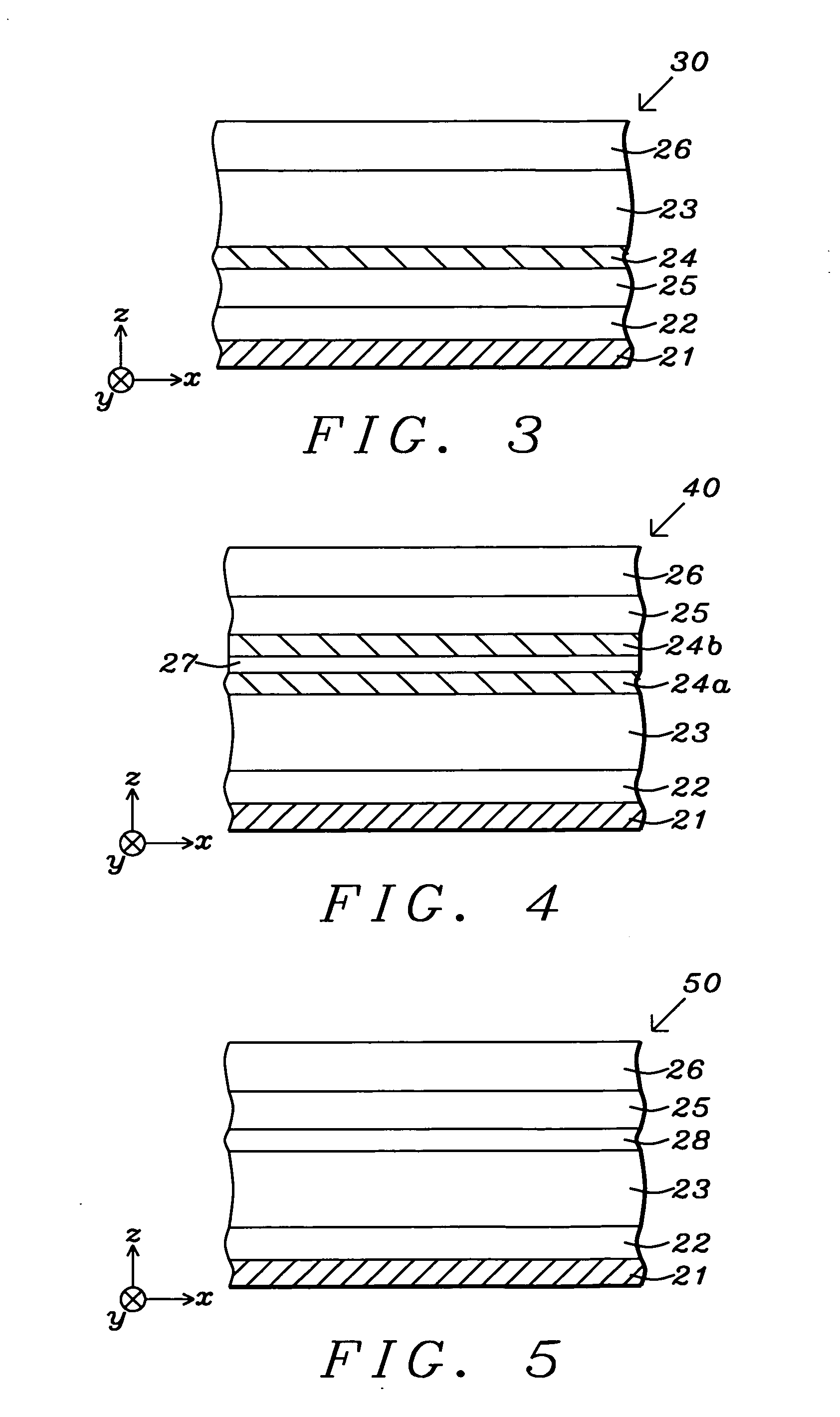
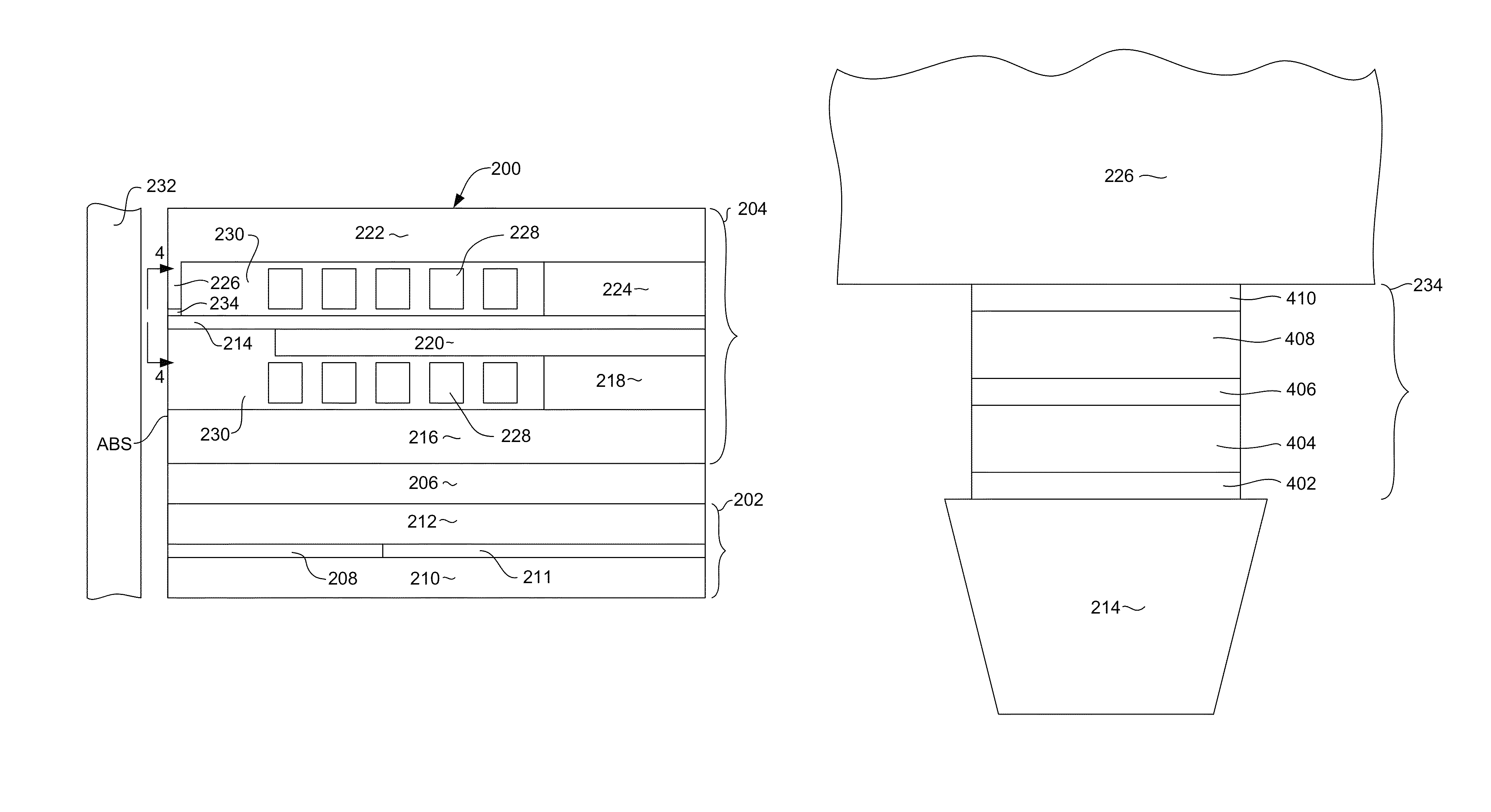
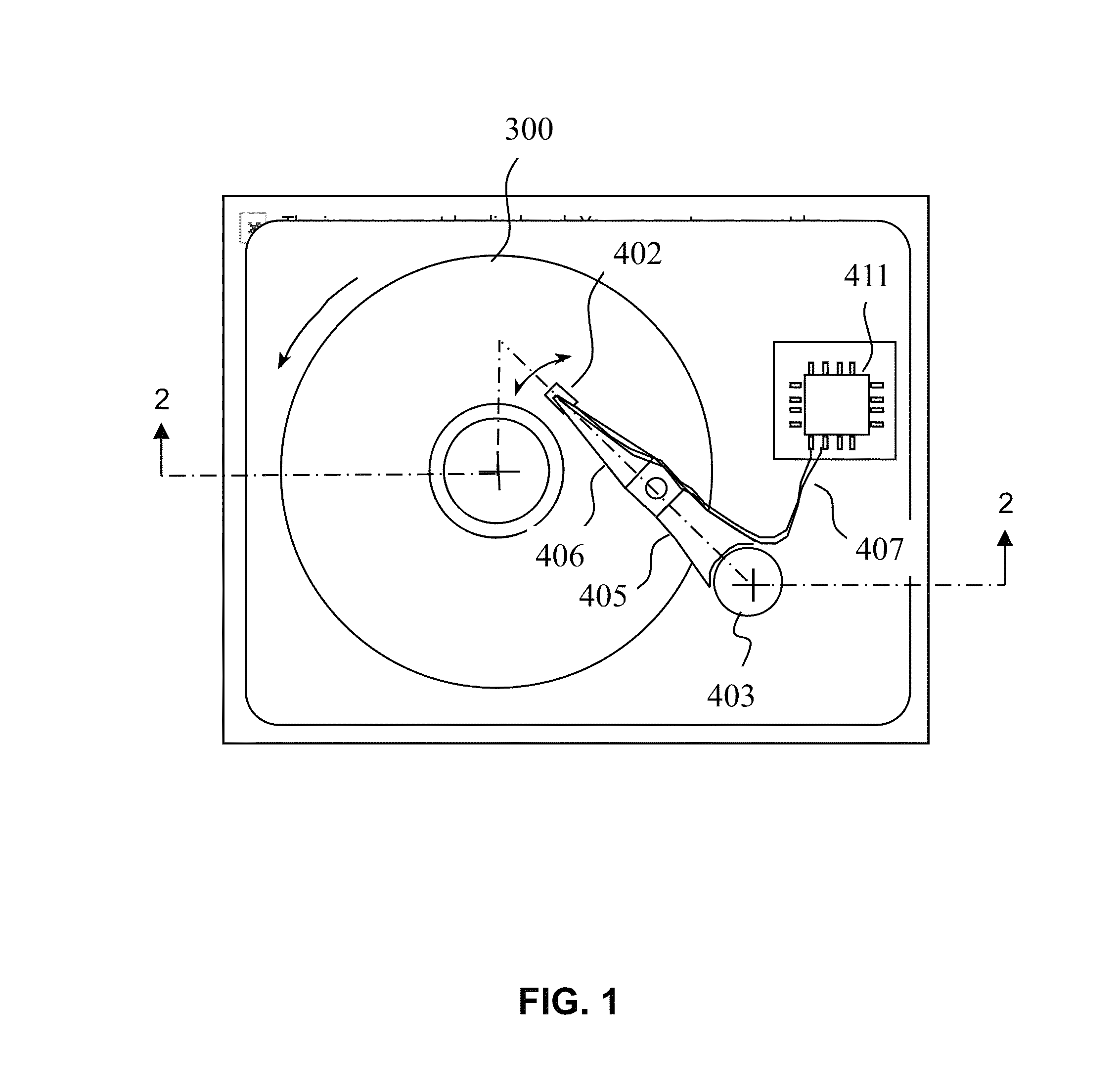
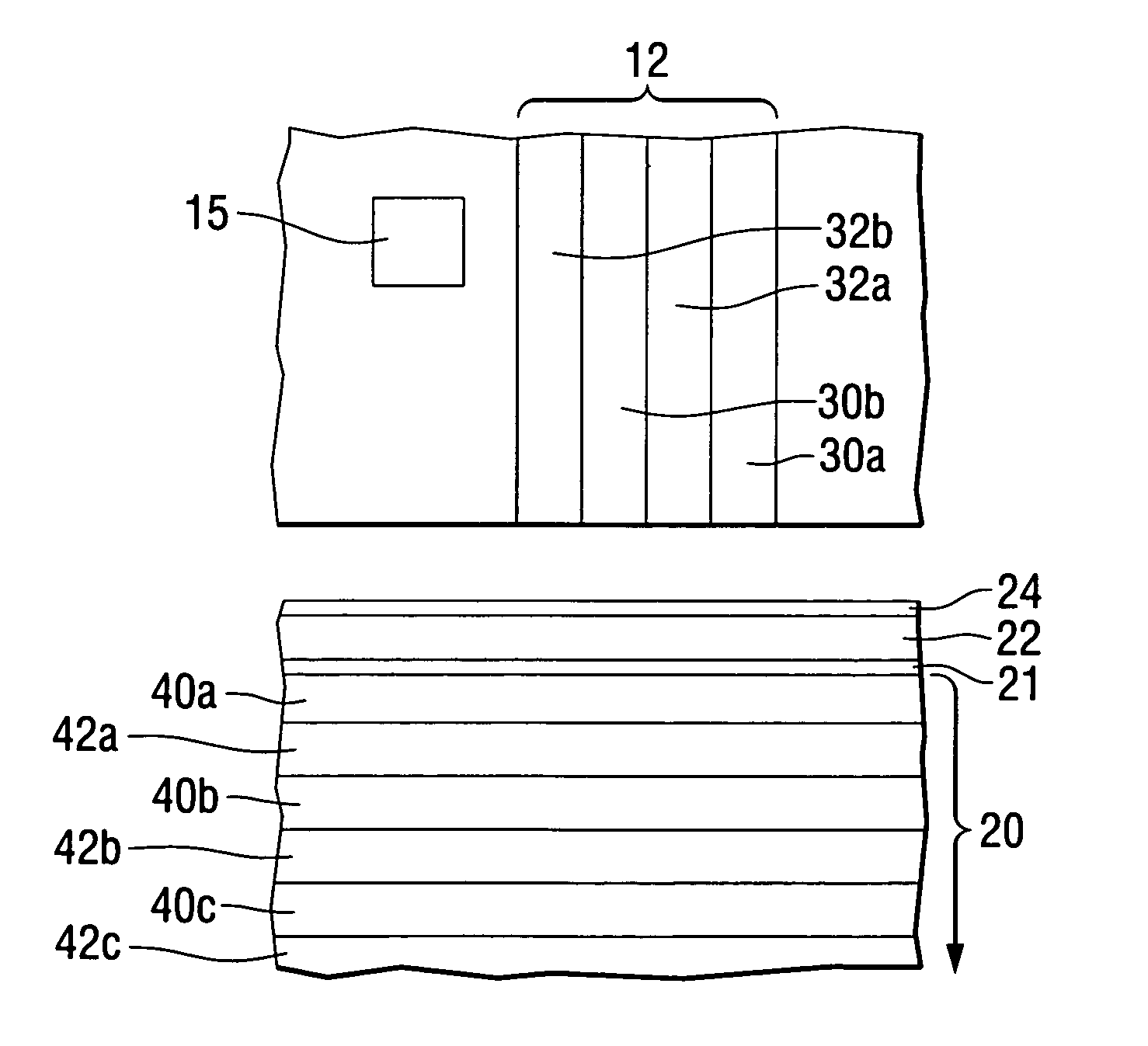
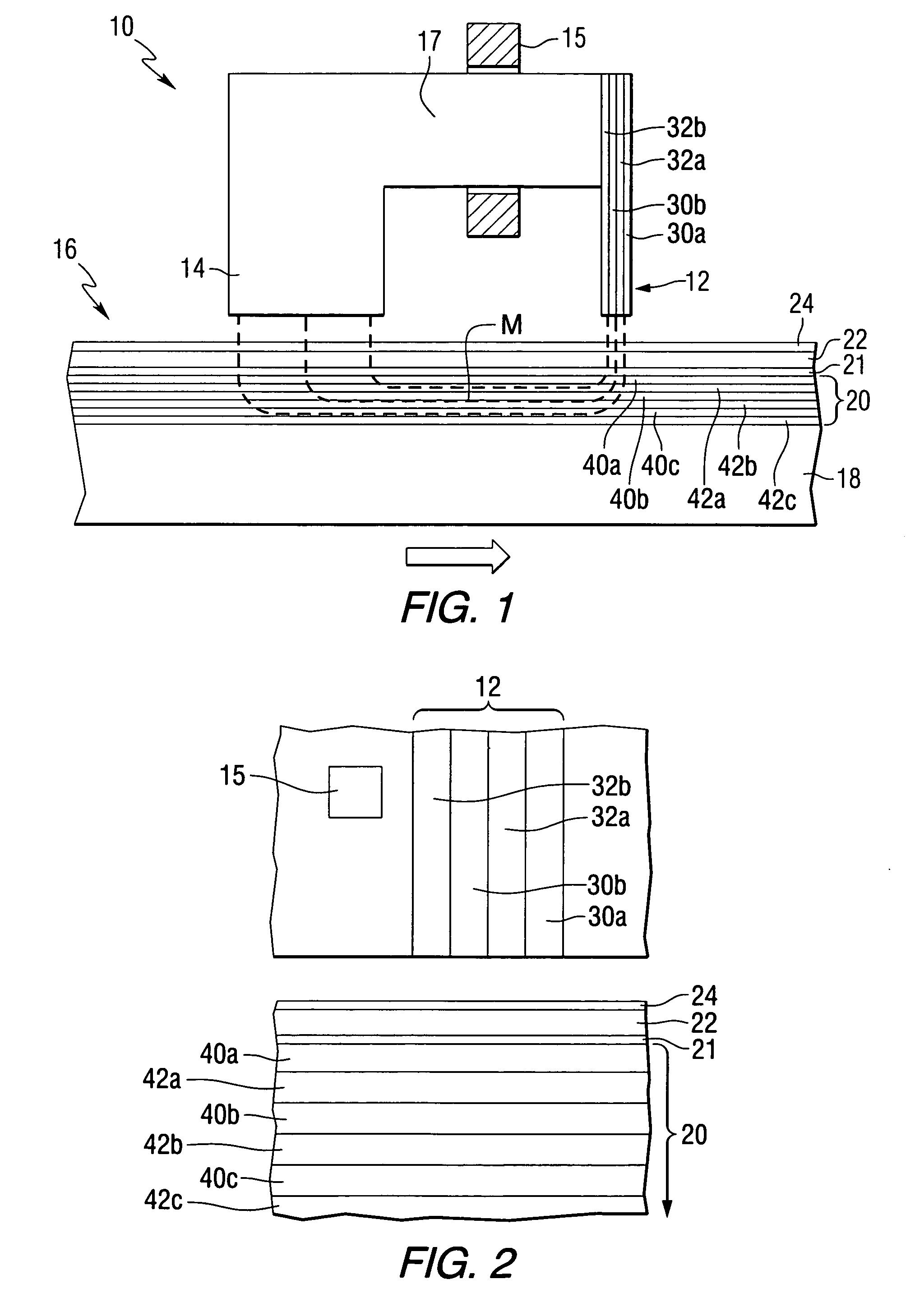
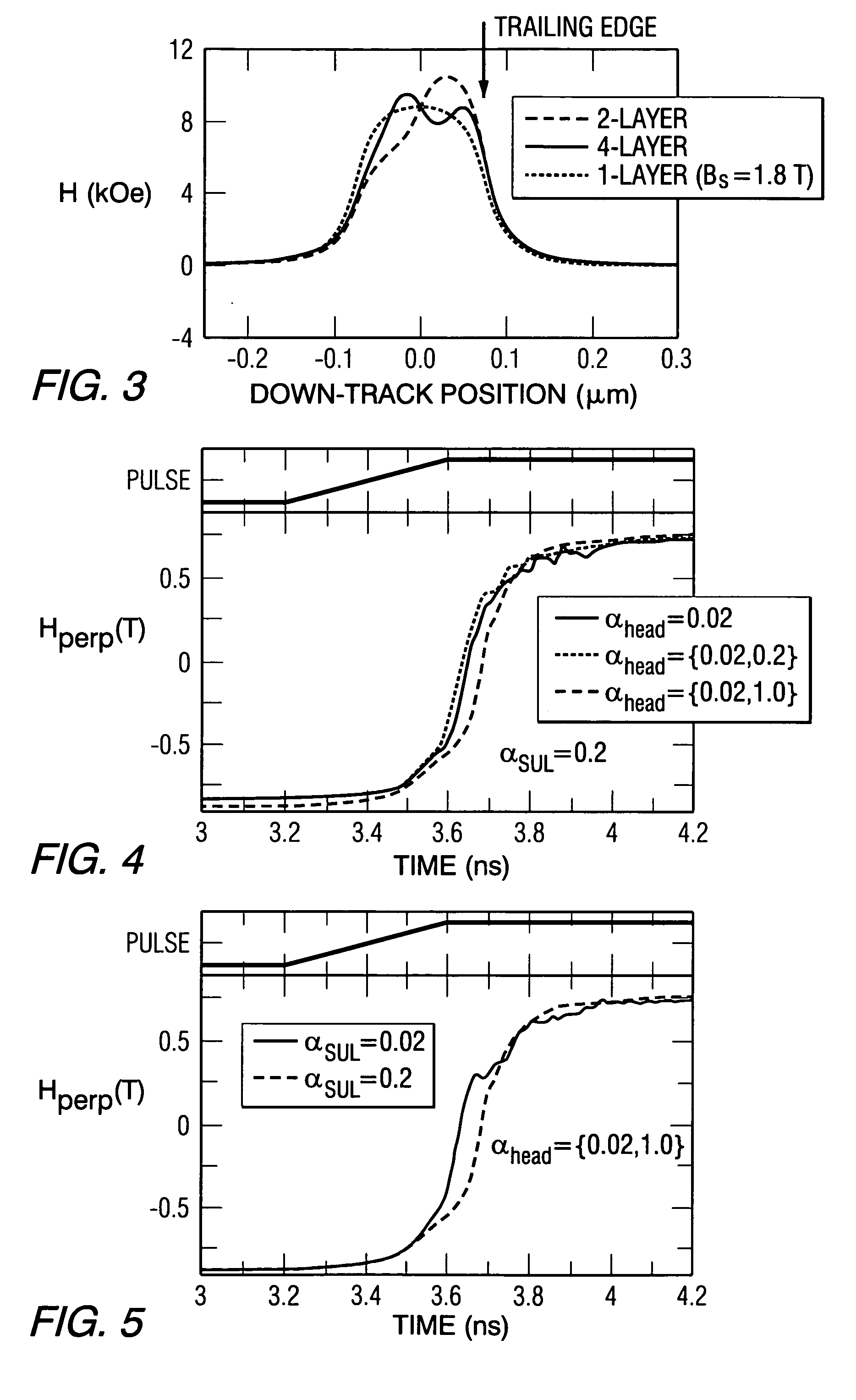
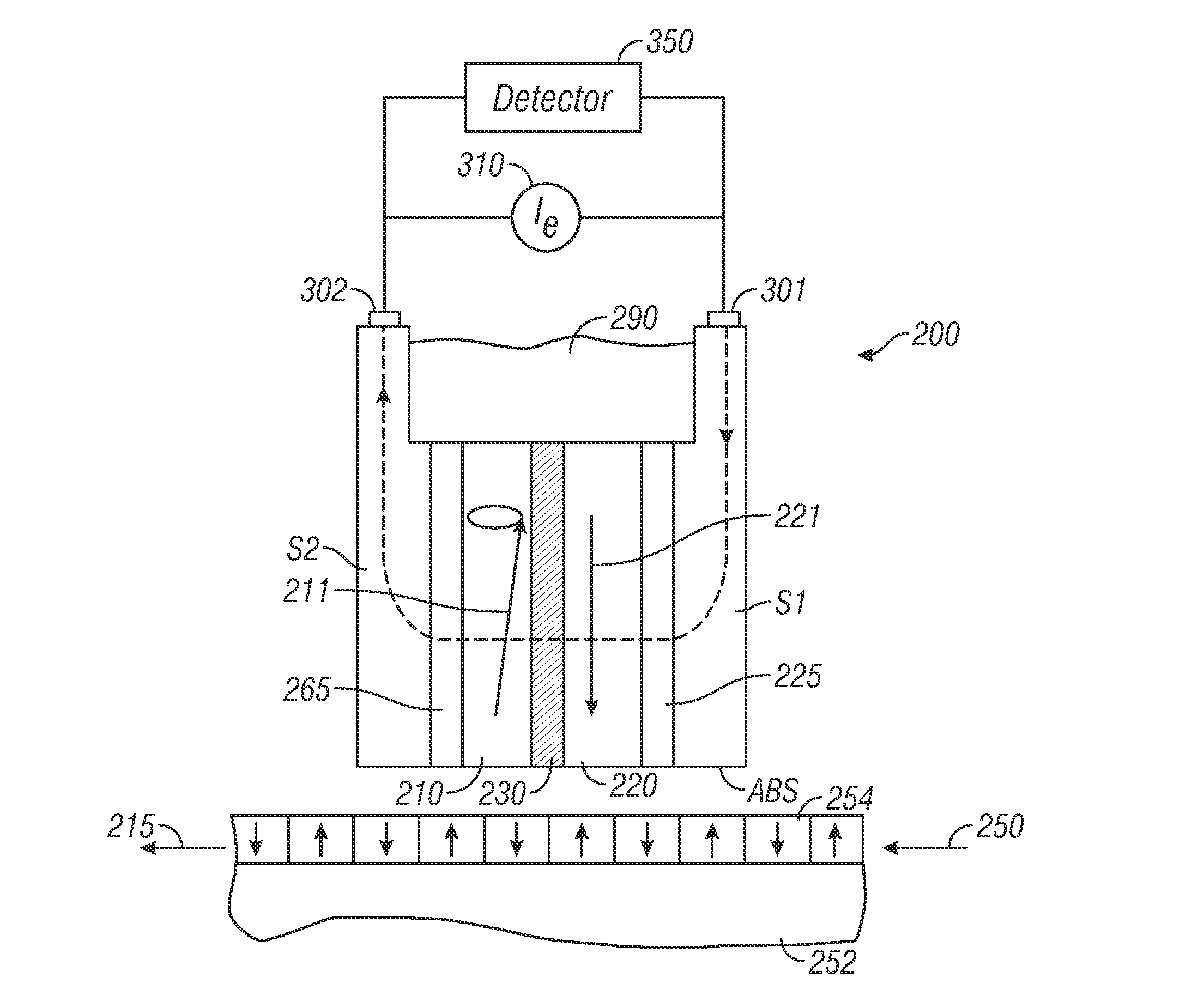
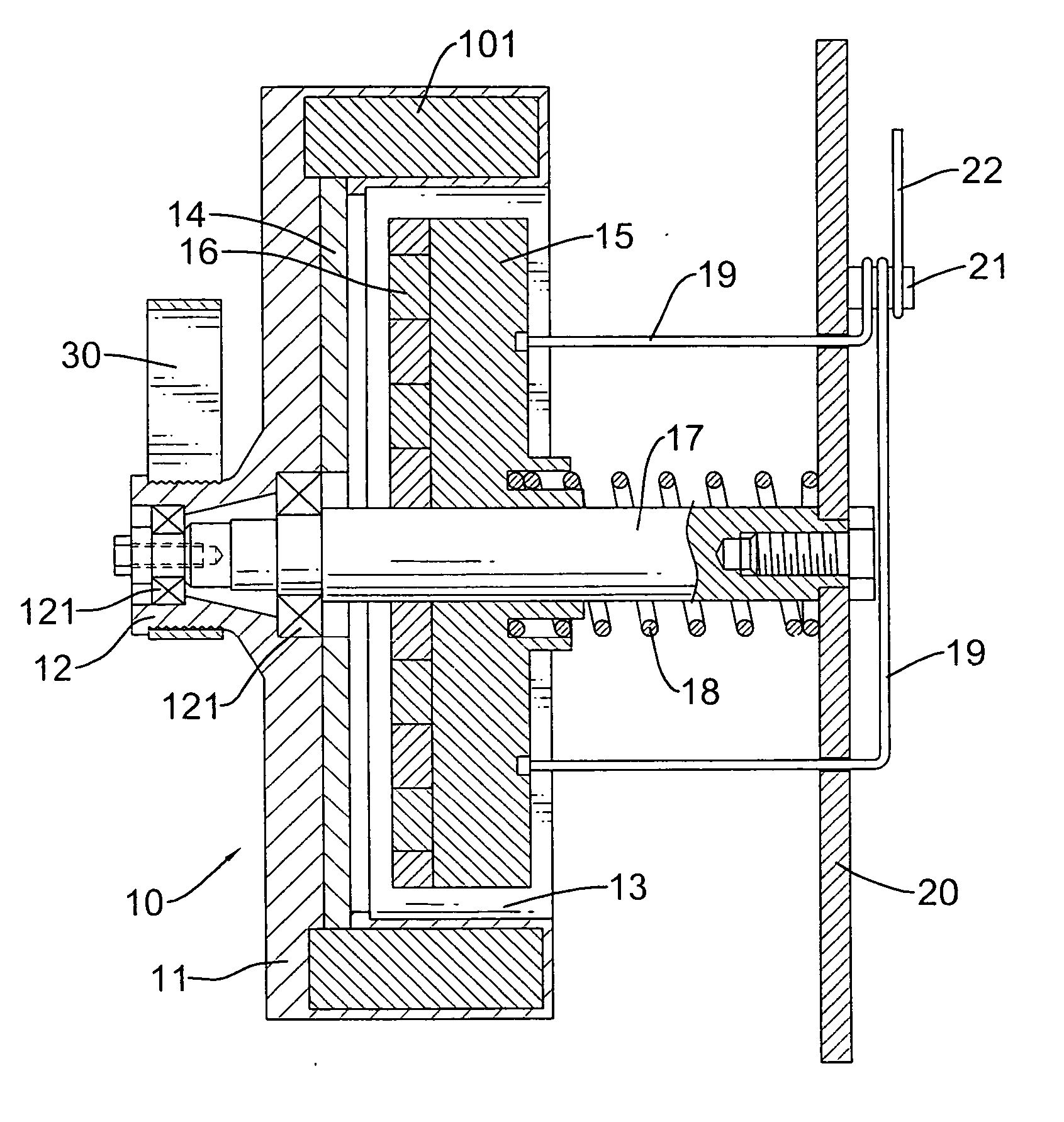
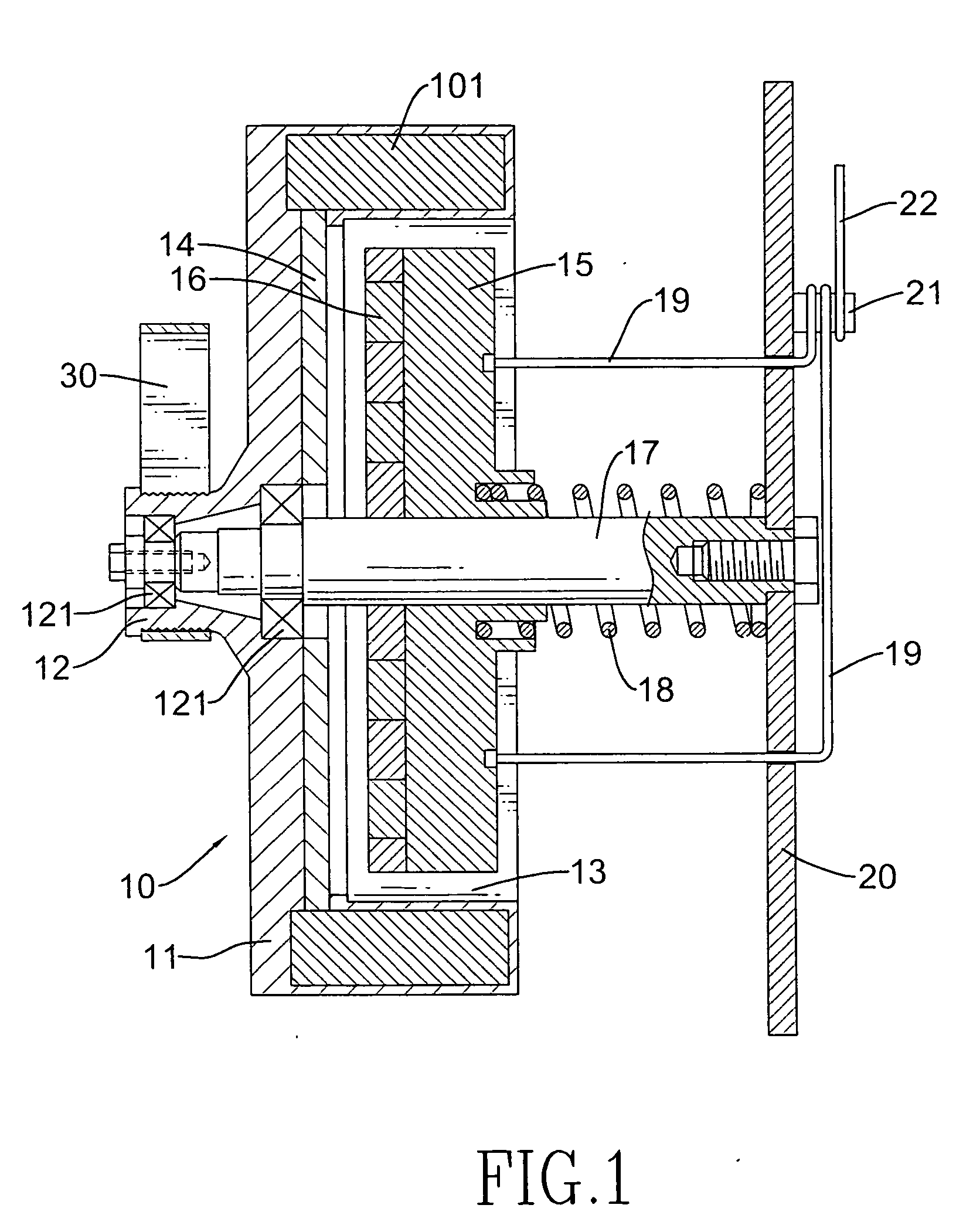
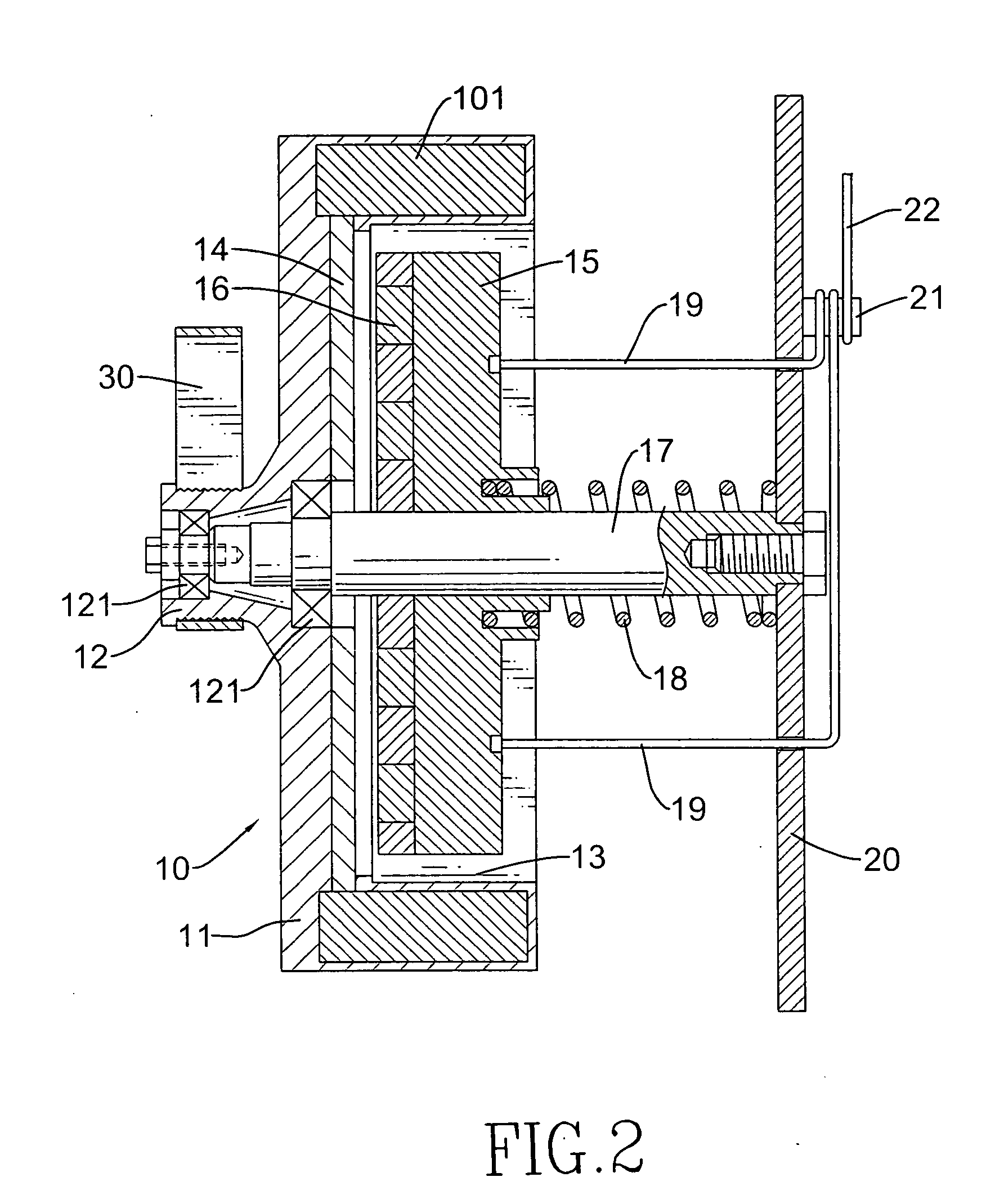
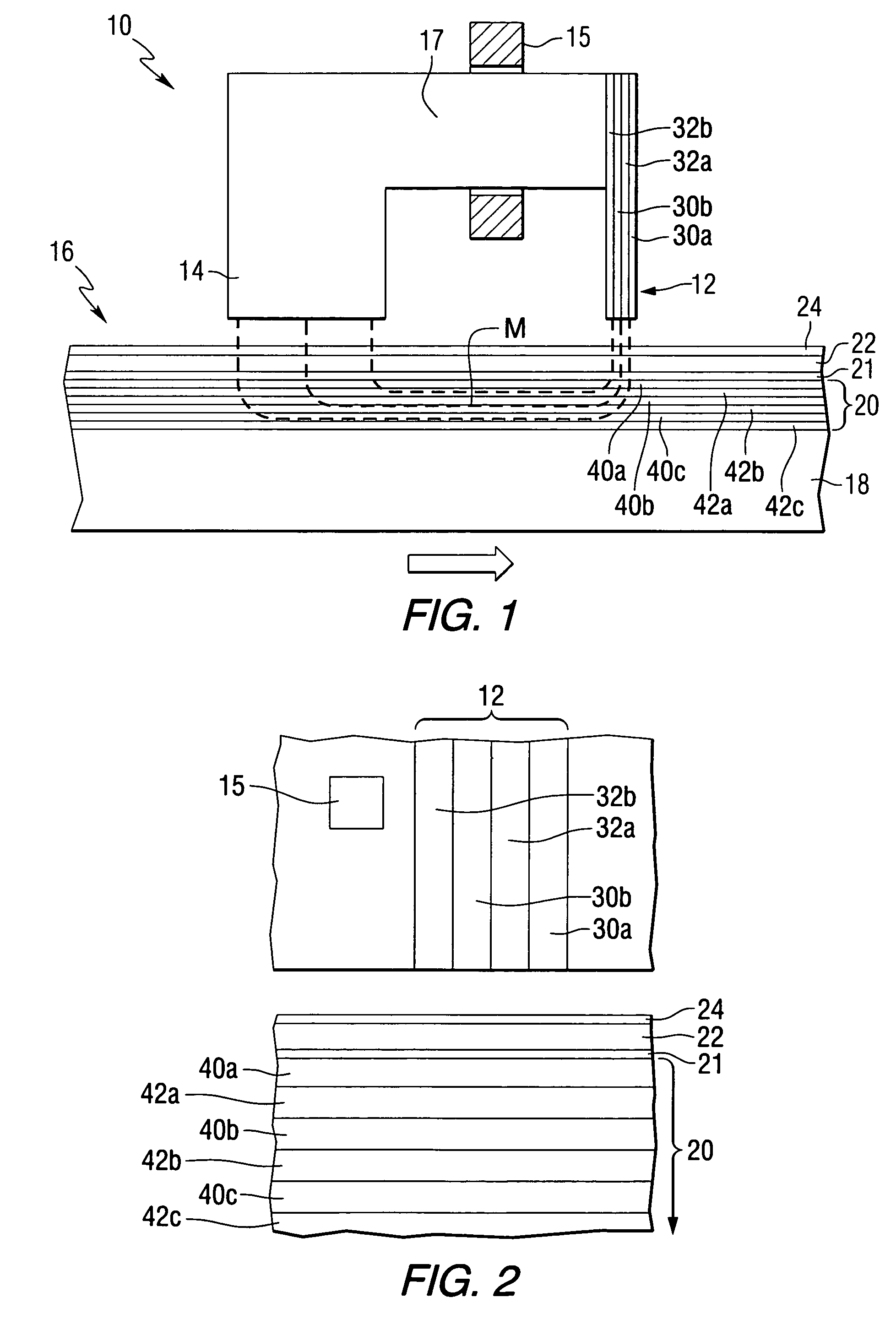
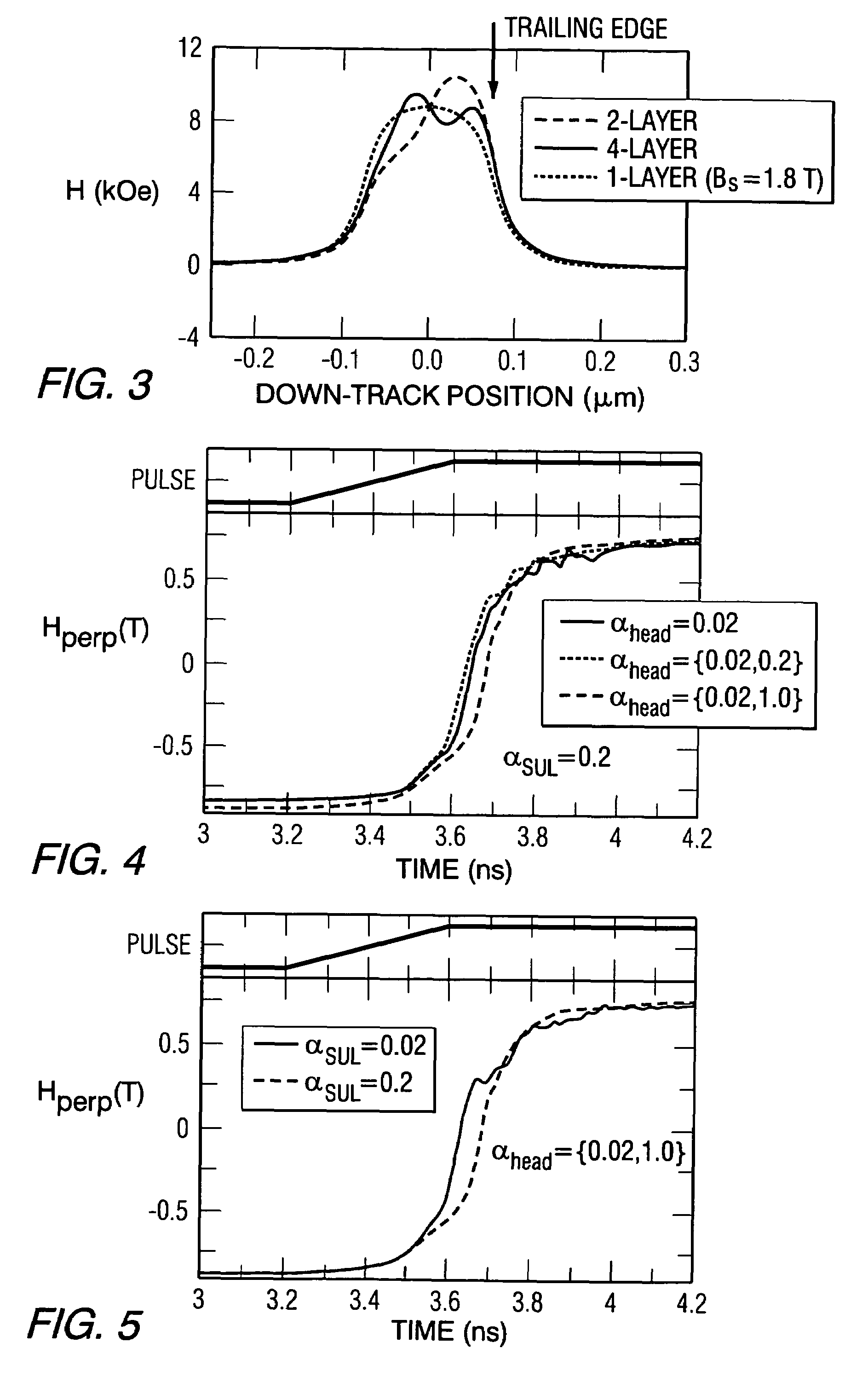
Damping control in magnetic recording systems
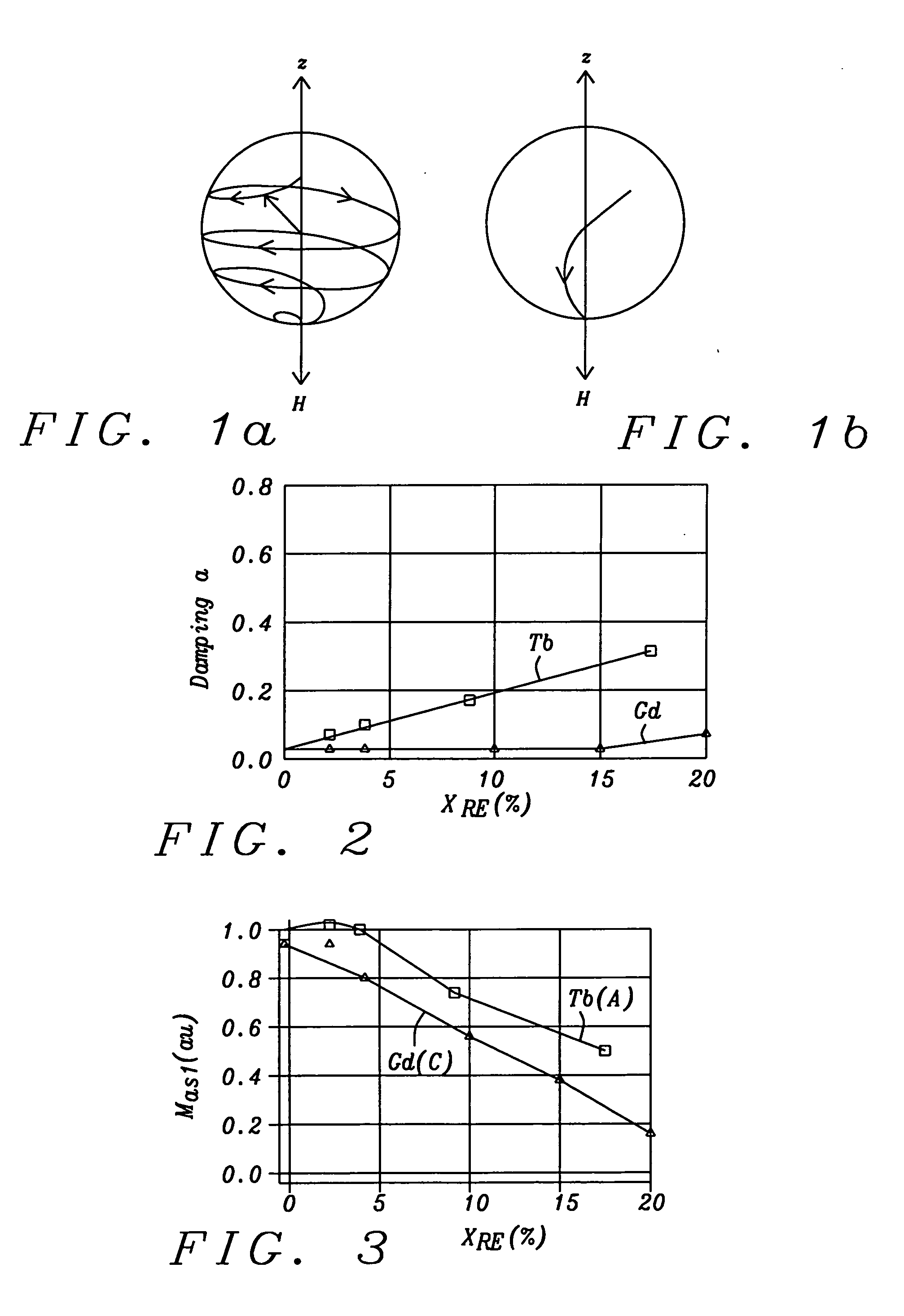
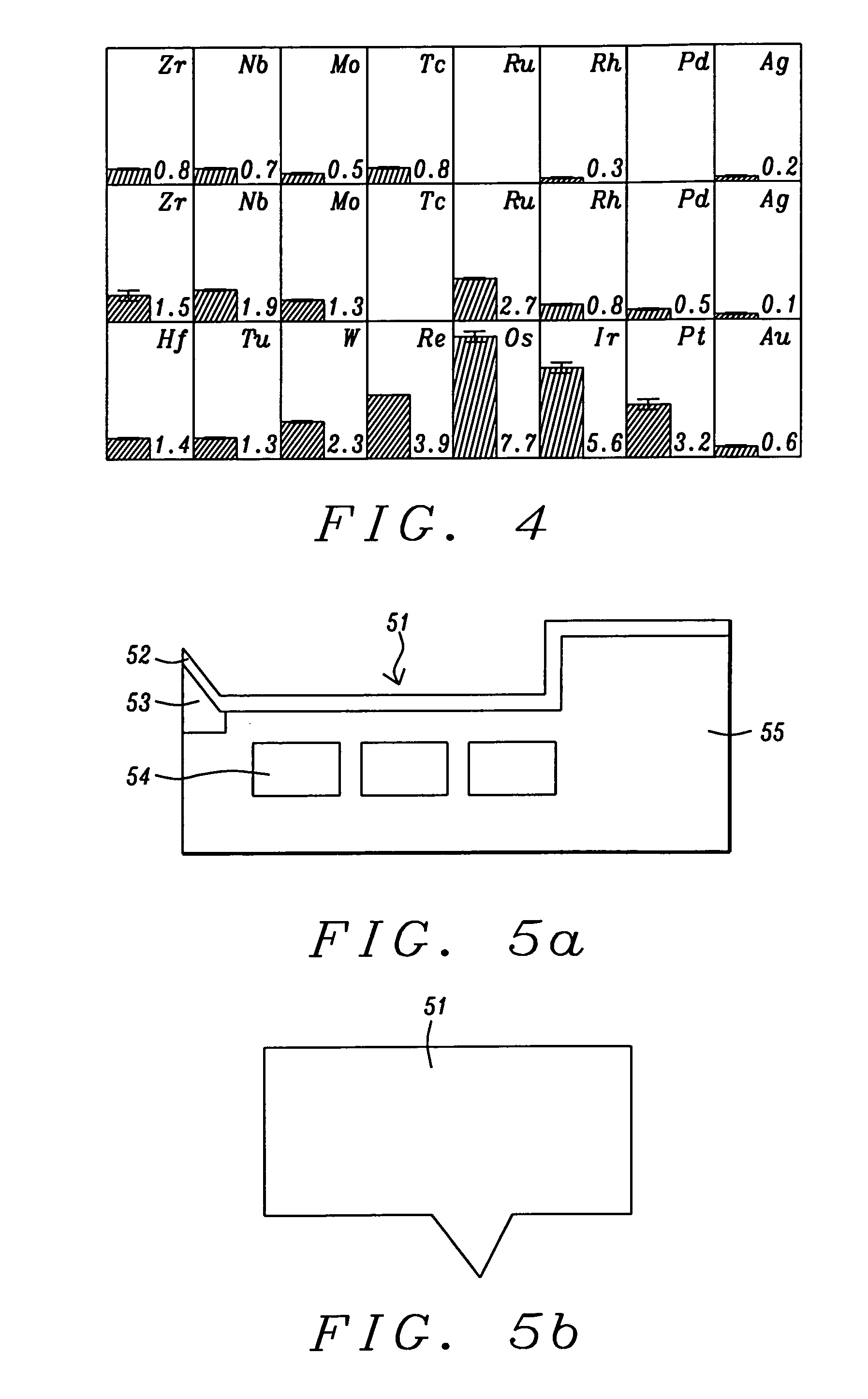
InactiveUS20070003792A1Reduction in transition jitterHigh magnetizationRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsMagnetic dampingRare earth
A magnetic recording system is disclosed in which the magnetization dynamics of the write head and recording medium are highly damped. The system may comprise a perpendicular recording head having a write pole, and a recording medium including a hard magnetic recording layer and a soft magnetic underlayer (SUL). The increased magnetic damping in the write pole and SUL suppresses precessional motion of the respective magnetizations, leading to a reduction in transition jitter caused by spurious head field fluctuations. The damping may be increased by providing films or multilayer structures that are doped with rare earth or transition metal elements. Exchange coupled laminates of doped and undoped layers may optimize both the effective damping and write field in the recording system.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Magnetic damper for vibration absorbers
