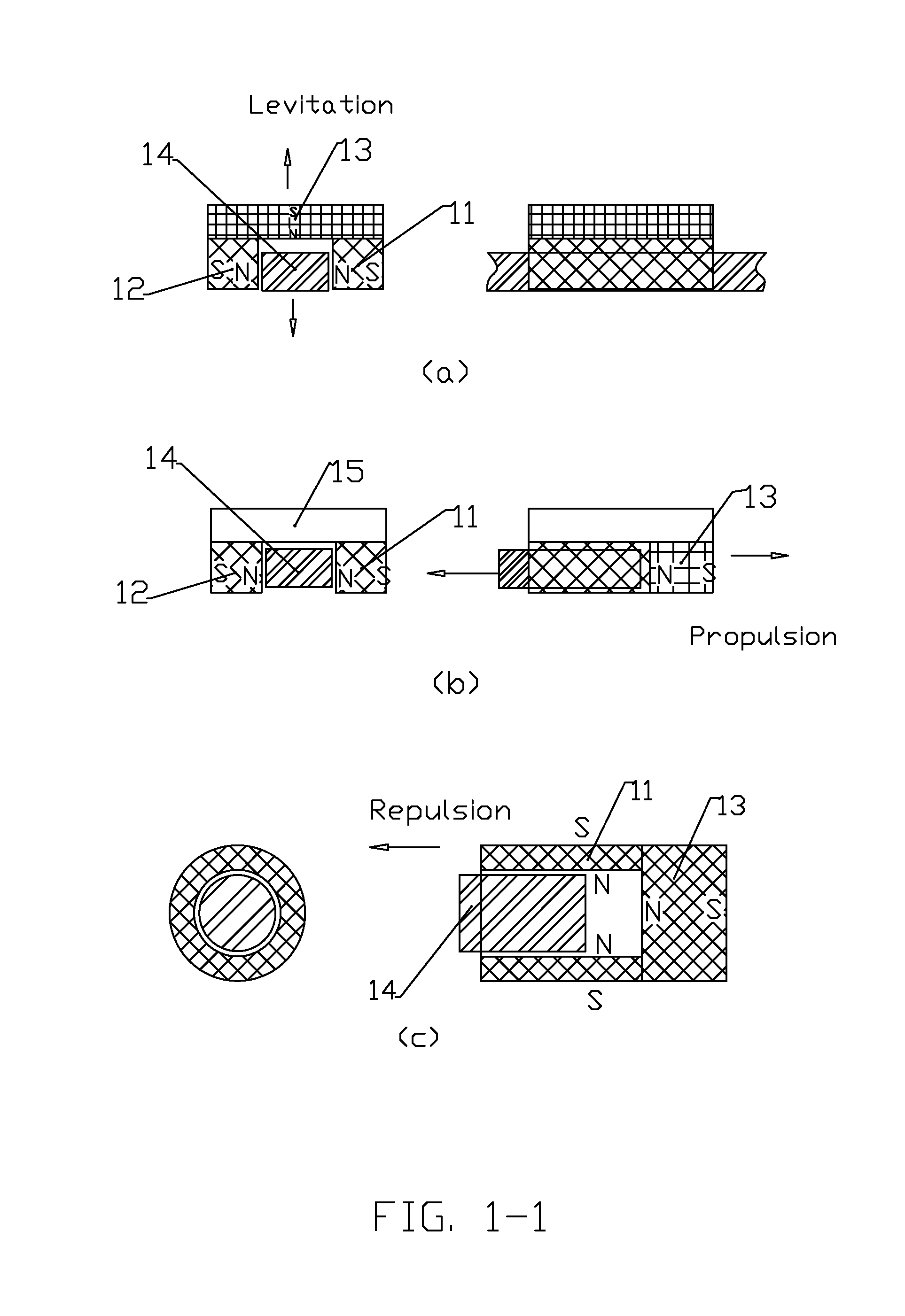
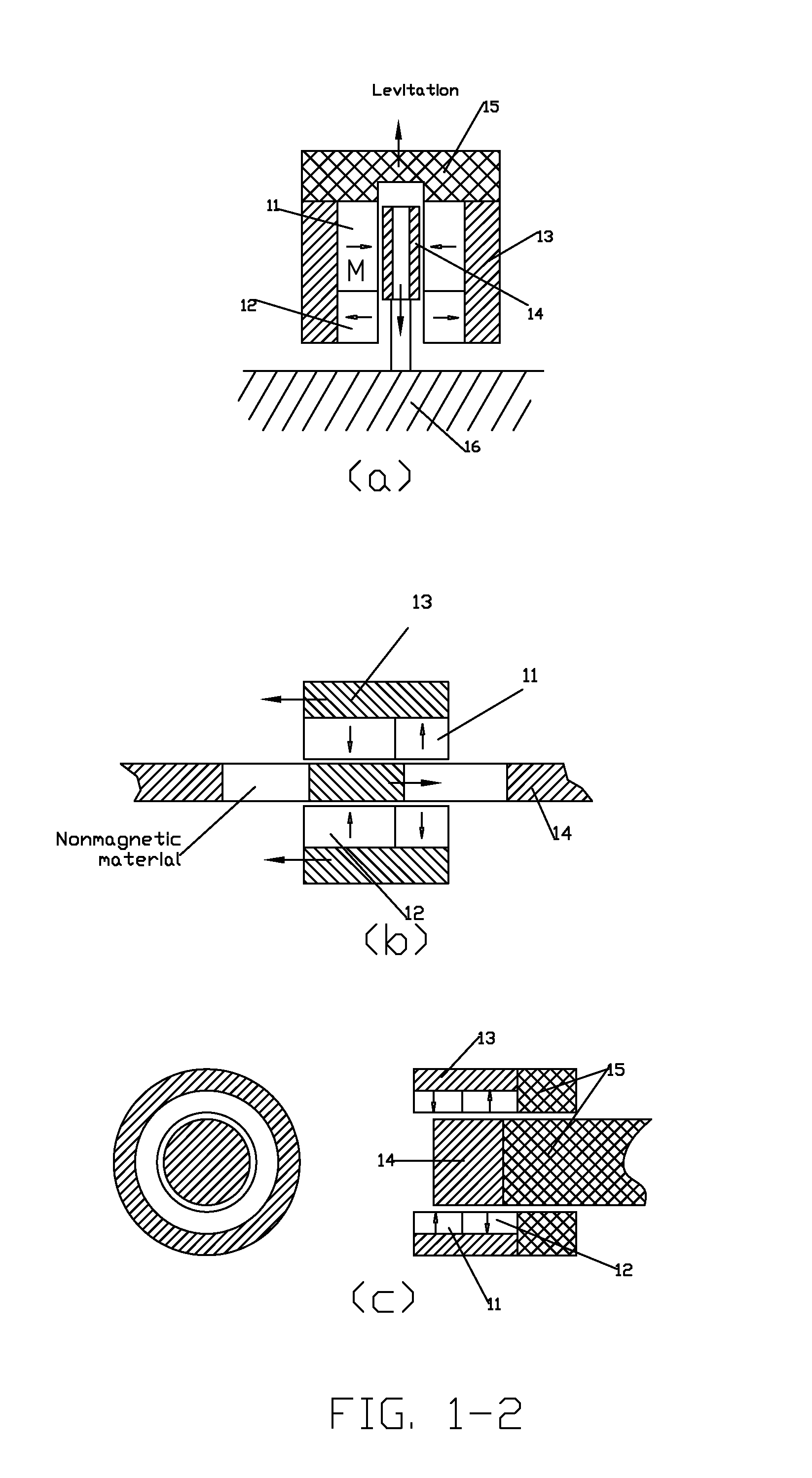
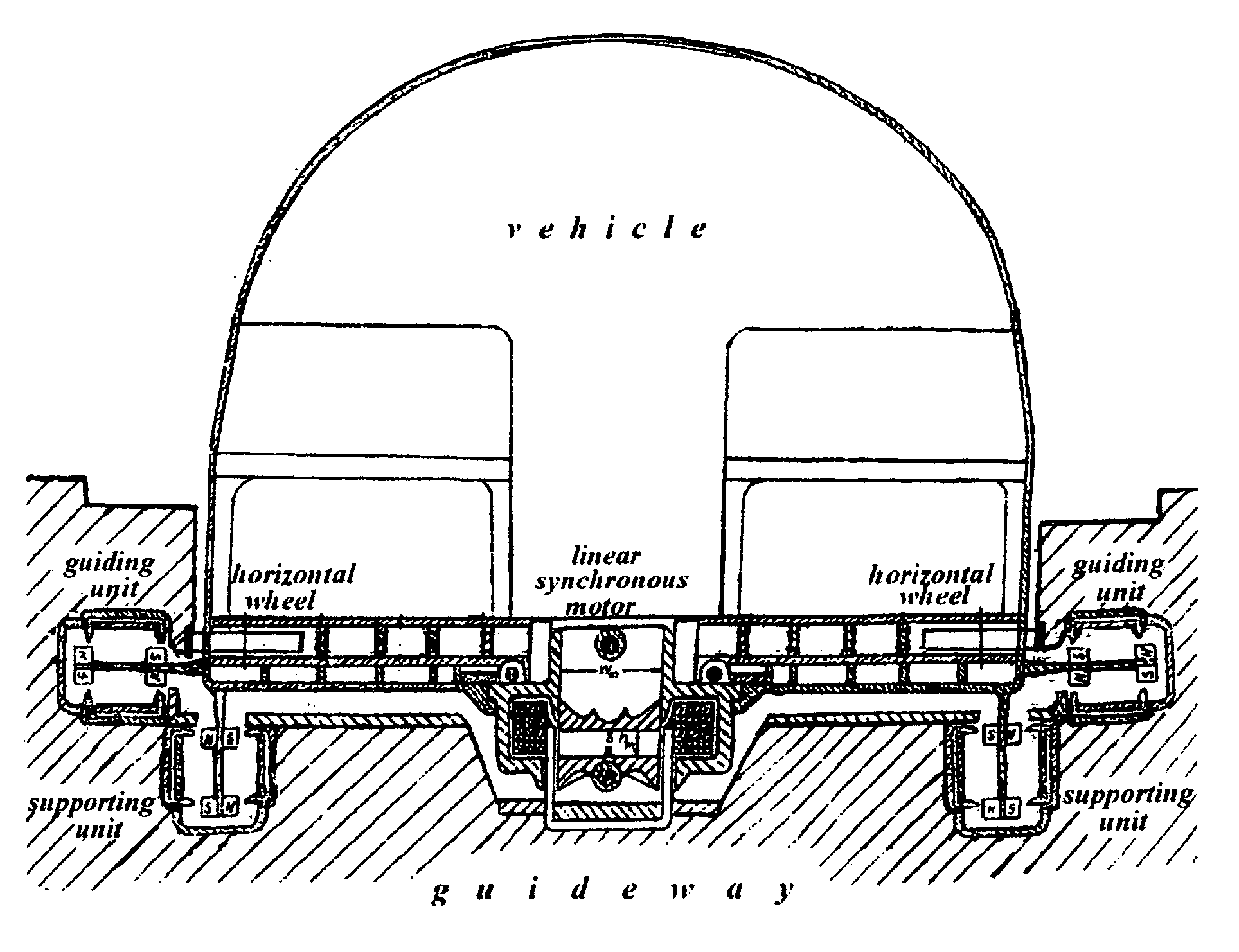
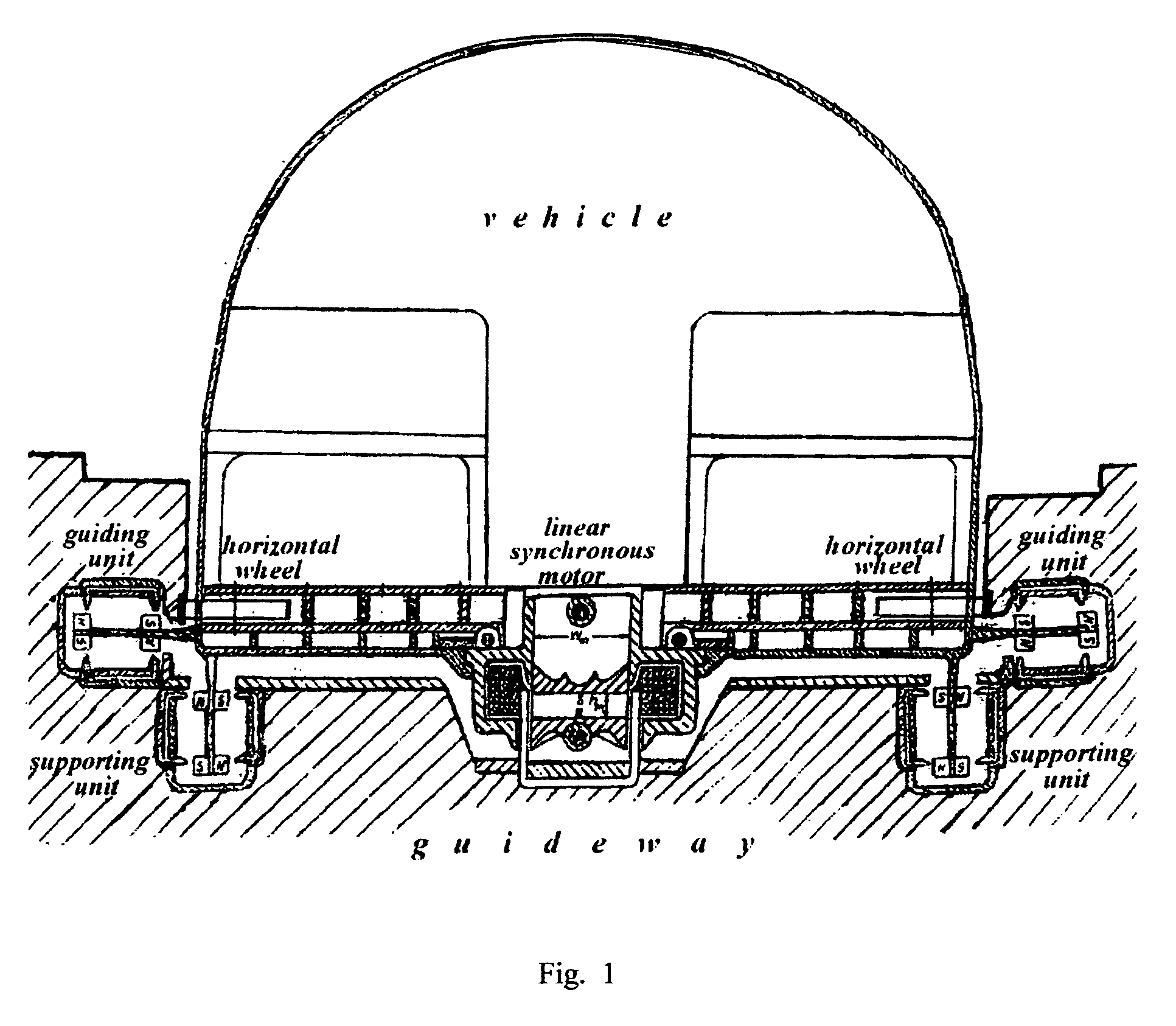
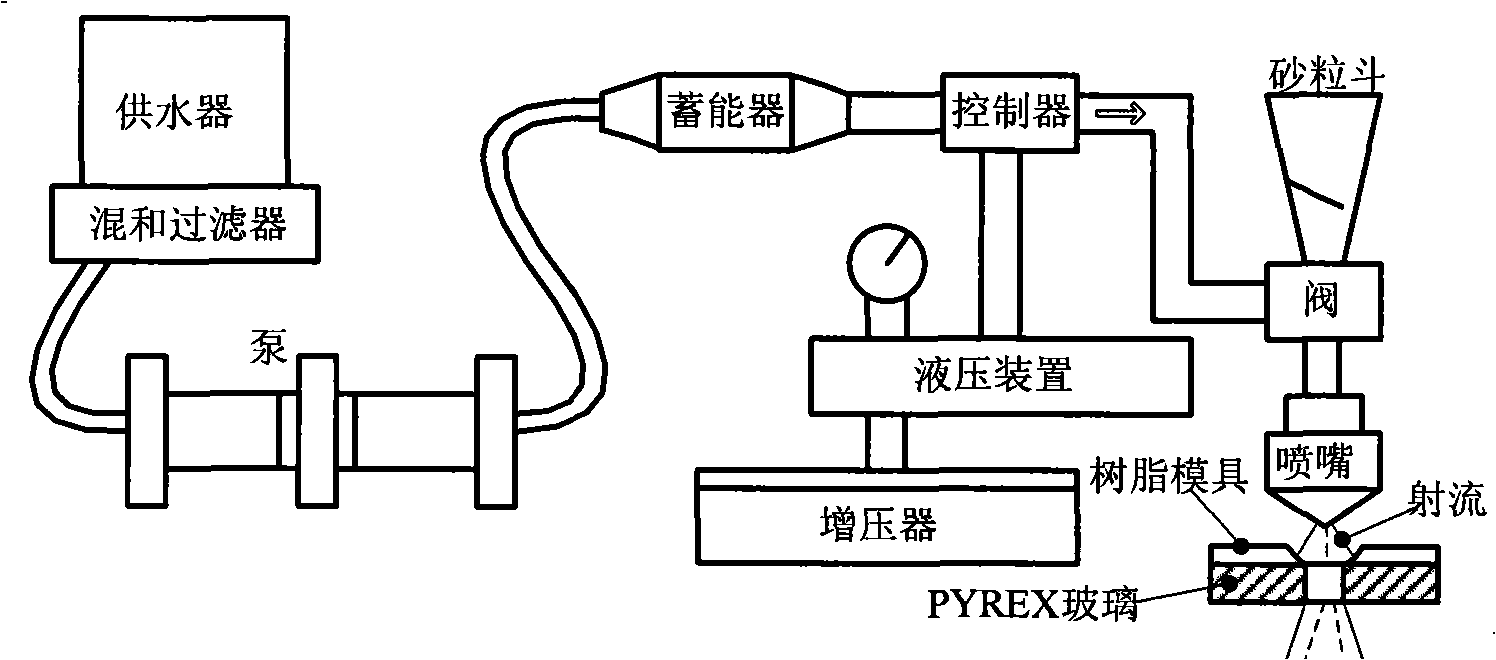
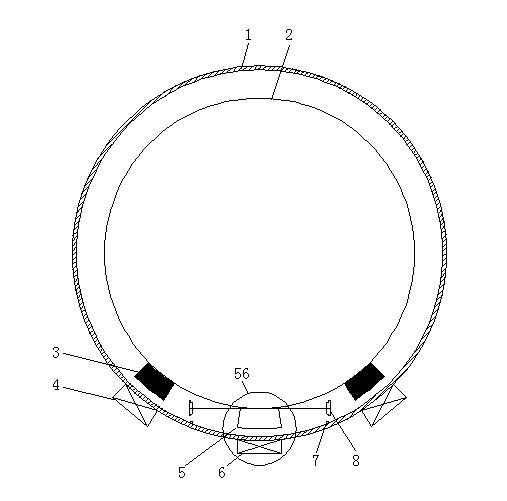
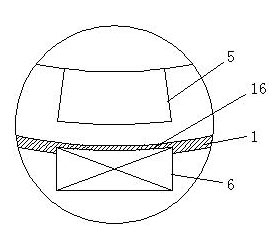
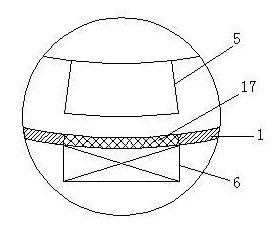
Patents
Literature
1071 results about "Levitation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Levitation (from Latin levitas "lightness") is the process by which an object is held aloft, without mechanical support, in a stable position. Levitation is accomplished by providing an upward force that counteracts the pull of gravity (in relation to gravity on earth), plus a smaller stabilizing force that pushes the object toward a home position whenever it is a small distance away from that home position. The force can be a fundamental force such as magnetic or electrostatic, or it can be a reactive force such as optical, buoyant, aerodynamic, or hydrodynamic.
