Patents
Literature
5879results about "Magnetic-field-controlled resistors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
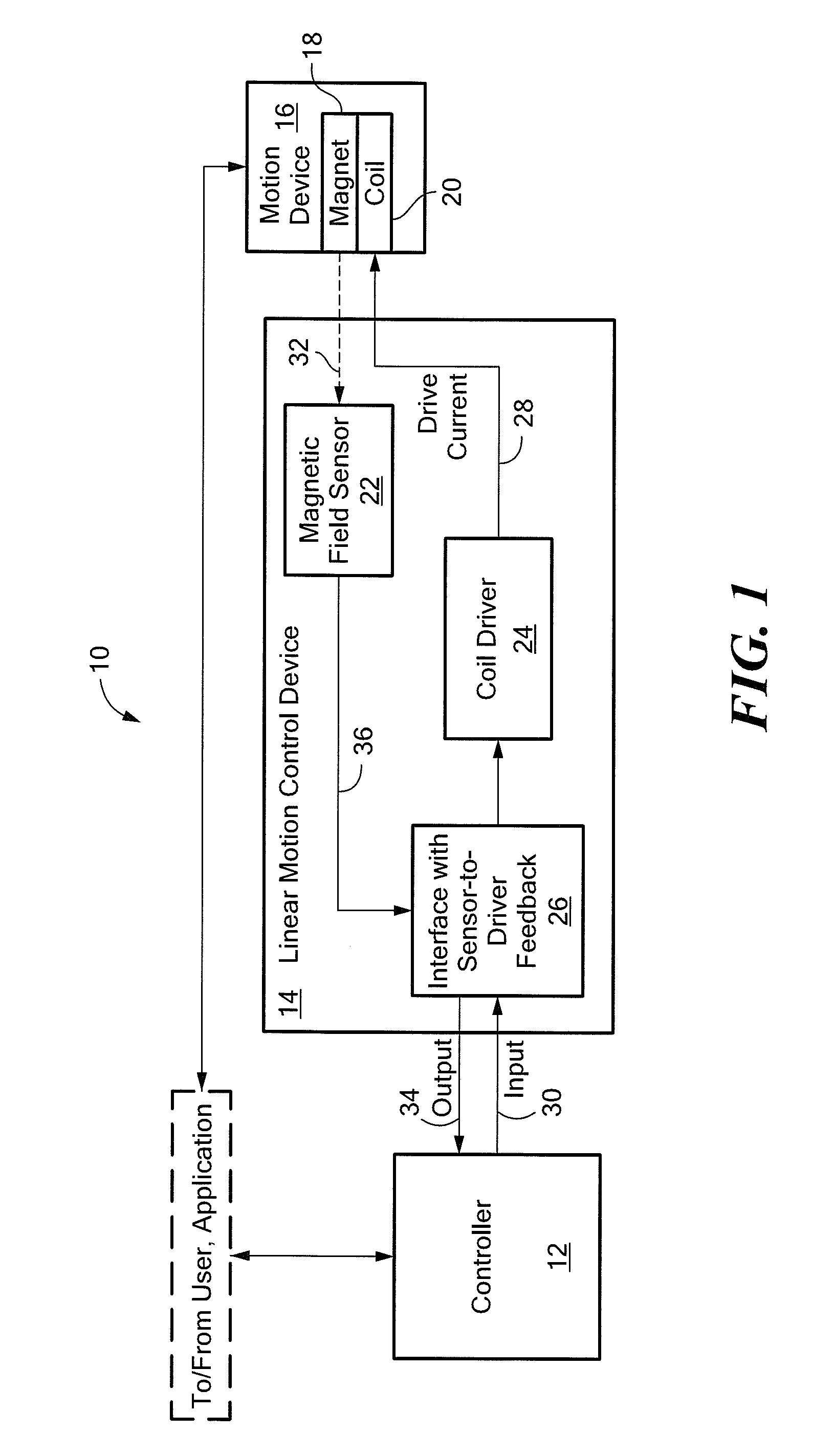
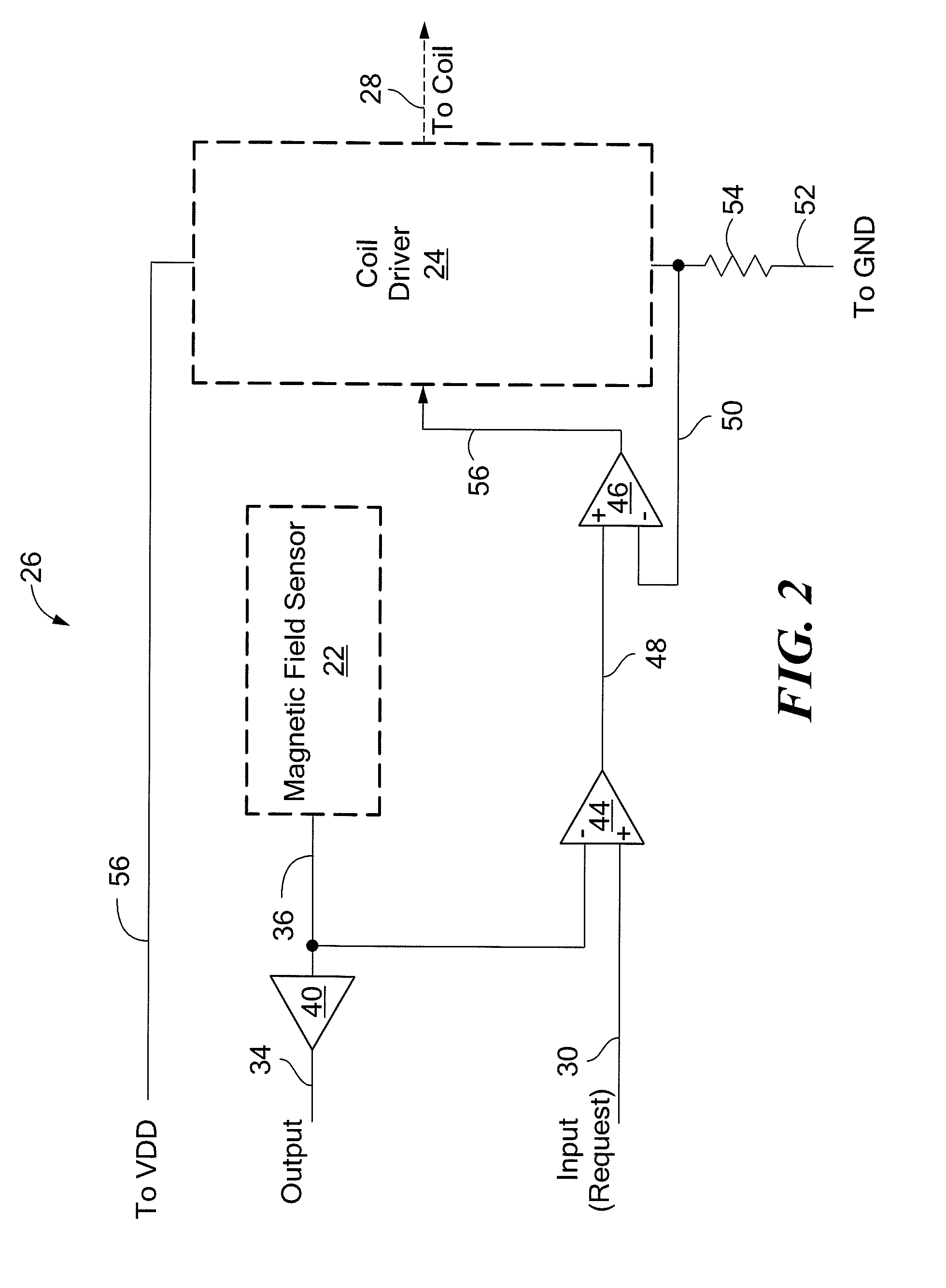
Position feedback system and method for use thereof
InactiveUS6625517B1Solid-state devicesSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringVirtual sensors
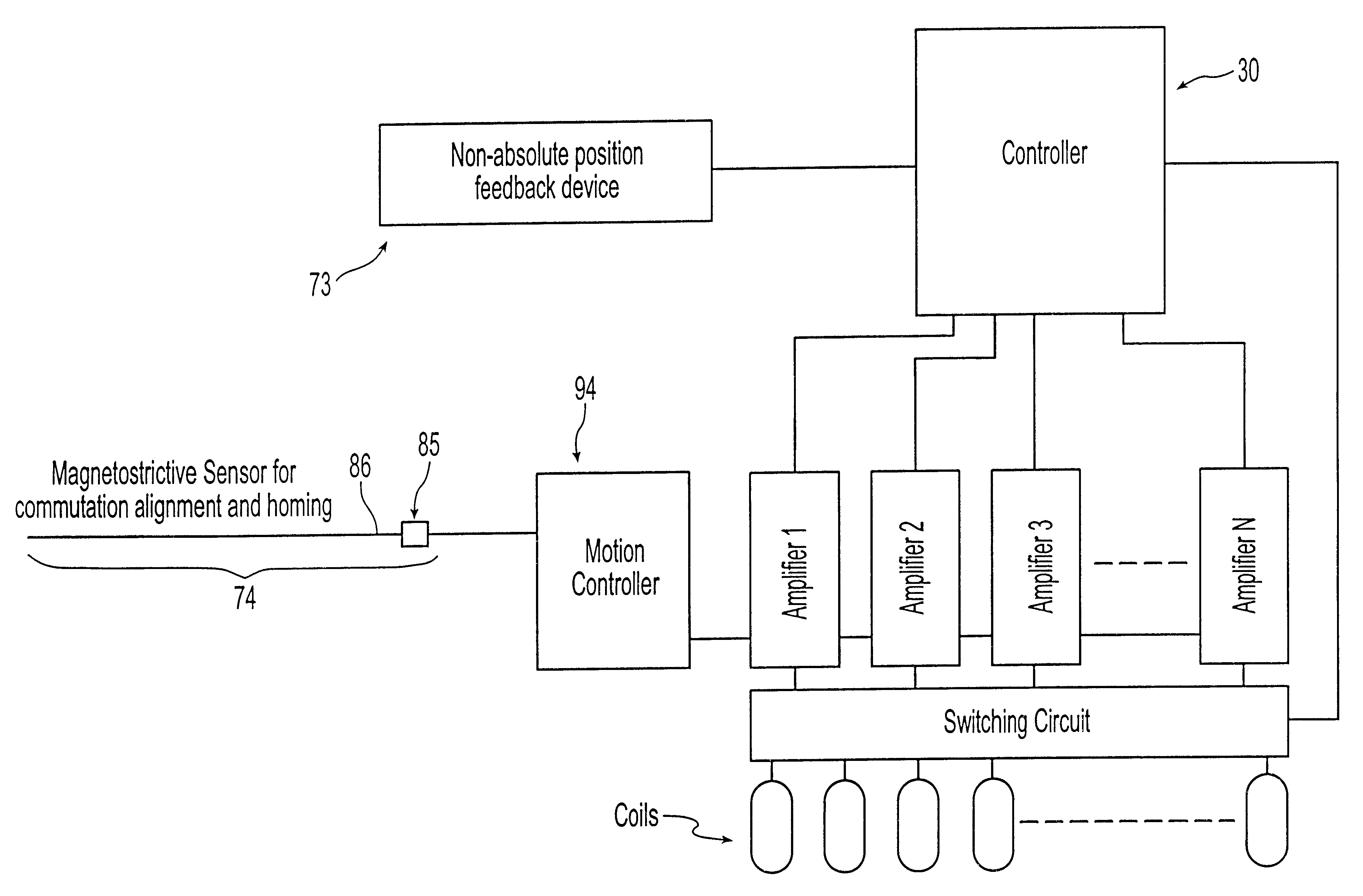
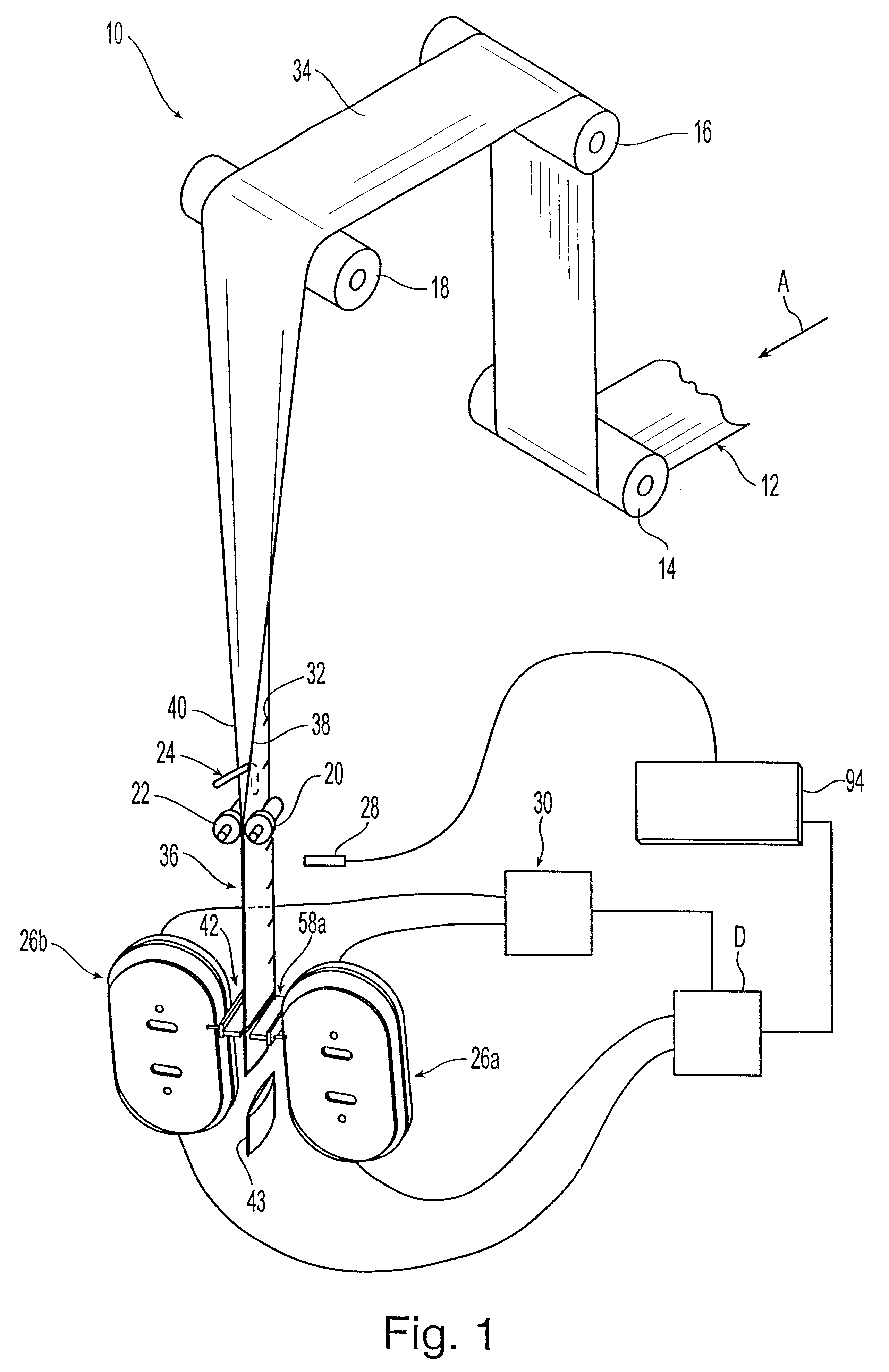
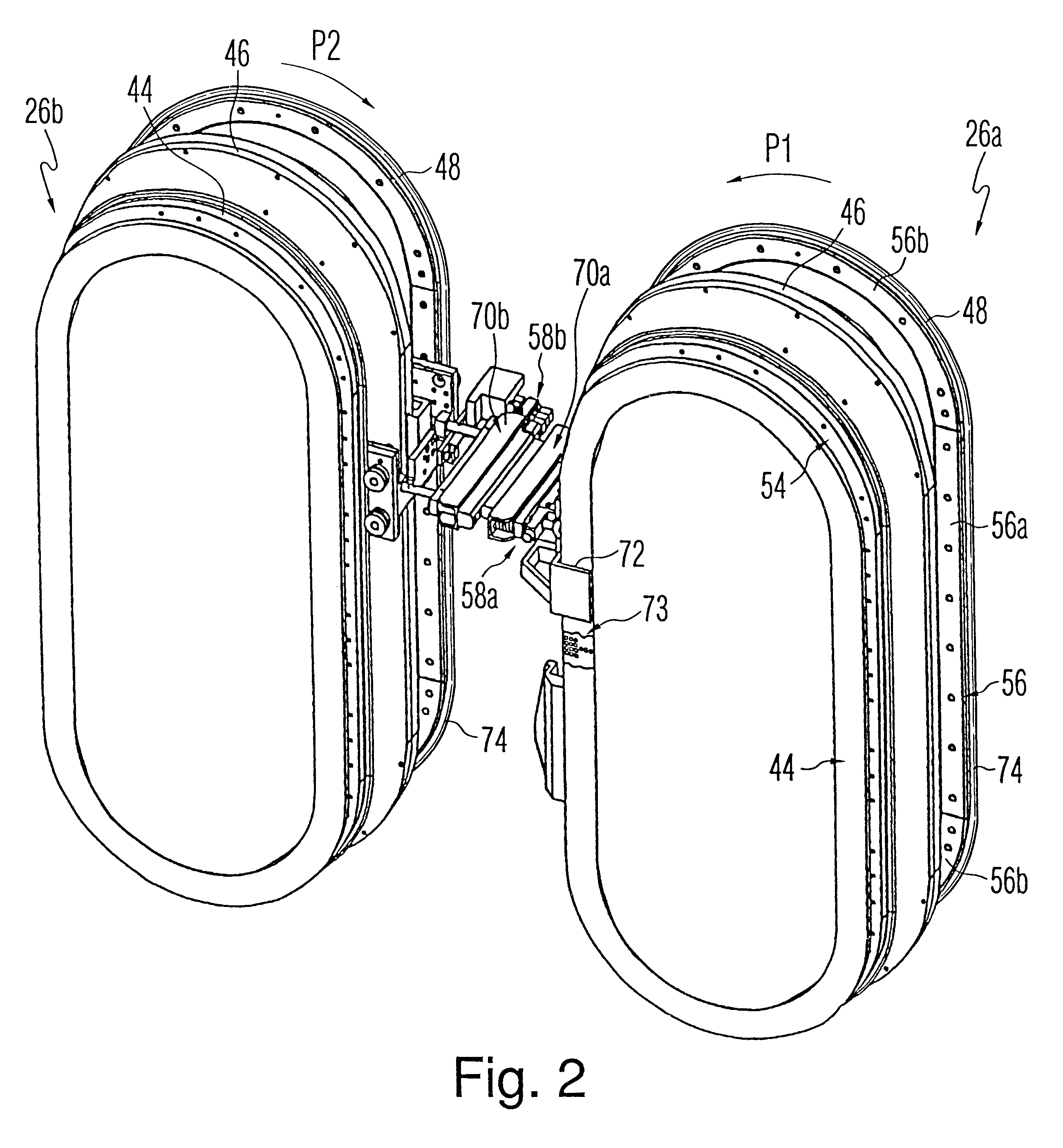
The present invention is directed to a machine with a position feedback system and a method for use thereof. The machine includes at least one movable element mounted for movement on a path and at least one programmable controller. The machine further includes at least two absolute or magnetostrictive sensors or the machine includes an absolute sensor and a non-absolute sensor. The programmable controller uses positional information from the sensors to determine the position of the movable elements on the path and control the movable elements. The method includes determining a known position for the movable elements, linking at least two magnetostrictive sensors into one virtual sensor, and / or performing commutation alignment for the movable elements. Determining the position and commutation alignment can occur when the movable elements are stationary or moving.
