Magnetism increasing type internal tangential adjustable flux motor
A magnetic flux motor and magnetic technology, applied in the direction of magnetic circuit shape/style/structure, magnetic circuit, electric components, etc., can solve the problems of uncontrollable demagnetization of alnico permanent magnets, etc., to ensure stability, controllability, change Air-gap flux, possibility reduction effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
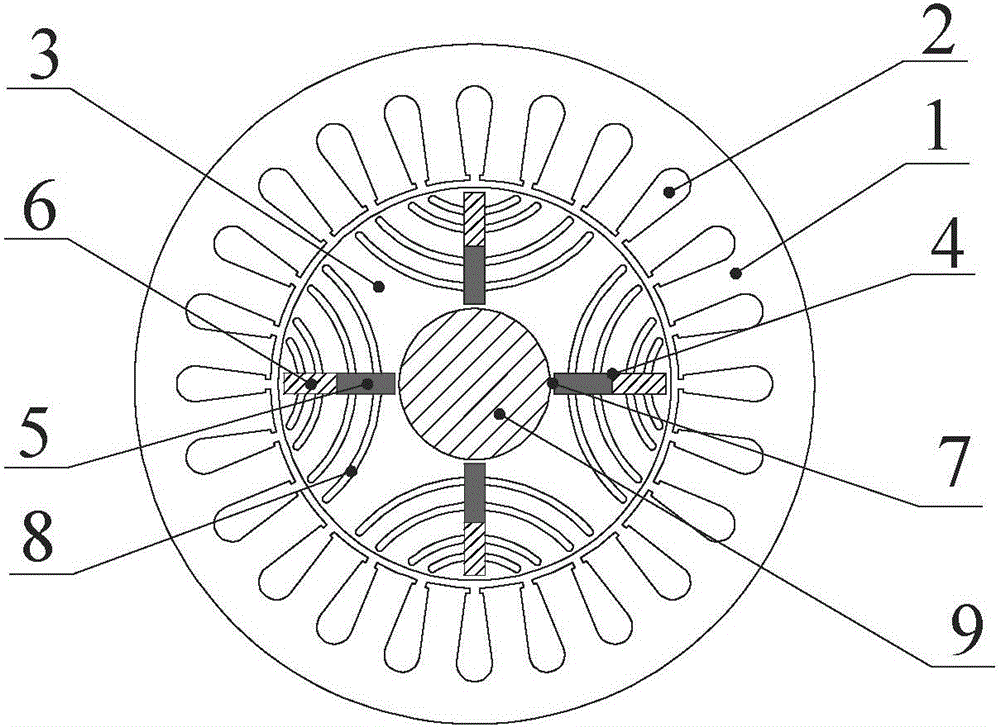
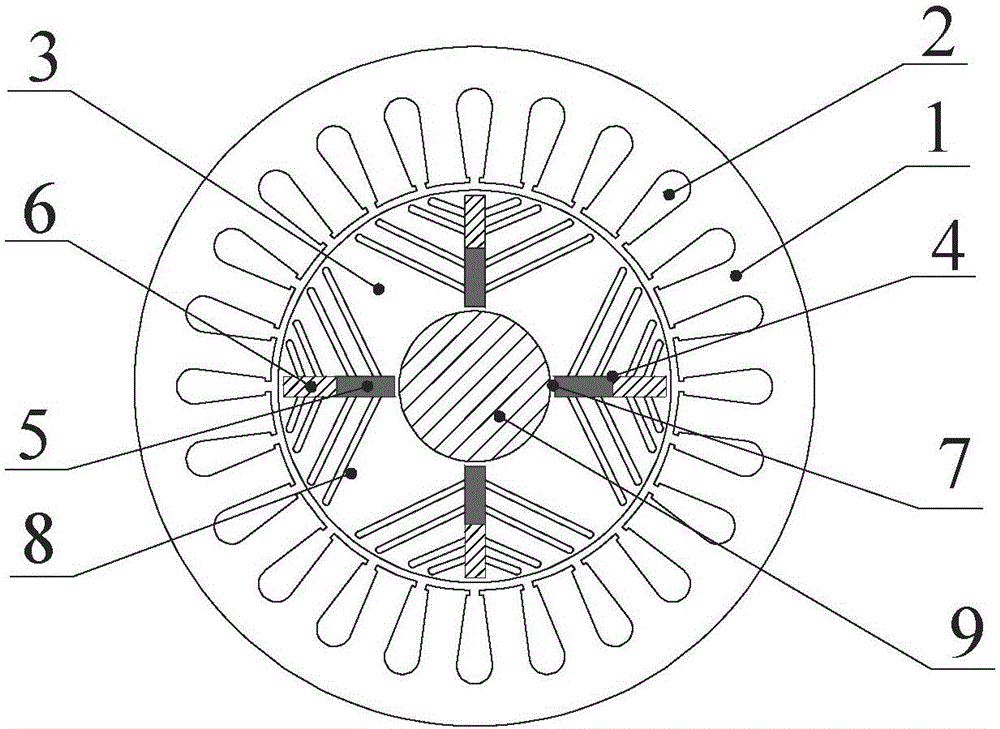
[0019] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination Figure 1 to Figure 3 Describe this embodiment, the magnetization type built-in tangentially adjustable flux motor described in this embodiment includes a stator core 1, an armature winding 2, a rotor core 3 and a rotating shaft 9; the rotor core 3 is fixed on the rotating shaft 9 and is located in the stator Inside the core 1, the armature winding 2 is arranged on the stator core 1;
[0020] It also includes tangential permanent magnet slots 4, p NdFeB magnetic poles 5, p AlNiCo magnetic poles 6 and p cross-axis magnetic barriers 8, p is an even number, and p tangential barriers are evenly arranged on the rotor core 3 along the circumference of the motor. permanent magnet slot 4 and p quadrature-axis magnetic barriers 8, and each quadrature-axis magnetic barrier 8 is a mirror-symmetrical structure centered on a tangential permanent magnet slot 4; the tangential permanent magnet slot 4 and the quadrature-axis m...