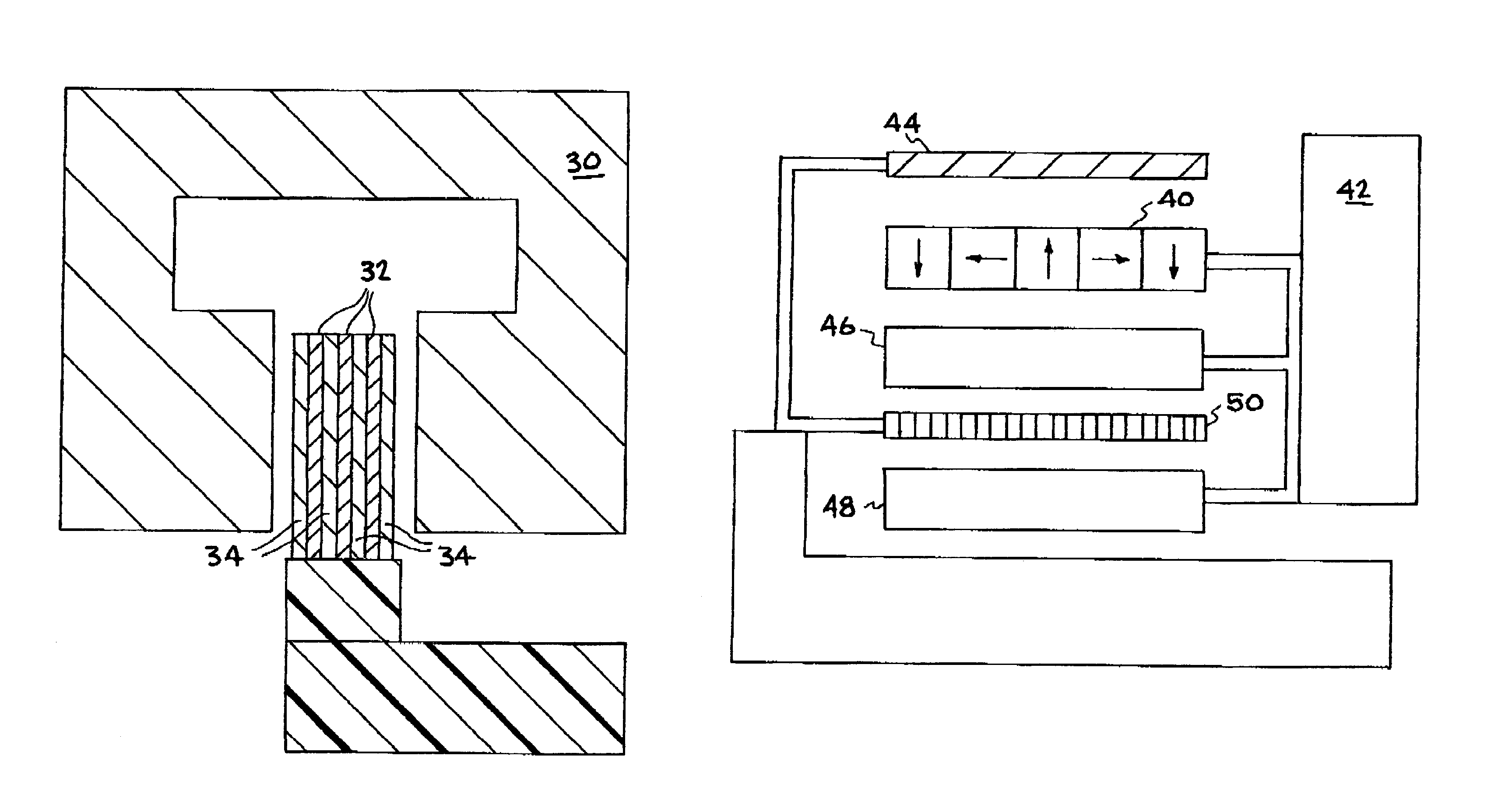
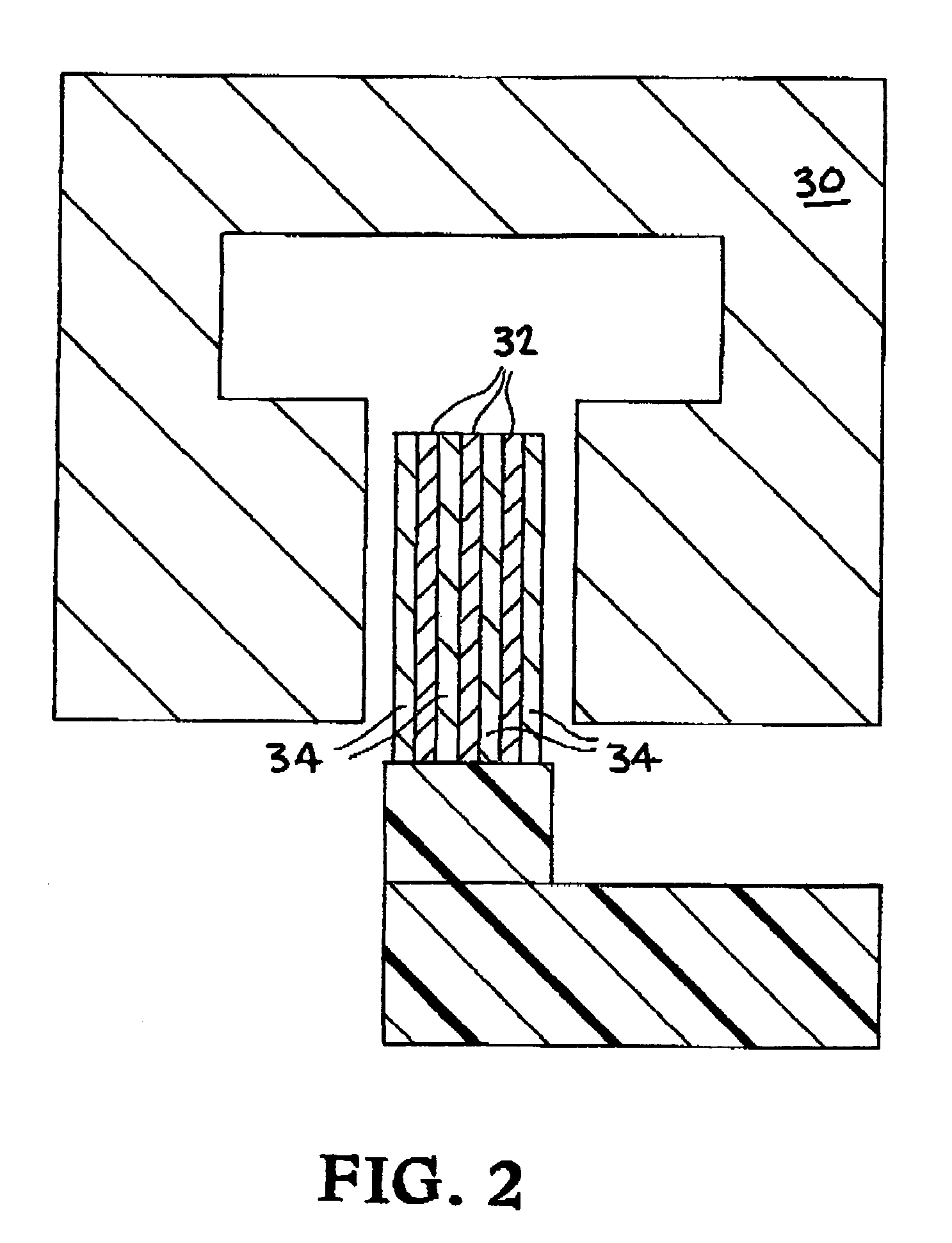
Levitation of objects using magnetic force
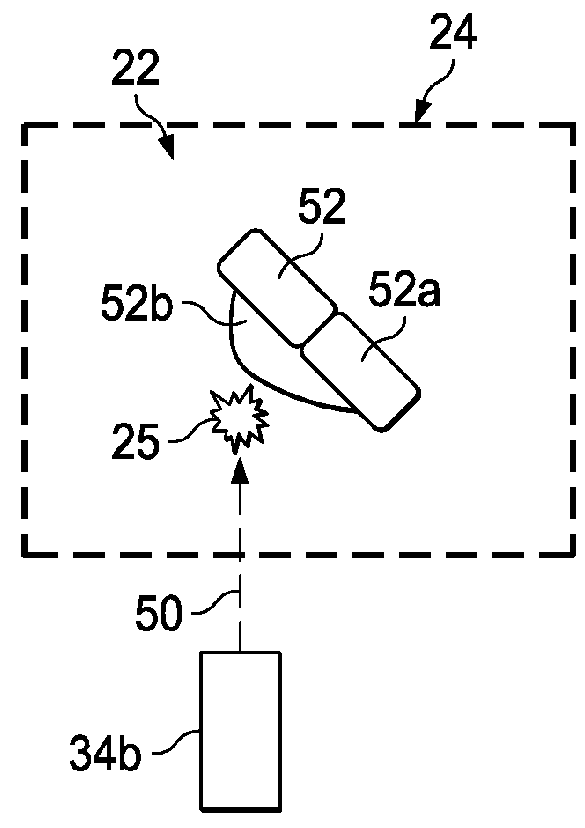
InactiveUS20060214756A1Enhancing its appealImprove stabilityPermanent magnetsMagnetic materialsMagnetic tension forceLevitation
The invention disclosed is a method of levitating one or both ends of an object permanently or temporarily, or altering the distance between two objects or the momentum of an object by manipulating the direction of the magnetic field of a permanent or electromagnet.
Owner:ELLIHAY CORP
System and method for servo control of nonlinear electromagnetic actuators
InactiveUS20060171091A1Eliminate impactRemove noiseElectrical controlAC motor controlResonance measurementInstability
Servo control using ferromagnetic core material and electrical windings is based on monitoring of winding currents and voltages and inference of magnetic flux, a force indication; and magnetic gap, a position indication. Third order nonlinear servo control is split into nested control loops: a fast nonlinear first-order inner loop causing flux to track a target by varying a voltage output; and a slower almost linear second-order outer loop causing magnetic gap to track a target by controlling the flux target of the inner loop. The inner loop uses efficient switching regulation, preferably based on controlled feedback instabilities, to control voltage output. The outer loop achieves damping and accurate convergence using proportional, time-integral, and time-derivative gain terms. The time-integral feedback may be based on measured and target solenoid drive currents, adjusting the magnetic gap for force balance at the target current. Incorporation of permanent magnet material permits the target current to be zero, achieving levitation with low power, including for a monorail deriving propulsion from the levitation magnets. Linear magnetic approximations lead to the simplest controller, but nonlinear analog computation in the log domain yields a better controller with relatively few parts. When servo-controlled solenoids provide actuation of a pump piston and valves, electronic LC resonance measurements determine liquid volume and gas bubble volume.
Owner:SEALE JOSEPH B +1
Stator field providing torque and levitation
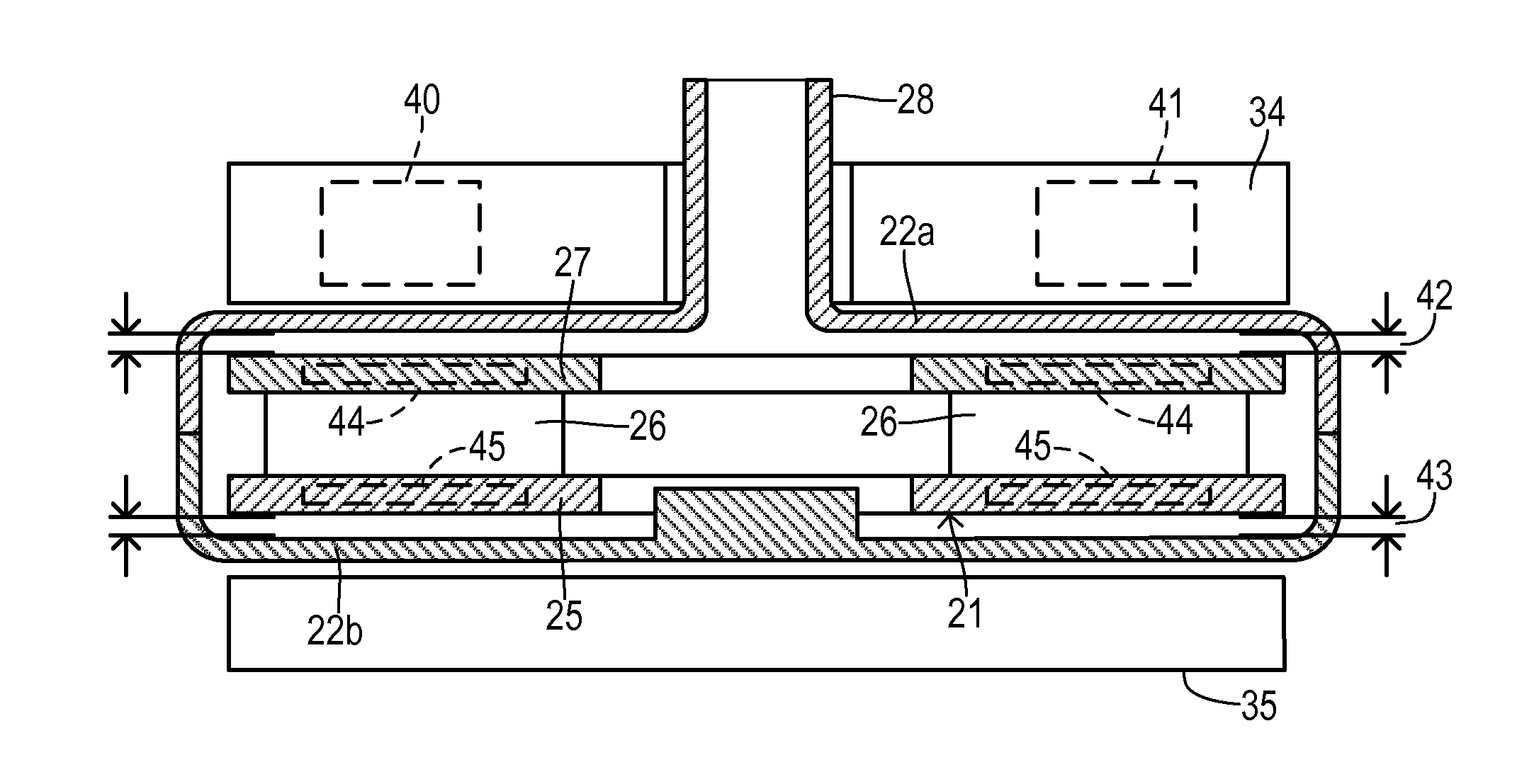
InactiveUS6879074B2Easy constructionSimple electrical controlShaftsMechanical energy handlingMagnetomotive forceLevitation
The invention relates to an economical, non-wearing, electrical permanent magnet drive for actively controlling the rotor position in three degree of freedom. The stator windings produce superimposed fields with different pole numbers in the pole pitches by unsymmetrical magnetomotive force distributions.
Owner:LEVITRONIX TECH +1
System using a levitating, rotating pumping or mixing element and related methods
InactiveUS7086778B2Eliminate deleterious thermal transferPrecise positioningShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersFlow mixersLevitationEngineering
A system for pumping or mixing a fluid using a levitating, rotating pumping or mixing element and various other components for use in a pumping or mixing system are disclosed. The pumping or mixing element is placed in a fluid-containing vessel in close proximity to a superconducting element. A cooling source thermally linked to the superconducting element provides the necessary cooling to induce levitation in the pumping or mixing element. The superconducting element may be thermally isolated, such that the pumping or mixing element, the vessel, and any fluid contained therein are not exposed to the cold temperatures required to produce the desired superconductive effects and the resulting levitation. By using means external to the vessel to rotate and / or stabilize the pumping or mixing element levitating in the fluid, including possibly rotating the superconducting element itself or moving it relative to the vessel, the desired effective pumping or mixing action may be provided.
Owner:PALL TECH UK
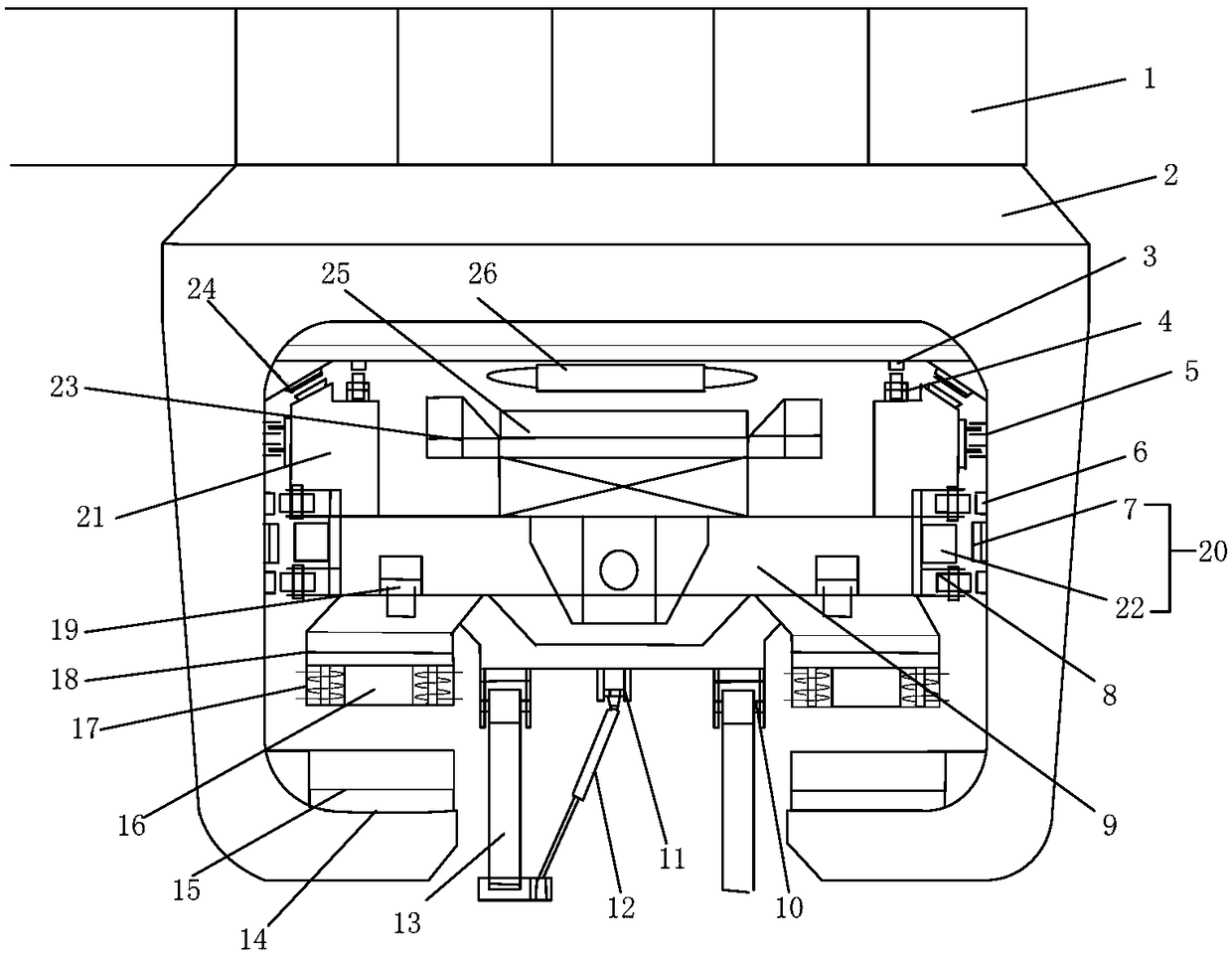
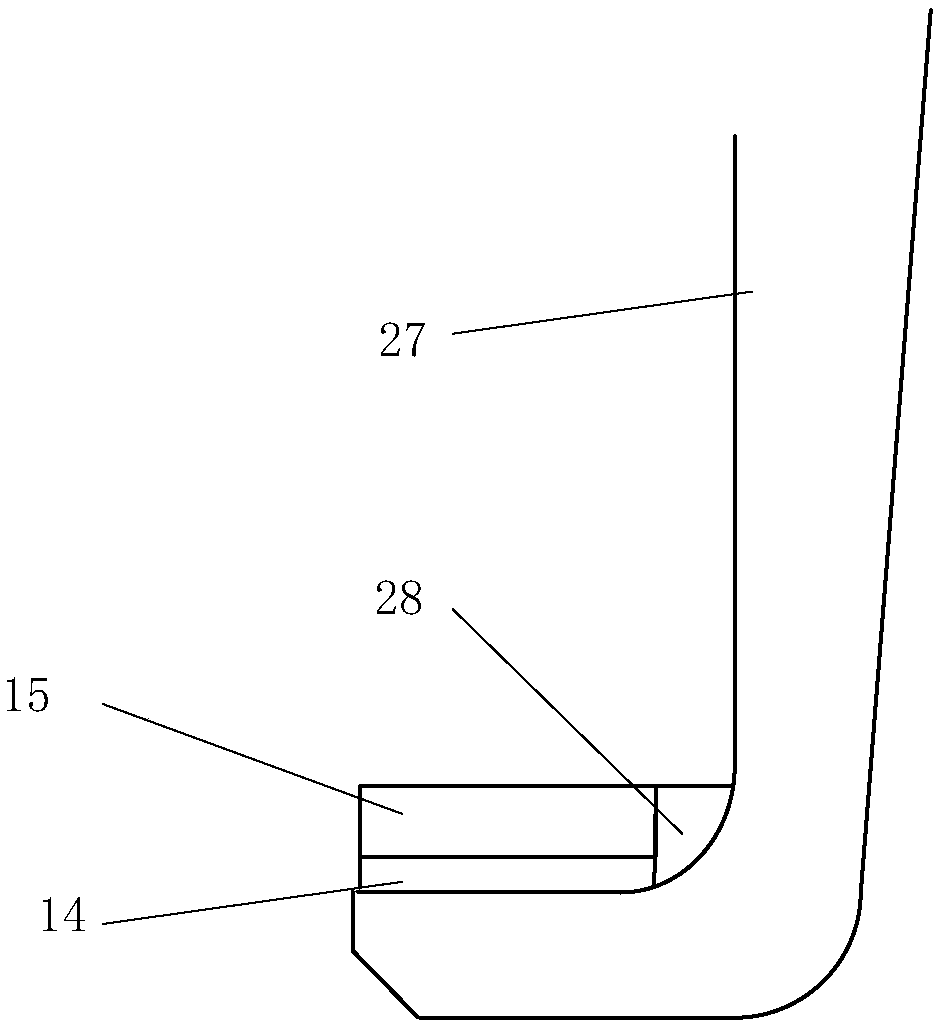
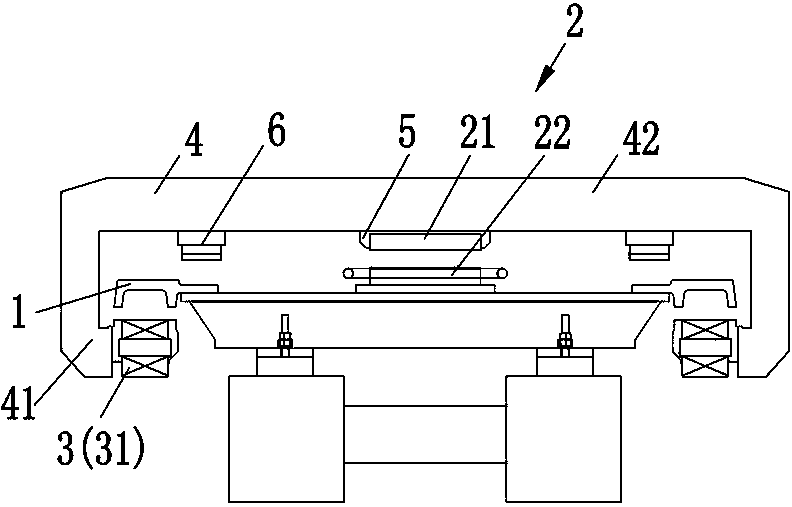
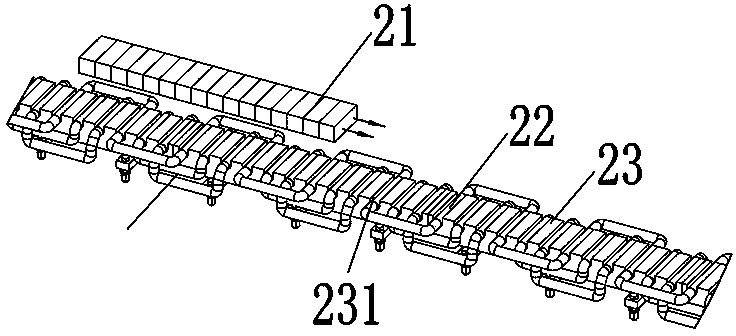
U-shaped rail double-safety running and levitation driving energy-saving mechanism
InactiveCN103612635AIncrease productivityImprove the level of precision controlRailway tracksSliding/levitation railway systemsLevitationAir spring
The invention belongs to the field of rail traffic and relates to a U-shaped rail double-safety running and levitation driving energy-saving mechanism which is suitable for low-medium-speed maglev train double-safety running and levitation driving energy saving. The mechanism is composed of a U-shaped rail 1, a self-locking hydraulic traveling wheel mechanism 2, a connecting frame 3, a train body 4, an air spring 5, a bogie arm 6, a spindle 7, an aluminum sensing plate 8 and levitation magnets 9. By designing a U-shaped rail structure, production efficiency of the U-shaped rail is improved, roller consumption in hot rolling production is reduced, and production cost is lowered. By combining the U-shaped rail structure with the self-locking hydraulic traveling wheel mechanism, a maglev train is enabled to have a magnetic levitation and rubber wheel double-safety running mechanism, levitation-starting energy consumption of the maglev train is reduced remarkably, traction levitation energy consumption is reduced by 10-15%, and energy-saving effect is obvious. Running safety and accident emergency response capability are improved remarkably, and when a full-levitation system is in a failure, driven by a linear motor, a rubber wheel supporting train still can safely get to a target station.
Owner:莱芜美澳冶金科技有限公司
Magnetically levitated motor and magnetic bearing apparatus
InactiveUS20030057784A1Reduce power consumptionForce is limitedShaftsMechanical energy handlingRotational axisLevitation
A magnetically levitating motor includes a rotor that is formed from a magnetic material and has a permanent magnet attached along a circumference thereof, and a stator core section having a first stator coil that generates a levitation control magnetic flux that controls levitation of the rotor in a radial direction and a second coil that generates rotational magnetic flux against the rotor. In one aspect of the present invention, a rotor side thrust bearing magnetic path section is formed on the rotor, and a stator side thrust bearing magnetic path section that is disposed opposite in the radial direction to the rotor side thrust bearing magnetic path section is provided on the stator. A bias magnetic flux that forms the radial levitation control magnetic flux is formed to pass a gap in the radial direction between the rotor side thrust bearing magnetic path section and the stator side thrust bearing magnetic path section. A thrust control coil that generates a supporting force to support the thrust bearing load is disposed in the bias magnetic flux that forms the radial levitation control magnetic flux, wherein the thrust control coil is wound about a rotational axis with respect to one of the rotor side thrust bearing magnetic path section and the stator side thrust bearing magnetic path section.
