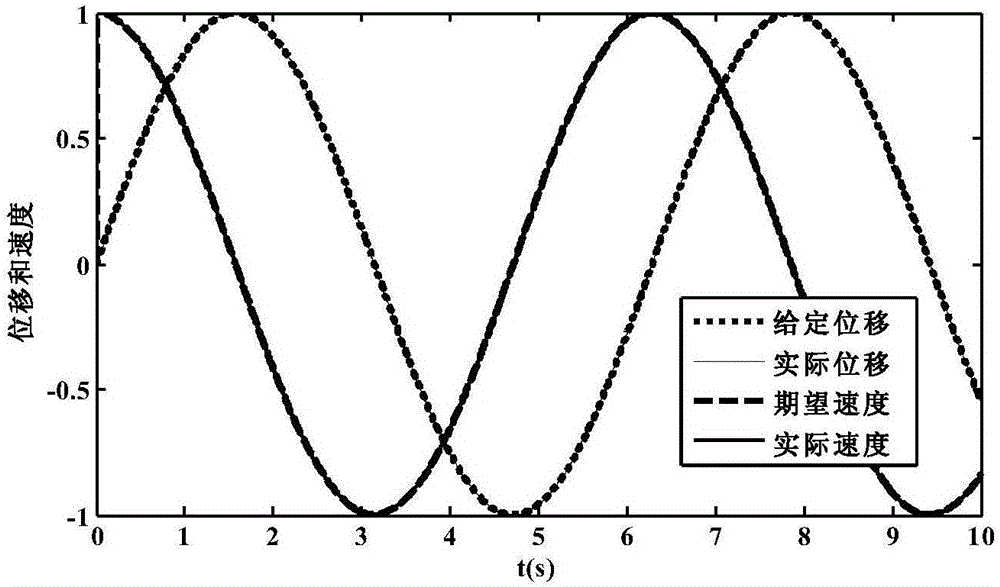
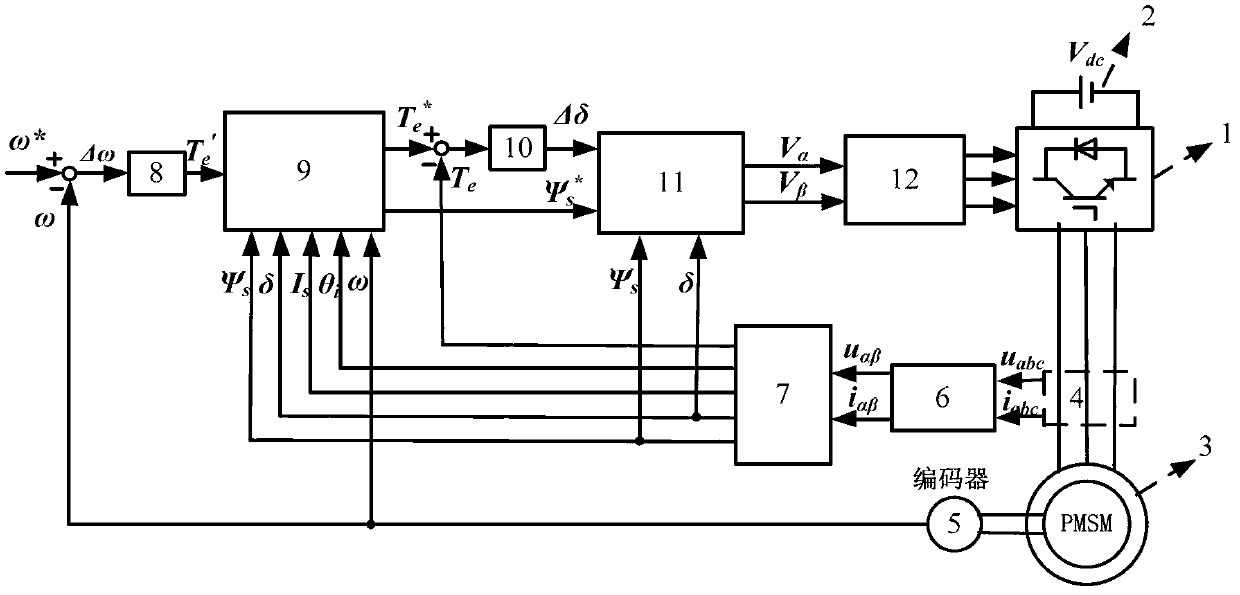
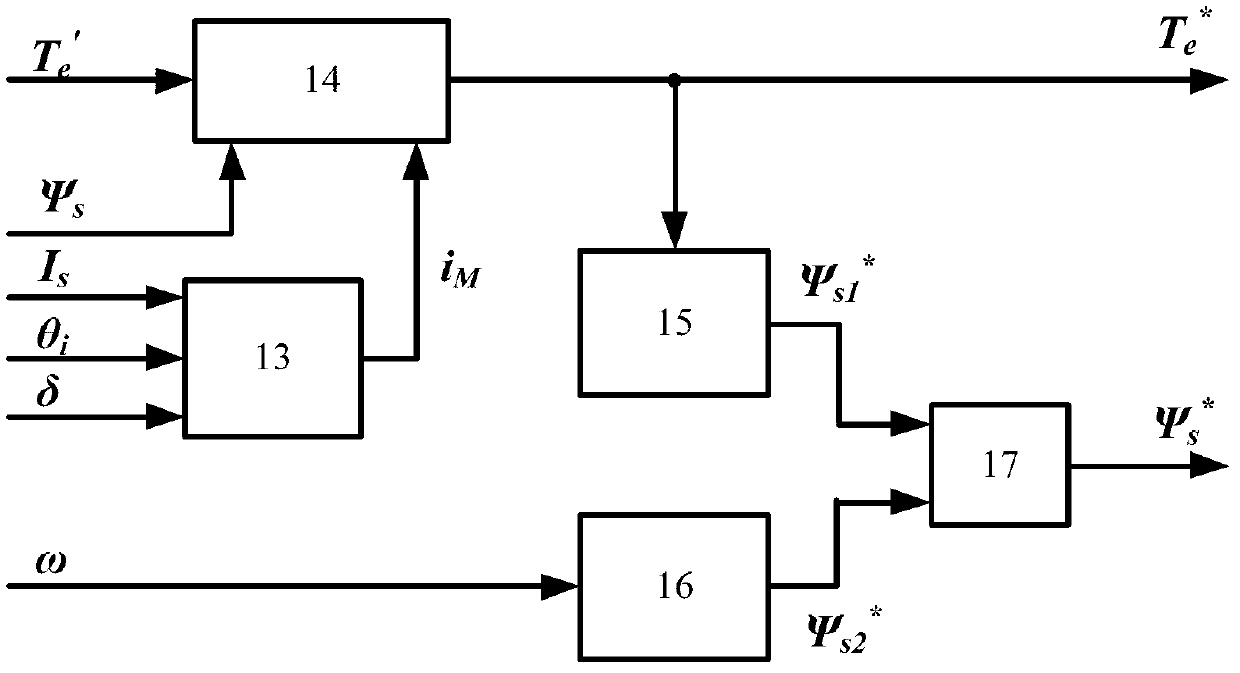
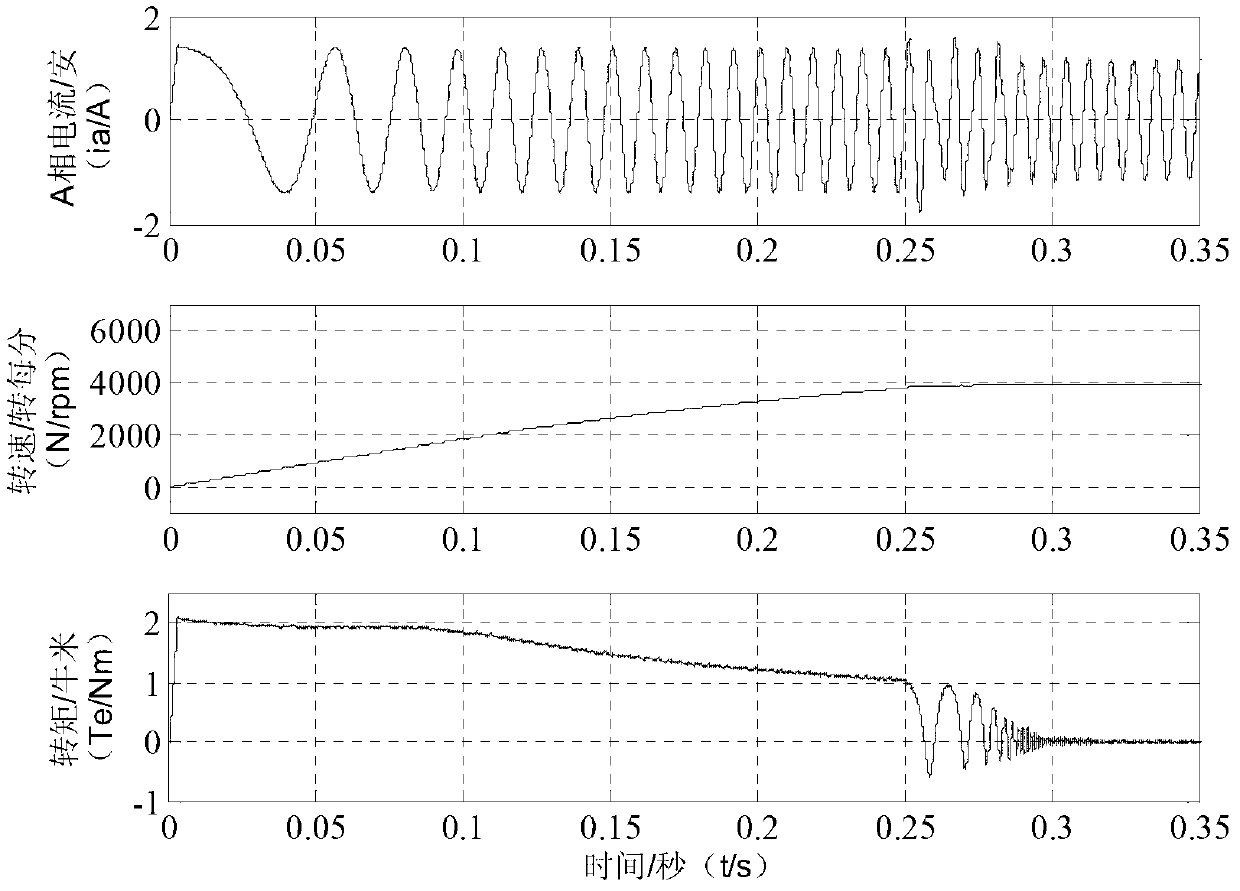
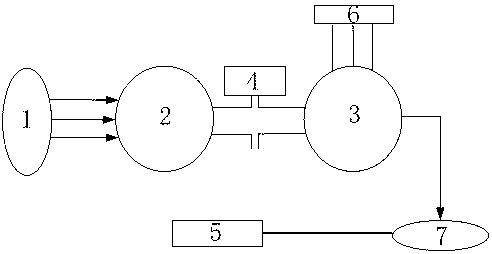
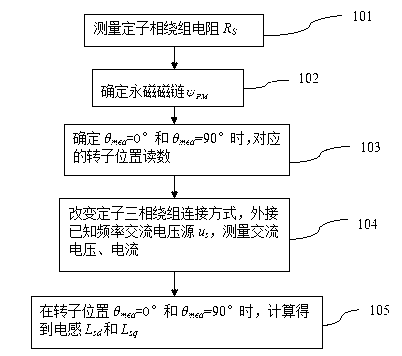
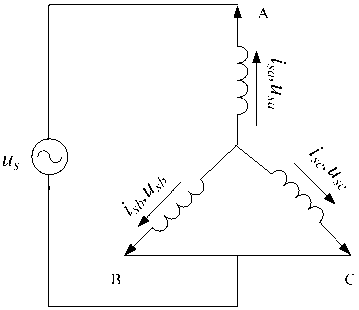
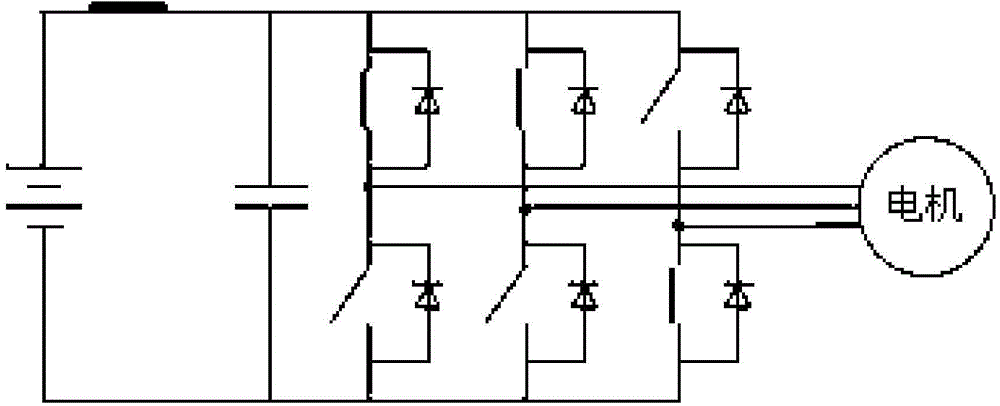
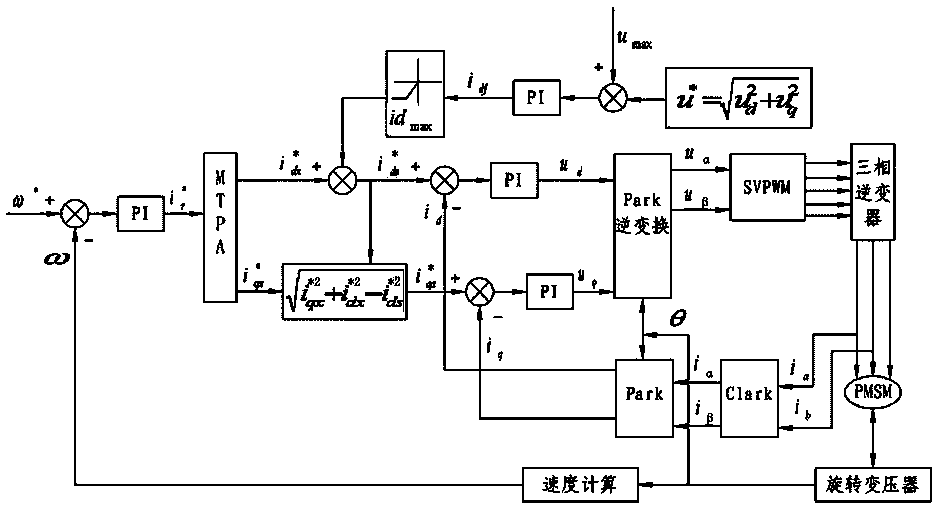
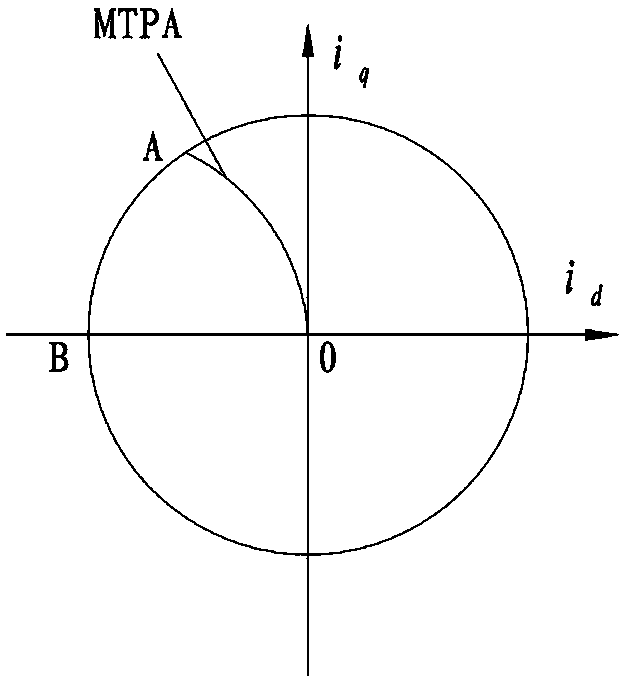
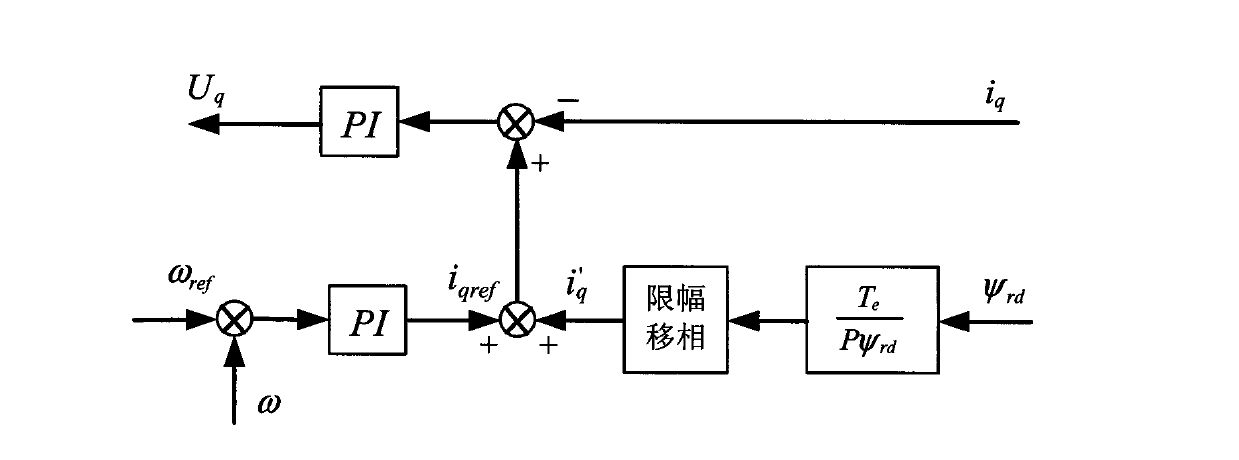
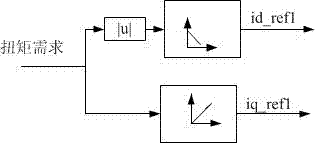
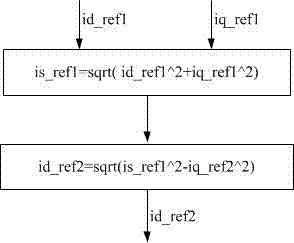
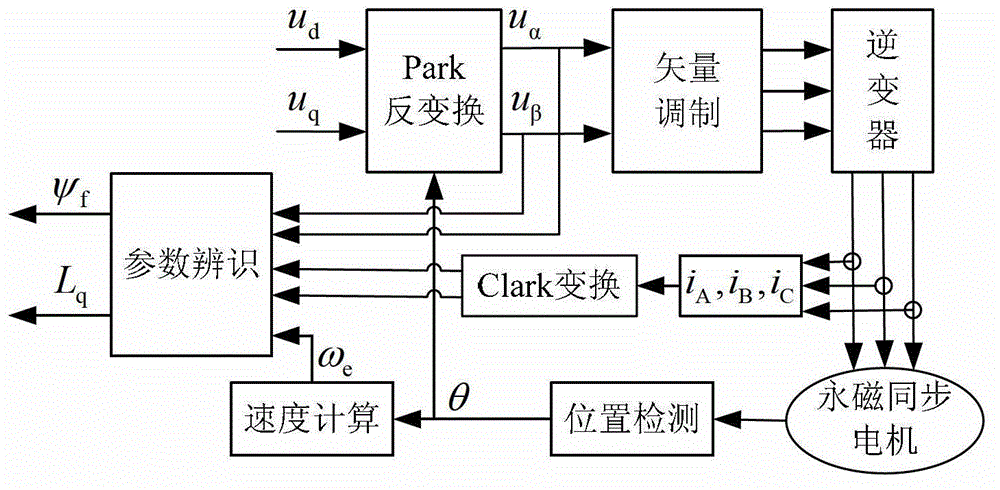
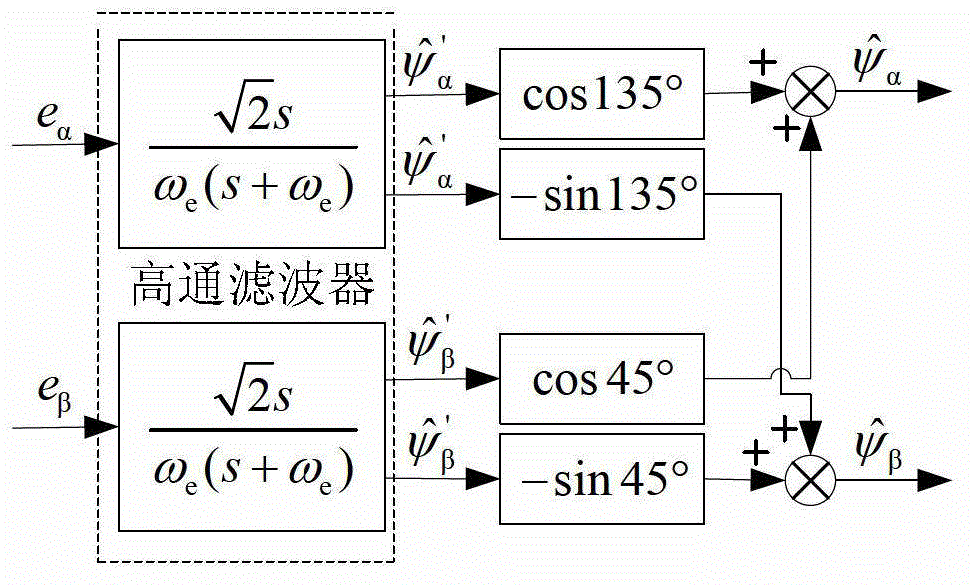
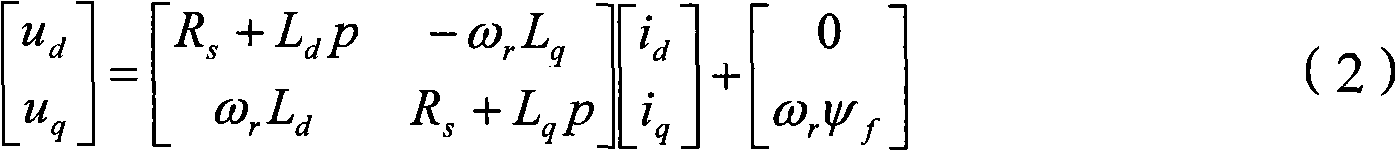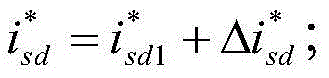Patents
Literature
405 results about "Permanent magnet linear synchronous motor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sensorless control system of permanent magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN101964624AImprove estimation accuracyPracticalElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsLow speedPermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention discloses a sensorless control system of a permanent magnet synchronous motor. The sensorless control system comprises a flux linkage / current state observer and a counter electromotive force measurement module, wherein the flux linkage / current state observer is a sliding mode observer; the sliding mode observer is controlled by a sliding mode variable structure; and the coordinate system of the sliding mode observer is an estimated rotary coordinate system, is rotated at an angular speed and lags behind an electrical angle of the coordinate system. In a control parameter computation module, the error of a rotor position is calculated. The sensorless control system of the permanent magnet synchronous motor, can be used on a low-speed observation occasion and a height observation occasion at the same time and has strong practicability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
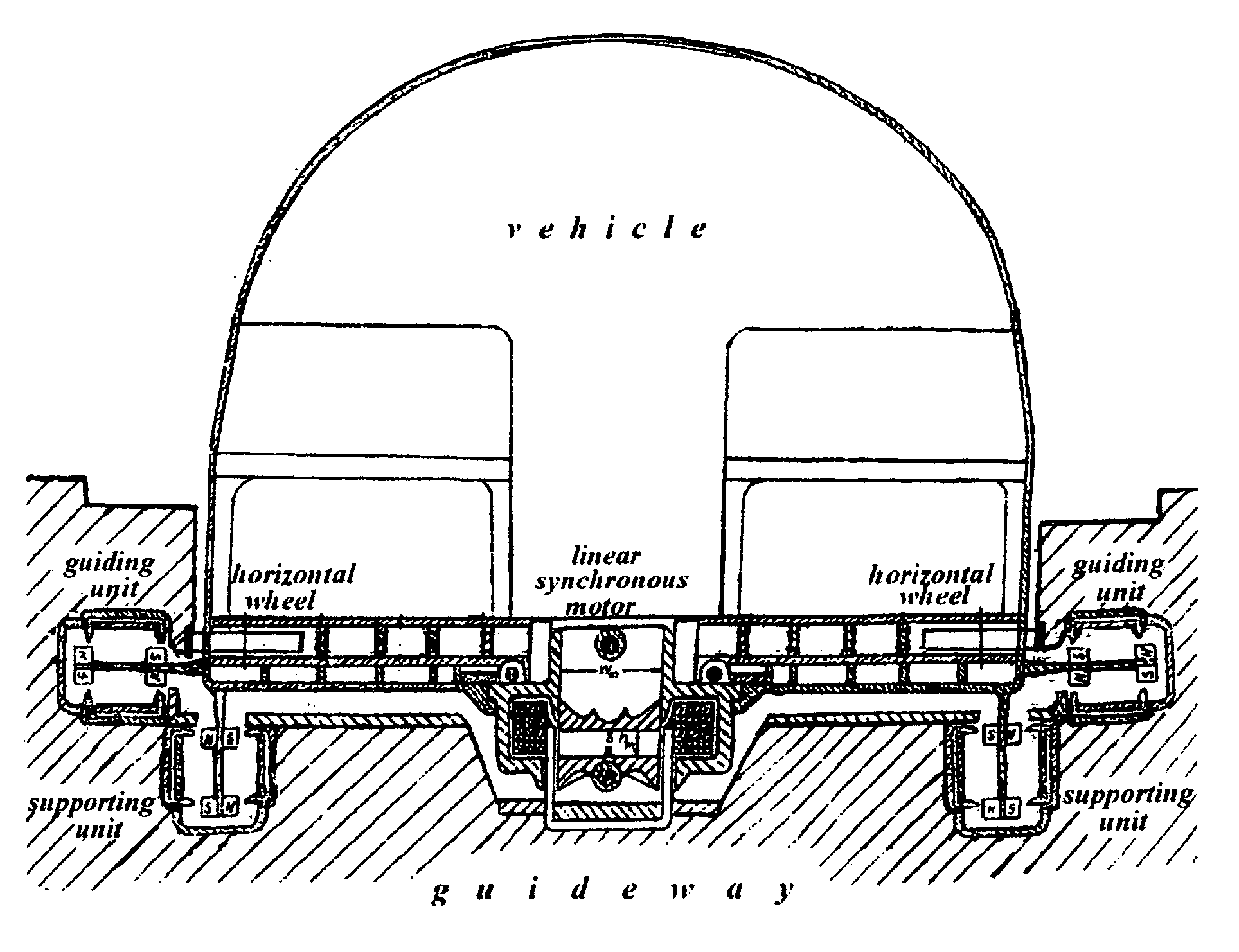
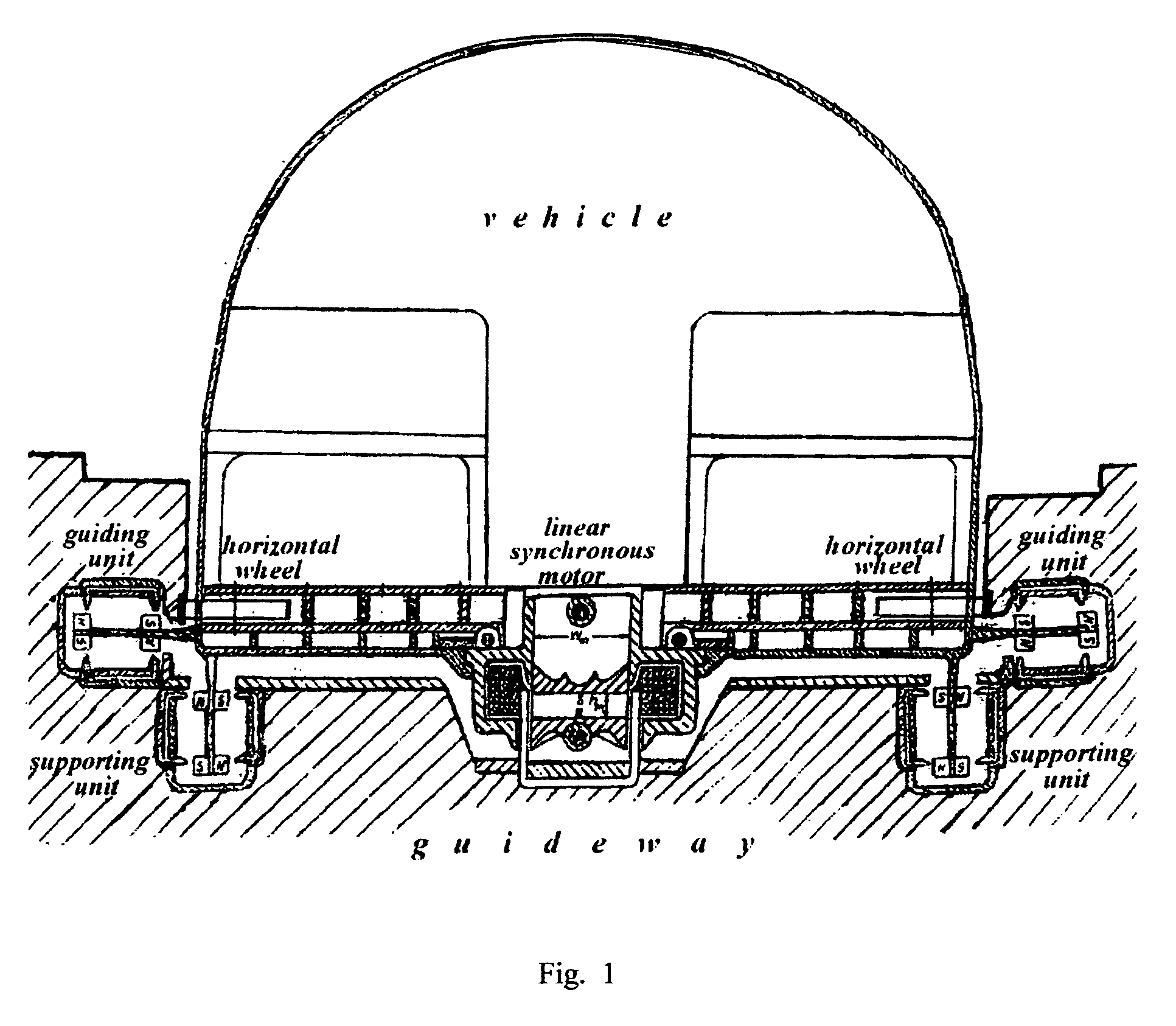
Amlev: Self-regulating type of Maglev high speed ground transportation based on permanent magnets and steel cores
