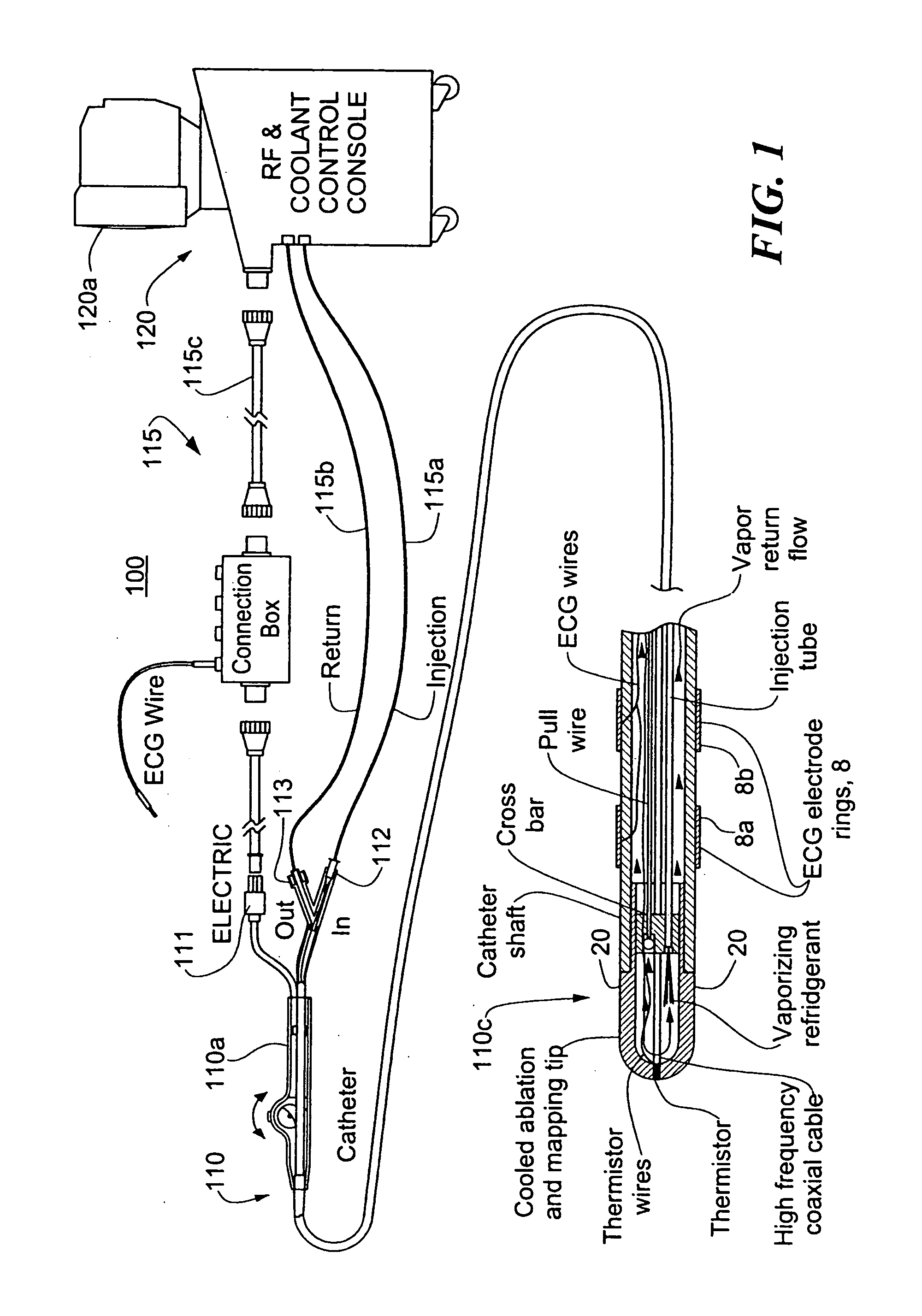
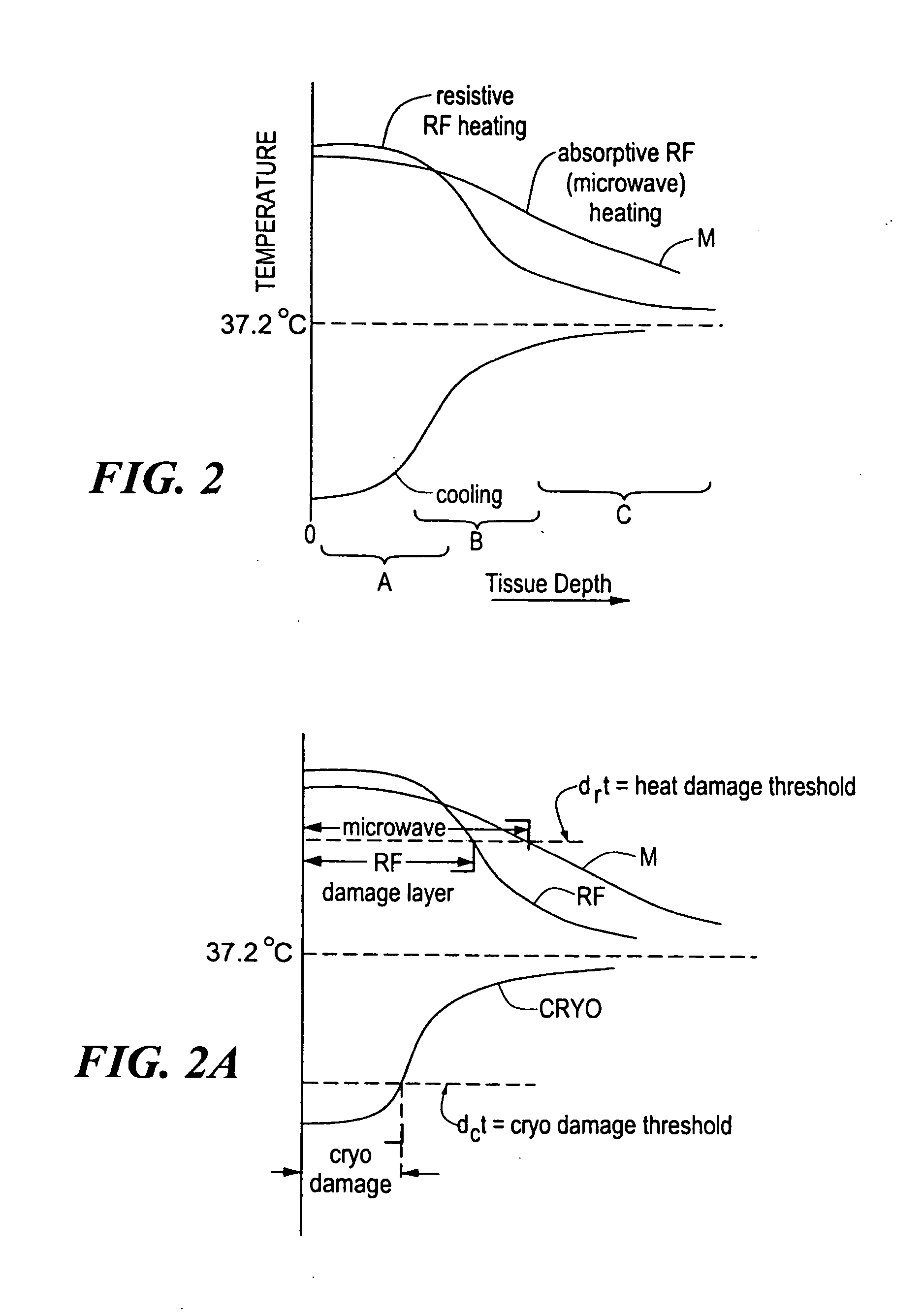
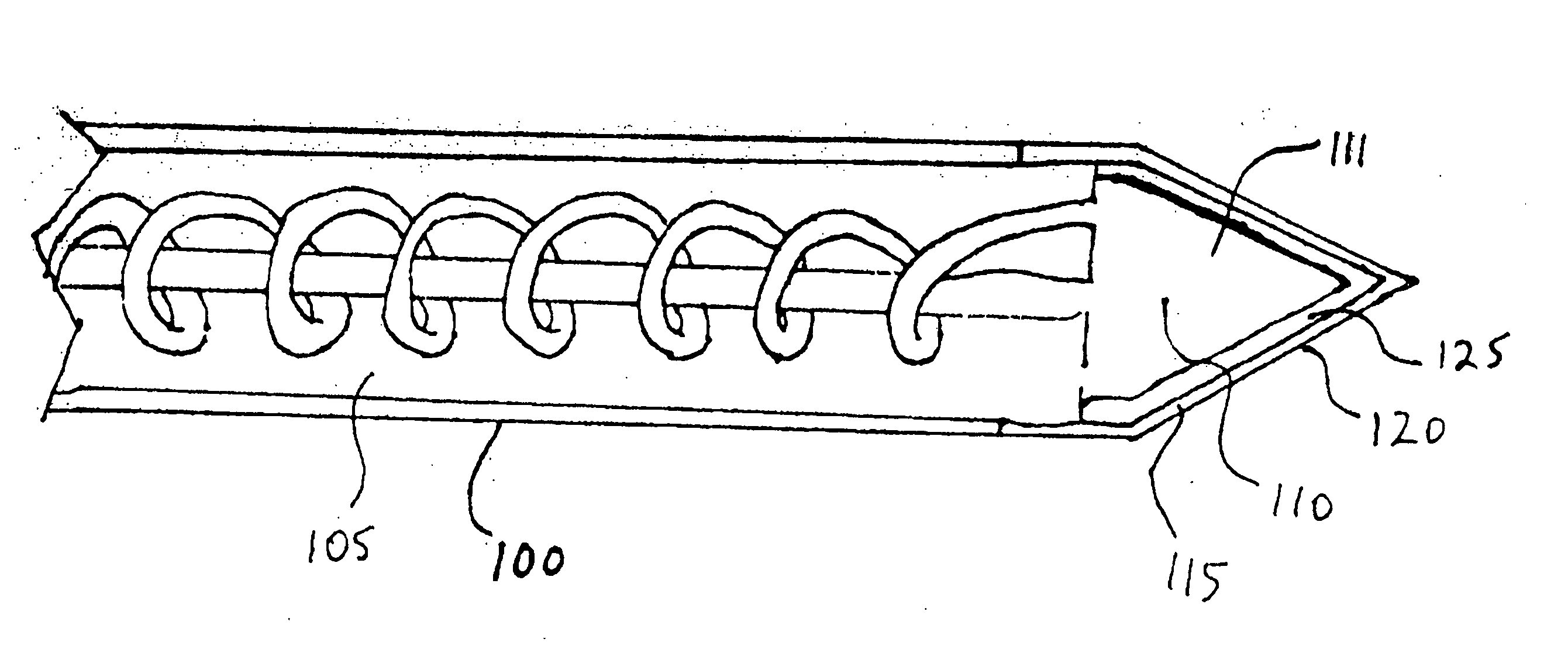
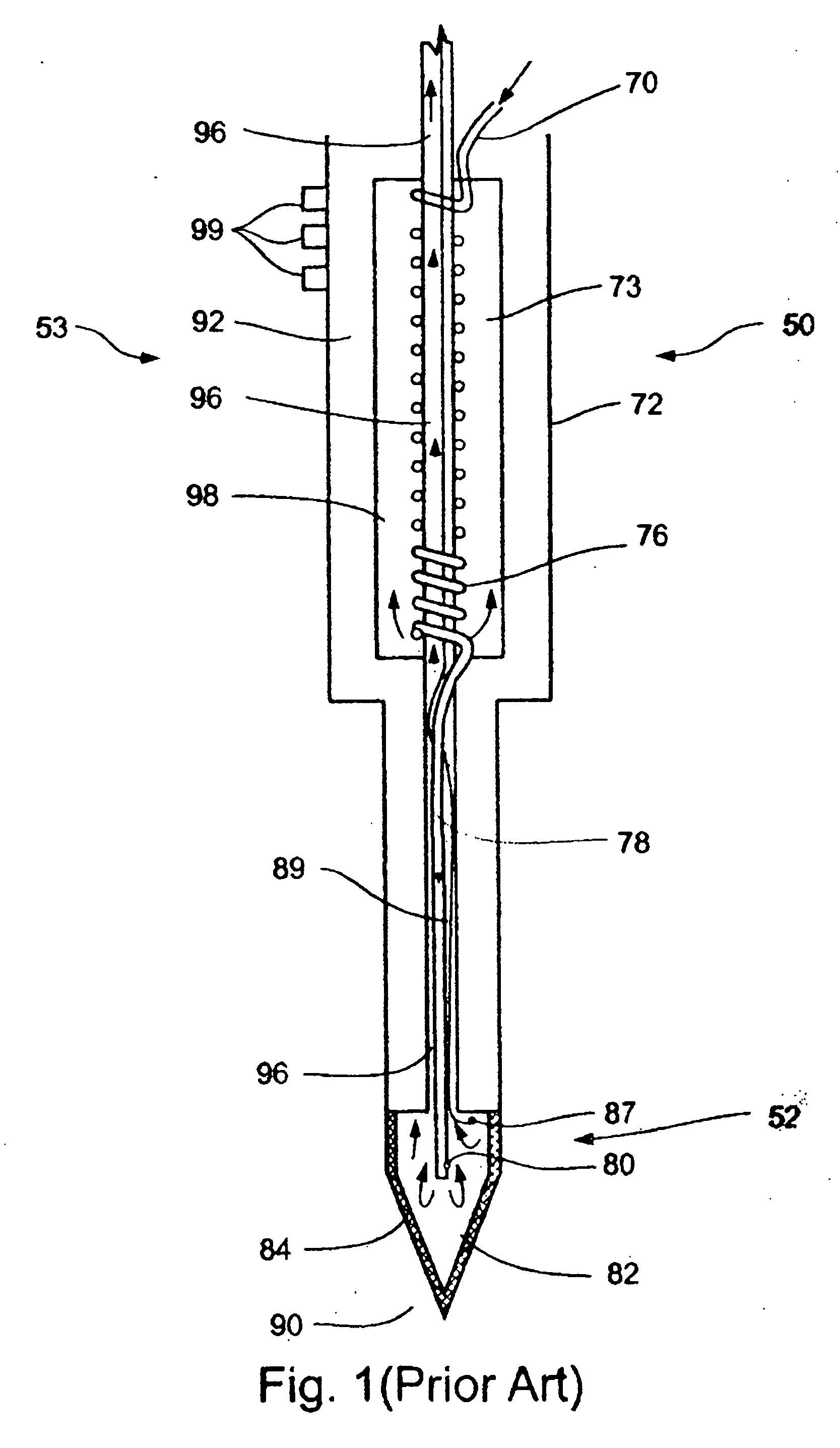
Patents
Literature
375 results about "Cryoablation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
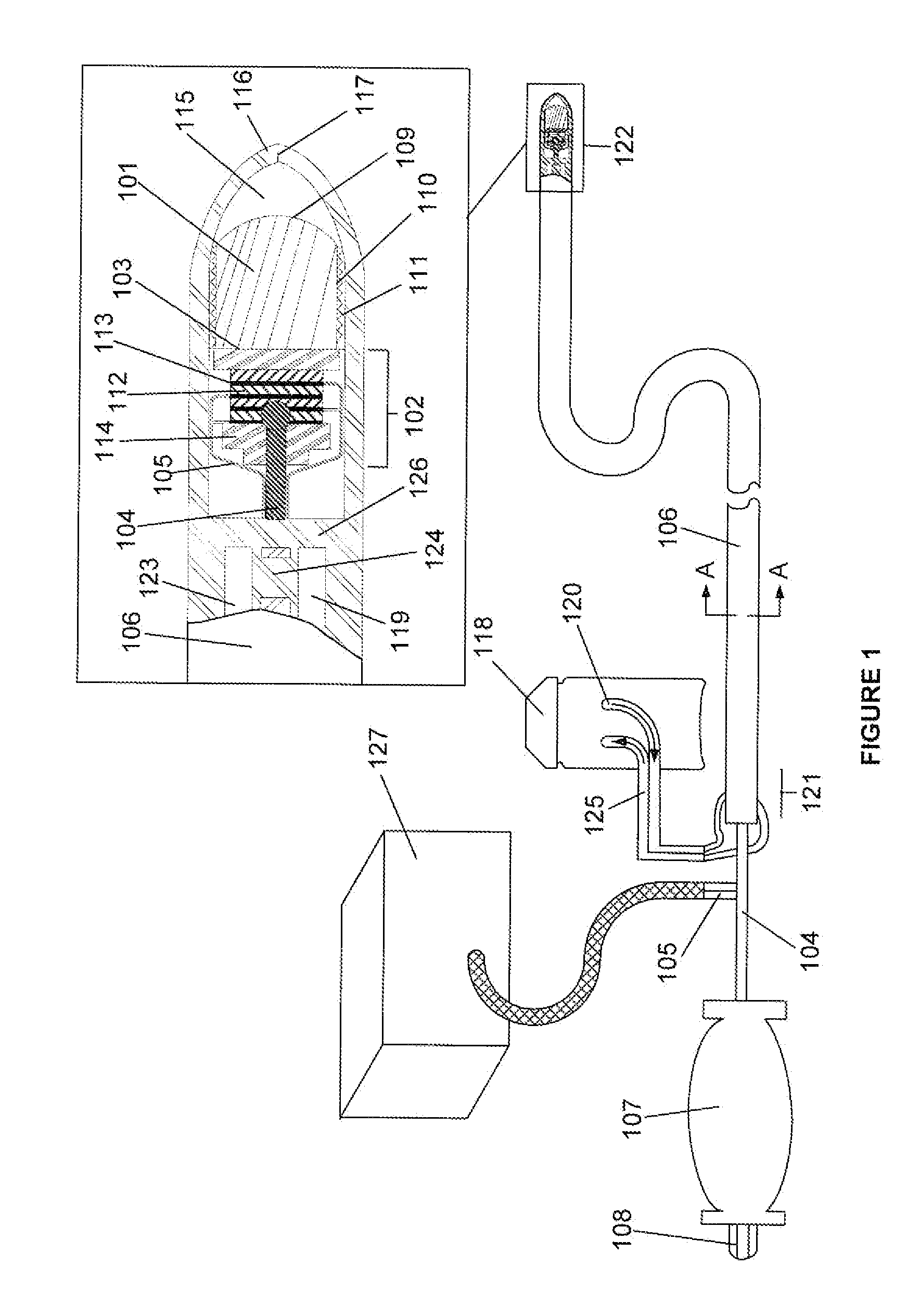
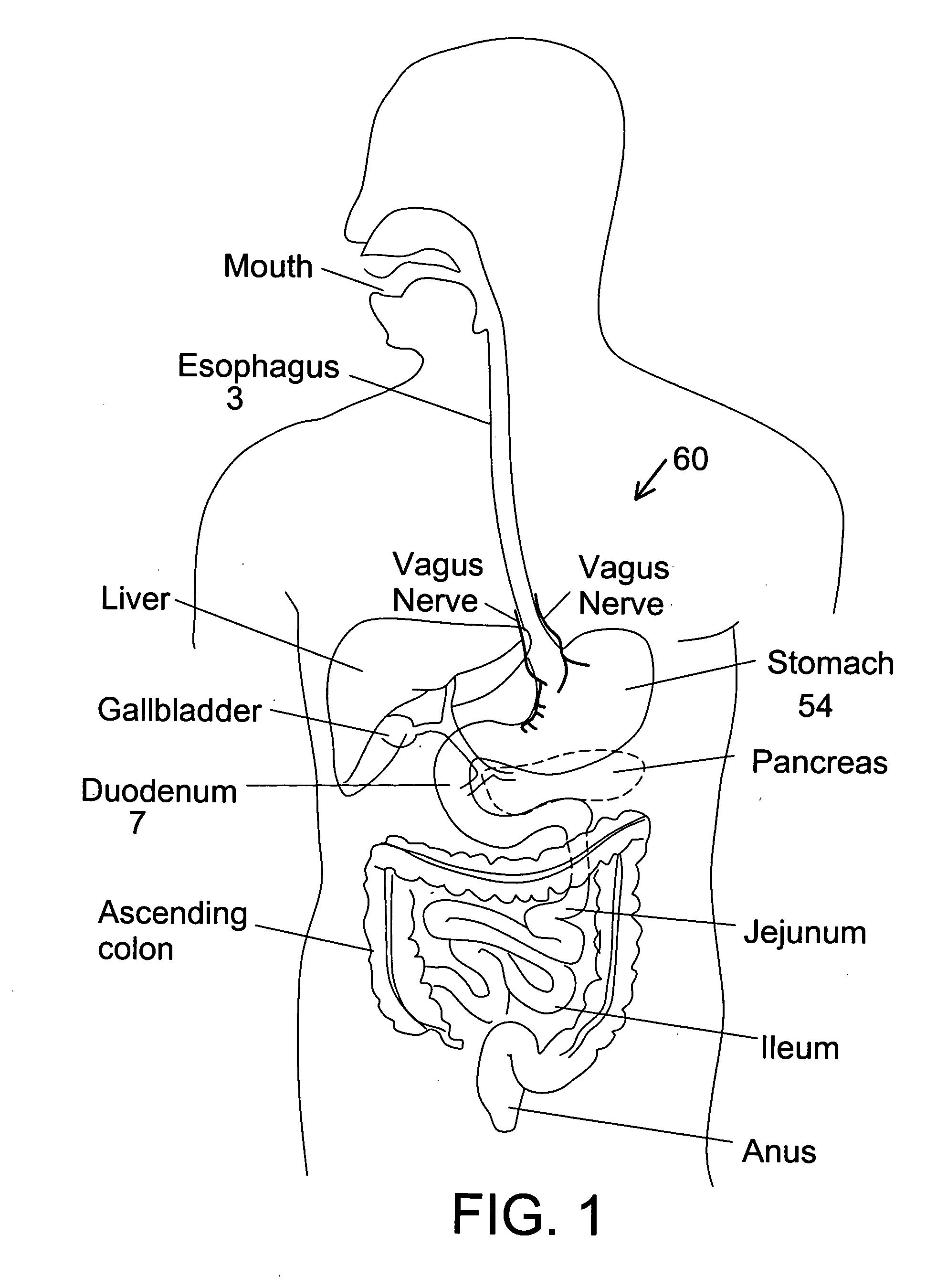
Cryoablation is a process that uses extreme cold to destroy tissue. Cryoablation is performed using hollow needles (cryoprobes) through which cooled, thermally conductive, fluids are circulated. Cryoprobes are positioned adjacent to the target in such a way that the freezing process will destroy the diseased tissue. Once the probes are in place, the attached cryogenic freezing unit removes heat from ("cools") the tip of the probe and by extension from the surrounding tissues.
High intensity ablation device
ActiveUS7179254B2Improve performanceOvercome limitationsUltrasound therapySurgical instruments for heatingMicrowaveHigh intensity
An apparatus for ablating tissue, the apparatus having first and second opposing jaws operative to compress tissue to be allayed therebetween, the first jaw having a first ablation surface directing ablative energy into the tissue and the second jaw having a second ablation surface reflecting incident ablative energy into the tissue. The ablative energy may be ultrasonic, microwave, cryoablation, radio-frequency, photodynamic, laser, and cautery energy. The instrument may also have a pointed tip for piercing tissue, allowing the instrument to clamp the tissue wall of a hollow organ before ablation. Alternately, the instrument may clamp two or more tissue layers of a hollow organ without piercing prior to clamping an ablation.
