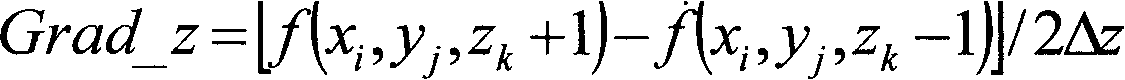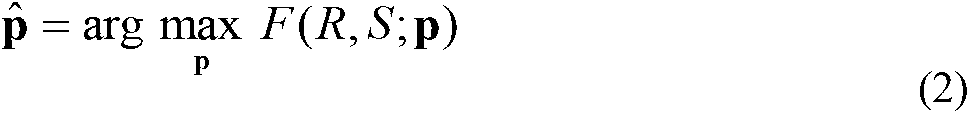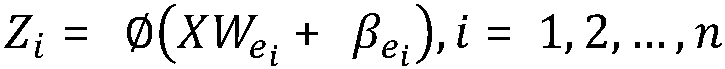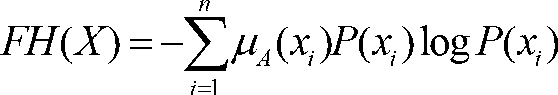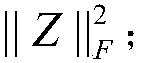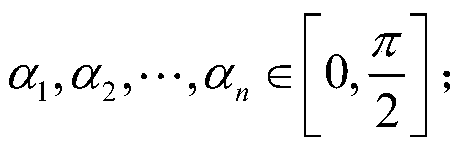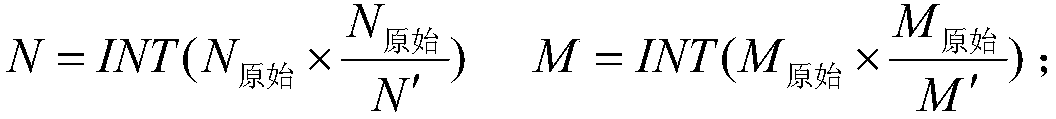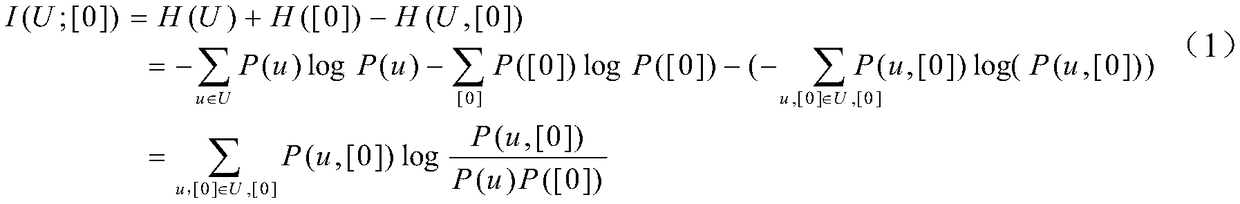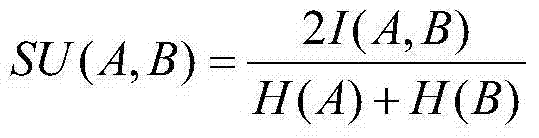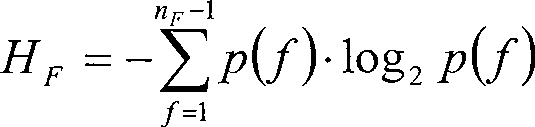Patents
Literature
65 results about "Normalized mutual information" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
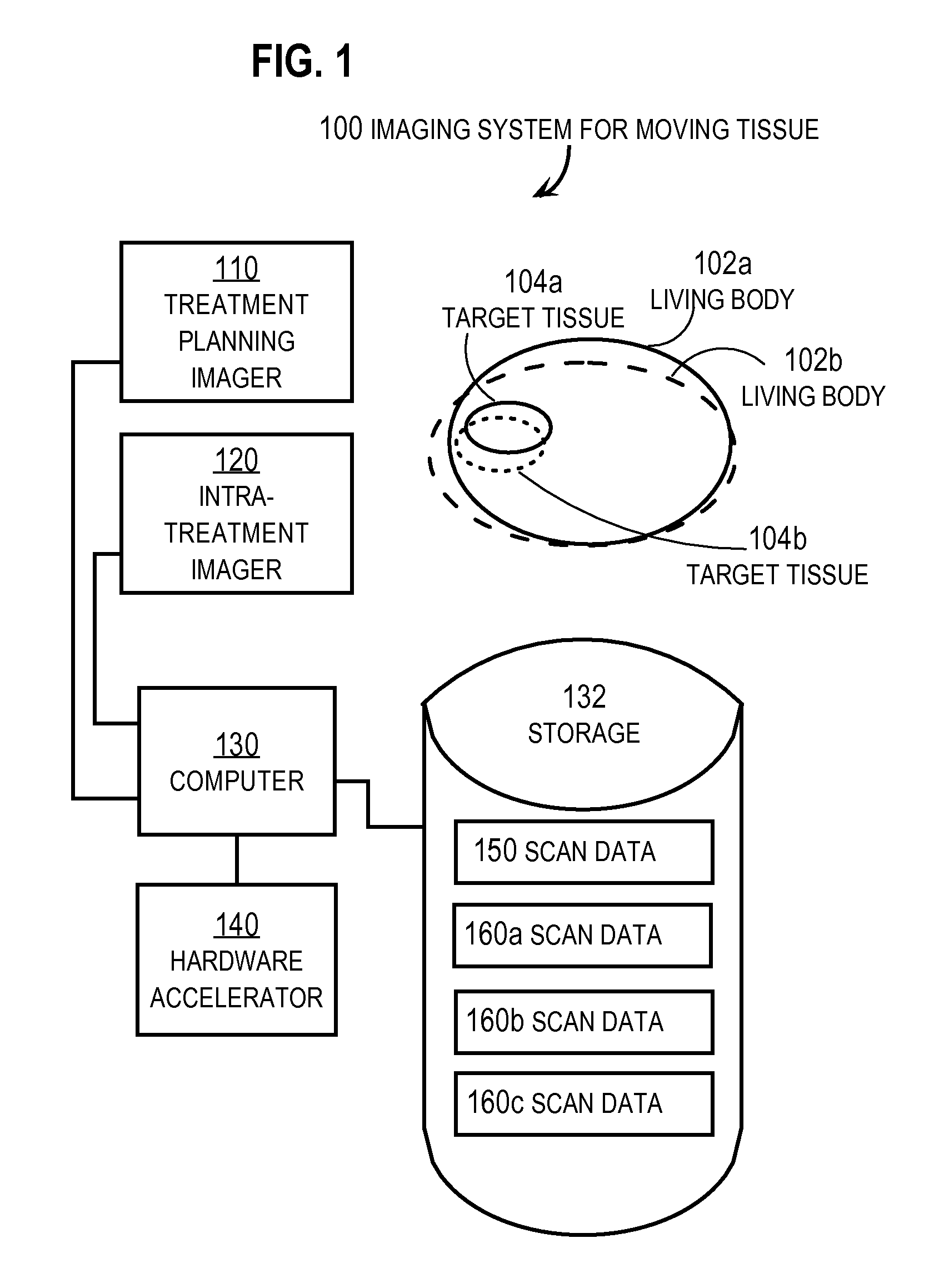
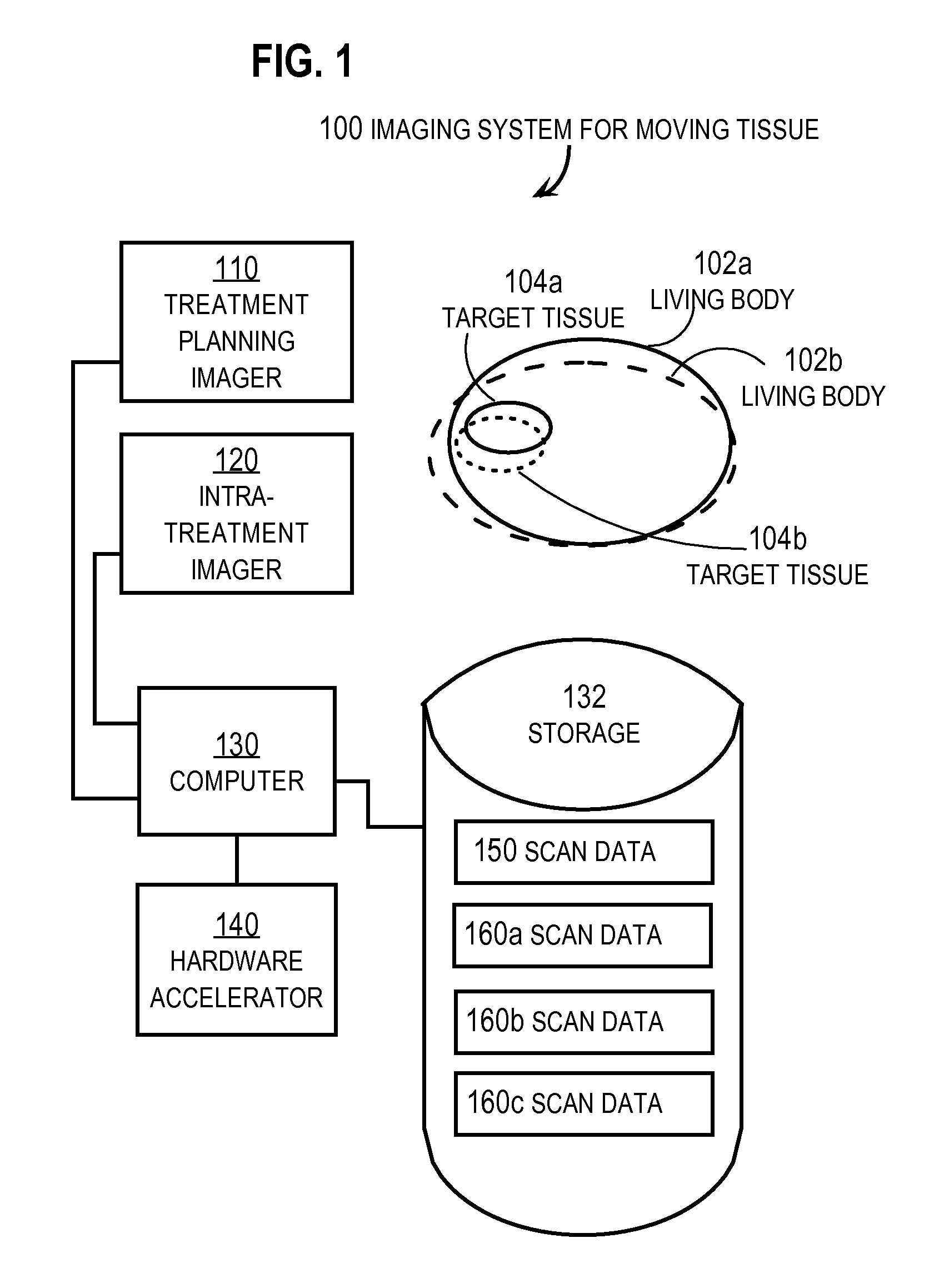
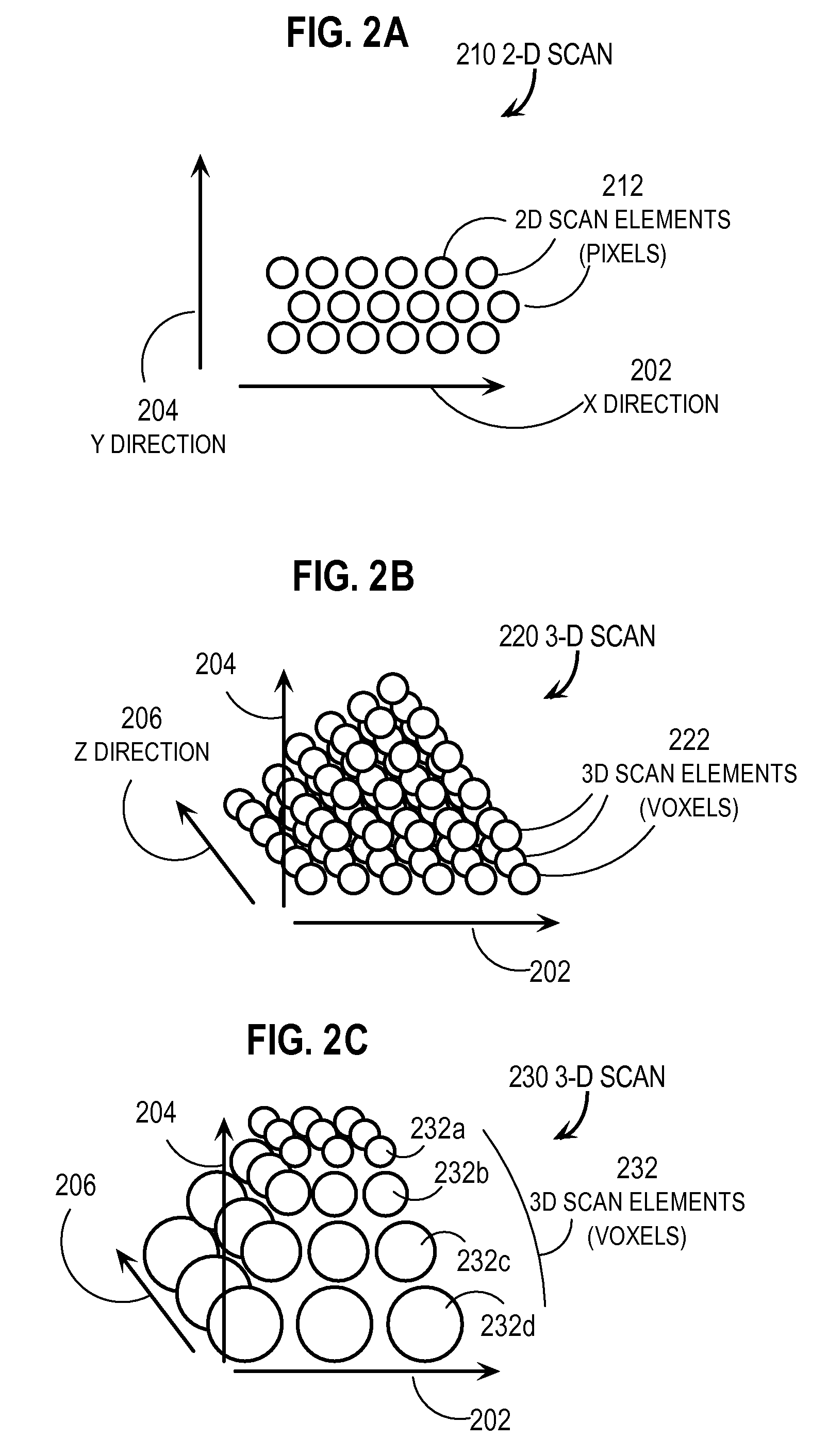
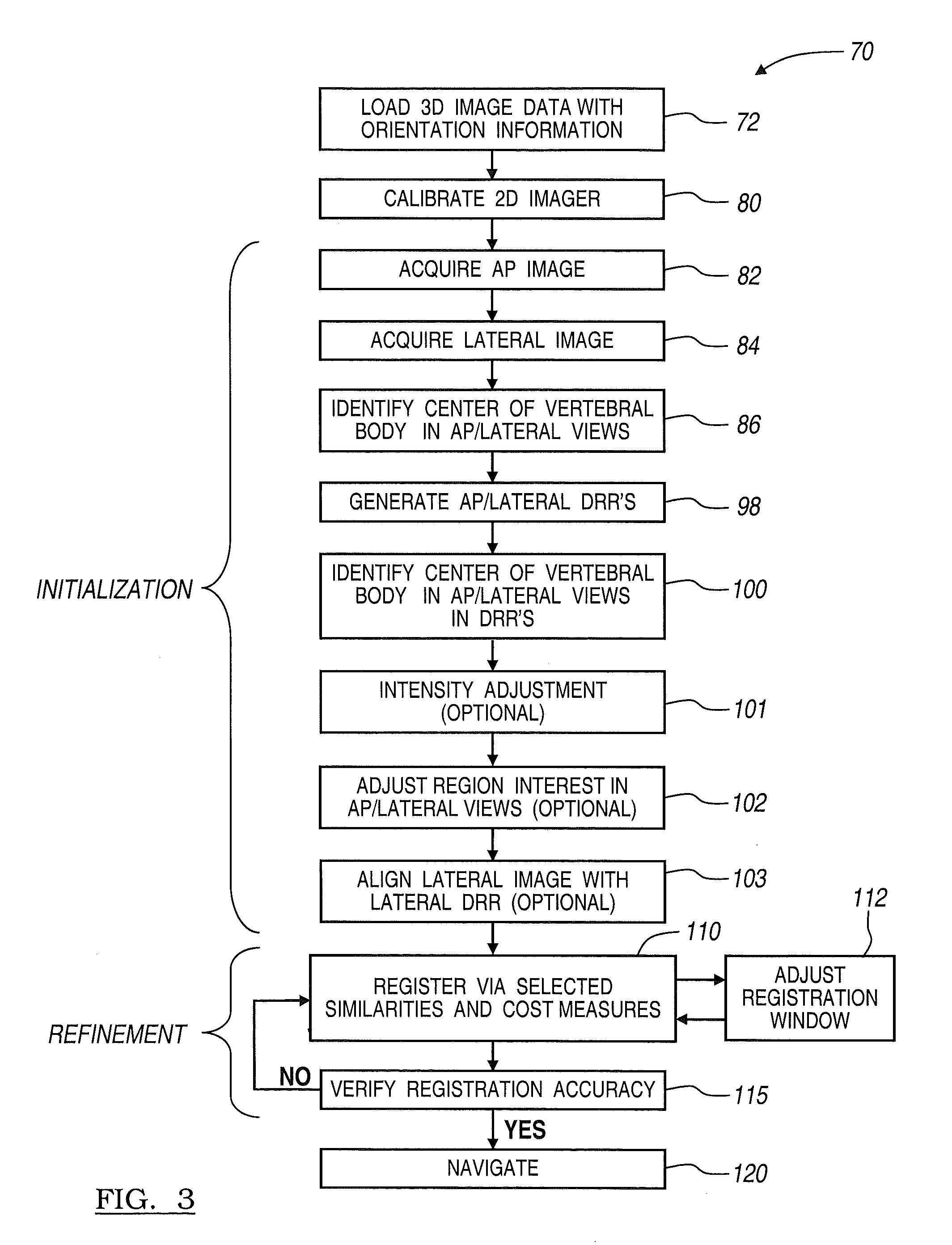
Method and apparatus for performing 2D to 3D registration
ActiveUS7570791B2Reduce the impactReduce impactSurgeryCharacter and pattern recognitionNormalized mutual informationNormalize mutual information
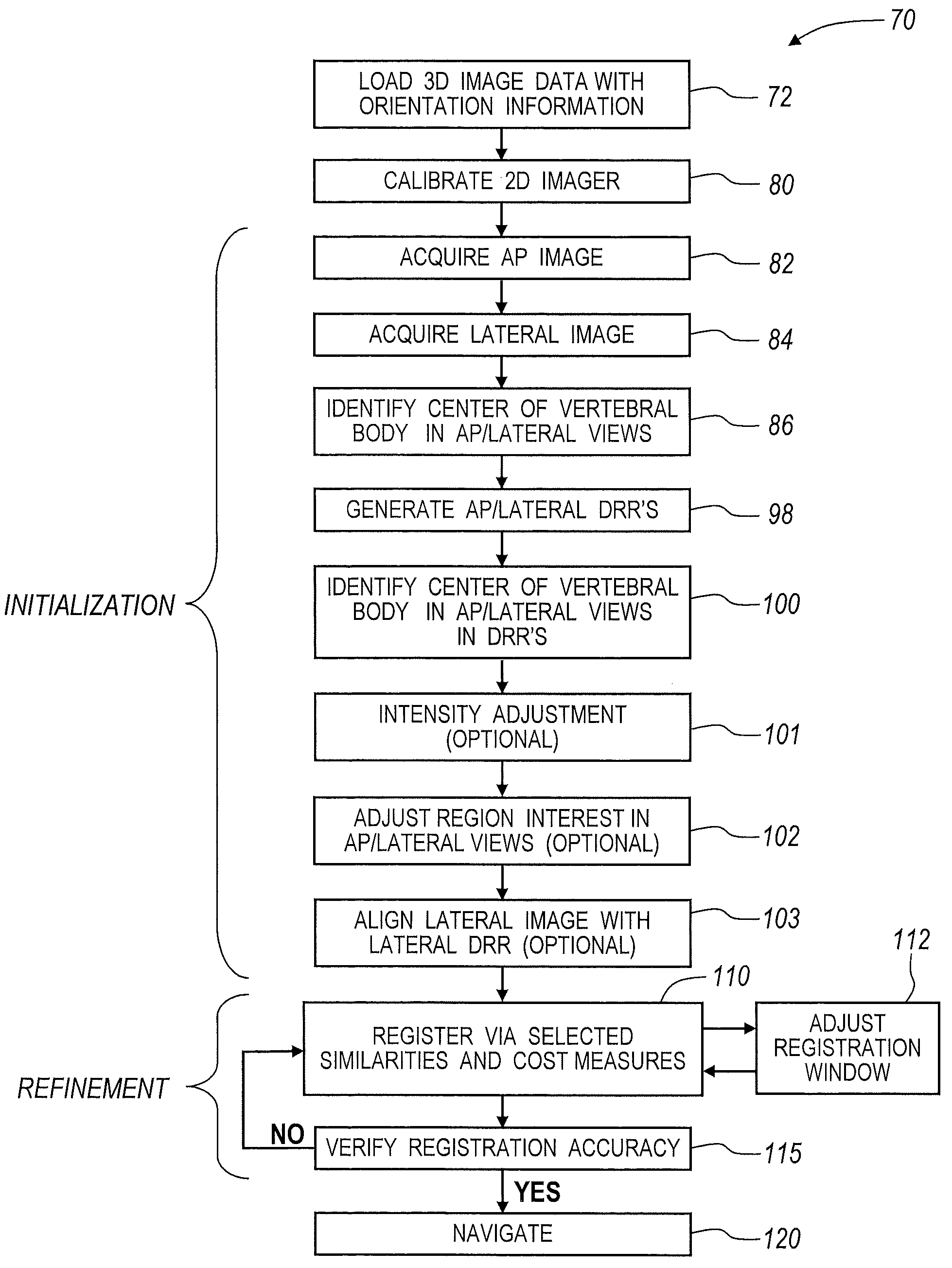
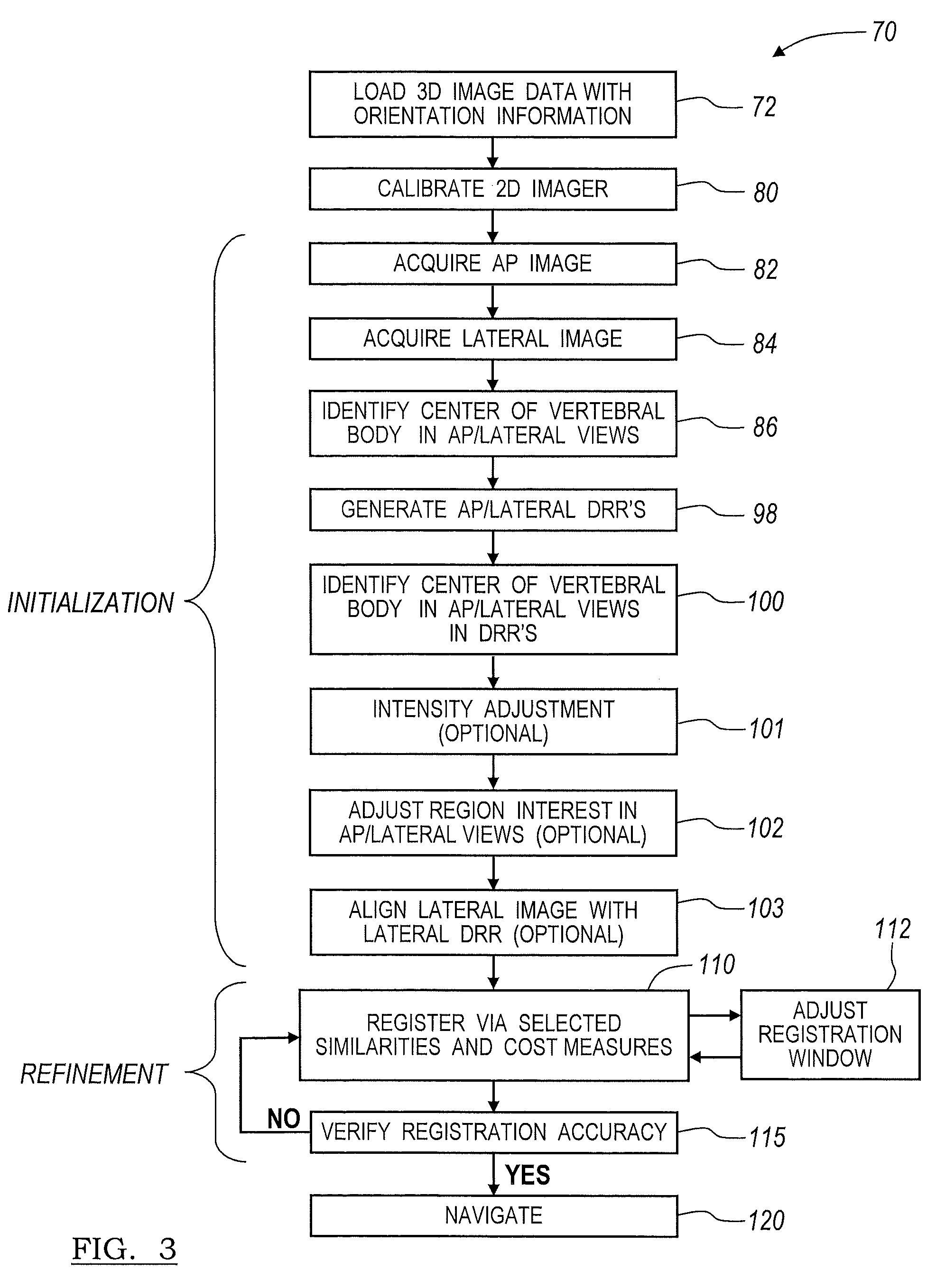
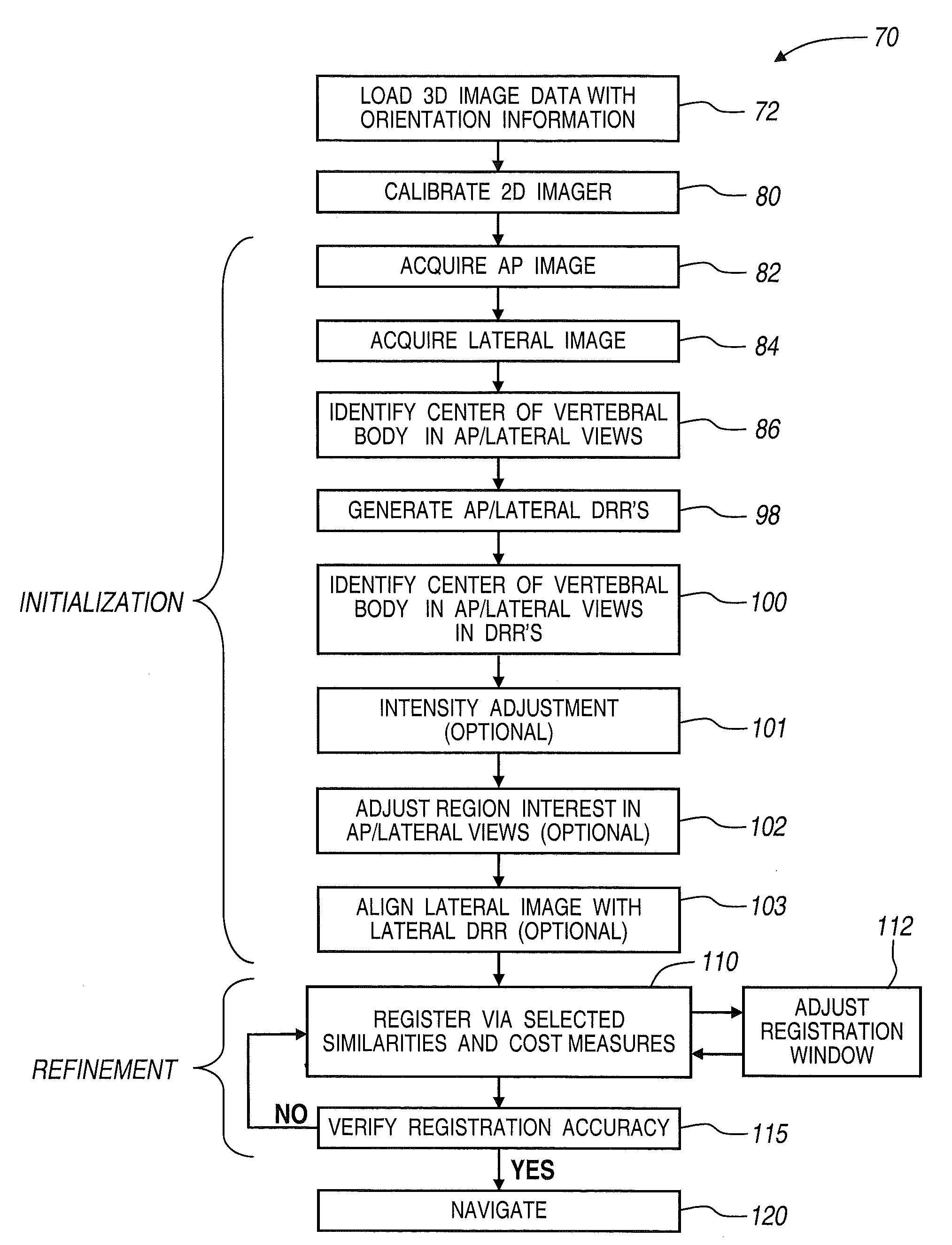
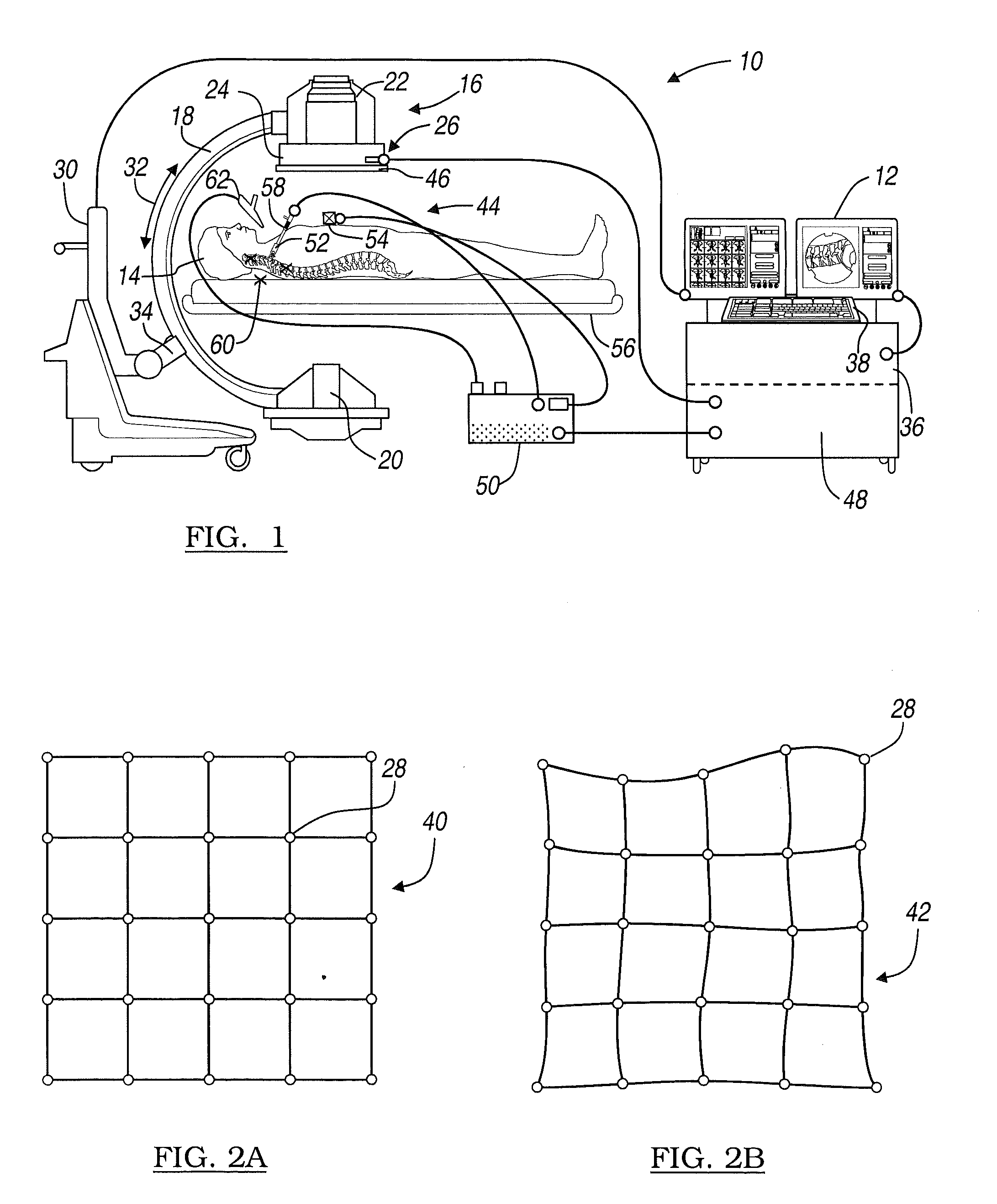
A method and apparatus for performing 2D to 3D registration includes an initialization step and a refinement step. The initialization step is directed to identifying an orientation and a position by knowing orientation information where data images are captured and by identifying centers of relevant bodies. The refinement step uses normalized mutual information and pattern intensity algorithms to register the 2D image to the 3D volume.
Owner:MEDTRONIC NAVIGATION
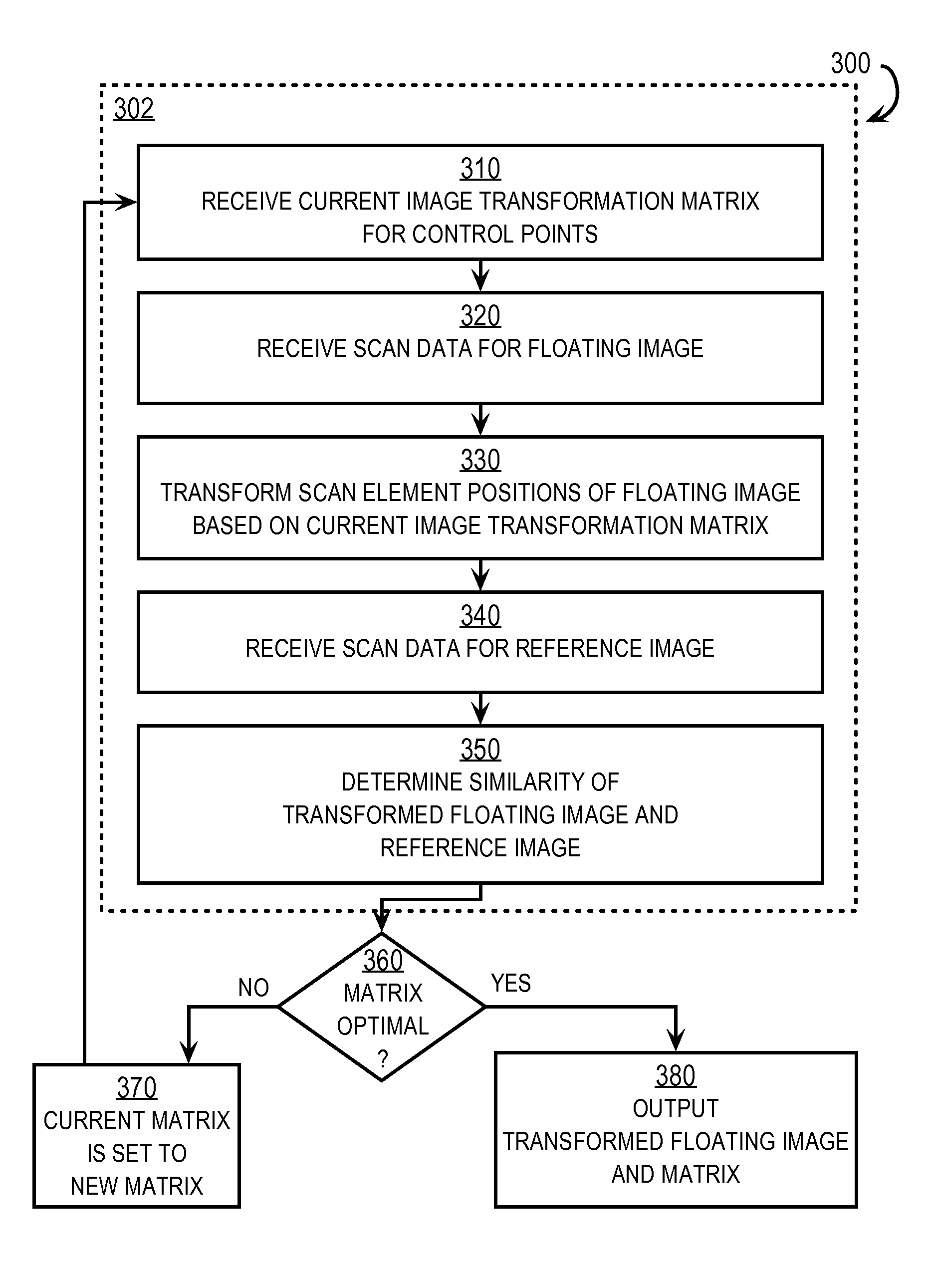
Method and Apparatus For Accelerated Elastic Registration of Multiple Scans of Internal Properties of a Body
InactiveUS20080317317A1Maximizing similarity measureLess timeImage enhancementImage analysisNormalized mutual informationContinuous scanning
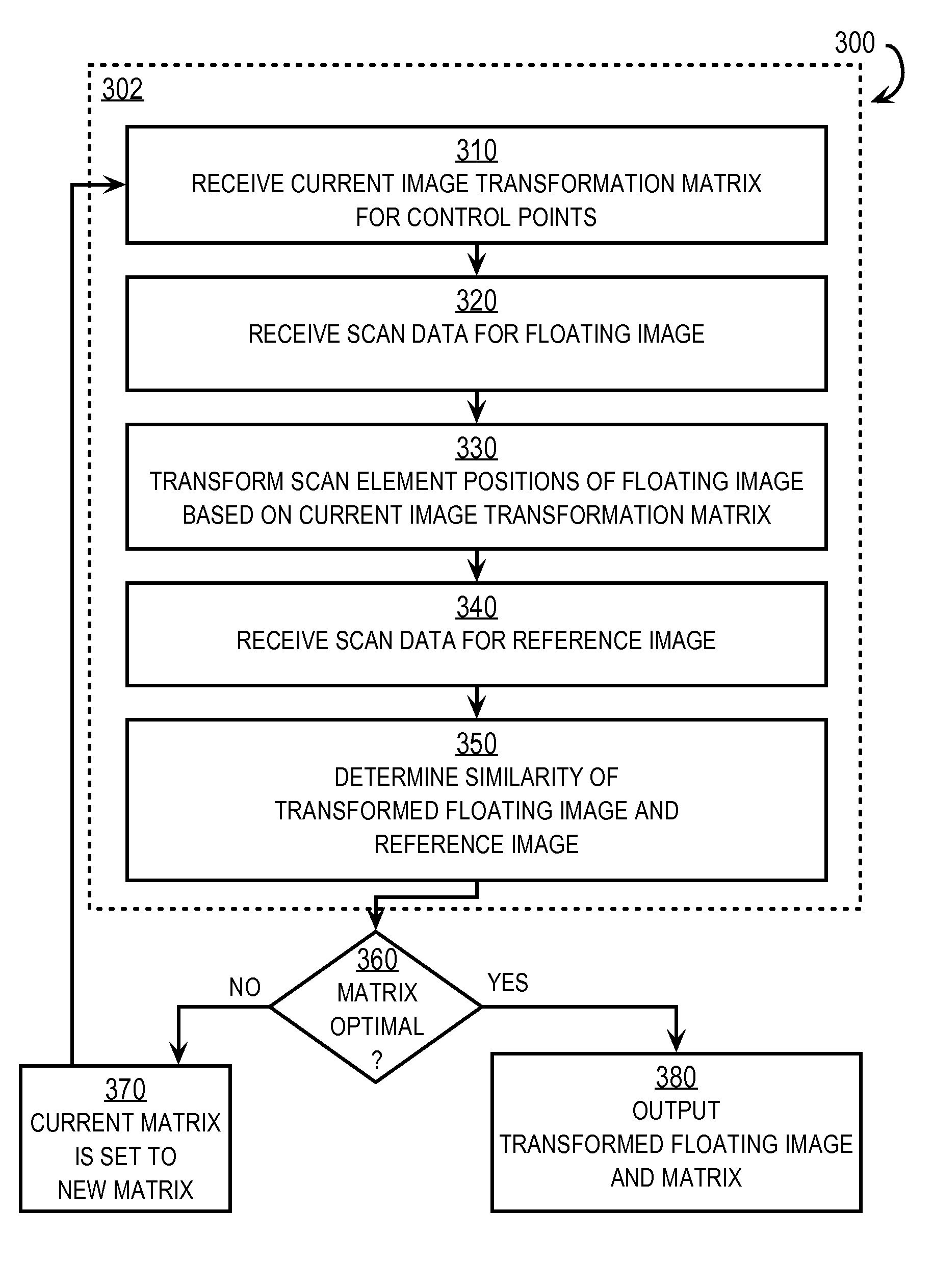
Techniques for accelerated elastic registration include receiving reference scan data and floating scan data, and a first transformation for mapping coordinates of scan elements from the first scan to coordinates of scan elements in the second scan. A subset of contiguous scan elements is determined. At least one of several enhancements is implemented. In one enhancement cubic spline interpolation is nested by dimensions within a subset. In another enhancement, a local joint histogram of mutual information based on the reference scan data and the floating scan data for the subset is determined and subtracted from an overall joint histogram to determine a remainder joint histogram. Each subset is then transformed, used to compute an updated local histogram, and added to the remainder joint histogram to produce an updated joint histogram. In another enhancement, a measure of similarity other than non-normalized mutual information is derived from the updated joint histogram.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
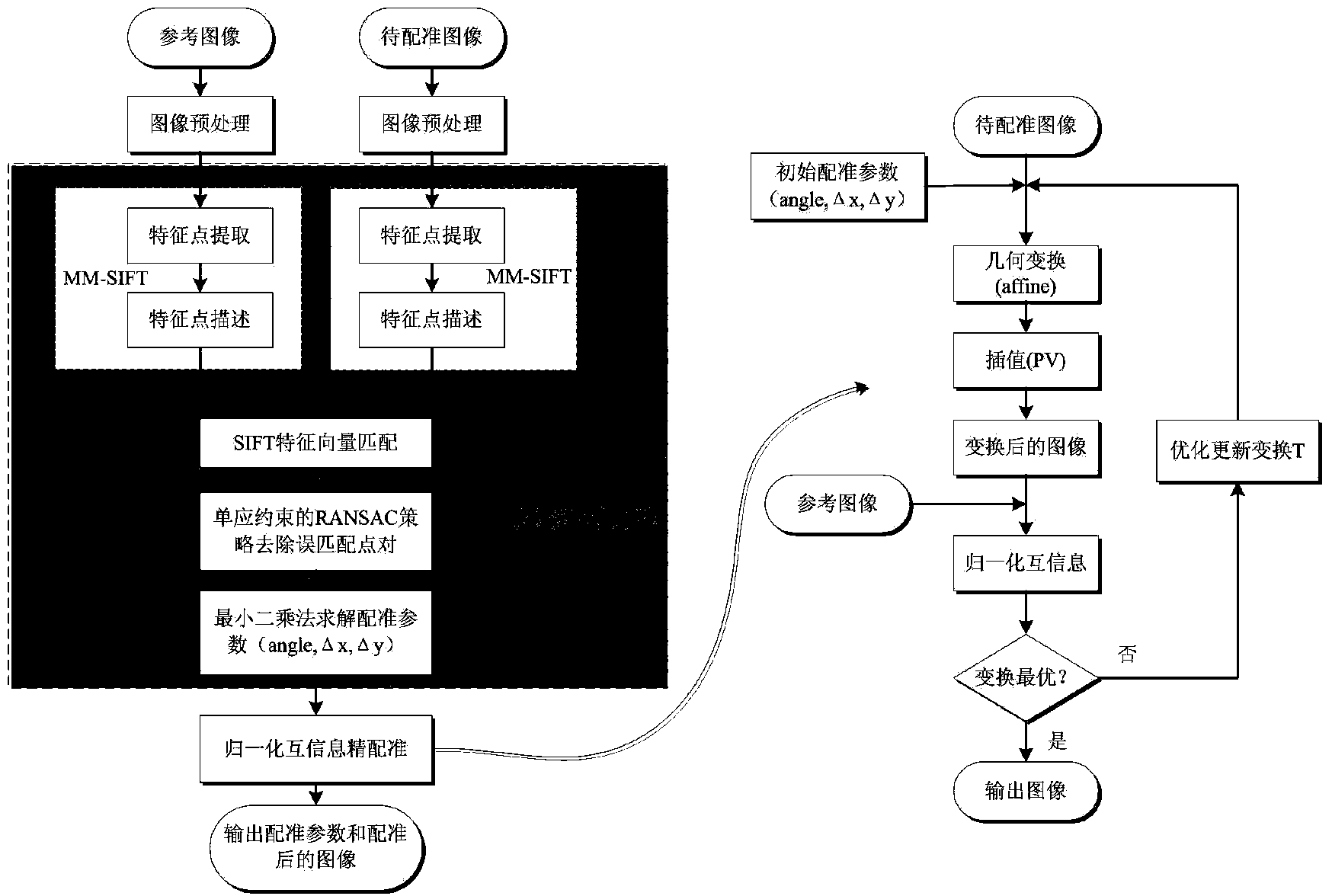
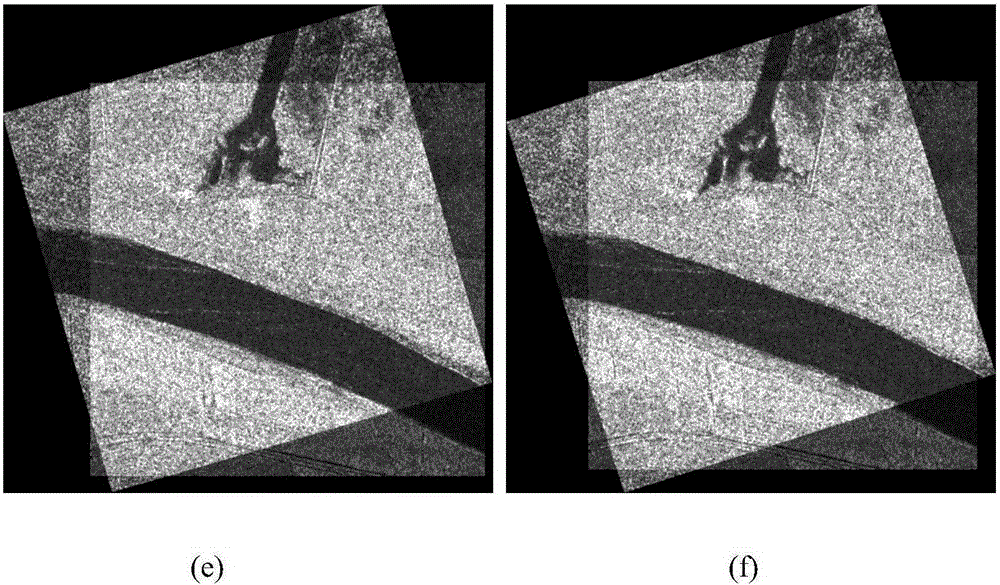
SAR image registration method based on SIFT and normalized mutual information
ActiveCN103839265AShorten the timeEnsure follow-up registration accuracyImage analysisFeature vectorNormalized mutual information
