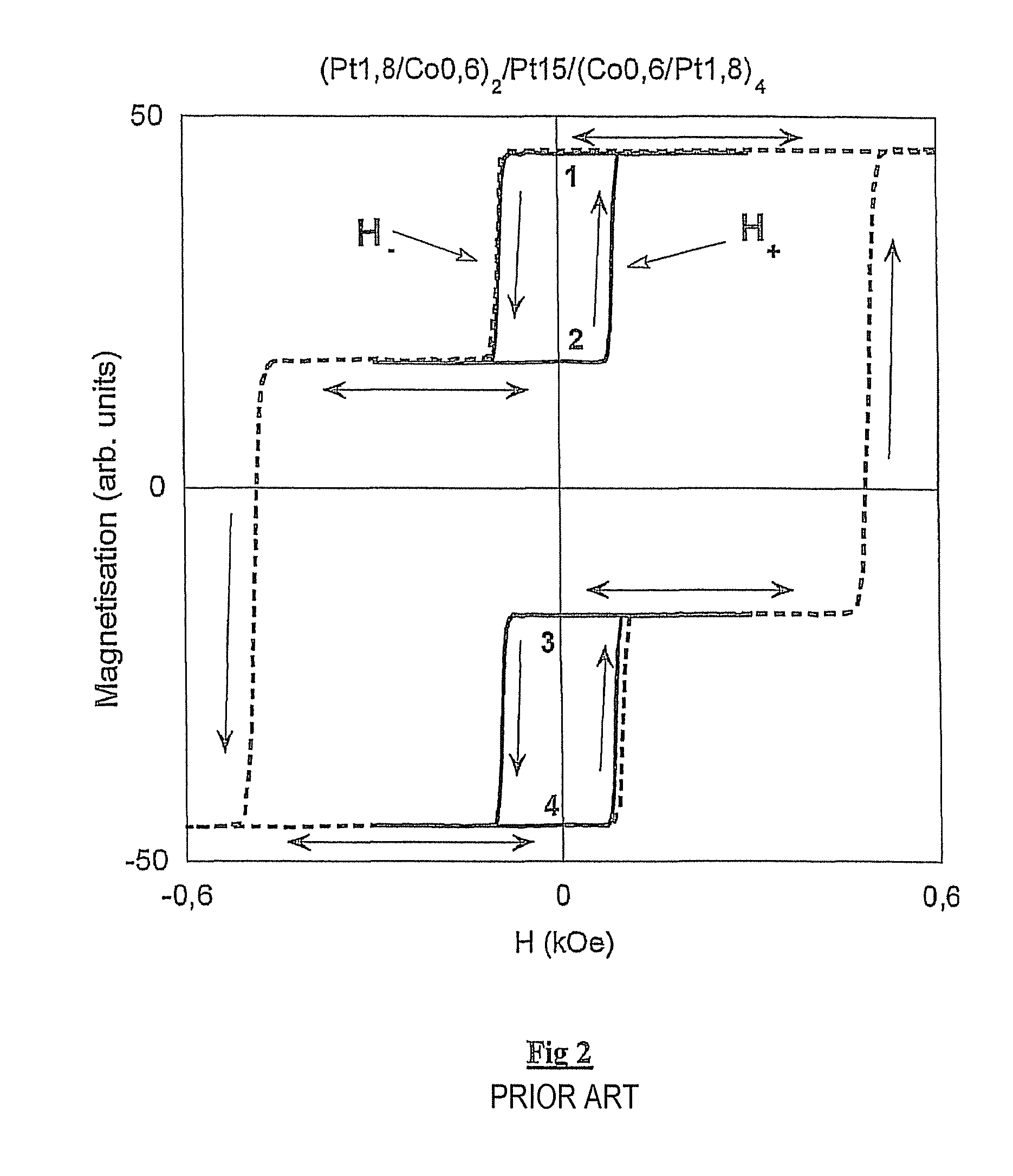
Patents
Literature
145 results about "Perpendicular magnetization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
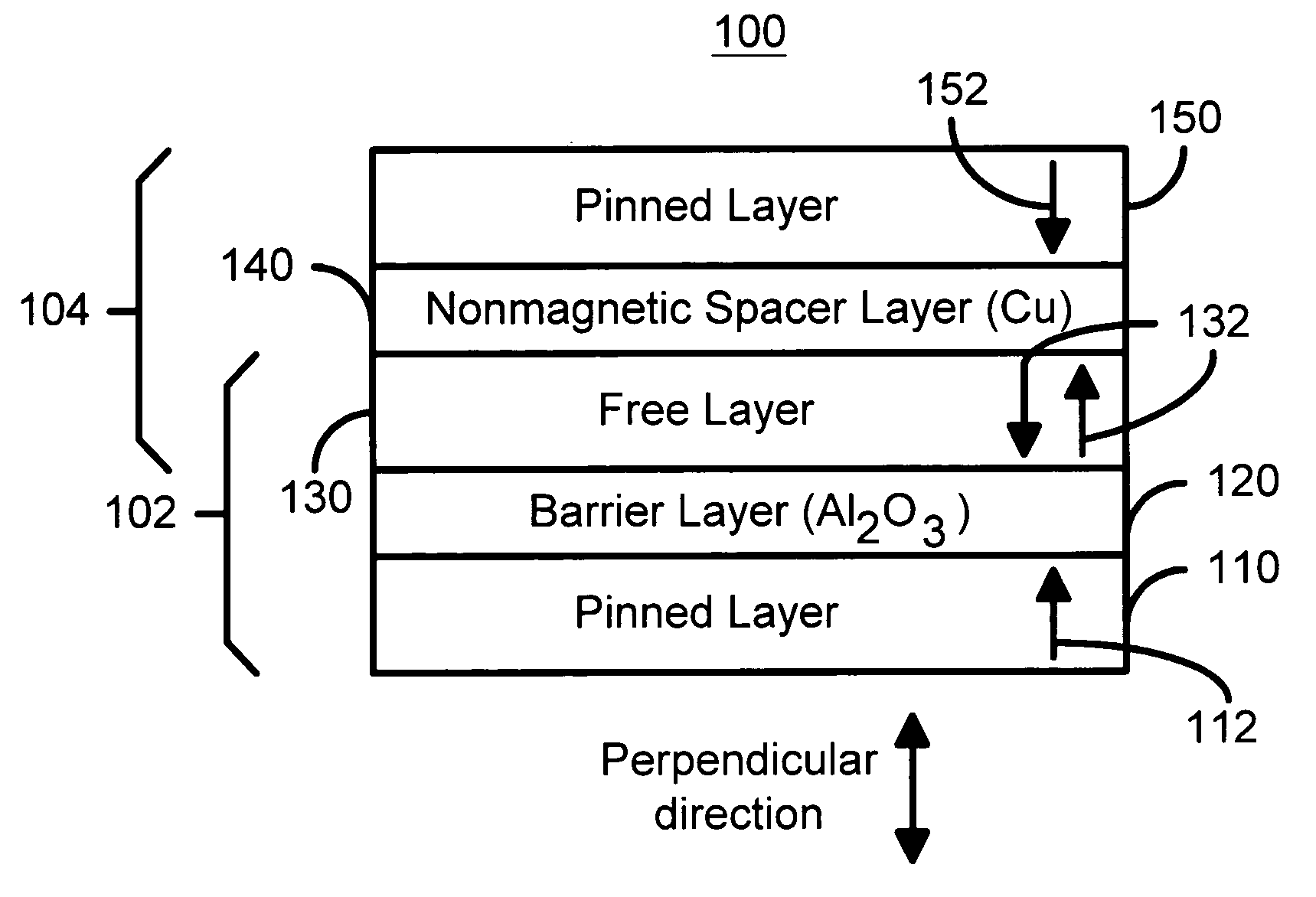
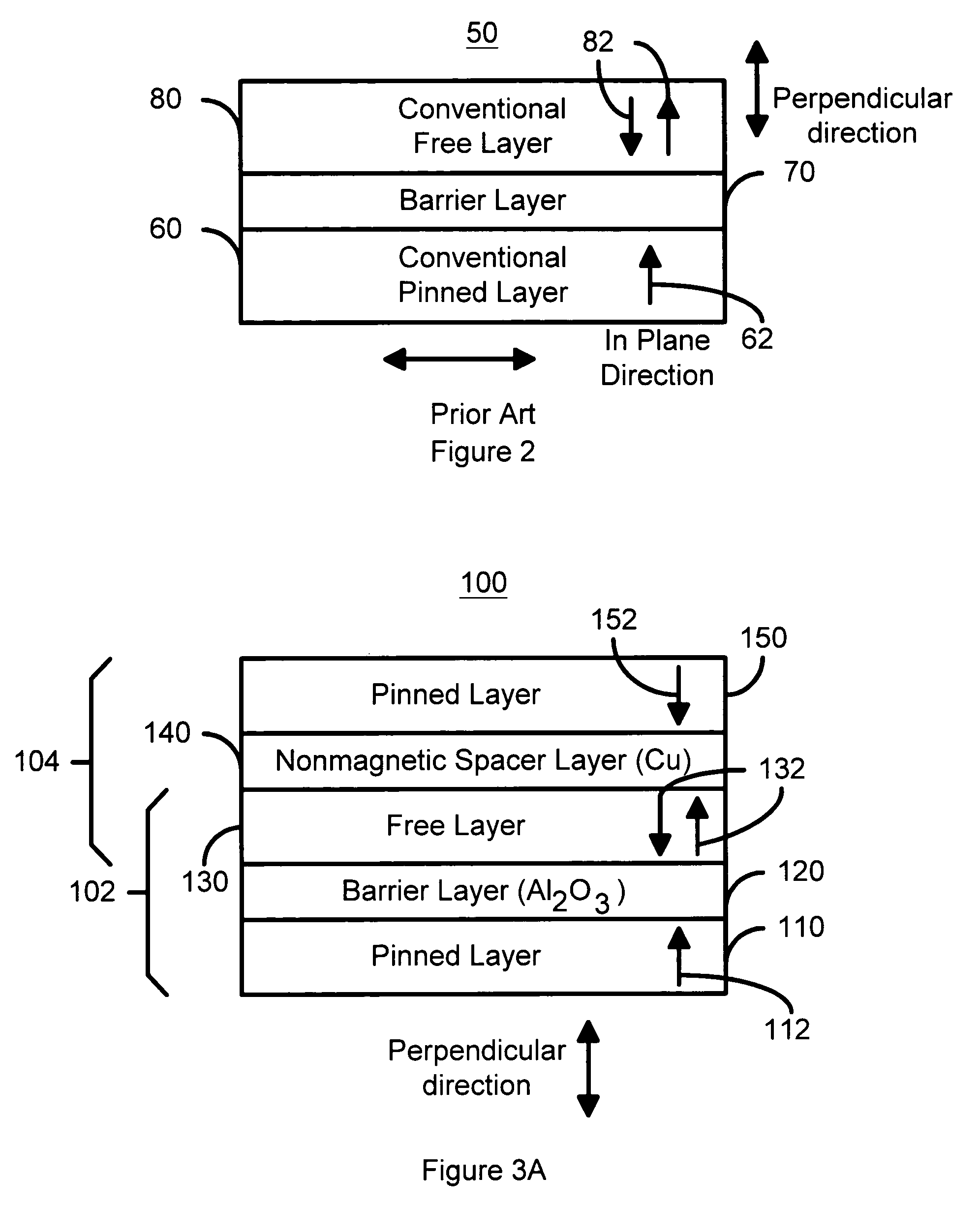
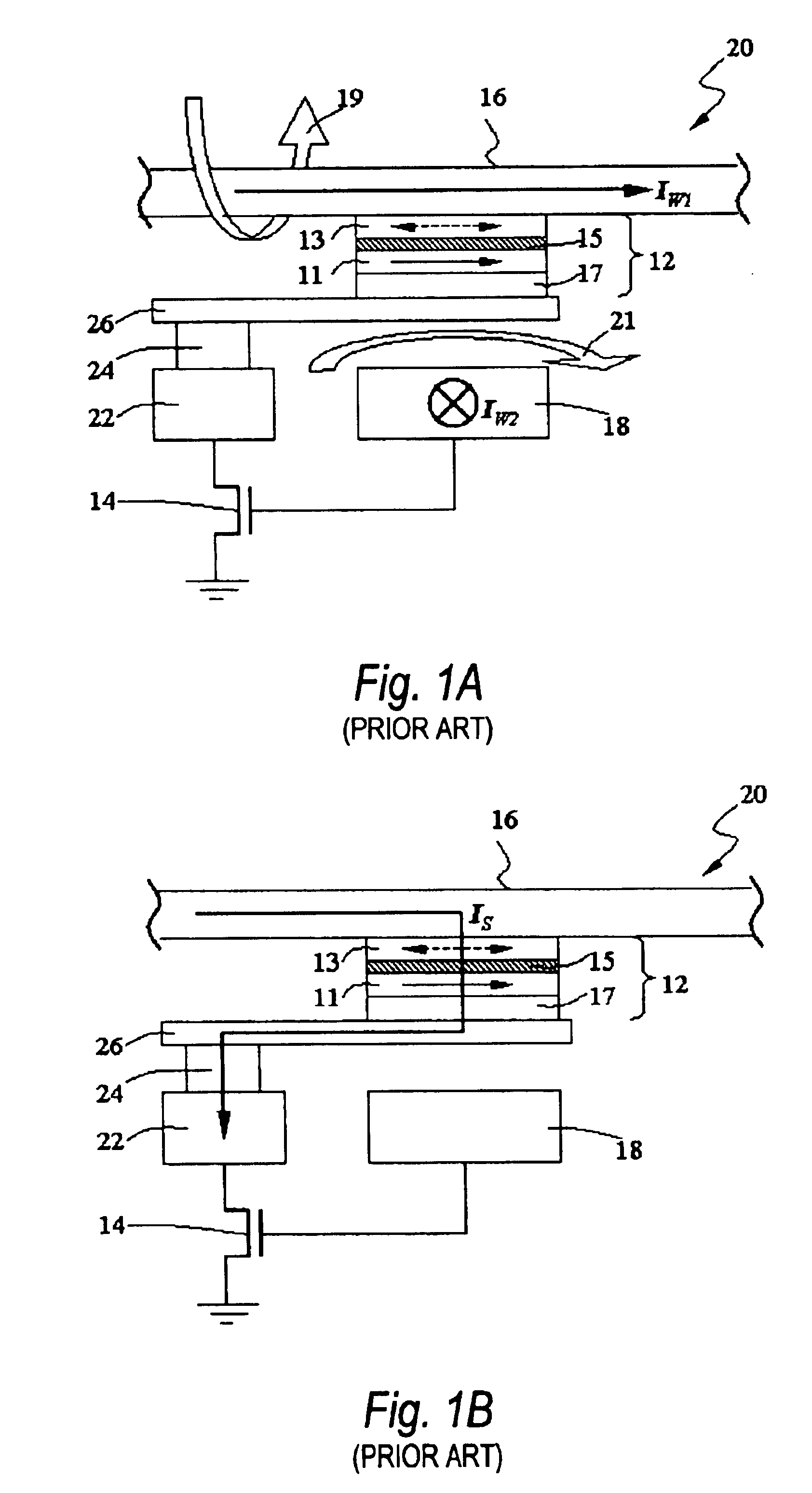
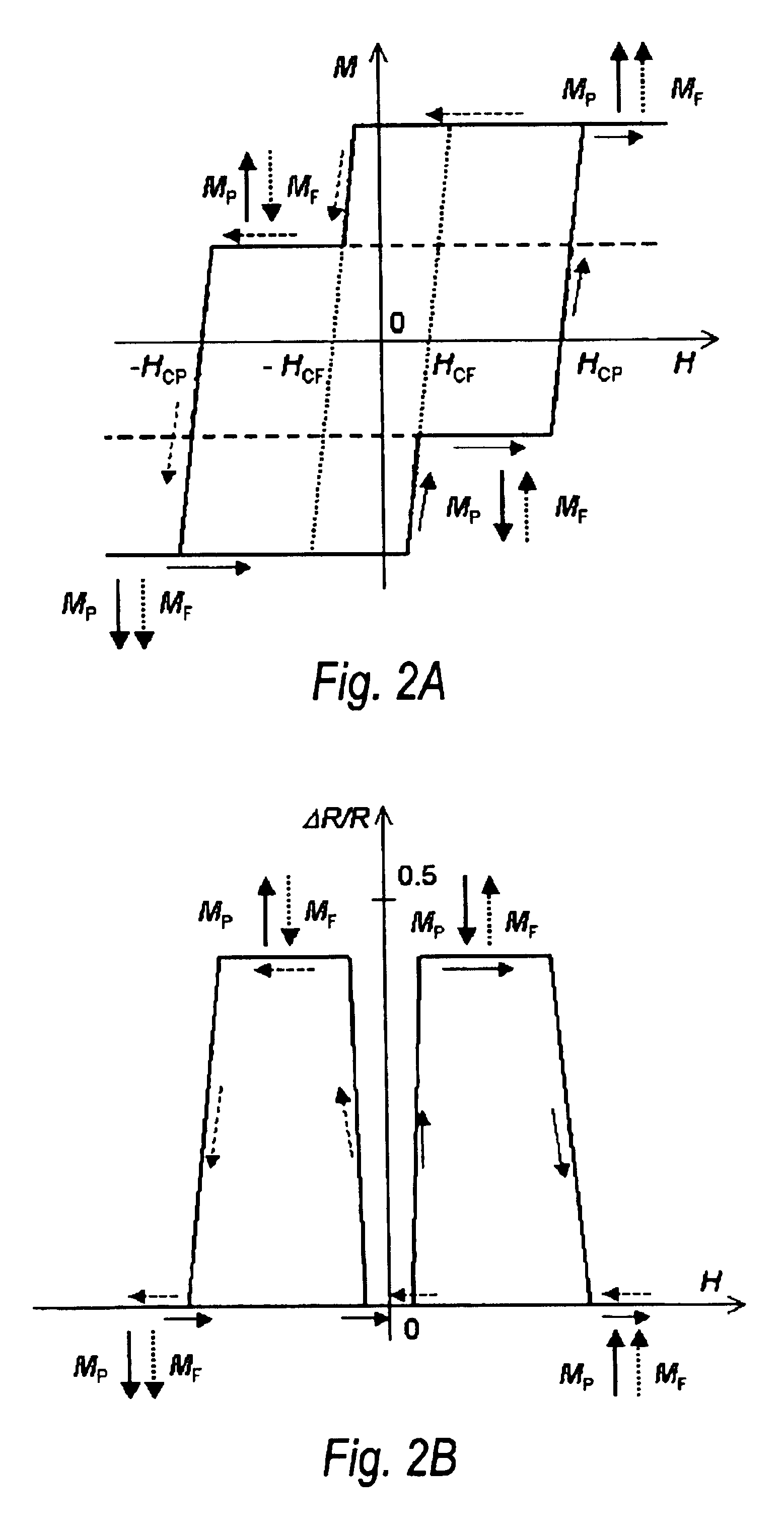
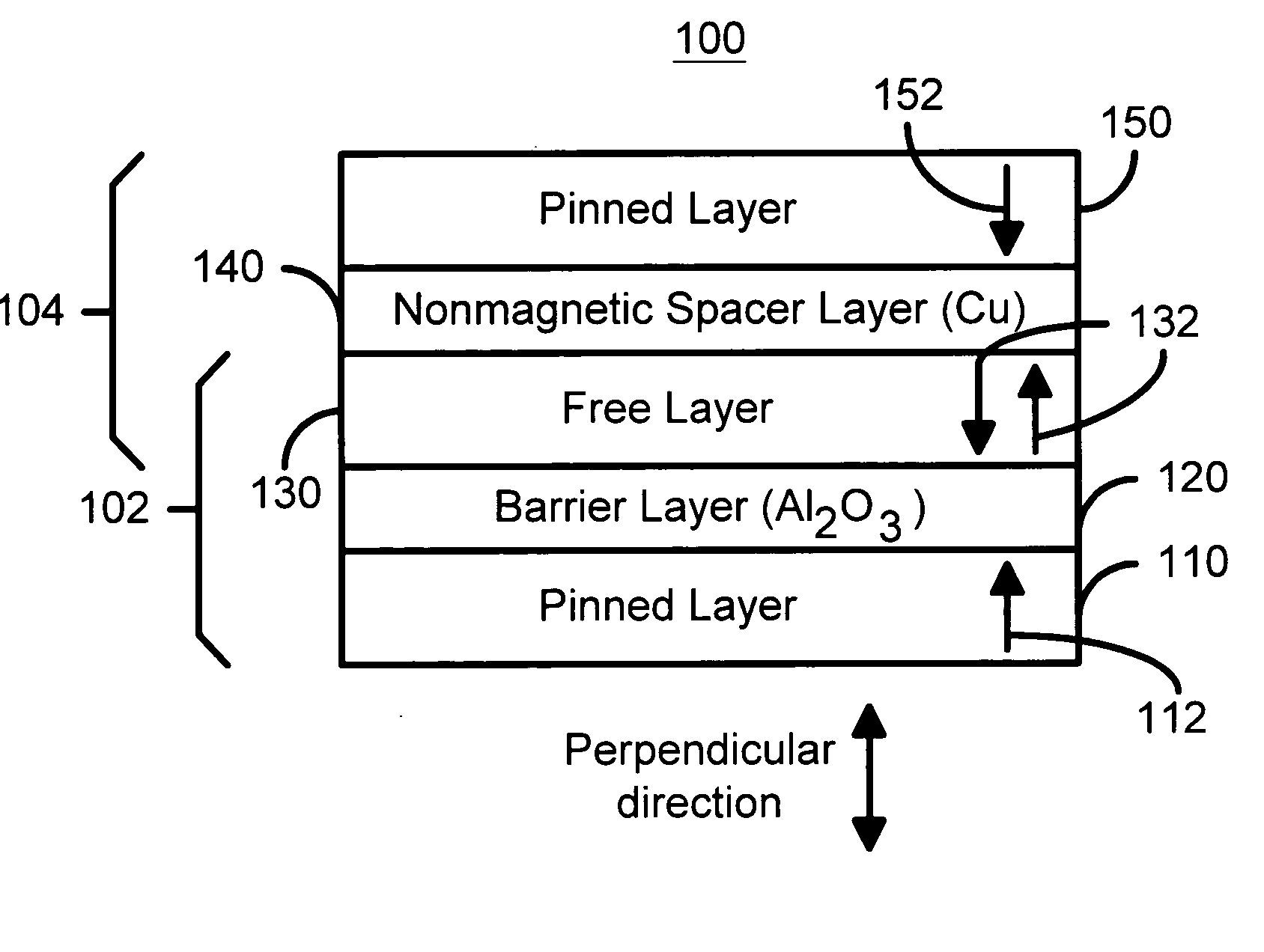
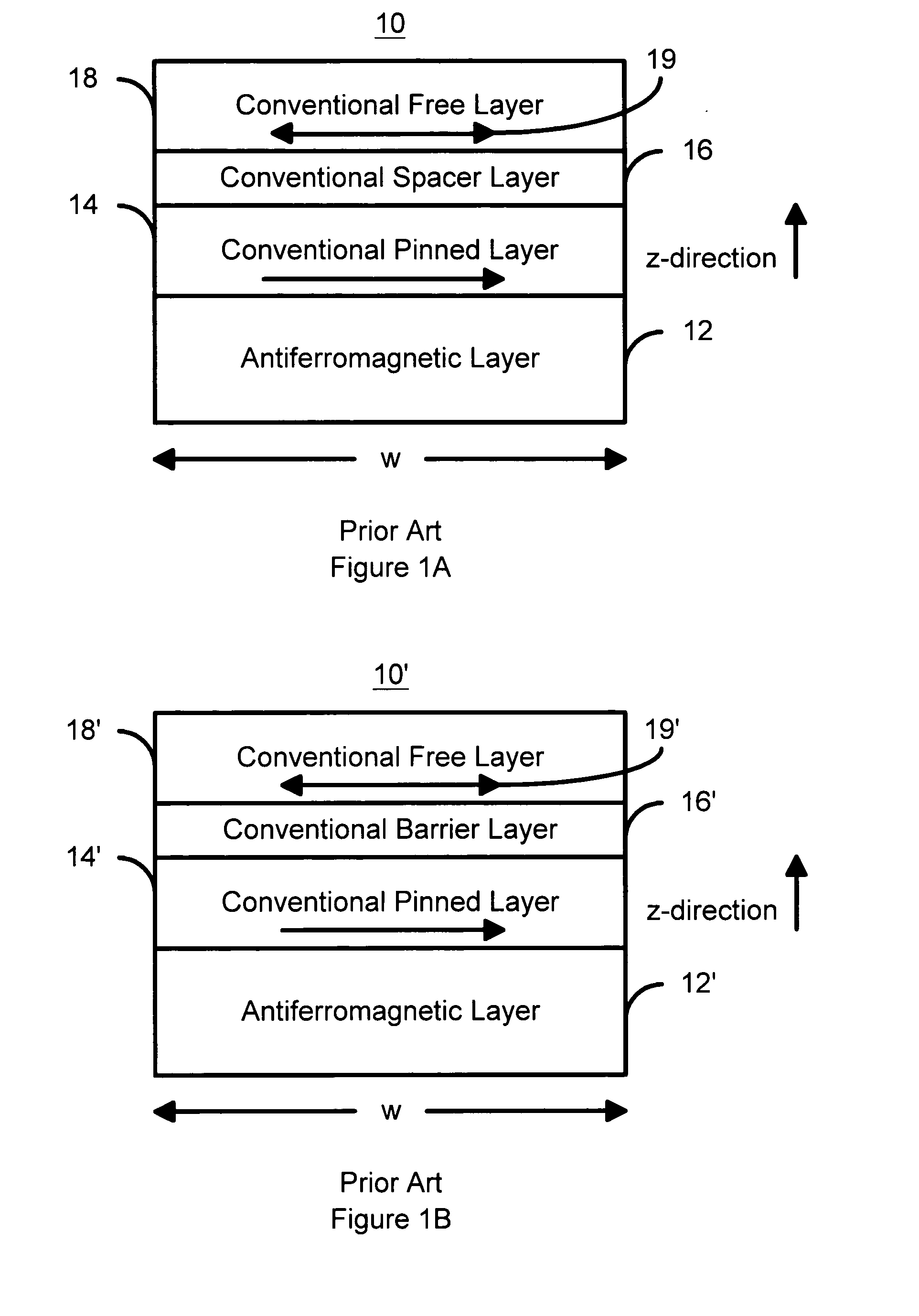
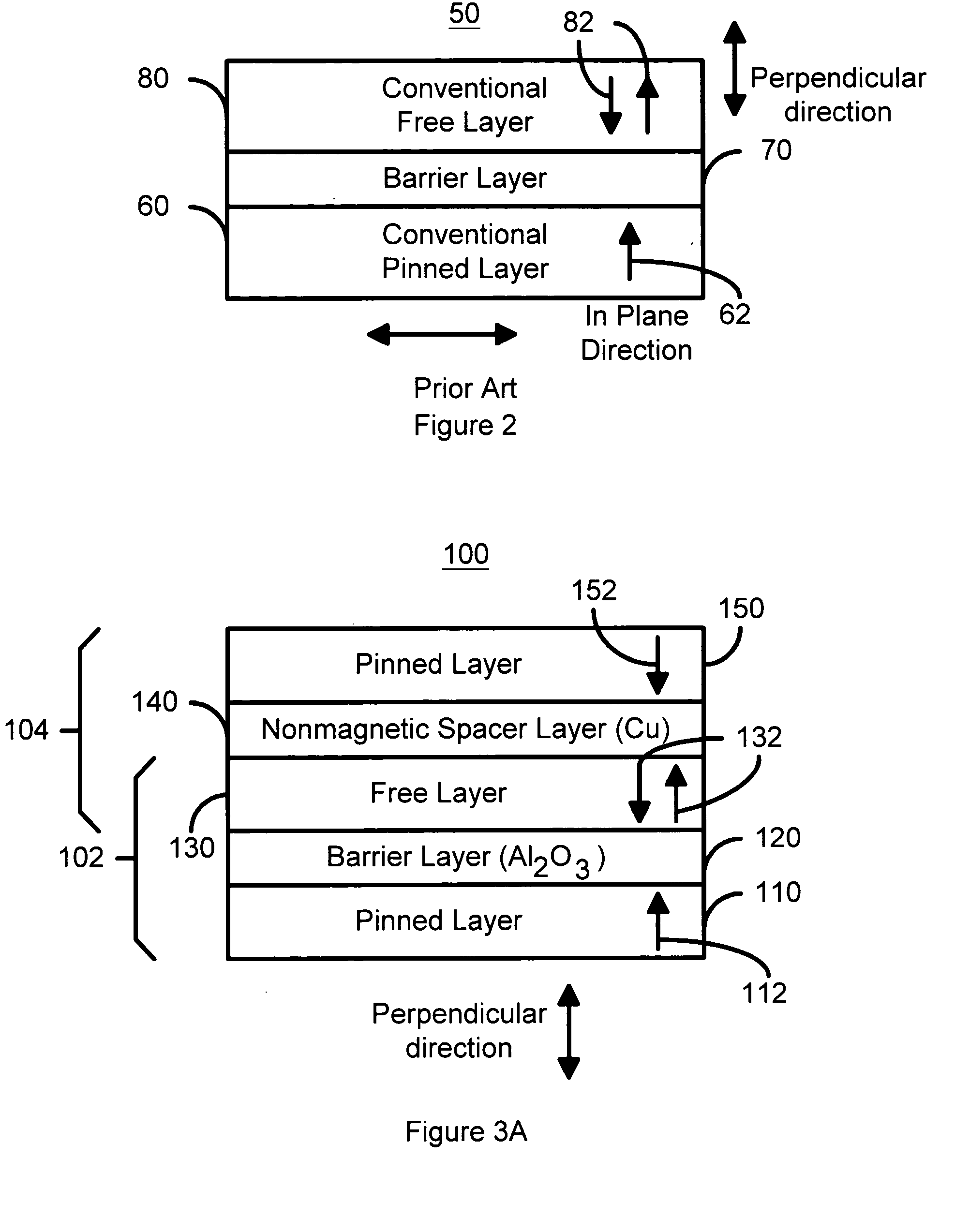
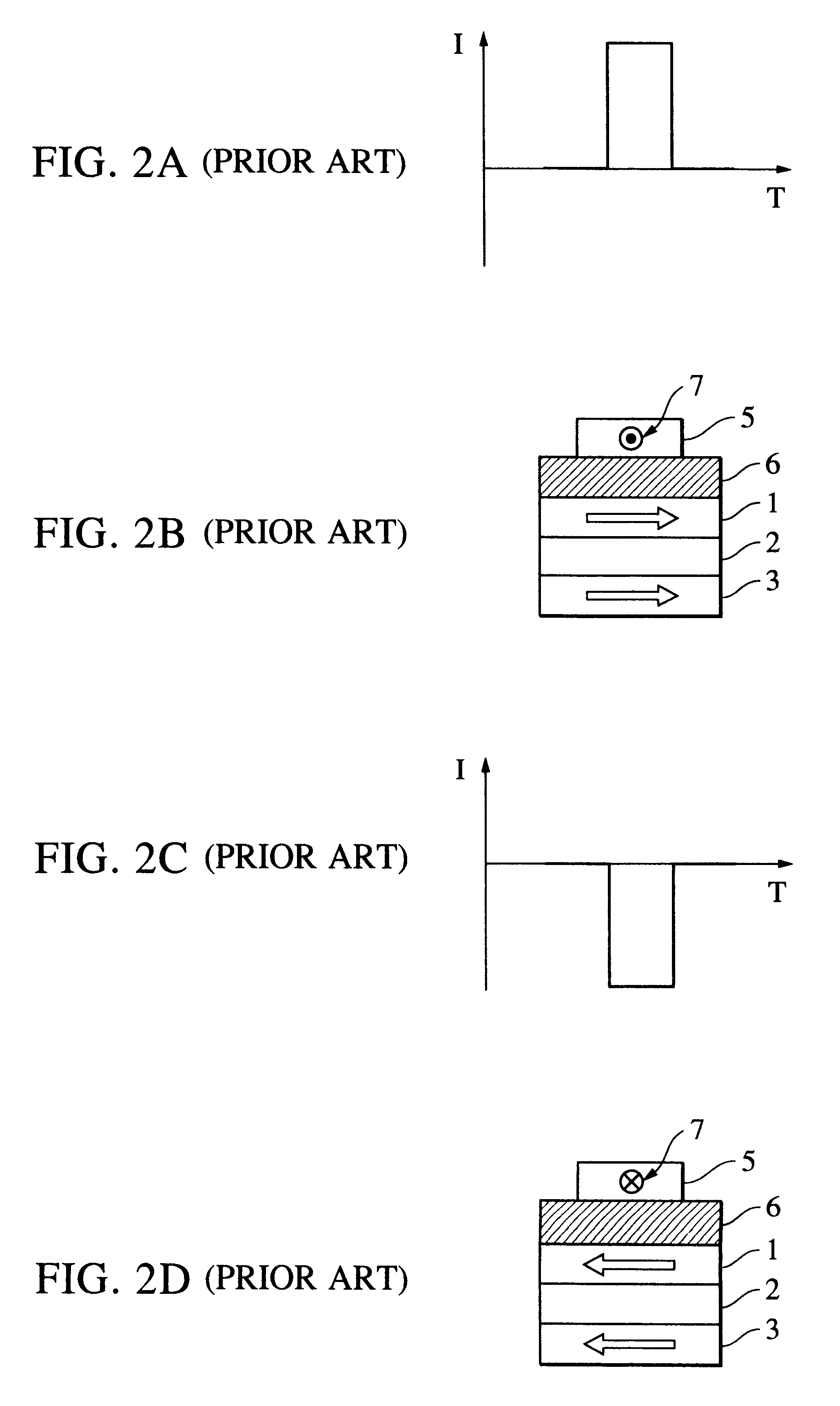
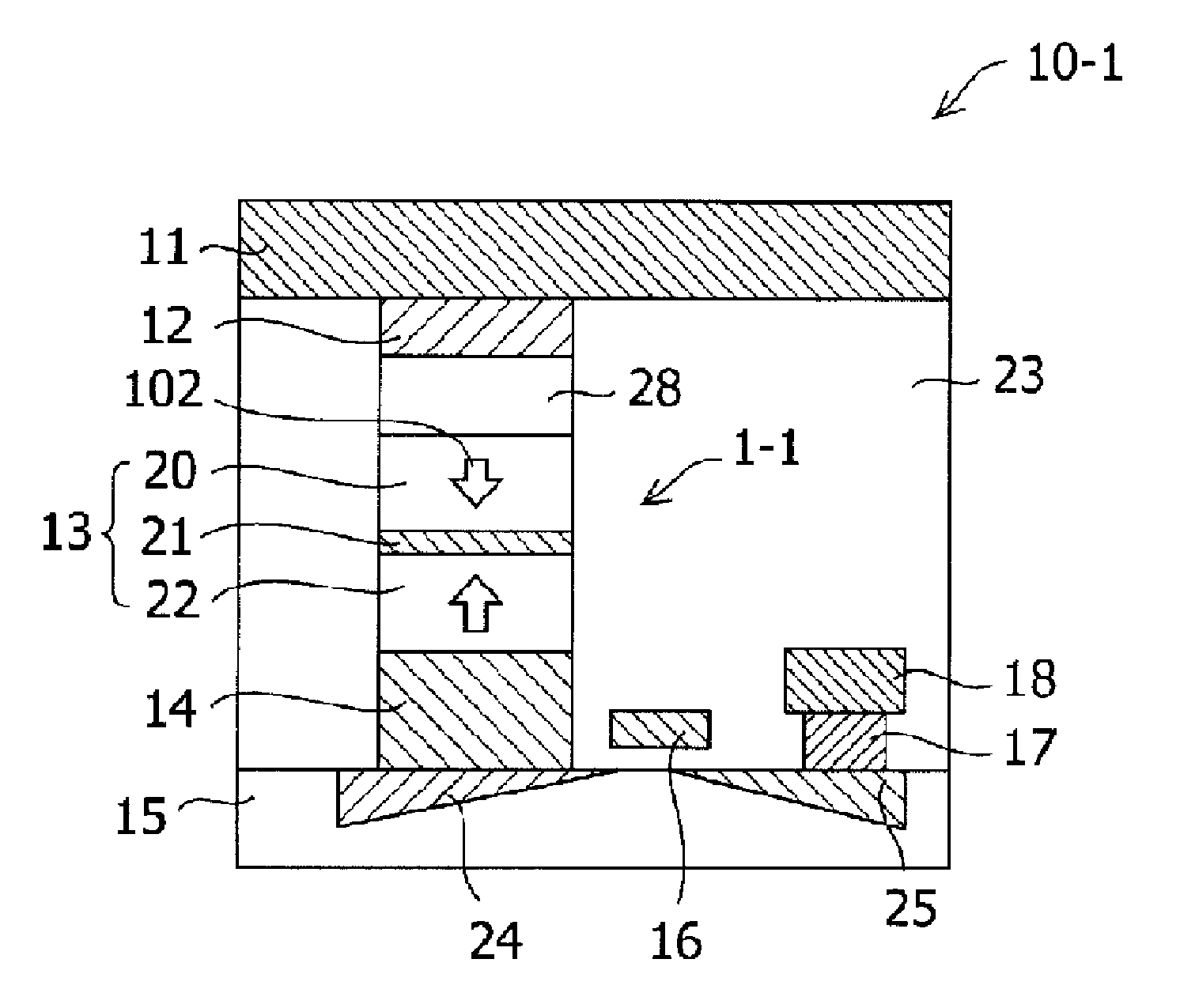
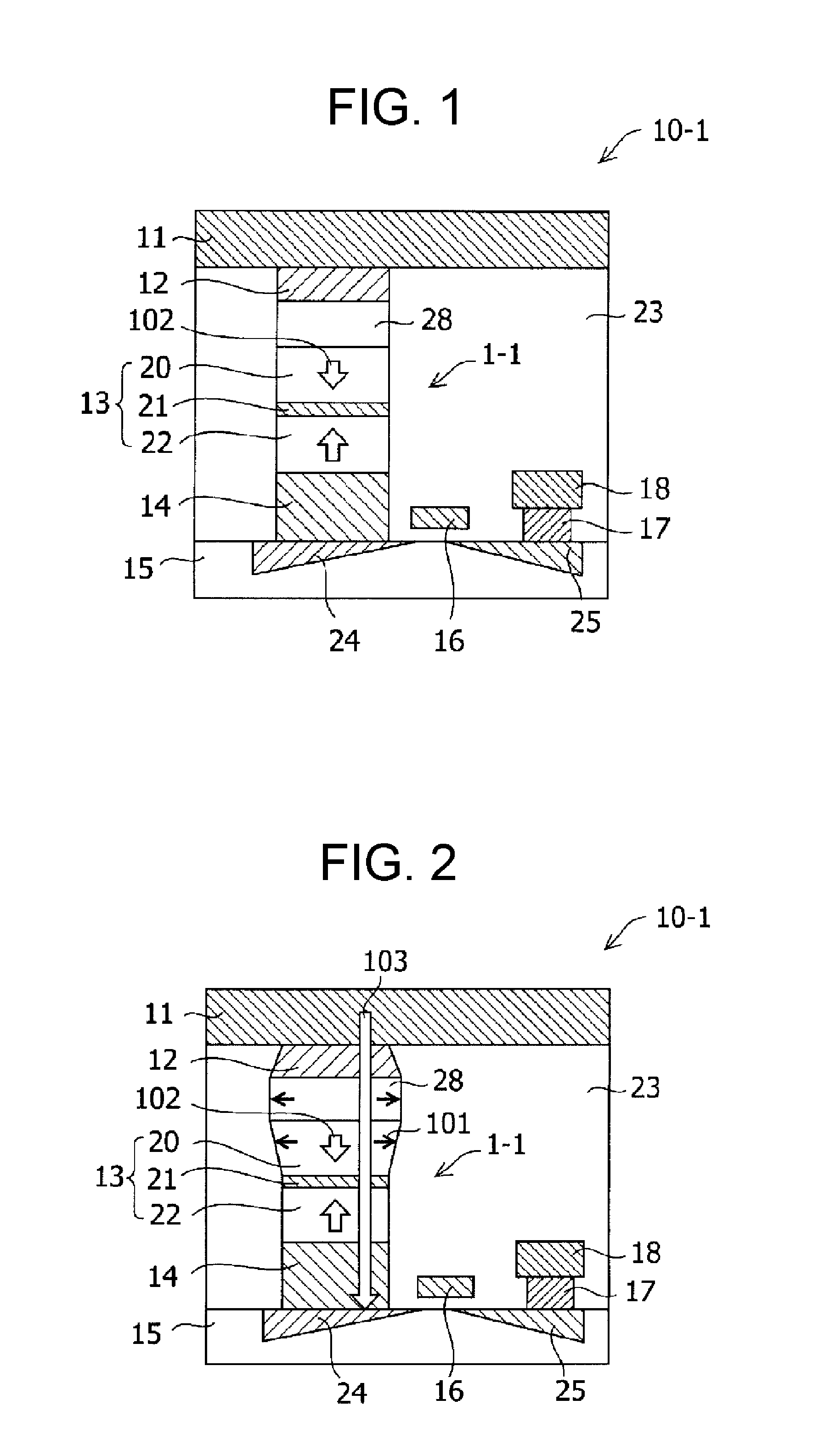
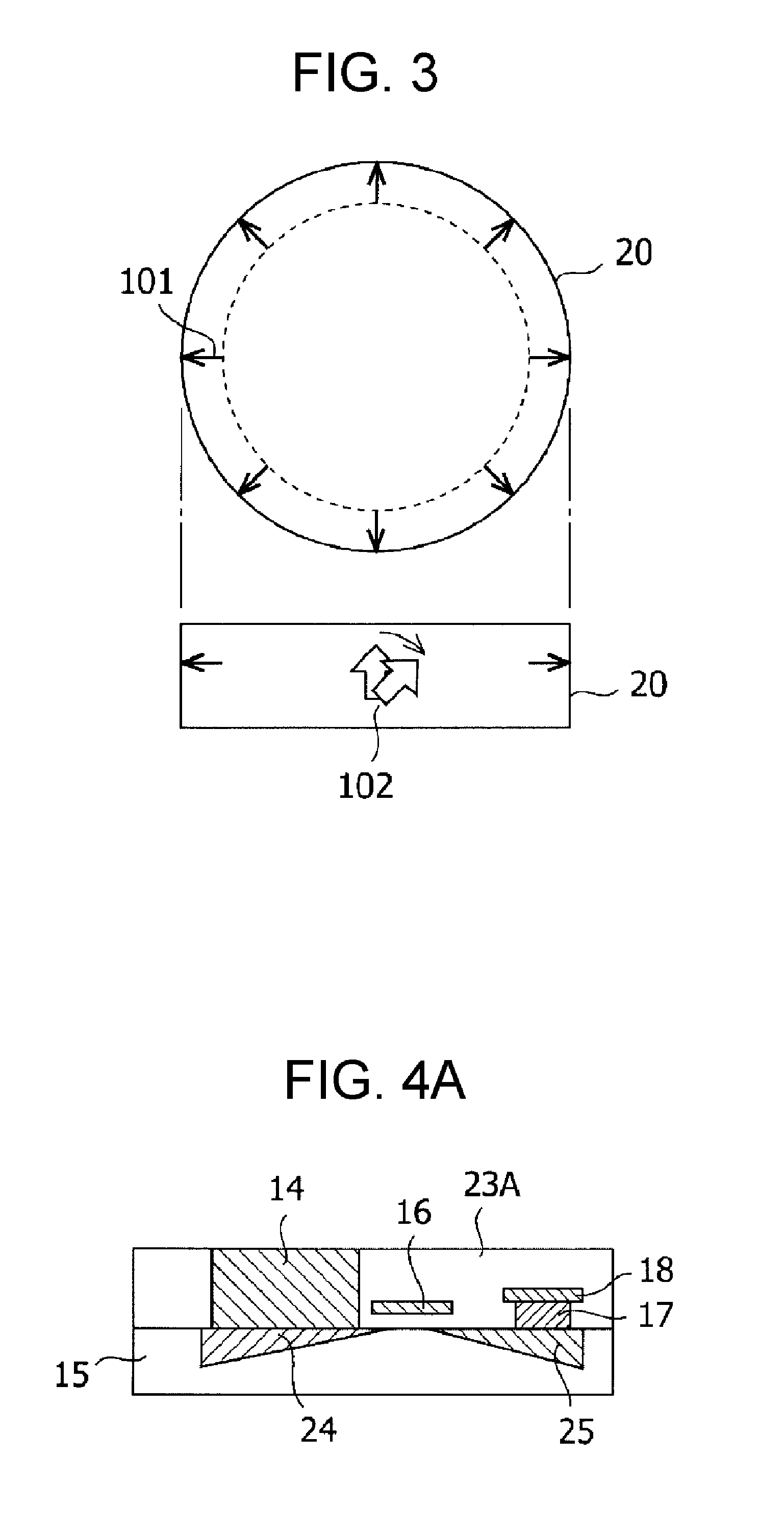
Perpendicular magnetization magnetic element utilizing spin transfer
ActiveUS6967863B2Reduce currentNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsPerpendicular magnetizationMagnetic memory
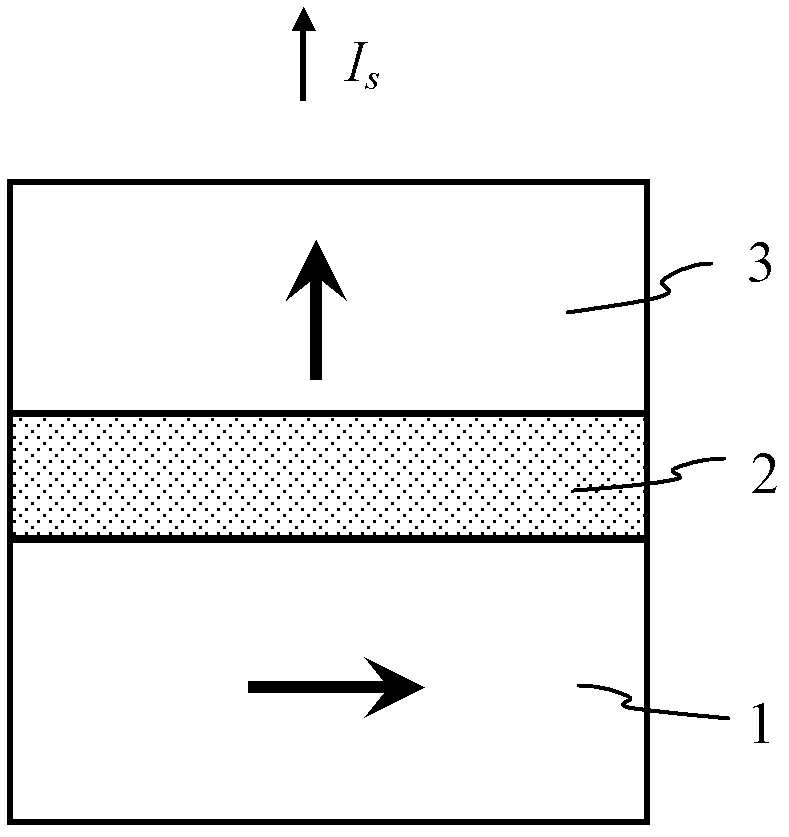
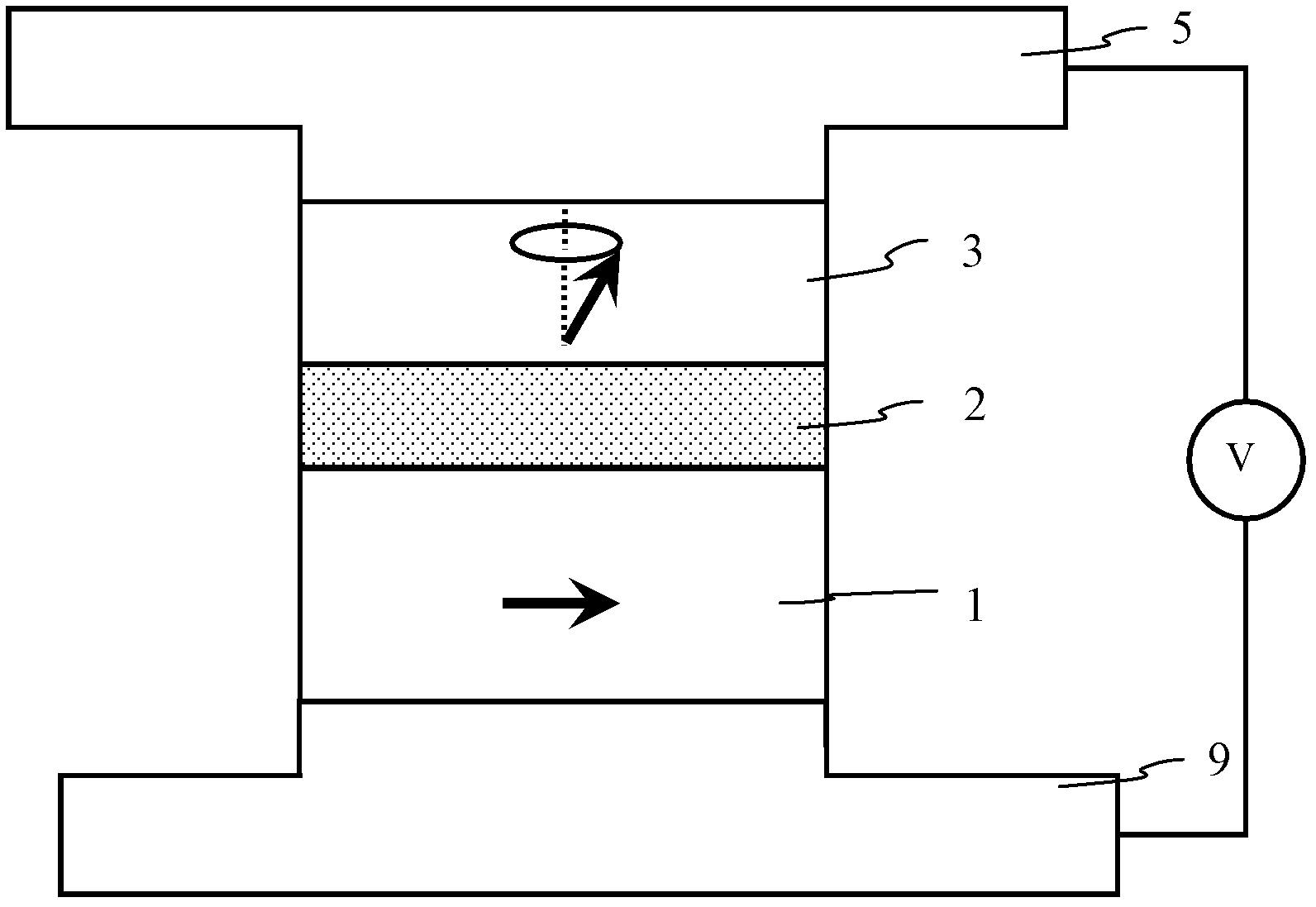
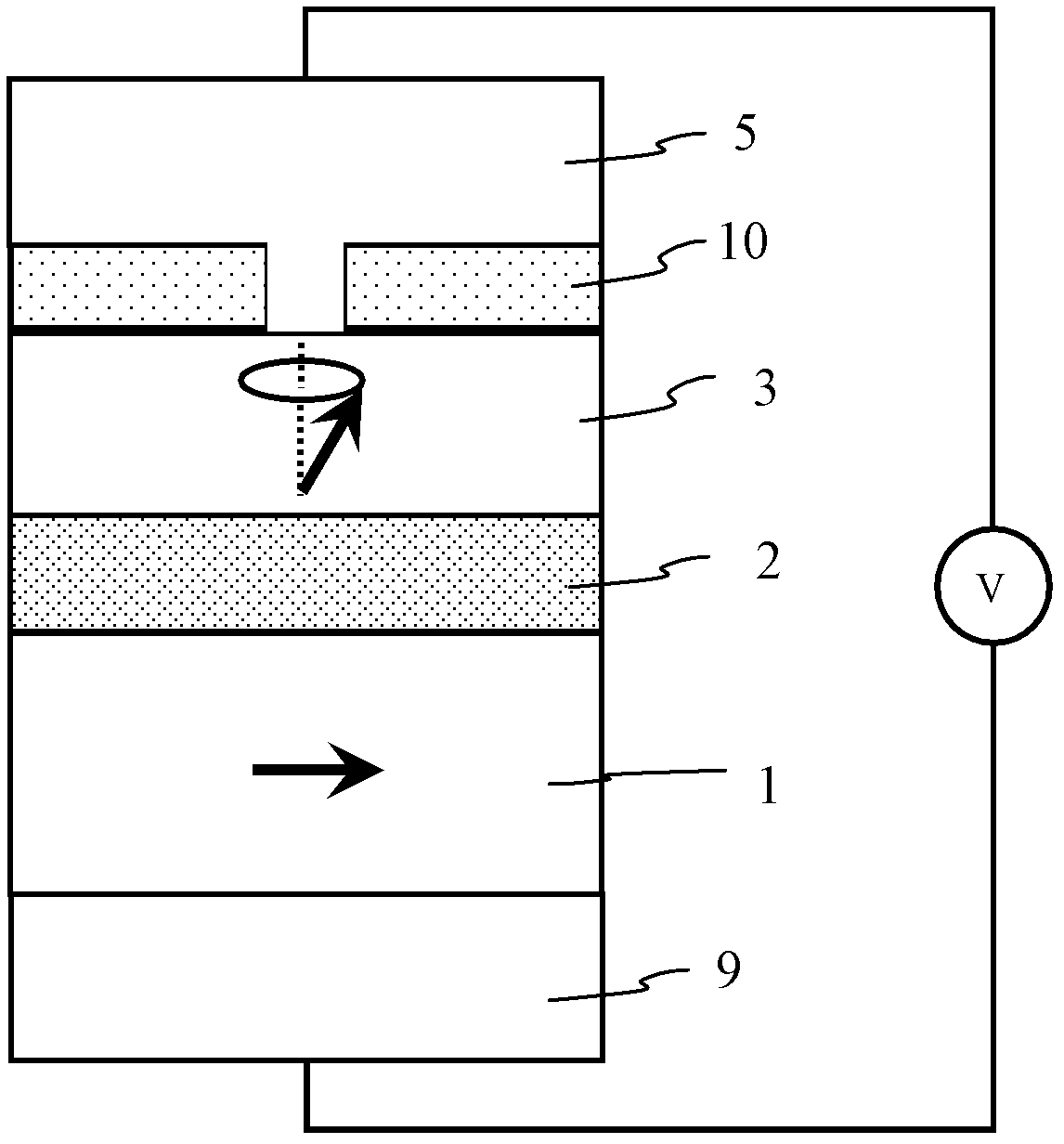
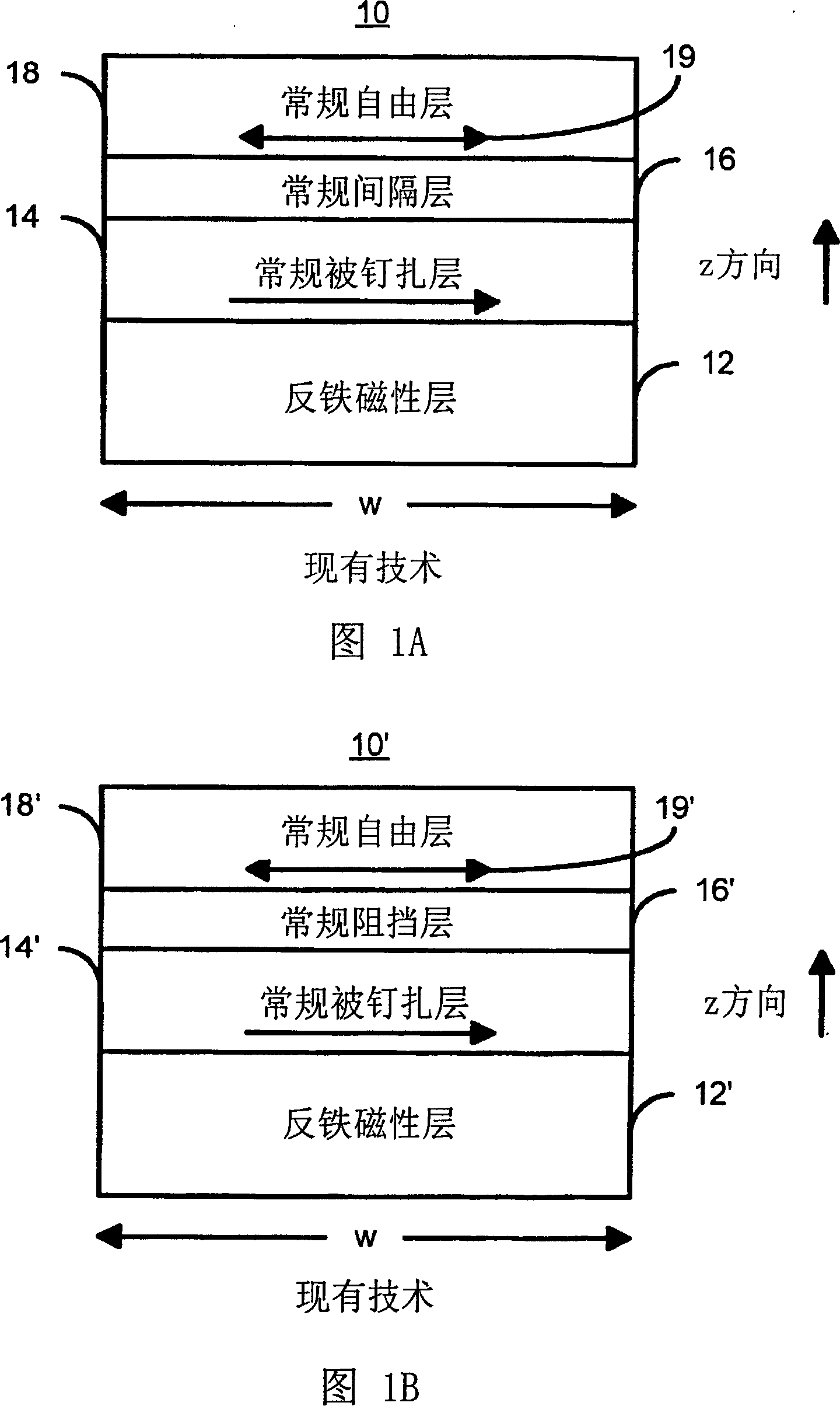
A method and system for providing a magnetic element that can be used in a magnetic memory is disclosed. The method and system include providing a first pinned layer, a barrier layer, a free layer, a conductive nonmagnetic spacer layer, and a second pinned layer. Each pinned layer has a pinned layer easy axis. At least a portion of the pinned layer easy axis is in a perpendicular direction. The barrier layer resides between the first pinned layer and the free layer. The spacer layer is between the free layer and the second pinned layer. The free layer has a free layer easy axis, at least a portion of which is in the perpendicular direction. The magnetic element is also configured to allow the free layer to be switched due to spin transfer effect when a write current is passed through the magnetic element. Because of the perpendicular magnetization(s), the writing current for spin transfer may be significantly reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
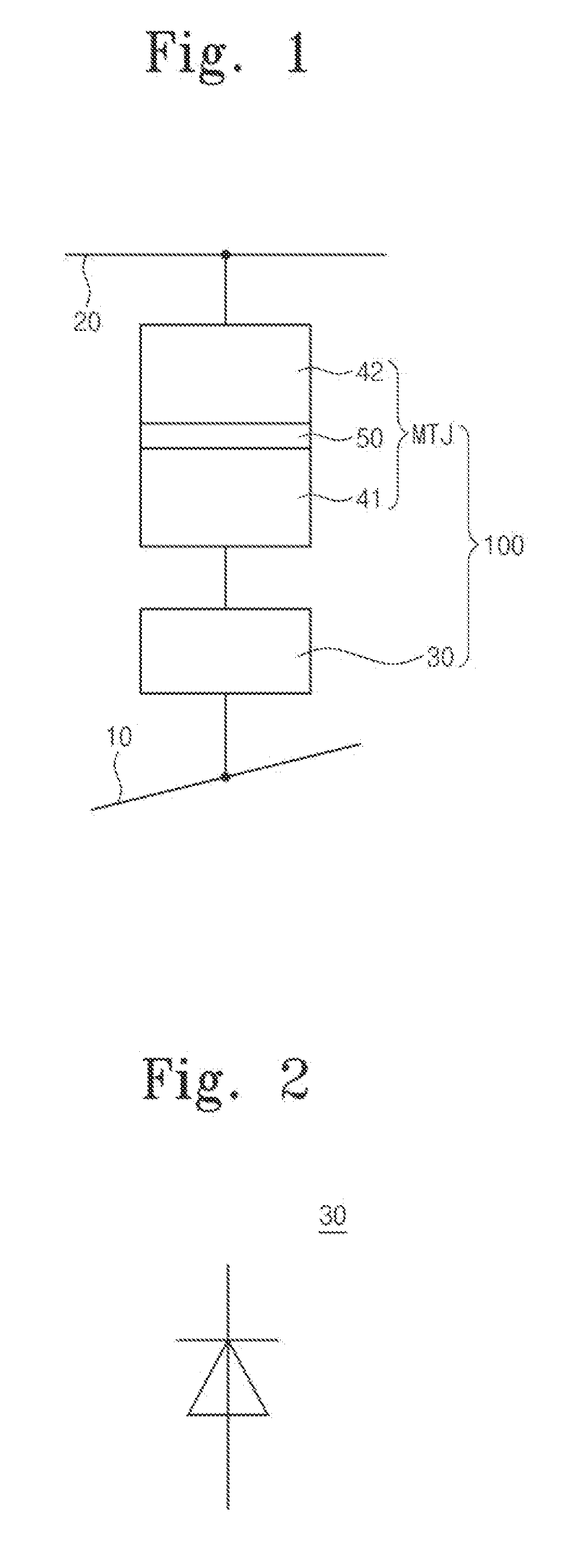
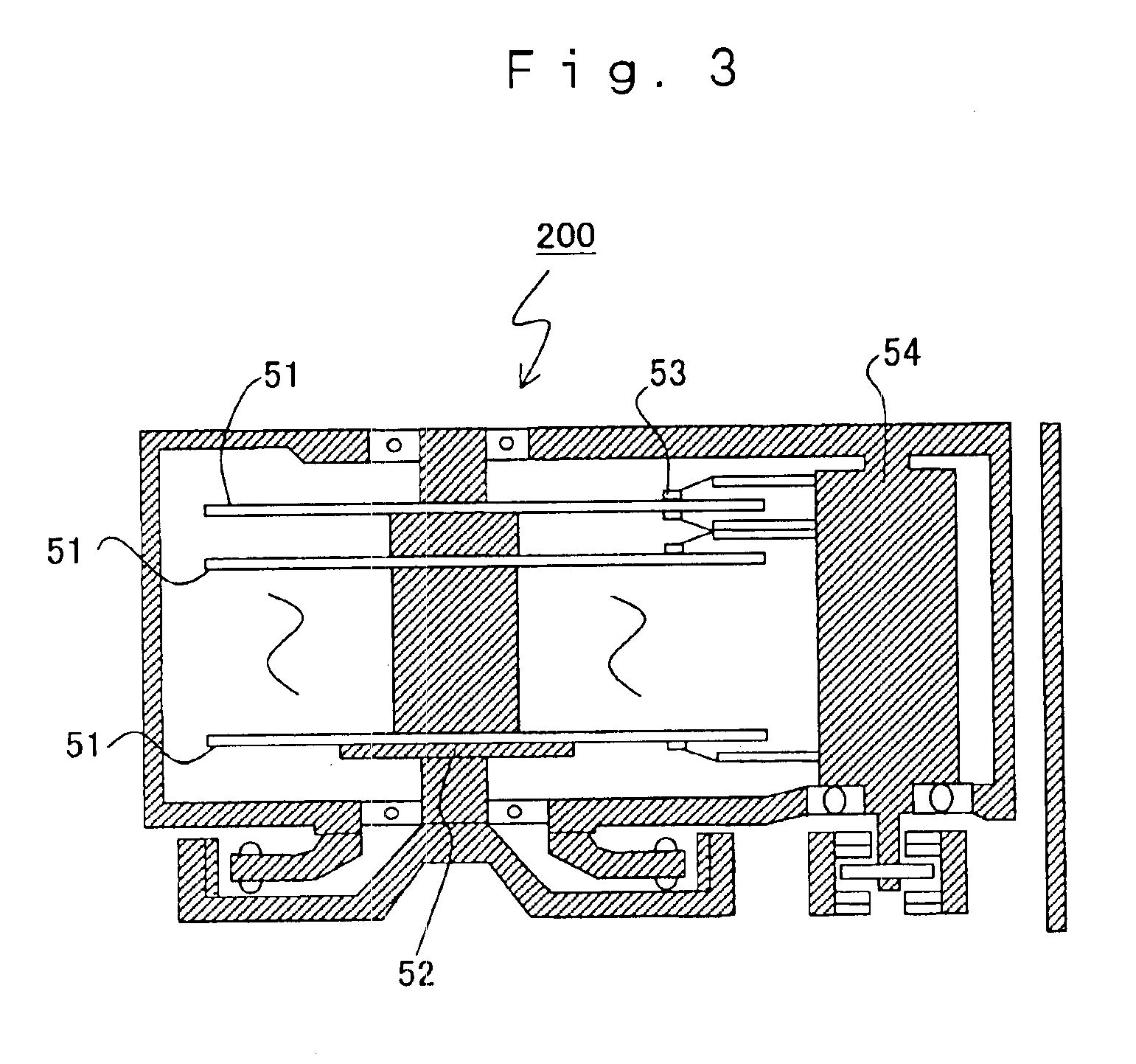
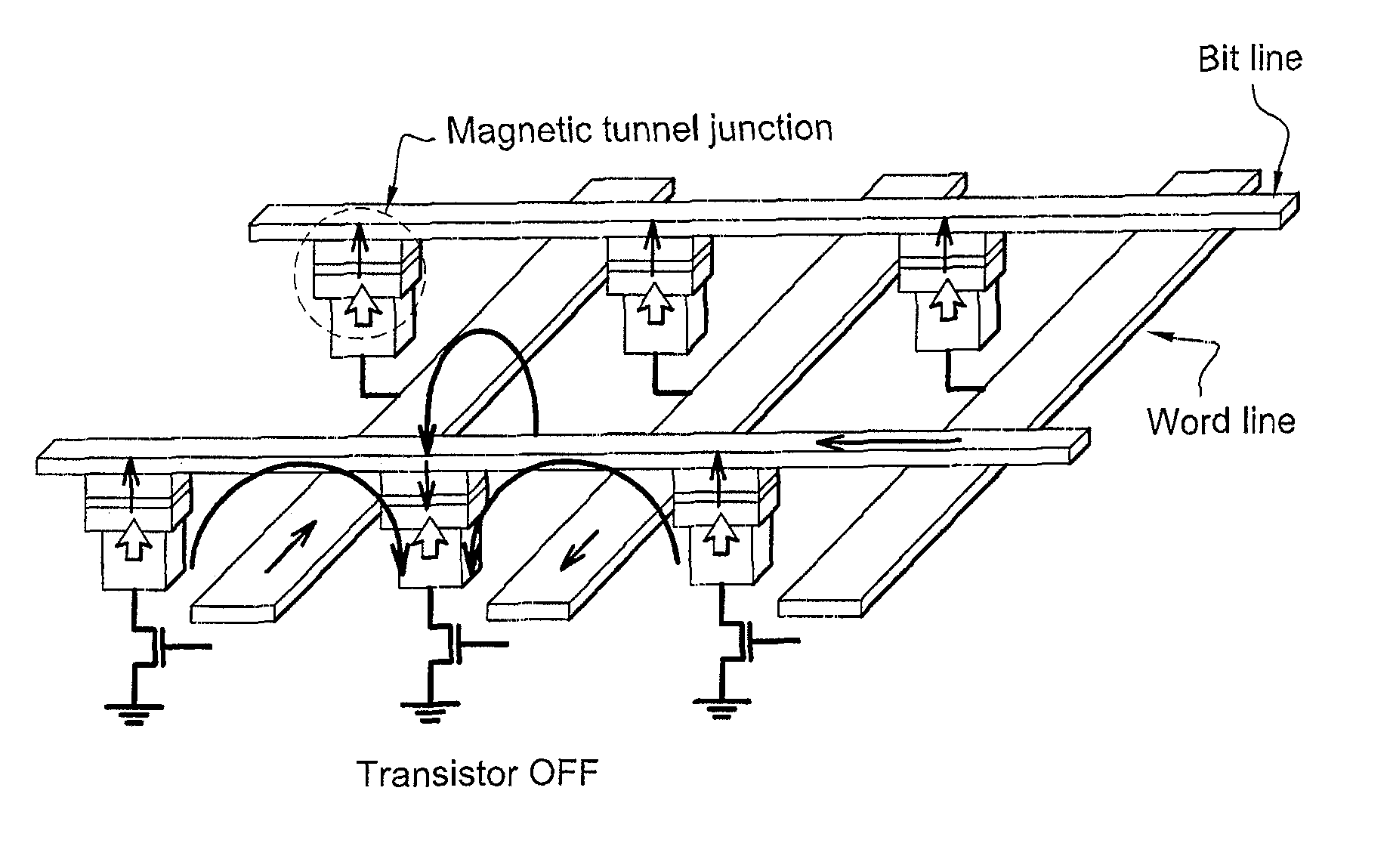
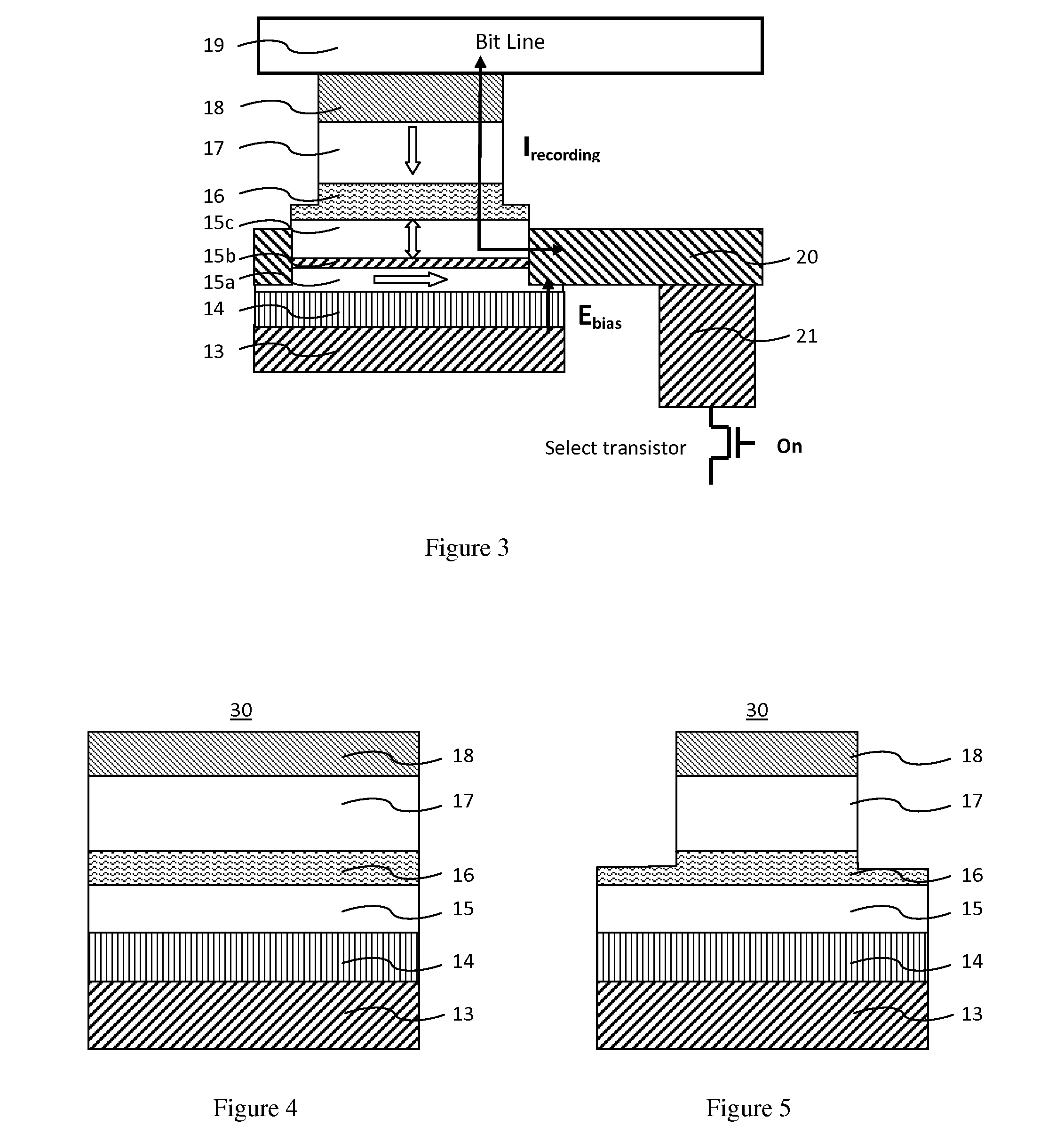
Magnetic tunnel junction memory device
