Patents
Literature
238 results about "Film plane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A film plane is the area inside any camera or image taking device with a lens and film or digital sensor upon which the lens creates the focused image. The film plane varies in distance from the lens focal point in cameras from different manufacturers. Thus each lens used has to be chosen carefully to assure that the image from the lens is focused on the exact place where the individual frame of film or digital sensor is positioned during exposure. It is sometimes marked on a camera body with the 'Φ' symbol where the vertical bar represents the exact location.
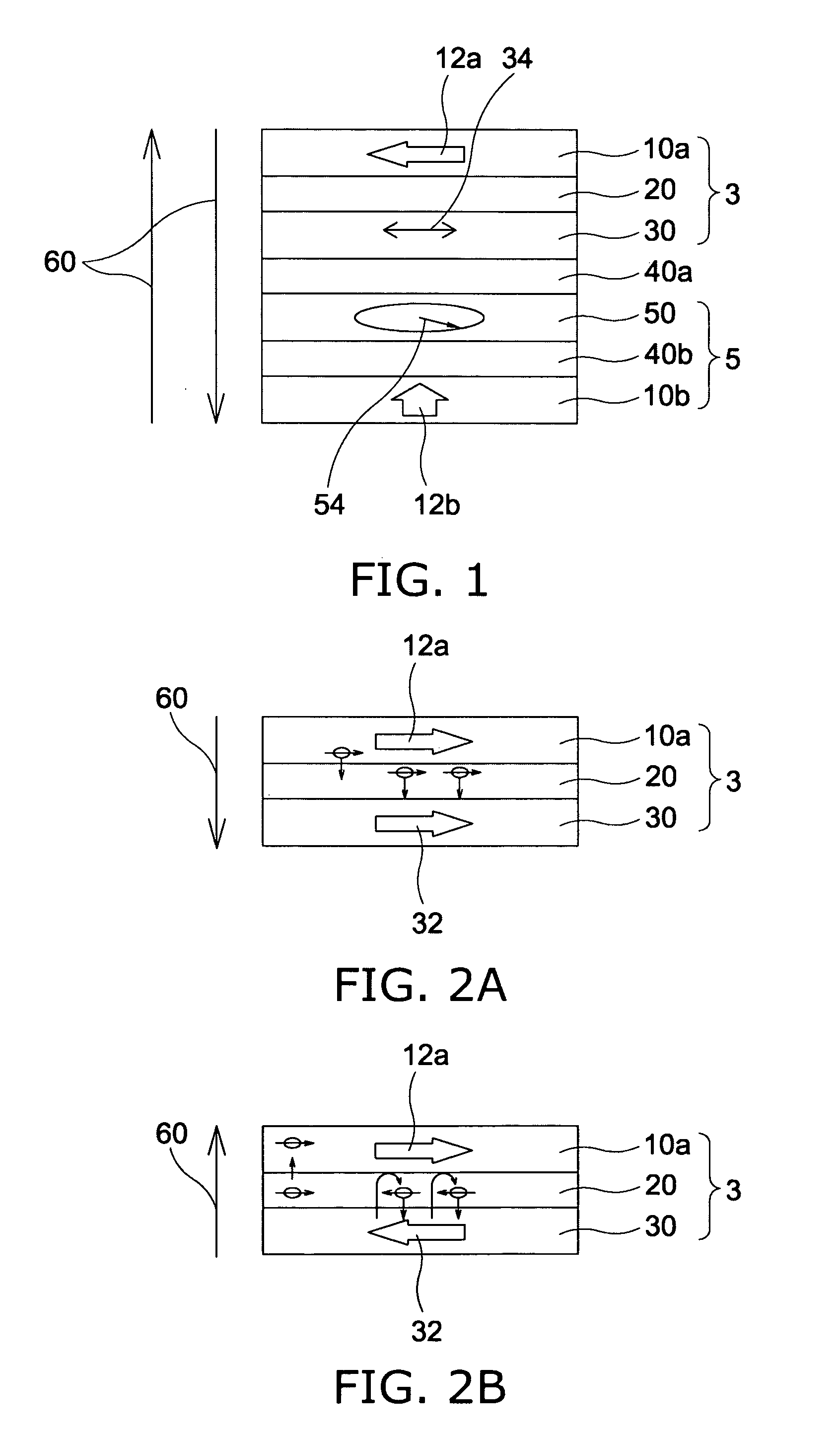
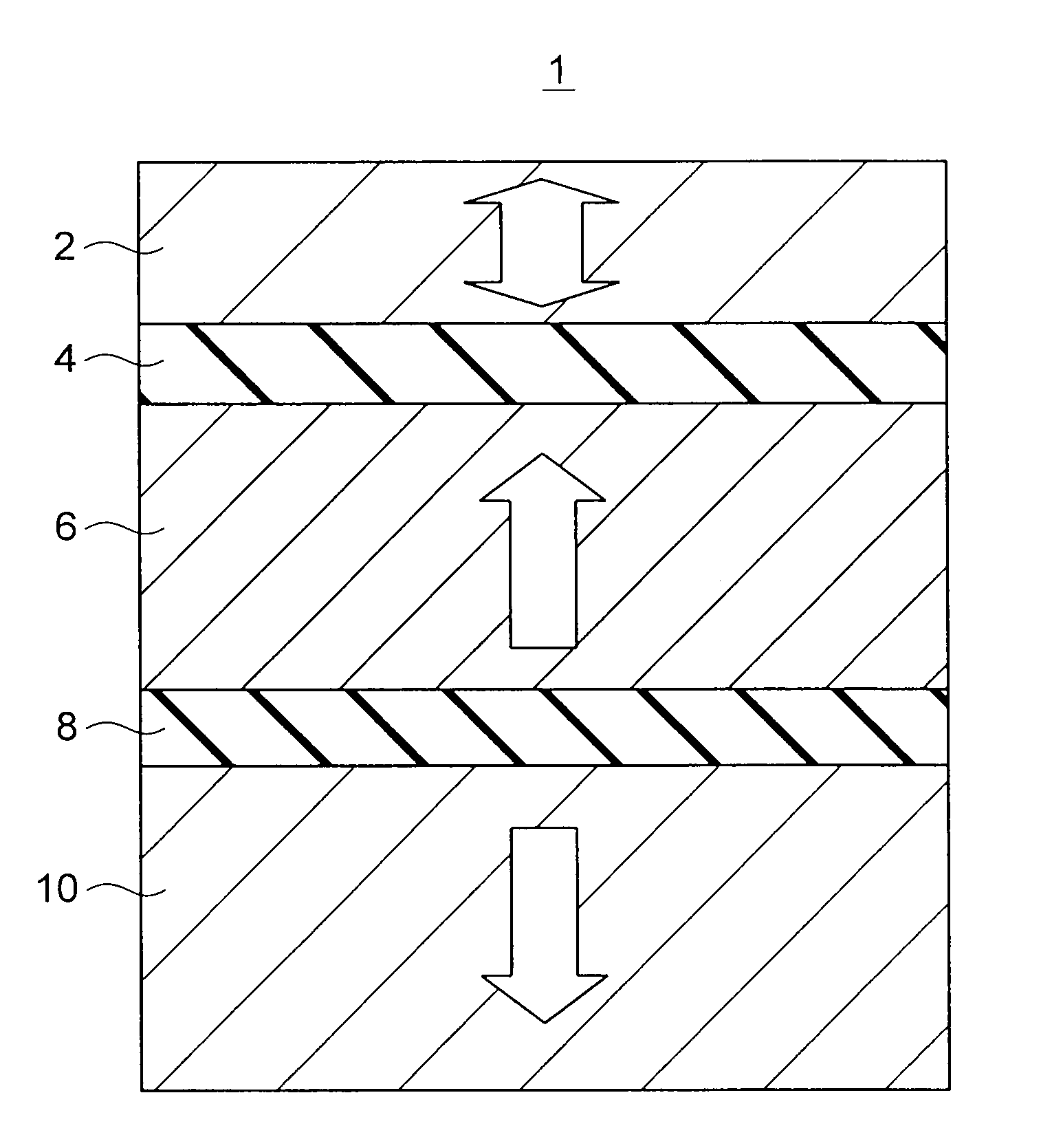
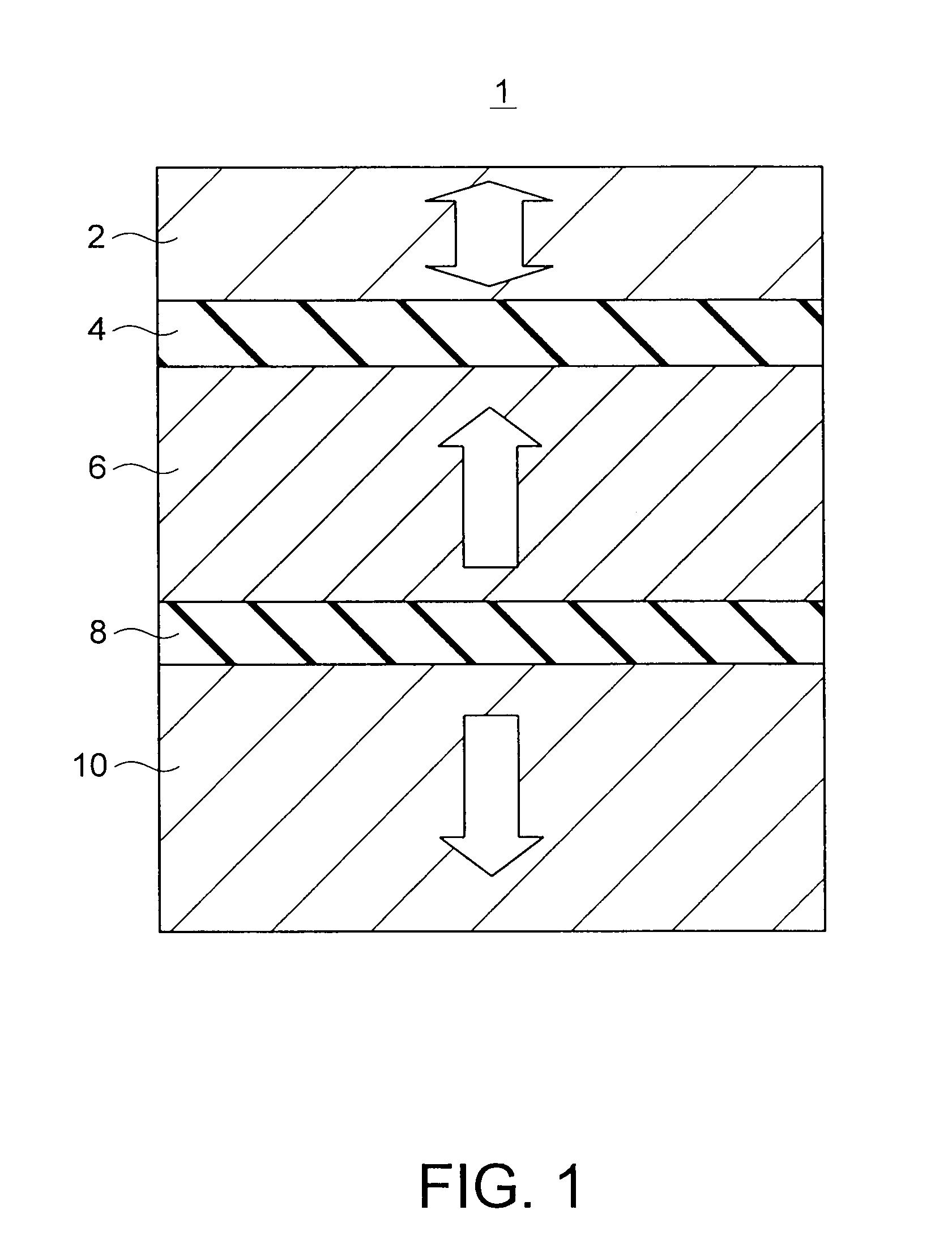
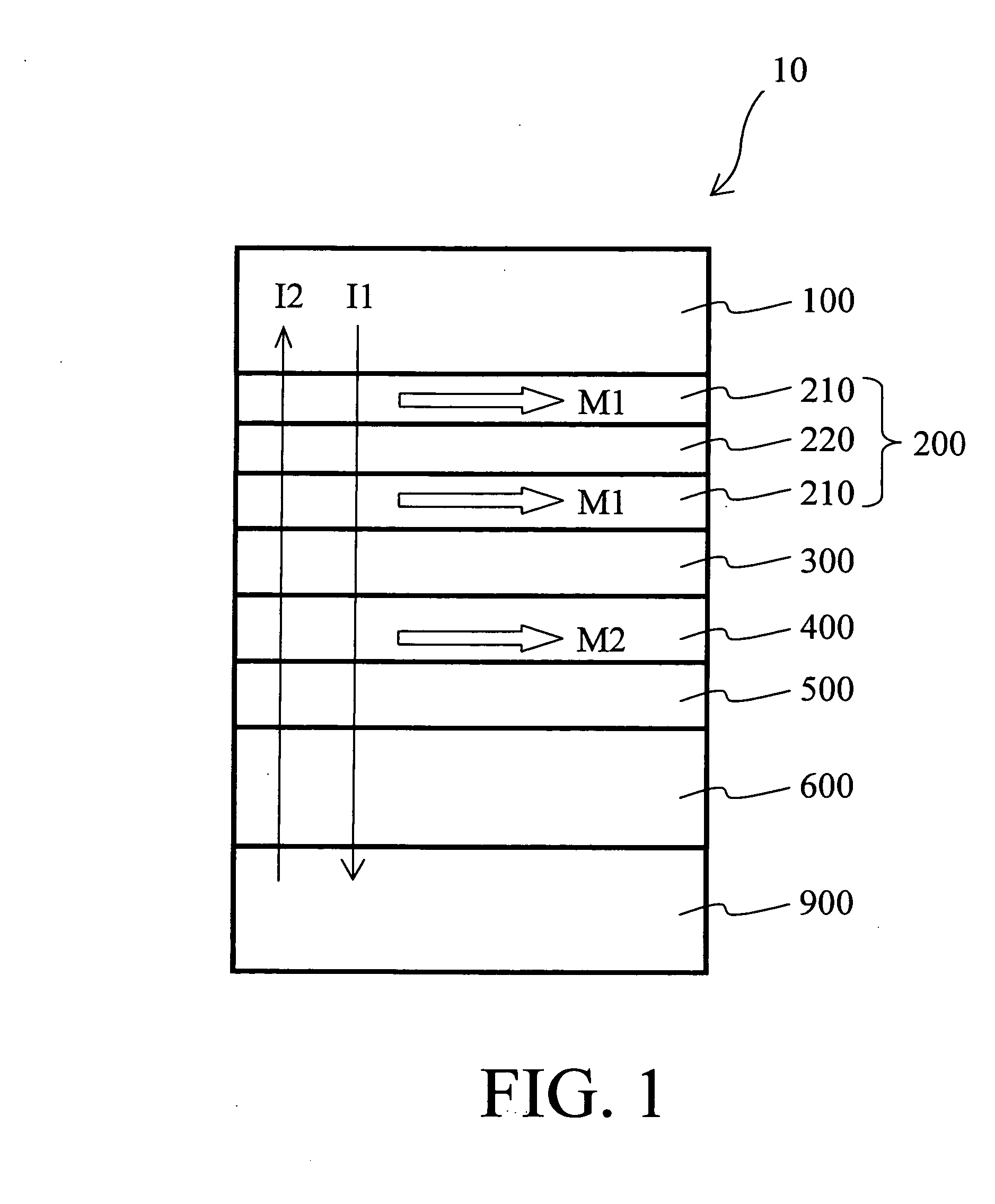
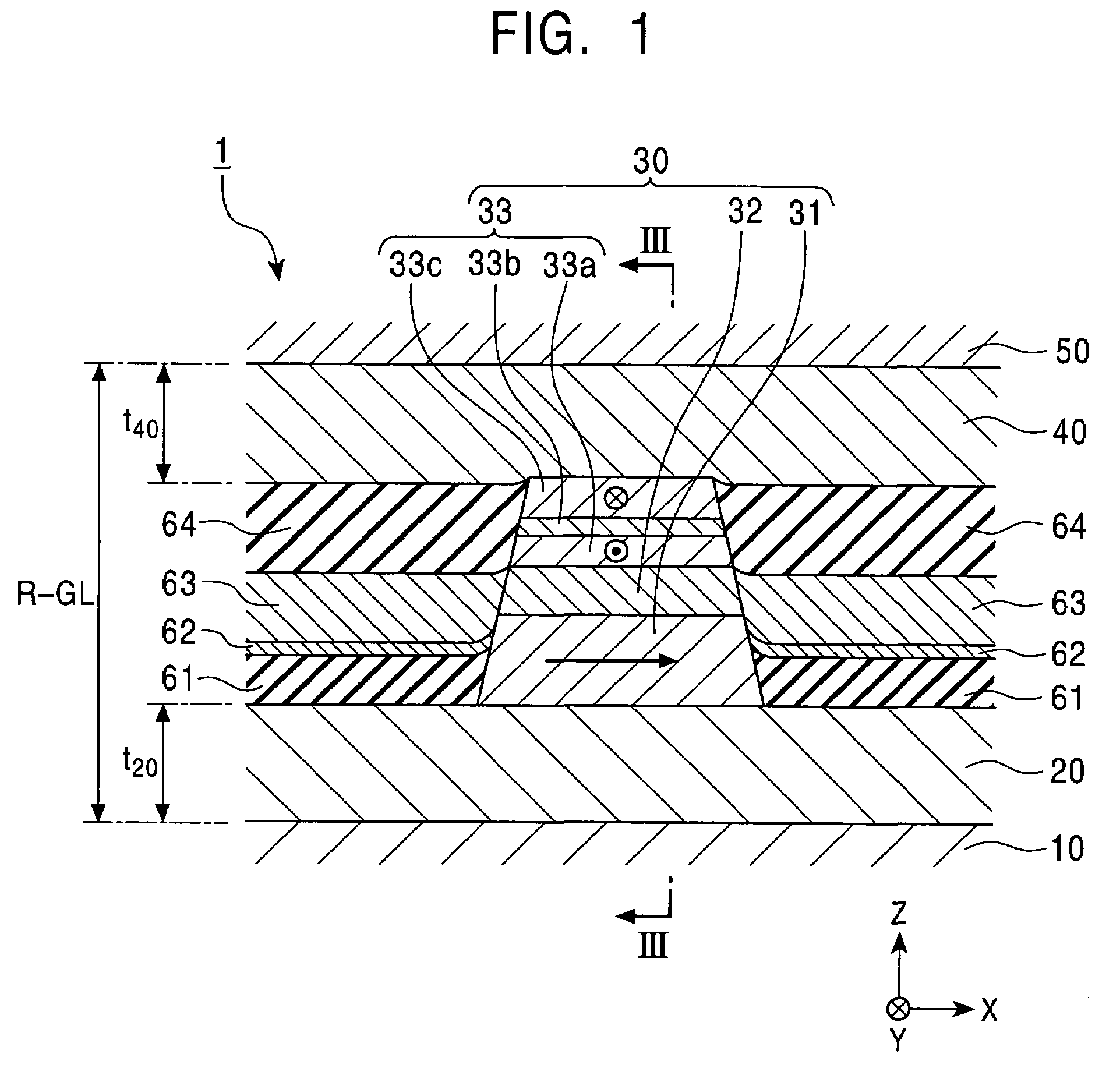
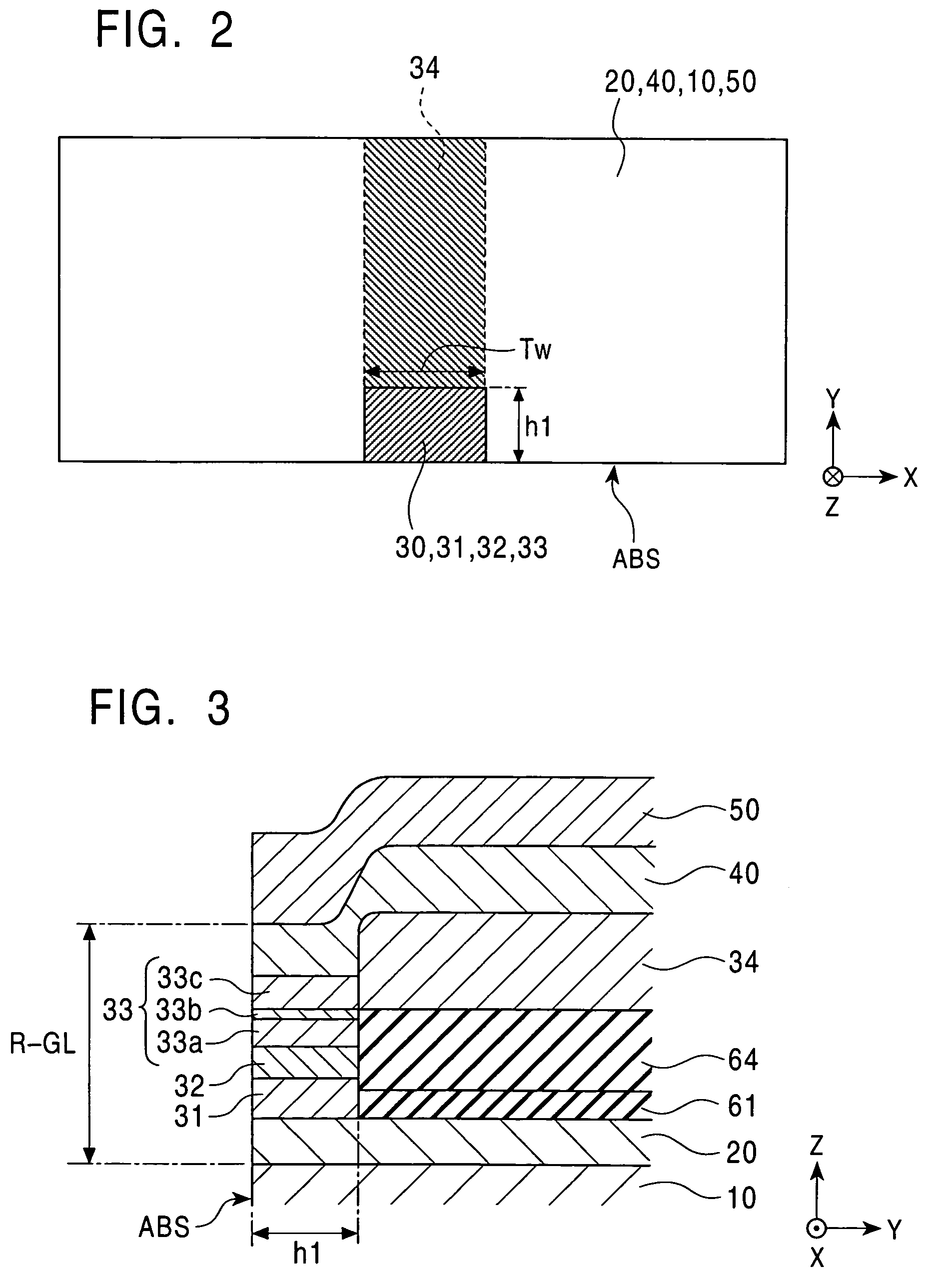
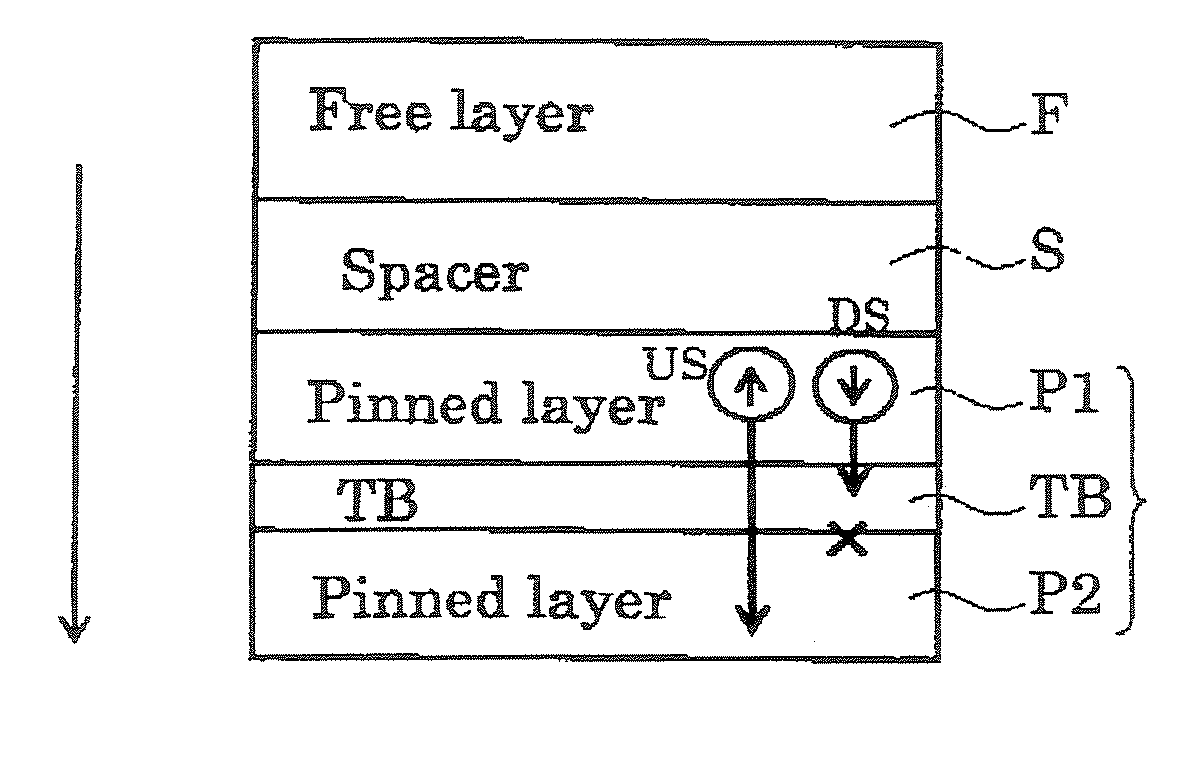
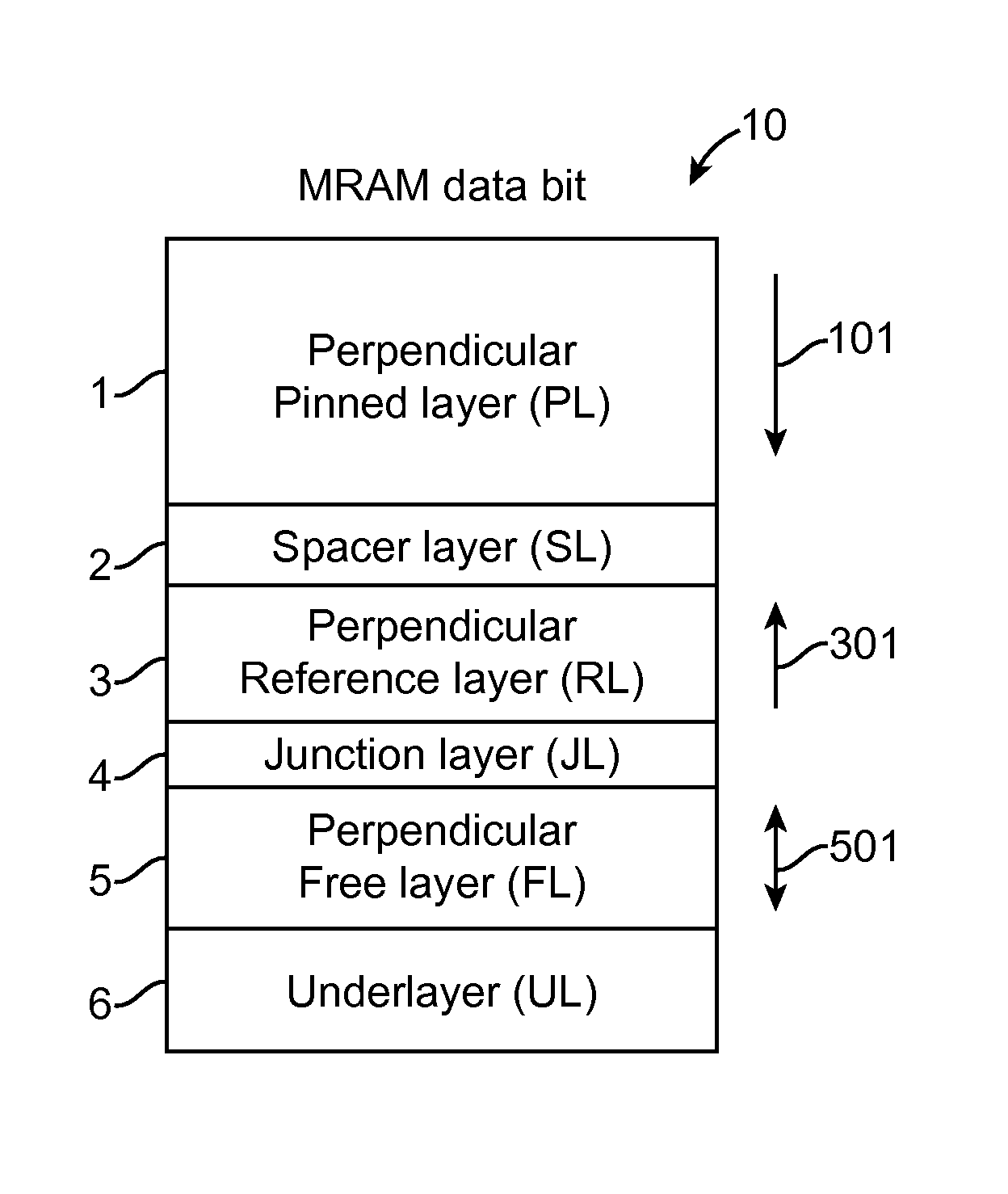
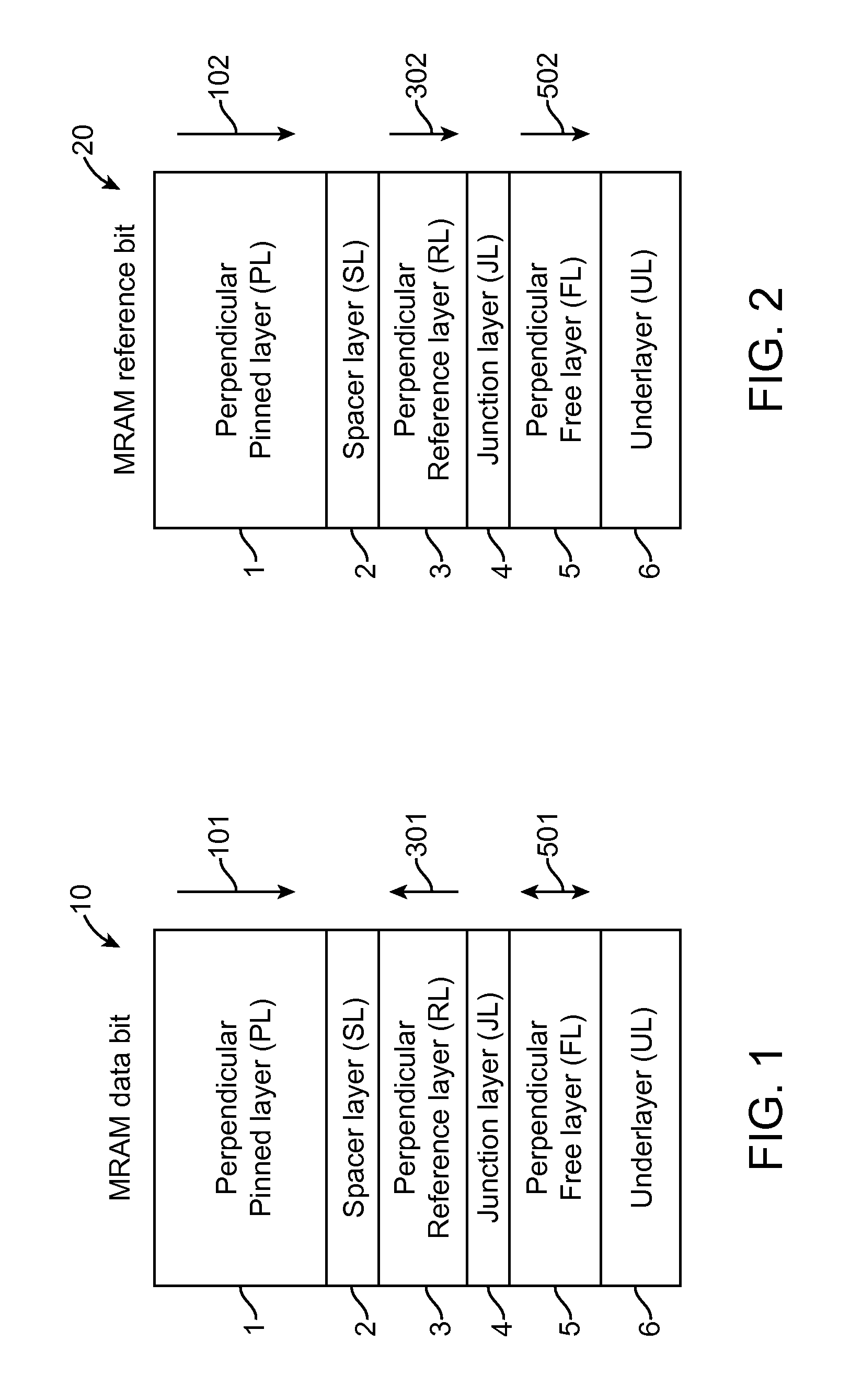
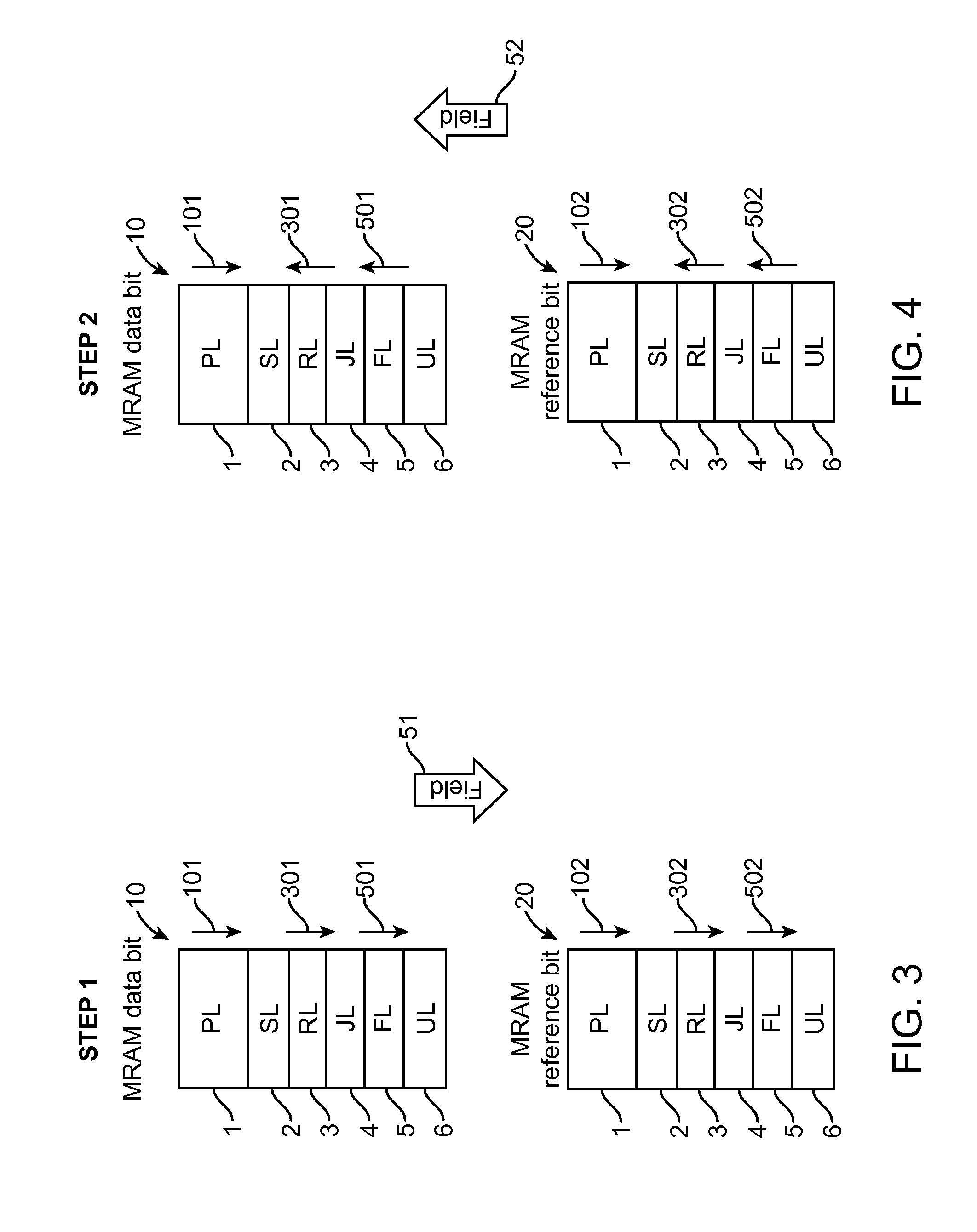
Magnetoresistive element and magnetic memory
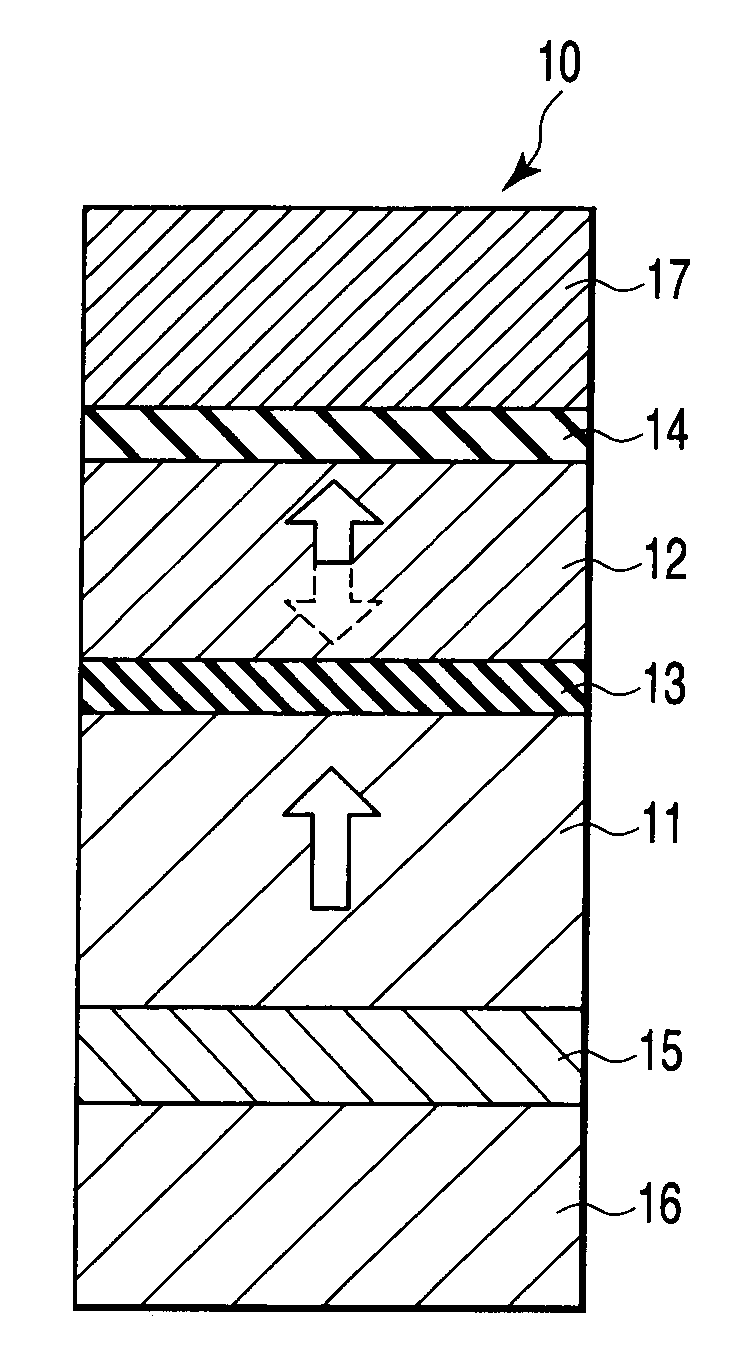
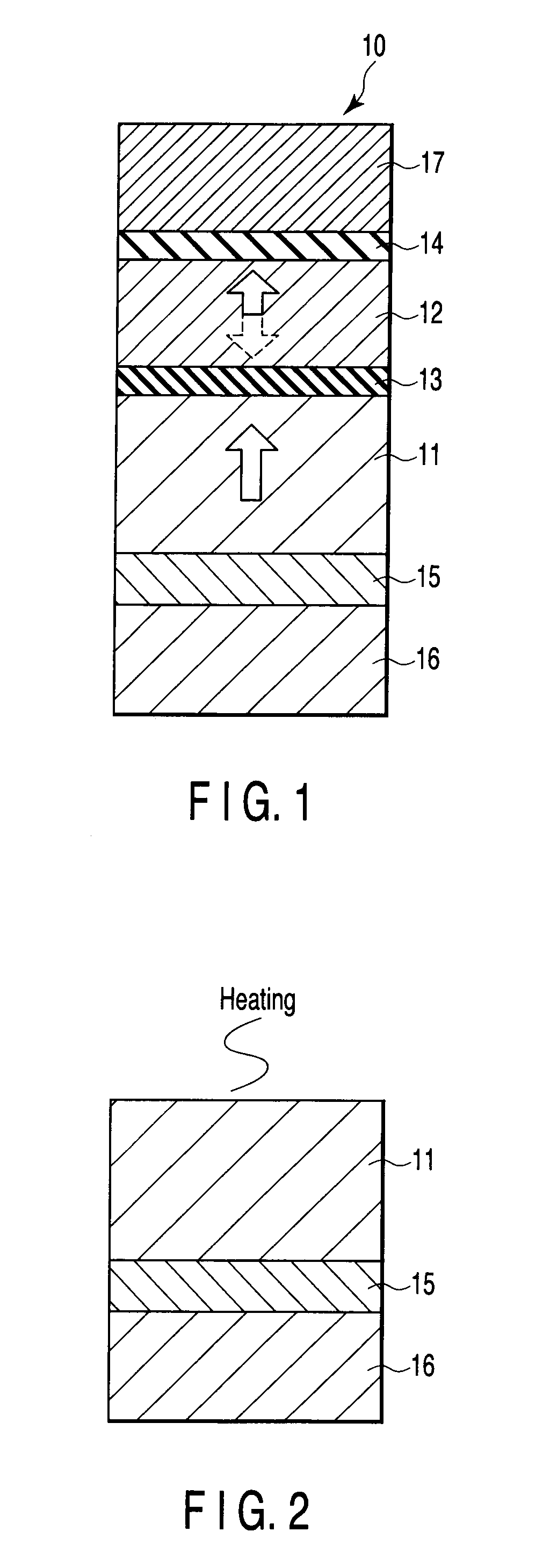
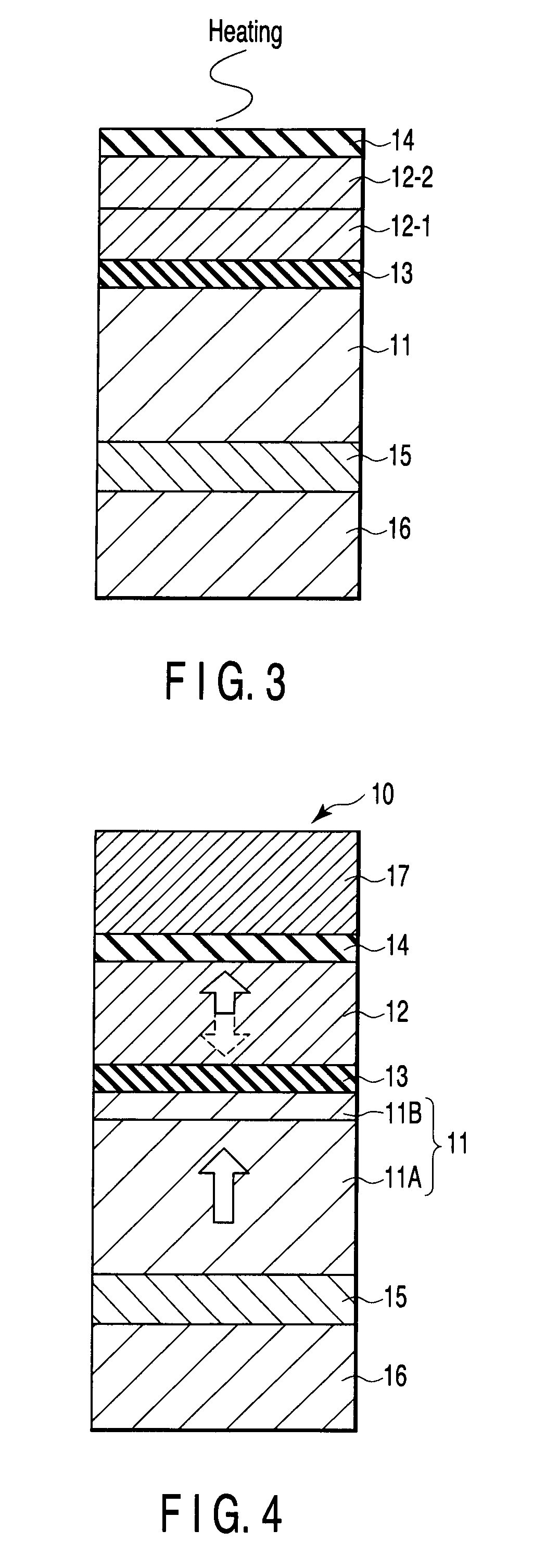
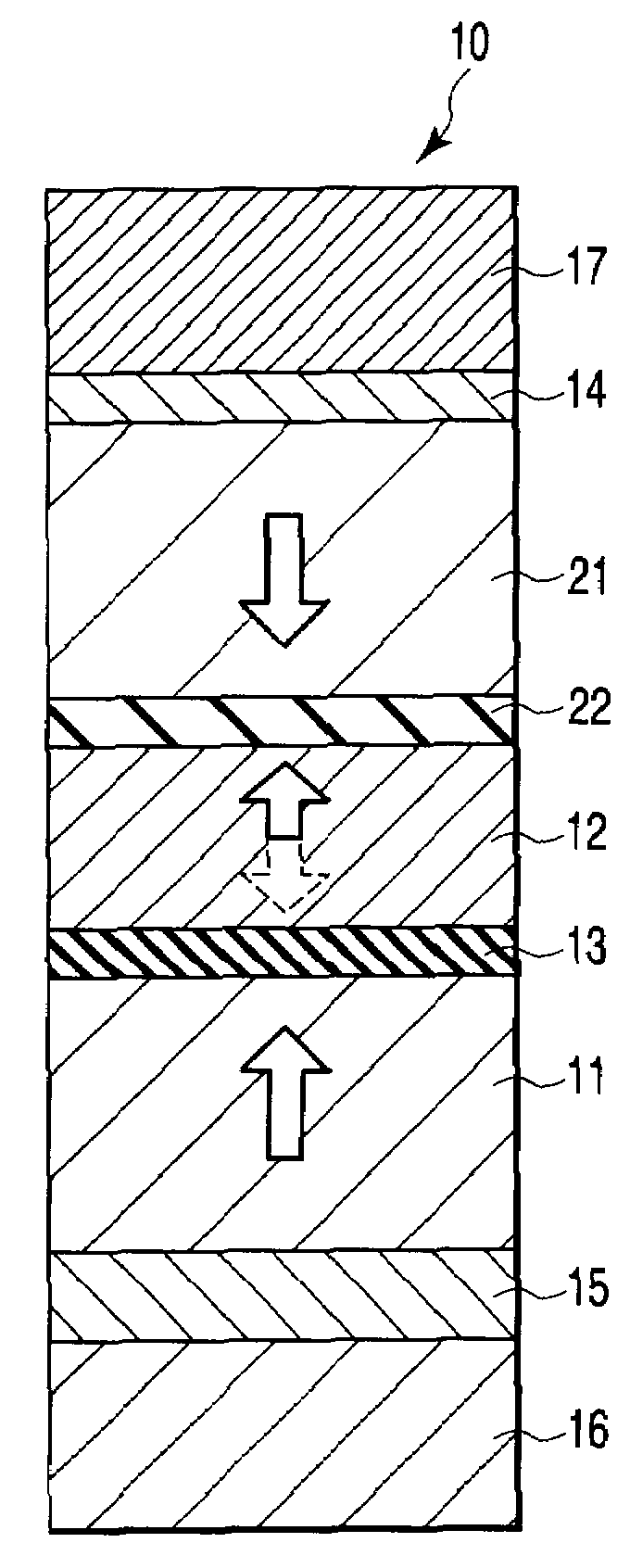
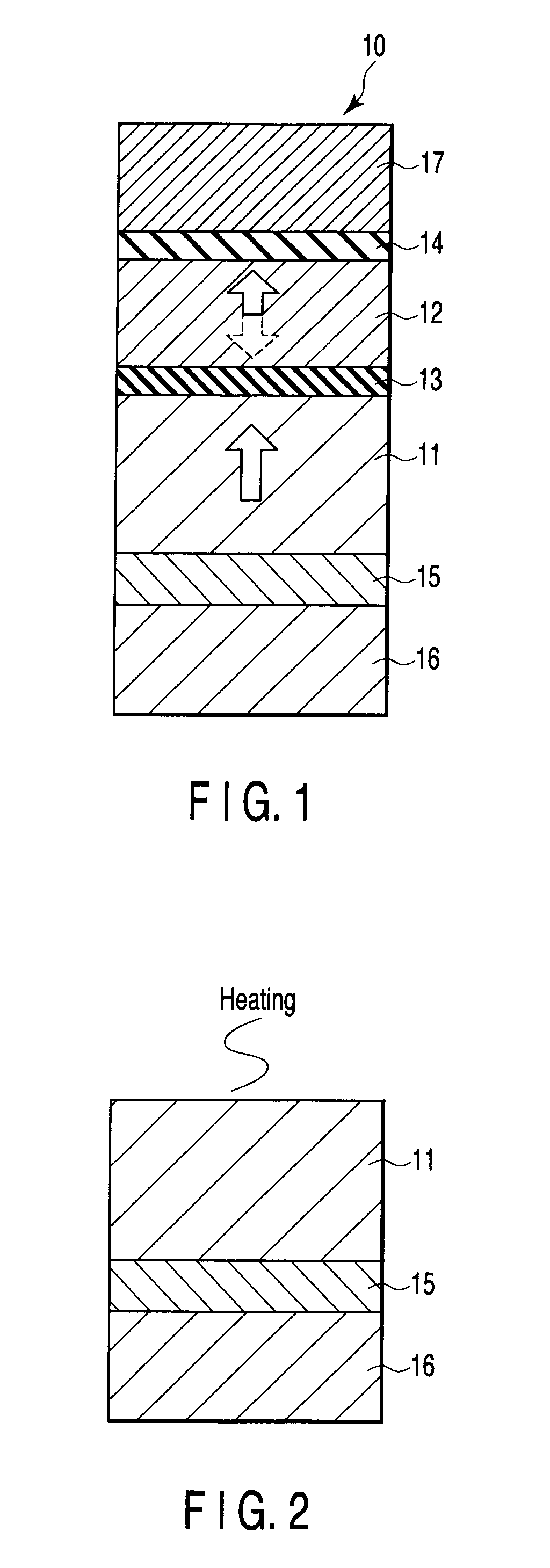
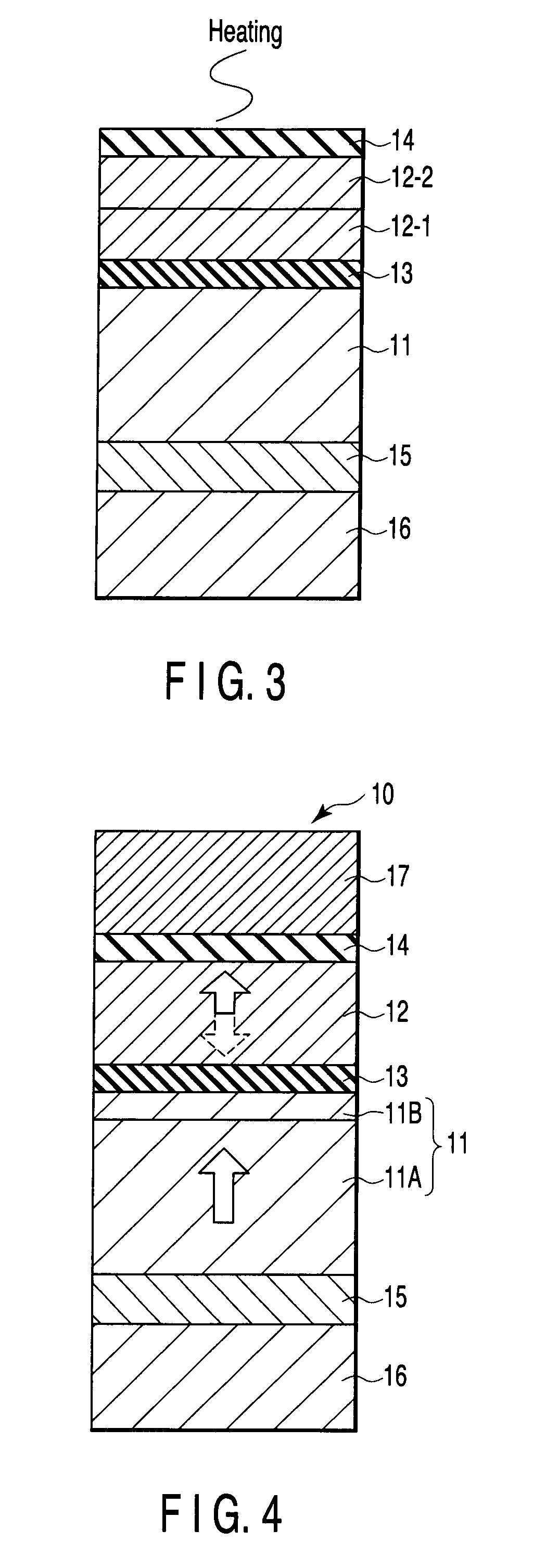
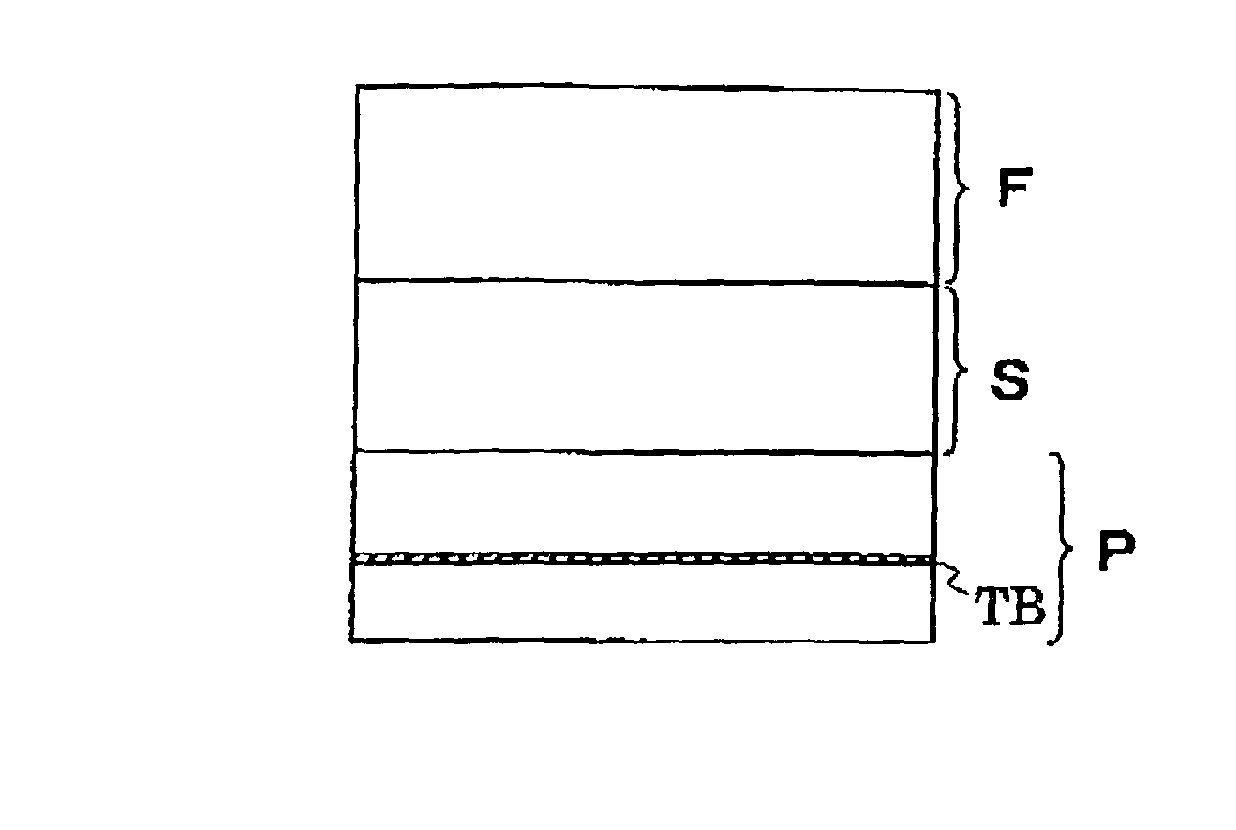
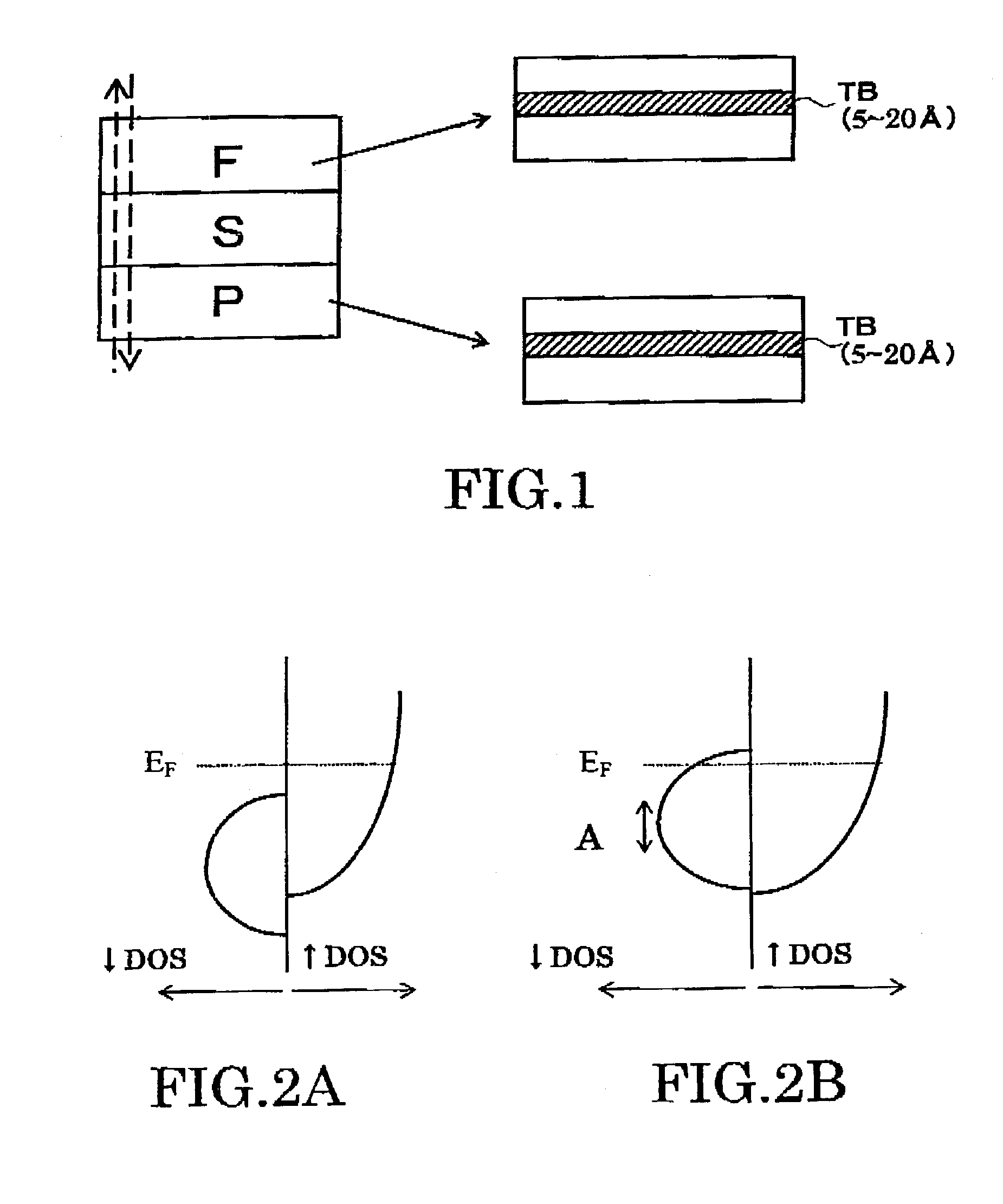
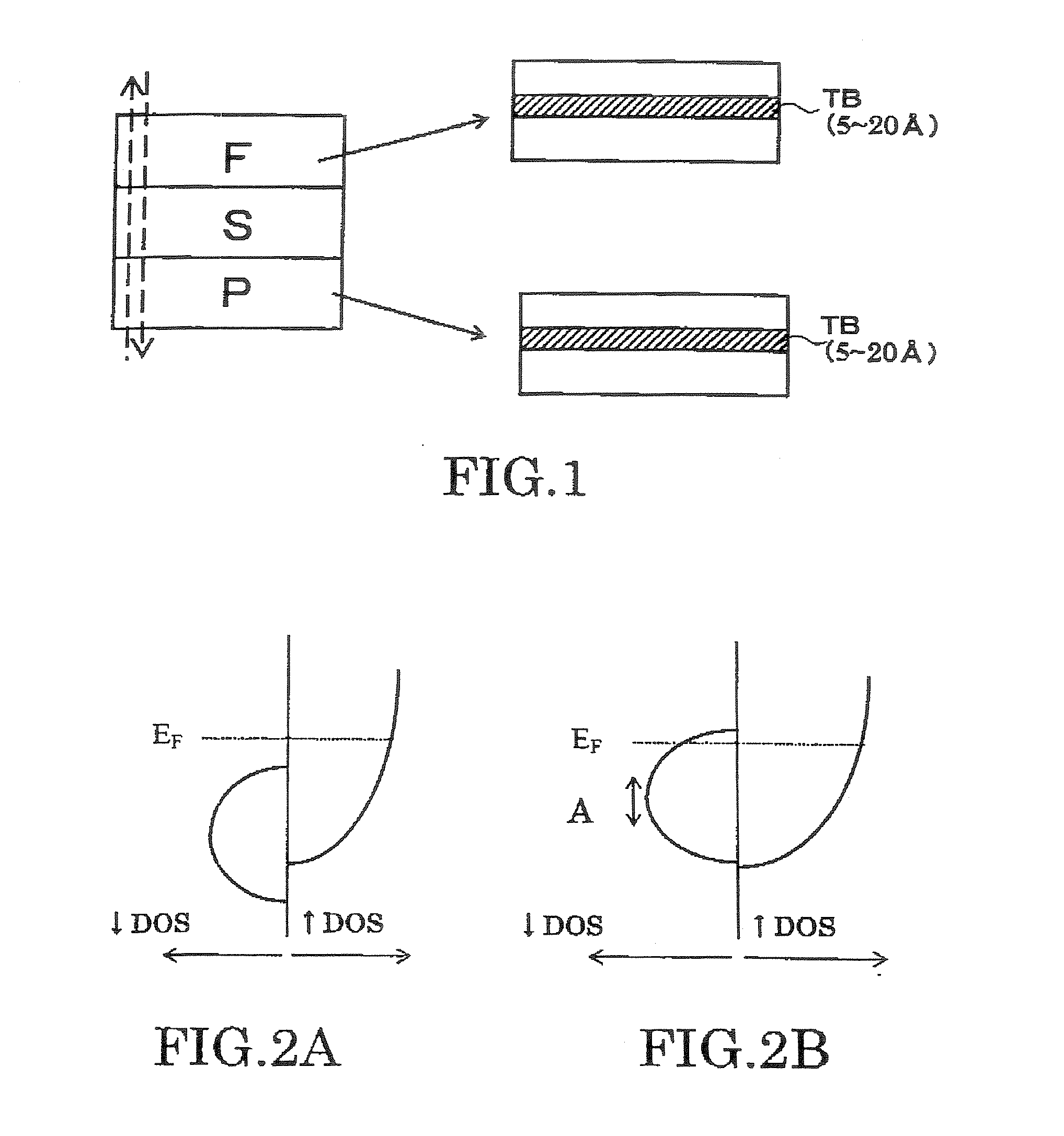
A magnetoresistive element includes a free layer which contains a magnetic material and has an fct crystal structure with a (001) plane oriented, the free layer having a magnetization which is perpendicular to a film plane and has a direction to be changeable by spin-polarized electrons, a first nonmagnetic layer and a second nonmagnetic layer which sandwich the free layer and have one of a tetragonal crystal structure and a cubic crystal structure, and a fixed layer which is provided on only one side of the free layer and on a surface of the first nonmagnetic layer opposite to a surface with the free layer and contains a magnetic material, the fixed layer having a magnetization which is perpendicular to a film plane and has a fixed direction.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
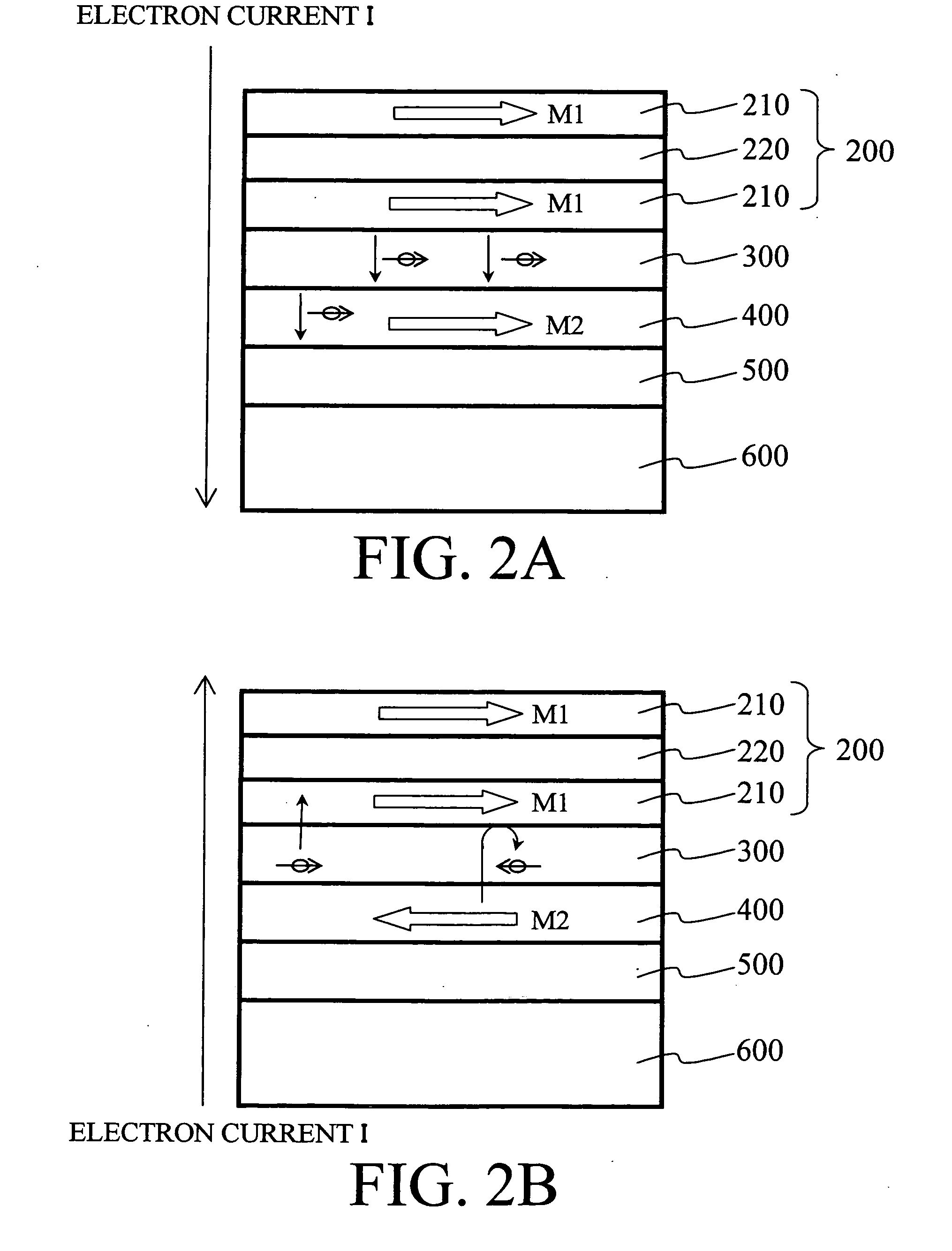
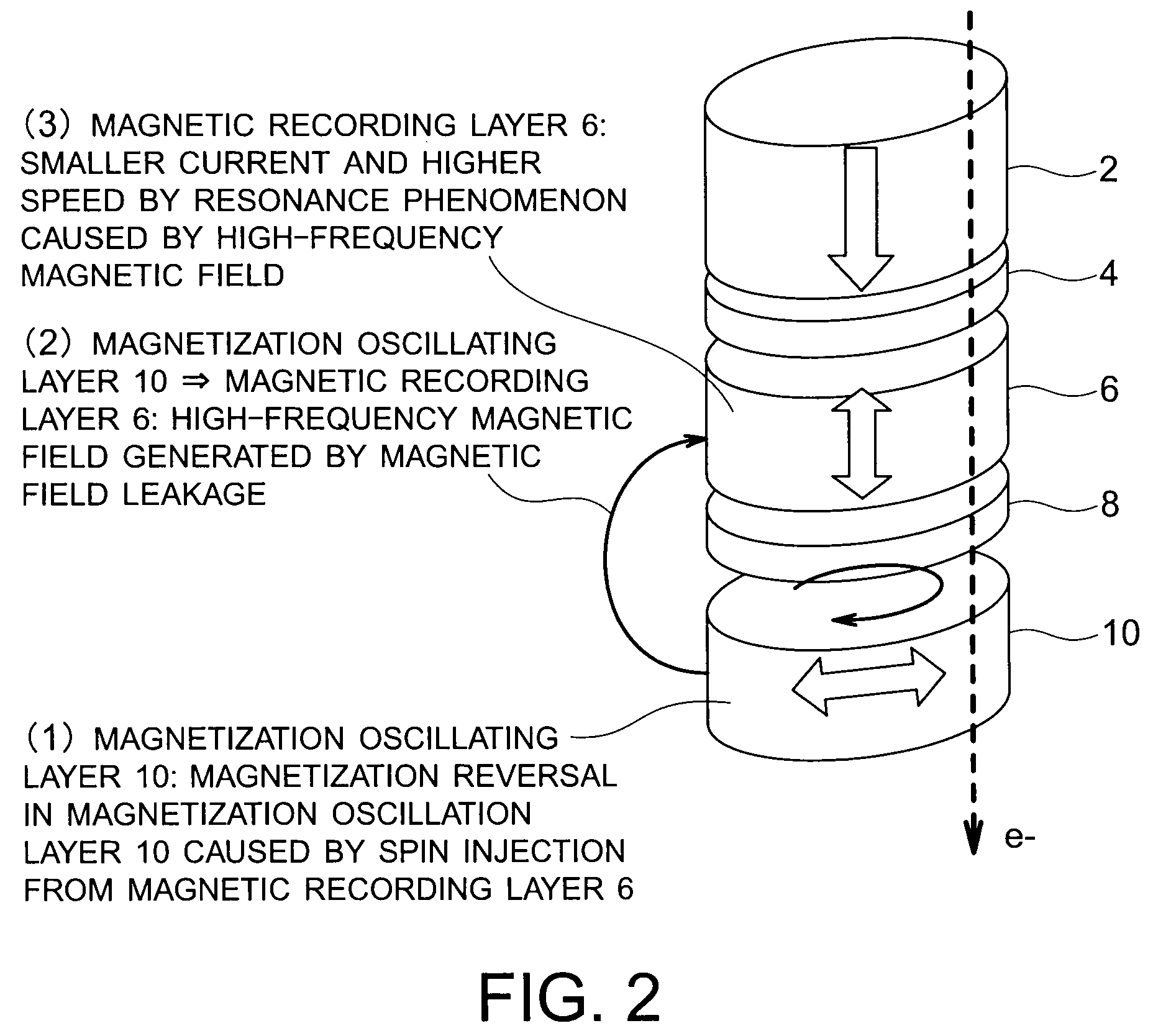
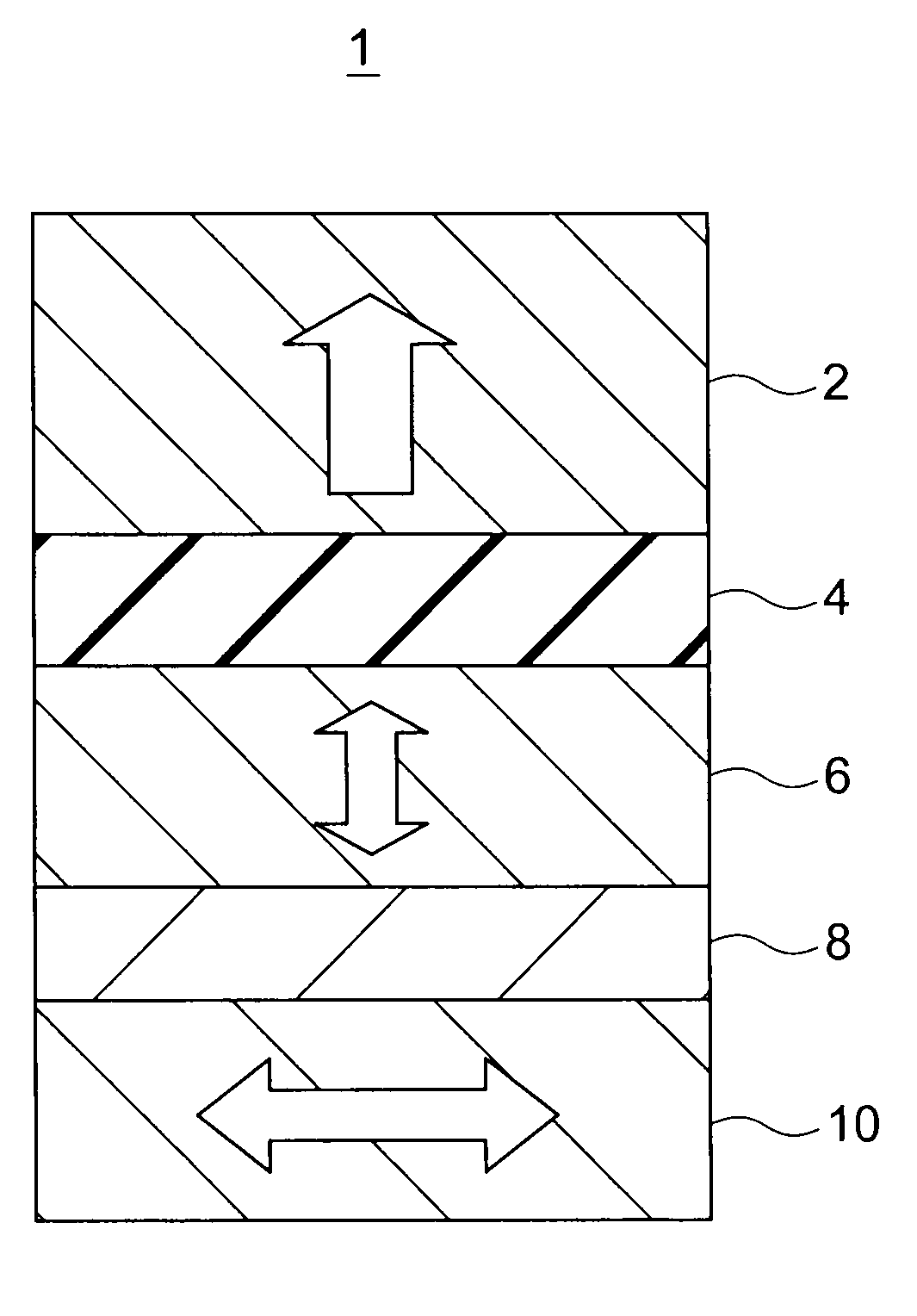
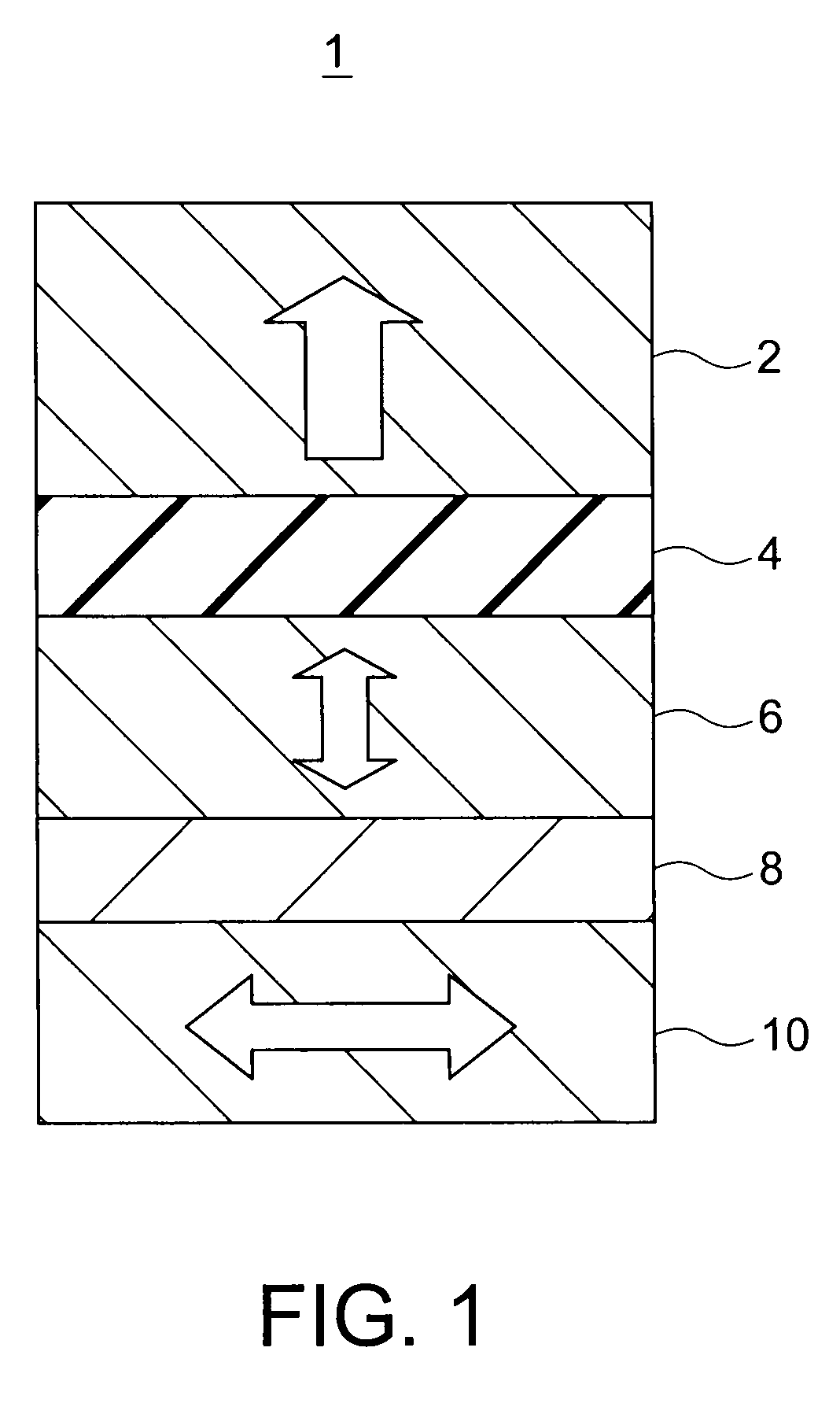
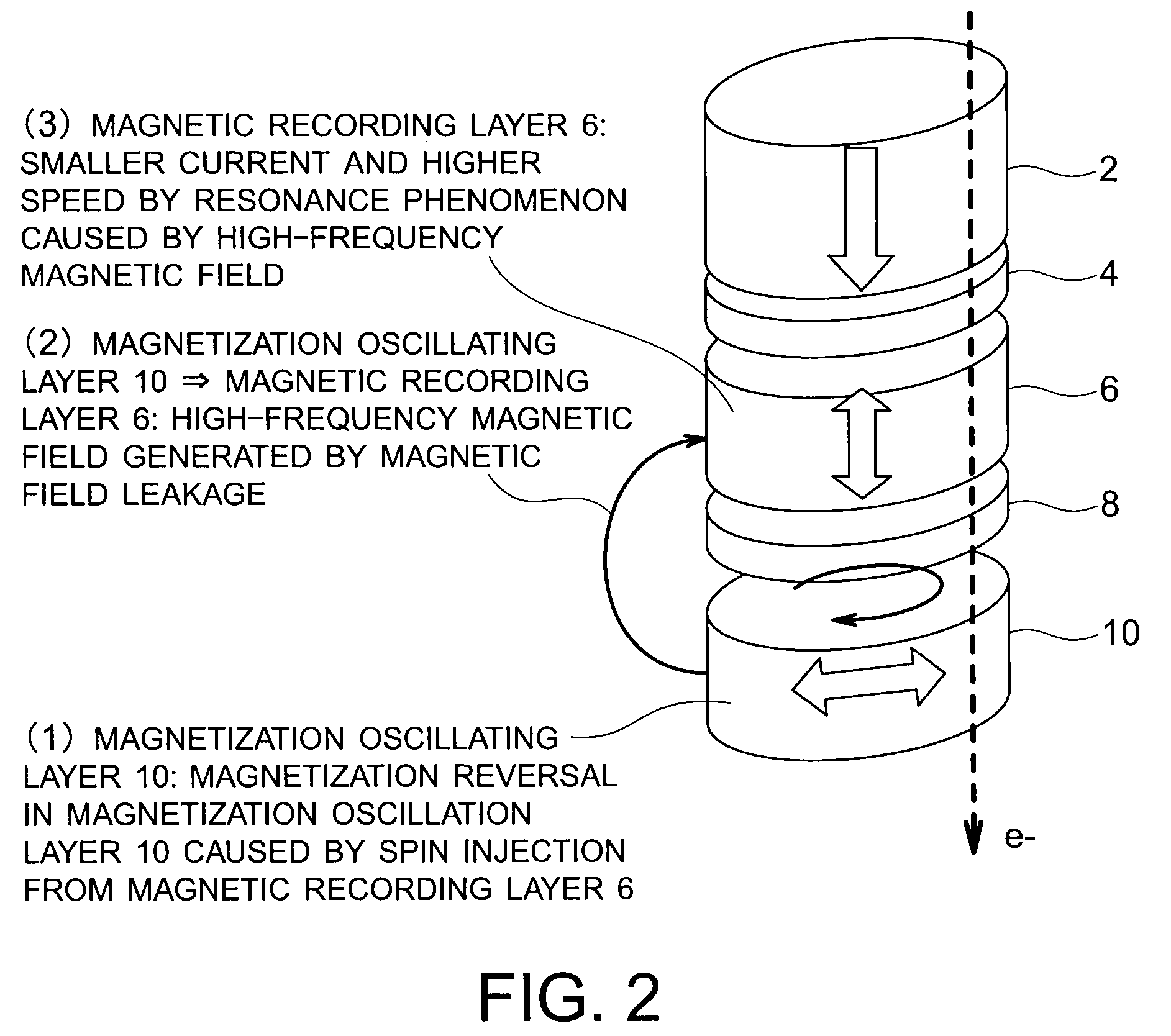
Magnetic recording device and magnetic recording apparatus
InactiveUS20090015958A1Record information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsPrecessionFilm plane