Owner:ETHICON INC
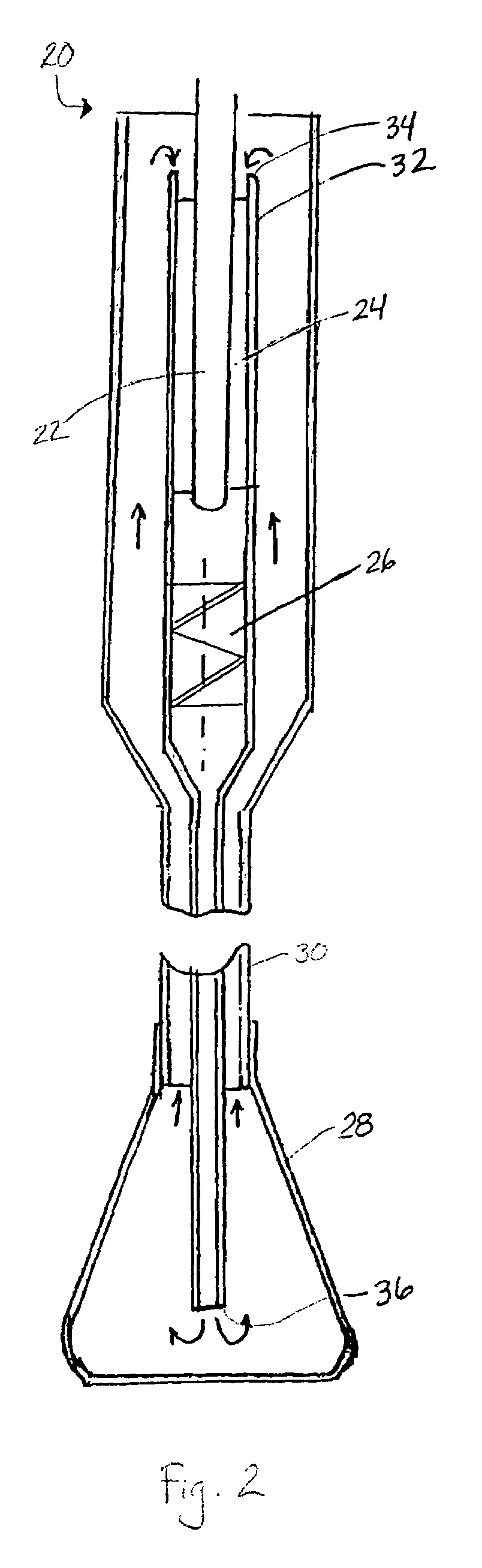
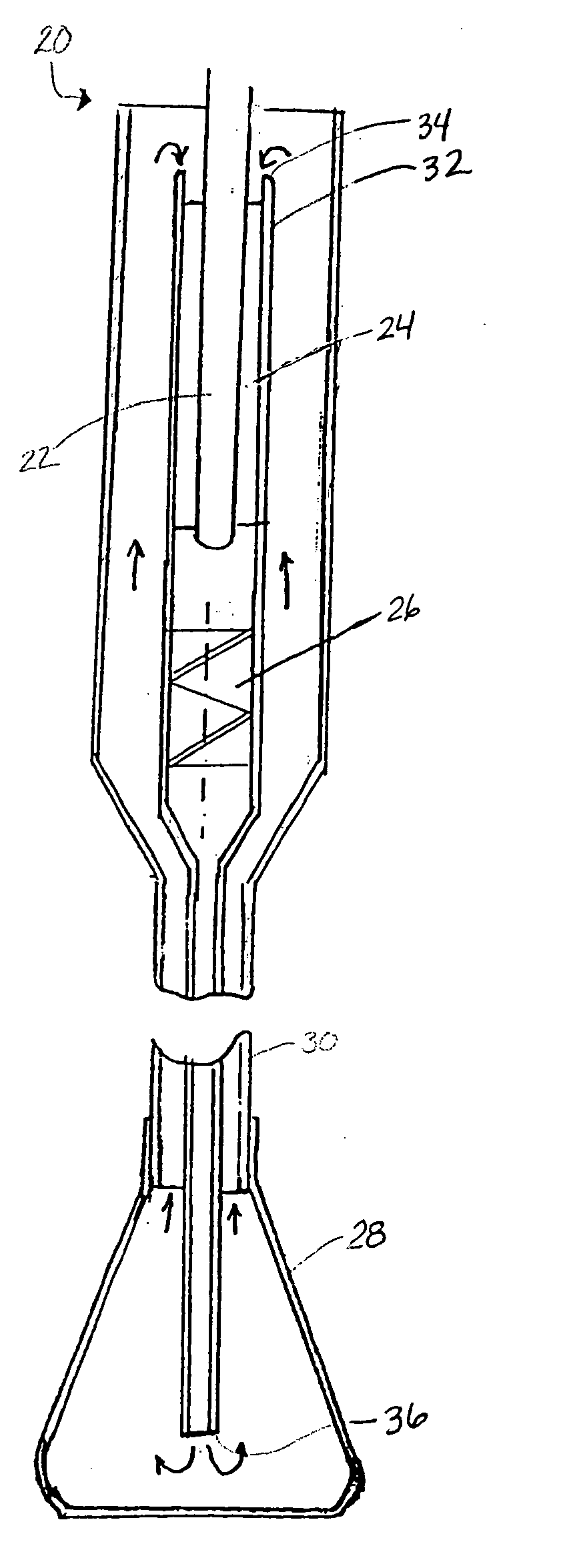
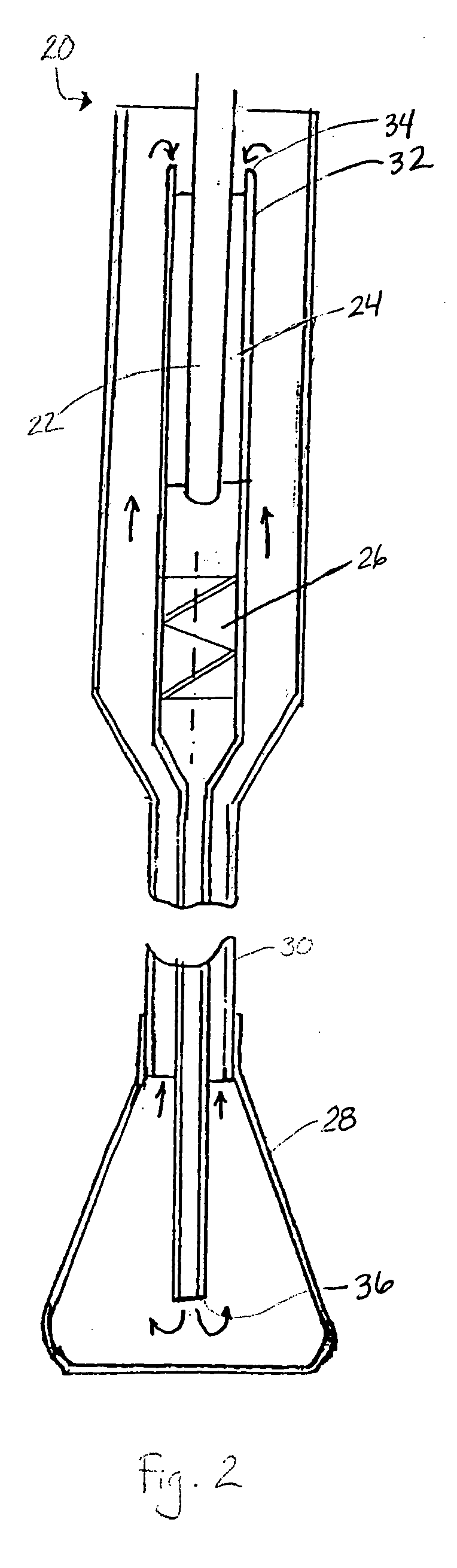
Cryo balloon
Devices and methods for performing cryo therapy, cryo ablation or cryoplasty. A cryo therapy apparatus may comprise an elongate shaft, a cooling member disposed at the distal end of the shaft, and a pressure gauge coupled to the cooling member.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
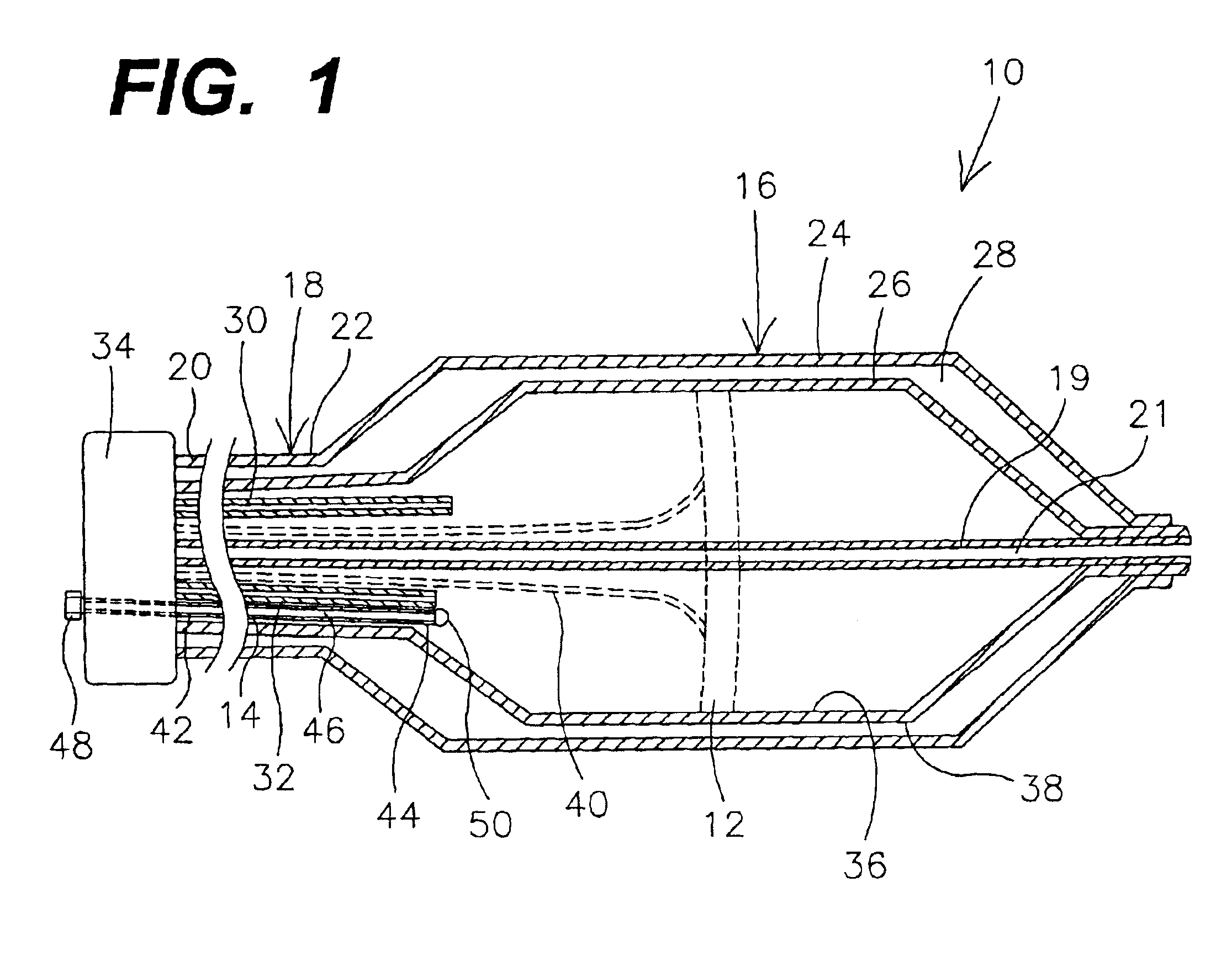
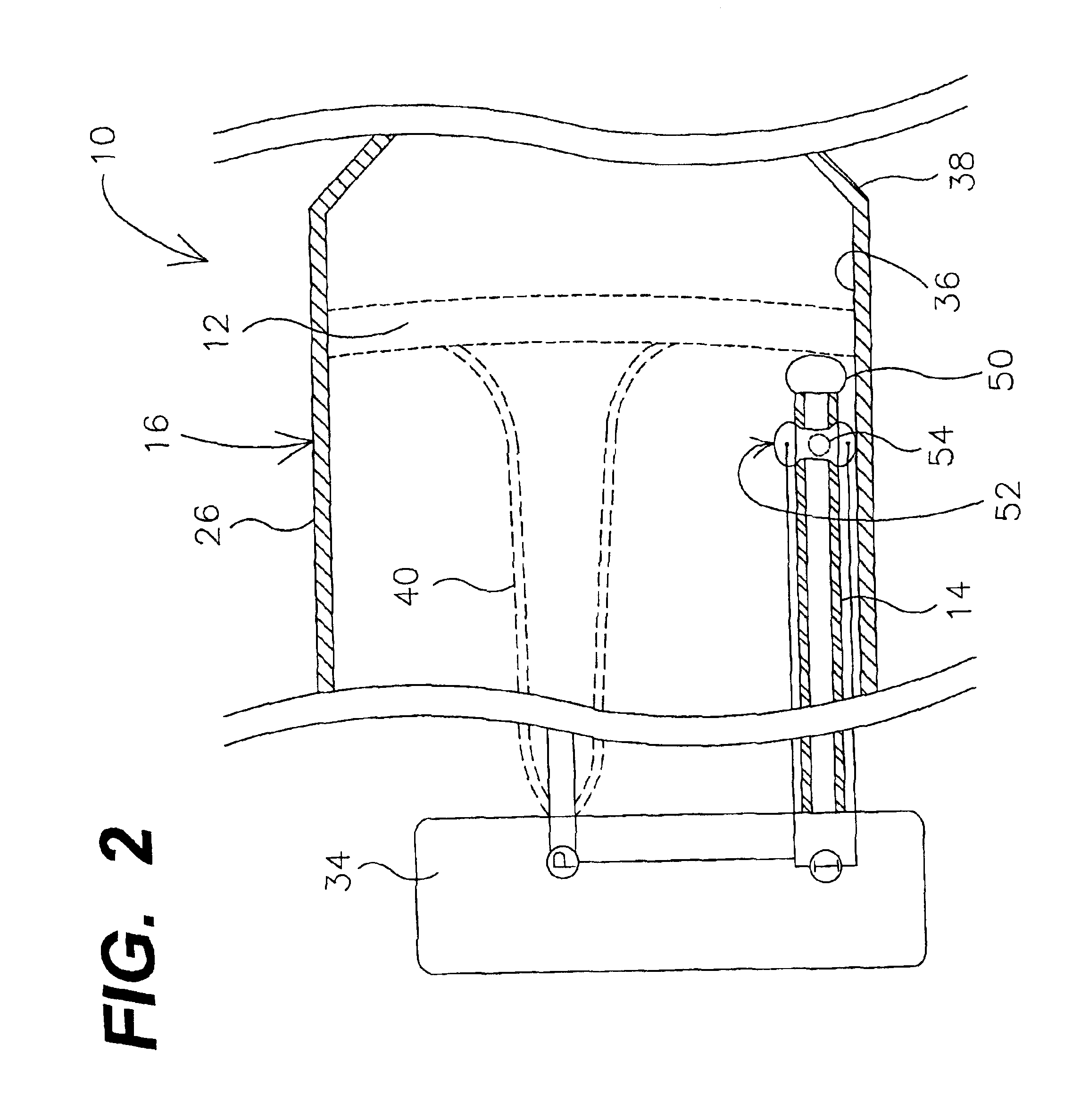
Catheter with cryogenic and heating ablation
InactiveUS7097641B1Improve versatilityEnhancing speed and placement lesionCatheterSurgical instruments for heatingTissue remodelingCelsius Degree
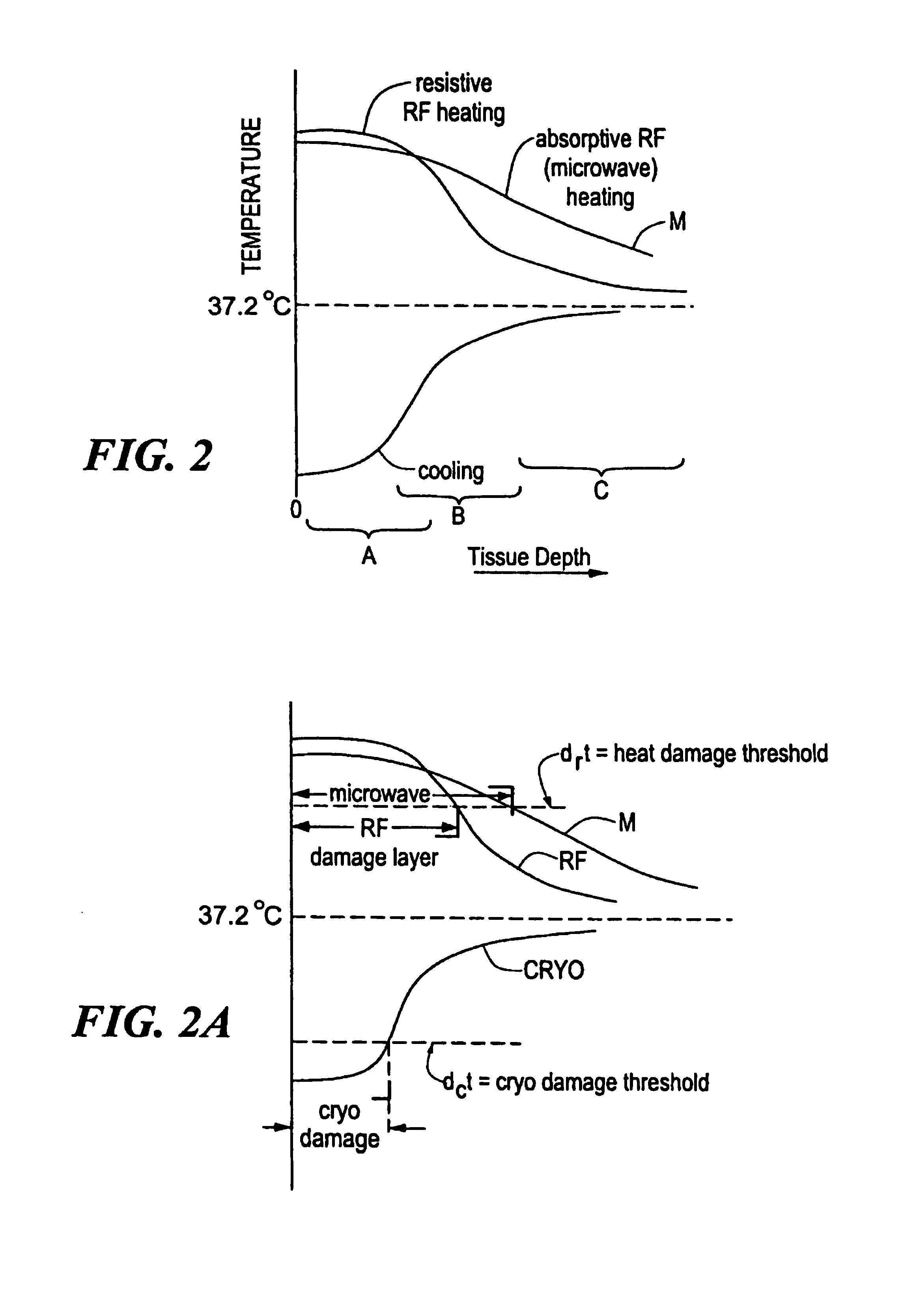
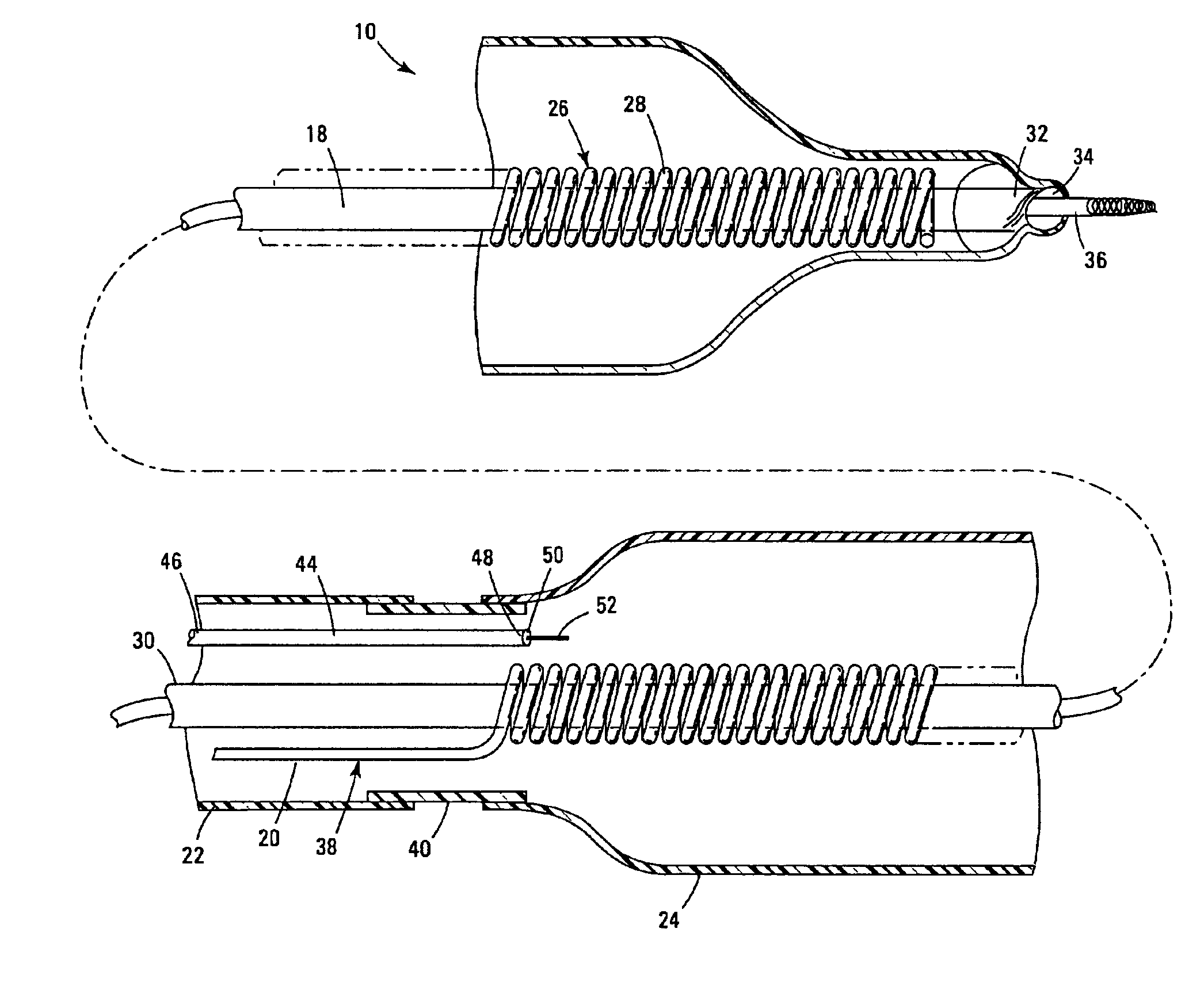
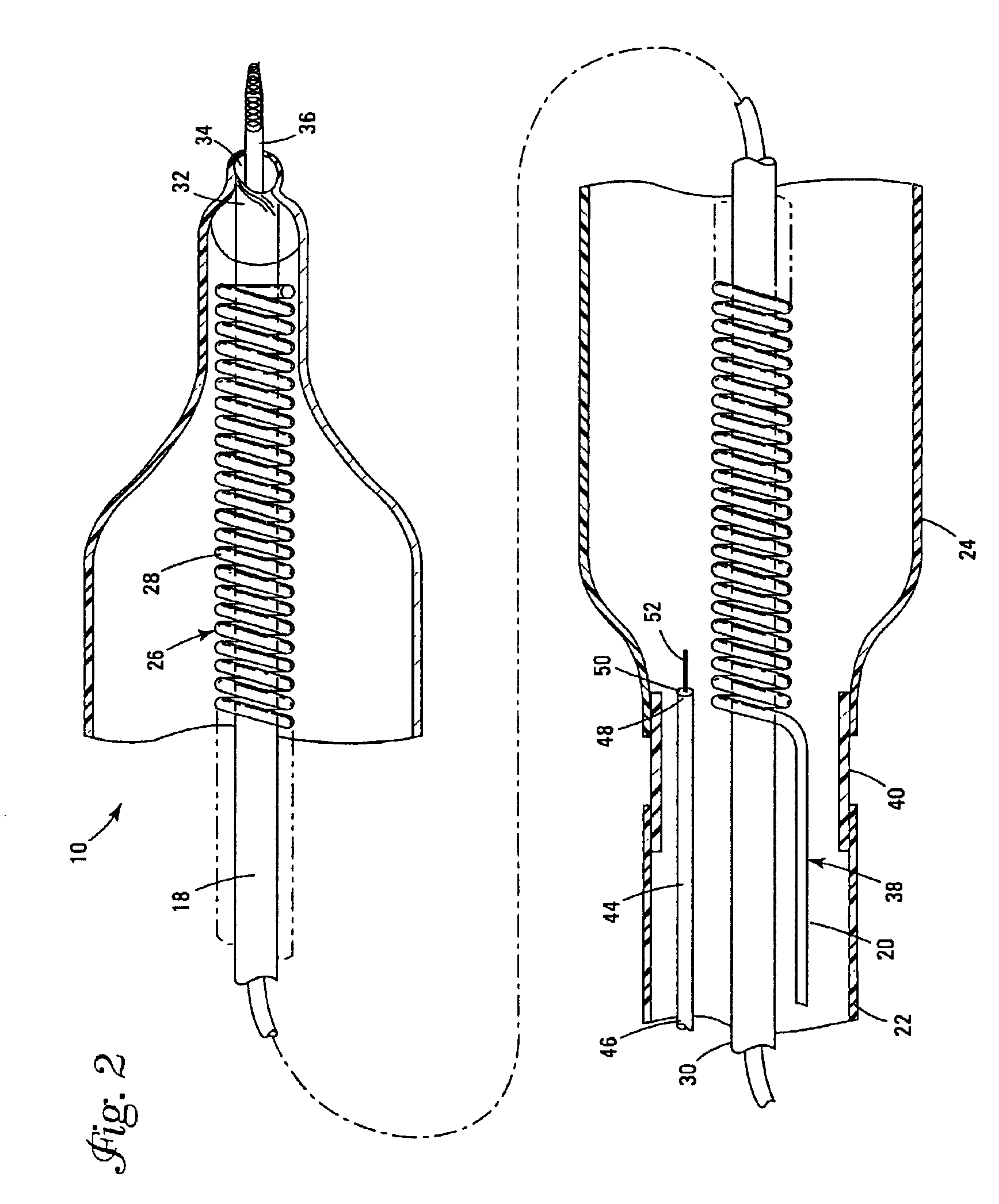
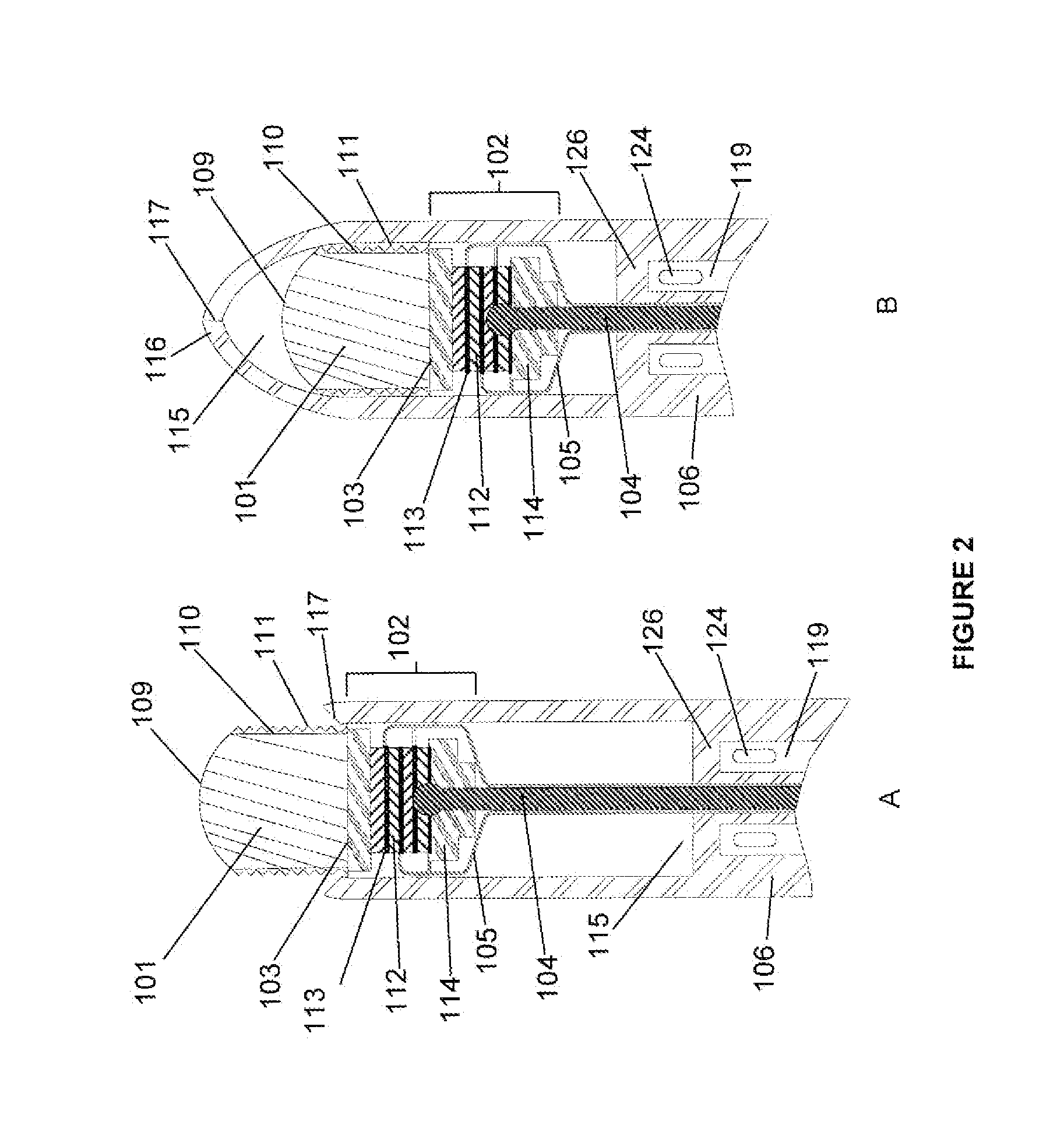
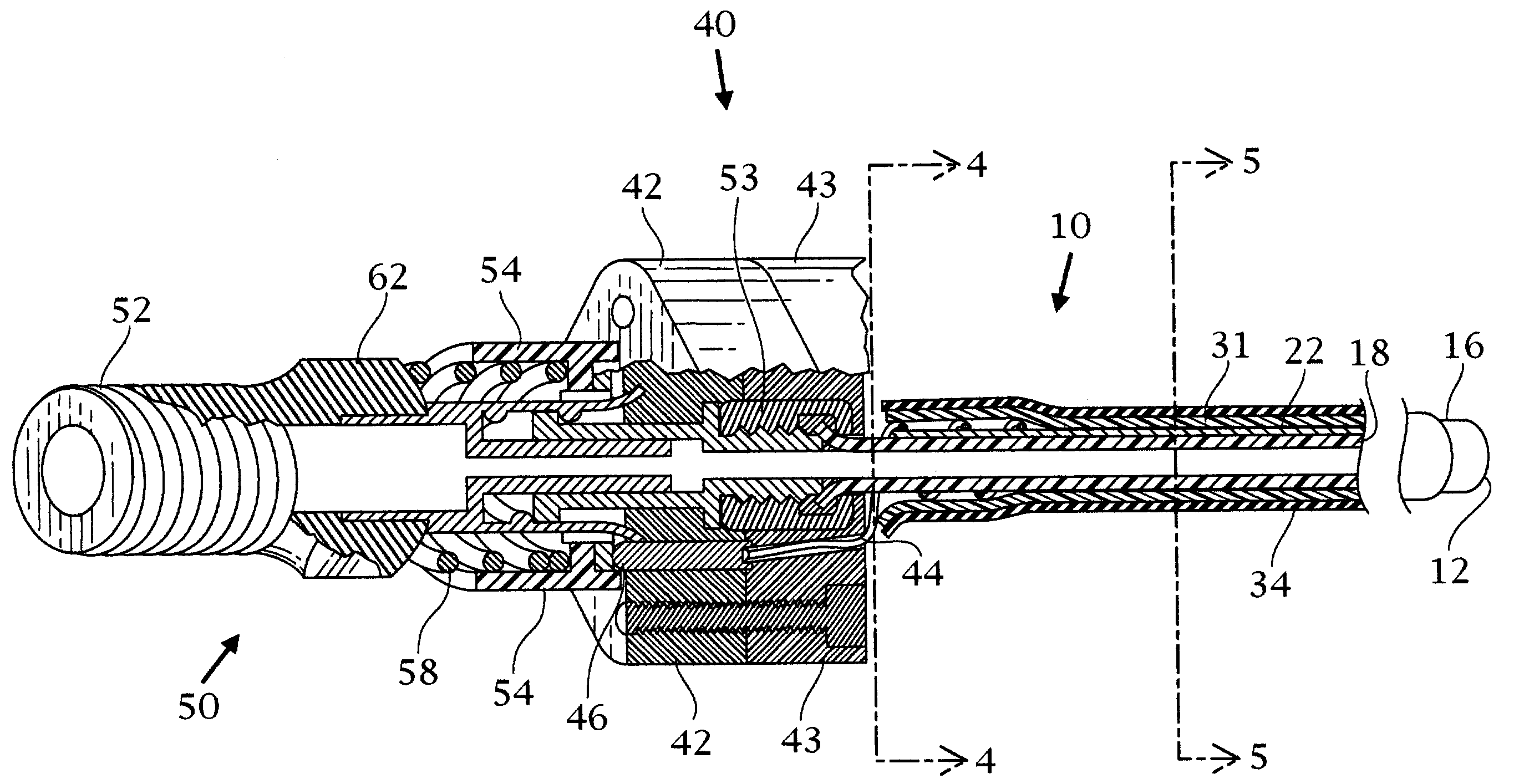
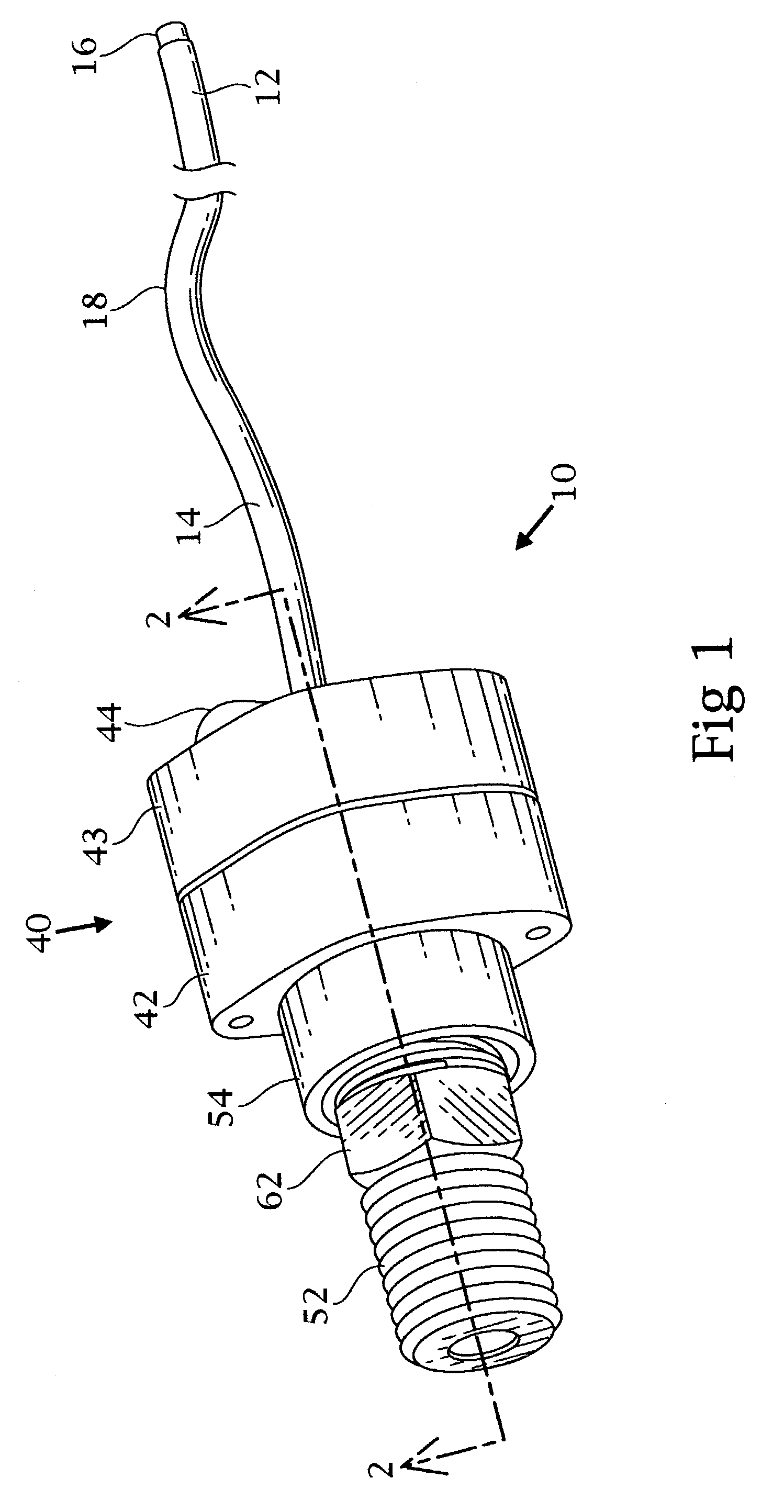
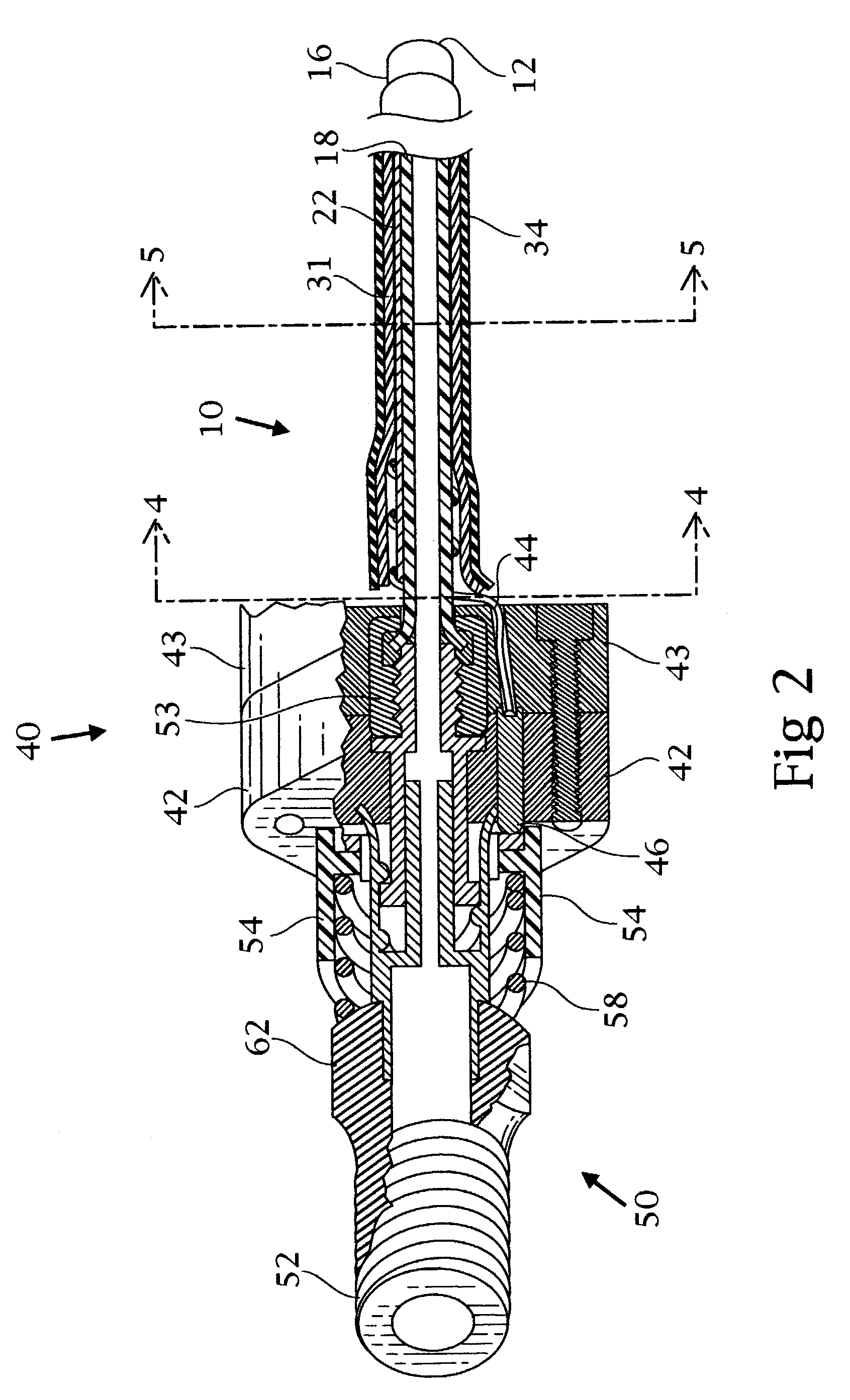
A catheter includes a cryoablation tip with an electrically-driven ablation assembly for heating tissue. The cryoablation tip may be implemented with a cooling chamber through which a controllably injected coolant circulates to lower the tip temperature, and having an RF electrode at its distal end. The RF electrode may be operated to warm cryogenically-cooled tissue, or the coolant may be controlled to conductively cool the tissue in coordination with an RF treatment regimen, allowing greater versatility of operation and enhancing the lesion size, speed or placement of multi-lesion treatment or single lesion re-treatment cycles. In one embodiment a microwave energy source operates at a frequency to extend beyond the thermal conduction depth, or to penetrate the cryogenic ice ball and be absorbed in tissue beyond an ice boundary, thus extending the depth and / or width of a single treatment locus. In another embodiment, the cooling and the application of RF energy are both controlled to position the ablation region away from the surface contacted by the electrode, for example to leave surface tissue unharmed while ablating at depth or to provide an ablation band of greater uniformity with increasing depth. The driver or RF energy source may supply microwave energy at a frequency effective to penetrate the ice ball which develops on a cryocatheter, and different frequencies may be selected for preferential absorption in a layer of defined thickness at depth in the nearby tissue. The catheter may operate between 70 and minus 70 degrees Celsius for different tissue applications, such as angioplasty, cardiac ablation and tissue remodeling, and may preset the temperature of the tip or adjacent tissue, and otherwise overlay or delay the two different profiles to tailor the shape or position where ablation occurs or to speed up a treatment cycle.
