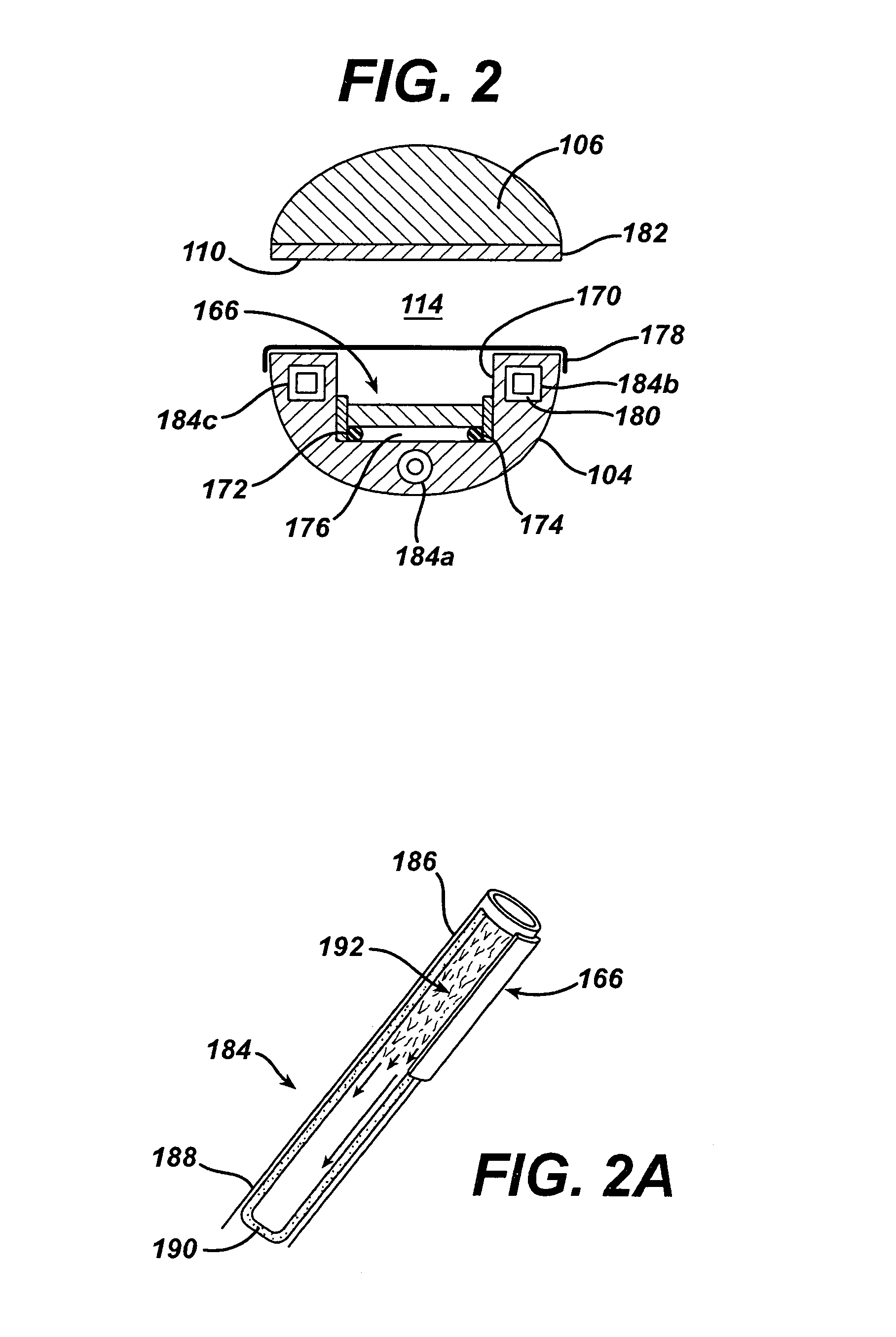
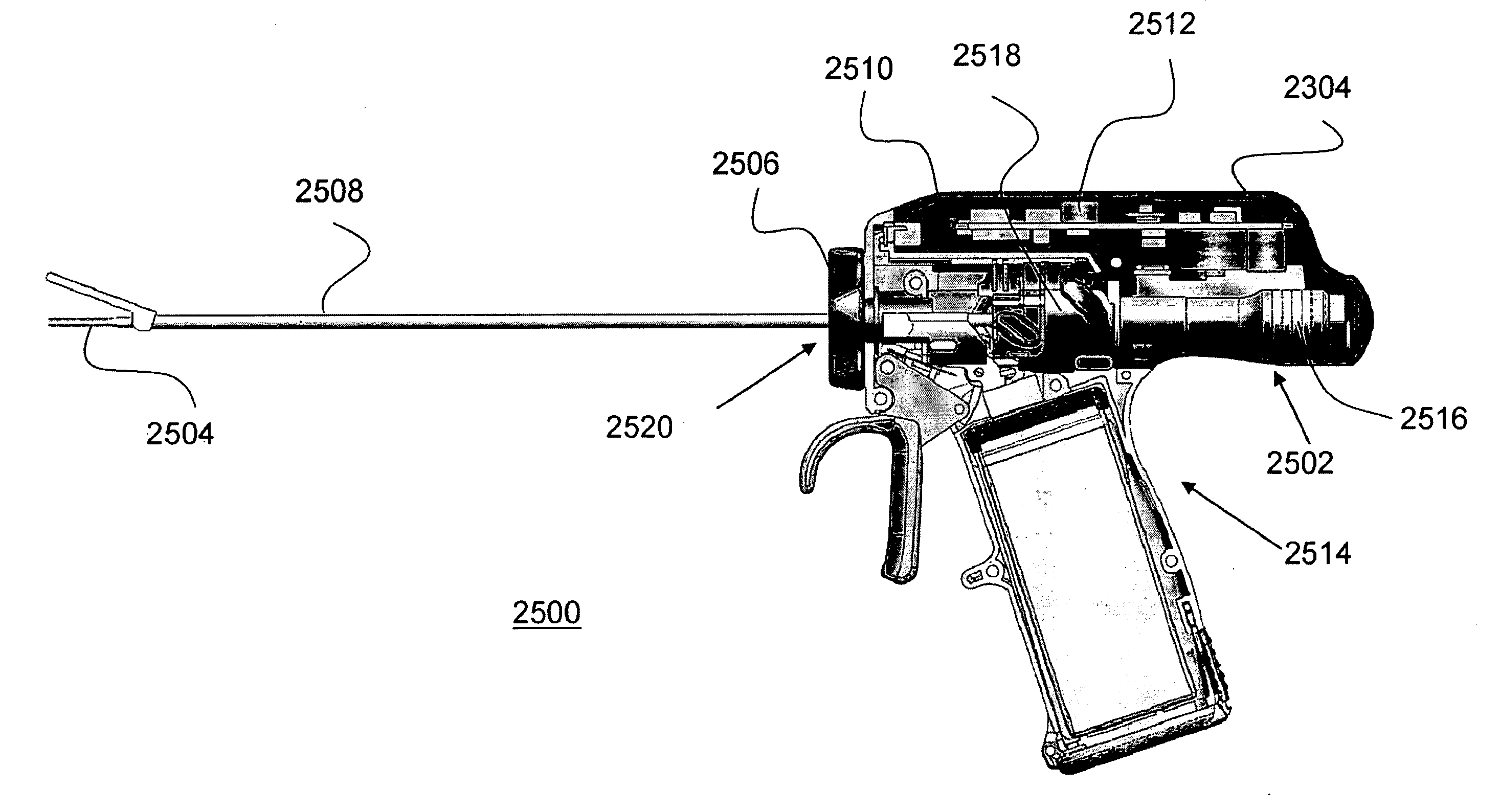
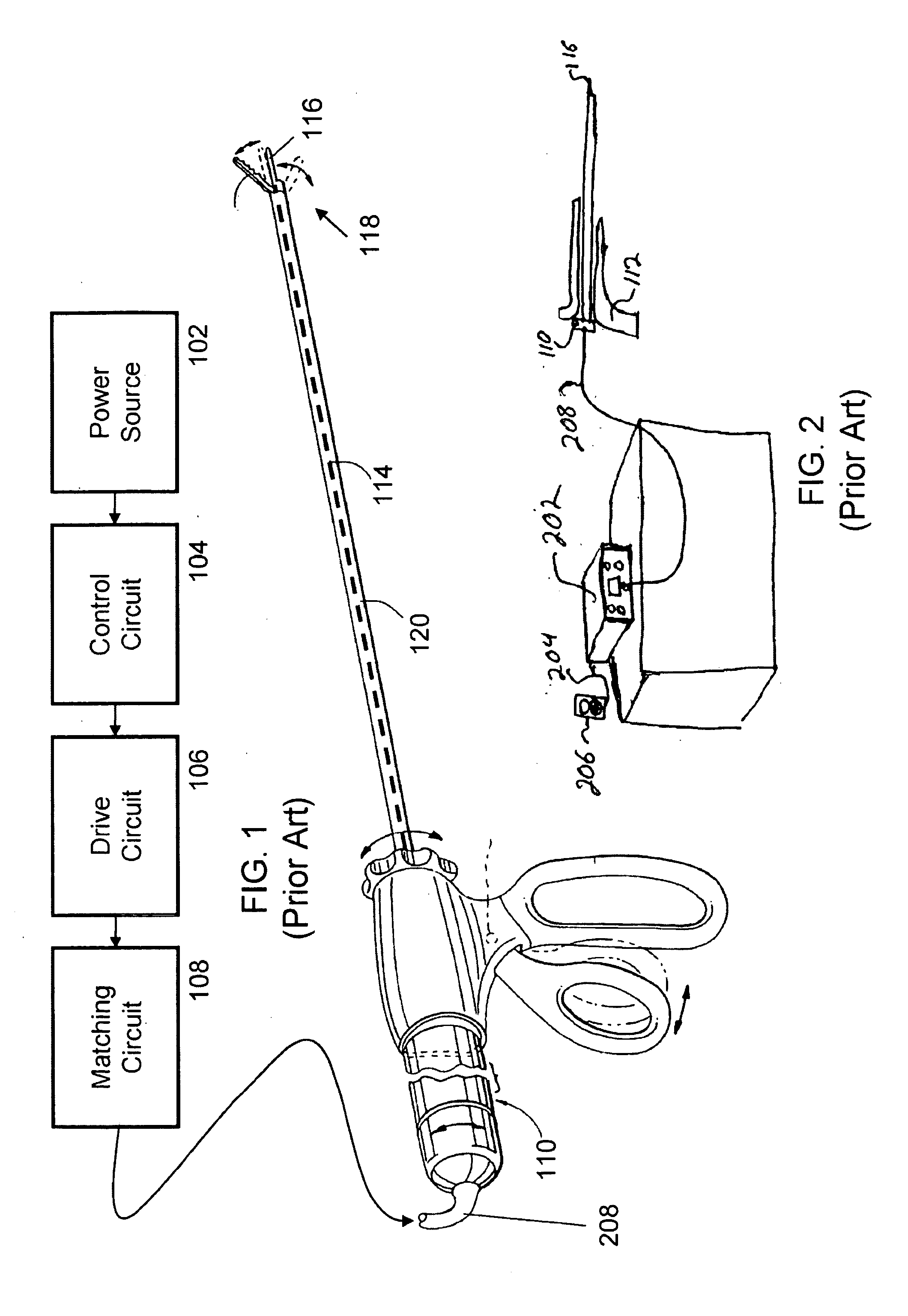
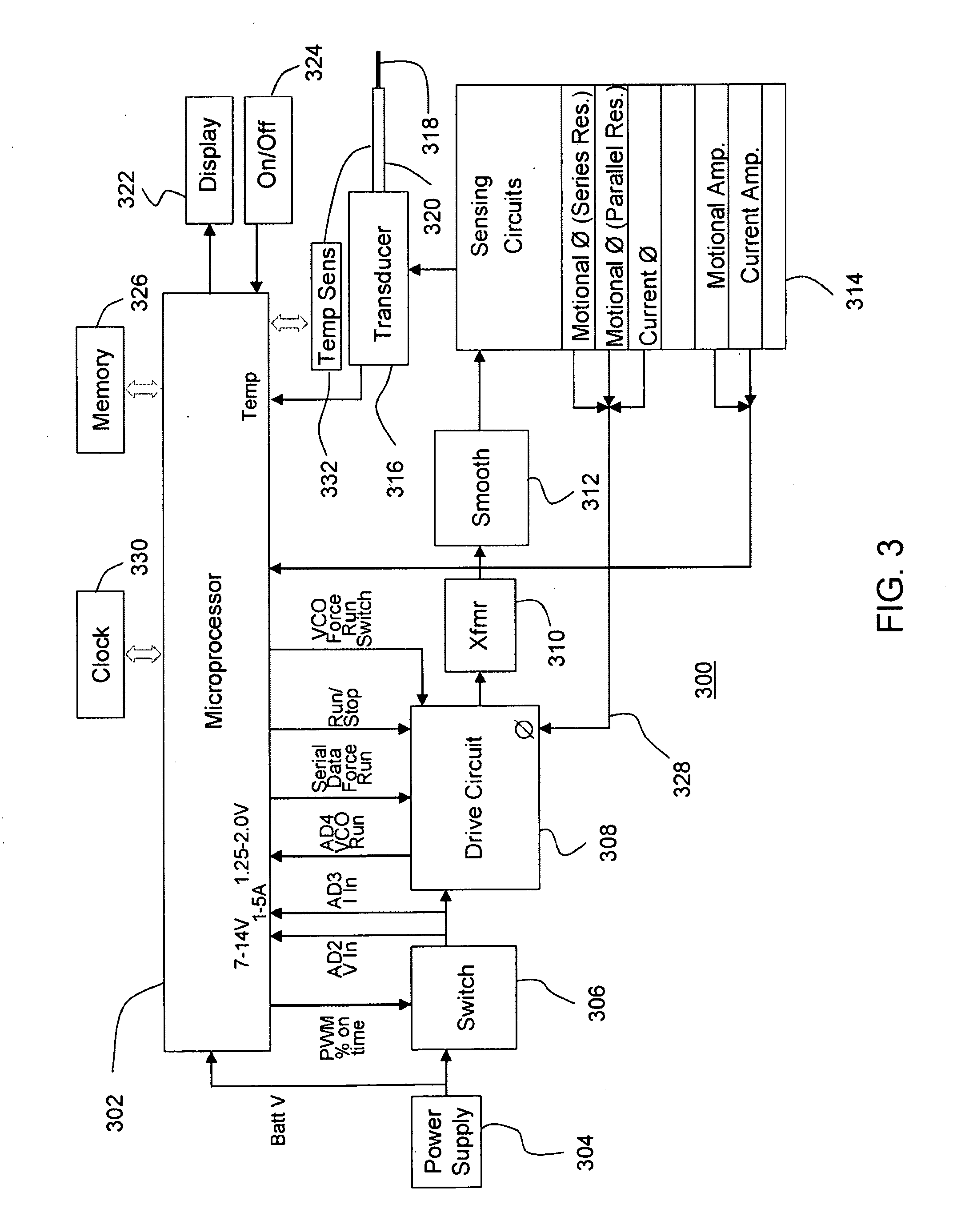
Patents
Literature
22370 results about "Ultrasound" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies from person to person and is approximately 20 kilohertz (20,000 hertz) in healthy young adults. Ultrasound devices operate with frequencies from 20 kHz up to several gigahertz.
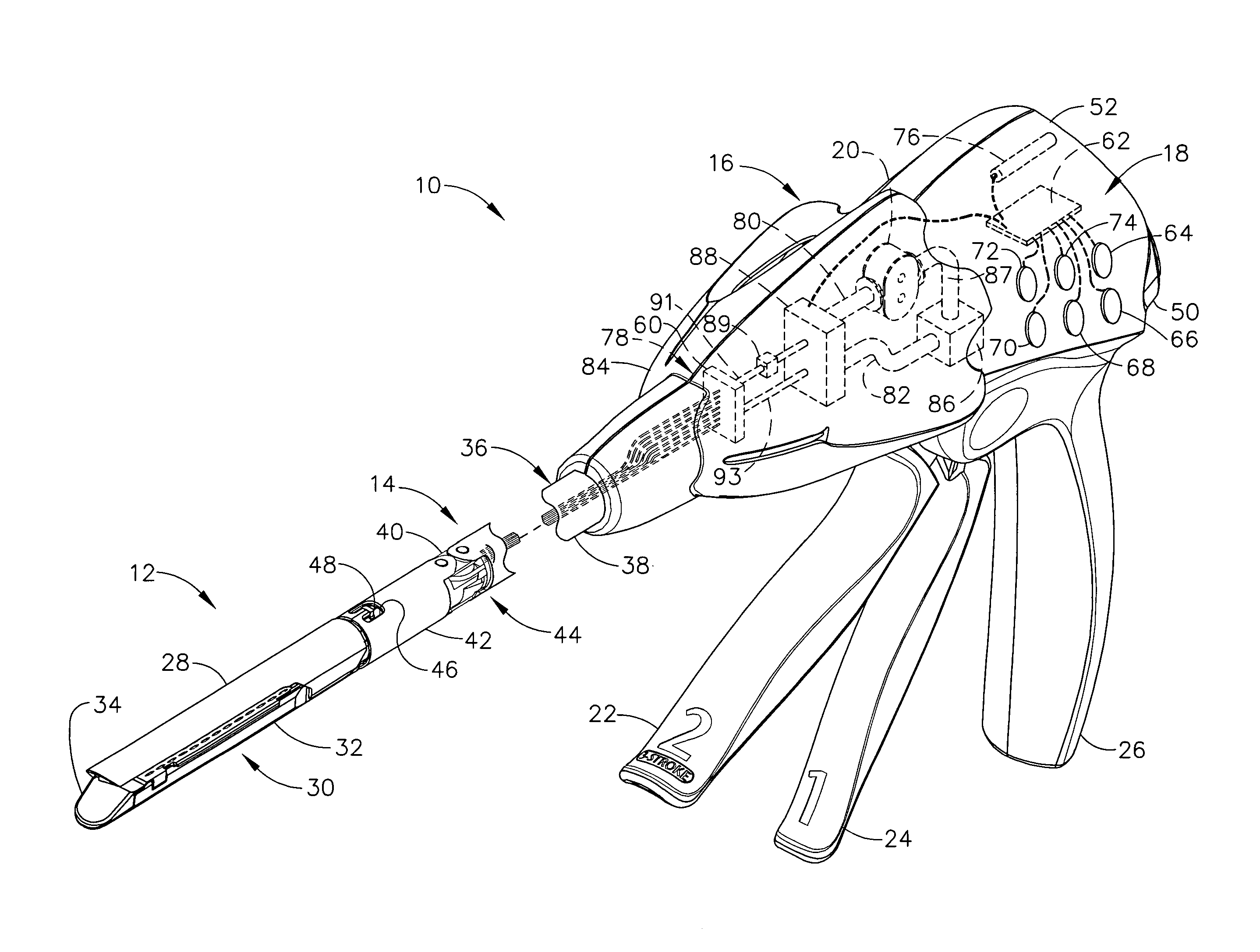
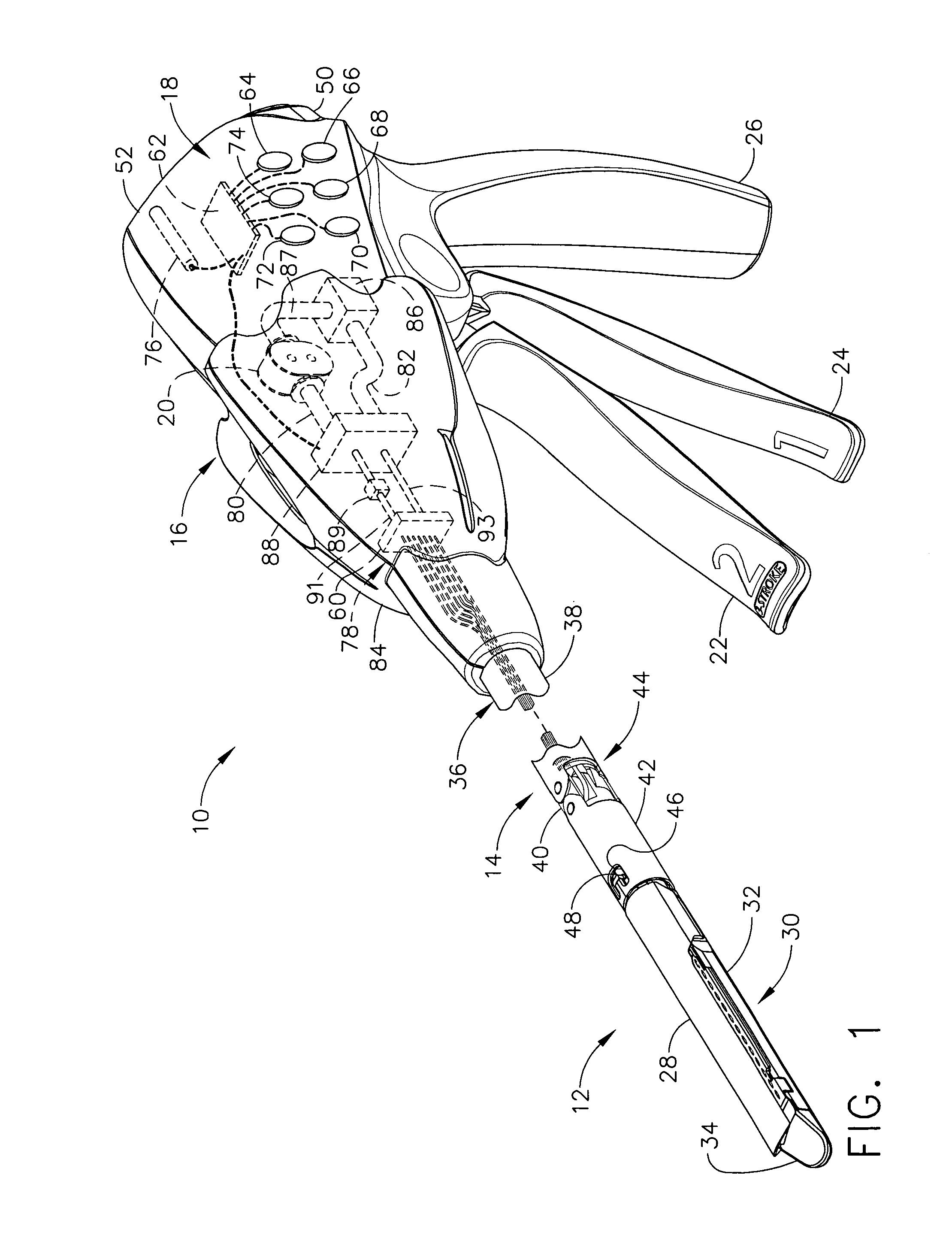
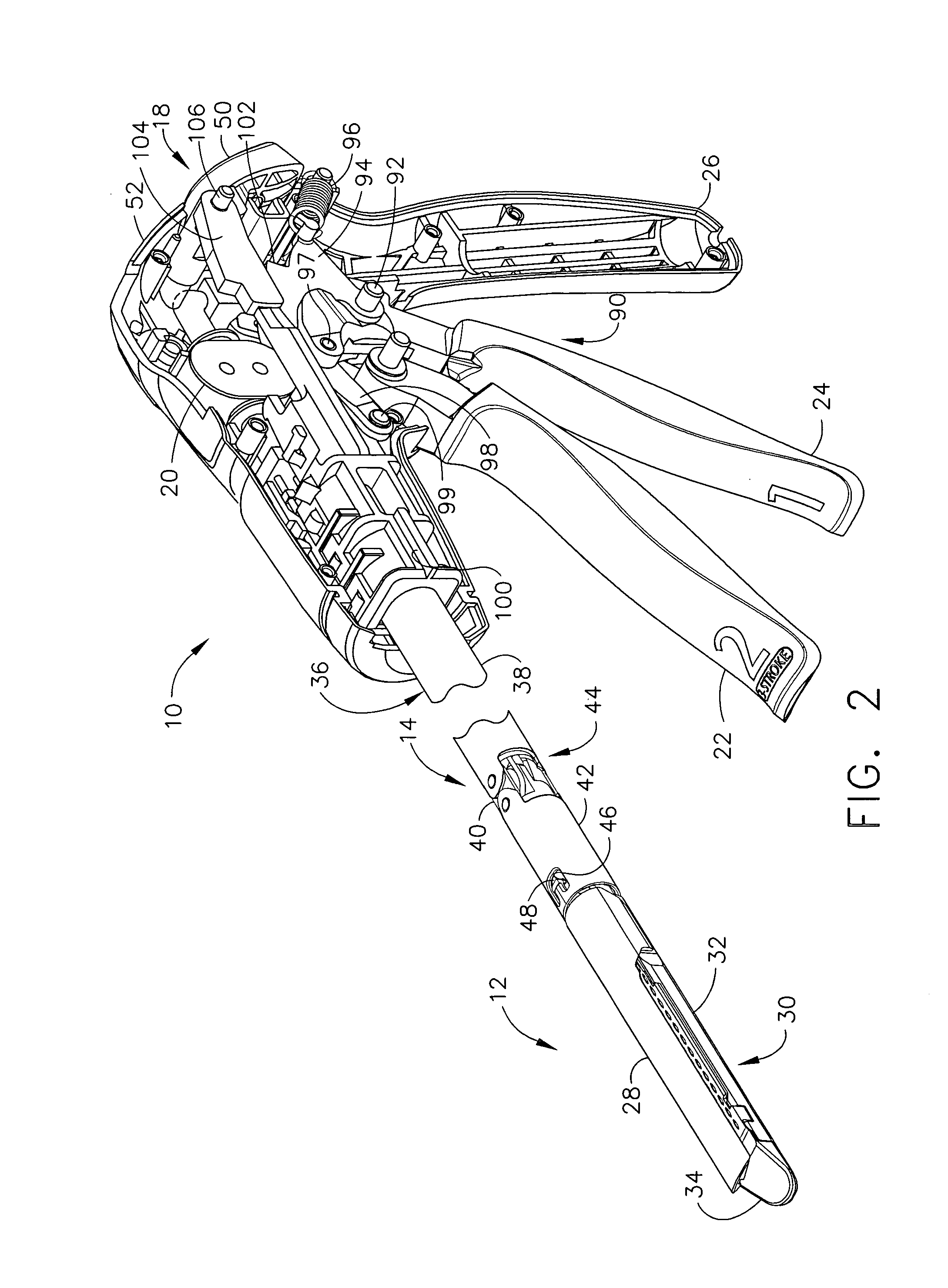
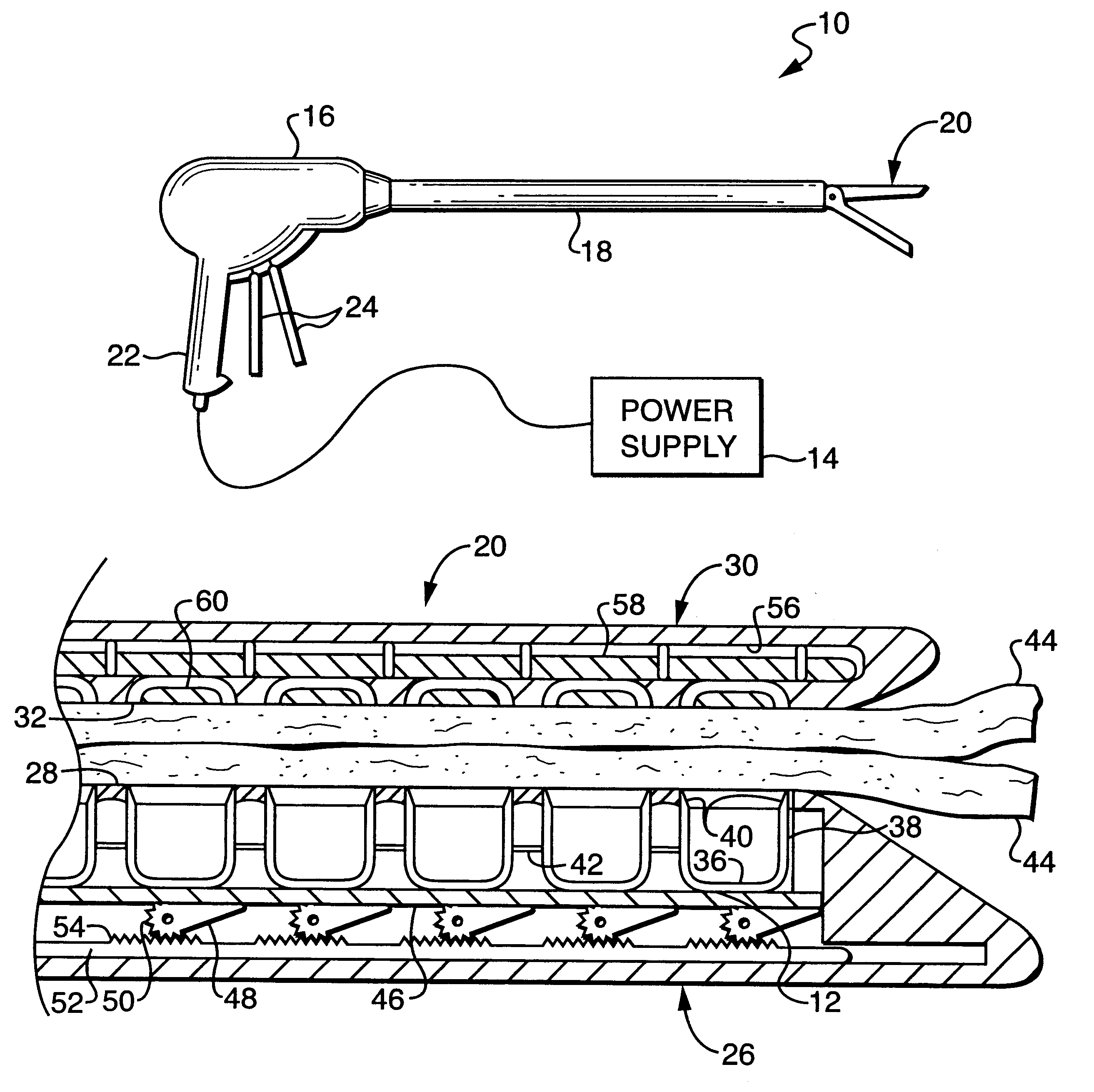
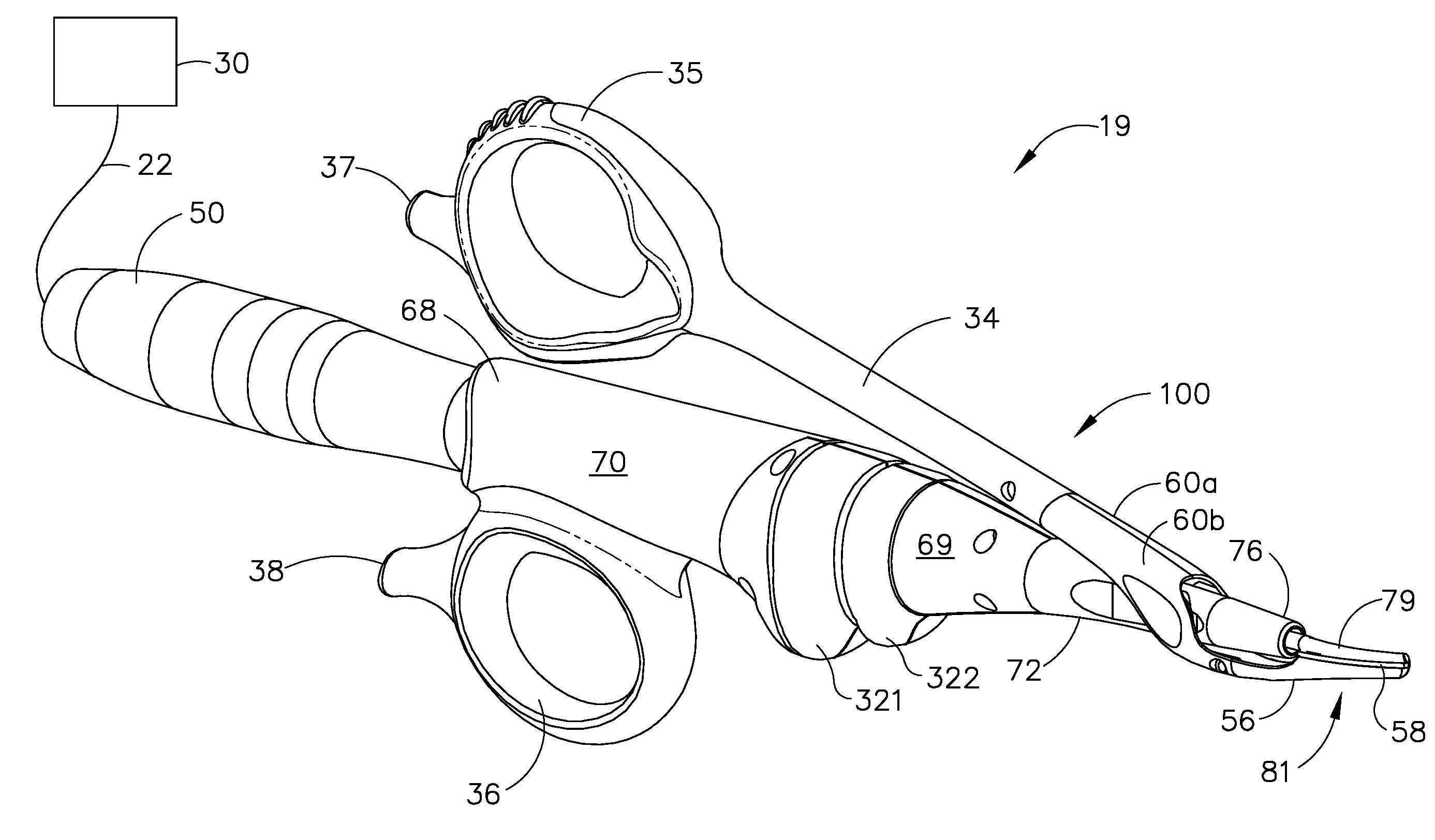
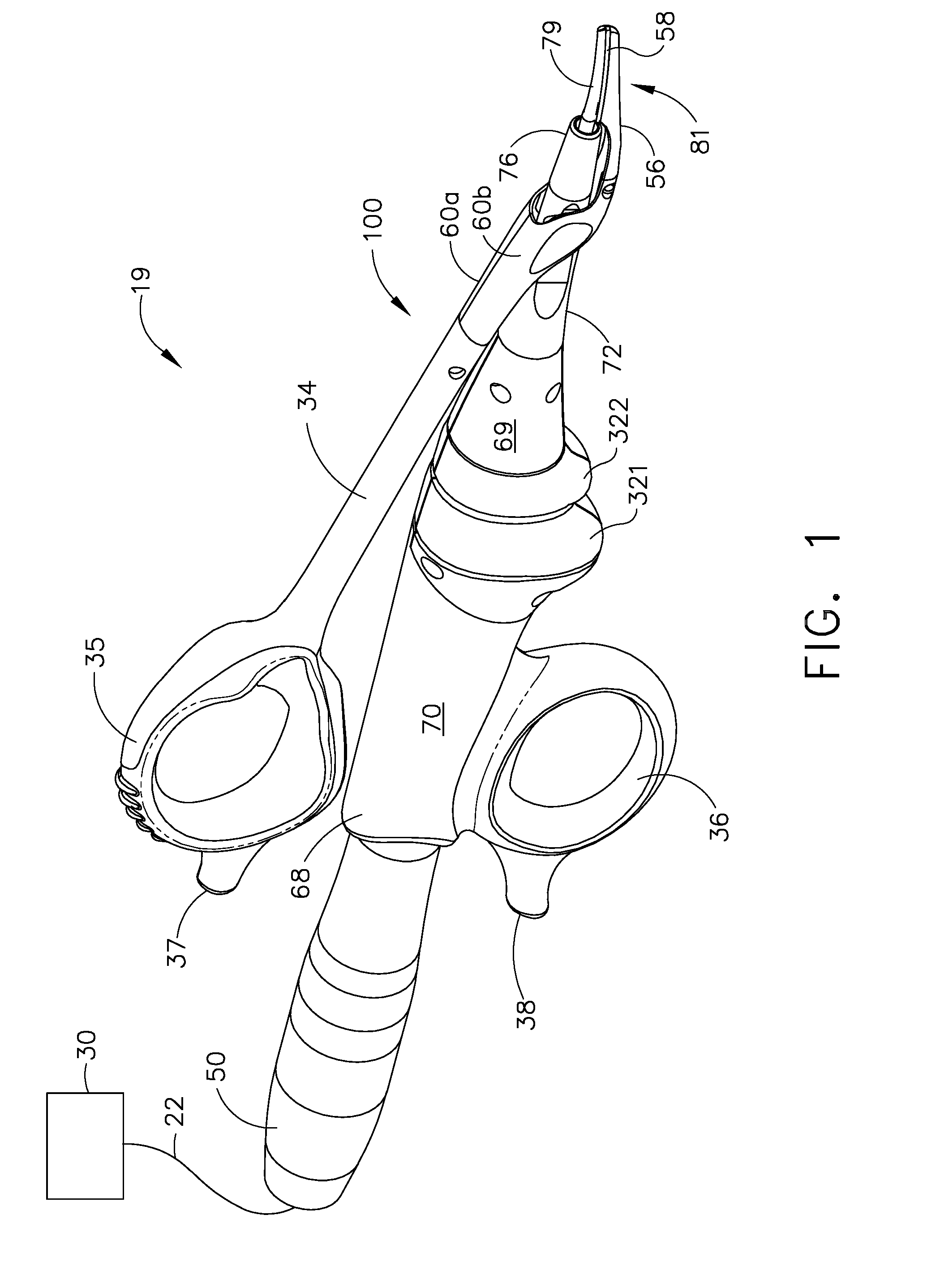
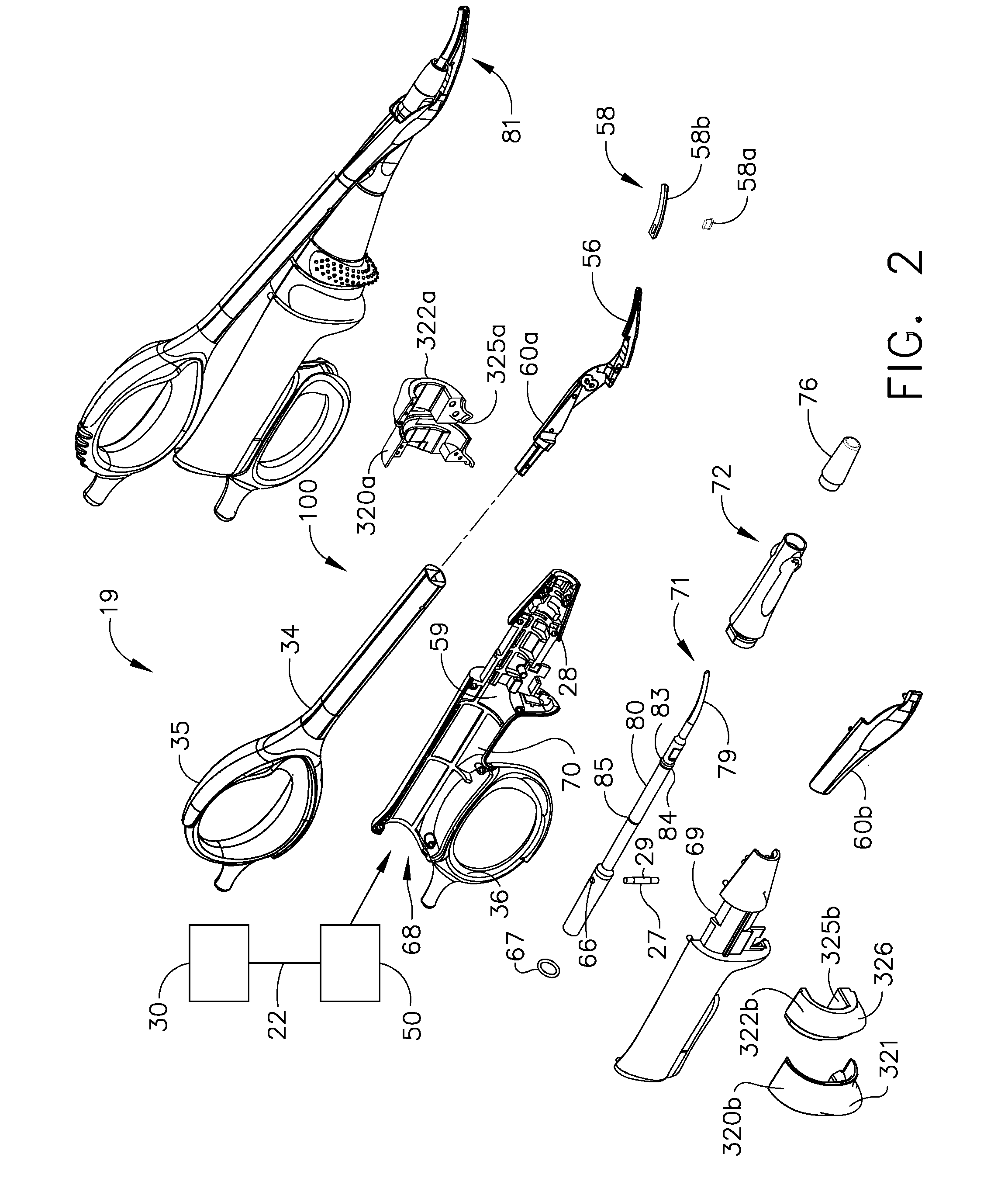
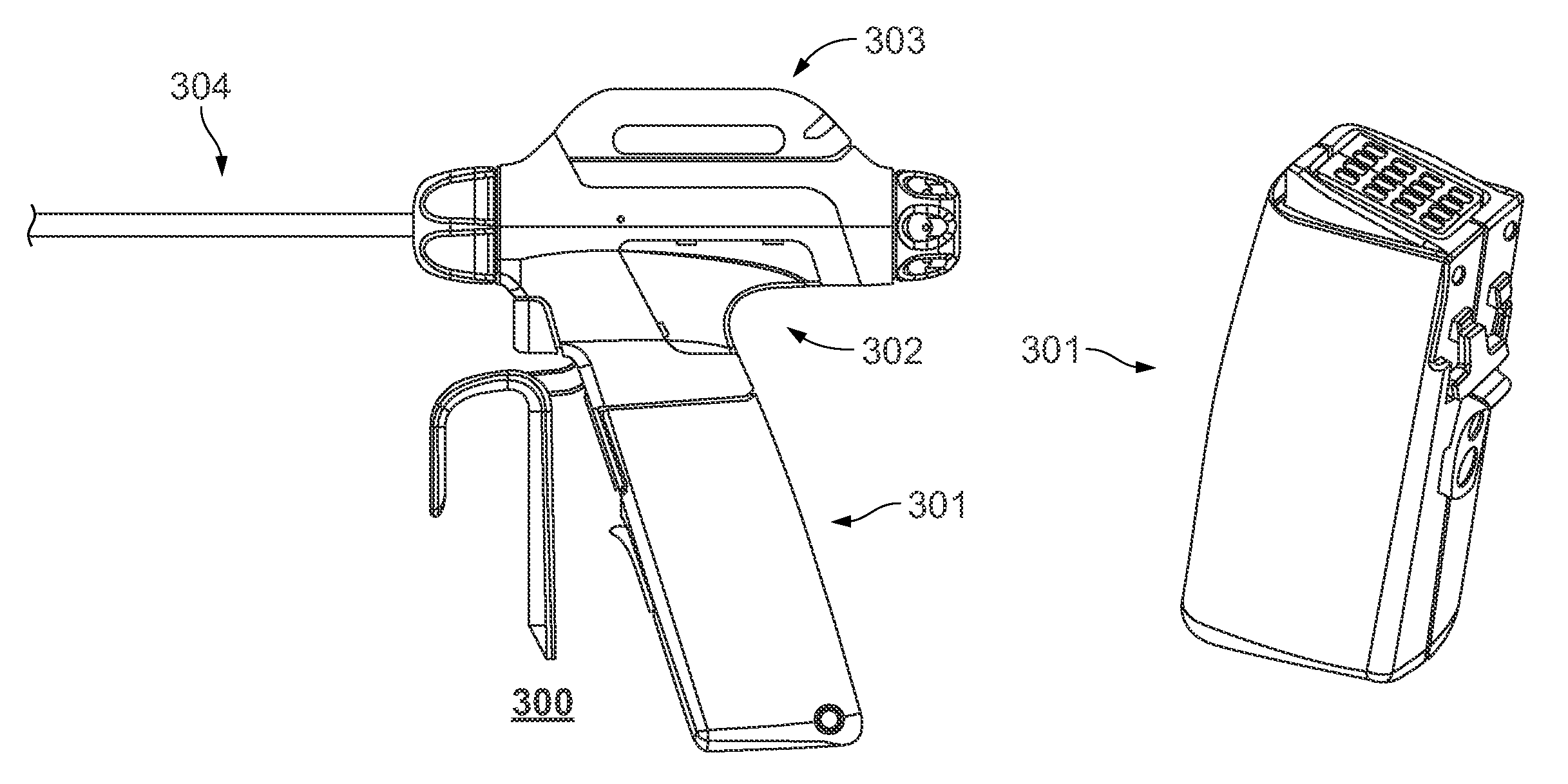
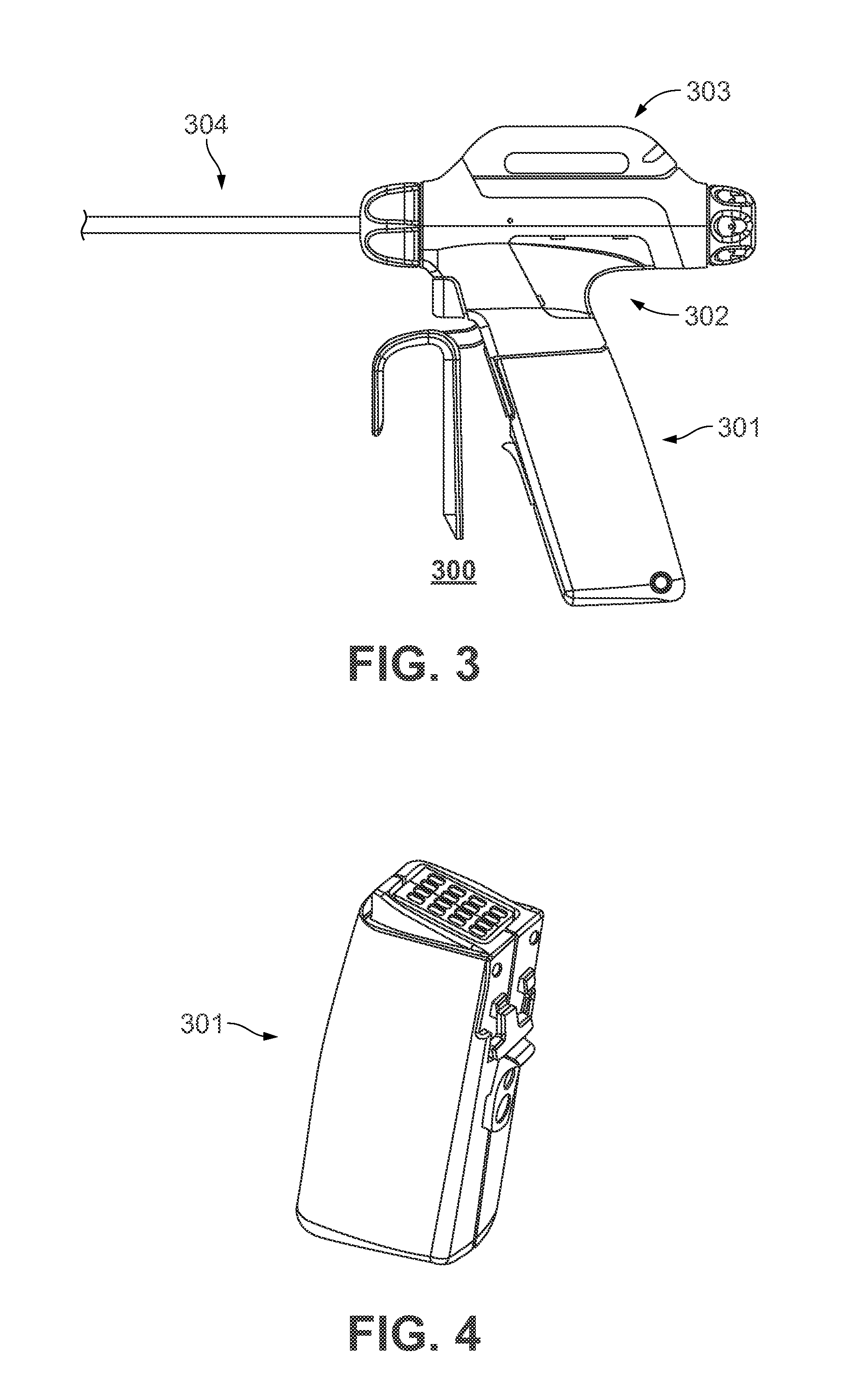
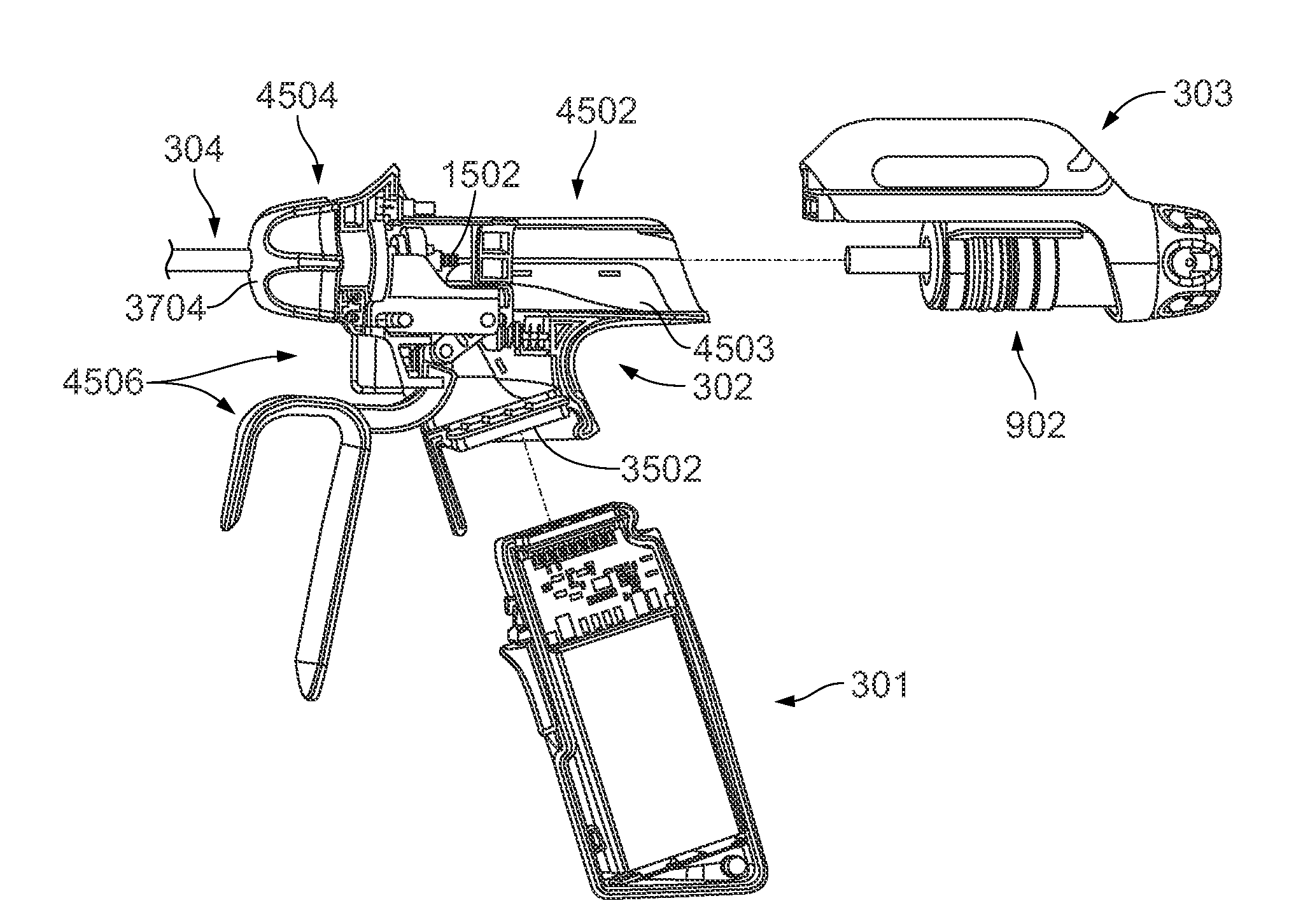
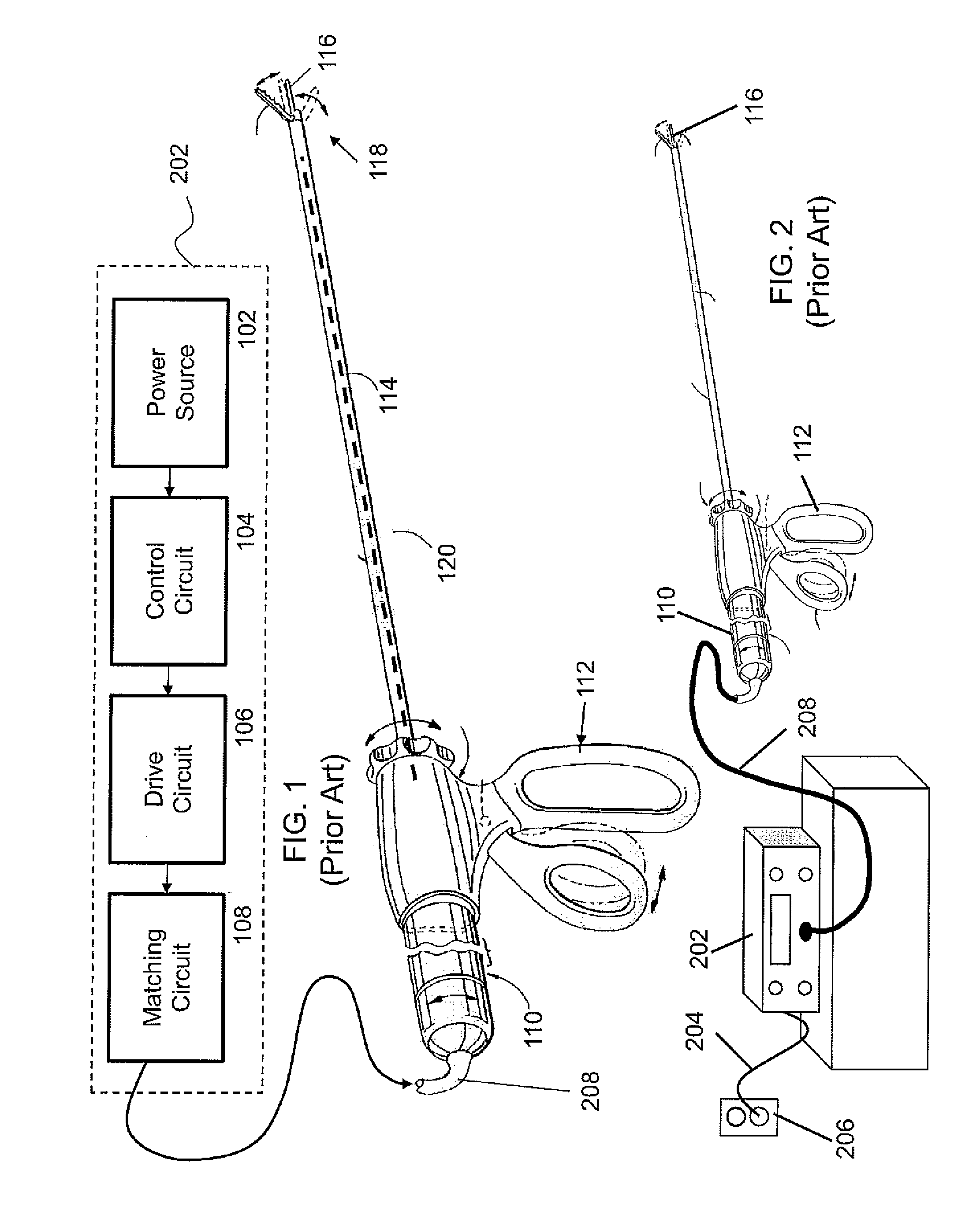
