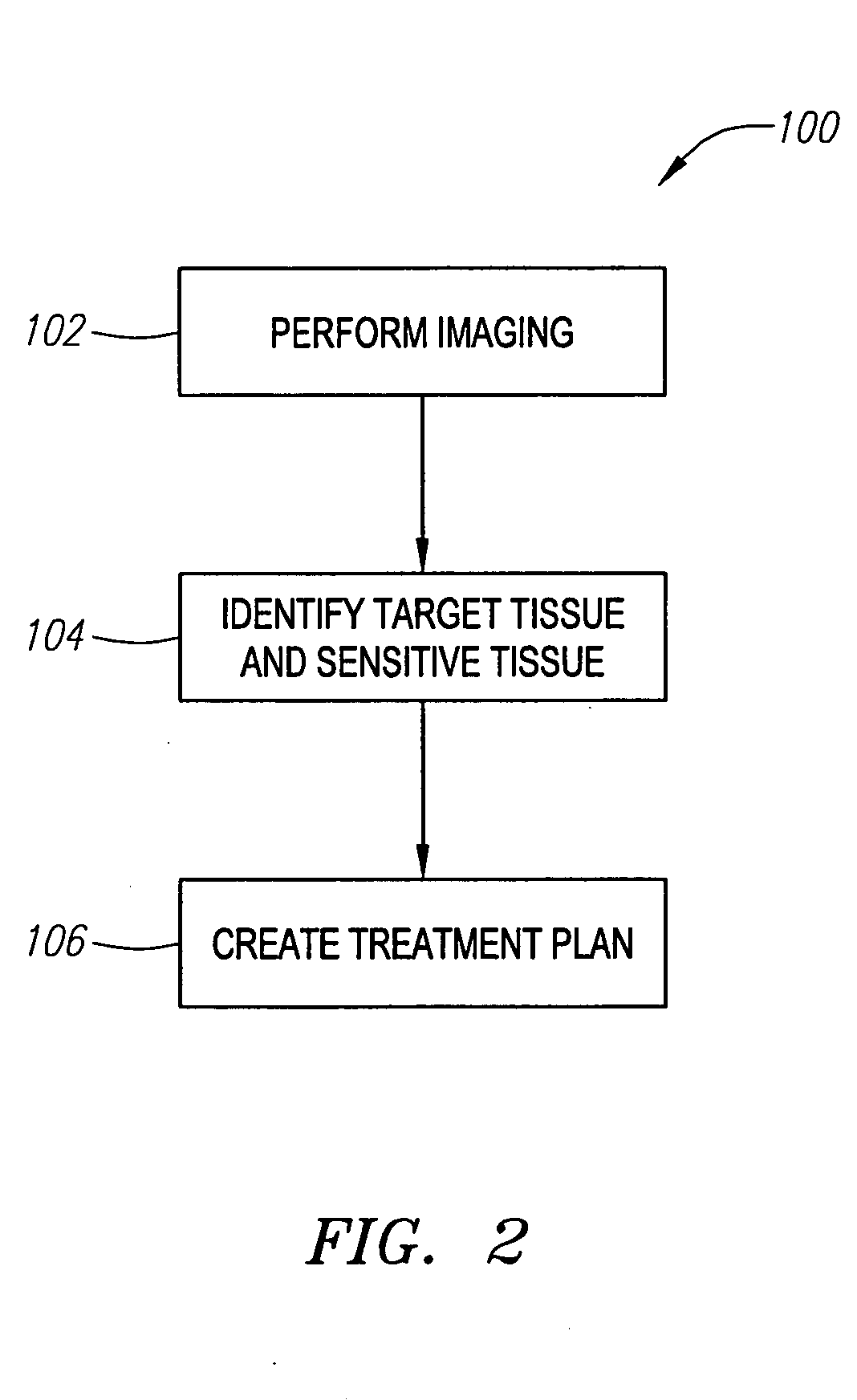
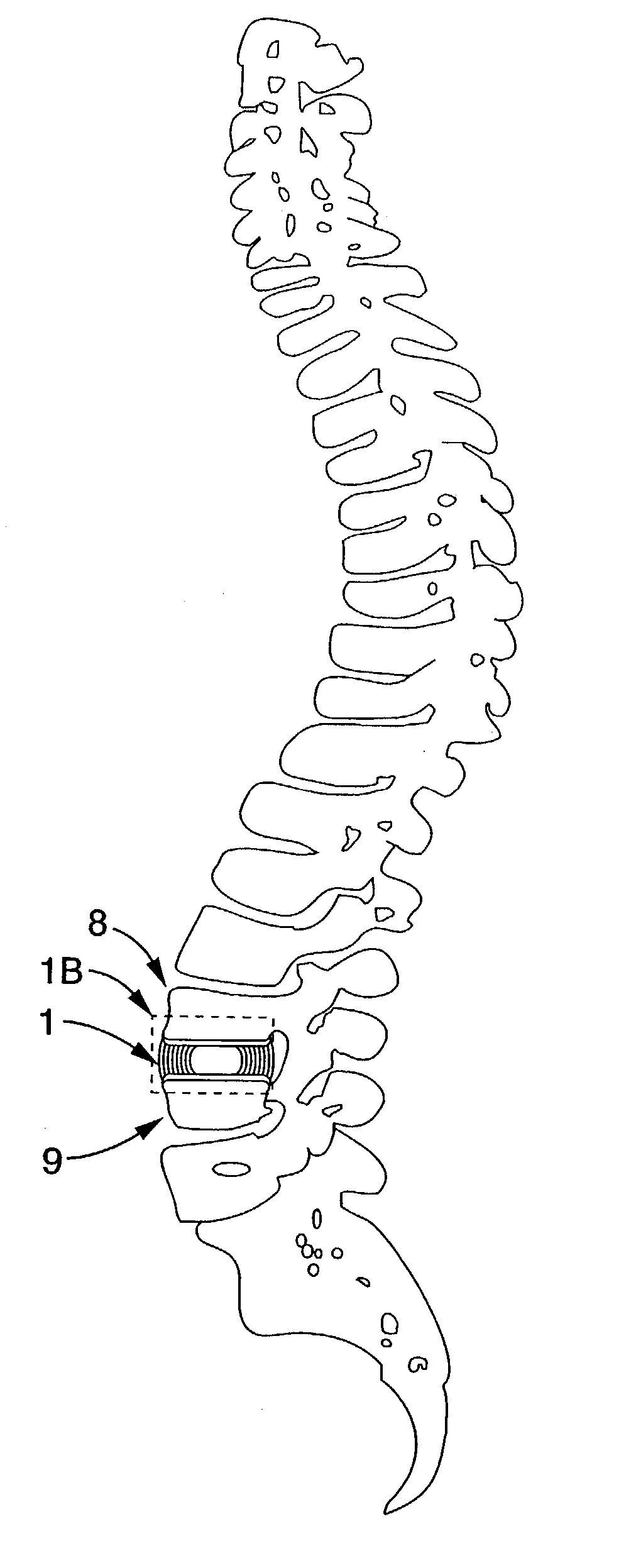
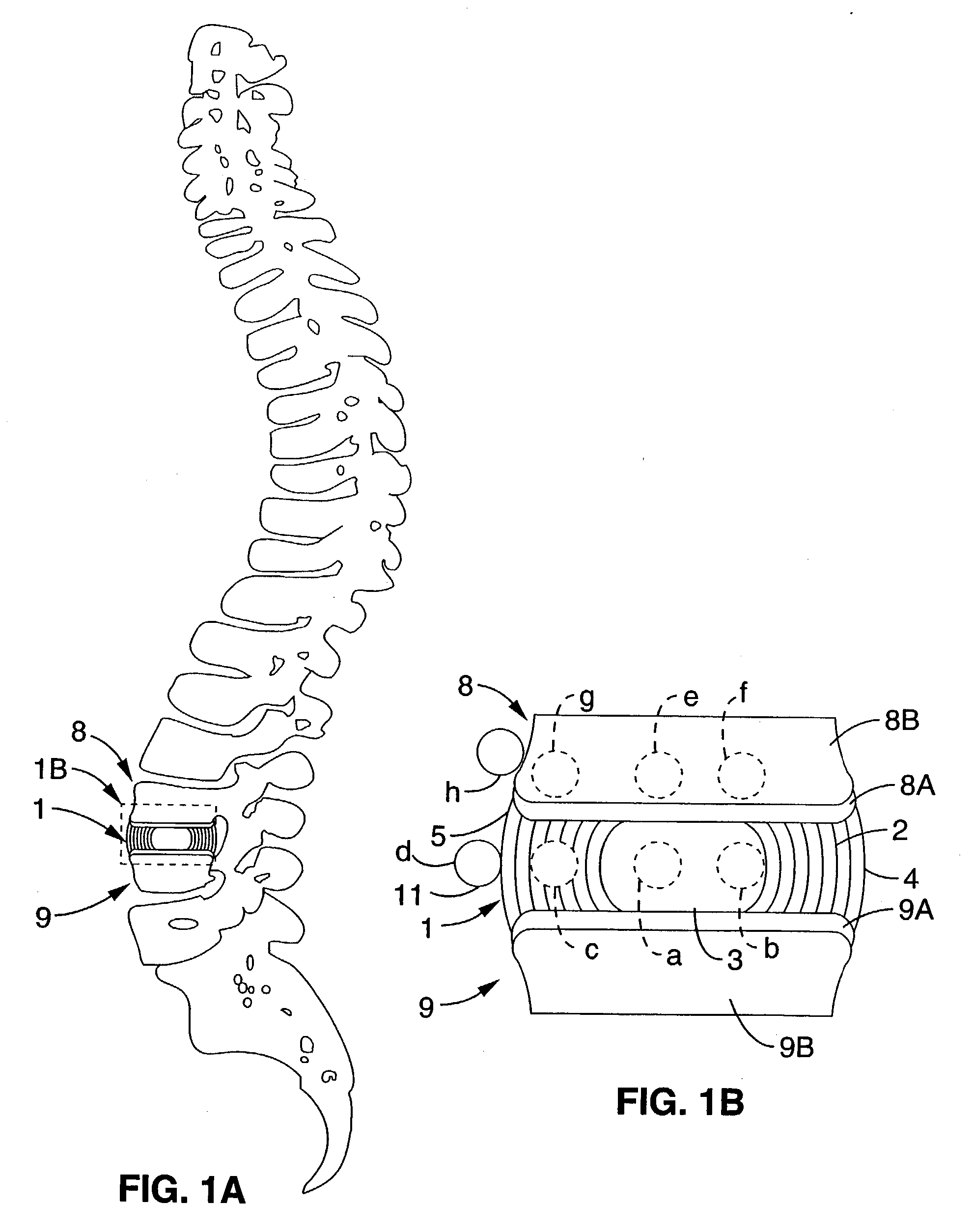
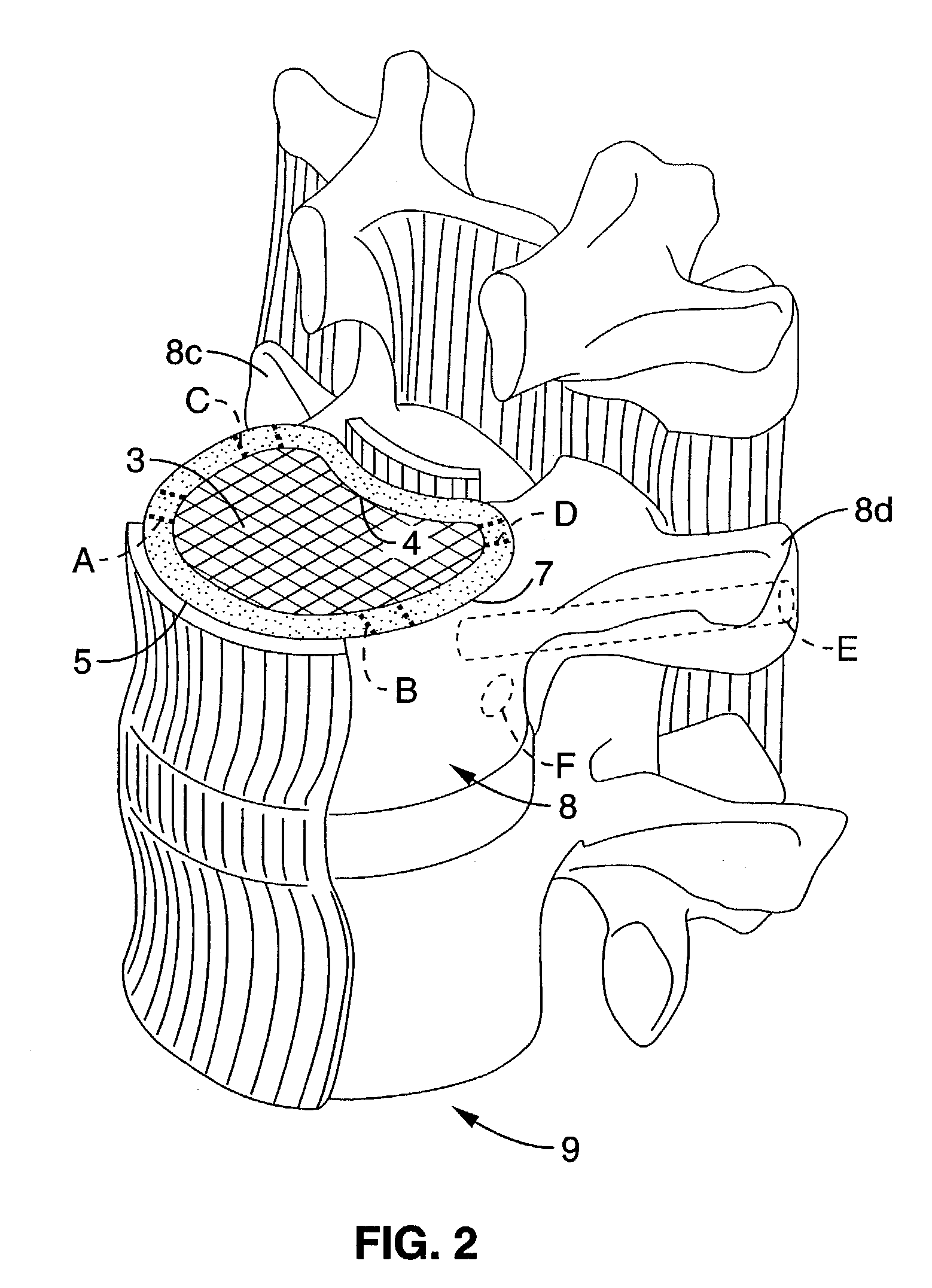
Patents
Literature
698 results about "Focused ultrasound" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
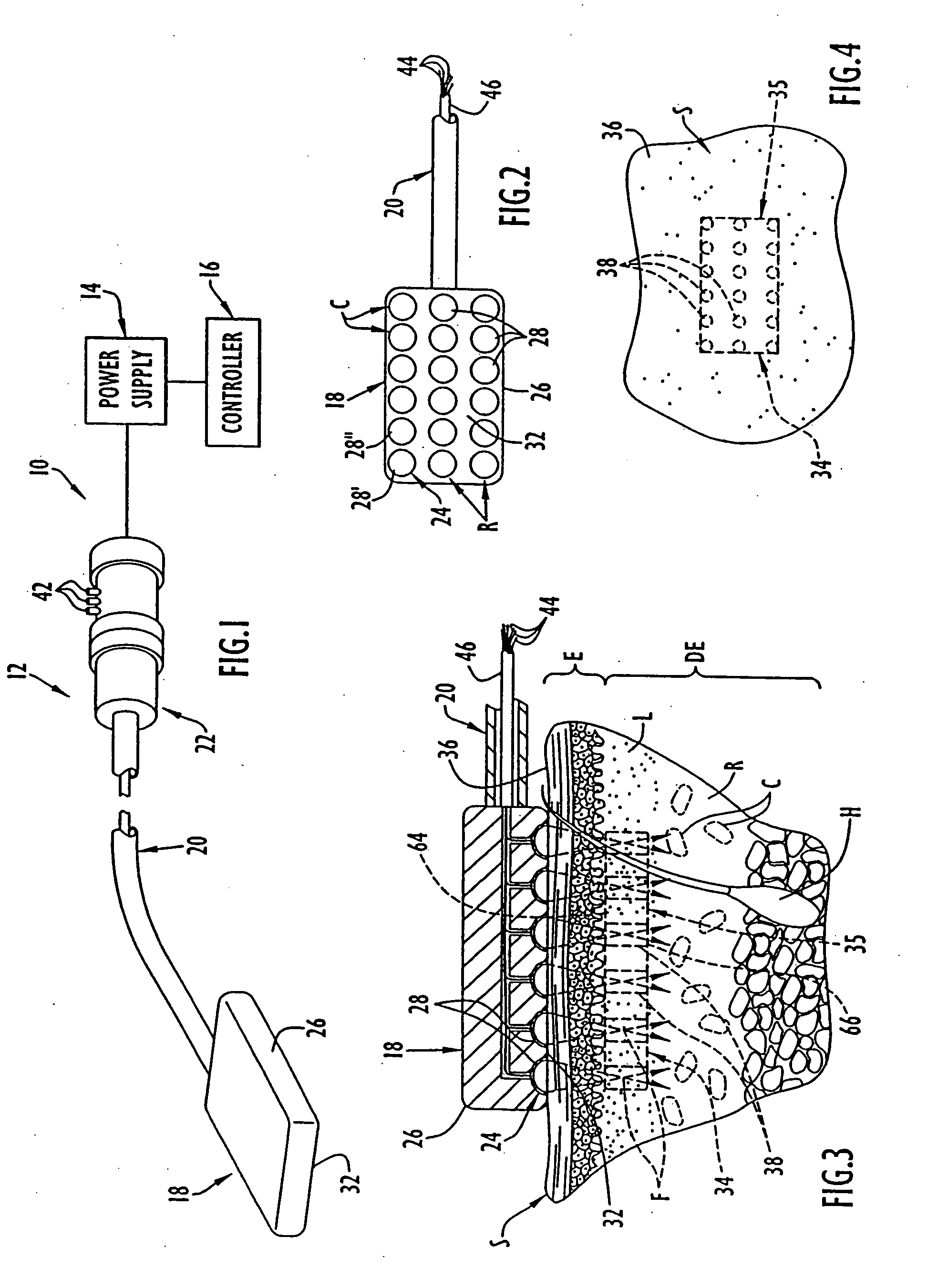
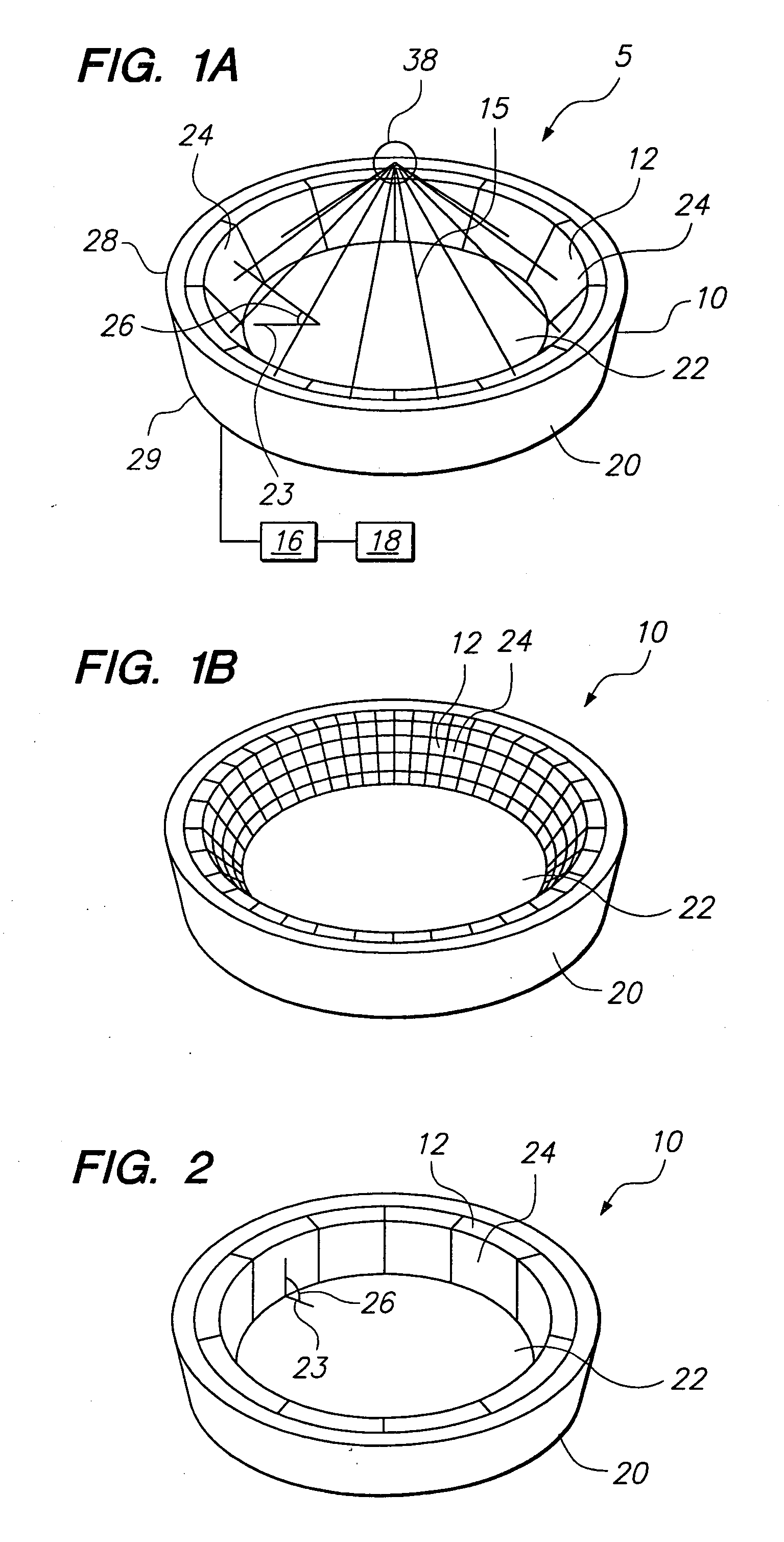
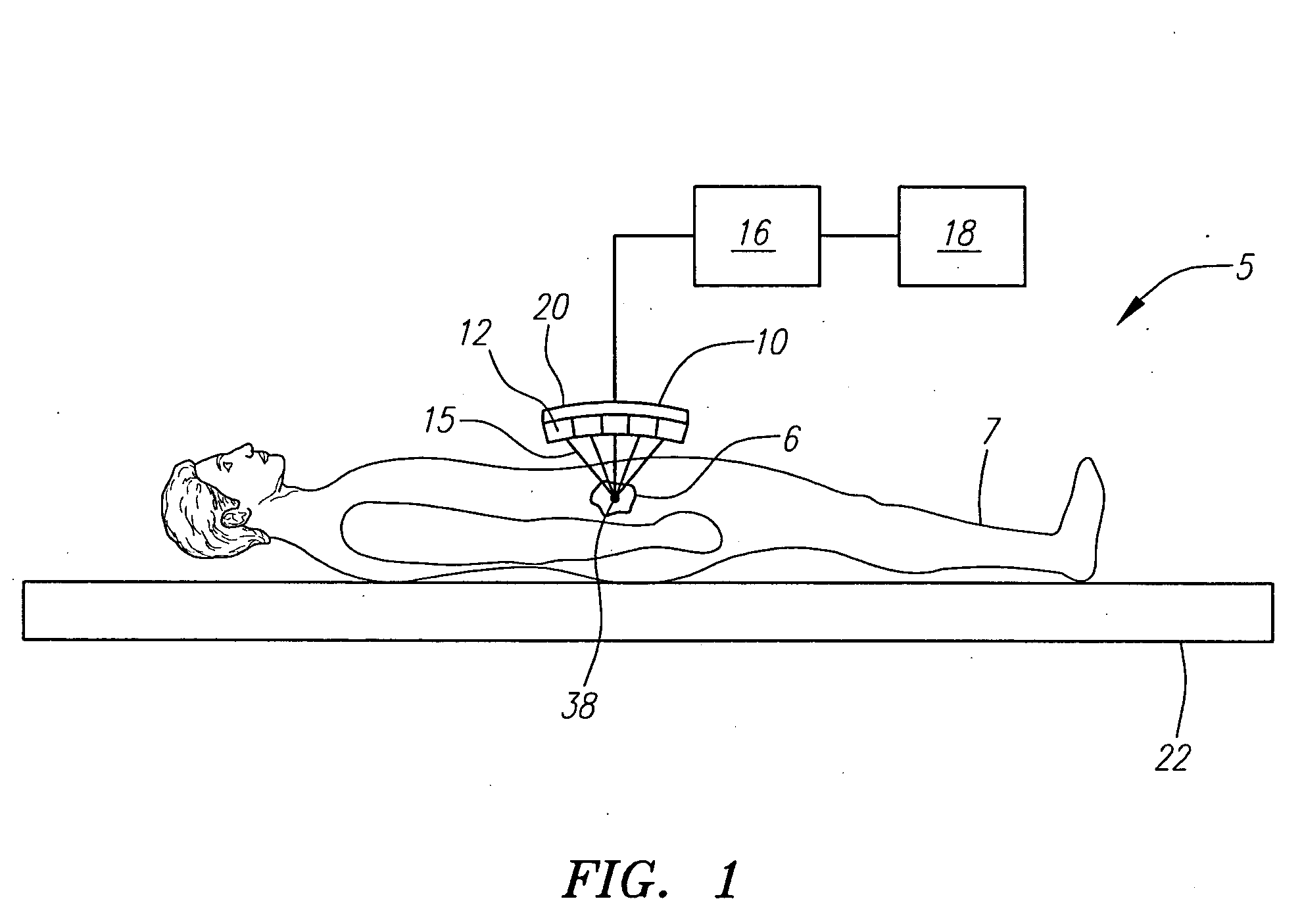
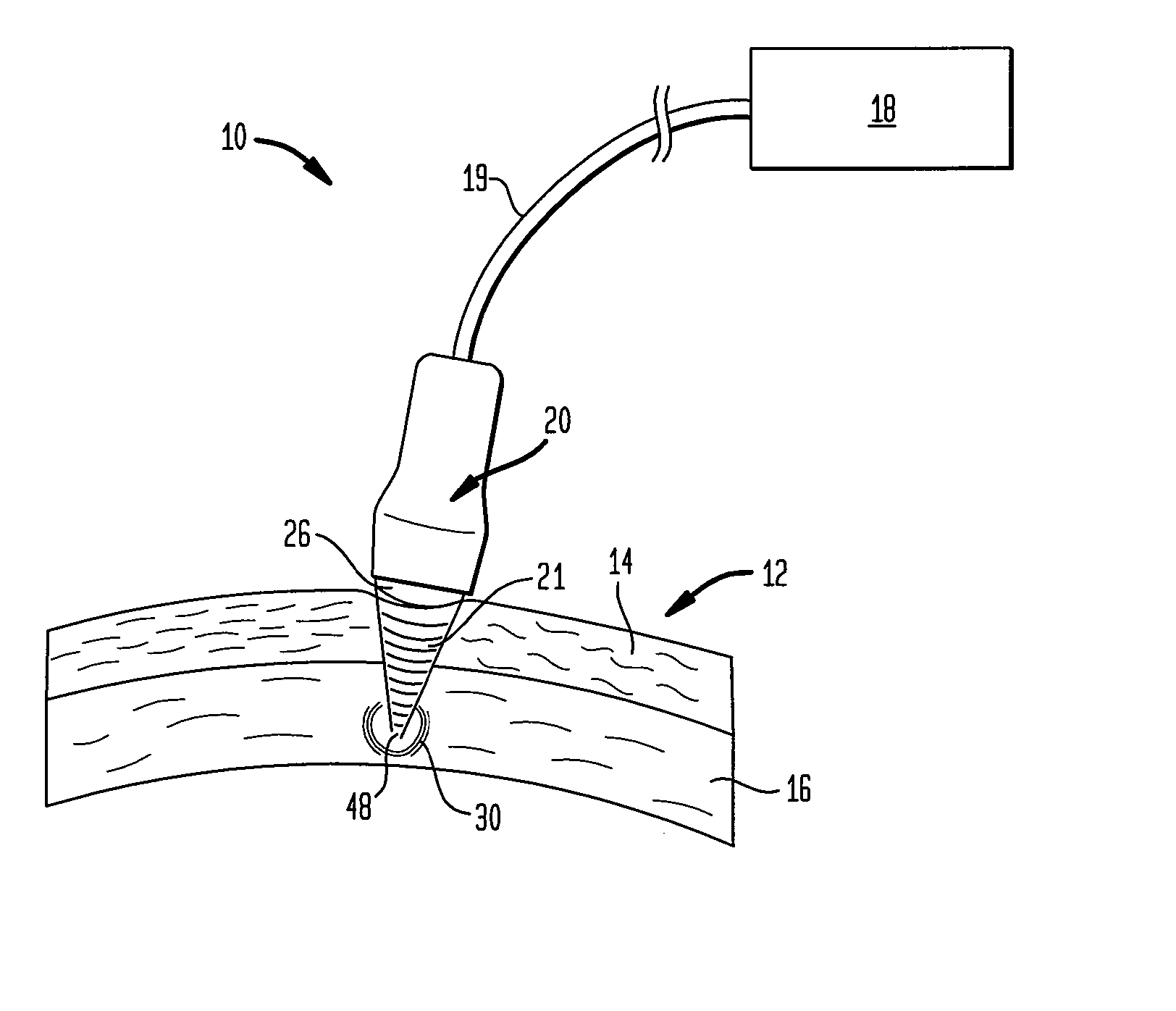
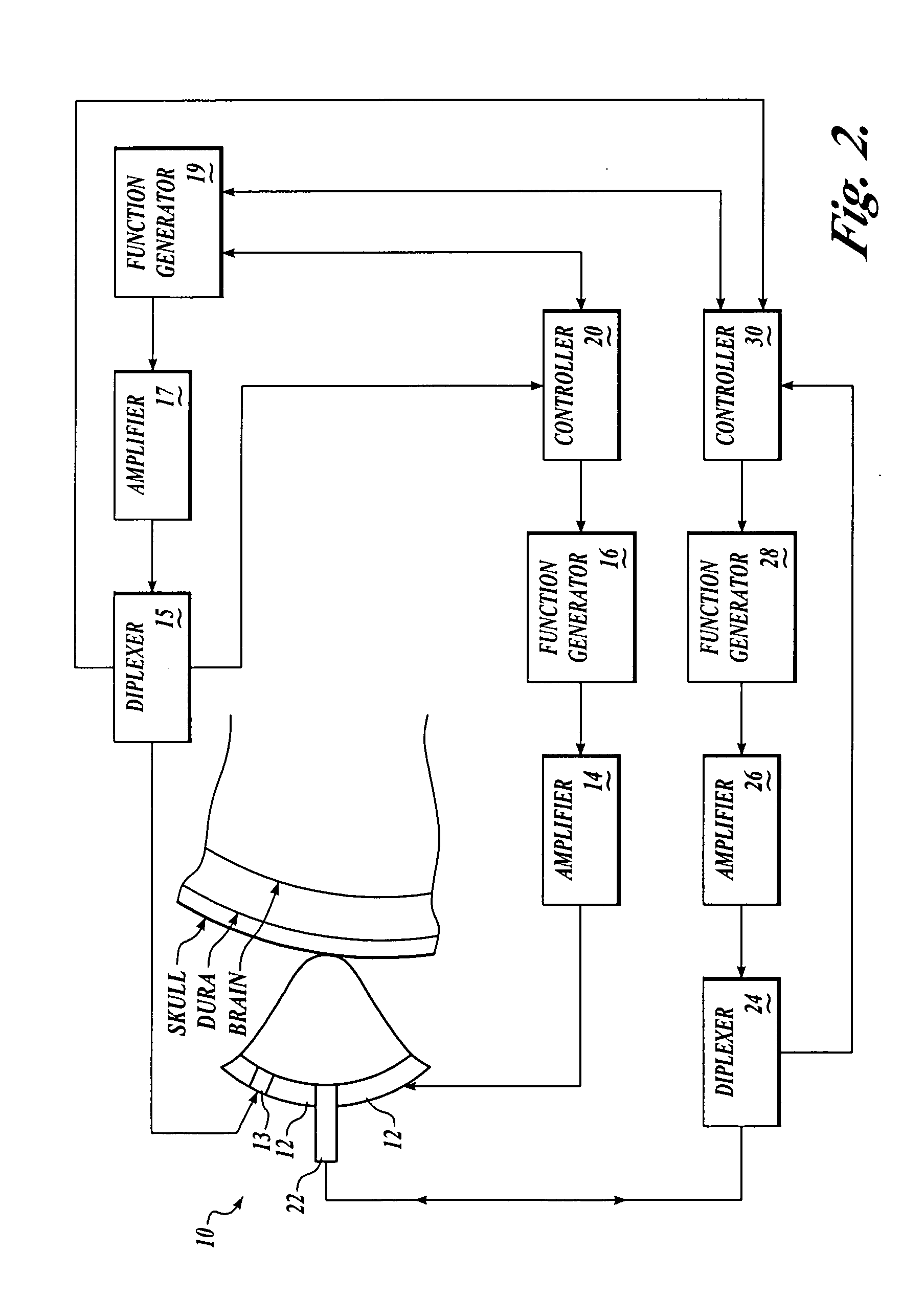
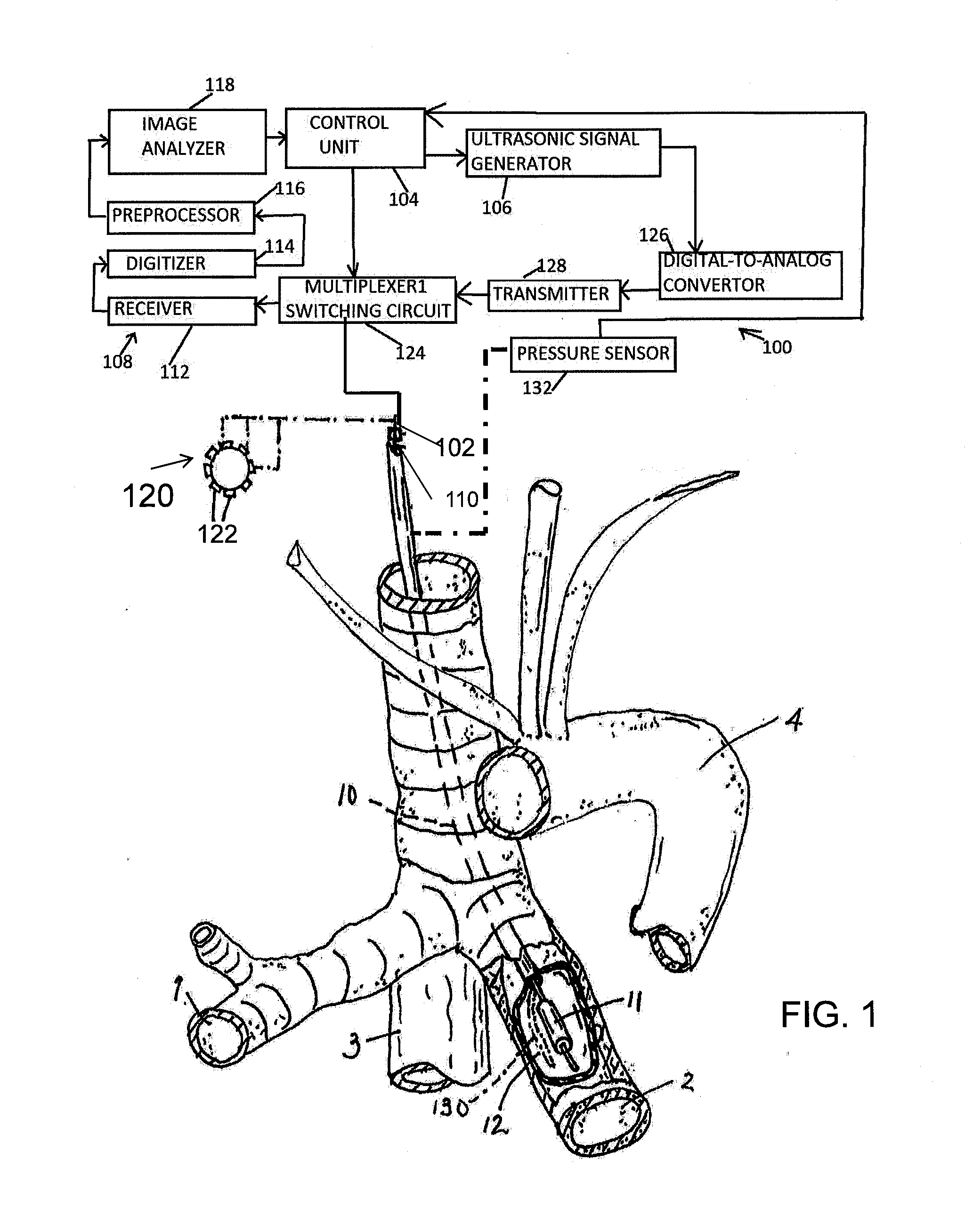
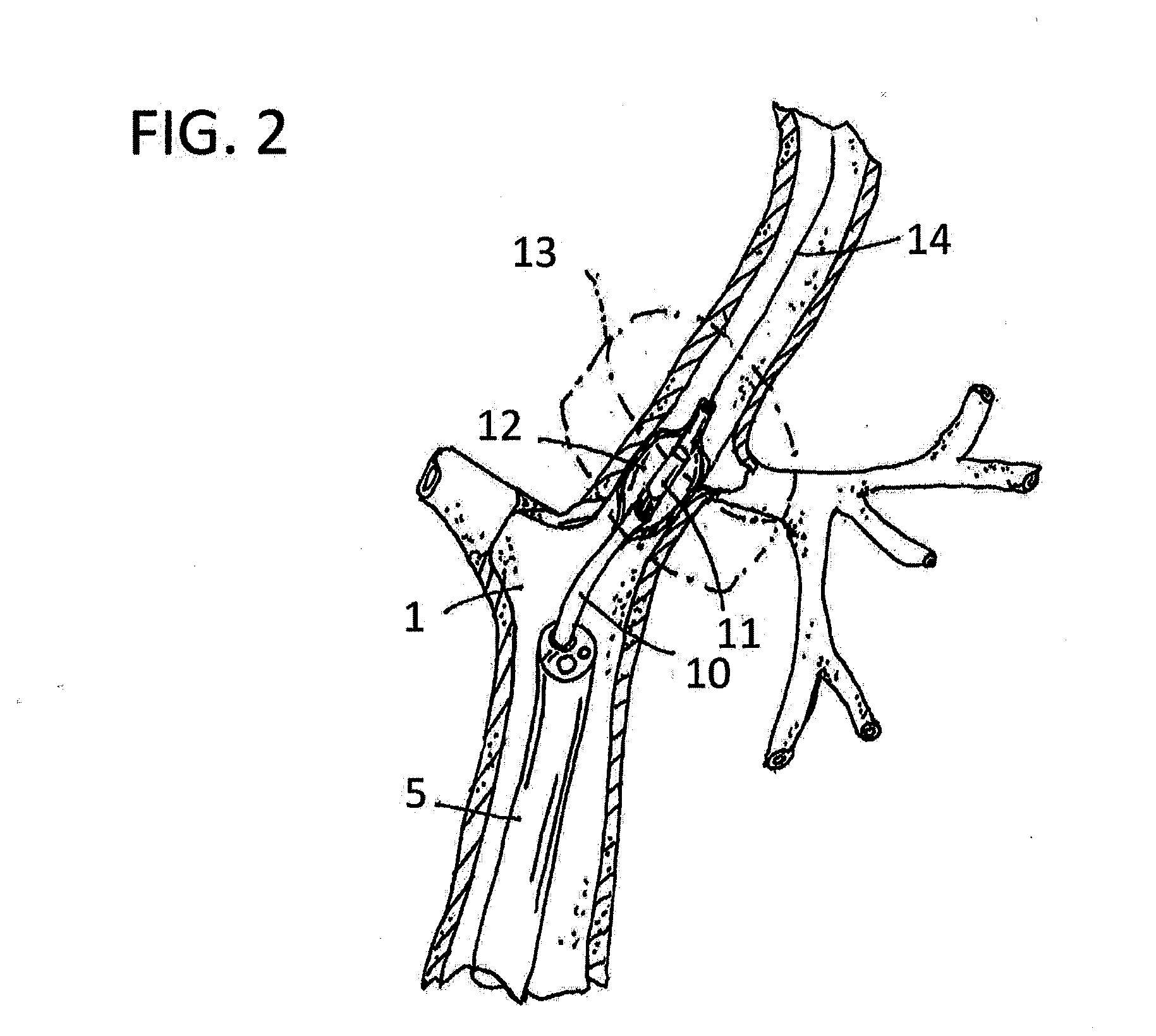
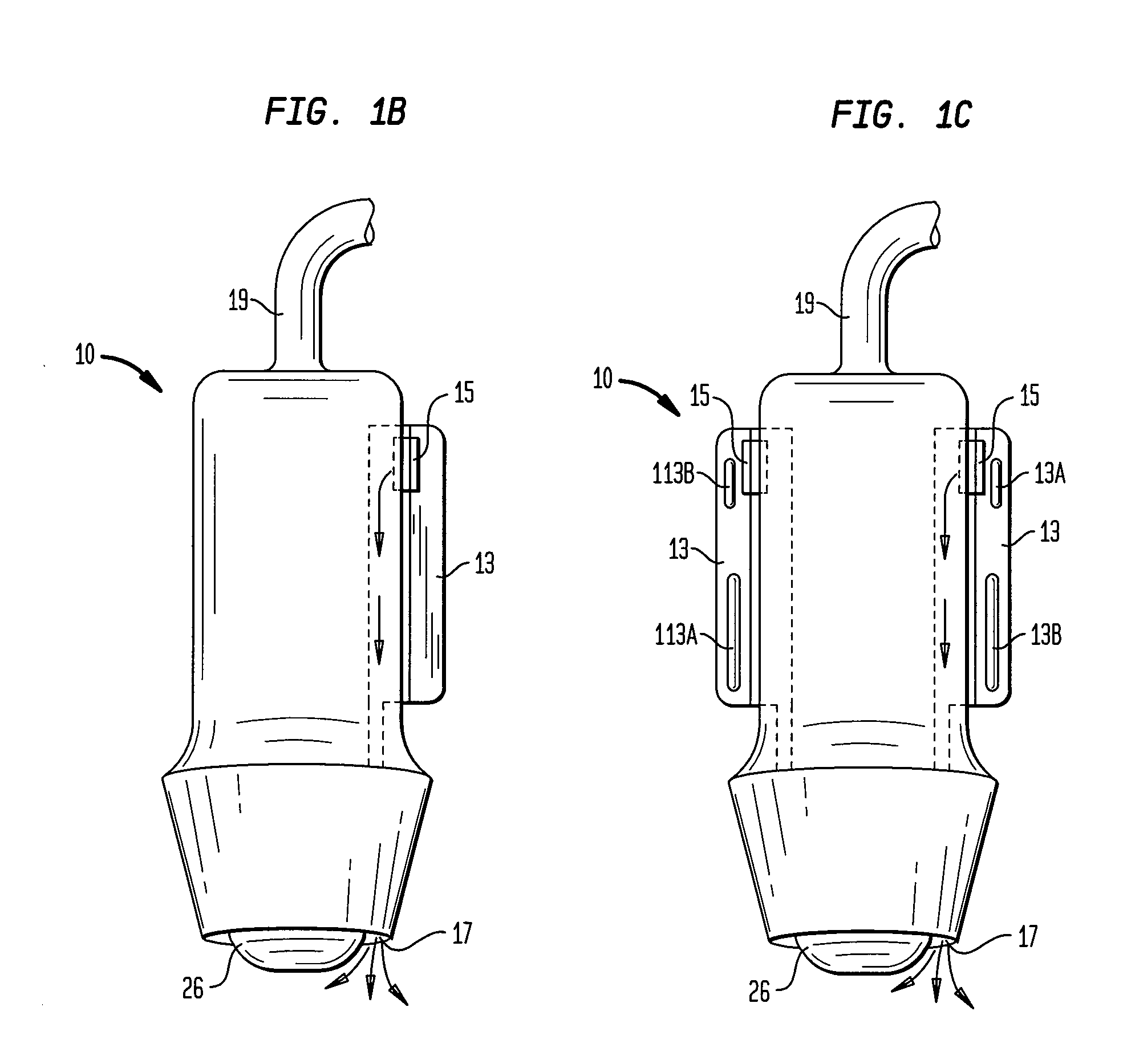
Systems and methods for making noninvasive physiological assessments
InactiveUS6875176B2Improve accuracySensitive highOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryDiseaseNon invasive
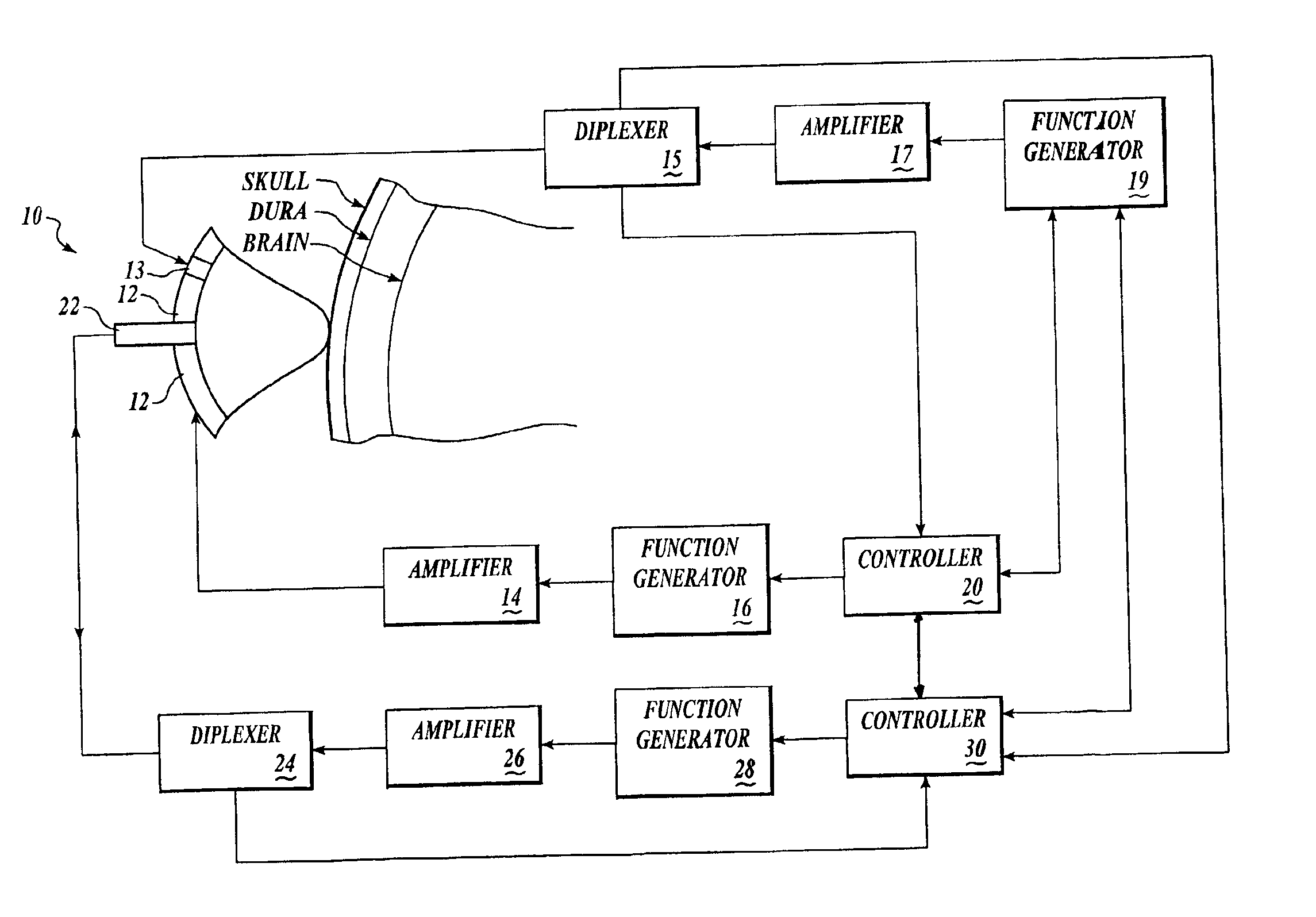
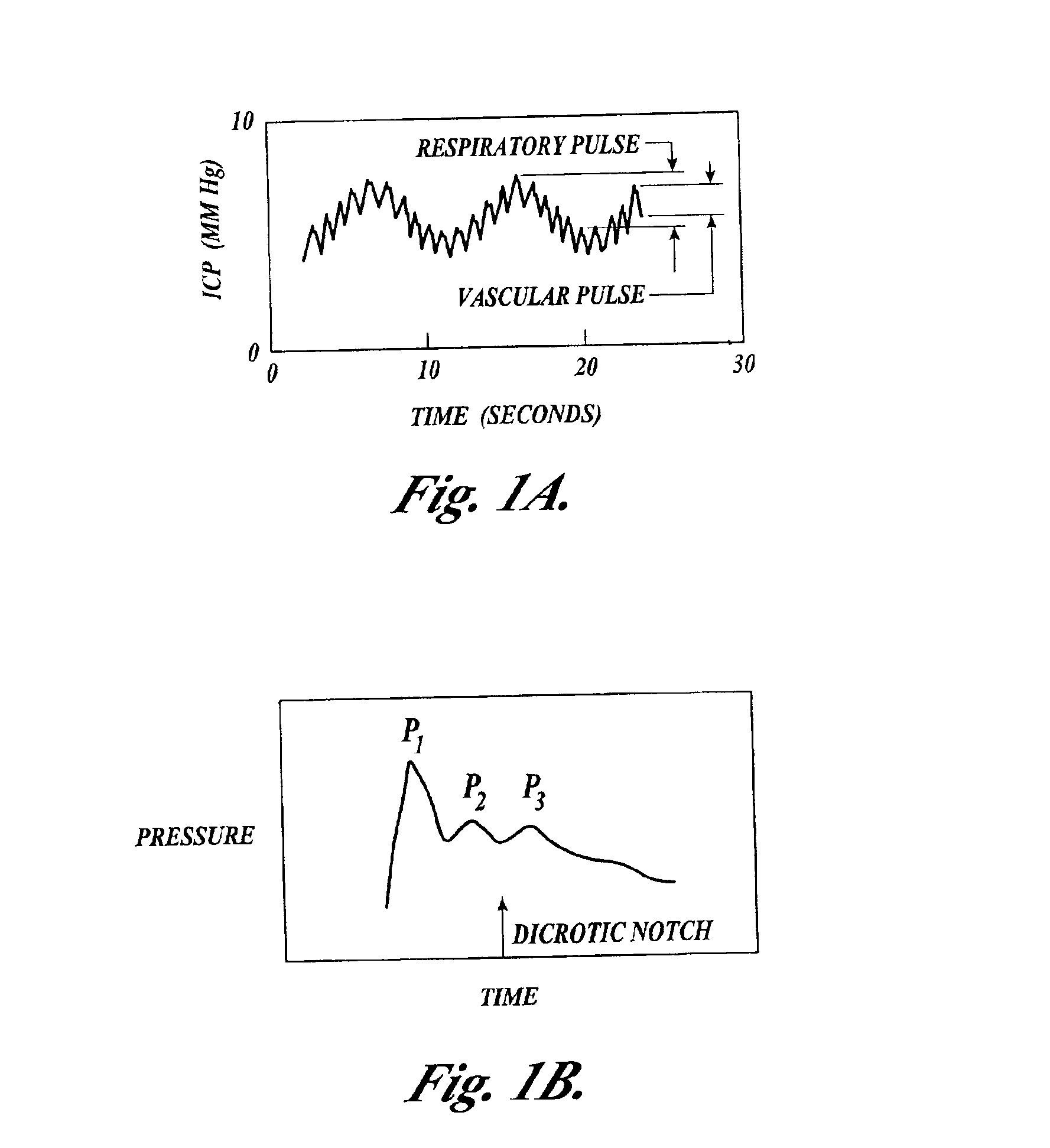
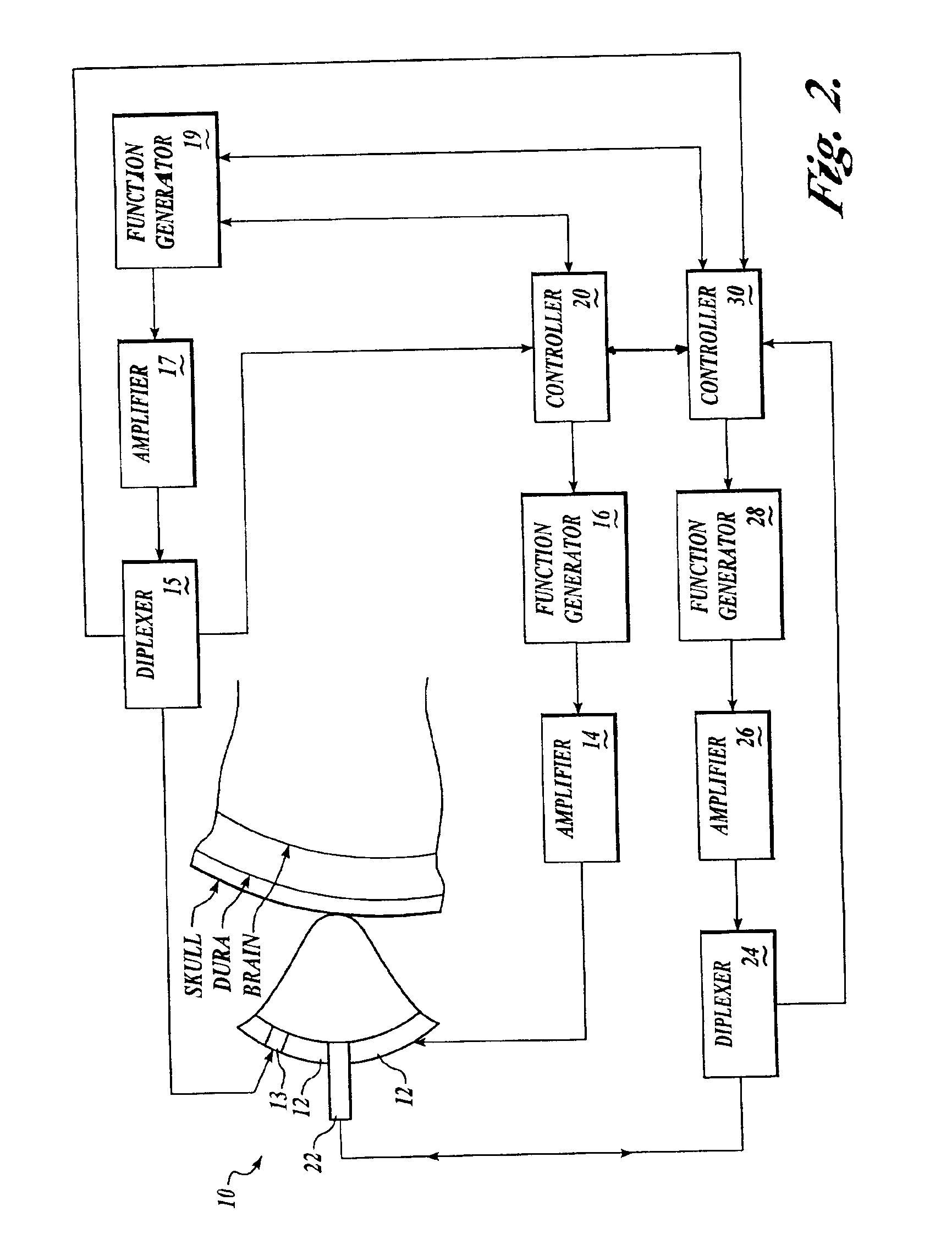
Systems and methods for assessment of tissue properties, noninvasively, by acquiring data relating to at least one aspect of intrinsic and / or induced tissue displacement, or associated biological responses, are provided. Data relating to tissue displacement and associated biological changes may be acquired by detecting acoustic properties of tissue using ultrasound interrogation pulses, preferably in a scatter or Doppler detection mode. Based on this data, tissue properties are assessed, characterized and monitored. Specific applications for systems and methods of the present invention include non-invasive assessment and monitoring of intracranial pressure (ICP), arterial blood pressure (ABP), CNS autoregulation status, vasospasm, stroke, local edema, infection and vasculitus, as well as diagnosis and monitoring of diseases and conditions that are characterized by physical changes in tissue properties. Methods and systems for localizing physiological condition(s) and / or biological response(s), such as pain, by targeting and selectively probing tissues using the application of focused ultrasound are also provided.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS
Ultrasonic radial focused transducer for pulmonary vein ablation
ActiveUS7066895B2Overcome disadvantagesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyVeinPulmonary vein ablation
A method for ablating tissue with ultrasonic energy is provided. The method including: generating ultrasonic energy from one or more ultrasonic transducers; and focusing the ultrasonic energy in the radial direction by one of: shaping the one or more ultrasonic transducers to focus ultrasonic energy in the radial direction; and arranging one or more lenses proximate the one or more ultrasonic transducers for focusing the ultrasonic energy from the one or more ultrasonic transducers in a radial direction.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Methods of using high intensity focused ultrasound to form an ablated tissue area containing a plurality of lesions
InactiveUS20050267454A1Improve the level ofWithout impairingUltrasound therapyChiropractic devicesHigh intensityHigh-intensity focused ultrasound
A method of thermal ablation using high intensity focused ultrasound energy includes the steps of positioning an ultrasound emitting member, emitting ultrasound energy from the ultrasound emitting member, focusing the ultrasound energy, ablating with the focused ultrasound energy to form an ablated tissue area and removing the ultrasound emitting member.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods of using high intensity focused ultrasound to form an ablated tissue area
InactiveUS20060025756A1Easy positioningEasily manipulateUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyHigh intensityHigh-intensity focused ultrasound