ActiveUS20170219045A1Eliminating avoiding vibrationVibration dampersNon-rotating vibration suppressionMagnetic dampingClassical mechanics
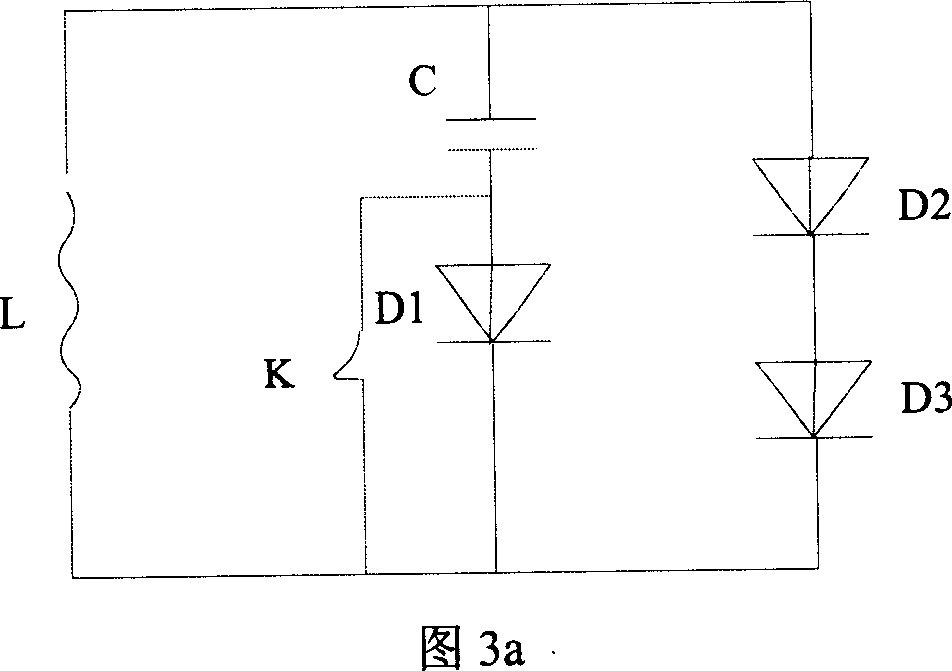
Rotationally symmetric dampers (FIG. 3A) of a new type for eliminating and avoiding vibrations in machines and installations, particularly wind turbines. The damping occurs by magnetically generated eddy currents. In addition, vibration absorbers, particularly pendulum absorbers (7), are equipped with such magnetic dampers, and to installations, particularly wind turbines, that are exposed to vibratory forces and that comprise such vibration absorbers.
Owner:ESM ENERGIE UND SCHWINGUNGSTECHN MITSCH
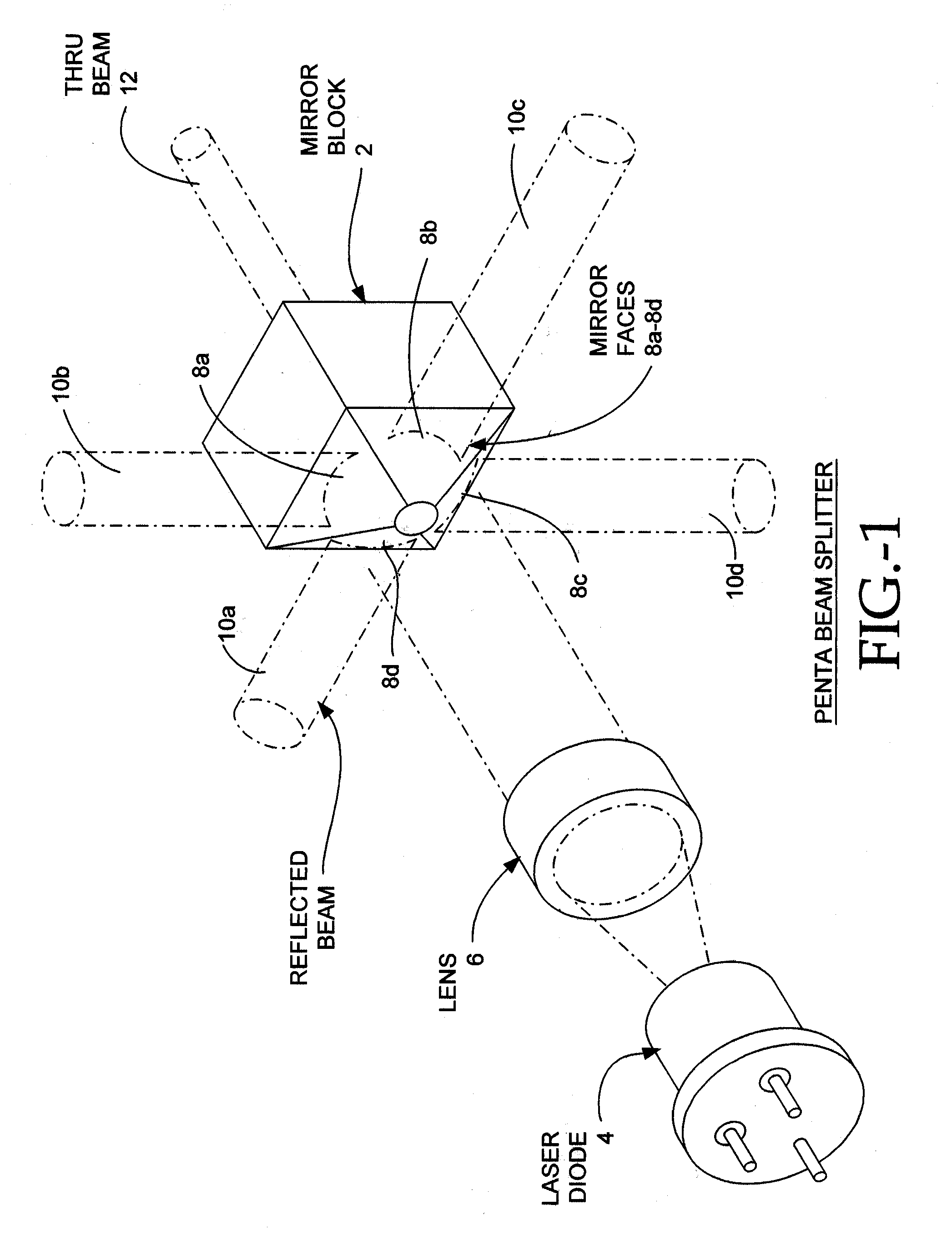
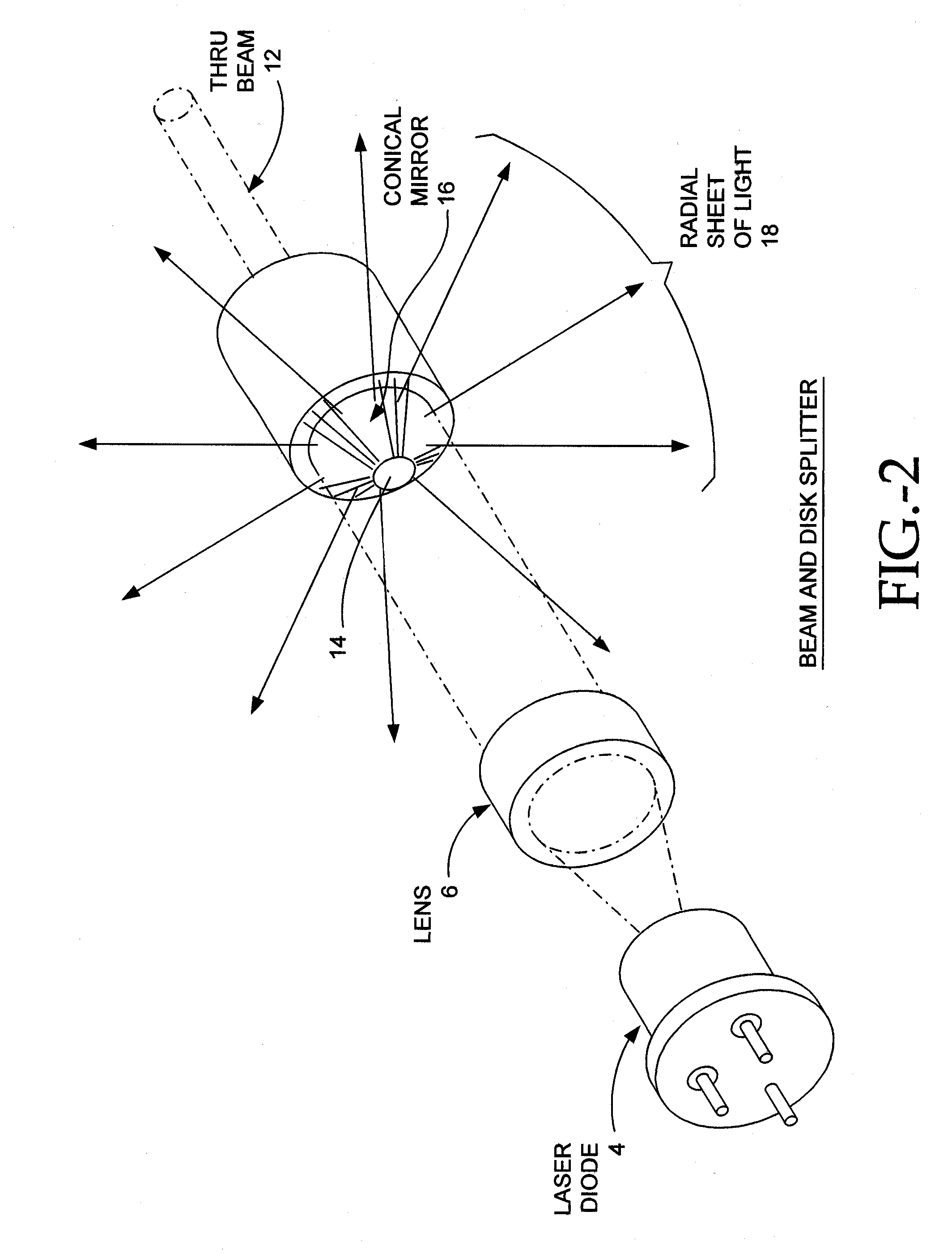
Laser Beam Device With Apertured or Non-Apertured Reflective Element
InactiveUS20020054433A1Simpler and stable and cost-effectiveAngle measurementUsing optical meansMagnetic dampingLight beam
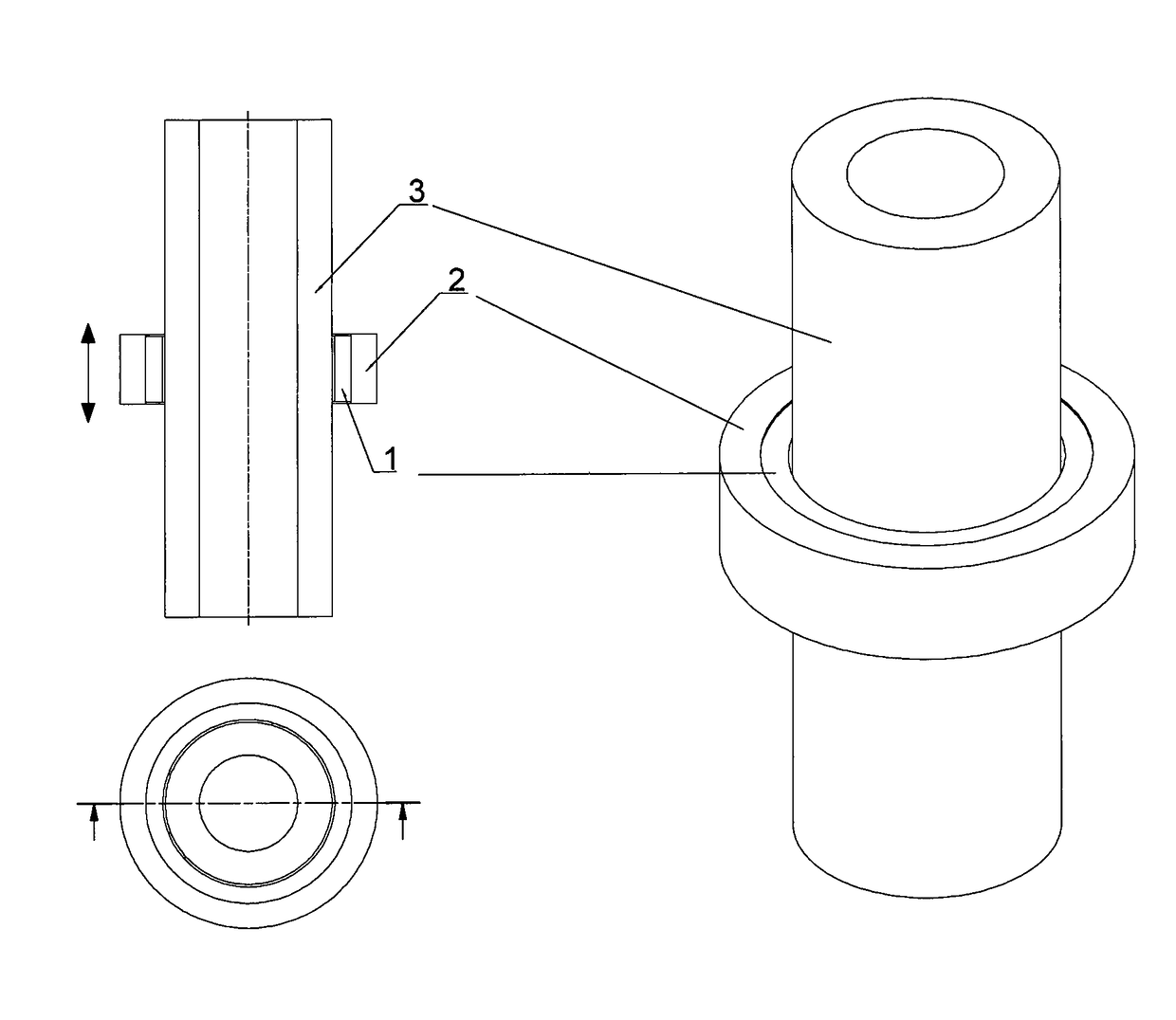
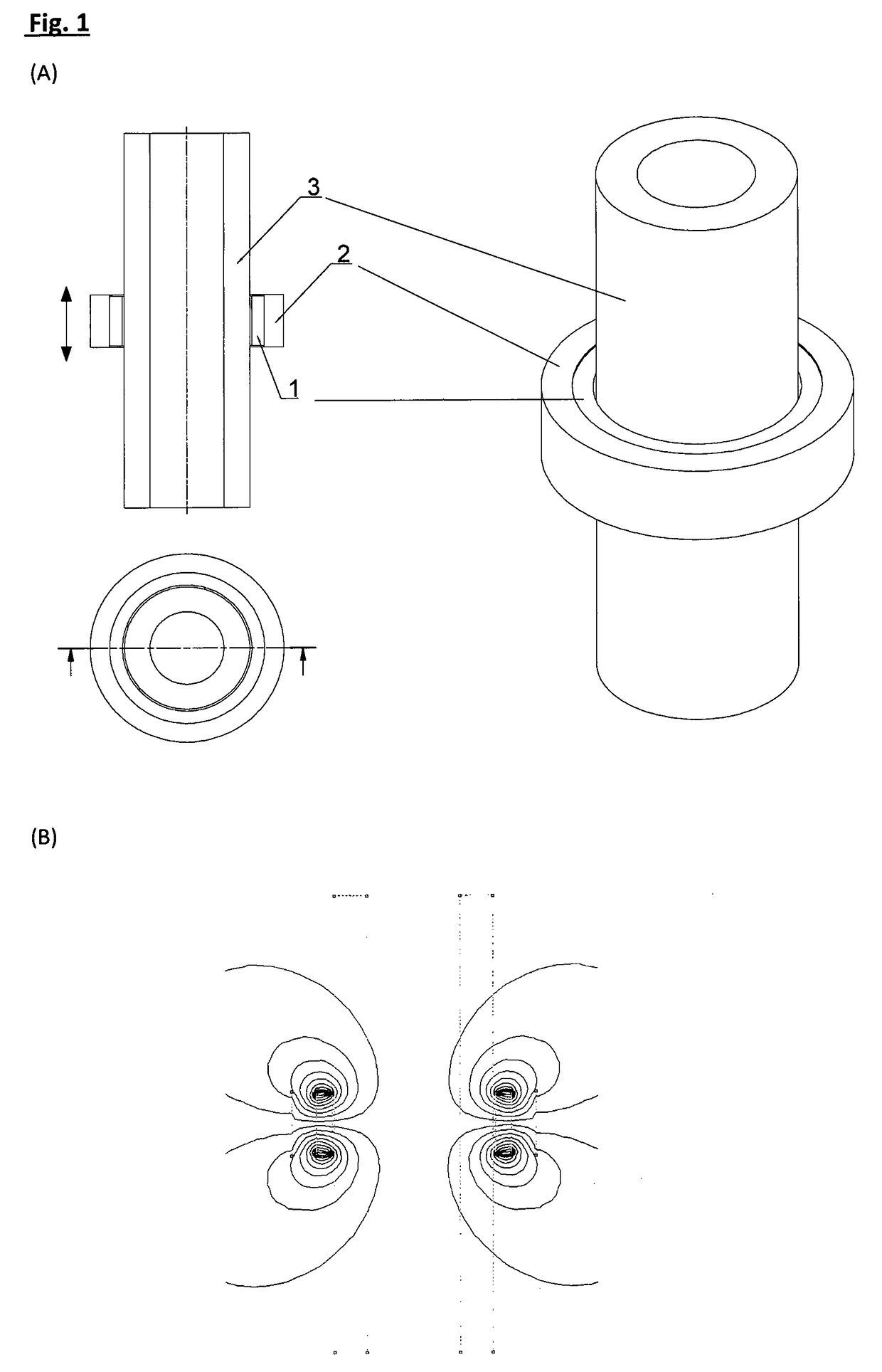
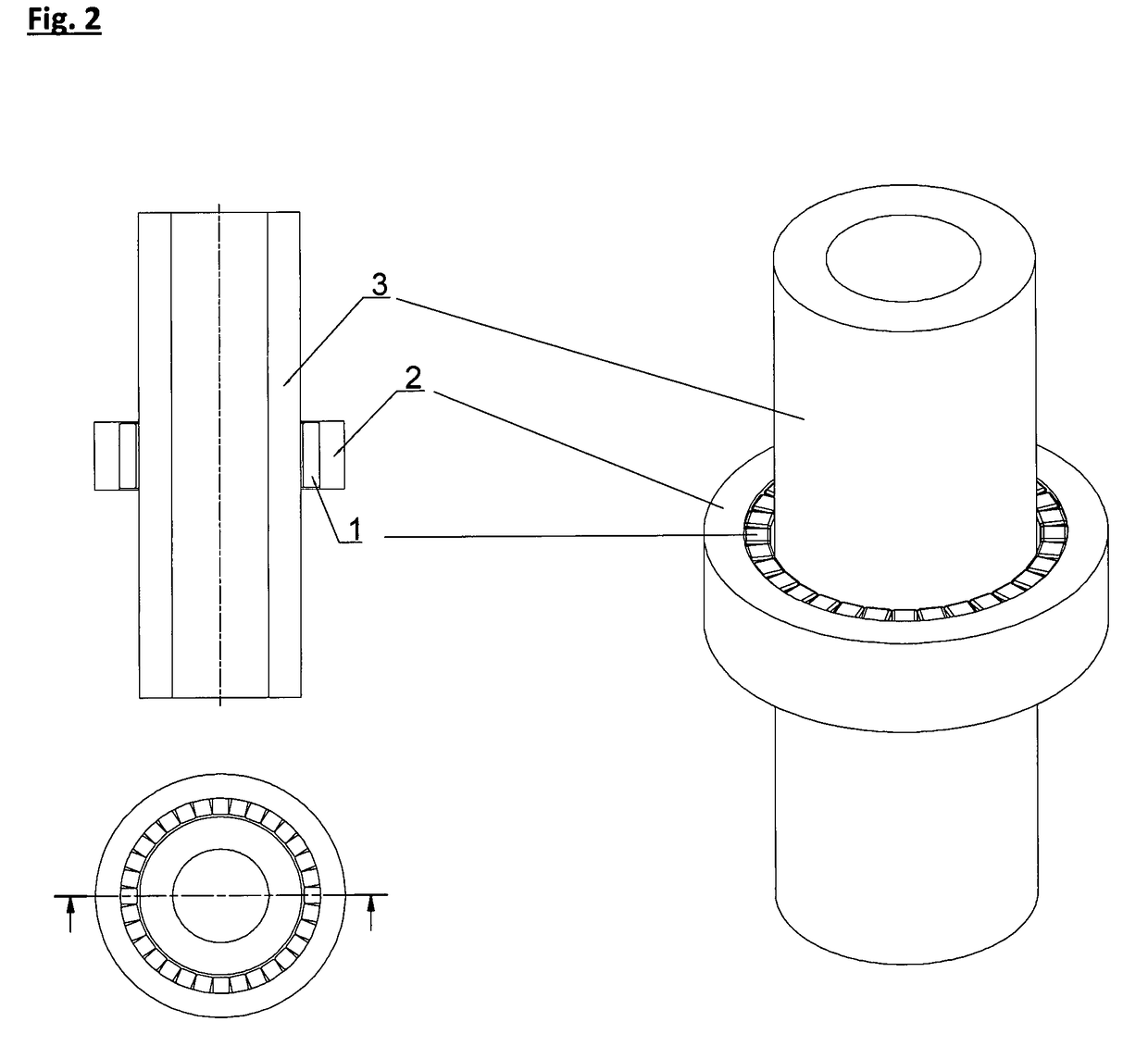
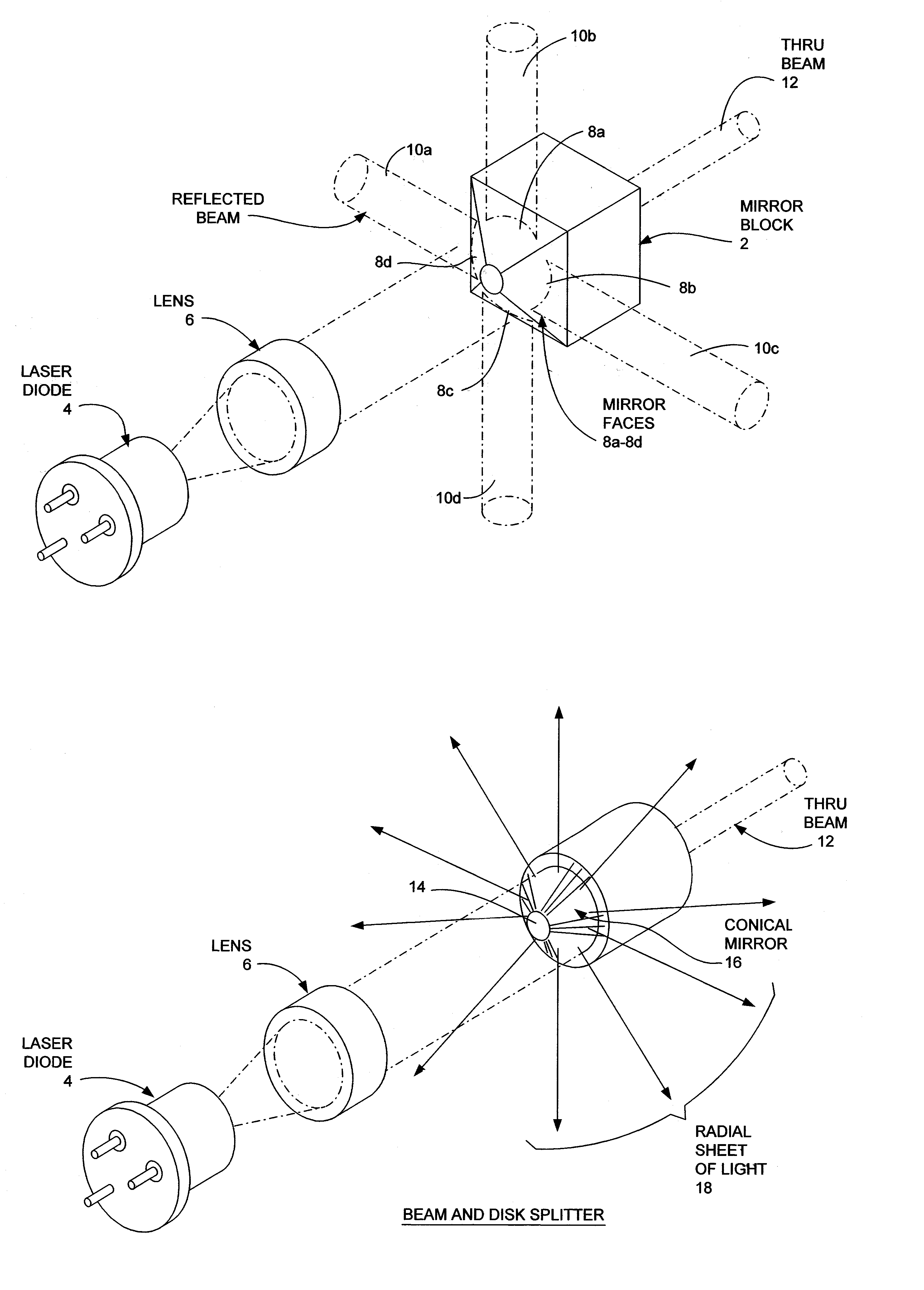
<heading lvl="0">Abstract of Disclosure< / heading> A multi-beam tool is disclosed which can perform square, plumb, and level function which may be required in a construction environment. The tool can generate in a preferred embodiment up to five orthogonal beams with two beams being plumb and three beams being leveled. Combinations of two level beams, or a level and a plumb beam in orthogonal arrangement can produce a square alignment set of beams. The tool includes in a preferred arrangement a self-leveling pendulum