A magnetic recording device includes: a laminated body including: a first ferromagnetic layer with a magnetization substantially fixed in a first direction; a second ferromagnetic layer with a variable magnetization direction; a first nonmagnetic layer disposed between the first ferromagnetic layer and the second ferromagnetic layer; and a third ferromagnetic layer with a variable magnetization direction. The magnetization direction of the second ferromagnetic layer is determinable in response to the orientation of a current, by allowing electrons spin-polarized by passing a current in a direction generally perpendicular to the film plane of the layers of the laminated body to act on the second ferromagnetic layer, and by allowing a magnetic field generated by precession of the magnetization of the third ferromagnetic layer to act on the second ferromagnetic layer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Magnetoresistance effect element, magnetic head, and magnetic reproducing apparatus
ActiveUS20040201929A1Reduce the amount of solutionMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsRecord information storageHigh concentrationInter layer
A magnetoresistance effect element comprises: a magnetoresistance effect film, a pair of electrodes, and a phase separation layer. The magnetoresistance effect film includes a first ferromagnetic layer whose direction of magnetization is pinned substantially in one direction, a second ferromagnetic layer whose direction of magnetization changes in response to an external magnetic field, and an intermediate layer provided between the first and second ferromagnetic layers. The pair of electrodes are electrically coupled to the magnetoresistance effect film and configured to supply a sense current perpendicularly to a film plane of the magnetoresistance effect film. The phase separation layer is provided between the pair of electrodes. The phase separation layer has a first phase and a second phase formed by a phase separation in a solid phase from an alloy including a plurality of elements. One of the first and second phases includes at least one element selected from the group consisting of oxygen, nitrogen, fluorine and carbon in higher concentration than other of the first and second phases.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
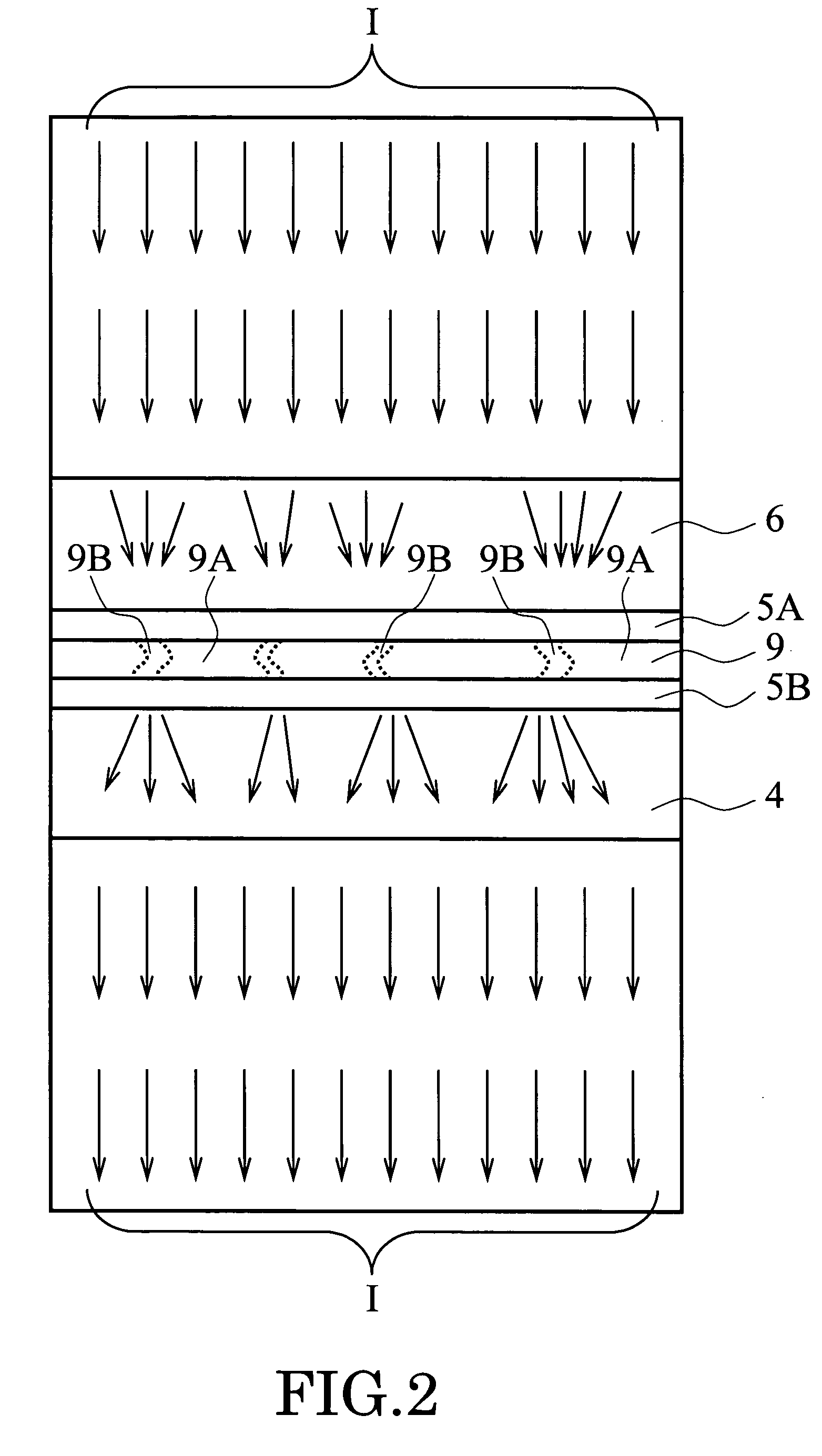
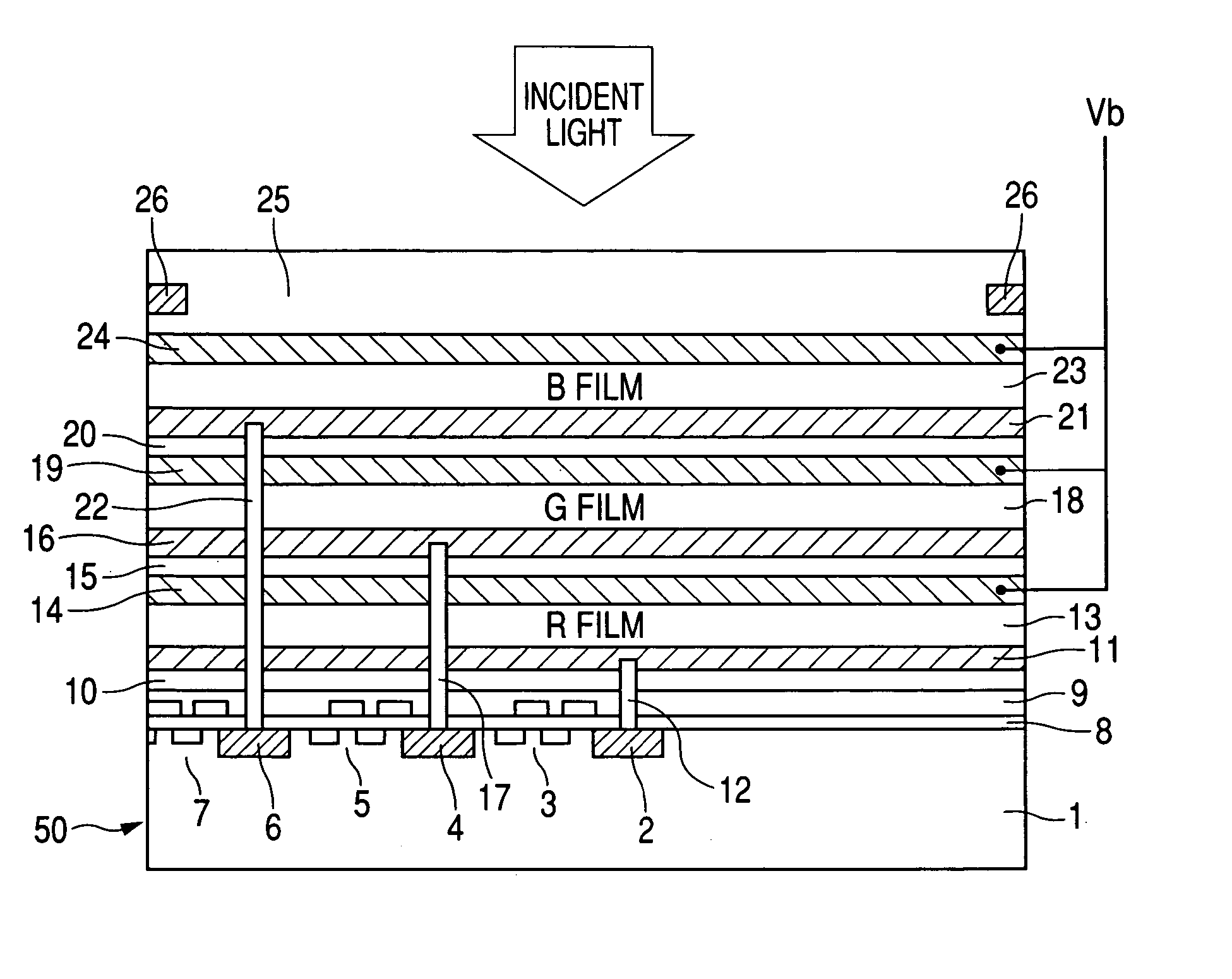
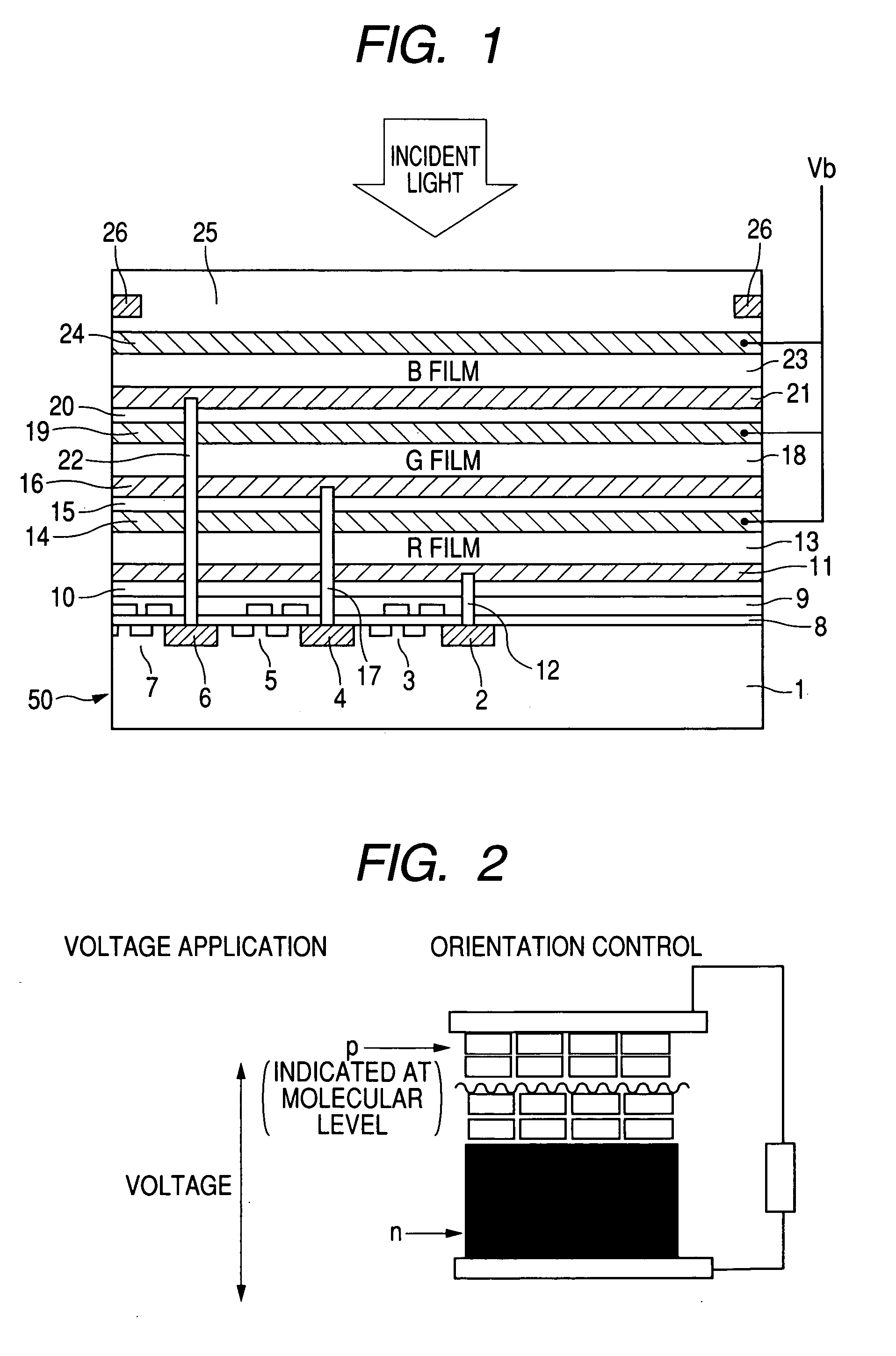
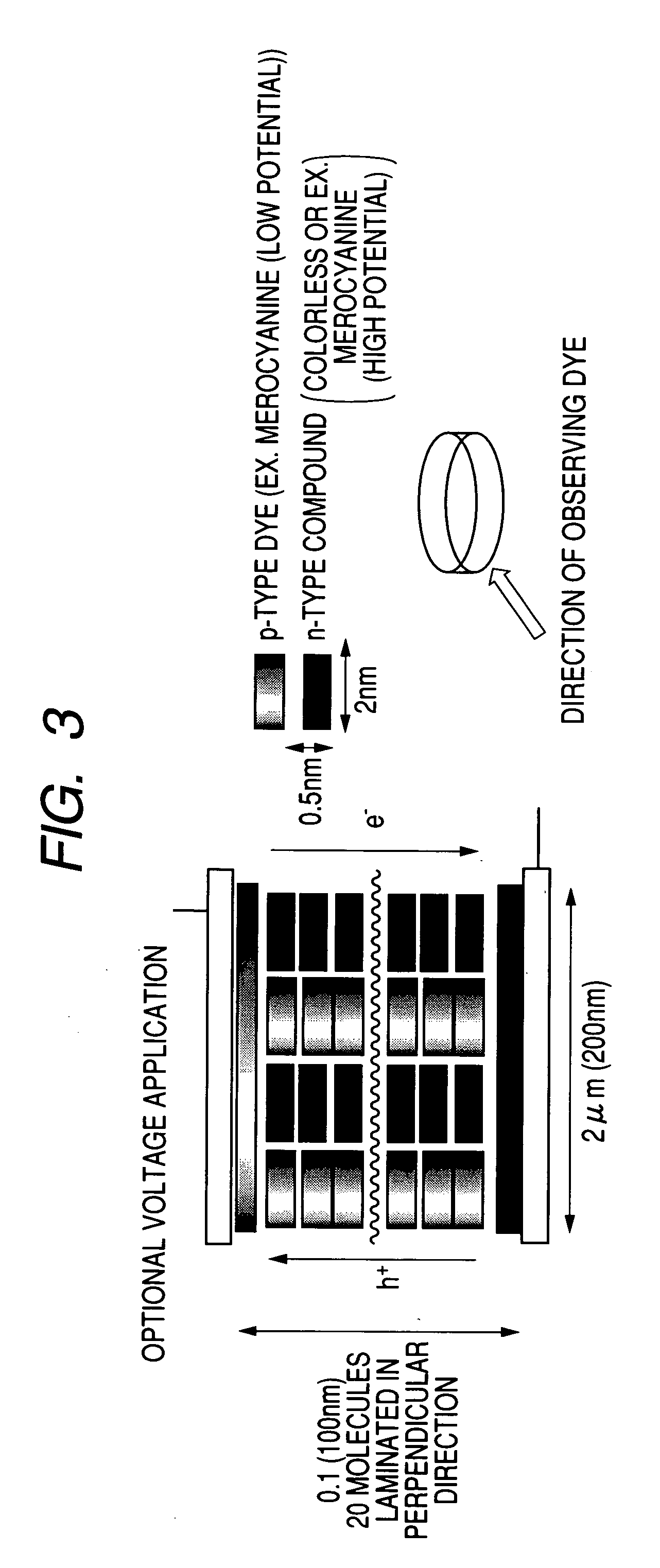
Photoelectric conversion film, photoelectric conversion element, imaging element, method of applying electric field thereto and electric field-applied element
ActiveUS20050205903A1High color reproductionHigh Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionOrganic dye
