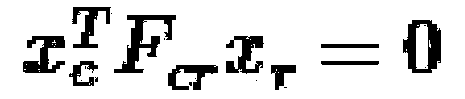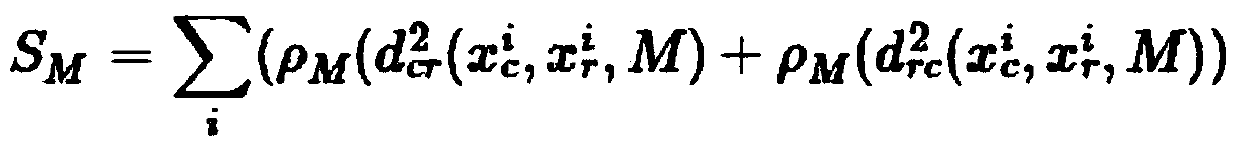Patents
Literature
592 results about "Homography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
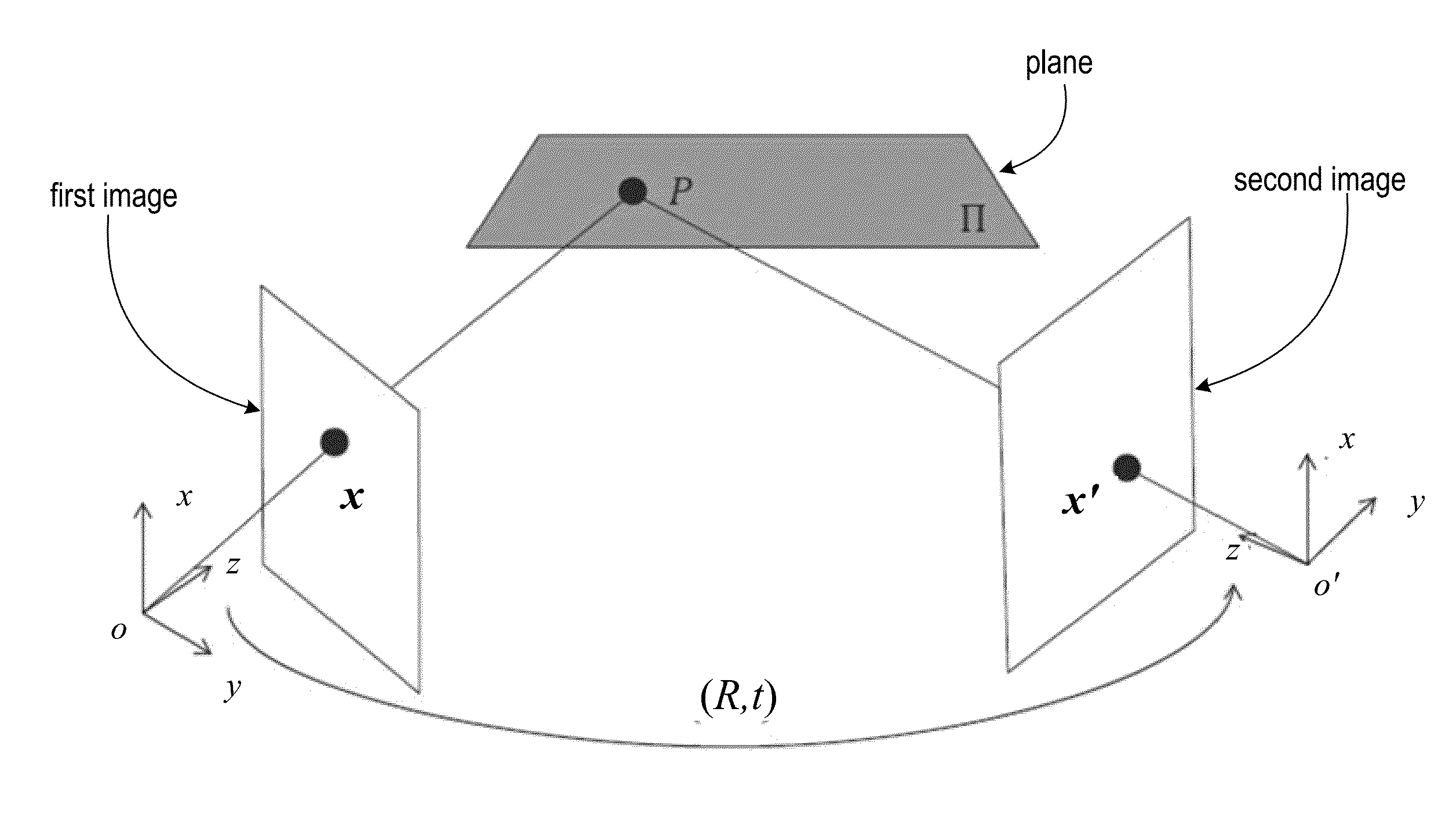
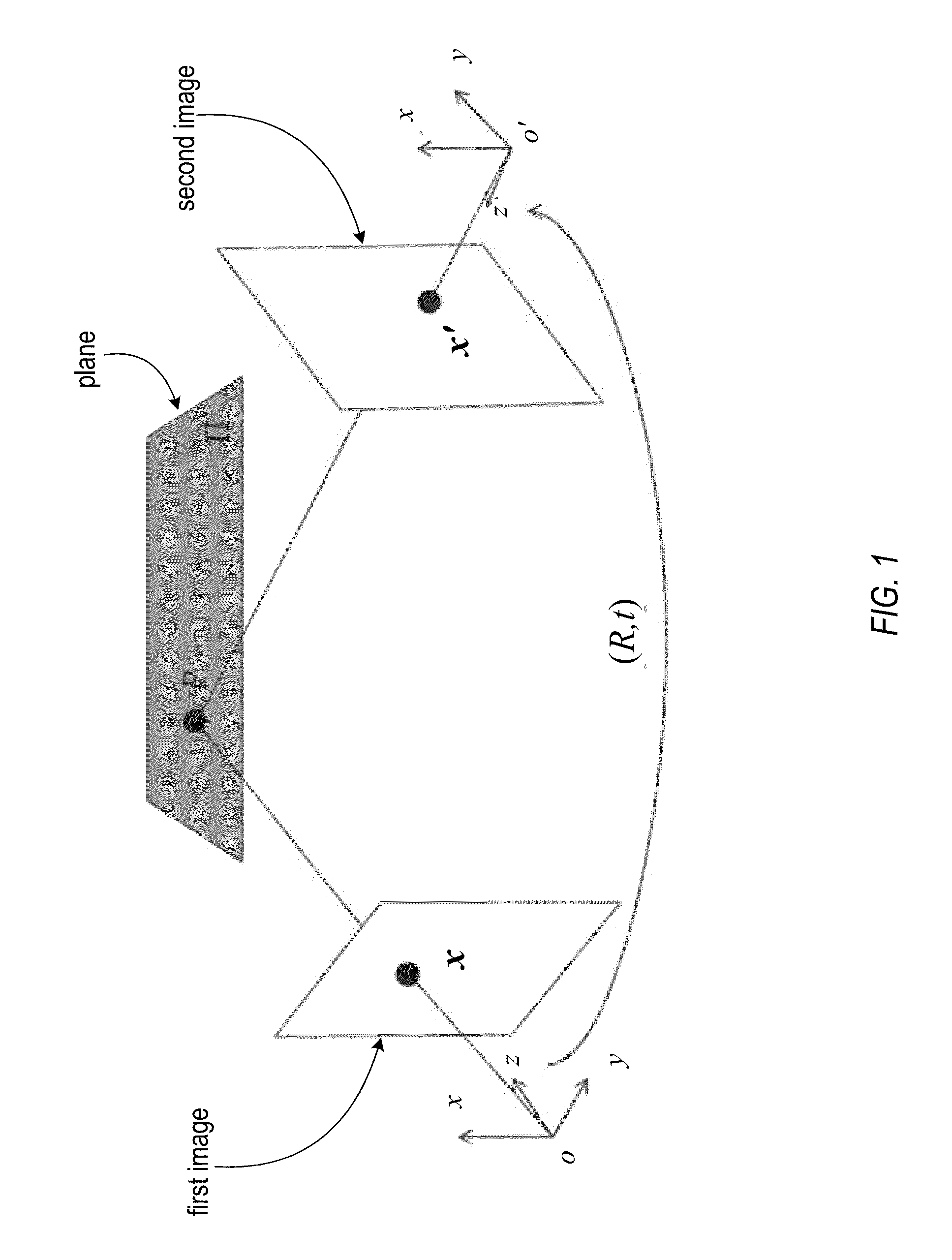
In projective geometry, a homography is an isomorphism of projective spaces, induced by an isomorphism of the vector spaces from which the projective spaces derive. It is a bijection that maps lines to lines, and thus a collineation. In general, some collineations are not homographies, but the fundamental theorem of projective geometry asserts that is not so in the case of real projective spaces of dimension at least two. Synonyms include projectivity, projective transformation, and projective collineation.
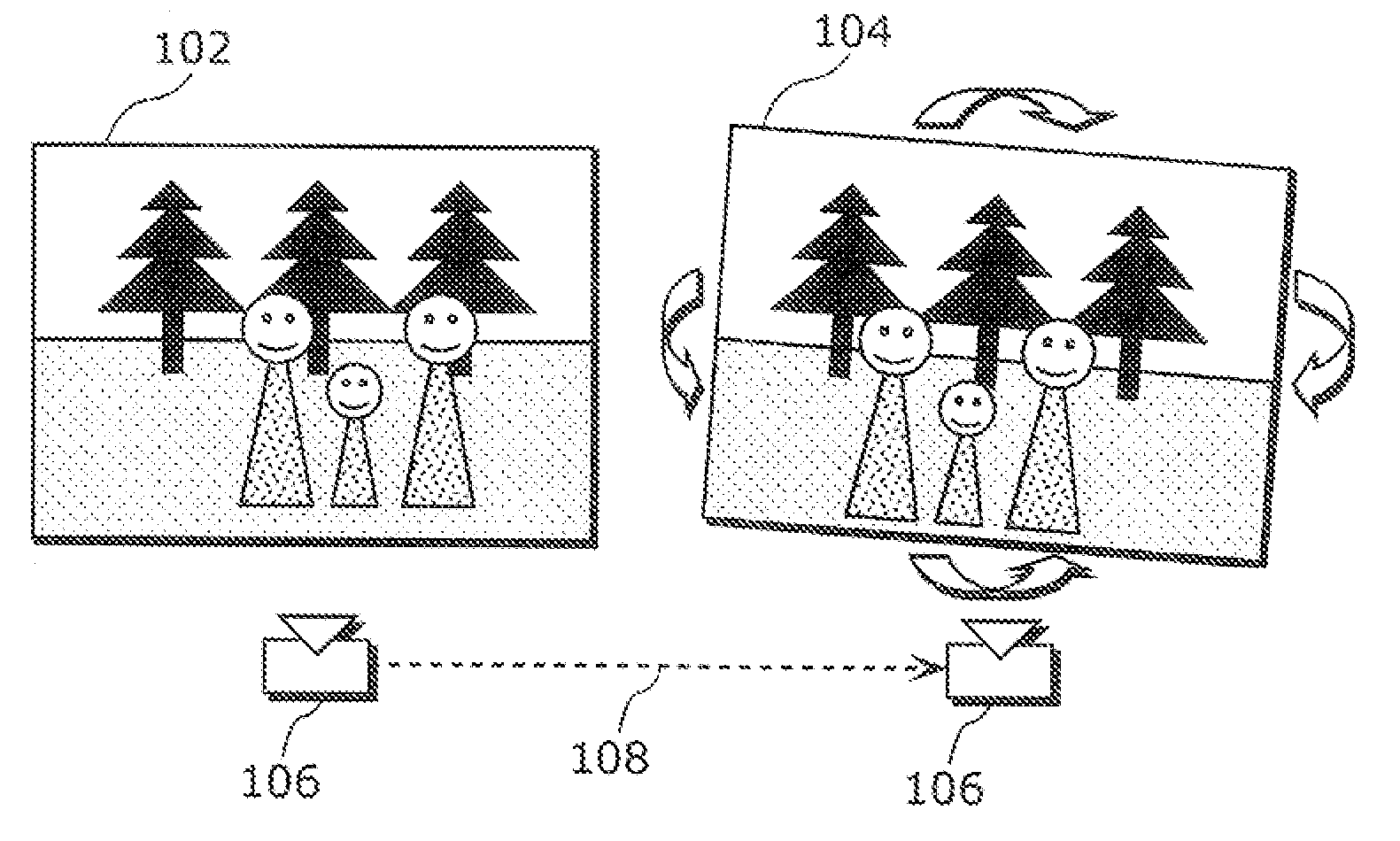
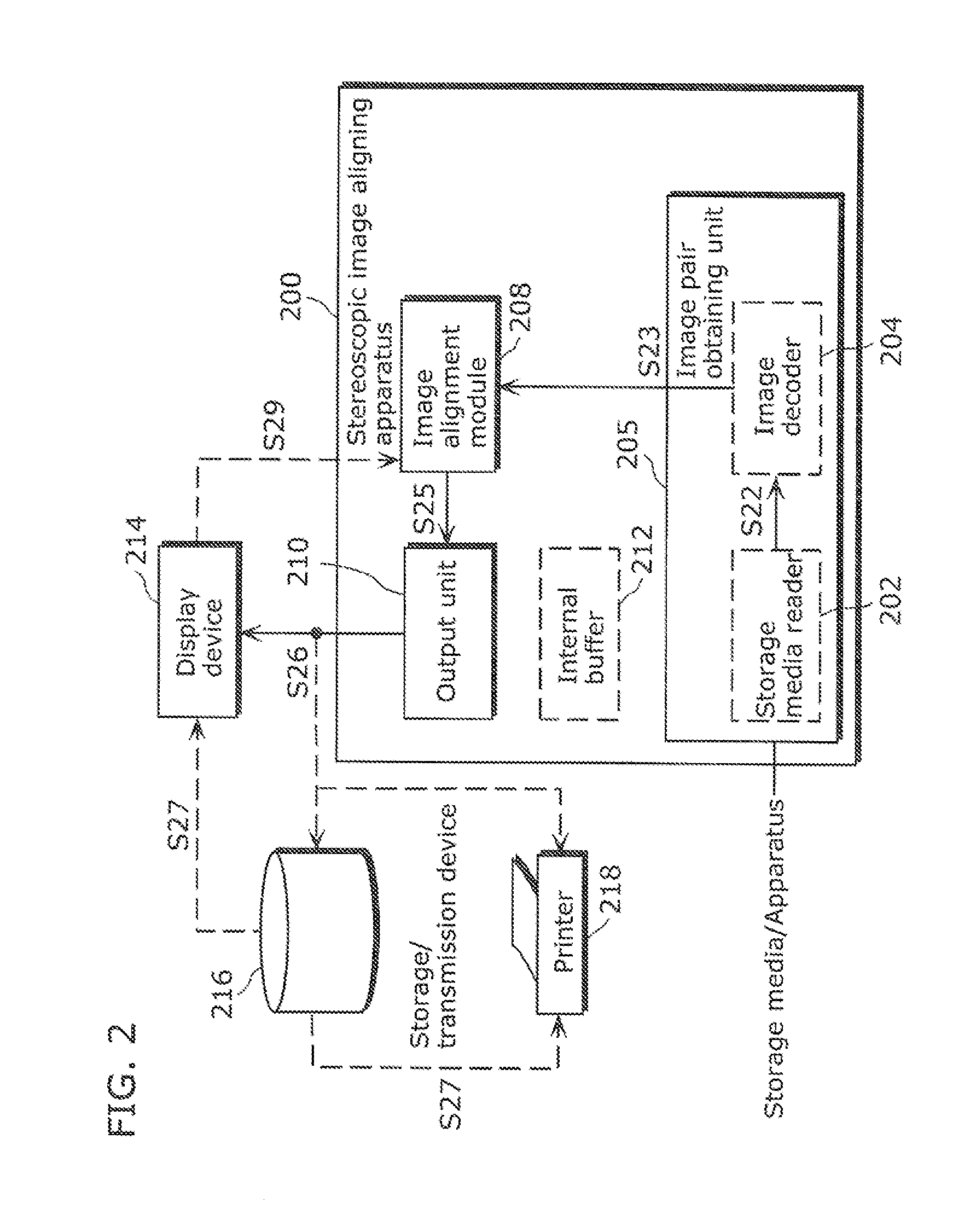
Stereoscopic image aligning apparatus, stereoscopic image aligning method, and program of the same
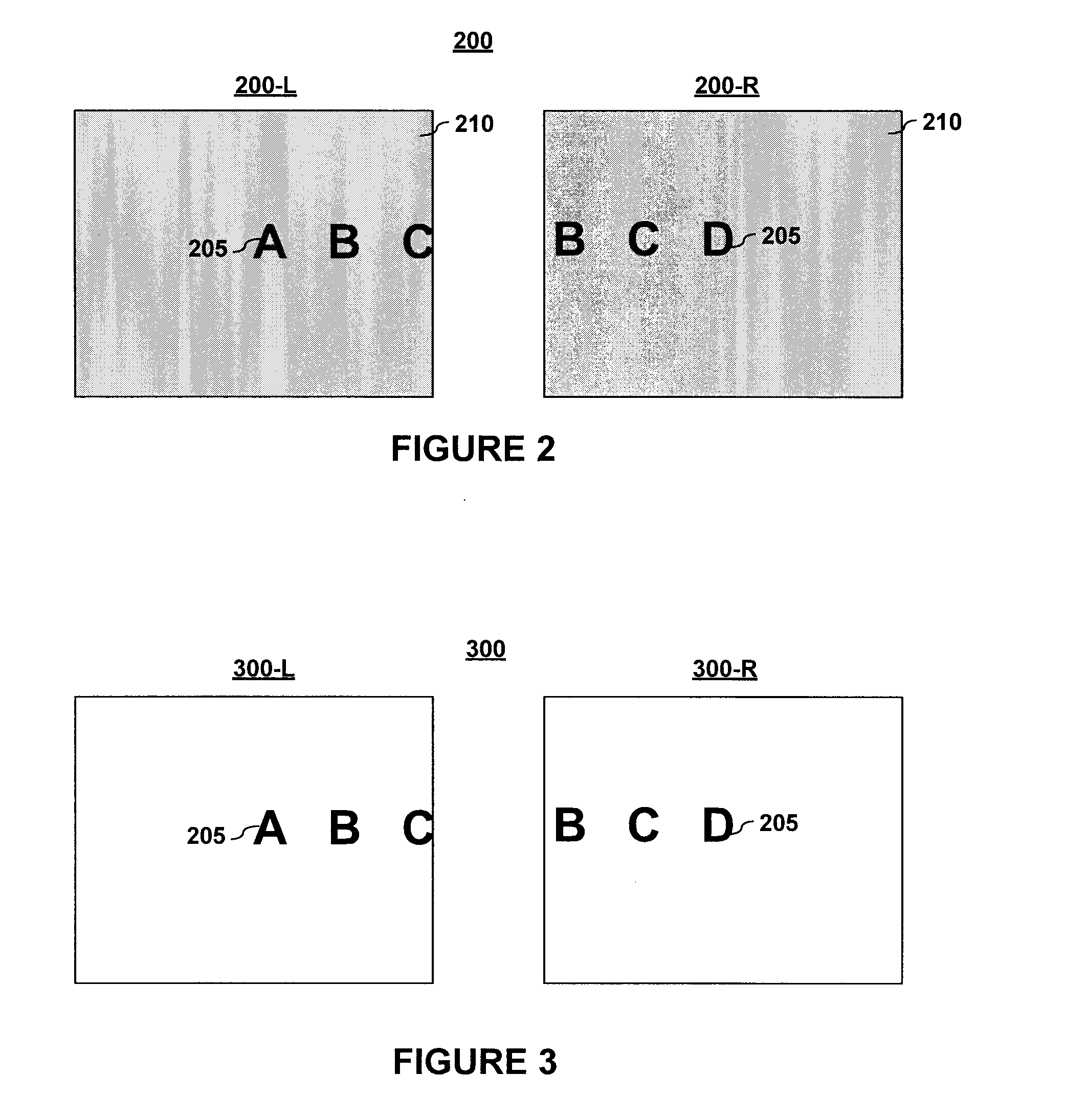
InactiveUS20120147139A1Short amount of timeFor automatic alignmentStereoscopic photographySteroscopic systemsParallaxImage pair
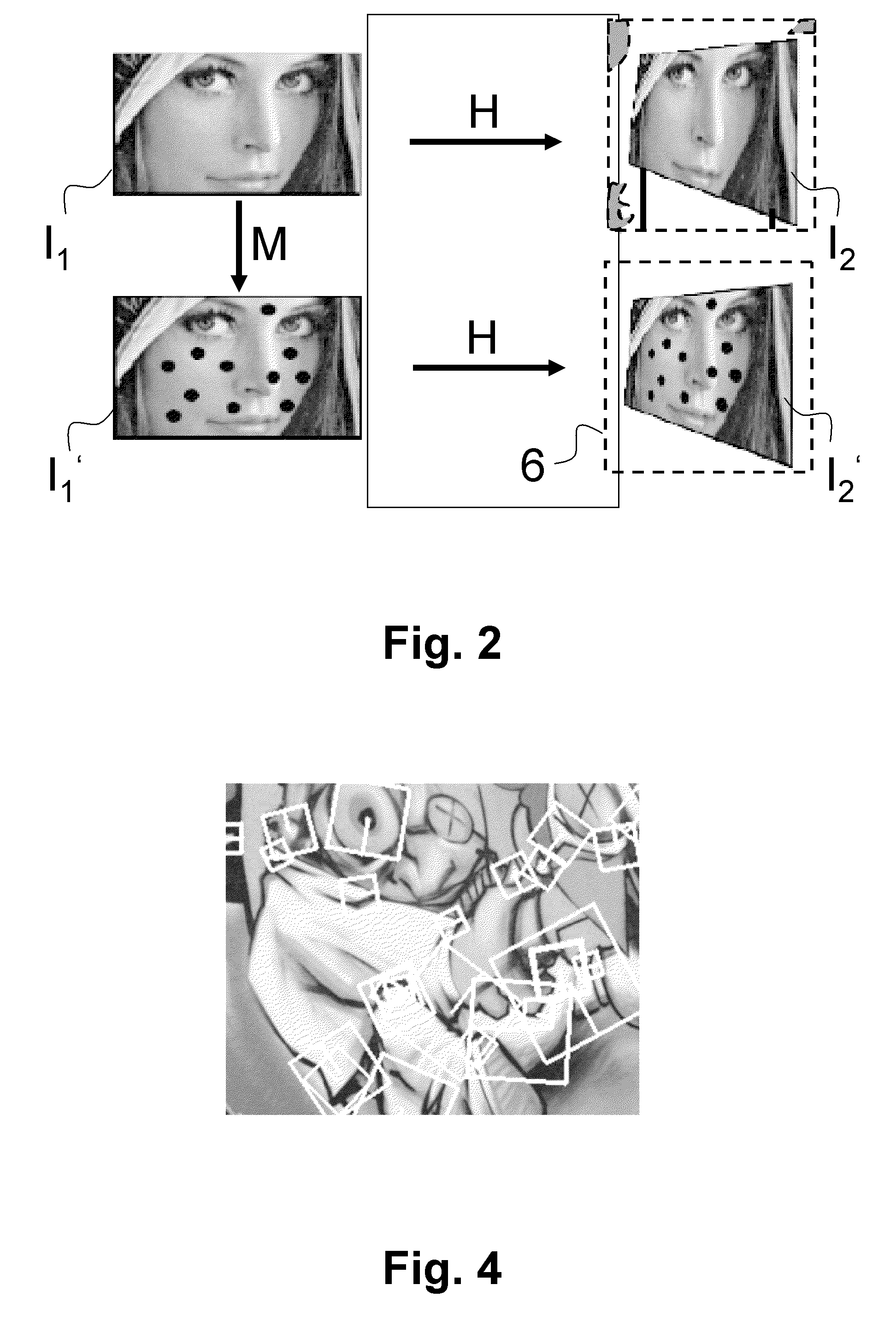
A stereoscopic image aligning apparatus (200) automatically aligns image pairs for stereoscopic viewing in a shorter amount of time than conventional apparatuses, which is applicable to image pairs captured by a single sensor camera or a variable baseline camera, without relying on camera parameters. The stereoscopic image aligning apparatus (200) includes: an image pair obtaining unit (205) obtaining an image pair including a left-eye image and a right-eye image corresponding to the left-eye image; a corresponding point detecting unit (252) detecting a corresponding point representing a set of a first point included in a first image that is one of the images of the image pair and a second point included in a second image that is the other of the images of the image pair and corresponding to the first point; a first matrix computing unit (254) computing a homography transformation matrix for transforming the first point such that a vertical parallax between the first and second points is smallest and an epipolar constraint is satisfied; a transforming unit (260) transforming the first image using the homography transformation matrix; and an output unit (210) outputting: a third image that is the transformed first image; and the second image.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Automatic multiscale image acquisition from a steerable camera
InactiveUS20060197839A1Eliminate needTelevision system detailsColor television detailsHigh resolution imageHomography
A system for automatically acquiring high-resolution images by steering a pan-tilt-zoom camera at targets detected in a fixed camera view is provided. The system uses automatic or manual calibration between multiple cameras. Using automatic calibration, the homography between the cameras in a home position is estimated together with the effects of pan and tilt controls and the expected height of a person in the image. These calibrations are chained together to steer a slave camera. The manual calibration scheme steers a camera to the desired region of interest and calculates the pan, tile and zoom parameters accordingly.
