Patents
Literature
151 results about "Multimodal image" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
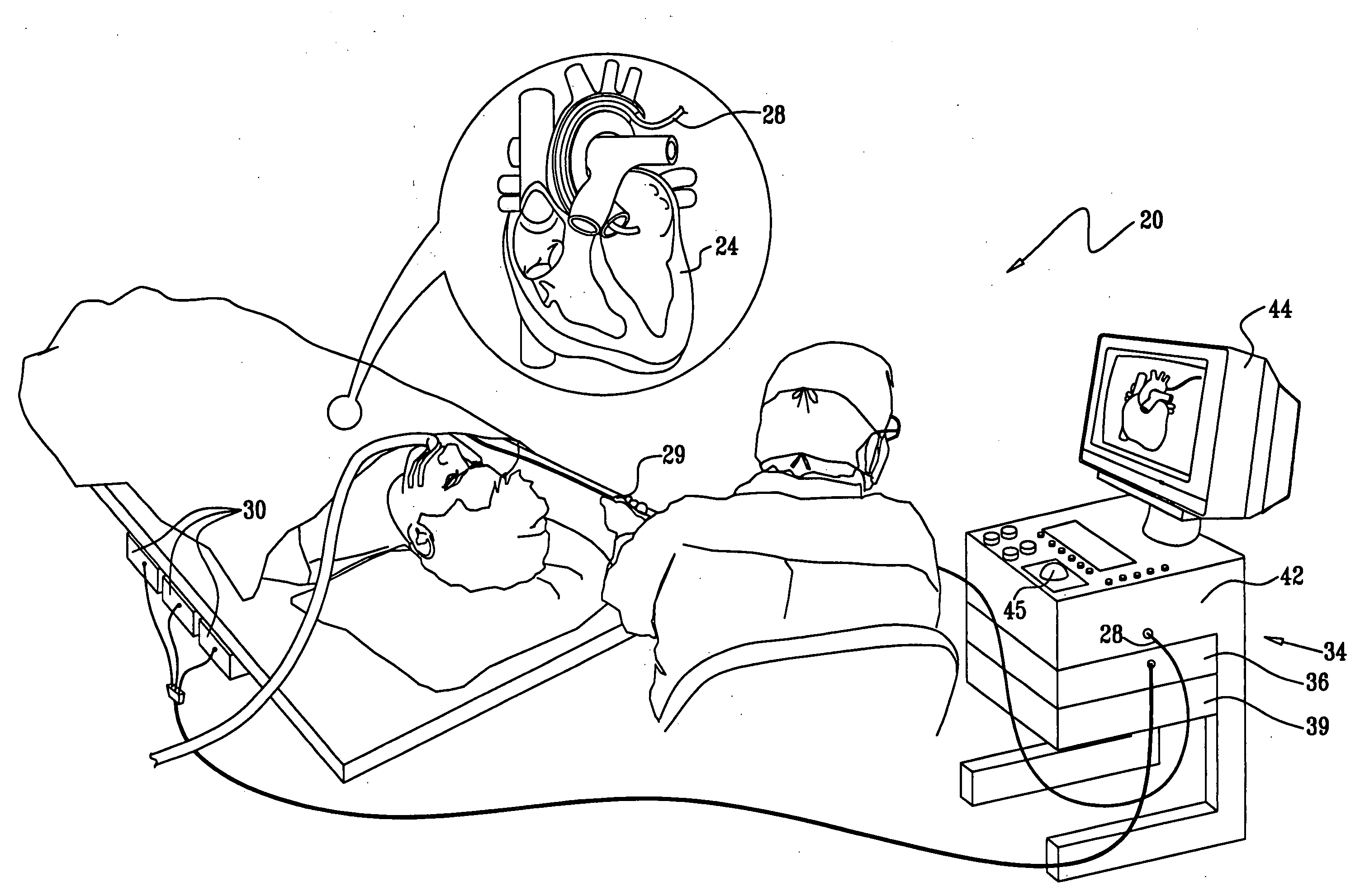
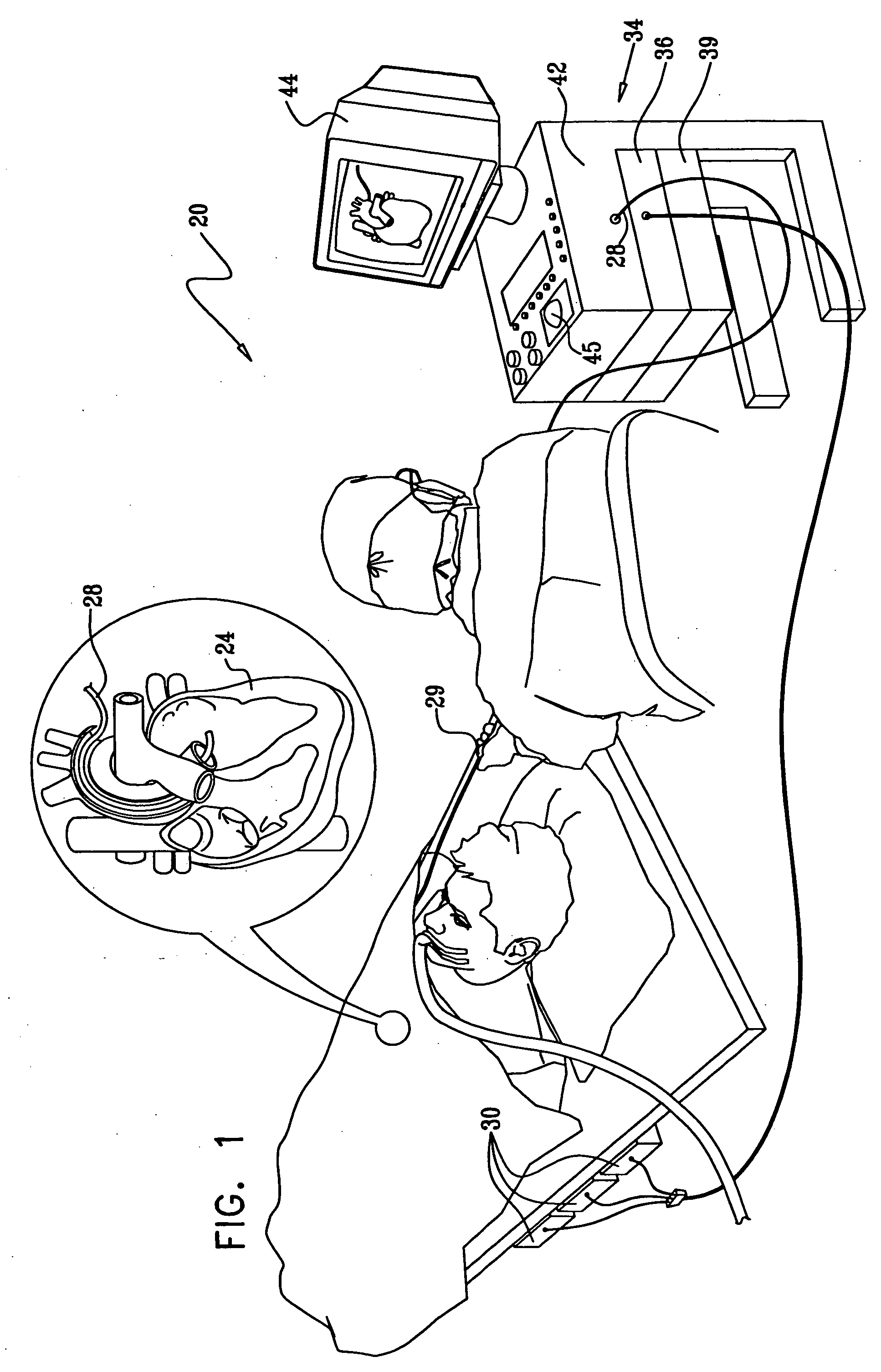
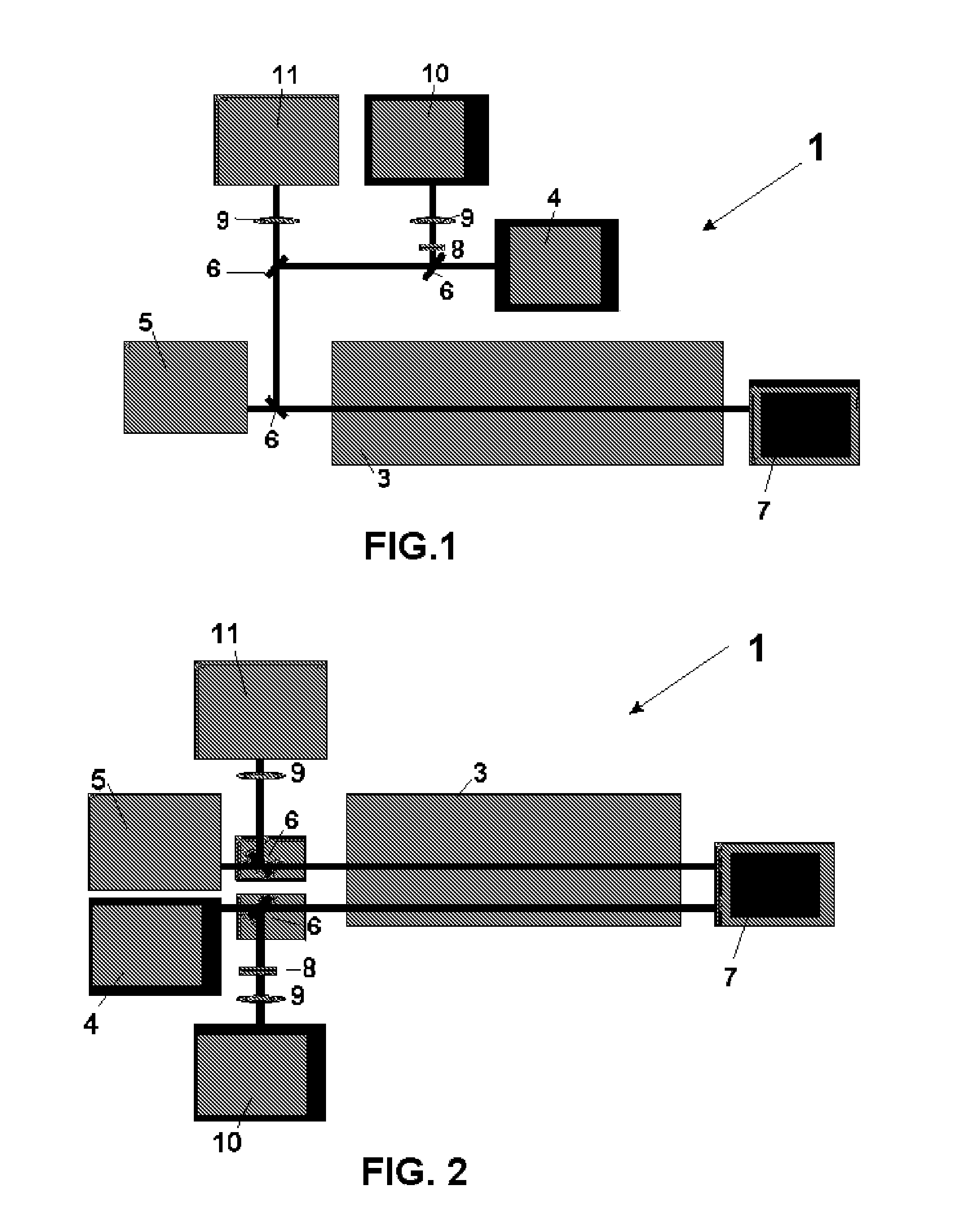
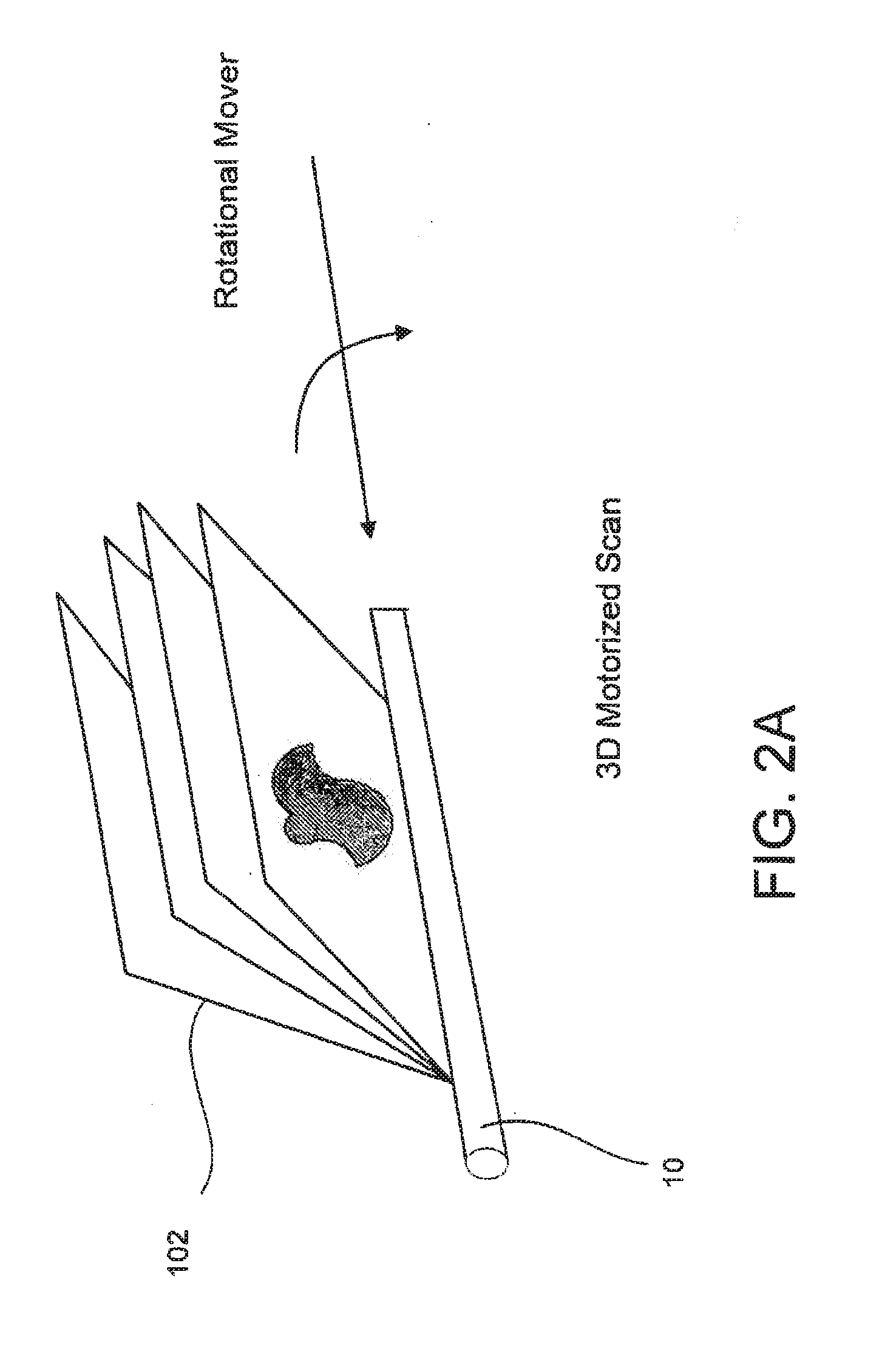
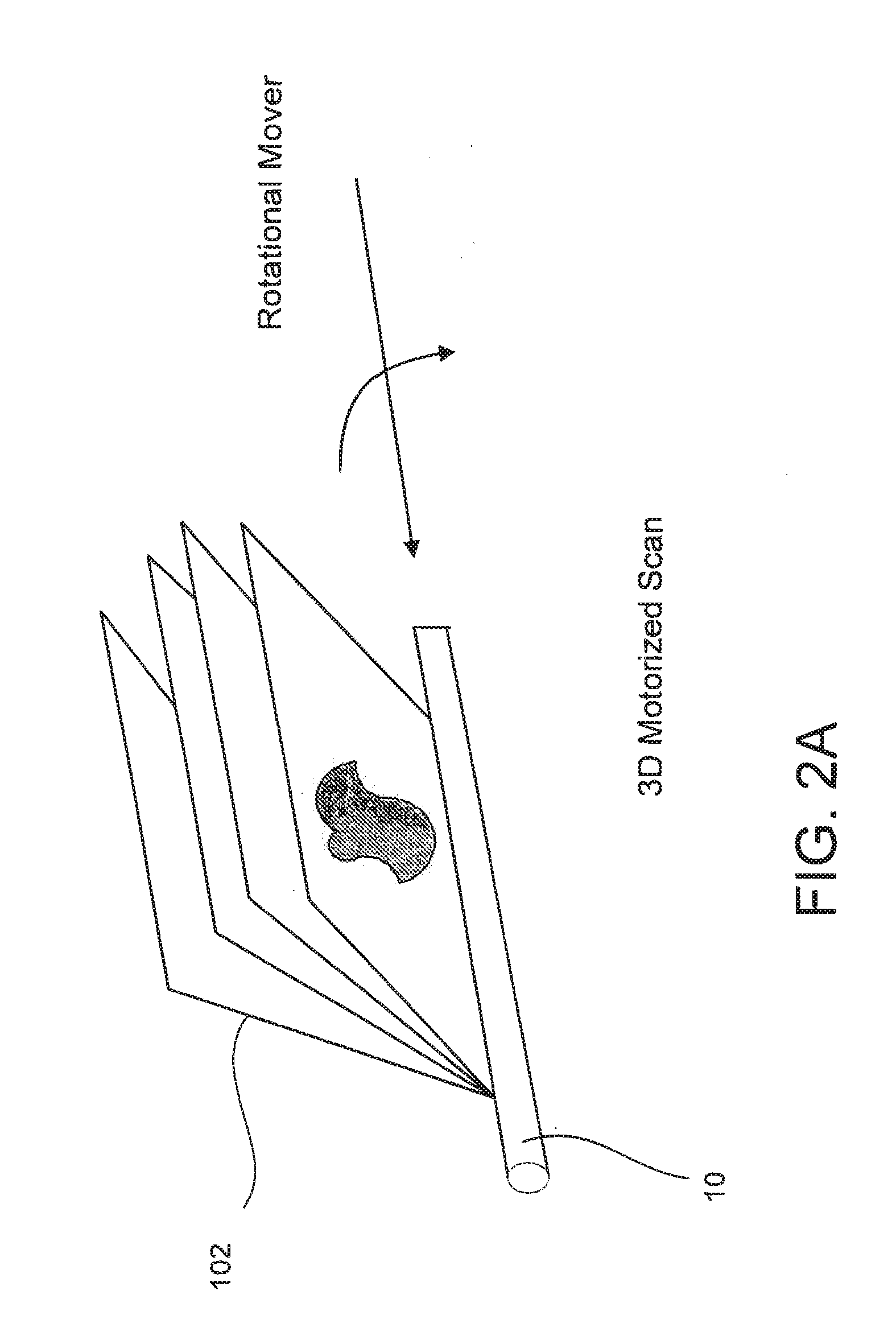
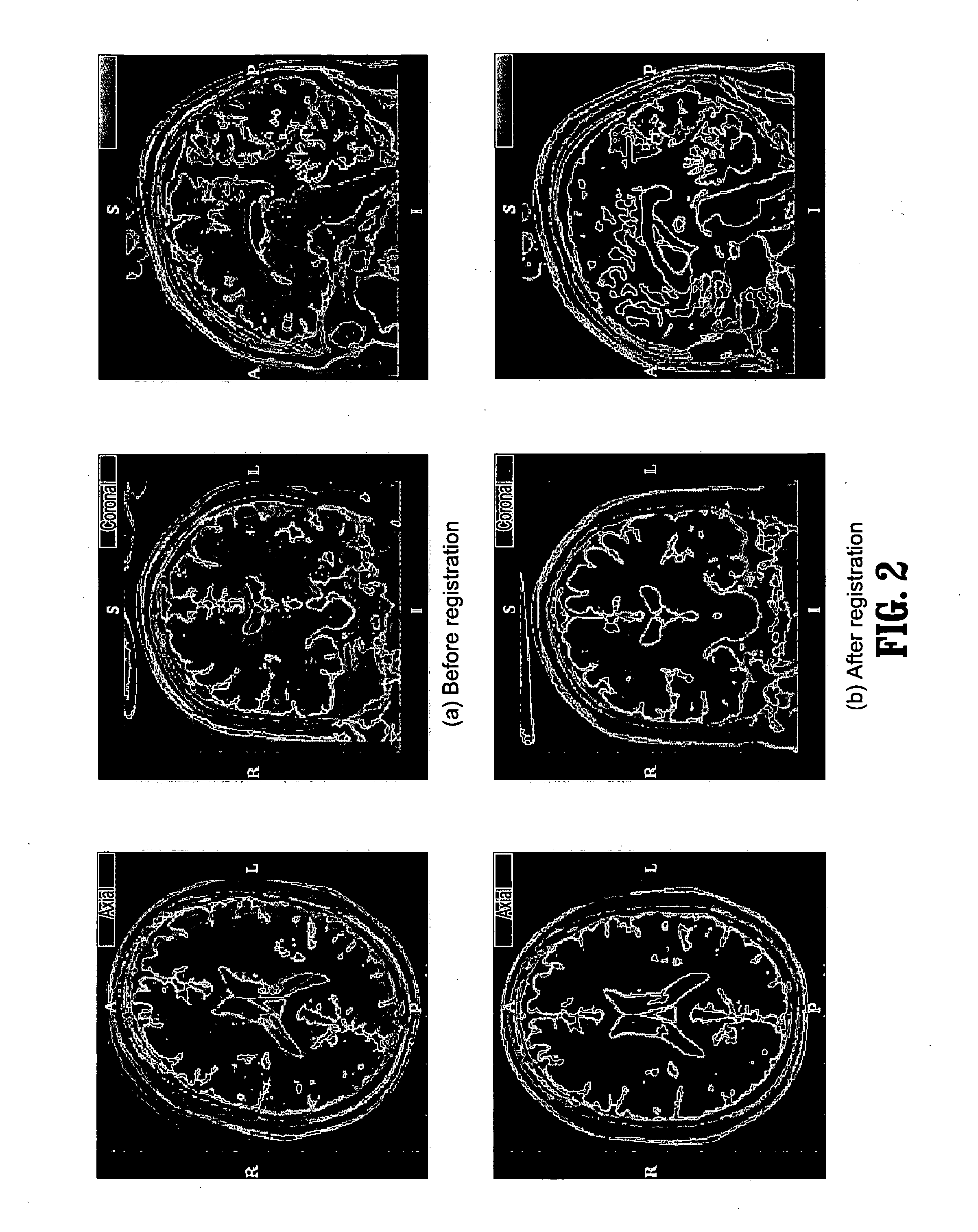
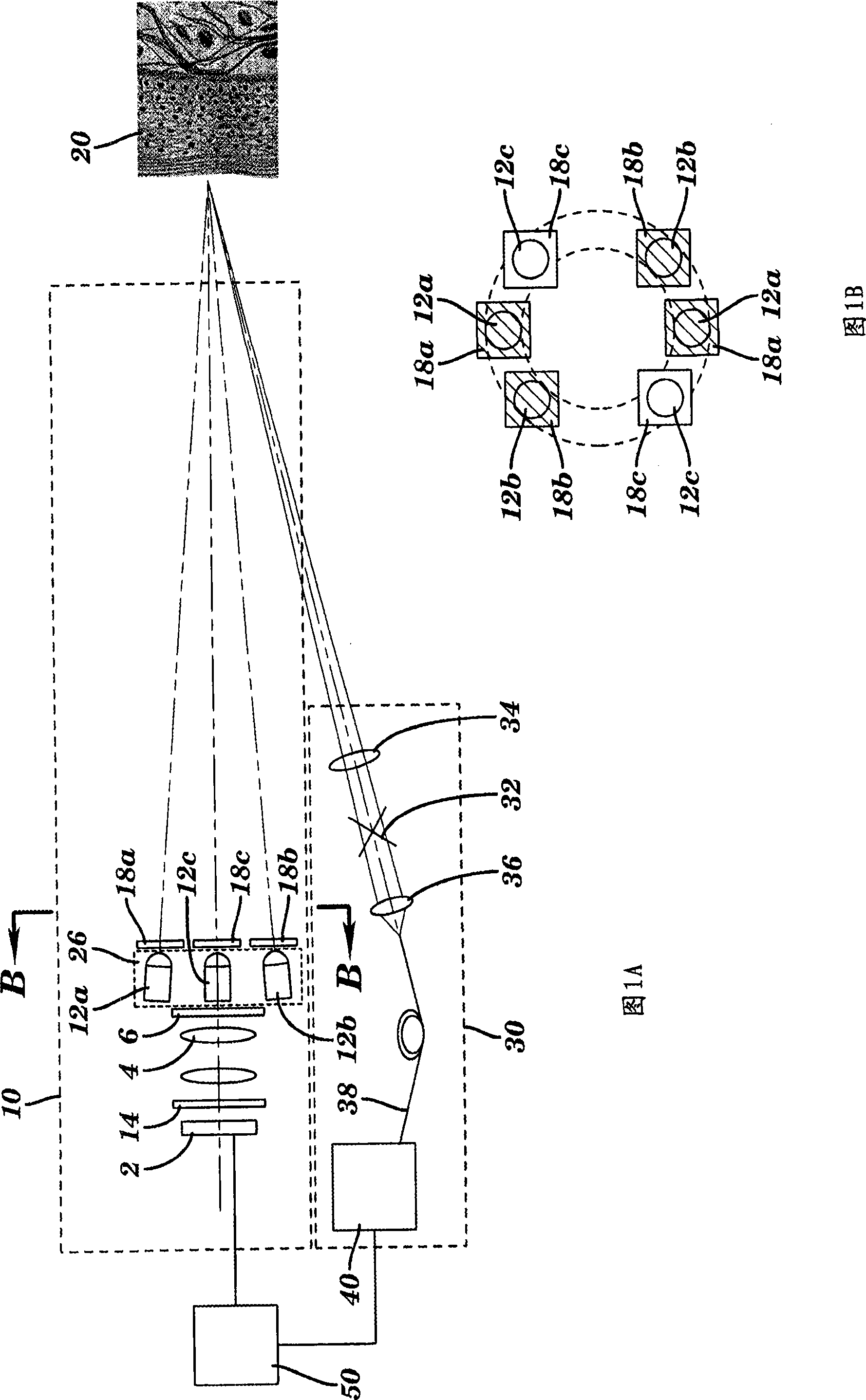
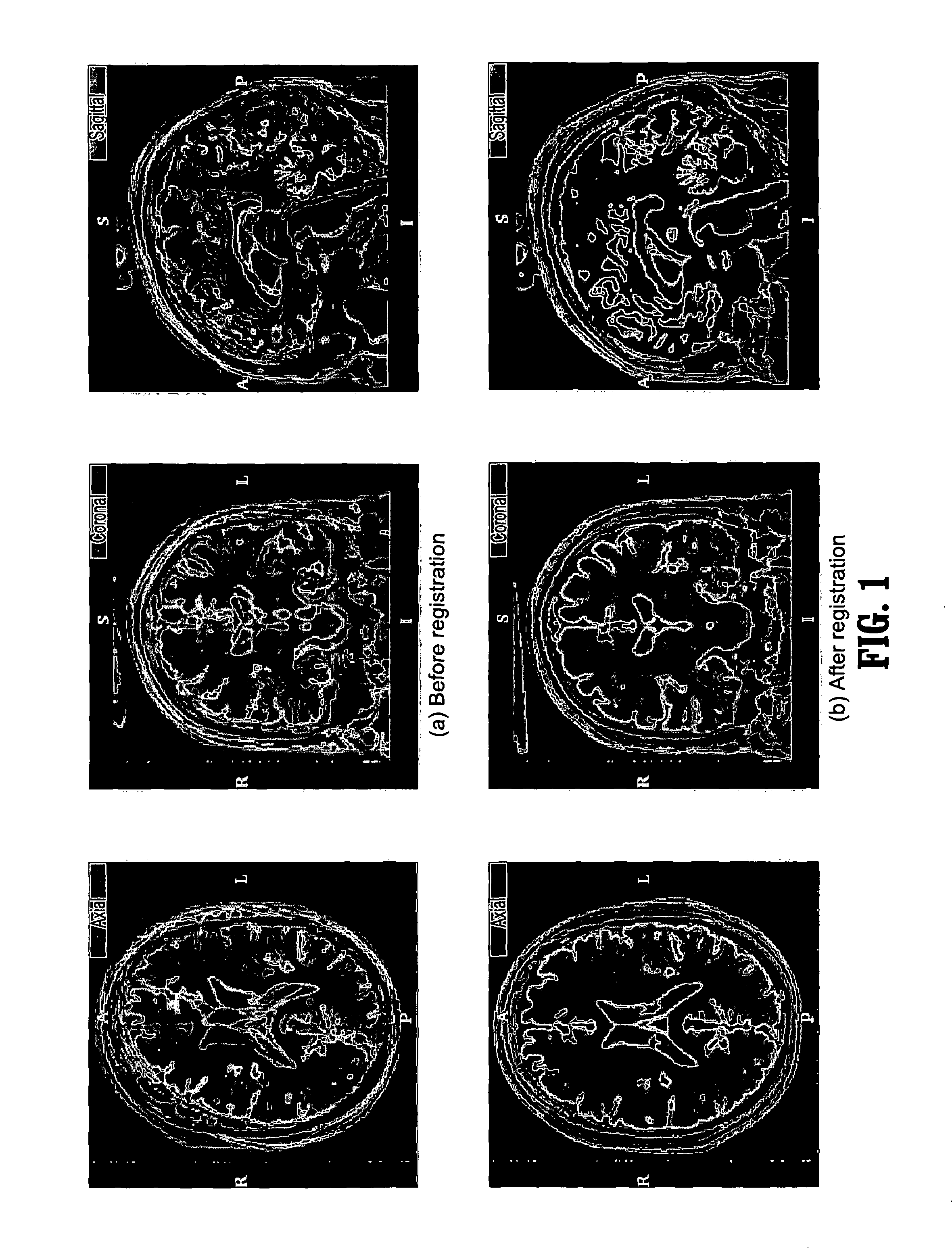
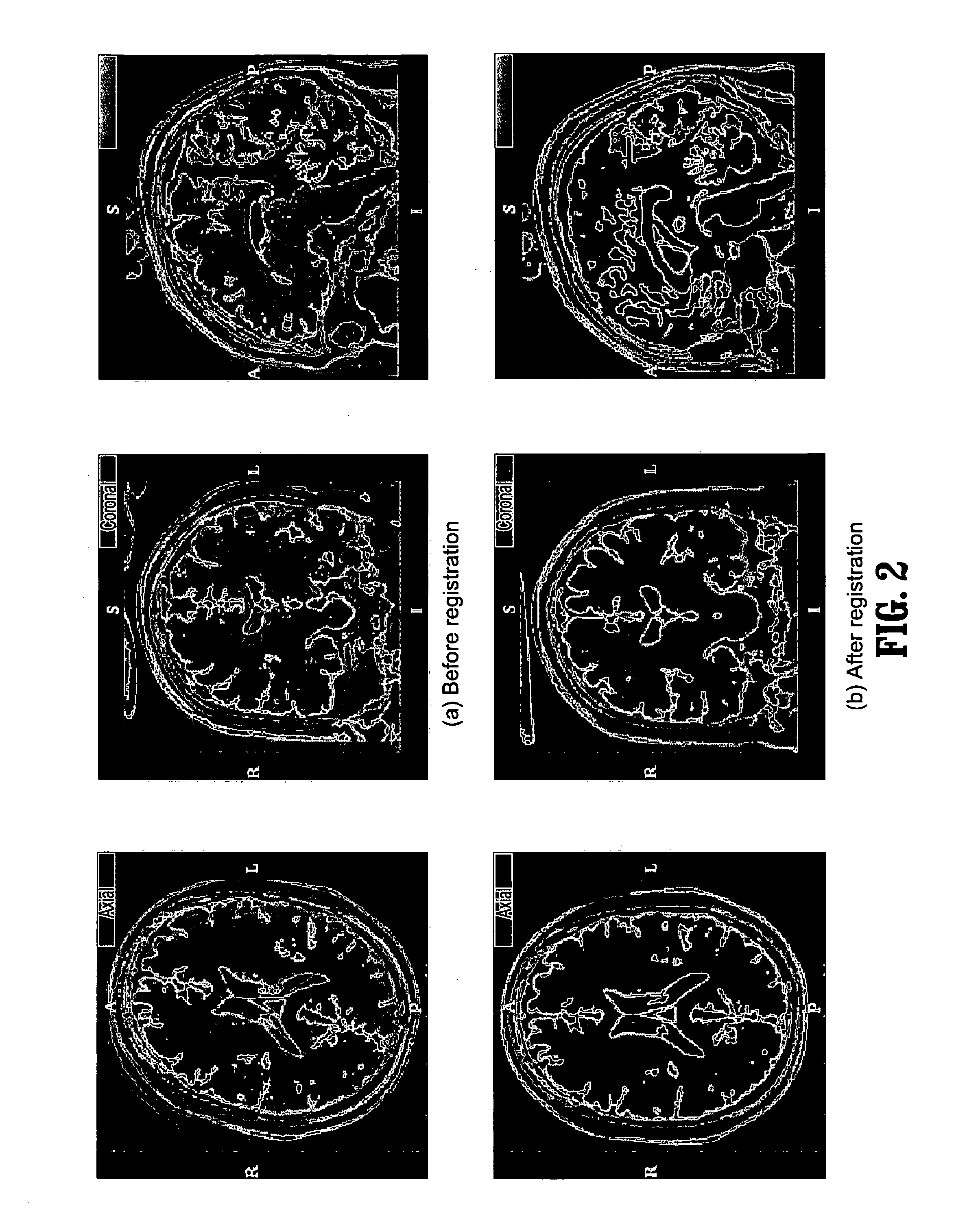
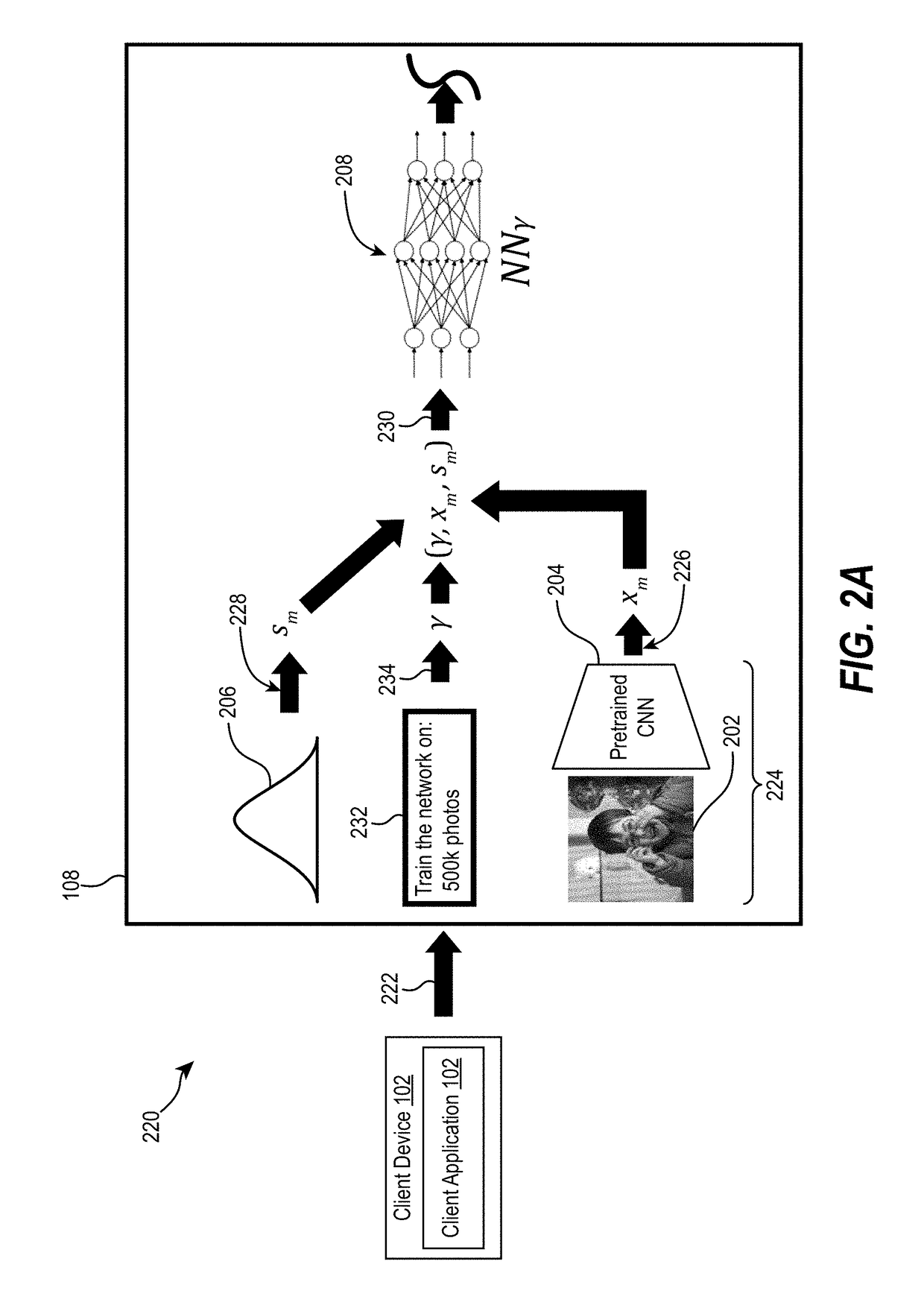
Segmentation and registration of multimodal images using physiological data
InactiveUS20070049817A1Improve accuracyMore rapidImage enhancementImage analysisComputer visionData system
Systems and methods are provided for registering maps with images, involving segmentation of three-dimensional images and registration of images with an electro-anatomical map using physiological or functional information in the maps and the images, rather than using only location information. A typical application of the invention involves registration of an electro-anatomical map of the heart with a preacquired or real-time three-dimensional image. Features such as scar tissue in the heart, which typically exhibits lower voltage than healthy tissue in the electro-anatomical map, can be localized and accurately delineated on the three-dimensional image and map.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Equipment for infrared vision of anatomical structures and signal processing methods thereof
InactiveUS20110295062A1Good repeatabilityImprove securityImage analysisDiagnostics using spectroscopyAnatomical structuresVisual perception