An imaging element having a photoelectric conversion film which has a laminated structure comprising a p-type semiconductor layer and an n-type semiconductor layer between a pair of electrodes, wherein at least one of the p-type semiconductor and the n-type semiconductor contains an organic compound with controlled orientation; a photoelectric conversion film having at least one organic dye compound, wherein the organic dye compound forms a J aggregate, or the angle between the spectral absorption transition dipolar moment of the organic dye compound and the photoelectric conversion film plane is 40° or less, a photoelectric conversion element and an imaging element; and a method of applying an electric field thereto, and an imaging element which comprises a photoelectric conversion film (a photosensitive layer) having a bulk heterojunction layer as an intermediate layer, or a photoelectric conversion film having two or more repeating structure units of a pn junction layer comprising a p-type semiconductor layer and an n-type semiconductor layer between a pair of electrodes.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Magnetoresistive element and magnetic memory
A magnetoresistive element includes a free layer which contains a magnetic material and has an fct crystal structure with a (001) plane oriented, the free layer having a magnetization which is perpendicular to a film plane and has a direction to be changeable by spin-polarized electrons, a first nonmagnetic layer and a second nonmagnetic layer which sandwich the free layer and have one of a tetragonal crystal structure and a cubic crystal structure, and a fixed layer which is provided on only one side of the free layer and on a surface of the first nonmagnetic layer opposite to a surface with the free layer and contains a magnetic material, the fixed layer having a magnetization which is perpendicular to a film plane and has a fixed direction.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Magnetic recording element and magnetic memory
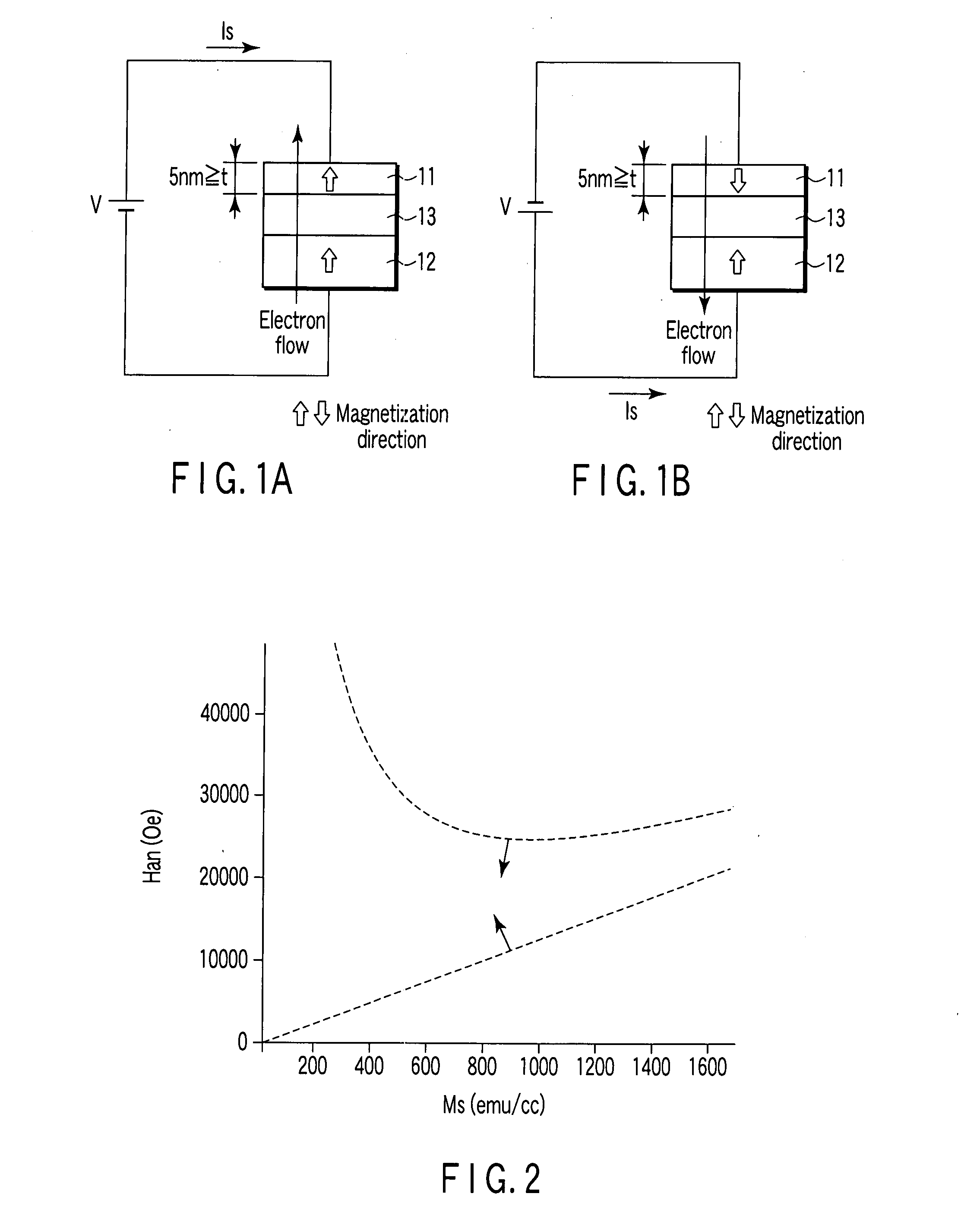
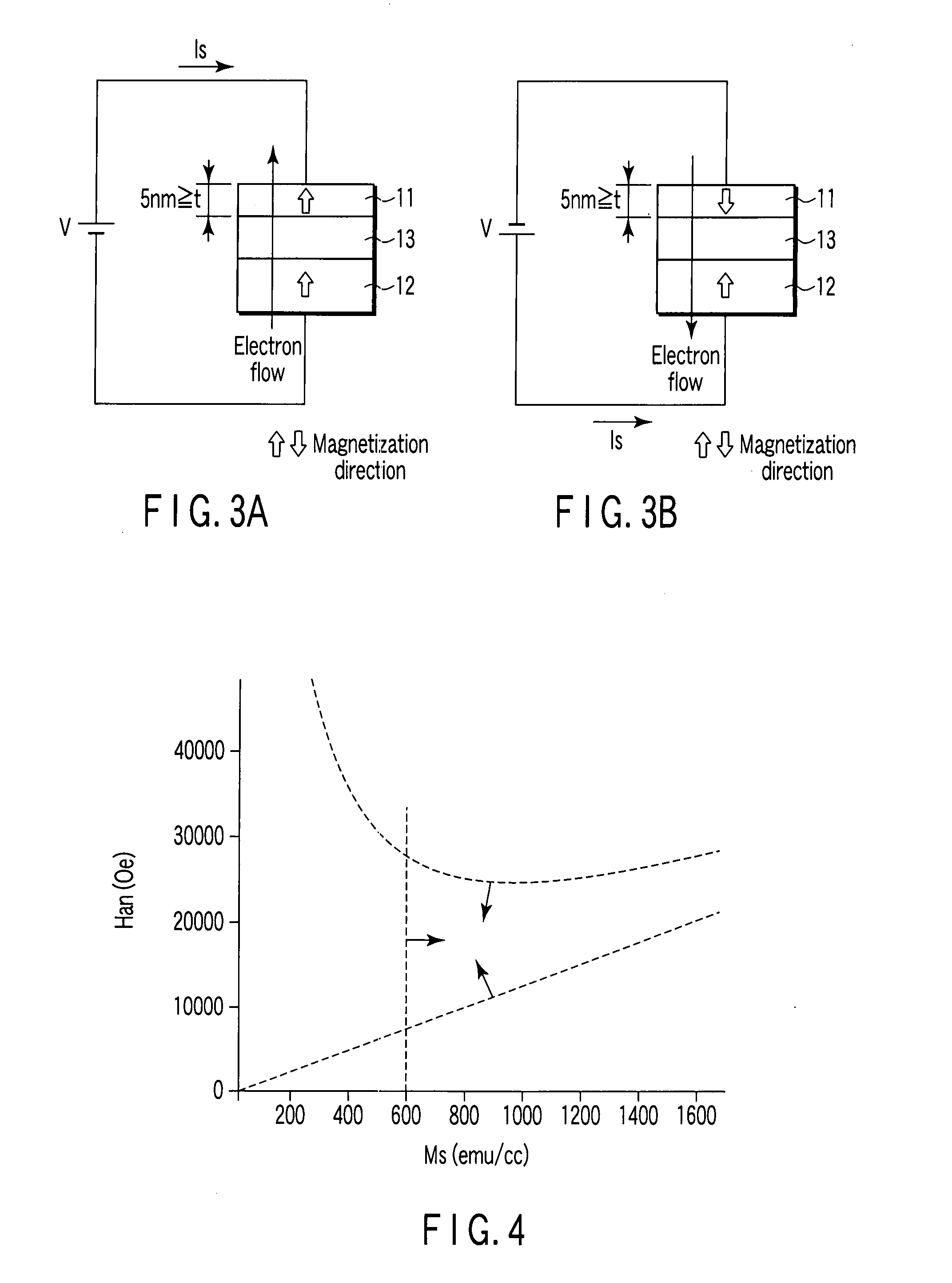
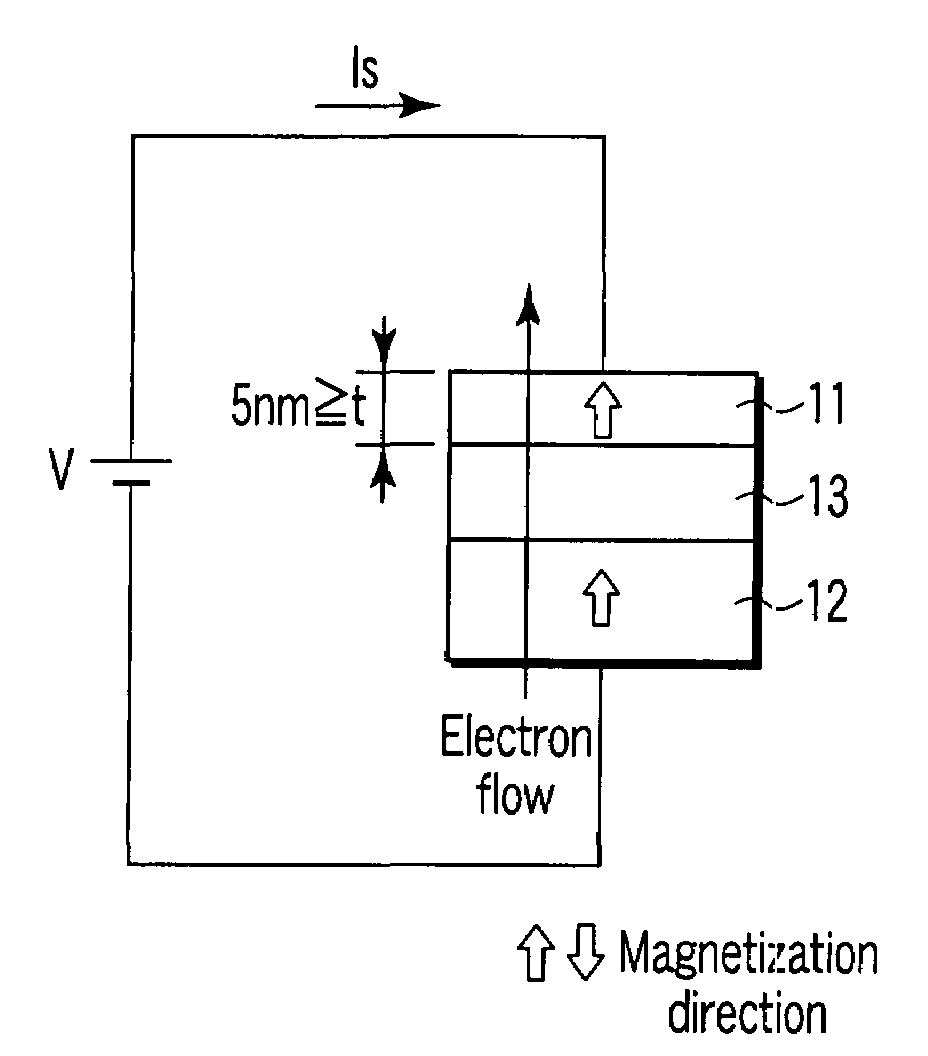
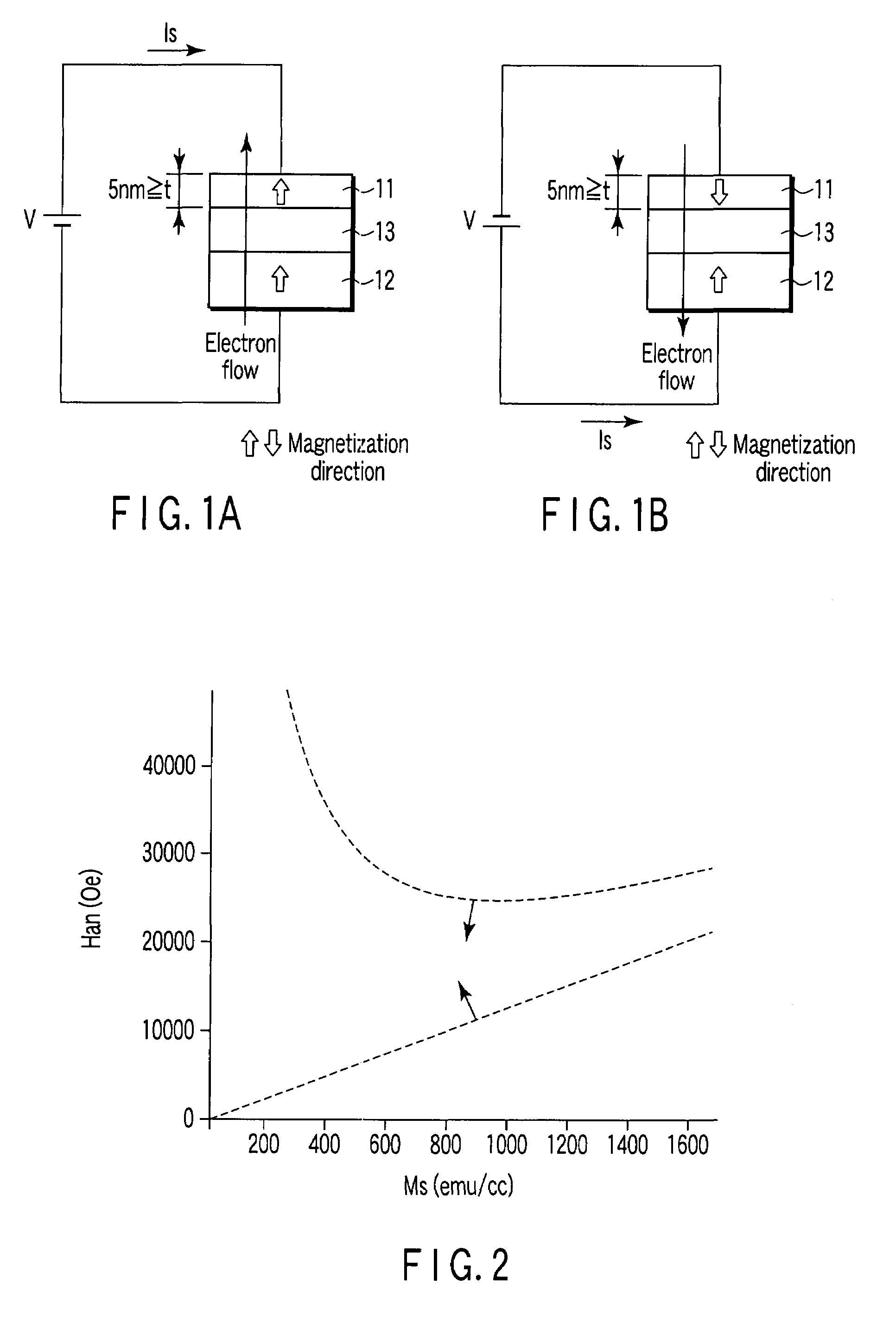
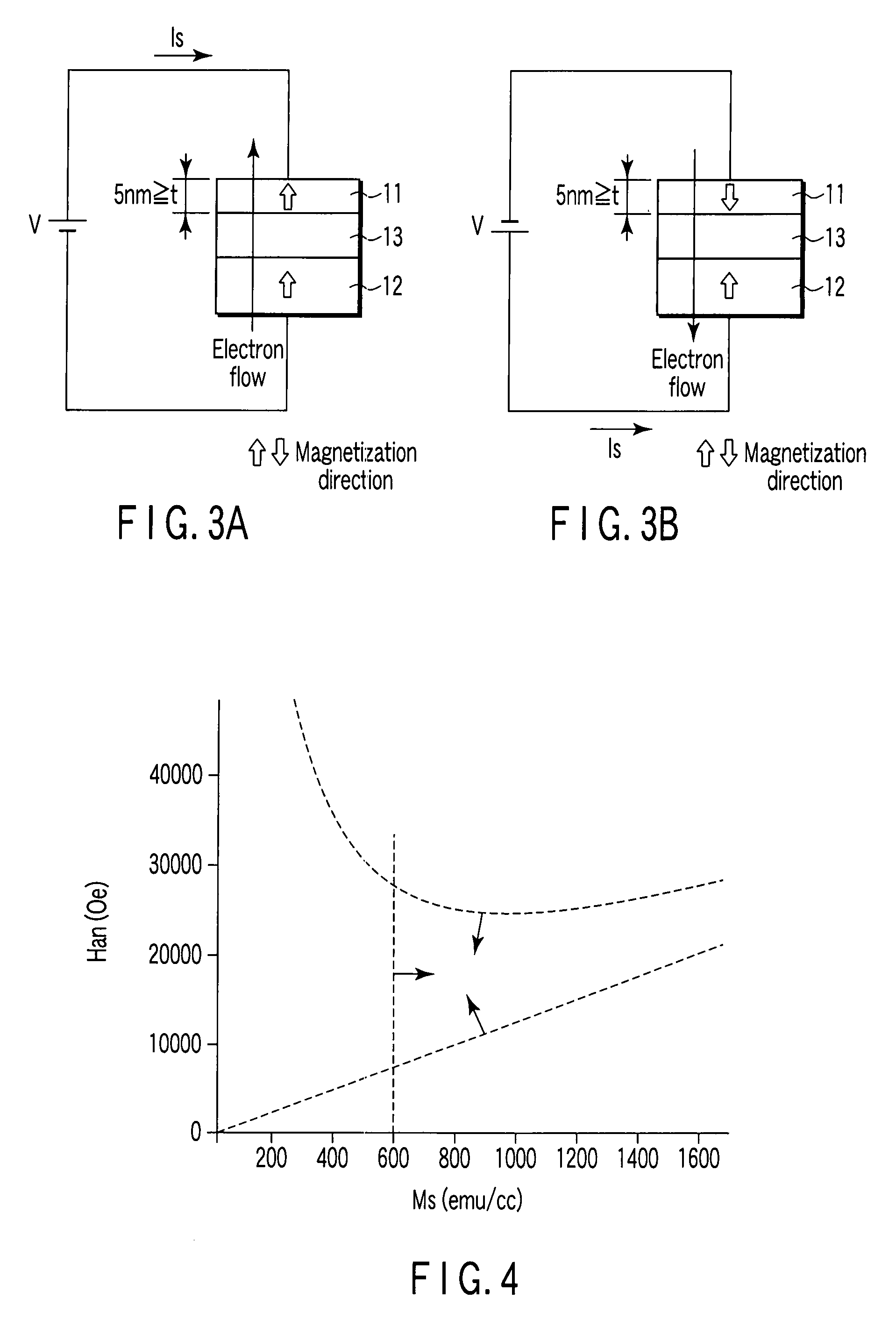
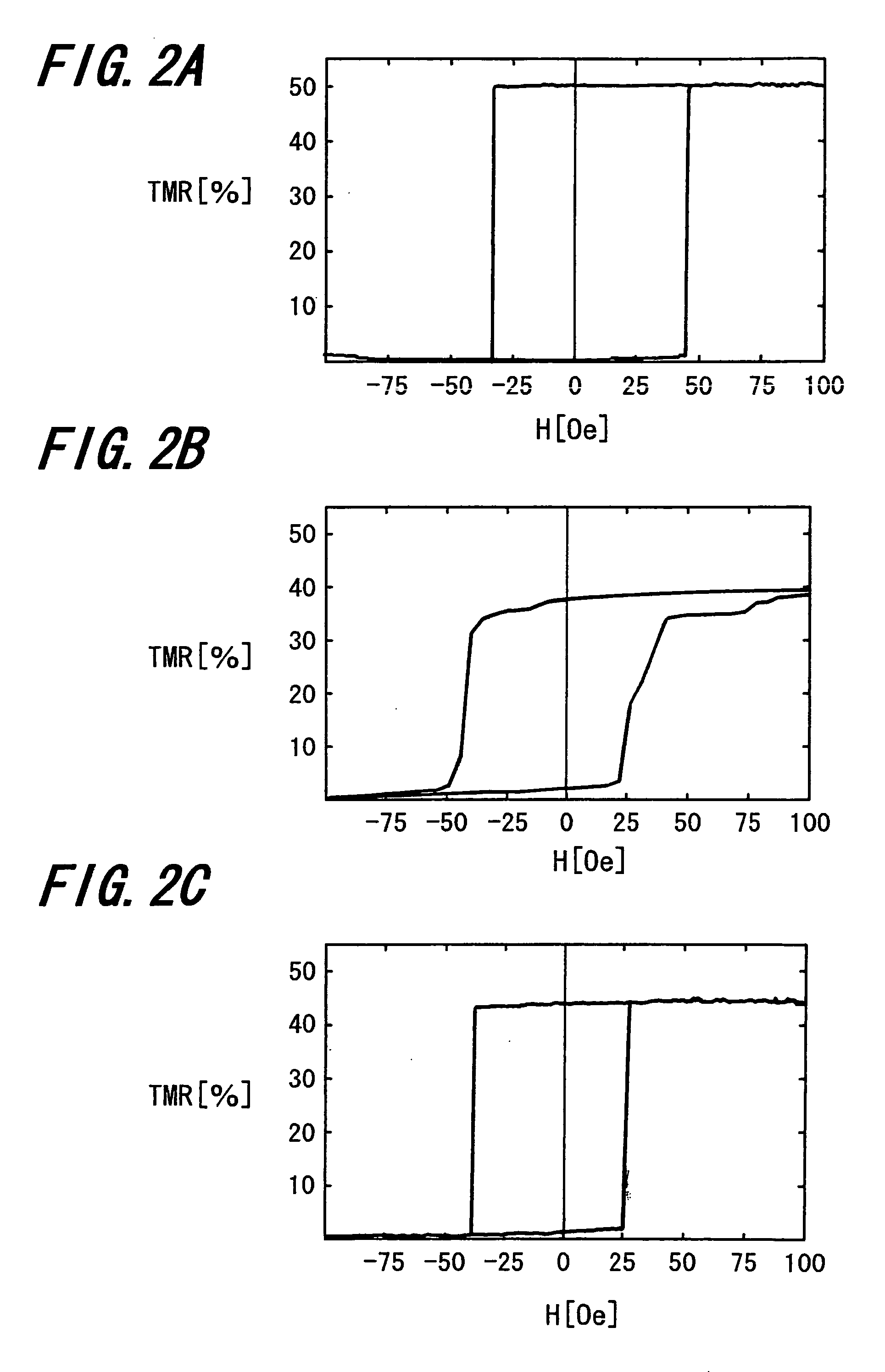
A magnetic recording element according to an example of the present invention includes a magnetic free layer whose magnetization is variable in accordance with a current direction passing through a film and whose direction of easy axis of magnetization is a direction perpendicular to a film plane, a magnetic pinned layer whose magnetization is fixed to a direction perpendicular to the film plane, and a non-magnetic barrier layer between the magnetic free layer and the magnetic pinned layer. In the magnetic free layer, a relation between a saturated magnetization Ms (emu / cc) and an anisotropy field Han (Oe) satisfies Han>12.57 Ms, and Han<1.2 E 7 MS-1+12.57 Ms.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Magnetic recording element and magnetic memory
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
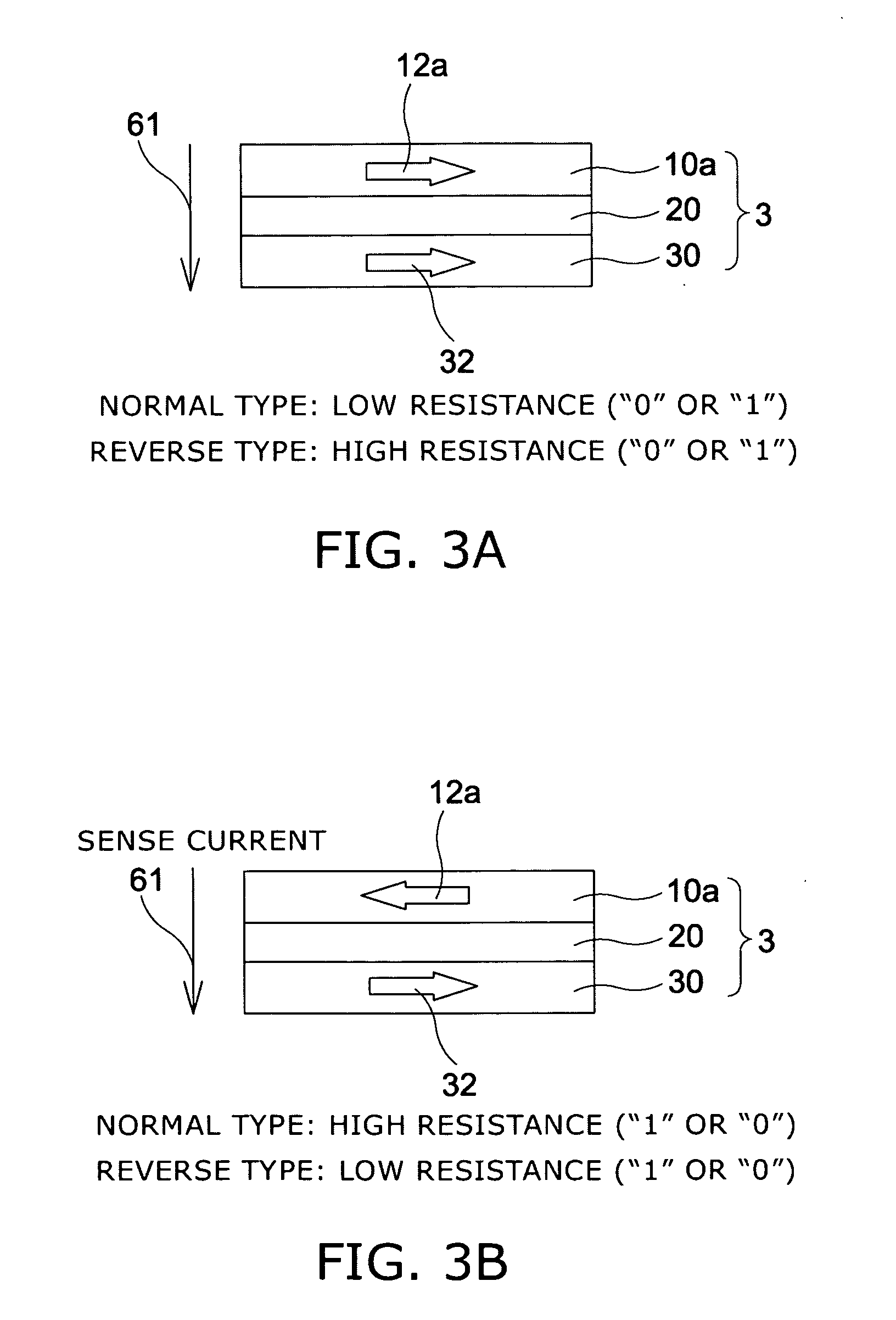
Cpp type giant magneto-resistance element and magnetic sensor
InactiveUS20080026253A1Lower resistanceRaise the ratioNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMagnetic reluctanceMagnetization