Owner:MEDTRONIC CRYOCATH LP
Cryo ablation coil
The present invention pertains to devices for causing cold-induced necrosis or apoptosis. The present invention includes a cryo therapy apparatus including a core member; a cryoplasty tube coupled to the core member, the cryoplasty tube having a proximal end and a distal end; wherein the distal end includes a coil disposed about at least a portion of the tubular sheath, the coil including at least one opening; an outer tube disposed over at least a portion of the cryoplasty tube; and a cooling member disposed over the coil and coupled to the outer tube. A method of causing cold-induced necrosis is also disclosed.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method and device for performing cooling or cryo-therapies, for, e.g., angioplasty with reduced restenosis or pulmonary vein cell necrosis to inhibit atrial fibrillation employing tissue protection
InactiveUS7001378B2Minimize and inhibit bio-chemical eventRobust designCatheterSurgical instruments for heatingPercent Diameter StenosisPercutaneous angioplasty
An enhanced method and device are provided to treat atrial fibrillation or inhibit or reduce restenosis following angioplasty or stent placement. A balloon-tipped catheter is disposed in the area treated or opened through balloon angioplasty immediately following angioplasty. The balloon, which can have a dual balloon structure, may be delivered through a guiding catheter and over a guidewire already in place. A fluid such as a perfluorocarbon flows into the balloon to freeze the tissue adjacent the balloon, this cooling being associated with reduction of restenosis. A similar catheter may be used to reduce atrial fibrillation by inserting and inflating the balloon such that an exterior surface of the balloon contacts at least a partial circumference of the portion of the pulmonary vein adjacent the left atrium. In another embodiment, blood perfusion is performed simultaneously. In another embodiment, tissue contacted by the cryoablation catheter, undesired to be ablated, is protected against damage by a separate heating step.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Method and device for performing cooling- or cryo-therapies for, e.g., angioplasty with reduced restenosis or pulmonary vein cell necrosis to inhibit atrial fibrillation employing tissue protection
InactiveUS6905494B2Minimize and inhibit biochemical eventRobust designCatheterSurgical instruments for heatingPercent Diameter StenosisPercutaneous angioplasty
An enhanced method and device are provided to treat atrial fibrillation or inhibit or reduce restenosis following angioplasty or stent placement. A balloon-tipped catheter is disposed in the area treated or opened through balloon angioplasty immediately following angioplasty. The balloon, which can have a dual balloon structure, may be delivered through a guiding catheter and over a guidewire already in place. A fluid such as a perfluorocarbon flows into the balloon to freeze the tissue adjacent the balloon, this cooling being associated with reduction of restenosis. A similar catheter may be used to reduce atrial fibrillation by inserting and inflating the balloon such that an exterior surface of the balloon contacts at least a partial circumference of the portion of the pulmonary vein adjacent the left atrium. In another embodiment, blood perfusion is performed simultaneously. In another embodiment, tissue contacted by the cryoablation catheter, undesired to be ablated, is protected against damage by a separate heating step.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Method and system for cryoablating fibroadenomas
InactiveUS6789545B2Improve performanceReduce the required powerDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for coolingFibroadenomaControl system
A cryosurgical system adapted for treatment of fibroadenomas within the breast of a patient. The system includes cryoprobes and a control system which operates the cryoprobes to accomplish freezing in two stages, including a high power freeze and a low power freeze.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Cryosurgical devices and methods for endometrial ablation
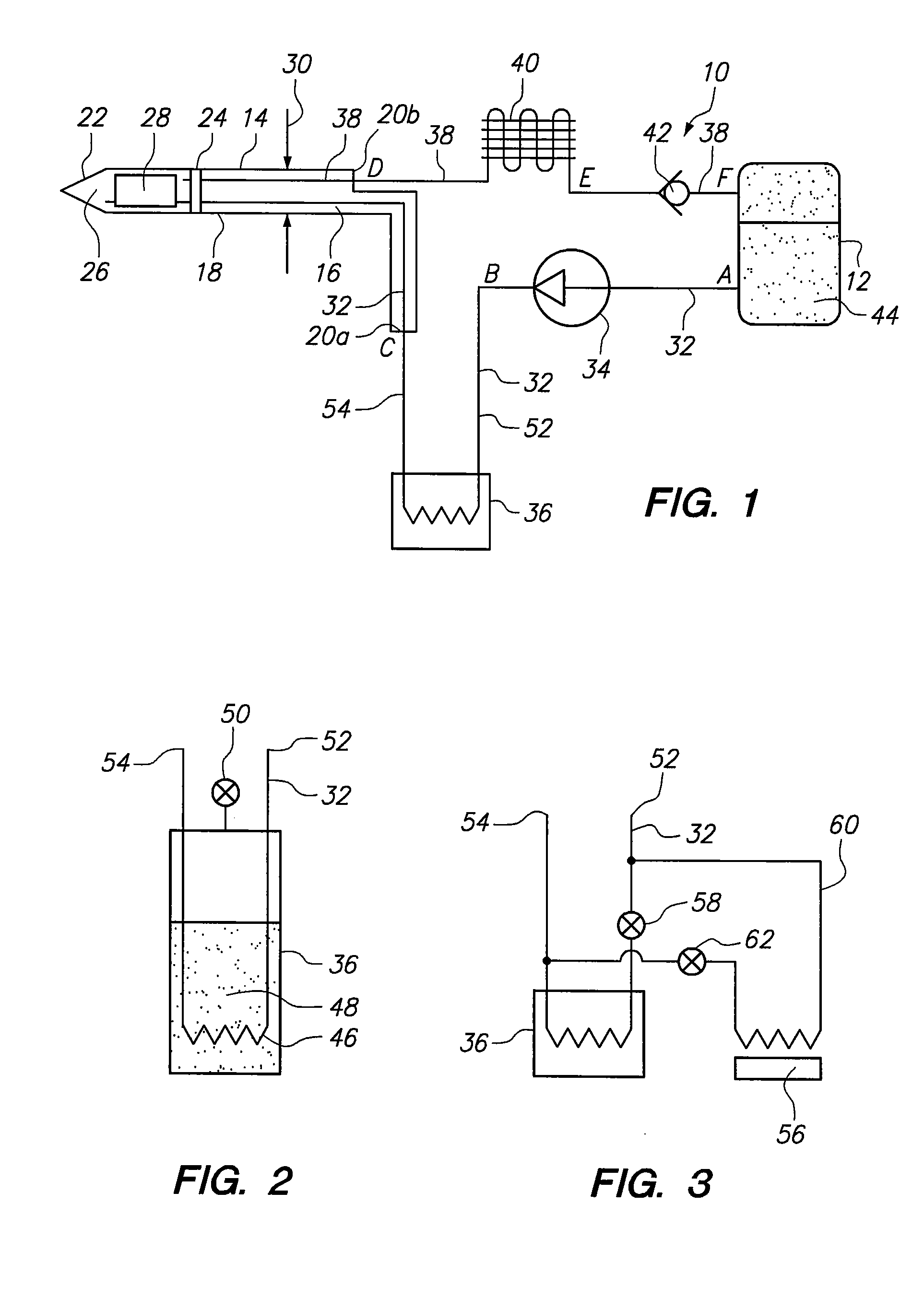
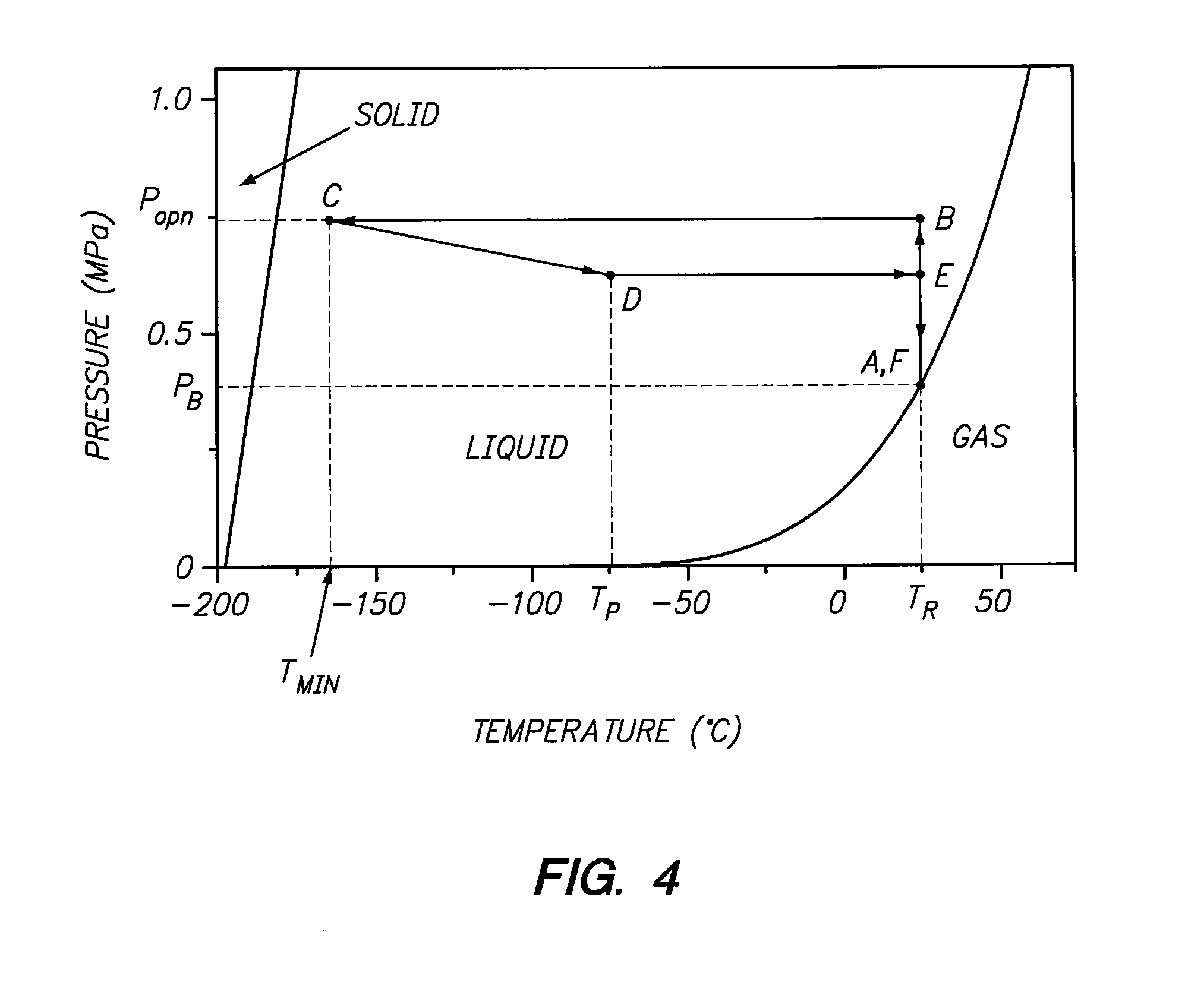
A cryoablation system including a cannula having a proximal end, a distal end, and a longitudinal axis, an expandable balloon extending from the distal end of the cannula and fluidly connected to a source of heat transfer fluid by at least one fluid path, a pump for circulating the heat transfer fluid into and out of the balloon, a probe handle coupled to the proximal end of the cannula and in fluidic communication with the balloon through the cannula, and a heat exchanger for varying the temperature of the heat transfer fluid, wherein the heat exchanger is fluidly connected to a secondary refrigerant source. The heat exchanger may be positioned within the probe handle, within the cannula, or at least partially within the balloon. The heat transfer fluid of this cryoablation system preferably has a freezing point lower than about −110° C. and a boiling point greater than about 50° C.
Owner:COOPERSURGICAL INC
Ablative ultrasonic-cryogenic apparatus
InactiveUS7540870B2Induced fastEasy to moveUltrasound therapyChiropractic devicesTransducerCardiac muscle
An ablative apparatus that can be used to treat atrial fibrillation and other cardiac arrhythmias by ablating cardiac tissue is disclosed. When the distal end of the apparatus reaches the tissue to be ablated, an ablation probe driven by a transducer is vibrated. Scratching the tissue with abrasive members, the vibrating ablation probe is capable of mechanically ablating tissues. This mechanical ablation may be utilized to penetrate epicardial fat, thereby exposing the underlying myocardium. The ablative apparatus may then be used subject the exposed myocardium to mechanical ablation, cryoablation, ultrasonic ablation, and / or any combination thereof.
Owner:BACOUSTICS LLC
Ablative ultrasonic-cryogenic methods
InactiveUS20090221955A1Induced fastEasy to moveUltrasound therapyChiropractic devicesCardiac muscleTransducer
An ablative apparatus and associated methods that can be used to treat atrial fibrillation and other cardiac arryhythmias by ablating cardiac tissue is disclosed. When the distal end of the apparatus reaches the tissue to be ablated, an ablation probe driven by a transducer is vibrated. Scratching the tissue with abrasive members, the vibrating ablation probe is capable of mechanically ablating tissues. This mechanical ablation may be utilized to penetrate epicardial fat, thereby exposing the underlying myocardium. The ablative apparatus may then be used subject the exposed myocardium to mechanical ablation, cryoablation, ultrasonic ablation, and / or any combination thereof.
Owner:BACOUSTICS LLC
System for MRI-guided interventional mammary procedures
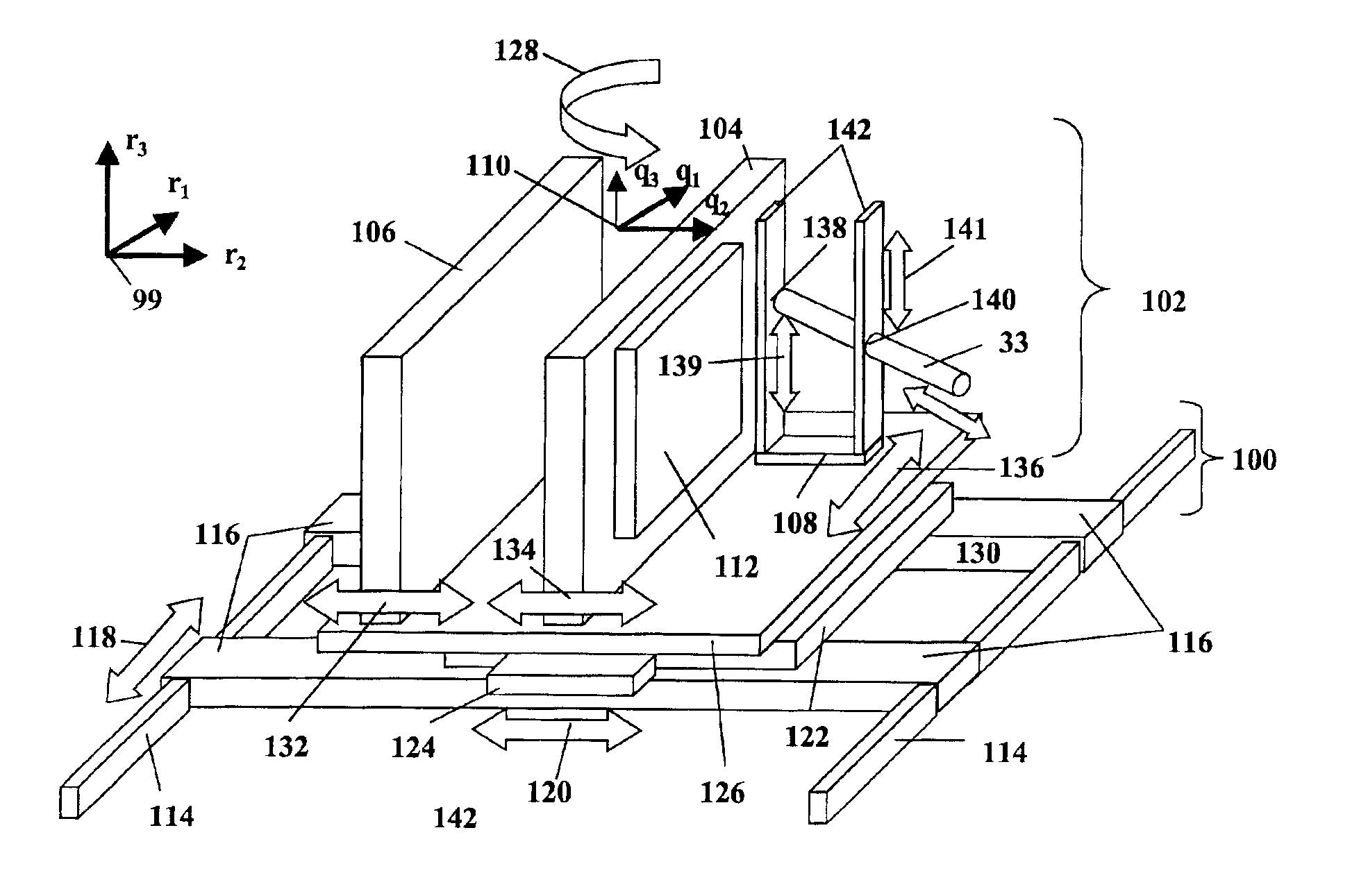
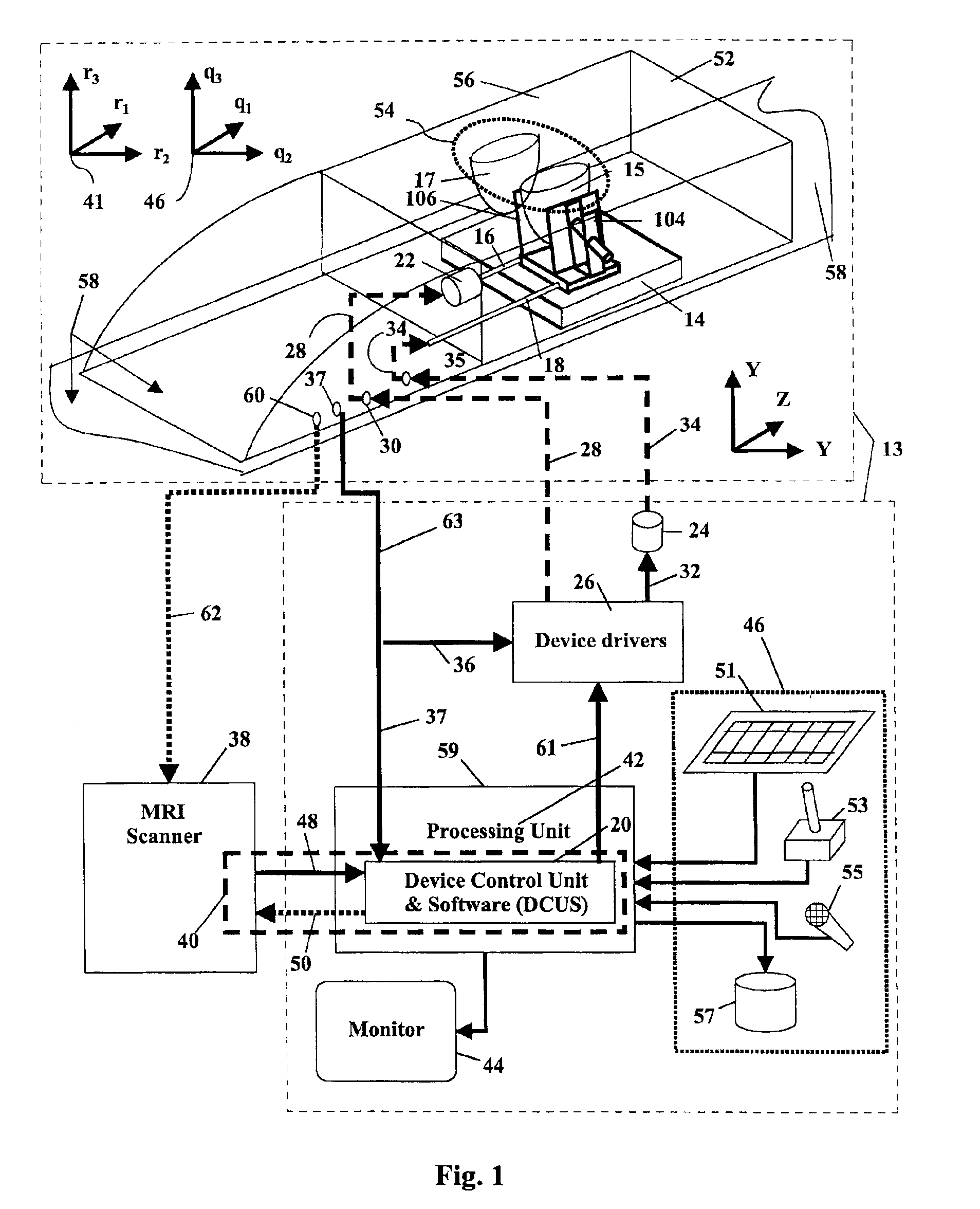
InactiveUS6904305B2Enhanced magnetic resonance imagingProvide flexibilitySurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsContrast-enhanced Magnetic Resonance ImagingSingle injection
The combination of contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and MR-guided subcutaneous core biopsy can be used as a robust approach for the diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer. MRI provides the means to accurately position and monitor interventional procedures such as biopsy, removal of tissue or other transcanular procedures. MRI may also be used in this invention to position and monitor the progress of breast conserving therapies (BCT), such as laser photo-ablation, cryoablation and localized hyperthermia. The general practice of this invention is to provide a remotely controlled apparatus for MR-guided interventional procedures in the breast. The apparatus allows the practice of a method that provides flexibility in conditioning the breast, i.e. orientation and degree of compression, and in setting the trajectory of the intervention. To that end, a robust conditioning / positioning device, fitted with the appropriate degrees of freedom, enhances the efficacy and efficiency of breast interventions by providing the flexibility in planning and executing an appropriate procedure strategy that better suits interventional procedures, either those in current use or yet to be developed. The novelty and potential commercial success of the device originates from its high maneuverability to set and perform the procedure strategy and its adaptability to accommodate an array of interventional probes. Remote control of this device can allow planning the operation and performing the relevant tasks in a short period, for example, within the contrast window provided by a single injection of a contrast agent, and this feature can be operator-independent.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Cryosurgical devices for endometrial ablation
A cryoablation system for performing endometrial ablation comprising an elongated tubular cannula having a proximal end, a distal end, and a longitudinal axis, an expandable balloon extending from the distal end of the cannula and fluidly connected to a source of heat transfer fluid by at least one fluid path, a pump for circulating the heat transfer fluid into and out of the balloon, a probe handle coupled to the proximal end of the cannula and in fluidic communication with the balloon through the cannula, and a heat exchanger for varying the temperature of the heat transfer fluid, wherein the heat exchanger is fluidly connected to a secondary refrigerant source, and wherein the heat exchanger comprises an outer tubular wall and a plurality of fins extending from the tubular wall toward the interior portion of the heat exchanger.
Owner:COOPERSURGICAL INC
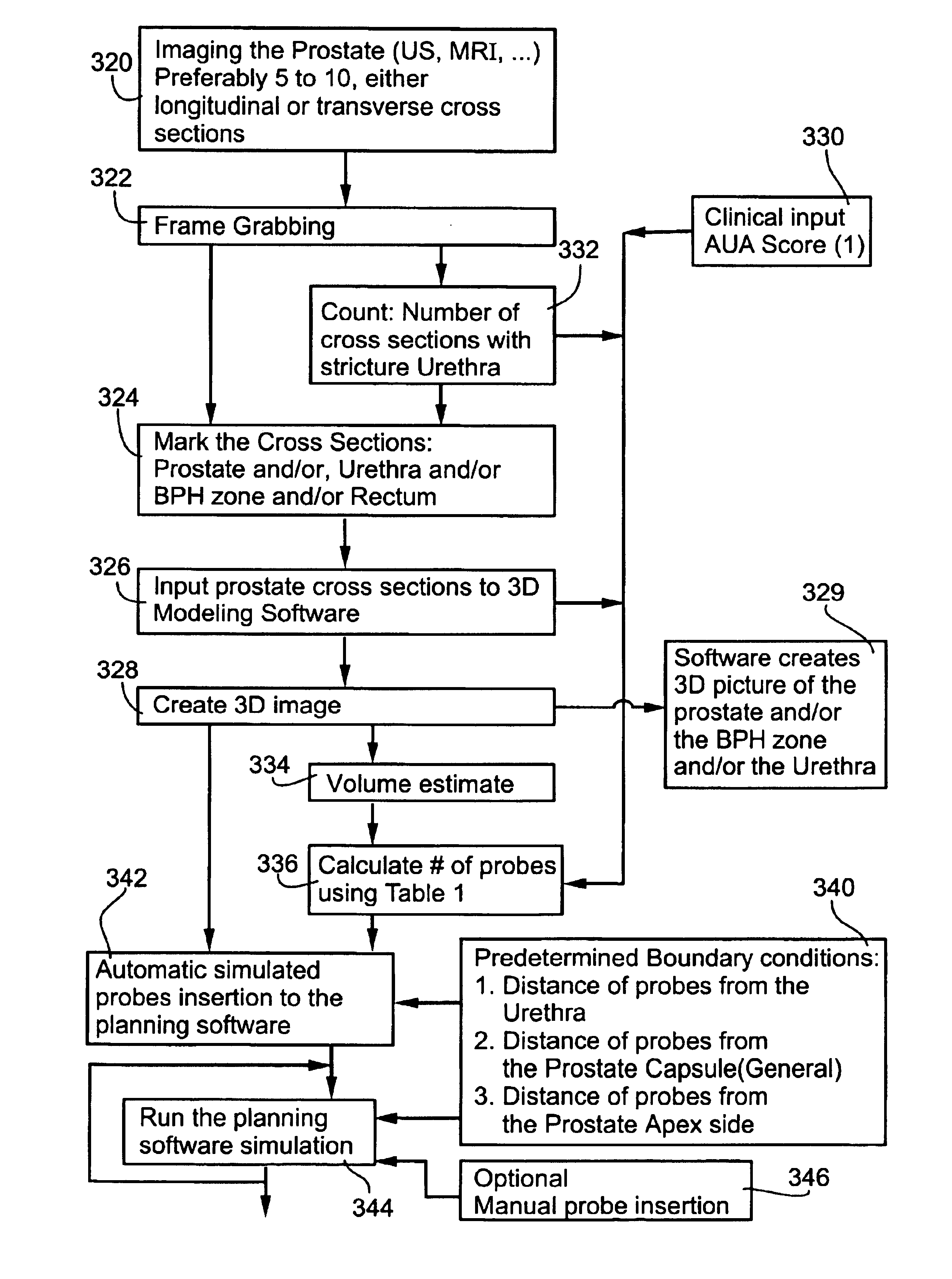
Planning and facilitation systems and methods for cryosurgery
InactiveUS6905492B2Effective planningEasy to interveneOrgan movement/changes detectionCatheterDiagnostic Radiology ModalityImaging modalities
Systems and methods for planning a cryoablation procedure and for facilitating a cryoablation procedure utilize integrated images displaying, in a common virtual space, a three-dimensional model of a surgical intervention site based on digitized preparatory images of the site from first imaging modalities, simulation images of cryoprobes used according to an operator-planned cryoablation procedure at the site, and real-time images provided by second imaging modalities during cryoablation. The system supplies recommendations for and evaluations of the planned cryoablation procedure, feedback to an operator during cryoablation, and guidance and control signals for operating a cryosurgery tool during cryoablation. Methods are provided for generating a nearly-uniform cold field among a plurality of cryoprobes, for cryoablating a volume with smooth and well-defined borders, thereby minimizing damage to healthy tissues.
