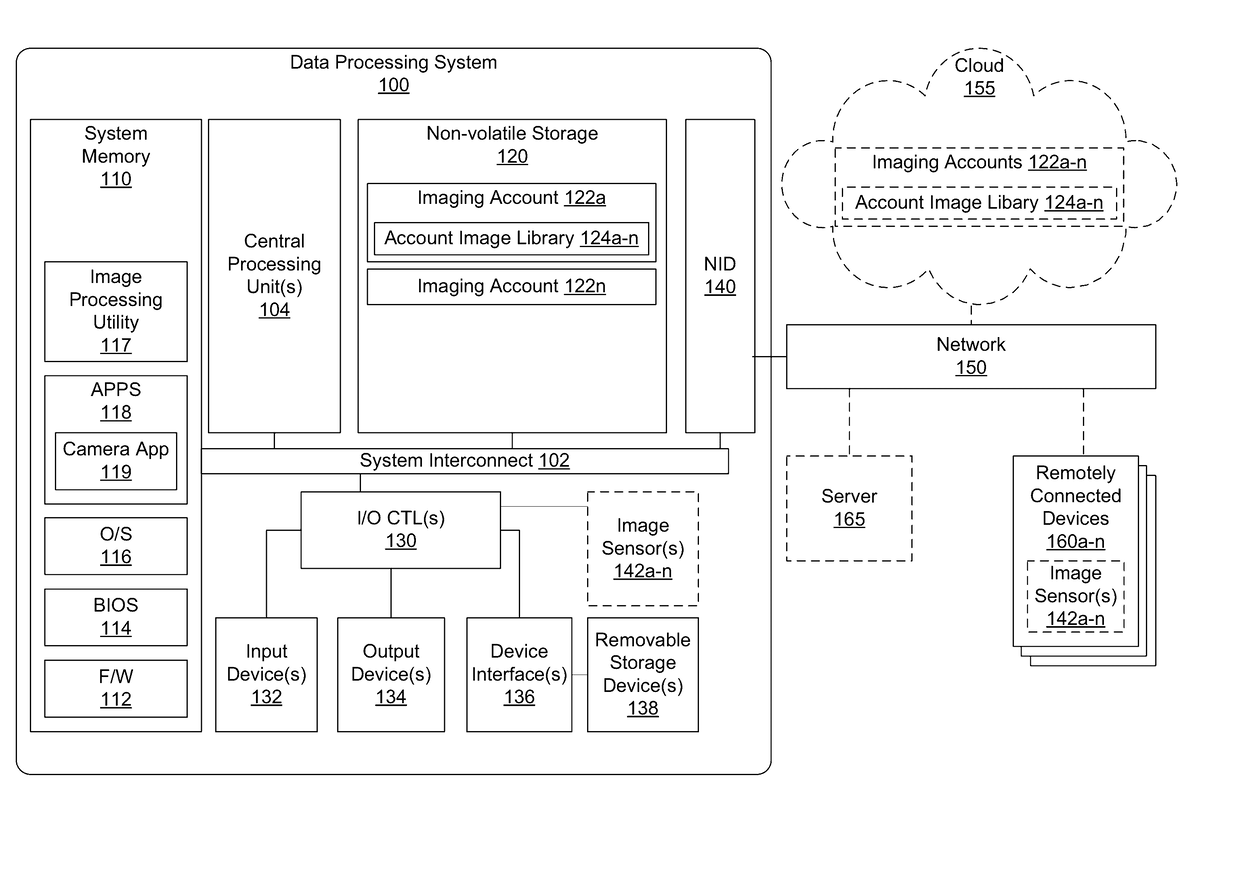
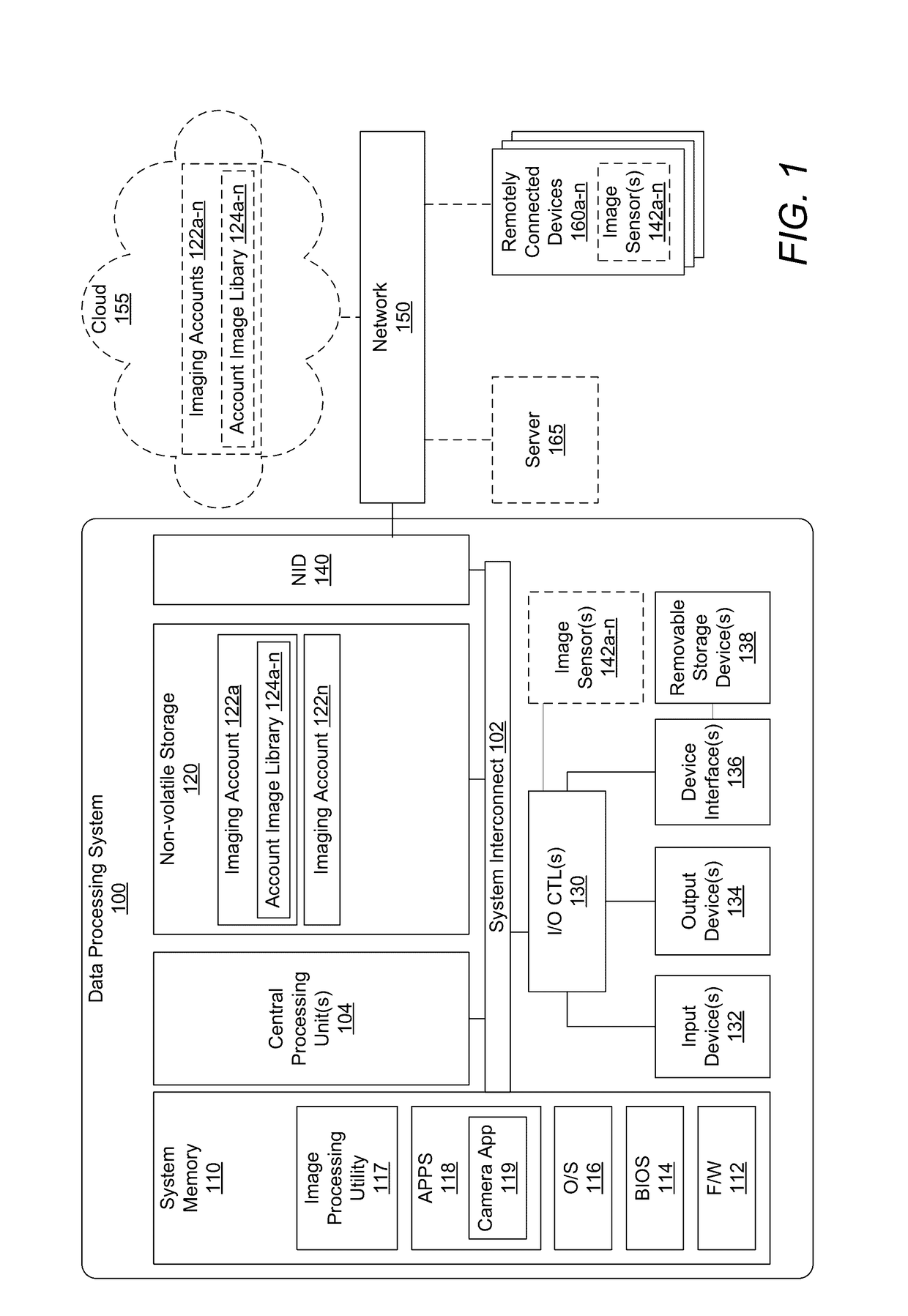
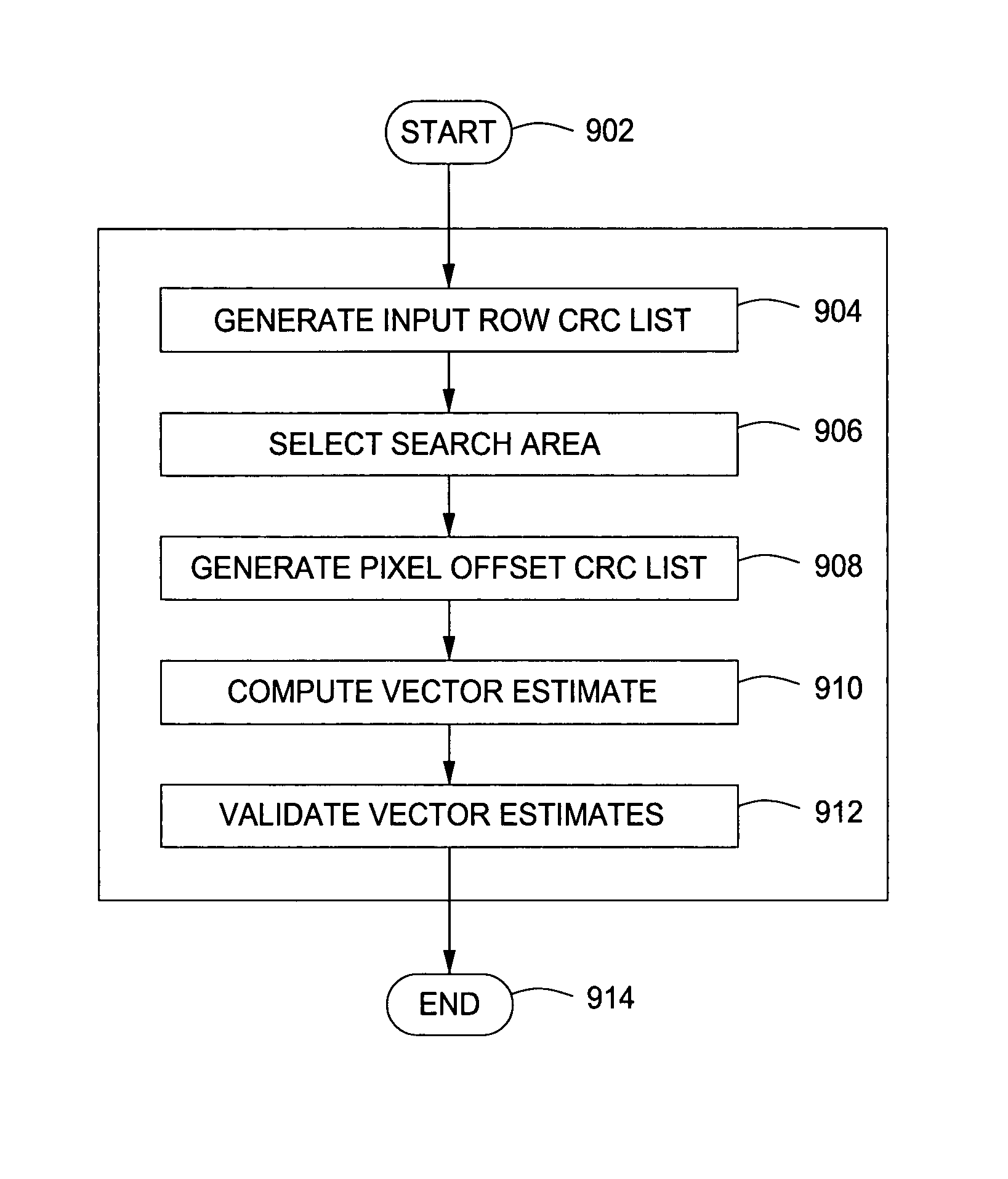
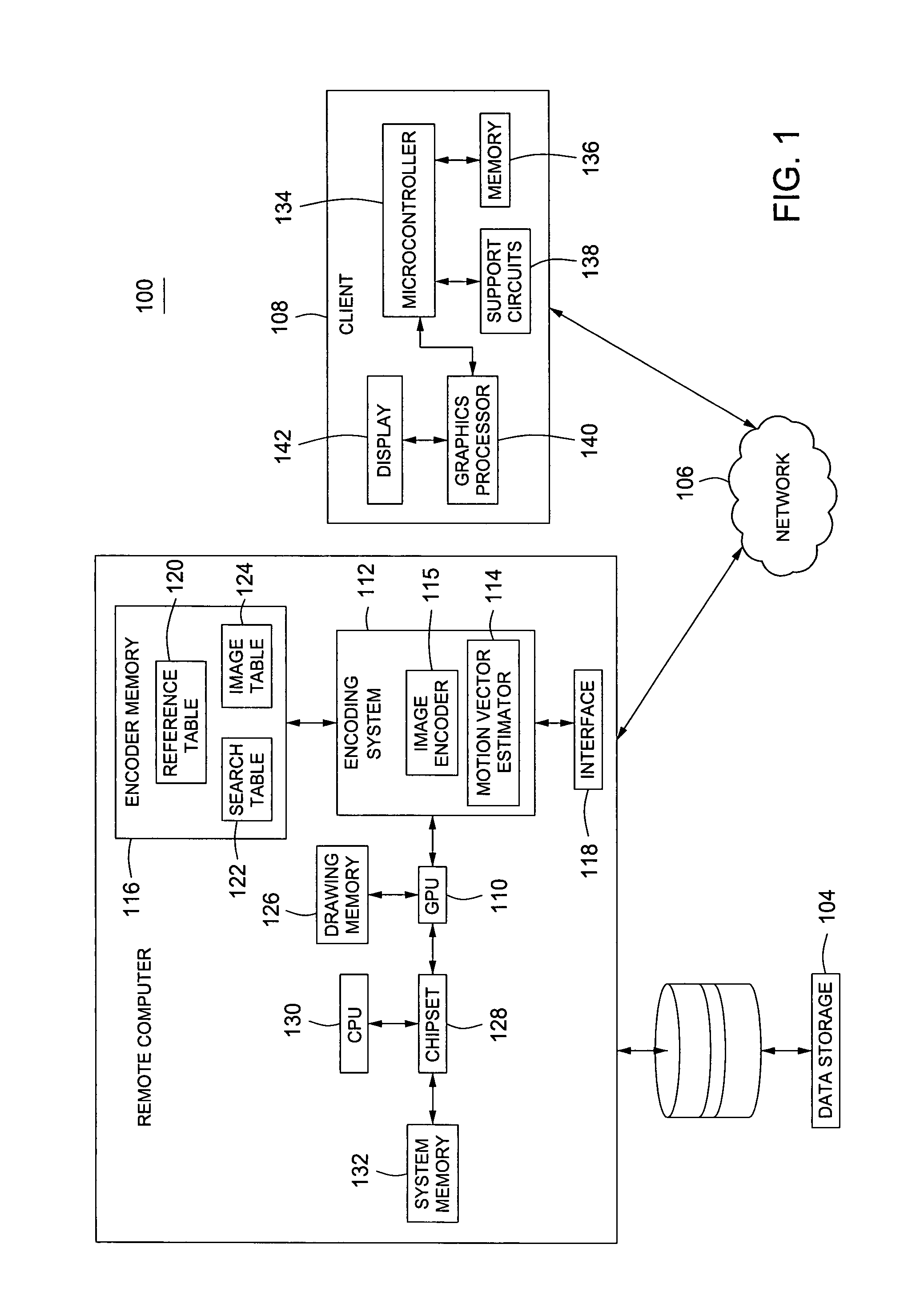
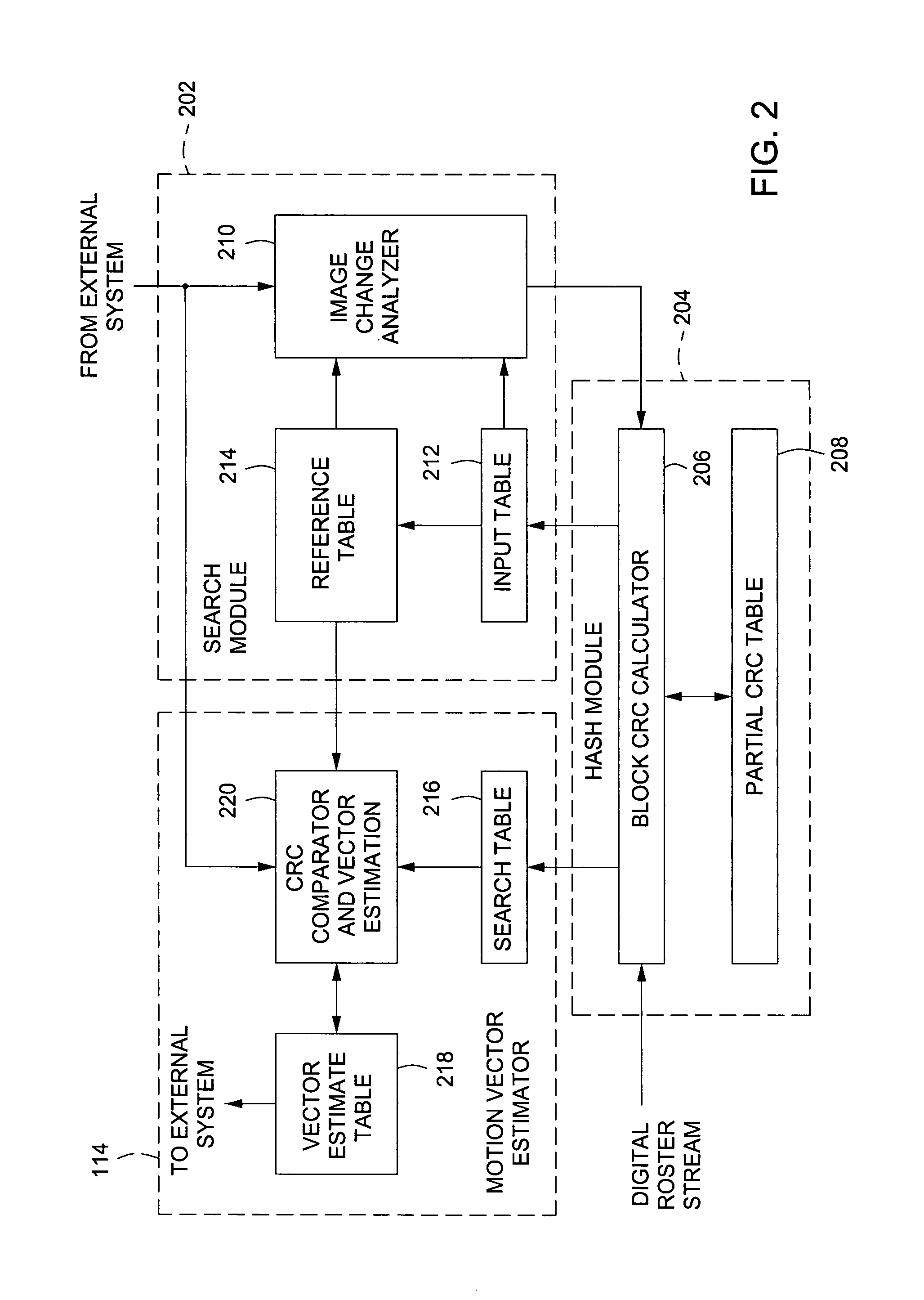
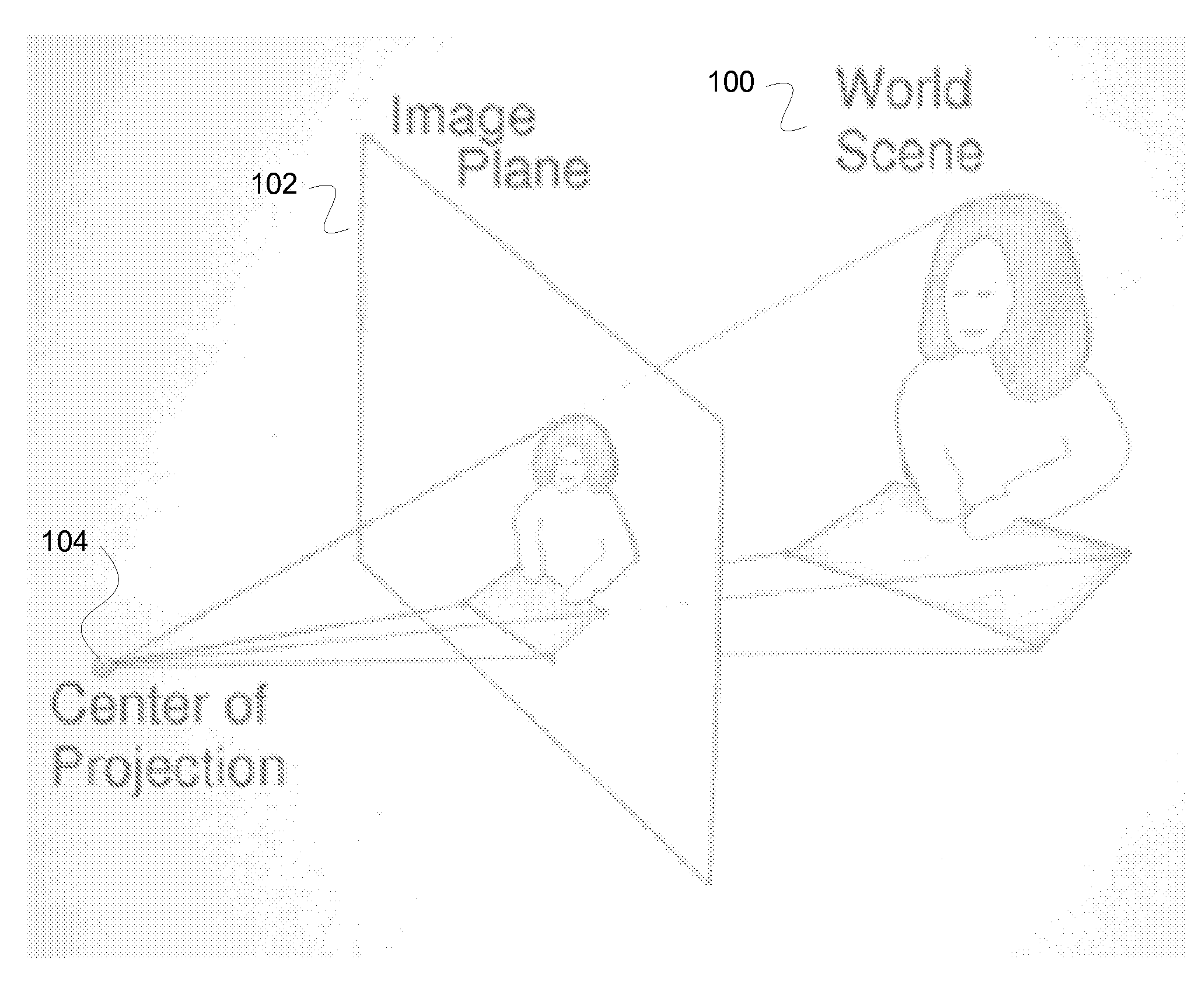
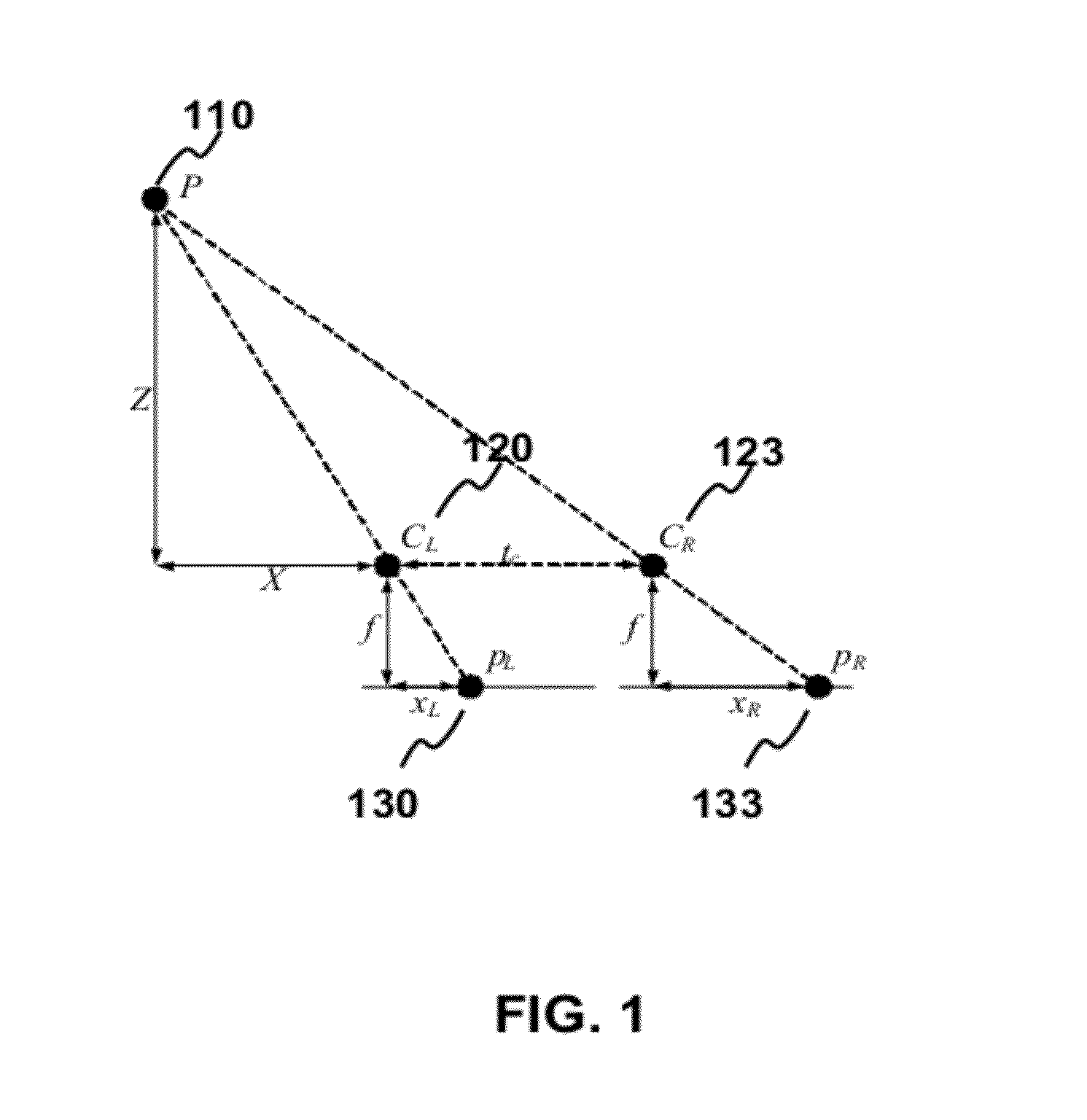
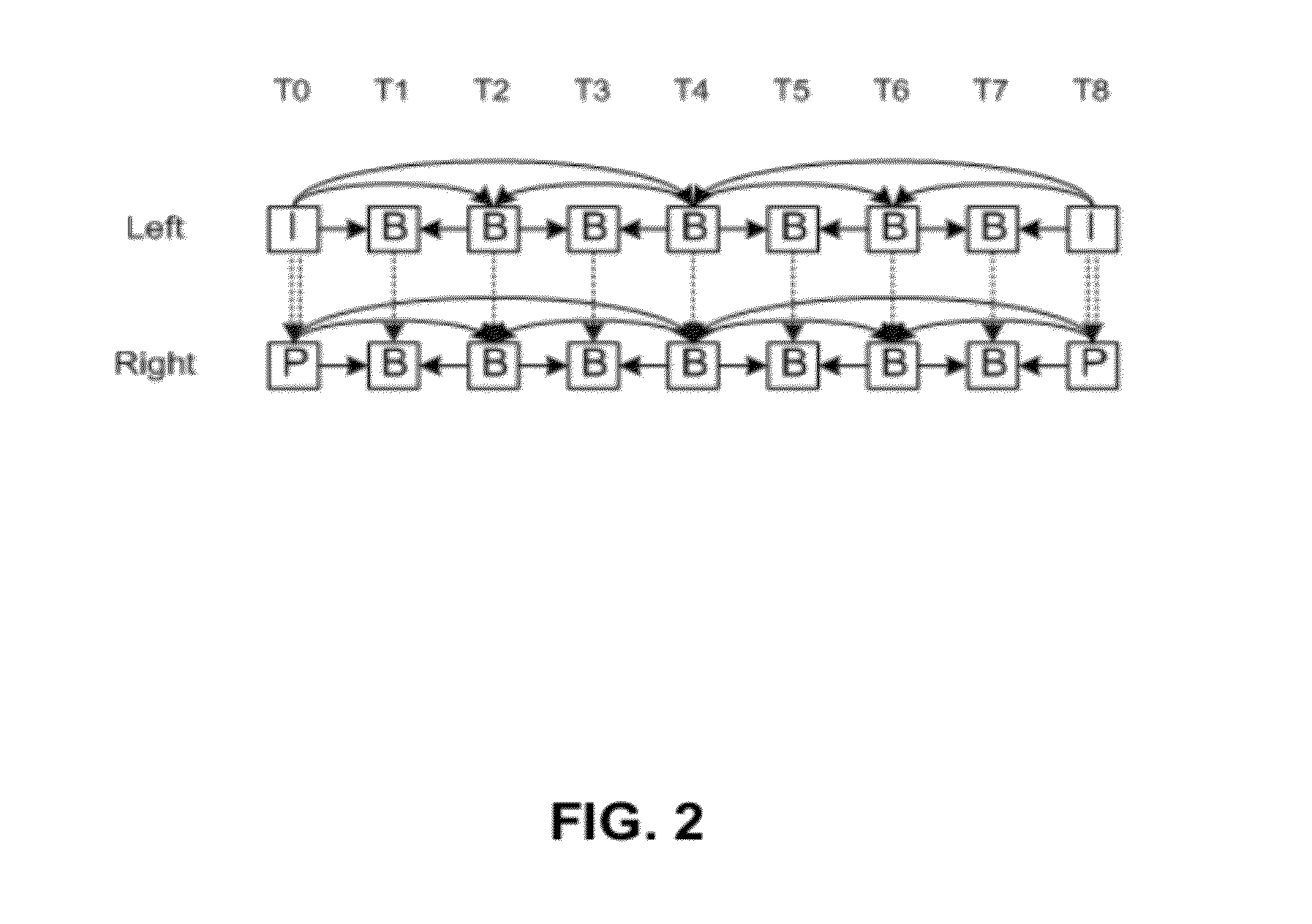
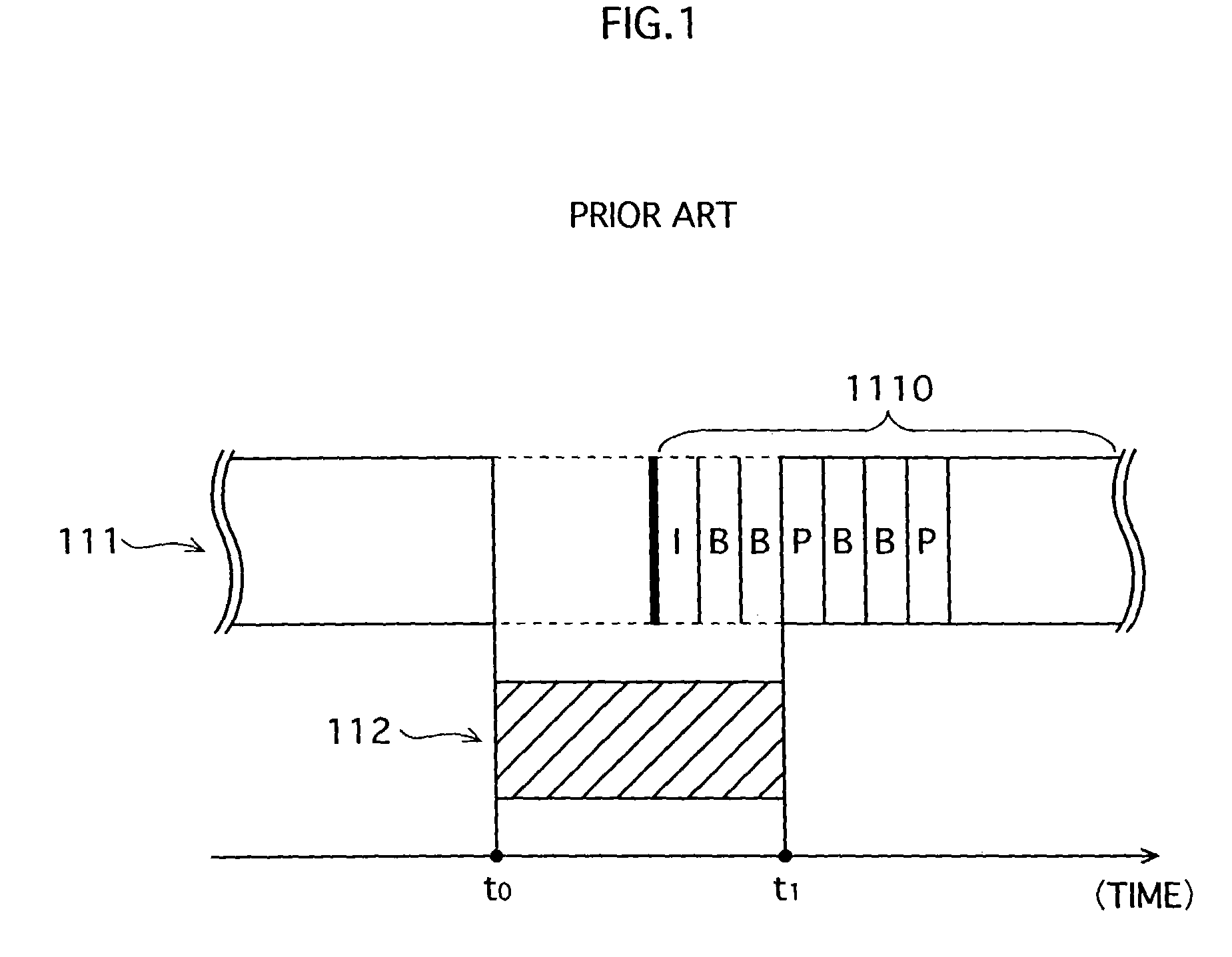
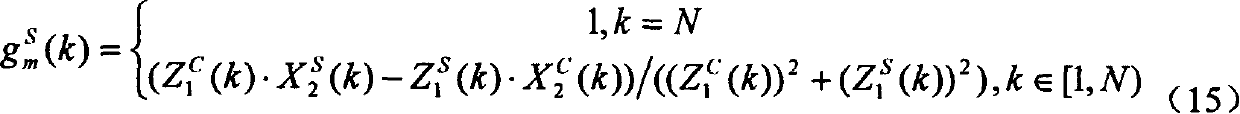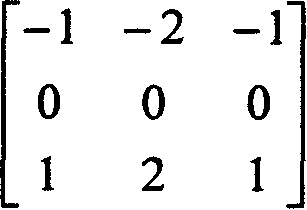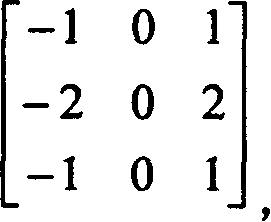Patents
Literature
1051 results about "Reference frame" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
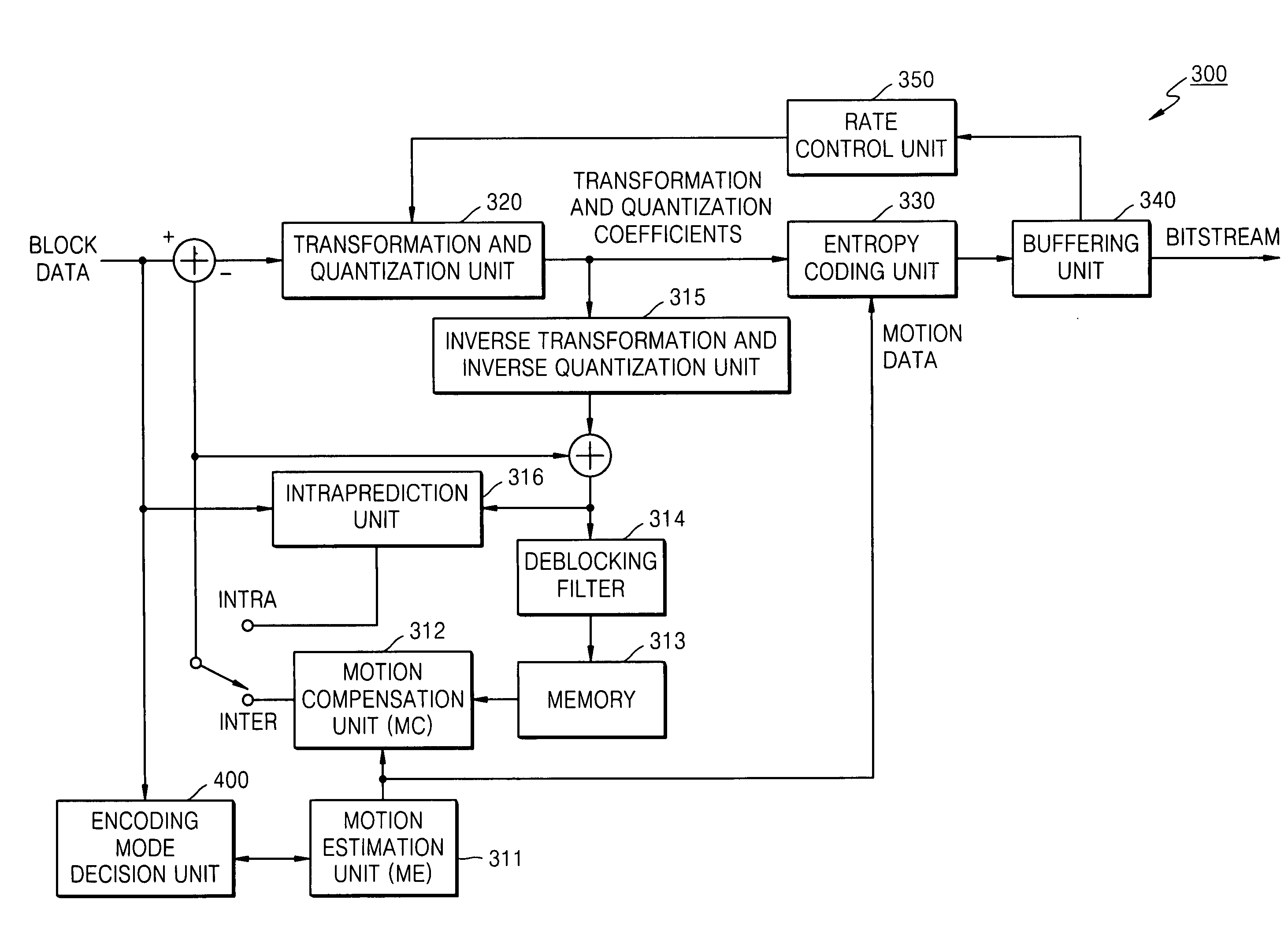
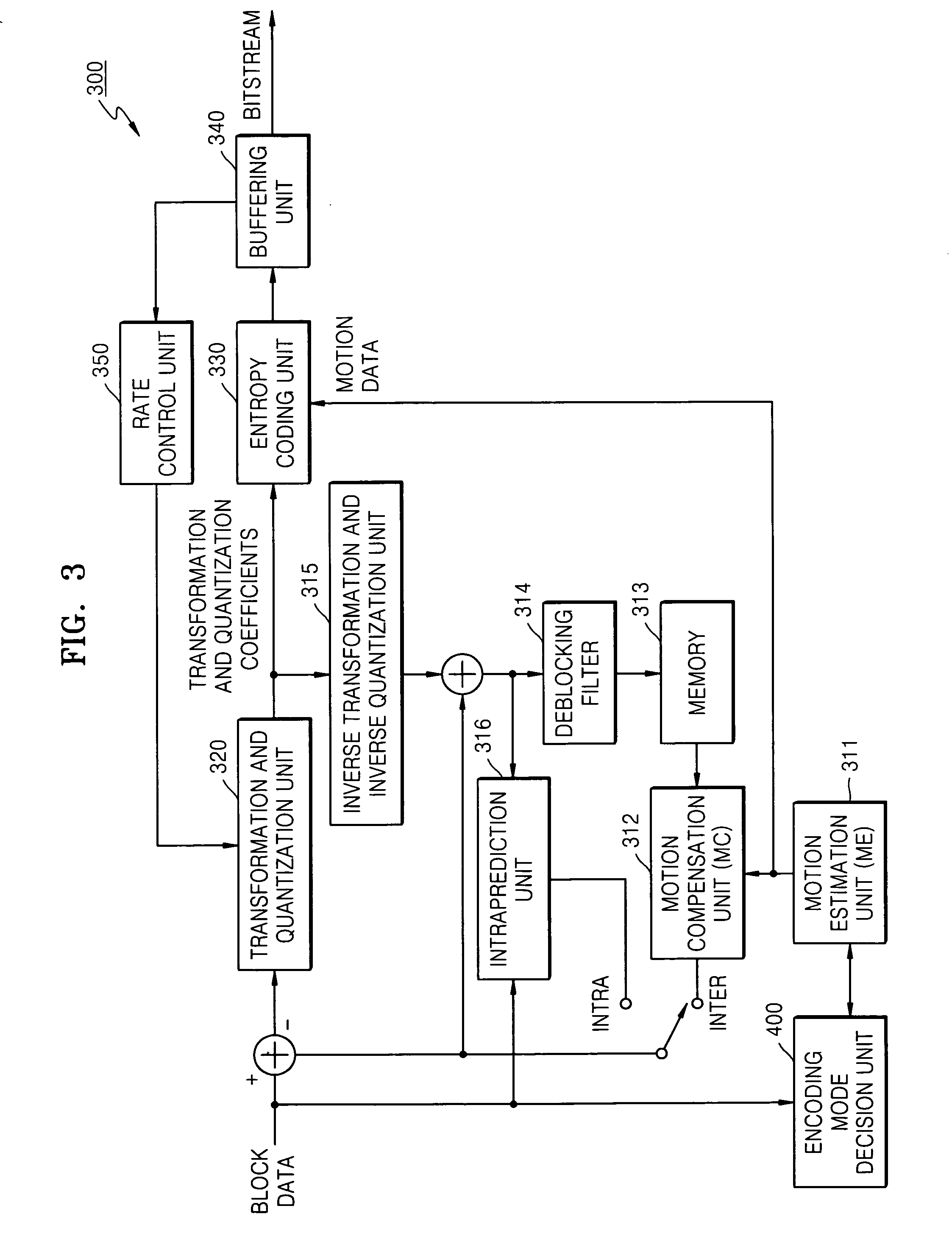
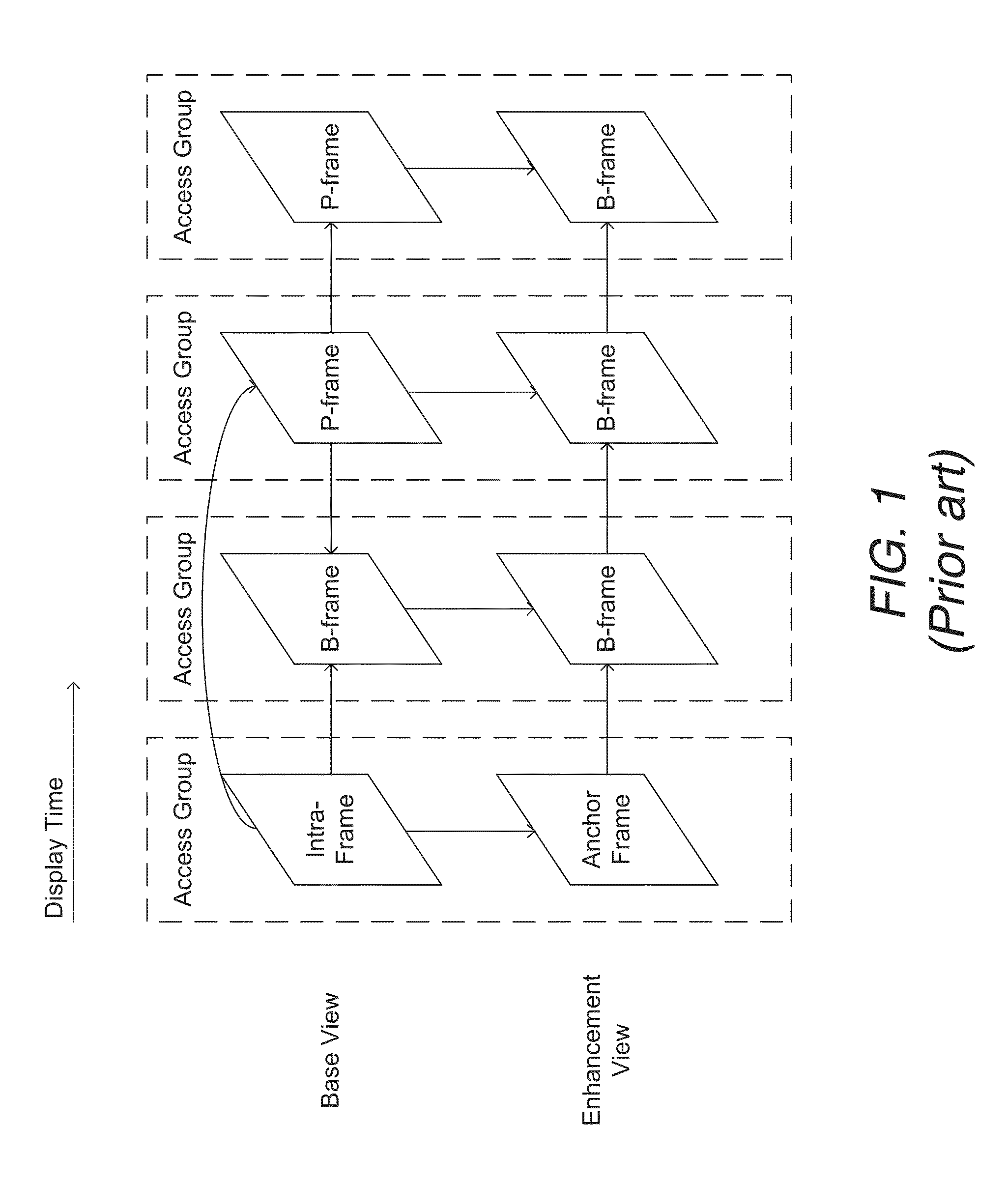
Reference frames are frames of a compressed video that are used to define future frames. As such, they are only used in inter-frame compression techniques. In older video encoding standards, such as MPEG-2, only one reference frame – the previous frame – was used for P-frames. Two reference frames (one past and one future) were used for B-frames.
Inter-layer prediction for extended spatial scalability in video coding
ActiveUS20080165855A1Improving inter-layer predictionReduce computational complexityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionInter layerMotion vector
An improved system and method for providing improved inter-layer prediction for extended spatial scalability in video coding, as well as improving inter-layer prediction for motion vectors in the case of extended spatial scalability. In various embodiments, for the prediction of macroblock mode, the actual reference frame index and motion vectors from the base layer are used in determining if two blocks should be merged. Additionally, multiple representative pixels in a 4×4 block can be used to represent each 4×4 block in a virtual base layer macroblock. The partition and motion vector information for the relevant block in the virtual base layer macroblock can be derived from all of the partition information and motion vectors of those 4×4 blocks.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
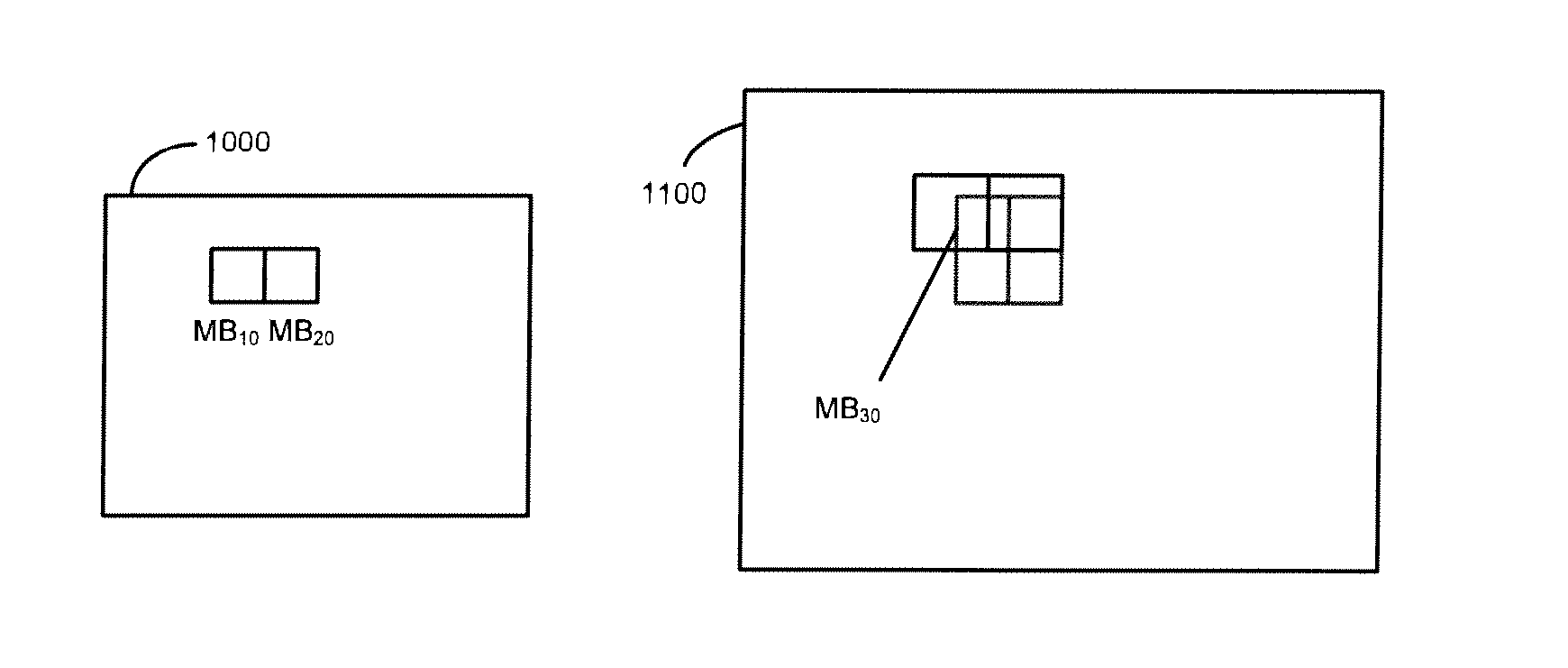
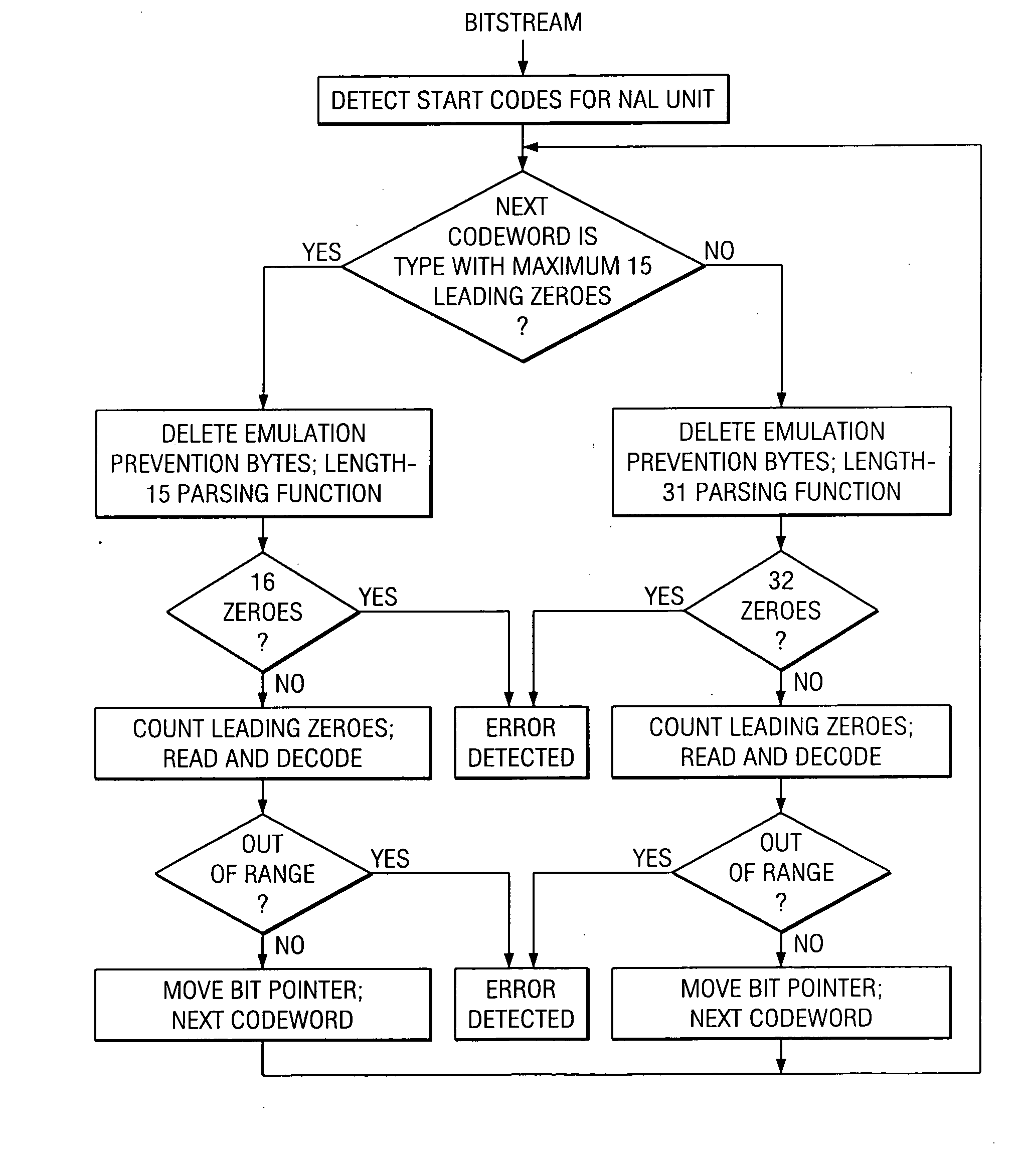
Video error detection, recovery, and concealment
InactiveUS20060013318A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer hardwareReference frame
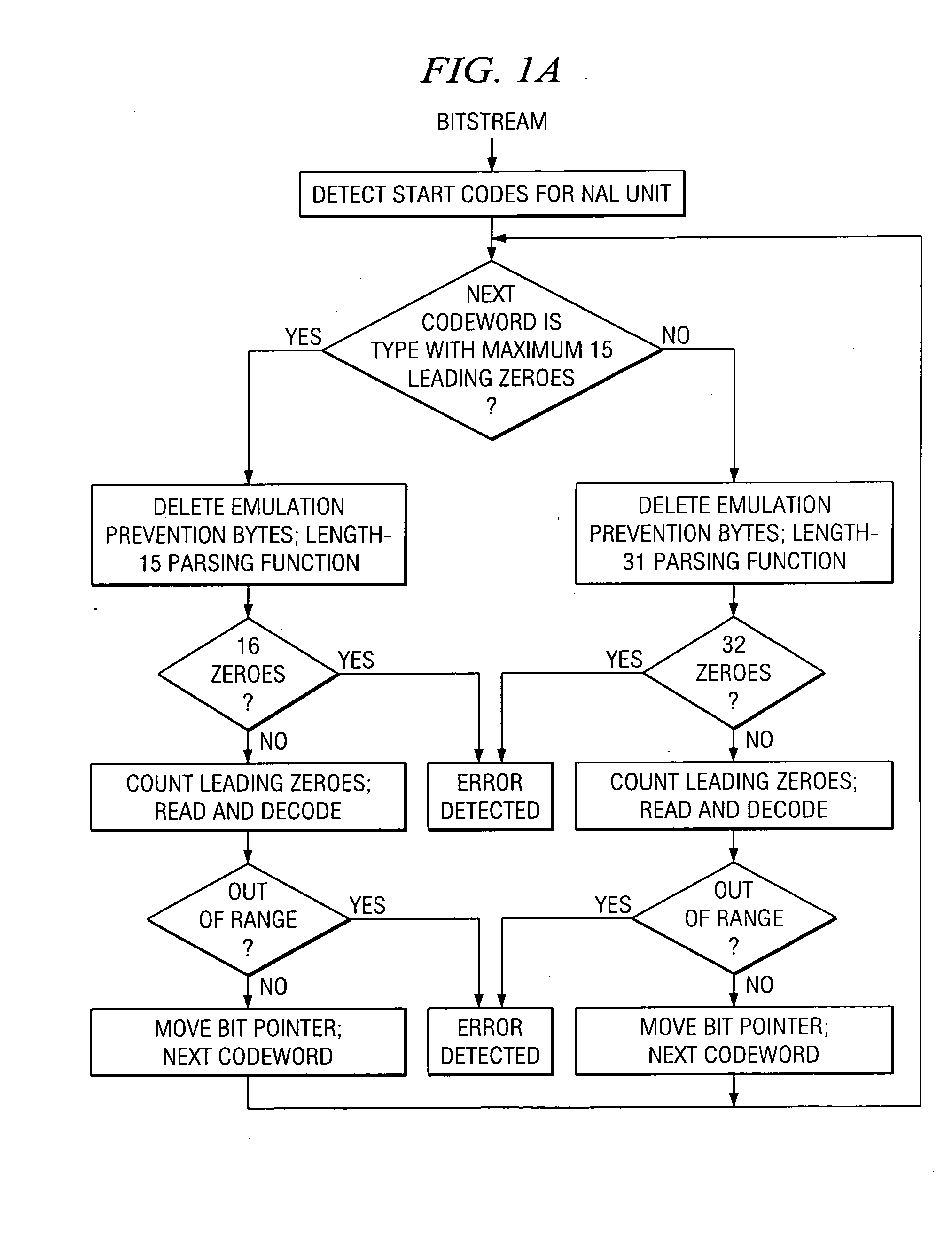