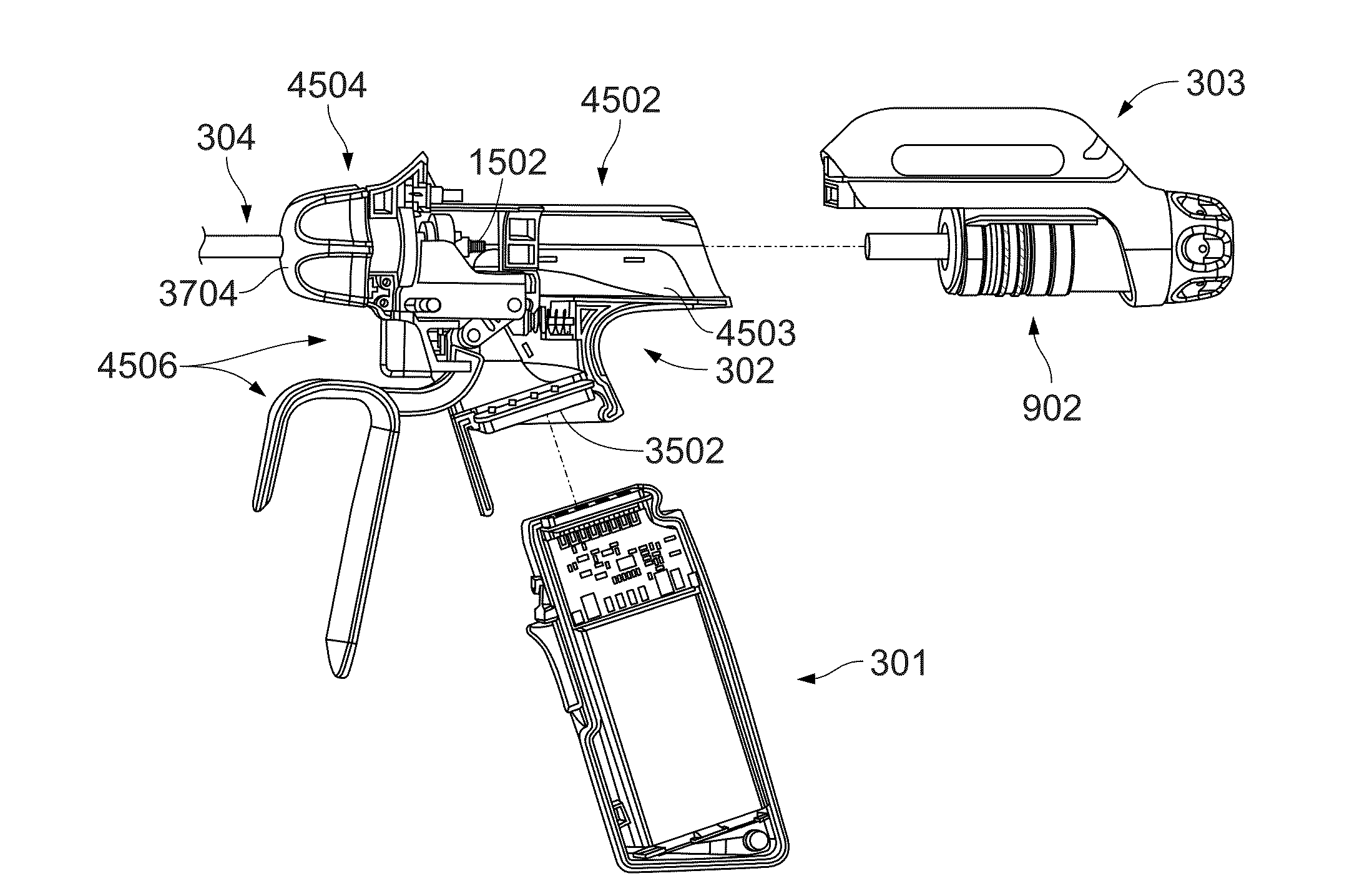
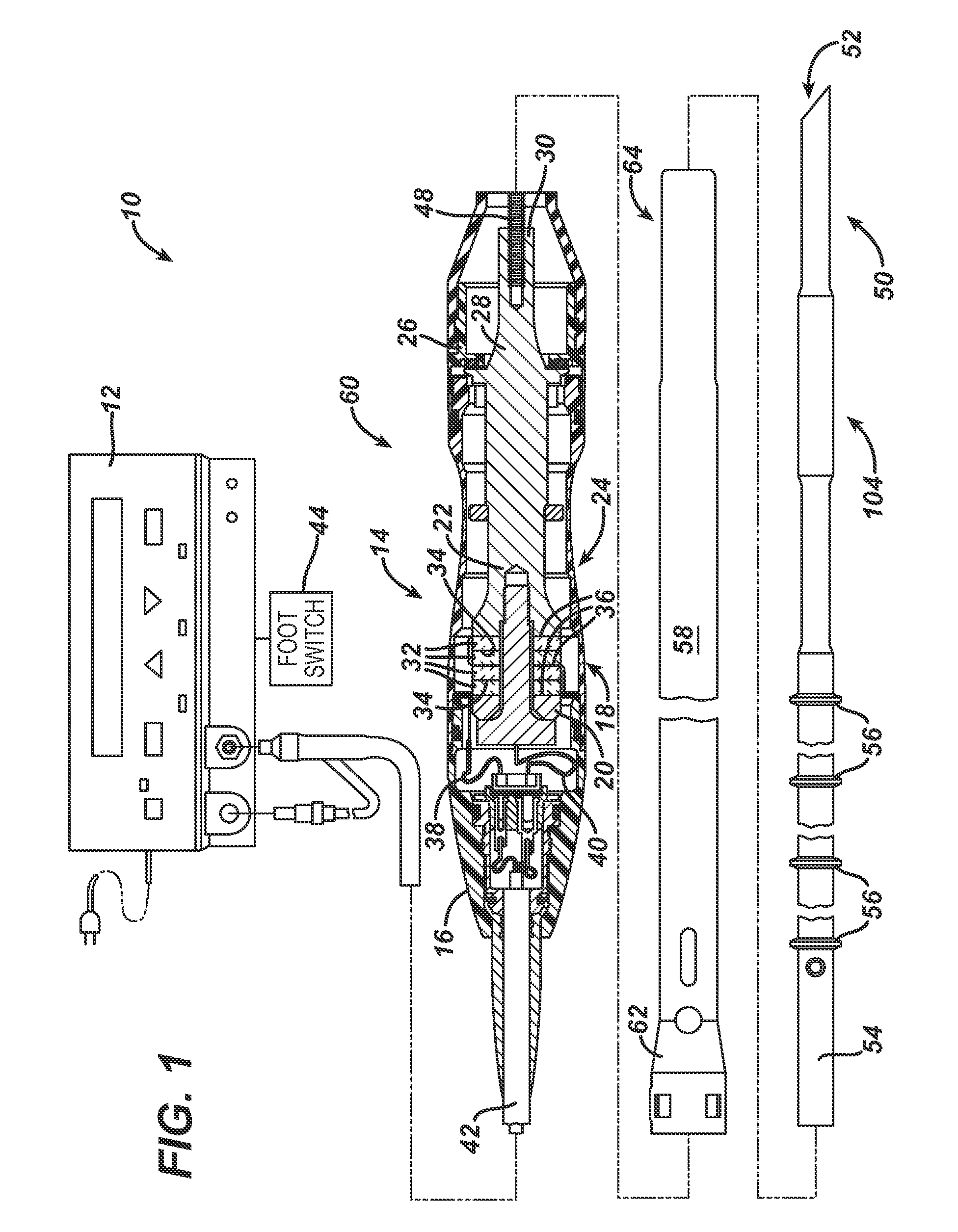
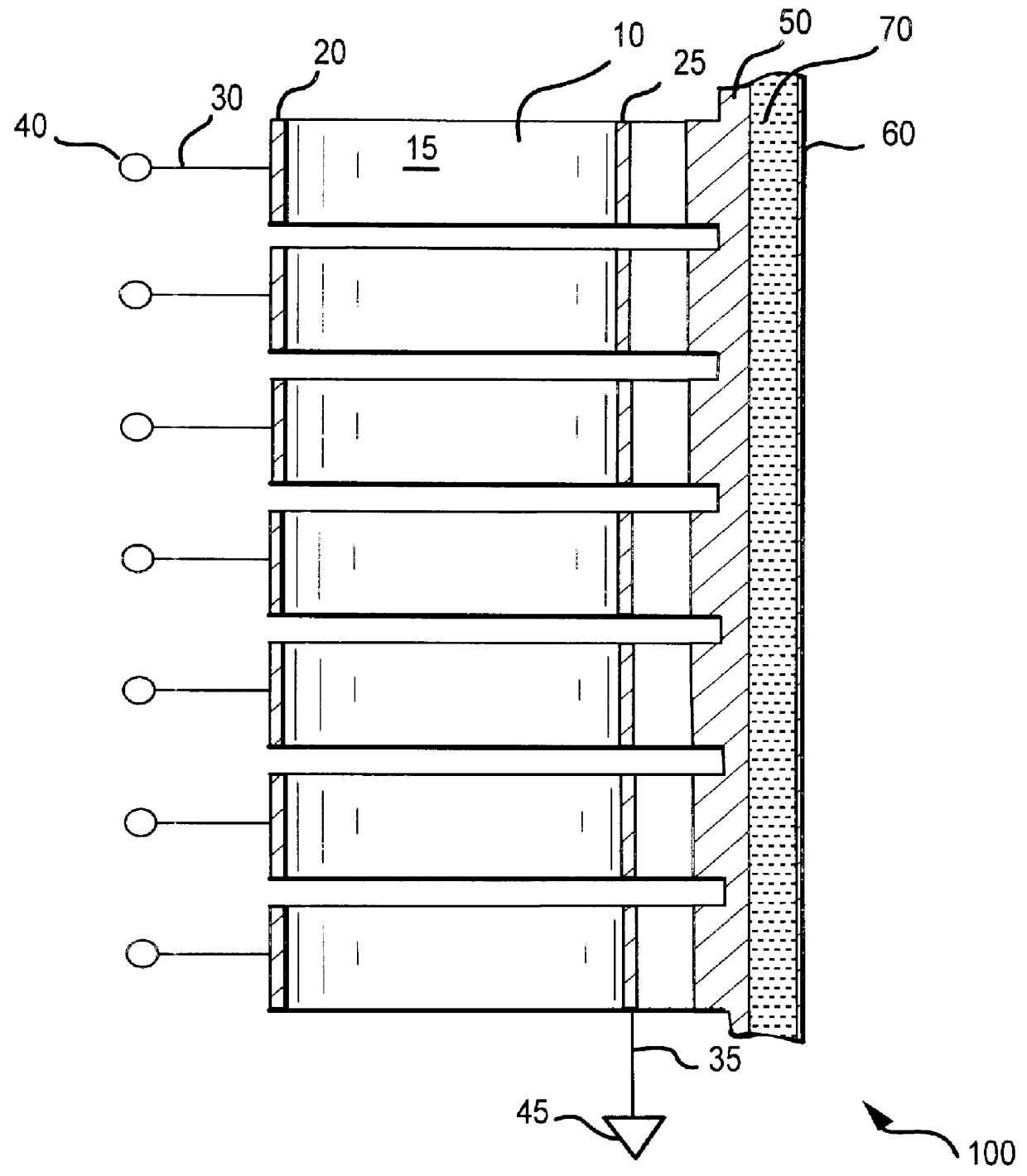
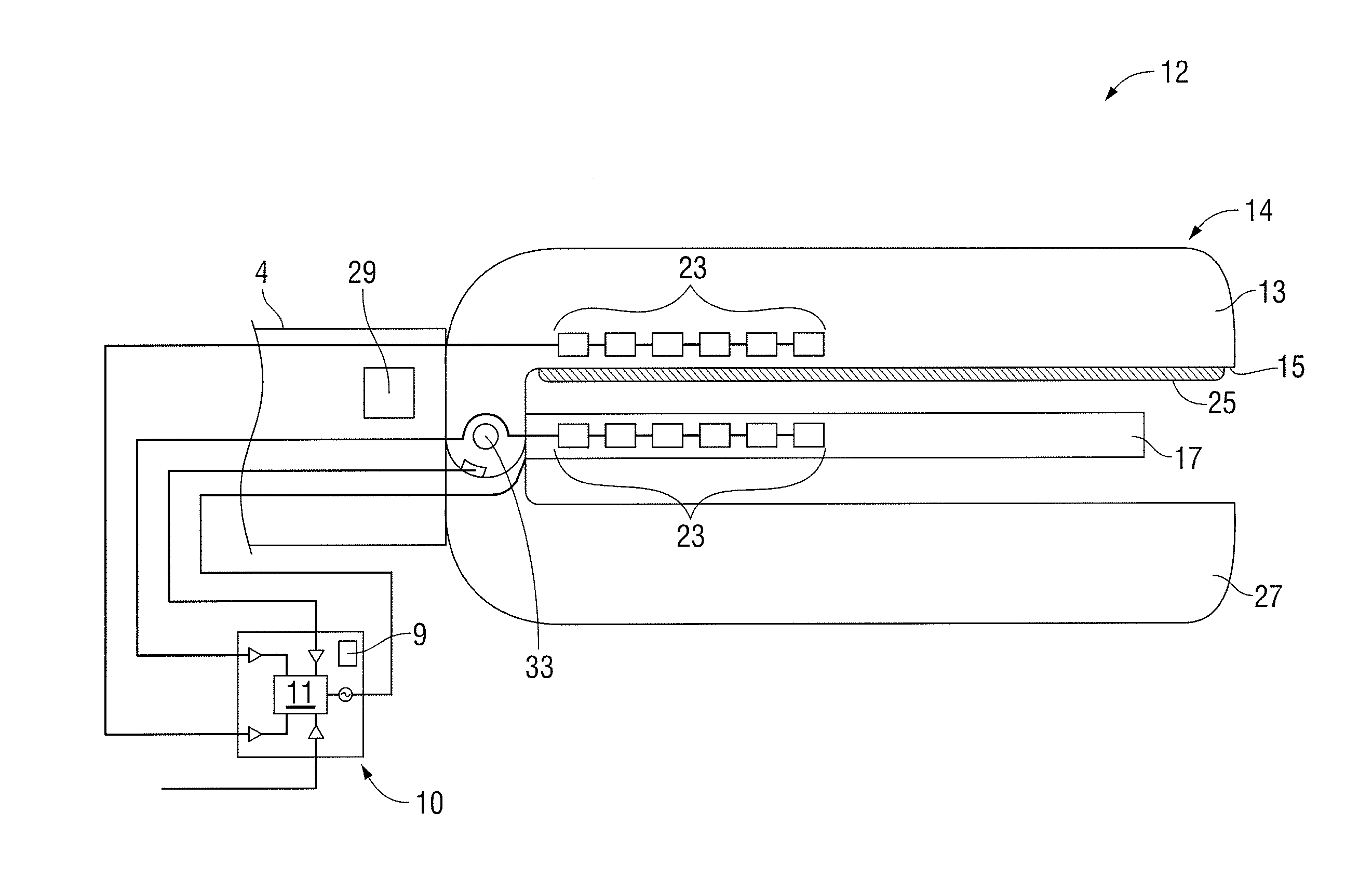
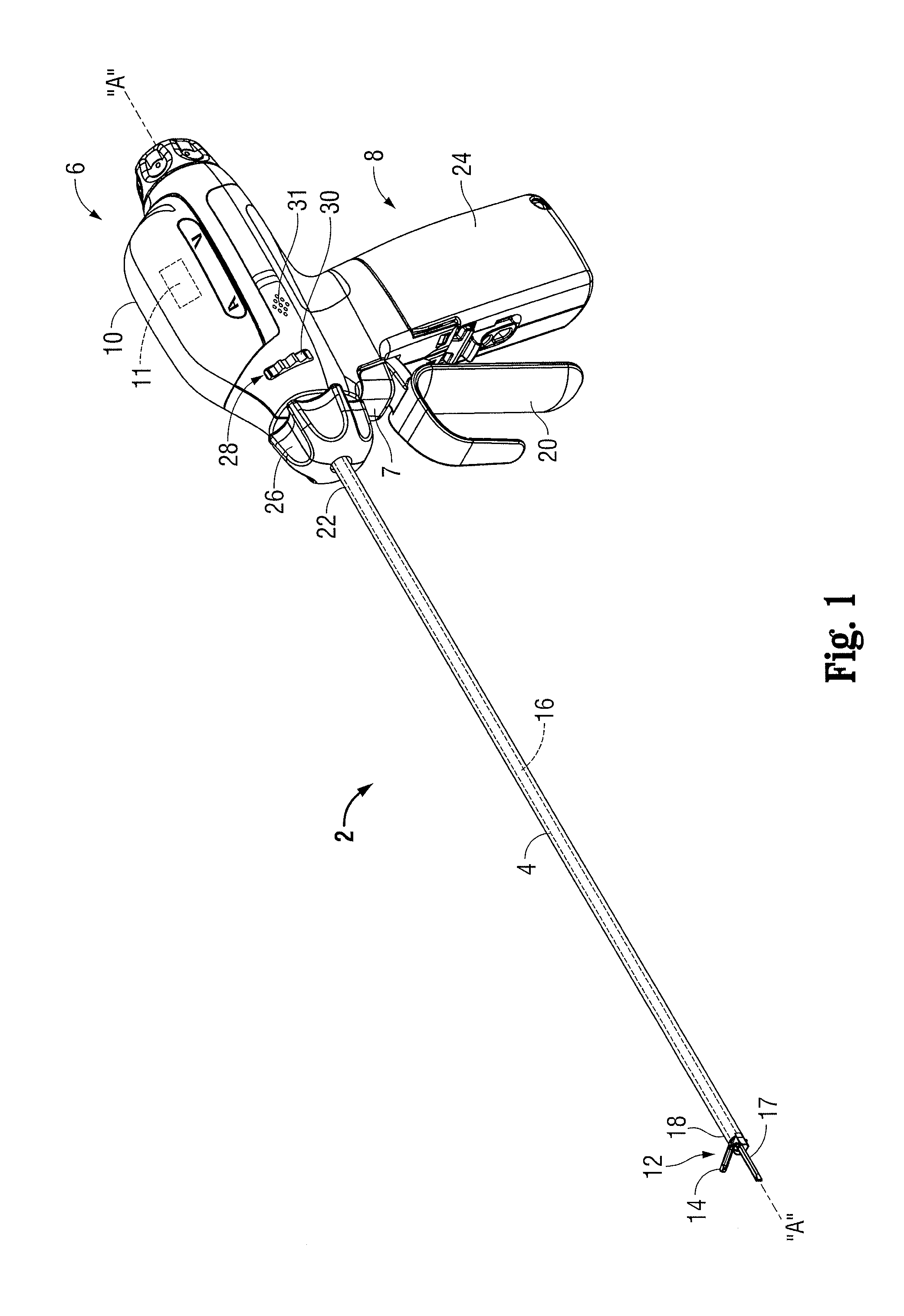
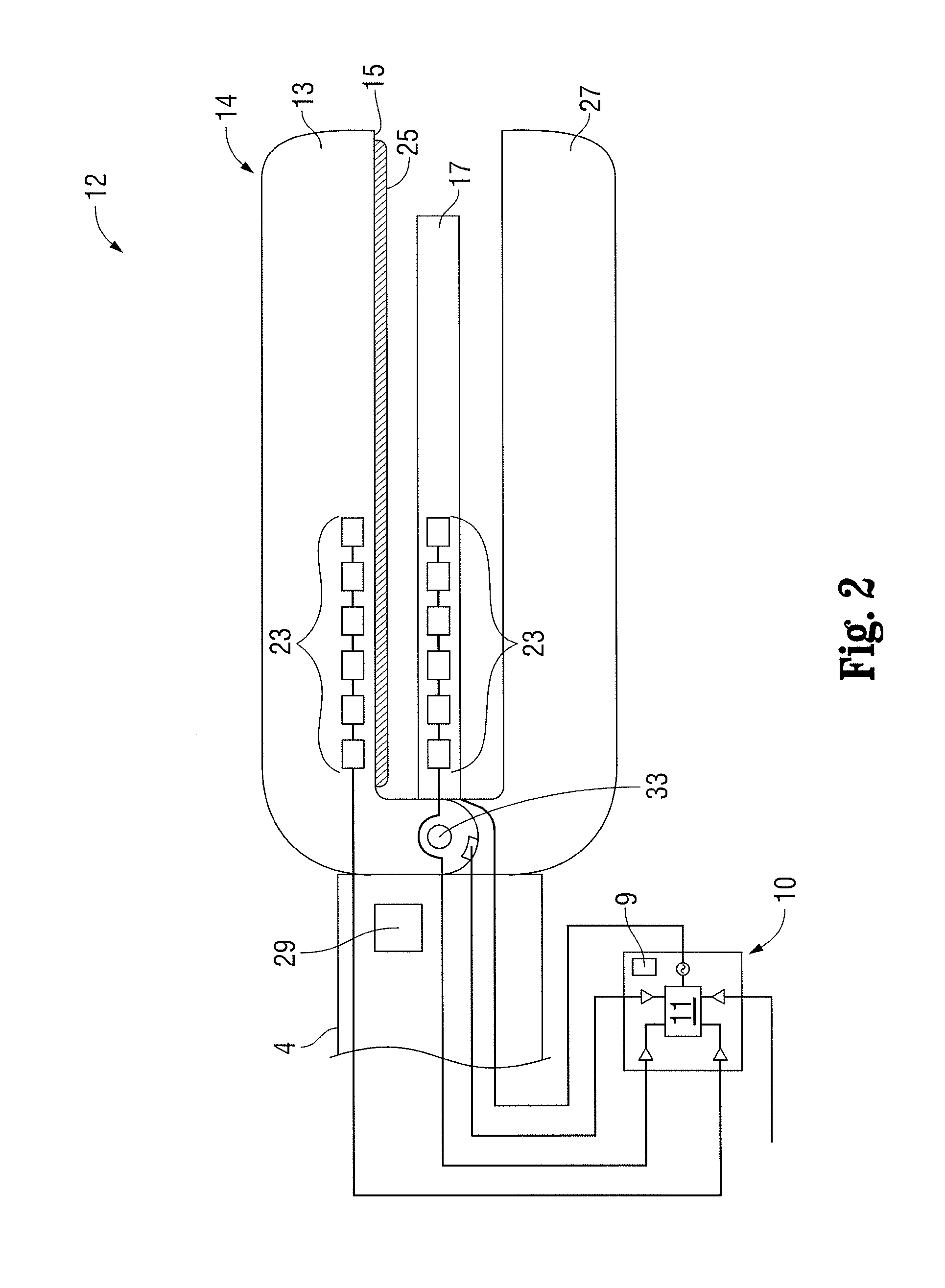
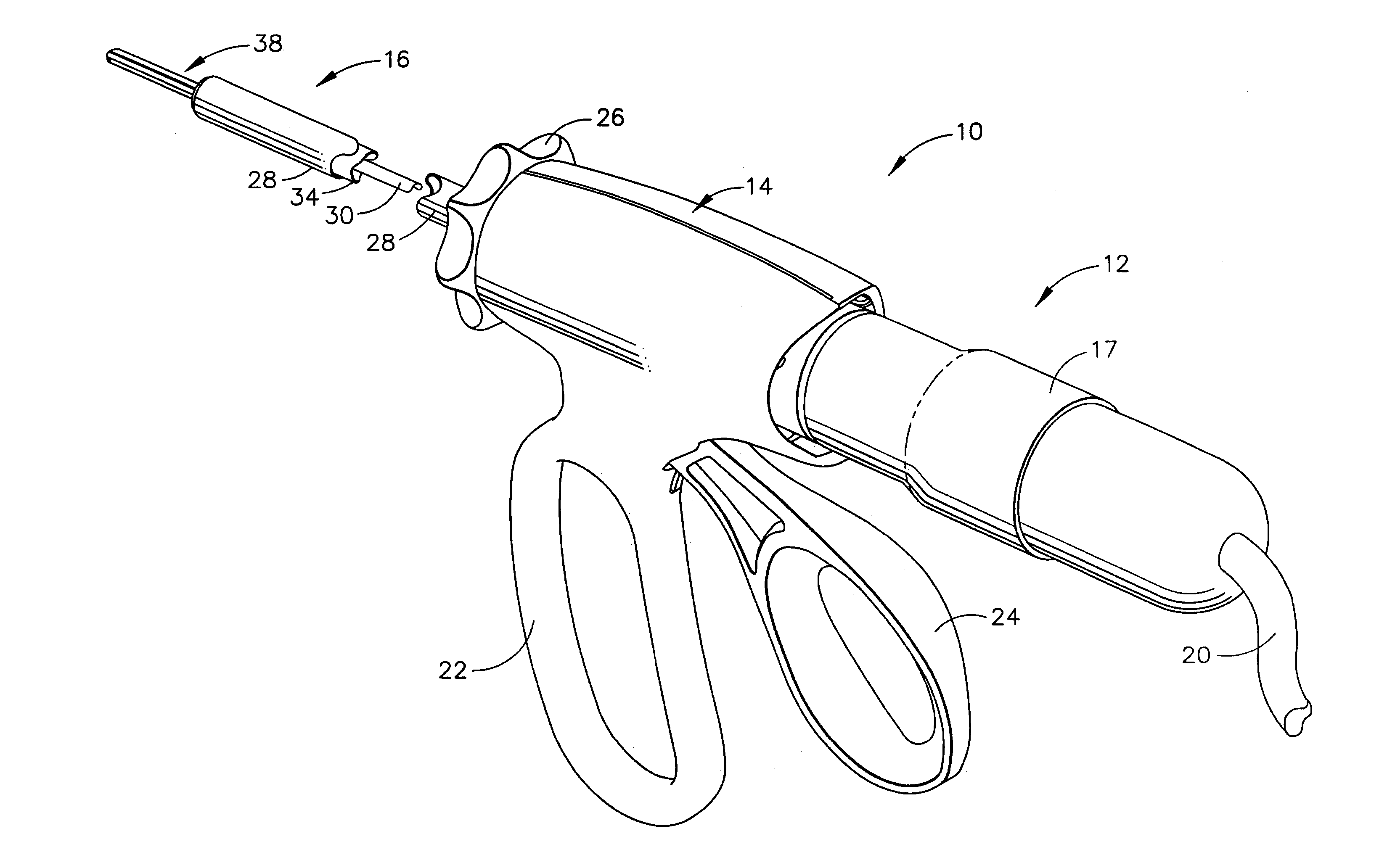
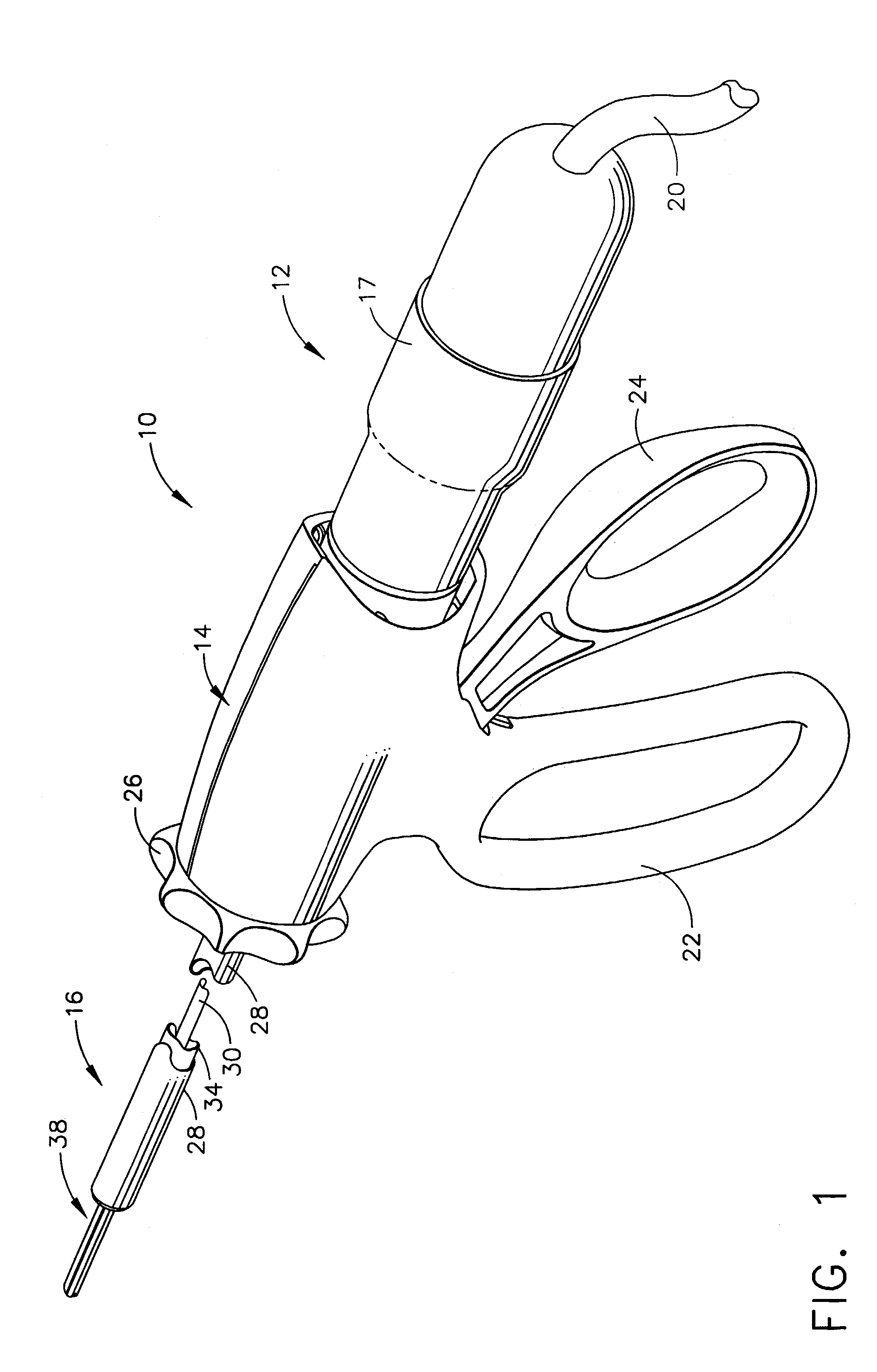
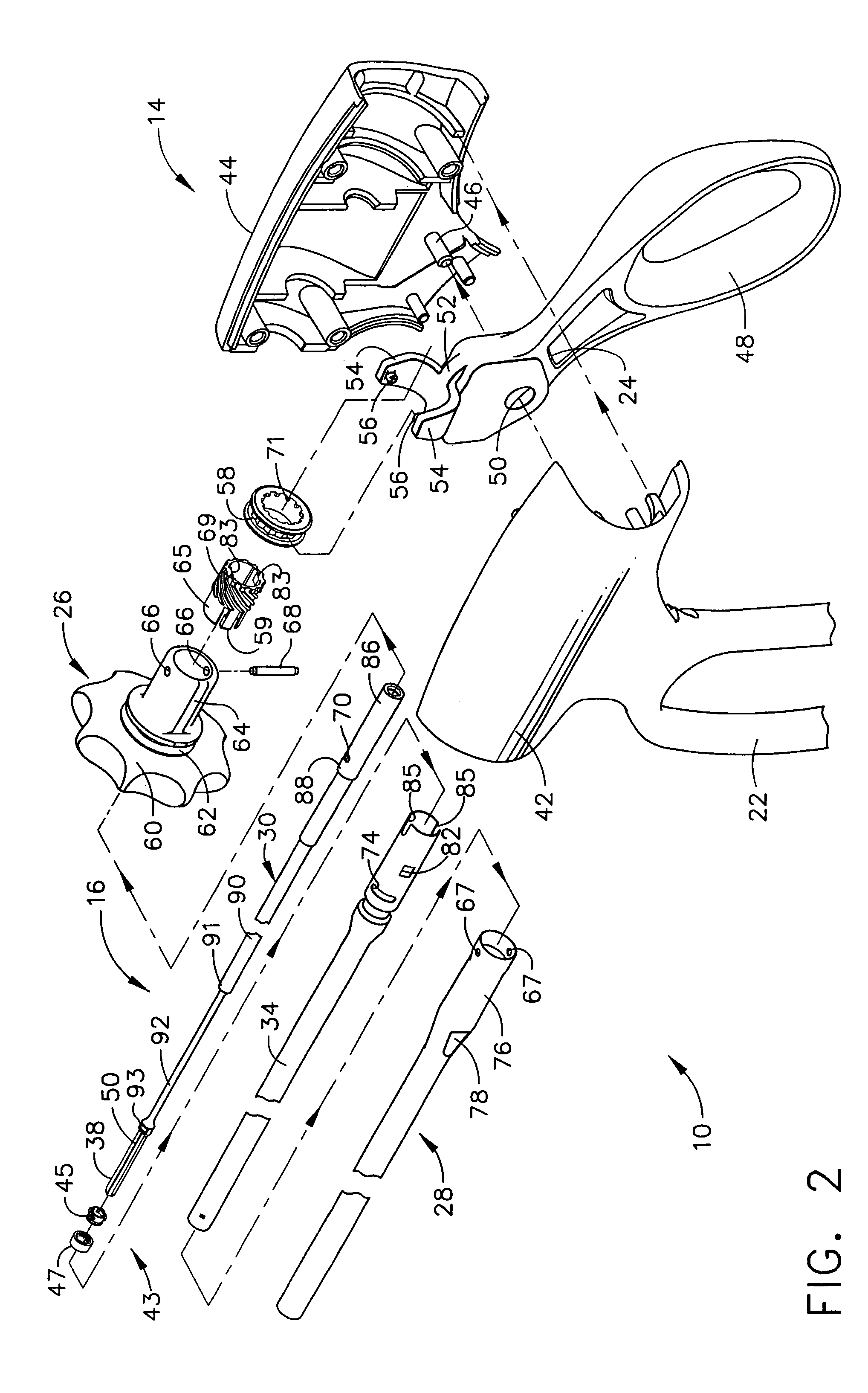
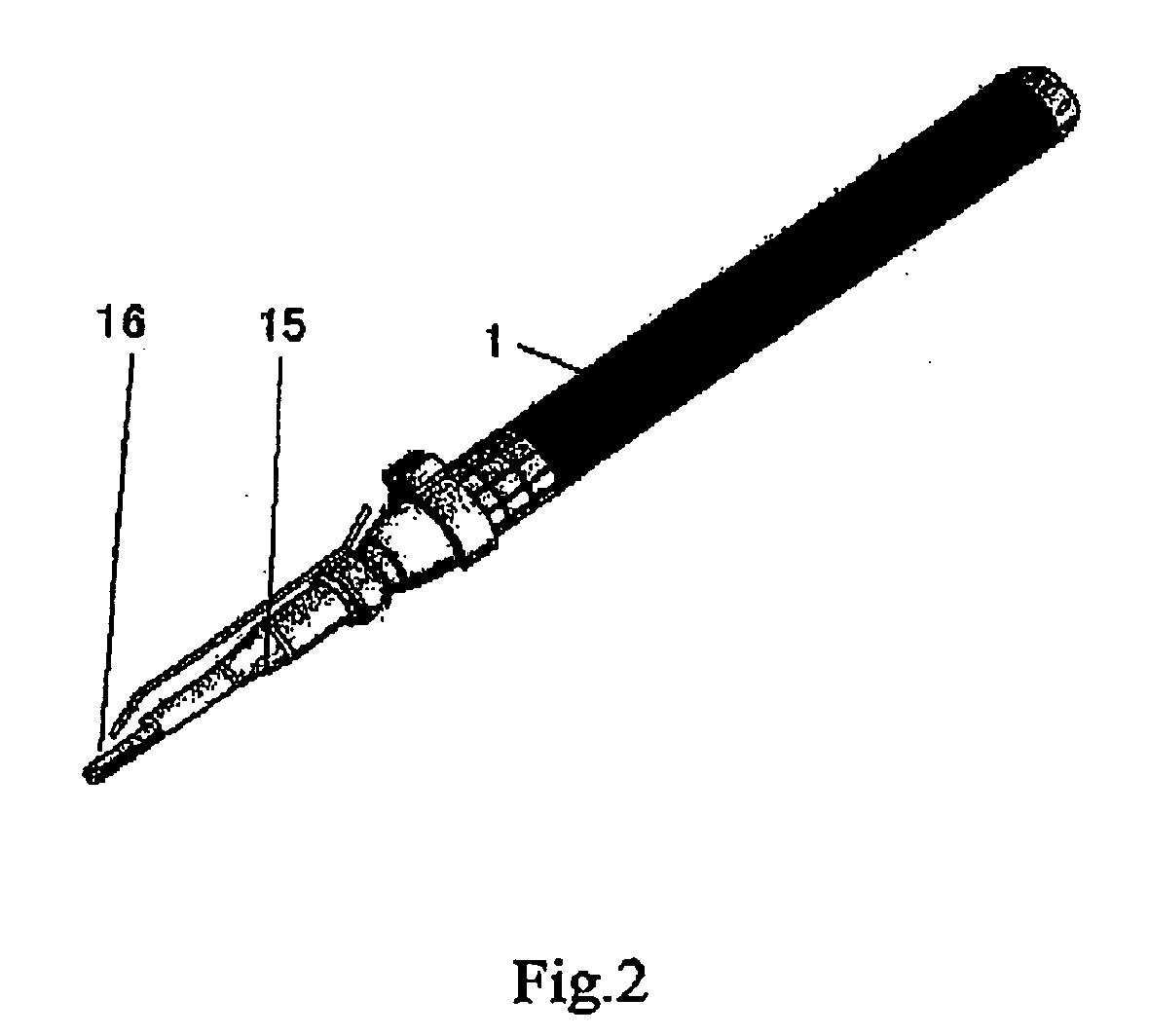
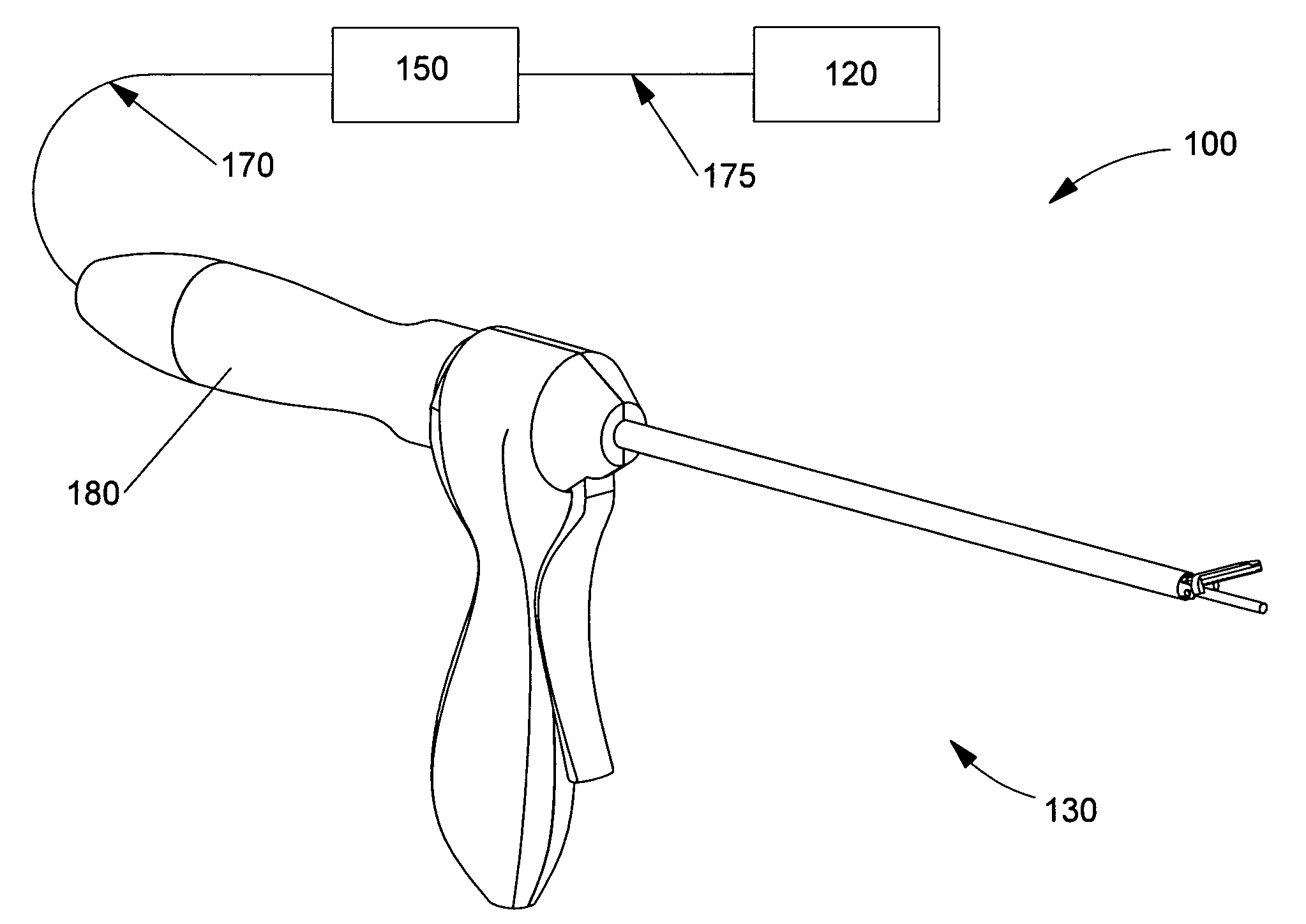
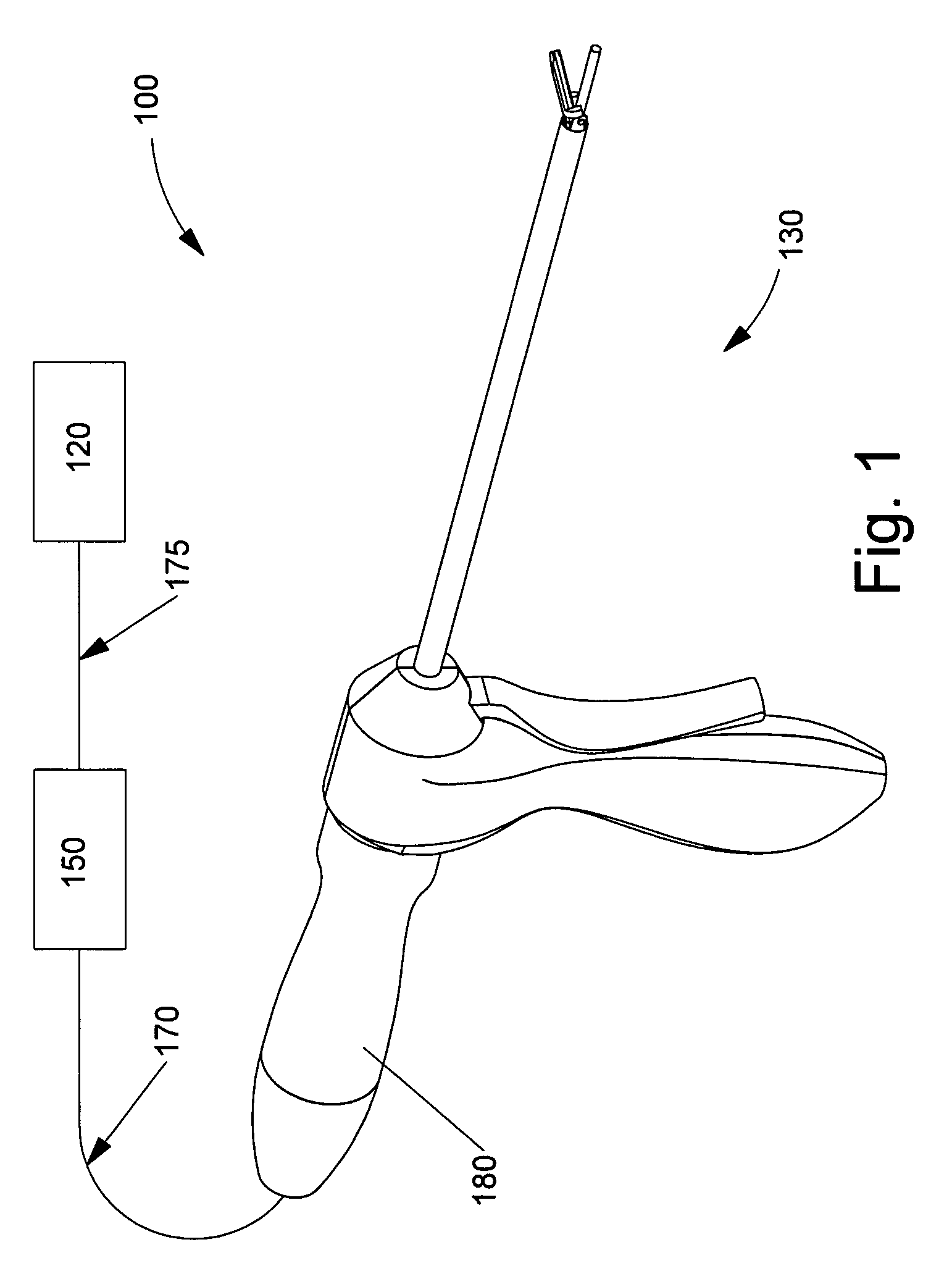
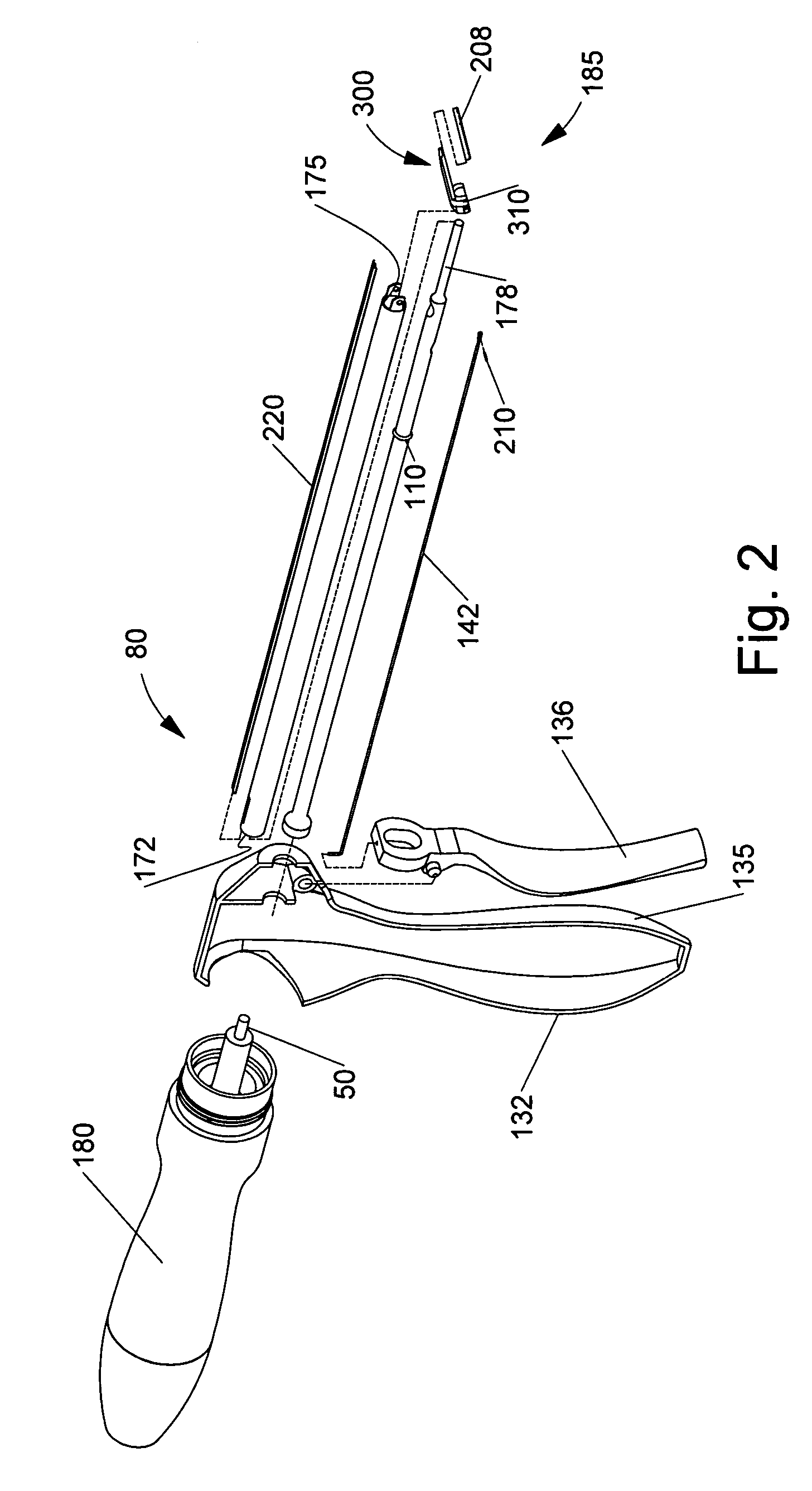
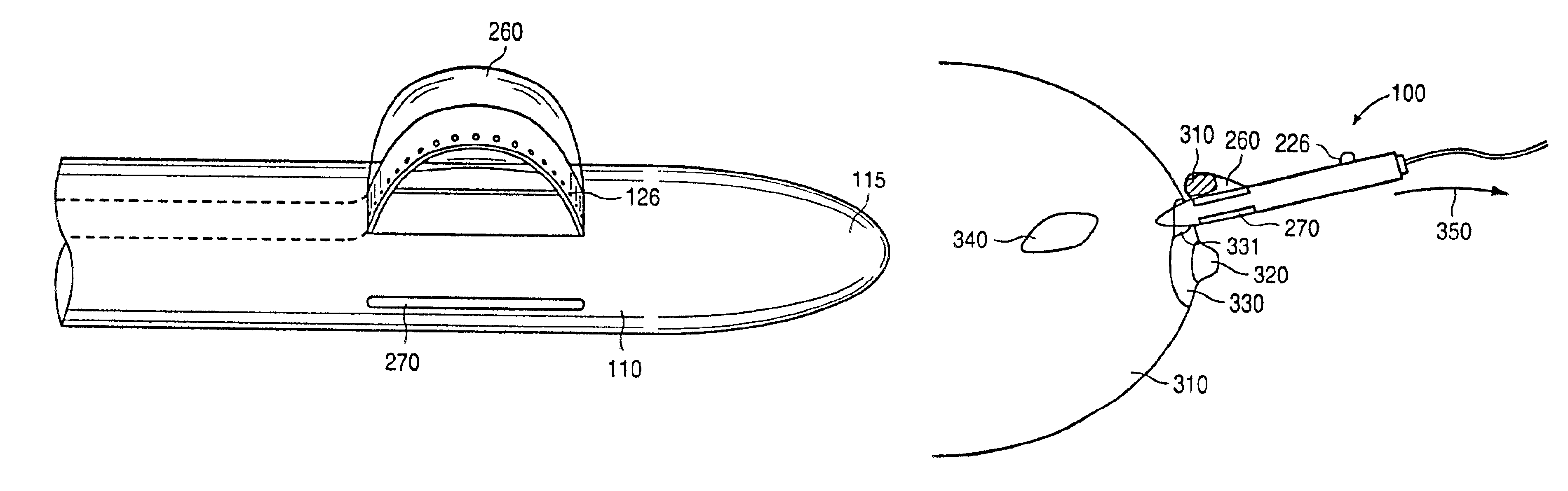
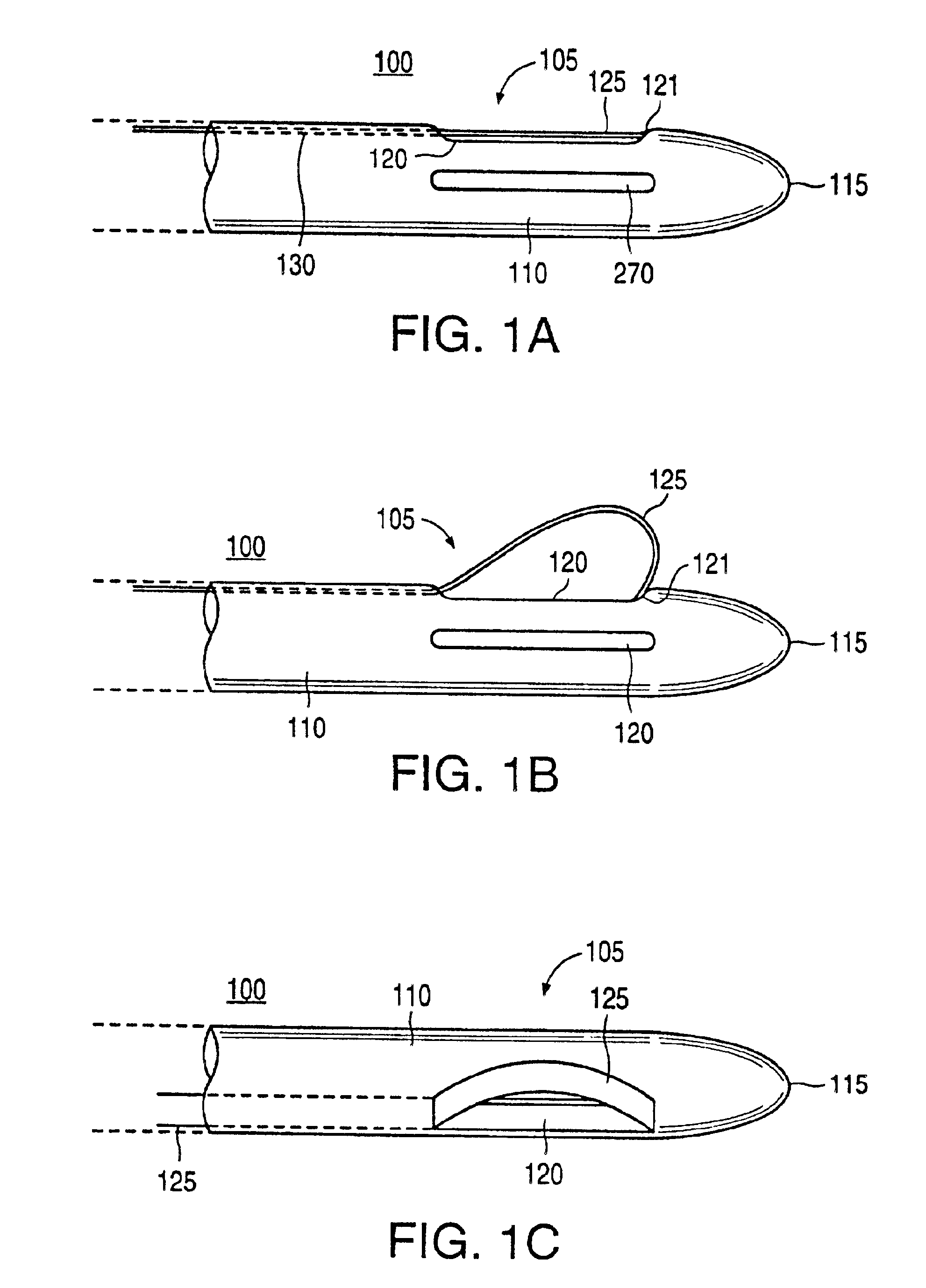
Rotary hydraulic pump actuated multi-stroke surgical instrument
A surgical instrument (e.g., endocutter, grasper, cutter, staplers, clip applier, access device, drug / gene therapy delivery device, and energy device using ultrasound, RF, laser, etc.) may