The proposed Amlev Self-Regulating System of High Speed Ground Transportation Based on Permanent Magnets and Steel Cores is designated for magnetic levitation, stabilization, and propulsion of vehicles moving without friction. The proposed system comprises subsystems: a Magneto-Dynamic Levitation and Stabilizing Self-Regulating System (MDLSS), and a Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor (PMLSM). Both systems comprise permanent magnets and steel cores. MDLSS provides levitation and stabilization of vehicle while PMLSM produces propulsion force providing the assigned alternative velocity of the vehicle along the stator winding powered by the current of constant frequency 50 Hz. Each of the subsystems comprises two main parts: a fixed part—guideway / stator including extended steel cores for MDLSS and windings for PMLSM, and moving part—permanent magnets of the levitator for MDLSS and the rotor for PMLSM—both affixed to the moving vehicle. Each of the subsystems is self-regulating and operates without fast response control system. A new model is proposed for measuring destabilizing forces impacting a flying vehicle at its shifts from an assigned trajectory that allows to eliminate the stage of full-scale modeling when designing Amlev system.
Owner:TOZONI MICHAEL
Method and system for measuring position compensation angles of permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor
ActiveCN102097988ALow costImprove reliabilityVector control systemsDynamo-electric converter controlVoltage vectorPermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention provides a method and device for measuring position compensation angles of a permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor, wherein the method comprises the following steps: setting a forcible magnetic field directional angle Theta Force; setting component instruction value of a d shaft voltage as u*d=0; inputting the component instruction value u*q of a q shaft voltage which can enable the permanent magnet synchronous motor to enter into a zero speed shaft locking state; according to the forcible magnetic field directional angle Theta Force, obtaining voltage vectors by virtue of PARK inverse transformation of u*d and u*q; generating a power device pulse-width signal needed by a voltage source inverter by a space vector pulse width modulation (SVPWM) algorithm; driving the permanent magnet synchronous motor to rote to a position of ThetaForcee+90 DEG by the voltage source inverter; obtaining the angle Theta xr read by an absolute encoder mounted on the rotor; and calculating the compensation angle that Theta c= Theta Force+ 90 DEG-Theta xr. The method provided by the invention can be simply, conveniently and easily realized; a current sensor is unnecessary to work, and the flitter is not existed during initial location.