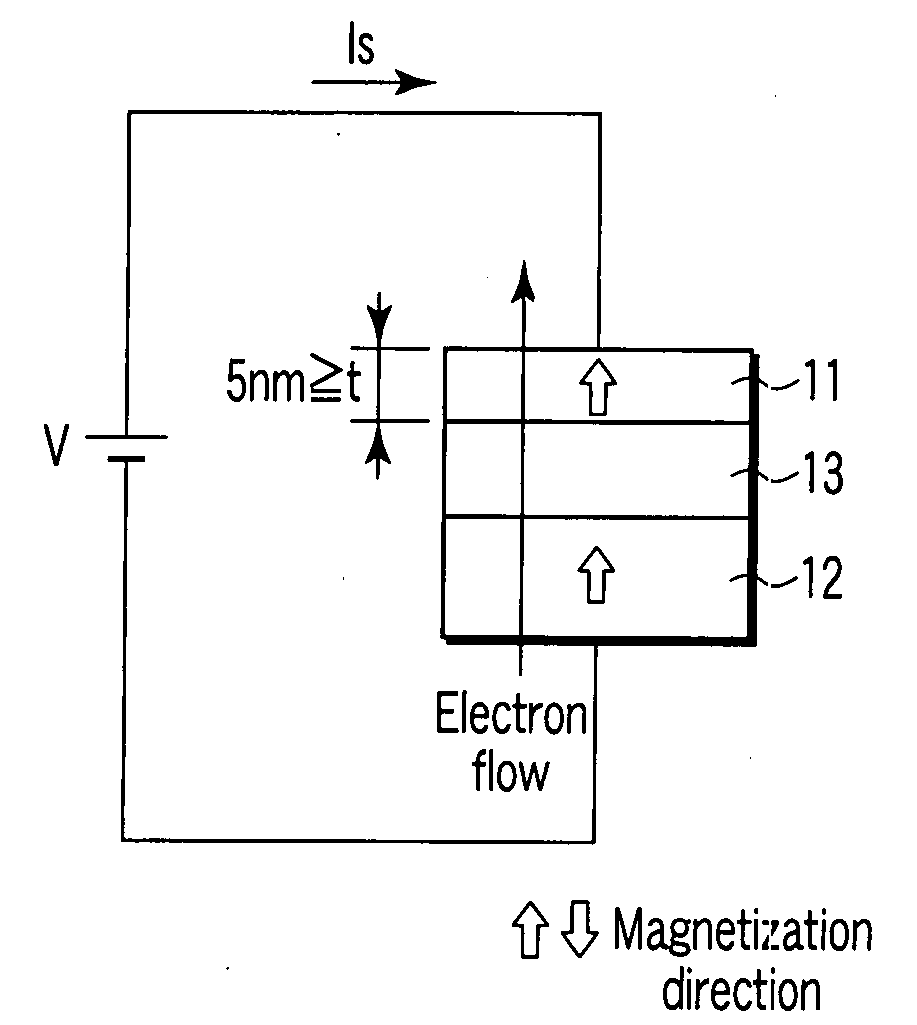
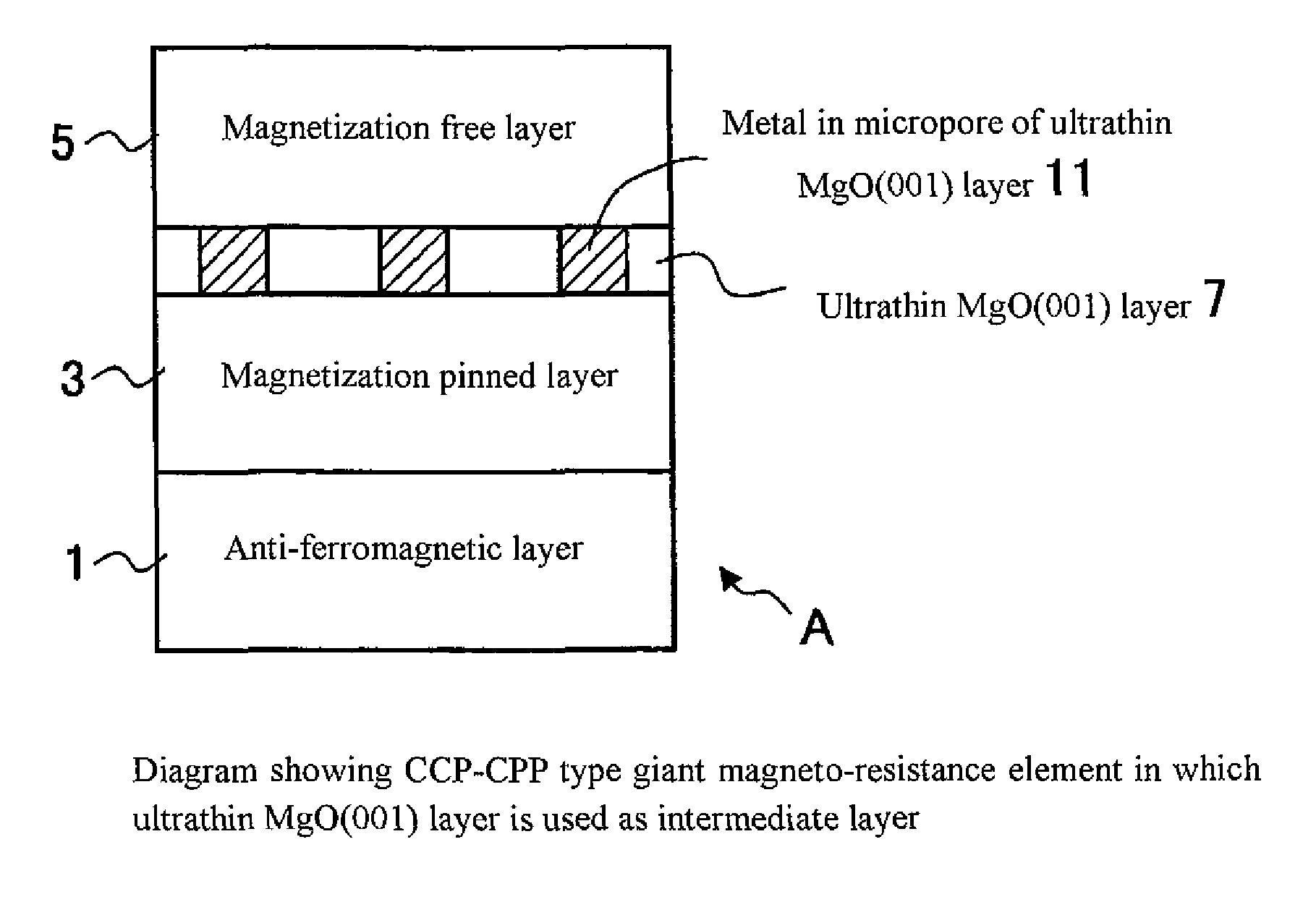
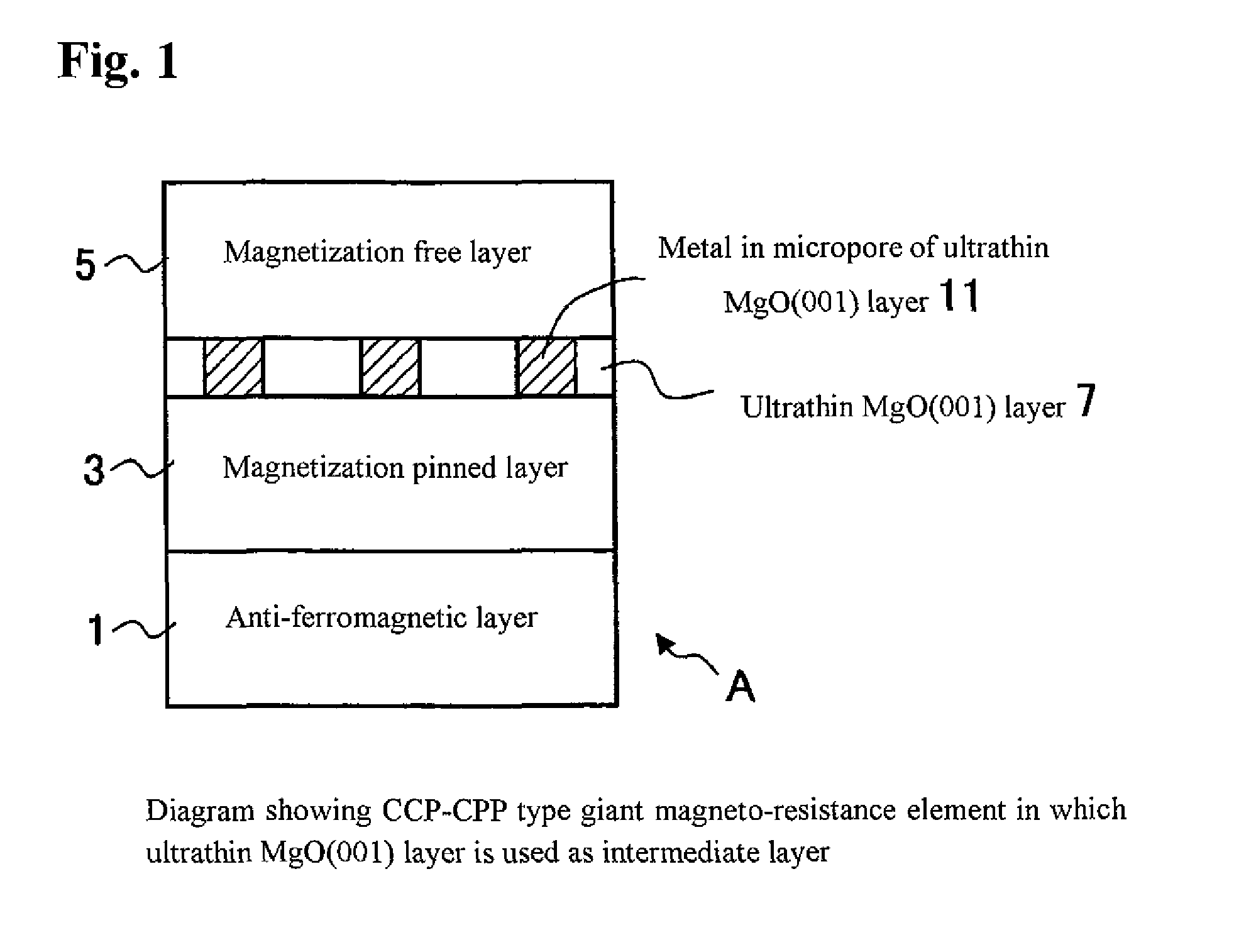
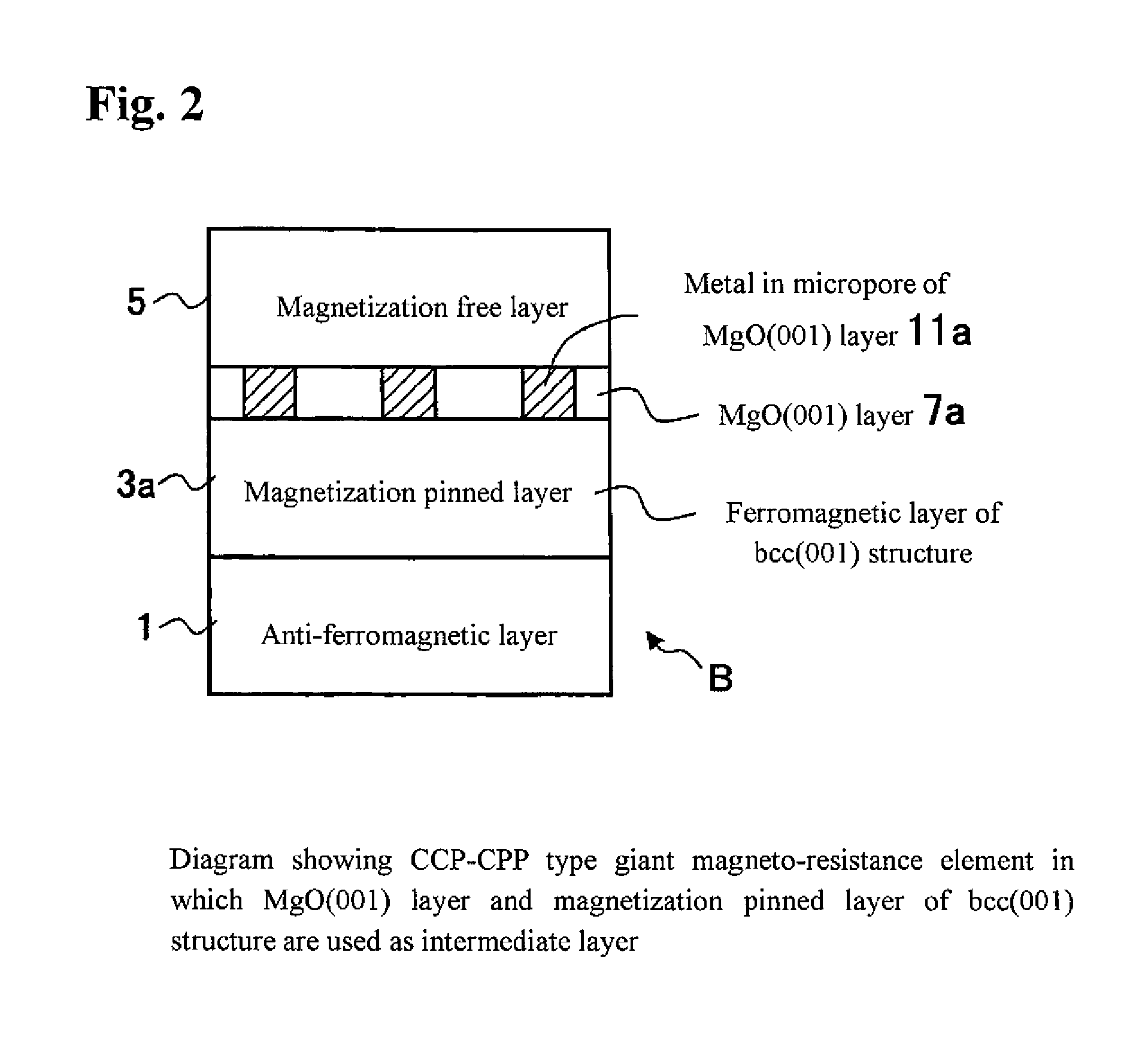
Provided are a CCP (current confined path)-CPP (current-perpendicular-to-plane) type giant magneto-resistance (GMR) element having a giant magneto-resistance ratio in a low resistance region (a region of not more than 1 ohm per square micrometer) and a magnetic sensor using this GMR element. The CCP-CPP type GMR element A has a laminated structure of an anti-ferromagnetic layer, a magnetization pinned layer, an intermediate layer and a magnetization free layer, and is formed to have a construction in which a current flows perpendicularly to a film plane. By using an ultrathin magnesium oxide layer having micropores that is preferentially oriented in the (001) direction as the intermediate layer, the magneto-resistance ratio is enhanced, because a current flowing from the magnetization free layer to the magnetization pinned layer (or in the opposite direction) is confined by the metal in the micropores.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
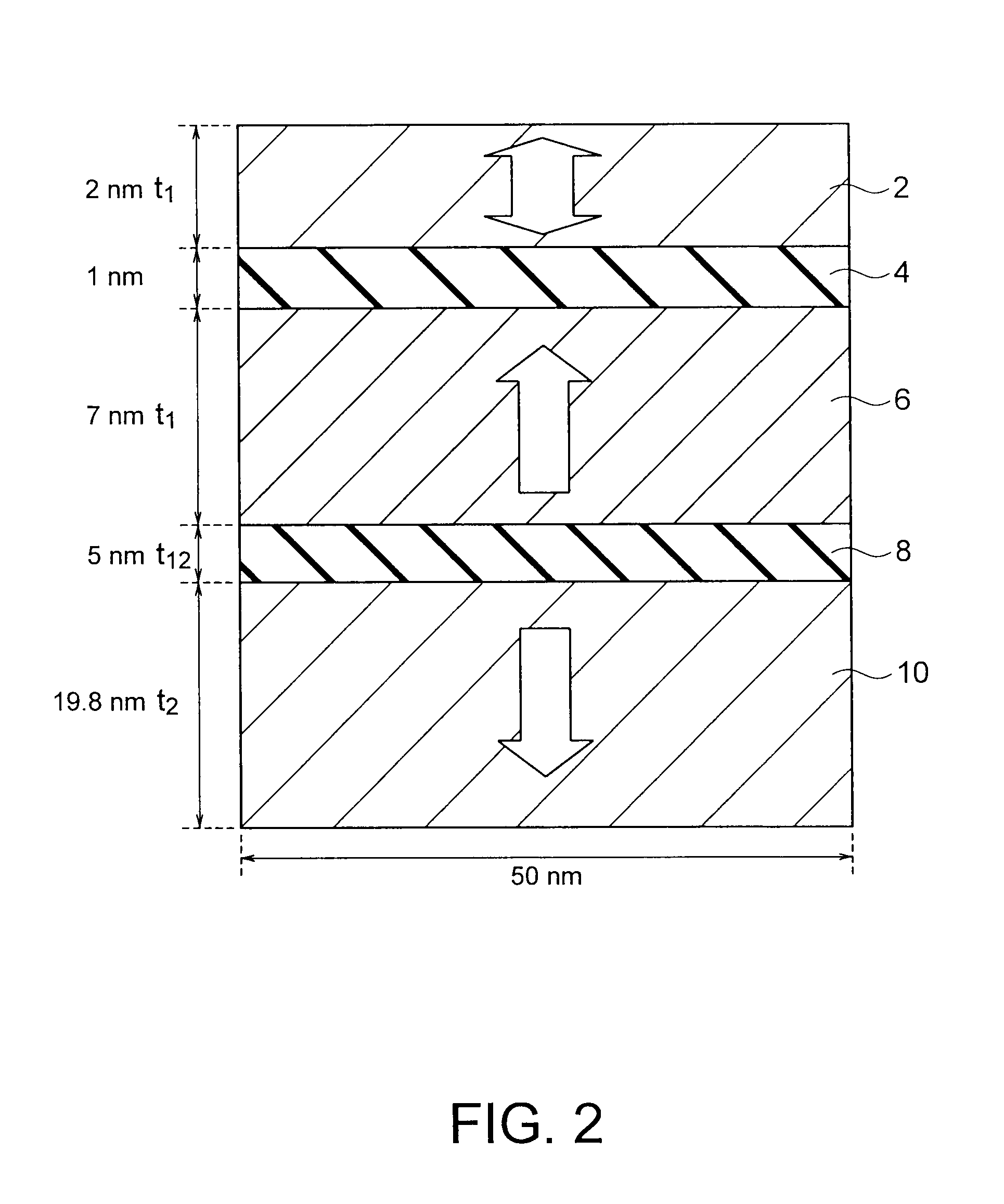
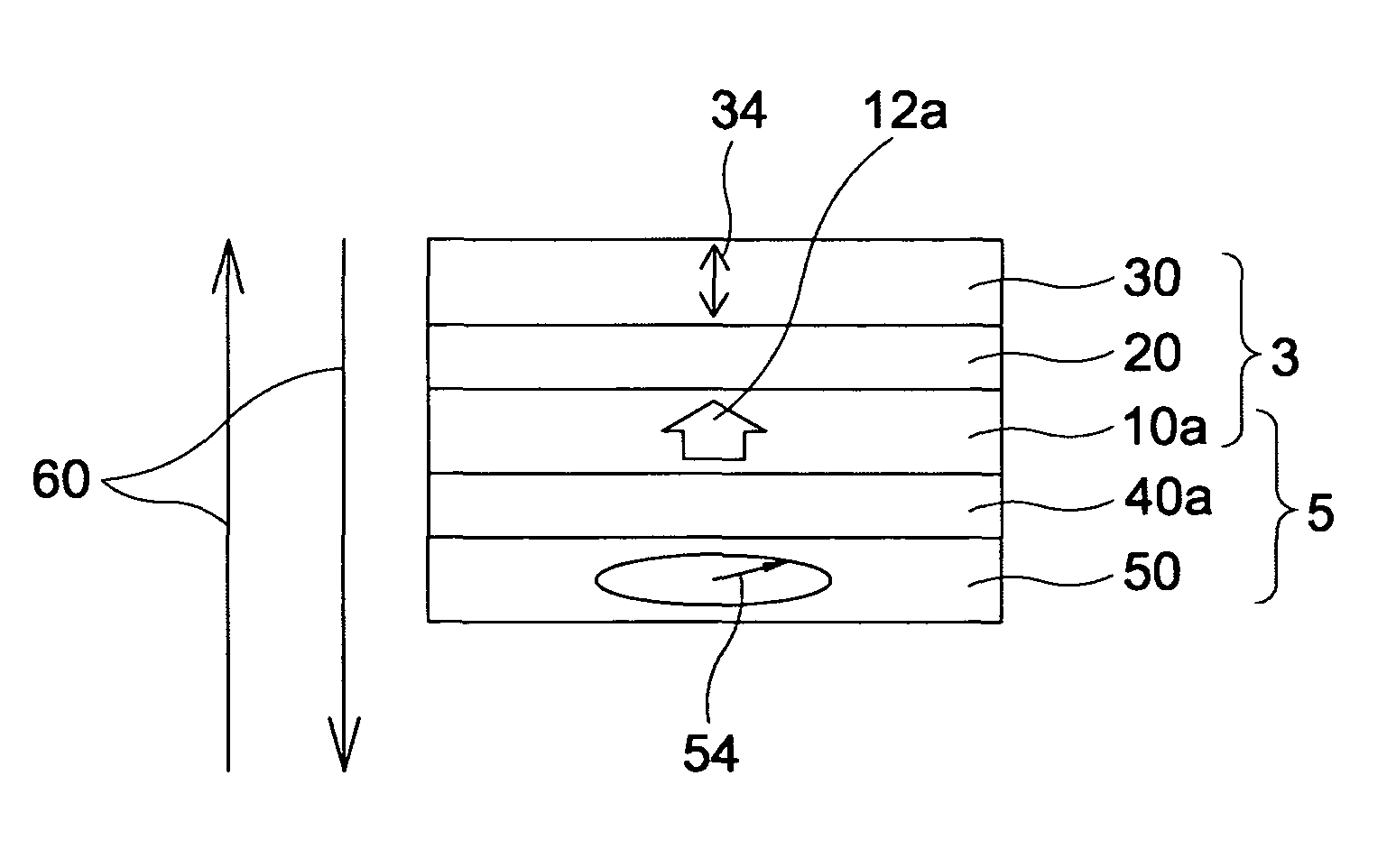
Magnetoresistive effect device and magnetic memory
ActiveUS20100080050A1MinimizingMinimizing leakage magnetic fieldNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsFilm planeMagnetic memory
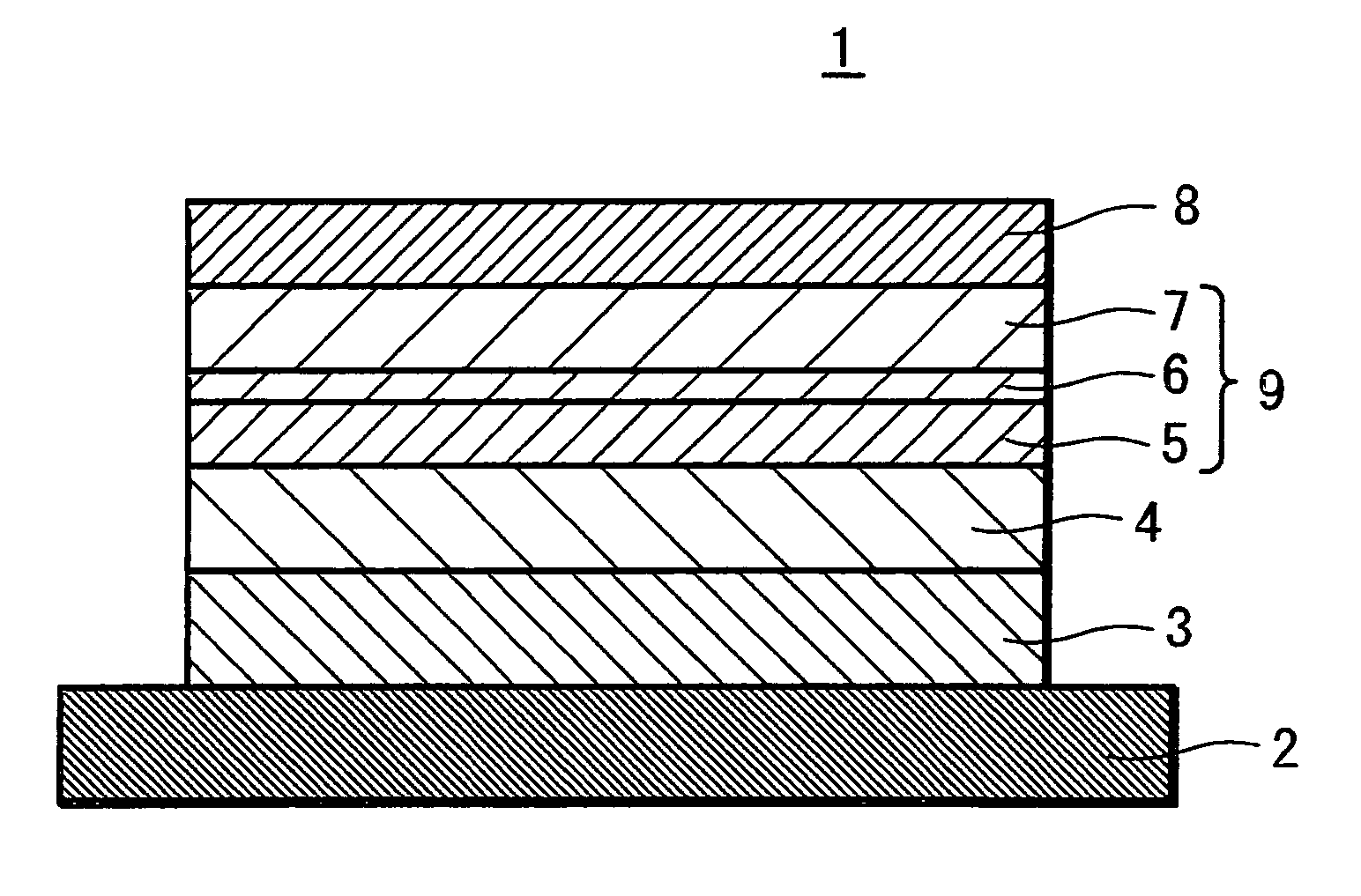
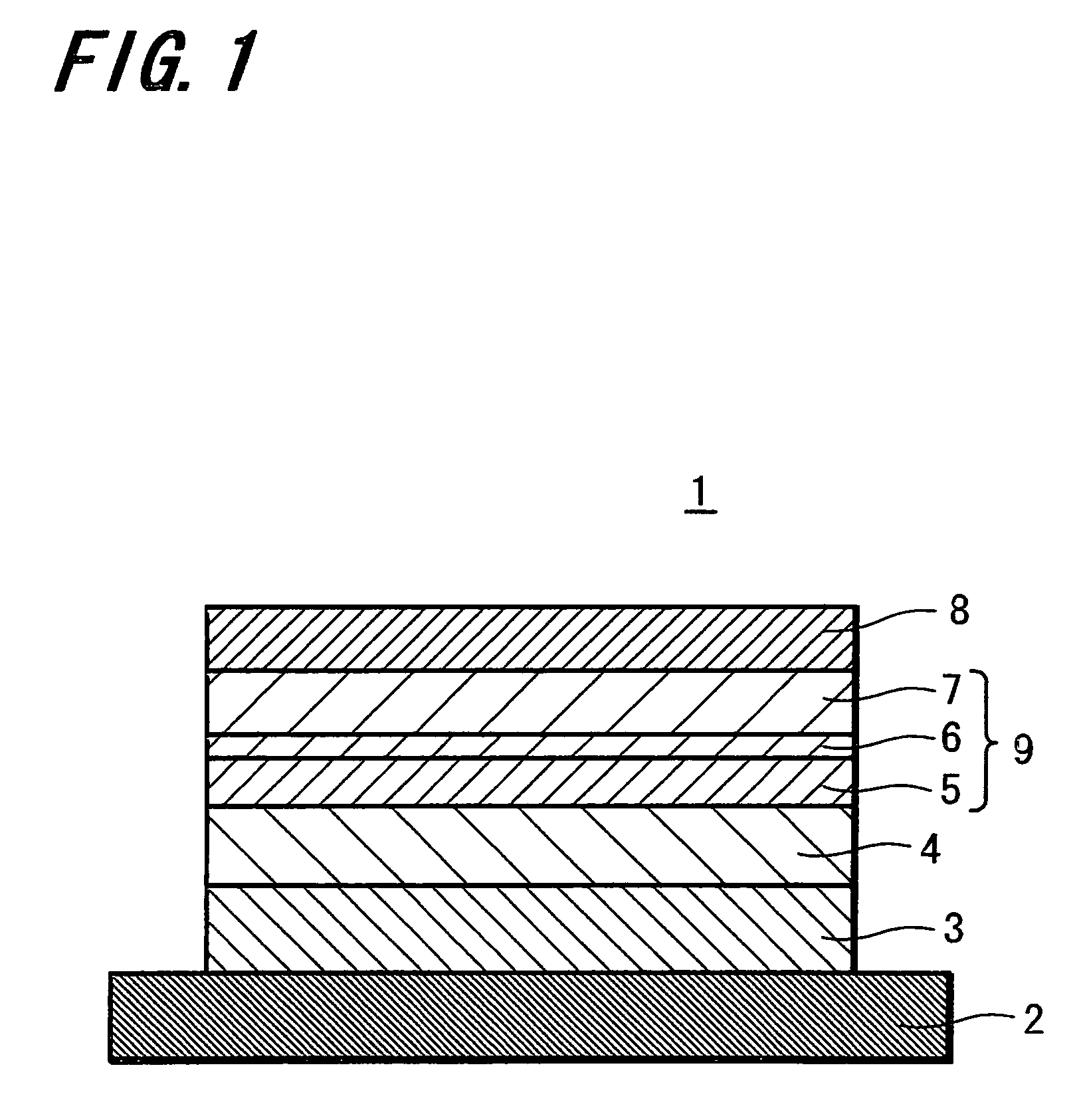
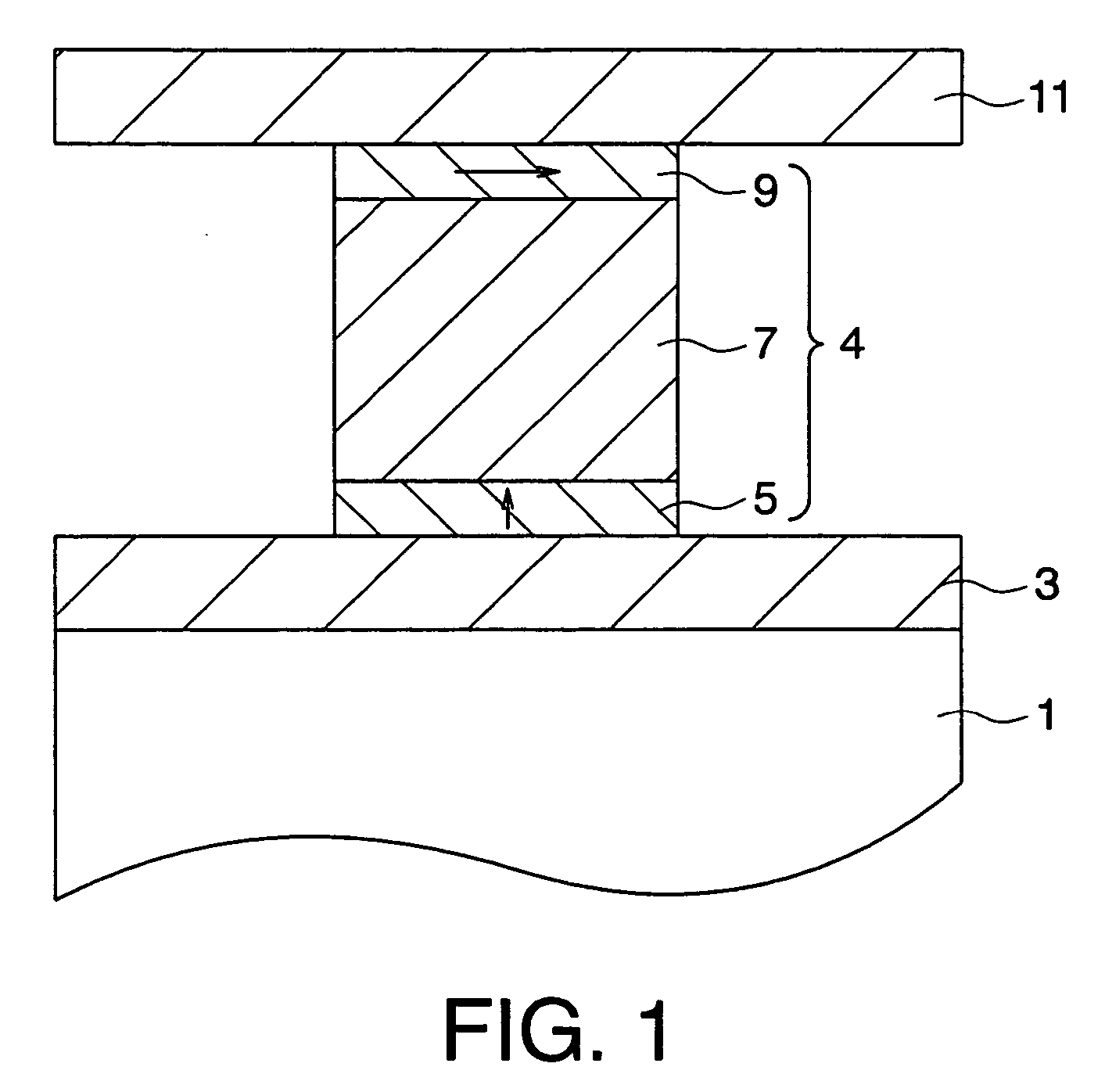
A magnetic memory includes a magnetoresistive effect device comprising: a first ferromagnetic layer that has magnetic anisotropy in a direction perpendicular to a film plane thereof; a first nonmagnetic layer that is provided on the first ferromagnetic layer; a first reference layer that is provided on the first nonmagnetic layer, has magnetic anisotropy in a direction perpendicular to a film plane thereof, has magnetization antiparallel to a magnetization direction of the first ferromagnetic layer, and has a film thickness that is 1 / 5.2 to 1 / 1.5 times as large as a film thickness of the first ferromagnetic layer in the direction perpendicular to the film plane; a second nonmagnetic layer that is provided on the first reference layer; and a storage layer that is provided on the second nonmagnetic layer, has magnetic anisotropy in a direction perpendicular to a film plane thereof, and has a magnetization direction varied by spin-polarized electrons caused by flowing the current to the magnetoresistive effect device.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Retardation film, process for producing the same, optical film, image display, liquid crystal panel and liquid crystal display
ActiveUS20060028601A1Retardation valueHard to cause a shift or an unevenness of a retardation valueOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsRefractive indexDisplay device