The invention provides an SAR image registration method based on SIFT and normalized mutual information. The method includes the steps that firstly, a standard image I1 and an image to be registered I2 are input and are respectively pre-processed; secondly, features of the pre-processed image I1 and features of the pre-processed image I2 are extracted according to the MM-SIFT method to acquire initial feature point pairs Fc and SIFT feature vectors Fv1 and Fv2; thirdly, initial matching is carried out through the Fv1 and the Fv2; fourthly, the Fc is screened for the second time according to the RANSAC strategy of a homography matrix model, final correct matching point pairs Fm are acquired, and a registration parameter pr is worked out according to the least square method; fifthly, I2 is subjected to space conversion through affine transformation, and a roughly-registered image I3 is acquired through interpolation and resampling; sixthly, pr serves as the initial value of normalization information registration, I1 and I2 are subjected to fine registration through the normalized mutual information method, a final registration parameter pr1 is worked out, and a registered image I4 is output. The method can be quickly, effectively and stably carried out, and SAR image registration precision and robustness are improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method and apparatus for accelerated elastic registration of multiple scans of internal properties of a body
InactiveUS8538108B2Less timeMaximizing similarity measureImage enhancementImage analysisNormalized mutual informationSerial scanning
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE
Multi-modality medical data three-dimensional visual method
InactiveCN1818974ANarrow searchHigh speedImage analysis2D-image generationDiagnostic Radiology ModalityNormalized mutual information
The invention involves a multi-mode medical body data three-dimensional video-method. Most the existing technologies are based on two-two-dimensional lay or two-three dimensional lay, which do not realize the integrated display course of medical body data aligning and amalgamation. The said method includes standardization mutual information-way aligning based on multi resolution ratio and single drop multi-mode straight body protracting-way amalgamation display. The previous one includes three approaches, such as coordinate transform, orientation criterion and multi resolution ratio optimize; the latter includes five approaches, such as impress function definition, the calculation of illumination model, image composition, single drop multi-mode show of the multi-mode data and amalgamation display. The invention can realize the integrated display course of medical body data aligning and amalgamation, and is a real two-three dimensional multi-mode video-method.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
A multi-resolution medical image registration method based on quantum behaviors particle swarm algorithm
InactiveCN101216939AAvoid difficultiesReduce the probability of mismatchImage analysisComputing modelsNormalized mutual informationImage resolution
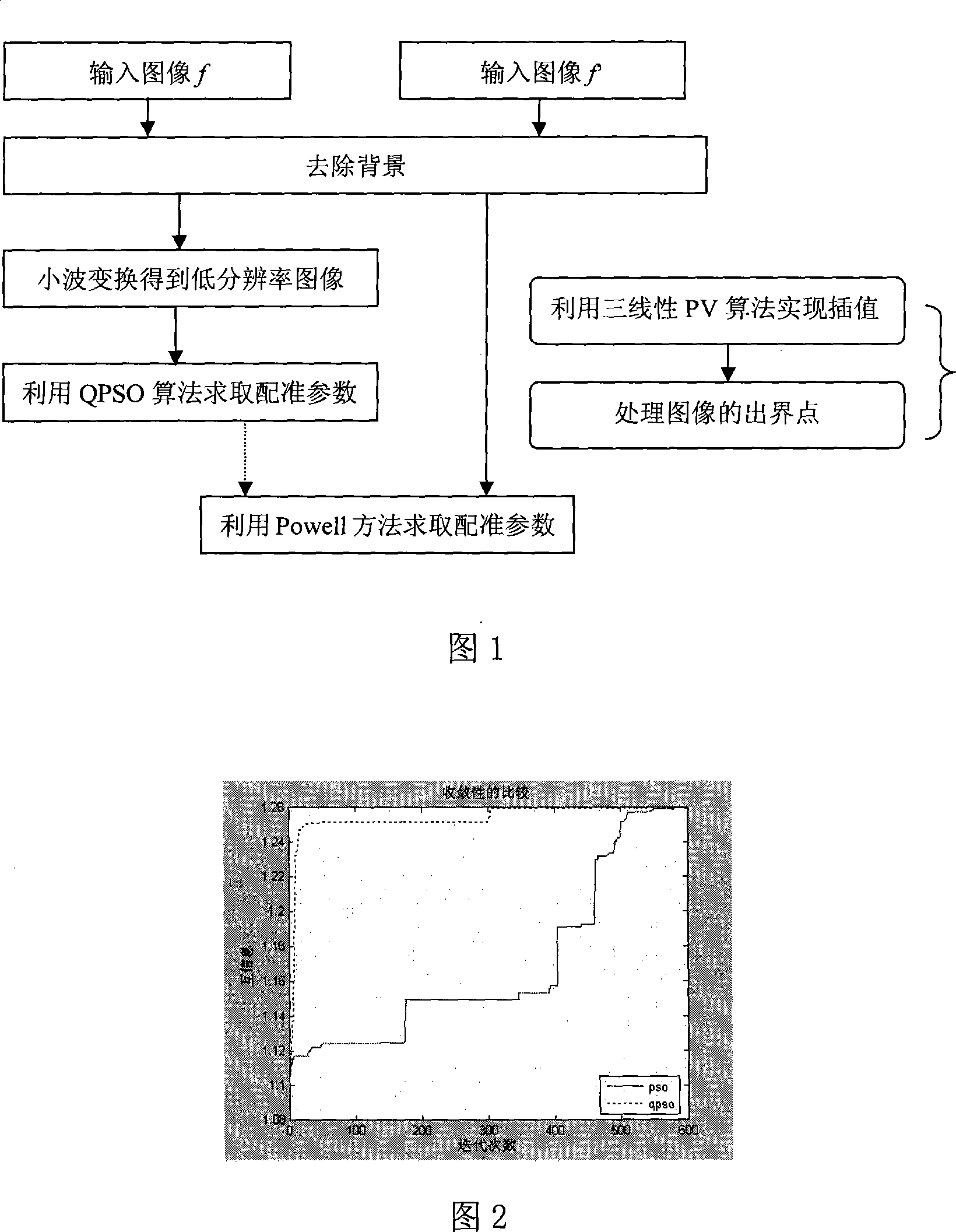
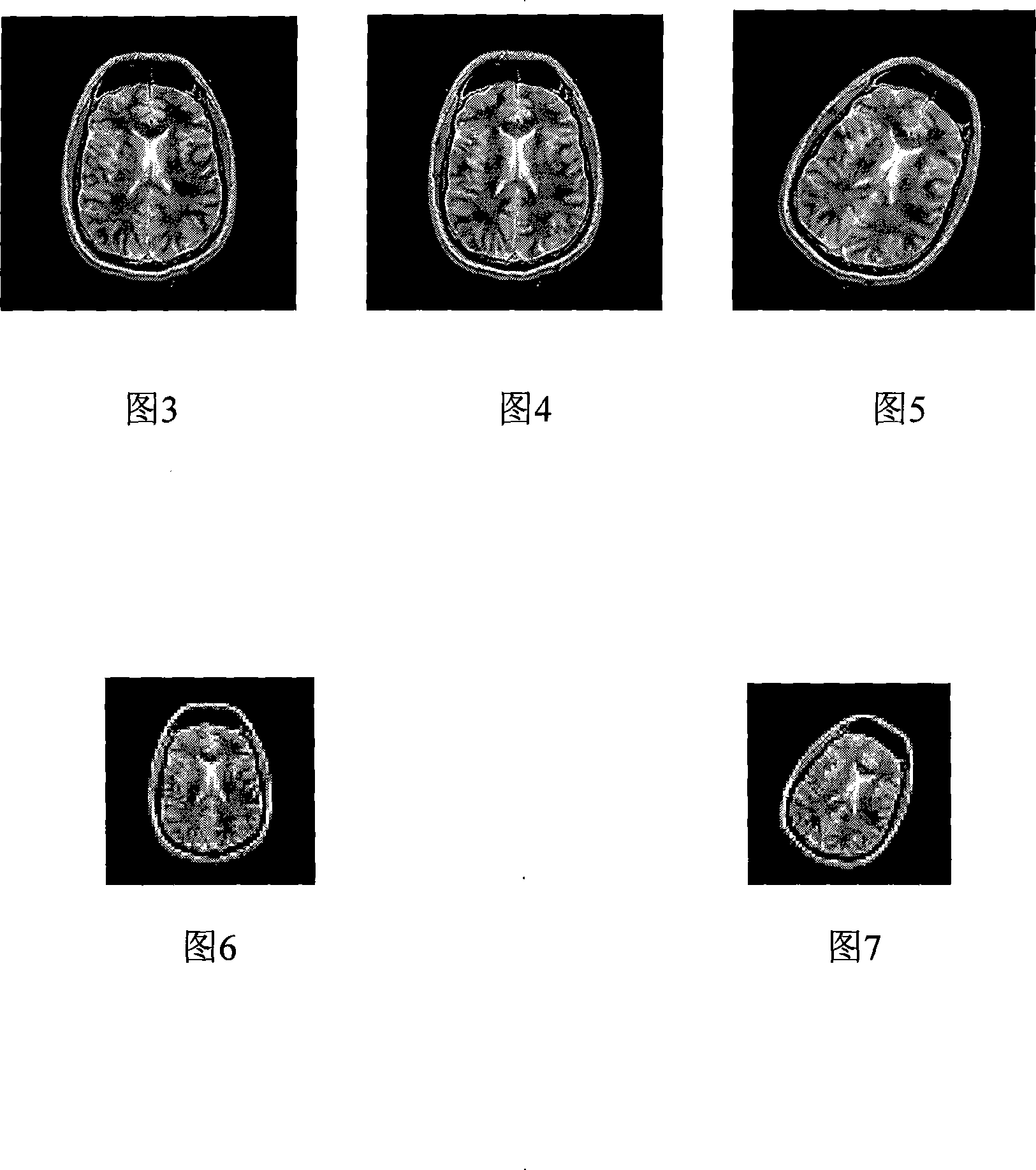
