Patents
Literature
564 results about "Large target" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
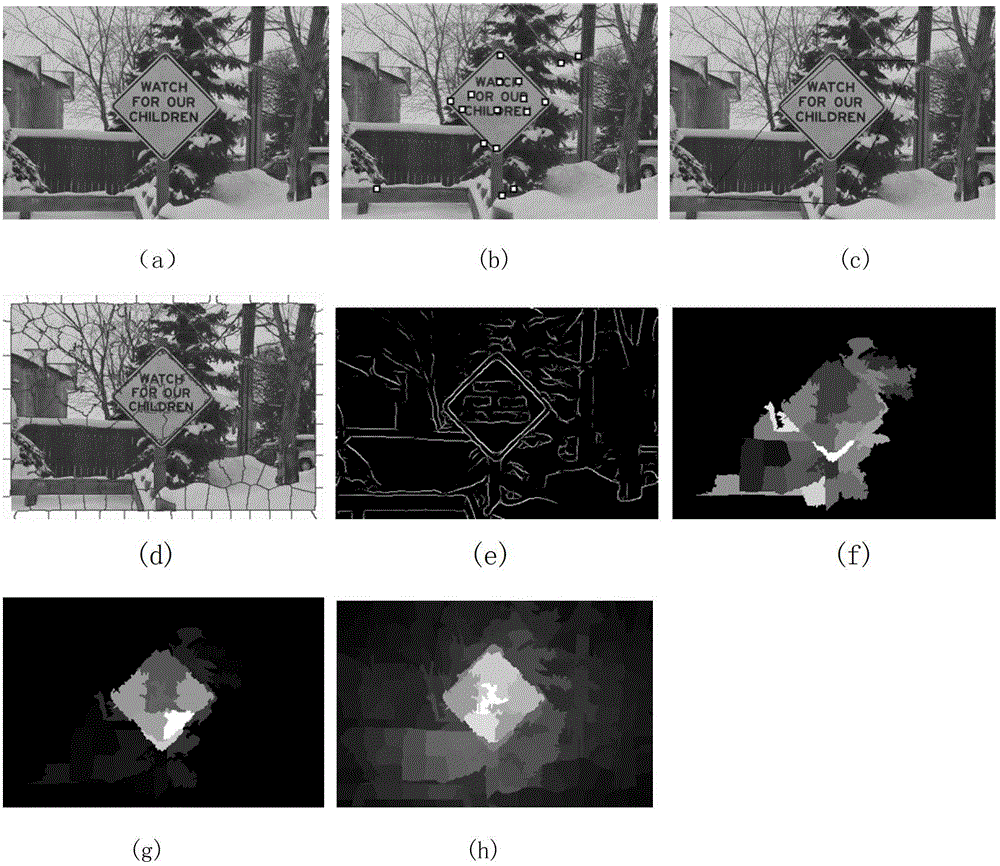
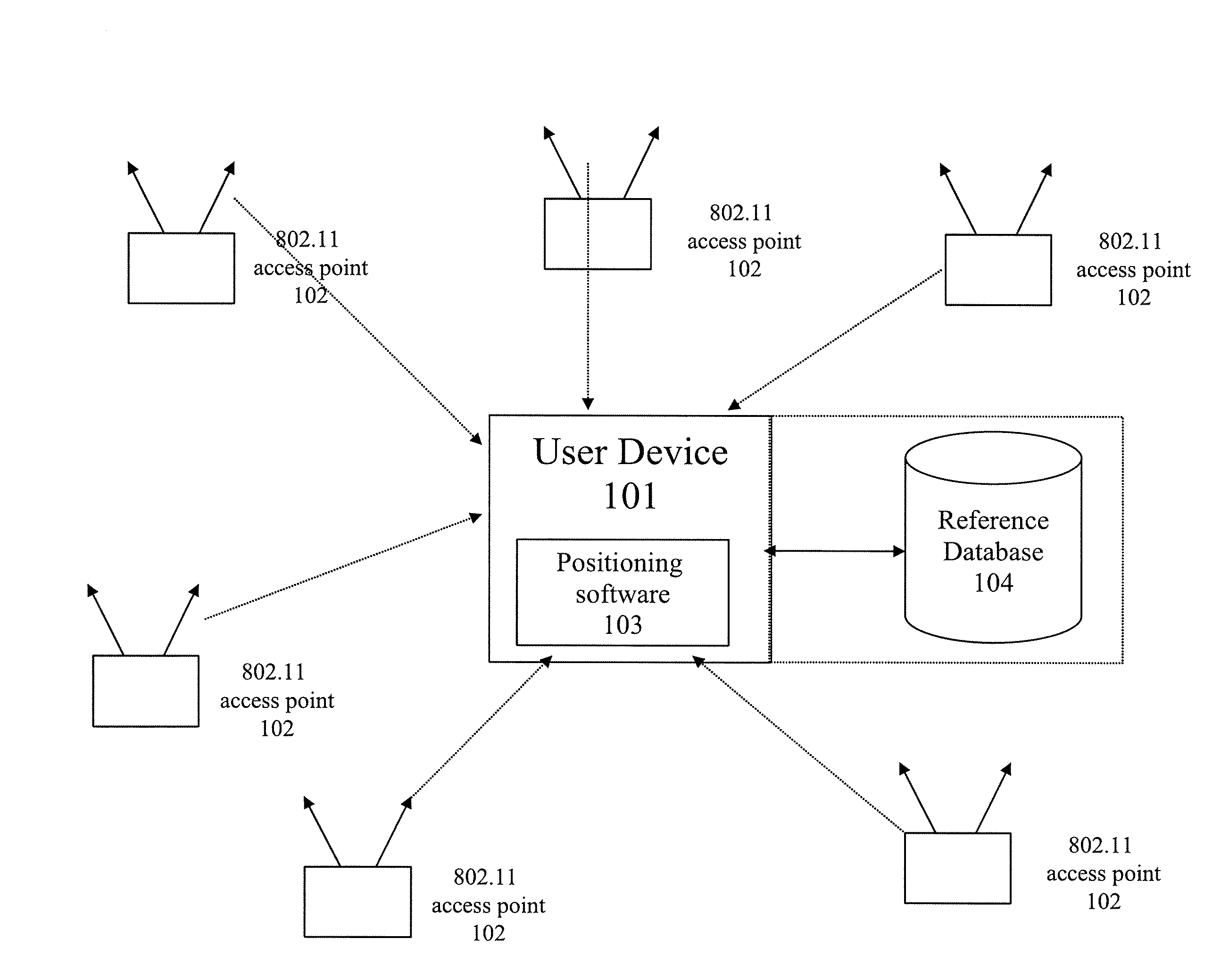
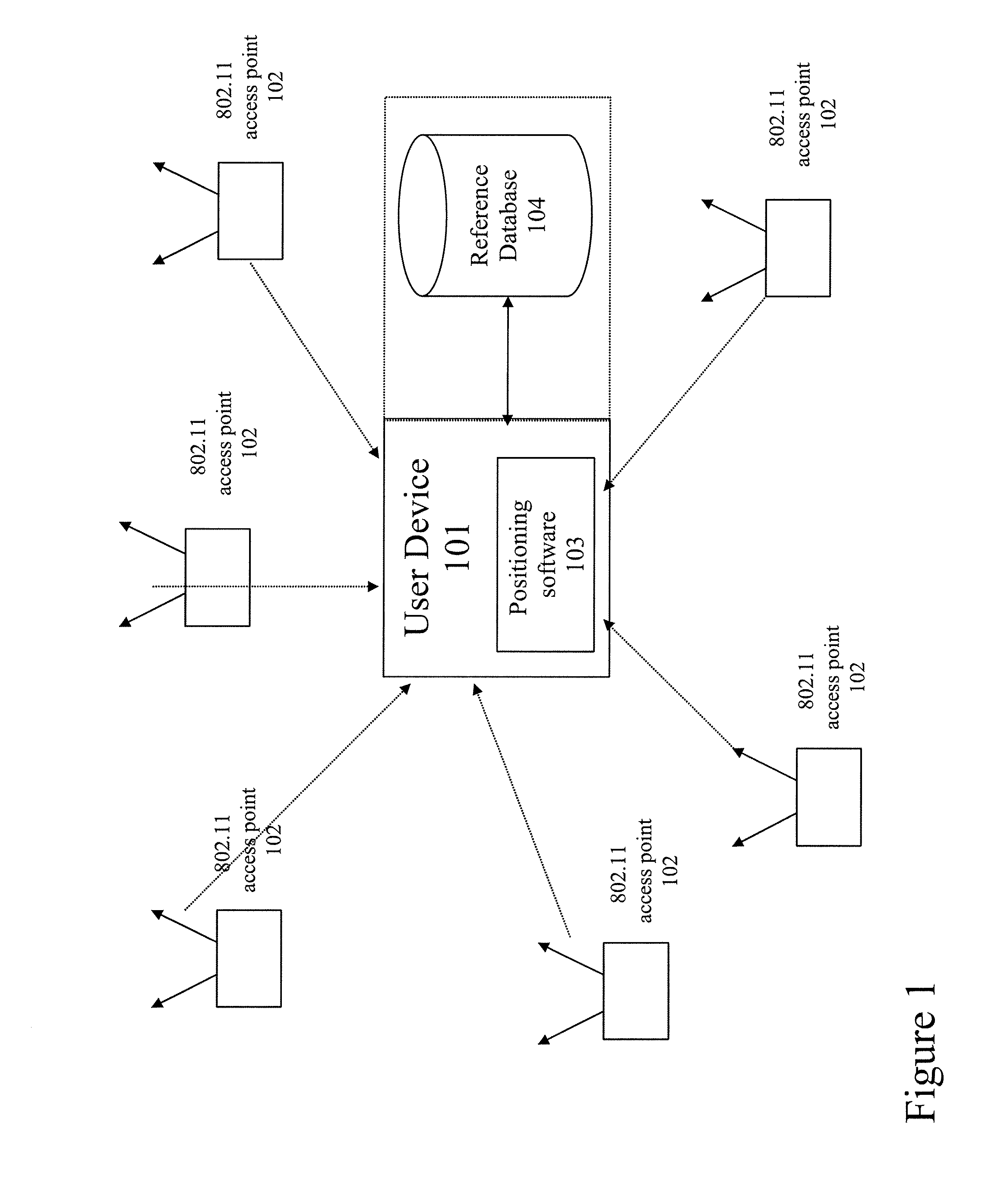
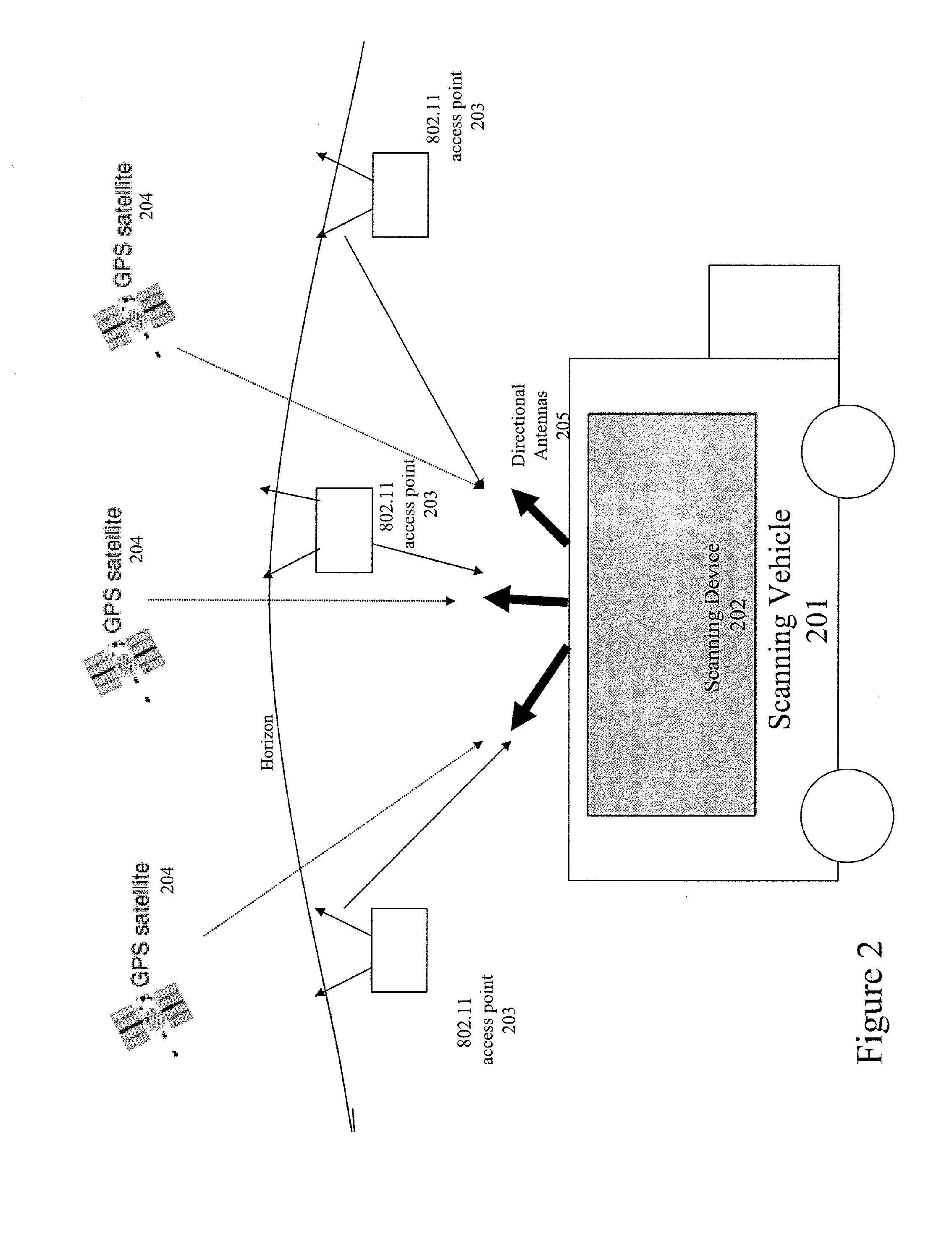
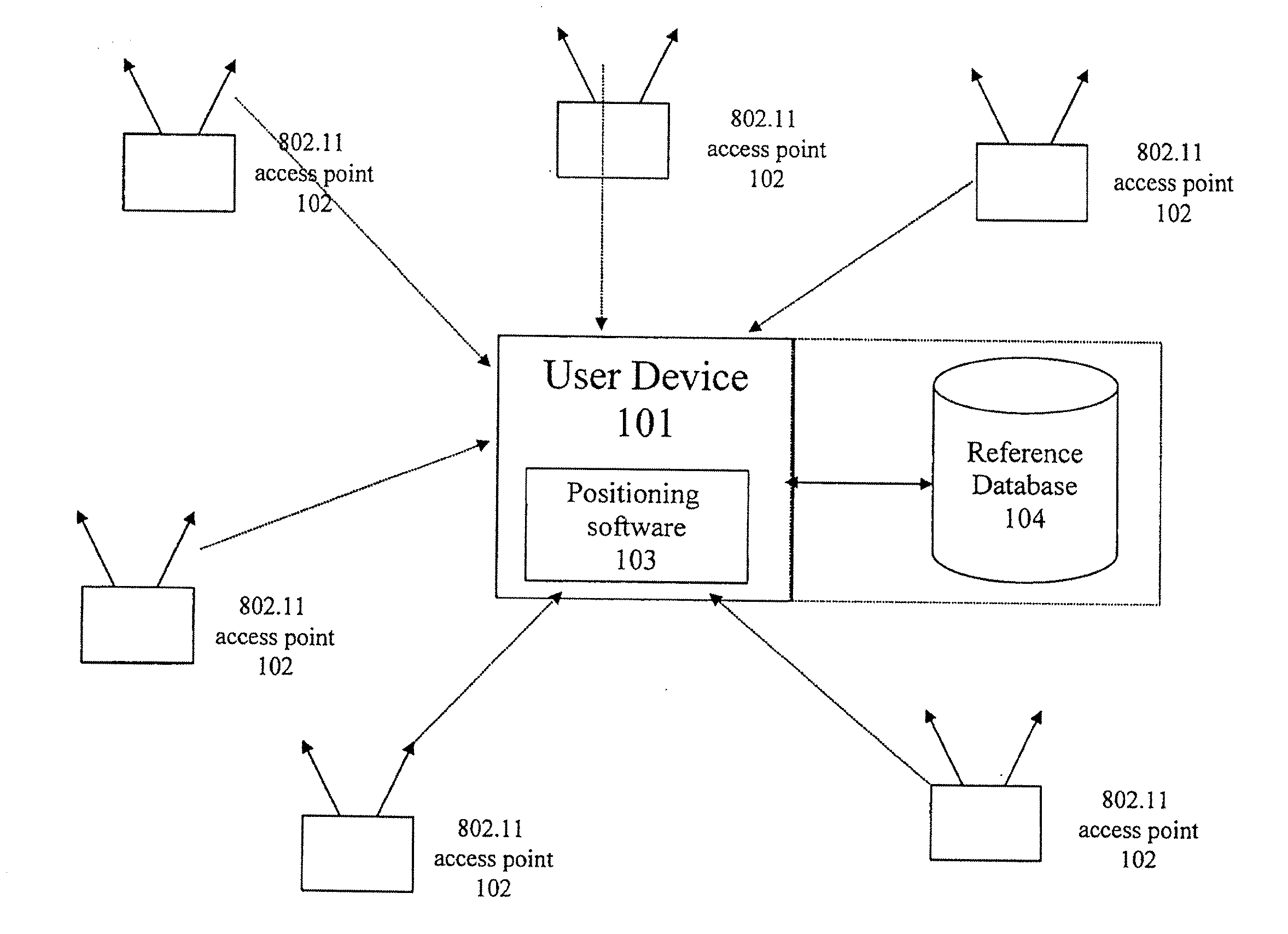
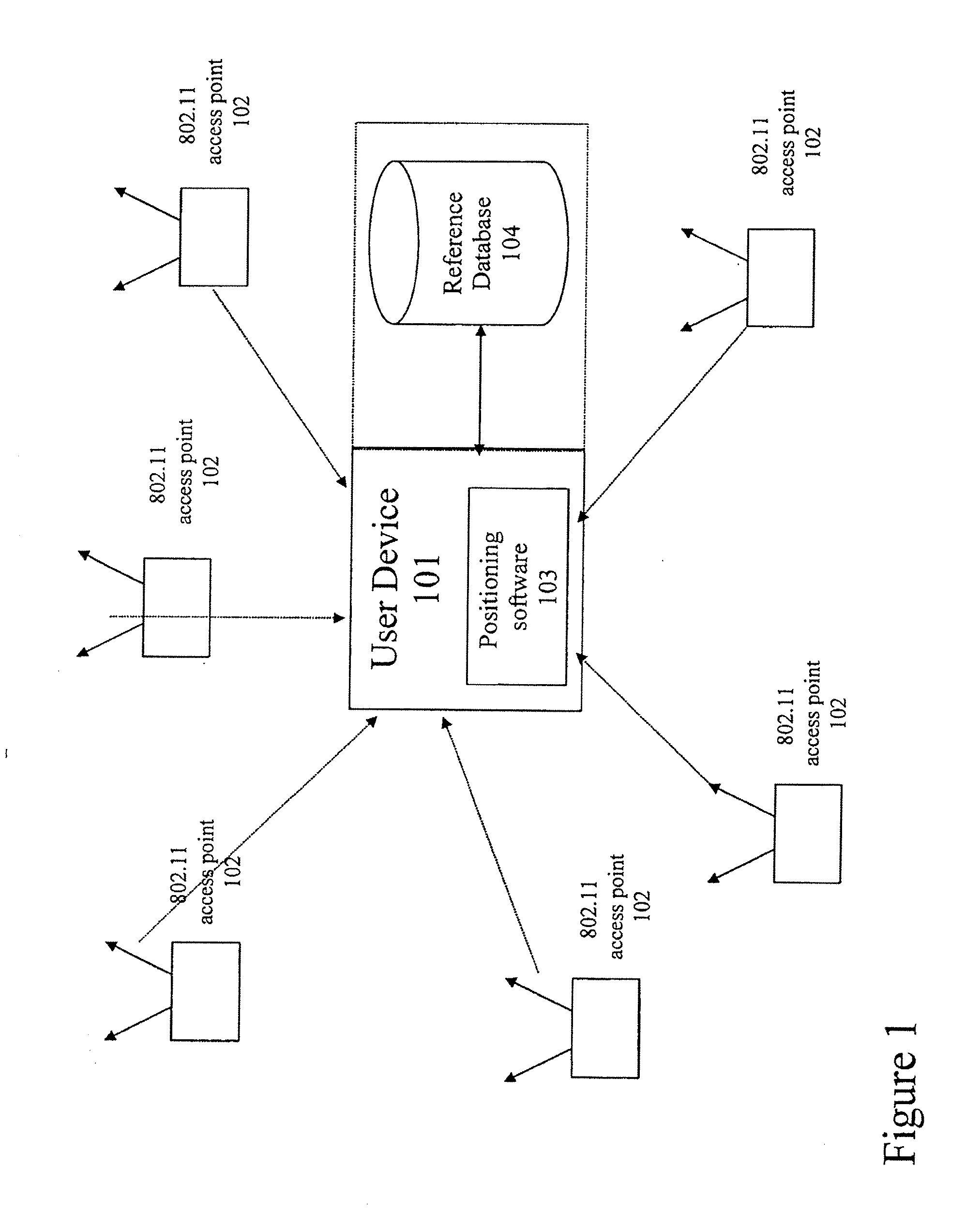
Method and system for selecting and providing a relevant subset of wi-fi location information to a mobile client device so the client device may estimate its position with efficient utilization of resources