Owner:NIDEC SANKYO CORP
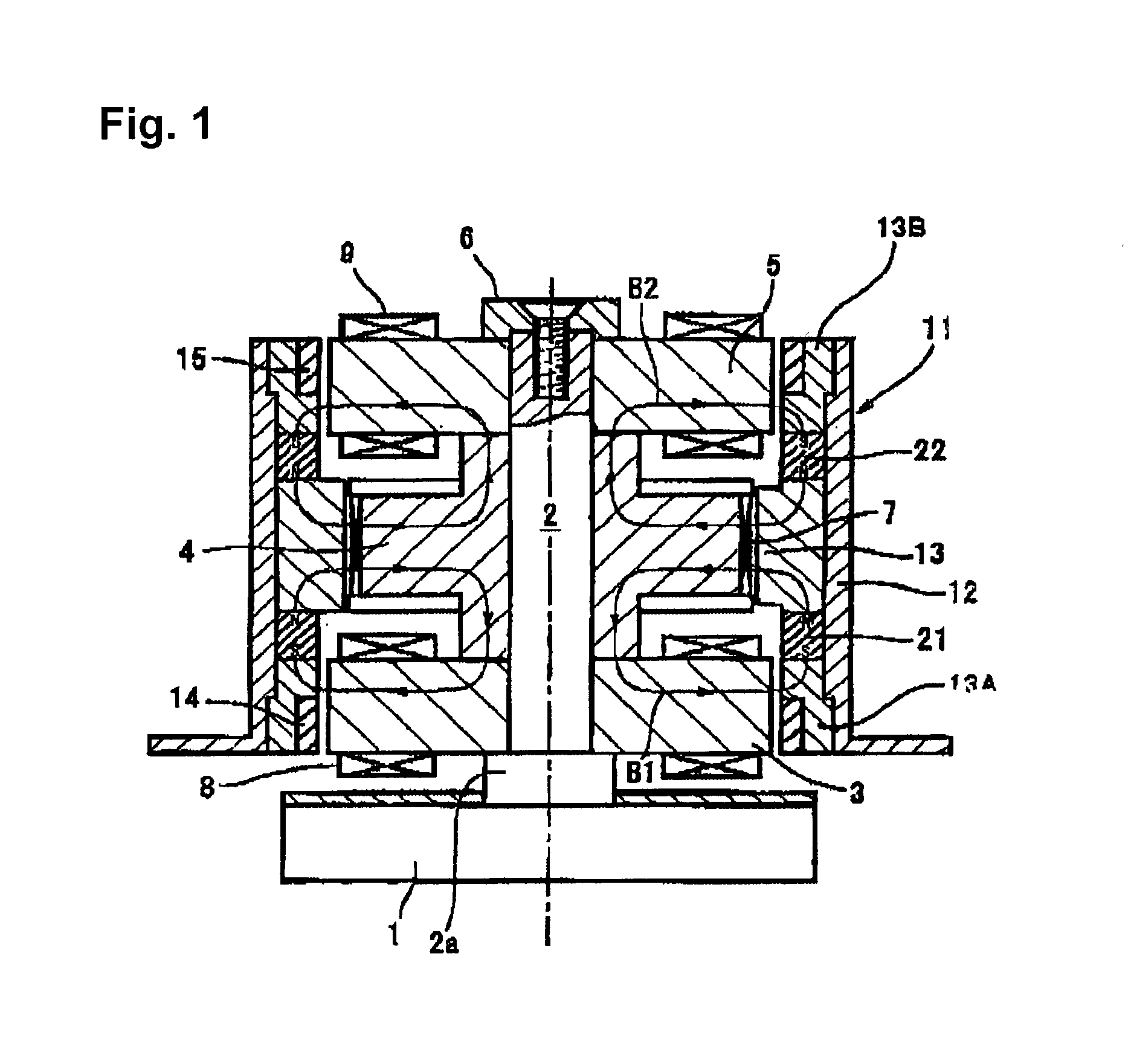
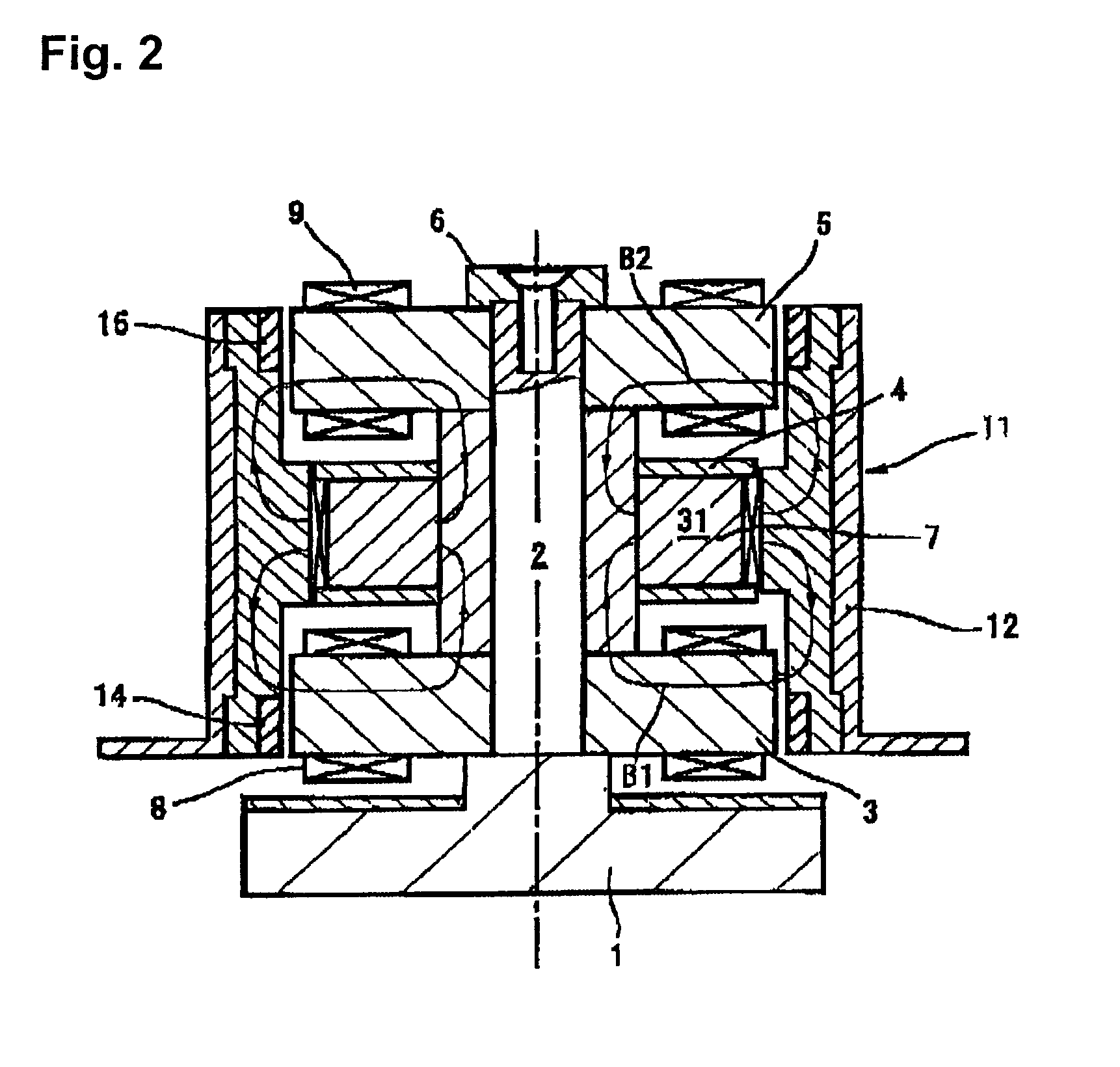
Centrifugal fluid pump apparatus
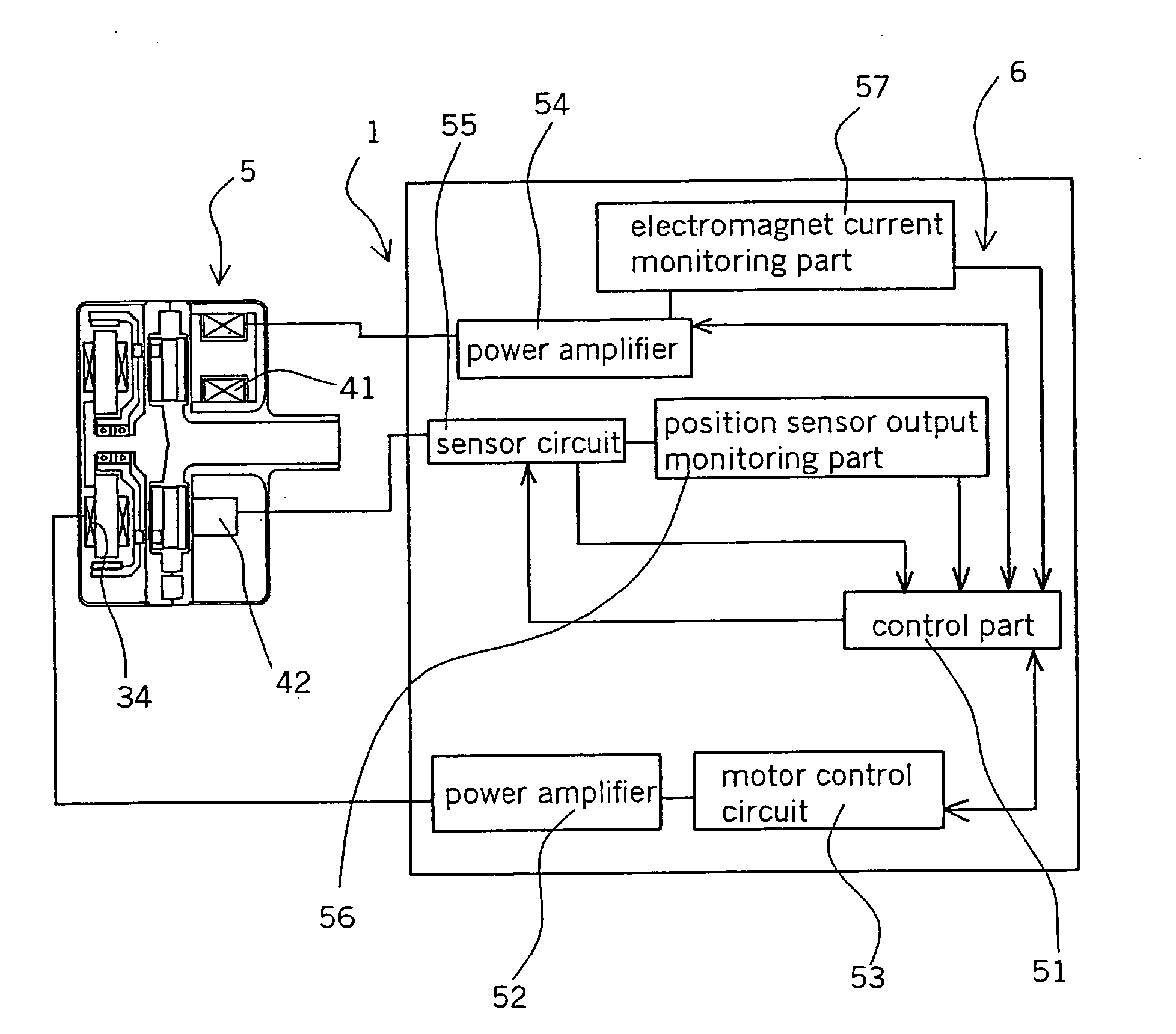
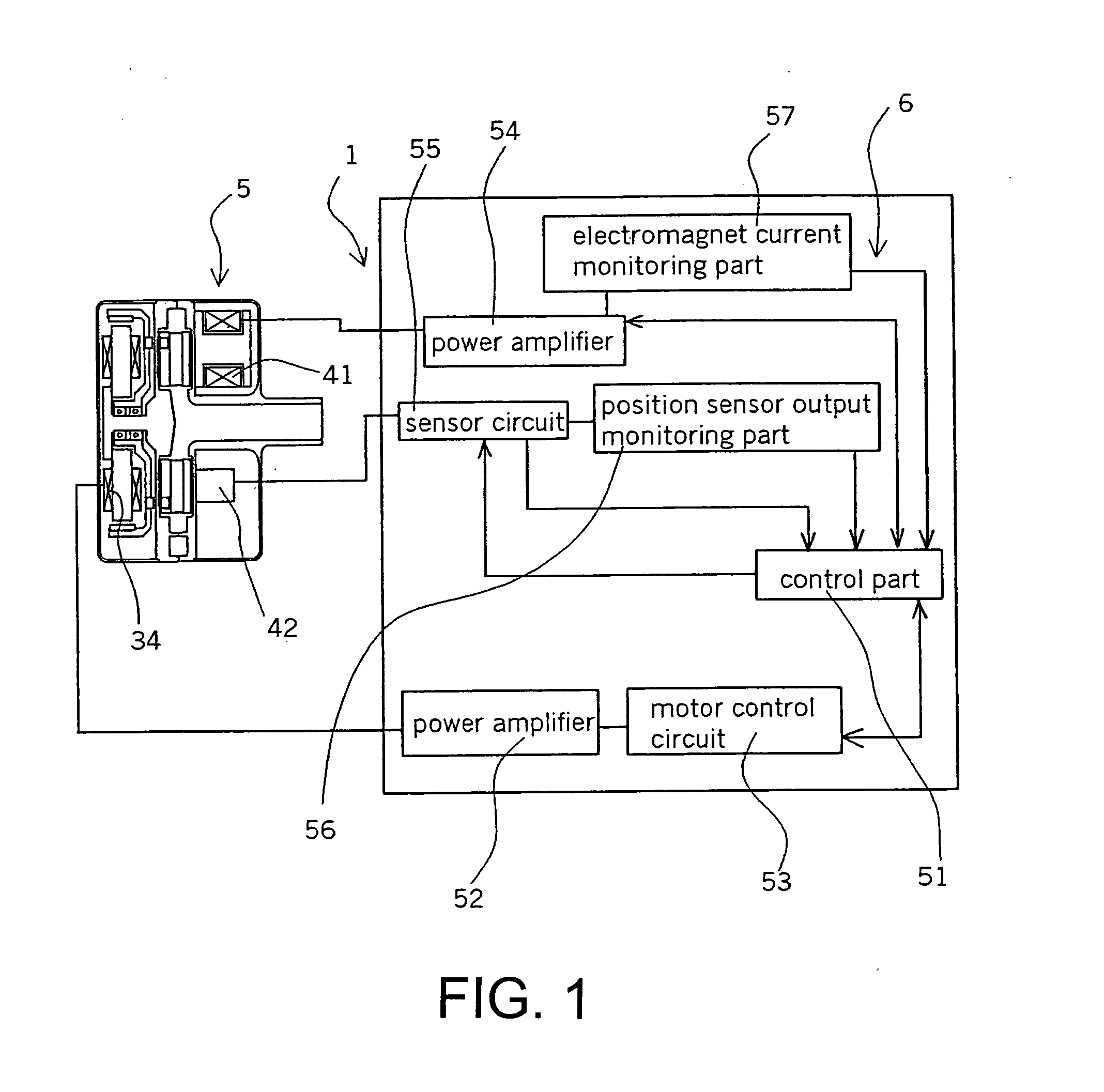
A centrifugal fluid pump apparatus includes a control mechanism including an emergency impeller rotation function. The emergency impeller rotation function includes a rotation termination function when the failure detection function detects a failure; impeller magnetic counterforce application function to apply a current to the electromagnet sufficient to overcome the magnetic attraction force of the rotor to the impeller caused by the magnet; hydrodynamic levitation control detection function to detect rotation of the impeller and the rotor by using a motor current monitored by the motor current monitoring function; motor speed control function for increasing the motor speed up to a predetermined value after the hydrodynamic levitation control detection function detects that the hydraulic bearing coupling between the impeller and the rotor has been made; and impeller magnetic counterforce termination function to terminate current to the electromagnet once the predetermined impeller rotation speed is reached.
Owner:TERUMO KK
Evacuated tube transport system with interchange capability
ActiveUS20140261054A1Reduces magnetic drag forceLightning protection is goodRailway tunnelsRailway componentsLevitationTransport system
A High Temperature Superconductor Maglev (HTSM) for Evacuated Tube Transport (ETT) with a magnetic levitation structure for ETT capsule vehicles traveling in an evacuated tube. At least one ETT capsule travels within an evacuated tube, an upper and a lower cryostat respectively mount at the top and bottom of said ETT capsule along the length thereof, at least a plurality of superconductor levitation force elements divided between said upper and lower cryostats. The levitation force being spread over the length of capsule, however substantially concentrated in a compact cross-sectional area. At least a pair of permanent magnetic elements mounted at the top and bottom of the evacuated tube to levitate the capsule. At least a pair of capsule based switchable diverge force elements cooperate with at least a pair of tube based diverge force elements to steer the capsule while in an interchange.
Owner:OSTER DARYL
Sliding load floor system with levitation mechanism
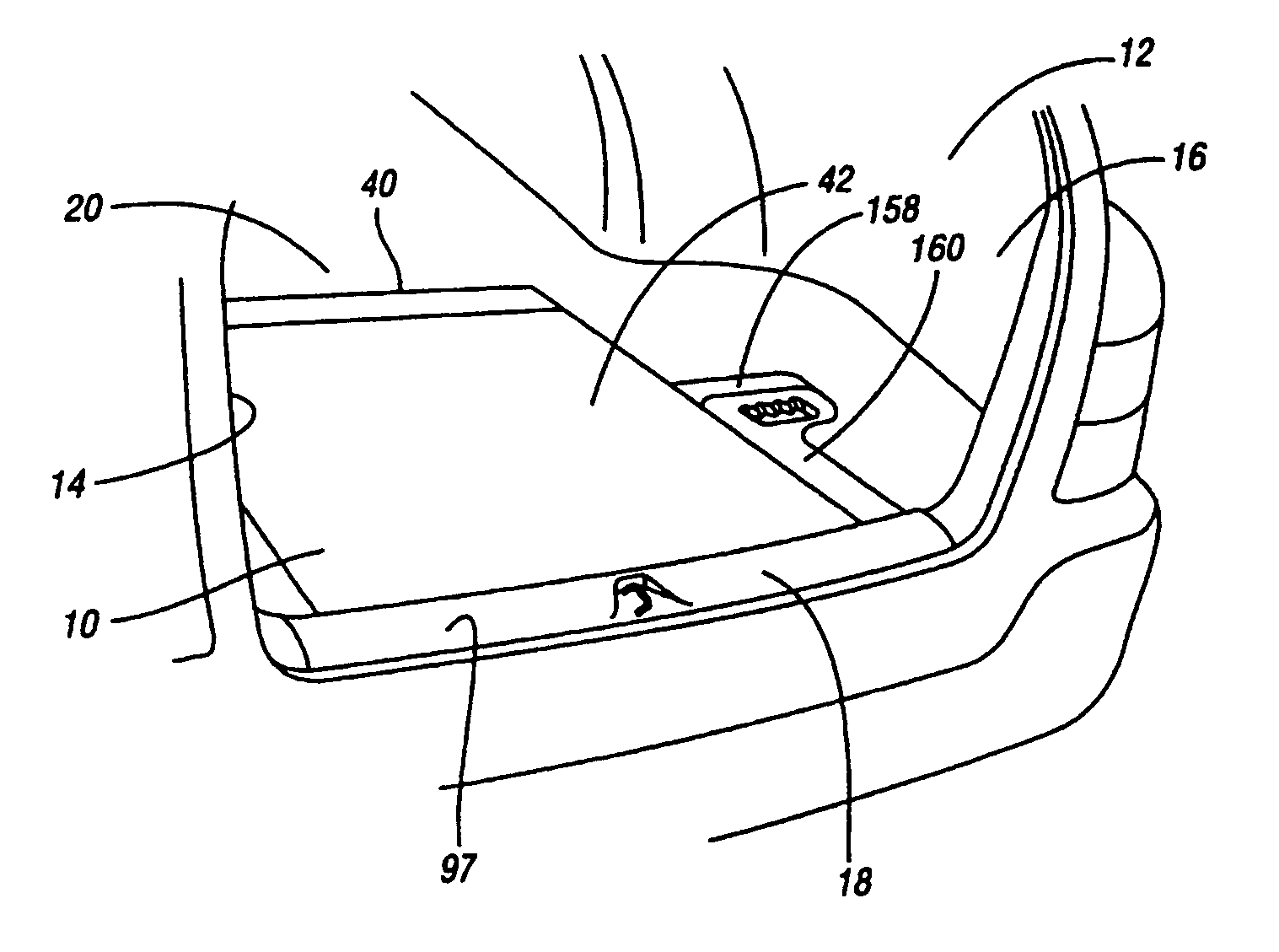
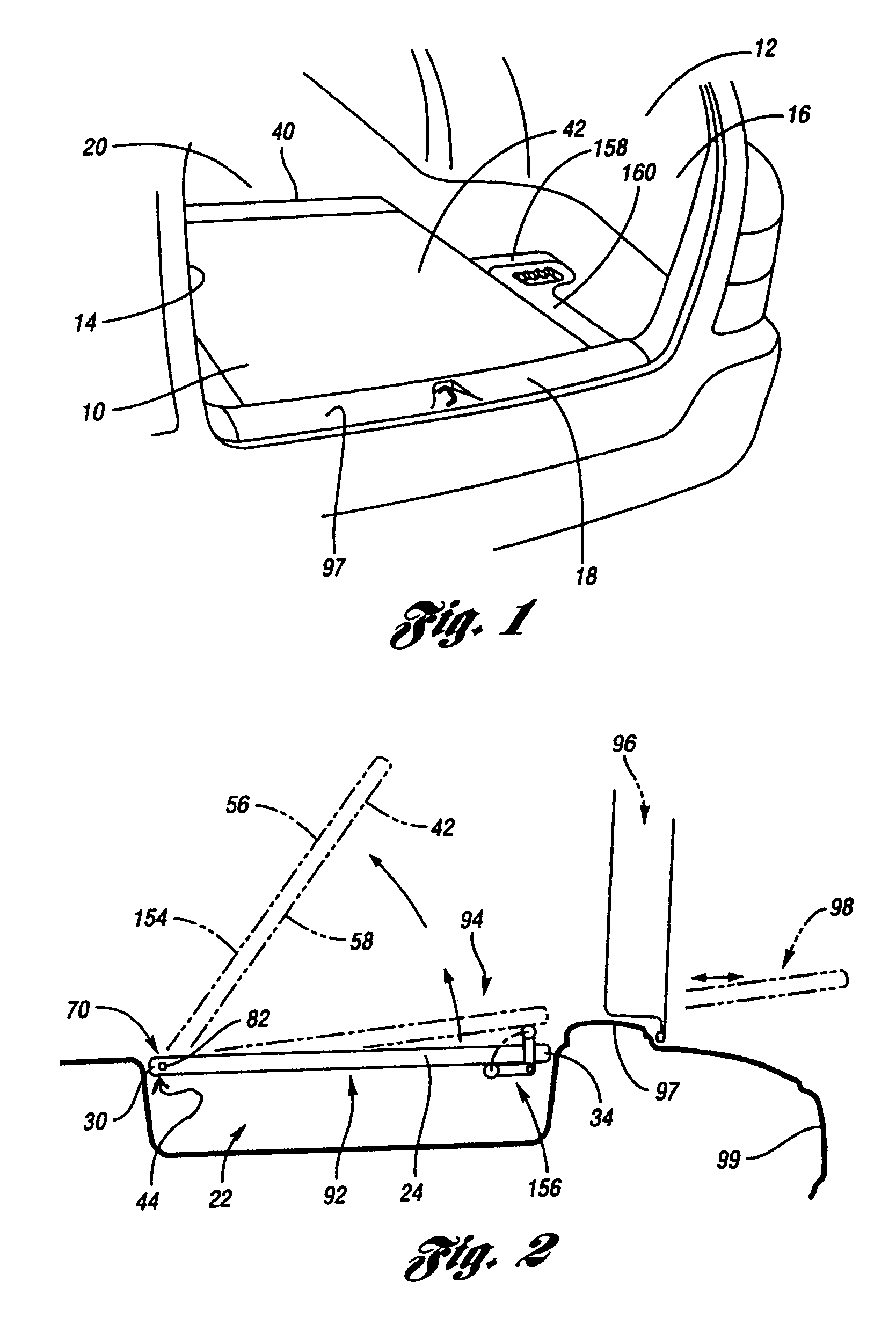
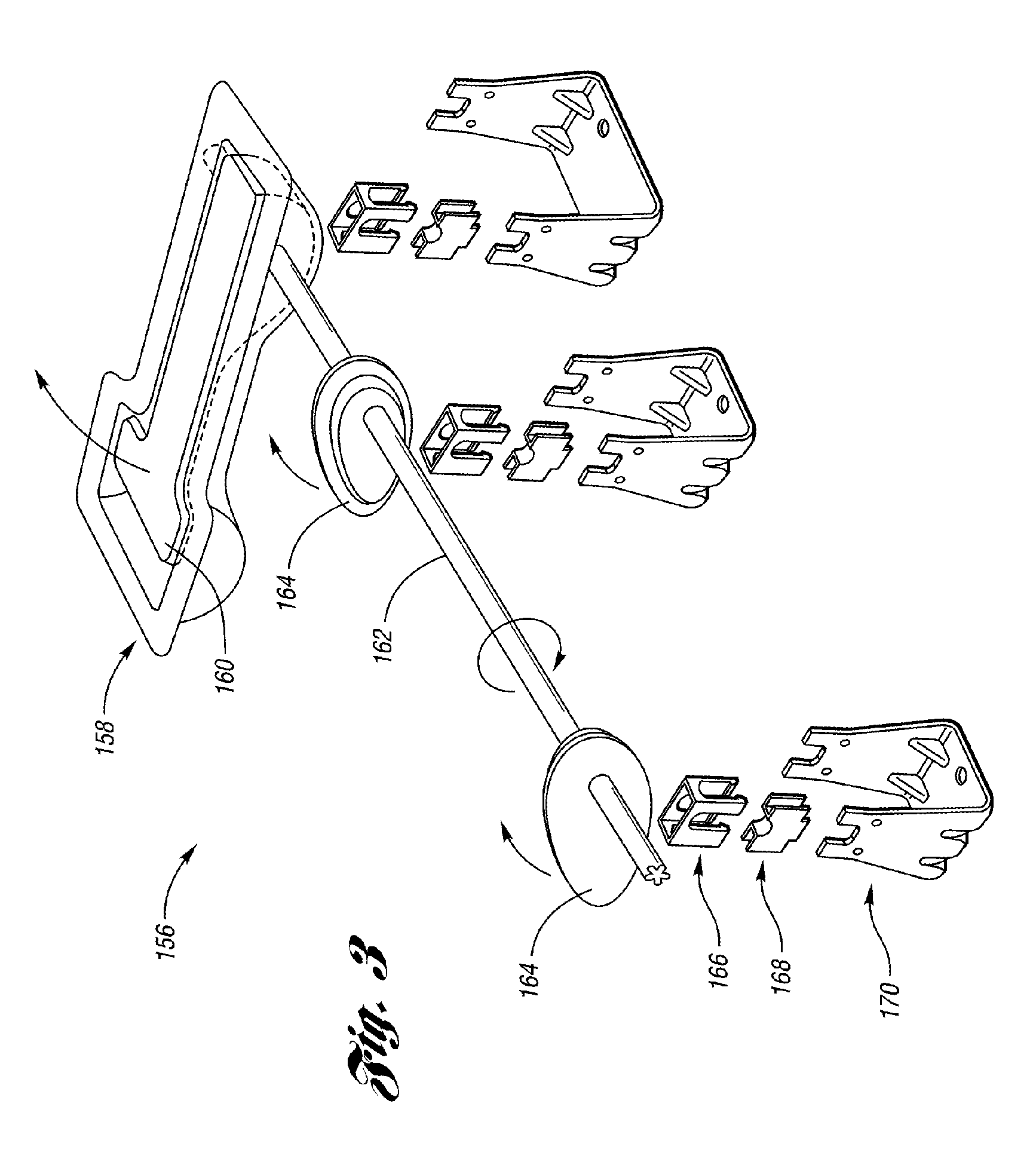
InactiveUS7188881B1Vehicle with living accommodationItem transportation vehiclesLevitationEngineering
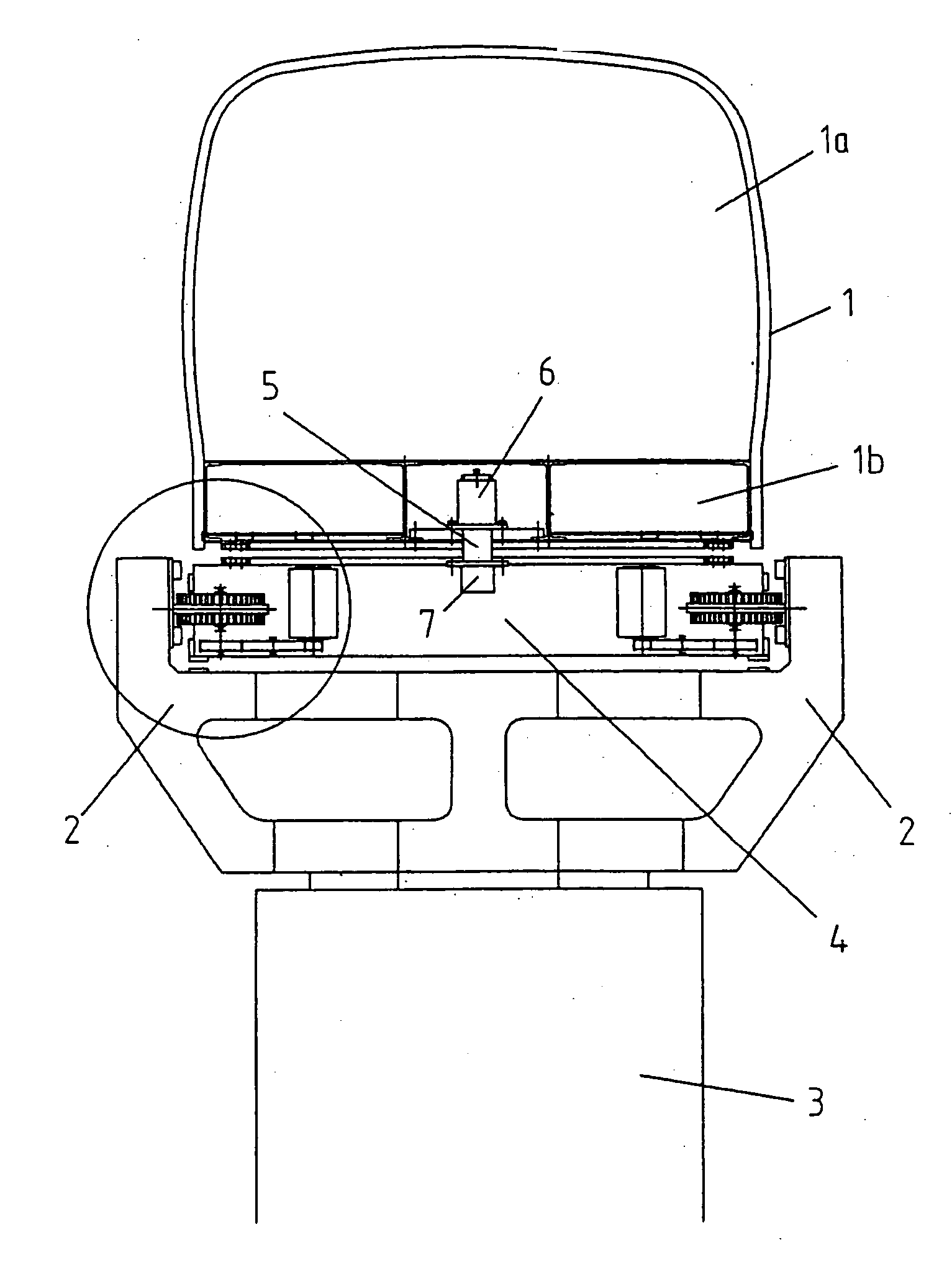
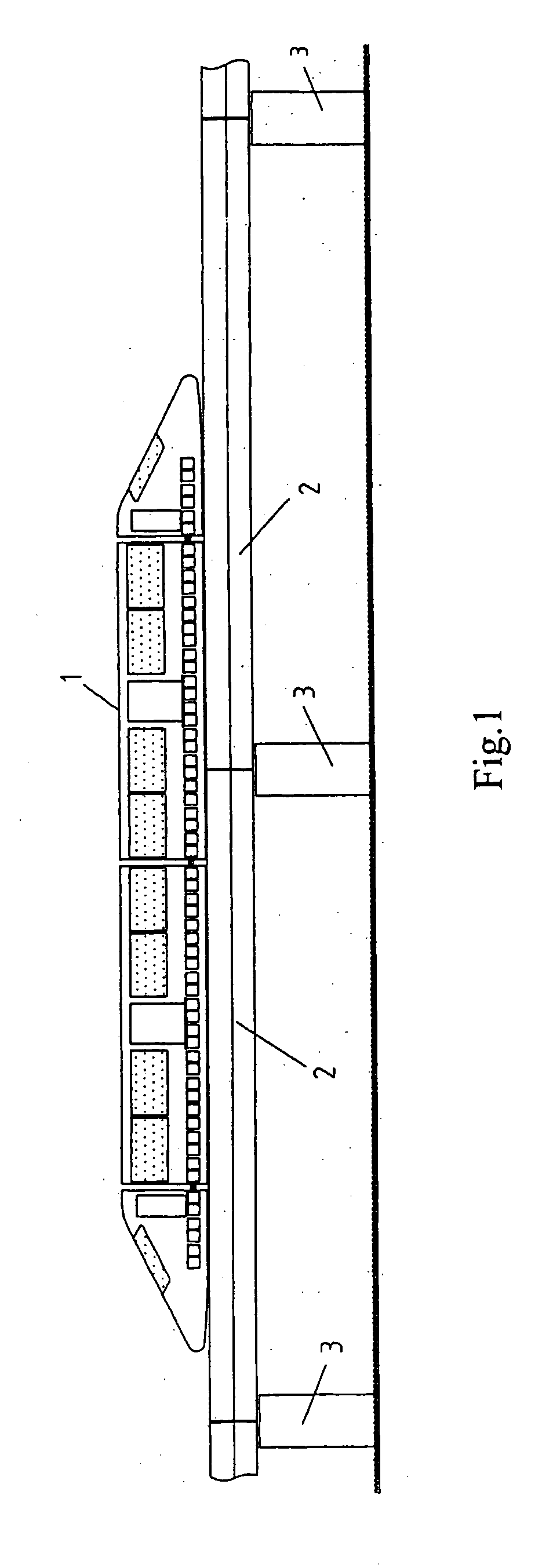