Owner:GALIL MEDICAL
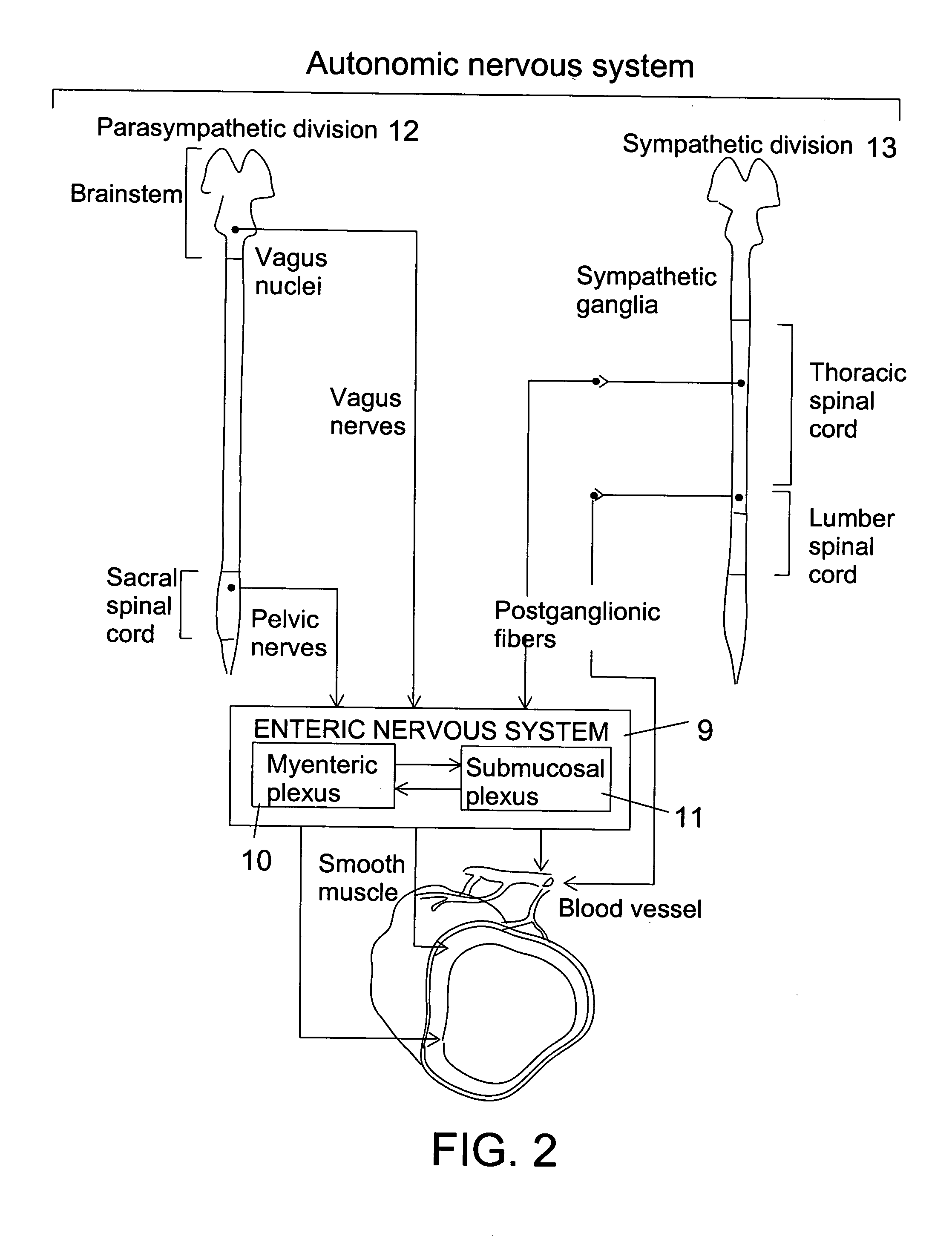
Method and system for gastric ablation and gastric pacing to provide therapy for obesity, motility disorders, or to induce weight loss
InactiveUS20050240239A1Avoid side effectsProviding therapyUltrasound therapyInternal electrodesCardiac pacemaker electrodeMotility
Method and system to provide therapy for obesity, gastric motility, or to induce weight loss comprises ablating the gastric tissue around the “pacemaker” region of the stomach, and electrically pacing the stomach with a pulse generator / stimulator to control the electrical activity of the gastric muscle. The ablation to the gastric tissue may be from the epigastric side, or may be from inside the stomach. The ablation may be performed utilizing any one of: radiofrequency catheter ablation; radiofrequency catheter ablation using an irrigated tip catheter; microwave ablation; cryoablation; high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) ablation; and laser ablation. The ablation of the “pacemaker” region of the stomach may be partial or complete. A gastric pulse generator / stimulator is implanted to provide electrical pulses to the stomach. The function of the gastric stimulator after complete ablation of the pacemaker region, is to provide a basic electrical rhythm (BER) to regulate and control electrical activity of the stomach. Alternatively, if partial ablation is performed the function of the gastric pulse generator / stimulator is to enhance the residual basic electrical rhythm (BER), or to interfere with the residual basic electrical rhythm (BER).
Owner:BOVEJA BIRINDER R +1
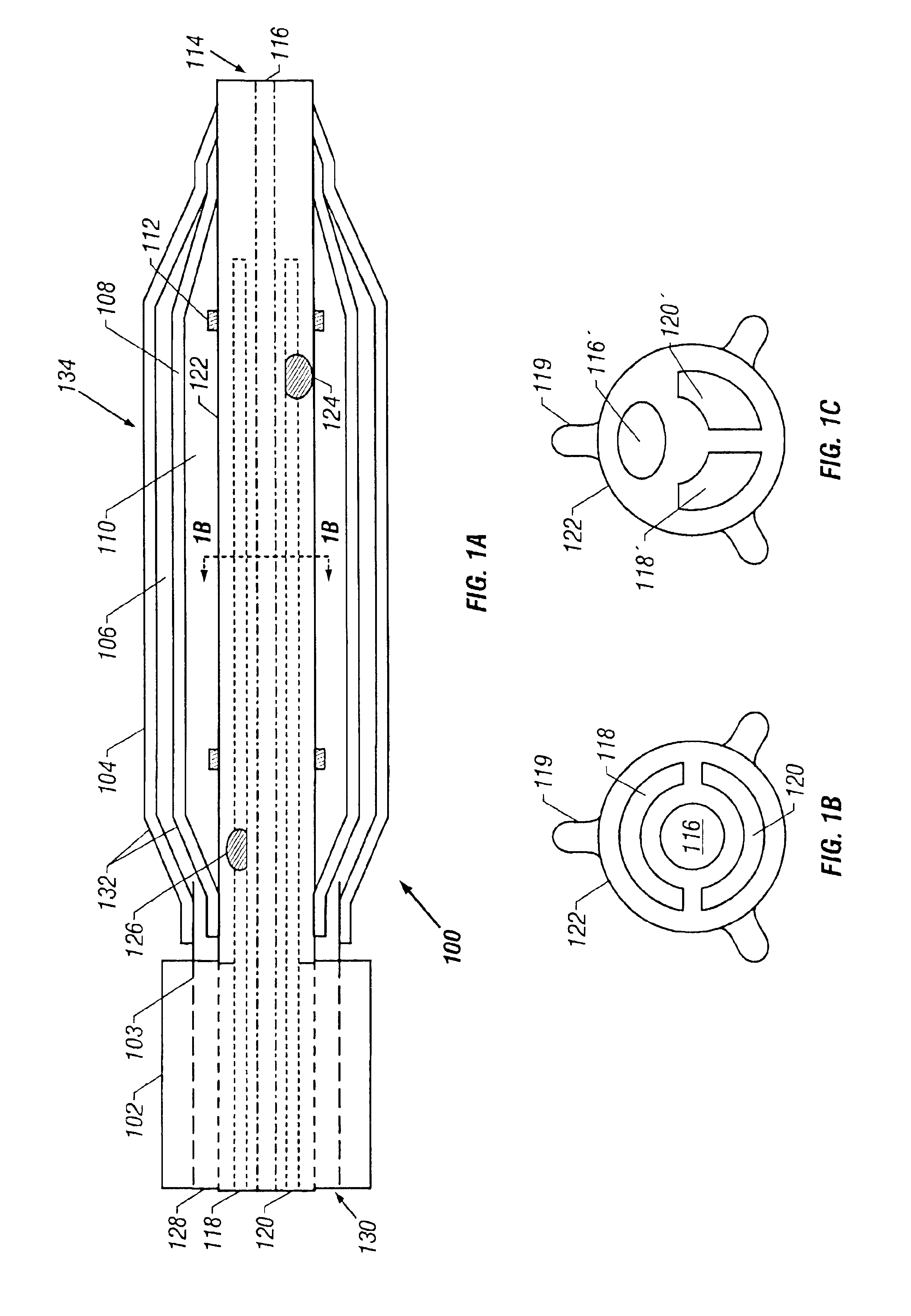
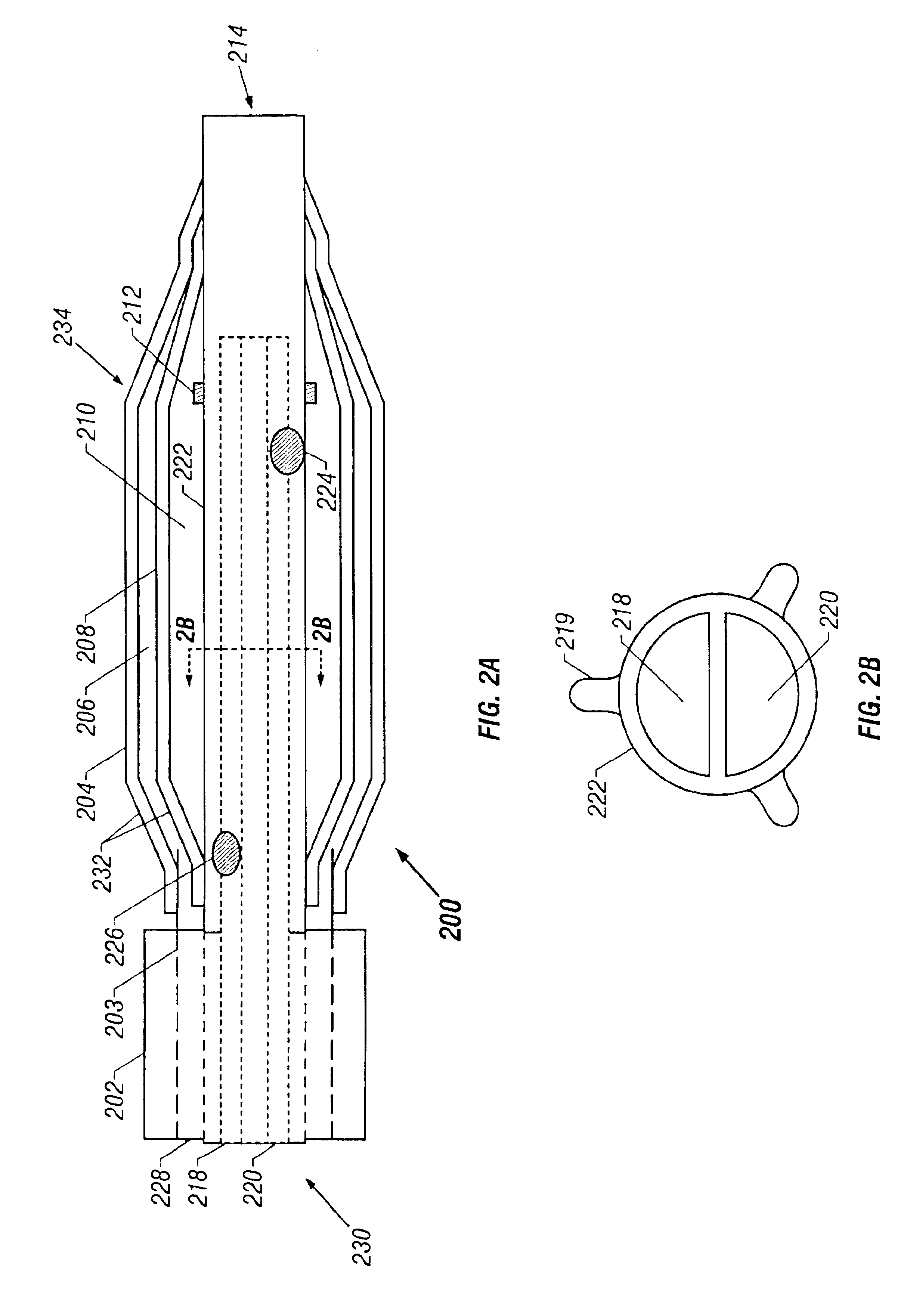
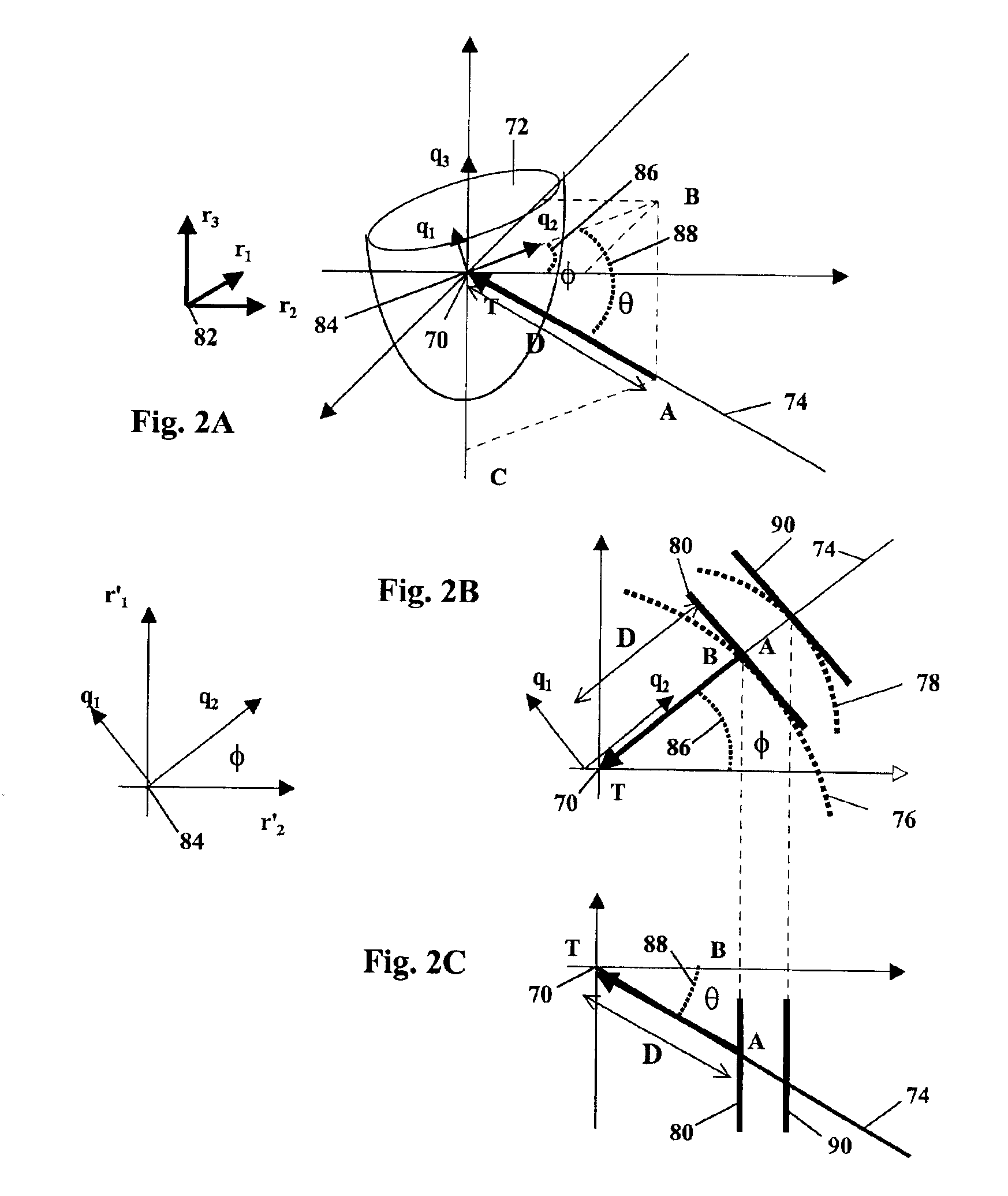
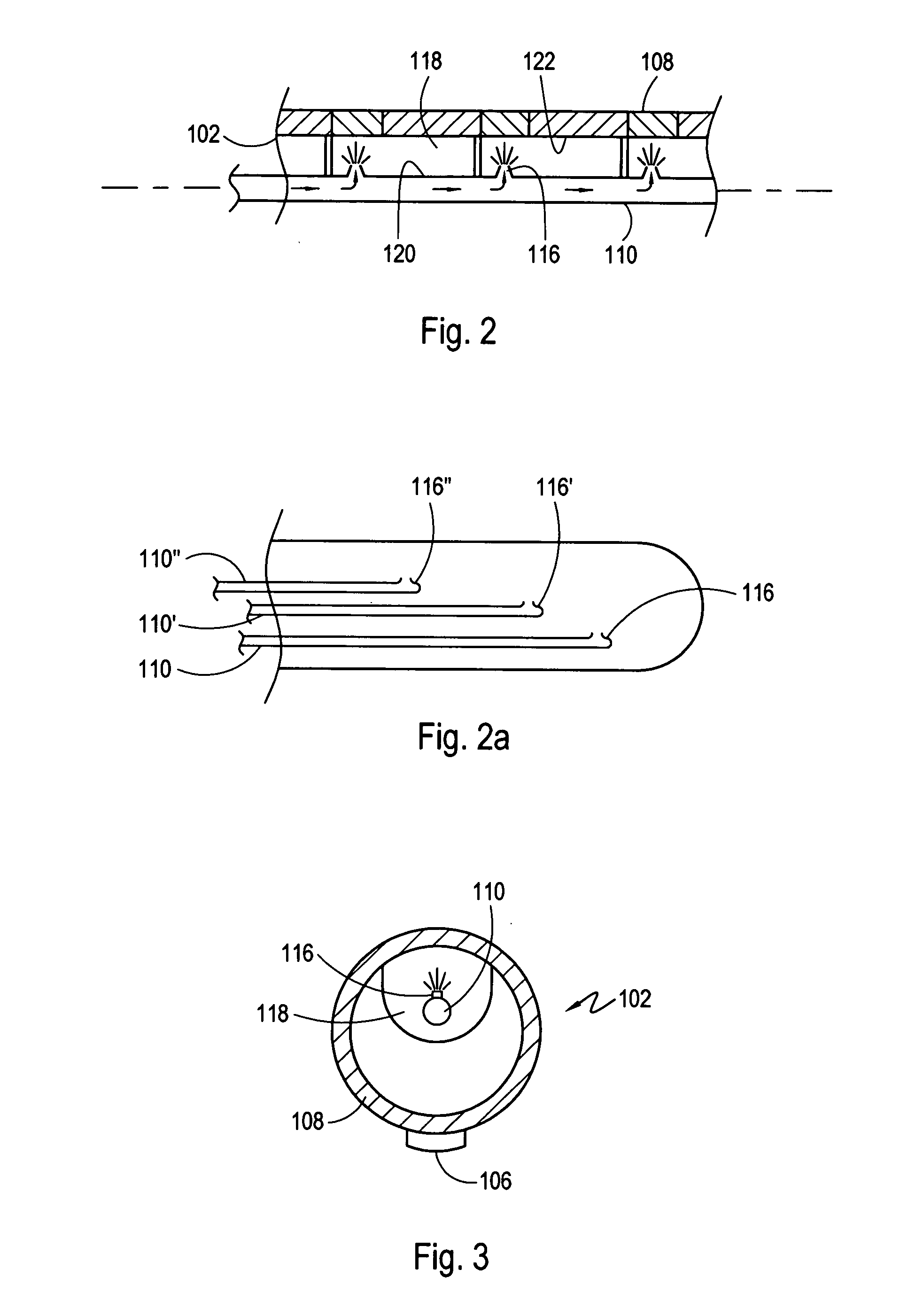
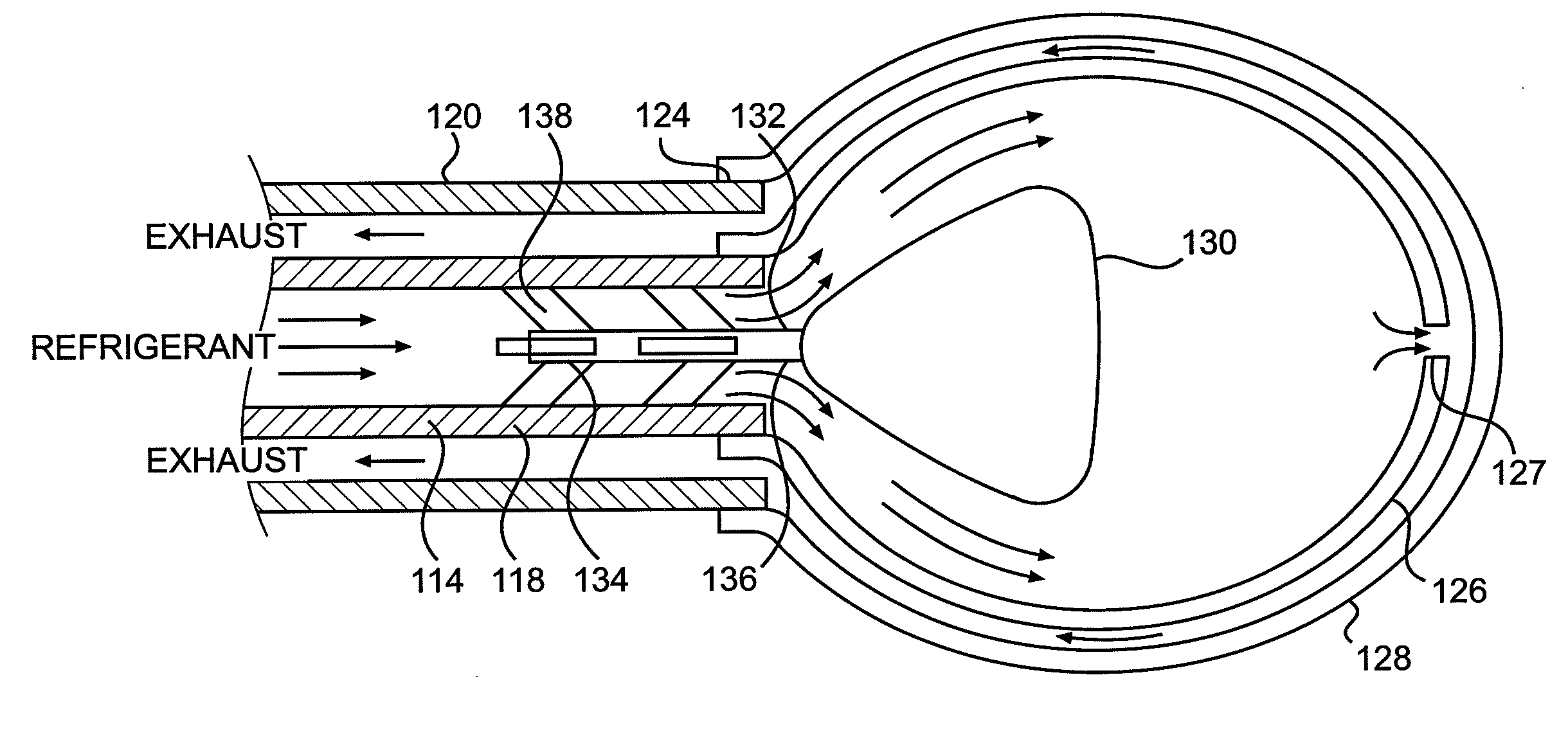
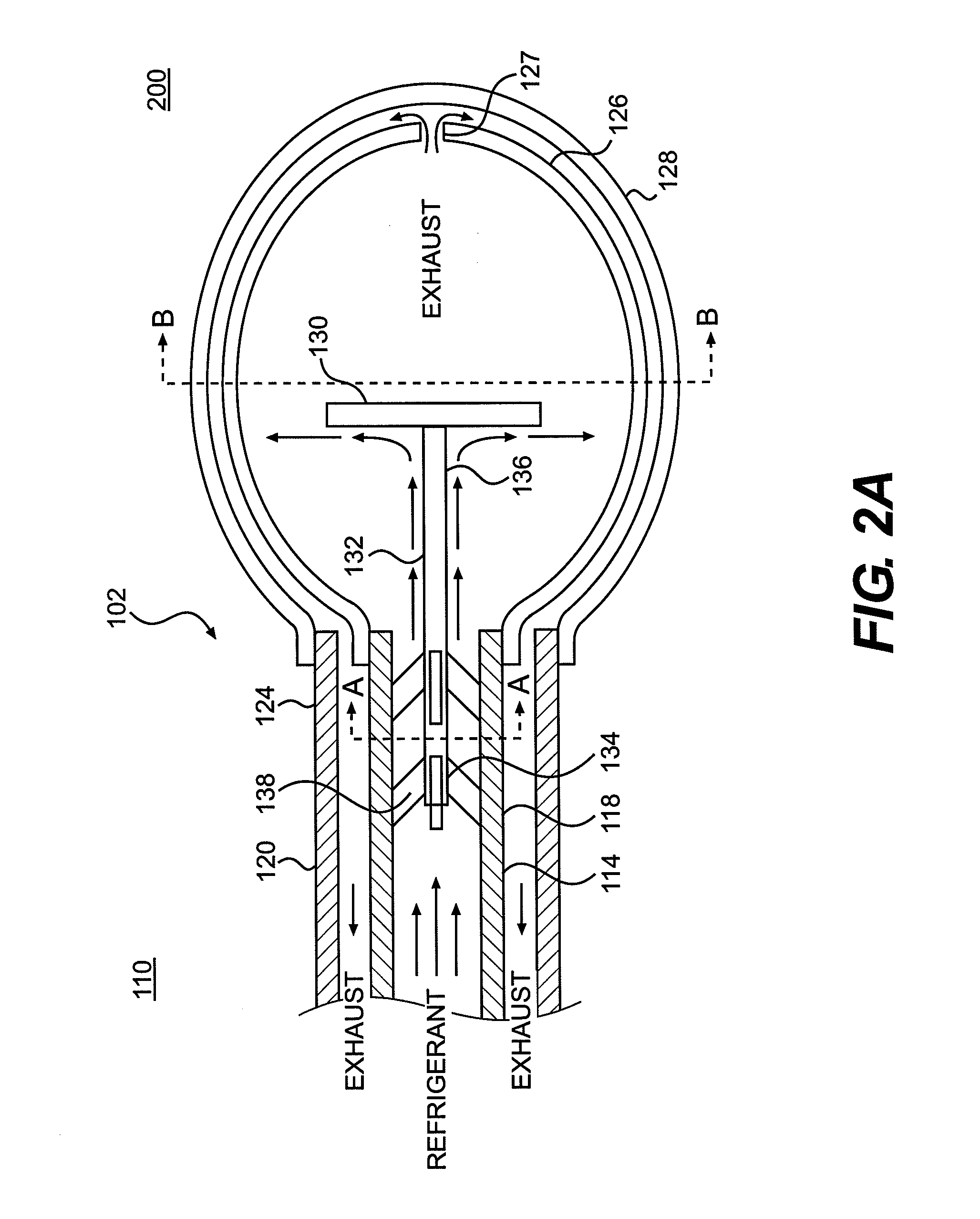
Apparatus and methods for cryogenically ablating tissue and adjusting cryogenic ablation regions
Apparatus and methods for performing cryogenic ablation of tissue and adjusting the size and / or location of a cryogenic cooling region. A cooling assembly may include tubes for dispensing and exhausting a coolant or refrigerant. One or both of the tubes may be moved, e.g., slidably adjusted, in order to adjust the location or size of a cryogenic ablation region. The cooling assembly may be integrated into cryogenic ablation devices including a cryogenic balloon device that includes an inner inflatable balloon and another balloon that is at least partially wrapped around the inner balloon and carries refrigerant for performing cryo-ablation. Electrodes permit electrical mapping of tissue before or after cryo-ablation to verify success of the procedure.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
High intensity ablation device
ActiveUS20050203499A1Improve performanceStructure can be compromisedUltrasound therapySurgical instruments for heatingHigh intensityRadio frequency
An apparatus for ablating tissue, the apparatus having first and second opposing jaws operative to compress tissue to be ablated therebetween, the first jaw having a first ablation surface directing ablative energy into the tissue and the second jaw having a second ablation surface reflecting incident ablative energy into the tissue. The ablative energy may be ultrasonic, microwave, cryoablation, radio-frequency, photodynamic, laser, and cautery energy. The instrument may also have a pointed tip for piercing tissue, allowing the instrument to clamp the tissue wall of a hollow organ before ablation. Alternately, the instrument may clamp two or more tissue layers of a hollow organ without piercing prior to clamping an ablation.