Owner:北京和利时电机技术有限公司
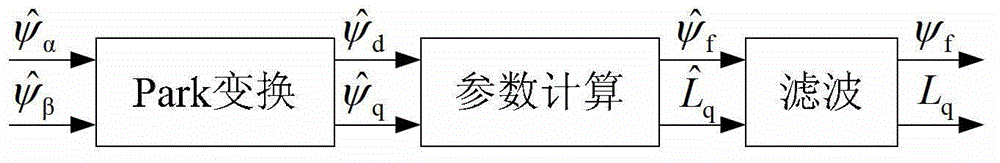
Method for acquiring parameters of permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM)
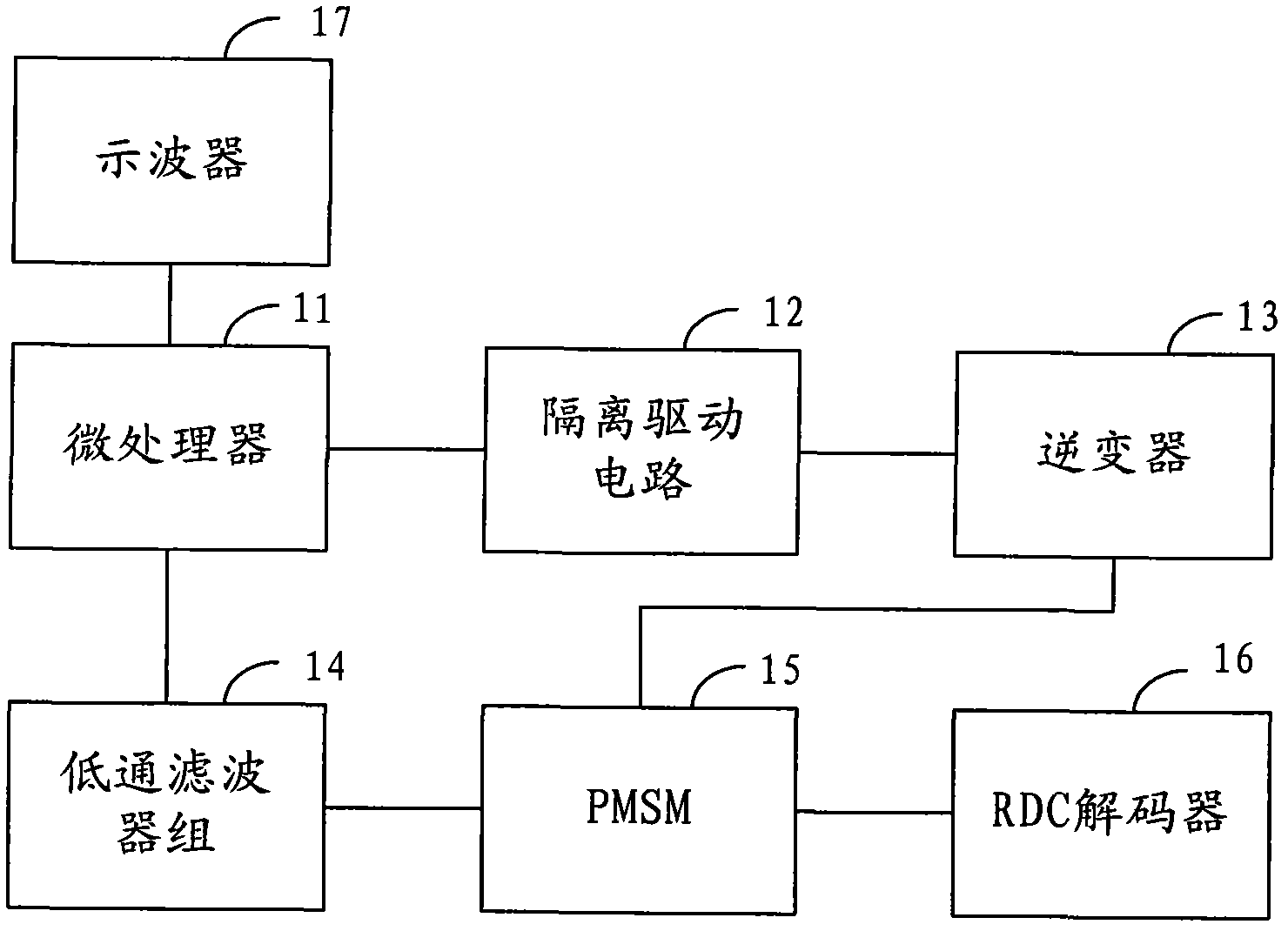
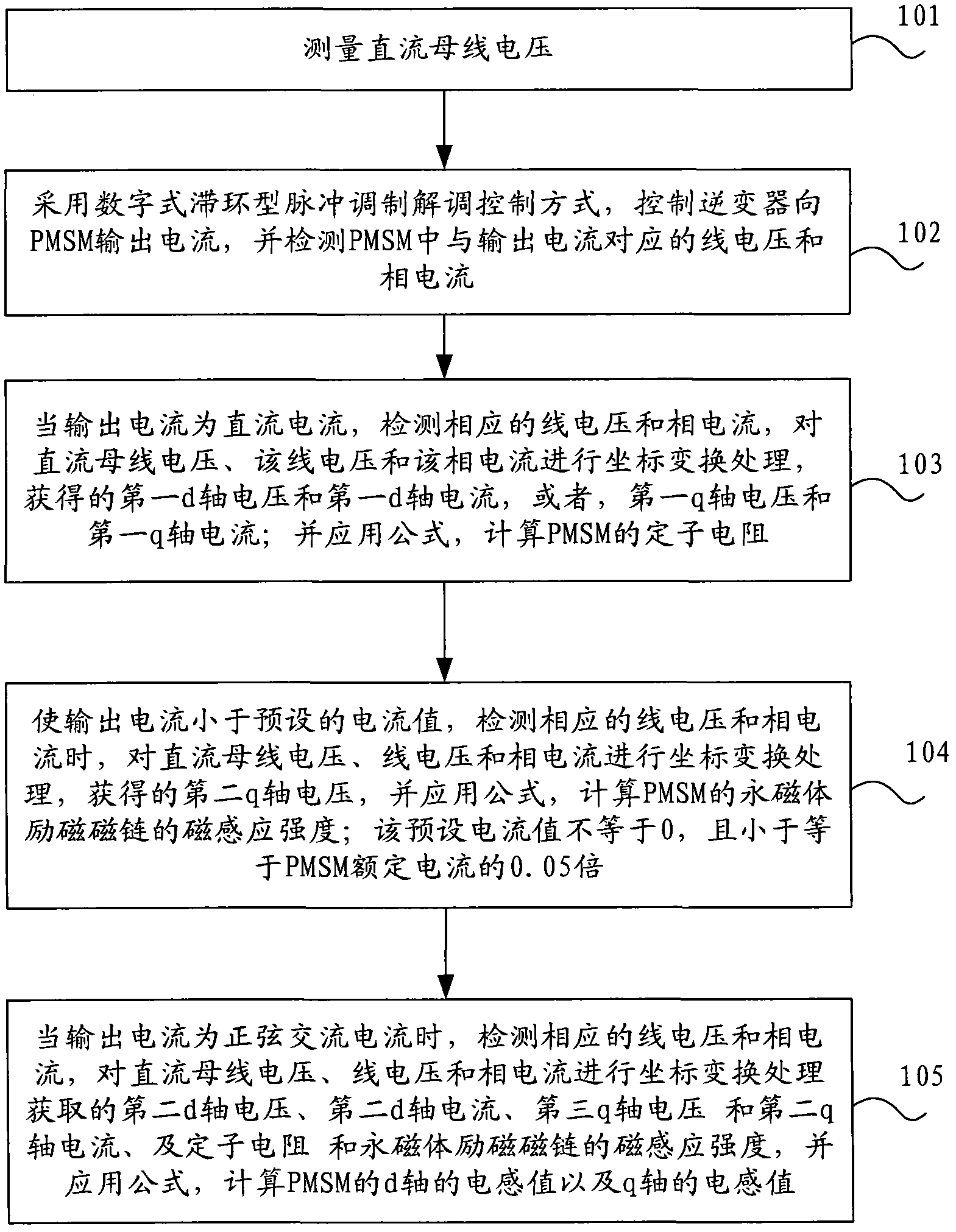
ActiveCN102386835AImprove controlAccurate acquisitionElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlHysteresisPhase currents
The invention provides a method for acquiring parameters of a permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM), which comprises the following steps: measuring direct-current bus voltage; controlling an inverter to output current to the PMSM by adopting a digital hysteresis loop-type pulse modulation demodulation control mode; detecting line voltage and phase current which correspond to input current in the PMSM; and calculating the stator resistance of the PMSM, the magnetic induction strength psif of a permanent magnet excitation flux linkage and / or the inductance value Ld of the d axis and the inductance value of the q axis according to different current output to the PMSM under controlling the inverter. By adopting the method for acquiring parameters of the PMSM, three parameters in the PMSM are accurately calculated, and the control effect of the vector control technology on the PMSM is effectively improved.
Owner:CRRC YONGJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Switching device of permanent magnet synchronous motor windings
InactiveCN105048888ALow costImprove reliabilityElectronic commutation motor controlTransient statePower flow
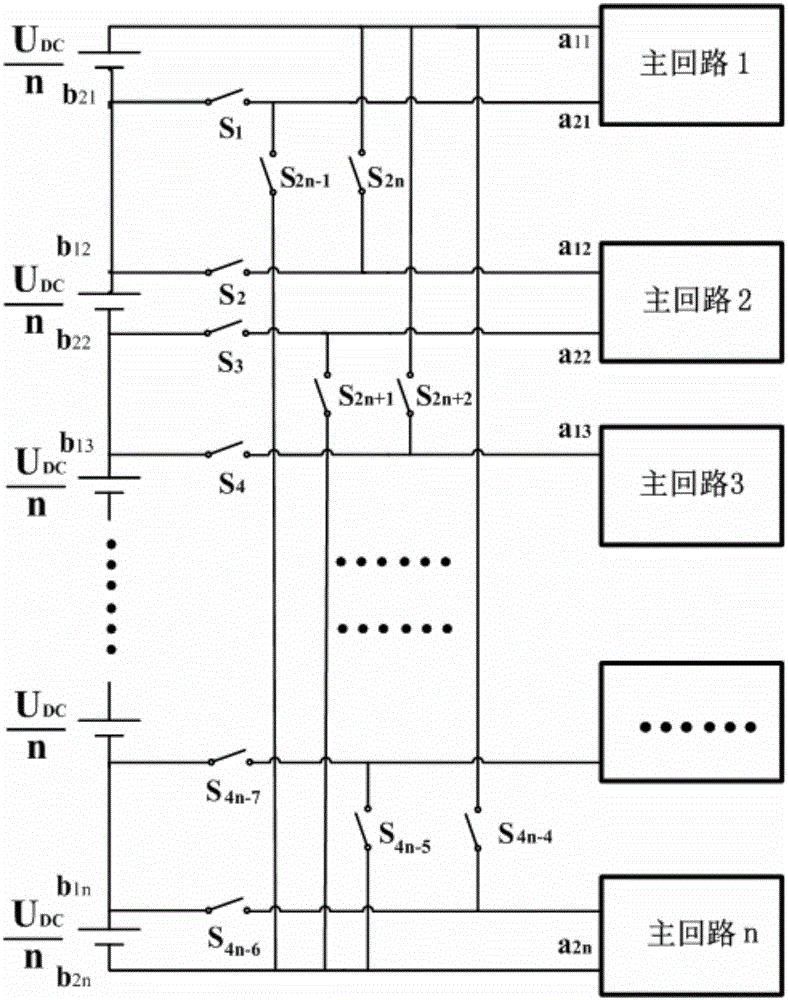
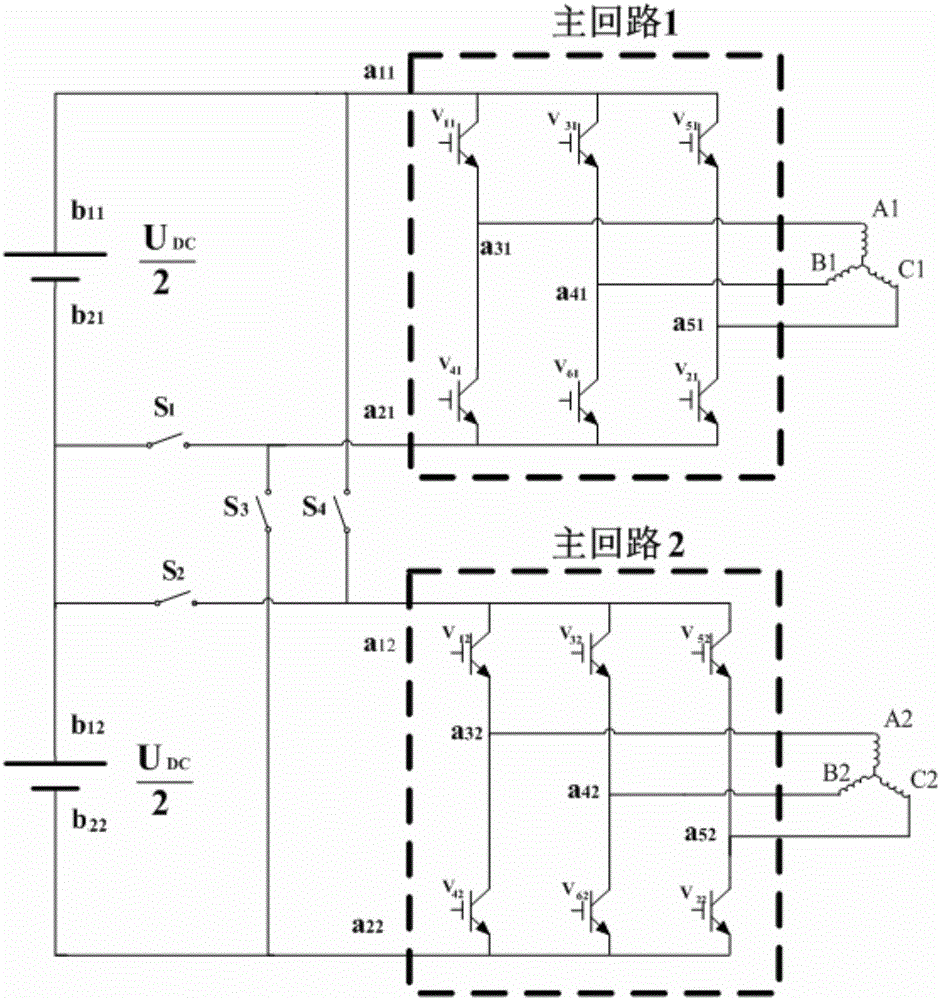
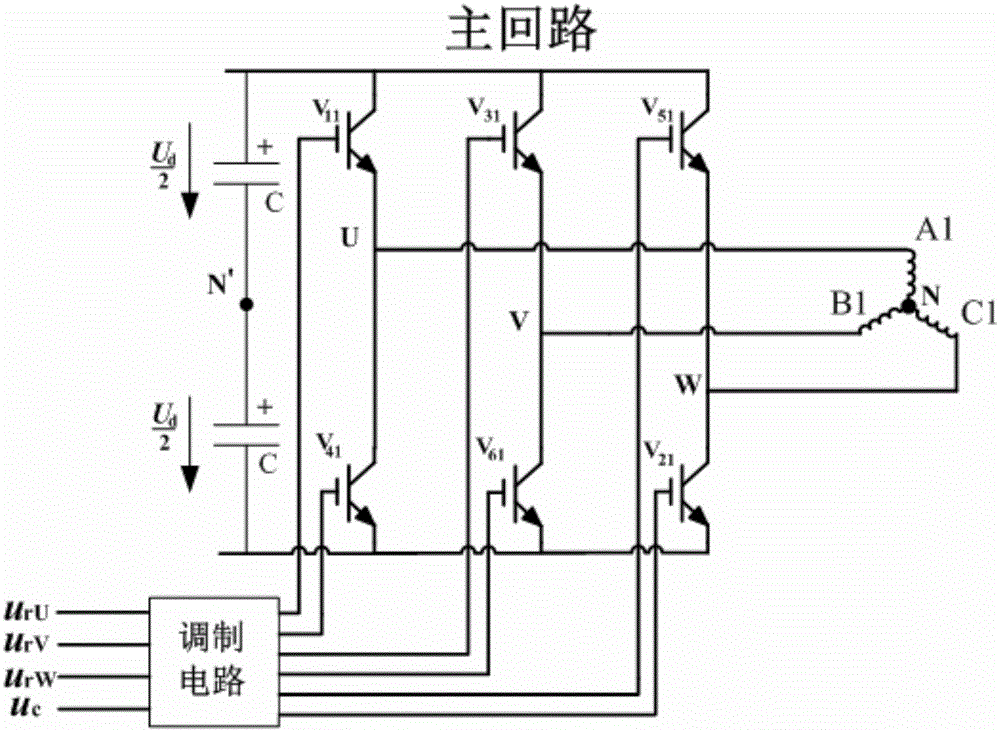
The invention provides a switching device of permanent magnet synchronous motor windings. The switching device has n sets of windings corresponding to n main loop units; and with the joint effort of (4n-4) switches, switching of series connection and parallel connection of the n sets of windings is realized. The switching device has the following characteristics: the cost of the switching system is lowered and reliability of the switching system is improved; the motor operation efficiency is improved, the speed regulation range of the motor is expanded, and the demand of the main loop capacity is reduced; the selection principle of the switching rotation speed is provided; and a switching strategy for reducing the transient impulse current during the switching process is also brought forward.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Miniature permanent magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN102751922ASimple structural designReduce startSingle motor speed/torque controlElectronic commutatorsPermanent magnet rotorAcute angle
The invention discloses a miniature permanent magnet synchronous motor which comprises a stator and a permanent magnet rotor which have equal number of poles. An alternating current source supplies power to the stator through a switch of a control circuit, and an air gap between the stator and the rotor narrows down from one pole to another pole along the rotating direction so that the axis of each pole of the rotor under free state deflects for an acute angle along the rotating direction by taking the axis of the nearest pole of the stator as the reference. A linear magnetic position sensor is installed at a set position on the circumference of the rotor so as to detect the polarity and the position of the rotor; the control circuit determines the axis direction of the permanent magnetic flux of all the poles of the rotor according to the output of the sensor and by taking the set position as the reference. The control circuit detects the polarity of the voltage supplied to the stator by the power source so as to determine the axis direction of the main fluxes generated by all the poles. The switch switches on the power source half-wave when the motor is started and the intersection angle between the axis direction of the main fluxes and the axis direction of the permanent magnetic fluxes is the above acute angle or when the motor runs and the axis direction of the main fluxes is opposite or approximately opposite to the axis direction of the permanent magnetic fluxes. The motor has good starting performance in preset rotating direction and good operational performance and the control structure of the motor is simple and reliable.
