Patents
Literature
315 results about "Magnetic barrier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
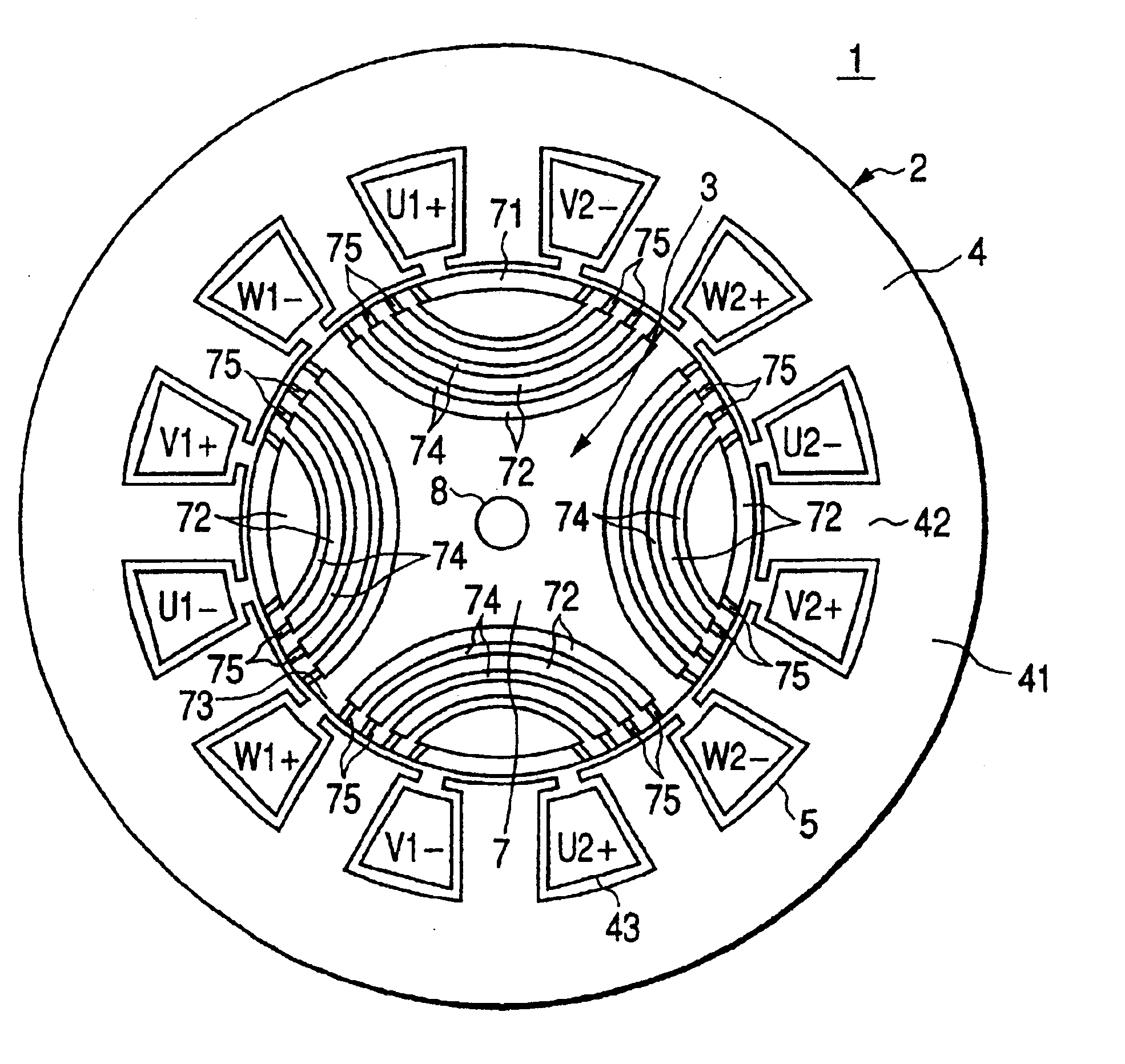
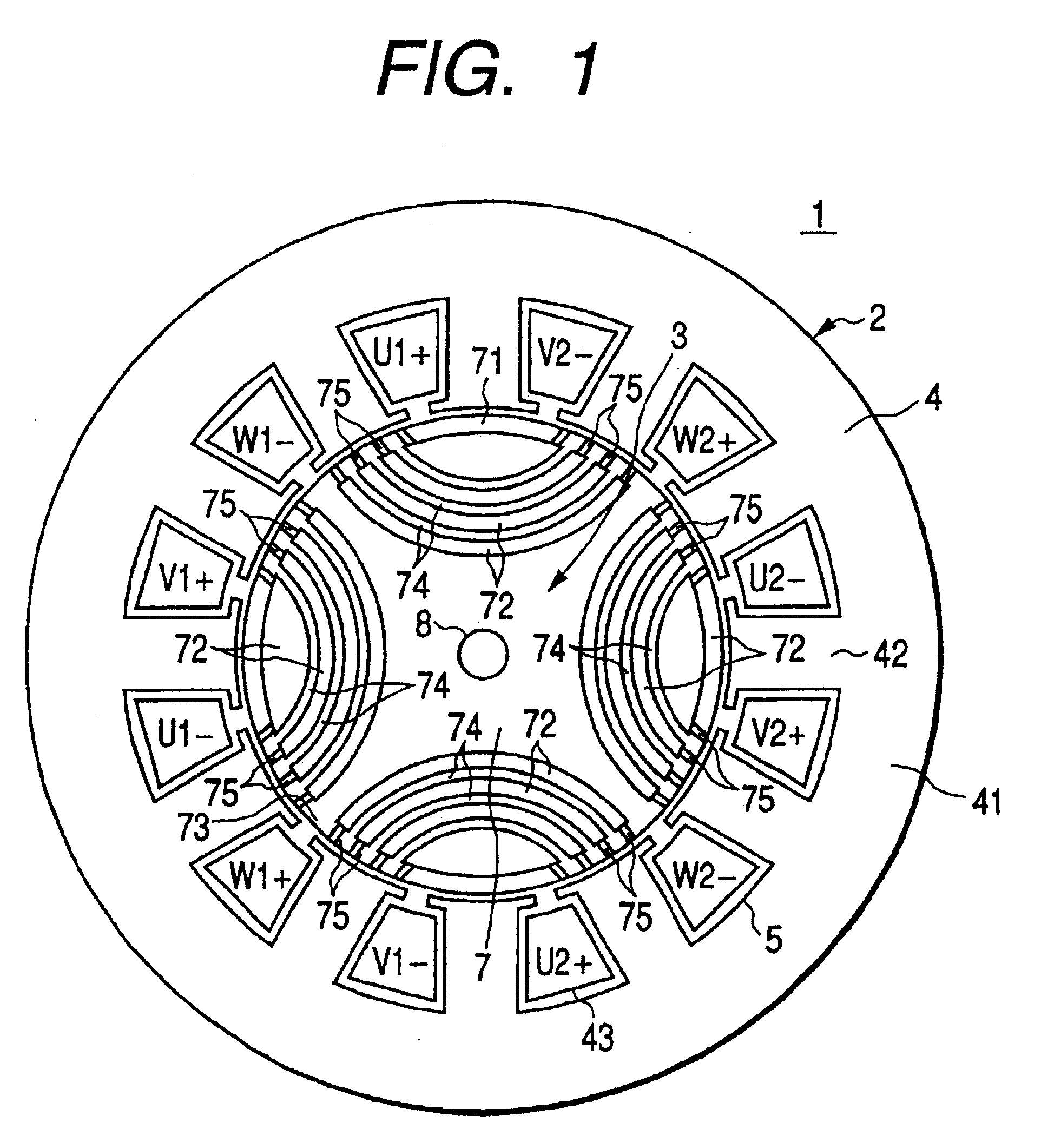
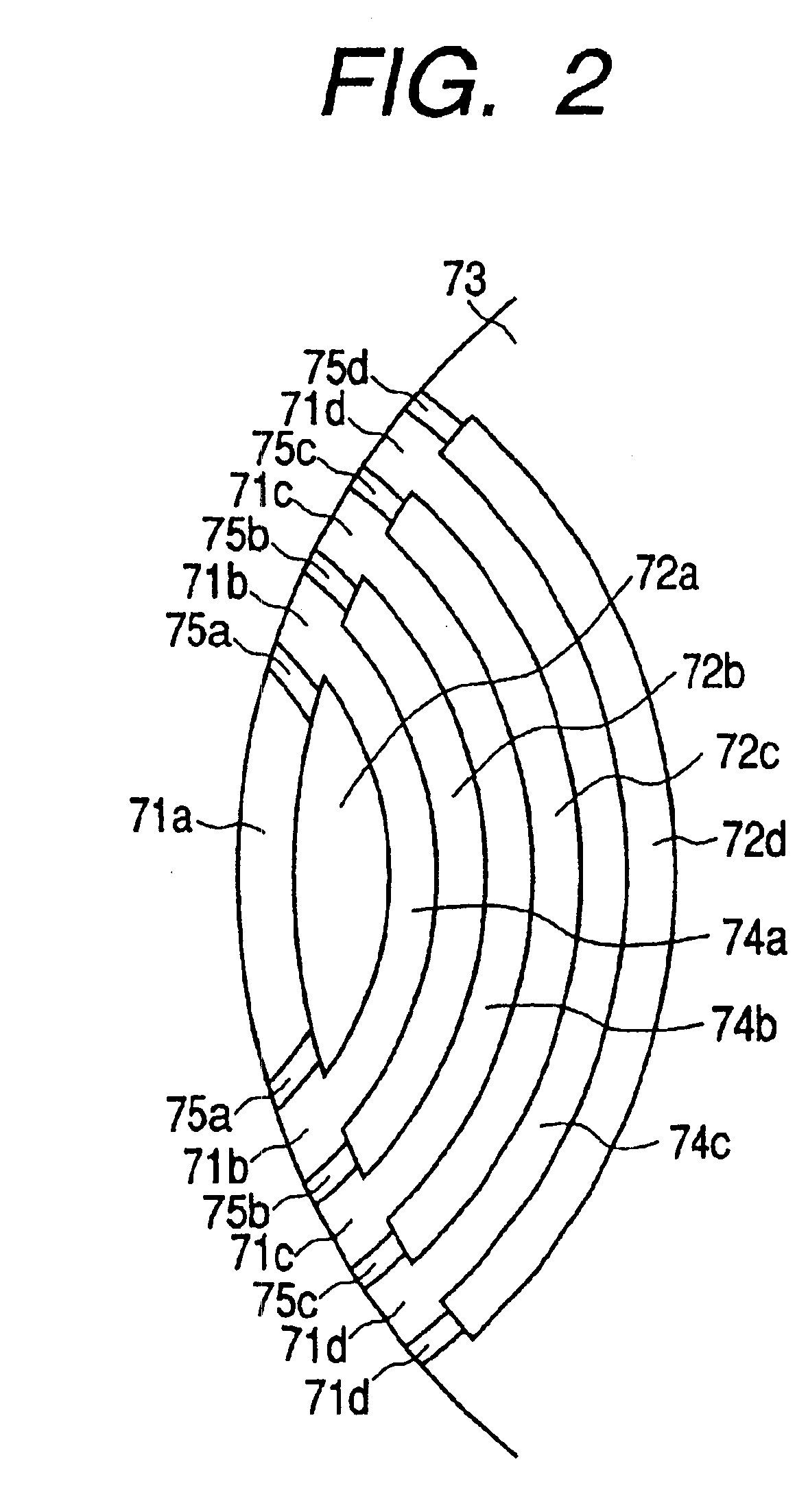
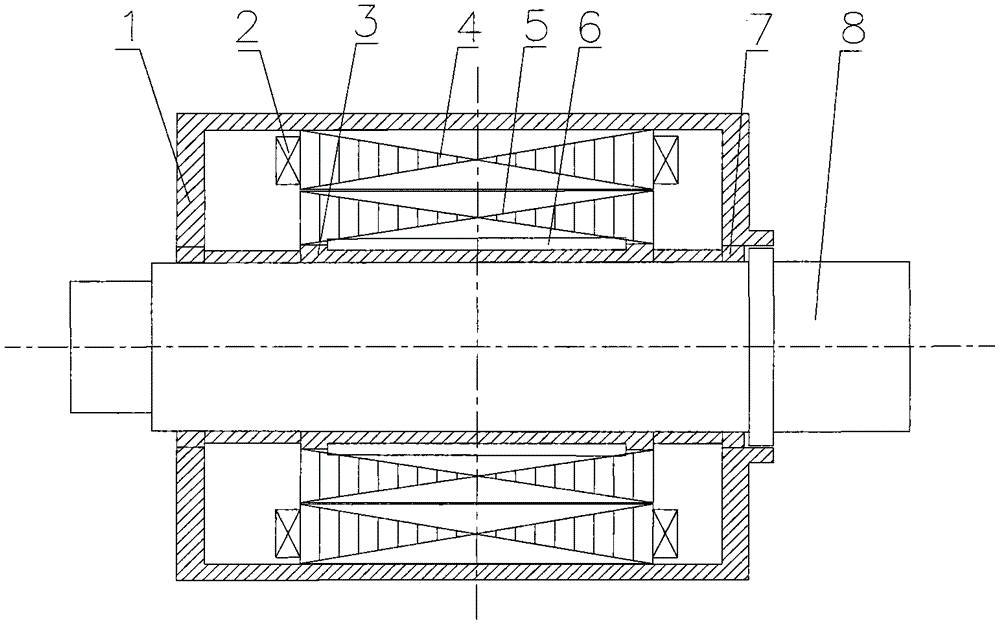
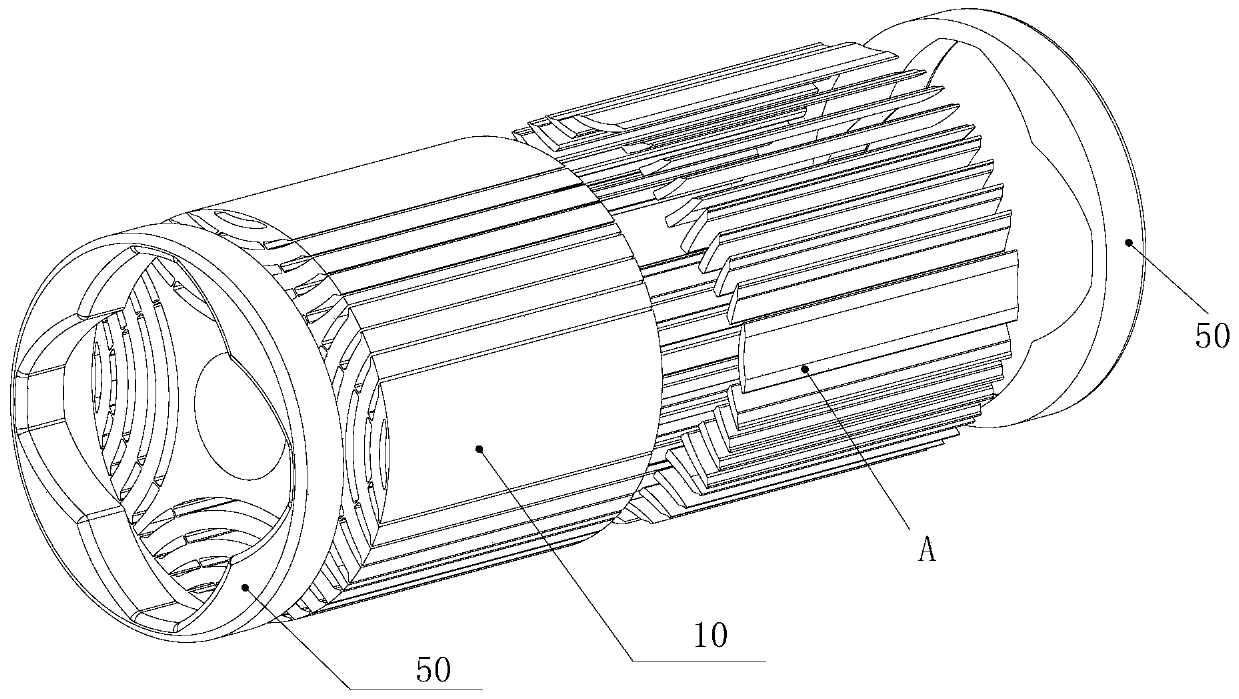
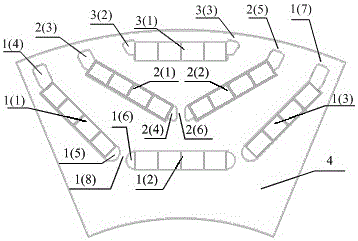
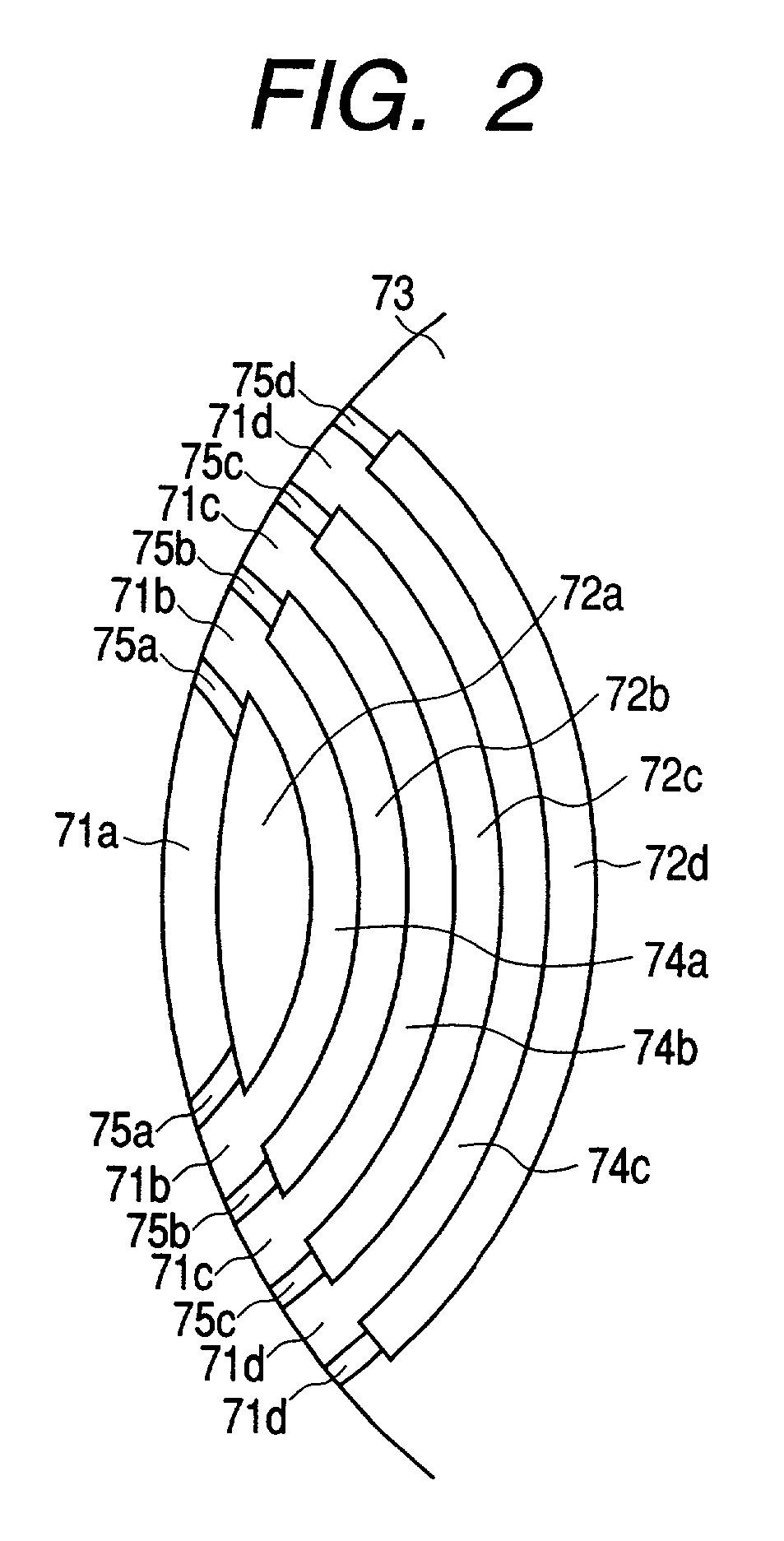
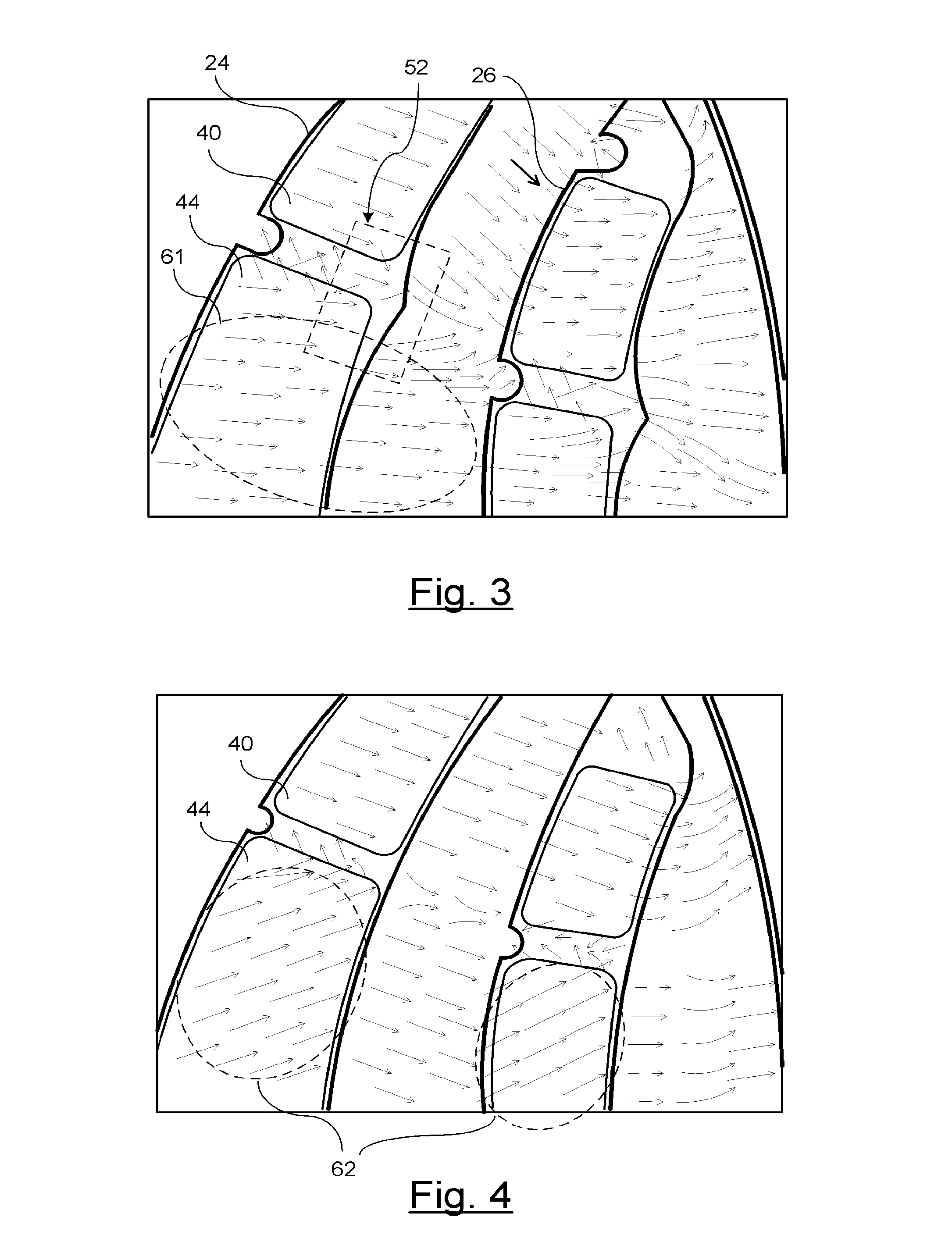
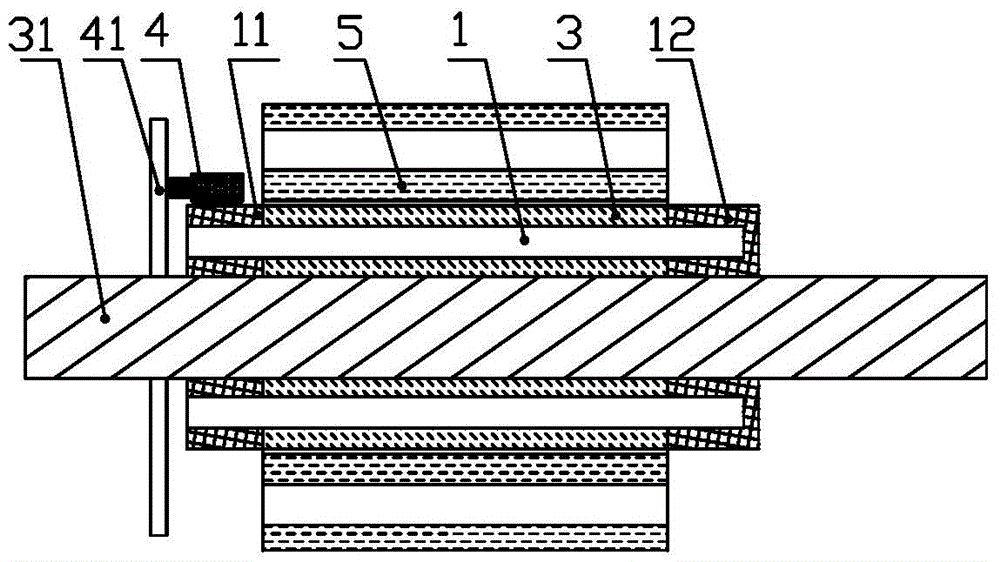
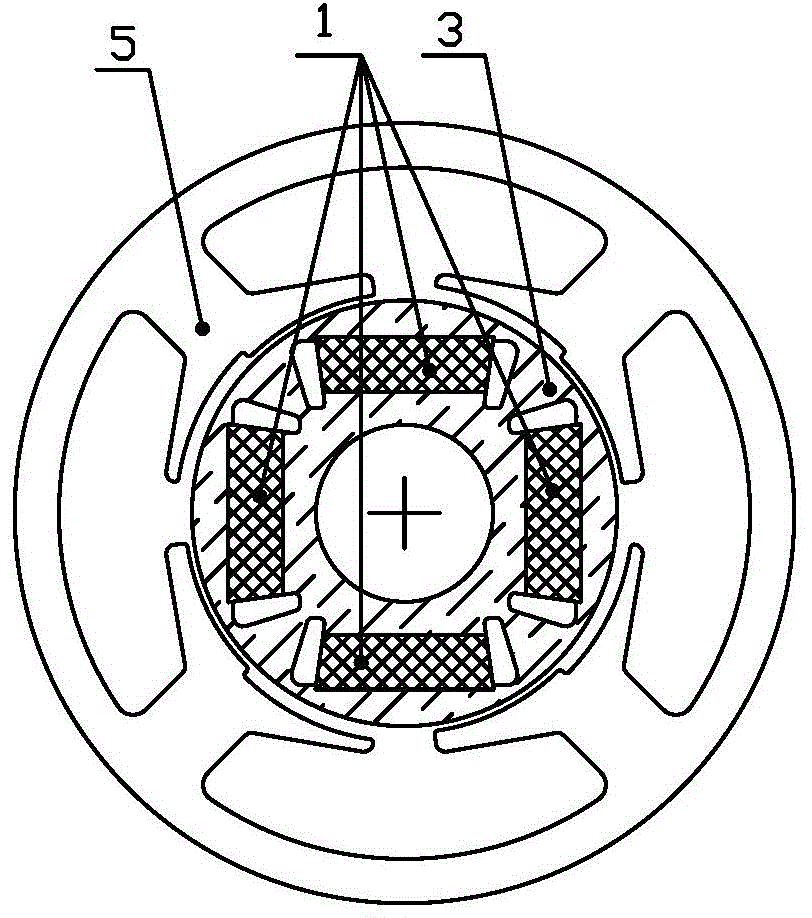
Rotary machine having bypath magnetic path blocking magnetic barrier
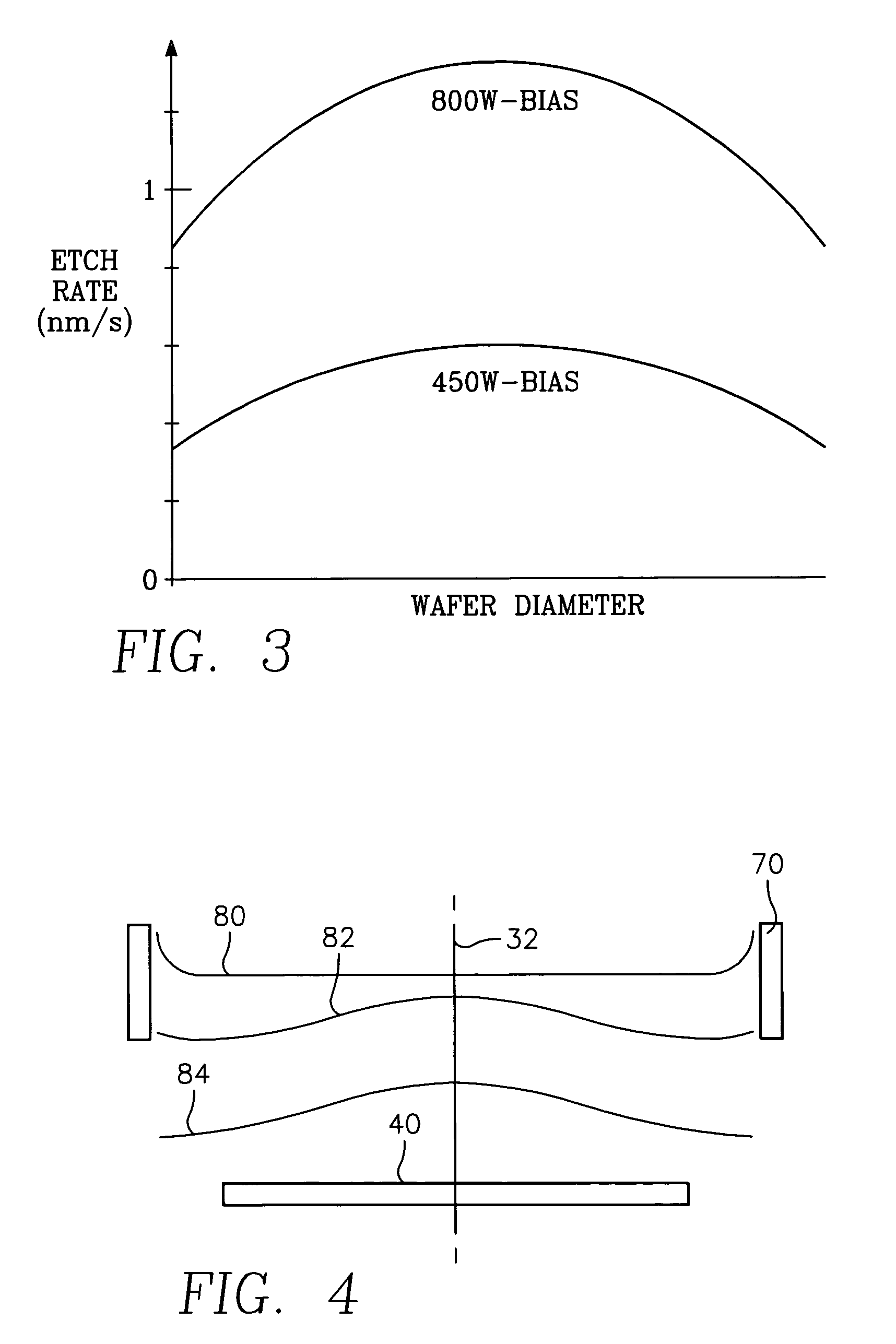
InactiveUS6849983B2Increase torqueHigh mechanical strengthSpeed controllerSynchronous generatorsMagnetic barrierMagnetic poles
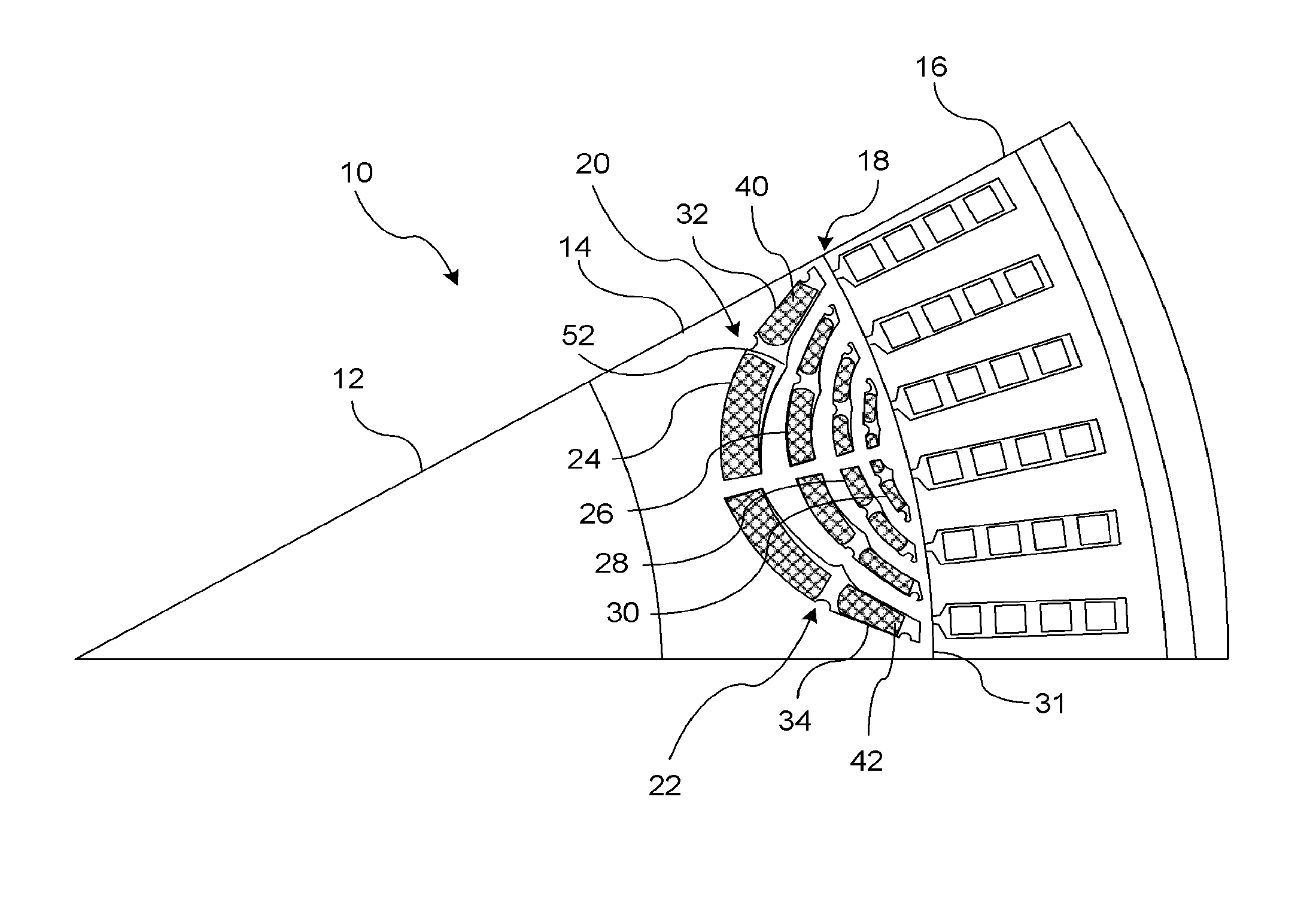
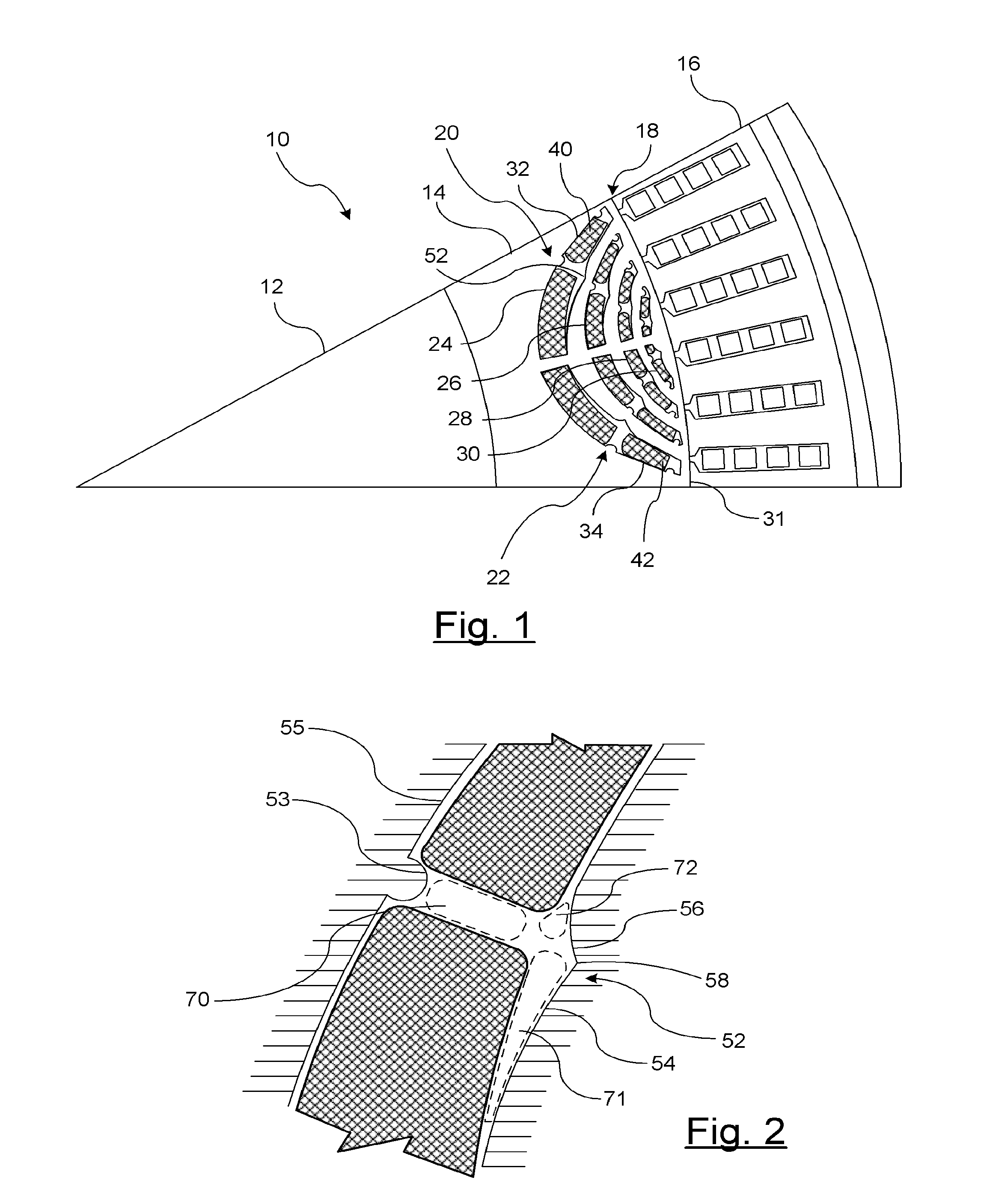
The rotary machine is composed of the rotor having magnetic poles and the stator having the stator yoke portion constituting the iron core tooth portion wound by the stator winding and the flux flow path of the magnetic poles. The rotor is composed of a metallic material having ferromagnetic parts and non-magnetic parts as a member and has a magnetic barrier area composed of the slit portion for blocking the bypath magnetic path in