Owner:ETHICON INC
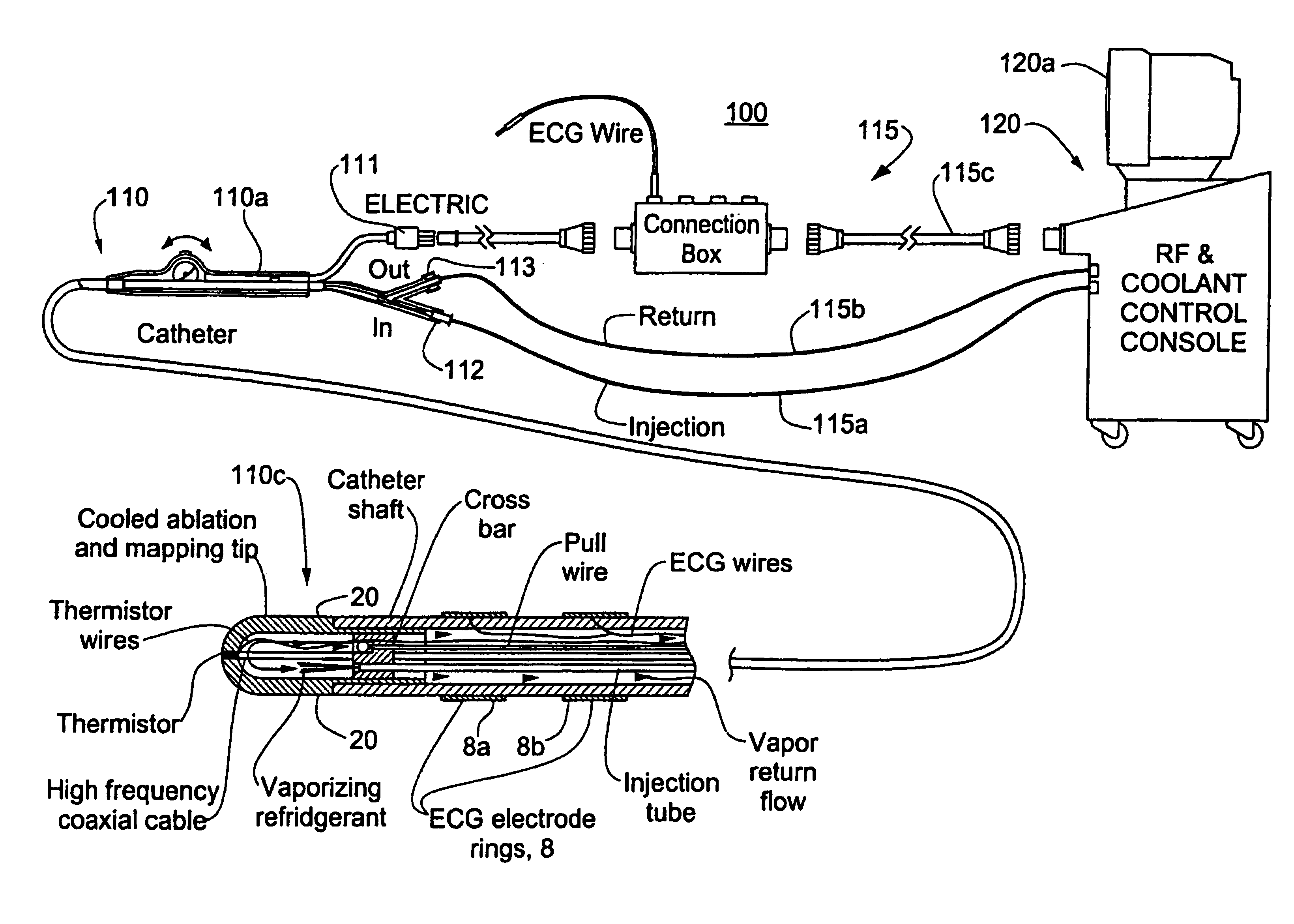
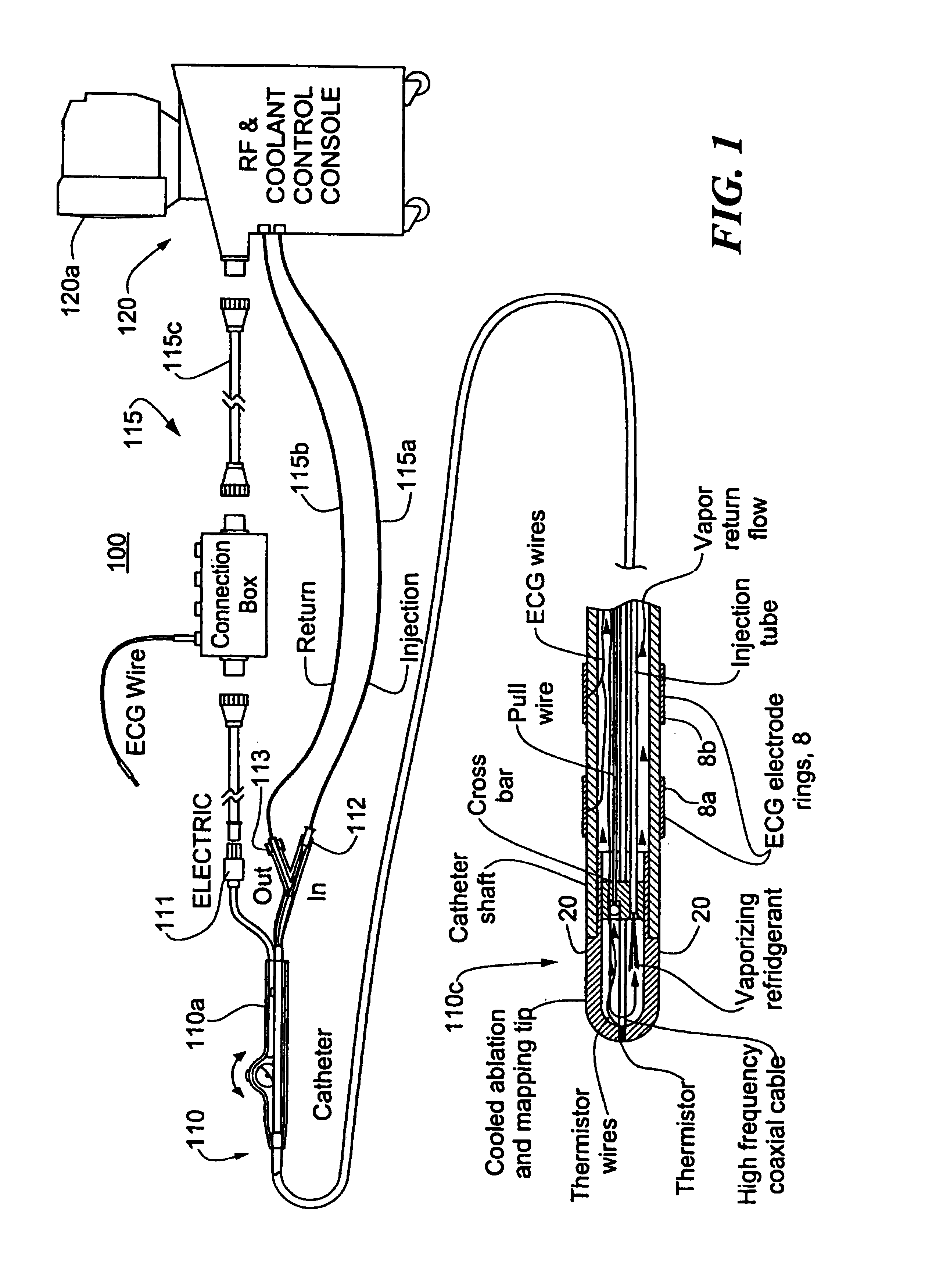
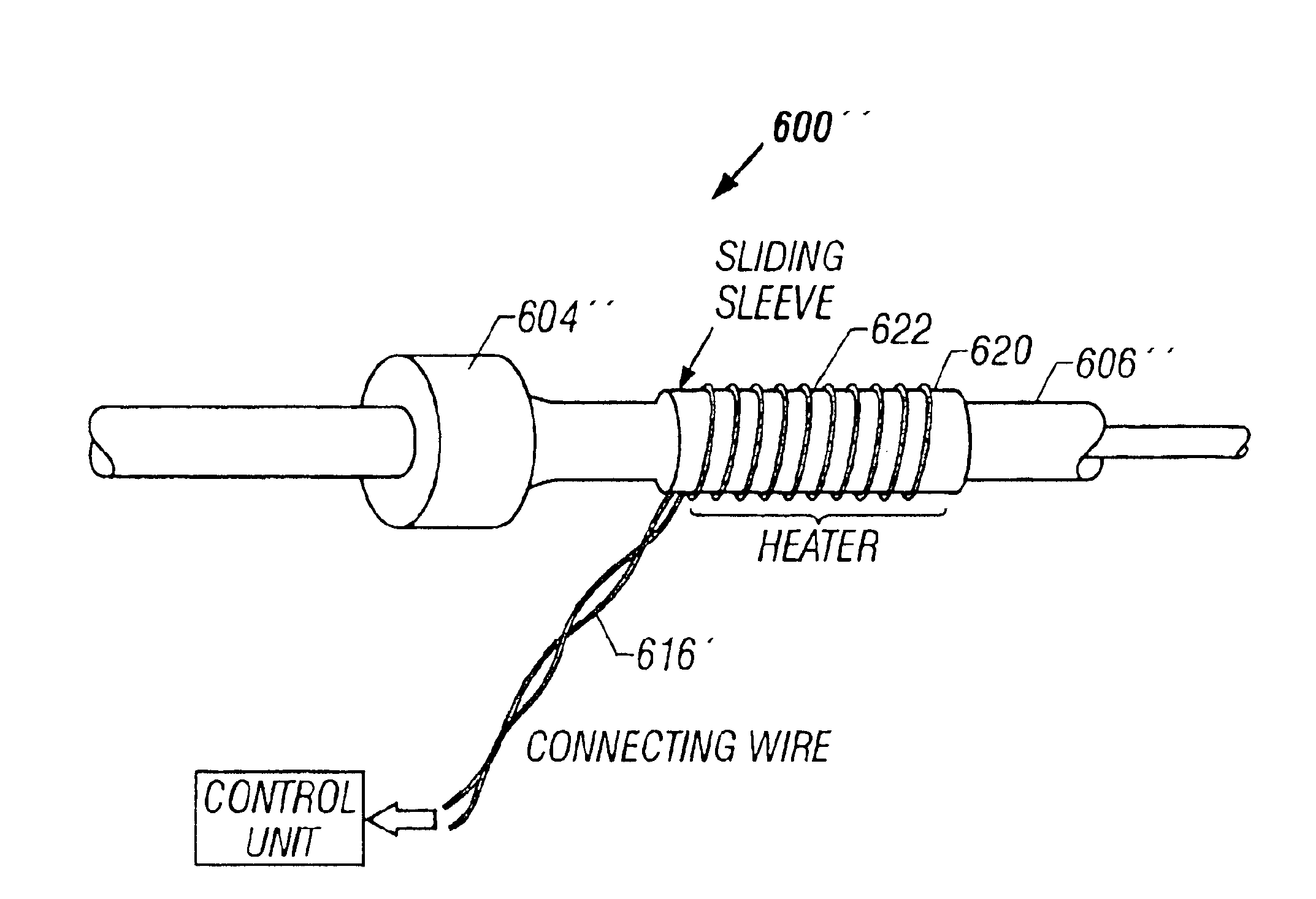
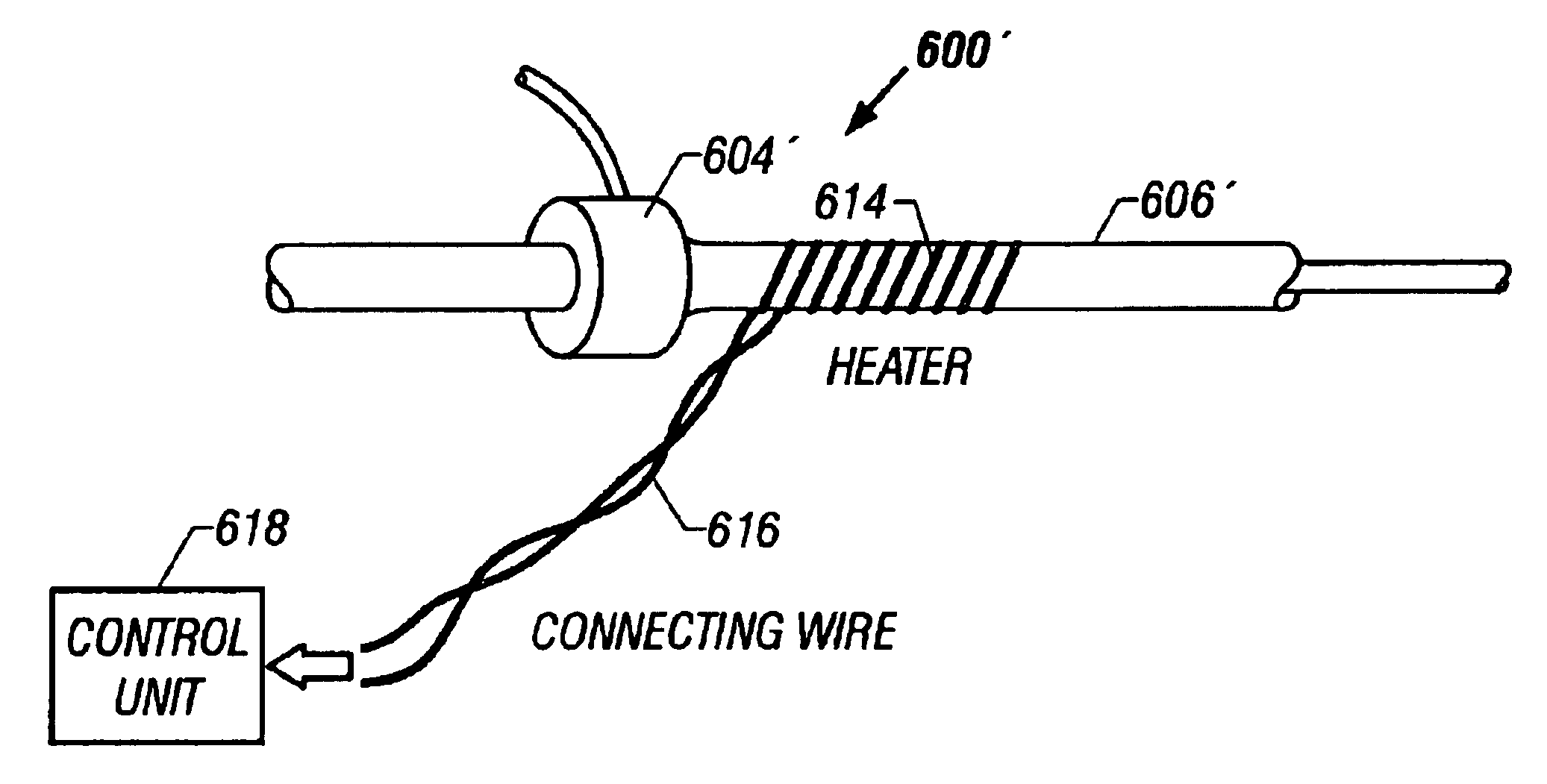
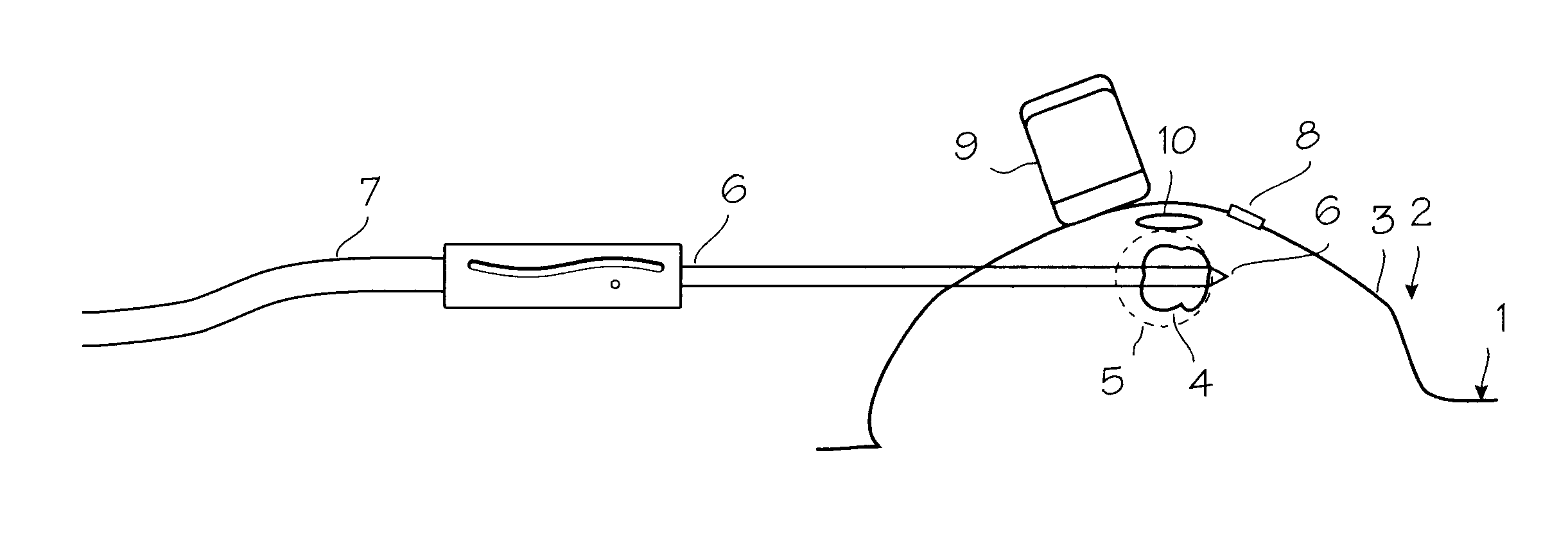
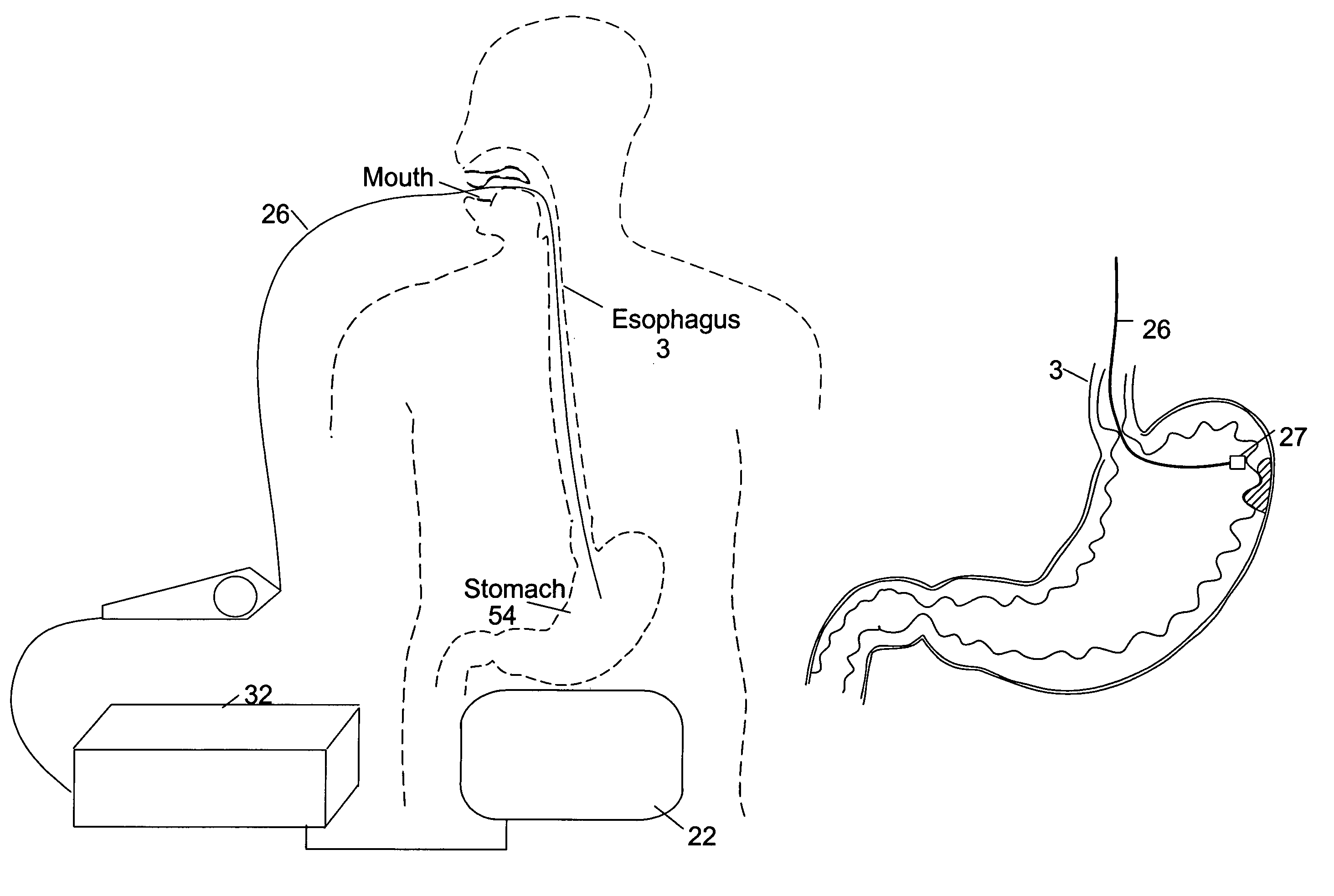
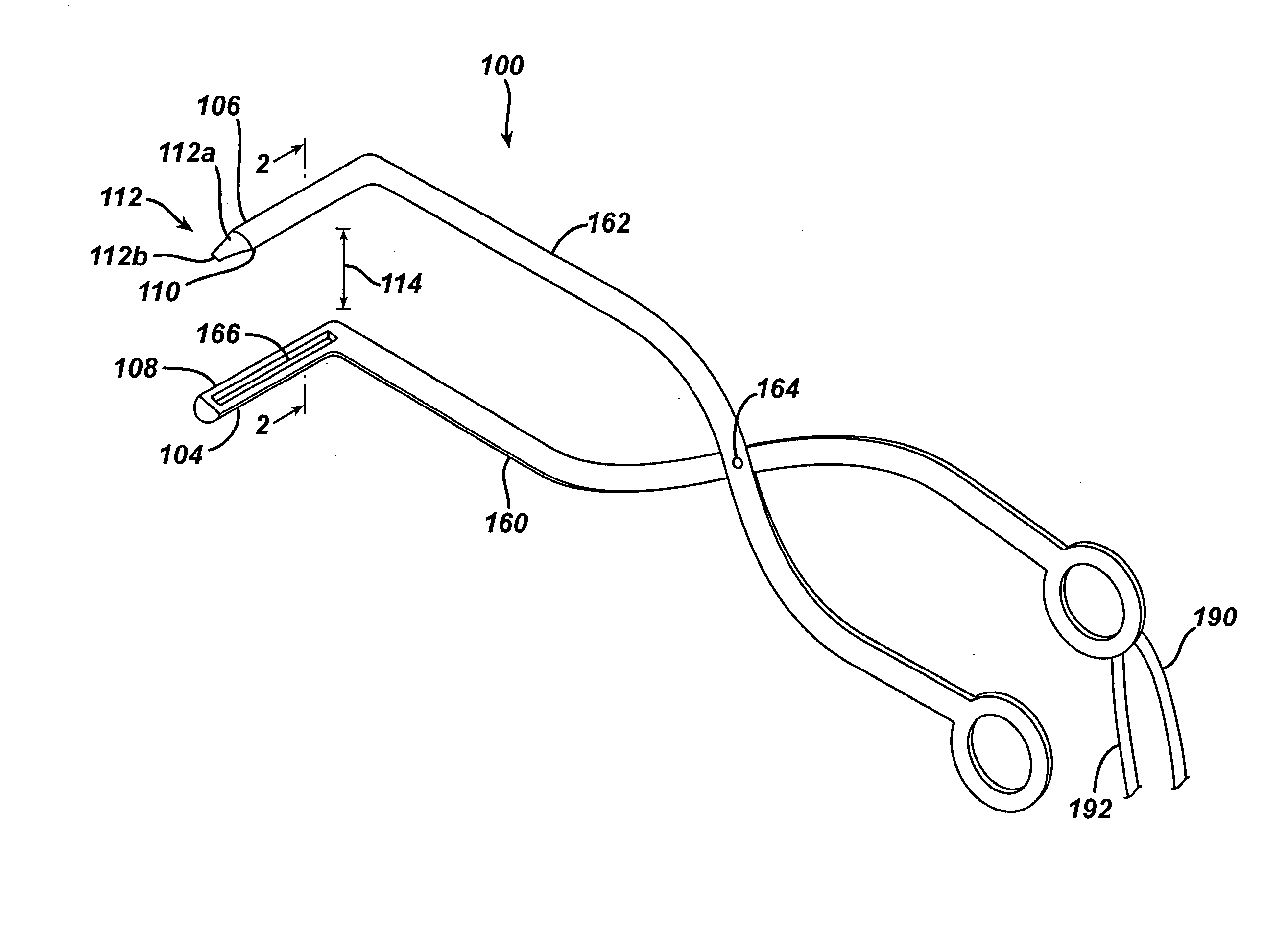
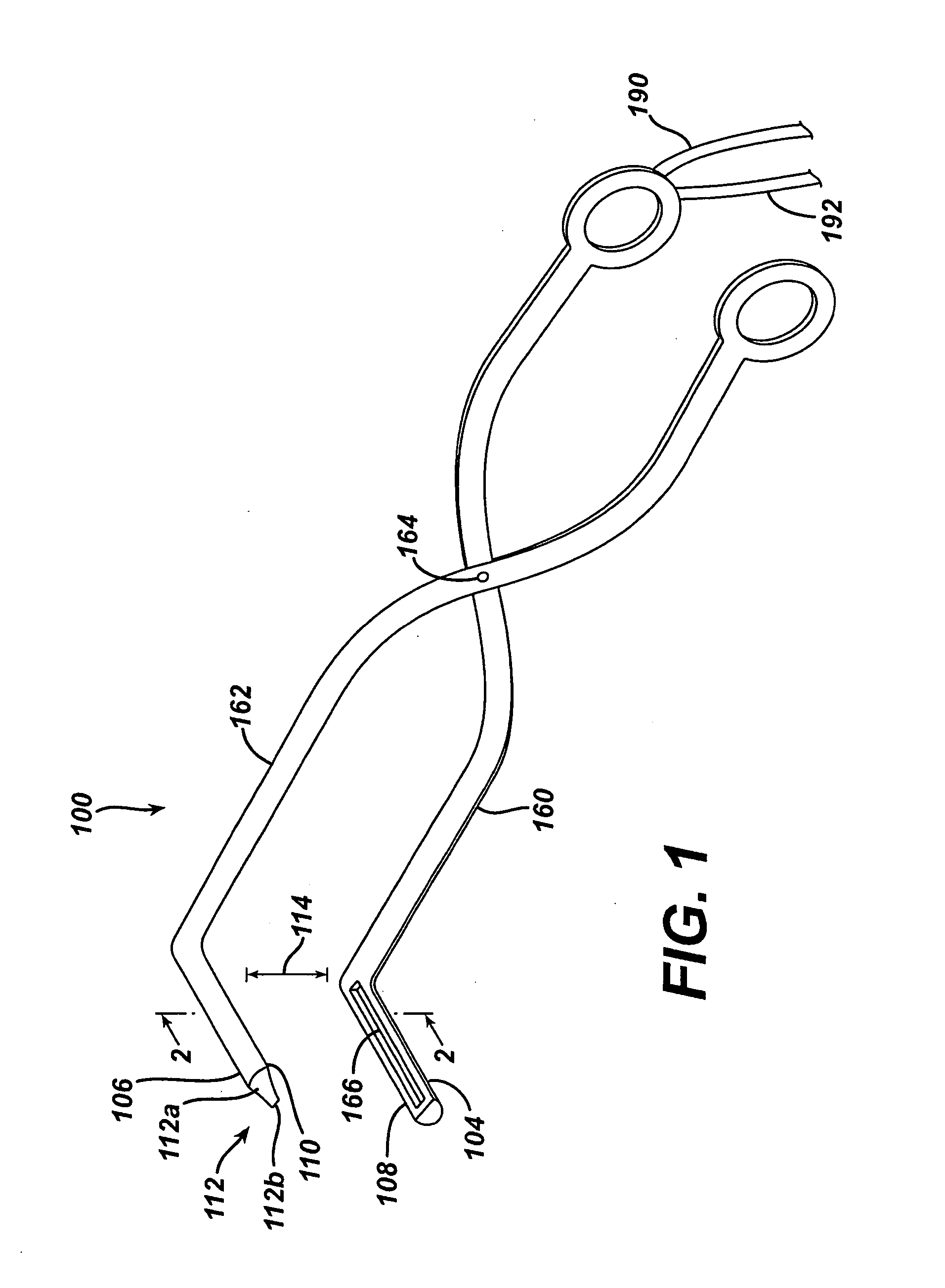
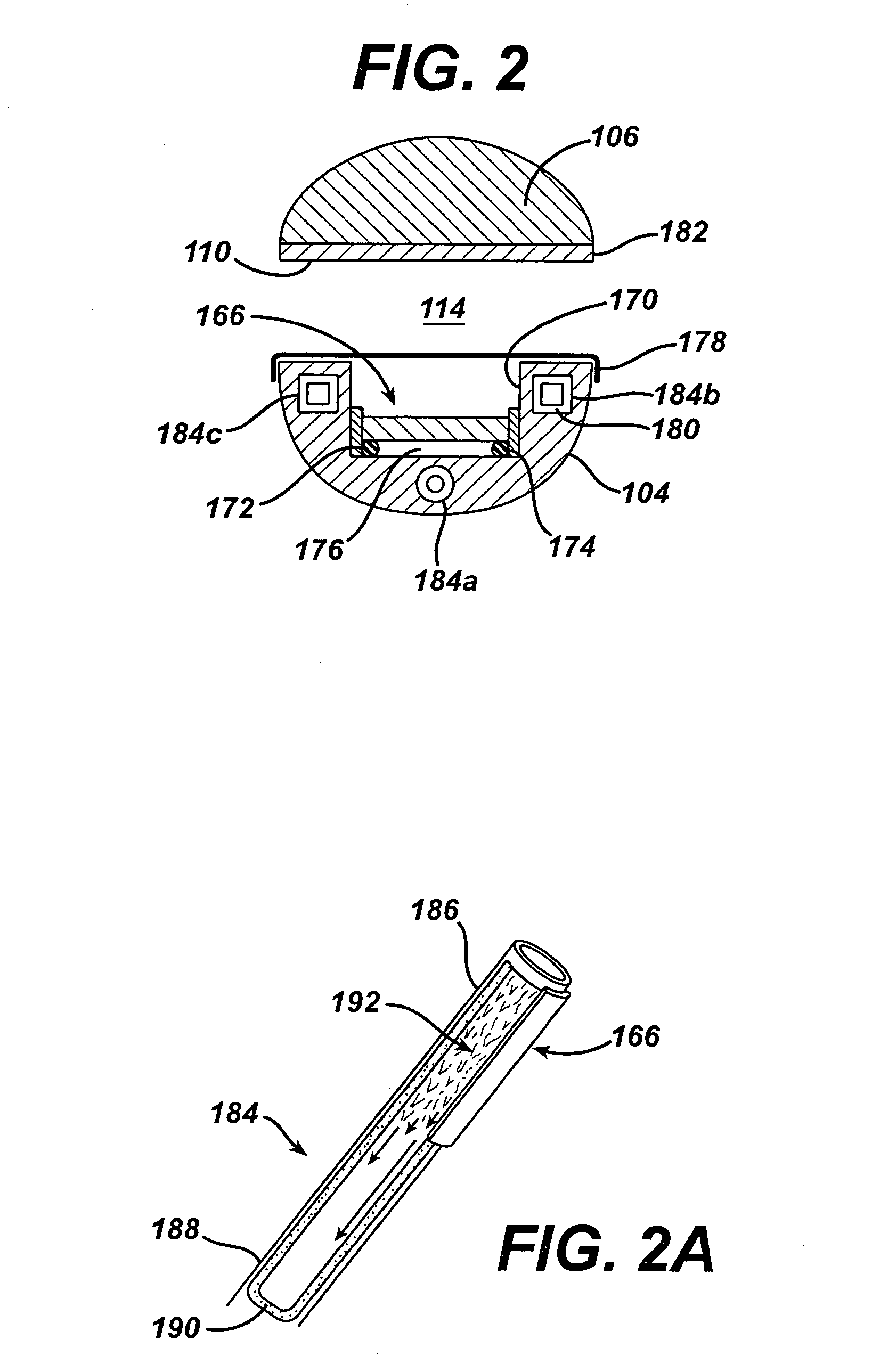
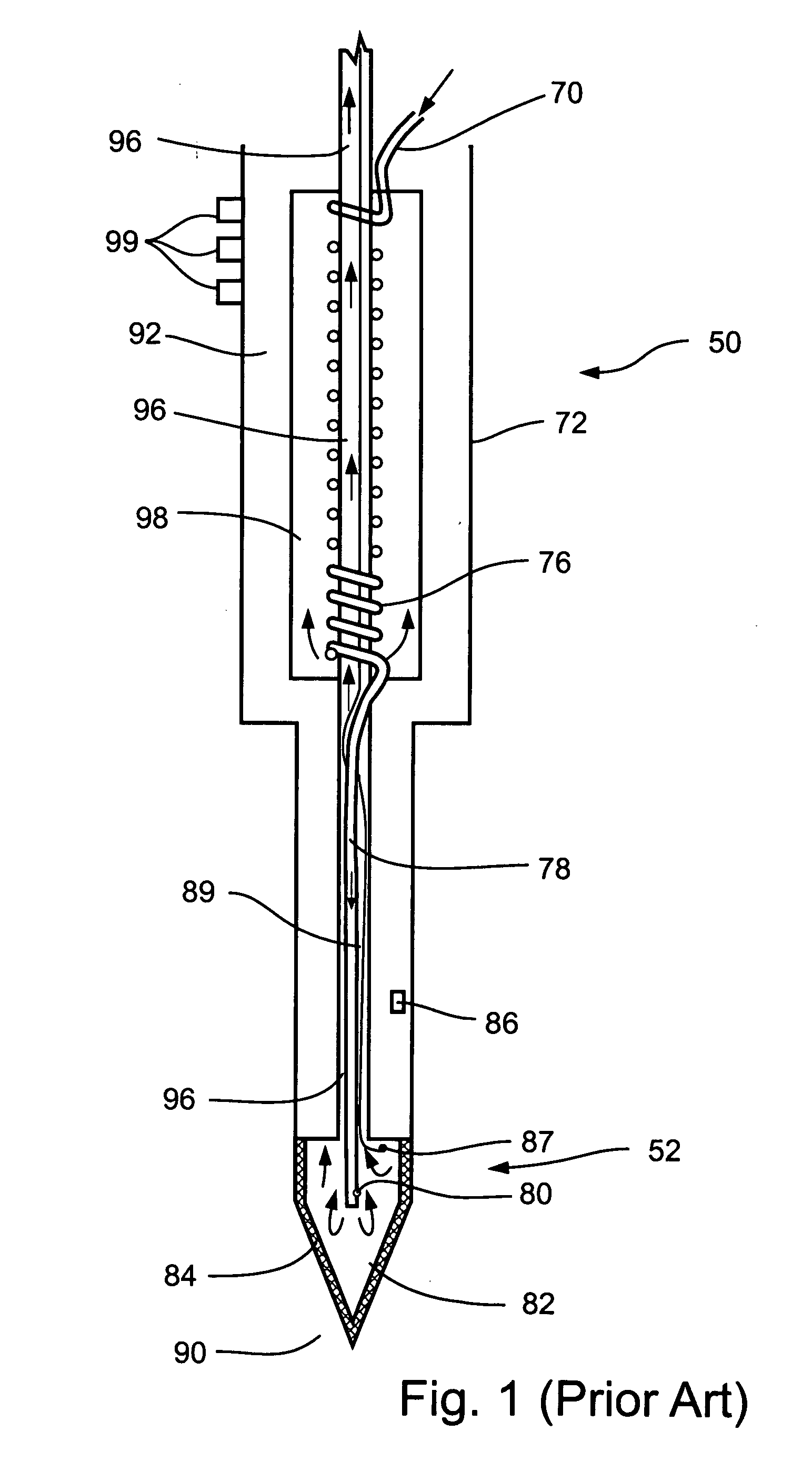
Heated catheter used in cryotherapy
InactiveUS7255693B1Constant visualizationEasy to viewCatheterSurgical instruments for heatingConductive coatingElectrical connection
Disclosed is a cryosurgical catheter which is heated in order to prevent its freezing within the lumen of an endoscope. The catheter is to be used with an endoscope to perform cryoablation on an internal tissue; e.g., the esophagus. Electric conductivity to produce heat employs an electrical conductive coating on the catheter. Also, disclosed is a fitting for use with a catheter comprising both a connection for receiving gas and an electrical connection.
