Patents
Literature
436 results about "Orthogonal coordinates" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, orthogonal coordinates are defined as a set of d coordinates q = (q¹, q², ..., q) in which the coordinate surfaces all meet at right angles (note: superscripts are indices, not exponents). A coordinate surface for a particular coordinate q is the curve, surface, or hypersurface on which q is a constant. For example, the three-dimensional Cartesian coordinates (x, y, z) is an orthogonal coordinate system, since its coordinate surfaces x = constant, y = constant, and z = constant are planes that meet at right angles to one another, i.e., are perpendicular. Orthogonal coordinates are a special but extremely common case of curvilinear coordinates.
Haptic interface for force reflection in manipulation tasks
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
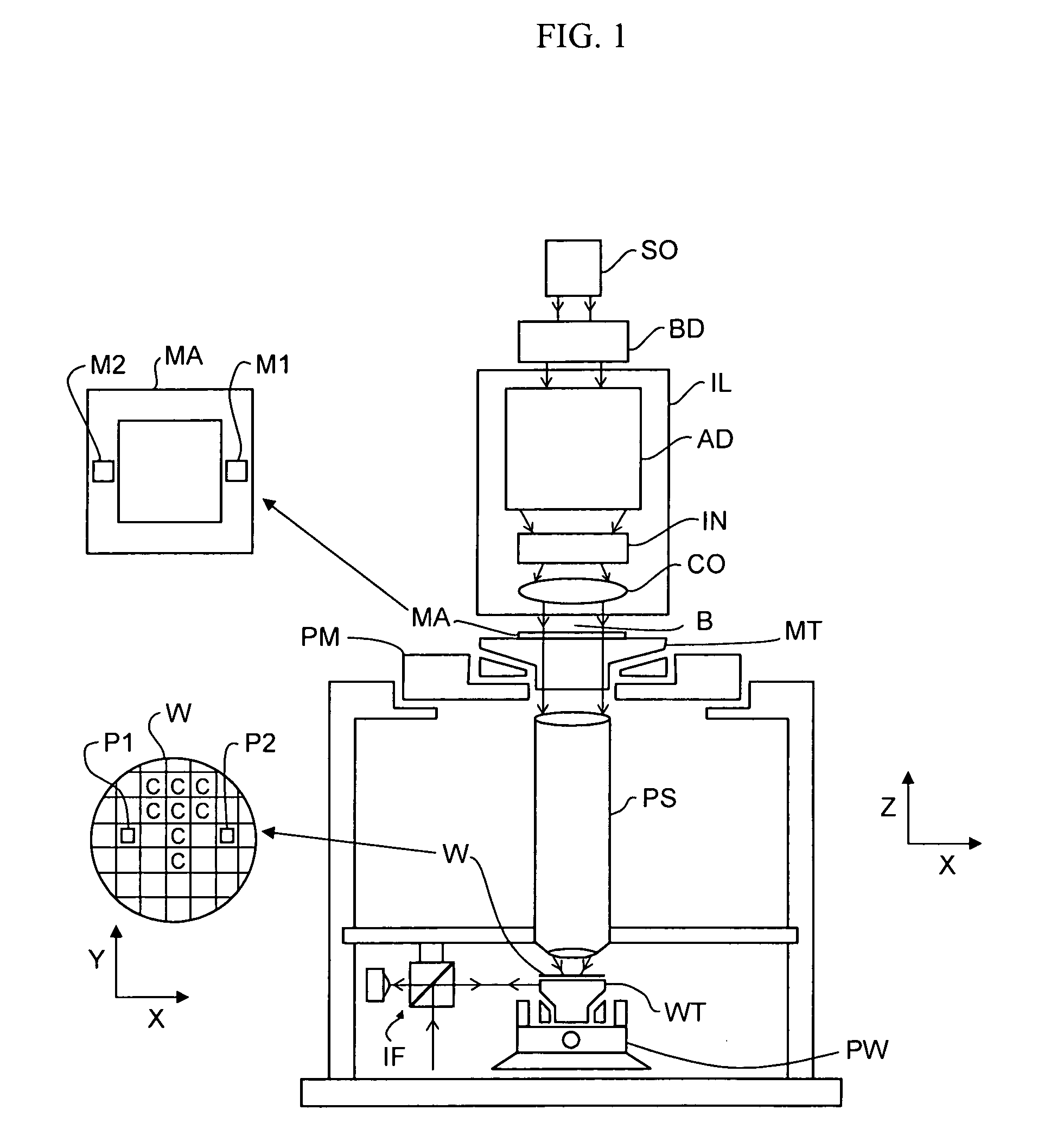
Lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method
ActiveUS20070195296A1Improve accuracyPhotomechanical apparatusUsing optical meansOrthogonal coordinatesEngineering
A lithographic apparatus includes a displacement measuring system to measure a position of a moveable object with respect to a reference frame of the lithographic apparatus, in at least three coplanar degrees of freedom (x, y, Rz) of an orthogonal x-y-z coordinate system centred in the center of the moveable object. The moveable object includes a support structure configured to support a patterning device or a substrate table configured to support a substrate. The displacement measuring system includes at least three sensor heads, each sensor head being positioned with a measuring direction substantially coplanar with the x-y plane of the coordinate system and each sensor head being furthermore positioned with the measuring direction substantially perpendicular to a connection line connecting the sensor head with the center of the movable object and extending coplanar with the x-y plane.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
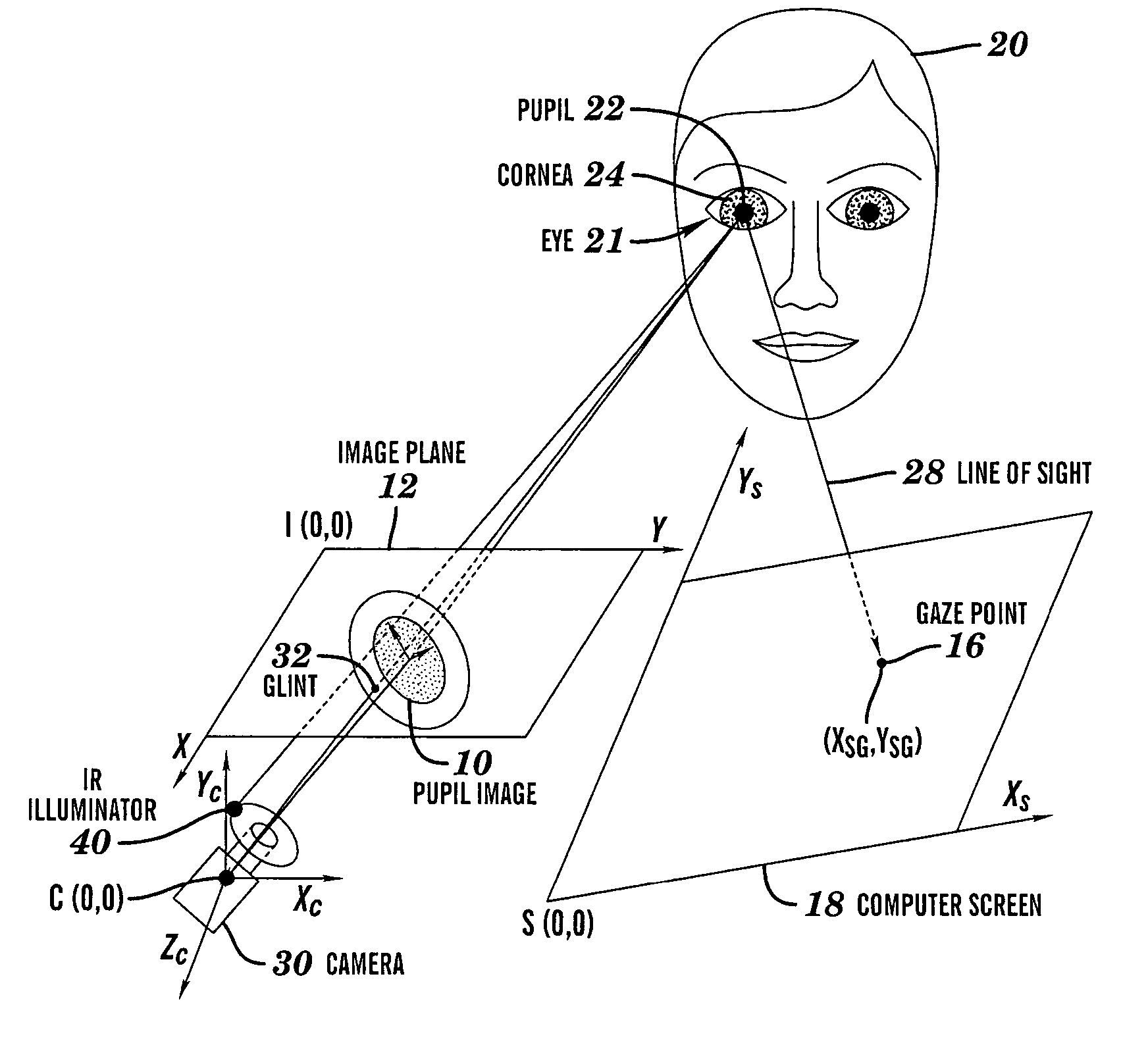
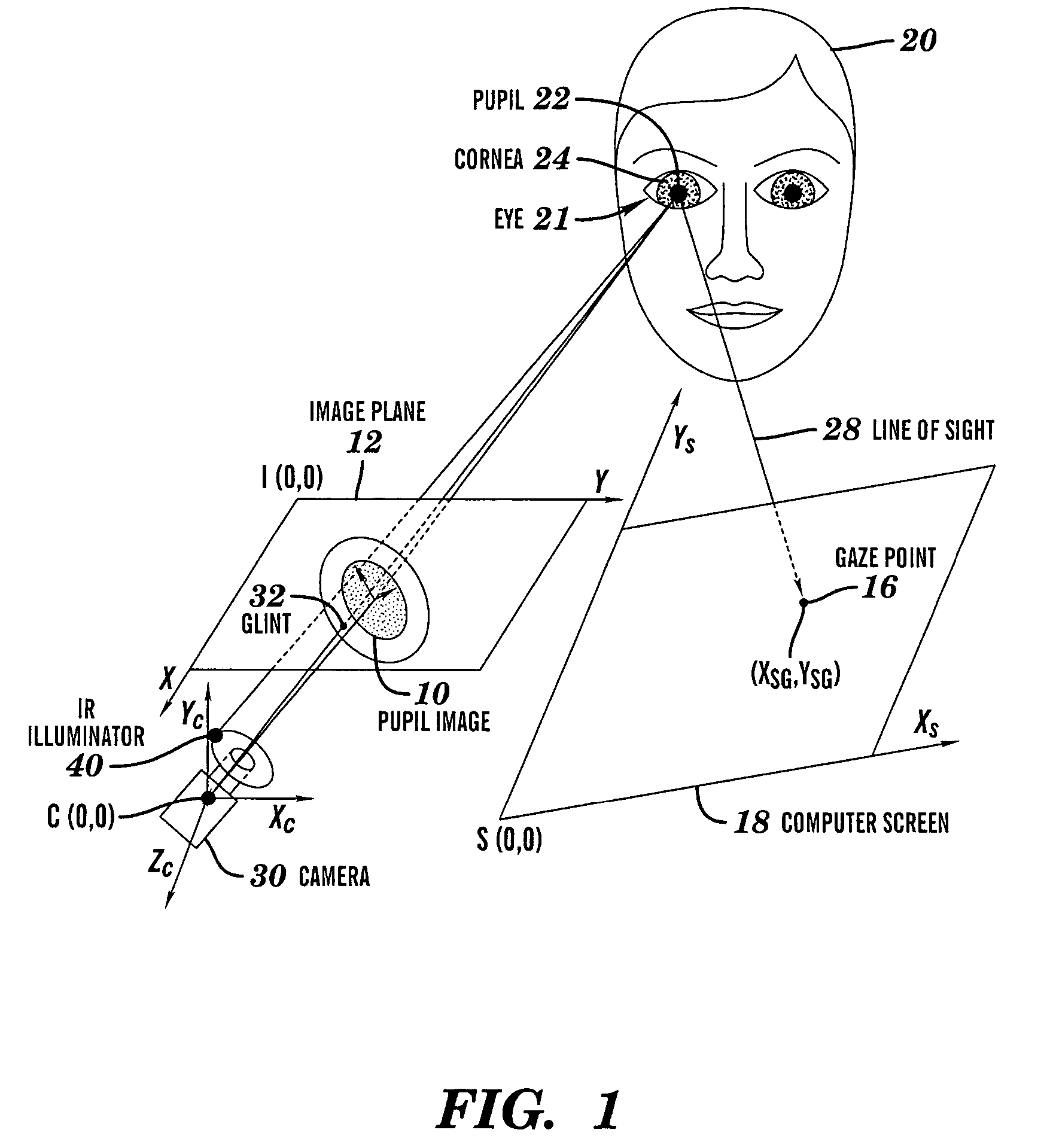
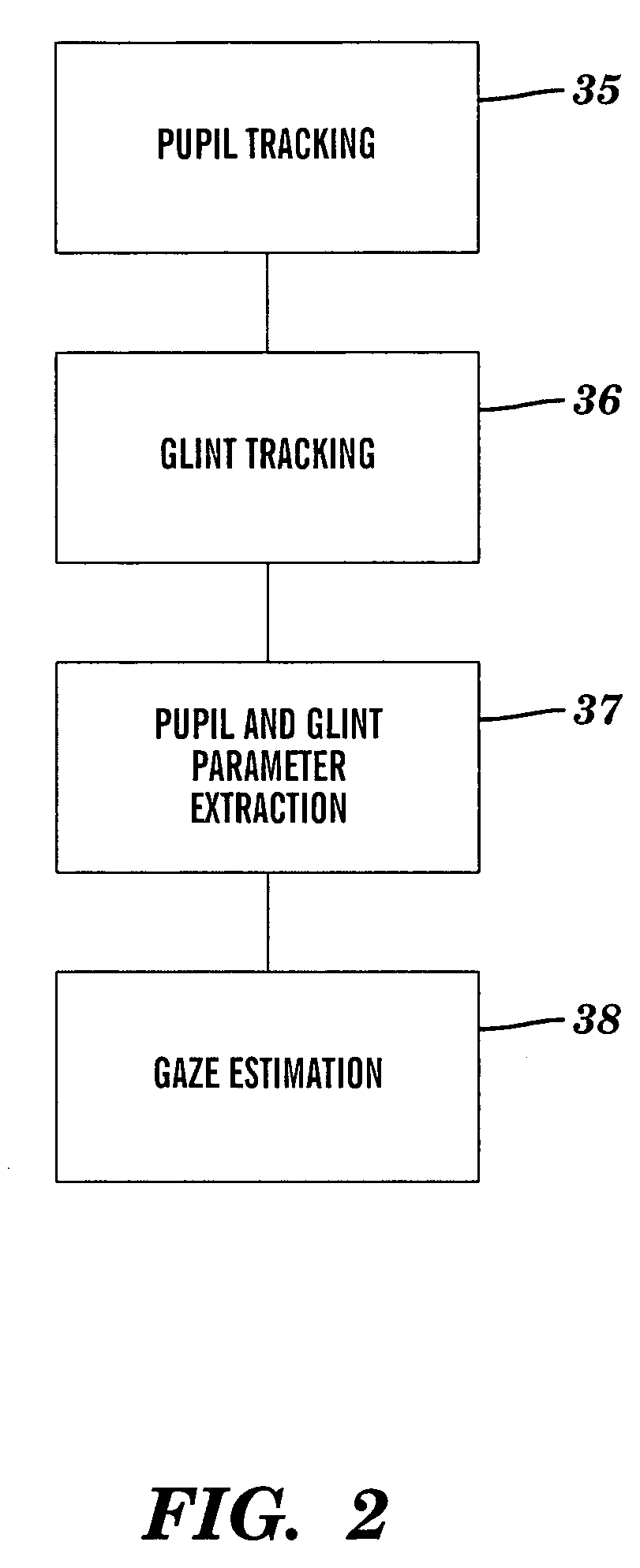
Calibration-free gaze tracking under natural head movement
ActiveUS7306337B2Overcomes and mitigates disadvantageInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionHead movementsOrthogonal coordinates
A method and computer system for tracking eye gaze. A camera is focused on an eye of subject viewing a gaze point on a screen while directing light toward the eye. Eye gaze data pertaining to a glint and pupil image of the eye in an image plane of the camera is sampled. Eye gaze parameters are determined from the eye gaze data. The determined eye gaze parameters include: orthogonal projections of a pupil-glint displacement vector, a ratio of a major semi-axis dimension to a minor semi-axis dimension of an ellipse that is fitted to the pupil image in the image plane, an angular orientation of the major semi-axis dimension in the image plane, and mutually orthogonal coordinates of the center of the glint in the image plane. The gaze point is estimated from the eye gaze parameters.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
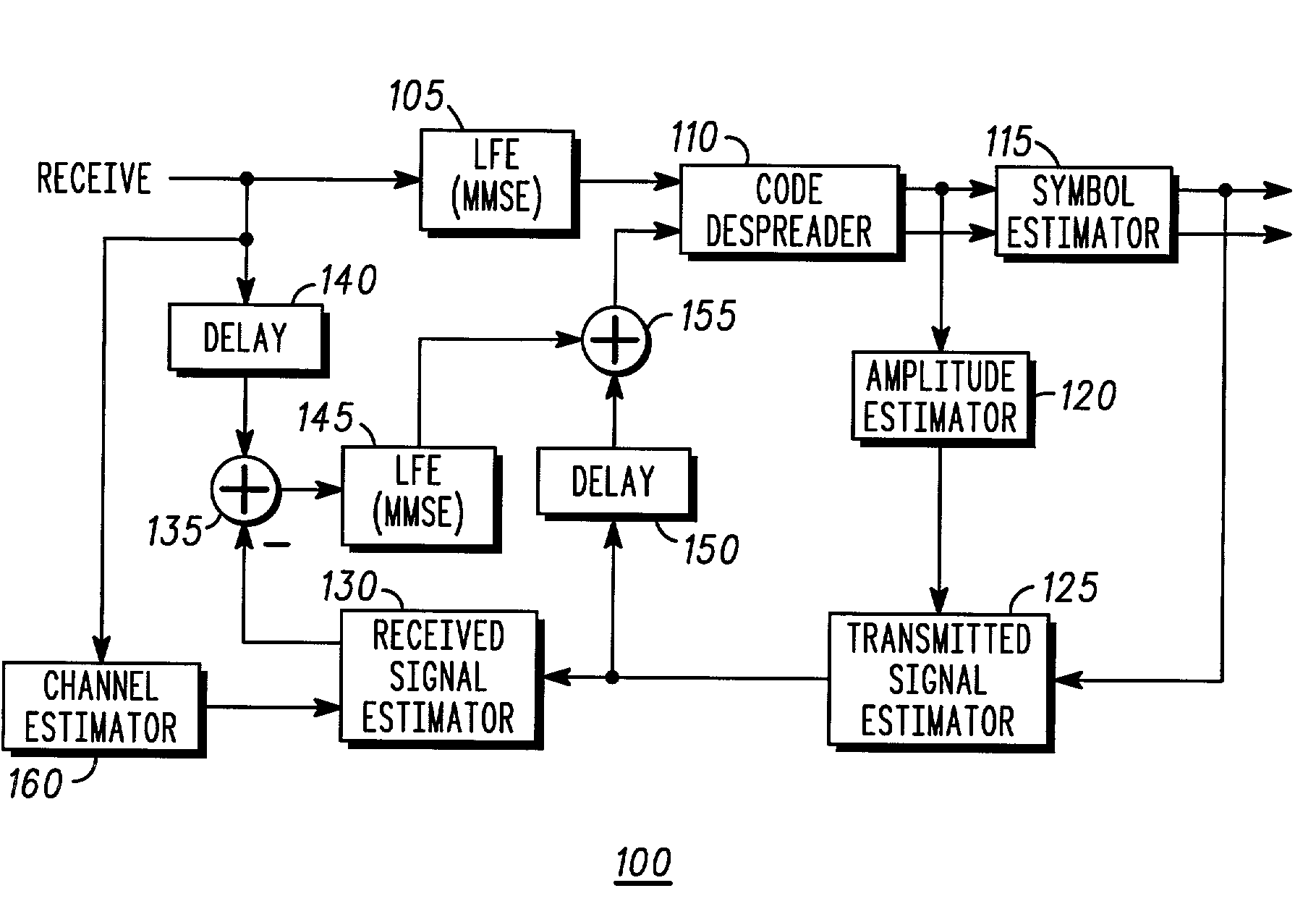
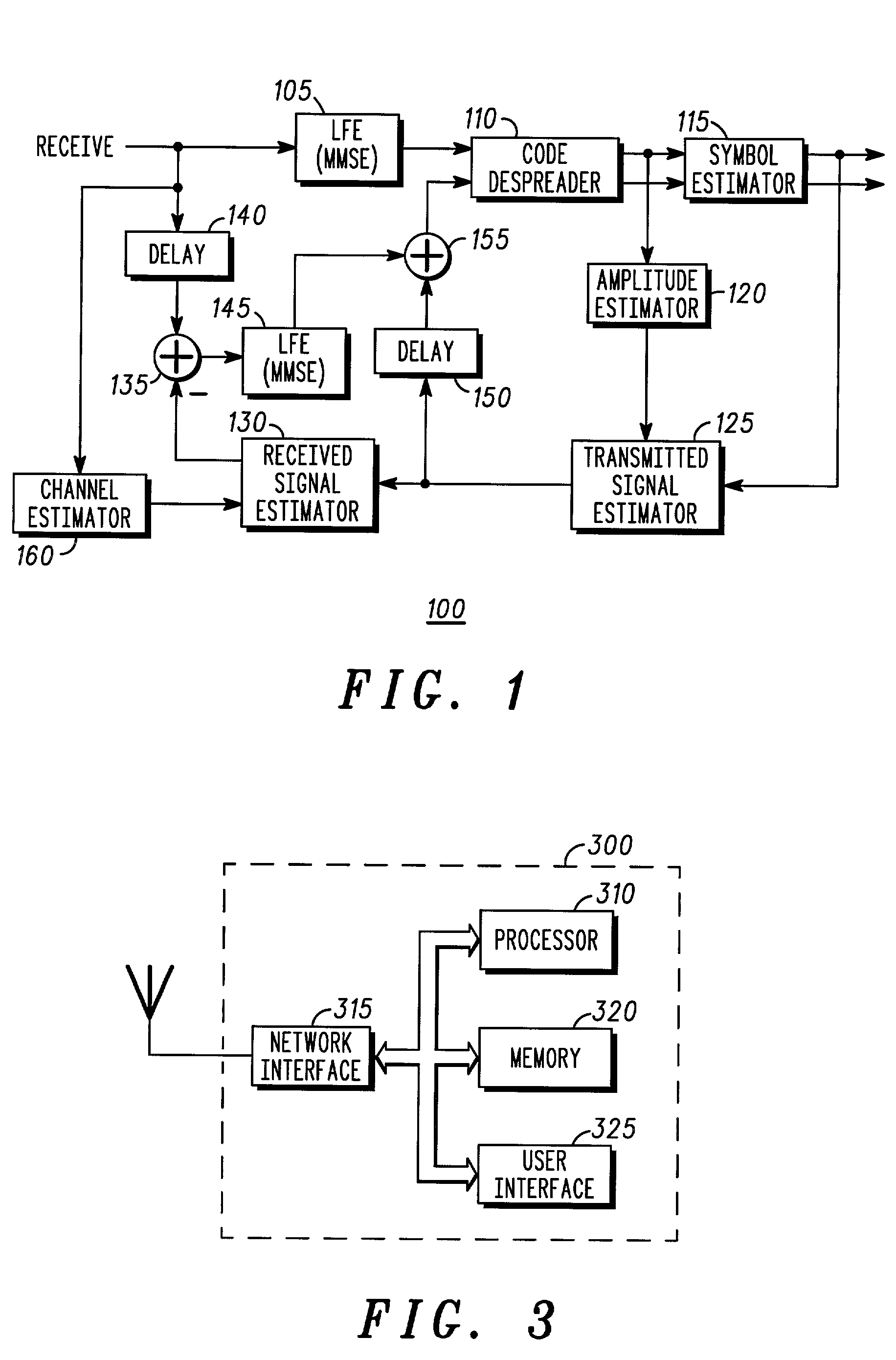
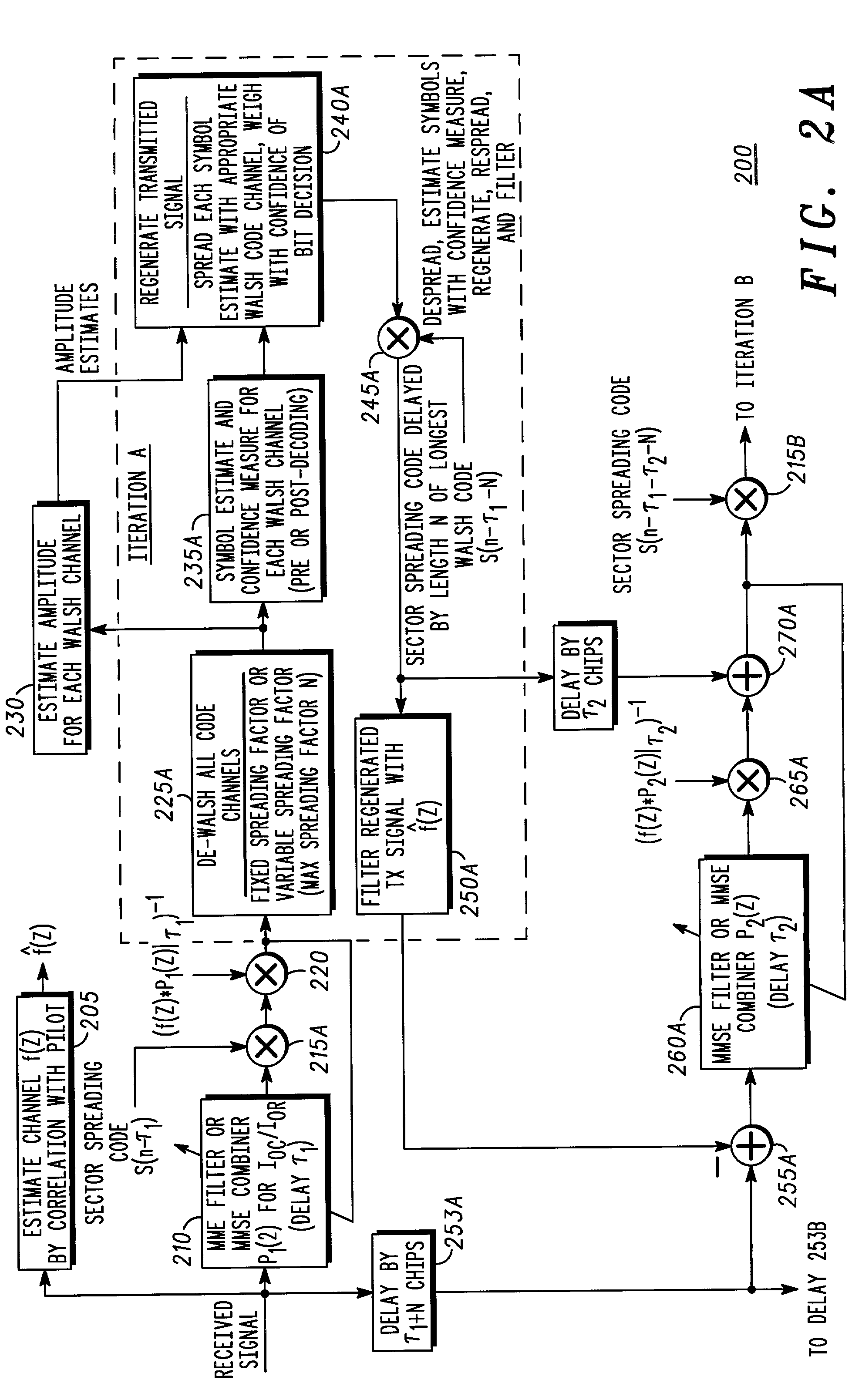
Linear minimum mean square error equalization with interference cancellation for mobile communication forward links utilizing orthogonal codes covered by long pseudorandom spreading codes
InactiveUS6956893B2Improve performanceLow power allocationMultiple-port networksError preventionOrthogonal coordinatesEngineering
The present invention provides linear MMSE equalization with parallel interference cancellation for symbol determination in a forward link of a CDMA communication system which has a plurality of code channels in use. Use of the linear MMSE equalization with parallel interference cancellation of the present invention provides significantly increased performance. The preferred method linearly filters a received signal to form a first filtered signal (410), despreads and demodulates the first filtered signal (415, 420) and provides a plurality of symbol estimates for all corresponding code channels (430). An estimated transmitted signal is generated from the plurality of symbol estimates (435), and with a channel estimate (405), an estimated received signal is generated (440). A residual signal is determined as a difference between the received signal and the estimated received signal, is linearly filtered (445), and then combined with the estimated transmitted signal to form a next, enhanced estimated transmitted signal (450). This next estimated transmitted signal is despread (455, 460) and utilized to provide a next plurality of symbol estimates, for a selected code channel of the plurality of channels, for subsequent use in error correction and decoding, and further use by a subscriber (465, 475).