Equipment for infrared vision of anatomical structures applicable to assist the physicians in endoscopic, fetoscopic or laparoscopic operations and methods for signal processing to enhance said vision, comprising two units that work together: a multimodal or multispectral imaging unit, constituted by a device comprising an endoscope or fetoscope or laparoscope, and additional optical systems to acquire multimodal images of the interior of the patient's body; and an image processing unit, to which said images are transferred, comprising processing devices with a navigation interface which process said images and display the patient's enhanced anatomical map image and the endoscope location, equipped with hardware and software that apply at least five different vision-enhancing methods, namely normalization, segmentation, tracking, mapping and fusion.
Owner:FCRB +2
Fused image moldalities guidance
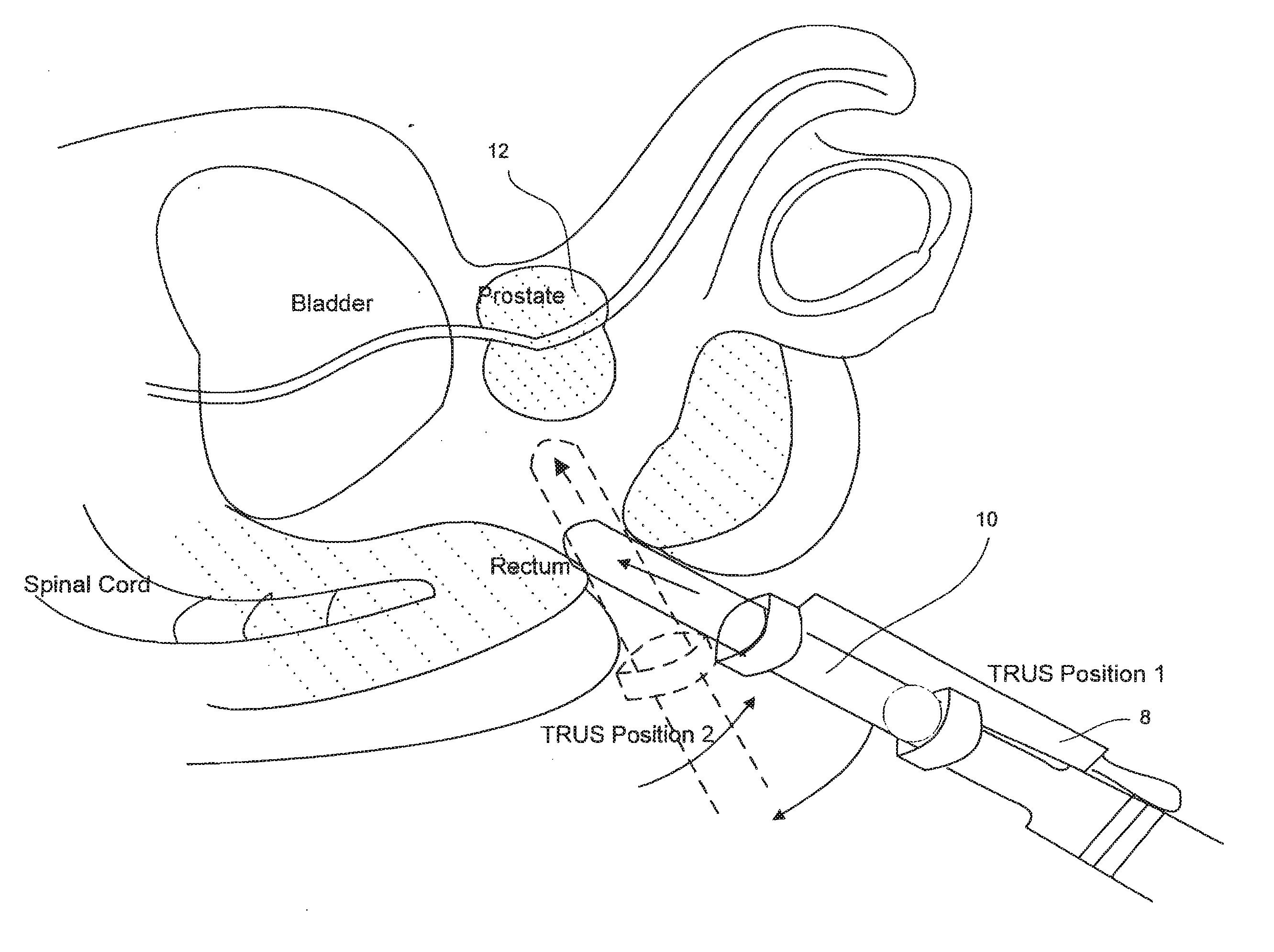
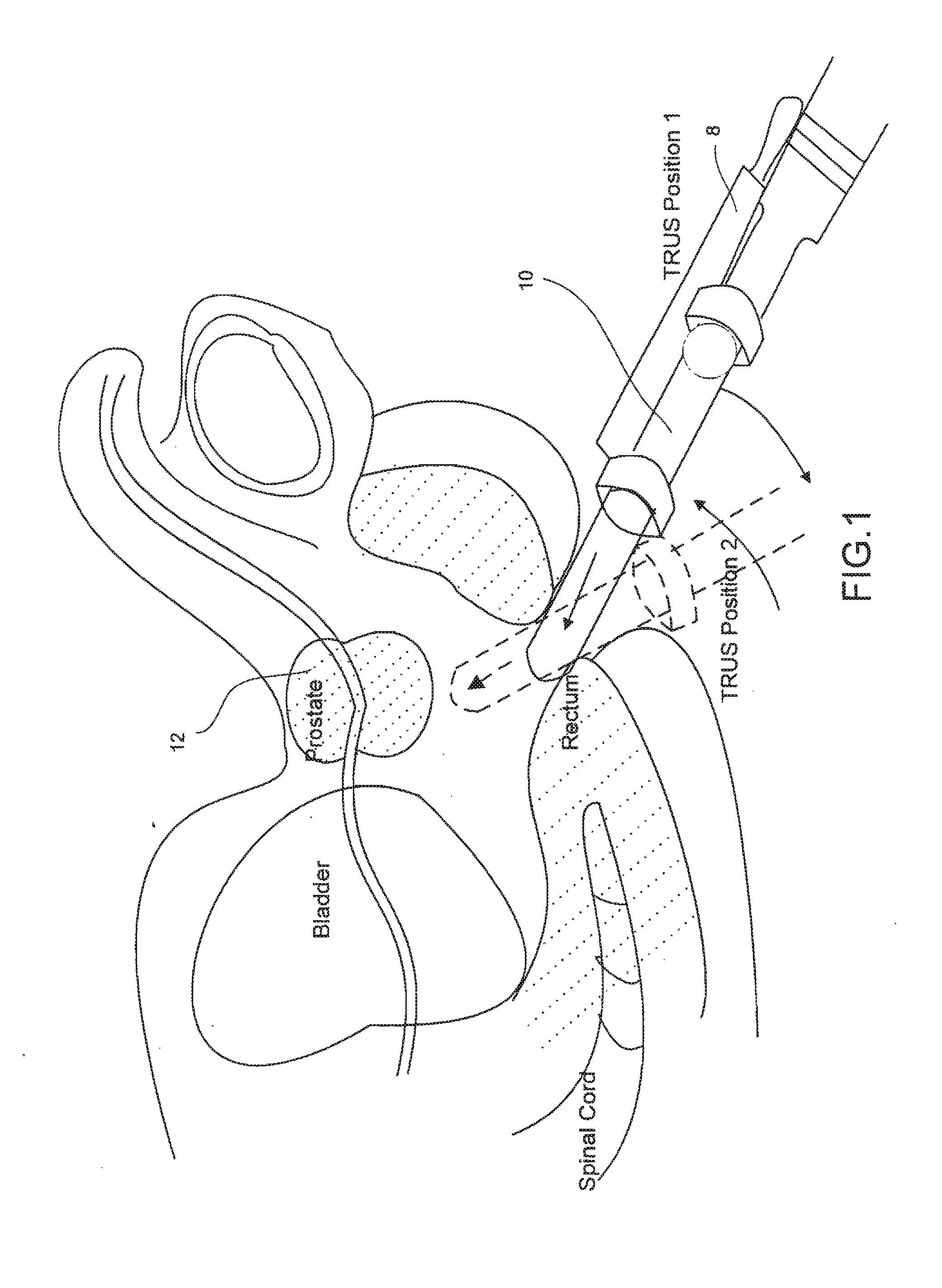
InactiveUS20110178389A1Impact registration qualityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementULTRASOUND PROCEDURESTrus image
An improved system and method (i.e. utility) for registration of medical images is provided. The utility registers a previously obtained volume (s) onto an ultrasound volume during an ultrasound procedure to produce a multimodal image. The multimodal image may be used to guide a medical procedure. In one arrangement, the multimodal image includes MRI information presented in the framework of a TRUS image during a TRUS procedure.