the periphery of the rotor and the non-magnetic parts. The rotary machine that produced torque can be increased sufficiently and the mechanical strength during high-speed running is improved and an electrical vehicle using it.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
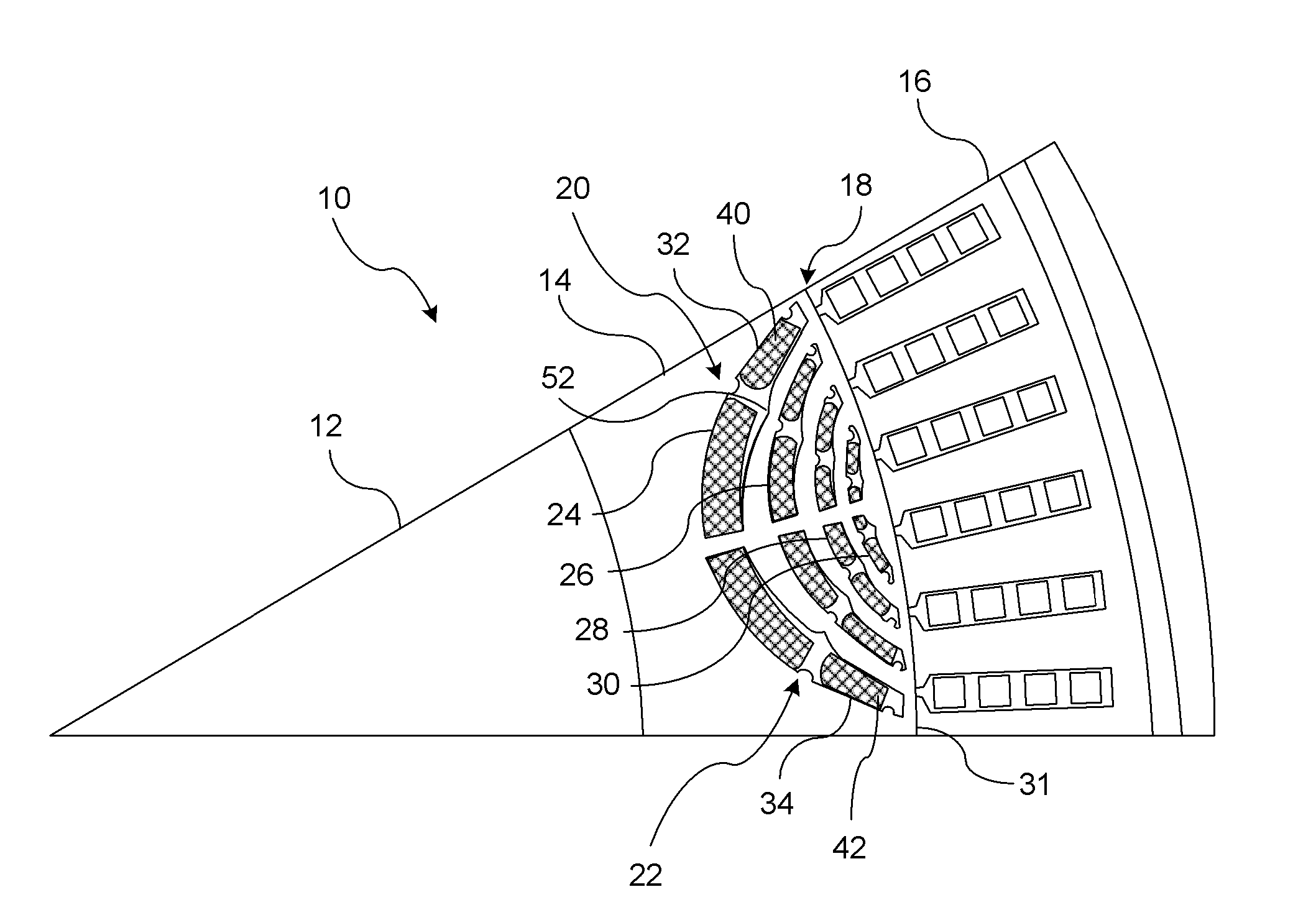
Magnetic barrier for minimizing demagnetization in bi-permanent magnet synchronous machines
ActiveUS20130320797A1Low costReduce in quantityMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsMagnetic barrierPermanent magnet synchronous machine
A rotor for a permanent synchronous machine includes a rotor having a plurality of arcuately-shaped cavities formed within a rotor core structure. The plurality of arcuately-shaped cavities substantially concentrically layered with respect to an outer cylindrical wall of the rotor core structure. A plurality of permanent magnets is inserted within the plurality of arcuately-shaped cavities. Each cavity layer retains a permanent magnet of a first magnetic field strength disposed in end sections and a permanent magnet of a second magnetic field strength in a center section of each cavity layer. Each respective cavity includes an air barrier formed between the magnets having different magnetic field