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
System and method for a three-axis MEMS accelerometer
InactiveUS7367232B2Low costHigh sensitivityAcceleration measurement using interia forcesAcceleration measurement in multiple dimensionsElectricityOrthogonal coordinates
A system and method for inputting motion measurement data into a computationally based device are provided. In a first version three-axis accelerometer determines components of an inertial force vector with respect to an orthogonal coordinate system. The accelerometer includes a sensor die made of a semiconductor substrate having a frame element, a proof mass element, and an elastic element mechanically coupling the frame and the proof mass. The accelerometer also has three or more stress-sensitive IC components integrated into the elastic element adjacent to the frame element for electrical connectivity without metal conductor traversal of the elastic element.
Owner:VAGANOV VLADIMIR +1
System and method for a three-axis MEMS accelerometer
InactiveUS20050160814A1Low cost productionLow-cost functional testingAcceleration measurement using interia forcesAcceleration measurement in multiple dimensionsElectricityOrthogonal coordinates
A system and method for inputting motion measurement data into a computationally based device are provided. In a first version three-axis accelerometer determines components of an inertial force vector with respect to an orthogonal coordinate system. The accelerometer includes a sensor die made of a semiconductor substrate having a frame element, a proof mass element, and an elastic element mechanically coupling the frame and the proof mass. The accelerometer also has three or more stress-sensitive IC components integrated into the elastic element adjacent to the frame element for electrical connectivity without metal conductor traversal of the elastic element.
Owner:VAGANOV VLADIMIR +1
Three-axis integrated MEMS accelerometer
InactiveUS7318349B2Low costHigh sensitivityAcceleration measurement using interia forcesAcceleration measurement in multiple dimensionsOrthogonal coordinatesAcceleration Unit
3D accelerometer for measuring three components of inertial force (or acceleration) vector with respect to an orthogonal coordinate system, which has high sensitivity due to a big proof mass located within a cavity beneath the surface of the sensor die. The size of the cavity and the size of the proof mass exceed the corresponding overall dimensions of the elastic element. The sensor structure occupies a very small area at the surface of the die increasing the area for ICs need to be integrated on the same chip.
Owner:VAGANOV VLADIMIR +1
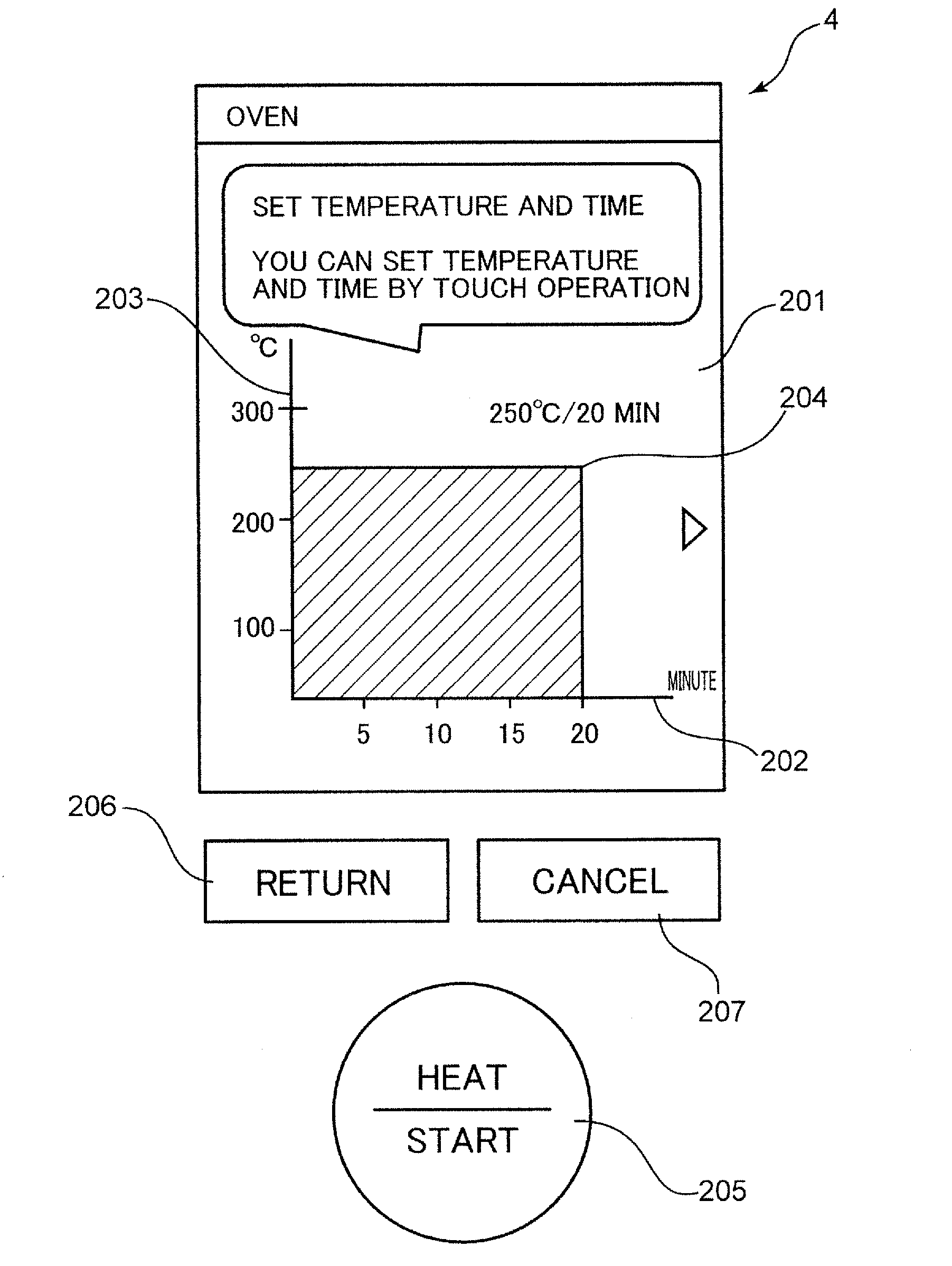
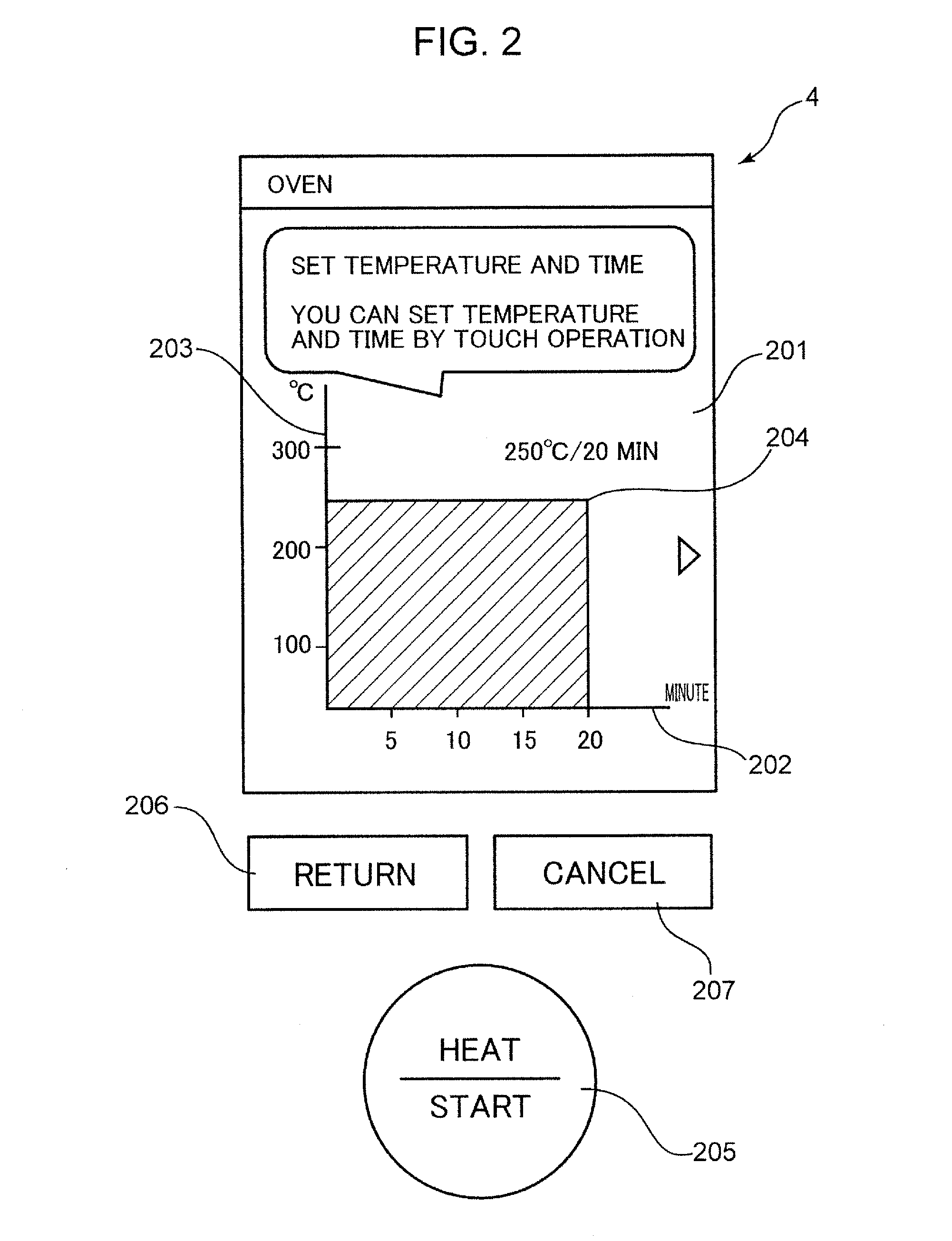
Operation device and operation method
ActiveUS20160253080A1Improve usabilityReduce the numberDomestic stoves or rangesLighting and heating apparatusOrthogonal coordinatesSimulation
An operation device is provided with a GUI display unit which displays a power setting value for defining an operation power of a household appliance, and a time setting value for defining an operation time of the household appliance on an orthogonal coordinate system; and a touch operation unit which simultaneously accepts an input of the power setting value and an input of the time setting value to be displayed on the GUI display unit by an operation of letting a predetermined object touch the GUI display unit.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Minisize rudders three-dimensional track emulation method under city environment
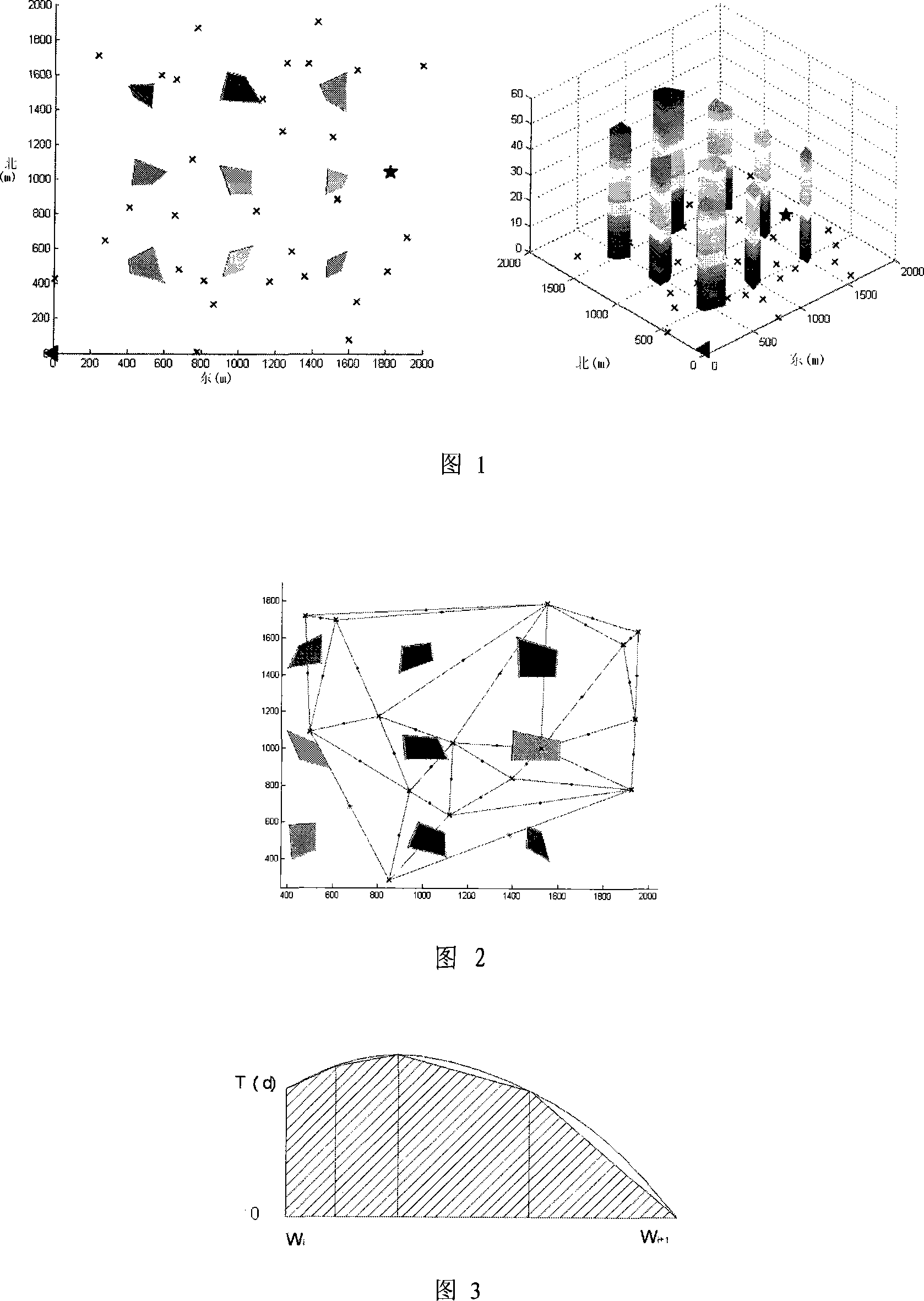
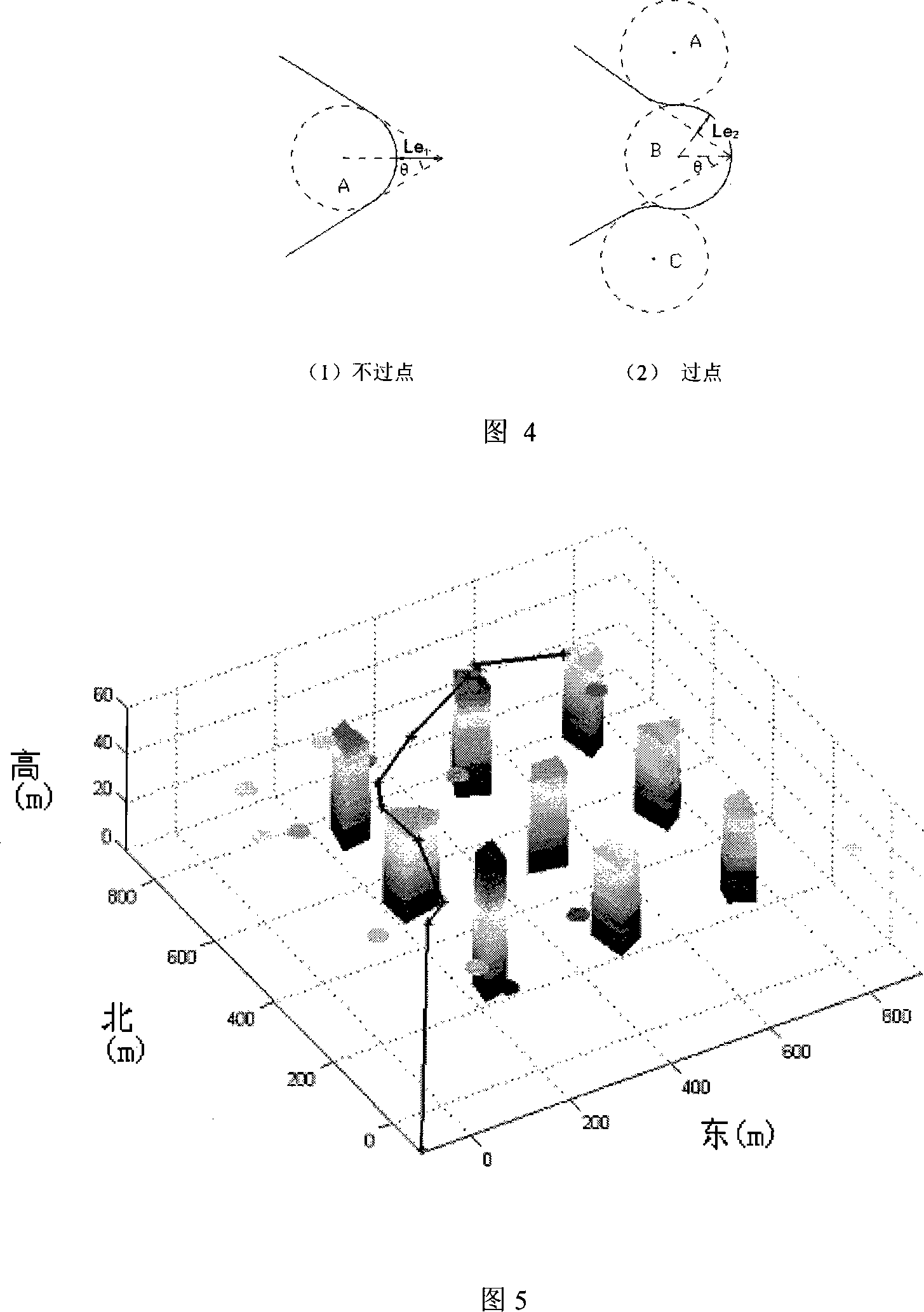
The present invention relates to a method of the 3D track simulation for a miniature aircraft under urban surroundings and belongs to the field of the 3D real-time route navigation technology for a miniature aircraft. The following modules are set in a computer: a map digitalized module, which digitalizes the 3D model of urban surroundings including threat points, buildings, the departure and target points of a miniature aircraft that is inputted by the graphical user interface (GUI), map parameters and the coordinate of a candidate navigation point composed of the 3D model of urban surroundings and the map parameters; a flight path programming module, which inputs the data from the map digitalized module, calculates the overall route index that takes the flight resource consumption rate and the survival rate into consideration, figures out the most feasible route using network optimizing algorithm under the condition of taking barriers into consideration, and then smooths the bevel at turnings and generates a realtime flight orbit; a data-collecting module, which collects the coordinate values of the aircraft positions and postures outputted by the flight path programming module and forms a posture coordinate value including orthogonal coordinate variables X, Y and Z, a pitch angle h, a yawing angle p and a roll angle r. The present invention saves flight resources and improves flights simultaneously.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
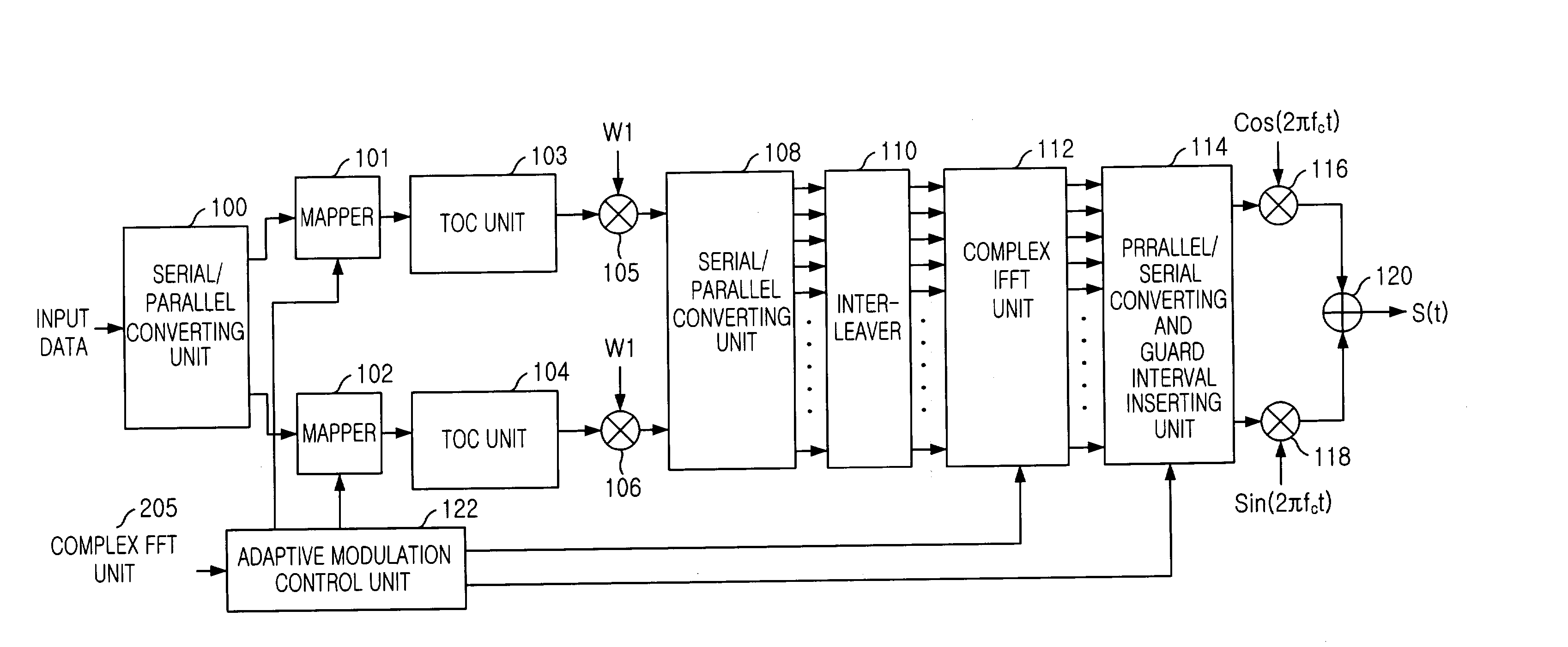
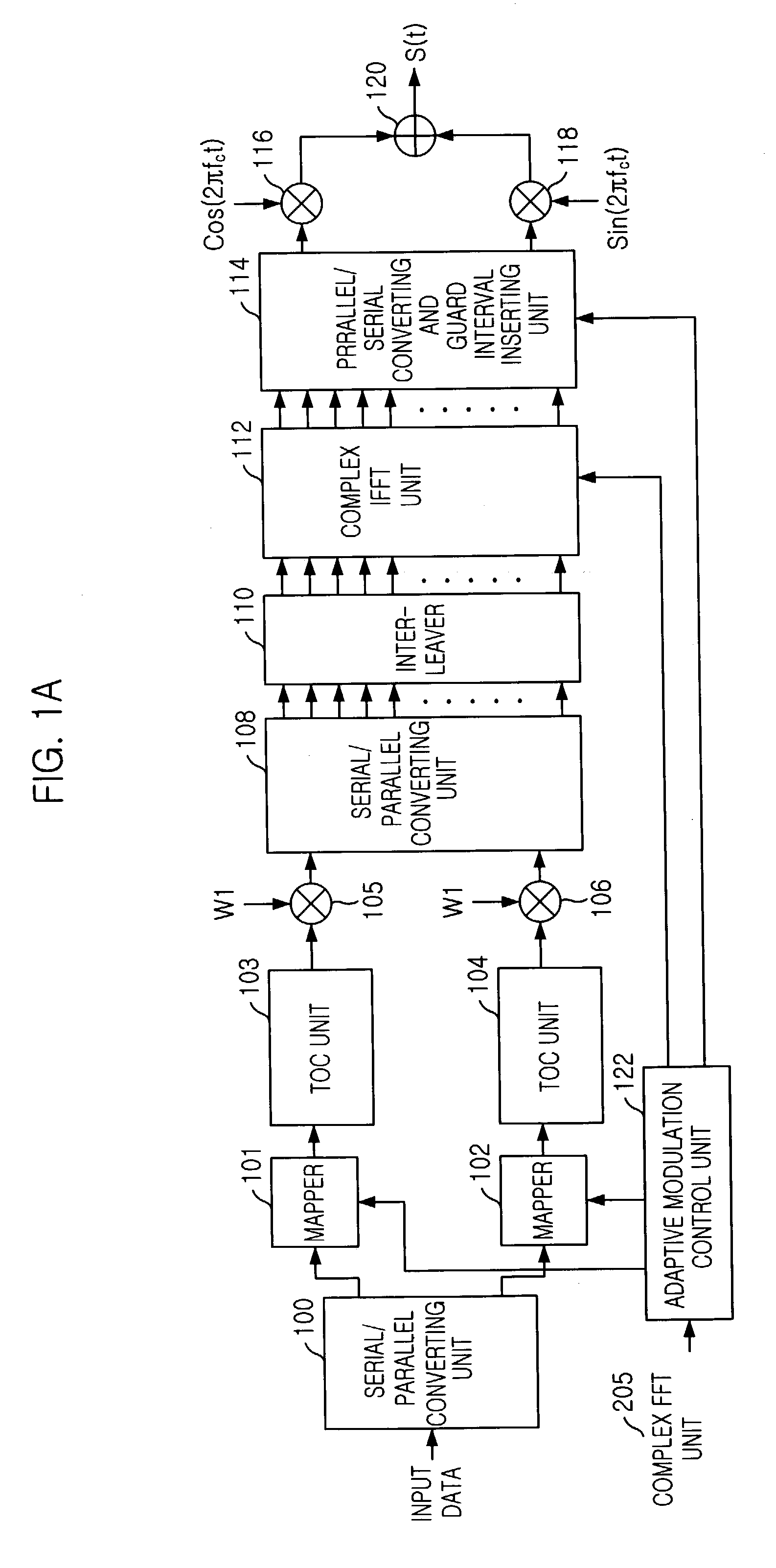
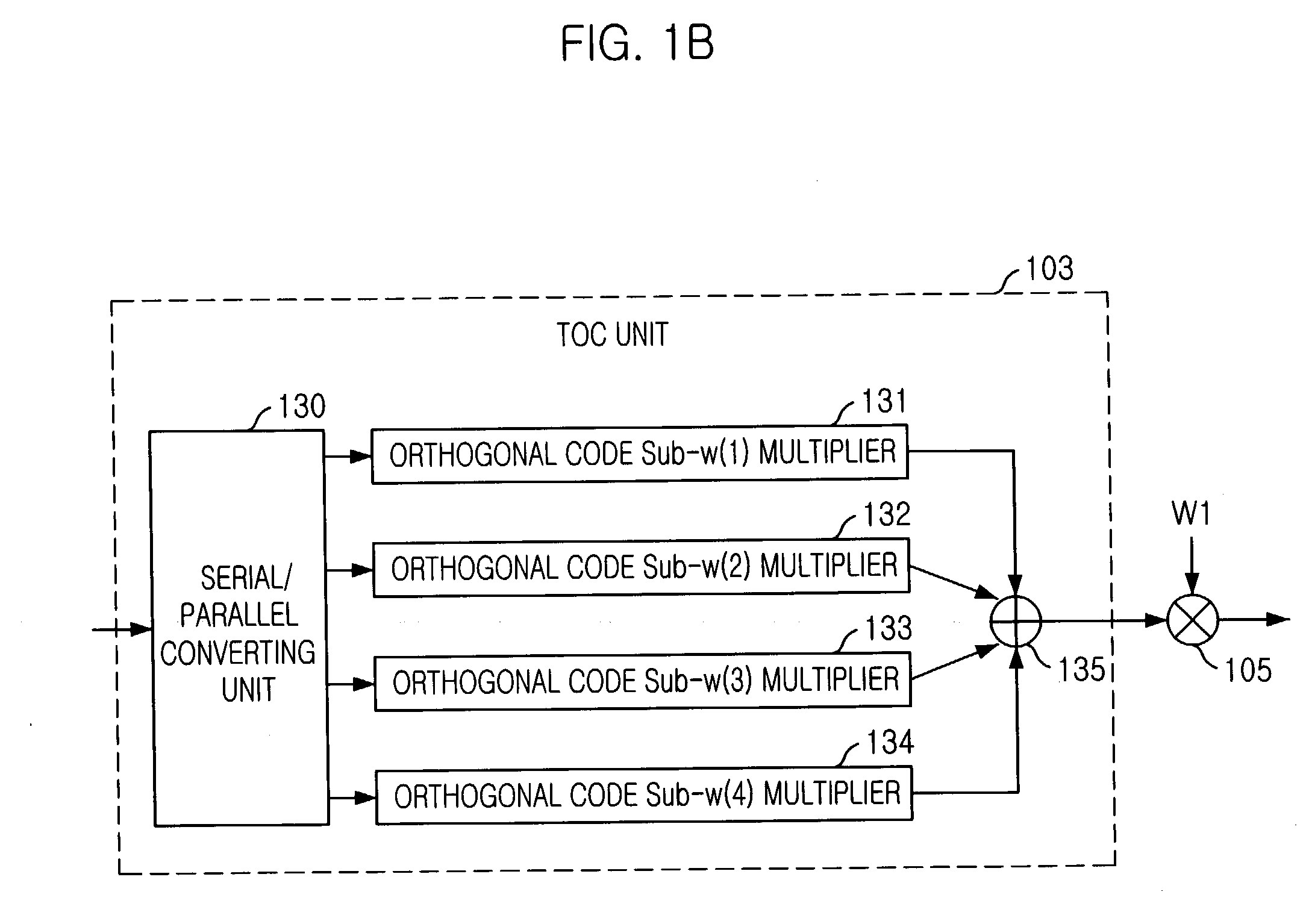
Apparatus for transmitting and receiving signal using orthogonal codes and non-binary values in CDMA/OFDM system and method thereof
ActiveUS20040085919A1Multiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsCriteria allocationOrthogonal coordinatesCode division multiple access
An apparatus for transmitting and receiving a signal in Code Division Multiple Access / Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (CDMA / OFDM) system is provided. The apparatus discriminates user signals with a unique spreading code and the orthogonal codes, increases data transmission rate with the non-binary value without increasing of entire bandwidth used by the users, solves signal interference with interleaver and diversity effect of interleaving and OFDM, and maximizes transmission efficiency by varying modulation schemes depending on channel states.