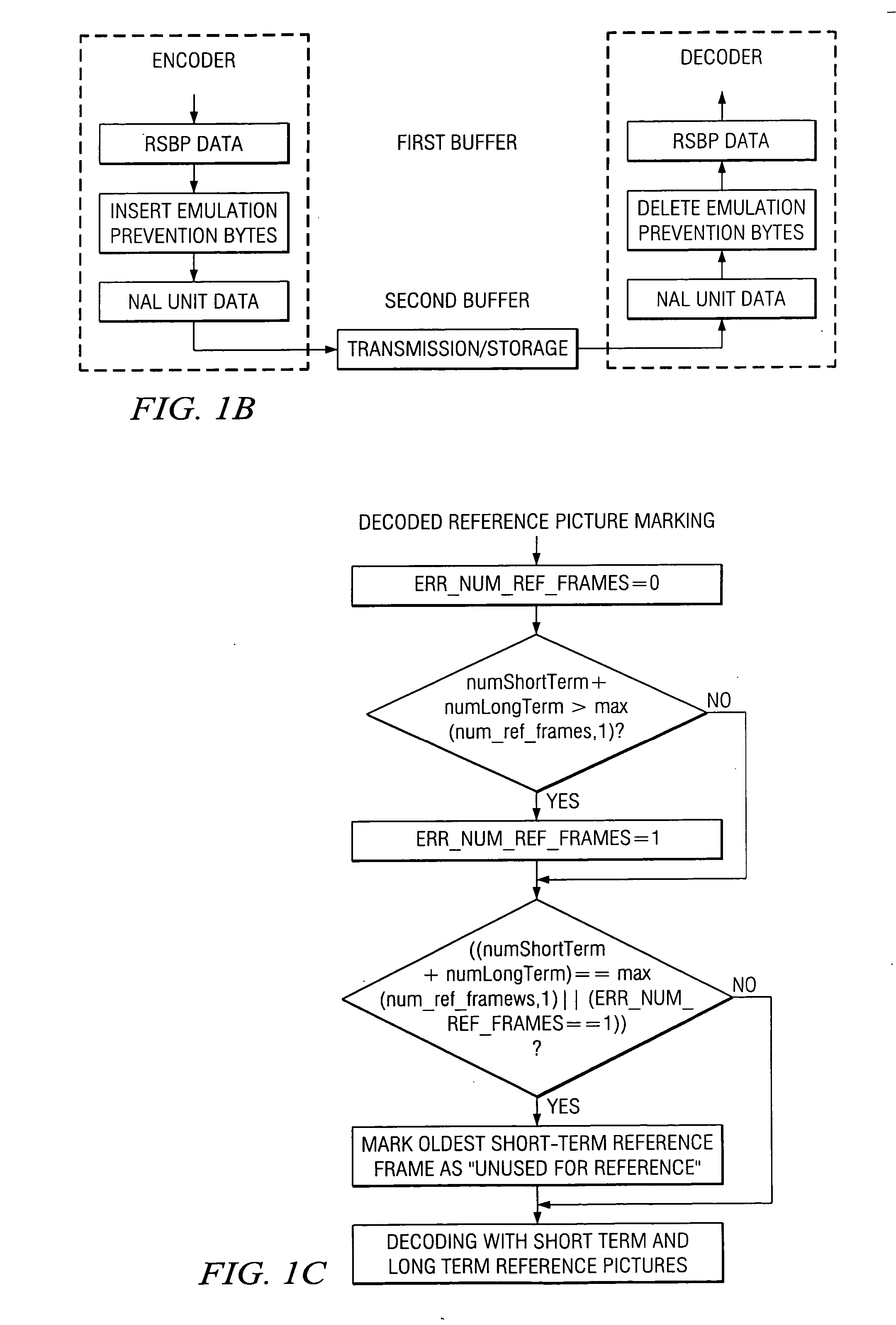
Decoding for H.264 with error detection, recovery, and concealment including two parsing functions for efficient detection of errors in exp-Golomb codewords, recovery for error in the number of reference frames, skipping to an uncorrupted SPS / PPS NAL unit, and concealment of invalid gaps in frame number by separate gap size 2 and greater than size 2 analysis.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Device and method for fast block-matching motion estimation in video encoders
InactiveUS20060245497A1Reduce complexityQuick estimateColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorVideo sequence
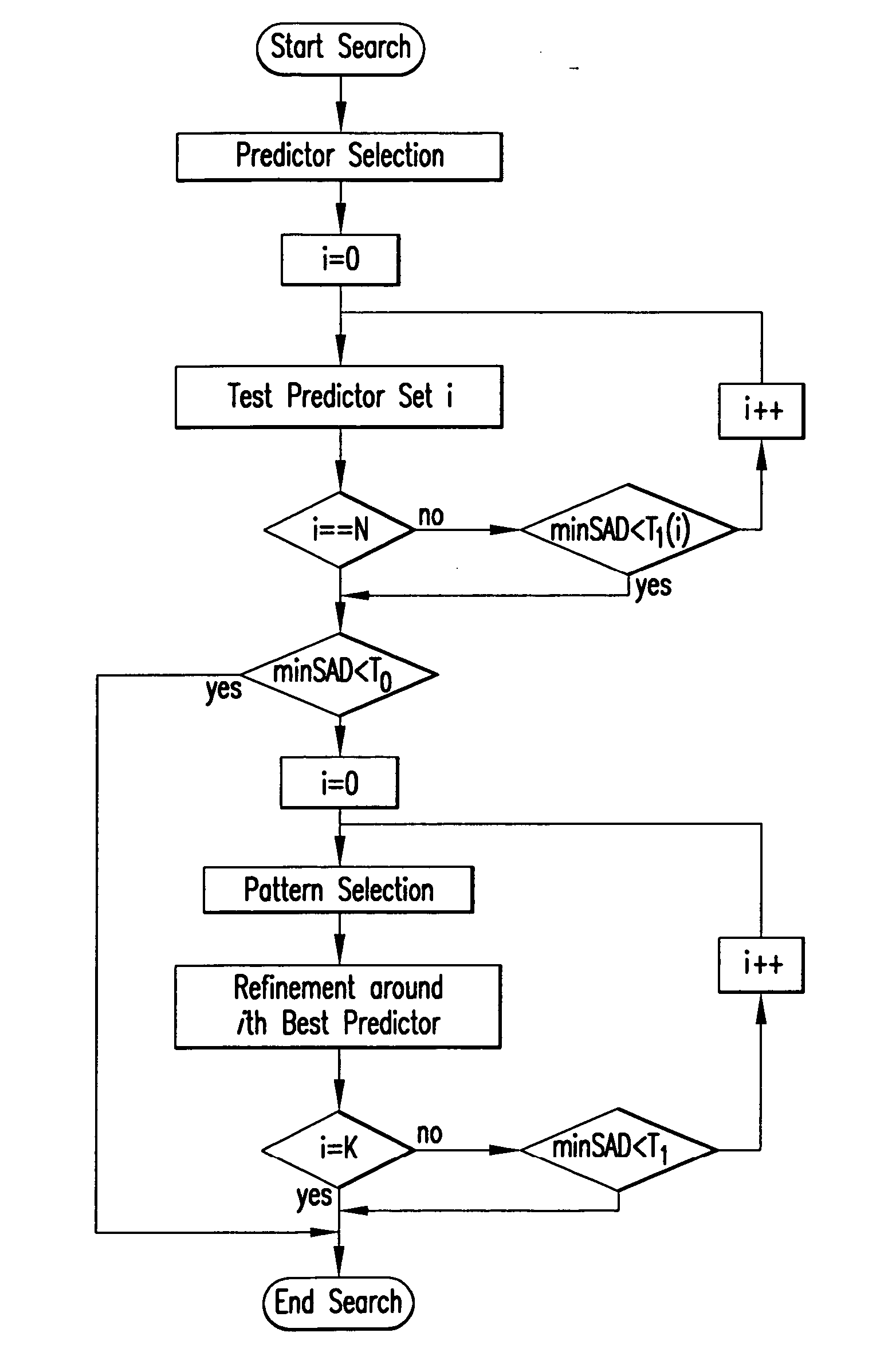
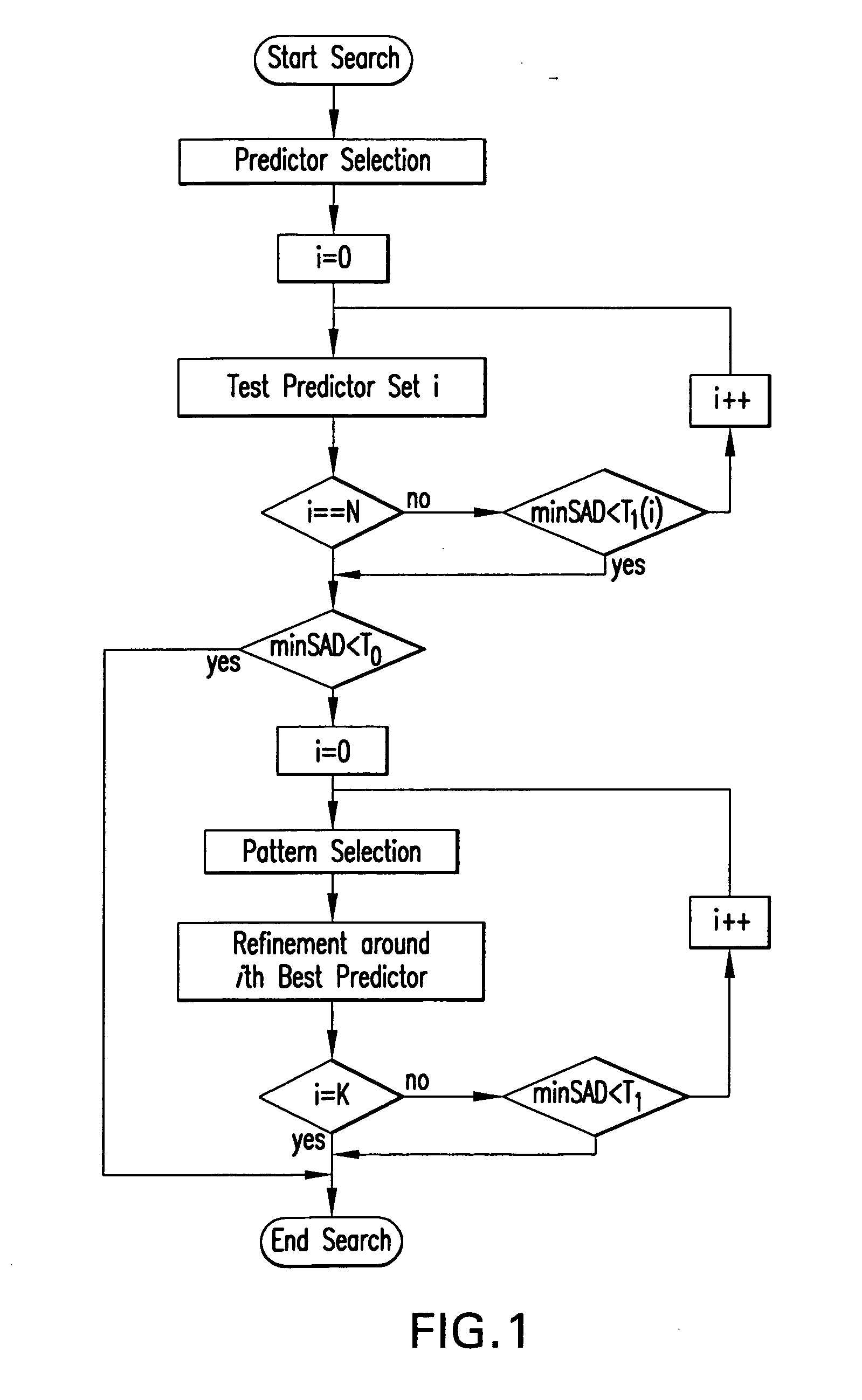
Motion estimation is the science of predicting the current frame in a video sequence from the past frame (or frames), by slicing it into rectangular blocks of pixels, and matching these to past such blocks. The displacement in the spatial position of the block in the current frame with respect to the past frame is called the motion vector. This method of temporally decorrelating the video sequence by finding the best matching blocks from past reference frames—motion estimation—makes up about 80% or more of the computation in a video encoder. That is, it is enormously expensive, and methods do so that are efficient are in high demand. Thus the field of motion estimation within video coding is rich in the breadth and diversity of approaches that have been put forward. Yet it is often the simplest methods that are the most effective. So it is in this case. While it is well-known that a full search over all possible positions within a fixed window is an optimal method in terms of performance, it is generally prohibitive in computation. In this patent disclosure, we define an efficient, new method of searching only a very sparse subset of possible displacement positions (or motion vectors) among all possible ones, to see if we can get a good enough match, and terminate early. This set of sparse subset of motion vectors is preselected, using a priori knowledge and extensive testing on video sequences, so that these “predictors” for the motion vector are essentially magic. The art of this method is the preselection of excellent sparse subsets of vectors, the smart thresholds for acceptance or rejection, and even in the order of the testing prior to decision.