A method of thermal ablation using high intensity focused ultrasound energy includes the steps of positioning one or more ultrasound emitting members within a patient, emitting ultrasound energy from the one or more ultrasound emitting members, focusing the ultrasound energy, ablating with the focused ultrasound energy to form an ablated tissue area and removing the ultrasound emitting member.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
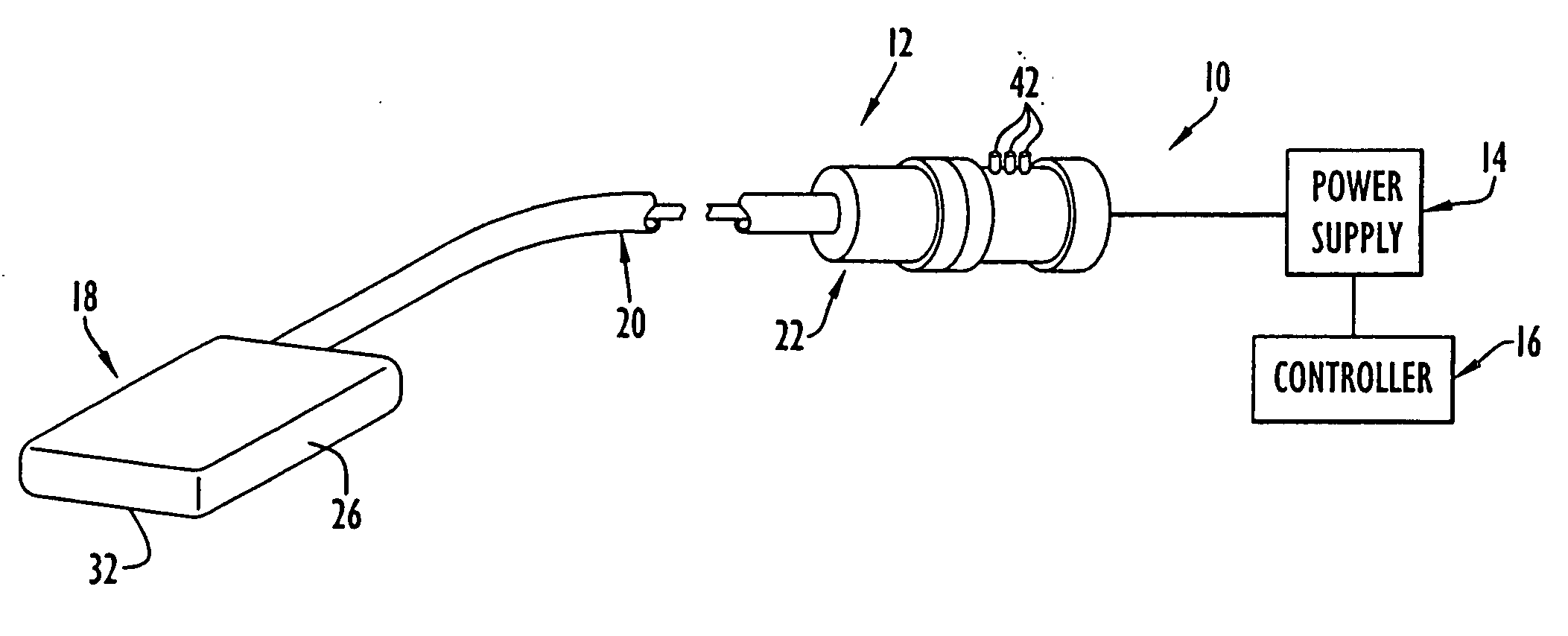
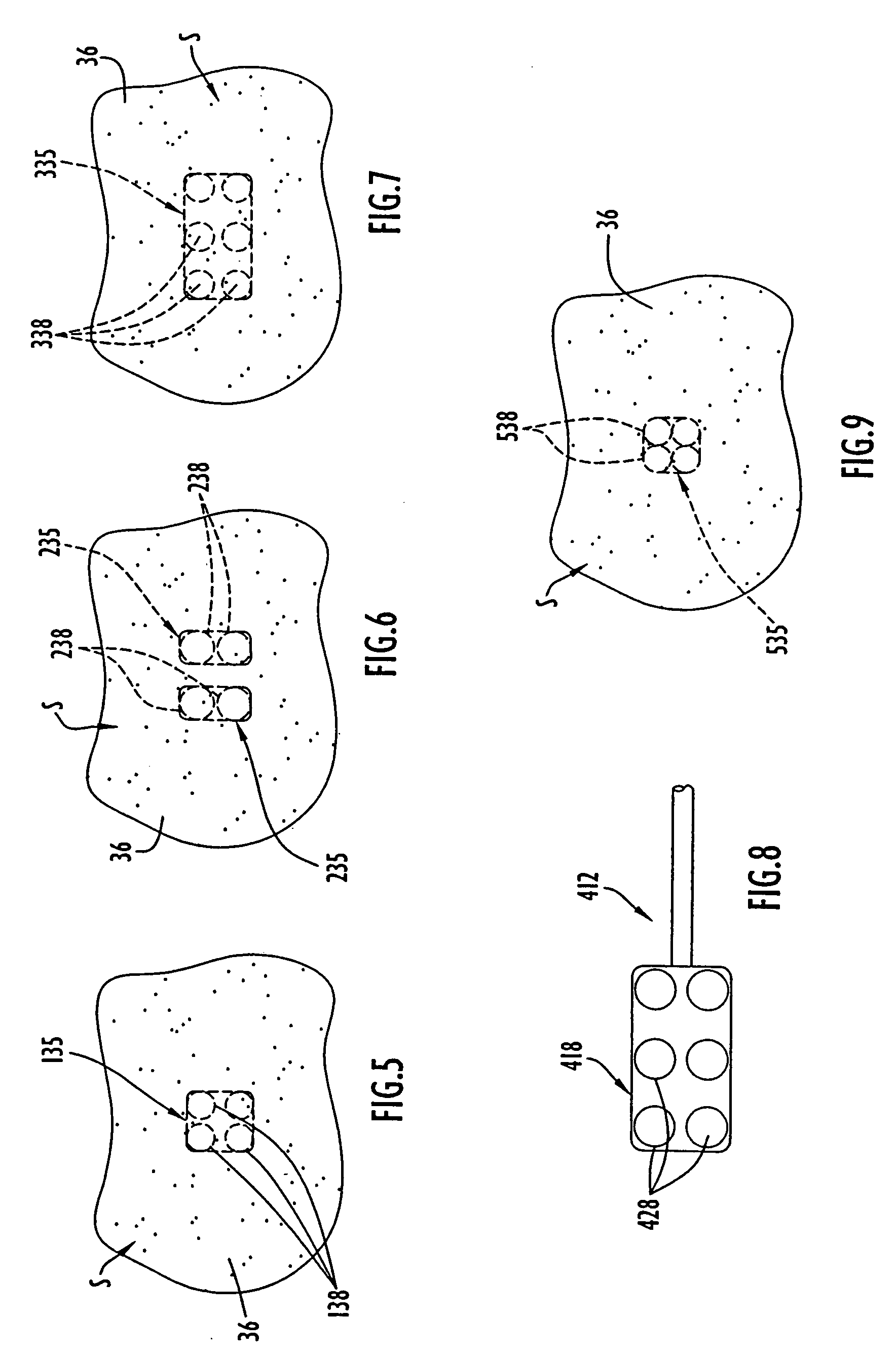
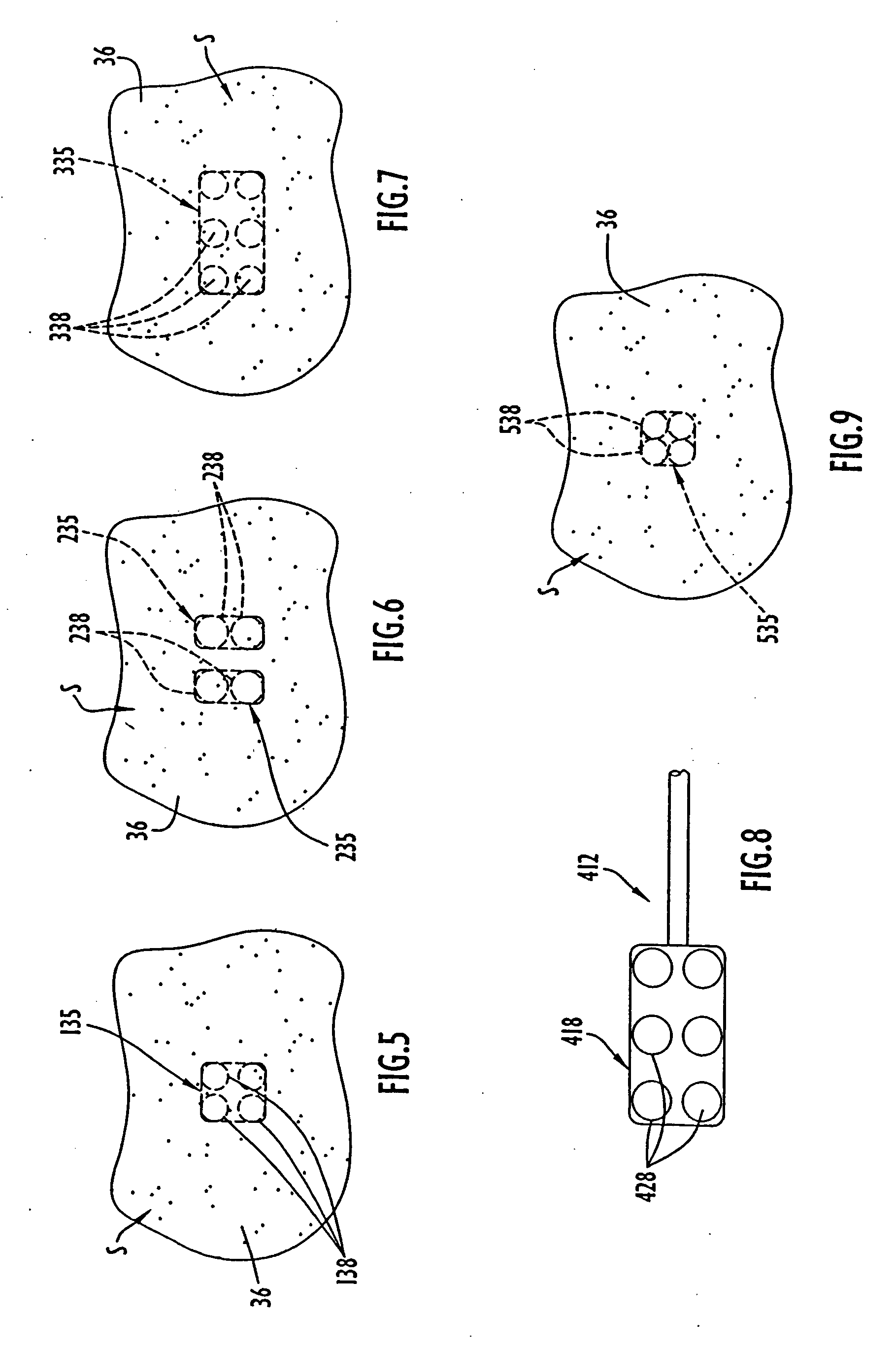
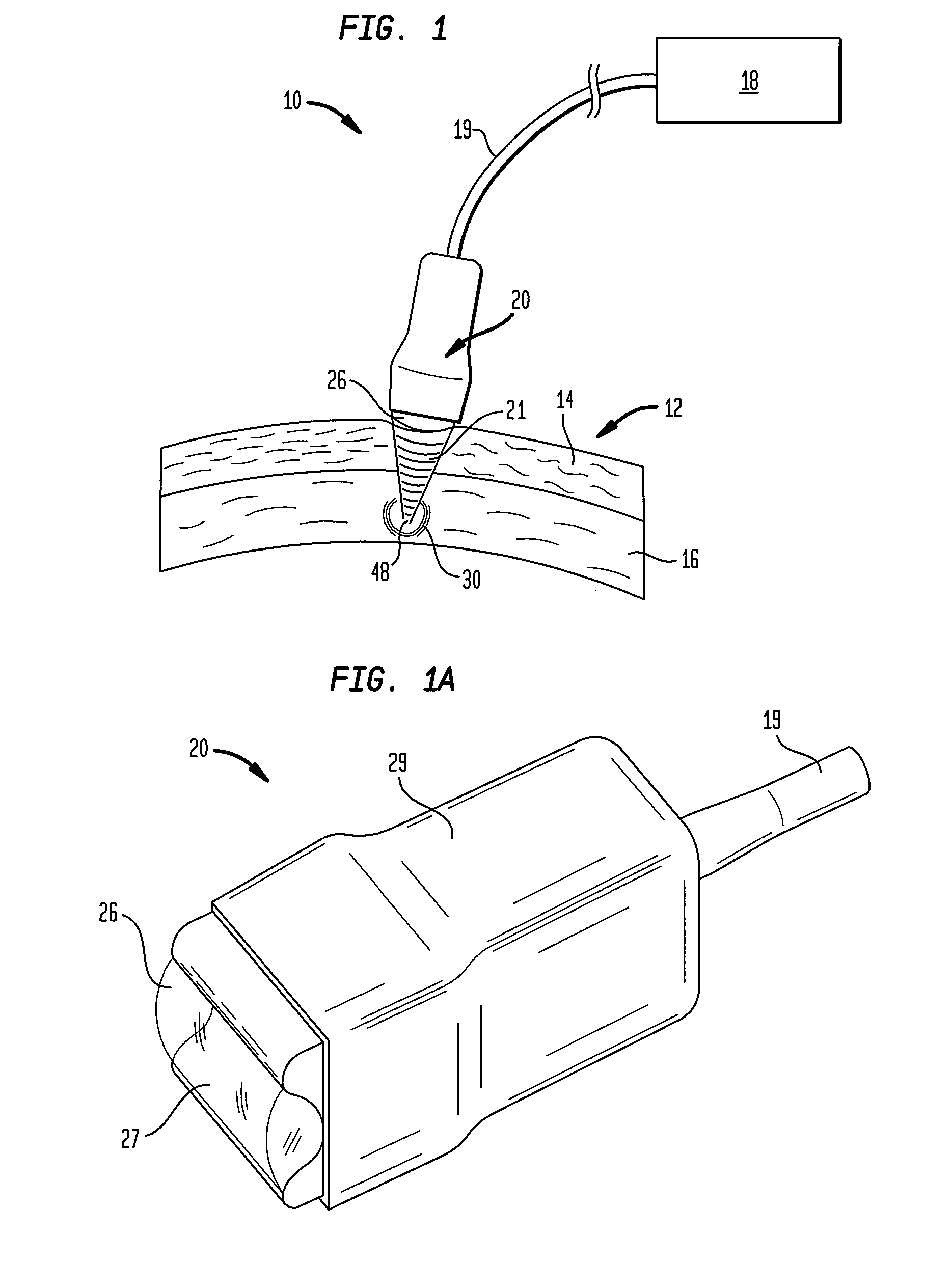
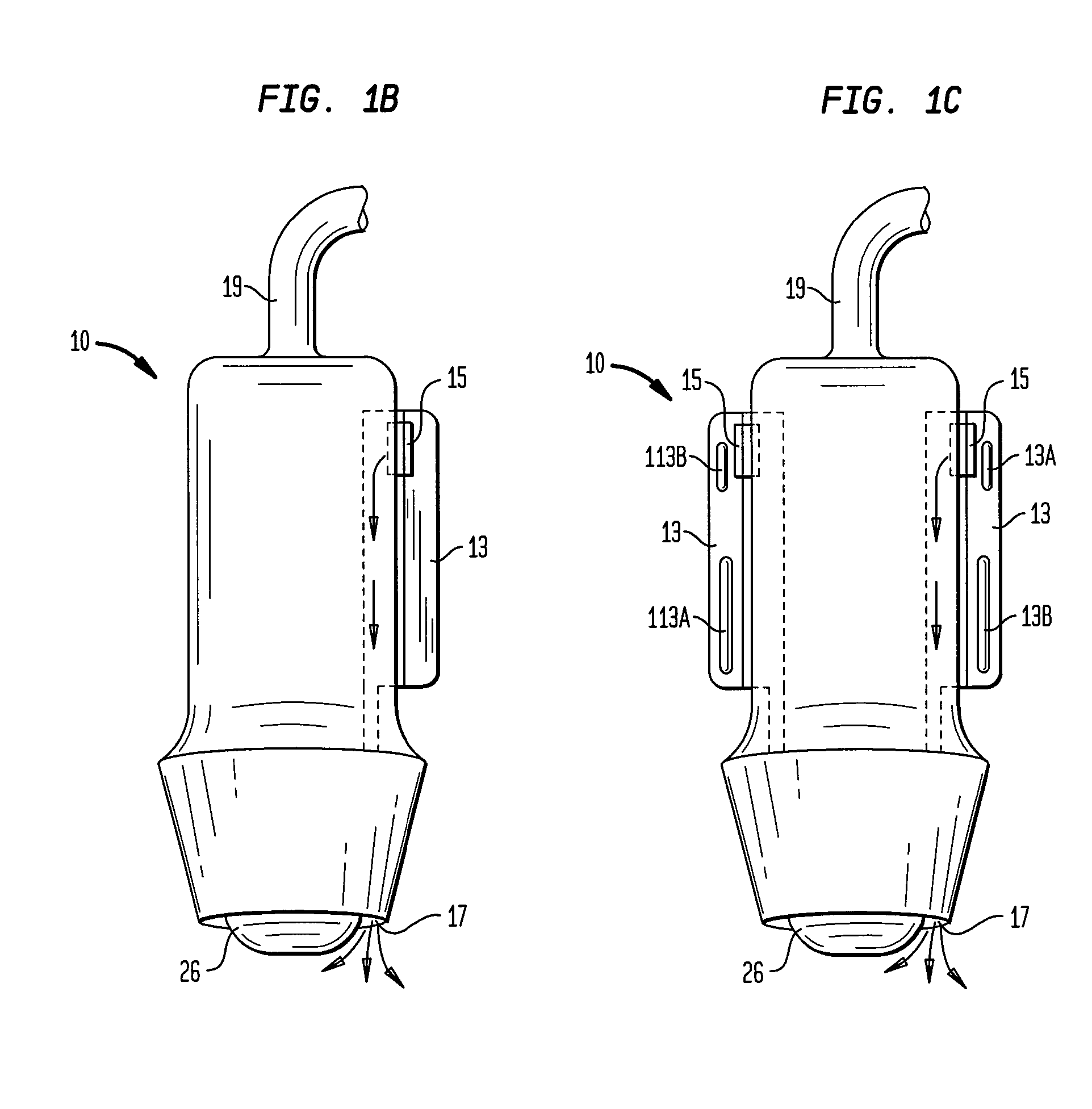
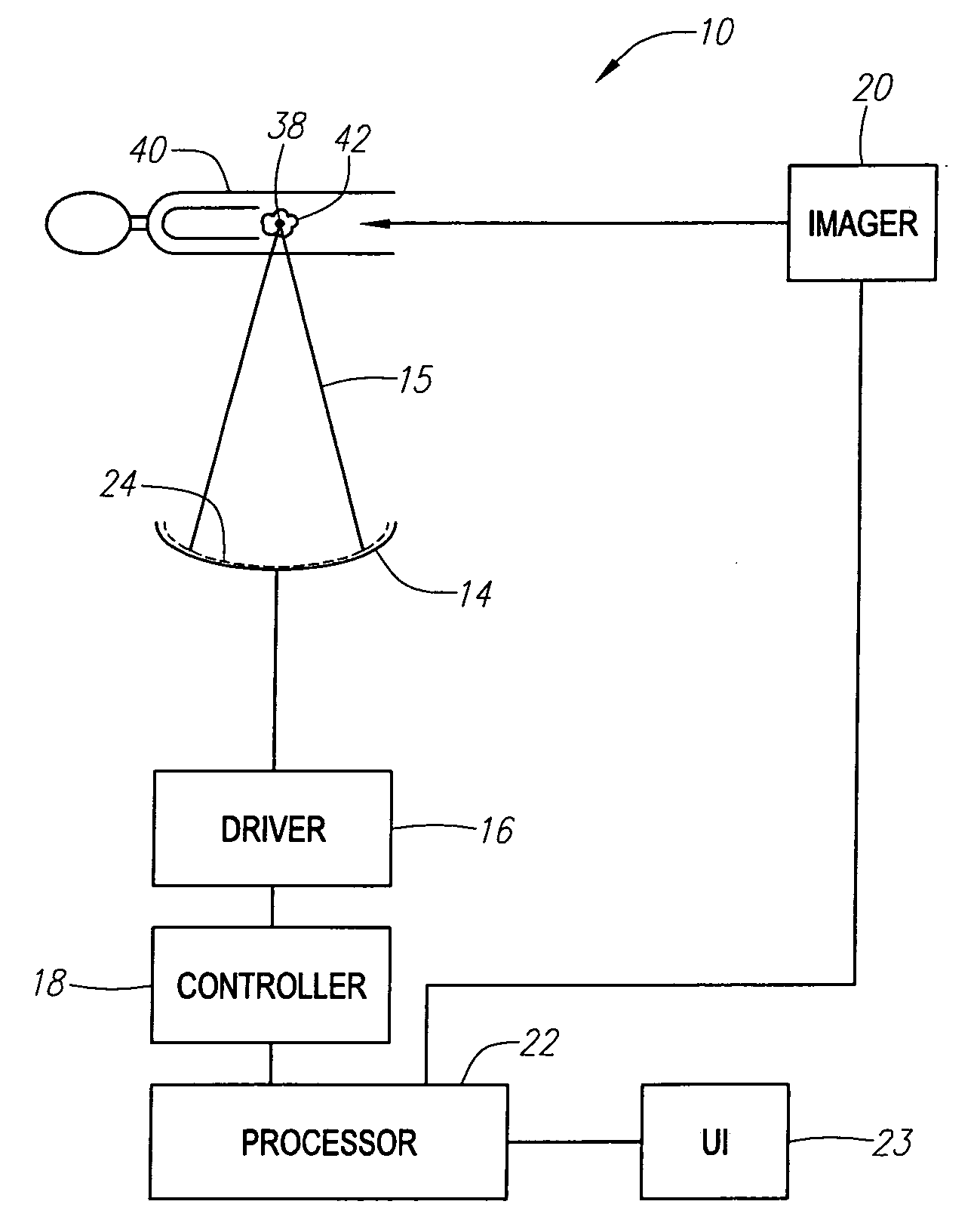
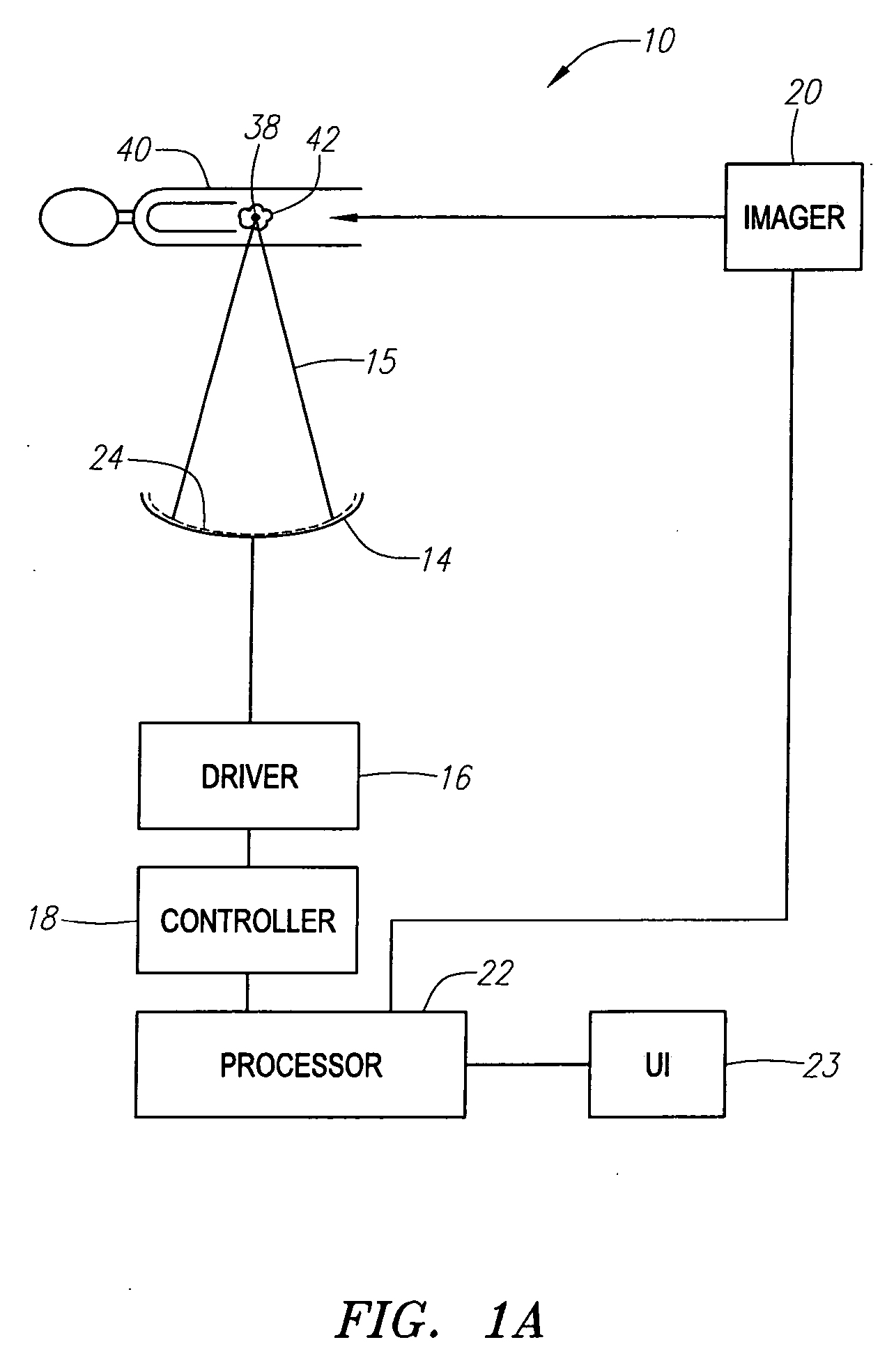
Focused ultrasound for pain reduction
InactiveUS20060184069A1Relieve painUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapySonificationTransducer
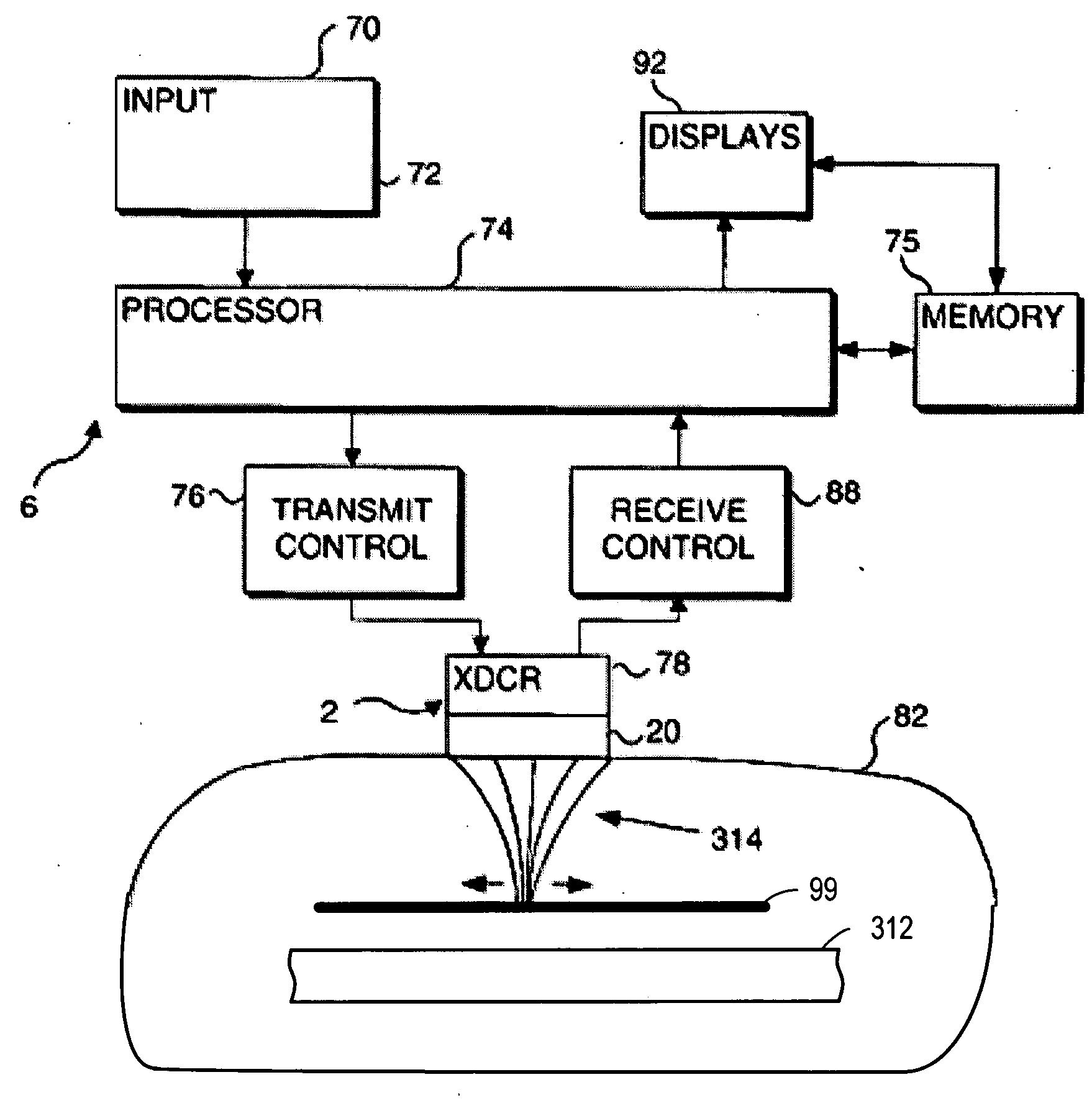
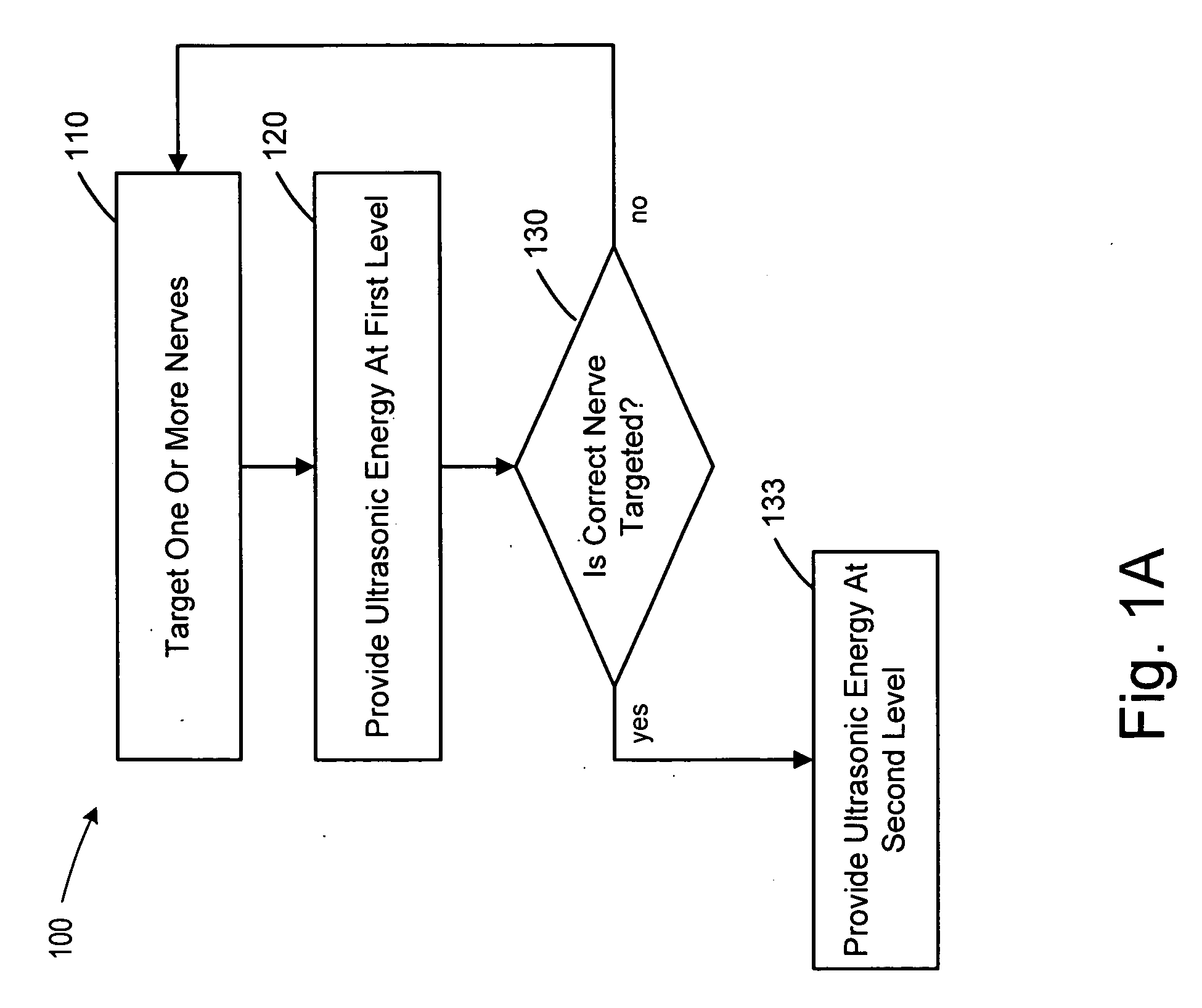
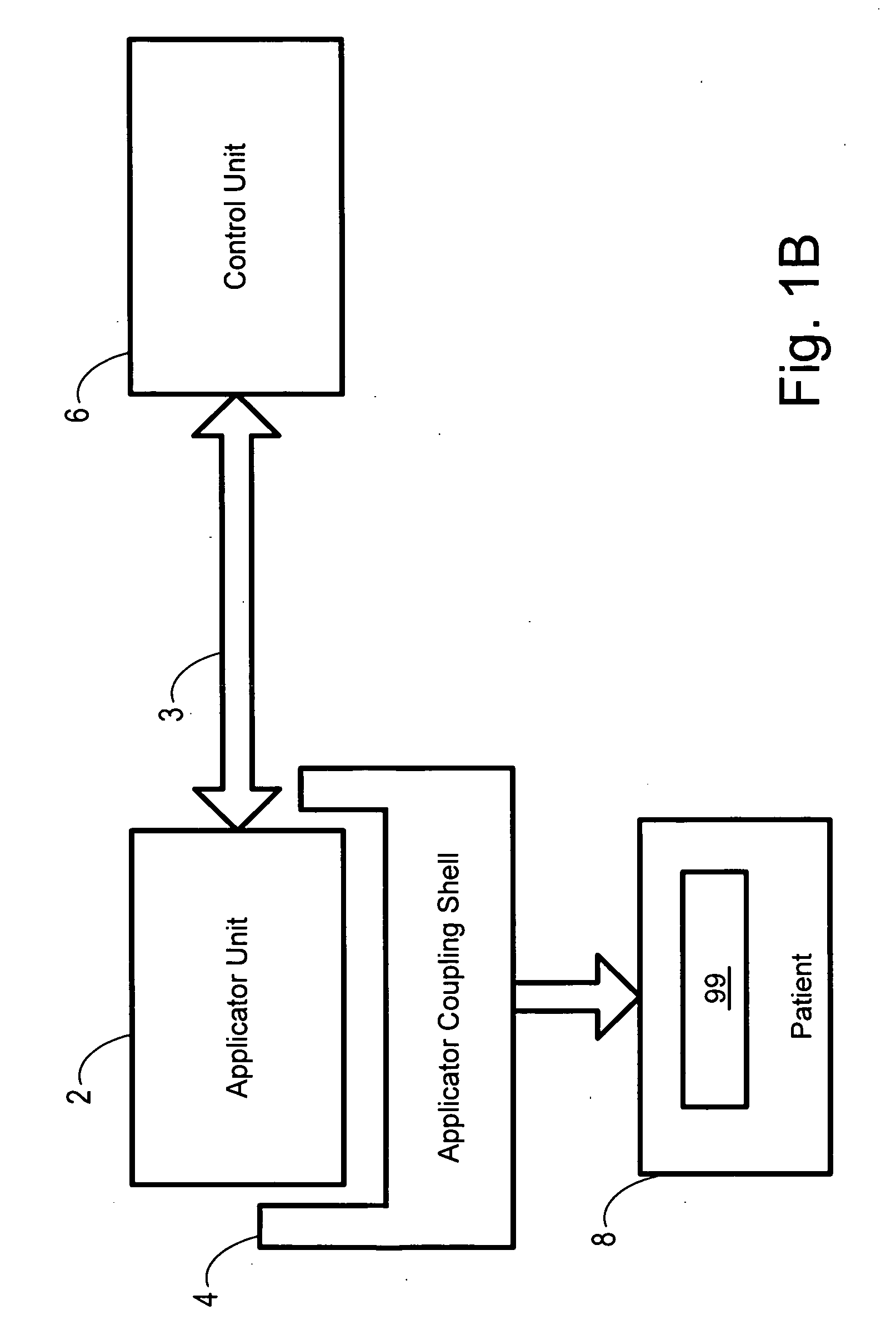
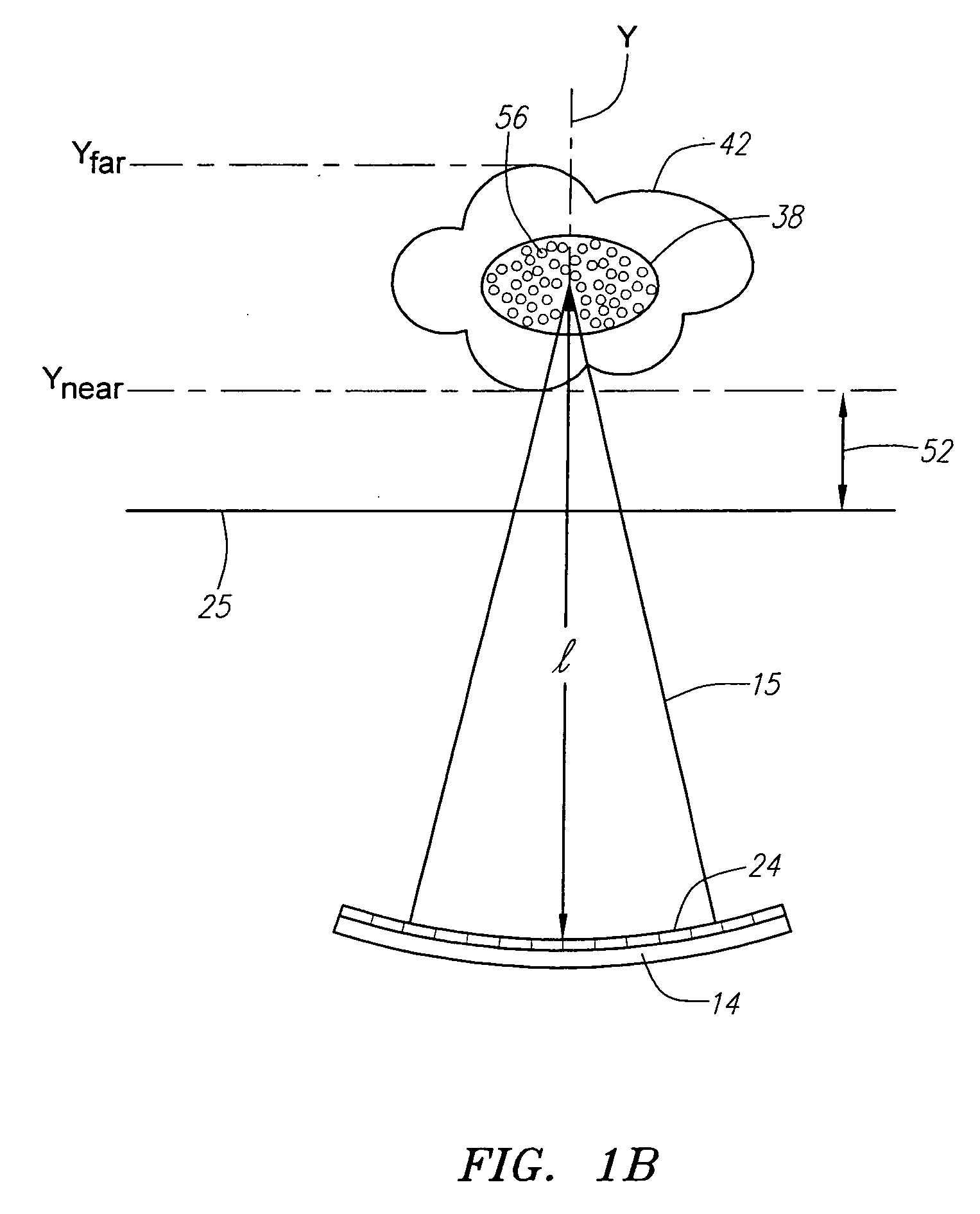
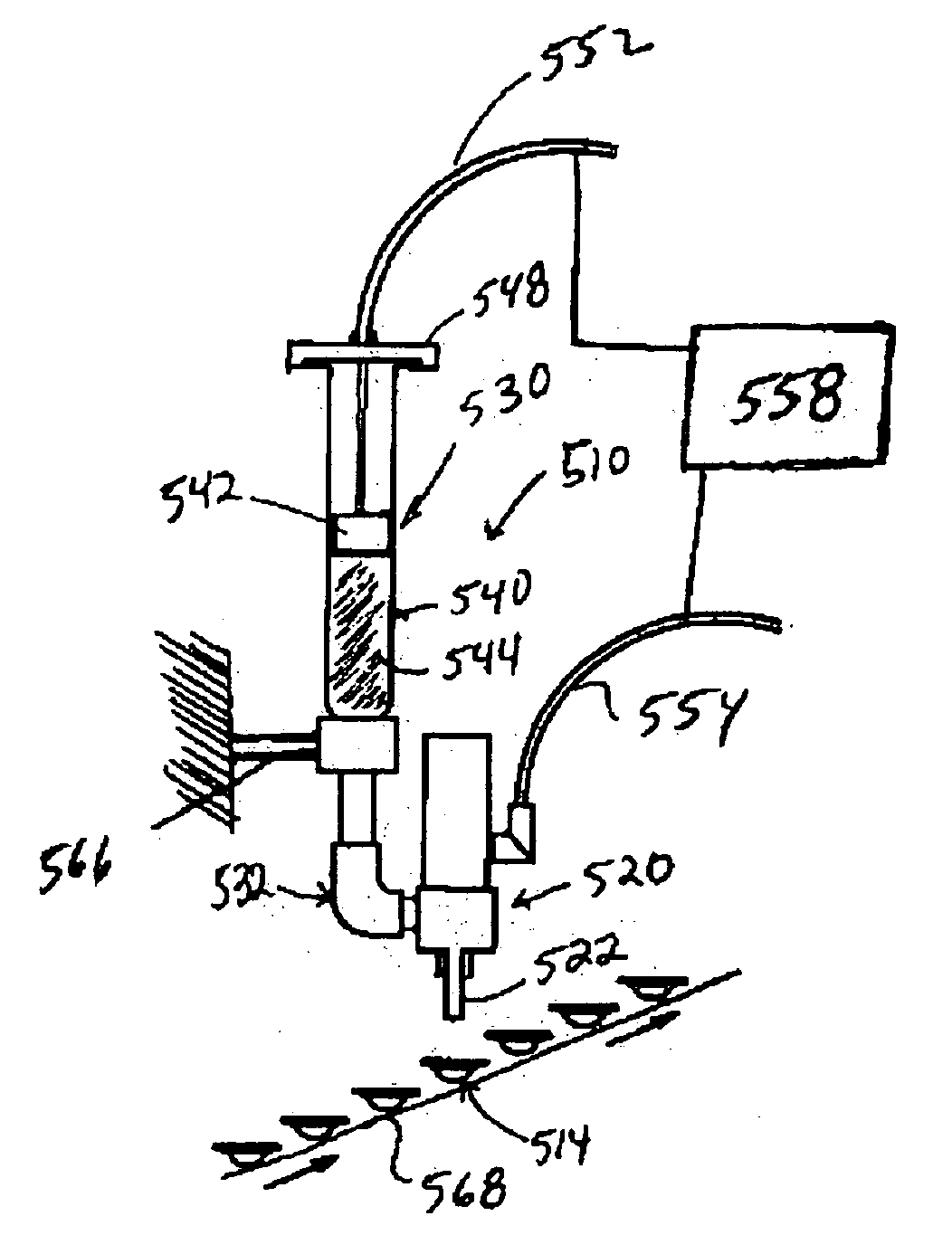
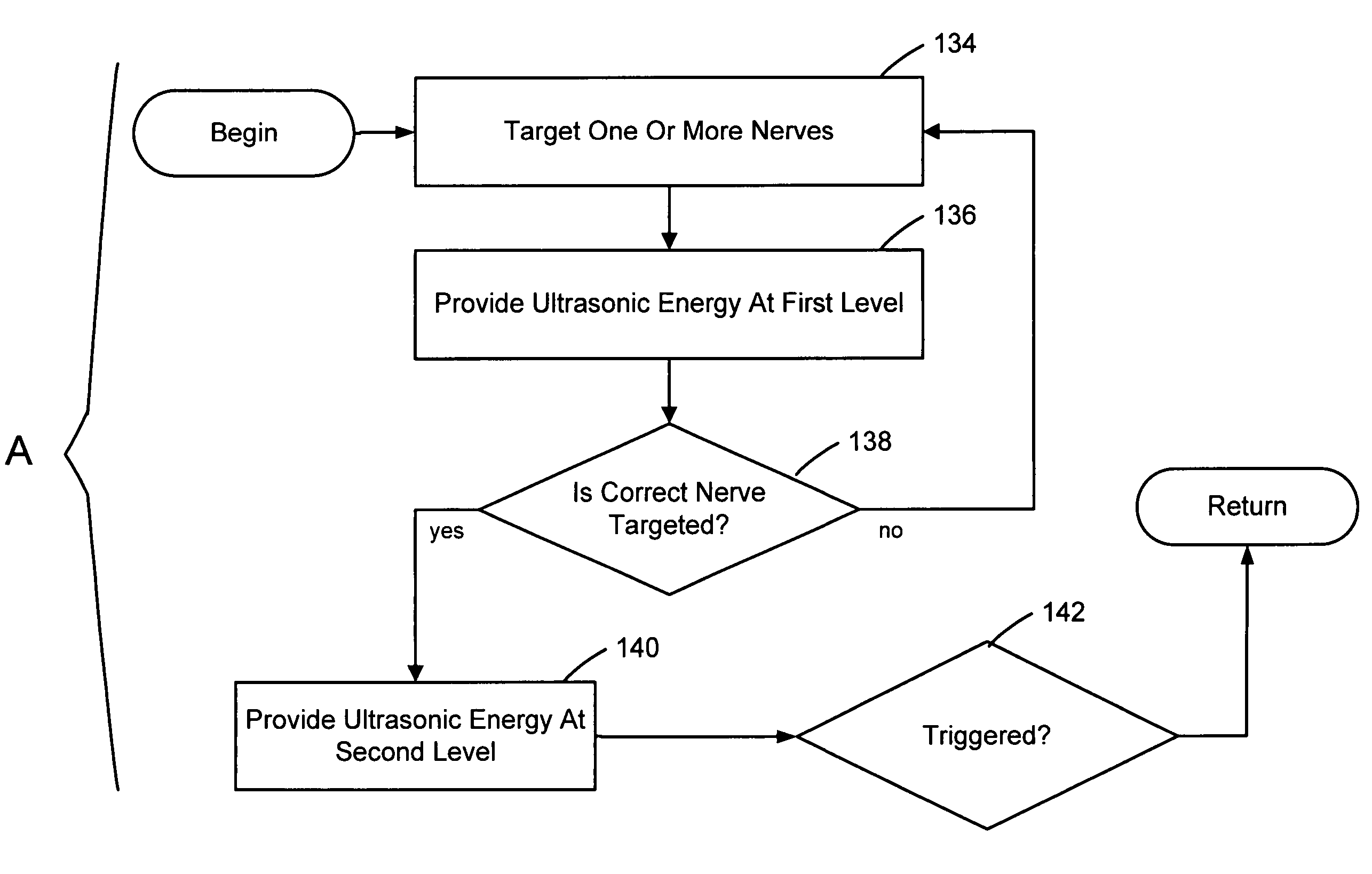
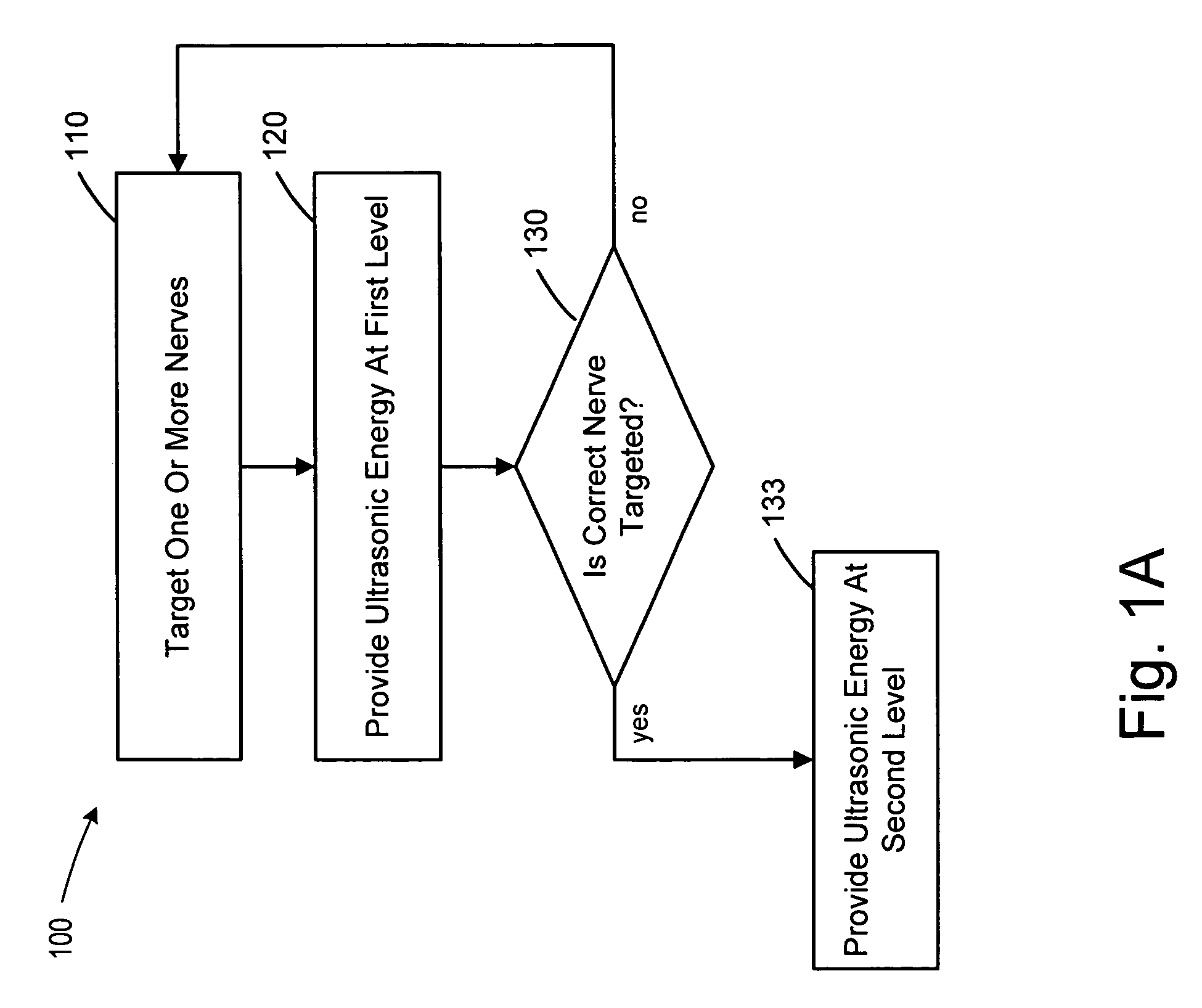
Methods and devices that provide ultrasonic energy used to cause one or more nerves to become dysfunctional. A nerve to be treated is placed in the focal zone of ultrasonic energy emitted by ultrasound transducer. A first level of ultrasonic energy is provided to the nerve using the ultrasound transducer, the first level sufficient to stimulate the nerve. A verification is made that the desired nerve is being stimulated by the first level of ultrasonic energy. For example, the patient may be asked to confirm that the ultrasonically stimulated nerve corresponds to the pain that is affecting the patient. Subsequent to verifying the stimulated nerve is the nerve desired for the reduction of pain, a second level of ultrasonic energy is delivered to the nerve using the ultrasound transducer, the second level of ultrasonic energy sufficient to cause nerve dysfunction.