Owner:IBM CORP
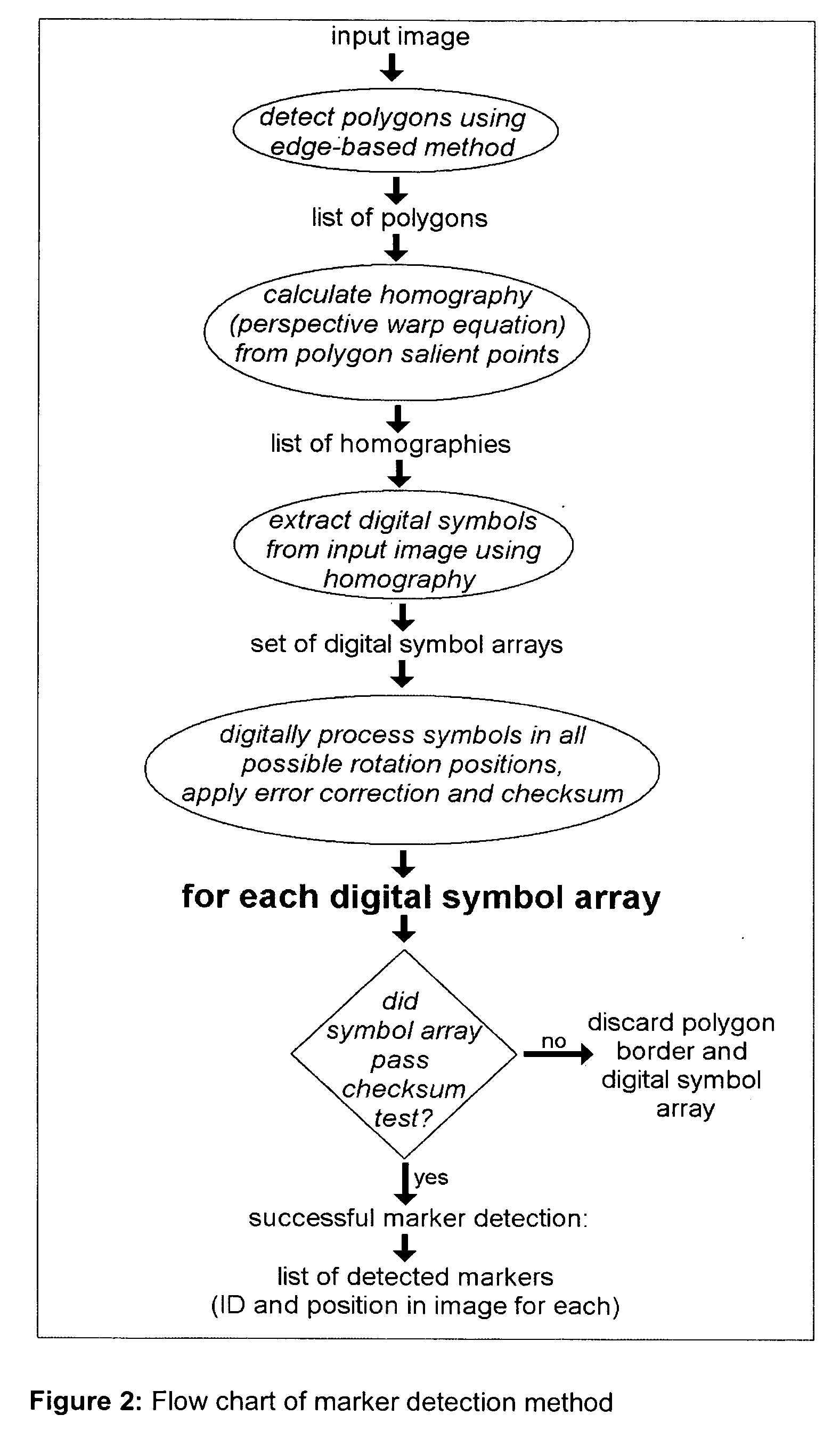
Marker and method for detecting said marker
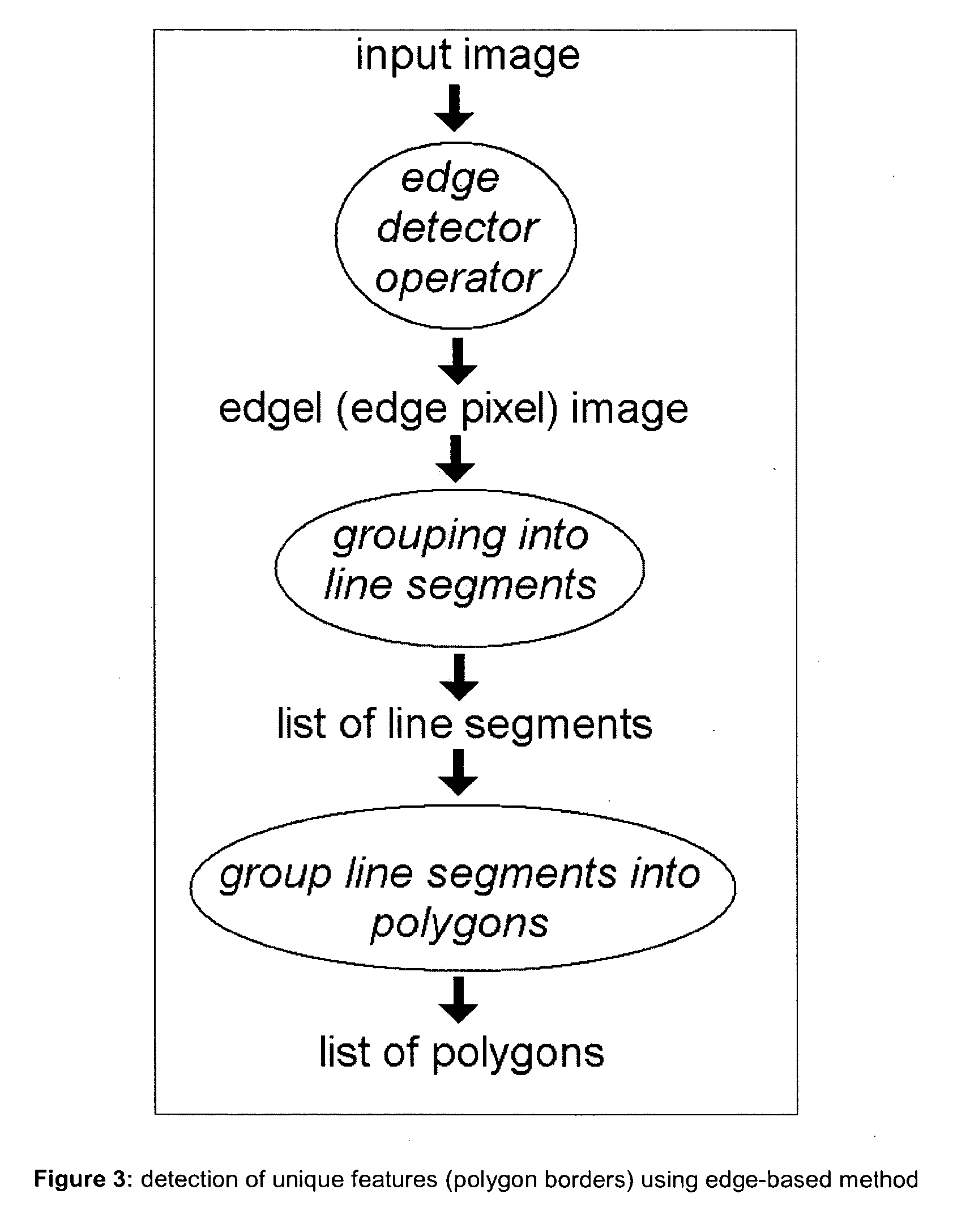
This invention discloses marker detectable by visual means comprising; a polygonal border having of at least four non collinear salient points. The marker has on it a pattern in binary digital code. The binary code data contains information data, checksum and error correction. The binary code data is on two levels; a first level of binary code readable at a first given distance, a second level of binary code readable at a second given distance, where the second given distance is less than the first given distance and the second level binary code is smaller in size than the first level binary code. The second level of binary code does not interfere with the reading of the first level binary code. It also discloses a method for detecting a marker comprising the steps of detecting an image, using an edge detector to detect an edge in said image, grouping more than one edge into a polygon having salient points, calculating homography from polygon salient points, generating a list of homographies, extracting binary data from input image having homographies, identifying and verifying binary data.
Owner:MILLENNIUM THREE TECH
Improved method of RGB-D-based SLAM algorithm
InactiveCN104851094AMatching result optimizationHigh speedImage enhancementImage analysisPoint cloudEstimation methods
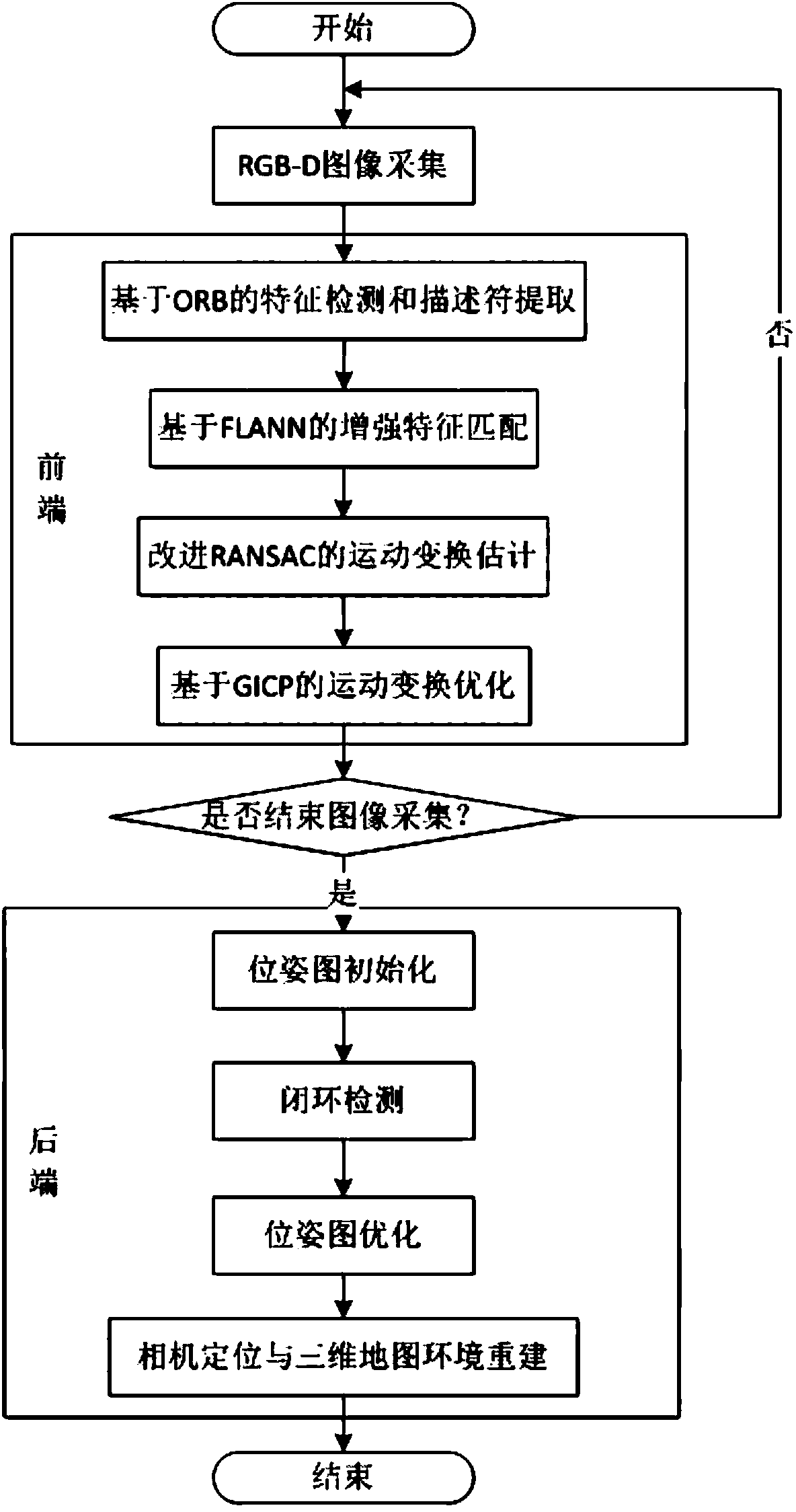
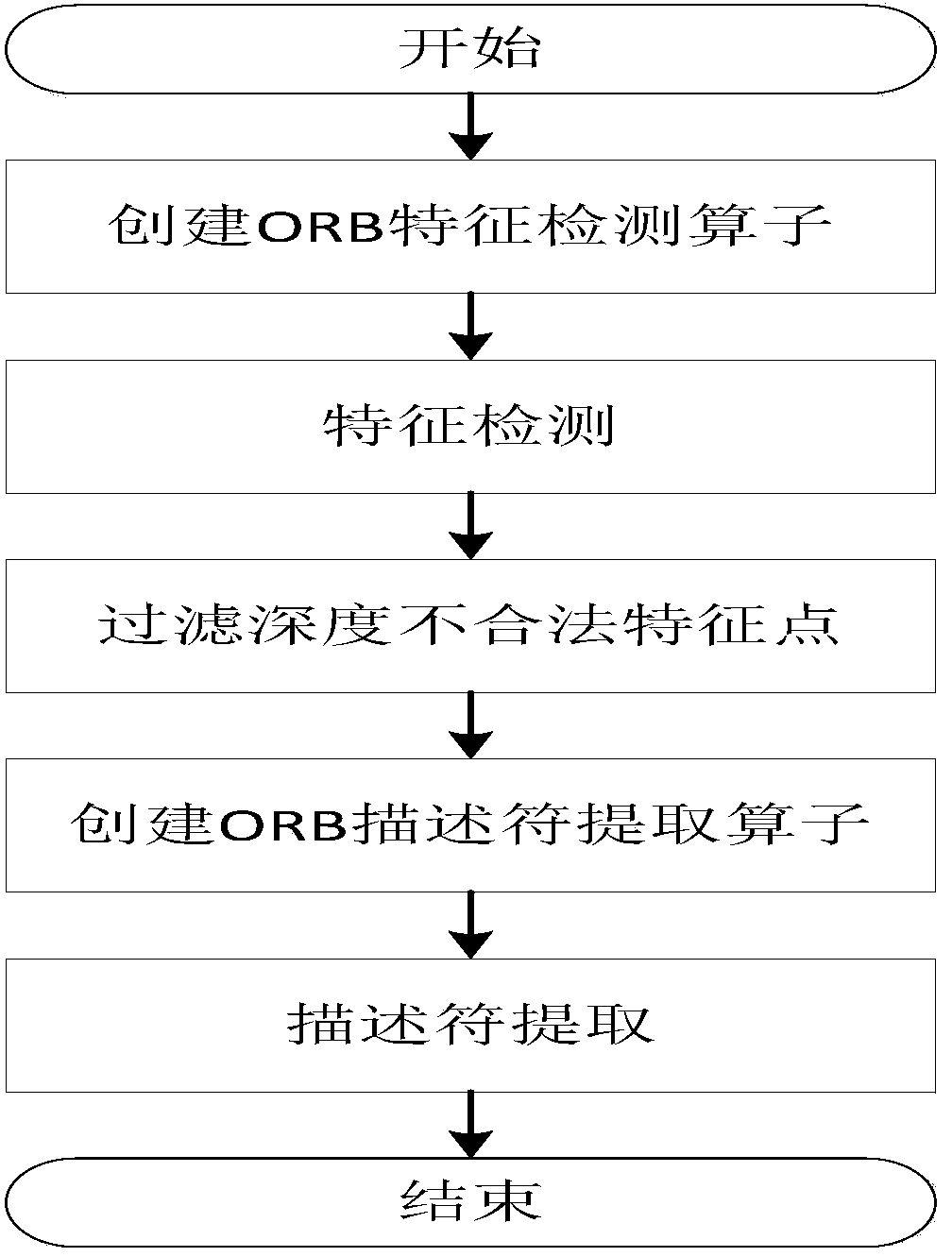
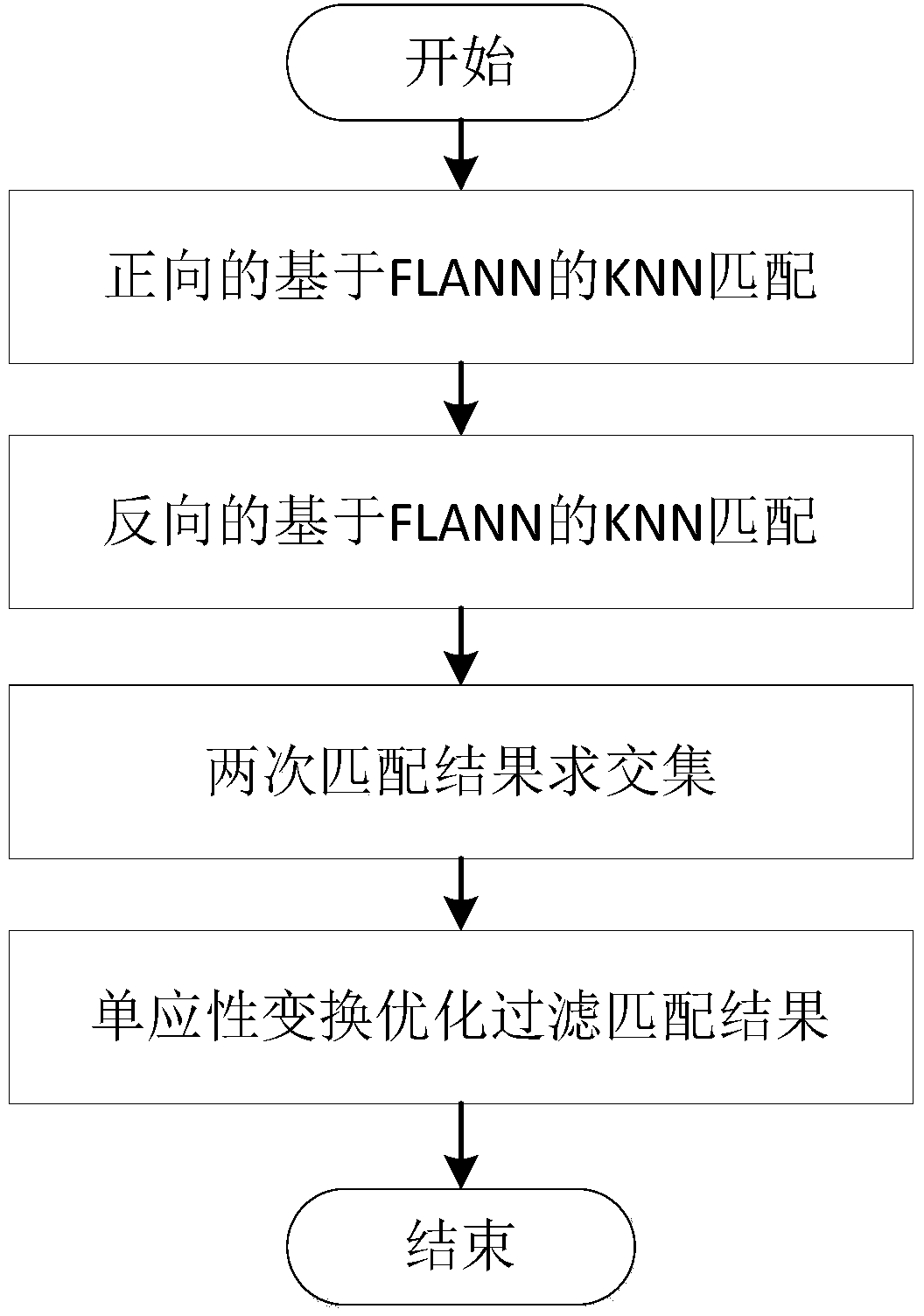
Disclosed in the invention is an improved method of a RGB-D-based simultaneously localization and mapping (SLAM) algorithm. The method comprises two parts: a front-end part and a rear-end part. The front-end part is as follows: feature detection and descriptor extraction, feature matching, motion conversion estimation, and motion conversion optimization. And the rear-end part is as follows: a 6-D motion conversion relation initialization pose graph obtained by the front-end part is used for carrying out closed-loop detection to add a closed-loop constraint condition; a non-linear error function optimization method is used for carrying out pose graph optimization to obtain a global optimal camera pose and a camera motion track; and three-dimensional environment reconstruction is carried out. According to the invention, the feature detection and descriptor extraction are carried out by using an ORB method and feature points with illegal depth information are filtered; bidirectional feature matching is carried out by using a FLANN-based KNN method and a matching result is optimized by using homography matrix conversion; a precise inliners matching point pair is obtained by using an improved RANSAC motion conversion estimation method; and the speed and precision of point cloud registration are improved by using a GICP-based motion conversion optimization method.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Reduced Homography for Recovery of Pose Parameters of an Optical Apparatus producing Image Data with Structural Uncertainty
A reduced homography H for an optical apparatus to recover pose parameters from imaged space points Pi using an optical sensor. The electromagnetic radiation from the space points Pi is recorded on the optical sensor at measured image coordinates. A structural uncertainty introduced in the measured image points is determined and a reduced representation of the measured image points is selected based on the type of structural uncertainty. The reduced representation includes rays {circumflex over (r)}i defined in homogeneous coordinates and contained in a projective plane of the optical apparatus. At least one pose parameter of the optical apparatus is then estimated by applying the reduced homography H and by applying a condition on the motion of the optical apparatus, the condition being consonant with the reduced representation employed in the reduced homography H.
Owner:ELECTRONICS SCRIPTING PRODS
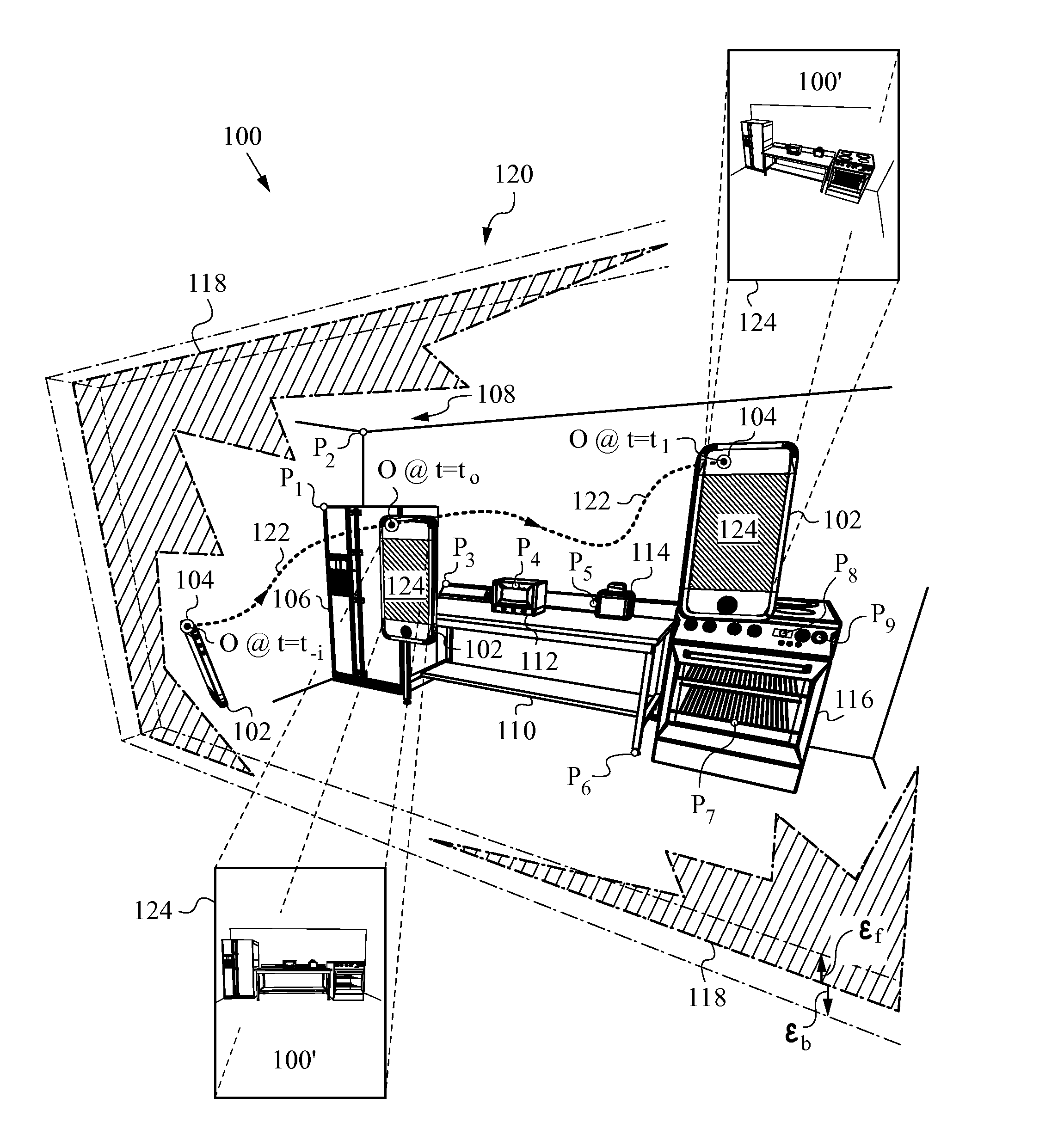
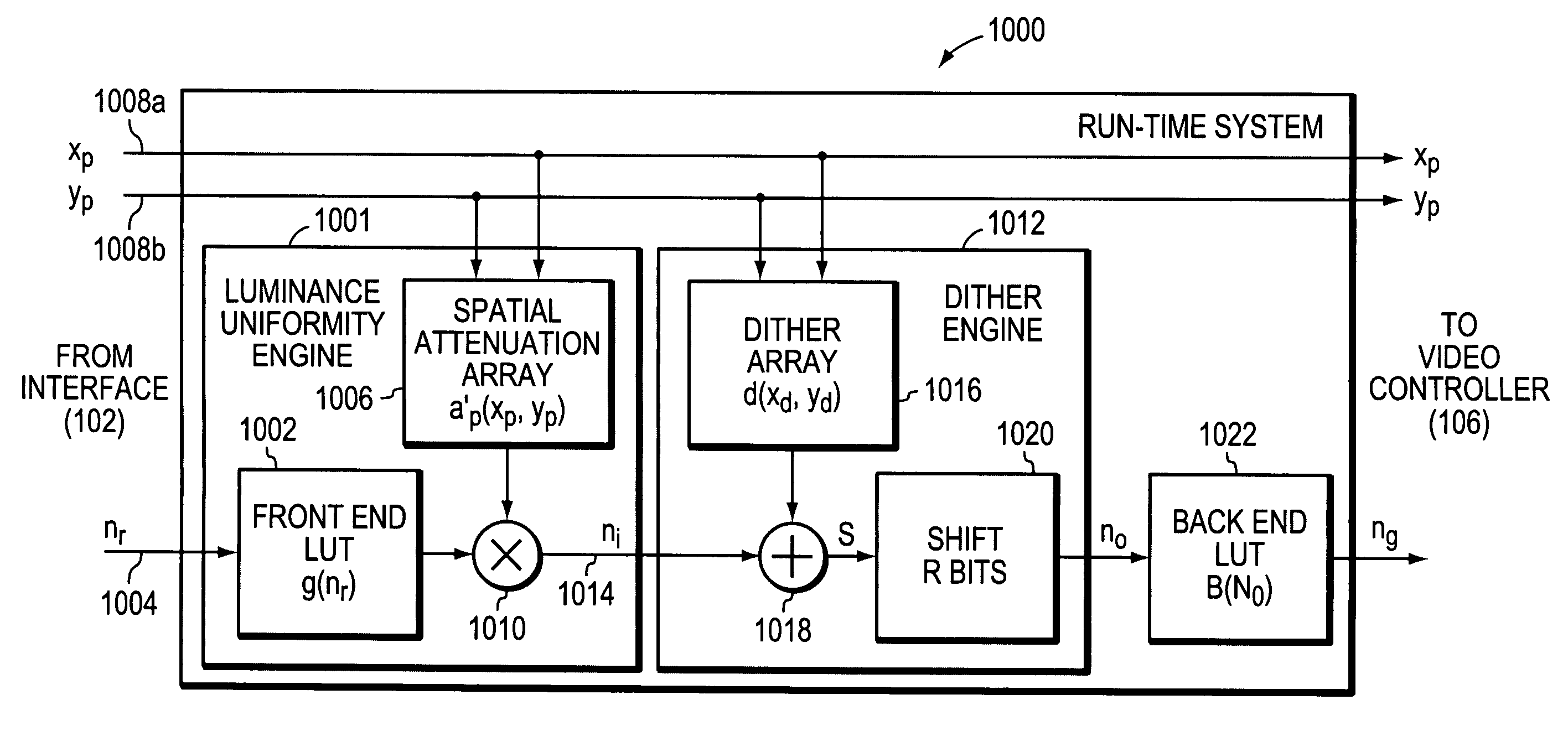
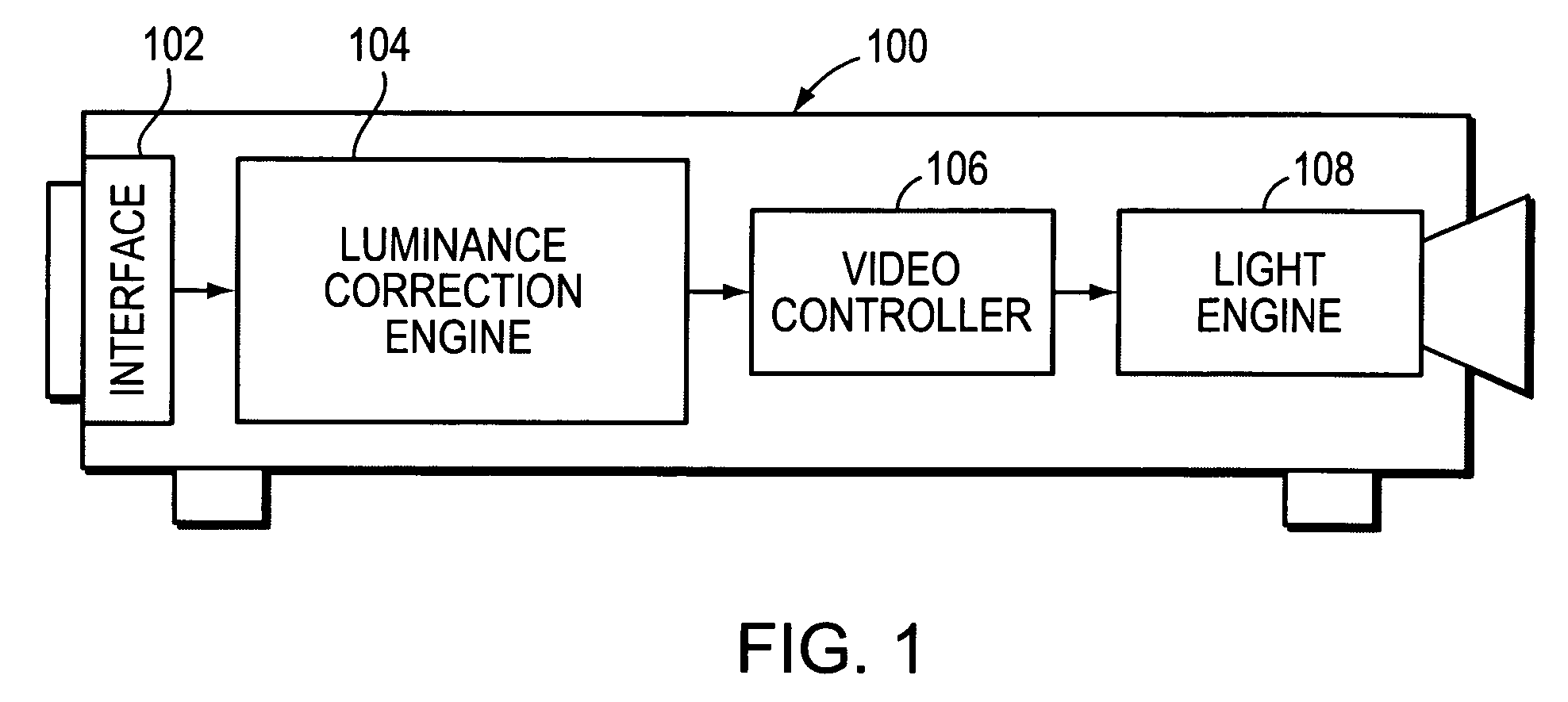