Owner:TETRA LAVAL HLDG & FINANCE SA
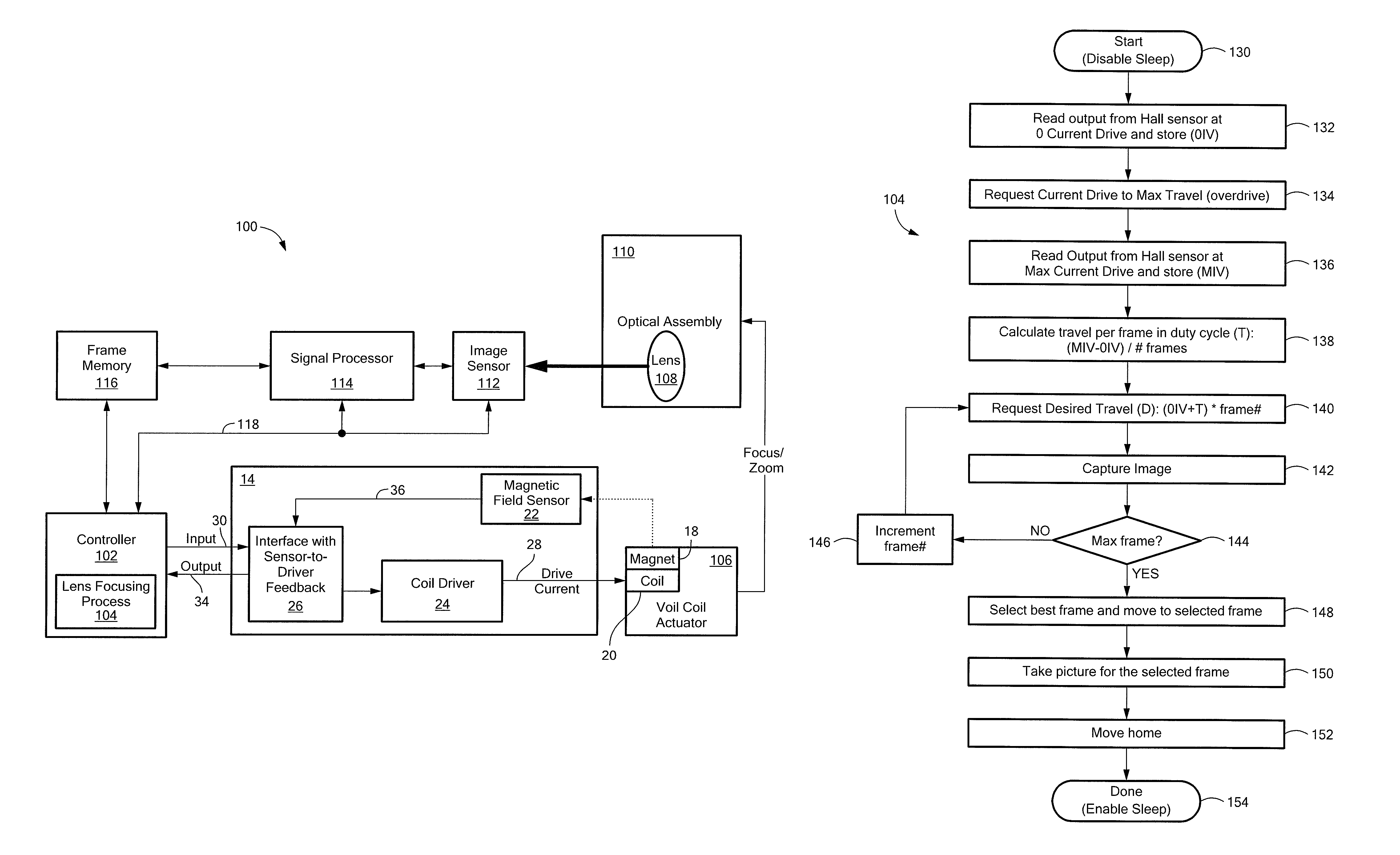
Hall-effect based linear motor controller
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
Current-induced magnetic switching device and memory including the same
InactiveUS6256223B1High bulk densitySimpler driving circuitsNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsNanoparticleConduction band
A magnetic switching device, includes a first electrode, a second electrode, and a nanoparticle having a magnetic moment and being disposed between the first and second electrodes. At least one of the first electrode and the second electrode includes a magnetic material which has a net spin polarization in its conduction band for injecting, into the nanoparticle, an electrical current including a net spin polarization for overcoming the magnetic moment of the nanoparticle upon selection of a predetermined magnitude for the electrical current.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
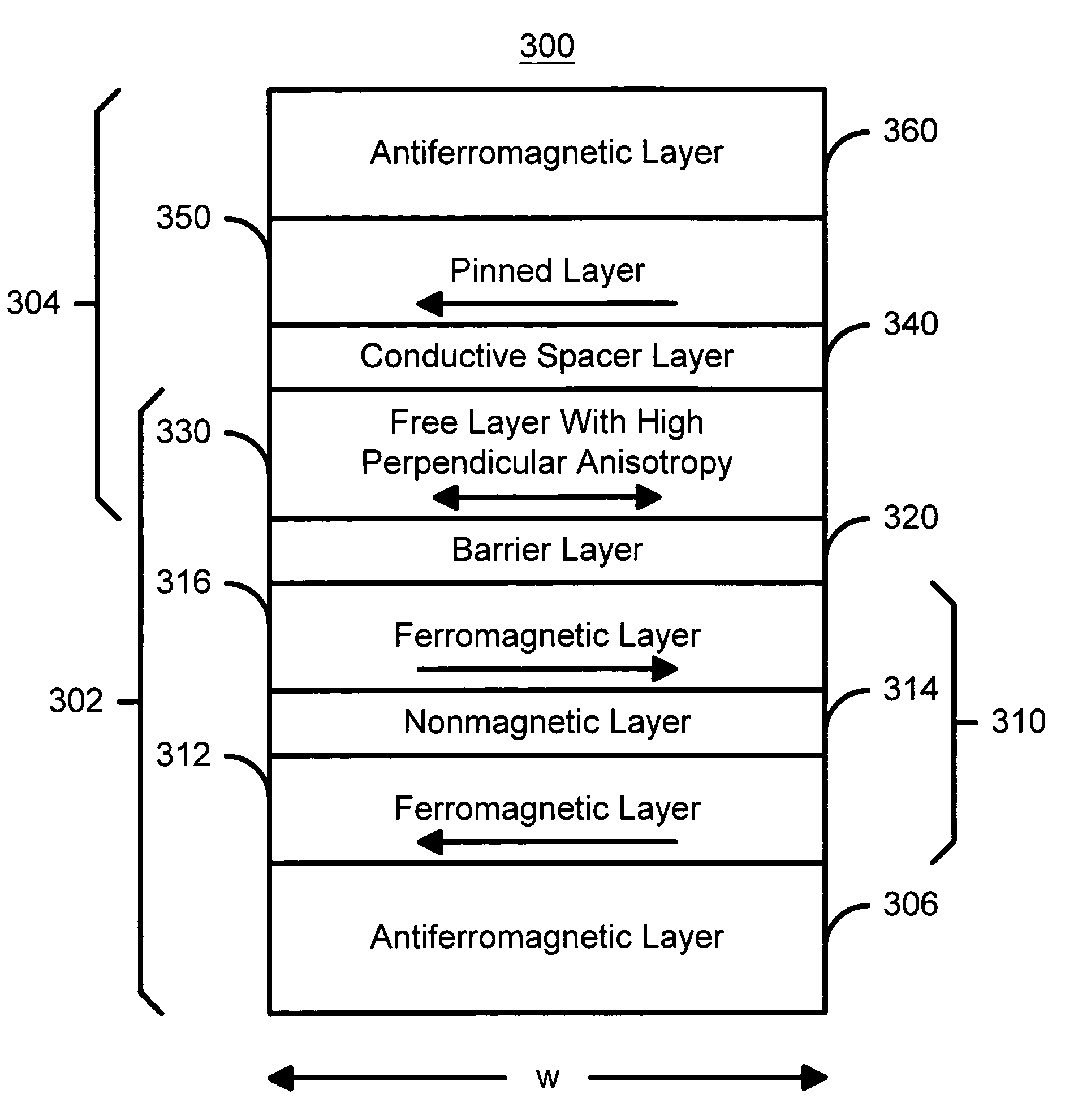
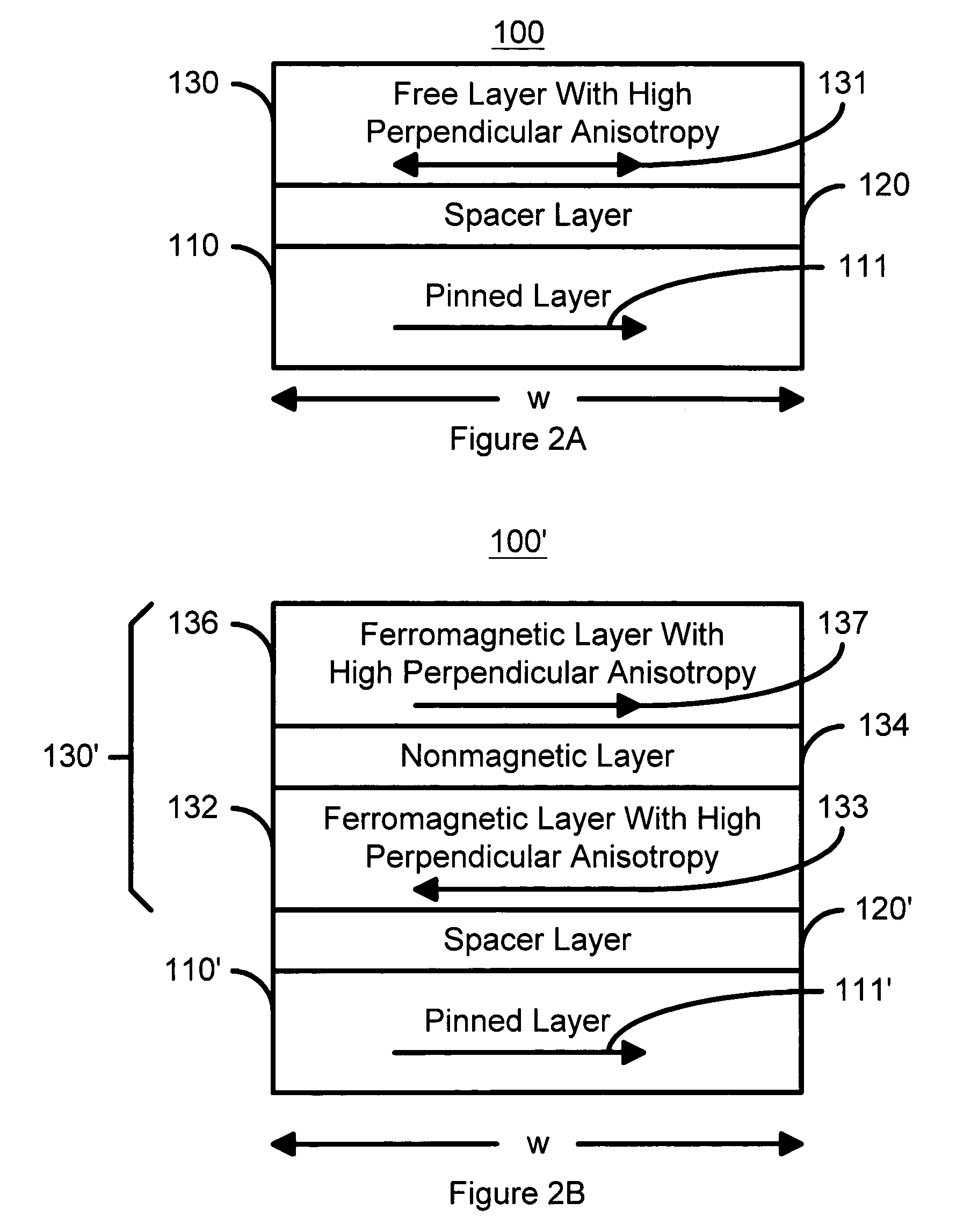
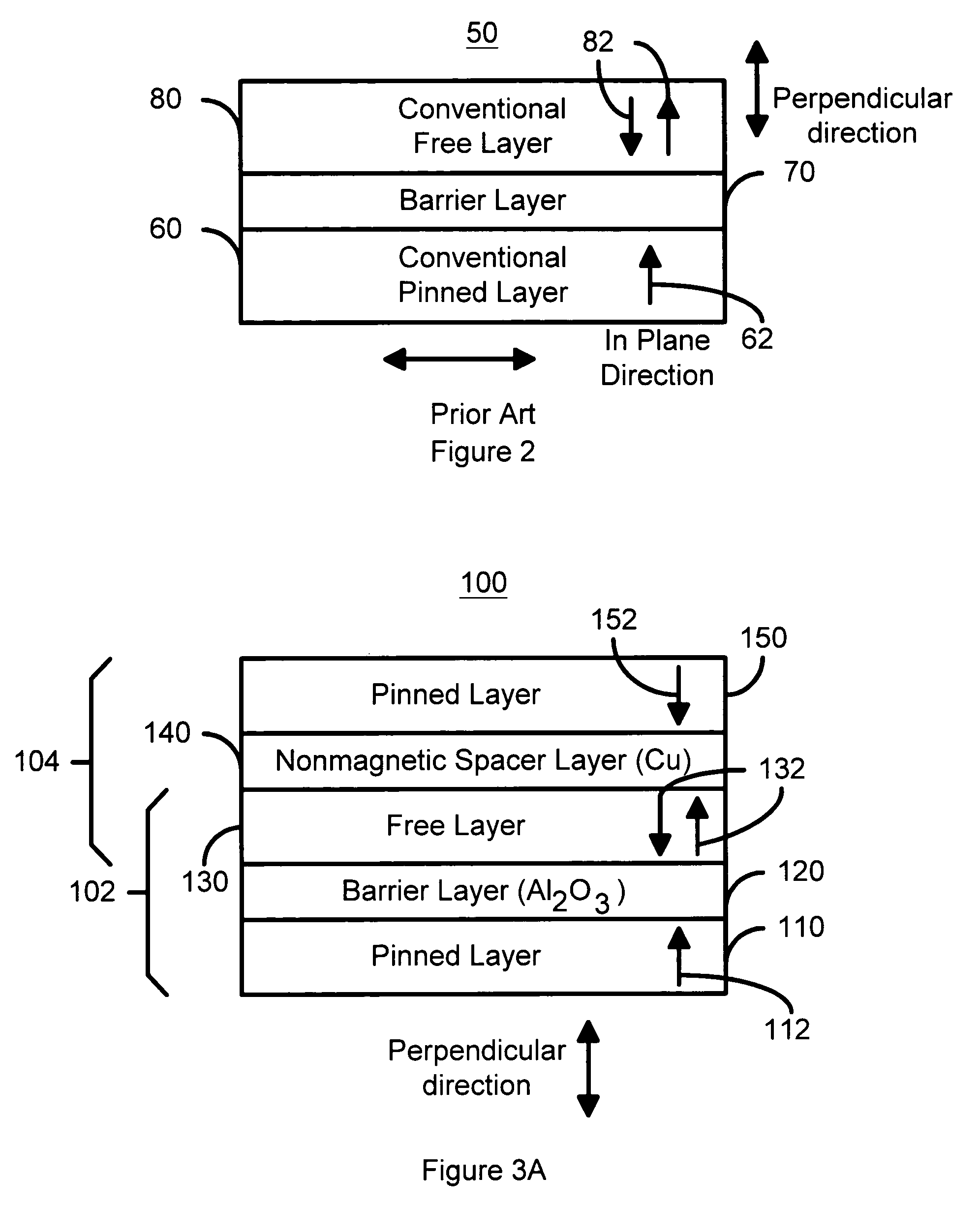
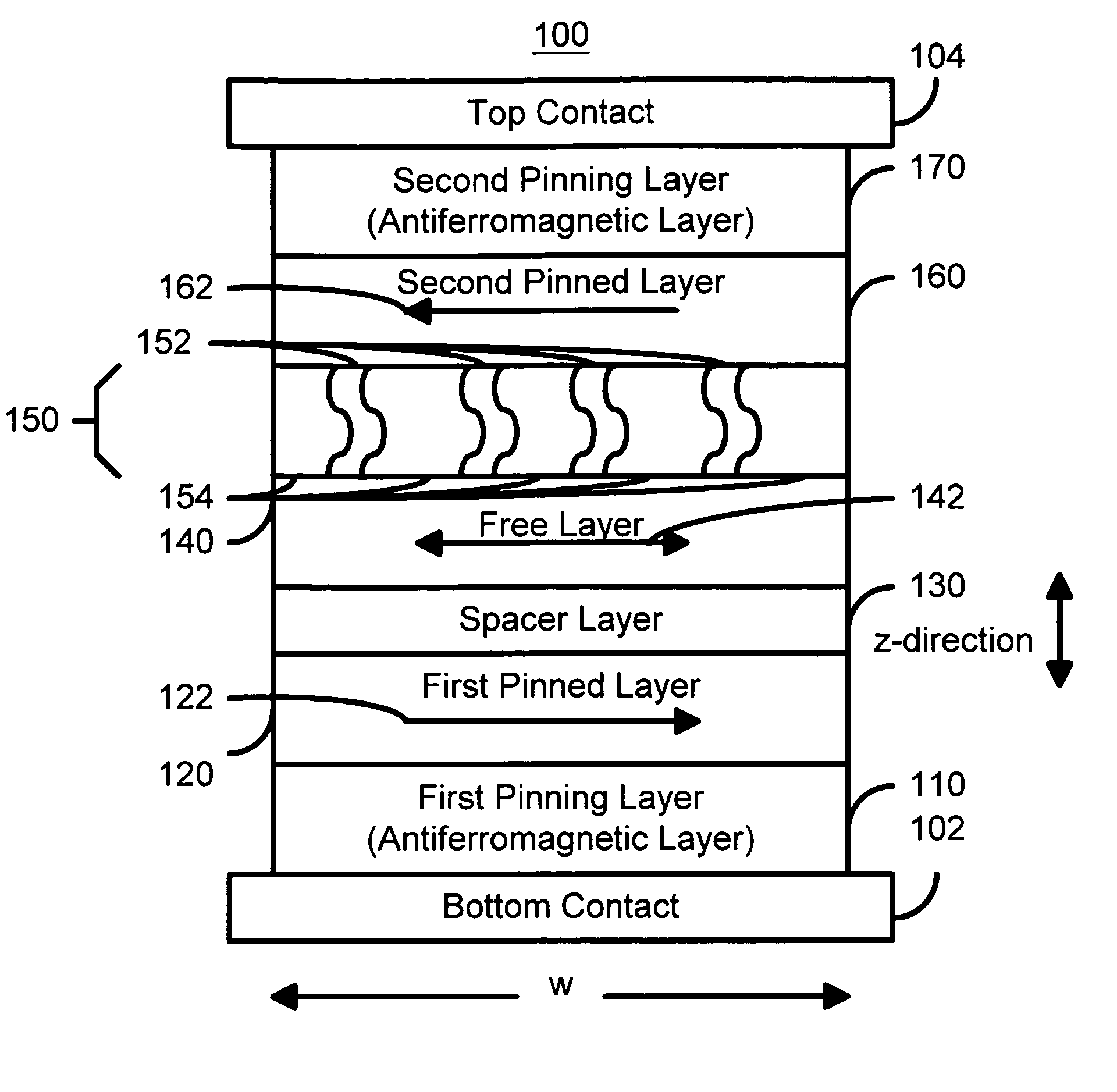
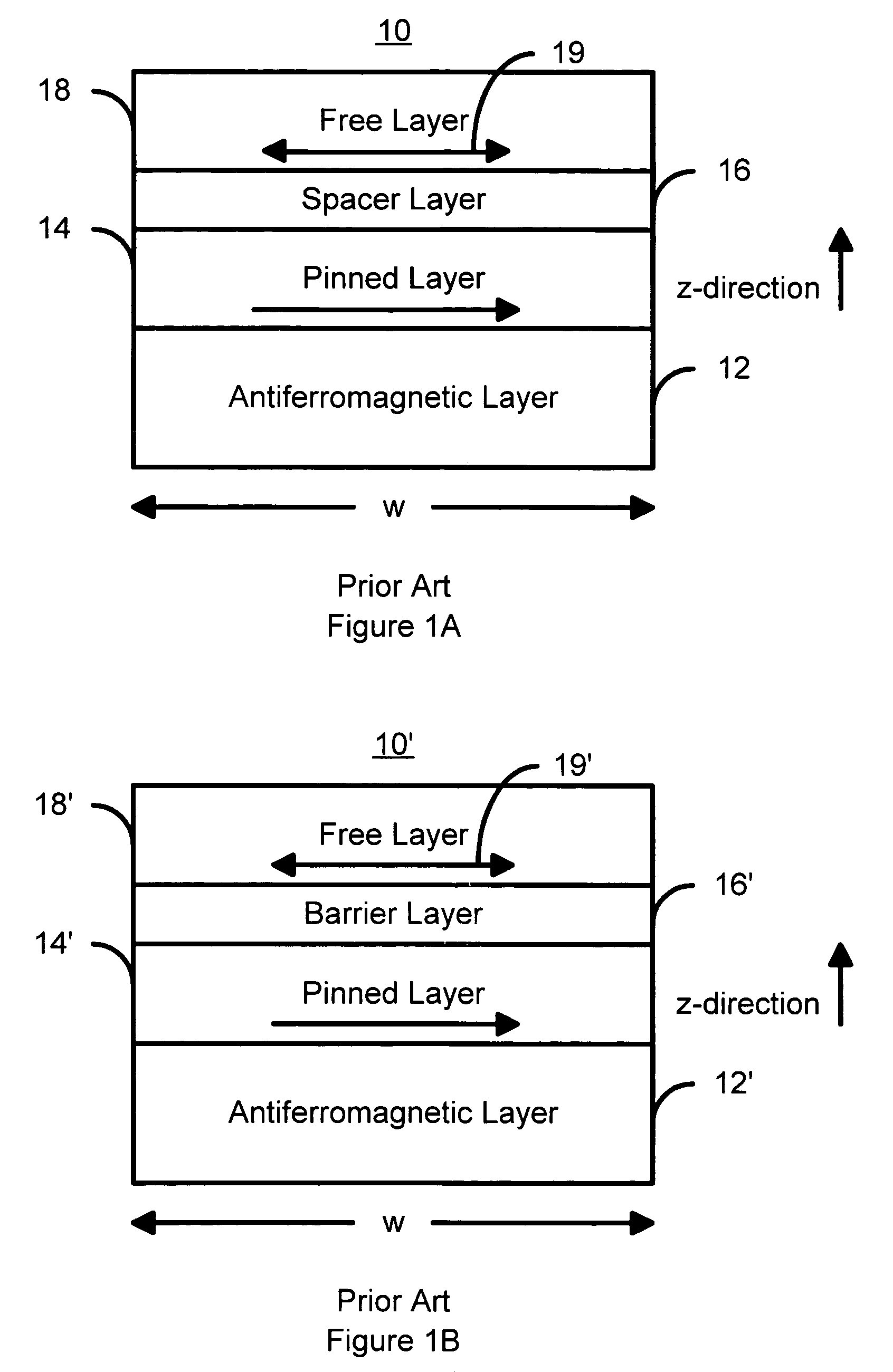
Spin transfer magnetic element with free layers having high perpendicular anisotropy and in-plane equilibrium magnetization
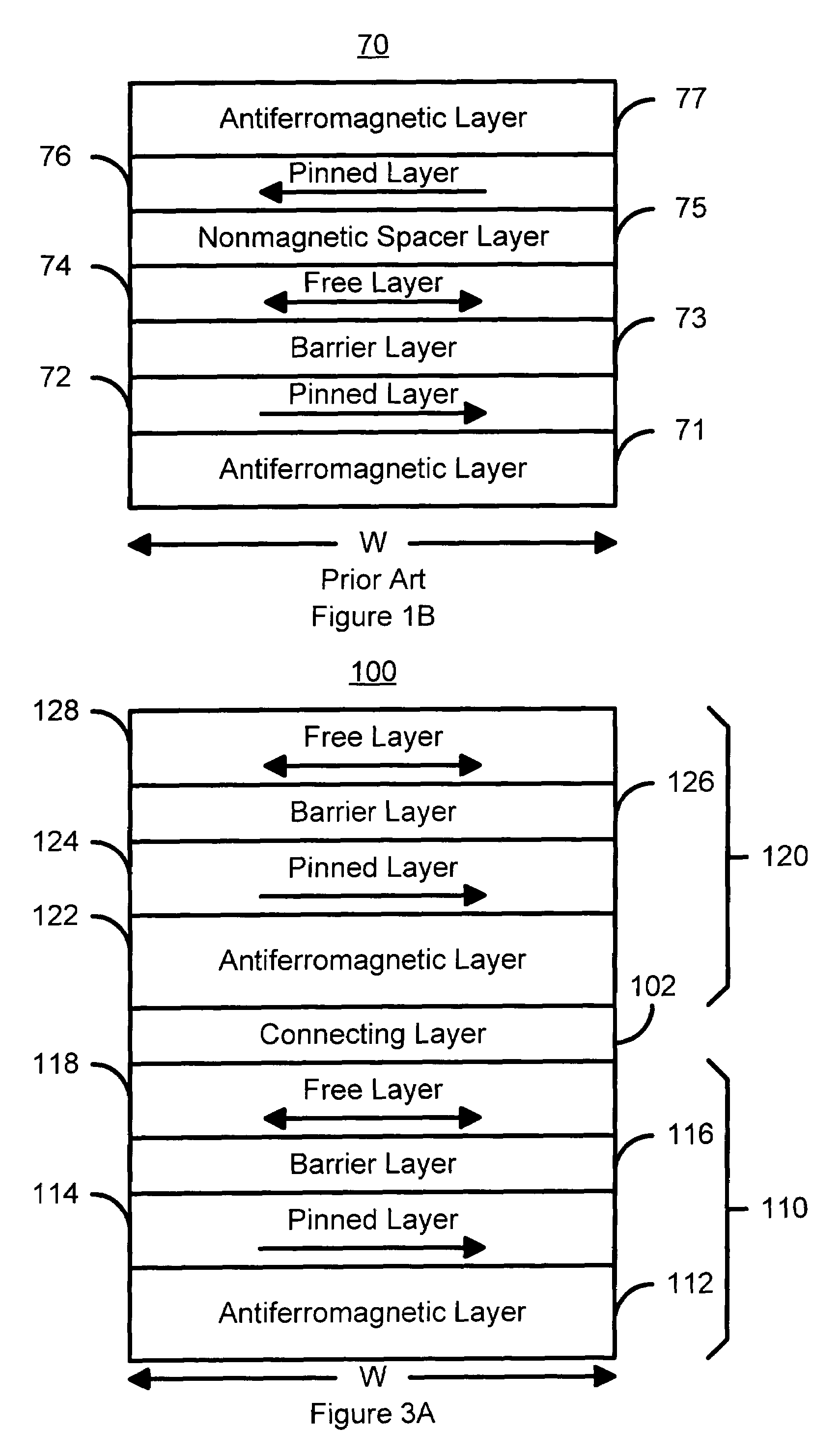
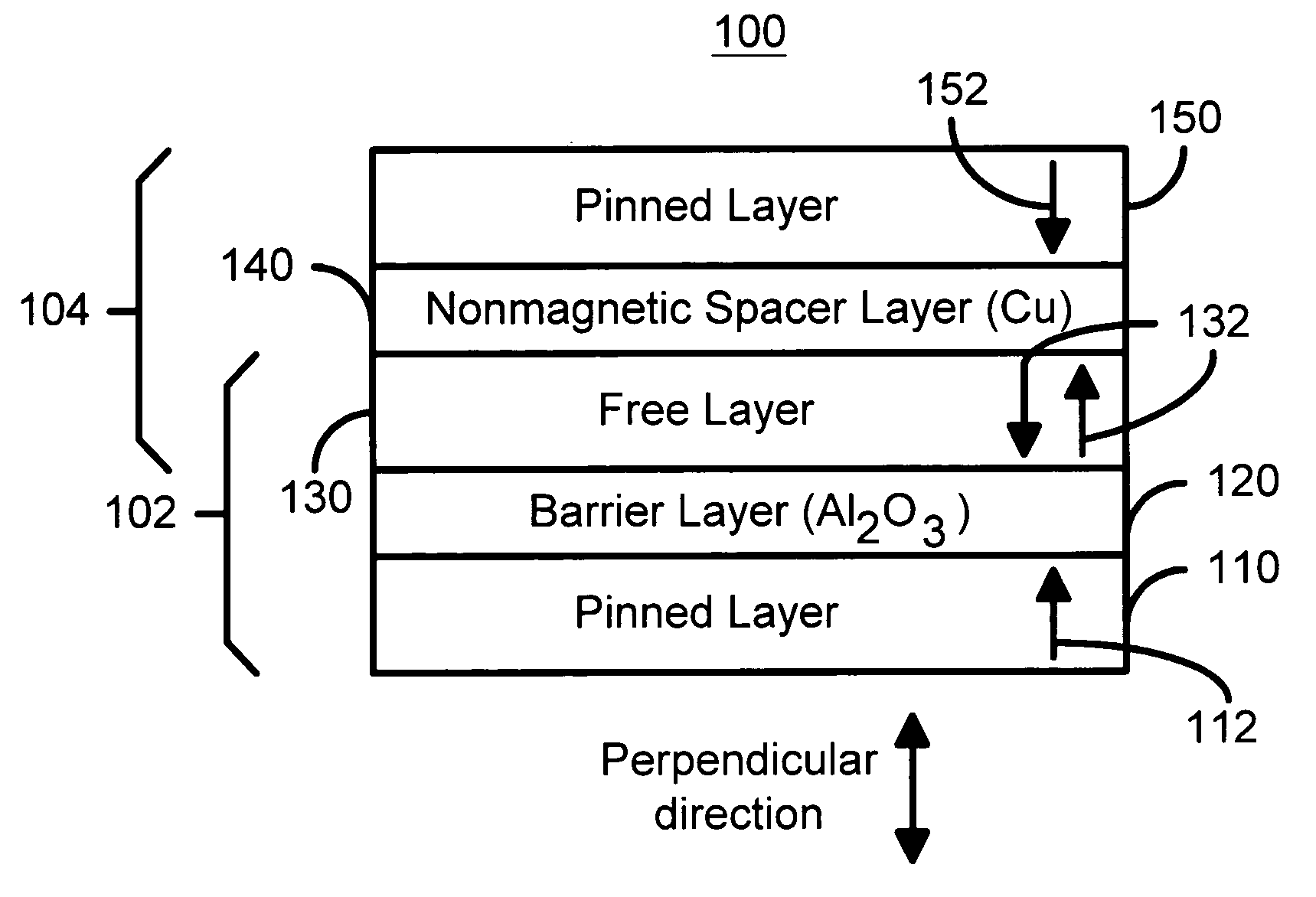
A method and system for providing a magnetic element that can be used in a magnetic memory is disclosed. The magnetic element includes pinned, nonmagnetic spacer, and free layers. The spacer layer resides between the pinned and free layers. The free layer can be switched using spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element. The magnetic element may also include a barrier layer, a second pinned layer. Alternatively, second pinned and second spacer layers and a second free layer magnetostatically coupled to the free layer are included. At least one free layer has a high perpendicular anisotropy. The high perpendicular anisotropy has a perpendicular anisotropy energy that is at least twenty and less than one hundred percent of the out-of-plane demagnetization energy.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
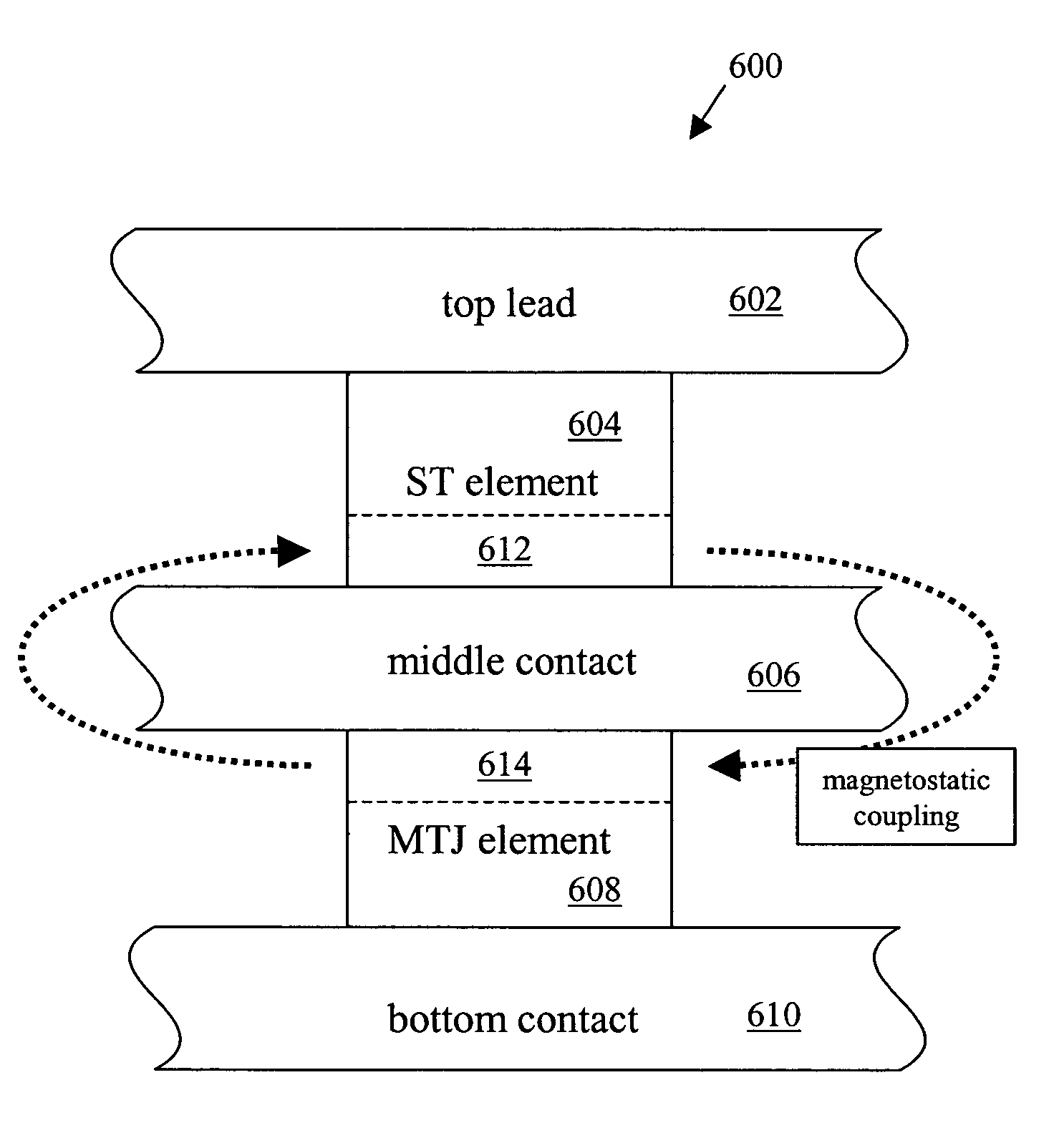
Three-terminal magnetostatically coupled spin transfer-based MRAM cell
A magnetic memory device for reading and writing a data state comprises at least three terminals including first, second, and third terminals. The magnetic memory device also includes a spin transfer (ST) driven element, disposed between the first terminal and the second terminal, and a readout element, disposed between the second terminal and the third terminal. The ST driven element includes a first free layer, and a readout element includes a second free layer. A magnetization direction of the second free layer in the readout element indicates a data state. A magnetization reversal of the first free layer within the ST driven element magnetostatically causes a magnetization reversal of the second free layer in the readout element, thereby recording the data state.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
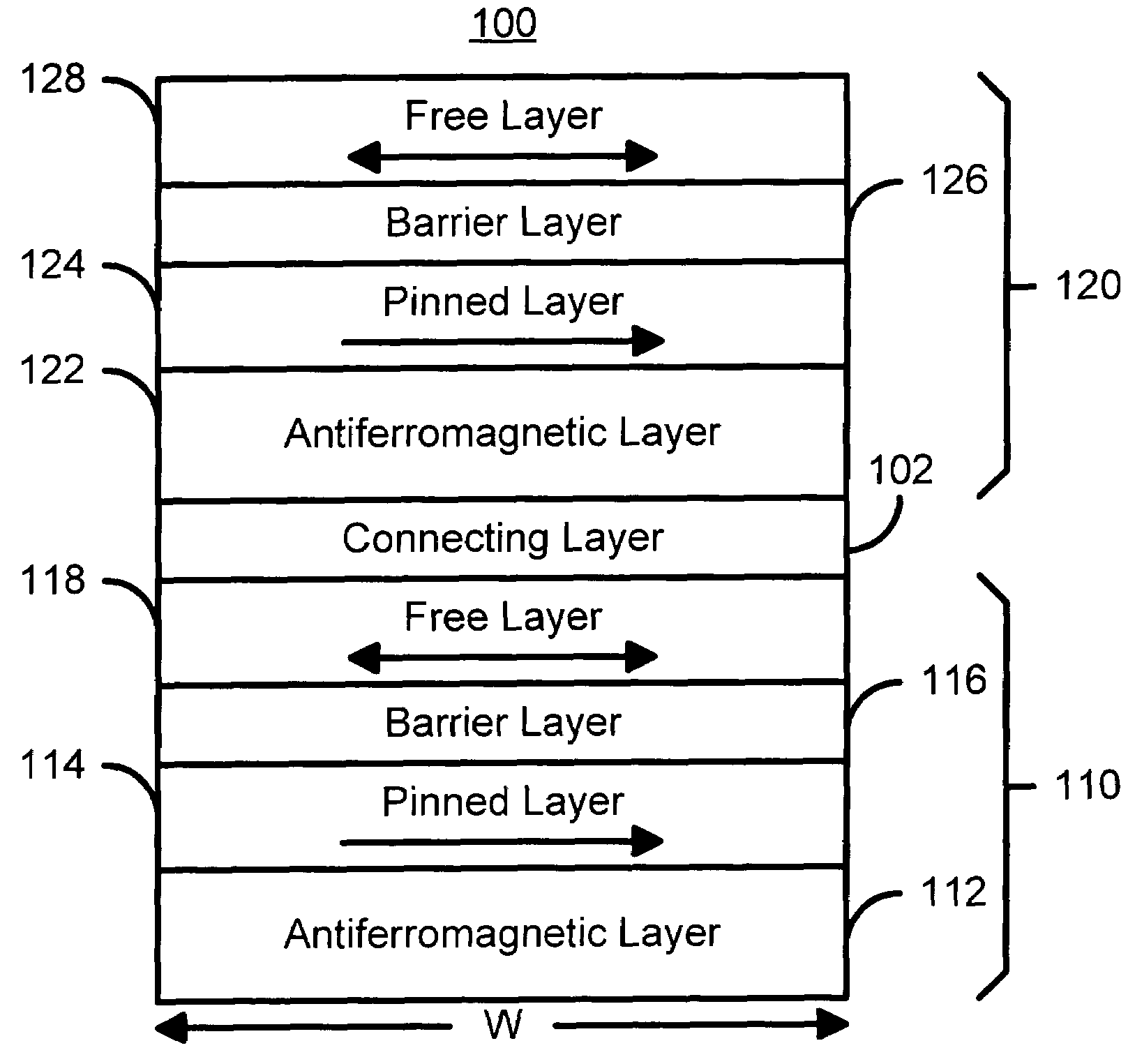
Magnetic memory element utilizing spin transfer switching and storing multiple bits
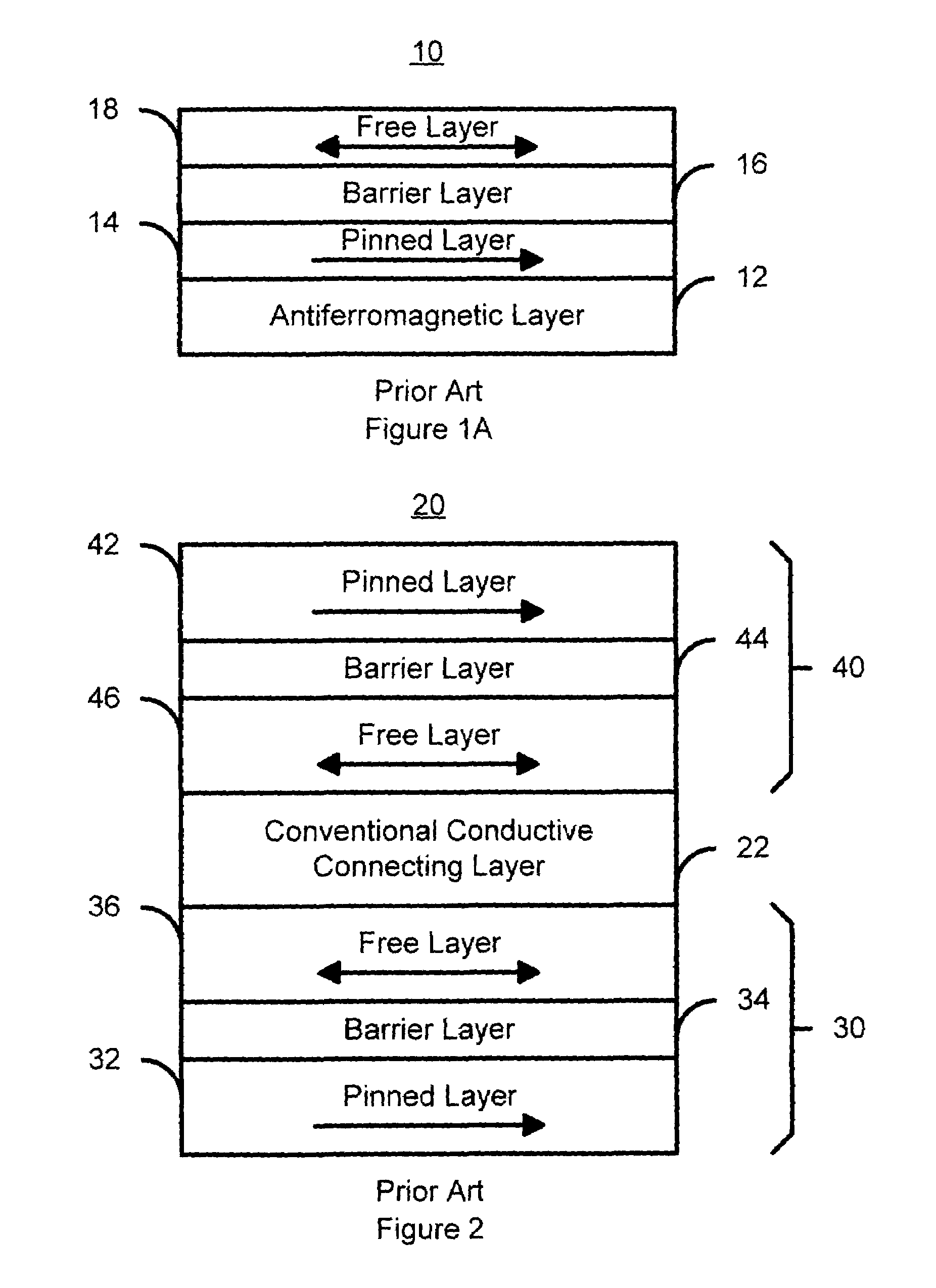
A method and system for providing a magnetic element capable of storing multiple bits is disclosed. The method and system include providing first pinned layer, a first nonmagnetic layer, a first free layer, a connecting layer, a second pinned layer, a second nonmagetic layer and a second free layer. The first pinned layer is ferromagnetic and has a first pinned layer magnetization pinned in a first direction. The first nonmagnetic layer resides between the first pinned layer and the first free layer. The first free layer being ferromagnetic and has a first free layer magnetization. The second pinned layer is ferromagnetic and has a second pinned layer magnetization pinned in a second direction. The connecting layer resides between the second pinned layer and the first free layer. The second nonmagnetic layer resides between the second pinned layer and the second free layer. The second free layer being ferromagnetic and having a second free layer magnetization. The magnetic element is configured to allow the first free layer magnetization and the second free layer magnetization to change direction due to spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