Owner:EIGEN INC
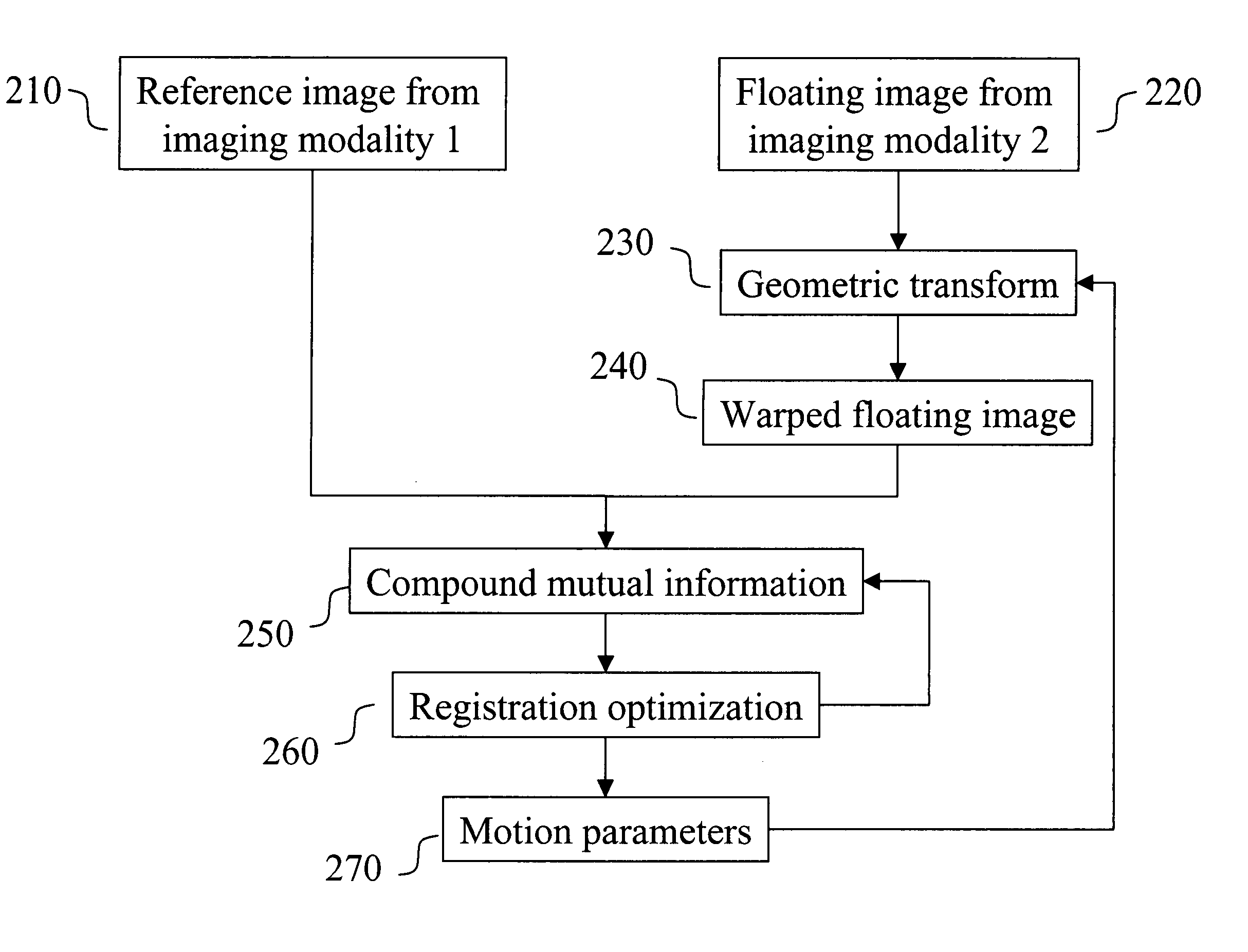
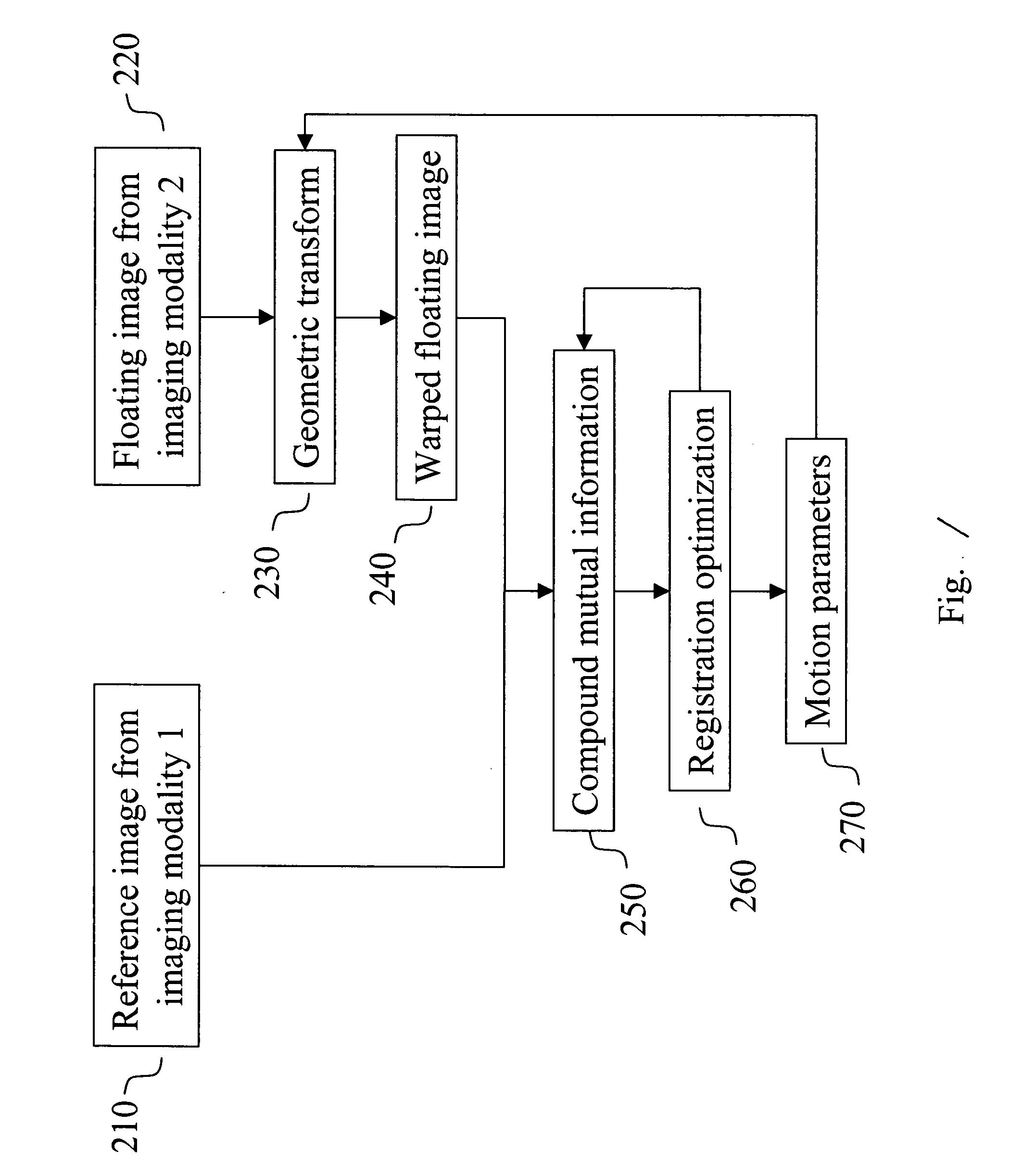
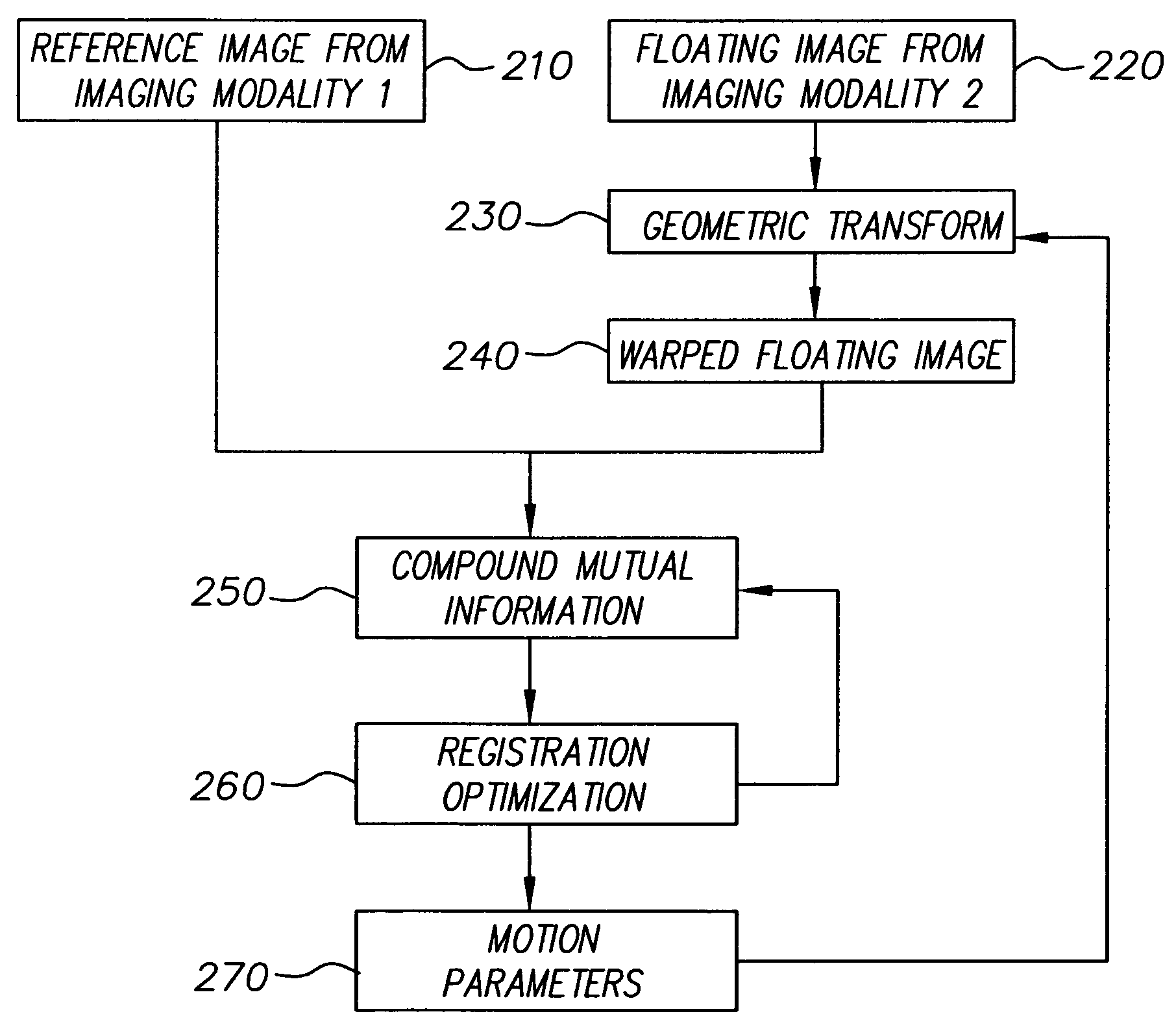
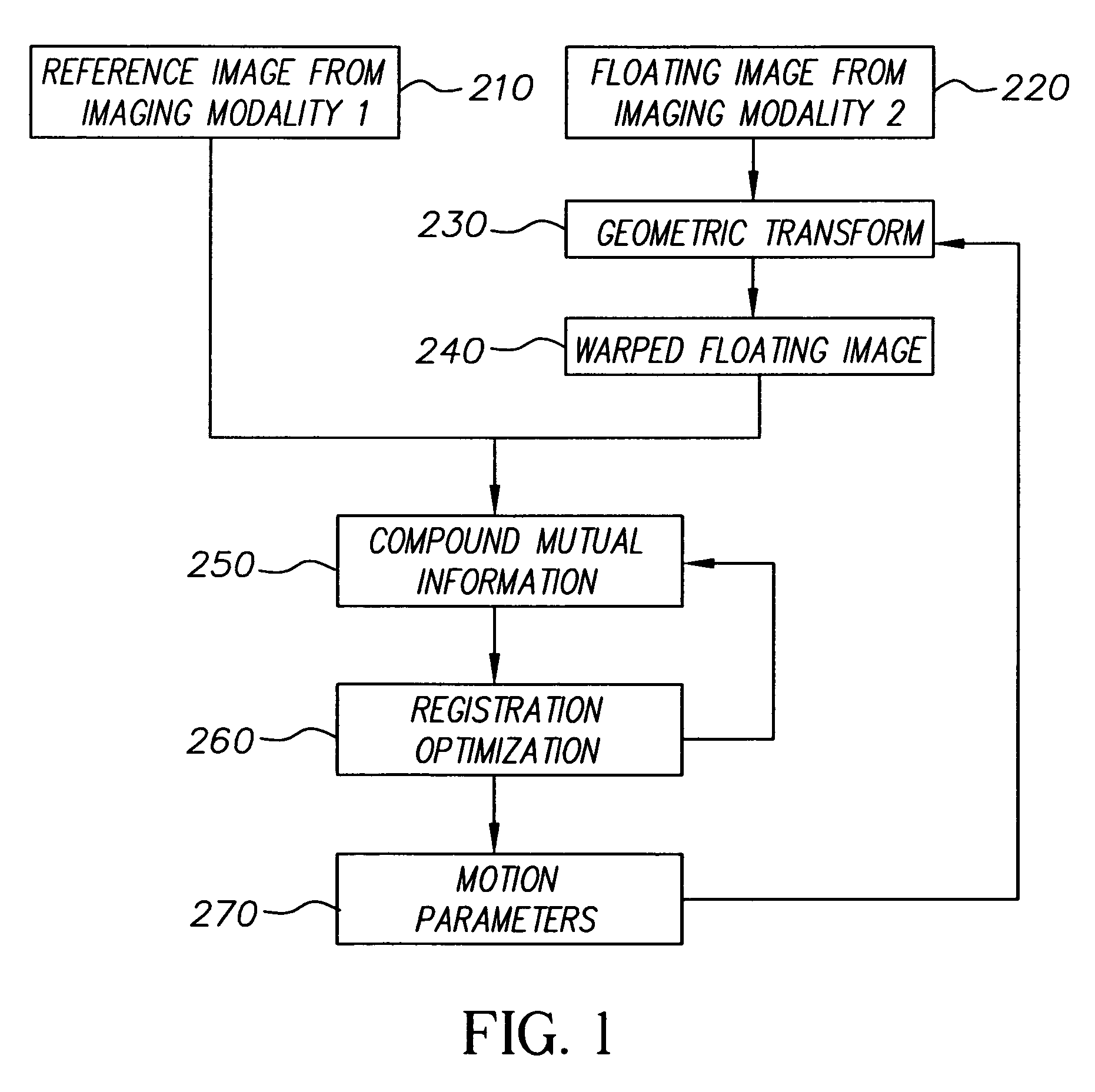
Multimodal image registration using compound mutual information
InactiveUS20060029291A1Simple methodCharacter and pattern recognitionMultimodality image registrationComputer vision
In a digital image registration method, a second digital image is transformed to be more like a first digital image using a modification function, resulting in a modified second digital image. A set of first features of each of the first and modified second digital images is determined. Zones are specified in each of the first and modified second digital images. A set of zonal features, of each of the zones is determined. Compound mutual information is computed from the first and zonal features. The modification function is altered. The transforming, determining, specifying, determining, computing, and altering are iterated until the compound mutual information is maximized.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
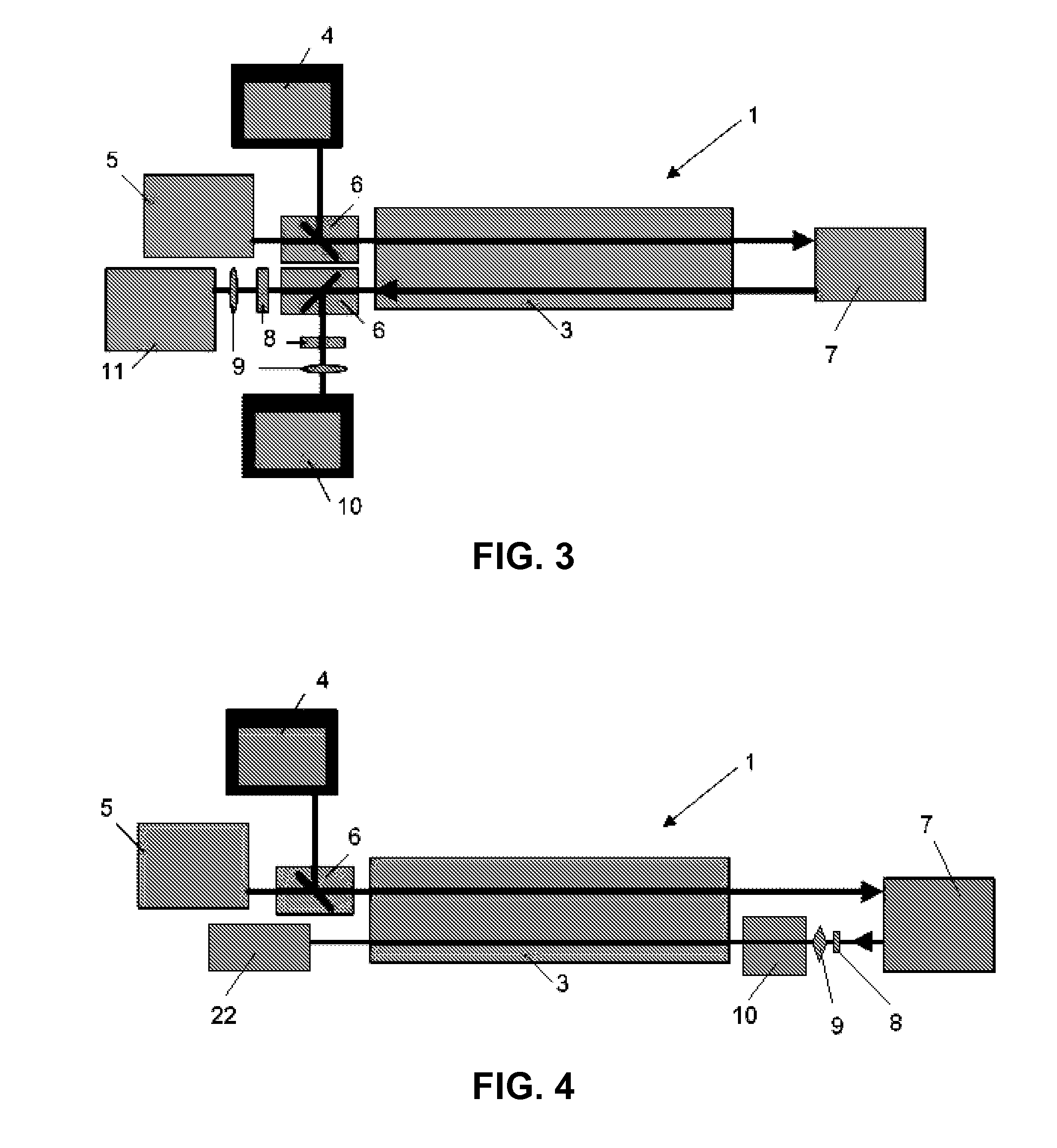
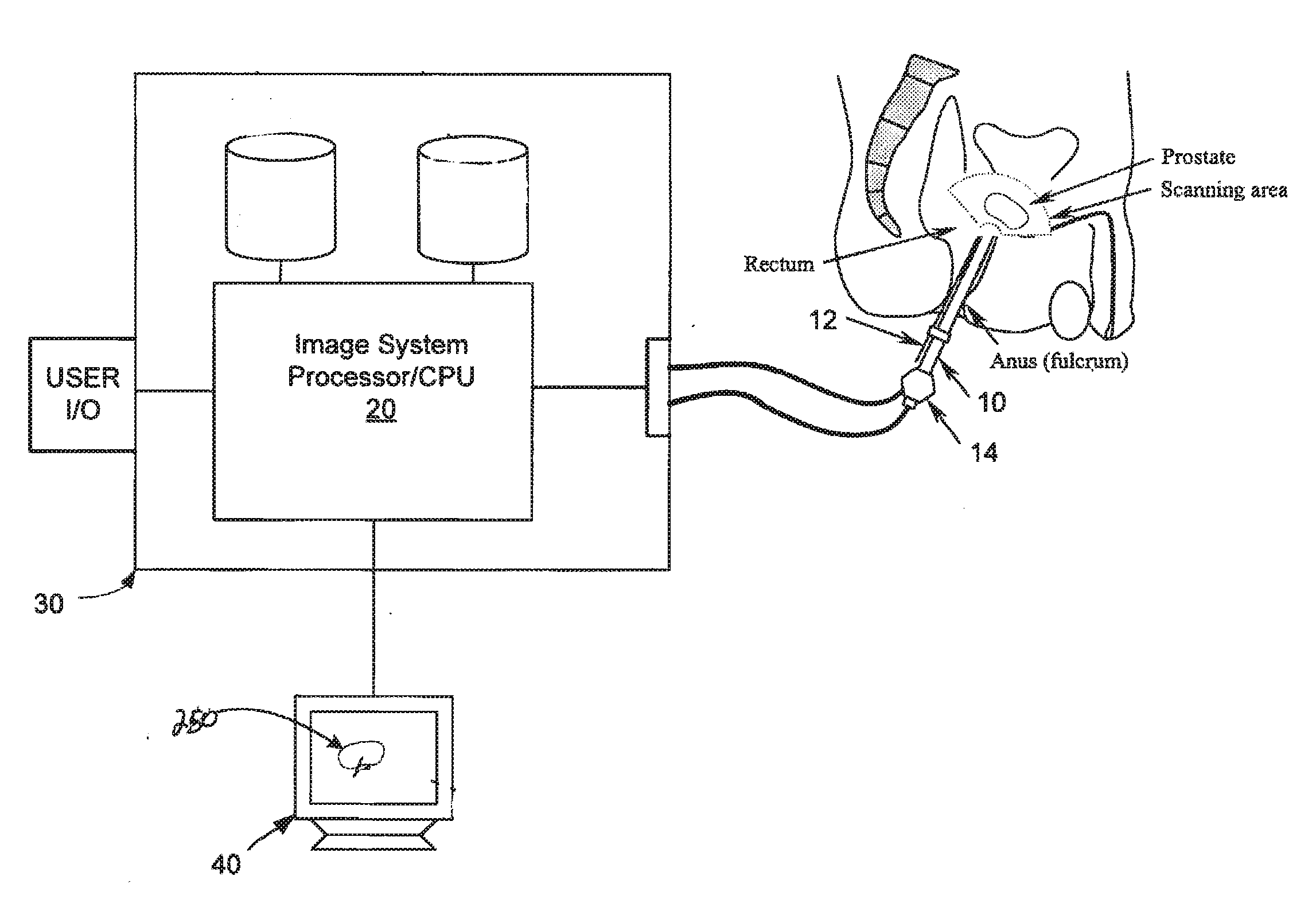
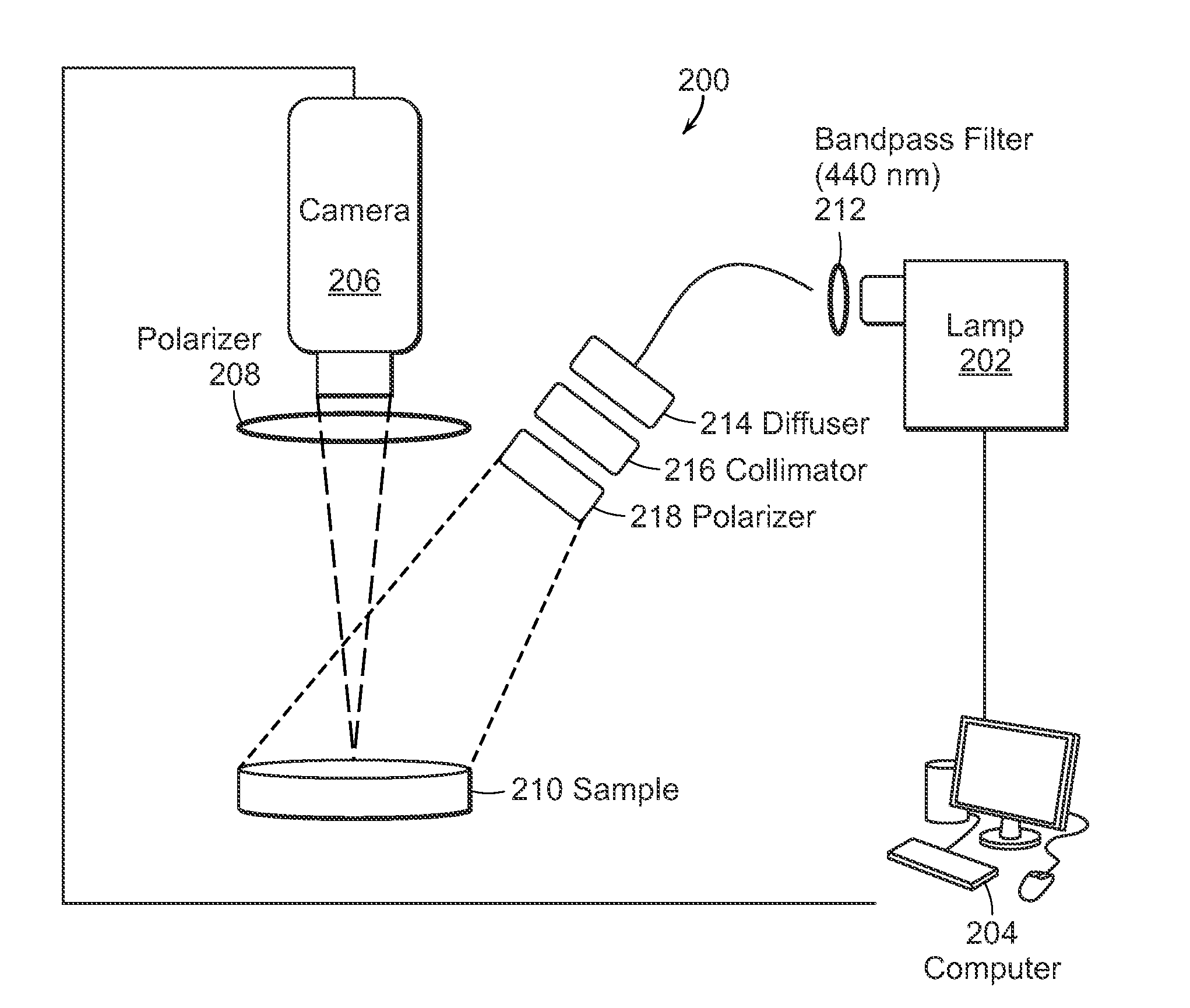
Multimodal imaging system for tissue imaging
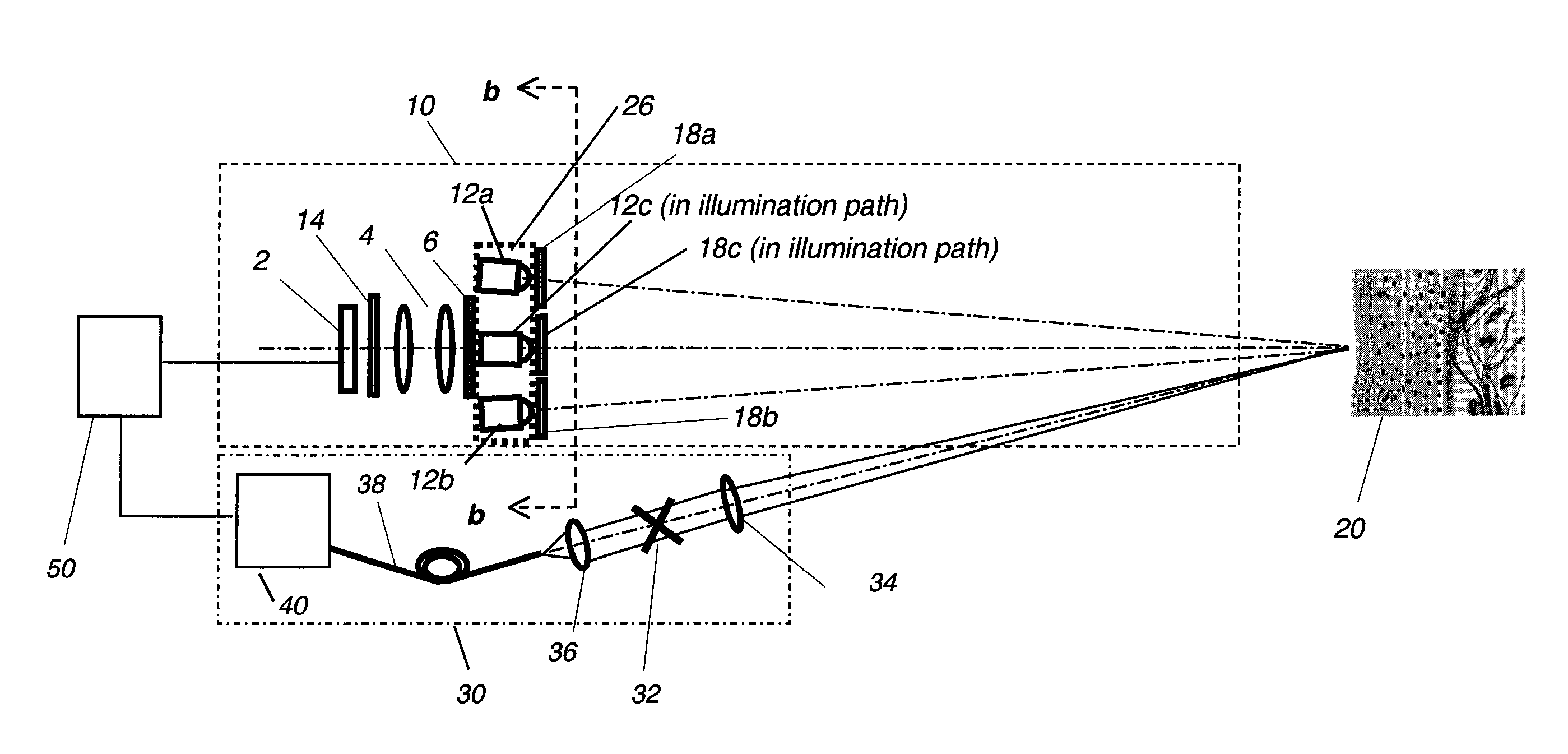
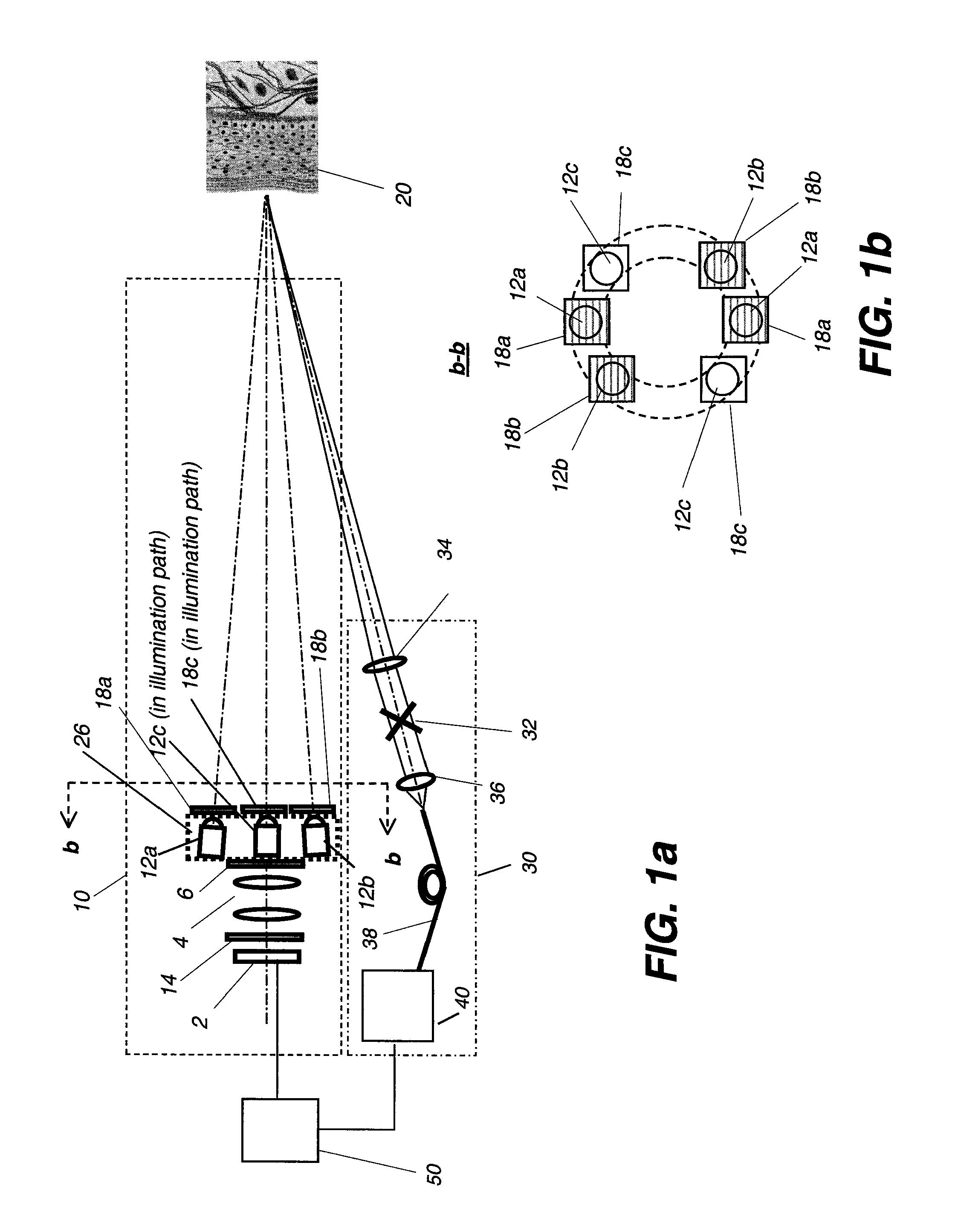
InactiveUS20090131800A1Eliminate specular reflectionsEnhance the imageDiagnostics using lightSensorsFluorescenceUltraviolet lights
An apparatus for obtaining area images and optical coherence tomography (OCT) image of a tissue comprises an image sensor, a first illumination means providing broadband polarized polychromatic light, a second illumination means providing narrow-band ultraviolet light, a third illumination means providing Near-Infrared light, an optical coherence tomography (OCT) imaging apparatus, one or more polarization elements, and an optical filter. An image processor identifies a region of interest according to area image, which can be a polarized reflectance image, a fluorescence light image, or both for the OCT imaging apparatus to obtain an OCT image over the region of interest.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Multi-modal image fusion method based on generative adversarial network and super-resolution network
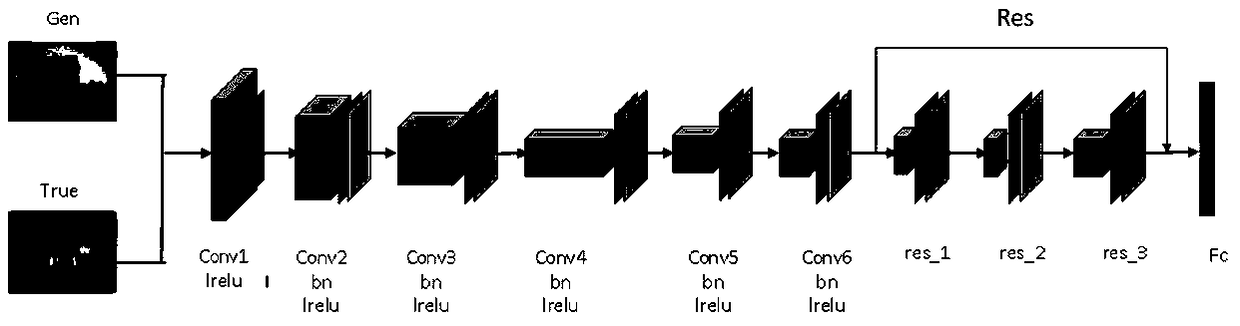
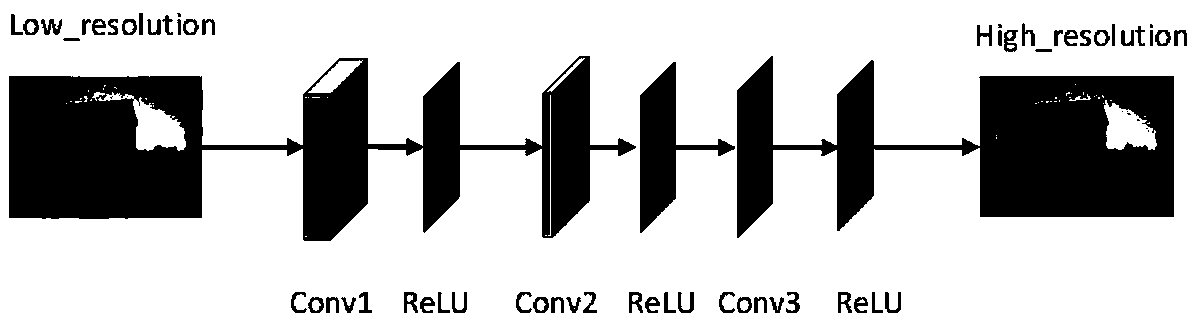
InactiveCN109325931AImprove performanceAchieve integrationImage enhancementImage analysisDiscriminatorPattern recognition
The present invention relates to an image fusion method, in particular to a multimodal image fusion method, especially a multi-modal image fusion method based on a generative adversarial network and asuper-resolution network. The method is carried out according to the following steps of designing and constructing the generative adversarial network, wherein the network structure adopts a conceiveddepth residual neural network, and obtaining a generating model through the dynamic balance training of a generator and a discriminator; constructing the super-resolution network based on the convolution layer; inputting the multi-band / multi-mode source image into the generating model to obtain the preliminary fusion image; and then inputting the image into the trained super-resolution network toget the final fusion image with high quality. The method realizes the end-to-end neural network fusion of multi-band / multi-mode images, avoids the difficulties of image multi-scale and multi-direction decomposition and fusion rule design based on prior knowledge, and realizes the adaptive network fusion.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Fused image modalities guidance
InactiveUS20090326363A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementULTRASOUND PROCEDURESTrus image
An improved system and method (i.e. utility) for registration of medical images is provided. The utility registers a previously obtained volume onto an ultrasound volume during an ultrasound procedure to produce a multimodal image. The multimodal image may be used to guide a medical procedure, In one arrangement, the multimodal image includes MRI and / or MRSI information presented in the framework of a TRUS image during a TRUS procedure.