Owner:UNILOC 2017 LLC
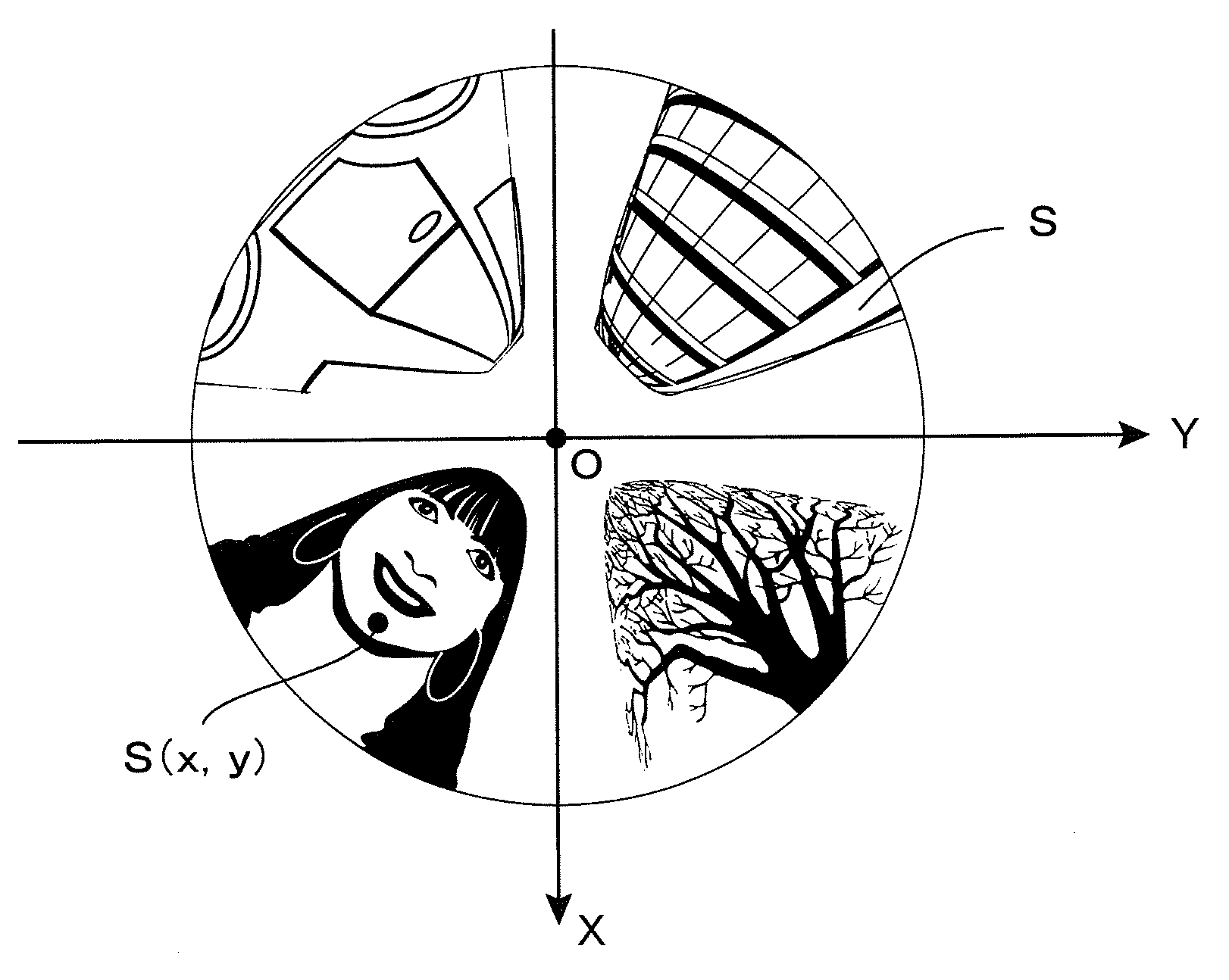
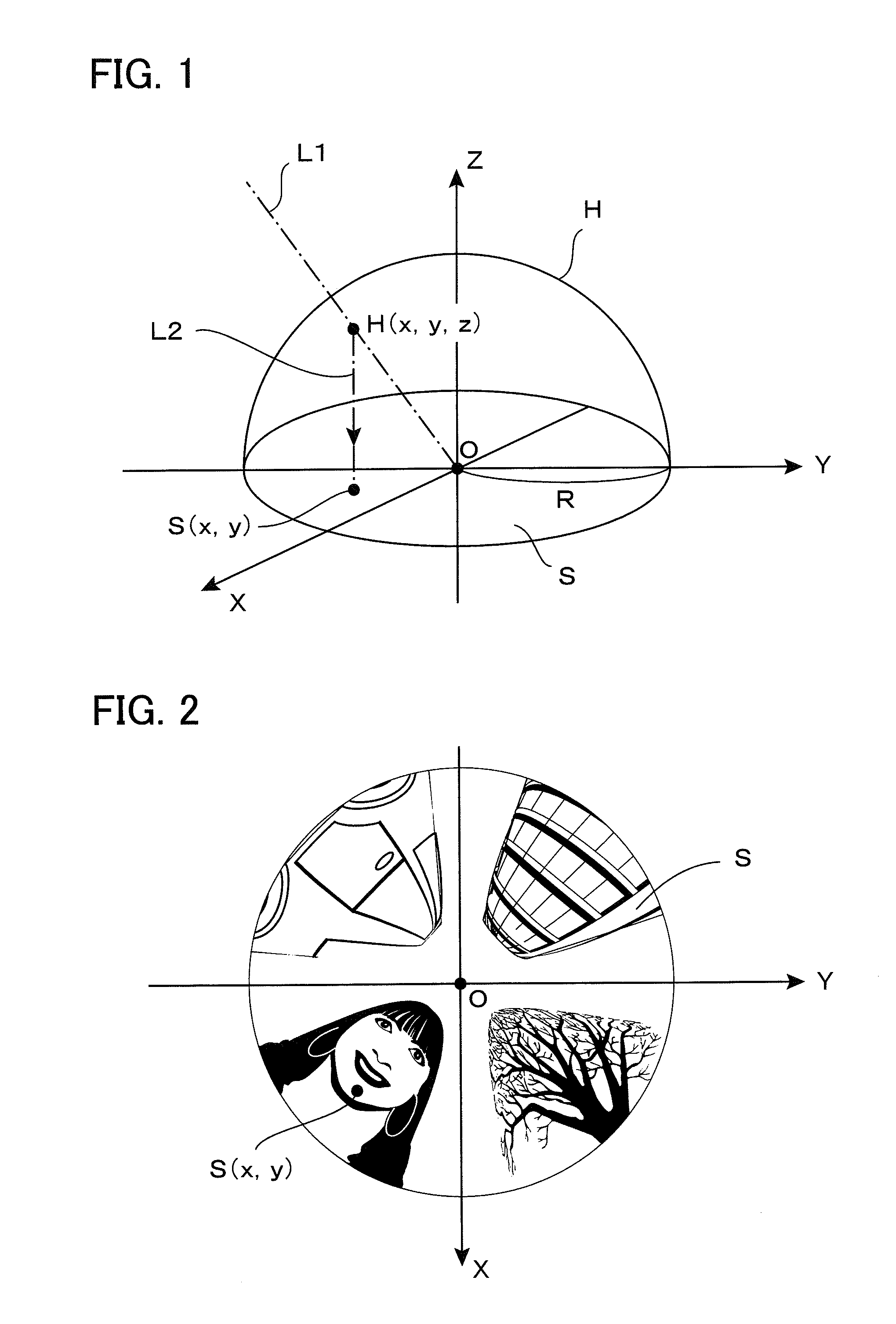
Image converter
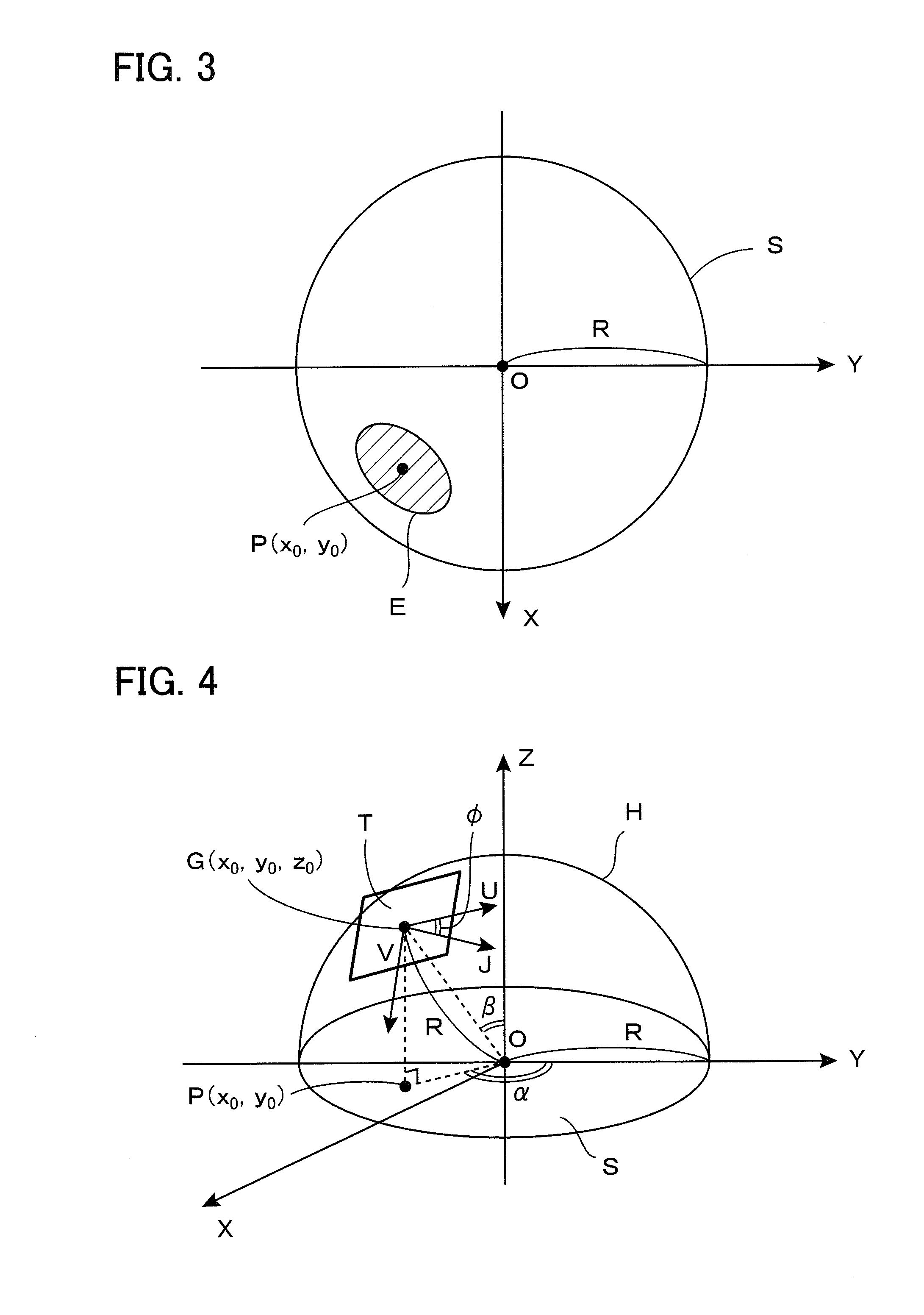
InactiveUS20100053325A1Less distortionImage enhancementGeometric image transformationFisheye lensOrthogonal coordinates
Any given part is cut out from a distorted circular image photographed by use of a fisheye lens and converted into a planar regular image with less distortion. A virtual sphere H having a radius R on a distorted circular image S on an XY plane is defined, thereby allowing a user to designate a cut-out center point P, a magnification m, and a planar inclination angle φ. A visual line vector n passing through an intersecting point Q immediately above the point P is determined to define an UV orthogonal coordinate system having an orientation depending on the angle φ on a plane orthogonal to a visual line vector n at a point G in which a distance between two points OG is given as m·R. The UV orthogonal coordinate system is curved along the side face C of a “virtual cylindrical column in which the point G forms one point on the side face to have a straight line V′ parallel to the V axis and also passing through the point O as a central axis,” thereby defining the UV curved coordinate system. Correspondence relationship equations between a point Ci (ui, vi) on the UV curved coordinate system and a point Si (xi, yi) on the XY coordinate system are used to obtain an image in the vicinity of a point P on the UV curved coordinate system, and the image is expanded on a plane T to obtain a planar regular image.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
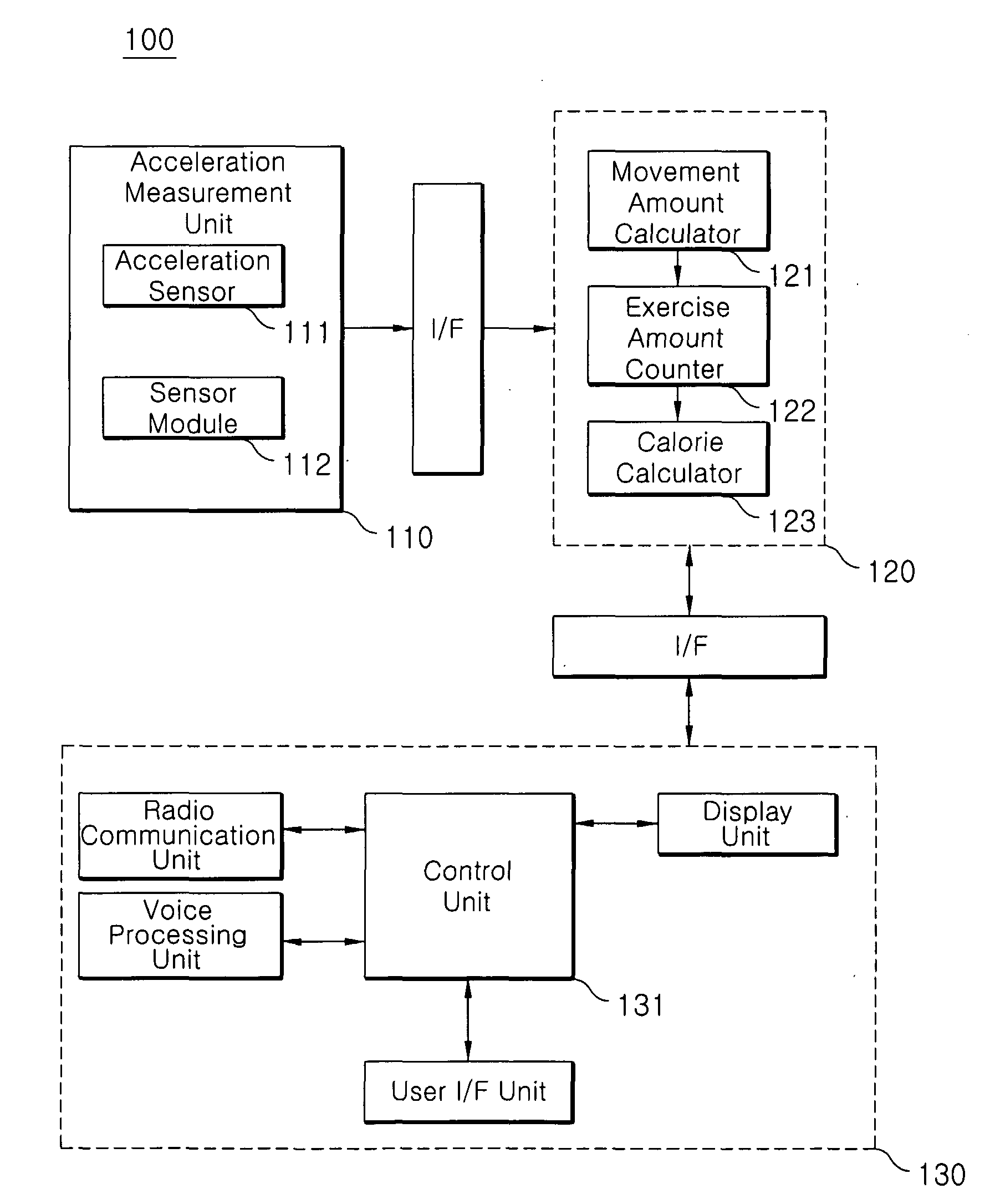
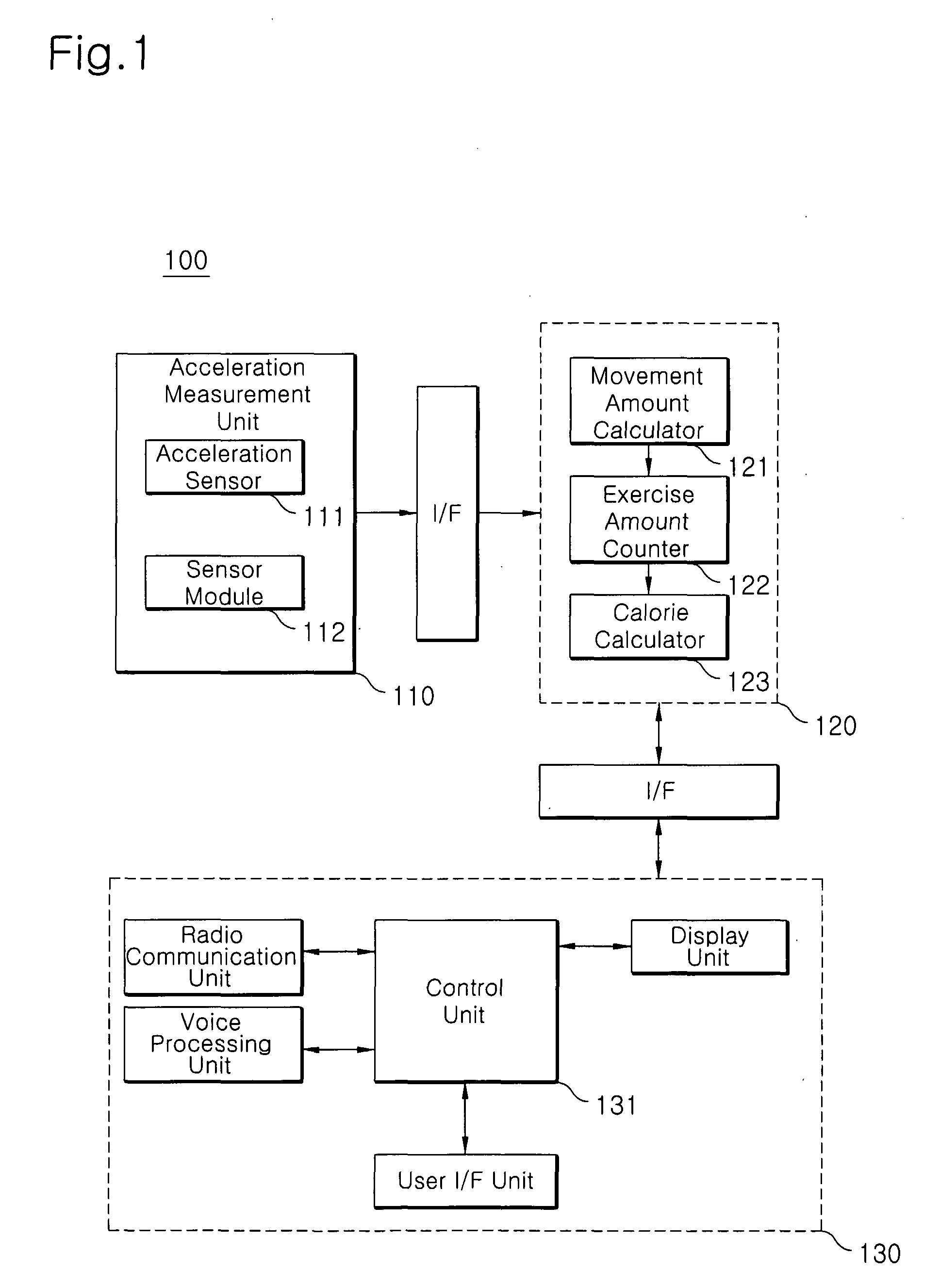
Mobile Communication Terminal Having Exercise Quantity Measurement Function and Method of Measuring Exercise Quantity Using the Same
InactiveUS20090005220A1Avoid low measurement accuracyInertial sensorsDiagnostic recording/measuringOrthogonal coordinatesClassical mechanics
Disclosed is a method of measuring the amount of exercise using a mobile communication terminal equipped with an acceleration sensor capable of measuring movement of a user. The method includes the steps of: a) measuring acceleration according to a change in the location of the mobile communication terminal by the acceleration sensor and detecting acceleration values of the terminal expressed in an orthogonal coordinate system where the acceleration sensor is set to a reference position; b) calculating gravitational acceleration direction values of the acceleration of the terminal from the acceleration values of the terminal detected in step a); c) detecting relative values of the acceleration values with respect to the gravitational acceleration direction values; and d) calculating the movement amount from the detected relative values.