strengths. The air barrier generates a reluctance within an air barrier gap for directing a flow of flux generated by each third permanent magnet in a preceding layer in a direction toward each third permanent magnet in a succeeding layer.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Sidewall magnet improving uniformity of inductively coupled plasma and shields used therewith
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
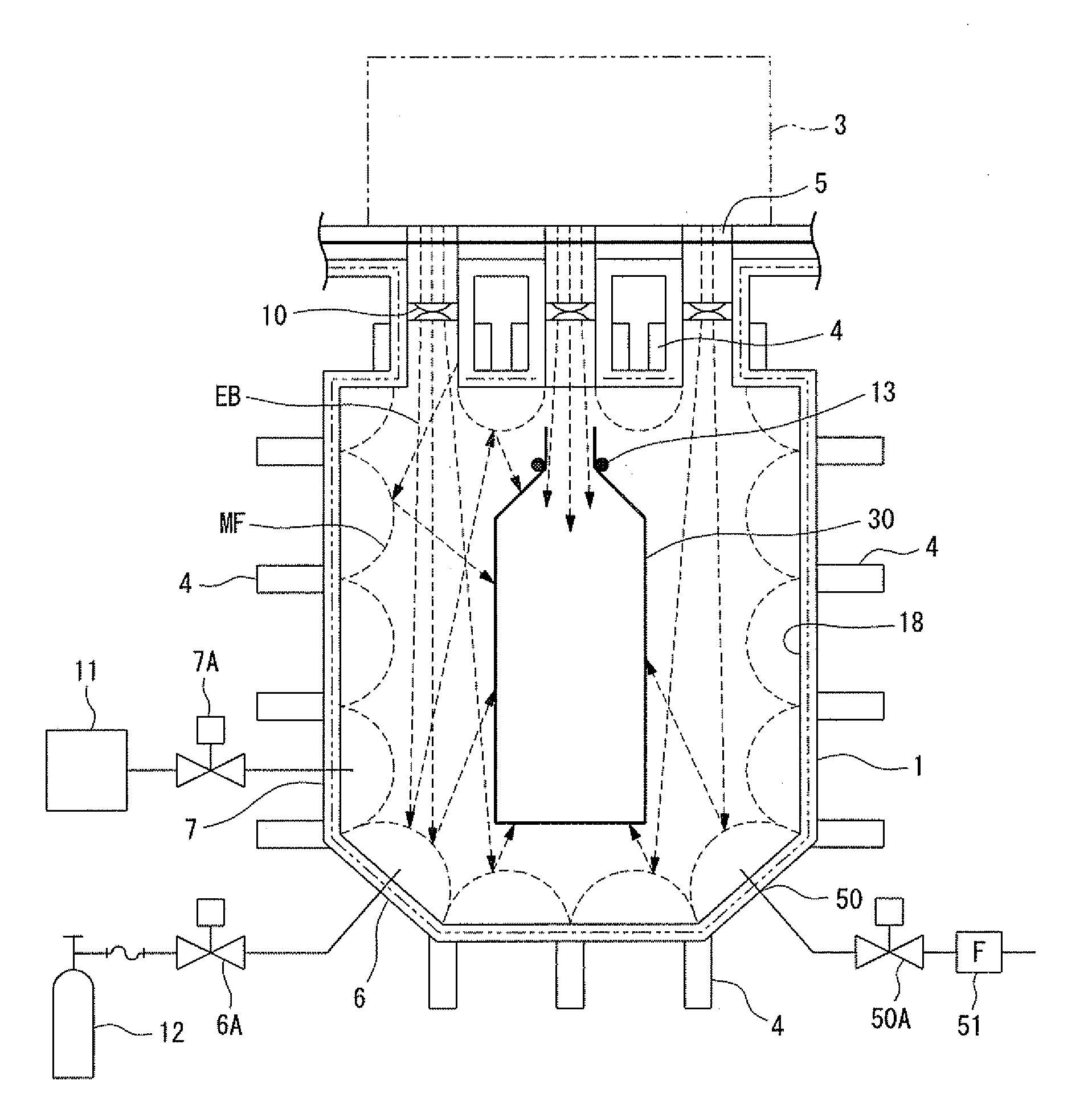
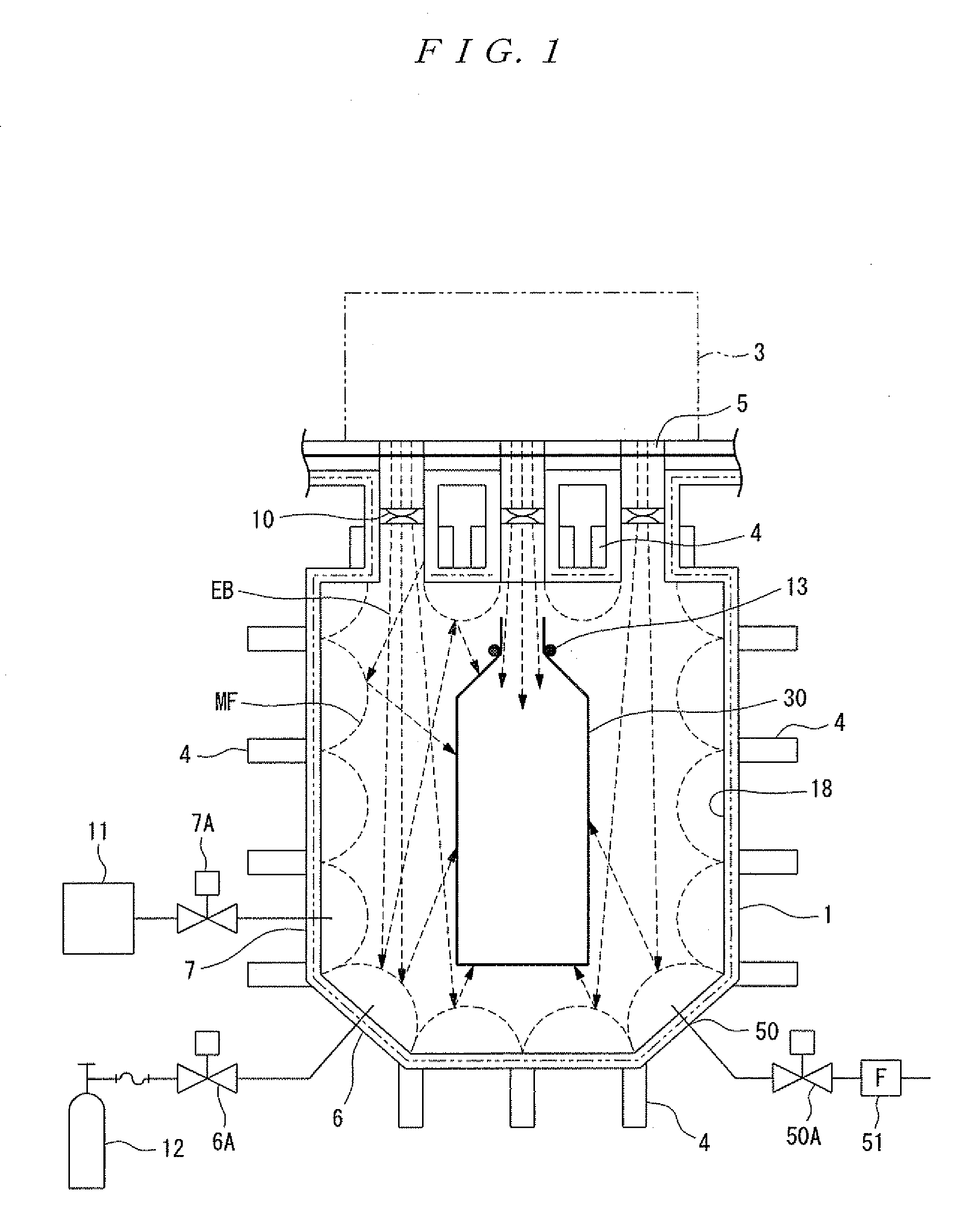
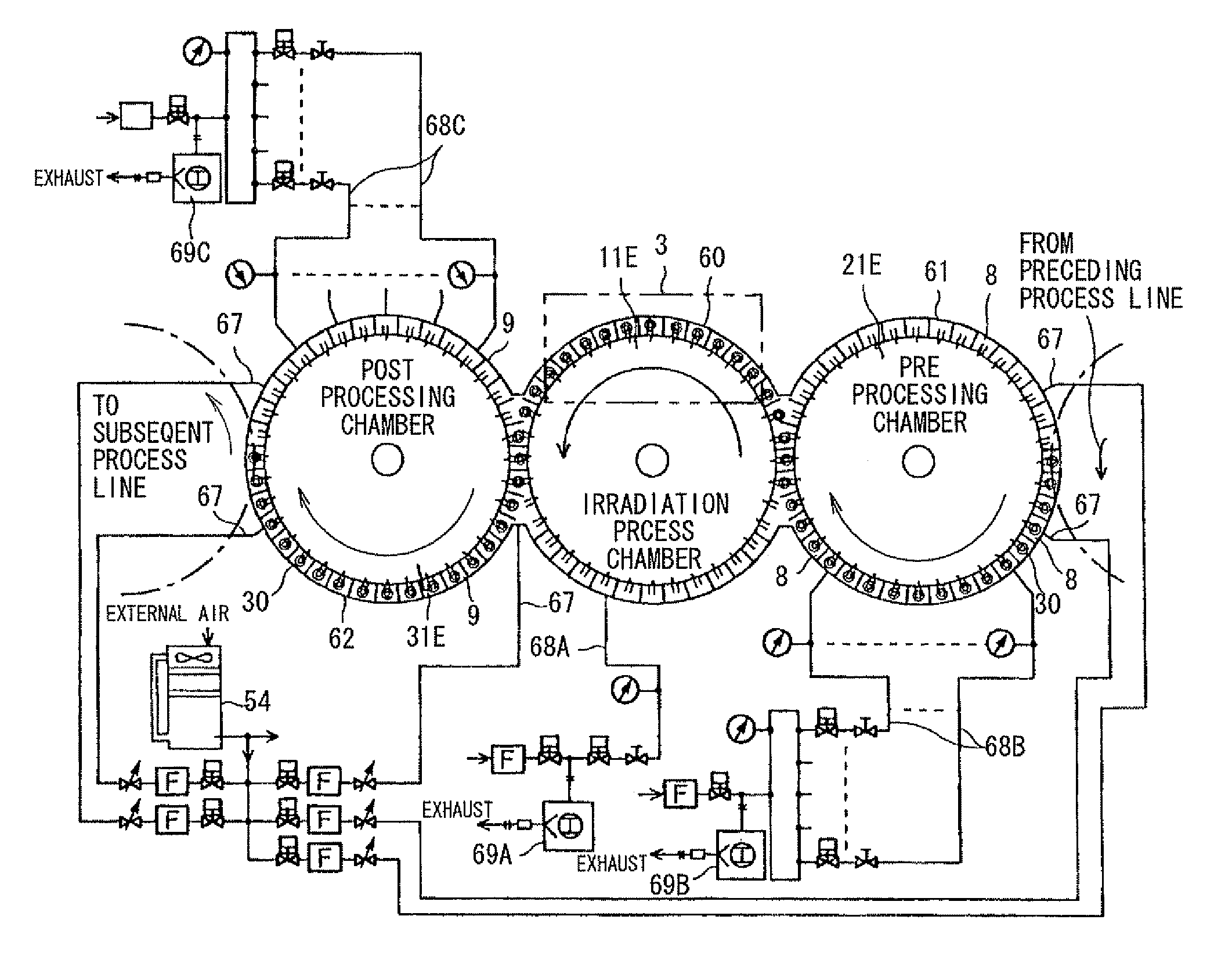
Electron Beam Irradiation Method, Electron Beam Irradiation Apparatus, and Electron Beam Irradiation Apparatus for Open-Mouthed Container
InactiveUS20090134338A1Reduce chanceSlightly wornParticle separator tubesPackage sterilisationMagnetic barrierElectron
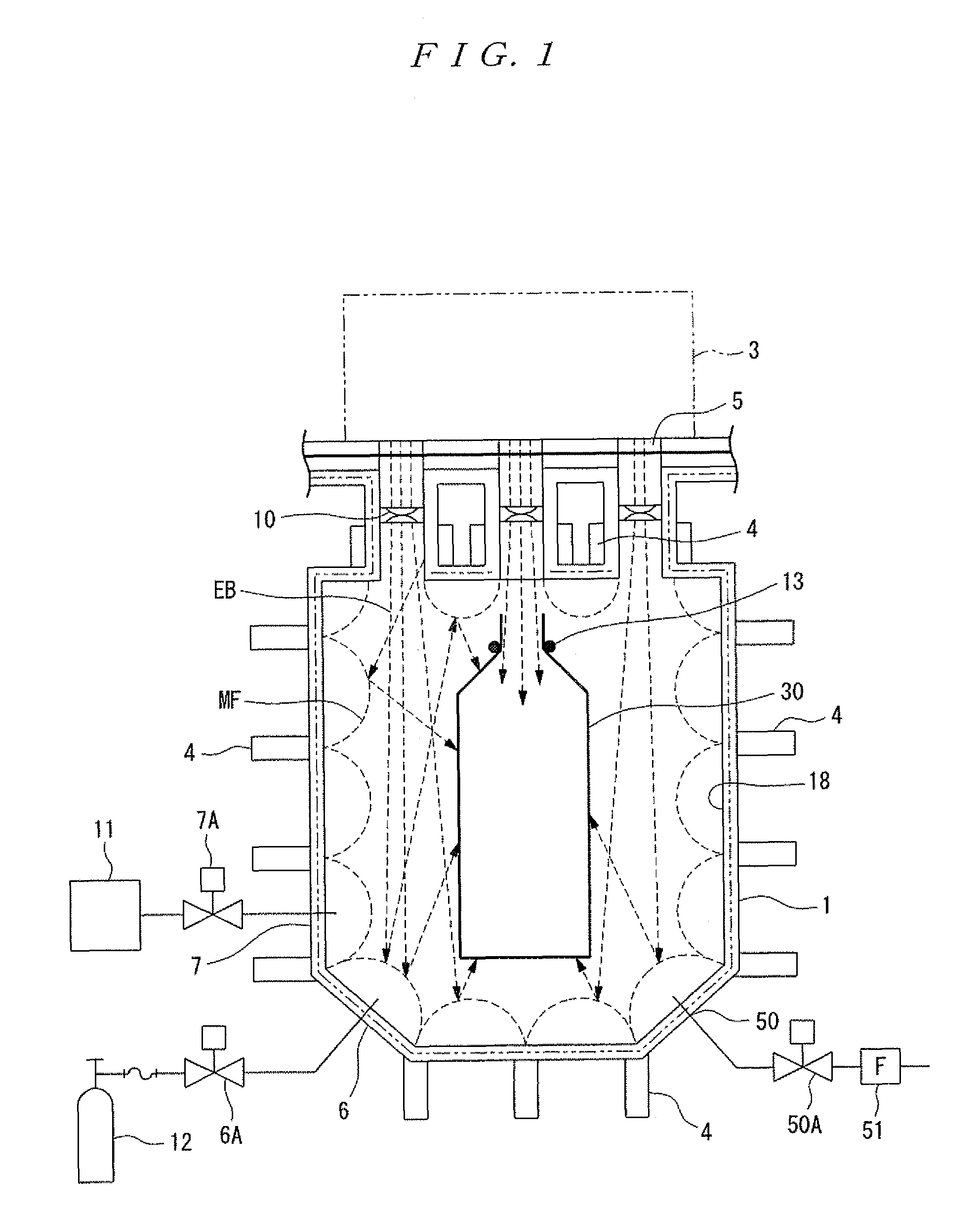
There are provided an electron beam application method and an electron beam application device capable of uniformly applying electron beams to an object even if the electron beams have a low energy. For this, electron beams (EB) are applied to a beverage container (30) (object) within a magnetic barrier (MF) formed by combining a plurality of magnetic fields generated in an electron beam application region.