The invention relates to a multi-resolution medical image registration method based on the quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization, which is characterized in that the method comprises the following step of: firstly removing the backgrounds of the two images to be registered to keep the images off the interference of noise; next obtaining the images with low resolution from the two background-removed images via the wavelet transform, using the low resolution to be the object, taking the normalized mutual information as the objective function, using the quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization, then the images with the high resolution to be the object, and obtaining the rotation amount and the translation amount between the two images to be registered to finish the image registration by using the Powell method. With solving a plurality of local extrema based on the objective function of the mutual information, the invention greatly improves the registration precision and speed, reaching up to the sub-pixel level; and is widely applicable to the fields of the image discrimination of the clinical diagnosis, the framing of the radiation treatment, the image guided surgical, etc.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Robust multi-source satellite remote sensing image registration method
InactiveCN103077527AAutomatic and reliable acquisitionHigh degree of automation of data processingImage analysisNormalized mutual informationImaging data
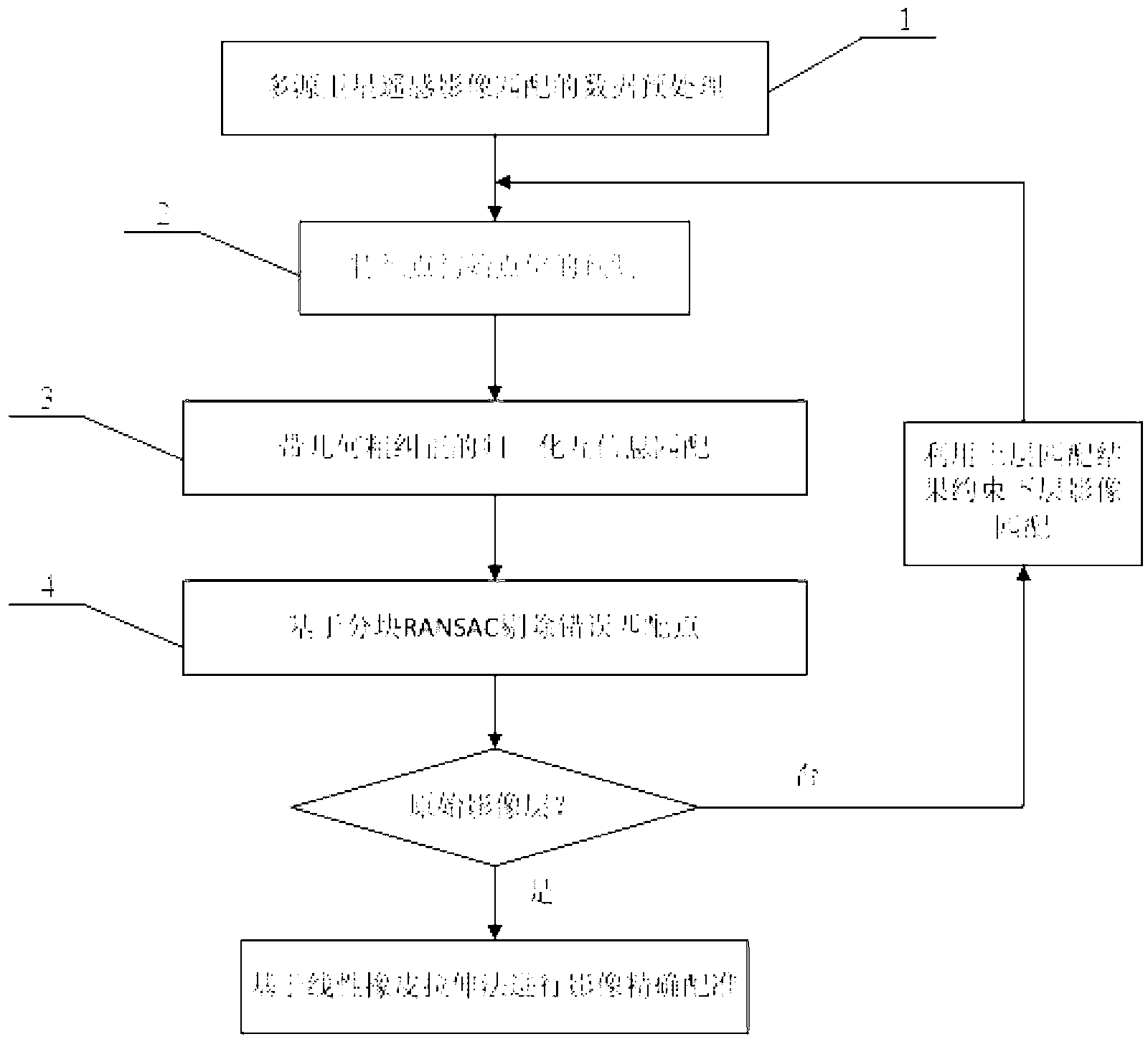
The invention discloses a robust multi-source satellite remote sensing image registration method based on mutual information and block random sample consensus. The method includes the following steps: (A) each layer of pyramid images are generated, and feature points are extracted; (B) on the highest layer of pyramid images, the global registration method is utilized to calculate affine transformation coefficients between the reference image and the slave image, and a rotation angle and a resolution difference coefficient between the images are estimated; (C) the initial positions of homonymy points are accurately predicted, geometric rough correction is carried out on matching window images, and normalized mutual information is utilized to search homonymy points; (D) a quadratic polynomial and a block RANSAC algorithm are utilized to eliminate false matching points; (E) step C and step D are repeated until the original image layer, and accurate image registration is implemented on the basis of the linear rubber sheeting method. The method greatly reduces the workload of manual editing in homonymy point measurement, increases the multi-source satellite remote sensing image data processing automation degree, and can bring remarkable economic and social benefits.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Method and Apparatus for Performing 2D to 3D Registration
InactiveUS20090290771A1Reduce impactSurgeryCharacter and pattern recognitionNormalized mutual informationNormalize mutual information
A method and apparatus for performing 2D to 3D registration includes an initialization step and a refinement step. The initialization step is directed to identifying an orientation and a position by knowing orientation information where data images are captured and by identifying centers of relevant bodies. The refinement step uses normalized mutual information and pattern intensity algorithms to register the 2D image to the 3D volume.