Perpendicular magnetization magnetic element utilizing spin transfer
ActiveUS6967863B2Reduce currentNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsPerpendicular magnetizationMagnetic memory
A method and system for providing a magnetic element that can be used in a magnetic memory is disclosed. The method and system include providing a first pinned layer, a barrier layer, a free layer, a conductive nonmagnetic spacer layer, and a second pinned layer. Each pinned layer has a pinned layer easy axis. At least a portion of the pinned layer easy axis is in a perpendicular direction. The barrier layer resides between the first pinned layer and the free layer. The spacer layer is between the free layer and the second pinned layer. The free layer has a free layer easy axis, at least a portion of which is in the perpendicular direction. The magnetic element is also configured to allow the free layer to be switched due to spin transfer effect when a write current is passed through the magnetic element. Because of the perpendicular magnetization(s), the writing current for spin transfer may be significantly reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
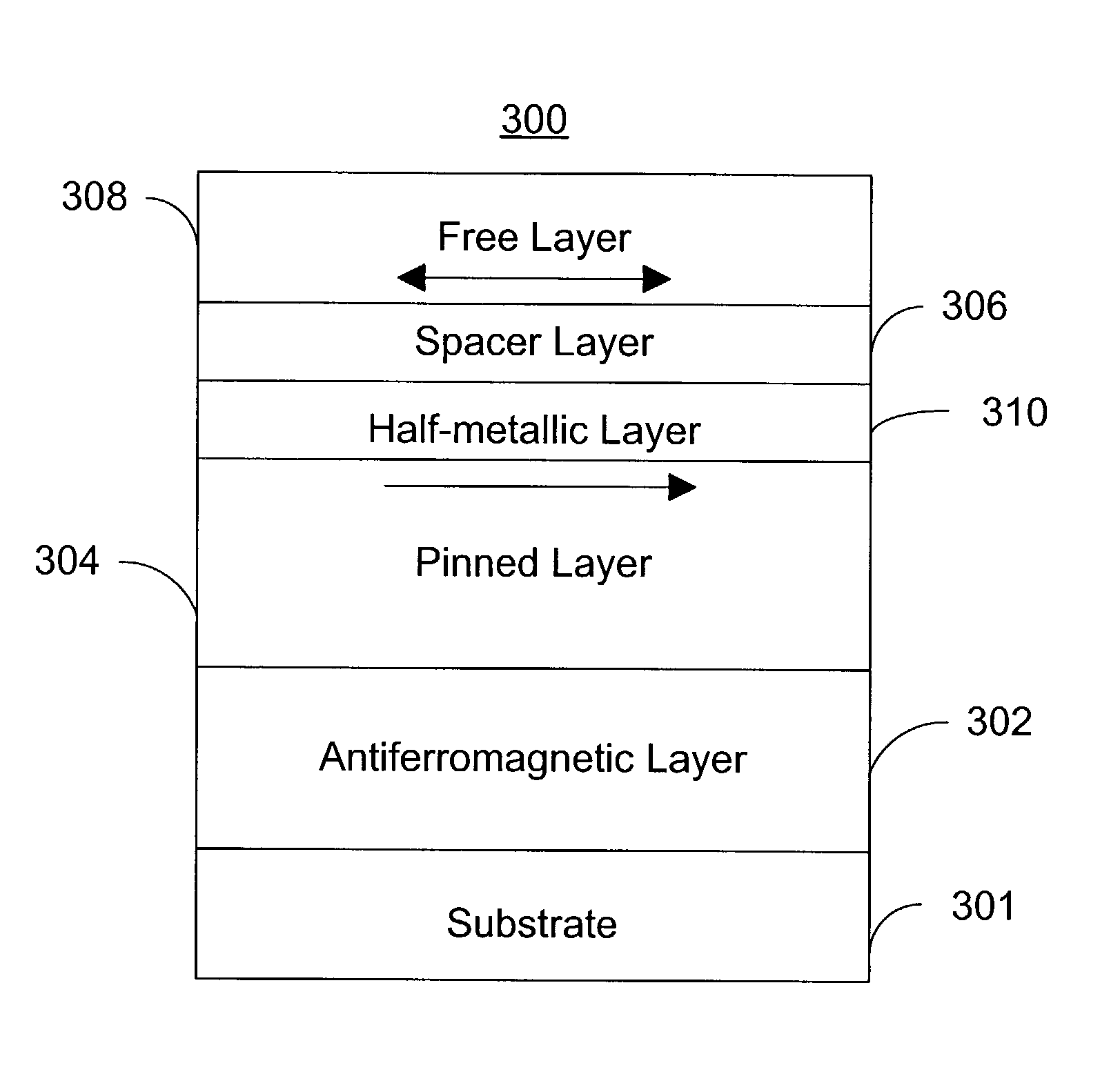
Magnetic element utilizing spin-transfer and half-metals and an MRAM device using the magnetic element
InactiveUS6958927B1Reduce high switching currentReduce power consumptionMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh densityHalf-metal
A magnetic element that can be used in a memory array having high density includes a pinned layer, a half-metallic material layer, a spacer (or a barrier) layer and a free layer. The half-metallic material layer is formed on the pinned layer and preferably has a thickness that is less than about 100 Å. The half-metallic material layer can be formed to be a continuous layer or a discontinuous on the pinned layer. The spacer (or barrier) layer is formed on the half-metallic material layer, such that the spacer (or barrier) layer is nonmagnetic and conductive (or insulating). The free layer is formed on the spacer (or barrier) layer and has a second magnetization that changes direction based on the spin-transfer effect when a write current passes through the magnetic element.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
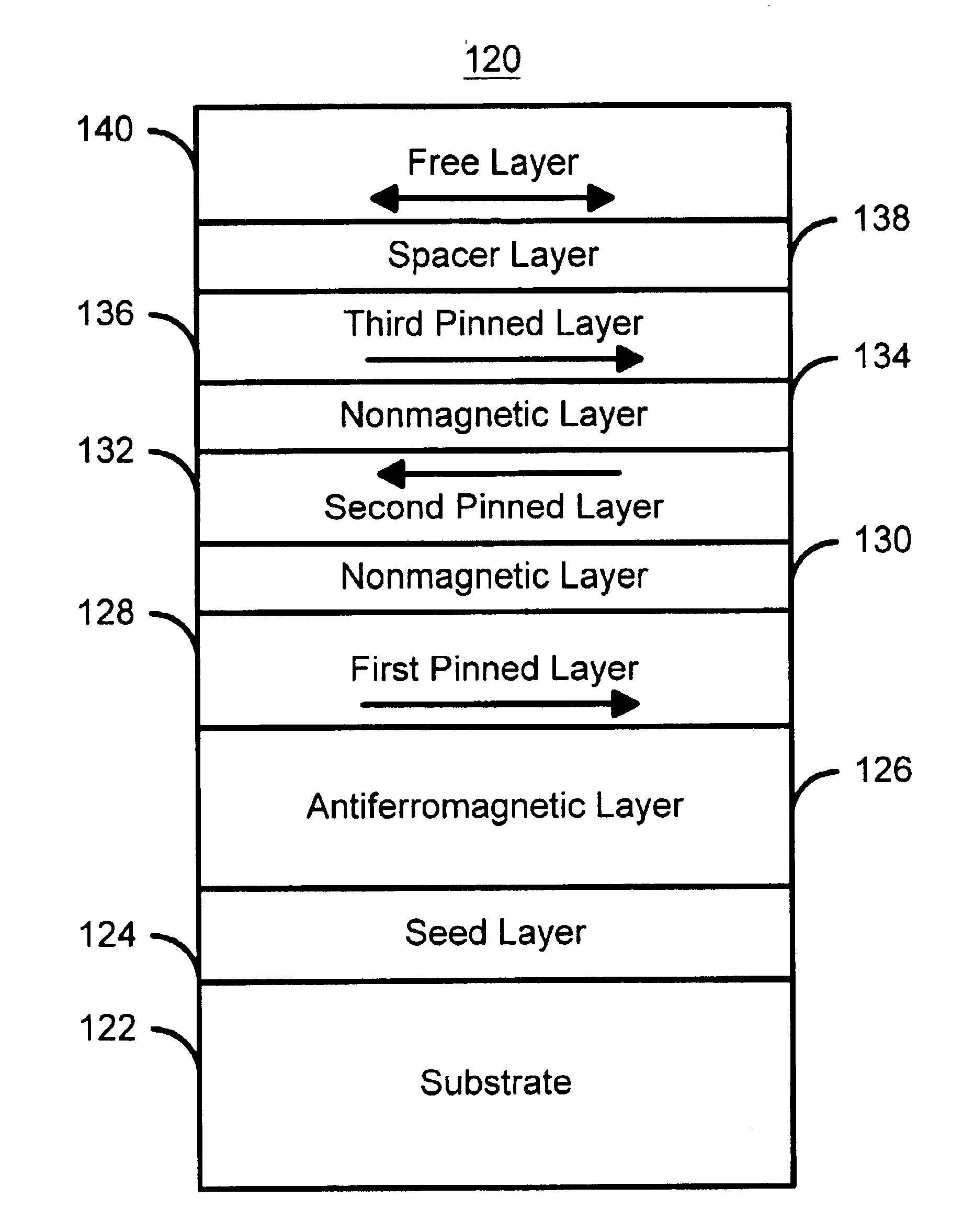
Thermally stable magnetic elements utilizing spin transfer and an MRAM device using the magnetic element
InactiveUS6838740B2Improve performanceImprove thermal stabilityTransistorNanomagnetismAntiferromagnetic couplingMagnetic memory
A method and system for providing a magnetic element capable of being written using spin-transfer effect while being thermally stable and a magnetic memory using the magnetic element are disclosed. The magnetic element includes a first, second and third pinned layers, first and second nonmagnetic layers, a free layer and a nonmagnetic spacer layers. The first, second and third pinned layers are ferromagnetic and have first, second and third magnetizations pinned in first, second and third directions. The first and second nonmagnetic layers include first and second diffusion barriers, respectively. The first and second nonmagnetic layers are between the first and second pinned layers and the second and third pinned layers, respectively. The first and second pinned layers and the second and third pinned layers are antiferromagnetically coupled. The nonmagnetic spacer layer is conductive and resides between the free layer and the third pinned layer. In addition, performance can be further improved by doping Co containing ferromagnetic layers with Cr and / or Pt.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
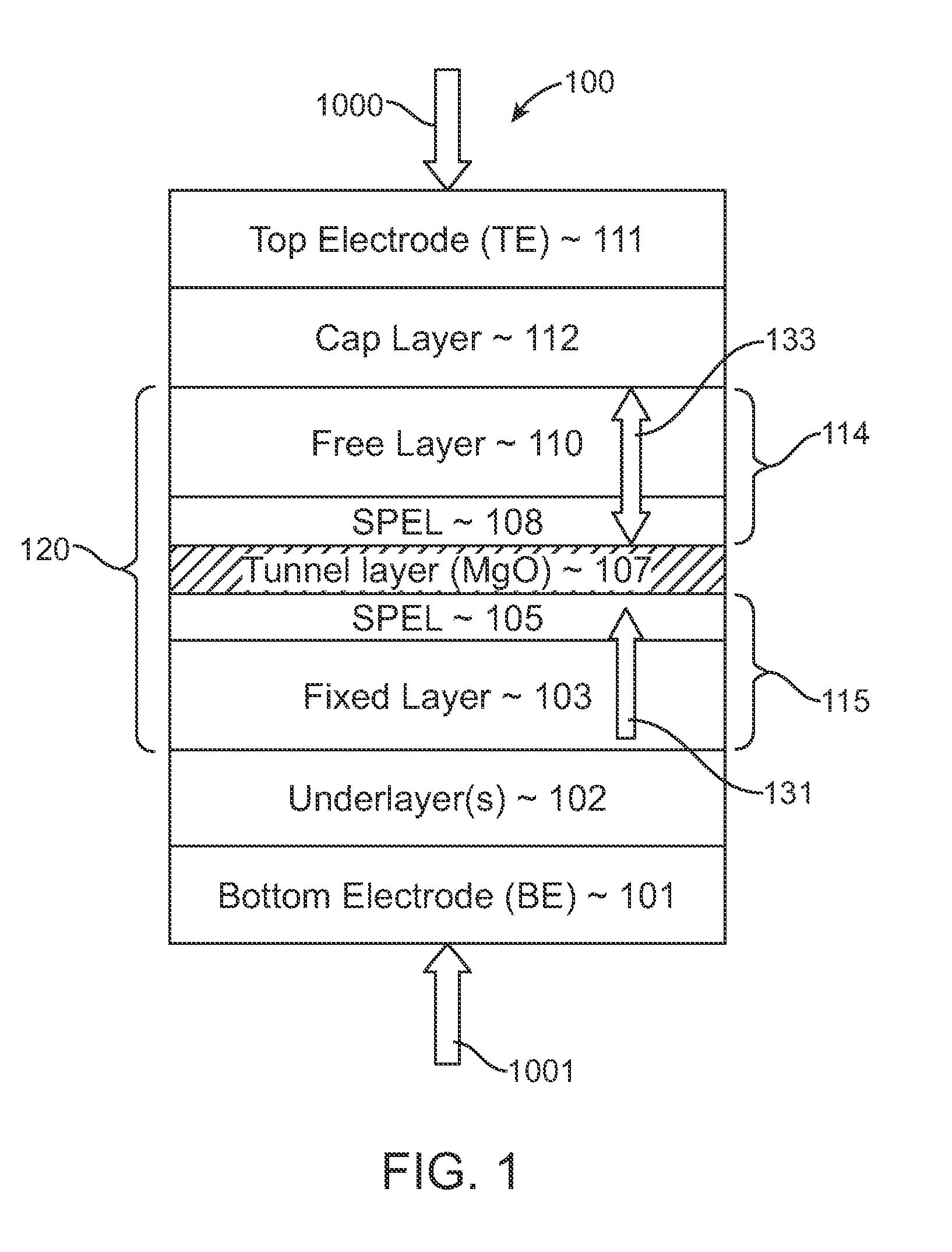
Magnetoresistive element