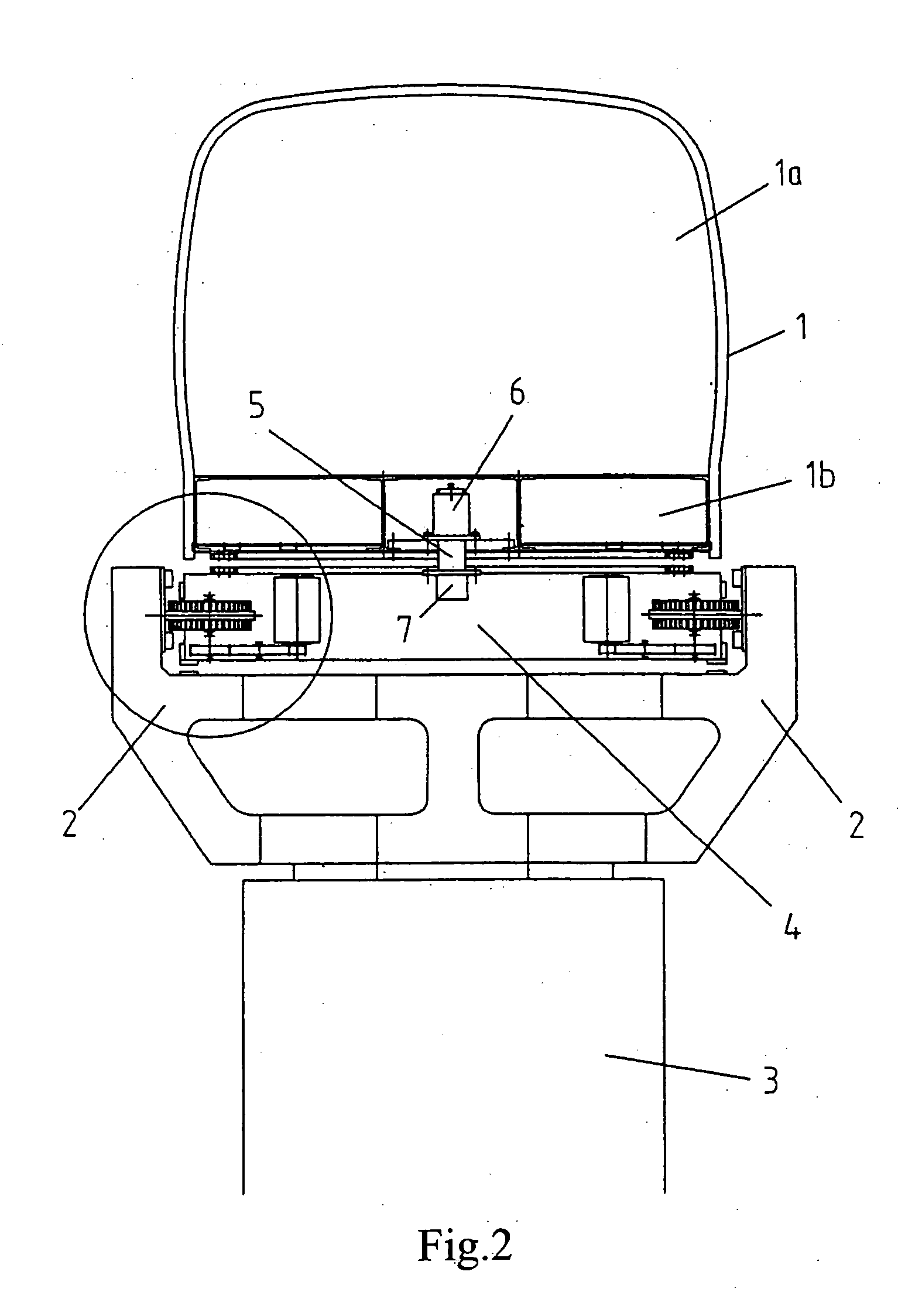
A sliding load floor system for use in the rear cargo area of a vehicle. The cargo area has a pair of opposing side portions that extend longitudinally in relation to the center line of the vehicle. A pair of opposing transverse portions extend laterally in relation to the vehicle. A storage area is positioned between and at a level below a plane including the side and transverse portions. The sliding load floor system comprises a slide mechanism including a pair of opposing rail members having a forward edge, and a removable load floor that is detachably positioned in relation to the slide mechanism; and a hinge assembly that is mounted to the side portions. The forward edges of the rail members are connected to the hinge assembly so that the slide mechanism, and the removable load floor may be moved arcuately in relation to the hinge assembly, and the load floor slid rearwardly. Also included is a levitation mechanism for raising a rear edge of the sliding load floor so that the load floor may be extended rearwardly outside the vehicle across a raised sill in the cargo area.
Owner:INT AUTOMOTIVE COMPONENTS GRP NORTH AMERICA INC
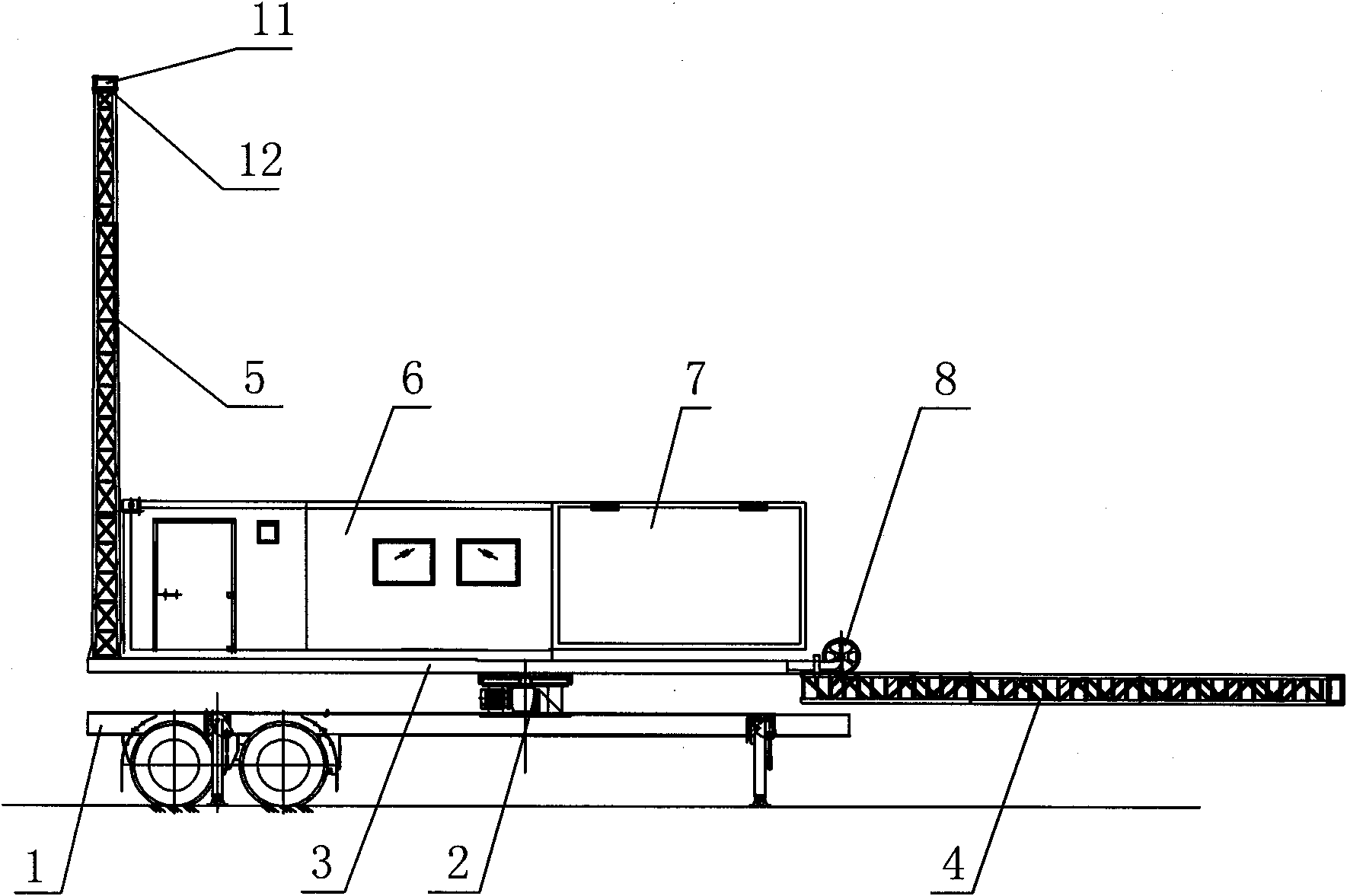
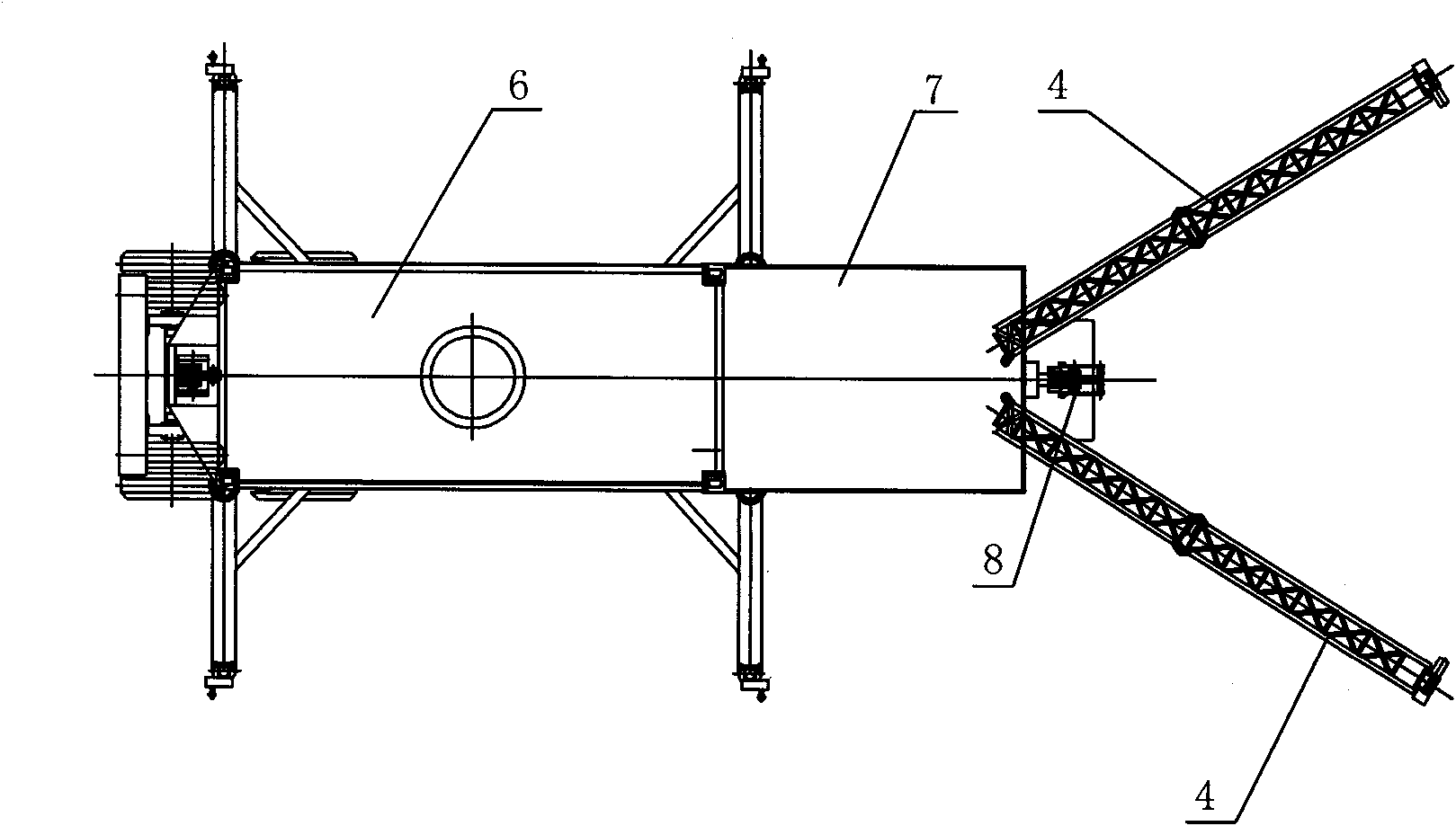
All-in-one anchoring trailer
InactiveCN101898633AImprove quick response abilityImprove mobilityItem transportation vehiclesLighter-than-air aircraftLevitationEngineering
The invention discloses an all-in-one anchoring trailer, and belongs to ground devices of medium and small-sized tethered balloons. The all-in-one anchoring vehicle comprises a semitrailer chassis, a pivoting platform fixed on the semitrailer chassis through a pivoting support and a mooring tower, a plurality of horizontal support arms and a capsule box which are arranged on the pivoting platform, and also comprises a shelter fixed to the front part of the pivoting platform, wherein a winch system is arranged in the shelter; the mooring tower is arranged at the front end of the pivoting platform; the horizontal support arms are hinged on both sides of the rear end of the pivoting platform; and the capsule box is fixed to the rear part of the pivoting platform. In the all-in-one anchoring trailer, all-in-one operation such as aeration, anchoring, levitation, air retention, recovery, roll-up and the like of the medium and small-sized tethered balloons can be performed on the pivoting platform directly, so the maneuverability of a tethered balloon system is improved greatly, the time of unfolding the system is reduced, the operation is simplified, the efficiency is improved and the quick-response capability of the tethered balloons is enhanced.
