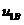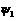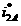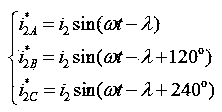Patents
Literature
92 results about "Air gap flux" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
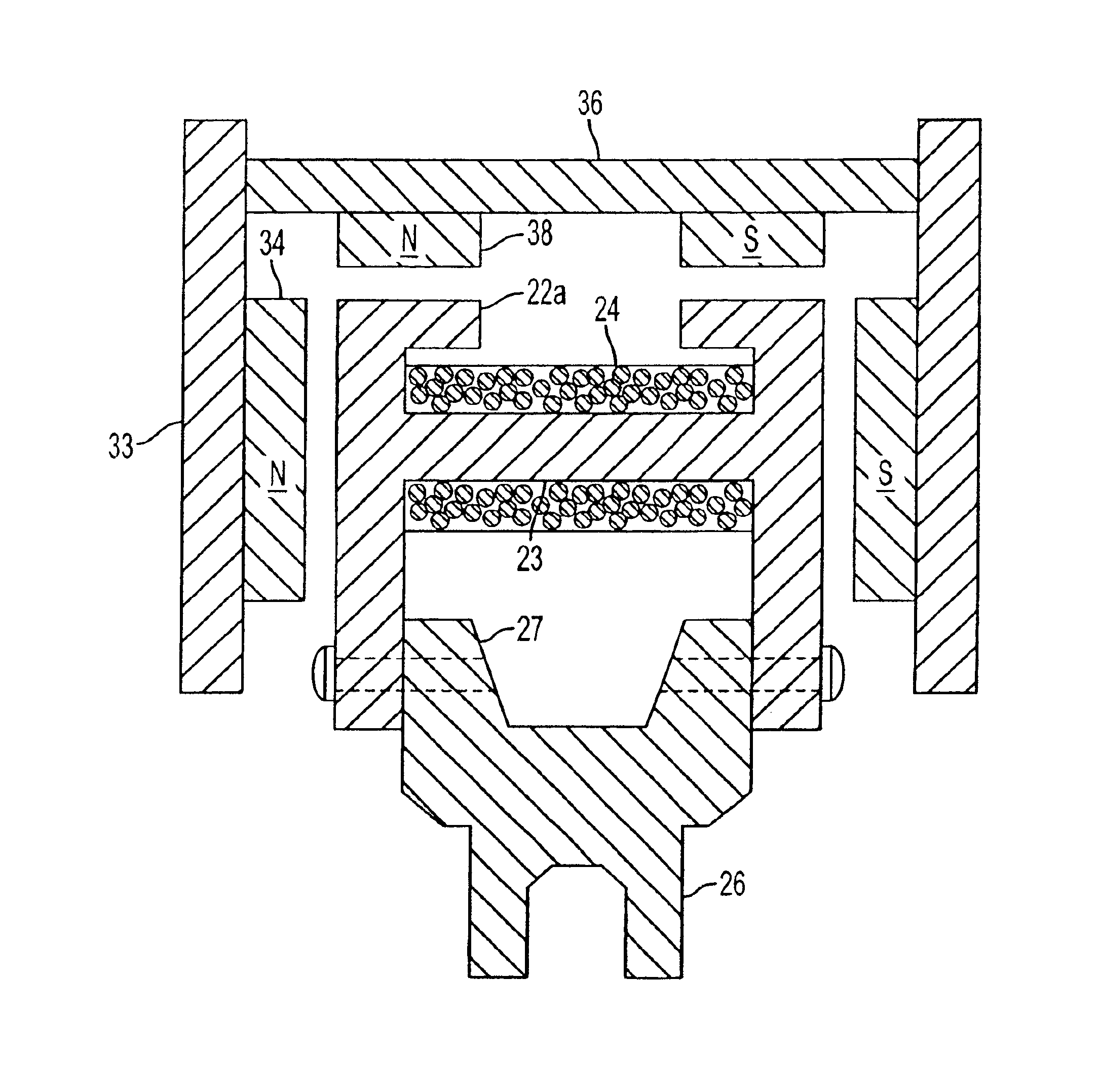
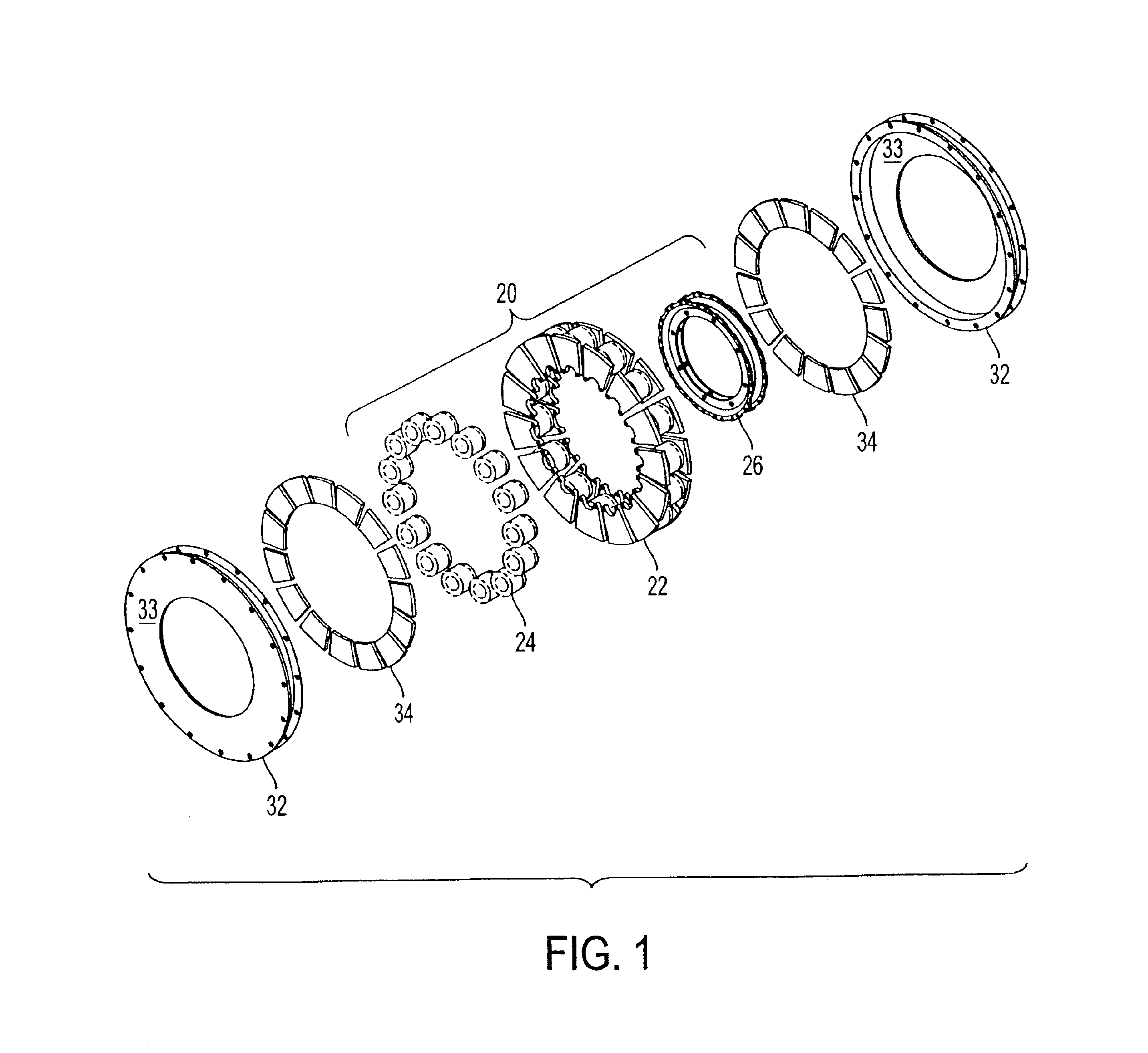
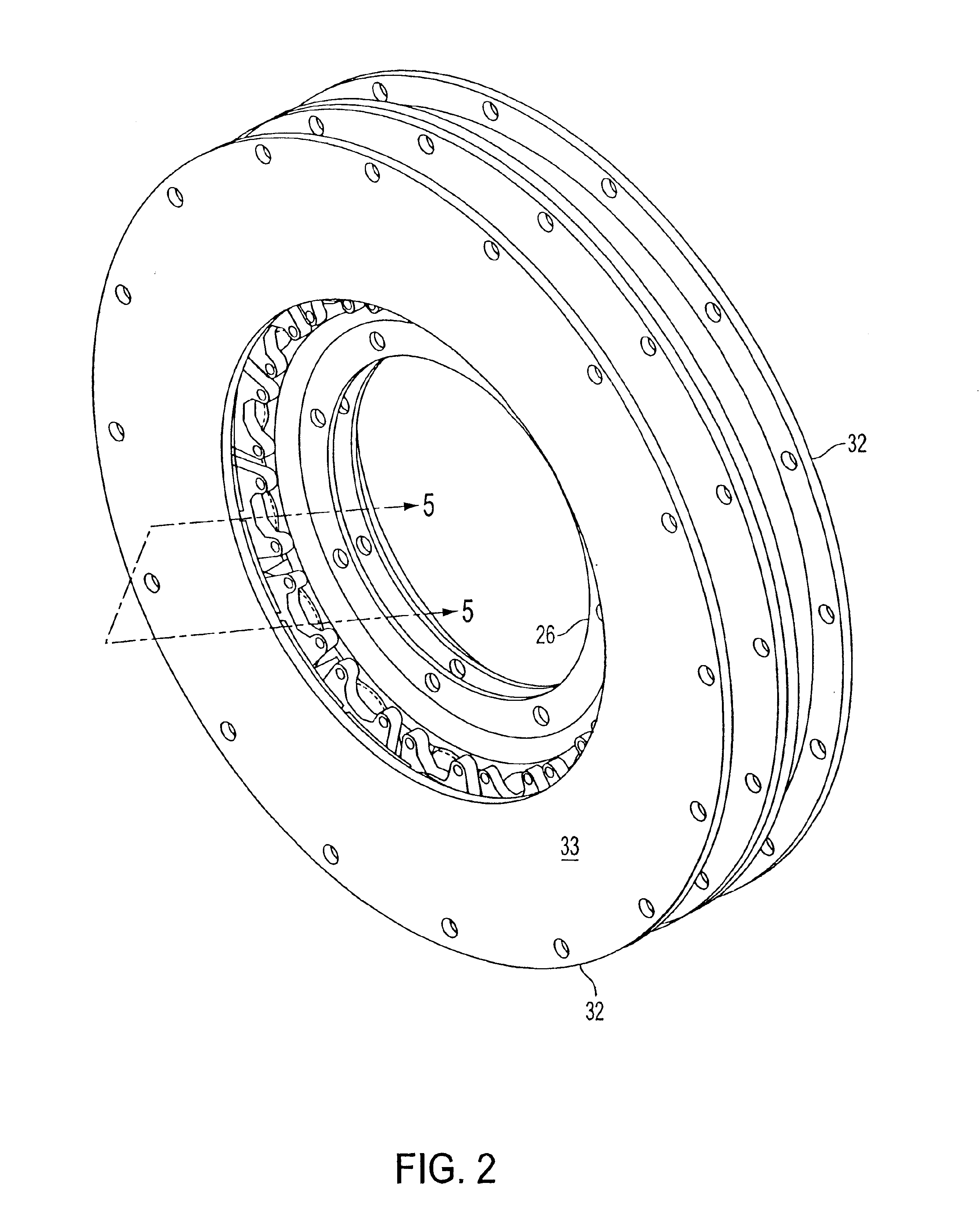
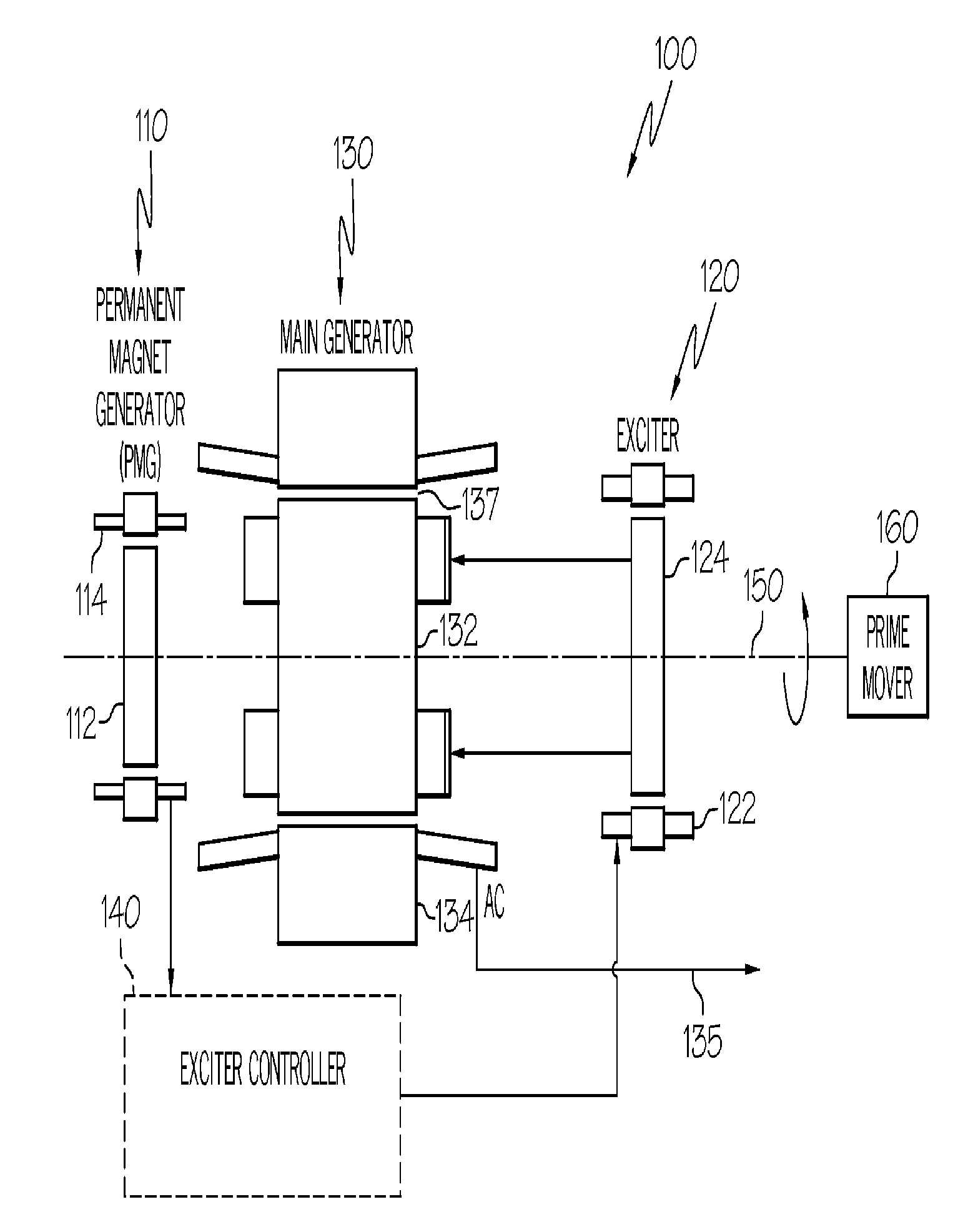
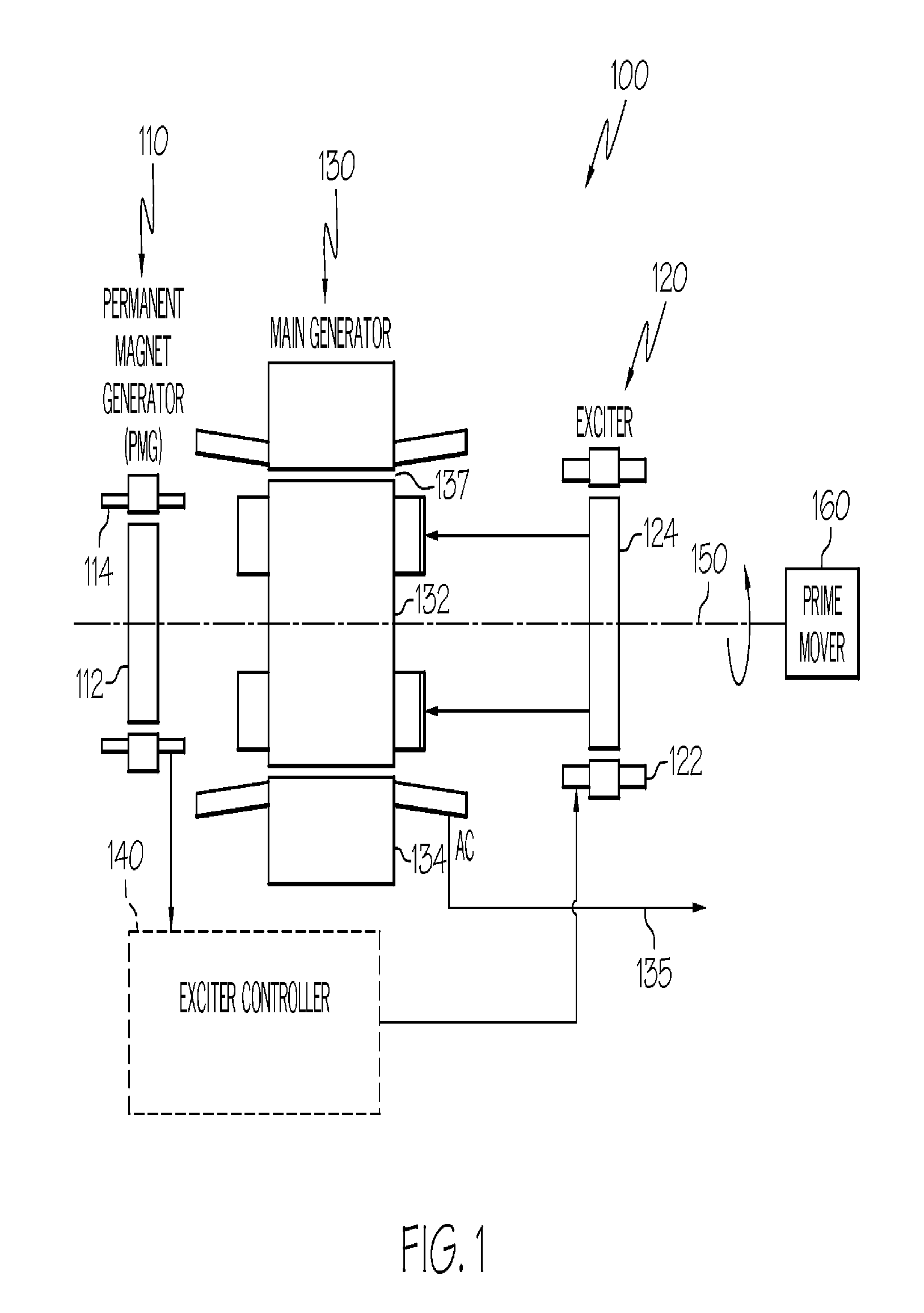
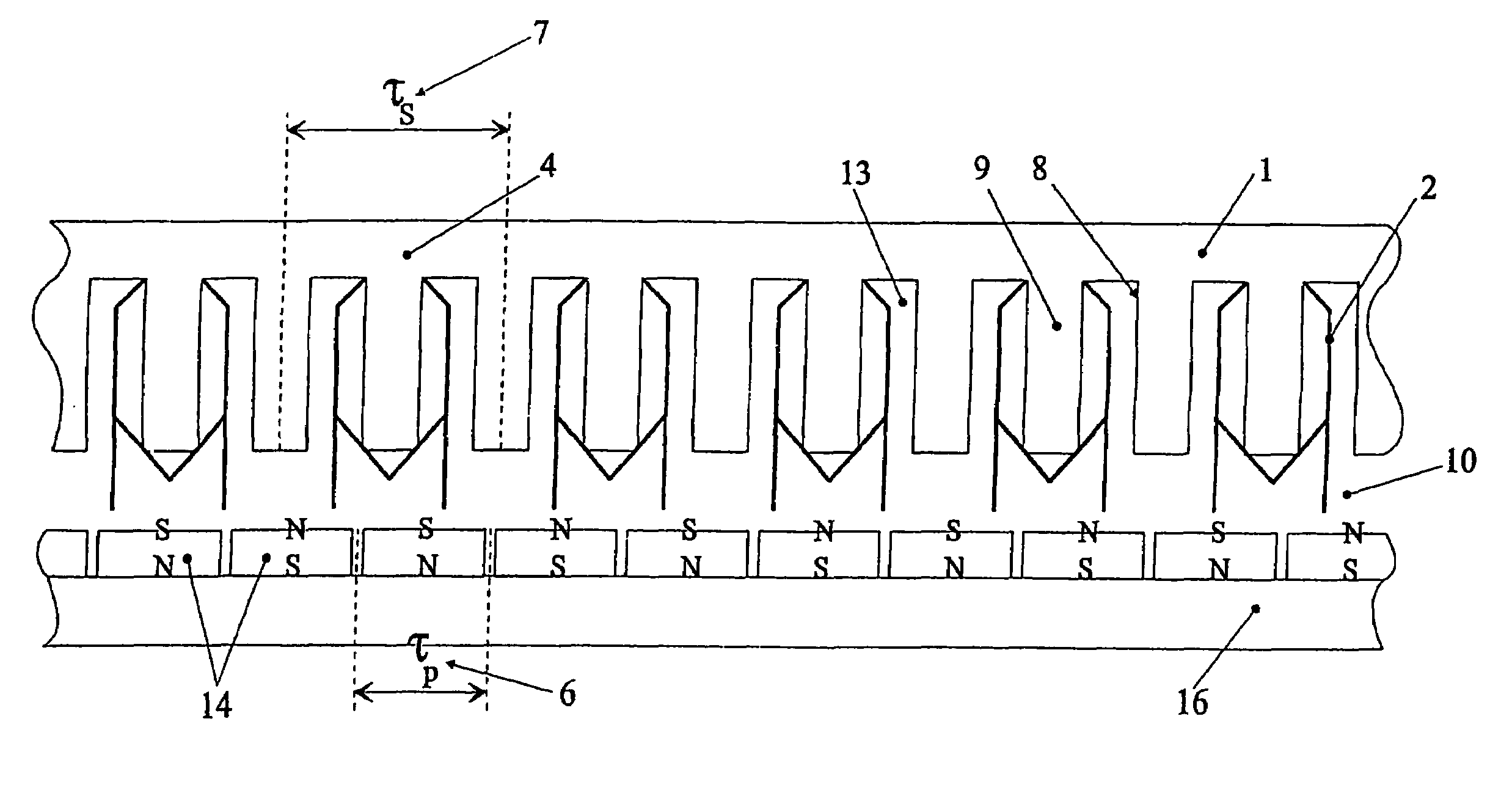
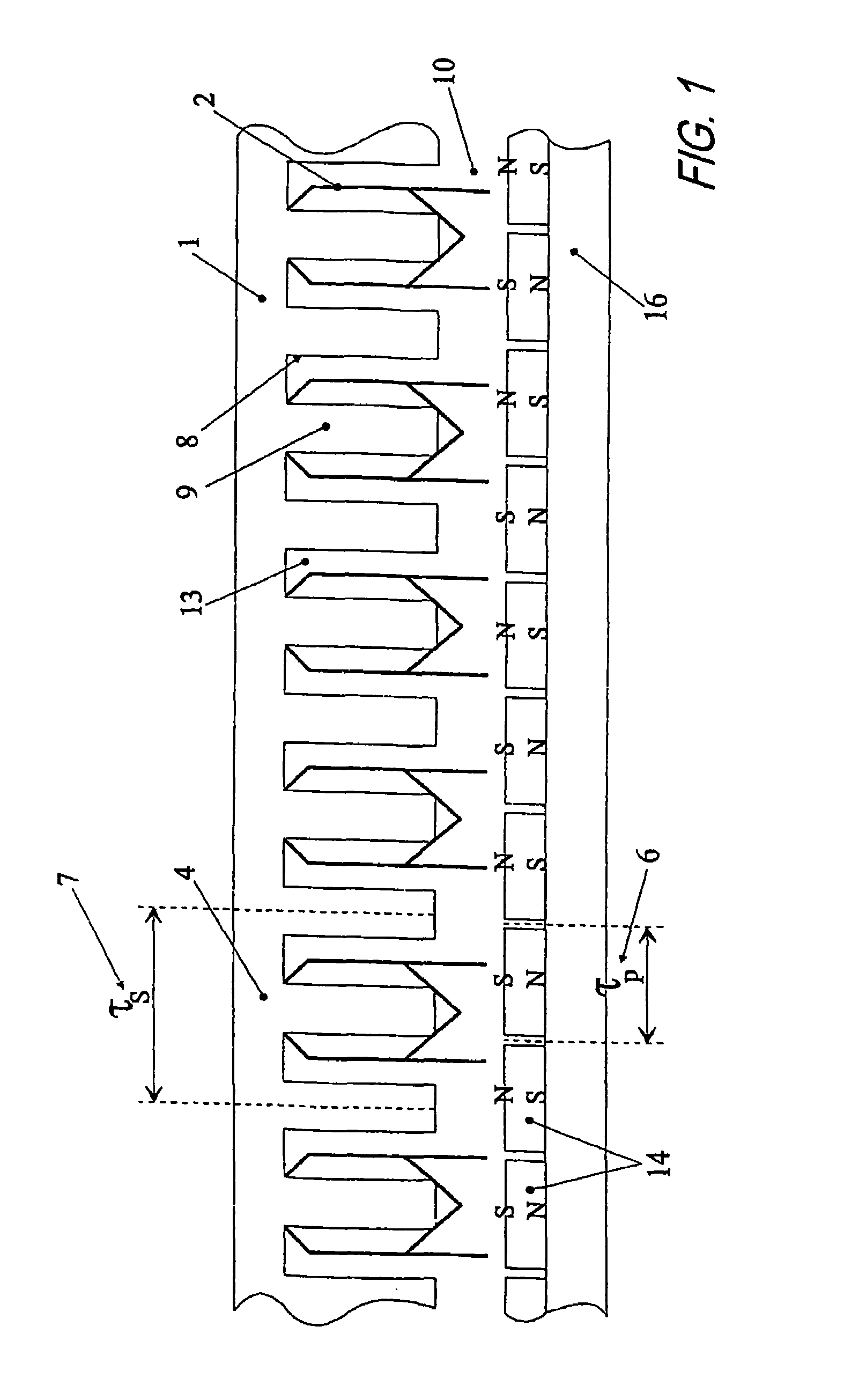
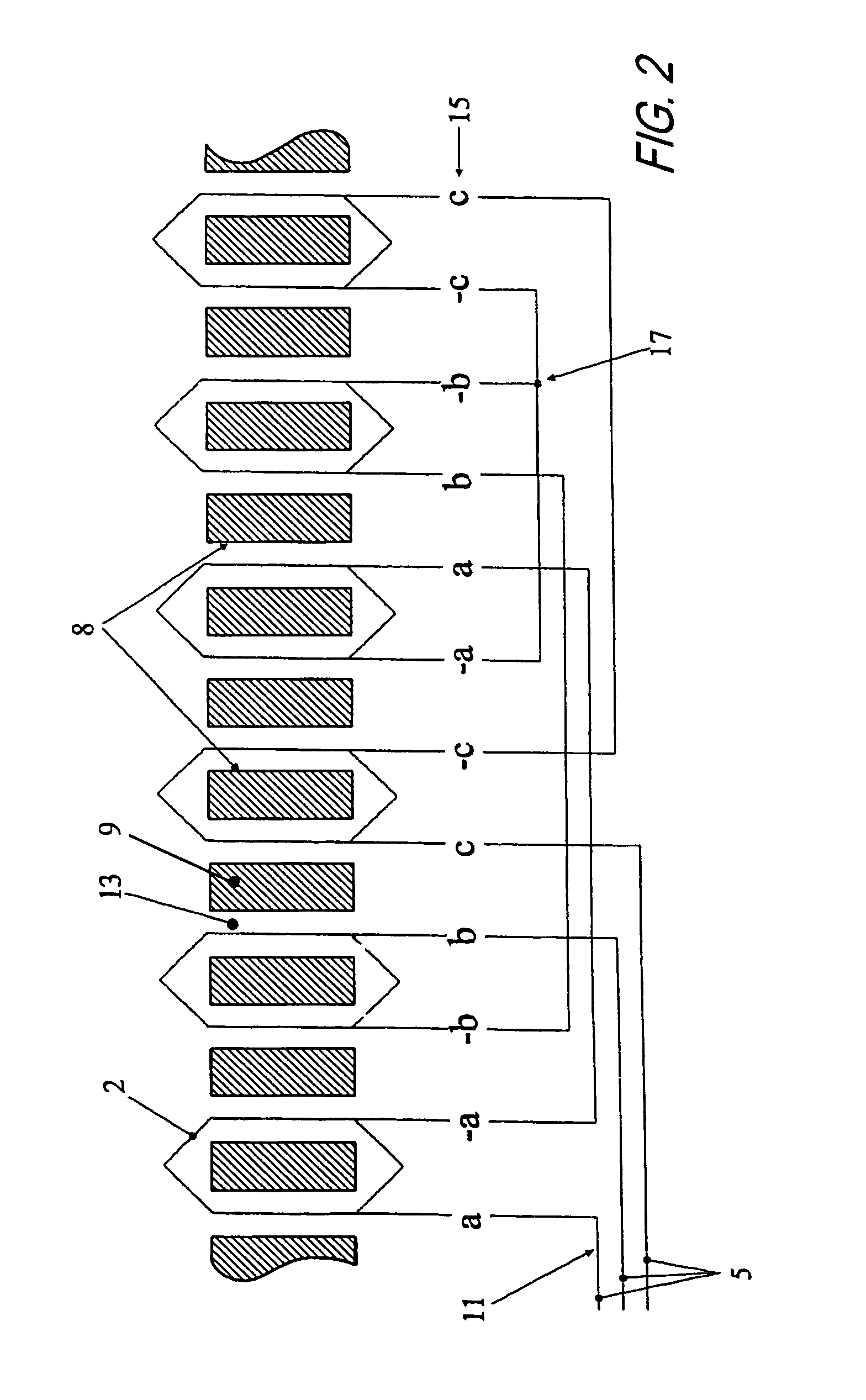
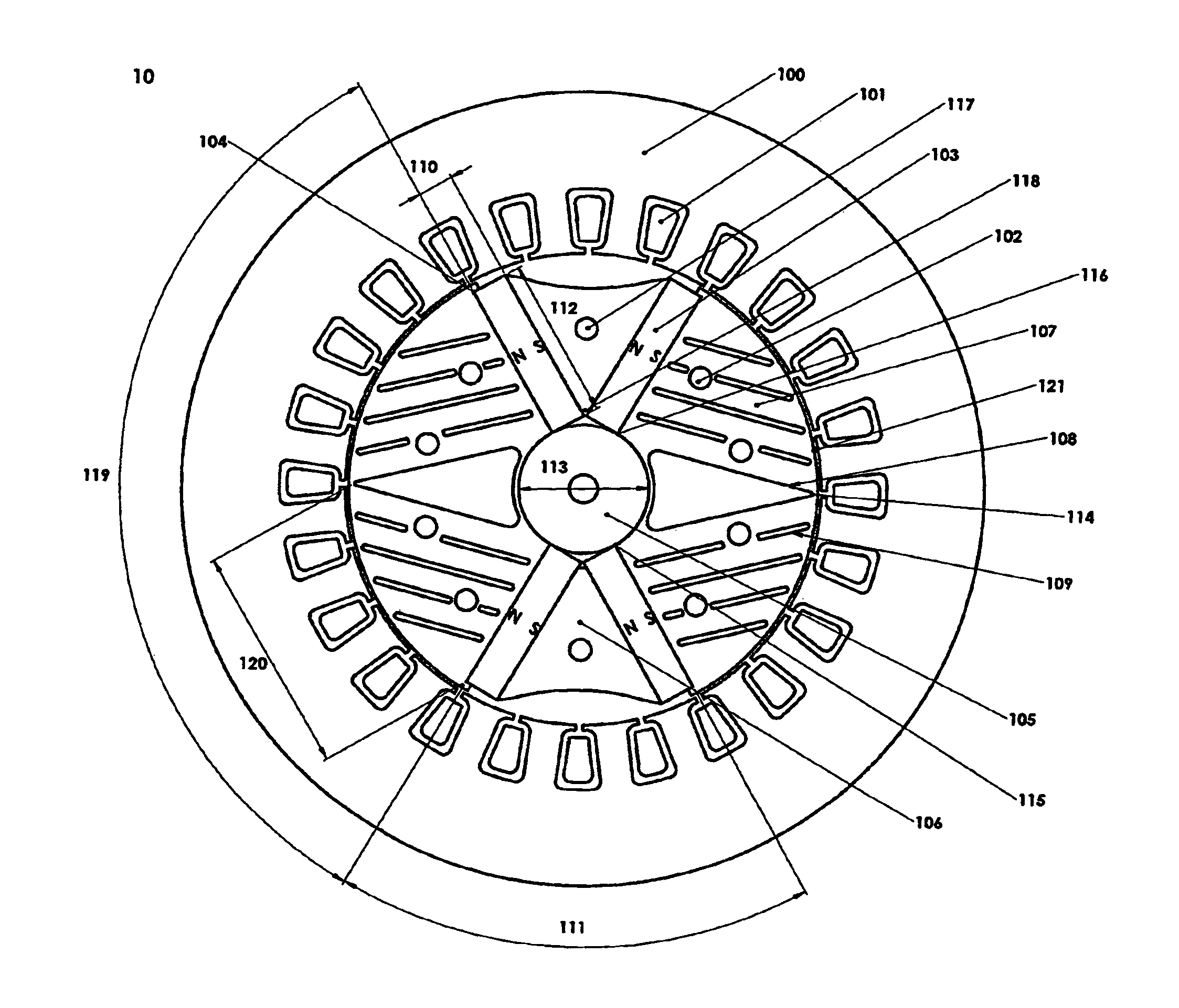
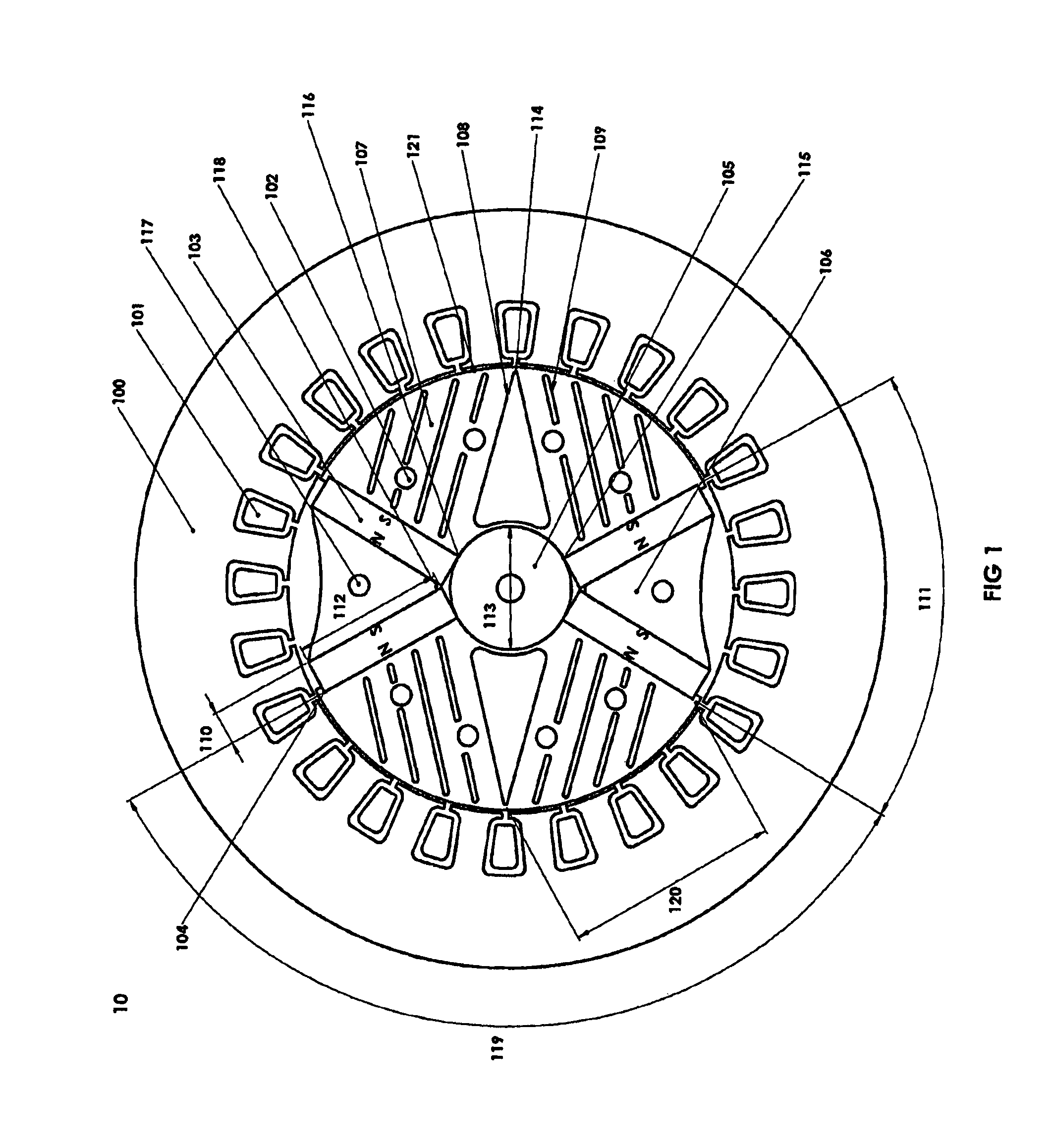
Rotary electric motor having both radial and axial air gap flux paths between stator and rotor segments
InactiveUS6891306B1Low flux lossEliminate the effects ofMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsMagnetic polesElectrical polarity
In a rotary electric motor, a stator contains a plurality of separate electromagnet core segments disposed coaxially about an axis of rotation. The core segments are affixed, without ferromagnetic contact with each other, to a non-ferromagnetic support structure. The rotor is configured in a U-shaped annular ring that at least partially surrounds the annular stator to define two parallel axial air gaps between the rotor and stator respectively on opposite axial sides of the stator and at least one radial air gap. Permanent magnets are distributed on each inner surface of the U-shaped rotor annular ring that faces an air gap. A winding is formed on a core portion that links axially aligned stator poles to produce, when energized, magnetic poles of opposite polarity at the pole faces.
Owner:BLUWAV SYST LLC
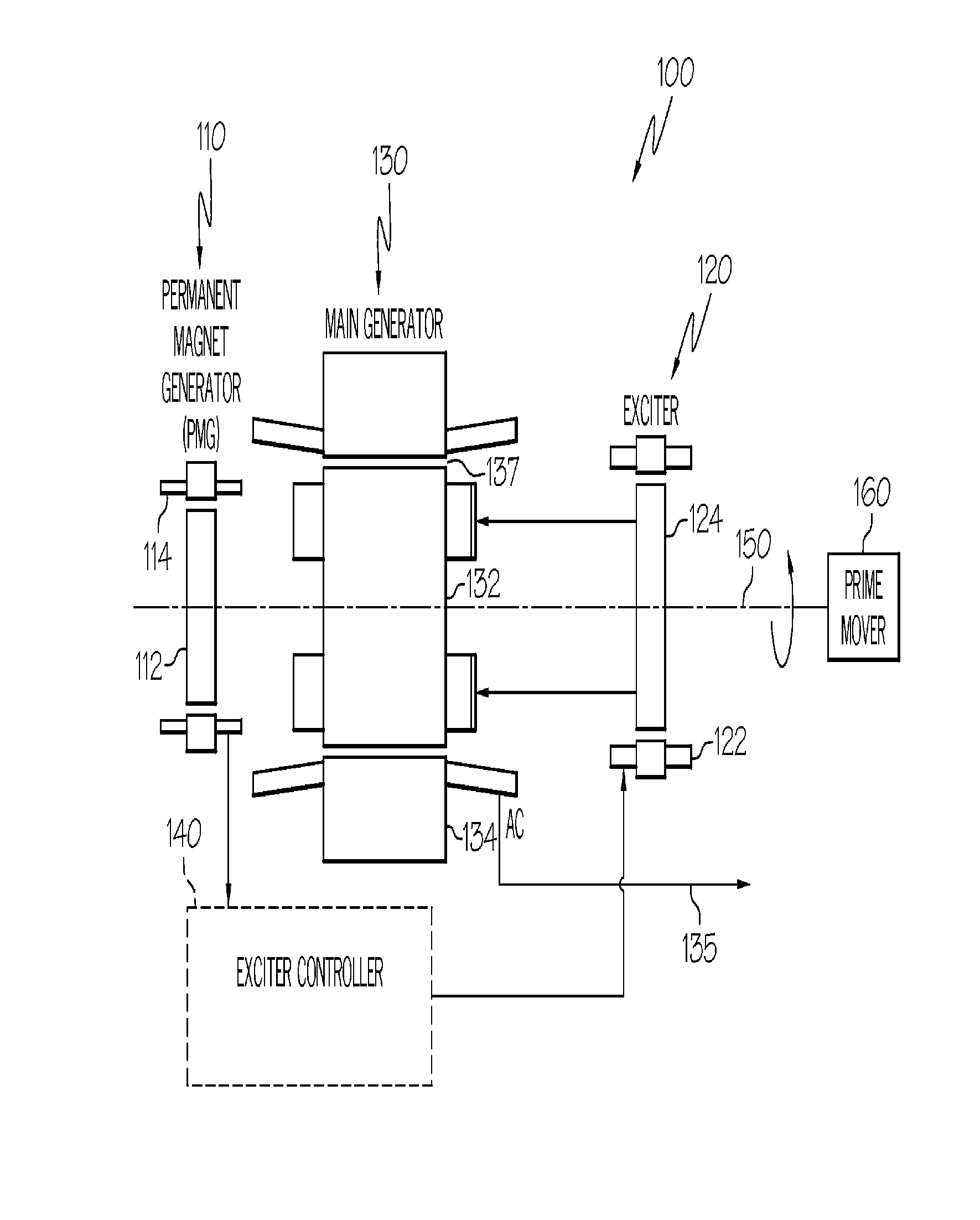
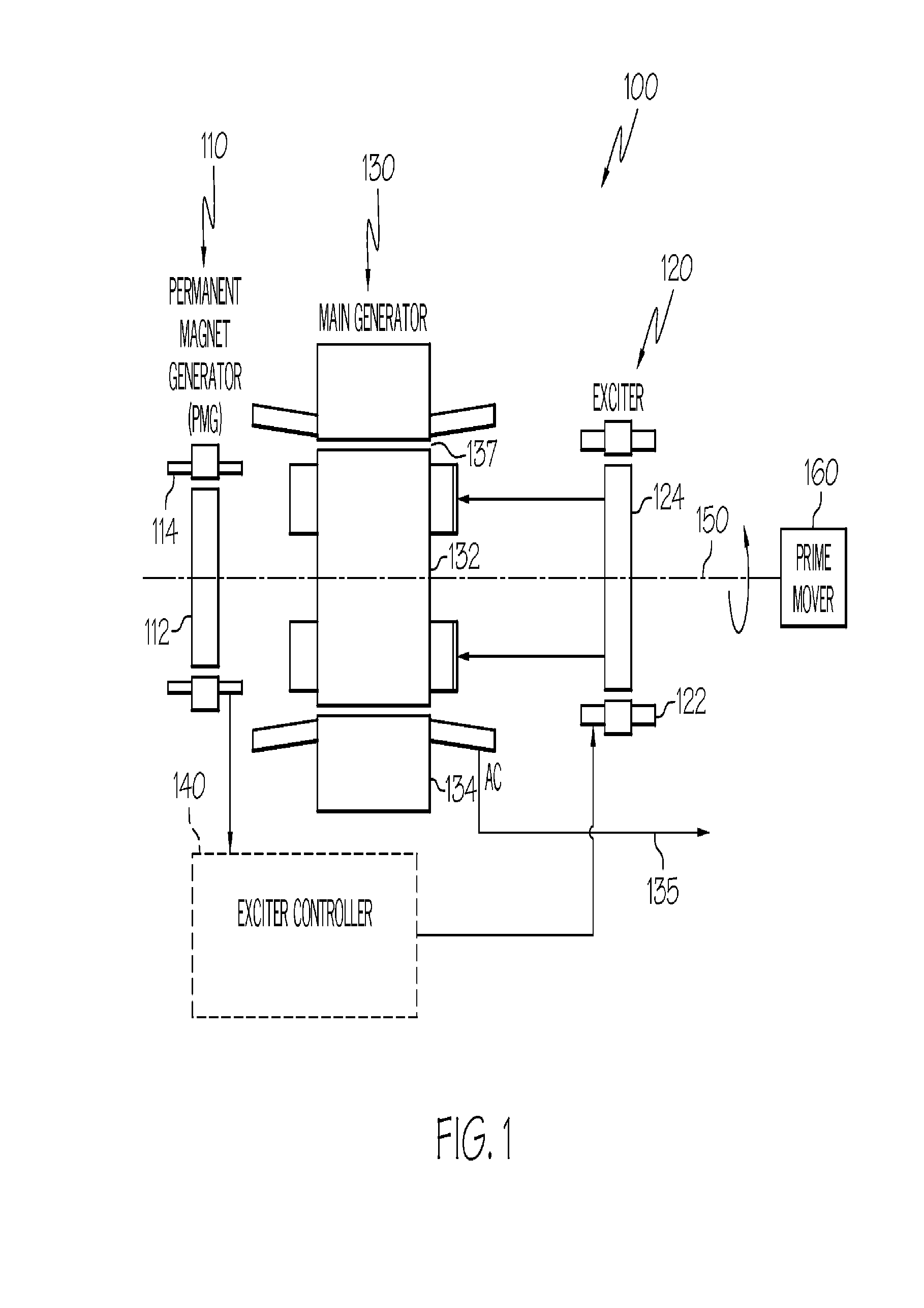
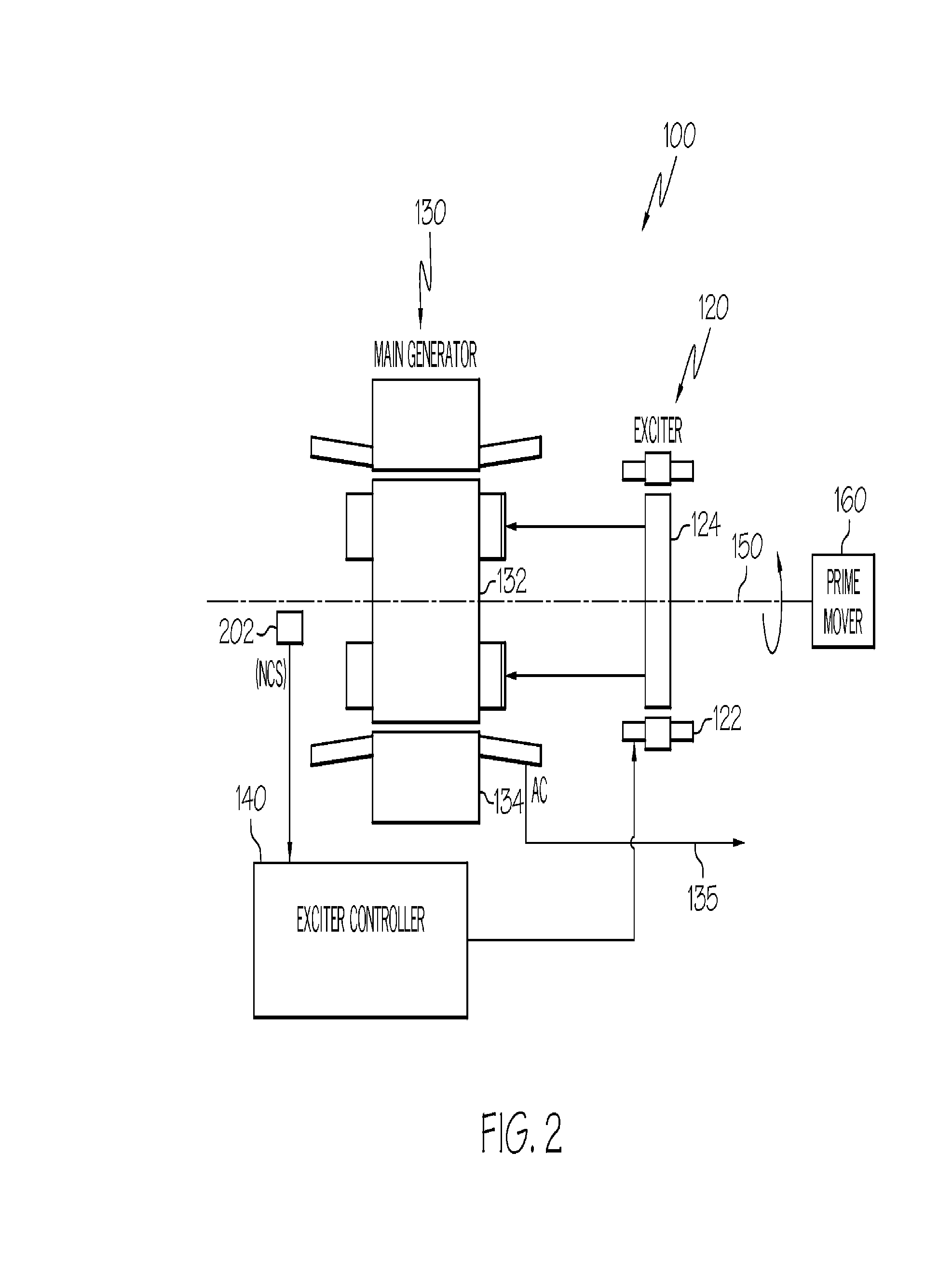
Engine start system with quadrature AC excitation
InactiveUS7514806B2Emergency protective circuit arrangementsDynamo-electric converter controlStarter generatorConstant frequency
A starter-generator system may be used to supply sufficient starting torque to start an aircraft main engine. The main starter-generator stator winding may be connected to a constant frequency (CF) power source to create a rotating field in the main starter-generator air gap. This rotating field, in turn, may induce current on the main rotor winding, which may be a closed circuit formed by main rotor field winding and exciter armature winding. The interaction between the main rotor current and the air gap flux may give rise to the starting torque to start the main engine. Adjusting the voltage supplied to the exciter stator field winding can modify the induced voltage and current on the rotor circuit to control the rotor current and starting torque. The starter-generator system may also be used to start an aircraft main engine by directly connecting the main stator winding to a power source without powering the exciter stator.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
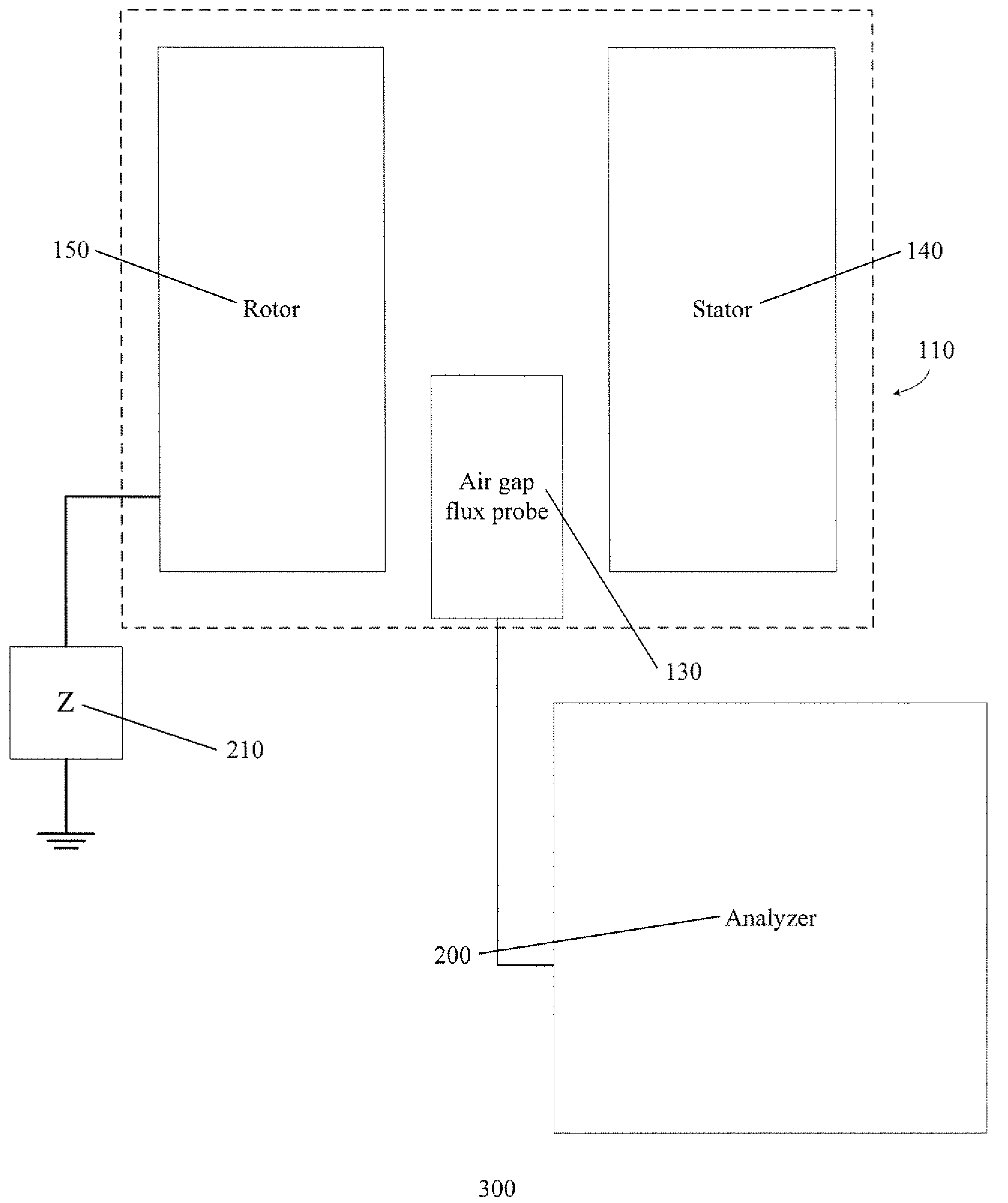
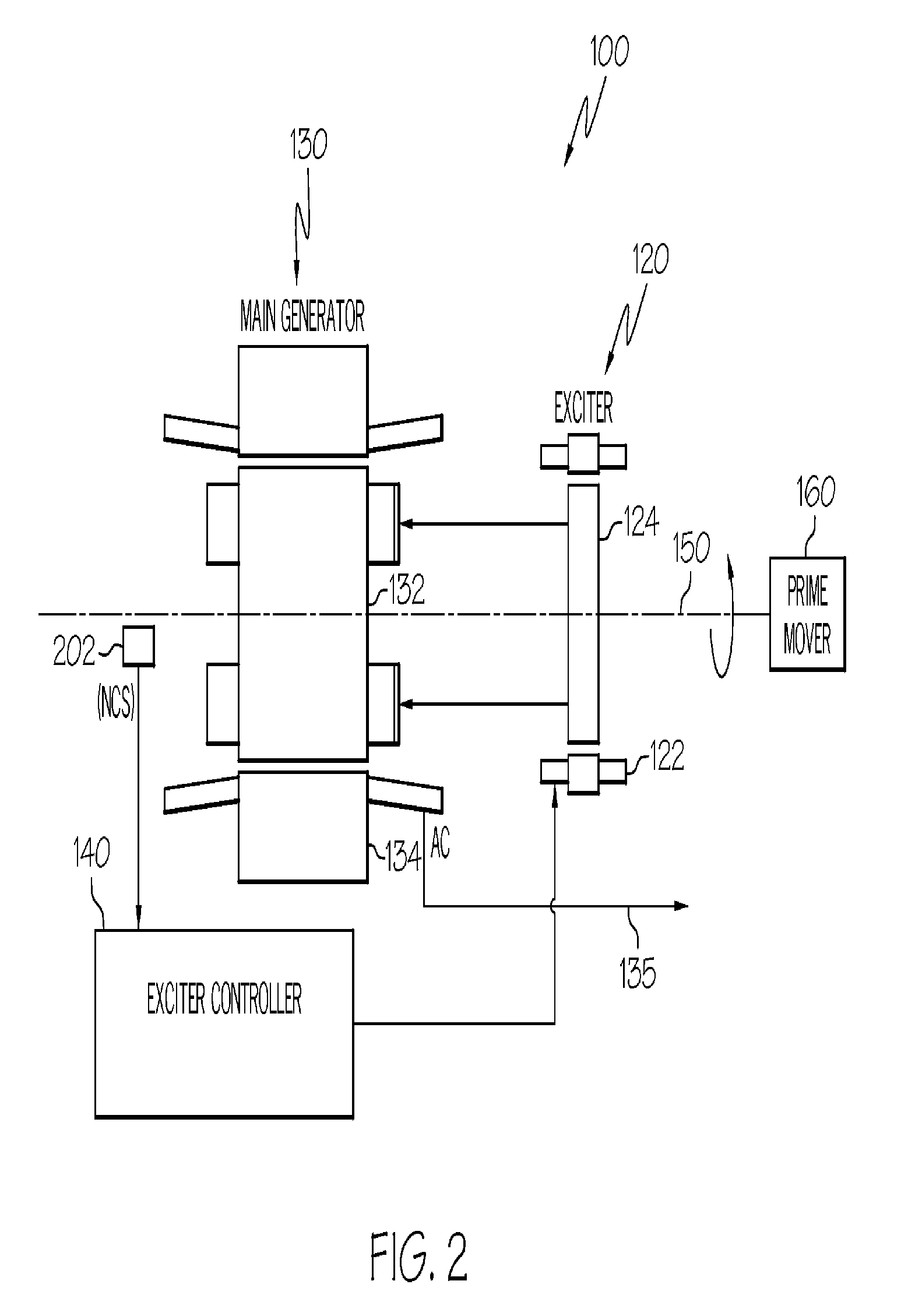
Methods and Systems for Detecting Rotor Field Ground Faults In Rotating Machinery
InactiveUS20090219030A1Electronic circuit testingEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectricityElectric machine
Embodiments of the invention can include methods and systems for detecting rotor field ground faults in rotating machinery. In one embodiment, a system can include a rotor of the rotating machine comprising a plurality of field windings substantially disposed therein and a stator of the rotating machine comprising a plurality of stator windings substantially disposed therein, with an air gap existing between the rotor and the stator. The system can include a high-impedance grounding circuit at least temporarily connected between the rotor and a ground. Additionally, the system can include an air gap flux probe positioned at least temporarily between the rotor and the stator for measuring a magnetic flux density generated in the air gap during operation of the rotating machine. Finally, the system can further include an analyzer in electrical communication with the air gap flux probe for receiving an output of the air gap flux probe.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
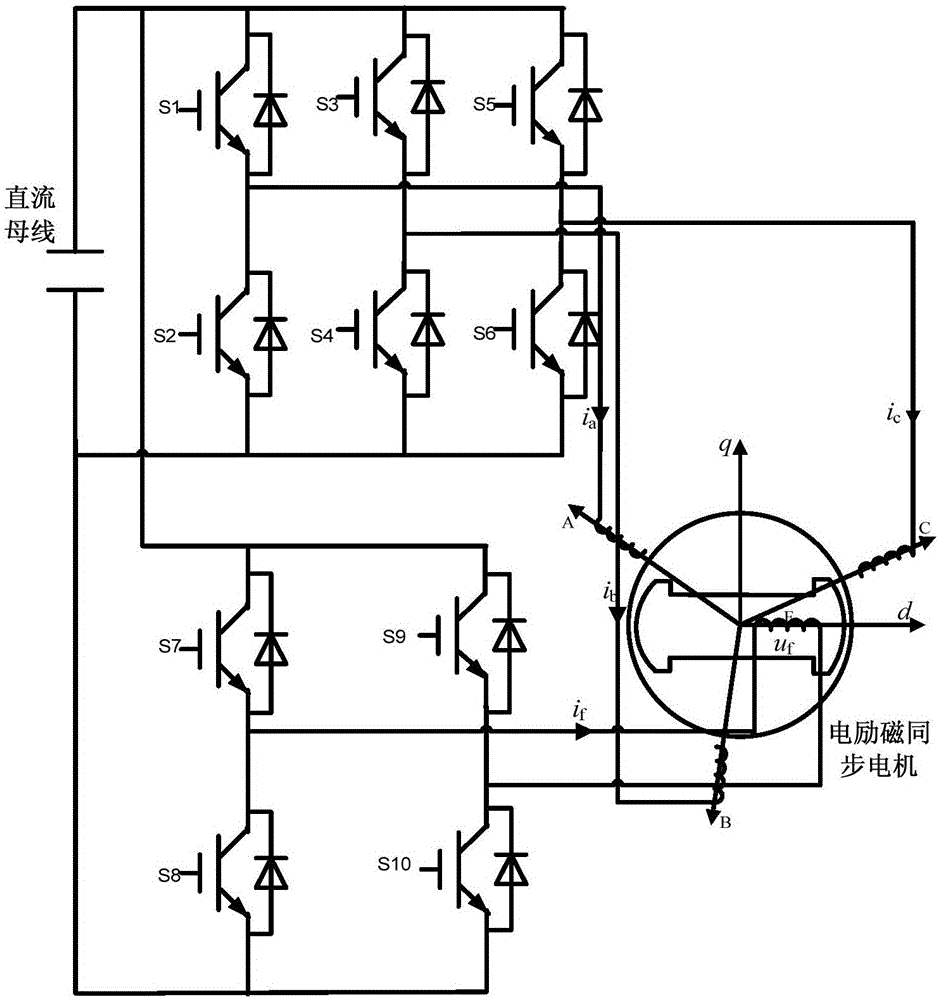
Mixed field excitation brushless synchronous motor with coordination structure