A magnetoresistive element which records information by supplying spin-polarized electrons to a magnetic material, includes a first pinned layer which is made of a magnetic material and has a first magnetization directed in a direction perpendicular to a film surface, a free layer which is made of a magnetic material and has a second magnetization directed in the direction perpendicular to the film surface, the direction of the second magnetization reversing by the spin-polarized electrons, and a first nonmagnetic layer which is provided between the first pinned layer and the free layer. A saturation magnetization Ms of the free layer satisfies a relationship 0≧Ms<√{square root over ( )}{Jw / (6nAt)}. Jw is a write current density, t is a thickness of the free layer, A is a constant.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
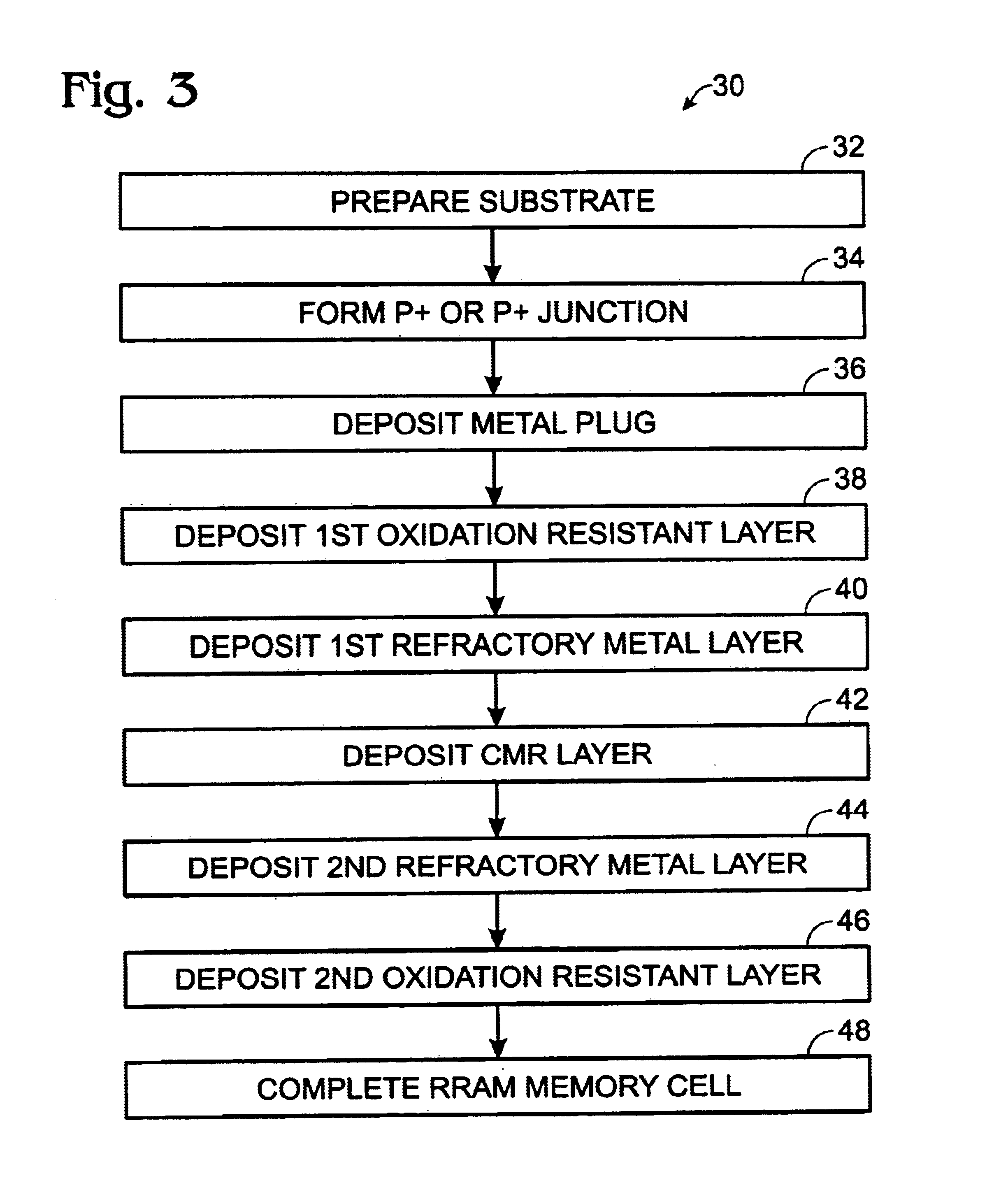
RRAM memory cell electrodes
ActiveUS6849891B1Improve device reliabilityImprove device device enduranceTransistorMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsOxidation resistantSilicon
A RRAM memory cell is formed on a silicon substrate having a operative junction therein and a metal plug formed thereon, includes a first oxidation resistive layer; a first refractory metal layer; a CMR layer; a second refractory metal layer; and a second oxidation resistive layer. A method of fabricating a multi-layer electrode RRAM memory cell includes preparing a silicon substrate; forming a junction in the substrate taken from the group of junctions consisting of N+ junctions and P+ junctions; depositing a metal plug on the junction; depositing a first oxidation resistant layer on the metal plug; depositing a first refractory metal layer on the first oxidation resistant layer; depositing a CMR layer on the first refractory metal layer; depositing a second refractory metal layer on the CMR layer; depositing a second oxidation resistant layer on the second refractory metal layer; and completing the RRAM memory cell.
Owner:XENOGENIC DEV LLC
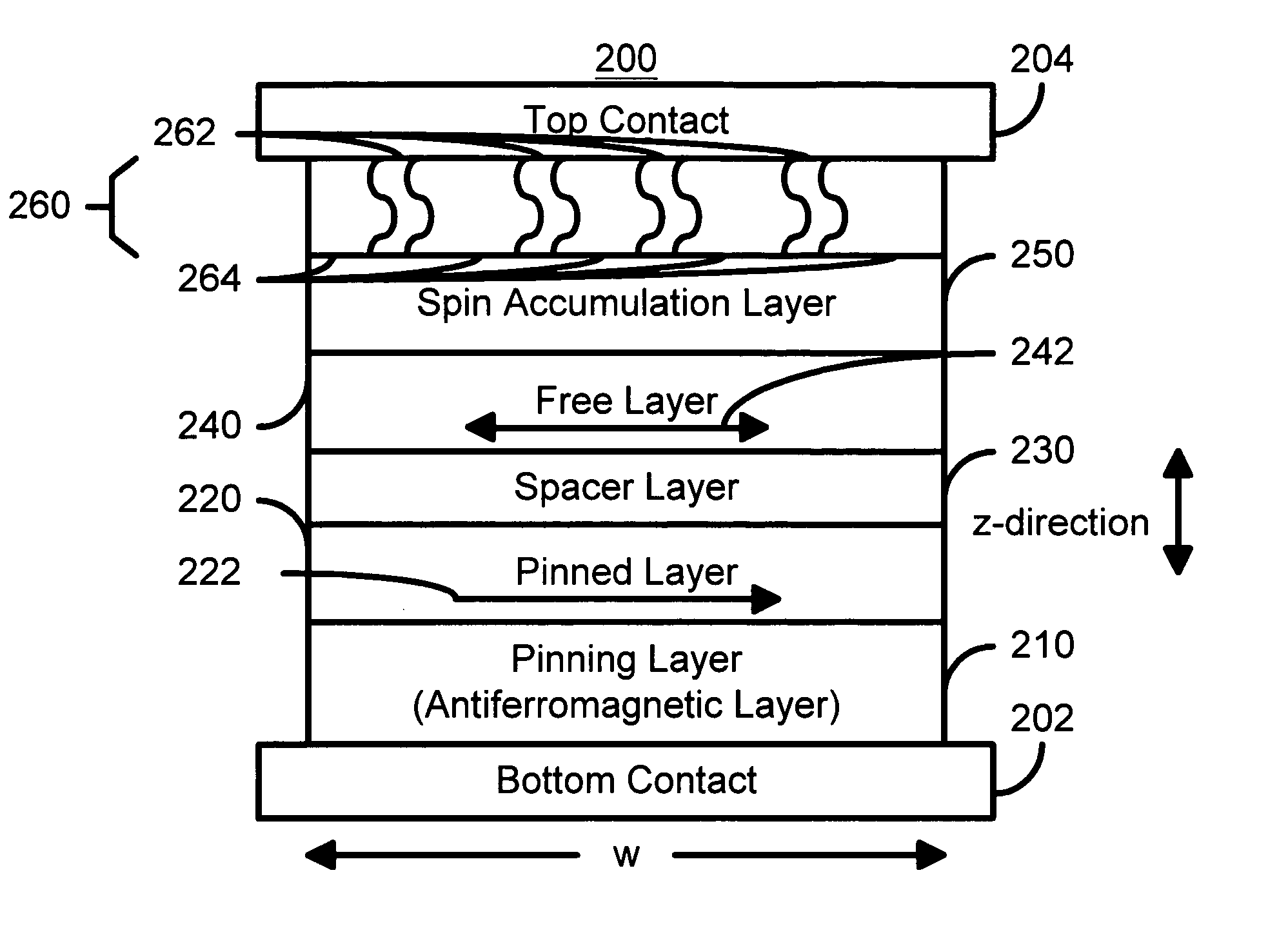
Spin barrier enhanced magnetoresistance effect element and magnetic memory using the same
ActiveUS7088609B2Reduce outer surfaceHigh areal resistanceNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsDamping constantMagnetic memory
A method and system for providing a magnetic element that can be used in a magnetic memory is disclosed. The magnetic element includes pinned, spacer, free, and spin barrier layers. The spacer layer is nonmagnetic and resides between the pinned and free layers. The free layer can be switched using spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element. The free layer resides between the spacer layer and the spin barrier layer. The spin barrier layer is configured to reduce an outer surface contribution to a damping constant of the free layer. In one aspect, the spin barrier layer has a high areal resistance and may substantially eliminate spin pumping induced damping. In another aspect, the magnetic element also includes a spin accumulation layer between the spin barrier and free layers. The spin accumulation layer has a high conductivity, preferably being metallic, and may have a long spin diffusion length.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
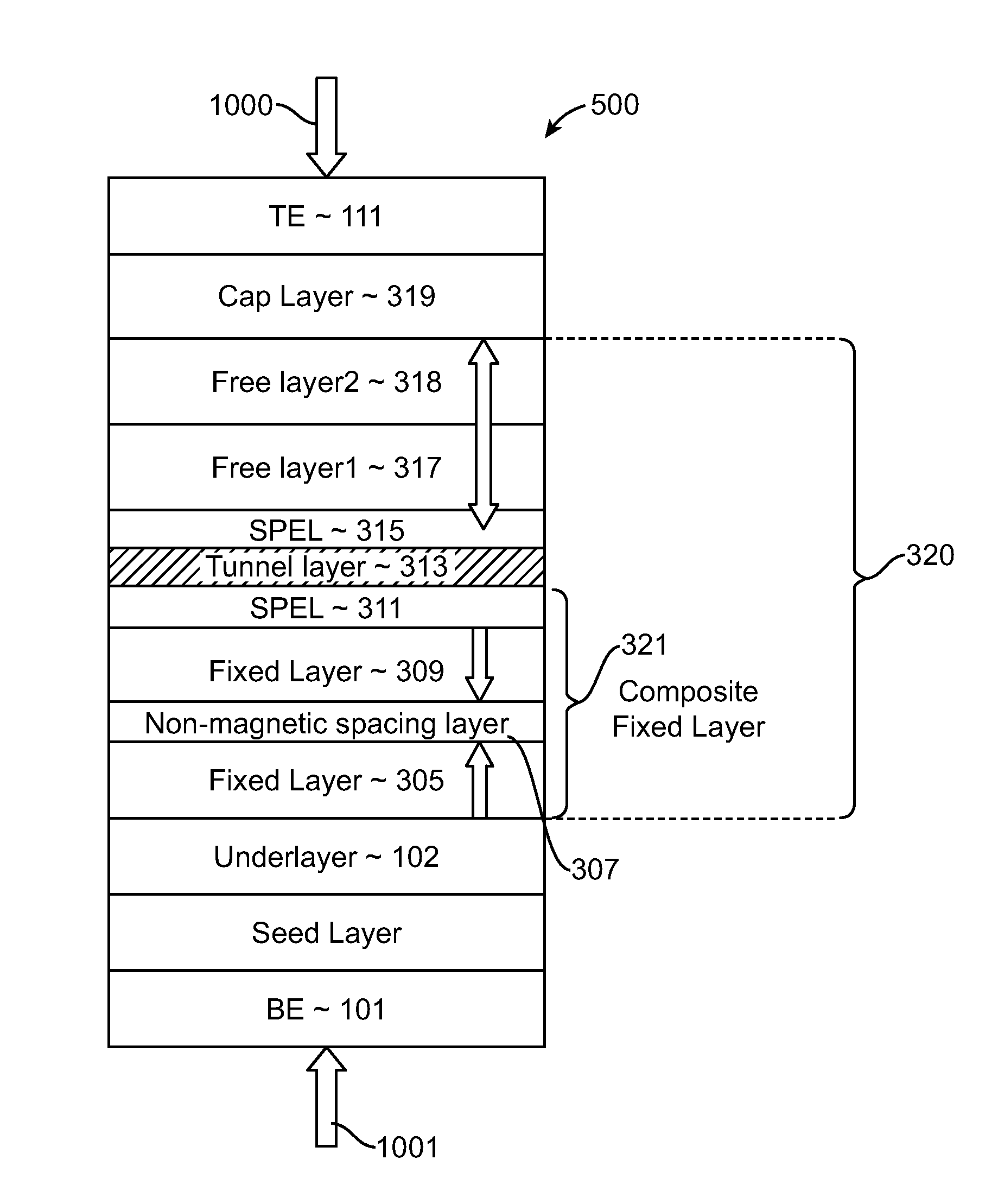
Spin-transfer torque magnetic random access memory having magnetic tunnel junction with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy
A spin-torque transfer memory random access memory (STTMRAM) element includes a fixed layer formed on top of a substrate and a a tunnel layer formed upon the fixed layer and a composite free layer formed upon the tunnel barrier layer and made of an iron platinum alloy with at least one of X or Y material, X being from a group consisting of: boron (B), phosphorous (P), carbon (C), and nitride (N) and Y being from a group consisting of: tantalum (Ta), titanium (Ti), niobium (Nb), zirconium (Zr), tungsten (W), silicon (Si), copper (Cu), silver (Ag), aluminum (Al), chromium (Cr), tin (Sn), lead (Pb), antimony (Sb), hafnium (Hf) and bismuth (Bi), molybdenum (Mo) or rhodium (Ru), the magnetization direction of each of the composite free layer and fixed layer being substantially perpendicular to the plane of the substrate.