Owner:VAITEKUNAS JEFFREY J
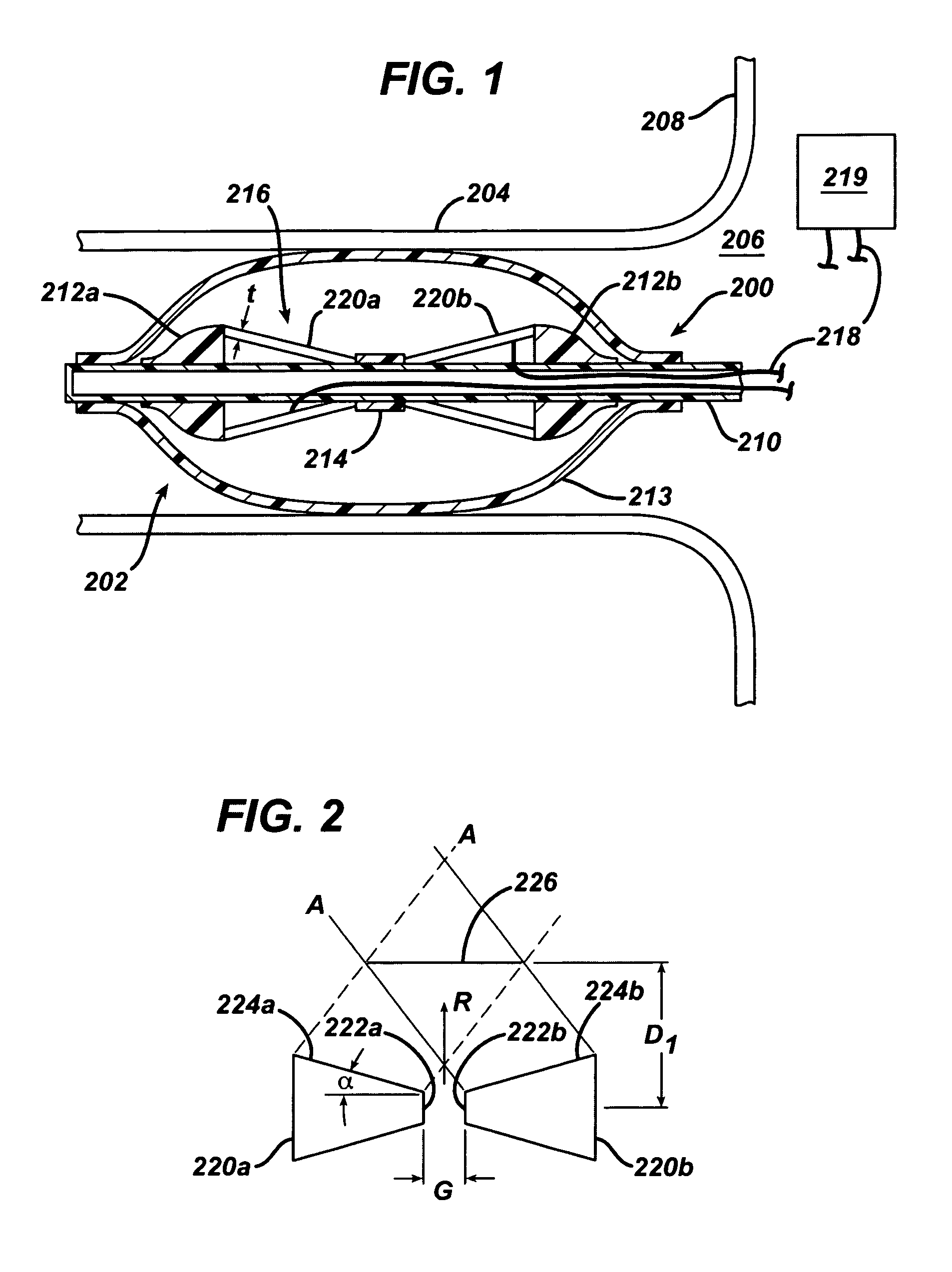
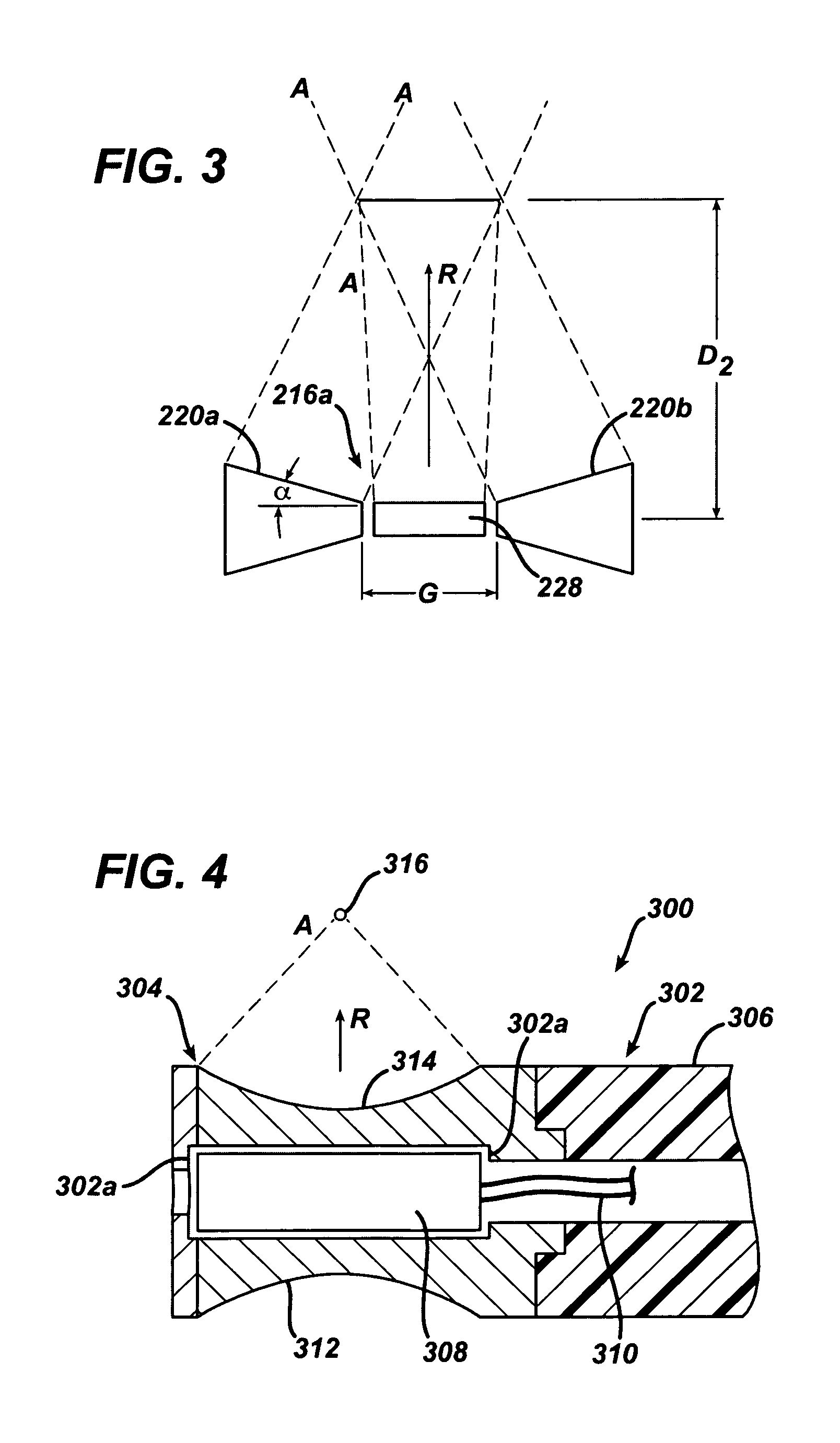
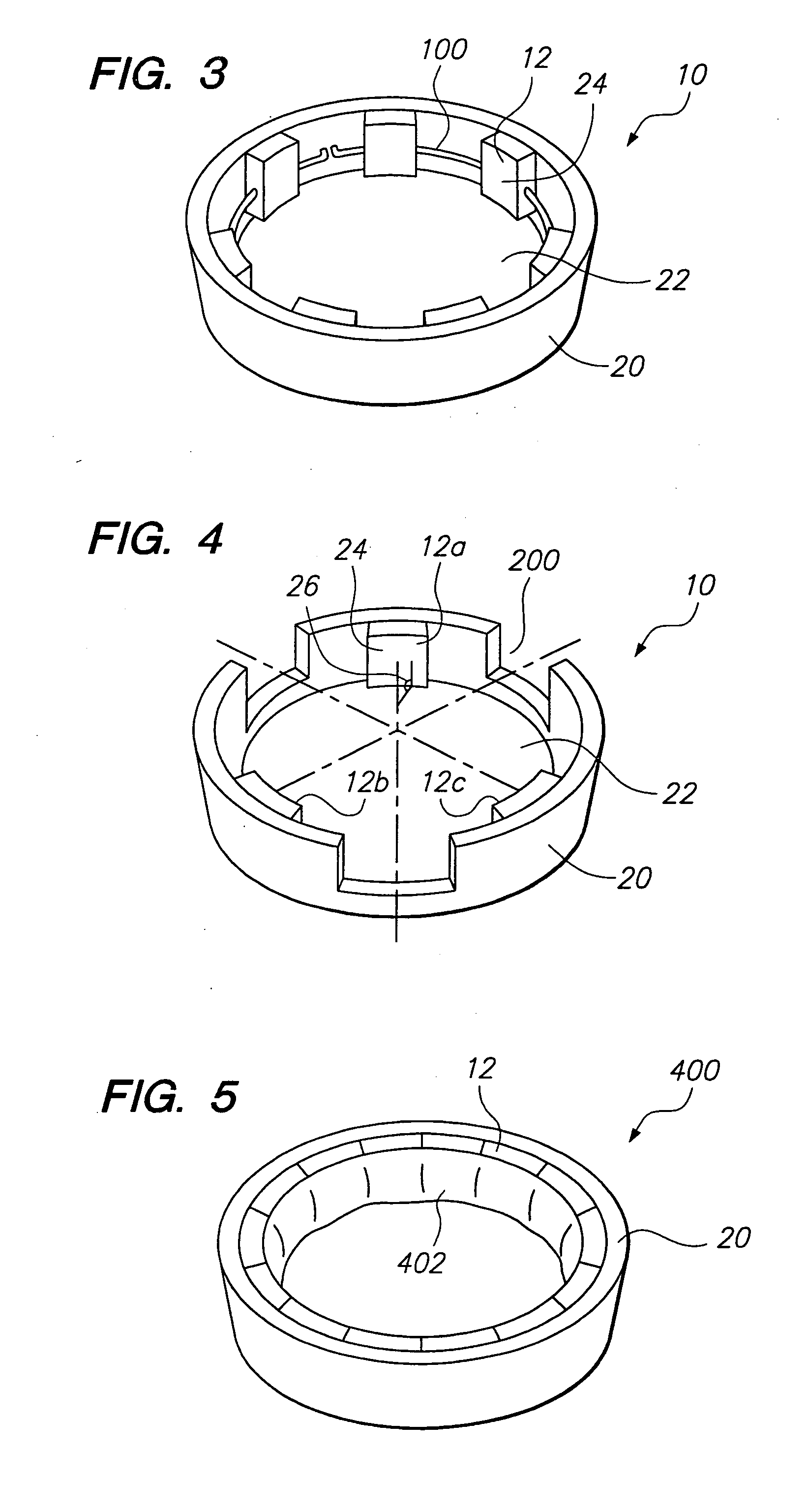
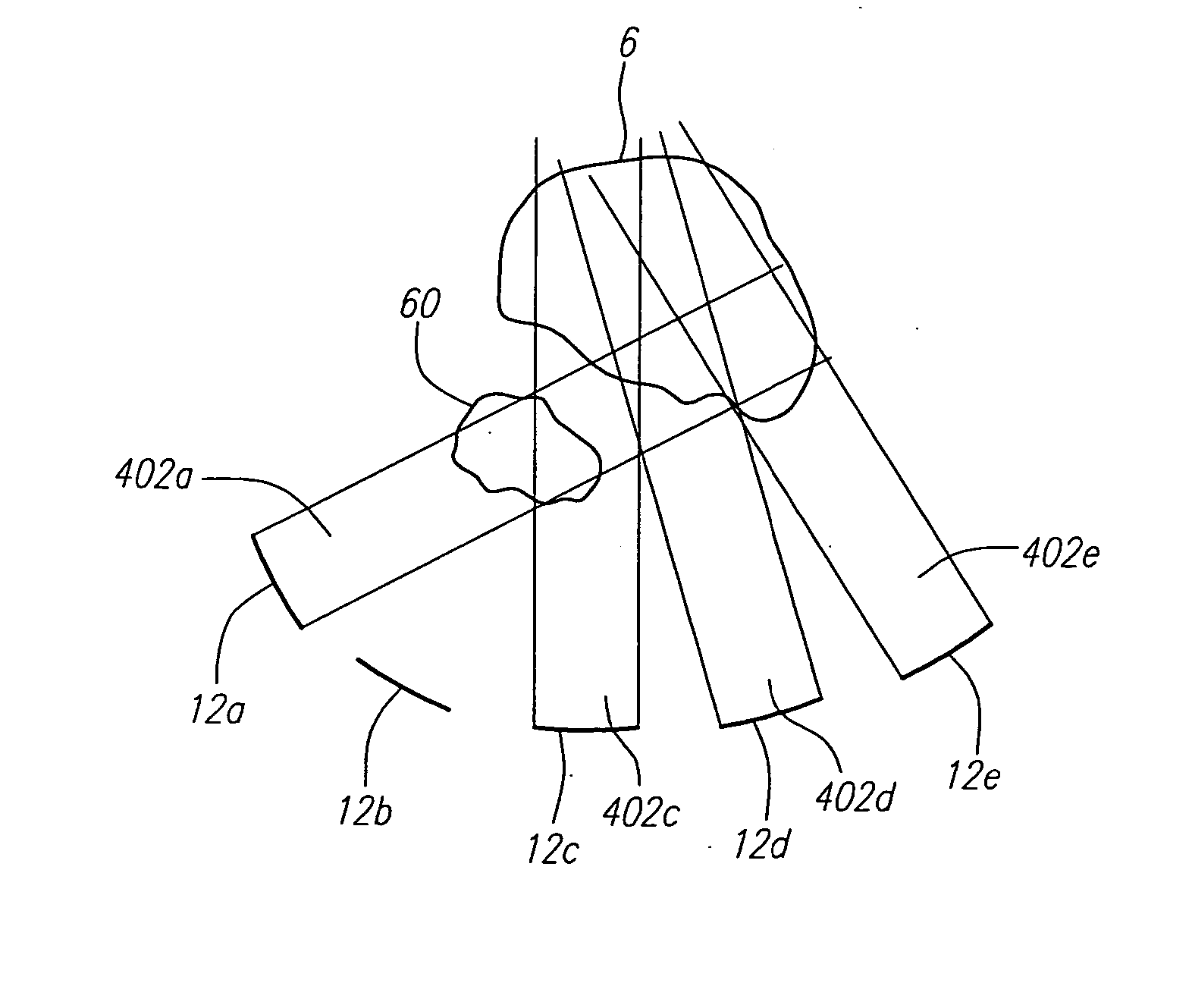
Focused ultrasound system for surrounding a body tissue mass
ActiveUS20060058678A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasonic sensorDevice form
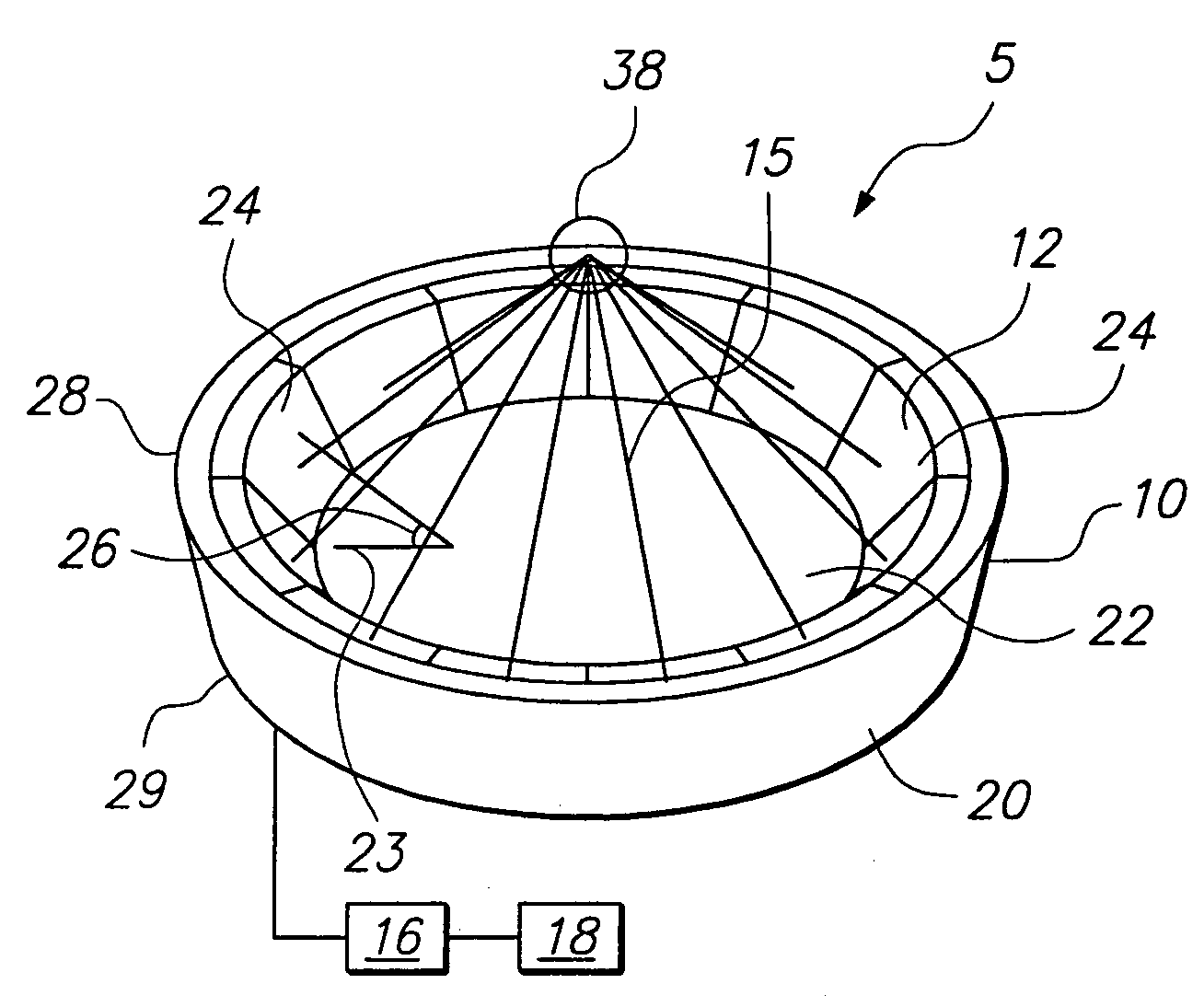
A focused ultrasound system includes an ultrasound transducer device forming an opening, and having a plurality of transducer elements positioned at least partially around the opening. A focused ultrasound system includes a structure having a first end for allowing an object to be inserted and a second end for allowing the object to exit, and a plurality of transducer elements coupled to the structure, the transducer elements located relative to each other in a formation that at least partially define an opening, wherein the transducer elements are configured to emit acoustic energy that converges at a focal zone.
Owner:INSIGHTEC
Focused ultrasound system with adaptive anatomical aperture shaping
ActiveUS20060058671A1Reducing ultrasound energyUltrasound therapyBlood flow measurement devicesSonificationTransducer
A method of treating tissue within a body includes directing an ultrasound transducer having a plurality of transducer elements towards target body tissue, and delivering ultrasound energy towards the target tissue from the transducer elements such that an energy intensity at the target tissue is at or above a prescribed treatment level, while an energy intensity at tissue to be protected in the ultrasound energy path of the transducer elements is at or below a prescribed safety level.