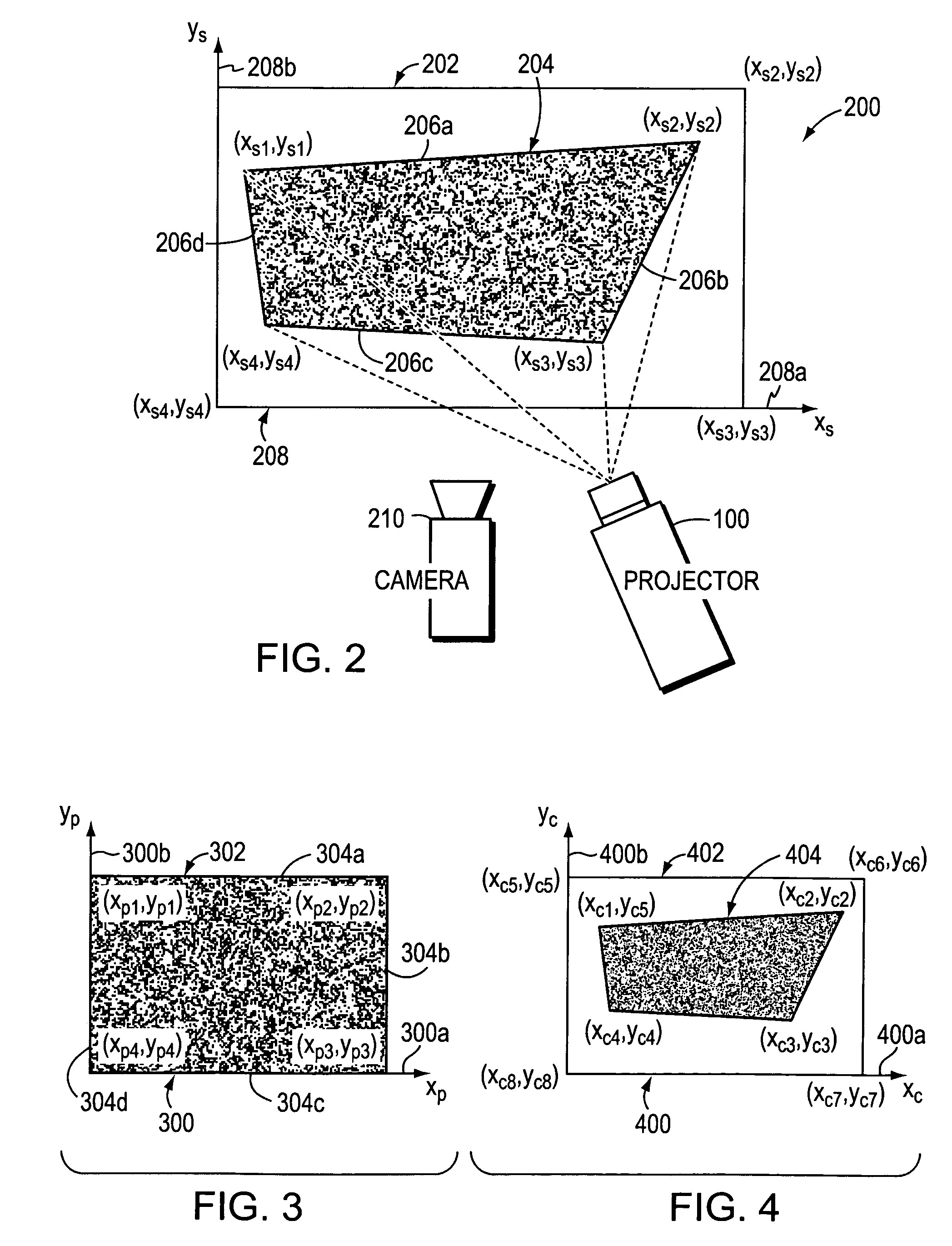
System and method for correcting luminance non-uniformity of obliquely projected images
A system and method corrects luminance non-uniformity caused by images being obliquely projected onto a screen. A camera is used to record the geometry of the obliquely displayed image. Utilizing this recorded geometry, a homography is then derived that maps pixels between the projector's coordinate system and the screen's coordinate system. Utilizing the homography, the projector pixel that attends to the largest projected area on the screen is identified. Next, the ratio of each pixel's projected area to the largest projected area is computed. These ratios are then organized into an attenuation array that is used to produce “corrected” luminance information from input image data. The projector is then driven with the “corrected” luminance information.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
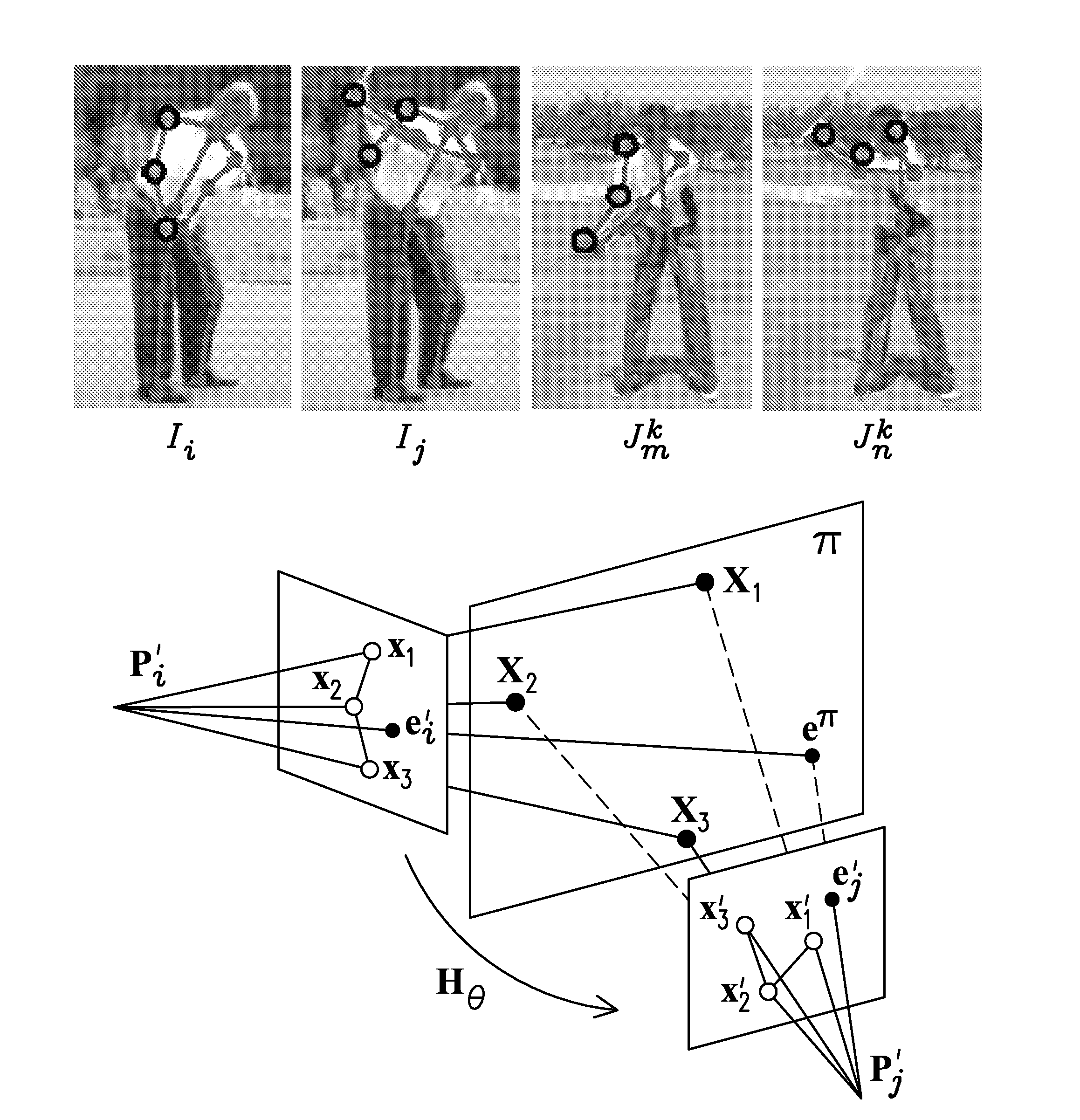
Methods for recognizing pose and action of articulated objects with collection of planes in motion
InactiveUS20100303303A1Reduce decreaseCharacter and pattern recognitionHuman bodyPattern recognition
The invention comprises an improved system, method, and computer-readable instructions for recognizing pose and action of articulated objects with collection of planes in motion. The method starts with a video sequence and a database of reference sequences corresponding to different known actions. The method identifies the sequence from the reference sequences such that the subject in performs the closest action to that observed. The method compares actions by comparing pose transitions. The cross-homography invariant may be used for view-invariant recognition of human body pose transition and actions.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
High-precision projector and camera calibration system and method
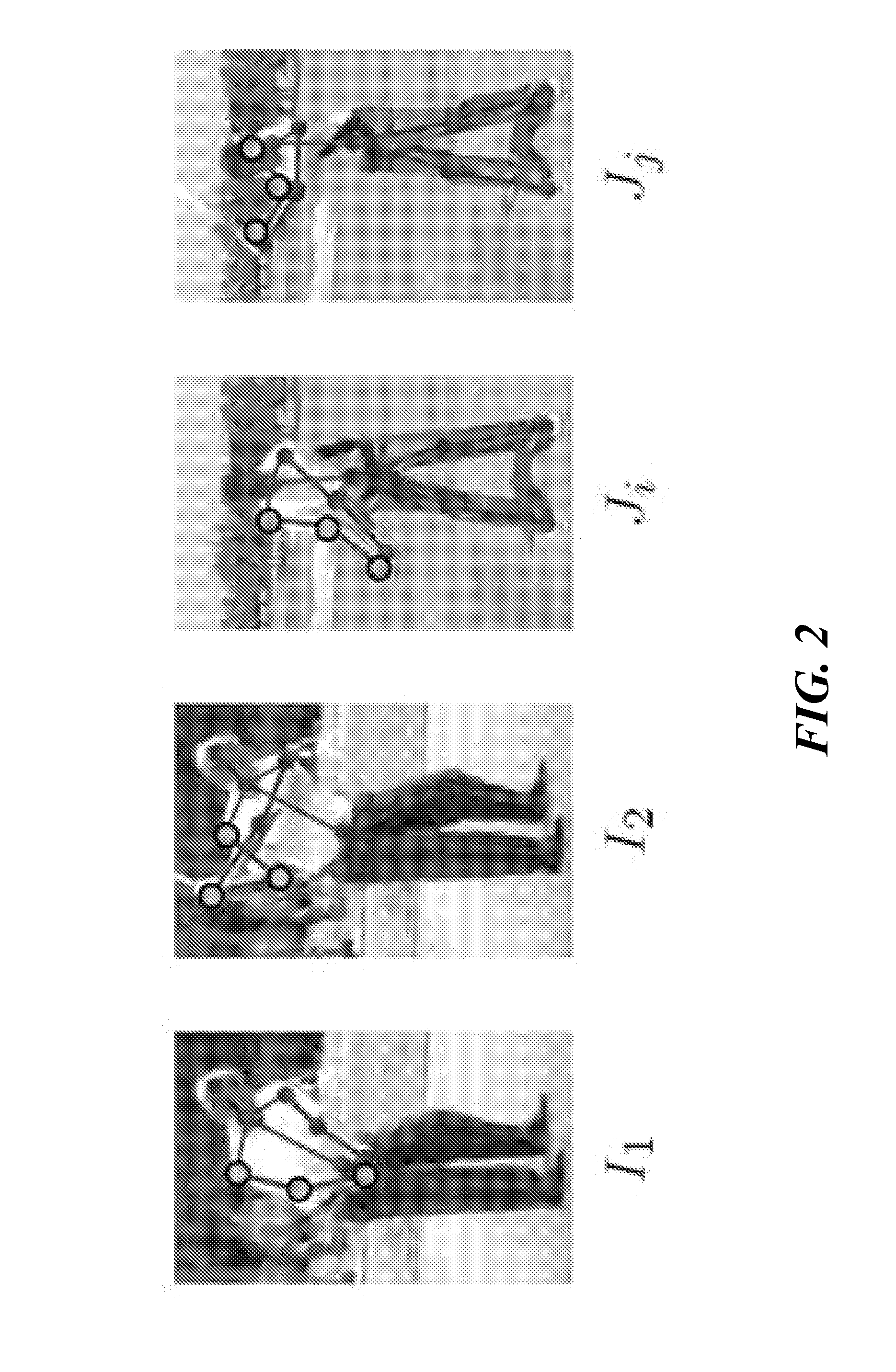
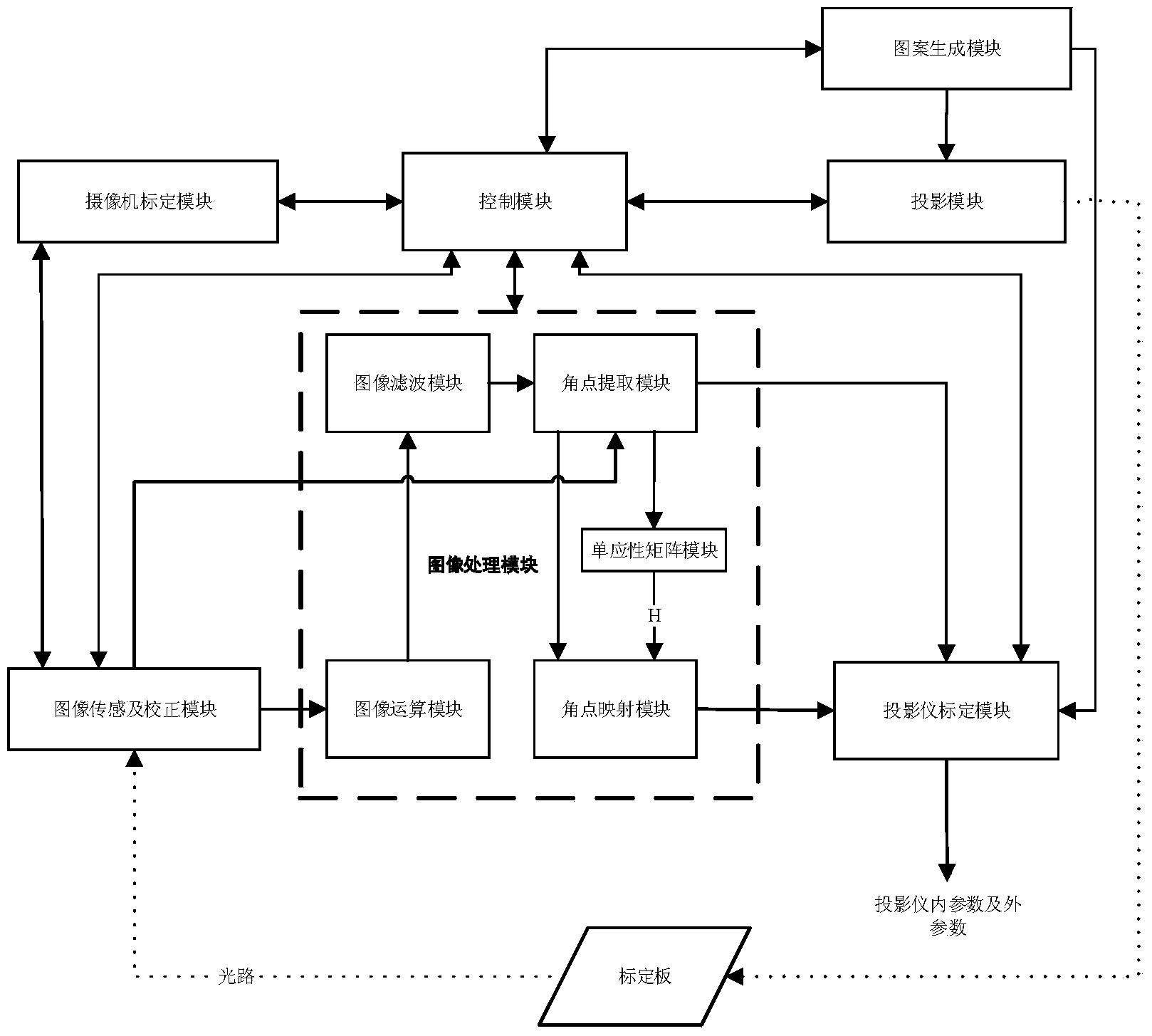
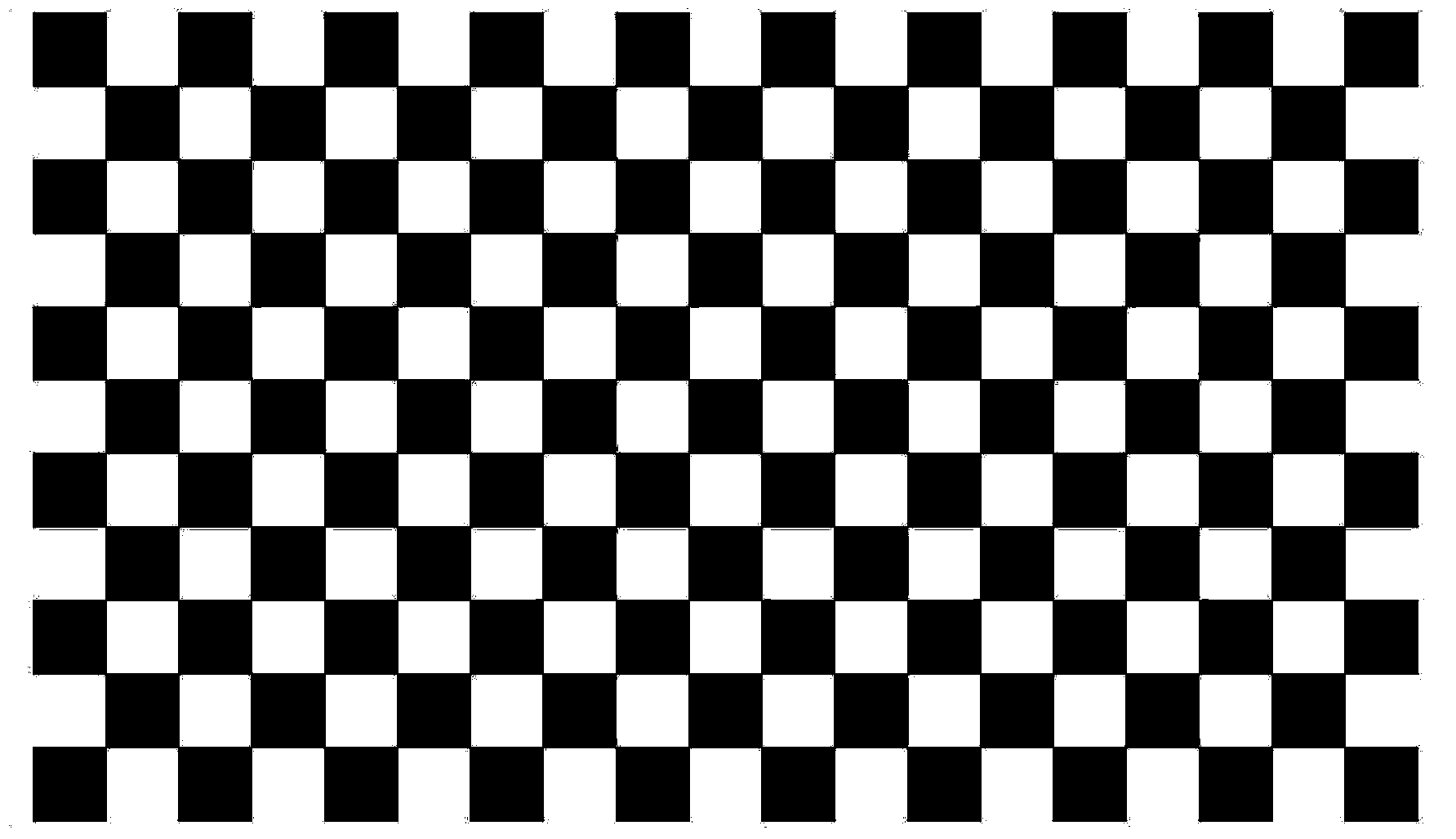
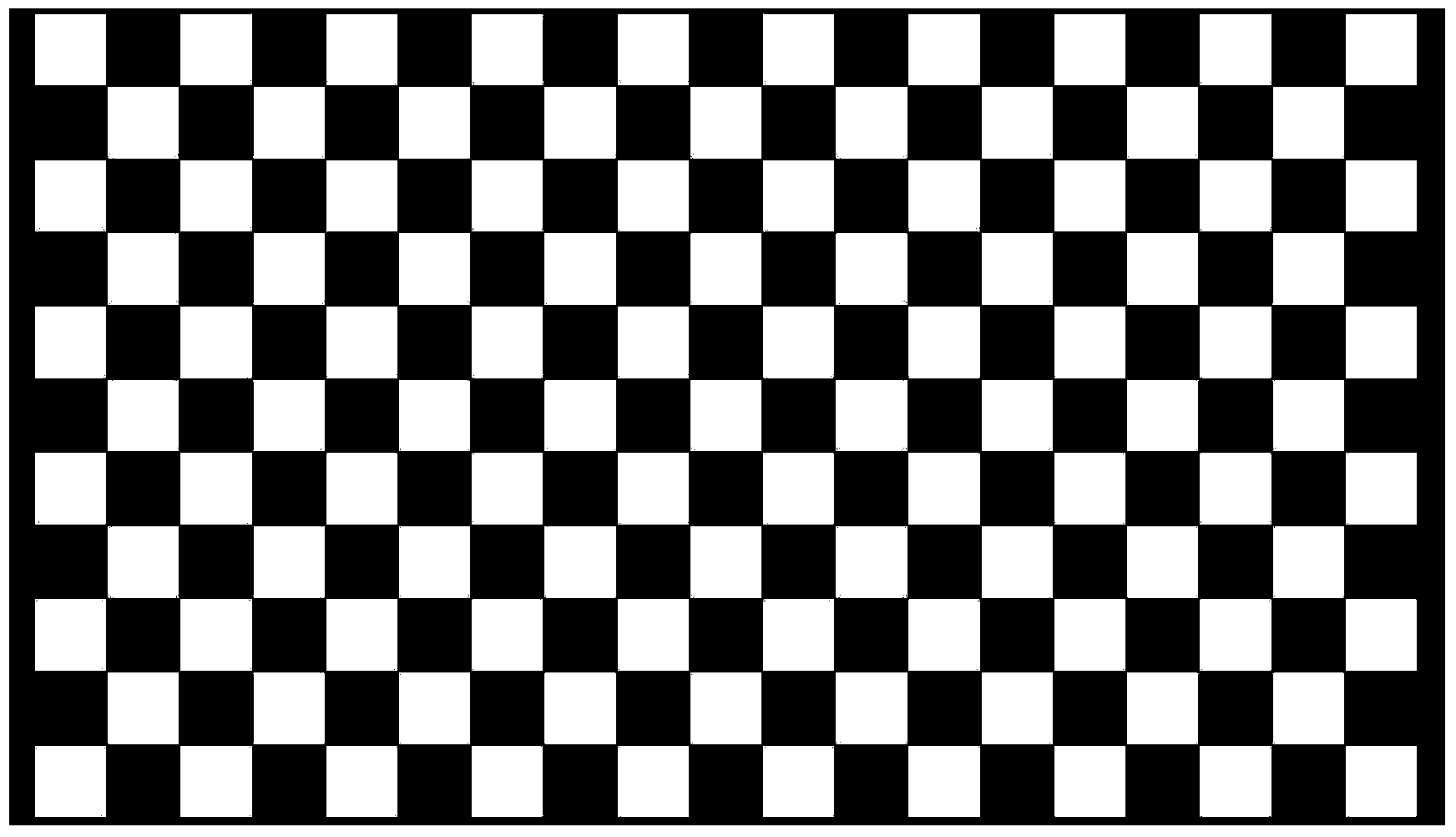
The invention discloses a high-precision projector and camera calibration system and method. The high-precision projector and camera calibration method comprises the steps that a camera is calibrated through a camera calibration method, so that camera internal parameters are obtained; a pure white pattern is projected onto a calibration board, the pattern and a pattern of the calibration board are overlaid, and a calibration area image is captured; image distortion is corrected through the camera internal parameters, and then angle point coordinates in the calibration area image are extracted; a homography matrix between a camera image plane and a calibration board plane is estimated according to the correspondence of angle points; different specific chessboard patterns are projected onto the calibration board in sequence, the chessboard patterns and the pattern of the calibration board are overlaid respectively, and calibration area images are captured; differential processing and filtering processing are carried out on the calibration area images, and then angle point coordinates on the calibration board plane are extracted; an average value of the angle point coordinates is obtained, and then the angle points are mapped to the calibration board plane through the homography matrix; the above steps are repeatedly executed according to the obtaining situations of the angle points. A projector is calibrated through the camera calibration method. According to the high-precision projector and camera calibration system and method, precision of an optical three-dimensional measuring system is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
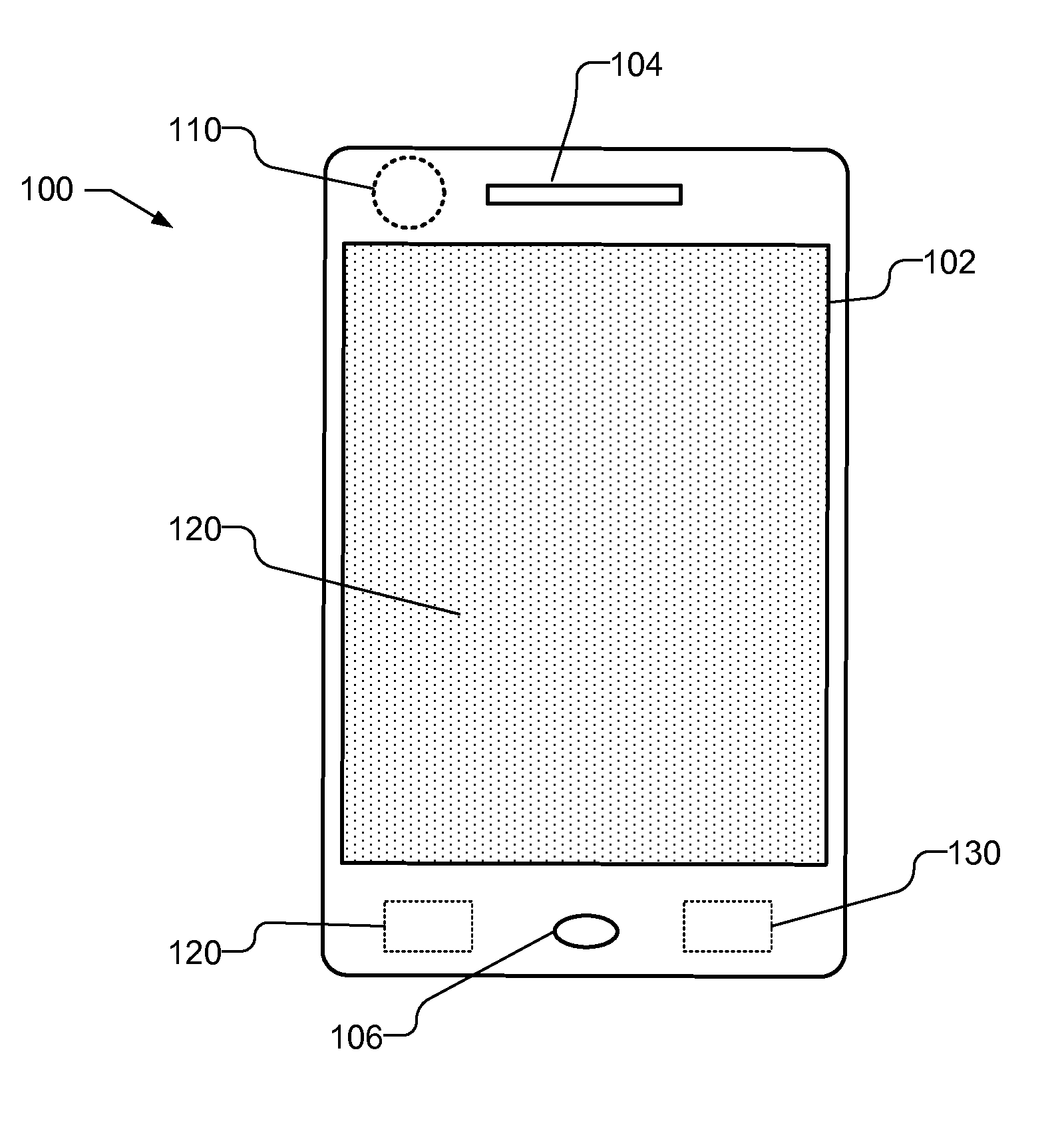
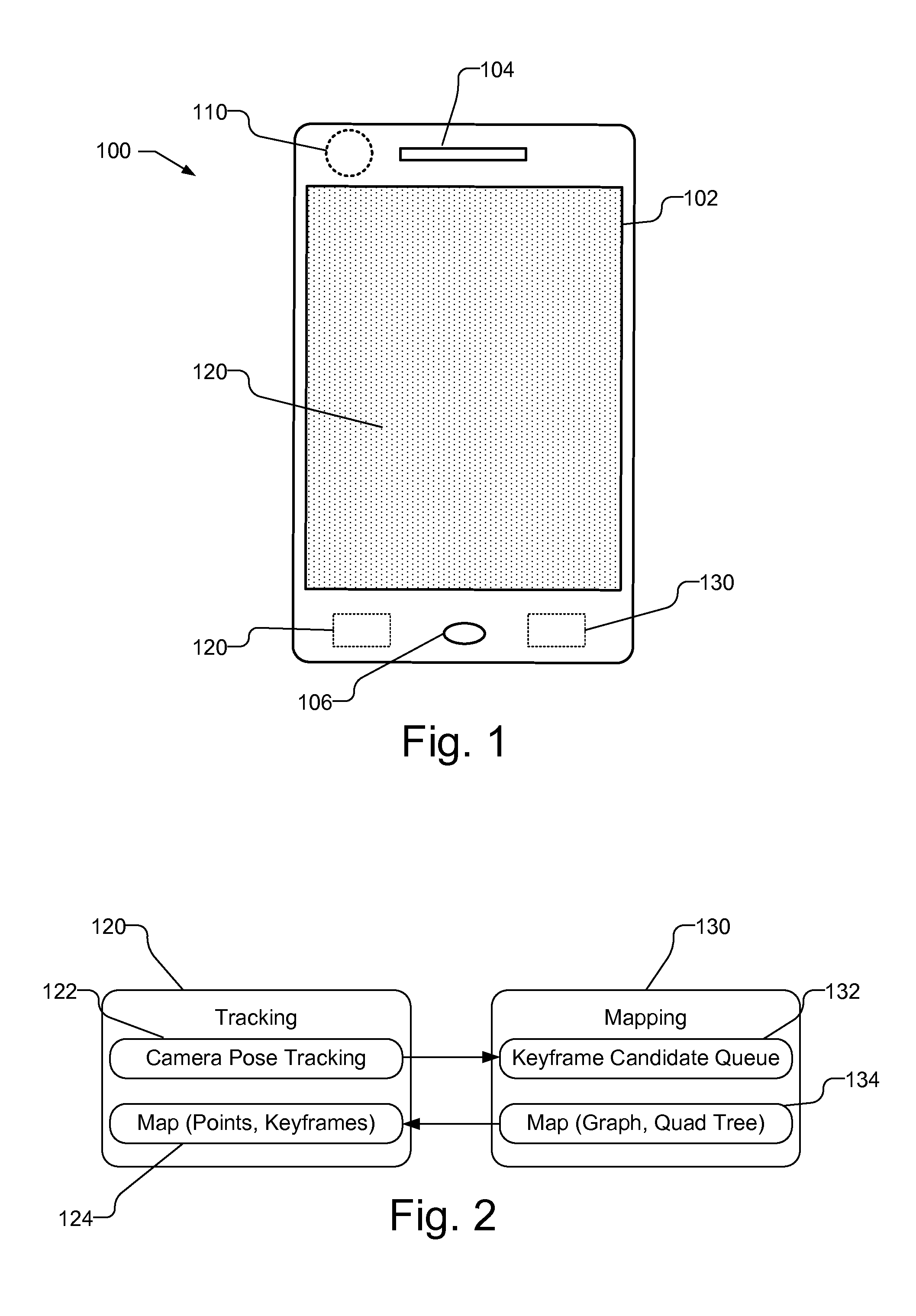
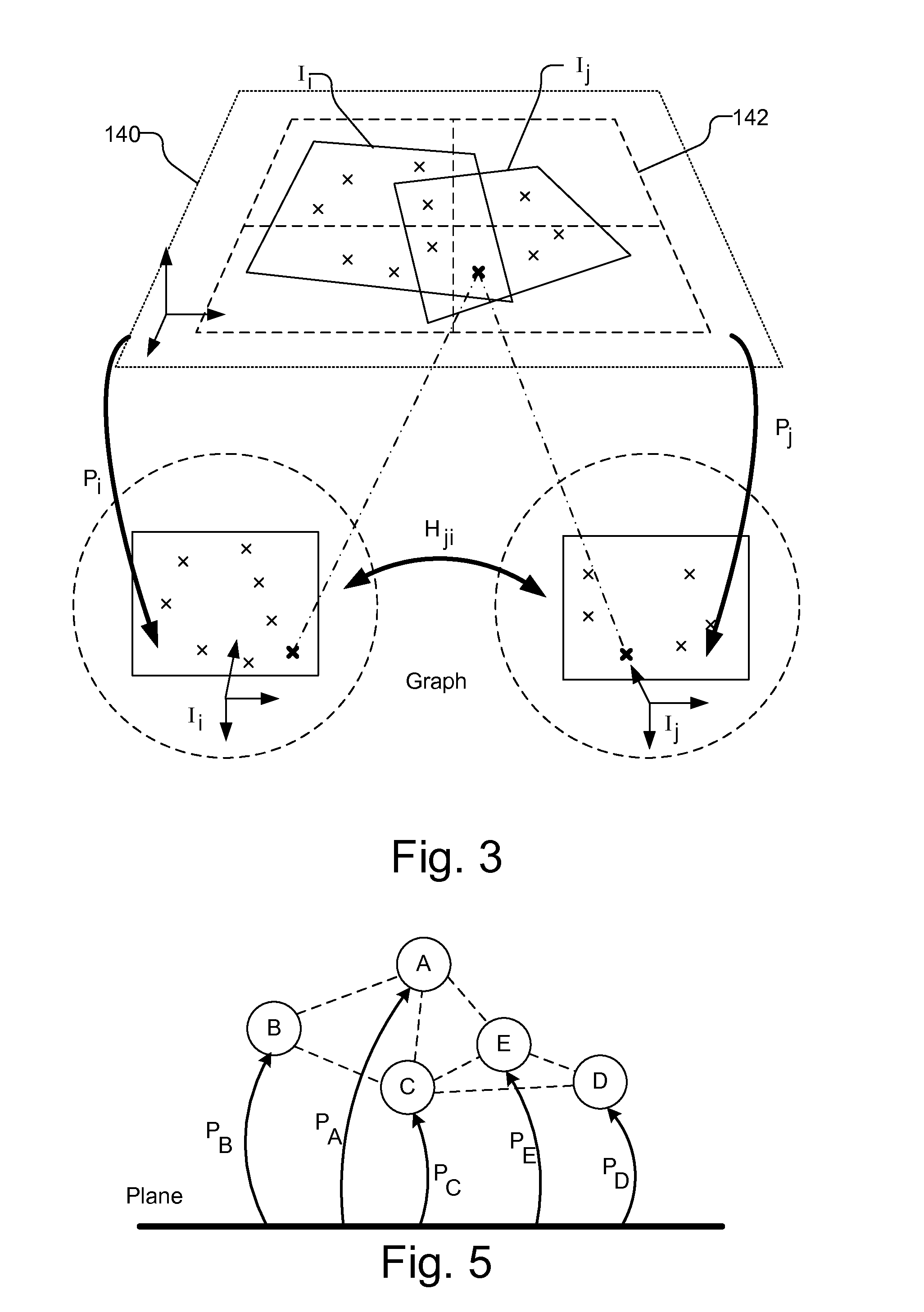
Planar mapping and tracking for mobile devices