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
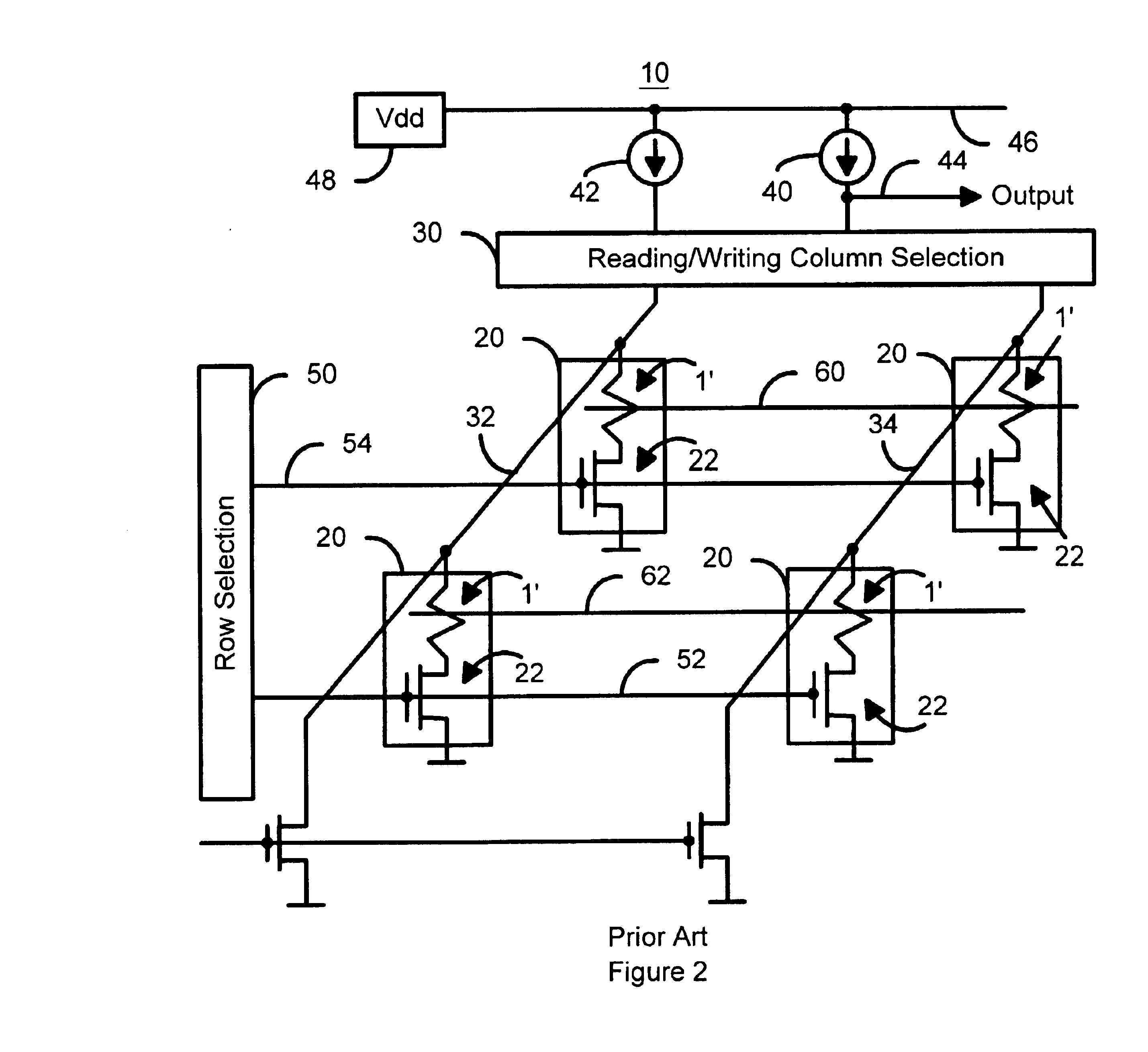
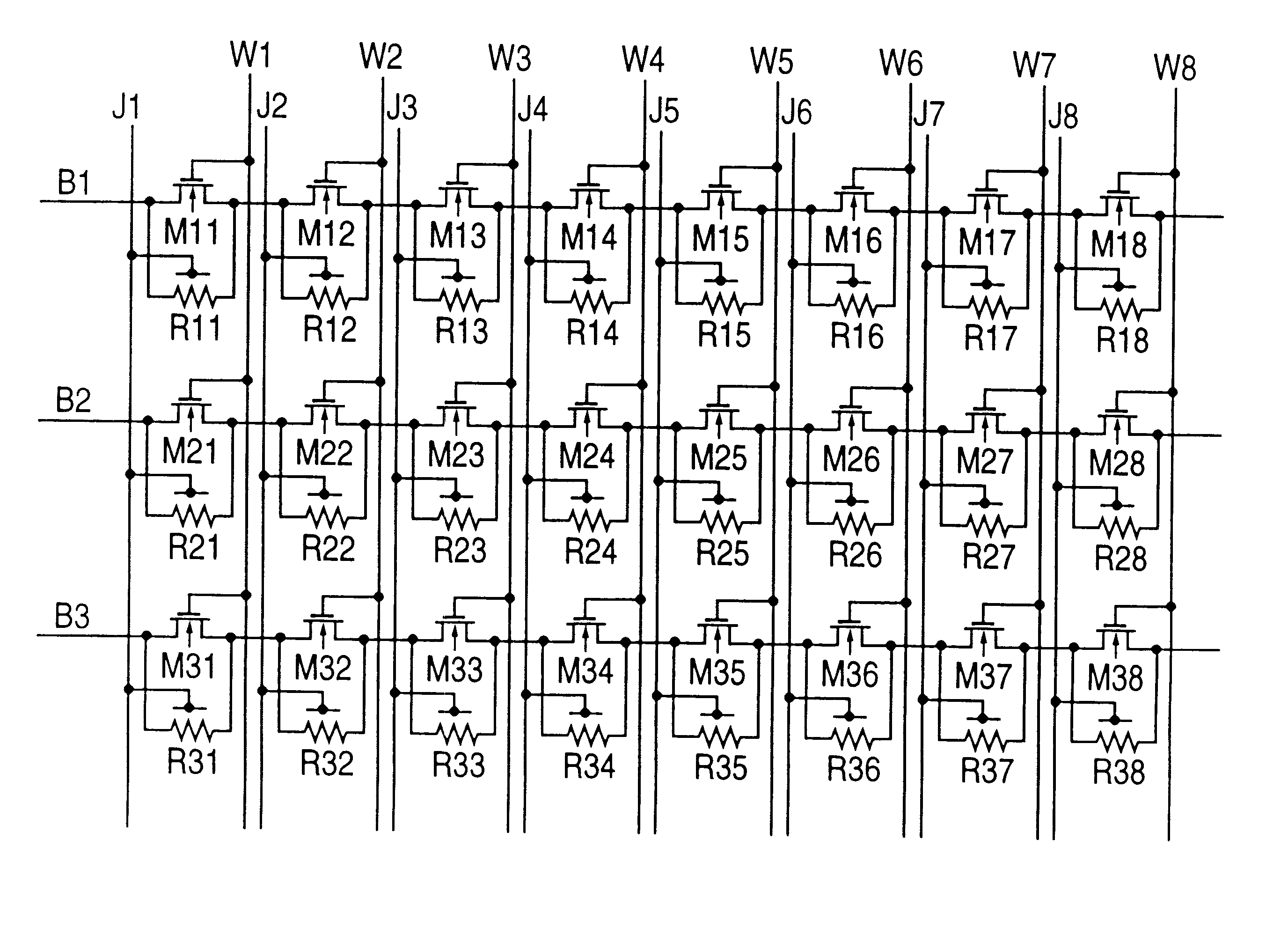
Magnetic thin film memory, method of writing information in it, and me
InactiveUS6226197B1NanoinformaticsMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMagnetic reluctanceField-effect transistor
The present invention relates to a magnetic thin film memory having a hybrid element including a field effect transistor and a magnetoresistive thin film connected to the field effect transistor in parallel. In the magnetic thin film memory, the hybrid element is preferably arranged in plurality in a matrix state. The present invention also relates to a method of writing information in this magnetic thin film memory, and a method of reading the information written in this magnetic thin film memory.
Owner:CANON KK
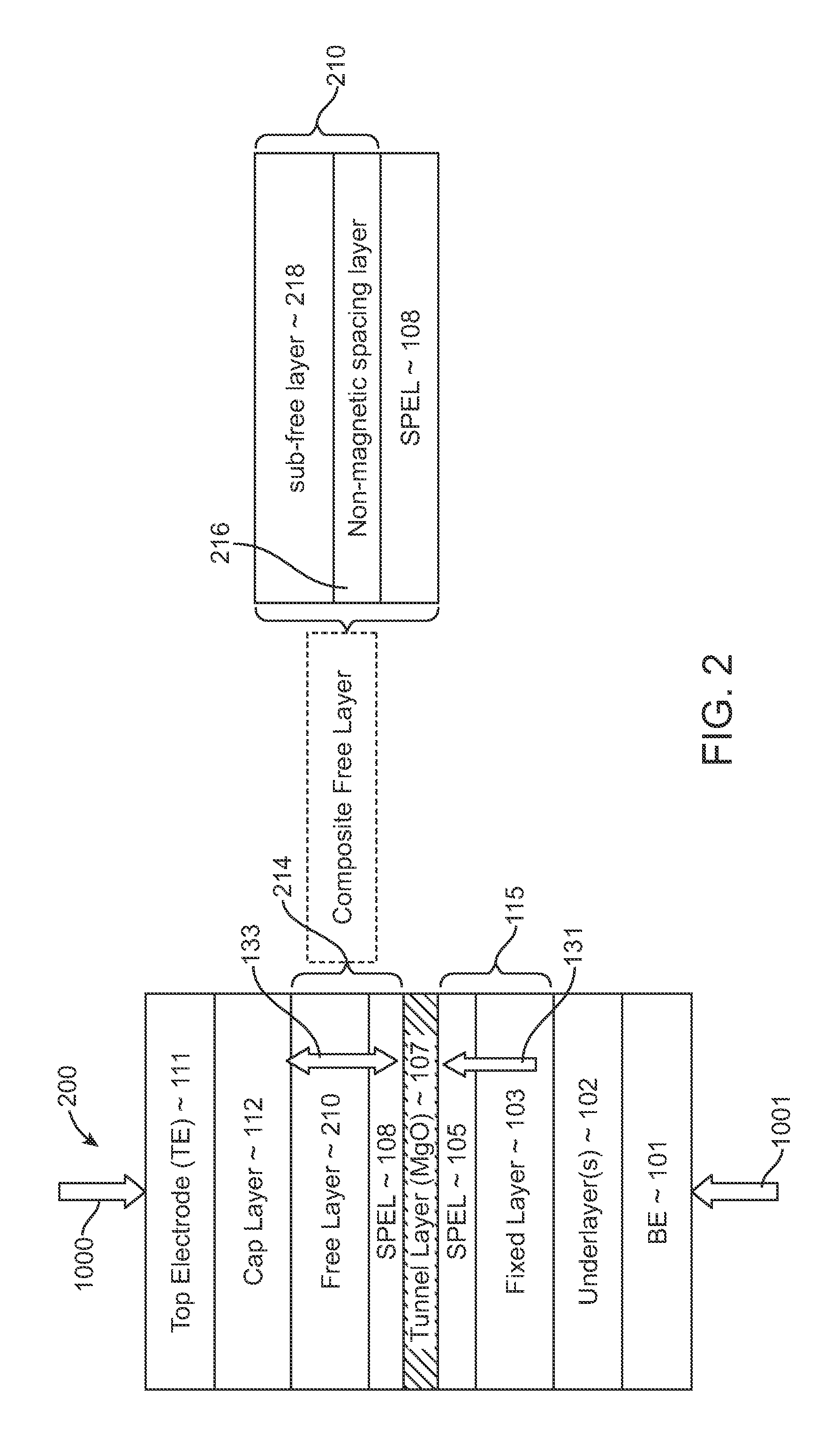
Multilayers having reduced perpendicular demagnetizing field using moment dilution for spintronic applications
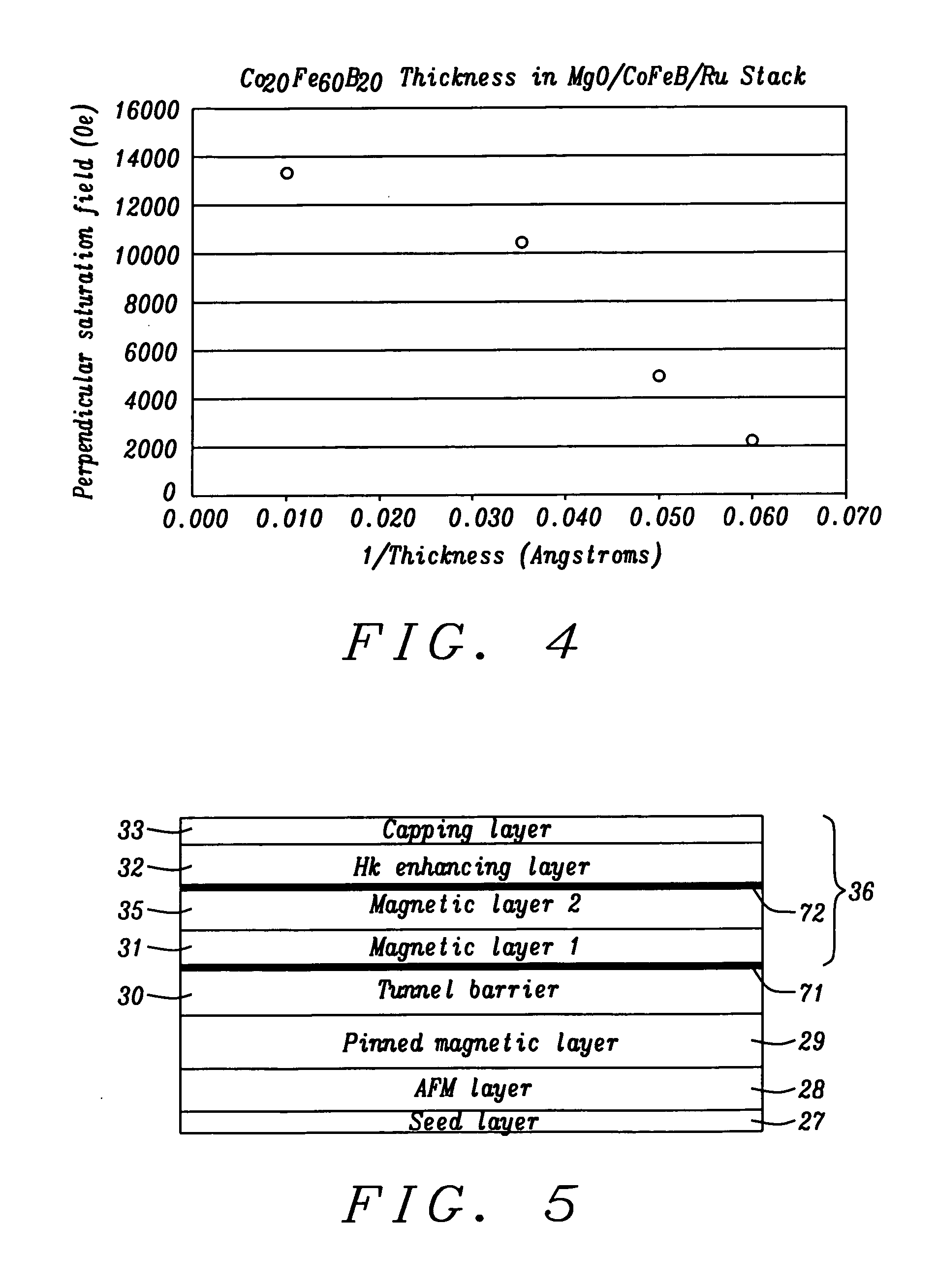
ActiveUS20120280336A1Improve thermal stabilityHigh MR ratioMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionPerpendicular anisotropyAlloy
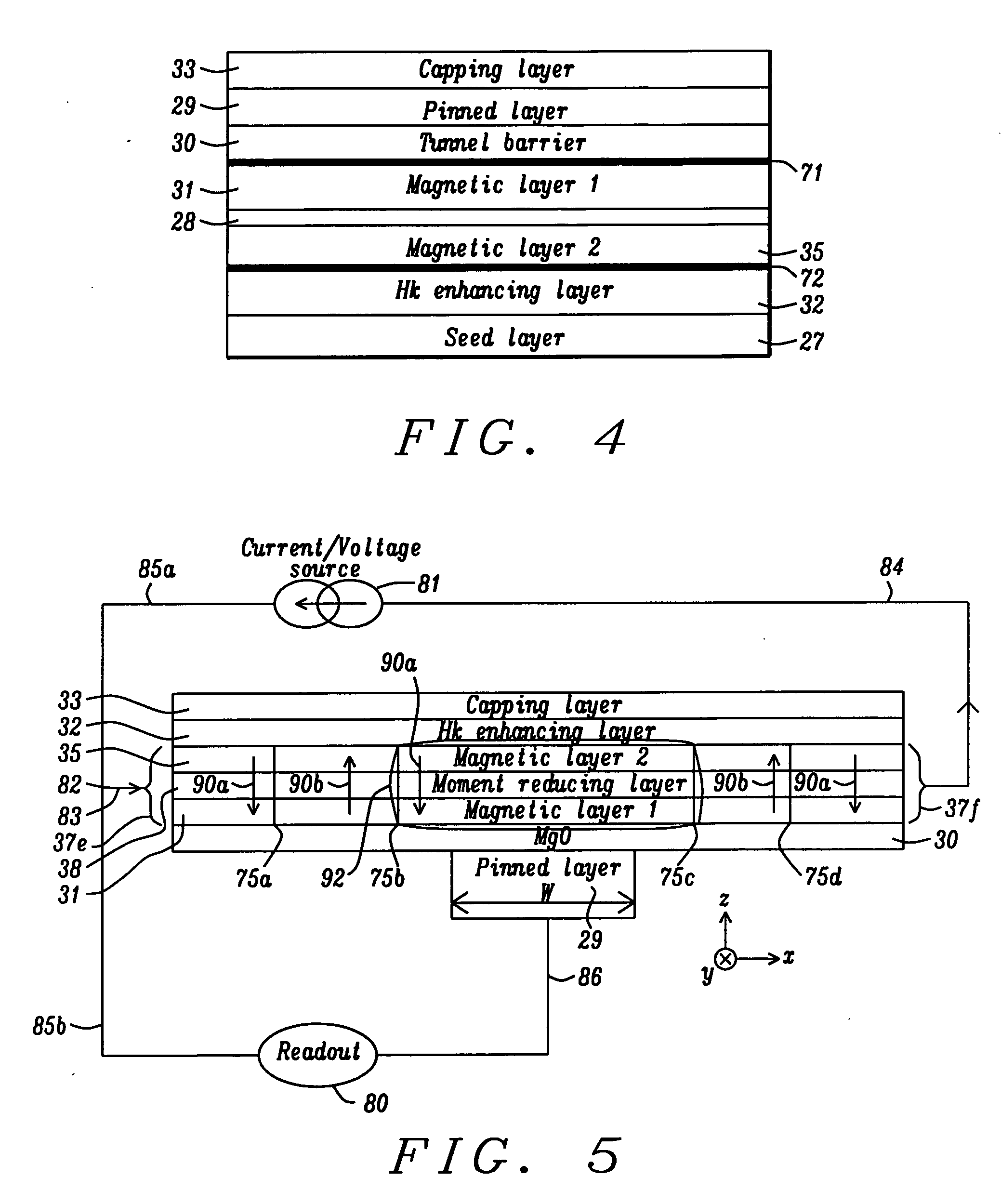
A magnetic element is disclosed that has a composite free layer with a FM1 / moment diluting / FM2 configuration wherein FM1 and FM2 are magnetic layers made of one or more of Co, Fe, Ni, and B and the moment diluting layer is used to reduce the perpendicular demagnetizing field. As a result, lower resistance x area product and higher thermal stability are realized when perpendicular surface anisotropy dominates shape anisotropy to give a magnetization perpendicular to the planes of the FM1, FM2 layers. The moment diluting layer may be a non-magnetic metal like Ta or a CoFe alloy with a doped non-magnetic metal. A perpendicular Hk enhancing layer interfaces with the FM2 layer and may be an oxide to increase the perpendicular anisotropy field in the FM2 layer. The magnetic element may be part of a spintronic device or serve as a propagation medium in a domain wall motion device.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
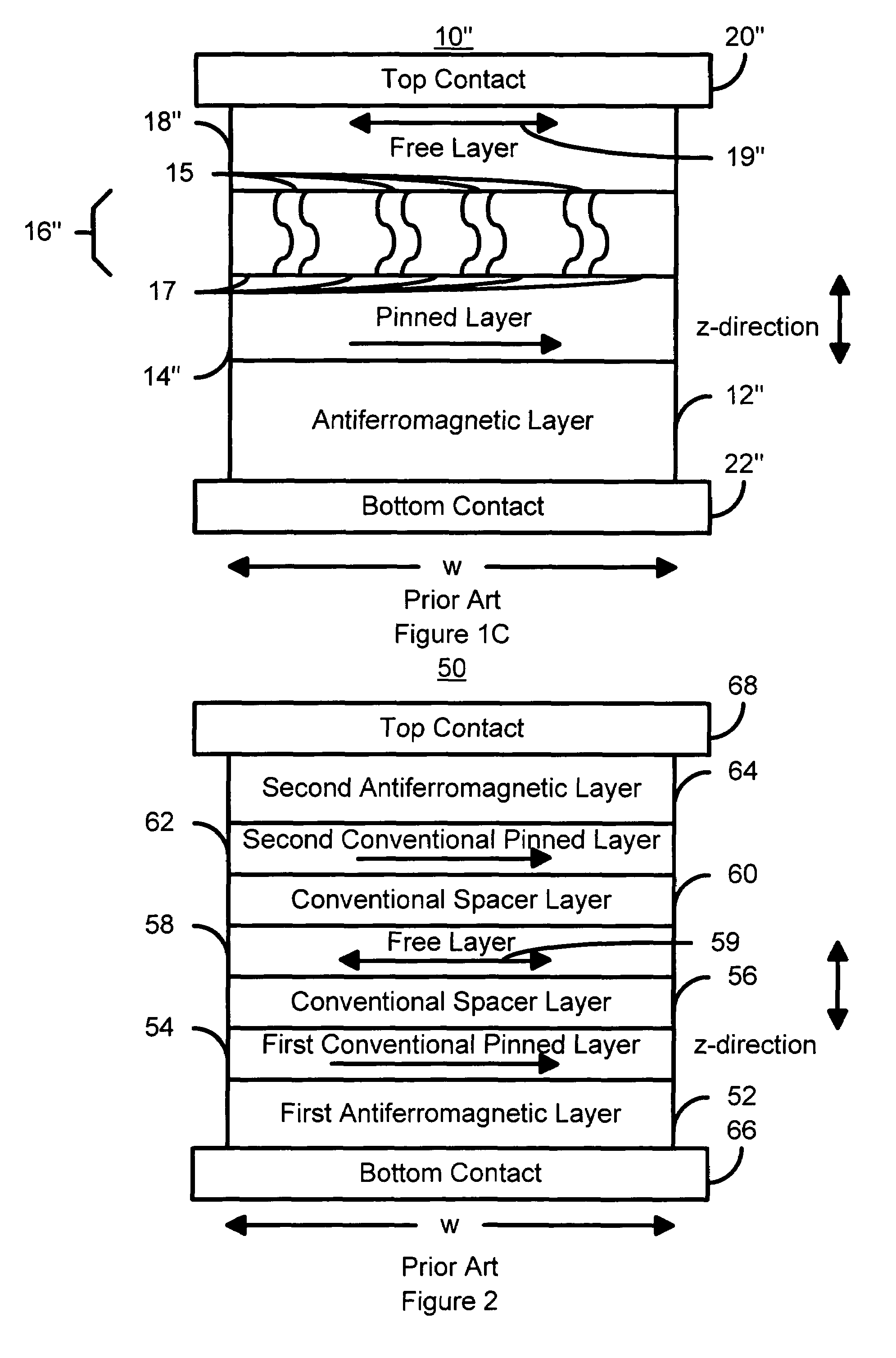
Magnetic tunnel junction magnetic device, memory and writing and reading methods using said device
InactiveUS6950335B2Good reproducibilityEliminate errorsNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMagnetizationSemiconductor
Magnetic tunnel junction magnetic device (16) for writing and reading uses a reference layer (20c) and a storage layer (20a) separated by a semiconductor or insulating layer (20b). The blocking temperature of the magnetisation of the storage layer is less than that of the reference layer. The storage layer is heated (22, 24) above the blocking temperature of its magnetisation. A magnetic field (34) is applied (26) to it orientating its magnetization with respect to that of the reference layer without modifying the orientation of the reference layer.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
High speed low power magnetic devices based on current induced spin-momentum transfer
InactiveUS6980469B2Operational advantageReduce the required powerNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsMagnetic memoryMagnetization
The present invention generally relates to the field of magnetic devices for memory cells that can serve as non-volatile memory. More specifically, the present invention describes a high speed and low power method by which a spin polarized electrical current can be used to control and switch the magnetization direction of a magnetic region in such a device. The magnetic device comprises a pinned magnetic layer with a fixed magnetization direction, a free magnetic layer with a free magnetization direction, and a read-out magnetic layer with a fixed magnetization direction. The pinned magnetic layer and the free magnetic layer are separated by a non-magnetic layer, and the free magnetic layer and the read-out magnetic layer are separated by another non-magnetic layer. The magnetization directions of the pinned and free layers generally do not point along the same axis. The non-magnetic layers minimize the magnetic interaction between the magnetic layers. A current is applied to the device to induce a torque that alters the magnetic state of the device so that it can act as a magnetic memory for writing information. The resistance, which depends on the magnetic state of the device, is measured to thereby read out the information stored in the device.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Magnetoresistive element and magnetic memory