Owner:INSIGHTEC
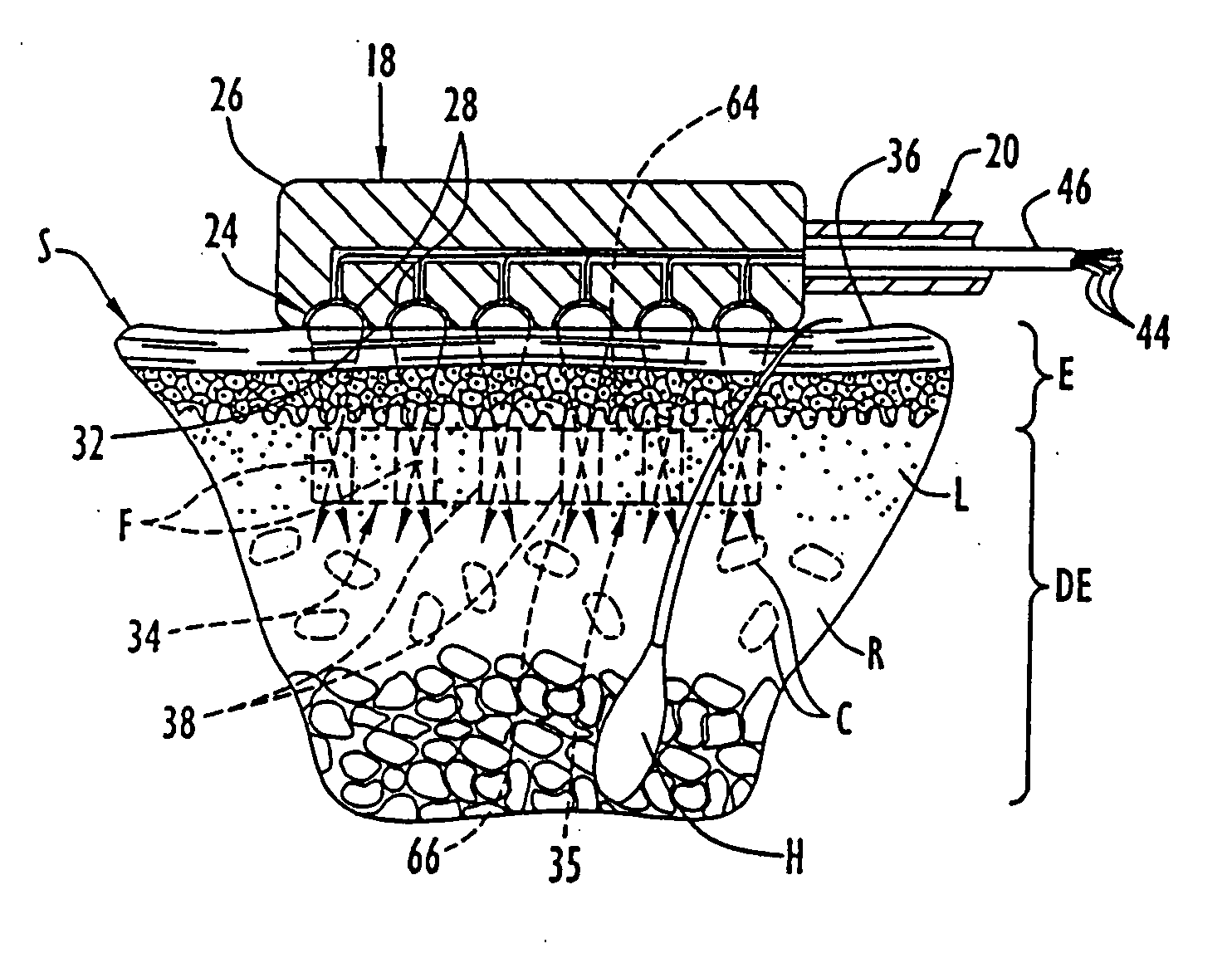
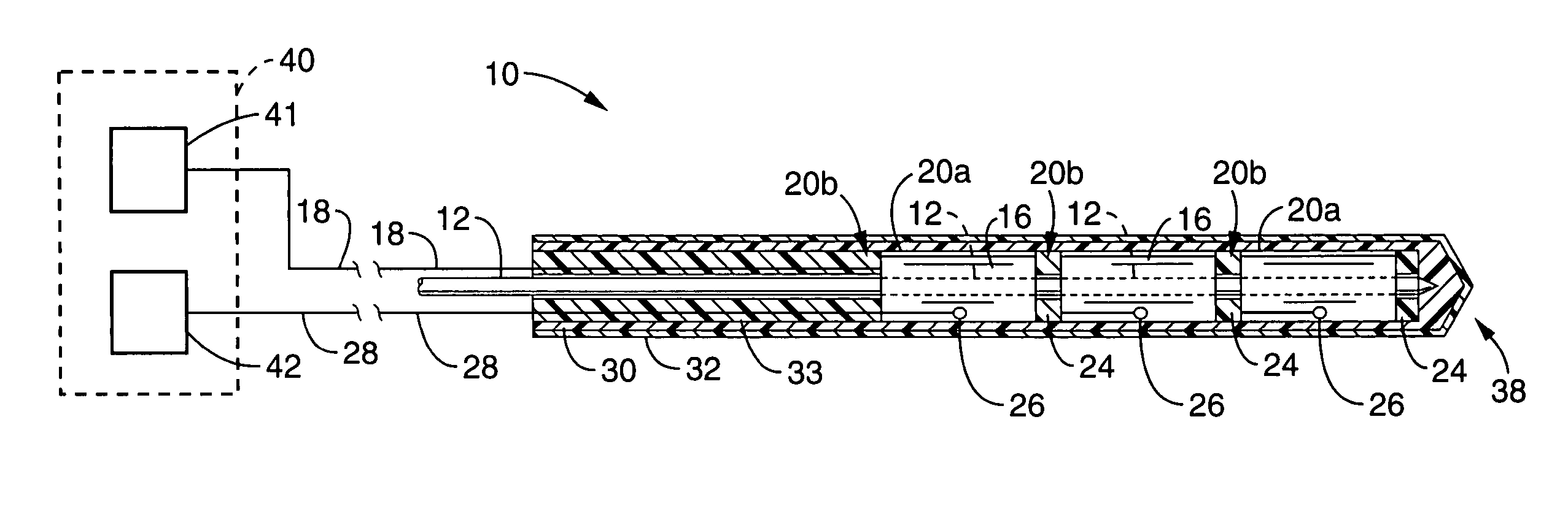
Implantable thermal treatment method and apparatus
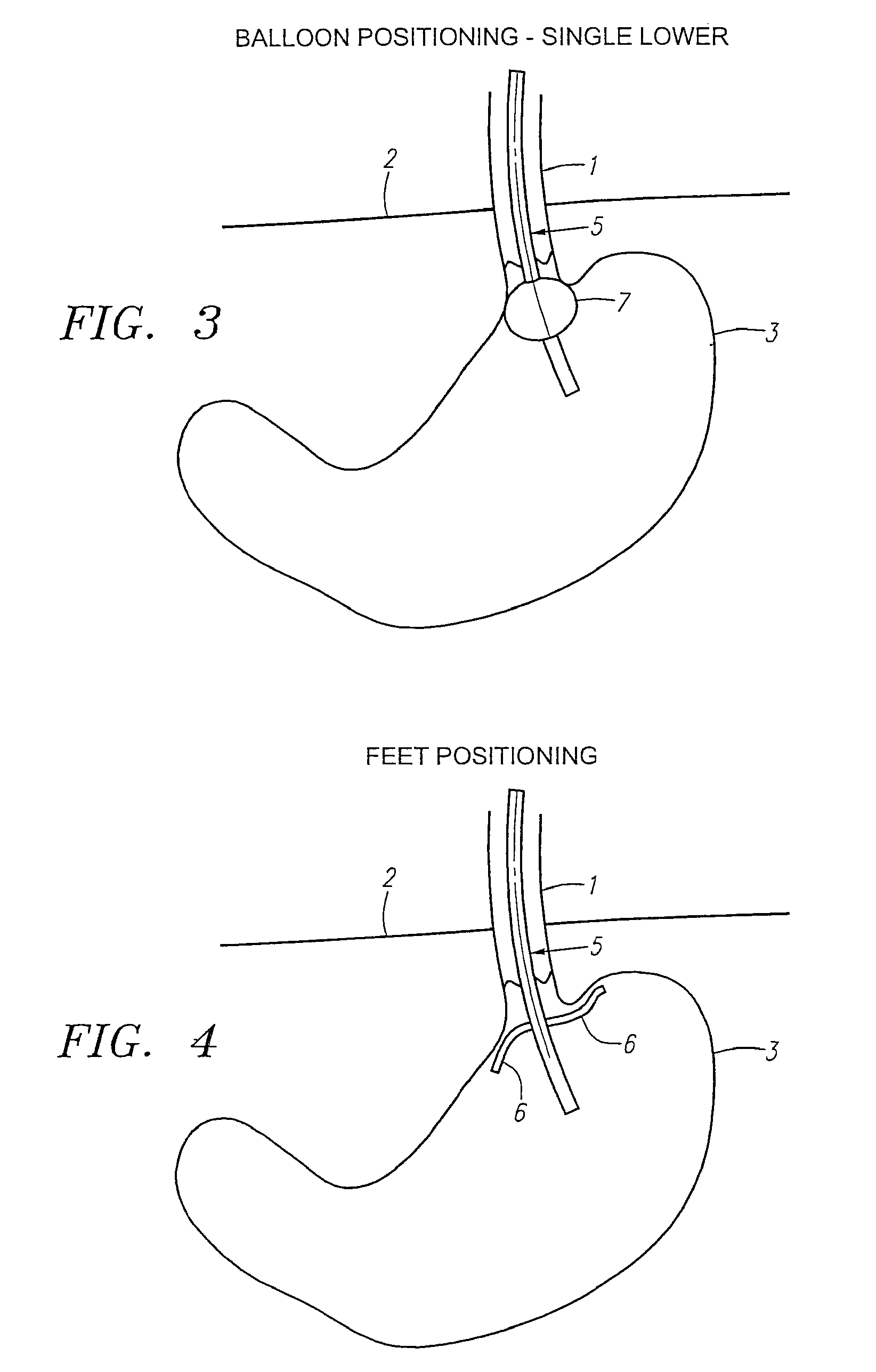
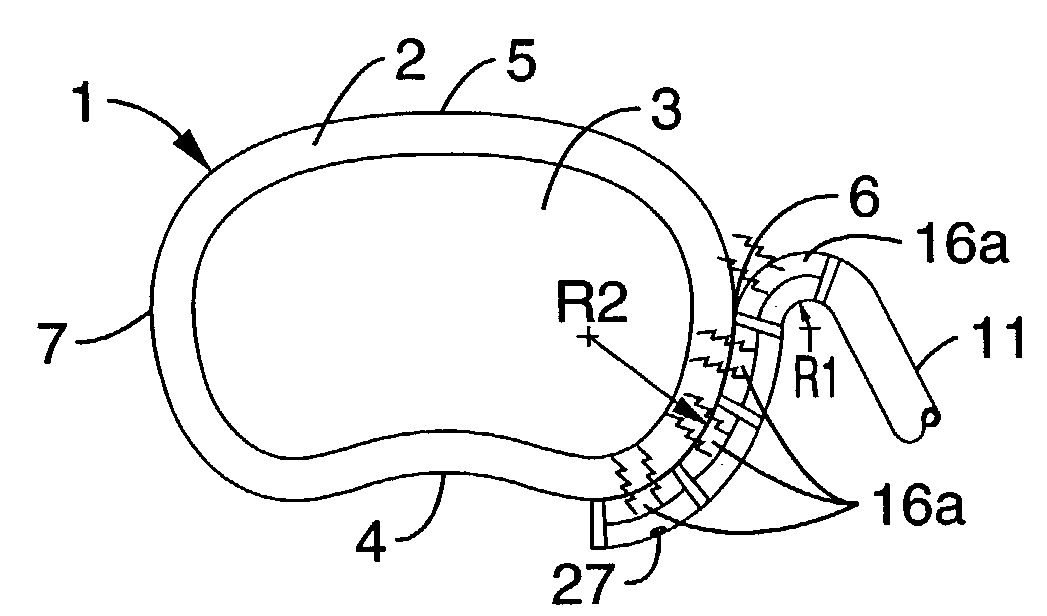
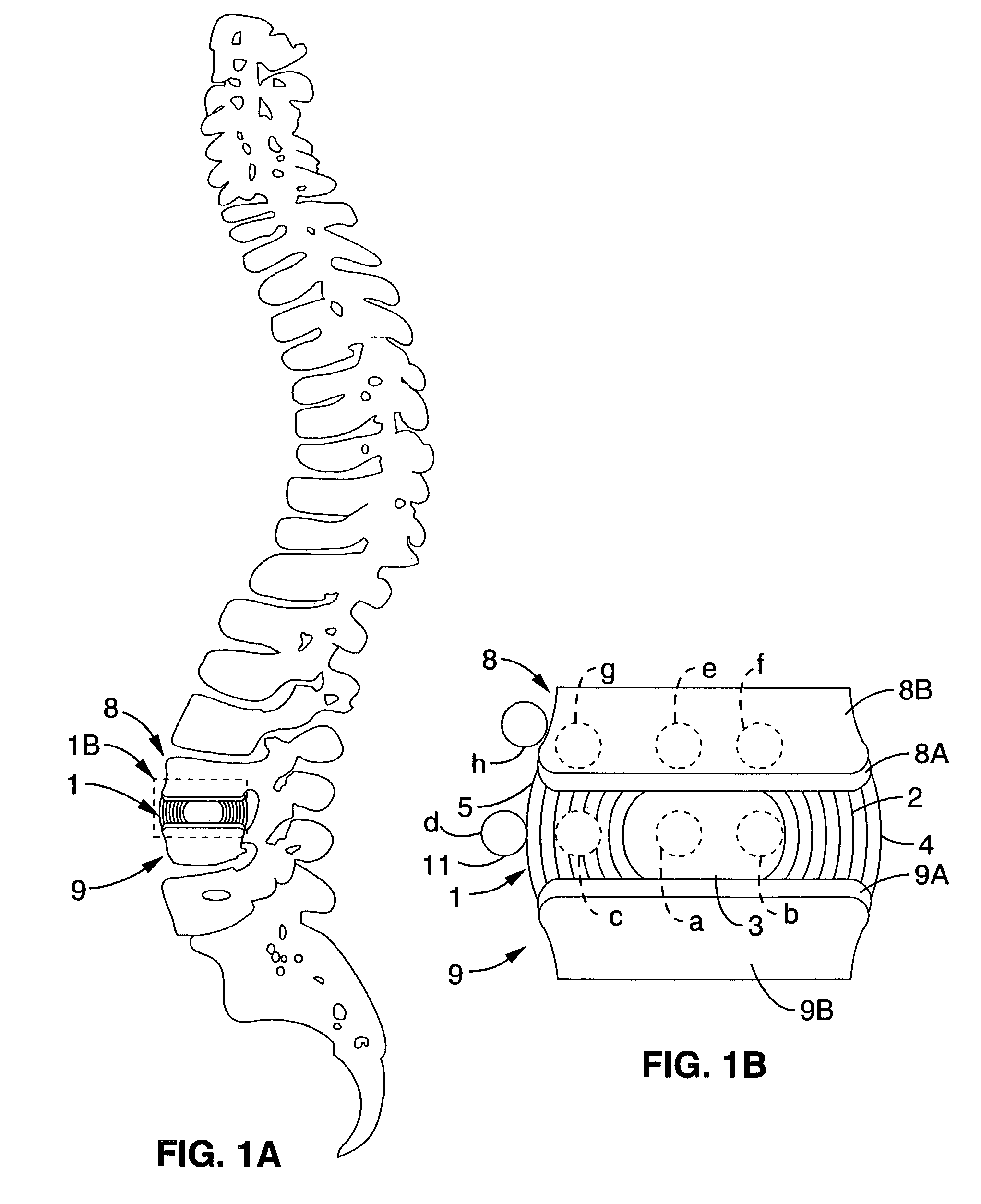
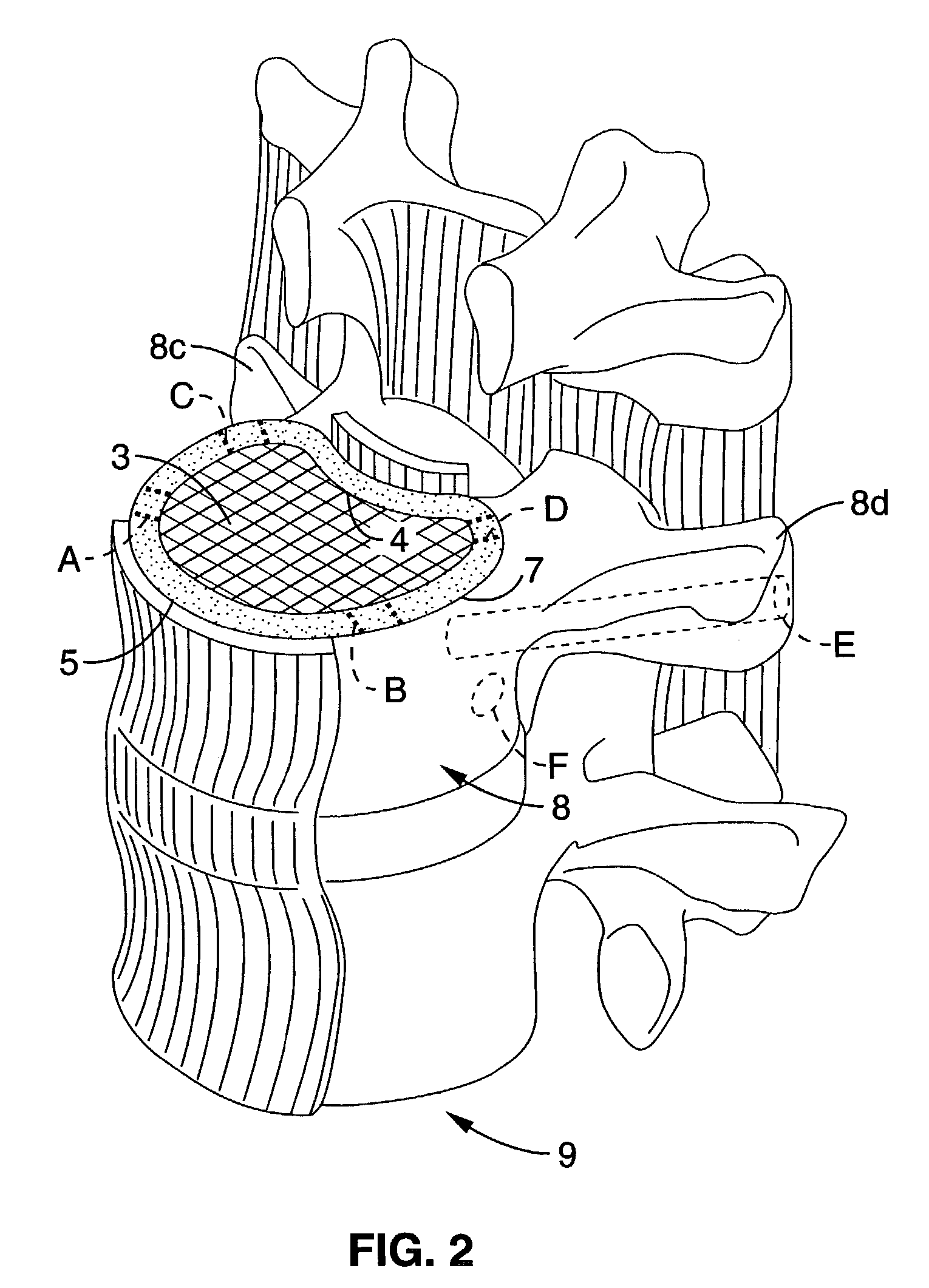
A long-term implantable ultrasound therapy system and method is provided that provides directional, focused ultrasound to localized regions of tissue within body joints, such as spinal joints. An ultrasound emitter or transducer is delivered to a location within the body associated with the joint and heats the target region of tissue associated with the joint from the location. Such locations for ultrasound transducer placement may include for example in or around the intervertebral discs, or the bony structures such as vertebral bodies or posterior vertebral elements such as facet joints. Various modes of operation provide for selective, controlled heating at different temperature ranges to provide different intended results in the target tissue, which ranges are significantly effected by pre-stressed tissues such as in-vivo intervertebral discs. In particular, treatments above 70 degrees C., and in particular 75 degrees C., are used for structural remodeling, whereas lower temperatures achieves other responses without appreciable remodeling.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
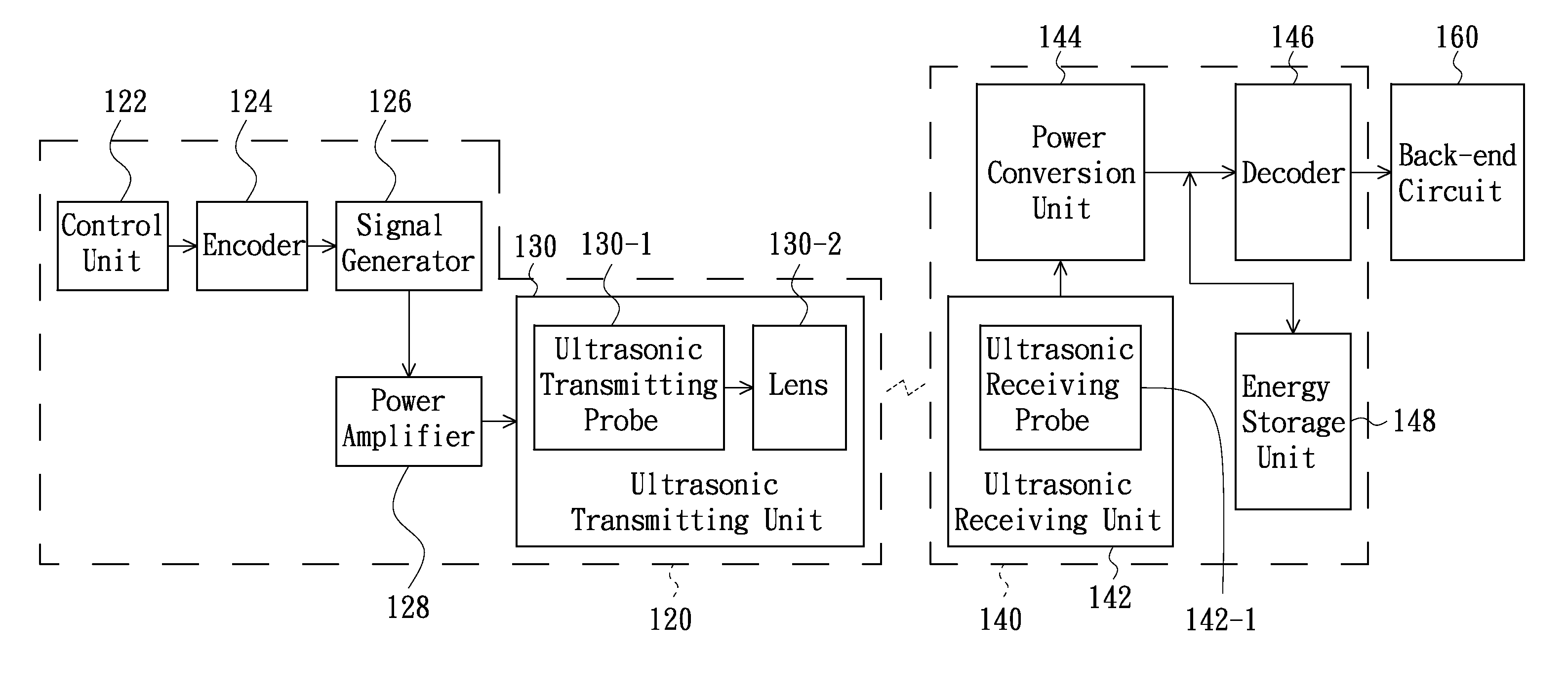
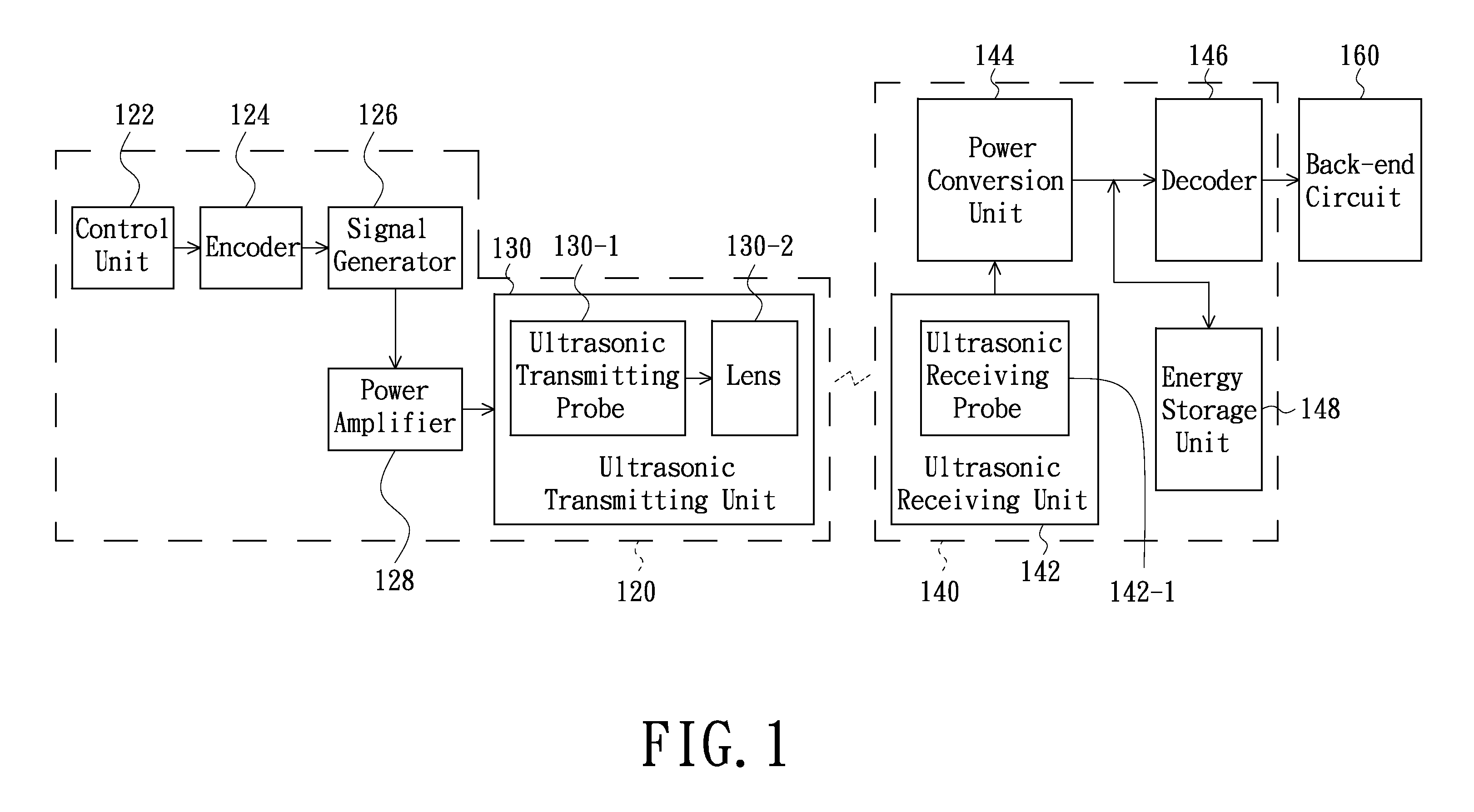
Wireless power transmission system, wireless power transmitting apparatus and wireless power receiving apparatus
InactiveUS20120157019A1Receiving of a sound field is facilitatedEasy to receivePower managementResonant long antennasElectric power transmissionEngineering
A wireless power transmission system includes a wireless power transmitting apparatus and a wireless power receiving apparatus. The wireless power transmitting apparatus includes a signal generator and an ultrasonic transmitting unit. The ultrasonic transmitting unit generates and outputs a focused ultrasonic wave according to a signal outputted from the signal generator. The wireless power receiving apparatus includes an ultrasonic receiving unit and a power conversion unit. The ultrasonic receiving unit receives the focused ultrasonic wave outputted from the wireless power transmitting apparatus and converts the focused ultrasonic wave into electrical power energy. The power conversion unit performs a power conversion on the electrical power energy and thereby provides the converted electrical power energy to a back-end circuit. The ultrasonic signal can also be encoded in the transmitting unit and subsequently decoded in the receiving unit as a means to remotely control the back-end circuit in the receiving unit.
Owner:LI PAI CHI
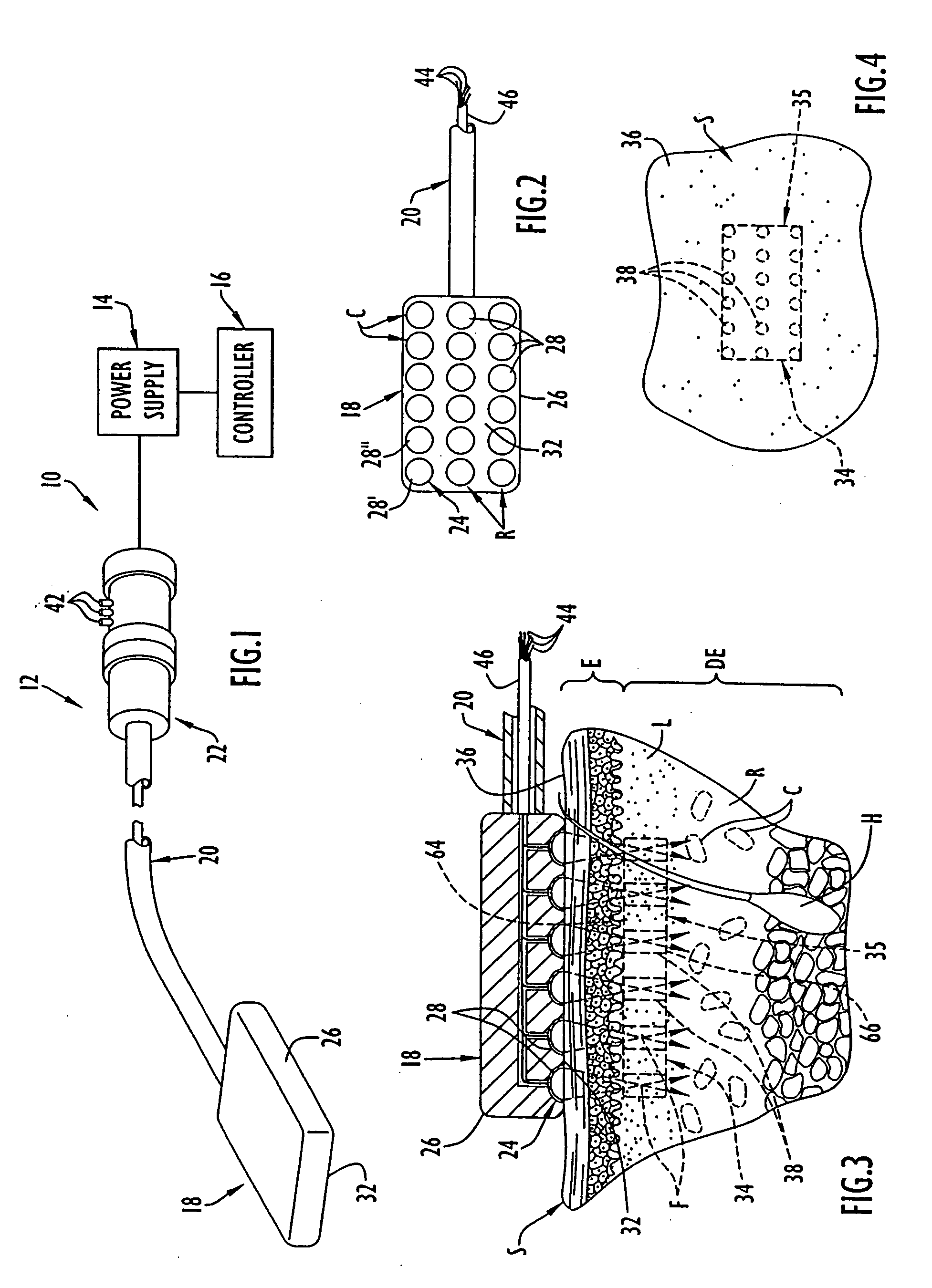
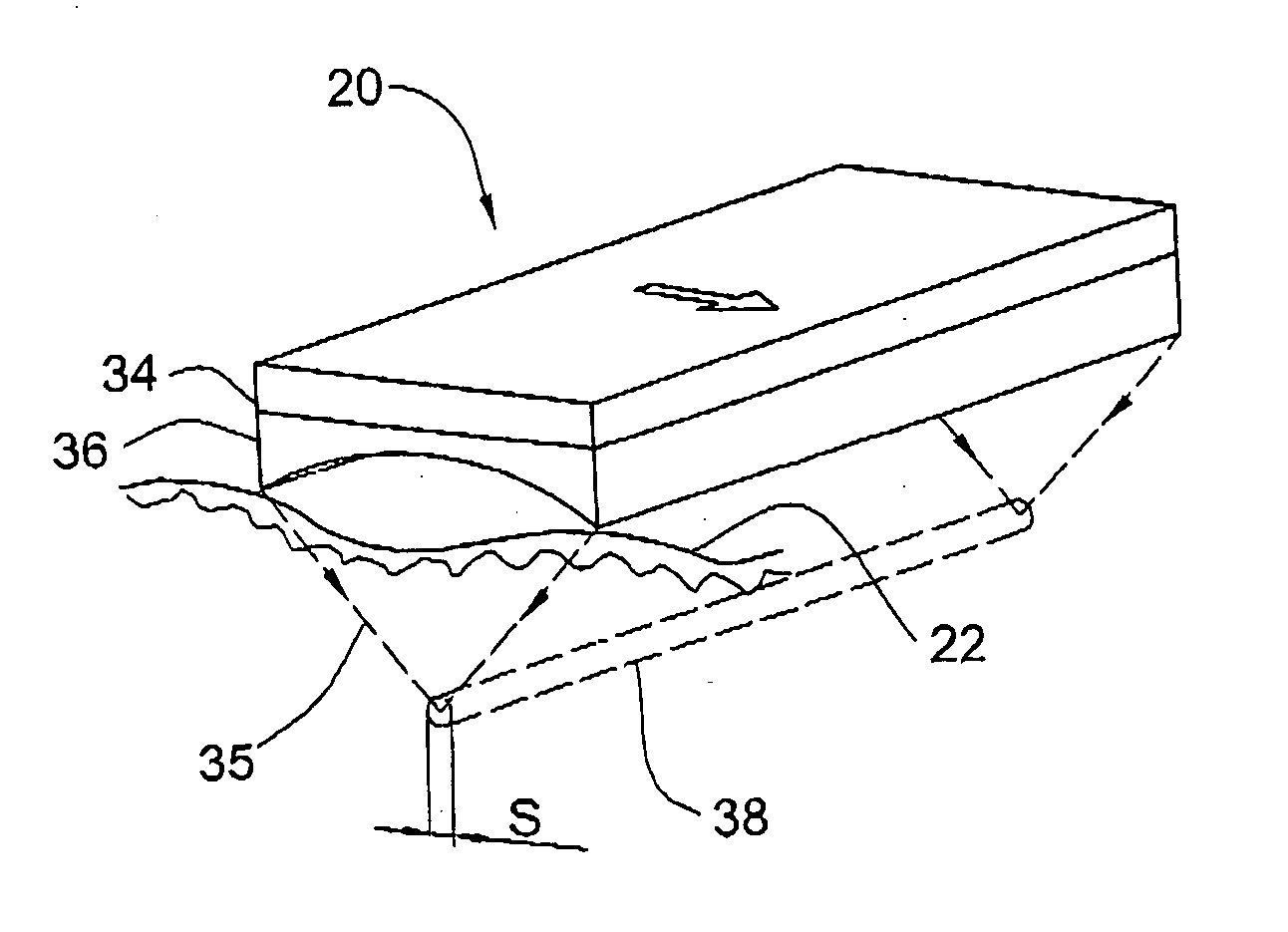
Multi-focal treatment of skin with acoustic energy
InactiveUS20080027328A1Reduce the possibilityIncrease contrastUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyFocal treatmentWavefront
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for applying acoustic energy to the skin. Acoustic waveguides with elements of varying thickness or shape are disclosed which deliver energy to more than one depth below a surface of the skin substantially simultaneously. The invention is especially useful with devices that focus ultrasound energy by condensing a propagating wavefront. The invention compensates for the mismatch in acoustic properties of the device's waveguide and the biological tissue that typically cause portions of the collapsing wavefront to lag behind other portions and, thereby, limit the focusing capabilities of acoustic treatment devices.