Owner:CSA MEDICAL
Catheter with cryogenic and electrical heating ablation
InactiveUS20060004351A1Reduce tip temperatureReduce movement sequenceCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringTissue remodelingCelsius Degree
A catheter includes a cryoablation tip with an electrically-driven ablation assembly for heating tissue. The cryoablation tip may be implemented with a cooling chamber through which a controllably injected coolant circulates to lower the tip temperature, and having an RF electrode at its distal end. The RF electrode may be operated to warm cryogenically-cooled tissue, or the coolant may be controlled to conductively cool the tissue in coordination with an RF treatment regimen, allowing greater versatility of operation and enhancing the lesion size, speed or placement of multi-lesion treatment or single lesion re-treatment cycles. In one embodiment a microwave energy source operates at a frequency to extend beyond the thermal conduction depth, or to penetrate the cryogenic ice ball and be absorbed in tissue beyond an ice boundary, thus extending the depth and / or width of a single treatment locus. In another embodiment, the cooling and the application of RF energy are both controlled to position the ablation region away from the surface contacted by the electrode, for example to leave surface tissue unharmed while ablating at depth or to provide an ablation band of greater uniformity with increasing depth. The driver or RF energy source may supply microwave energy at a frequency effective to penetrate the ice ball which develops on a cryocatheter, and different frequencies may be selected for preferential absorption in a layer of defined thickness at depth in the nearby tissue. The catheter may operate between 70 and minus 70 degrees Celsius for different tissue applications, such as angioplasty, cardiac ablation and tissue remodeling, and may preset the temperature of the tip or adjacent tissue, and otherwise overlay or delay the two different profiles to tailor the shape or position where ablation occurs or to speed up a treatment cycle.
Owner:MEDTRONIC CRYOCATH LP
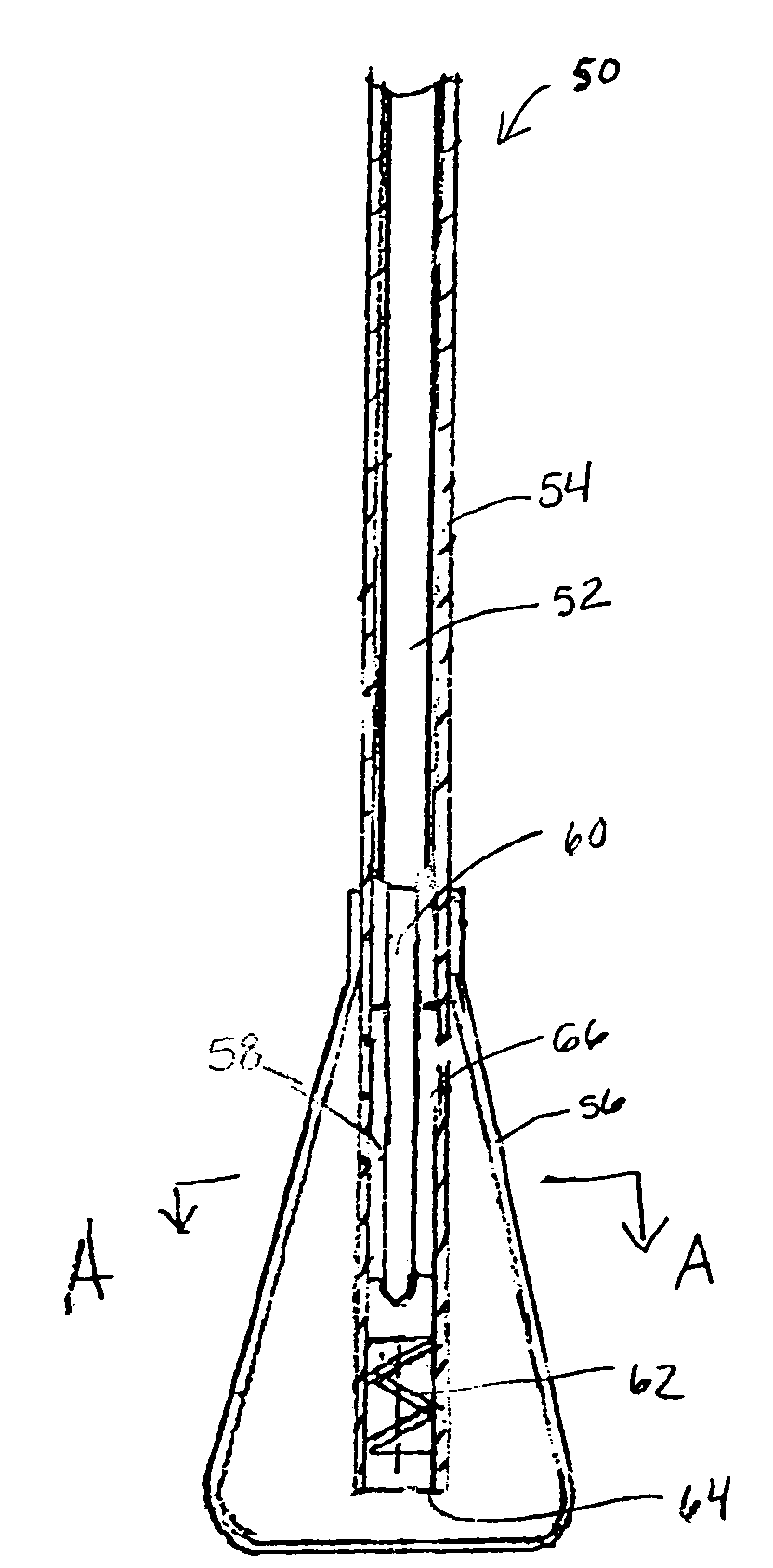
Cryoprobe with reduced adhesion to frozen tissue, and cryosurgical methods utilizing same
The present invention relates to devices and methods for cryosurgery. More particularly, the present invention relates to a cryoprobe which does not form strong adhesive or mechanical bonds with body tissues when such tissues are frozen by cooling action of the probe. Embodiments of the present invention include a cryoprobe having a distal cooling module with an outer surface layer of non-polar molecules, a probe having a distal cooling module with a microscopically smooth outer surface, and a cryoprobe comprising a mechanism for coating a distal cooling module thereof with non-polar lubricant during movement of the cryoprobe within body tissues of a patient. Also presented are methods utilizing disclosed cryoprobes to facilitate cryosurgery and to enhance accuracy of cryoablation of user-selected cryoablation targets.
Owner:GALIL MEDICAL
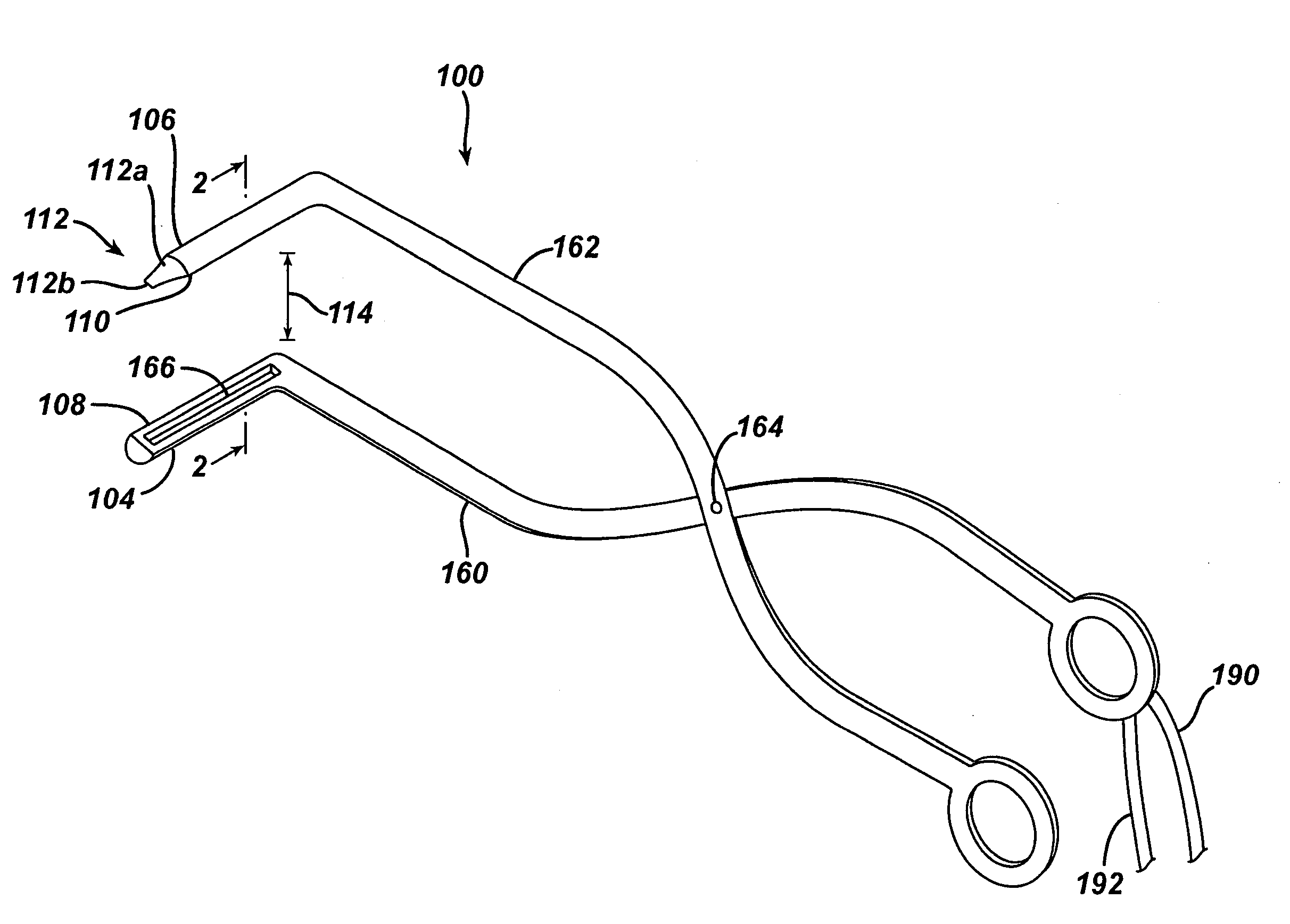
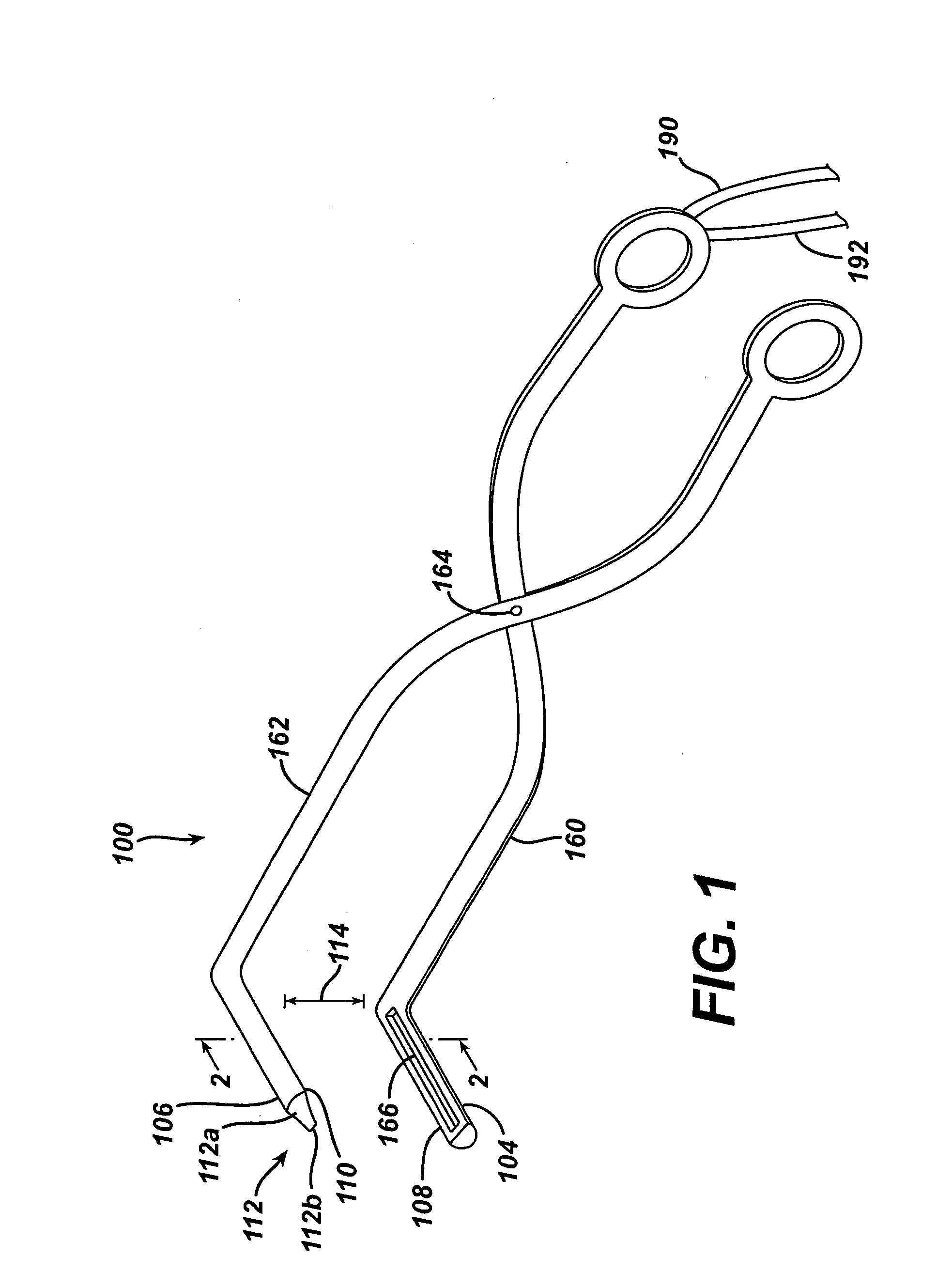
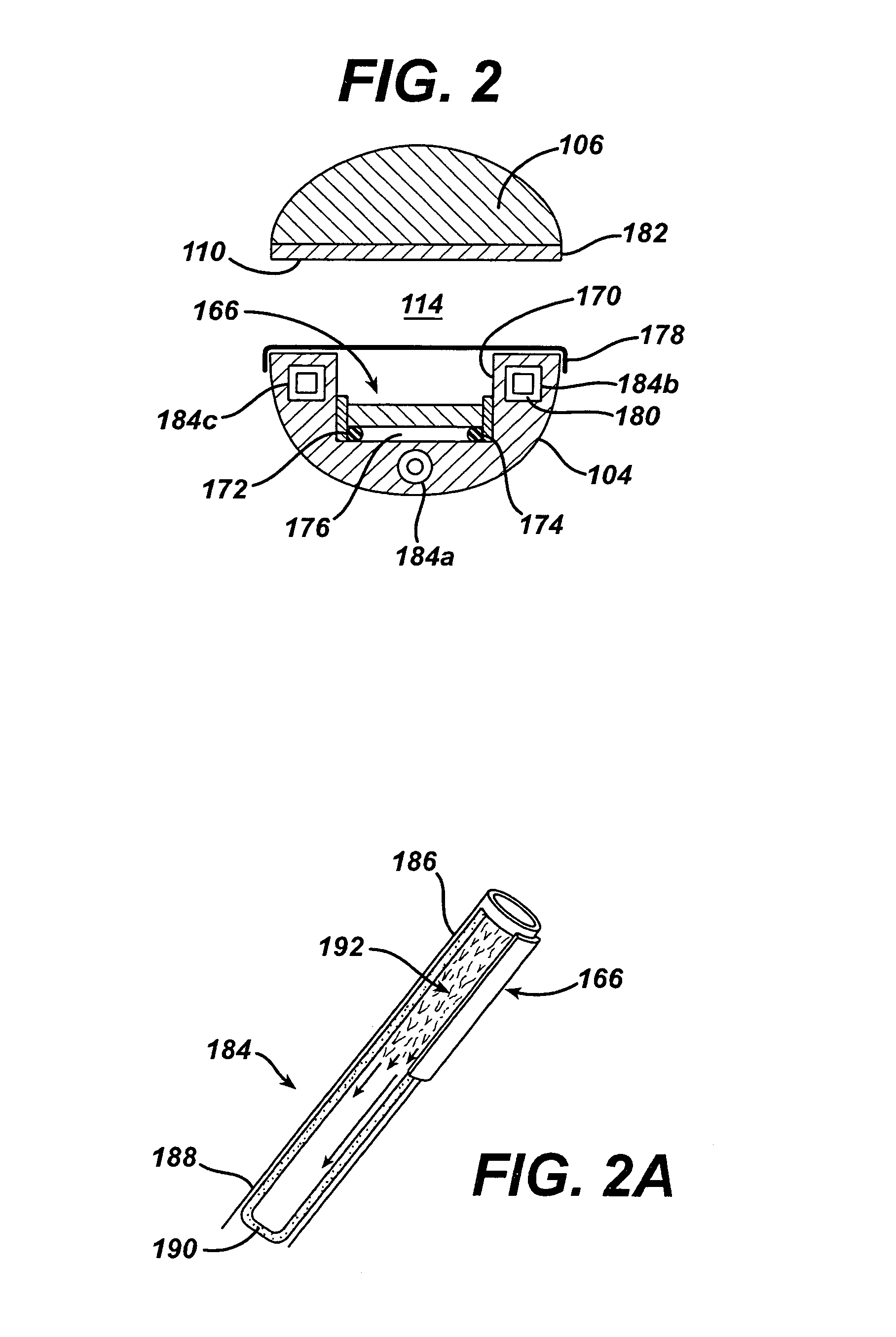
System for bi-directionally controlling the cryo-tip of a cryoablation catheter
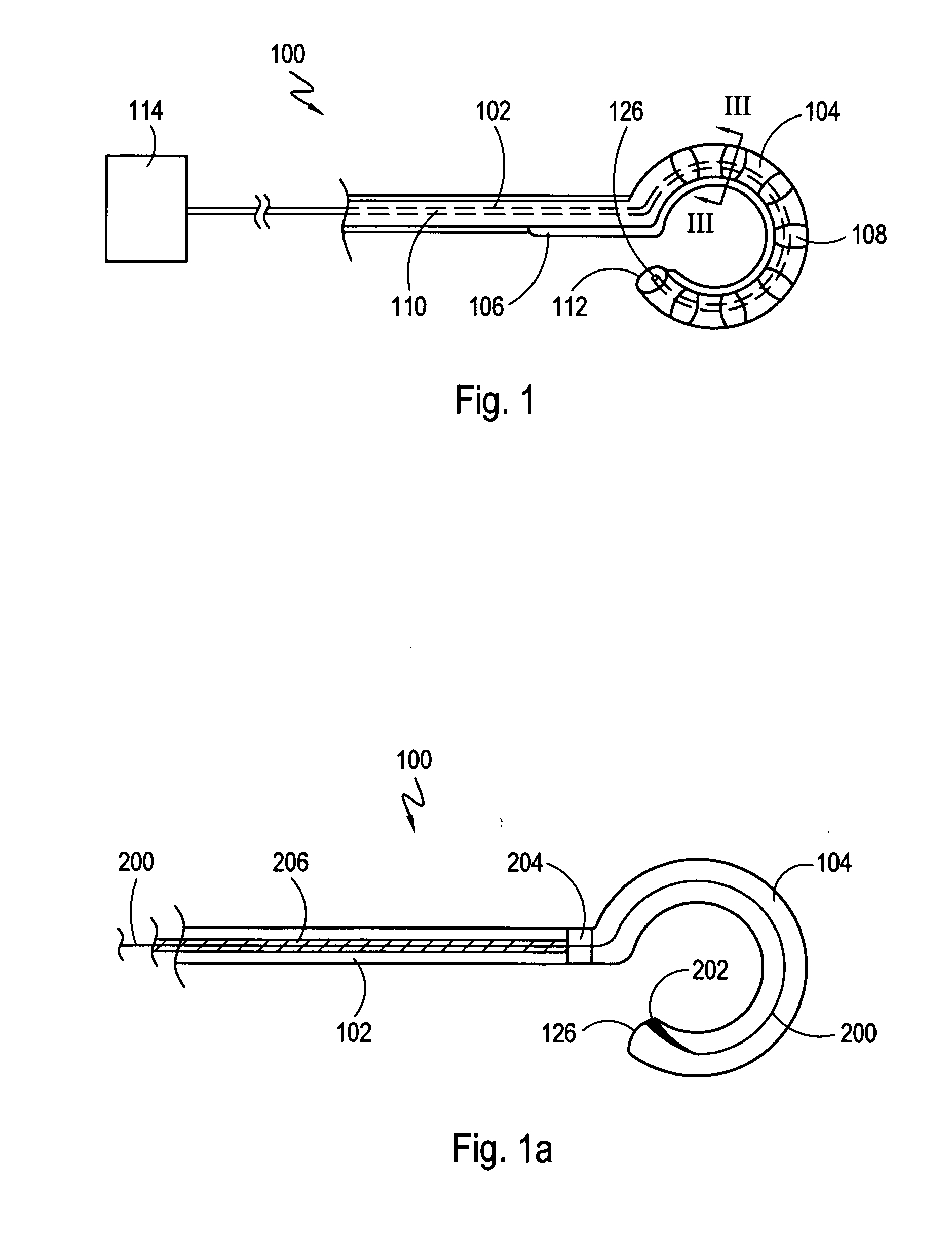
InactiveUS20050288656A1Restore fluencyMaximum recoveryMedical devicesCatheterCryoablationLarge deflection
A bi-directional system for actively deflecting the distal tip of a catheter includes a reconfigurable tube that is positioned proximal to the catheter's distal tip. The tube is formed with slits that are arranged to allow the tube to be transformed from a relaxed, cylindrical configuration to a plurality of deflected configurations. First and second pull wires are provided, with each wire having a respective distal end that is attached to the distal end of the tube. Each wire extends to a catheter handle where it is attached to a respective reel. The reels can be rotated, back and forth, to selectively deflect or relax the tube. To ensure a smooth recovery after a relatively large deflection, a mechanism is disclosed for delaying an application of tension on one of the pull wires until at least a portion of any tension on the other pull wire is released.
Owner:CRYOCOR
Cryosurgical devices for endometrial ablation
ActiveUS20050177148A1Improve cooling effectHigh trafficCatheterSurgical instruments for coolingEndometriumHeat transfer fluid
A cryoablation system for performing endometrial ablation comprising an elongated tubular cannula having a proximal end, a distal end, and a longitudinal axis, an expandable balloon extending from the distal end of the cannula and fluidly connected to a source of heat transfer fluid by at least one fluid path, a pump for circulating the heat transfer fluid into and out of the balloon, a probe handle coupled to the proximal end of the cannula and in fluidic communication with the balloon through the cannula, and a heat exchanger for varying the temperature of the heat transfer fluid, wherein the heat exchanger is fluidly connected to a secondary refrigerant source, and wherein the heat exchanger comprises an outer tubular wall and a plurality of fins extending from the tubular wall toward the interior portion of the heat exchanger.