to which a laser and quad-mirror arrangement is secured. The self-leveling pendulum is damped in order to allow the tool to settle down and provide alignment after the tool is positioned as desired. The quadmirror, the magnetic damping, and the coiled wire allowing power to be provided to the laser assembly, each separately, and also in combination, provide for a compact tool.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH CO LTD
Spin-torque oscillator for microwave assisted magnetic recording
ActiveUS20140085753A1Reduced magnetic damping constantGenerate efficientlyRecord information storageFluid-dynamic spacing of headsNuclear magnetic resonanceInter layer
A microwave assisted magnetic recording write head having a spin torque oscillator capable of producing high strength high frequency magnetic oscillations with reduced applied current. The spin torque oscillator uses a magnetic field generation layer with a high moment material including such as Fe and Co that is formed on an interlayer having a face centered cubic (fcc) crystal structure, that functions as an under-layer. The high moment magnetic field generation layer has also reduced magnetic damping.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
High data rate magnetic writer design
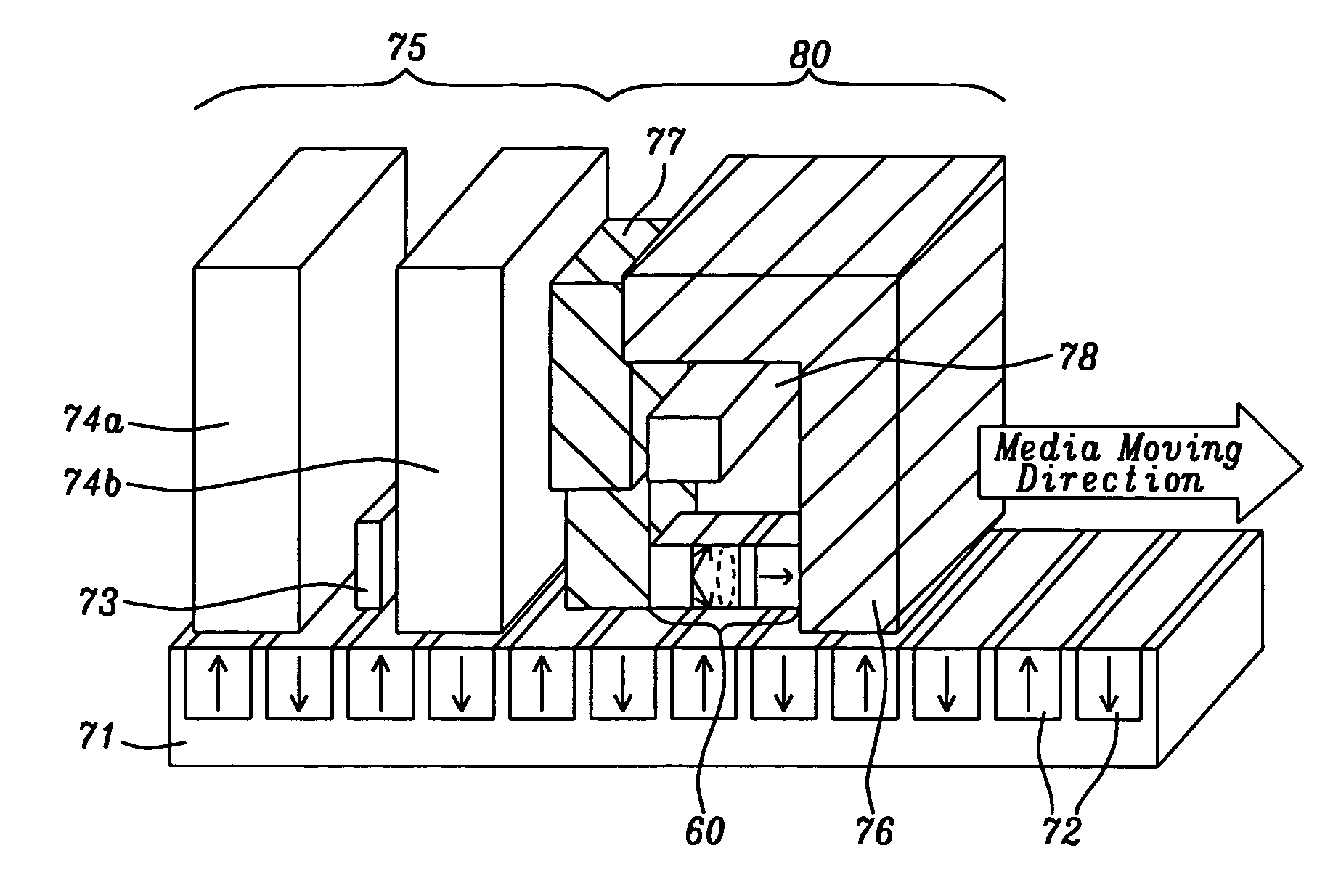
ActiveUS20130027809A1Increase data rateHigh damping constantManufacture head surfaceRecord information storageMagnetic dampingHigh saturation magnetization