Owner:JAPAN AE POWER SYST
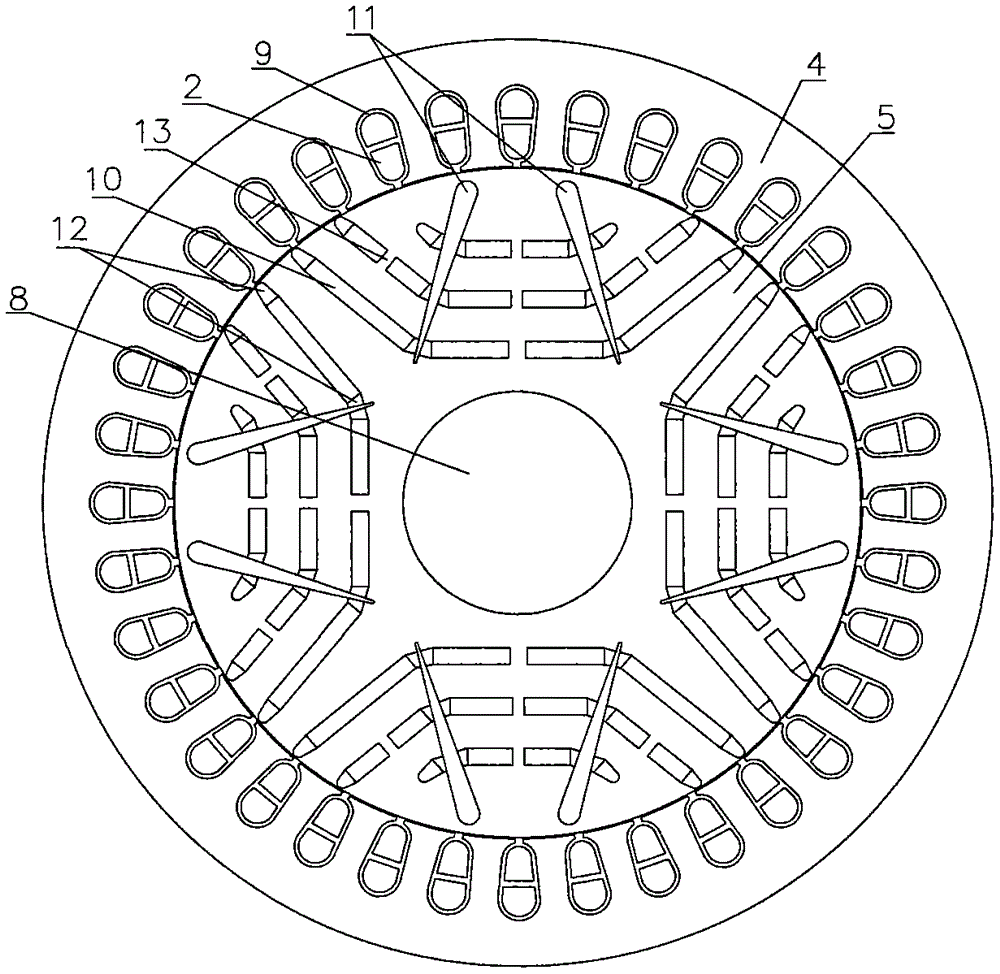
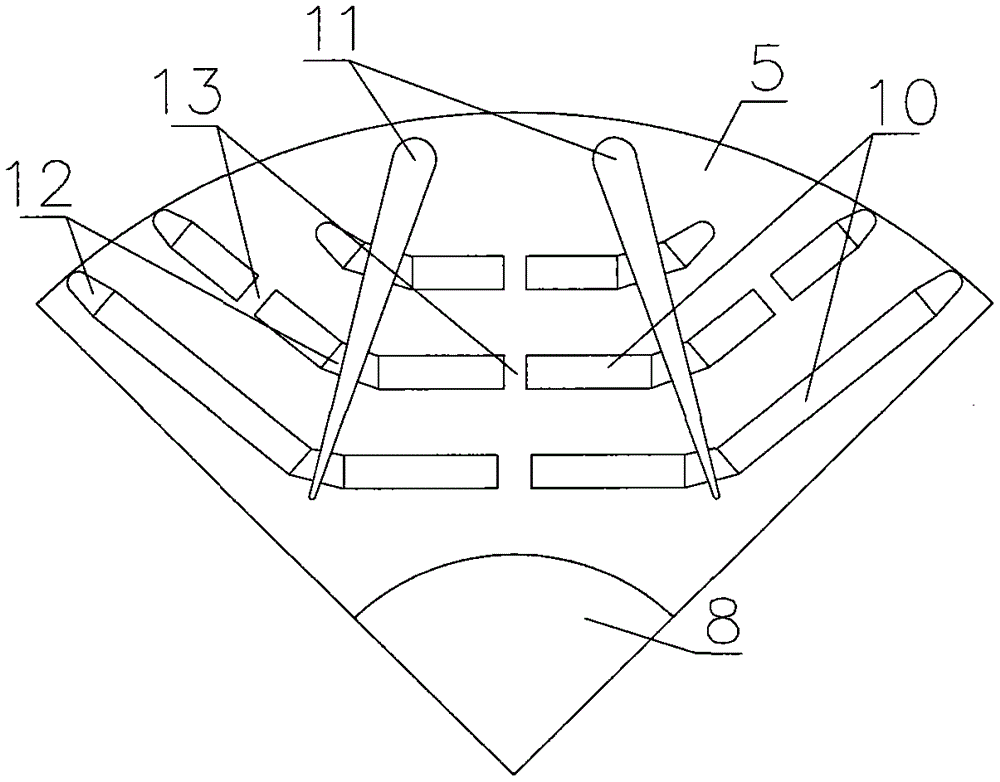
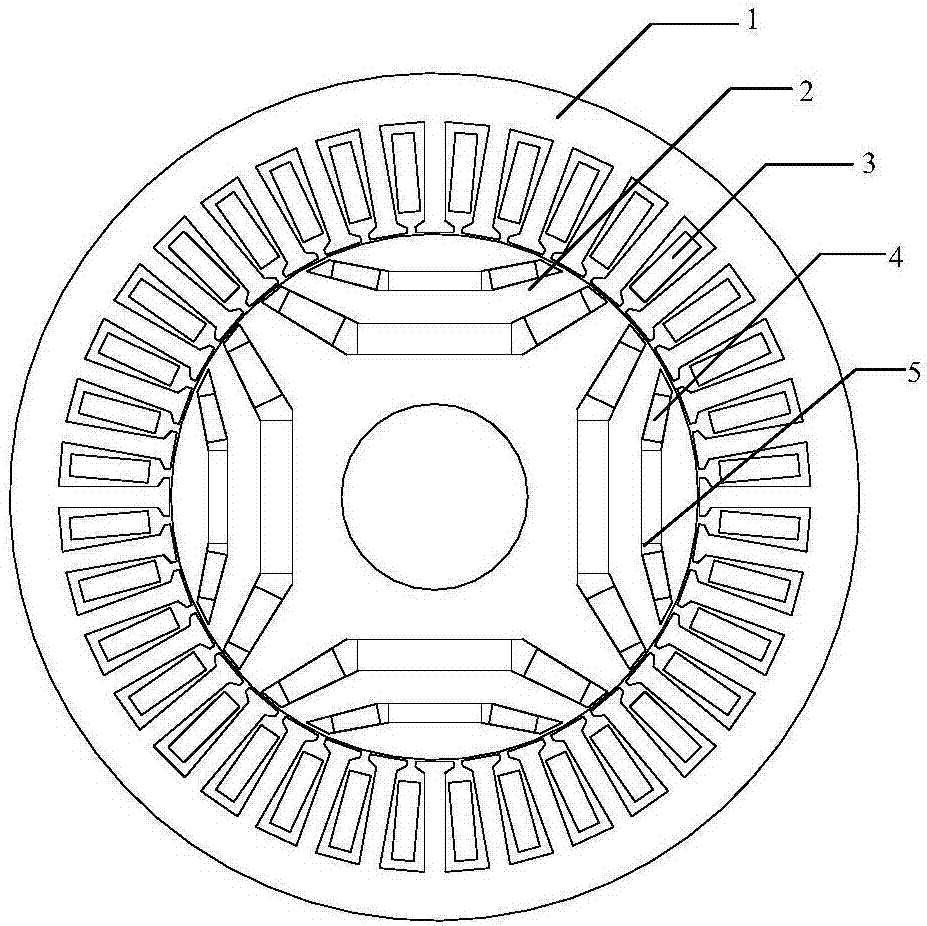
Built-in magnetic barrier type magnetic field enhanced permanent magnet brushless motor
ActiveCN106026597AIncrease profitModerate thicknessMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machine detailsMagnetic barrierBrushless motors
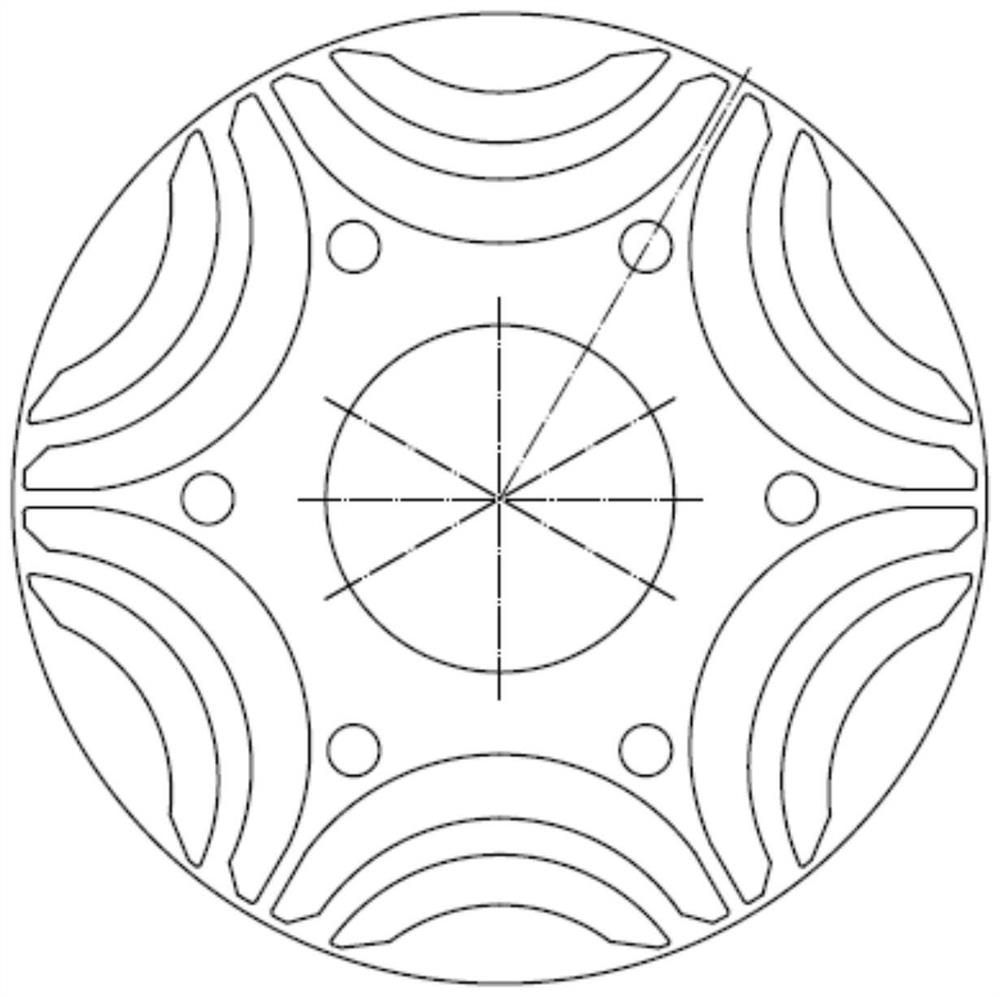
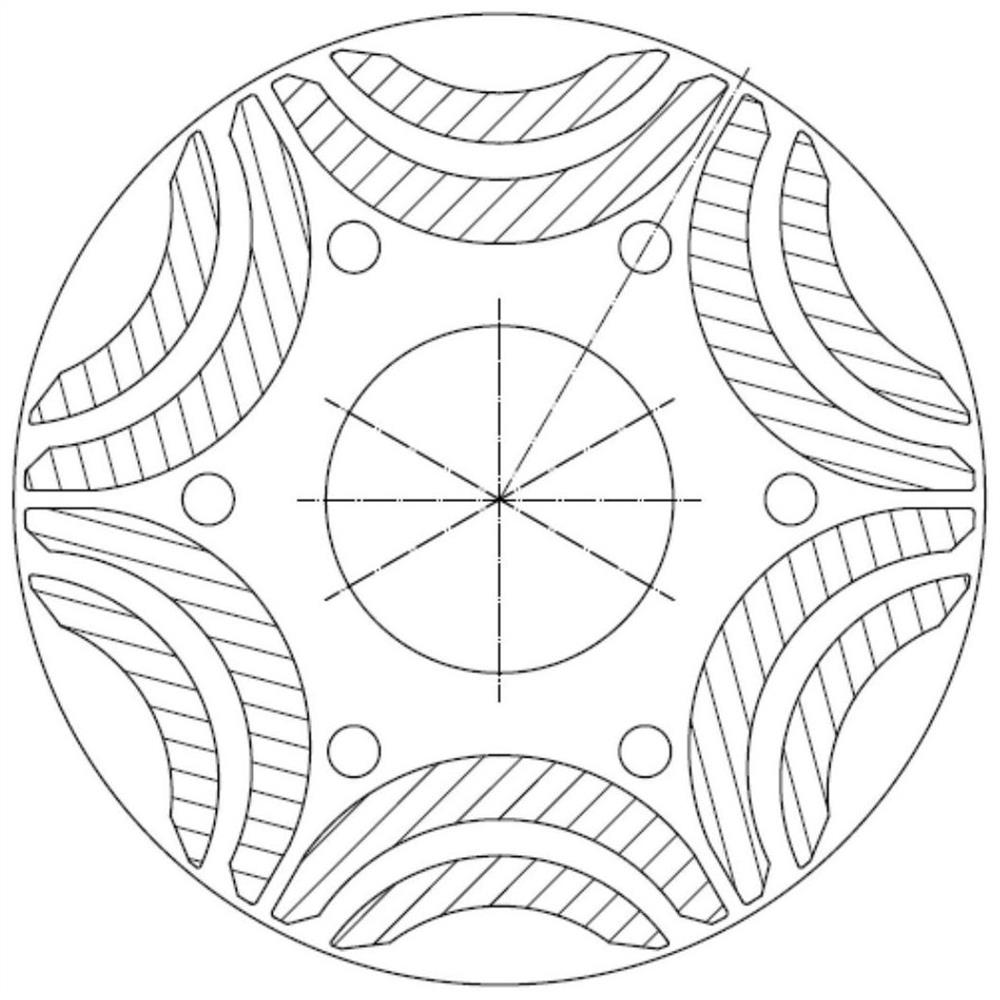
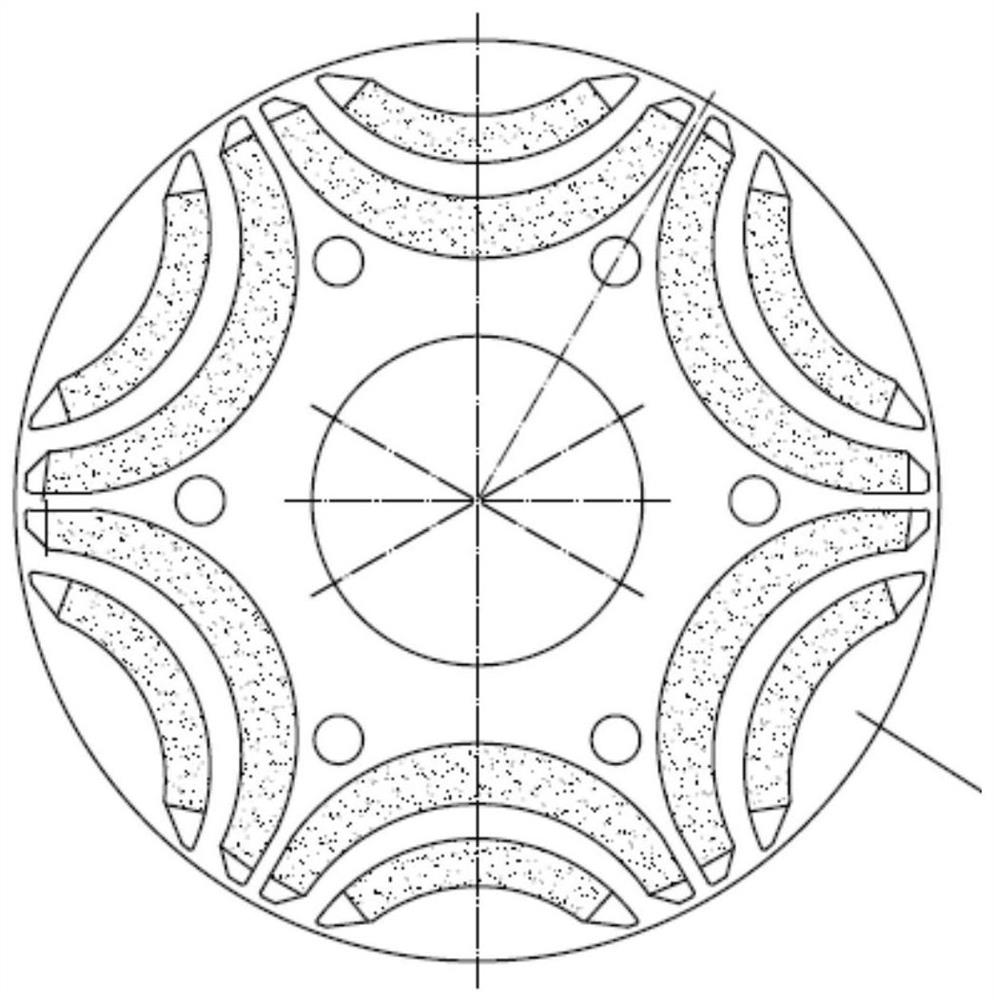
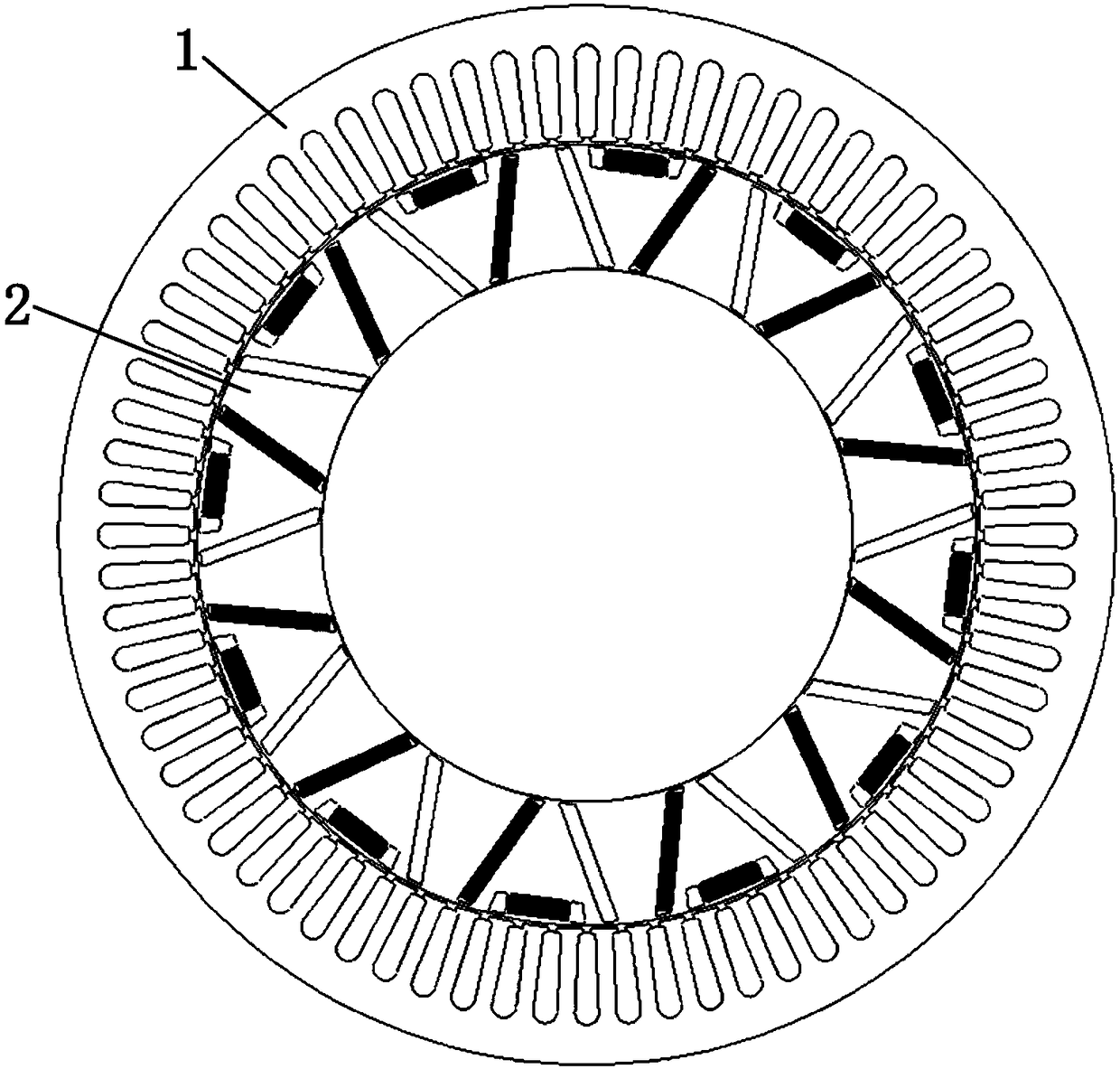
The invention discloses a built-in magnetic barrier type magnetic field enhanced permanent magnet brushless motor, comprising a stator and a rotor coaxially sleeved inside the stator. The rotor is evenly embedded with a plurality of pairs of permanent magnetic steels along the circumference, and each pair of the permanent magnetic steels are composed of two blocks of neodymium iron boron permanent steels of the same rectangular structure and placed in a V manner. The V-shaped opening faces an air gap and the adjacent two pairs of permanent magnetic steels are arranged symmetrically on the two sides of a cross axis; the inner part of the rotor between adjacent two pairs of permanent magnetic steels is provided with a first group of arc shaped built-in magnetic barriers whose arc openings face the air gap; a second group of arc shaped built-in magnetic barriers and a third group of arc shaped built-in magnetic barriers whose arc openings face the air gap and whose structures are identical and are symmetrically arranged around a straight axis are arranged between the two neodymium iron boron permanent steels of each pair of the permanent magnetic steels. Each group of the arc shaped built-in magnetic barriers contains an inner magnetic barrier and an outer magnetic barrier. The adjacent two pairs of permanent magnetic steels alternate for tangential magnetization, and the tangential magnetization directions of two blocks of neodymium iron boron permanent steels in each pair of the permanent magnetic steels are opposite to each other, which improves the driving performance and reliability of the motor.