InactiveUS6845038B1Improve permeabilityLow resistivityDigital storageBit linePerpendicular magnetization
A memory cell for magnetic random access memory devices based on a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) memory element with a perpendicular orientation of magnetization in pinned and free magnetic layers, and a tunnel barrier layer sandwiched between the pinned and free layers. The memory cell can include the MTJ memory element, a magnetic flux guide in series with selection devices, such as a bit line, a word line, and a transistor. The magnetic flux guide can have two electrically conductive magnetic portions with the MTJ memory element positioned between the magnetic portions. The MTJ memory element is magnetically isolated from the magnetic flux guide by thin non-magnetic conductive spacers. The MTJ memory element is arranged in a vertical space between the intersecting bit and word lines at their intersection region. The memory cell also includes write and excitation lines. The write line is parallel to the bit line and the excitation line is parallel to the word line. The write and excitation lines also intersect each other and define a corner. The MTJ memory element is positioned in the corner of the intercepting write and excitation lines.
Owner:SHUKH ALLA MIKHAILOVNA
Perpendicular magnetization magnetic element utilizing spin transfer
ActiveUS20050185455A1Reduce currentNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsPerpendicular magnetizationMagnetic memory
A method and system for providing a magnetic element that can be used in a magnetic memory is disclosed. The method and system include providing a first pinned layer, a barrier layer, a free layer, a conductive nonmagnetic spacer layer, and a second pinned layer. Each pinned layer has a pinned layer easy axis. At least a portion of the pinned layer easy axis is in a perpendicular direction. The barrier layer resides between the first pinned layer and the free layer. The spacer layer is between the free layer and the second pinned layer. The free layer has a free layer easy axis, at least a portion of which is