A retardation film of the present invention comprises a stretched film of a polymer film containing a norbornene-based resin, wherein the stretched film satisfies the following equation (1) and the equation (2); 100 nm≦(nx−ny)·d≦350 nm . . . (1),0.1≦(nx−nz) / (nx−ny)≦0.9 . . . (2), where the refractive indices in the slow axis direction, the fast axis direction and the thickness direction of the film are nx, ny and nz, respectively, d(nm) is thickness of the film, and the slow axis direction is a direction that the refractive index in film plane is maximum. The retardation film is hard to cause a shift or an unevenness of a retardation value due to a stress.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
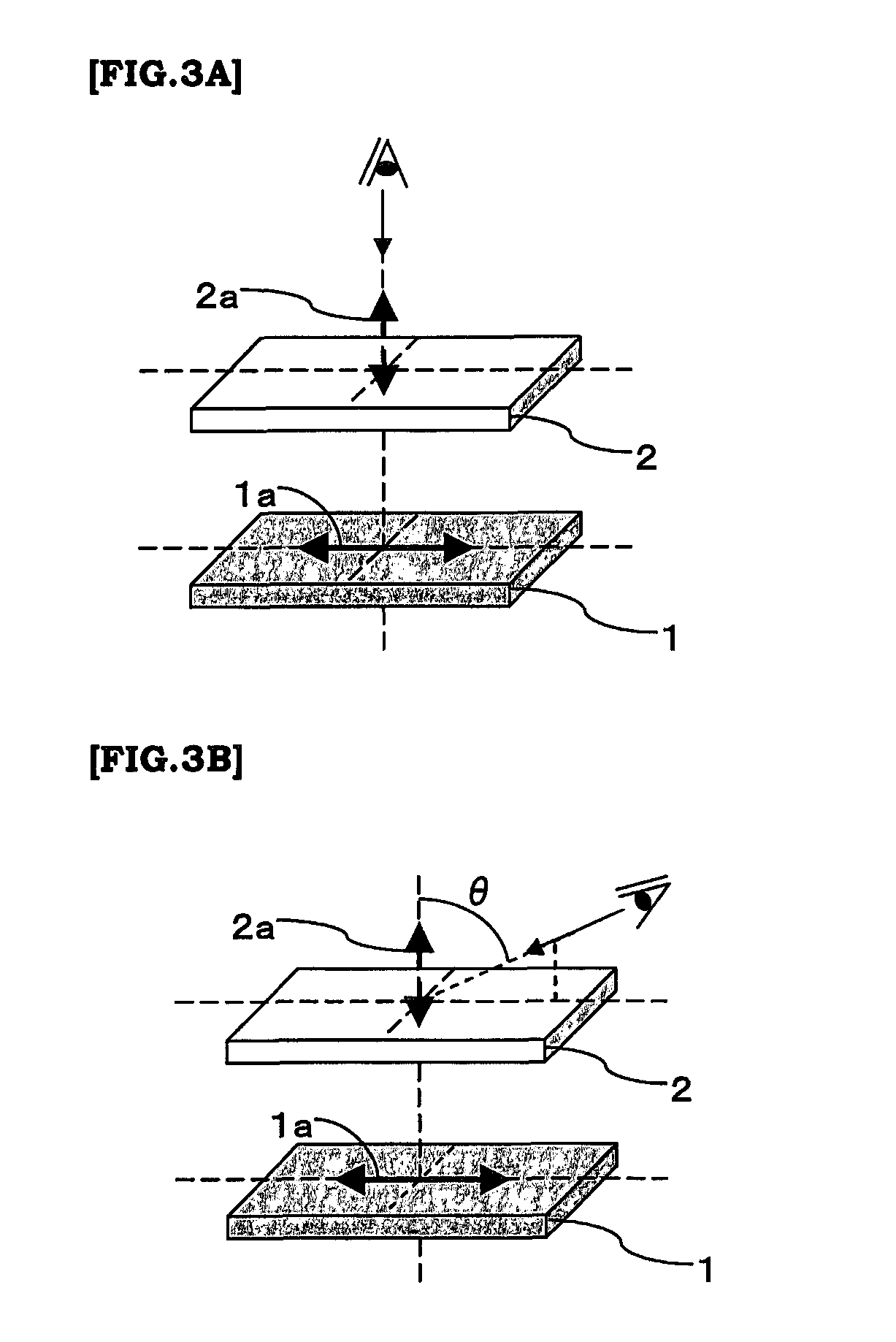
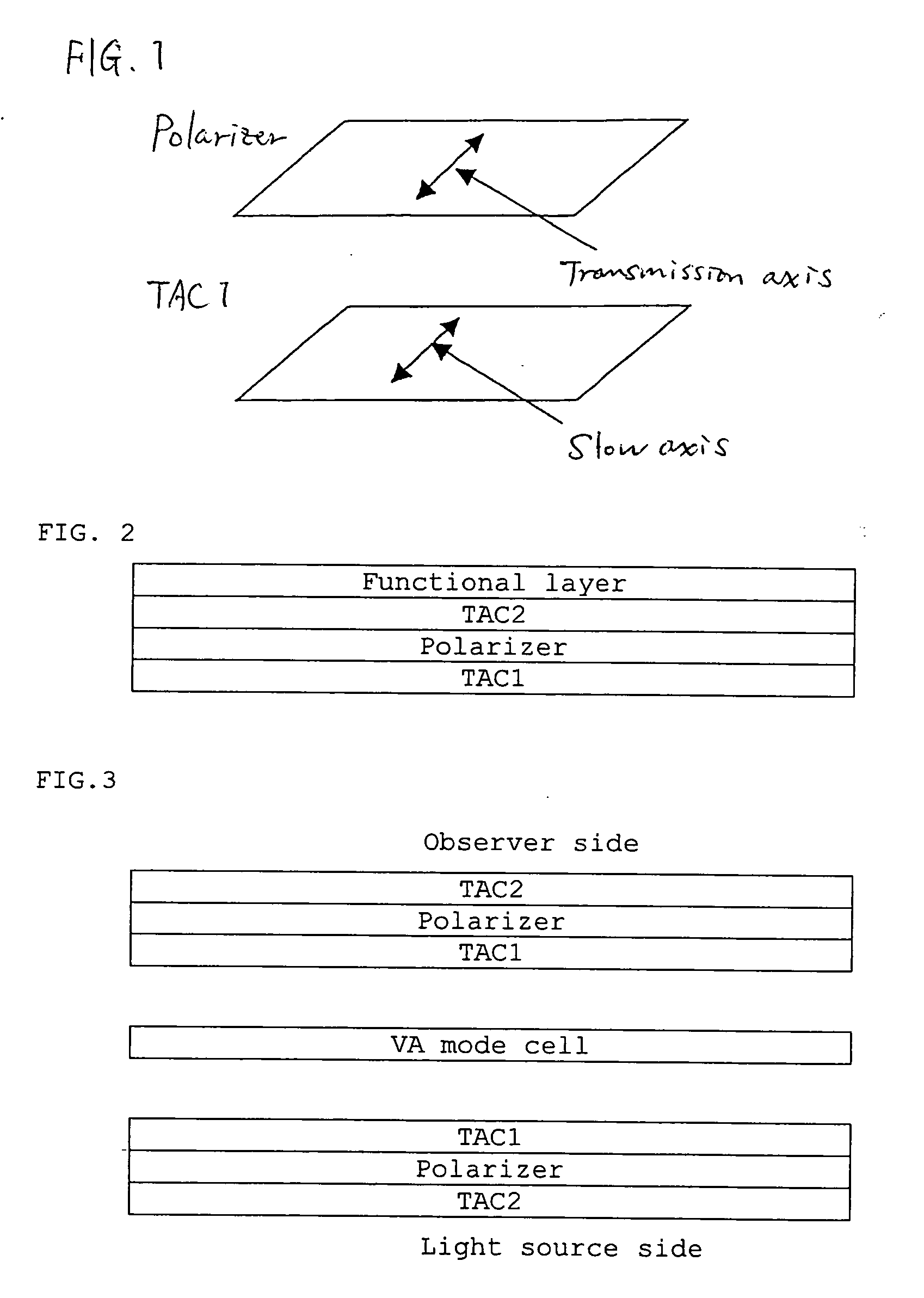
Viewing angle controlling system, and image display device using the same
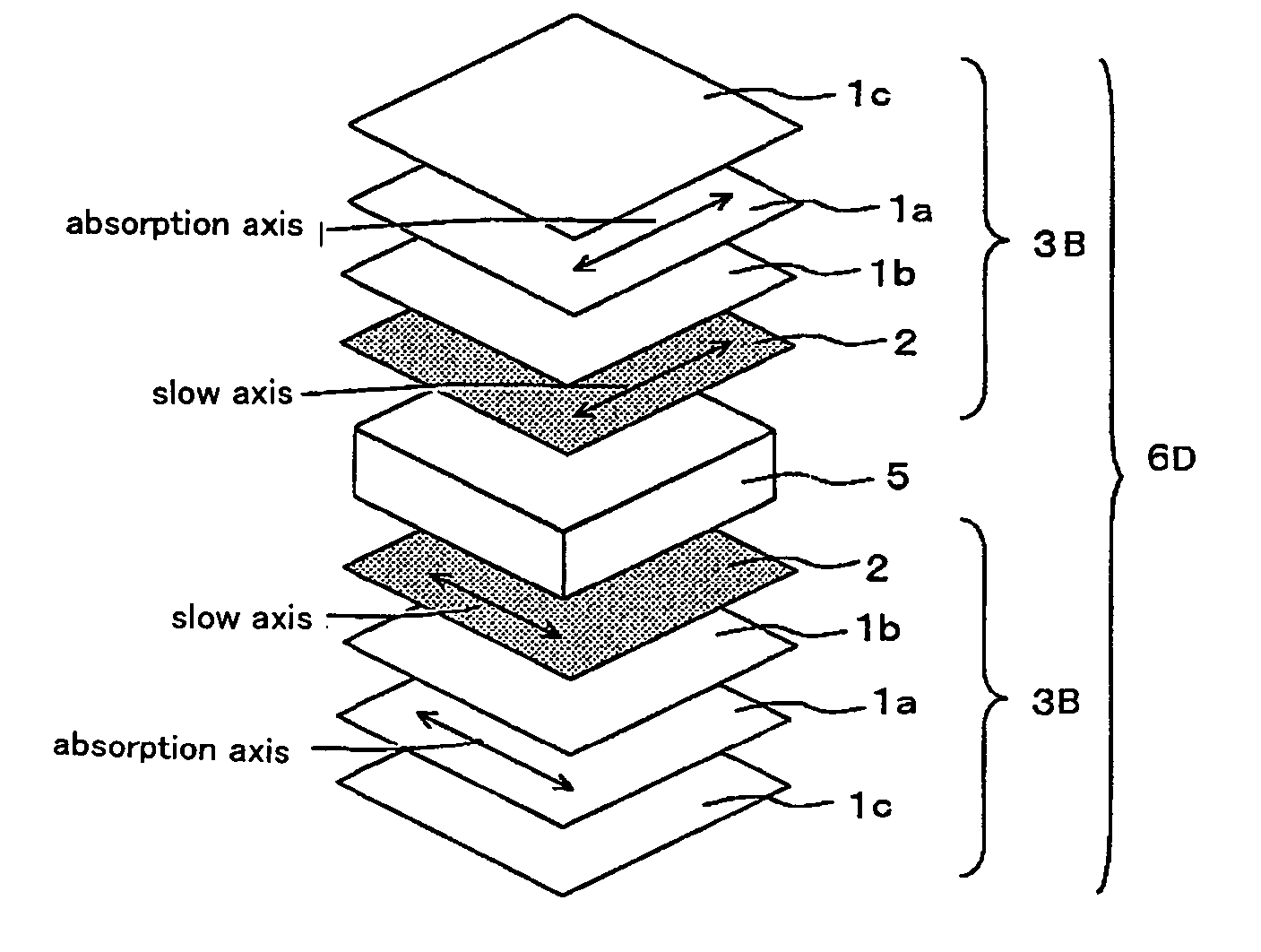
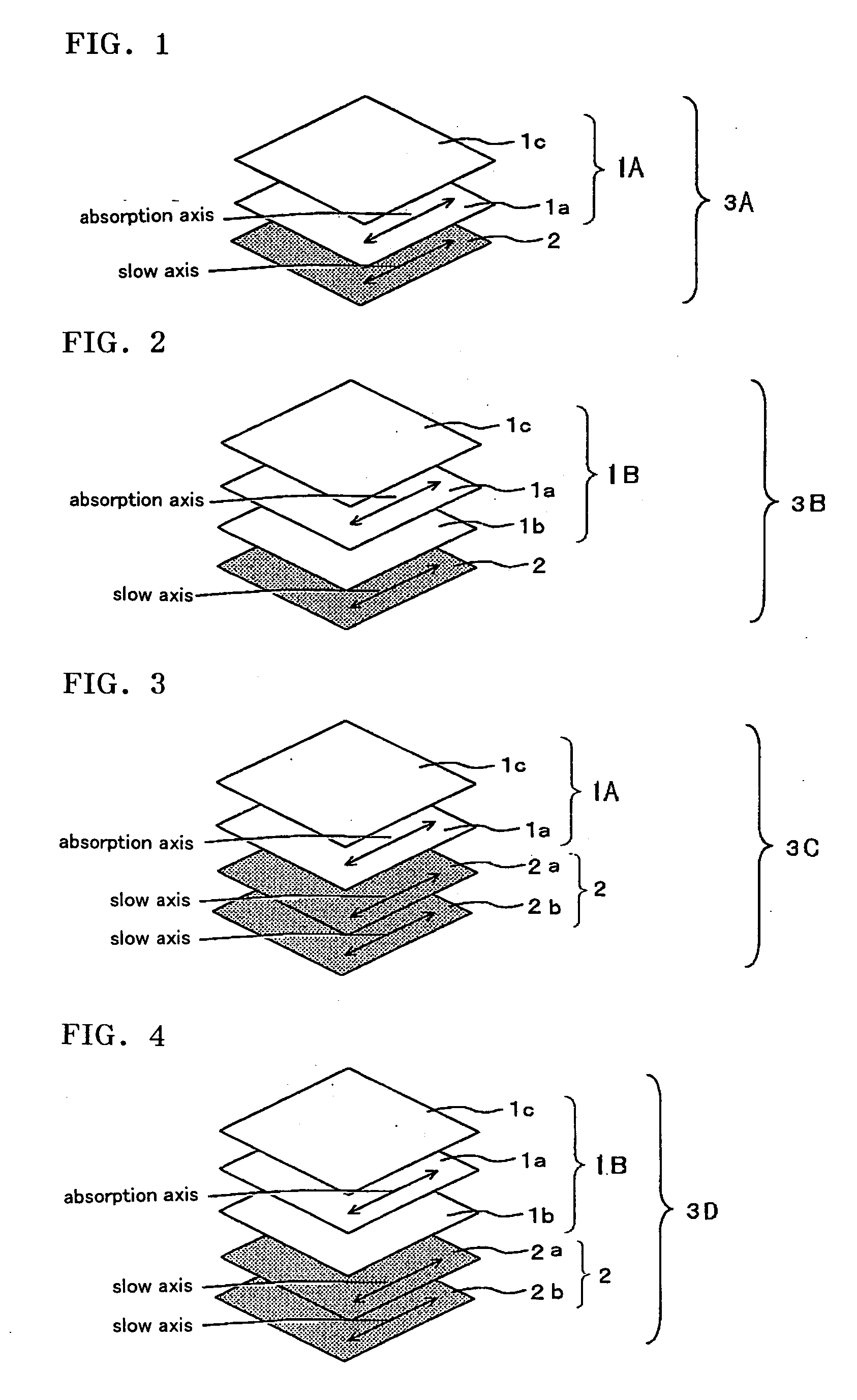
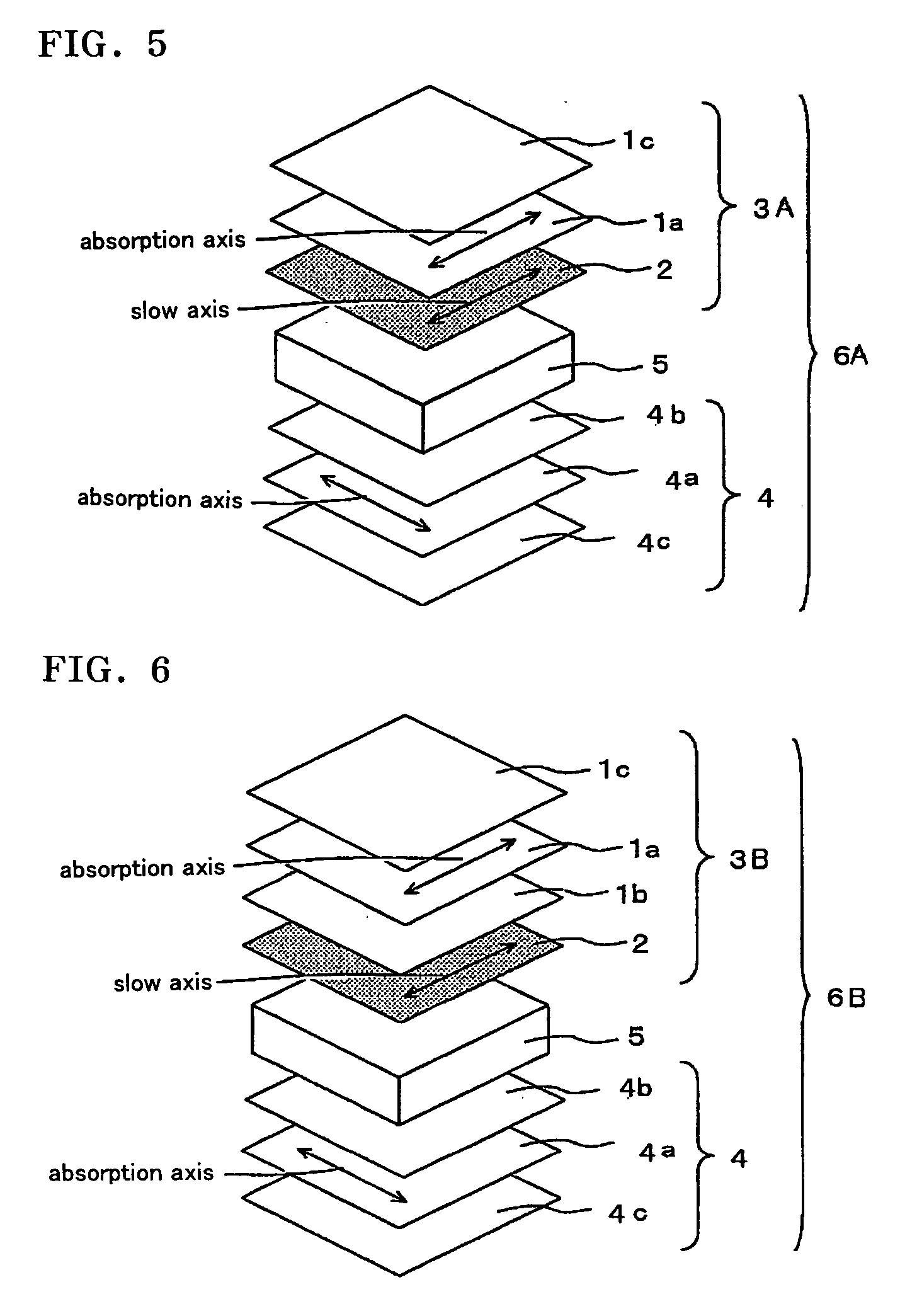
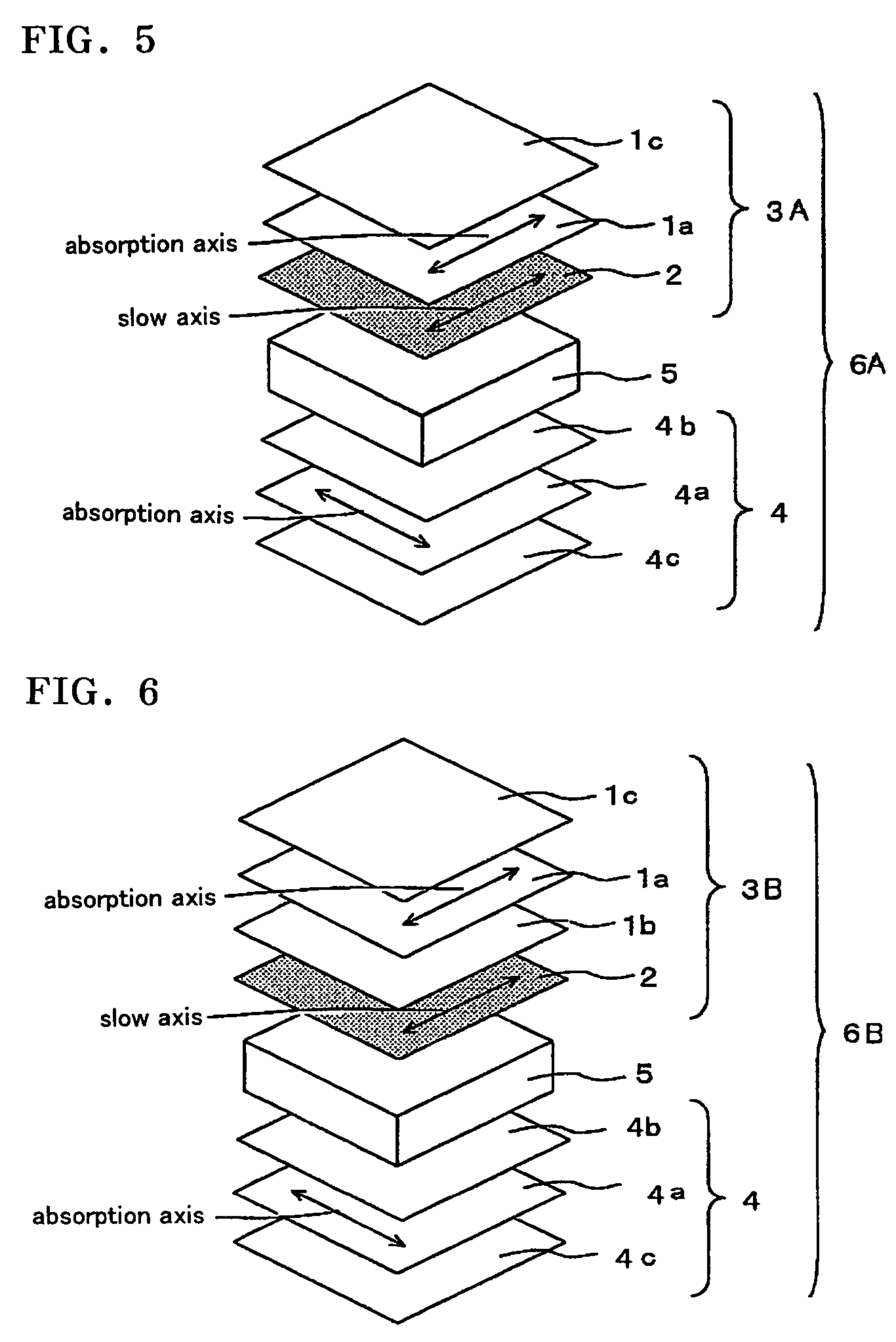
InactiveUS20090153783A1Reduce in quantityMeet thin and lightPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsControl systemFilm plane
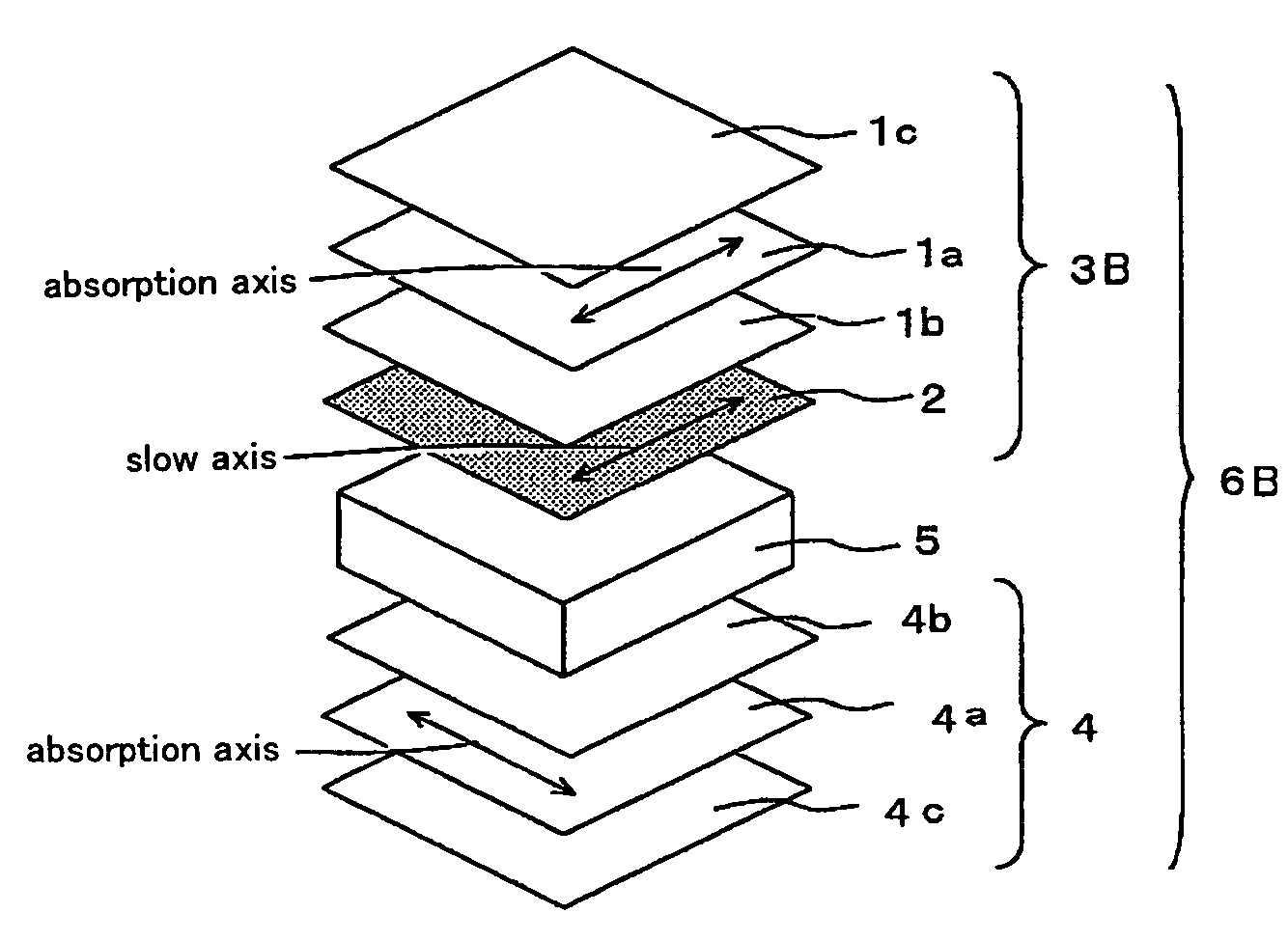
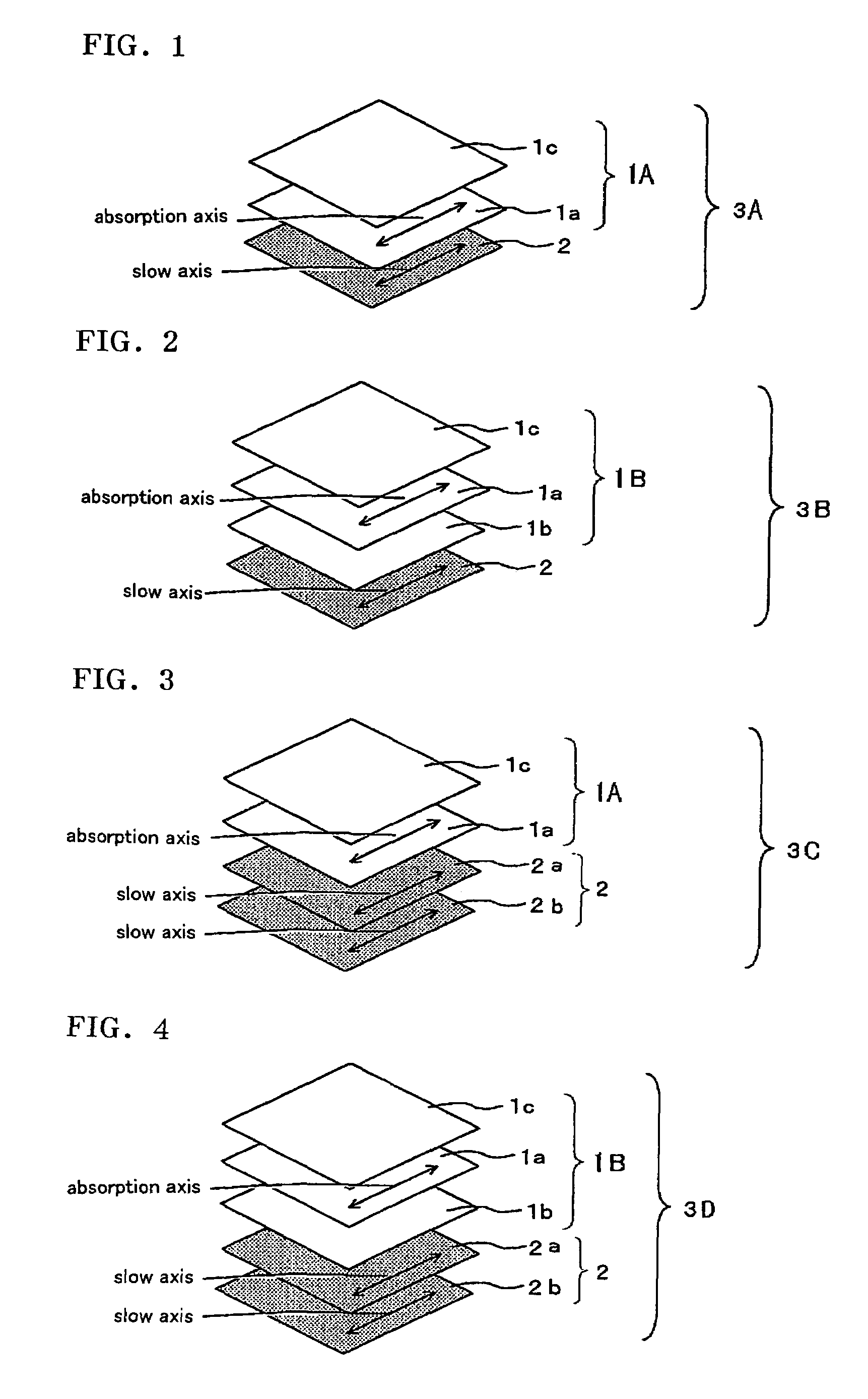
There are provided a viewing angle controlling system which can be used in a display device for which peep-prevention and viewing-angle-control are required, and makes it possible to control the viewing angle of a display, and an image display device using the same.The viewing angle controlling system includes: a first polarizer and a second polarizer which are each in the form of a film comprising an absorption dichroic material. The first polarizer has an absorption axis in its film plane, and the second polarizer has an absorption axis in the range of angle from 0 to 45° to the normal line of its film plane.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Reflective film
The invention relates to a process as described in claim of preparing a reflective film comprising a layer of a polymerized mesogenic material with helically twisted structure, wherein the helix axis is perpendicular to the film plane, and containing regions with varying helical pitch, to a reflective film obtainable by such a process, to the use of such a reflective film as reflective broadband or notch polarizer or as a multicolored film or image in liquid crystal displays, as color filter, in effect pigments, for decorative or security applications, and to a liquid crystal display comprising a liquid crystal cell and a reflective polarizer as described in the foregoing and the following, and optionally further comprising one or more compensaters or polarizers.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
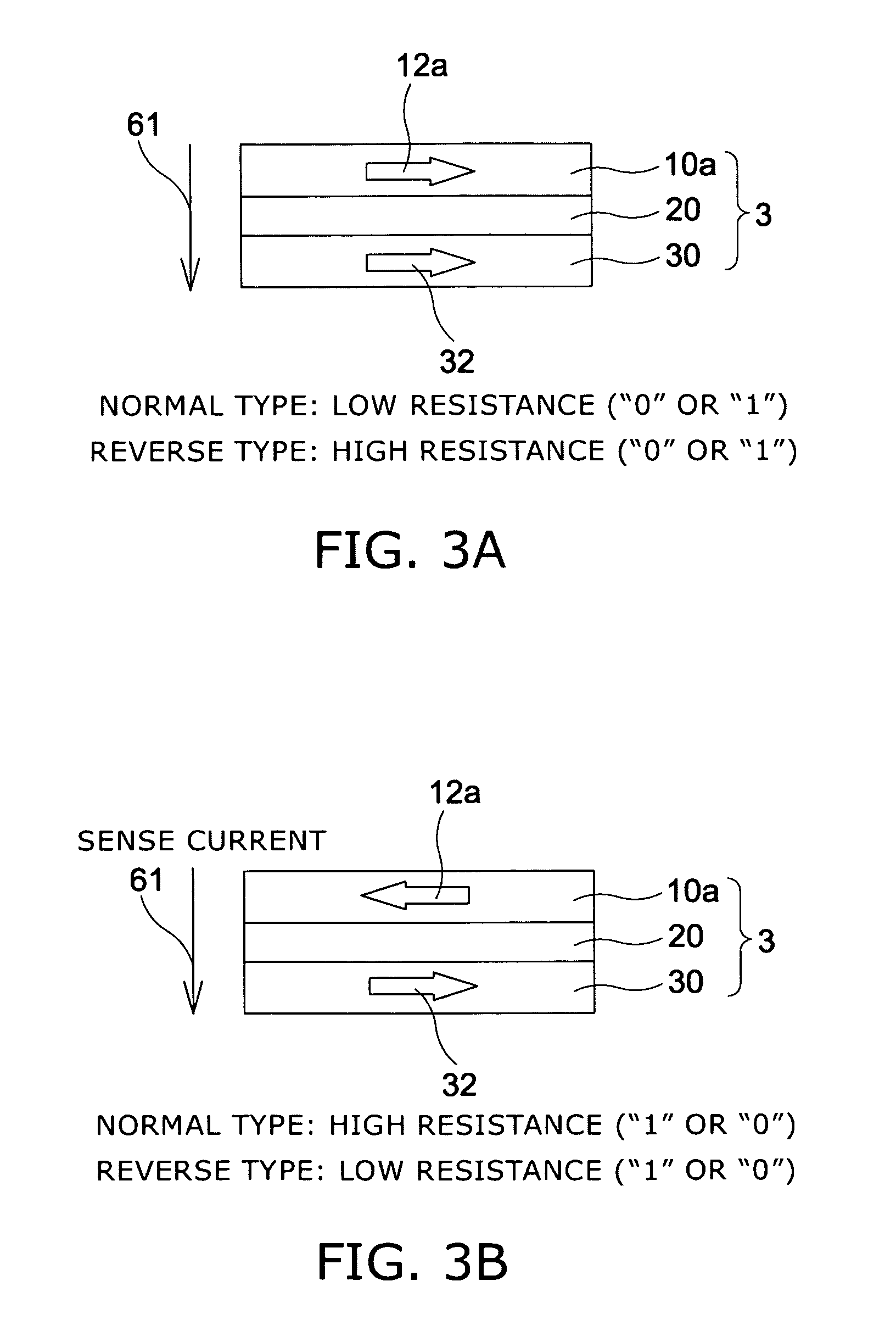
Magnetoresistance effect element, magnetic head, magnetic reproducing apparatus, and magnetic memory