Owner:EIGEN INC
Multimodal image registration using compound mutual information
InactiveUS7639896B2Simple methodCharacter and pattern recognitionMultimodality image registrationDigital image
In a digital image registration method, a second digital image is transformed to be more like a first digital image using a modification function, resulting in a modified second digital image. A set of first features of each of the first and modified second digital images is determined. Zones are specified in each of the first and modified second digital images. A set of zonal features, of each of the zones is determined. Compound mutual information is computed from the first and zonal features. The modification function is altered. The transforming, determining, specifying, determining, computing, and altering are iterated until the compound mutual information is maximized.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
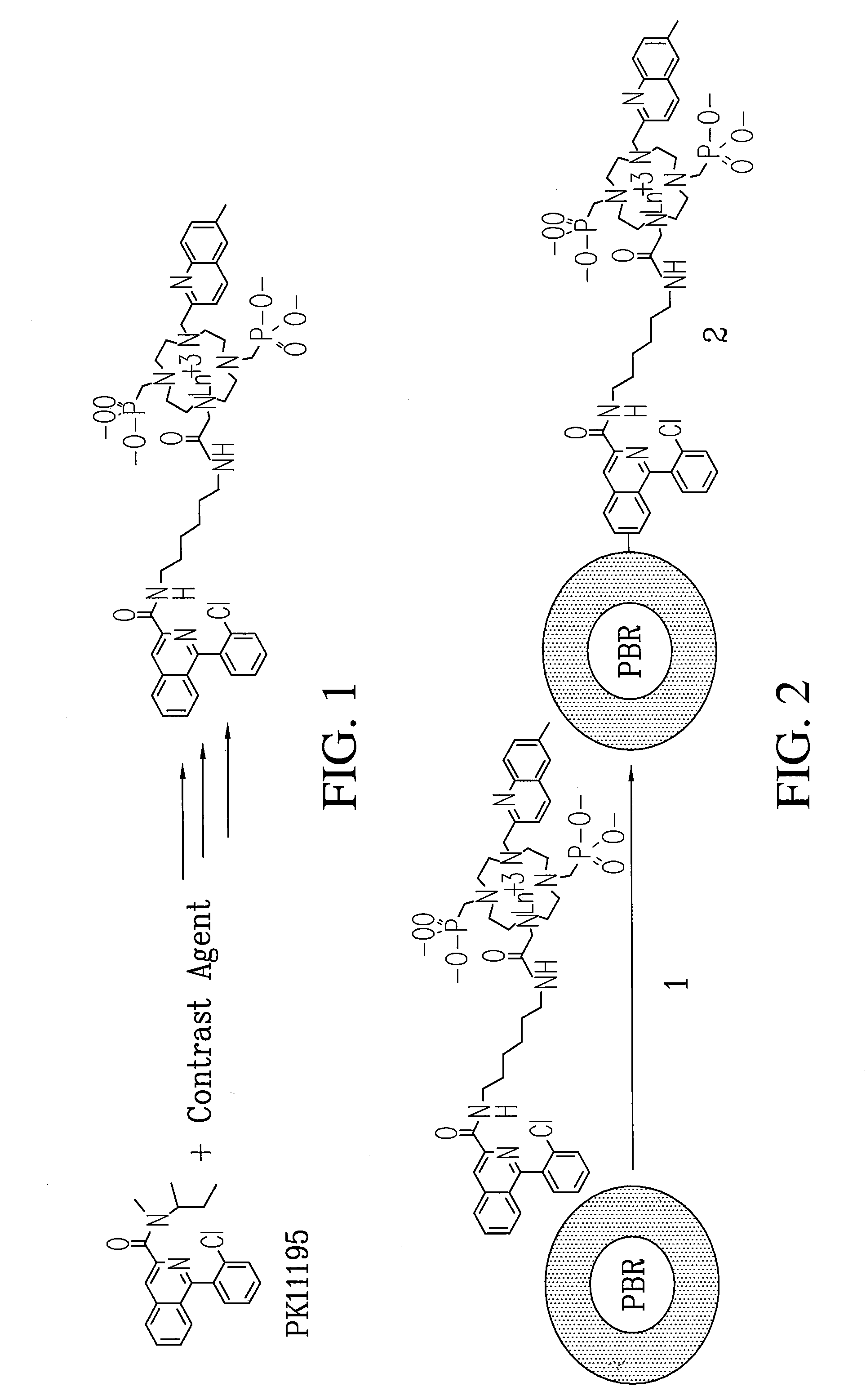
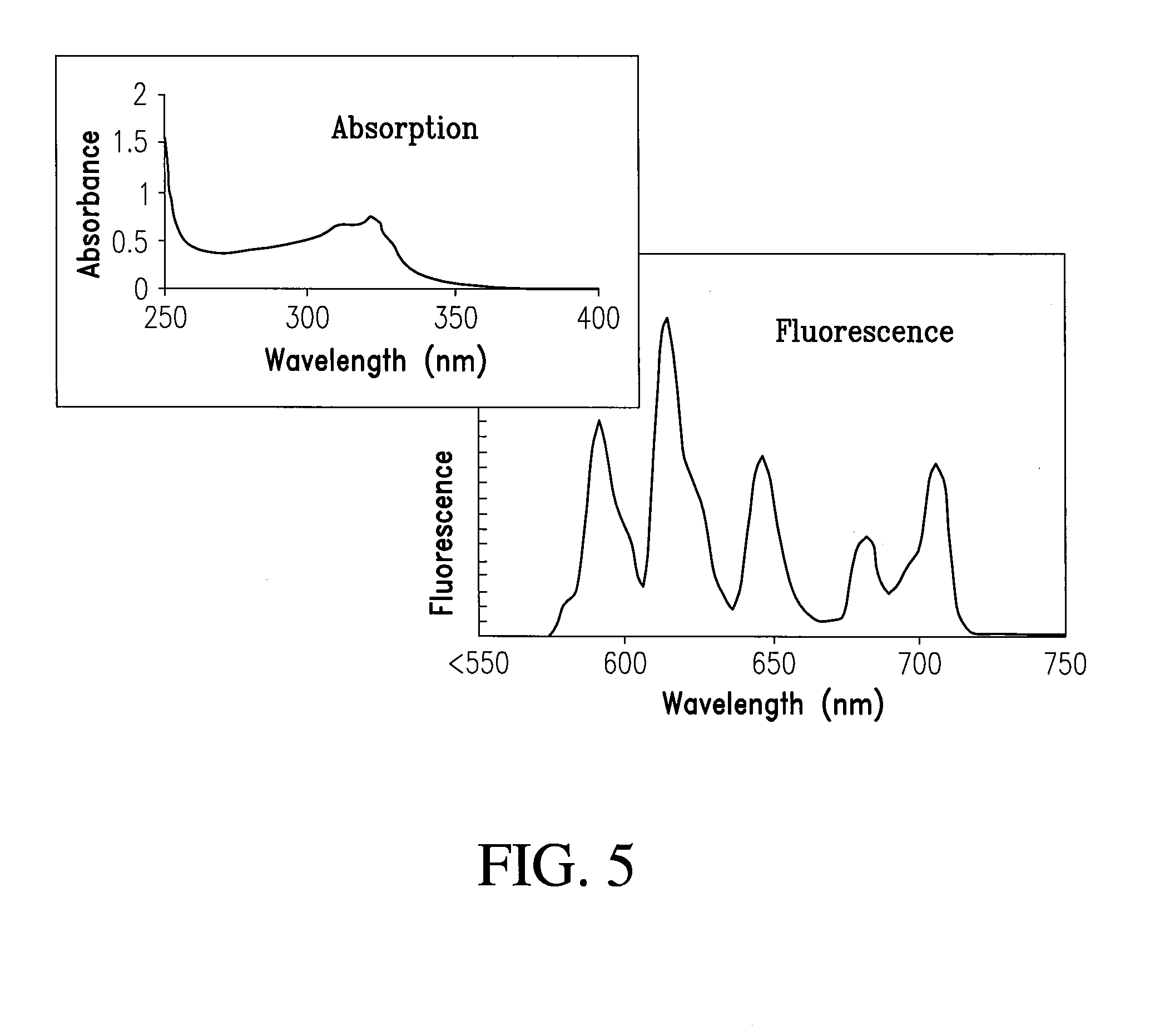
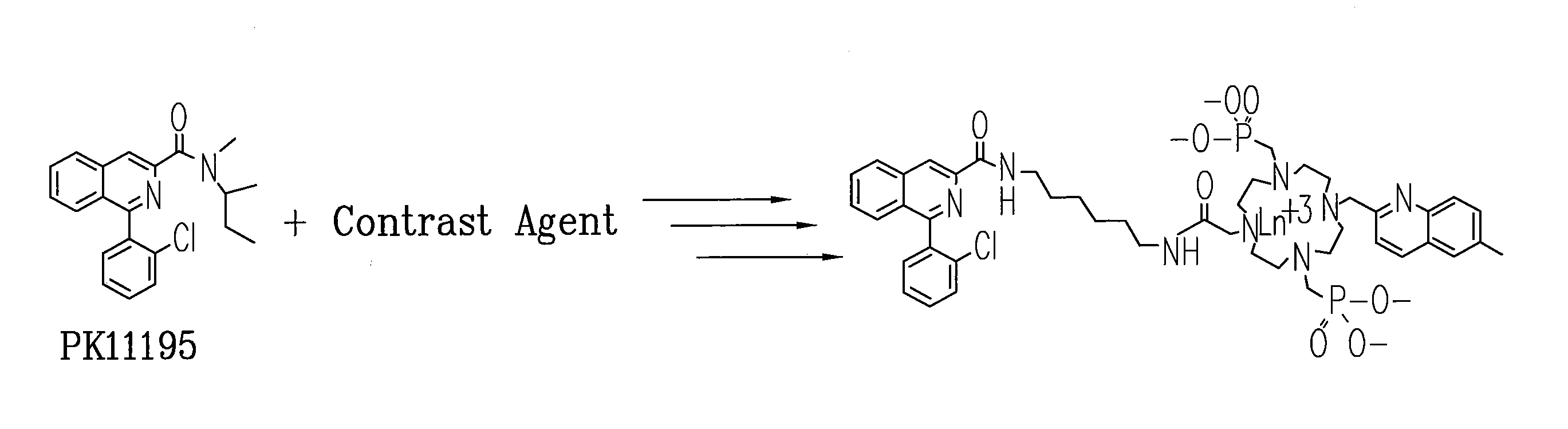
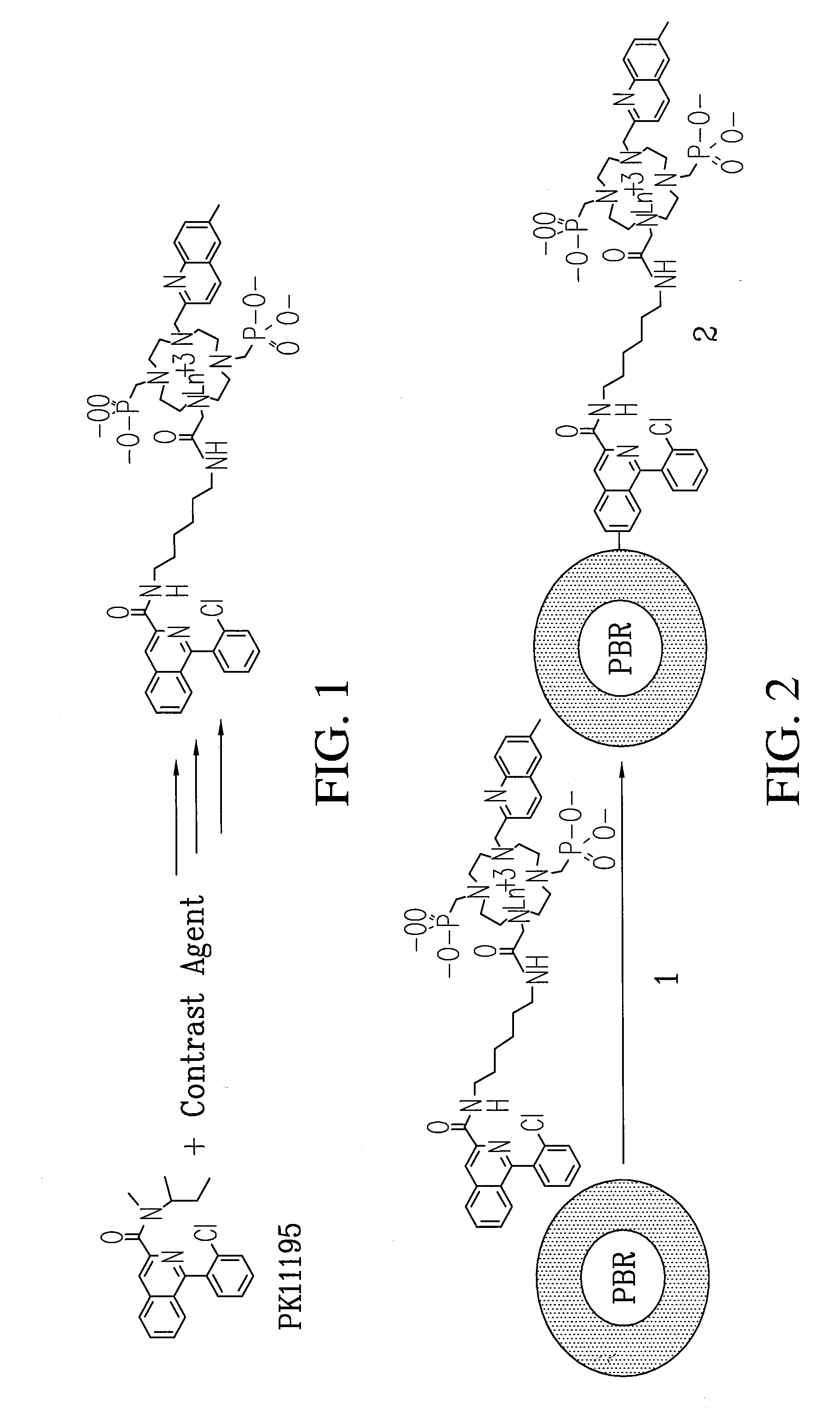
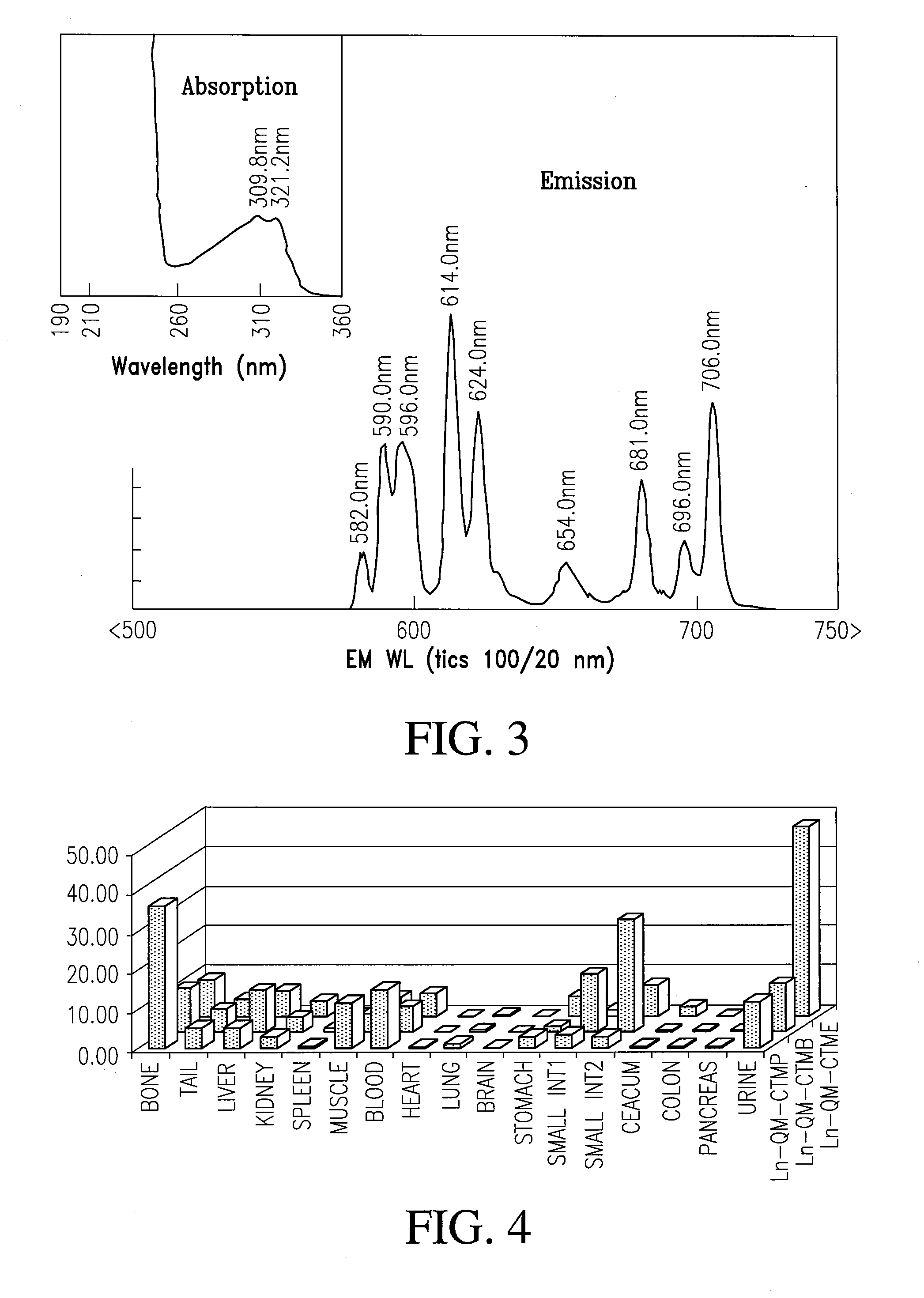
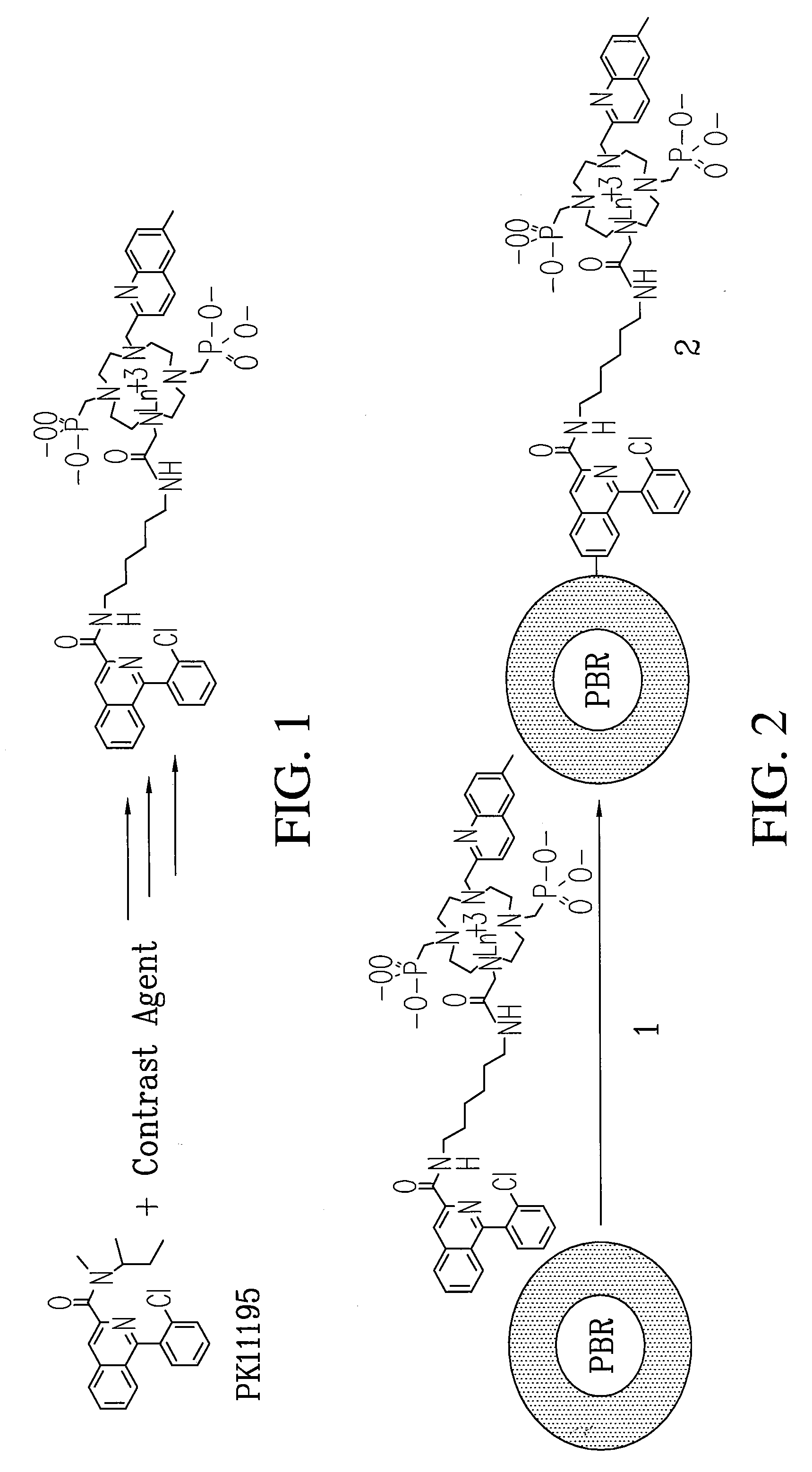
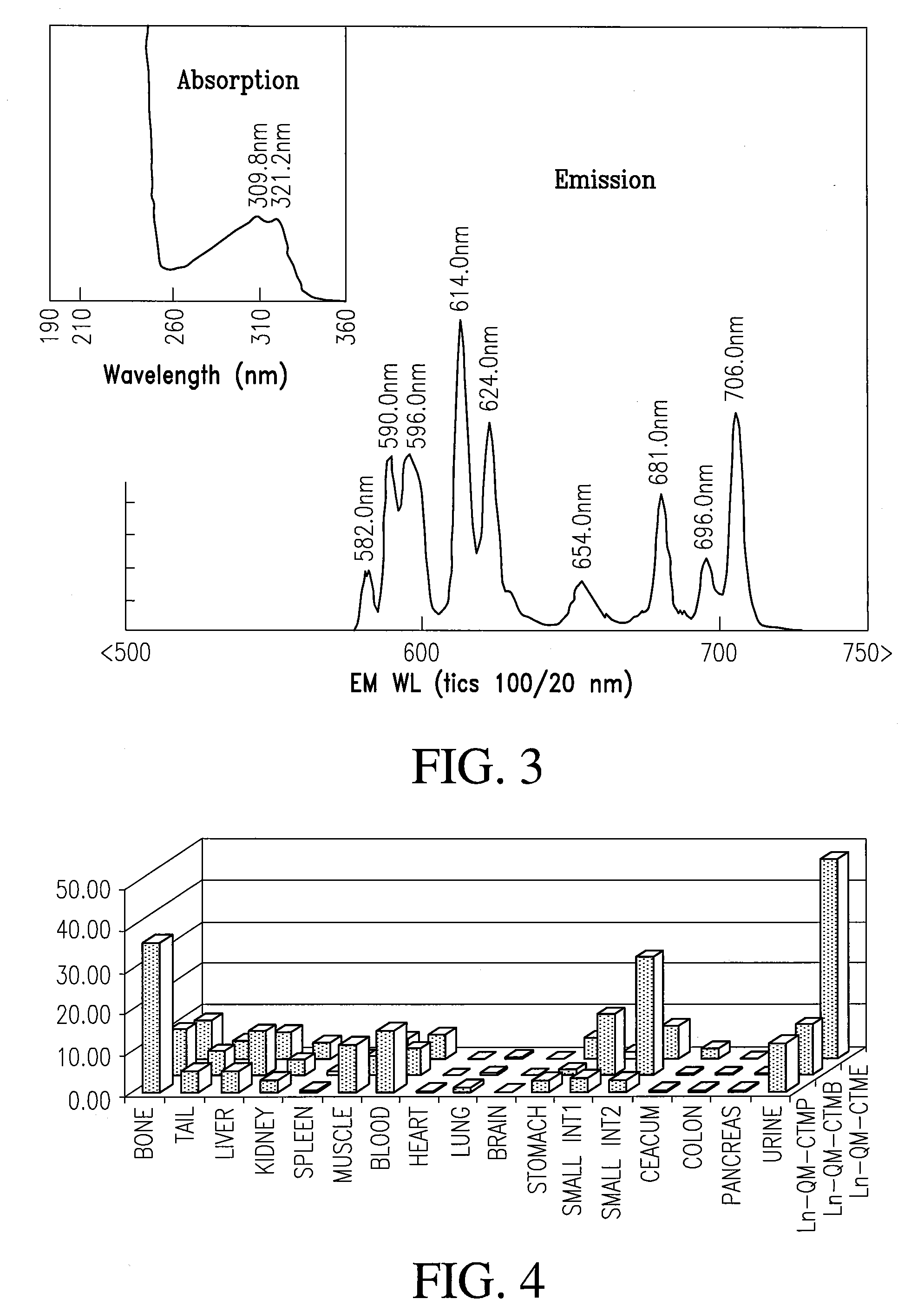
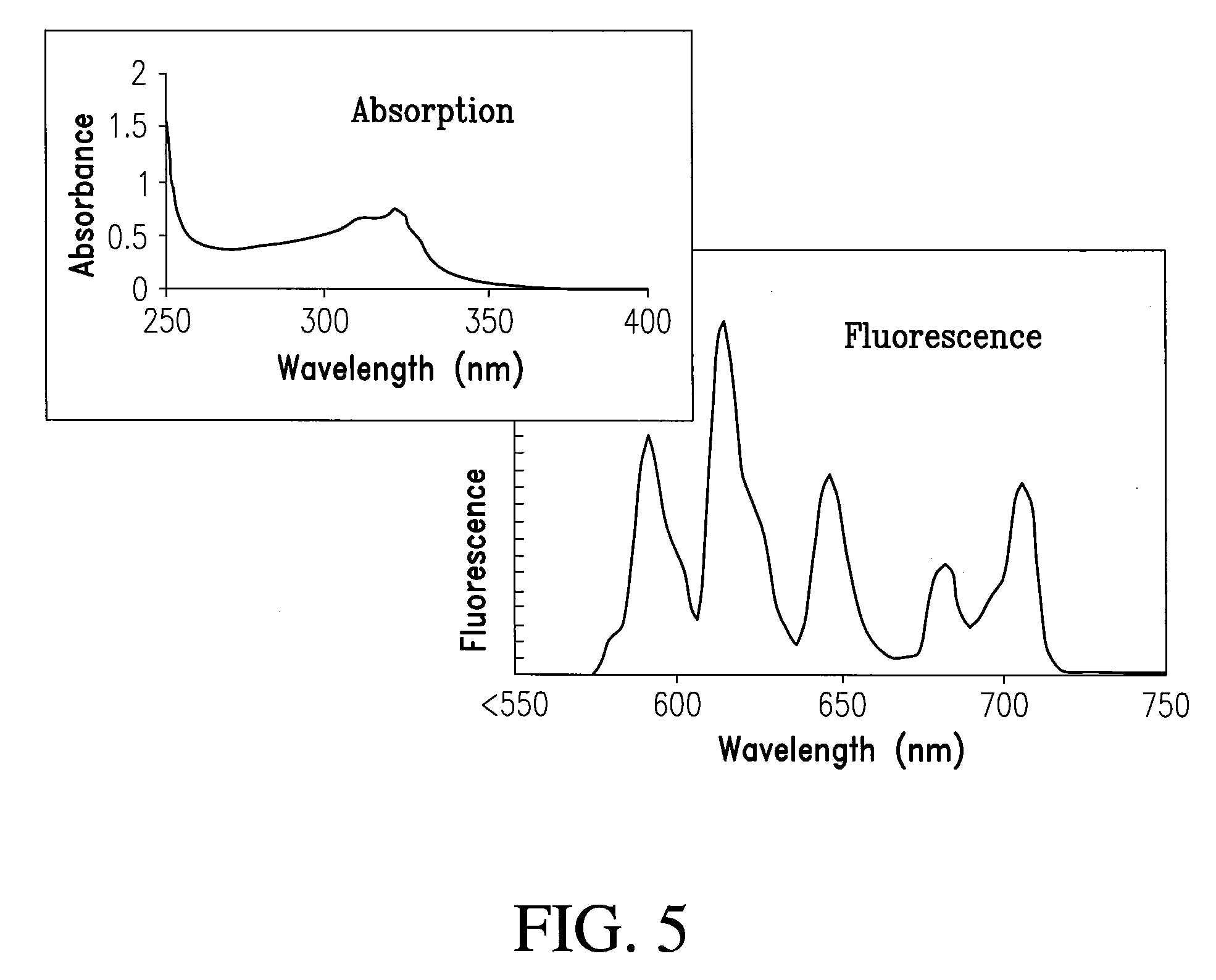
Multi-use multimodal imaging chelates
InactiveUS7338651B2Improve discriminationEasy to detectUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsOrganic active ingredientsCancer cellFluorescence
Cyclen-based chelates can be used as contrast agents for multi-modal imaging of tissue cells. The cyclen-based chelates are preferably polyazamacrocyclic molecules formed from 1,4,7,10 tetraazacyclododecane (“cyclen”) having varying chelating ions, phosphoester chains, and light harvesting moieties. By changing the chelating ion, phosphoester chain length and / or the light harvesting moiety different imaging techniques, such as MRI, CT, fluorescence and absorption, x-ray and NIR, may be employed to image the tissue cells. Additionally, the cyclen-based chelates may be conjugated to provide for site-specific delivery of the cyclen-based chelate to the desired tissue cells. The cyclen-based chelates may also be delivered to the tissue cells by attaching the cyclen-based chelates to a polymeric delivery vehicle. Although these cyclen-based chelates have a wide variety of application, the preferred use is for imaging of cancer cells, such as brain cancer, for improving resection of a cancerous tissue.