in the perpendicular direction. The magnetic element is also configured to allow the free layer to be switched due to spin transfer effect when a write current is passed through the magnetic element. Because of the perpendicular magnetization(s), the writing current for spin transfer may be significantly reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
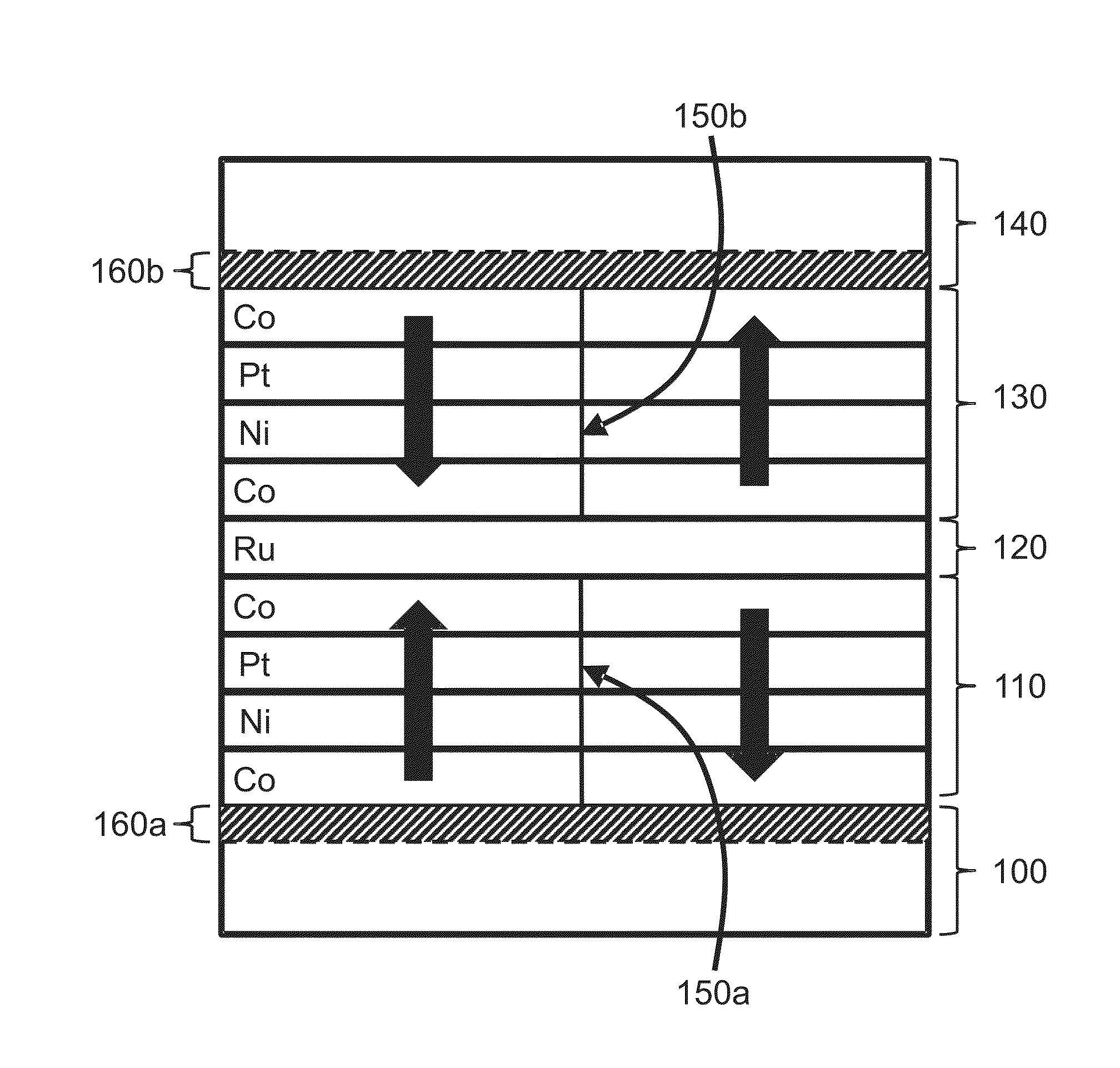
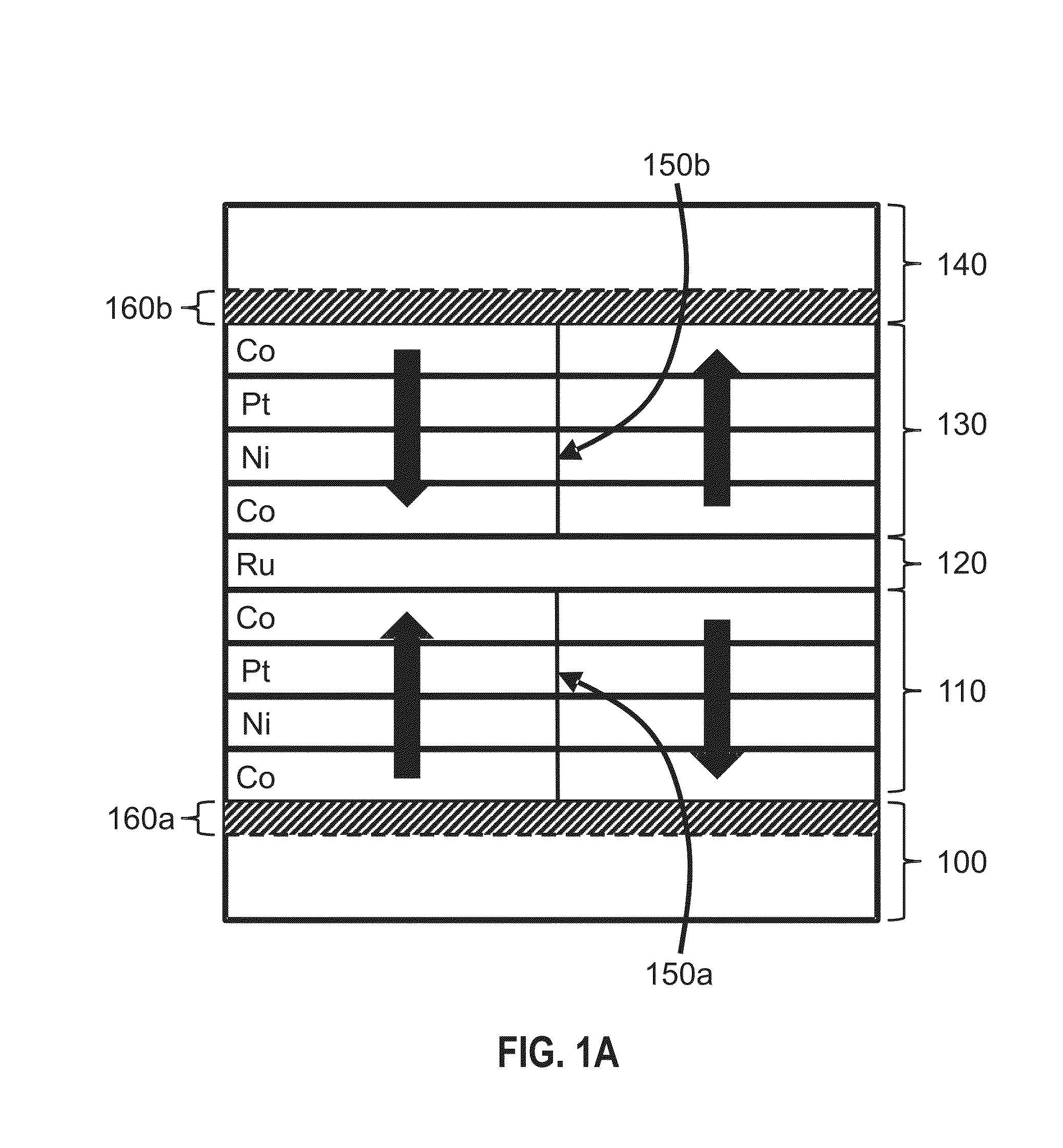
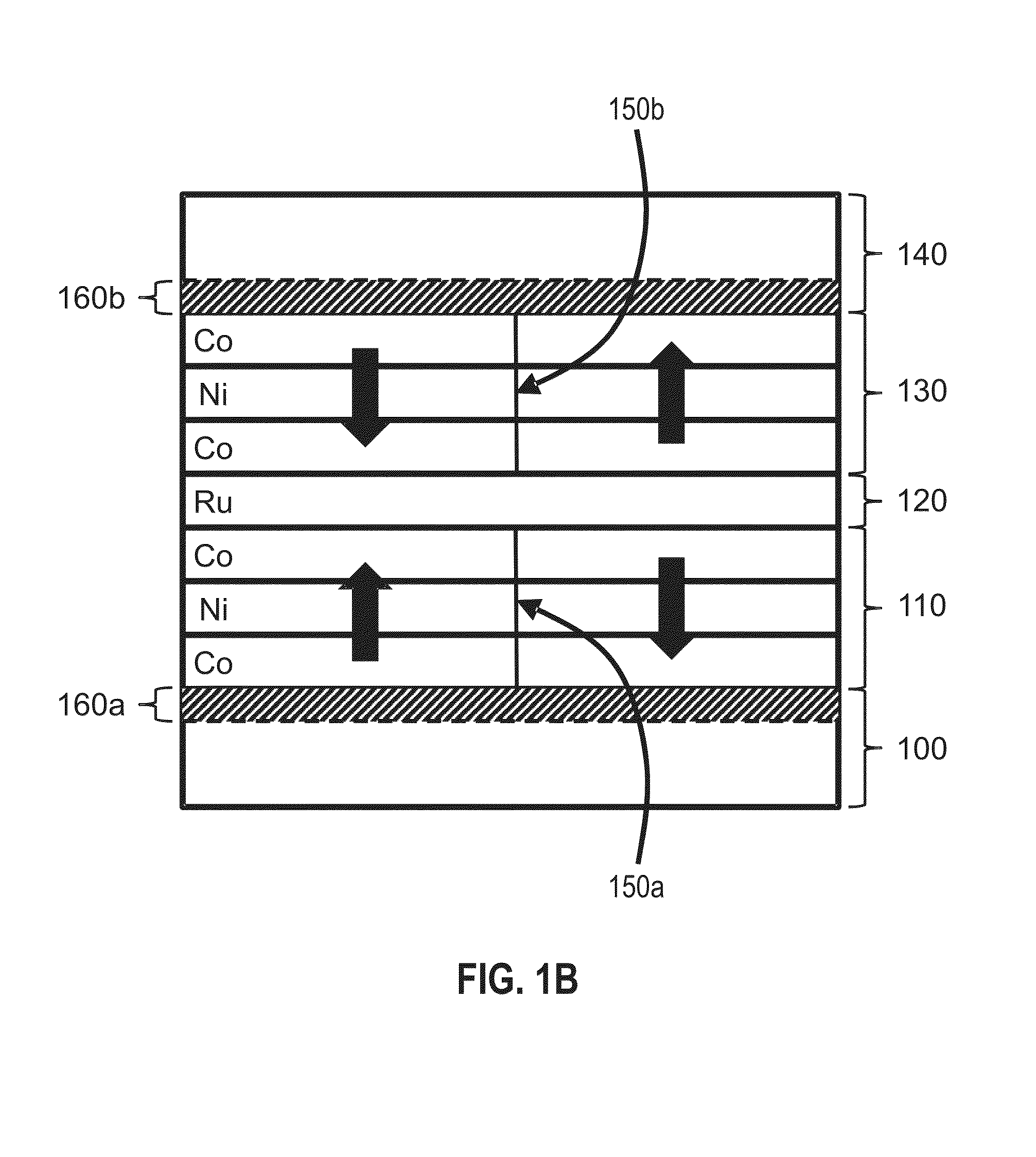
Domain wall motion in perpendicularly magnetized wires having artificial antiferromagnetically coupled multilayers with engineered interfaces
ActiveUS20140009994A1Digital storageThin magnetic filmsPerpendicular magnetizationAntiferromagnetic coupling
Magnetic wires that include two antiferromagnetically coupled magnetic regions show improved domain wall motion properties, when the domain walls are driven by pulses of electrical current. The magnetic regions preferably include Co, Ni, and Pt and exhibit perpendicular magnetic anisotropy, thereby supporting the propagation of narrow domain walls. The direction of motion of the domain walls can be influenced by the order in which the wire's layers are arranged.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Perpendicular magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS6270885B1Decrease cancellationReduce noiseRecord information storageDisk carriersPerpendicular magnetizationMagnetization
In a perpendicular magnetic recording medium, a soft magnetic film playing the role of an back layer, but not having a domain wall structure, is positioned beneath a perpendicular magnetization film. Such a back layer improves the envelope characteristic of the medium at the time of recording and reproduction. Moreover, the medium is free from spike noise and the decrease or cancellation of recorded magnetization ascribable to the movement of the domain wall of a back layer. The medium of the present invention is therefore a drastic solution to the problems particular to a conventional perpendicular magnetic recording medium and realizes desirable recording and reproducing characteristics.