Owner:HANYU GRP CO LTD
Permanent magnet linear synchronous motor slip form control system based on linear expansion state observer
ActiveCN106849795AAccurate trackingImprove robustnessElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlLyapunov stabilityOrthogonal coordinates
The invention discloses a permanent magnet linear synchronous motor slip form control system based on a linear expansion state observer, and belongs to the technical field of linear motor control. The system comprises the following steps that: firstly, establishing the dynamic equation of a permanent magnet linear synchronous motor on a two-phase synchronous rotation orthogonal coordinate system; secondly, simplifying the dynamic equation into a special two-order integral series type mathematical model; thirdly, designing the linear expansion state observer to obtain a disturbance estimated value, and considering the estimated value in the design of a slip form control law to eliminate a chattering phenomenon; and finally, applying a Lyapunov stability theory to analyze the stability of the system. The system has the most important characteristics that the state and the disturbance of the system can be accurately estimated by the linear expansion state observer. In addition, the control system is high in robustness, and a given displacement signal can be accurately tracked. In addition, the chattering phenomenon of slip form control can be greatly improved so as to be suitable for designing the permanent magnet linear synchronous motor servo control system.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Method for controlling direct torsion/ flux linkage of permanent magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN103269191AExtended operating rangeOvercoming the crashVector control systemsSingle motor speed/torque controlPermanent magnet synchronous motorPermanent magnet synchronous generator
The invention discloses a method for controlling direct torsion / flux linkage of a permanent magnet synchronous motor. The method comprises the steps of collecting three-phase stator voltage and currents of the motor, and obtaining voltage and currents under a two-phase static coordinate system through three-phase / two-phase static coordinate conversion; calculating actual feedback value of electromagnetism torsion and stator flux linkage according to the voltage and the currents under the two-phase static coordinate system; obtaining initial given value of the electromagnetism torsion through a PI controller according to difference between given rotating speed and feedback rotating speed; obtaining given value of the electromagnetism torsion and the stator flux linkage according to a given electromagnetism torsion and stator flux linkage calculating module; obtaining given voltage on an alpha beta shaft of the two-phase static coordinate system through a given voltage calculating module; generating switching signals of an inverter through space vector pulse width modulation, triggering a switching device of the inverter, and realizing direct torsion / flux linkage control of the permanent magnet synchronous motor. The method realizes low, medium and high speed wide range operation of the permanent magnet synchronous motor, does not need to rotate coordinate conversion, and has the advantages of being convenient to calculate, quick in dynamic response, strong in robustness, and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Transverse flux cylinder type permanent magnet linear synchronous motor
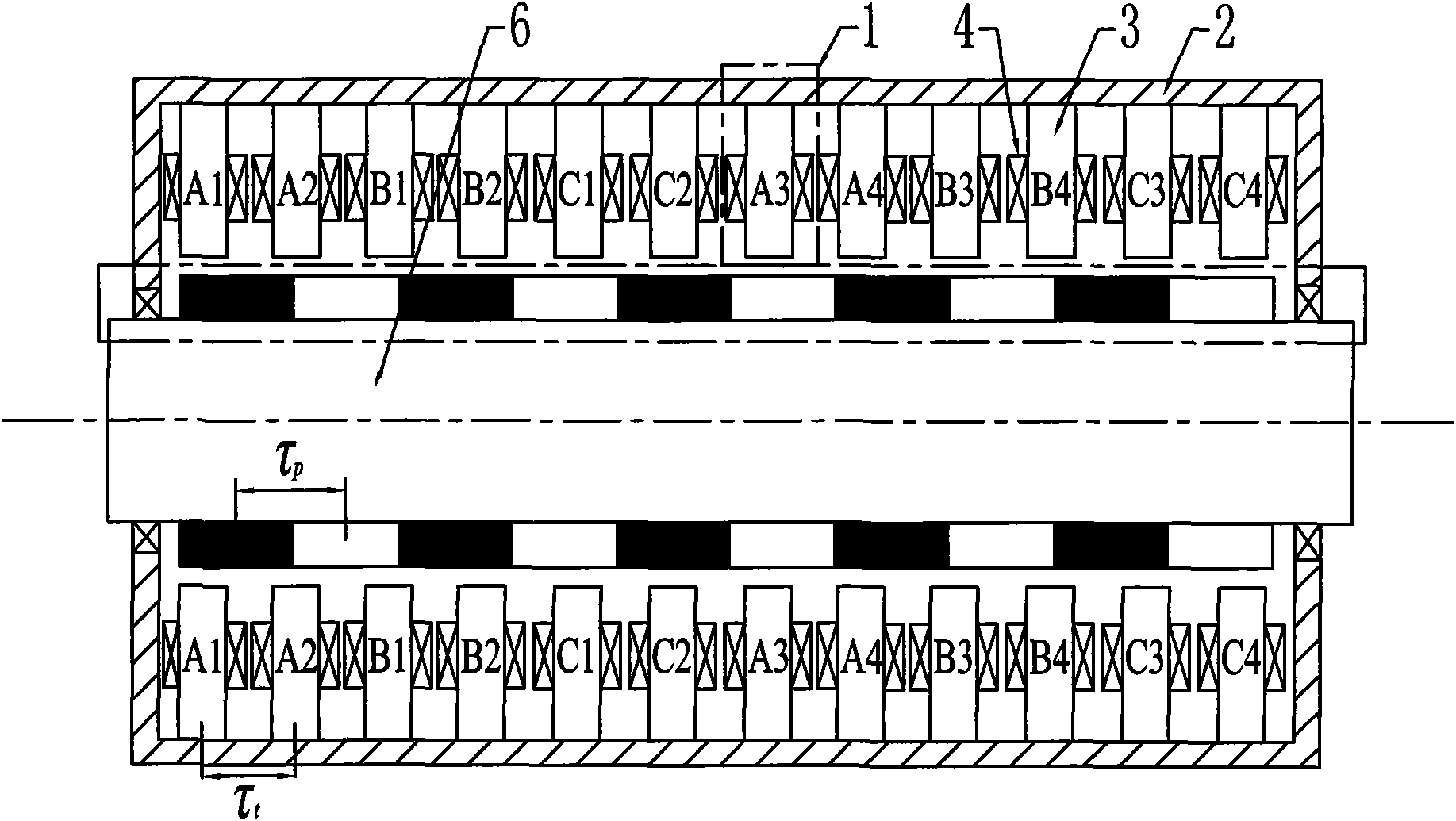
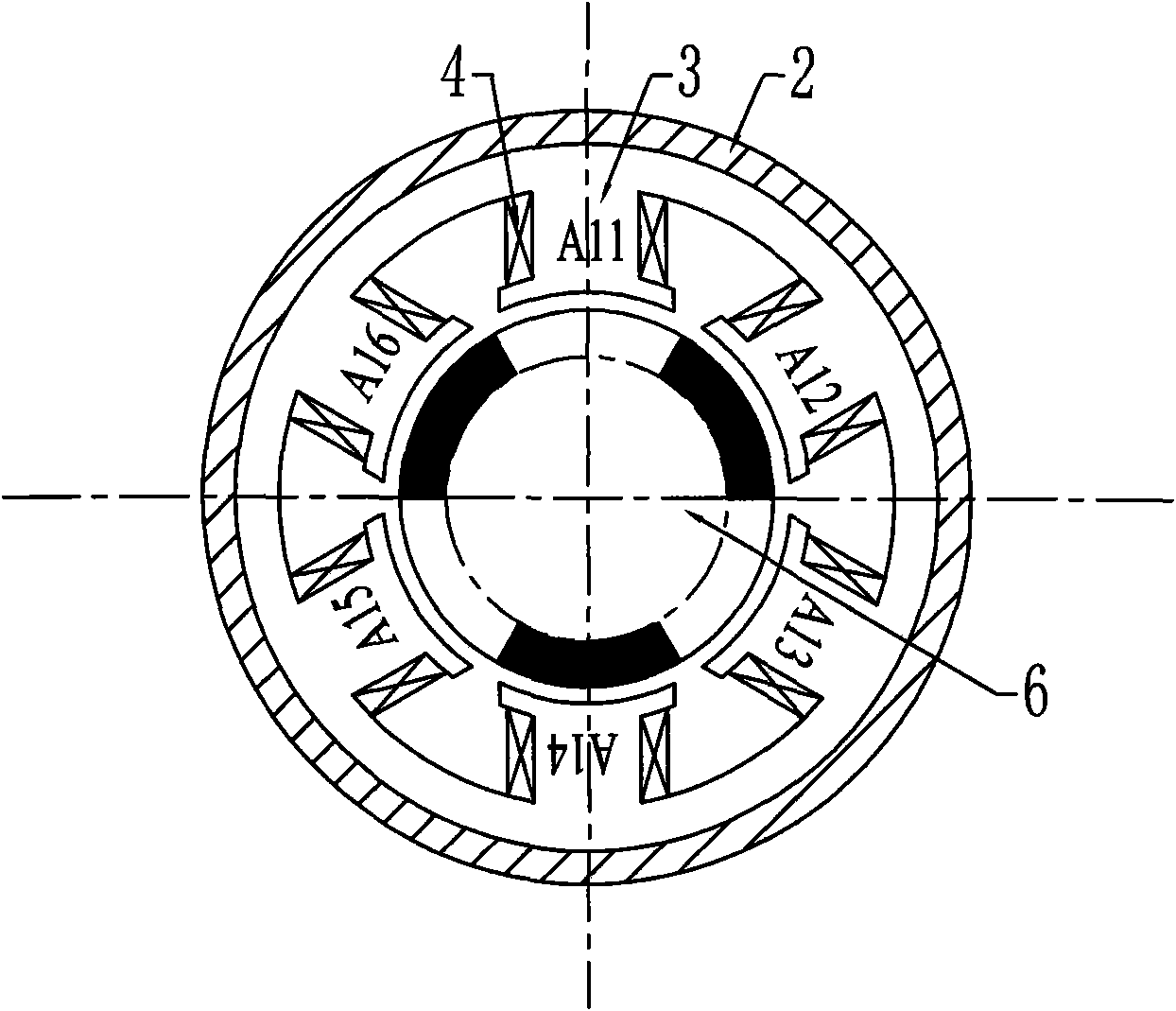
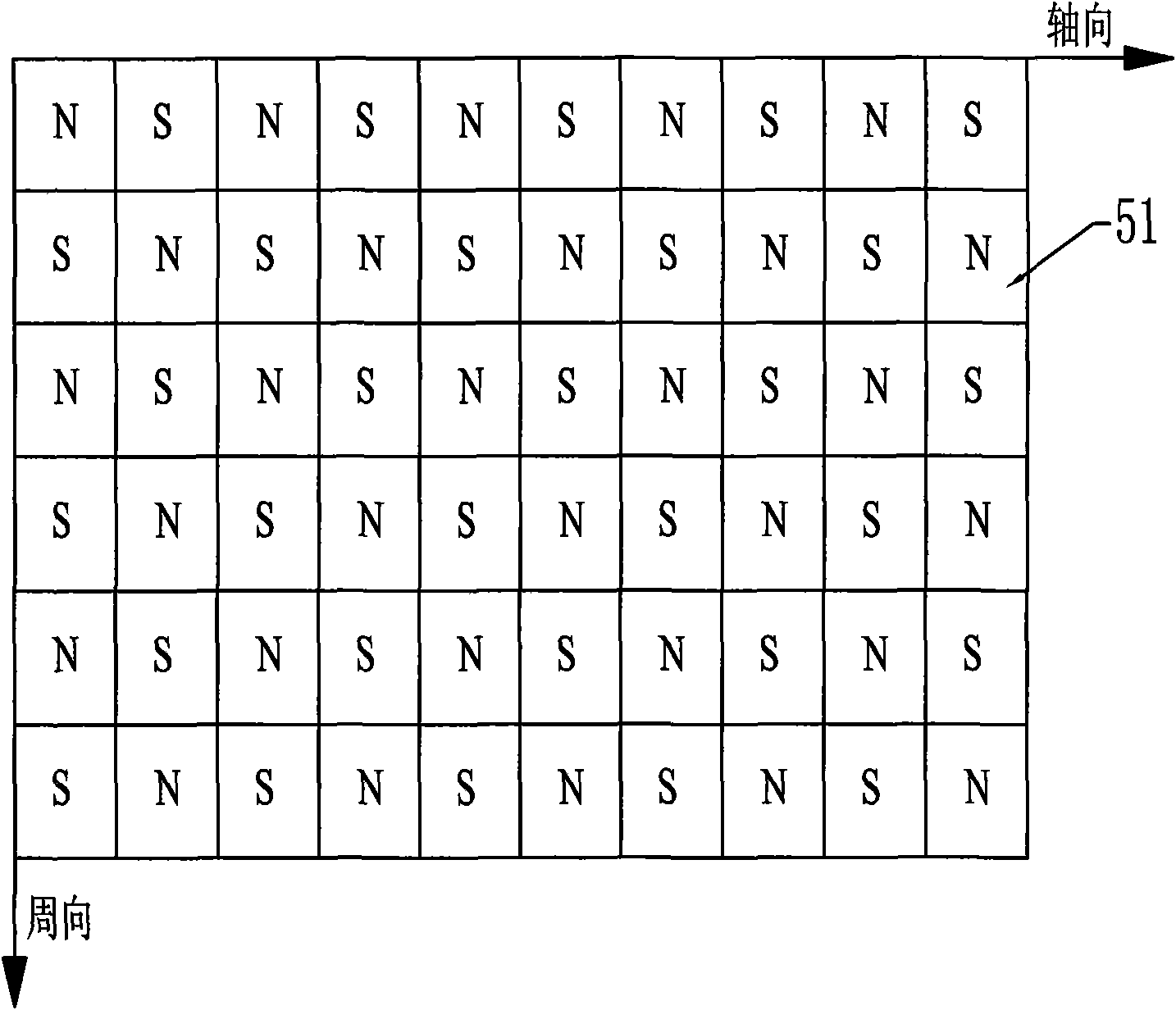
A transverse flux cylinder type permanent magnet linear synchronous motor relates to the field of motor, and settles the problems of low efficiency, large eddy current loss, complex technique and effect to the control precision and dynamic characteristic. The transverse flux cylinder type permanent magnet linear synchronous motor of the invention comprises a primary stage, a secondary stage and an air gap. The number of phase armature units is S=nm, wherein n is a natural number. The number of axial magnetic poles formed by secondary permanent magnets is P=2i, wherein is a natural number. When no common divisor exists between S and P, the S phase armature units are equally divided to m groups along the axial direction, and each n adjacent phase armature units belong to one phase. When a highest common divisor j exists between S and P, the S phase armature units are equally divided into mj parts along the axial direction, and windings on each adjacent n / j phase armature units belong to one phase. The phase unit armature core tooth pitch taut between two adjacent phase armature units along the axial direction and the pole distance taup along the axial permanent magnet satisfy a relationship mktaut=(mk+ / -1)taup, wherein m and k are natural numbers, and m is the phase number of motor. The motor not only can be used as an electric motor, but also can be used as a generator.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
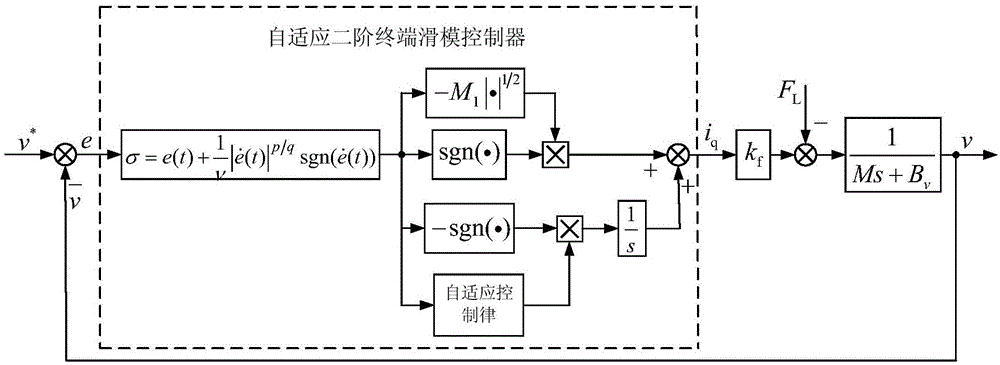
Adaptive second-order terminal sliding-mode control system and method of permanent magnet linear synchronous motor
InactiveCN104917436ALimitations of Overcoming Uncertainty Bounds to DetermineOvercome limitationsElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsRobustificationControl system