A high speed magnetic data writer containing a stitched pole tip that works in conjunction with the main pole is disclosed, together with a process for their manufacture. The material composition of each of these two sub-structures is slightly different; one sub-structure is optimized for high magnetic damping while the other sub-structure is optimized for high saturation magnetization.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Spin-torque oscillator (STO) with magnetically damped free layer
ActiveUS20130009712A1Enhance layeringIncrease currentMagnetic measurementsSolid masersDopantSpin torque oscillators
A spin-torque oscillator (STO) has increased magnetic damping of the oscillating free ferromagnetic layer. The Gilbert magnetic damping parameter (a) is at least 0.05, and preferably greater than 0.05. The free layer may be a any type of conventional ferromagnetic material, but contains one or more damping elements as a dopant. The damping element is selected from the group consisting of Pt, Pd and the 15 lanthanide elements. The free layer damping may also be increased by a damping layer adjacent the free layer. One type of damping layer may be an antiferromagnetic material, like a Mn alloy. As a modification to the antiferromagnetic damping layer, a bilayer damping layer may be formed of the antiferromagnetic layer and a nonmagnetic metal electrically conductive separation layer between the free layer and the antiferromagnetic layer. Another type of damping layer may be one formed of one or more of the elements selected from Pt, Pd and the lanthanides.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Scissoring-type current-perpendicular-to-the-plane giant magnetoresistance (CPP-GMR) sensors with damped free layer structures