InactiveUS7301733B1Enhanced couplingEasy to adjustNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsFilm planeMagnetic memory
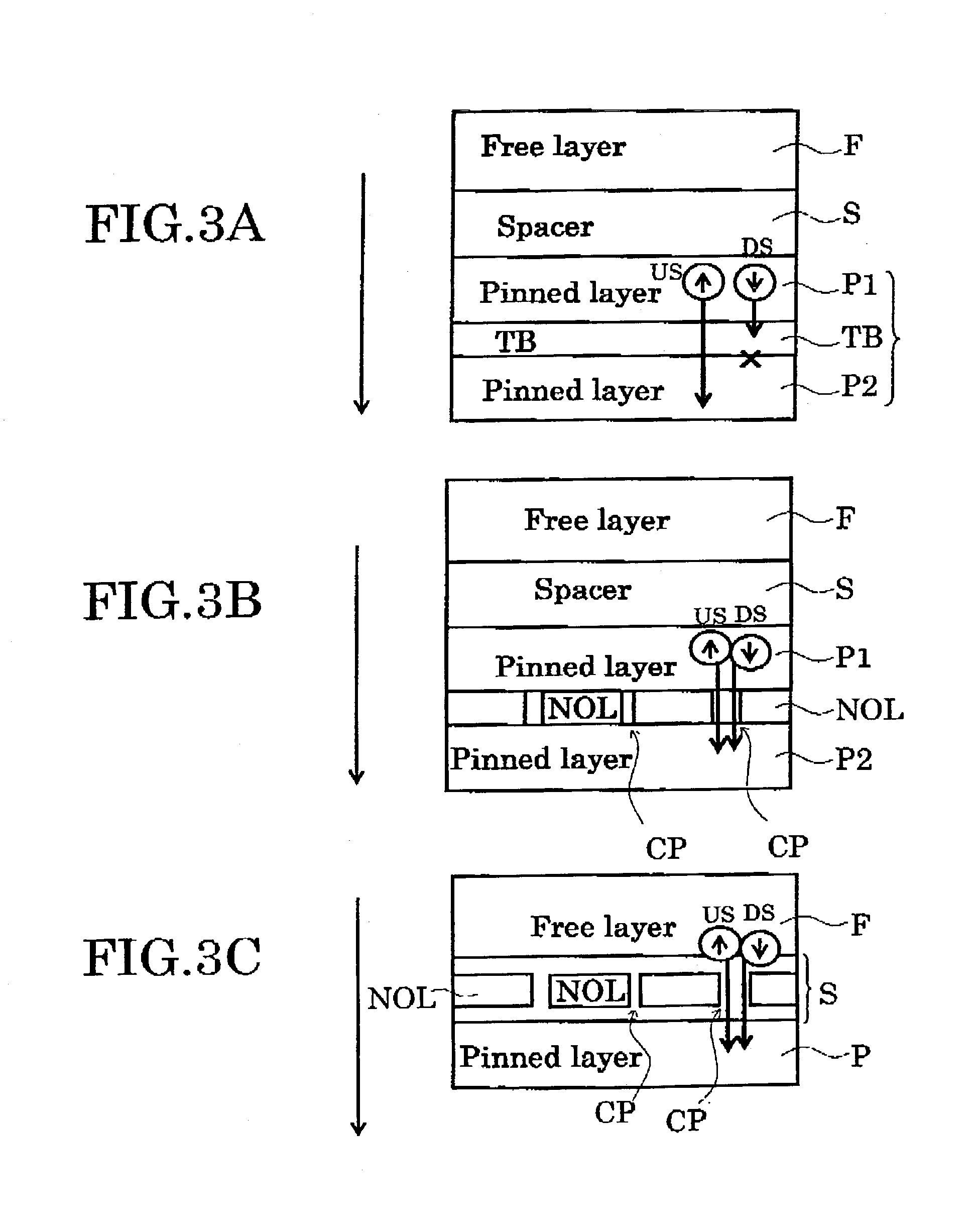
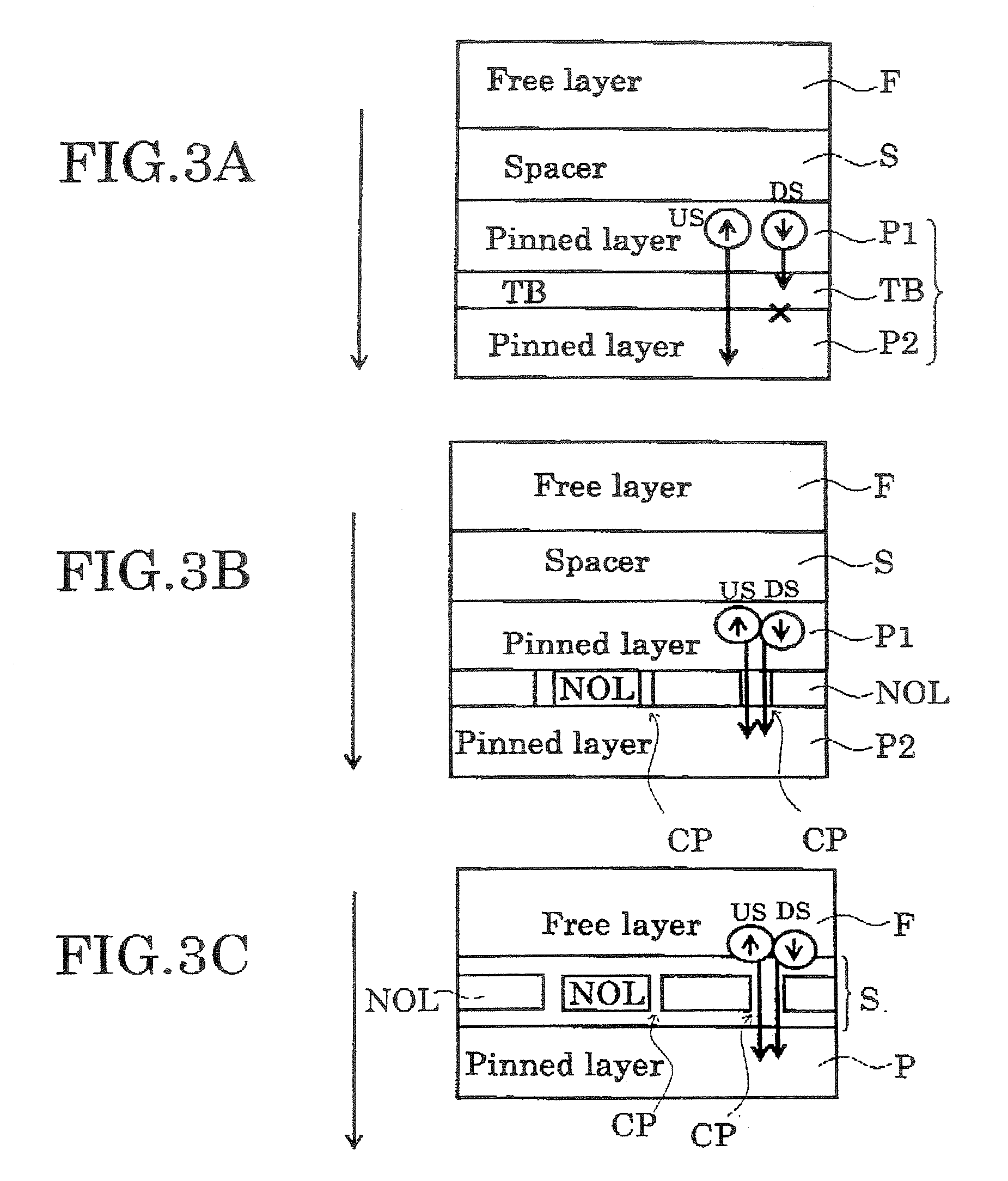
A magnetoresistance effect element comprises a magnetoresistance effect film and a pair of electrode. The magnetoresistance effect film having a first magnetic layer whose direction of magnetization is substantially pinned in one direction; a second magnetic layer whose direction of magnetization changes in response to an external magnetic field; a nonmagnetic intermediate layer located between the first and second magnetic layers; and a film provided in the first magnetic layer, in the second magnetic layer, at a interface between the first magnetic layer and the nonmagnetic intermediate layer, and / or at a interface between the second magnetic layer and the nonmagnetic intermediate layer, the film having a thickness not larger than 3 nanometers, and the film has as least one selected from the group consisting of oxide, nitride, oxinitride, phosphide, and fluoride. The pair of electrodes are electrically connected to the magnetoresistance effect film to supply a sense current perpendicularly to a film plane of said magnetoresistance effect film.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
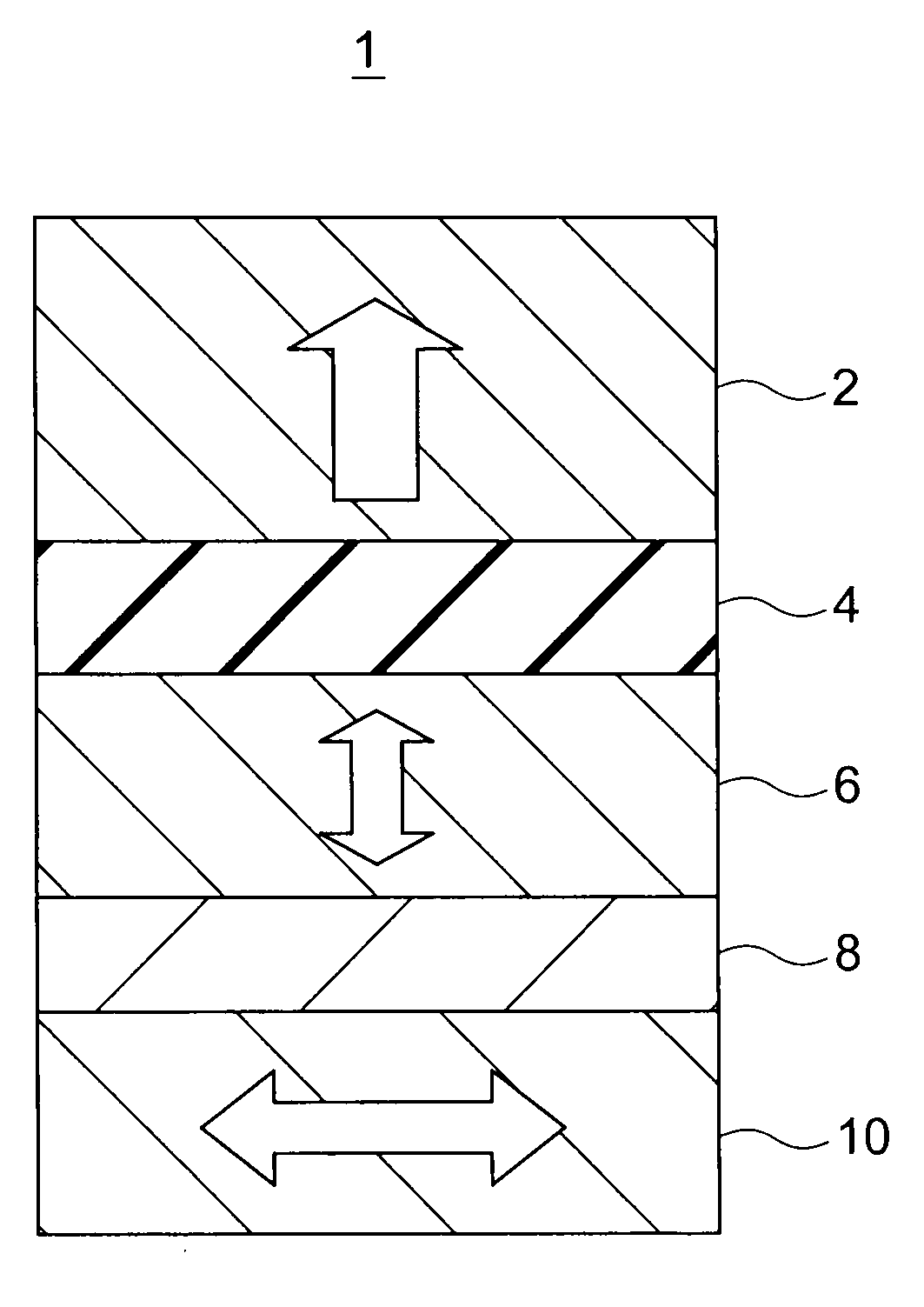
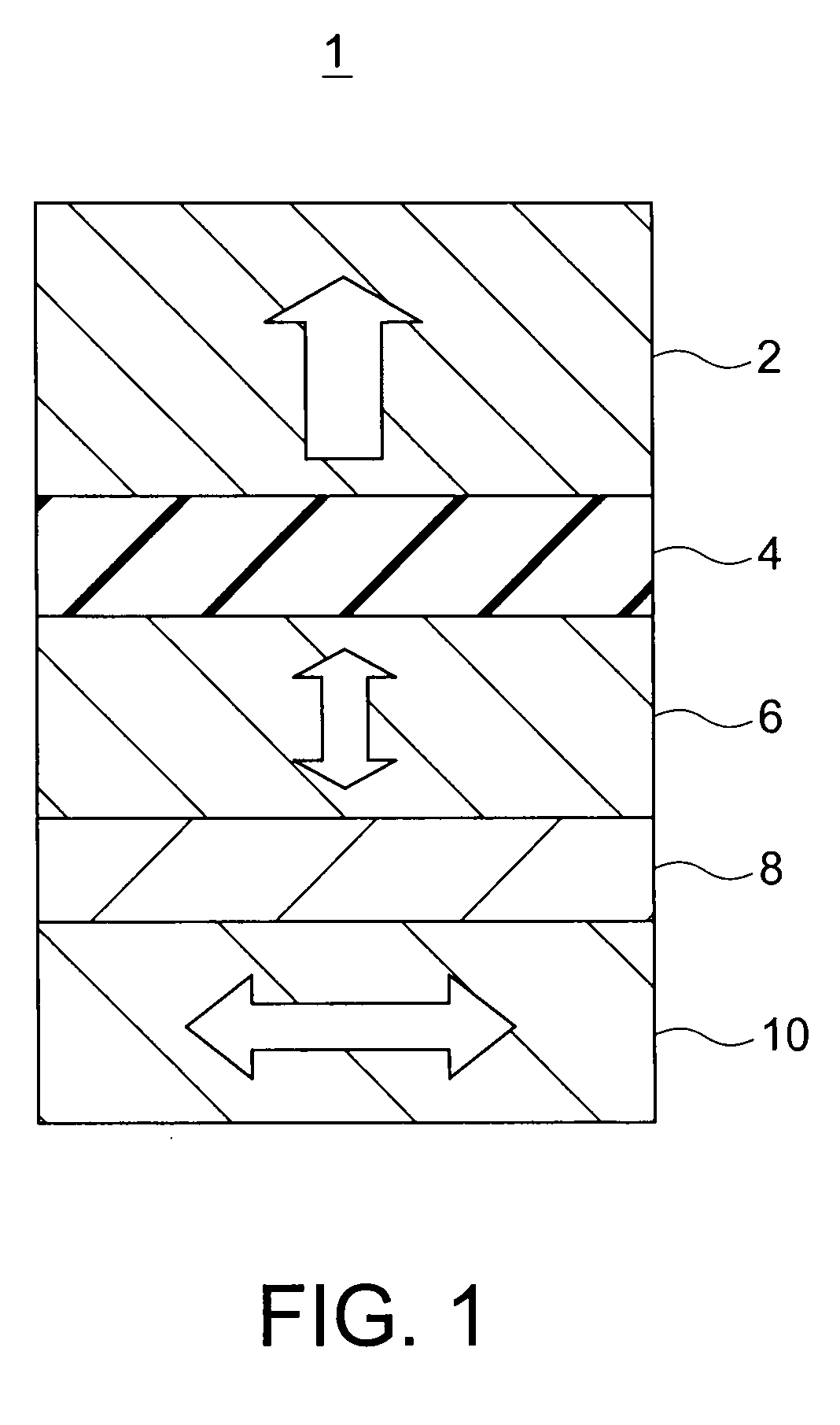
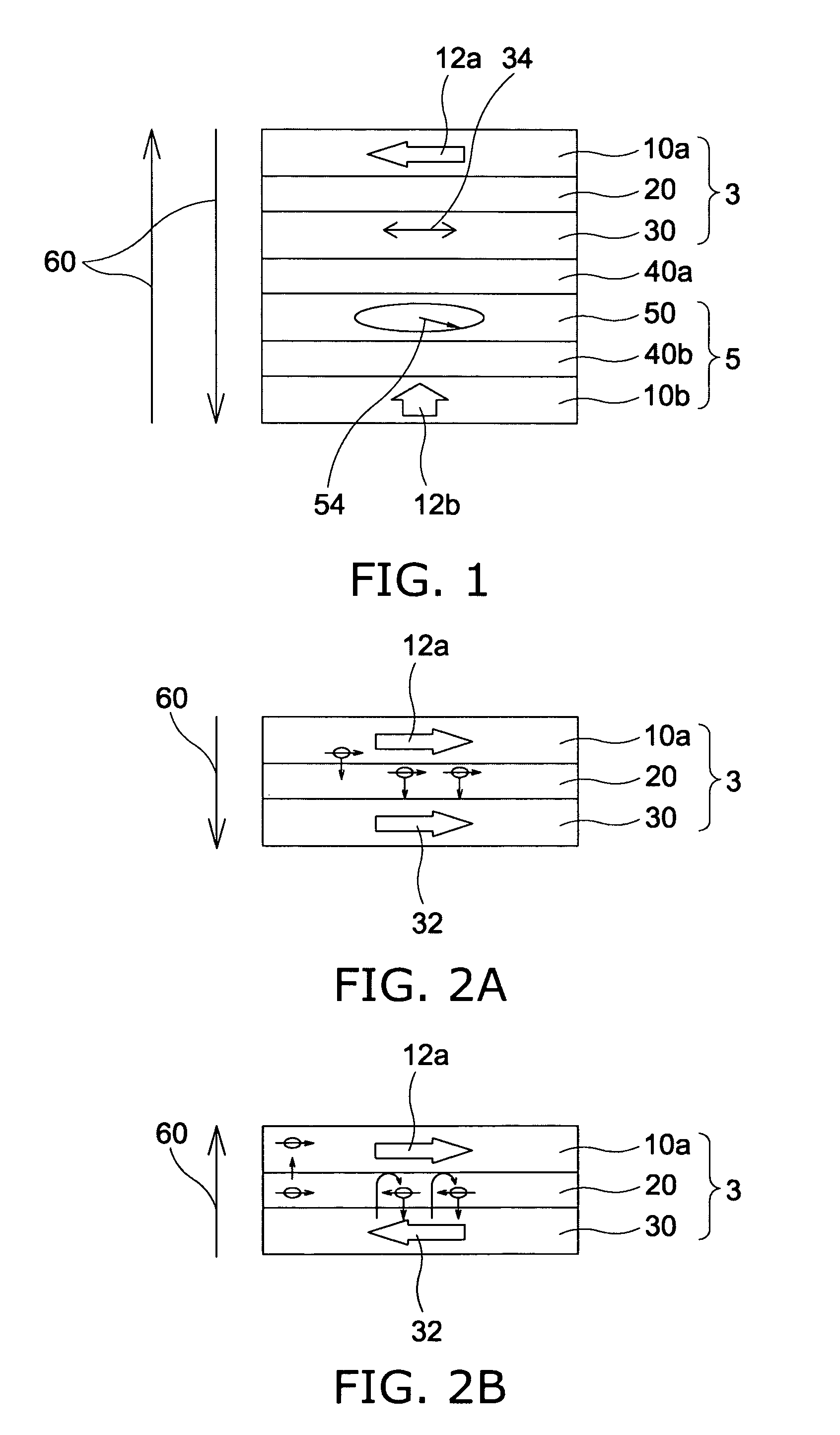
Magnetic device and magnetic memory
ActiveUS20050099724A1Maintain alignmentMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesMagnetic memoryMagnetization
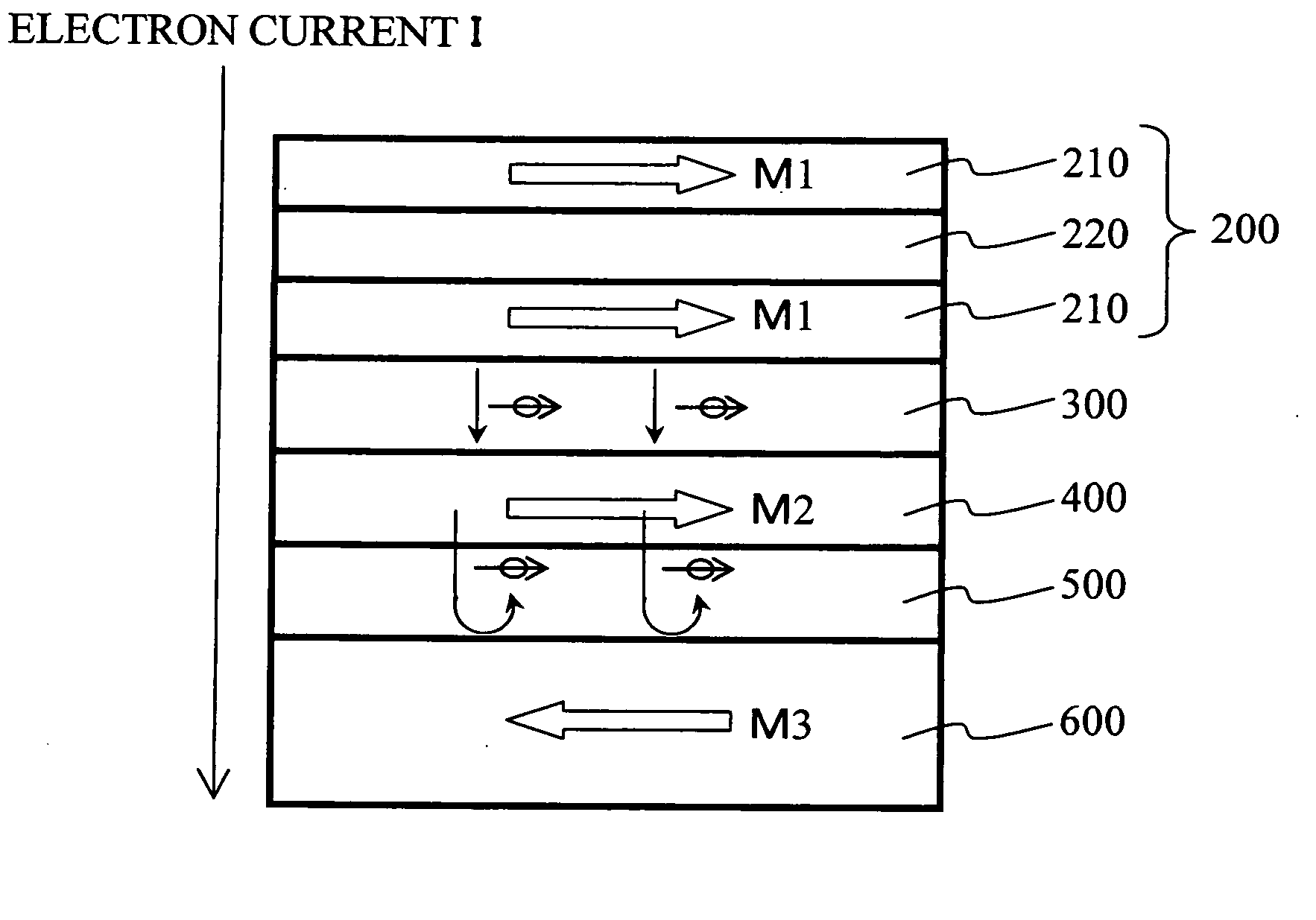
A magnetic device comprises first through third ferromagnetic layers, first and second intermediate layers and a couple of electrodes. The first ferromagnetic layer includes magnetic layers and one or more nonmagnetic layers which are alternately stacked, at least one layer of the magnetic layers has magnetization substantially fixed to a first direction, and two or more layers of the magnetic layers are ferromagnetically coupled via the nonmagnetic layers while having easy axes of magnetization parallel to a film plane. The second ferromagnetic layer has magnetization substantially fixed to a second direction. The third ferromagnetic layer is provided between the first ferromagnetic layer and the second ferromagnetic layer. The third ferromagnetic layer has a variable direction of magnetization. The first and second intermediate layers are provided between the ferromagnetic layers. The electrodes are configured to provide write current between the first and second ferromagnetic layers to cause spin-polarized electrons to act on the third ferromagnetic layer so that the direction of magnetization of the third ferromagnetic layer is determined depending on a direction of the current. The ferromagnetic coupling has a strength such that a parallel magnetic alignment of the magnetic layers is maintained when the write current.