Owner:FASTVDO
System and method for reconstruction of the human ear canal from optical coherence tomography scans
InactiveUS20060276709A1High-resolution imageAccurate modelingSurgeryHearing aid design aspectsOffset distanceScan line
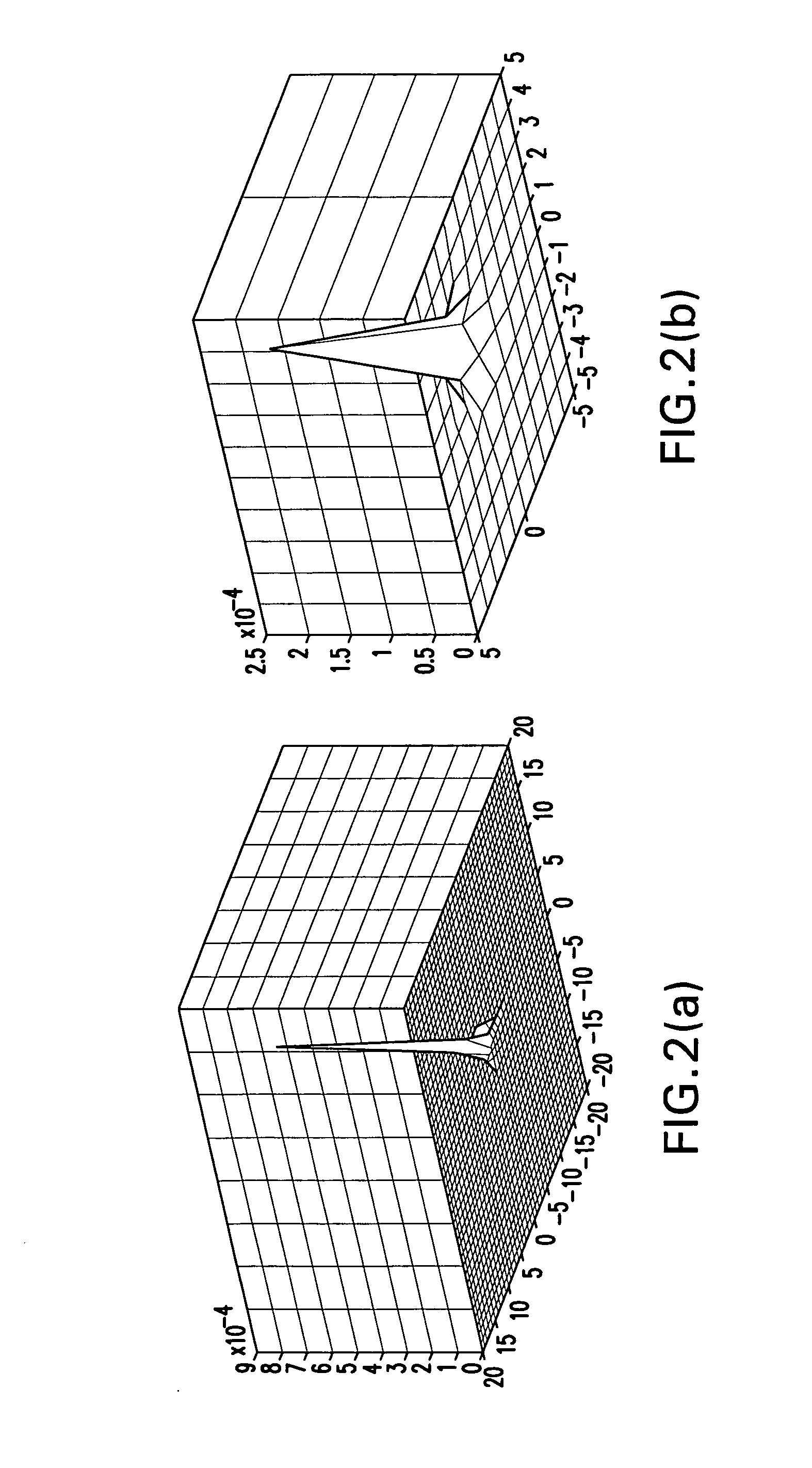
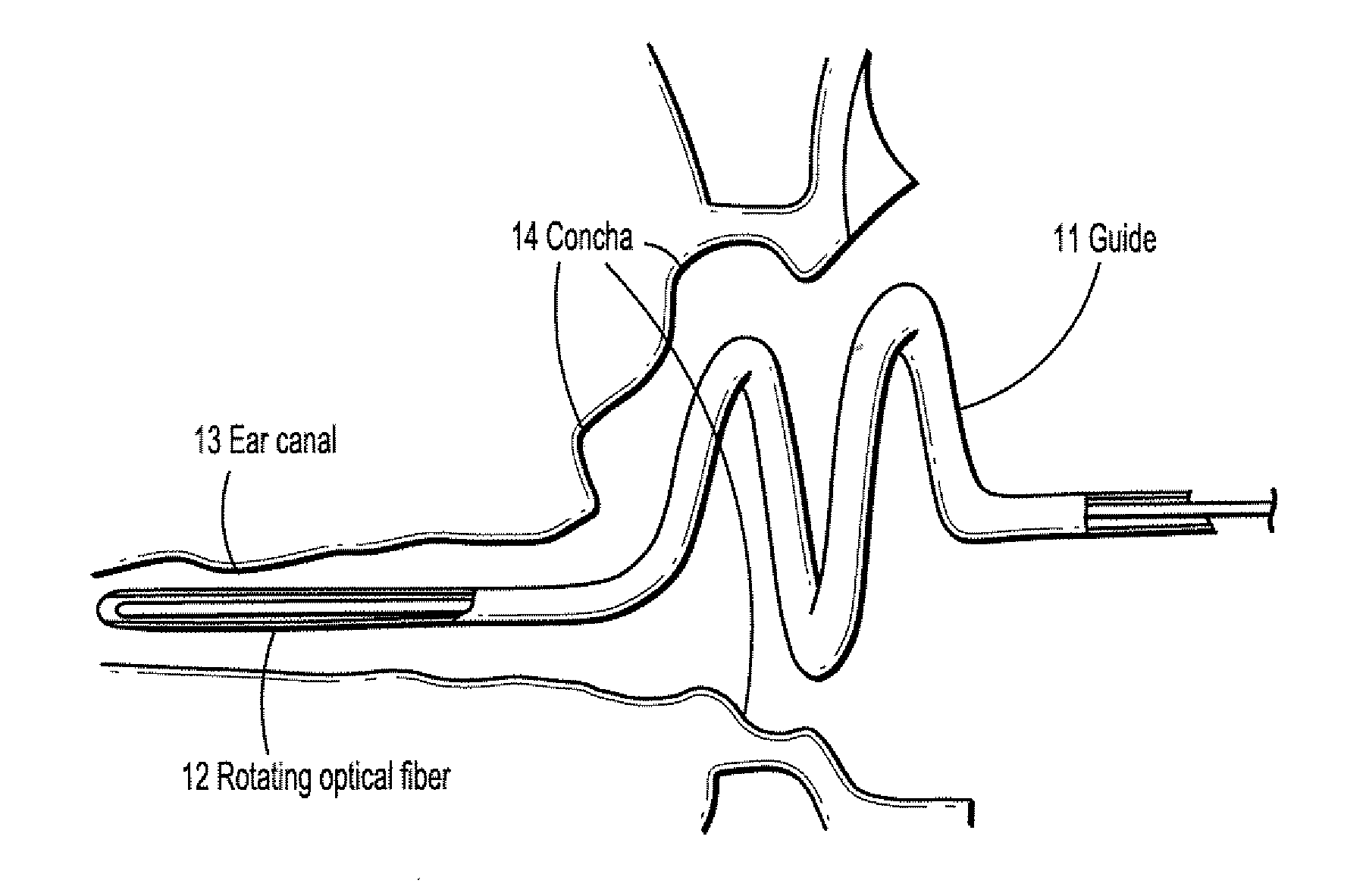
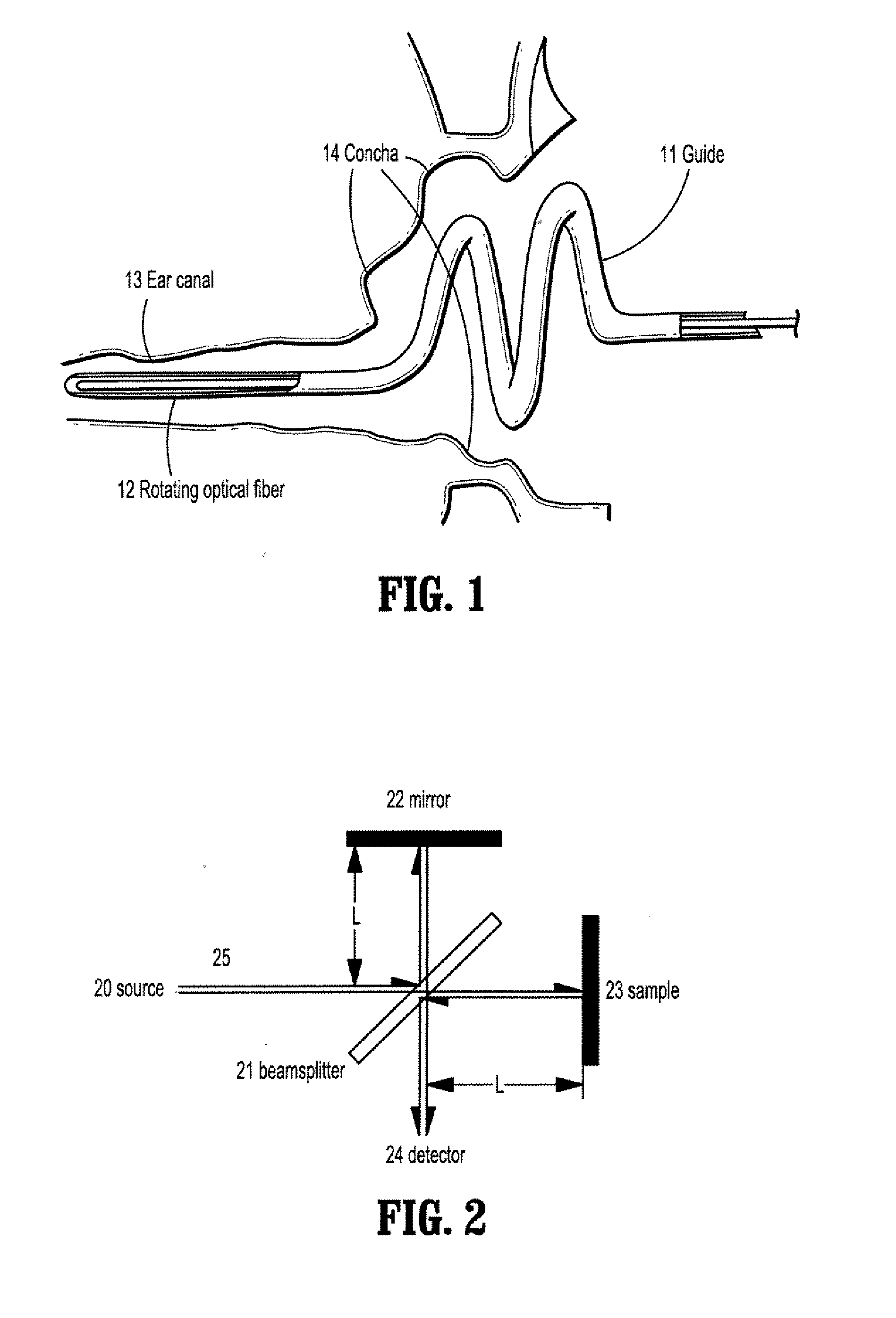
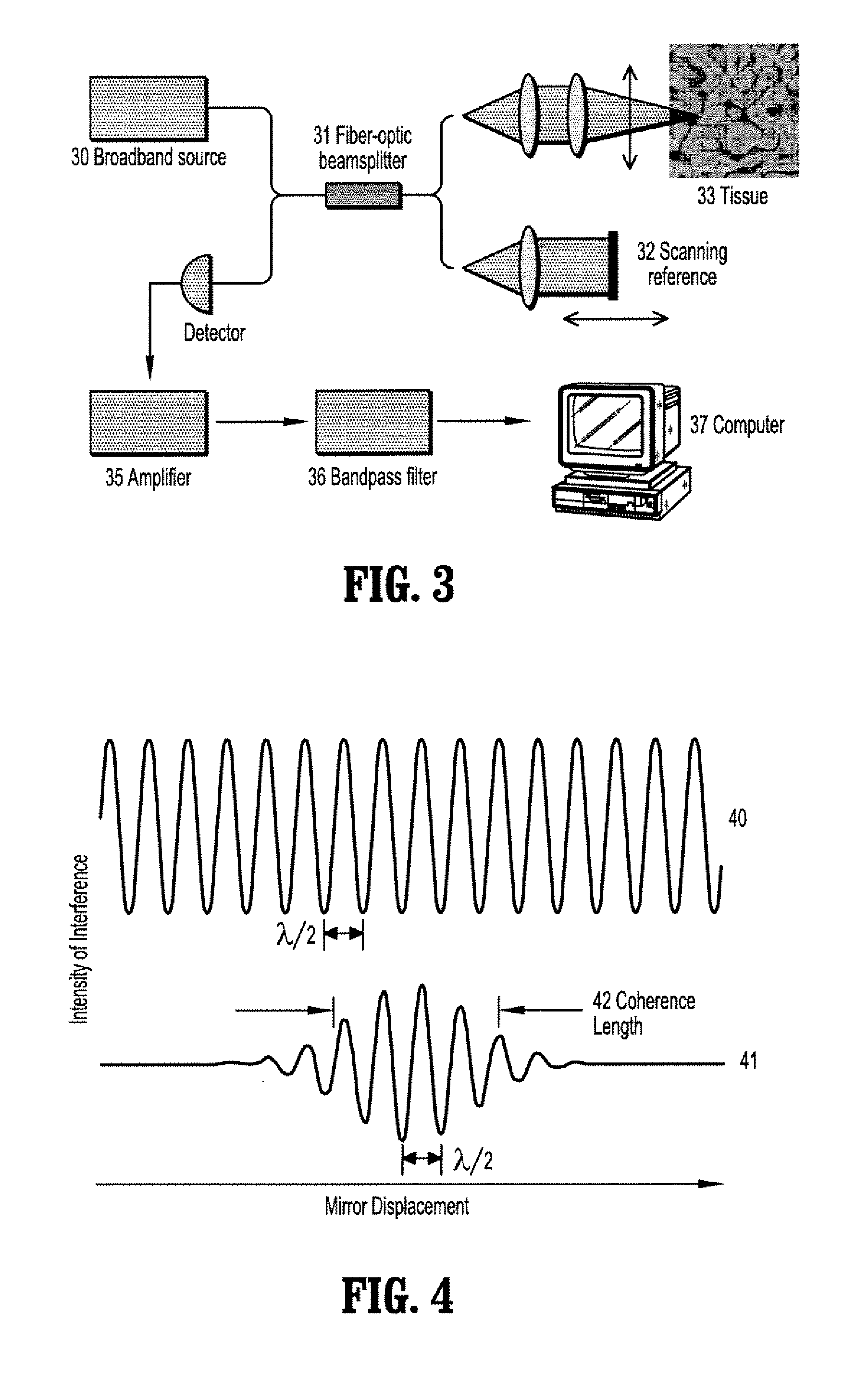
A method for reconstructing an ear canal from optical coherence tomography (OCT) scan data of an ear comprises extracting frame numbers and line numbers of interference intensities corresponding to one or more markers on an OCT scan guide, receiving reference frame numbers and lines numbers for one or more markers, determining a starting position and direction for the OCT ear scan from the ear scan marker frame and line numbers and the reference marker frame and line numbers, for each scan line, finding a pixel number of a maximum interference intensity value, and determining an offset distance of said pixel from said scan guide, and reconstructing a surface of the ear canal from the distance offset data.
Owner:SIEMENS HEARING INSTRUMENTS +1
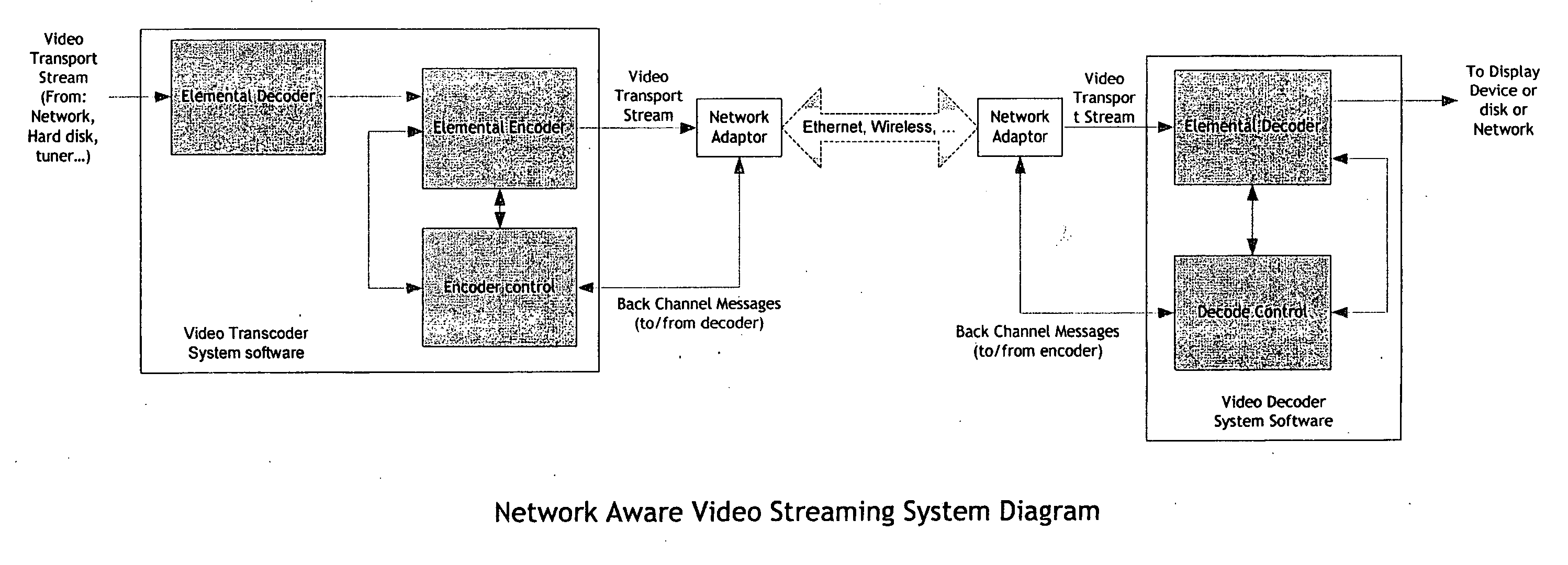
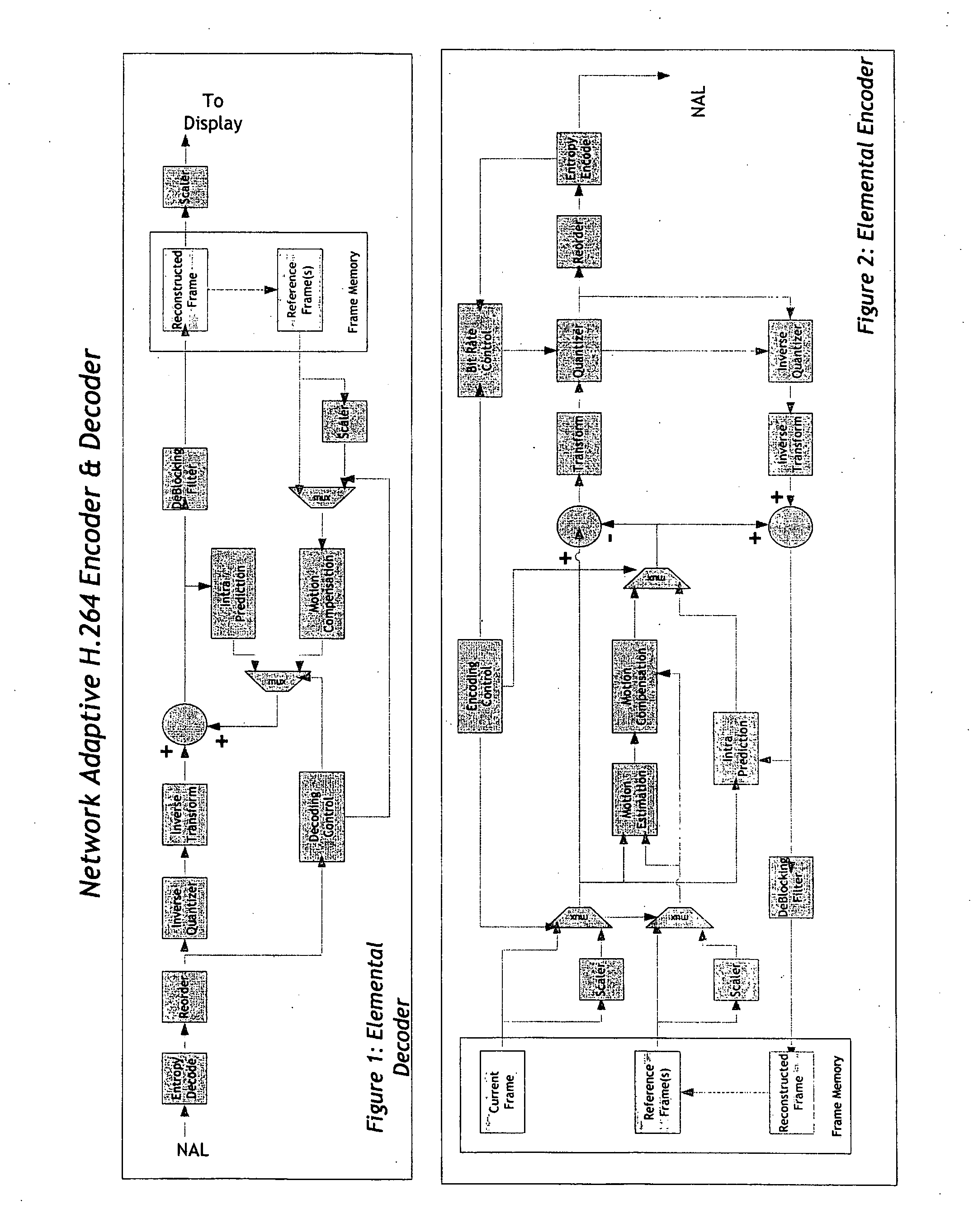
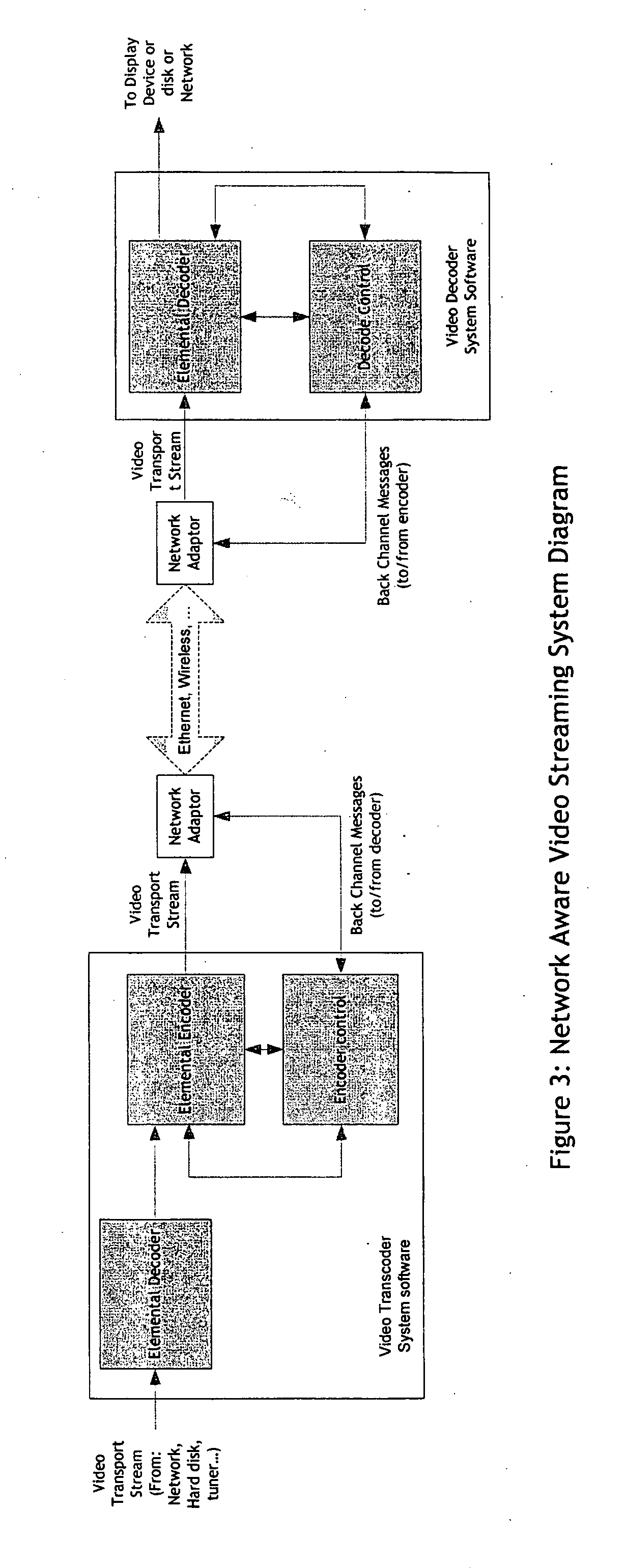
Real-time network adaptive digital video encoding/decoding
ActiveUS20080084927A1Lowering scale factorLow data ratePulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesDigital videoImaging quality
A method for real time video transmission over networks with varying bandwidth is described. Image quality is maintained even under degrading network performance conditions through the use of image scaling in conjunction with block based motion compensated video coding (MPEG2 / 4, H.264, et. Al.). The ability to quickly switch resolutions without decreasing reference frame correlation is shown enabling a fast switch to reduce the required bandwidth for stable image quality.