benefit from having a plurality of hydraulically actuated subsystems (e.g., severing, stapling, articulation, locking / unlocking, lockout enabling / disabling, grasping, etc.) supplied with hydraulic power from a trigger actuated rotary pump (e.g., lobe pump, rotary gear pump, internal rotating gear pump, flexible vane rotor pump, rotary vane pump). Thereby, an available amount of mechanical advantage available at a firing trigger may be optimally distributed to various end effector components, perhaps sequenced by an electroactive polymer or piezoelelectrically actuated function switch block.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
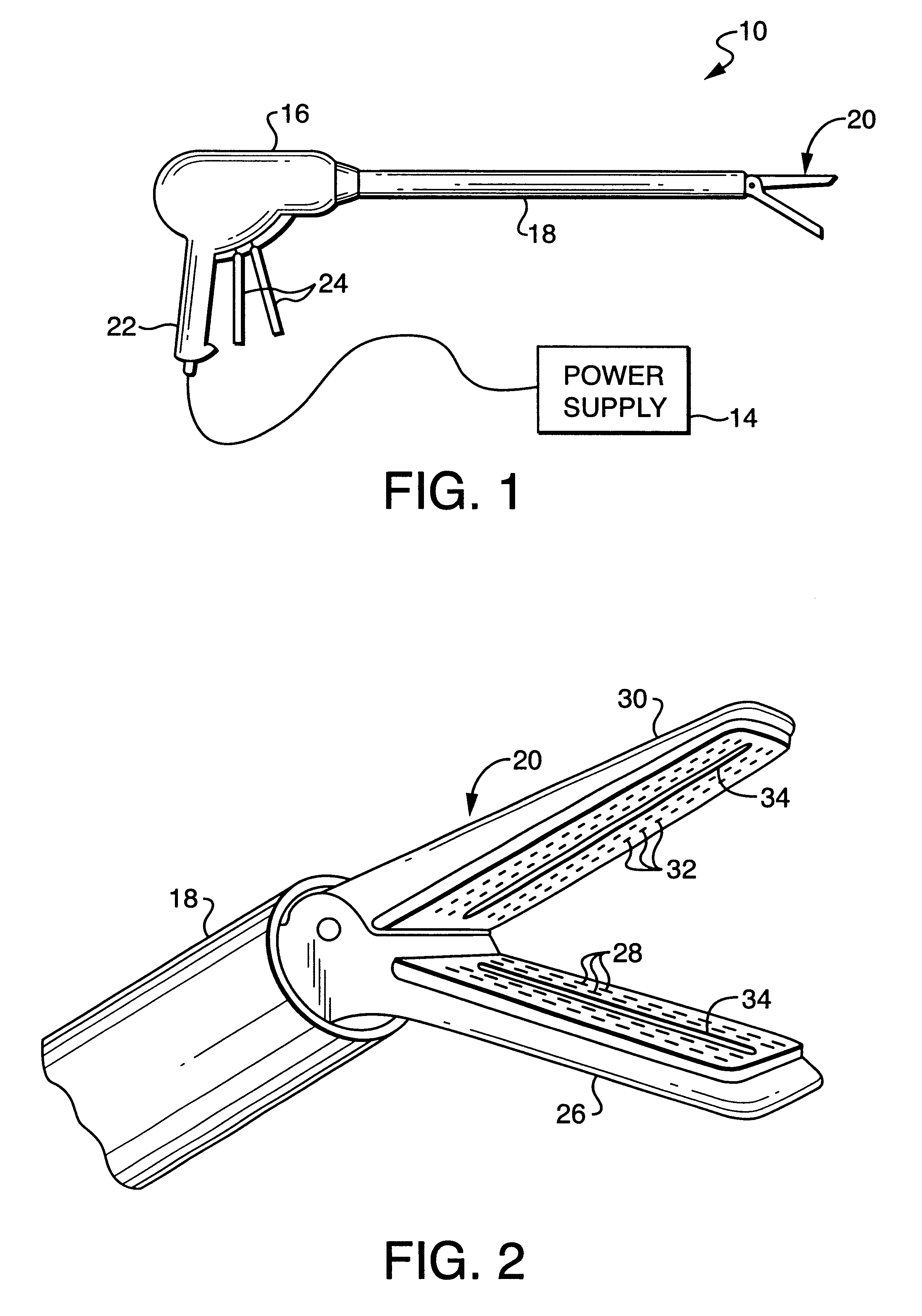
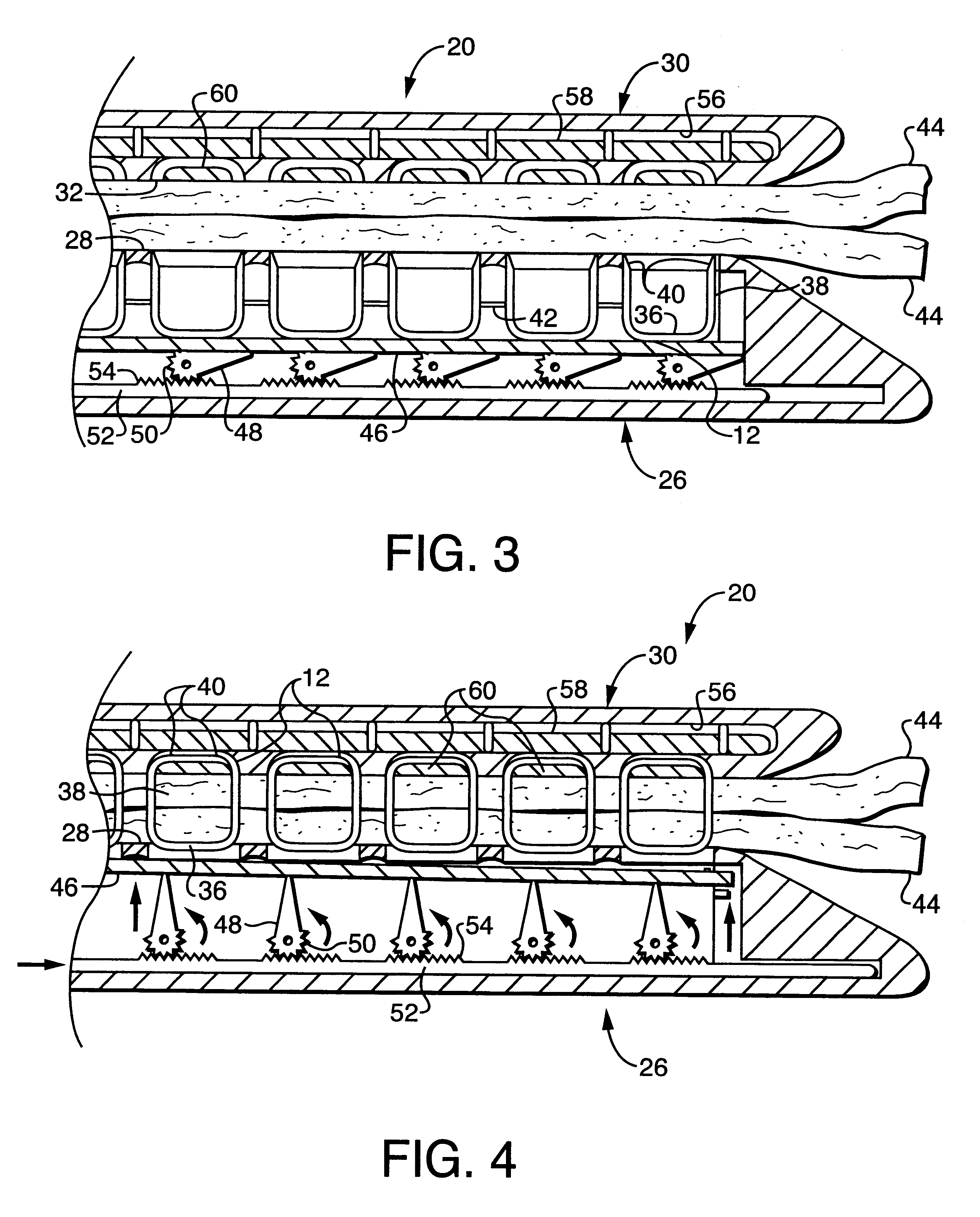
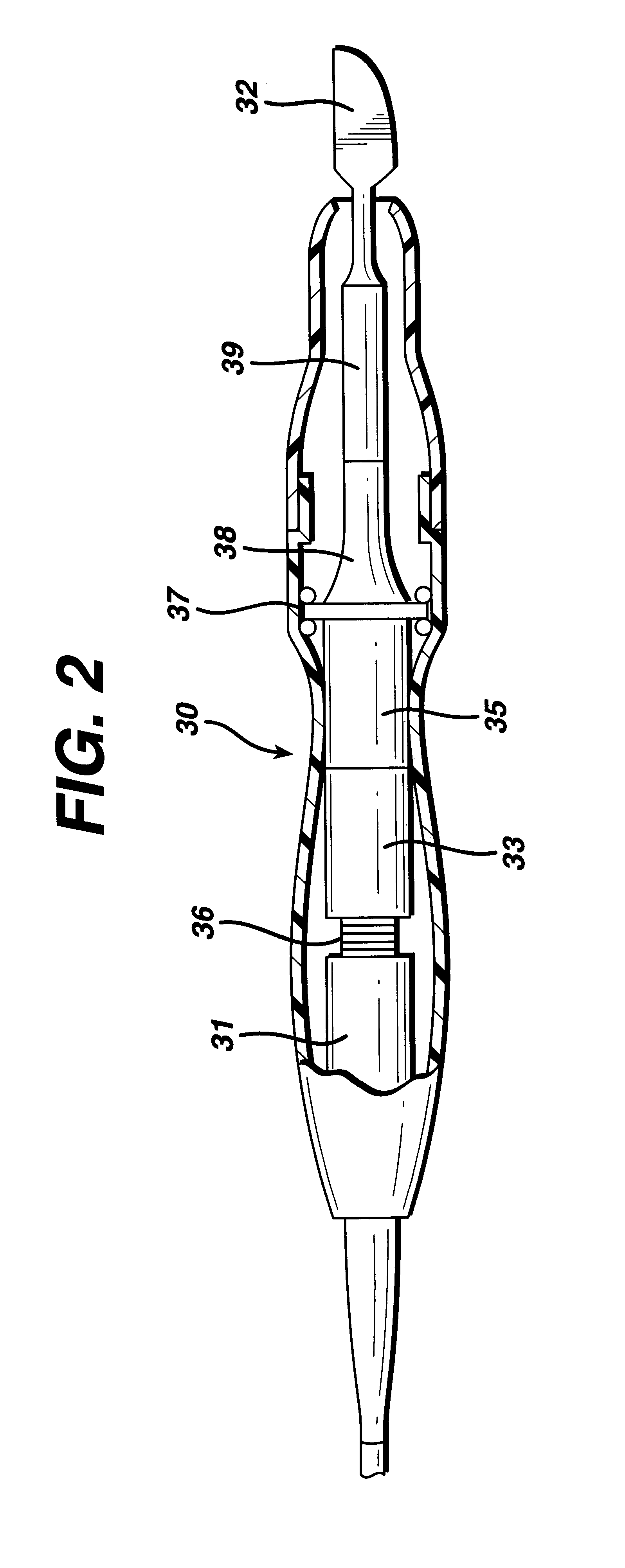
Surgical stapler and method of applying plastic staples to body tissue
A surgical stapler utilizing plastic staples and ultrasonic welding to secure the staples in body tissue. The stapler includes a pair of jaws movable between open and closed positions, a handle and trigger assembly for controlling operation of the jaws, and an elongated tubular structure connecting the handle and trigger assembly to the jaws. The stapler also includes an ejection assembly for ejecting at least one staple from one of the jaws against the other of the jaws. An anvil and a horn are positioned in the other of the jaws and are arranged to receive ends of the ejected staple such that the ends overlap between the anvil and the horn. The horn is for melting and bonding at least a portion of the overlapping ends of the staple upon being energized by a predetermined form of energy, and one of the anvil and the horn is movable from within the bonded staple to allow the jaws to be moved to an open position.