Embodiment 1
[0024] combine figure 1 To illustrate this embodiment, the magnetized built-in tangentially adjustable flux motor includes a stator, a rotor, and a rotating shaft. The stator in the present invention includes a stator core 1 and an armature winding 2. The armature winding 2 is arranged in the slot of the stator iron core, and the rotating shaft 9 is made of cast steel, and the stator and shaft 9 are the same as those of conventional permanent magnet synchronous motors; the rotor includes tangential permanent magnet slots 4, NdFeB magnetic poles 5, AlNiCo magnetic poles 6, magnetic bridges 7 and quadrature-axis magnetic barriers 8 , the tangential permanent magnet slots 4 and the quadrature-axis magnetic barriers 8 are alternately and evenly arranged on the rotor along the circumferential direction, and the tangential permanent magnet slots 4 and the quadrature-axis magnetic barriers 8 both run through the entire motor in the axial direction, and each tangential permanent magnet...
Embodiment 2
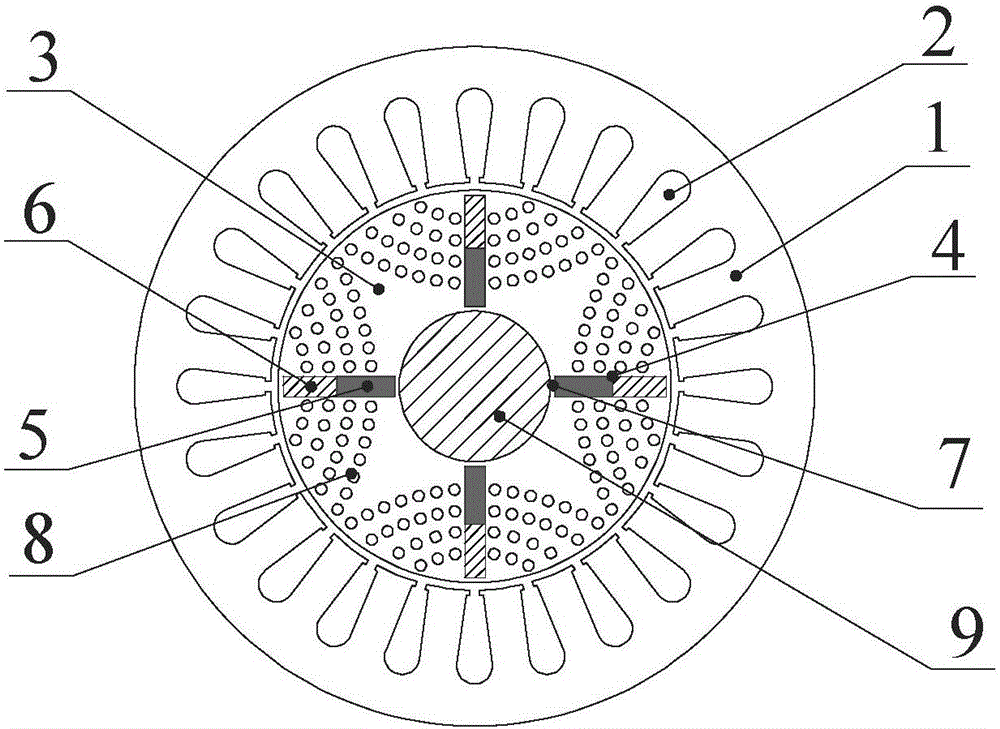
[0026] combine figure 2 Note that the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the quadrature-axis magnetic barrier 8 is a series of radially arranged circular groove arrays, the array is formed by multiple arc structures, and each arc structure is provided with Multiple circular slots, the number of circular slots in each circular arc structure gradually increases from outside to inside along the rotor radius direction, multiple circular arc structures take the tangential permanent magnet slot 4 as the line of symmetry, and are symmetrically arranged on the tangential permanent magnet slot 4. On both sides of the magnet slot 4, the number of circular slots can be flexibly designed on the basis of taking into account the mechanical strength of the rotor and reducing the magnetic flux path of the quadrature axis of the motor. The inside of the circular magnetic barrier can also be made of epoxy resin, carbon fiber, etc. Non-conductive material fill.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com