Owner:COOPERSURGICAL INC
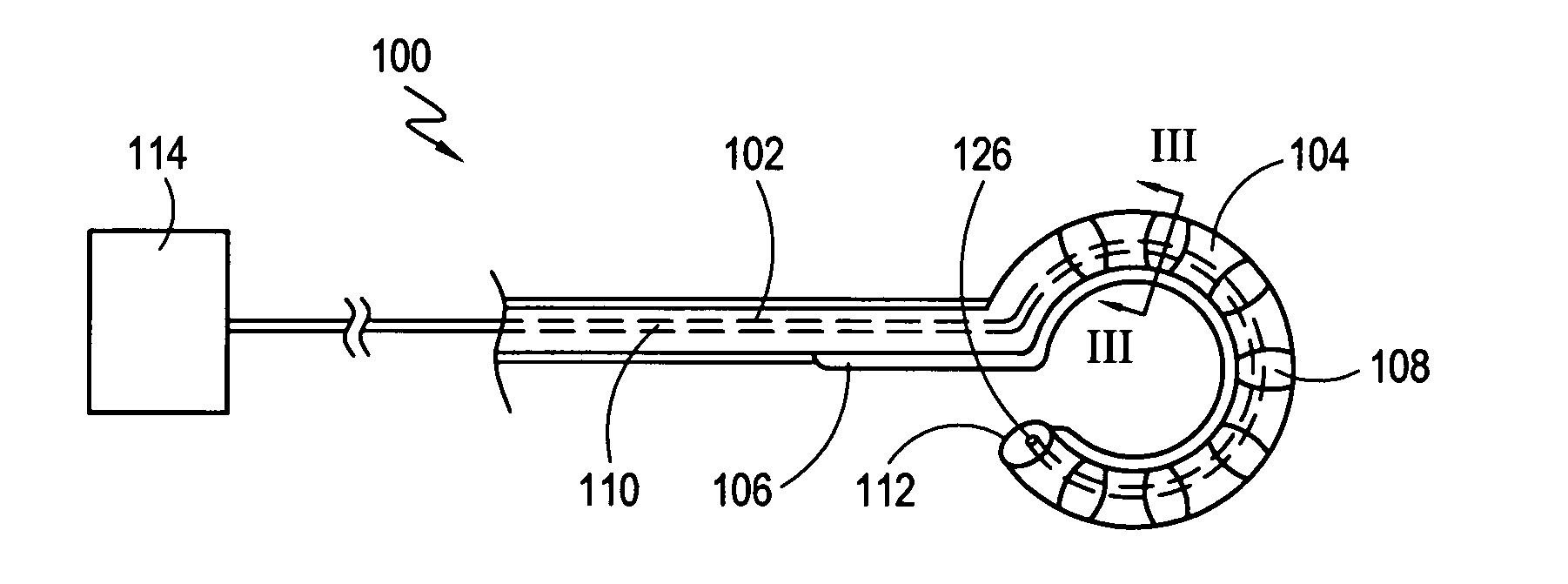
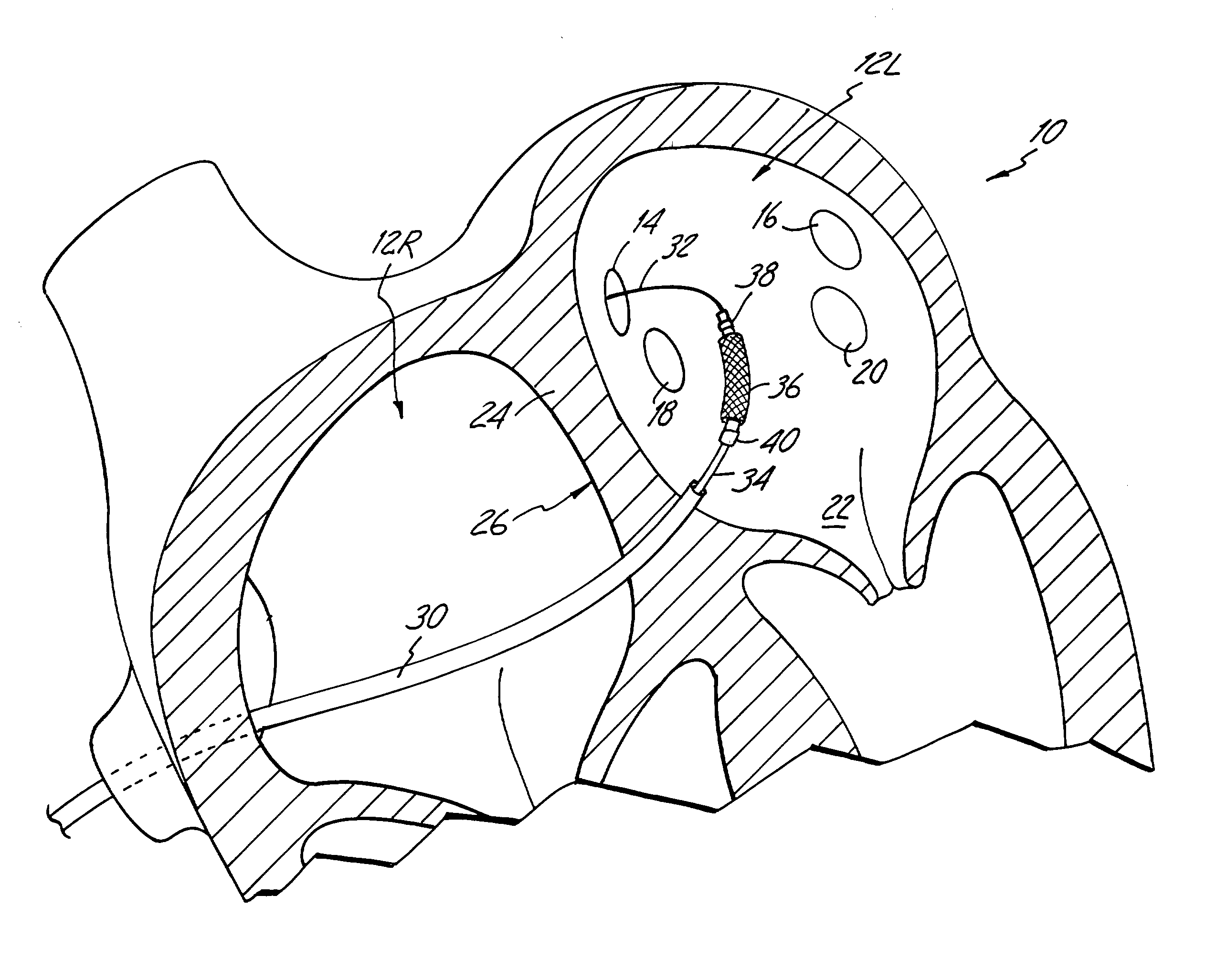
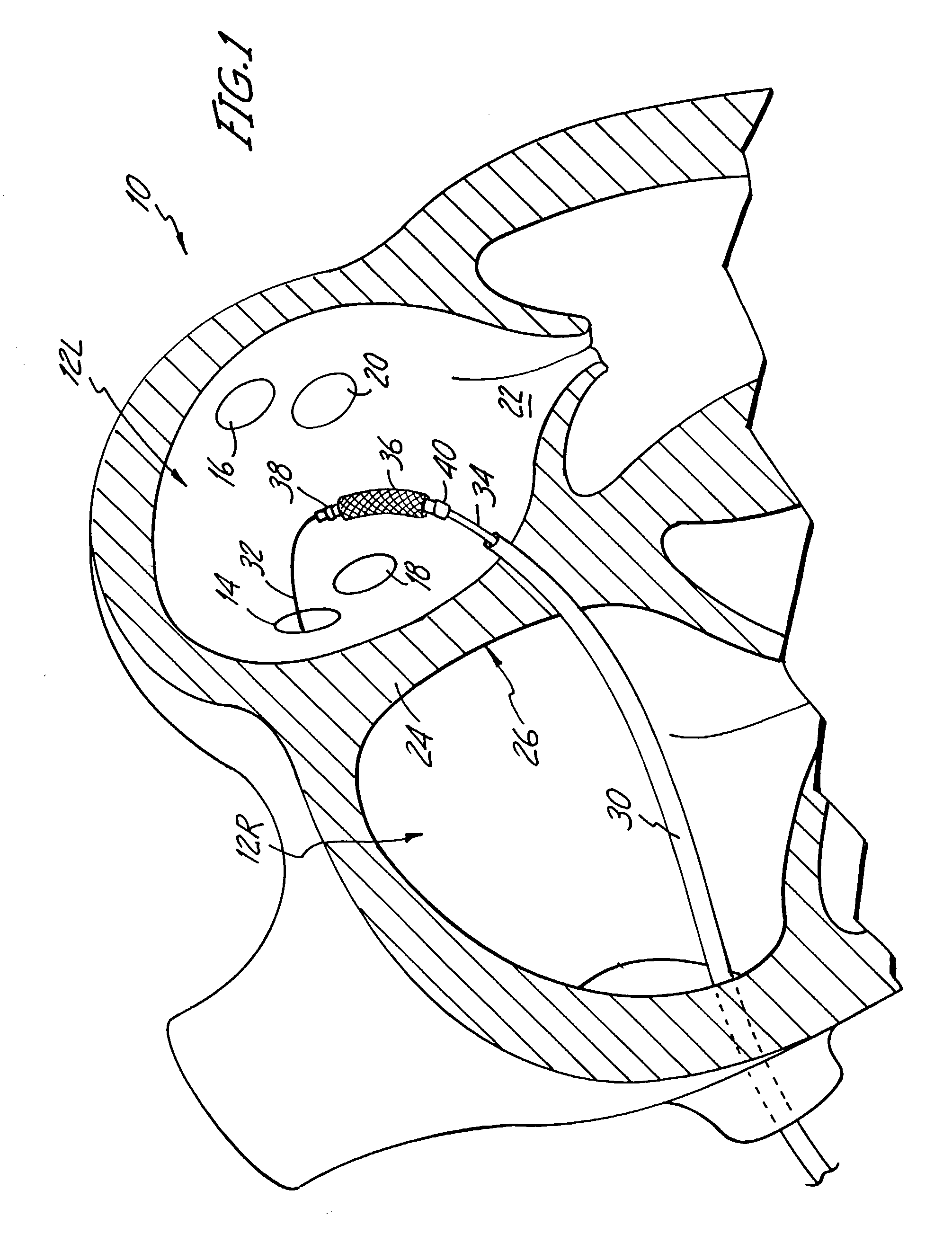
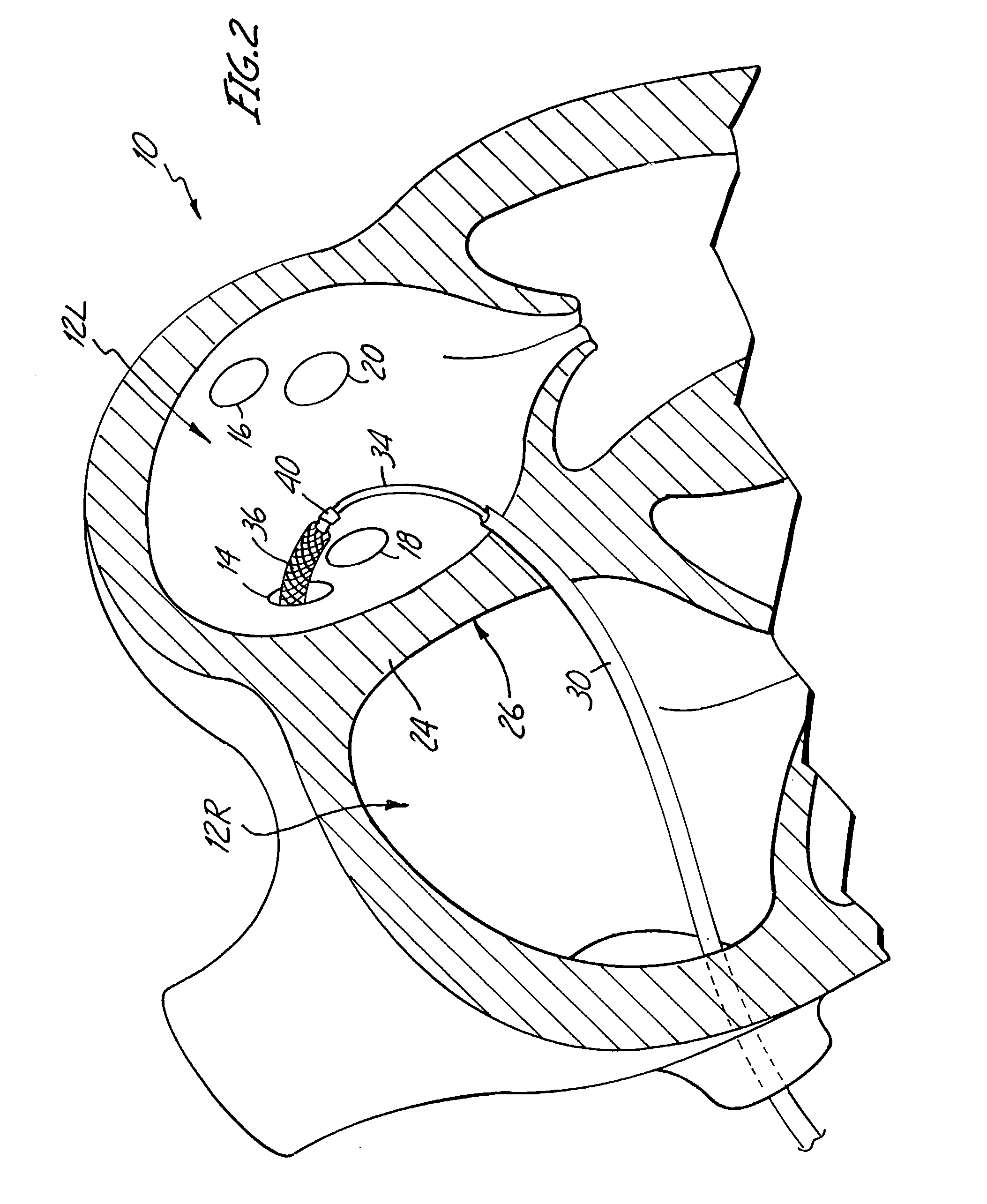
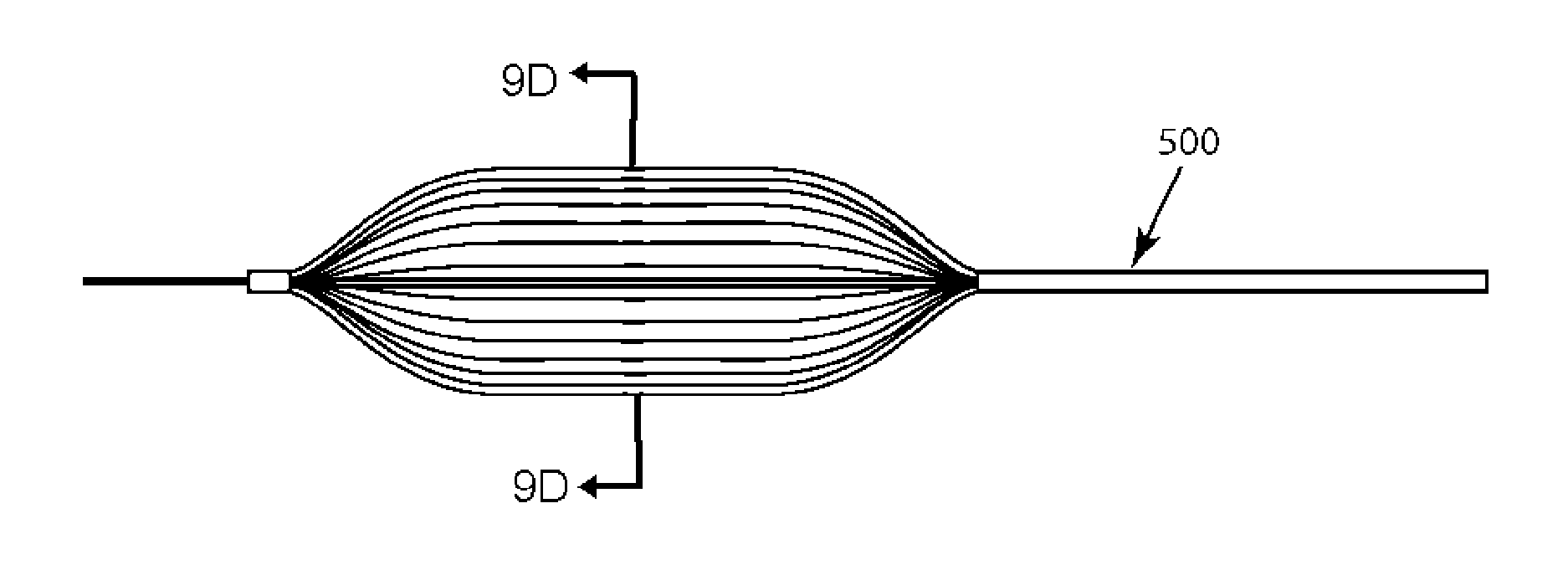
Cryoablation systems and methods
Systems and methods for treating an arrhythmia originating in a pulmonary vein of a patient are described. The system includes a rigid sheath and an elongated catheter that defines an axis and has an ablating distal section. The distal section includes a plurality of conductive bands, with each band establishing an enclosed chamber. The ablating distal section is reconfigurable between a first compact configuration in which each band is positioned relatively near the axis for transit through the sheath and second expanded configuration in which each band is positioned relatively far from the axis. Once in the second configuration, a fluid refrigerant is expanded into each enclosed chamber to cool the bands and cryoablate tissue. The second configuration is particularly useful for ablating a circumferential band of tissue, for example, a band of tissue surrounding the opening (i.e. ostium) where a pulmonary vein connects with the left atrium.
Owner:CRYOCOR
Atrial fibrillation therapy with pulmonary vein support
ActiveUS7195628B2Prevent stenosisAvoid conductive propertiesElectrotherapyHeart valvesAtrial cavityAblation Techniques
A system and method for treatment of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation by destruction of conductive pathways between the pulmonary veins and the left atrium. A stent is delivered by catheter to the left atrium and to the ostium of a pulmonary vein to be treated. The stent is positioned in the pulmonary vein and is deployed to engage and support the pulmonary vein. The stent prevents stenosis of the pulmonary vein as a result of ablation of tissue. The ablation is produced by a coating of a biologically active material on the stent which destroys tissue or slows electrophyisiologic conduction through the tissue. Alternatively, ablation is performed using RF energy, cryoablation, laser energy, or other ablation techniques.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Apparatus and method for accurately delimited cryoablation
ActiveUS20060079867A1Choose accuratelyMinimize damageDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for coolingRadiologySurgical department
The present invention is of a system and method for accurate cryoablation, useable to enhance a surgeon's ability to accurately cryoablate a selected cryoablation target and to limit cryoablation to that selected target. Presented are apparatus and method for accurately delimiting a cryoablation volume, for minimizing damage to tissues surrounding a cryoablation volume, and for real-time visualization of a border of a cryoablation volume during cryoablation. Also presented are a method for mildly heating tissues during cryoablation, cryoprobes operable to simultaneously cool first tissues while heating second tissues, and cryoprobes operable to cool tissues extending in a first lateral direction from those probes while not substantially cooling tissues extending in a second lateral direction from those probes.
Owner:GALIL MEDICAL
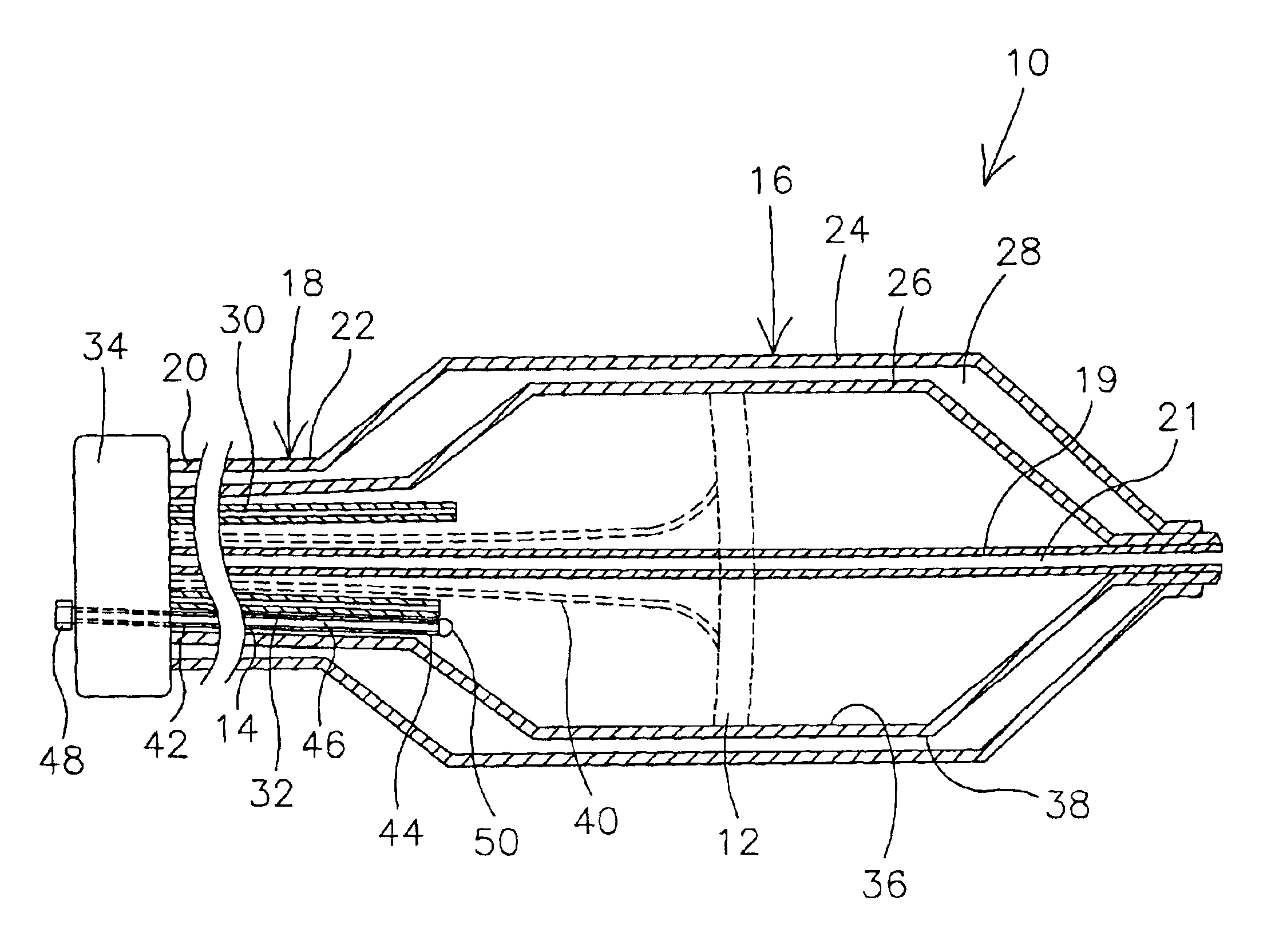
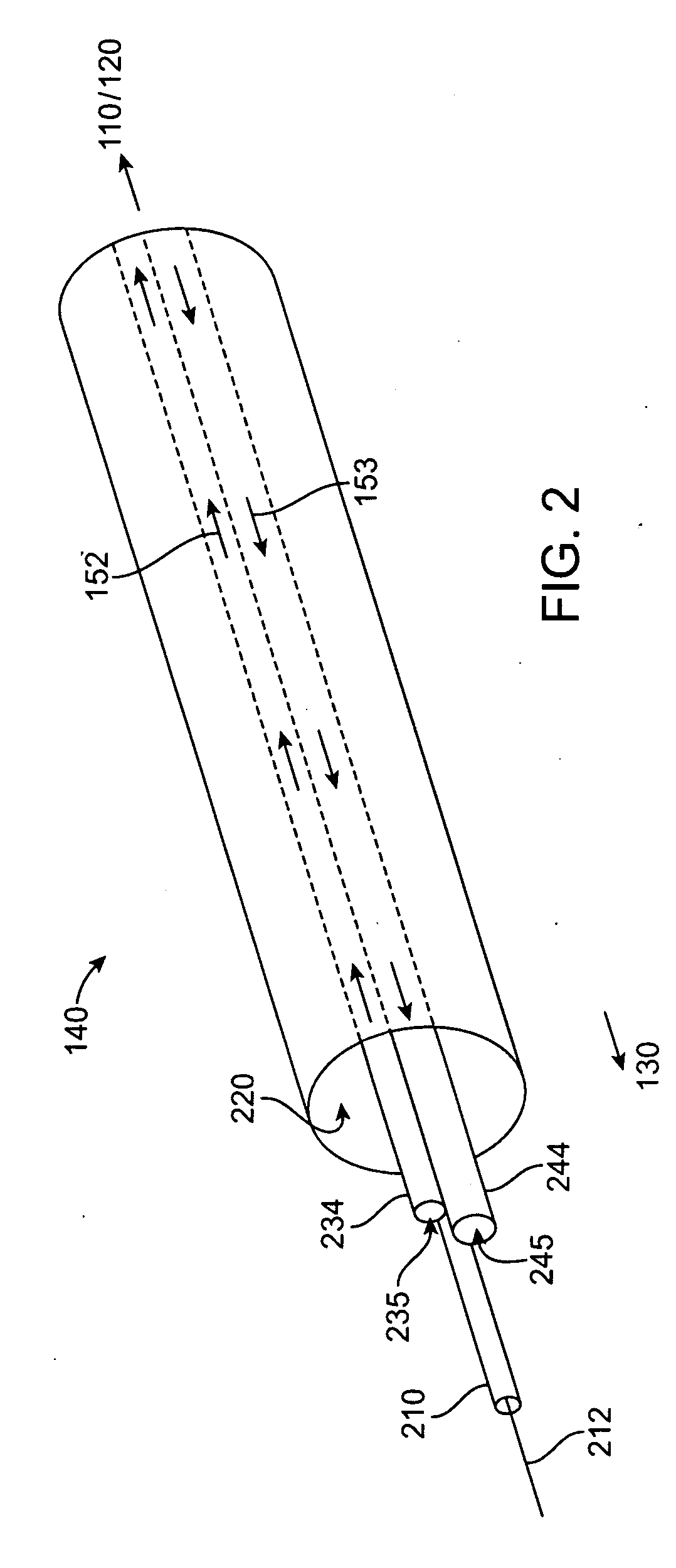
Cryo-ablation refrigerant distribution catheter
Described herein are methods and devices for performing ablation via a cryoablation catheter. An ablation catheter having a cyroablation chamber at its distal end can be used to achieve a uniform ablation band in or around the pulmonary veins. The cyrochamber can house a dispersion member in fluid communication with a refrigerant supply and can function to evenly distribute received refrigerant over some portion of the inner wall of the cryochamber. As a result of this even distribution of refrigerant within the cyrochamber, uniform ablation of the targeted tissue of the patient can be achieved.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
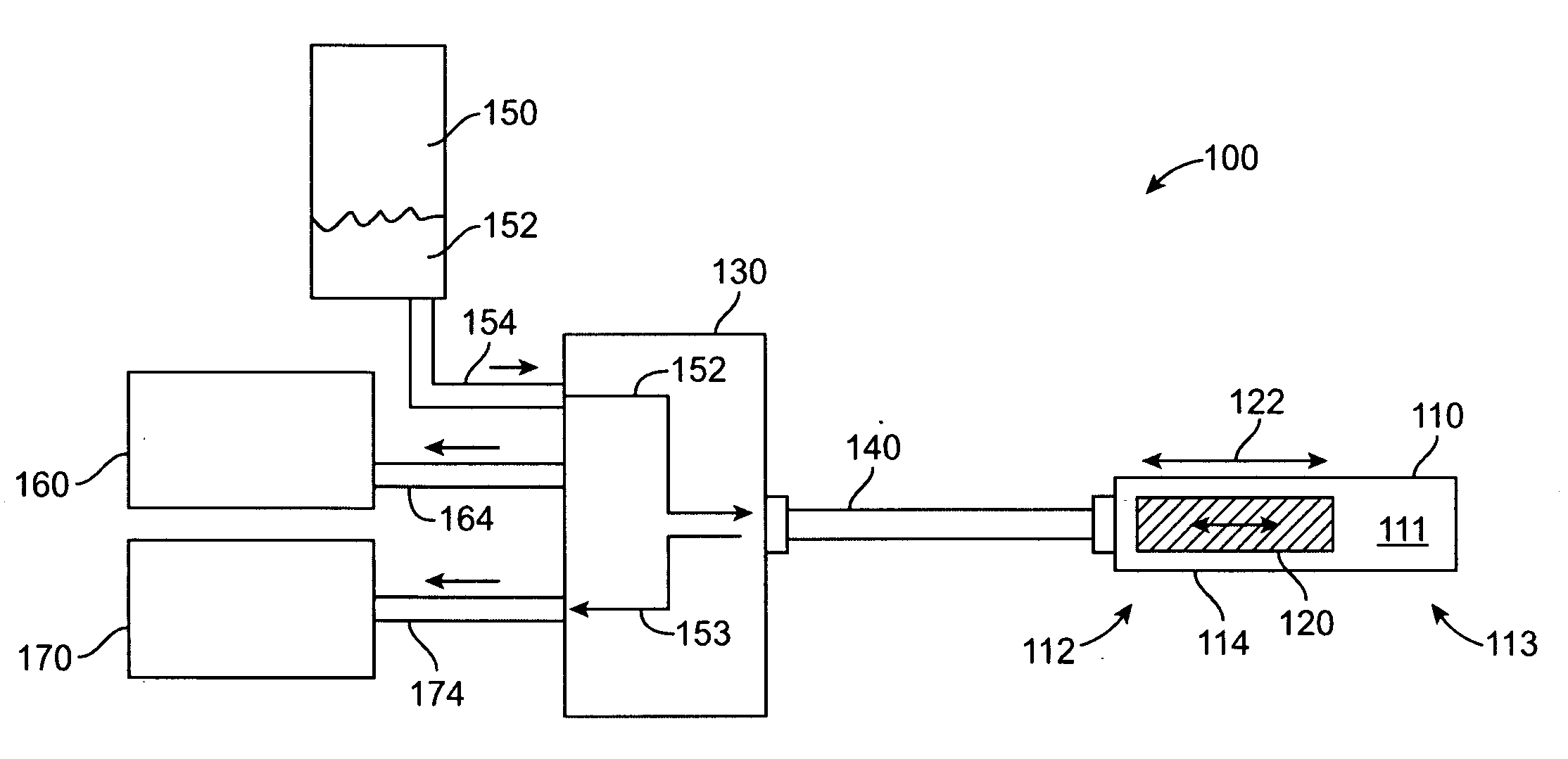
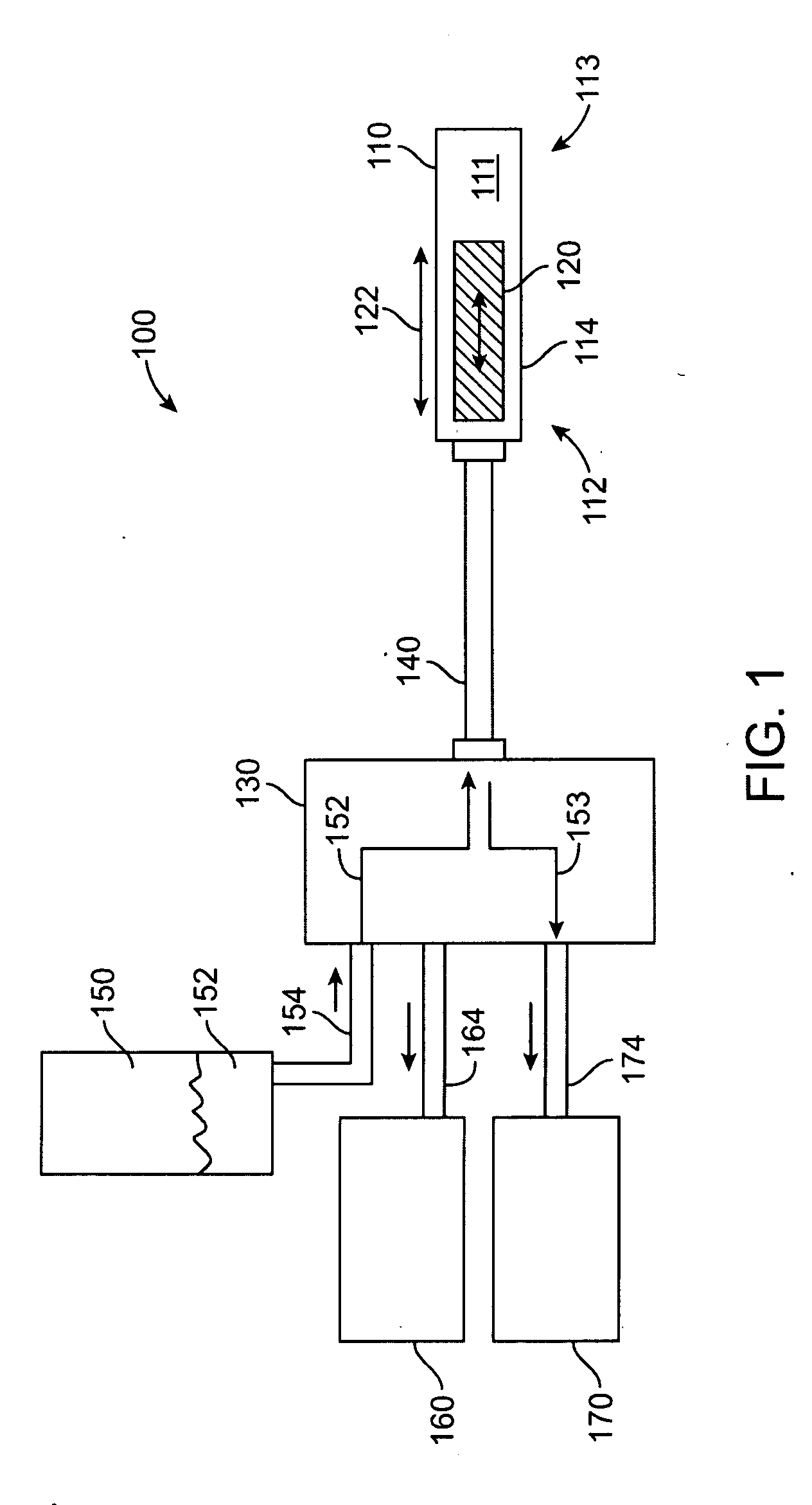
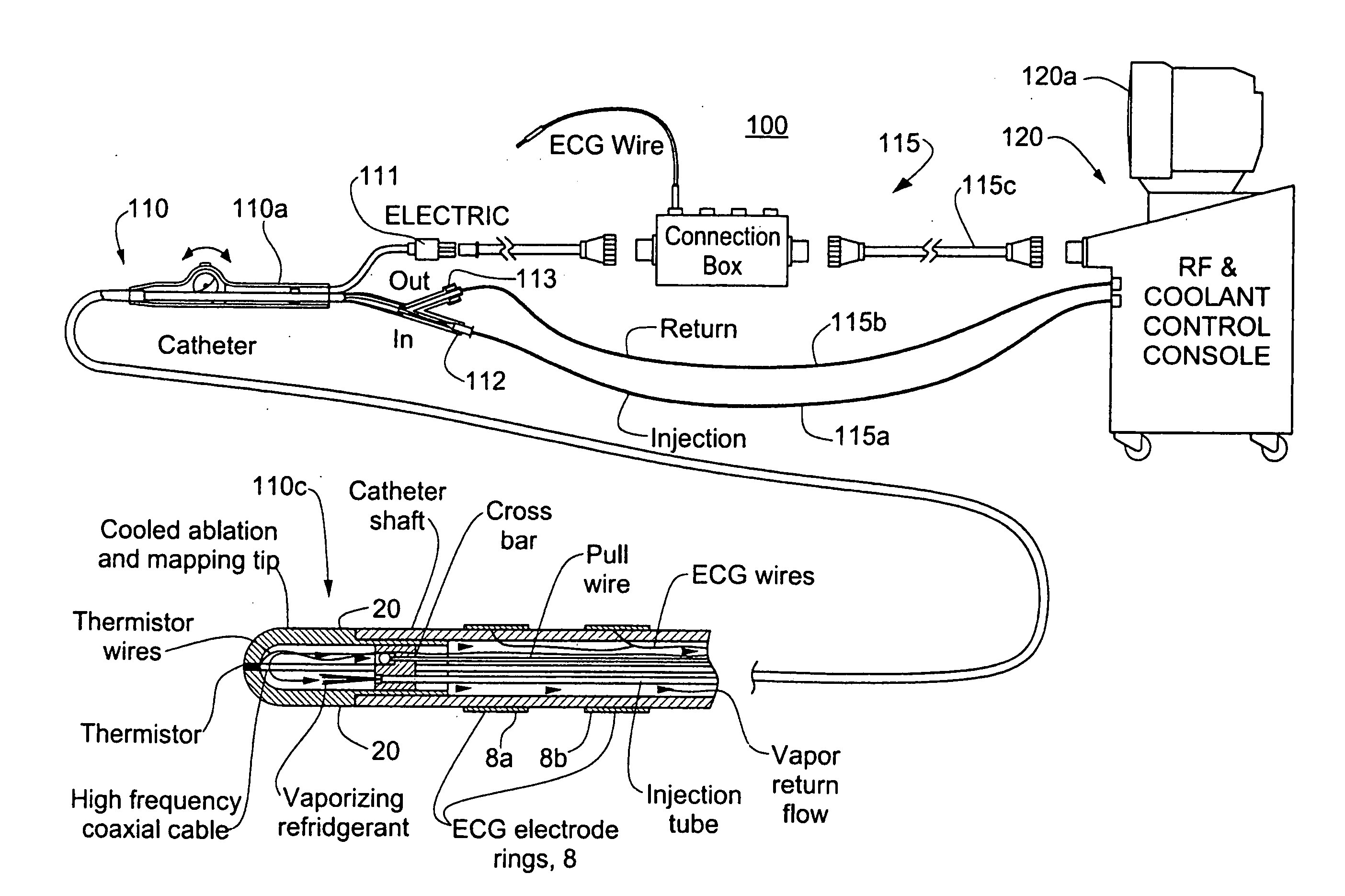
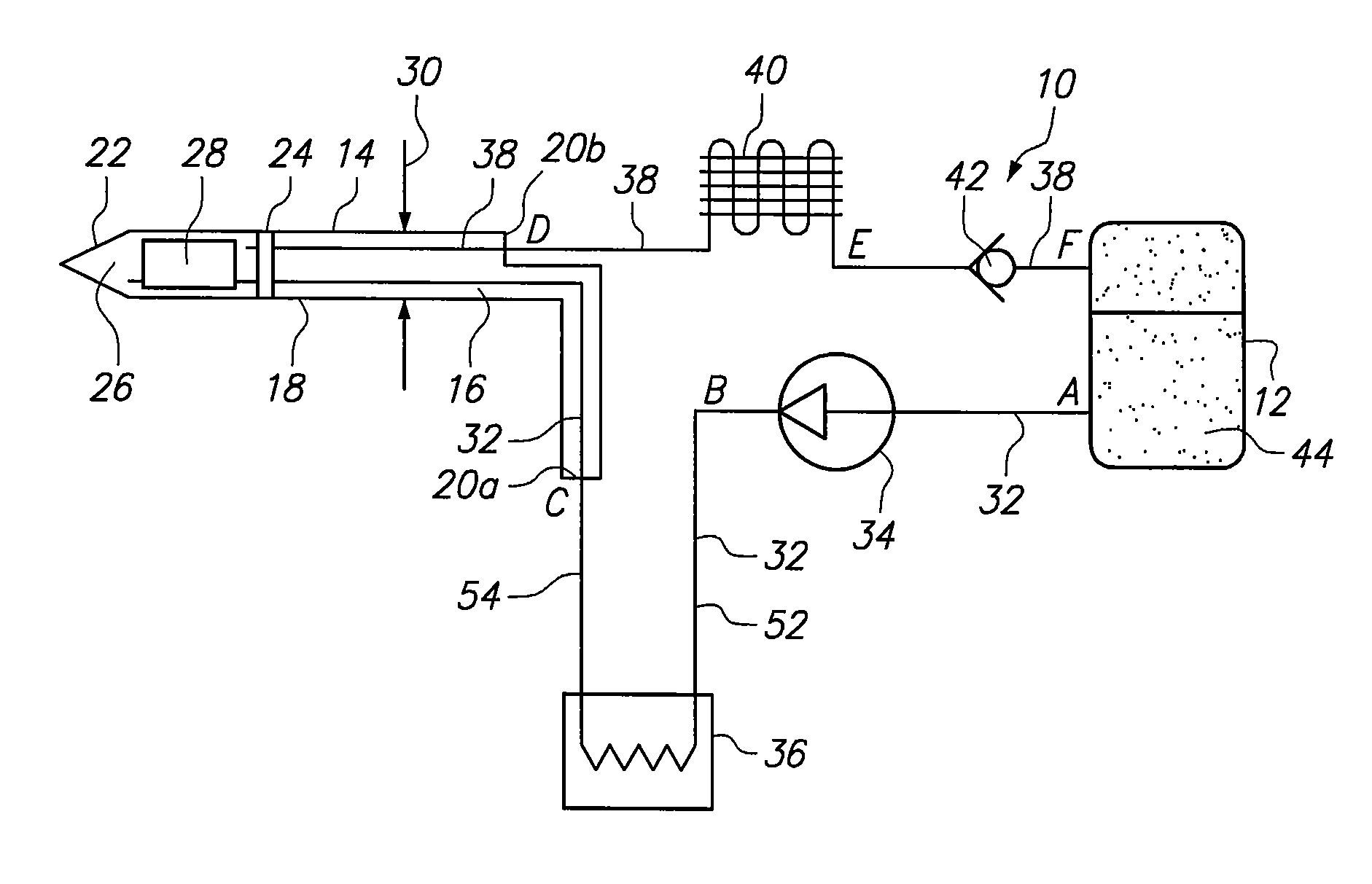
Closed loop catheter coolant system
A coolant system for a cryoablation or treatment probe such as a mapping or ablation catheter, or a treatment wand, includes a compressor and condenser having a low pressure inlet side and a high pressure outlet side, wherein the outlet side passes through a heat exchanger and is cooled by the inlet side and conditioned for injection to a catheter inlet. A vacuum return system connectable to the catheter outlet draws thermally expended coolant from the catheter and returns it to the low pressure inlet side. A motorized pressure regulator between the heat exchanger and the catheter inlet determines the pressure of coolant passing into the catheter and thus regulates the cooling rate for a selected mapping or ablation regimen. The low pressure compressor inlet supply preferentially conditions the pressurized coolant to ambient temperature or lower before injection into the catheter, allowing the coolant to travel through the body at ambient before expansion in the tip.