A “scissoring-type” current-perpendicular-to-the-plane giant magnetoresistive (CPP-GMR) sensor has magnetically damped free layers. In one embodiment each of the two free layers is in contact with a damping layer that comprises Pt or Pd, or a lanthanoid (an element selected from the group consisting of La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Pm, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Th, Yb, and Lu). Each of the two free layers has one of its surfaces in contact with the sensor's electrically conducting nonmagnetic spacer layer and its other surface in contact with its associated damping layer. A nonmagnetic film may be located between each free layer and its associated damping layer. In another embodiment the damping element is present as a dopant or impurity in each of the two free layers. In another embodiment a nanolayer of the damping element is located within each of the two free layers.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Magnetically damped isolator and pointing mount
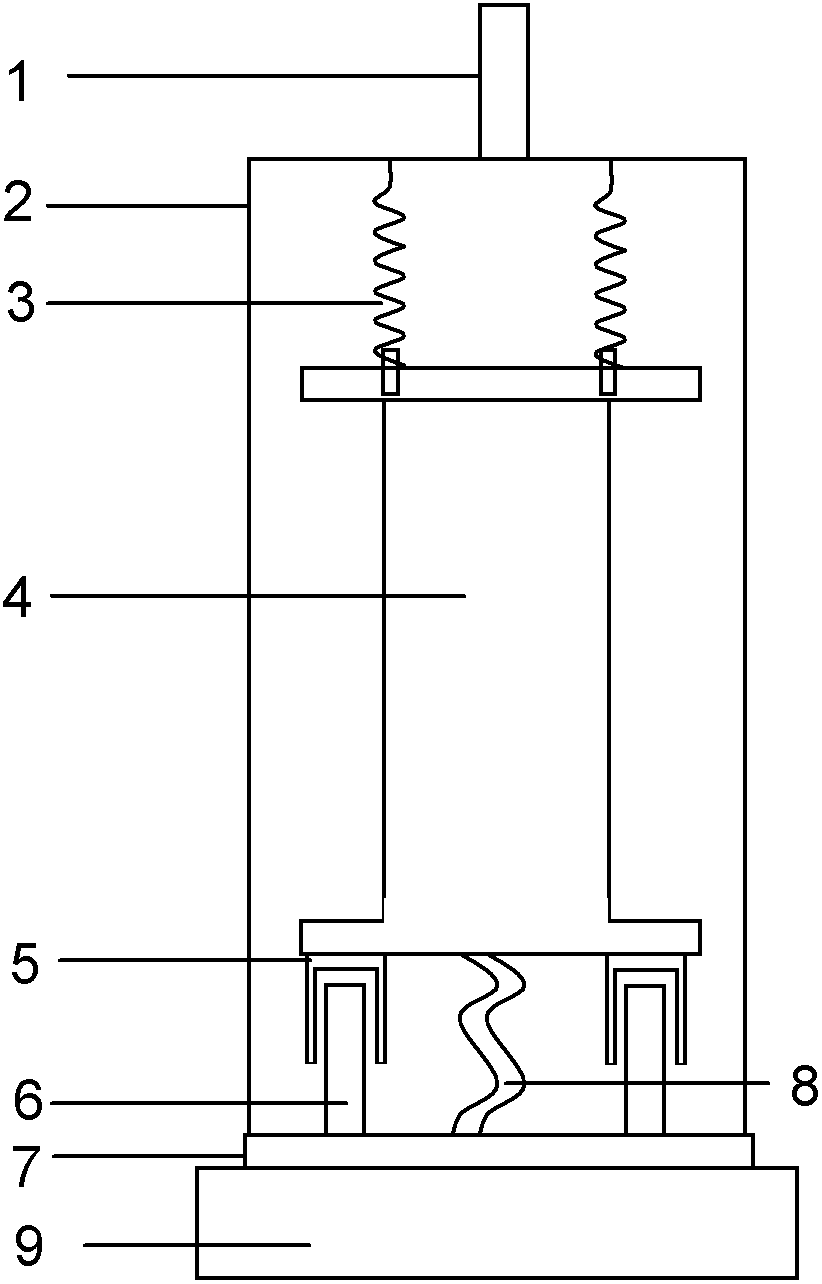
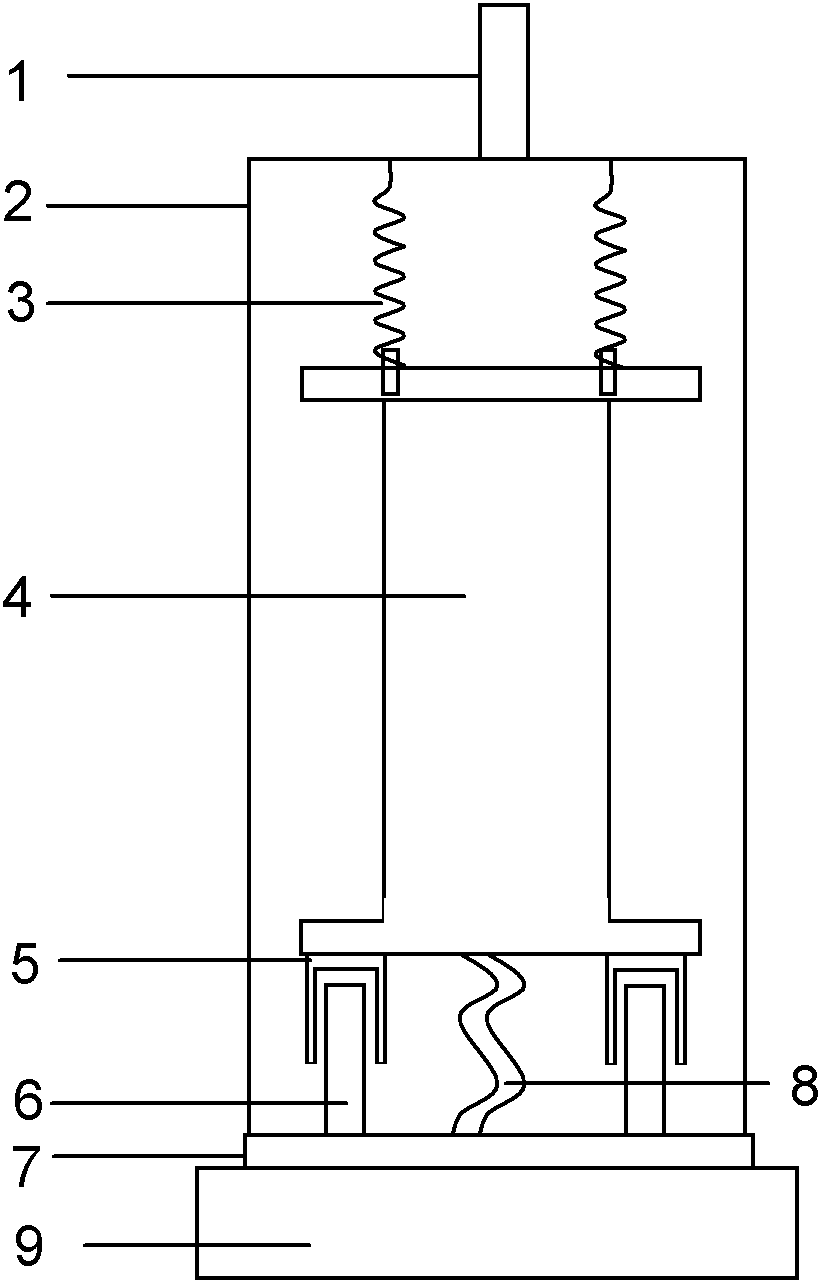
ActiveUS20160047433A1Optimize normal mode of vibrationIncrease magnetic damping effectivenessCosmonautic vehiclesNon-rotating vibration suppressionMagnetic reluctanceEngineering
A magnetically damped mounting and isolation system with pointing capability. A payload is mounted to an isolator plate, a base plate is mounted to a satellite or other space vehicle, and the isolation system provides damping of all six degrees of freedom of isolator plate motion relative to the base plate. Three bidirectional magnetic dampers are connected between the isolator plate and the base plate and arranged