The invention relates to an adaptive second-order terminal sliding-mode control system and method. On the basis of comparison of a given speed signal and a feedback speed signal of a servo system of a permanent magnet linear synchronous motor, an error amount is obtained; a terminal sliding mode surface is designed based on the error amount and a super-coiling algorithm controlled by the second-order sliding mode is used for realizing the input of a speed controller; and an adaptive control way is introduced to carry out dynamic adjustment on a control gain of the super-coiling algorithm. Therefore, the rapid response of the system is realized; and the system robustness is improved. With the control method, the system can have the high robustness and the system buffeting can be weakened effectively.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
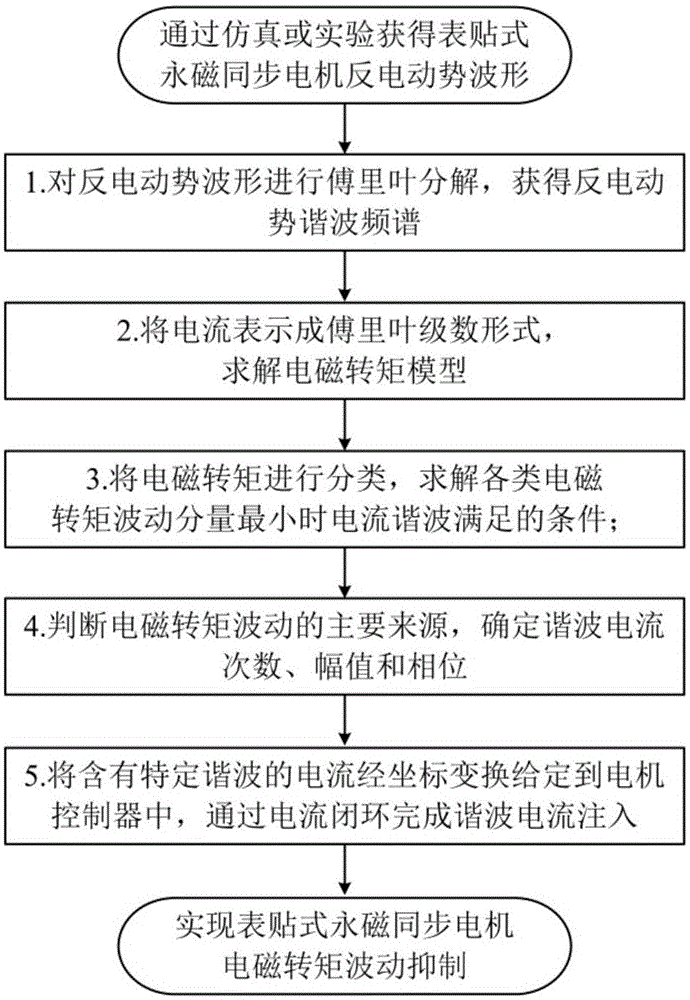
Method for restraining torque ripple of surface-mounted permanent magnet synchronous motor by use of current harmonic waves
ActiveCN105071717ASimplified Current Harmonic SchemeTorque ripple controlFrequency spectrumDecomposition
The invention discloses a method for restraining torque ripple of a surface-mounted permanent magnet synchronous motor by use of current harmonic waves. The method comprises steps of performing Fourier decomposition on back EMF waveforms of the permanent magnet synchronous motor to obtain a frequency spectrum of the back EMF and the amplitude of harmonic waves every time; representing current as Fourier series and solving an electromagnetic torque model based on three-phase back EMF and the current expression; classifying the electromagnetic torque according to different components of harmonic waves and solving conditions that the current harmonic waves satisfy during the smallest electromagnetic torque ripple; judging the main sources of the electromagnetic torque ripple and determining numbers, amplitudes and phase positions of the current harmonic waves according to characteristics of the back EMF waveforms; and accessing current containing specific harmonic waves into a three-phase winding of the permanent magnet synchronous motor to restrain electromagnetic torque ripple of the motor. Thus, the electromagnetic torque ripple of the surface-mounted permanent magnet synchronous motor can be effectively restrained; a new idea is provided for restraining of the electromagnetic torque ripple; and the method can be further used for torque ripple restraining of other types of surface-mounted permanent magnet synchronous motor.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
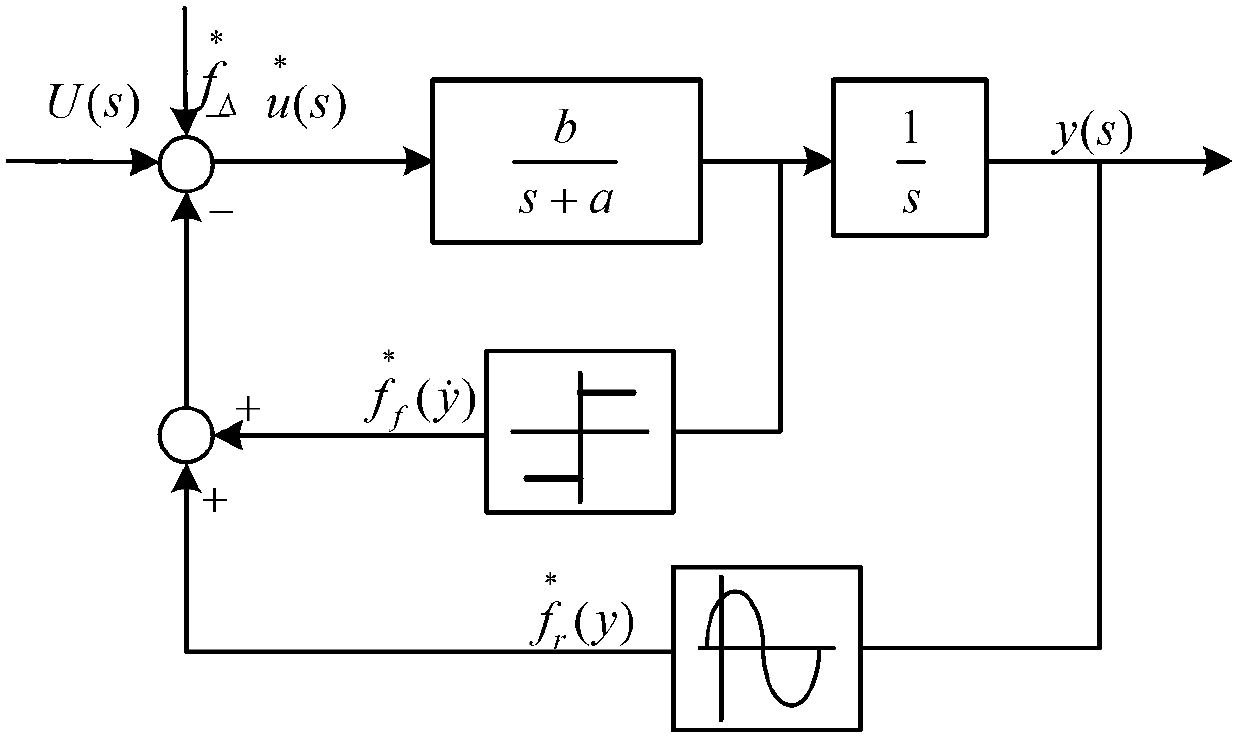
Nonlinear interference control method and control system for permanent magnet linear synchronous motor
InactiveCN102710214AIncreased non-linear interferenceImprove robustnessAC motor controlDigital signal processingControl system
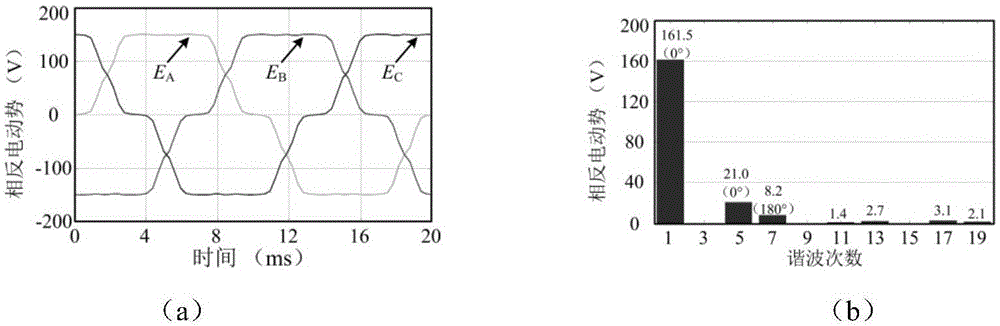
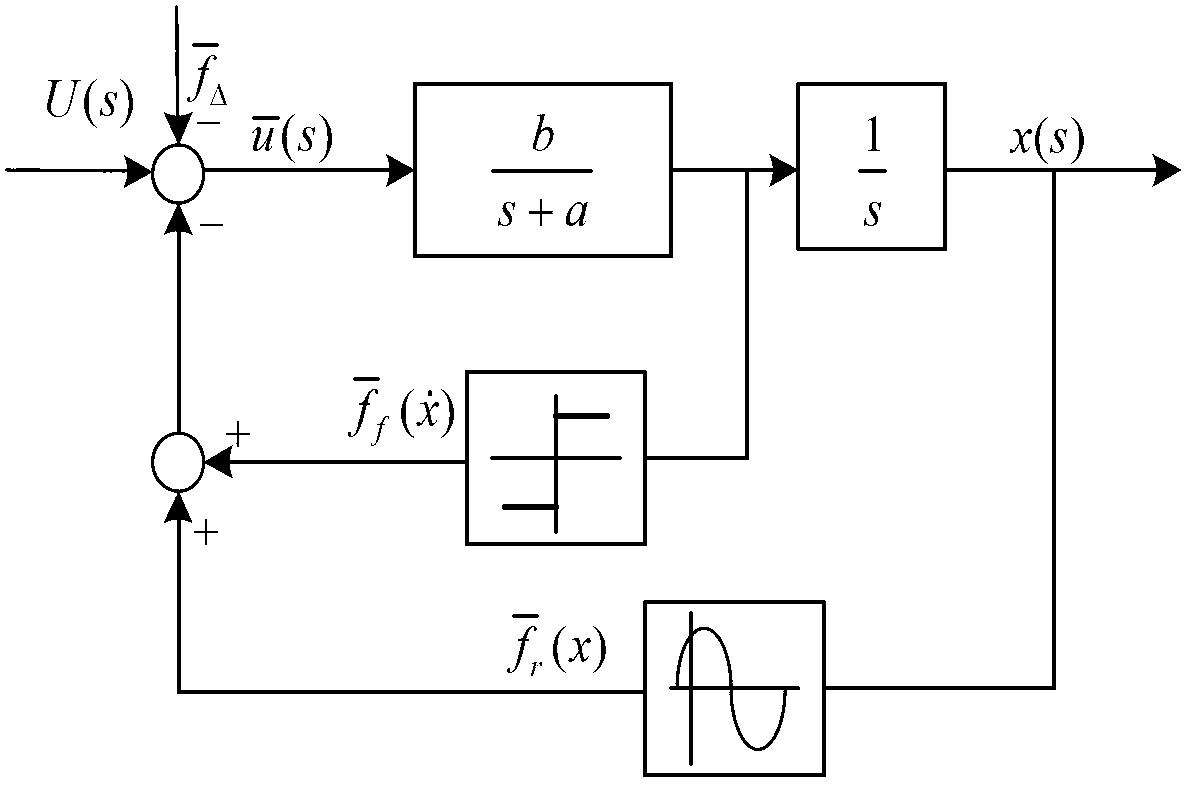
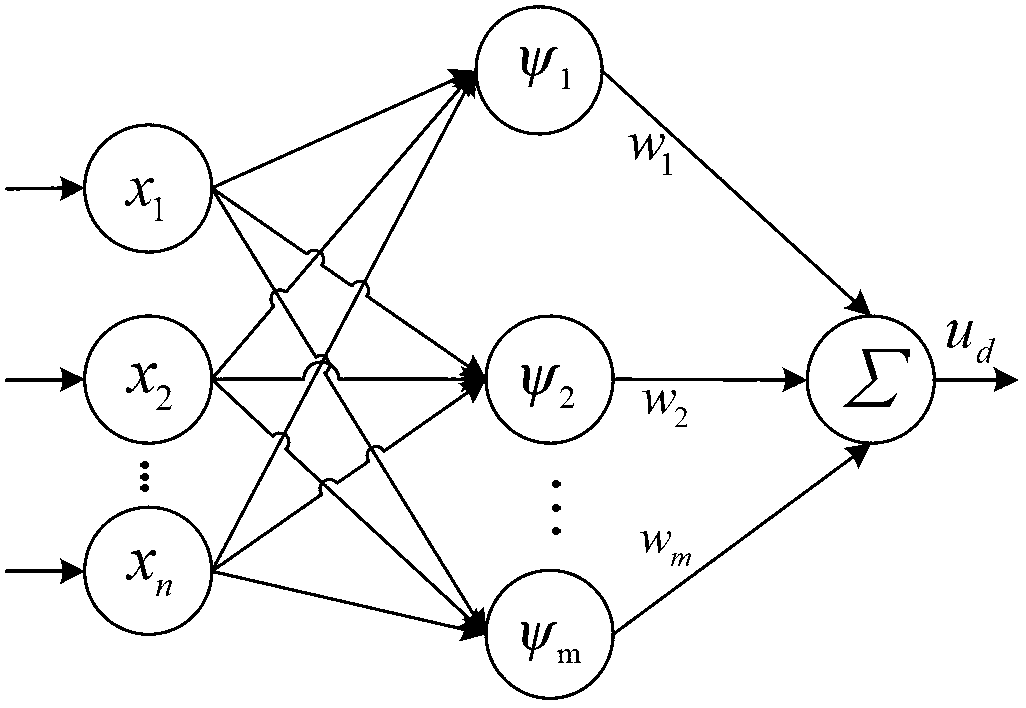
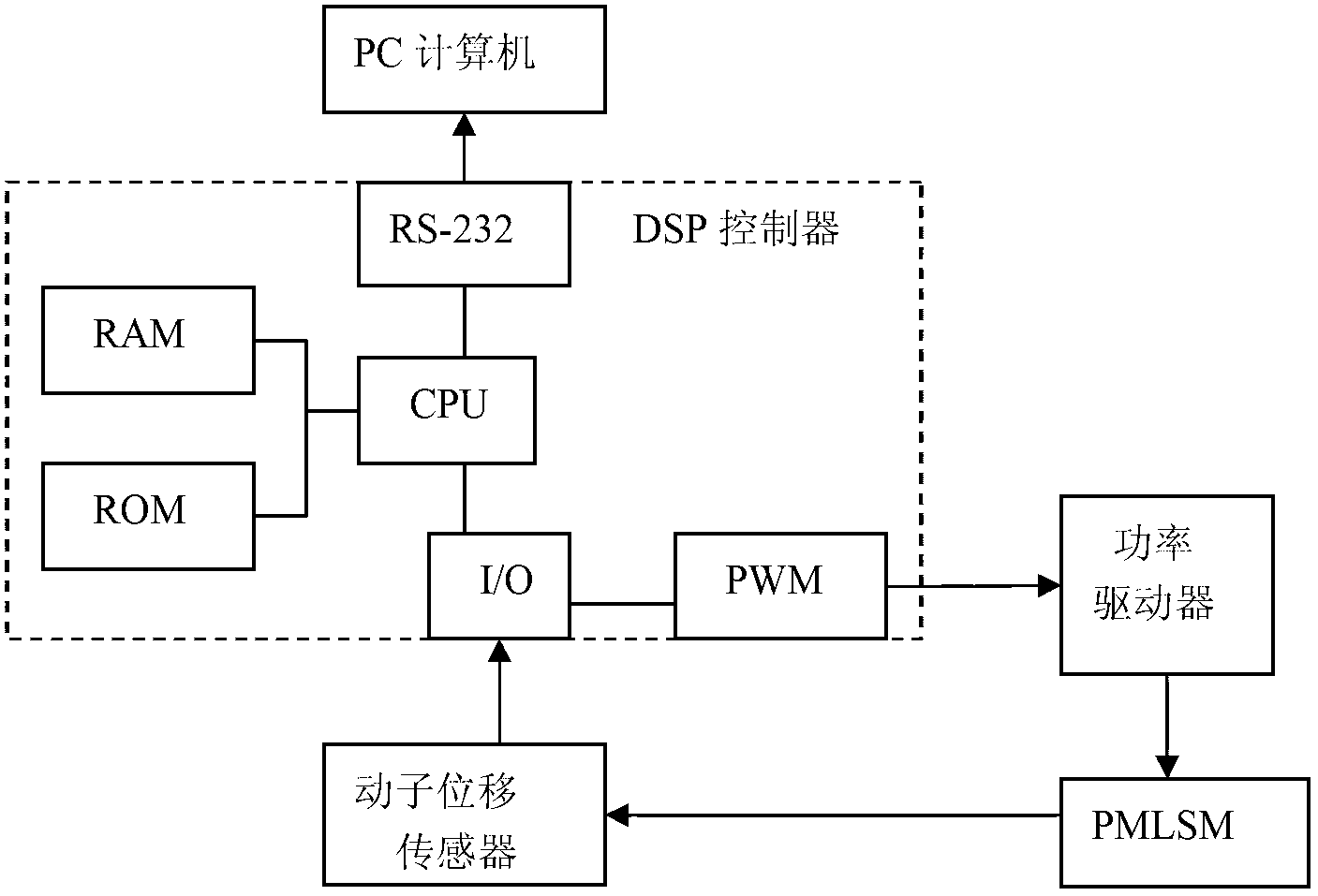
The invention discloses a nonlinear interference control method and a nonlinear interface control system for a permanent magnet linear synchronous motor (PMLSM). According to the control method, an online estimated compensating voltage value ud of a wavelets neural network (WNN) is added on the basis of up+uf of the conventional composite feedforward proportional differential control, and the sum of up, uf and ud is used as the control voltage U(t) of a stator of the PMLSM, namely the control voltage U(t) is equal to up+uf+ud. The WNN is a three-layer forward network, and ud is the sum of omega1psi1, omega2psi2, ..., omegajpsij, ..., and omegampsim. A learning signal of the WNN is an output value of a proportional differential controller. The control system comprises a digital signal processing controller, a power driving module connected with the stator of the PMLSM, and a rotor displacement sensor arranged on the PMLSM. The WNN is used for effectively compensating interference such as PMLSM thrust fluctuation and frictional force and errors of a fixed parameter model, and tracking accuracy can be improved by more than 2.7 times; and the control system can be implemented by universal hardware, and is convenient to popularize and use.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Control method and system for permanent magnet synchronous motor
InactiveCN104734592AImprove stabilityFactors that eliminate current instability problemsElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsLower limitPermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention provides a control method and system for a permanent magnet synchronous motor. The control method and system are characterized in that firstly, initial given currents are obtained according to the given angular speed and the actual angular speed of the permanent magnet synchronous motor; initial quadrature-axis currents are obtained according to the initial given currents; initial direct-axis currents are obtained according to the initial given currents; first direct-axis currents are obtained according to the initial direct-axis currents and the negative compensation quantity; second direct-axis currents are obtained according to the first direct-axis currents, and the second direct-axis currents are not smaller than a preset lower limit value; given direct-axis voltages are obtained according to the second direct-axis currents; the difference between the first direct-axis currents and the second direct-axis currents is acquired, ratio calculation is conducted on the differencing result, and the quadrature-axis current compensation quantity is acquired through calculation; the difference between the initial quadrature-axis currents and the quadrature-axis current compensation quantity, and first quadrature-axis currents are obtained; given quadrature-axis voltages are obtained according to the first quadrature-axis currents; the negative compensation quantity is acquired according to the given quadrature-axis currents and the given quadrature-axis voltages. The stability of the permanent magnet synchronous motor can be improved, and current oscillation is avoided.