Owner:AXYA MEDICAL INC
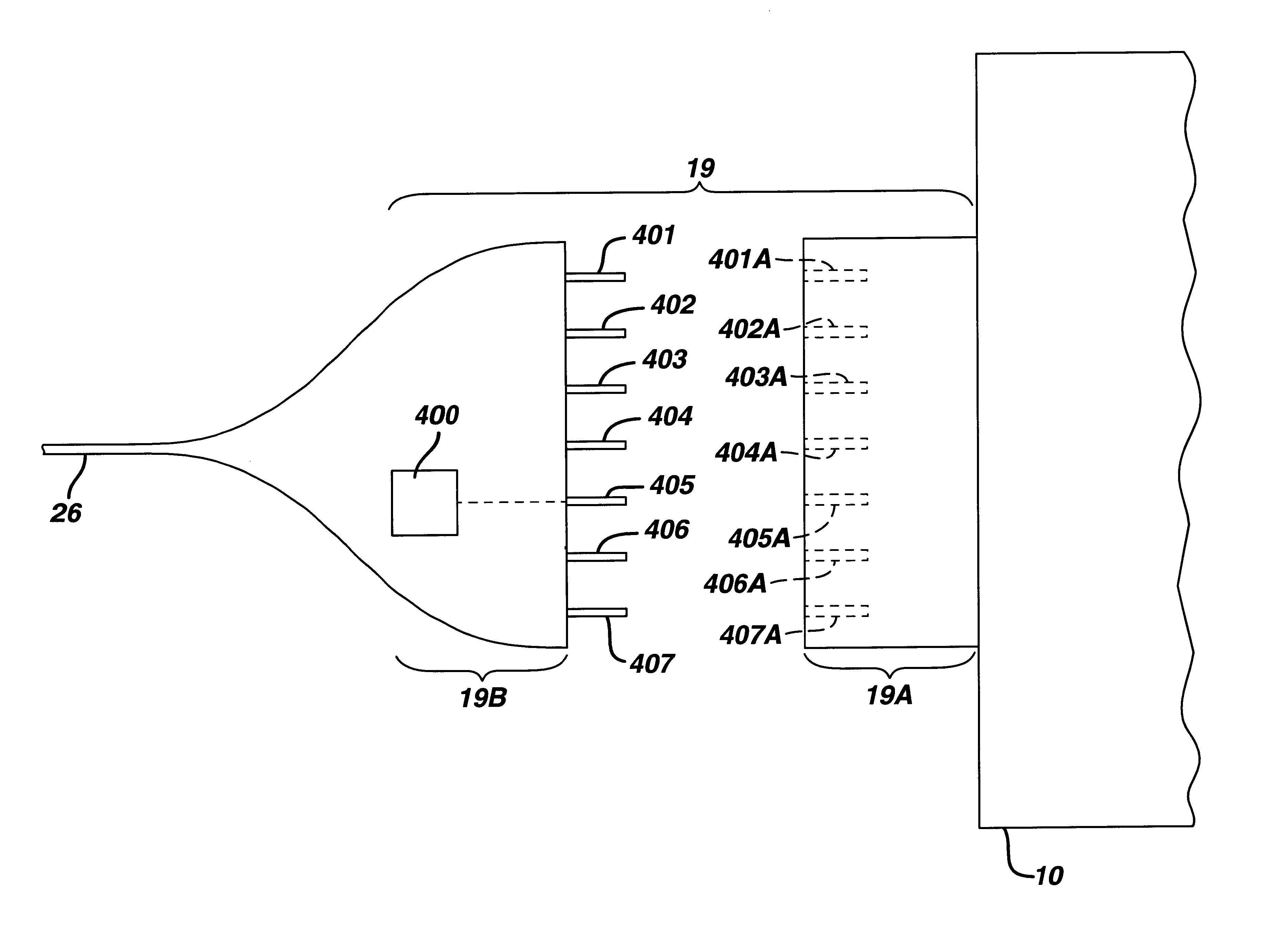
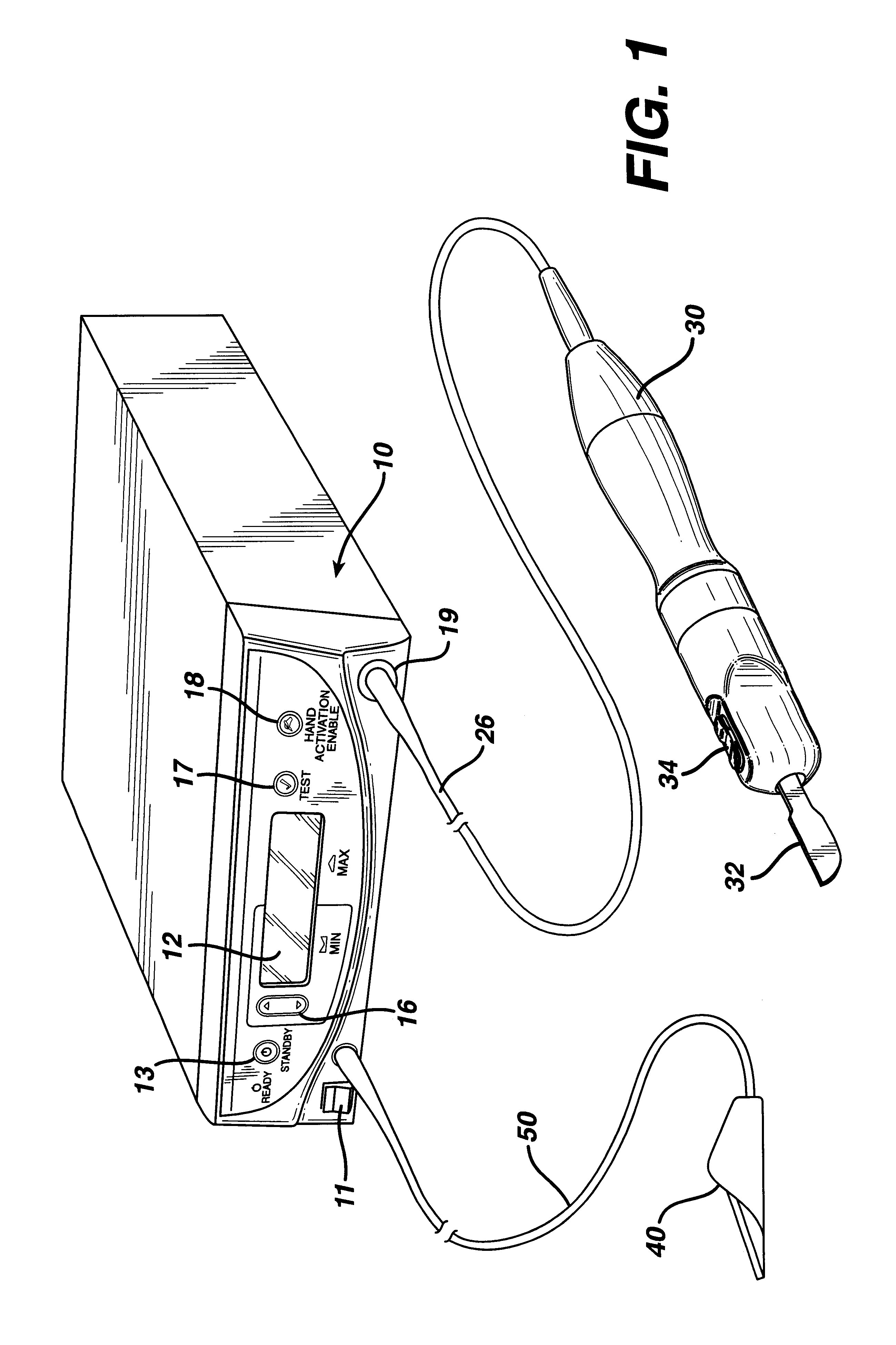
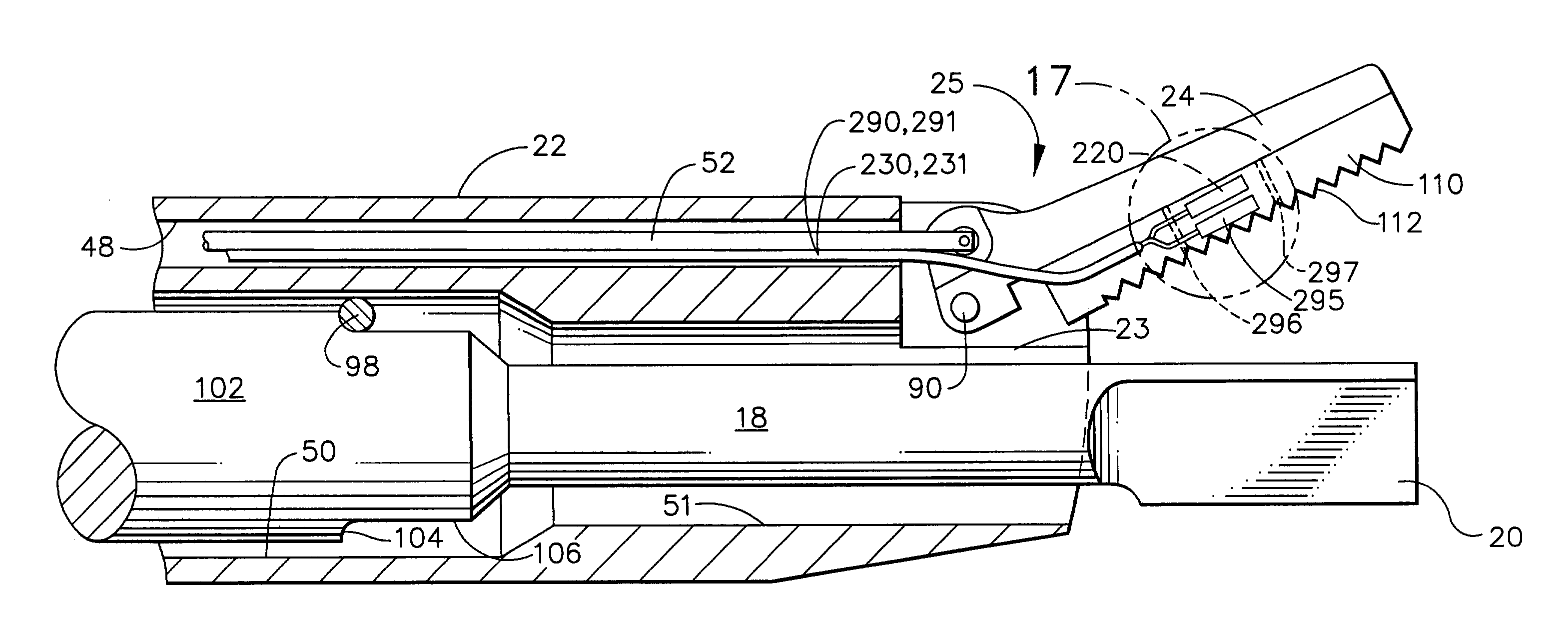
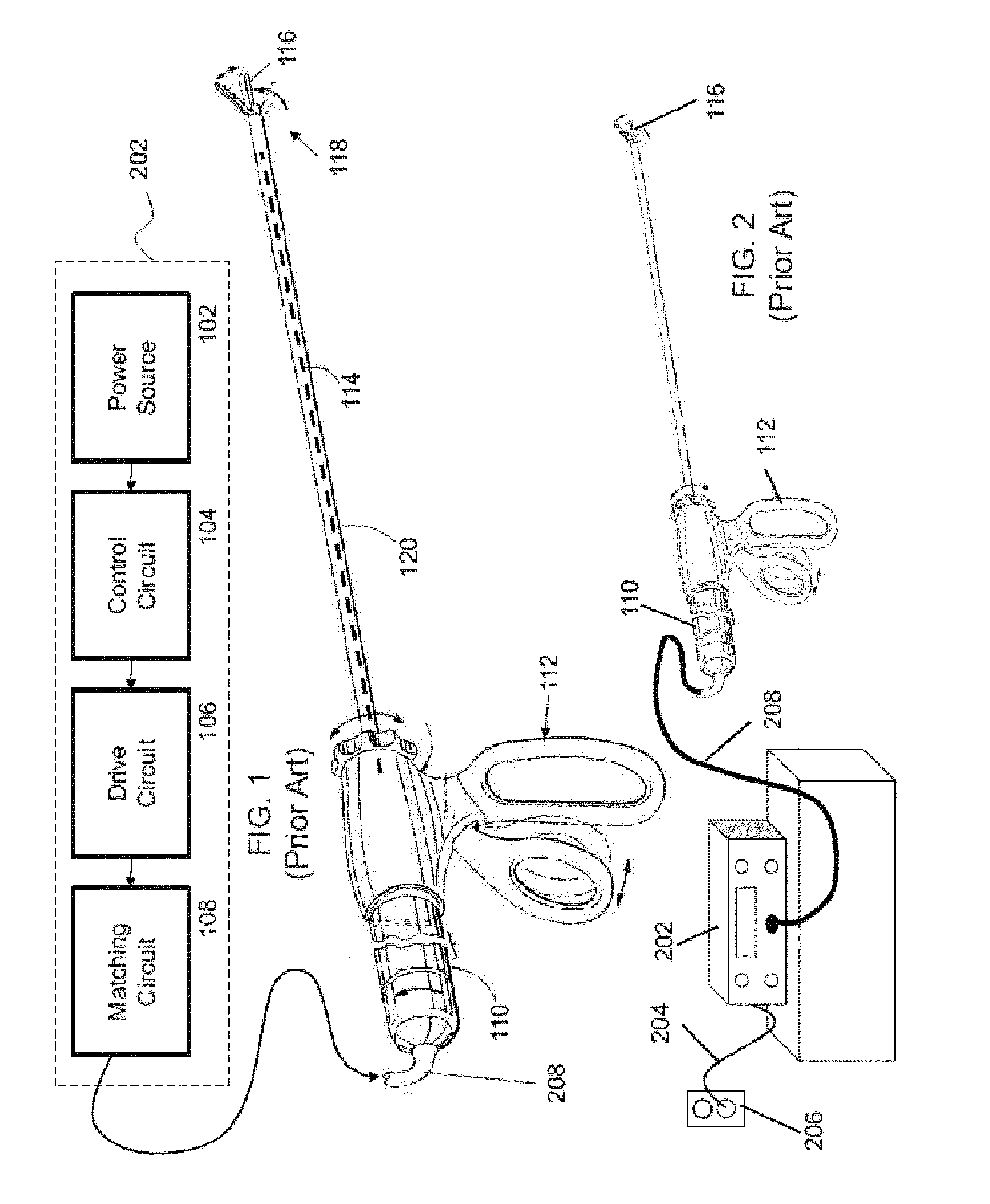
Apparatus and method for altering generator functions in an ultrasonic surgical system
InactiveUS6908472B2Avoid mistakesNew system functionalityIncision instrumentsDiagnosticsDriving currentElectricity
The present invention provides a system for implementing surgical procedures which includes an ultrasonic surgical hand piece having an end-effector, a console having a digital signal processor (DSP) for controlling the hand piece, an electrical connection connecting the hand piece and the console, and a memory, such as an EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory), disposed in the electrical connection. The console sends a drive current to drive the hand piece which imparts ultrasonic longitudinal movement to the blade. The console reads the memory and authenticates the hand piece for use with the console if particular or proprietary data are present in the memory. Moreover, to prevent errors in operating the hand piece, the memory can store certain diagnostic information which the console can utilize in determining whether the operation of the hand piece should be handicapped or disabled. Furthermore, the memory can be used to reprogram the console, if needed.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
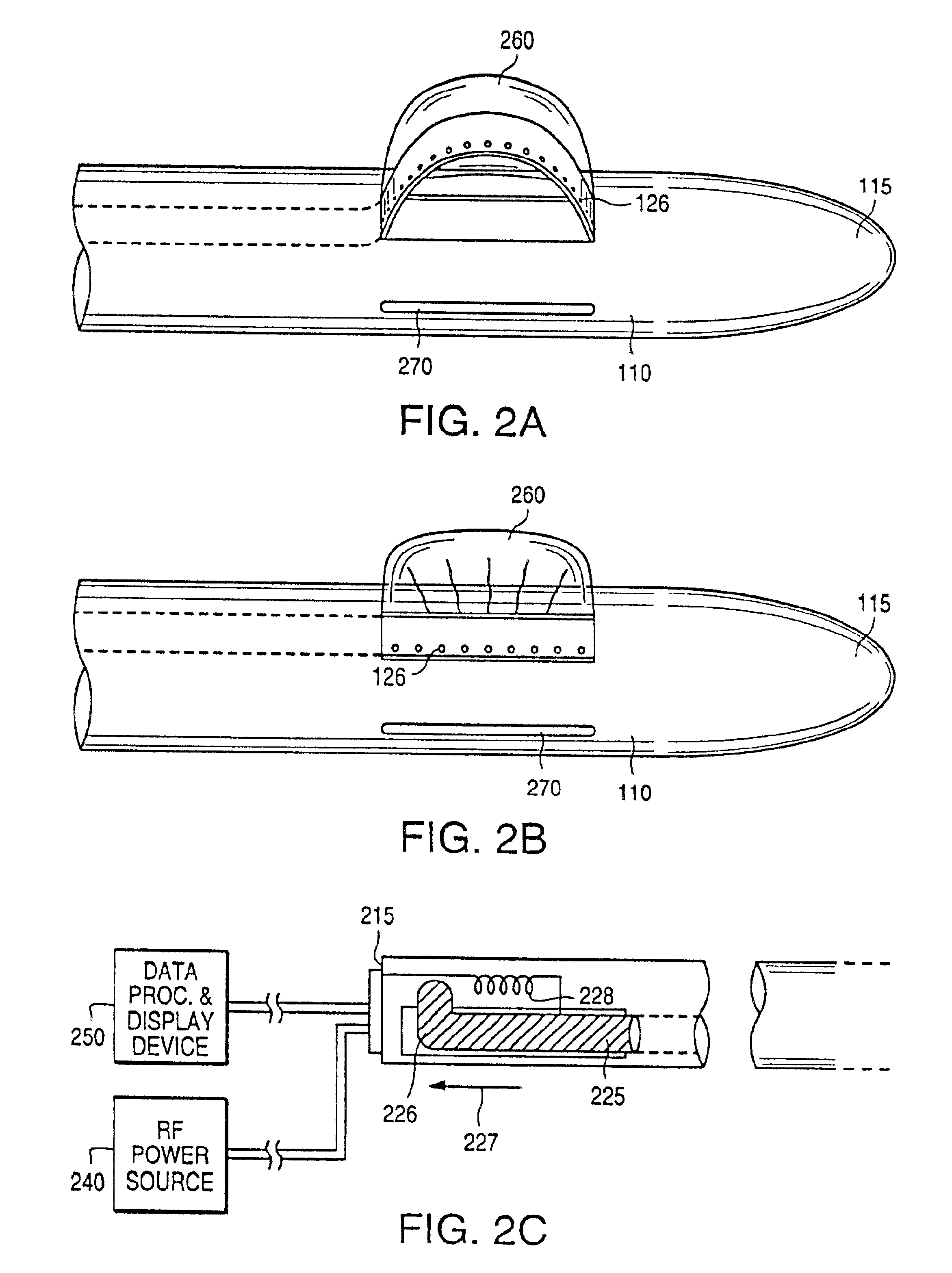
Feedback control in an ultrasonic surgical instrument for improved tissue effects
A temperature monitoring device and / or method which control the tissue temperature at the end-effector of a therapeutic ultrasonic cutting and coagulating instrument as the tissue is being heated with ultrasonic vibrations from the end-effector. One or more temperature sensors are located at the end-effector, preferably on a clamping member. The temperature sensors measure the temperature of the tissue engaged by the end-effector either directly or indirectly. An alternate method and apparatus provides an electrical tissue impedance measure in combination with an ultrasonic cutting and coagulating instrument to provide active feedback control of an ultrasonic generator.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Ultrasonic device for cutting and coagulating
InactiveUS20070191713A1Improve wear resistanceLoad moreUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsBack cuttingBiological activation
An ultrasonic clamp coagulator assembly that is configured to permit selective cutting, coagulation, and fine dissection required in fine and delicate surgical procedures. The assembly includes a clamping mechanism, including a clamp arm cam-mounted at the distal portion of the instrument, which is specifically configured to create a desired level of tissue clamping forces. The balanced blade provides a functional asymmetry for improved visibility at the blade tip and a multitude of edges and surfaces, designed to provide a multitude of tissue effects: clamped coagulation, clamped cutting, grasping, back-cutting, dissection, spot coagulation, tip penetration and tip scoring. The assembly also features hand activation configured to provide an ergonomical grip and operation for the surgeon. Hand switches are placed in the range of the natural axial motion of the user's index or middle fingers, whether gripping the surgical instrument right-handed or left handed.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT +1
Catheter for conducting a procedure within a lumen, duct or organ of a living being
In an embodiment, the invention provides a catheter suitable for use in performing a procedure within a vessel, lumen or organ of a living having a distal end which is steerable, such as upon the application of compression. The catheter may be of the over the wire type, or alternatively may be a rapid exchange catheter. The catheter may provide for a rotating element which may be used to open a clogged vessel, or alternatively to provide information about adjacent tissues, such as may be generated by imaging or guiding arrangements using tissue detection systems known in the art, e.g., ultrasound, optical coherence reflectometry, etc. For rapid exchange catheters having a rotating element, there is provided an offset drive assembly to allow the rotary force to be directed from alongside the guidewire to a location coaxial to and over the guidewire.
Owner:KENSEY NASH CORP
Surgical instrument
A surgical instrument has a first grasping member, a second grasping member which is provided to the first grasping member to open and close to the first grasping member, and grasps a living tissue between them, an ultrasonic coagulation-cutting unit which includes an ultrasonic vibrating portion provided in one of the first and second grasping members and connected to an ultrasonic transducer to generate ultrasonic vibration, and a pressing portion provided in the other of the first and second grasping members, and facing the ultrasonic vibrating portion, the pressing portion and the ultrasonic vibrating portion pressing the living tissue between them, and a high-frequency coagulation unit which includes a first electrode provided in the first grasping member, and a second electrode provided in the second grasping member, the first electrode and the second electrodes facing each other to coagulate the living tissue.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Ultrasonic coagulation and cutting apparatus
An ultrasonic coagulation and cutting apparatus includes: an ultrasonic transducer for a treatment using ultrasonic vibrations on body tissue; a probe for transmitting generated ultrasonic vibrations to the distal end thereof; a movable gripping member for cooperating with the outer surface of the probe in gripping therebetween body tissue; an operation unit operated to move the gripping member; an operation transmitting member for transmitting the operation of the operation unit to the gripping member; and high frequency power supply connecting portions for electrically connecting the probe and the gripping member to predetermined portions of a high frequency power supply for a treatment using high frequency current on the body tissue. At least coagulation of the body tissue using high frequency current is started in a first gripping state. Cutting of the body tissue using ultrasonic vibrations generated by the ultrasonic transducer is started in a second gripping state.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Battery-powered hand-held ultrasonic surgical cautery cutting device
ActiveUS9107690B2Alter functionAlter performanceBatteries circuit arrangementsBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsReal-time clockElectrical battery
A battery assembly for use with a surgical device having a battery terminal and operational parameters includes a housing having a shape formed to removably connect with the terminal. The housing contains a modular battery operable to supply power to the device at the terminal and has a control circuit with a microprocessor, a memory, and a real-time clock. The control circuit is communicatively coupled to the battery and is operable to detect an identity of the surgical device, to determine at least one piece of information pertaining to at least one of the operational parameters of the surgical device based upon the detected identity, to record the piece of information at least in the memory, and to selectively allow or prevent the battery from supplying power to the surgical device dependent upon the piece of information.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Battery-powered hand-held ultrasonic surgical cautery cutting device
ActiveUS9017355B2Alter functionAlter performanceChiropractic devicesEye exercisersSurgical operationHand held