Owner:WD MEDIA SINGAPORE PTE
Perpendicular magnetic recording medium and manufacturing process therefor
InactiveUS6387483B1Improve perpendicular orientation of perpendicularReduce noiseMagnetic materials for record carriersBase layers for recording layersPerpendicular magnetizationEngineering
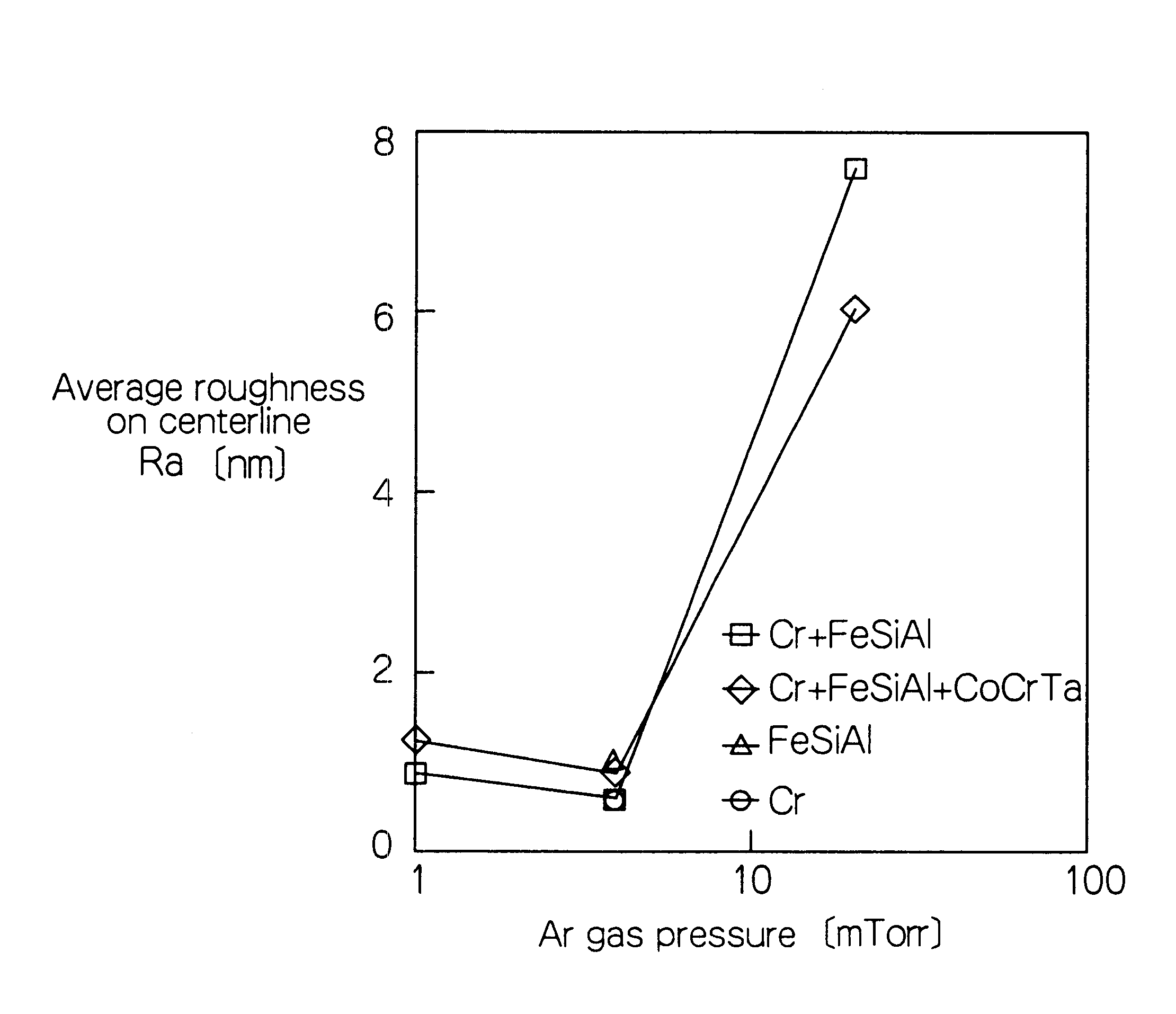
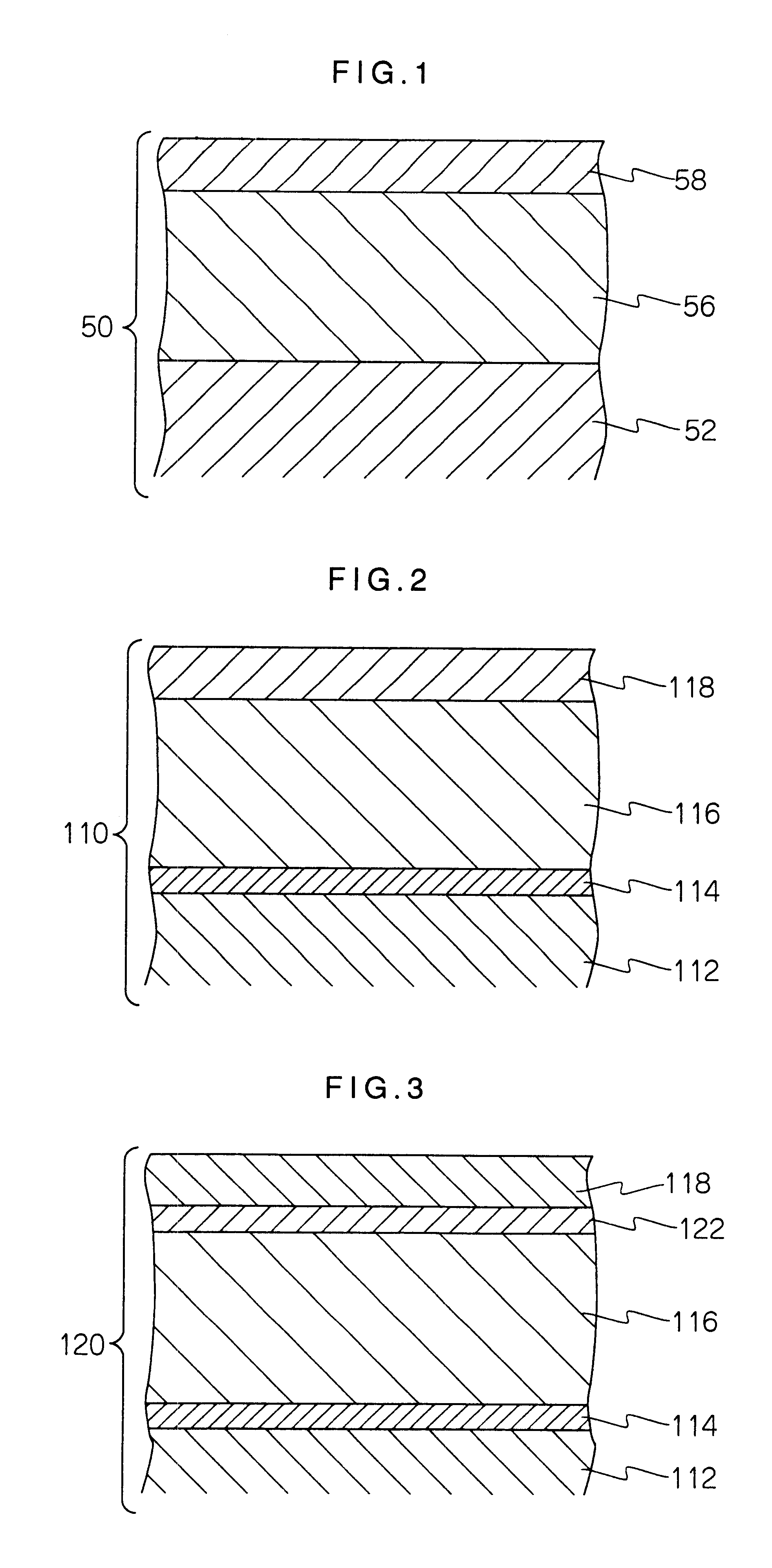
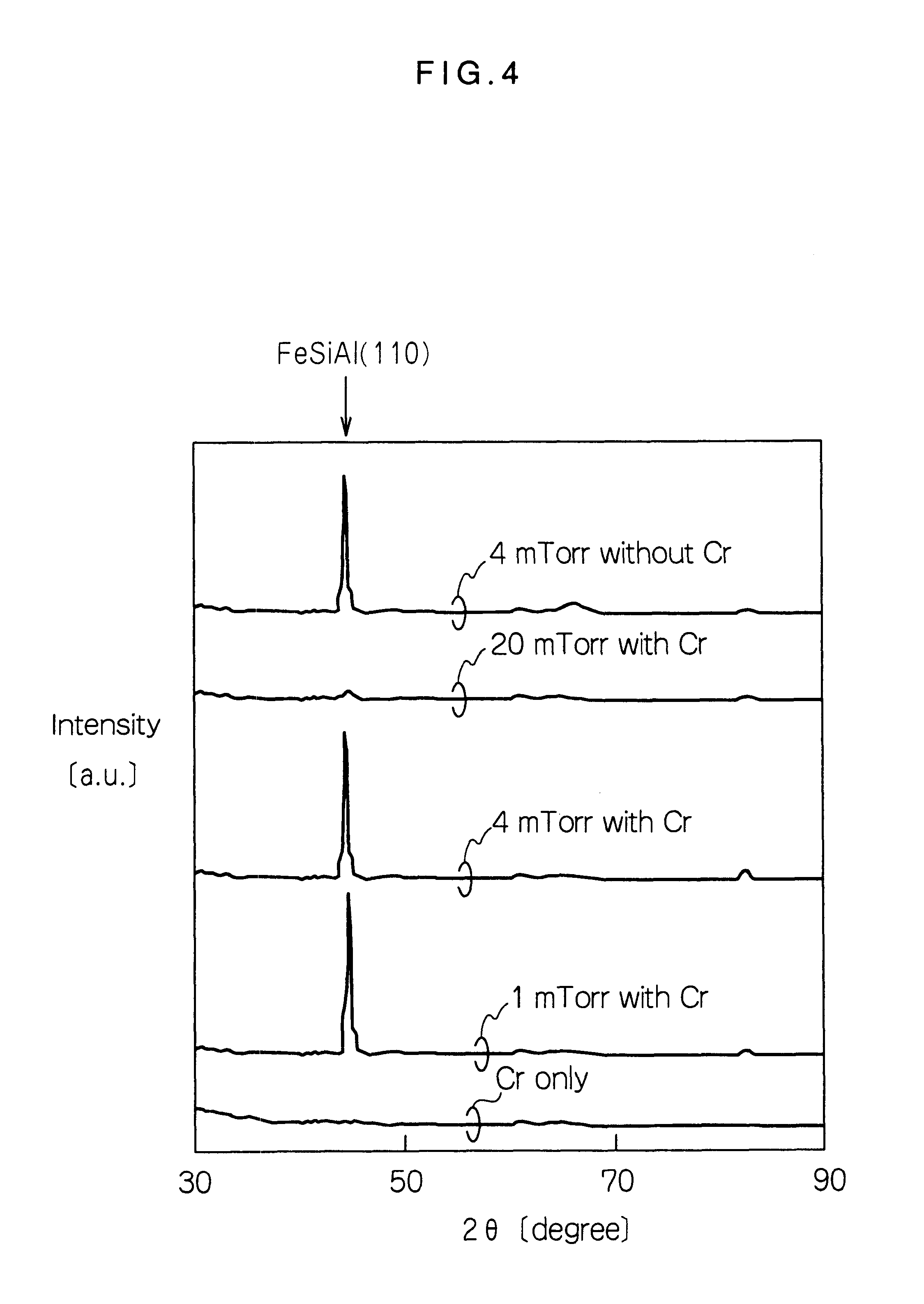
It is intended to reduce the media noise, and to improve the recording density dependence of read output voltage. The present invention provides a perpendicular magnetic recording media and its manufacturing process, wherein a perpendicular magnetic recording medium comprises a soft magnetic underlayer film and a perpendicular magnetizing film, these films being formed on a substrate in this order, a smoothness control film such as Cr film, being inserted between the substrate and the soft magnetic underlayer film. Therefore, perpendicular orientation and surface smoothness are improved for the perpendicular magnetizing film laminated on the smooth surface of the soft magnetic underlayer film. As the perpendicular orientation is improved for the perpendicular magnetizing film, the initial layer is reduced, thereby media noise being lowered and recording density dependence of read output voltage being improved. In addition, as the surface smoothness is improved for the perpendicular magnetizing film, sliding characteristics of a recording / reproducing head is also improved, thereby this also lowering the media noise.
Owner:WD MEDIA SINGAPORE PTE
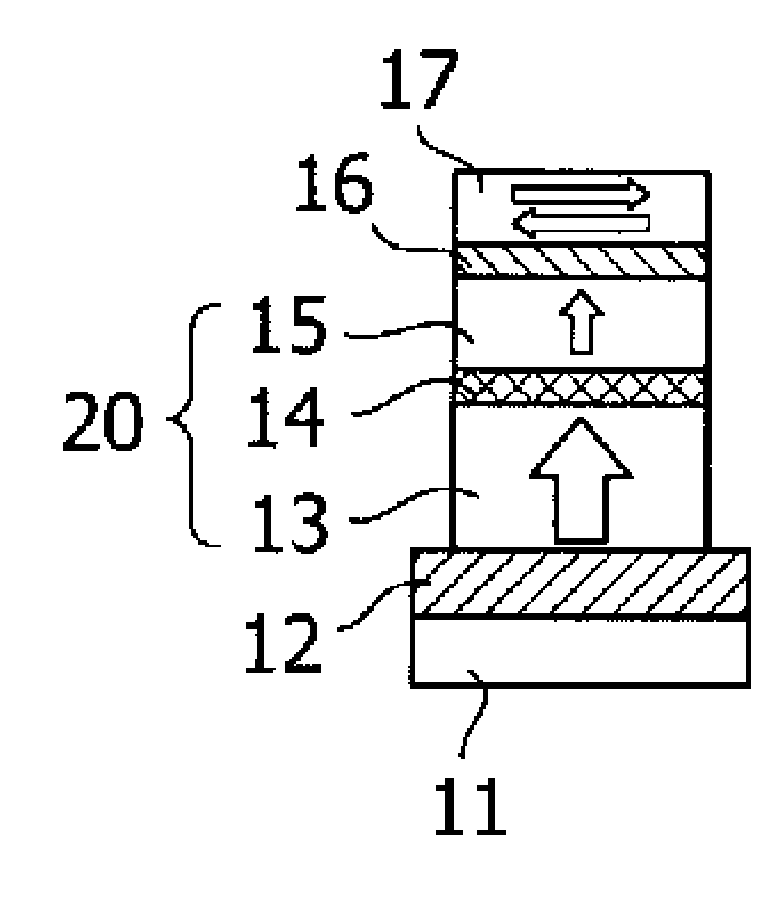
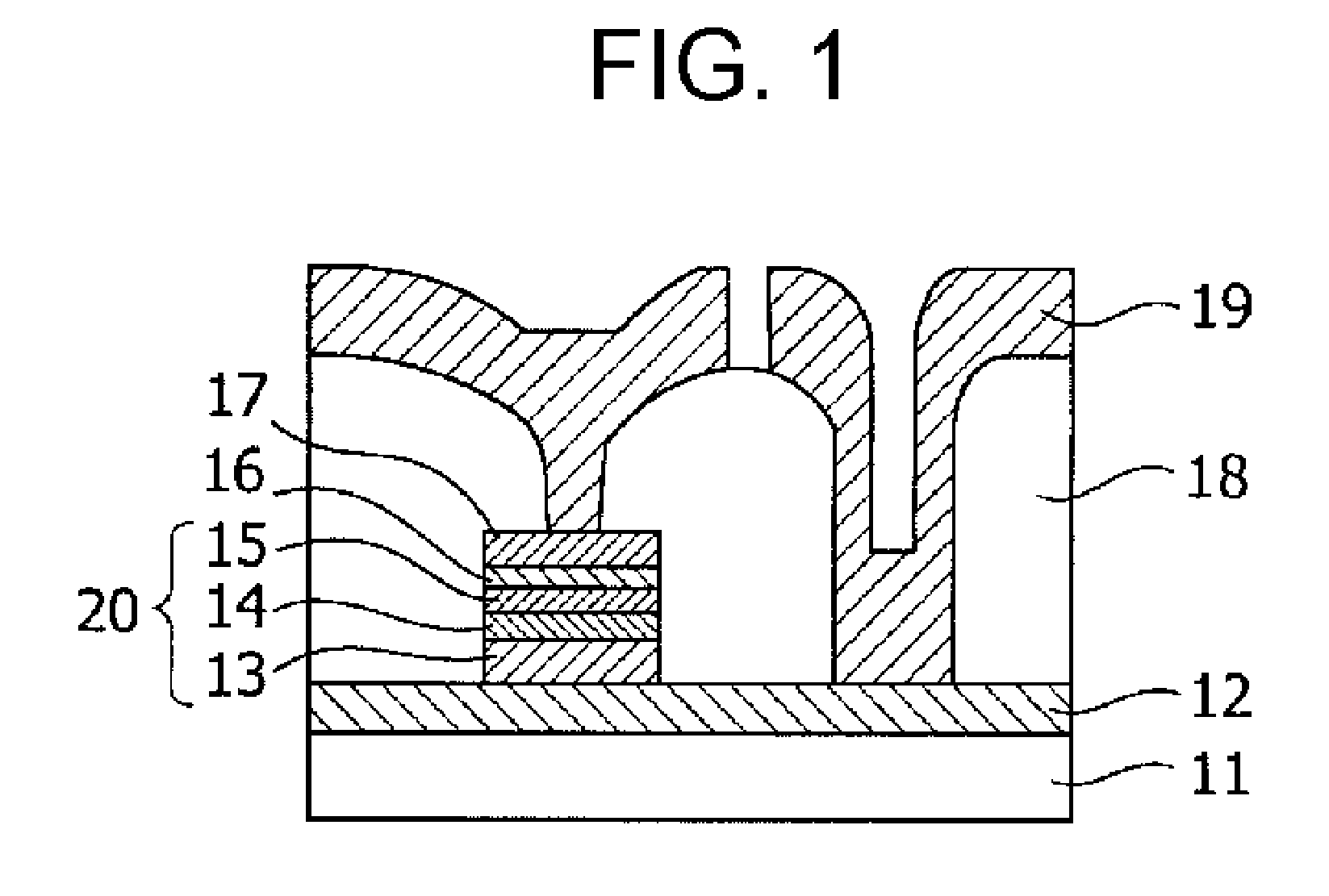
Magnetic thin film element, memory element using the same, and method for recording and reproducing using the memory element
A magnetic thin film element is provided with a magnetoresistive film including a first magnetic layer composed of a perpendicular magnetization film, a second magnetic layer composed of a perpendicular magnetization film having a higher coercive force than that of the first magnetic layer, and a nonmagnetic layer interposed between the first magnetic layer and the second magnetic layer. The resistance of the magnetoresistive film varies depending on whether or not the magnetic spins of the first magnetic layer and the second magnetic layer are in the same direction.
Owner:CANON KK
Magnetic memory element and storage device using the same
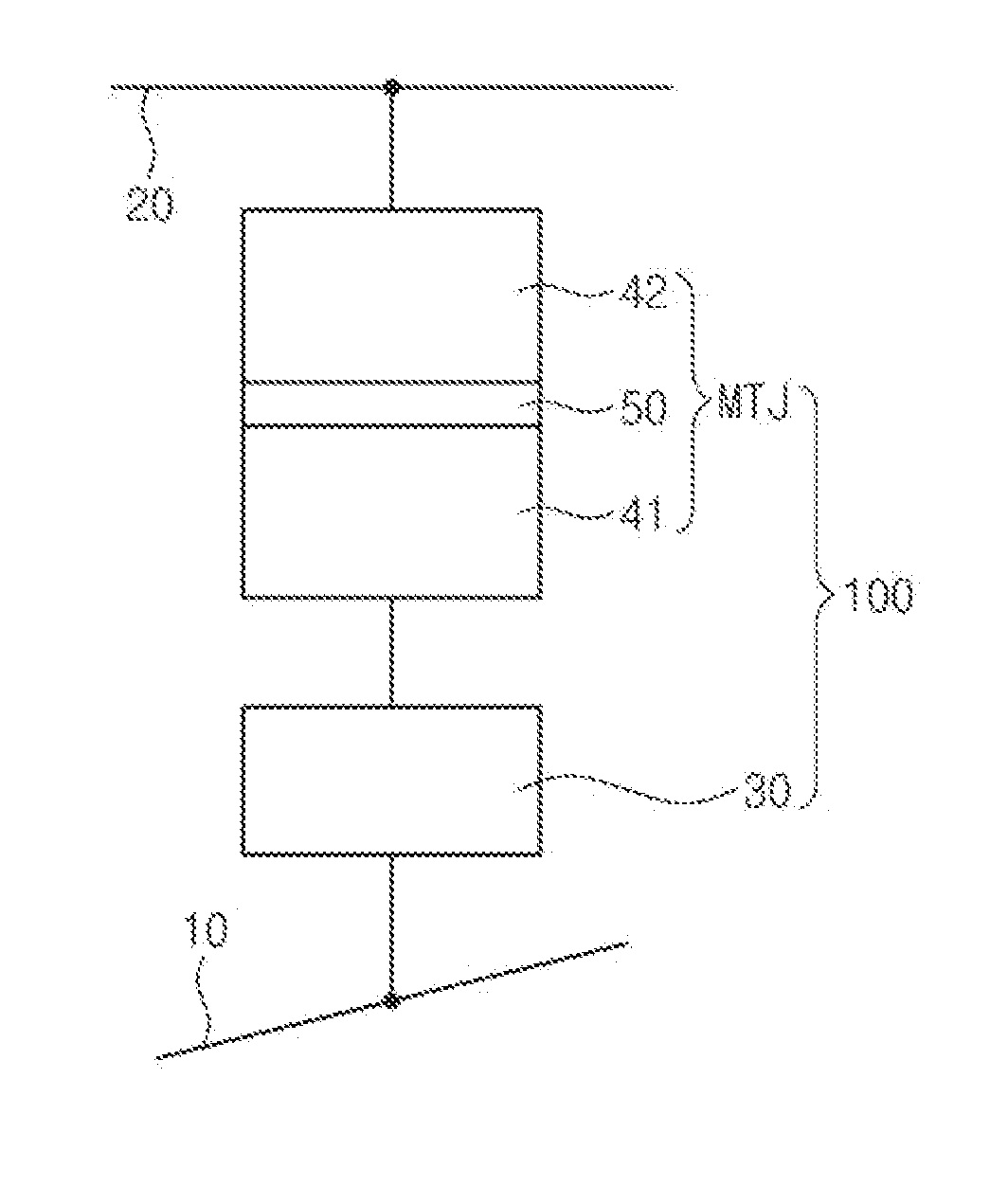
ActiveUS20120075922A1Magnetic anisotropic energy decreaseImprove thermal stabilityNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsPerpendicular magnetizationSwitched current
A magnetic memory element capable of maintaining high thermal stability (retention characteristics) while reducing a writing current. The magnetic memory element includes a magnetic tunnel junction having a first magnetic body including a perpendicular magnetization film, an insulating layer, and a second magnetic body serving as a storage layer including a perpendicular magnetization film, which are sequentially stacked. A thermal expansion layer is disposed in contact with the magnetic tunnel junction portion. The second magnetic body is deformed in a direction in which the cross section thereof increases or decreases by the thermal expansion or contraction of the thermal expansion layer due to the flow of a current, thereby reducing a switching current threshold value required to change the magnetization direction.
Owner:III HLDG 3
Magnetic random access memory
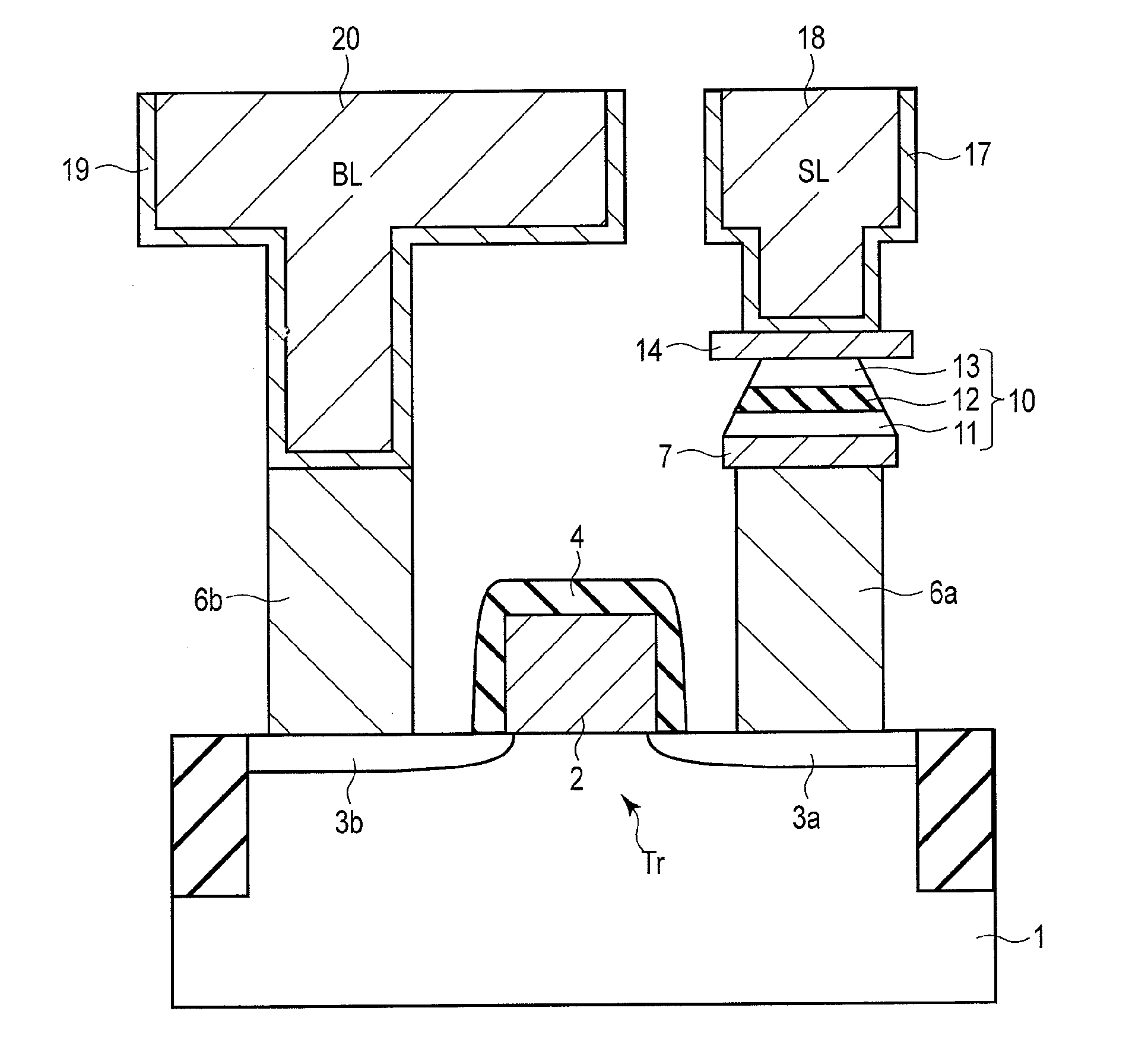
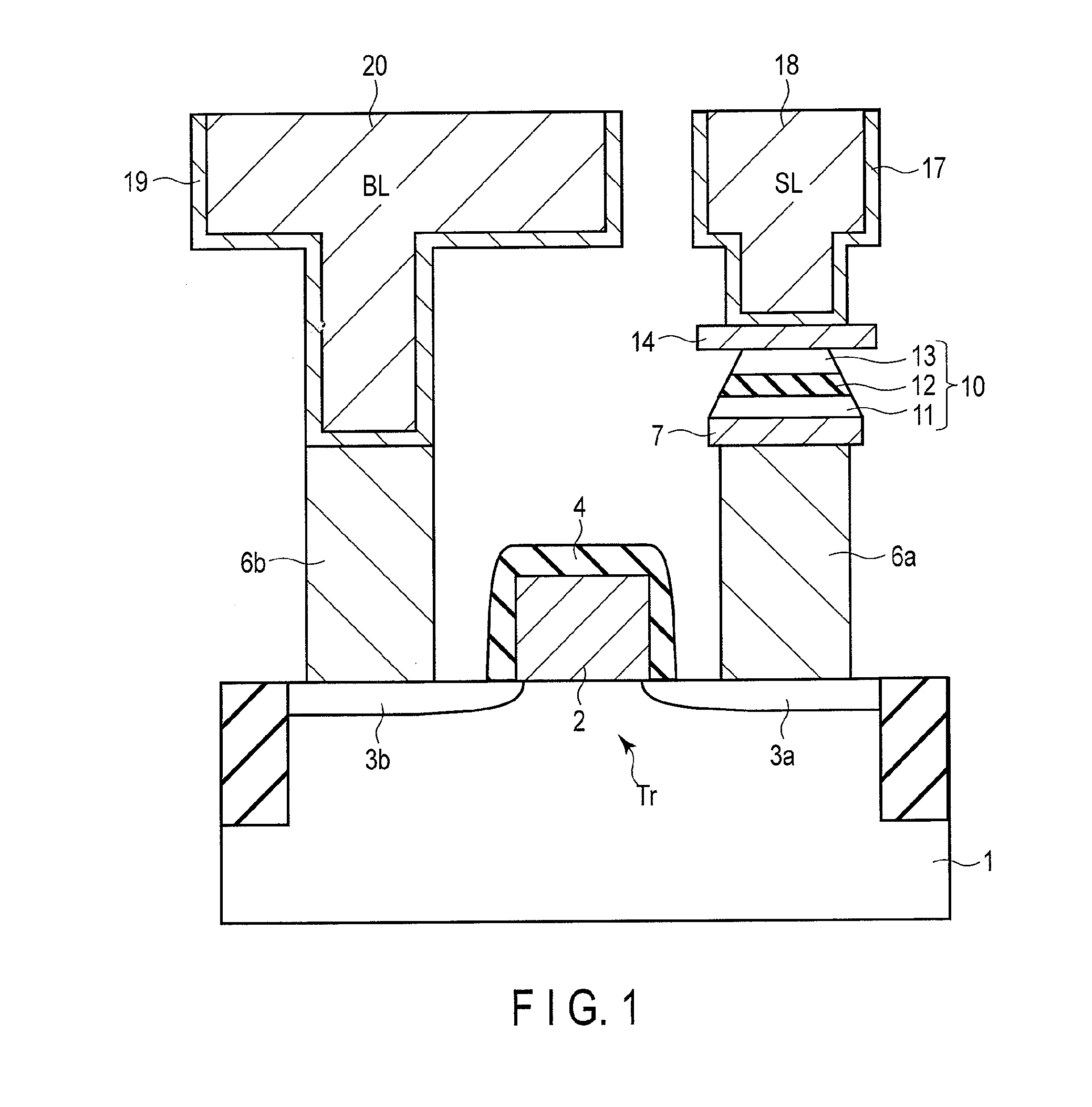
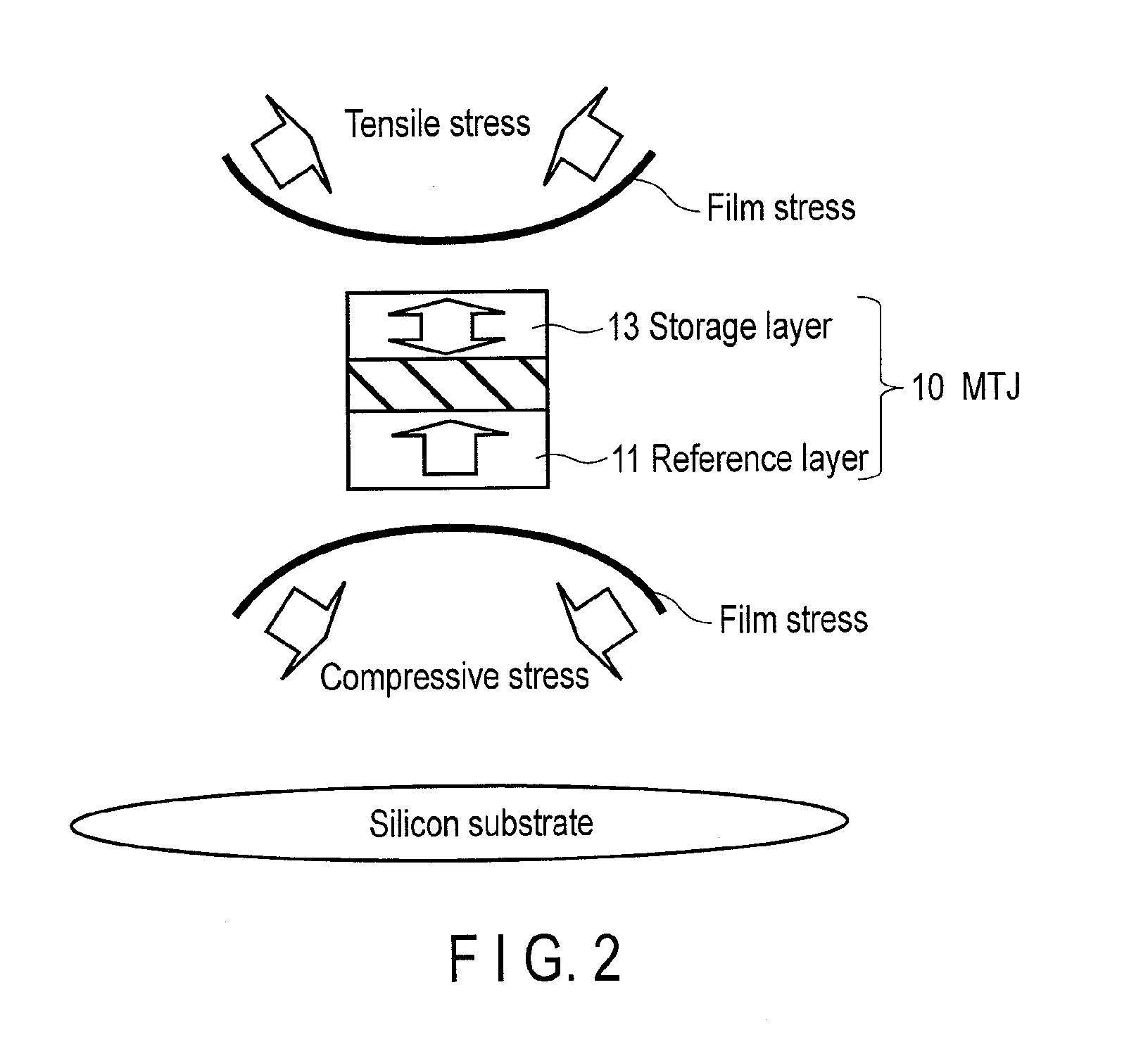
ActiveUS20120217594A1Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesPerpendicular magnetizationRandom access memory
According to one embodiment, a magnetic random access memory includes a semiconductor substrate, an MTJ element formed from a perpendicular magnetization film and arranged above the semiconductor substrate, and a stress film including at least one of a tensile stress film arranged on an upper side of the MTJ element to apply a stress in a tensile direction with respect to the semiconductor substrate and a compressive stress film arranged on a lower side of the MTJ element to apply a stress in a compressive direction with respect to the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Magnetic tunneling junction devices, memories, memory systems, and electronic devices
ActiveUS20130042081A1Improve thermal stabilityMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionPerpendicular magnetizationElectron
Provided is a magnetic tunneling junction device including a first structure including a magnetic layer; a second structure including at least two extrinsic perpendicular magnetization structures, each including a magnetic layer and; a perpendicular magnetization inducing layer on the magnetic layer; and a tunnel barrier between the first and second structures.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Magnetic memory element and driving method for same
ActiveUS20120134201A1Reduce switchingLow densityNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsPerpendicular magnetizationIn plane
A magnetic memory element and a method of driving such an element are disclosed. The magnetic memory element has a magnetic tunnel junction portion with a spin-valve structure having a perpendicular magnetization free layer formed of a perpendicular magnetization film, a perpendicular magnetization pinned layer formed of a perpendicular magnetization film, and a nonmagnetic layer sandwiched between the perpendicular magnetization free layer and the perpendicular magnetization pinned layer, and records information by application of an electric pulse to the magnetic tunnel junction portion. An in-plane magnetization film, interposed in the path of the electric pulse, is disposed in the magnetic tunnel junction portion. The in-plane magnetization film is configured so as to exhibit antiferromagnetic (low-temperature)-ferromagnetic (high-temperature) phase transitions depending on temperature changes based on application of the electric pulse to the magnetic tunnel junction portion.