Real time tracking and mapping is performed using images of unknown planar object. Multiple images of the planar object are captured. A new image is selected as a new keyframe. Homographies are estimated for the new keyframe and each of a plurality of previous keyframes for the planar object that are spatially distributed. A graph structure is generated using the new keyframe and each of the plurality of previous keyframes and the homographies between the new keyframe and each of the plurality of previous keyframes. The graph structure is used to create a map of the planar object. The planar object is tracked based on the map and subsequently captured images.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and system for image-based information retrieval
InactiveUS20100309226A1User privacy is enhancedNarrow down the search spaceStill image data retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionProjection imageReference image
For retrieving information based on images, a first image is taken (S1) using a digital camera associated with a communication terminal (1). Query data related to the first image is transmitted (S3) via a communication network (2) to a remote recognition server (3). In the remote recognition server (3) a reference image is identified (S4) based on the query data. Subsequently, in the remote recognition server (3), a Homography is computed (S5) based on the reference image and the query data, the Homography mapping the reference image to the first image. Moreover, in the remote recognition server (3), a second image is selected (S6) and a projection image is computed (S7) of the second image using the Homography. By replacing a part of the first image with at least a part of the projection image, an augmented image is generated (S8, S10) and displayed (S11) at the communication terminal (1). Efficient augmentation of the first image taken with the camera is made possible by remaining in the planar space and dealing with two-dimensional images and objects only.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Image stitching method and device
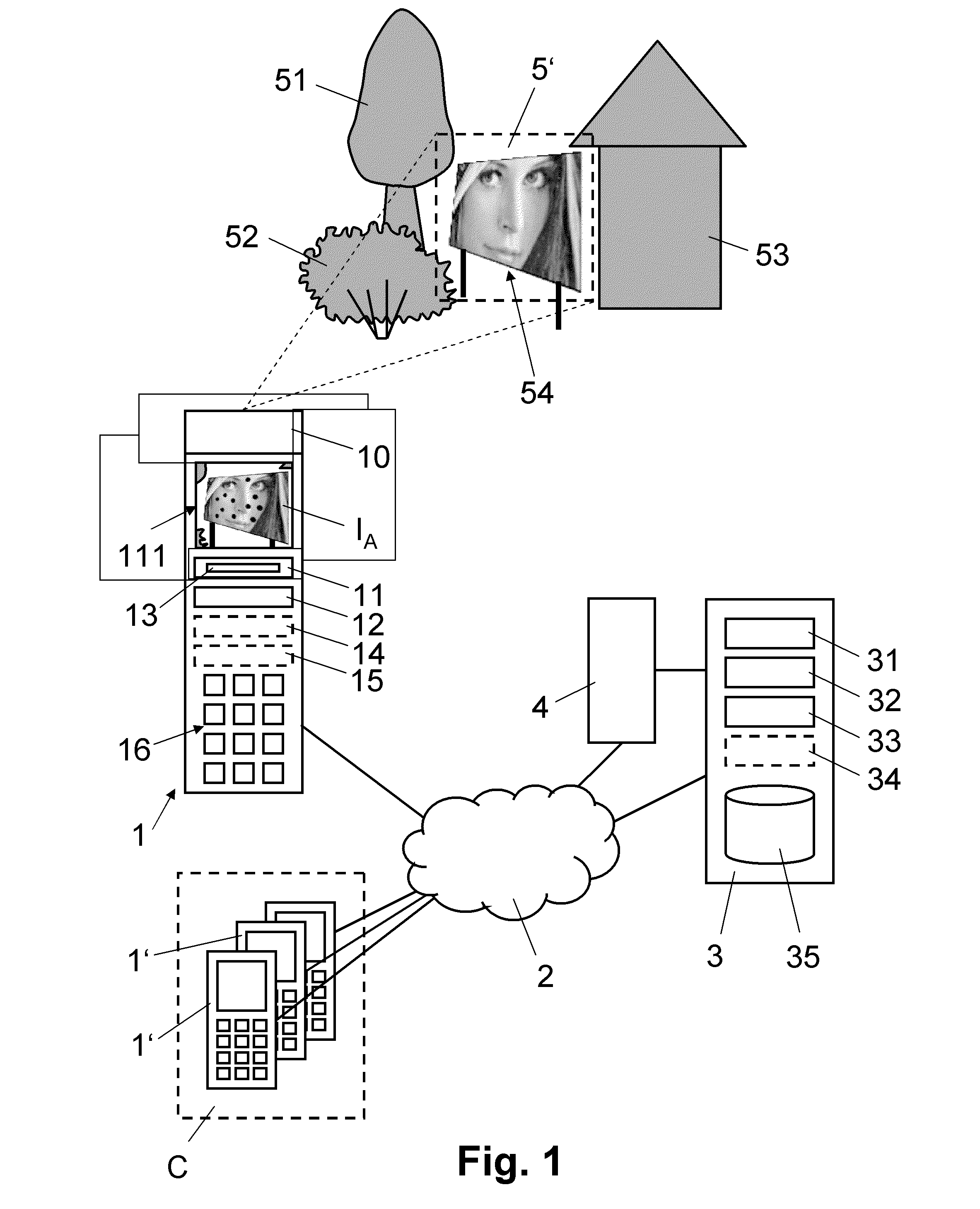
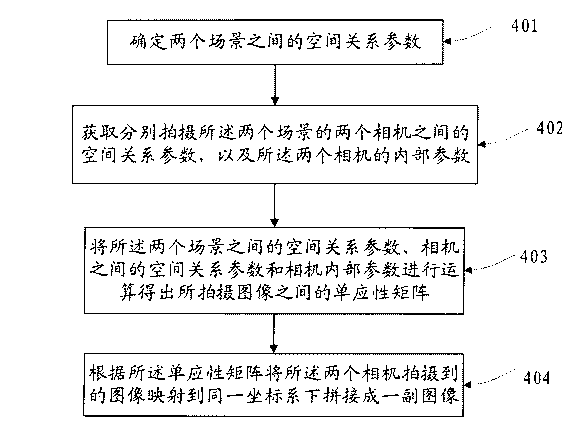
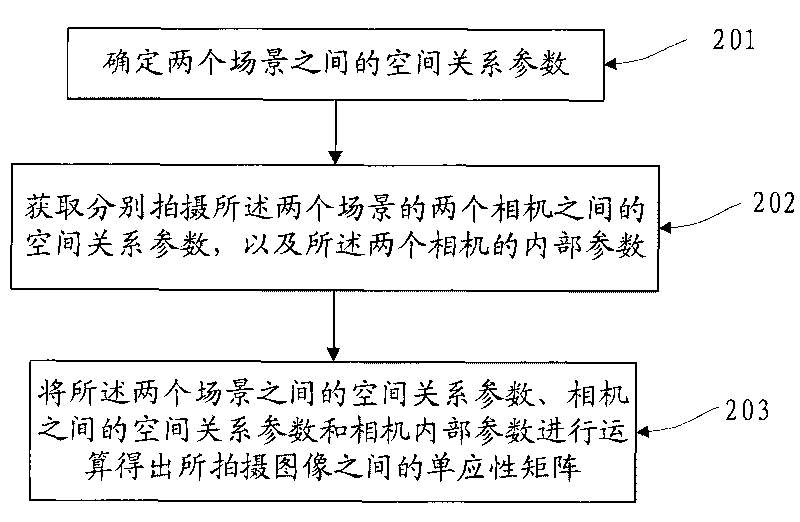
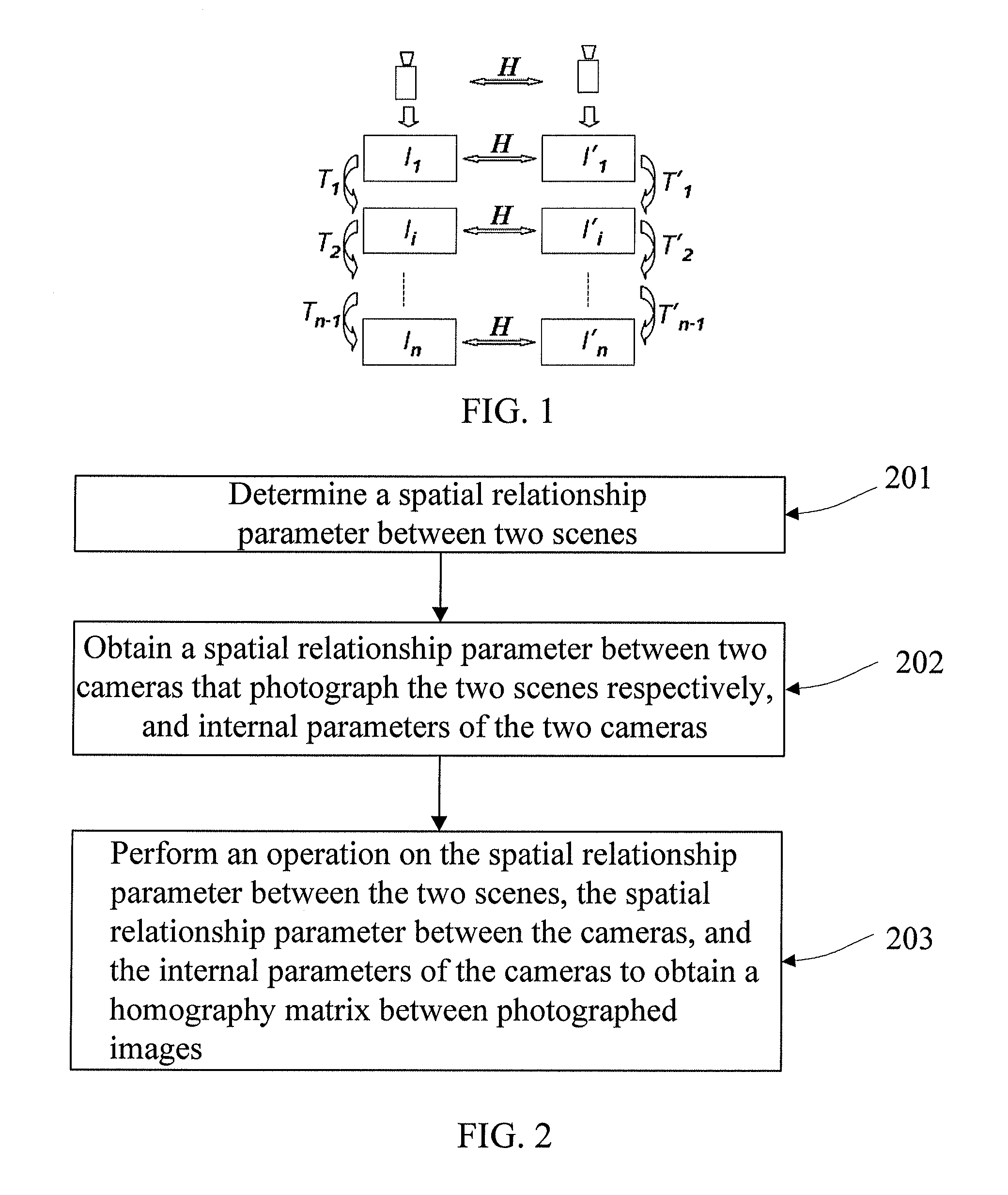
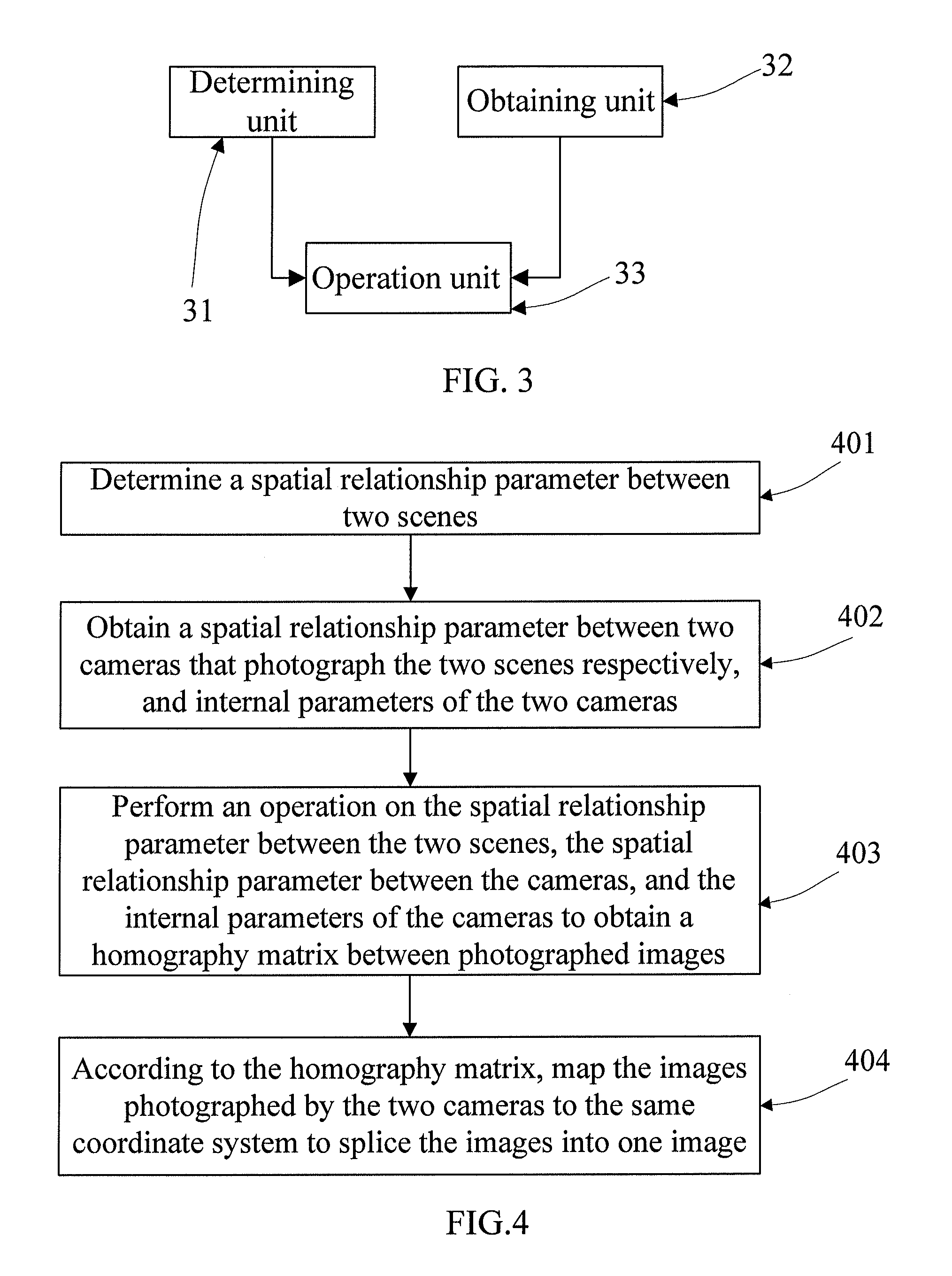
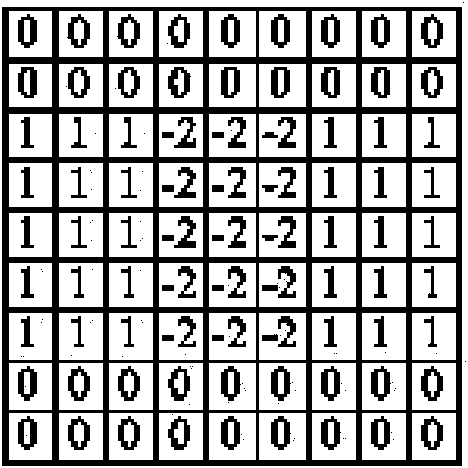
The invention discloses an image stitching method and a device, relating to the field of image processing technology, and solves the problem the existing homography matrix needs an overlap area between the images or a video sequence; in the embodiment of the invention, spatial relationship parameters between two scenes are firstly determined; the spatial relationship parameters between two cameras for respectively shooting the two scenes and internal parameters of the two cameras are obtained; the homography matrix among the shot images is obtained by operating the spatial relationship parameters between the two scenes, the spatial relationship parameters between the cameras and the internal parameters of the camera; the images shot by the two cameras are mapped to the same coordinate system, so as to stitch one image according to the homography matrix; the embodiment of the invention is mainly applied to the calculation of the homography matrix between two images, especially applied to the calculation of the homography matrix in the image stitching process.
Owner:GLOBAL INNOVATION AGGREGATORS LLC
Dense structure from motion
ActiveUS20140161323A1Reduce image resolutionReduce resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisStructure from motionHomography
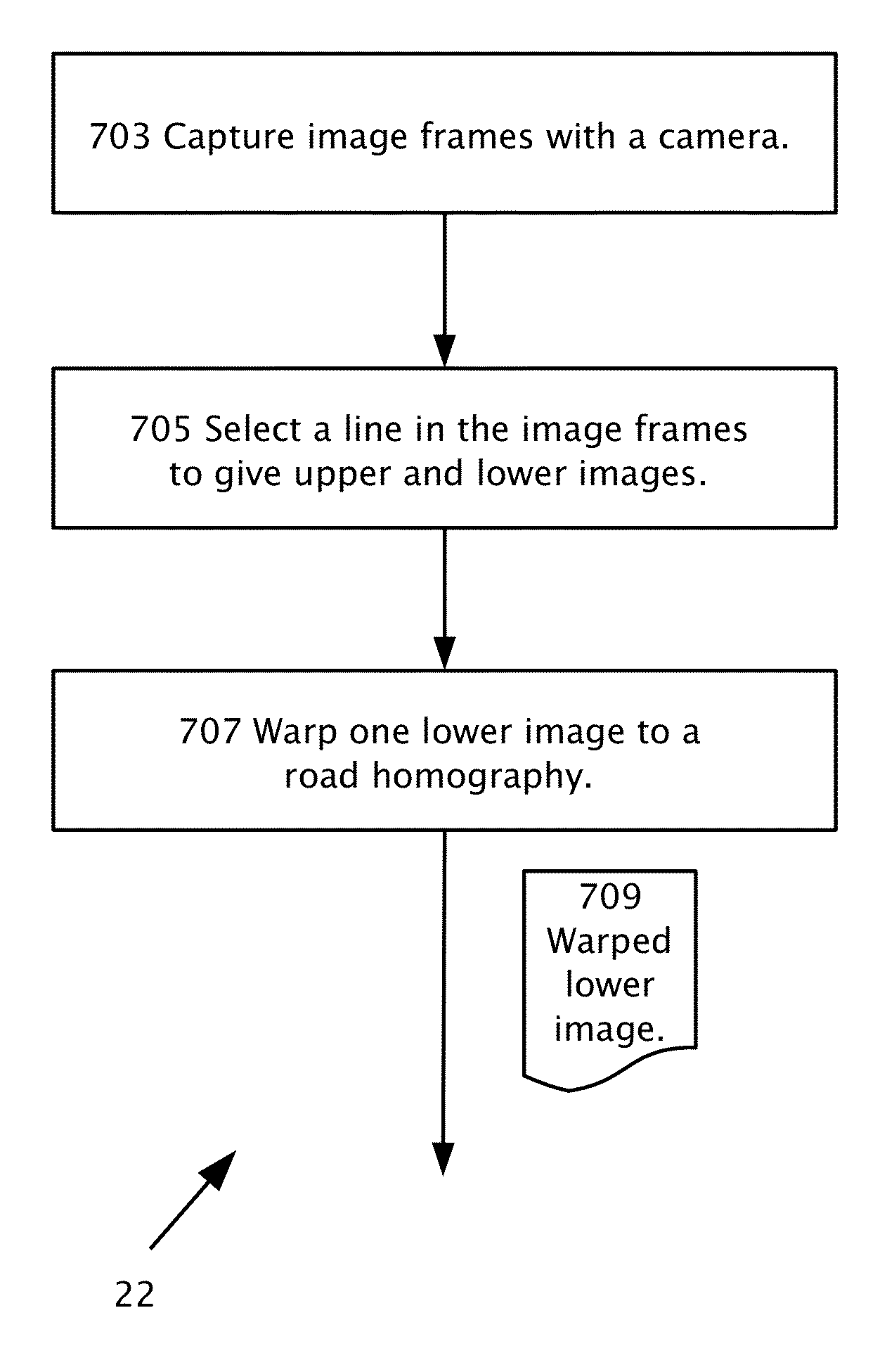
Determining three-dimensional structure in a road environment using a system mountable in a host vehicle including a camera connectible to a processor. Multiple image frames are captured in the field of view of the camera. In the image frames, a line is selected below which the road is imaged. The line separates between upper images essentially excluding images of the road and lower images essentially including images of the road. One or more of the lower images is warped, according to a road homography to produce at least one warped lower image. The three-dimensional structure may be provided from motion of a matching feature within the upper images or from motion of a matching feature within at least one of the lower images and at least one warped lower image.