A battery-powered, modular surgical device includes an electrically powered surgical instrument operable to surgically interface with human tissue and a handle assembly connected to the surgical instrument. The handle assembly has a removable hand grip and a handle body. The hand grip is shaped to permit handling of the surgical device by one hand of an operator, has an upper portion and a cordless internal battery assembly that powers the surgical instrument. The internal battery assembly has at least one energy storage cell. The handle body is operable to removably connect at least the upper portion of the hand grip thereto and create an aseptic seal around at least a portion of the hand grip when connected thereto and electrically couple the internal battery assembly of the hand grip to the surgical instrument and thereby power the surgical instrument for interfacing surgically with the human tissue.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
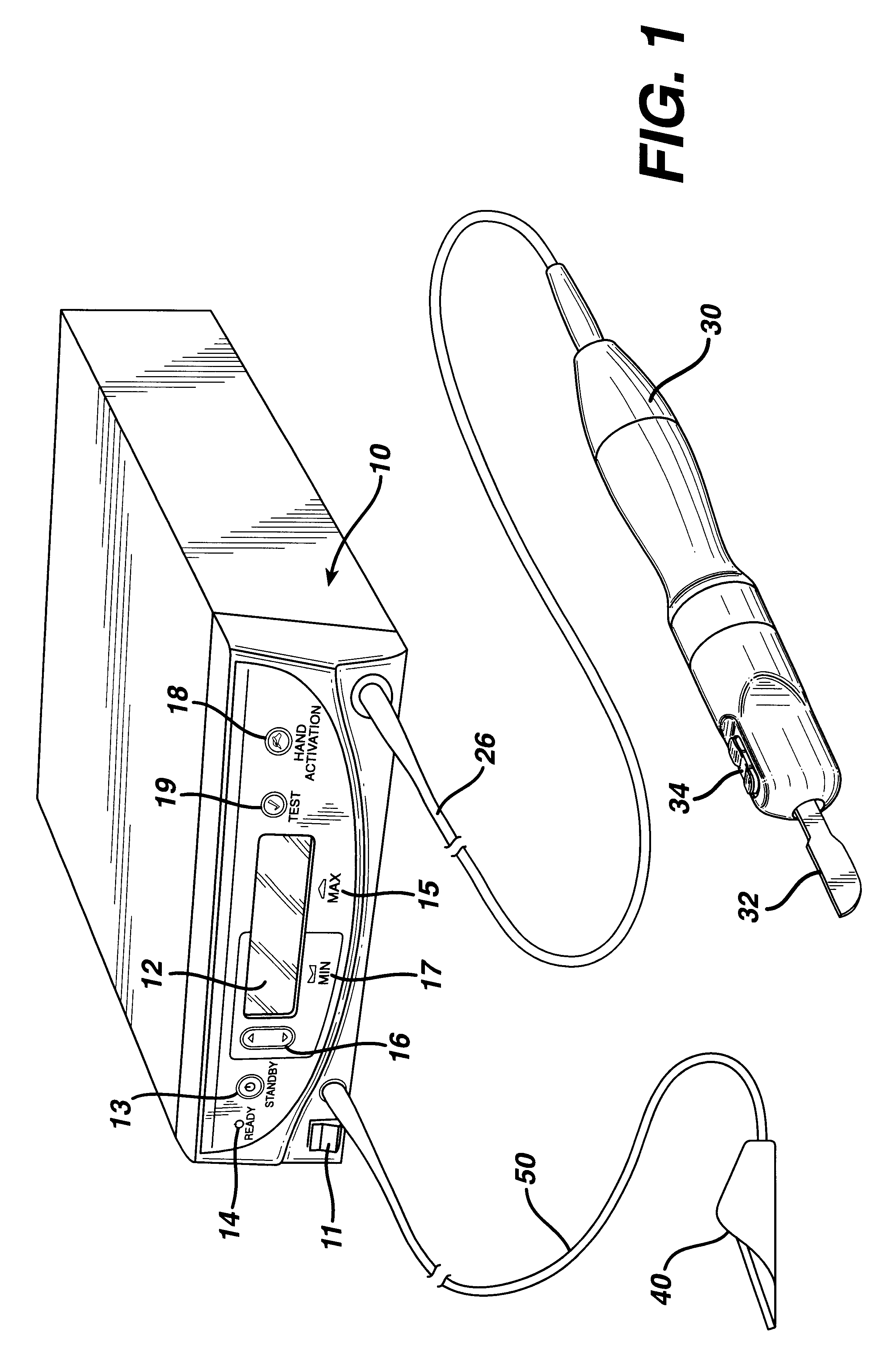
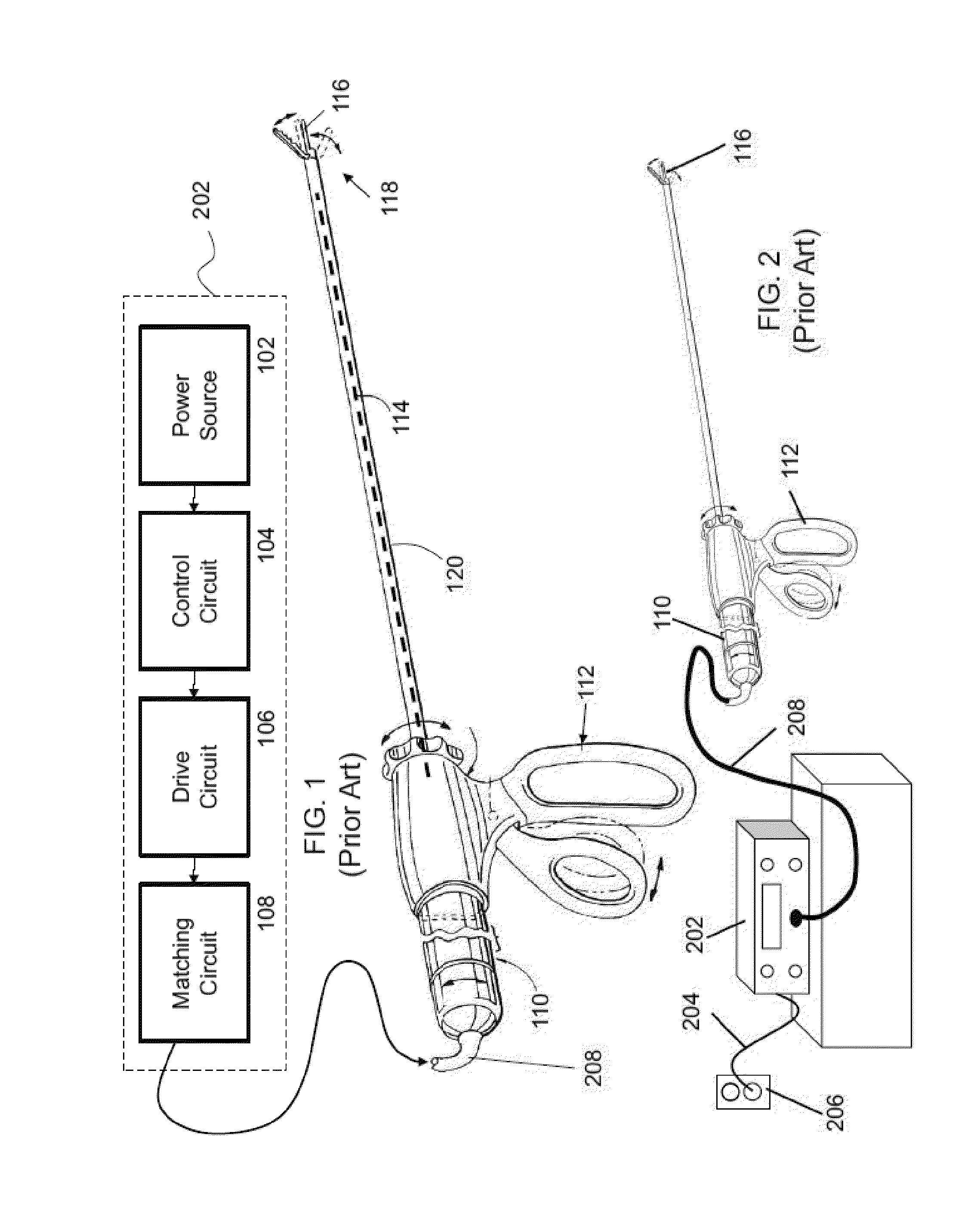
Method for detecting transverse mode vibrations in an ultrasonic hand piece/blade
InactiveUS6588277B2Low costRecuperation increasedVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesResonanceEngineering
A method for detecting transverse mode vibrations in an ultrasonic hand piece / blade for determining the existence of unwanted vibration in the hand piece / blade. A tracking filter centered at the drive frequency of the generator, is used to monitor the drive frequency of the ultrasonic generator and attenuate the drive signal when it exceeds a predetermined level. The tracking filter has a wide pass band. Alternatively, a tracking filter having a pass band which is divided into several regions is used to avoid other longitudinal resonances, such as a resonance at a second harmonic, or other spectral features that would otherwise detract from the tracking accuracy of the filter.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
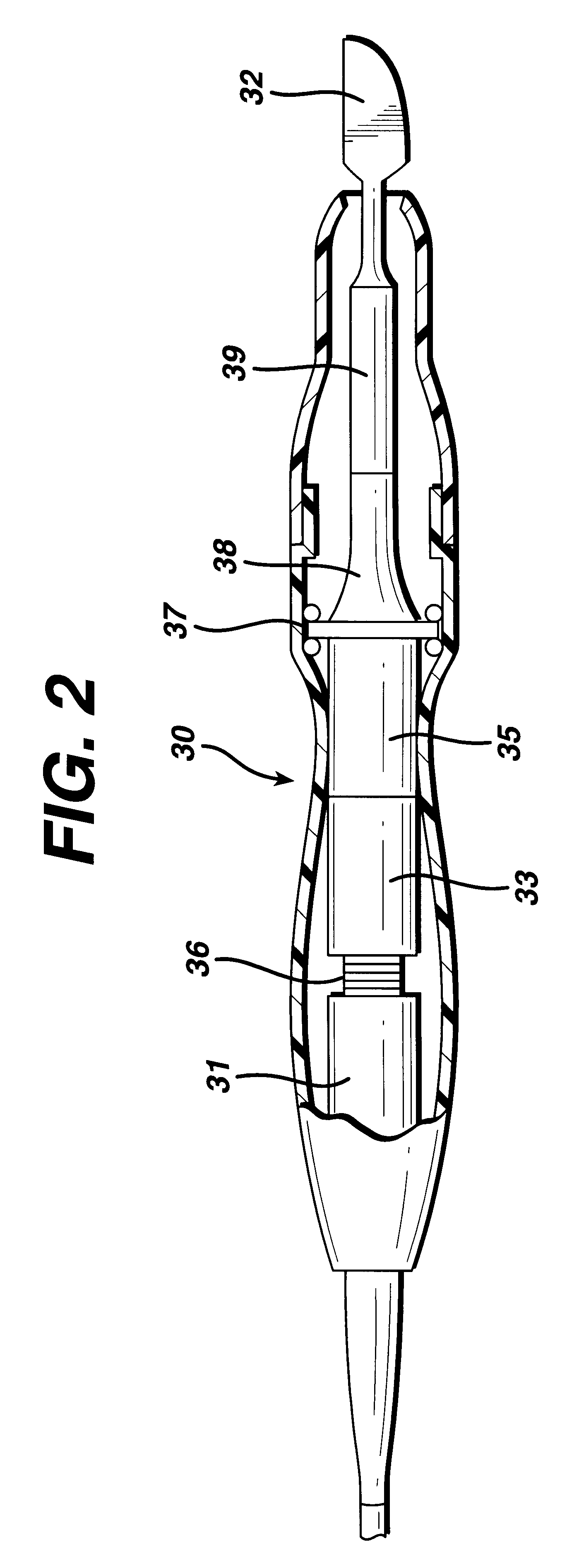
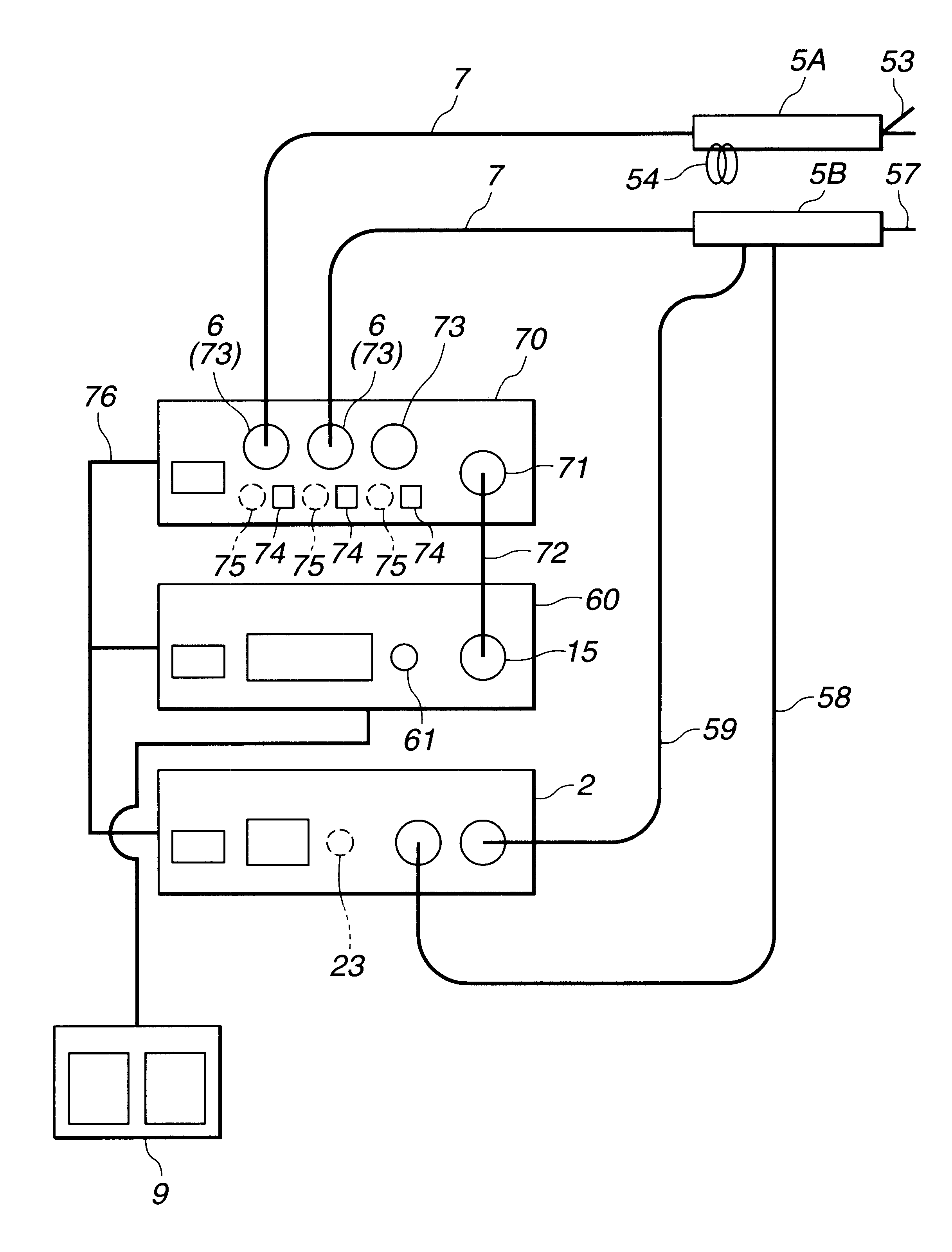
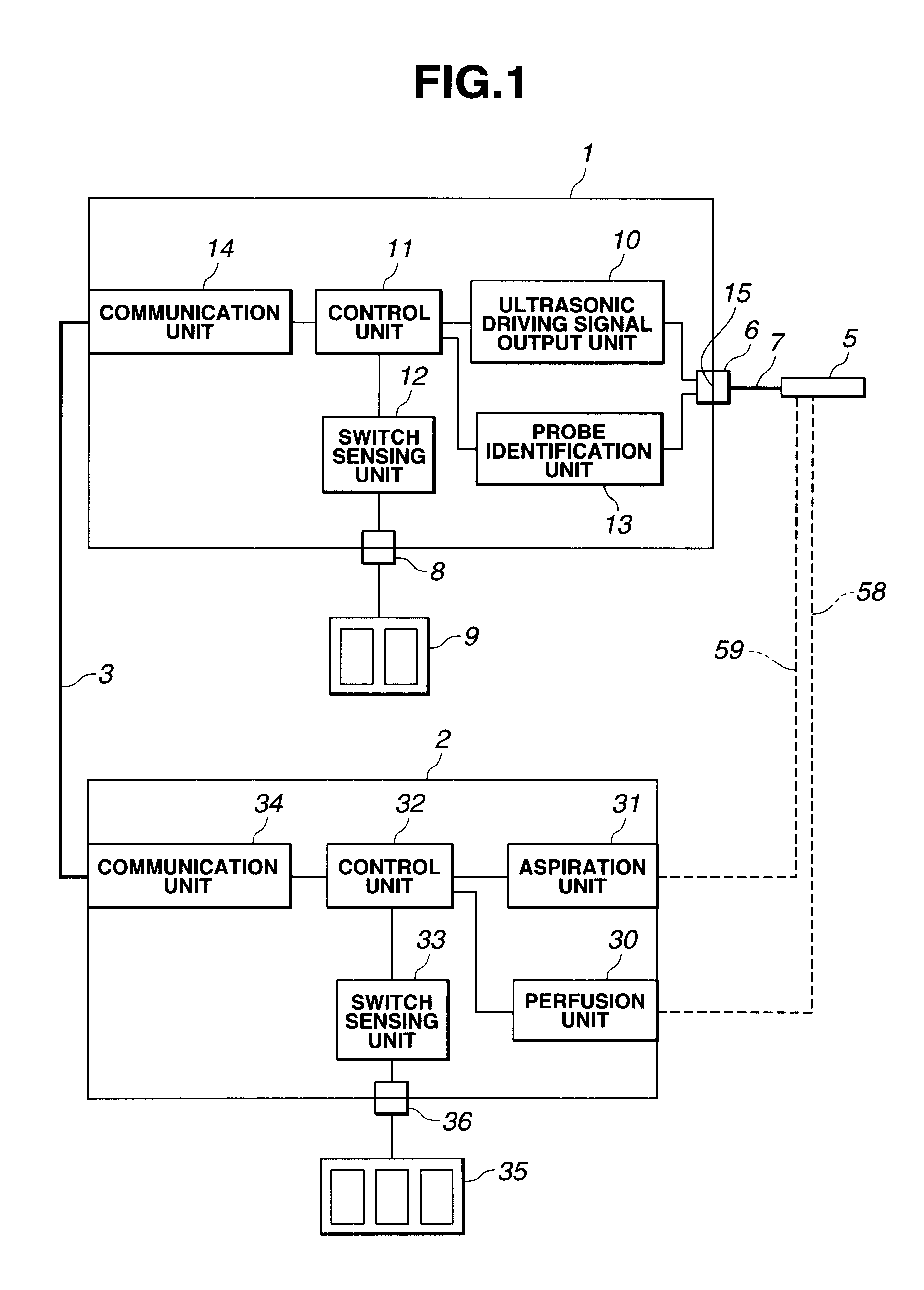
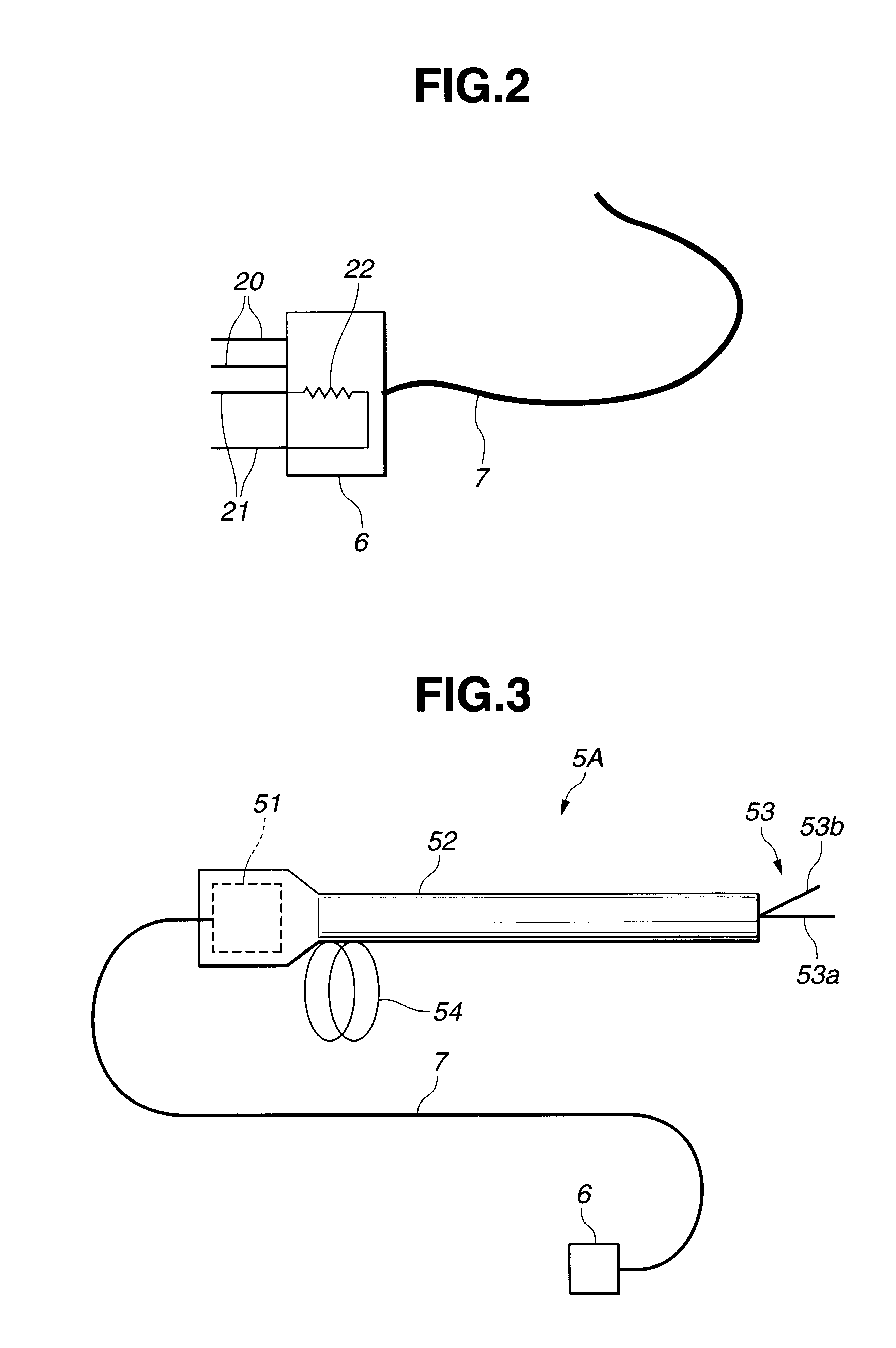
Electric treatment system
InactiveUS6666860B1Work lessAvoid uneven performanceSurgical instruments for heatingSuction devicesElectricityEngineering
A treatment tool for performing a treatment for a curative procedure with ultrasonic waves, high frequency current and so on is provided with an identifier formed of a resistor or the like for indicating the type of the treatment tool. A medical instrument such as an ultrasonic wave output apparatus discriminates the type of a treatment tool connected thereto from the identifier to automatically set operating parameters such as an output value suitable for the treatment tool and to associatively operate an ancillary medical instrument such as a perfusion / aspiration apparatus depending on the treatment tool, thereby reducing extra work such as manual setting to allow for a smooth treatment.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Battery-powered hand-held ultrasonic surgical cautery cutting device
ActiveUS9314261B2Alter functionAlter performanceSurgical furnitureMechanical vibrations separationElectrical batteryHand held
A battery-powered, modular surgical device comprising an electrically powered surgical instrument that requires a pre-determined minimum amount of electrical energy to complete a surgical procedure, and a power module assembly that has a battery that powers the surgical instrument and has a current state of electrical charge, and a control circuit that is electrically coupled to the battery and the surgical instrument and has a memory and a microprocessor. The microprocessor determines the current state of electrical charge of the battery, compares the current state of electrical charge to the pre-determined minimum amount of electrical energy, permits the battery to discharge if the current state of electrical charge is above the pre-determined minimum amount of electrical energy, and maintains the battery in a non-discharge state if the current state of electrical charge is below the pre-determined minimum amount of electrical energy.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Ultrasonic surgical blade
An ultrasonic surgical blade includes a body having an external surface, at least one cutting edge, and a distal end. In at least one embodiment, the cutting edge can be defined by first and second surfaces which define an angle therebetween. In various embodiments, at least a portion of the cutting edge comprises a sharp point. In other embodiments, at least a portion of the cutting edge and surface comprise a sharp point and or a beveled surface.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT +1
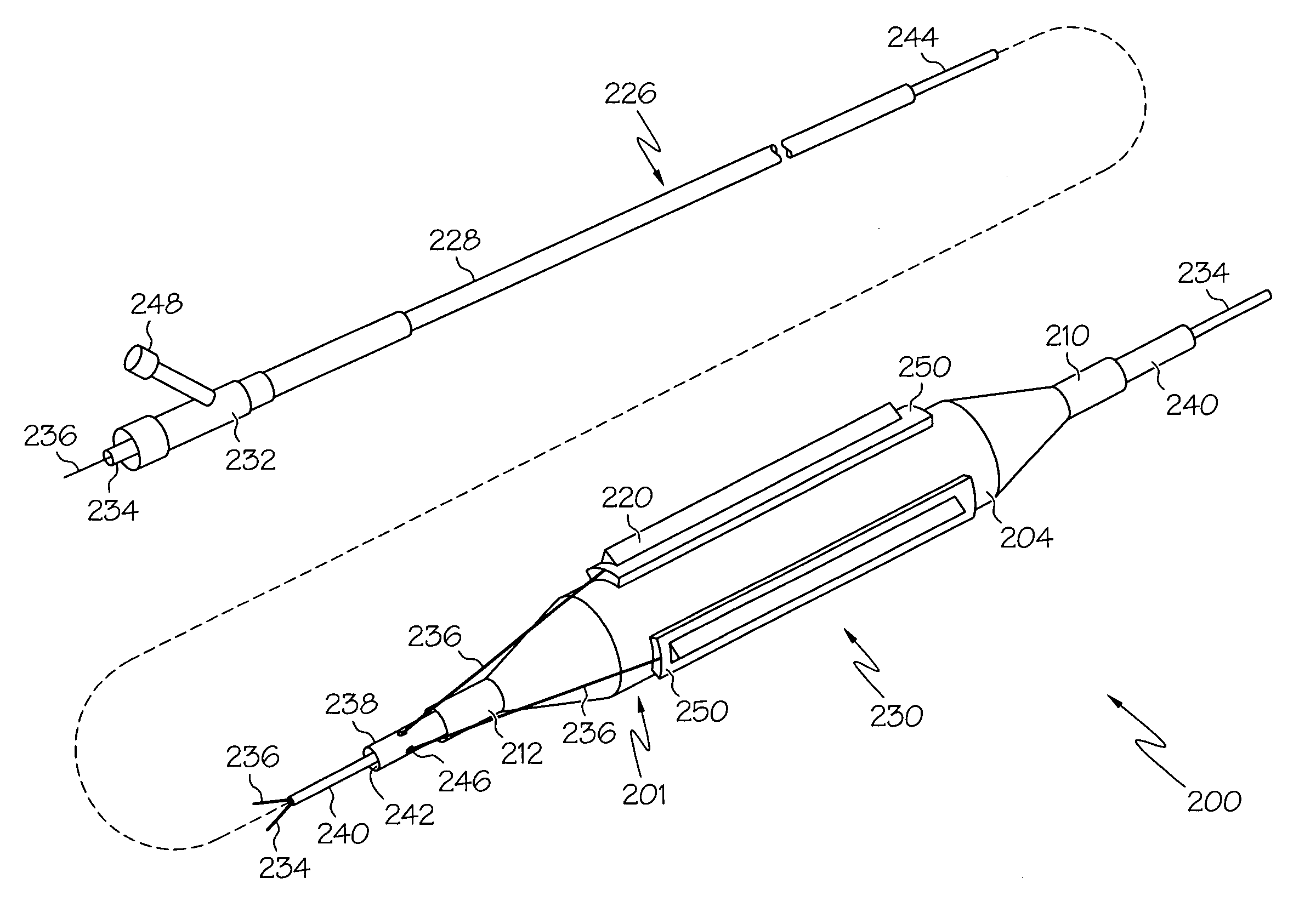
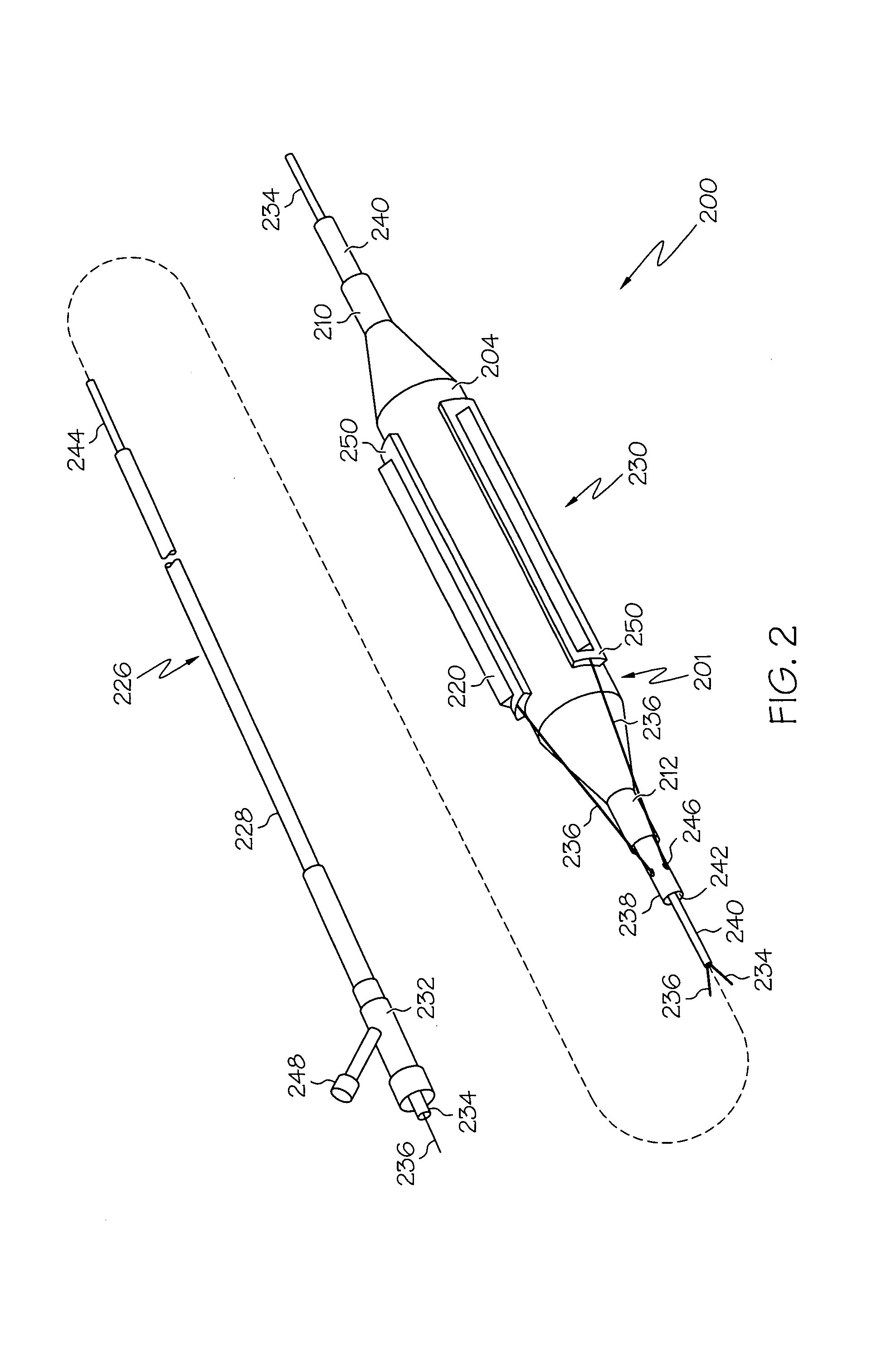
Medical device comprising alignment systems for bringing two portions into alignment
The invention is a medical device comprising an insertion shaft having an articulation section located near its distal end. The medical device comprises one or more alignment systems to assist in bringing two portions of the insertion shaft that are located on opposite sides of the articulation section into alignment. The alignment systems are selected from the following: a) a mechanical system comprising one or more alignment pins or screws and two or more locking screws located in one of the portions and a corresponding number of funnels and receptacles into which the alignment pins and the locking screws can be inserted or advanced respectively located in the other of the portions; b) an ultrasound system comprising an ultrasound reflecting mirror having one or more steps located on one of the portions and a ultrasound transmitter / receiver located on the other of the portions; and c) an optical system comprising one or more light sources that emit light from one of the portions and an image sensor located on the other of the portions.
Owner:MEDIGUS LTD
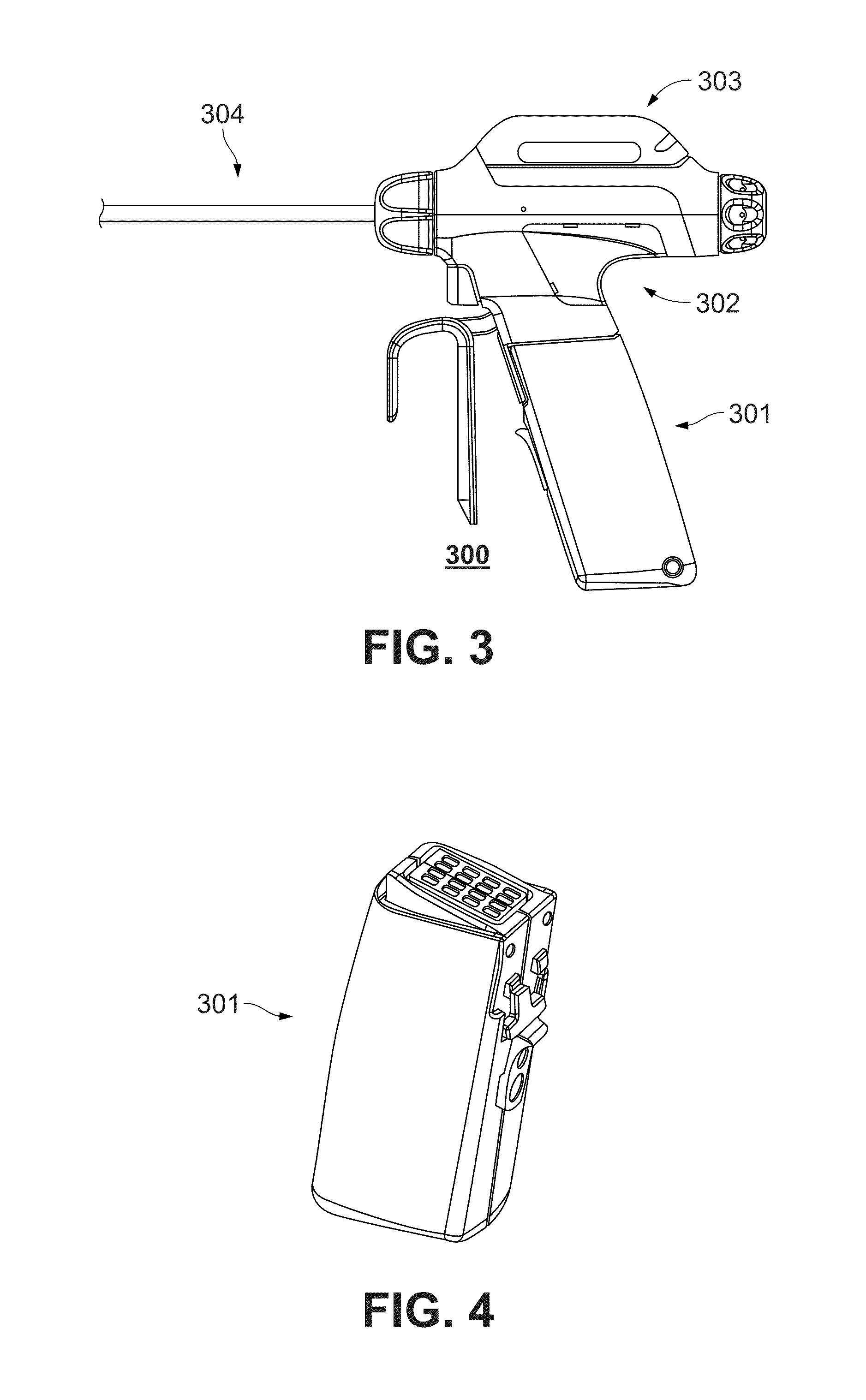
Ultrasonic surgical system and method
ActiveUS20070239028A1Automatically performUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSurgical operationSurgical site
An ultrasonic surgical system has an ultrasonic unit including an instrument operatively connected to an ultrasonic generator, wherein the instrument has an ultrasonic end effector on the distal end of a shaft. The system further includes a positioning unit including a movable arm adapted for releasably holding the instrument, whereby an operator may direct the positioning unit to position the end effector at a surgical site inside a body cavity of a patient for performing a plurality of surgical tasks. The system further includes a control unit operatively connected to the ultrasonic and positioning units, wherein the control unit is programmable with a surgical subroutine for performing the surgical tasks. The system further includes a user interface operatively connected to the control unit for initiating an operative cycle of the surgical subroutine such that the surgical tasks are automatically performed during the operative cycle.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
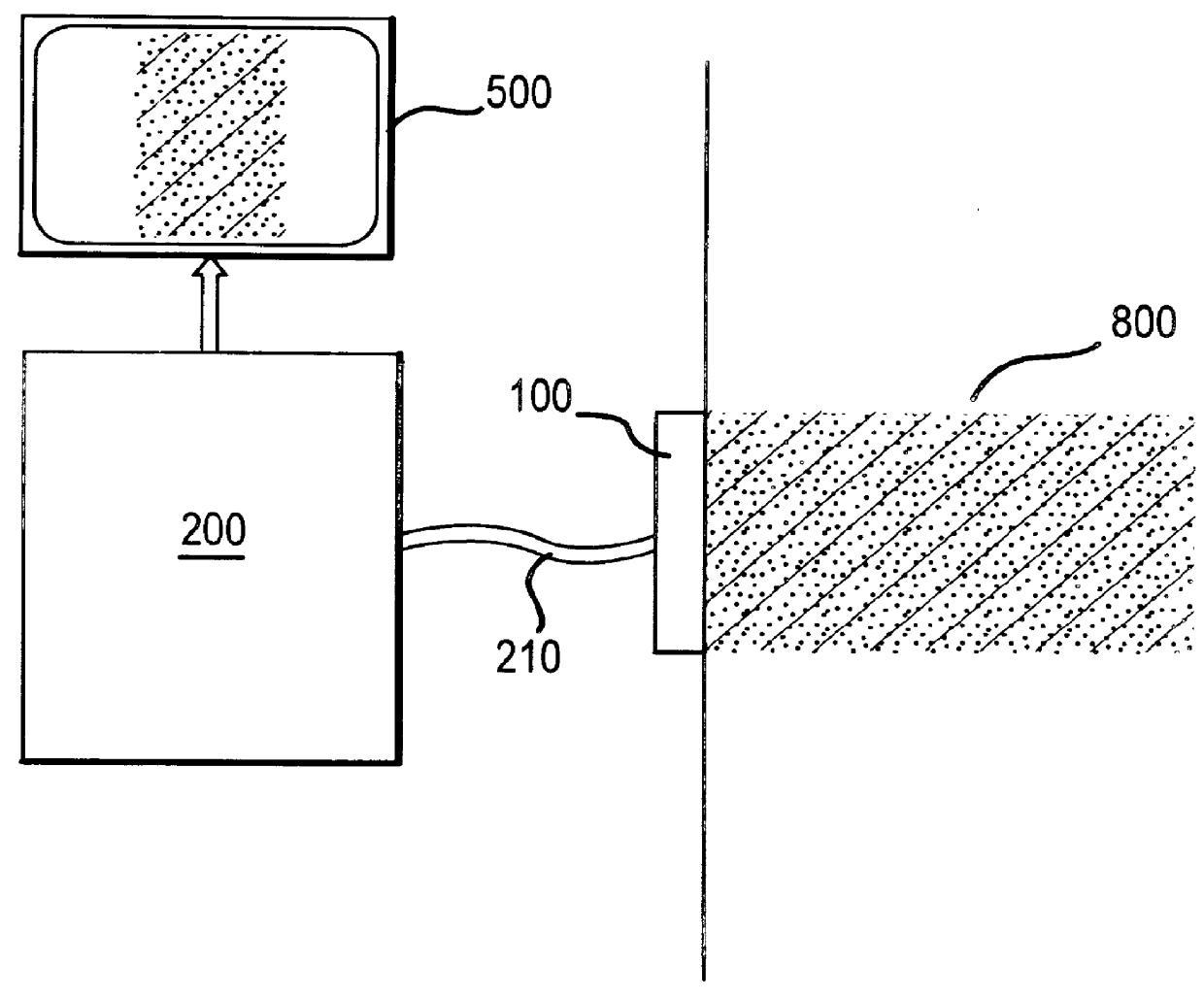
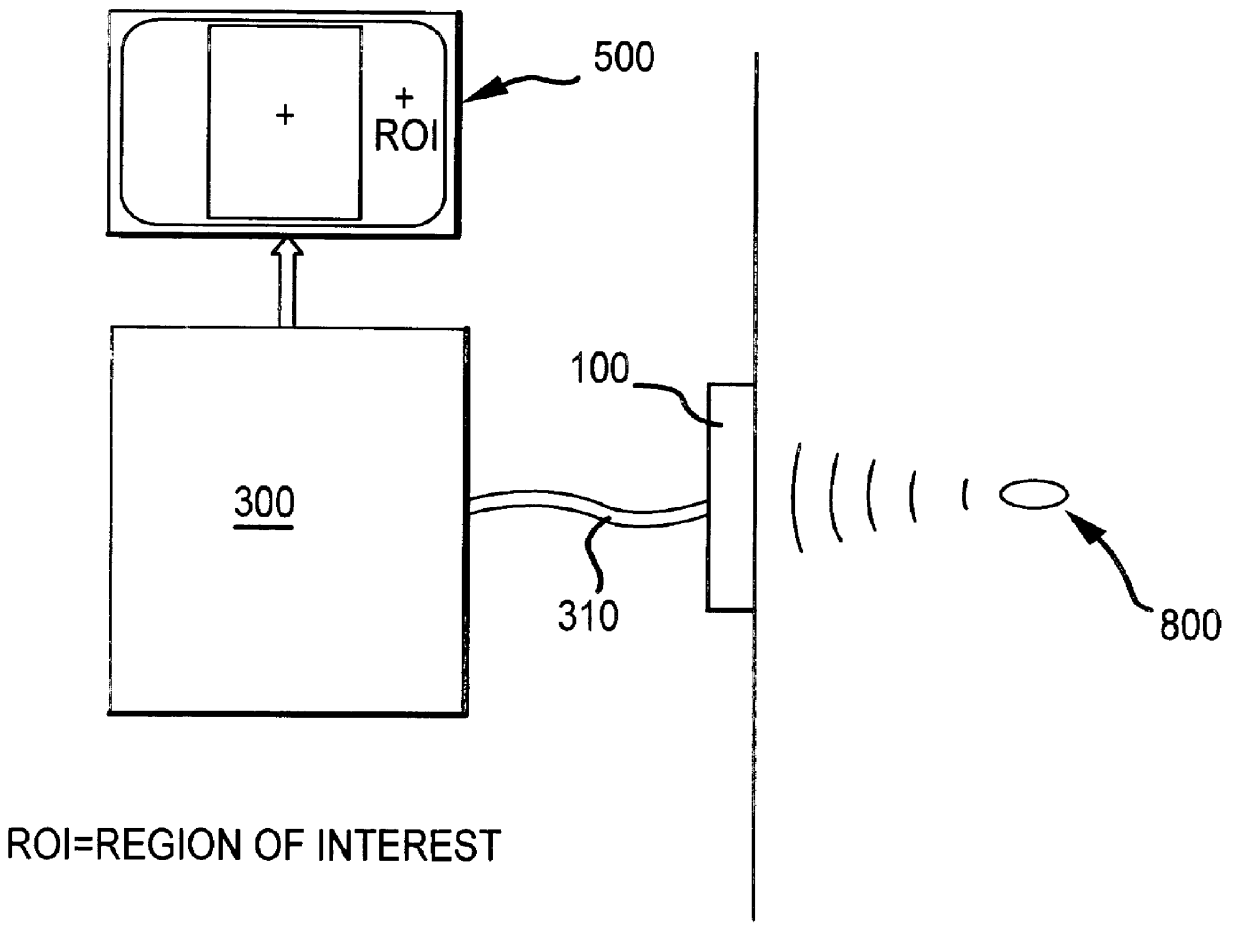
Imaging, therapy, and temperature monitoring ultrasonic system
An ultrasonic system useful for providing imaging, therapy and temperature monitoring generally comprises an acoustic transducer assembly configured to enable the ultrasound system to perform the imaging, therapy and temperature monitoring functions. The acoustic transducer assembly comprises a single transducer that is operatively connected to an imaging subsystem, a therapy subsystem and a temperature monitoring subsystem. The ultrasound systems may also include a display for imaging and temperature monitoring functions. An exemplary single transducer is configured such that when connected to the subsystems, the imaging subsystem can generate all image of a treatment region on the display, the therapy subsystem can generate high power acoustic energy to heat the treatment region, and the temperature monitoring subsystem can map and monitor the temperature of the treatment region and display the temperature on the display, an through the use of the single transducer. Moreover, the acoustic transducer assembly is configured such that the imaging, therapeutic heating and temperature monitoring of the treatment region can be conducted substantially simultaneously.