Owner:MEDTRONIC NAVIGATION INC
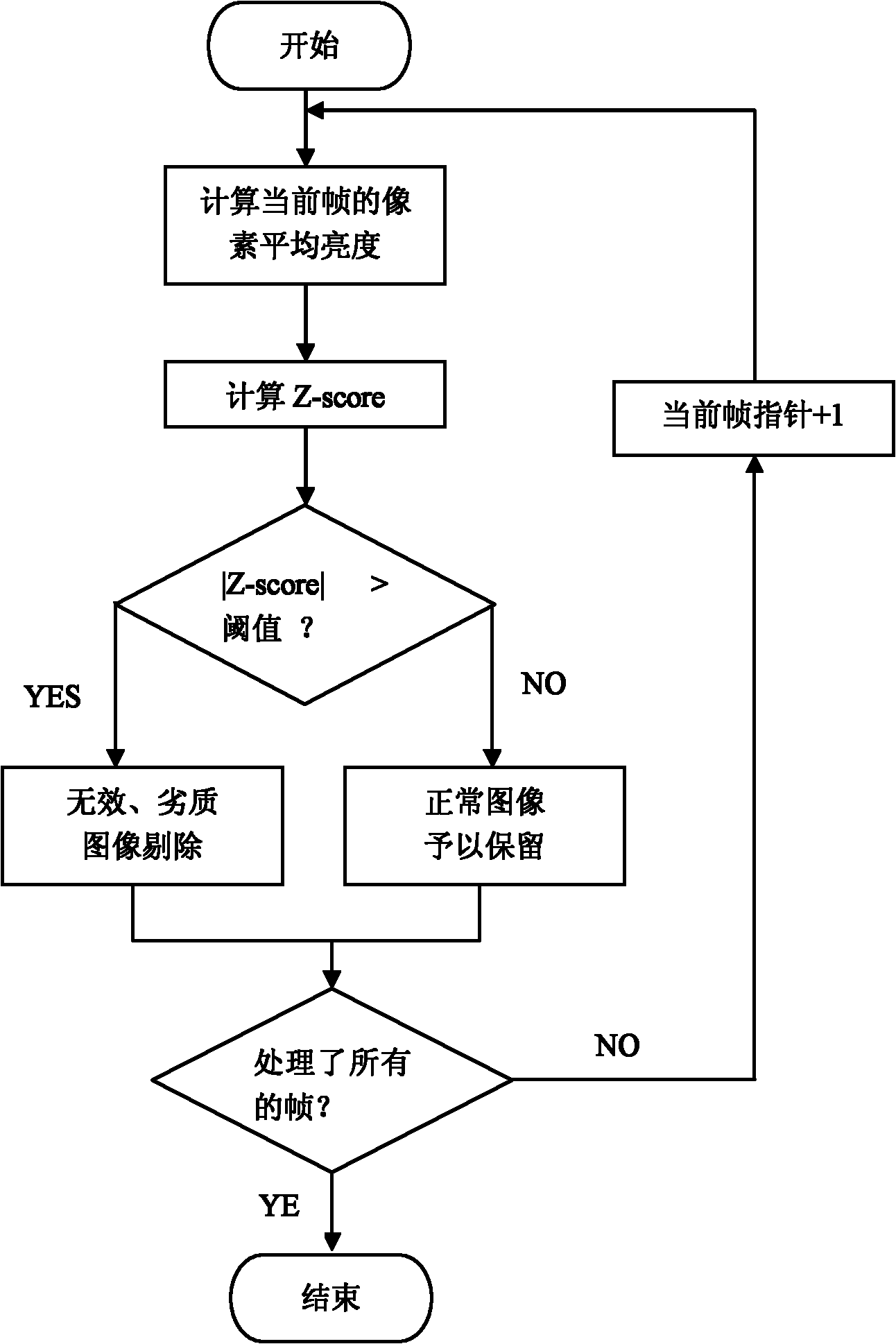
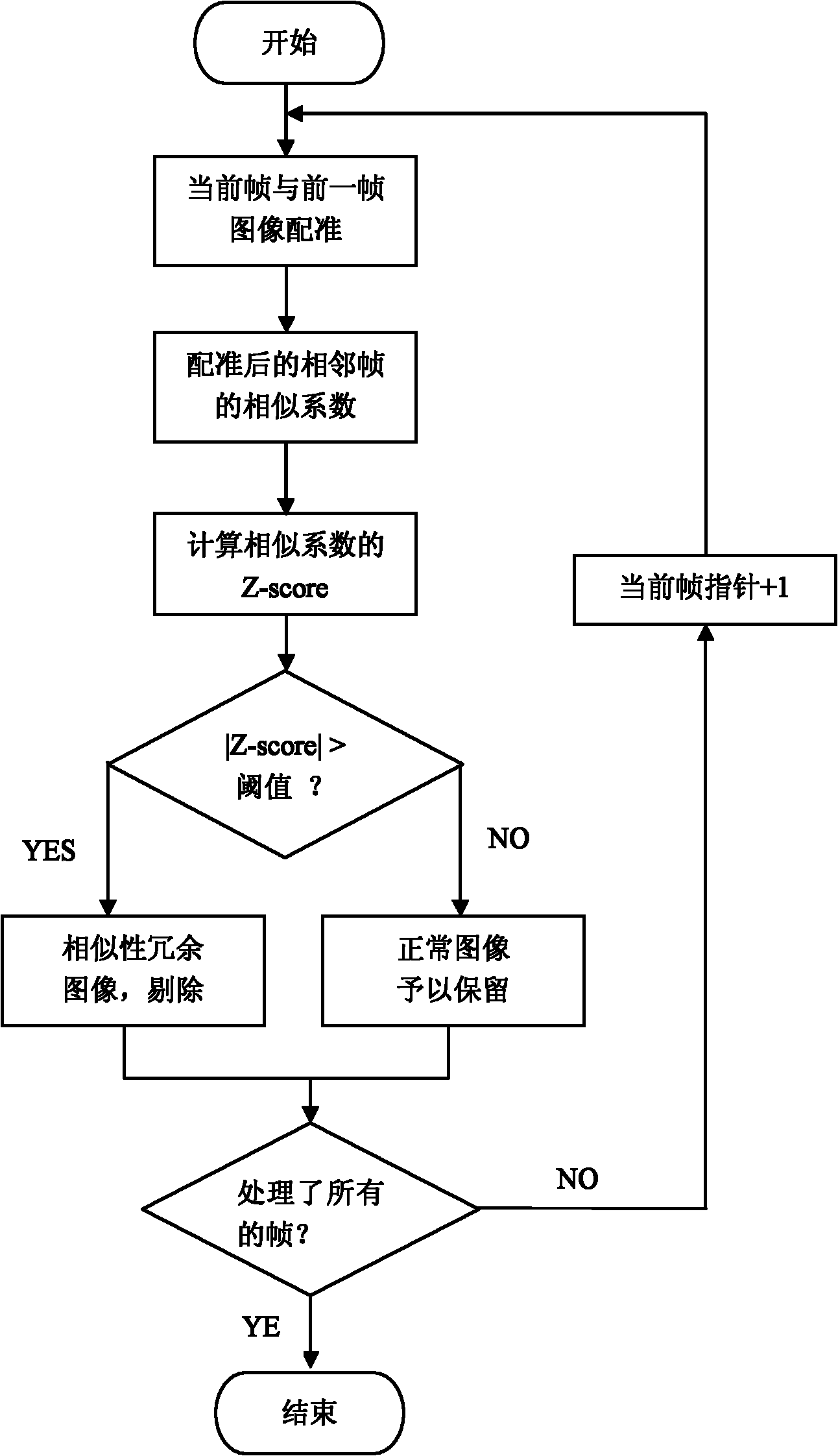
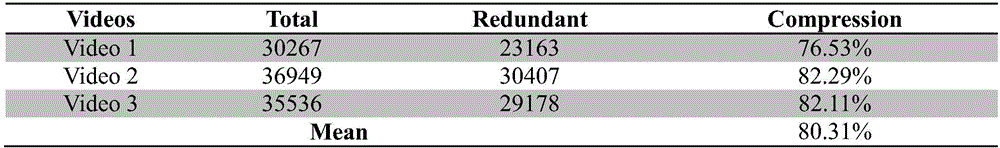
Automatic eliminating method for redundant image data of capsule endoscope
InactiveCN102096917ANo data reductionEasy to calculateImage analysisSurgeryNormalized mutual informationSkew normal distribution
The invention discloses an automatic eliminating method for redundant image data of a capsule endoscope, and the method comprises the following steps: firstly, selecting a normal image sample to obtain the mean value and variance of the average gray distribution of image pixels, computing the average gray value of the pixels of each frame of the image in picture data to be judged, judging whether the image is an image with abnormal exposure according to the characteristic of the standard normal distribution, and eliminating the image with the abnormal exposure; then, supposing that the normalized related coefficient or normalized mutual information quantity between every two adjacent frames of the images is submitted to the normal distribution; evaluating the mean value and the variance from an image sample to be processed; rigidly registering the images which are adjacent to the image to be processed; and judging whether the contents of the two adjacent frames of the images are highly repeated according to the characteristic of the standard normal distribution, and delimiting the repeated images. The method is performed before the content-based image retrieval is carried out, so that the searching efficiency can be preferably improved, the interference can be eliminated as much as possible, and the film reading time can be shortened, therefore, the diagnosis efficiency of a doctor is improved.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Different-source image registration method for X-ray image and laser image
InactiveCN102208109AAccurate and effective registrationImage enhancementImage analysisSoft x rayNormalized mutual information
The invention relates to a different-source image registration method for an X-ray image and a laser image. When an object is irradiated with an X-ray, the X-ray can transmit the object to obtain and collect the X-ray image of the object. When the same object is irradiated with a laser beam, the laser beam can be reflected by the surface of the object so as to obtain and store the laser image of the object. The different-source image registration method comprises the following steps: (1) preprocessing the collected X-ray image and laser image to suppress the interference of noise points of the images; (2) modifying the image edge; (3) respectively extracting the features of the X-ray image and the laser image, and carrying out rough matching; and (4) performing precise registration on the X-ray image with the laser image. Compared with the prior art, the method provided by the invention can achieve accurate and effective registration of the X-ray image and the laser image based on the extreme result of normalized mutual information by firstly carrying out rough registration and then carrying out precise registration of the X-ray image and the laser image of a calibration block with a regular shape.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Image registration method based on improved structural similarity
InactiveCN102509114AGood convex function characteristicsImprove registration accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionNormalized mutual informationNormalize mutual information
The invention provides an image registration method based on improved structural similarity. According to the invention, the improved structural similarity serves as the objective function of the image registration for the first time; four parameters of the two-dimensional image rigid body transformation are obtained through translation, rotation and consistent scaling along the X-axis and Y-axis; and the single-modal and multimodal images are analyzed in detail based on the registration algorithm and performance of the structural similarity and are compared with that based on a normalized mutual information registration algorithm. The result shows that when an absolute value is extracted during defining the structural similarity, the structural similarity has favorable features of a convex function; for either the single-modal image registration or the multimodal image registration, the structural similarity serving as the measure function can achieve the sub-pixel registration with registration precision and robustness better than that based on the classic normalized mutual information registration algorithm; and if K1 is less than or equal to 0.000001, and K2 is less than or equal to 0.000003, the two-value image can achieve the pixel registration.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
High-resolution remote sensing image registration method with control points distributed in adaptive manner
InactiveCN104361590AAccurate extractionImprove registration accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisNormalized mutual informationContourlet
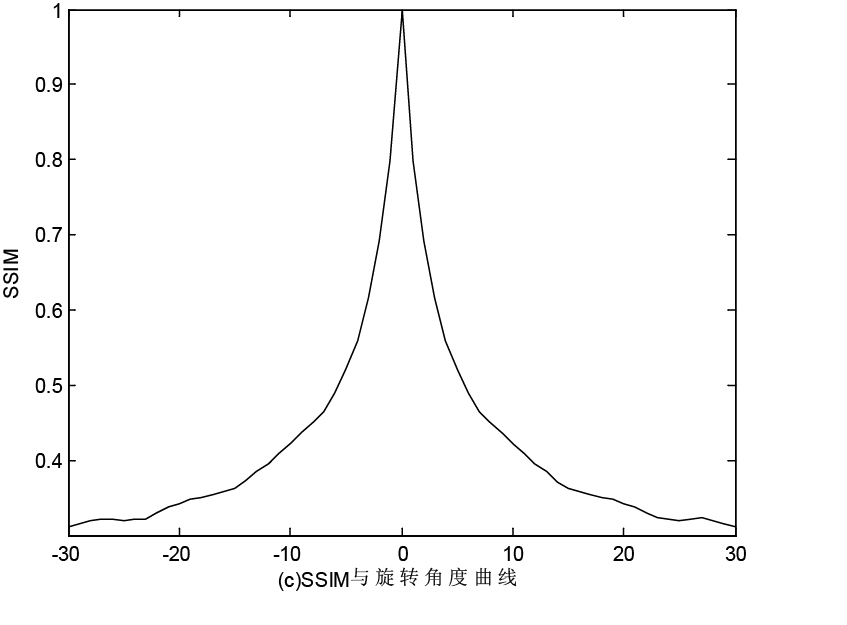
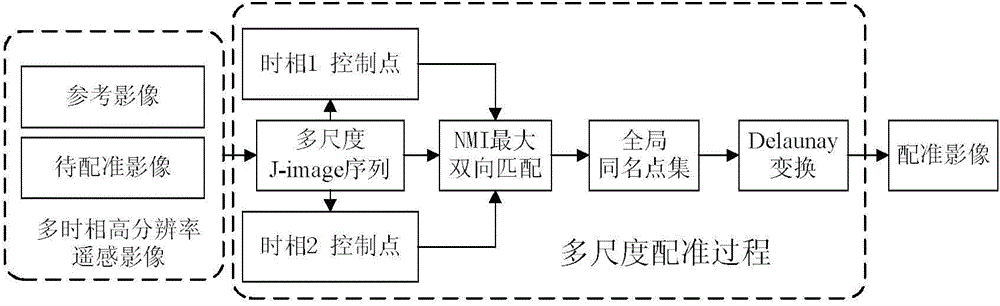
The invention discloses a high-resolution remote sensing image registration method with control points distributed in an adaptive manner. By the use of the high-resolution remote sensing image registration method, a multi-scale J-image is introduced into image registration. A self-adaptive control points extracting method based on a partitioning strategy is provided to extract the control points of the multi-scale J-image image, thus the defect that the control points only sense specific directional high-frequency information is overcome. A self-adaptive control points extracting strategy is defined so as to limit control point distribution. The control points are subjected to multi-scale matching by NMI (normalized mutual information measure), allowing registration function smooth. Geometric correction is realized by adopting Delaunay triangle local transformation. In the following text, basic principle and key steps of the algorithm are introduced, and three remote-sensing image groups of different types are subjected to experiment and analysis and comparison experiments with various registration methods based on wavelet transform and NSCT (non-subsampled contourlet transform).