to provide the required amount of temperature-independent damping. The bidirectional magnetic dampers can be connected to the base plate and the isolator plate in different configurations based on desired mass and natural frequency characteristics. Flexures which statically position the isolator plate are also designed to optimize normal modes of vibration. The isolation system may include a motion amplification feature to increase magnetic damping effectiveness, and the isolation system may also include active positioning of the payload relative to the satellite.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Magnetic dampening unit for an exercise gym apparatus
InactiveUS20060128533A1Easily configureOptimizationMovement coordination devicesMuscle exercising devicesMagnetic disksExercise equipment
A magnetic dampening unit for an exercise gym apparatus includes a plate and an axle secured on the plate. A flywheel is rotatably mounted on the axle and has a hub. A stub is formed at a central portion of the hub and opposed to the plate. A non-magnetic metal member is provided in the flywheel and faces the plate. A disk is rotatably mounted on the axle and between the flywheel and the plate. A resilient member is mounted on the axle and between the disk and the plate. Multiple permanent magnets are provided on the disk with an alternate arrangement of N-polarities and S-polarities and facing the non-magnetic metal member. Two cables are provided on the disk and extend out from the plate. When drilling the flywheel for a dynamic balance, material waste will not be drawn to the magnets and the flywheel can be easily cleaned.