Methods and systems for selecting and providing a relevant subset of Wi-Fi location information to a mobile client device so the client device may estimate its position with efficient utilization of resources.A method of providing a relevant subset of information to a client device is based in part on scanning for Wi-Fi access points within range of the client device, using a Wi-Fi database that covers a large target region to retrieve information about these access points, using this information to estimate the position of the mobile client device, selecting a limited region in the vicinity of the estimated location of the client device, and providing information about Wi-Fi access points within this limited region to the client. For efficient transfer and maintenance of data, the target region may be divided into a hierarchy of fixed geographical tiles.
Owner:SKYHOOK WIRELESS
Paired end sequencing
The present invention provides for a method of preparing a target nucleic acid fragments to produce a smaller nucleic acid which comprises the two ends of the target nucleic acid. Specifically, the invention provides cloning and DNA manipulation strategies to isolate the two ends of a large target nucleic acid into a single small DNA construct for rapid cloning, sequencing, or amplification.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
Implantable injection port
InactiveUS6039712AMedical devicesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismInjection portBiomedical engineering
An implantable injection port consists of a very low profile housing with virtually no residual volume while maintaining a large target area for the needle.
Owner:FOGARTY TERENCE M
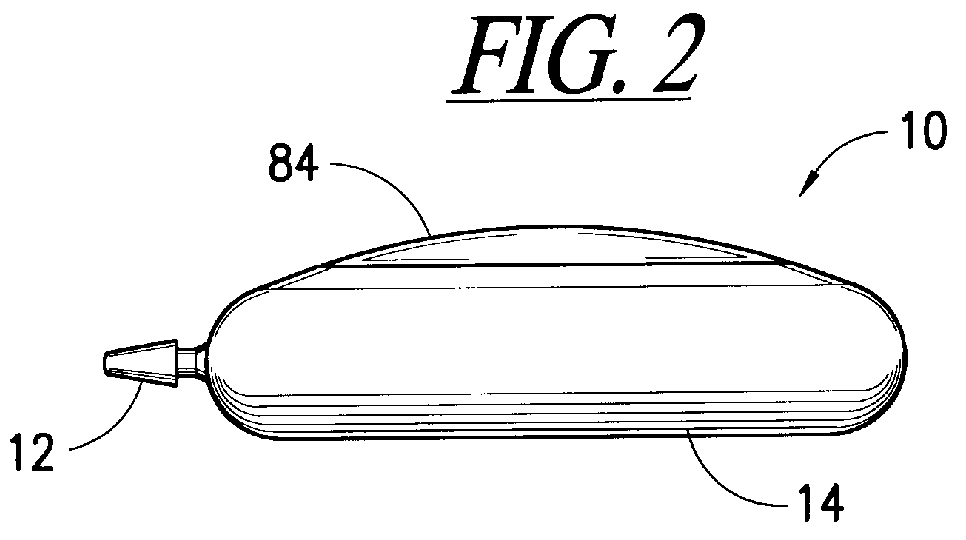