Owner:III HLDG 3
Bipolar spin-transfer switching
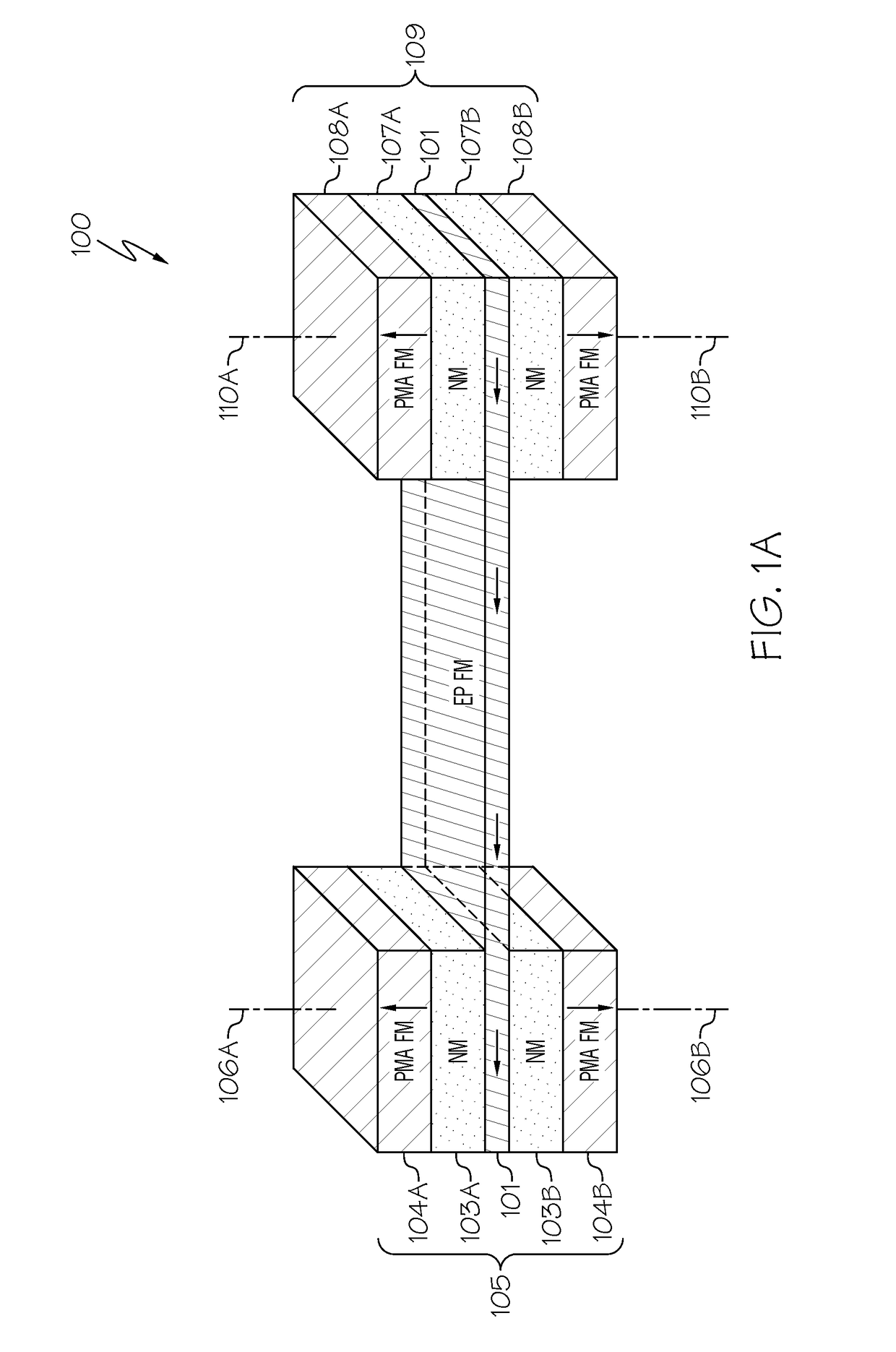
InactiveUS8755222B2Enhanced informationOperational advantageDigital storageSemiconductor devicesPerpendicular magnetizationRandom access memory
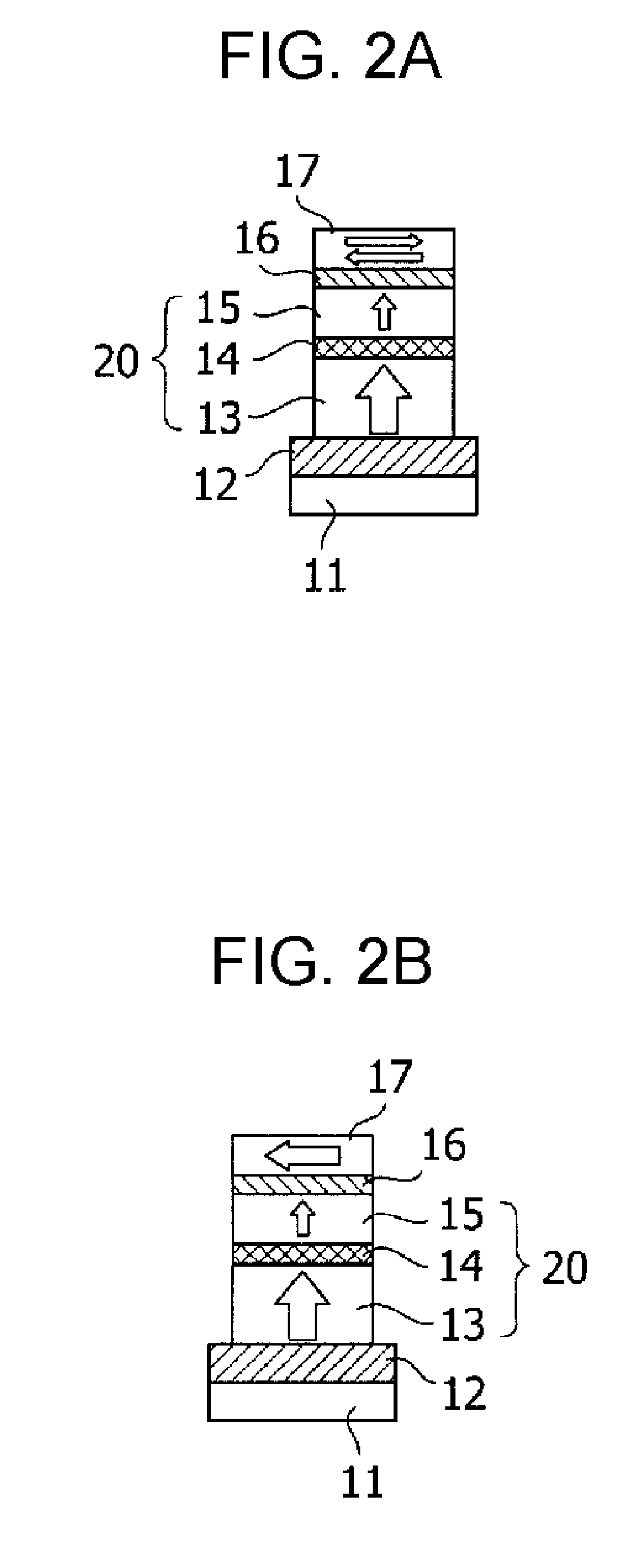
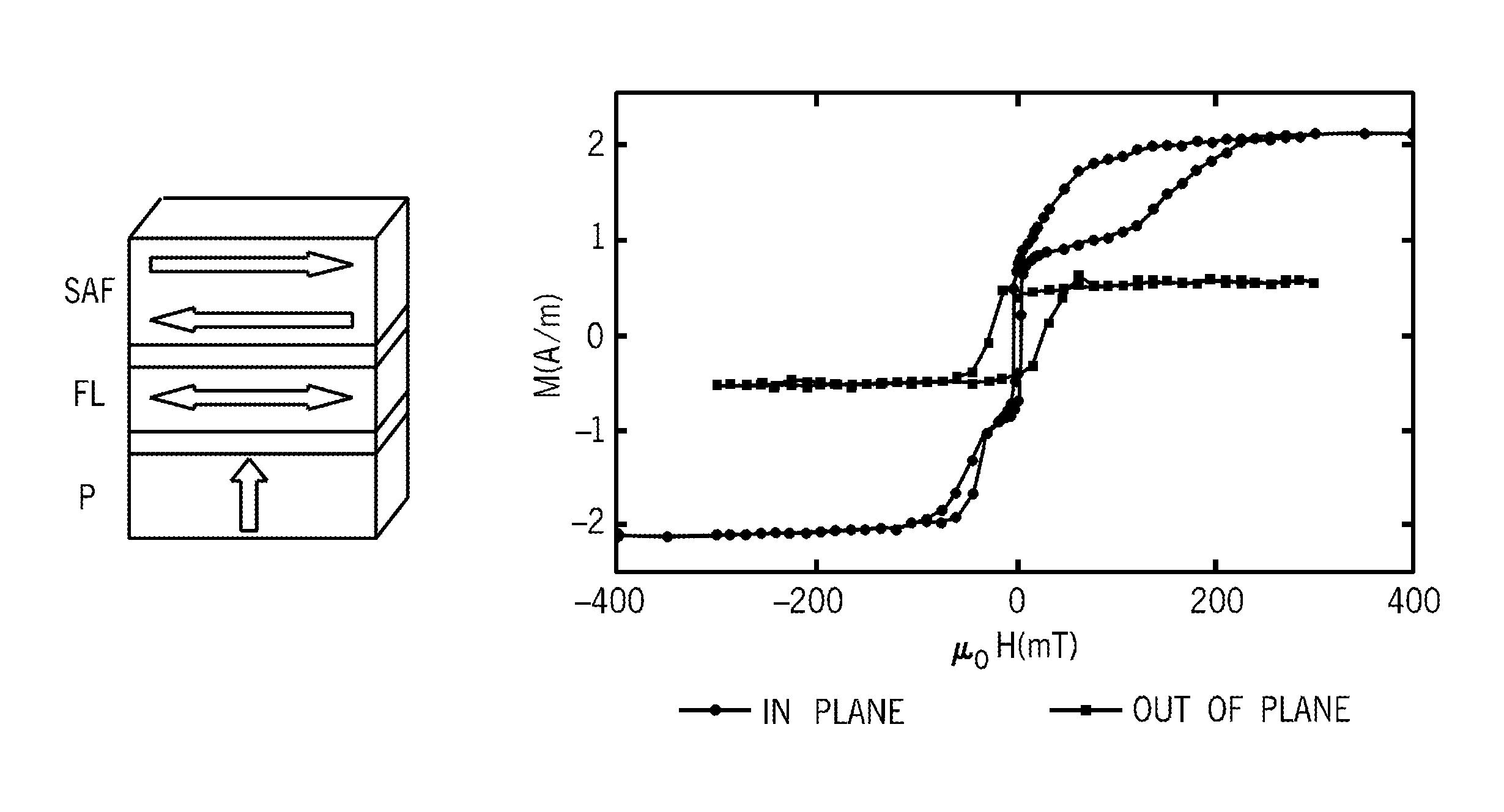
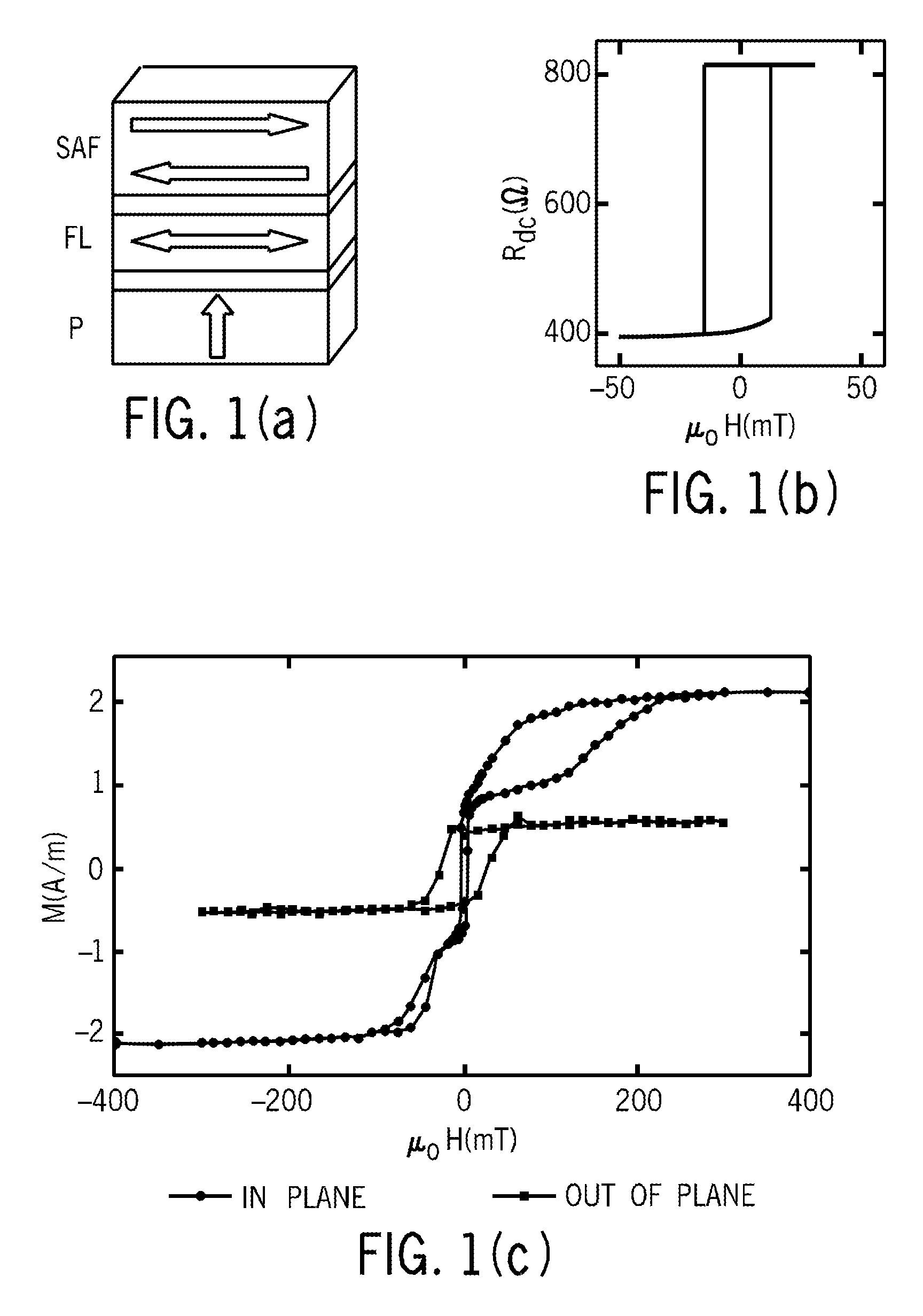
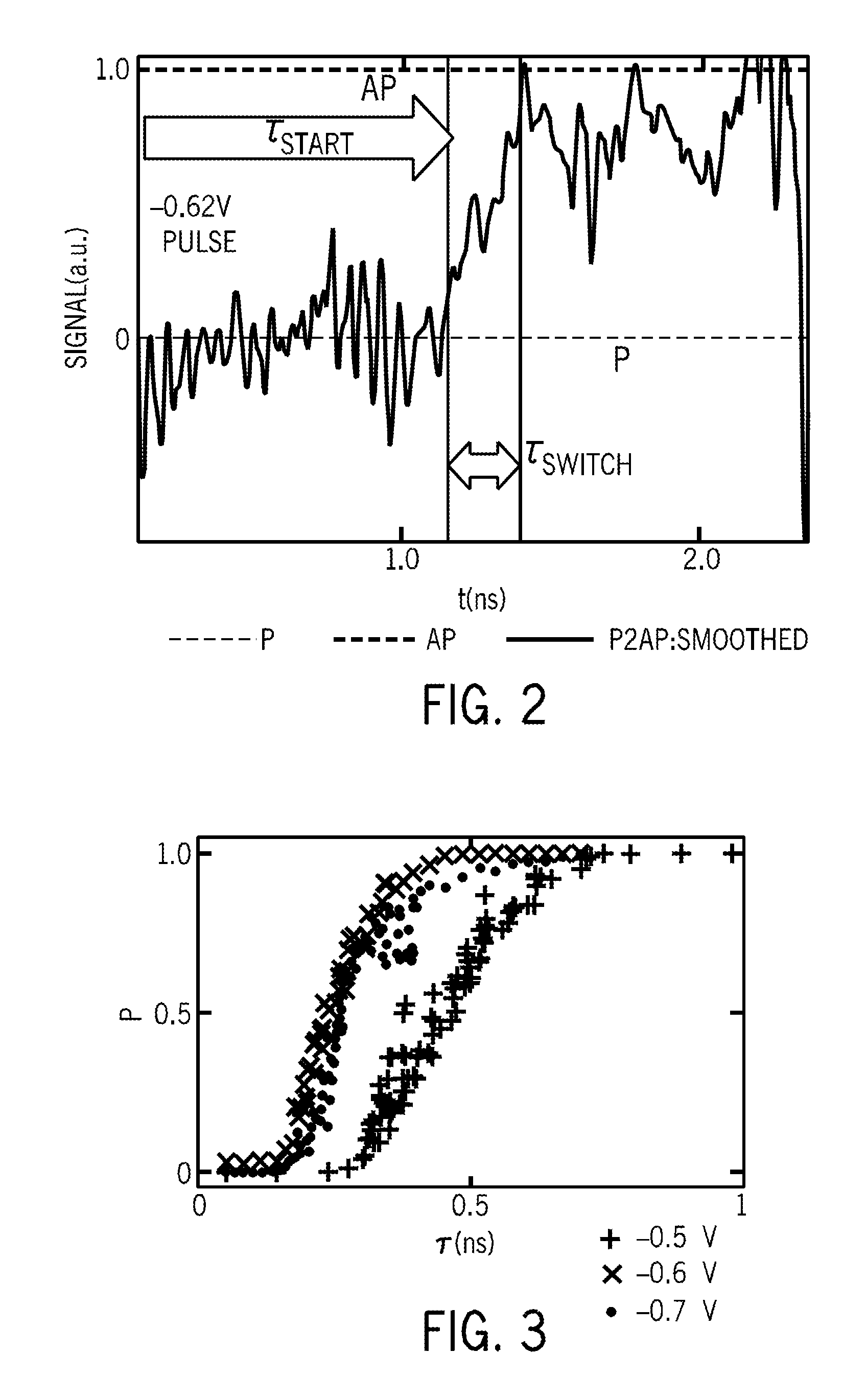
Orthogonal spin-transfer magnetic random access memory (OST-MRAM) uses a spin-polarizing layer magnetized perpendicularly to the free layer to achieve large spin-transfer torques and ultra-fast energy efficient switching. OST-MRAM devices that incorporate a perpendicularly magnetized spin-polarizing layer and a magnetic tunnel junction, which consists of an in-plane magnetized free layer and synthetic antiferromagnetic reference layer, exhibit improved performance over prior art devices. The switching is bipolar, occurring for positive and negative polarity pulses, consistent with a precessional reversal mechanism, and requires an energy less than 450 fJ and may be reliably observed at room temperature with 0.7 V amplitude pulses of 500 ps duration.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Multibit Cell of Magnetic Random Access Memory With Perpendicular Magnetization
ActiveUS20120155164A1Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesPerpendicular magnetizationBit line
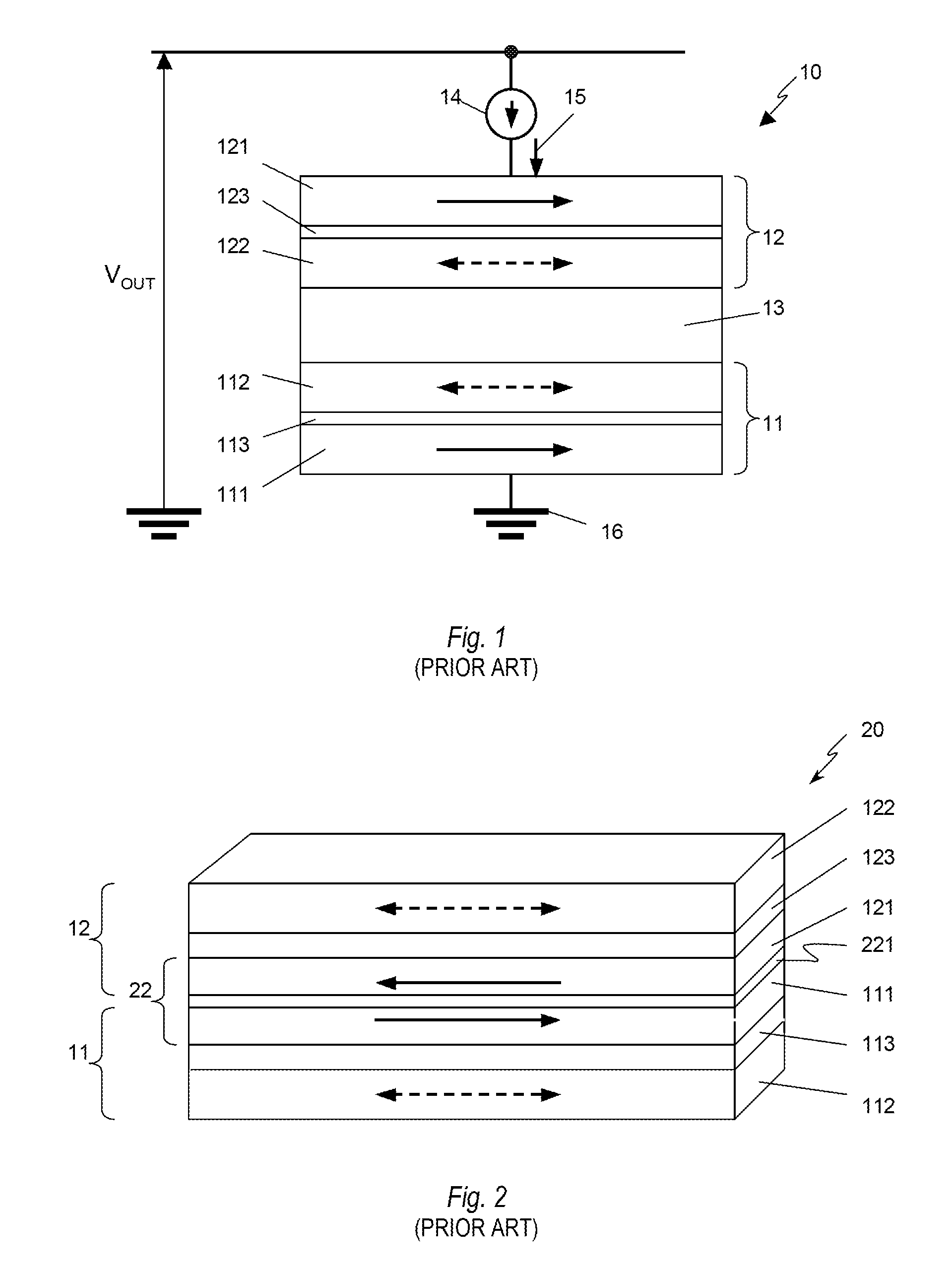
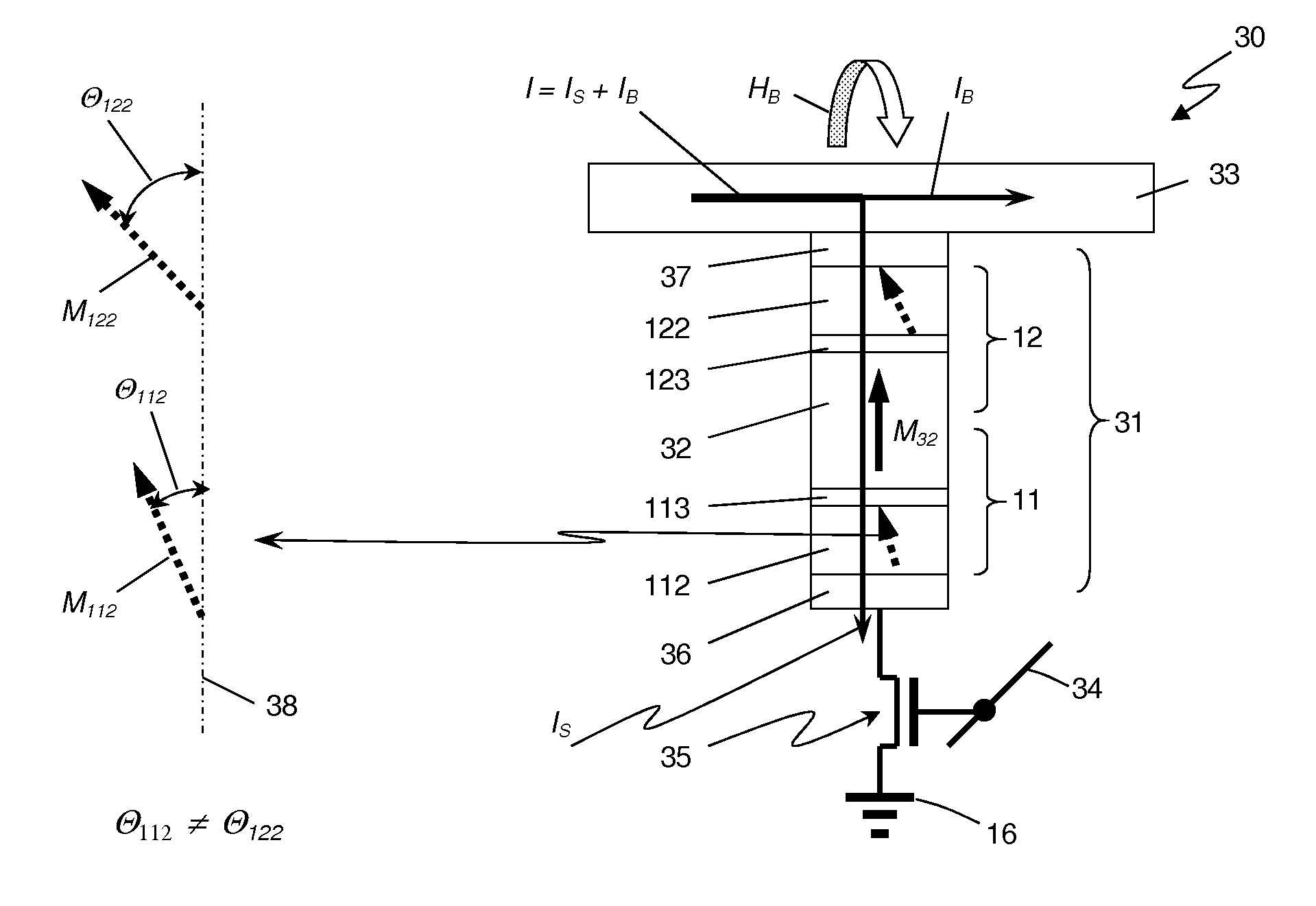
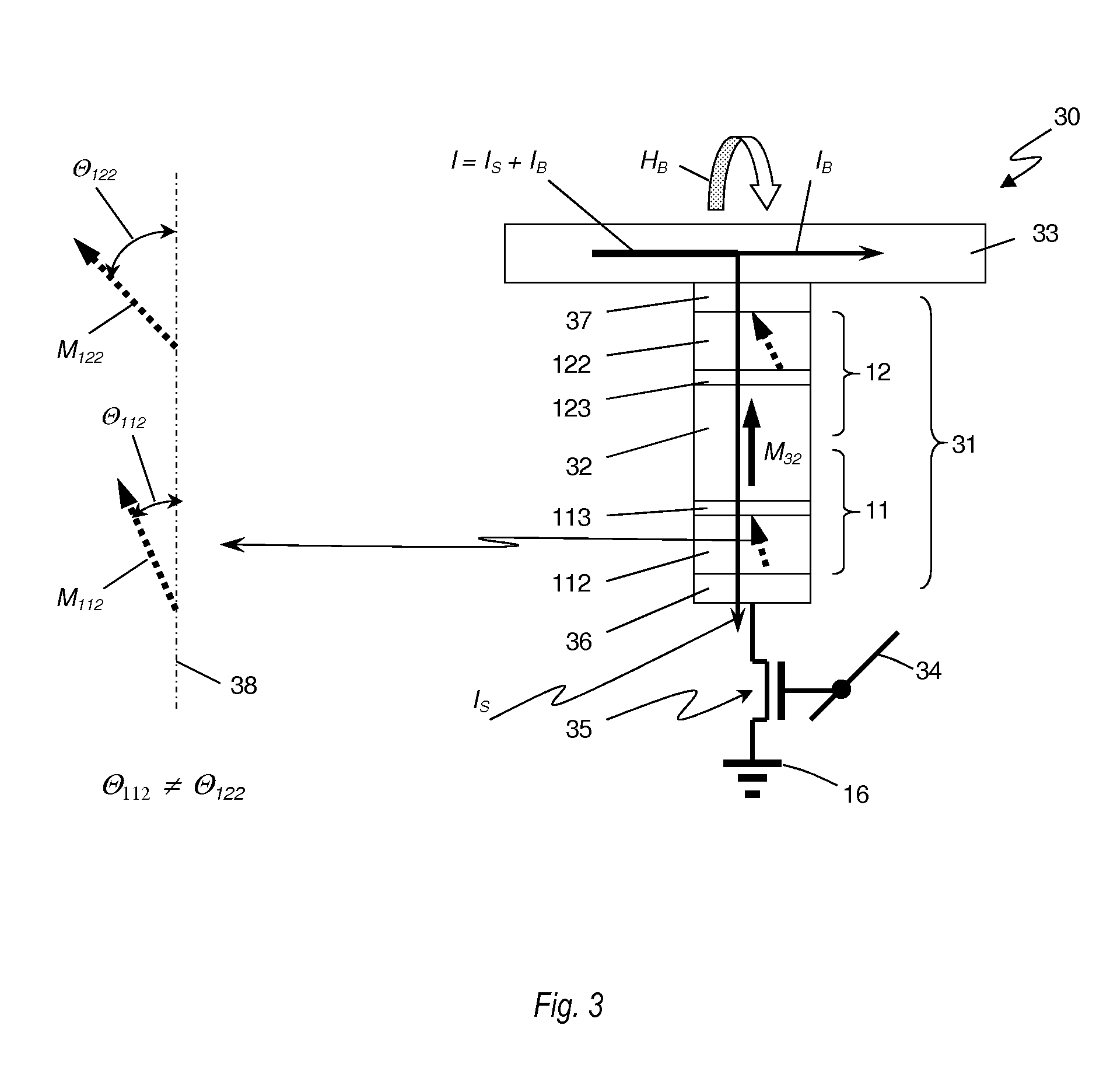
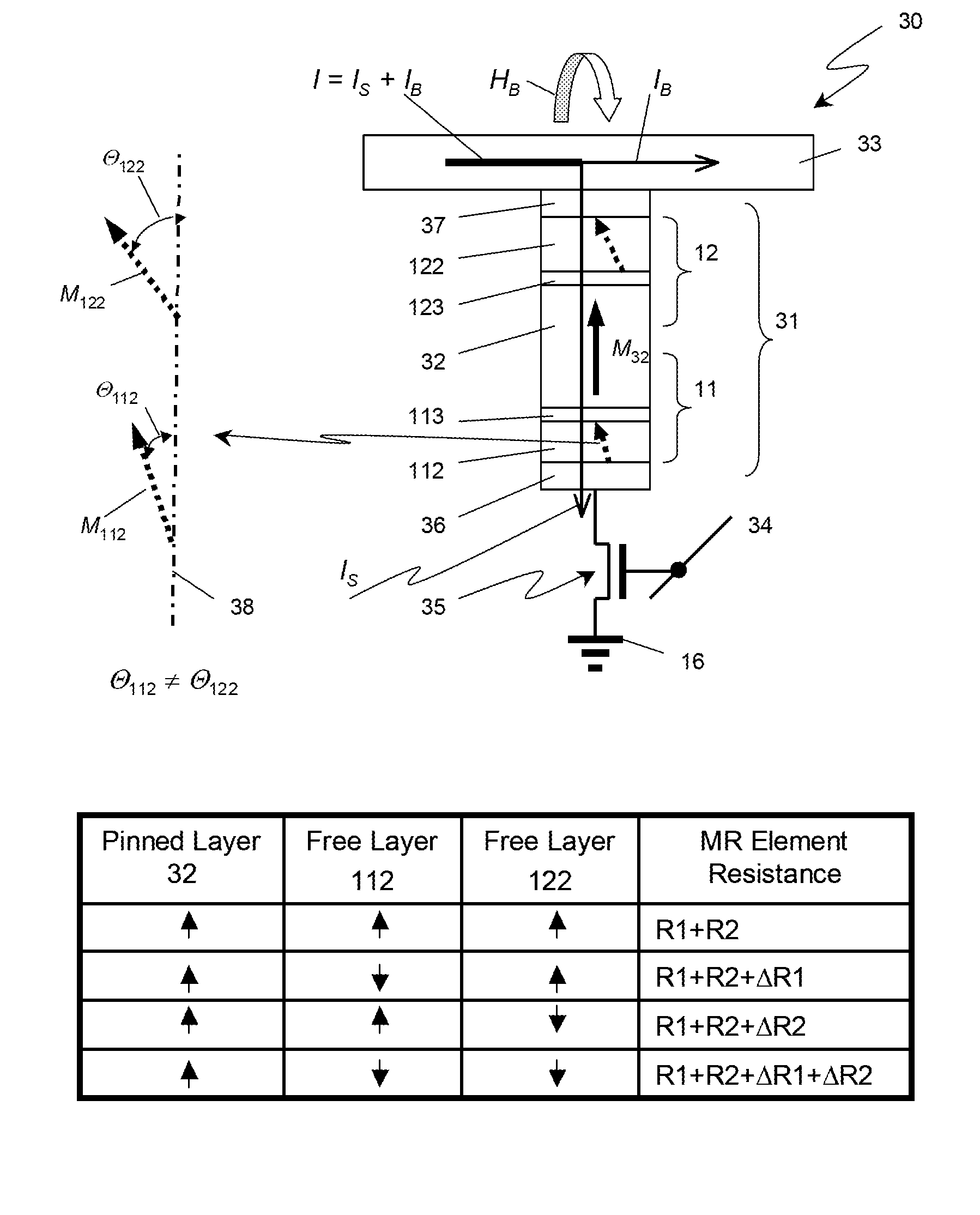
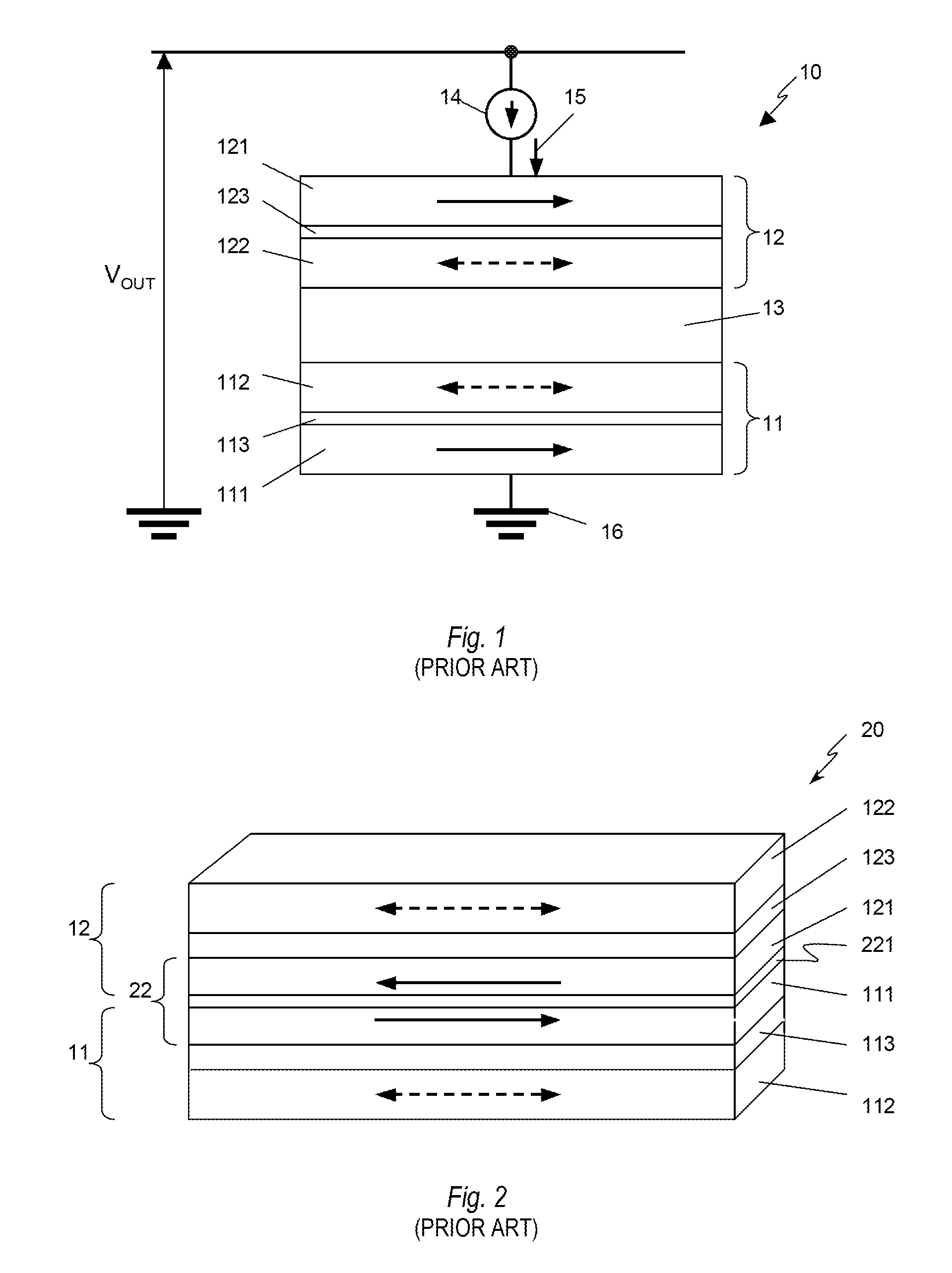
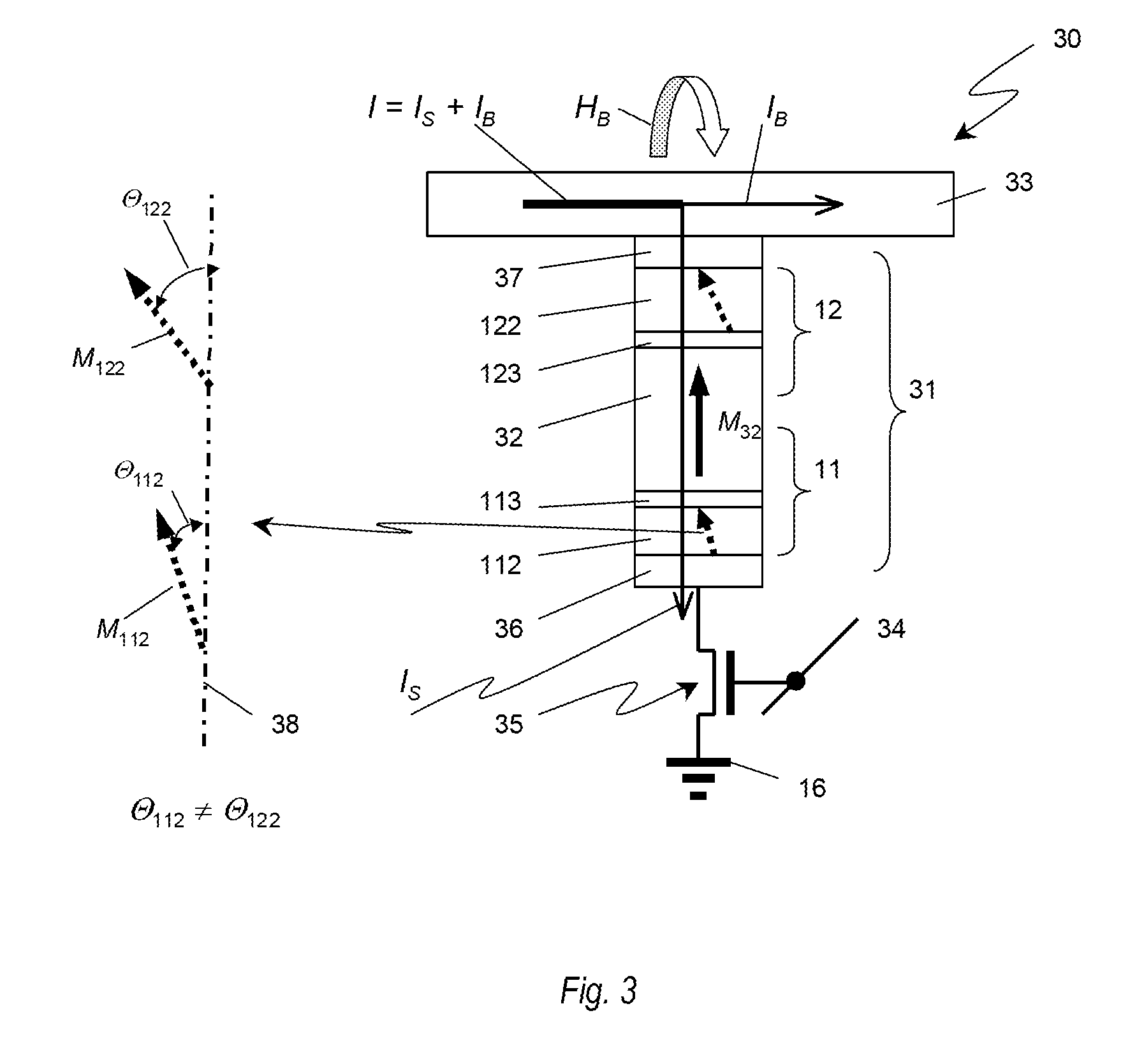
A multi-bit cell of magnetic random access memory comprises a magnetic tunnel junction element including a first and second free layer comprising a changeable magnetization oriented substantially perpendicular to a layer plane in its equilibrium state and a switching current, a first and second tunnel barrier layer, and a pinned layer comprising a fixed magnetization oriented substantially perpendicular to a layer plane, the pinned layer is disposed between the first and second free layers and is separated from the free layers by one of the tunnel barrier layers, a selection transistor electrically connected to a word line, and a bit line intersecting the word line. The magnetic tunnel junction element is disposed between the bit line and the selection transistor and is electrically connected to the bit line and the selection transistor, wherein the first and second free layers have substantially different switching currents.
Owner:SHUKH ALEXANDER MIKHAILOVICH
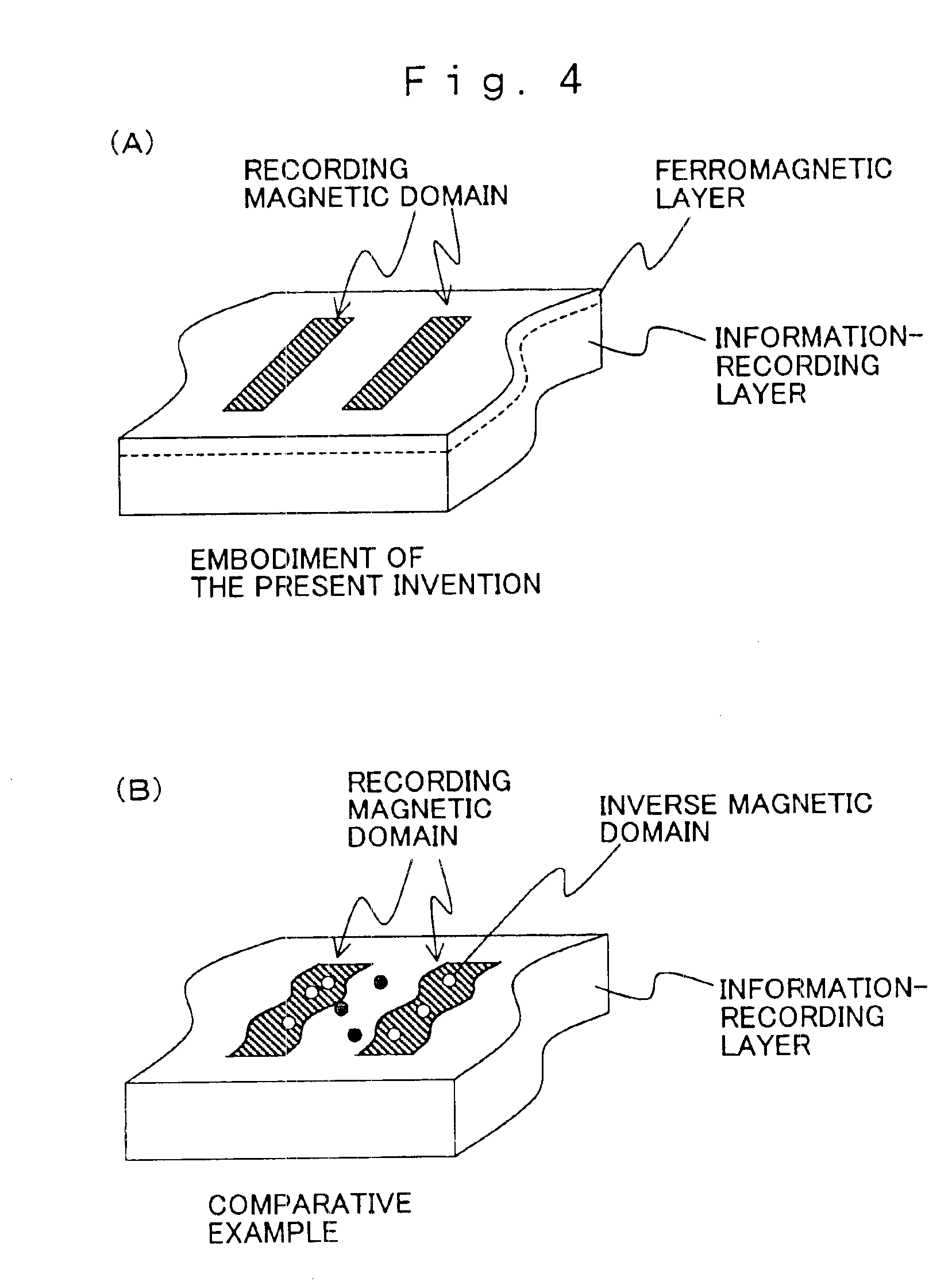
Magnetic recording medium with high thermal stability, method for producing the same, and magnetic recording apparatus
InactiveUS6893746B1Large anisotropyHigh densityRecord information storageDisk carriersPerpendicular magnetizationHigh density
A magnetic recording medium comprises an information-recording film and a ferromagnetic film on a substrate. The information-recording film is composed of, for example, an amorphous ferrimagnetic material having perpendicular magnetization. Further, the ferromagnetic film is composed of a magnetic material which has saturation magnetization larger than that of the information-recording film. Accordingly, the leak magnetic flux from the ferromagnetic film is larger than that from the information-recording film. The magnetic recording medium and a magnetic recording apparatus are obtained, which are excellent in thermal stability and which are preferred to perform super high density recording.
Owner:HITACHT MAXELL LTD
Magnetic device having perpendicular magnetization and interaction compensating interlayer