Owner:ELEMENTAL TECH LLC
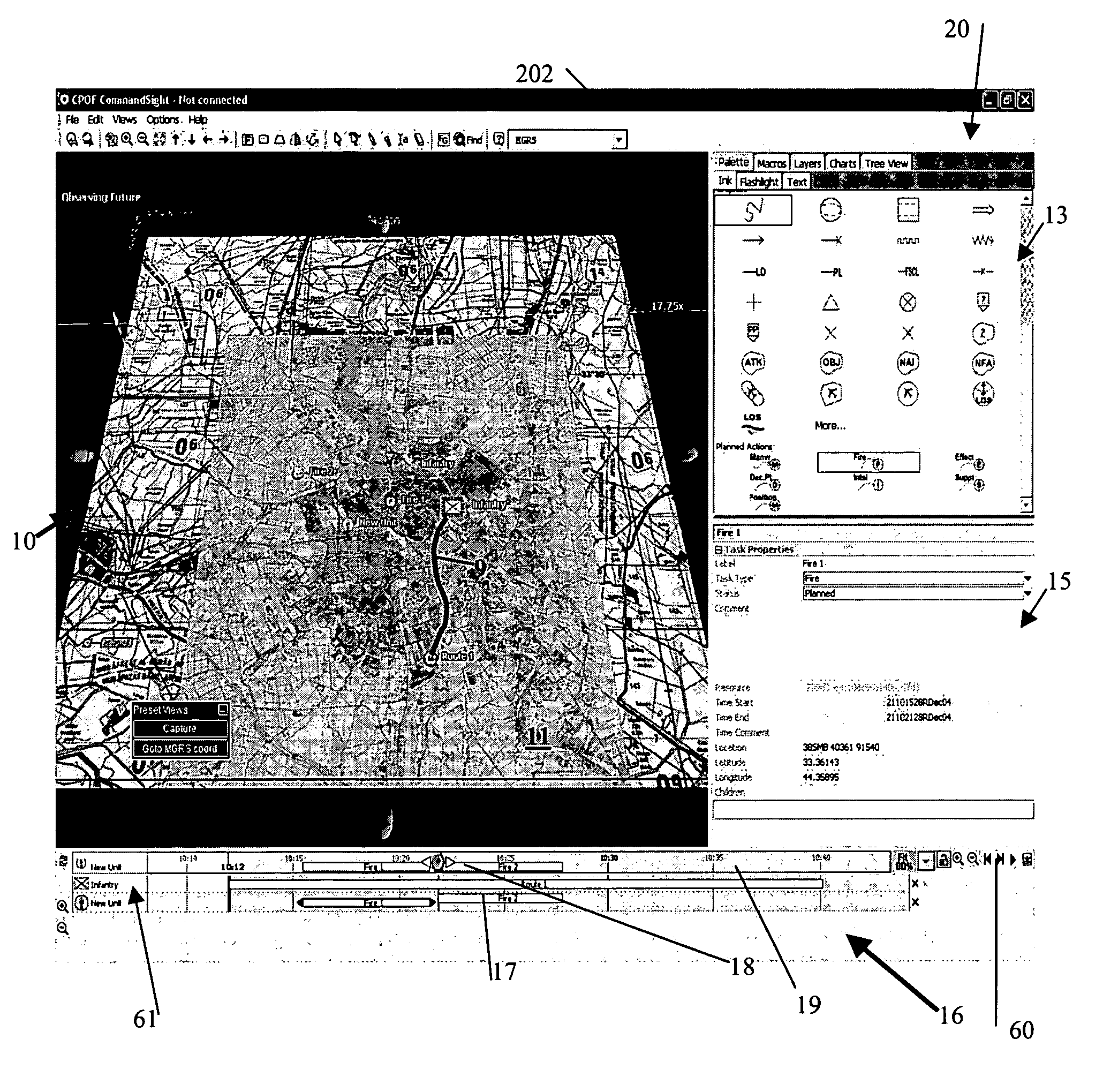
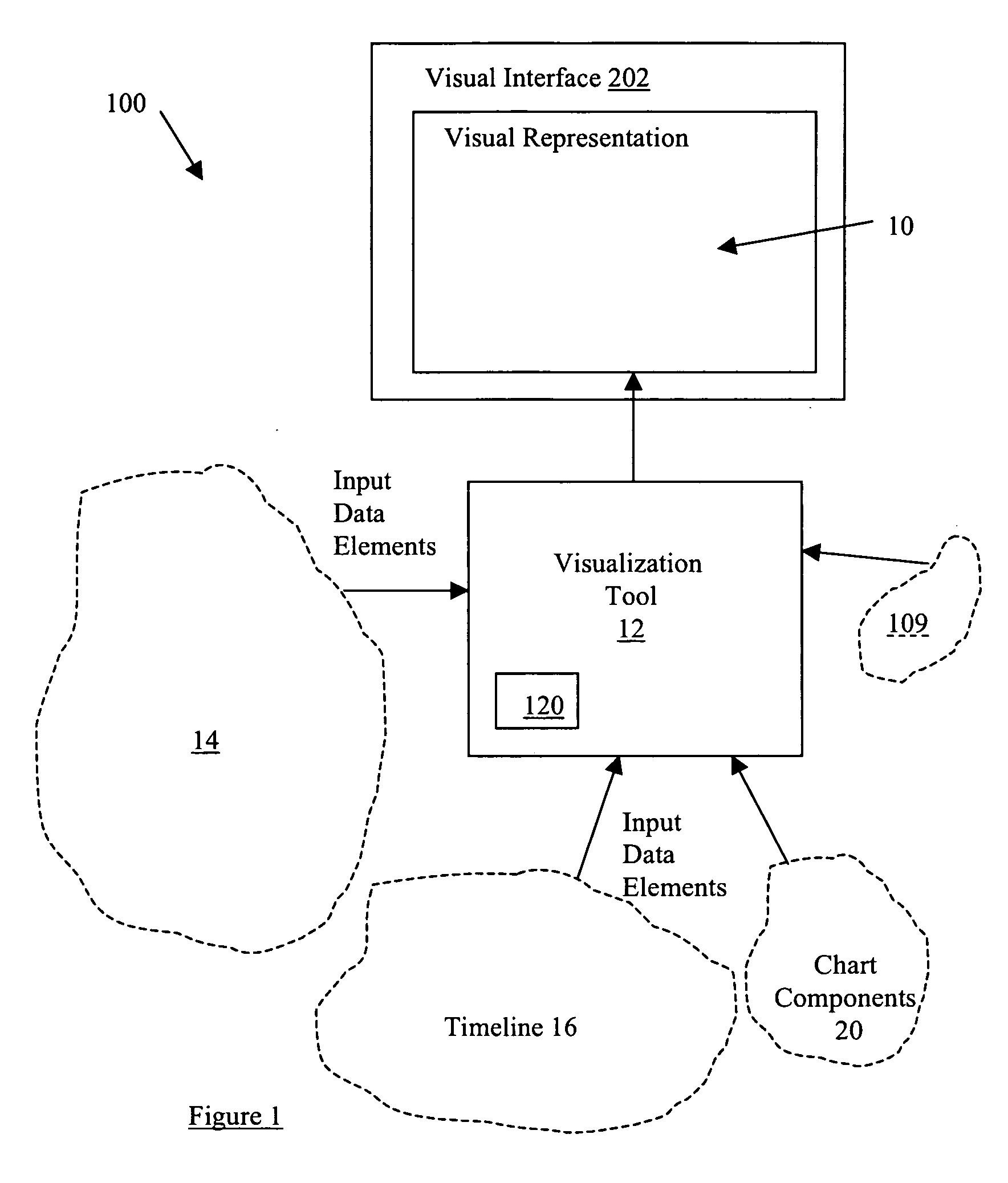
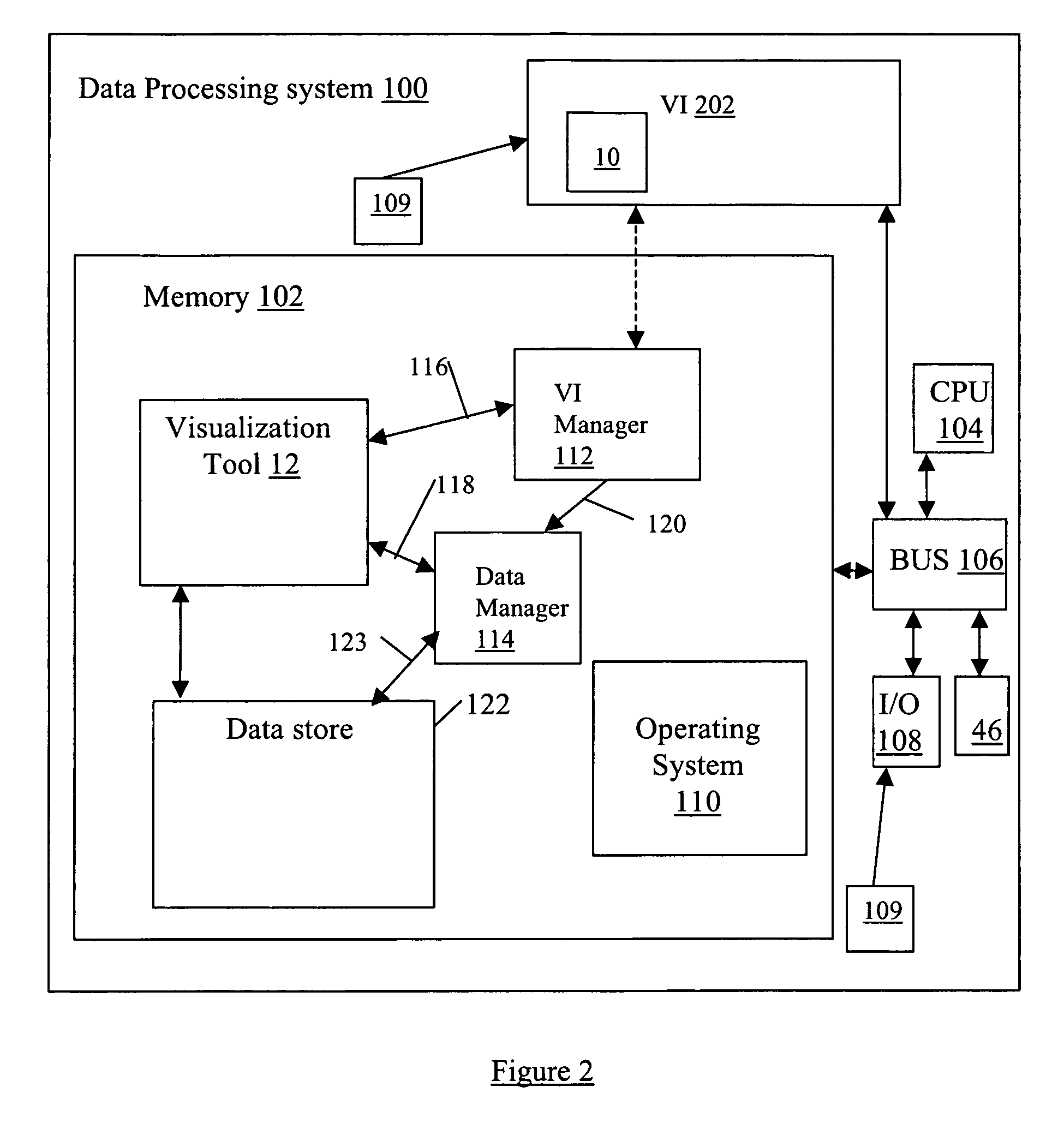
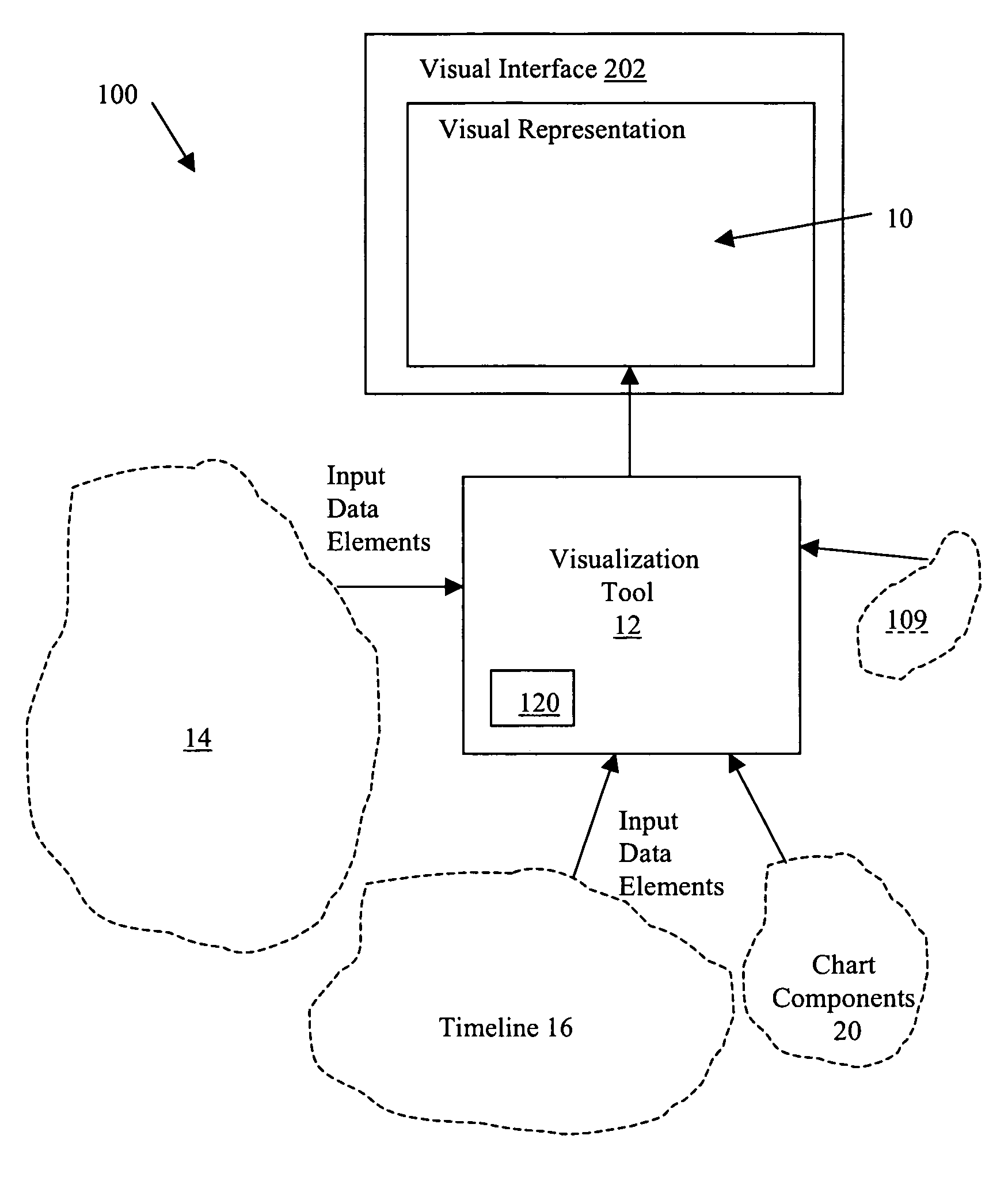
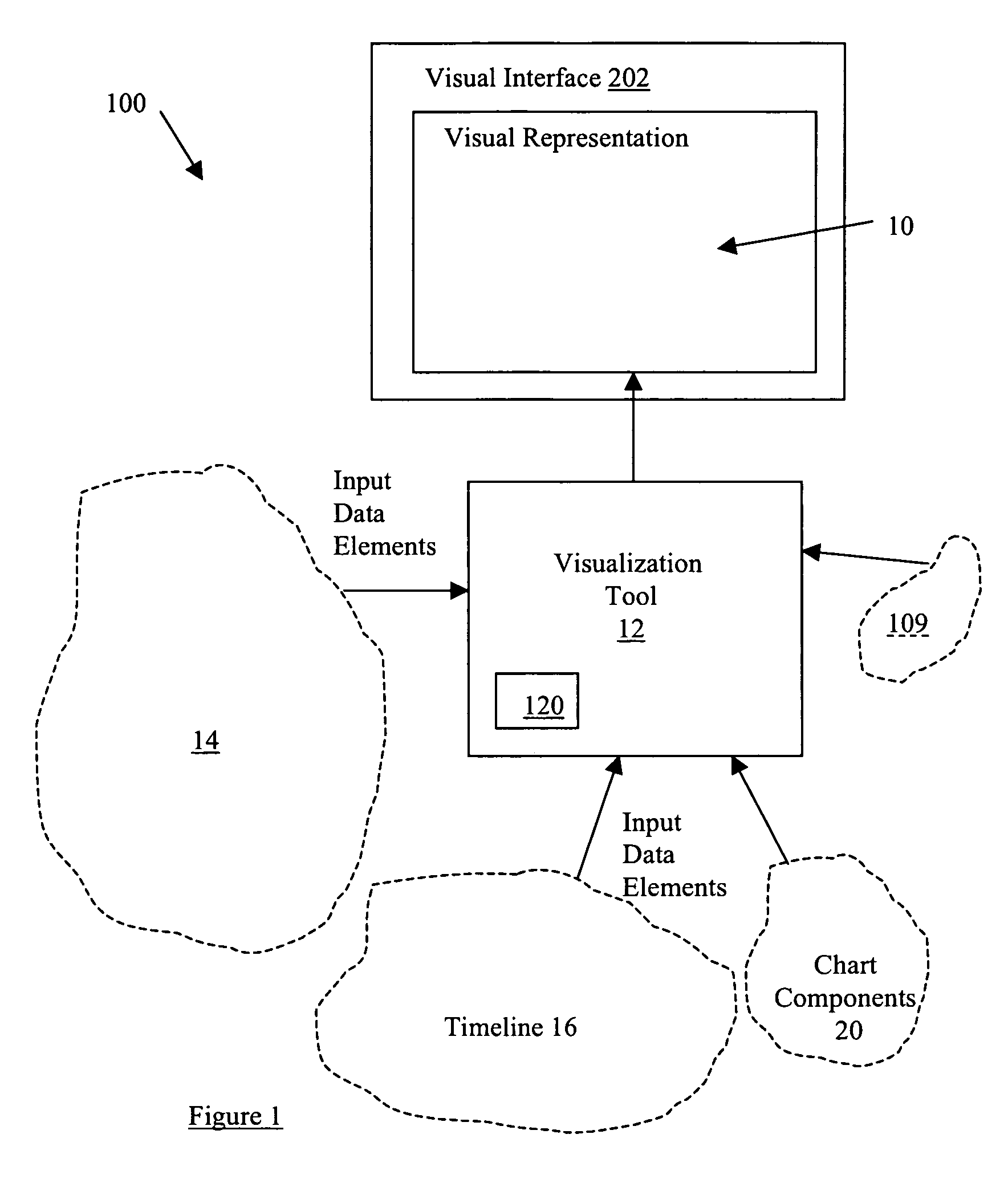
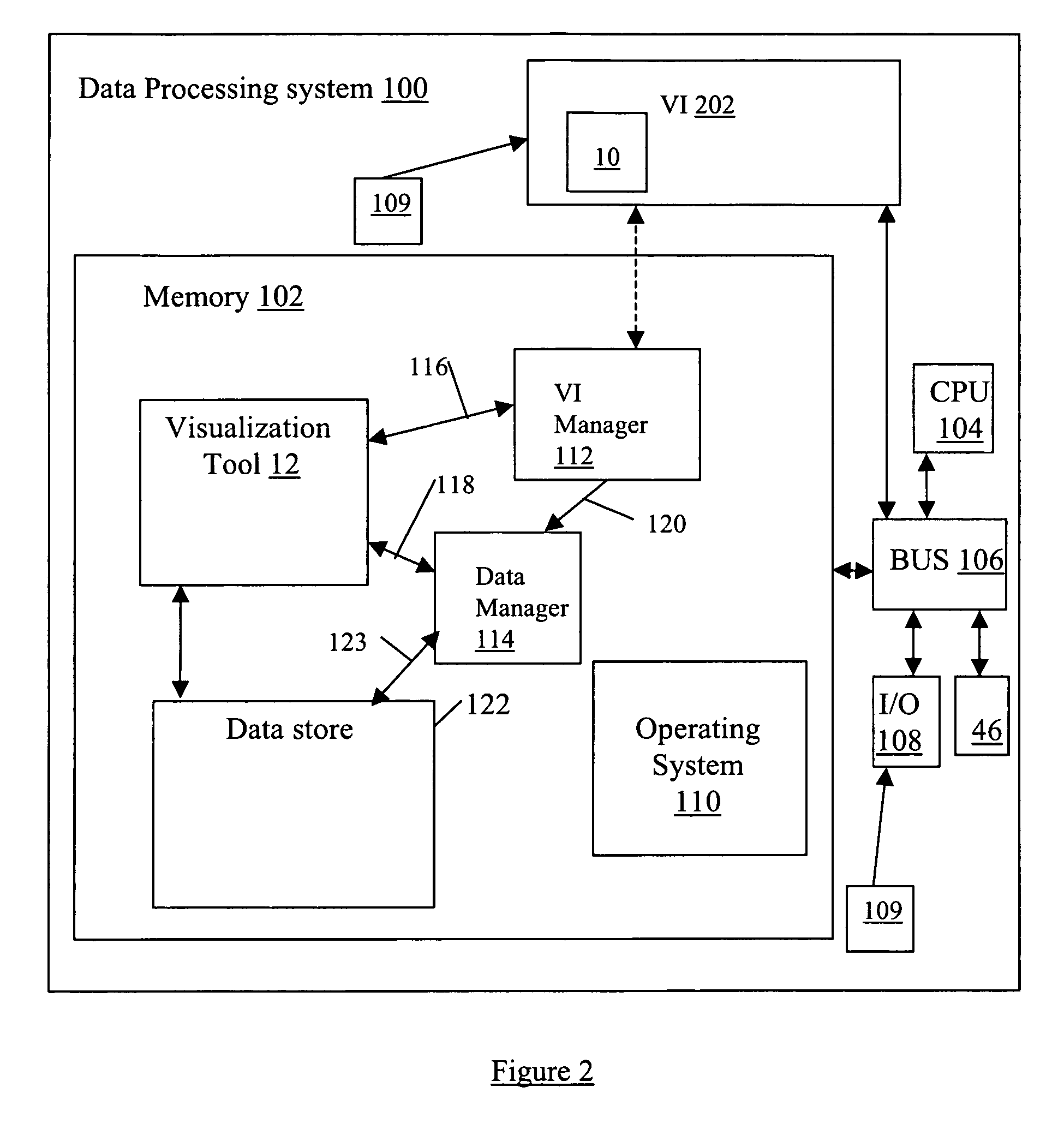
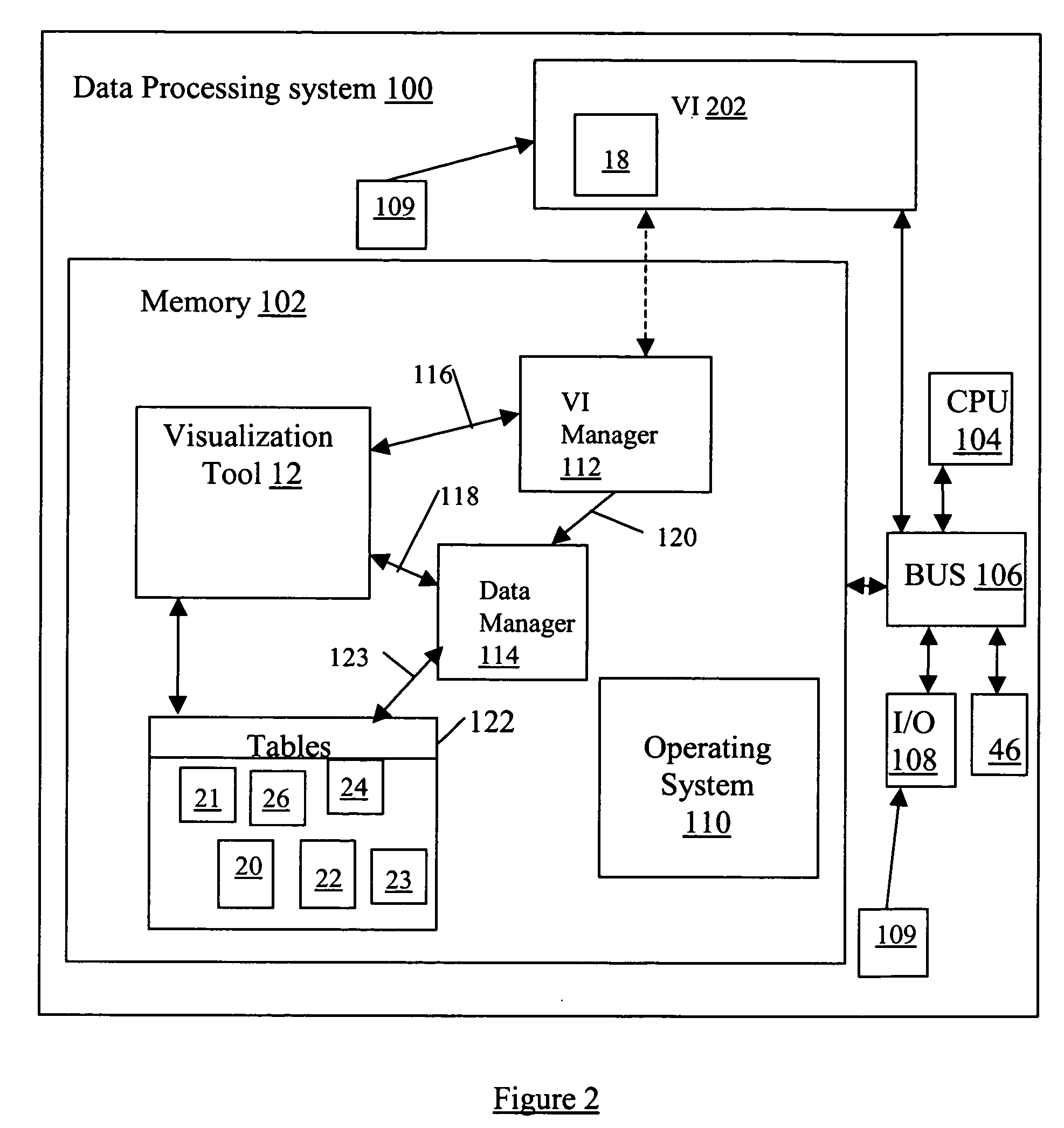
System and method for data visualization using a synchronous display of sequential time data and on-map planning
InactiveUS20060238538A1Easy to navigateDrawing from basic elementsOffice automationData visualizationData element
A system and method is provided for coordinating display of synchronized spatial information and time-variant information on a visual interface as a visual representation of a multi-dimensional planned process. The system and method comprise a data store configured for storing the time-variant information, such that the data store is further configured for storing the spatial information as a plurality of data elements for representing visual elements for display in the visual representation with respect to a reference surface. Each of the visual elements is operatively coupled to at least one sequenced element of a plurality of sequenced elements. The system and method also include a synchronization module coupled to the data store and is configured for synchronizing a displayed state on the visual interface of the spatial information with a displayed state on the visual interface of the time-variant information. The time-variant information includes timeline data including at least two of the plurality of sequenced elements having overlapping time spans with respect to a common temporal reference frame, and includes a marker for facilitating navigation of the plurality of sequenced elements with respect to the common temporal reference frame. Changes in the displayed state of the time-variant information are reflected in changes to the displayed state of the spatial information.
Owner:UNCHARTED SOFTWARE INC
System and method for data visualization using a synchronous display of sequential time data and on-map planning
InactiveUS7688322B2Easy to navigateDrawing from basic elementsOffice automationData memoryReference range
A system and method is provided for coordinating display of synchronized spatial information and time-variant information on a visual interface as a visual representation of a multi-dimensional planned process. The system and method comprise a data store configured for storing the time-variant information, such that the data store is further configured for storing the spatial information as a plurality of data elements for representing visual elements for display in the visual representation with respect to a reference surface. Each of the visual elements is operatively coupled to at least one sequenced element of a plurality of sequenced elements. The system and method also include a synchronization module coupled to the data store and is configured for synchronizing a displayed state on the visual interface of the spatial information with a displayed state on the visual interface of the time-variant information. The time-variant information includes timeline data including at least two of the plurality of sequenced elements having overlapping time spans with respect to a common temporal reference frame, and includes a marker for facilitating navigation of the plurality of sequenced elements with respect to the common temporal reference frame. Changes in the displayed state of the time-variant information are reflected in changes to the displayed state of the spatial information.
Owner:UNCHARTED SOFTWARE INC
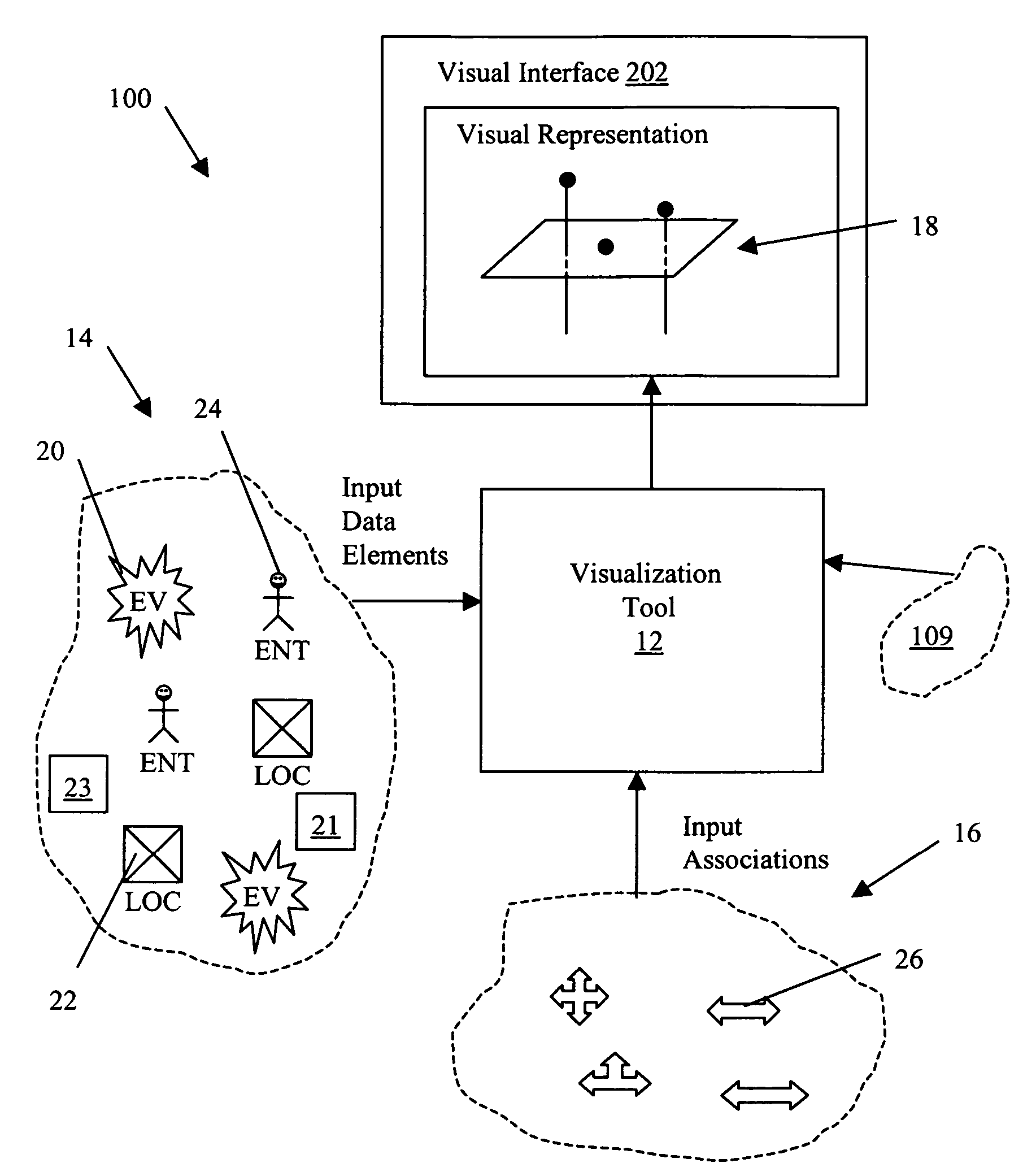
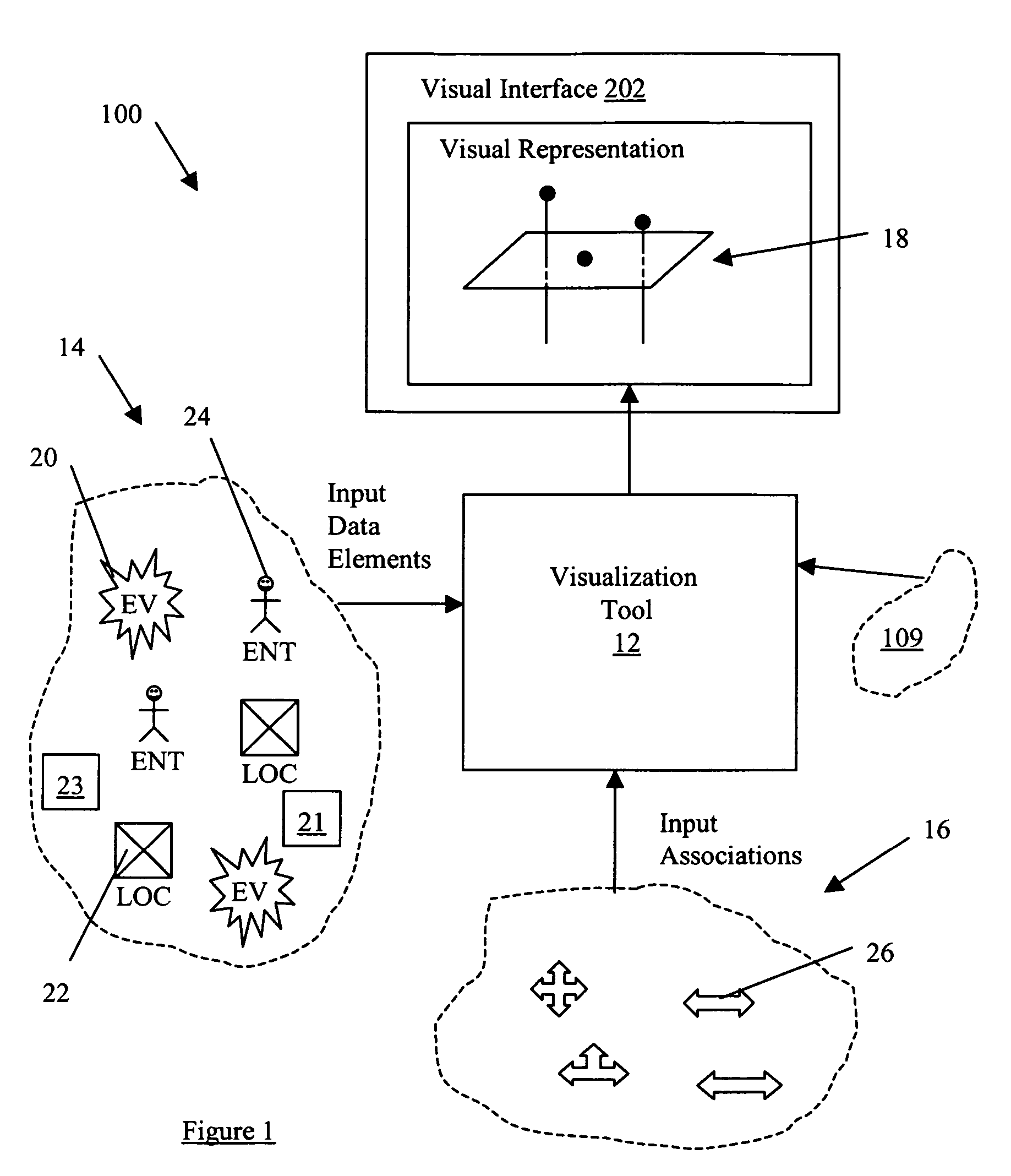
System and method for applying link analysis tools for visualizing connected temporal and spatial information on a user inferface
ActiveUS20070055782A1Drawing from basic elementsMultiple digital computer combinationsTime domainData element
A system and method for analyzing a plurality of data elements having both temporal and spatial properties, where a first data element and a second data element of the plurality of data elements are linked by at least one association element. The system and method include selecting the first data element from the plurality of data elements and providing at least one search criteria for use in analyzing the properties of the plurality of data elements with respect to at least one property of the first data element. An analysis module is used to apply the at least one search criteria to the properties of the plurality of data elements for identifying the second data element from the plurality of data elements and the corresponding at least one association element. The at least one association element is configured for representing a connection between the first data element and the second data element, such that the connection has a first property common to a property of the first data element and a second property common to a property of the second data element. A visualization module is used to generate a visual representation of the first and second data elements and the association element configured for display on a user interface for subsequent interaction with user events. The visual representation includes a spatial domain including a reference surface for providing a spatial reference frame having at least two spatial dimensions and a temporal domain operatively coupled to the spatial domain for providing a common temporal reference frame for locations of interest in the spatial domain.