InactiveCN101345453AAchieve brushlessImprove reliabilityMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric machinesAviationSynchronous motor
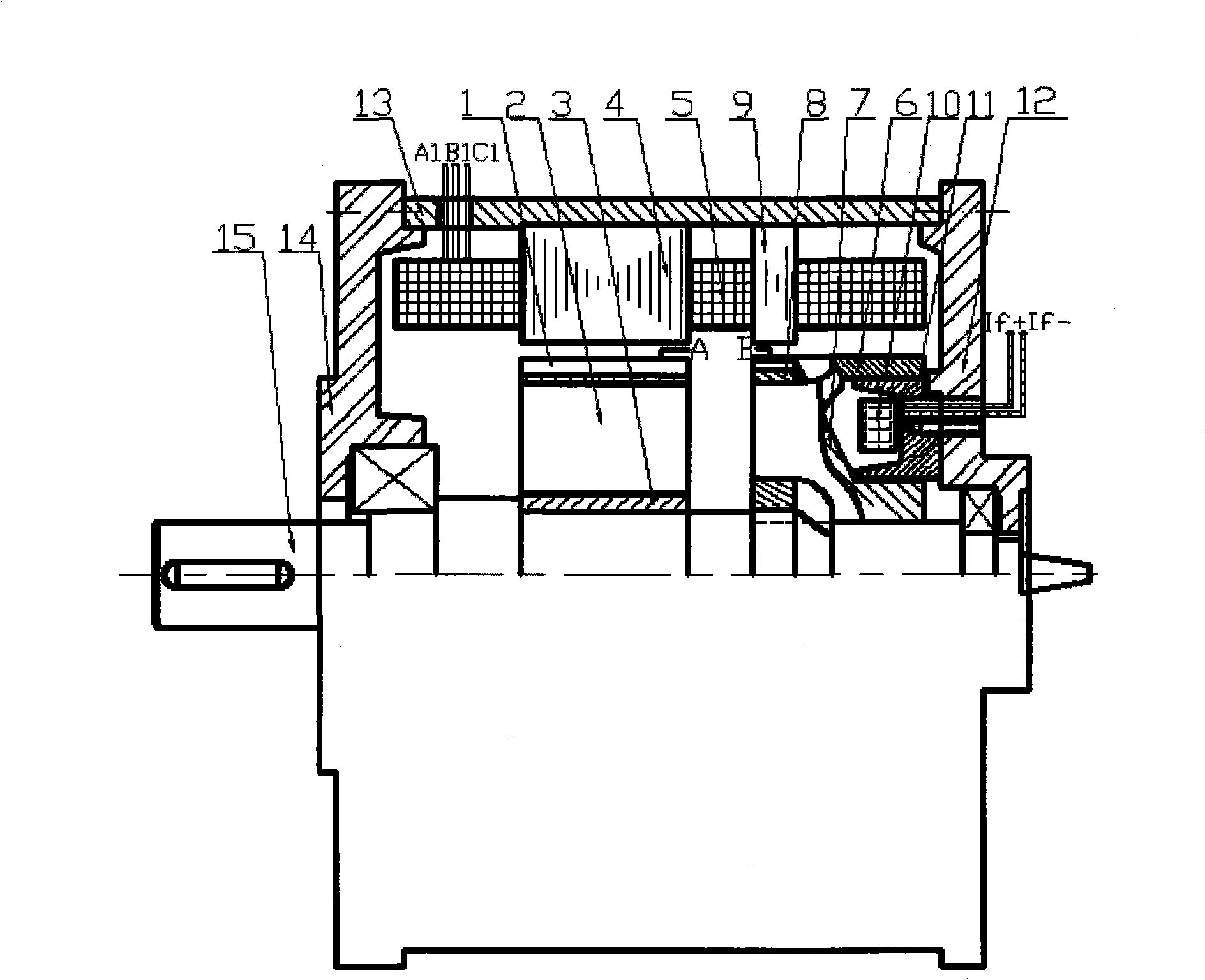
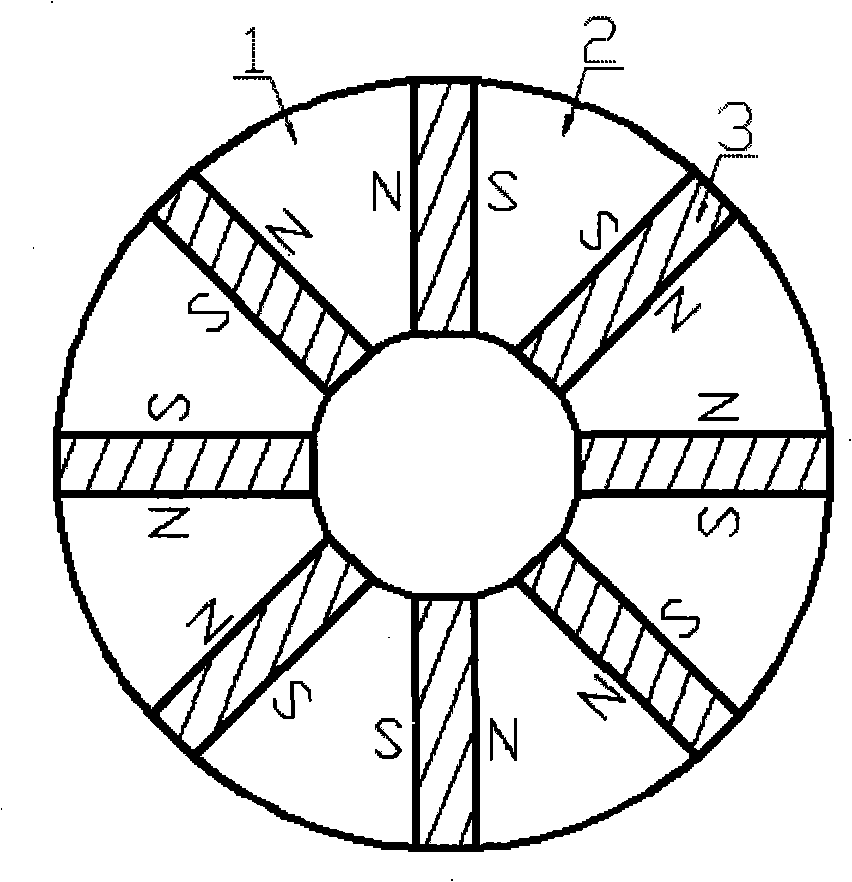
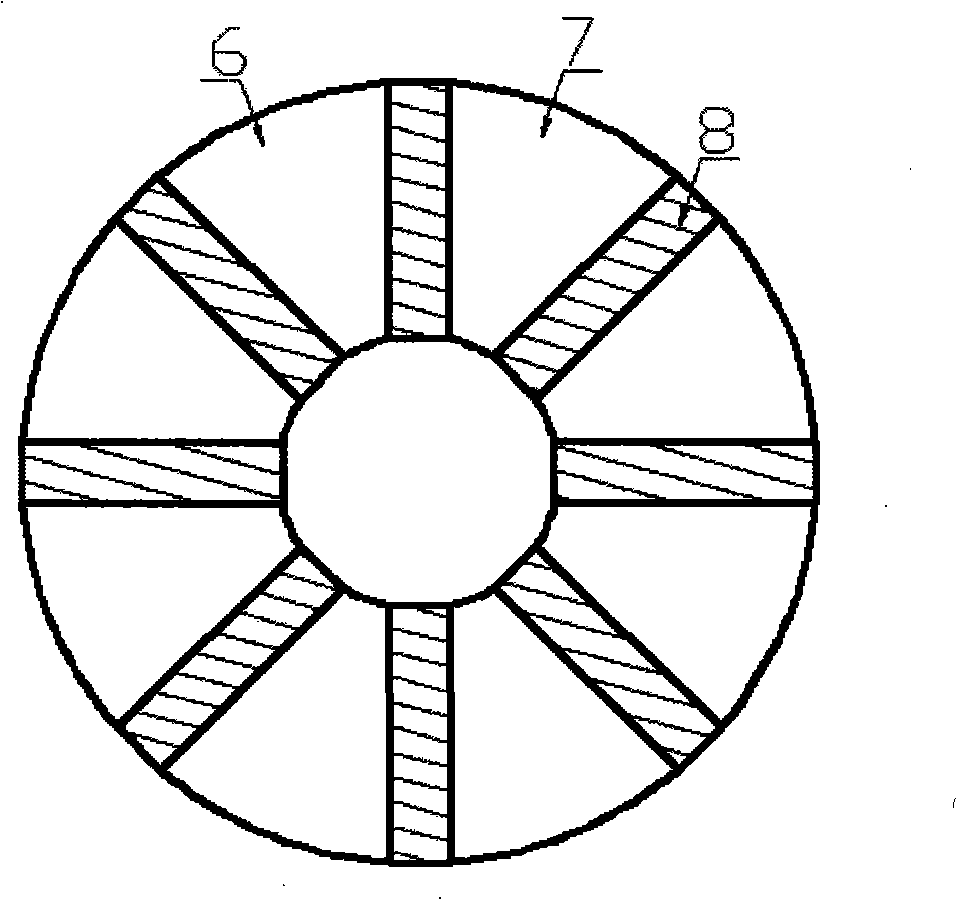
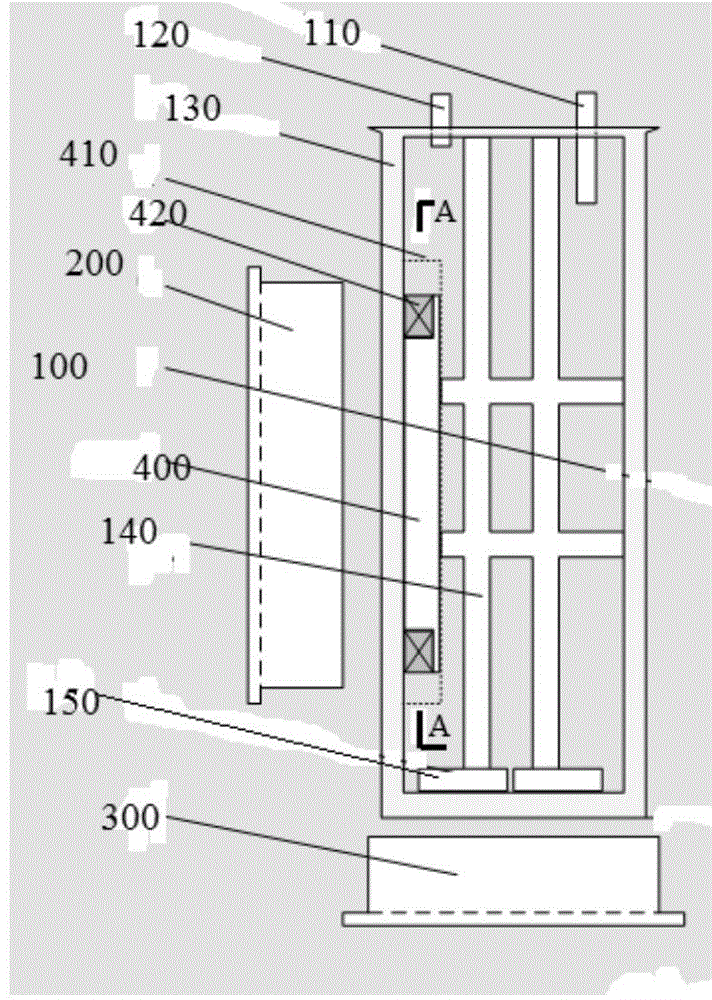
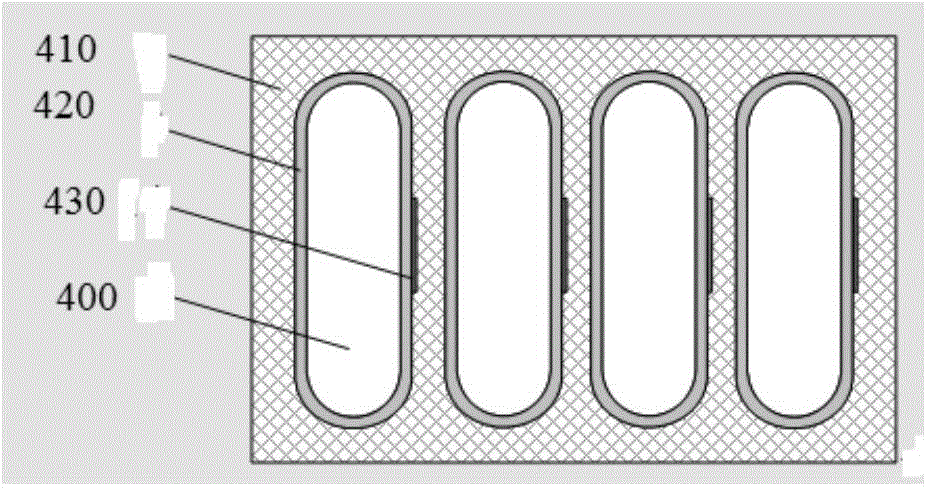
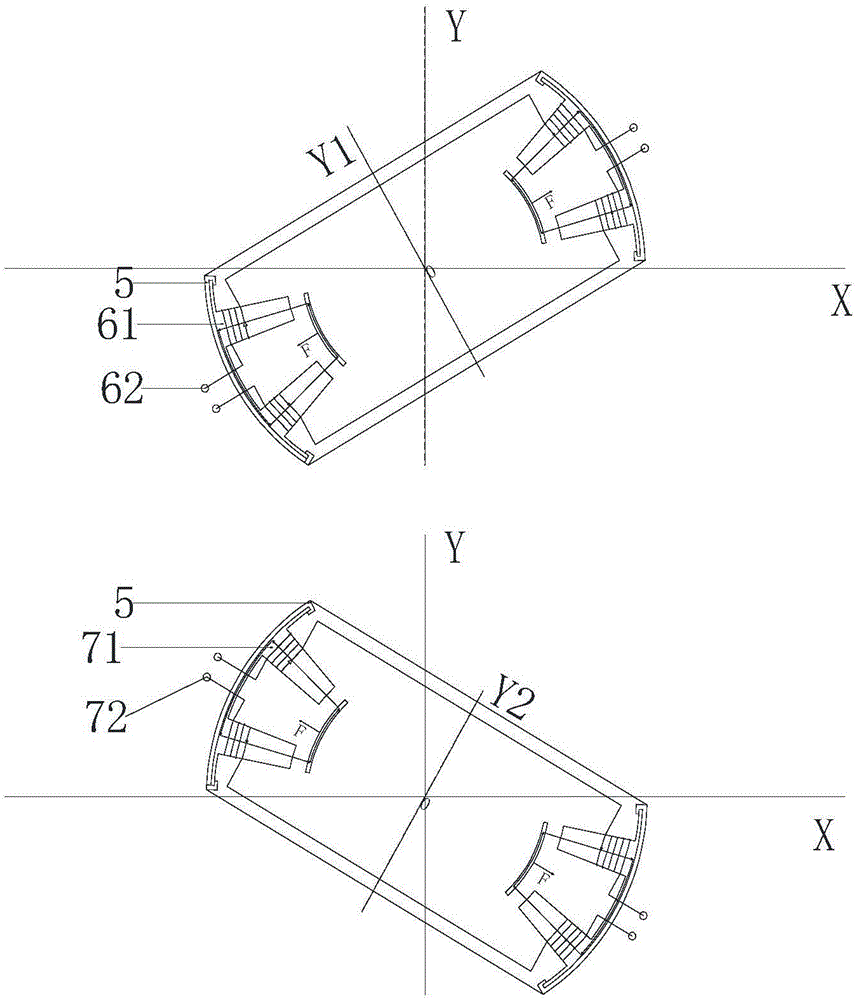
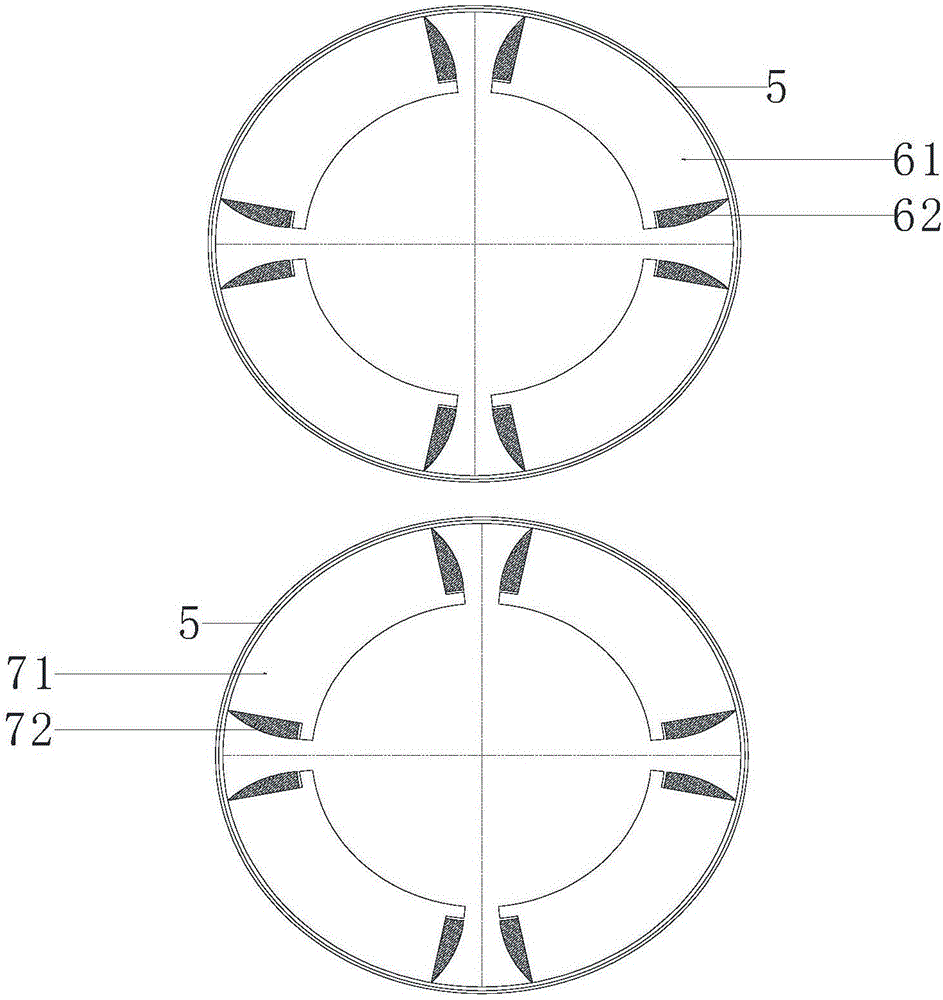
The invention discloses a hybrid excitation brushless synchronous machine with a coordinate structure belonging to the hybrid excitation synchronous machine. The machine comprises a permanent magnet synchronous motor and an electric excitation brushless synchronous motor. An armature winding (5) is sleeved on a permanent magnet synchronous stator core (4) and an electric excitation brushless synchronous stator core (9). The permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor is composed of an N pole shoe (1), an S pole shoe (2) and a permanent magnet steel (3). The electric excitation brushless synchronous motor rotor is composed of a magnetizer A(6), a magnetizer B(7) and a stainless steel block (8). An excitation winding (10) and a magnetic conductive bridge (11) are also included. The rotor magnetic circuit and stator magnetic circuit of the two motor are independent with each other but share the armature winding (5) and a shaft (15). The excitation current bidirectionally regulates the air gap flux in the electric excitation brushless synchronous motor to regulate the induced potential or output torque of the armature winding. The motor of the invention not only can be a brushless ac generator, but also a brushless dc generator by external connecting with a rectification circuit, furthermore as a motor for the aviation frequency power with a wide rotation speed range, the wind generator system and the electric automobile drive system.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Engine start system with quadrature ac excitation
InactiveUS20080303280A1Aircraft power plantsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsStarter generatorConstant frequency
A starter-generator system may be used to supply sufficient starting torque to start an aircraft main engine. The main starter-generator stator winding may be connected to a constant frequency (CF) power source to create a rotating field in the main starter-generator air gap. This rotating field, in turn, may induce current on the main rotor winding, which may be a closed circuit formed by main rotor field winding and exciter armature winding. The interaction between the main rotor current and the air gap flux may give rise to the starting torque to start the main engine. Adjusting the voltage supplied to the exciter stator field winding can modify the induced voltage and current on the rotor circuit to control the rotor current and starting torque. The starter-generator system may also be used to start an aircraft main engine by directly connecting the main stator winding to a power source without powering the exciter stator.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
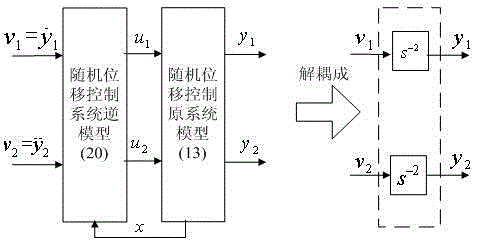
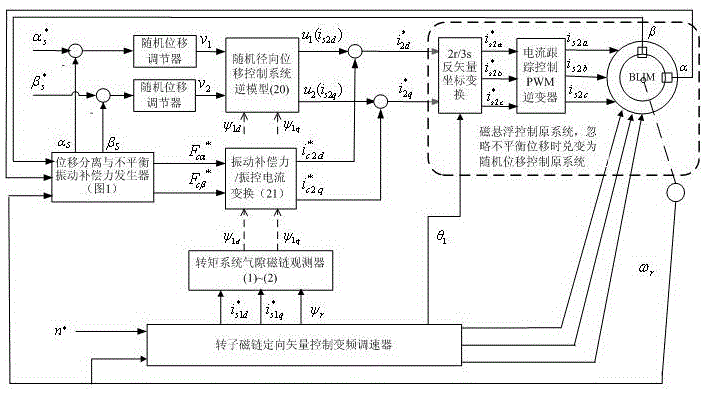
Current compensation-based unbalance vibration control system for bearingless asynchronous motor
InactiveCN105048913ANovel structureGuaranteed real-timeElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlMotor speedVibration control
The invention discloses a current compensation-based unbalance vibration control system for a bearingless asynchronous motor. A rotor flux linkage-oriented vector control variable-frequency governor provides current to a torque winding to control the rotating speed of the motor and the rotor flux linkage; torque winding stator current components and rotor flux linkage signals are output to an air gap flux linkage observer; two linear integration sub-systems are formed before a random displacement control inverse system is connected to the original system in series; rotor radial displacement is fed into a displacement separation and unbalance vibration compensation force generator to obtain random displacement and unbalance vibration compensation force; the random displacement is fed into the inverse system through a random displacement adjustor to form closed loop control; the inverse system outputs random displacement control current; the unbalance vibration compensation force is subjected to force / flow transformation to obtain unbalance vibration compensation control current; the unbalance vibration compensation control current is correspondingly compared with the random displacement control current to obtain synthetic magnetic levitation control current; and the synthetic magnetic levitation control current is fed into the original system to generate three-phase magnetic levitation control current, so that the unbalance vibration current compensation control on the bearingless asynchronous motor is realized.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Multi-pattern high temperature superconducting motor using flux trapping and concentration