Owner:MEDTRONIC CRYOCATH LP
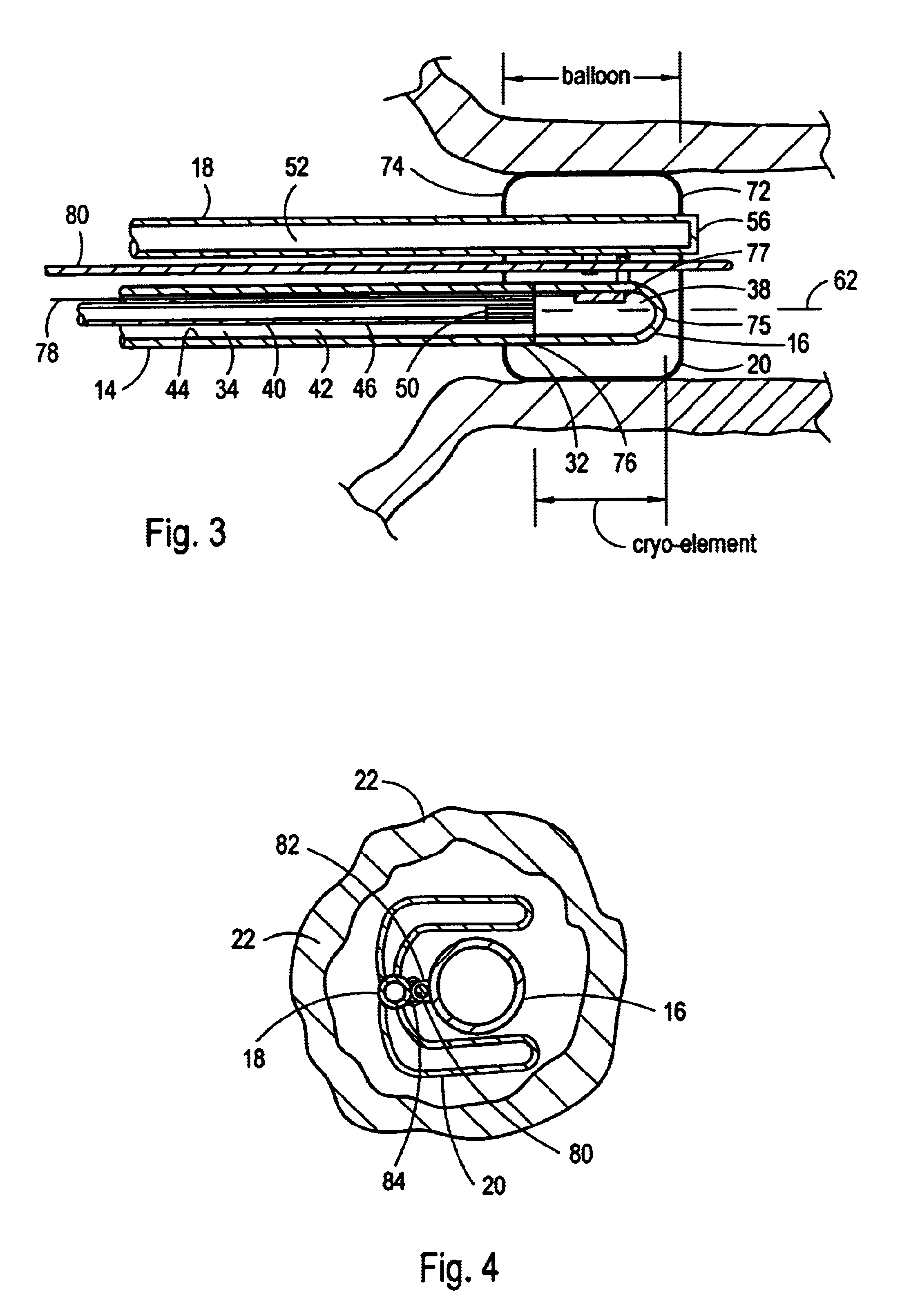
System and method for performing a single step cryoablation
A system for cryoablating target tissue at a treatment site includes a cryo-element mounted at the distal end of a cryo-catheter. A balloon catheter is provided having a U-shaped balloon attached thereon. The cryo-element is threaded onto a pre-positioned guidewire and advanced within the patient's vasculature until the cryo-element is positioned at the treatment site. Next, the balloon is threaded onto the guidewire and advanced within the patient's vasculature using the balloon catheter. At the treatment site, the U-shaped balloon is interposed between the cryo-element and the target tissue. Saline solution is pumped into the balloon causing the U-shaped balloon to expand and contact both the cryo-element and the surrounding target tissue. Next, a refrigerant is expanded to cool the cryo-element, which in turn, freezes the saline solution. The resulting “ice ball” extracts heat from surrounding tissue resulting in the cryoablation of a substantially circumferential portion of tissue.
Owner:CRYOCOR
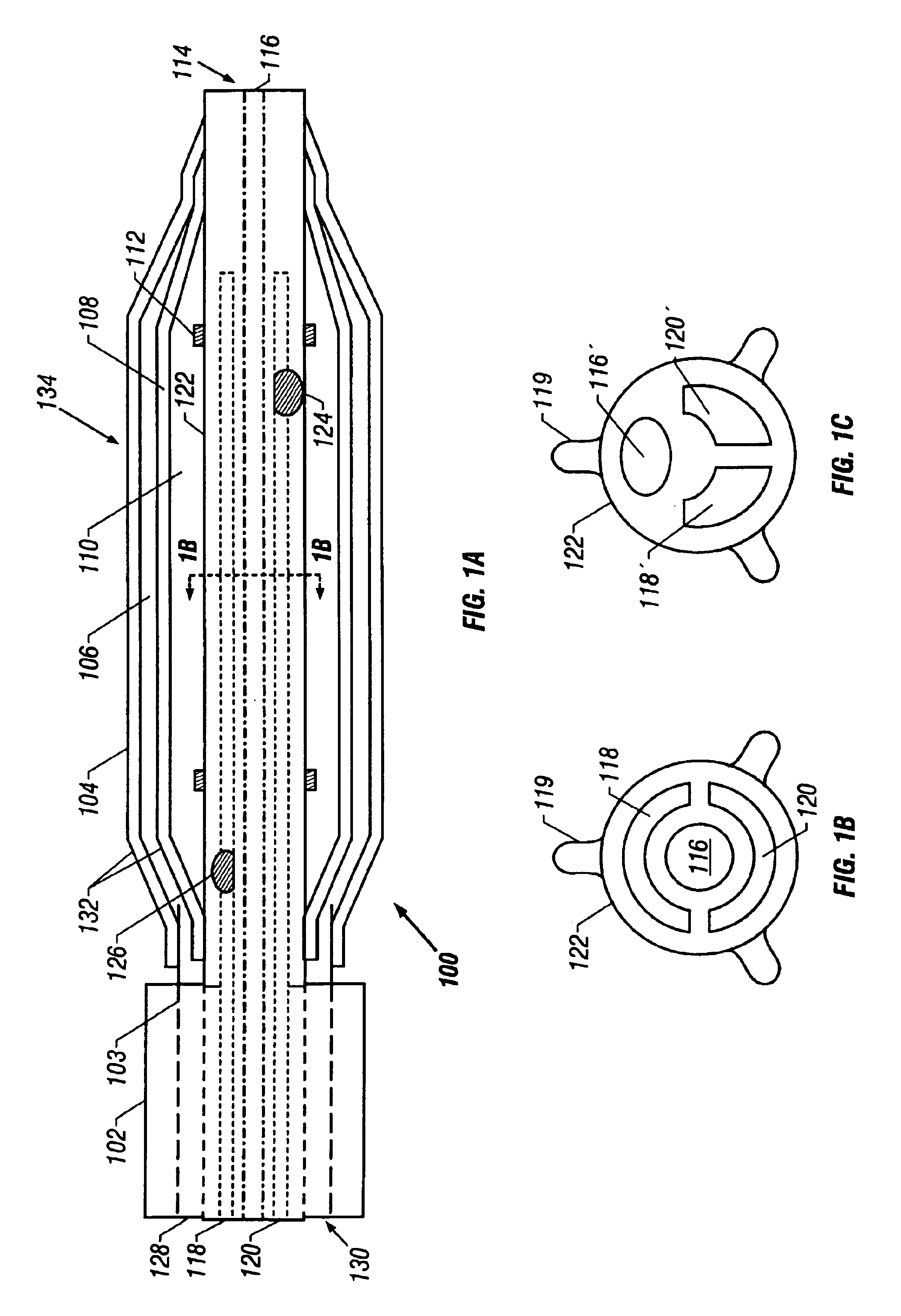
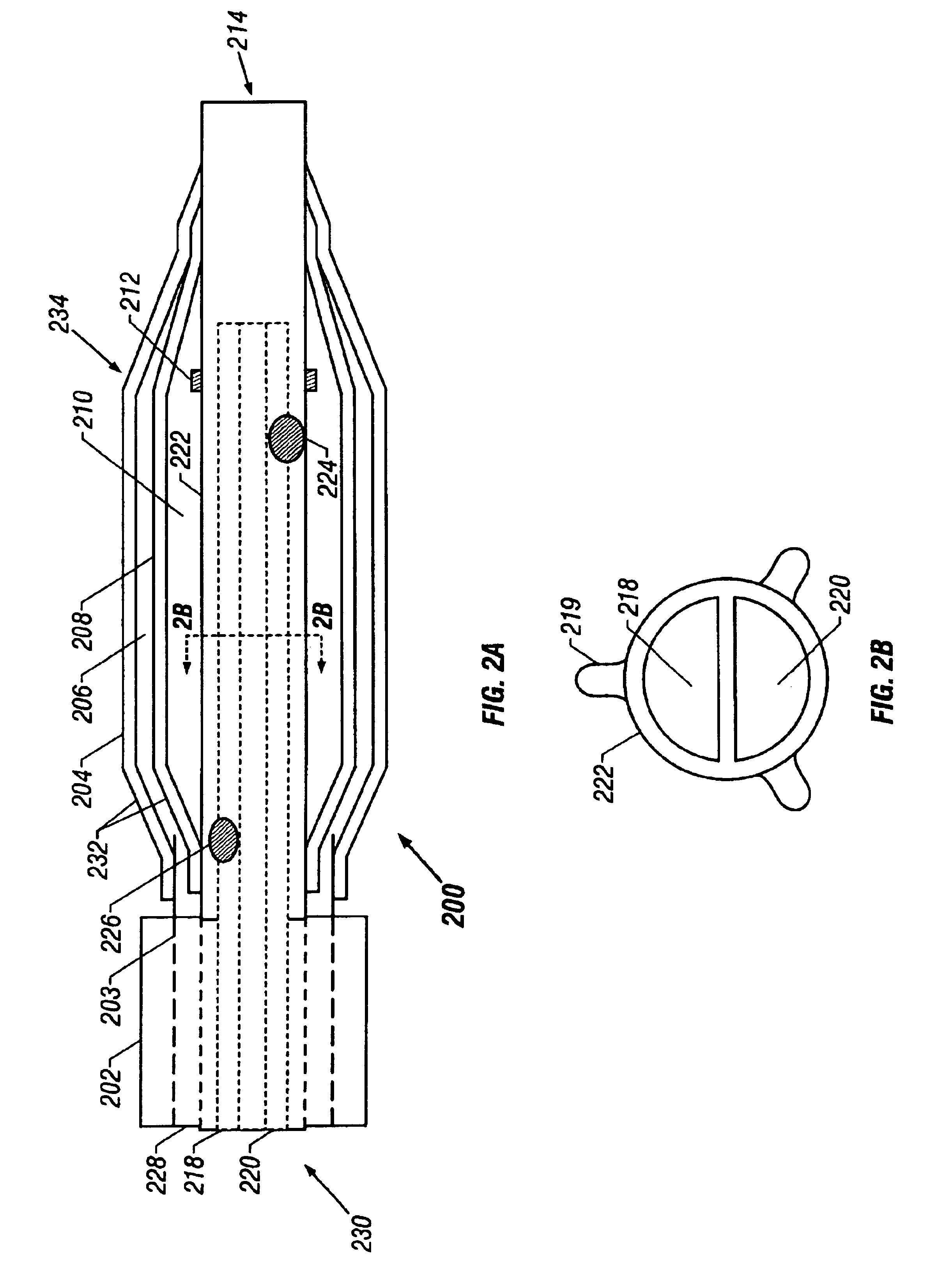
Cryoablation balloon catheter and related method
Cryoablation balloon catheters and methods are described herein. The cryoablation balloon catheter comprises a distal end section and an inflatable balloon member disposed along the distal end section for contacting a target tissue. The balloon member may be inflated with a thermally conductive liquid. One or more cooling microtubes are positioned within the balloon and a single phase liquid coolant is transported from a liquid source, through the microtubes to the distal section, and returned to a reservoir. Cryogenic energy is transferred from the microtubes, through the conductive liquid filling the balloon, through the wall of the balloon, and to the tissue. In a cryoablation balloon catheter, a plurality of flexible microtubes are adhered to a surface of the expandable balloon. Cryoenergy from the microtubes is directly transferred to the tissue.
Owner:CRYOMEDIX
Method and System for Cryoablation Treatment
A system and a method for its use are provided to cool a cryotip at the distal end of a probe for a cryosurgical procedure. In particular, the cryotip is cooled by a liquid refrigerant to cryogenic temperatures in order to perform a cryosurgical procedure on biological tissue. The system is closed-loop, and during transit of the liquid refrigerant through the entire system, the liquid refrigerant always remains in a liquid state at a relatively low pressure.
Owner:CRYOMEDIX
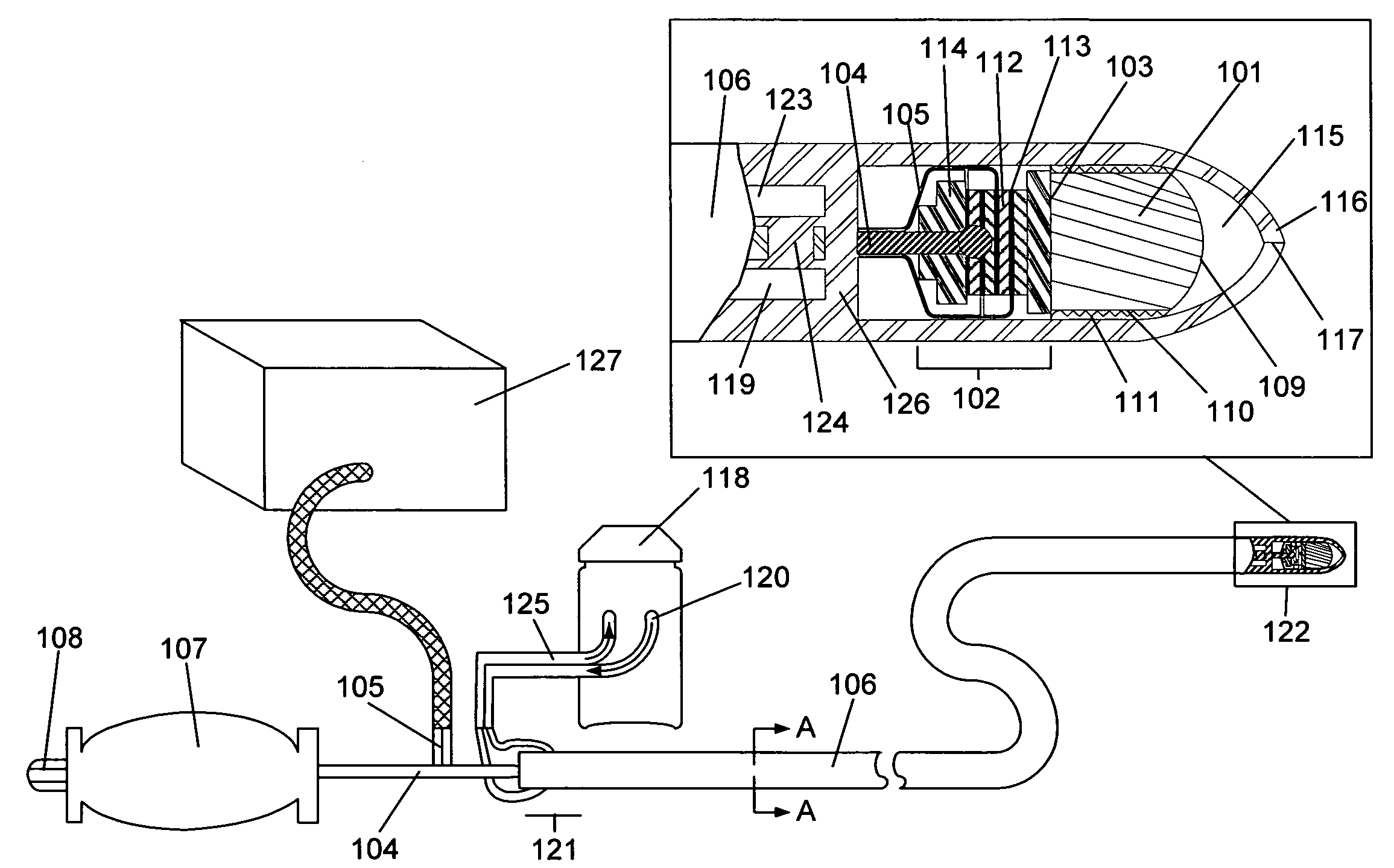
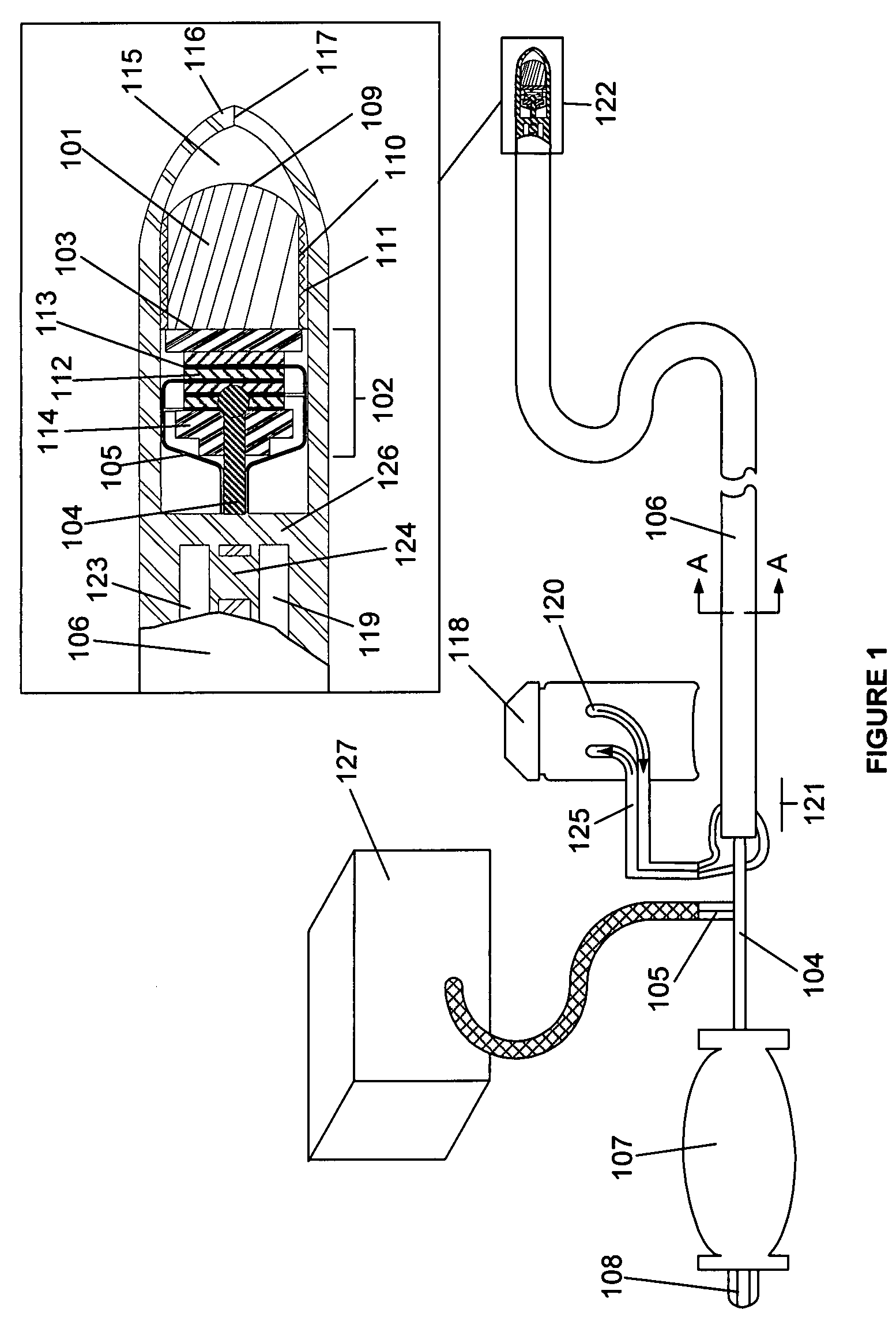
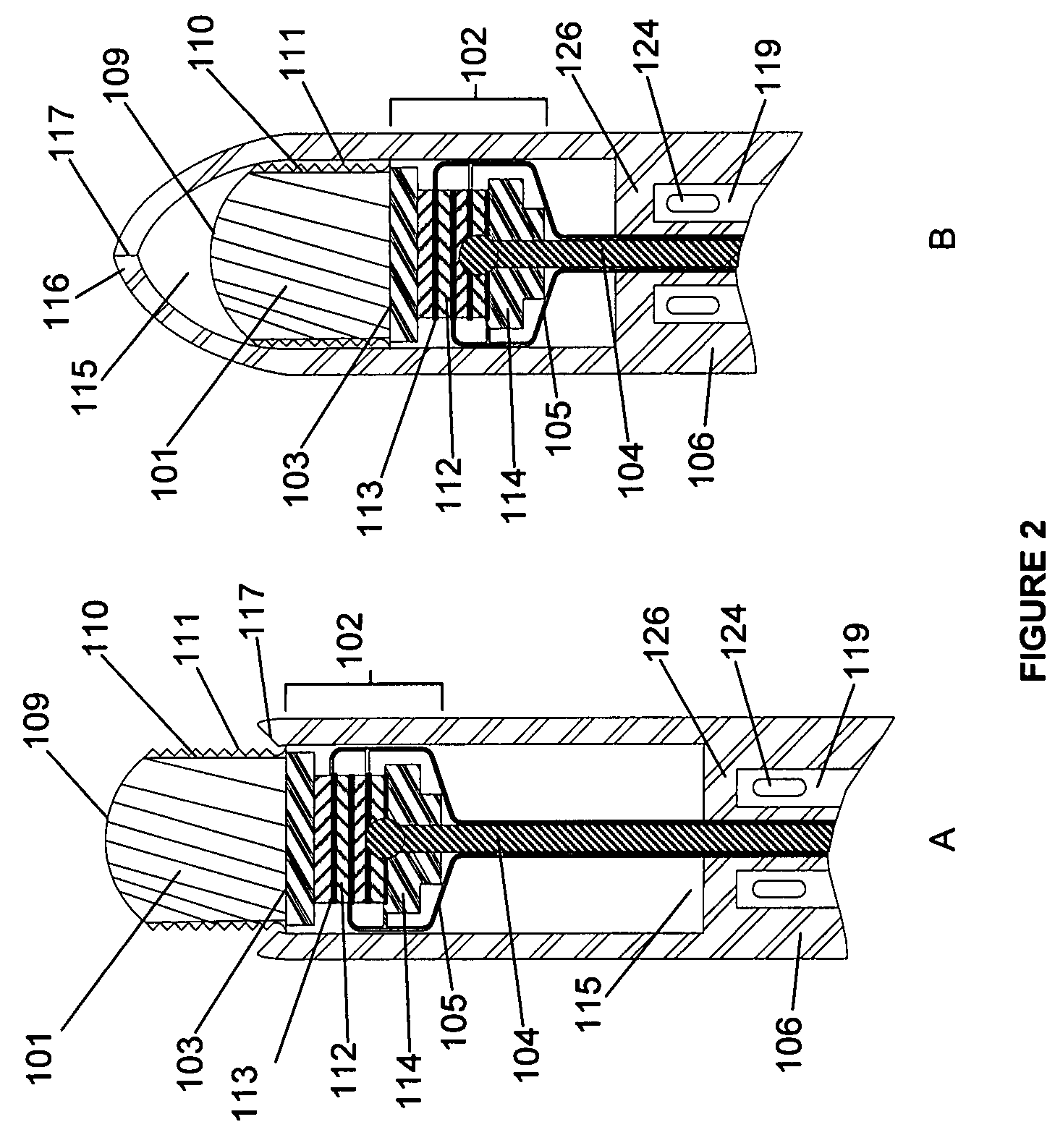
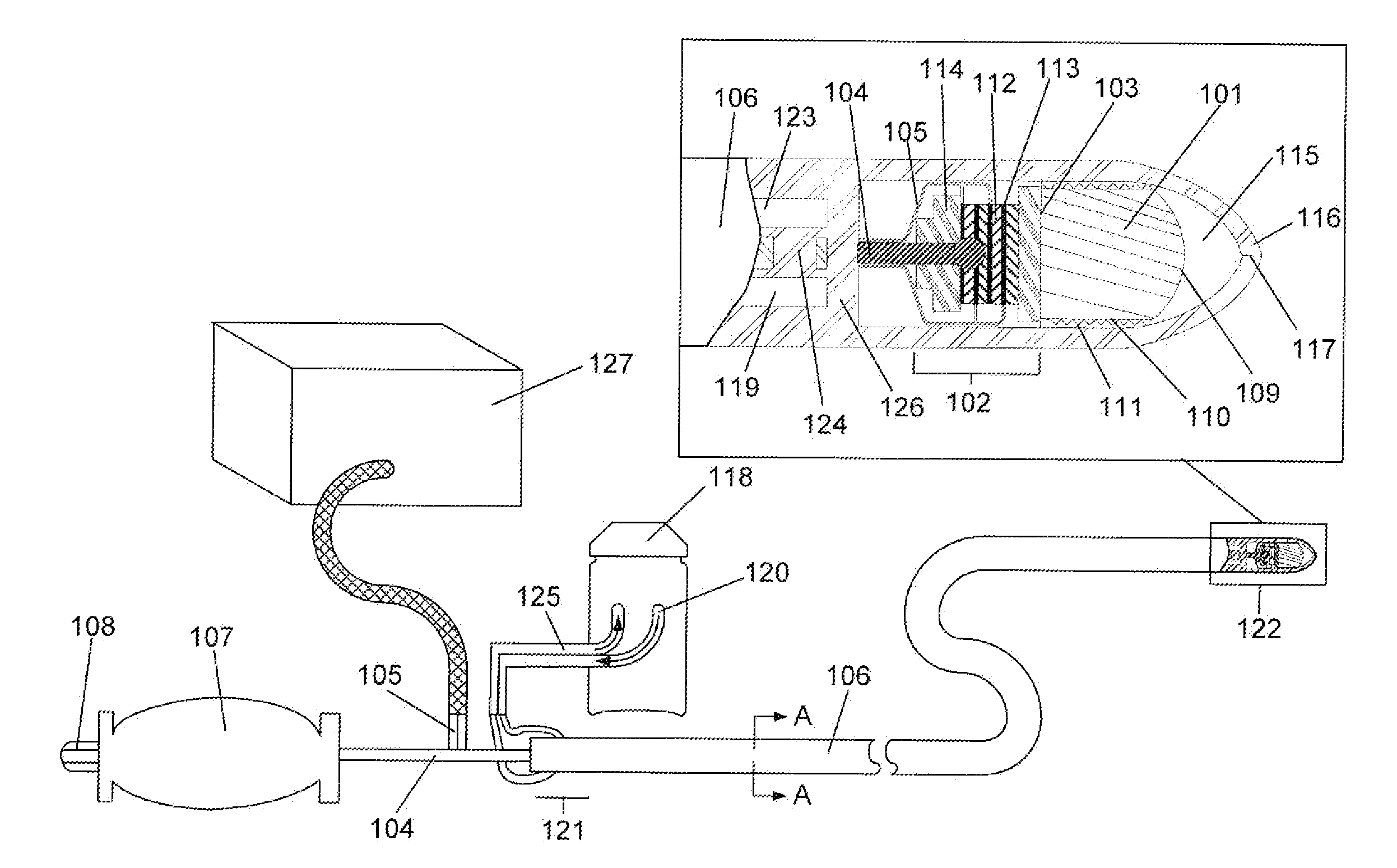
Distal end for cryoablation catheters
Owner:CRYOCOR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com