Owner:HEALTHPIA +2
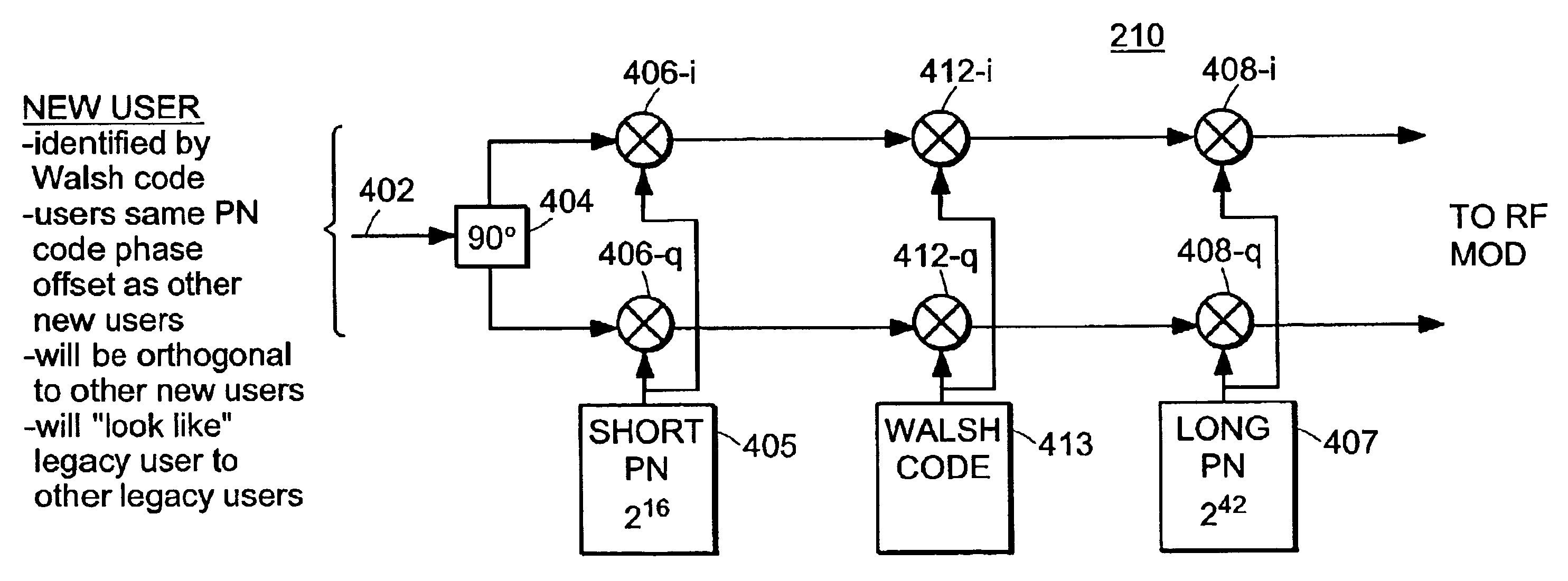
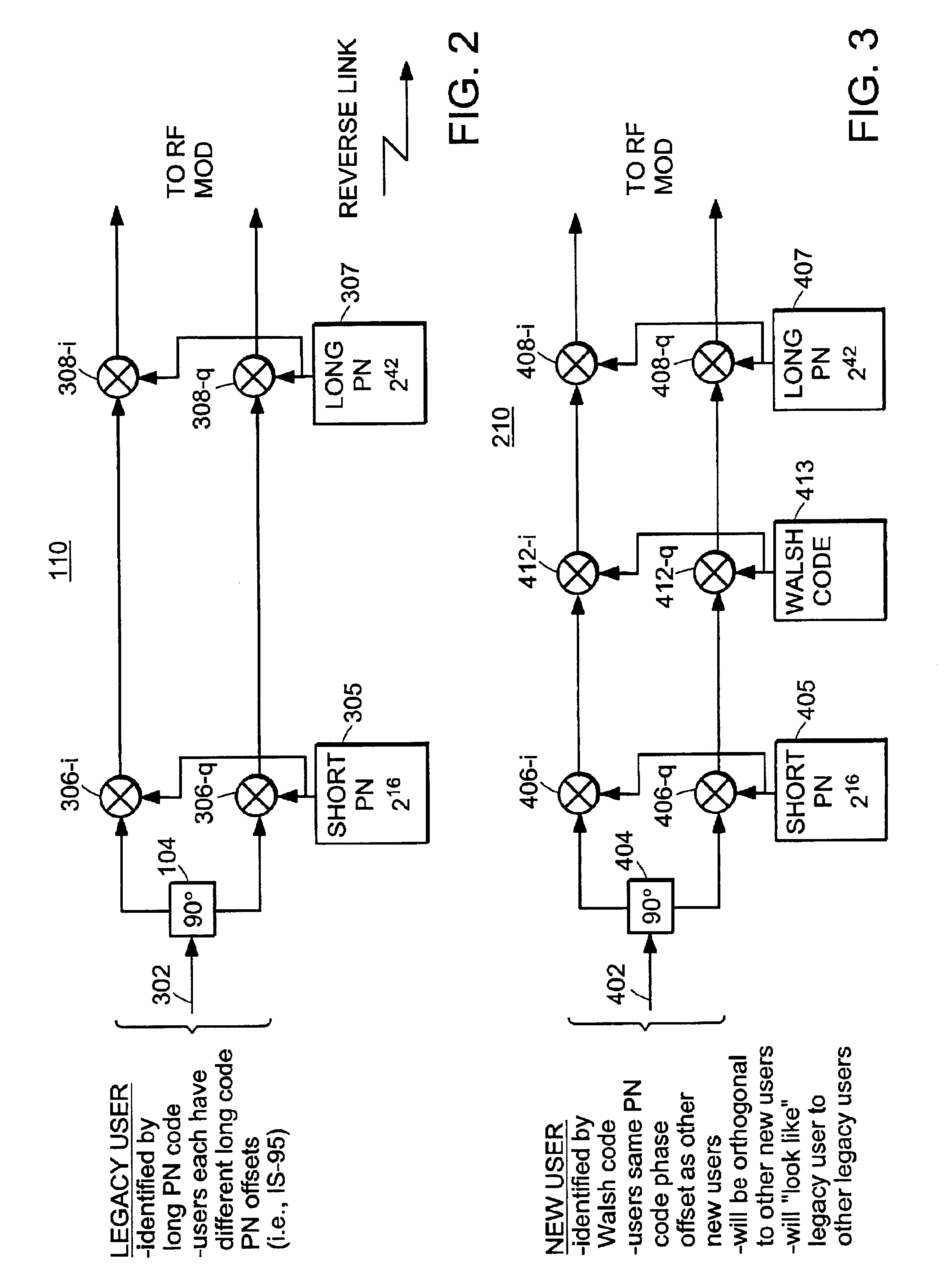
Use of orthogonal or near orthogonal codes in reverse link
InactiveUS6917581B2Increase data rateMinimal interferenceSynchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementOrthogonal coordinatesRadio channel
A technique for allowing a first and second group of users to share access to a communication channel such as a wireless radio channel is disclosed. The first group of users can be a group of legacy users such as those that use digital CDMA cellular telephone equipment based on the IS-95 standard. The second group of users can be a group of web surfers that code their transmissions using one of multiple formats. The first group of users can share one modulation structure such as, on a reverse link, using unique phase offsets of a common pseudorandom noise (PN) code. The second group of users can share another modulation structure, but in a manner that is consistent and compatible with the users of the first group. Specifically, the users of the second group may all use the same PN code and code phase offset. Each channel used by the second group of users can be uniquely identified by a corresponding unique orthogonal code.
Owner:IPR LICENSING INC
CDMA system using quasi-orthogonal codes
InactiveUS7133353B2Reduce performance varianceImprove performanceError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransmission systemsOrthogonal coordinatesComputer science
A CDMA communication system uses a set of quasi-orthogonal codes to supplement the standard set of Walsh codes used in conventional systems. Users are assigned a code selected from the set of Walsh codes, if available. If the number of users exceeds the number of available Walsh codes, selected users are assigned to quasi-orthogonal codes. The users assigned quasi-orthogonal codes are chosen based on user mobility.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
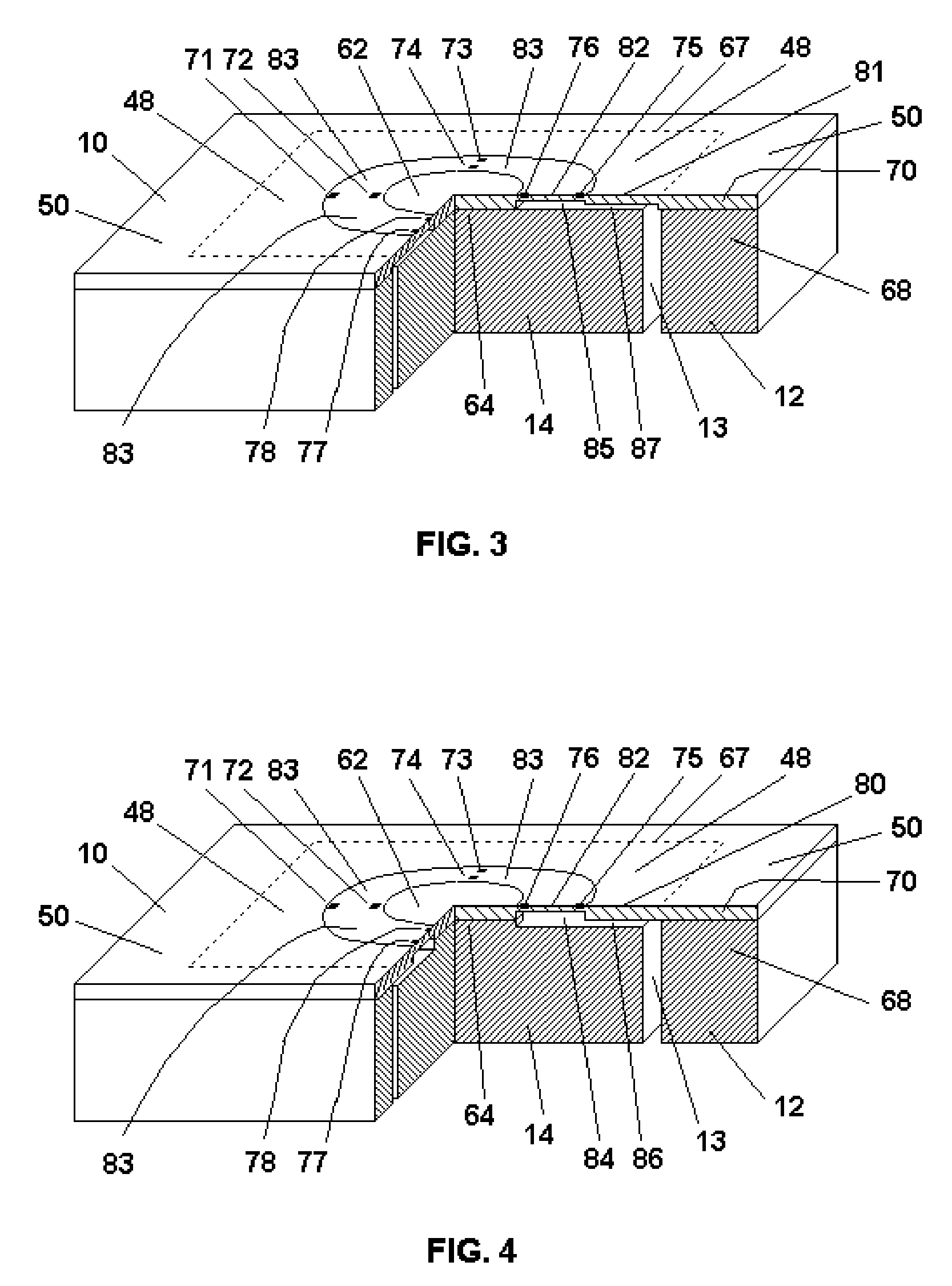
Active and passive type ankle joint rehabilitative apparatus
InactiveCN103041546AMeet Rehabilitation Training RequirementsGuarantee the effect of rehabilitation trainingGymnastic exercisingChiropractic devicesOrthogonal coordinatesThree degrees of freedom
The invention provides active and passive type ankle joint rehabilitative apparatus which uses orthogonal coordinates and three degrees of freedom to respectively achieve dorsal stretch and plantar flexion, inversion and eversion, and intorsion and extorsion motions of ankle joints. Every degree of freedom is respectively driven by a motor so that single degree of freedom motions of ankle joints are achieved and the linkage of three motor can achieve complex motions of ankle joints. Force sensors are arranged on pedals of the ankle joint rehabilitative apparatus. During a rehabilitation process, foot motions of a trainee are controlled by detecting stresses of the pedals so that active and passive type ankle trainings are achieved, besides, stress safety protections are performed and secondary injuries to the trainee are avoided. The active and passive type ankle joint rehabilitative apparatus meets rehabilitative training requirements of single degree of freedom and multiple degrees of freedom motions of ankle joints with a simple and reliable structure. Intelligent control, effect evaluation and intelligent protection are achieved due to an adoption of force sensors so that effects and safety of rehabilitative trainings of a patient are guaranteed.
Owner:三亚哈尔滨工程大学南海创新发展基地
Navigational aid system for fishermen
InactiveUS20080103695A1Easy to findGood prospectsRoad vehicles traffic controlClimate change adaptationOrthogonal coordinatesLongitude
A navigational aid system for fishermen comprises a computer that is connected to the Internet. The computer accesses a high resolution map in the vicinity of a fishing boat. The map depicts the ocean temperature and depth profile in relation to marked latitude and longitudinal indicators. A specialized GPS system in communication with the computer depicts the latitudinal and longitudinal position of the fisherman's boat. The computer executes a separate program that has a transparent window overlaying the map. A user selects two points, one point at a time, on the map and enters corresponding latitude and longitude bearings consistent with those shown on the map. The separate program receives the GPS data and plots the boat position in an orthogonal coordinate system based on the two points selected and their corresponding coordinates. The map is optionally provided with data concerning weather and buoy or wreck hazards in the vicinity of the boat, together with details concerning the coastline.
Owner:WHITING JONATHAN MERRILL
Link actuation device
ActiveUS20150088308A1Large working rangeAccurate operationProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorOrthogonal coordinatesProximal point
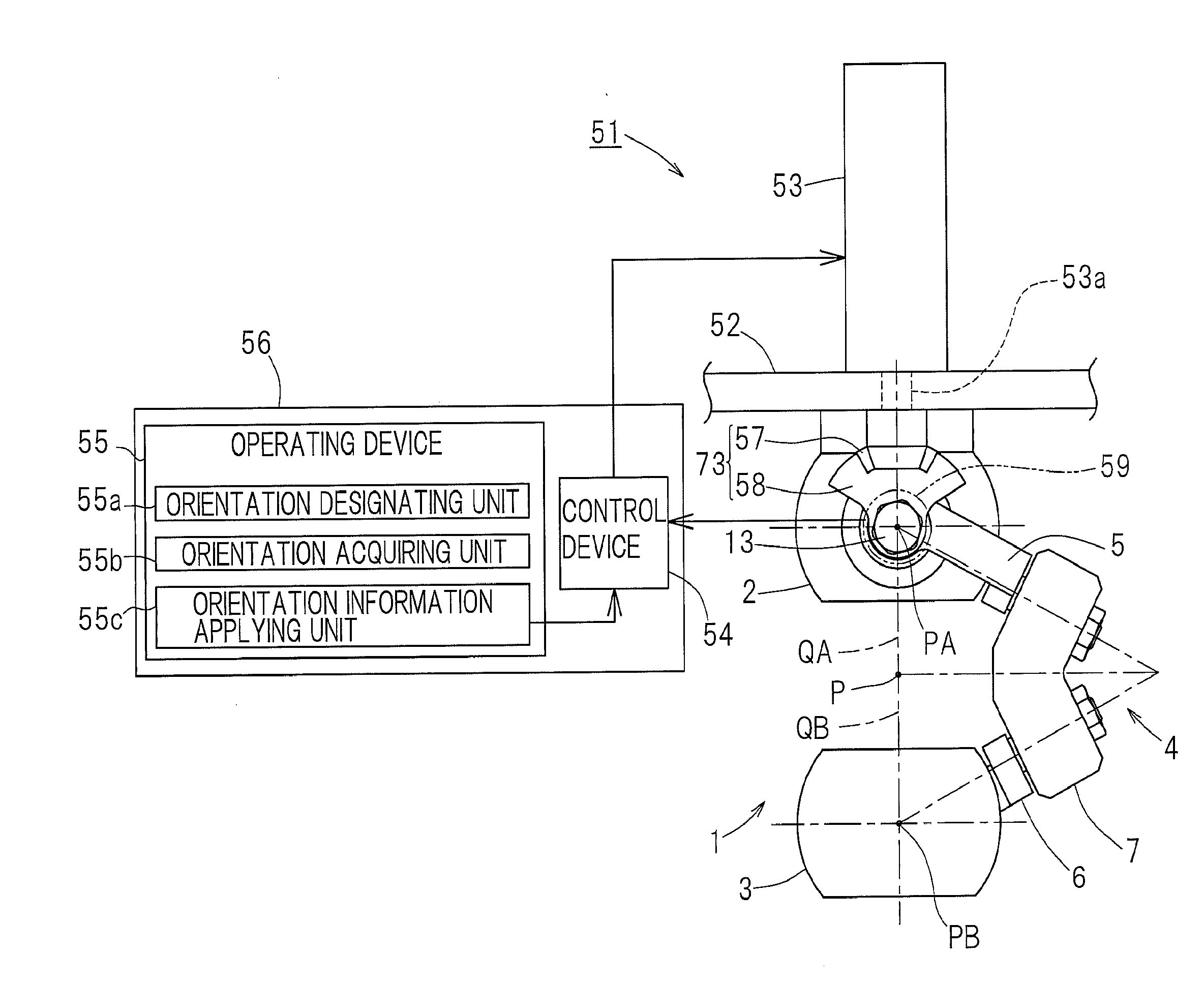
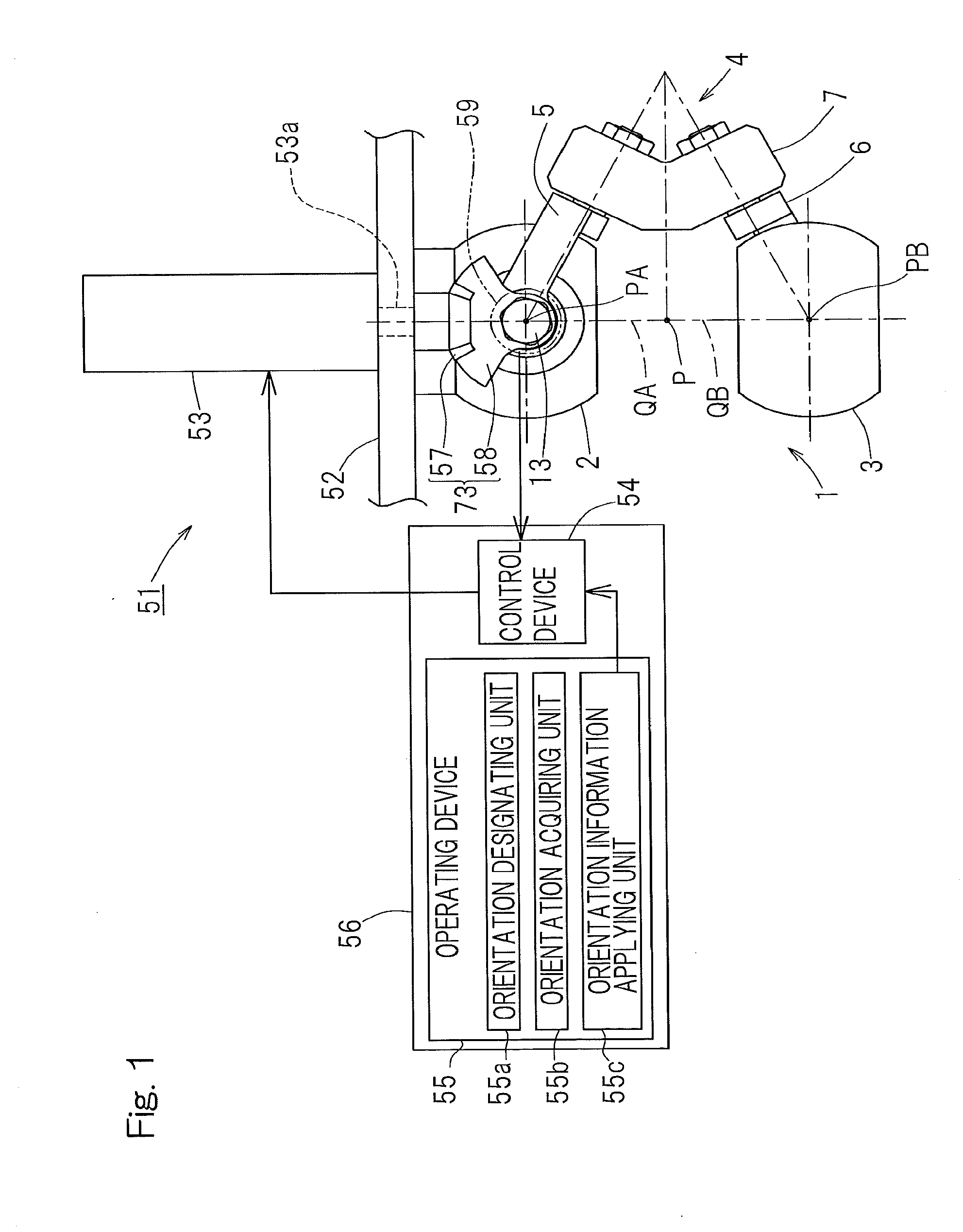
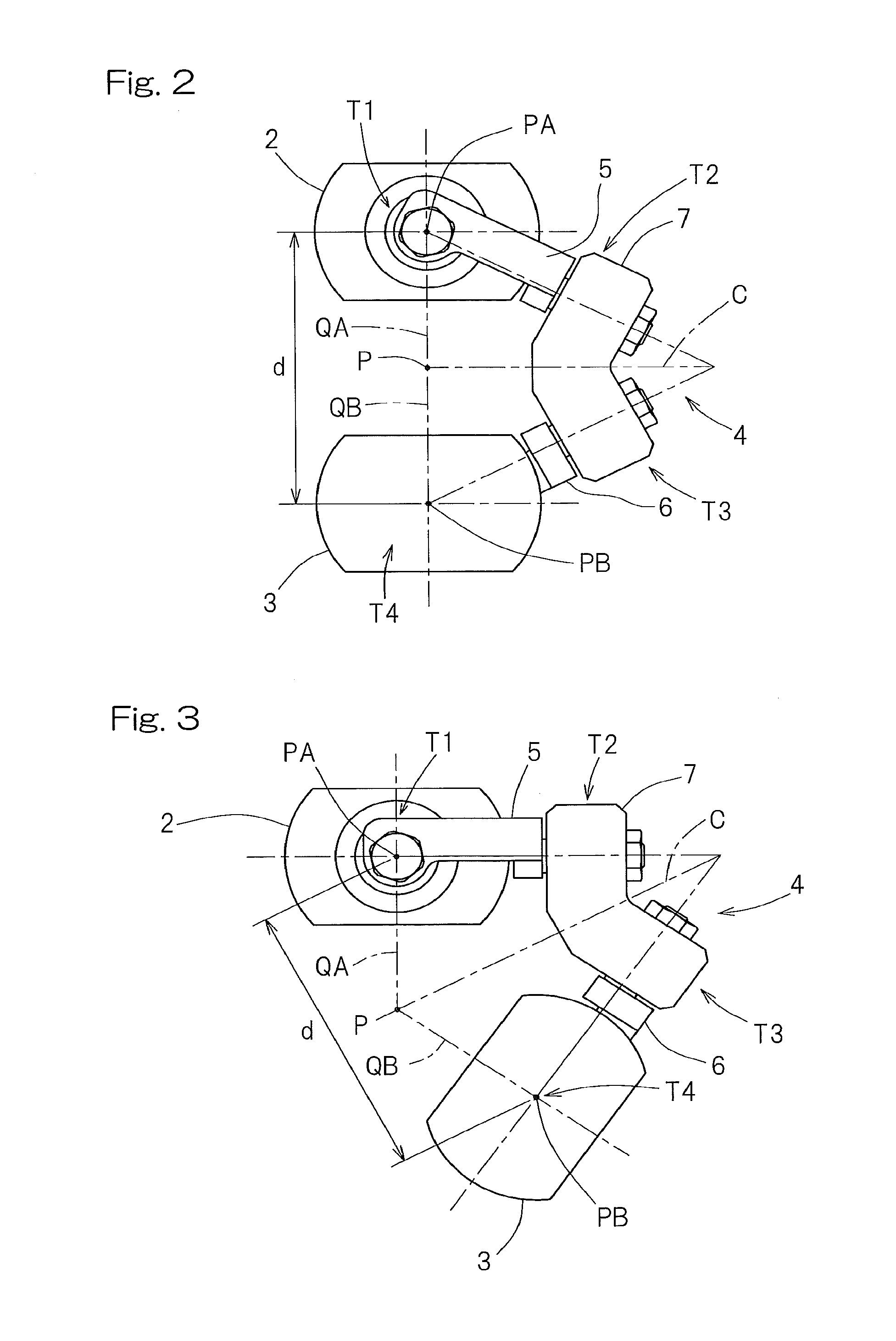
A link actuation device includes a distal end side link hub connected with a proximal end side link hub through three or more sets of link mechanisms for alteration in orientation. By means of an actuator provided in the two or more set of the link mechanism, the distal end orientation, which is the orientation of the distal end side link hub relative to the proximal end link hub, is changed arbitrarily. The operating device includes an orientation designating unit for designating the distal end orientation aimed at by means of a coordinate position on the orthogonal coordinate system by an artificial manipulation, an orientation acquiring unit for acquiring the distal end orientation that is expressed by an angular coordinate system through calculation, and an orientation information applying unit for applying information on the distal end orientation so acquired to a control device for controlling the actuator.