Owner:GUIDED THERAPY SYSTEMS LLC
Ultrasonic surgical instruments
ActiveUS9375230B2Reduce heat damageImprove cooling effectDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsSurgical deviceUltrasonic Surgery
An ultrasonic surgical instrument is provided. The ultrasonic surgical instrument includes a housing having an elongated shaft extending therefrom. The shaft defines a longitudinal axis therethrough and has at least one jaw member disposed at a distal end thereof. The jaw member(s) is movable between open and clamping configurations. A probe extends through the shaft and operably couples to the housing. The probe includes a cutting blade at a distal end thereof adjacent the jaw member(s) to treat tissue of interest. The jaw member(s) and cutting blade are configured such that heat damage to tissue adjacent tissue of interest that has been treated by the cutting blade is reduced and / or eliminated.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Ultrasonic surgical instruments
An ultrasonic surgical instrument is provided. The ultrasonic surgical instrument includes a housing having an elongated shaft extending therefrom. The shaft has a jaw member disposed at a distal end thereof. The jaw member is movable between an open configuration and a clamping configuration and includes a tissue contacting surface thereon. A cutting blade extends from a distal end of the shaft and operably couples to the housing and adjacent the jaw member to treat tissue. At least one sensor is configured to sense at least one operational parameter of the ultrasonic surgical instrument. At least one controller in operable communication with the at least one sensor is configured to terminate delivery of ultrasonic energy to the cutting blade when the at least one sensor senses the at least one operational parameter.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
High intensity ablation device
ActiveUS7179254B2Improve performanceOvercome limitationsUltrasound therapySurgical instruments for heatingMicrowaveHigh intensity
An apparatus for ablating tissue, the apparatus having first and second opposing jaws operative to compress tissue to be allayed therebetween, the first jaw having a first ablation surface directing ablative energy into the tissue and the second jaw having a second ablation surface reflecting incident ablative energy into the tissue. The ablative energy may be ultrasonic, microwave, cryoablation, radio-frequency, photodynamic, laser, and cautery energy. The instrument may also have a pointed tip for piercing tissue, allowing the instrument to clamp the tissue wall of a hollow organ before ablation. Alternately, the instrument may clamp two or more tissue layers of a hollow organ without piercing prior to clamping an ablation.
Owner:ETHICON INC
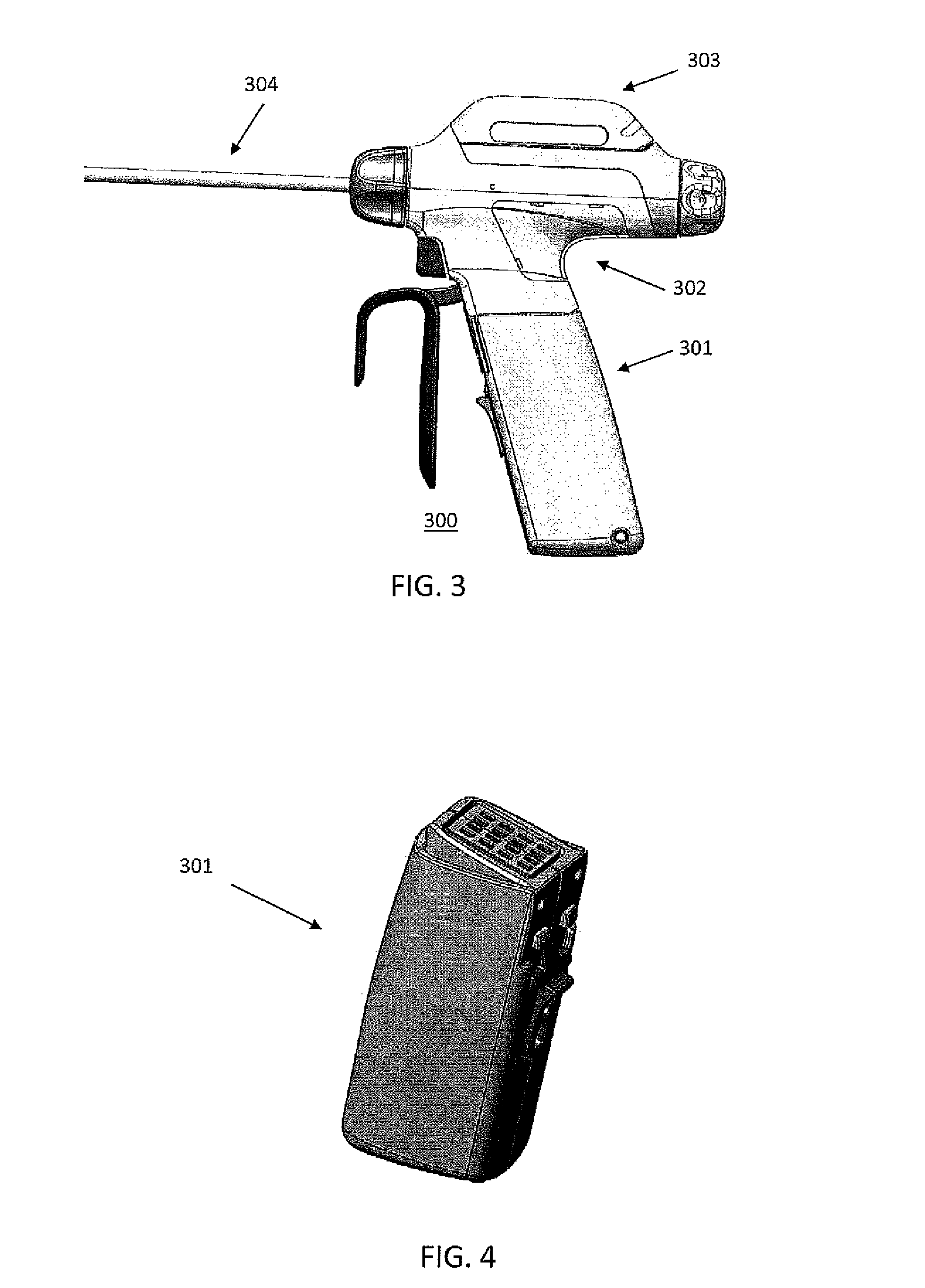
Cordless Hand-Held Ultrasonic Cautery Cutting Device
ActiveUS20090143805A1Alter functionAlter performanceUltrasound therapySurgical instruments for heatingHand heldWaveguide
A disposable ultrasonic surgical handle connectable to an ultrasonic waveguide, a battery, and an ultrasonic-movement-generator assembly includes a first handle body portion defining therein an aseptically sealable battery-holding compartment shaped to receive the battery therein, a second handle body portion connected to the first handle body portion, and an electrical couple. The second handle body portion has a waveguide attachment dock exposed to the environment and an ultrasonic-movement-generator assembly dock exposed to the environment and shaped to connect the ultrasonic waveguide in the waveguide attachment dock to the ultrasonic-movement-generator assembly through the second handle body portion. The electrical couple is operable to connect a battery within the battery-holding compartment to the ultrasonic-movement-generator-assembly when the ultrasonic-movement-generator assembly is docked at the ultrasonic-movement-generator assembly dock.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Catheter balloon with ultrasonic microscalpel blades
InactiveUS7153315B2Much sharper and cleaner incisionsCutting precision can be improvedCannulasSurgical instrument detailsBalloon catheterMedical treatment
The present invention provides a catheter balloon, and balloon catheter incorporating the catheter balloon, useful in medical dilation procedures. The catheter balloon includes at least one microscalpel operatively disposed on an outer surface thereof. The microscalpel may advantageously be operatively disposed relative to a power source so as to be controllably activatable. Also provided are methods of making the inventive balloon and / or catheter as well as methods of using the inventive catheter in a dilation / incising treatment.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
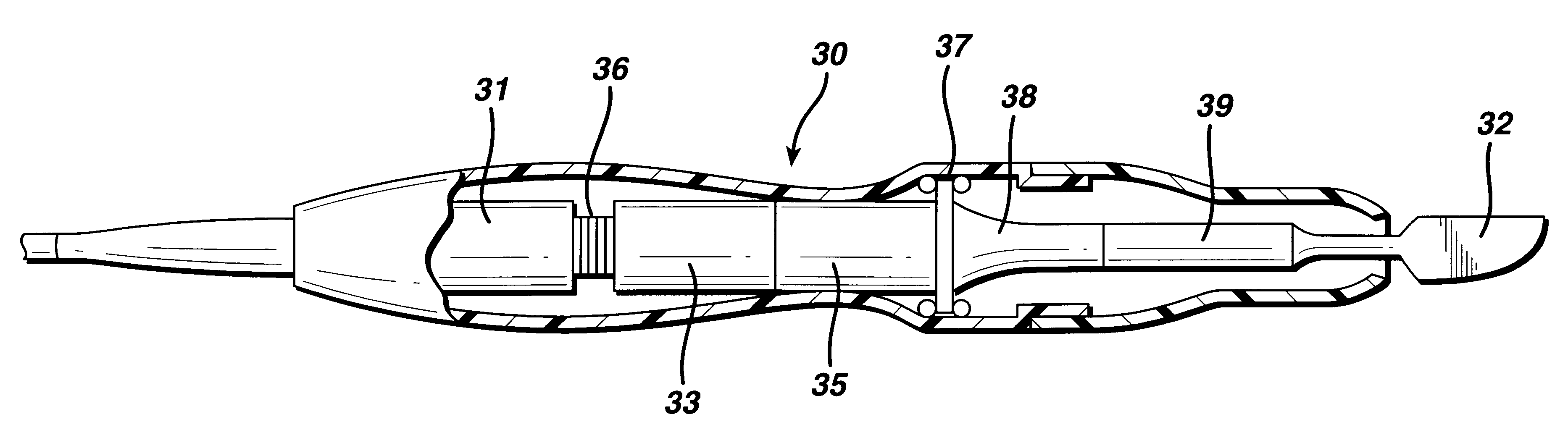
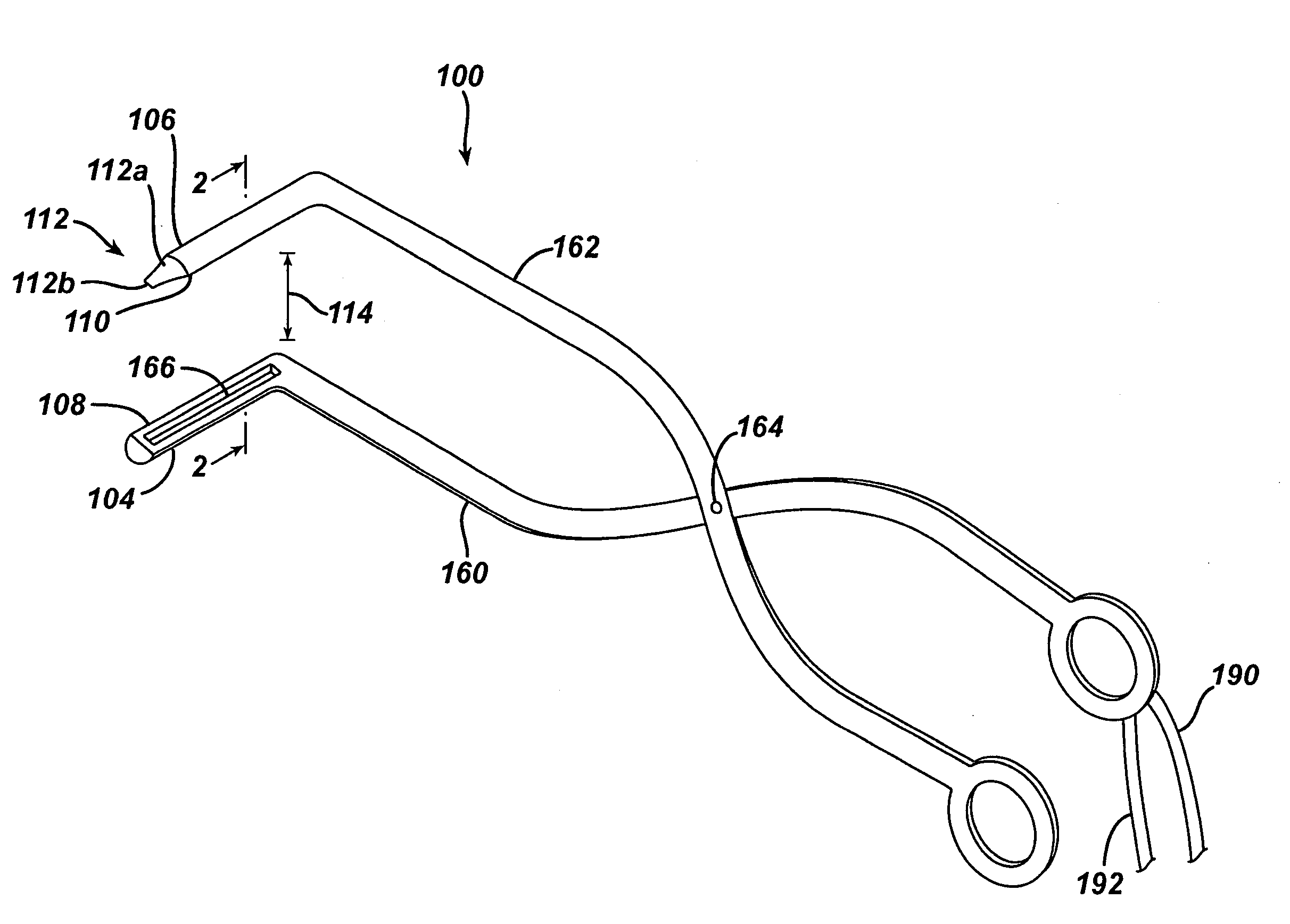
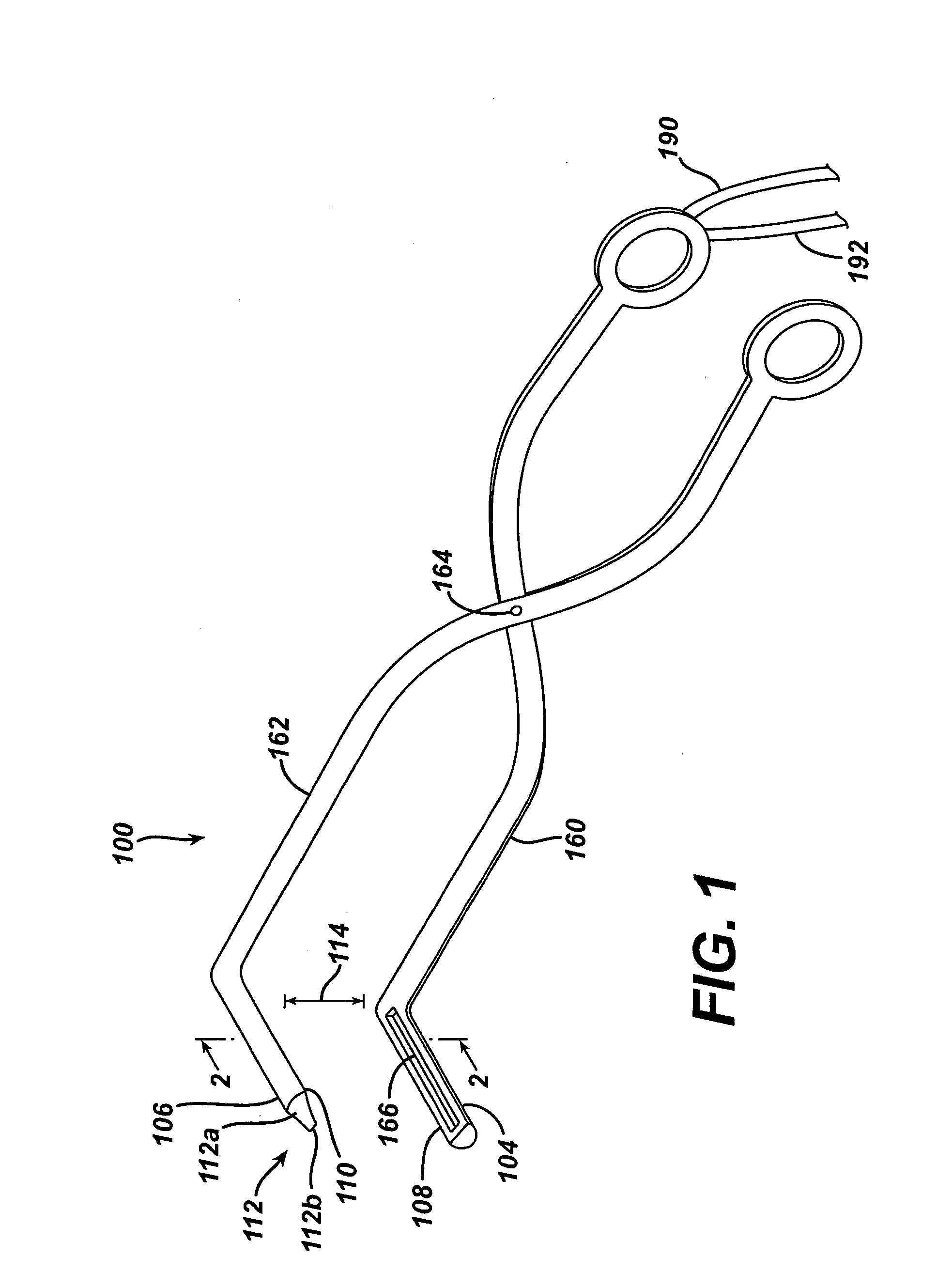
Articulating ultrasonic surgical shears
An ultrasonic surgical instrument is described which incorporates an articulating shearing end-effector. The instrument comprises an ultrasonic transducer, an ultrasonically activated end-effector, and a substantially solid ultrasonic waveguide that connects the ultrasonic transducer to the end-effector. The waveguide comprises a transmission section extending from the transducer to a fixed node, and an articulation section extending from the fixed node to a pivoting node. The end-effector includes a bifurcated waveguide segment. A handle is adapted to hold the transducer. An outer sheath extends from the handle to the end-effector and surrounds the waveguide. An actuation trigger is rotatably positioned on the handle, and an actuation arm extends from a distal end of the actuation trigger to the pivoting node.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Ultrasonic orthopedic surgical device with compound ultrasound vibration
InactiveUS20060030797A1Improve cutting efficiencyAvoid local accumulationChiropractic devicesEye exercisersVibration amplitudeDrive motor
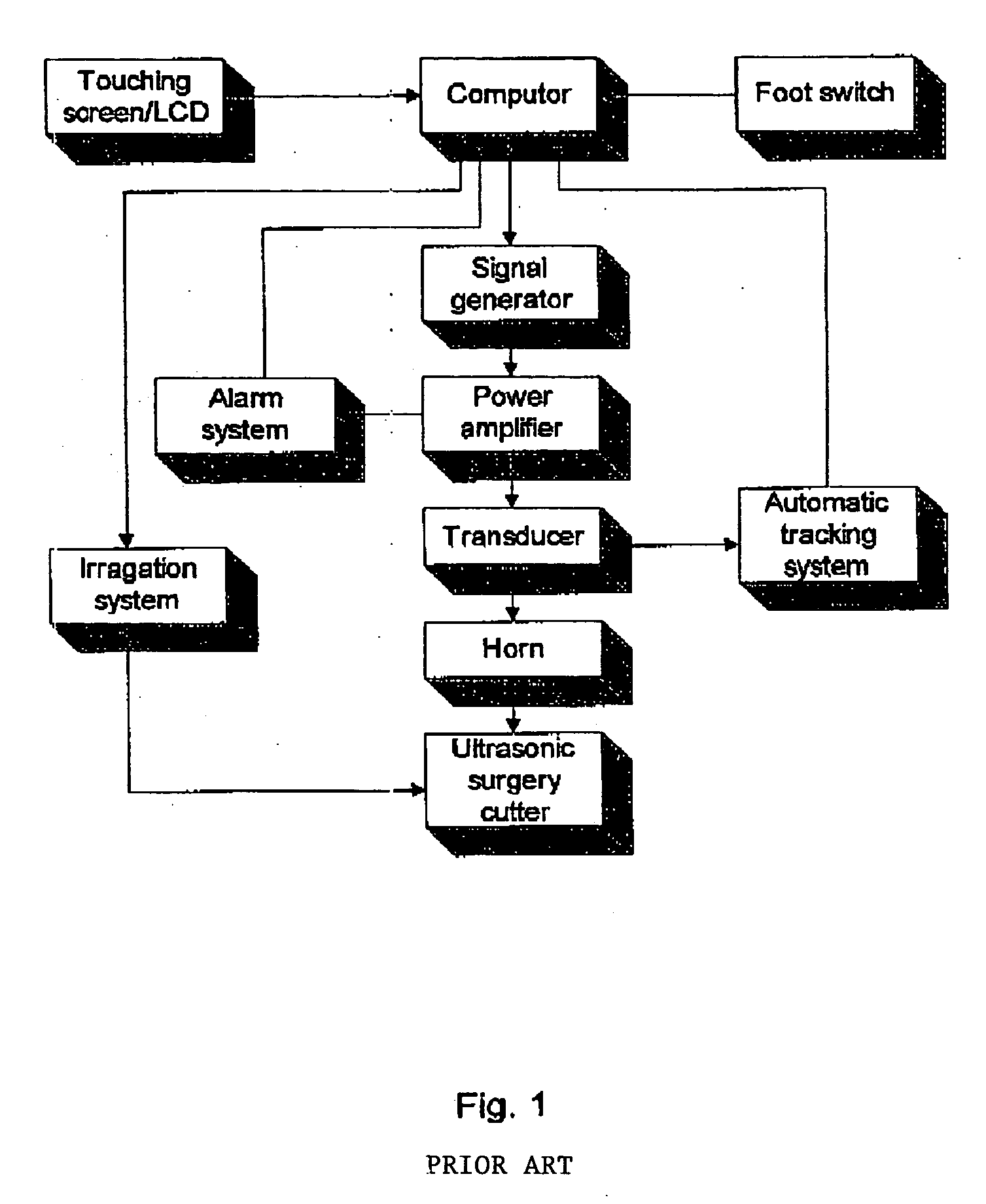
An orthopedic surgical device with compound ultrasound vibration that comprises a handpiece, a surgical cutter fixed on the anterior top of the handpiece, and an ultrasound signal generator. Inside the outer casing of said handpiece, there are provided: an ultrasound transducer for transforming the ultrasound signals from said ultrasound signal generator into ultrasound mechanical waves; a horn (or amplitude transformer) for amplifying vibration amplitude of ultrasound mechanical waves generated from said transducer and then transmitting the amplified ultrasound mechanical waves to said surgical cutter to lead to longitudinal vibration of the surgical cutter; a driving motor fixed in the back end of said handpiece for driving said ultrasound transducer and horn to accomplish the movement of swing and rotation; an adapter provided between said driving motor and said transducer for supplying ultrasonic electrical signals generated by said ultrasound signal generator to said ultrasound transducer.
Owner:ZHOU ZHAOYING +3
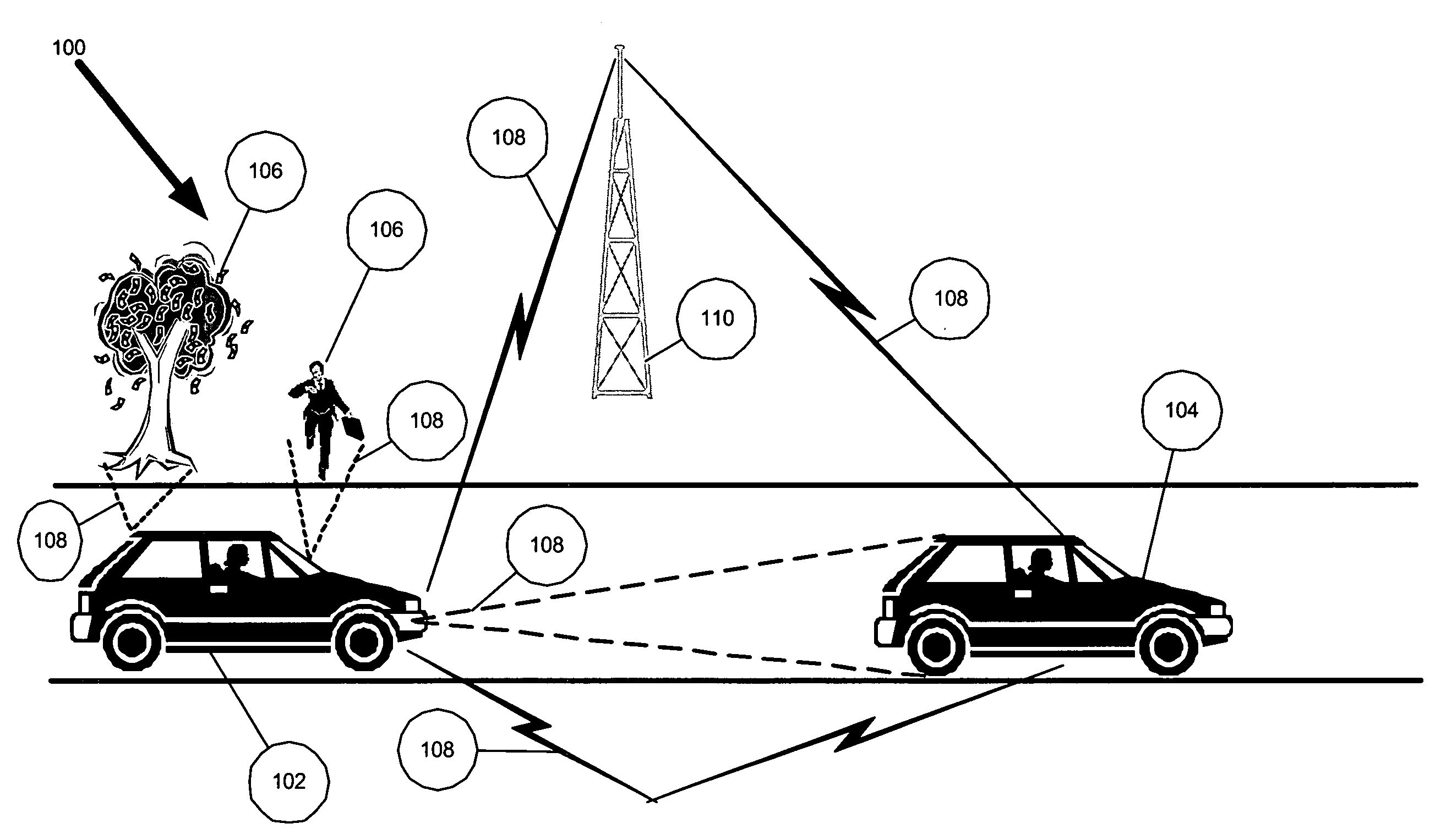
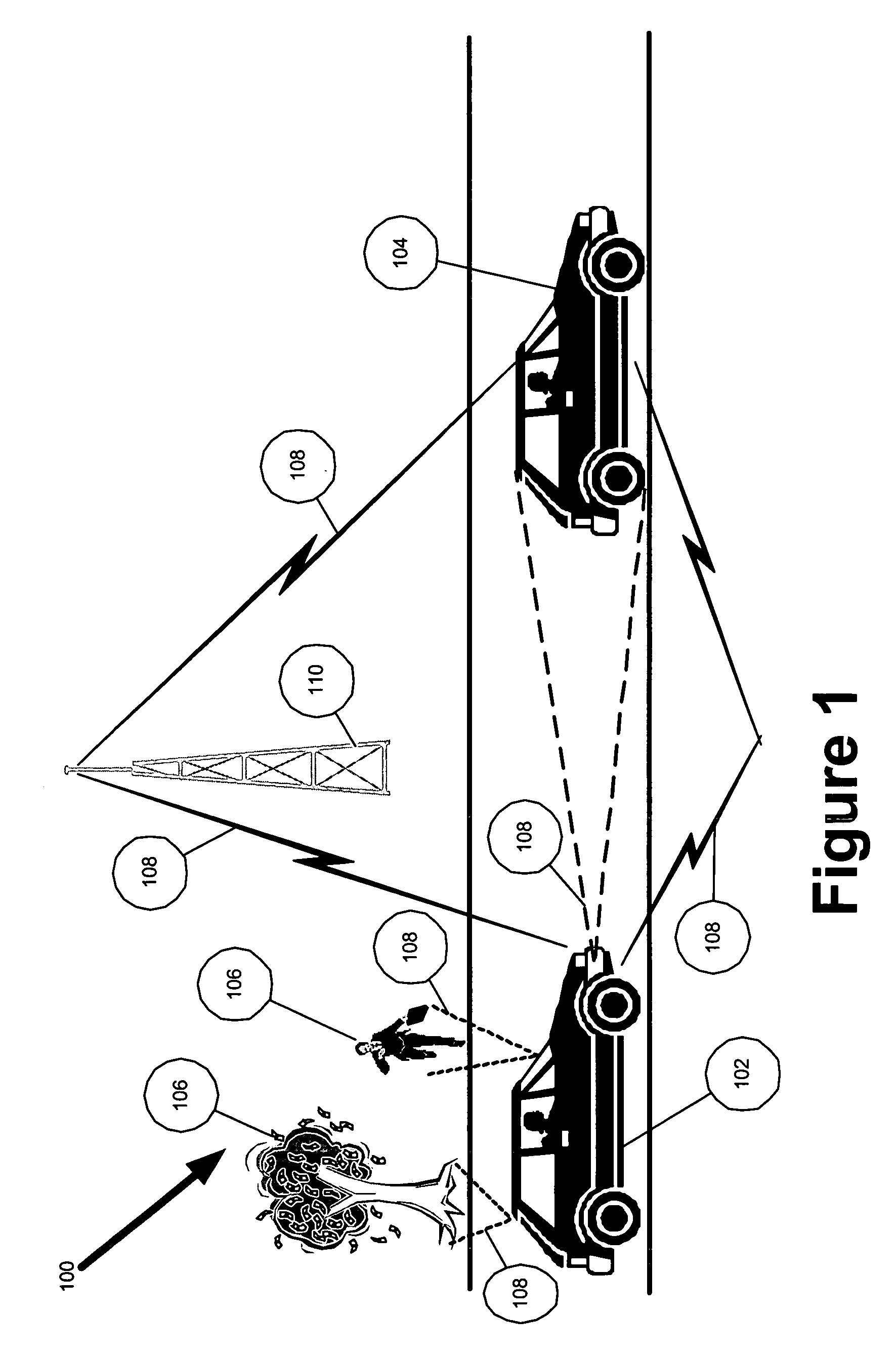
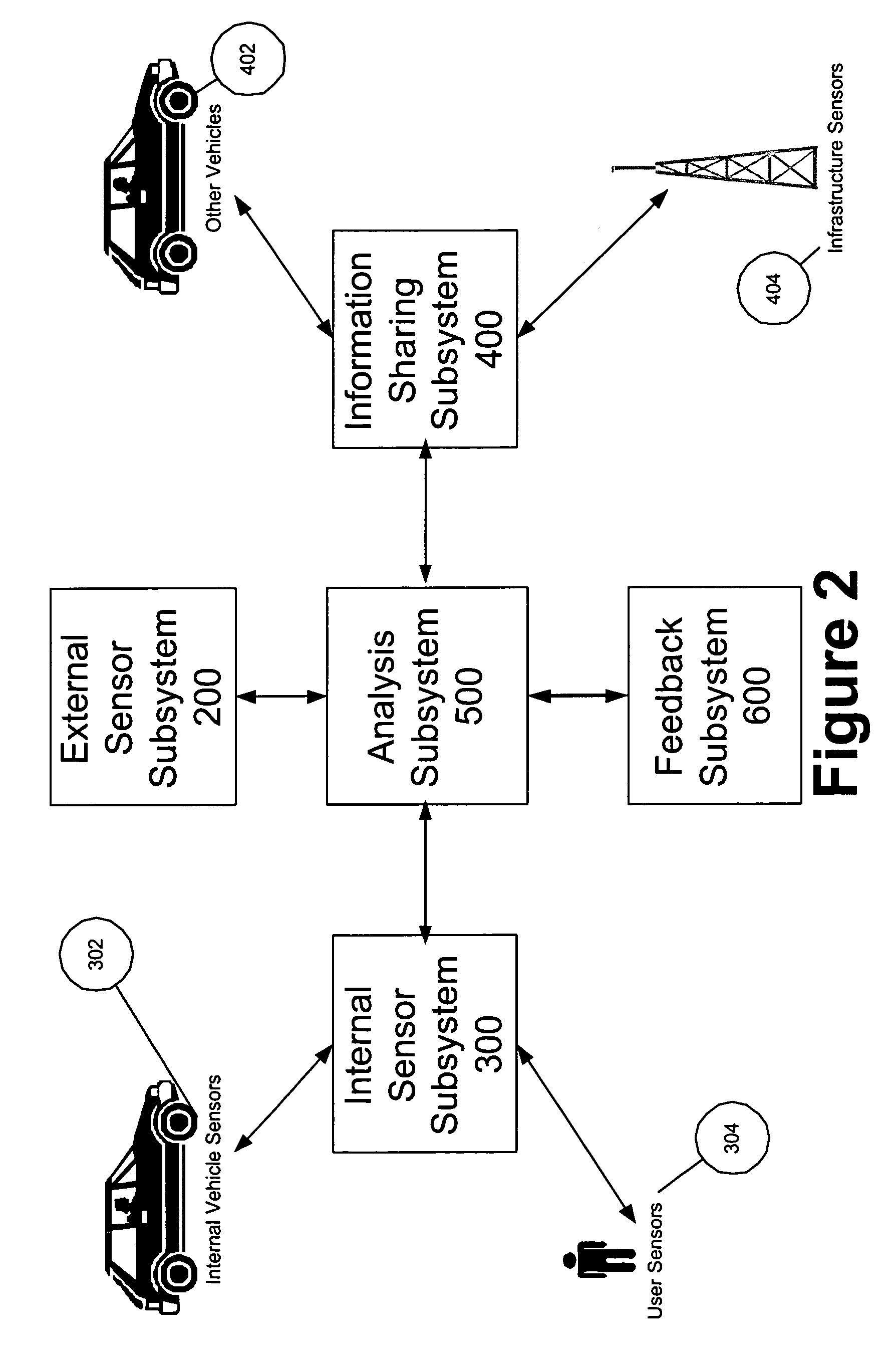