Owner:SUMEC HARDWARE & TOOLS
Mid-series type hybrid permanent-magnet adjustable flux motor having passive adjustable flux magnetic barrier
ActiveCN108110980AIncrease working pointImprove power densityMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machine detailsMagnetic barrierElectric machine
The invention discloses a mid-series type hybrid permanent-magnet adjustable flux motor having passive adjustable flux magnetic barriers, and belongs to the field of permanent-magnet motors, and solves the problem that advantages of serial and parallel hybrid permanent-magnet adjustable flux motors cannot be combined. The mid-series type hybrid permanent-magnet adjustable flux motor comprises a stator iron core, an armature winding, a rotor iron core and a rotating shaft; the rotor iron core is fixed on the rotating shaft, and is positioned inside the stator iron core; the armature winding isarranged on the stator iron core; the mid-series type hybrid permanent-magnet adjustable flux motor further comprises low-coercivity permanent-magnet slots, low-coercivity permanent magnets, radial slots, high-coercivity permanent magnets and the passive adjustable flux magnetic barriers; the low-coercivity permanent-magnet slots and the radial slots are distributed on the rotor iron core alternately and uniformly along a circumferential direction; the low-coercivity permanent-magnet slots and the radial slots are penetrated through the whole motor along an axial direction; the low-coercivitypermanent magnets are installed in the low-coercivity permanent-magnet slots; and the high-coercivity permanent magnets and the passive adjustable flux magnetic barriers are jointly installed in the radial slots.
Owner:黑龙江省工研院资产经营管理有限公司
Modular vernier permanent magnetic linear motor based on Halbach permanent magnetic structure
ActiveCN106411096AReduce thrust fluctuationImprove the unbalanced three-phase potential problemPropulsion systemsMagnetic barrierPhase difference
The invention discloses a modular vernier permanent magnetic linear motor based on a Halbach permanent magnetic structure. The modular vernier permanent magnetic linear motor comprises 3k mover modules and one stator, there are air gaps between the two, the stator comprises a permanent magnet which is provided with a stator core, is surface-mounted to the stator core and has a Halbach array structure, armature windings are arranged in grooves of the mover modules, positions of each phase of the armature windings in the different mover modules are different, positions of axles of the same phase of the armature windings in each module correspondingly relative to the stator permanent magnet are maintained consistent, each module can work as an individual complete vernier permanent magnetic linear motor, two adjacent mover modules are connected by use of a magnetic barrier made of a non-magnetic material, the different mover modules respectively generate push forces with certain phase differences with the stator, through modular combination of movers and variation of positions of the windings in the different modules, each phase of the windings is enabled to have a completely symmetric structure in an overall view, and thus the effect of offsetting and weakening thrust fluctuations is realized.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Permanent magnet assisted synchronous reluctance motor rotor which can be used in high-speed situation
ActiveCN104901452ASafe high-speed operation capabilityMaximize output capacityMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machine detailsMagnetic barrierSynchronous reluctance motor
The present invention discloses a permanent magnet assisted synchronous reluctance motor rotor which can be used in a high-speed situation. The permanent magnet assisted synchronous reluctance motor rotor comprises a rotor core, magnetic barriers distributed on the rotor core and magnetic steels arranged in the magnetic barriers. Four layers of ship-shaped magnetic barriers are distributed under each pole of the rotor core, and each layer of magnetic barriers is formed by the connection closing of a straight line part which is in the middle and is perpendicular to a d axis direction and oblique straight line parts which are at two ends and are in an alpha angle direction with the d axis. According to the permanent magnet assisted synchronous reluctance motor rotor, the optimal design of the motor rotor is carried out, and thus a motor has the advantages of high efficiency, high torque density, high power factor, strong anti-demagnetization ability and convenient manufacture.
Owner:SHANGHAI GIE EM
Spindle synchronous motor with wide speed regulation range for lathe
InactiveCN104410234ASimple designIncrease armature reactionMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsMagnetic barrierSynchronous motor
The invention provides a spindle synchronous motor with a wide speed regulation range for a lathe. The spindle synchronous motor comprises a stator core, three-phase windings in stator grooves, a rotor core and permanent magnets which are embedded into the rotor core and are in special structures, wherein the stator core and the rotor core are formed by laminating silicon steel sheets and fixed by rivets; conductors in the stator grooves are the three-phase symmetrical windings; the permanent magnets are in layered and segmented structures; slender and nonuniform-width hollow holes are reserved into a rotor structure to form double-layer magnetic barriers; the hollow holes are symmetrically distributed on the two sides, close to the bottom of a rotating shaft, of each concave permanent magnet, and transversely arranged into quadrature axis magnetic circuits; a chamfered angle close to a stator side is larger; and a chamfered angle close to a rotating shaft side is smaller. According to the spindle synchronous motor, a new method of selecting the number of the stator conductors is provided, the magnetic potential of an armature reaction is improved by a novel rotor structure, the main magnetic flux is reduced, the output characteristic of the motor is optimized, and effects of improving the weak magnetism and increasing the maximum rotating speed are achieved, so that the speed regulation range of the spindle synchronous motor is greatly widened.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Direct-axis magnetic field enhanced type wide-range speed control permanent magnet brushless motor for electric automobile
ActiveCN104253499AMeet high torque performance requirementsImprove driving abilityMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric machinesMagnetic barrierBrushless motors
The invention discloses a direct-axis magnetic field enhanced type wide-range speed control permanent magnet brushless motor for an electric automobile. A magnetic barrier fills each slot of a rotor, and the magnetic barriers are symmetrical relative to a centerline, i.e., a quadrature axis, of slot parts of the rotor; four sections of arc-shaped permanent magnet steel are fixedly embedded on each tooth part of the rotor, the four sections of arc-shaped permanent magnet steel are divided into an inner layer and an outer layer, two sections are arranged on each layer, the two sections of permanent magnet steel on each layer are the same in structure and are symmetrical relative to a centerline, i.e., a direct axis of the tooth parts of the rotor, the two sections of permanent magnet steel on the same layer do not run through each other and are not connected with each other, and an arc-shaped magnetic bridge is formed between the two sections of permanent magnet steel; a circle center of each section of permanent magnet steel is located on the diameter of the rotor; the direct-axis inductance of the motor is larger than the quadrature-axis inductance, so that the motor can adopt a control method with zero direct-axis current and can also adopt a direct-axis magnetic field enhanced control method during low-speed operation or startup, and can adopt a coordinated control method of direct-axis magnetic field enhancement and slight direct-axis magnetic field weakening during high-speed operation, and the speed control range is wider.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