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
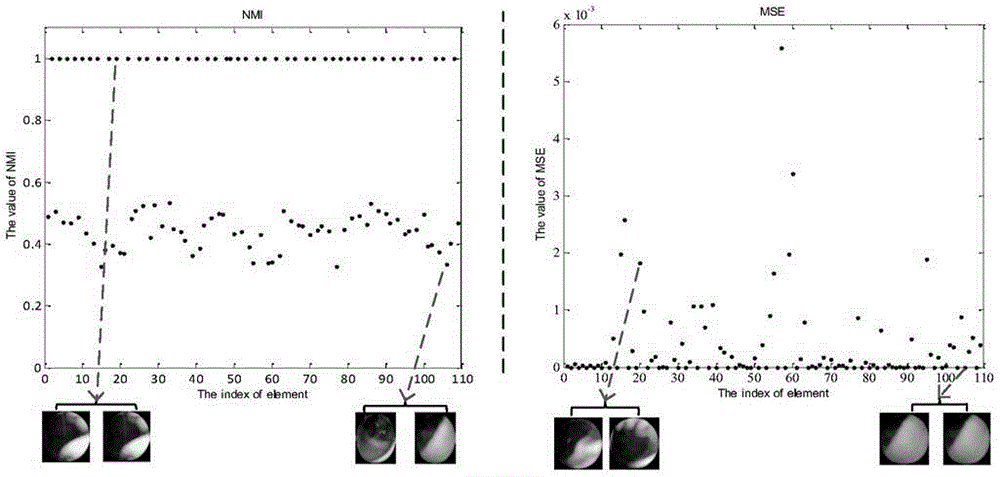
Wireless capsule endoscopy redundant image screening method based on multi-feature fusion
InactiveCN105469383AEfficient screeningImprove work efficiencyImage analysisSurgeryNormalized mutual informationMulti feature fusion
The present invention provides a wireless capsule endoscopy redundant image screening method based on multi-feature fusion. The method comprises the steps of extracting the color feature vector and the texture feature vector of an image through an HSV color feature histogram and a gray level co-occurrence matrix, a step of calculating the color feature normalized mutual information amount of an adjacent image and a texture feature mean square error value as similarity measurement, a step of considering the robustness of the method, a step of proposing the mean value method setting adaptive similarity determination threshold based on a W parameter, a step of dividing an WCE image with certain time correlation and color-texture similarity into a same sub image segment through comparing the similarity measurement value of the adjacent WCE image and a judgment threshold value orderly, and a step of using an adaptive K-means clustering algorithm to carry out key frame extraction on each sub image clip to achieve the purpose of filtering a redundant image. According to the method, the redundant image can be effectively filtered, and thus the efficiency of doctors is improved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
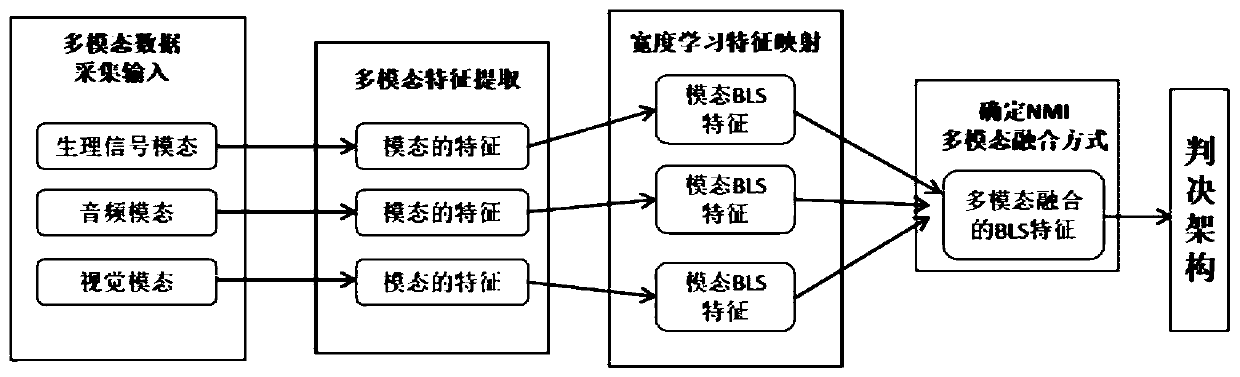
Multi-modal fusion method and device based on normalized mutual information, medium and equipment
ActiveCN111461176ASolve difficult trainingSolve hard-to-reason problemsCharacter and pattern recognitionNormalized mutual informationHuman body
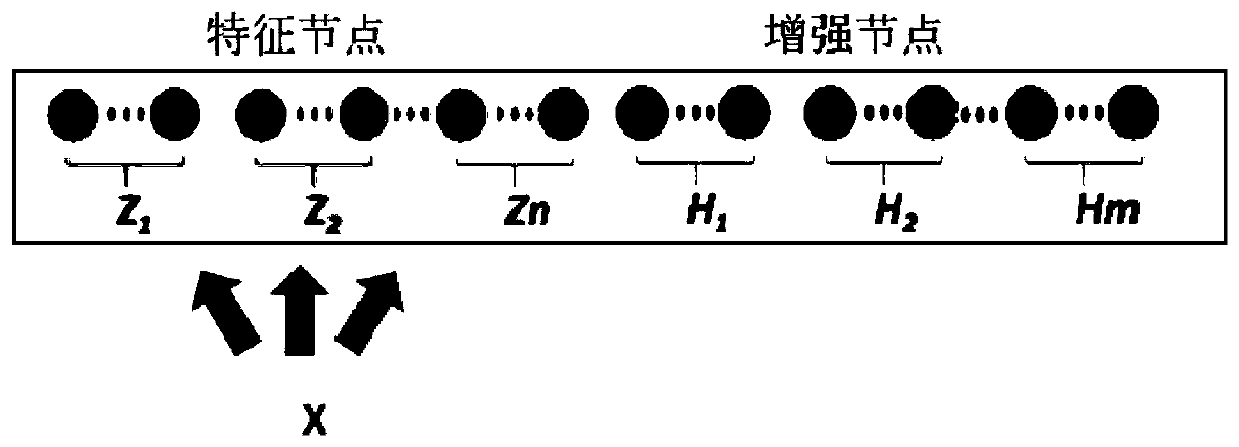
The invention provides a multi-modal fusion method and device based on normalized mutual information, a medium and equipment. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a plurality of modal data sets of a human body, wherein data in each modal data set is provided with a label; preprocessing the various modal data sets; respectively carrying out feature extraction on the preprocessed various modal data sets; obtaining width learning feature mapping of each modal data set through a width learning system; determining a multi-modal fusion mode of normalized mutual information; training and testing a width learning system; and carrying out modal feature fusion and final decision output according to the trained and tested multi-modal fusion mode and the discrimination architecture model. The method is high in training speed and low in resource consumption, and can quickly construct an incremental learning model; information complementation between modals can be realized, and redundant modal information can be reduced; and the method has good reliability, accuracy and robustness.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
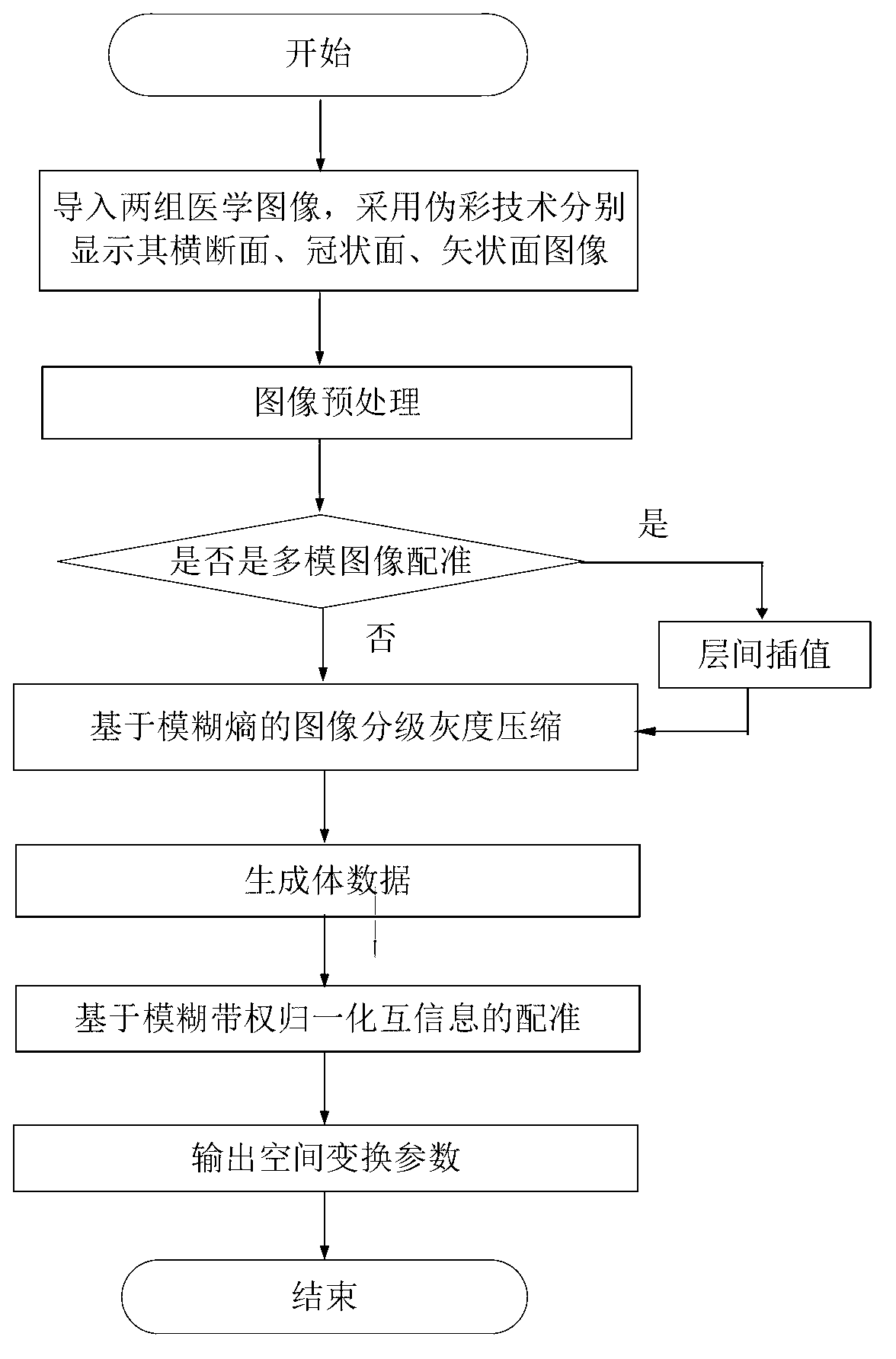
Method and system for registering three-dimensional medical images on basis of weighted fuzzy mutual information
ActiveCN103020976ACalculation speedHigh speedImage analysisNormalized mutual informationCoronal plane
The invention provides a method and a system for registering three-dimensional medical images on the basis of weighted fuzzy mutual information, and relates to the technical field of image-guided radiotherapy and medical image analysis. The method mainly includes steps of 1, guiding the medical images; 2, displaying the medical images; 3, processing the medical images; and 4, registering the medical images. In the step of guiding the medical images, single-mode image registration and multi-mode image registration are supported; in the step of displaying the medical images, cross section, coronal plane and sagittal plane images of the medical images to be registered are colored differently by a pseudo-color technology; in the step of processing the medical images, grayscales of the medical images are classified and compressed on the basis of a concept of fuzzy entropy, and mutual information calculation is reduced; and in the step of registering the medical images, normalized mutual information measures are modified on the basis of the fuzzy entropy, and the robustness of medical image registration is improved. The method and the system have the advantages that the measure method on the basis of the mutual information is adopted, the method and the system are applicable to single-mode image registration, and a good effect can also be realized for multi-mode image registration.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Matching curve feature based image registration evaluating method
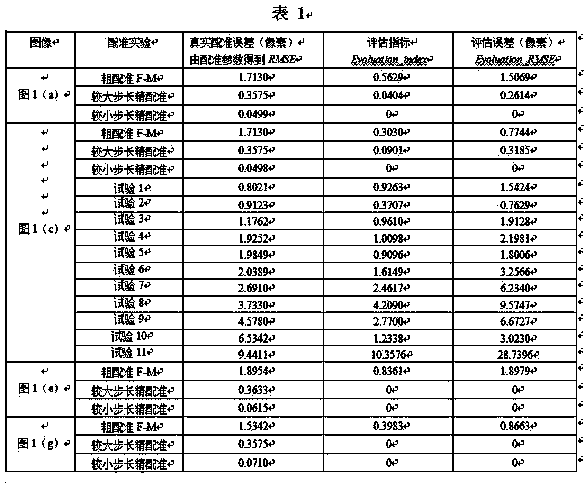
InactiveCN103632338AThe assessment results are accurateAccurate and quantitative assessment of resultsGeometric image transformationNormalized mutual informationCorrelation coefficient
Quantitative evaluation on registration results is an important content in the field of image registration. Many scholars propose to evaluate the registration results with pixel physical coordinates RMSE (root mean square error) and MSE (mean square error), or pixel gray level CC (correlation coefficient) and NMI (normalized mutual information) and the like, however, those methods are normally used for evaluating registration of single-modal or retrospective multi-modal images, but quantitative evaluation results are difficult to give to real multi-modal image registration due to lack of accurate measurement criteria. Through research on image matching curves, the invention provides a novel registration evaluating method, namely a matching curve feature evaluating method. Peaks, peak deviations and peak values of matching curves and RMSEs among the peak values are taken as quantitative evaluation indexes, and quantitative evaluation results are given on the basis of the peak deviations and the peak values. By the method, registration performance is visually described from features of smoothness, sharpness and the like of the curves, registration effect can be evaluated quantitatively via feature indexes of the curves, and given evaluation results for sub-pixel registration are accurate.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Right ventricle multi-map partitioning method based on cardiac magnetic resonance movie minor-axis image
InactiveCN108564590AImprove robustnessImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisExpectation–maximization algorithmNormalized mutual information