Owner:NTN CORP
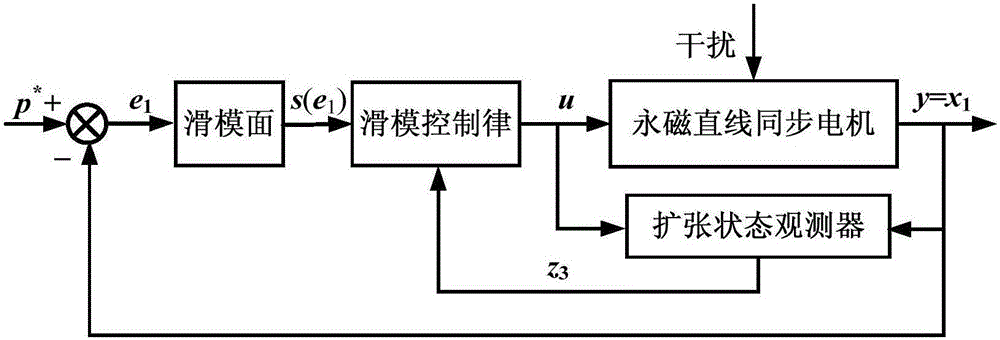
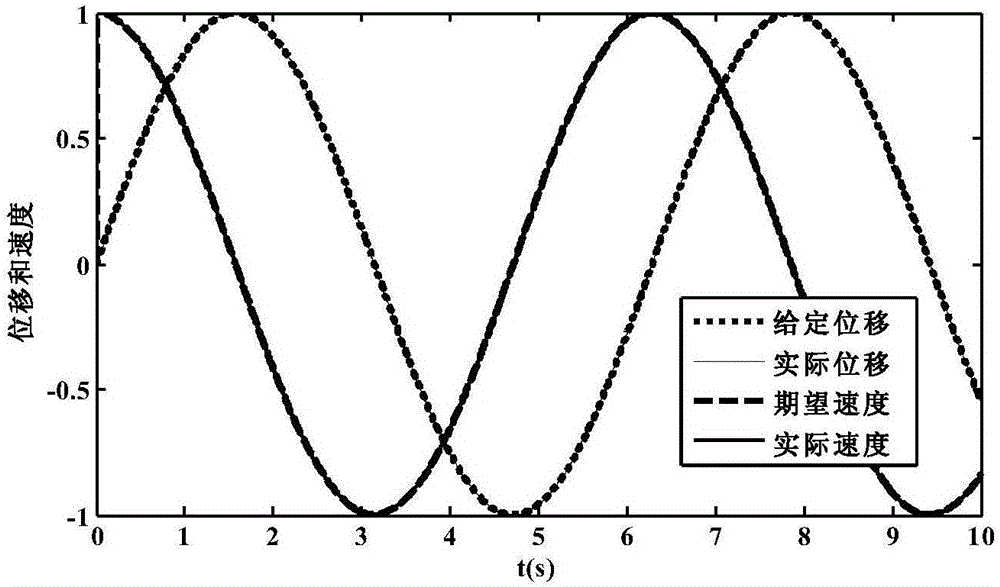
Permanent magnet linear synchronous motor slip form control system based on linear expansion state observer
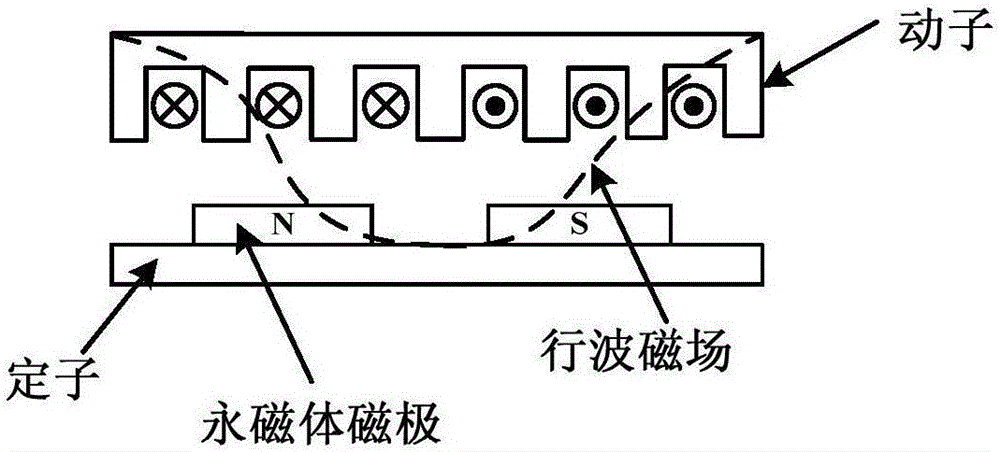
ActiveCN106849795AAccurate trackingImprove robustnessElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlLyapunov stabilityOrthogonal coordinates
The invention discloses a permanent magnet linear synchronous motor slip form control system based on a linear expansion state observer, and belongs to the technical field of linear motor control. The system comprises the following steps that: firstly, establishing the dynamic equation of a permanent magnet linear synchronous motor on a two-phase synchronous rotation orthogonal coordinate system; secondly, simplifying the dynamic equation into a special two-order integral series type mathematical model; thirdly, designing the linear expansion state observer to obtain a disturbance estimated value, and considering the estimated value in the design of a slip form control law to eliminate a chattering phenomenon; and finally, applying a Lyapunov stability theory to analyze the stability of the system. The system has the most important characteristics that the state and the disturbance of the system can be accurately estimated by the linear expansion state observer. In addition, the control system is high in robustness, and a given displacement signal can be accurately tracked. In addition, the chattering phenomenon of slip form control can be greatly improved so as to be suitable for designing the permanent magnet linear synchronous motor servo control system.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
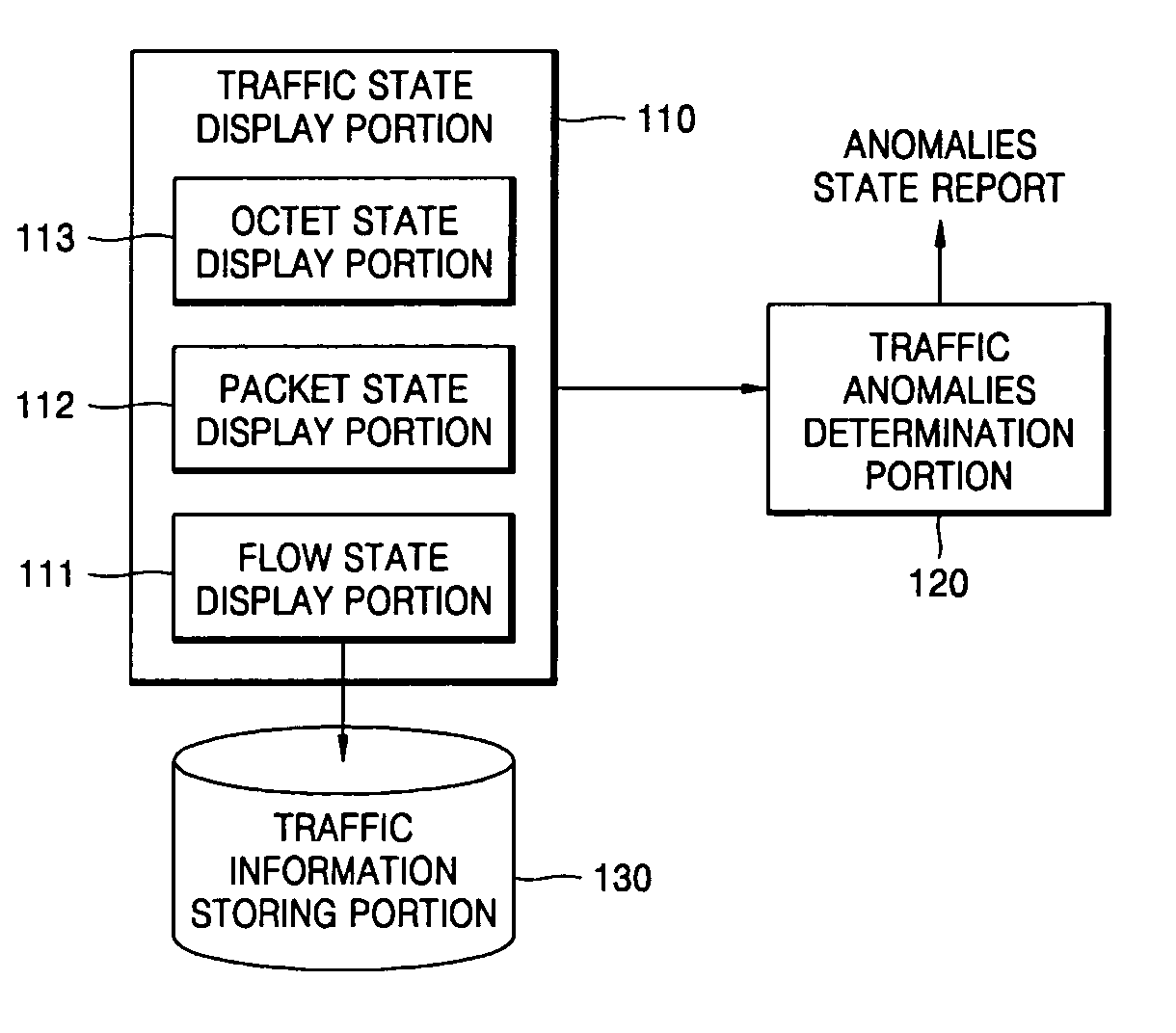
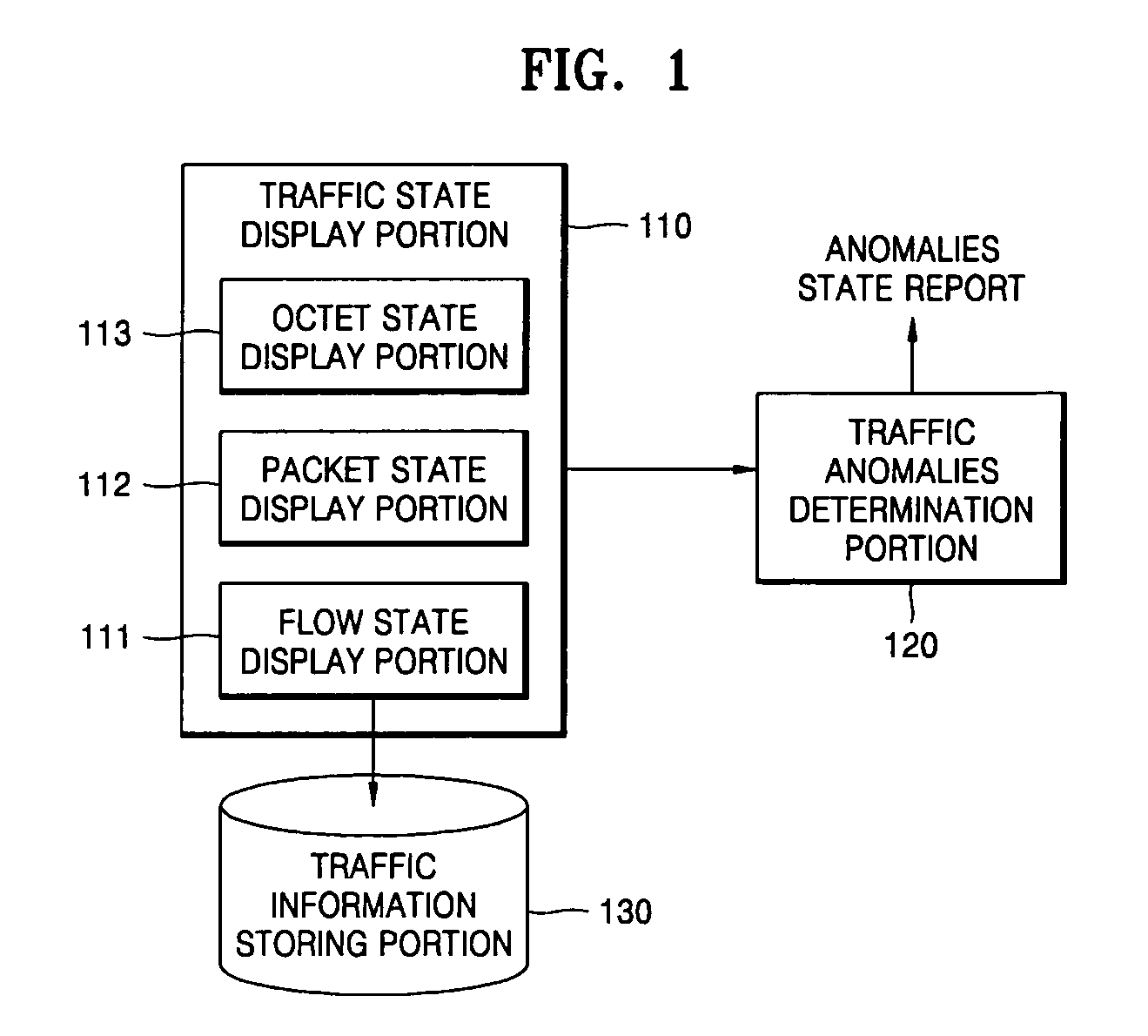
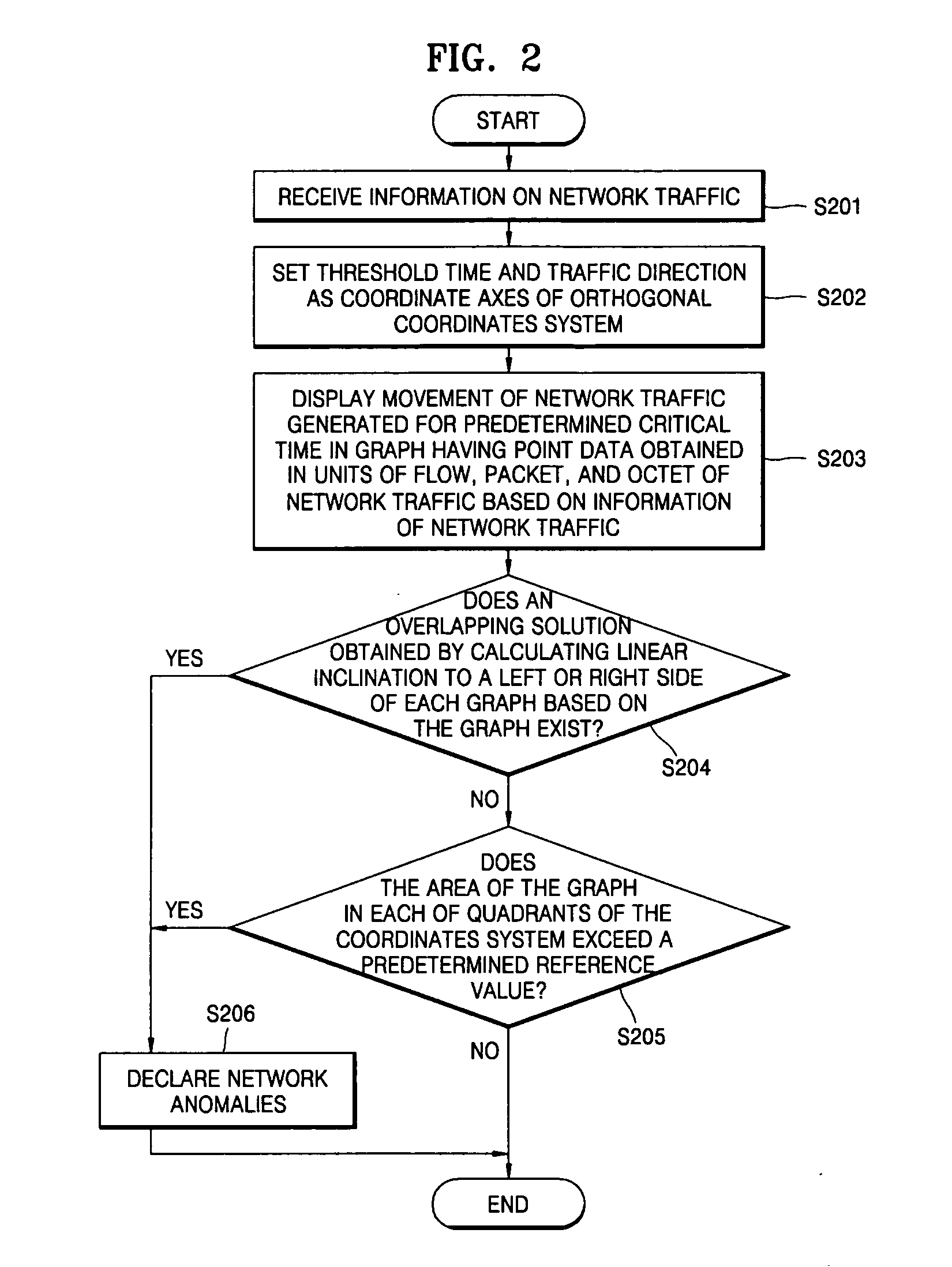
Apparatus and method for detecting and visualizing anomalies in network traffic
InactiveUS20060098579A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsGraphicsOrthogonal coordinates
Provided is an apparatus for detecting and visualizing anomalies in network traffic which includes a traffic information storing portion storing information on network traffic, a traffic state display portion presenting a status of the network traffic generated for a predetermined threshold time based on the information on network traffic on an orthogonal coordinates system in a form of a graph connecting at least one point data as a coordinate value, and a traffic anomalies determination portion determining an existence of anomalies in the network traffic based on a shape of the graph.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
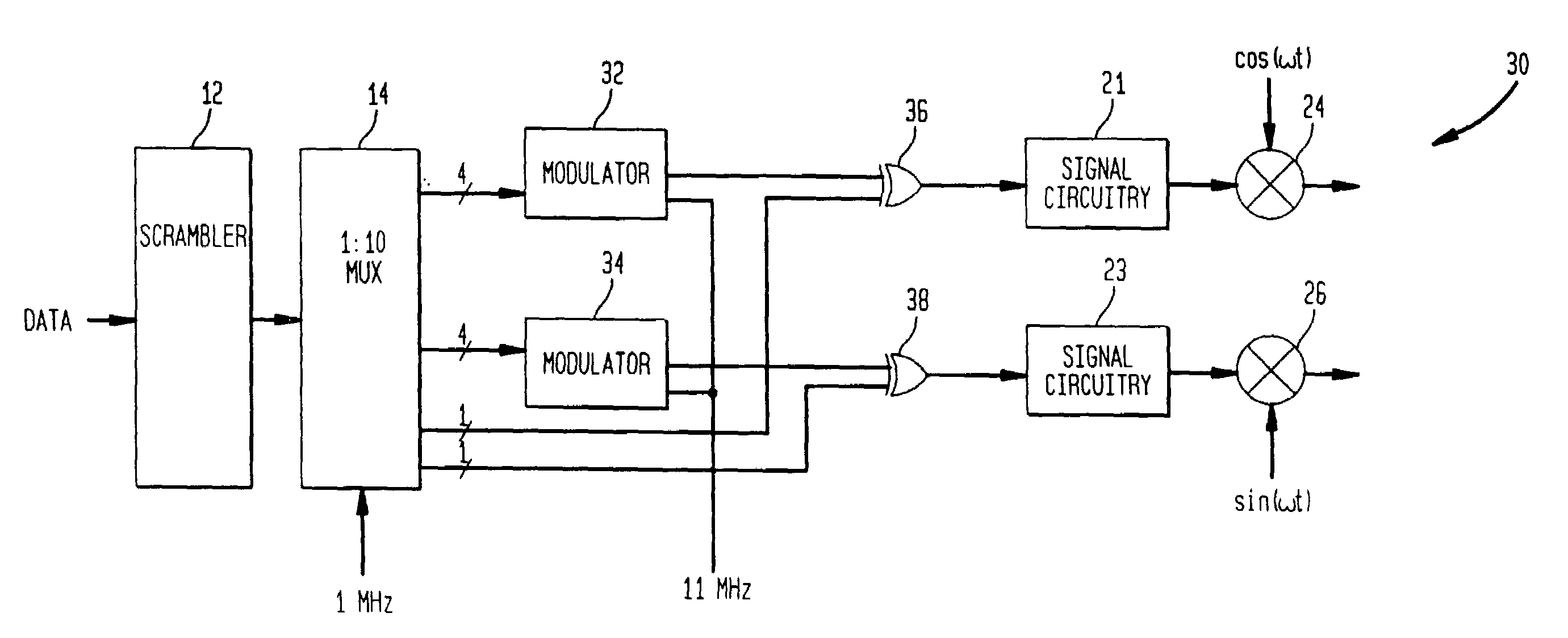
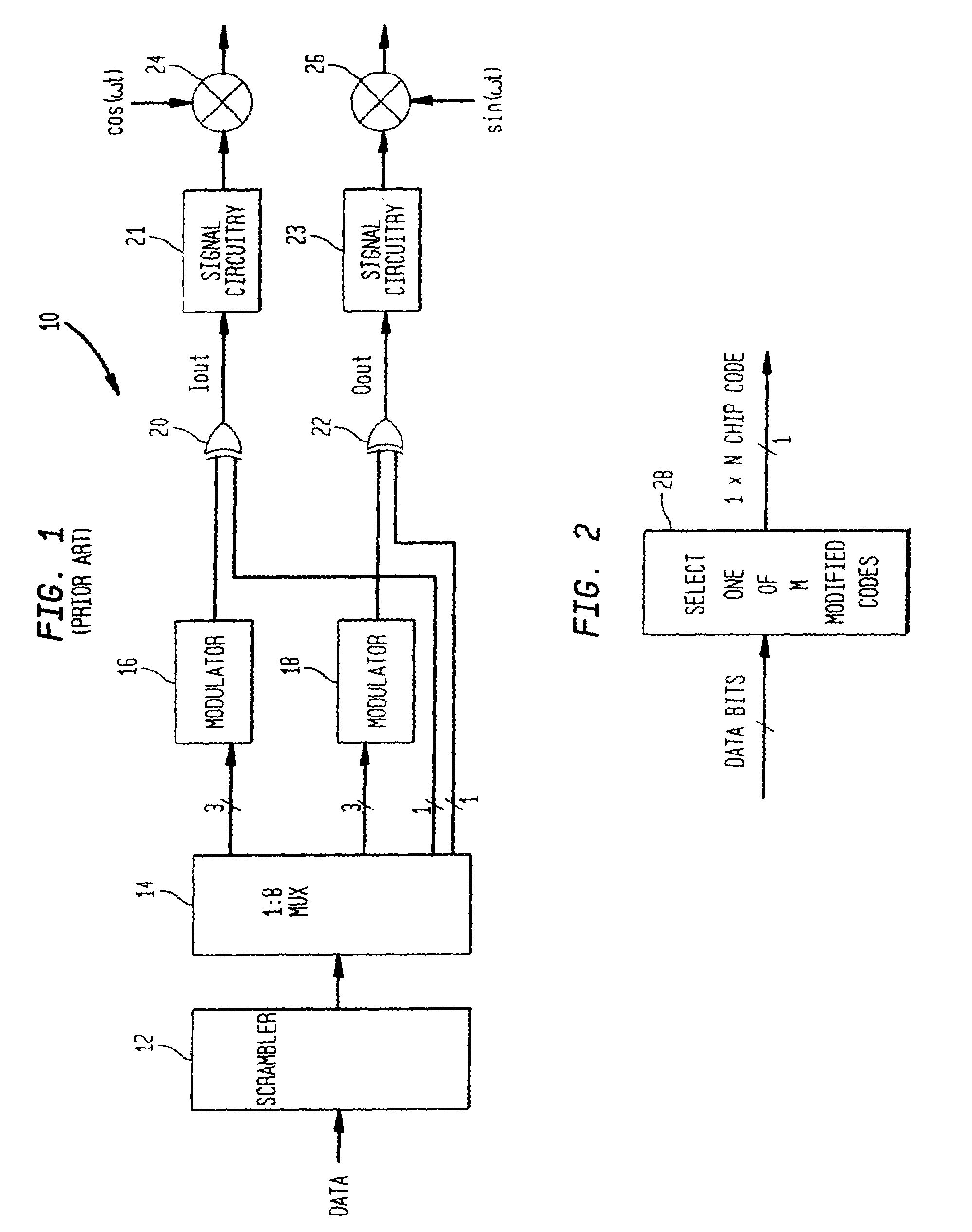
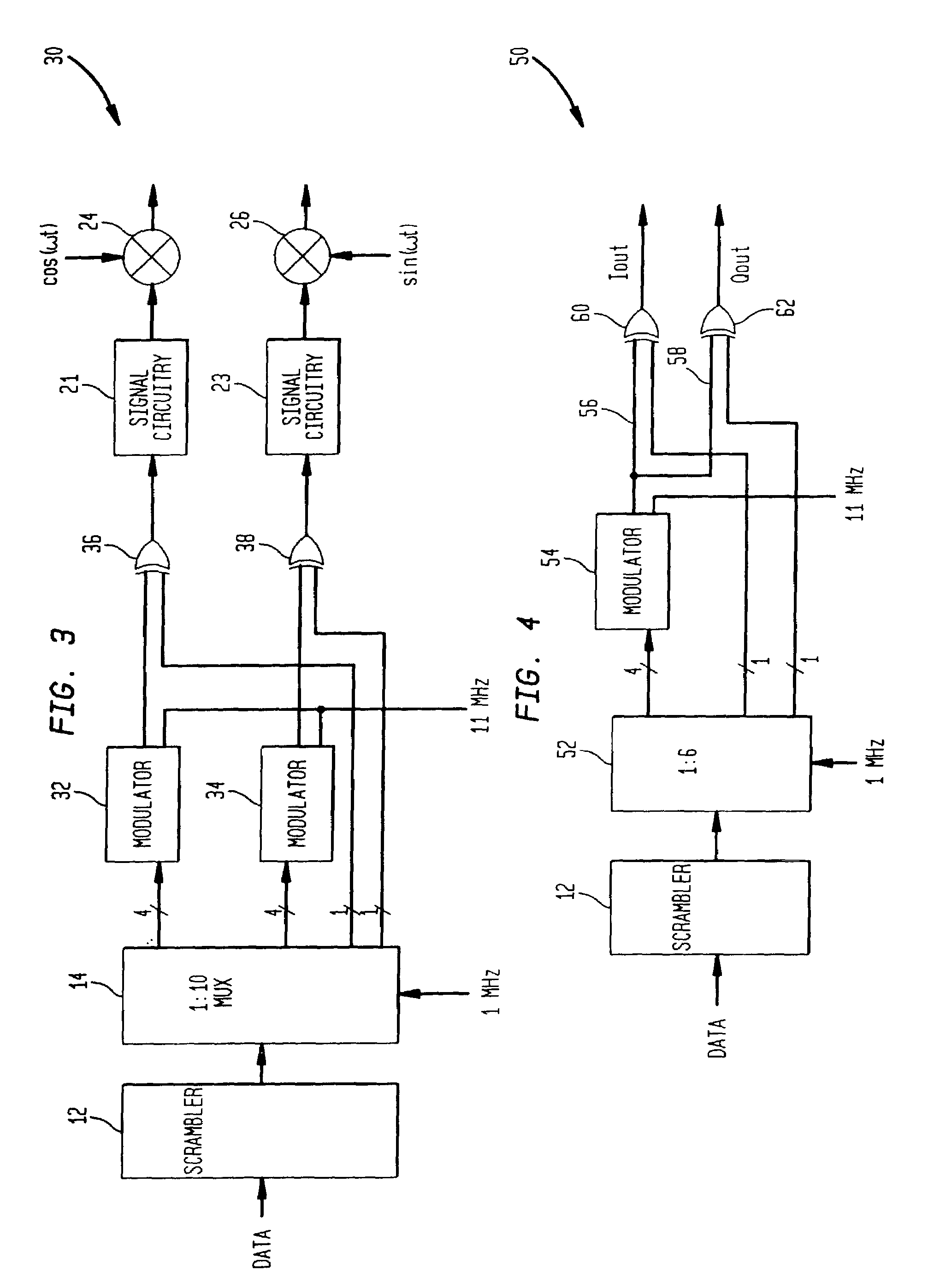
Digital modulation system using extended code set
InactiveUS7079567B2High data rateMaintaining coding gainAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsMultiplex code generationProgramming languageOrthogonal coordinates
A digital (de)modulation system uses a larger code set of M codes for N length codes, where M>N, to provide an increased data rate while maintaining the coding gain. For example, the system can use 16 different codes each having a length of 11 chips in a code set while the conventional M-ary keying systems use a code set size of 8 for 11-chip codes or 8-chip codes. By extending the code set size, the system increases the data rate of the system. With 16 codes and the ability to change the sign of the code to be transmitted, the system can encode 5 data bits on both I and Q, so a total of 10 data bits can be encoded per code symbol. In this embodiment, a code symbol contains an 11 chip code on a I modulation branch and an 11 chip code on a Q modulation branch. As such, using 11 chip codes and a chip rate of 11 Mhz, the system provides a data rate of 10 Mbps while conventional M-ary keying systems can only achieve 8 Mbps using the same code length and chip rate. By extending the code length, the processing gain is increased. The extended code set is not orthogonal, so a non-zero cross-correlation value results between the different codes of the code set. However, the resulting noise and multipath performance degradation can be kept small by choosing code sets with small cross-correlation values (nearly orthogonal). The magnitudes of both cross-correlation values and auto-correlation sidelobes should preferably be below half a code length. In some embodiments, the code set is derived from orthogonal codes which are modified to reduce the autocorrelation sidelobes associated with the orthogonal codes. In other embodiments, the code set is derived using a complementary code which provides low autocorrelation sidelobes and is modified to reduce the cross-correlation values between the codes.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Image processing apparatus and image processing method
InactiveUS20100008580A1Improve accuracyReduce necessityDigitally marking record carriersGeometric image transformationImaging processingPhase shifted
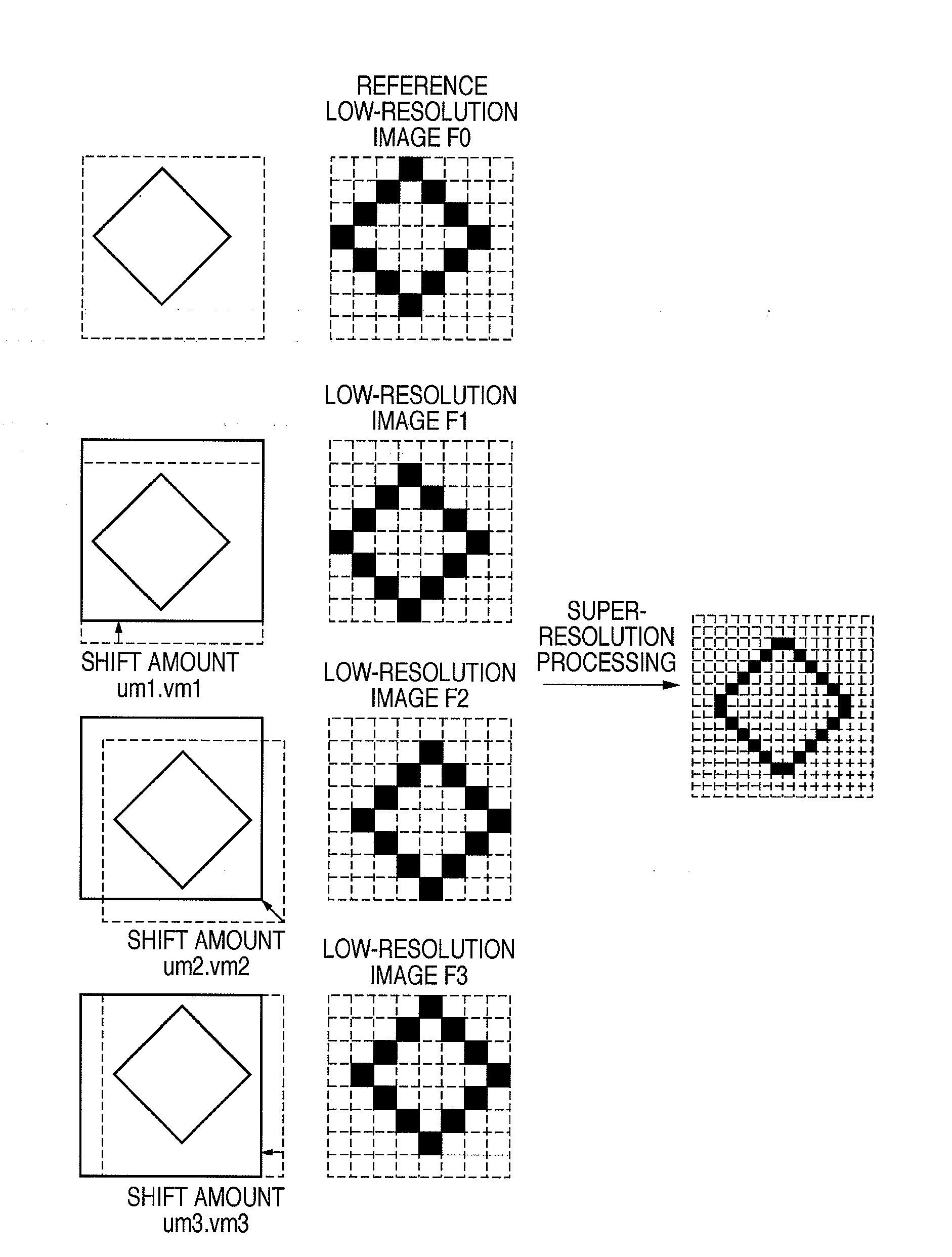
An image scanner using an area sensor having a tilt reads a plurality of low-resolution image data having phase shifts from each other, and the low-resolution image data are converted into those on an orthogonal coordinate system by affine transformation. The number of data to be used is decided based on one of these low-resolution image data. The low-resolution image data as many as the designated number of data are saved, and high-resolution image data is generated by executing super-resolution processing.