Owner:CSR ZHUZHOU ELECTRIC LOCOMOTIVE RES INST
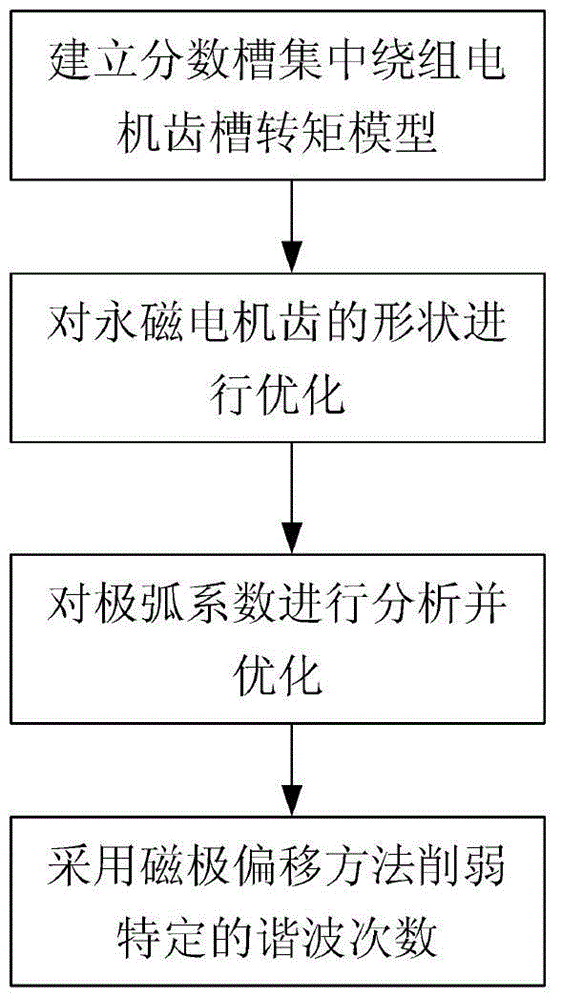
Method for weakening cogging torque of permanent magnet synchronous generator
ActiveCN104617720AReduce cogging torqueReduce starting torqueManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesWind energy generationElement modelPermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention belongs to the permanent magnet synchronous generator technology field, and particularly relates to a method for weakening cogging torque of a permanent magnet synchronous generator. The method for weakening the cogging torque of the permanent magnet synchronous generator includes: firstly, optimizing the shape of a permanent magnet motor tooth so as to reduce the cogging torque; then, optimizing a pole arc coefficient; next, using a magnet pole shifting method to reduce a harmonic component of the cogging torque so as to achieve the purpose of reducing the cogging torque; finally, combining the above three steps so as to minimize the cogging torque, building a finite element model of the permanent magnet synchronous generator, and performing analysis and finite element verification on a provided cogging torque suppression method. The method for weakening the cogging torque of the permanent magnet synchronous generator has the advantages of reducing the cogging torque of the permanent magnet synchronous generator on the premise of slightly influencing other properties of the permanent magnet synchronous generator by changing the shape of the tooth and using an optimal pole arc coefficient method and a magnetic pole shifting method in combination, and then reducing starting resistance torque of a direct drive permanent magnet synchronous wind generator, and improves usage rate of wind energy.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
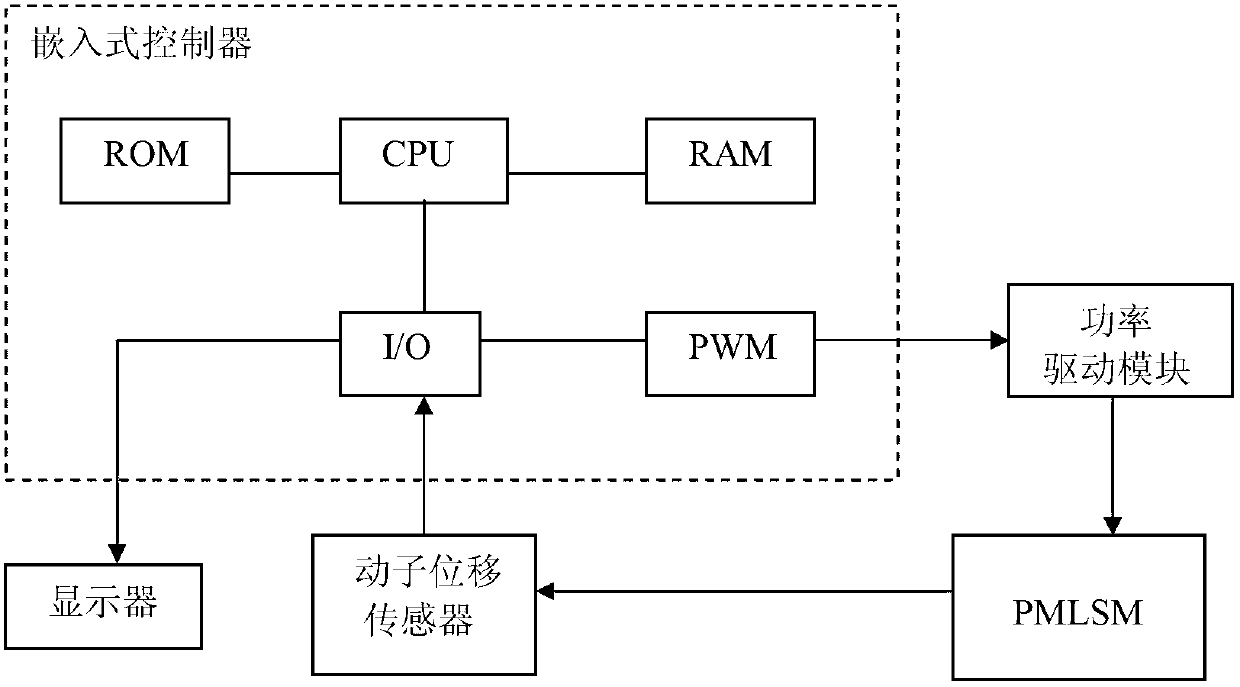
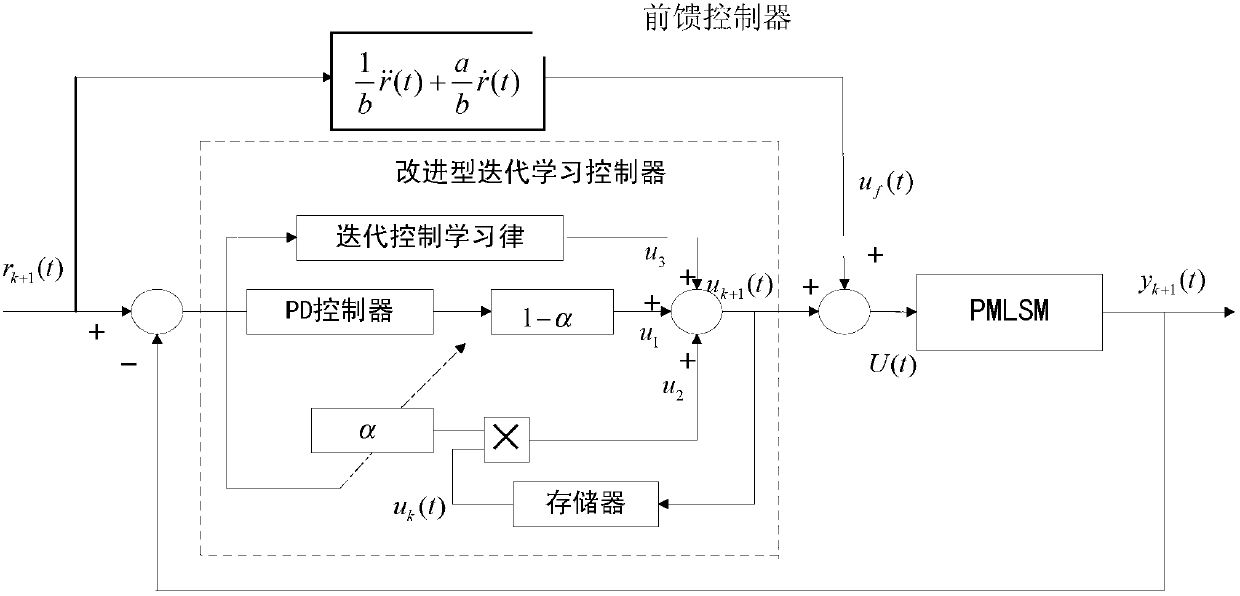
Improved iterative learning control method and control system for permanent magnet linear synchronous motor
InactiveCN102710212AAvoid large swingsReduce excessive vibrationMotor parameters estimation/adaptationElectronic commutatorsPermanent magnet synchronous motorVoltage control
The invention discloses an improved iterative learning control method and an improved iterative learning control system for a permanent magnet linear synchronous motor (PMLSM). The control method comprises the following steps of: calculating the control voltage of a stator of the PMLSM by adopting a time axis and iteration axis superposed iterative control law algorithm; introducing an initial control variable u0 on the time axis of the iterative control law algorithm, and designing an adaptive factor alpha; and adding a feedforward control variable to the (k+1)-iterated control voltage of the PMLSM following an iterative learning law. The control system comprises an embedded controller, a power driving module connected with the stator of the PMLSM, and a rotor displacement sensor arranged on the PMLSM. The oscillation of an initial iteration track is avoided, and an iterative convergence speed is increased; and control accuracy is improved to be 0.55 percent.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Method for measuring parameters of permanent magnet synchronous motor
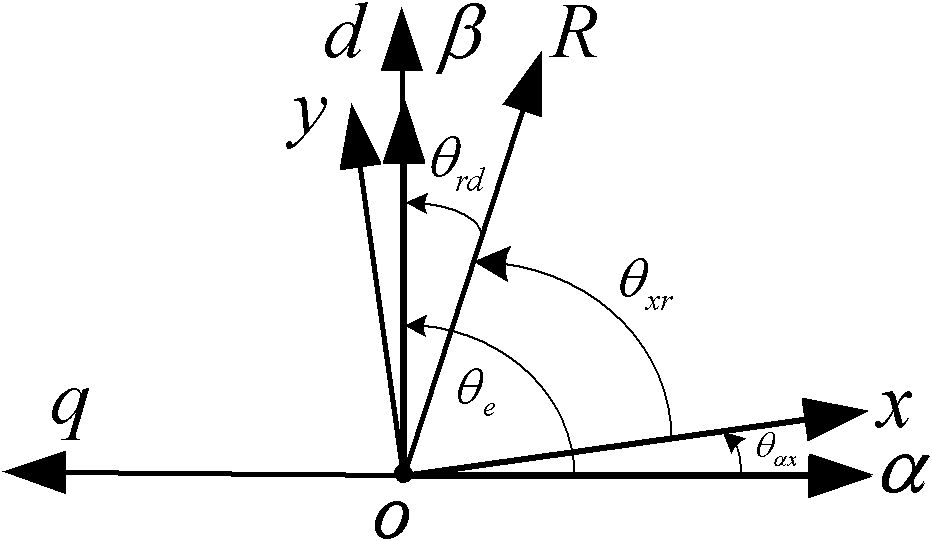
ActiveCN103018577APhysical concepts are clearHigh measurement accuracyResistance/reactance/impedencePermanent magnet synchronous motorAngular degrees
The invention discloses a method for measuring parameters of a permanent magnet synchronous motor and belongs to the field of motor parameter measurement. The method includes utilizing the A phase no-load counter EMF (Electromotive Force) of a motor and the electric angular velocity of the motor to obtain a permanent magnet flux linkage, utilizing the wave form of the A phase no-load counter EMF and a position sensor to read the corresponding electric angular positions of the 90-degree angle and 0-degree angle of a motor rotor, changing the connection type of a stator winding, and utilizing the alternating voltage, current and frequency to respectively obtain corresponding direct-axis inductance and quadrature-axis inductance. The apparatus used in the method are conventional apparatus and the method has the advantages of clear physical concept, easy operation, high measurement accuracy and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
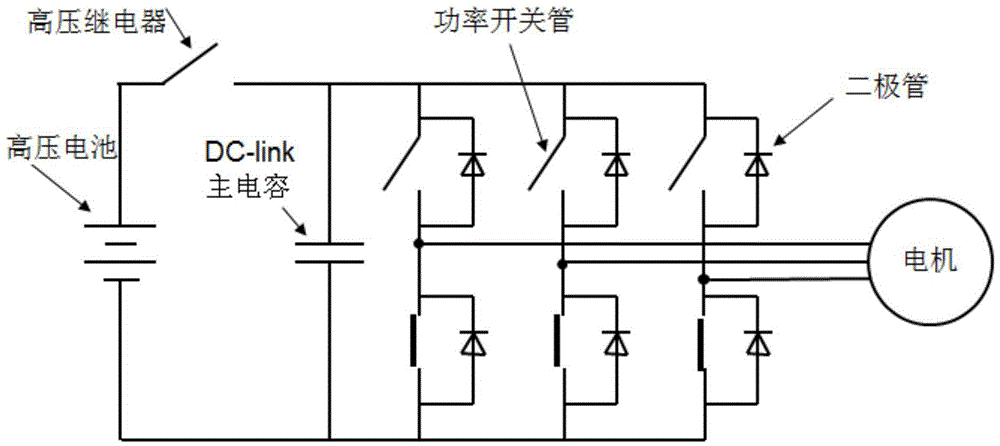
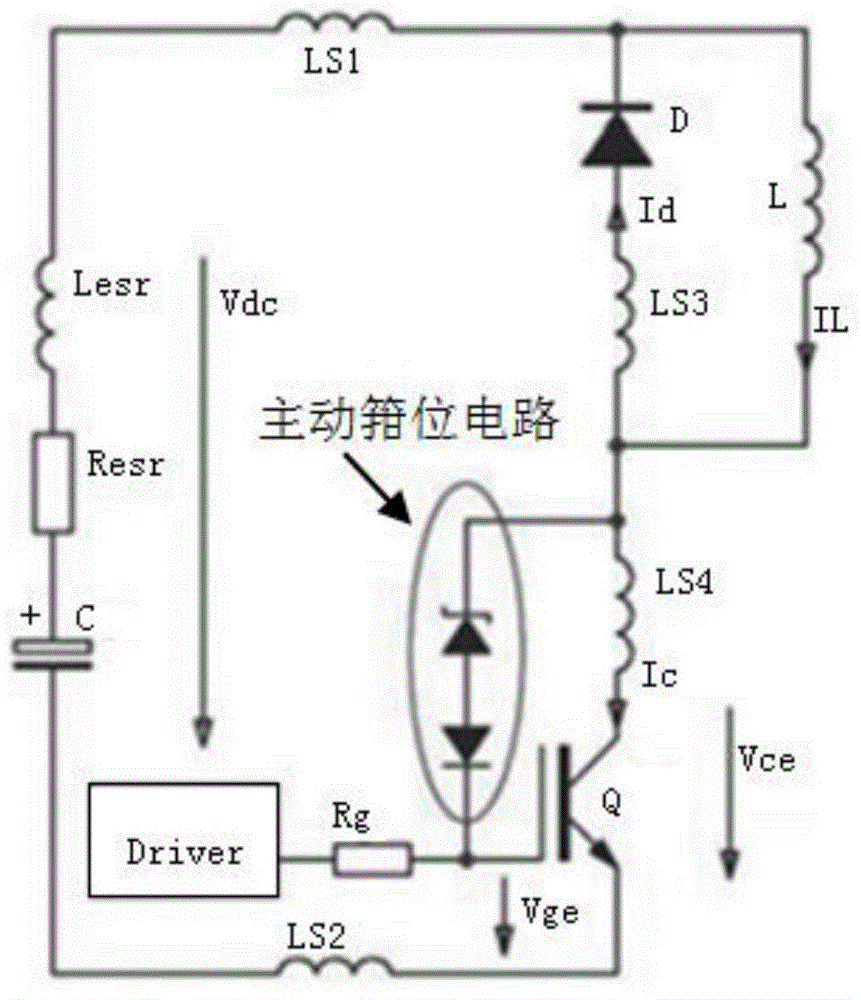
Driving system of high-voltage permanent magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN104410337ASingle motor speed/torque controlEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentCapacitancePermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention discloses a driving system of a high-voltage permanent magnet synchronous motor. A main capacitor and a high-voltage relay are connected in series at two ends of a high-voltage battery after the main capacitor is in parallel connection with three bridge arms of a three-phase bridge-type alternating-current inverter circuit; an active clamping circuit is arranged between gate poles and collectors of three IGBTs (insulated gate bipolar transistors) of upper bridge arms of the bridge arms of the three-phase bridge-type alternating-current inverter circuit; a motor controller enters a rapid active discharging mode after the high-voltage relay is switched off; if the voltage at two ends of the main capacitor exceeds a clamping threshold, all the six IGBTs of the bridge arms of the three-phase bridge-type alternating-current inverter circuit are immediately controlled to be switched off, and after n milliseconds, all the three IGBTs of the lower bridge arms are controlled to be switched on and all the three IGBTs of the upper bridge arms are controlled to be switched off. The driving system of the high-voltage permanent magnet synchronous motor protects power devices from being broken down by transient-state high voltages when the high-voltage relay is switched off and protects the power devices from being broken down by transient-state high-voltage surges when the high-voltage relay is switched on unexpectedly.
Owner:UNITED AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRONICS SYST
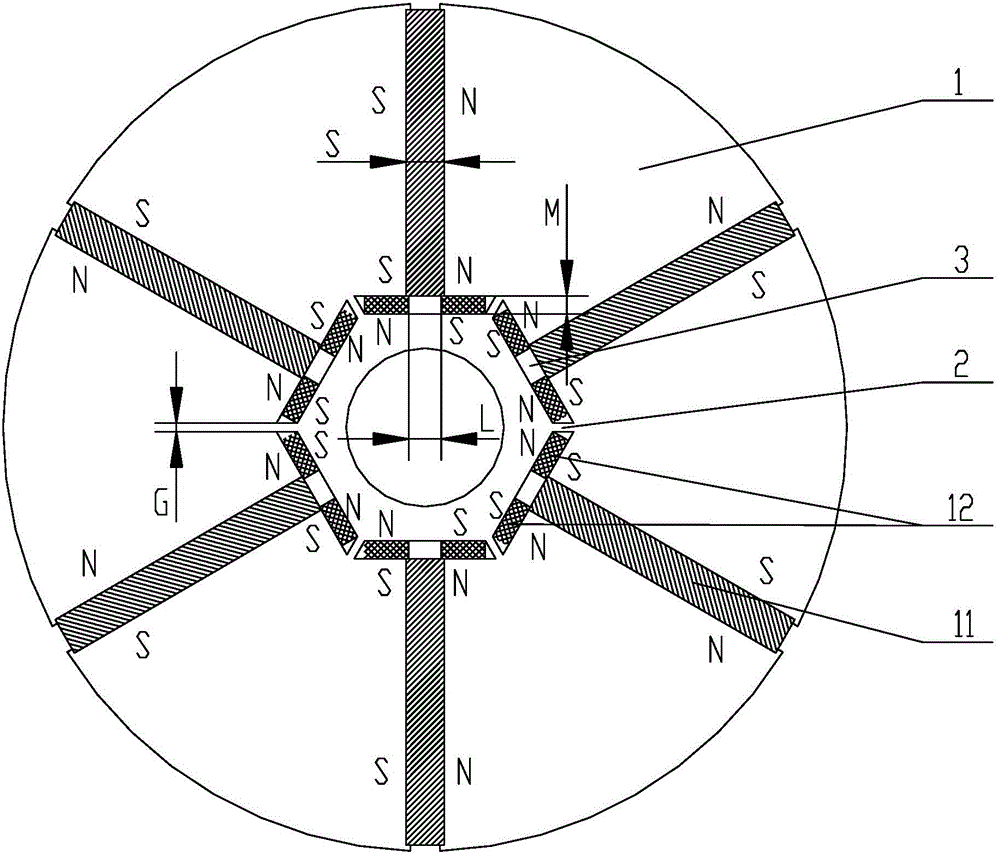
Rotor of permanent magnet synchronous motor and permanent magnet synchronous motor provided with same
ActiveCN104485762AHigh mechanical strengthReduce Flux LeakageSynchronous machine detailsMagnetic circuit rotating partsPermanent magnet synchronous motorPermanent magnet synchronous generator
The invention discloses a rotor of a permanent magnet synchronous motor and the permanent magnet synchronous motor, which belong to the technical field of the permanent magnet synchronous motors, and are designed in order to solve the problems of high leakage flux, low permanent magnet utilization rate, influence on motor performance and efficiency and the like in existing rotor of the permanent magnet synchronous motor. The rotor of the permanent magnet synchronous motor comprises a rotor core, wherein an even number n of tangential permanent magnets are distributed evenly in radial direction on the rotor core, and the same polarities of two adjacent tangential permanent magnets are opposite; radial permanent magnets are arranged symmetrically on two sides of one end of each tangential permanent magnet close to the inner side of the rotor core respectively; every two radial permanent magnets sandwiched between two adjacent tangential permanent magnets have the same polarity in the direction facing to a stator, and a magnetic isolating bridge is arranged between every two radial permanent magnets. The invention further discloses a permanent magnet synchronous motor provided with the rotor. By utilizing the rotor, the leakage flux of the tangential permanent magnets on the inner side of the rotor is reduced, the utilization rate of the permanent magnets is improved, and the motor efficiency and the motor structural intensity are enhanced.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC +1
Electric vehicle-used built-in permanent magnet synchronous motor flux weakening control method
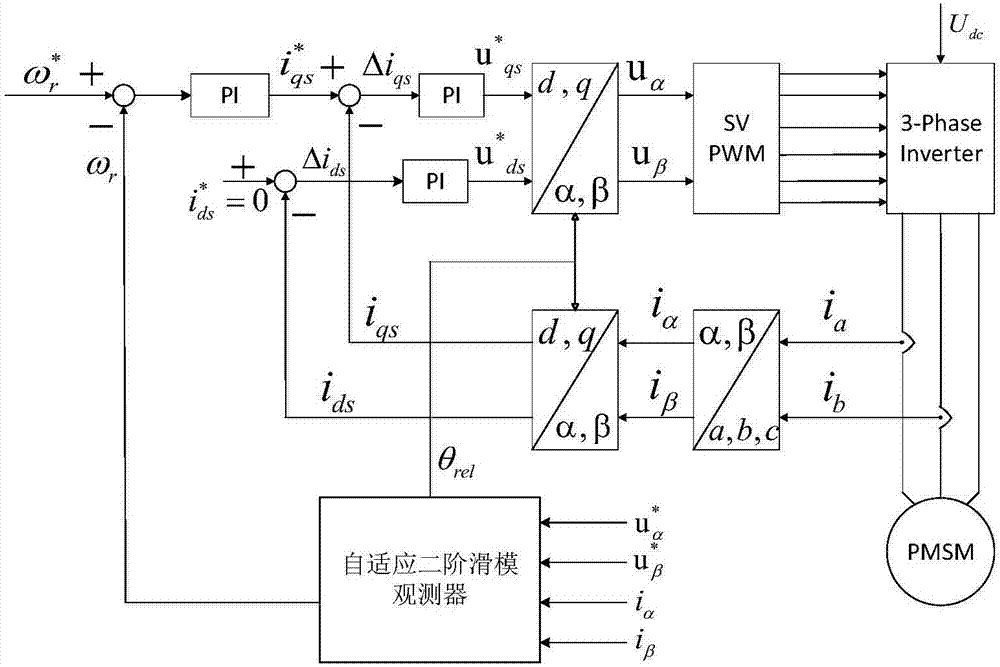
InactiveCN105071715AHigh control precisionImprove stabilityAC motor controlVector control systemsElectric machineryPermanent magnet synchronous generator
The invention discloses an electric vehicle-used built-in permanent magnet synchronous motor flux weakening control method. Two phases of current and a real-time rotor position of the motor are acquired, after Clarke transformation, Park transformation, an current ring PI adjustor, d-axis reference voltage ud and q-axis reference voltage uq are obtained, and output u* as described in the description of a current controller and reference voltage umax are compared to judge whether to enter flux weakening control. The method of the invention has the beneficial effects that the control precision of torque and speed and stability of the system are improved without depending on parameters of the motor.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU AIRCRAFT EQUIP +1
Method for restraining torque pulsation of permanent magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN103378789AImprove controlPlay a protective effectElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsCompensation effectPermanent magnet synchronous motor
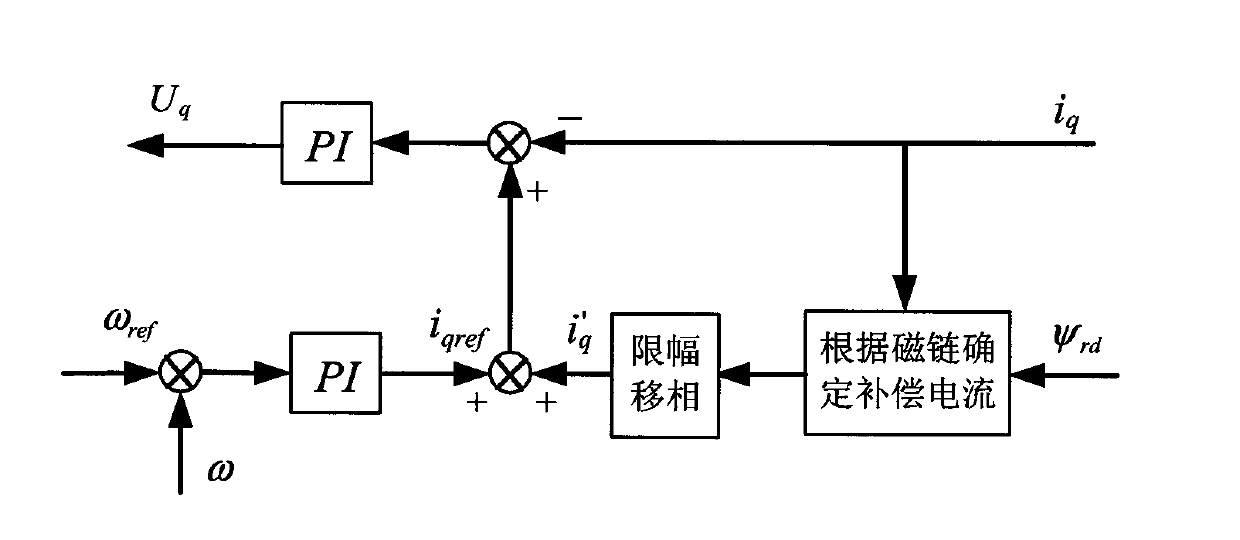
The invention discloses a method for restraining torque pulsation of a permanent magnet synchronous motor. Original reference signals and q axis current signals are adopted, and the method is characterized in that a superposition q axis current compensation method is adopted for restraining the torque of the permanent magnet motor. The q axis current compensation method can be conducted in the following two modes respectively: under the condition that the output torque Te is given, the q axis compensation current can be calculated on the basis of an electromagnetic torque formula; when the electromagnetic torque needed by the motor can not be accurately known, the compensation current can be determined according to a flux linkage formula. According to the method for restraining torque pulsation of the permanent magnet synchronous motor, the control performance of the permanent magnet synchronous motor is improved by increasing the compensation current, the good compensation effect is achieved through a phase shifting link, and through an amplitude limiting link, the compensation effect can be prevented from being affected when current glitches are large, and the protection function is achieved.