InactiveUS20070297220A1Easily magnetizedNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsIn planeInter layer
A magnetoresistive includes a first magnetic reference layer having a fixed magnetization direction, a magnetic free layer having a magnetization direction which is changeable by being supplied with spin polarized electrons, a second magnetic reference layer having a fixed magnetization direction, a first intermediate layer provided between the first magnetic reference layer and the magnetic free layer, and a second intermediate layer provided between the magnetic free layer and the second magnetic reference layer. The magnetic free layer and the first magnetic reference layer have directions of easy magnetization perpendicular or parallel to an in-plane direction. The first magnetic reference layer and the second magnetic reference layer have directions of easy magnetization perpendicular to each other.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
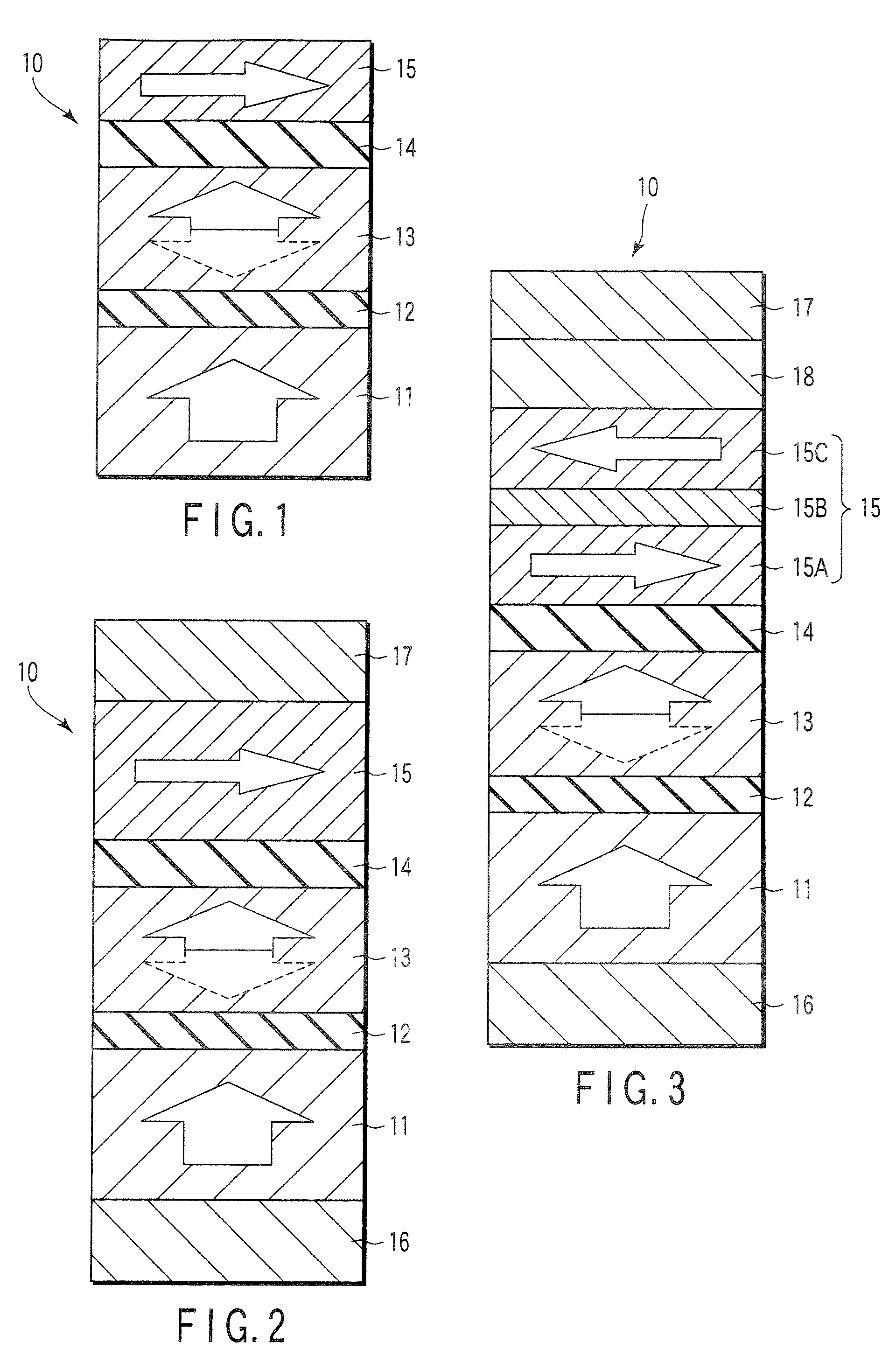
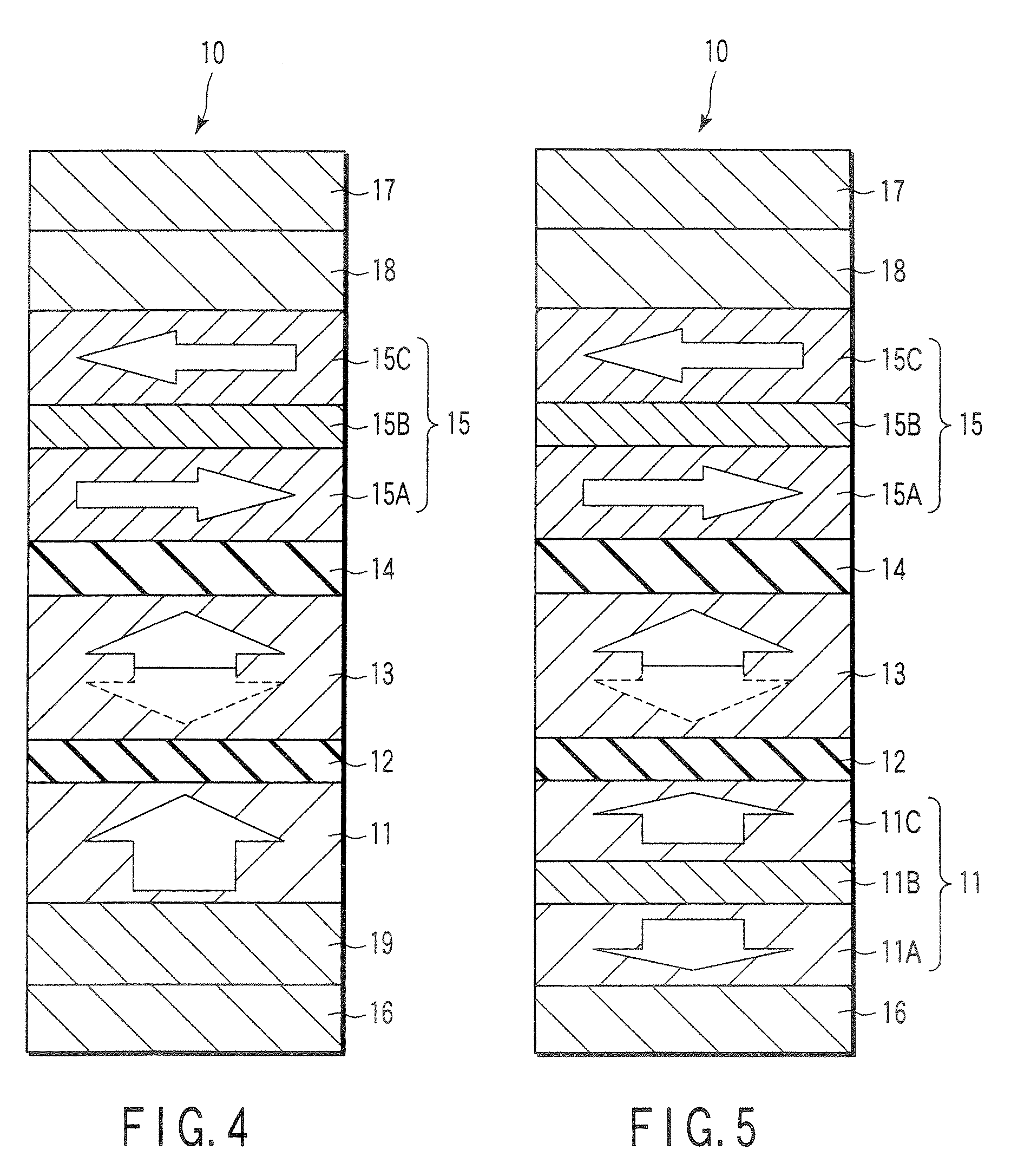
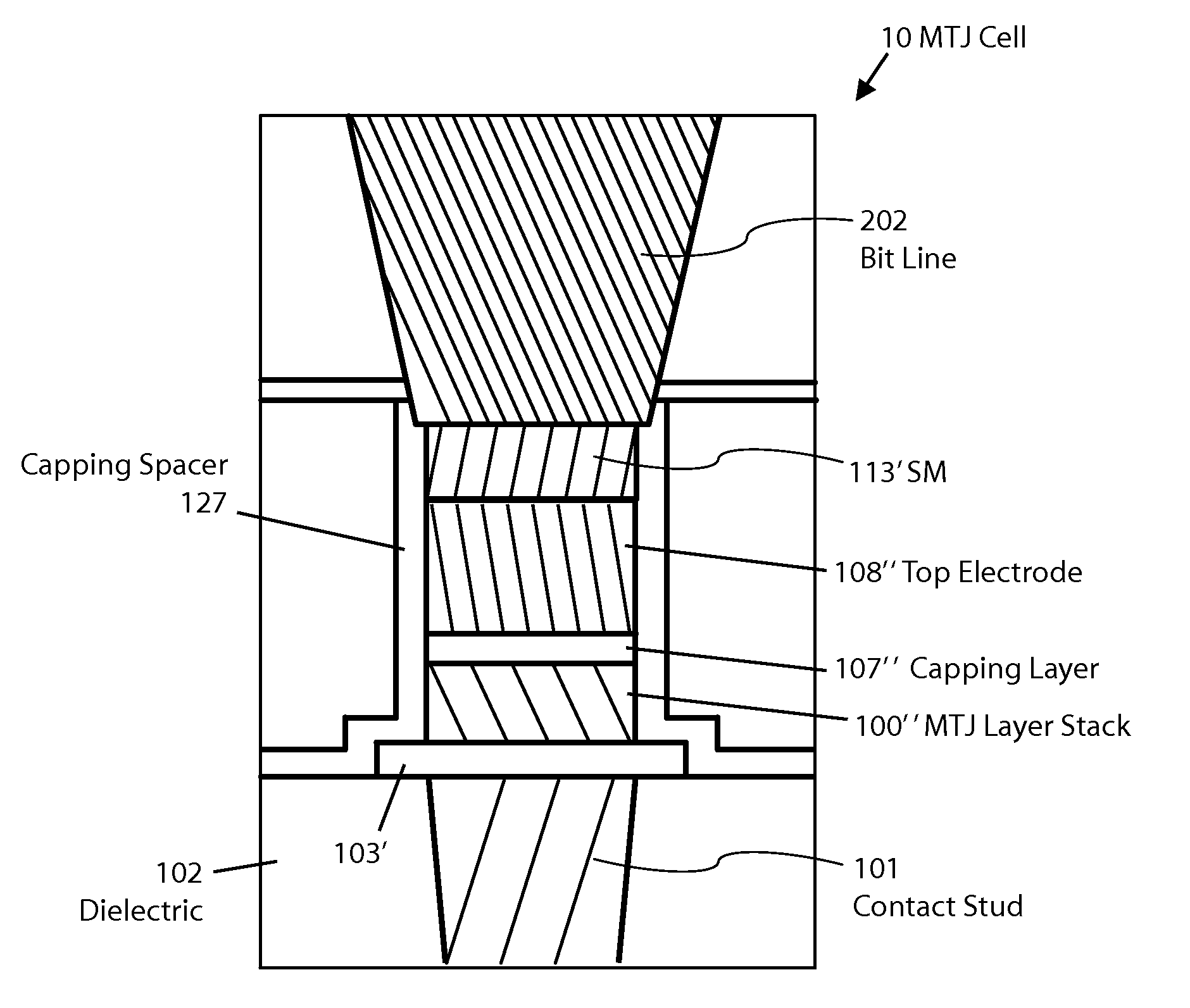
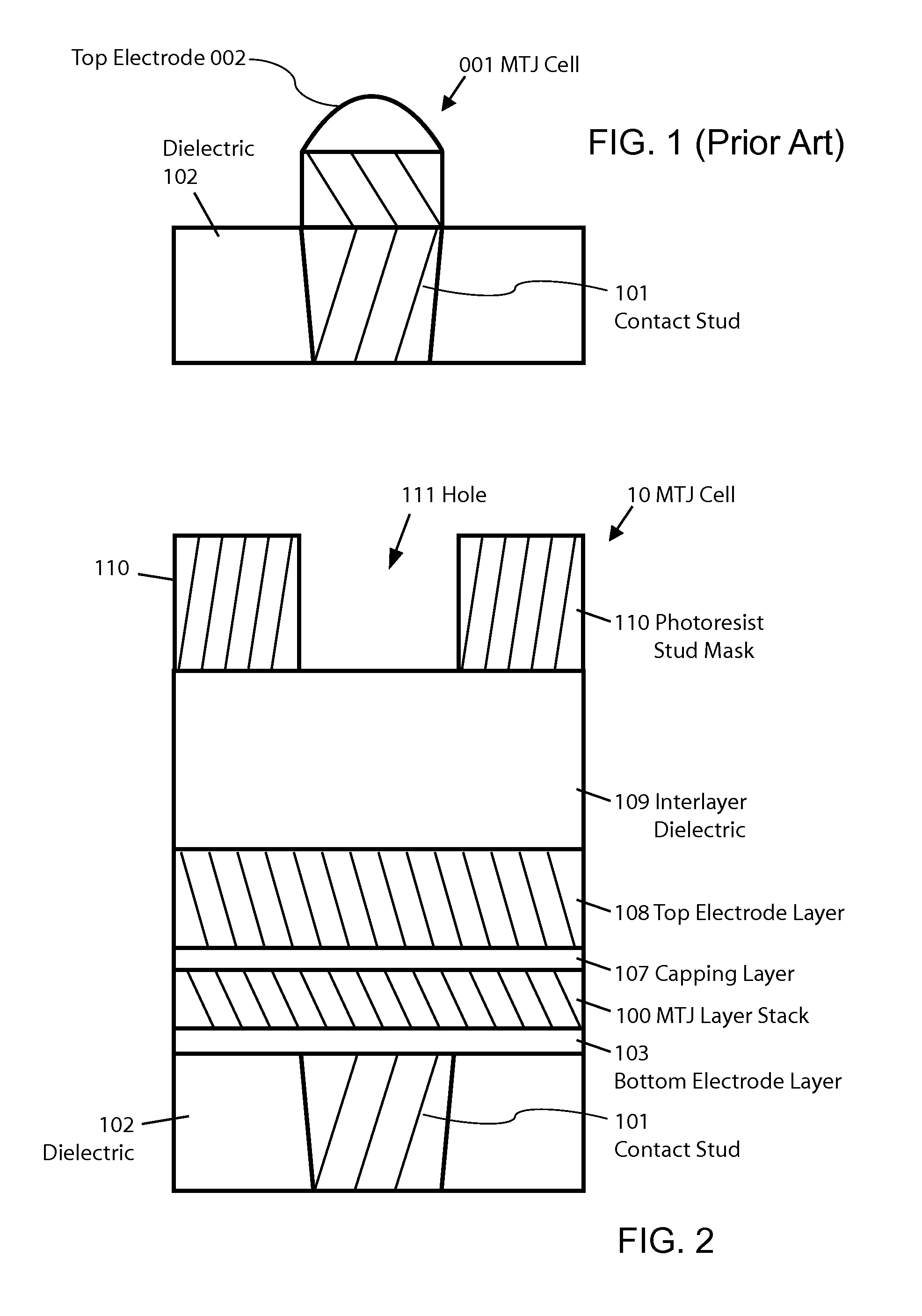
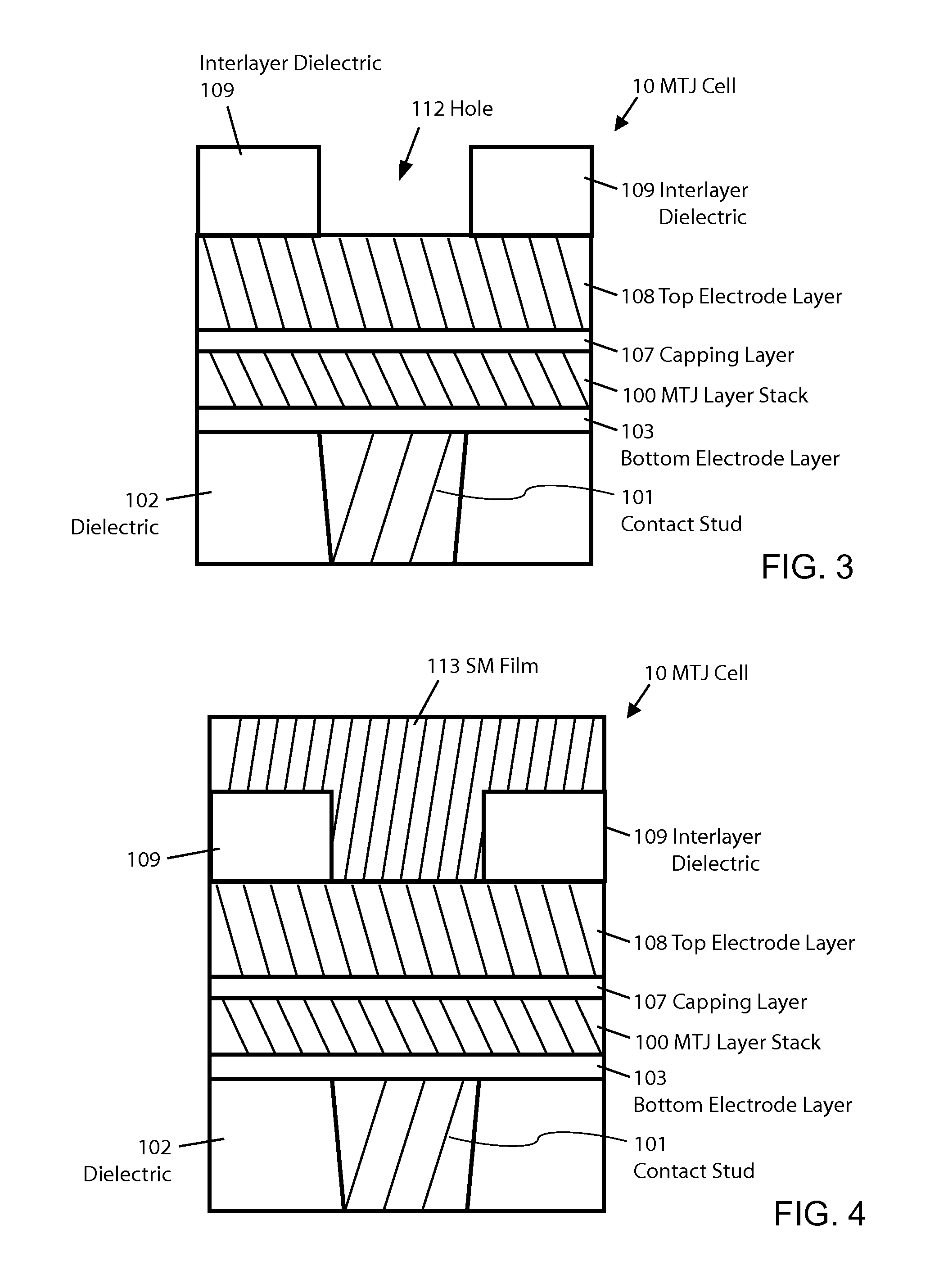
MTJ MRAM with stud patterning
ActiveUS8772888B2Reduce widthImprove errorMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesEtchingConductive materials
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
Spin barrier enhanced dual magnetoresistance effect element and magnetic memory using the same
ActiveUS7057921B2Reduce outer surfaceHigh areal resistanceNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsDamping constantMagnetic memory
A method and system for providing a magnetic element that can be used in a magnetic memory is disclosed. The magnetic element includes first pinned, spacer, free, spin barrier, and second pinned layers. The spacer layer is nonmagnetic and resides between the pinned and free layers. The free layer can be switched using spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element. The free layer resides between the spacer and spin barrier layers. The spin barrier layer is between the free and second pinned layers. The spin barrier layer is configured to reduce an outer surface contribution to the free layer damping constant. In one aspect, the spin barrier layer has a high areal resistance and may substantially eliminate spin pumping induced damping. In another aspect, the magnetic element also includes a spin accumulation layer between the spin barrier and free layers. The spin accumulation layer has a high conductivity and may have a long spin diffusion length.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
Spin-current switched magnetic memory element suitable for circuit integration and method of fabricating the memory element
A magnetic memory element switchable by current injection includes a plurality of magnetic layers, at least one of the plurality of magnetic layers having a perpendicular magnetic anisotropy component and including a current-switchable magnetic moment, and at least one barrier layer formed adjacent to the plurality of magnetic layers (e.g., between two of the magnetic layers). The memory element has the switching threshold current and device impedance suitable for integration with complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) integrated circuits.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
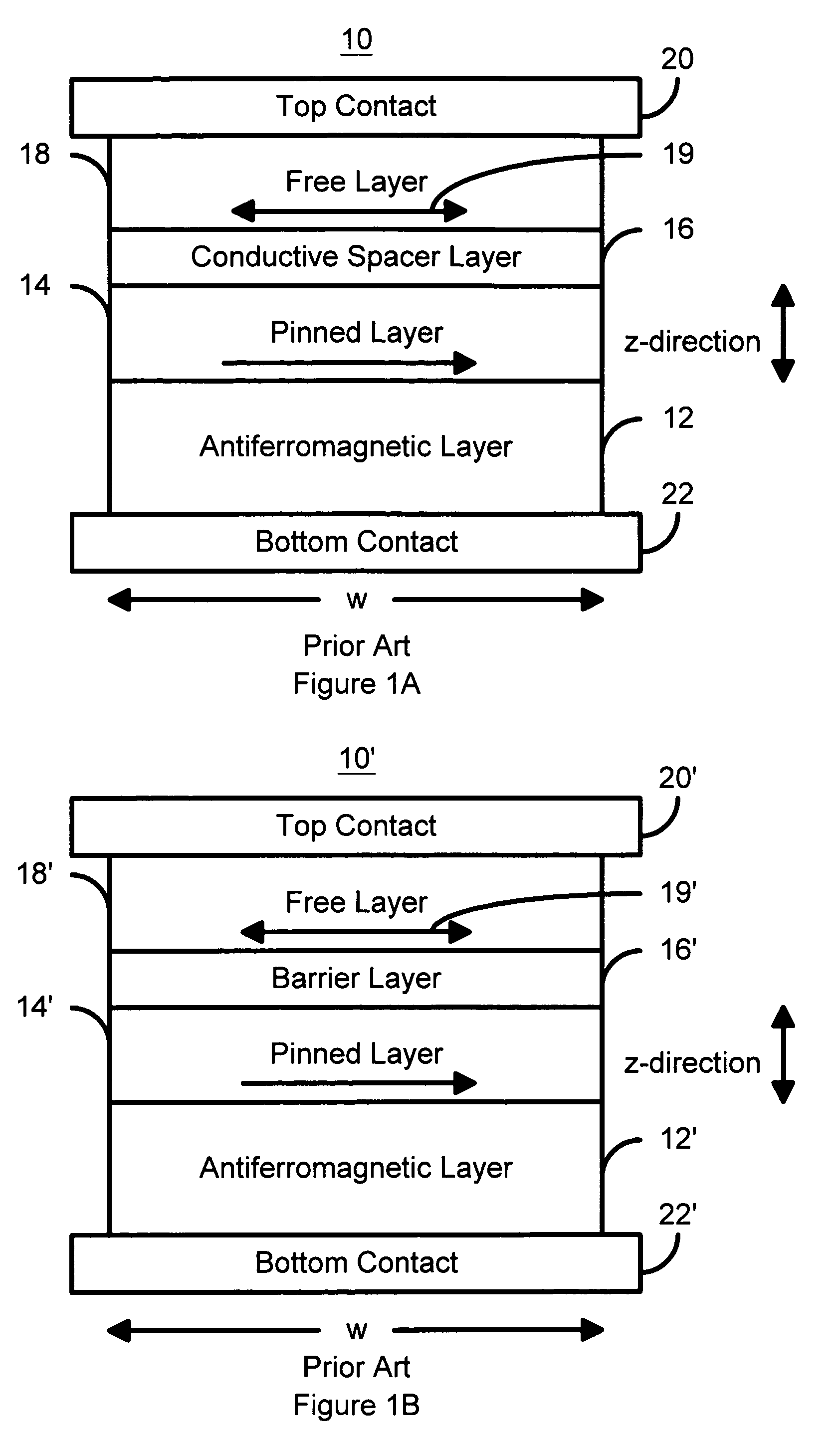
Magnetic element utilizing spin transfer and an MRAM device using the magnetic element
InactiveUS6920063B2Efficient and localized phenomenonEnhanced output signalNanostructure applicationNanomagnetismMagnetic memorySpin transfer
A method and system for providing a magnetic element capable of being written using spin-transfer effect while generating a high output signal and a magnetic memory using the magnetic element are disclosed. The magnetic element includes a first ferromagnetic pinned layer, a nonmagnetic spacer layer, a ferromagnetic free layer, an insulating barrier layer and a second ferromagnetic pinned layer. The pinned layer has a magnetization pinned in a first direction. The nonmagnetic spacer layer is conductive and is between the first pinned layer and the free layer. The barrier layer resides between the free layer and the second pinned layer and is an insulator having a thickness allowing electron tunneling through the barrier layer. The second pinned layer has a magnetization pinned in a second direction. The magnetic element is configured to allow the magnetization of the free layer to change direction due to spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