Owner:CANON KK
Receiving apparatus and method for digital multi-carrier transmission
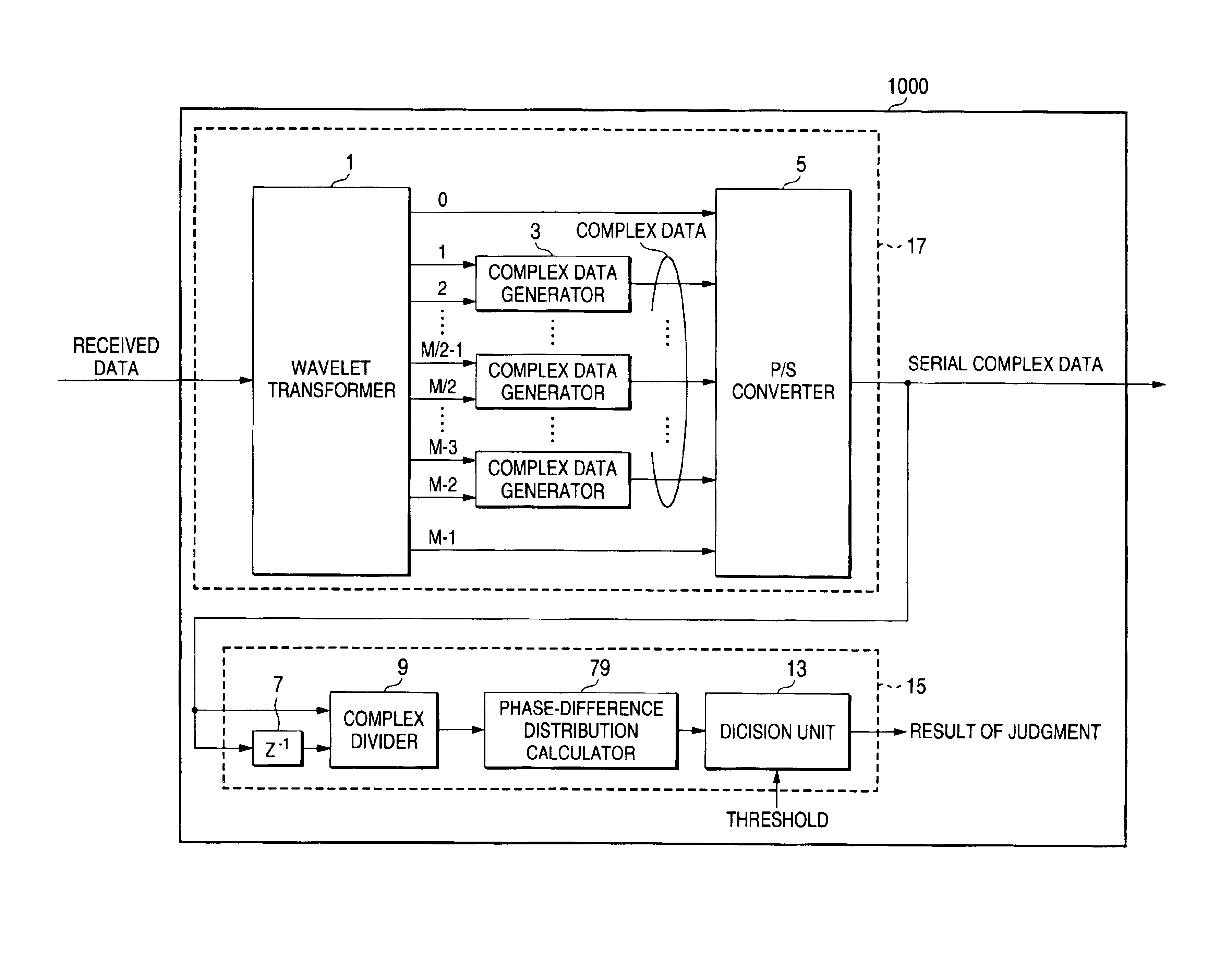
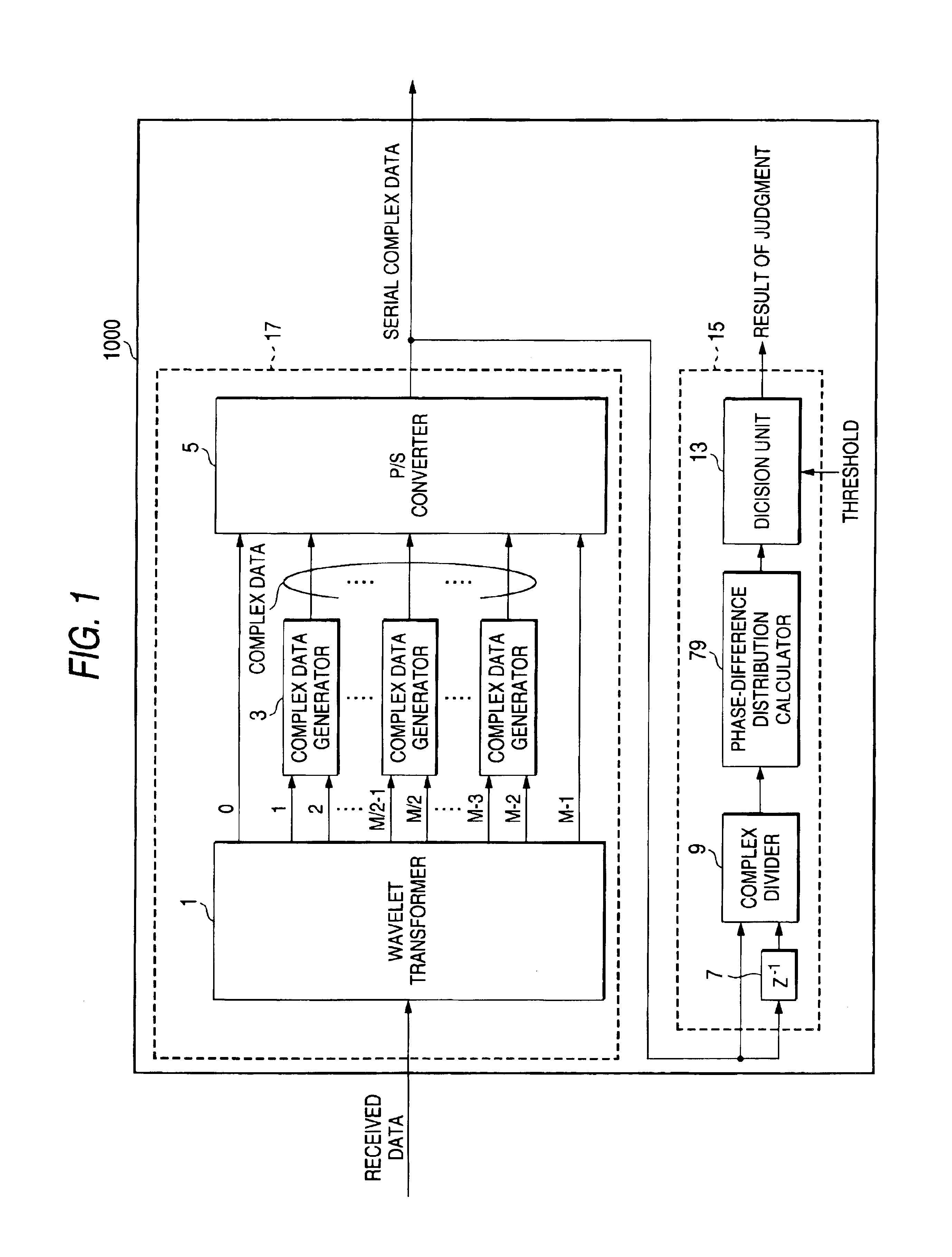
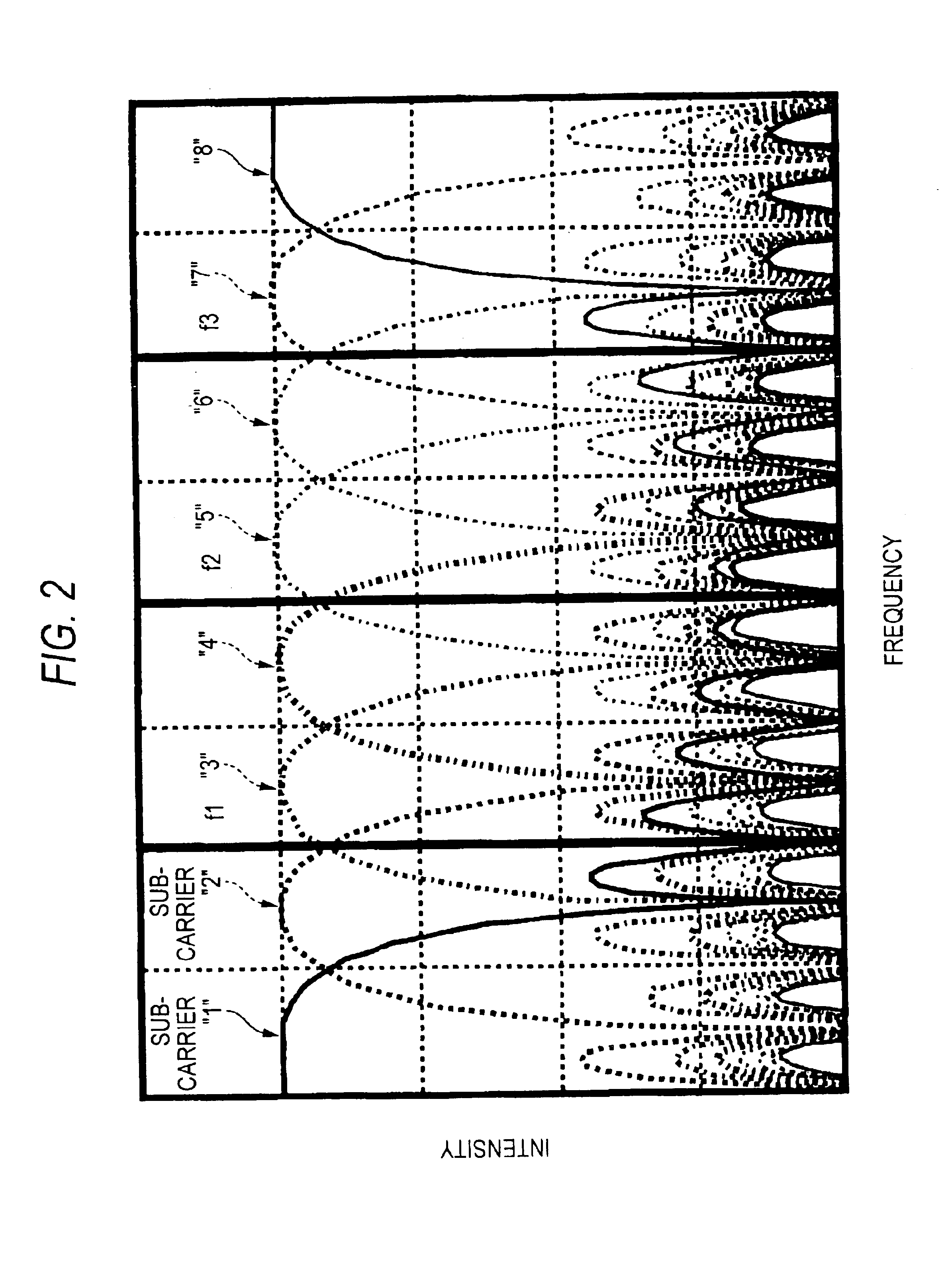
InactiveUS6944232B2Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningOrthogonal coordinatesAlgorithm
A receiving apparatus and method for performing carrier detection in a frequency domain for a digital wavelet multi-carrier transmission. A wavelet transform of received data is performed to output complex data and then the complex data is delayed for one sampling period. Subsequently, the delayed complex data and delayed complex data are divided. A number of the divided complex data present within each of plural quadrants on orthogonal coordinates is calculated and a maximum number of data present within one of the quadrants is selected and compared with a threshold in order to decide whether the received data is intended data.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Motor control apparatus and motor control method
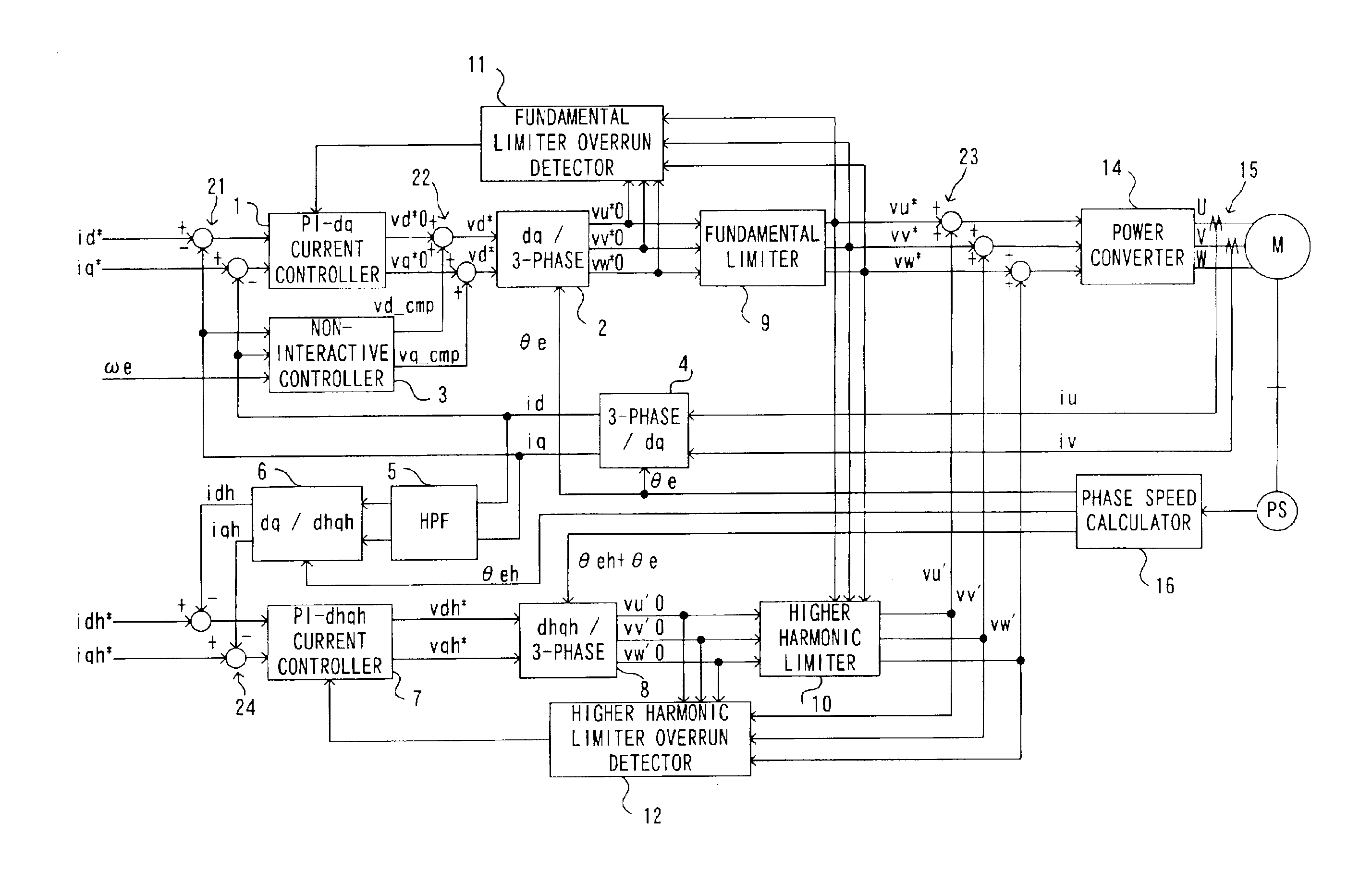
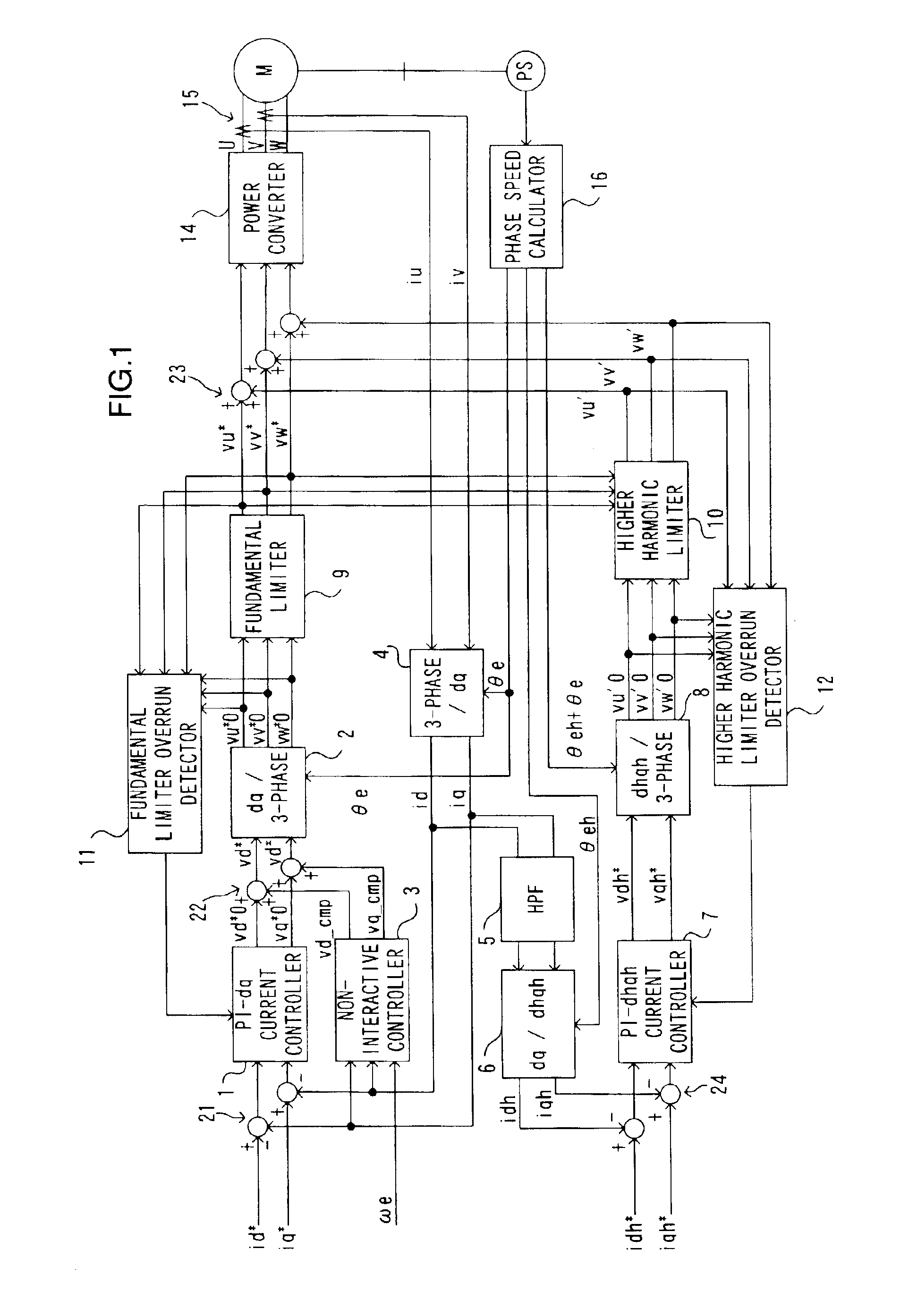
InactiveUS6861813B2Reduced responseImprove responseDC motor speed/torque controlSynchronous motors startersOrthogonal coordinatesEngineering
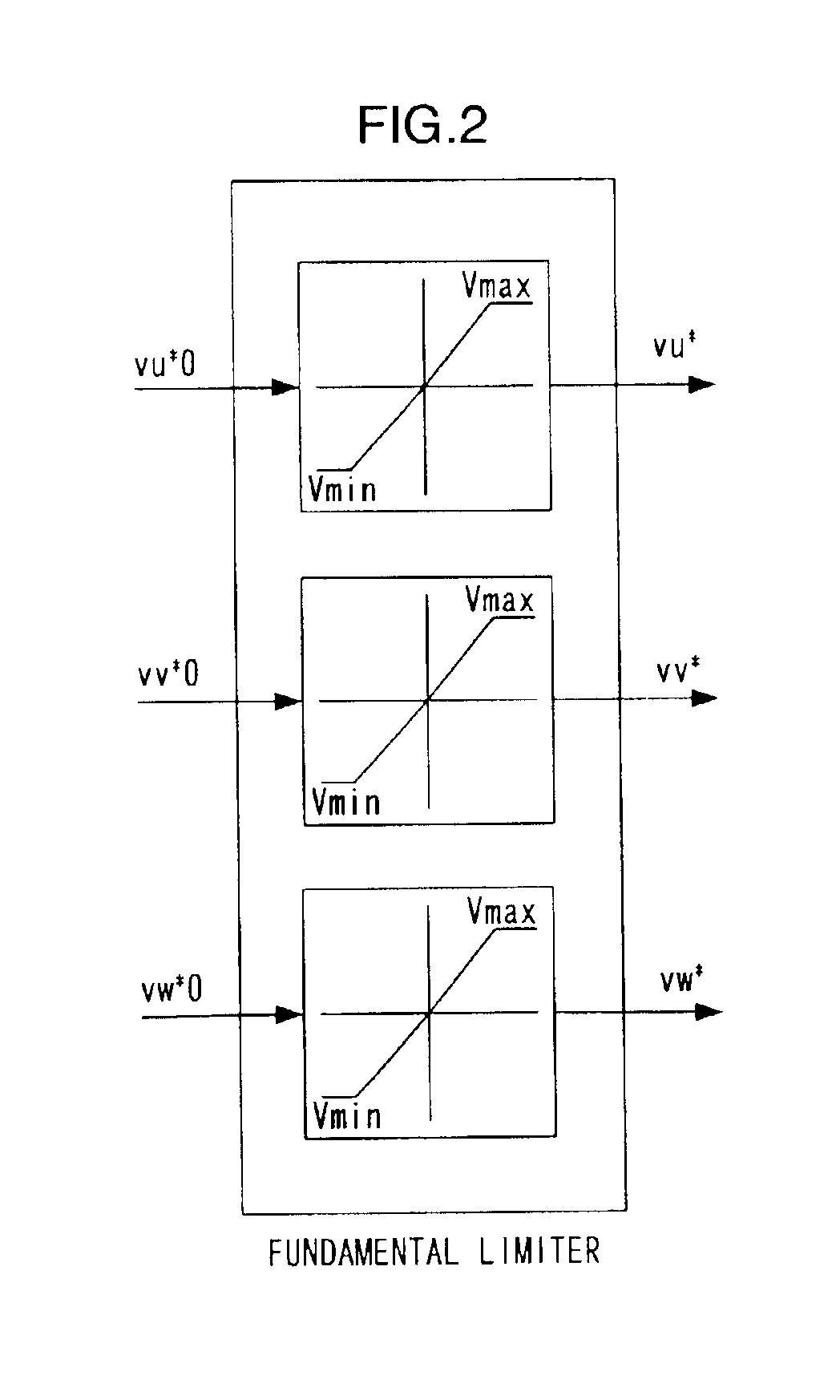
Limits are imposed on a fundamental voltage command value calculated at a fundamental current control circuit that controls a fundamental component of a 3-phase AC motor current in a dq-axis coordinate system rotating in synchronization with the rotation of the 3-phase AC motor by using predetermined limit values and limits are imposed on a higher harmonic voltage command value calculated in an orthogonal coordinate system (a higher harmonic coordinate system) rotating at a frequency set to an integral multiple of the frequency of the fundamental component in the 3-phase AC motor current by using a predetermined limit values. The voltage command values resulting from the limit processing are added together and a voltage corresponding to the sum is applied to the AC motor for drive control.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and magnetic resonance imaging method
InactiveUS20050070784A1Improve accuracy reliabilityReliable temperature measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceOrthogonal coordinates
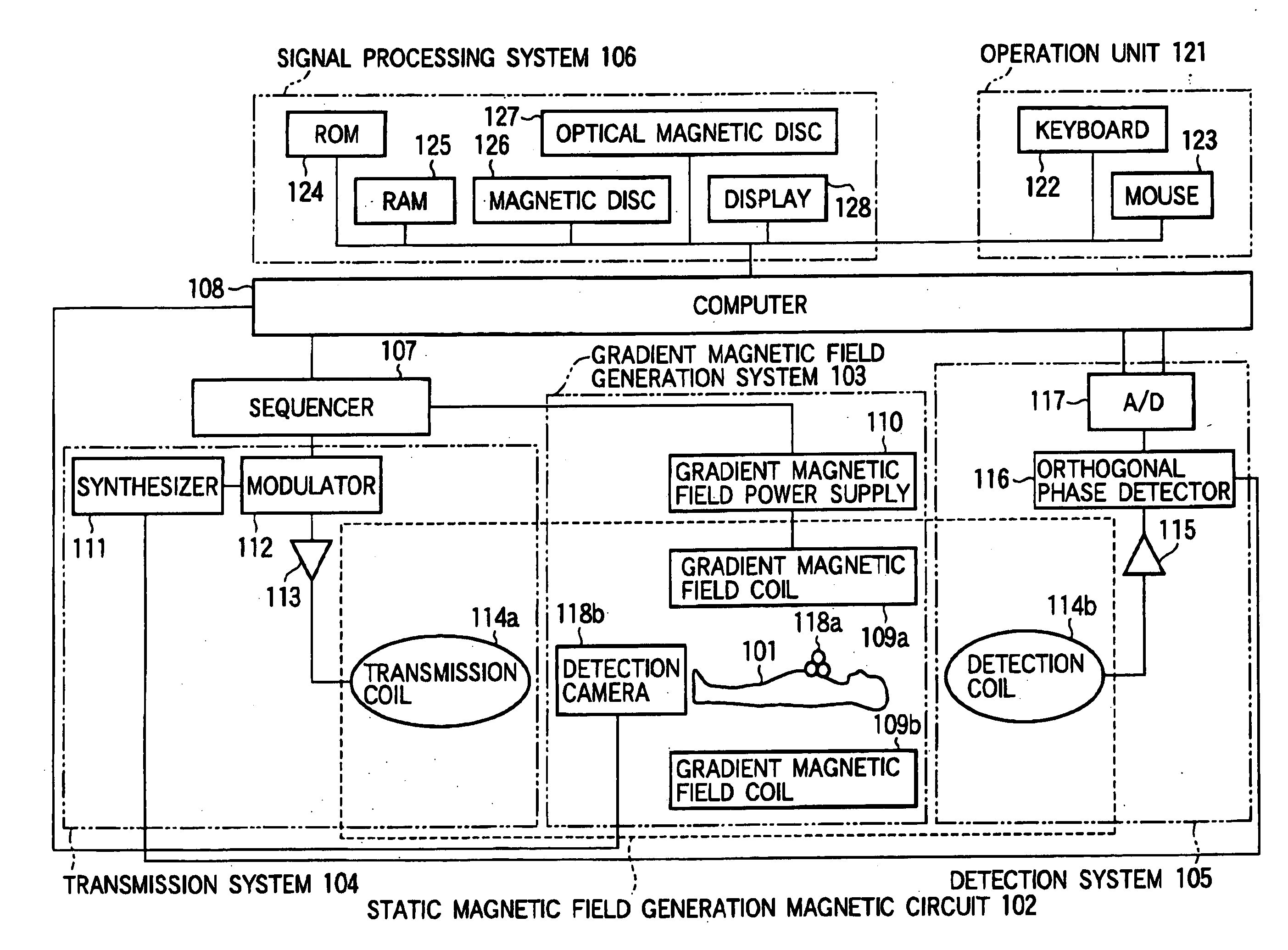
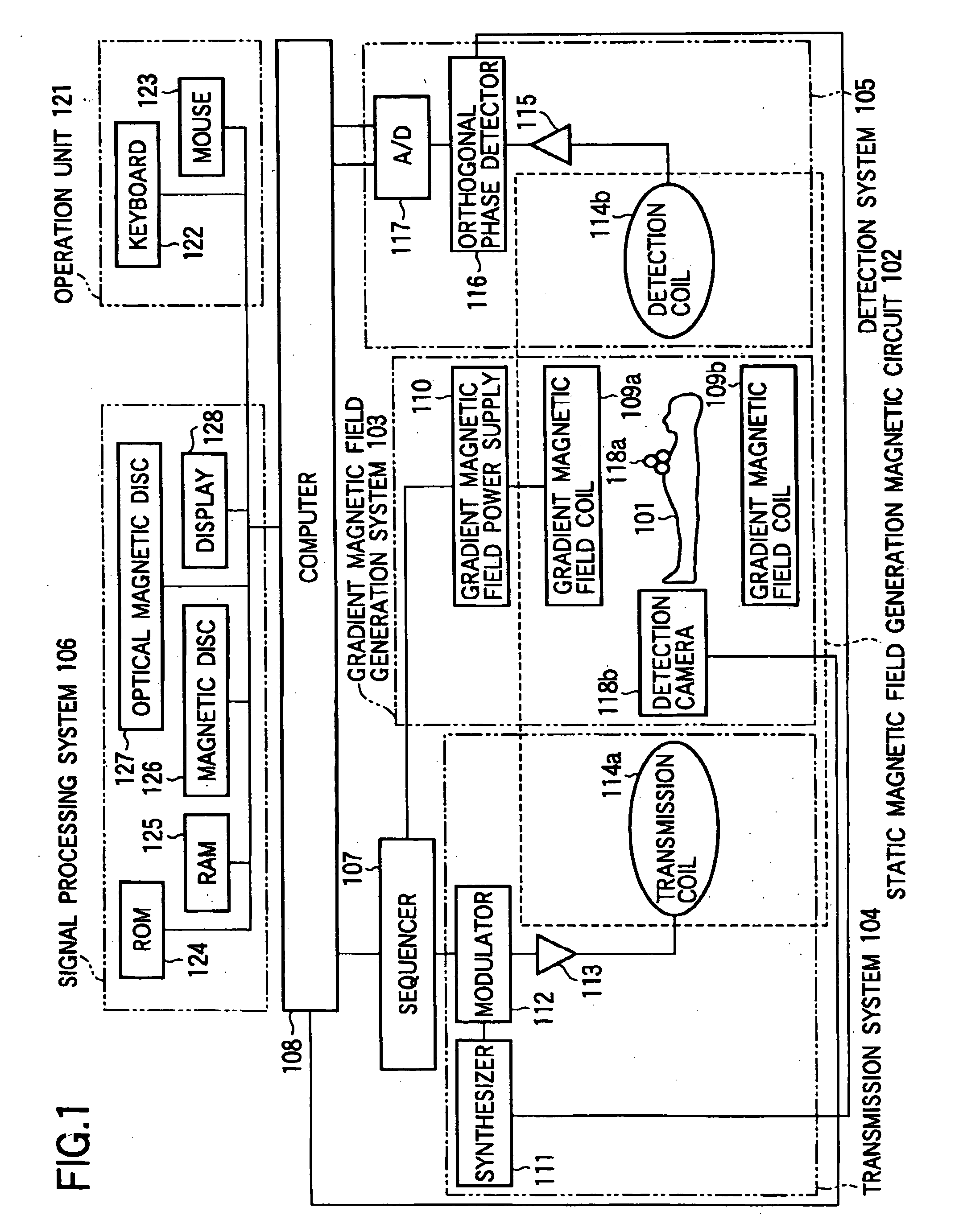
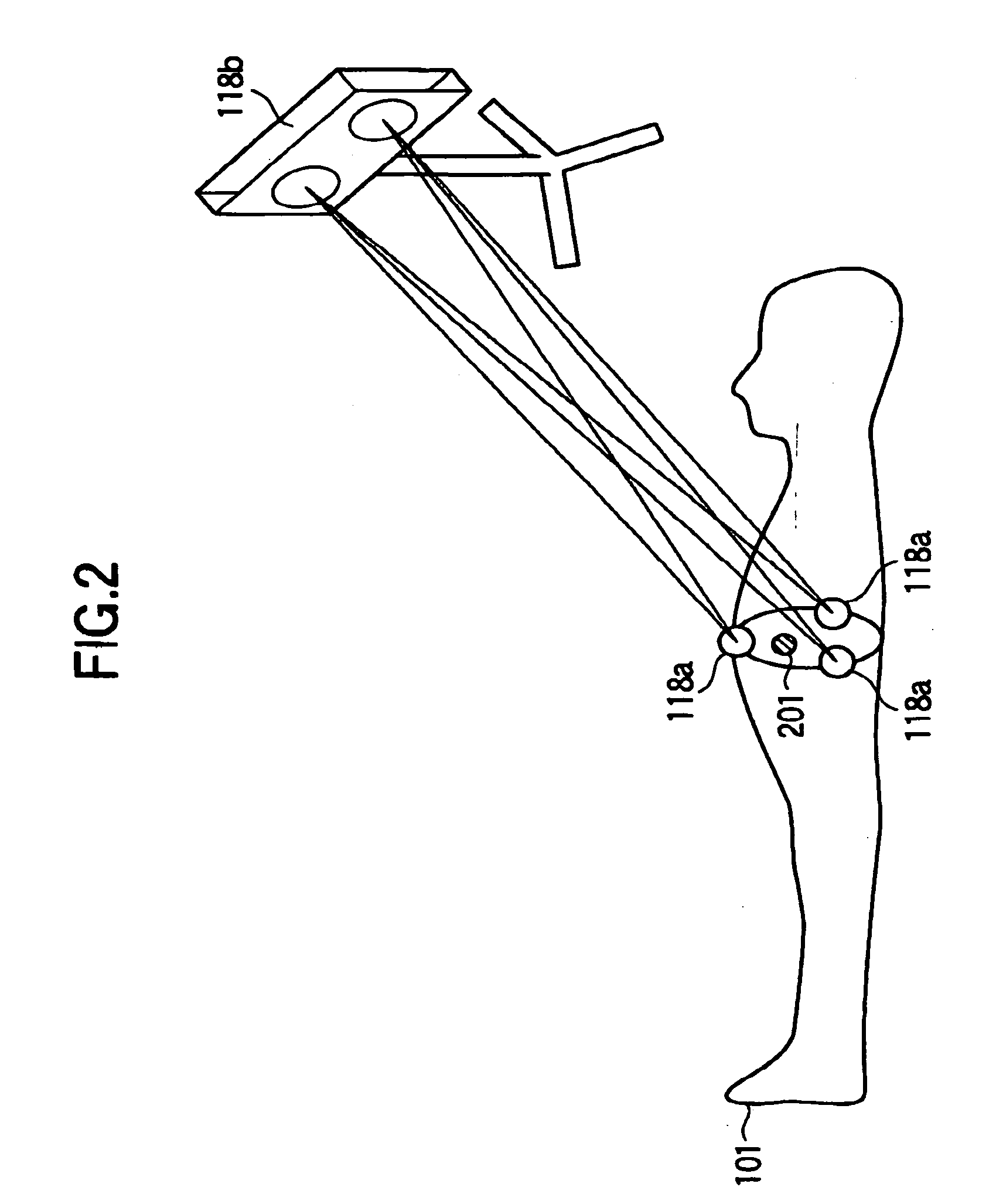
A magnetic resonance imaging apparatus includes control means 107 and 108 for continuously performing magnetic resonance imaging of a cross section including a portion subjected to measurement of an examinee (101) at a predetermined time interval, operation means 108 for calculating diagnosis information related to the portion subjected to measurement by using a plurality of sets of nuclear magnetic resonance signals related to cross sections imaged at different time points by measuring nuclear magnetic resonance signals generated from the examinee 101, and a position detection device 118 having a detection camera 118b for detecting in non-contact manner the position (three-dimensional position and rotation angle around an orthogonal coordinate axis) of a pointer 118a provided outside the examines body and moving while interlocked with the biological movement of the examinee 101. The control means 108 sets the position of the cross section according to the position of the pointer 118a detected by the position detection device 118, thereby eliminating an affect of the biological movement and improving the accuracy and the reliability of the diagnosis information including differential processing of a portion subjected to measurement.