Owner:PEN LINK LTD
Method of and apparatus for deciding encoding mode for variable block size motion estimation
InactiveUS20070171974A1Reduce the amount of calculationRapid encoding mode decisionColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion estimationMacroblock
Provided are a method of and an apparatus for deciding an encoding mode for variable block size motion estimation, which can decide an encoding mode quickly and with less computation during variable block size motion estimation. The method includes searching in a reference frame for a macroblock that is most similar to a current macroblock, selecting a temporary encoding mode candidate group for encoding of the current macroblock from among a plurality of encoding mode candidate groups including at least one encoding mode, using encoding mode information of the searched-for macroblock of the reference frame, selecting the decided temporary encoding mode candidate group or an encoding mode candidate group including an encoding mode using a smaller block than the decided temporary encoding mode candidate group as a final encoding mode candidate group, based on the temporary encoding mode candidate group, the complexity of the current macroblock or sub-blocks obtained by dividing the current macroblock, and the difference between the current macroblock or each of the sub-blocks and the reference frame, and performing motion estimation in encoding mode included in the final encoding mode candidate group and deciding an encoding mode of the current macroblock.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
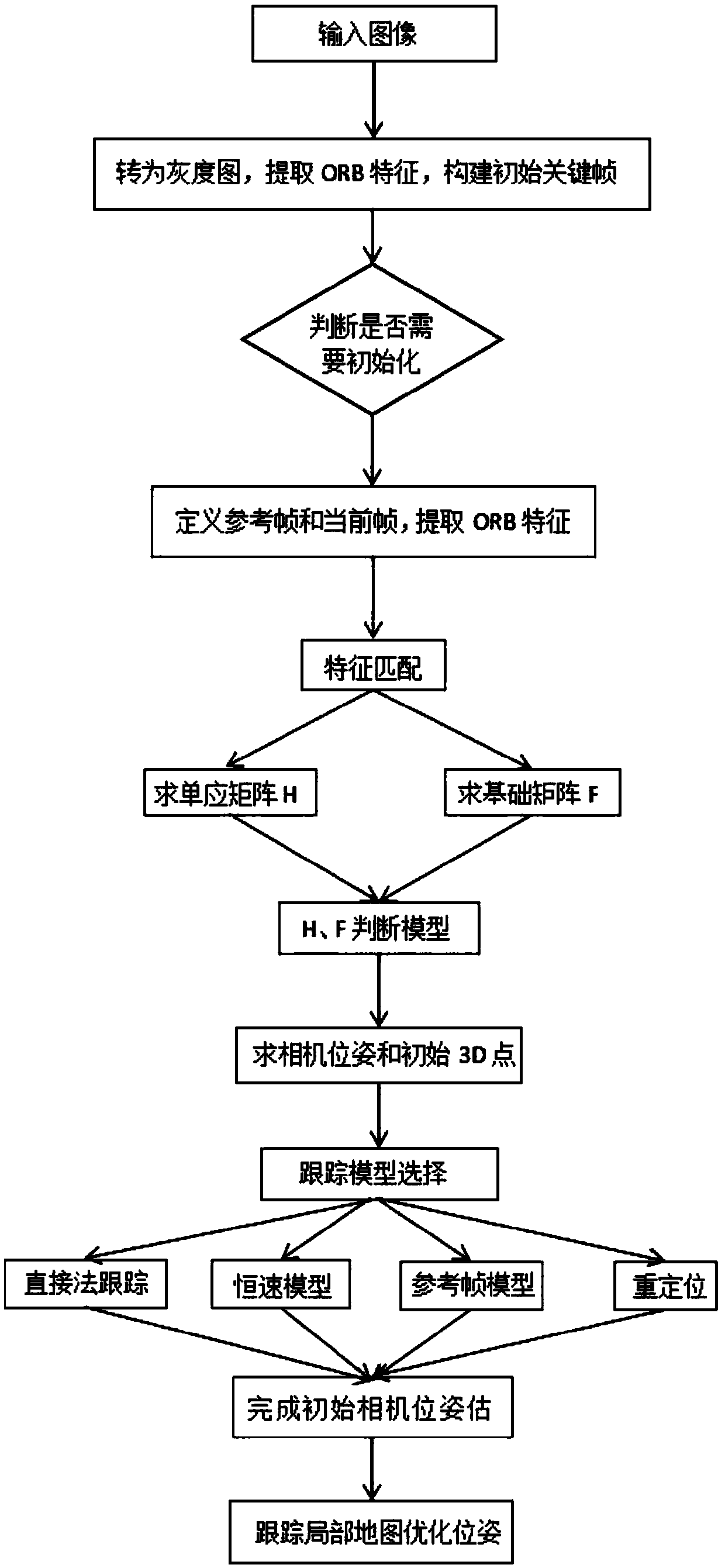
A fast monocular vision odometer navigation and positioning method combining a feature point method and a direct method
ActiveCN109544636AAccurate Camera PoseFeature Prediction Location OptimizationImage enhancementImage analysisOdometerKey frame
The invention discloses a fast monocular vision odometer navigation and positioning method fusing a feature point method and a direct method, which comprises the following steps: S1, starting the vision odometer and obtaining a first frame image I1, converting the image I1 into a gray scale image, extracting ORB feature points, and constructing an initialization key frame; 2, judging whether thatinitialization has been carry out; If it has been initialized, it goes to step S6, otherwise, it goes to step S3; 3, defining a reference frame and a current frame, extracting ORB feature and matchingfeatures; 4, simultaneously calculating a homography matrix H and a base matrix F by a parallel thread, calculating a judgment model score RH, if RH is great than a threshold value, selecting a homography matrix H, otherwise selecting a base matrix F, and estimating a camera motion according to that selected model; 5, obtaining that pose of the camera and the initial 3D point; 6, judging whetherthat feature point have been extracted, if the feature points have not been extracted, the direct method is used for tracking, otherwise, the feature point method is used for tracking; S7, completingthe initial camera pose estimation. The invention can more precisely carry out navigation and positioning.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
Methods and Systems for Determining Coordinates of an Underwater Seismic Component in a Reference Frame
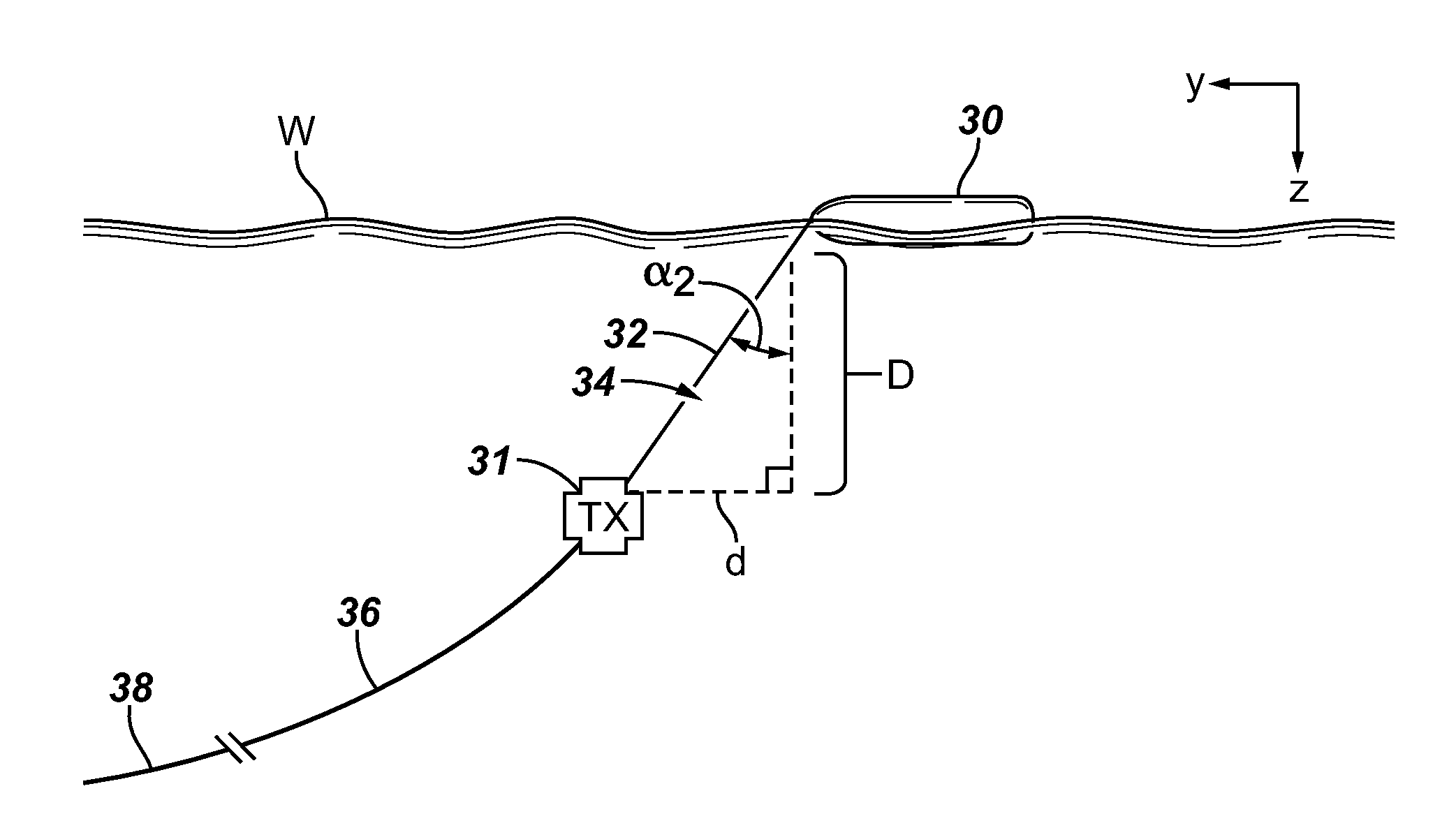
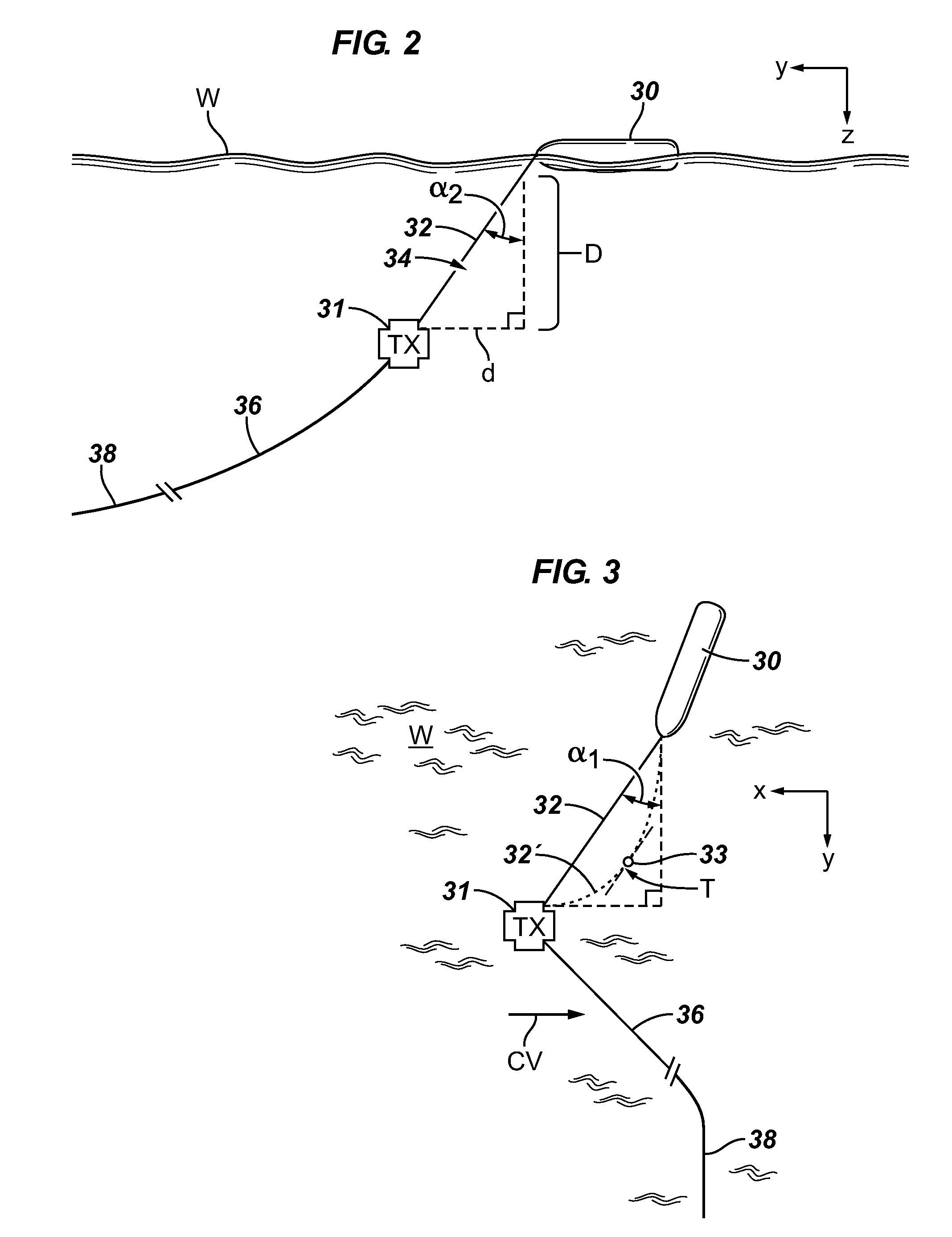
ActiveUS20090231953A1Improve long-term stabilitySeismology for water-covered areasEngineeringReference frame
A method comprising determining coordinates of a first point rigidly attached to a rigid body floating on the sea surface in a desired coordinate reference frame; measuring orientation parameters of the rigid floating body to determine 3D offset in the coordinate reference frame of the first point to any point on or rigidly attached to the body; applying a 3D coordinate shift from the first point to a second point rigidly attached to the body, thus determining coordinates of the second point in the desired reference frame; determining a distance from the second point to one or more devices that are components of a seismic acquisition spread, by comparing transmission times of a signal to recording times of transmitted signals and multiplying by a signal propagation rate; and determining relative positions of components of the spread to each other and to devices rigidly attached to the rigid body.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Mixture resolution encoding and decoding method and device