InactiveUS20070052304A1Increase flux densityMore powerSynchronous machinesCooling/ventillation arrangementSynchronous motorSuperconducting electric machine
A high temperature superconducting synchronous motor having an inductor topology that increases the air gap flux density in direct relation to motor power density by trapping flux and concentrating it in the air gap to obtain more power in the same volume or smaller volume for the same power, and whose geometry enables the induction motor to be lighter than superconducting motors without the inductor topology, the motor being positioned in a housing, and the motor comprising: a) stator means having an armature winding to provide a stator field; b) rotor means positioned within the stator field and on which is disposed at least two polygon shaped ring or coil means along the same axis to provide separated and spaced apart relationship field solenoids; c) at least three high temperature superconducting plate means disposed in alternating relationship between the ring or coil means to hold the ring or coil means together to trap magnetic field and shape flux lines; and d) cooling means to cool the superconducting in the rotor to a temperature below the critical temperature of the superconducting plate means.
Owner:MASSON PHILIPPE +1
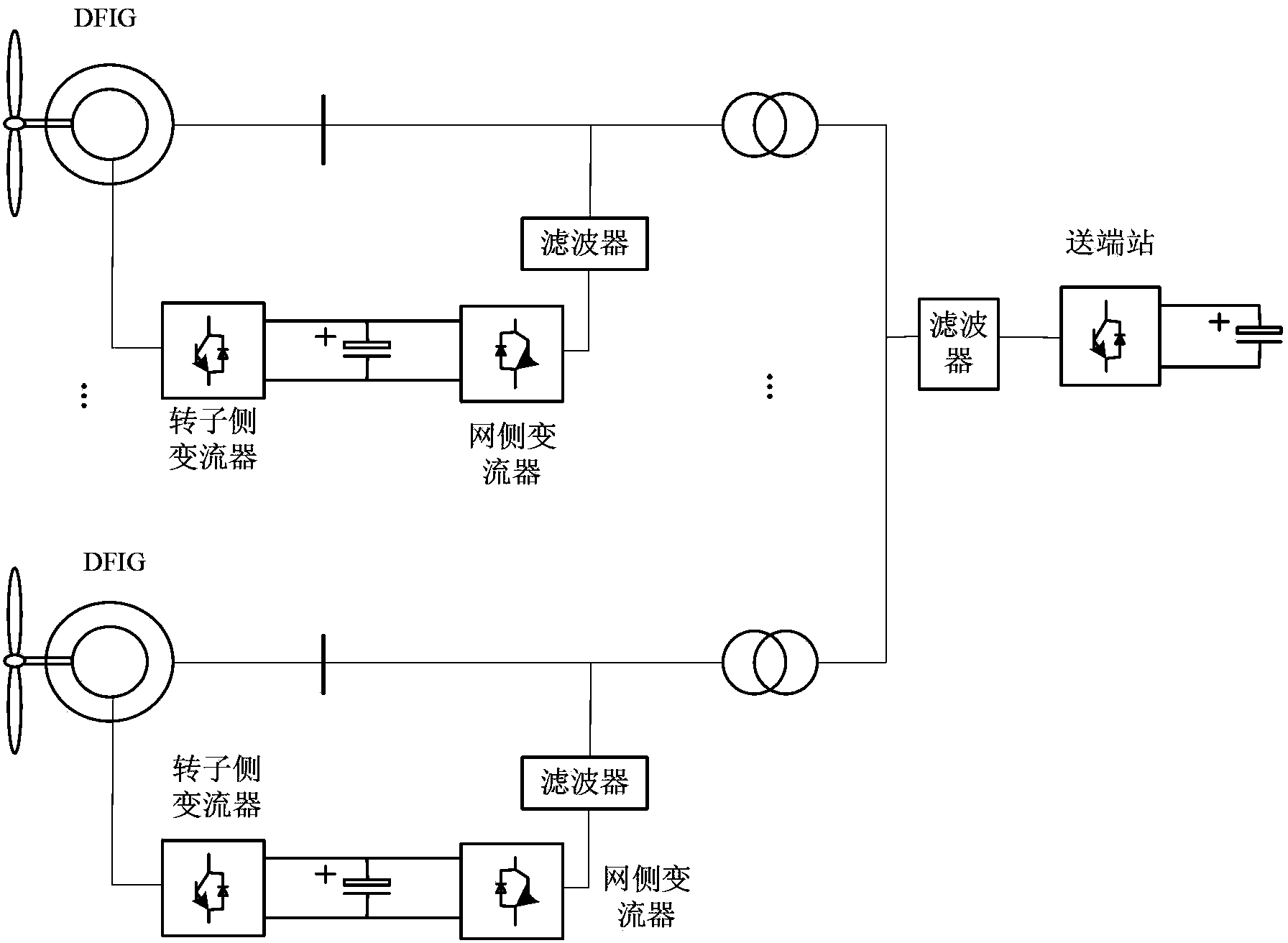
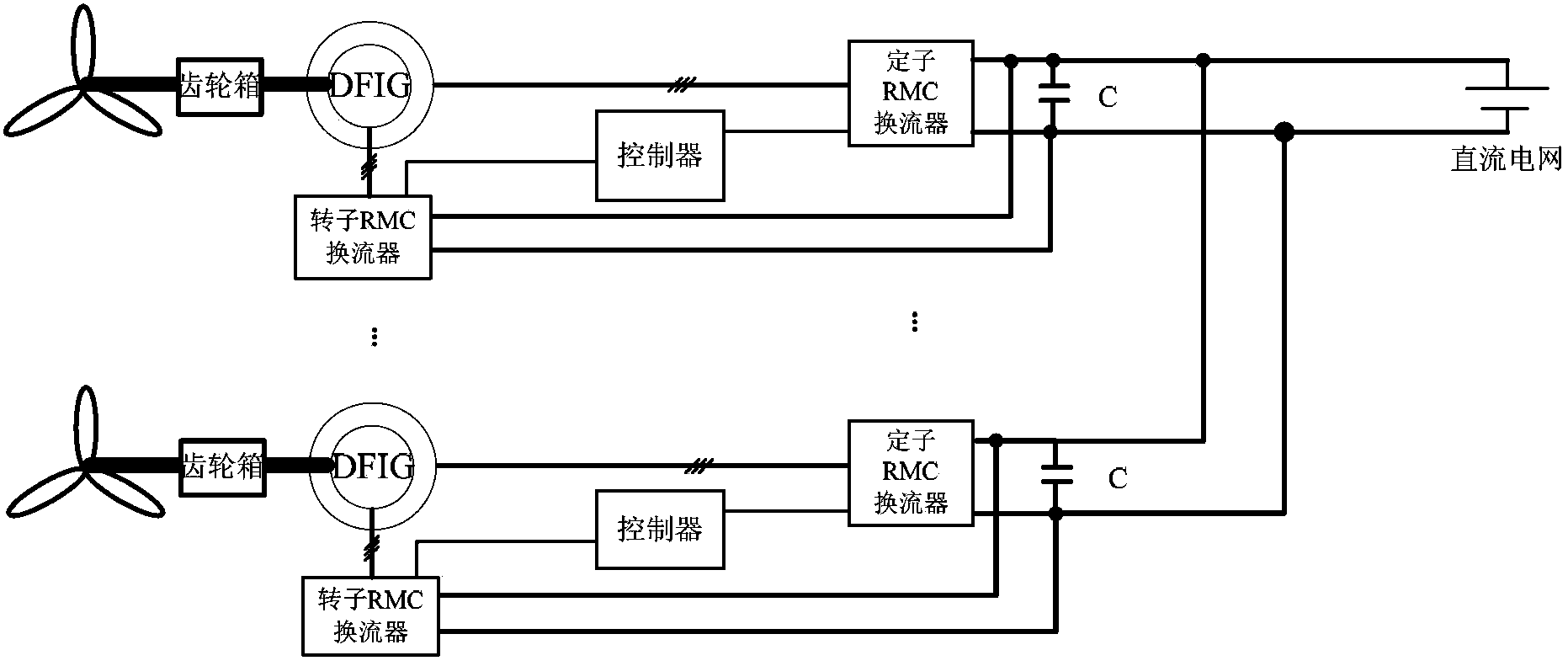
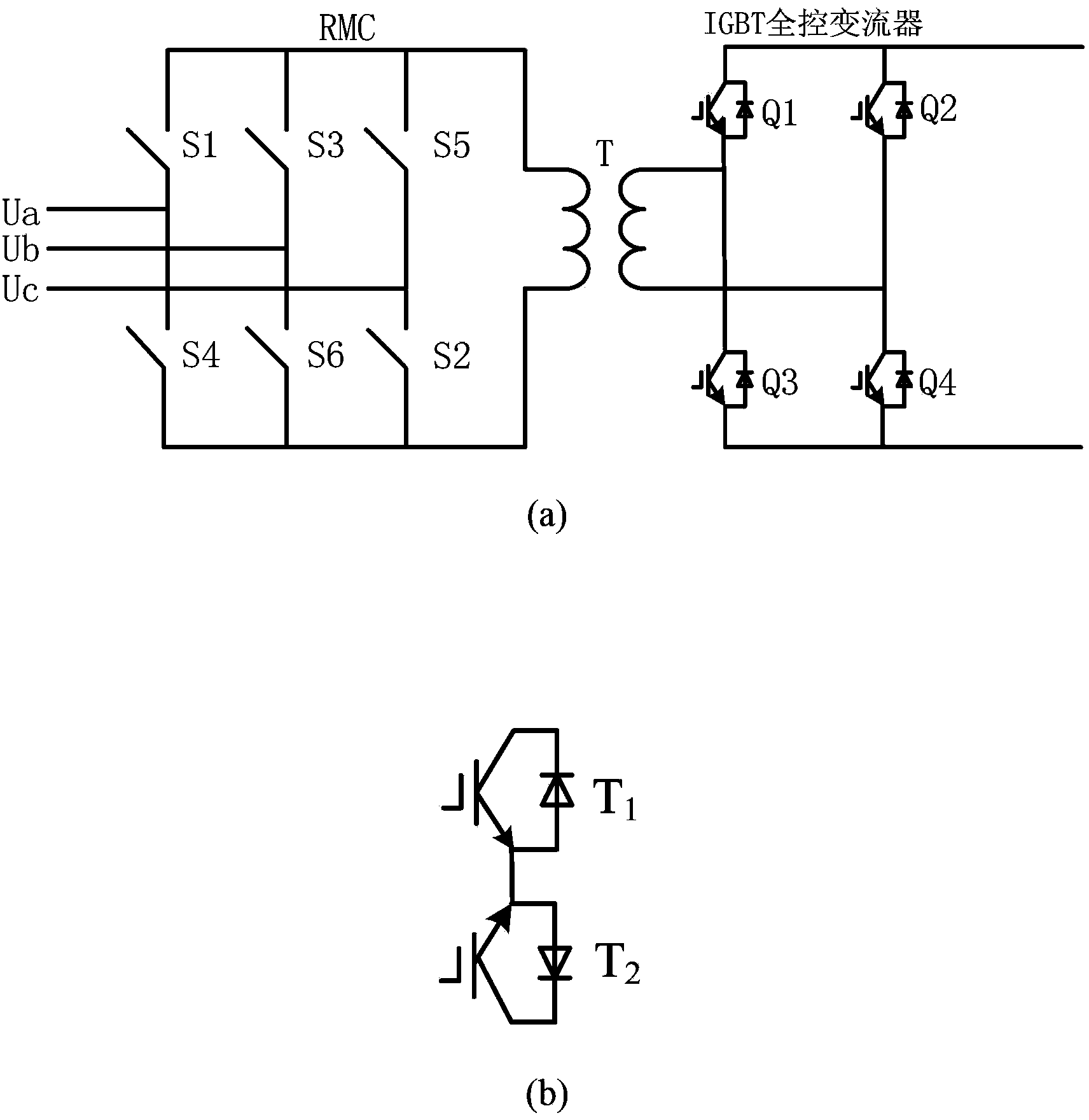
DFIG direct current grid-connected power generation system based on RMC and torque control method of DFIG direct current grid-connected power generation system
ActiveCN103414209AReduce harmonic effectsReduce volumeElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsCapacitanceElectric machine
The invention discloses a DFIG direct current grid-connected power generation system based on an RMC. The DFIG direct current grid-connected power generation system comprises a plurality of DFIGs and a high-voltage direct current power grid; each DFIG is connected with a stator RMC converter and a rotor RMC converter; each stator RMC converter and the corresponding rotor RMC converter share one controller. Compared with a traditional DFIG grid-connected system, the DFIG system enables an industrial frequency transformer to be smaller in size and lighter in weight. According to the DFIG system, the number of levels of the converters is reduced, a voltage stabilizing capacitor with the large size is replaced by a filter capacitor with the small size and the light weight, and the system is simple in structure and stable in operation performance. The invention further discloses a torque control method of the system, through the synergistic effect of the stator RMC converters and the rotor RMC converters, the constant electromagnetic torque output by the DFIGs and the constant amplitude of air gap flux linkage are guaranteed, and the output active power and the input reactive power of the stator side and the rotor side of a motor are controlled to be equal.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
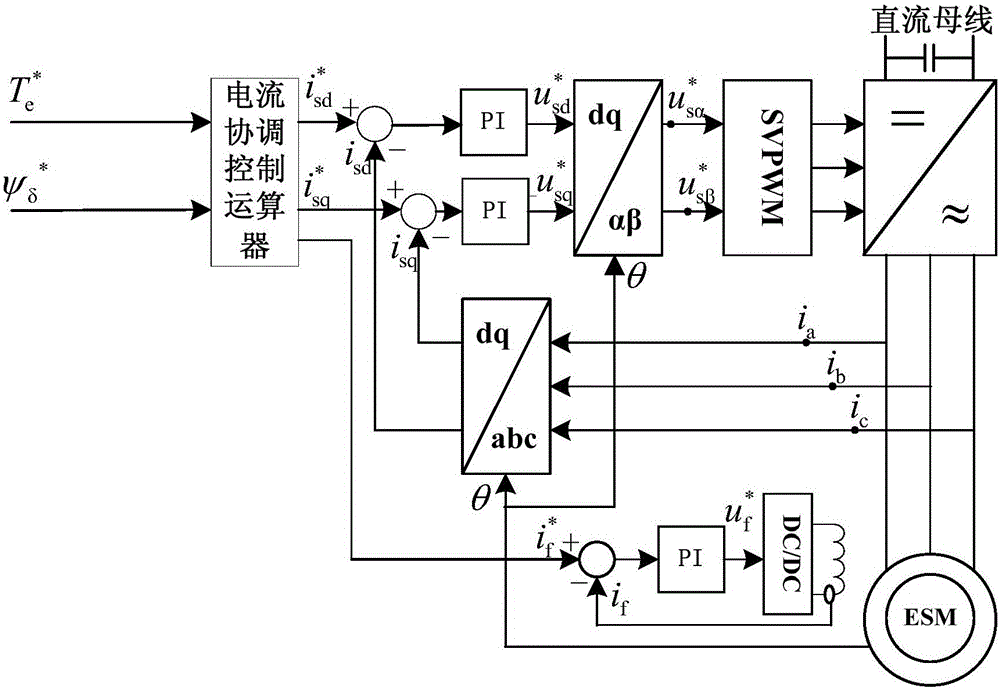
Current coordination control method of electrically-excited synchronous motor
InactiveCN105099316AAvoid saturationGuaranteed linear relationshipElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsSynchronous motorEngineering