The invention provides a right ventricle multi-map partitioning method based on a cardiac magnetic resonance movie minor-axis image. A magnetic resonance imaging system is used for collecting a certain number of heart original magnetic resonance images of a tested person, and a region of interest is extracted. A fixed number of map images of right ventricle are selected from the original magneticresonance images to be added into a map set, and an expert manual partitioning result is obtained by an expert manually partitioning the map image. The map images and target images obtain a right ventricle coarse partitioning result by adopting B sample conversion based on normalized mutual information, COLLATE fusion is adopted for the coarse partitioning result, firstly log likelihood estimationis carried out on complete data, and then iterative solution is carried out by using a maximum expectation algorithm until convergence, so that the right ventricle final partitioning result is obtained through amending treatment. The method has higher robustness, the accuracy and precision of fusion can be improved, and the method is used for accurately partitioning the heart right ventricle minor-axis image.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
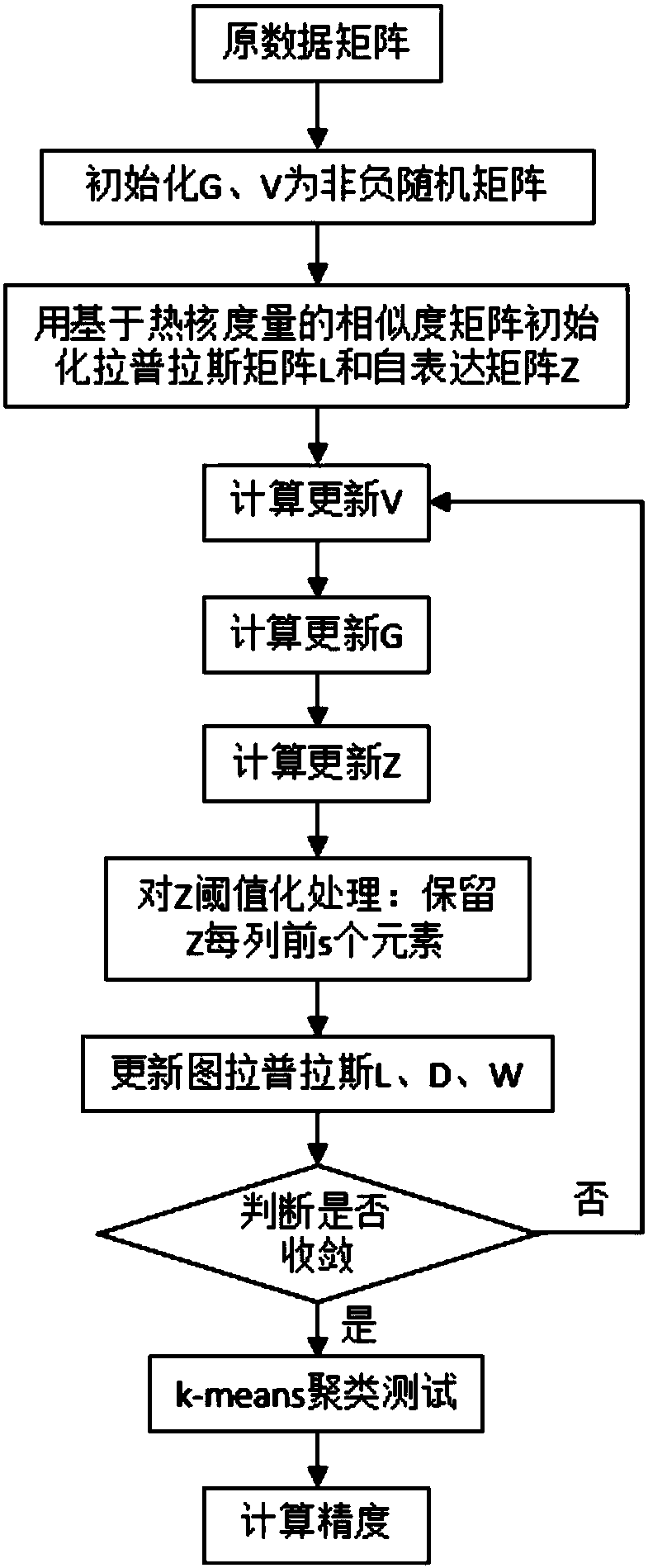
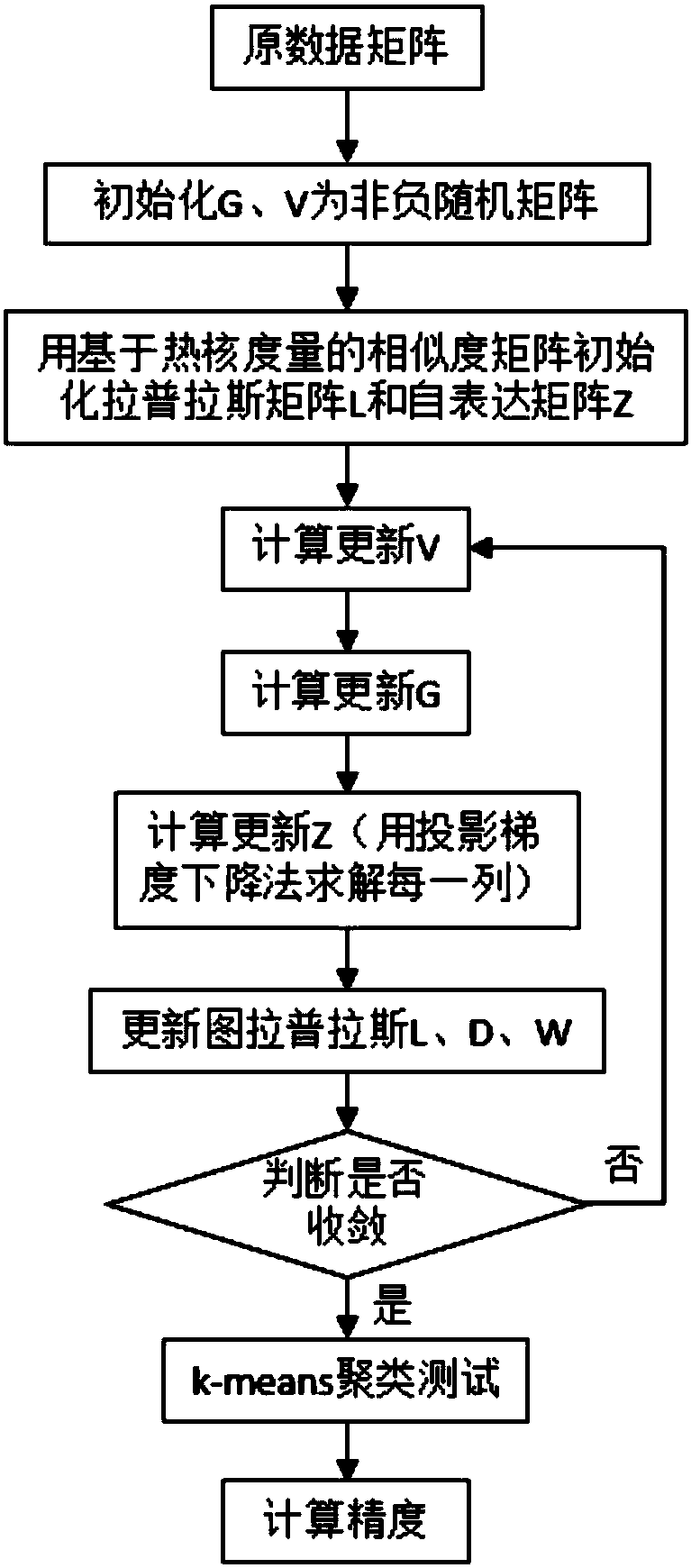
Convex nonnegative matrix factorization method based on subspace clustering
ActiveCN108415883ADecomposition improvementLow-dimensional data represent goodCharacter and pattern recognitionComplex mathematical operationsNormalized mutual informationAlgorithm
The invention discloses a convex nonnegative matrix factorization method based on subspace clustering. The method comprises the implementation steps of (1) stretching an image in an original databaseinto vectors to compose an original data matrix; (2) performing convex nonnegative matrix factorization based on spectral clustering on the original data matrix, solving by use of two optimization methods to obtain a basis matrix and an encoding matrix; and (3) performing a clustering test of a k-means clustering algorithm on the encoding matrix, counting experimental results, calculating two measure criteria of clustering precision and normalized mutual information. According to the convex nonnegative matrix factorization method based on subspace clustering, compared with an existing method,subspace structural information inside data is explored and utilized, meanwhile the local subspace constraints exerted to the algorithm enhances robustness of the algorithm and improves the clusteringeffect of the image; and the method can be widely applied to the field of data mining and data analysis.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
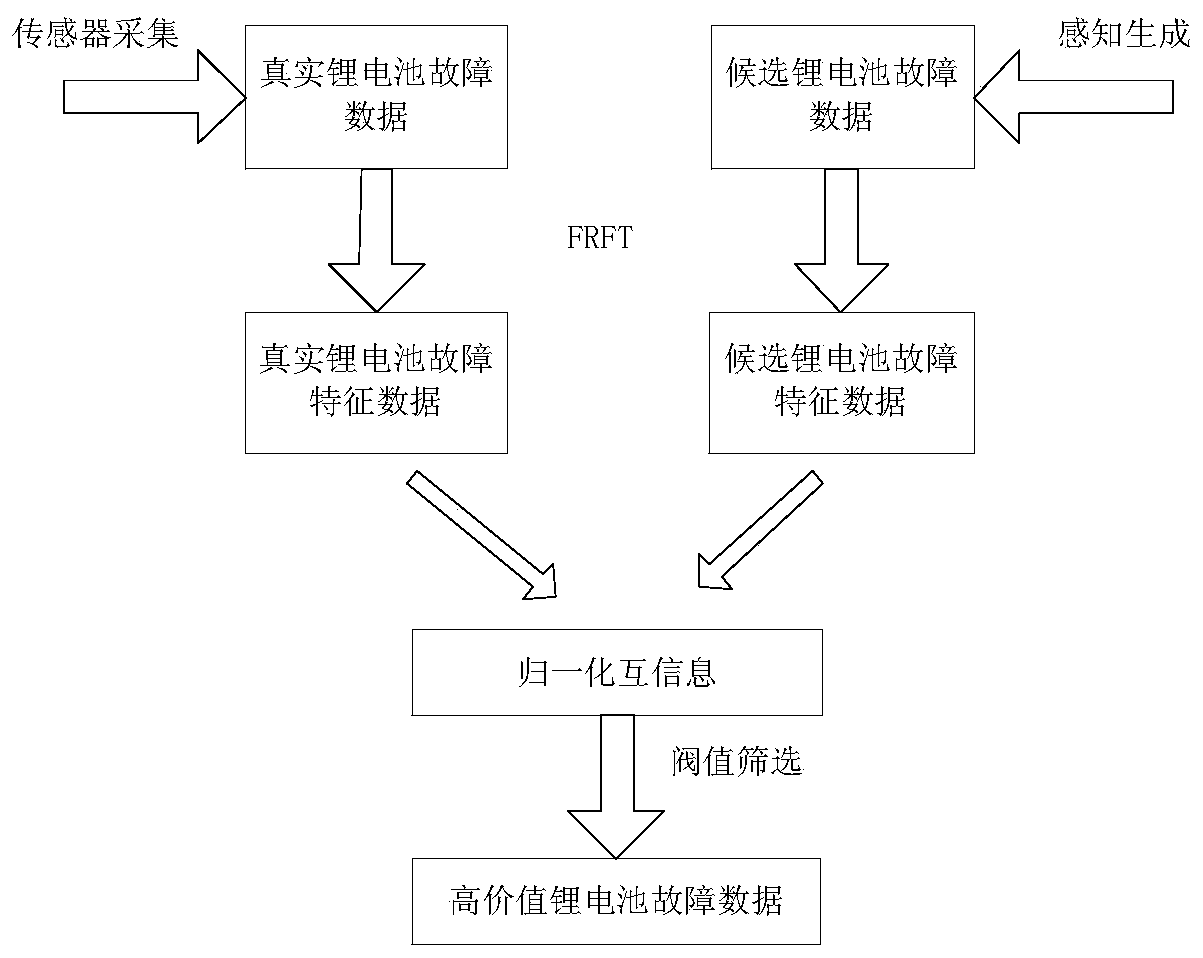
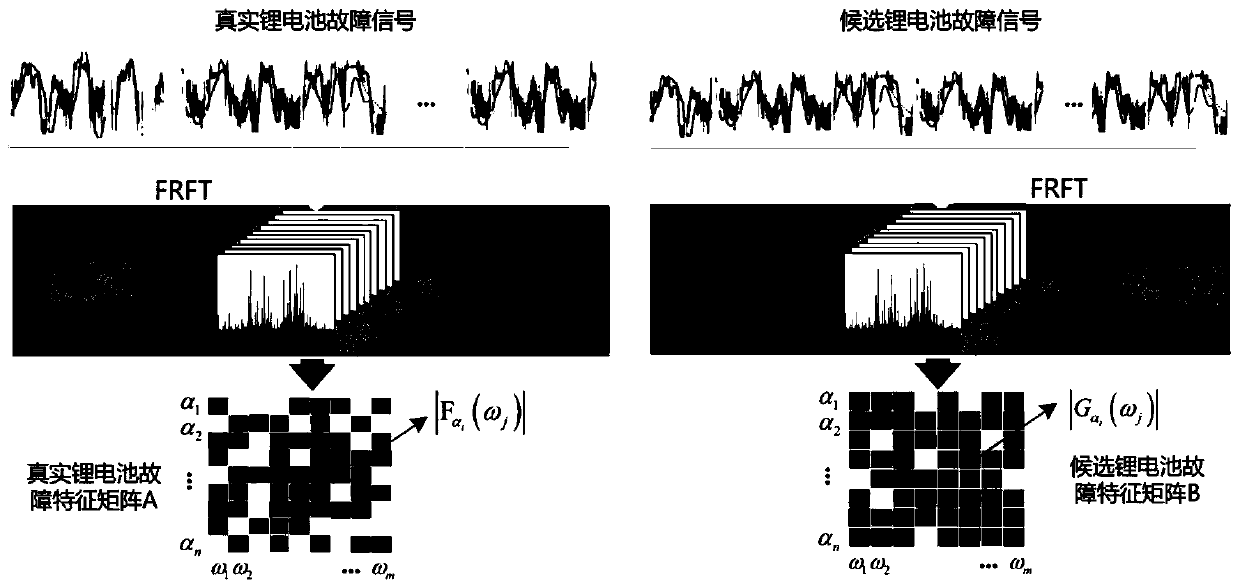
Lithium battery fault data screening method constrained by normalized mutual information criterion
ActiveCN110412467ARefined fault spectrum characterizationQuality improvementElectrical testingCharacter and pattern recognitionNormalized mutual informationNormalize mutual information
The invention relates to a lithium battery fault data screening method constrained by a normalized mutual information criterion, and belongs to the field of lithium battery fault diagnosis. The methodcomprises the following steps that S1, data is collected, wherein the real lithium battery fault data is collected through a sensor, and the candidate lithium battery fault data is generated by meansof a perceptual generation network; S2, fractional Fourier transform is adopted for extracting characteristics of the lithium battery fault data; S3, normalized mutual information between a real lithium battery fault characteristic matrix A and a candidate lithium battery fault characteristic matrix B is calculated and adopted as a screening measure for the lithium battery fault data; S4, a screening threshold value is selected through a fault diagnosis experiment. According to the method, the screened lithium battery fault data can be real and effective, the screening speed can be increasedat the same time, and a high-quality data guarantee is provided for a deep learning method of fault diagnosis.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
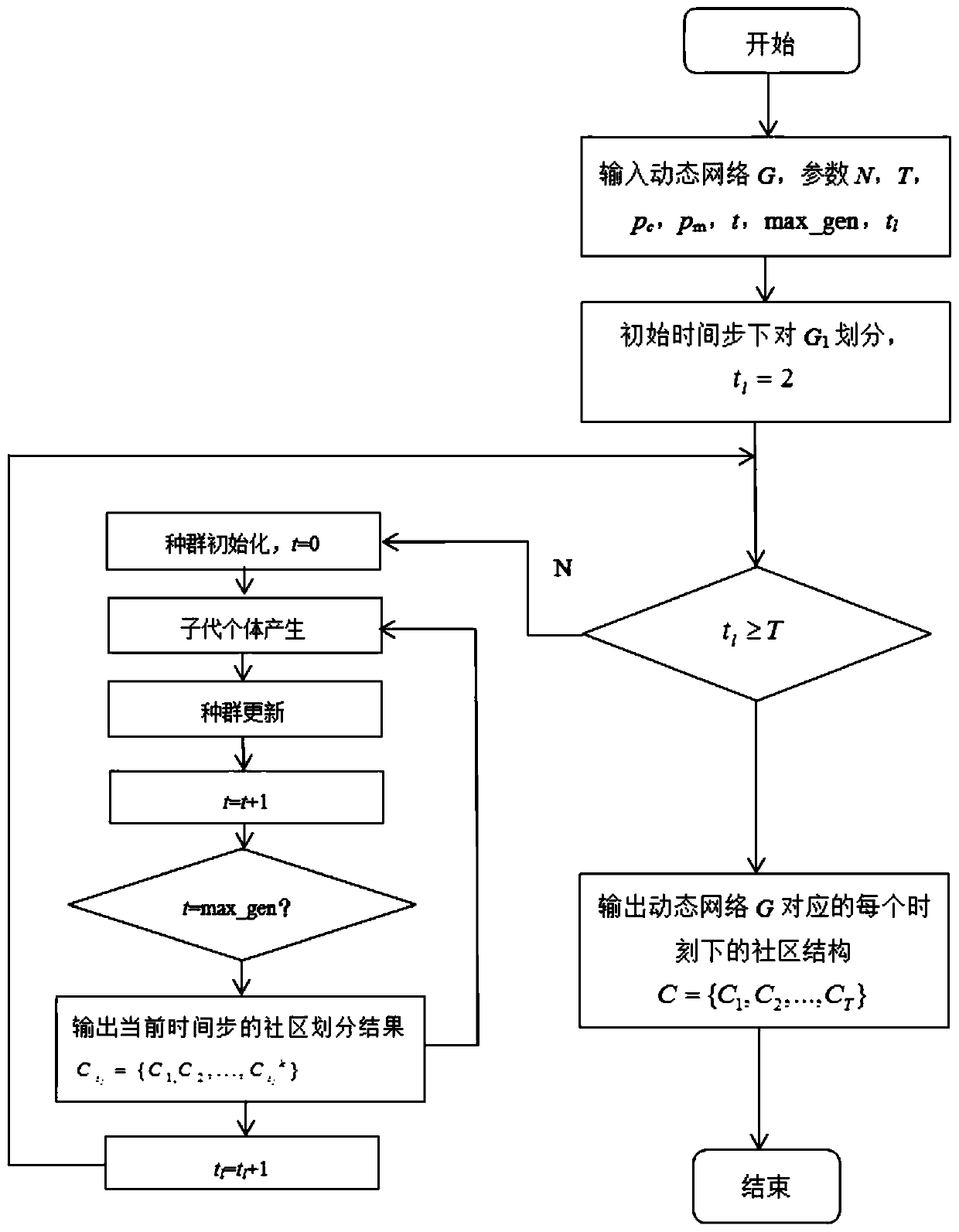
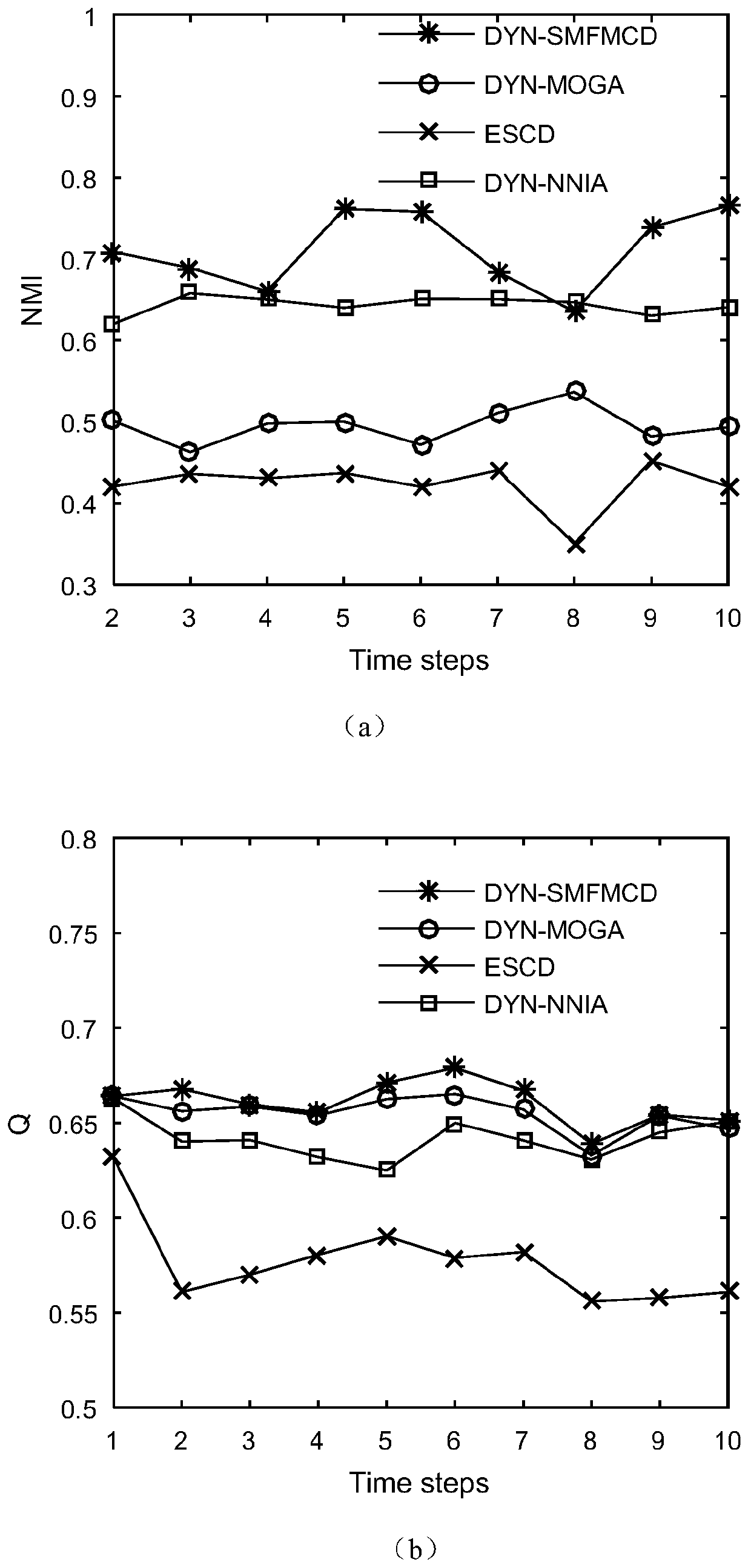
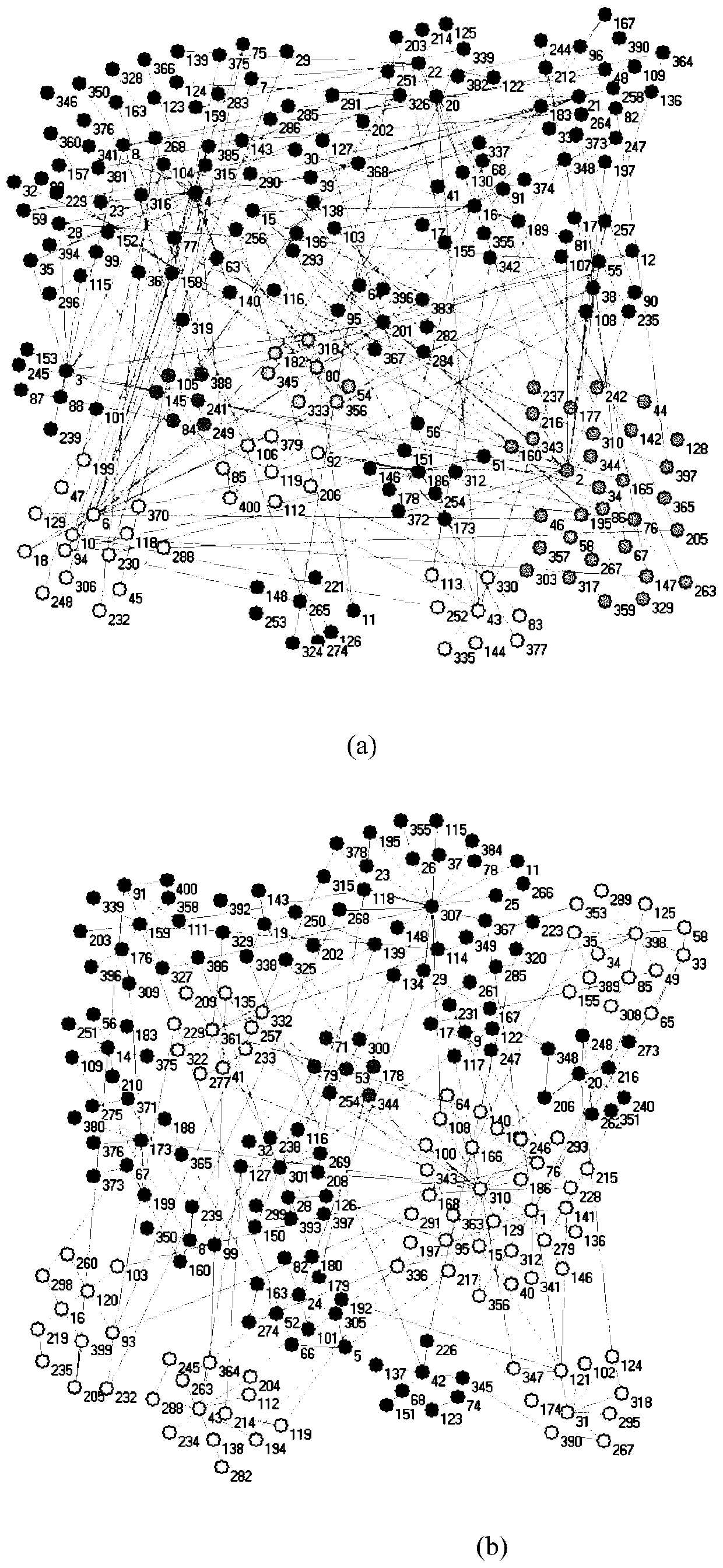
A multi-target dynamic network community division method based on a memetic framework
InactiveCN109921936AImprove efficiencyIncrease diversityData switching networksMemetic algorithmNormalized mutual information
The invention discloses a memetic framework-based multi-target dynamic network community division method, which comprises the following three steps of: step 100, establishing a memetic algorithm framework; Step 200, under a memetic framework, weighting the modularity density function D to obtain an optimized modularity density function D, and embedding the optimized modularity density function D and the normalized mutual information NMI into a cost objective function to obtain a minimized optimization objective function; Step 300, adopting direct integer coding mode, combining an initialization mechanism based on identifier transmission, a two-way cross genetic algorithm and a searching mode of a self-climbing algorithm to obtain the optimal community structure, the population diversity ishigh, the searching space is small, fine division of the community structure can be achieved, meanwhile, the algorithm efficiency is high, and the community division precision is fine.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
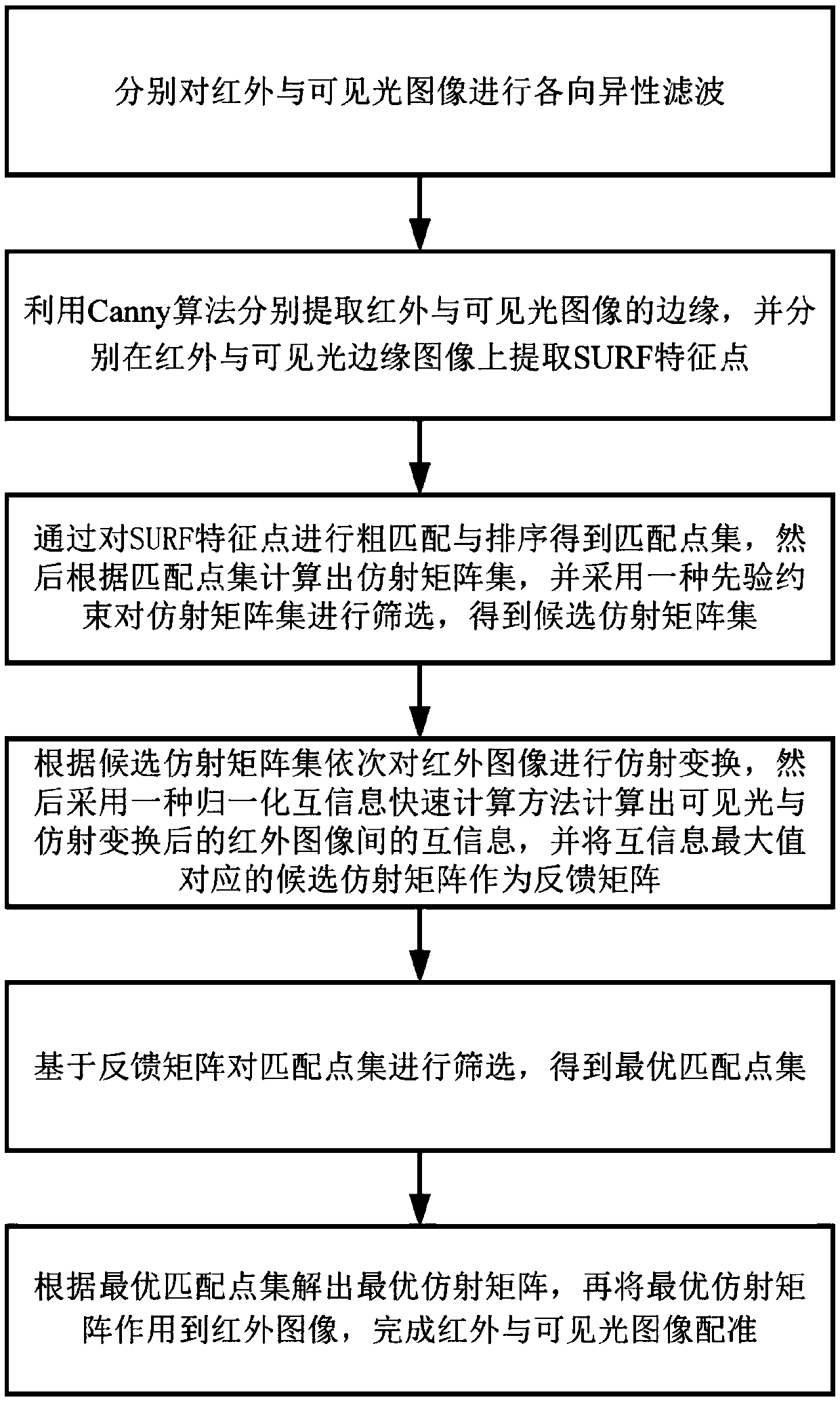
An infrared and visible image registration method for power equipment based on feedback mechanism
ActiveCN109523583APrecise positioningStrong complementarityImage enhancementImage analysisNormalized mutual informationElectric power equipment
The invention discloses infrared and visible image registration method for power equipment based on feedback mechanism, which respectively extracts edges of infrared and visible images by using a Canny algorithm, and respectively extracts SURF feature points on the infrared and visible edge images. After rough matching and sorting the SURF feature points, the set of matching points is obtained, and the affine matrix set is calculated according to the set of matching points. The set of affine matrix is screened by prior constraints, and the candidate affine matrix set is obtained. According tothe set of candidate affine matrices, the infrared images are transformed in turn, and the mutual information between the visible light and the infrared images after affine transformation is calculated by using the normalized mutual information fast calculation method, and the candidate affine matrices corresponding to the maximum mutual information are used as feedback matrices. The mutual information between the visible light and the infrared images after affine transformation is calculated by using the normalized mutual information fast calculation method. The optimal set of matching pointsis obtained by selecting the set of matching points based on the feedback matrix. The method adopted by the invention can effectively improve the registration accuracy of infrared and visible light images of the electric power equipment.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