Owner:湖南航天管理局
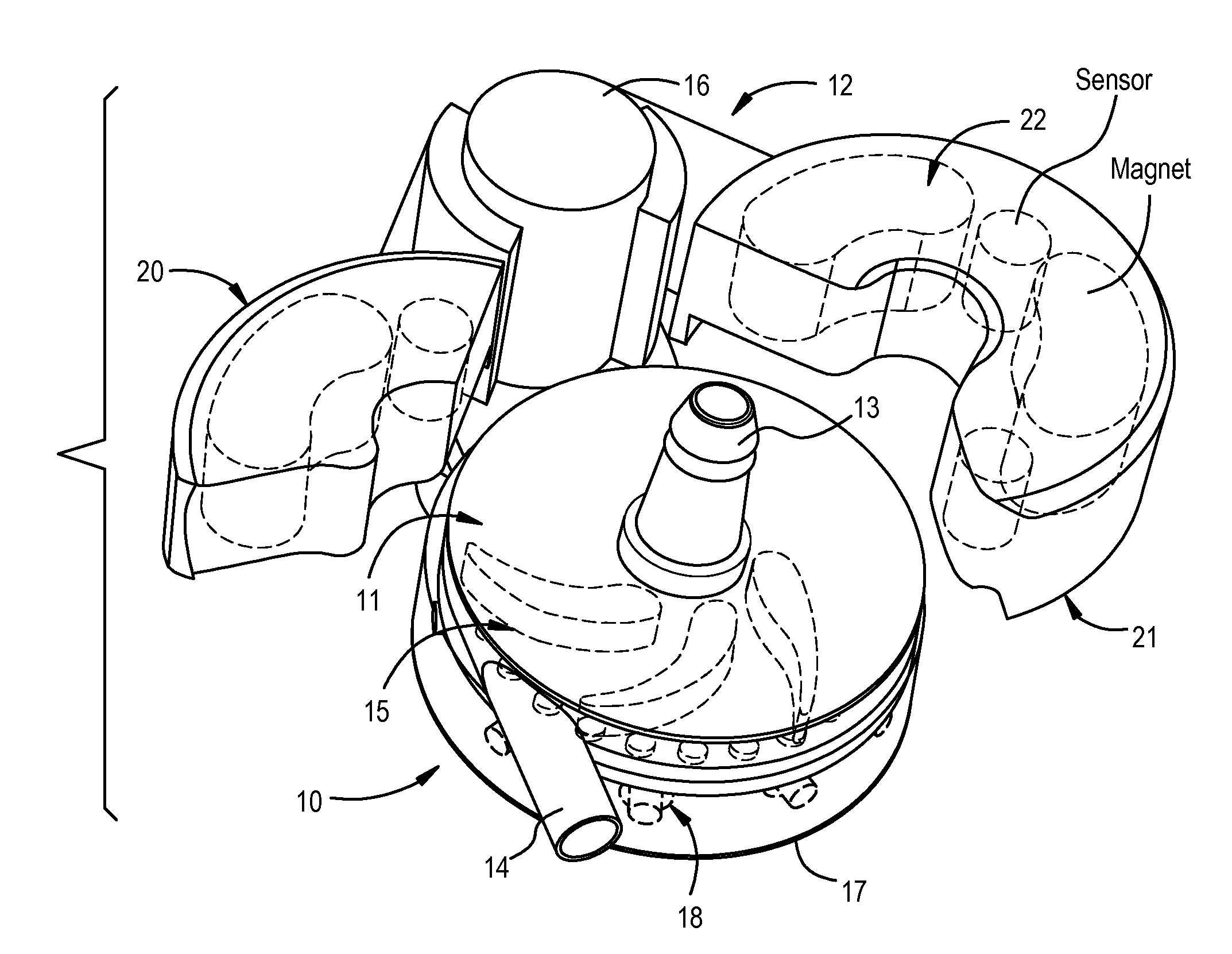
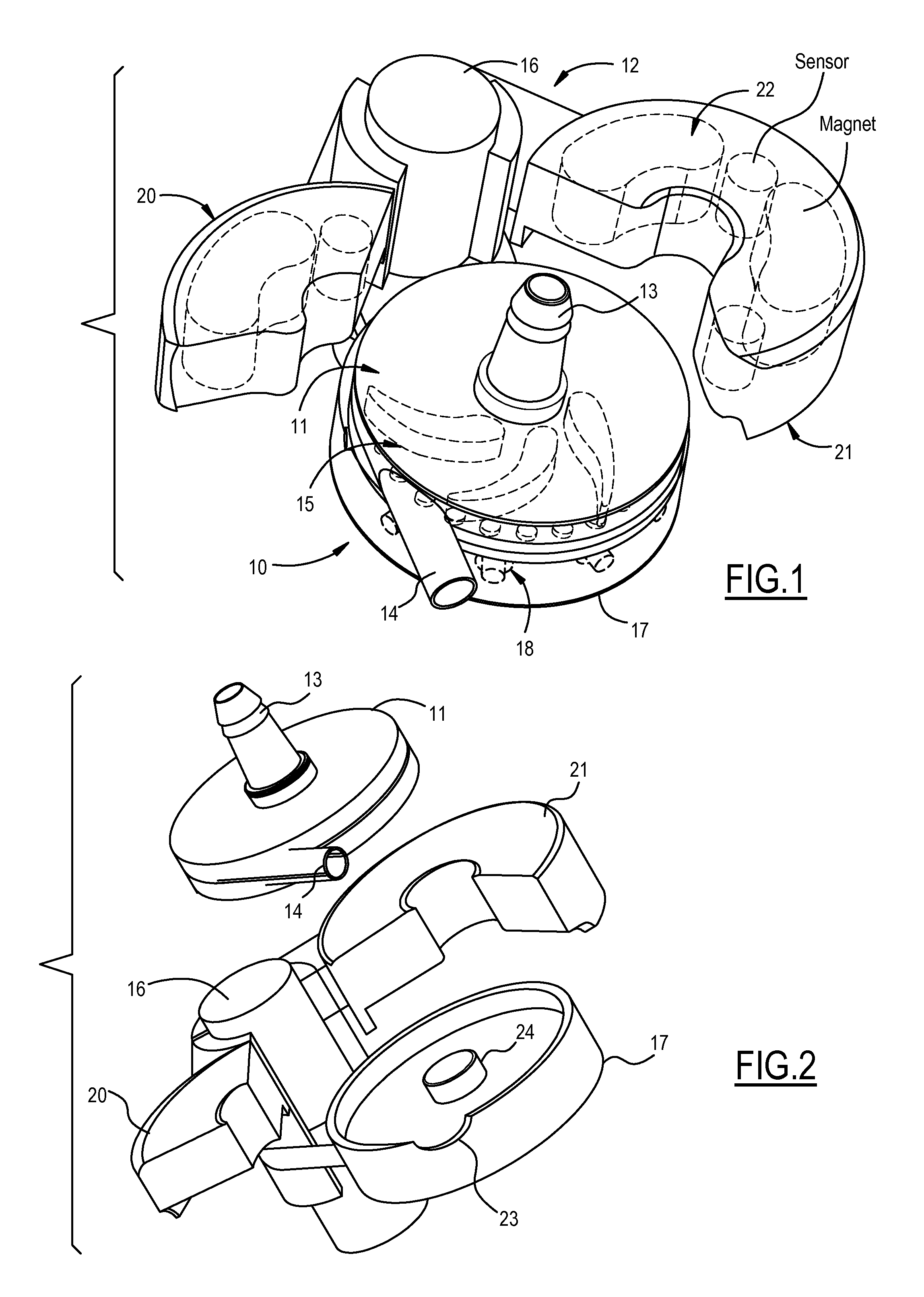
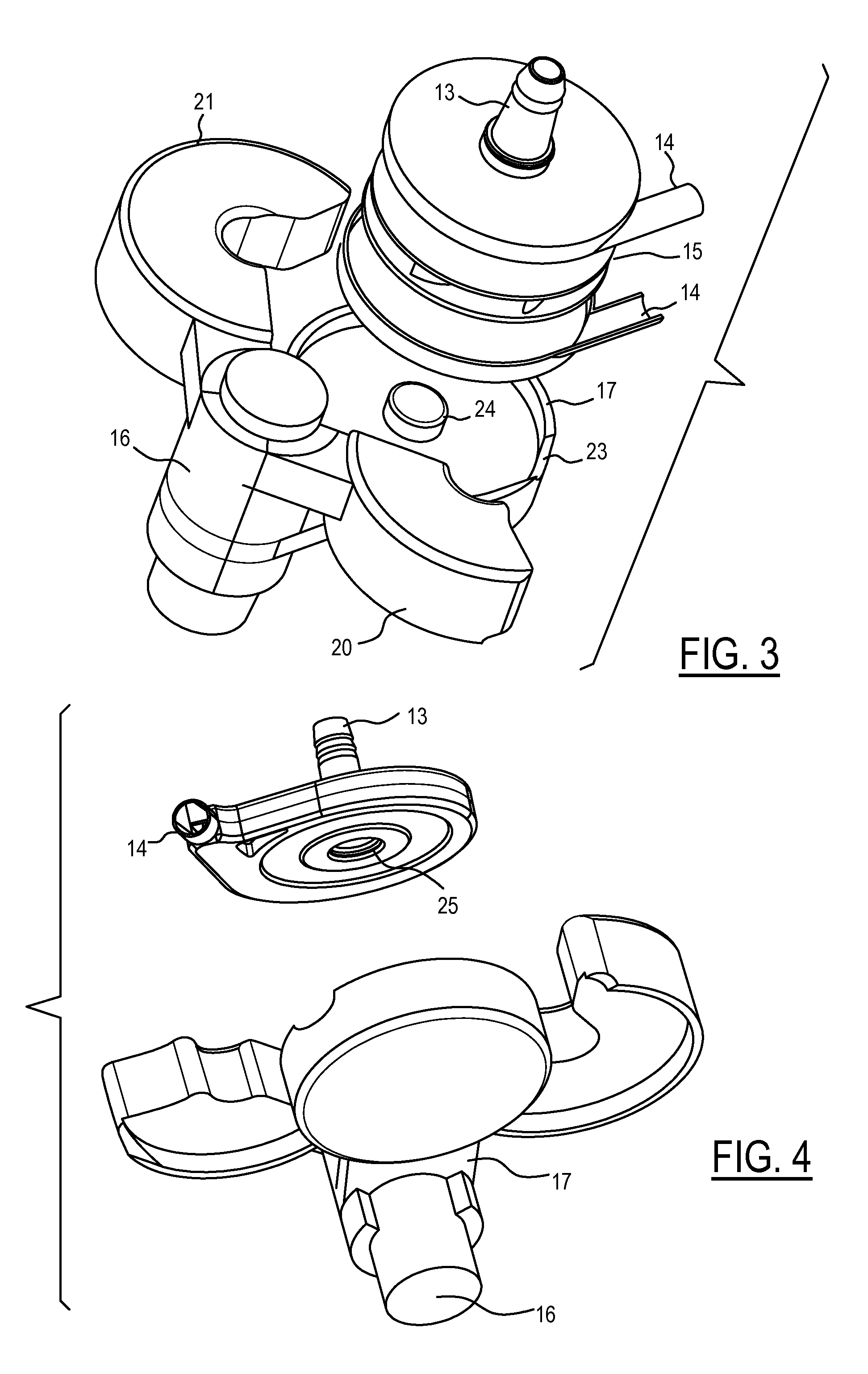
Extracorporeal Blood Pump with Disposable Pump Head Portion Having Magnetically Levitated Impeller
A pump drive unit has an openable housing that accommodates a disposable impeller unit which is pre-connected with tubing, while maintaining the tight tolerances and close spacing. A levitation system (magnets and sensors), drive motor and drive magnets, and control electronics are all re-usable and housed within relatively permanent structures. In one embodiment, a hinged top separates the levitating magnets to allow the impeller unit to be captured and retained with positional accuracy and in close proximity to the desired locations when the hinged top is closed. The top may be separated into sections covering unequal arcs to coincide with the organization of the magnetic subcomponents in the upper drive unit housing.
Owner:TERUMO CARDIOVASCULAR SYST CORP
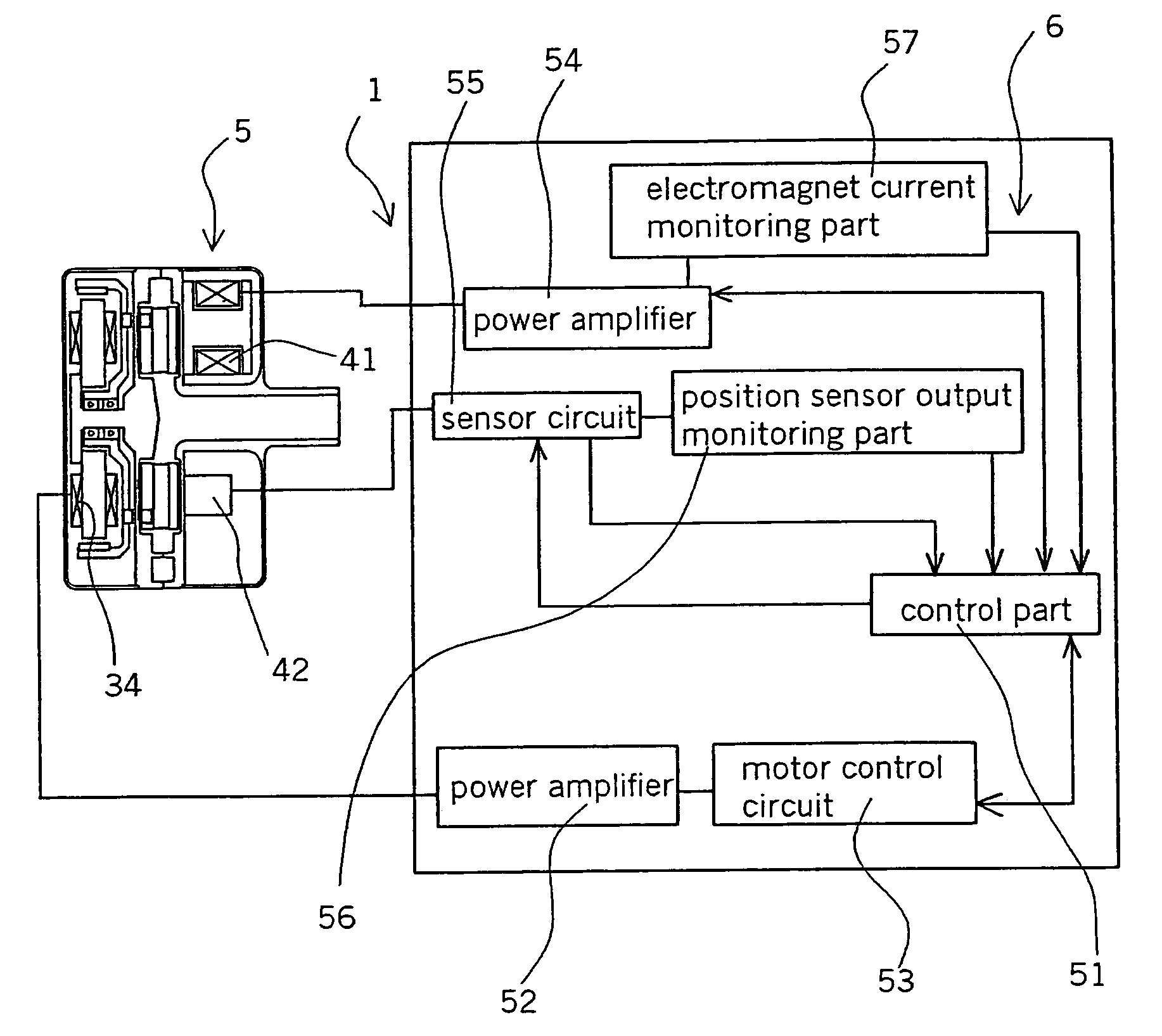
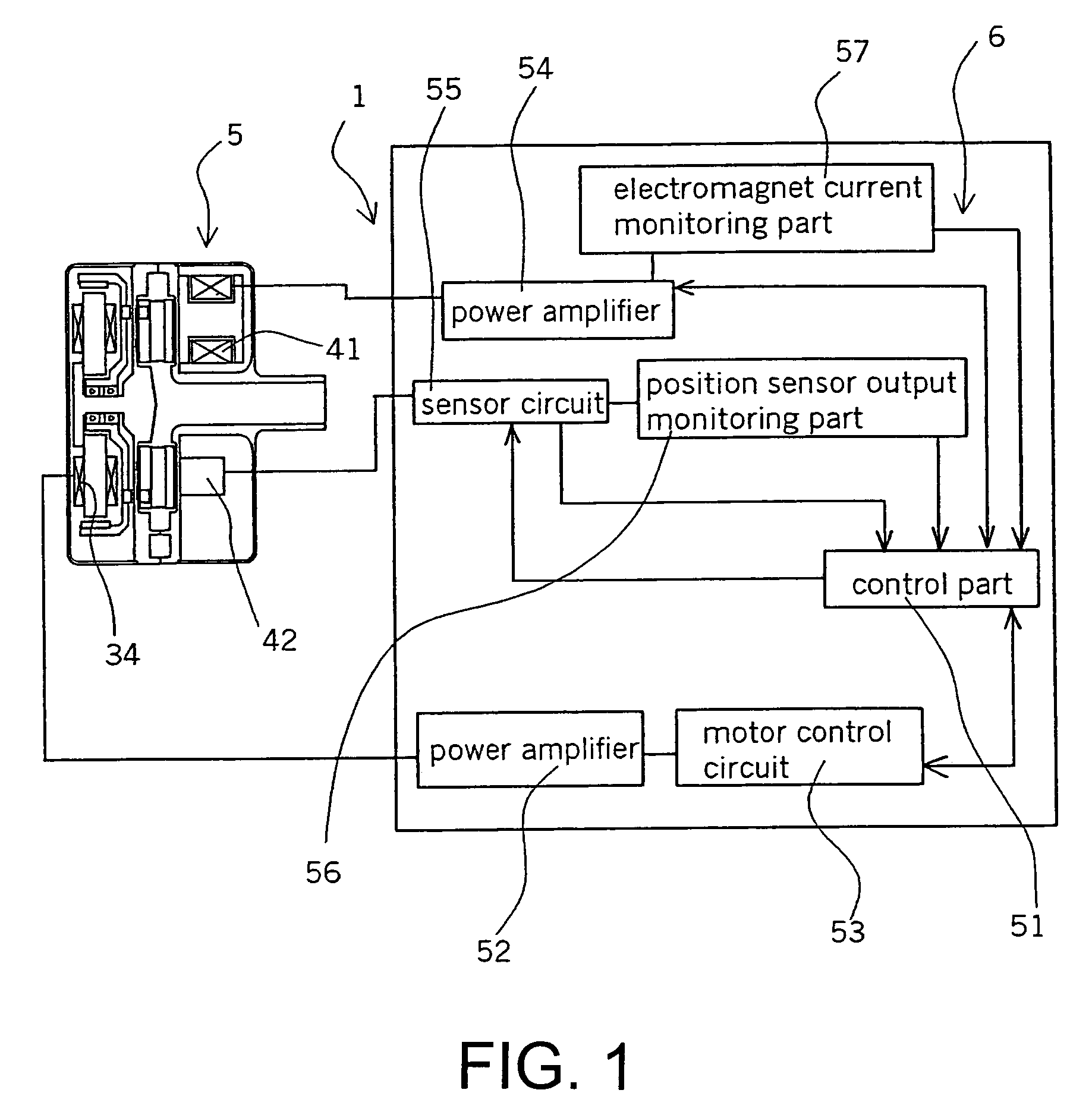
Centrifugal fluid pump apparatus
A centrifugal fluid pump apparatus includes a control mechanism; and a body including a pump section having an impeller rotating inside a housing; a rotor having an impeller attraction magnet; a motor for rotating the rotor; an impeller attraction electromagnet for attracting the impeller thereto; an impeller-position detection sensor; and hydrodynamic bearing means provided on an inner surface of the housing. The control mechanism has a position sensor output monitoring function or an electromagnet current monitoring function, a motor current monitoring function; and an emergency impeller rotation function. The emergency impeller rotation function includes a rotation termination function of terminating current to the motor and the electromagnet when the failure detection function detects a failure to thereby terminate rotation of the rotor and the impeller; impeller magnetic counterforce application function to apply a current to the electromagnet sufficient to overcome the magnetic attraction force of the rotor to the impeller caused by the magnet; hydrodynamic levitation control detection function to detect rotation of the impeller and the rotor by using a motor current monitored by the motor current monitoring function; motor speed control function for increasing the motor speed and hence the impeller rotation speed up to a predetermined value after the hydrodynamic levitation control detection function detects that the hydraulic bearing coupling between the impeller and the rotor has been made; and impeller magnetic counterforce termination function to terminate current to the electromagnet once the predetermined impeller rotation speed is reached.