Owner:TEXAS TECH UNIV SYST +1
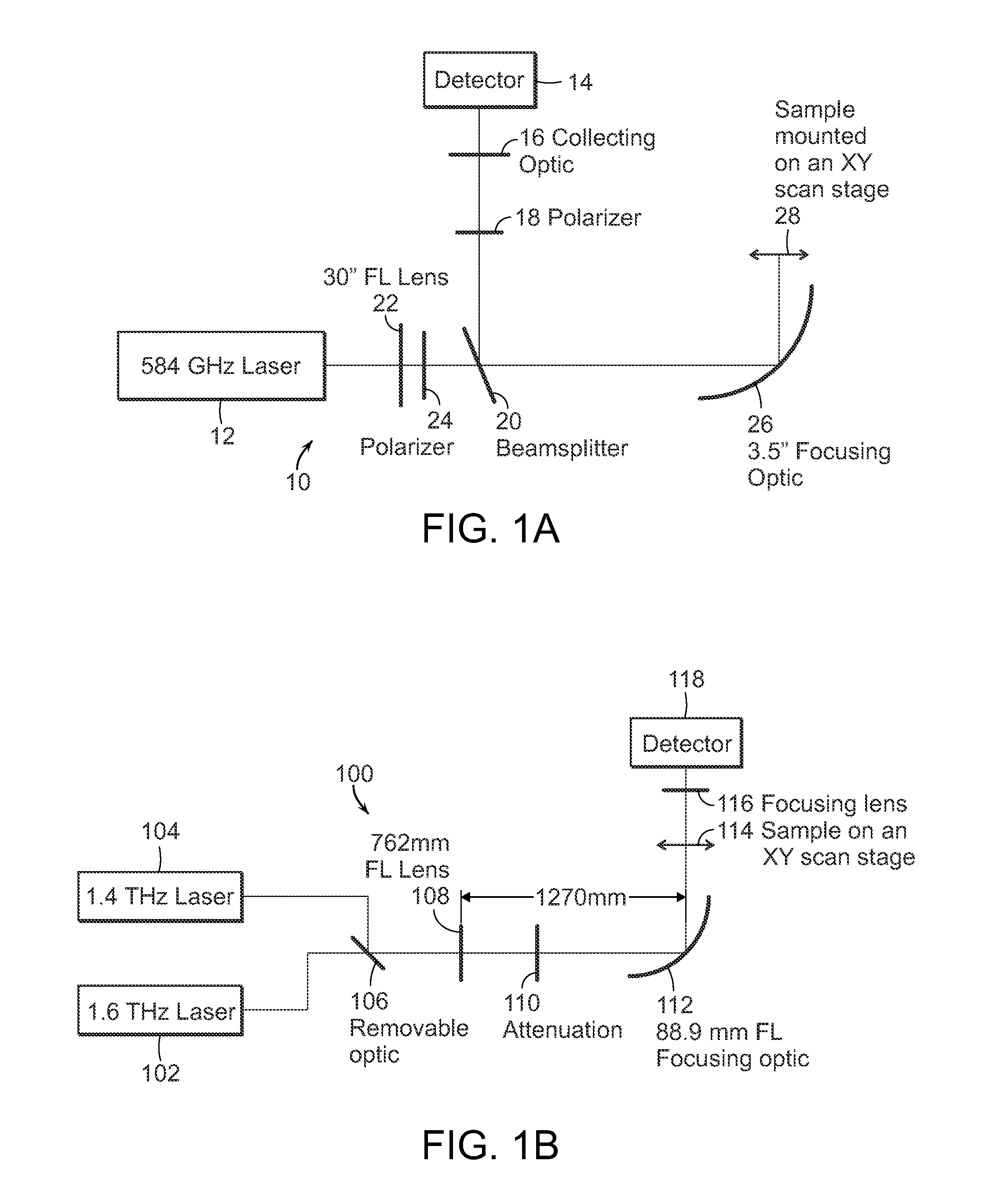
Multimodal imaging for the detection of tissue structure and composition
InactiveUS20150164327A1Accurately presentedSolution value is not highMedical imagingPolarisation-affecting propertiesTumor marginLight delivery
The present invention relates to the use of optical and terahertz imaging of tissue for measuring characteristics to assist in diagnosis. A light delivery and collection system is used that can aid in the detection of tumor margins, for example. A data processor processes the image data to determine characteristics of a region of tissue.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Enhanced multi-protocol analysis via intelligent supervised embedding (empravise) for multimodal data fusion
ActiveUS20140037172A1Image analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmDimensionality reduction
The present invention provides a system and method for analysis of multimodal imaging and non-imaging biomedical data, using a multi-parametric data representation and integration framework. The present invention makes use of (1) dimensionality reduction to account for differing dimensionalities and scale in multimodal biomedical data, and (2) a supervised ensemble of embeddings to accurately capture maximum available class information from the data.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Cloud computation based early oncotherapy efficacy evaluation system and method
The invention discloses a cloud computation based early oncotherapy efficacy evaluation system and method. The system comprises a multimodal imaging acquisition device in the oncotherapy process, a voxel-based multimodal image registration and fusion cloud computation device, a voxel-based early evaluation cloud computation device for efficacies in the oncotherapy process, and a posttreatment cloud computation evaluation device. The system and method provides more accurate, reliable and real-time information abundant in information amount to doctors, and accurate bases are provided for establishing patient-orientated personalized treatment programs. By establishment of a molecular image guided early oncotherapy efficacy evaluation cloud system with high-speed processing capacity, a posttreatment historical data reference platform is provided for medical staff, and a platform used for providing bases to timely adjustment, fast tracking or implementation of treatment schemes on the basis of real-time data in the current treatment course can be provided.
Owner:苏州动影信息科技有限公司
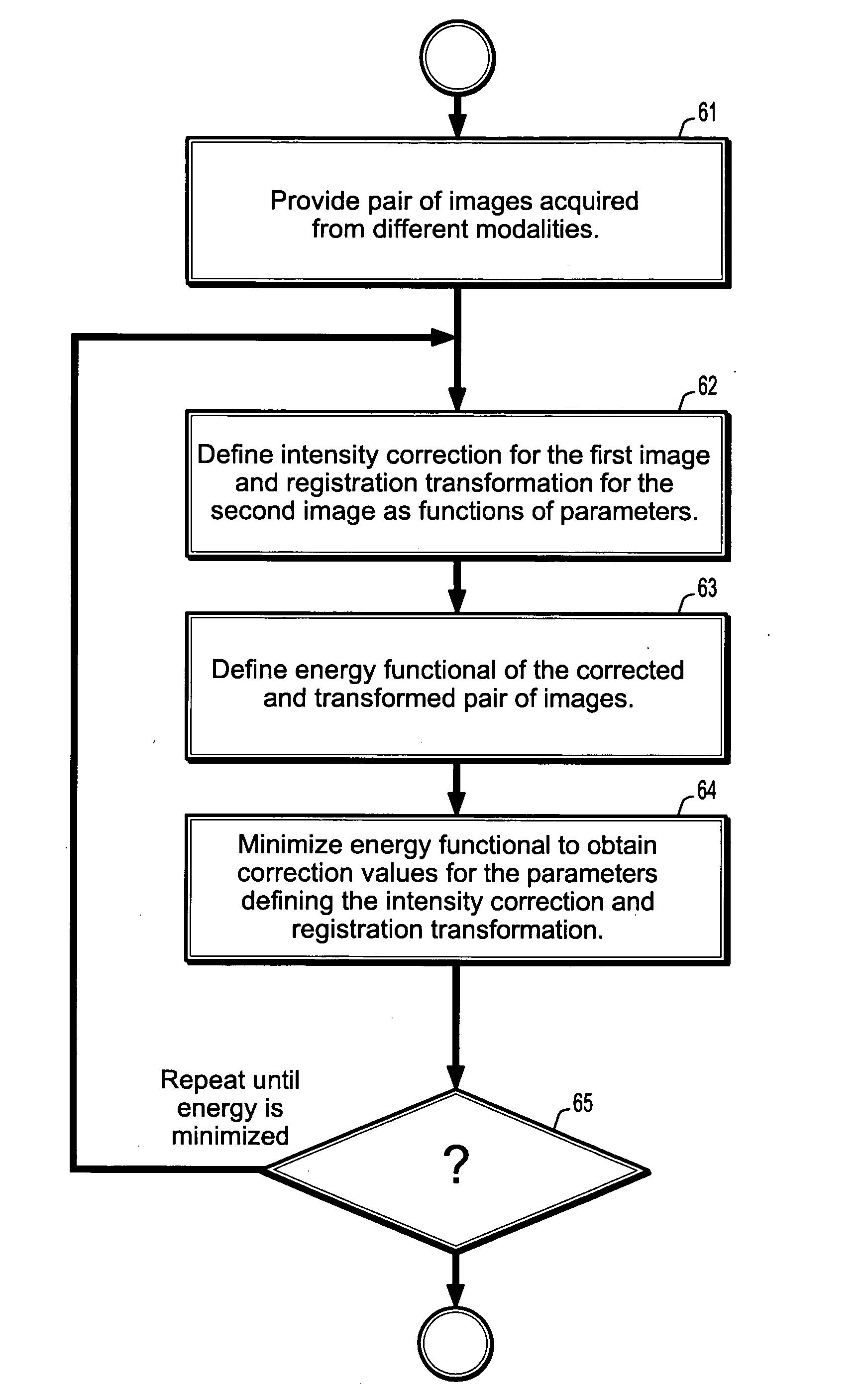
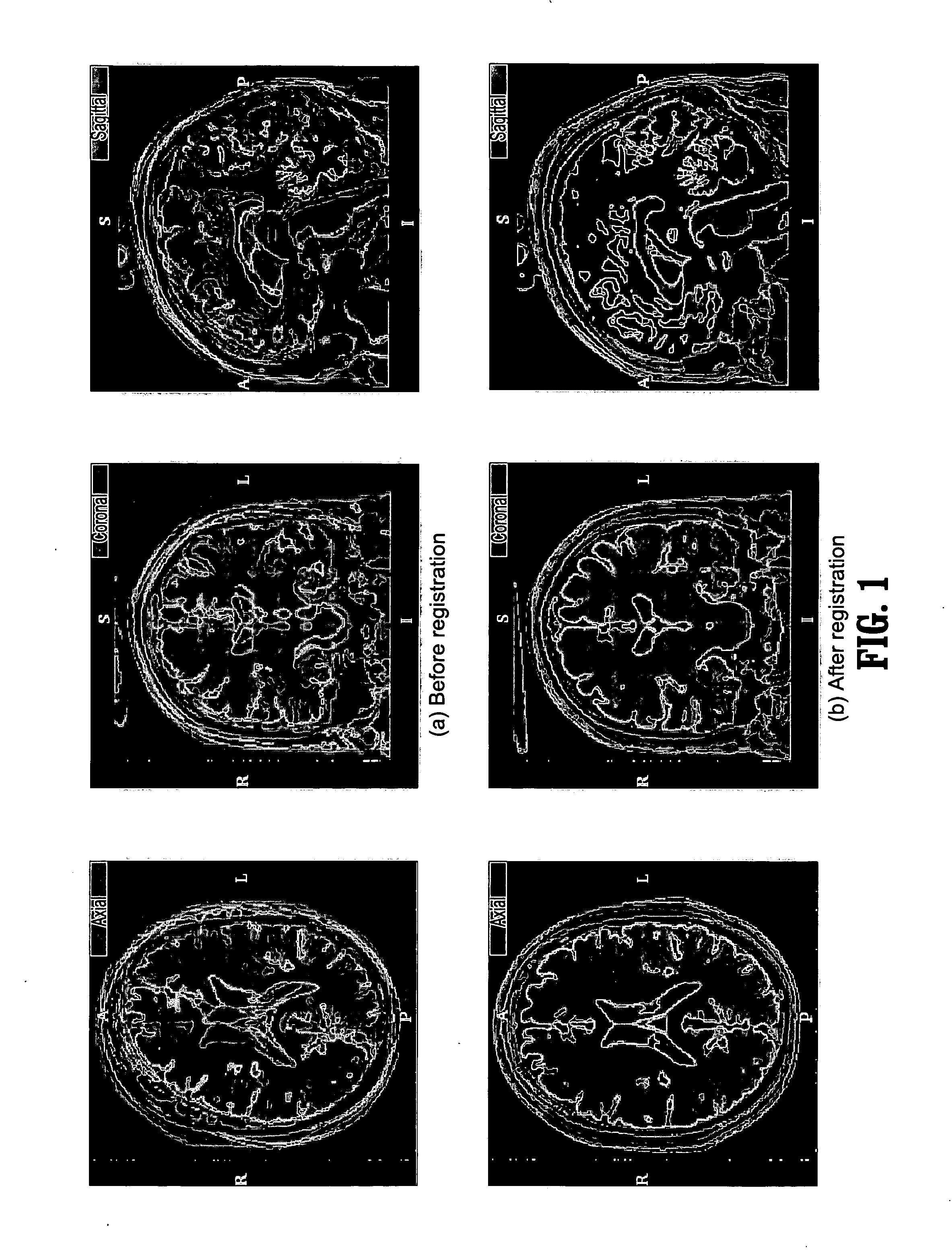
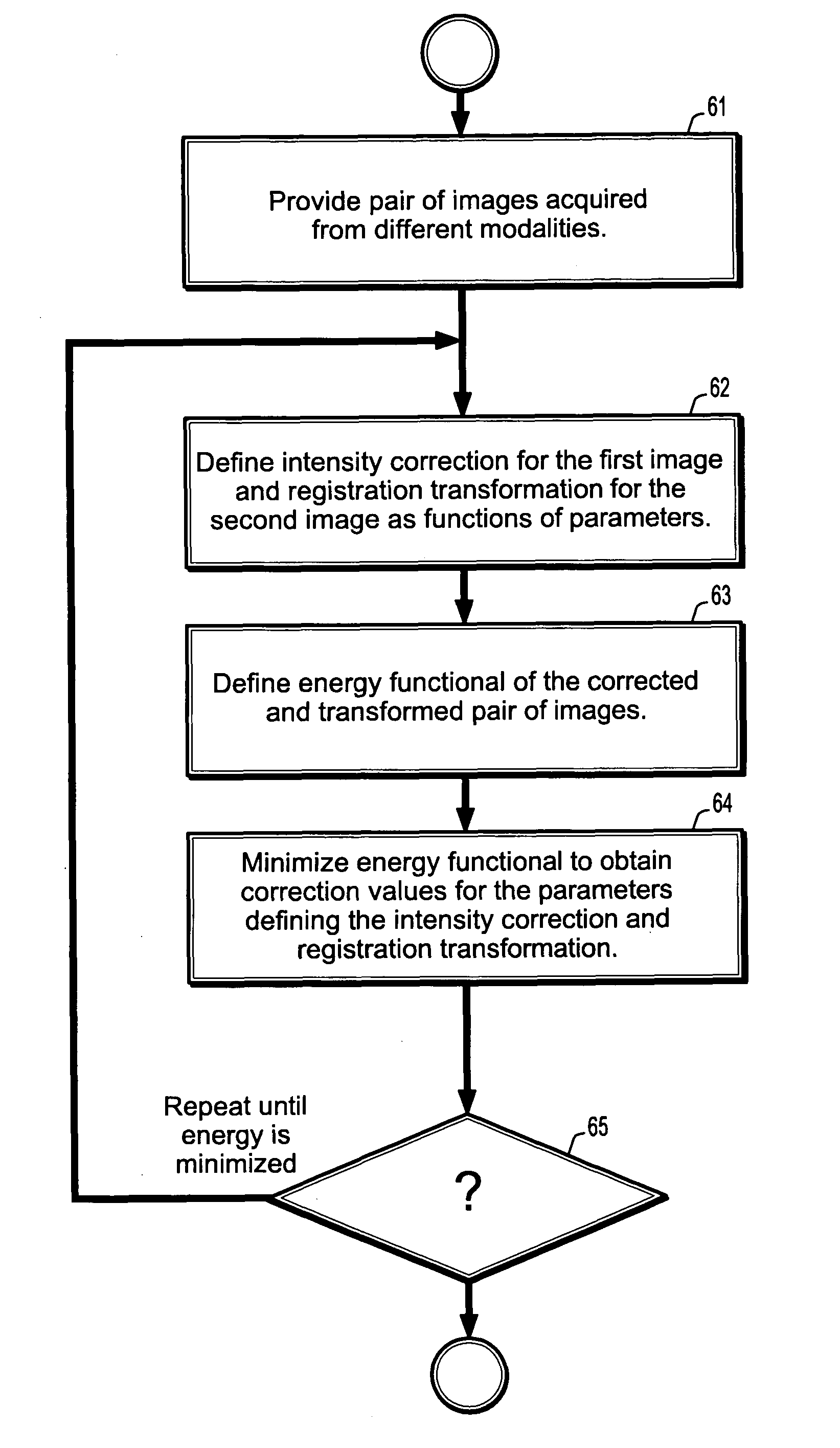
System and method for fast multimodal registration by least squares
InactiveUS20070086678A1Minimize energy functionPrecise functionImage enhancementImage analysisImaging modalitiesMultimodality image registration
A method for multimodal image registration includes providing a pair of images acquired from differing imaging modalities, defining an intensity correction function that corrects the intensities of a first image in terms of the intensities of the second image, defining a registration transformation function that registers the second image with the first image, wherein said intensity correction function and transformation function are functions of a plurality of parameters, obtaining corrections to the plurality of parameters by minimizing an energy functional of a square difference of the intensity corrected first image and the registration transformed second image, and updating the intensity correction function and the registration transformation function based on the corrected plurality of parameters.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
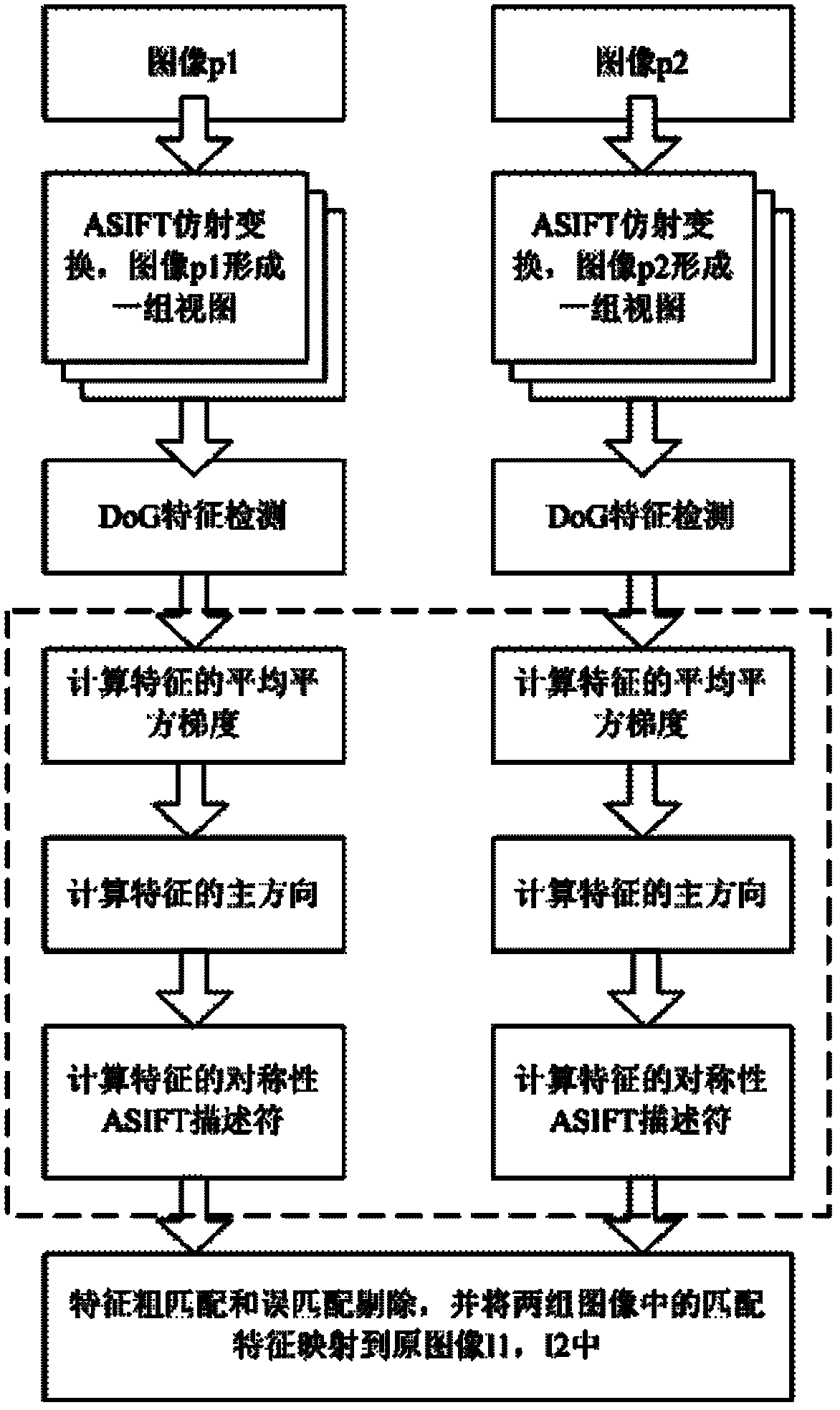
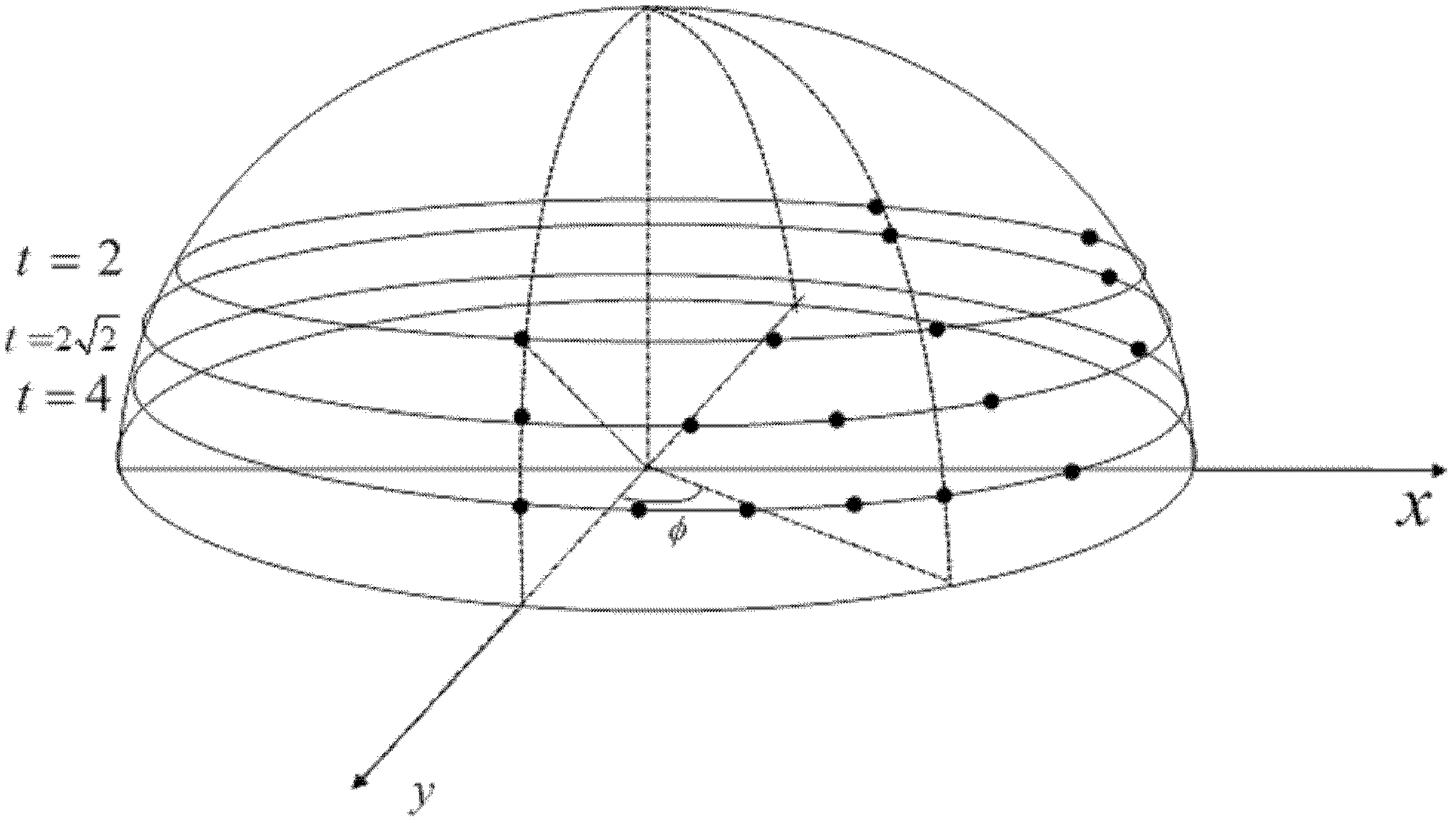
Multimodal image feature extraction and matching method based on ASIFT (affine scale invariant feature transform)
InactiveCN102231191AHas a completely affine invariant propertySolve the unsolvable affine invariance problemImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorScale-invariant feature transform
The invention discloses a multimodal feature extraction and matching method based on ASIFT (affine scale invariant feature transform), and the method is mainly used for realizing the point feature extraction and matching of the multimodal image which cannot be solved in the prior art. The method can be realized through the following steps: carrying out sampling on the ASIFT affine transformational model tilting value parameters and longitude parameters, thus obtaining two groups of views of two input images; adopting a difference of Gauss (DoG) feature detection method to detect the position and size of the feature point on the two groups of views; using an average squared-gradient method to set the principle directions of the features and setting the feature vector amplitude by a counting method; calculating the symmetric ASIFT descriptor of the features; and adopting a nearest neighborhood method to carry out coarse matching on the symmetric ASIFT descriptor, and using an optimized random sampling method to remove mis-matching features. In the invention, features can be extracted and matched in the images sensed by various sensors, and the method provided by the invention has the characteristic of invariability after complete affine, and can be applied to the fields of object recognition and tracking, image registration and the like.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Multimodal imaging system for tissue imaging
An apparatus for obtaining area images and optical coherence tomography (OCT) image of a tissue comprises an image sensor, a first illumination means providing broadband polarized polychromatic light, a second illumination means providing narrow-band ultraviolet light, a third illumination means providing Near-Infrared light, an optical coherence tomography (OCT) imaging apparatus, one or more polarization elements, and an optical filter. An image processor identifies a region of interest according to area image, which can be a polarized reflectance image, a fluorescence light image, or both for the OCT imaging apparatus to obtain an OCT image over the region of interest.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