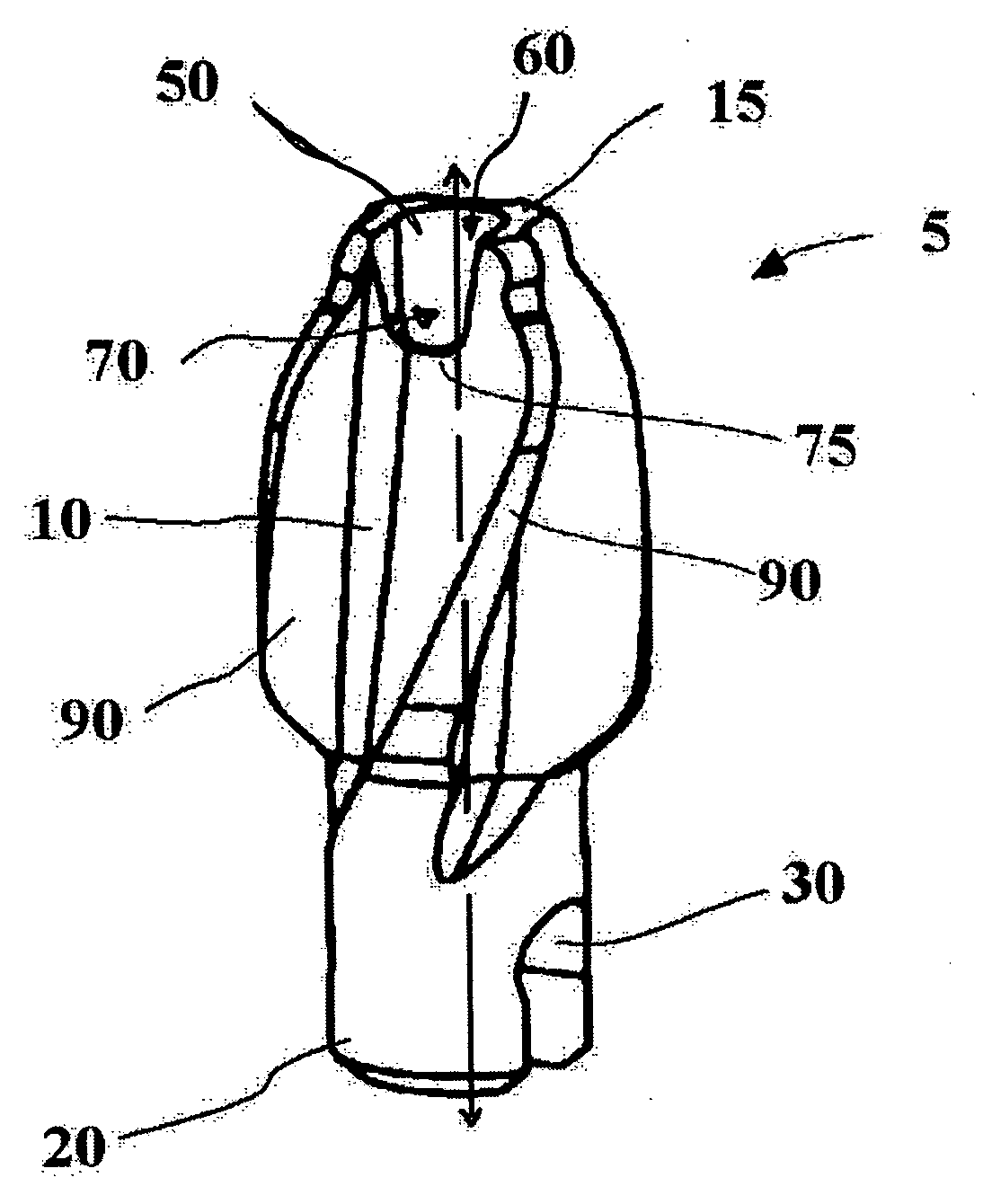
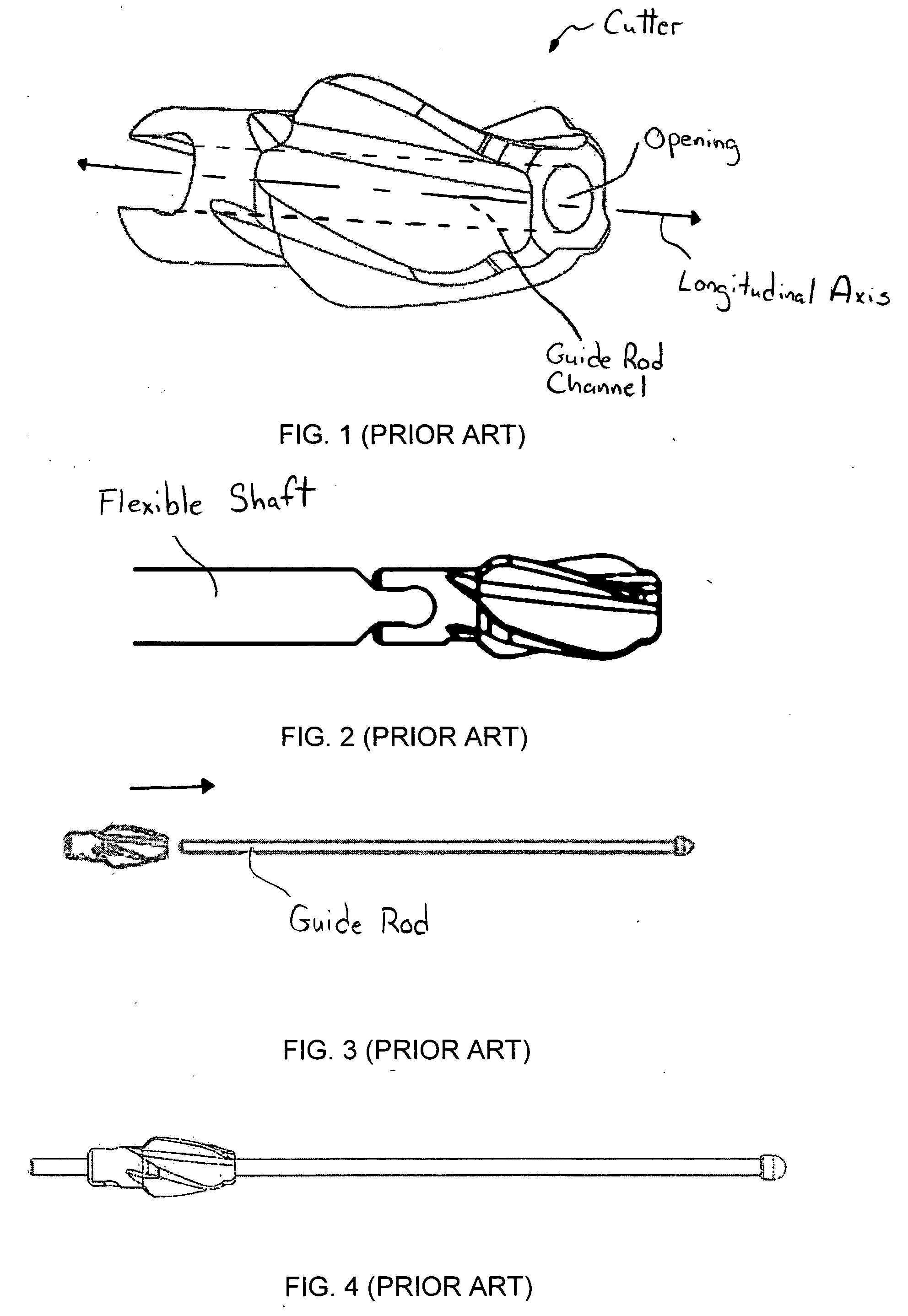
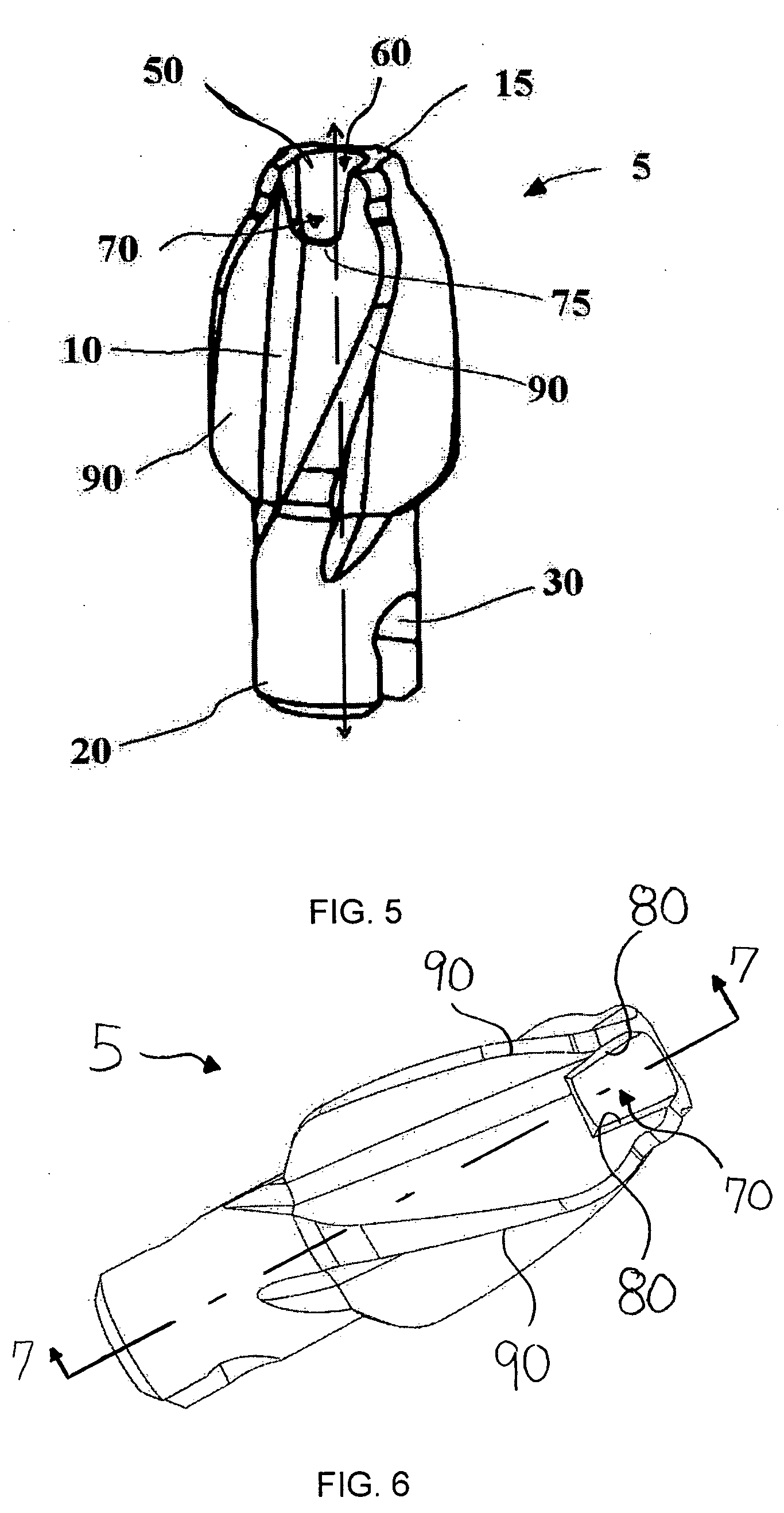
Cutting device
A cutter for reaming of the bone canal is provided. The cutter facilitates connection with a guide rod by having a larger target for insertion of the guide rod into the cutter channel of the cutter. The cutter can have an opening with a first portion that is substantially orthogonal to the longitudinal axis of the cutter channel and a second portion that is non-orthogonal to the longitudinal axis. The first and second portions can be orthogonal to each other.