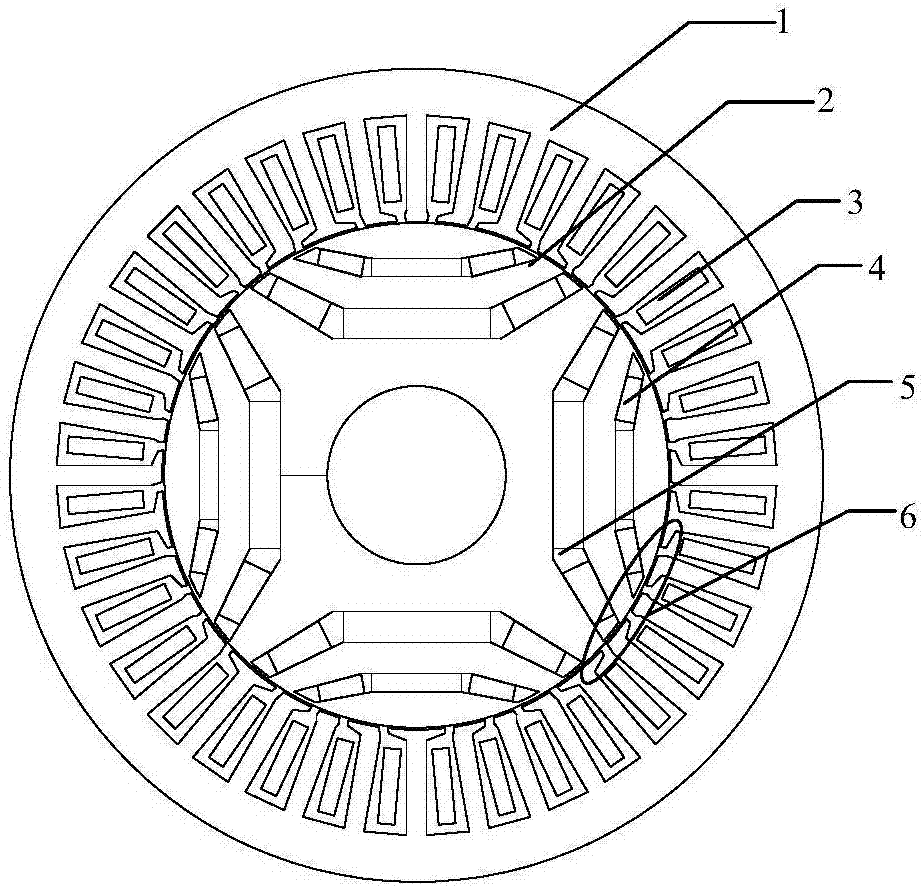
Synchronous reluctance motor rotor structure, motor and manufacturing method of rotor structure
ActiveCN110138117AReduced torque rippleReduce vibration and noiseMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous motorsMagnetic barrierSynchronous reluctance motor
The invention provides a synchronous reluctance motor rotor structure, a motor and a manufacturing method of the rotor structure. The synchronous reluctance motor rotor structure comprises a rotor core which is provided with multiple slit slots, two ends of each of the slit slots are provided with two filling grooves to form a magnetic barrier layer, a first end of each of the filling grooves is adjacent to a slit slot, a second end of each of the filling grooves extends in the radial direction of the rotor core, and the outer peripheral surface of the rotor core is provided with a notch communicating with an end of the second end each of the filling grooves. By setting notches and bevels at the ends of the filling grooves, the reluctance torque of the motor can be increased, the torque ripples generated by a rotor and a stator tooth space can be weakened by each other, the purpose of reducing the torque ripple of the motor is achieved, the vibration noise of the motor is reduced, theefficiency of the motor with the rotor structure is improved, and the starting ability of the motor is improved.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
Motor
ActiveUS20150171683A1Reduced strengthSynchronous machine detailsMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic barrierMagnetic flux
A motor including a stator, and a rotor adapted to rotate, wherein the stator includes a stator body, a plurality of teeth protruding from the stator body toward the rotor, and at least one stator magnetic barrier provided to each of the teeth to interrupt magnetic flux. A magnetic field produced in a direction parallel to the outer circumferential surface of the rotor is attenuated, and therefore demagnetization of permanent magnets included in the rotor may be prevented.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multilayer segmented built-in permanent magnet synchronous motor used for electric automobile driving
InactiveCN106329774AReduce harmonic contentImprove weak magnetic propertiesMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric machinesMagnetic barrierCar driving
The invention discloses a multilayer segmented built-in permanent magnet synchronous motor used for electric automobile driving. A built-in rotor part comprises a rotor iron core, a three-layer segmented neodymium-iron-boron magnetic steel and a magnetic barrier. By optimizing a pole-arc coefficient of every layer of a permanent magnet, the harmonic content of the gap flux density of the built-in permanent magnet synchronous motor is minimized, and therefore the torque ripple and the iron core loss of the built-in permanent magnet synchronous motor are reduced. By adopting the multi-layer mechanism, the salient pole rate of the motor reaches more than three, and the flux weakening capability of the motor is improved. Each permanent magnet is divided into four segments, and therefore the eddy current loss of the permanent magnet is reduced, the heating of the permanent magnet is reduced, and an anti-irreversible demagnetization capability is improved, and the reliability of the motor is improved. Compared with the prior art, the torque ripple and the iron core loss of the permanent magnet synchronous motor, and the permanent magnet eddy current loss are reduced, and the noises of the operation of the motor are reduced, and the operation efficiency and the reliability of the electric automobile driving motor are improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
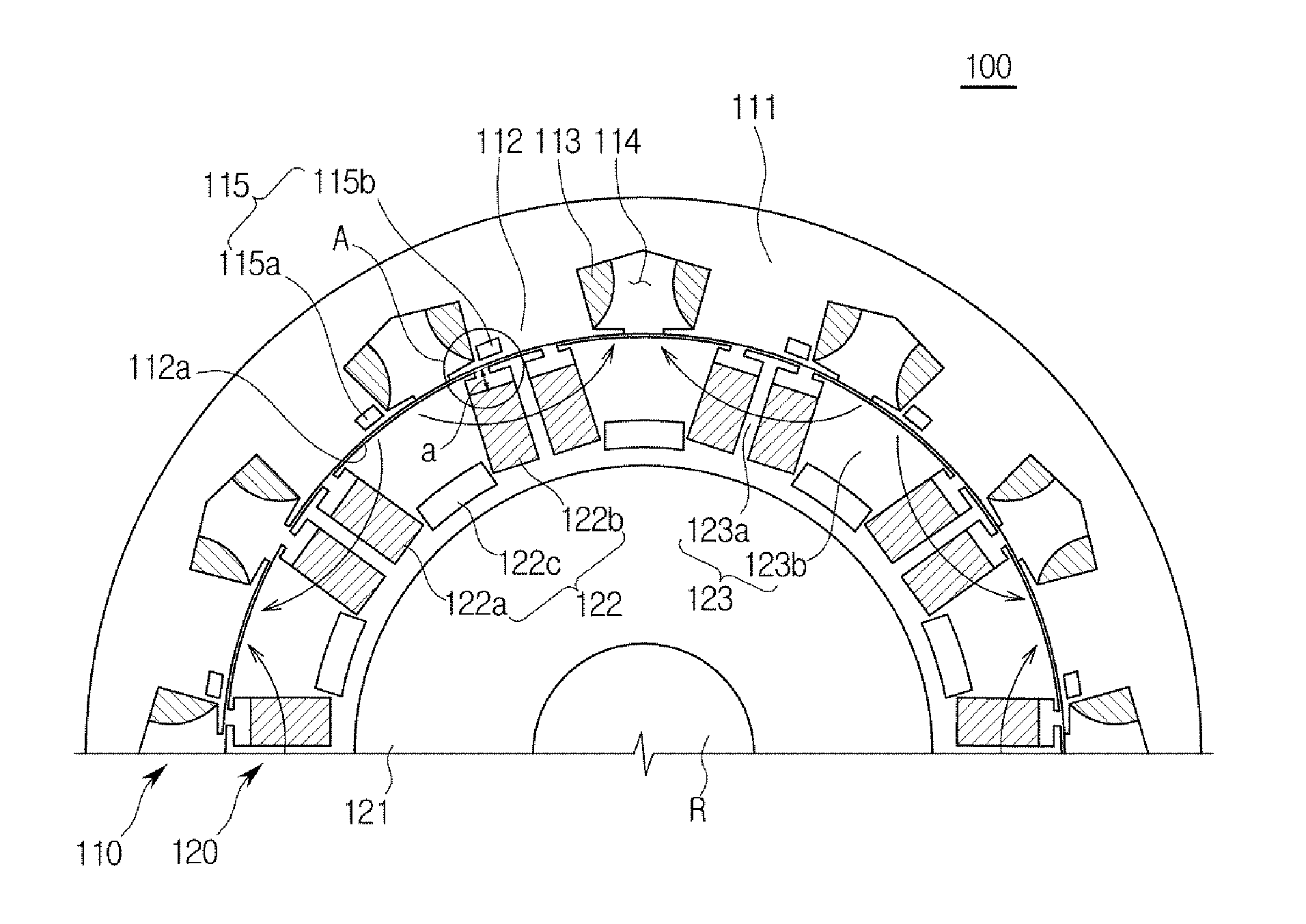
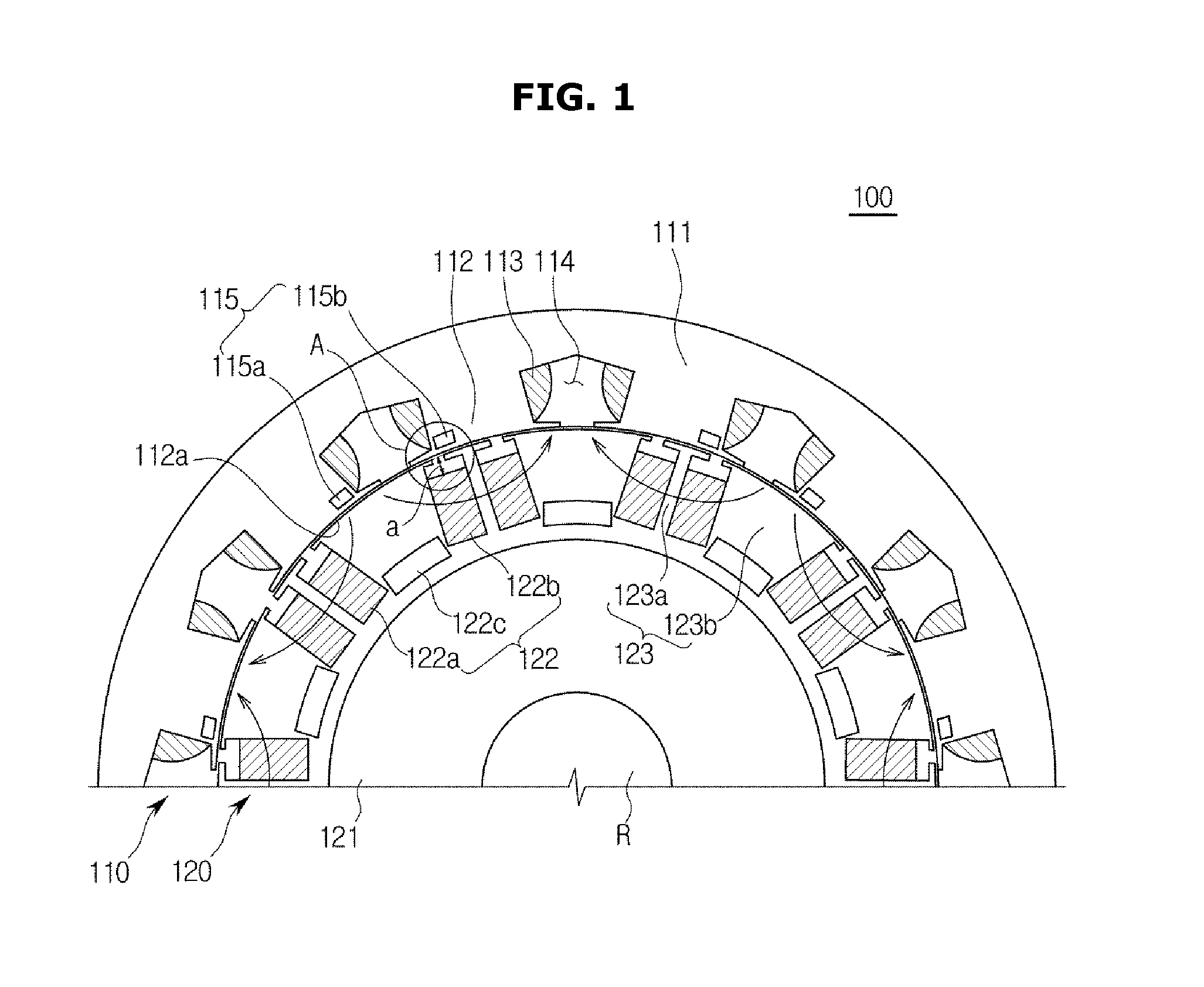
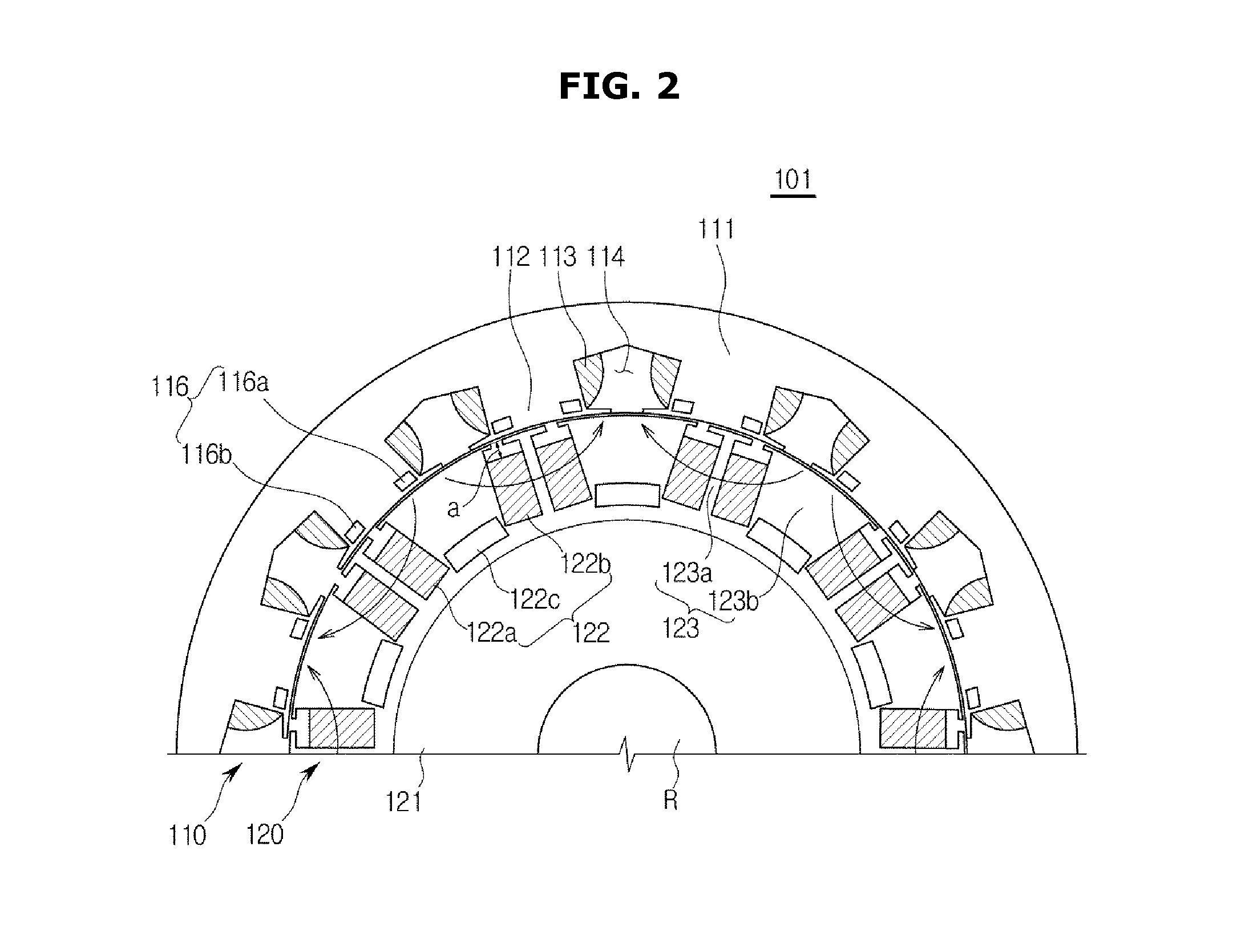
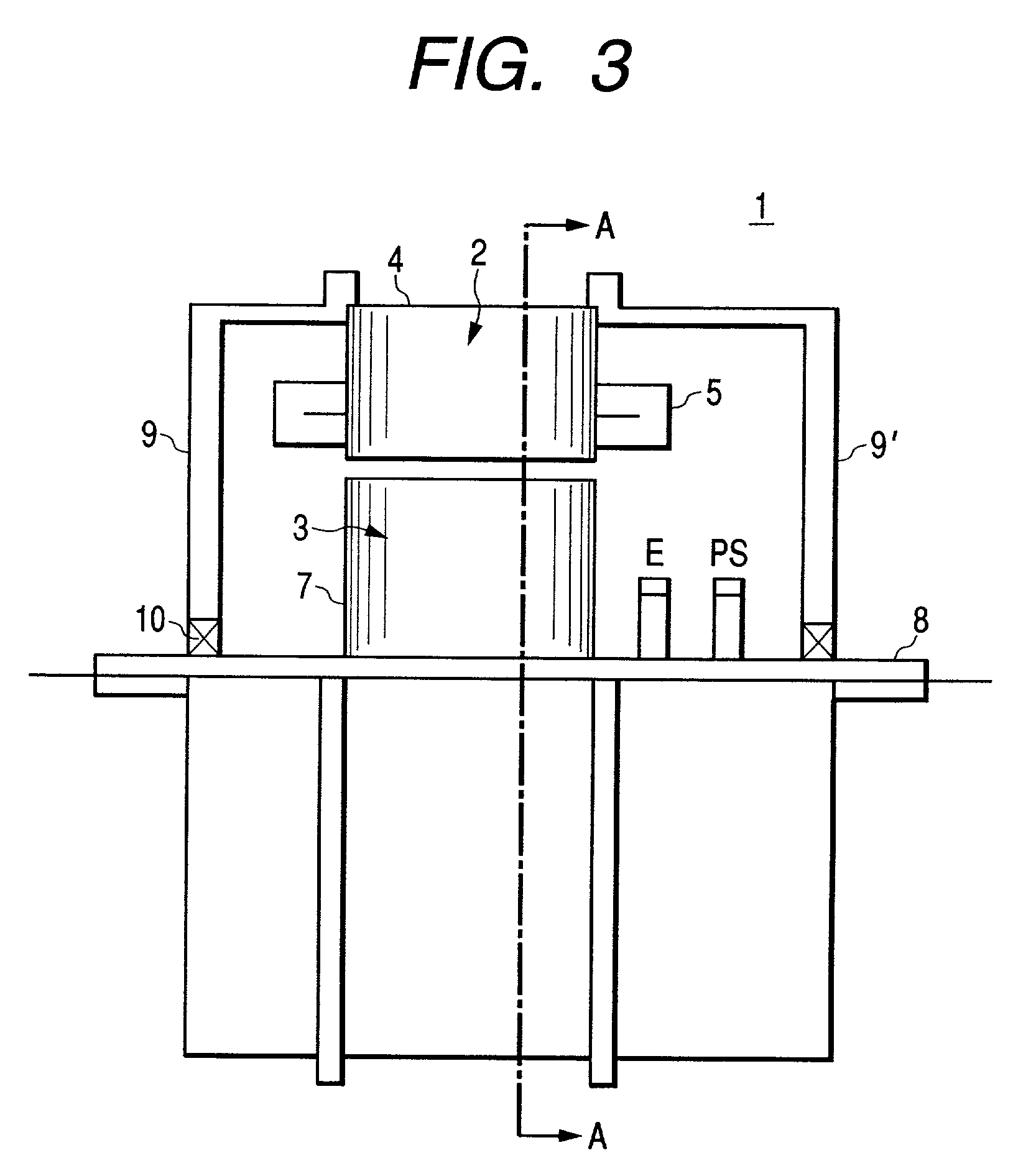
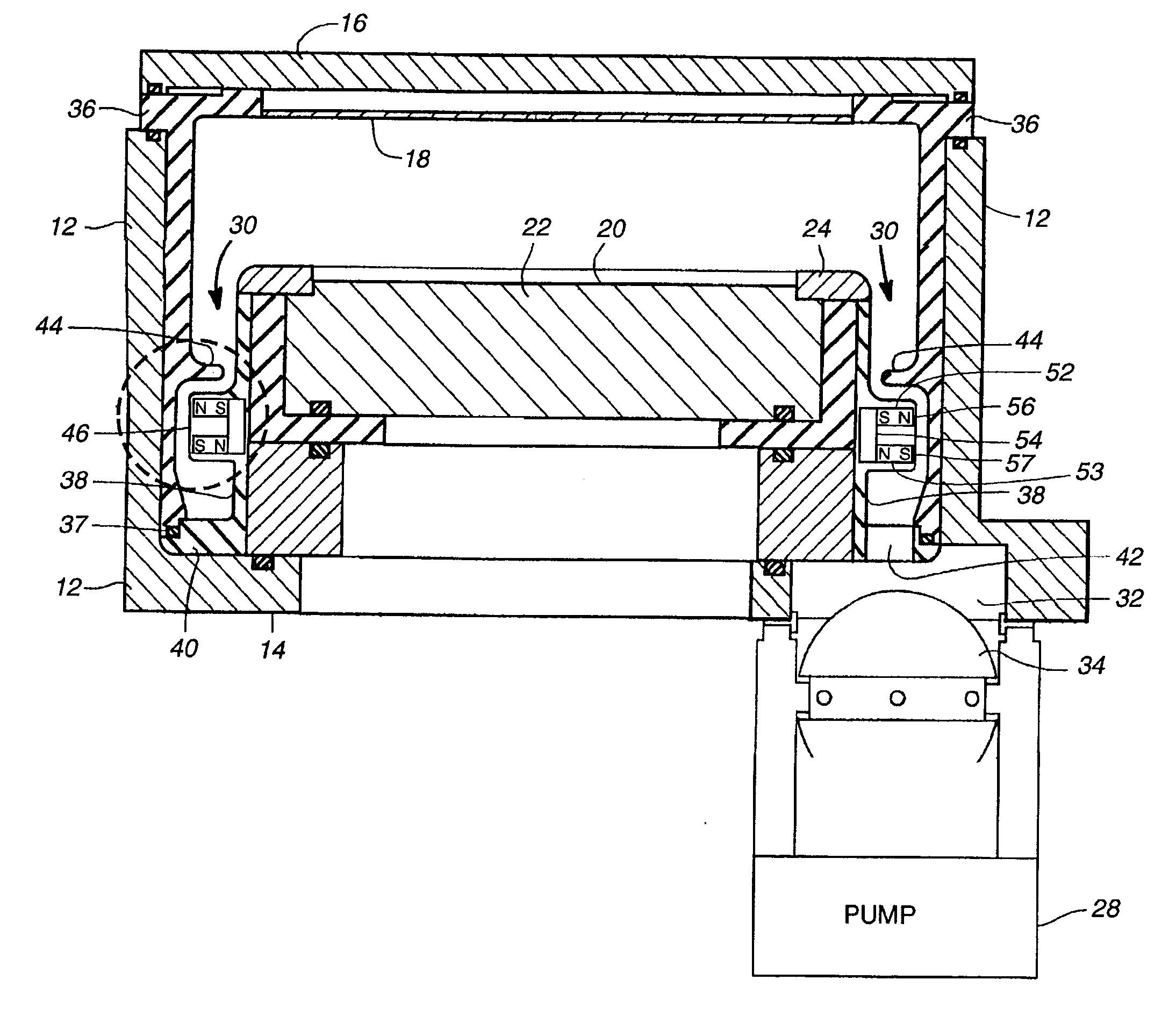
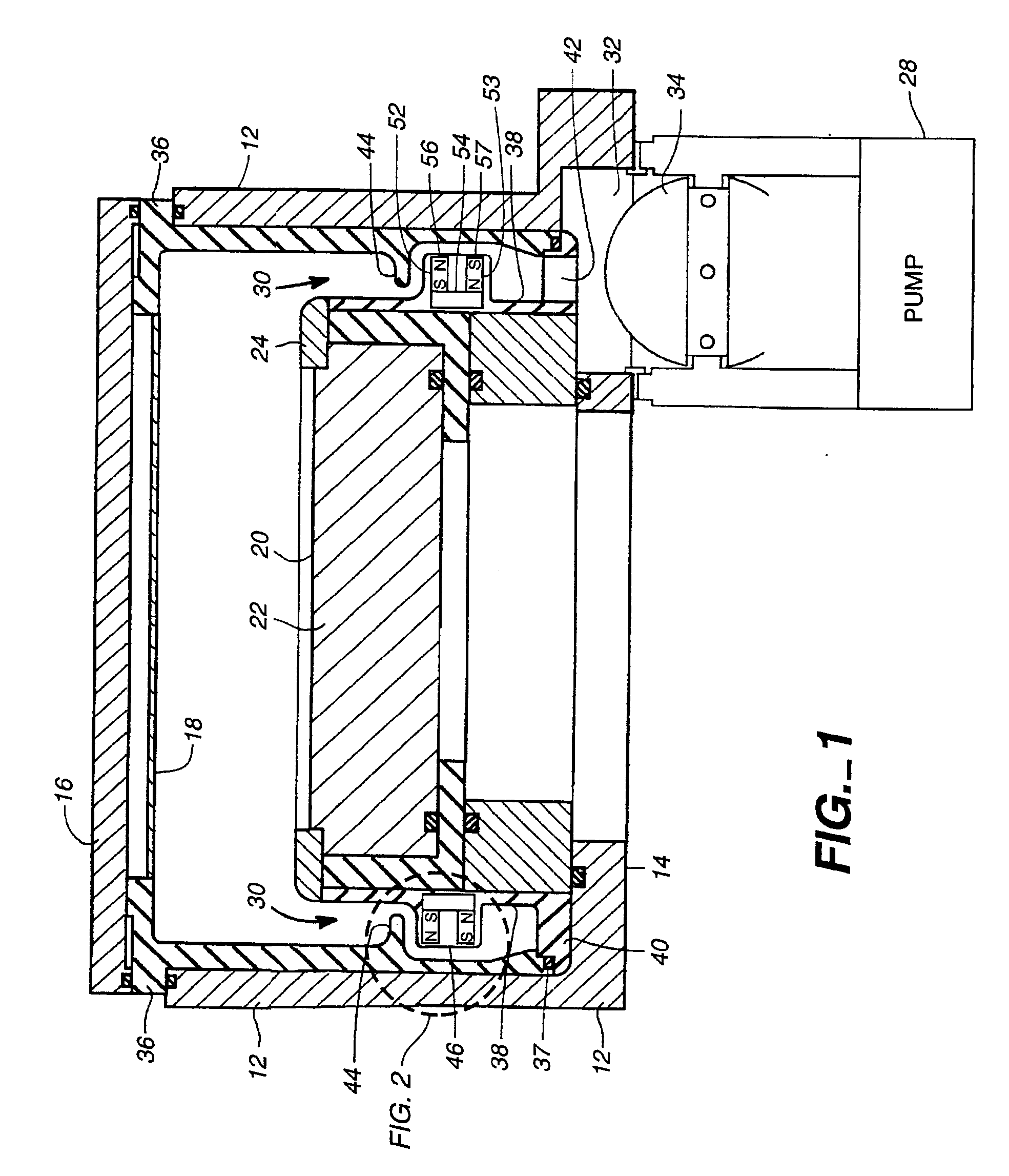
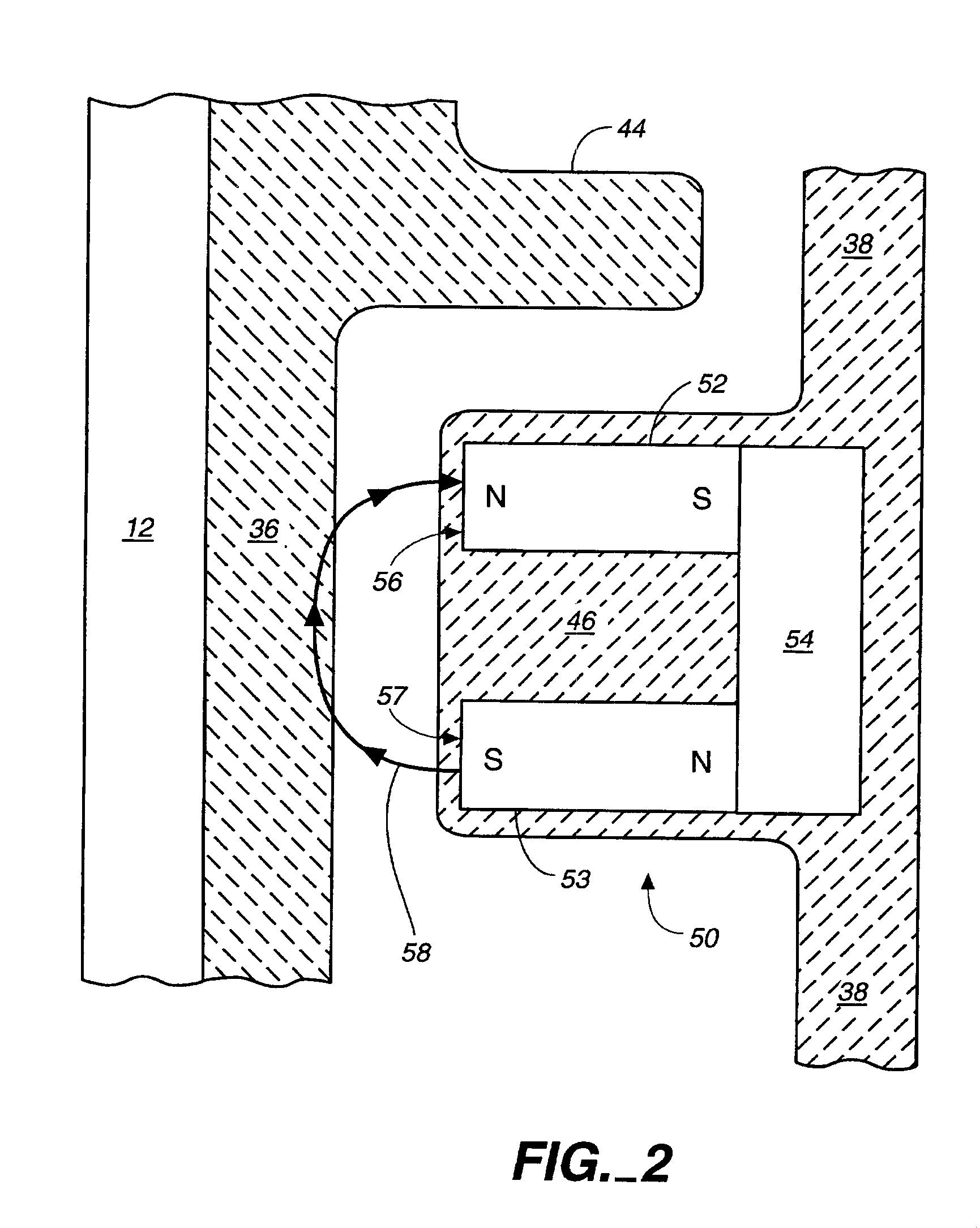
Rotary machine and electrical vehicle using the same
InactiveUS20010026108A1Raise the ratioProduced torque is increasedSynchronous generatorsSpeed controllerMagnetic barrierMagnetic poles
The rotary machine 1 is composed of the rotor 3 having magnetic poles and the stator 4 having the stator yoke portion 41 constituting the iron core tooth portion 42 wound by the stator winding 5 and the flux flow path of the magnetic poles. The rotor 3 is composed of a metallic material having ferromagnetic parts and non-magnetic parts as a member and has a magnetic barrier area composed of the slit portion 72 for blocking the bypath magnetic path in the periphery of the rotor and the non-magnetic parts 75. The rotary machine that produced torque can be increased sufficiently and the mechanical strength during high-speed running is improved and an electrical vehicle using it.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
Cylindrical permanent-magnet linear motor with modular C-shaped stator cores
ActiveCN102938603AReduce positioning forceImprove thrust performancePropulsion systemsIsolation effectFault tolerance
The invention discloses a cylindrical permanent-magnet linear motor with modular C-shaped stator cores, which is used in a small linear propulsion system. An inner stator ring is composed of armature windings, a magnetic barrier and two C-shaped cores, wherein the magnetic barrier is made of a non-magnetic material; the two C-shaped cores are made of a magnetic material and are the same in structure; the magnetic barrier is fixedly sandwiched between the two C-shaped cores; the two C-shaped cores are arranged in the axial direction; the distance between each C-shaped core and an outer rotor ring is the same; each C-shaped core is provided with a C-shaped groove; the opening of the C-shaped groove faces the outer rotor ring; one armature winding is embedded in each C-shaped groove; the axial length of the two C-shaped cores is one rotor polar pitch; and the axial width of the magnetic barrier is 1 / 4 of one rotor polar pitch. Thus, the two modular C-shaped core structures and a rotor generate positioning forces which are opposite in phase, thus realizing the counteraction of the positioning forces; the winds of the two phases achieve a physical circuit isolation effect and a temperature isolation effect, thereby being capable of realizing operation even in the case of a failure; and the magnetic barrier physically isolates the two modular C-shaped cores and decouples the magnetic circuit, thereby improving the operation fault tolerance of the motor.