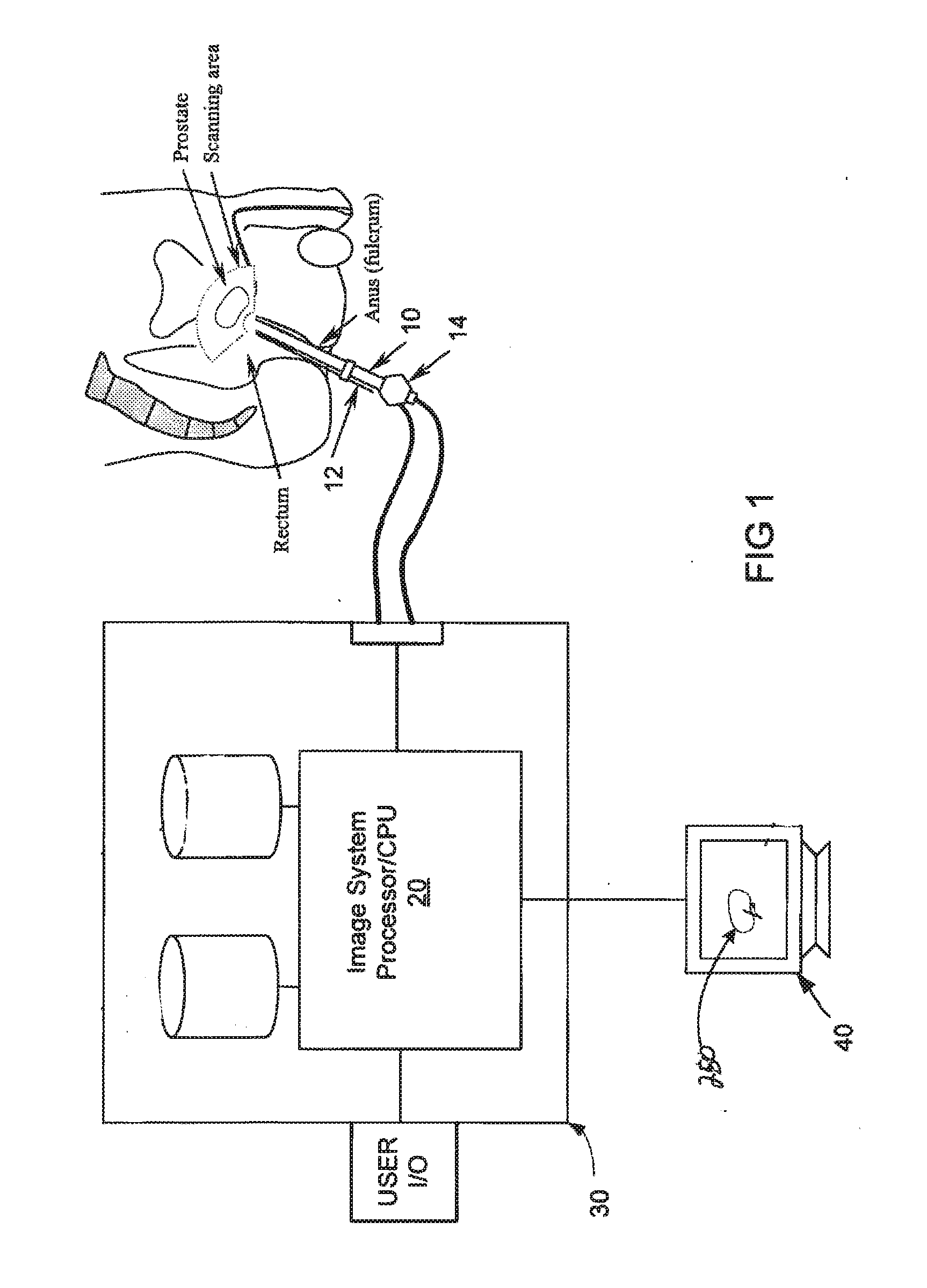
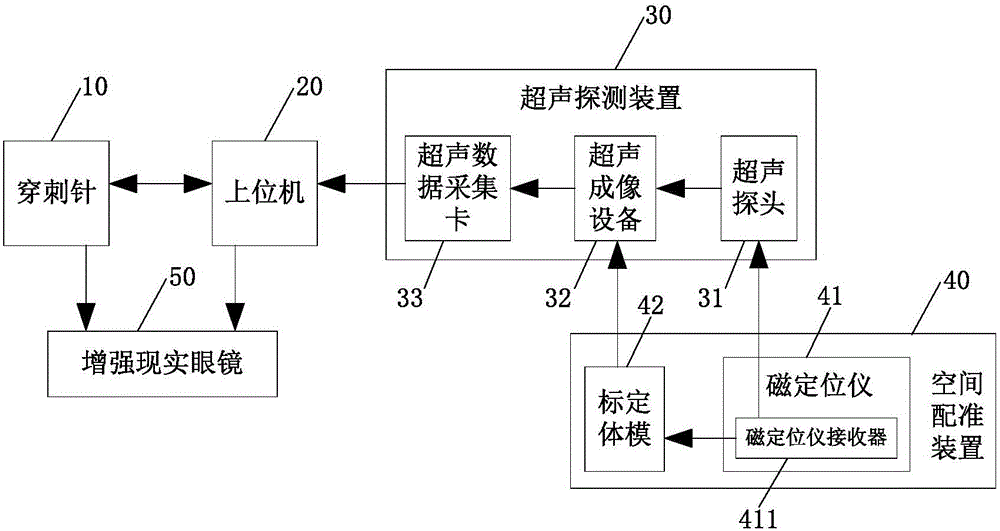
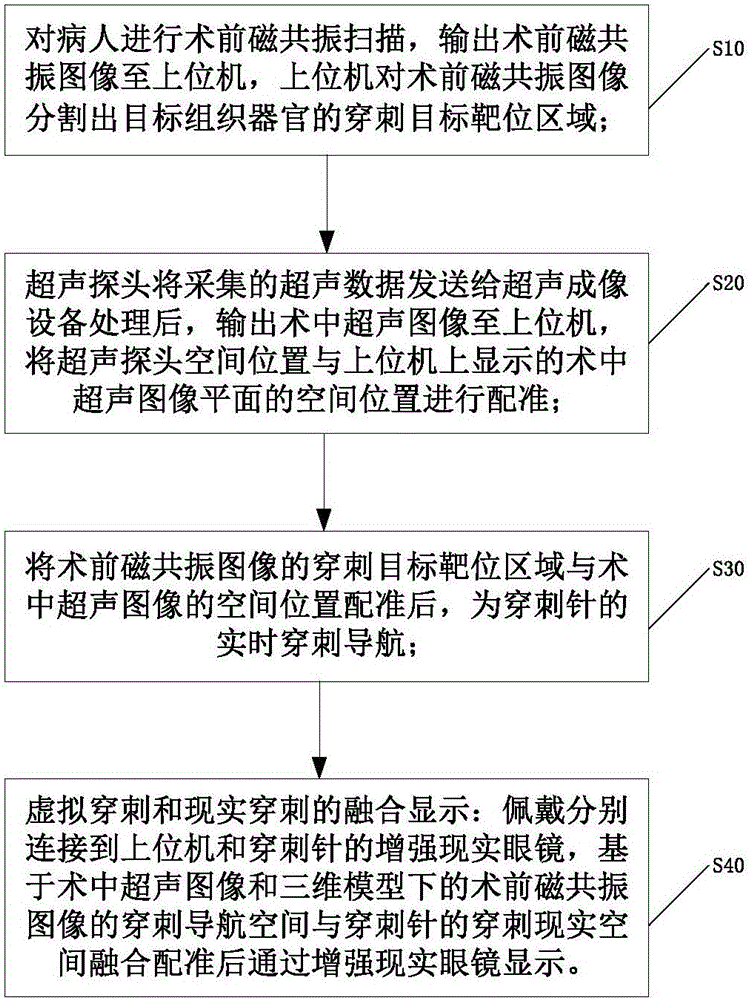
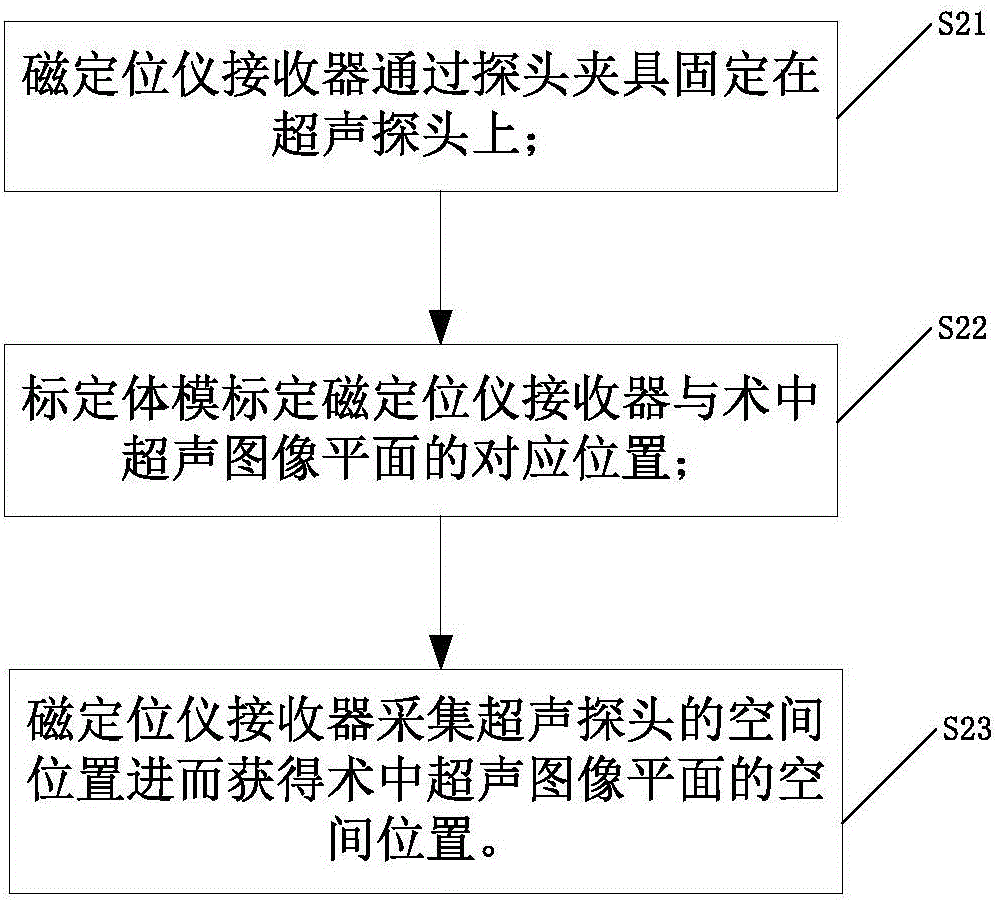
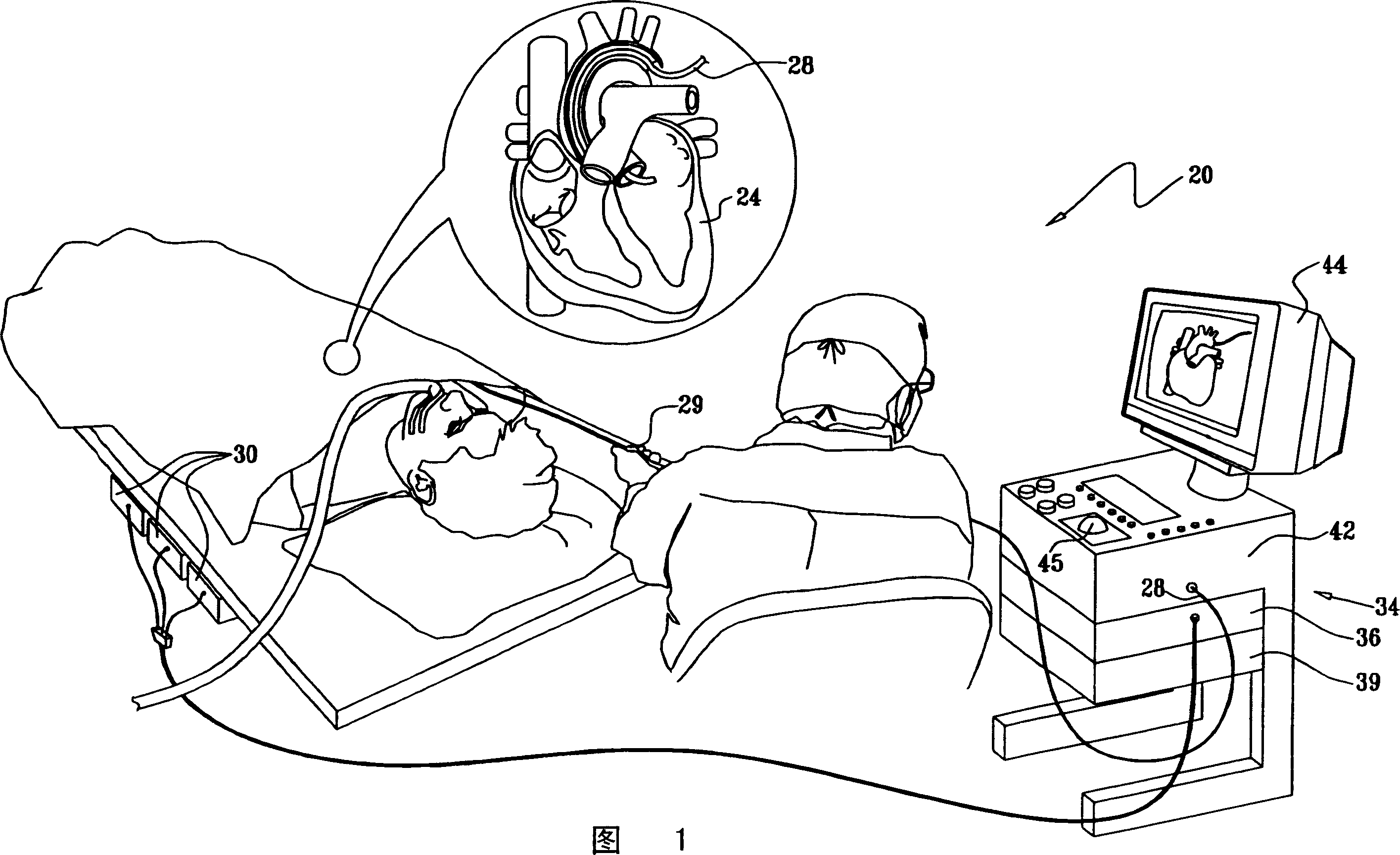
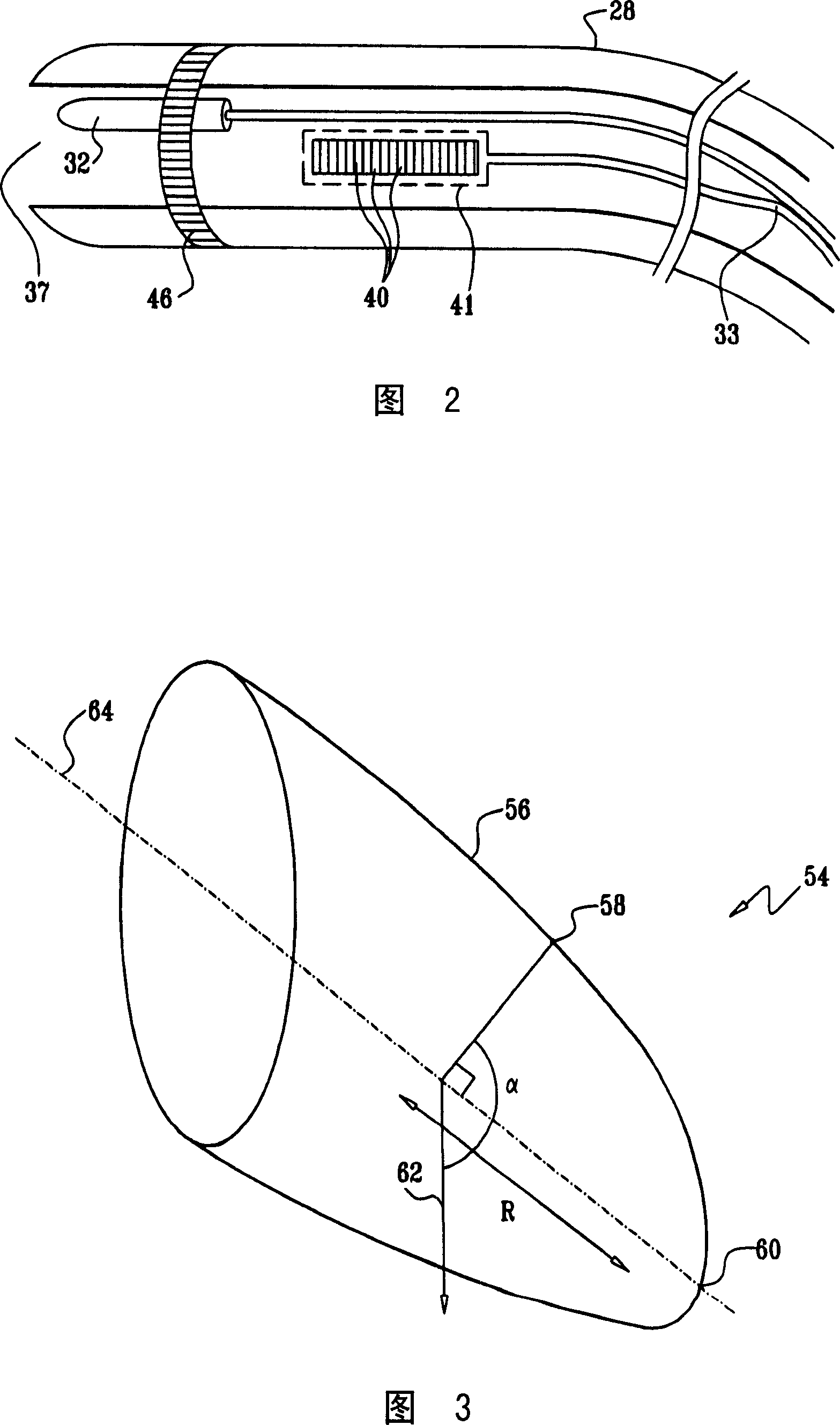
Real-time puncture navigation system and navigation method thereof
ActiveCN106063726AImprove convenienceImprove accuracySurgical needlesSurgical navigation systemsUltrasound imagingResonance
The invention discloses a real-time puncture navigation system, which comprises a puncture needle; a host computer to display puncture navigation space of a multimodal image based on the fusion of a magnetic resonance image prior to a surgery and an ultrasonic image during the surgery; an ultrasonic detecting device comprising an ultrasonic probe and an ultrasonic imaging apparatus wherein the ultrasonic probe sends acquired ultrasonic data to the ultrasonic imaging apparatus for processing and outputs the ultrasonic image during the surgery for display and transmission to the host computer; a space registering device comprising a magnetic locator and a calibration body die wherein the magnetic locator receiver is fixedly arranged on the ultrasonic probe through a probe fixture, the calibration body die calibrates the corresponding positions of the magnetic locator receiver and the ultrasonic image plane during the surgery and the magnetic locator receiver acquires the space position of the ultrasonic probe so as to further obtain the space position of the ultrasonic image plane during the surgery; and reality augmented glasses in connection with the host machine and the puncture needle. According to the invention, no special ultrasonic probe and imaging apparatus are needed, making the system not limited to specific puncture parts, and achieving convenient and high puncture navigation.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Segmentation and registration of multimodal images using physiological data
Systems and methods are provided for registering maps with images, involving segmentation of three-dimensional images and registration of images with an electro-anatomical map using physiological or functional information in the maps and the images, rather than using only location information. A typical application of the invention involves registration of an electro-anatomical map of the heart with a preacquired or real-time three-dimensional image. Features such as scar tissue in the heart, which typically exhibits lower voltage than healthy tissue in the electro-anatomical map, can be localized and accurately delineated on the three-dimensional image and map.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Image registration method based on improved structural similarity
InactiveCN102509114AGood convex function characteristicsImprove registration accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionNormalized mutual informationNormalize mutual information
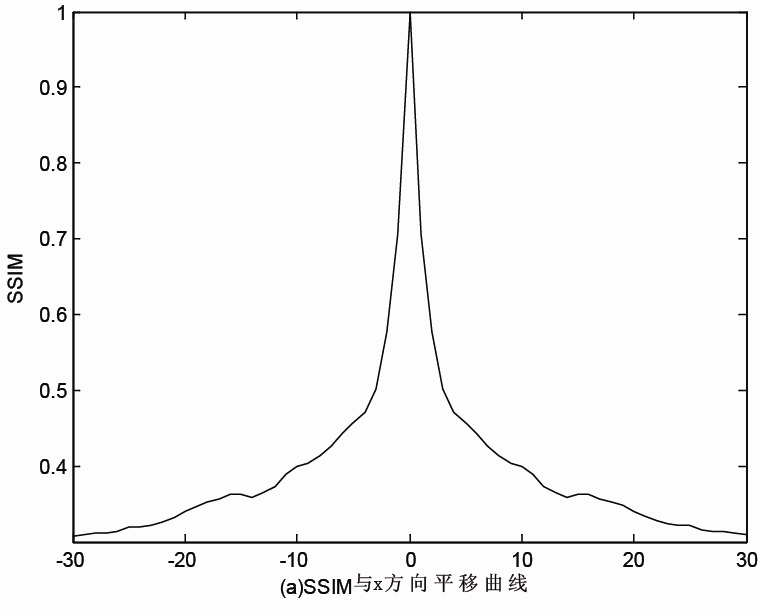
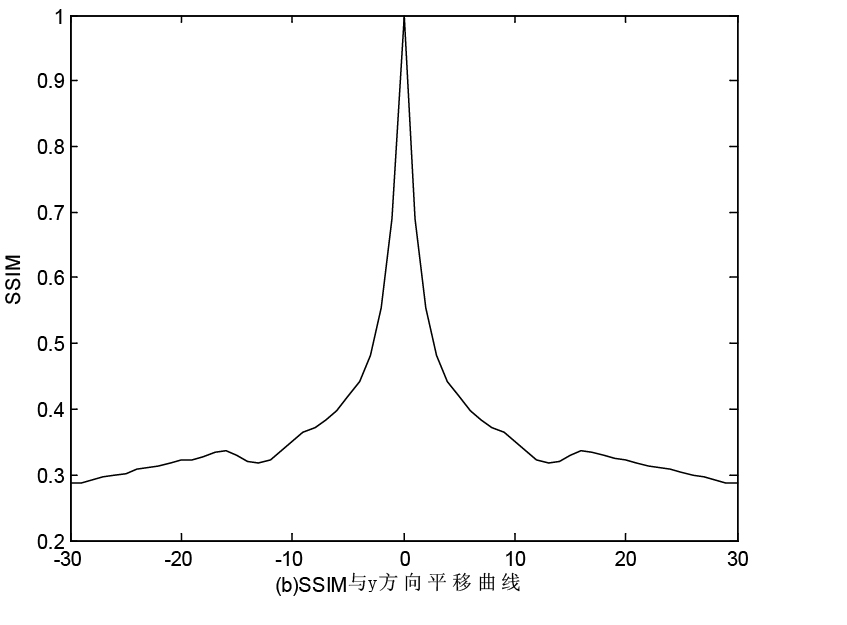
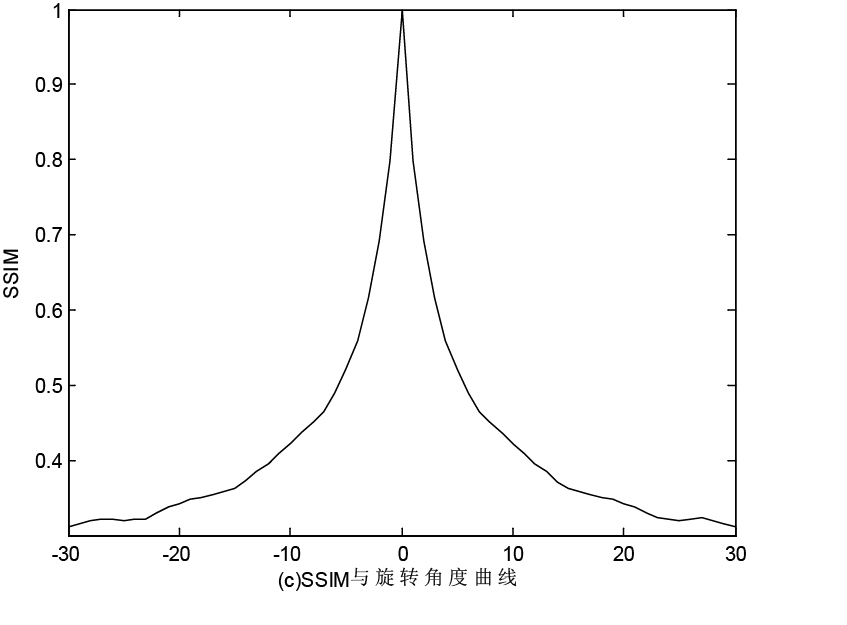
The invention provides an image registration method based on improved structural similarity. According to the invention, the improved structural similarity serves as the objective function of the image registration for the first time; four parameters of the two-dimensional image rigid body transformation are obtained through translation, rotation and consistent scaling along the X-axis and Y-axis; and the single-modal and multimodal images are analyzed in detail based on the registration algorithm and performance of the structural similarity and are compared with that based on a normalized mutual information registration algorithm. The result shows that when an absolute value is extracted during defining the structural similarity, the structural similarity has favorable features of a convex function; for either the single-modal image registration or the multimodal image registration, the structural similarity serving as the measure function can achieve the sub-pixel registration with registration precision and robustness better than that based on the classic normalized mutual information registration algorithm; and if K1 is less than or equal to 0.000001, and K2 is less than or equal to 0.000003, the two-value image can achieve the pixel registration.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Real-time scene-modeling combining 3D ultrasound and 2d x-ray imagery
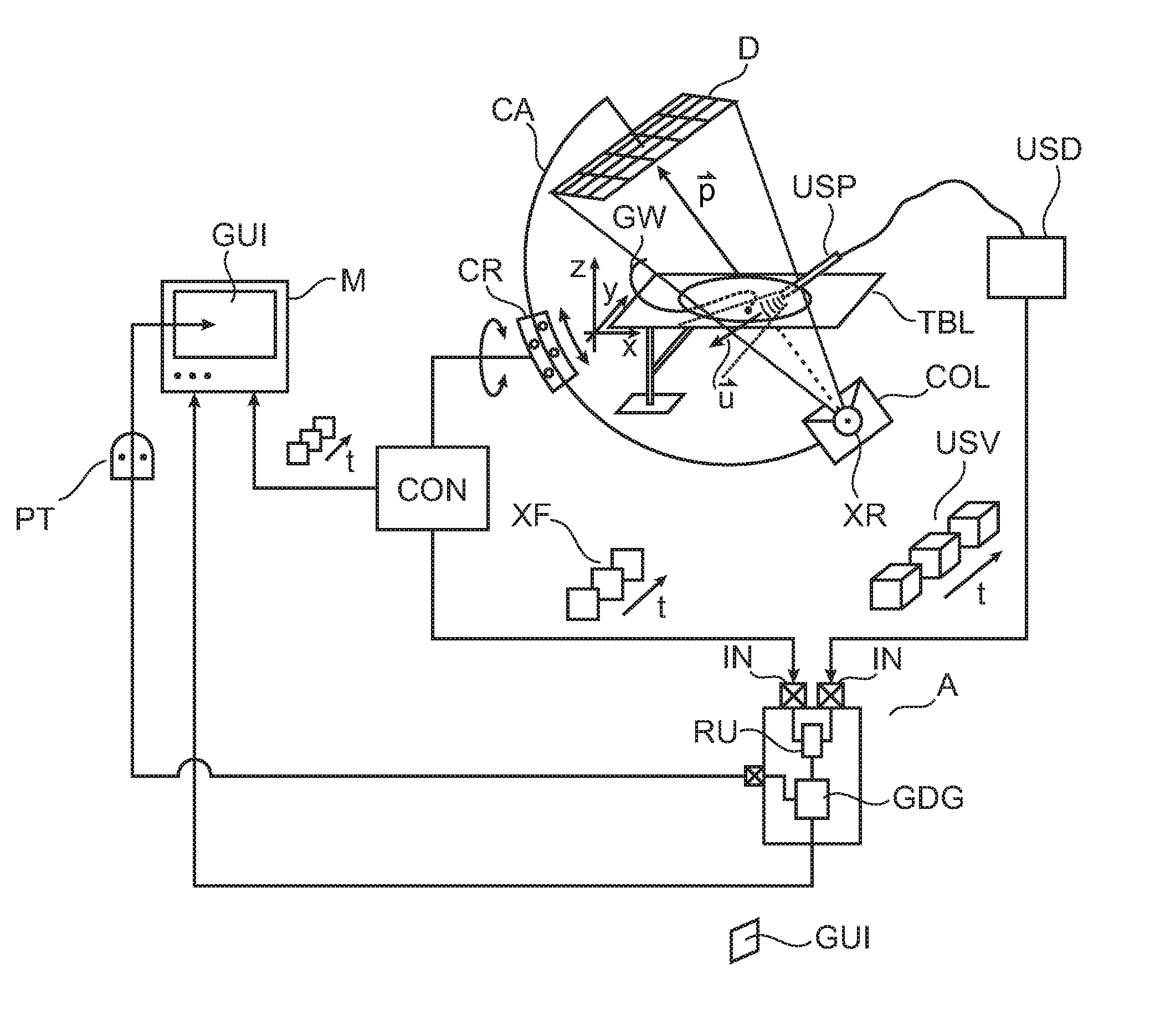
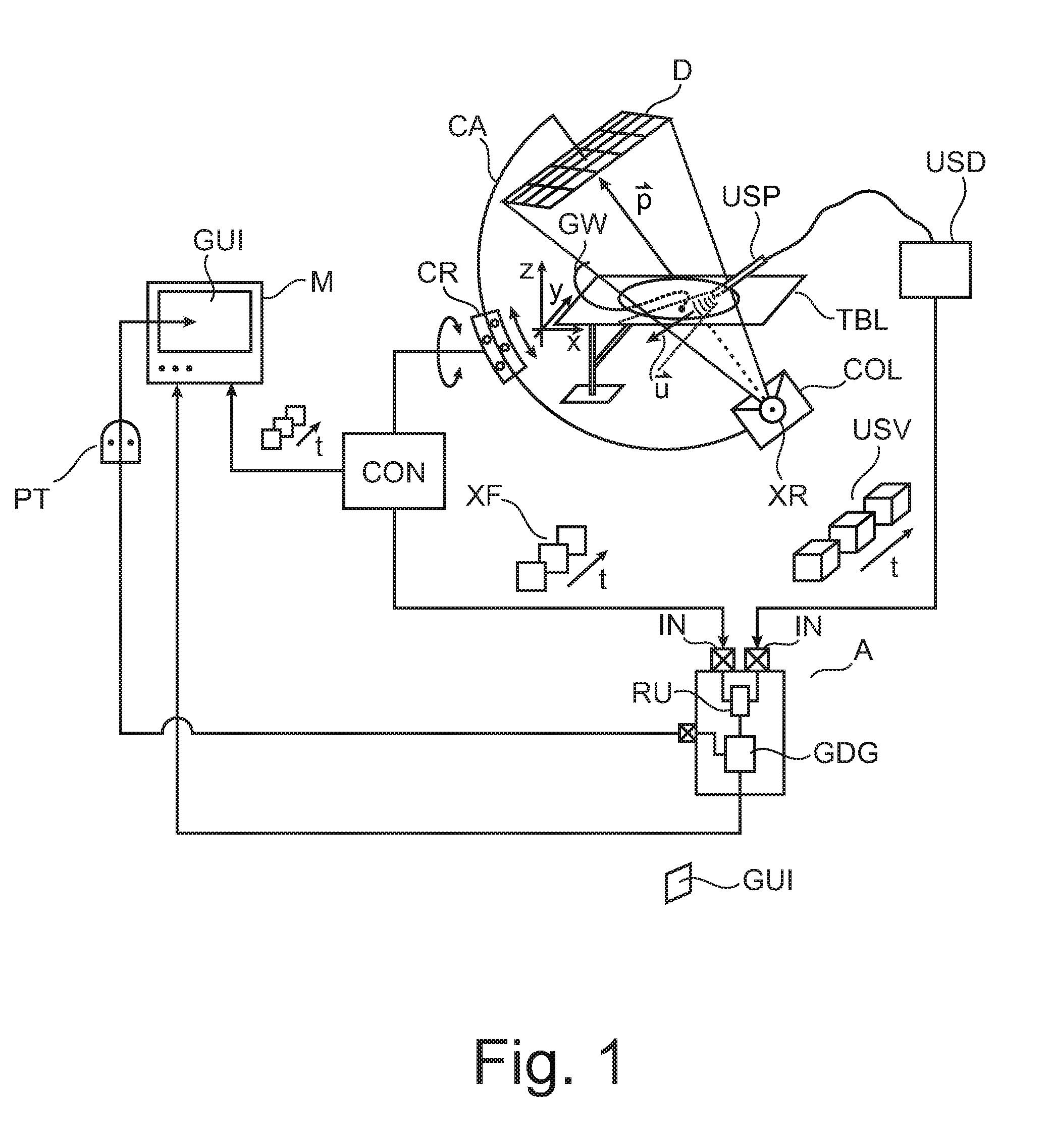
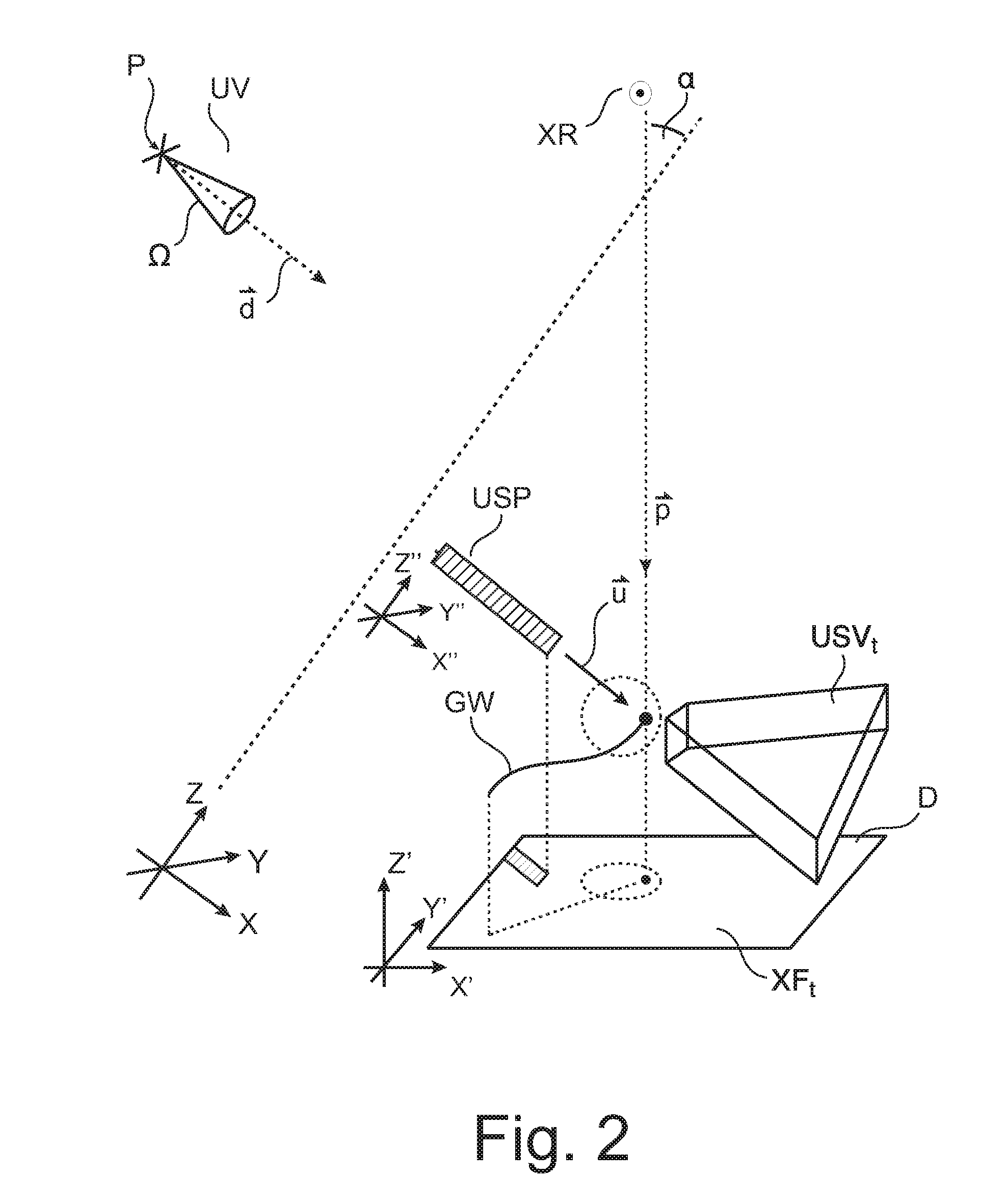
ActiveUS20150302634A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementInteractive graphicsSonification
An apparatus for visualizing image material in a multimodal imaging environment. Images (XF, USV) from an X-ray imager (100) and an ultrasound probe (USP) are fused into an interactive graphics display (GUI) to form a 3D scene, where, alongside to a 3D rendering (USS) of an ultrasound volume (USV) an X-Ray projection plan (XF) is displayed in perspective within the same scene. The rendering is according to a user selected view (UV) which is changeable upon user interaction with the interactive graphics display (GUI).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
System and method for fast multimodal registration by least squares
InactiveUS7715654B2Minimize energy functionImage enhancementImage analysisImaging modalitiesMultimodality image registration
A method for multimodal image registration includes providing a pair of images acquired from differing imaging modalities, defining an intensity correction function that corrects the intensities of a first image in terms of the intensities of the second image, defining a registration transformation function that registers the second image with the first image, wherein said intensity correction function and transformation function are functions of a plurality of parameters, obtaining corrections to the plurality of parameters by minimizing an energy functional of a square difference of the intensity corrected first image and the registration transformed second image, and updating the intensity correction function and the registration transformation function based on the corrected plurality of parameters.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