Owner:PEPPER JOHN R
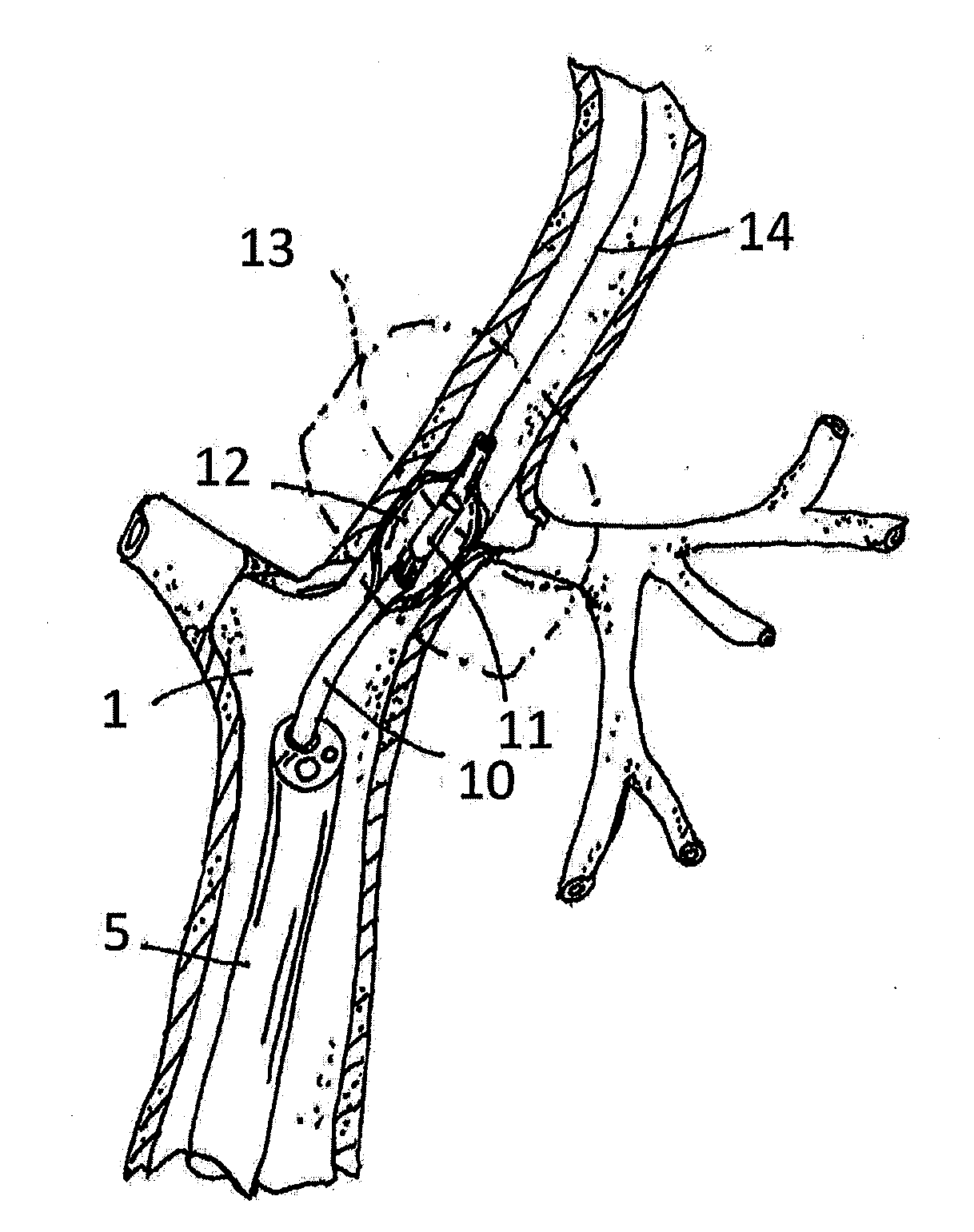
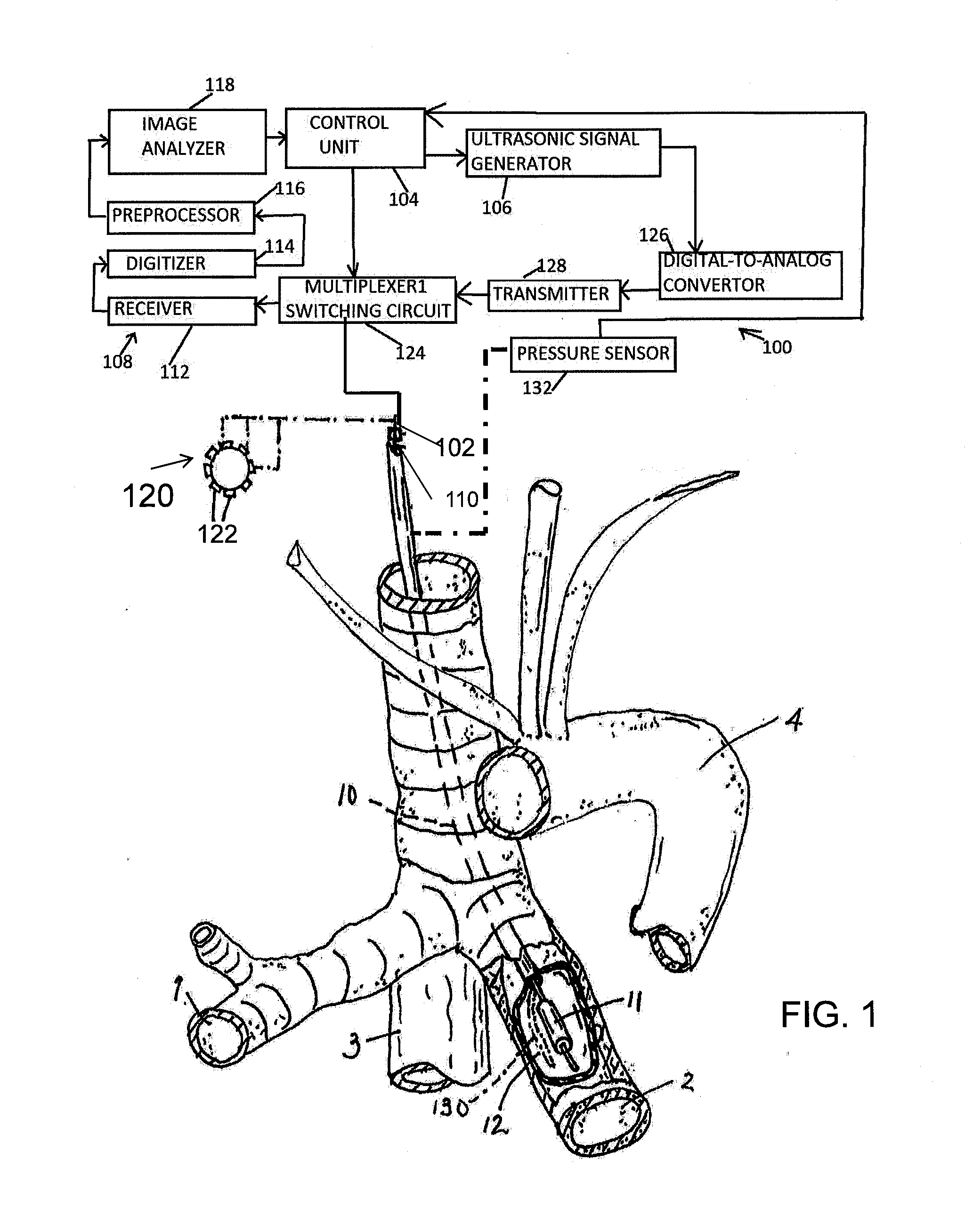
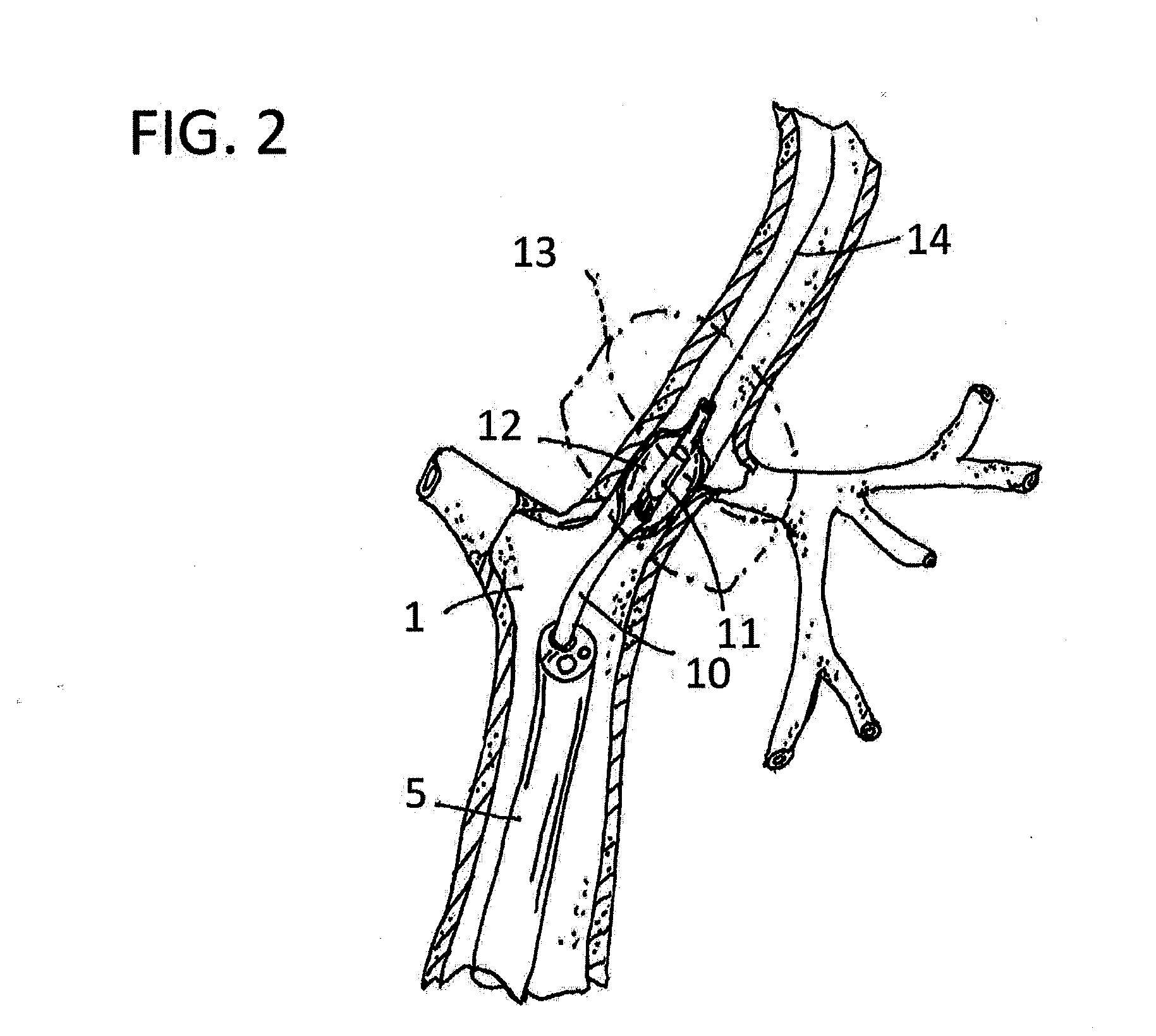
Method and apparatus for performance of thermal bronchiplasty with unfocused ultrasound
InactiveUS20160287912A1Reduce the possibilityAvoid insufficient temperatureUltrasound therapyBronchoscopesSonificationLarge target
Apparatus and methods for deactivating bronchial nerves and smooth muscle extending along a bronchial branch of a mammalian subject to treat asthma and related conditions. An electromechanical transducer (11) is