Owner:TERUMO KK
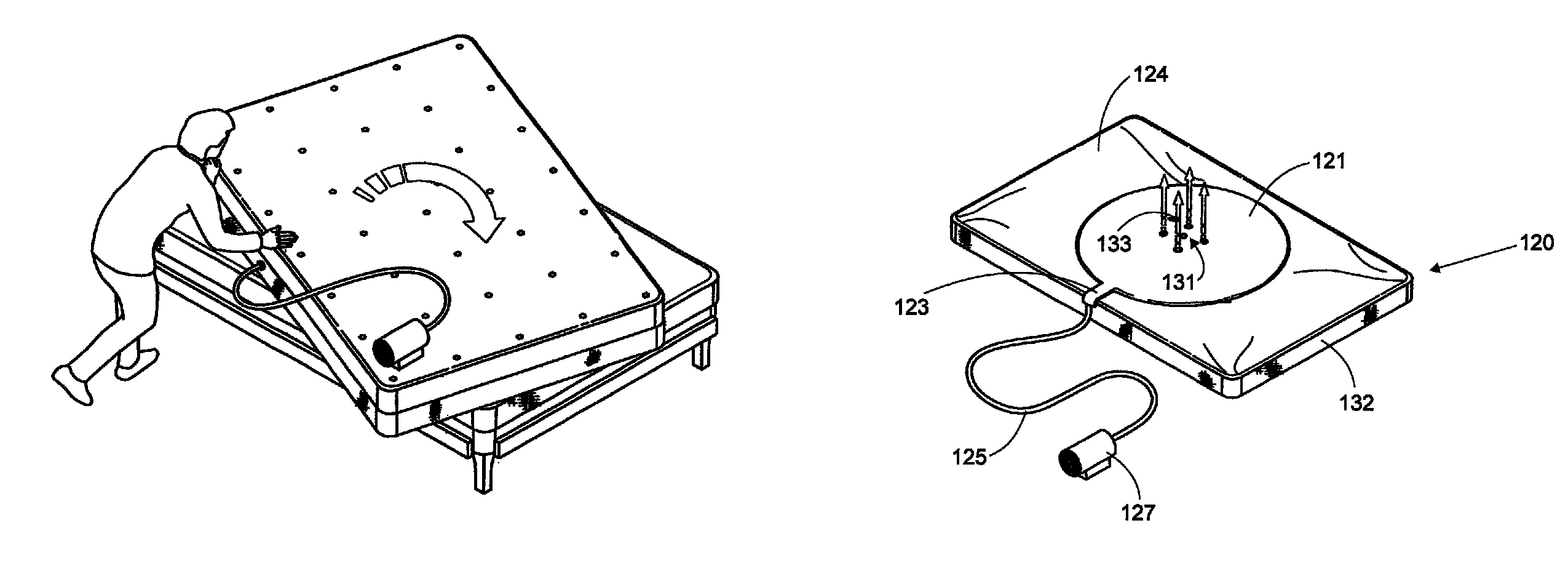
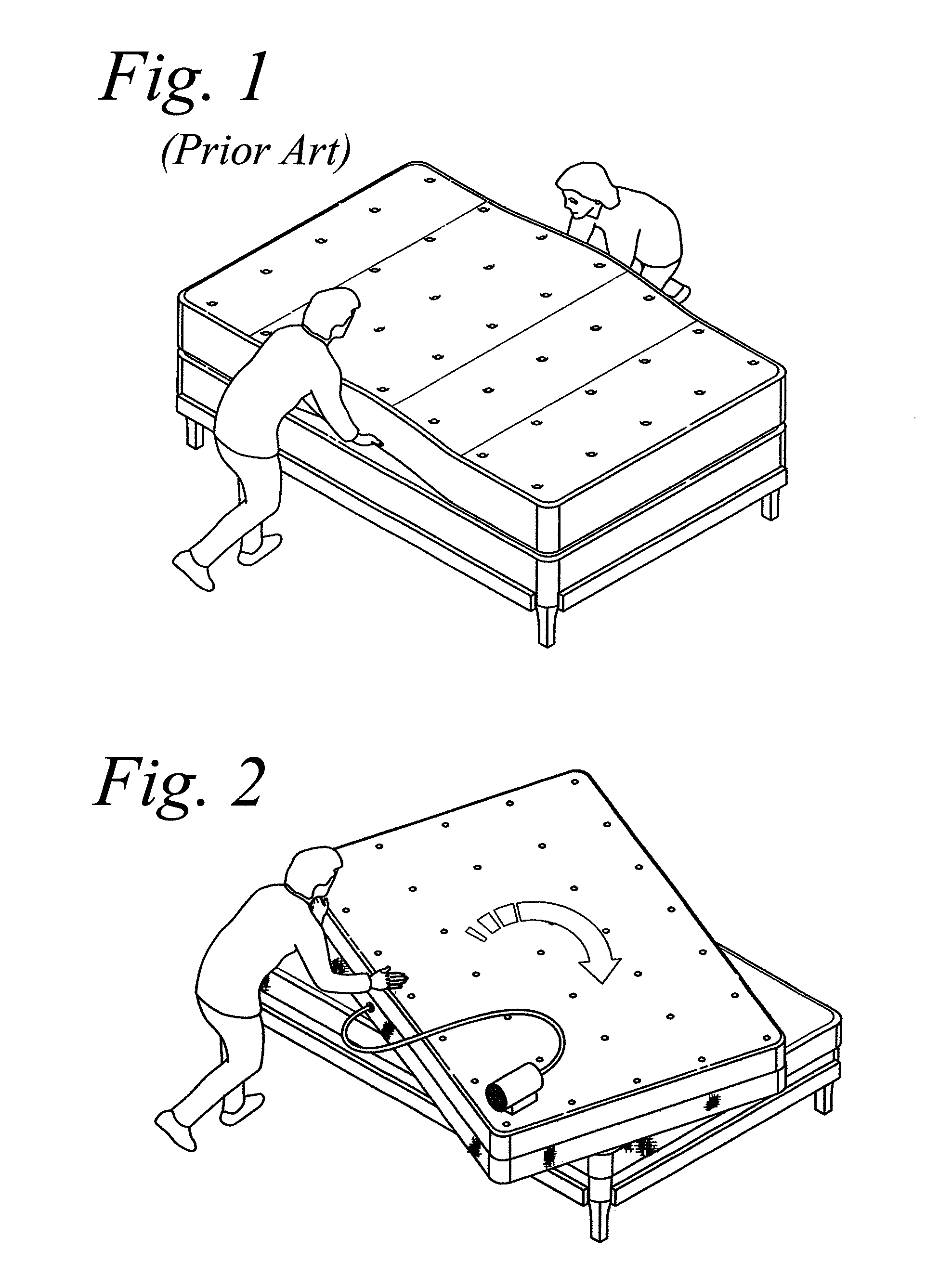
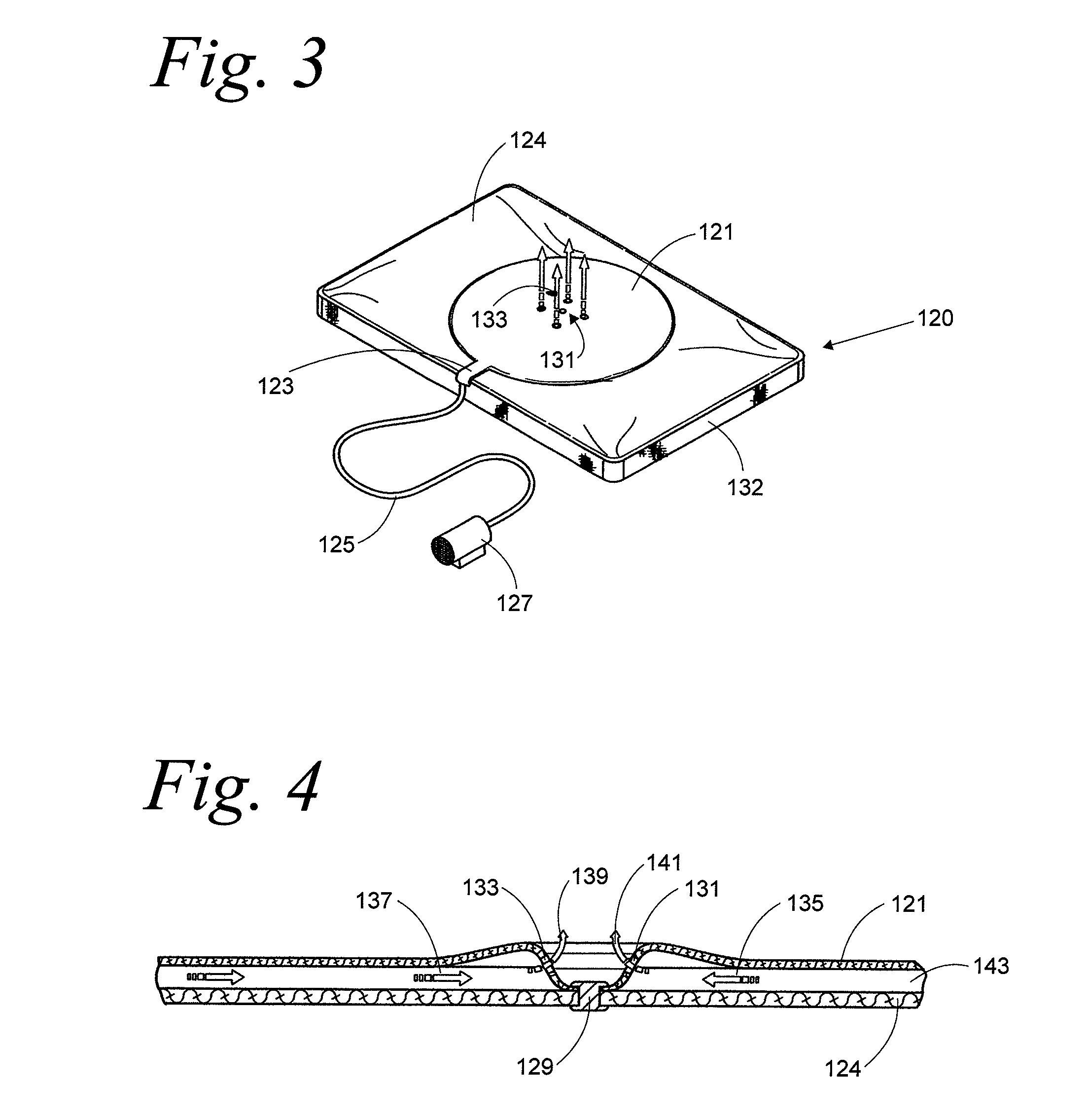
Active mattress spinner
A device is disclosed for facilitating rotation of a mattress in a horizontal plane carried by a box spring or a platform. In order to facilitate rotation, slick surfaces between the mattress and the box spring or platform are selectively placed in contact in order to reduce the normal friction therebetween. The slick surfaces may be provided by two (2) separate covers; one cover for the mattress and one cover for the box spring or platform. A first cover is provided with a slick and non-slick surface. In order to further facilitate rotation, a second cover includes a slick surface on one side and forms part of a levitation device. The other side of the second cover may be formed with a slick or a non-slick surface. A levitation device creates an air cushion between the mattress and the box spring under the influence of an air supply which lifts the mattress and allows the mattress to be rotated in a horizontal plane virtually effortlessly.
Owner:LEVITATION SCI
Magnetostatic levitation and propulsion systems for moving objects
InactiveUS20100126374A1High levitating force outputRemove complexitySliding/levitation railway systemsMachines/enginesMagnetic tension forceMagnetic bearing
The present invention relates to a novel magnetic suspension and propulsion technologies, which are named as Magnetostatic Suspension (MSS) and Magnetostatic Propulsion (MSP) respectively because of their magnetostatic nature of forces generated. A spring-like magnetic force is produced through interactions between magnets and ferrous materials such as steel. To apply the technologies, four key embodiments of the invention have been invented and described: a MSS and MSP maglev vehicle system in which a vehicle body is lifted up and stabilized by magnetostatic forces above a steel rail both horizontally and vertically; a MSP long-stator linear motor system in which a rotor can be driven up along a magnet-free steel rail or long steel stator; a MSS Permanent Magnet Magnetic Bearing System (PMMB) system in which a steel shaft is levitated standstill by a fully permanent magnets assembly for frictionless rotating; a MSS maglev wind turbine system in which a magnet-free turbine body can hover standstill over a permanent magnet base assembly spinning frictionlessly with low inertia and low cut-in wind speed threshold.
Owner:JI QIGEN
Amlev: Self-regulating type of Maglev high speed ground transportation based on permanent magnets and steel cores
The proposed Amlev Self-Regulating System of High Speed Ground Transportation Based on Permanent Magnets and Steel Cores is designated for magnetic levitation, stabilization, and propulsion of vehicles moving without friction. The proposed system comprises subsystems: a Magneto-Dynamic Levitation and Stabilizing Self-Regulating System (MDLSS), and a Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor (PMLSM). Both systems comprise permanent magnets and steel cores. MDLSS provides levitation and stabilization of vehicle while PMLSM produces propulsion force providing the assigned alternative velocity of the vehicle along the stator winding powered by the current of constant frequency 50 Hz. Each of the subsystems comprises two main parts: a fixed part—guideway / stator including extended steel cores for MDLSS and windings for PMLSM, and moving part—permanent magnets of the levitator for MDLSS and the rotor for PMLSM—both affixed to the moving vehicle. Each of the subsystems is self-regulating and operates without fast response control system. A new model is proposed for measuring destabilizing forces impacting a flying vehicle at its shifts from an assigned trajectory that allows to eliminate the stage of full-scale modeling when designing Amlev system.
Owner:TOZONI MICHAEL
Magnetic levitation motor and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20010030471A1Convenience to workHigh outputSynchronous generatorsWindingsLevitationConductor Coil
A magnetic levitation motor includes a rotor and a stator disposed opposite to the rotor. The rotor has a main body formed from a magnetic member and a permanent magnet attached to a peripheral surface of the main body. The stator has a first stator winding that generates a levitation control magnetic flux for controllably levitating the rotator body, a second stator winding that generates a rotation magnetic flux for rotating the rotator body and a stator core having the first stator winding and the second stator winding. A direct current magnetic field generation device is provided to generate a magnetic flux radially spreading from the rotor to the stator. The stator core is formed from a plurality of individual stator core sections. Each of the individual stator core sections has a base section and a salient pole section extending from a central section of the base section. The first winding and the second winding are wound around the salient pole section of each of the individual stator core sections. Then, the stator core sections are joined together to form the stator core.
Owner:SANKYO SEIKI MFG CO LTD
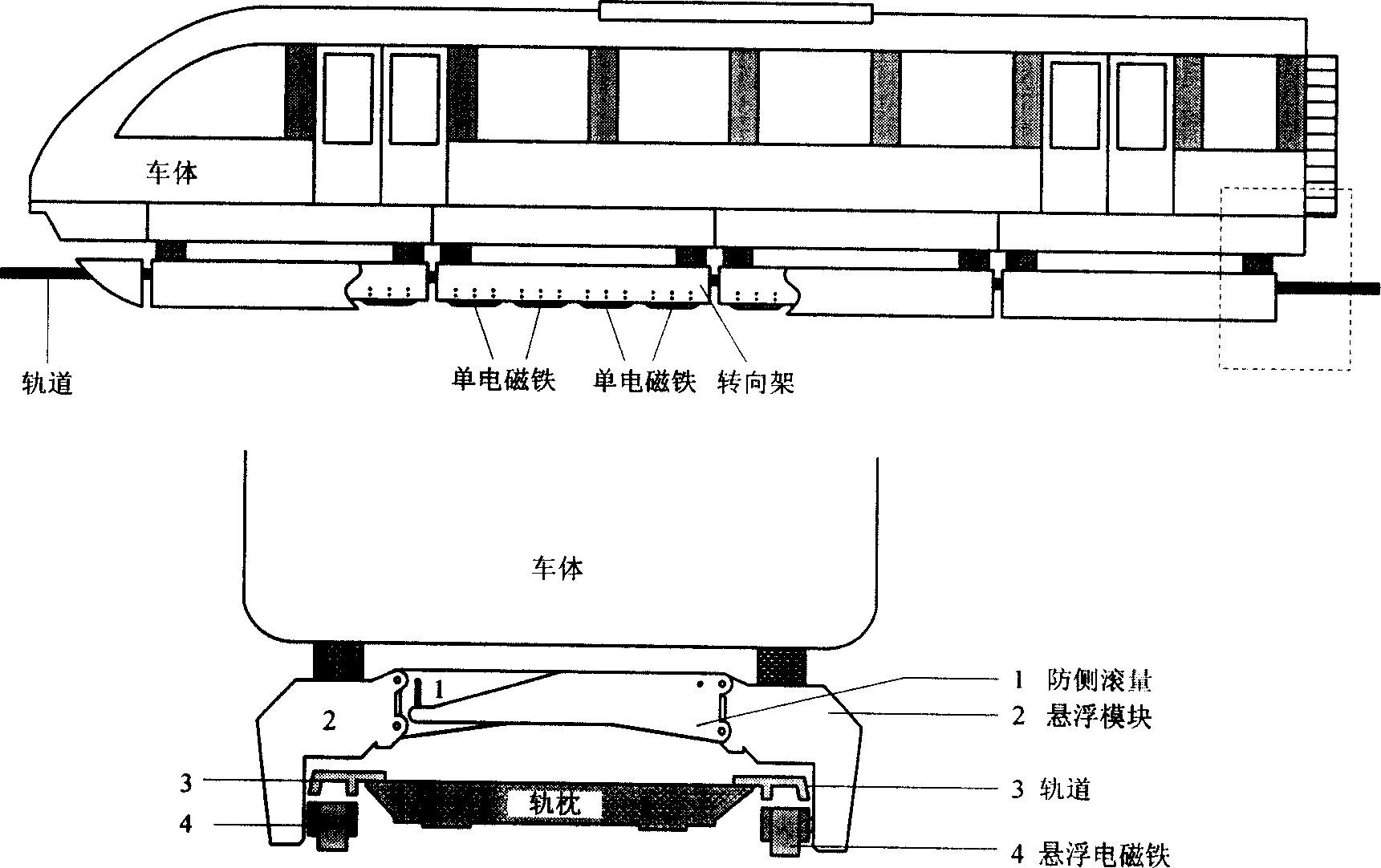
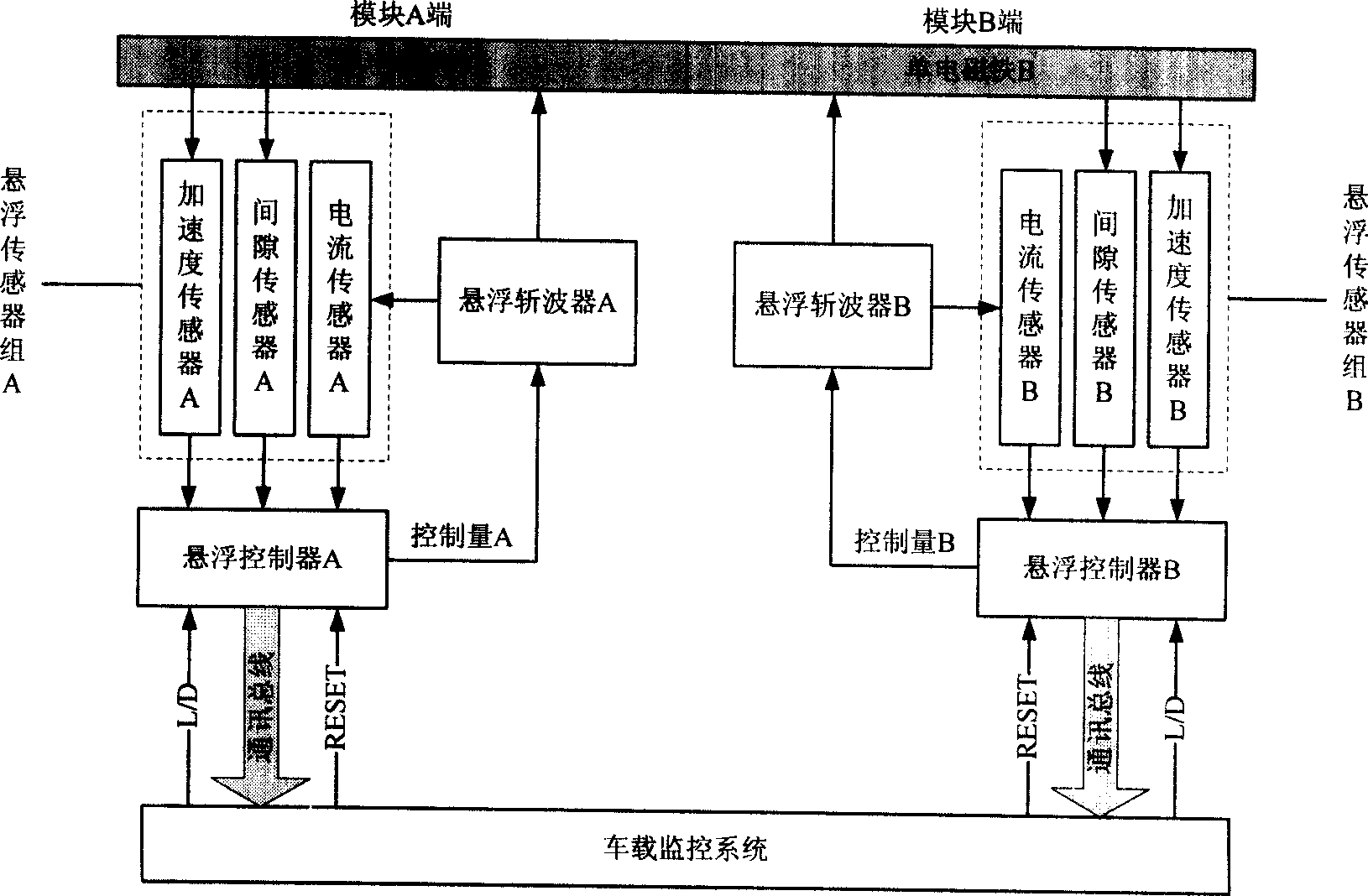
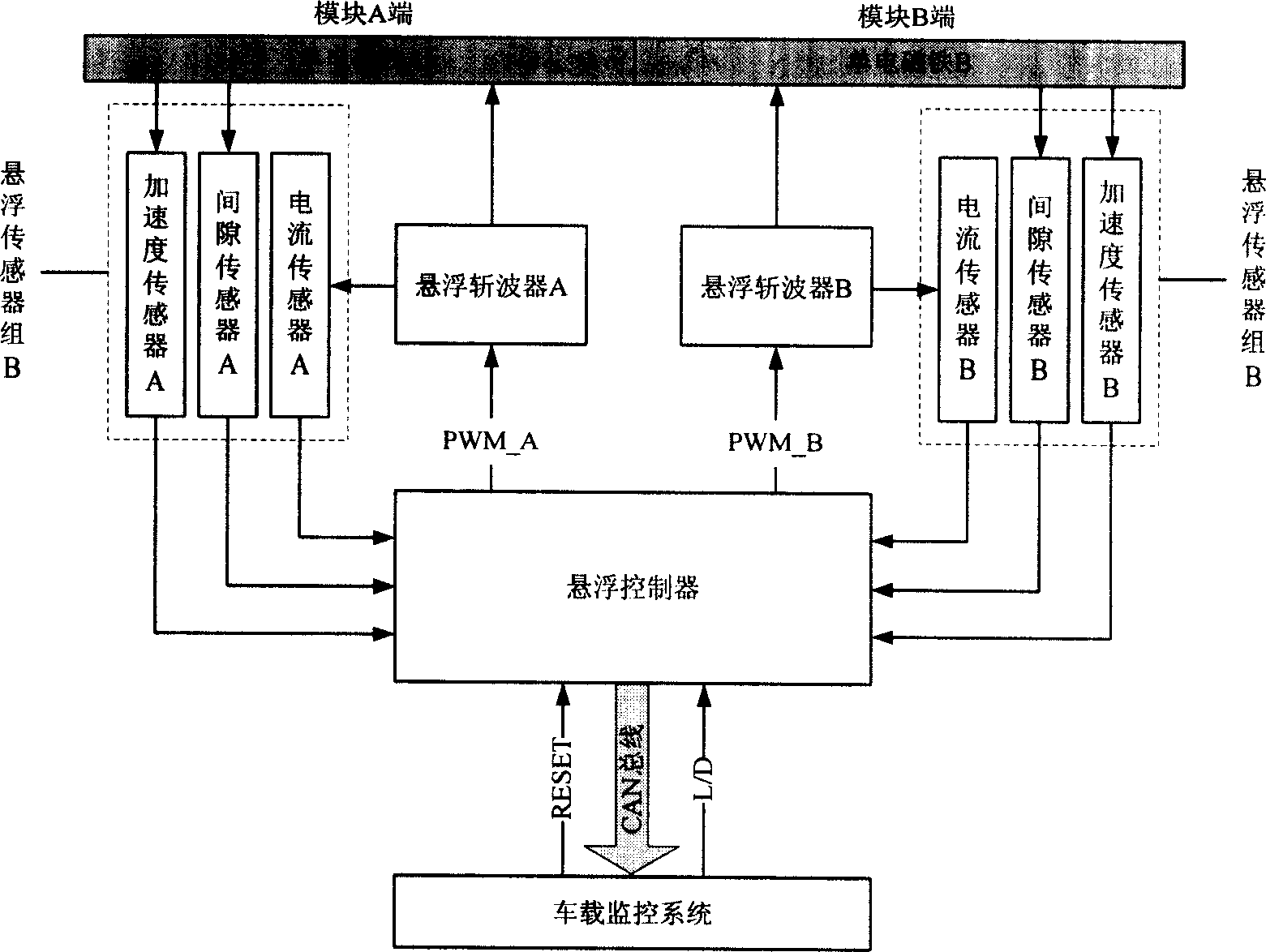
Suspension method for controling module of electromagnetism type magnetic suspension train in normal conduction and low temperature
InactiveCN1915704AAvoid interactionOvercome inherent flaws that existElectric propulsionMagnetic tension forceElectricity
A module levitation control method for the frequently conducting electromagnetic-type low-speed magnetic levitation train features that a levitation control system has only one levitation controller consisting of signal processing unit, A / D converter, clock signal generator, master DSP unit, PWM wave generator and auxiliary DSP unit. Said method includes such steps as measuring the levitation states of ends A and B of a module by two levitation sensors, calculating their control values, and controlling the current values of electromagnets A and B and in turn their electromagnetic forces, so ensuring the gap between module and track to be constant.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Impeller position compensation using field oriented control
A centrifugal pump system having an impeller rotating with first and second magnetic structures on opposite surfaces. A levitation magnetic structure is disposed at a first end of a pump housing having a levitating magnetic field for axially attracting the first magnetic structure. A multiphase magnetic stator at a second end of the pump housing generates a rotating magnetic field for axially and rotationally attracting the second magnetic structure. A commutator circuit provides a plurality of phase voltages to the stator. A sensing circuit determines respective phase currents. A controller calculates successive commanded values for the phase voltages in response to the determined phase currents and a variable commutation angle. The angle is selected to correspond to an axial attractive force of the stator that maintains a levitation of the impeller at a centered position within the pumping chamber.