Method and system for providing a dual spin filter
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
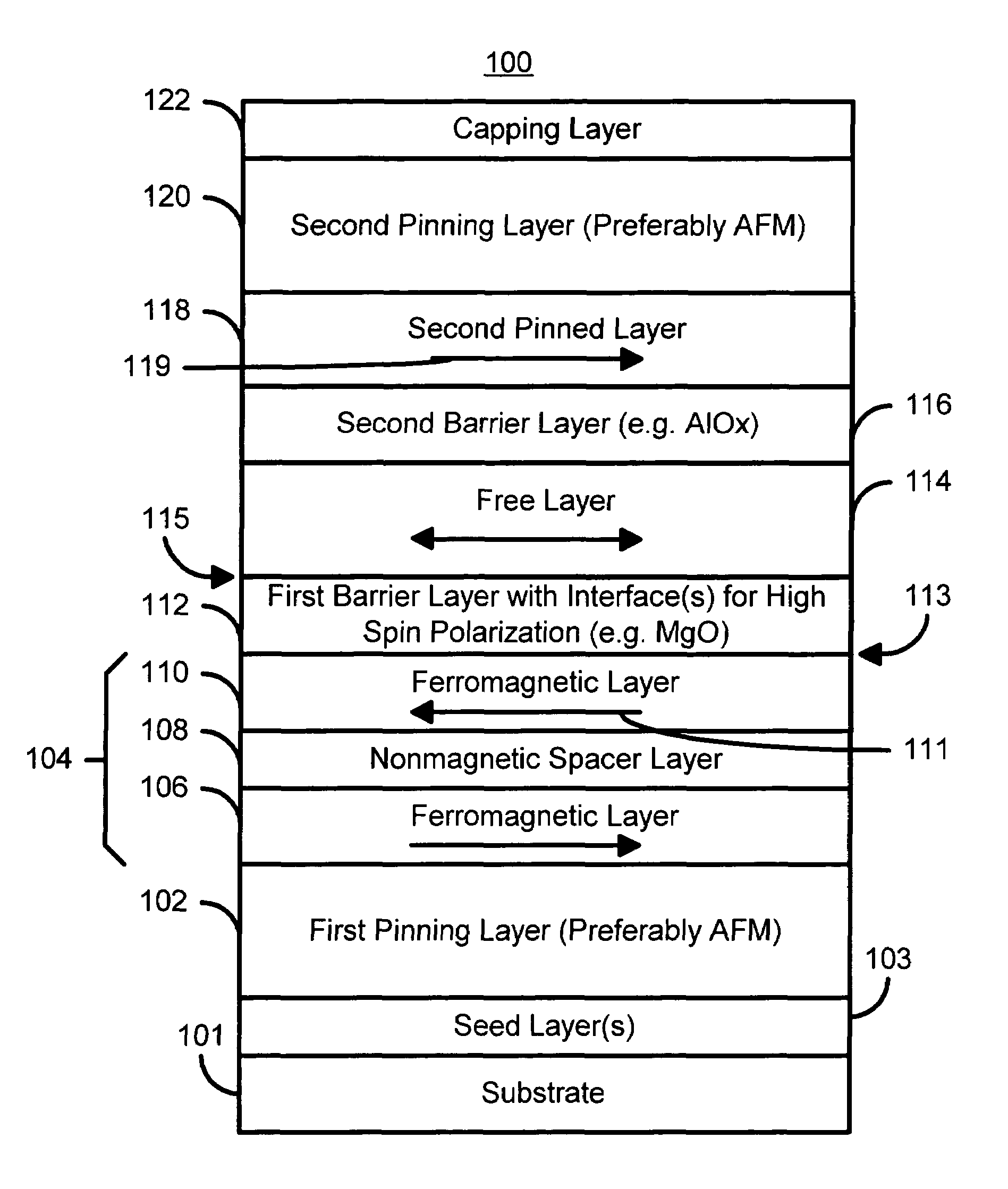
MTJ elements with high spin polarization layers configured for spin-transfer switching and spintronics devices using the magnetic elements
ActiveUS20060141640A1Write currentEnhanced signalNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSpin transferSpin polarization
A method and system for providing a magnetic element are disclosed. The method and system include providing first and second pinned layers, a free layer, and first and second barrier layers between the first and second pinned layers, respectively, and the free layer. The first barrier layer is preferably crystalline MgO, which is insulating, and configured to allow tunneling through the first barrier layer. Furthermore, the first barrier layer has an interface with another layer, such as the free layer or the first pinned layer. The interface has a structure that provides a high spin polarization of at least fifty percent and preferably over eighty percent. The second barrier layer is insulating and configured to allow tunneling through the second barrier layer. The magnetic element is configured to allow the free layer to be switched due to spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
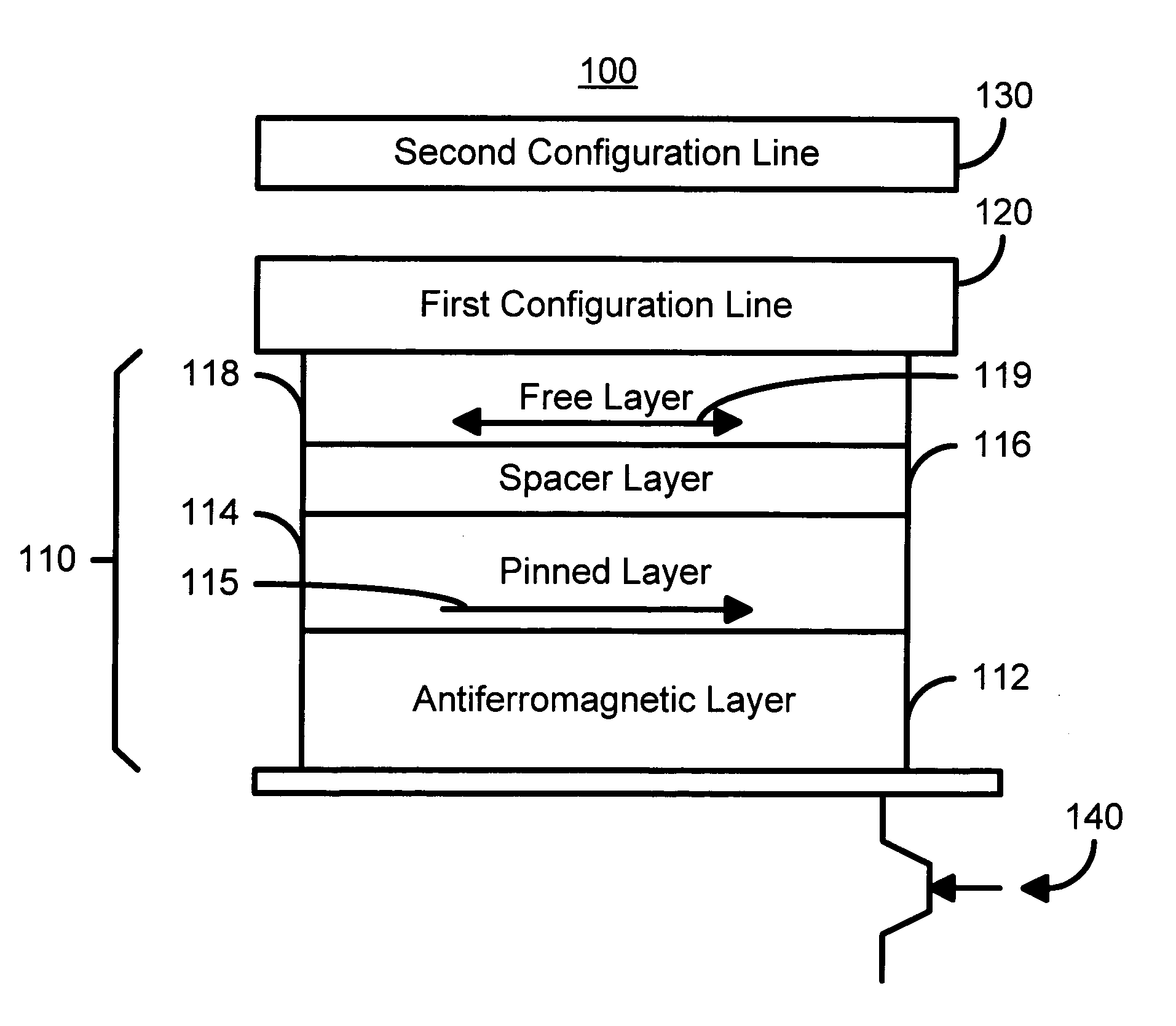
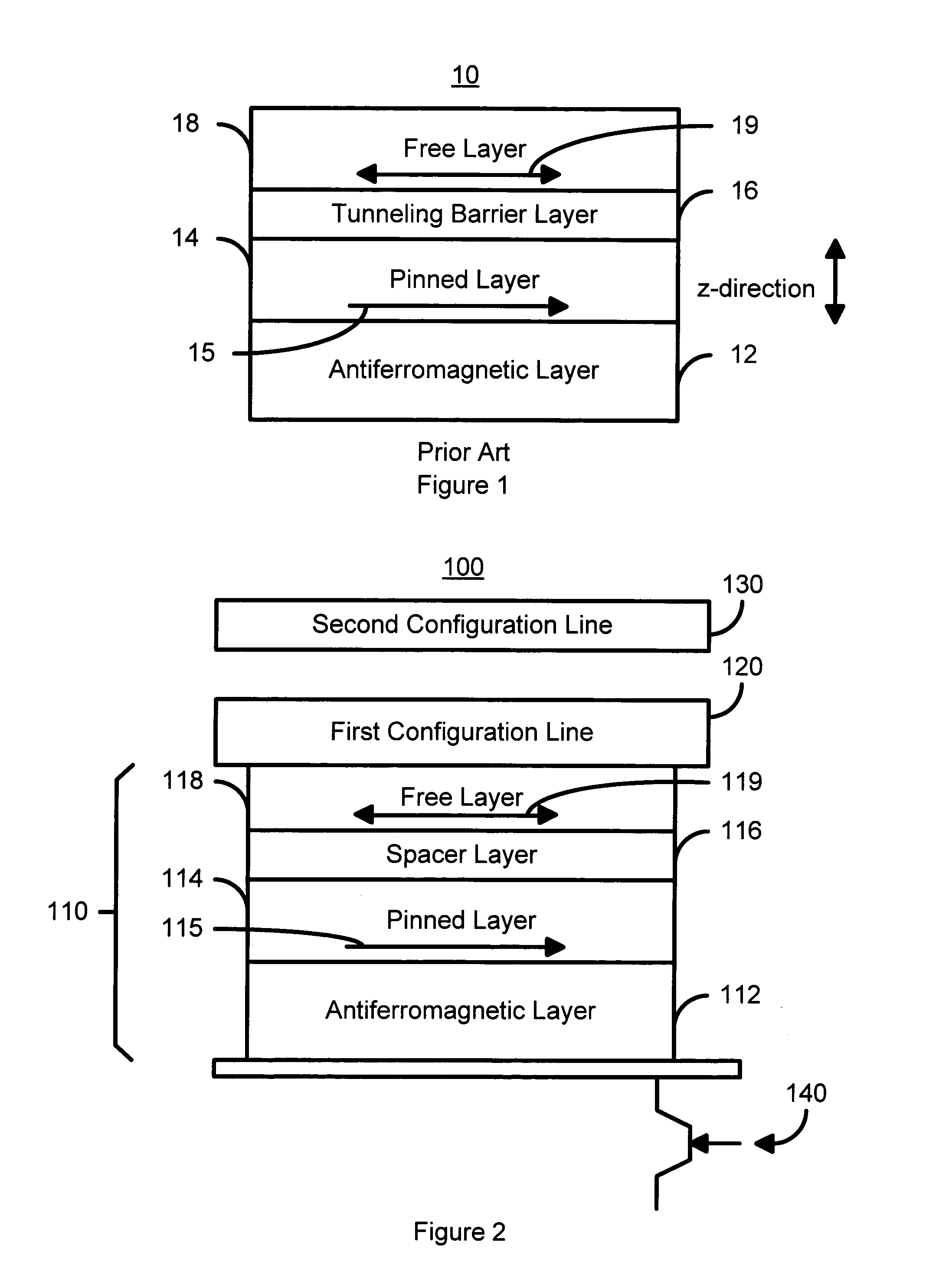
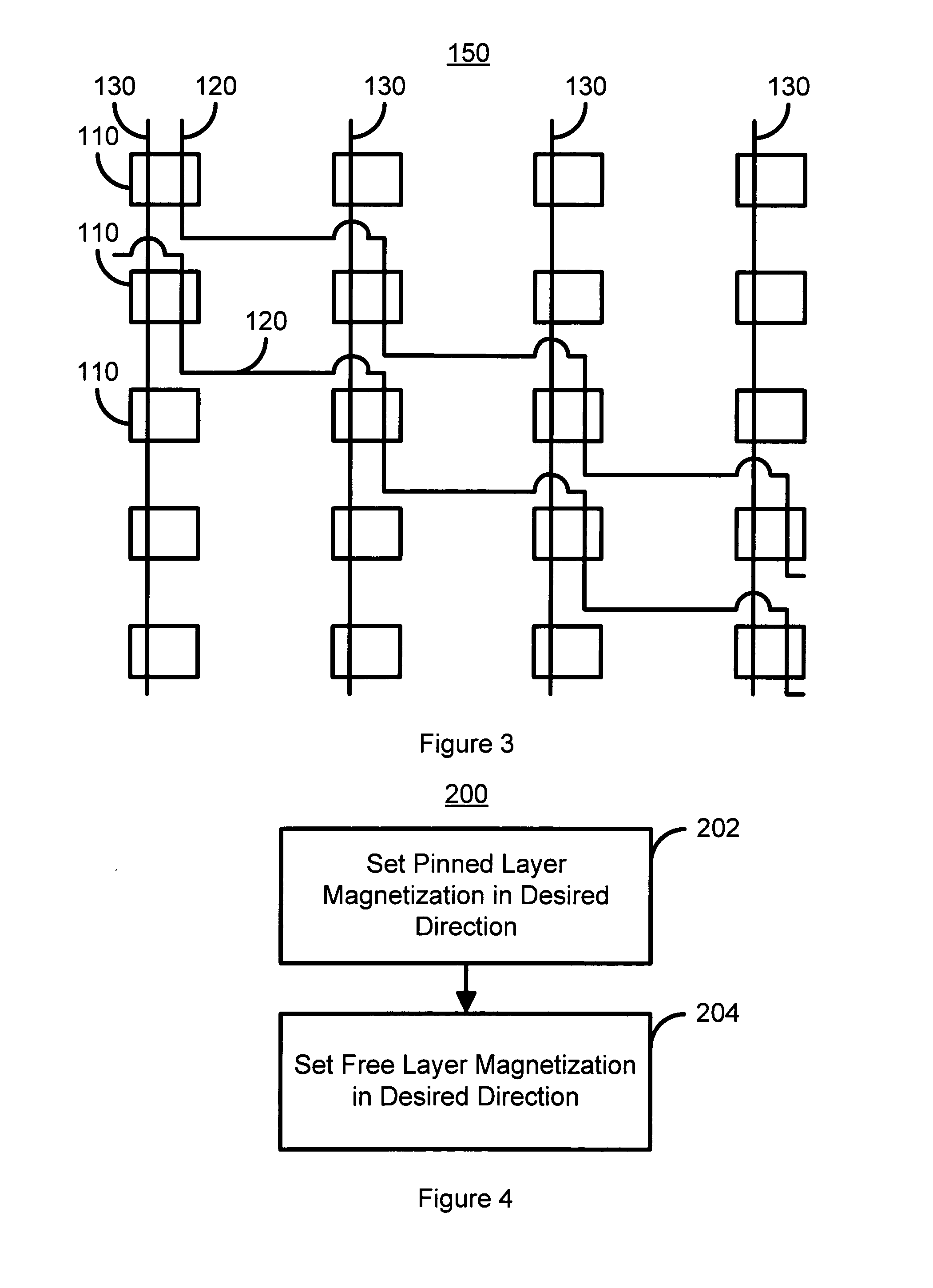
Re-configurable logic elements using heat assisted magnetic tunneling elements
A magnetic logic cell includes a magnetic element having a pinned layer, a free layer, and a spacer layer. The pinned and free layers have pinned and free layer magnetizations. The spacer layer resides between the pinned and free layers. In one aspect, the magnetic logic cell includes a first configuration line that is electrically connected to the magnetic element and carries a first current and a second configuration line electrically that is insulated from the magnetic element and the first configuration line and carries a second current. The first or second current alone cannot switch the free layer magnetization. The first and second currents together can switch the free layer magnetization. When the first current is driven through the magnetic element and the second current is provided, the combination sets the pinned layer magnetization direction. In one aspect, the pinned layer magnetization is set by heating the AFM layer to approximately at or above the blocking temperature. In order to configure the logic cell, an initial direction for the free layer magnetization is also set.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
MTJ elements with high spin polarization layers configured for spin-transfer switching and spintronics devices using the magnetic elements
ActiveUS7241631B2Write currentEnhanced signalNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSpin transferSpin polarization
A method and system for providing a magnetic element are disclosed. The method and system include providing first and second pinned layers, a free layer, and first and second barrier layers between the first and second pinned layers, respectively, and the free layer. The first barrier layer is preferably crystalline MgO, which is insulating, and configured to allow tunneling through the first barrier layer. Furthermore, the first barrier layer has an interface with another layer, such as the free layer or the first pinned layer. The interface has a structure that provides a high spin polarization of at least fifty percent and preferably over eighty percent. The second barrier layer is insulating and configured to allow tunneling through the second barrier layer. The magnetic element is configured to allow the free layer to be switched due to spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
Magnetic element with improved out-of-plane anisotropy for spintronic applications
ActiveUS20120205758A1Without degrading thermal stability and MR ratioEnhanced interfacial perpendicular anisotropyMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionPerpendicular anisotropyAlloy