InactiveUS7772659B2Improve stabilityLess sensitiveSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPerpendicular magnetizationAntiferromagnetic coupling
The magnetic device comprises a least two layers made of a magnetic material that are separated by at least one interlayer made of a non-magnetic material. The layers made of a magnetic material each have magnetization oriented substantially perpendicular to the plane of the layers. The layer of non-magnetic material induces an antiferromagnetic coupling field between the layers made of a magnetic material, the direction and amplitude of this field attenuating the effects of the ferromagnetic coupling field of magnetostatic origin that occurs between the magnetic layers.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECH SCI 15
Magnetic memory using perpendicular magnetization film
InactiveUS6844605B2NanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsPerpendicular magnetizationMagnetic reluctance
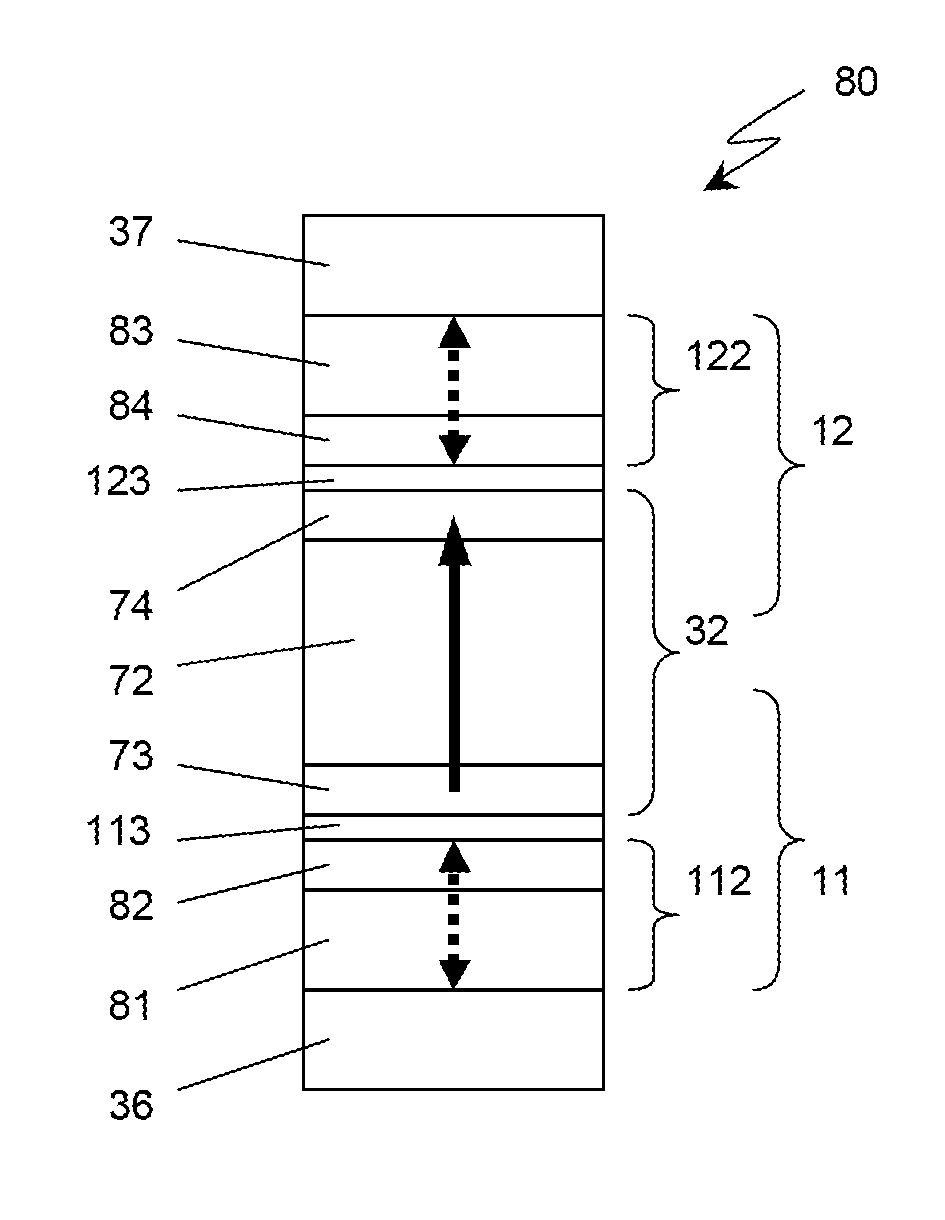
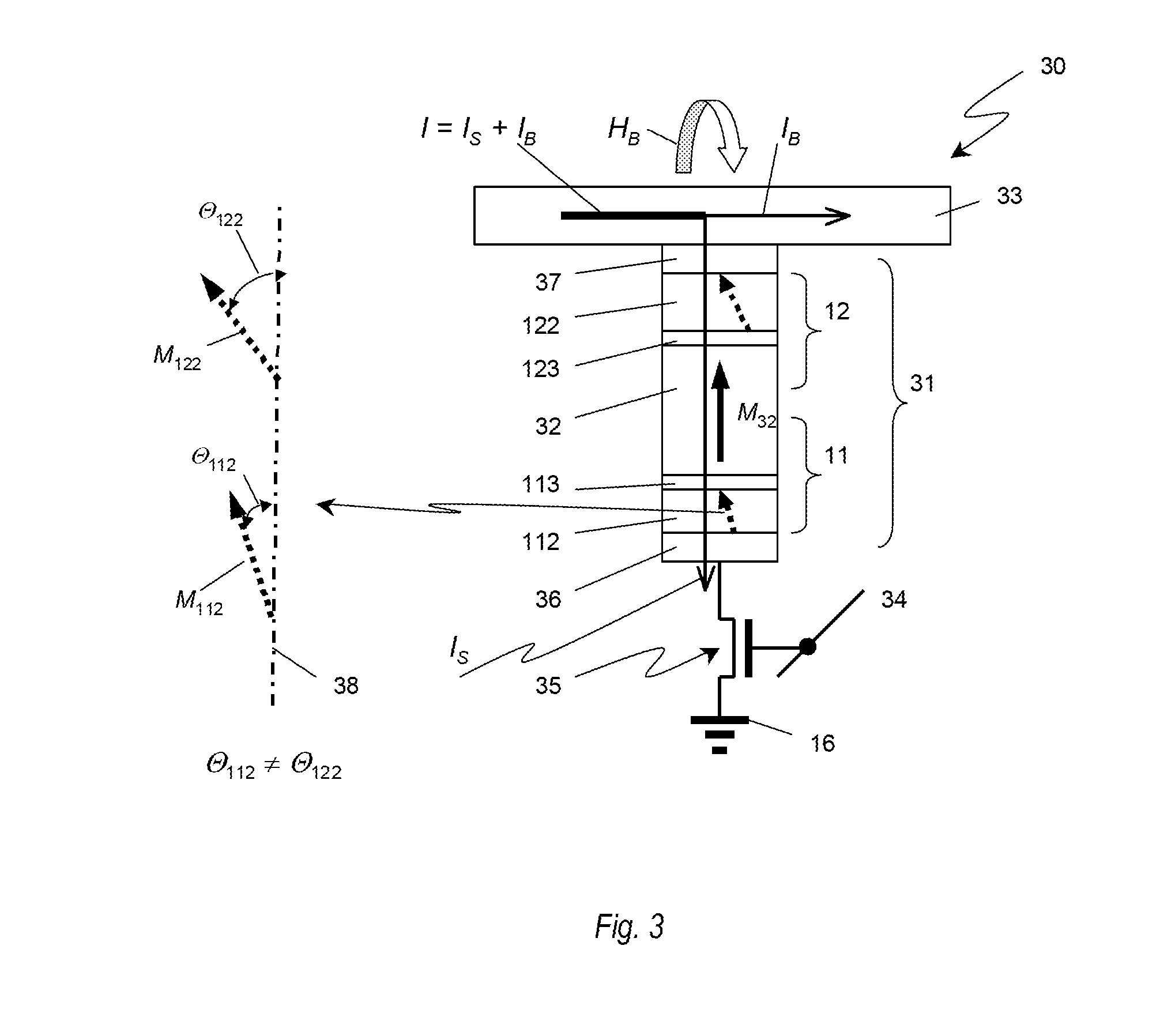
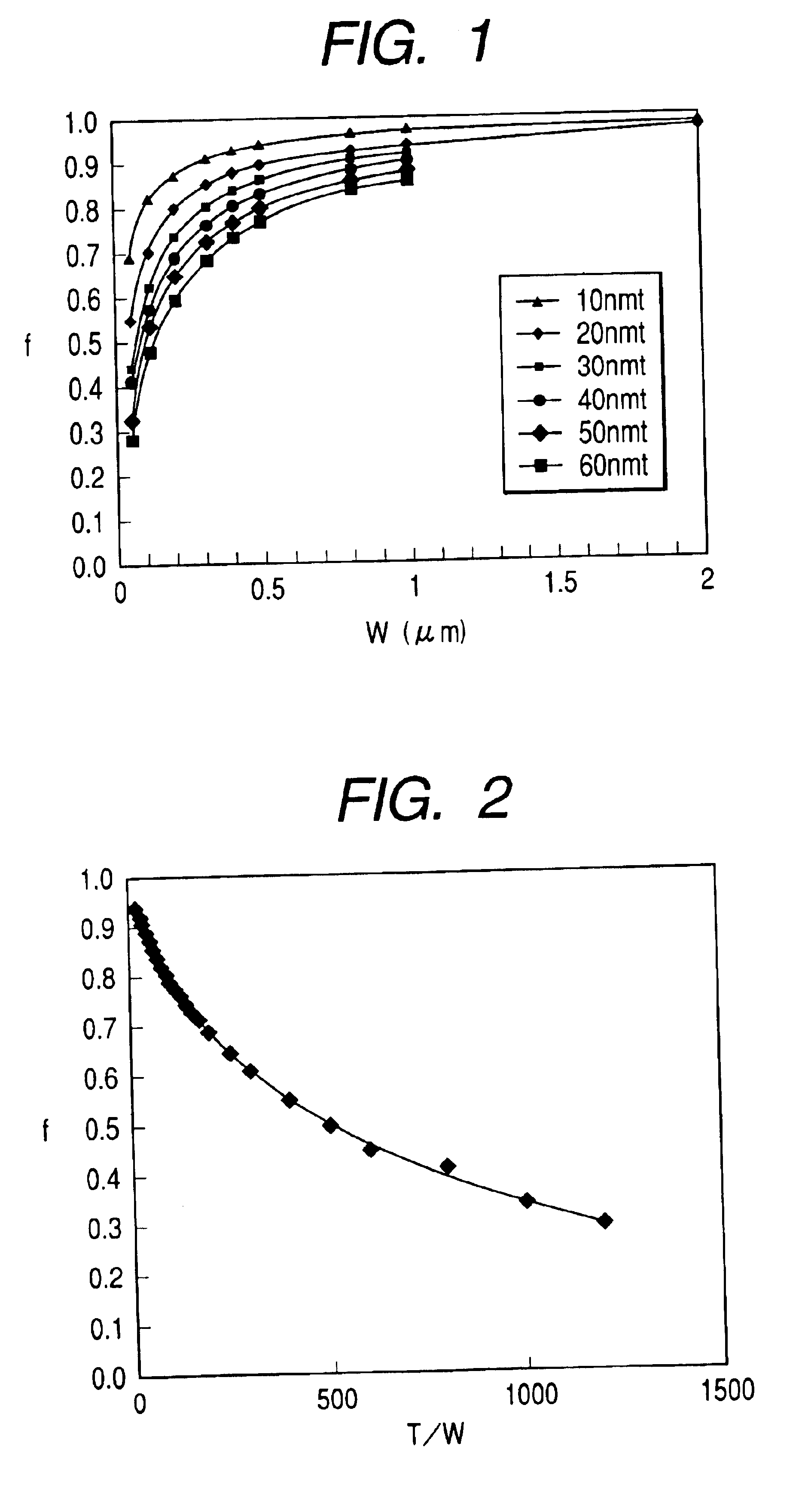
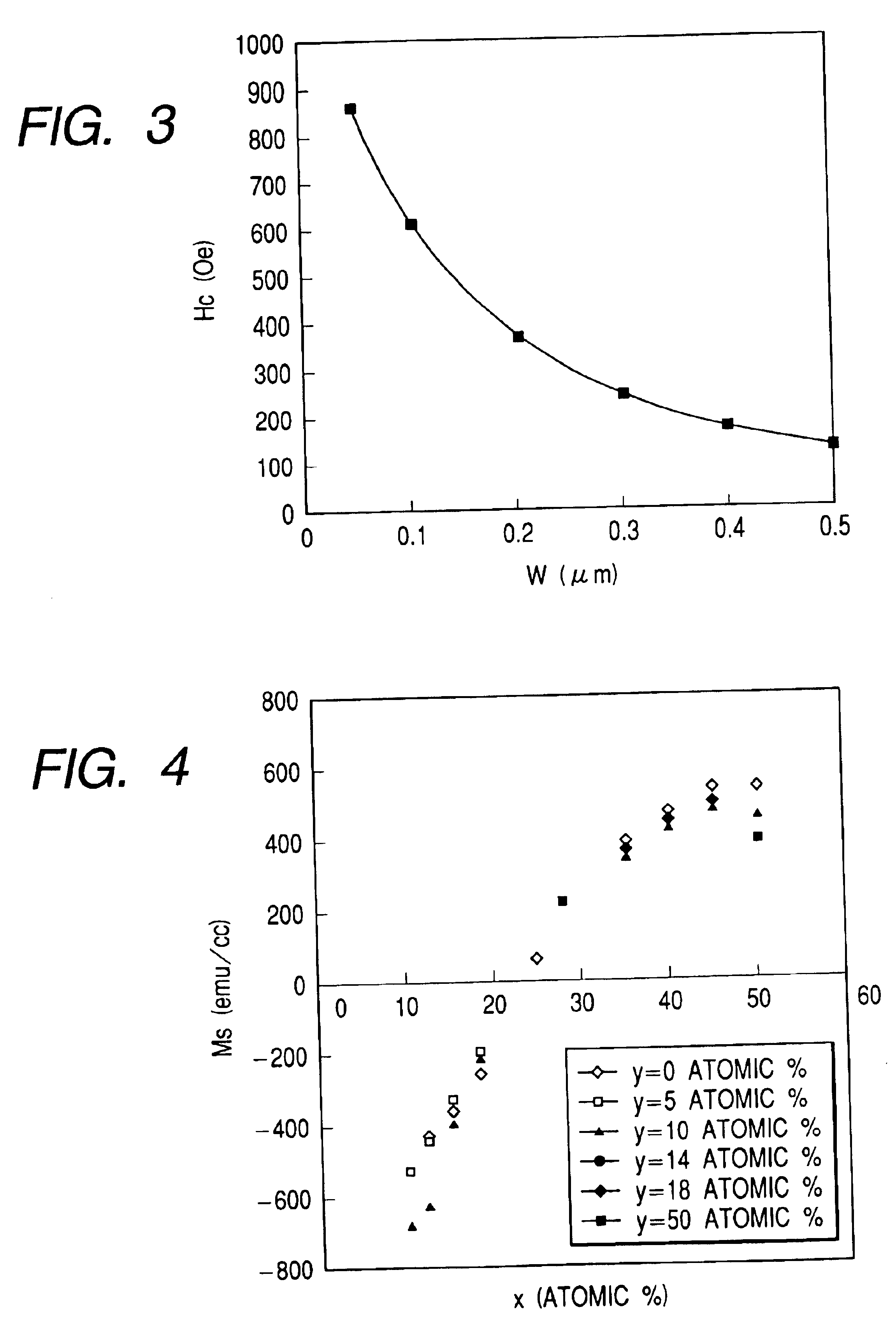
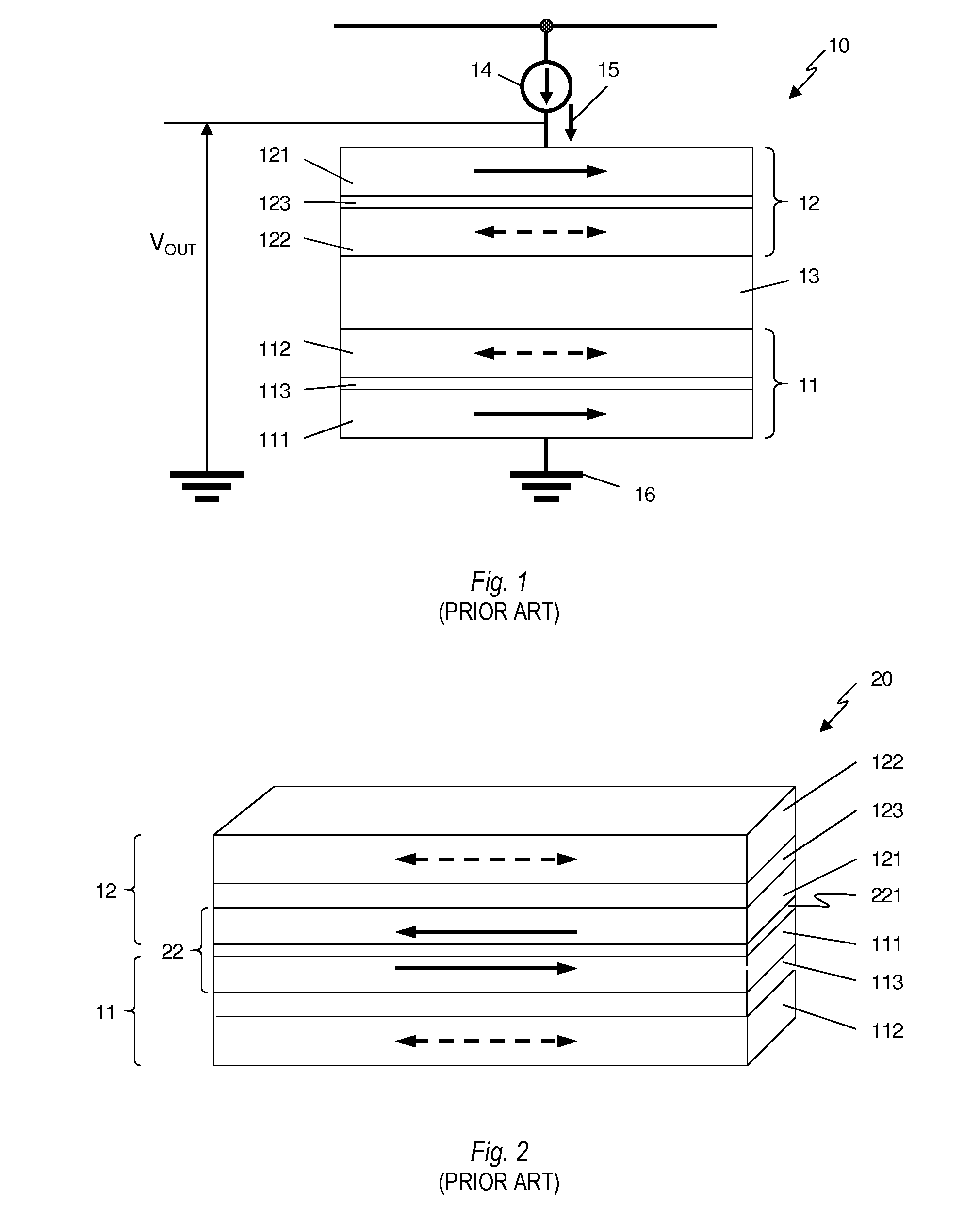
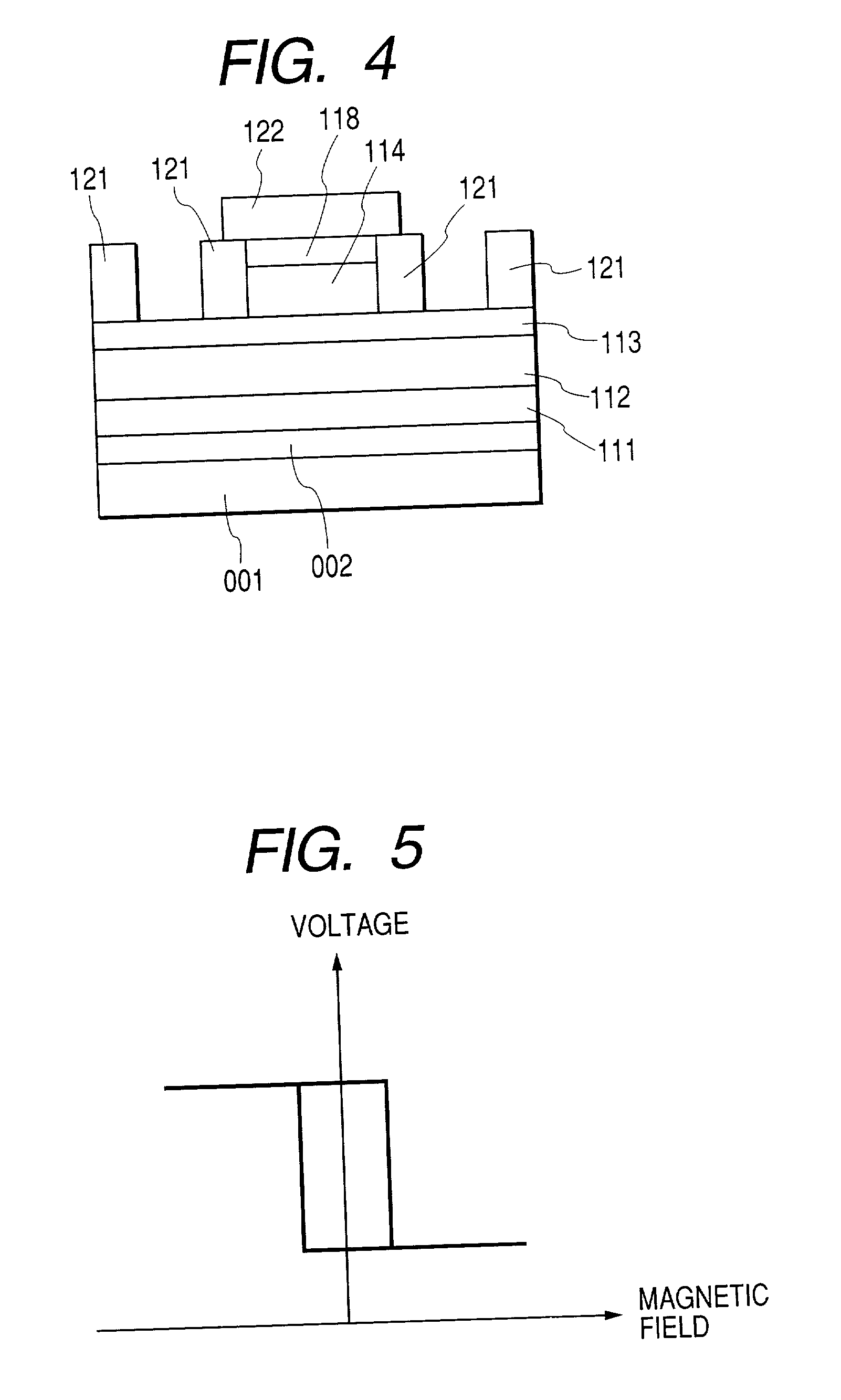
In a magnetoresistive element of a magnetic memory, a inversion field Hc of at least a first magnetic layer is given by Hc=2(Ku-2π Ms2f)Mswhere Ku and Ms are the perpendicular magnetic anisotropy constant and saturation magnetization of the first magnetic layer. The inversion field Hc is set smaller than a magnetic field generated by a magnetic field generation mechanism. Letting T be the film thickness of the first magnetic layer and W be the width and length, f is a factor given byf=7×10−13(T / W)4−2×10−9(T / W)3+3×10−6(T / W)2−0.0019(T / W)+0.9681A magnetic memory manufacturing method is also disclosed.
Owner:CANON KK
Multibit Cell of Magnetic Random Access Memory with Perpendicular Magnetization
A multi-bit cell of magnetic random access memory comprises a magnetoresistive element including first and second free layers, each free layer comprising a reversible magnetization direction directed substantially perpendicular to a layer plane in its equilibrium state and a switching current, first and second tunnel barrier layers, and a pinned layer comprising a fixed magnetization direction directed substantially perpendicular to the layer plane, the pinned layer is disposed between the first and second free layers and is separated from the free layers by one of the tunnel barrier layers; a selection transistor electrically connected to a word line, and a bit line intersecting the word line; the magnetoresistive element is disposed between the bit line and the selection transistor and is electrically connected to the bit line and the selection transistor, wherein the first and second free layers have substantially different switching currents.
Owner:SHUKH ALEXANDER MIKHAILOVICH
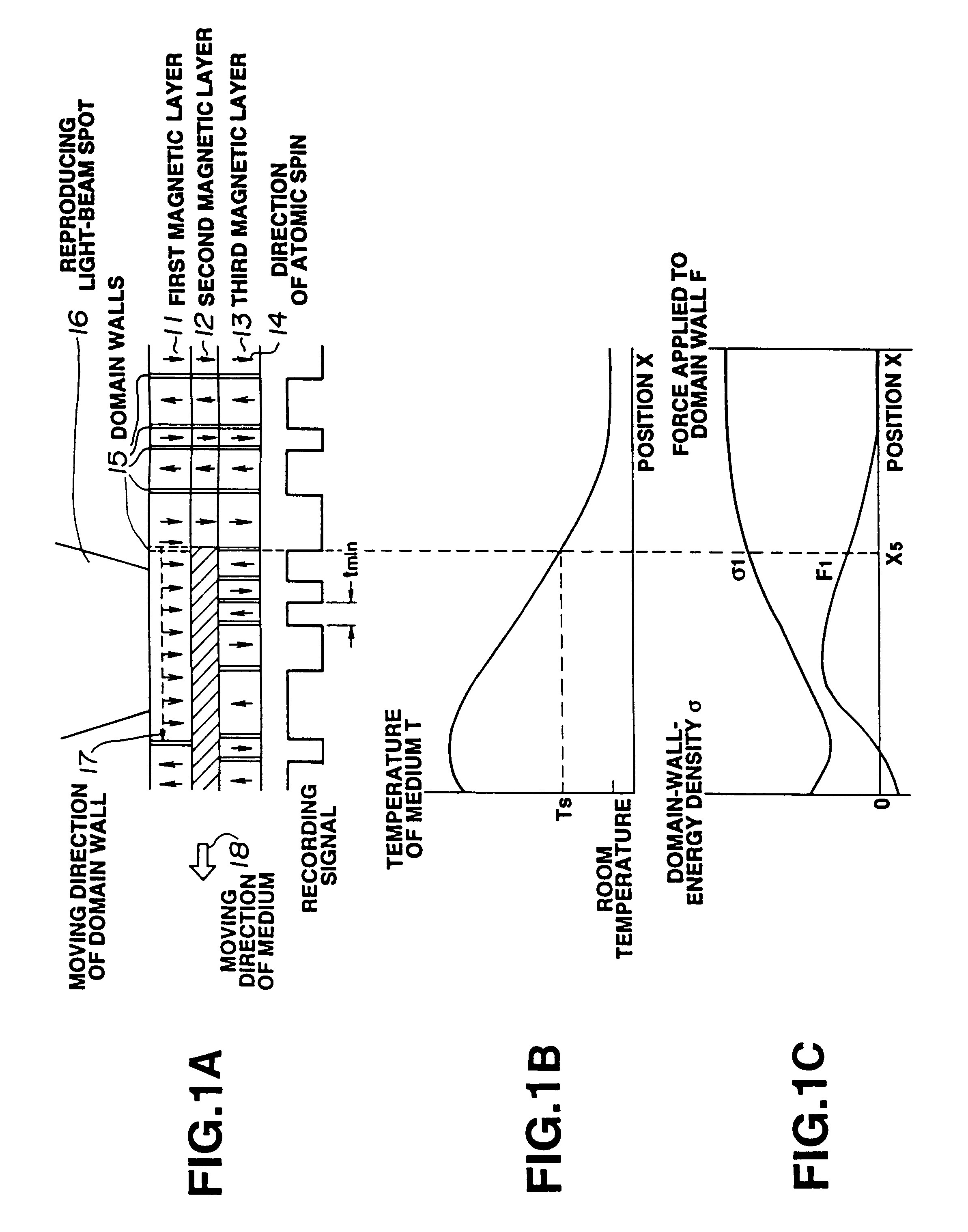
Magnetooptical recording medium on which high-density information can be recorded and method of reproducing the recorded information
InactiveUS6399174B1High densityRaise transfer toLayered productsRecord information storagePerpendicular magnetizationHigh density
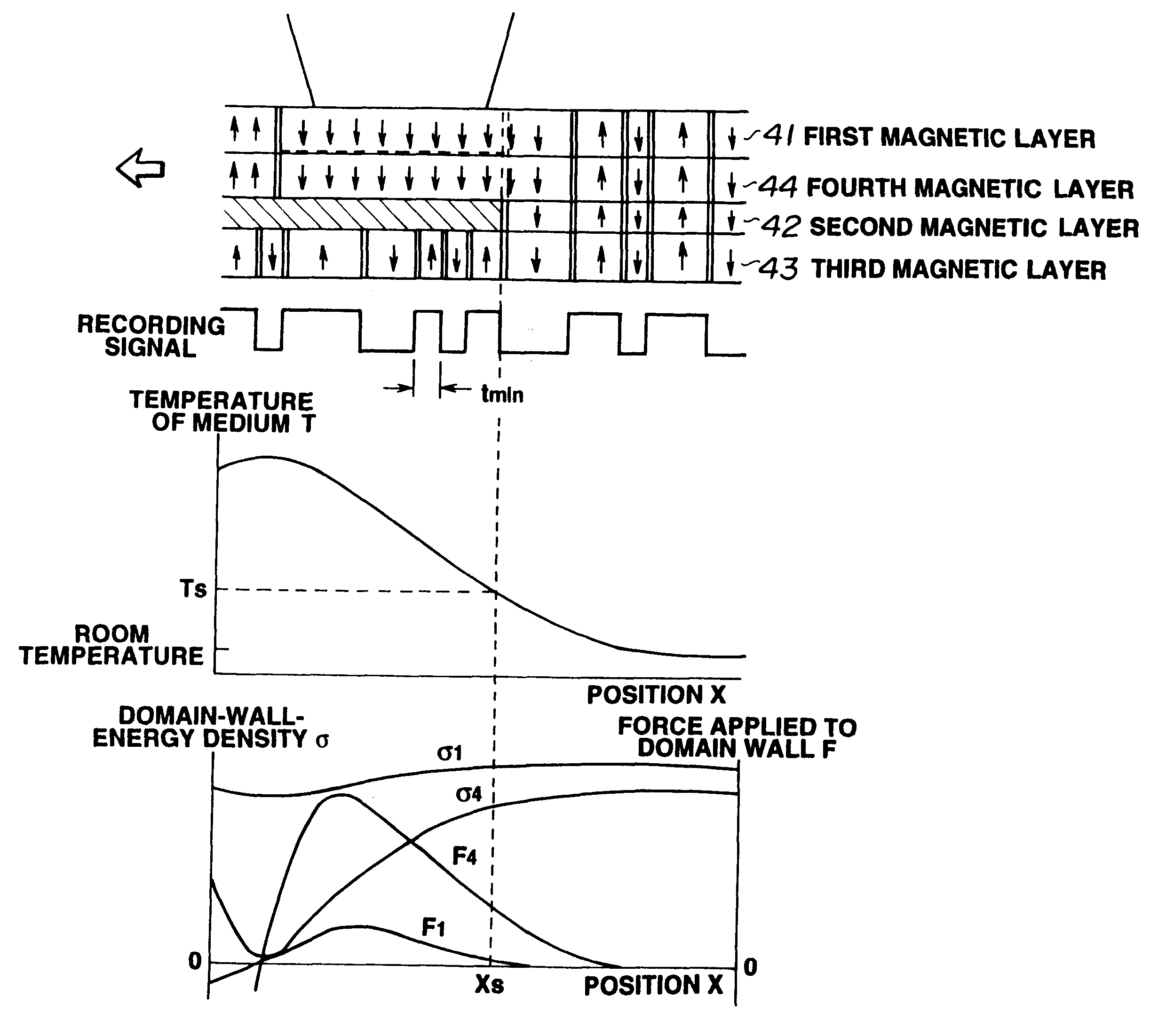
A magnetooptical recording medium includes a first magnetic layer, a second magnetic layer whose Curie temperature is lower than that of the first magnetic layer, and a third magnetic layer, comprising a vertically-magnetizing film, whose Curie temperature is higher than that of the second magnetic layer. The first magnetic layer, the second magnetic layer and the third magnetic layer are in a state of exchange coupling with each other at a portion of a vertically-magnetizing film. A domain walls formed in the first magnetic layer moves when the temperature of the medium has been raised to at least the Curie temperature of the second magnetic layer.