Owner:HUAWEI TEHCHNOLOGIES CO LTD
Magnetism increasing type internal tangential adjustable flux motor
InactiveCN106208450AWide speed rangeNot easy to saturateMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsMagnetic barrierMagnetic poles
The invention discloses a magnetism increasing type internal tangential adjustable flux motor, belongs to the field of permanent magnet motors and solves a problem that uncontrollable demagnetization of an aluminum nickel cobalt permanent magnet is easy to occur when a flux weakening type adjustable flux motor runs at high load. The magnetism increasing type internal tangential adjustable flux motor comprises a stator core, an armature winding, a rotor core, a rotating shaft, tangential permanent magnet slots, p neodymium iron boron magnetic poles, p aluminum nickel cobalt magnetic poles and p quadrature axis magnetism barriers, wherein p is an even number; the p tangential permanent magnet slots and the p quadrature axis magnetism barriers are uniformly arranged on the rotor core along the circumferential direction of the motor, and each quadrature axis magnetism barrier is of a mirror symmetry structure centering on one tangential permanent magnet slot; the tangential permanent magnet slots and the quadrature axis magnetism barriers axially penetrate through the whole rotor core; one neodymium iron boron magnetic pole and one aluminum nickel cobalt magnetic pole are both arranged in each tangential permanent magnet slot; each neodymium iron boron magnetic pole is arranged in a position close to the inner circle of a rotor in the tangential permanent magnet slot; and each aluminum nickel cobalt magnetic pole is arranged in a position close to the outer circle of a rotor in the tangential permanent magnet slot.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Rotor structure of self-starting hybrid excitation permanent magnet auxiliary reluctance motor and motor
PendingCN111614181AAvoid feverImprove efficiencySynchronous machine detailsMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic barrierElectrical conductor
The invention provides a rotor structure of a self-starting hybrid excitation permanent magnet auxiliary reluctance motor and the motor. The rotor structure comprises a rotor iron core, a plurality ofmagnetic barrier grooves are formed in the rotor iron core, a permanent magnet is arranged in at least one magnetic barrier groove in the plurality of magnetic barrier grooves, and a non-magnetic conductor is arranged in at least one magnetic barrier groove in the rest of the plurality of magnetic barrier grooves. The permanent magnet auxiliary reluctance motor with the structure has an out-of-step protection function. Due to the fact that the non-magnetic conductor is arranged in the rotor iron core, the non-magnetic conductor has a damping winding effect, when the motor operates synchronously, transient impact currents of the rotor in various abnormal states can be guided to the end of the rotor to be offset and returned to zero, and the effects of avoiding rotor structure heating and magnetic steel demagnetization are achieved. By adopting the rotor structure of the structure, the efficiency and the practicability of the motor are effectively improved.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC +1
Electron beam irradiation method, electron beam irradiation apparatus, and electron beam irradiation apparatus for open-mouthed container
InactiveUS7767987B2Reduce energy lossKeep for a long timePackage sterilisationChemical conversion by chemical reactionMagnetic barrierElectron
There are provided an electron beam application method and an electron beam application device capable of uniformly applying electron beams to an object even if the electron beams have a low energy. For this, electron beams (EB) are applied to a beverage container (30) (object) within a magnetic barrier (MF) formed by combining a plurality of magnetic fields generated in an electron beam application region.
Owner:JAPAN AE POWER SYST
Magnetic barrier for minimizing demagnetization in bi-permanent magnet synchronous machines
ActiveUS8664823B2Low costReduce in quantityMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsMagnetic barrierPermanent magnet synchronous machine
A rotor for a permanent synchronous machine includes a rotor having a plurality of arcuately-shaped cavities formed within a rotor core structure. The plurality of arcuately-shaped cavities substantially concentrically layered with respect to an outer cylindrical wall of the rotor core structure. A plurality of permanent magnets is inserted within the plurality of arcuately-shaped cavities. Each cavity layer retains a permanent magnet of a first magnetic field strength disposed in end sections and a permanent magnet of a second magnetic field strength in a center section of each cavity layer. Each respective cavity includes an air barrier formed between the magnets having different magnetic field strengths. The air barrier generates a reluctance within an air barrier gap for directing a flow of flux generated by each third permanent magnet in a preceding layer in a direction toward each third permanent magnet in a succeeding layer.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Asymmetric permanent magnet auxiliary synchronous reluctance motor and design method for improving torque performance
ActiveCN107979196AImprove performanceNo reduction in average torqueMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsMagnetic barrierSynchronous reluctance motor
The invention discloses an asymmetric permanent magnet auxiliary synchronous reluctance motor and a design method for improving torque performance. A stator includes a plurality of tooth portions arranged in the circumferential direction, a plurality of stator slots, and an armature winding embedded in the slots. The slots are composed of repeating units. Each slot is symmetrical about a centerline. The opening corresponding to each slot is not symmetrical about the centerline. The repeating unit is composed of four stator slots. The openings of the four stator slots are successively deflectedby a specific angle in the clockwise circumferential direction. A rotor includes a rotor core, a plurality of permanent magnets, and groups of magnetic barriers. Each group of magnetic barriers is atwo-layer U-shaped structure. The permanent magnets are placed in the magnetic barrier structures. The asymmetric stator slot opening structure weakens the cogging torque, the reluctance torque rippleand total torque ripple of the permanent magnet synchronous motor. The method of the invention does not cause the reduction of the average torque, and there is no asymmetry of three-phase no-load back-EMF due to the asymmetrical stator slot distribution, thereby improving the overall performance of the motor.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Magnetic barrier for plasma in chamber exhaust
InactiveUS6863835B1Efficient designEffective blockingElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsMagnetic barrierPlasma confinement
A plasma chamber apparatus and method employing a magnet system to block the plasma within the chamber interior from reaching the exhaust pump. An exhaust channel between the chamber interior and the pump includes a magnet and at least one deflector that creates turbulence in the flow of exhaust gases. The magnetic field and the turbulence produced by the deflector both increase the rate of recombination of charged particles in the gases, thereby reducing the concentration of charged particles sufficiently to quench the plasma downstream of the magnet and deflector, thereby preventing the plasma body within the chamber from reaching the exhaust pump. The plasma confinement effect of the magnetic field permits the use of a wider and / or less sinuous exhaust channel than would be required to block the plasma without the magnetic field. Therefore, the pressure drop across the exhaust channel can be reduced in comparison with prior art designs that rely entirely on the sinuousness of the exhaust channel to block the plasma. Alternatively, if the magnetic field is strong enough, the magnetic field alone can block the plasma from reaching the exhaust pump without the need for any deflector in the exhaust channel.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Permanent magnet assisted bearingless synchronous reluctance motor
PendingCN106533103AIncreased torque densityEasy field weakening controlMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machine detailsMagnetic barrierSynchronous reluctance motor
The invention discloses a permanent magnet assisted bearingless synchronous reluctance motor in the field of motor manufacturing. Four groups of magnetic barrier bodies are uniformly arranged inside a rotor along the peripheral direction; each group of magnetic barrier bodies consists of circular arc-shaped inner magnetic barriers and circular arc-shaped outer magnetic barriers which are arranged at intervals along the radial direction, a permanent magnet mounting groove is formed in the middle section of each inner magnetic barrier and the middle section of each outer magnetic barrier respectively, and a permanent magnet is embedded in each permanent magnet mounting groove; the inner magnetic barriers, the outer magnetic barriers and the permanent magnets are symmetrically distributed along the d axis of the motor; a torque winding is wound on the outer layer of a stator, and a suspension force winding is wound on the inner layer of the stator; the magnetizing directions of the permanent magnets in two adjacent groups of magnetic barrier bodies are opposite, the magnetizing directions of the permanent magnets in the same group of magnetic barrier bodies are the same, the end, close to an air gap, of each permanent magnet is N pole, and the end, close to a rotating shaft, of each permanent magnet is S pole; the magnetic barriers are added onto a direct-axis magnetic circuit of the rotor, and meanwhile layered rectangular permanent magnet structures are adopted on the direct-axis magnetic circuit of the rotor, so that the direct-axis inductance of the motor is greater than the quadrature-axis inductance, and the torque density of the motor is increased.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Axially parallel hybrid rotor motor
InactiveCN107579636AIncreased torque densityIncrease profitMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsMagnetic barrierElectric machine
The invention discloses an axially parallel hybrid rotor motor, which comprises a stator (1), a permanent magnetic rotor (2) and a reluctance rotor (3). The permanent magnetic rotor (2) and the reluctance rotor (3) are characterized in that the two rotors are in an axially parallel relation spatially and are coaxially installed, and angle deviation exists between axial lines in straight axes of the two rotors. The stator (1) is arranged outside the permanent magnetic rotor (2) and the reluctance rotor (3), and comprises armature core teeth (1.1), a stator yoke (1.2) and an armature winding (4)arranged on the armature core teeth (1.1). The permanent magnetic rotor (2) comprises surface-mounted NbFeB permanent magnets (2.1) and a rotor core back yoke (2.2). The reluctance rotor (3) is of amulti-layer magnetic barrier structure, and comprises a rotor core (3.1), an air groove (3.2) and magnetic conductive bridges (3.3). The axially parallel hybrid rotor motor can solve the vulnerabilityof low utilization rate of permanent-magnet torque component and reluctance torque component of a traditional built-in permanent magnet motor, and realizes the effect that permanent-magnet torque component and reluctance torque component reach the maximum at the same inner power factor angle by means of straight axis deviation of the two rotors, so as to increase torque density; and the permanentmagnetic rotor is convenient in installation and high in mechanical strength, thereby being conducive to high-speed operation.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Multiphase direct-current uncoupling integrated inductor
InactiveCN103489569AReduce volumeReduce weightTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsInductance with magnetic coreMagnetic barrierInductor
The invention relates to a multiphase direct-current uncoupling integrated inductor which comprises an iron core, inductive windings and magnetic barriers. The iron core of a vertical structure is formed by laminating laminations. The n-phase inductive windings are laid on n iron core columns on the two sides of the iron core respectively. The n magnetic barriers are arranged in the vertical structure of the iron core. The n magnetic barriers are located over the n-phase inductive windings. Anti-saturation air gaps in the iron core are used as the magnetic barriers at the same time, the numerical values of the magnetic barriers are reasonably selected, magnetic flux linkages generated by the inductive windings are separated, and the uncoupling between a plurality of inductor bodies of the same iron core is achieved. The problems that according to the independent inductor bodies, when each inductor body is wound by one independent magnetic core, the number of the magnetic cores is large, and the size is larger are solved. Due to the adoption of the multiphase direct-current uncoupling integrated inductor, the size of the magnetic core is reduced, the size and the weight of the inductor are reduced, meanwhile, the cost of the inductor is greatly reduced, and the more the number of phases of the uncoupling direct-current integrated inductor is, the more obvious the benefits are.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Low frequency strong magnetic field shield material
InactiveCN103171184AImprove the level ofImprove the ability to resist low-frequency strong magnetic field interferenceMagnetic/electric field screeningMetal layered productsMagnetic barrierFerromagnetism
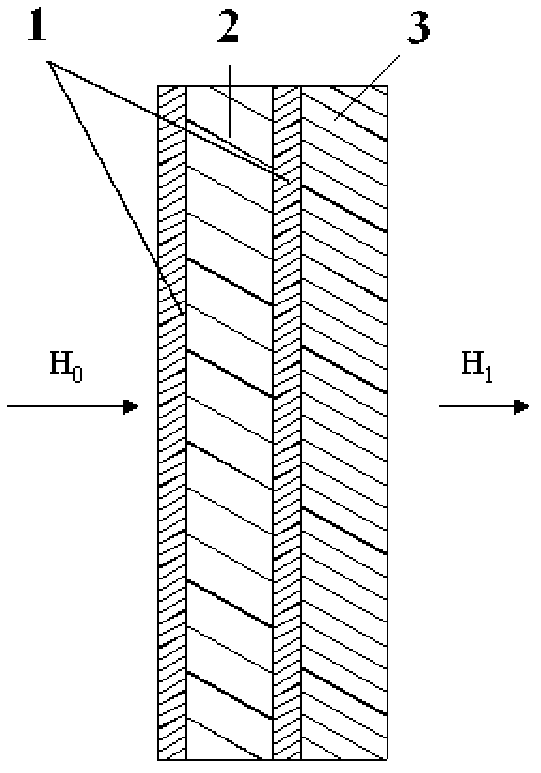
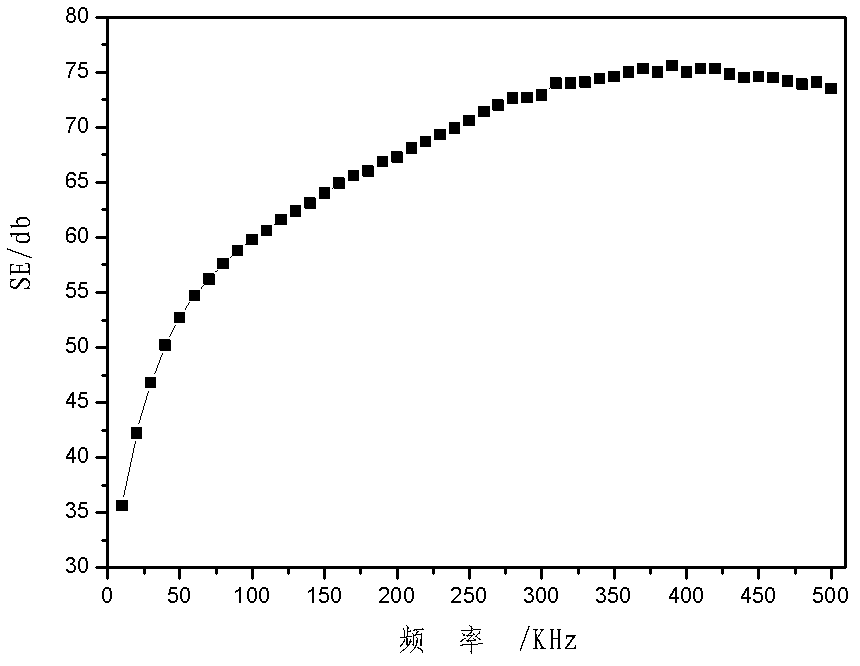
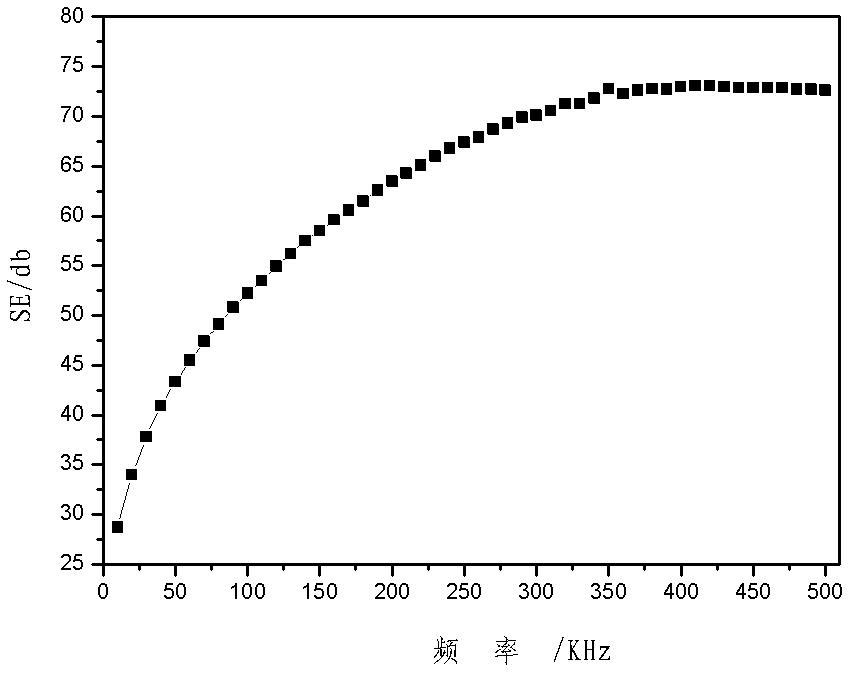
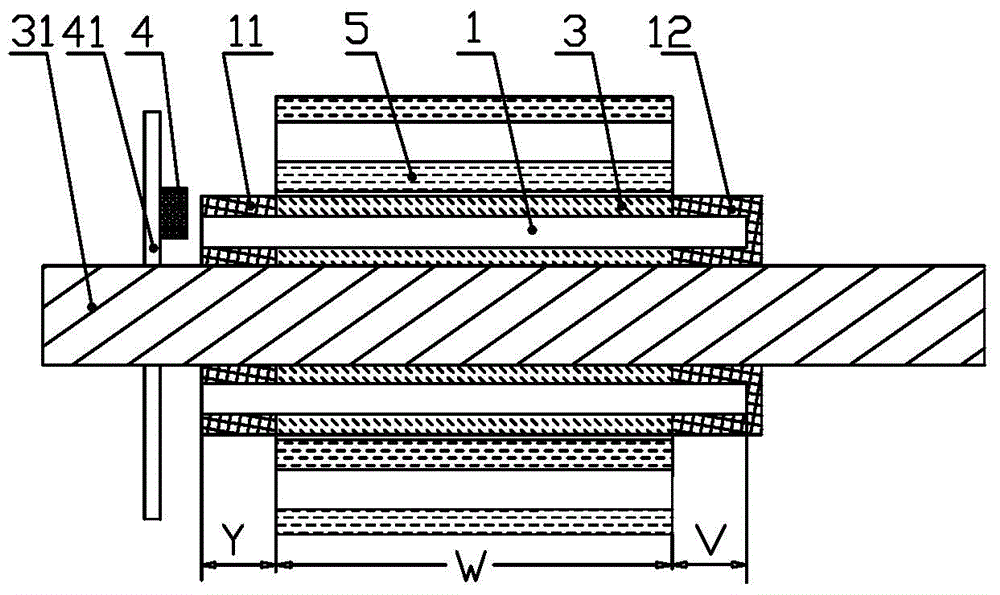
The invention relates to a low frequency strong magnetic field shield material, which is composed of a single layer or multiple layers high conductivity material and a ferromagnetism material. The shield material is combined by the high conductivity material and the ferromagnetism material according to different orders, layers and thicknesses. The ferromagnetism material is performed with heat processing during the process for preparing the shield material. Considering the easy generation of magnetic saturation phenomenon of high magnetic permeability ferromagnetism material under strong magnetic field environment, a highly resistance magnetic saturation material is selected to reduce the strong magnetic field, then the high magnetic permeability material is employed to shield attenuated magnetic field, The high conductivity material is employed as a magnetic barrier layer between the highly resistance magnetic saturation material and the high magnetic permeability material layer, and the low frequency strong magnetic field shield material can partially shield the alternating magnetic field. According to the invention, the thickness of the shield material is about 0.2mm, the shield efficiency of the low frequency strong magnetic field at 10 kHz-500 kHz can reach 40 dB, and a technical problem that how to increase the shield efficiency of the low frequency strong magnetic field under the condition that the shield material allowanced thickness is limited can be solved.