Owner:MOBILEYE VISION TECH LTD
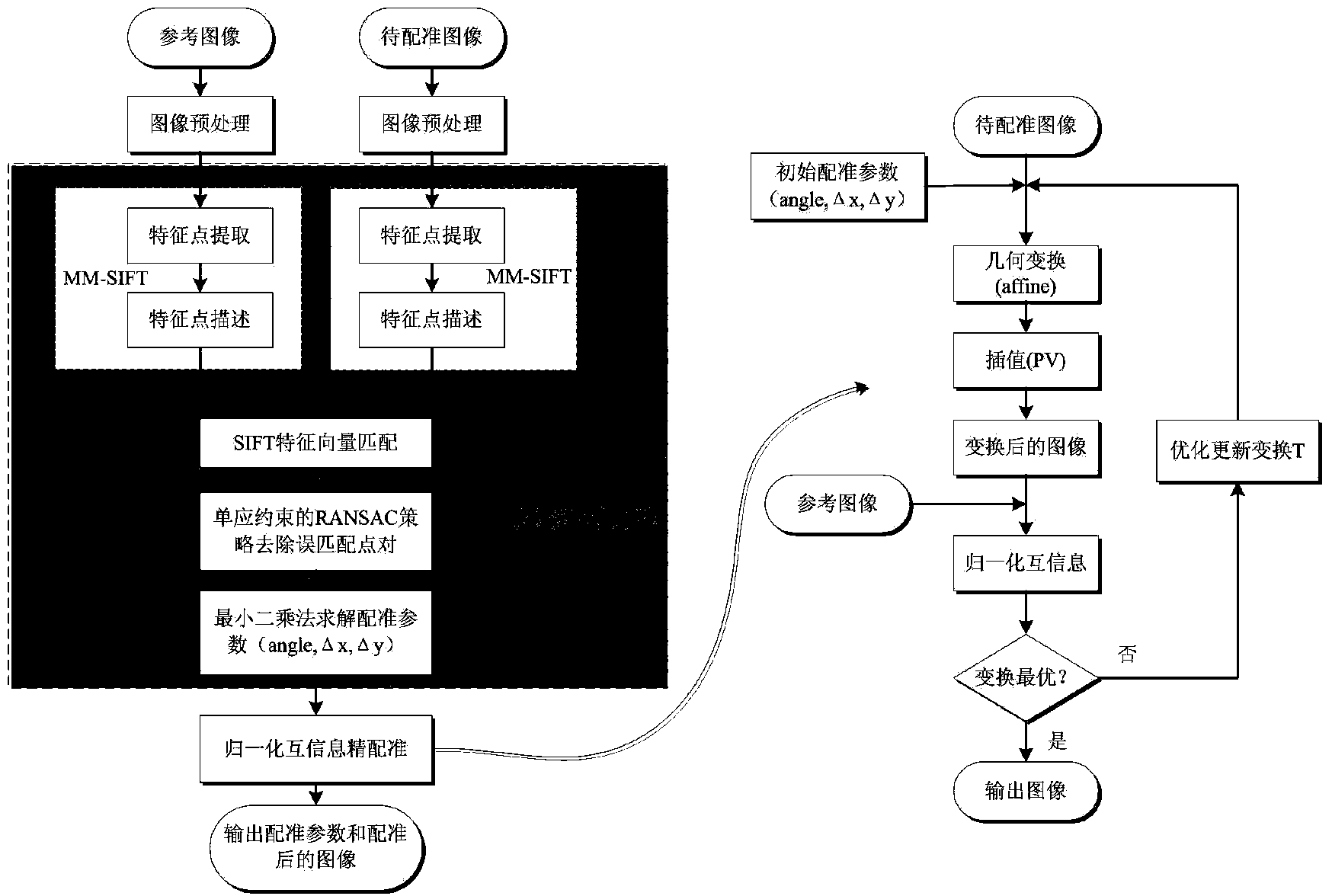
SAR image registration method based on SIFT and normalized mutual information
ActiveCN103839265AShorten the timeEnsure follow-up registration accuracyImage analysisFeature vectorNormalized mutual information
The invention provides an SAR image registration method based on SIFT and normalized mutual information. The method includes the steps that firstly, a standard image I1 and an image to be registered I2 are input and are respectively pre-processed; secondly, features of the pre-processed image I1 and features of the pre-processed image I2 are extracted according to the MM-SIFT method to acquire initial feature point pairs Fc and SIFT feature vectors Fv1 and Fv2; thirdly, initial matching is carried out through the Fv1 and the Fv2; fourthly, the Fc is screened for the second time according to the RANSAC strategy of a homography matrix model, final correct matching point pairs Fm are acquired, and a registration parameter pr is worked out according to the least square method; fifthly, I2 is subjected to space conversion through affine transformation, and a roughly-registered image I3 is acquired through interpolation and resampling; sixthly, pr serves as the initial value of normalization information registration, I1 and I2 are subjected to fine registration through the normalized mutual information method, a final registration parameter pr1 is worked out, and a registered image I4 is output. The method can be quickly, effectively and stably carried out, and SAR image registration precision and robustness are improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Multiple video cameras synchronous quick calibration method in three-dimensional scanning system
A synchronous quick calibration method of a plurality of video cameras in a three-dimensional scanning system, which includes: (1) setting a regular truncated rectangular pyramid calibration object, setting eight calibration balls at the vertexes of the truncated rectangular pyramid, and respectively setting two reference calibration balls at the upper and lower planes; (2) using the video cameras to pick-up the calibration object, adopting the two-threshold segmentation method to respectively obtain the corresponding circles of the upper and lower planes, extracting centers of the circles, obtaining three groups of corresponding relationships between circle center points in the image and the centres of calibration ball in the space, solving the homography matrix to obtain the internal parameter matrix and external parameter matrix and obtaining the distortion coefficient, taking the solved video camera parameter as the initial values, and then using a non-linear optimization method to obtain the optimum solution of a single video camera parameter; (3) obtaining in sequence the external parameter matrix between a plurality of video cameras and a certain video camera in the space, using the polar curve geometric constraint relationship of the binocular stereo vision to establish an optimizing object function, and then adopting a non-linear optimization method to solve to get the optimum solution of the external parameter matrix between two video cameras.
Owner:NANTONG TONGYANG MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL MFR +1
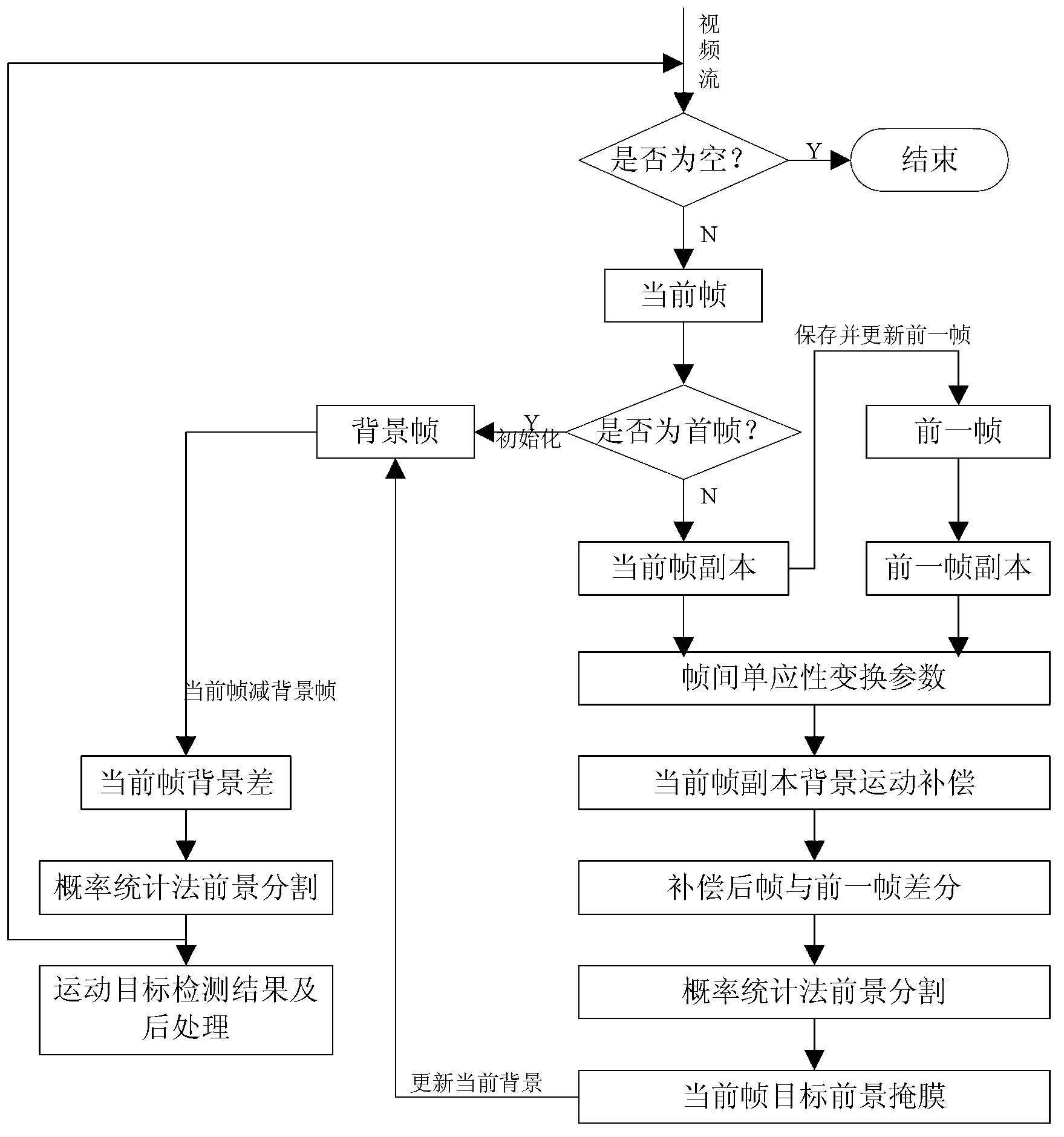
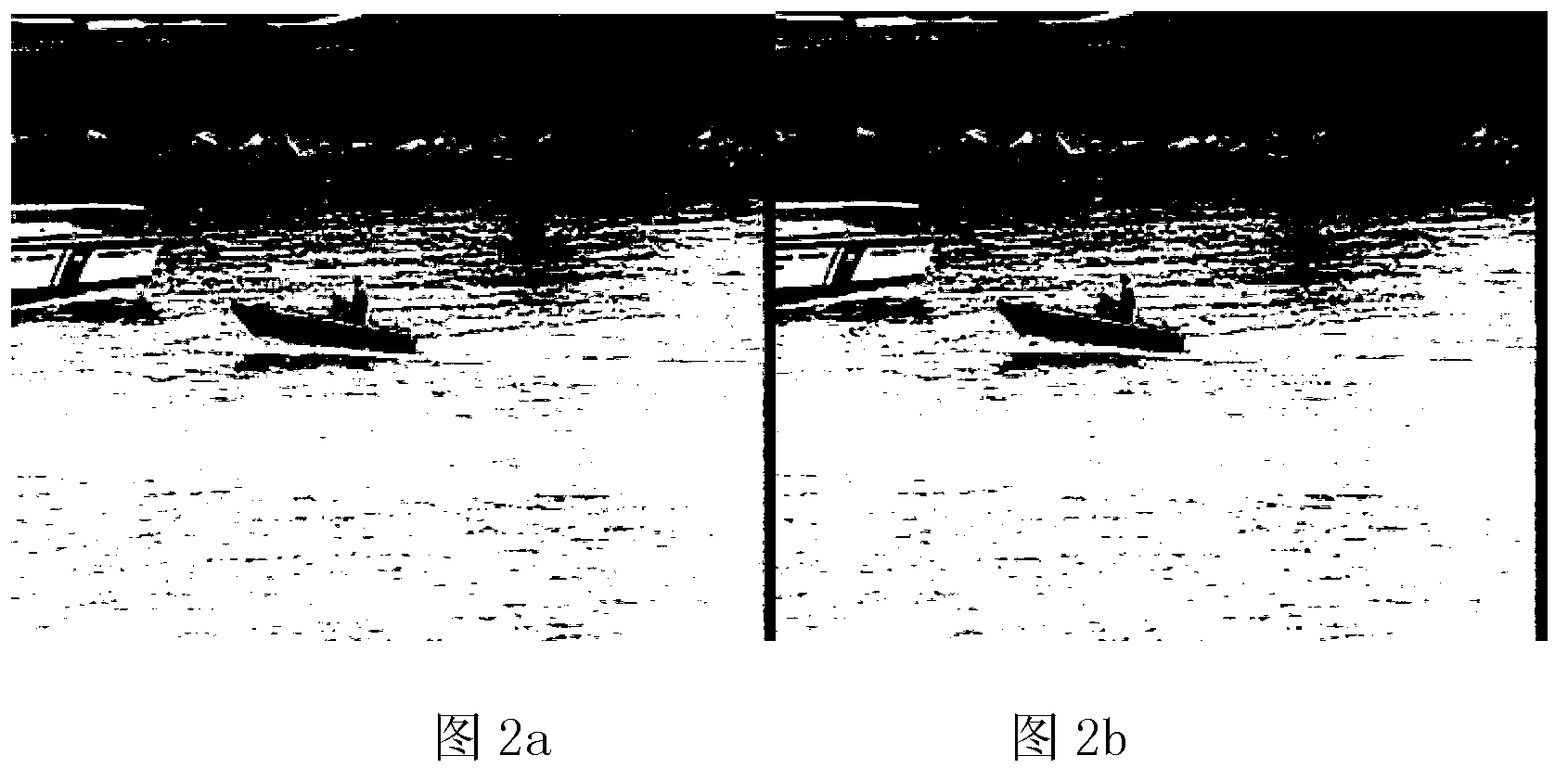
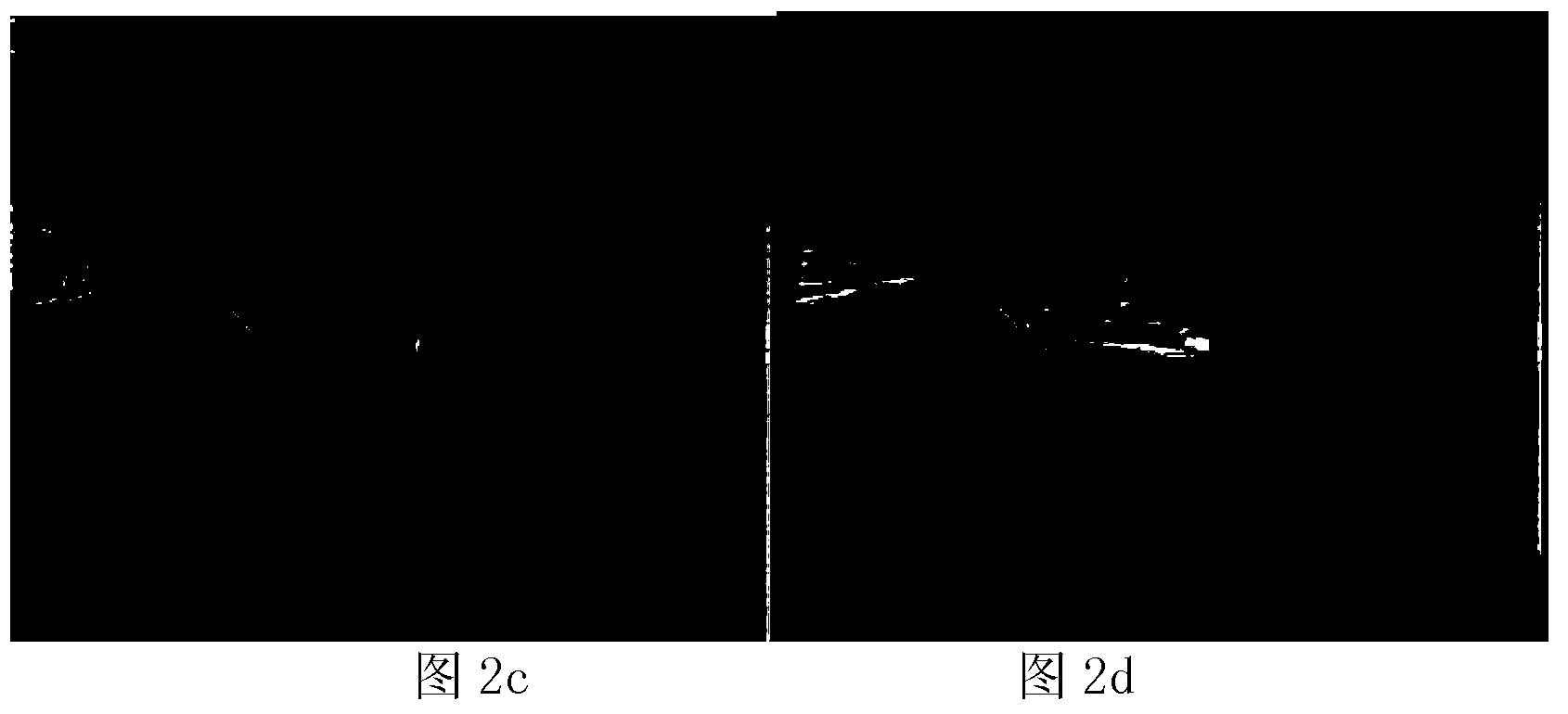
Quick detecting method for moving objects in dynamic scene
InactiveCN103325112AComplete exercise goalsSatisfy the rapidityImage analysisFrame differenceGray level
Provided is a quick detecting method for moving objects in a dynamic scene. The quick detecting method for the moving objects in the dynamic scene comprises carrying out sequence interframe registration on moving images by utilizing CenSurE feature points and a homography transformation model, obtaining a registering frame of a former frame taking a current frame as reference, carrying out subtraction on the registering frame with the current frame to obtain a frame difference image to generate a foreground mask, building a dynamic background updated in real time according to space distribution information of the foreground mask in the current frame, obtaining a background subtraction image based on a background subtraction method, carrying out statistics on the probability density of the gray level of each pixel in the frame difference image, when the sum of the probability density of the gray level of a pixel is larger than 2phi(k)-1, taking the gray level as a self-adaptation threshold value, judging pixels with values of gray levels larger than the threshold value as foreground pixels, and otherwise judging the pixels as background pixels. The quick detecting method for the moving objects in the dynamic scene can reach the processing speed of 15frame / s and can obtain relatively integral moving objects under the premise that the detecting speed is ensured, and therefore, index requirements such as rapidity, noise immunity, illumination adaptation, target integrity and the like of the detection of the moving objects in the dynamic scene can be met.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
Image splicing method and apparatus
The present invention discloses an image splicing method and apparatus, and relates to the field of image processing technologies. In embodiments of the present invention, first, a spatial relationship parameter between two scenes is determined; a spatial relationship parameter between two cameras that photograph the two scenes respectively, and internal parameters of the two cameras are obtained; and then, an operation is performed on the spatial relationship parameter between the two scenes, the spatial relationship parameter between the cameras, and the internal parameters of the cameras to obtain a homography matrix between photographed images; and according to the homography matrix, the images photographed by the two cameras are mapped to the same coordinate system to splice the images into one image. The embodiments of the present invention are mainly applied to calculation of a homography matrix between two images, especially to calculation of a homography matrix in image splicing process.
Owner:HUAWEI DEVICE CO LTD
Method for splicing video in real time based on multiple cameras
InactiveCN102006425AReduce the amount of splicing calculationsSplicing speed is fastTelevision system detailsColor television detailsColor imageNear neighbor
The invention discloses a method for splicing a video in real time based on multiple cameras, which comprises the following steps of: acquiring synchronous multi-path video data; preprocessing frame images at the same moment; converting a color image into a grayscale image; enhancing the image, and expanding the dynamic range of grayscale of the image by a histogram equalization method; extracting the characteristic points of corresponding frames by using a speeded up robust features (SURF) algorithm; solving matched characteristic point pairs among corresponding frame images of the video by using a nearest neighbor matching method and a random sample consensus matching algorithm; solving an optimal homography matrix of initial k frames of the video; determining splicing overlapping regions according to the matched characteristic point pairs; taking a homography matrix corresponding to a frame with highest overlapping region similarity as the optimal homography matrix, and splicing subsequent video frame scenes; and outputting the spliced video. The method can reduce the calculated amount of splicing the video frame single-frame image, improves the splicing speed of traffic monitoring videos and achieves real-time processing effect.
Owner:RES INST OF HIGHWAY MINIST OF TRANSPORT
Three-dimensional surface generation method
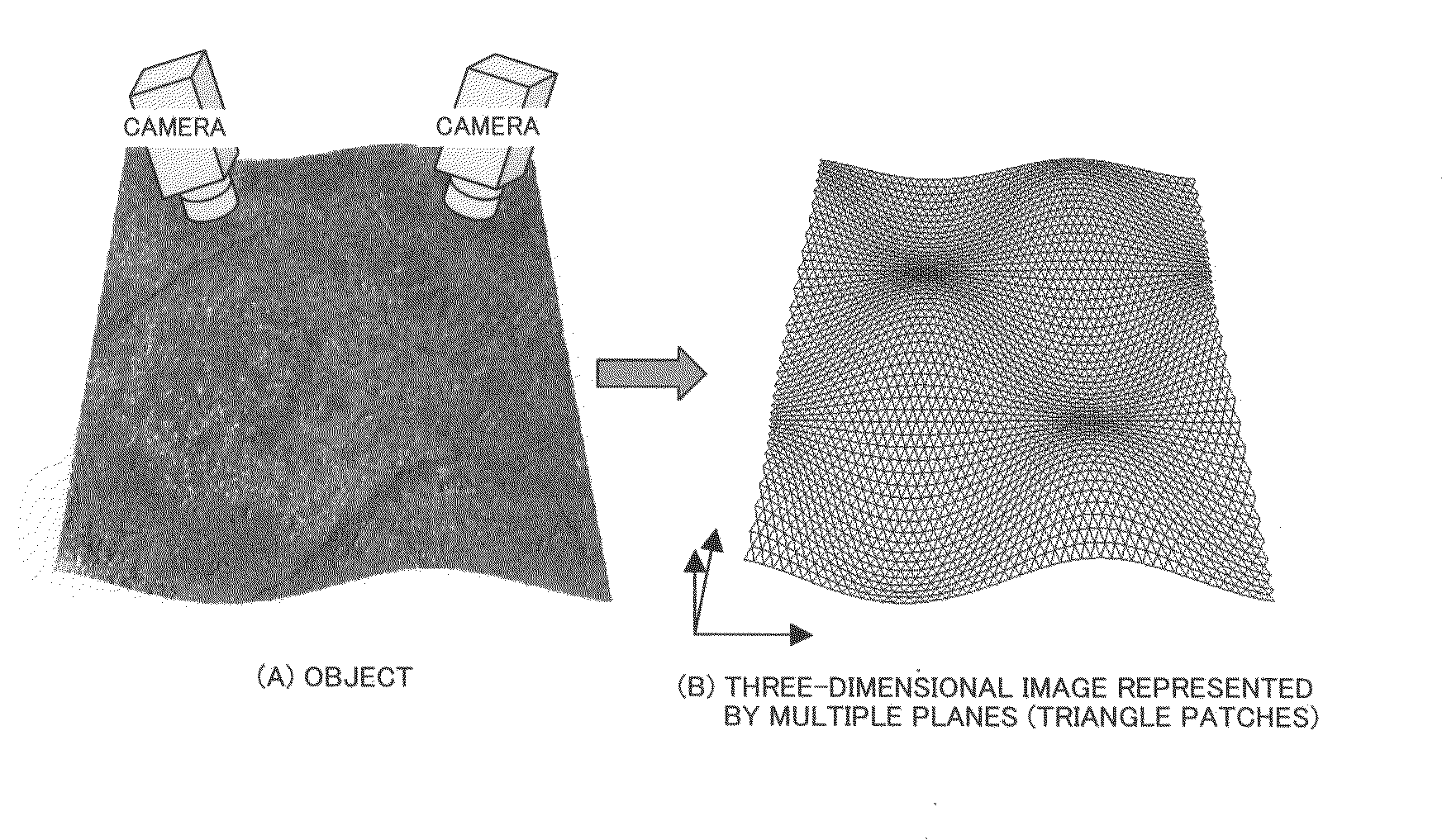
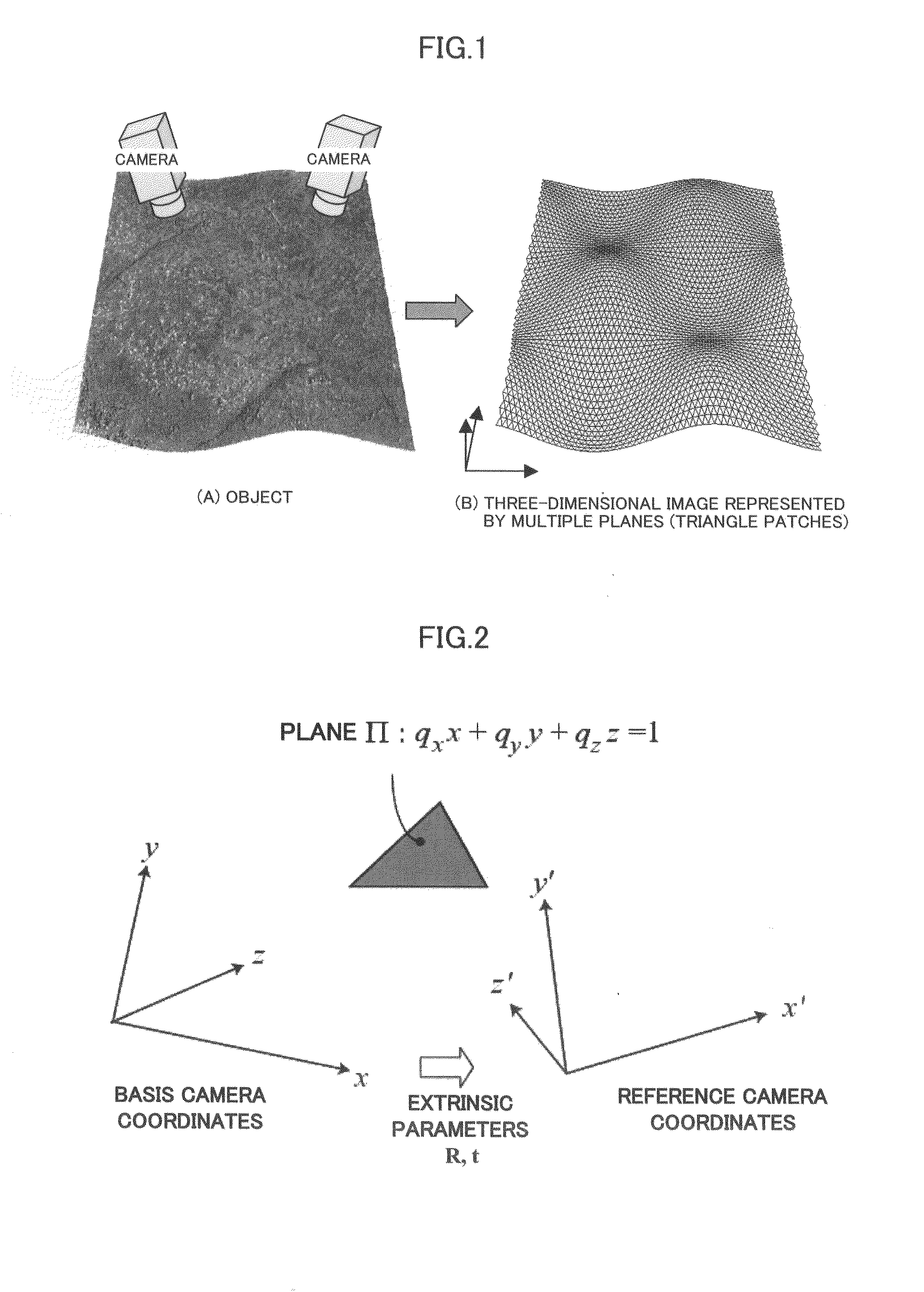
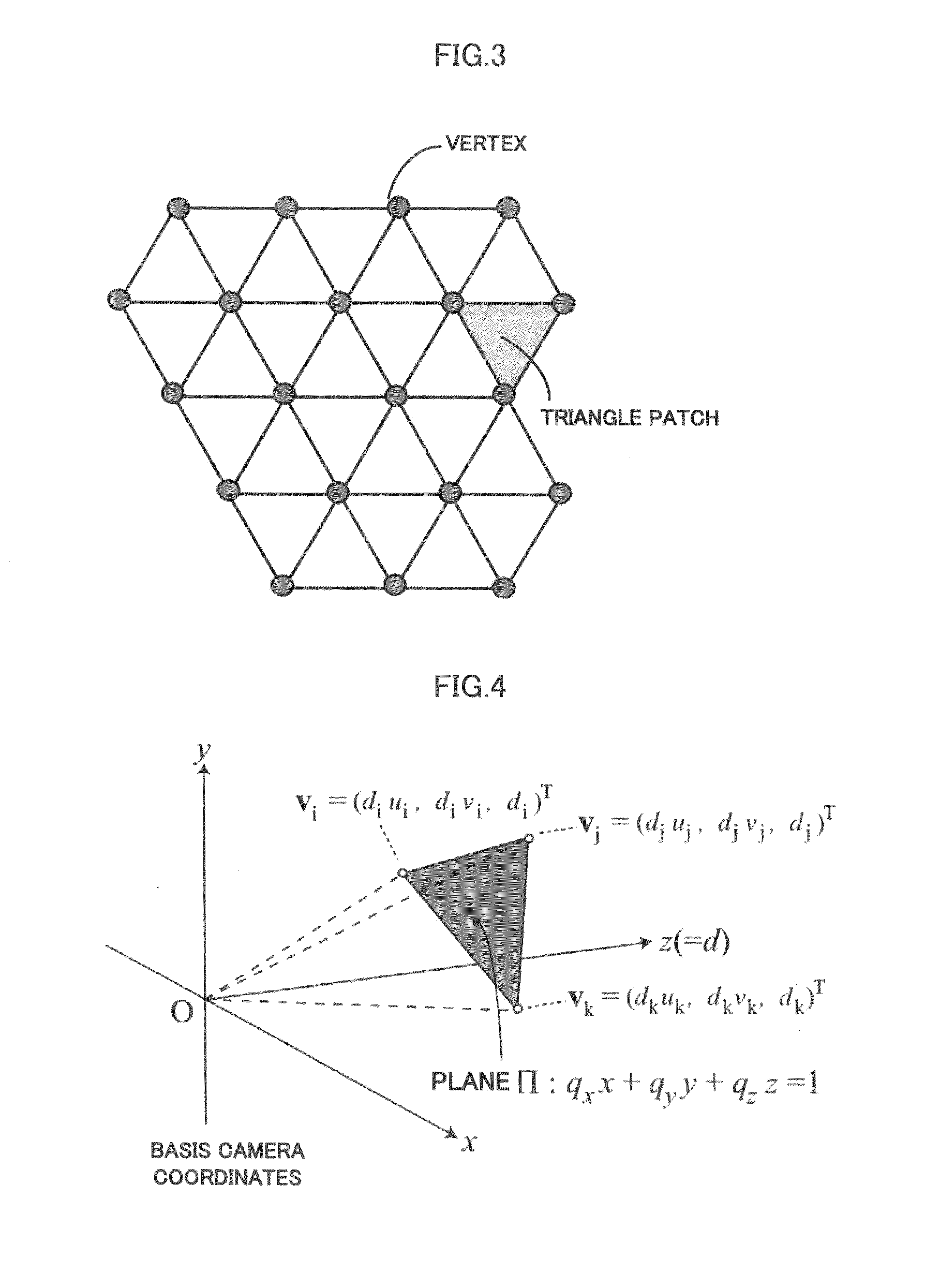
InactiveUS20100054579A1Increase speedDetails involving processing stepsImage analysisViewpointsReference image
The present invention provides a three-dimensional surface generation method that directly and efficiently generates a three-dimensional surface of the object surface from multiple images capturing a target object.The three-dimensional surface generation method of the present invention sets one image as a basis image from multiple images obtained by capturing the target object from different viewpoint positions and sets other images as reference images, and then generates two-dimensional triangle meshes on the basis image. Next, the method of the present invention sets a distance between a vector whose elements are pixel values of an image obtained by deforming the reference image by a homography determined by an all-vertices depth parameter of meshes and camera parameters and a vector whose elements are pixel values of the basis image, as a term of a cost function, and computes the all-vertices depth parameter that a value of the cost function becomes smallest by iteratively performing the computation of the small variation of the all-vertices depth parameter and the update of the current value of the all-vertices depth parameter by using an optimization method that sets the multiple images, the camera parameters and the initial value of the all-vertices depth parameter as inputs till a predetermined condition is satisfied.