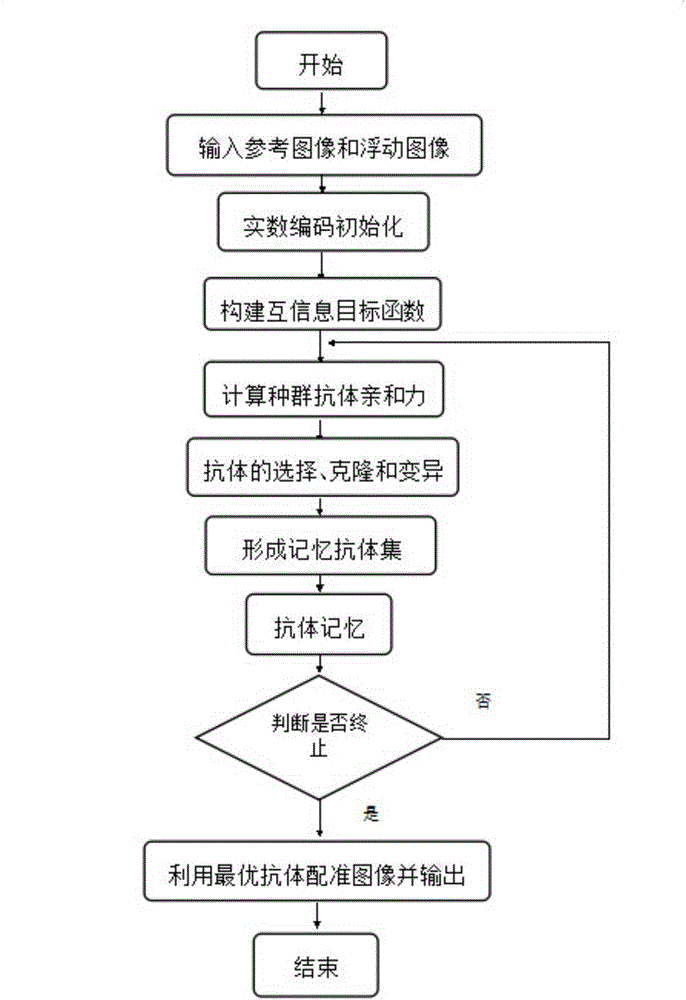
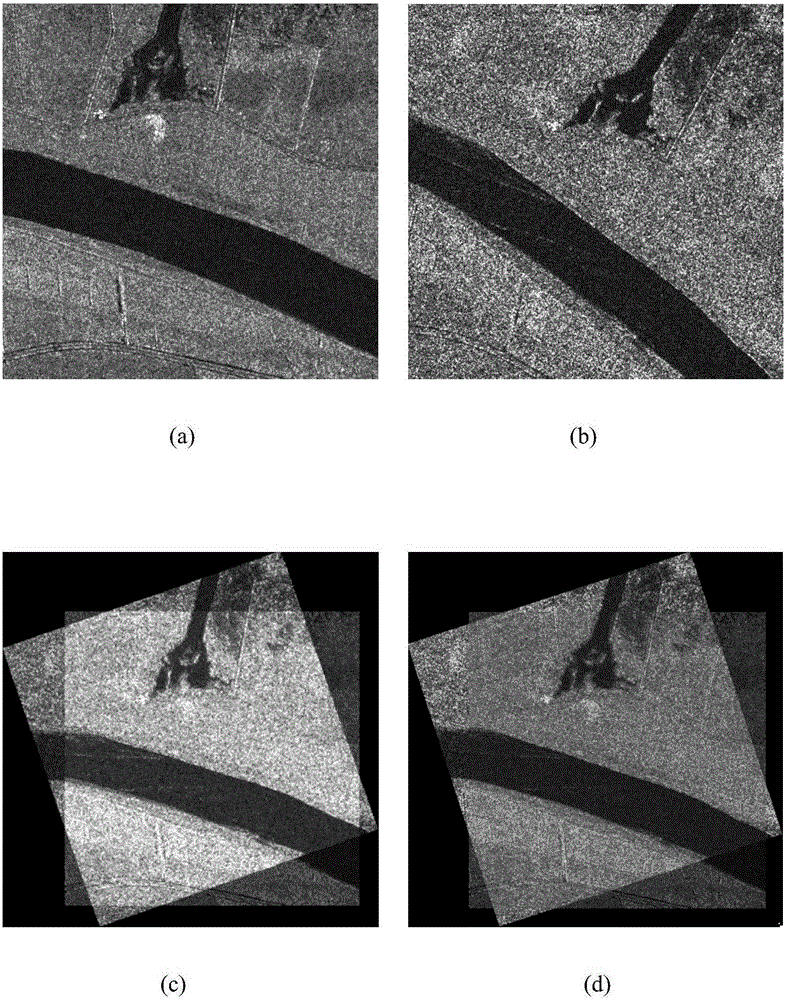
Image registering method in real number coding based clonal selection algorithm
ActiveCN105184764AOvercome the shortcoming of easy to fall into local optimumImprove operational efficiencyImage analysisNormalized mutual informationLocal optimum
The invention discloses an image registering method in a real number coding based clonal selection algorithm, and mainly solves the problem that the image registering accuracy is not high due to the fact that function optimization tends to local optimization in the prior art. The method comprises the steps that (1) a reference image and a floating image are input; (2) an antibody population is initialized in a real number coding method; (3) a normalized mutual information function is constructed and serves as an objective function; (4) the affinity of population antibodies is calculated; (5) selection, clone and variation are carried out on the antibodies; (6) a memory antibody set is formed; (7) the antibodies are memorized; (8) whether a termination condition is reached is determined, if no, the step (4) is returned to, and otherwise, a step (9) is turned to; and (9) an image is registered by utilizing the optimal antibody, and a result is output. The mutual information function is optimized in the real number coding based clonal selection algorithm, the problem that function optimization tends to local optimization in the prior art is solved, and the image registering accuracy is improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Node-activity-based asymmetrical cell group expansion overlapping cell discovering and predicting method in complex network
ActiveCN107240028AImprove detection accuracyImprove detection success rateData processing applicationsComplex mathematical operationsNODALNormalized mutual information
The invention aims to the research on the discovery of overlapping cell in the evolution of a complex network, which does not consider the dynamic evolution, the uneven activity distribution and the multi-scaling of individuals so that the overlapping cell could not improve the NMI (Normalized Mutual Information) and the F-score. Therefore, the method discloses a node-activity-based asymmetrical cell group expansion overlapping cell discovering and predicting method, comprising: first, defining the activity of the nodes; using the activity of the nodes on the objective function for overlapping cell expansion; then, expanding the cell and using the biggest cell group as the expanding seed; and finally, working out the asymmetrical cell group expansion algorithm based on the node activity. According to the invention, it is possible to radically increase the detection accuracy for the overlapping cell in a complex network and to possess a better predicting capability for an overlapping community in the future.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
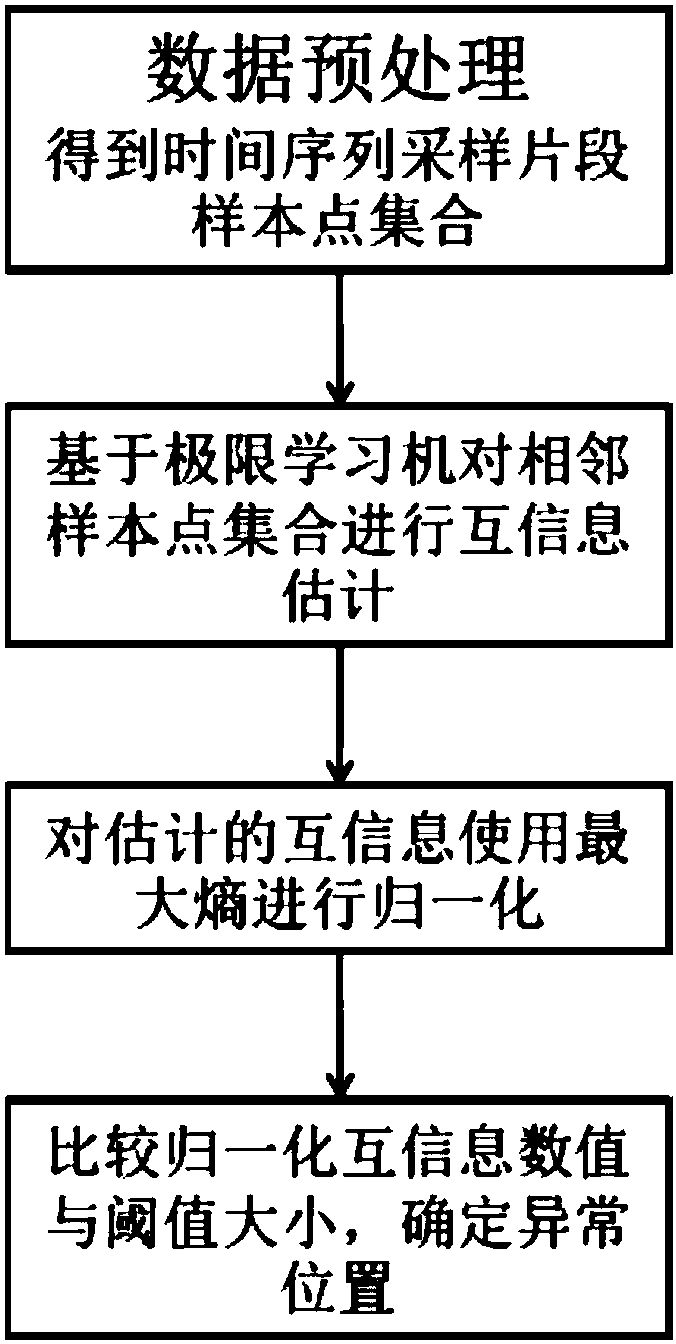
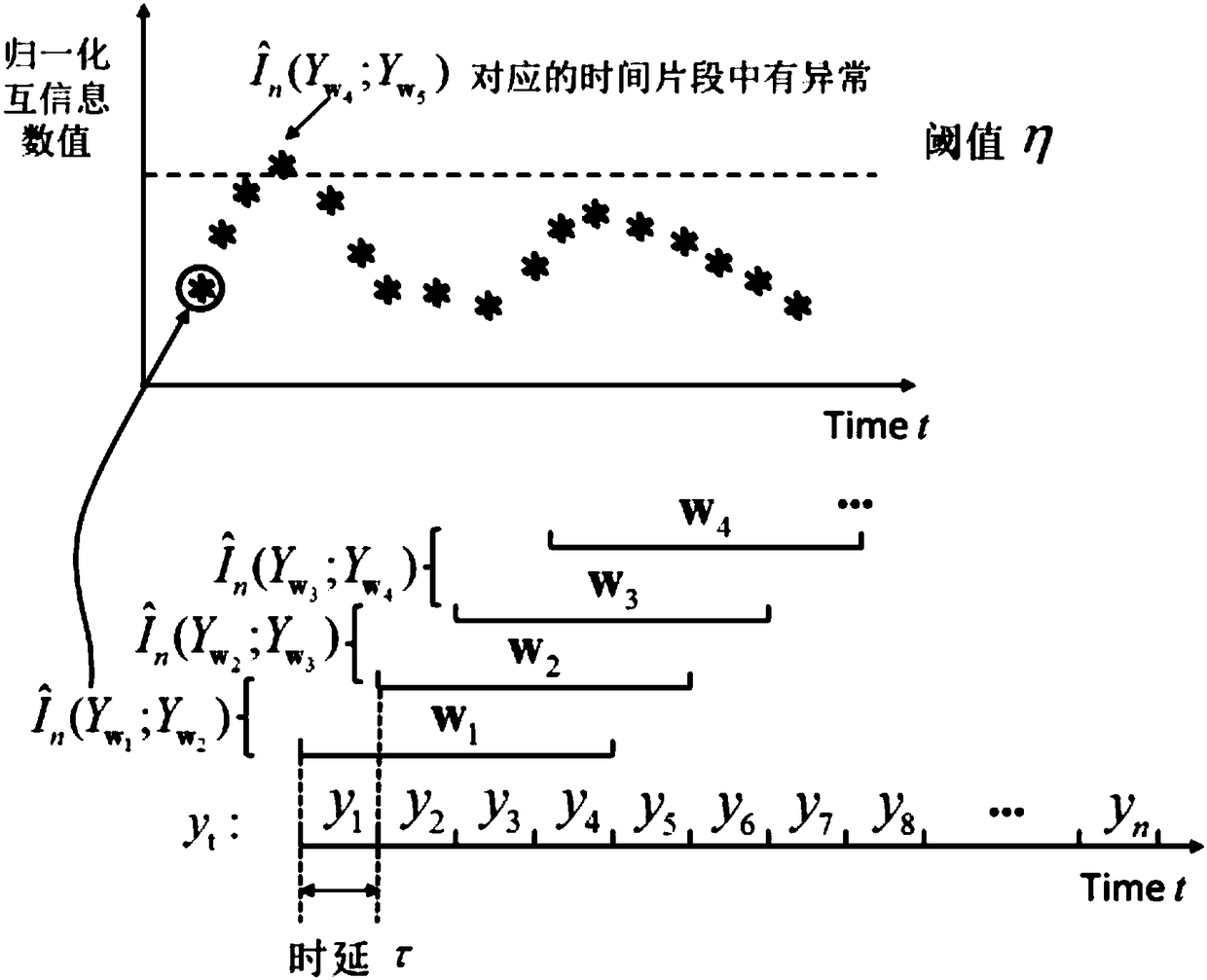
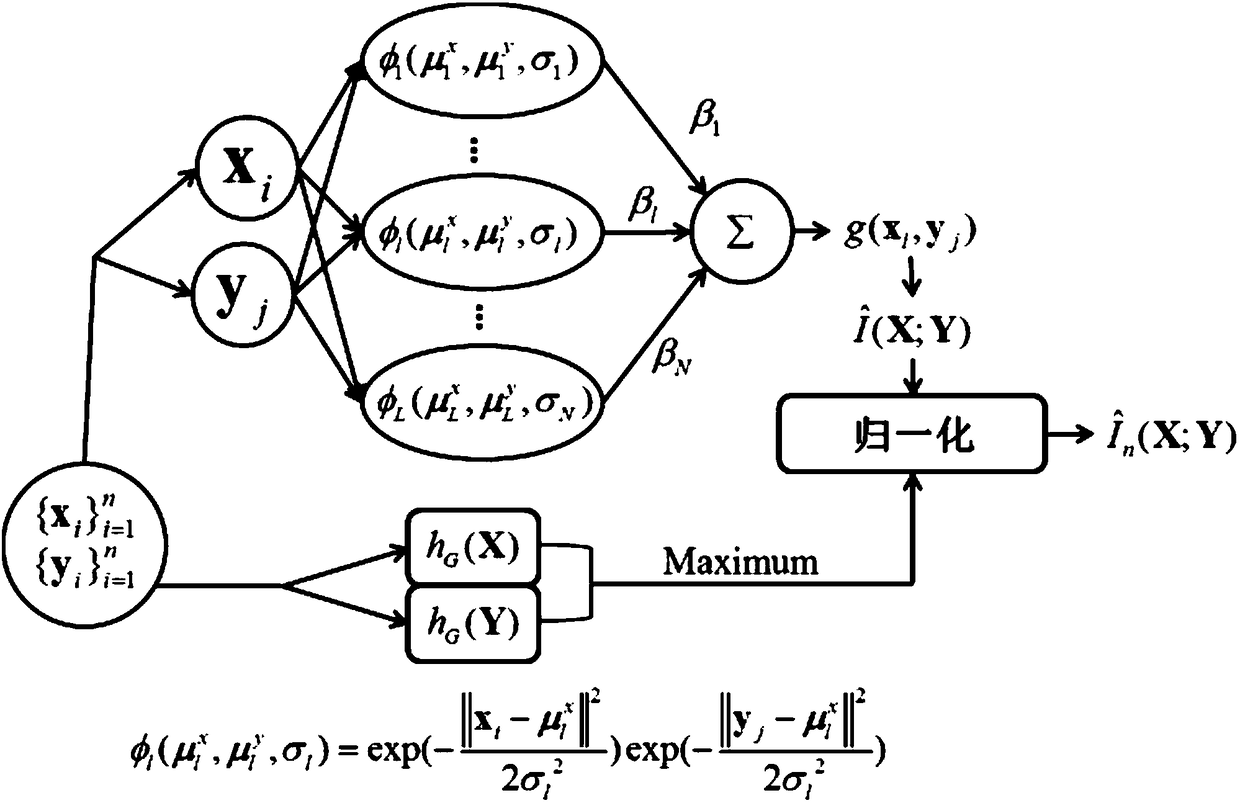
Time sequence anomaly detection method based on normalized mutual-information estimation
InactiveCN108491559AGuaranteed execution efficiencyReduced execution timeComputing modelsDesign optimisation/simulationData dredgingLearning machine
The invention relates to a time sequence anomaly detection method based on normalized mutual-information estimation, and belongs to the technical fields of time sequence anomaly detection, informationtheory and data mining. The method comprises: A, carrying out data preprocessing to obtain sample point sets corresponding to time sequence sampling segments; B, carrying out mutual-information estimation on sample point sets, which correspond to every two adjacent sampling segments, on the basis of an extreme learning machine; C, using maximum entropy to normalize obtained mutual information; and D, repeating the step B and the step C to obtain a normalized mutual-information sequence, and determining a location of sequence mutation through comparison with a threshold value. The method describes an algorithm which does not need parameter optimization and training, and the algorithm uses the extreme learning machine for estimation of the mutual information, uses randomly generated parameter setting, reduces execution time, and ensures execution efficiency of an algorithm model; and at the same time, the maximum entropy is used to normalize the mutual information obtained by estimation, and accuracy of anomaly detection is guaranteed.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
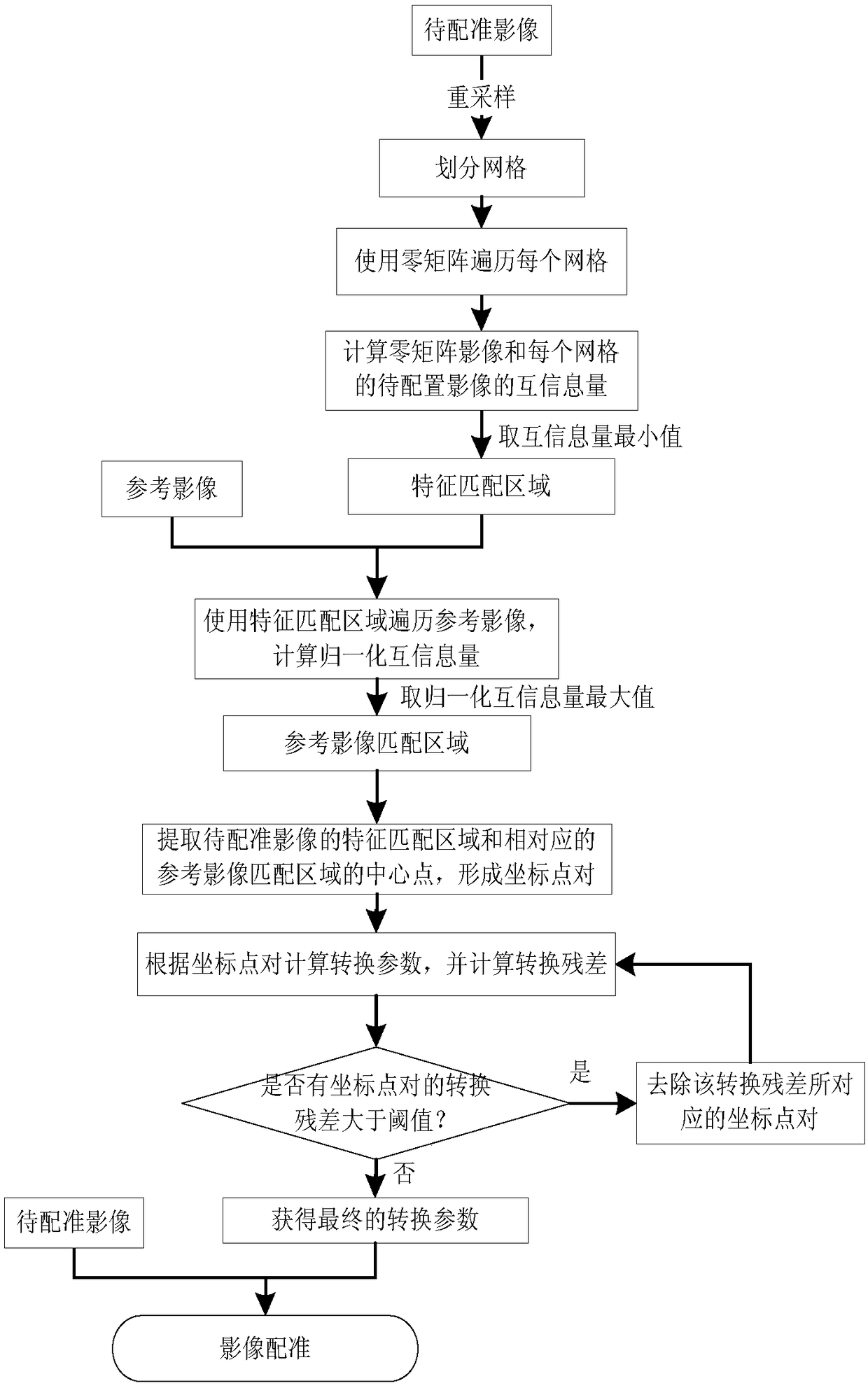
An automatic geometric registration method for multi-source high spatial resolution images
ActiveCN109191501AEvenly distributedImprove registration accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisNormalized mutual informationImage resolution
An automatic geometric registration method for multi-source high spatial resolution images comprises the following steps: (1) resampling an image to be registered by using a reference image; (2), dividing the processed image to be registered into grids; (3) calculating mutual information quantity between the image to be registered and the zero matrix image in each grid, wherein the region corresponding to the minimum mutual information quantity is taken as the feature matching region in the image to be registered; (4) traversing a reference image by using a feature matching area, calculating the normalized mutual information amount between the feature matching area in each grid and the reference image, and taking the area corresponding to the maximum value of the normalized mutual information amount as the reference image matching area; (5), extracting the center point coordinates of the feature matching area and the reference image matching area, and calculating the final conversion parameters; (6) that image to be register using the final conversion parameter to obtain the result of image registration. The homonymous points are evenly distributed, and the registration accuracy ishigh and the speed is fast.