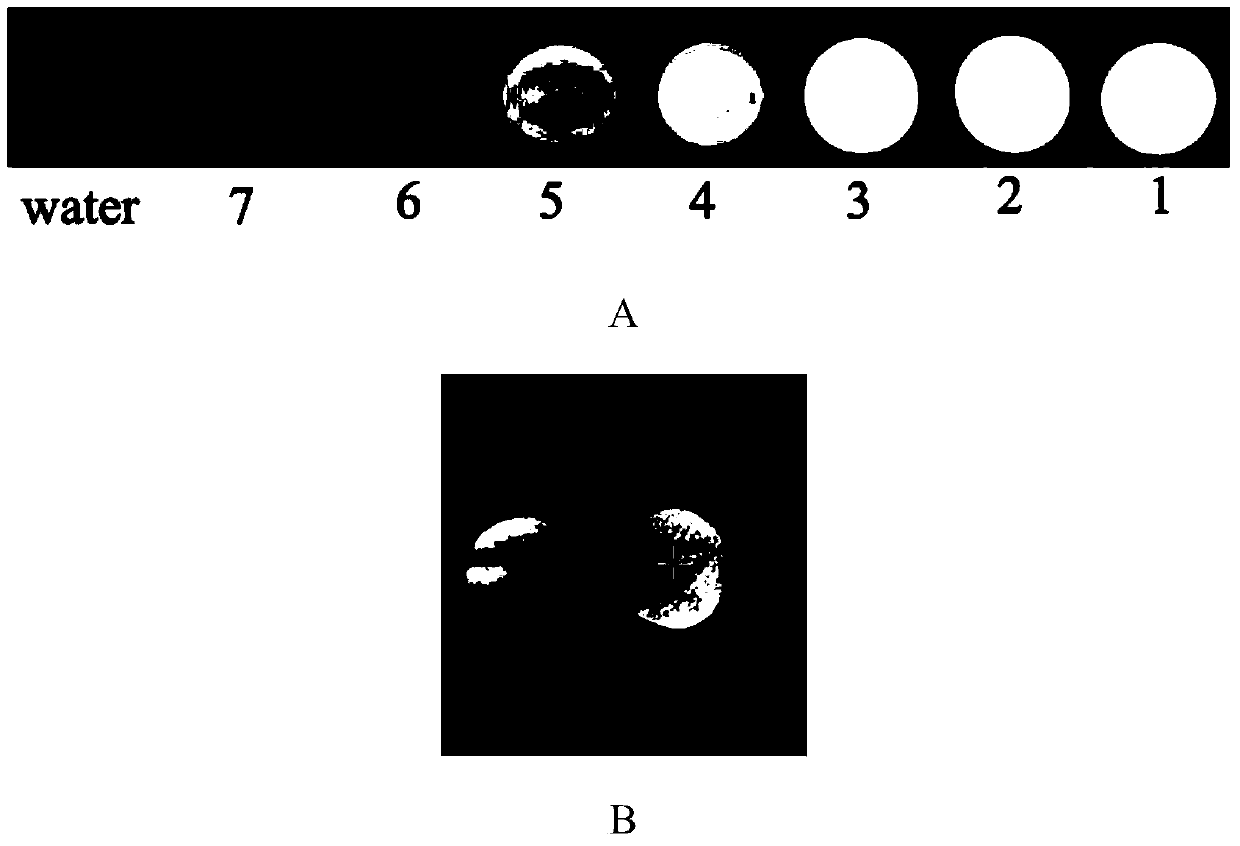
Multifunctional nano probe for multimodal images and photothermal therapy of liver cancer and application of multifunctional nano probe
ActiveCN103721271AHigh molecular weightImprove spatial resolutionEnergy modified materialsX-ray constrast preparationsSide effectLight energy
Owner:FUZHOU HOSPITAL FOR INFECTIOUS DISEASE
Multi-use multimodal imaging chelates
InactiveUS20080241873A1Improve discriminationEasy to detectOrganic active ingredientsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsCancer cellFluorescence
Cyclen-based chelates can be used as contrast agents for multi-modal imaging of tissue cells. The cyclen-based chelates are preferably polyazamacrocyclic molecules formed from 1,4,7,10 tetraazacyclododecane (“cyclen”) having varying chelating ions, phosphoester chains, and light harvesting moieties. By changing the chelating ion, phosphoester chain length and / or the light harvesting moiety different imaging techniques, such as MRI, CT, fluorescence and absorption, x-ray and NIR, may be employed to image the tissue cells. Additionally, the cyclen-based chelates may be conjugated to provide for site-specific delivery of the cyclen-based chelate to the desired tissue cells. The cyclen-based chelates may also be delivered to the tissue cells by attaching the cyclen-based to a polymeric delivery vehicle. Although these cyclen-based chelates have a wide variety of application, the preferred use is for imaging of cancer cells, such as brain cancer, for improving resection of a cancerous tissue.
Owner:BORNHOP DARRYL J +2
Multi-use multimodal imaging chelates
InactiveUS20080241074A1Improve discriminationEasy to detectUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsOrganic active ingredientsCancer cellDelivery vehicle
Cyclen-based chelates can be used as contrast agents for multi-modal imaging of tissue cells. The cyclen-based chelates are preferably polyazamacrocyclic molecules formed from 1,4,7,10 tetraazacyclododecane (“cyclen”) having varying chelating ions, phosphoester chains, and light harvesting moieties. By changing the chelating ion, phosphoester chain length and / or the light harvesting moiety different imaging techniques, such as MRI, CT, fluorescence and absorption, x-ray and NIR, may be employed to image the tissue cells. Additionally, the cyclen-based chelates may be conjugated to provide for site-specific delivery of the cyclen-based chelate to the desired tissue cells. The cyclen-based chelates may also be delivered to the tissue cells by attaching the cyclen-based to a polymeric delivery vehicle. Although these cyclen-based chelates have a wide variety of application, the preferred use is for imaging of cancer cells, such as brain cancer, for improving resection of a cancerous tissue.
Owner:TEXAS TECH UNIV SYST +1
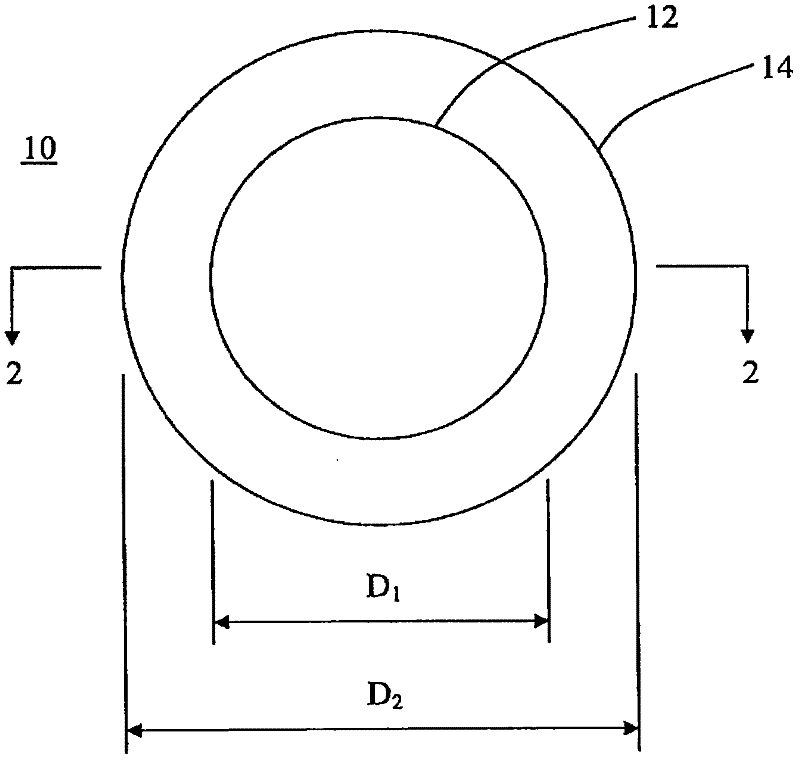
Multimodal imaging fiducial marker
A multimodal fiducial marker (10) for registration of data is disclosed. The multimodal fiducial marker (10) generally comprises a first portion (12) made from at least one radiopaque material and a second portion (14) made from a porous material capable of absorbing at least one radioactive material. The second portion (14) at least partially surrounds the first portion (12).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Prussian blue based nanoparticle as multimodal imaging contrast material
The invention relates to a Prussian Blue based nanoparticle comprising a Prussian Blue based metal core doped with one or more metal isotope and an organic biocompatible coating. The invention relates furthermore to a process for the preparation of said nanoparticle, and the use thereof as imaging contrast material or in the therapy.
Owner:SEMMELWEIS EGYETEM
Formulation and Methods for Enhanced Interventional Image-Guided Therapy of Cancer
InactiveUS20120277517A1Reducing field inhomogenitiesImprove permeabilityBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsMagnetite NanoparticlesTherapeutic effect
An embodiment in accordance with the present invention provides a thermo-chemoembolization formulation and method for enhanced interventional image-guided therapy for cancer. The T-C formulation includes magnetic iron oxide nano-particles (MIONs) that heat when exposed to an alternating magnetic field (AMF), a liquid tumorphilic drug carrier that enhances tumor retention of the T-C formulation, and a chemotherapeutic or radiotherapeutic agent. The T-C formulation enhances delivery of heat and chemo- or radio-therapeutic agents with hyperthermia produced by magnetic nanoparticles to improve therapeutic outcomes. The magnetic nanoparticles and tumorphilic drug carrier also allow for multimodal image-guided monitoring of treatment and patient follow-up. The method for enhanced interventional image-guided therapy for cancer includes using an AMF to heat the T-C formulation and activate the thermotherapy.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
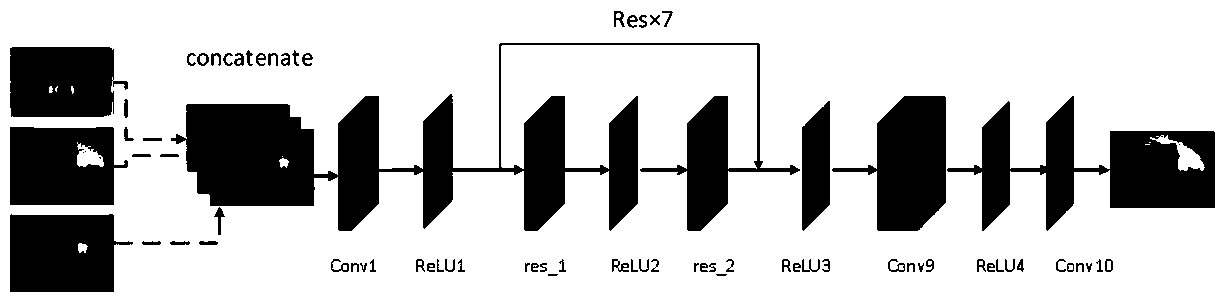
Generating multimodal image edits for a digital image
The present disclosure is directed towards methods and systems for determining multimodal image edits for a digital image. The systems and methods receive a digital image and analyze the digital image. The systems and methods further generate a feature vector of the digital image, wherein each value of the feature vector represents a respective feature of the digital image. Additionally, based on the feature vector and determined latent variables, the systems and methods generate a plurality of determined image edits for the digital image, which includes determining a plurality of set of potential image attribute values and selecting a plurality of sets of determined image attribute values from the plurality of sets of potential image attribute values wherein each set of determined image attribute values comprises a determined image edit of the plurality of image edits.