Owner:GENERAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR NONFERROUS METALS BEIJNG
Magnetic circuit structure of brushless DC motor and embedded rotor of permanent magnet of magnetic circuit structure
InactiveCN104578663AImprove riding performanceImprove reliabilityMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic barrierMagnetic effect
The invention relates to a magnetic circuit structure of a brushless DC motor and an embedded rotor of a permanent magnet of the magnetic circuit structure and relates to a motor which is provided with a non-mechanical reversing device and a magnetic circuit part of the motor, in particular to a brushless DC motor which applies a magnetic effect device and a magnetic circuit part structure which is provided with the embedded rotor of the permanent magnet. The magnetic circuit structure comprises a stator iron core, a rotor iron core, a permanent magnet and a magneto-dependent sensor, wherein the length of the permanent magnet is greater than that of the rotor iron core, the magneto-dependent sensor is arranged in a position which is close to an extension part of the rotor iron core and far from magnetic field interference of the stator, magnetic barriers and positioning bumps for fixing the permanent magnet are arranged at two ends of a permanent magnet groove, and the magneto-dependent sensor induces the end magnetic field of the permanent magnet rather than a combined magnetic field of the rotor iron core and the permanent magnet, so that hall signal jitter caused by an irregular and clear boundary between two magnetic poles on the surface of the rotor is effectively reduced; according to the improved structure, the magneto-dependent sensor is far from influence of the stator magnetic field and temperature, so that the operating smoothness and reliability of motor are further improved.
Owner:HAMMER ELECTRIC POWER TOOLS
STT-MRAM storage unit
ActiveCN106783862AMiniaturizationUniform structureSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesMiniaturizationEngineering
The invention discloses an STT-MRAM storage unit. The STT-MRAM storage unit comprises a transistor and an MTJ unit, wherein the transistor is arranged on a substrate, and a drain electrode of the transistor is in drain contact with the MTJ unit through a metal wire; the MTJ unit comprises an inner electrode, and a seed layer, a ferromagnetism pinning layer, a non-magnetic barrier layer, a ferromagnetism free layer and an outer electrode which are wrapped on the periphery of the inner electrode; the metal wire is connected with the inner electrode; the seed layer, the ferromagnetism pinning layer, the non-magnetic barrier layer, the ferromagnetism free layer and the outer electrode are not parallel to a plane where the substrate is respectively; and the seed layer, the ferromagnetism pinning layer, the non-magnetic barrier layer, the ferromagnetism free layer and the outer electrode are arranged at intervals with the metal wire. Through the setting form of the MTJ unit in the STT-MRAM storage unit, the thermal stability factor delta is weakened into linear change along with the square change relation of the original plane structure dimensions, so that the thermal stability factor delta can be compensated by using height, and MTJ miniaturization is facilitated. According to the STT-MRAM storage unit, the space can be effectively utilized, high heat stability is guaranteed, the storage density is improved, various storage modes are provided, and the STT-MRAM storage unit has application prospect for storage devices below 20 nm technology nodes.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Antenna assembly for a vehicle
ActiveUS10511086B1Cross-talk/noise/interference reductionAntenna supports/mountingsMagnetic barrierModem device
An antenna assembly comprising a base, a modem, a top lid and a housing is disclosed herein. The antenna assembly is for a vehicle. The base is composed of an aluminum material. The modem is disposed within the base. The top lid is for the base, and the top lid comprises at least one antenna element disposed on an exterior surface thereof. The housing covers the top lid and base. The top lid and base act as an electro-magnetic barrier for the modem.
Owner:AIRGAIN INC
Permanent magnetism motor with asymmetric rotor
InactiveCN108418321AReduce dosageIncreased torque output capabilityMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsMagnetic barrierPermanent magnet motor
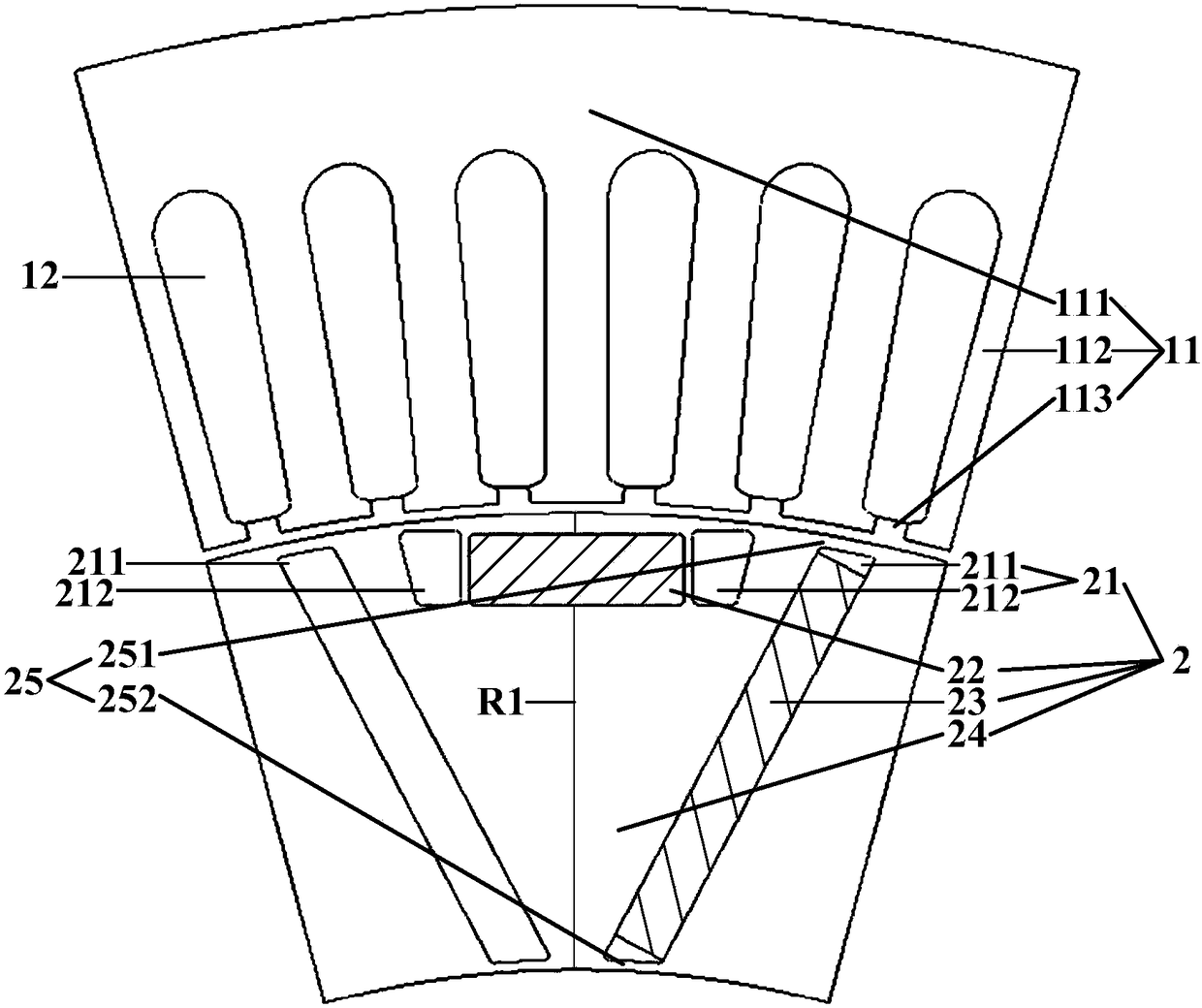
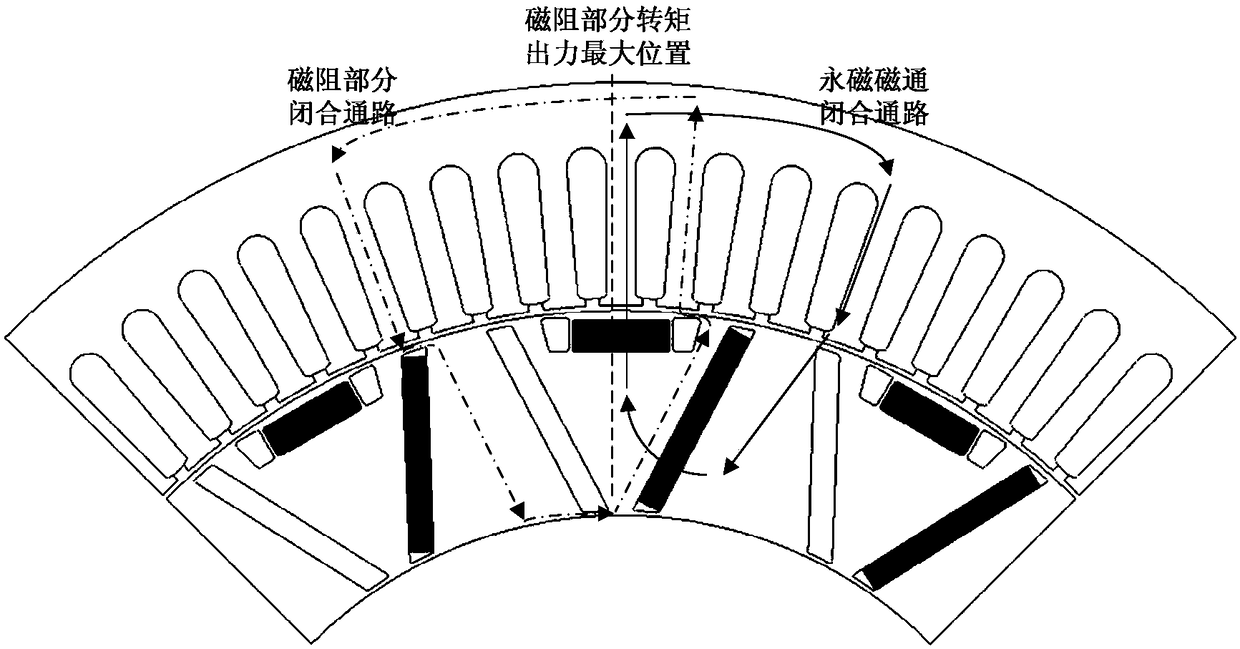
The invention discloses a permanent magnetism motor with an asymmetric rotor. The motor comprises a stator and the rotor which includes permanent magnets arranged in an asymmetric way, the stator is arranged outside the rotor, an air gap is arranged between the stator and the rotor, and the rotor is fixed to a rotating shaft; the stator comprises a stator core and a three-phase armature winding, the stator core comprise a stator yoke and stator teeth which extend from the stator yoke to the rotor, and stator grooves are formed between the adjacent stator teeth; the rotor is provided with multiple permanent magnetism unit structures, and each permanent magnetism unit structure comprises an air magnetic barrier, a first permanent magnet built in a rotor yoke and a second permanent magnet arranged in the air magnetic barrier; and the central axis of the permanent magnetism unit structures is a rotor radial axis R1 crossing the center of the rotating shaft, and the permanent magnetism unitstructures are divided into left and right permanent magnetism unit structures of different structures by the central axis. The second permanent magnets of the rotor are arranged in the asymmetric way to overcome the disadvantage that the utilization rate of permanent magnetic and magnetic resistance torques of a built-in motor is not high, and thus, the torque output capability of the motor is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Semi-magnetic barrier type dual-field excitation linear synchronous generator
InactiveCN101179223AReduce Flux LeakageGood suspensionReciprocating/oscillating/vibrating magnetic circuit partsPropulsion systemsMagnetic barrierLevitation
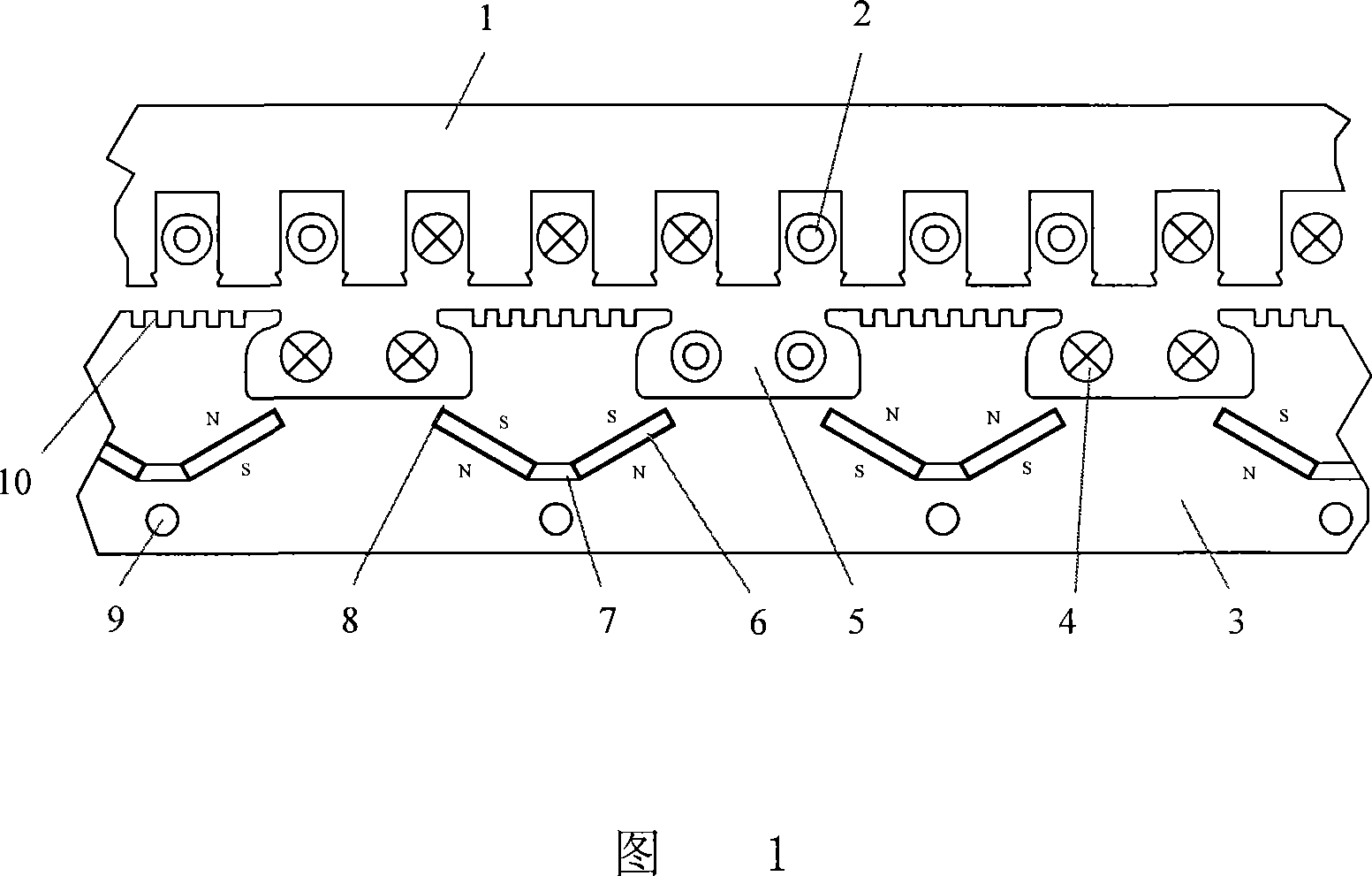
The invention discloses a semi-magnet-isolated double-excitation linear synchronous motor. It includes primary iron core, primary winding, secondary iron core, secondary excitation winding, secondary excitation winding slot, permanent magnet, generator and cogging, and secondary excitation winding is wound on the core teeth and placed on the secondary excitation In the winding slot, the characteristic is that there are two permanent magnets for excitation under each magnetic pole, placed obliquely, corresponding to each other, fixed in the embedded groove in the middle of the secondary yoke, and facing upward at an angle of 120°. There is a trapezoidal magnetic isolation air between the adjacent ends of each pair of permanent magnets; the faces of the same polarity of the two permanent magnets under the same magnetic pole are facing the same direction, and the N and S magnetic poles are alternately distributed along the length direction of the secondary yoke; the permanent magnets The upper end is close to the secondary excitation winding slot and connected by the magnetic bridge of the secondary iron core. The integrity of the secondary iron core is good, and the levitation force and thrust of the motor are significantly increased under the same conditions. It is mainly used in various occasions of maglev transportation system drive and logistics line drive.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com