Owner:HITACHI MEDICAL CORP
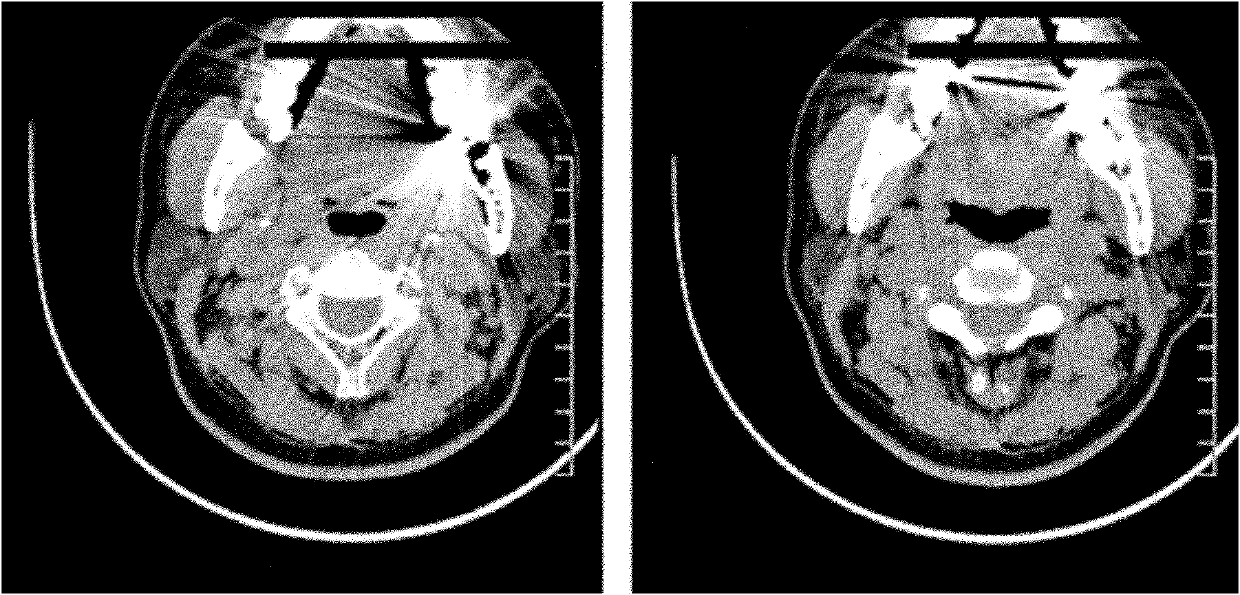
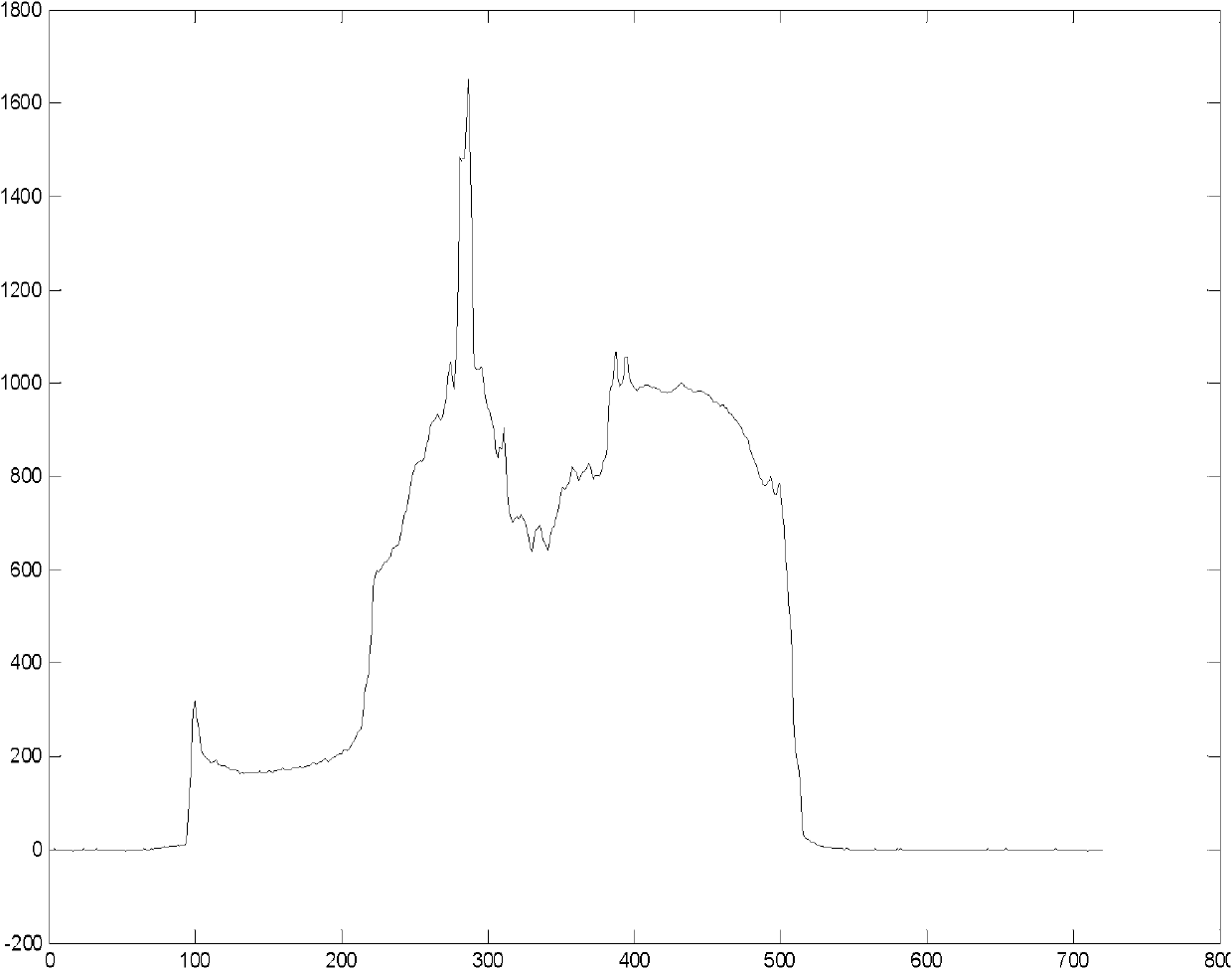
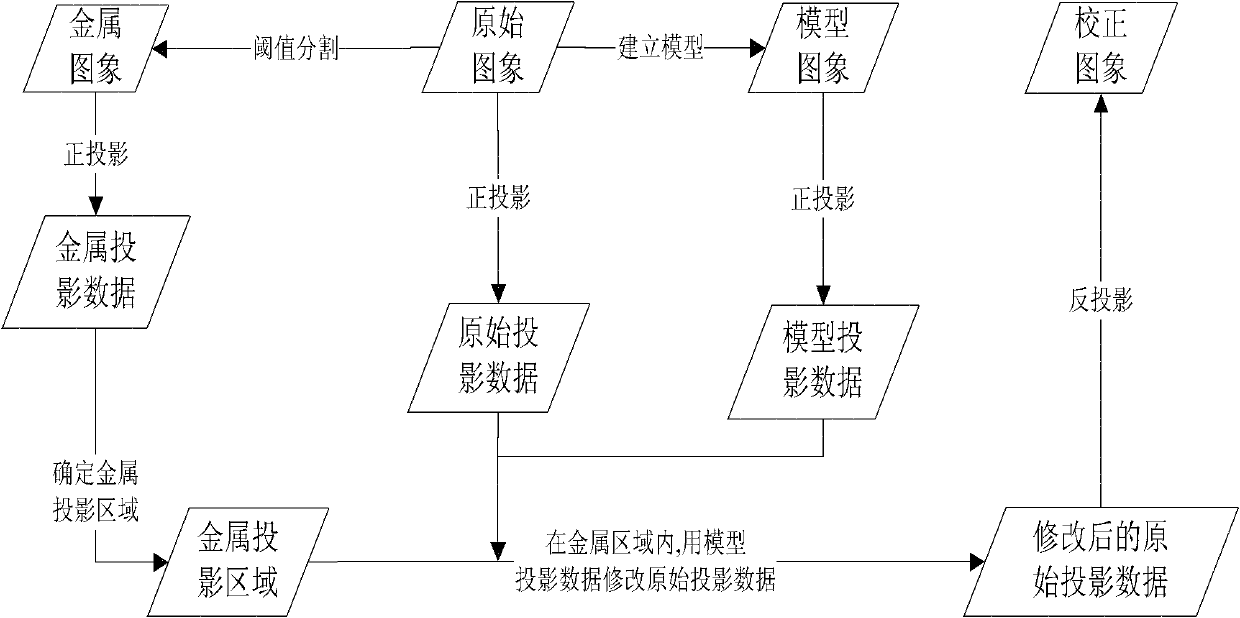
Image postprocessing method for removing metal artifact from computed tomography (CT) image
ActiveCN102567958AImprove calibration resultsThe result after calibration is goodImage enhancementMetal ArtifactOrthogonal coordinates
The invention relates to an image postprocessing method for removing a metal artifact from a computed tomography (CT) image, which comprises the following steps of: converting an original CT image into a polar coordinate image from an orthogonal coordinate image; determining a metal projection region in the polar coordinate image; establishing a model in the polar coordinate image; performing model correction by adopting the model; correcting front and back projection errors brought into the model correction; and converting the polar coordinate image into the orthogonal coordinate image. According to a model establishing method provided by the invention, the good model can be established, and finally, a good correction result can be obtained; the errors brought in by front and back projection are corrected, so that the result after the correction is better, and the processing speed is ensured.
Owner:PHILIPS CHINA INVESTMENT
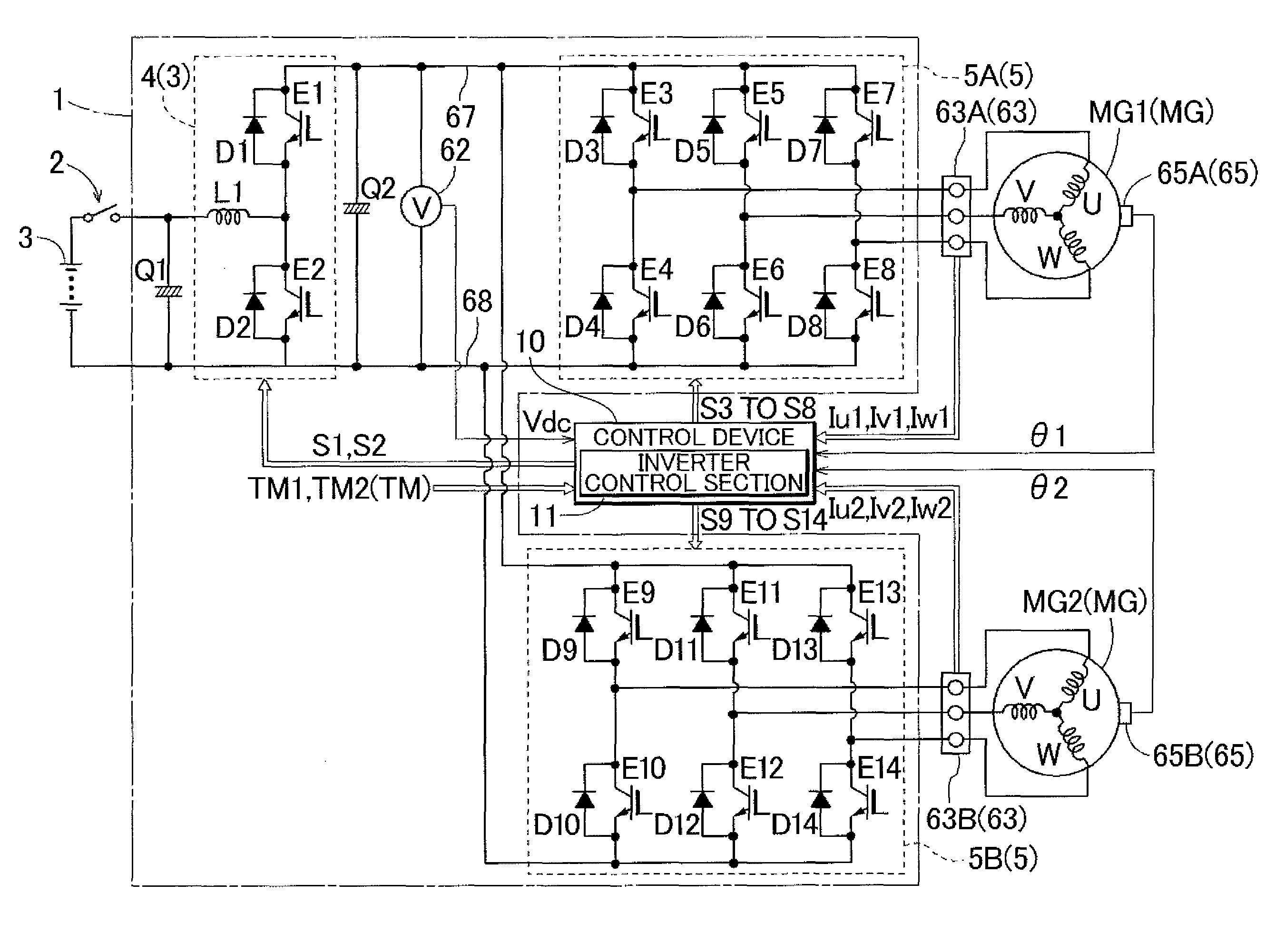
Rotary electrical machine control device
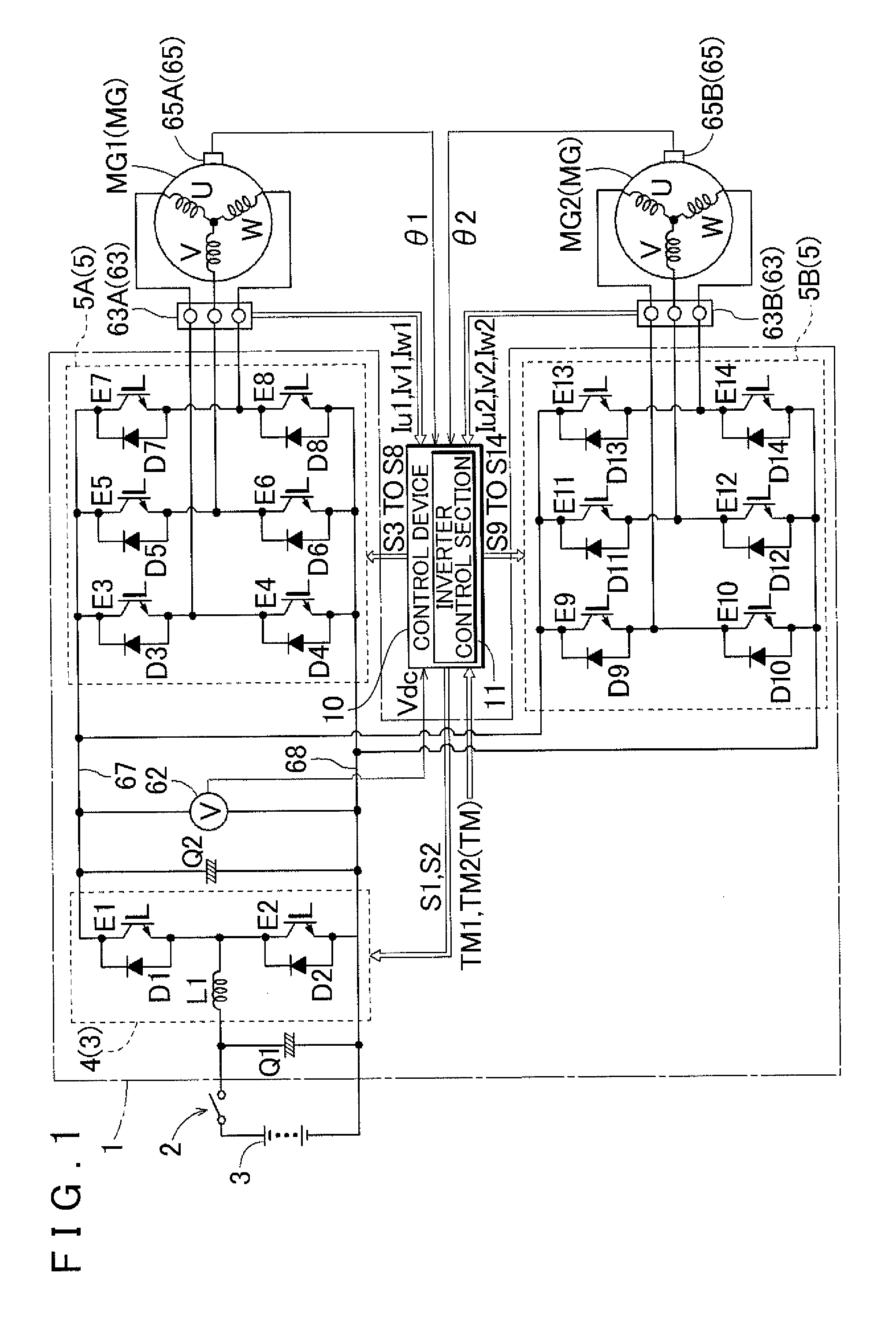
ActiveUS20140232304A1Regenerative power is greatly reducedSecure performanceAC motor controlSynchronous motors startersPower inverterDriving current
Regenerated power fed from a rotary electric machine is immediately reduced where connection between an electric machine and a DC power source is blocked. An inverter control section controls the inverter by controlling an armature current in a two-axis orthogonal coordinate system that rotates in synchronization with the rotary electric machine, the armature current being a vector obtained by synthesizing a field current and a drive current extending along respective axes of the orthogonal coordinate system. If it is determined that connection between the DC power source section and the inverter is in a blocked state, the inverter control section executes zero-torque control in which the inverter is controlled such that torque regenerated by the rotary electric machine becomes zero, and executes high-loss control in which the field current is varied so as to increase the armature current while maintaining a torque command provided in the zero-torque control.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
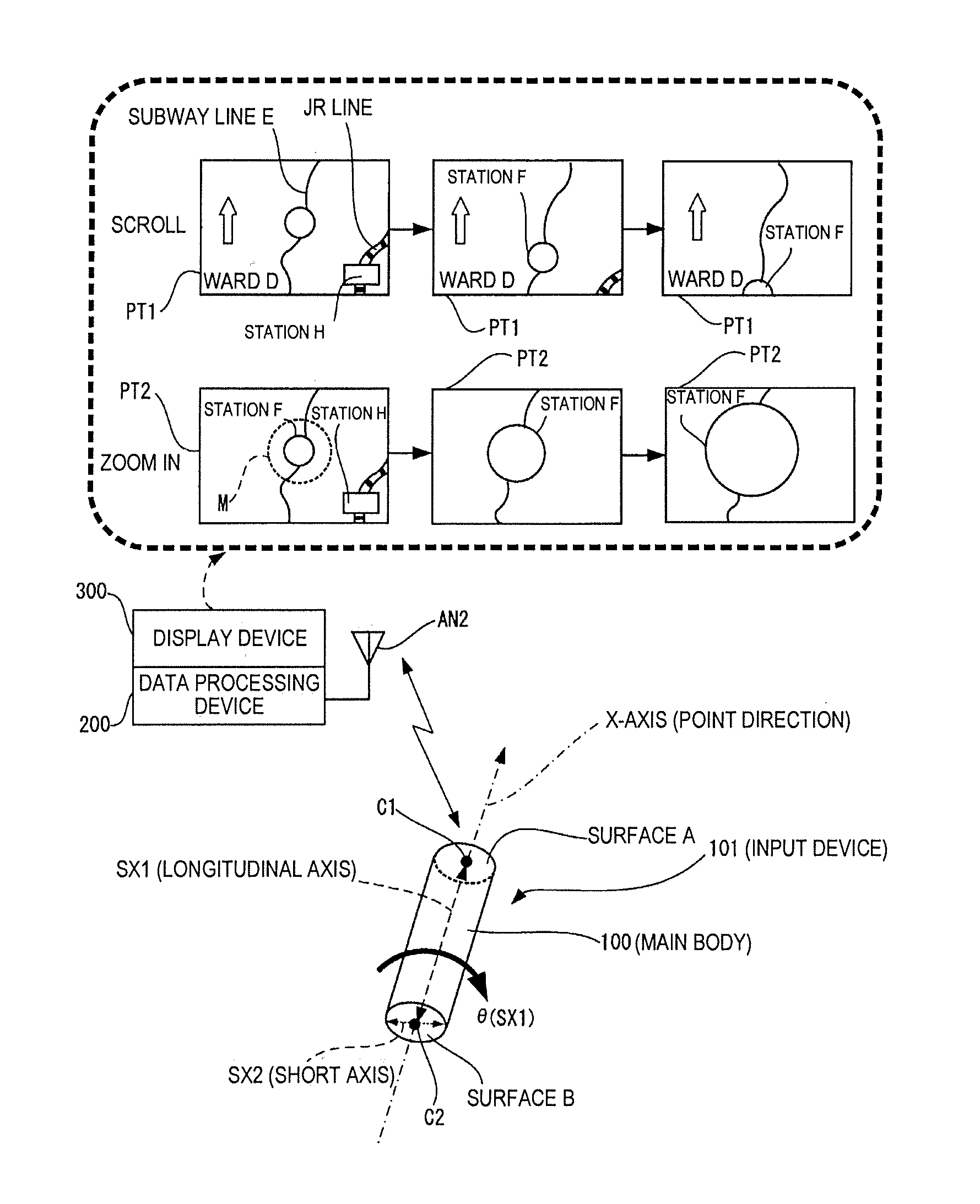
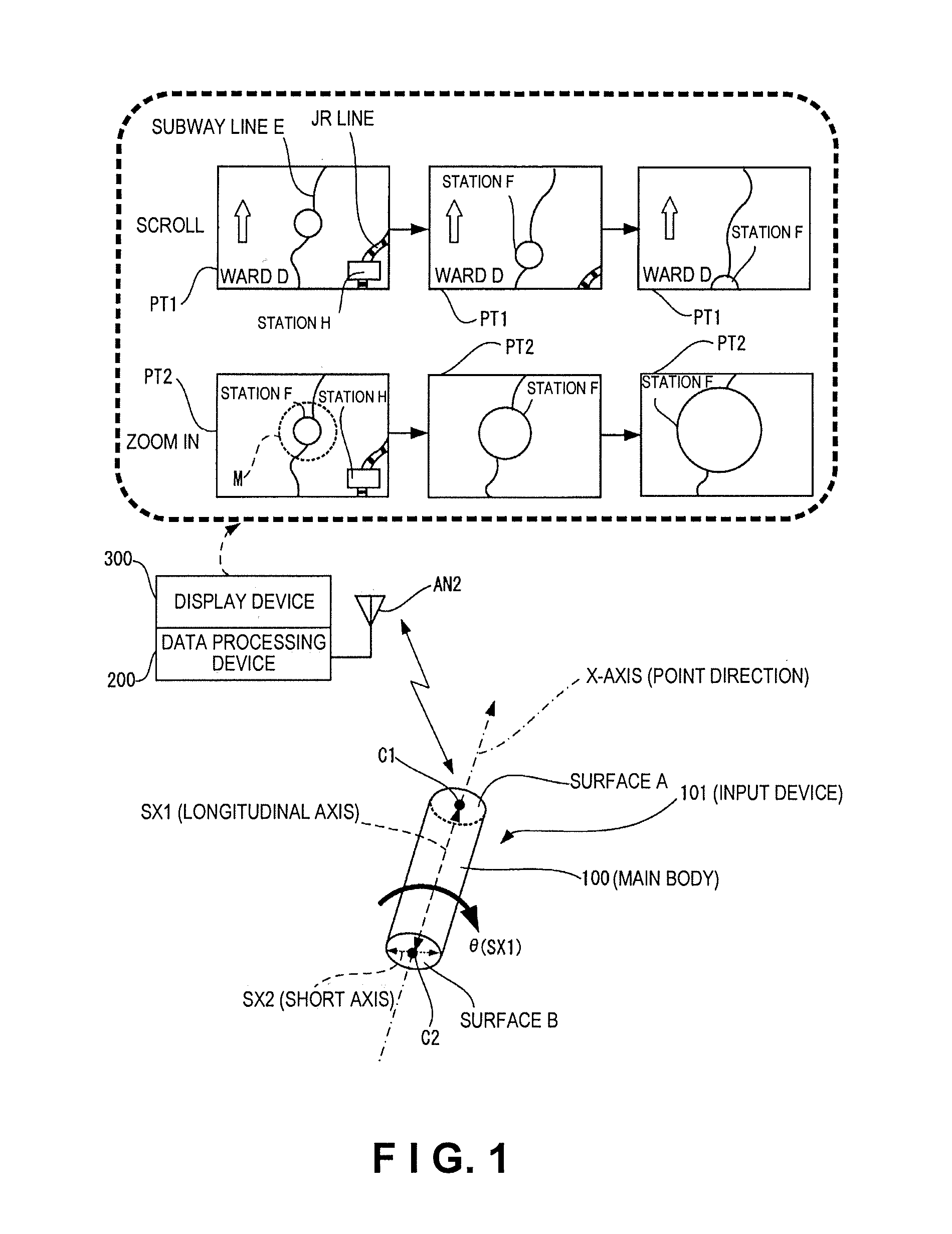
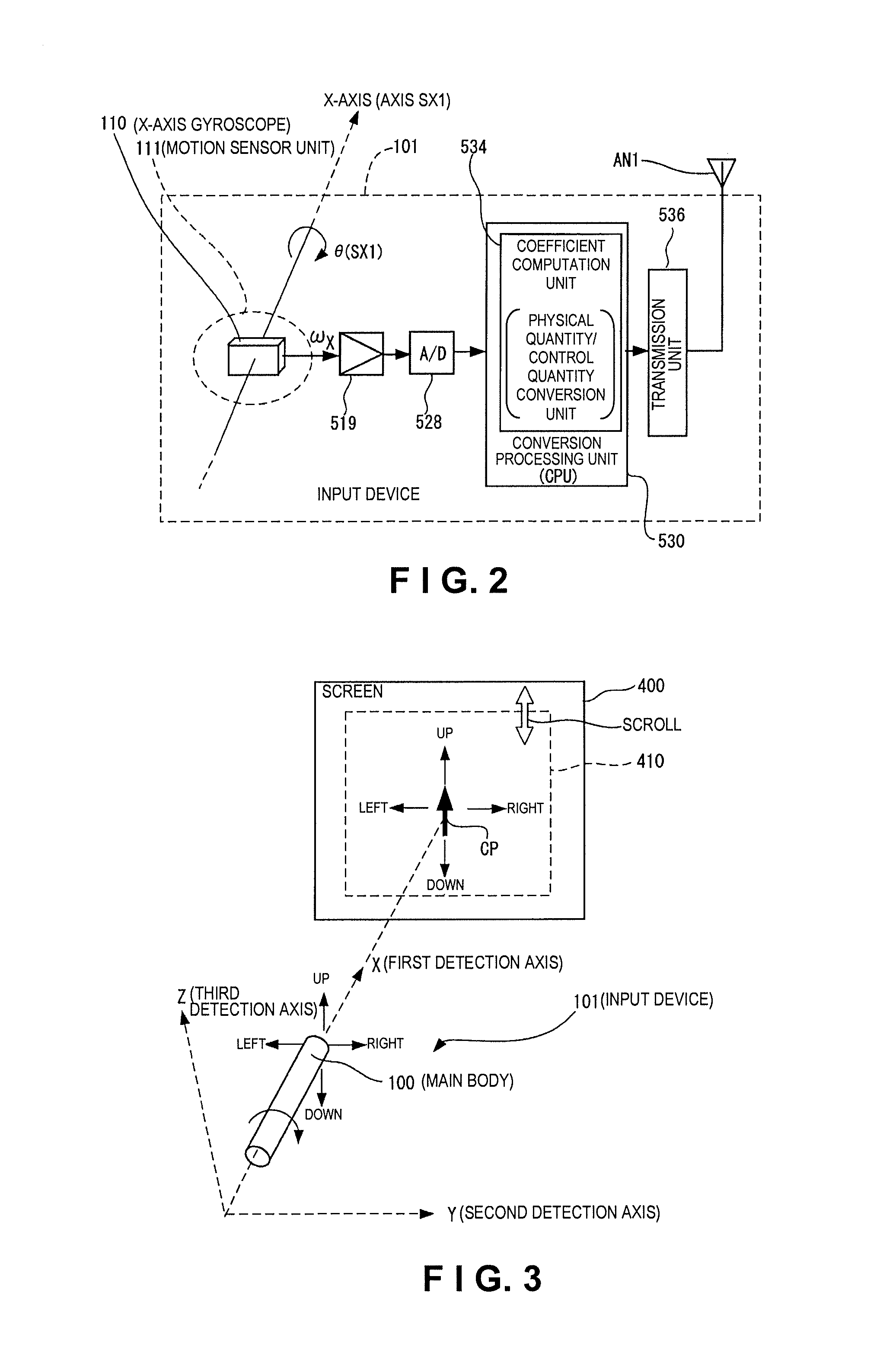
Input device and data processing system
ActiveUS20100156785A1Easy to operateImprove convenienceDigital computer detailsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsAxis–angle representationData processing system
An input device includes a main body and a motion sensor unit. The main body has a longitudinal axis. The motion sensor unit is configured and arranged to detect rotation of the main body about the longitudinal axis. The motion sensor unit has an X-axis angular velocity sensor configured and arranged to detect an angular velocity of the main body about an X-axis in a three-dimensional orthogonal coordinate system defined by the X-axis, a Y-axis and a Z-axis. The X-axis coincides with the longitudinal axis of the main body and the Y-axis and the Z-axis being orthogonal to each other in a first plane perpendicular to the X-axis.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Multi-axes synchronous mechanism