Owner:宁波市测绘和遥感技术研究院 +1
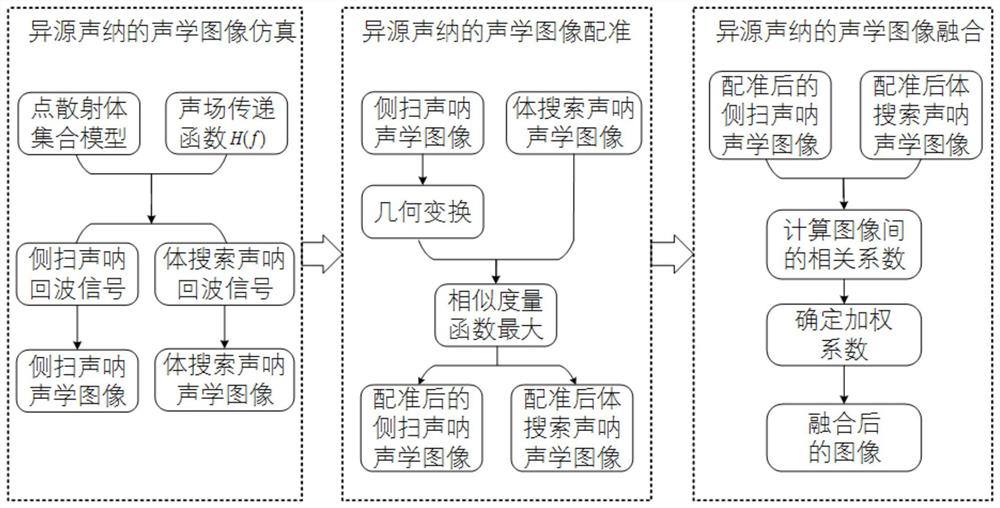
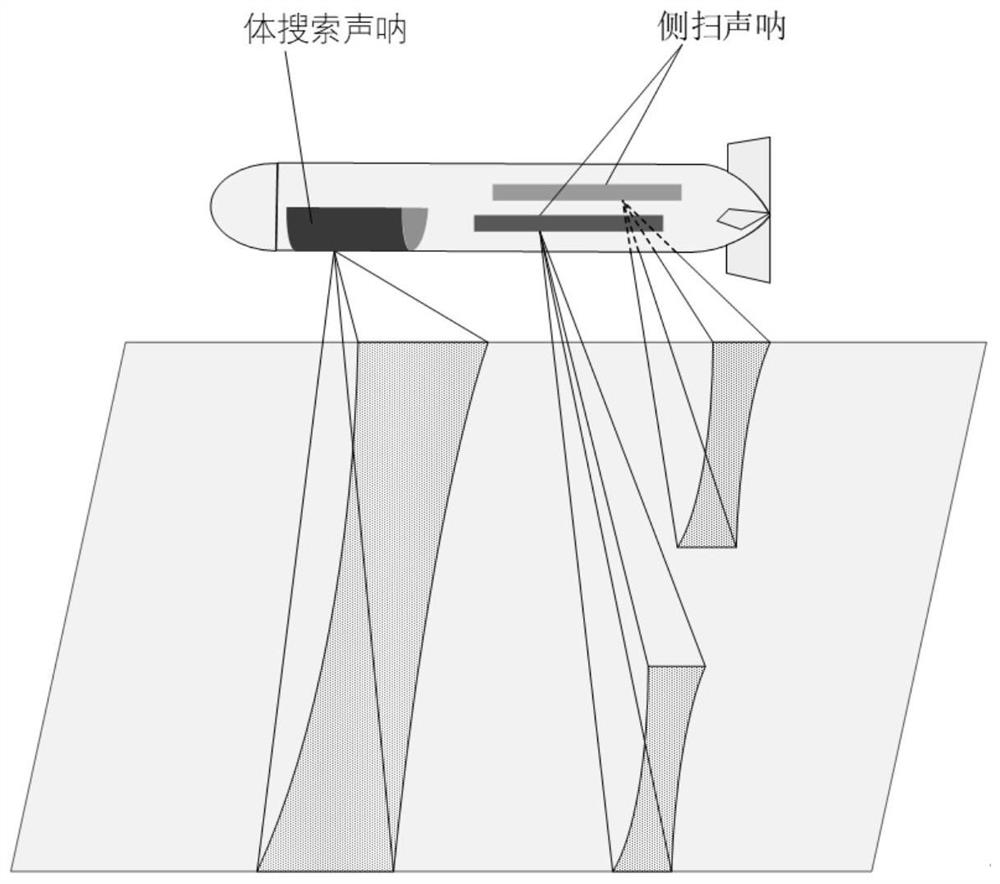
Acoustic image splicing method for same-platform different-source sonar
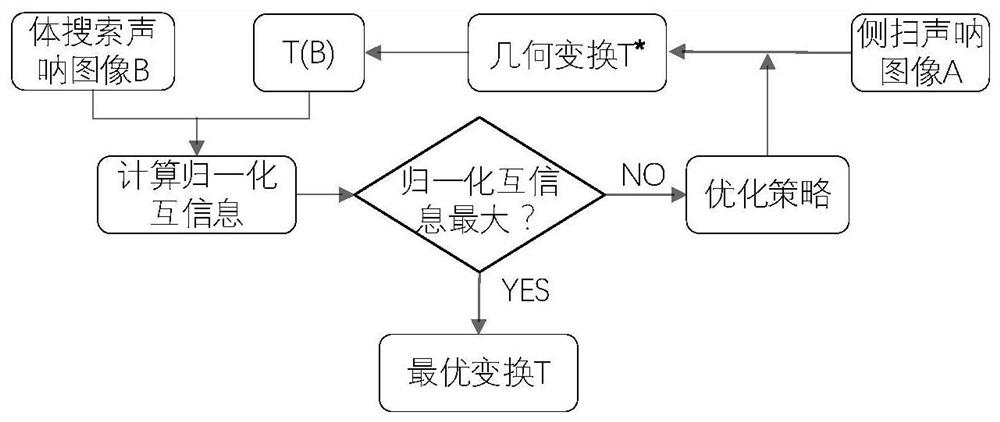
PendingCN112862677AGood splicing effectAvoid negative effectsImage enhancementImage analysisNormalized mutual informationImaging processing
The invention discloses a same-platform different-source sonar acoustic image splicing method, which comprises the following steps: firstly, researching an echo modeling method of an observation area by a different-view-angle sonar system on the same underwater platform, acquiring corresponding acoustic images of a side-scan sonar and a body search sonar by combining a conventional acoustic imaging method, and then carrying out image splicing on the basis; an image registration algorithm based on normalized mutual information is introduced into sonar image processing, and the normalized mutual information is used as a similarity measurement function to solve optimal transformation between two images, so that image registration is realized; and finally, carrying out image fusion on the matched sonar image by adopting a weighted average method so as to obtain a seabed target imaging image with relatively high resolution and position precision. According to the invention, an image registration algorithm based on normalized mutual information is introduced into the field of heterogeneous sonar acoustic image splicing, and the problems of large acoustic image registration error and poor subsequent image fusion effect caused by a traditional feature-based acoustic image registration method are solved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Multi-modal brain image registration method based on GAN
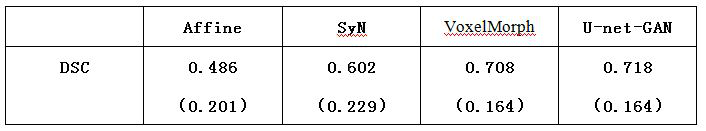
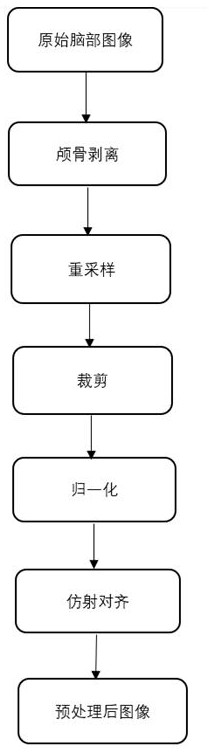
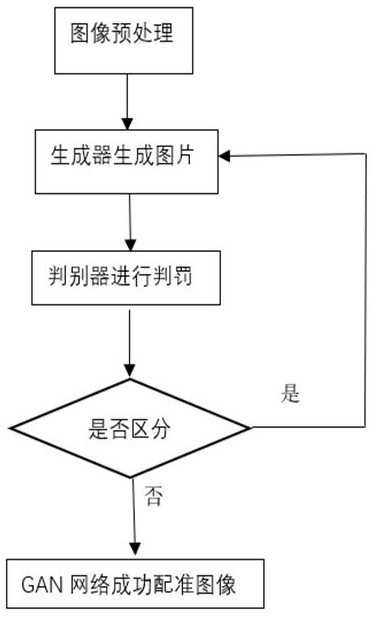
PendingCN113744234AFast registrationEffective registrationImage enhancementImage analysisNormalized mutual informationData set
With the development of the imaging technology, the appearance of various imaging devices makes a great contribution to the progress of modern medicine, but due to the limitation of the imaging principle, the single-mode imaging technology generally can only provide single and limited information, and therefore, in order to improve the accuracy of diagnosis and the effectiveness of treatment, doctors often need to fuse information of images of different modalities to know comprehensive information of diseased tissues or organs. The invention provides a registration method based on a generative adversarial network in order to realize efficient and rapid registration of brain images and facilitate treatment of doctors. A U-Net encoder-decoder structure is adopted in a generator, an encoder obtains transformation parameters from a floating image to a fixed image, a decoder recovers the size of a feature map, medical image registration based on normalized mutual information is used in similarity measurement, a gradient descent method is used as an optimization algorithm of image registration, and tests are respectively performed in CT single-mode and CT-MRI multi-mode sequence images, and registration results obtained by using an original normalized mutual information calculation method and an improved normalized mutual information method are compared. According to the disclosed method, the generalization ability of the model can be enhanced by automatically learning the mapping relation between the same data set. According to the invention, accurate and rapid registration can be realized.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
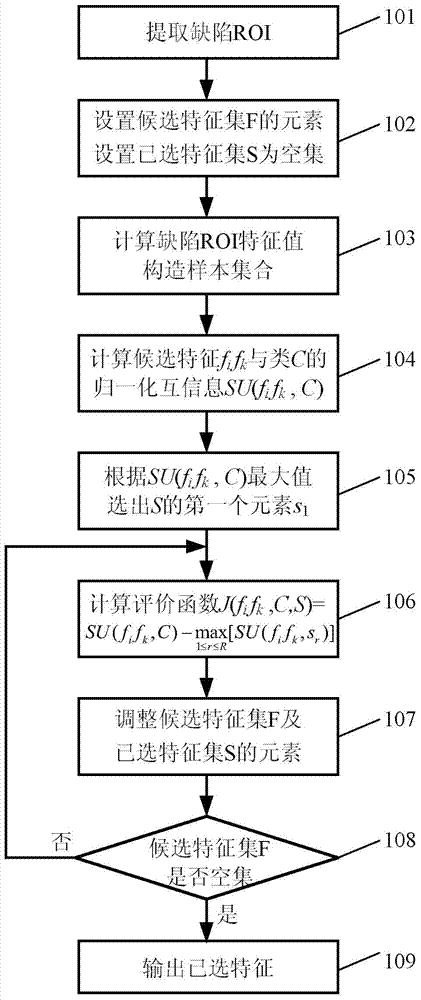
Entropy method for filter defect characteristic parameter selection
ActiveCN103500336AImprove selection accuracyOvercome the problem that the selection result may not be optimalCharacter and pattern recognitionNormalized mutual informationFeature parameter
The invention discloses an entropy method for filter defect characteristic parameter selection, which comprises the steps of segmenting a bounding rectangle containing defects from defective filter images to form defects ROI; setting elements of a candidate characteristic set F and setting a selected characteristic set S as an empty set; calculating the characteristic values of the defects ROI and constructing a sample set; calculating normalized mutual information SU (fifk, C) of candidate characteristic fifk and class C; selecting a first element s1 of the S according to the maximum of SU (fifk, C); removing characteristics which are selected in the S from the candidate characteristic set F and the candidate characteristics with normalized mutual information SU (fifk, C) which is smaller than a threshold; calculating the value of an evaluation function J (fifk, C, S) of each candidate characteristic fifk in the candidate characteristic set F; selecting a next element of the selected characteristic set S according to the maximum of the evaluation function J (fifk, C, S); removing the characteristics which are selected in the S from the candidate characteristic F and the candidate characteristics with the evaluation function J (fifk, C, S) which is smaller than a threshold; judging whether the candidate characteristic set F is an empty set or not; outputting the selected characteristics.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
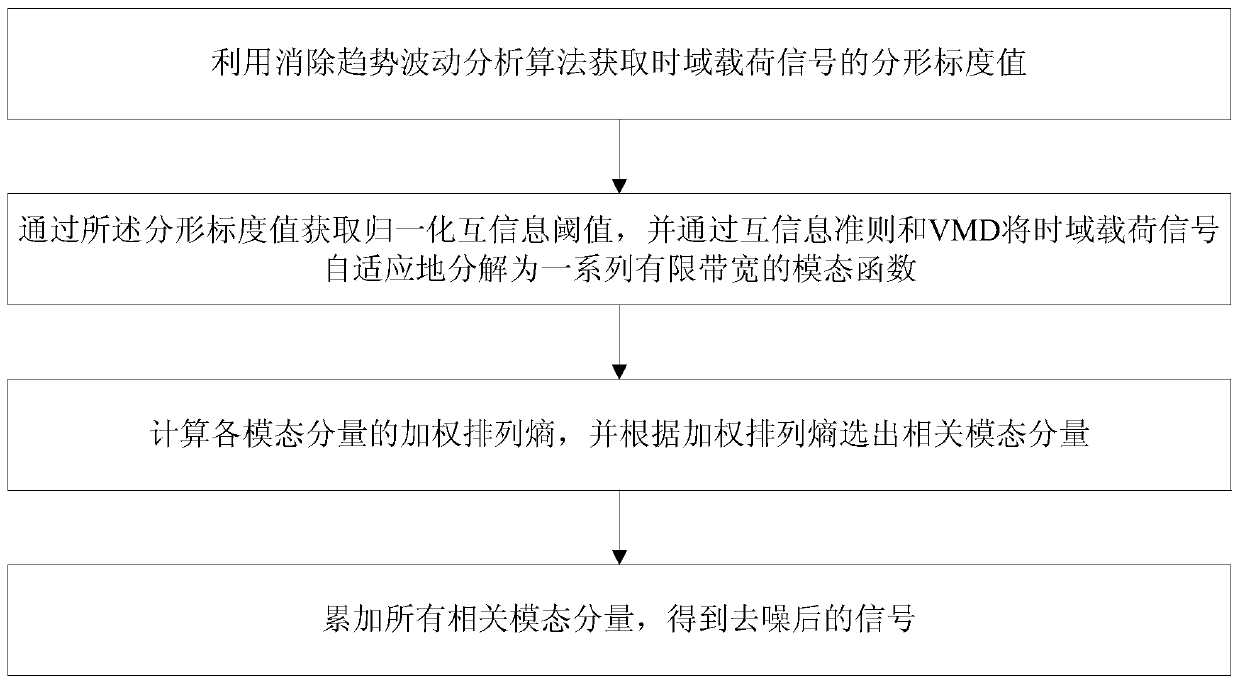
Denoising method for time domain load signal based on VMD
ActiveCN111144230AImprove adaptabilityImprove denoising effectCharacter and pattern recognitionComplex mathematical operationsTime domainNormalized mutual information
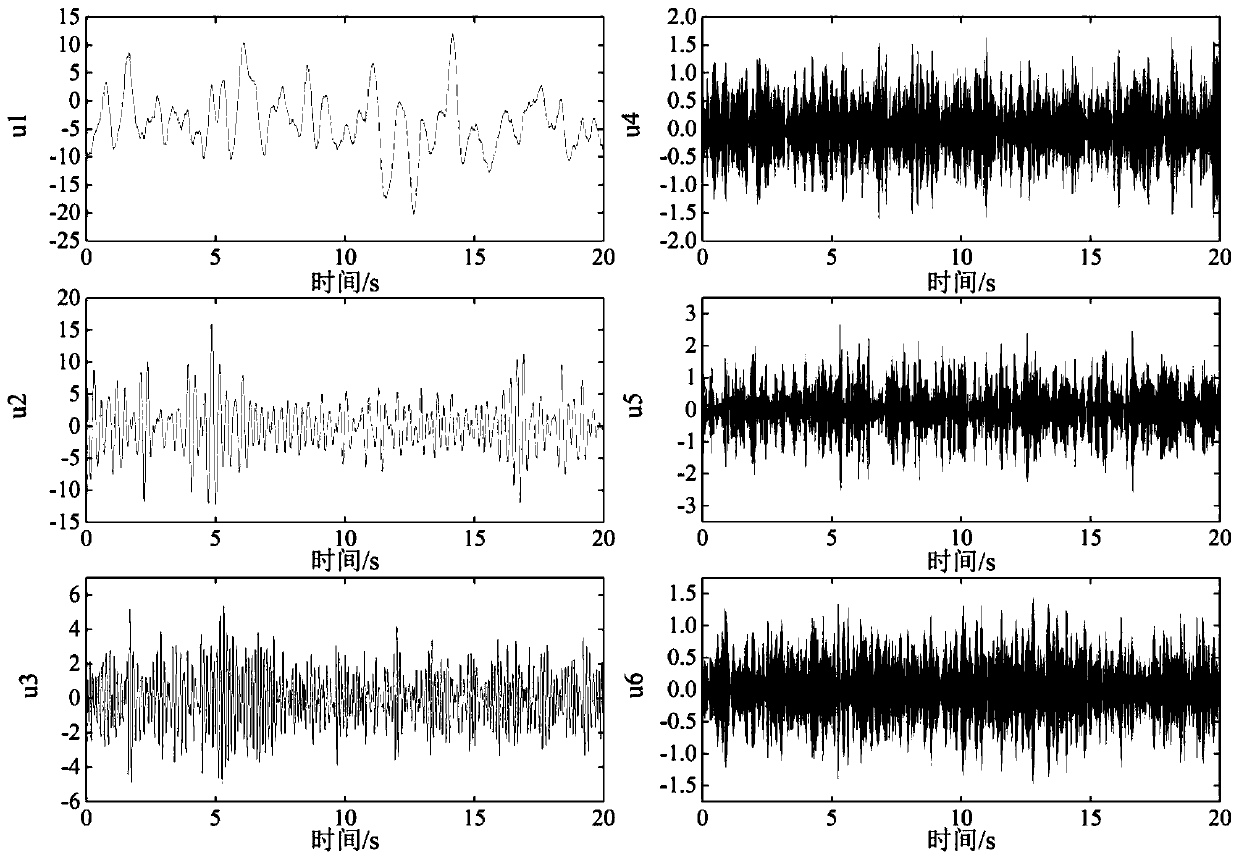
The invention discloses a denoising method for a time domain load signal based on VMD. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a fractal scale value of the time domain load signal by usinga trend fluctuation elimination analysis algorithm; obtaining a normalized mutual information threshold value through the fractal scale value, and adaptively decomposing the time domain load signal into a series of modal functions with limited bandwidth through a mutual information criterion and VMD; calculating a weighted permutation entropy of each modal component, and selecting a related modalcomponent according to the weighted permutation entropy; and accumulating all the related modal components to obtain a denoised signal. According to the method, the number of the VMD modes can be adaptively determined, and the time domain load signal is denoised by identifying the related mode components through the weighted permutation entropy, so that the analysis precision of the time domain load signal under strong background noise and complex electromagnetic interference is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Multi-modality medical data three-dimensional visualization method
InactiveCN100498839CSolve the insurmountable problem of variability in overlapping regionsAddress variabilityImage analysis2D-image generationDiagnostic Radiology ModalityNormalized mutual information
The invention involves a multi-mode medical body data three-dimensional video-method. Most the existing technologies are based on two-two-dimensional lay or two-three dimensional lay, which do not realize the integrated display course of medical body data aligning and amalgamation. The said method includes standardization mutual information-way aligning based on multi resolution ratio and single drop multi-mode straight body protracting-way amalgamation display. The previous one includes three approaches, such as coordinate transform, orientation criterion and multi resolution ratio optimize; the latter includes five approaches, such as impress function definition, the calculation of illumination model, image composition, single drop multi-mode show of the multi-mode data and amalgamation display. The invention can realize the integrated display course of medical body data aligning and amalgamation, and is a real two-three dimensional multi-mode video-method.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com