Owner:JULIA THERAPEUTICS
Controlled, non-linear focused ultrasound treatment
InactiveUS20070016039A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyMicrobubblesRadiology
A system for treating tissue within a body is configured to deliver a first level of ultrasound energy to a target tissue region for a first duration resulting in the generation of microbubbles in the target tissue region, determine one or more characteristics of the target tissue region in the presence of the microbubbles, and deliver a second level of ultrasound energy to the target tissue region for a second duration, wherein one or both of the second energy level and the second duration are based, at least in part, on the determined one or more characteristics of the target tissue region.
Owner:INSIGHTEC
Device and method for forming a lesion
InactiveUS20020128639A1Minimize complexityLow costUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCannulasControl systemEngineering
A control system alters one or more characteristics of an ablating element to ablate tissue. In one aspect, the control system delivers energy nearer to the surface of the tissue by changing the frequency or power. In another aspect, the ablating element delivers focused ultrasound which is focused in at least one dimension. The ablating device may also have a number of ablating elements with different characteristics such as focal length.
Owner:EPICOR
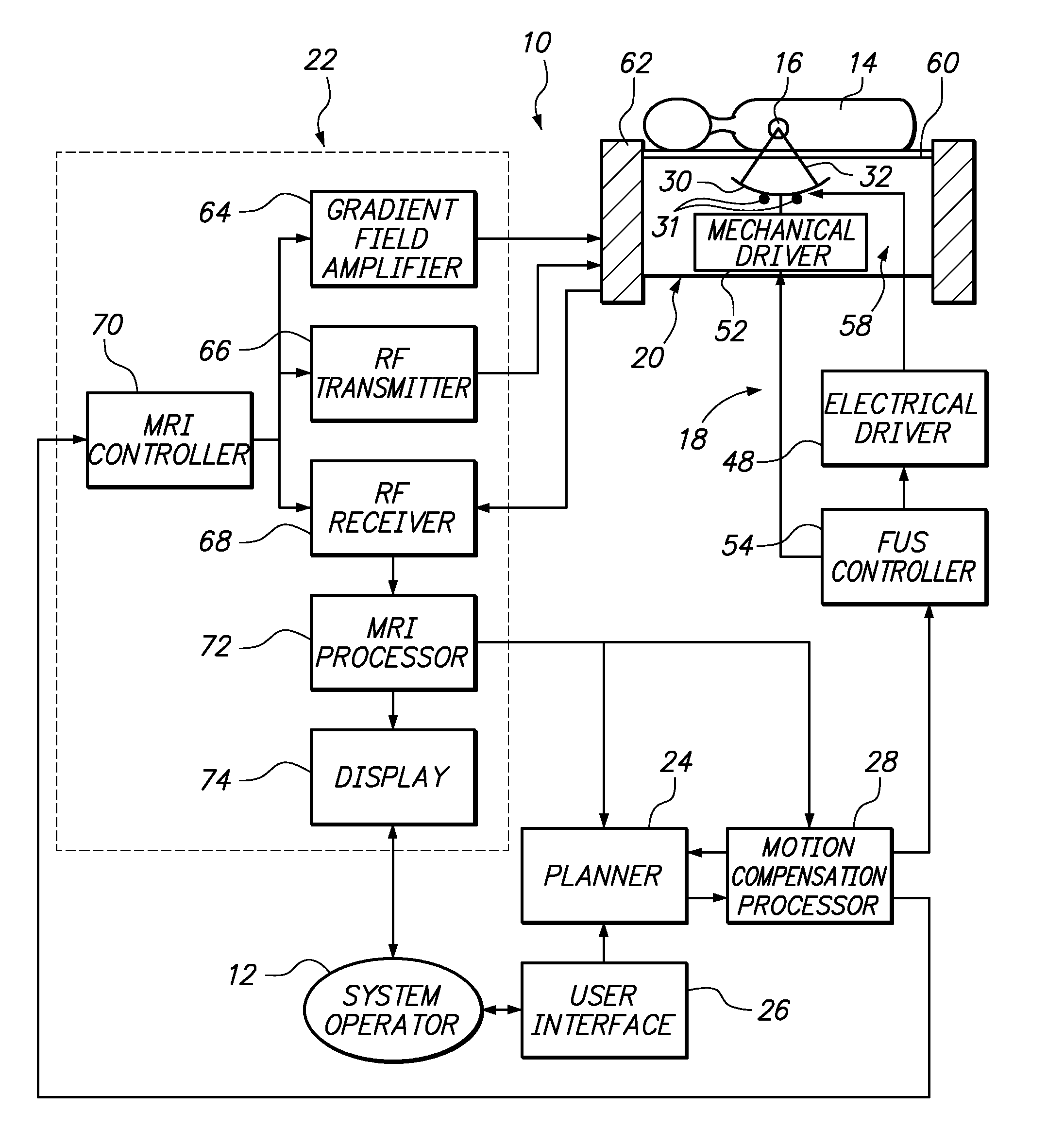
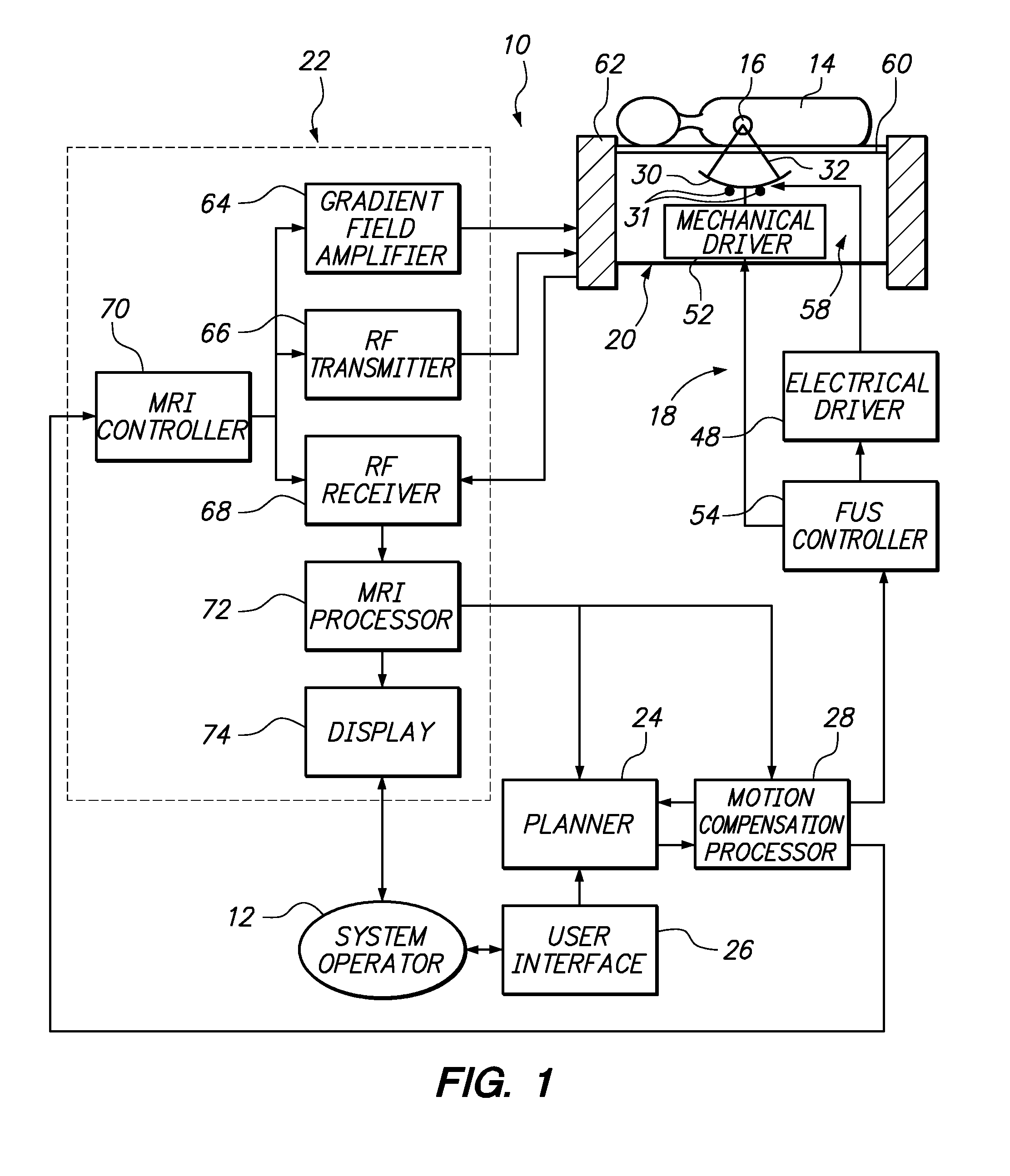
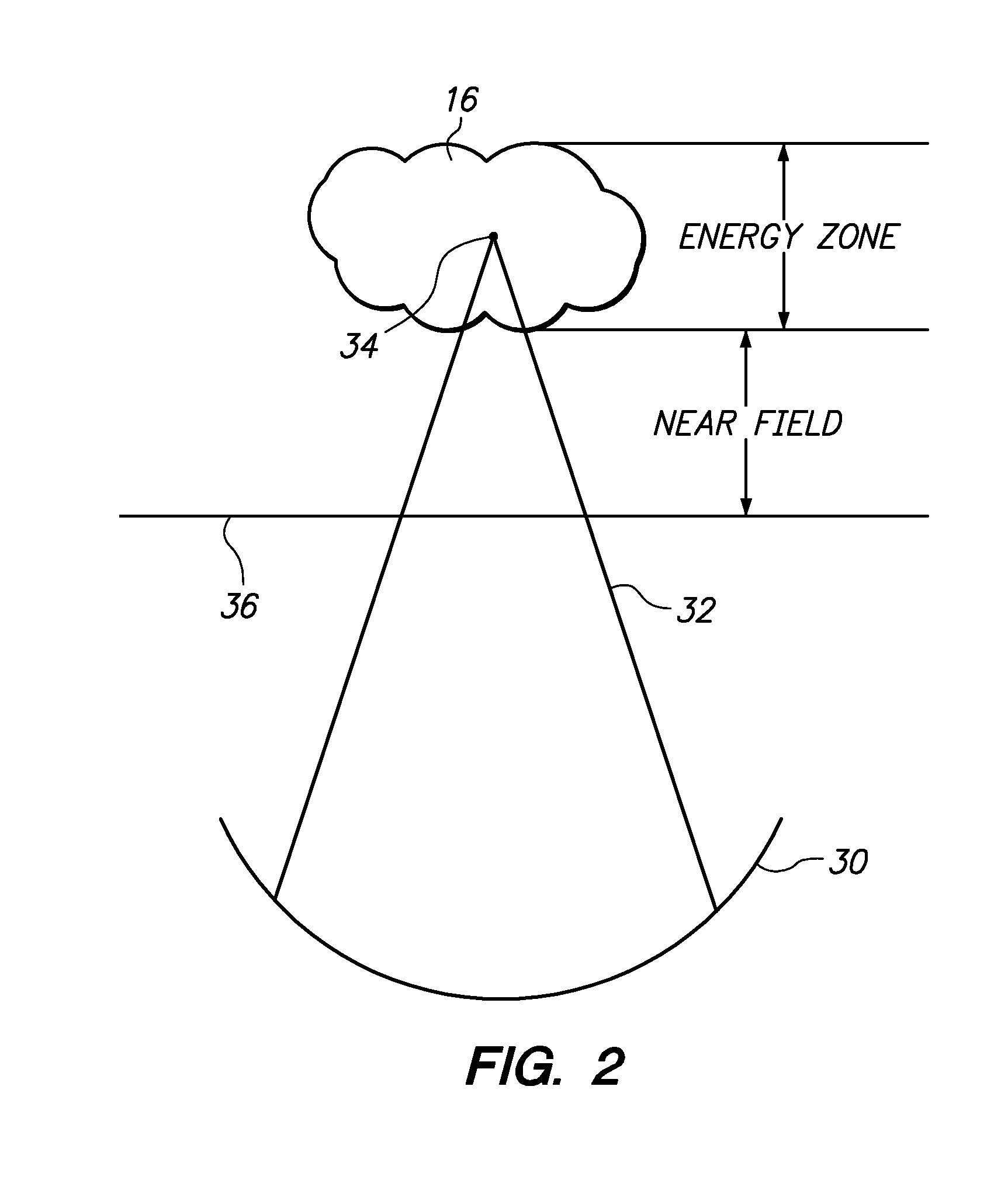
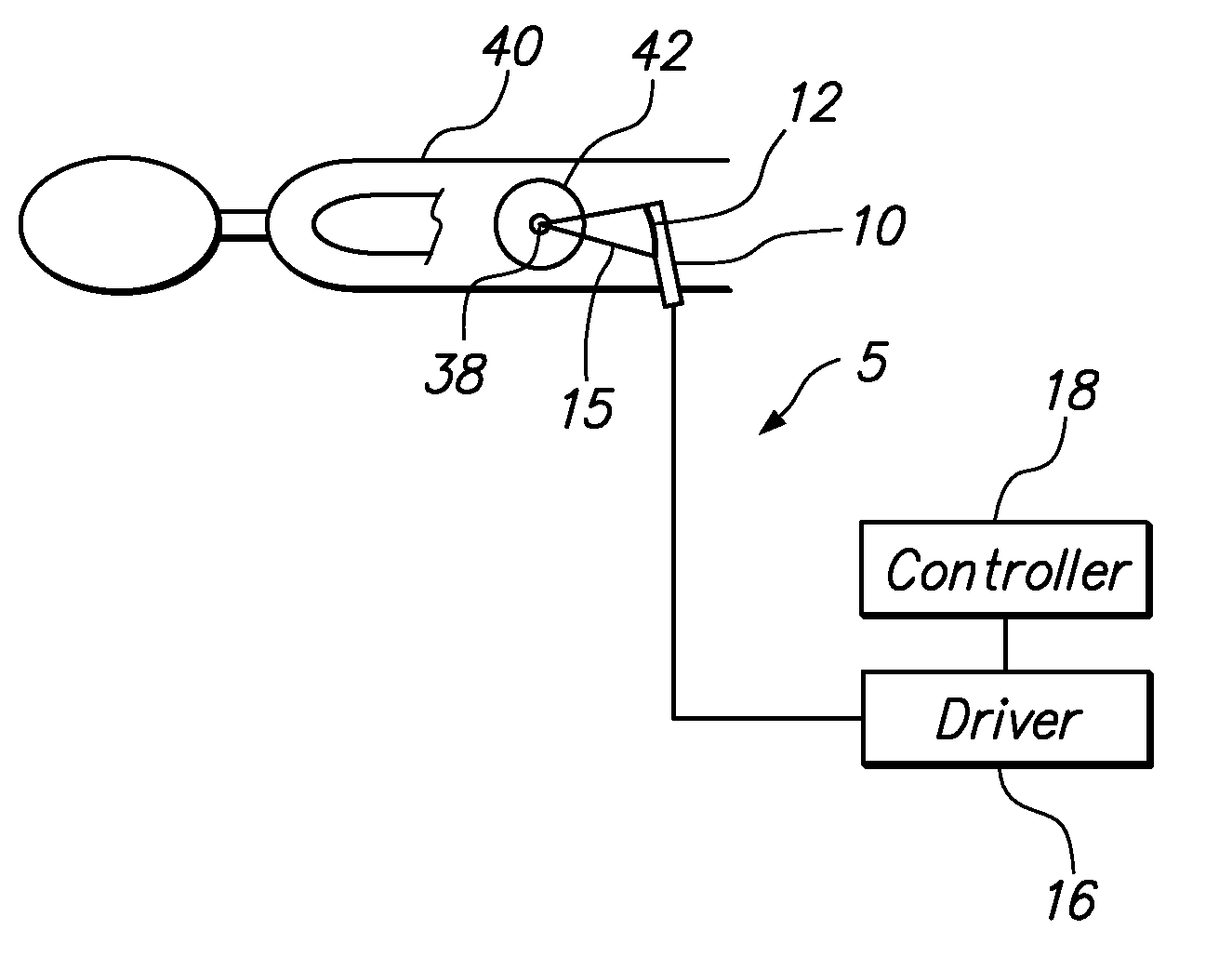
Motion compensated image-guided focused ultrasound therapy system
ActiveUS20090088623A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasonic sensorTherapeutic Devices
An image-guide therapy system comprises a thermal treatment device (e.g., an ultrasound transducer) configured for transmitting a therapeutic energy beam, and The system further comprises an imaging device (e.g., a magnetic resonant imaging (MRI) device) configured for acquiring images of the target tissue mass and the thermal treatment device. The system further comprises a controller configured for controlling thermal dose properties of the thermal treatment device to focus the energy beam on a target tissue mass located in an internal body region of a patient, and a processor configured for tracking respective positions of the thermal treatment device and the target tissue mass in a common coordinate system based on the acquired images. The system may optionally comprise a display configured for displaying the acquired images.
Owner:INSIGHTEC
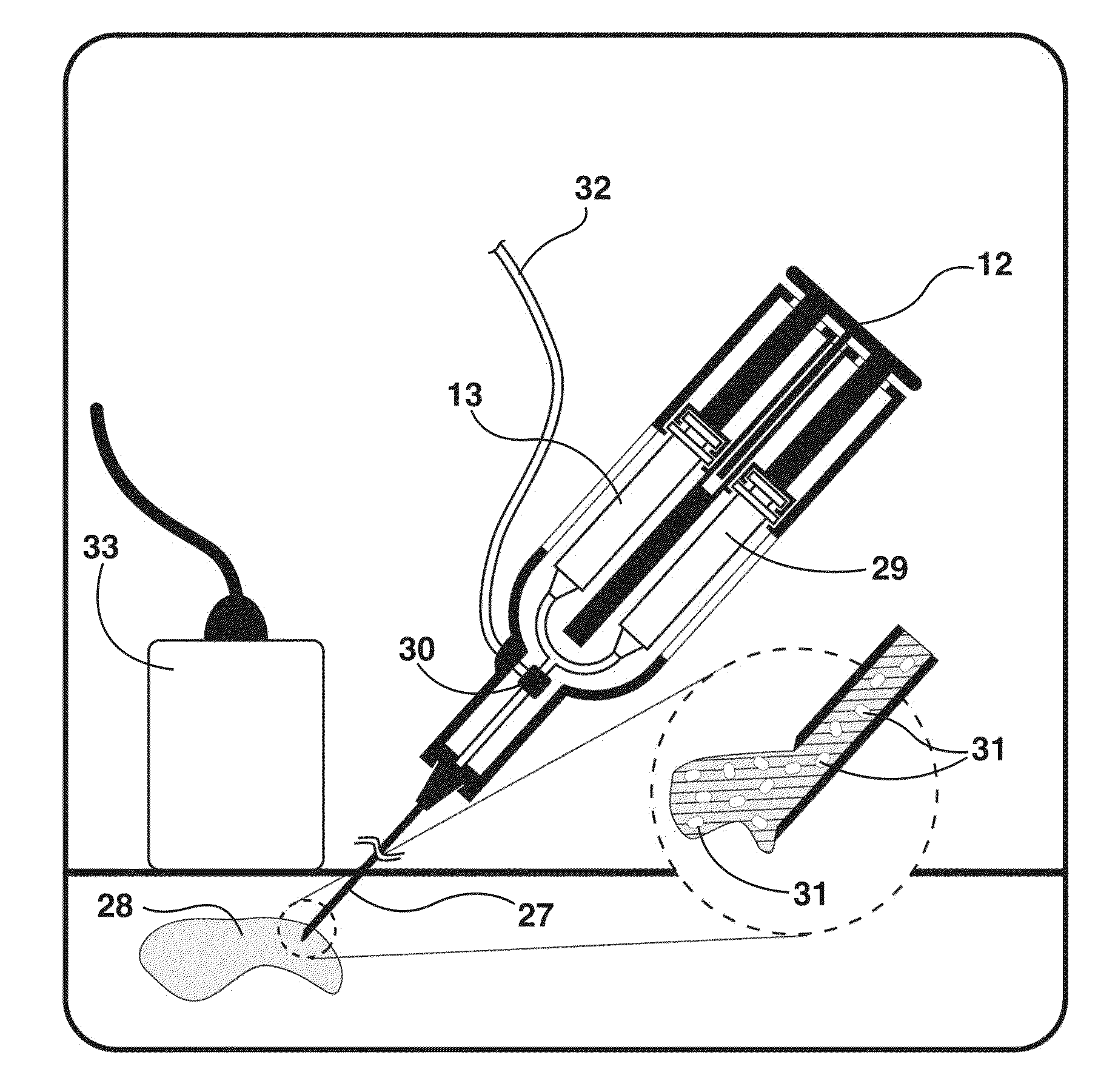
Endo-cavity focused ultrasound transducer
InactiveUS20070197918A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasonic sensorAcoustic energy
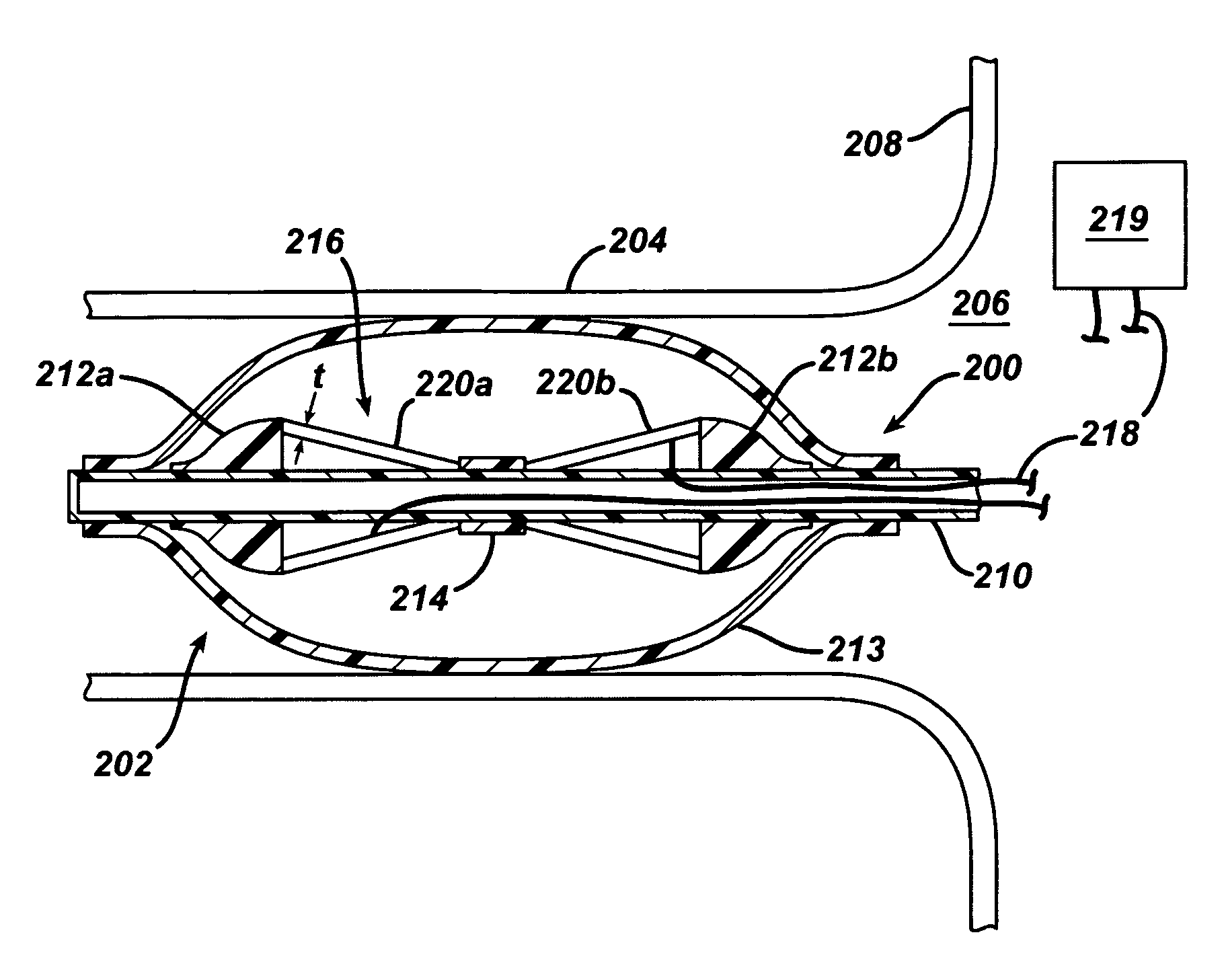
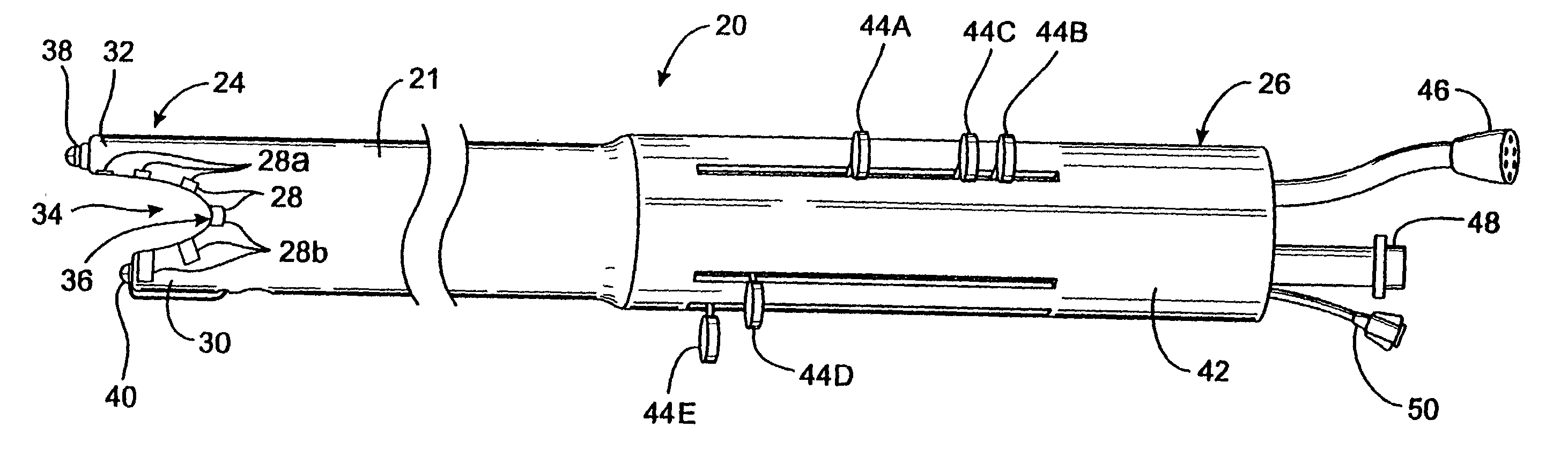
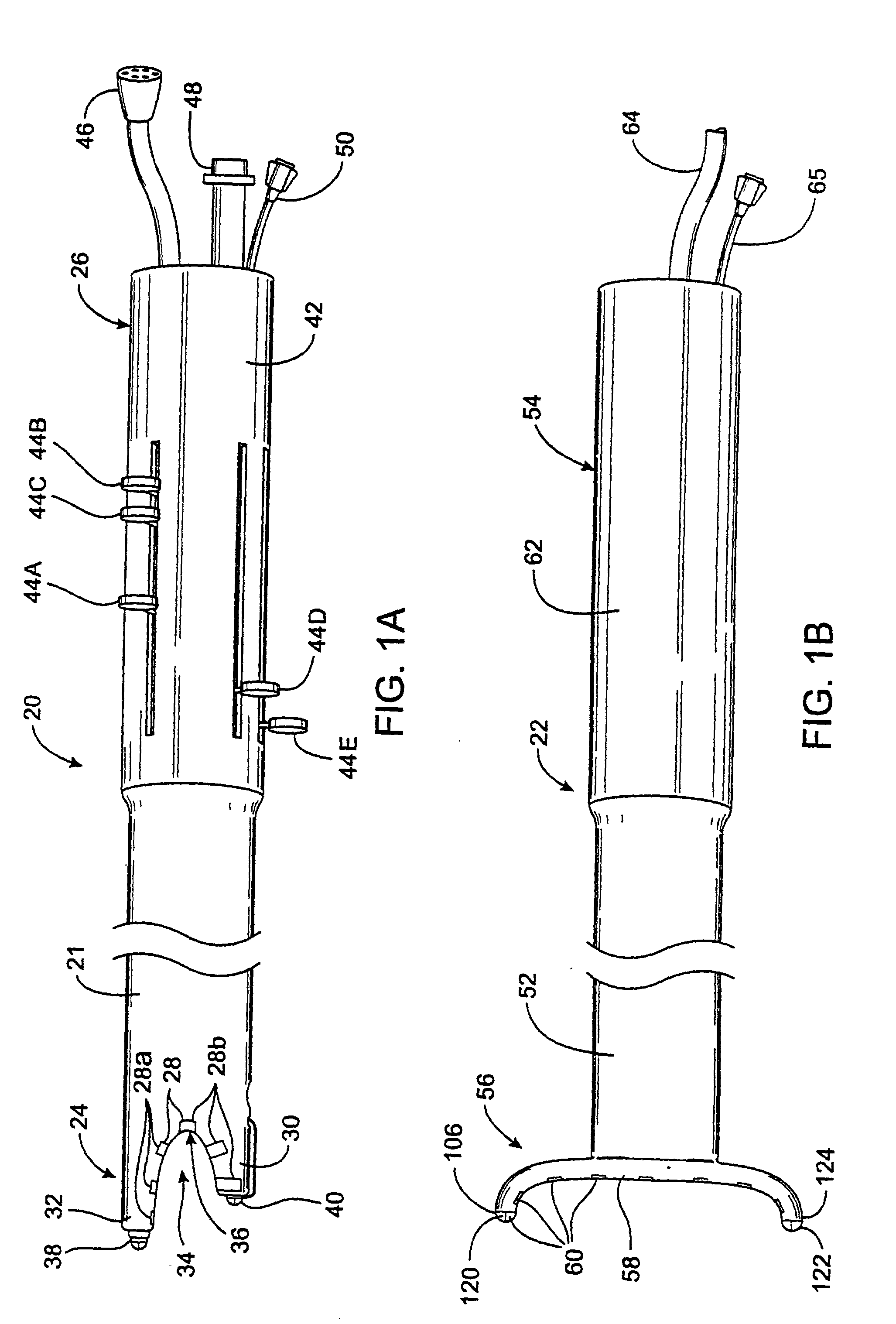
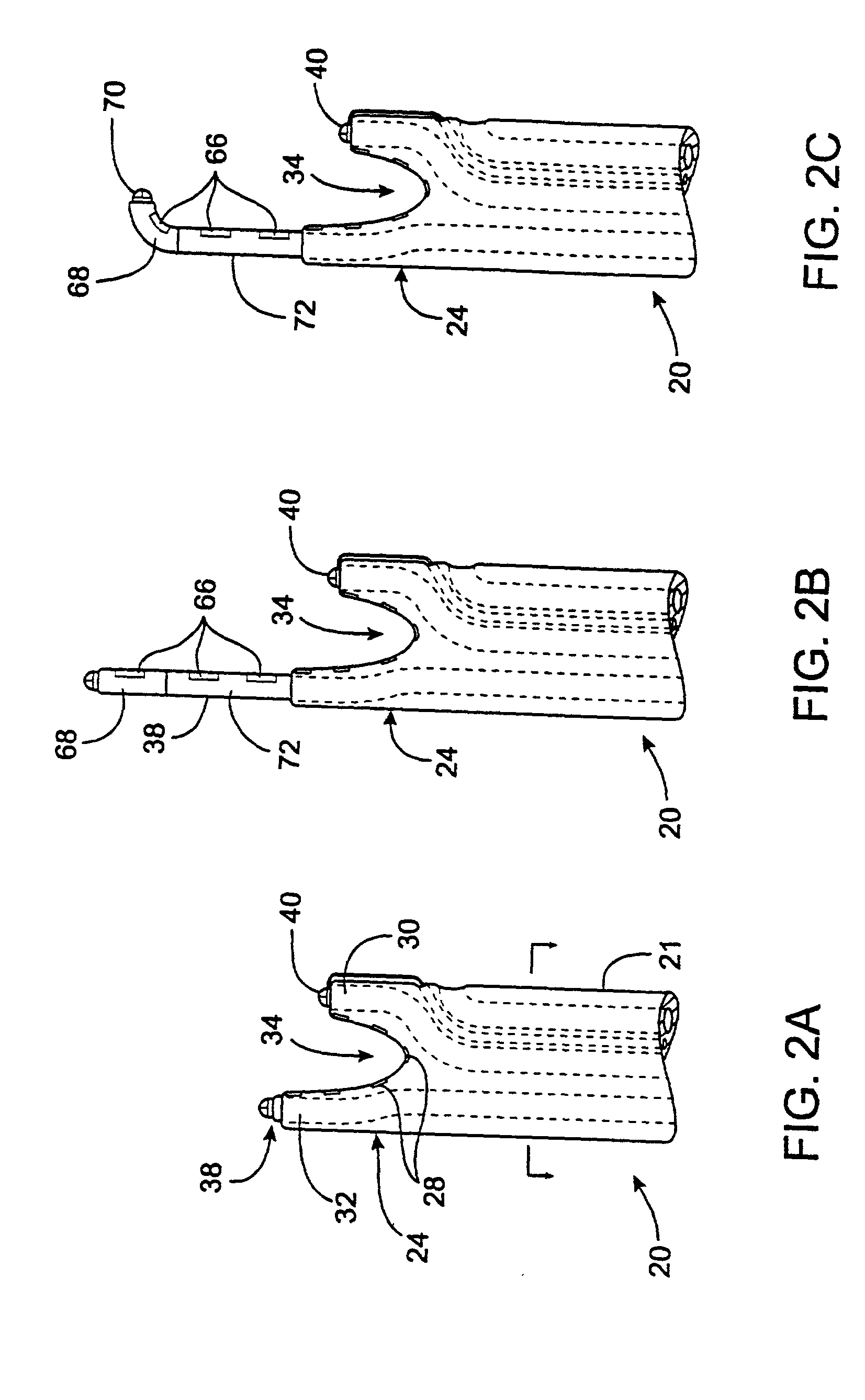
An apparatus for delivering acoustic energy to a target site adjacent a body passage includes first and second elongate members, each carrying one or more transducer elements on their distal ends. The first and / or second elongate members include connectors for securing the first and second elongate members together such that the transducer elements together define a transducer array. The first and second elongate members are introduced sequentially into a body passage until the transducer elements are disposed adjacent a target site. Acoustic energy is delivered from the transducer elements to the target site to treat tissue therein. In another embodiment, the apparatus includes a tubular member and an expandable structure carrying a plurality of transducer elements. The structure is expanded between a contracted configuration during delivery and an enlarged configuration when deployed for delivering acoustic energy to a target site adjacent the body passage.