Owner:TOKYO INST OF TECH
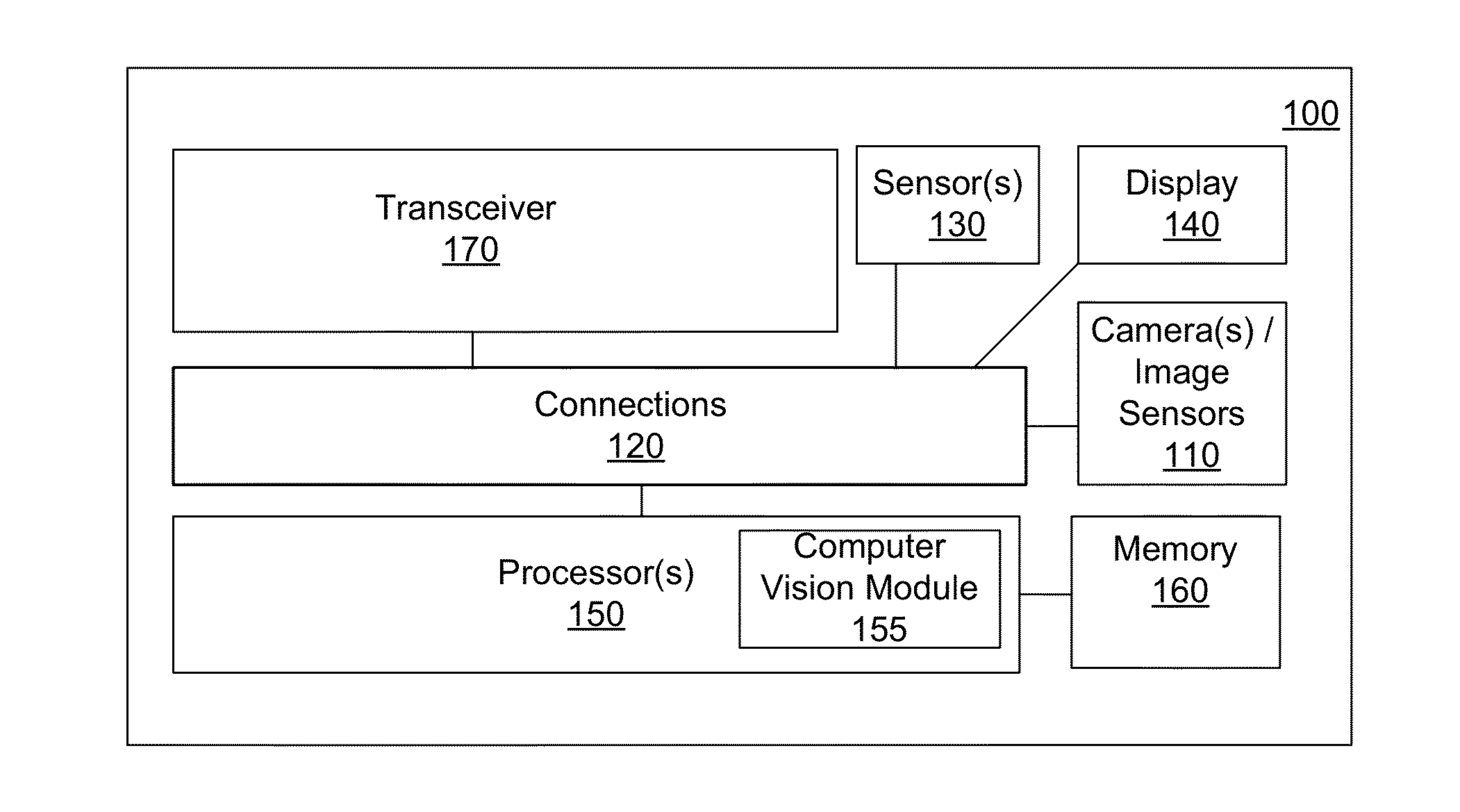
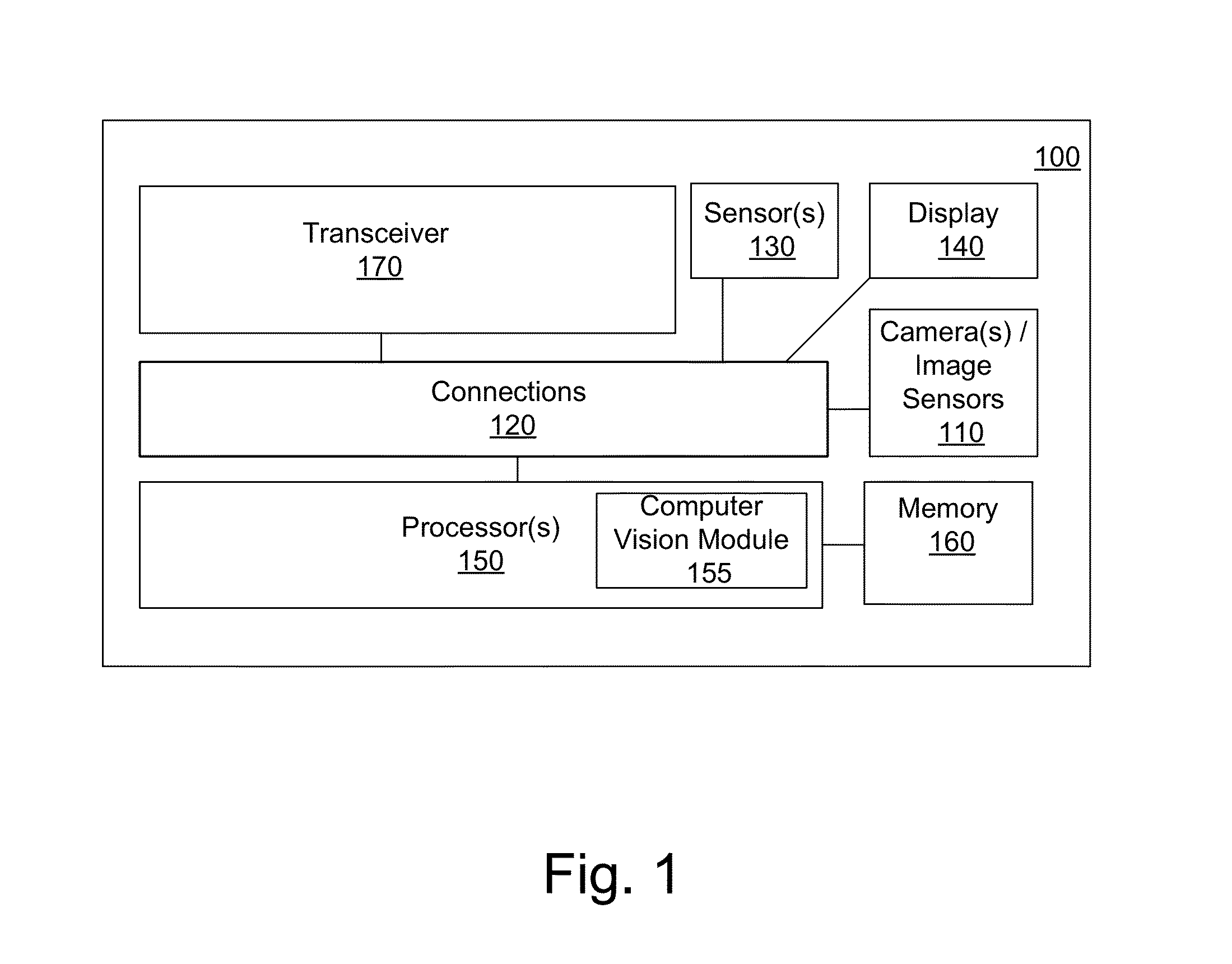
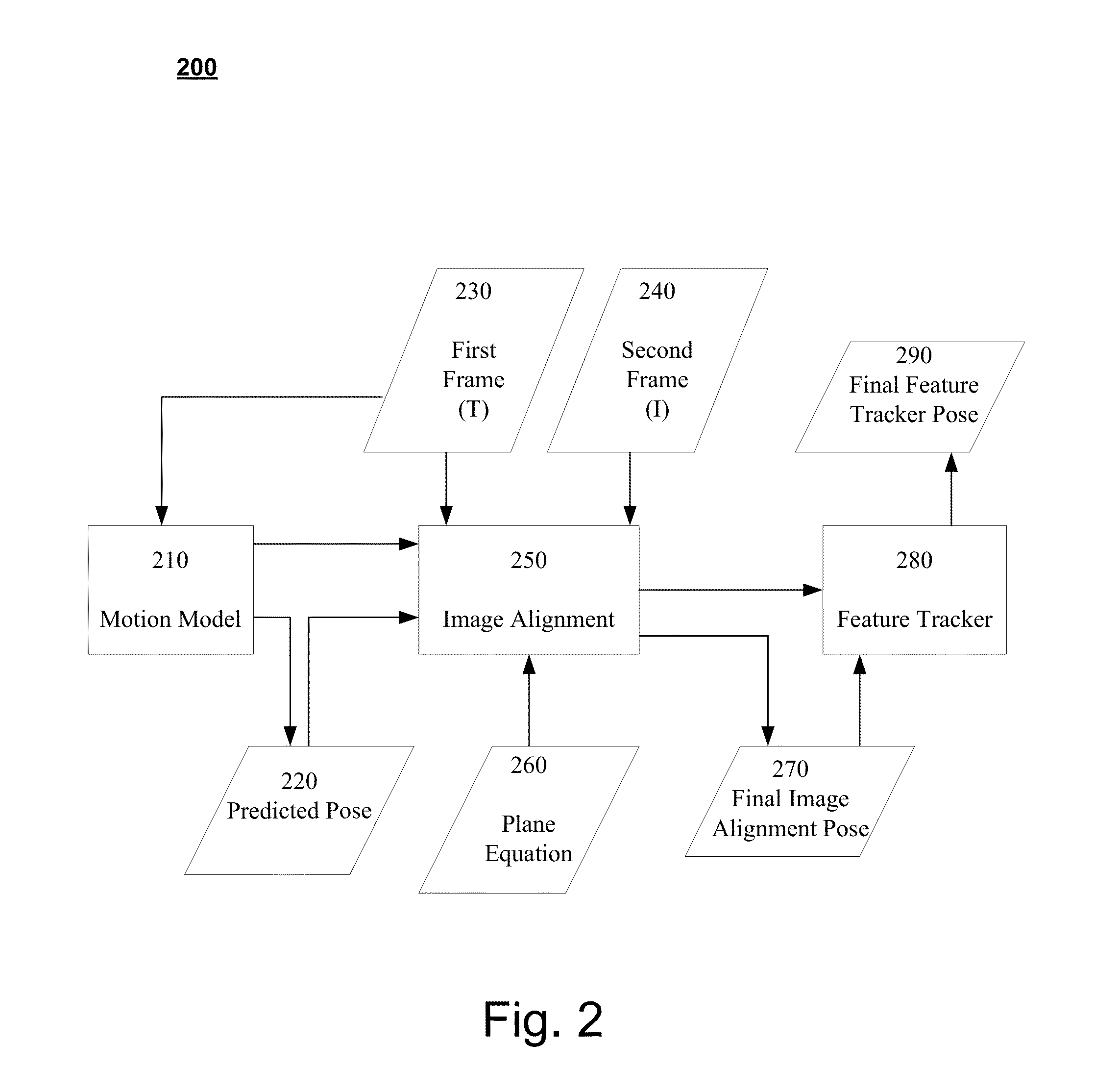
Systems and Methods for Feature-Based Tracking
Disclosed embodiments pertain to feature based tracking. In some embodiments, a camera pose may be obtained relative to a tracked object in a first image and a predicted camera pose relative to the tracked object may be determined for a second image subsequent to the first image based, in part, on a motion model of the tracked object. An updated SE(3) camera pose may then be obtained based, in part on the predicted camera pose, by estimating a plane induced homography using an equation of a dominant plane of the tracked object, wherein the plane induced homography is used to align a first lower resolution version of the first image and a first lower resolution version of the second image by minimizing the sum of their squared intensity differences. A feature tracker may be initialized with the updated SE(3) camera pose.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Plane-based Self-Calibration for Structure from Motion
Robust techniques for self-calibration of a moving camera observing a planar scene. Plane-based self-calibration techniques may take as input the homographies between images estimated from point correspondences and provide an estimate of the focal lengths of all the cameras. A plane-based self-calibration technique may be based on the enumeration of the inherently bounded space of the focal lengths. Each sample of the search space defines a plane in the 3D space and in turn produces a tentative Euclidean reconstruction of all the cameras that is then scored. The sample with the best score is chosen and the final focal lengths and camera motions are computed. Variations on this technique handle both constant focal length cases and varying focal length cases.
Owner:ADOBE INC
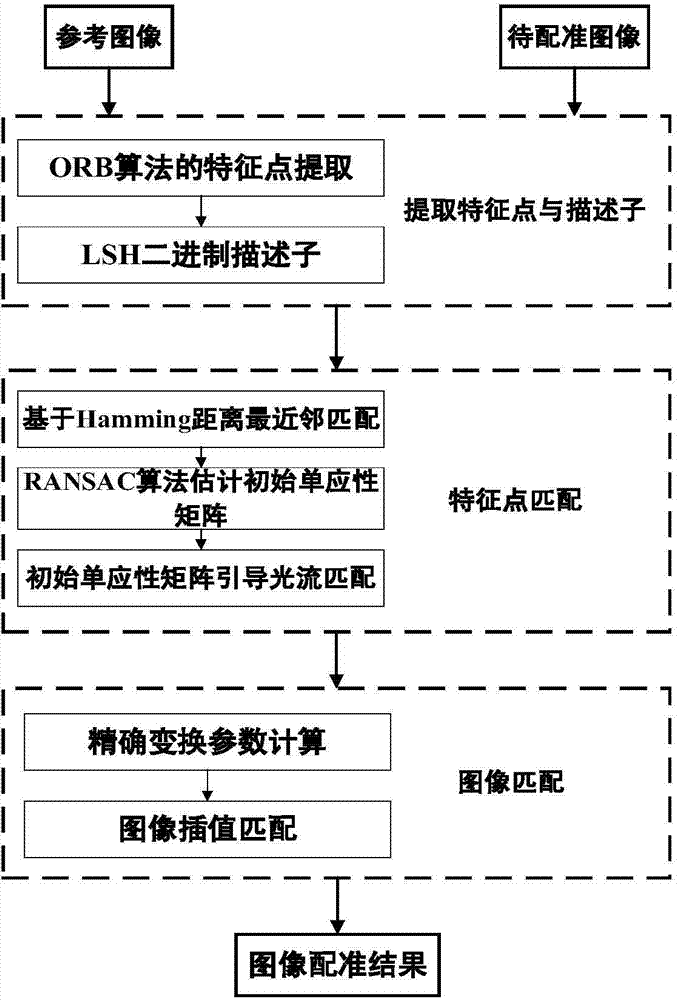
ORB (oriented brief) image feature registration method based on LK (Lucas-Kanade) optical flow constraint
InactiveCN104751465ASimple calculationReduce computationImage analysisImaging processingImaging Feature
The invention relates to an ORB (oriented brief) image feature registration method based on LK (Lucas-Kanade) optical flow constraint. The method includes three phases; in the first phase, ORB feature matching, ORB feature points in an image are extracted and matched to obtain a homography matrix; in the second phase, LK optical-flow precision matching, local optimal points are searched for by means of multiple iterations by the LK sparse optical flow method and used as optimal matching points, subjected to precision matching; in the third phase, image interpolation registration, two images are subjected to precision matching using the renewed homography matrix by means of bilinear interpolation. The method has the advantages that images of different scenes or images acquired by different sensors are automatically matched by means of image processing, registration precision directly determines quality of following image fusion, the high precision matching is maintained, and an algorithm is enabled to meet the demand for timely processing is met.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
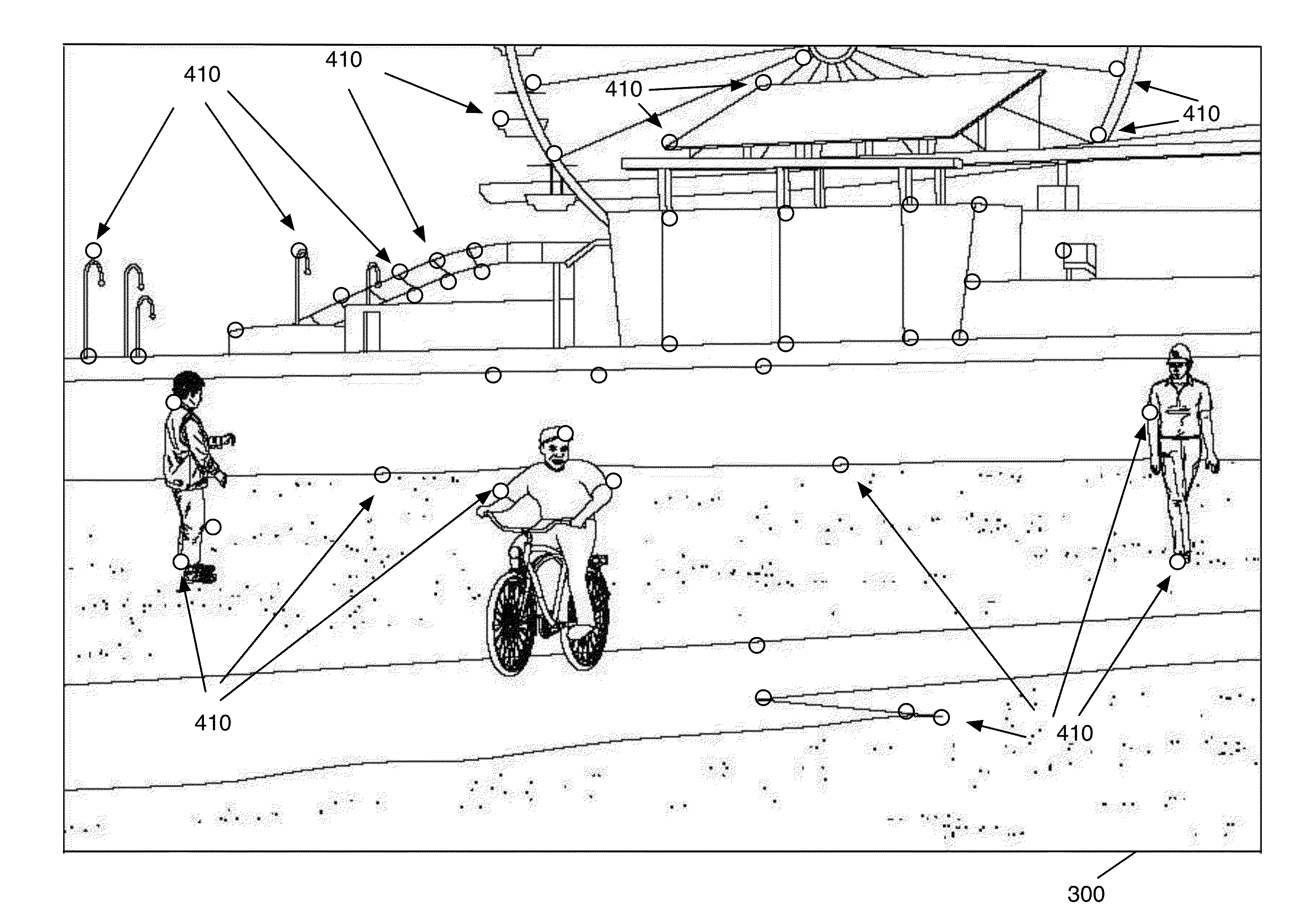
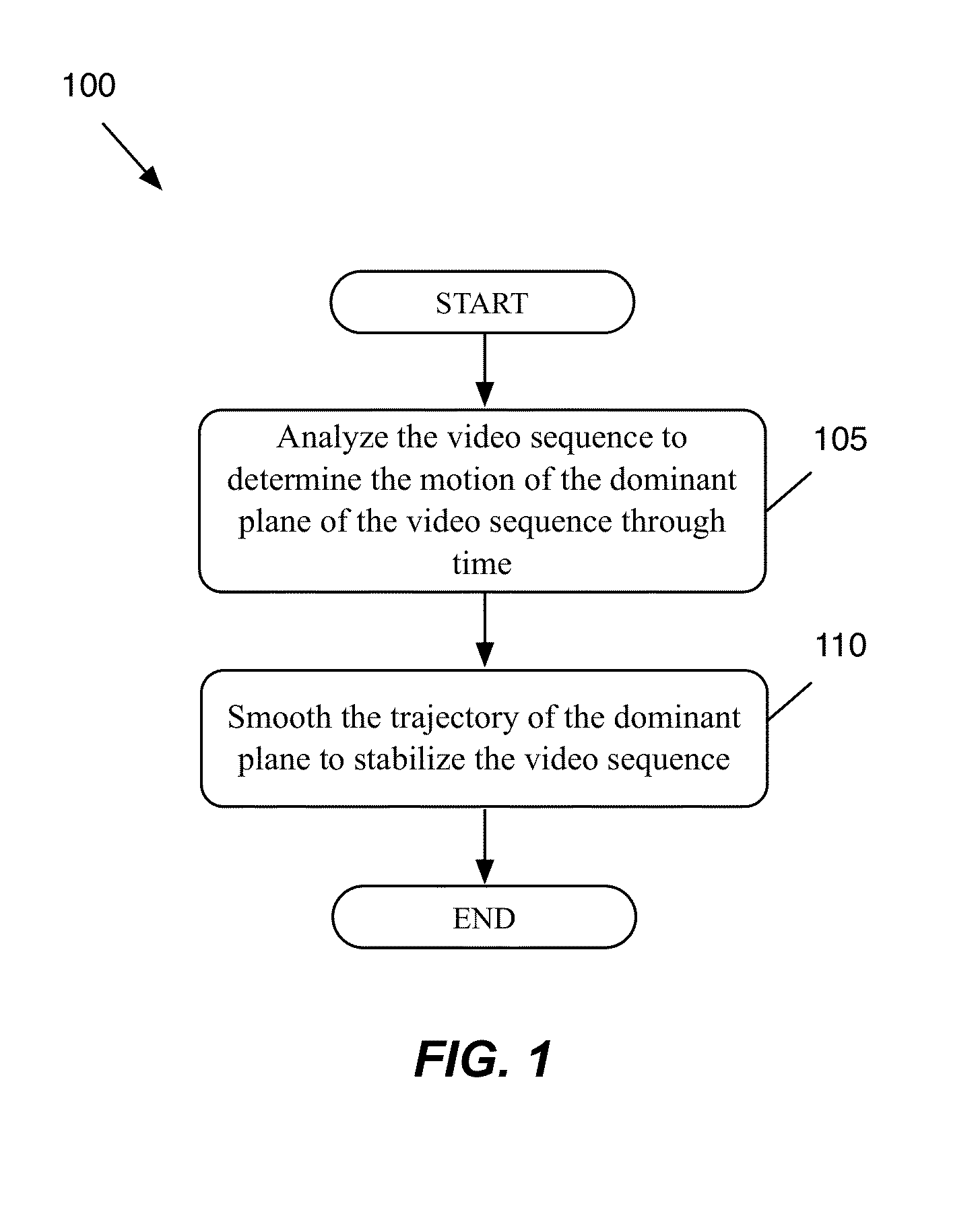
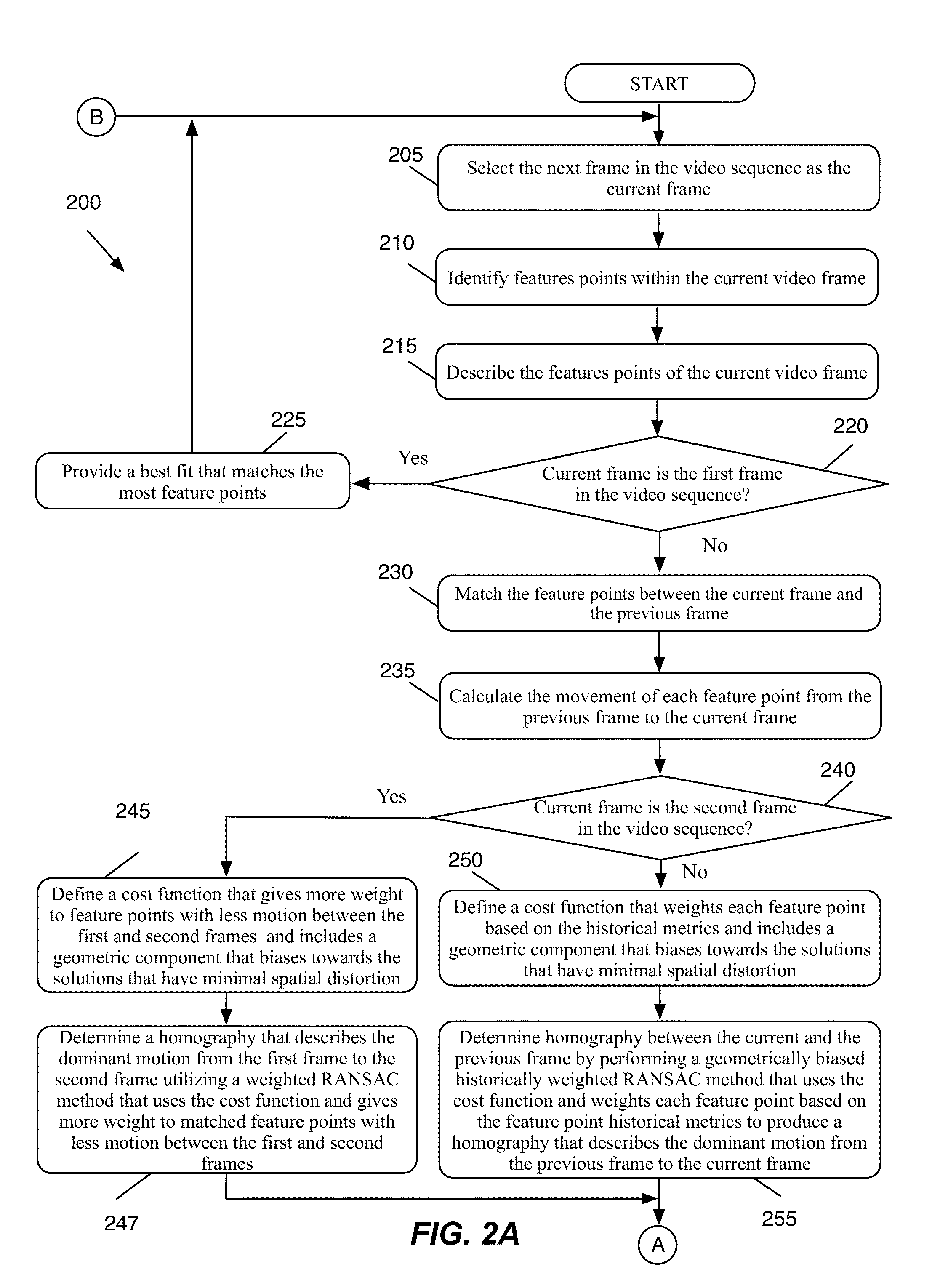
Robust Image Feature Based Video Stabilization and Smoothing
ActiveUS20140362240A1Eliminate relative motionLow densityImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionVideo sequence
A method of removing unwanted camera motion from a video sequence is provided. The method matches a group of feature points between each pair of consecutive video frames in the video sequence. The method calculates the motion of each matched feature point between the corresponding pair of consecutive video frames. The method calculates a set of historical metrics for each feature point. The method, for each pair of consecutive video frames, identifies a homography that defines a dominant motion between the pair of consecutive frames. The homography is identified by performing a geometrically biased historically weighted RANSAC on the calculated motion of the feature points. The geometrically biased historically weighted RANSAC gives a weight to the calculated motion of each feature point based on the historical metrics calculated for the feature point. The method removes he unwanted camera motion from the video sequence using the identified homographies.