Owner:ADOBE INC
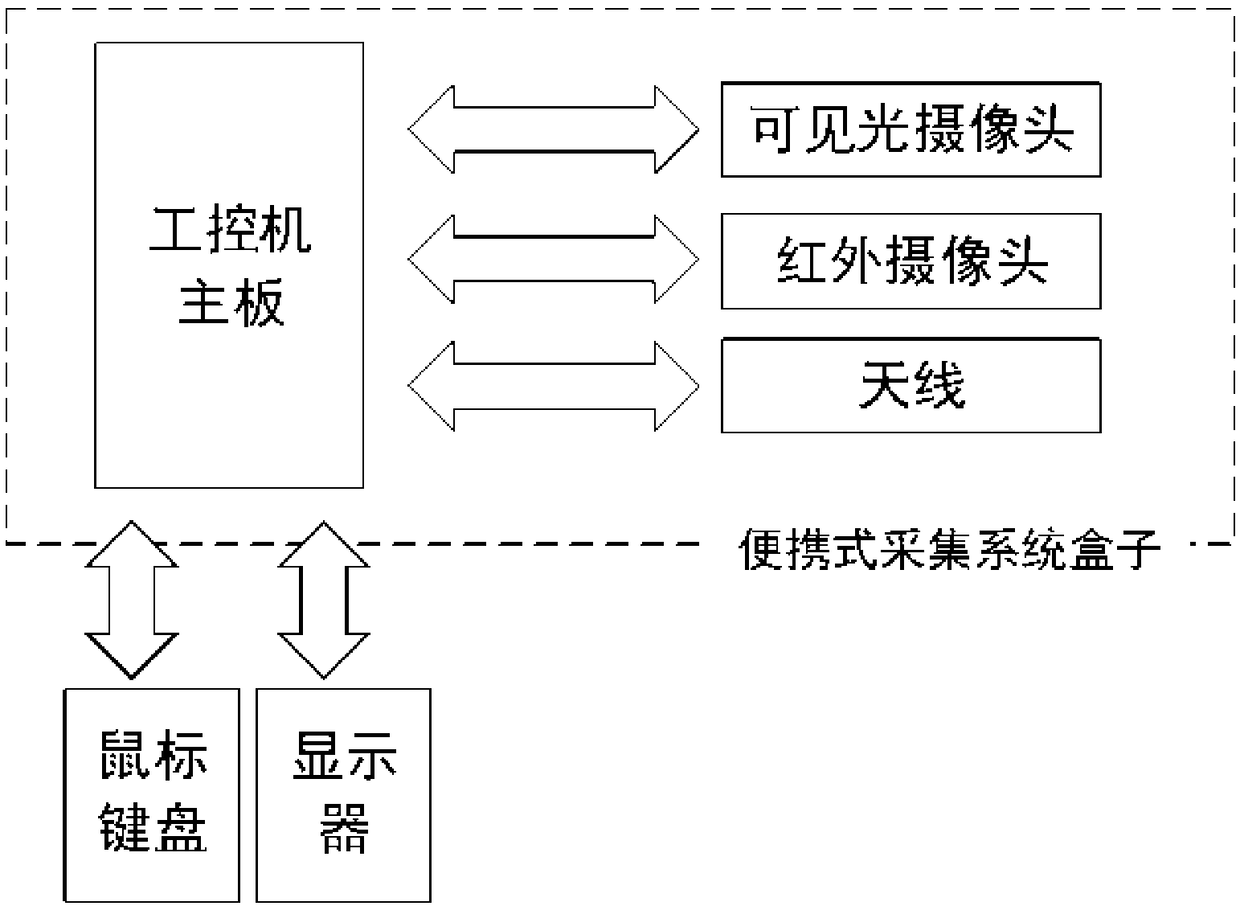
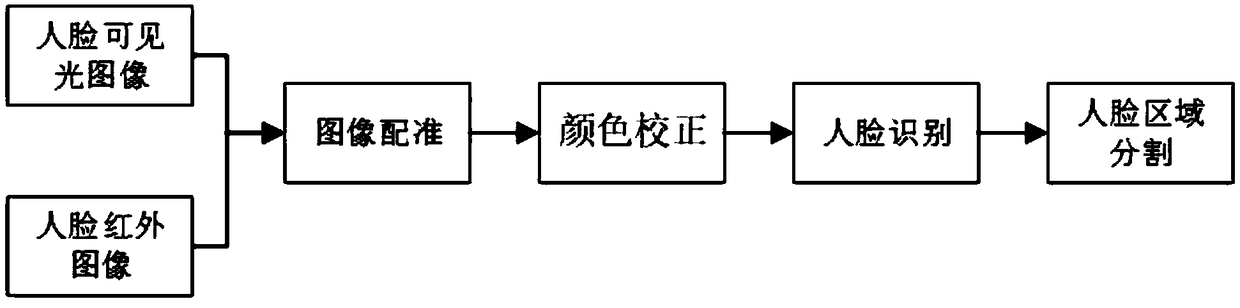
Face multimodal image acquisition and processing device and method
InactiveCN109192302AAchieve matchingPrecise registrationHealth-index calculationCharacter and pattern recognitionColor correctionPersonal computer
The invention discloses a face multimodal image acquisition and processing device and method. The face multimodal image acquisition and processing device comprises a box body; an industrial personal computer main board for processing face images, as well as a visible light camera and an infrared camera which are used for collecting the face images and are electrically connected with the industrialpersonal computer main board are installed in the box body; the visible light camera and the infrared camera are arranged side by side; through holes corresponding to the visible light camera and theinfrared camera are formed in the box body; the industrial personal computer main board comprises a control module; the control module is connected with an image registration module for aligning visible light images collected by the visible light camera with infrared images collected by the infrared camera, a color correction module for normalizing the colors of the collected face images, a faceidentification module for precisely positioning a face region, and a face region segmentation module used for segmenting the face region so as to put the temperature of each area into statistics.
Owner:杭州体光医学科技有限公司
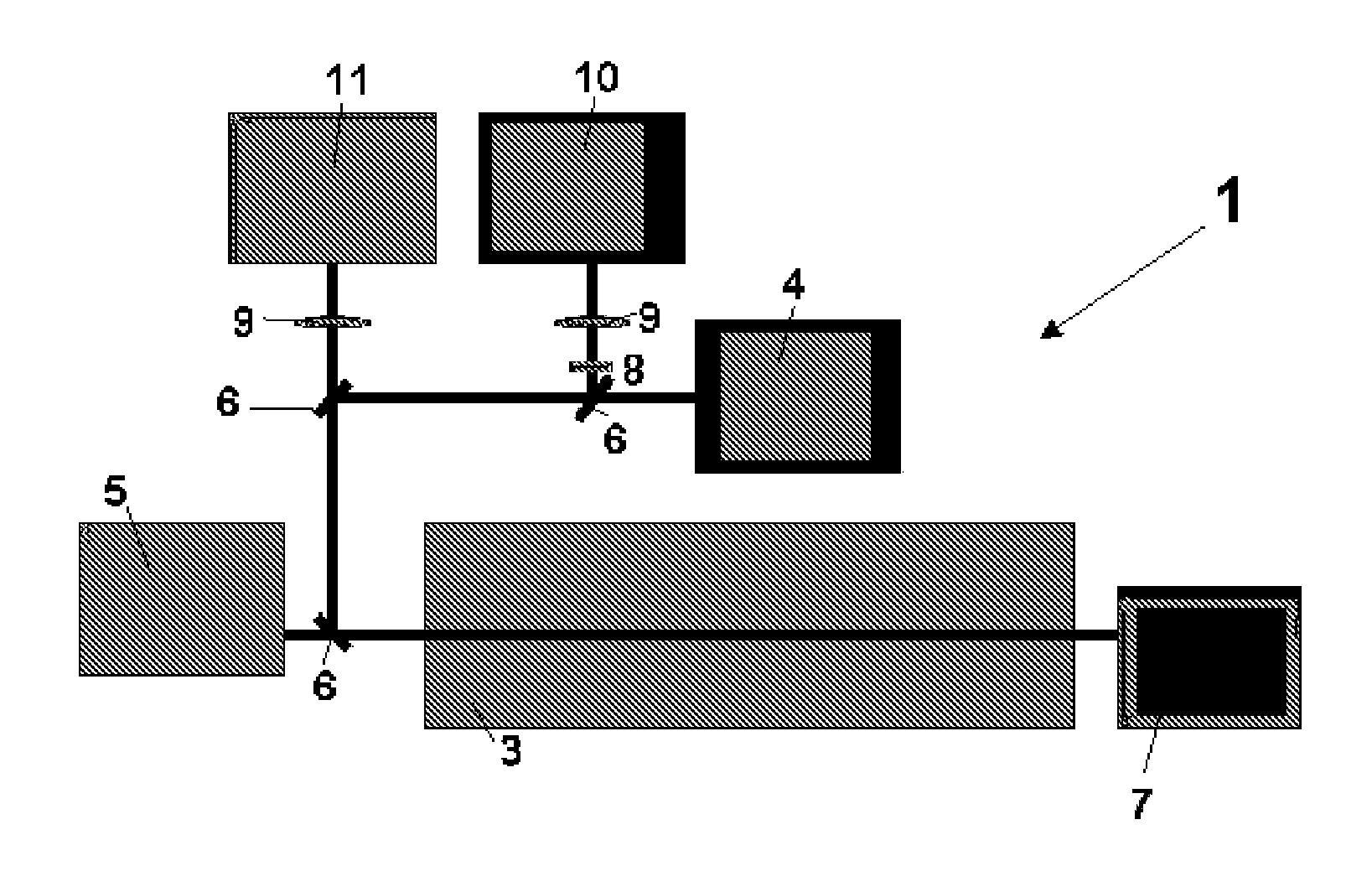
Multimodal imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20160209515A1Conserve costReduce the amount requiredMaterial analysis by optical meansComputerised tomographsRadioactive tracerPhotodetector
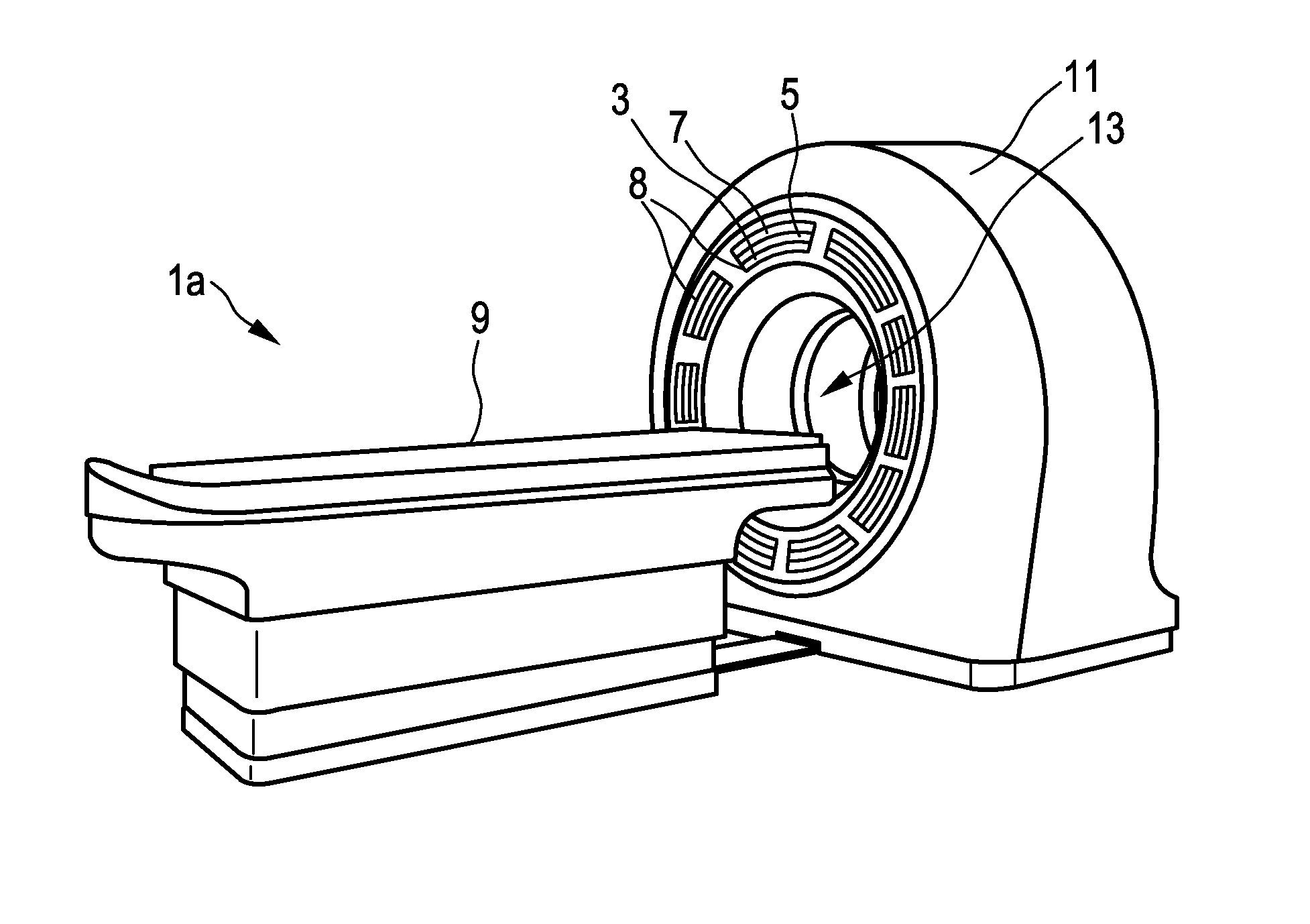
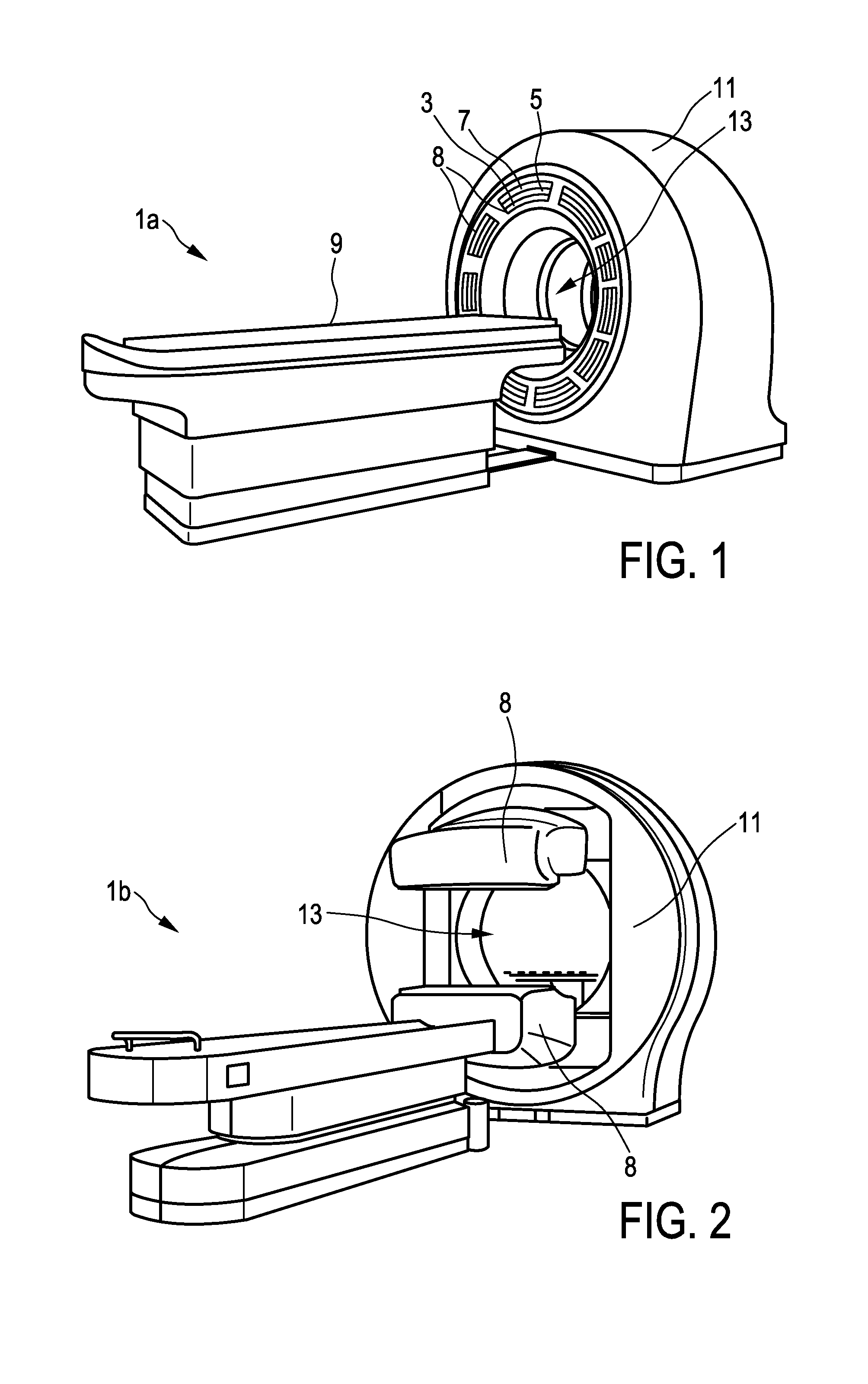
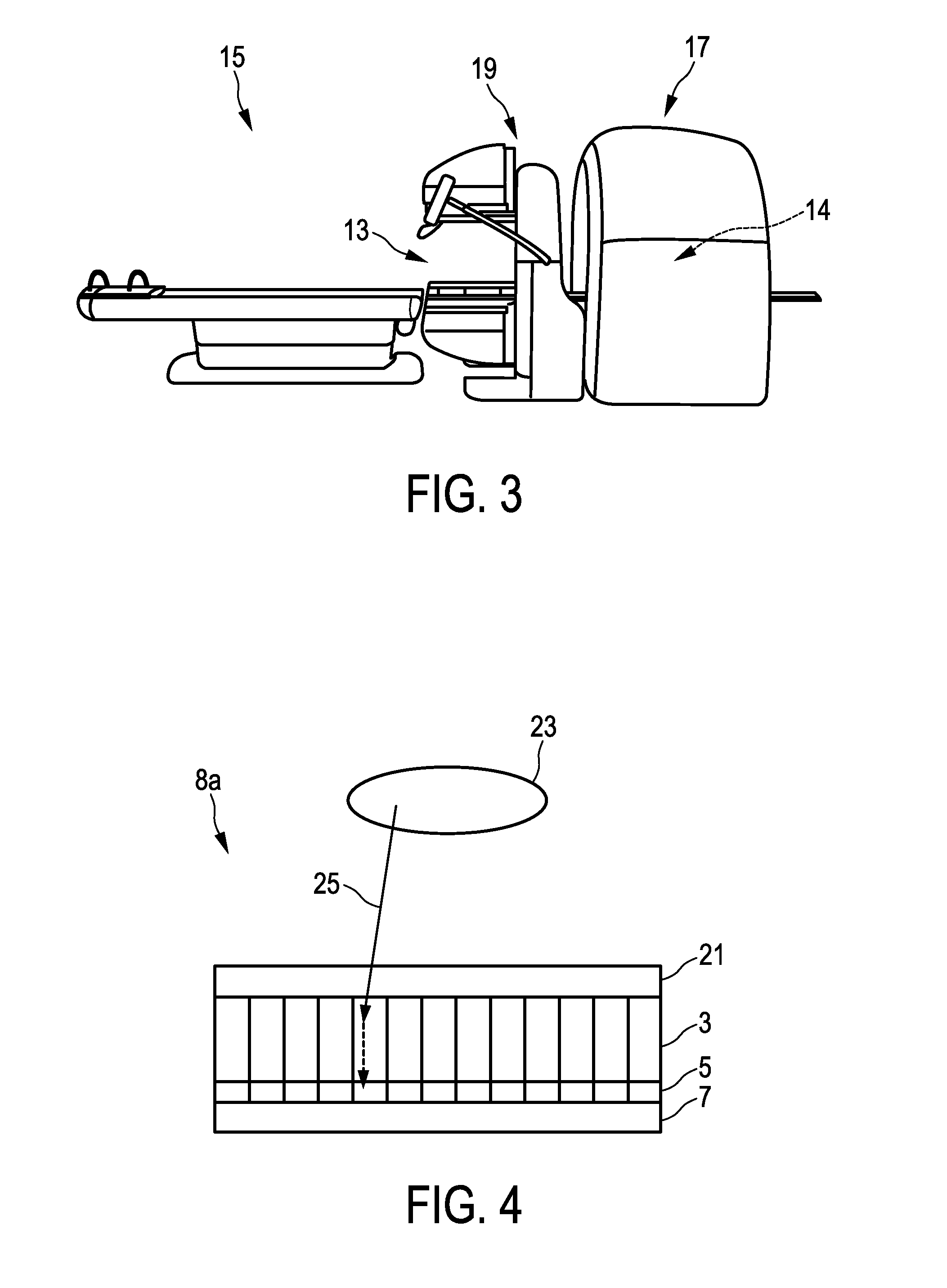
The present invention relates to a multimodal imaging apparatus (1a, 1b) for imaging a process (63) in a subject (23), said process (63) causing the emission of gamma quanta (25, 61), said apparatus (1a, 1b) comprising a scintillator (3) including scintillator elements (31) for capturing incident gamma quanta (25, 61) generated by the radiotracer and for emitting scintillation photons (26) in response to said captured gamma quanta (25, 61), a photodetector (5) including photosensitive elements (33) for capturing the emitted scintillation photons (26) and for determining a spatial distribution of the scintillation photons, and a readout electronics (7) for determining the impact position of an incident gamma quantum in the scintillator (3) and / or a parameter indicative of the emission point of the gamma quantum (25, 61) in the subject (23) based on the spatial distribution of the scintillation photons, wherein the imaging apparatus (1a, 1b) is configured to be switched between a first operation mode for detecting low energy gamma quanta and a second operation mode for detecting high energy gamma quanta, wherein the high energy gamma quanta have a higher energy than the low energy gamma quanta, and the scintillator (3) is arranged to capture incident gamma quanta (25, 61) from the same area of interest (65) in the first operation mode and in the second operation mode without requiring a relative movement of the subject (23) versus the scintillator (3), wherein the scintillator (3) comprises an array of scintillator elements (31) including a first region with high energy scintillator elements (27) for capturing high energy gamma quanta and a second region with low energy scintillator elements (29) for capturing low energy gamma quanta; and / or the apparatus (1a, 1b) further comprises a positioning mechanism (35) for changing the orientation and / or position of the scintillator elements (31), in particular for tilting the scintillator elements (31), to switch the imaging apparatus (1a, 1b) between the first operation mode and the second operation mode.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Multispectral-based fundus image registration method and system
ActiveCN110544274ACorrect space transformationAvoid fit problemsImage enhancementImage analysisDiagnostic Radiology ModalityPattern recognition
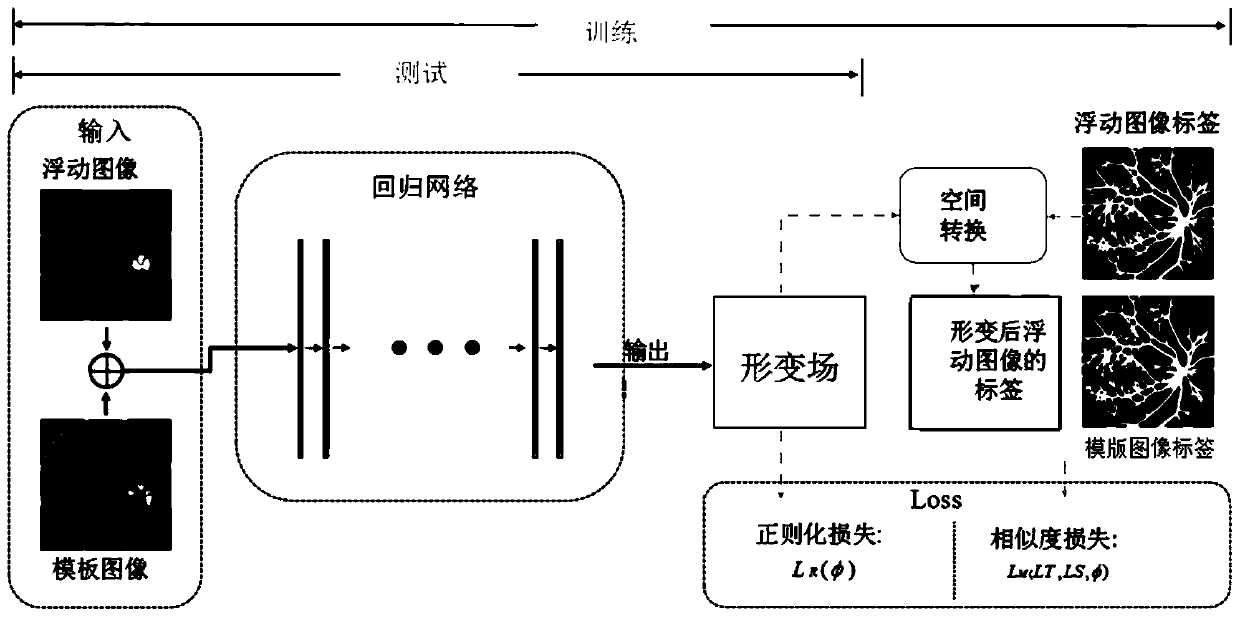
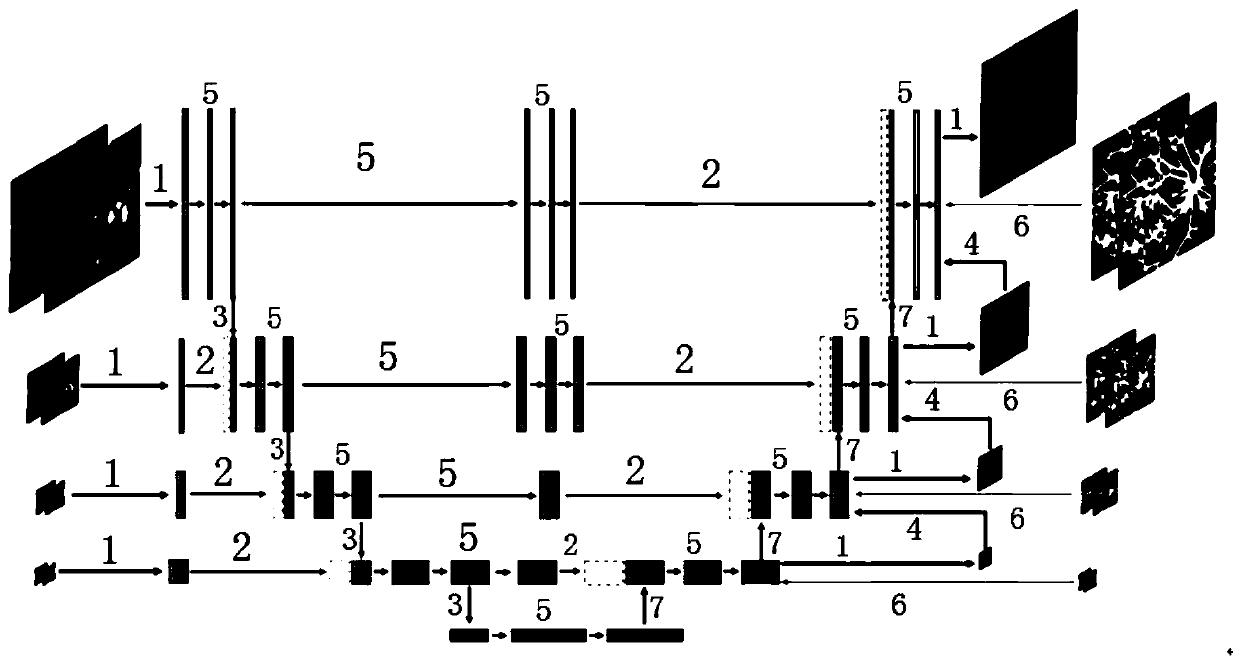
The invention provides a multispectral-based fundus image registration method, comprising the steps: acquiring the multispectral fundus image through RHA, and selecting a template fundus image and a fundus image to be registered; constructing a regression network for obtaining a deformation field between the template fundus image and the fundus image to be registered, and adding a feature balancelayer and a pyramid structure into the regression network; constructing a loss function, wherein the loss function comprises similarity loss of the blood vessel label graph and flattening constraint of a deformation field; and training the network in a weak supervision mode, and taking the processed segmentation image of the fundus image as a label of the training network. According to the multispectral-based fundus image registration method, the registration model is trained by taking the segmentation image as guidance and adopting a weak supervision mode, and practice proves that the methodcan effectively solve the problem of multispectral fundus image registration, and a good effect can be achieved, and the weak supervision segmentation oriented registration method can be expanded to more multimodal image registration problems.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com