Owner:KATANA SILICON TECH LLC
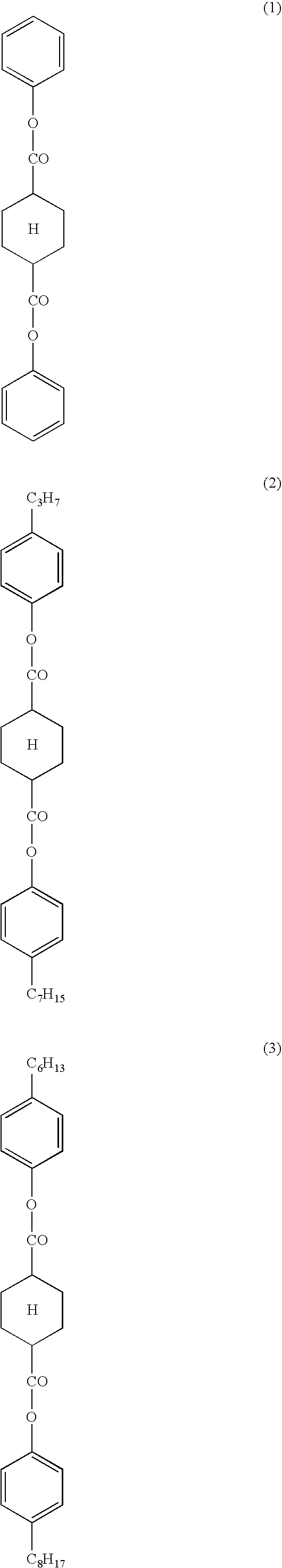
Optical cellulose acylate film, polarizing plate and liquid crystal display
ActiveUS20050142304A1Favorable retardation valueLittle changeLiquid crystal compositionsPolarising elementsCelluloseMixed fatty acid
To provide an optical film which exhibits excellent retardation values both in the film plane and along the direction perpendicular to the film plane and shows little change in retardation values depending on environmental factors such as humidity, a liquid crystal display showing little change in viewing angle characteristics due to an environmental (humidity) change, and a polarizing plate to be used in the liquid crystal display, the cellulose acylate contains a cellulose acylate which is a mixed fatty acid ester of a cellulose and satisfies formulae specified in the specification, and a polarizing plate and a liquid crystal display using this cellulose acylate film.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetoresistive element and magnetic memory
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Lens-fitted film unit with plastic taking lens
InactiveUS6188841B1Simple structureIncrease changeProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementCamera lensFilm plane
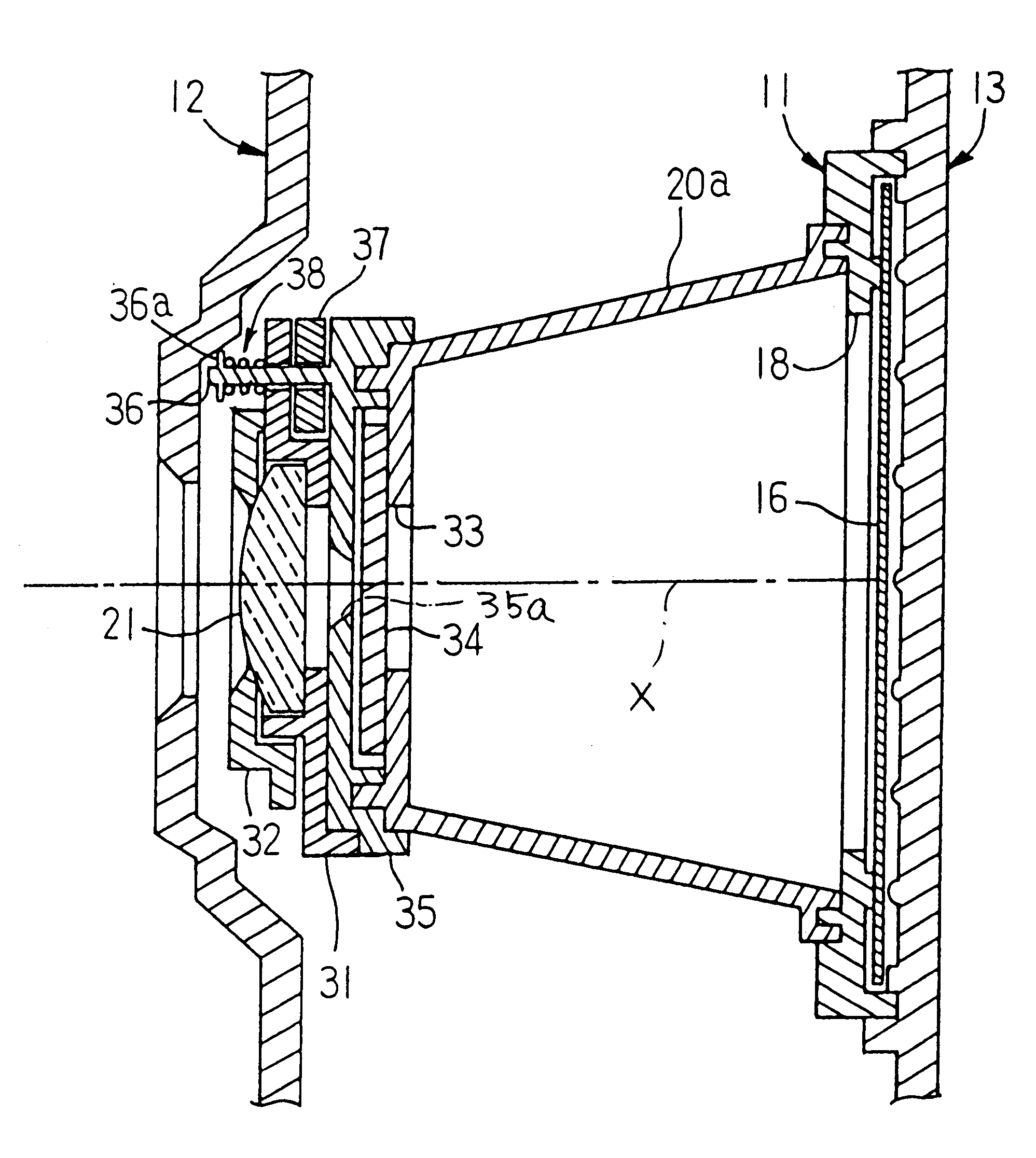
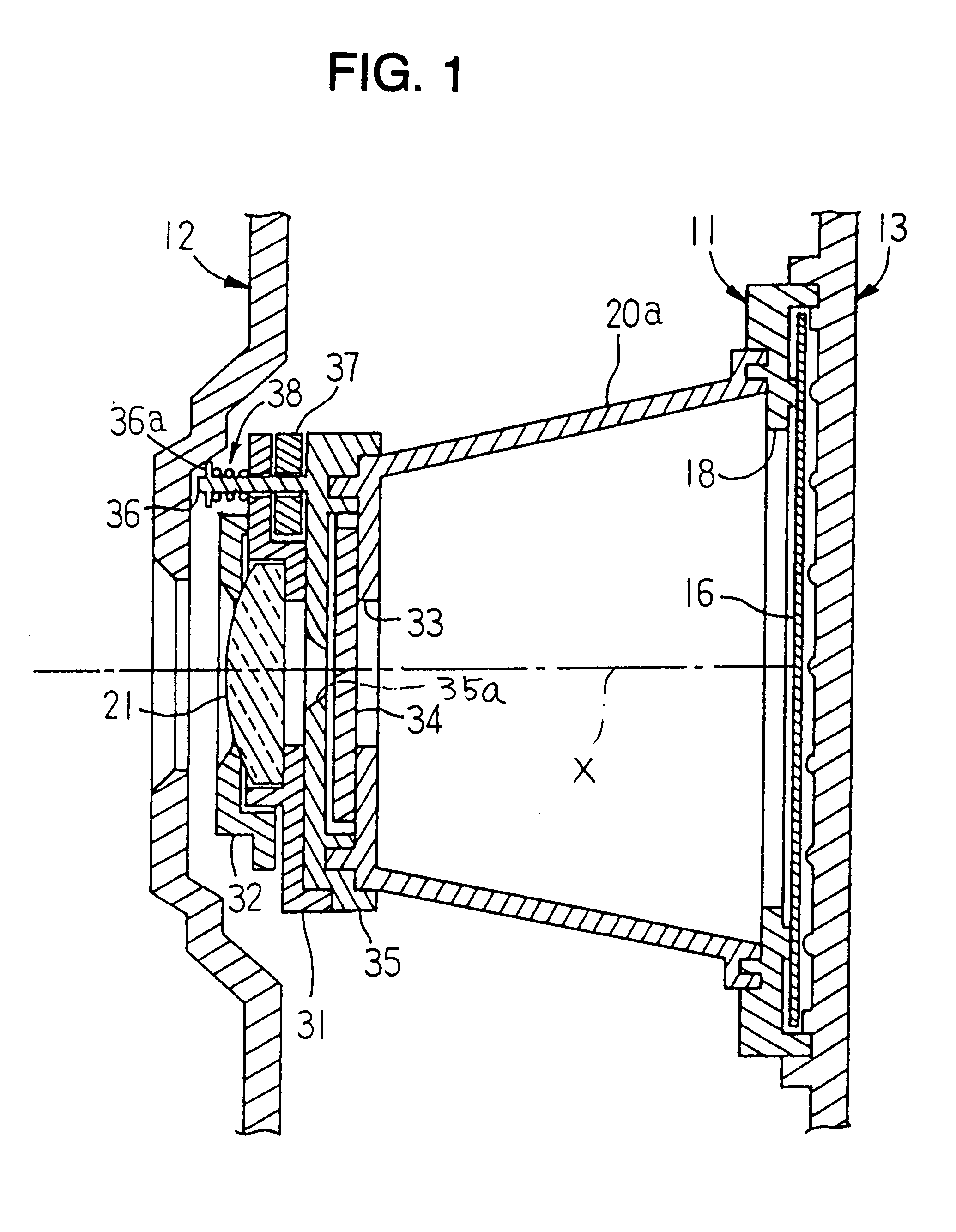
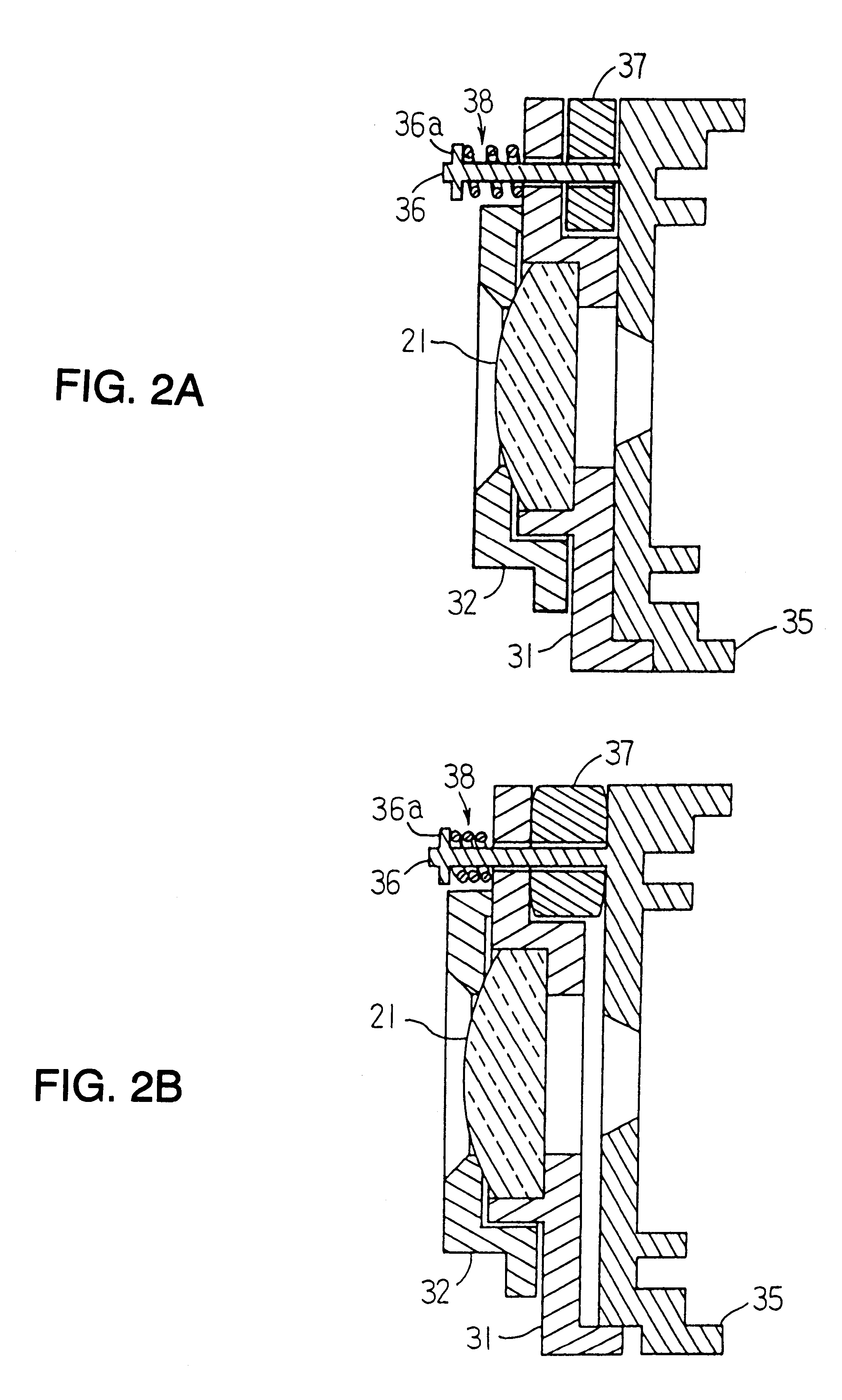
A lens-fitted film unit is provided with a thermally expandable axial distance adjusting member which has a thermal expansion coefficient greater than plastic lens elements of a taking lens held by an axially movable lens holder and disposed between the lens holder and a stationary shutter cover and which expands or contracts in accordance with a change in ambient temperature to change an axial distance between the lens holder and a film plane so as thereby to shift a focal point of the taking lens in an axial direction to compensate a variation of the focal length of the taking lens due to a change in refractive power of the plastic lens element which is caused by axial expansion or axial contraction of the plastic lens element due to the change in ambient temperature.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
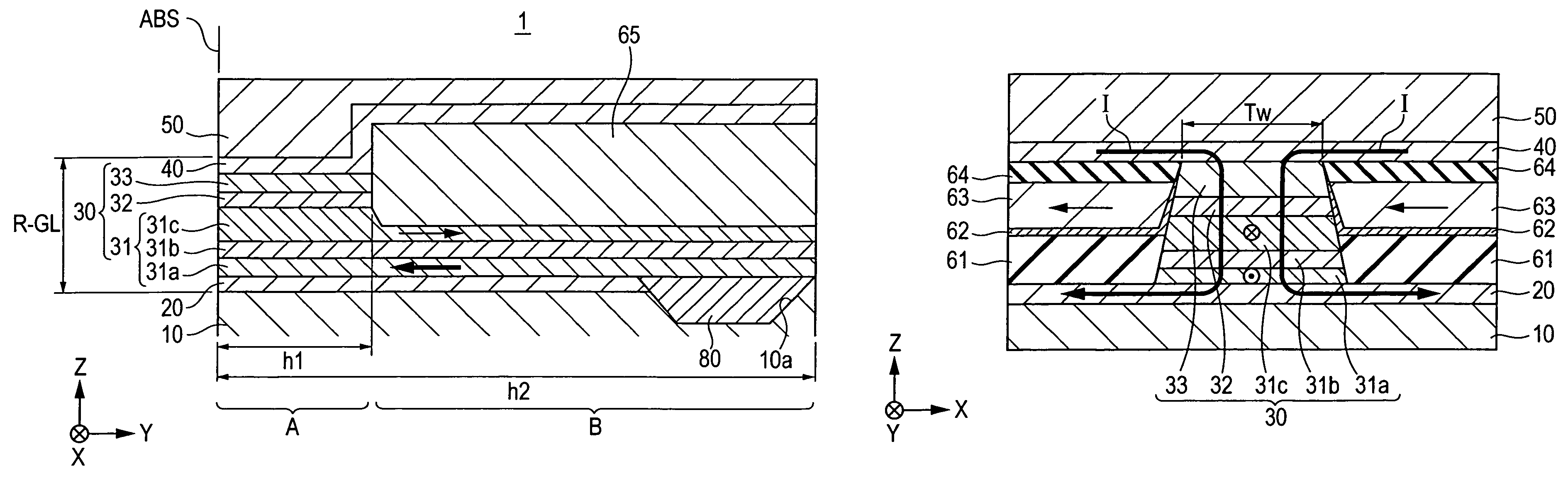
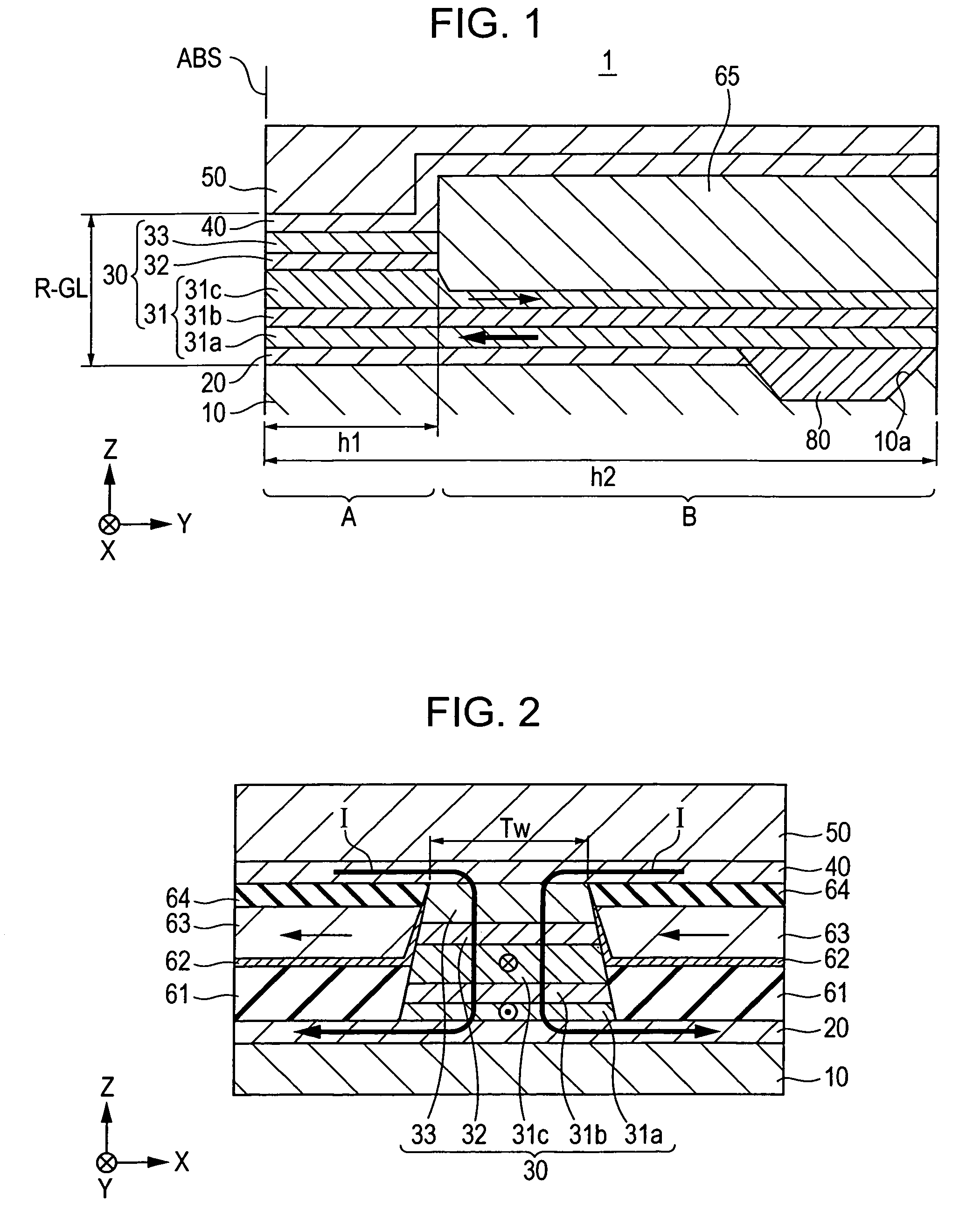
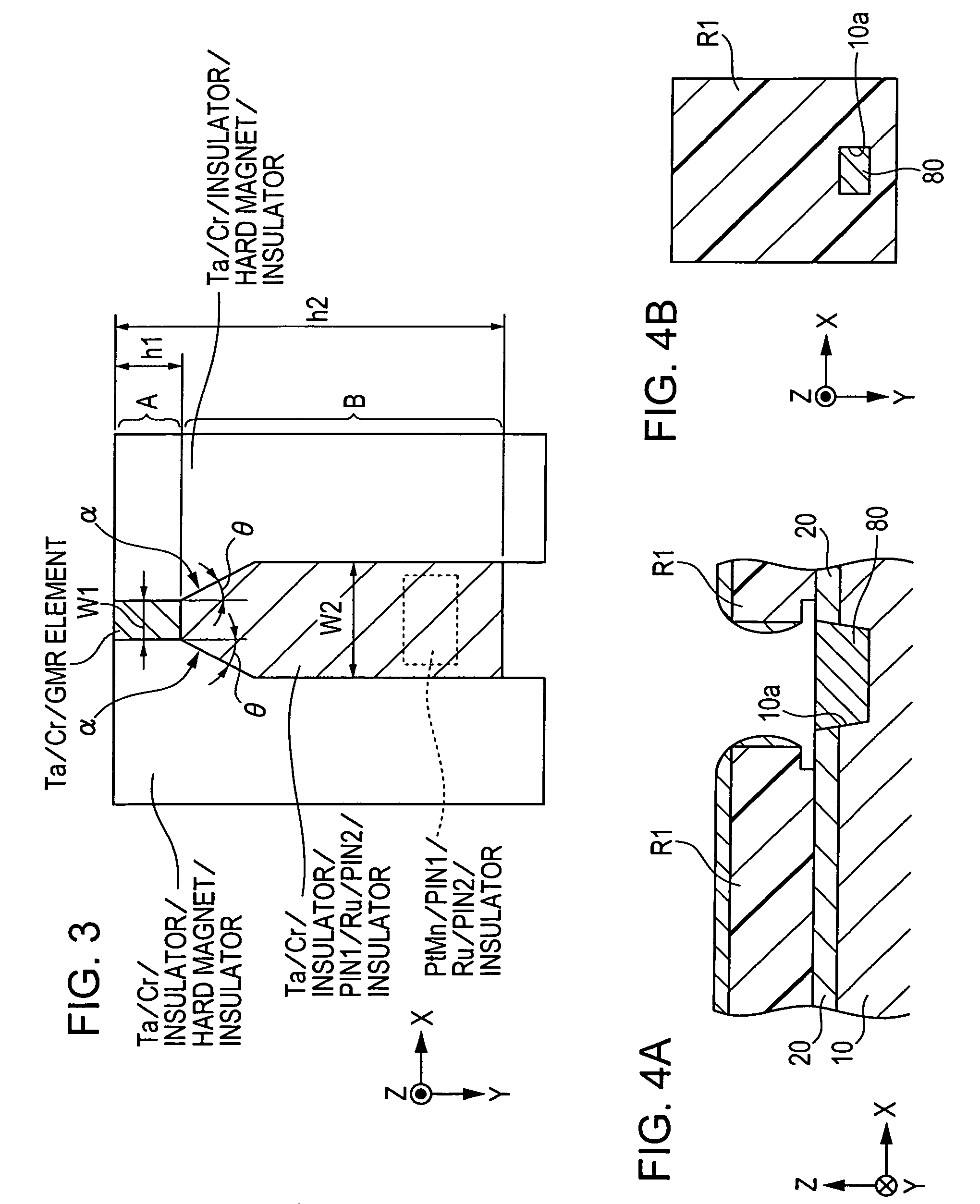
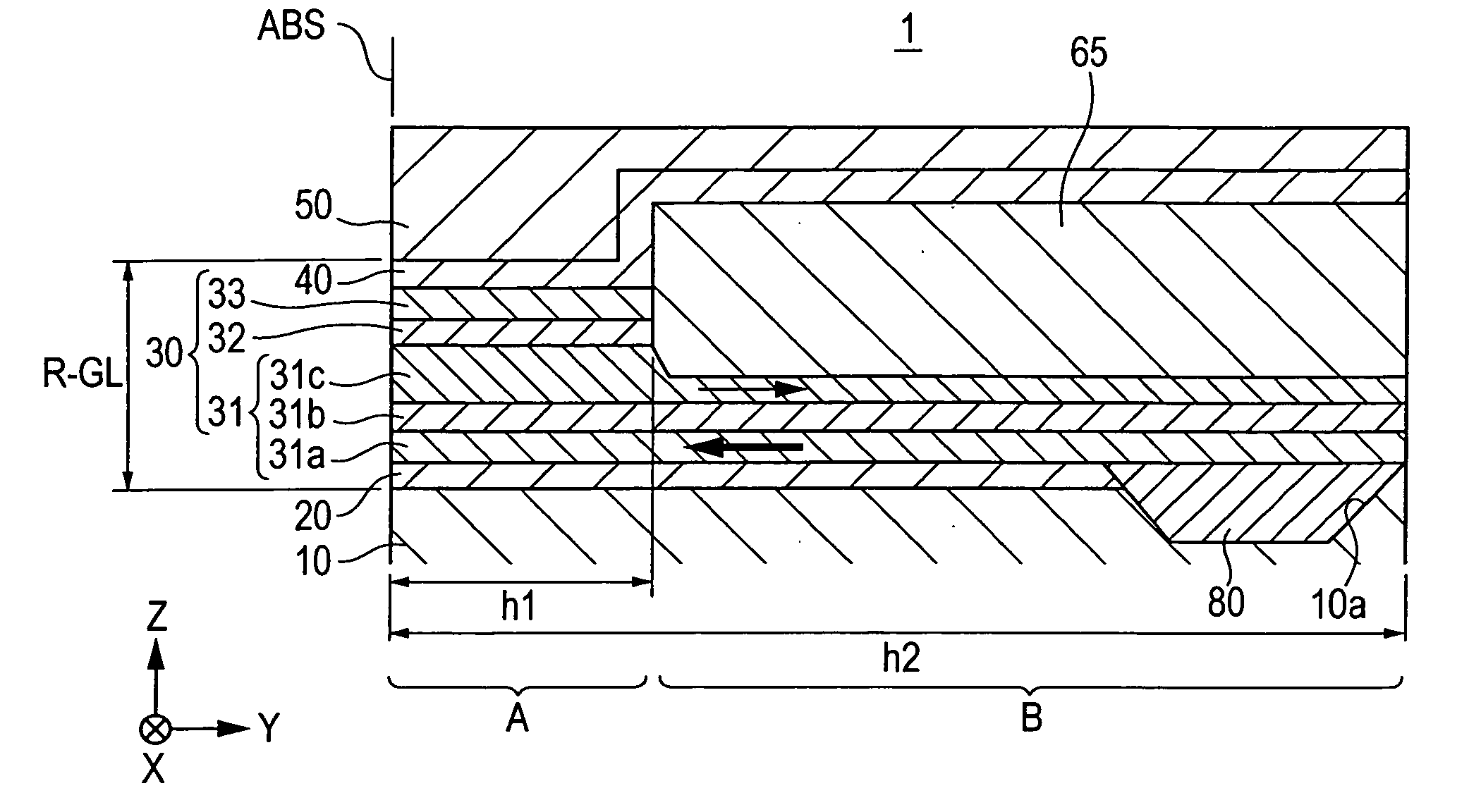
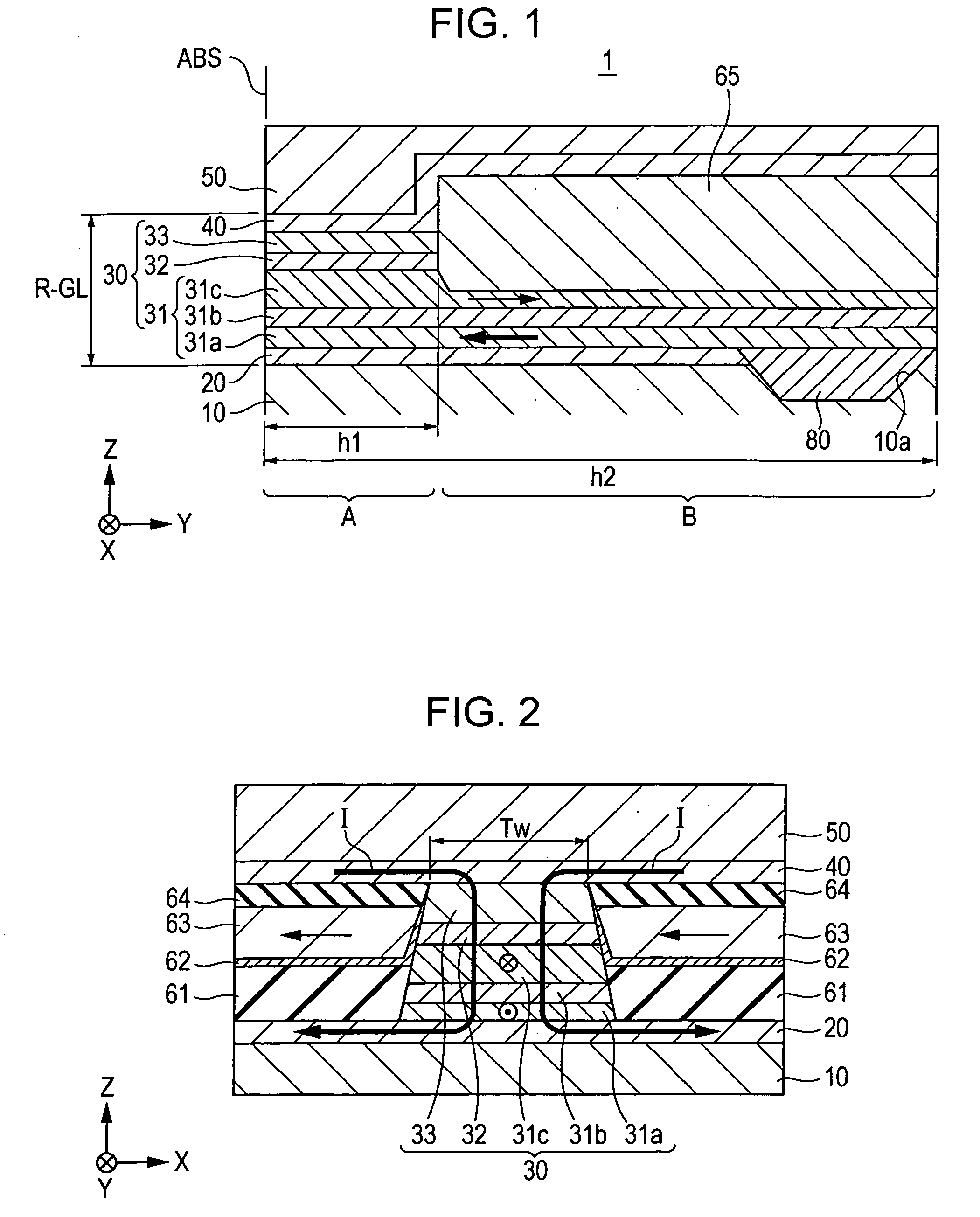
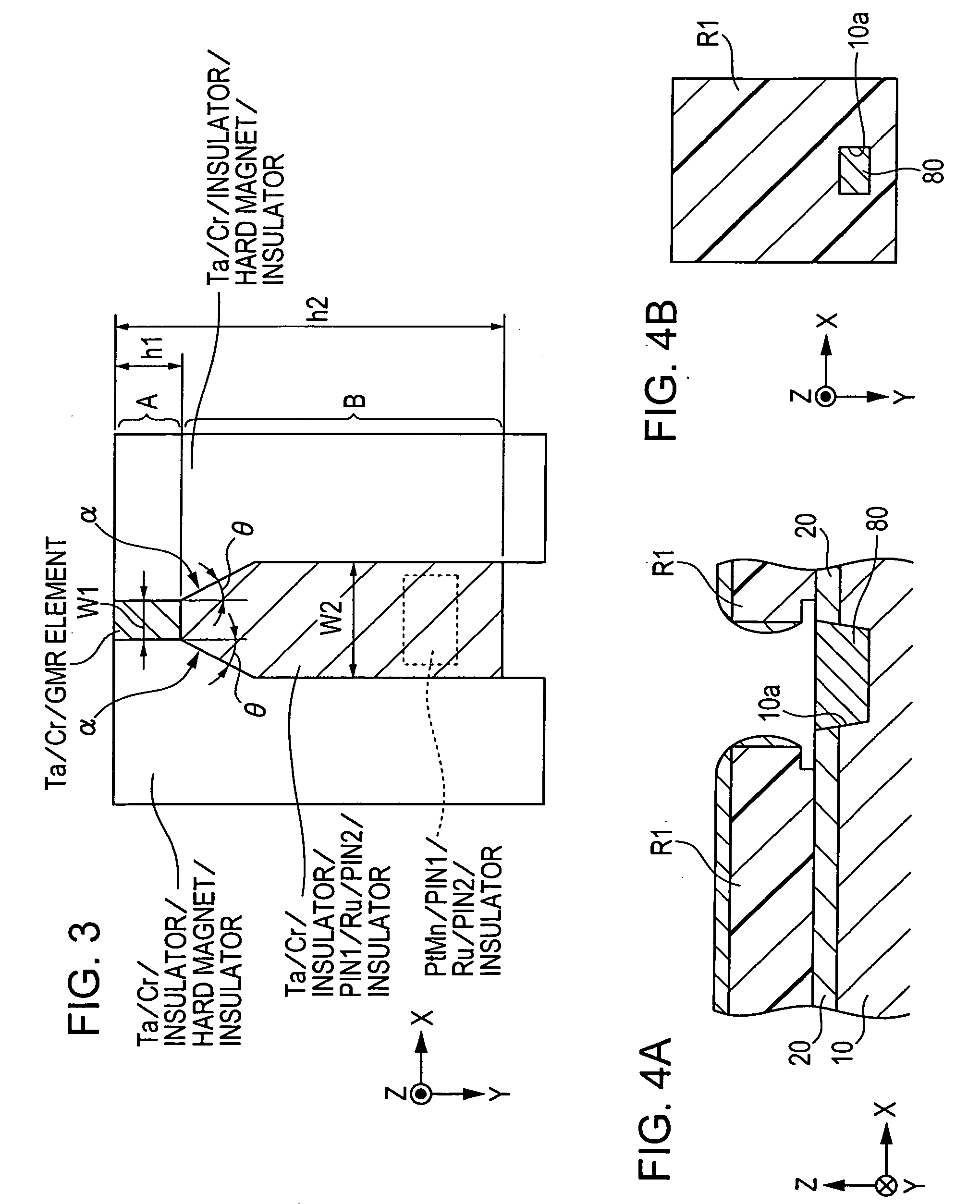
CPP giant magnetoresistive head having antiferromagnetic film disposed in rear of element
ActiveUS7220499B2Avoid feverSuppresses component temperature riseNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsFilm planeMagnetization
A CPP giant magnetoresistive head includes lower and upper shield layers with a predetermined distance therebetween, and a giant magnetoresistive element (GMR) including pinned and free magnetic layers disposed between the upper and lower shield layers with a nonmagnetic layer interposed between the pinned and free magnetic layers. A current flows perpendicularly to the film plane of the GMR. The magnetoresistive head further includes an antiferromagnetic layer (an insulating AF of Ni—O or α-Fe2O3) provided in the rear of the GMR in a height direction to make contact with the upper or lower surface of a rear portion of the pinned magnetic layer which extends in the height direction, and an exchange coupling magnetic field is produced at the interface with the upper or lower surface, so that the magnetization direction of the pinned magnetic layer is pinned by the exchange coupling magnetic field in the height direction.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Magnetoresistance effect element and magnetic random access memory
ActiveUS20090244792A1Minimize current required for writingHigh-speed writingMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryMicrowave
A magnetoresistance effect element includes: a first ferromagnetic layer having invariable magnetization perpendicular to a film plane; a second ferromagnetic layer having variable magnetization perpendicular to the film plane; a first nonmagnetic layer interposed between the first ferromagnetic layer and the second ferromagnetic layer; a third ferromagnetic layer provided on an opposite side of the second ferromagnetic layer from the first nonmagnetic layer, and having variable magnetization parallel to the film plane; and a second nonmagnetic layer interposed between the second and third ferromagnetic layers. Spin-polarized electrons are injected into the second ferromagnetic layer by flowing a current in the direction perpendicular to the film planes between the first and third ferromagnetic layers, precession movement is induced in the magnetization of the third ferromagnetic layer by injecting the spin-polarized electrons, and a microwave magnetic field of a frequency corresponding to the precession movement is applied to the second ferromagnetic layer.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Magnetic recording device and magnetic recording apparatus
InactiveUS8085582B2Record information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsFilm planePrecession
A magnetic recording device includes: a laminated body including: a first ferromagnetic layer with a magnetization substantially fixed in a first direction; a second ferromagnetic layer with a variable magnetization direction; a first nonmagnetic layer disposed between the first ferromagnetic layer and the second ferromagnetic layer; and a third ferromagnetic layer with a variable magnetization direction. The magnetization direction of the second ferromagnetic layer is determinable in response to the orientation of a current, by allowing electrons spin-polarized by passing a current in a direction generally perpendicular to the film plane of the layers of the laminated body to act on the second ferromagnetic layer, and by allowing a magnetic field generated by precession of the magnetization of the third ferromagnetic layer to act on the second ferromagnetic layer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Compensating film for a liquid crystal display and an OCB mode liquid crystal display incorporating the compensating film
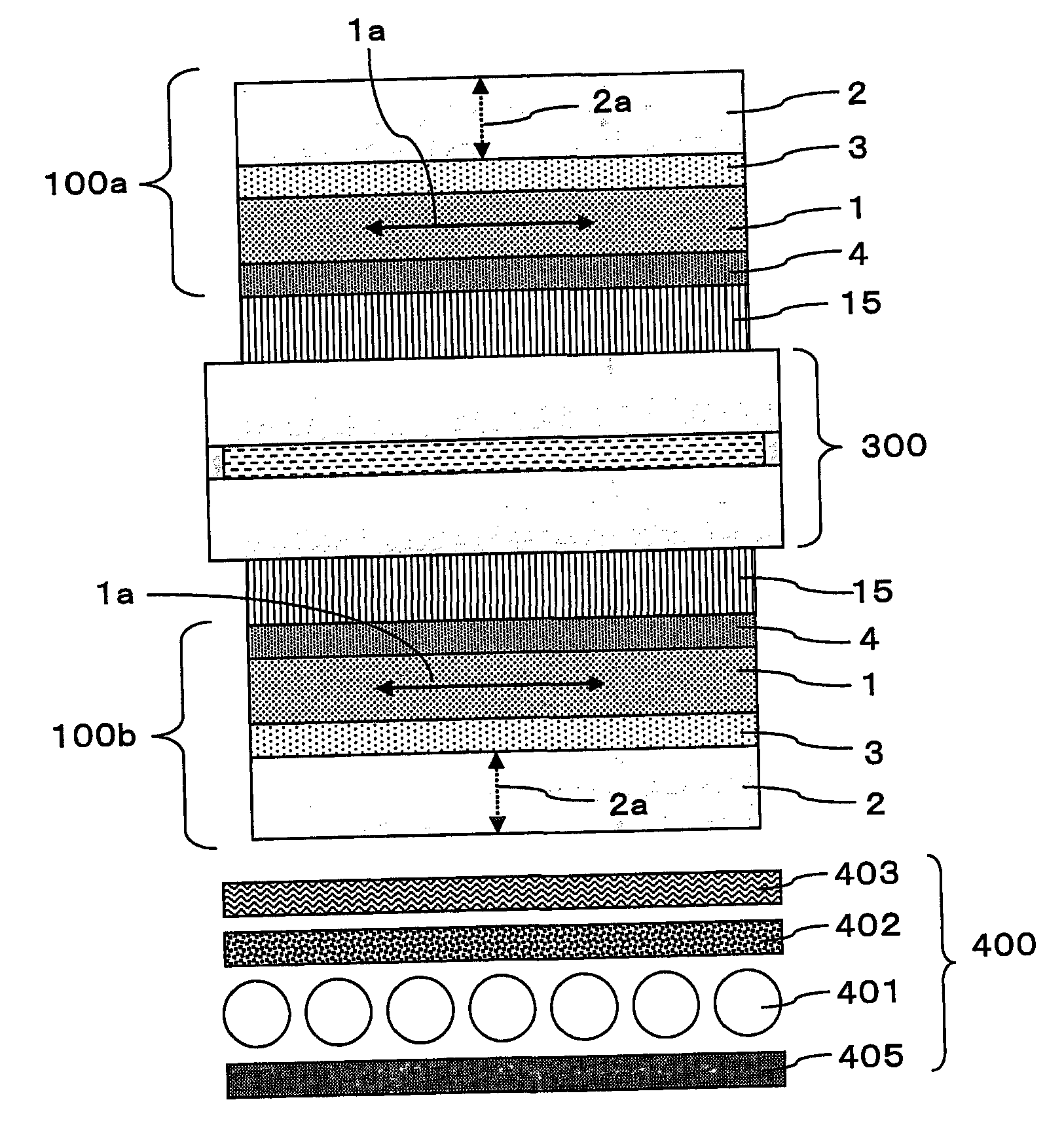
InactiveUS6124913AGood compensationSet freeLiquid crystal compositionsDiffusing elementsColor compensationFilm plane
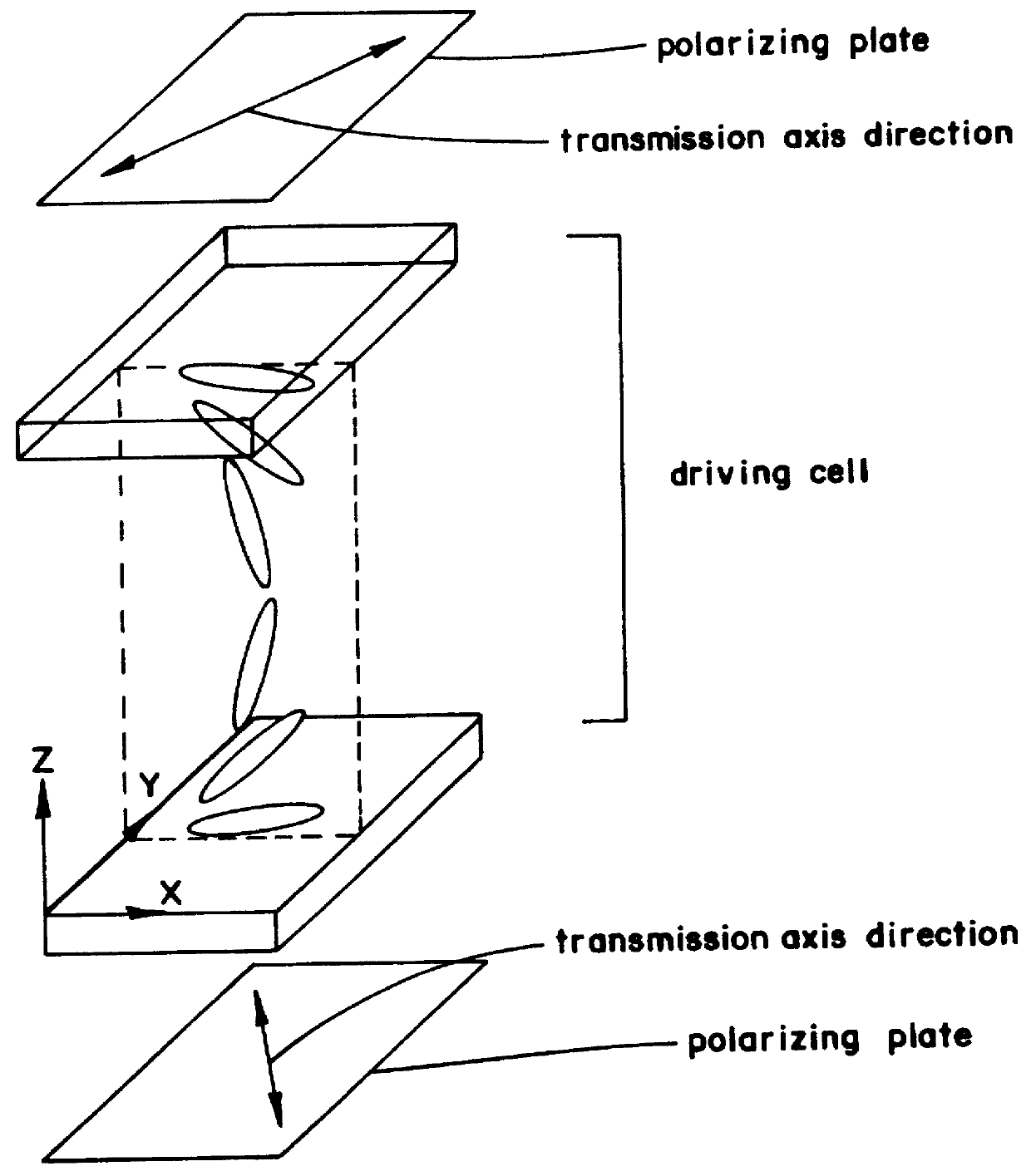
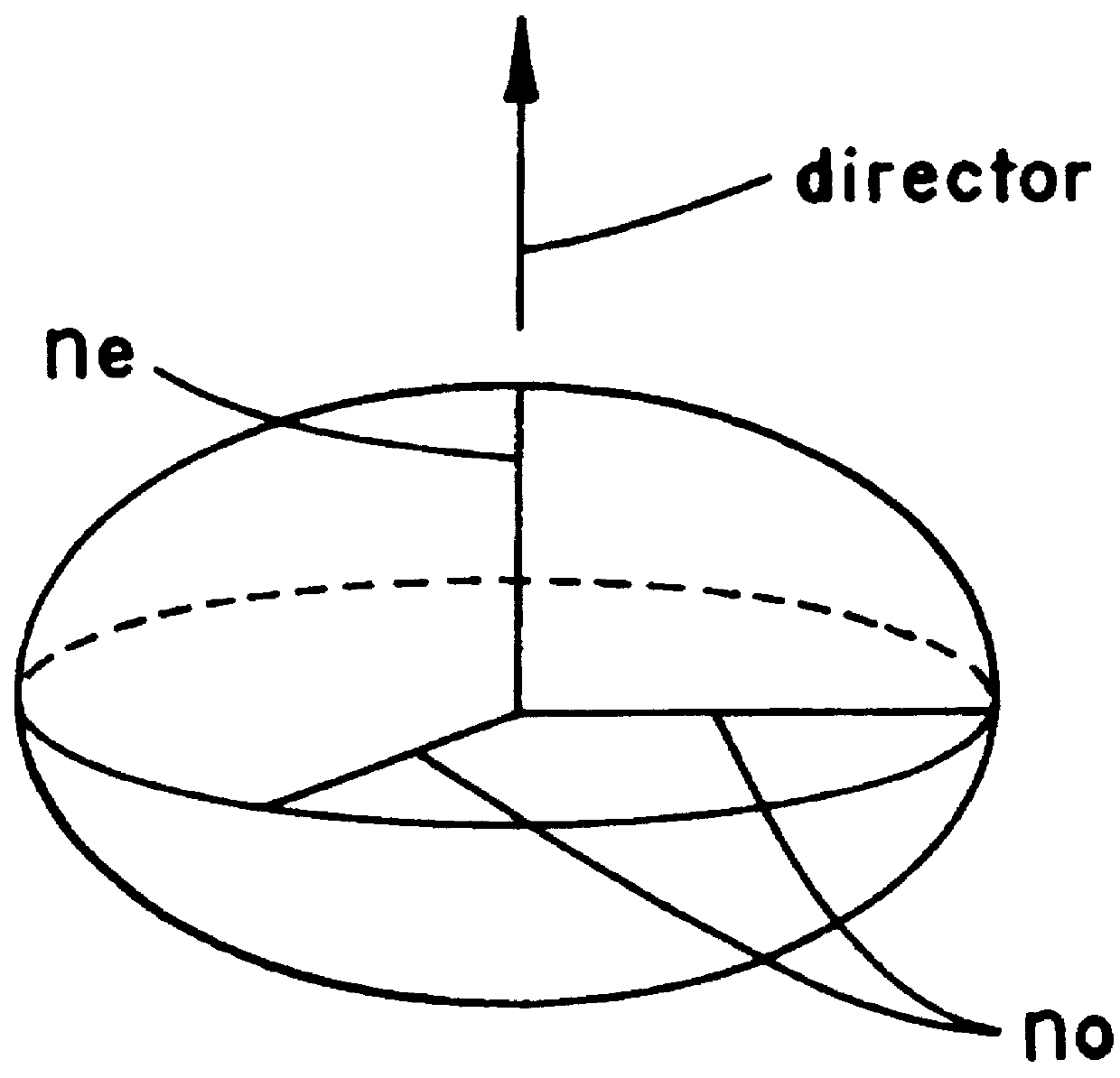
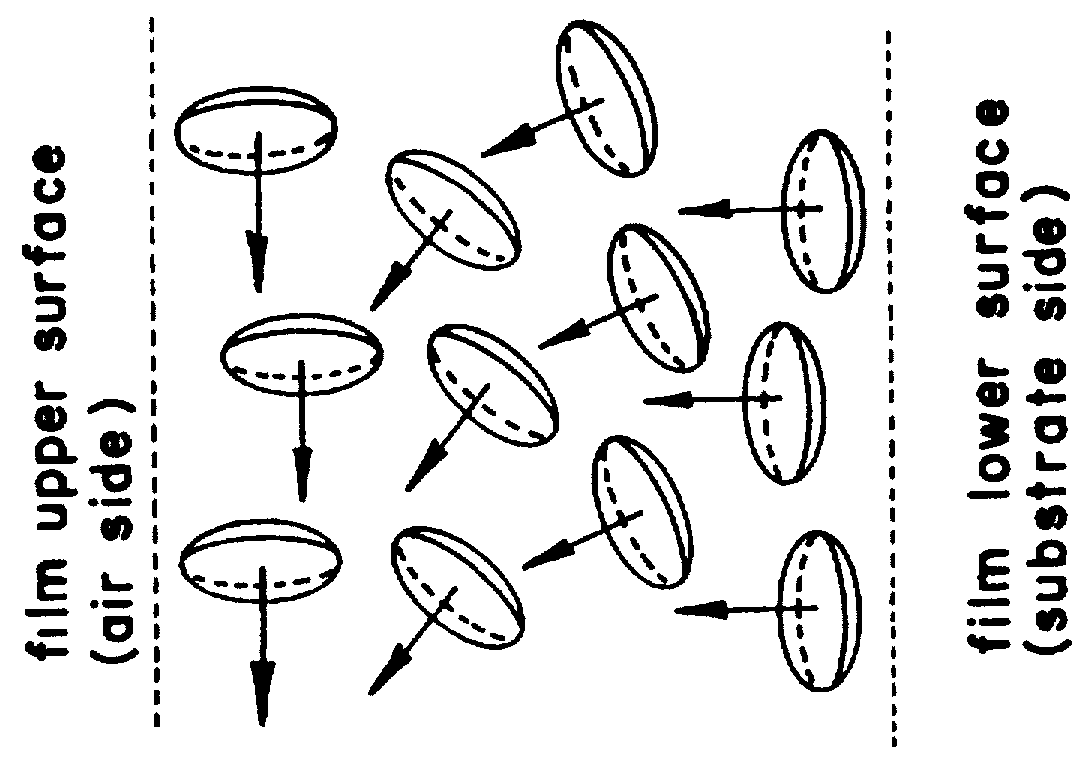
As a compensator for use in an OCB mode liquid crystal display there is provided a compensating film capable of making color compensation and attaining such a viewing angle expansion as has not been attainable heretofore. A compensating film for a liquid crystal display, constituted by at least one layer of a compensating film to be used in an OCB mode liquid crystal display, the compensating film being formed by a discotic liquid crystalline material having a fixed orientation form of a discotic liquid crystal, the compensating film being disposed between a driving liquid crystal cell and a pair of upper and lower polarizing plates, and the orientation form being a hybrid orientation in which the angle between discotic liquid crystal directors near the upper interface of the film and the film plane and the angle between discotic liquid crystal directors near the lower interface of the film and film plane are different from each other.
Owner:NIPPON MITSUBISHI OIL CORP
Magnetoresistance effect element, magnetic head, magnetic reproducing apparatus, and magnetic memory
InactiveUS20070081276A1High sensitivityReduce power consumptionNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsFilm planeMagnetic memory