Owner:DORNA TECH
Detecting method of rotor position and rotating speed of permanent magnet synchronous motor
InactiveCN107482977ASuppress chatterAccurate estimateElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlPermanent magnet synchronous motorPermanent magnet synchronous generator
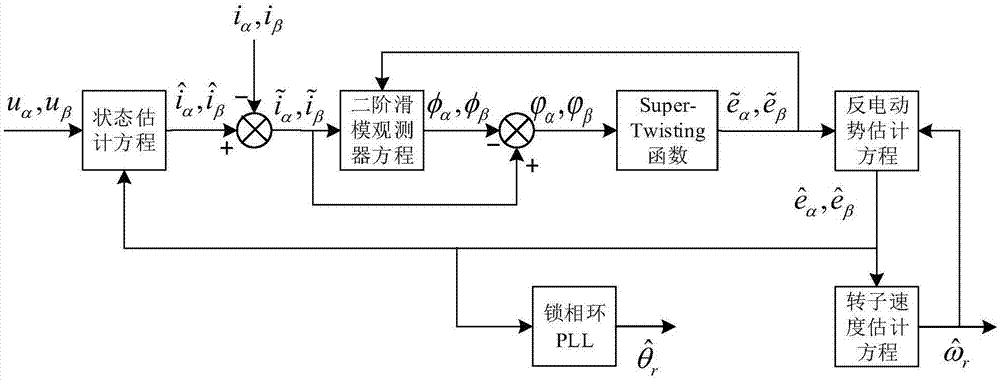
The invention relates to a detecting method of the rotor position and rotating speed of a permanent magnet synchronous motor, and belongs to the field of permanent magnet synchronous motor control. The detecting method includes the following steps that a counter electromotive force equation and a state equation of the permanent magnet synchronous motor are set up; matrix-vector arrangement is carried out on the state equation set up, and a state estimating equation is set up according to the state equation obtained after arrangement to obtain a state error equation; a second-order sliding-mode observer equation is set up according to the state error equation to obtain a counter electromotive force error equation; the sigmoid function is used for replacing the control function signum to correct the counter electromotive force error equation; a counter electromotive force estimating equation is set up according to the counter electromotive force error equation obtained after correction; the counter electromotive force estimating equation is subtracted from the counter electromotive force equation, the Lyapunov equation is used for analyzing stability to obtain and correct a rotor rotating speed estimating equation; rotor position information is extracted through the phase-locked loop technology. A model reference adaption and second-order sliding-mode combined observer is used for estimating counter electromotive force and rotor speed of the permanent magnet synchronous motor and replacing a traditional sliding-mode observer to obtain the rotor speed through counter electromotive force numerical calculation.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Permanent magnet synchronous motor
InactiveCN102420475AReduce cogging torqueEasy to manufacture and assembleMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machine detailsPermanent magnet synchronous motorMagnetic poles
A purpose of the present invention is providing a permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor structure which has high air gap flux density and is easy to generate back electromotive force with a sine wave. In a permanent magnet synchronous motor, a circumferential surface of the rotor is uniformly provided with a plurality of magnetic steel grooves which are independently enclosed and do not contact mutually. Every two magnetic steel grooves are arranged to form a V shape, an opening of the V shape faces excircle of the rotor, and a tip of the V shape faces a rotor center. Each magnetic steel groove is provided with magnetic steel. In each group of V-shaped magnetic steel grooves, two magnetic steel facing the excircle of the rotor core have a same magnetic pole, and magnetic poles of magnetic steel facing the excircle of the rotor core in two adjacent groups of V-shaped magnetic steel grooves are opposite with the magnetic pole of the two magnetic steel. The excircle of the rotor goes down toward the center with depth delta and smooth transition at a crossing position of axes, which means that air gap width at the crossing position is less than air gap width at a straight axis position by delta. Through improving the rotor, the permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor has high mechanical strength and a large salient pole ratio, and weakened magnetism speed expansion is facilitated.
Owner:TIANJIN SANTROLL ELECTRIC SCI & TECH
Driving system of permanent magnet synchronous motor
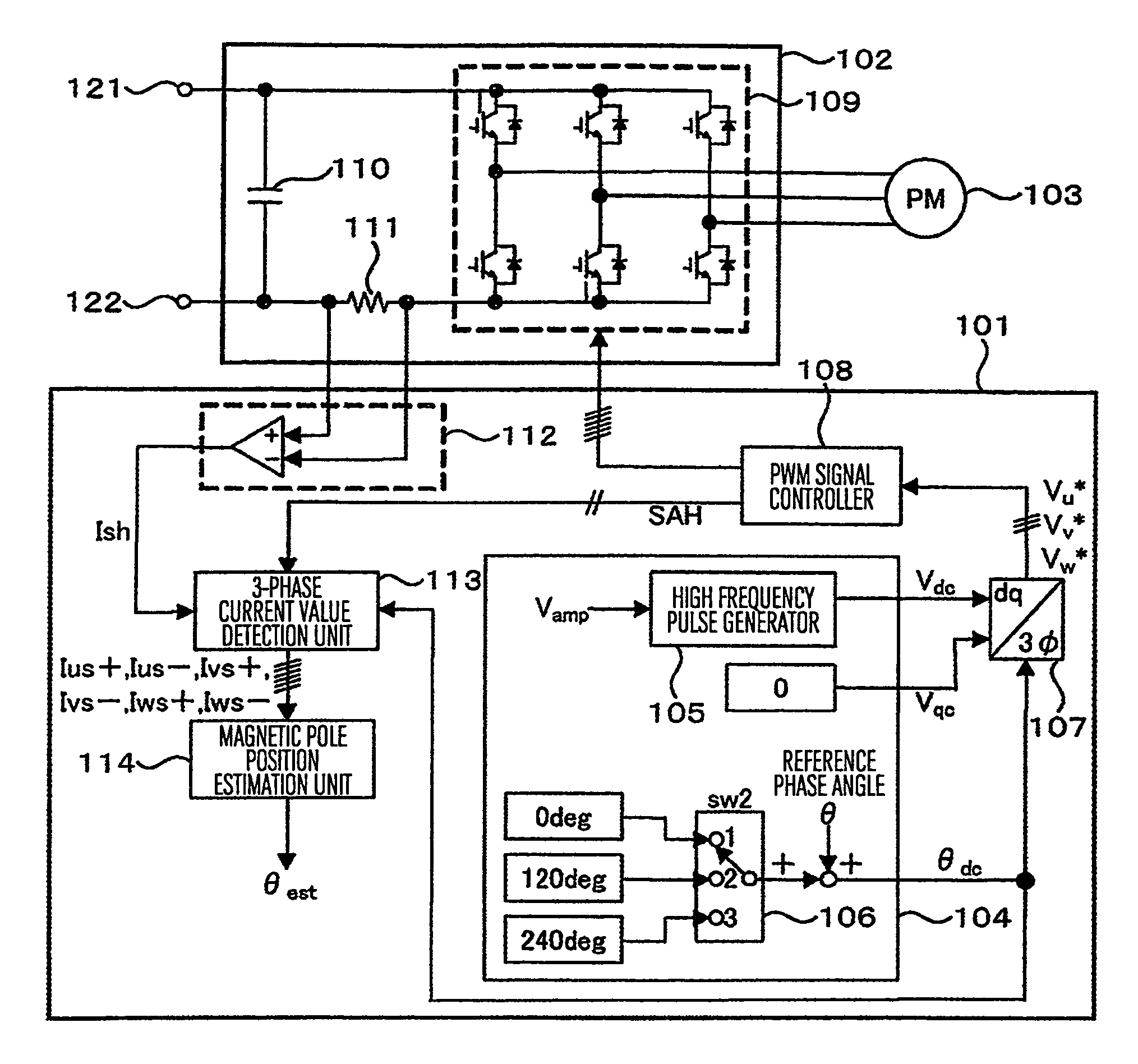
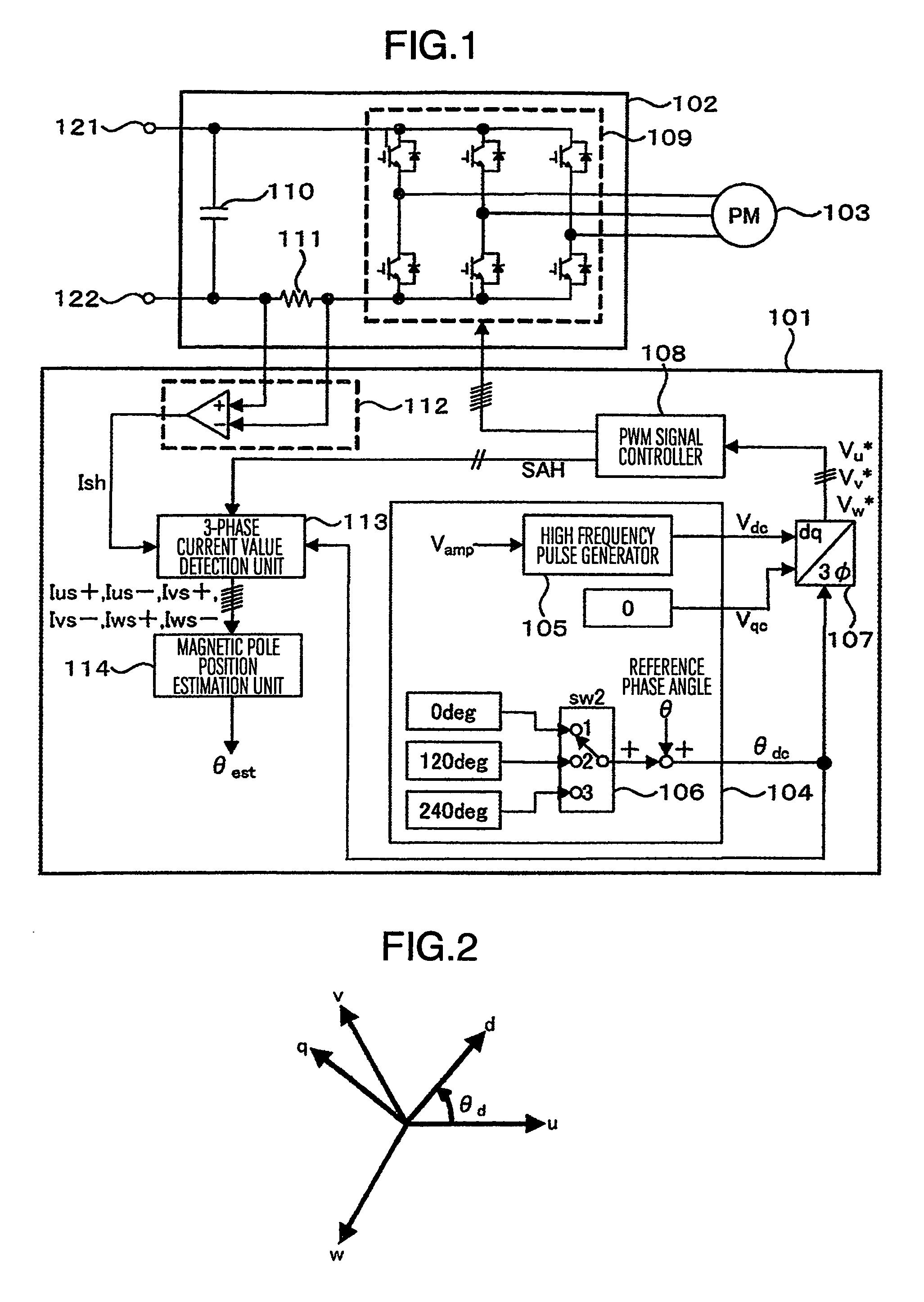
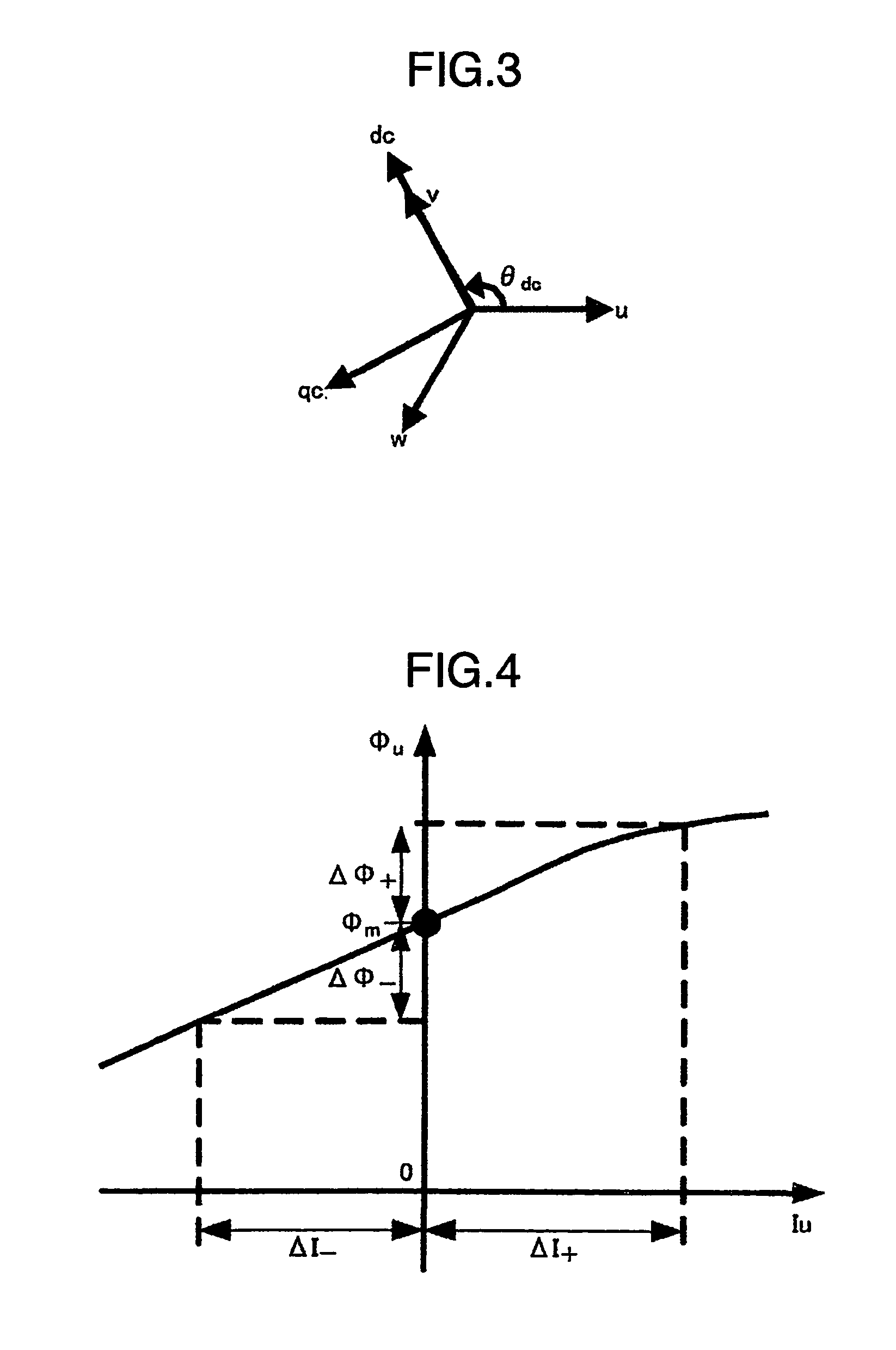
ActiveUS8541971B2Improve positionIncrease the number ofCommutation monitoringSynchronous motors startersPhase currentsMagnetic poles
Owner:HITACHI IND EQUIP SYST CO LTD
Torque output control system of permanent magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN103762924ASolving Torque Accuracy IssuesAvoid complex processElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsElectricityPower inverter
The invention provides a torque output control system of a permanent magnet synchronous motor. The system comprises a modulation module, an inverter and the permanent magnet synchronous motor, wherein the modulation module, the inverter and the permanent magnet synchronous motor are electrically connected in sequence. The system further comprises a 3 / 2 conversion module, a torque calculation module, a required current calculation module, a torque comparator, a torque current compensation integral adjustment module, a torque current adder, a magnetic flow current calculation module, a torque current comparator, a magnetic flow current comparator and a current PI regulating module. On the basis of controlling torque output, and by using actual output torque as a target, the torque output control system is used for calculating torque deviation and correcting the matching relation between magnetic flow current and torque current according to the torque deviation so as to enable motor torque output to track target torque.