Owner:APPLE INC
Image Stitching
InactiveUS20080298718A1Improve accuracyIncrease speedImage enhancementImage analysisImage pairPoint pair
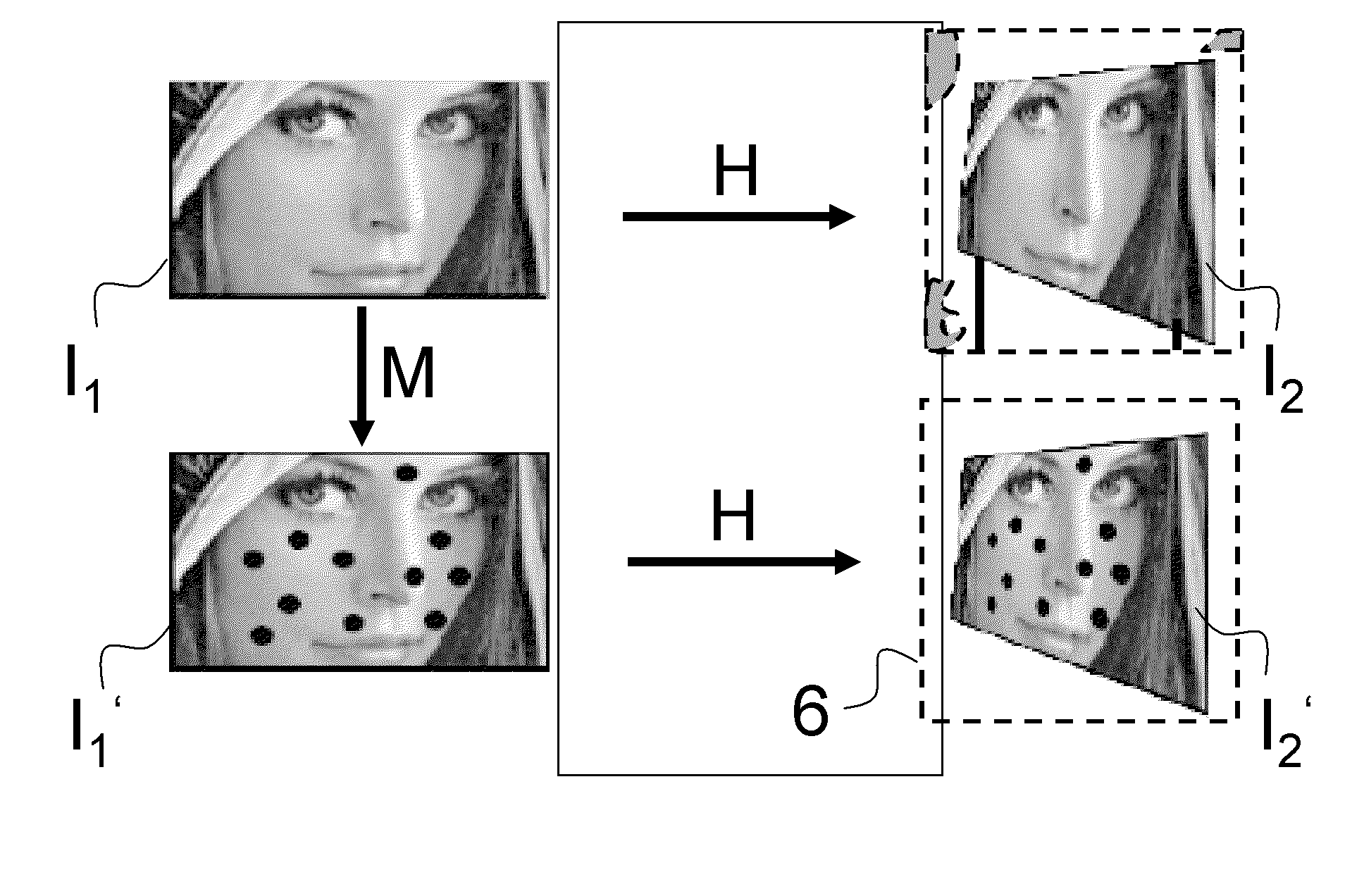
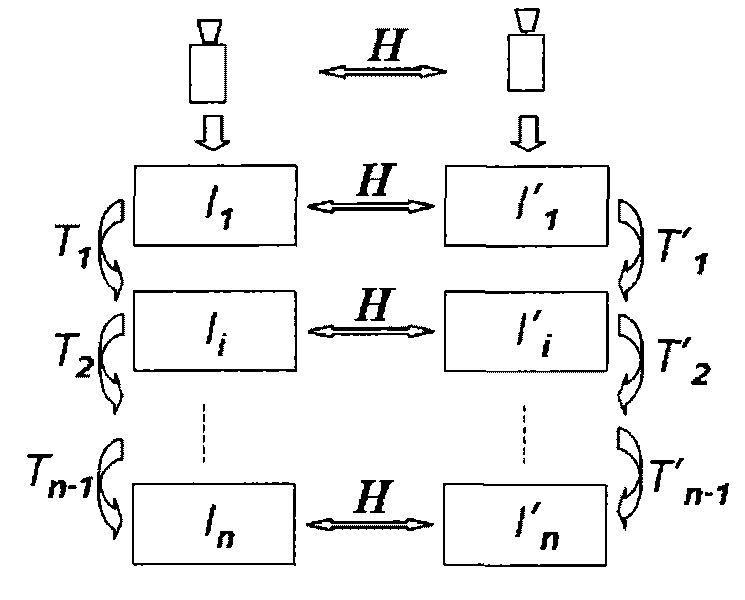
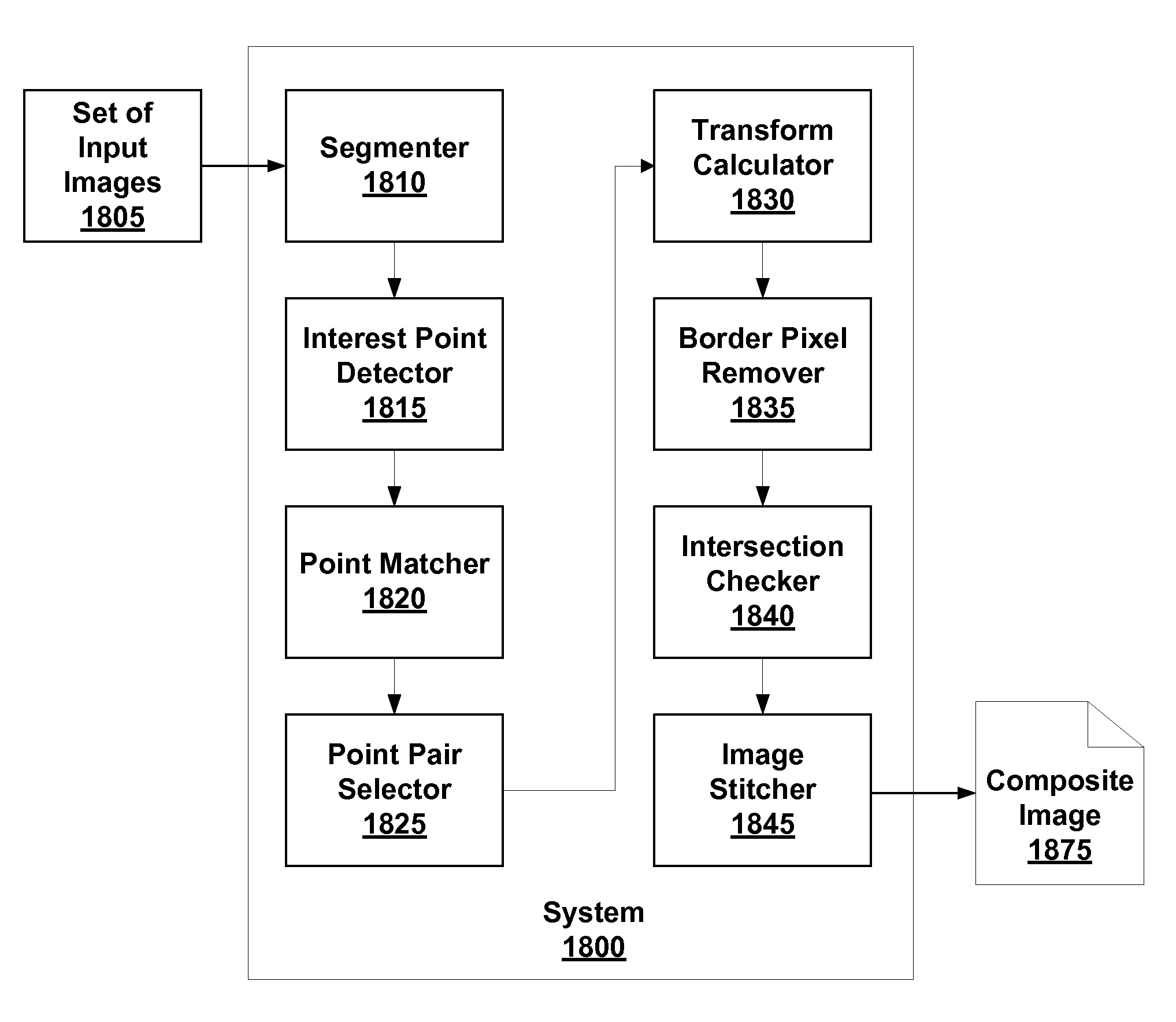
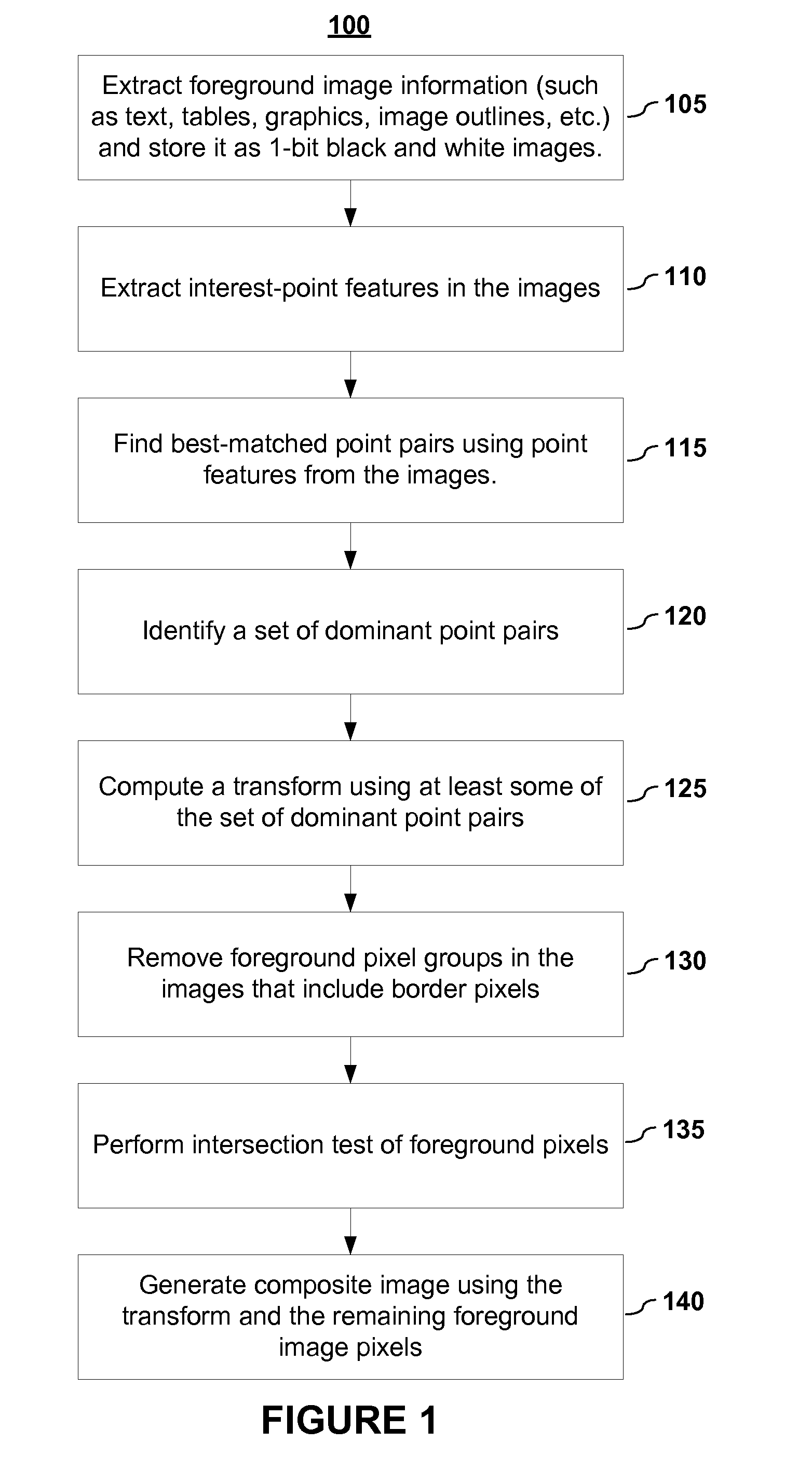
Disclosed are embodiments of systems and methods to stitch two or more images together into a composite image. By finding matching point pairs for a pair of images, a homography transform may be obtained for the pair of images. The homography transform may be used to generate a composite image of the image pair. In an embodiment, the process of identifying a homography transform may be iterated. In an embodiment, when forming the composite image, the transformed foreground regions may be selected such that there is no intersection of foreground pixel regions. In an embodiment, foreground pixel regions on the border of an image may be removed. The resulting composite image is a larger image generated from the selected regions from the input images. In embodiments, the process may be repeated for sets of images with more than two images.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
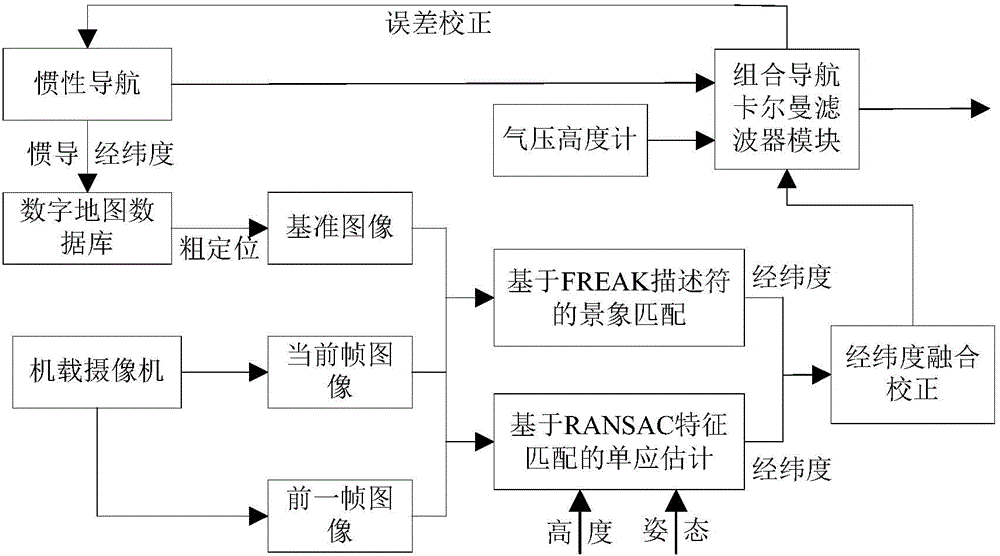
Scene matching/visual odometry-based inertial integrated navigation method
ActiveCN103954283AHigh positioning accuracyStrong autonomyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsVisual perceptionHomography
The invention relates to a scene matching / visual odometry-based inertial integrated navigation method. The method comprises the following steps: calculating the homography matrix of an unmanned plane aerial photography real time image sequence according to a visual odometry principle, and carrying out recursive calculation by accumulating a relative displacement between two continuous frames of real time graph to obtain the present position of the unmanned plane; introducing an FREAK characteristic-based scene matching algorithm because of the accumulative error generation caused by the increase of the visual odometry navigation with the time in order to carry out aided correction, and carrying out high precision positioning in an adaption zone to effectively compensate the accumulative error generated by the long-time work of the visual odometry navigation, wherein the scene matching has the advantages of high positioning precision, strong automaticity, anti-electromagnetic interference and the like; and establishing the error model of the inertial navigation system and a visual data measuring model, carrying out Kalman filtering to obtain an optimal estimation result, and correcting the inertial navigation system. The method effectively improves the navigation precision, and is helpful for improving the autonomous flight capability of the unmanned plane.
Owner:深圳市欧诺安科技有限公司
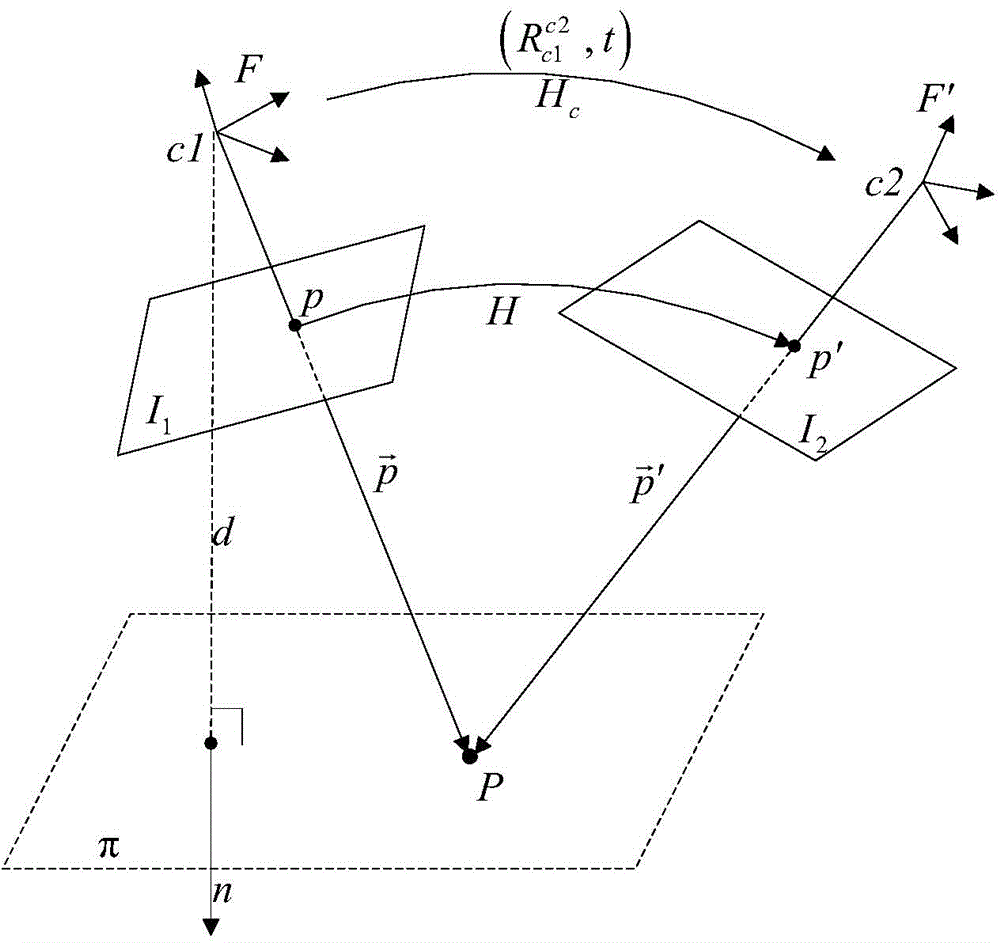
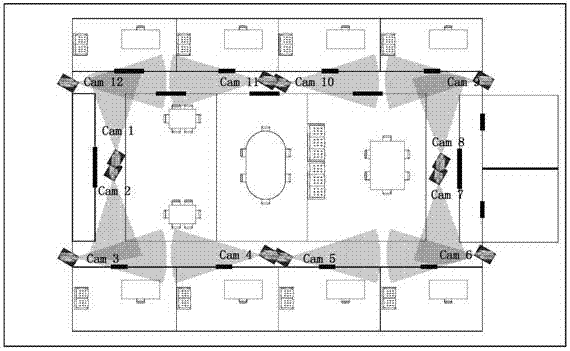
Multi-target positioning method based on camera network
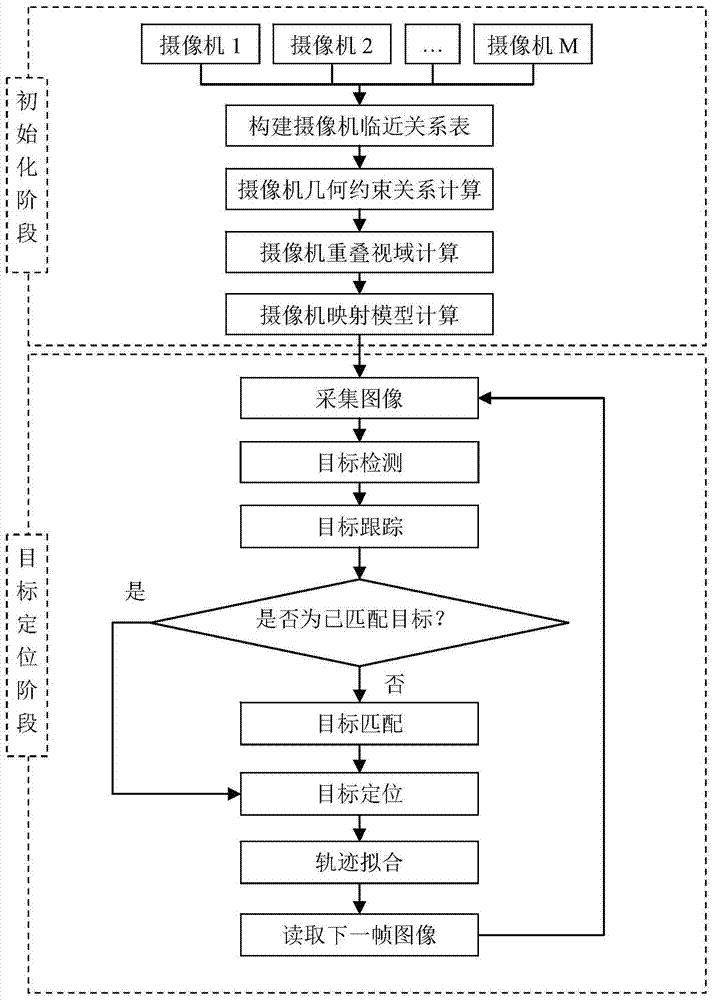
ActiveCN104778690AImprove accuracyPrevent degradationImage analysisClosed circuit television systemsSafety monitoringHomography
The invention discloses a multi-target positioning method based on a camera network and belongs to the technical field of multimedia sensor networks. The multi-target positioning method comprises steps as follows: firstly, at the initialization stage, camera network initialization is completed through four steps of establishment of a camera unit, computation of camera homography conversion, computation of camera overlapping vision fields and computation of a camera mapping model; secondary, at the target positioning stage, target detection and tracking of a single camera are completed, and target matching is realized through comprehensive utilization of the topological relation among the cameras, as well as geometric constraint and target characteristic information; finally, physical location of targets is computed by the aid of the camera model, and multi-target positioning is realized. According to the multi-target positioning method based on the camera network, stable tracking of multiple targets can be realized, and the method has the characteristics of low cost, high positioning accuracy, stable operation and the like and has broad application prospect in the fields of battlefield reconnaissance, safety monitoring, boundary protection and the like.