Owner:CANON KK
Magnetic memory bits with perpendicular magnetization switched by current-induced spin-orbit torques
ActiveUS9343658B2Easy to switchImprove efficiencyMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic device detailsIn planeMagnetic memory
A basic Spin-Orbit-Torque (SOT) structure with lateral structural asymmetry is provided that produces a new spin-orbit torque, resulting in zero-field current-induced switching of perpendicular magnetization. More complex structures can also be produced incorporating the basic structure of a ferromagnetic layer with a heavy non-magnetic metal layer having strong spin-orbit coupling on one side, and an insulator layer on the other side with a structural mirror asymmetry along the in-plane direction. The lateral structural asymmetry and new spin-orbit torque, in effect, replaces the role of the external in-plane magnetic field. The direction of switching is determined by the combination of the direction of applied current and the direction of symmetry breaking in the device.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Perpendicular magnetic recording medium and magnetic recording and reproducing apparatus using the same
InactiveUS20090073599A1High resolutionImprove the immunityRecord information storageAlignment for track following on disksPerpendicular magnetizationHigh density
Embodiments of the present invention provide a perpendicular magnetic recording medium suitable for high density recording. According to one embodiment, a magnetic recording layer comprises four layers in which a first magnetic layer, a magnetic coupling layer, a second magnetic layer, and a third magnetic layer are formed above a substrate. The first magnetic layer and the second magnetic layer are perpendicular magnetization films containing an oxide, and ferromagnetically coupled with each other by way of the magnetic coupling layer, and they are, more preferably, a Co alloy layer containing an oxide. The third magnetic layer is ferromagnetically coupled with the second magnetic layer. The concentration of the oxide contained in the third magnetic layer is lower than the concentration of the oxide in the second recording layer, or the third magnetic layer does not contain the oxide. In this case, magnetic property is set for the anisotropic magnetic field Hk1 of the first magnetic layer and the anisotropic magnetic field Hk2 of the second magnetic layer, so as to satisfy: Hk1>Hk2.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Perpendicular spin torque oscillator FMR frequency measurement method
ActiveUS20130069626A1Magnetic measurementsRecord information storageIn planeElectrical resistance and conductance
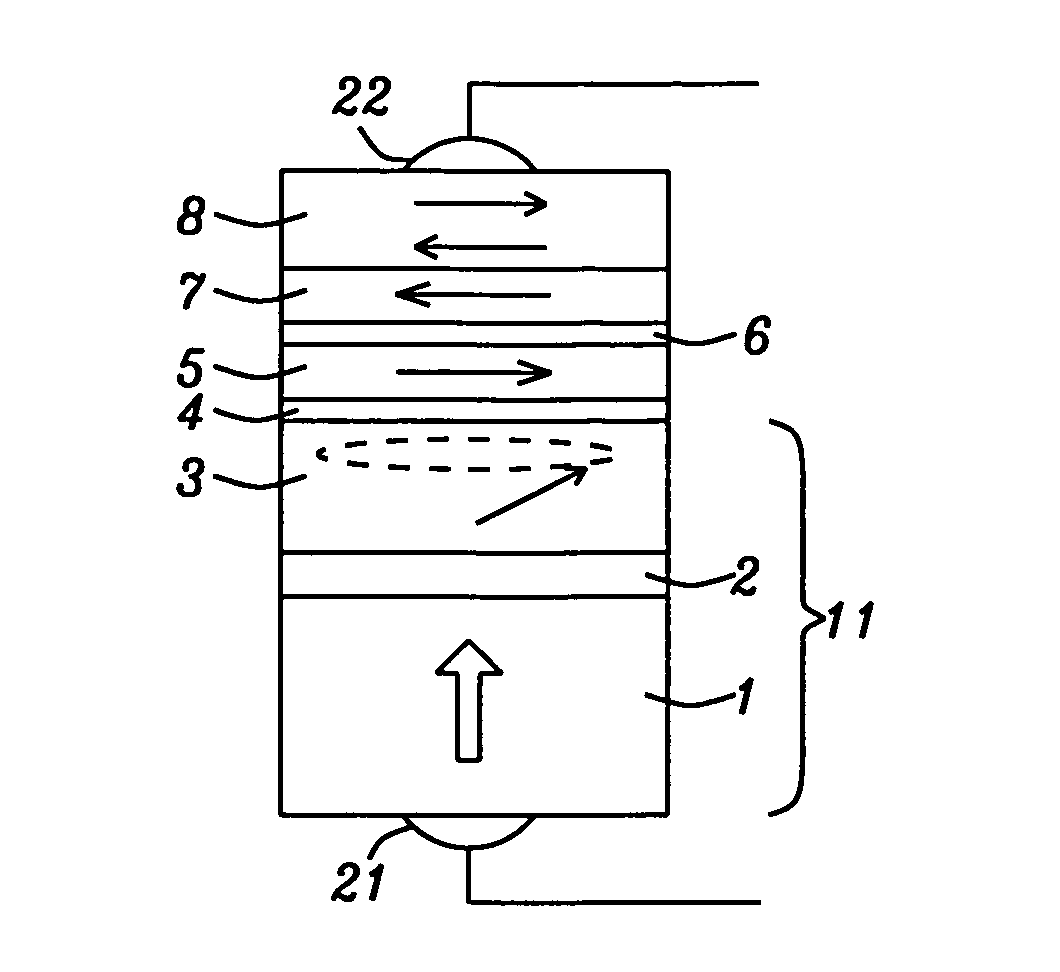
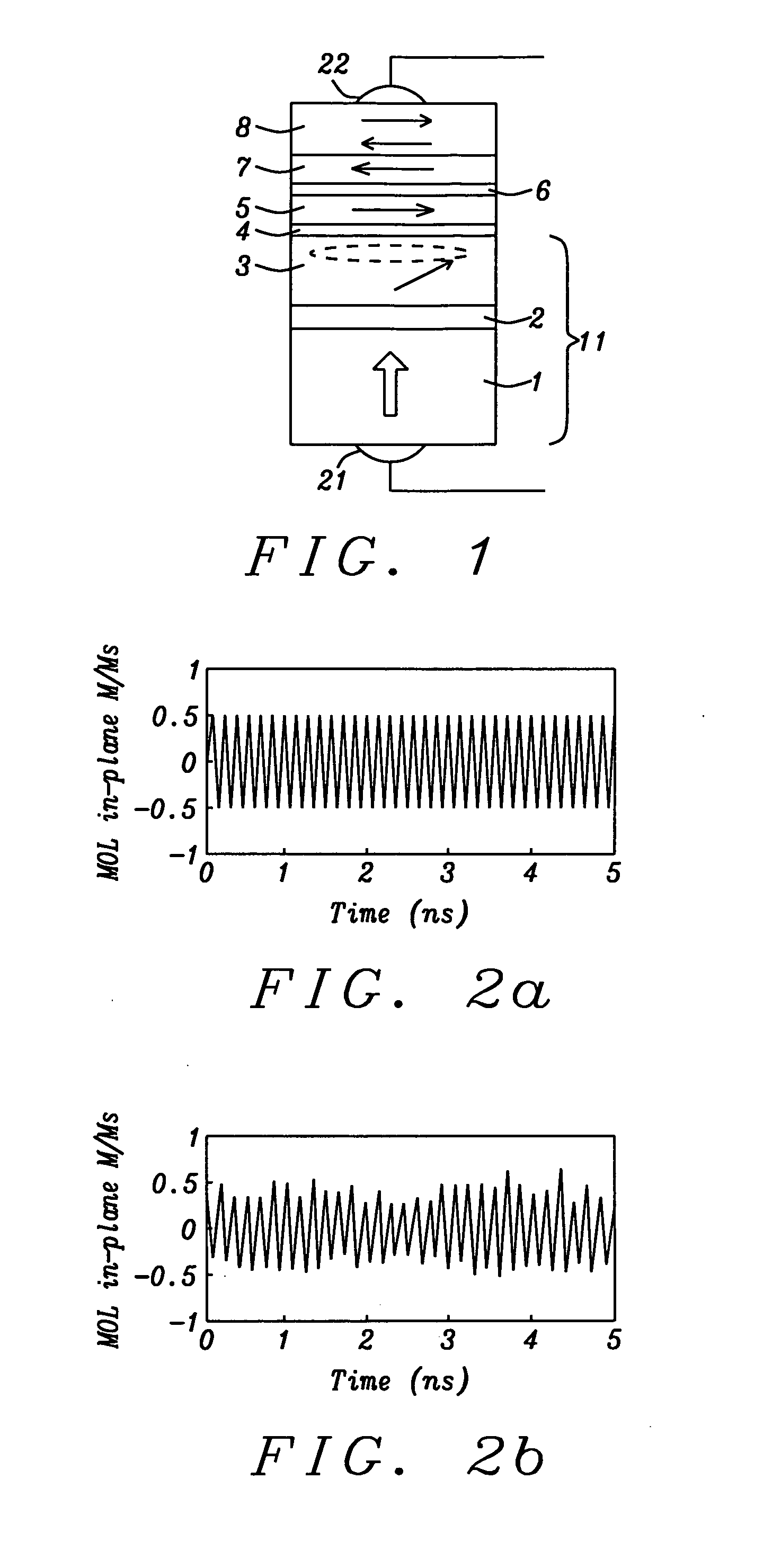
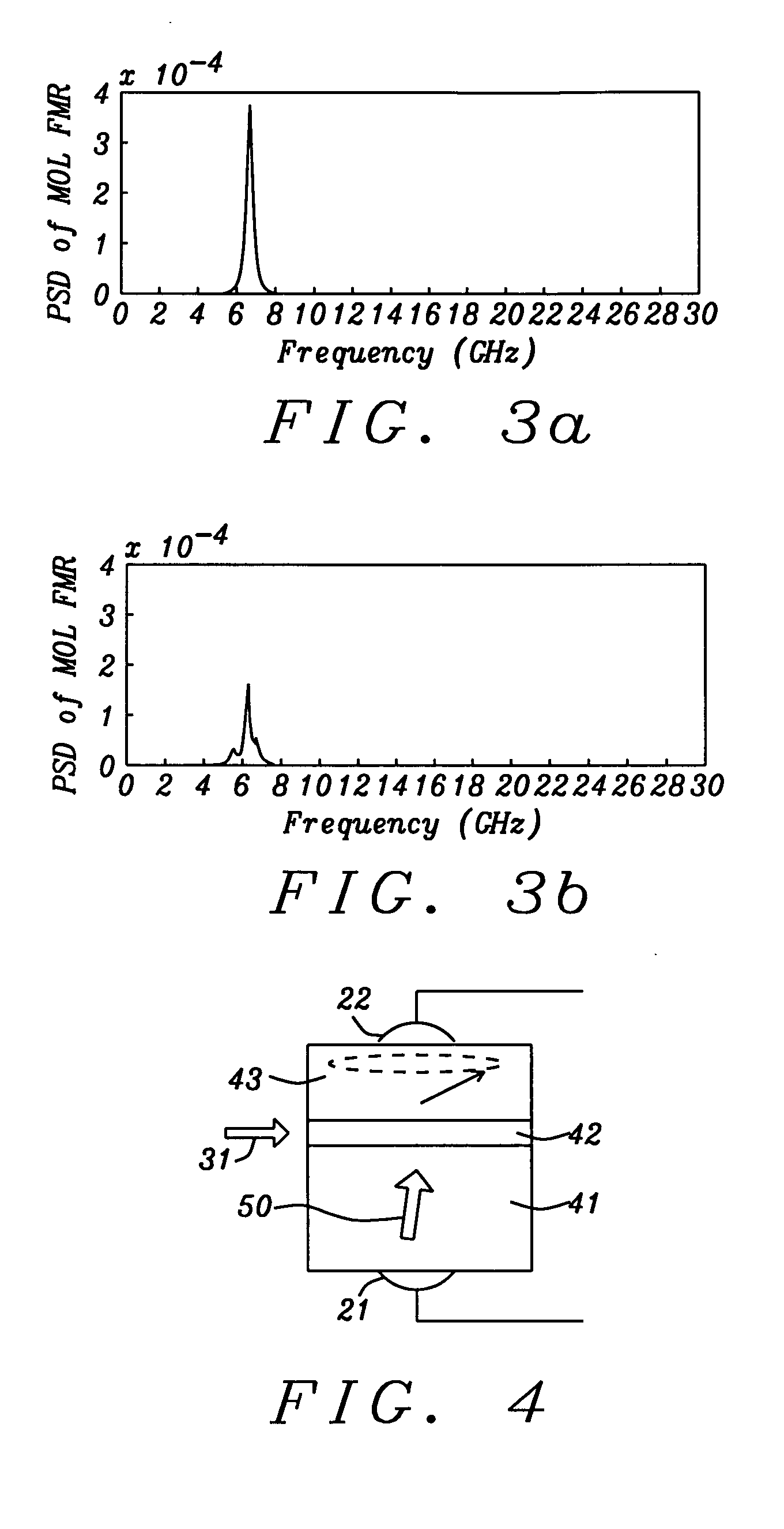
A method for measuring the frequency in a spin torque oscillator having at least a magnetic oscillation layer (MOL), junction layer, and magnetic reference layer (MRL) is disclosed. In a first embodiment, a small in-plane magnetic field is applied to the STO after a DC current is applied to excite the MOL into an oscillation state. The MRL has a perpendicular magnetization that is tilted slightly to give an in-plane magnetization component to serve as a reference layer for measuring the oscillation frequency of the MOL in-plane magnetization component. An AC voltage change is produced in the DC current as a result of variable STO resistance and directly correlates to MOL oscillation frequency. Alternatively, a field having both perpendicular and in-plane components may be applied externally or by forming the STO between two magnetic poles thereby producing an in-plane magnetization reference component in the MRL.
