Spinning microwave oscillator based on vertical magnetizing free layer and manufacturing method thereof
A microwave oscillator, vertical magnetization technology, applied in resonators, waveguide-type devices, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem of low output power of spin microwave devices, and achieve the effects of broadband adjustable integration, low cost, and small size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
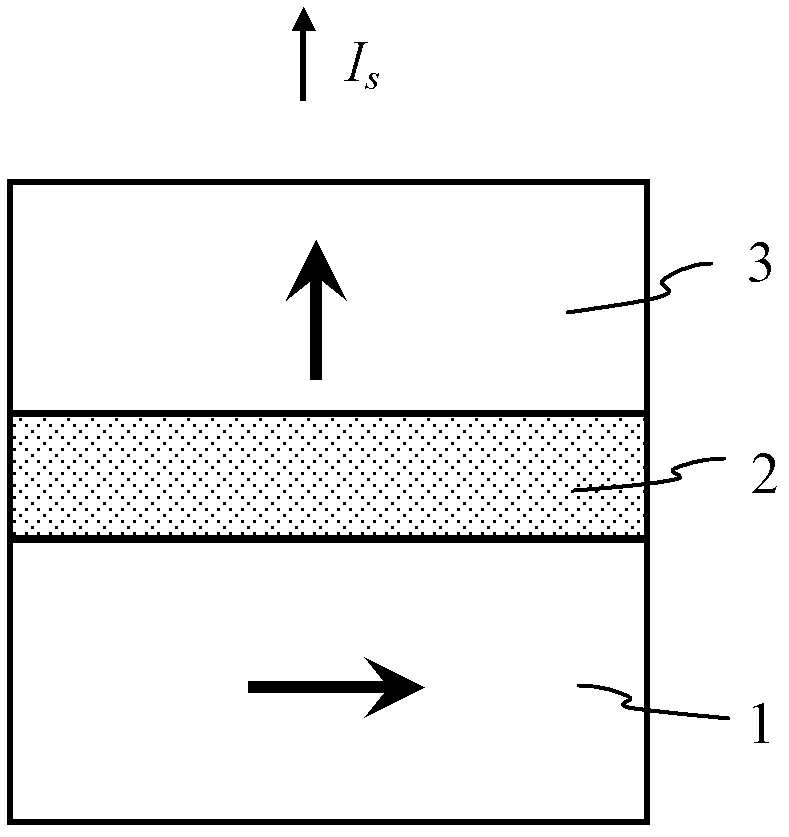
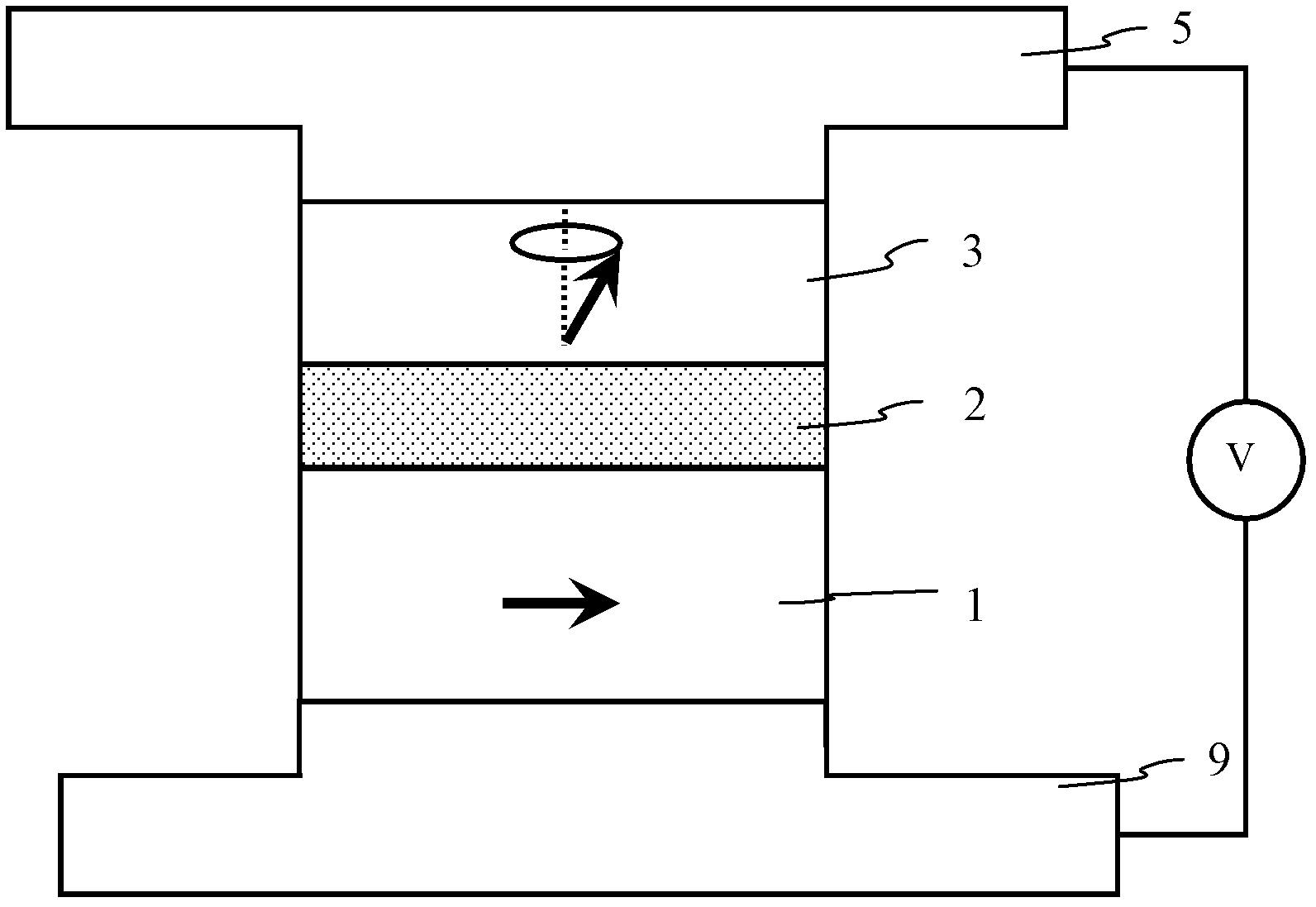
[0041] Example 1 refer to figure 2 , the structure of the spin microwave oscillator based on the perpendicular magnetization free layer and in-plane magnetization fixed layer structure is as follows: firstly a CuN seed layer 9 is formed on the substrate; then a lower ferromagnetic Co 40 Fe 40 B 20 layer, its thickness is 2 nm, and the magnetization direction of the layer is parallel to the surface of the film; one formed on the ferromagnetic Co 40 Fe 40 B 20 A spacer layer above the spacer layer, that is, a MgO barrier layer with a thickness of 0.8 nm; another magnetic Co 20 Fe 60 B 20 layer and a CuN capping layer formed over the second ferromagnetic layer. co 20 Fe 60 B 20 The