The invention discloses a current coordination control method of an electrically-excited synchronous motor, which belongs to the field of motor control. In the method, an exciting current, a torque current and a compensation current in a electrically-excited synchronous motor system are defined. Under coordination control of the currents, a stator q shaft current serves as the exciting current and is used for generating an air gap magnetic field so as to keep a stator air gap flux linkage constant; a rotor current serves as the torque current and acts with the air gap magnetic field to generate electromagnetic torque; and a stator d shaft current serves as the compensation current, and a certain proportion relation is maintained between the stator d shaft current and the rotor current, so that a stator air gap magnetomotive force and a rotor air gap magnetomotive force in the direction of a d shaft are cancelled. The realization mode of the method is simple, the magnetic circuit saturation problem under a heavy duty is overcome, the linear relation between the electromagnetic torque and the torque current can be basically maintained if multiple overload torque is output, and the torque output capability is substantially improved; in addition, the torque response speed is greatly improved, and the problem of an insufficient inverter output voltage under the heavy duty condition is solved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
BSRM modeling method considering edge diffusion effect
ActiveCN105373014AEnable accurate modelingImprove modeling accuracySimulator controlLevitationModel method
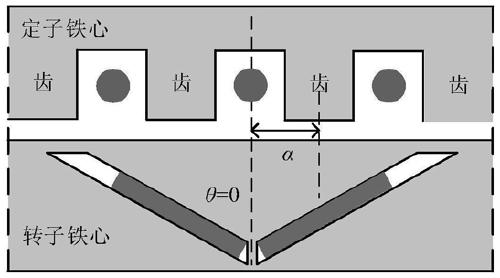
The invention relates to a BSRM modeling method considering the edge diffusion effect. The method includes the following steps that: Maxwell stress method integral paths considering the edge diffusion effect are selected respectively according to a stator movement region and a rotor movement region of a BSRM air gap when an angle theta by which rotor tooth poles deviate from stator tooth poles is equal to 0 degree and when the theta is not equal to 0 degree; based on the Maxwell stress method integral paths, air gap flux densities when theta is equal to 0 degree and when the theta is not equal to 0 degree are calculated; alpha-direction levitation forces and beta-direction levitation forces which are borne by the rotor tooth poles, and electromagnetic torques can be obtained through calculation according to the air gap flux densities; and an alpha-direction and beta-direction levitation force and electromagnetic torque analytical model of a BSRM is established. With the BSRM modeling method adopted, BSRM analytical modeling is realized, and the edge diffusion effect is considered, and therefore, modeling accuracy is high.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
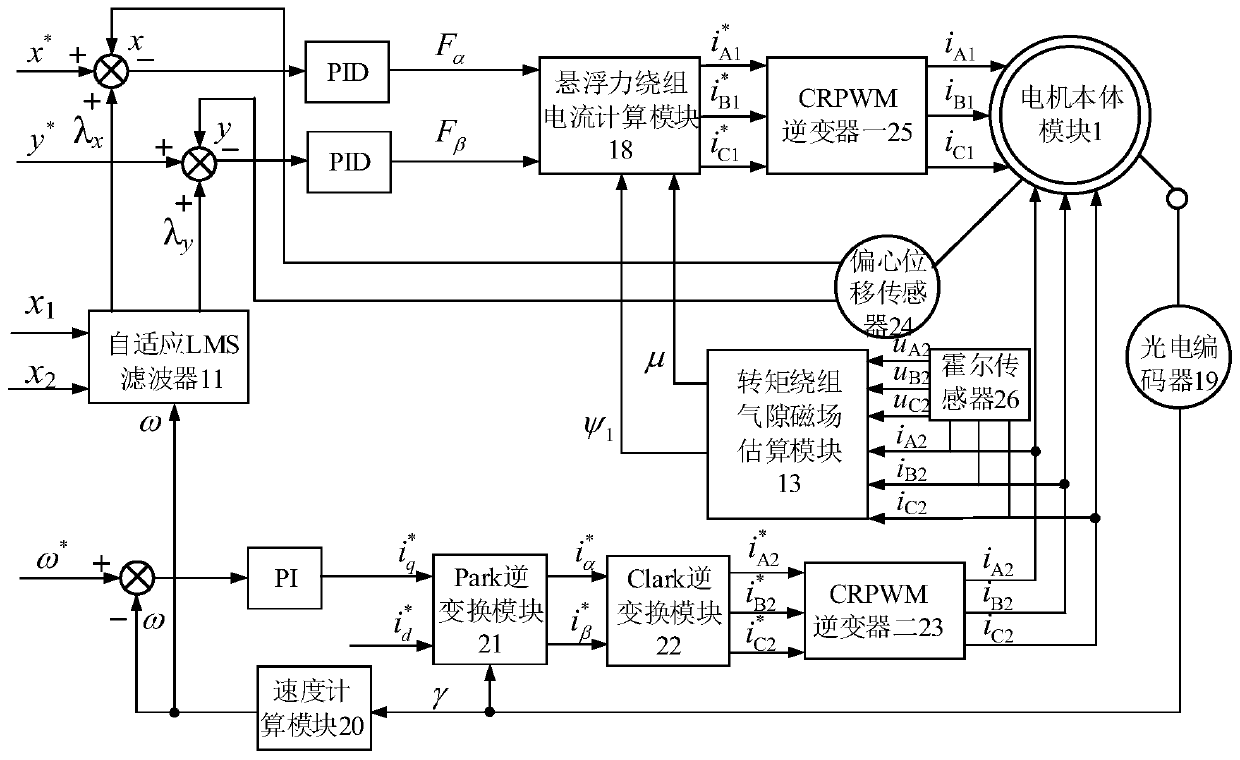
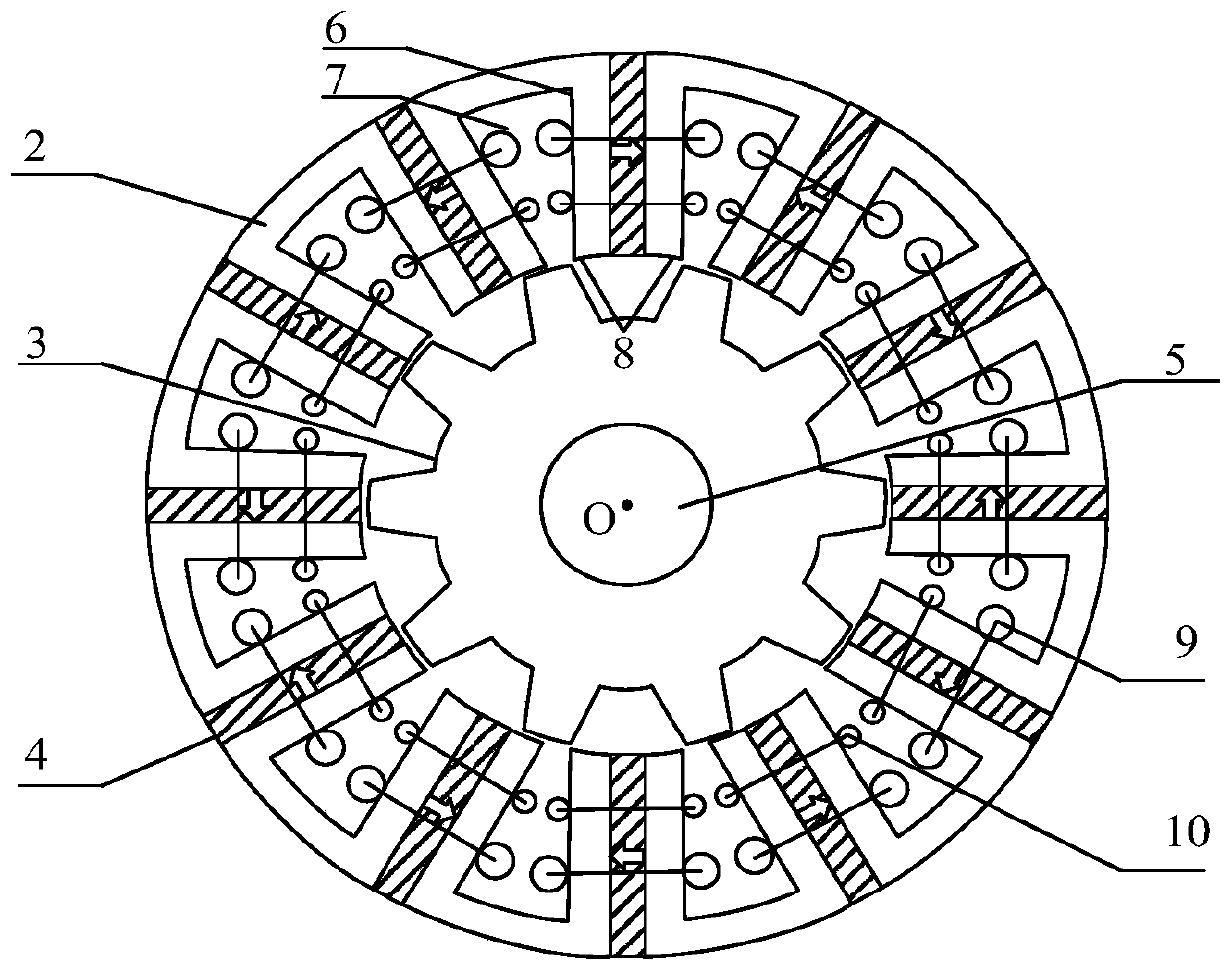
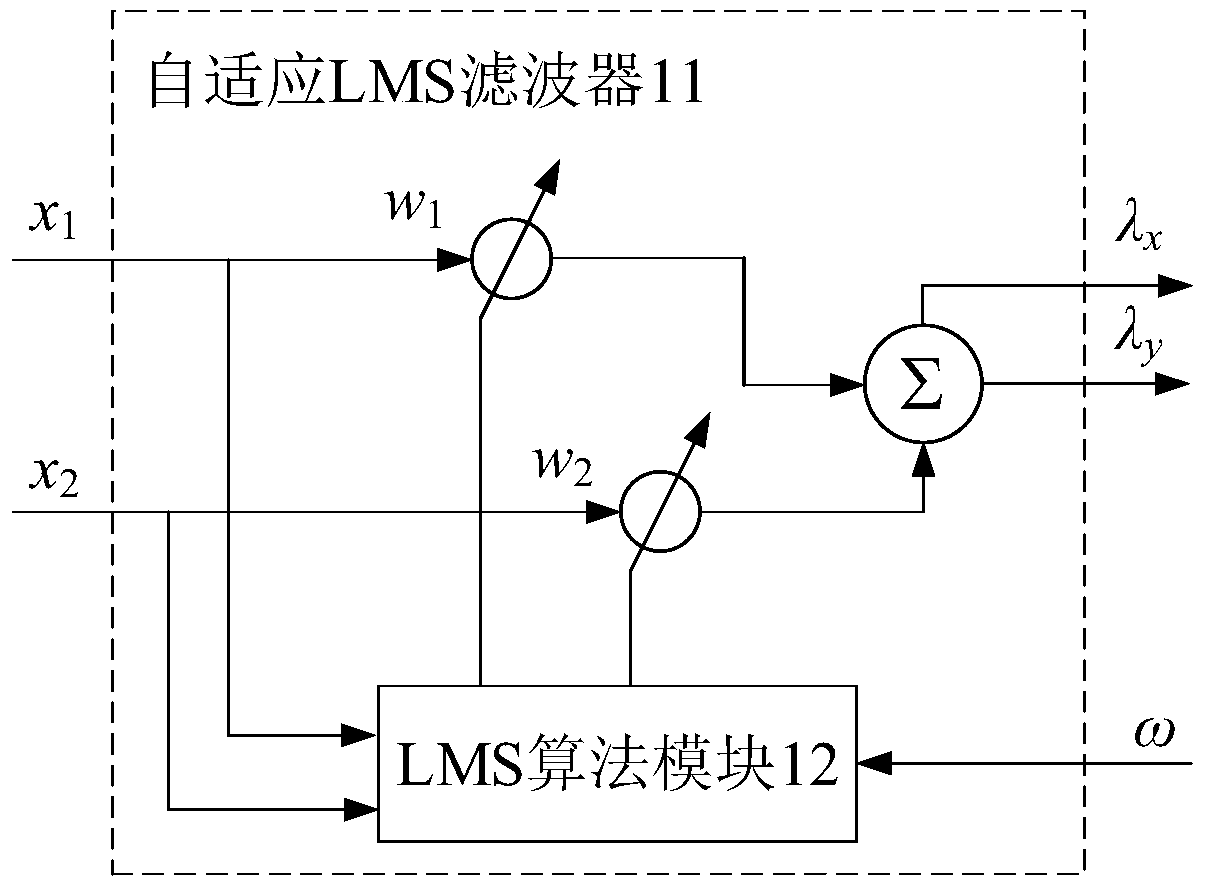
Bearing-free magnetic flux switching permanent magnet motor rotor eccentric displacement compensation controller
InactiveCN110380658AImprove detection accuracyGuaranteed accuracy and reliabilityElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlPermanent magnet motorThree-phase
The invention discloses a bearing-free magnetic flux switching permanent magnet motor rotor eccentric displacement compensation controller. A real-time rotating speed is input into an adaptive LMS filter, and the output of the adaptive LMS filter is a displacement compensation value; a rotor radial eccentric displacement and a rotor displacement command value and a displacement compensation valueare subjected to error comparison, and an error value is input into a corresponding PID controller; the PID controller converts the error value into two control components of the suspension force andinputs the suspension force into a suspension force winding current calculation module; a three-phase torque winding control current and a three-phase torque winding phase voltage are input into a torque winding air gap magnetic field estimation module, and the torque winding air gap magnetic field estimation module obtains rotor winding air gap flux linkage amplitude and phase and inputs the rotor winding air gap flux linkage amplitude and phase into the suspension force winding current calculation module; the suspension force winding current calculation module obtains a suspension force winding control current command value, and an inverter performs compensation control on the eccentric displacement of the suspension force rotor; the actual eccentric position center of the rotor does notneed to be detected, and the detection precision is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Linear Halbach permanent magnet-arranged superconductive eddy-current brake device with superconductive switch
InactiveCN103552473AIncrease profitIncrease electromagnetic forceElectrodynamic brake systemsEngineeringControllability