Owner:THE 28TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
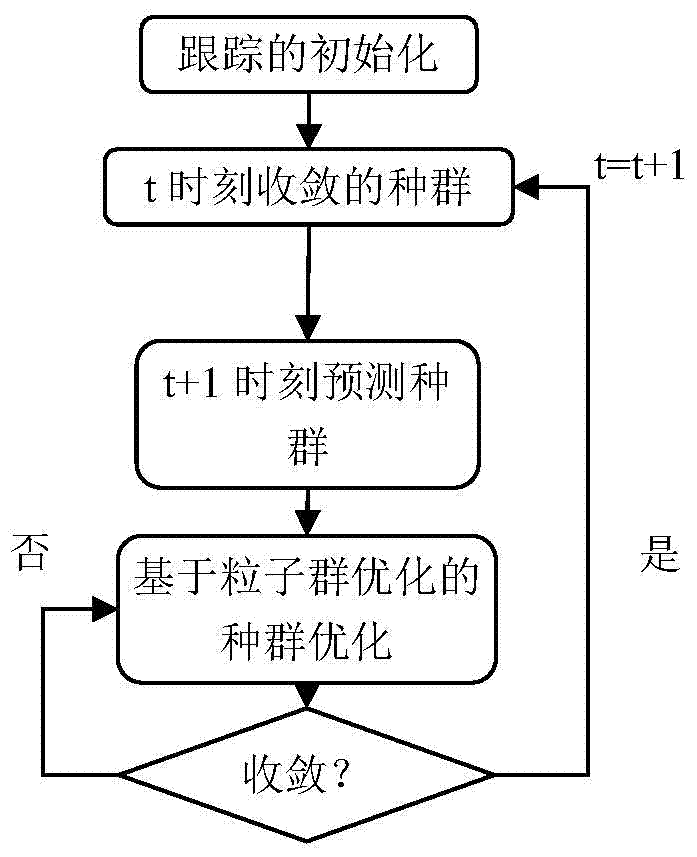
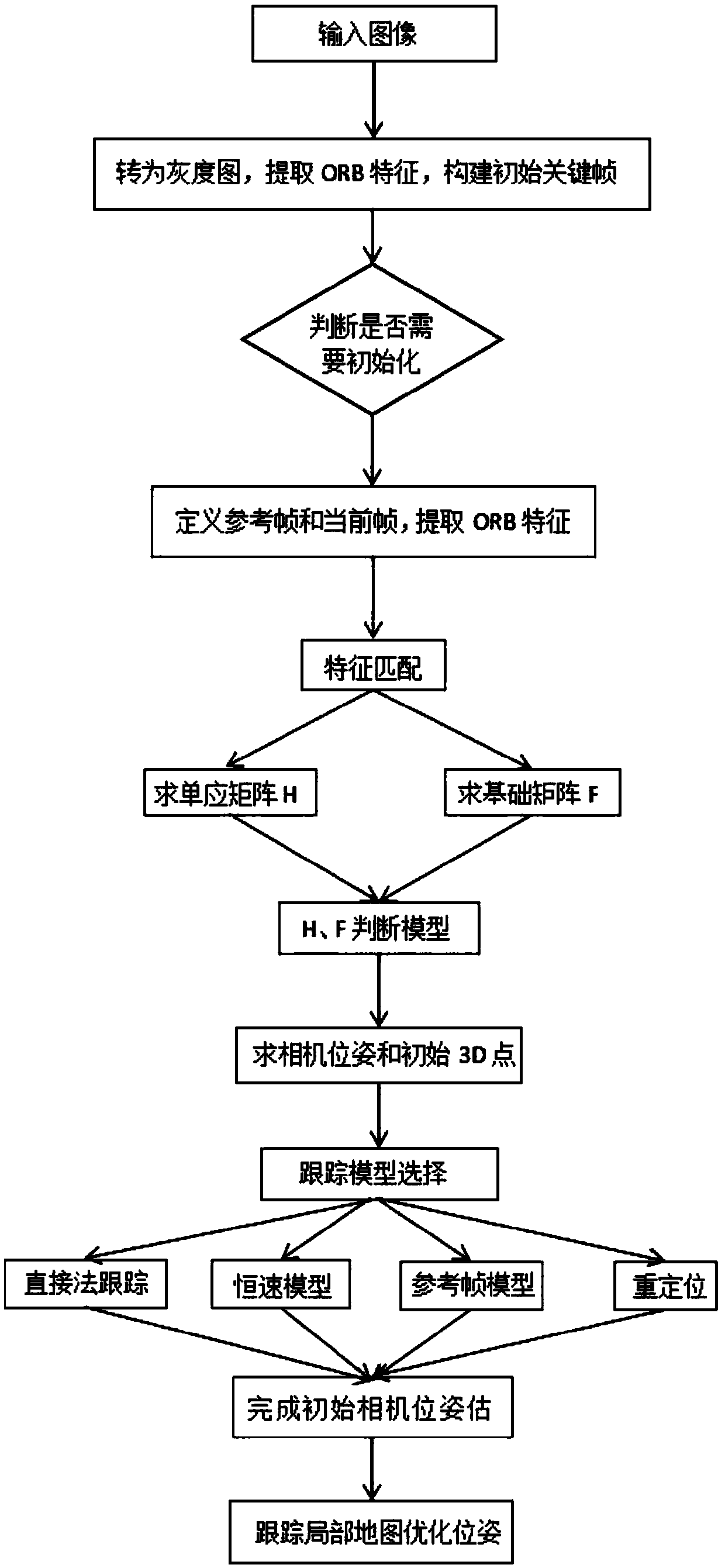
A fast monocular vision odometer navigation and positioning method combining a feature point method and a direct method
ActiveCN109544636AAccurate Camera PoseFeature Prediction Location OptimizationImage enhancementImage analysisOdometerKey frame
The invention discloses a fast monocular vision odometer navigation and positioning method fusing a feature point method and a direct method, which comprises the following steps: S1, starting the vision odometer and obtaining a first frame image I1, converting the image I1 into a gray scale image, extracting ORB feature points, and constructing an initialization key frame; 2, judging whether thatinitialization has been carry out; If it has been initialized, it goes to step S6, otherwise, it goes to step S3; 3, defining a reference frame and a current frame, extracting ORB feature and matchingfeatures; 4, simultaneously calculating a homography matrix H and a base matrix F by a parallel thread, calculating a judgment model score RH, if RH is great than a threshold value, selecting a homography matrix H, otherwise selecting a base matrix F, and estimating a camera motion according to that selected model; 5, obtaining that pose of the camera and the initial 3D point; 6, judging whetherthat feature point have been extracted, if the feature points have not been extracted, the direct method is used for tracking, otherwise, the feature point method is used for tracking; S7, completingthe initial camera pose estimation. The invention can more precisely carry out navigation and positioning.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
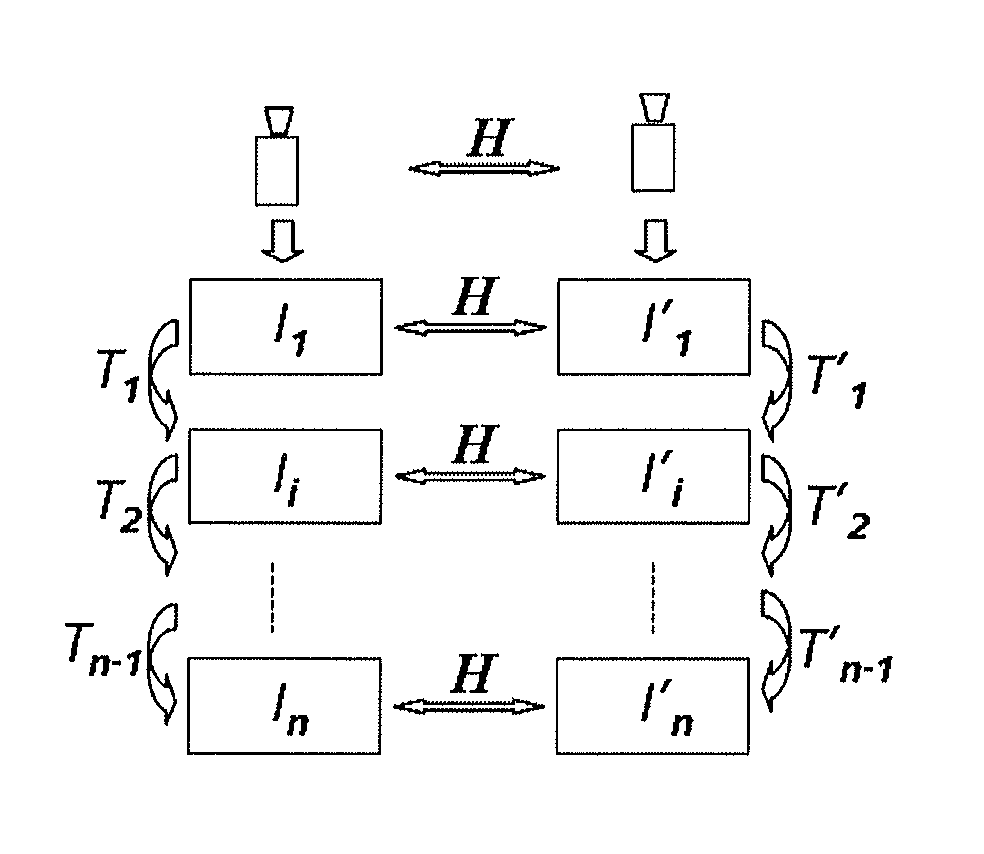
System and method for calibrating multiple cameras without employing a pattern by inter-image homography
InactiveUS20060024041A1Computer processing power becomes strongNetwork bandwidth becomes broadImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionHomographyType of service
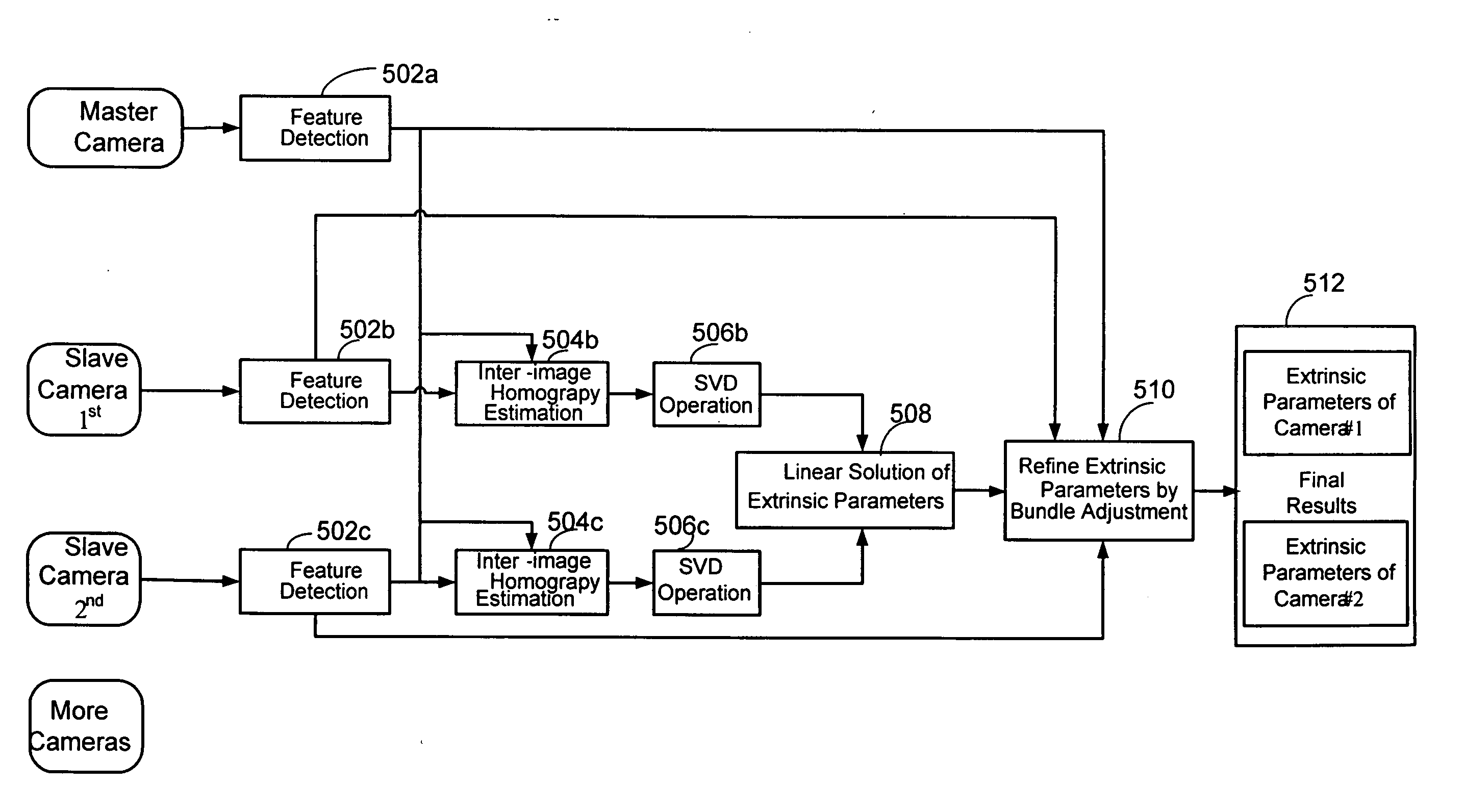
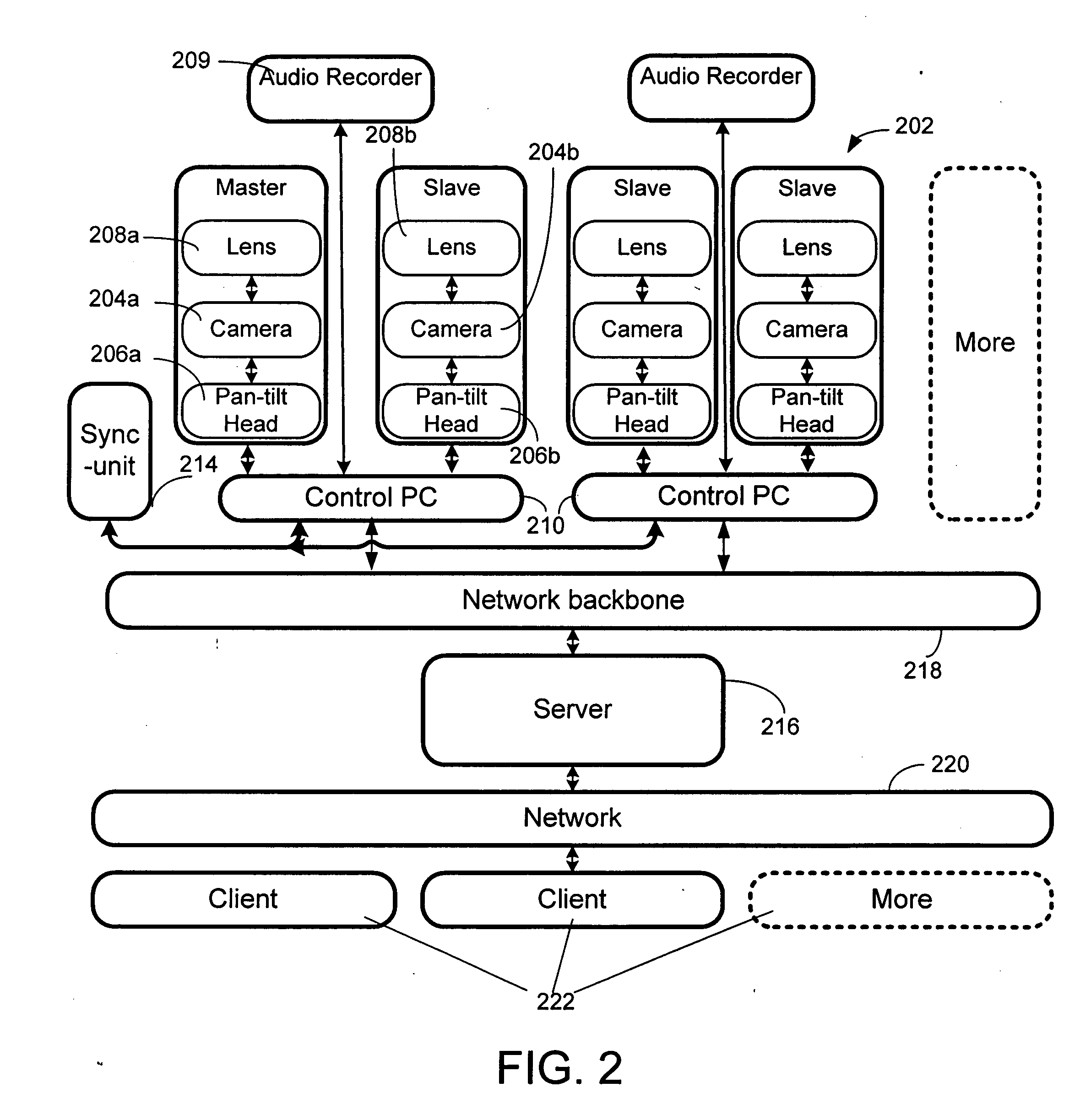
Interactive multi-view video presents new types of video capture systems, video formats, video compression algorithms, and services. Many video cameras are allocated to capture an event from various related locations and directions. The captured videos are compressed in control PCs and are sent to a server in real-time. Users can subscribe to a new type of service that allows users to connect to the servers and receive multi-view videos interactively. In one embodiment of the invention, an automatic pattern-free calibration tool is employed to calibrate the multiple cameras. In contrast with a pattern-based method which uses the correspondences between image points and pattern points, the pattern-free calibration method is based on the correspondences between image points from different views.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
A real time panorama video splicing method based on ORB characteristics and an apparatus
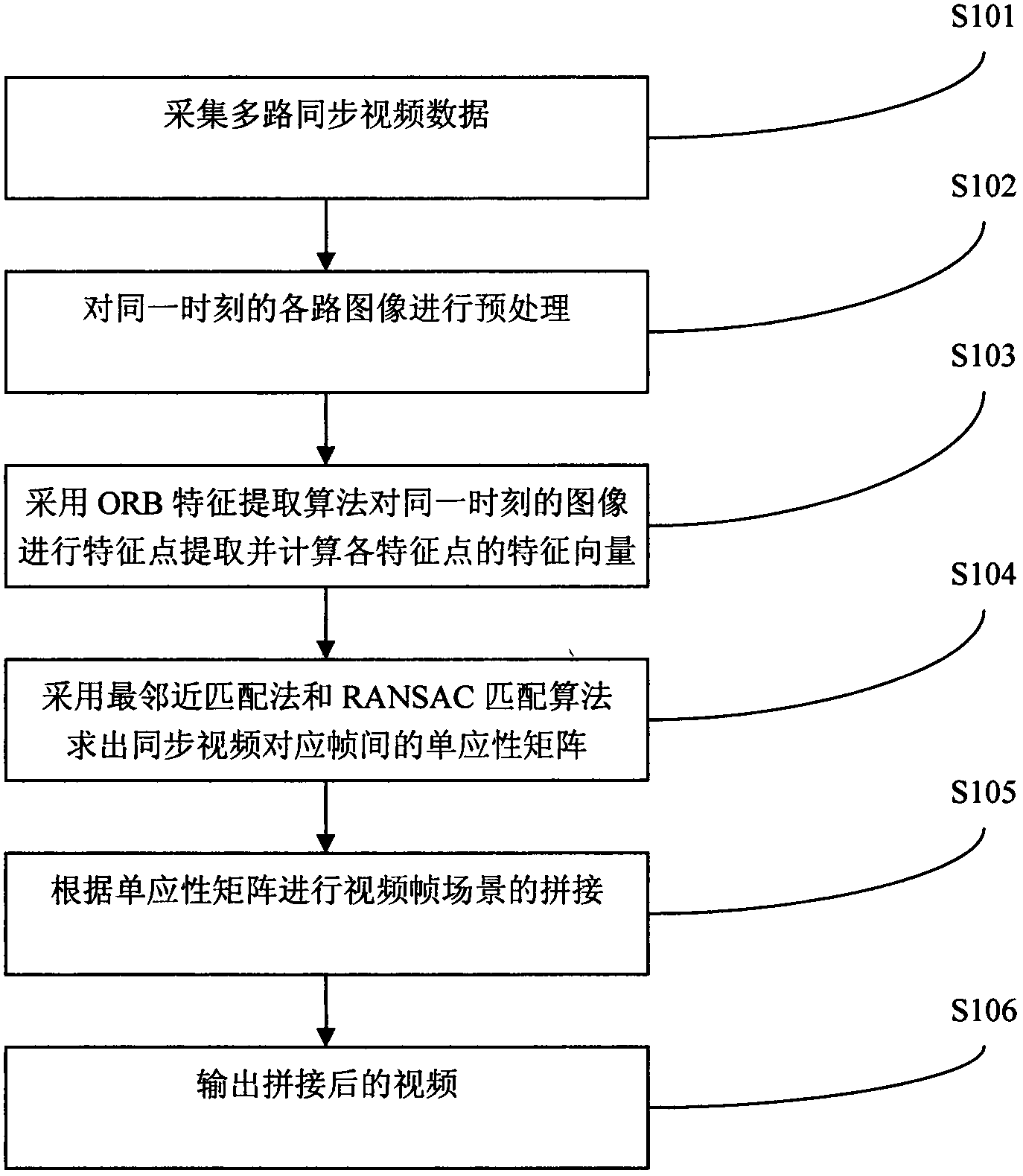
InactiveCN103516995AFast extractionReal-time panorama stitching processingTelevision system detailsColor television detailsColor imageFeature extraction algorithm
The invention discloses a real time panorama video splicing method based on ORB characteristics. The real time panorama video splicing method based on the ORB characteristics comprises the following steps: acquisition of multipath synchronized video data is started; pretreatment is carried out on images in various paths at a same moment, and color images are changed into gray scale images of 256 levels, and a de-noising processing is carried out on the images through employing a Gaussian filter; the ORB feature extraction algorithm is employed to carry out feature point extraction on the images in the various paths at the same moment, and ORB characteristic vectors of the feature points are calculated; through the adoption of the nearest neighborhood matching method and the RANSAC (random sample consensus) matching method to determine a homography matrix array between corresponding frames of the synchronized videos; frame scene splicing is carried out according to the homography matrix array; and finally spliced videos are output. The real time panorama video splicing method based on ORB characteristics and the apparatus are advantageous in that: the feature extraction speed and the coupling effect are improved in the image splicing process.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Auto-calibration method for a projector-camera system
ActiveUS20090245690A1Quality improvementImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionProjector camera systemsVisual perception
A method for self-recalibration of a structured light vision system including a camera and a projector. A camera plane and a projector plane are defined, a Homography matrix between the camera plane and the projector plane is computed, and a translation vector and a rotation matrix are determined from Homography-based constraints. A computer vision system implementing the method is also described.
Owner:CITY UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
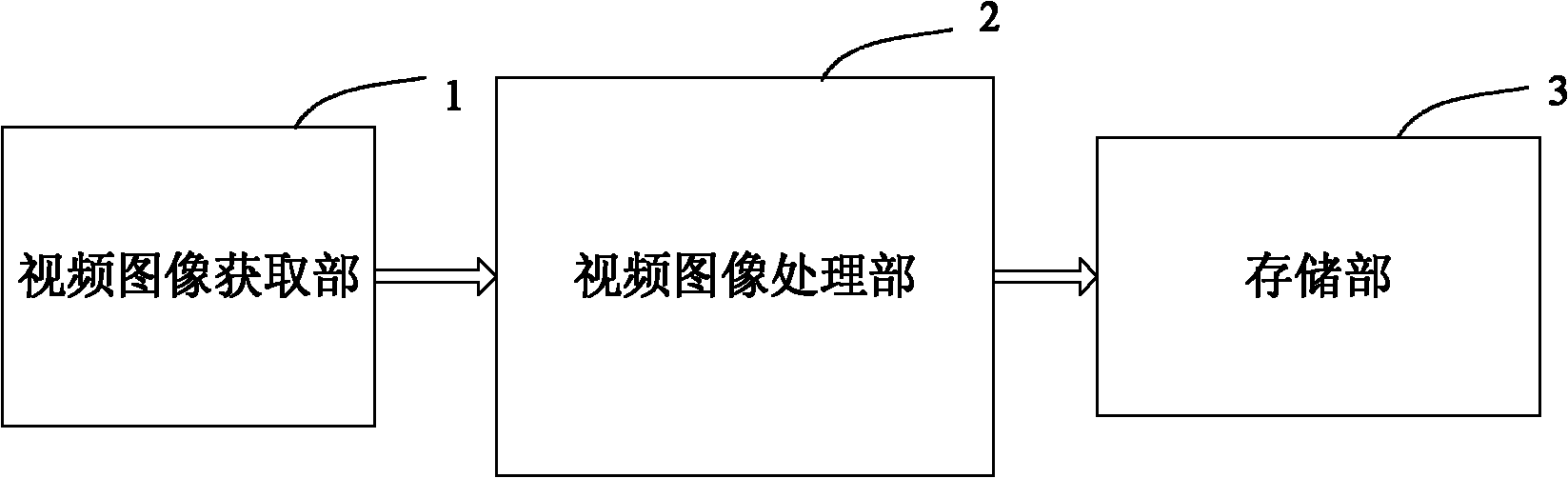
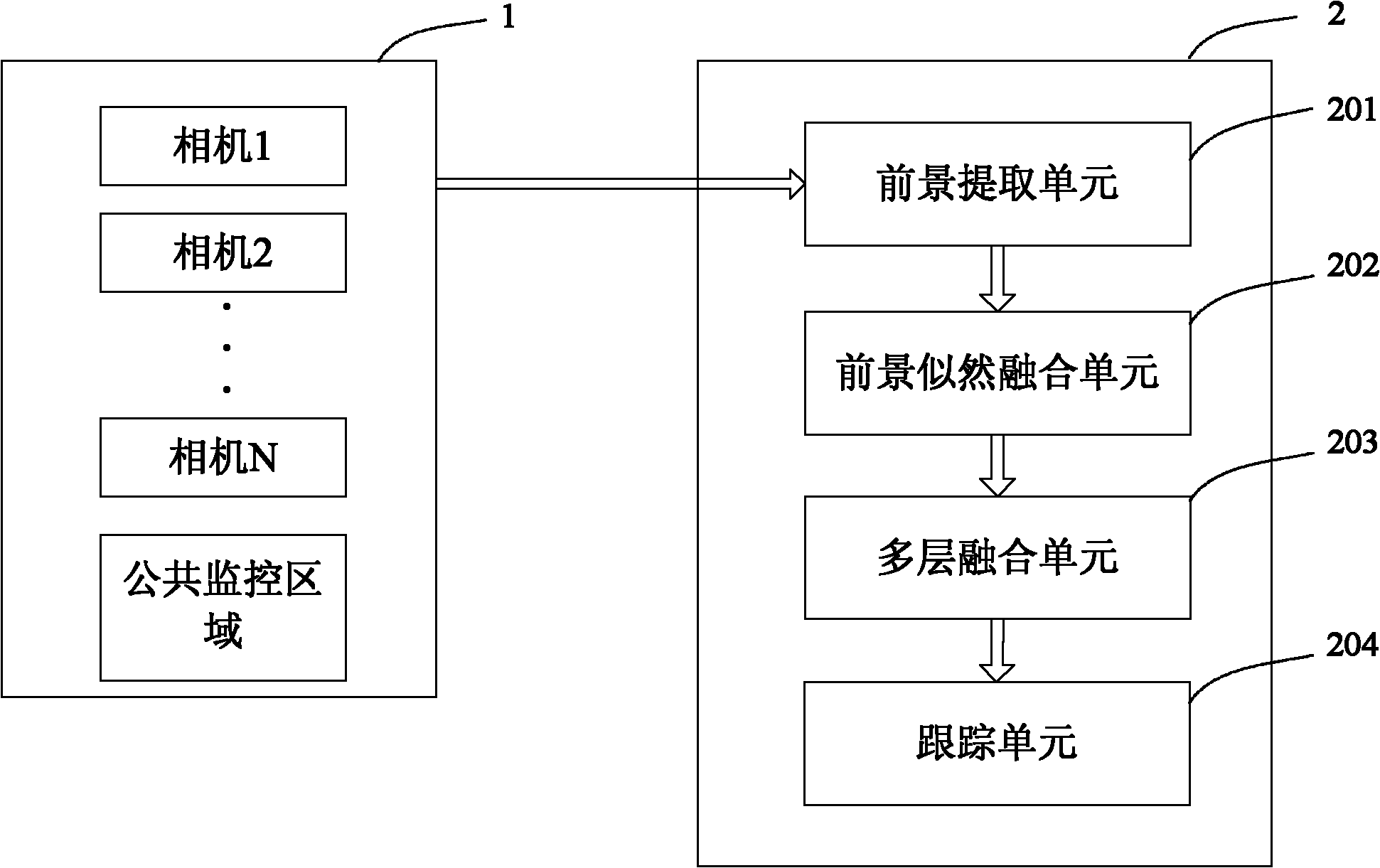
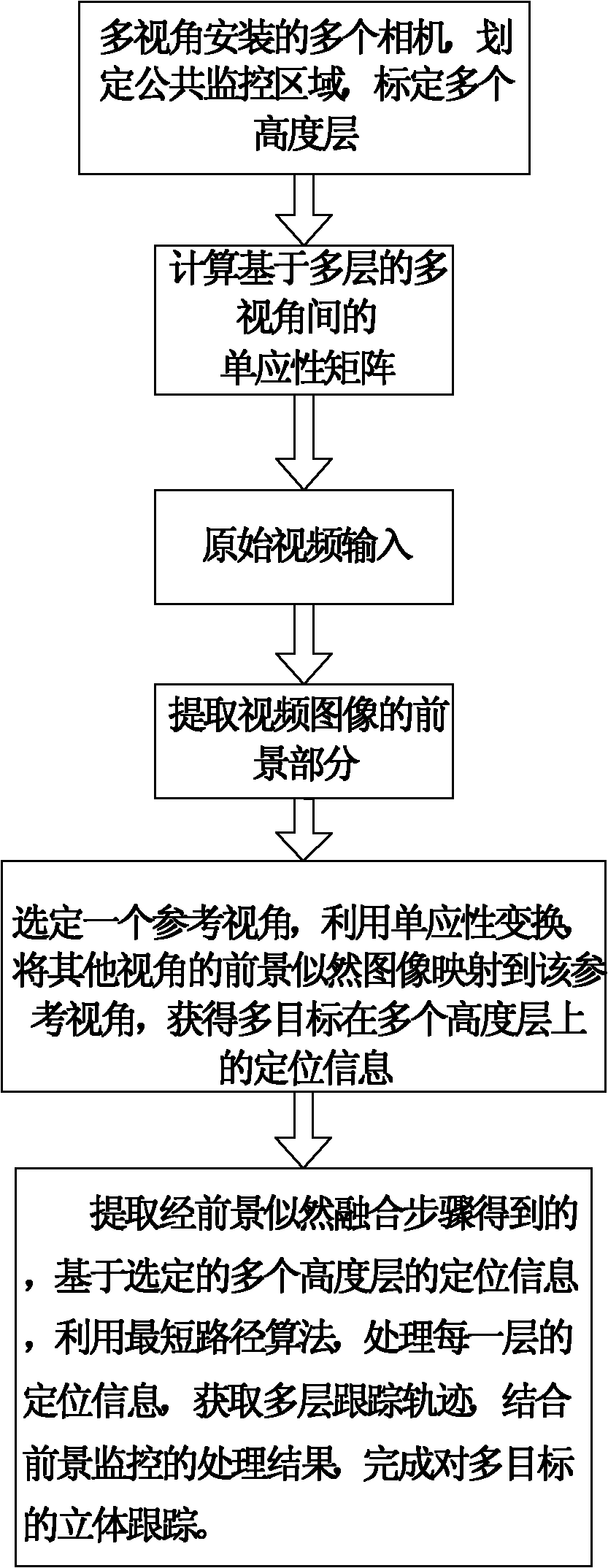
Multi-camera-based multi-objective positioning tracking method and system
InactiveCN102243765AImprove accuracyHigh precisionImage analysisClosed circuit television systemsMulti cameraShort path algorithm
The invention discloses a multi-camera-based multi-objective positioning tracking method. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: installing a plurality of cameras at a plurality of visual angles firstly, planning a public surveillance area for the cameras, and calibrating a plurality of height levels; sequentially implementing the steps of foreground extraction, homography matrix calculation, foreground likelihood fusion and multi-level fusion; extracting positioning information which is based on selected a plurality of height levels and obtained in the step of foreground likelihood fusion; processing the positioning information of each level by using the shortest path algorithm so as to obtain the tracking paths of the levels; and after combining with the processing results of foreground extraction, completing the multi-objective three-dimensional tracking. By using the method disclosed by the invention, in the process of tracking, the vanishing points of the plurality of cameras are not required to be calculated, and a codebook model is introduced for the first time for solving the multi-objective tracking problem, thereby improving the accuracy of tracking; and the method has the characteristics of good stability, good instantaneity and high precision.
Owner:DALIAN NATIONALITIES UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com