InactiveCN101474734AIncrease costLow costWelding/cutting auxillary devicesArc welding apparatusRotational axisOrthogonal coordinates
The invention relates to a multiaxial linkage mechanism, comprising a X ,Y and Z triaxial mechanical system of triaxial orthogonal coordinate, working ends, an A axis rotary mechanism comprising an A rotary axis, a servo driving system and a control system, wherein the servo driving system controlled by the control system drives the X, Y and Z triaxial mechanical system, the A axis rotary mechanism drives the working ends to rotate around the rotary axis A , and the X, Y and Z mechanical system and the A axis rotary mechanism drive the working ends to any spatial position. The multiaxial linkage mechanism of the invention has the advantages of low production and maintenance cost, thereby benefiting market popularization; and the multiaxial linkage mechanism has relatively good versatility and high resetting precision, and is applicable for occasions requiring higher precision.
Owner:SHENZHEN NEW CANGHAI MACHINERY
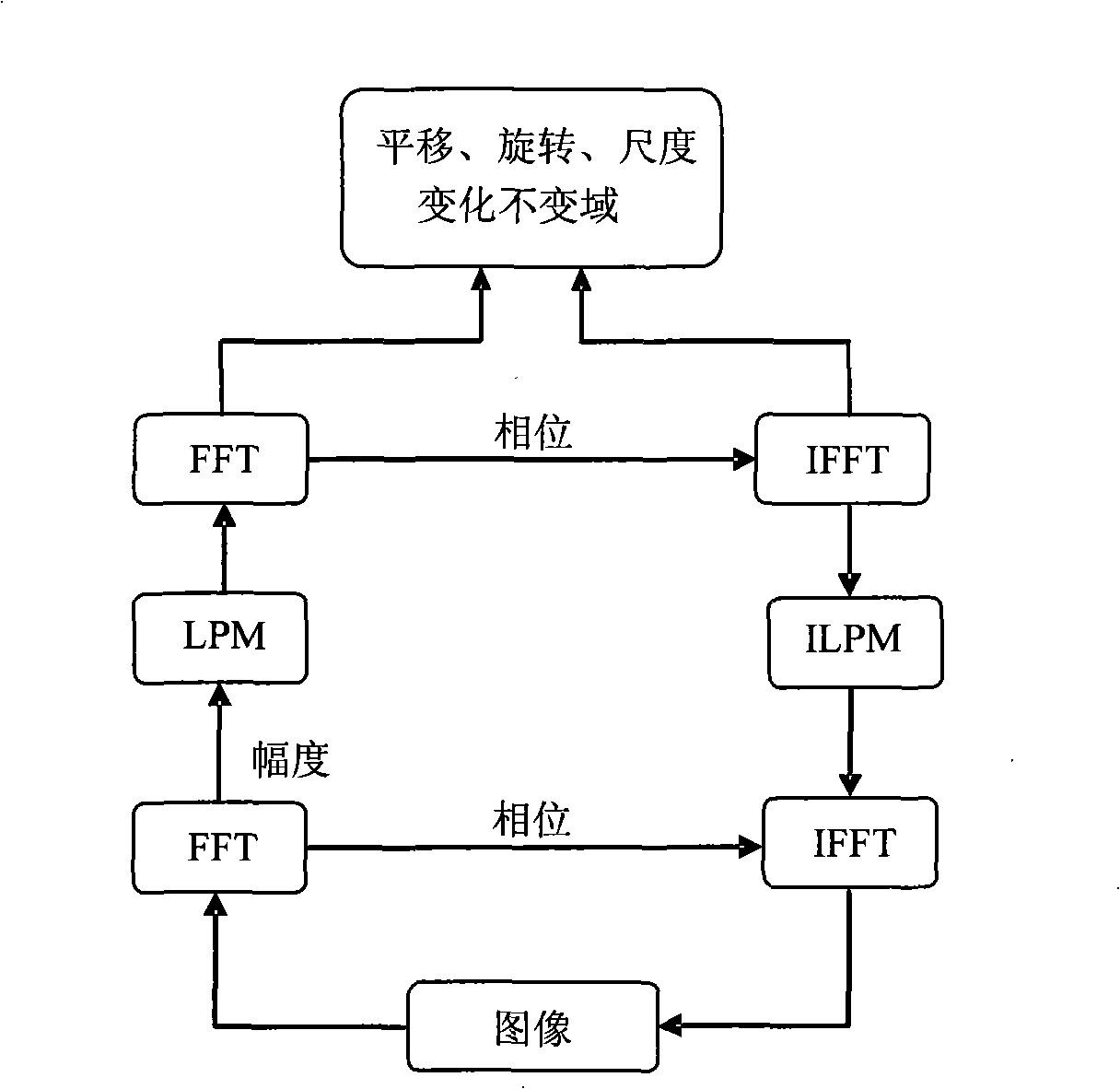
Method and apparatus for embedding and extracting watermark as well as processing system
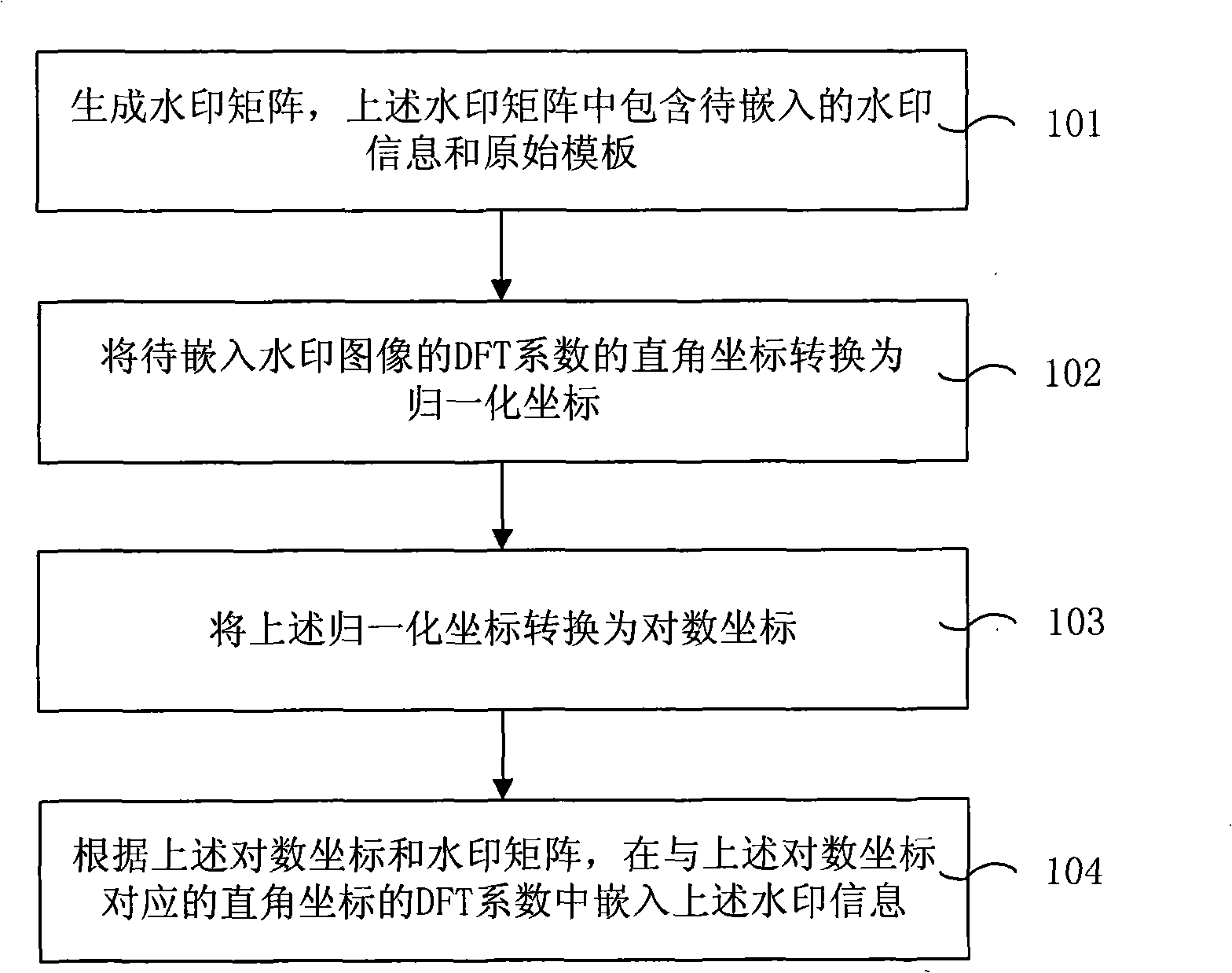
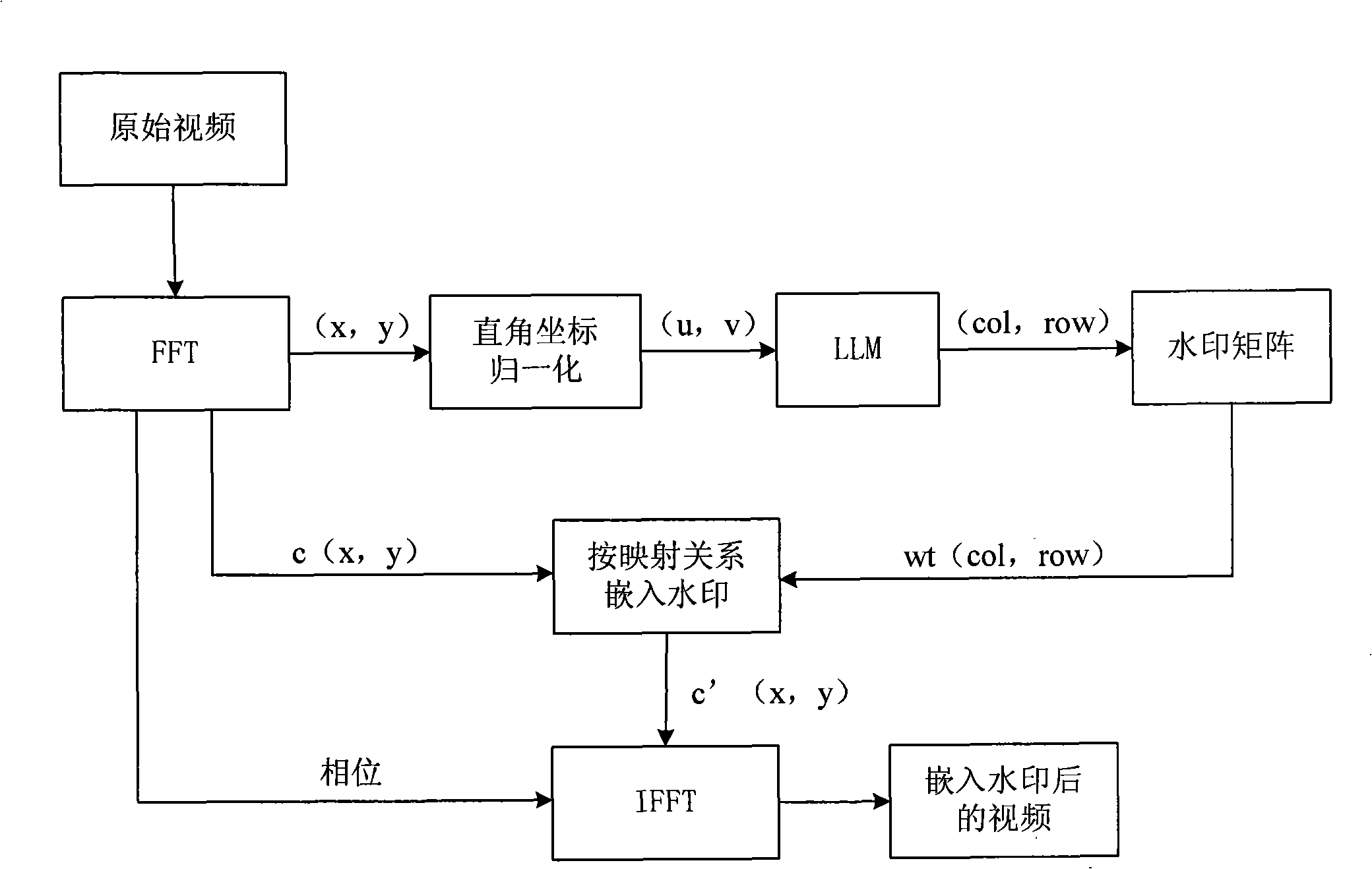
InactiveCN101330610AShorten the timeImprove visibilityPulse modulation television signal transmissionImage data processing detailsComputation complexityOrthogonal coordinates
The embodiment of the invention relates to a method and a device for embedding a watermark, a method and a device for extracting the watermark, and a processing system, wherein the method for embedding the watermark comprises the following steps: a watermark matrix is generated; an orthogonal coordinate of a DFT coefficient for the watermark image to be embedded is transformed into a logarithmic coordinate; and the watermark information is embedded in the DFT coefficient of the orthogonal coordinate corresponding to the logarithmic coordinate according to the logarithmic coordinate and the watermark matrix. The method and the device for embedding a watermark and the method and the device for extracting the watermark ensure that the video watermark can ensure better visual imperceptibility and resist various geometric attacks, such as adding noise, scaling, intraframe clipping, intraframe parallel movement, blended attacks of scaling and clipping, simultaneously better reduce the computational complexity in the watermark extraction and save the time of the watermark extraction.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
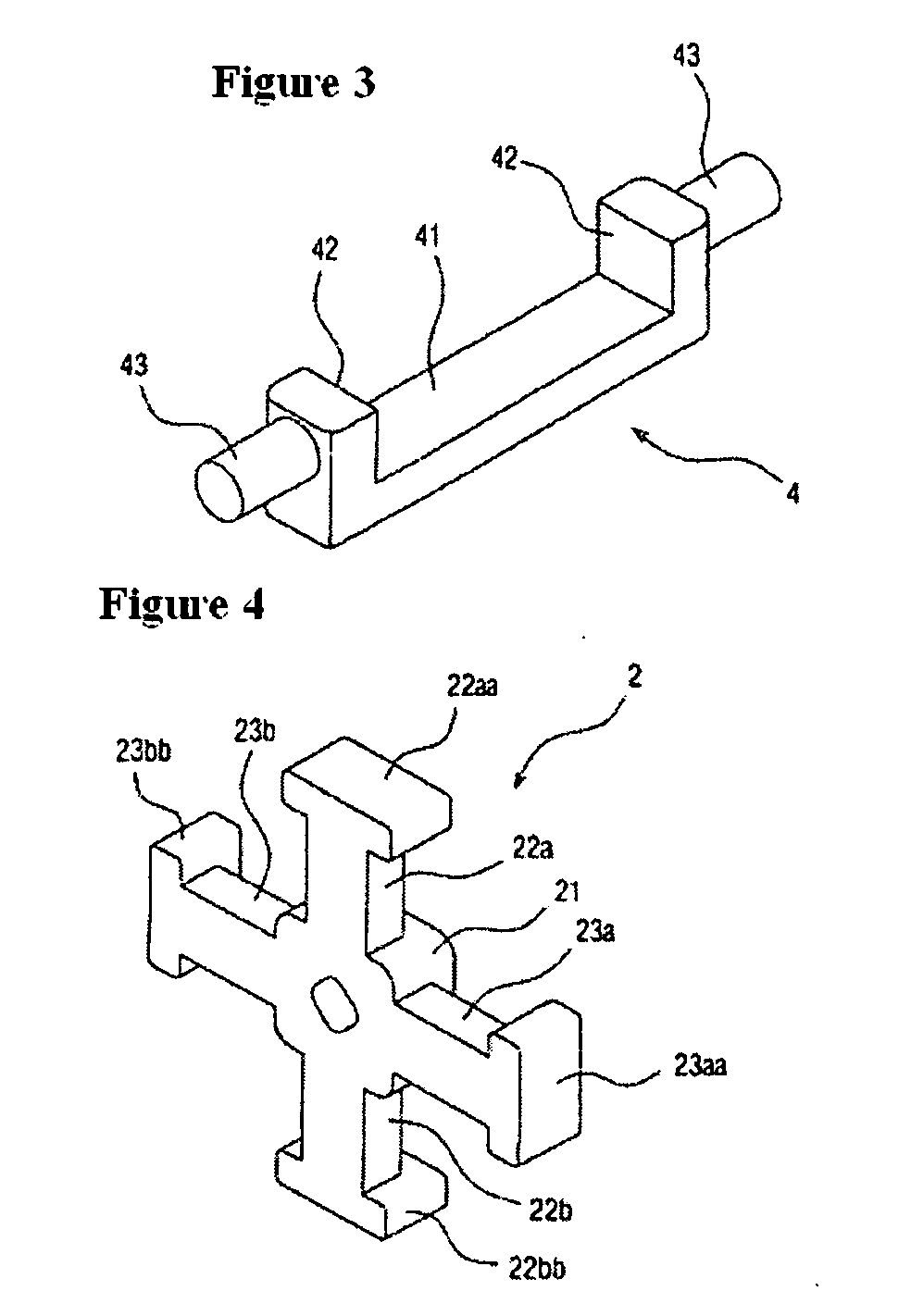
Three-axis antenna, antenna unit, and receiving device
ActiveUS20070195001A1Precise positioningAvoid couplingLoop antennas with ferromagnetic coreAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesOrthogonal coordinatesEngineering
To achieve sensitivity not deviating in any of XYZ directions. A three-axis antenna with a cross-shaped core (2) having a pair of X-axis arms (22a, 22b) projecting in the X-axis direction in an orthogonal coordinate system and a pair of Y-axis arms (23a, 23b) projecting in the Y-axis direction orthogonal to the X-axis direction, and having Z-axis winding wire (26) provided in a substantially rectangular frame shape, outside the head sections of the X-axis arms (22a, 22b) and the head sections of the Y-axis arms (23a, 23b). The Z-axis winding wire is housed in a case having the bottom so as to cover the entire parts of head surfaces of the X-axis arms (22a, 22b) and of head surfaces of the Y-axis arms (23a, 23b).
Owner:SUMIDA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com