Owner:INSIGHTEC
Systems and methods for making non-invasive physiological assessments by detecting induced acoustic emissions
InactiveUS20060079773A1Improve accuracyPositive diagnosisDiagnostics using vibrationsOrgan movement/changes detectionDiseaseNon invasive
Systems and methods for assessing a physiological parameter of a target tissue wherein a pulse of focused ultrasound is applied to a target tissue site thereby inducing oscillation of the target tissue. By these systems and methods, a property of an acoustic signal emitted from the oscillating target tissue is measured and related to a physiological property of the tissue. Specific applications for systems and methods of the present invention include the assessment and monitoring of intracranial pressure (ICP), arterial blood pressure (ABP), CNS autoregulation status, vasospasm, stroke, local edema, infection and vasculitus, as well as diagnosis and monitoring of diseases and conditions that are characterized by physical changes in tissue properties.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
Microbubble medical devices
ActiveUS20100228122A1Enhance heat ablation effectSimple procedureUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersFocus ultrasoundLight activation
Method and medical devices for generating and stabilizing micro- or nano-bubbles, and systems and methods for therapeutic applications using the bubbles, are provided. The micro-bubbles may be used to enhance therapeutic benefits such as ultrasound-guided precision drug delivery and real-time verification, acoustic activation of large tumour masses, enhanced acoustic activation through longer retention of therapeutic agents at the point of interest, enhancement of high intensity focused ultrasound treatments, light activation of photodynamic drugs at a depth within a patient using extracorporeal light sources, probes, or sonoluminescence, and initiation of time reversal acoustics focused ultrasound to permit highly localized treatment.
Owner:ARTENGA
Methods of using high intensity focused ultrasound to form an ablated tissue area
InactiveUS7706882B2Easily position and manipulate and stabilize and holdAvoid unwanted damageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapySonificationHigh intensity
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and apparatus for performance of thermal bronchiplasty with unfocused ultrasound
InactiveUS20160287912A1Reduce the possibilityAvoid insufficient temperatureUltrasound therapyBronchoscopesSonificationLarge target
Apparatus and methods for deactivating bronchial nerves and smooth muscle extending along a bronchial branch of a mammalian subject to treat asthma and related conditions. An electromechanical transducer (11) is inserted into the bronchus as, for example, by advancing the distal end of a catheter (10) bearing the transducer into the bronchial section to be treated. The electromechanical transducer emits unfocused mechanical vibratory energy of one or more ultrasonic frequencies so as to heat tissues throughout a relatively large target region (13) as, for example, at least about 1 cm3 encompassing the bronchus to a temperature sufficient to inactivate nerves but insufficient to cause rapid ablation or necrosis of organic tissues. The treatment can be performed without locating or focusing on individual bronchial nerves.
Owner:GUIDED INTERVENTIONS
Gel dispensers for treatment of skin with acoustic energy
InactiveUS20080146970A1Lower capability requirementsCompensation DistortionUltrasound therapySurgeryWavefrontAcoustic energy
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for dispensing fluid in an apparatus for applying acoustic energy to the skin. Acoustic waveguides are disclosed which compensate for distortions that otherwise occur when a focused acoustic beam crosses a boundary, such as the transition from a treatment device to a target region of skin. The invention is especially useful with devices that focus ultrasound energy by condensing a propagating wavefront. The invention compensates for the mismatch in acoustic properties of the device's waveguide and the biological tissue that typically cause portions of the collapsing wavefront to lag behind other portions and, thereby, limit the focusing capabilities of acoustic treatment devices.
Owner:JULIA THERAPEUTICS
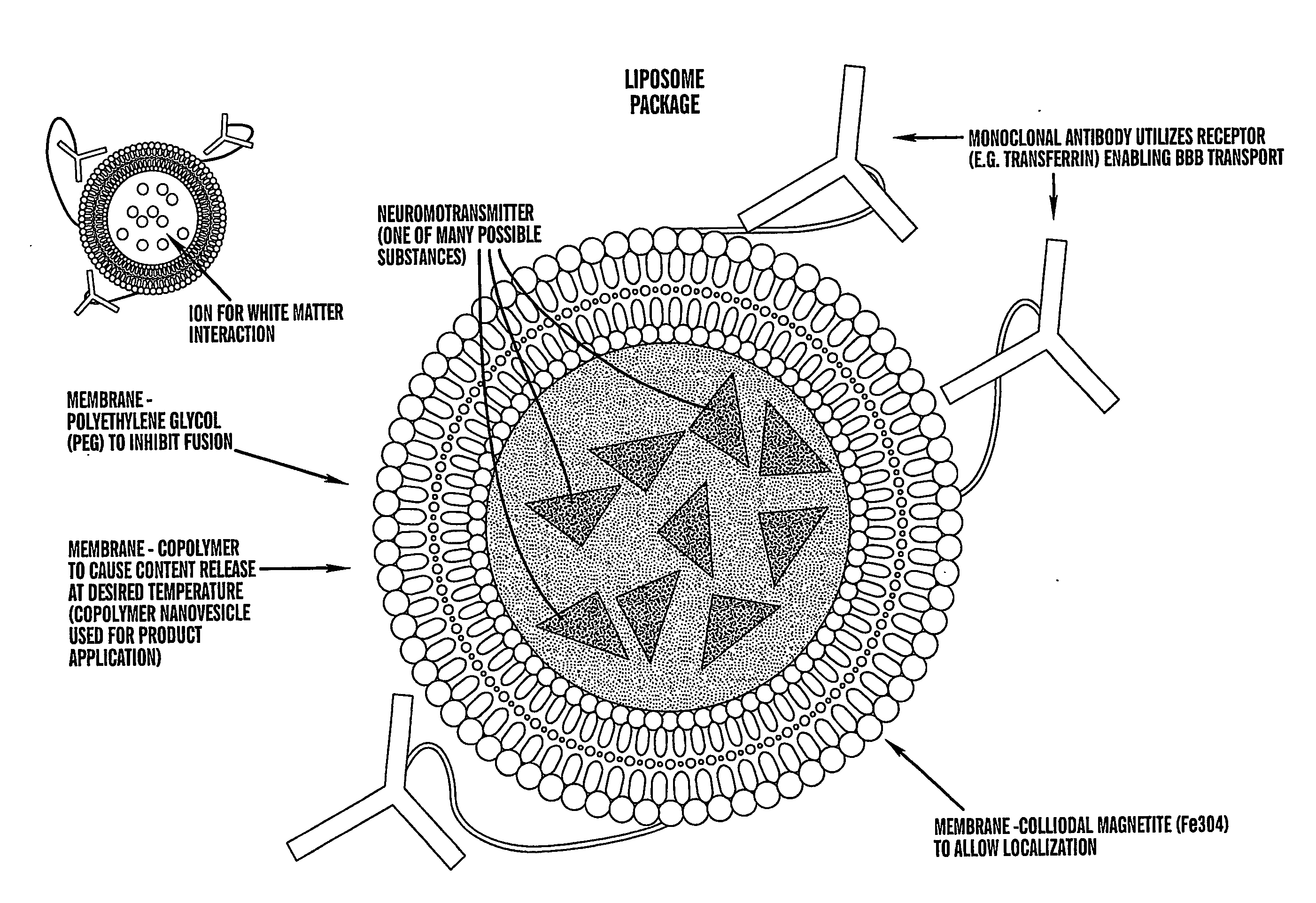
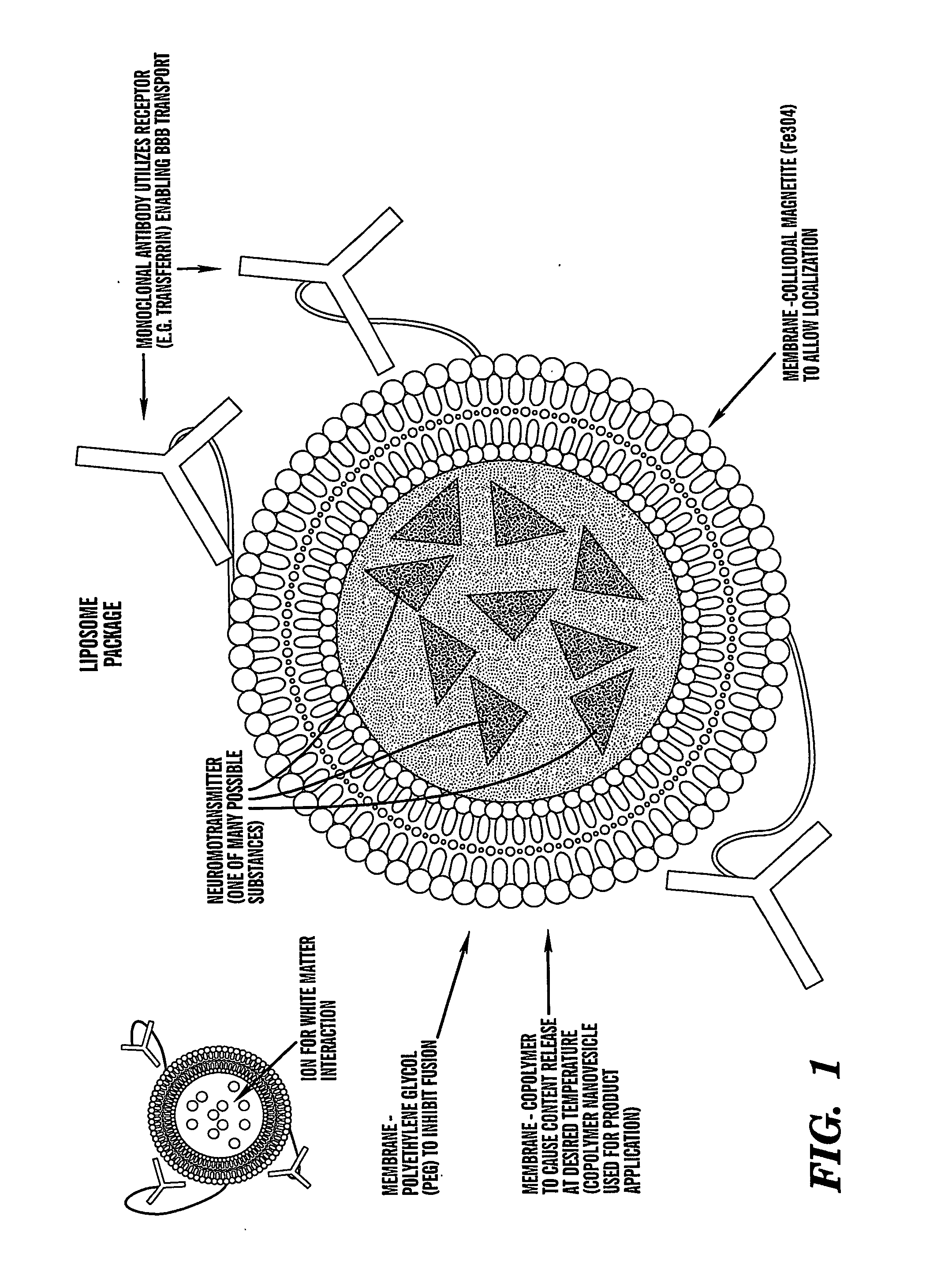
Localized non-invasive biological modulation system
The present invention provides methods for non-invasive localized delivery of biologically active molecules, comprising packaging a molecule(s) of interest inside a thermosensitive particle, administering said particles to a subject, and inducing localized release of said molecules from said particles using a focused heat source. The thermosensitive particles may be thermosensitive polymer nanoparticles or thermosensitive liposomes. The particles may be delivered to a subject by any technique, including infusion. The molecules may be released from the particles using any method which induces localized hyperthermia, including focused ultrasound.
Owner:SAOIRSE CORP
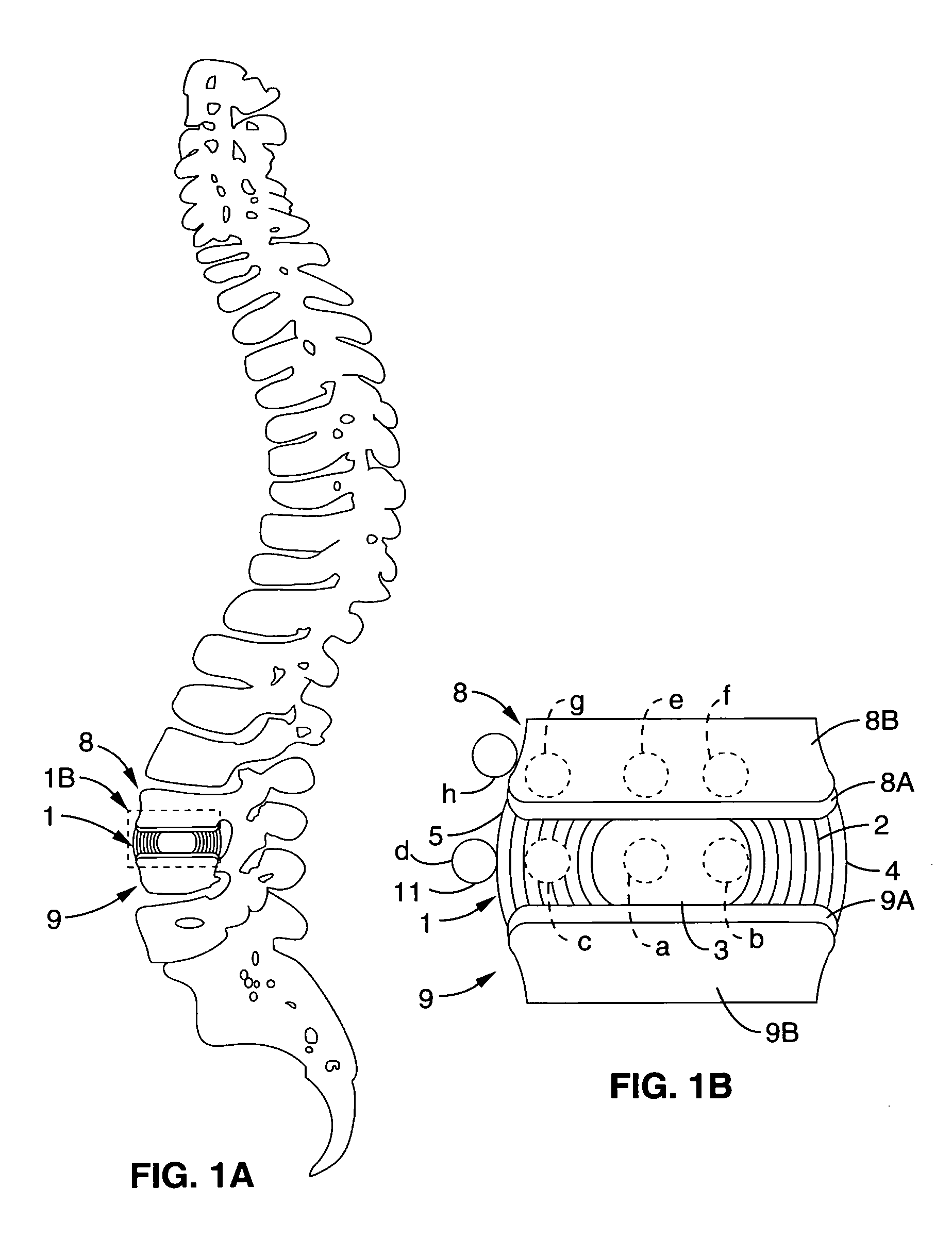
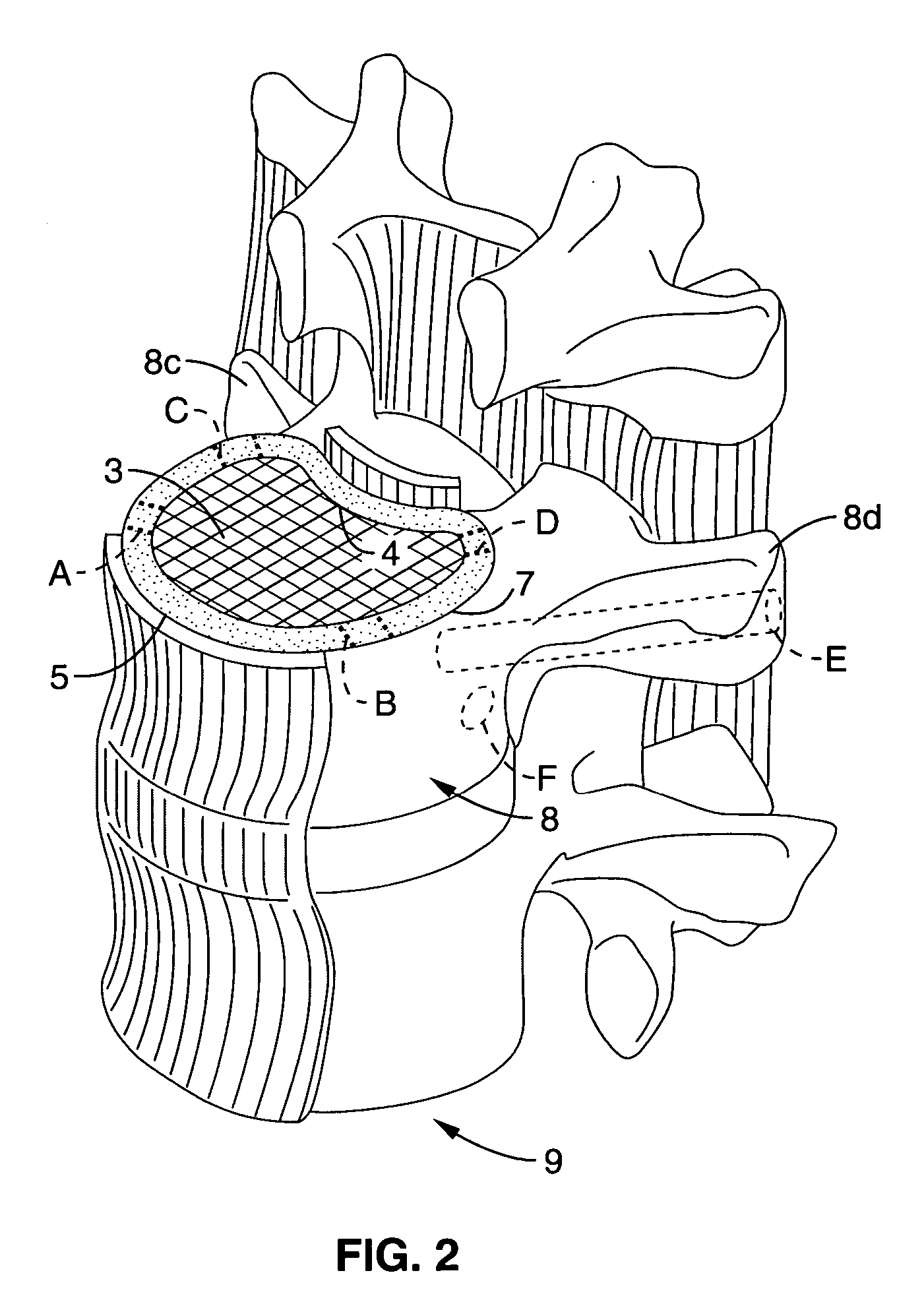
System and method providing directional ultrasound therapy to skeletal joints
InactiveUS20060241576A1Sufficient energy levelUltrasound therapyDiagnosticsBody jointsUltrasonic sensor
An ultrasound therapy system and method is provided that provides directional, focused ultrasound to localized regions of tissue within body joints, such as spinal joints. An ultrasound emitter or transducer is delivered to a location within the body associated with the joint and heats the target region of tissue associated with the joint from the location. Such locations for ultrasound transducer placement may include for example in or around the intervertebral discs, or the bony structures such as vertebral bodies or posterior vertebral elements such as facet joints. Various modes of operation provide for selective, controlled heating at different temperature ranges to provide different intended results in the target tissue, which ranges are significantly affected by pre-stressed tissues such as in-vivo intervertebral discs. In particular, treatments above 70 degrees C., and in particular 75 degrees C., are used for structural remodeling, whereas lower temperatures achieve other responses without appreciable remodeling.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
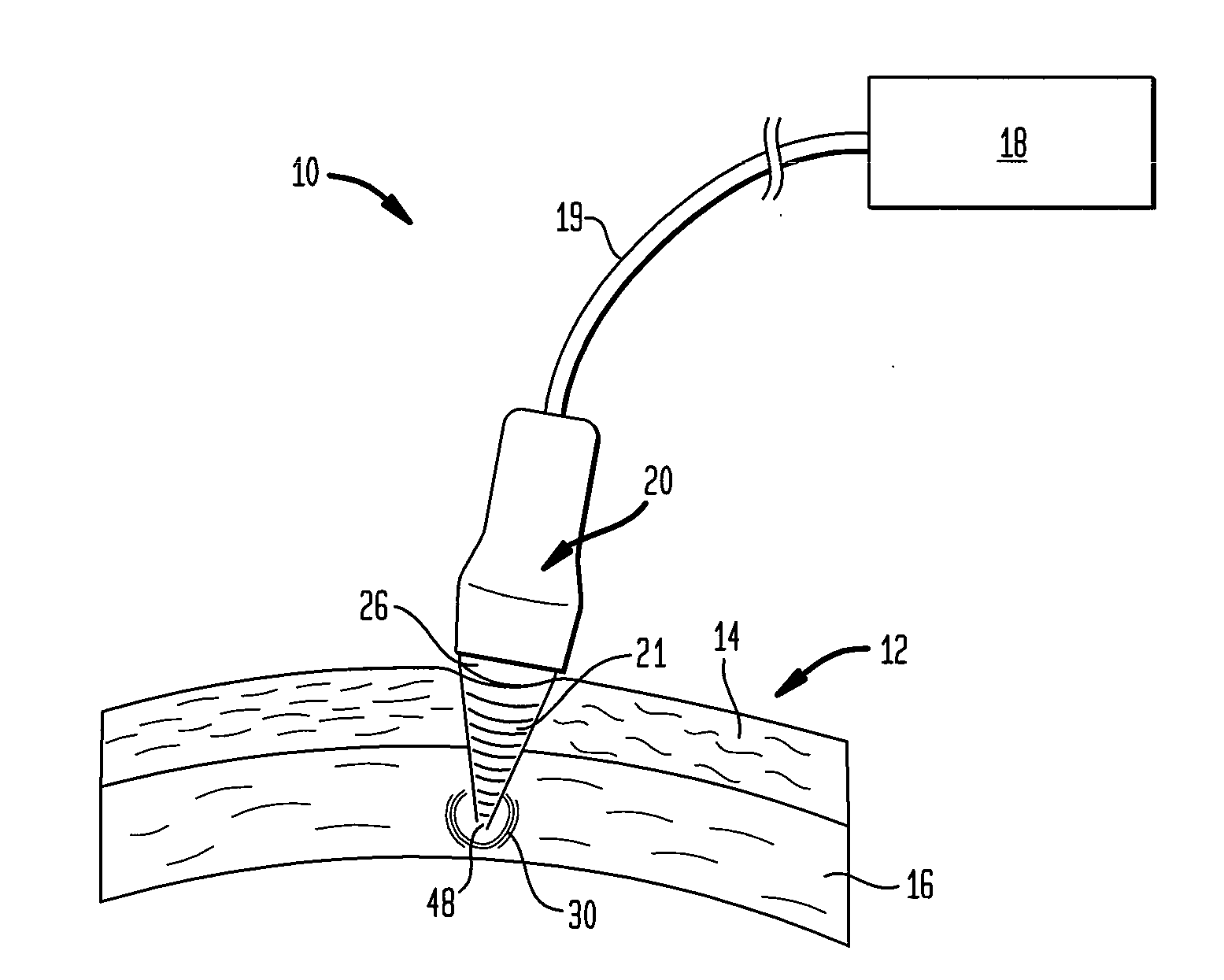
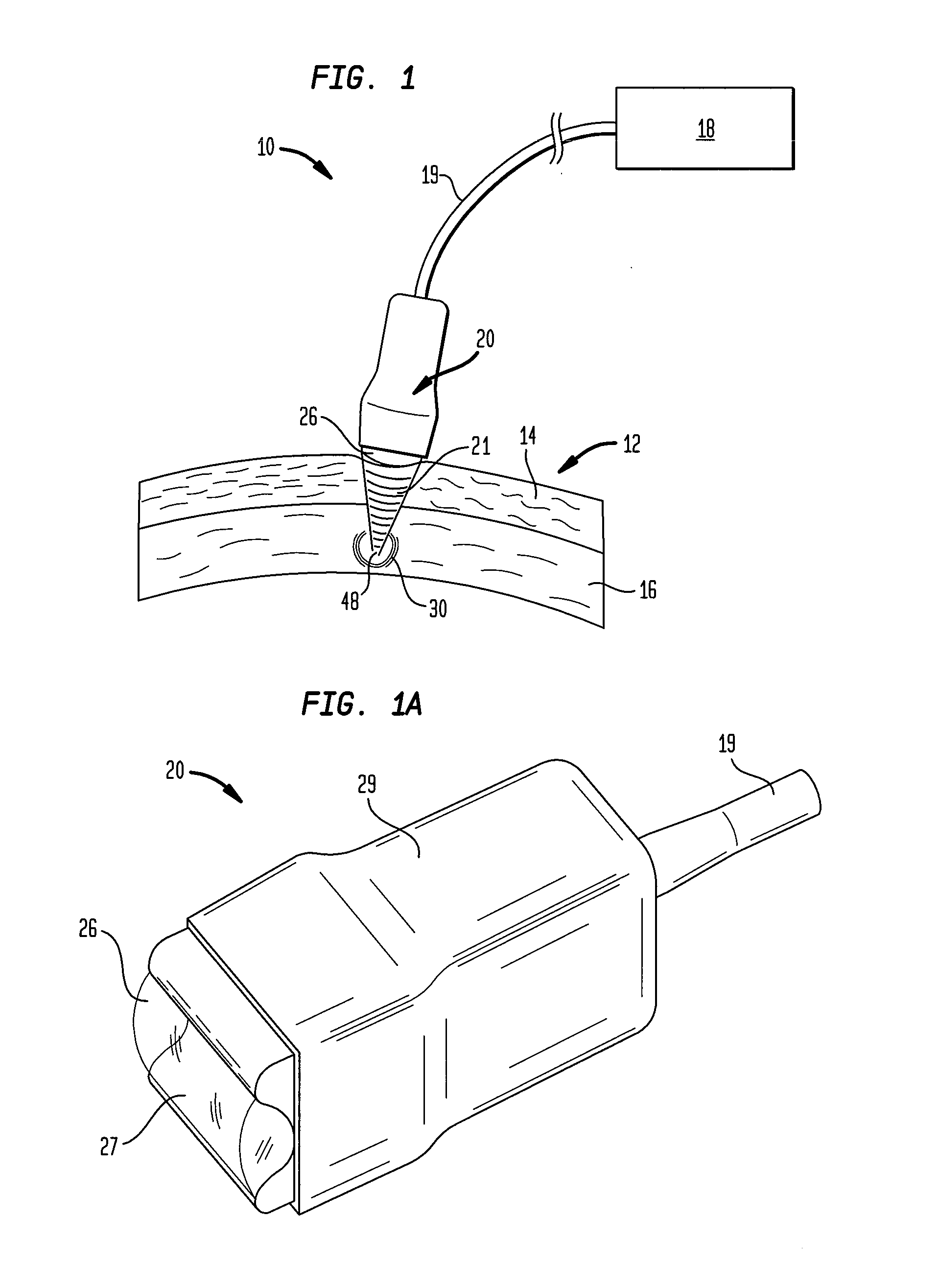
Method and device for sub-dermal tissue treatment
InactiveUS20050055018A1Avoid heat damageAvoid tissue damageUltrasound therapySurgical instruments for heatingCavitationHand held
System and method for non-invasive lysis of sub-dermal tissue by means of focused ultrasonic energy, the system comprising: a source of ultrasonic energy adapted to operate in continuous wave mode and to focus ultrasonic energy in a focal zone within the sub-dermal tissue, the ultrasonic energy being adapted to induce tissue cavitation in the focal zone; means for continuous displacement of the source over the skin surface; and means for determining a safe speed for the displacement, the safe speed allowing to avoid thermal tissue damage. The source of ultrasonic energy is accommodated in a hand-held applicator including a wheeled traction system powered by an electric drive.