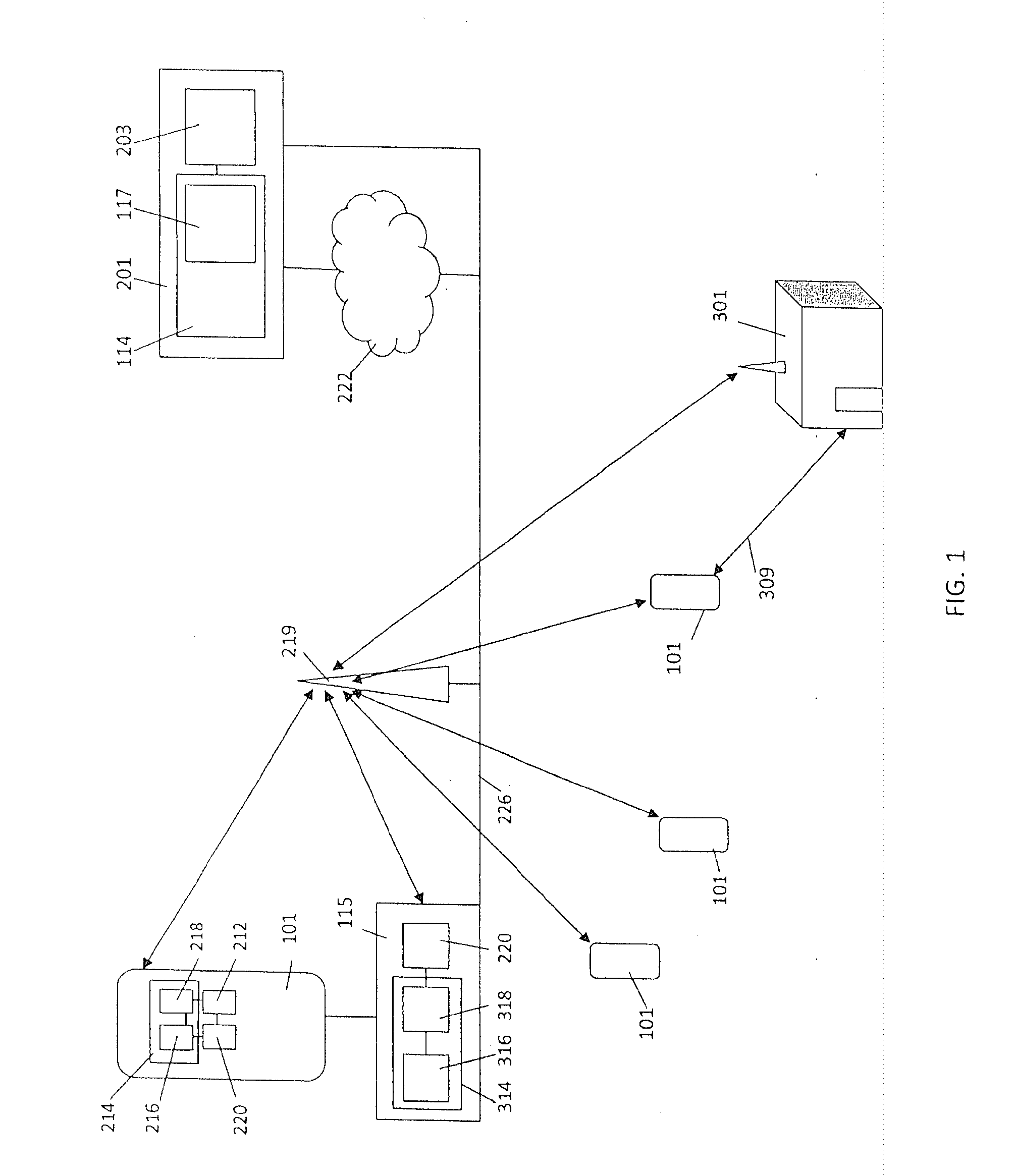
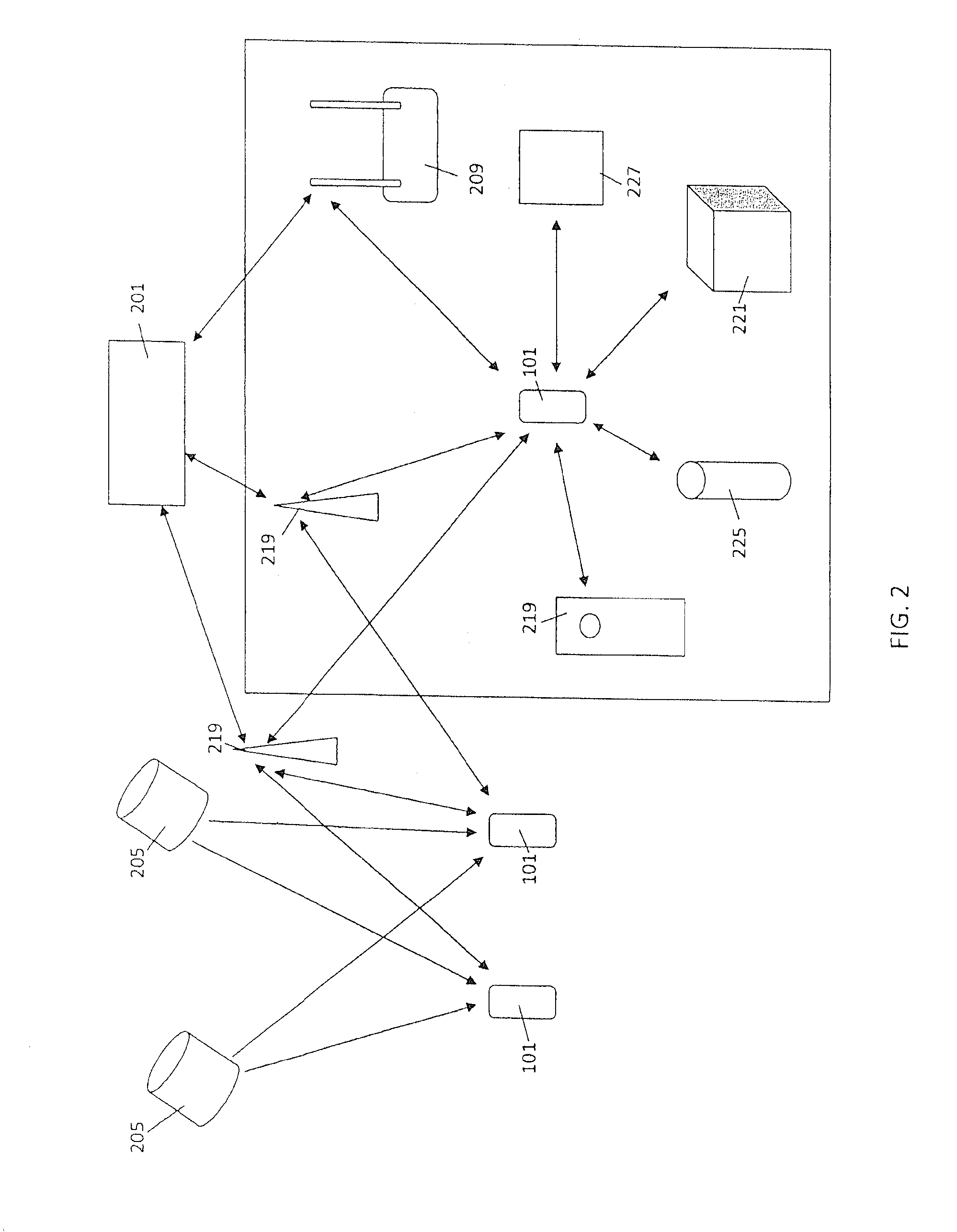
Multi-sensor integration for a vehicle
A sensor system for use in a vehicle that integrates sensor data from more than one sensor in an effort to facilitate collision avoidance and other types of sensor-related processing. The system include external sensors for capturing sensor data external to the vehicle. External sensors can include sensors of a wide variety of different sensor types, including radar, image processing, ultrasonic, infrared, and other sensor types. Each external sensor can be configured to focus on a particular sensor zone external to the vehicle. Each external sensor can also be configured to focus primarily on particular types of potential obstacles and obstructions based on the particular characteristics of the sensor zone and sensor type. All sensor data can be integrated in a comprehensive manner by a threat assessment subsystem within the sensor system. The system is not limited to sensor data from external sensors. Internal sensors can be used to capture internal sensor data, such a vehicle characteristics, user attributes, and other types of interior information. Moreover, the sensor system can also include an information sharing subsystem of exchanging information with other vehicle sensor systems or for exchanging information with non-vehicle systems such as a non-movable highway sensor system configured to transmit and receive information relating to traffic, weather, construction, and other conditions. The sensor system can potentially integrate data from all different sources in a comprehensive and integrated manner. The system can integrate information by assigning particular weights to particular determinations by particular sensors.
Owner:YAZAKI NORTH AMERICA
Ultrasonic shear with asymmetrical motion
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Excisional biopsy devices and methods
InactiveUS6863676B2Efficiently and safely exciseMinimize complicationCannulasSurgical needlesUltrasonic sensorTissue Collection
An excisional biopsy system includes a tubular member that has a proximal end and a distal end in which one or more windows are defined. A first removable probe has a proximal portion that includes a cutting tool extender and a distal portion that includes a cutting tool. The first removable probe may be configured to fit at least partially within the tubular member to enable the cutting tool to selectively bow out of and to retract within one of the windows when the cutting tool extender is activated. A second removable probe has a proximal section that includes a tissue collection device extender and a distal section that includes a tissue collection device. The second removable probe may also be configured to fit at least partially within the tubular member to enable the tissue collection device to extend out of and to retract within one of the windows when the tissue collection device extender is activated. A third removable probe may also be provided. The third removable probe may also be configured to fit at least partially within the tubular member and may include an imaging device, such as an ultrasound transducer, mounted therein. By selectively activating the cutting tool and the tissue collection device while rotating the excisional device, a tissue specimen may be cut from the surrounding tissue and collected for later analysis.
Owner:ENCAPSULE MEDICAL
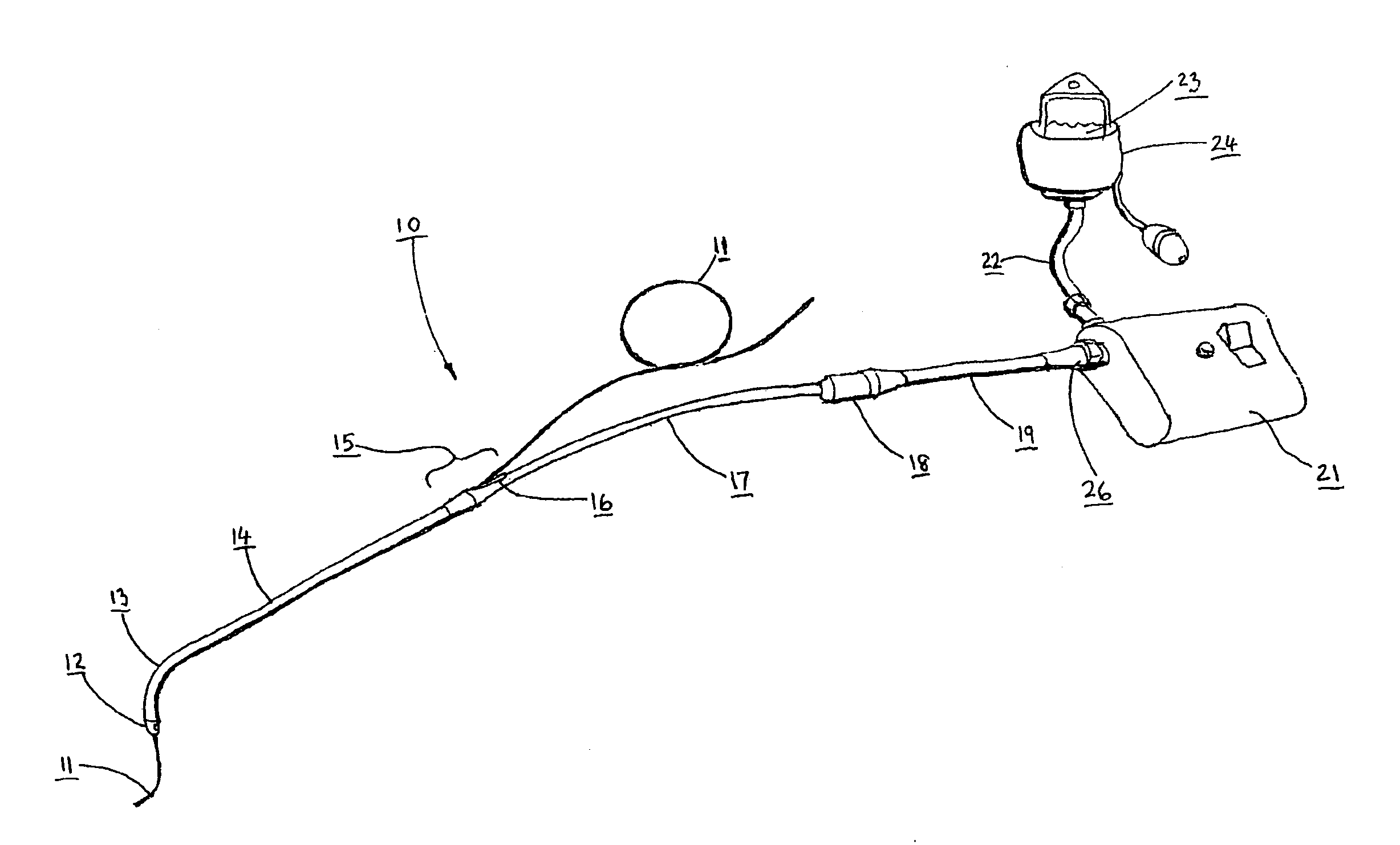
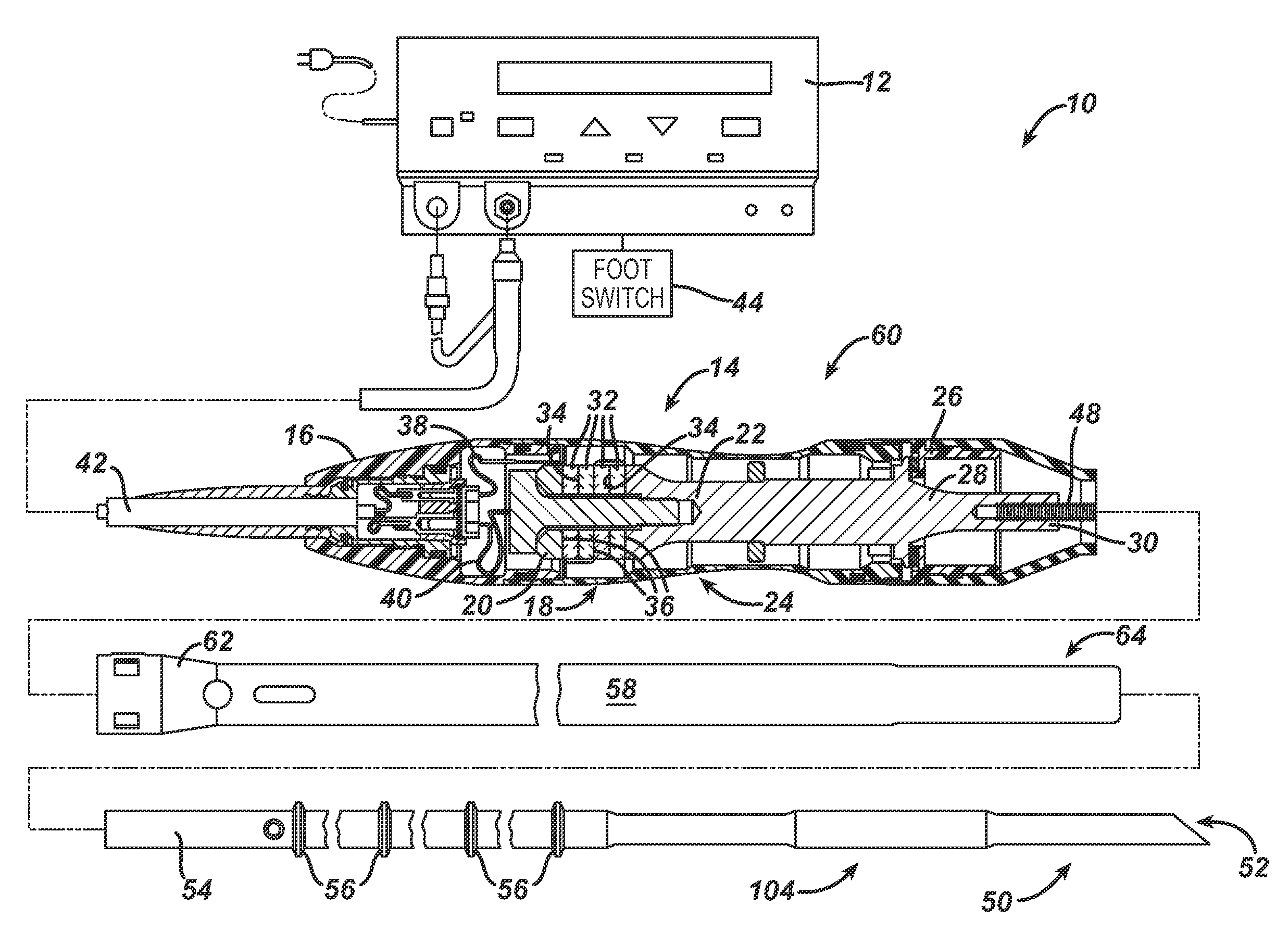
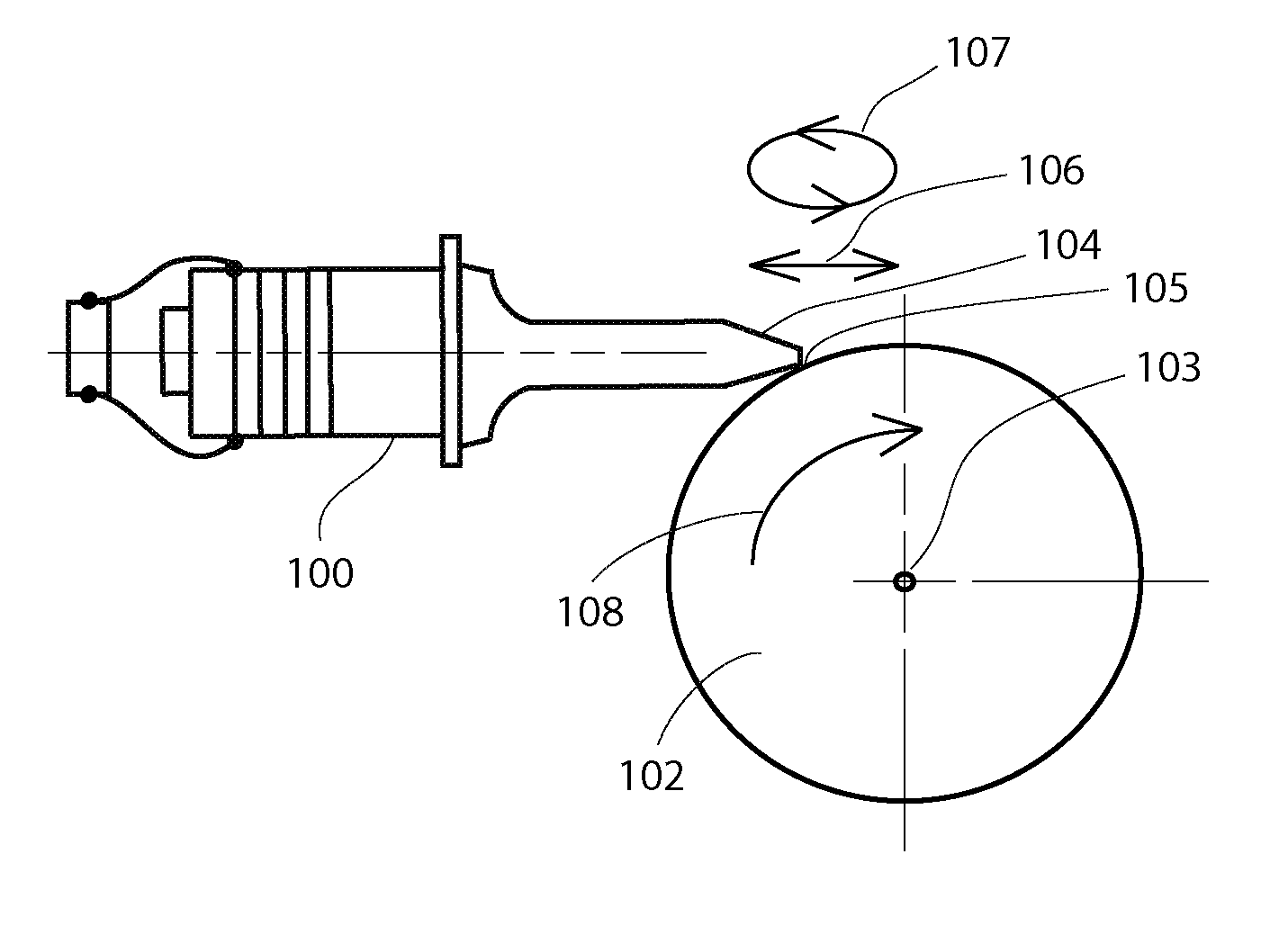
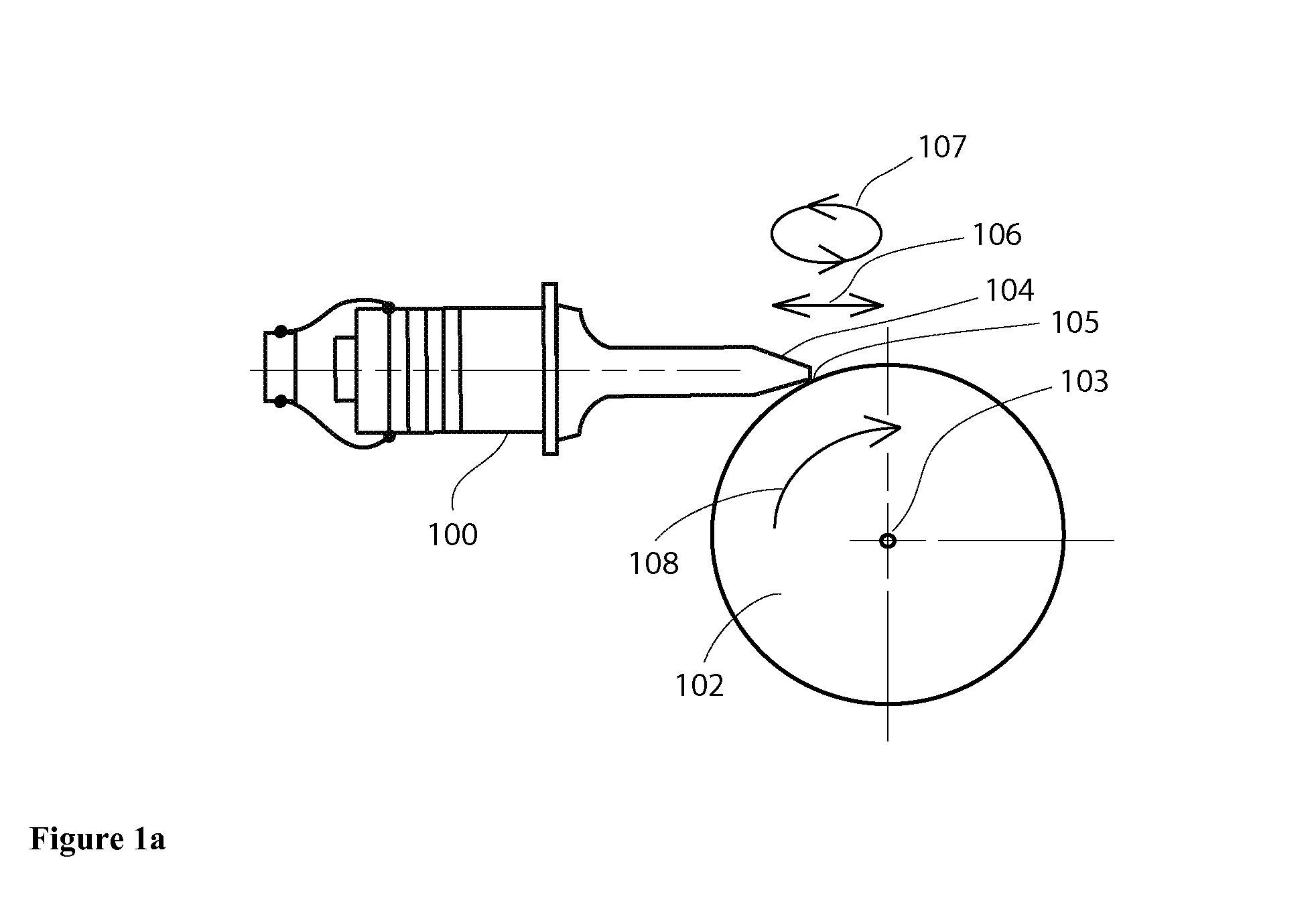
Ultrasonically Powered Medical Devices and Systems, and Methods and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20070149881A1Improve patient safetyLow costUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesActuatorHand held devices
The present invention provides a new family of ultrasonically powered medical devices and systems for powering such devices. Disclosed are methods for improving the overall power transfer efficiency of devices according to the present invention, as well as a wide variety of medical uses for such devices and systems. Devices of the present invention comprise a transducer that, during operation, converts electrical energy into high frequency, low amplitude mechanical vibrations that are transmitted to a driven-member, such as a wheel, that produces macroscopic rotary or linear output mechanical motions. Such motions may be further converted and modified by mechanical means to produce desirable output force and speed characteristics that are transmitted to at least one end-effector that performs useful mechanical work on soft tissue, bone, teeth and the like. Power systems of the present invention comprise one or more such handheld devices electrically connected to a power generator. Examples of powered medical tools enabled by the present invention include, but are not limited to, linear or circular staplers or cutters, biopsy instruments, suturing instruments, medical and dental drills, tissue compactors, tissue and bone debriders, clip appliers, grippers, extractors, and various types of orthopedic instruments. Devices of the present invention may be partly or wholly reusable, partly or wholly disposable, and may operate in forward or reverse directions, as well as combinations of the foregoing. The devices and systems of the present invention provide a safe, effective, and economically viable alternative source for mechanical energy, which is superior to AC or DC (battery) powered motors, compressed air or compressed gas, and hand powered systems.
Owner:RABIN BARRY HAL
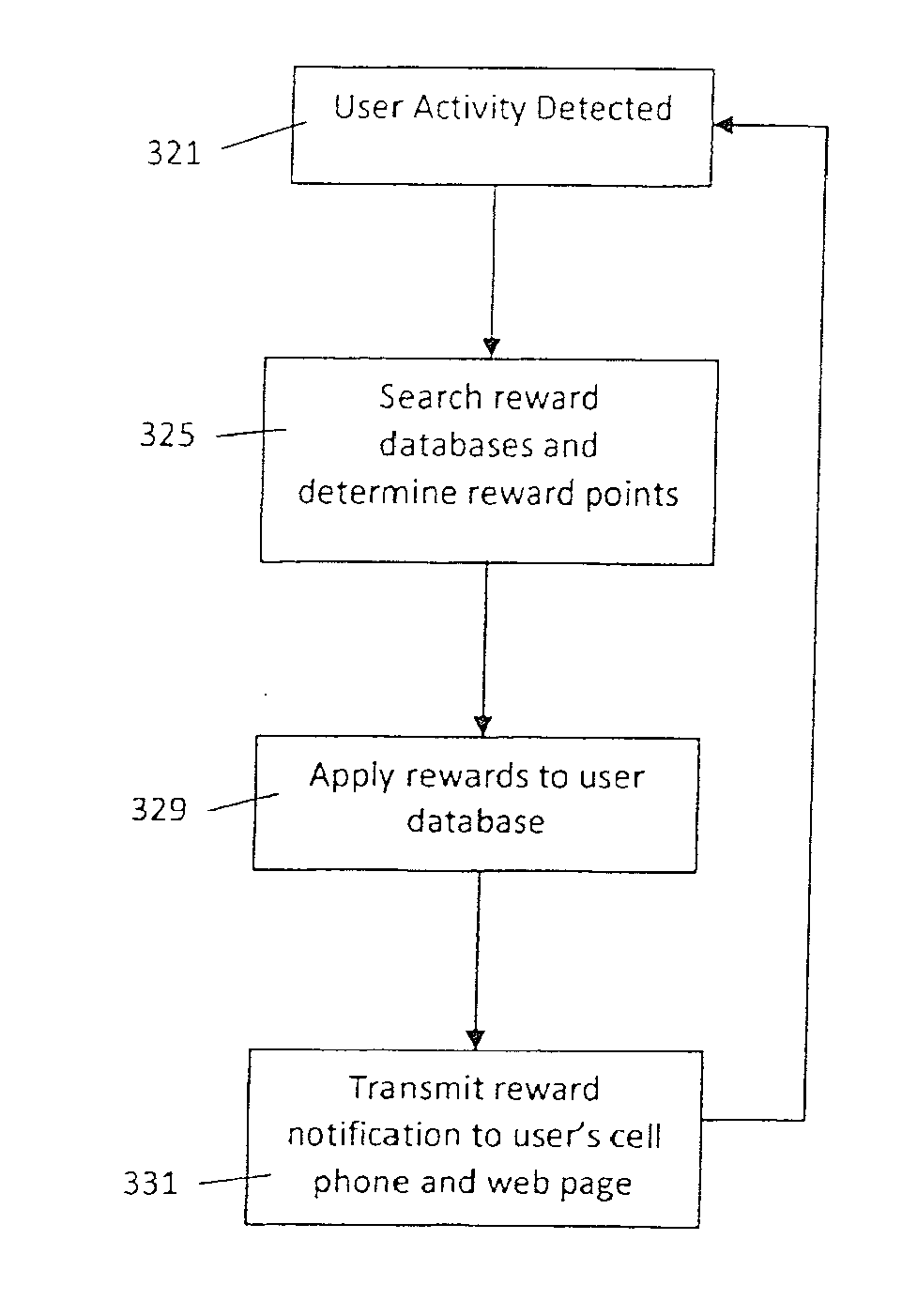
Method and system for presence detection
ActiveUS20110029370A1Improve consumer experienceImprove efficiencyDiscounts/incentivesSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionUltrasonic sensorPosition dependent
The transmission system transmits an encrypted identifier ultrasonically in an open-air environment using an ultrasonic transmitter. The ultrasonic identifier is associated with a location, which may be a store or a department within a store, and may be received by a microphone on a mobile phone. The identifier may be used to infer presence of the mobile phone user at the location associated with the identifier. The transmitter may include an ultrasonic transducer. The system may further provide a reward, responsive to inferring presence at the location.
Owner:SHOPKICK
Ultrasonic device for tissue ablation and sheath for use therewith
InactiveUS7503895B2Prevent relapseImprove permeabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyCavitationTransverse mode
A transverse mode ultrasonic probe is provided which creates a cavitation area along its longitudinal length, increasing the working surface of the probe. Accessory sheaths are also provided for use with the probe to enable a user to select from features most suited to an individual medical procedure. The sheaths provide acoustic enhancing and aspiration enhancing properties, and / or can be used as surgical tools or as medical access devices, protecting tissue from physical contact with the probe.
Owner:CYBERSONICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com