The invention discloses a linear Halbach permanent magnet-arranged superconductive eddy-current brake device with a superconductive switch, which is used for the non-contact electromagnetic braking of levitated bodies and comprises linear Halbach combination magnets and a superconductive eddy-current brake, and the superconductive eddy-current brake is arranged on a levitated body for braking. The two linear Halbach combination magnets adopted as the sidewalls of a linear Halbach combination magnet track are vertically mounted over the sides of permanent magnet guide rails for levitation along the longitudinal extension direction of a line; and eddy-current coils of the superconductive eddy-current brake adopt superconductive material to form superconductive coils. The linear Halbach permanent magnet-arranged superconductive eddy-current brake device can obtain higher air gap flux than the conventional arrangement method within an available space, and meanwhile, a good magnetic shielding effect can effectively reduce the affection of a magnetic field on a magnetic levitation system. Moreover, the linear Halbach permanent magnet-arranged superconductive eddy-current brake device has the advantages of high eddy-current braking electromagnetic force and controllability.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Electromagnetic property testing simulator for hydro-generator
Owner:HARBIN ELECTRIC MASCH CO LTD
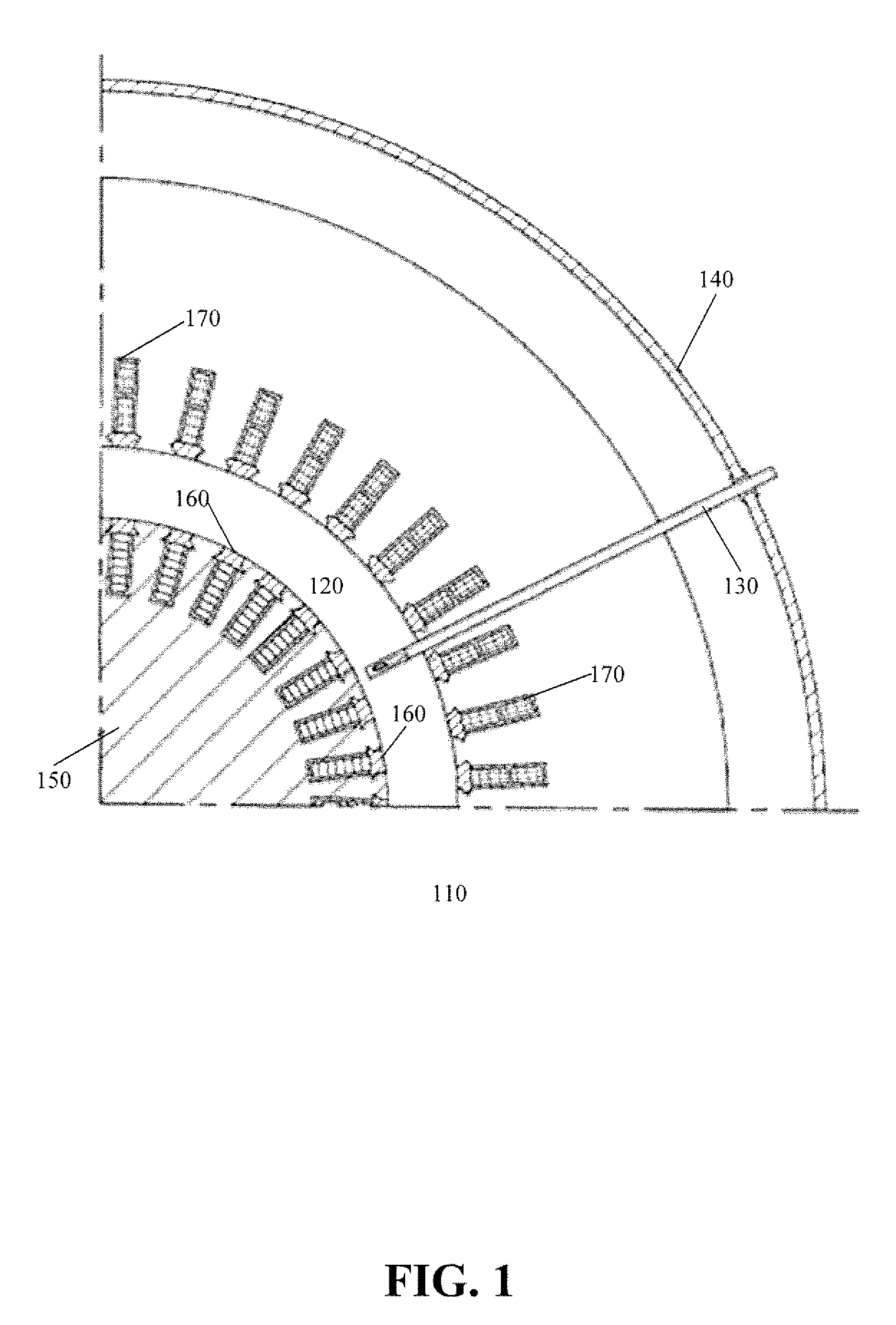
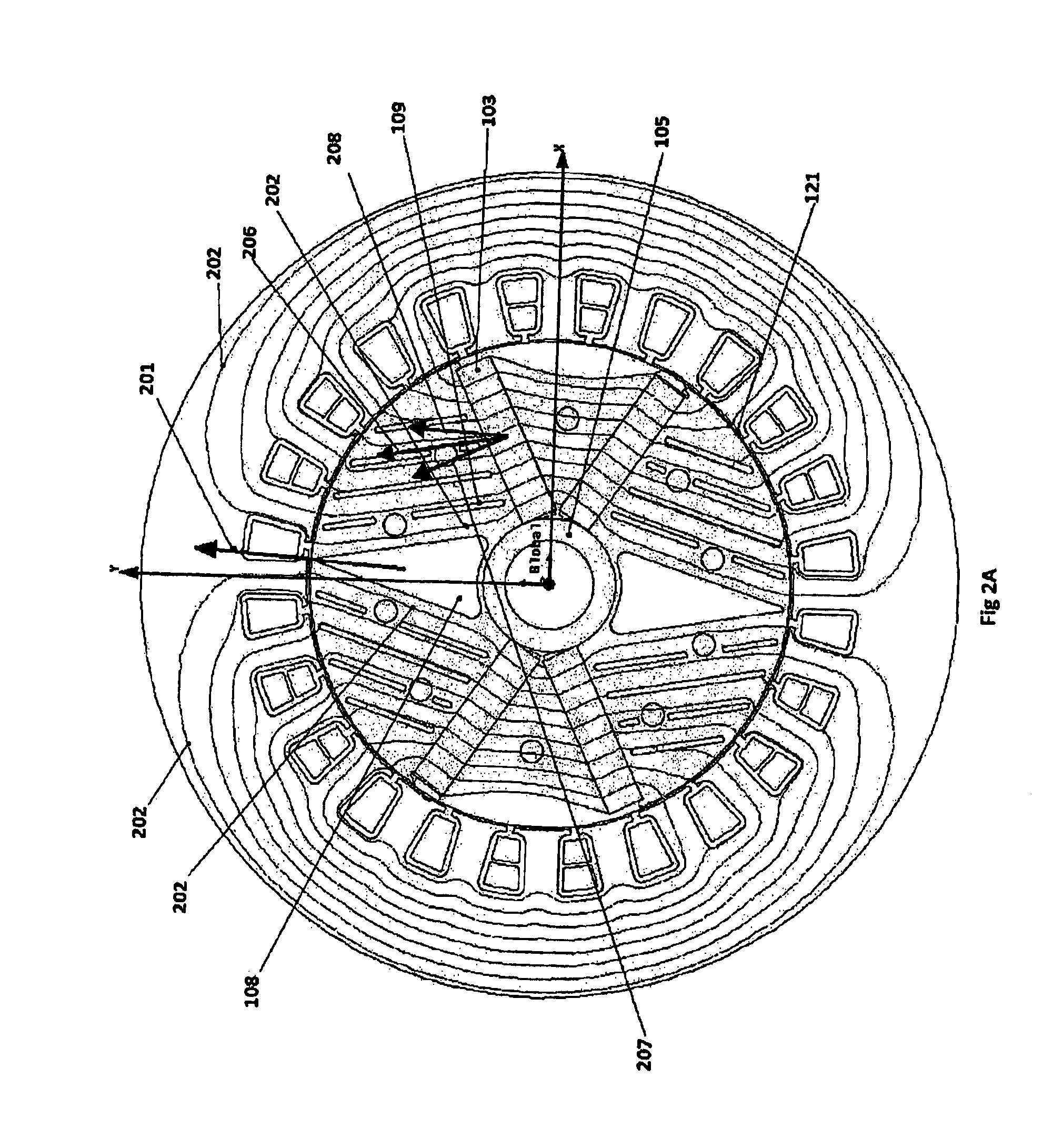
Permanent magnet electrical machine
ActiveUS20140246938A1Magnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsMagnetic polesPole piece
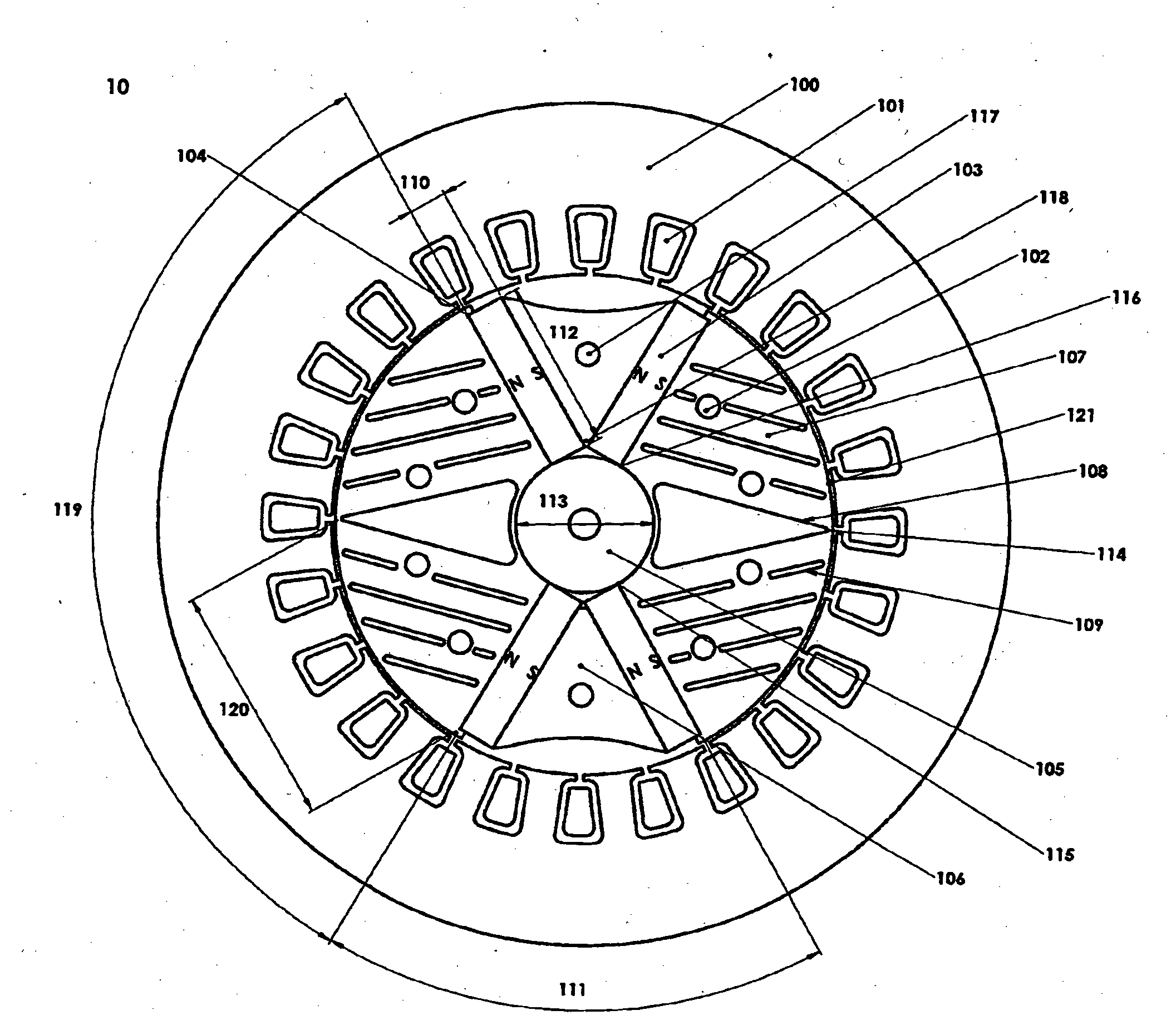
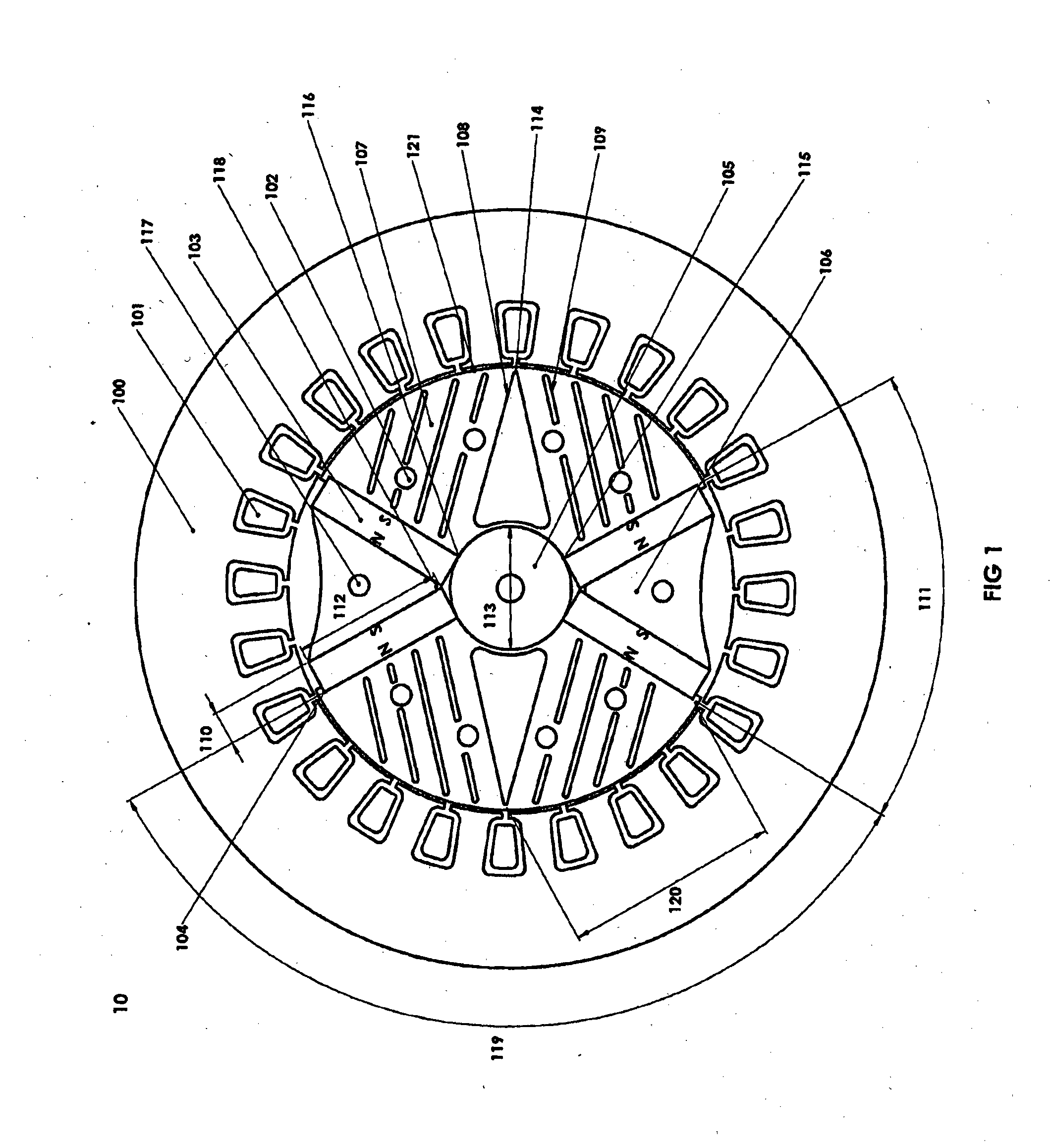
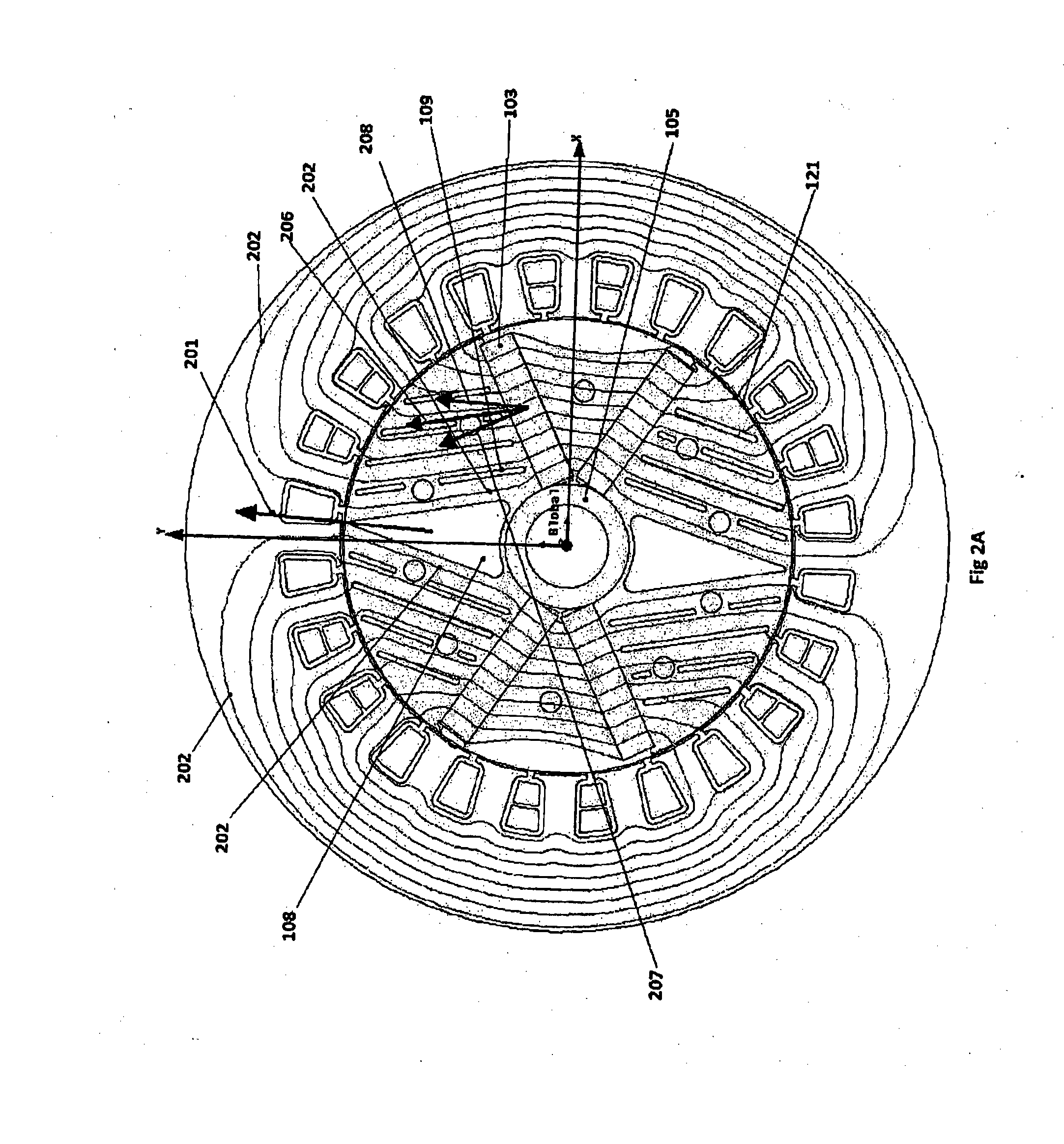
A 2-pole machine arrangement (10) has a stator (100) with windings (101) in conventional form, wound either in a single phase or three phase configuration. The rotor is formed of stacked laminations. The laminations include rotor pole pieces (107) located between the two magnetic poles. Each pole is formed by a pair of (embedded) permanent magnets (103), angularly spaced-apart by inter-magnet segments (106). The rotor pole pieces (107) include a series of evenly-spaced slots (109) and a central void (108). The slots (109) are of various lengths to direct the flux from the magnets (103) into the air gap (121) at a desired angle normal to the rotor surface. The slots 109 may be varied in width and angle to achieve the desired lowest waveform distortion under load and the highest air gap flux. The slots (109) also contribute to changing the saliency of the rotor.
Owner:RADIAL FLUX LAB
A multi-air-gap axial flux-magnetic field modulated permanent magnet motor
InactiveCN105406669BSmooth torque outputImprove power factorDynamo-electric machinesPermanent magnet rotorPower factor
The invention discloses a multi-air-gap axial magnetic flow-magnetic field modulation permanent magnet motor, which comprises a plurality of stators and a plurality of rotors, wherein the stators and the rotors are sequentially in staggered arrangement in the axial direction; the two ends of the permanent magnet motor are two surface-mounted permanent magnet rotors; the other rotors are embedded permanent magnet rotors; the structure dimensions of the plurality of stators are identical; the stators are subjected to two-edge grooving and use annular windings; and each stator sequentially deviates for the mechanical angle of the half groove distance relative to the former stator in the circumference direction. The multi-air-gap axial magnetic flow-magnetic field modulation permanent magnet motor realized according to the invention can comprehensively solve the inherent problems of magnetic field modulation motor torque density limitation and low power factor on the basis of remaining good performance of a magnetic field modulation motor.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
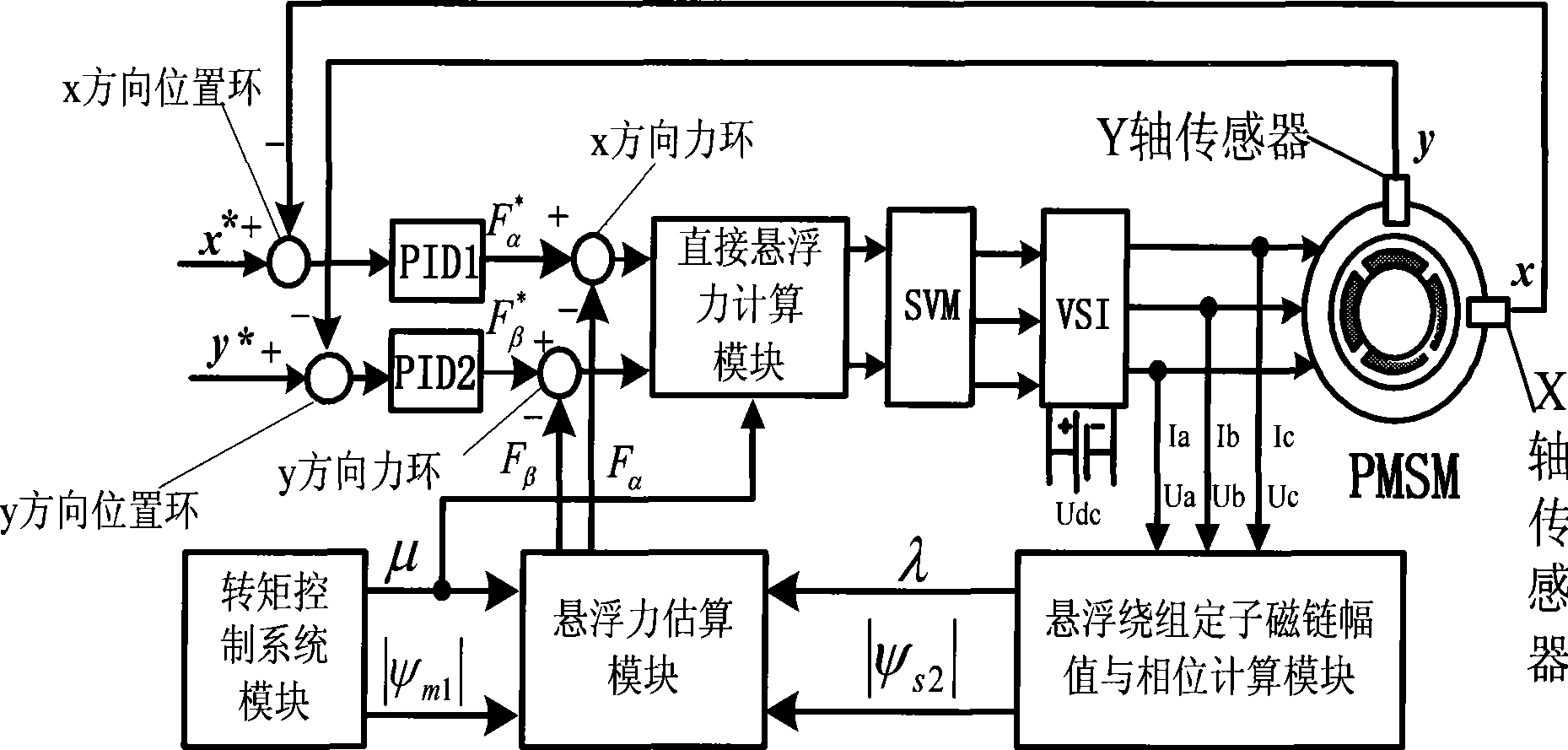
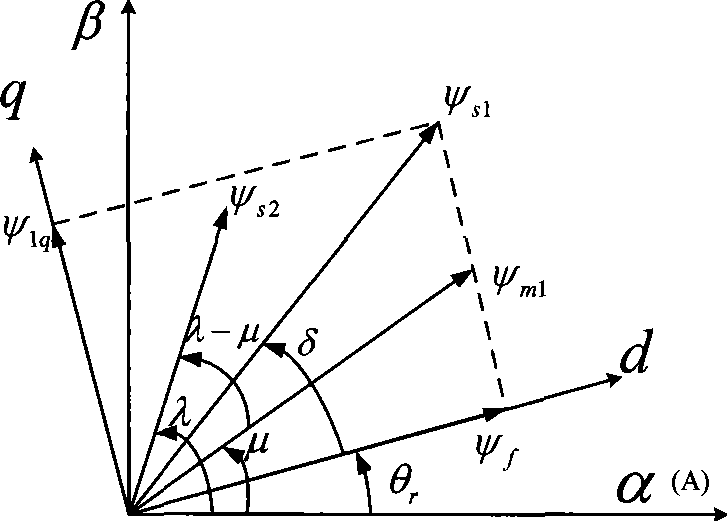
Direct suspending power control method for permanent magnet type non-bearing motor
InactiveCN101383573AImprove accuracyImprove dynamic response speedMagnetic holding devicesElectric machineClosed loop
The invention discloses a direct suspension force control method for a permanent-magnet-type bearing-free motor, and the method belongs to a bearing-free motor control method. The method controls the crest value and the direction of the space vector of a suspension winding stator flux through properly selecting the switch state of an inverter while maintaining the invariableness of an air-gap-flux composed by motor winding, and the suspension is controlled by adopting a closed loop, thereby further decoupling the torque control winding and the suspension winding. The invention is a control method with high suspension control precision, fast dynamic response and small motor parameter influence.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