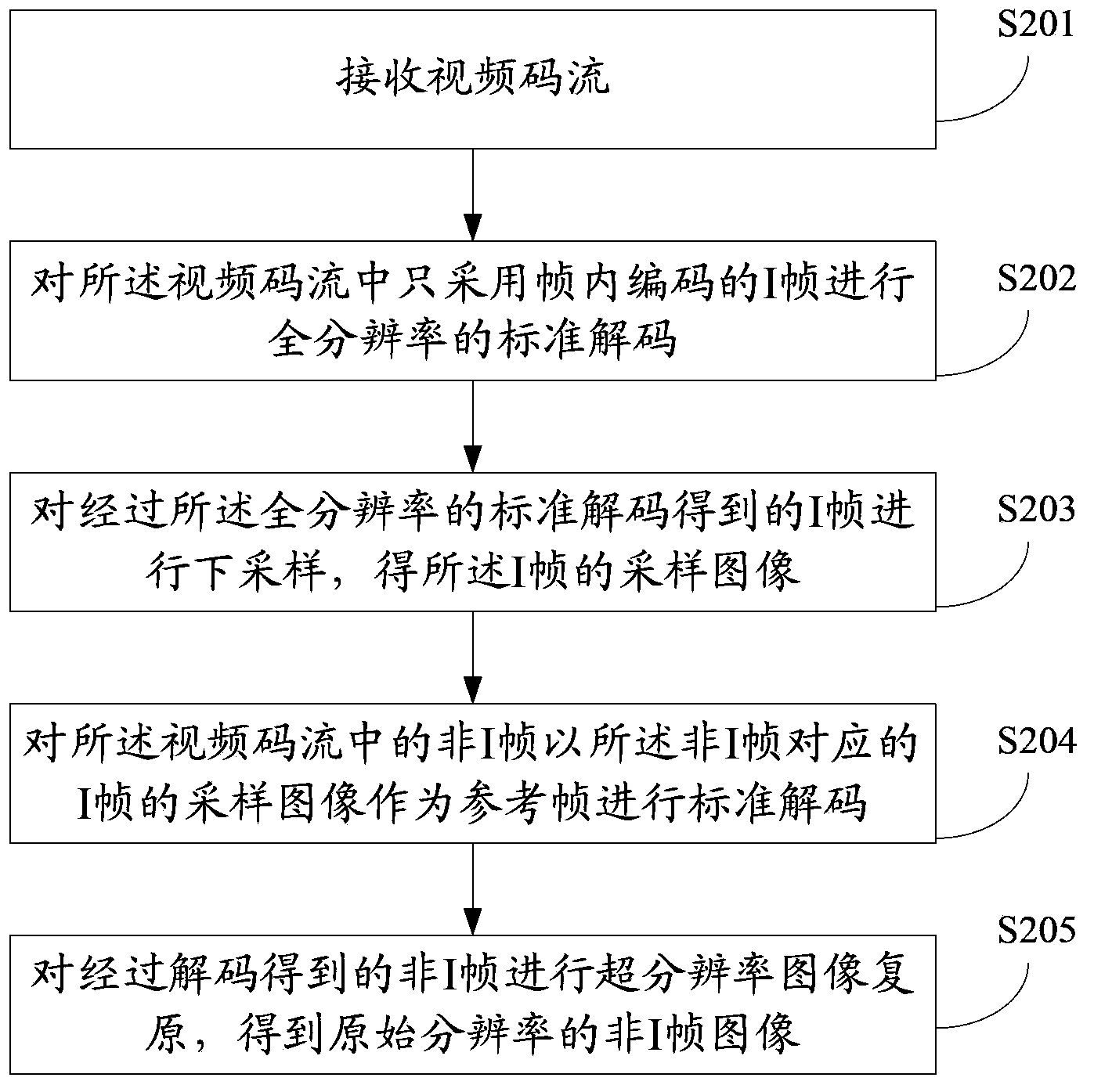
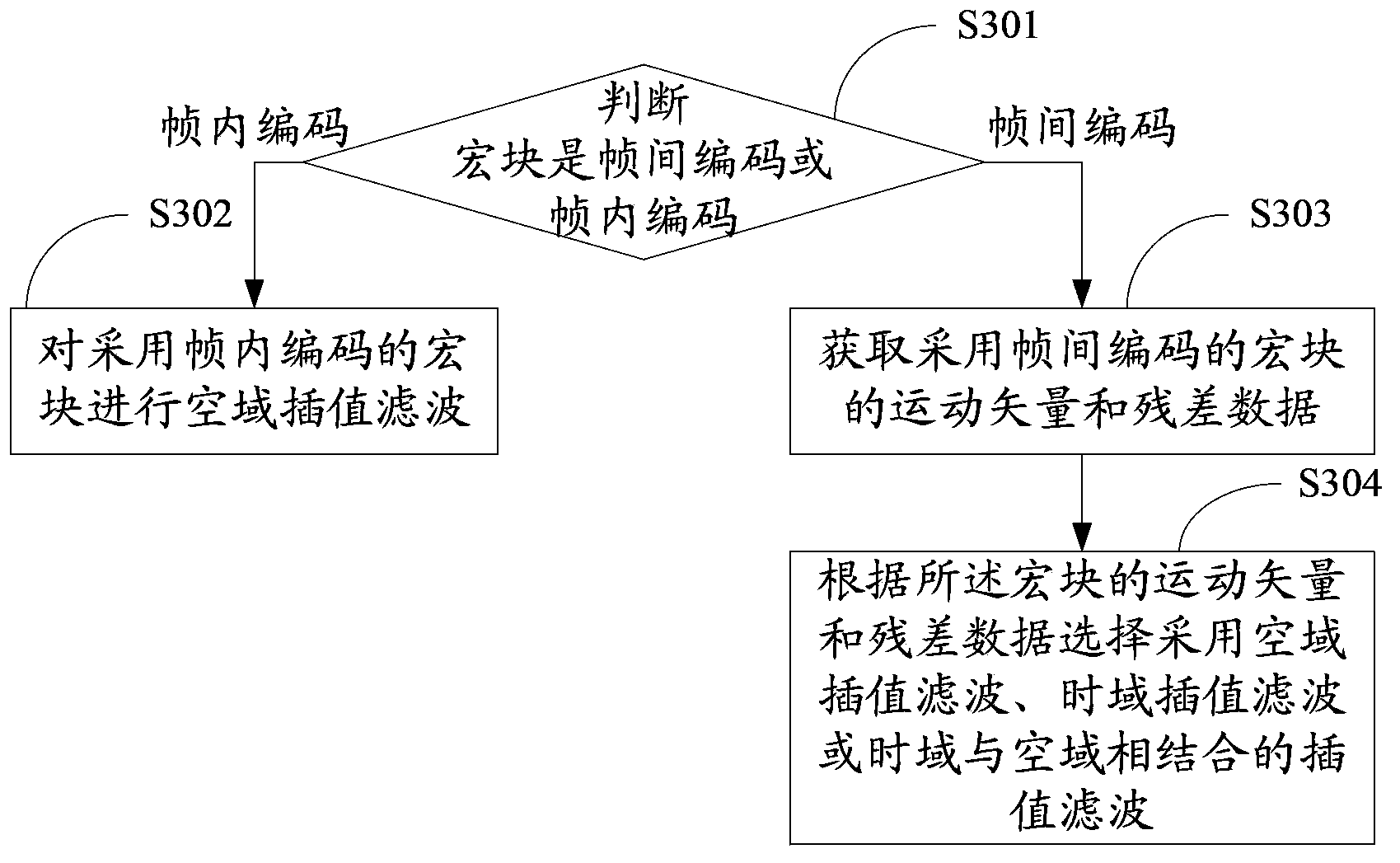
ActiveCN103813174AReduced amount of encoded dataReduce computational complexityDigital video signal modificationDecoding methodsFrame sequence
An embodiment of the invention provides a mixture resolution encoding and decoding method. The mixture resolution encoding and decoding method comprises performing full resolution standard encoding and frame reconstruction on video frame sequence I frames which only adopt intraframe coding and obtaining reconstructed frames of the I frames; performing down sampling on the reconstructed frames of the I frames and obtaining sampling images of the reconstructed frames of the I frames; performing down sampling on non-I frames in a video frame sequence and obtaining sampling images of the non-I frames; performing standard encoding on the sampling images of the non-I frames with the sampling images of the reconstructed frames of the I frames which are corresponding to the non-I frames serving as reference frames; sending video code frames which comprise the I frames and non-I frames which are obtained through encoding. The invention also discloses a corresponding mixture resolution encoding and decoding device. According to the mixture resolution encoding and decoding method and device, encoding and decoding calculation complexity can be reduced and encoding and decoding speed and efficiency are greatly improved.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
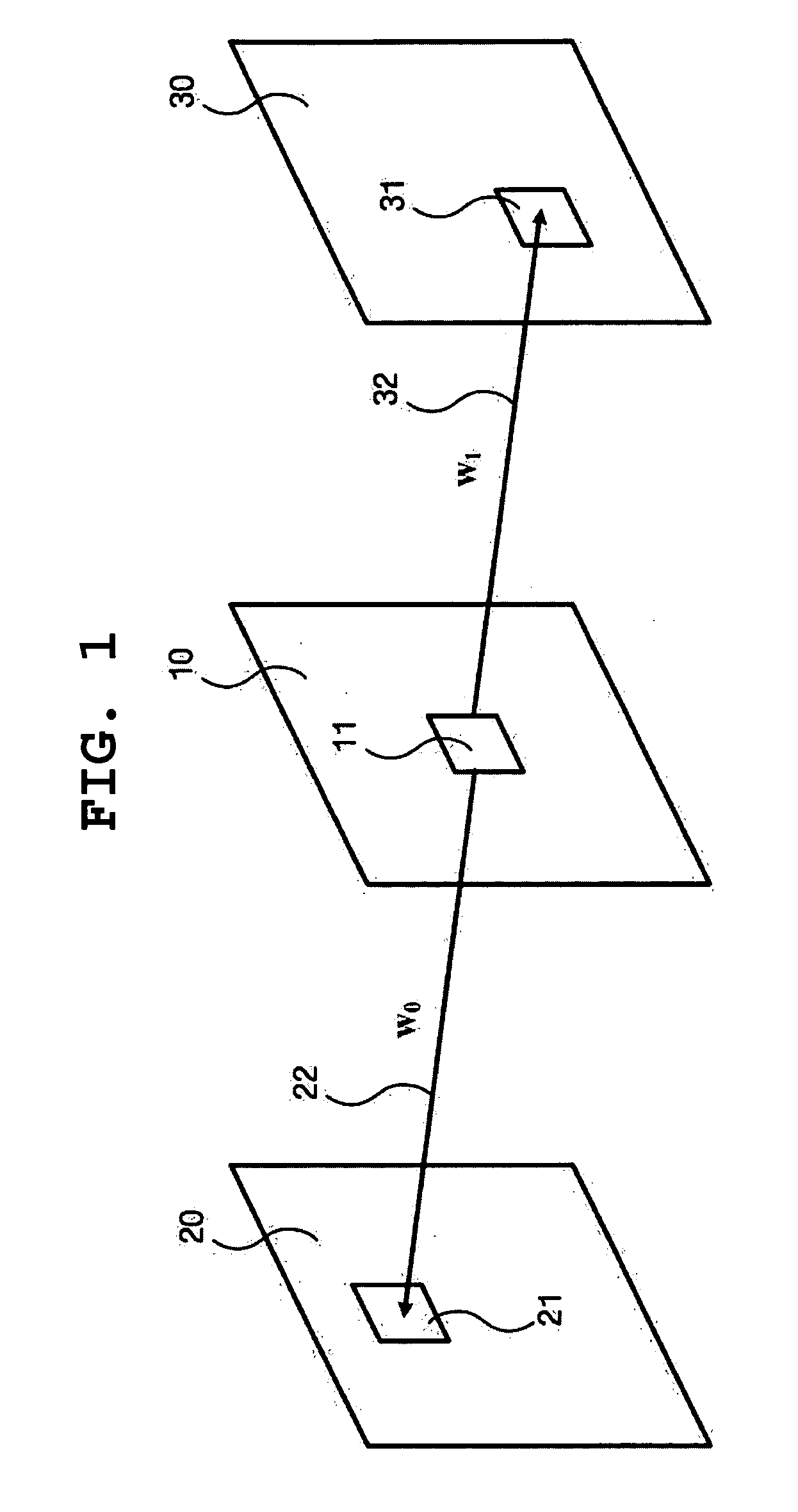
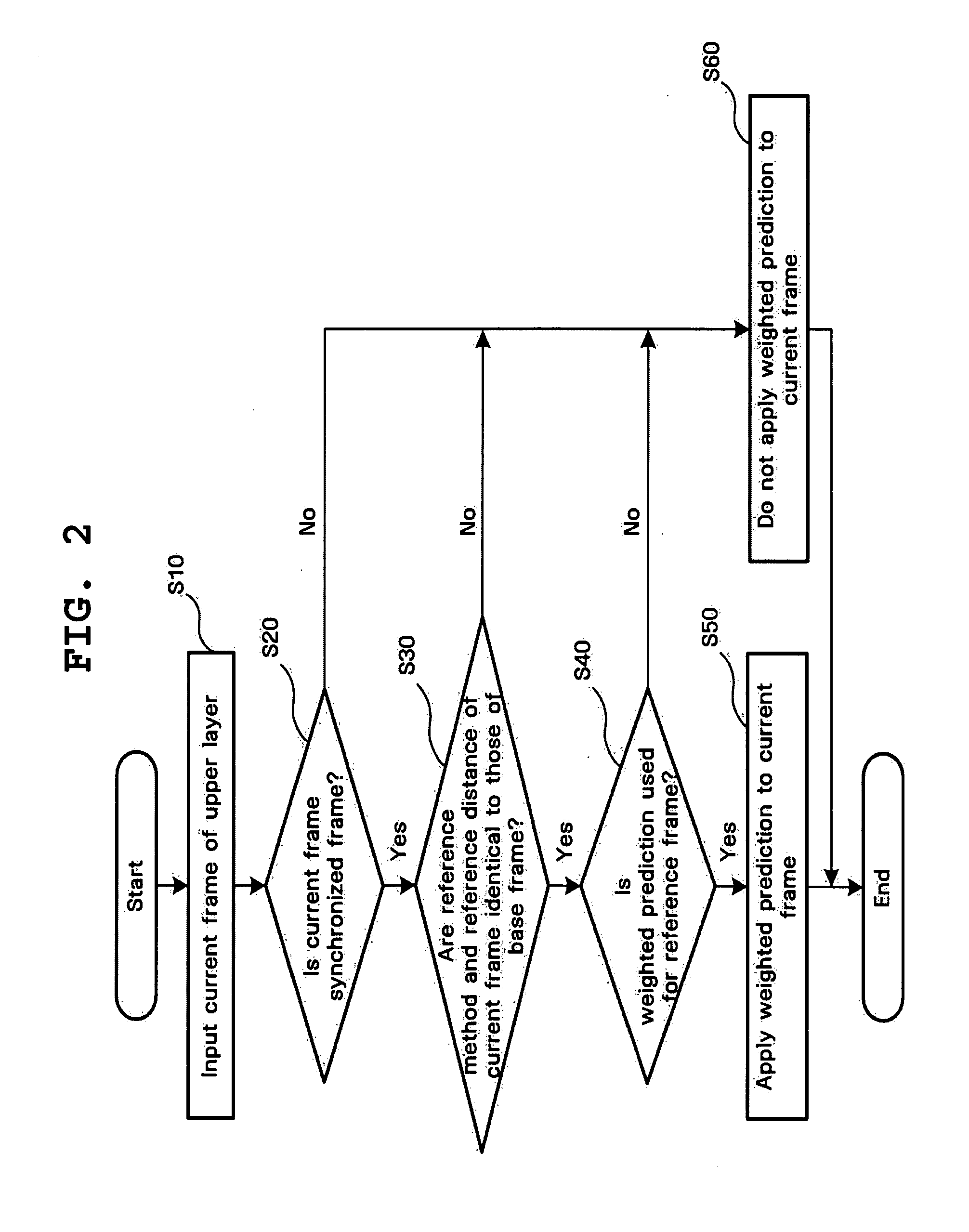
Video coding method and apparatus using multi-layer based weighted prediction
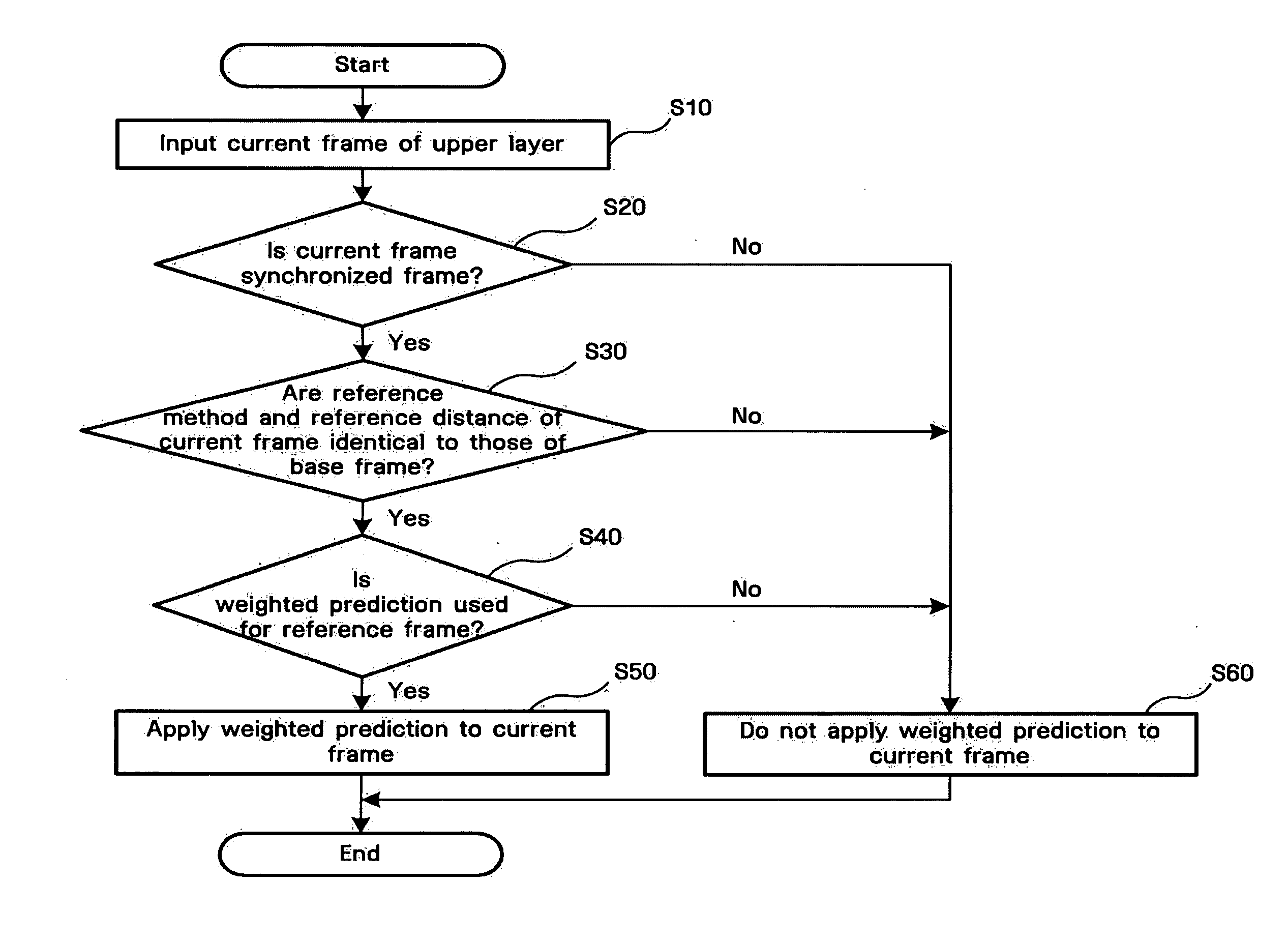
InactiveUS20060291562A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionFrame basedWeight factor
A method and apparatus for efficiently encoding a plurality of layers using inter-layer information in a multi-layer based video codec are disclosed. The video encoding method includes operations of reading the weighting factors of one layer; performing motion compensation on reference frames for the current frame based on a motion vector; generating a predicted frame for the current frame by acquiring a weighted sum of the motion-compensated reference frames using the read weighting factors; and encoding the difference between the current frame and the predicted frame.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
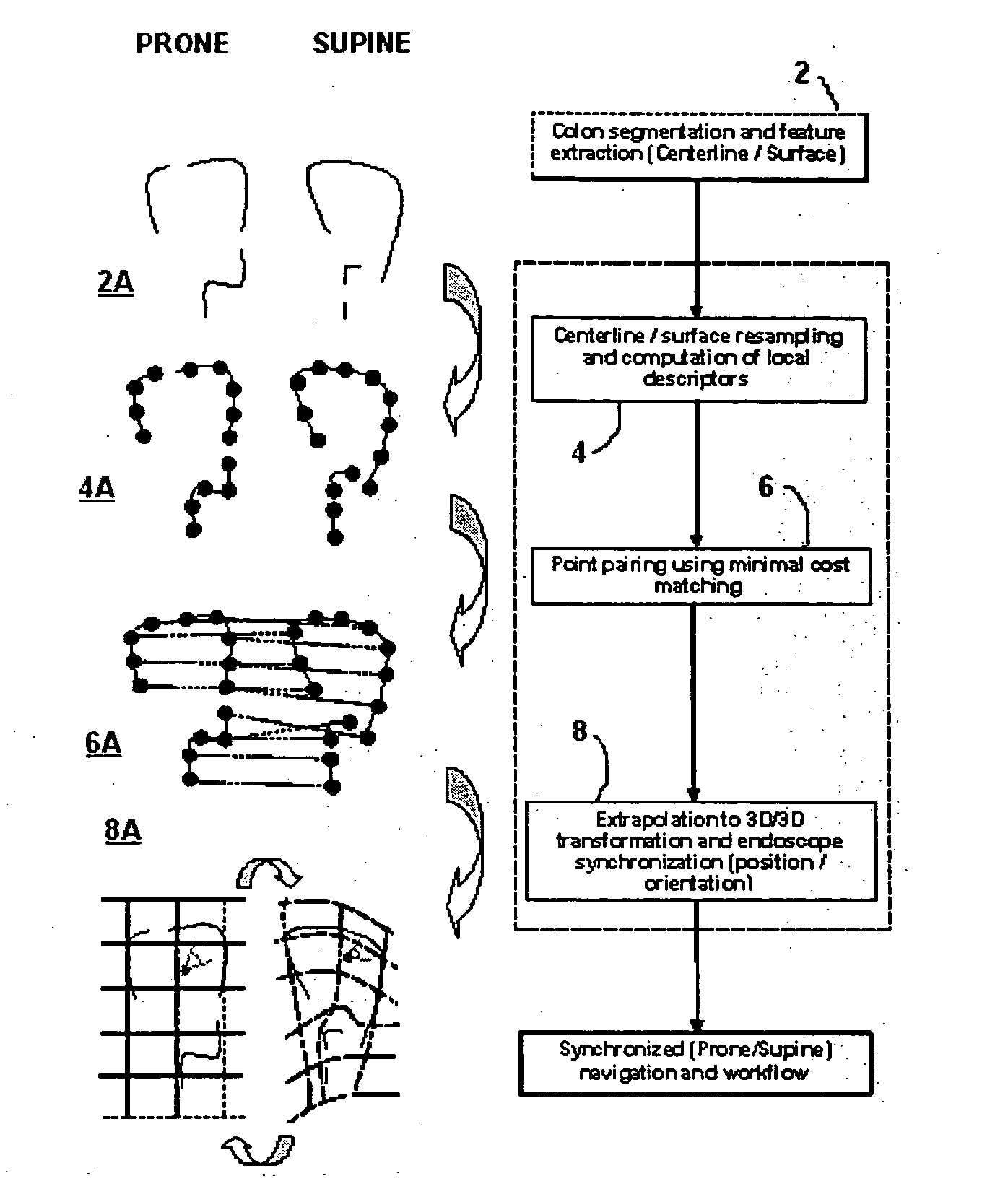
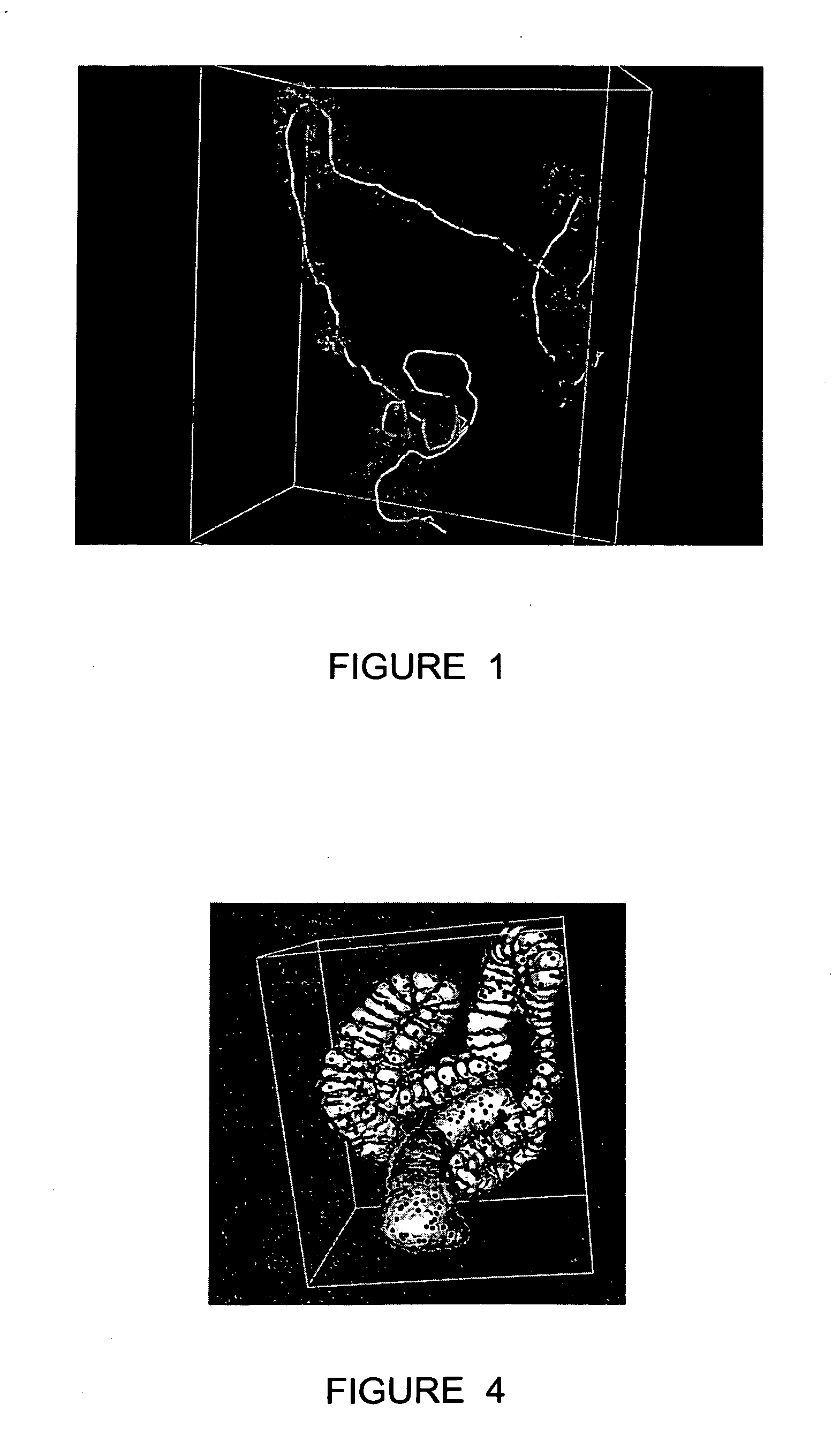
Method and apparatus for registration of virtual endoscopic images
InactiveUS20050048456A1Minimal cost matchingImage enhancementImage analysisFeature extractionReference frame
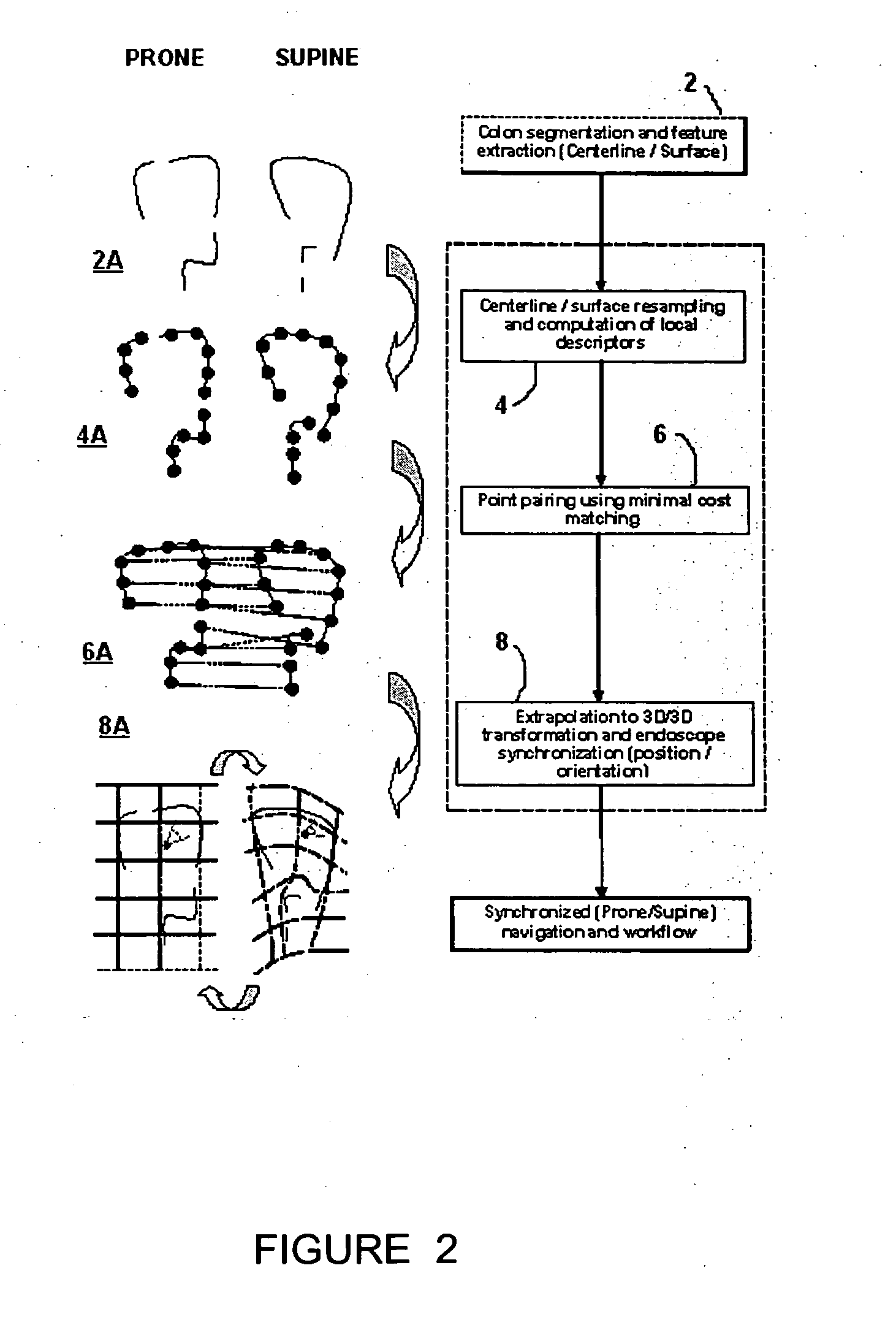
A method for registration of virtual endoscopy images in first and second patient positions comprises performing colon segmentation and feature extraction, including centerline and colon surface data for each of the images; resampling the centerline and colon surface data; computing respective local descriptors; pairing point correspondences on the centerlines between the first and second images by minimal cost matching; extrapolating the centerline point correspondences to a 3-dimensional / 3-dimensional (3D / 3D) transformation between the first and second images. The method also includes selecting a position for a virtual endoscope in one of the images; associating an orthogonal reference frame with the virtual endoscope; and applying the 3D / 3D transformation to the orthogonal reference frame so as to derive a corresponding transformed reference frame for the virtual endoscope in the other of the images.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
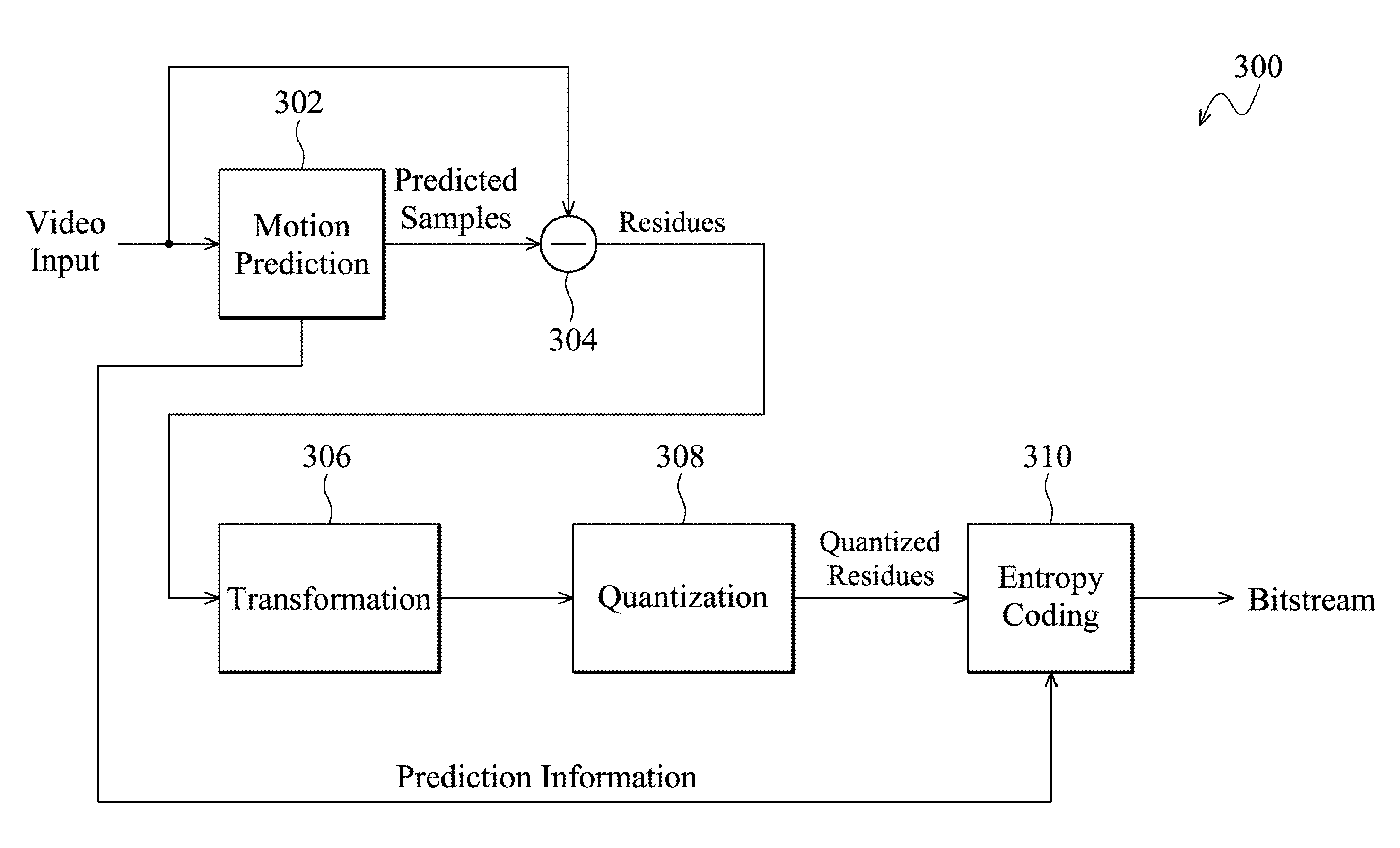
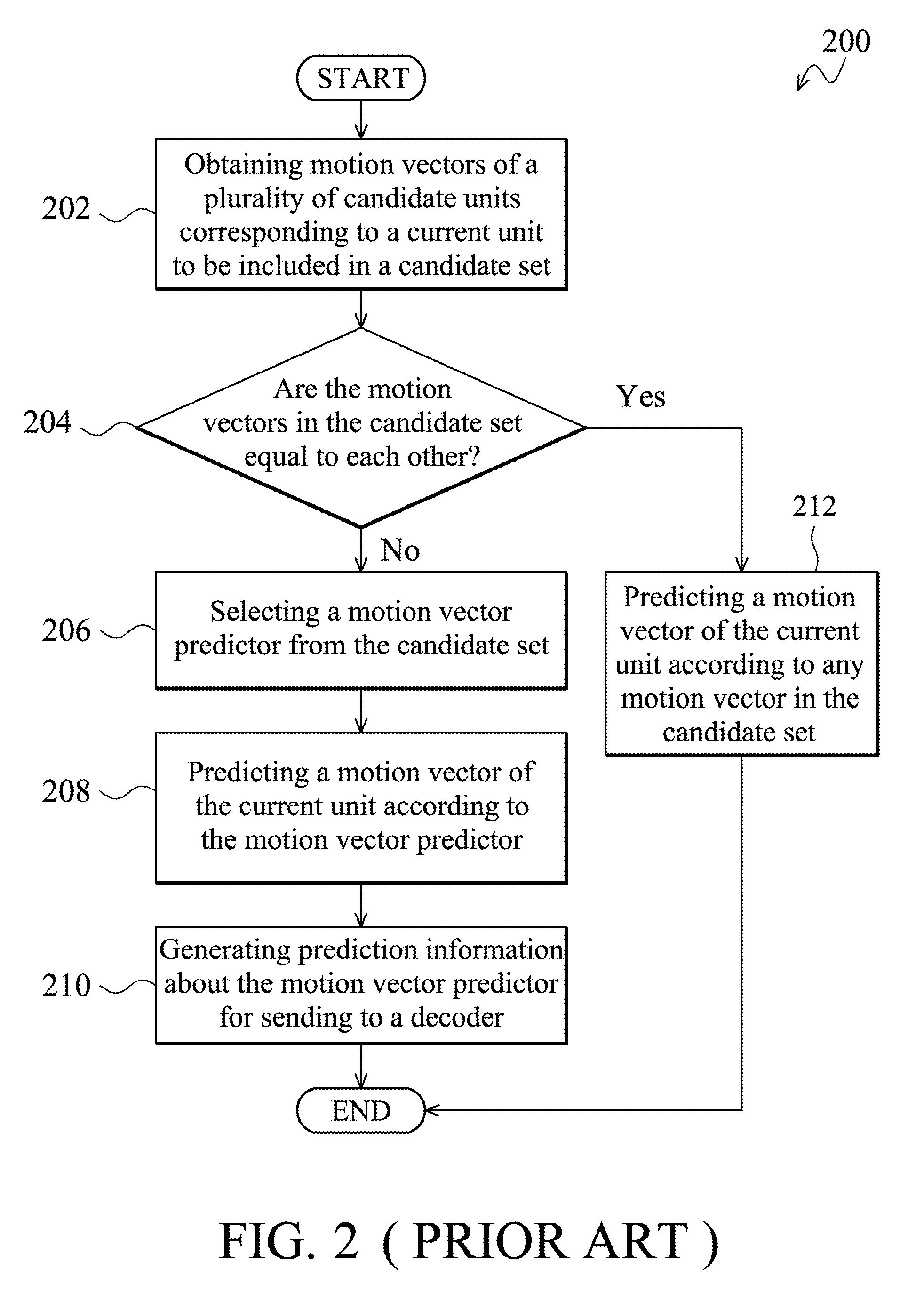
Motion Prediction Method and Video Encoding Method
ActiveUS20110176613A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo encodingMotion vector
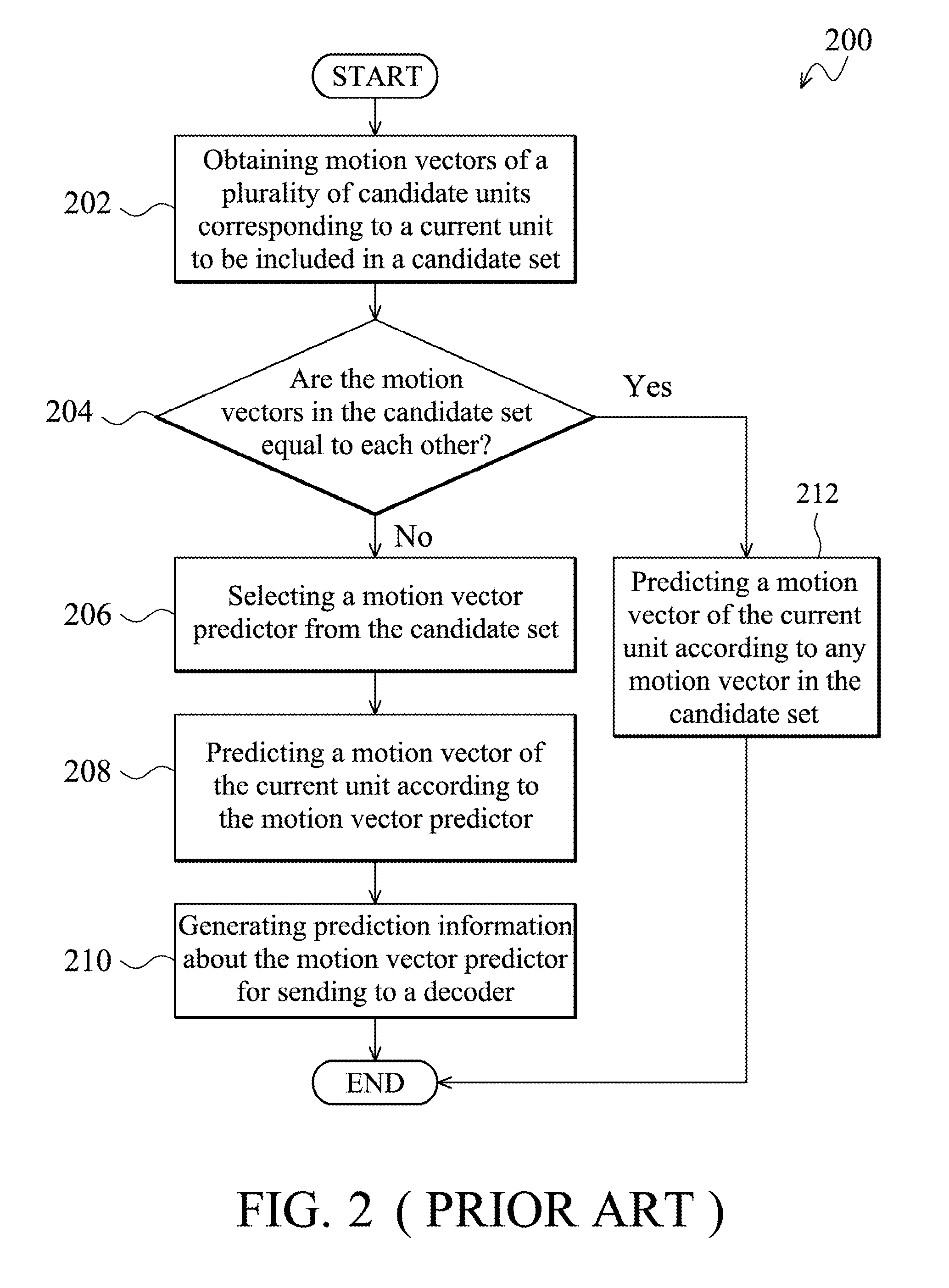
The invention provides a motion prediction method. First, a plurality of motion vector predictors is obtained to be included in a candidate set for motion prediction of a current unit of a current frame. Whether the current frame is a non-reference frame which is not referred to by other frames for motion prediction is then determined. When the current frame is not the non-reference frame, any motion vector predictor corresponding to a previously coded frame is removed from the candidate set, and a motion vector of the current unit is predicted according to the motion vector predictors of the candidate set.