Owner:SHENZHEN HANGSHENG ELECTRONICS
Method for identifying permanent magnet flux and quadrature axis inductance of permanent magnet synchronous motor
InactiveCN103338002ASimple methodSuitable for engineering realizationElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsControl systemDirect effects
The invention discloses a method for identifying permanent magnet flux and quadrature axis inductance of a permanent magnet synchronous motor. The method comprises the steps as follows: designing a filter based on an identification algorithm and calculating identification parameters. The accuracy of the permanent magnet flux and quadrature axis inductance parameters directly influences the control performance of a vector control system of the permanent magnet synchronous motor. But the existence of a saturation effect and the like enables the motor parameters to be non-linearly changed. Therefore, a change curve of the motor parameters is necessarily measured or identified on line. The invention discloses the simple and easy method for identifying the permanent magnet flux and the quadrature axis inductance, and the control performance of the system is improved on the basadopts not increasing the system cost.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
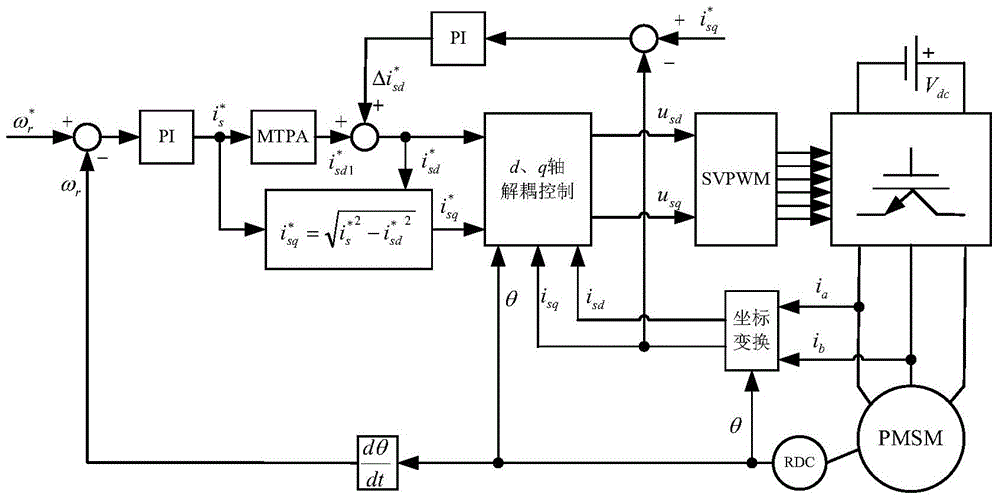
Flux-weakening control method of permanent magnet synchronous motor
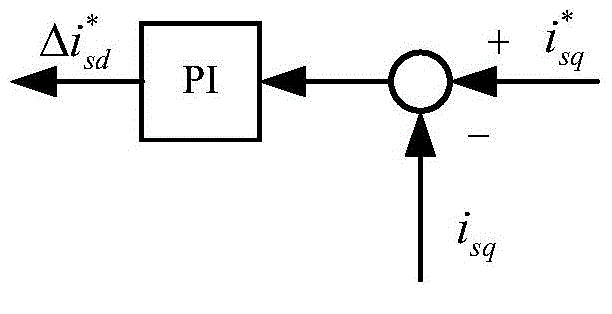
InactiveCN104135202AEasy to understandLower control costsElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsCurrent sensorPermanent magnet synchronous generator
The invention belongs to the technical field of vector control of a permanent magnet synchronous motor. Total control current I*s is obtained by adjusting PI (Proportional-Integra) of a given motor rotational speed w*r and a motor rotational speed wr; a basic given current i*sdl of d axis is obtained by control of MTPA (Maximum Torque Per Ampere); current feedback isd and isq of the d axis and q axis are obtained by detection of a current sensor; the given current i*sq of the q axis is equal to square root of the difference of (i*s)2 and (i*sd)2; the given adjustment current DELTAi*sd of the d axis is obtained by passing the current feedback isq of q axis through a flux-weakening control module; the given current i*sd of d axis is equal to the sum of i*sdl and DELTAi*sd; the currents of the d axis and q axis are subjected to decoupling control and voltages u*sd and u*sq are output; and an SVPWM (Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation) inverter is controlled to obtain three-phase alternating current to drive the permanent magnet synchronous motor. Through PI adjustment on the given current i*sq of q axis and the current feedback isq of the q axis, the given adjustment current DELTAi*sd of the d axis is obtained, optimal flux weakening of the permanent magnet synchronous motor is achieved, the flux-weakening control method is easy to understand and implement, control cost is low, and a good flux-weakening control effect is achieved.
Owner:SANHONG HEAVY IND SCI & TECH
Double-stator permanent magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN108390529AImprove efficiencyImprove reliabilityMagnetic circuit stationary partsWindings conductor shape/form/constructionMagnetomotive forceElectric machine
The invention discloses a double-stator permanent magnet synchronous motor, and relates to the field of motors. The invention aims at solving problems that a conventional double-stator permanent magnet synchronous motor usually employs a fractional-slot concentrated winding, the number of coils of the fractional-slot concentrated winding is large and the manufacturing cost is larger; and problemsthat the big eddy-current loss of a rotor permanent magnet and the rising of the temperature of the permanent magnet are liable to cause the irreversible demagnetization because the harmonic content of the magnetomotive force of the fractional-slot concentrated winding is large when the power-on frequency of a motor winding is higher and the overload multiples is large. The double-stator permanentmagnet synchronous motor provided by the invention enables the harmonic contents of a synthetic magnetomotive force and the magnetomotive force of two armatures to be small through the correspondingstaggering of double-stator windings, and is small in eddy-current loss of the rotor permanent magnet. Moreover, the end parts of the windings are not overlapped, thereby improving the motor efficiency and reliability.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Permanent magnet synchronous motor unposition sensor control method
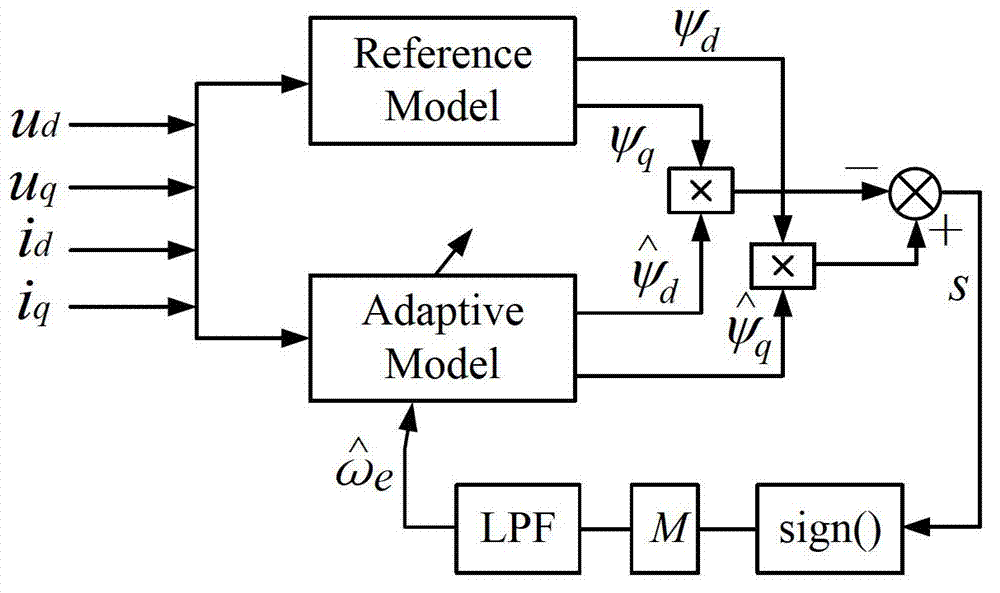
InactiveCN103051271ALow costSimple control strategyElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsControl vectorPower flow
The invention discloses a permanent magnet synchronous motor unposition sensor control method, which concretely comprises the following steps of: step 10, collecting three-phase voltage of a permanent magnet synchronous motor, switching the three-phase voltage to a dd coordinate system, and obtaining voltage ud and uq in a dq axis; step 20, collecting three-phase current of the permanent magnet synchronous motor, switching the three-phase current to a dq coordinate system, and obtaining current id and iq in the dq axis; step 30, adopting a sliding mode variable structure model reference adaptive system-based algorithm to obtain a rotor estimated electric angle speed and a rotor position of the permanent magnet synchronous motor; and step 40, according to the rotor estimated electric angle speed and the rotor position obtained in the step 30, realizing unposition sensor rotation speed close-loop vector control of the motor. The permanent magnet synchronous motor unposition sensor control method has the advantages of low cost, simple control algorithm, high rotation speed and position estimation speed, high estimation accuracy, and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Apparatus and method for measuring position deviation of rotor of permanent magnet synchronous motor
ActiveUS20140145654A1Simple methodImprove efficiencyElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersControl signalPermanent magnet synchronous motor
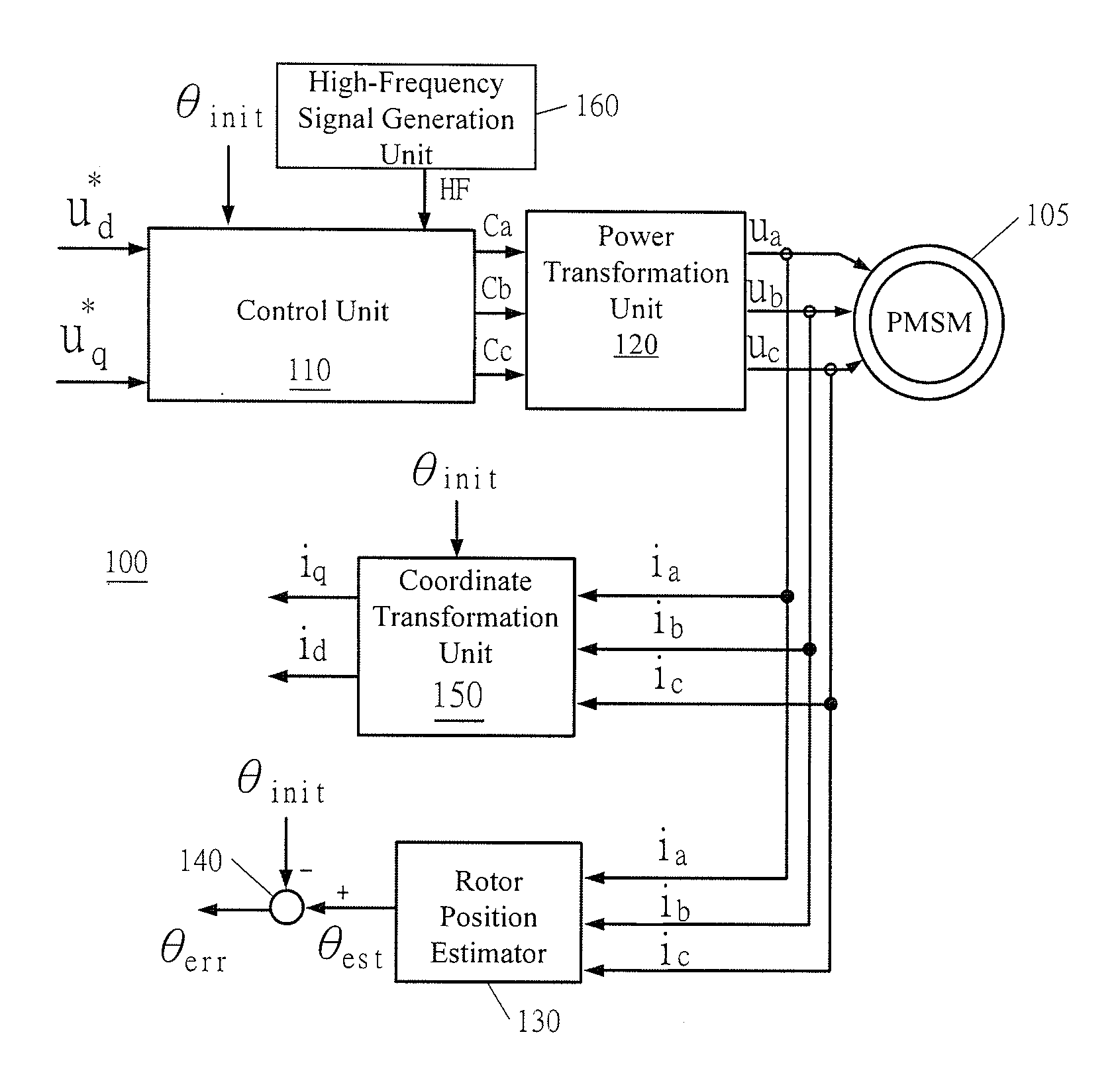
An apparatus for measuring a position deviation of a rotor of a permanent magnet synchronous motor includes a control unit, a power transformation unit, a rotor position estimator and a calculation unit. The control unit receives a d-axis DC voltage signal and a q-axis AC voltage signal and receives an initial value of the rotor position and a high-frequency signal to output a three-phase command signal. The power transformation unit receives the three-phase command signal and outputs a three-phase control signal for controlling the motor. The rotor position estimator receives a three-phase current feedback signal corresponding to an operation of the motor and generates an estimation value of the rotor position. The calculation unit performs calculation to the initial value and the estimation value to generate a deviation value of the rotor position. Moreover, a method for measuring the position deviation is also disclosed herein.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Permanent magnet synchronous motor simulator considering nonlinear characteristics and control method thereof
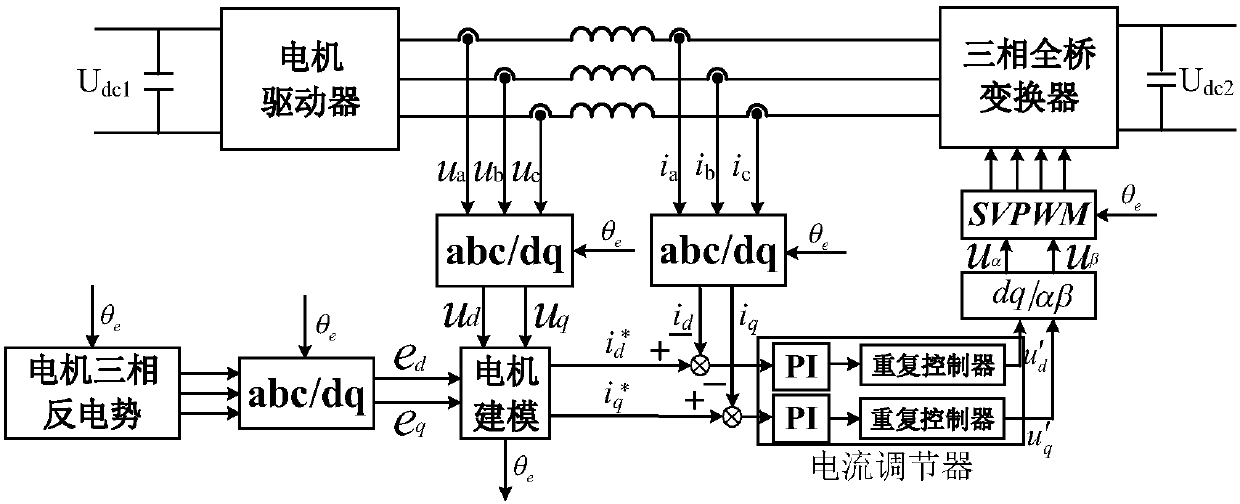
ActiveCN107943121ARealize static error-free trackingDynamo-electric machine testingSpeed/accelaration control using electric meansMathematical modelAngular velocity
The invention discloses a permanent magnet synchronous motor simulator considering nonlinear characteristics and a control method thereof. The method includes the steps of outputting three-phase voltages and currents, and obtaining q-axis and d-axis voltage and current components respectively through coordinate transformation and combined with a current cycle electrical angle; obtaining q-axis andd-axis counter electromotive force (EMF) components; establishing a nonlinear permanent magnet synchronous motor mathematical model, taking the q-axis and d-axis voltages and q-axis and d-axis counter EMF as the input to calculate the mechanical angular velocity, electrical angle, motor rotation speed, and q-axis and d-axis currents of a next cycle, and taking the q-axis and d-axis currents as command currents for the closed-loop control of the next cycle; and regulating differences between the command currents and the q-axis and d-axis current components by using a current regulator, and connecting the reference voltage obtained after the inverse Park transformation of the results to an SVPWM modulation module such that a three-phase full-bridge converter actually outputs the command currents. According to the invention, the operation characteristics of various working conditions under the condition of non-linear counter EMF can be effectively simulated, and the tracking without static error of high frequency signals contained in the higher harmonic currents can be achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com