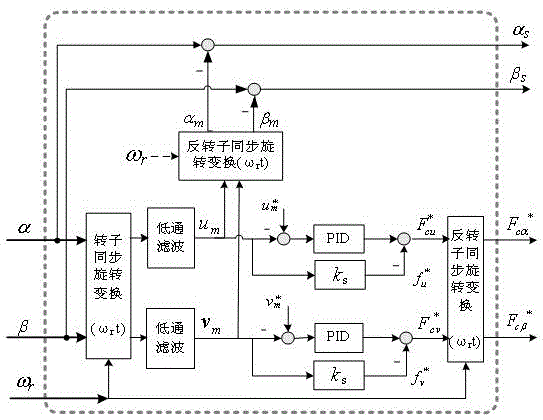
An air gap field oriented control method and system for an electrically excited synchronous motor
ActiveCN109217764AOrientation is accurateDirectional control is accurateElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlSynchronous motorFlux linkage
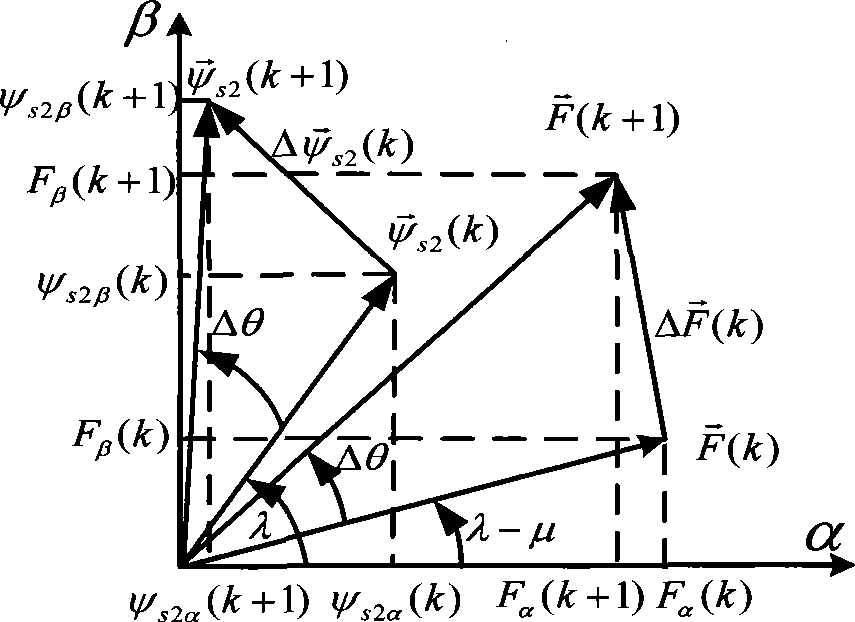
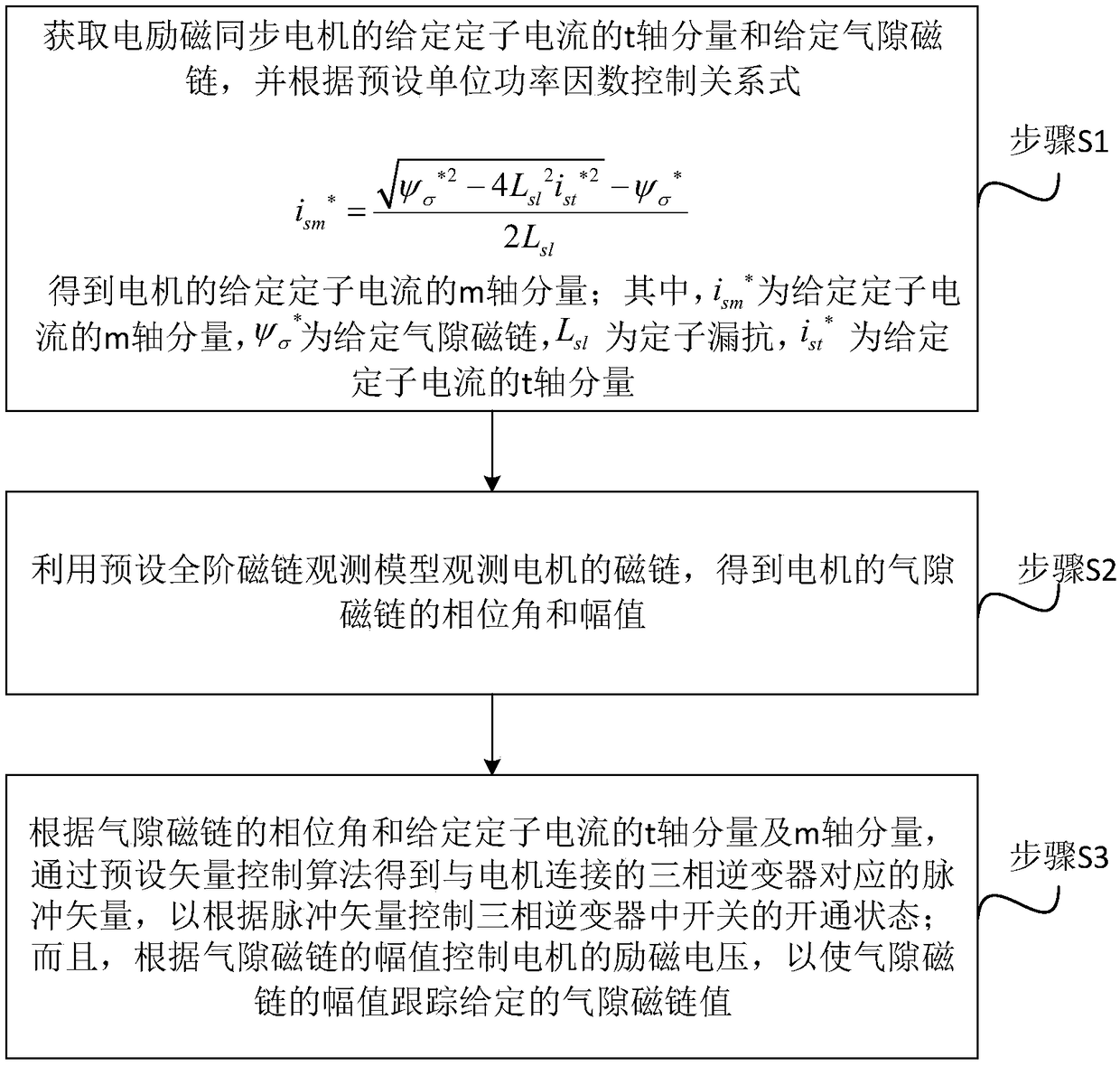
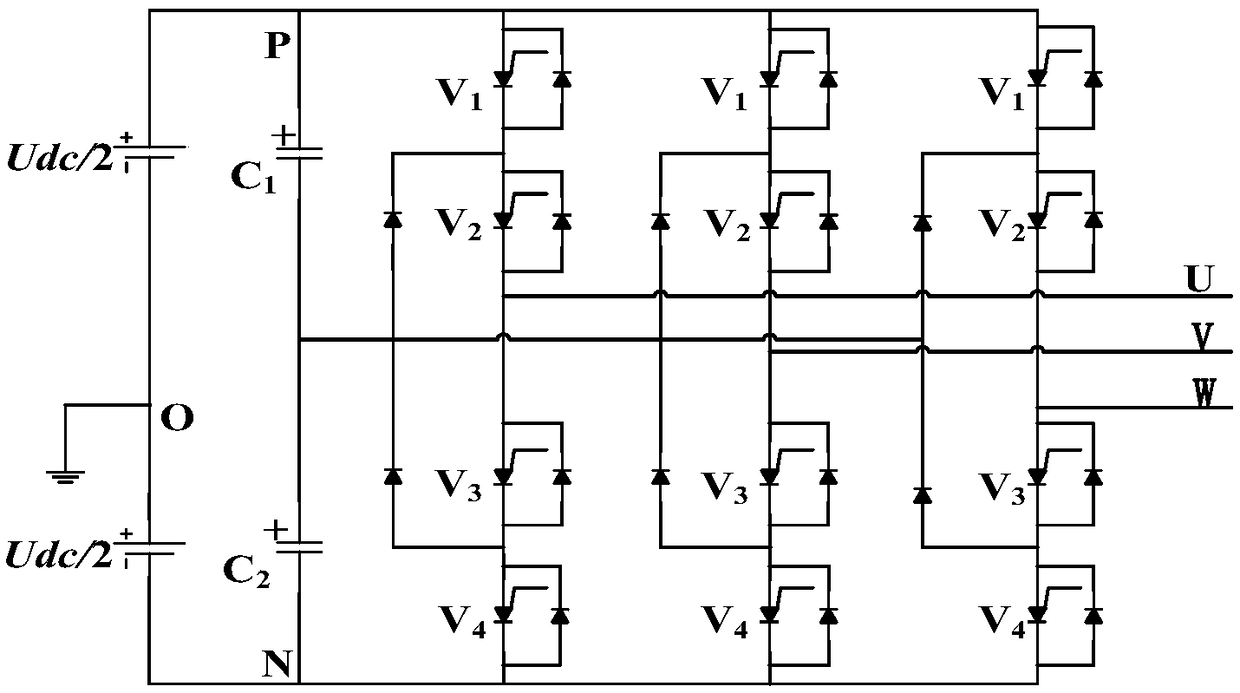
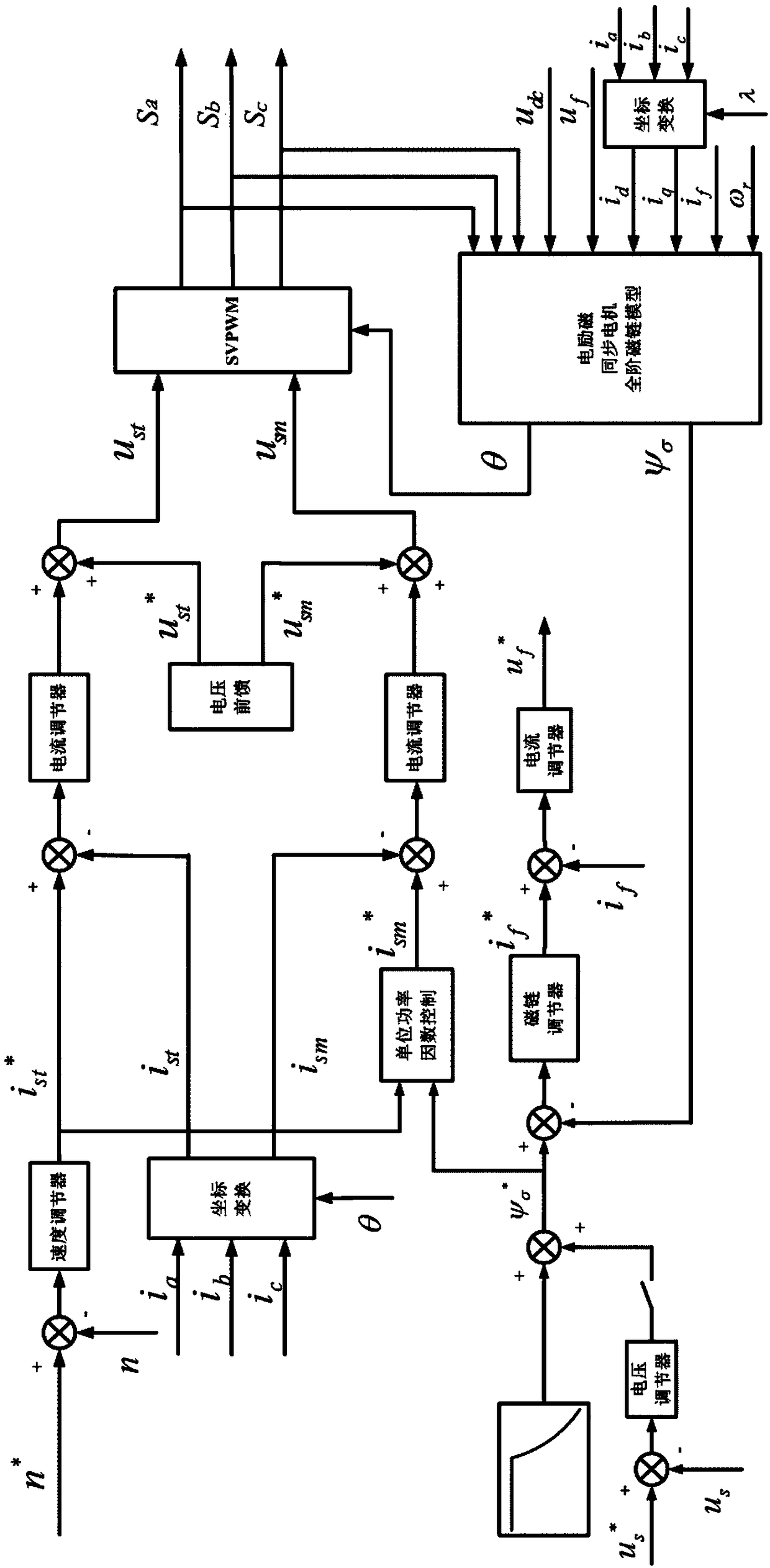
The invention discloses an air-gap field oriented control method and a system of an electrically excited synchronous motor, comprising the following steps: obtaining t-axis component of a given statorcurrent and a given air-gap flux linkage of the electrically excited synchronous motor, and obtaining m-axis component of the given stator current according to a unit power factor control relation; The phase angle and amplitude of the air-gap flux linkage are obtained by observing the flux linkage of the motor with the full-order flux linkage observation model. According to the phase angle of theair-gap flux linkage and the t-axis and m-axis components of the stator current, the pulse vector corresponding to the three-phase inverter connected with the motor is obtained by the vector controlalgorithm, so as to control the on-state of the switch in the three-phase inverter according to the pulse vector. The excitation voltage of the motor is controlled according to the magnitude of the air-gap flux linkage so that the magnitude of the air-gap flux linkage tracks a given air-gap flux linkage value. The present application can realize unity power factor control, and based on a full-order flux linkage observation model, the air gap magnetic field is accurately oriented, is less affected by parameters, can realize complete decoupling control, and has better performance.
Owner:ZHUZHOU CSR TIMES ELECTRIC CO LTD
Initiative risk protection system for variable flow type vector control device of high-capacity thyristor
InactiveCN103208962AEnsure safetyImprove the ability to resist exhaustive attacksElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsTime informationSynchronous motor
An initiative risk protection system for a variable flow type vector control device of a high-capacity thyristor comprises a chip-level encryption and decryption control unit, a multisource / heterogeneous type industrial control network gateway, a compact type embedding type processing unit, an embedding type analyzing system, a risk evaluation and typical operation state analyzing unit and the like. The chip-level encryption and decryption control unit is used for supplying high-capacity synchronous motor rotor mechanical positions and rotating speed data information. The compact type embedding type processing unit is used for performing flow control and filtering on dynamic data of alternating current. The embedding type analyzing system is used for analyzing a current regulating type expert type rule base within half cycle of natural commutation. The risk evaluation and typical operation state analyzing unit is used for obtaining real-time information of voltage feedforward compensation and air gap flux linkage tracks. The initiative risk protection system aims at solving the problem of security holes, attack and virus invasion of industrial control networks of main mills and the like in the steel and iron industry, can perform initiative protection and remote real-time monitoring, and is safe, reliable, autonomous and controllable. An industrial equipment level information security control technique of the initiative risk protection system is further provided.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Modeling method of variable magnetic flux leakage permanent magnet synchronous motor based on multi-working-condition operation
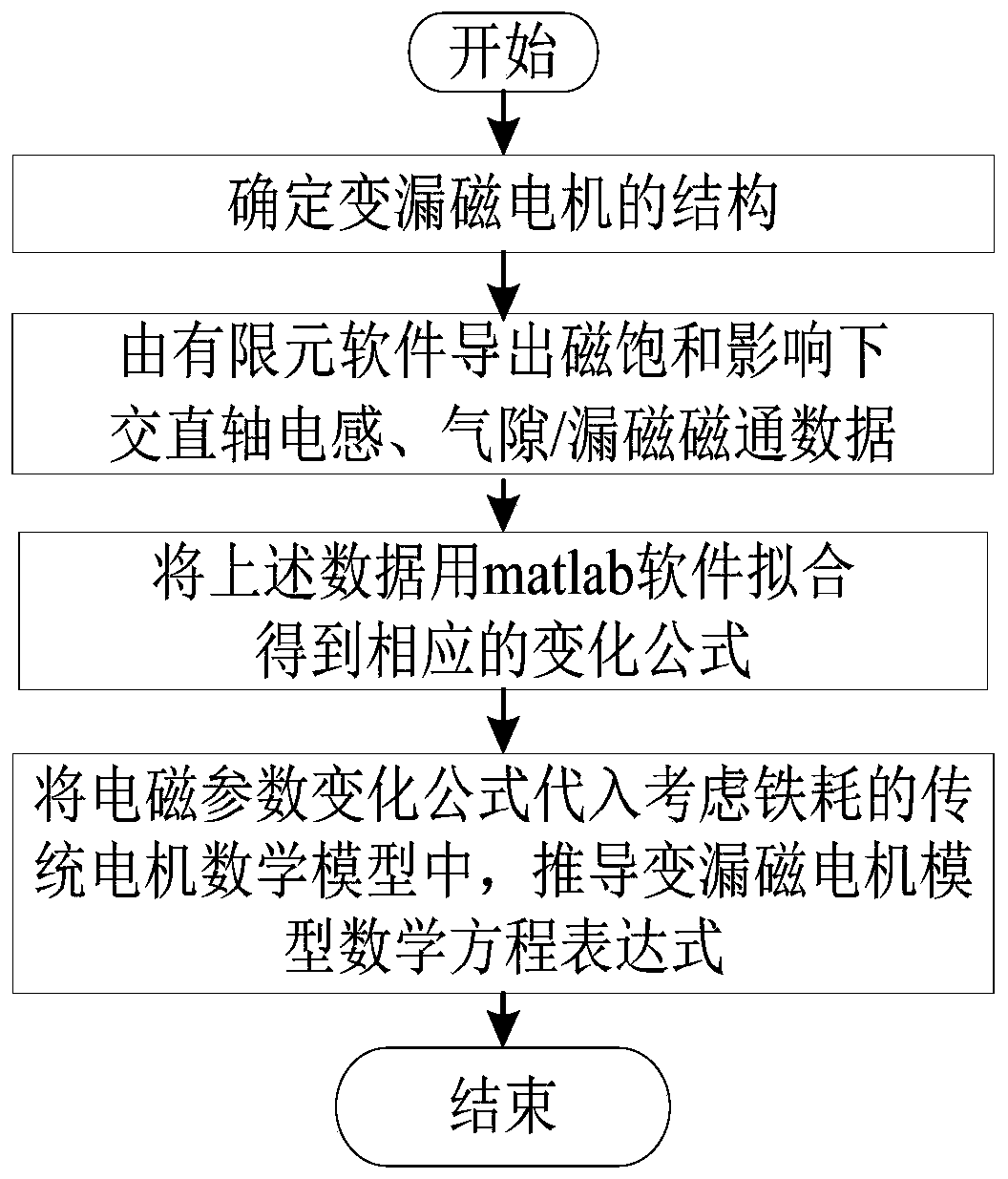
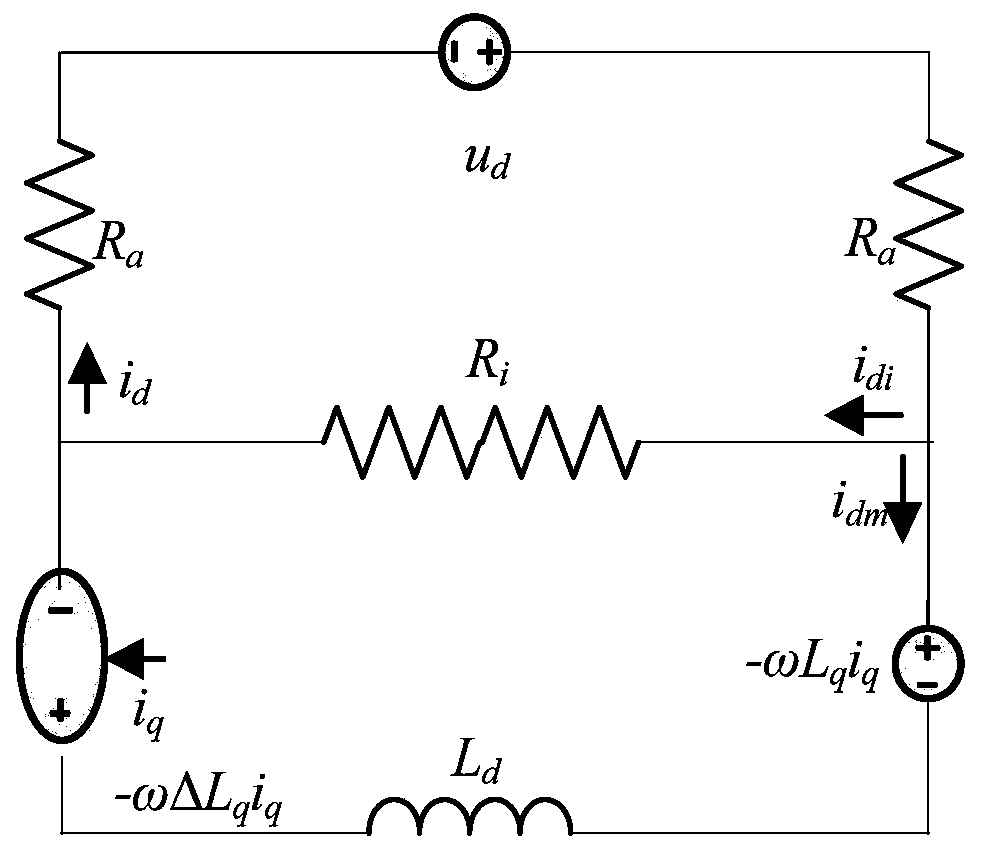
ActiveCN110442944AThe actual running effect of the reactionIncreased sensitivitySpecial data processing applicationsElement modelMathematical model