Owner:MA CHI HSIU +1
Composite magnetic damping vibration absorber
InactiveCN101012860AImprove bearing capacityImprove flexibilityMagnetic springsMagnetic dampingAir spring
The invention provides a composite magnetic floating damping vibration reducer, comprising a bottom plate and an upper cover above. The sides of the bottom plate and the upper cover are arranged with guide side plates between them to guide each other. The bottom plate and the upper cover are arranged with a main spring between to support the upper cover. The bottom plate is mounted with a cylinder which contains an upper and a lower permanent magnets with same polarity. The upper permanent magnet is arranged with a piston above, while the piston is connected to the upper cover via the piston rod. The upper permanent magnet and the piston are arranged with an auxiliary spring between. The invention has the advantage in the combination between main spring, damping structure, magnetic floating structure, and air spring, to improve the bearing function, improve the flexibility of main spring, and reduce the size of invention, with adjustable mounting height.
Owner:CHANGSHU INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Recording heads including a magnetically damped write pole and recording systems including such heads
InactiveUS7595959B2Optimize both the effective damping and write fieldIncreased magnetic dampingRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsMagnetic dampingMagnetic reluctance
A magnetic recording system is disclosed in which the magnetization dynamics of the write head and recording medium are highly damped. The system may comprise a perpendicular recording head having a write pole, and a recording medium including a hard magnetic recording layer and a soft magnetic underlayer (SUL). The increased magnetic damping in the write pole and SUL suppresses precessional motion of the respective magnetizations, leading to a reduction in transition jitter caused by spurious head field fluctuations. The damping may be increased by providing films or multilayer structures that are doped with rare earth or transition metal elements. Exchange coupled laminates of doped and undoped layers may optimize both the effective damping and write field in the recording system.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Magnetic damping life-saving apparatus
InactiveCN1990064AAdjust the speed of descentEnsure safetyBuilding rescueMagnetic dampingMechanical energy
The invention is a magnetic damping life apparatus which includes shell, spool, insurance ropes and driving device. The spool support on the shell through rotation shaft, one end of insurance ropes is fixed and wound on the spools. Said magnetic damping life apparatus also includes electrical and mechanical conversion device and energy receiving device, the spool drives the electrical and mechanical conversion device through the driving device, electrical and mechanical conversion device transforms the mechanical energy into electrical energy which is received by the receiving device to increasing the safety and practicality of magnetic damping life apparatus.
Owner:白孝林
Vibration reduction structure of low-temperature scanning near-field optical microscope
InactiveCN102434621ARealize the effect of 2 vibration reductionNon-rotating vibration suppressionScanning probe microscopyMagnetic dampingOptical instrument
The invention discloses a vibration reduction structure of a low temperature scanning near-field optical microscope (SNOM), and belongs to the field of manufacture of near-field optical instruments. The vibration reduction structure is characterized in that a vacuum cavity of the low temperature scanning near-field optical microscope is internally provided with a metal sleeve, a low temperature SNOM scanning head is hung on the top in the metal sleeve so as to play the role of primary vibration reduction action; further a magnetic damping vibration reduction device is arranged on the vibration reduction structure, a U-shaped copper frame of the magnetic damping vibration reduction device is partially fixed on the lower surface of a scanning head pedestal, and a corresponding magnet is fixed on a heat conduction copper disc; when the vibration reduction structure is vibrated, one edge of the U-shaped copper frame does a motion of cutting the magnetic line of force along one edge of the magnet so as to cause magnetic damping, thereby playing a secondary vibration reduction action. The vibration reduction structure provided by the invention can be used for reducing of the low temperature scanning near-field optical microscope.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
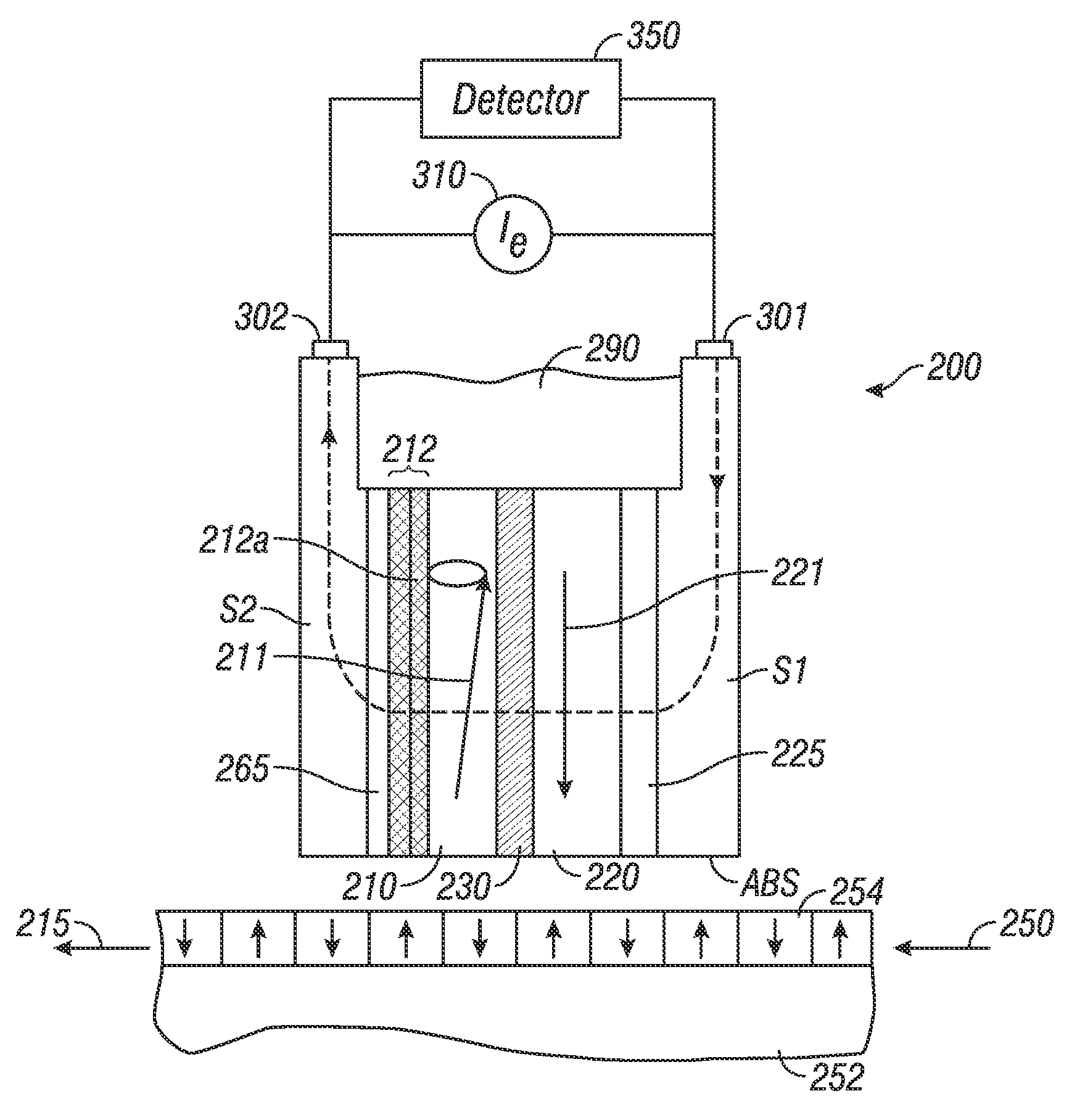
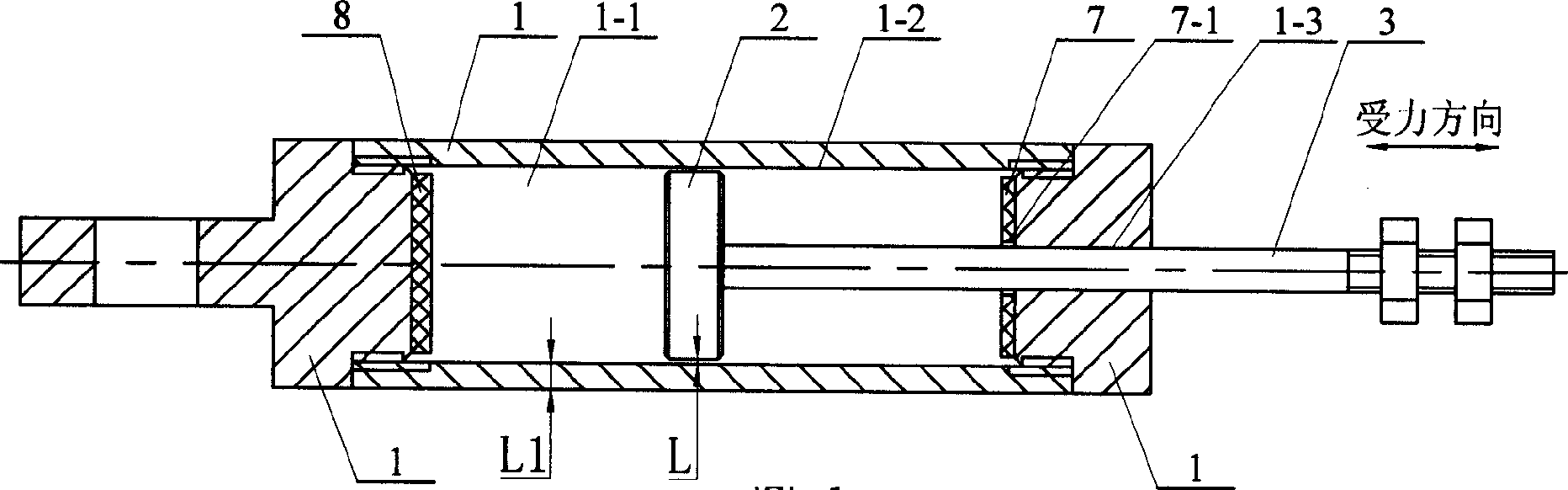
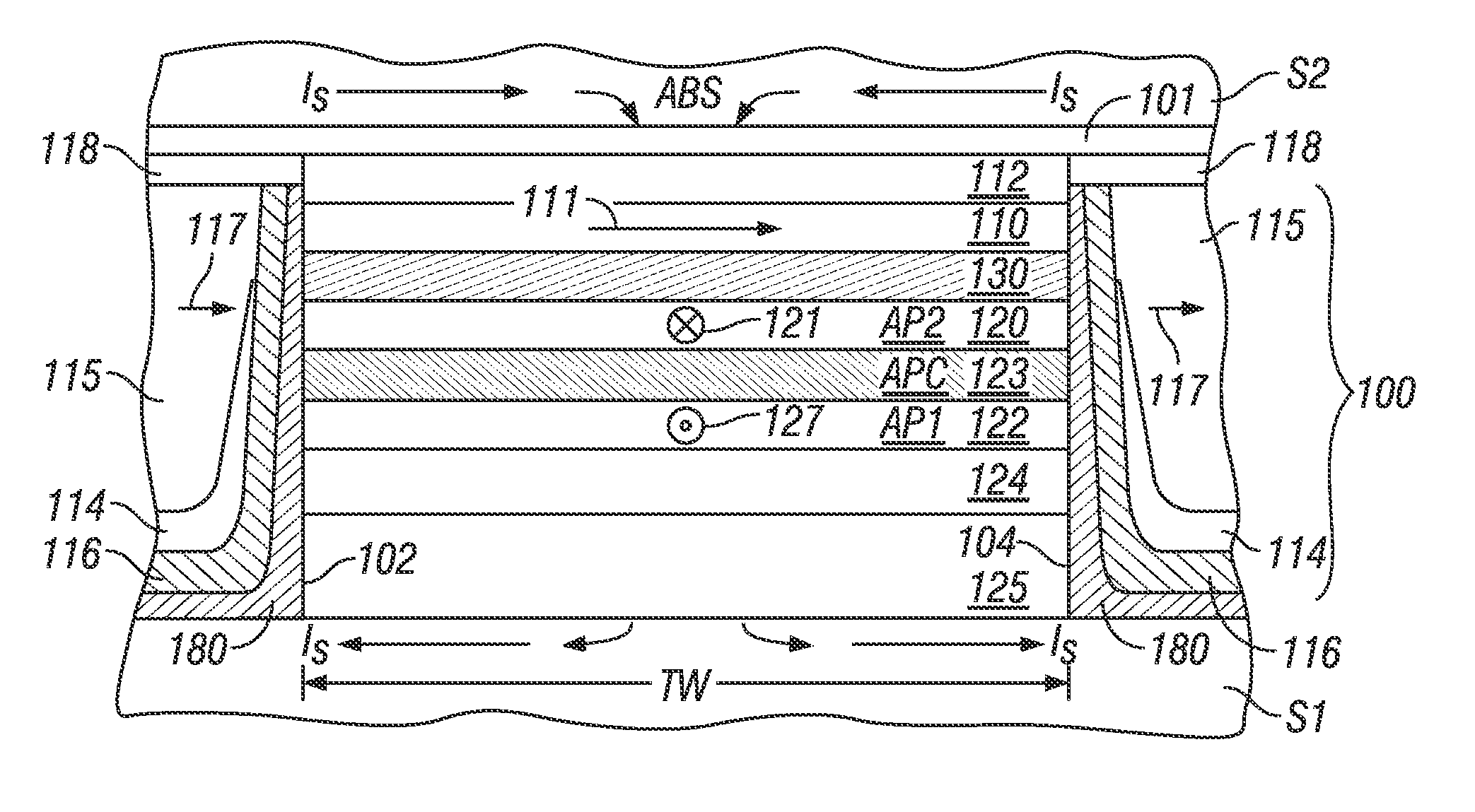
Tunneling magnetoresistive (TMR) read head with low magnetic noise
ActiveUS20110043950A1Reduce noiseLow magnetic dampingNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsDamping constantMagnetic damping
A tunneling magnetoresistance (TMR) device, like a TMR read head for a magnetic recording disk drive, has low magnetic damping, and thus low mag-noise, as a result of the addition of a ferromagnetic backing layer to the ferromagnetic free layer. The backing layer is a material with a low Gilbert damping constant or parameter α, the well-known dimensionless coefficient in the Landau-Lifshitz-Gilbert equation. The backing layer may have a thickness such that it contributes up to two-thirds of the total moment / area of the combined free layer and backing layer. The backing layer may be formed of a material having a composition selected from (CoxFe(100-x))(100-y)Xy, (Co2Mn)(100-y)Xy and (Co2FexMn(1-x))(100-y)Xy, where X is selected from Ge, Al and Si, and (Co2Fe)(100-y)Aly, where y is in a range that results in a low damping constant for the material.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Eddy magnetic damping type damper