A magnetic element is disclosed wherein first and second interfaces of a free layer with a Hk enhancing layer and tunnel barrier, respectively, produce enhanced surface perpendicular anisotropy to lower switching current or increase thermal stability in a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ). In a MTJ with a bottom spin valve configuration where the Hk enhancing layer is an oxide, the capping layer contacting the Hk enhancing layer is selected to have a free energy of oxide formation substantially greater than that of the oxide. The free layer may be a single layer or composite comprised of an Fe rich alloy such as Co20Fe60B20. With a thin free layer, the interfacial perpendicular anisotropy may dominate the shape anisotropy to generate a magnetization perpendicular to the planes of the layers. The magnetic element may be part of a spintronic device or serve as a propagation medium in a domain wall motion device.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
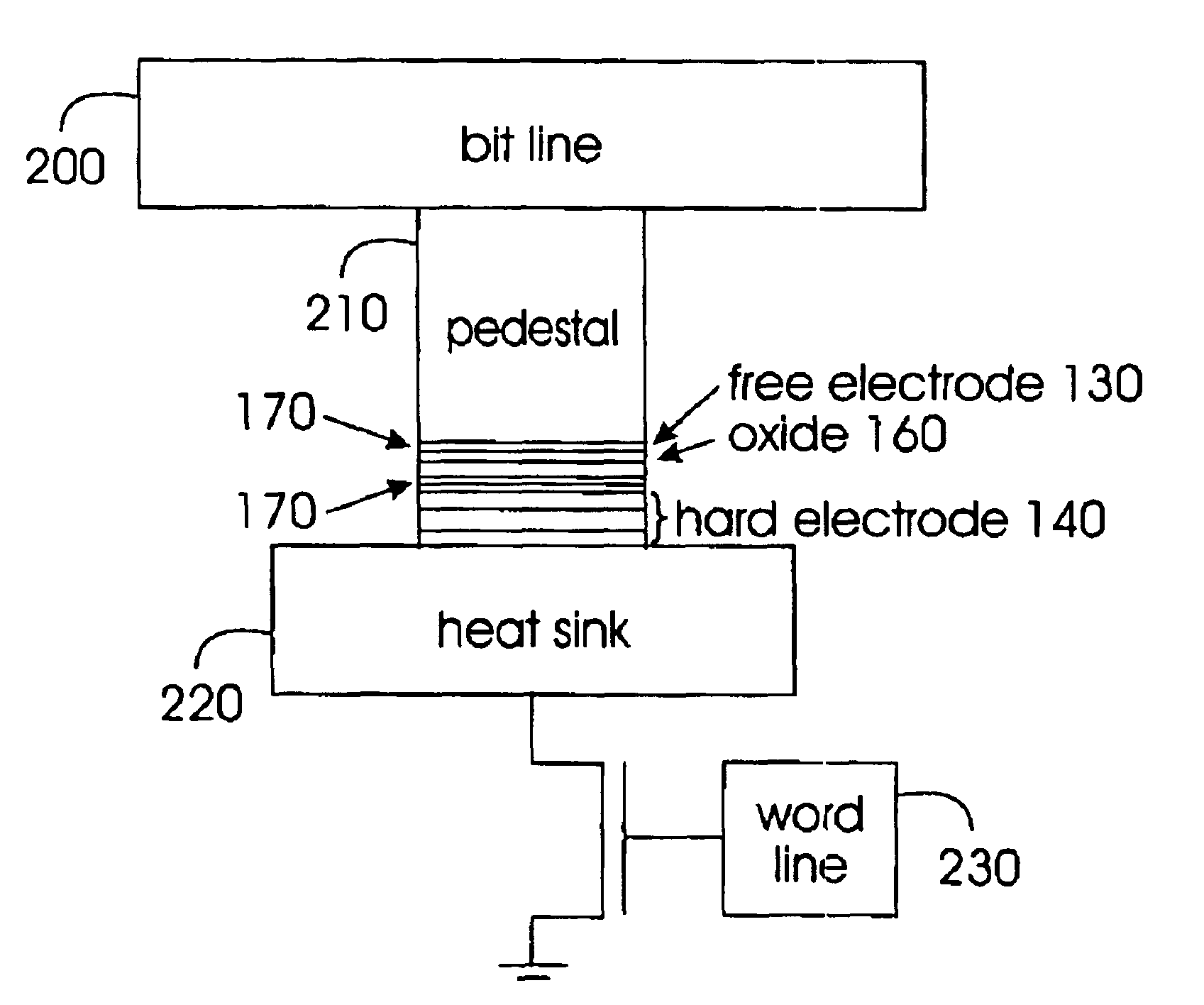
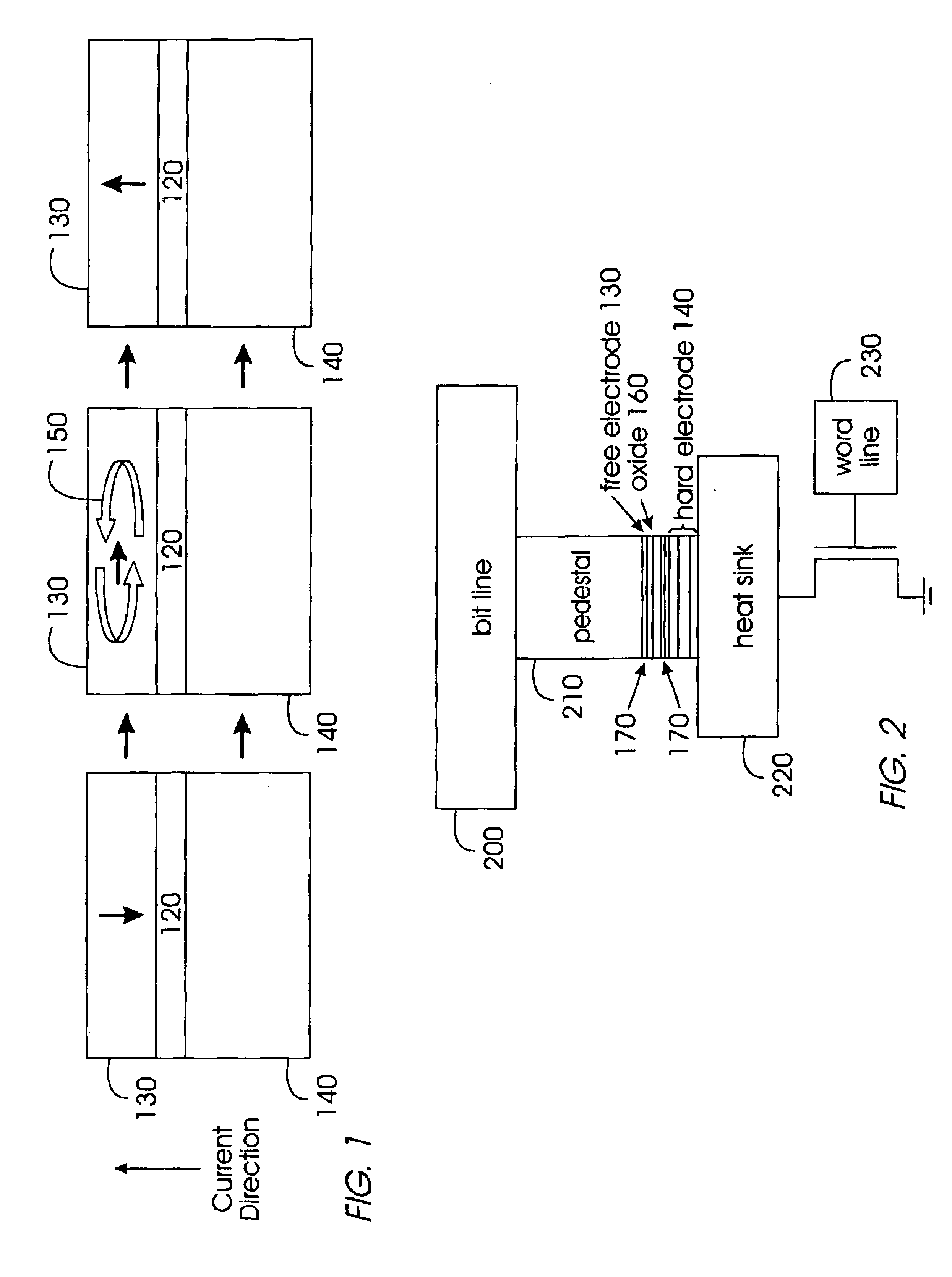
Thermally-assisted magnetic writing using an oxide layer and current-induced heating
InactiveUS6771534B2Increase in sizeIncrease in coercivityNanostructure applicationNanomagnetismElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrical conductor
A method and structure for a non-volatile magnetic random access memory (MRAM) device that has a stable magnetic electrode, an oxide layer adjacent the stable magnetic electrode, and a free magnetic electrode. The oxide layer is between the stable magnetic electrode and the free magnetic electrode. In the invention, a conductor is connected to a stable magnetic electrode. The oxide layer has a resistance at levels to allow sufficient power dissipation to lower the anisotropy of the free magnetic electrode through current induced heating. Current-induced heating is used in combination with spin-transfer torque or a magnetic field to switch the free magnetic electrode.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
High performance MTJ element for STT-RAM and method for making the same
ActiveUS20090027810A1Low angular dispersionEasy to operateNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSpin angular momentum of lightDamping factor
We describe the structure and method of forming a STT-MTJ MRAM cell that utilizes transfer of spin angular momentum as a mechanism for changing the magnetic moment direction of a free layer. The device includes an IrMn pinning layer, a SyAP pinned layer, a naturally oxidized, crystalline MgO tunneling barrier layer that is formed on an Ar-ion plasma smoothed surface of the pinned layer and, in one embodiment, a free layer that comprises an amorphous layer of Co60Fe20B20. of approximately 20 angstroms thickness formed between two crystalline layers of Fe of 3 and 6 angstroms thickness respectively. The free layer is characterized by a low Gilbert damping factor and by very strong polarizing action on conduction electrons. The resulting cell has a low critical current, a high dR / R and a plurality of such cells will exhibit a low variation of both resistance and pinned layer magnetization angular dispersion.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
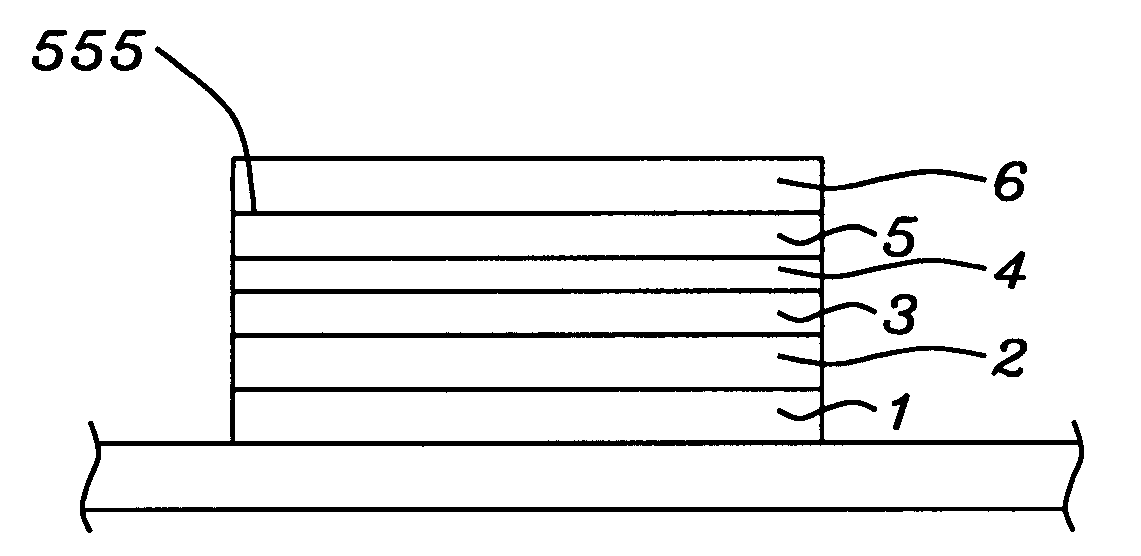
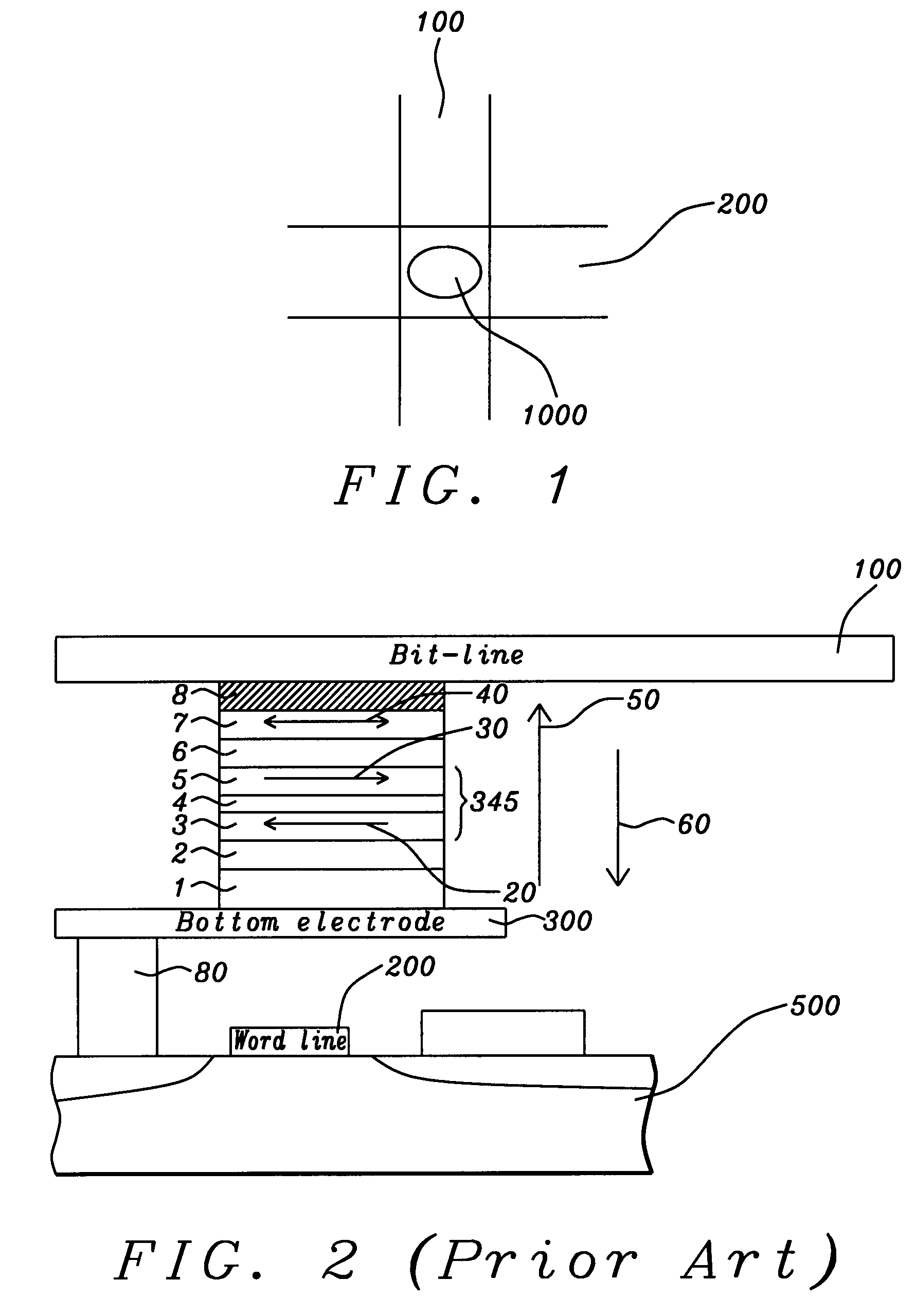
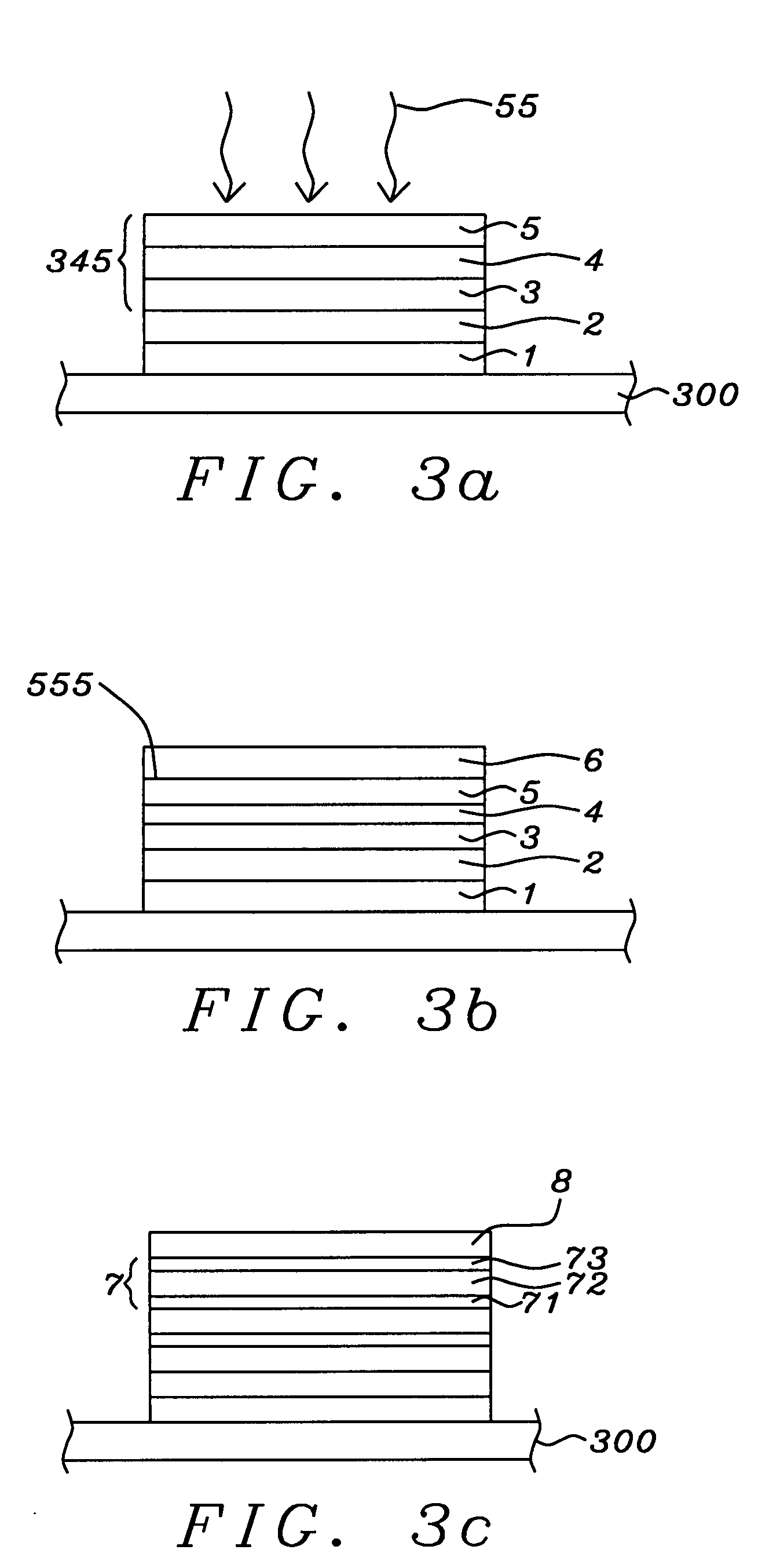
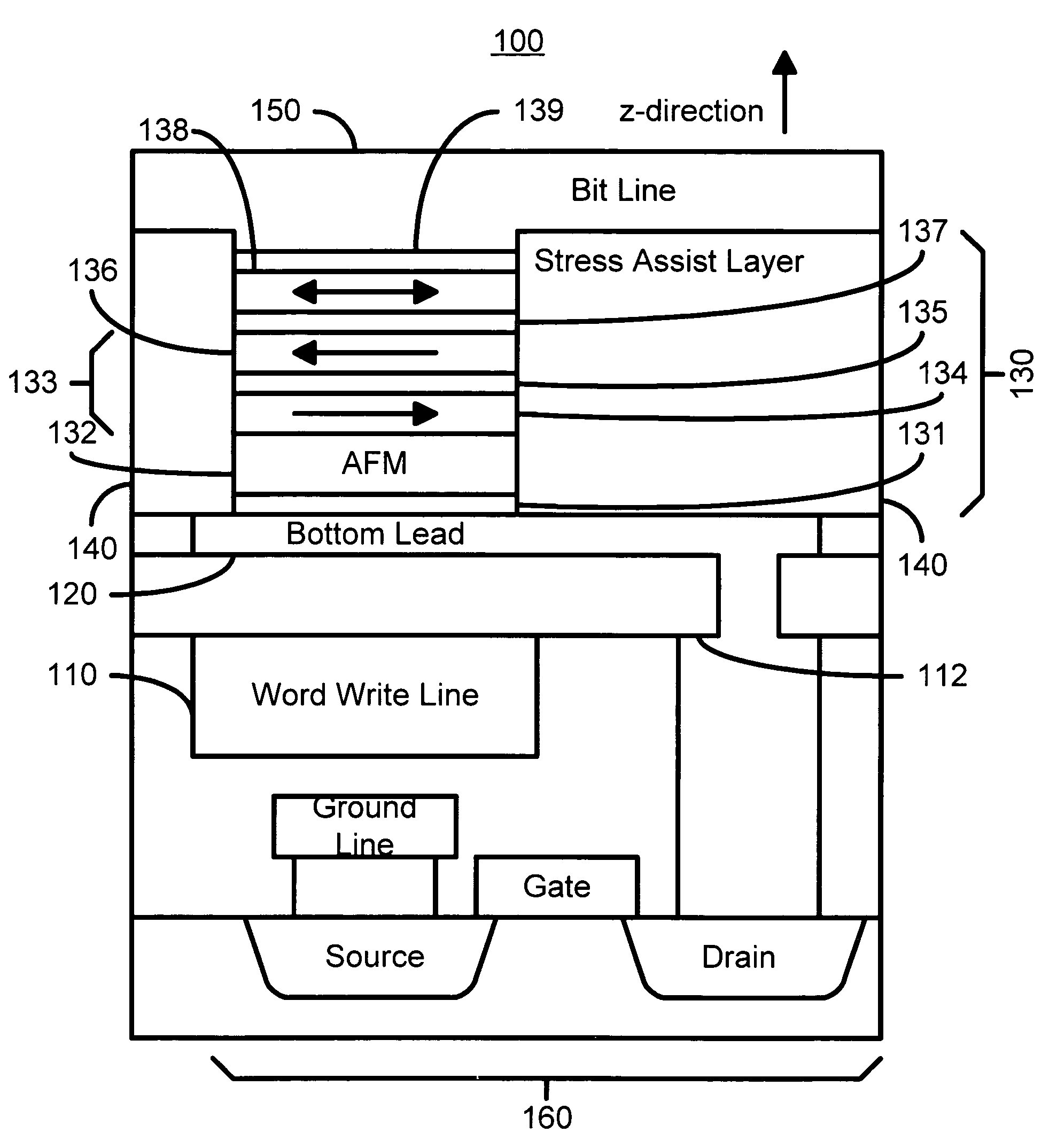
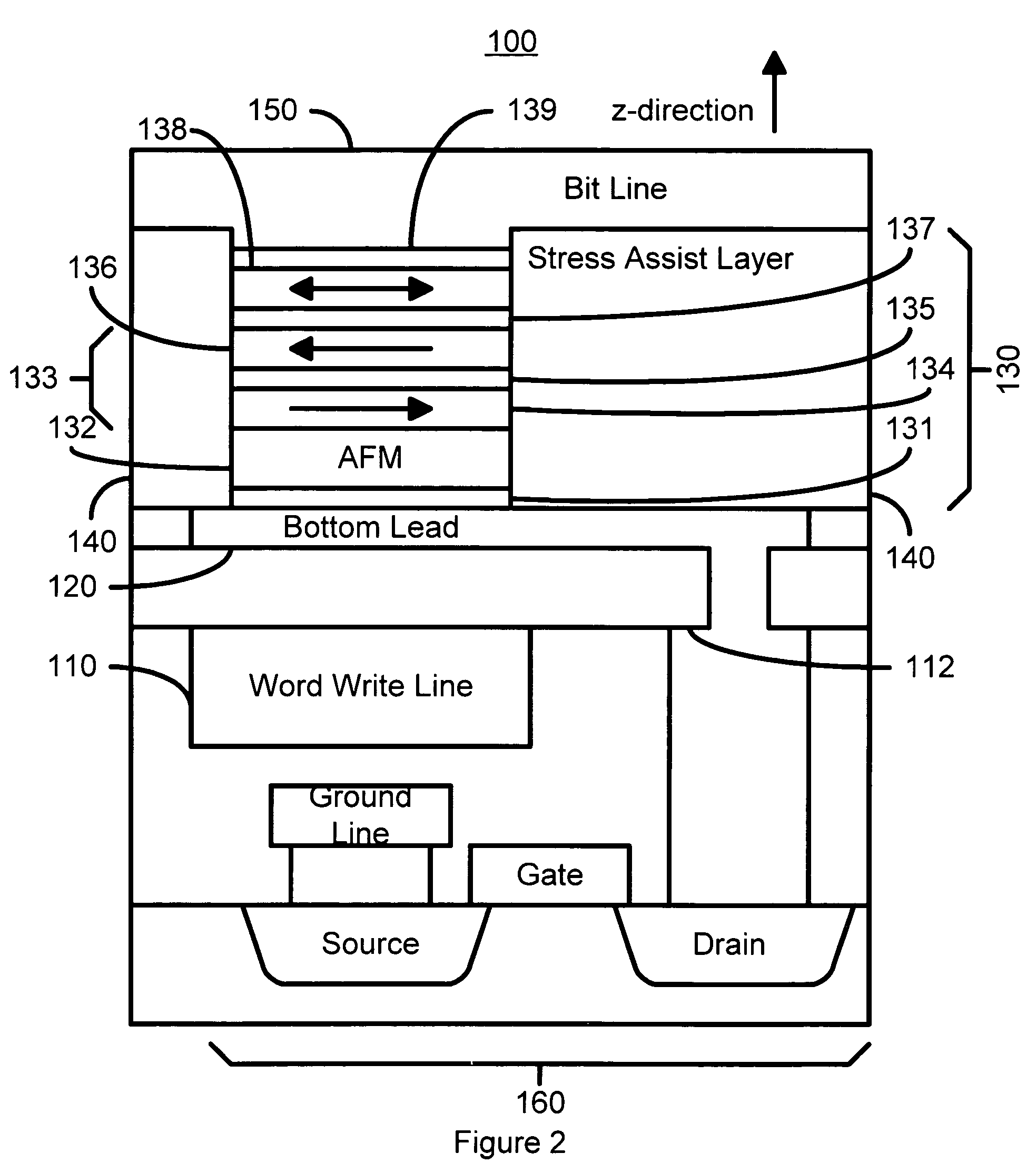
Stress assisted current driven switching for magnetic memory applications
A method and system for providing a magnetic memory is disclosed. The method and system include providing a plurality of magnetic elements and providing at least one stress-assist layer. Each of the plurality of magnetic elements is configured to be written using spin transfer. The at least one stress-assist layer is configured to exert at least one stress on at least one magnetic element of the plurality of magnetic elements during writing. The reduction of spin-transfer switching current is due to stress exerted by the stress-assist layer on the magnetic elements during writing. Stability of the magnetic memory with respect to thermal fluctuations is not compromised because the energy barrier between the two magnetization states is unchanged once the switching current is turned off.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com