Owner:TC1 LLC
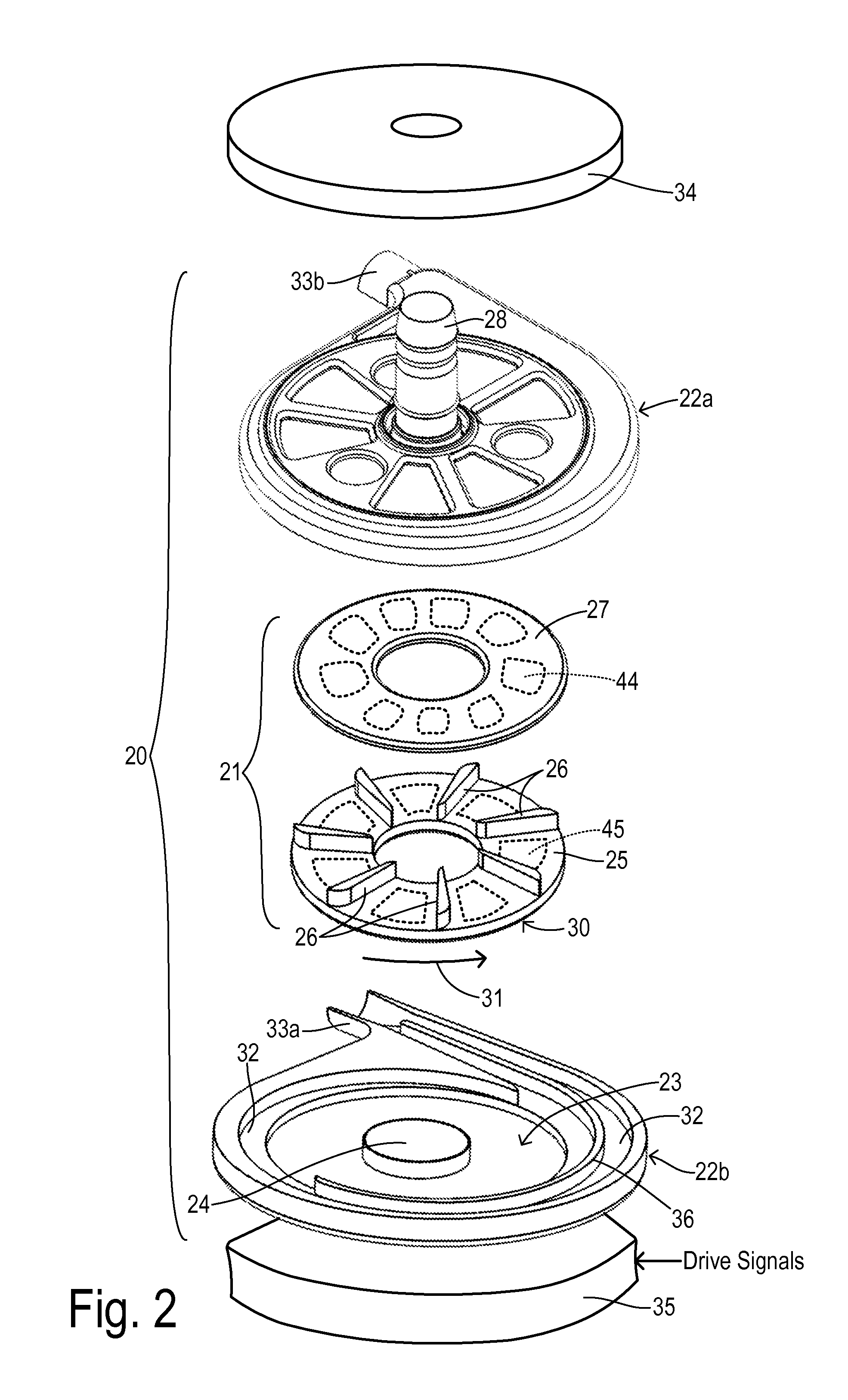
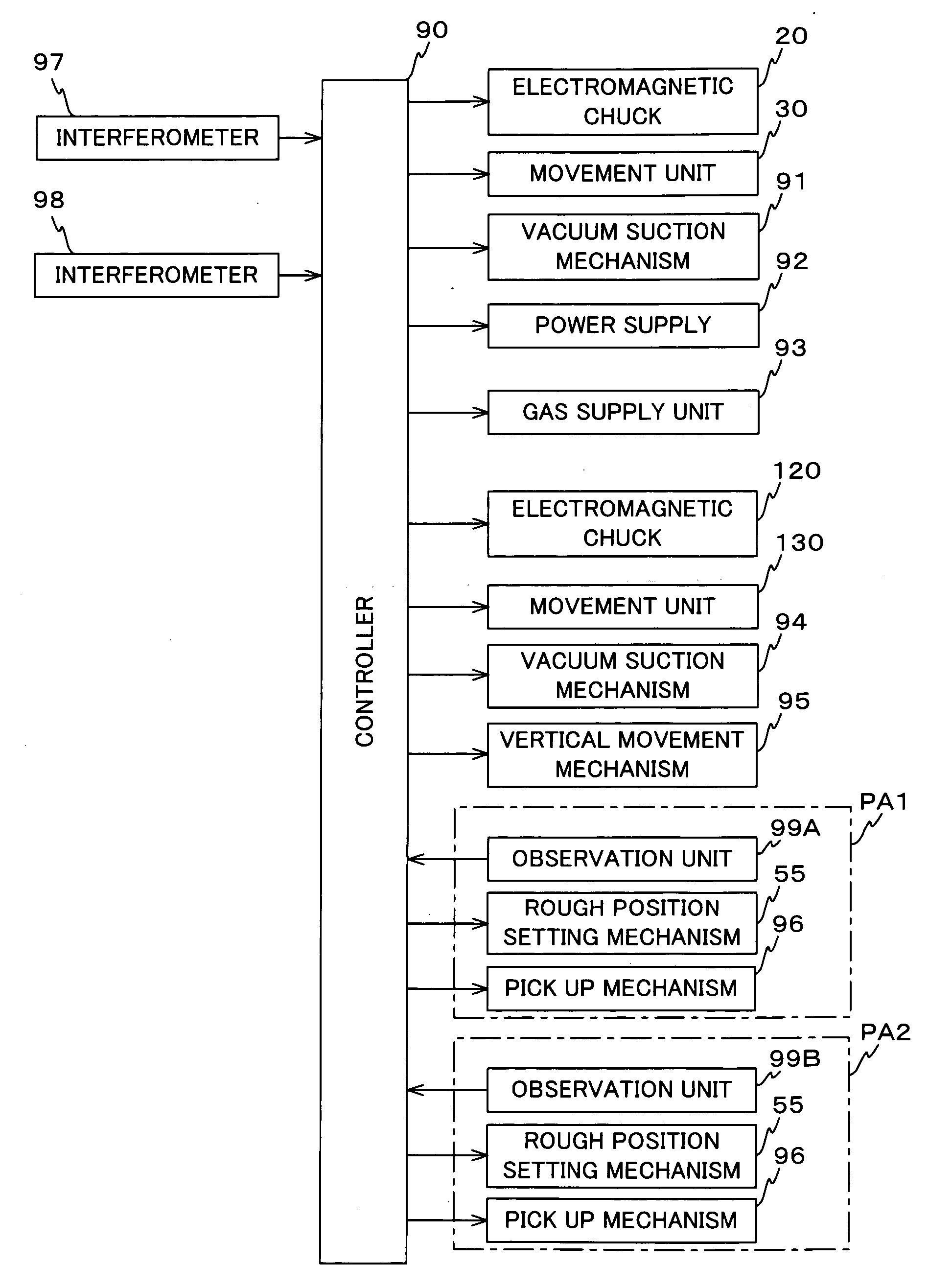
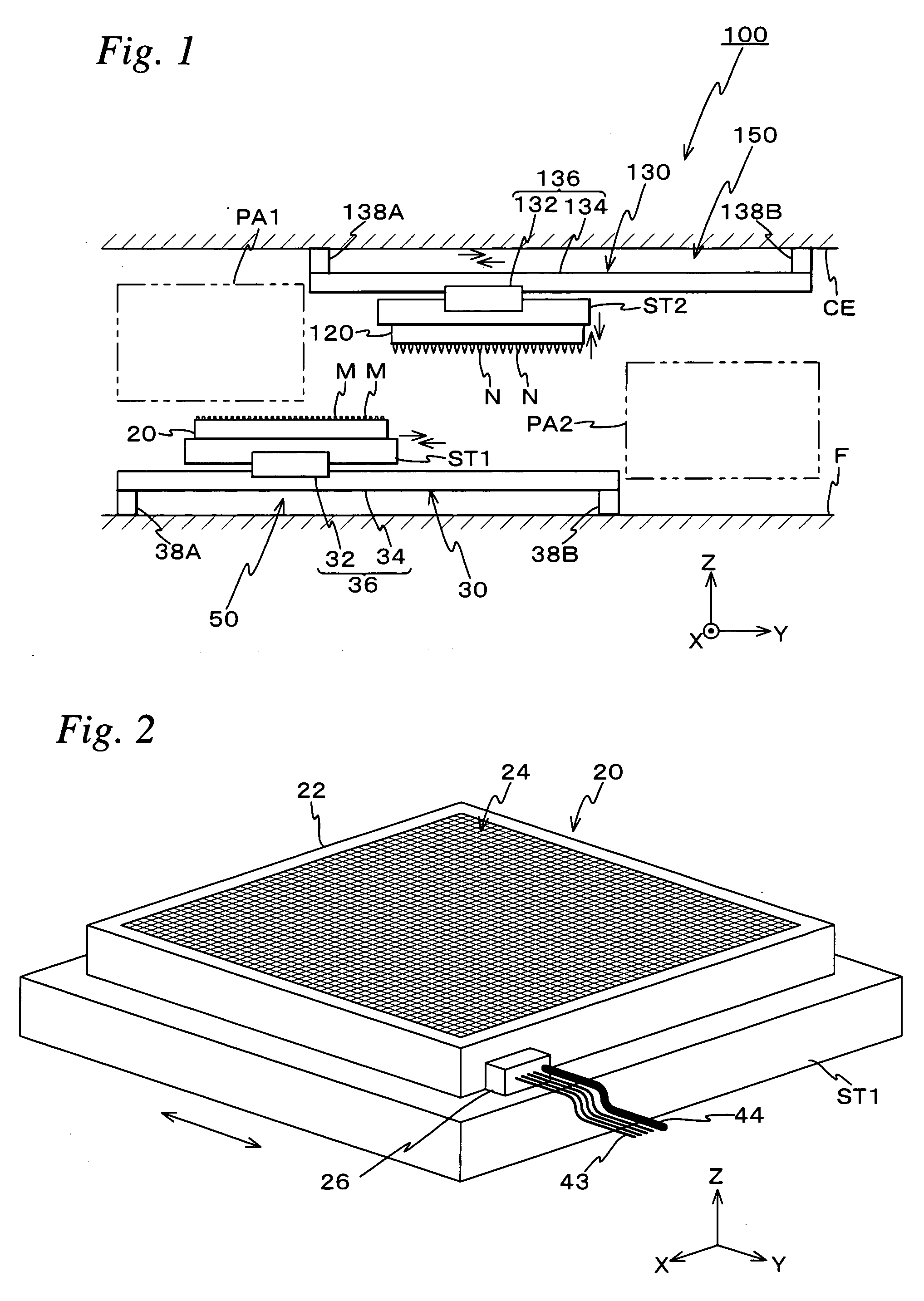
Holding unit, assembly system, sputtering unit, and processing method and processing unit
Because an electromagnetic chuck supplies current to a specific microcoil among a plurality of microcoils and makes an object exert an electromagnetic force working together with a magnet of the object, the object can be held in a state where the object is set at a desired position (a position that corresponds to the microcoil to which current has been supplied) on a base surface. Further, by gas that blows out from a gas supply passage, a levitation force is given to the object, which can reduce effects of a friction force that acts between the object and an upper surface of the electromagnetic chuck when the position of the object is set.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Construction method for erecting steel truss girder on uplift pushing tow
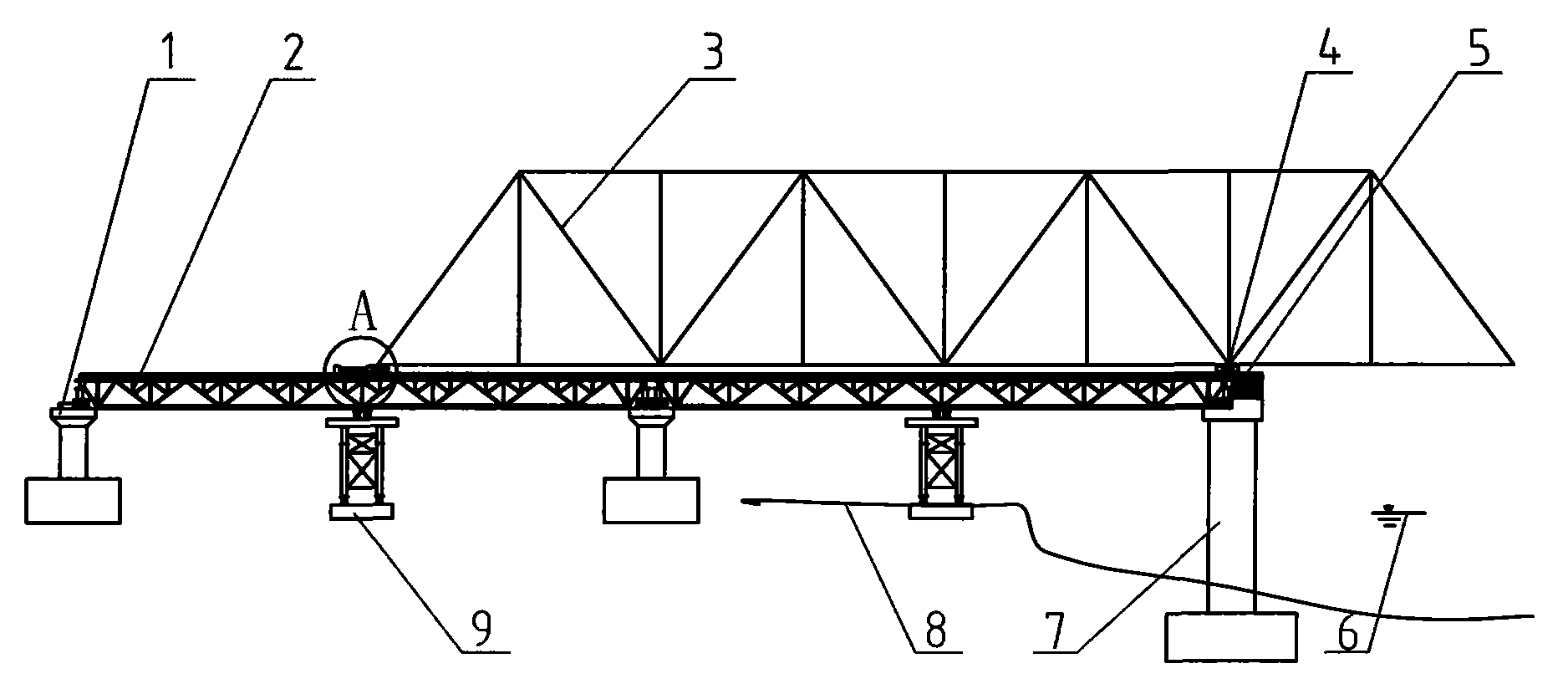
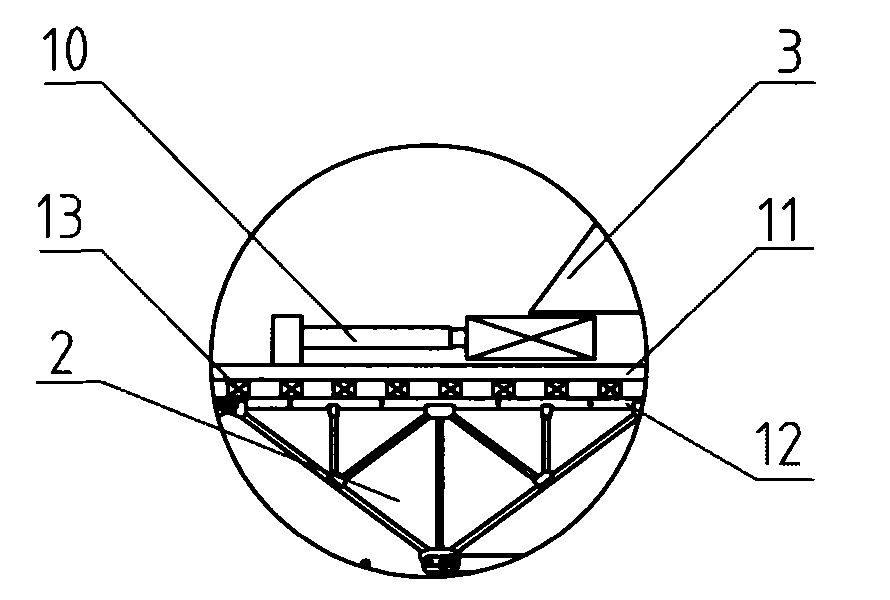
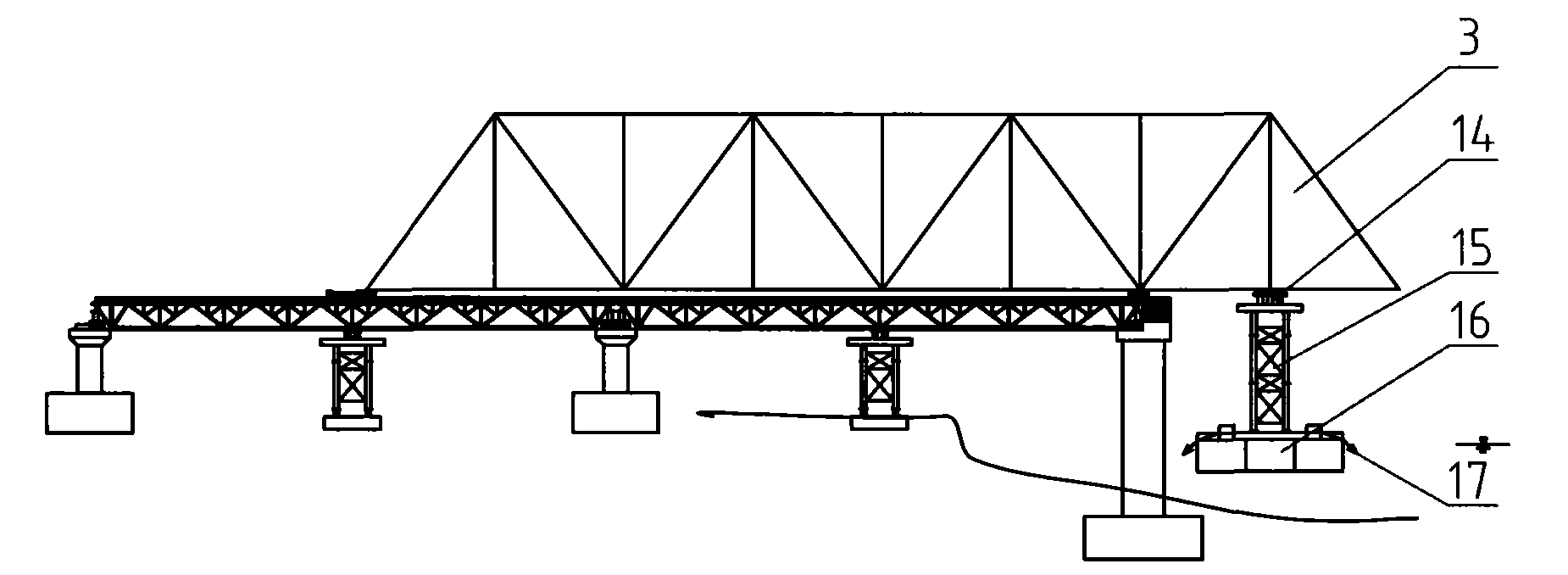
The invention discloses a construction method for erecting a steel truss girder. In the technical proposal of the invention, a buoyancy tank group serves as a carrier for levitation support; buoyancy tanks in the central part thereof are used to fill or drain water to ballast water to adjust elevation in a convenient manner; in addition, the proposal of using pushing tow construction is adopted, so that the steel truss girder can be assembled on a falsework on the spot in a convenient manner, hoisting of members is convenient and construction safety is high; the invention provides a construction method for erecting steel truss girder on uplift pushing tow, which features short construction cycle, convenient operation, short navigation closure period and low cost of erecting the steel truss girder and solves the problems that in the construction of the pushing tow, deflection of the steel truss girder is overlarge and internal stress of the steel truss girder is also overlarge.
Owner:RAILWAY NO 10 ENG GRP CO LTD
Inductrack configuration
InactiveUS7096794B2Improve rendering capabilitiesLittle strengthLinear bearingsRailway vehiclesHorizontal forceLevitation
A simple permanent-magnet-excited maglev geometry provides levitation forces and is stable against vertical displacements from equilibrium but is unstable against horizontal displacements. An Inductrack system is then used in conjunction with this system to effect stabilization against horizontal displacements and to provide centering forces to overcome centrifugal forces when the vehicle is traversing curved sections of a track or when any other transient horizontal force is present. In some proposed embodiments, the Inductrack track elements are also employed as the stator of a linear induction-motor drive and braking system.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Suspension maglev rail transit system
ActiveCN109131370AReduce frictionReduced forward resistanceSliding/levitation railway systemsElevated railway with suspended vehicleGuidance systemRepulsion force
A suspension maglev rail transit system includes an orbital system, a suspension system, a control system and a car system, wherein the control system comprises a drive system, a guidance system and asuspension control system, wherein the track system is suspended in the air through upright posts, the car system is suspended vertically below the track system through the suspension system, and thedrive system and the guidance system cooperate to drive the car system to operate in the track system. The invention utilizes the levitation force with the permanent magnet repulsion force as the main force and the electromagnetic regulation as the auxiliary force to suspend the car on the air track, and realizes the stable operation through the non-contact traction of the linear motor. The invention has the advantages of low energy consumption, high safety, no land occupation, low cost, strong climbing ability, small turning radius and wide adaptability.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Track component for maglev train
InactiveCN104029686AIncrease usageIncrease installation spaceSliding/levitation railway systemsElectric propulsionBogieLevitation
The invention discloses a track component for a maglev train. The track component comprises a track, a bogie arranged on a maglev train body, a traction module, and levitation guide modules arranged on two sides of the track. The traction module is disposed in the middle of the track and comprises array structured permanent magnets in corresponding arrangement and a long stator coil; power supply is controlled for the long stator coil via the ground; the array structured permanent magnets are mounted on the bogie; the long stator coil is mounted on the track; the long stator coil and the array structured permanent magnets interact to produce tractive force for the maglev train. The track component has the advantages that utilization rate of energy resources is increased, energy consumption is lowered and vehicular equipment is simplified.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
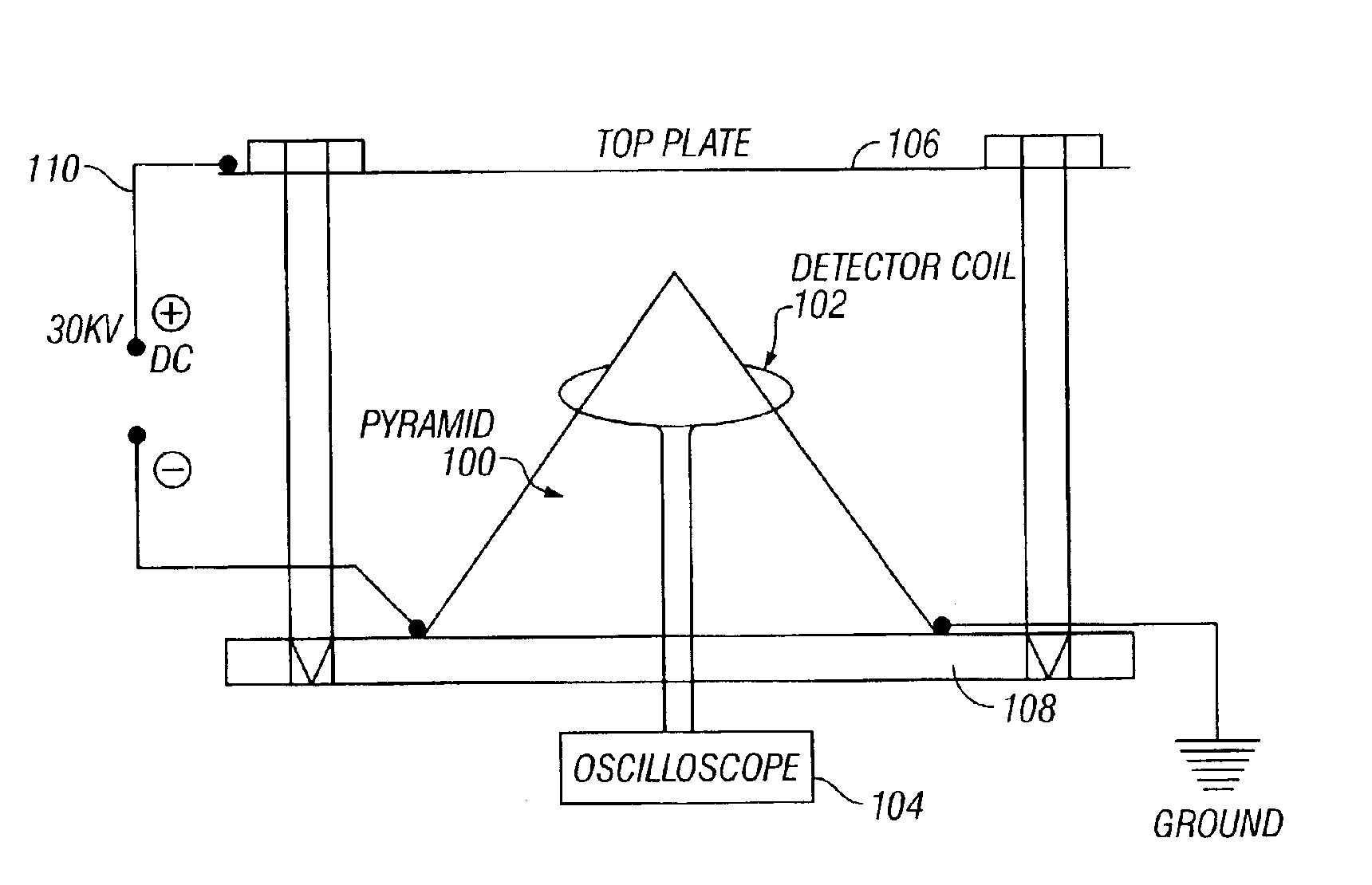
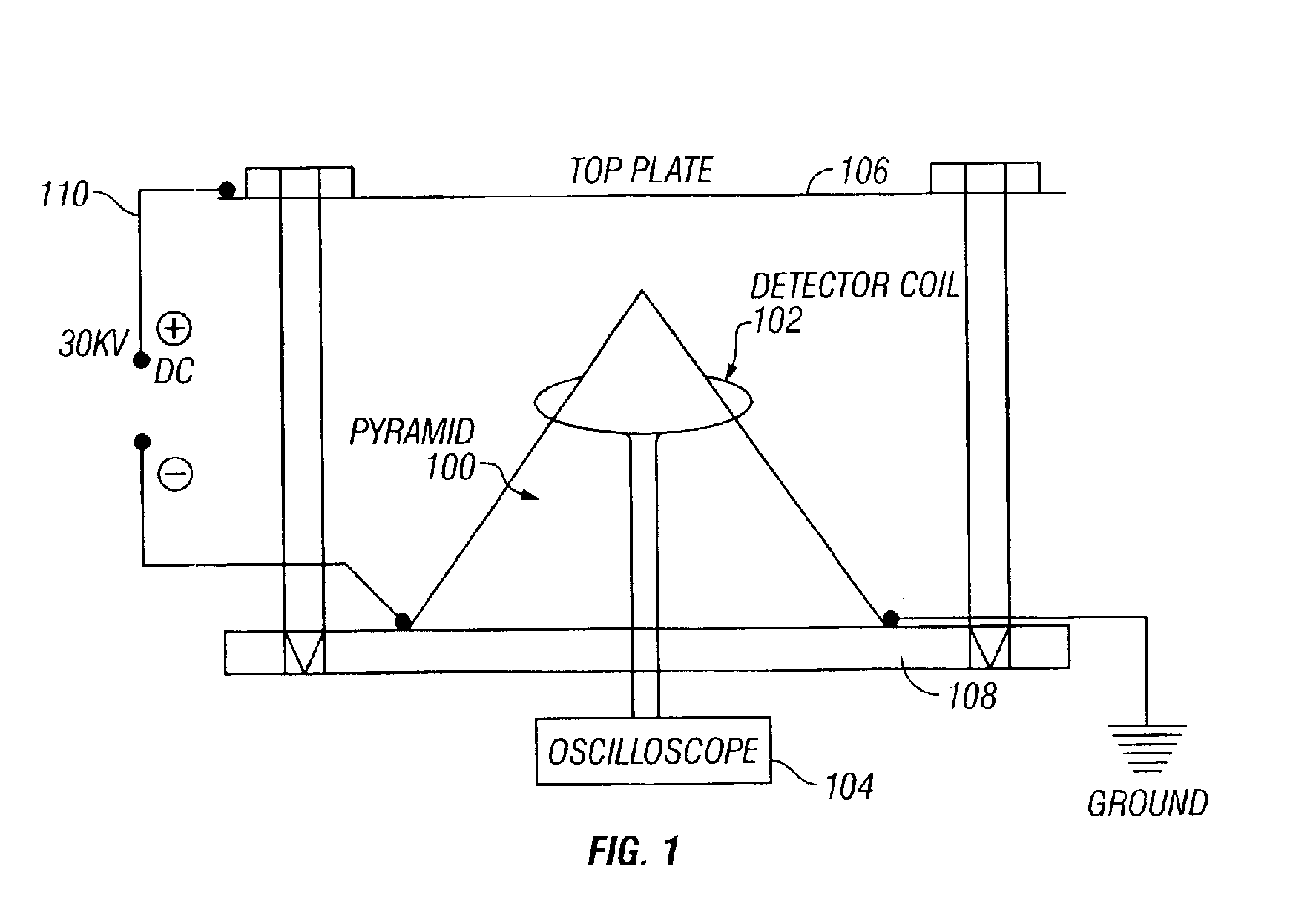
Method and apparatus for converting electrostatic potential energy
InactiveUS6974110B2Provide controlAircraft navigation controlCosmonautic vehiclesLevitationMechanical energy
A new method is described to produce useful electrical energy from DC electrostatic fields using a pyramid-shaped capacitor. The system uses no moving parts and no mechanical energy is introduced. Also, when a pyramid-shaped electrode is charged with DC high voltage, a propulsive force is generated. This will allow the manufacture of vehicles capable of levitation and flight.