Owner:HFI INNOVATION INC
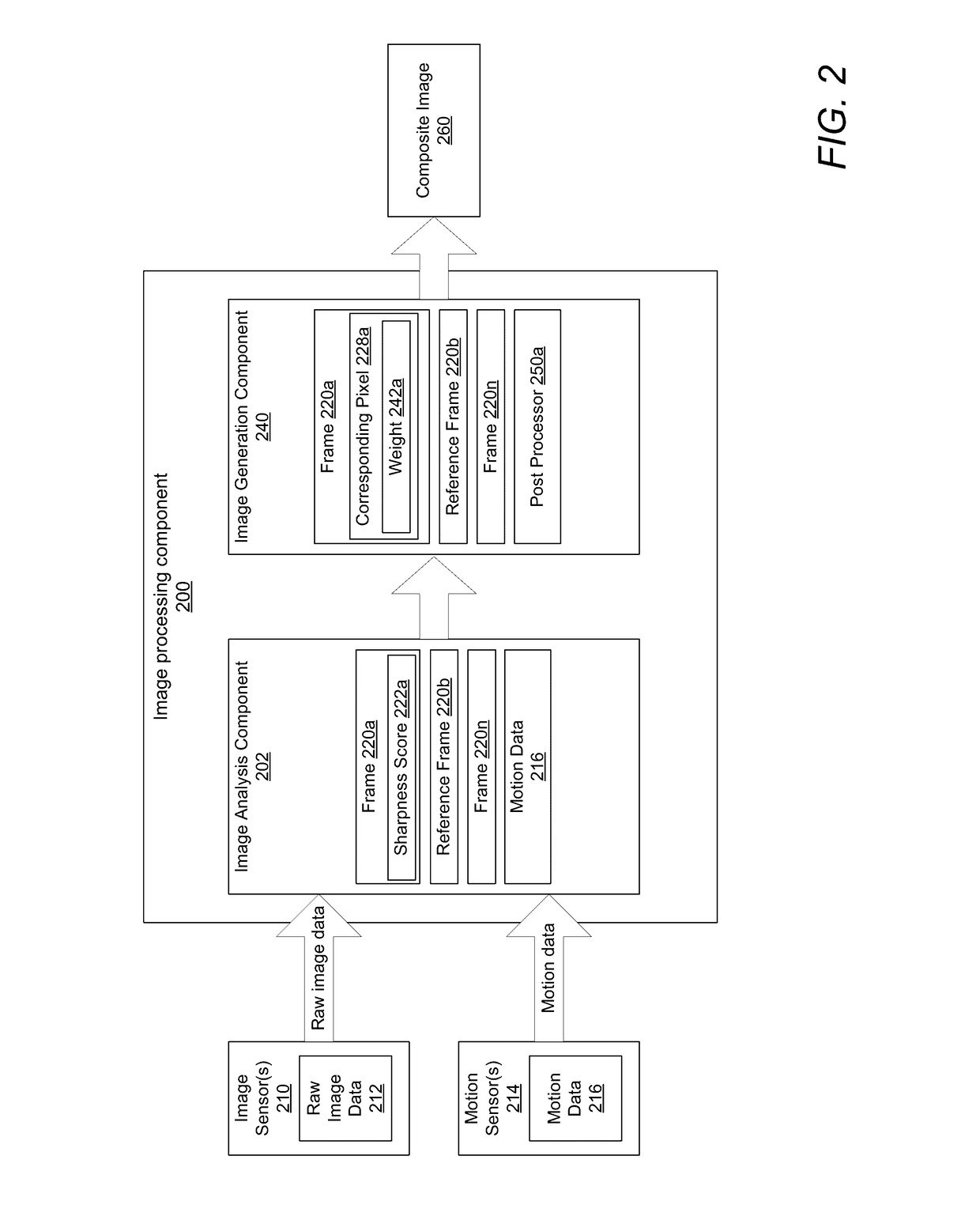
Creating a composite image from multi-frame raw image data
A method, a system, and computer program product for creating a composite image from multi-frame raw image data. The method includes extracting each individual frame from a plurality of frames within raw image data and determining a sharpness score for a region of each individual frame. A particular frame that has a sharpest region from among the plurality of frames is then selected as a reference frame. Each pixel in the reference frame is then registered to a plurality of corresponding pixels from non-reference frames of the plurality of frames. Equivalent pixels from the reference frame and each non-reference frame are then summed to create a composite image.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
Video compression coding-decoding method
InactiveCN1658673ALess importantRaise the importanceTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationMotion vectorVideo encoding
A compressing encoding and decoding method which includes the following: encode the video compressed signals with the programs, discrete cosine transform DCT; transform and quantitate; set the channel buffer storage before the encoding bit flow gets into the channel; the buffer storage must have a control mechanism; movement estimate; the position excursion is described by the movement vector, and a movement vector represents the displacement in the two actinic and vertical directions; as movement estimating, the P frame image uses the former most recent decoded I frame or P frame as the referenced image called the forward forecast; the movement compensation; the movement vector calculated by the movement estimate moves the macro piece in the referenced image to the corresponding position in the actinic and vertical direction, then namely produce the forecast to the compressed image; and search and calculate the subpels; the quantitation, storage and movement search after the sampling signals are made the discrete cosine transform DCT transform are all completed in the frequency field. The video encoder finishes all the calculation in the frequency field. The compressed rate is high, and the calculating quantity is small.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method of and system for improving temporal consistency in sharpness enhancement for a video signal
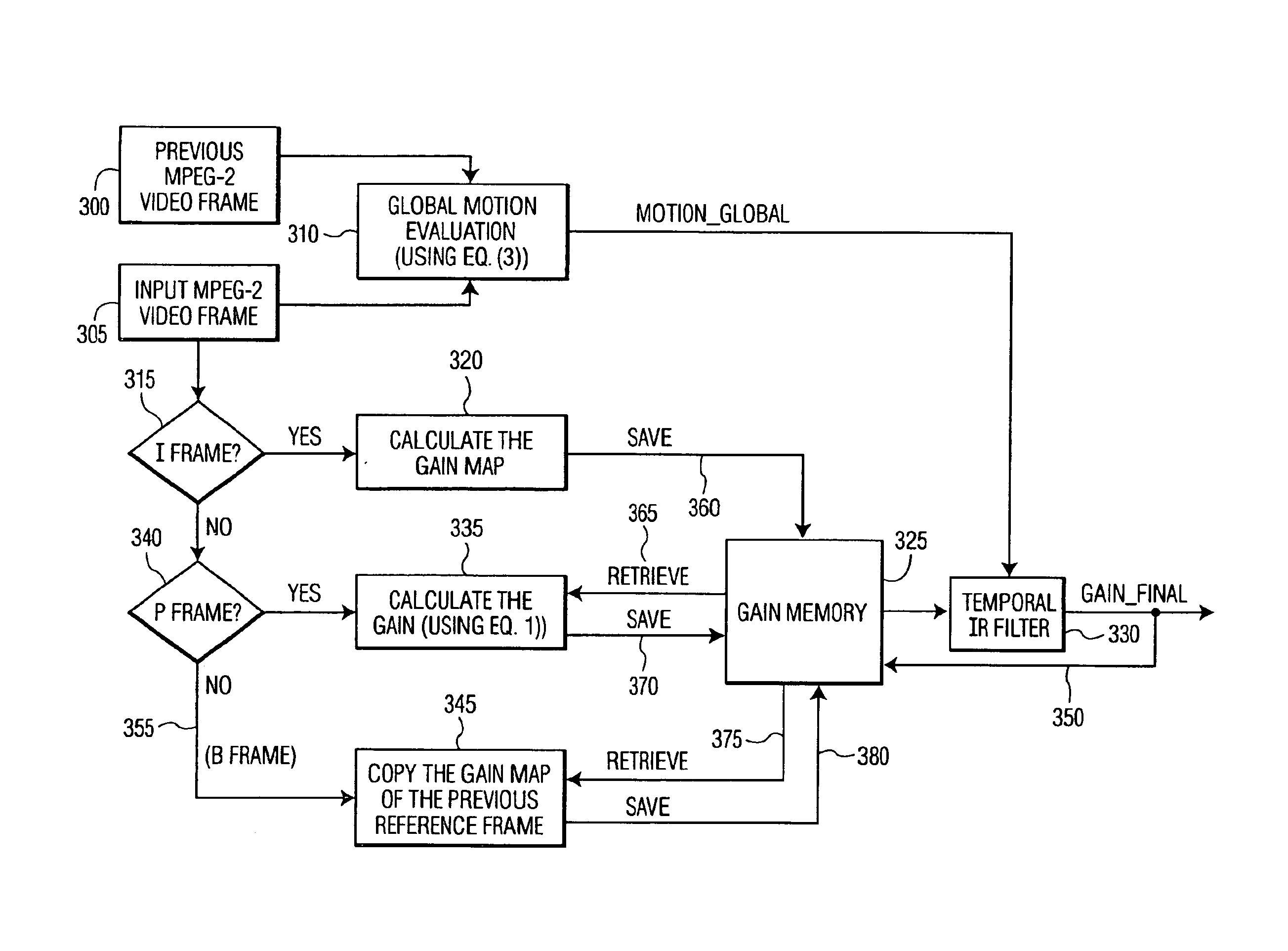
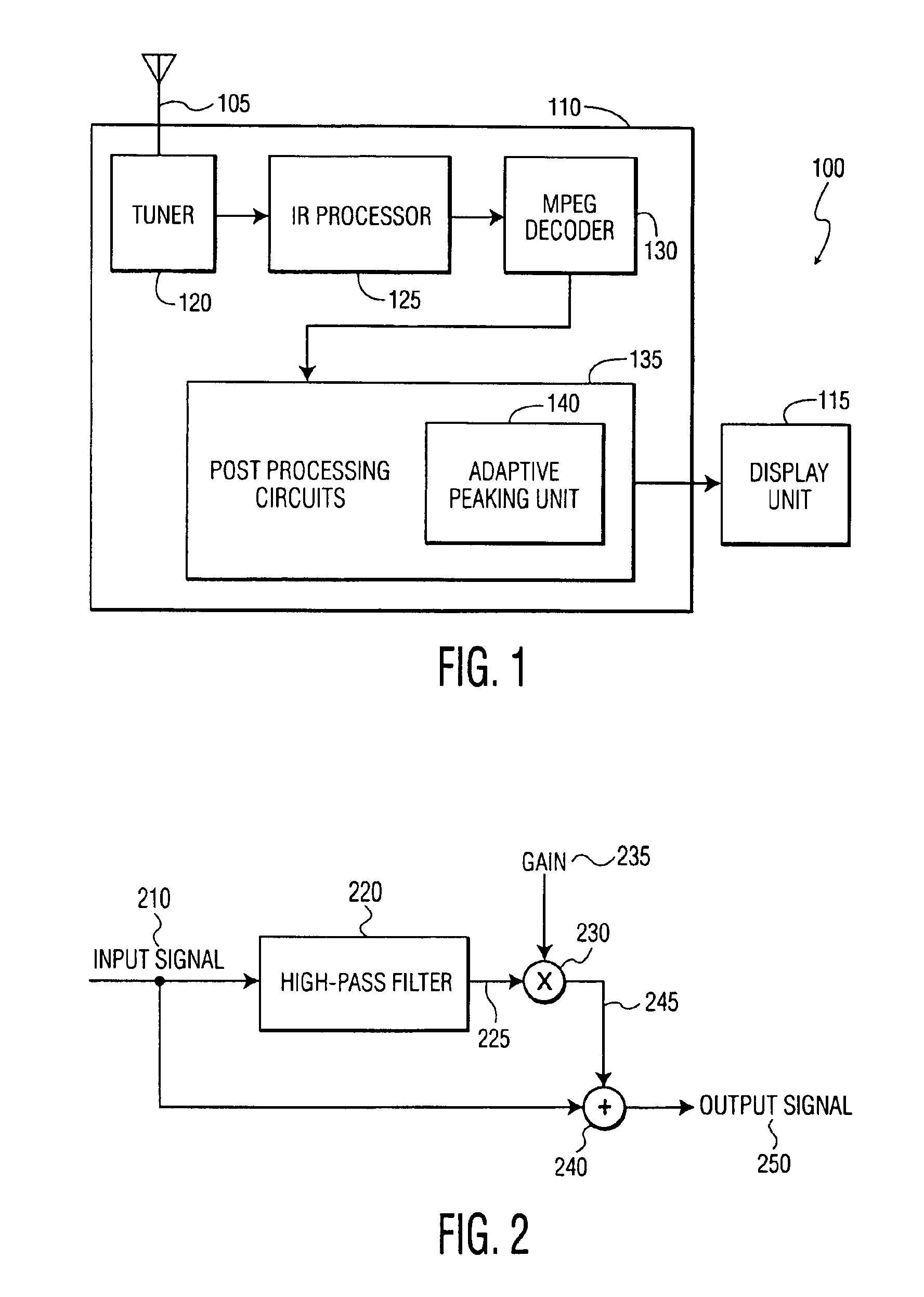
ActiveUS6873657B2Improving temporal consistencyHigh gainTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesIir filteringMotion vector
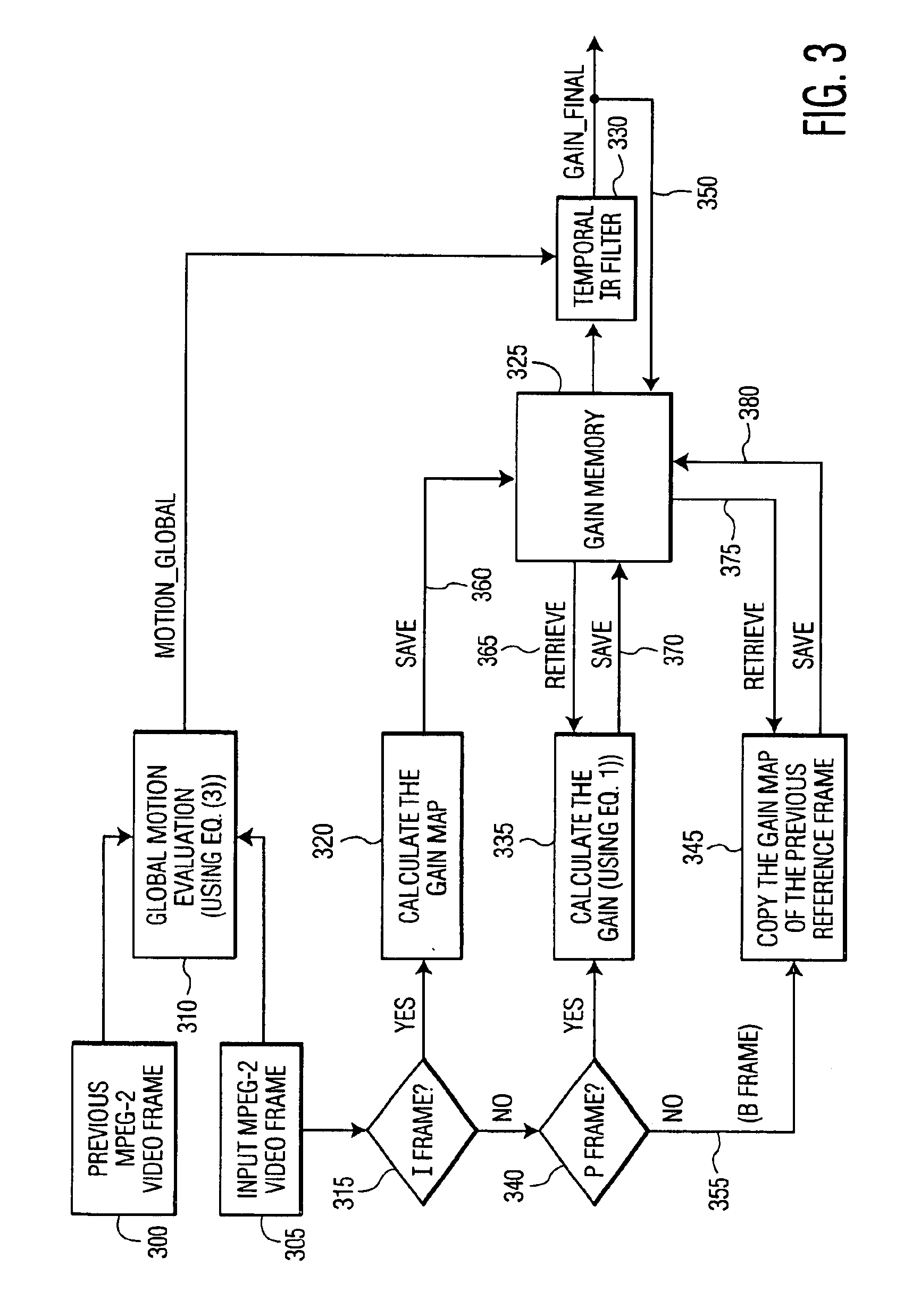
In accordance with the preferred embodiment of the present invention, a method of and system for improving temporal consistency of an enhanced signal representative of at least one frame using a sharpness enhancement algorithm with an enhancement gain are provided. The method comprises the steps of: receiving the enhanced signal comprising at least one frame, obtaining an enhancement gain for each pixel in the frame, retrieving an enhancement gain value of each pixel in a reference frame from a gain memory using motion vectors, identifying if the frame is an I, P or B frame type and determining an updated enhancement gain for an I frame type by calculating a gain map for use in the sharpness enhancement algorithm. The updated enhancement gain of each pixel is equal to enhancement gain previously determined for use in the sharpness enhancement algorithm. In addition, the method includes storing the updated enhancement gain to gain memory, and applying the updated enhancement gain to the sharpness enhancement algorithm to improve temporal consistency of the enhanced signal. The method may further comprise the step of further improving the updated enhancement gain by applying a motion adaptive temporal IIR filter on the updated enhancement gain.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
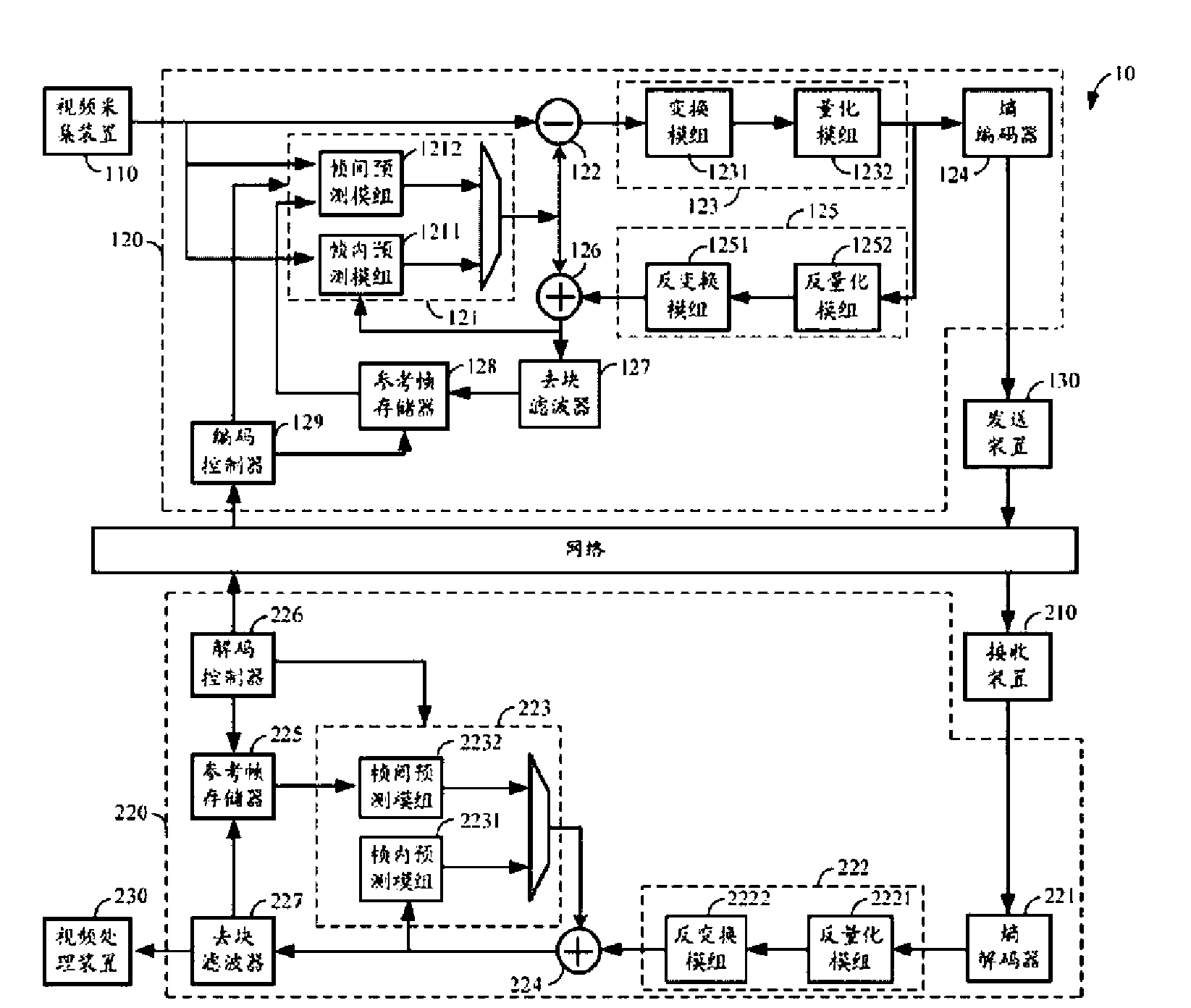
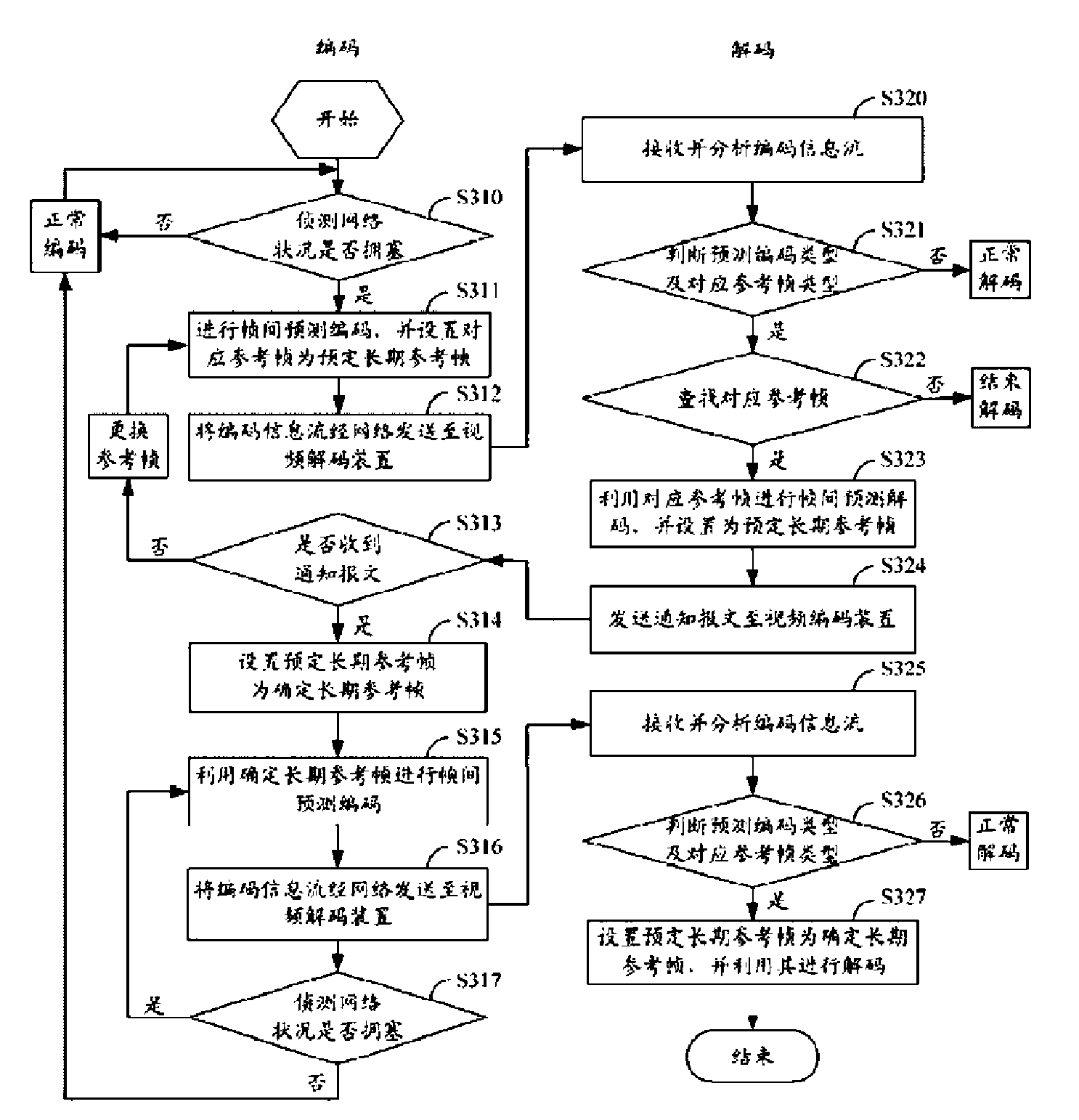
Video encoding and decoding method and video encoding device and decoding device thereof
InactiveCN102045557AImprove image qualityAvoid decoding errorsTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationComputer hardwarePacket loss
The invention relates to a video encoding and decoding method which is used in a video communication system, wherein the predictive encoding type and reference frame type of a video encoding device are controlled according to the network state and a notice message of a video decoding device. When a network is congested, the video encoding device utilizes a reference frame as a long-term reference frame to perform interframe prediction encoding and judges whether the video decoding device receives the corresponding reference frame according to the notice message of the video decoding device, thus the video encoding device and the video decoding device can utilize the same reference frame. The invention also provides the video encoding device and video decoding device which are used in the method in the invention. The video encoding and decoding method, video encoding device and video decoding device provided by the invention are used to encode and decode a video image by determining the long-term reference frame, thus the video encoding device and the video decoding device can utilize the same reference frame, the decoding error phenomenon caused by packet loss can be avoided and the quality of the video image in video communication can be increased.
Owner:NANNING FUGUI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Method and apparatus for motion vector estimation for an image sequence
ActiveUS8787460B1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionImage analysisMotion vectorImage sequence
A method and apparatus for motion vector estimation for a plurality of image frames including retrieving a reference hash value associated with a reference frame, wherein the reference hash value represents a spatially oriented block of pixels, generating a plurality of image hash values including a first hash value for a first area represented by a spatially oriented block of pixels of an image frame and computing a motion vector estimate using a plurality of first hash values and the reference hash value is disclosed.
Owner:TERADICI CORP
Camera calibration using an easily produced 3D calibration pattern
A system for computing one or more calibration parameters of a camera is disclosed. The system comprises a processor and a memory. The processor is configured to provide a first object either marked with or displaying three or more fiducial points. The fiducial points have known 3D positions in a first object reference frame. The processor is further configured to provide a second object either marked with or displaying three or more fiducial points. The fiducial points had known 3D positions in a second object reference frame. The processor is further configured to place the first object and the second object in a fixed position such that the fiducial point positions of the first and second objects are non-planar. The processor is further configured to compute one or more calibration parameters of the second camera using computations based on images taken of the fiducials.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Frequency domain registration and convex set projection-based multi-frame image super-resolution reconstruction method
InactiveCN101980289AHigh-resolutionImprove visual effectsImage enhancementRelative displacementIntermediate frequency
The invention discloses a frequency domain registration and convex set projection-based super-resolution reconstruction method. The method comprises the following steps of: reading a multi-frame image, selecting a reference frame serving as registration, and registering the image to obtain relative displacement of each frame of image, wherein a frequency domain-based rapid registration algorithm is used as the registration algorithm; performing super-resolution reconstruction on the multi-frame image by using a convex set projection method according to the relative displacement of each frame; and finally outputting the image, wherein a video sequence sampling speed is high and the displacement of neighboring frames is small, so that by the method, the registration process is simplified, and the translational motion is estimated by using intermediate frequency domain information of the image and the rotation angle is not estimated to greatly reduce the amount of operation of the registration algorithm. Meanwhile, by the method, the convex set projection reconstruction method is simplified, the entire amount of operation of the super-resolution algorithm is greatly reduced by only using high-brightness amplitude constraint of the image and apriori constraint of a Gaussian point spread function, and the reconstruction quality can be guaranteed.
Owner:上海格州电子股份有限公司
Systems and methods for encoding video using higher rate video sequences
InactiveUS20140003523A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionHigh rate
Systems and methods for encoding video sequences using frames from a higher rate video sequence in accordance with embodiments of the invention are disclosed. One embodiment of the invention includes encoding frames in a first video sequence by selecting a frame in the first video sequence and selecting a frame in a second video sequence as a reference frame by comparing the similarity of the content of the selected frame from the first video sequence with the content of at least one frame in the second video sequence. The selected frame from the first sequence is then encoded using predictions that include references to the reference frame from the second sequence. Information identifying the reference frame from the second sequence is then associated with the encoded frame from the first sequence to enable decoding of the first sequence using the second sequence.
Owner:SONIC IP
Movement detection and construction of an "actual reality" image
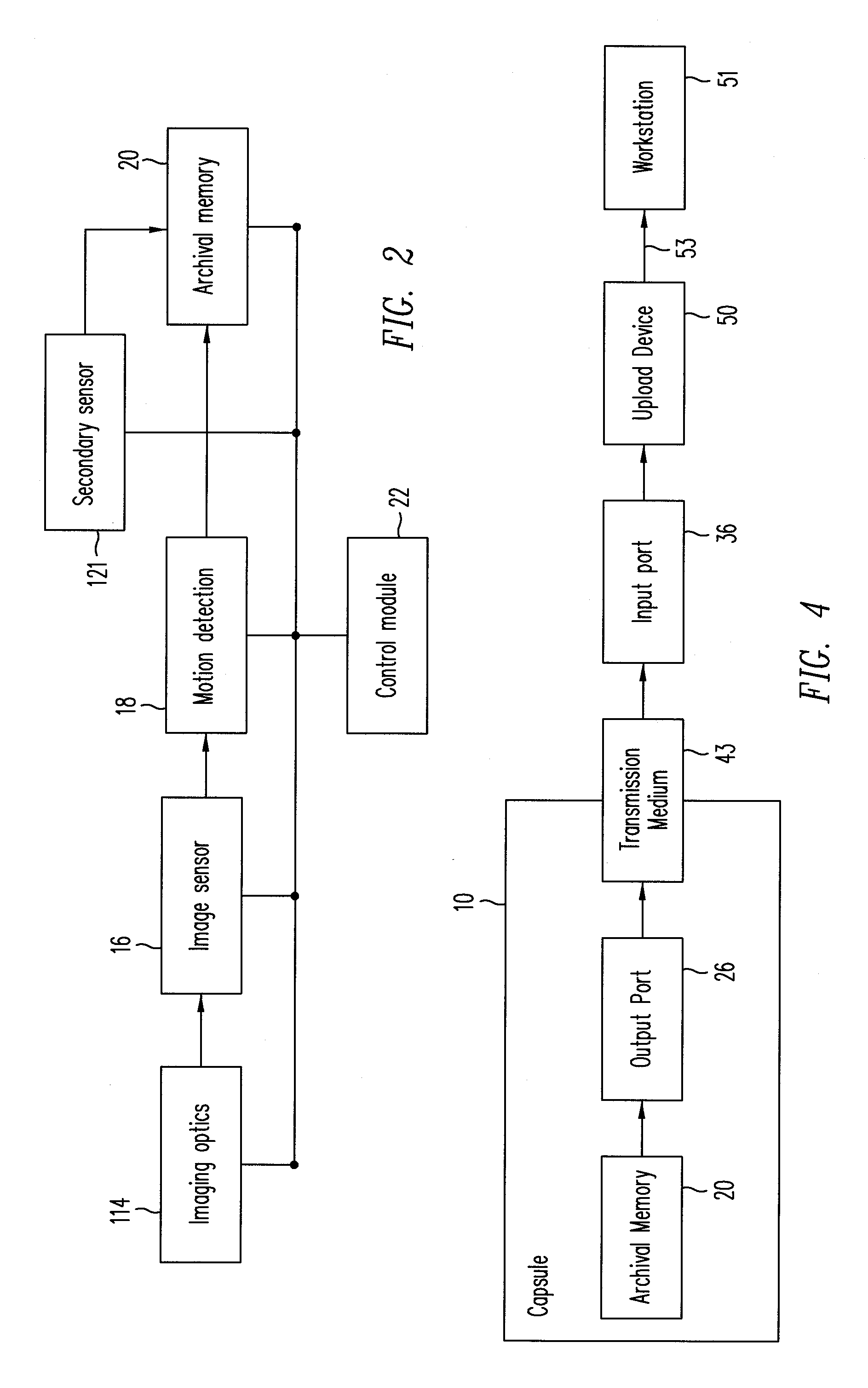
InactiveUS20080117968A1Minimize cost functionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesEndoscopesComputer graphics (images)Image compression
A method for intraframe image compression of an image is combined with a method for reducing memory requirements for an interframe image compression. The intraframe image compression includes (a) dividing the image into blocks; (b) selecting a block according to a predetermined sequence; and (c) processing each selected block by: (1) identifying a reference block from previously processed blocks in the image according to an activity metric; and (2) using the reference block, compressing the selected block. The selected block may be compressed by compressing a difference between the selected block and the reference block, where the difference may be offset by a predetermined value. The difference is compressed after determining that an activity metric of the difference block. The activity metric depends on elements of a difference block, which is a block in which elements are each a difference between an element of the current image frame and a corresponding element of the reference frame. The activity metric is a function of the sum of (a) the sum over all rows of all differences between two successive consecutive elements of each row of the difference block; and (b) the sum over all columns of all differences between two consecutive elements of each column of the difference block. The reference block is identified by minimizing a cost function based on the activity metric and either a sum of absolute differences function or a sum of square differences function. The cost function may be a weighted sum of the activity metric and either a sum of absolute differences function or a sum of square differences function, or a weighted sum of the activity function and either a sum of absolute differences function or a sum of square differences function.