The invention discloses a modeling method of a variable magnetic flux leakage permanent magnet synchronous motor based on multi-working-condition operation, which comprises the following steps of: establishing a finite element model of the variable magnetic flux leakage permanent magnet synchronous motor and simulating to obtain change data between quadrature-axis current iq and direct-axis inductance Ld, quadrature-axis inductance Lq, air gap flux psi delta and magnetic flux leakage psi sigma; performing data fitting on the quadrature-axis current iq and change data among the direct-axis inductance Ld, the quadrature-axis inductance Lq, the air-gap flux psi delta and the leakage flux psi sigma to obtain a corresponding change formula; substituting the change formula into a mathematical model of a traditional motor considering iron loss change to obtain a flux linkage equation, a voltage equation and a torque equation. A model of the variable flux leakage permanent magnet synchronous motor is established, neglected influence factors of magnetic field changes on modeling in a traditional motor model are taken into consideration, the established motor model is established based on multi-working-condition operation of the motor for the electric automobile, and the actual operation effect of the motor under multi-factor driving can be reflected more truly.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Direct controller of radial displacement of bearing-less asynchronous motor rotor
The invention discloses a direct controller of a radial displacement of a bearing-less asynchronous motor rotor. The direct controller is composed of a rotary speed controller, a radial displacement closed-loop controller and a torque winding air gap flux linkage estimation module; the rotary speed controller outputs a three-phase current to an electric motor torque winding; the radial displacement closed-loop controller is composed of a rotor eccentric displacement and eccentric angle computing module, a neuron PID controller, a levitation force winding current computing module, a three-phase power pulse-width modulation (PWM) inverter, a radial displacement sensor and a photoelectric encoder; according to the levitation force winding current computing module, five variables such as the radial levitation force amplitude, the rotor eccentric angle, the torque winding air gap flux linkage amplitude, the phase and the rotor position angle serve as inputs, three-phase levitation force winding current command values i'<2A>, i'<2B> and i'<2C> serve as outputs, and three-phase levitation force winding currents i<2A>, i<2B> and i<2C> required for stable rotor levitation are obtained through the three-phase power PWM inverter; the direct controller is simple and practical in structure, and independent control of the electromagnetic torque and the radial levitation force of a bearing-less asynchronous motor is achieved.
Owner:江阴智产汇知识产权运营有限公司
Bearingless synchronous reluctance motor rotor eccentric displacement controller and construction method thereof
The invention discloses a bearingless synchronous reluctance motor rotor eccentric displacement controller and a construction method thereof. The motor rotor eccentric displacement controller comprises a rotation speed controller, a torque winding air gap flux linkage estimation module and an eccentric displacement controller body. A rotation speed given value is taken as an input value of the rotation speed controller, three-phase torque winding drive current values are taken as output values, torque winding three-phase phase voltage values and phase current values are taken as input values of the torque winding air gap flux linkage estimation module, an amplitude and a phase position of a torque winding air gap flux linkage are taken as output values of the torque winding air gap flux linkage estimation module, the amplitude and the phase position of the torque winding air gap flux linkage, rotor displacement given values X* and Y* and a rotor position angle are taken as input values of the eccentric displacement controller body, three-phase suspension force winding drive current values are taken as output values of the eccentric displacement controller body, and then the bearingless synchronous reluctance motor rotor eccentric displacement controller is constructed. Therefore, an electromagnetic torque and radial direction suspension force of a bearingless synchronous reluctance motor can be independently controlled, and control performance of the whole system is effectively improved.