Owner:SYNERON MEDICAL LTD
Methods and apparatus for treatment of obesity with an ultrasound device movable in two or three axes
InactiveUS20050203501A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasound deviceTransducer
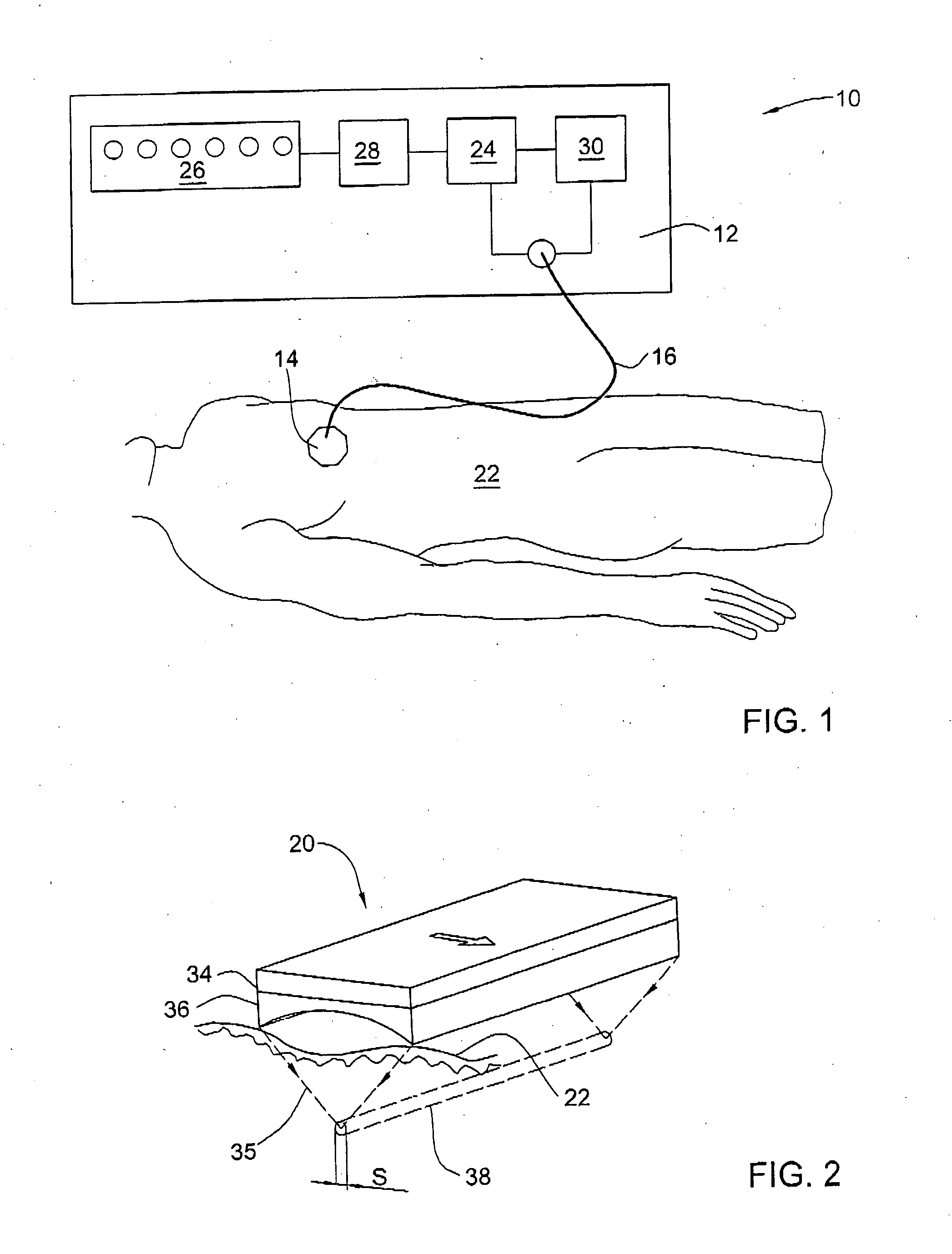
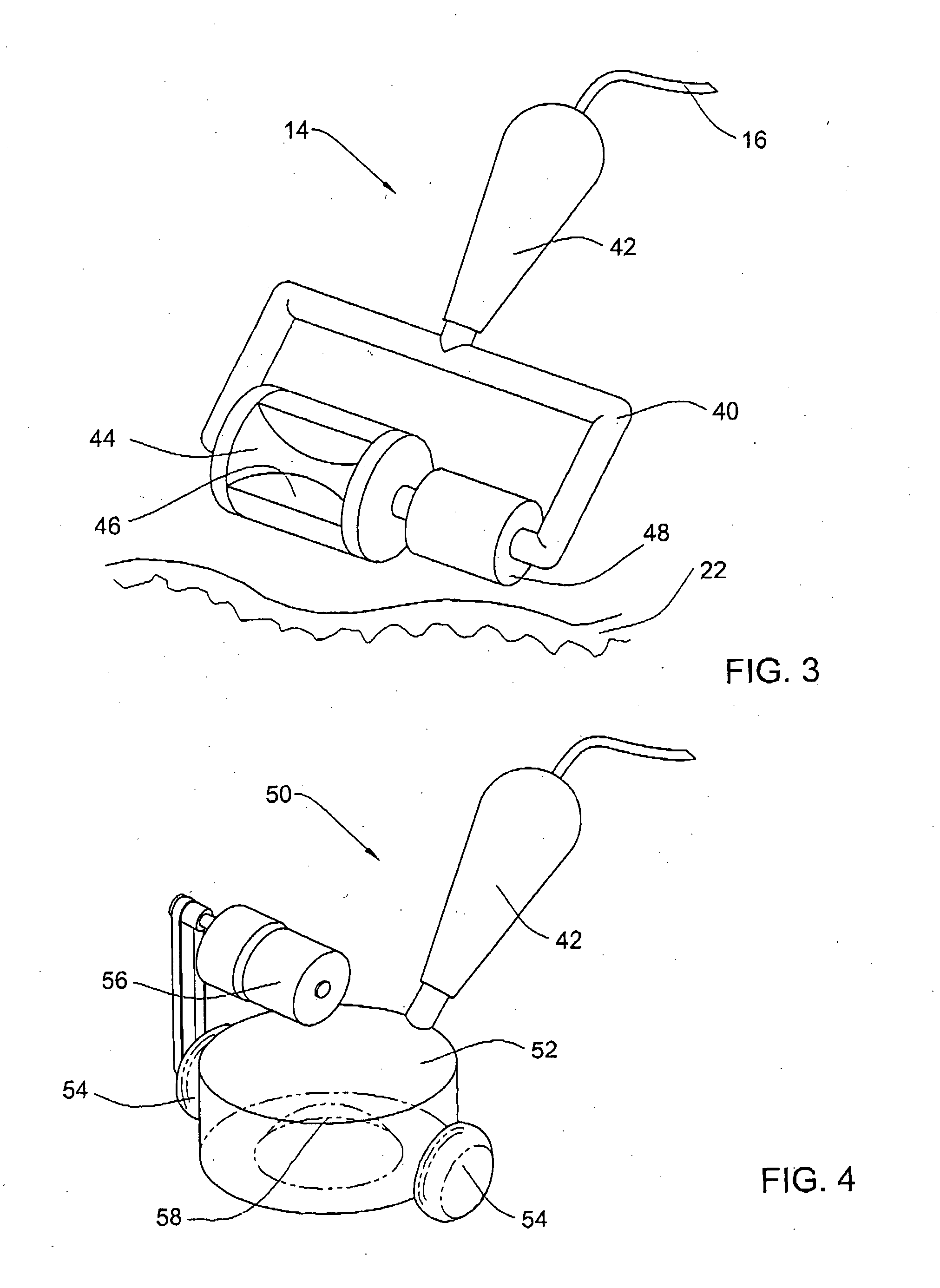
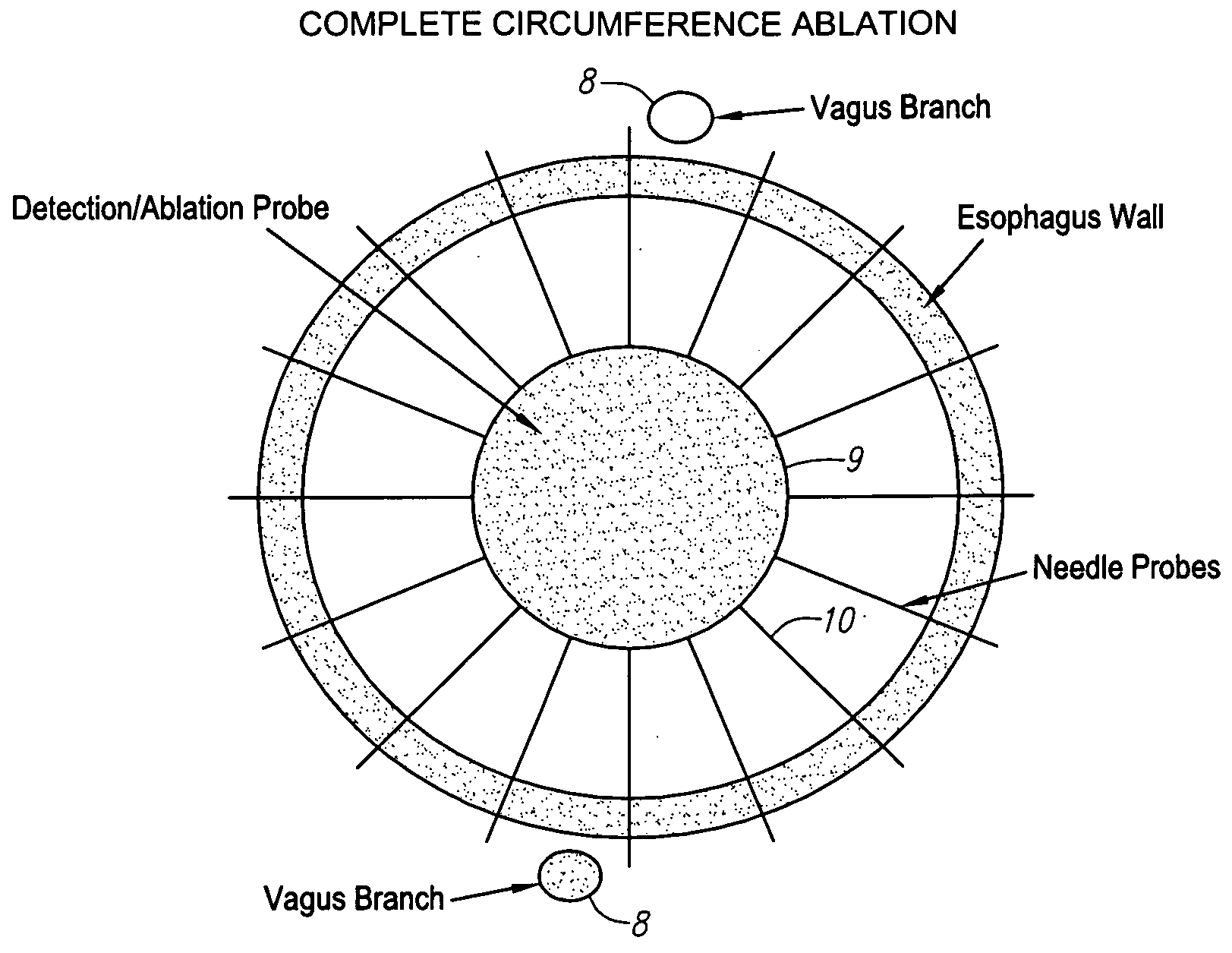
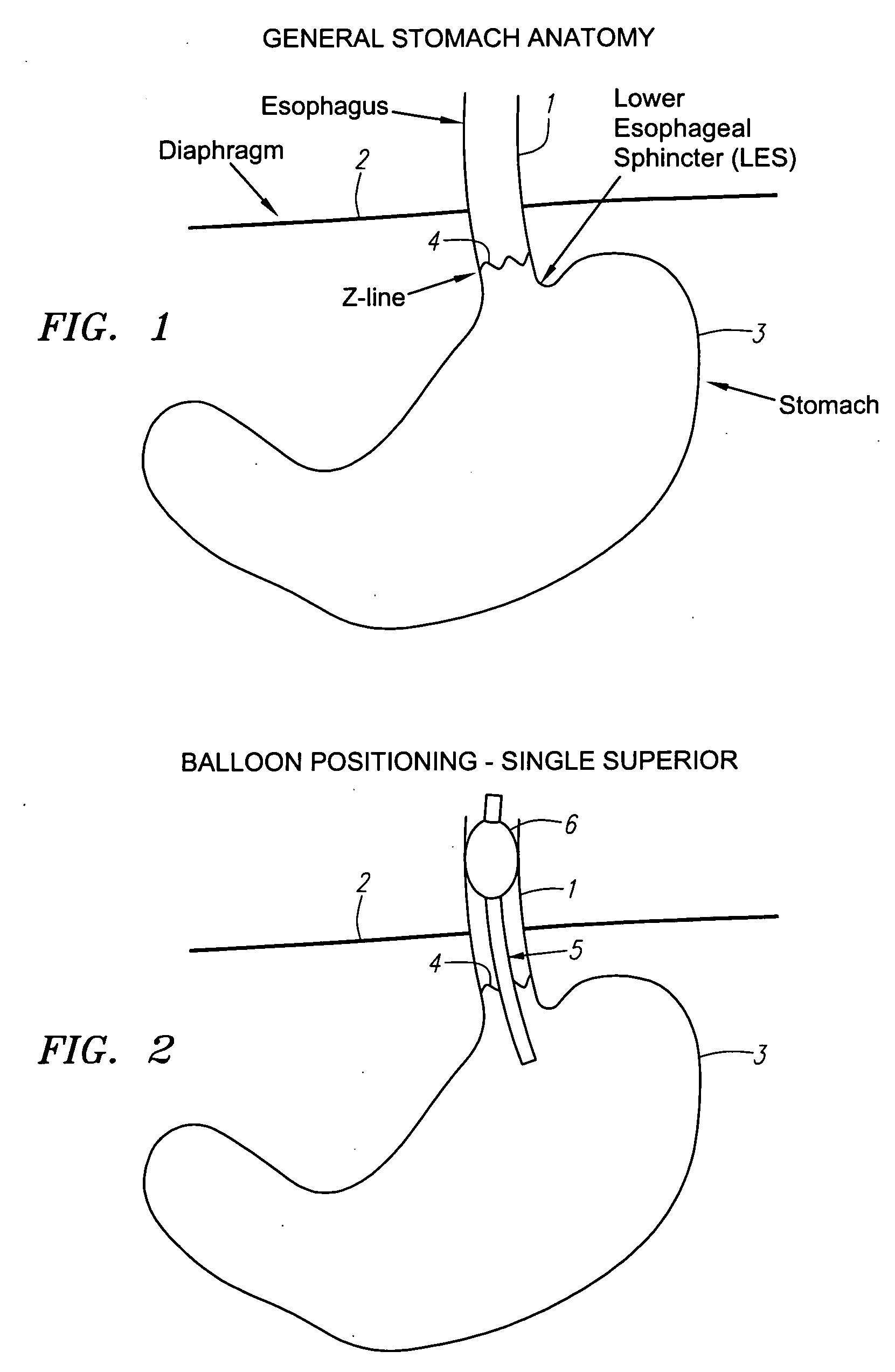
Method and apparatus for treating obesity by an energy delivery device, such as a high focus ultrasound transducer, mounted for movement along two or three axes relative to the esophagus to deliver transesophageal energy to interrupt the function of vagal nerves. Preferably, movement along a longitudinal axis of the esophagus changes the site to which the energy is directed and movement transversely along a radius of the esophagus focuses the energy on a vagal nerve. The third degree of freedom relative to the esophagus is to rotate the transducer about the longitudinal axis of the esophagus.
Owner:ENDOVX
Endo-cavity focused ultrasound transducer
InactiveUS7377900B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasonic sensorAcoustic energy
Owner:INSIGHTEC
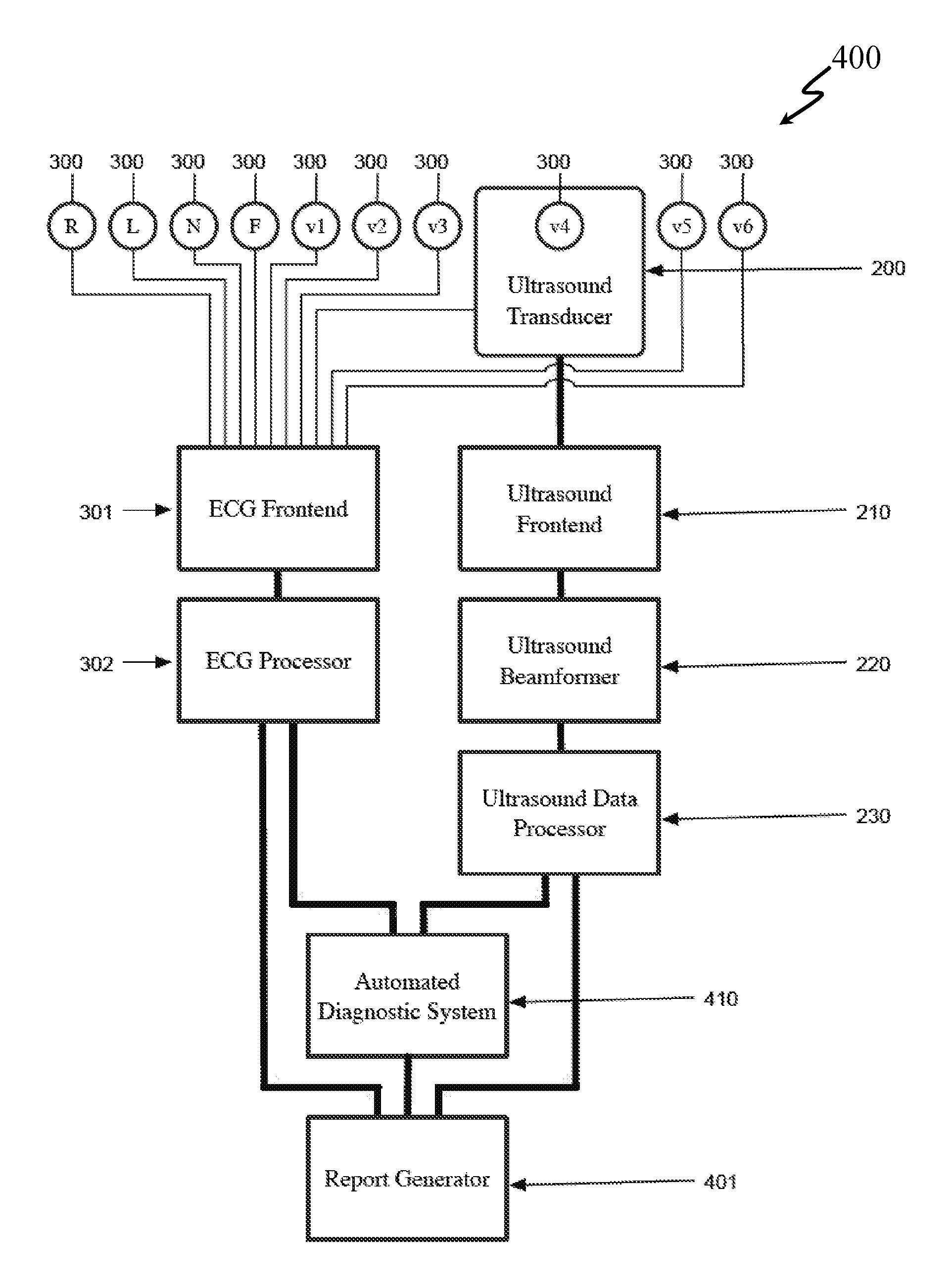
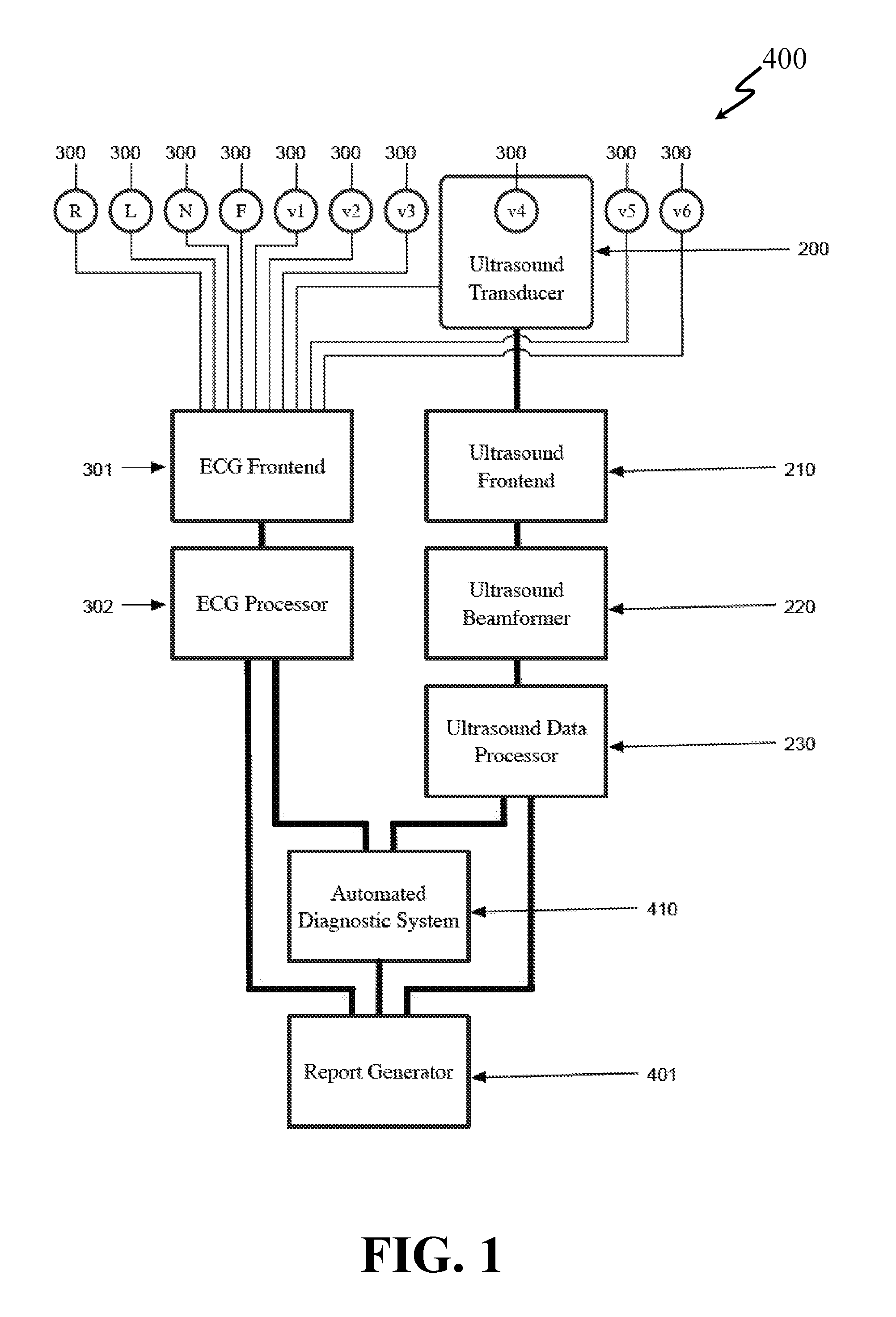
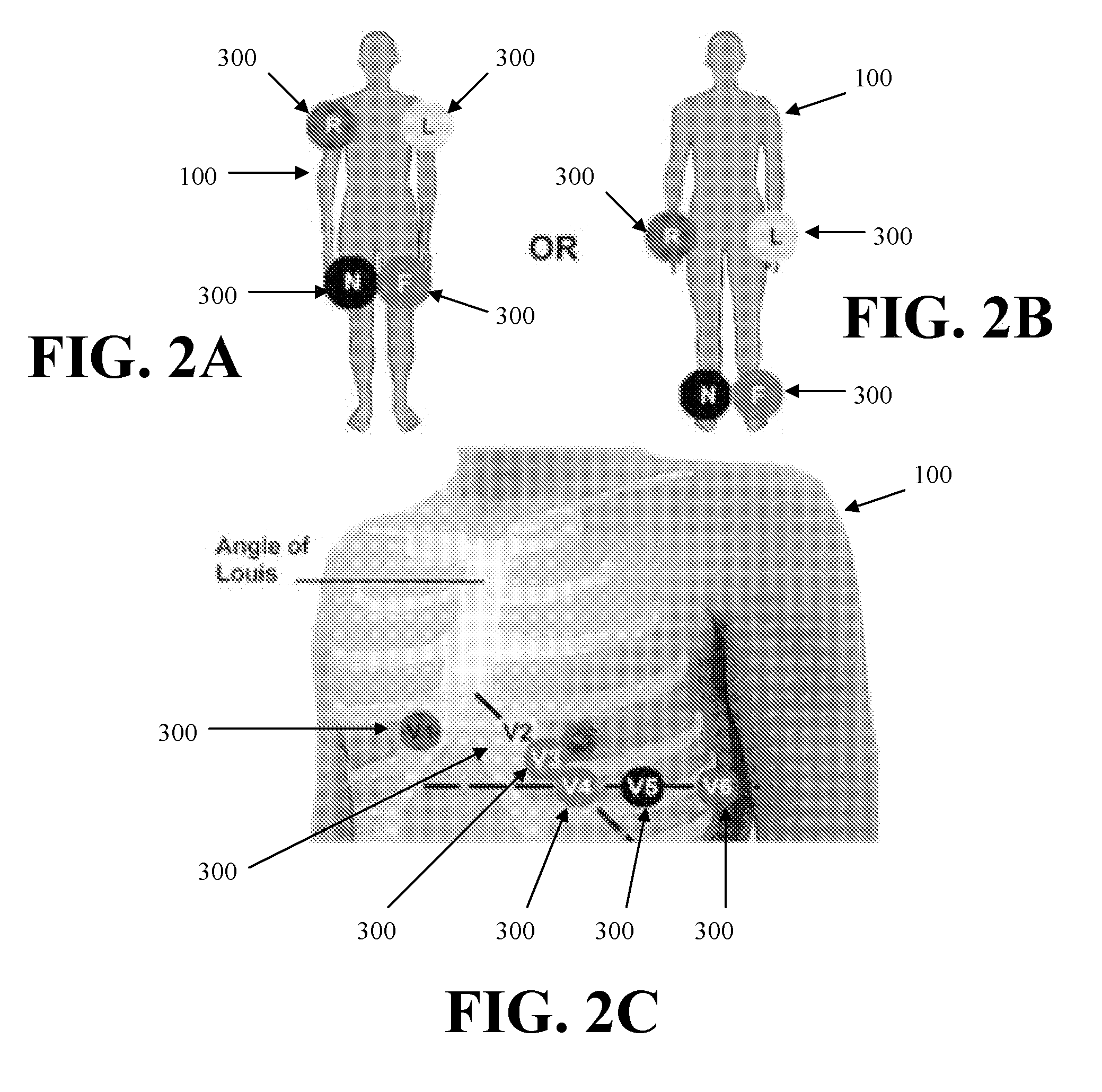
System and Method for Combined ECG-Echo for Cardiac Diagnosis
InactiveUS20100168578A1Low costSmall sizeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringSonificationCardiac muscle
A system and related method for obtaining volumetric cardiac data of a subject. The data is generated by forming a plurality of focused ultrasound images corresponding to a series of ranges, generating myocardial boundary data for each of the plurality of ultrasound images, calculating the area of the region defined by said myocardial boundary data for each of the plurality of ultrasound images, multiplying the area for each of the plurality of ultrasound images by a slice depth corresponding to said ultrasound image to obtain the slice volume of each slice, and summing the slice volumes to obtain a total volume. In an alternative embodiment the system and related method combine an automated volumetric ultrasound system for finding chamber volumes and myocardial thicknesses, with a diagnostic electrocardiogram system to enable simultaneous diagnosis of mechanical and electrical cardiac problems.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
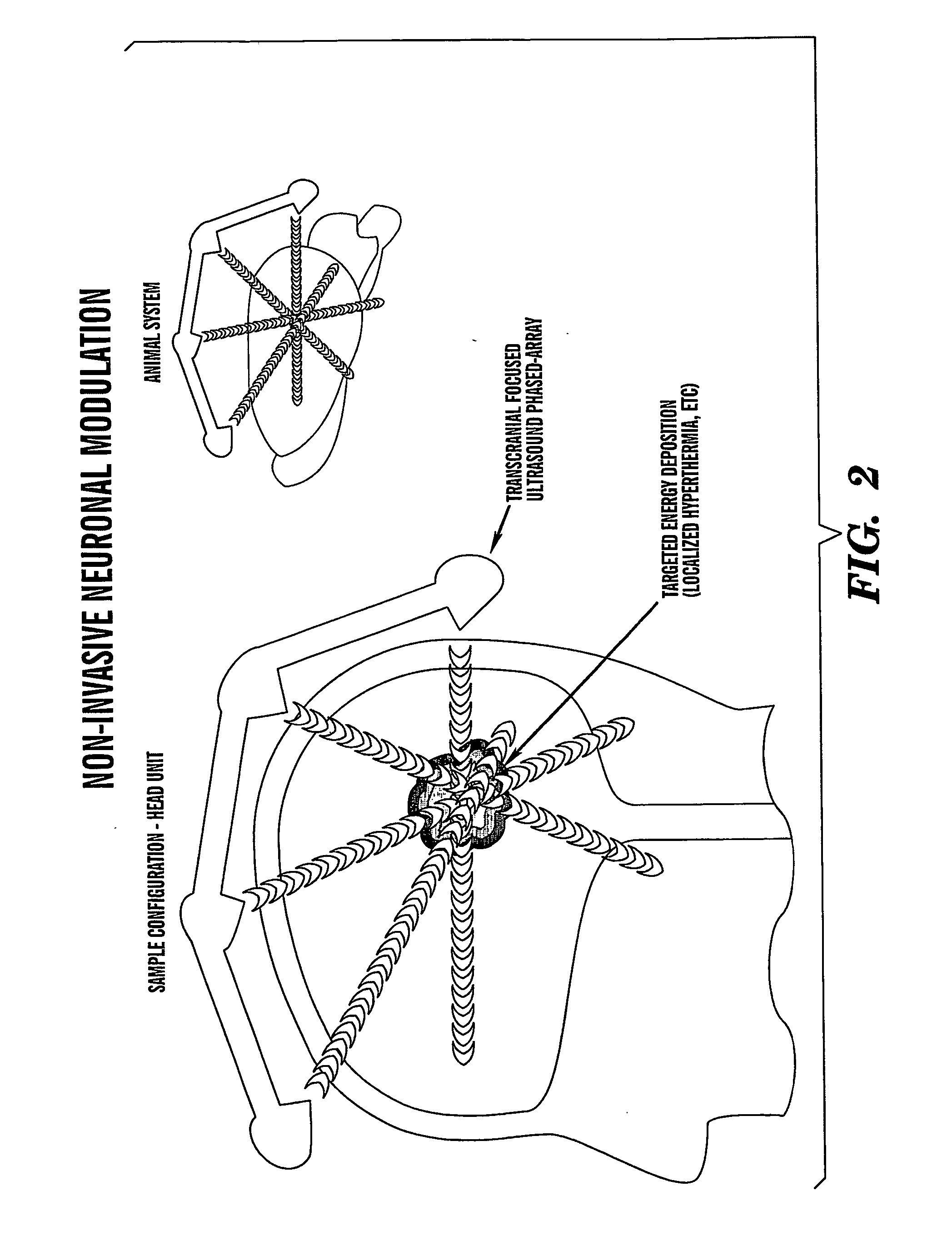
Methods for modifying electrical currents in neuronal circuits
InactiveUS20070299370A1Change propertiesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyBrain circuitNeuronal circuits
Disclosed herein are methods for modifying electrical currents in brain circuits through the simultaneous use of focused ultrasound pulse (FUP) and an existing brain-imaging system, such as a functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) system. The methods are used for research, treatment and diagnosis of psychiatric, neurological, and neuroendocrine disorders whose biological mechanisms include brain circuits. The methods include the simultaneous steps of applying FUP to a live neuronal circuit within a brain and monitoring a brain image produced by a brain imaging system during the application of FUP.
Owner:BRAINSONIX CORP
Methods and apparatus for treatment of obesity
Method and apparatus for treating obesity by use of transesophageal delivery of energy to interrupt the function of vagal nerves. The energy, which may be highly focused ultrasound energy or other types of energy is delivered through the wall of the esophagus by a device placed in the esophagus. The energy delivered is sufficient to ablate a vagal nerve on the outer wall of the esophagus.
Owner:ENDOVX
System and method providing directional ultrasound therapy to skeletal joints
An ultrasound therapy system and method is provided that provides directional, focused ultrasound to localized regions of tissue within body joints, such as spinal joints. An ultrasound emitter or transducer is delivered to a location within the body associated with the joint and heats the target region of tissue associated with the joint from the location. Such locations for ultrasound transducer placement may include for example in or around the intervertebral discs, or the bony structures such as vertebral bodies or posterior vertebral elements such as facet joints. Various modes of operation provide for selective, controlled heating at different temperature ranges to provide different intended results in the target tissue, which ranges are significantly effected by pre-stressed tissues such as in-vivo intervertebral discs. In particular, treatments above 70 degrees C., and in particular 75 degrees C., are used for structural remodeling, whereas lower temperatures achieves other responses without appreciable remodeling.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Contact lens mold assemblies and systems and methods of producing same
ActiveUS20070035051A1Prevent materialEnhanced cavitationOptical articlesStereotype platesEngineeringContact lens
Methods and apparatus are provided for making an ophthalmic lens. Apparatus are provided for filling contact lens shaped cavities of contact lens molding assemblies. Methods of coupling and fusing contact lens mold sections are also provided and generally include providing first and second mold sections which when coupled together are effective to form a lens-shaped cavity and contact regions between the mold sections. One or both of the mold sections may include one or more recessed regions or projections which provide areas of non-fusion and areas of fusion, respectively, when the mold sections have been filled with a contact lens precursor material and are fused together, for example, by means of focused ultrasound energy.
Owner:COOPERVISION INT LTD
Focused ultrasound for pain reduction
Methods and devices that provide ultrasonic energy used to cause one or more nerves to become dysfunctional. A nerve to be treated is placed in the focal zone of ultrasonic energy emitted by ultrasound transducer. A first level of ultrasonic energy is provided to the nerve using the ultrasound transducer, the first level sufficient to stimulate the nerve. A verification is made that the desired nerve is being stimulated by the first level of ultrasonic energy. For example, the patient may be asked to confirm that the ultrasonically stimulated nerve corresponds to the pain that is affecting the patient. Subsequent to verifying the stimulated nerve is the nerve desired for the reduction of pain, a second level of ultrasonic energy is delivered to the nerve using the ultrasound transducer, the second level of ultrasonic energy sufficient to cause nerve dysfunction.
Owner:VAITEKUNAS JEFFREY J
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com