Owner:CAPSO VISION INC
Adjustable compressing method for realizing video code stream frame rate
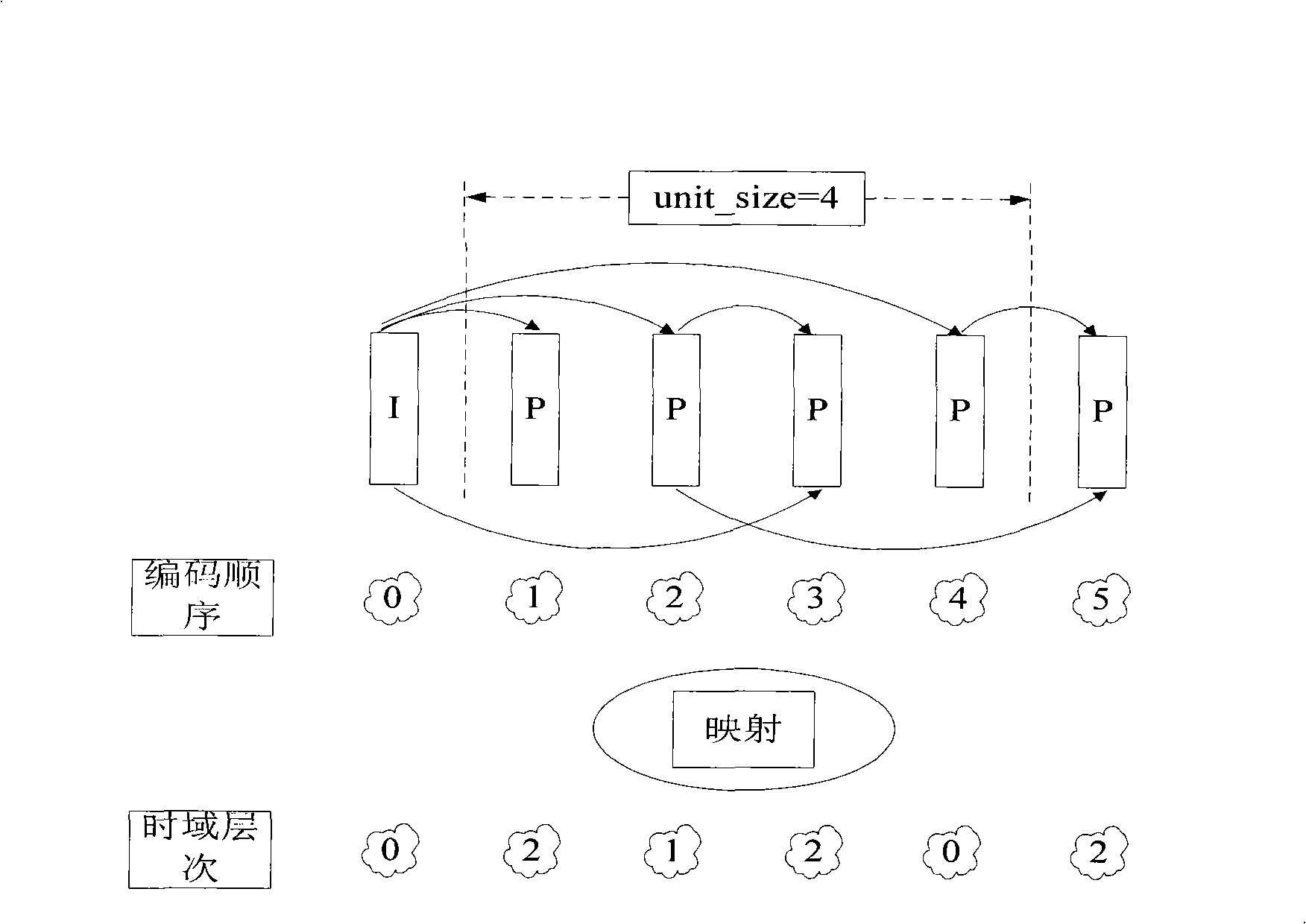
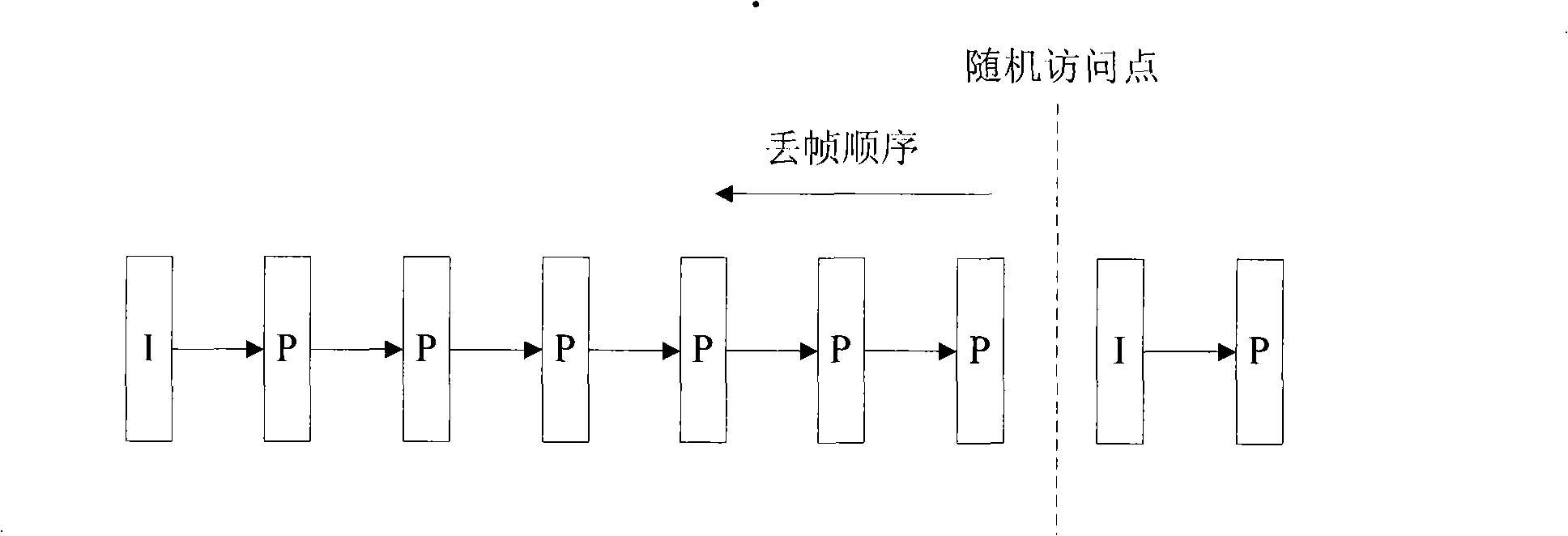
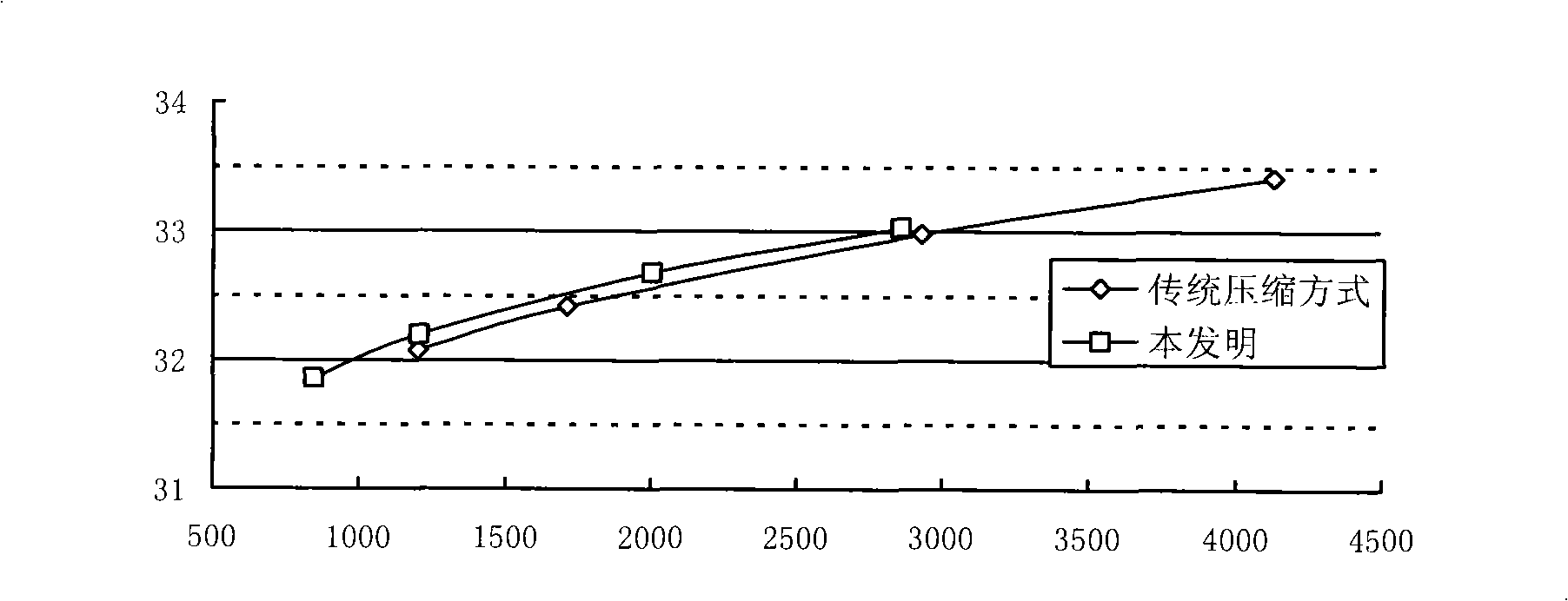
InactiveCN101257628AReduce latencySave bandwidthTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationTime domainFrame time
The invention provides a method of implementing video code stream frame rate adjustable compression, the type of the compression image comprises I frame, non-I frame, P frame, non-P frame and B frame, in the process of decoding, time domain level of each frame image of I frame or P frame is varied periodically as the size of unit group; in the process of coding, the time domain level of current frame image is determined according to the current frame image coding sequence firstly, and then the reference frame image of current frame image is obtained according to reference frame selection strategy, the current frame image is encoded, the reference frame caching is updated according the reference frame updating strategy after accomplishing coding; in decoding, the time domain level of current frame image is determined according to the current frame image decoding sequence, and then the reference frame image of current frame image is obtained according to reference frame selection strategy, the current frame image is decoded, the reference frame caching is updated according the reference frame updating strategy after accomplishing decoding. The compressed code stream has the function of adjustable frame rate, which is capable of adapting transmission of different networks and display of different terminal device.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
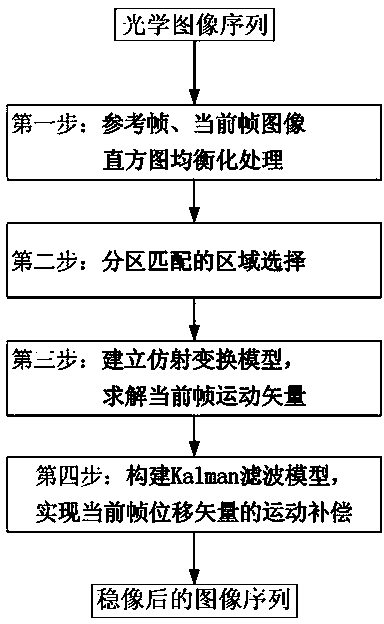
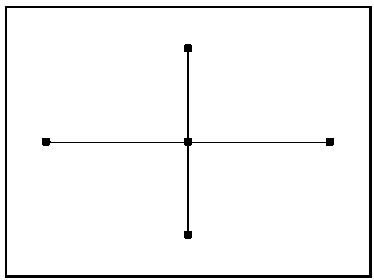
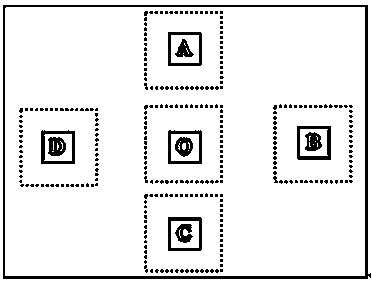
Image de-spin and stabilization method based on subarea matching and affine model
InactiveCN103402045ASuppress random noiseReduce computationTelevision system detailsImage analysisMotion vectorComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses an image de-spin and stabilization method based on subarea matching and an affine model, which comprises the steps that 1, a reference frame and a current frame are subjected to image histogram equalization processing; 2, four areas distributed crosswise and an image center area are selected as matching areas of motion estimation; 3, an affine transformation model is established, and a current frame motion vector is solved; and 4, a kalman filter model is established, and motion compensation of a current frame displacement vector is achieved. In Step 2, the operand is less; a speed is high; the motion estimation capacity is favorable when translation and rotation motion coexist in an image; and an interframe estimated error is less than one pixel. According to the method, the random motion quantity of a video image can be removed with high precision; scanning motion inherent in a platform or a load is kept; and the smoothness of a dynamic image sequence is improved. The method can effectively improve the video image and inhibit random noise.
Owner:CHANGSHA CHAOCHUANG ELECTRONICS TECH
Method and Apparatus for Multiview Video Coding
InactiveUS20120114036A1Lower requirementReduce complexityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionParallaxBlock match
The present invention relates to method and apparatus for multiview video coding. In particular, the present invention describes a disparity compensated prediction to exploit the inter-view correlation in multiview video coding by providing stretching, compression, and shearing (SCSH) disparity compensation to approximate the actual disparity effects in addition to the translational disparity. A sub-sampled block-matching disparity estimation technique is provided to implement the SCSH disparity compensation which makes use of the interpolated reference frames for subpixel motion and disparity estimation in conventional hybrid video coding structure.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
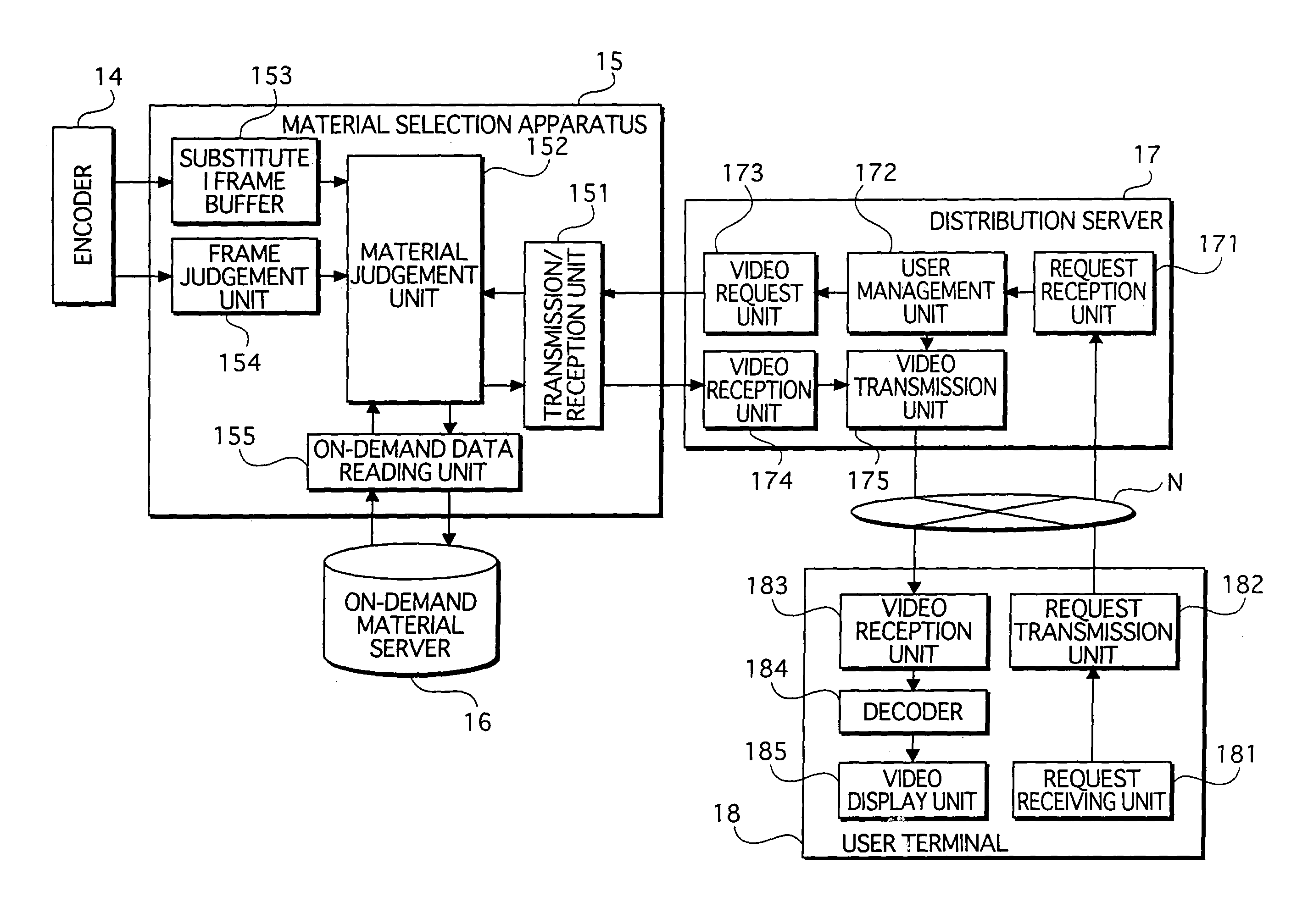
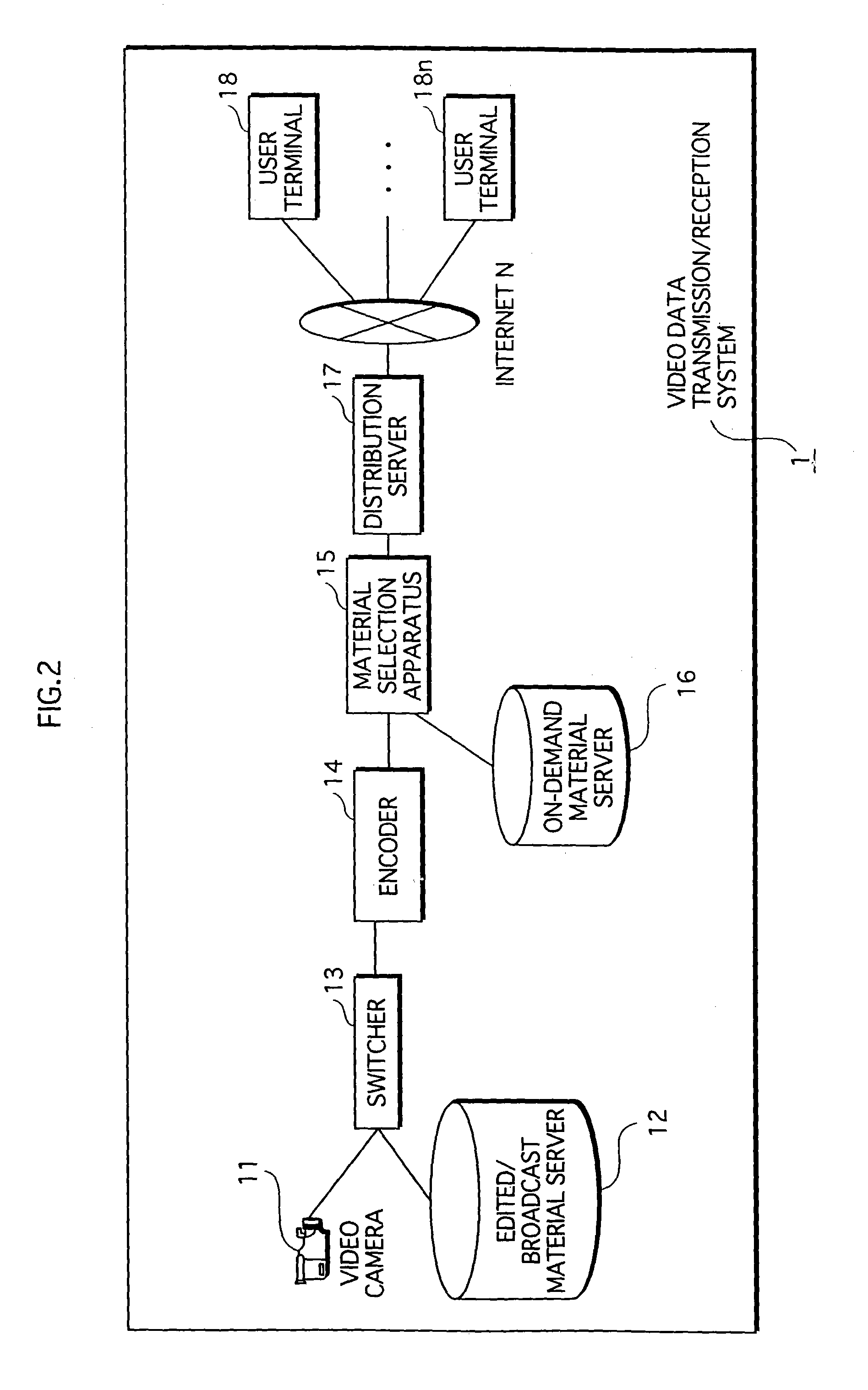
Video data transmission/reception system in which compressed image data is transmitted from a transmission-side apparatus to a reception-side apparatus
InactiveUS7743400B2High processing loadIncrease loadPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesReference frameData transmission
When transmission of on-demand video data interrupts transmission of broadcast video data from a distribution server 17 to a user terminal 18, the distribution server 17 transmits substitute I frame data to the terminal 18 after on-demand video data transmission in complete and before resuming broadcast video data transmission. The user terminal 18 decodes and displays the substitute I frame data, and then uses the decoded substitute I frame data as a reference frame to decode and display the first several frames of broadcast video data received directly after resumption of transmission.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Motion prediction method and video encoding method
ActiveUS9008182B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo encodingMotion vector
The invention provides a motion prediction method. First, a plurality of motion vector predictors is obtained to be included in a candidate set for motion prediction of a current unit of a current frame. Whether the current frame is a non-reference frame which is not referred to by other frames for motion prediction is then determined. When the current frame is not the non-reference frame, any motion vector predictor corresponding to a previously coded frame is removed from the candidate set, and a motion vector of the current unit is predicted according to the motion vector predictors of the candidate set.
Owner:HFI INNOVATION INC
Image stabilizer
InactiveUS20090256918A1Smooth effectLess memoryTelevision system detailsImage analysisPattern recognitionDigital video
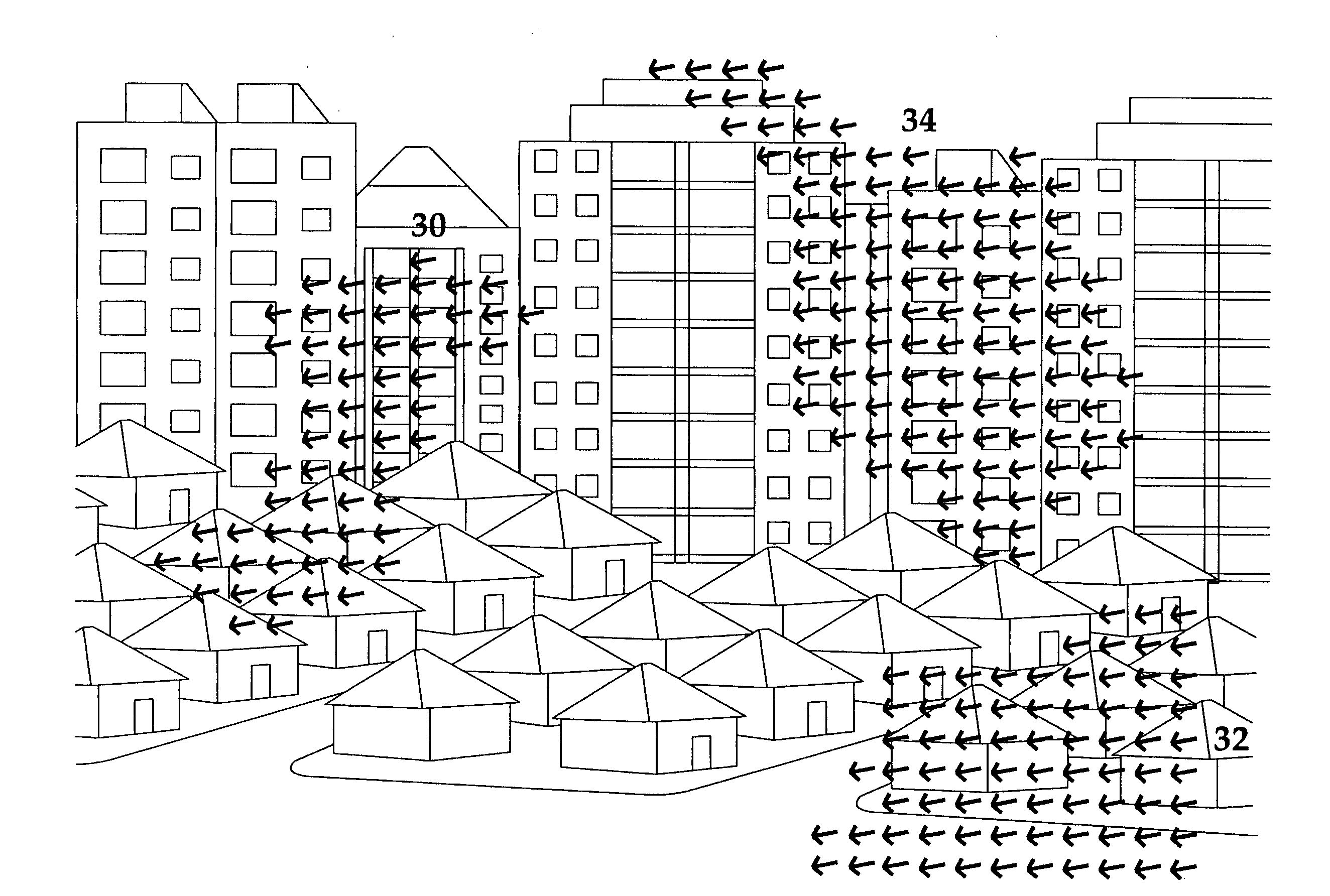
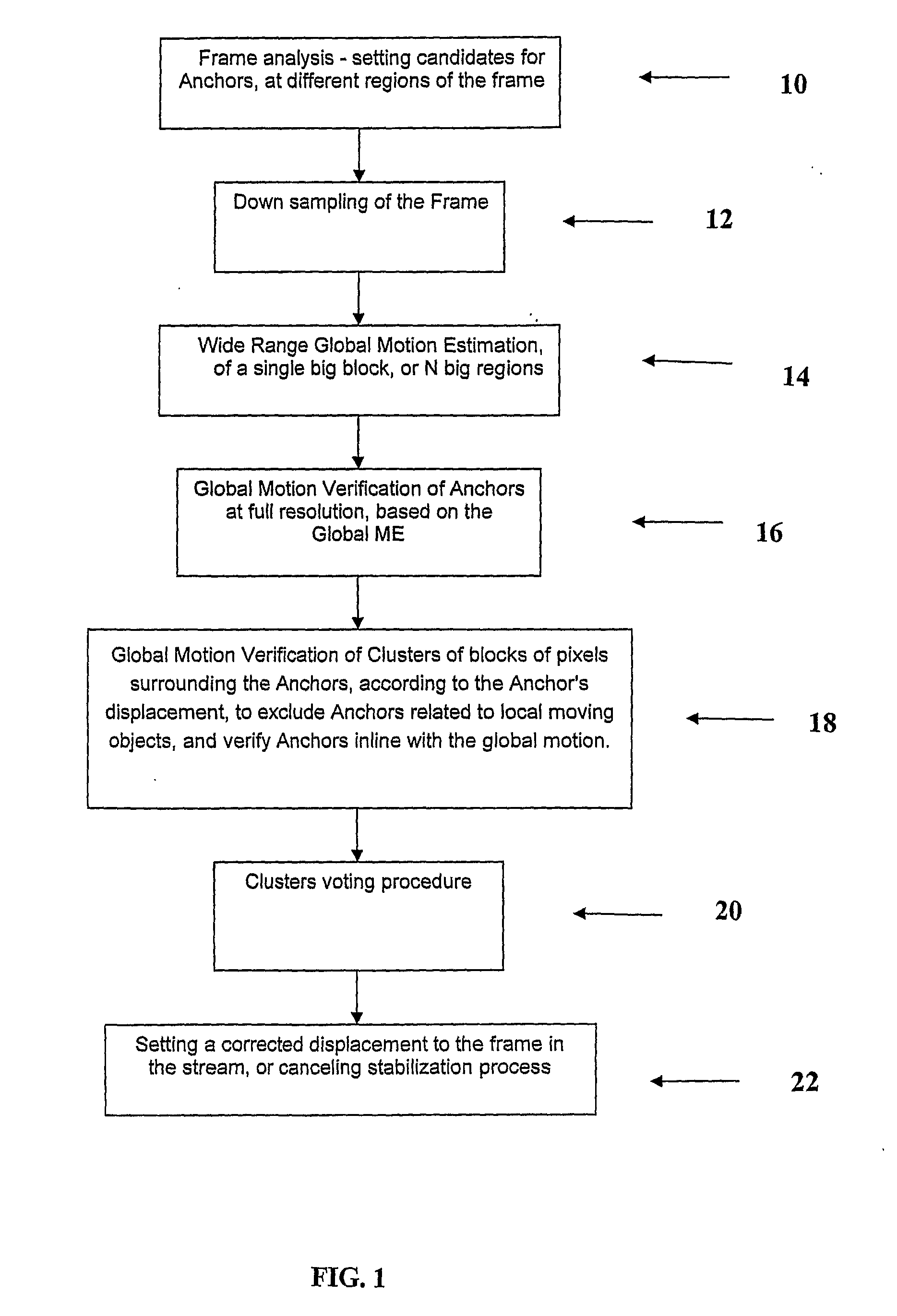
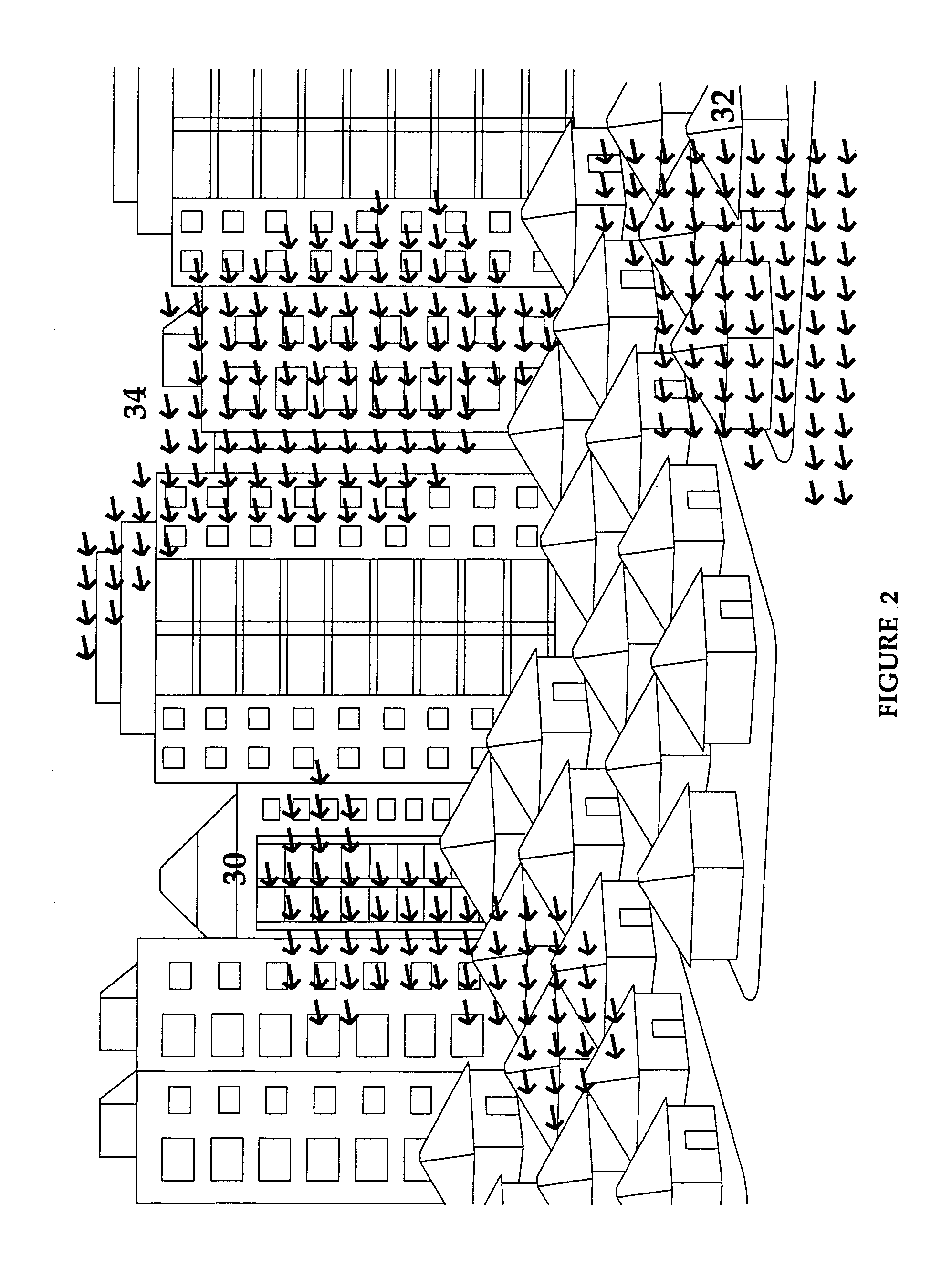
A method for digital video image stabilization, the method including: estimating, from at least one portion of a frame, global frame displacement between an initial reference digital video frame and a current frame in a video sequence of frames; verifying, for the entire frame, the validity of the estimated frame displacement; and compensating for the estimated frame displacement by aligning at least one frame in the sequence with respect to the initial reference frame; wherein the step of aligning includes producing a corrected motion vector for the frame to be aligned and displacing the frame within the video frames sequence in accordance with the corrected motion vector.
Owner:HUMAN MONITORING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com