Owner:GRANDICS PETER
Manufacturing method for floating type micro-silicon electrostatic gyro/accelerometer sensitive structure
InactiveCN101279713AInhibit sheddingThickness loss is negligibleAcceleration measurement using interia forcesDecorative surface effectsLevitationAccelerometer
The invention relates to a method for preparing a levitation-type micro-silicon electrostatic gyro / accelerometer sensitive structure, which belongs to the technical field of silicon structure processing. The method comprises the steps: glass etching; glass gold splashing: a metal layer raising 400-600 tenthmeters higher than a glass surface; perforating the glass; a first and a second RIE etching for the silicon slice; film beam process: high-temperature dry oxidation and surface corrosion; a first electrostatic bonding for glass and silicon; thinning and polishing to the silicon slice; ICP etching for the silicon slice; a third RIE etching for the silicon slice; a fourth RIE etching for the silicon slice; a second electrostatic bonding for glass and silicon; ICP removal for film beam to prepare the levitation-type micro-silicon electrostatic gyro / accelerometer sensitive structure. The method adopts the proposal of sandblasting perforating for perforating the glass, introduces the silicon dioxide film beam as a sacrificial layer and adopts the ICP film beam removal process; the method can effectively solve the problem of adherence of a sandwich microstructure in the second electrostatic bonding and does not need post treatment so that the method has higher efficiency and better compatibility with the MEMS process.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
External thin-wall vacuum duct maglev traffic system of power system
The invention provides an external thin-wall vacuum duct maglev traffic system of a power system. A vacuum duct with small wall thickness is adopted, a linear motor coil, a track levitation mechanism and other communication, detecting and control devices are arranged outside the duct and provide power, levitation force and control to vehicles in the duct in the state that one thin duct wall is used for separation. The material of the duct wall is required to have no effect on the electromagnetic field of a linear motor and the levitation magnetic field of a levitation device, for example, non-magnetized stainless steel, carbon alloy, glass fiber reinforced plastics or high-strength organic materials are adopted, or the duct is made of a composite material. The arrangement has the advantages that the installation construction of a linear motor stator and the levitation mechanism can be conveniently performed outside the duct; routine maintenance and repair during operation can also be performed outside the duct; mechatronic systems can be well cooled, and heat aggregation in the vacuum duct is avoided; and the space in the duct is not occupied; and the construction, maintenance and system operation costs of the vacuum duct high-speed maglev traffic system can be lowered.
Owner:张耀平
Magnetic levitation guideway-train system
InactiveUS20070095245A1Meet convenient maintenanceConvenient to examineRailway vehiclesElectric propulsionLevitationEngineering
A magnetic levitation guideway-train system is provided. The levitation power chambers located at a lower portion of the train are fitted in the grooved guideway, and the side permanent magnets of the levitation power chambers and the ferromagnetic balance levitation tracks correspond to one another so as to generate upward or downward balance attractive force for the train. Wing permanent magnets at the bottom of the levitation power chamber and the permanent magnet tracks correspond to one another so that the identical poles of the wing permanent magnets and the permanent magnet tracks repel one another to provide the train with an upward repulsion levitation force.
Owner:LI LINGQUN
Startup sequence for centrifugal pump with levitated impeller
A centrifugal pump system having an impeller rotating with first and second magnetic structures on opposite surfaces. A levitation magnetic structure is disposed at a first end of a pump housing having a levitating magnetic field for axially attracting the first magnetic structure. A multiphase magnetic stator at a second end of the pump housing generates a rotating magnetic field for axially and rotationally attracting the second magnetic structure. A commutator circuit provides a plurality of phase voltages to the stator. A sensing circuit determines respective phase currents. A controller calculates successive commanded values for the phase voltages during a running state in response to a desired impeller speed and an actual impeller phase. The controller has a startup interval during which the commanded values of the phase voltages are determined in response to a pseudo impeller phase and in response to a ramping gain factor.
Owner:TC1 LLC
Free-Form Spatial 3-D Printing Using Part Levitation
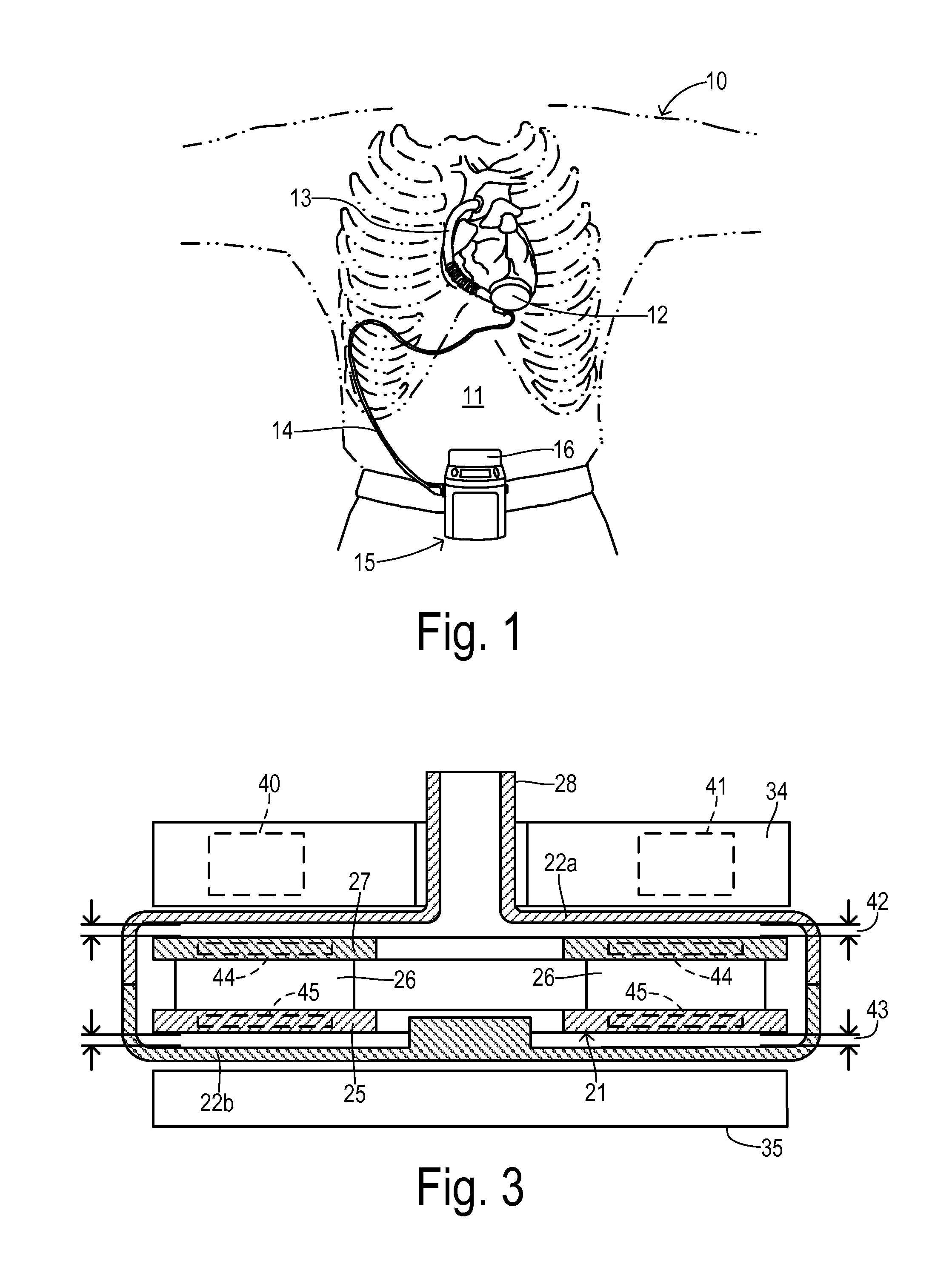
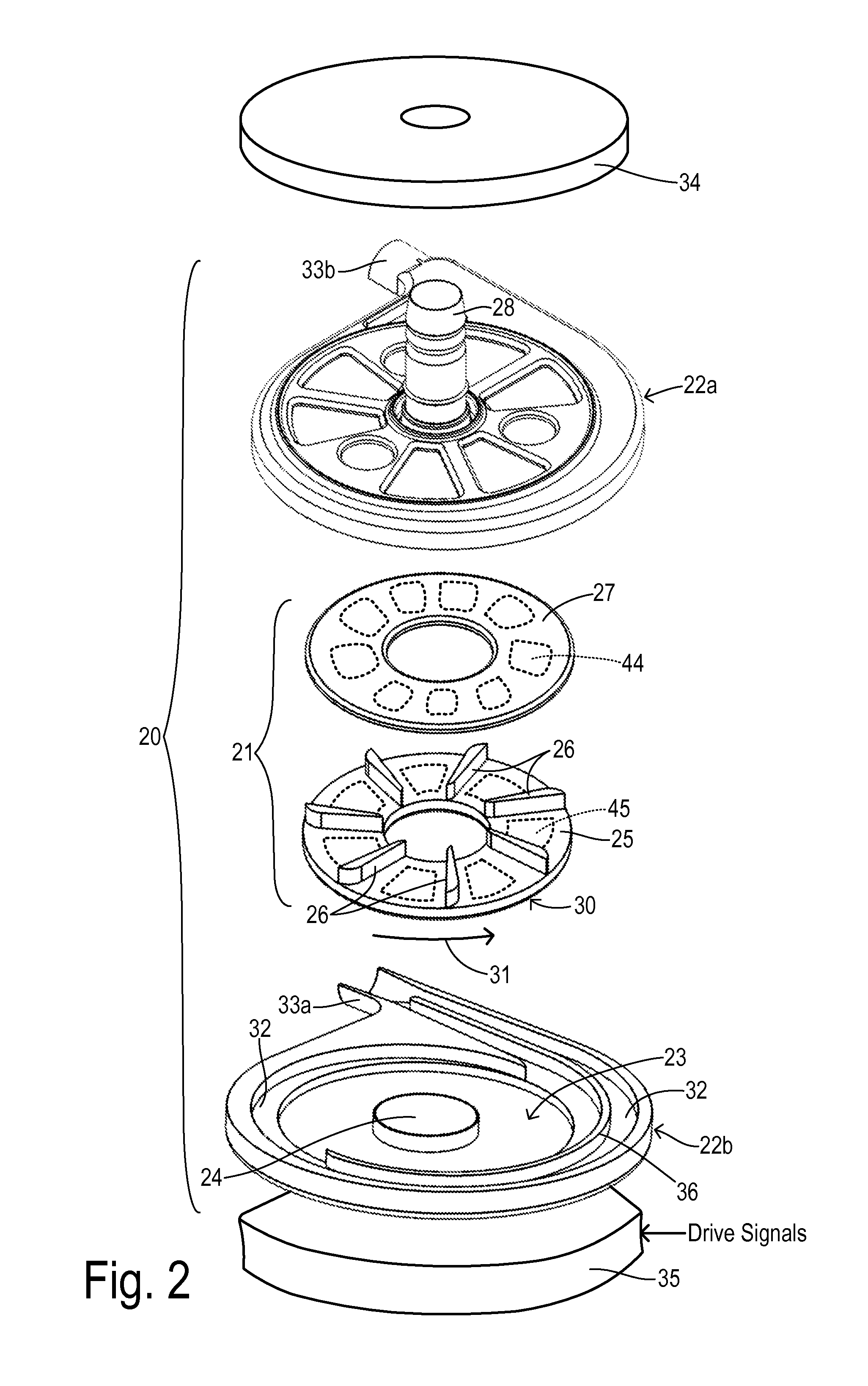
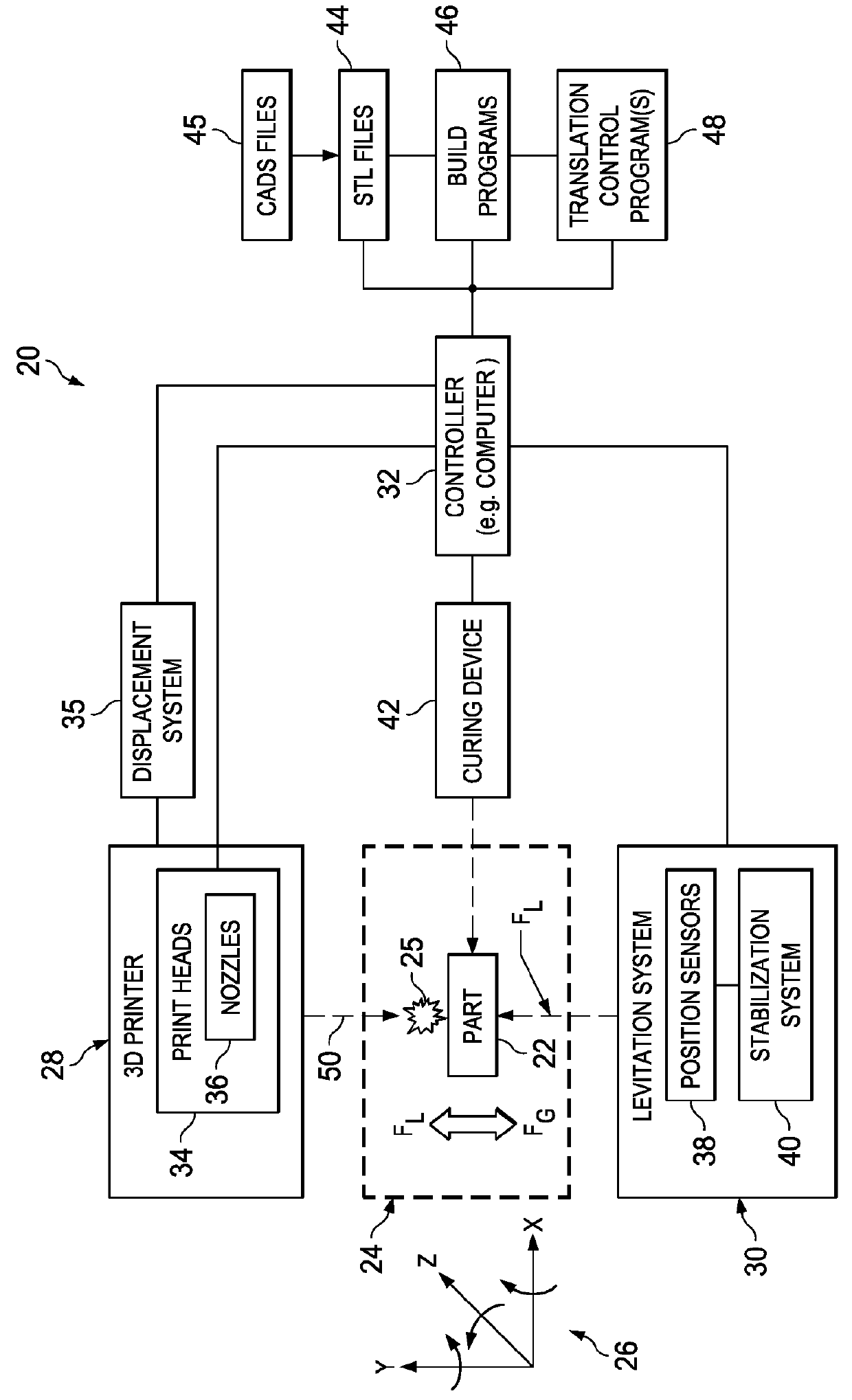
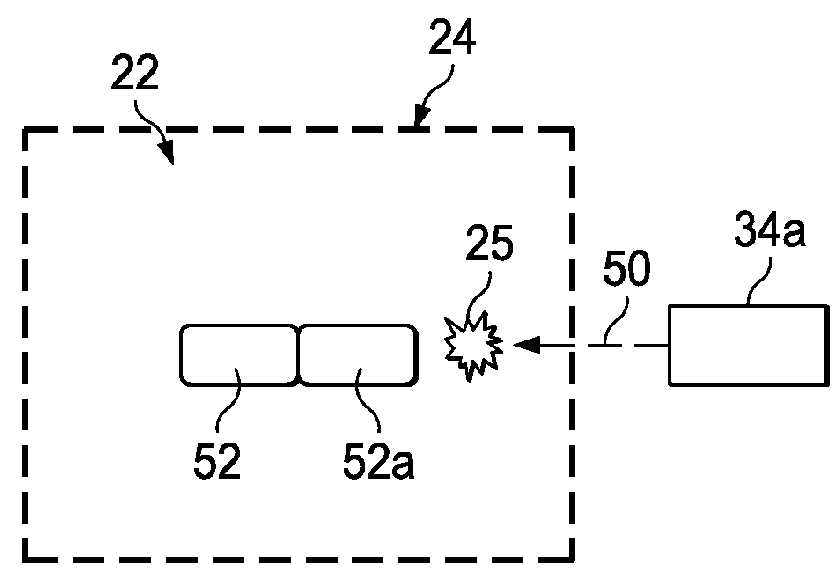
ActiveUS20160031156A1Improve manufacturing speedAdditive manufacturing apparatusElectric discharge heatingSpatial OrientationsLevitation
A part is fabricated by an additive manufacturing process while levitating in space. Constituent features of the part are formed by 3-D printing. A part levitation system allows the spatial orientation of the part to be manipulated relative to one or more print heads.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
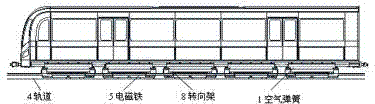
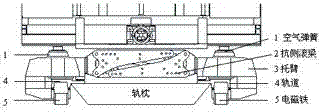
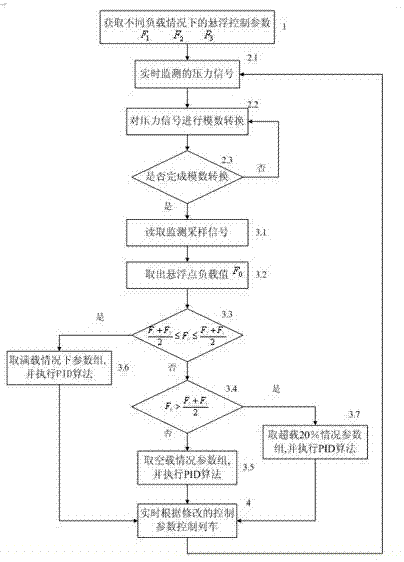
Suspension control method for low and middle speed magnetic-levitation train
ActiveCN102303544ASuspension unchangedSolve the problem of suspension instabilityMagnetic holding devicesElectric propulsionPressure measurementControl parameters
The invention discloses a suspension control method for a low and middle speed magnetic-levitation train. The suspension control method comprises the following steps of: firstly, acquiring suspension control parameters when the train is positioned at different loads by a suspension controller; secondly, acquiring a load pressure value signal which is monitored by a pressure measuring device by the suspension controller; thirdly, changing the suspension control parameters according to load change of a suspension point, which is monitored by the suspension controller according to the pressure measuring device; and fourthly, carrying out real-time suspension control by the suspension controller and turning into the second step. According to the suspension control method disclosed by the invention, the pressure measuring device is used for measuring the pressure value of the suspension point and the suspension controller is used for automatically adjusting the suspension control parameters according to load change conditions, thus the problem that the suspension is instable when the load of a low and middle speed electro-magnet suspension train fluctuates in a wide range and the train passes a transition curve and a circular curve is effectively solved, further the suspension performance is kept unchanged when the electro-magnet suspension train fluctuates in a wide range and the train passes the transition curve and the circular curve and control performance of the suspension controller is improved.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com