Owner:TOSHIBA ELECTRONICS DEVICES & STORAGE CORPORARTION +1
Spinning microwave oscillator based on vertical magnetizing free layer and manufacturing method thereof
The invention discloses a spinning microwave oscillator based on a vertical magnetizing free layer and a manufacturing method of the spinning microwave oscillator. The spinning microwave oscillator comprises a magnetic multilayer film and electrodes connected with the magnetic multilayer film, wherein the magnetic multilayer film comprises a seed layer, a first magnetic layer, a non-magnetic isolating layer, a magnetic free layer and a protecting layer; the first magnetic layer is formed on the seed layer and has an in-plane balanced magnetizing state; the non-magnetic isolating layer is formed on the first magnetic layer; the magnetic free layer with vertical magnetization is formed on the non-magnetic isolating layer; and the protecting layer is formed on the free layer. The manufacturing method of the spinning microwave oscillator comprises the steps of: forming the magnetic multilayer film on a substrate according to a magnetron sputtering method; processing the magnetic multilayer film into a nanometer columnar or point contact structure according to microelectronic technology; and arranging upper and lower electrodes on the magnetic multilayer film so as to form a target product. The spinning microwave oscillator can obtain high microwave power output without externally added magnetic field; the spinning microwave oscillator has the characteristics of small size, simple structure, adjustable broadband, easiness in integration and the like; the preparation is easily realized; and the cost is low.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Perpendicular magnetization magnetic element utilizing spin transfer
InactiveCN1938780AWrite lessNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsPerpendicular magnetizationMagnetic memory
A method and system for providing a magnetic element that can be used in a magnetic memory is disclosed. The method and system include providing a first pinned layer, a barrier layer, a free layer, a conductive nonmagnetic spacer layer, and a second pinned layer. Each pinned layer has a pinned layer easy axis. At least a portion of the pinned layer easy axis is in a perpendicular direction. The barrier layer resides between the first pinned layer and the free layer. The spacer layer is between the free layer and the second pinned layer. The free layer has a free layer easy axis, at least a portion of which is in the perpendicular direction. The magnetic element is also configured to allow the free layer to be switched due to spin transfer effect when a write current is passed through the magnetic element. Because of the perpendicular magnetization(s), the writing current for spin transfer may be significantly reduced.
Owner:GRANDIS
Electric field assisted perpendicular stt-mram
ActiveUS20140203341A1Decreasing perpendicular anisotropy strengthEasy to switchSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMagnetic reluctanceRecording layer
A perpendicular STT-MRAM comprises apparatus, a method of operating and a method of manufacturing a spin-torque magnetoresistive memory and a plurality of magnetoresistive memory element having a recording layer which has an interface interaction with an underneath dielectric functional layer. The energy switch barrier of the recording layer is reduced under an electric field applying along a perpendicular direction of the functional with a proper voltage on a digital line from a control circuitry; accordingly, the perpendicular magnetization of the recording layer is readily reversible in a low spin-transfer switching current.
Owner:SHANGHAI CIYU INFORMATION TECH
Spin Transistor Using Perpendicular Magnetization
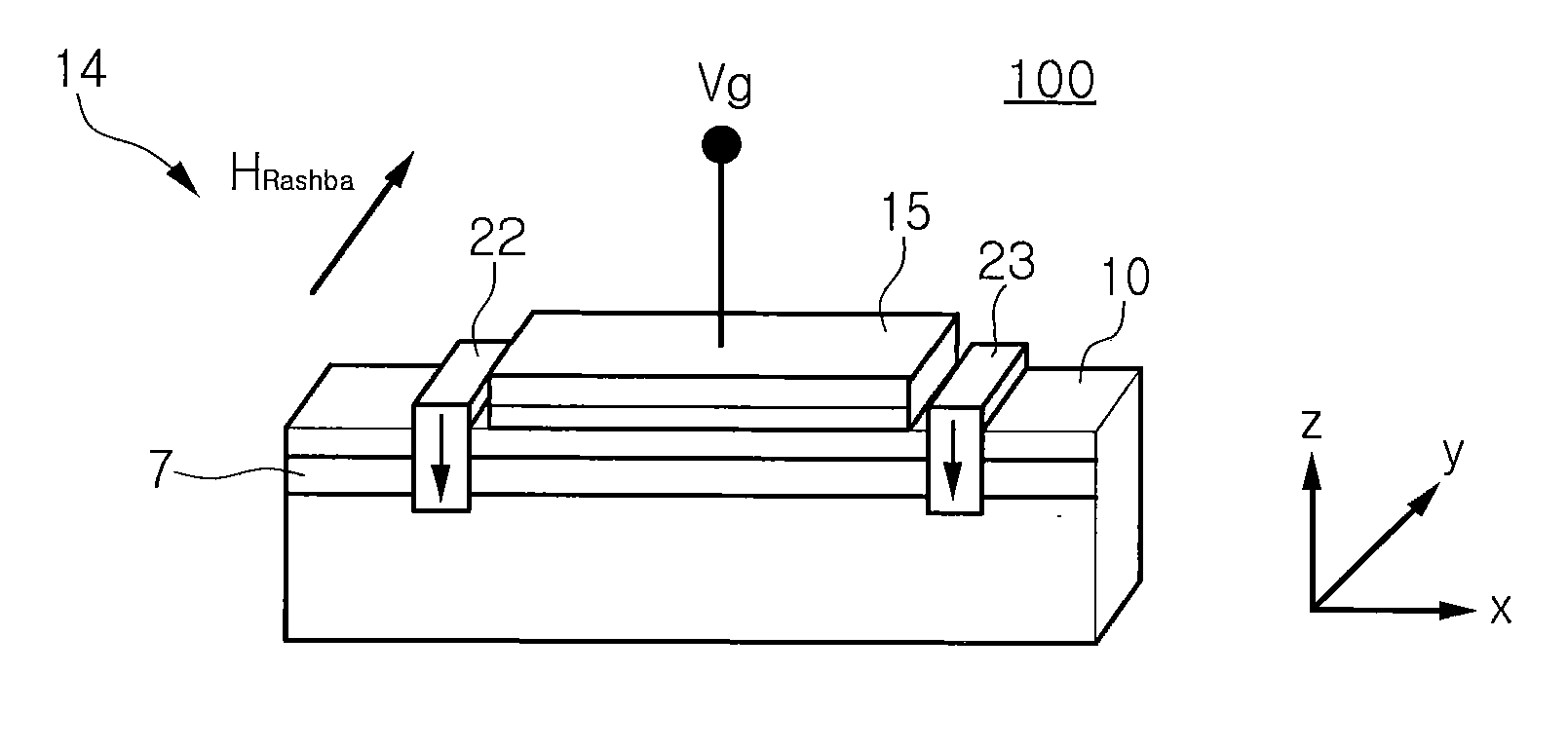
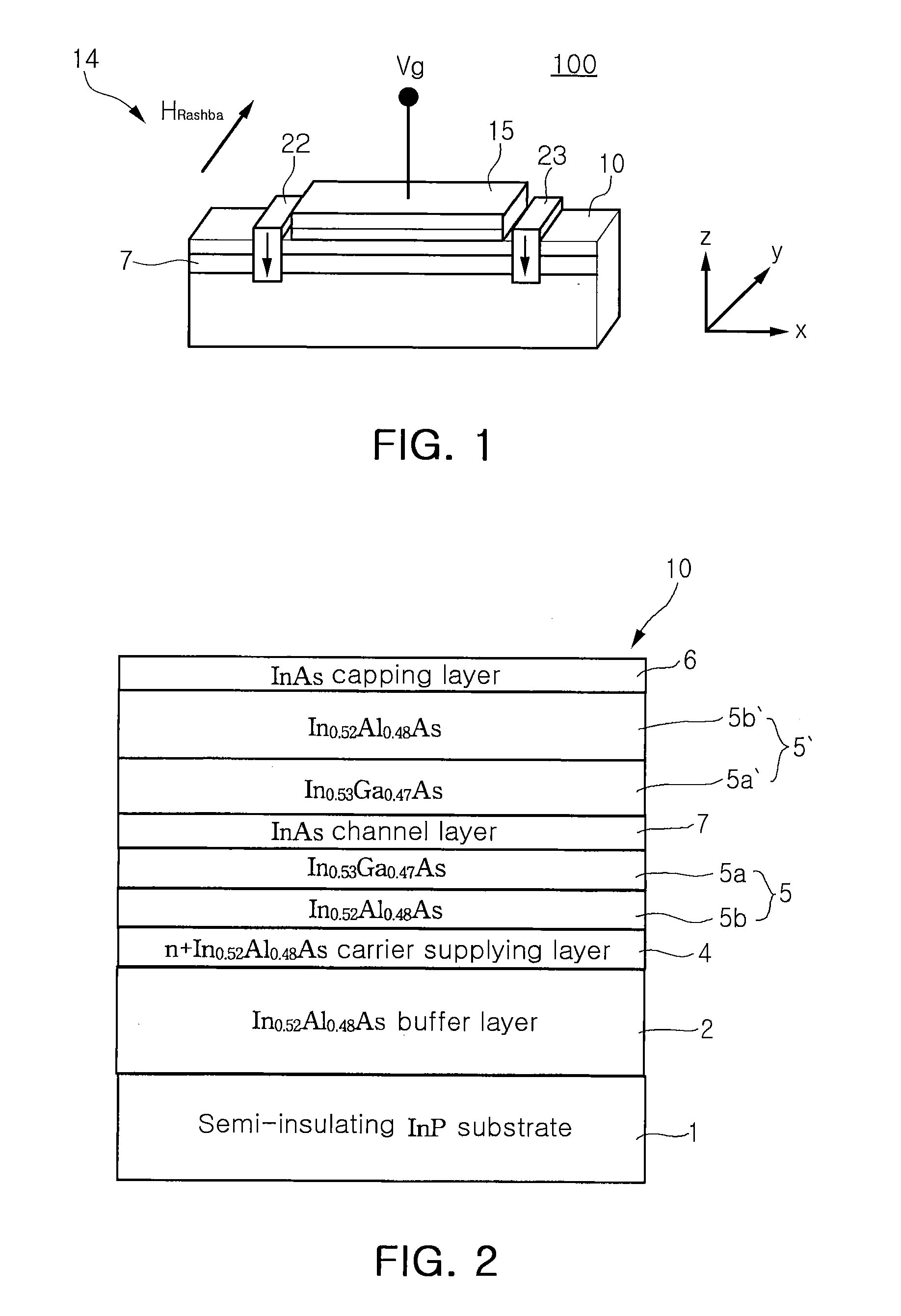
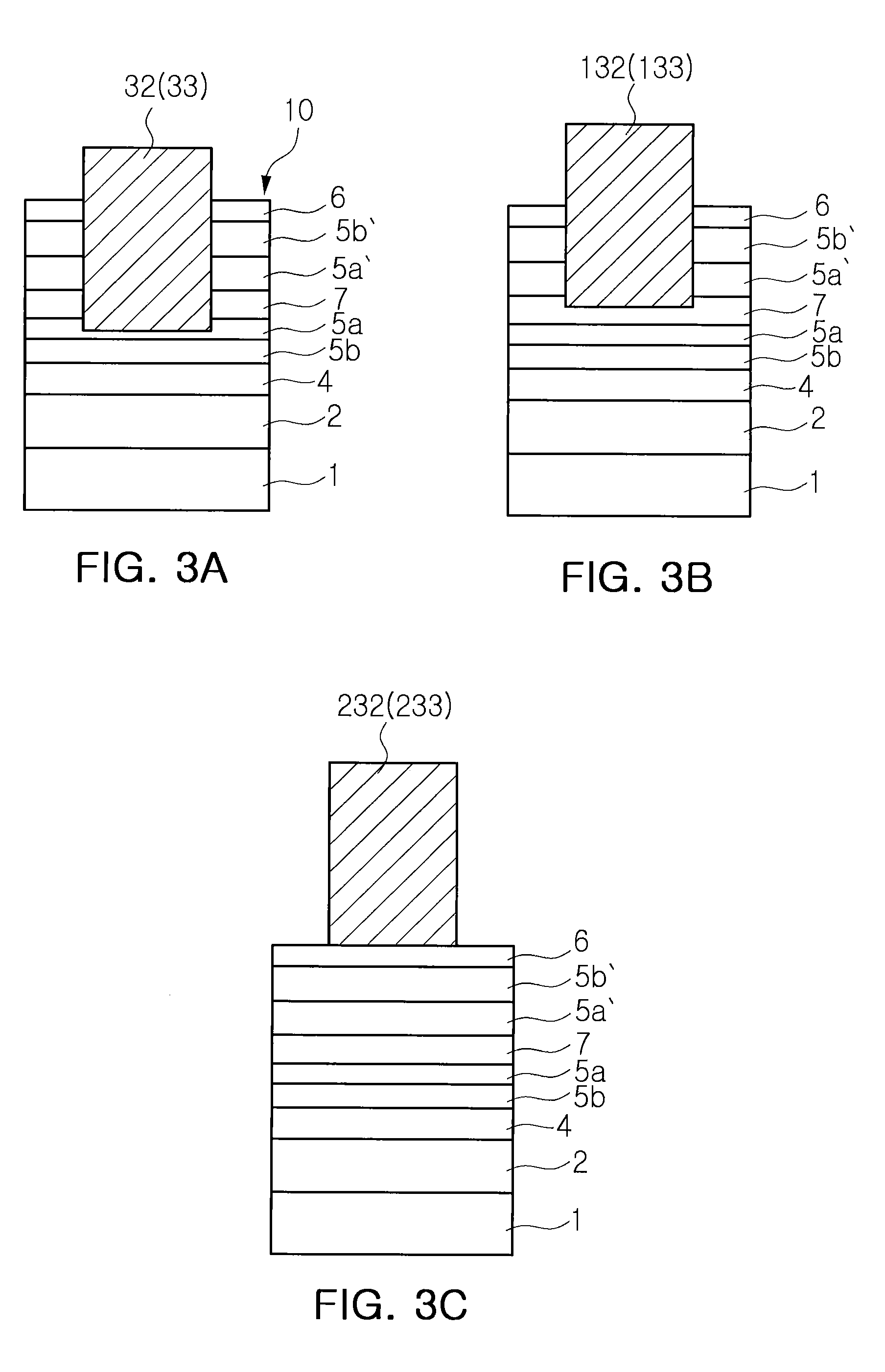
InactiveUS20080308844A1Limited resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectronTransistor
A spin transistor useful for device miniaturization and high-density integration is provided. The spin transistor includes: a semiconductor substrate including a channel layer; ferromagnetic source and drain disposed on the semiconductor substrate to be separated from each other and to be magnetized in a direction perpendicular to a surface of the channel layer; a gate formed on the semiconductor substrate between the source and the drain to adjust spins of electrons passing through the channel layer, wherein spin-polarized electrons are injected from the source to the channel layer, and the electrons injected into the channel layer pass though the channel layer and are injected into the drain, and wherein the spins of the electrons passing through the channel layer undergo precession due to a spin-orbit coupling induced magnetic field according to a voltage of the gate.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Transistor that employs collective magnetic effects thereby providing improved energy efficiency
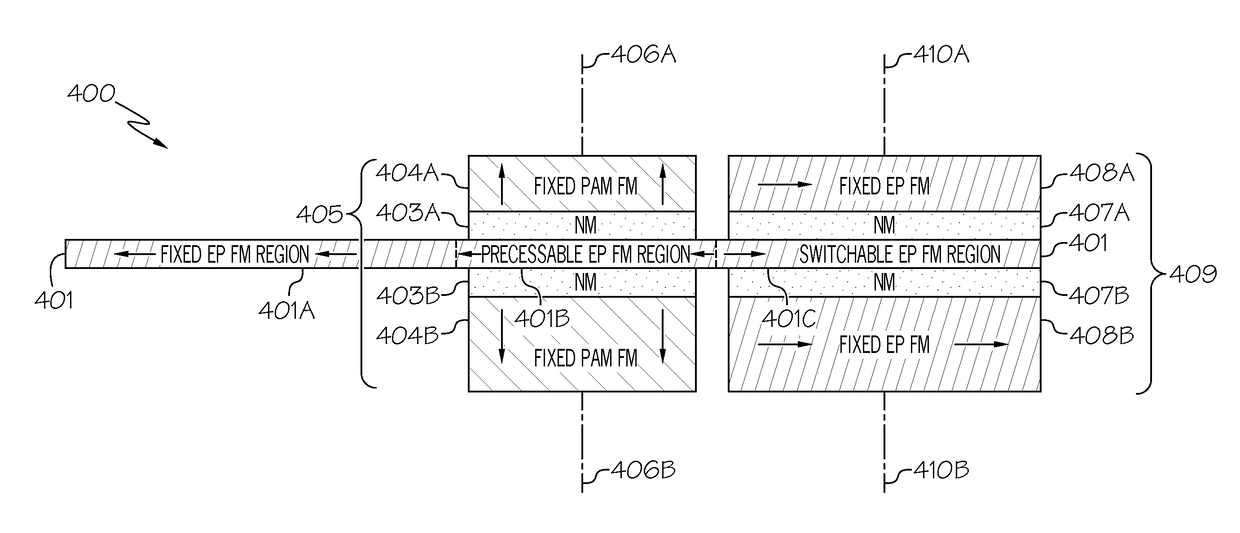
ActiveUS20170104151A1Increase currentLower magnetic strengthSolid-state devicesGalvano-magnetic material selectionMOSFETIn plane
A device or class of devices that provides a mechanism for controlling charge current flow in transistors that employs collective magnetic effects to overcome voltage limitations associated with single-particle thermionic emission as in conventional MOSFETs. Such a device may include two or more magnetic stacks with an easy-in-plane ferromagnetic film sandwiched between oppositely magnetically oriented perpendicular magnetization anisotropy (PMA) ferromagnets. Each stack includes two non-magnetic layers separating the easy-plane ferromagnetic film from the PMA layers. Charge current flow through one of these stacks controls the current-voltage negative differential resistance characteristics of the second stack through collective magnetic interactions. This can be exploited in a variety of digital logic gates consuming less energy than conventional CMOS integrated circuits. Furthermore, the easy-in-plane magnetic films may be subdivided into regions coupled through exchange interactions and the in-plane fixed magnetic layers in the input magnetic stacks can be used in non-volatile logic and memory.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS
Magnetoresistive element, memory element having the magnetoresistive element, and memory using the memory element
InactiveUS20020182442A1Layered productsRecord information storagePerpendicular magnetizationMagnetic reluctance
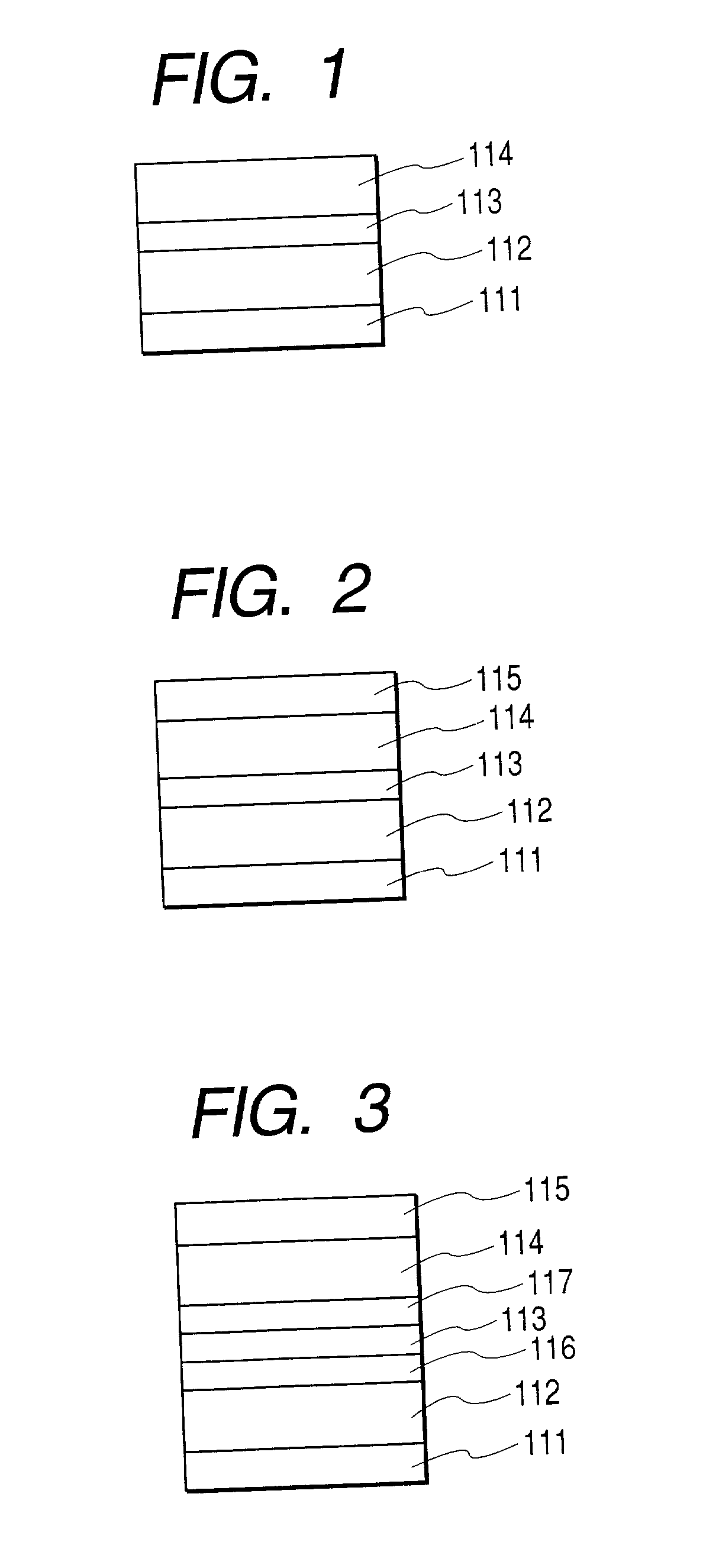
A magnetoresistive film includes a nonmagnetic film, and a structure in which magnetic films are formed on the two sides of the nonmagnetic film. At least one of the magnetic films is a perpendicular magnetization film. A magnetic film whose easy axis of magnetization is inclined from a direction perpendicular to the film surface is formed at a position where the magnetic film contacts the perpendicular magnetization film but does not contact the nonmagnetic film. A memory, magnetic element, magnetoresistive element, and magnetic element manufacturing method are also disclosed.
Owner:CANON KK
Thin film magnet, cylindrical ferromagnetic thin film and production method thereof
InactiveUSRE36517E1Improve magnetic propertiesSmall sizeFixed microstructural devicesVolume/mass flow measurementPerpendicular magnetizationGas phase
A thin film magnet and a cylindrical ferromagnetic thin film having a high maximum energy product (greater than 120 kJ / m3) and thus suitable for use in miniature high performance devices are provided. The thin film magnet is produced by means of physical vapor deposition. The thin film magnet is an (Nd1-xRx)yM1-y-zBz alloy having a ferromagnetic compound of the Nd2Fe14B type as its main phase, wherein R is Tb, Ho, and Dy and M is Fe metal or an Fe-based alloy including at least one of Co and Ni, 0.04< / =x< / =0.10,0.11< / =y< / =0.15, and 0.08< / =z< / =0.15. A perpendicular magnetization film having such a composition is deposited on the side wall of a substrate in the columnar (or cylindrical) form thereby obtaining a cylindrical ferromagnetic thin film having radial anisotropy.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Perpendicular magnetization film, perpendicular magnetization film structure, magnetoresistance element, and perpendicular magnetic recording medium
ActiveUS20160314825A1Improve flatnessLow saturation magnetizationMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionPerpendicular magnetizationNitrogen
Provided is a structure having a perpendicular magnetization film which is an (Mn1-x,Gax)4N1-y (0<x≦0.5, 0<y<1) thin film having a nitrogen-deficient composition which is formed by controlling and introducing nitrogen N into an MnGa alloy or a thin film containing at least one of Ge, Zn, Sb, Ni, Ag, Sn, Pt, and Rh, instead of Ga. The perpendicular magnetization film exhibits a Curie temperature sufficiently higher than room temperature, has saturation magnetization smaller than that of existing materials, and is capable of being fabricated as a very flat film.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI +1
Multibit cell of magnetic random access memory with perpendicular magnetization
ActiveUS8331141B2Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesPerpendicular magnetizationStatic random-access memory
A multi-bit cell of magnetic random access memory comprises a magnetic tunnel junction element including a first and second free layer comprising a changeable magnetization oriented substantially perpendicular to a layer plane in its equilibrium state and a switching current, a first and second tunnel barrier layer, and a pinned layer comprising a fixed magnetization oriented substantially perpendicular to a layer plane, the pinned layer is disposed between the first and second free layers and is separated from the free layers by one of the tunnel barrier layers, a selection transistor electrically connected to a word line, and a bit line intersecting the word line. The magnetic tunnel junction element is disposed between the bit line and the selection transistor and is electrically connected to the bit line and the selection transistor, wherein the first and second free layers have substantially different switching currents.
Owner:SHUKH ALEXANDER MIKHAILOVICH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com