A magnetoresistance effect element comprises a magnetoresistance effect film and a pair of electrode. The magnetoresistance effect film having a first magnetic layer whose direction of magnetization is substantially pinned in one direction; a second magnetic layer whose direction of magnetization changes in response to an external magnetic field; a nonmagnetic intermediate layer located between the first and second magnetic layers; and a film provided in the first magnetic layer, in the second magnetic layer, at a interface between the first magnetic layer and the nonmagnetic intermediate layer, and / or at a interface between the second magnetic layer and the nonmagnetic intermediate layer, the film having a thickness not larger than 3 nanometers, and the film has as least one selected from the group consisting of nitride, oxinitride, phosphide, and fluoride. The pair of electrodes are electrically connected to the magnetoresistance effect film to supply a sense current perpendicularly to a film plane of said magnetoresistance effect film.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
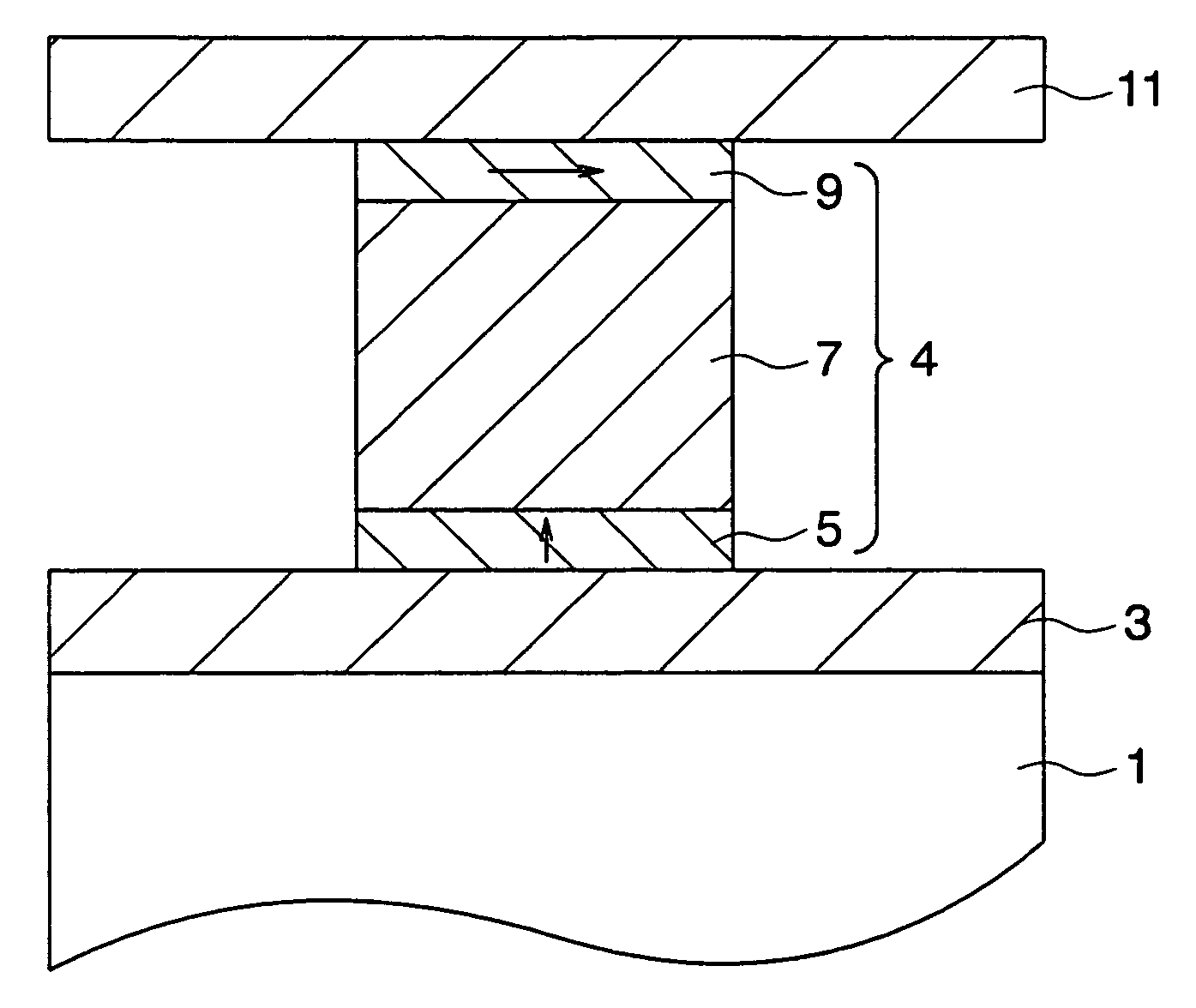
Magnetoresistant device and magnetic memory device further comments
InactiveUS20060125034A1Low coercivityRectangle property can be improvedNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsBit lineFilm plane
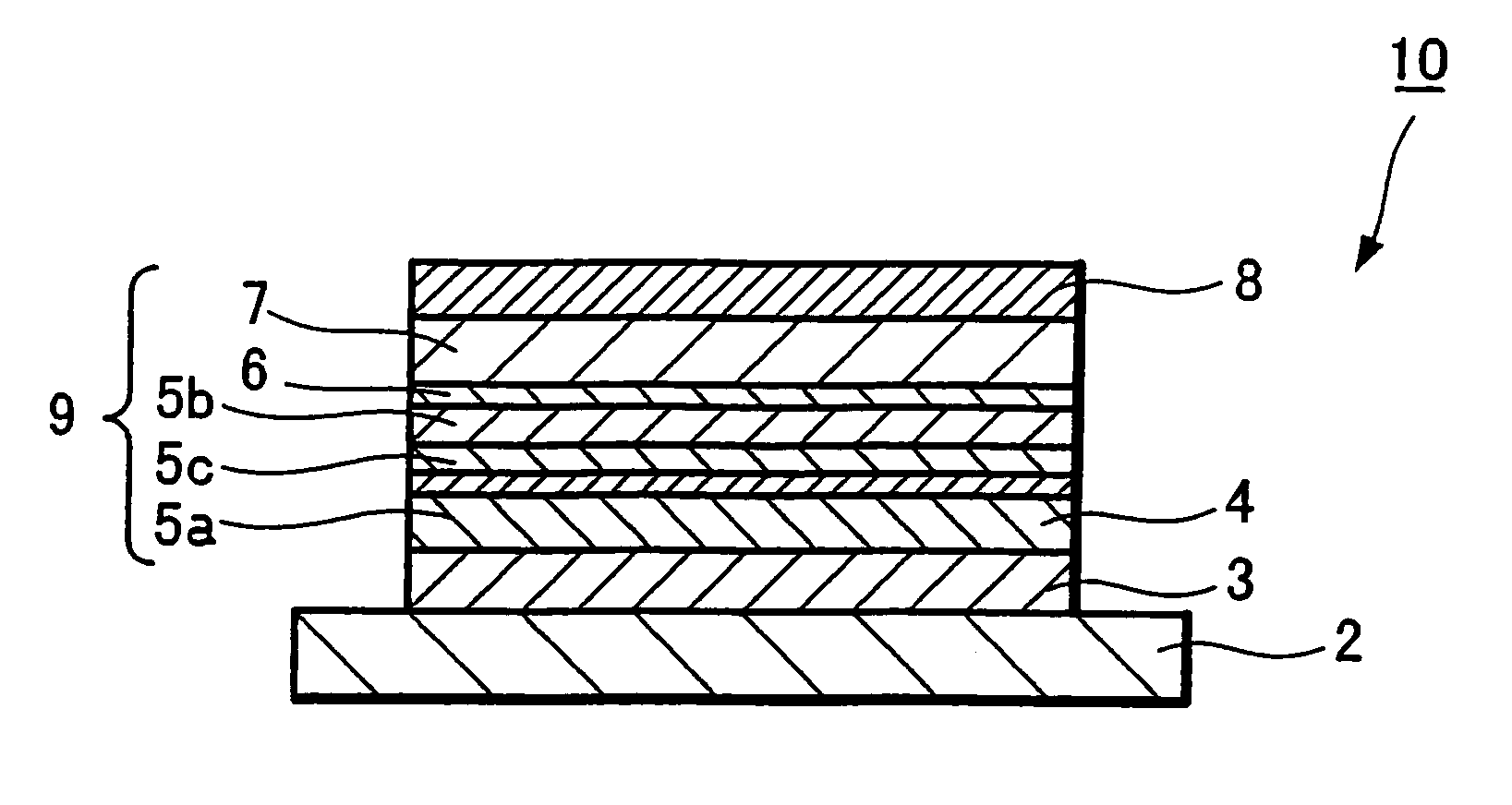
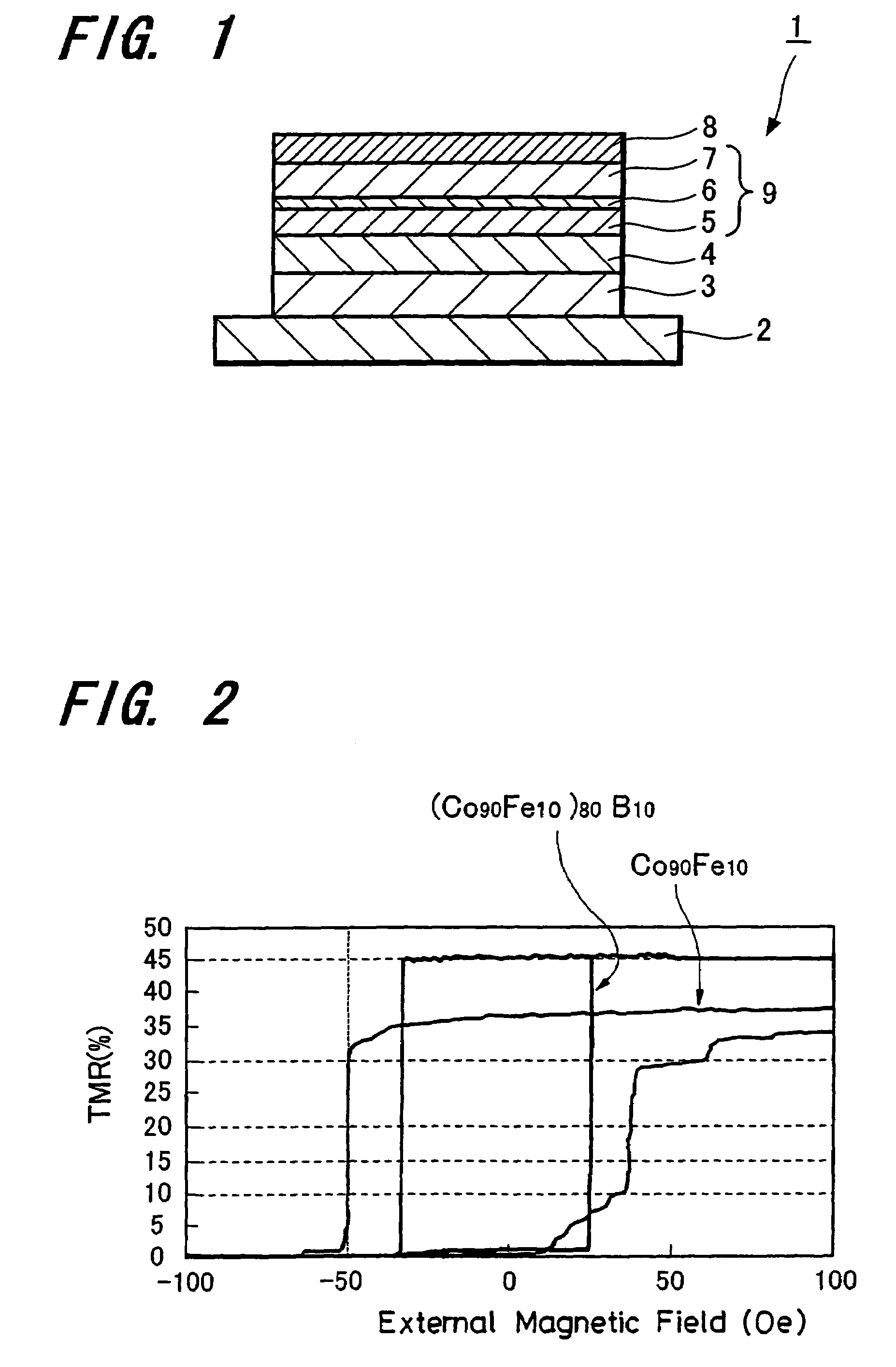
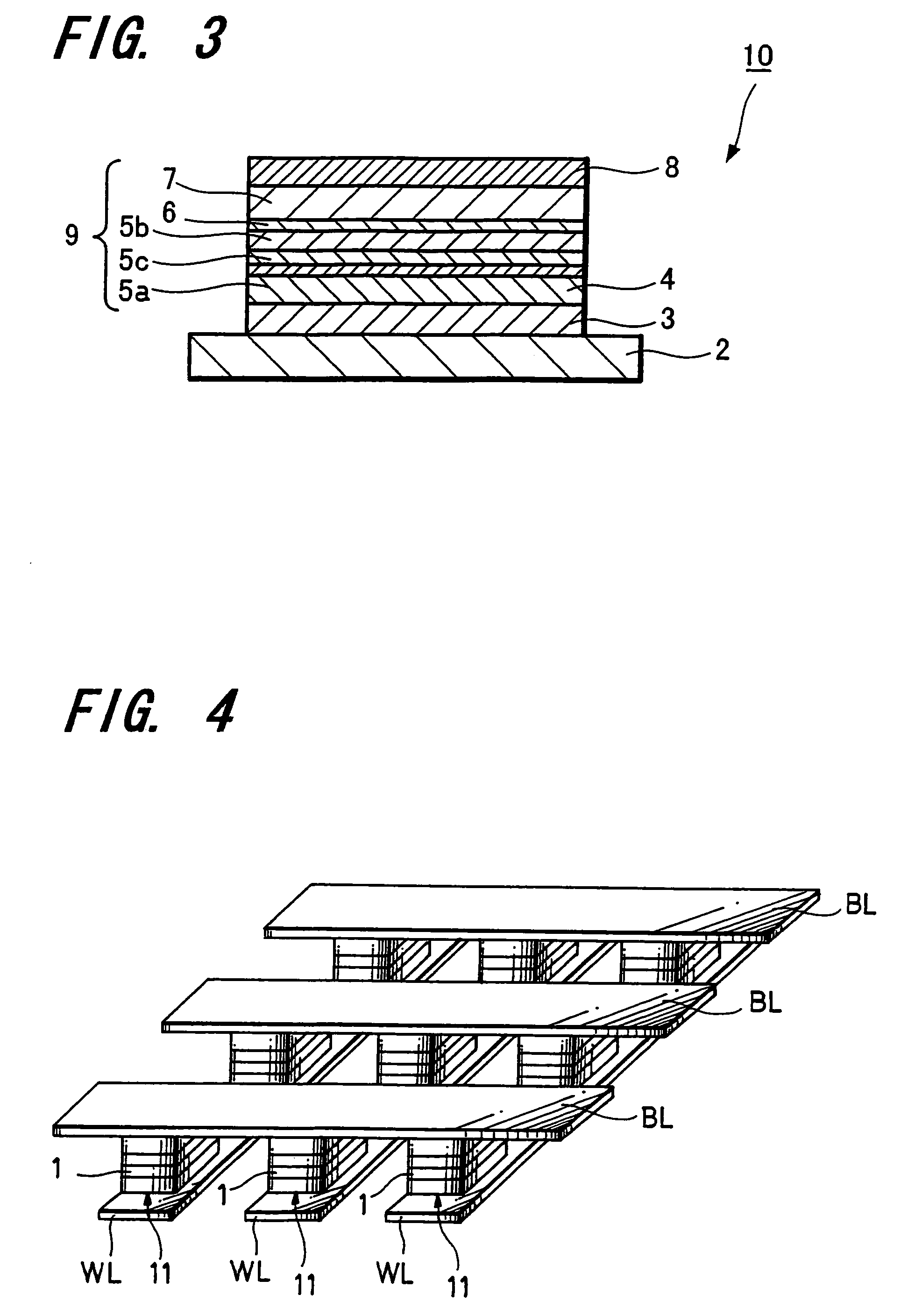
There are provided a magnetoresistive device having excellent magnetic properties and a magnetic memory apparatus including this magnetoresistive device and which has excellent read and write characteristics. A magnetoresistive device has an arrangement including a pair of ferromagnetic layers (magnetization fixed layer 5 and magnetization free layer 7) being opposed to each other through an intermediate layer 6 to obtain variations in magnetoresistance by an electric current flowing in the direction perpendicular to the film plane. This magnetoresistive device 1 has the pair of ferromagnetic layers 5, 7 composed of the magnetization fixed layer 5 made of a crystalline ferromagnetic layer provided under the intermediate layer 6 and the magnetization free layer 7 being made of an amorphous ferromagnetic layer being provided above the intermediate layer 6, and the magnetic memory apparatus is composed of this magnetoresistive device 1 and a bit line and a word line sandwiching the magnetoresistive device 1 in the thickness direction.
Owner:SONY CORP
Magnetoresistive effect element and magnetic memory device
InactiveUS7315053B2Improve featuresBias voltage dependence can be improvedNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsFilm planeMagnetic memory
Write characteristics and read characteristics can be improved at the same time by applying novel materials to ferromagnetic layers. In a magnetoresistive effect element having a pair of ferromagnetic layers being opposed to each other through an intermediate layer to cause a current to flow in the direction perpendicular to the film plane to obtain a magnetoresistive change, at least one of the ferromagnetic layers contains a ferromagnetic material containing Fe, Co and B. The ferromagnetic material should preferably contain FeaCobNicBd (in the chemical formula, a, b, c and d represent atomic %. 5≦a≦45, 35≦b≦85, 0<c≦35, 10≦d≦30. a+b+C+d=100).
Owner:SONY CORP
Magnetoresistance effect element and magnetic random access memory
ActiveUS8014193B2Minimise currentHigh-speed writingMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryMicrowave
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Magnetic oscillator, magnetic head, and magnetic recording and reproducing apparatus
The present invention is to be capable of suppressing magnetic white noises as far as possible. A resonant magneto-resistance effect element includes a first magnetic layer whose magnetization direction is substantially parallel to a film plane, a second magnetic film whose magnetization direction is substantially perpendicular to the film plane, and a non-magnetic layer which is provided between the first and second layers.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Retardation film, process for producing the same, optical film, image display, liquid crystal panel and liquid crystal display
ActiveUS7215839B2Hard to cause a shift or an unevenness of a retardation valueOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayFilm plane
A retardation film of the present invention comprises a stretched film of a polymer film containing a norbornene-based resin, wherein the stretched film satisfies the following equation (1) and the equation (2); 100 nm≦(nx−ny)·d≦350 nm . . . (1), 0.1≦(nx−nz) / (nx−ny)≦0.9 . . . (2), where the refractive indices in the slow axis direction, the fast axis direction and the thickness direction of the film are nx, ny and nz, respectively, d(nm) is thickness of the film, and the slow axis direction is a direction that the refractive index in film plane is maximum. The retardation film is hard to cause a shift or an unevenness of a retardation value due to a stress.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
CPP giant magnetoresistive head including pinned magnetic layer that extends in the height direction
ActiveUS7365949B2Simple processIncrease productionMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsRecord information storageFilm planeMagnetic layer
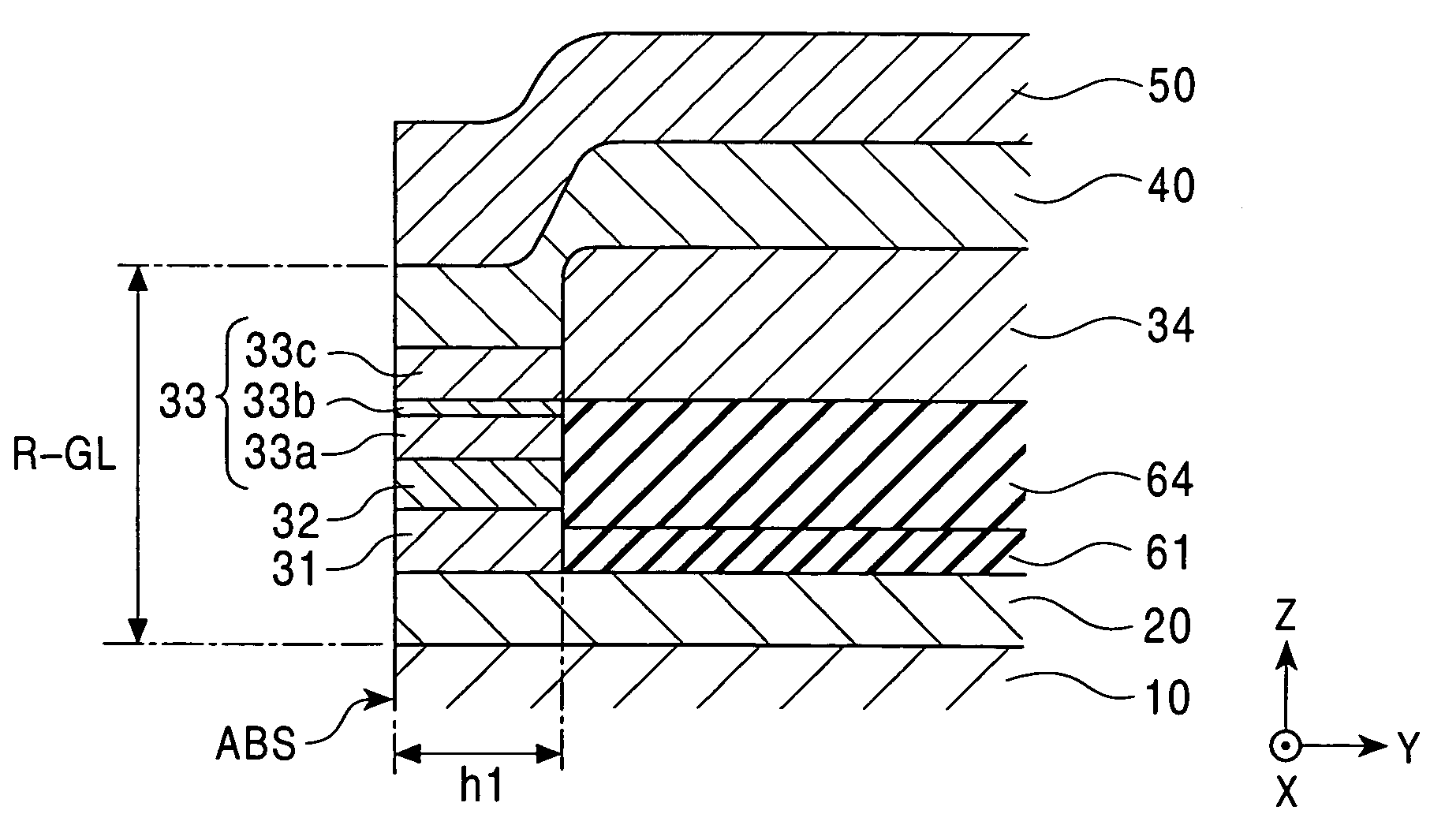
A CPP giant magnetoresistive head includes a lower shield layer; an upper shield layer; and a giant magnetoresistive element (GMR) between the lower shield layer and the upper shield layer. The GMR includes a nonmagnetic material layer; a pinned magnetic layer; and a free magnetic layer. The pinned layer and the free layer are laminated with the nonmagnetic layer provided therebetween. A current flows perpendicularly to a film plane of the GMR, the pinned magnetic layer extends in the height direction longer than in a track-width direction and includes a first portion in the GMR. The first portion is disposed above or below the nonmagnetic layer and the free layer. A second portion is behind the nonmagnetic layer and the free layer in the height direction. The first and second portions are in the same plane. The width of the pinned layer in the track-width direction in the first portion is greater than that in the second portion.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
CPP giant magnetoresistive head including pinned magnetic layer that extends in the height direction
ActiveUS20050270703A1Reducing magnetic fluctuation of magneticLongitudinal width can be reducedMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsRecord information storageFilm planeMagnetic layer
A CPP giant magnetoresistive head includes a lower shield layer; an upper shield layer; and a giant magnetoresistive element (GMR) between the lower shield layer and the upper shield layer. The GMR includes a nonmagnetic material layer; a pinned magnetic layer; and a free magnetic layer. The pinned layer and the free layer are laminated with the nonmagnetic layer provided therebetween. A current flows perpendicularly to a film plane of the GMR, the pinned magnetic layer extends in the height direction longer than in a track-width direction and includes a first portion in the GMR. The first portion is disposed above or below the nonmagnetic layer and the free layer. A second portion is behind the nonmagnetic layer and the free layer in the height direction. The first and second portions are in the same plane. The width of the pinned layer in the track-width direction in the first portion is greater than that in the second portion.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com