Owner:江阴智产汇知识产权运营有限公司
Bearingless asynchronous motor direct suspension force control method based on model prediction
InactiveCN110266231ALoad torque constantSolve the accuracy problemElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlRectangular coordinatesElectric machine
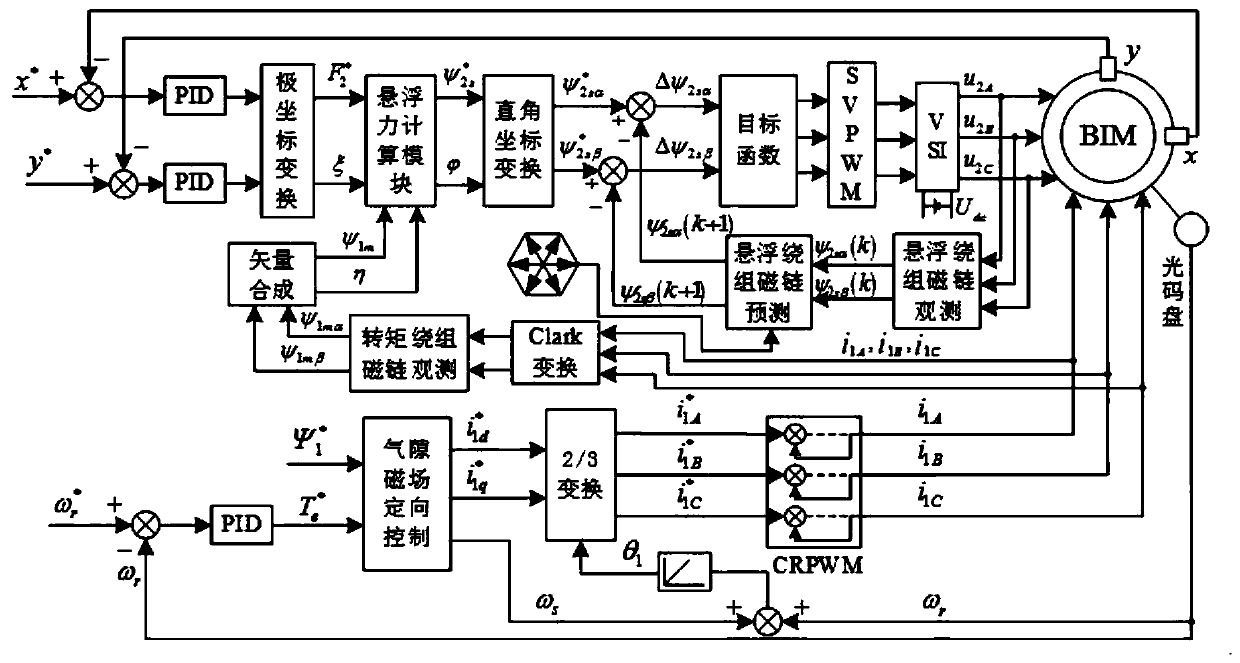
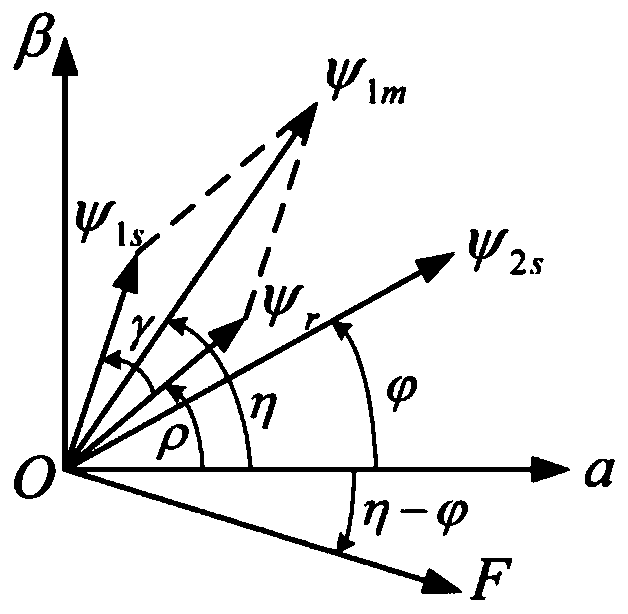
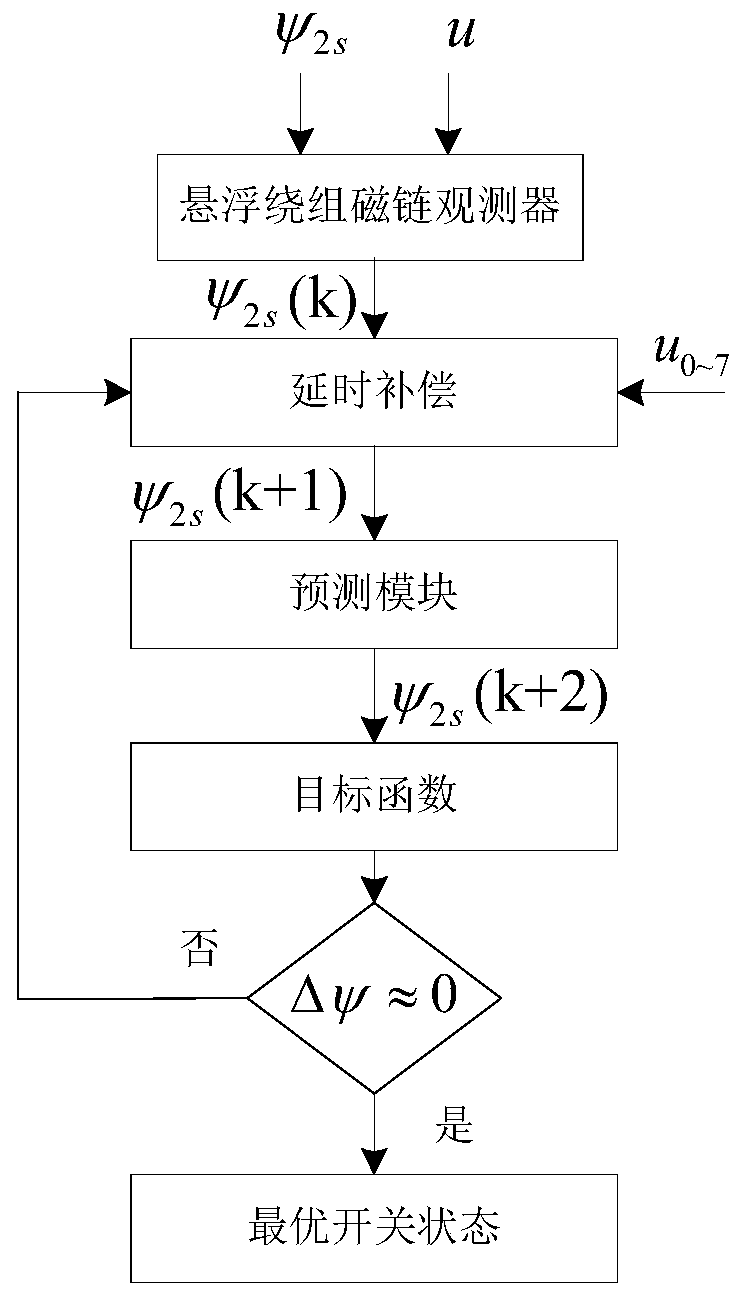
The invention discloses a bearingless asynchronous motor direct suspension force control method based on model prediction. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining radial suspension force amplitude and phase xi after PID adjustment and polar coordinate conversion of difference values of displacement signals x and y and given displacement signals x* and y* through suspension control; calculating synthesis air gap flux linkage psi 1m and phase eta through torque winding flux observer and vectorial resultant of three-phase current; inputting radical suspension force amplitude and phase xi, air gap flux linkage psi and phase eta into a suspension force calculating module, carrying out rectangular coordinate conversion treatment to obtain a suspension winding flux linkage reference value, screening a difference value with a suspension winding flux linkage reference value at the next moment through a target function to obtain a flux linkage in an optimal switch state, obtaining the voltage signal of a drive inverter after SVPWM modulation of the flux linkage, and finally obtaining three-phase voltage required for a control motor so as to realize bearingless asynchronous motor direct suspension force control. The method can solve the problem that precision is insufficient and is greatly influenced by motor parameters caused by traditional suspension force indirect control.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Halbach permanent magnet linear oscillation motor and operation method thereof
InactiveCN105006941AReduce thicknessIncrease profitMagnetic circuit rotating partsConductor CoilMagnet
The present invention relates to a Halbach permanent magnet linear oscillation motor, which comprises a housing, a stator main iron core, a rotor iron core and a linear axis. The stator main iron core is fixedly held in the housing and a winding is wound onto the stator main iron core. The rotor iron core is accommodated in the housing and is arranged opposite to the stator main iron core. A Halbach permanent magnet array is arranged outside the rotor iron core. The linear axis runs through the housing and is pivotably connected with the housing through a pair of linear bearings. The rotor iron core is fixedly arranged onto the linear axis and is in linkage with the linear axis. The Halbach permanent magnet array is adopted by the Halbach permanent magnet linear oscillation motor, so that an air gap flux larger than that of a conventional magnet can be obtained. Meanwhile, the Halbach permanent magnet linear oscillation motor is good in magnetic shielding effect and can reduce the thickness of a rotor magnetic-conductive yoke.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Current harmonic injection type vernier reluctance motor and system
ActiveCN107707093AIncrease profitAC motor controlMagnetic circuit rotating partsAlternating currentConductor Coil
The invention discloses a current harmonic injection type vernier reluctance motor and system. The vernier reluctance motor body comprises a stator, a rotor and a winding. The stator and the rotor arein salient pole structures. The winding is a single-layer concentrated winding. Two sinusoidal alternating currents with different frequencies are injected into each phase of the winding. On the basis that the current in the winding is three-phase symmetrical current, two sinusoidal alternating current components with different frequencies in the winding are used to produce armature magnetomotiveforces with the same number of pole-pairs but different rotation speed. One magnetomotive force produce a space magnetic field with the same number of pole-pairs and the same rotation speed with theother armature magnetomotive force through the modulation of an air-gap flux guide, and a certain angle is between the space magnetic field and the other armature magnetomotive force. The magnetic field interacts with the other armature magnetomotive force to generate torque and realize electromechanical energy conversion. Compared with the prior art, the motor has the advantage that the current utilization ratio is increased by 11% compared with a direct current injection type vernier reluctance motor. In addition, the complexity of the controller part of the motor system is significantly reduced, and the cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Travelling field synchronous AC motor
InactiveUS7095141B2Strong and stable structureMaximise output torqueSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuitPhase currentsEngineering
The invention relates to a synchronous AC electric motor with concentrated windings (2), whereby one primary side pole is comprised of a series of toothed-modules (4) with each toothed-module (4) being connected in the correct electrical phase sequence to a corresponding phase (11) of the motor electrical supply (5). In order to provide a highly optimized concentrated winding motor design applicable equally to either linear or rotating machines, which retains the performance benefits of existing concentrated-winding motors it is proposed that neighboring modules (4) are wound so as to have alternating polarities, whereby the number of toothed-modules (4) comprising a primary side pole is exactly equal to twice the number of motor phases (5), and that the motor is designed to operate using an air-gap flux component which is harmonic of the fundamental phase current frequency.
Owner:REXROTH INDRAMAT
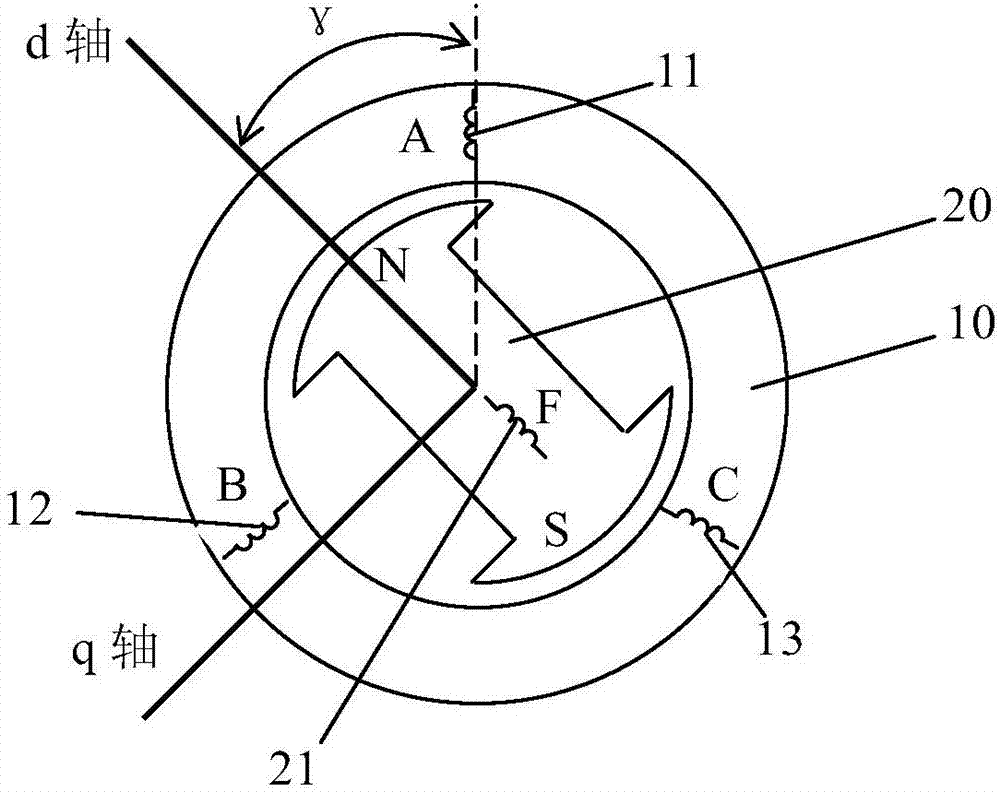
Excitation synchronous motor rotor initial position estimation method
ActiveCN107070345ASmall estimation errorNo hardware signal interference issuesElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsSynchronous motorPosition angle
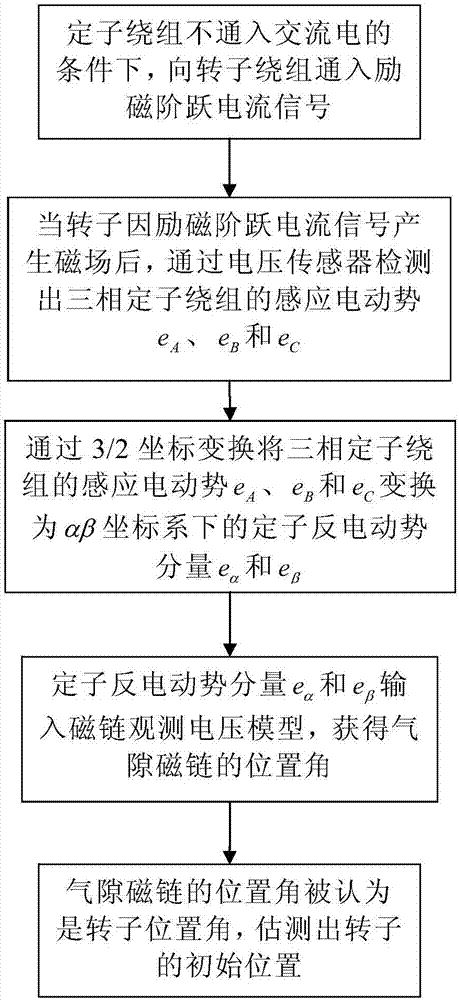
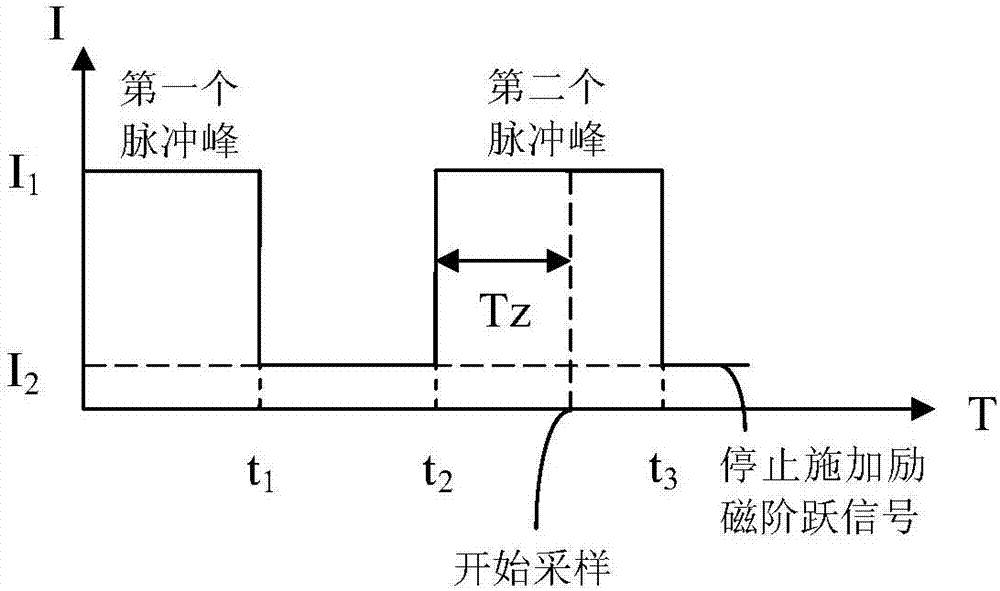
The invention discloses an excitation synchronous motor rotor initial position estimation method. The method includes the following steps that: under a condition that alternating current is not introduced into stator windings, excitation step current signals are introduced into a rotor winding; after an excitation synchronous motor generates a magnetic field due to the excitation step current signals, the induced electromotive forces of the three-phase stator windings are detected through a voltage sensor, and the induced electromotive forces of the three-phase stator windings are transformed into stator back-electromotive force components in an alpha-beta coordinate system through 3 / 2 coordinate transformation, and the stator back-electromotive force components are inputted into a voltage model, the position angle of air gap flux is obtained, and the position angle of the air gap flux is a rotor position angle, and therefore, the initial position of a rotor can be estimated. According to the method of the invention, the initial position of the rotor can be realized without a position sensor required, and therefore, the method is simple and practical, can accurately estimate the initial position of the rotor and is suitable for various kinds of electric excitation synchronous motors.
Owner:BEIJING LEADER & HARVEST ELECTRIC TECH
Method for calculating load electromagnetic excitation force waves of built-in permanent magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN111241735AReduce computing timeAccurately get the frequencySynchronous machine detailsDesign optimisation/simulationMagnetomotive forcePermanent magnet synchronous motor
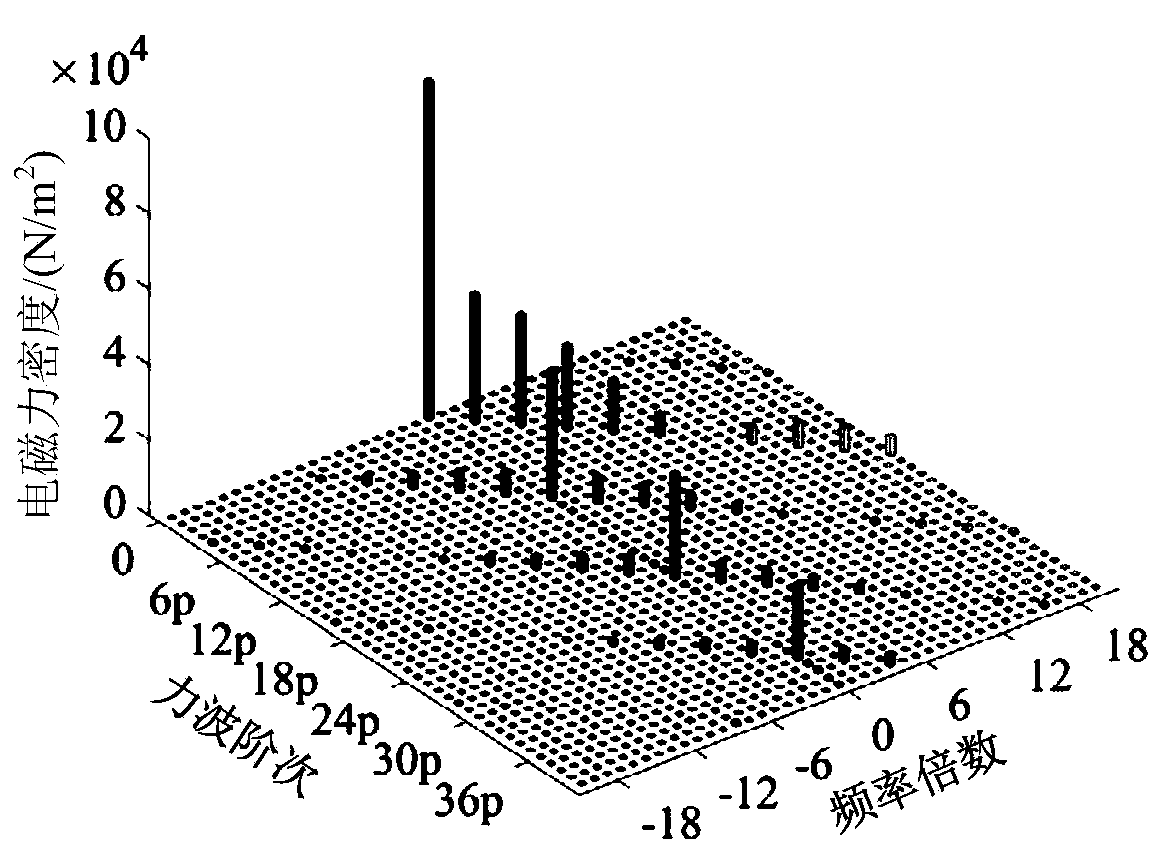
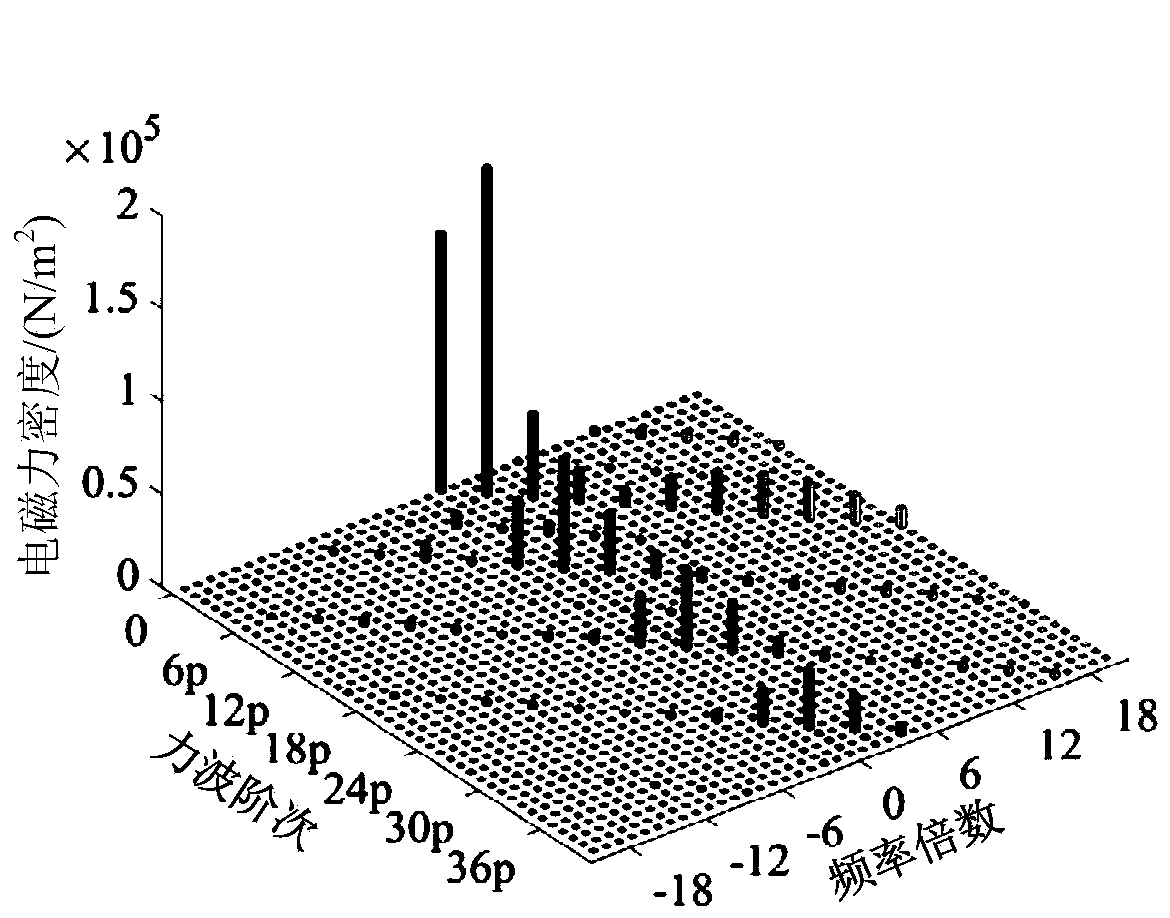
The invention provides a method for calculating load electromagnetic excitation force waves of a built-in permanent magnet synchronous motor, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the calculation of air gap flux density under a no-load condition through a finite element to obtain the relation between magnetomotive force and magnetic conductance under the no-load condition; simulating toobtain a d-axis magnetic conductance model of an armature magnetic field by utilizing a method of freezing magnetic conductivity, accurately calculating a magnetomotive force and magnetic conductancerelationship generated by independent action of a winding under a load condition according to the model, and solving an air gap flux density generated by the winding; superposing the air gap flux densities generated by the permanent magnet and the armature winding by using a superposition principle to obtain a built-in load air gap flux density expression; according to a Maxwell tensor method, putting magnetomotive force and air gap magnetic conductance component results into an electromagnetic force density expression to accurately obtain force wave amplitudes under different frequencies anddifferent orders.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Permanent magnet synchronous machine (PMSM) possessing assembled magnetic effect
InactiveCN102255460AImprove distributionImprove approachMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsPermanent magnet synchronous machinePermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention provides a permanent magnet synchronous machine (PMSM) possessing an assembled magnetic effect. The PMSM comprises a stator and a rotor. Air gaps exist between the stator and the rotor. The stator includes a stator core and a stator winding. The rotor includes a rotor core, a rotating shaft and permanent magnet steel. The stator winding is a centralized winding. The rotor is an eccentric rotor. Ends of the permanent magnet steel are directly connected with each other. The air gaps between the stator and the rotor are non-uniform air gaps. The invention has the following positive effects that: (1) distribution of air-gap flux density can be optimized through improving a rotor structure and the air gap flux can be very close to a sinusoidal waveform by using the non-uniform air gaps; (2) magnetic flux leakage on the ends can be effectively reduced because the ends of the permanent magnet steel are directly connected with each other, and simultaneously a magnetic isolation bushing is not needed to be installed on a rotating shaft side so that a requirement of a rotating shaft material can be reduced, wherein the rotating shaft can adopt a magnetic conductive material and / or a non magnetic conductive material.
Owner:SHANGHAI DIANJI UNIV
Permanent magnet electrical machine
A 2-pole machine arrangement (10) has a stator (100) with windings (101) in conventional form, wound either in a single phase or three phase configuration. The rotor is formed of stacked laminations. The laminations include rotor pole pieces (107) located between the two magnetic poles. Each pole is formed by a pair of (embedded) permanent magnets (103), angularly spaced-apart by inter-magnet segments (106). The rotor pole pieces (107) include a series of evenly-spaced slots (109) and a central void (108). The slots (109) are of various lengths to direct the flux from the magnets (103) into the air gap (121) at a desired angle normal to the rotor surface. The slots 109 may be varied in width and angle to achieve the desired lowest waveform distortion under load and the highest air gap flux. The slots (109) also contribute to changing the saliency of the rotor.
Owner:RADIAL FLUX LAB
Control method of spherical electric vehicle use magnetic suspended flywheel battery
ActiveCN106849479AHigh control precisionIncreased control torque rangeElectric machinesMechanical energy handlingPower flowEngineering
The invention discloses a control method of a spherical electric vehicle use magnetic suspended flywheel battery. In the working processing of the spherical flywheel battery, a control mode that a magnetic field laminates differential is adopted, that is, a pair of upper stator poles and a pair of lower stator poles are provided with bias coils and control coils respectively, the bias coils of the two stator poles are in series connection, and through a constant current, a bias magnetic field for a magnetic spherical faced bearing to work is provided; the control coils on each pair of the stator poles are in series connection, magnetic fluxes generated by the control coil and the control current in the control coil are added up in the pair of stator poles, and the magnetic fluxes of the control coil and the control current generated in the control coil are subtracted in the other pair of stator poles, therefore an air gap flux between the pair of the stator poles and a spherical flywheel is increased, an air gap flux between the other pair of the stator poles and the spherical flywheel is reduced, according to a formula I, B is a magnetic induction intensity, S is a stator spherical face area of the spherical faced bearing, mu0 is an air permeability, electromagnetic force bore at one side is increased, and electromagnetic force bore at the other side is reduced, therefore the position of the spherical faced flywheel is adjusted to be always at a balanced position.
Owner:江苏良基集团有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com