magnetization direction of the layer is perpendicular to the film plane and forms an angle of about 90 degrees with the first magnetic material layer without a magnetic field, Co 20 Fe 60 B 20 The magnetization direction of the layer changes in response to an applied magnetic field as w...
Embodiment 2
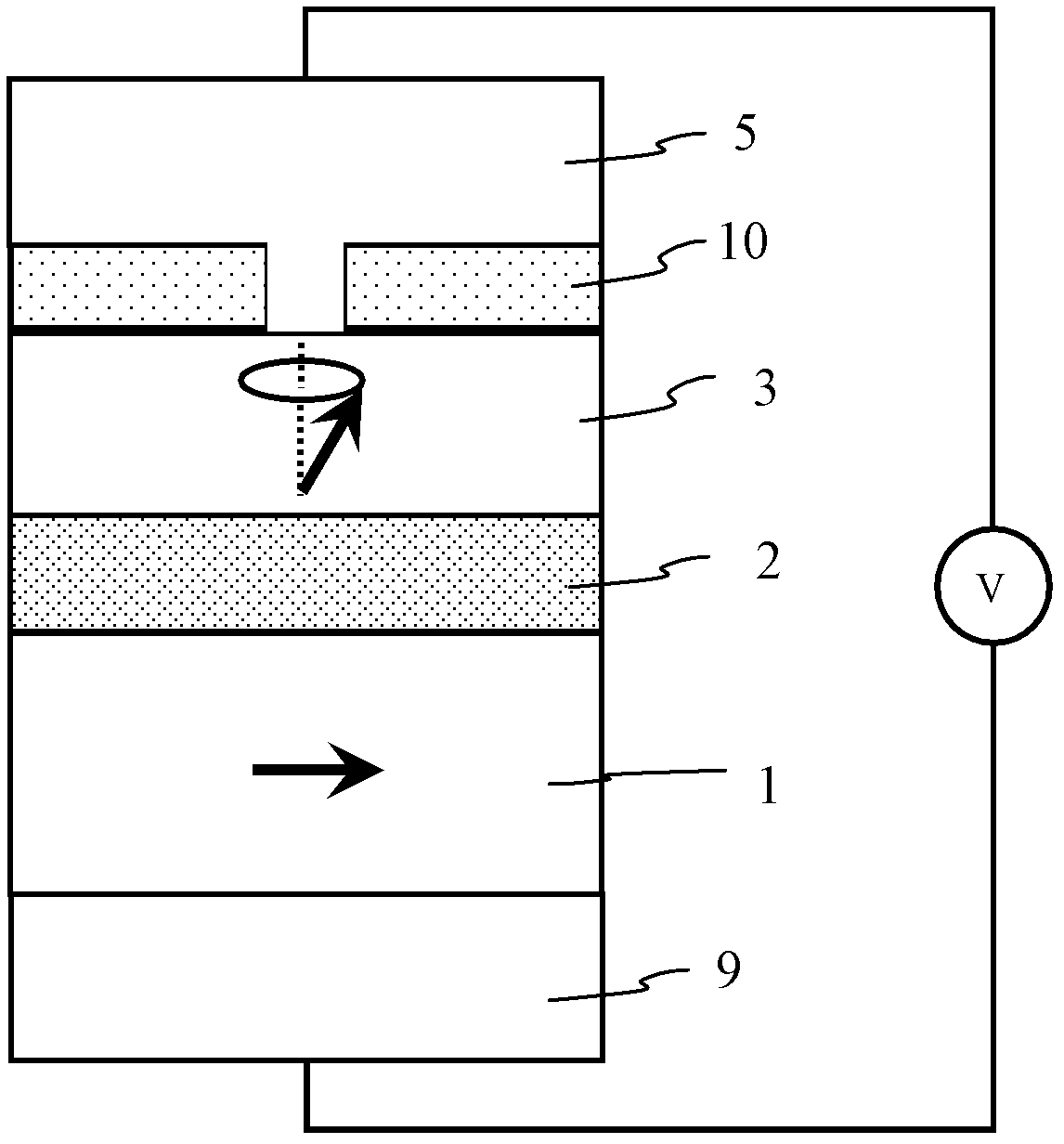
[0043] Example 2 In the foregoing embodiments, the balanced magnetization direction of the first magnetic layer is determined by the in-plane magnetization of the material, and its direction is relatively fixed. But when its coercive force is small, its magnetization direction can be reversed under the action of a small external field, thereby affecting the microwave performance of the microwave oscillator. In view of the above problems, this embodiment further proposes a pinned microwave oscillator, the structure of which is as follows Figure 4 As shown, that is: firstly a seed layer is formed on the substrate; then an antiferromagnetic layer is formed on the seed layer, and the lower ferromagnetic layer or semi-metal layer (reference layer) is formed on the antiferromagnetic layer, and the reference layer’s The equilibrium magnetization direction is relatively fixed due to the pinning effect of antiferromagnetism; a nonmagnetic isolation layer formed on the reference laye...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Example 3 In the foregoing embodiment 2, the antiferromagnetic layer 4 pinning the ferromagnetic or half-metal layer 1 can also be composed of the antiferromagnetic layer 4 and the ferromagnetic layer / nonmagnetic metal layer / ferromagnetic layer (FM / NM / FM) The FM / NM / FM composite multilayer film forms an artificial antiferromagnetic coupling layer, so that the magnetization direction of the magnetic layer 1 is fixed. Here FM is similar to the material of the lower magnetic layer 1 in Example 1, and NM is composed of non-magnetic metals such as Ru, Cu, Ag, etc., and its thickness is about 0.8 nm, which meets the requirements of FM / NM / FM composite multilayer film to form artificial antiferromagnetism The coupling condition, its basic structure is as Figure 5 shown. An example of a specific material is given here, in Si / SiO 2 On the substrate, a seed layer (3 nm Ta / 10 nm CuN / 5 nm Ta), an antiferromagnetic layer 4 (15 nm IrMn), an artificial antiferromagnetic coupling ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com