InactiveCN1715701ANon-rotating vibration suppressionMagnetic springsMagnetic dampingWorking temperature
The present invention relates to eddy magnetic damping technology, and aims at providing eddy magnetic damper superior to available hydraulic buffering damper. The eddy magnetic damper includes metal casing with inside cylindrical cavity, axially magnetized circular permanent magnet with outer surface slide connecting the inner wall of the cylindrical cavity, and guide rod with left end connected to the right magnetic pole of the circular permanent magnet and right end penetrating the through hole on the right end of the metal casing and exposing one section. Compared with available hydraulic buffering damper, the present invention has the advantages of simple structure, relaxed part machining requirement, no need of liquid, low cost, wide work temperature range from -80 deg c to +100 deg c and long service life.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for preparing nano magnetic ferrite particle and magnetic damping rubber thereof
InactiveCN101186761AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove magnetic propertiesPigment treatment with macromolecular organic compoundsActivator 1Polymer science
The invention relates to magnetic shock-absorption rubber and nanophase magnetic ferrite particles, specifically a process for preparing the nanophase magnetic ferrite particles and magnetic shock-absorption rubber prepared by using the nanophase magnetic ferrite particles. The invention is used for resolving the problems that the existing magnetic particles can not meet the physically mechanical property and magnetic shock-absorption effect of magnetic shock-absorption rubber and materials of the existing magnetic shock-absorption rubber are not properly selected and matched. 1.4-5.11g FeCl3, 6H2O, 1.75-6g FeSO4, 7H2O and 0.00025 mol polyethylene glycol with molecular weight of 400-10000 are added into 560ml distilled water, and further sodium hydroxide solution is added into the mixture, thereby nanophase magnetic ferrite particles which has certain shape and is coated by polyethylene glycol is achieved. The magnetic shock-absorption rubber is composed of components with percentage by weight of plantation rubber 15-60%, ethylene-propylene-diene monomer 15-60%, nanophase magnetic ferrite particles 5-50%, vulcanized agent 1-10%, vulcanizing activator 1-10%, vulcanization accelerator 1-10%, aging inhibitor 0.1-5% and reinforcing agent 10-40%.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Current-perpendicular-to-the-plane (CPP) magnetoresistive (MR) sensor with magnetic damping material at the sensor edges
ActiveUS8576519B1Reduce the impactReduce impactMagnetic measurementsMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMagnetic dampingSpin-transfer torque
A current-perpendicular-to-the-plane magnetoresistive sensor has magnetic damping material located adjacent either or both of the sensor side edges and back edge to reduce the effect of spin transfer torque. The damping material may be Pt, Pd, Os, or a rare earth metal from the 15 lanthanoid elements. The damping material may be an ultrathin layer in contact with the sensor edges. An insulating layer is deposited on the damping layer and isolates the sensor's ferromagnetic biasing layer from the damping layer. Instead of being a separate layer, the damping material may be formed adjacent the sensor edges by being incorporated into the material of the insulating layer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Vibration isolator capable of achieving horizontal decoupling
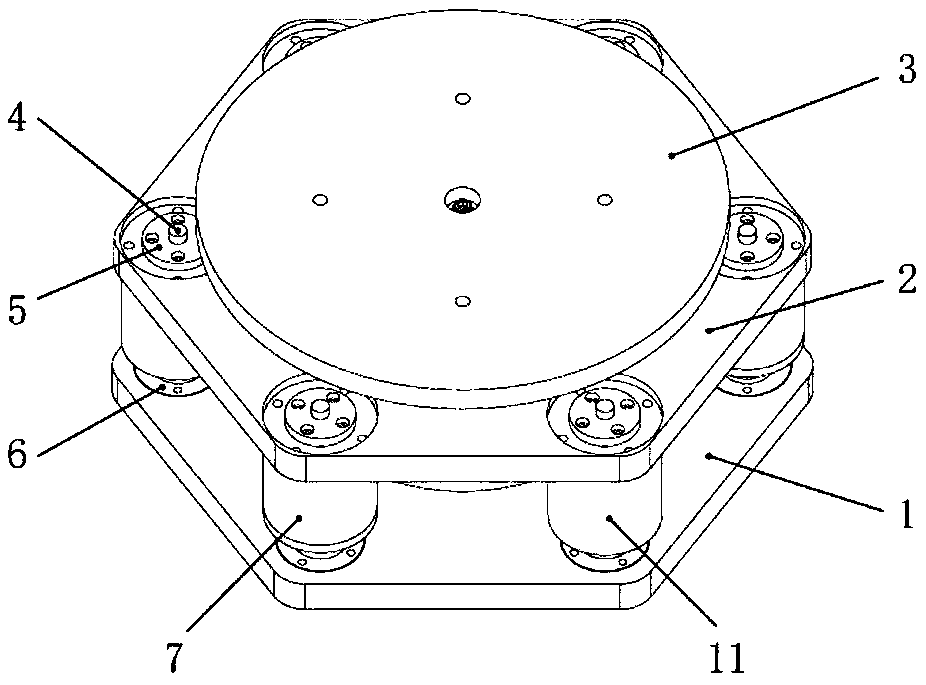
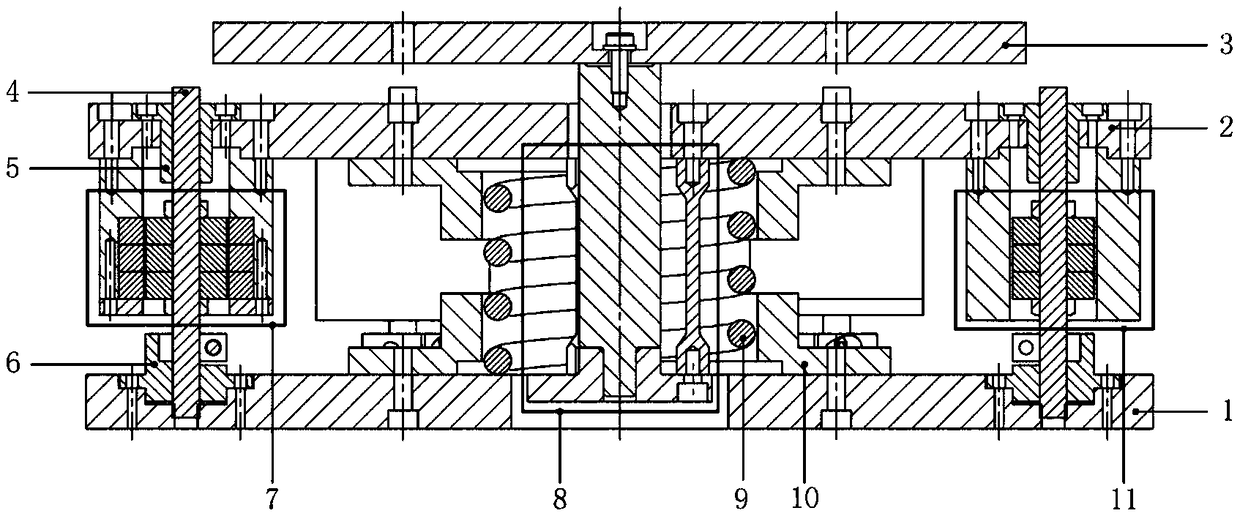
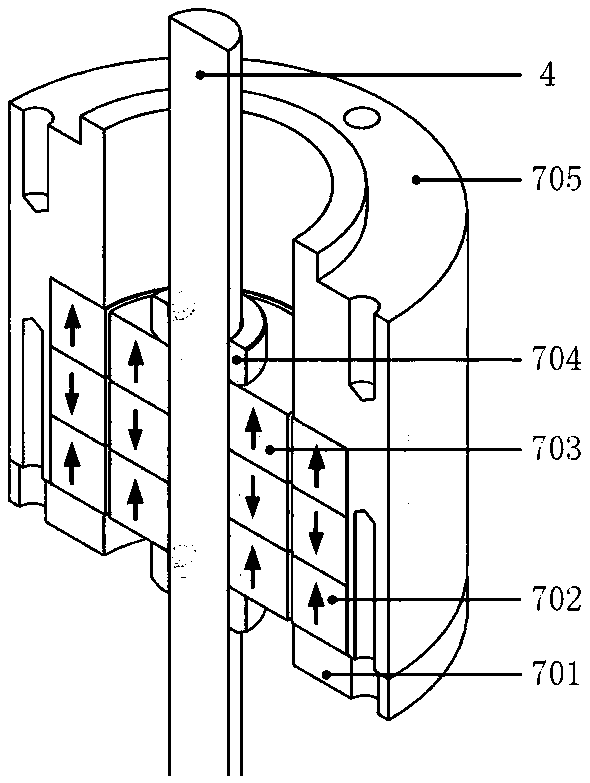
ActiveCN108953473AAchieve ultra-low frequency vibration isolationLower natural frequencyNon-rotating vibration suppressionMagnetic springsDynamic stiffnessMagnetic damping
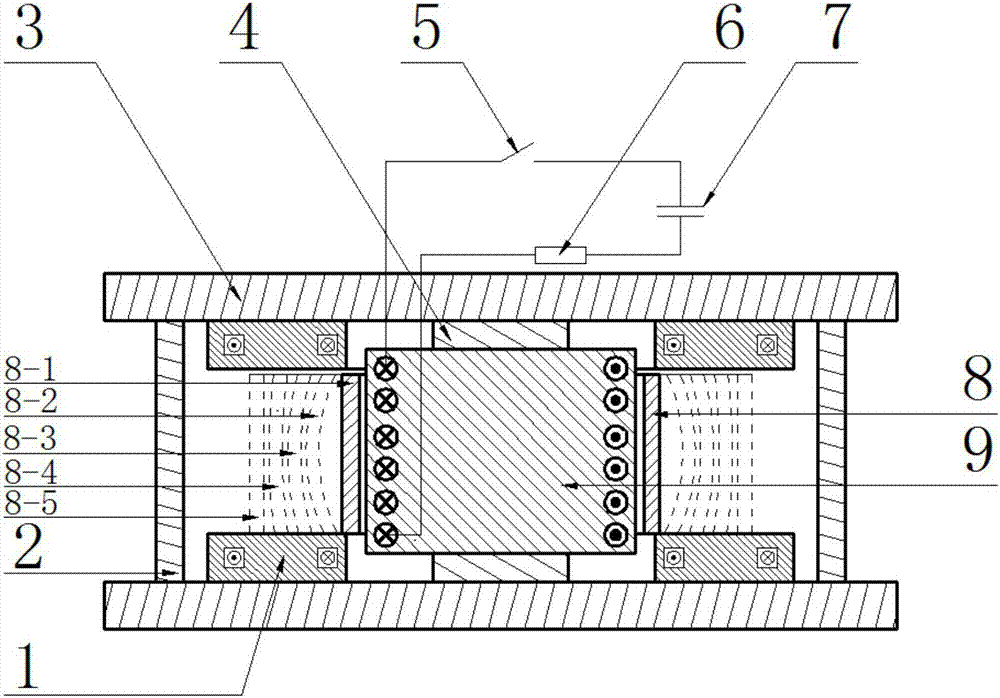
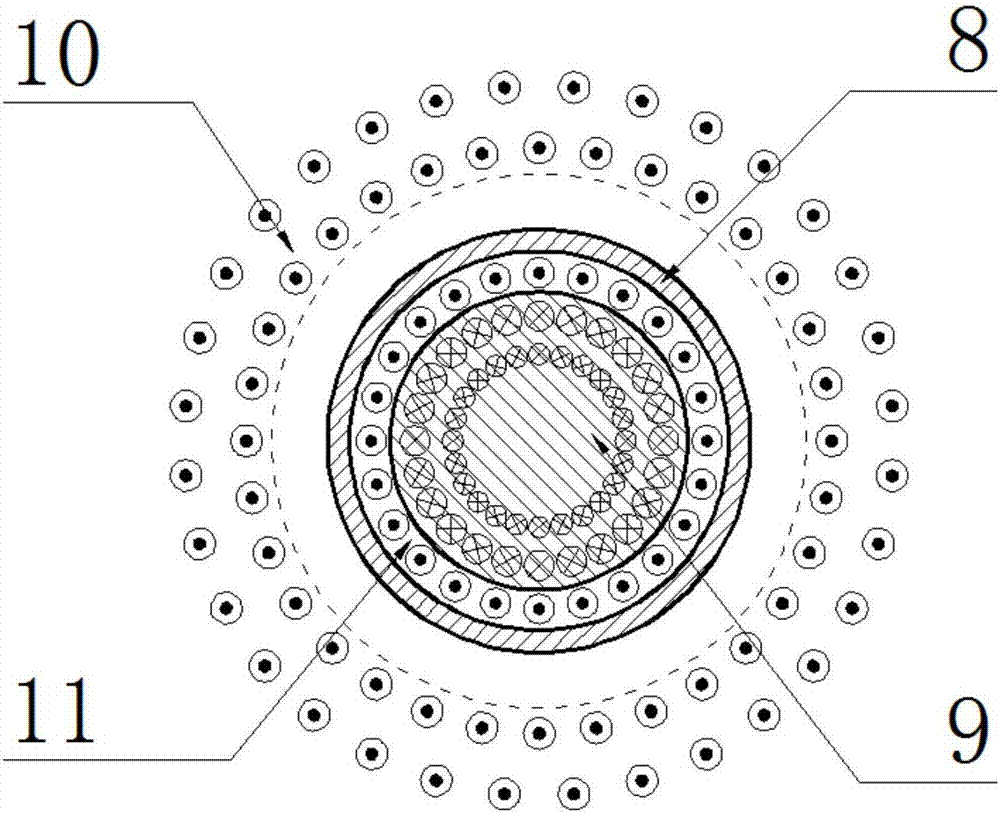
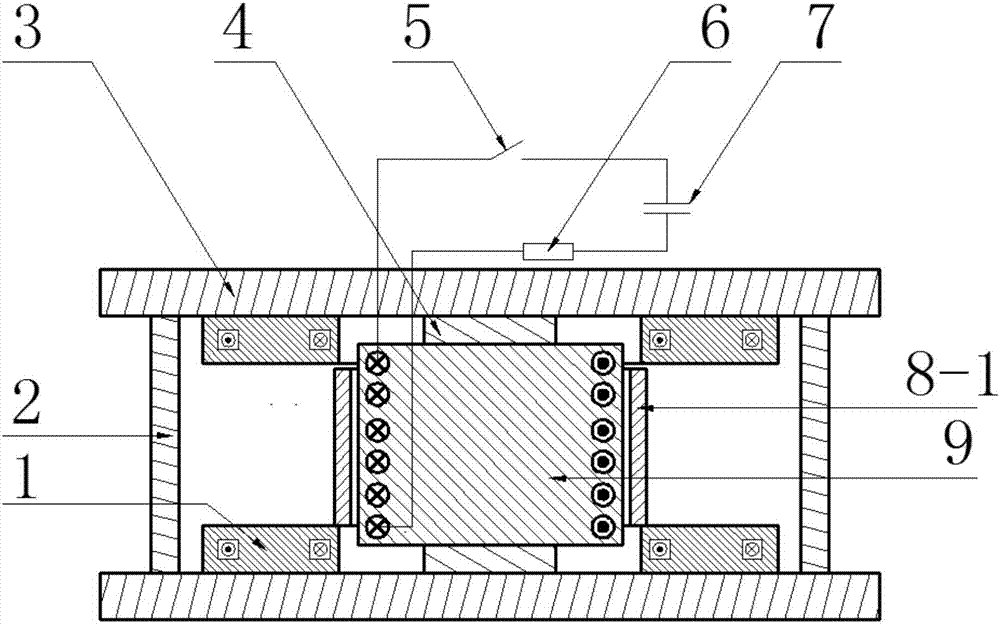
The invention discloses a vibration isolator. A positive stiffness component, magnetic damping components and magnetic negative stiffness components of the vibration isolator are arranged between a base board and a middle board in parallel; the magnetic damping components and the magnetic negative stiffness components are evenly arranged on the edge of the base board in the circumferential direction; one swing mechanism penetrates through the center of the positive stiffness component to be connected with the positive stiffness component in series; the swing mechanism isolates vibration in thehorizontal direction through low horizontal stiffness of a flexible swing rod; and each magnetic damping component and each magnetic negative stiffness component are each divided into two coaxial parts which are fixedly connected with the base board and the middle board separately and generate action through electromagnetic force, and no mechanical contact or abrasion is generated. The vibrationisolator capable of achieving horizontal decoupling can achieve high static stiffness and low dynamic stiffness in the vertical direction and vibration decoupling in the horizontal direction and the vertical direction.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com