inserted into the bronchus as, for example, by advancing the distal end of a catheter (10) bearing the transducer into the bronchial section to be treated. The electromechanical transducer emits unfocused mechanical vibratory energy of one or more ultrasonic frequencies so as to heat tissues throughout a relatively large target region (13) as, for example, at least about 1 cm3 encompassing the bronchus to a temperature sufficient to inactivate nerves but insufficient to cause rapid ablation or necrosis of organic tissues. The treatment can be performed without locating or focusing on individual bronchial nerves.
Owner:GUIDED INTERVENTIONS
Paired end sequencing
The present invention provides for a method of preparing a target nucleic acid fragments to produce a smaller nucleic acid which comprises the two ends of the target nucleic acid. Specifically, the invention provides cloning and DNA manipulation strategies to isolate the two ends of a large target nucleic acid into a single small DNA construct for rapid cloning, sequencing, or amplification.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
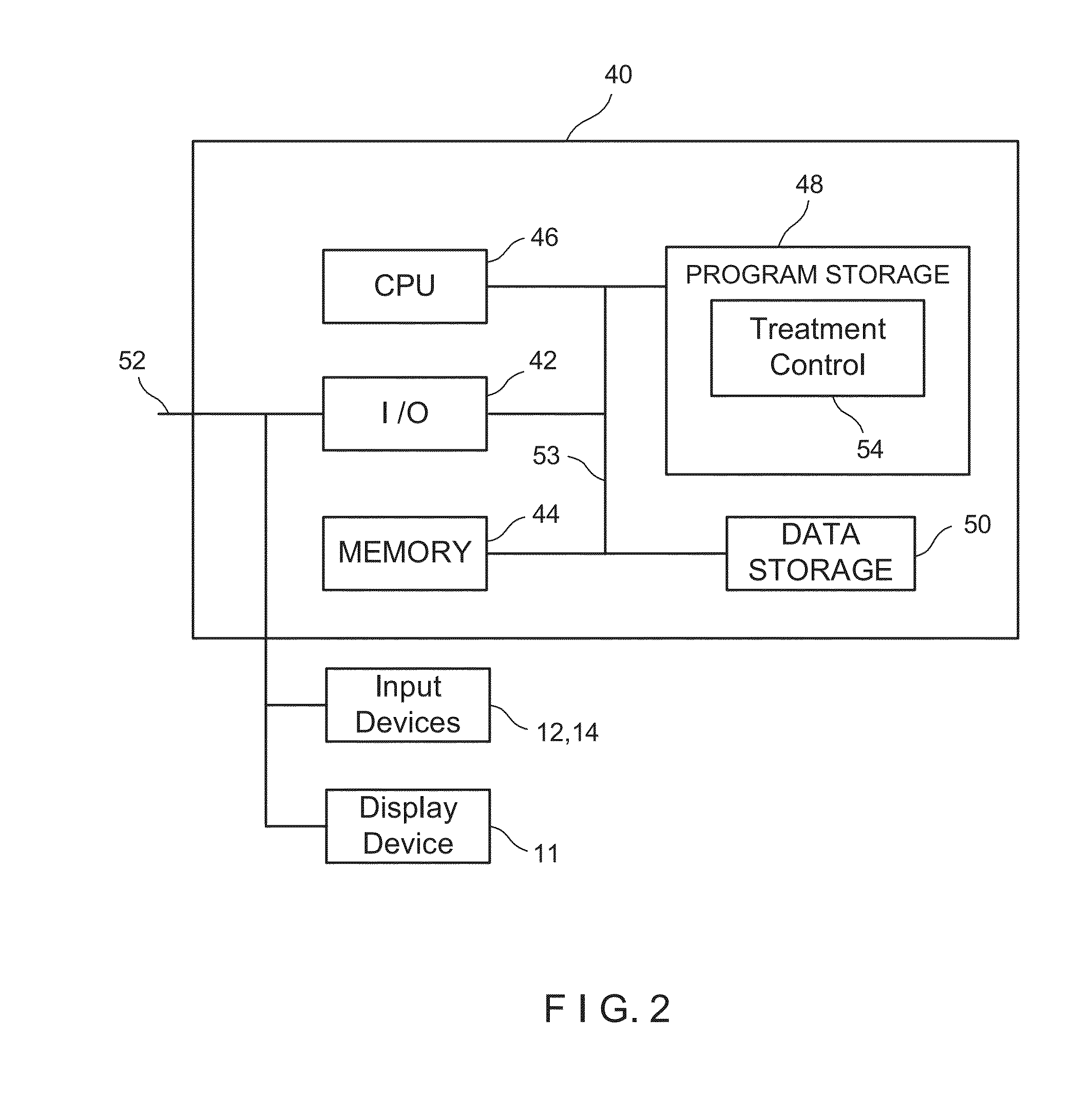
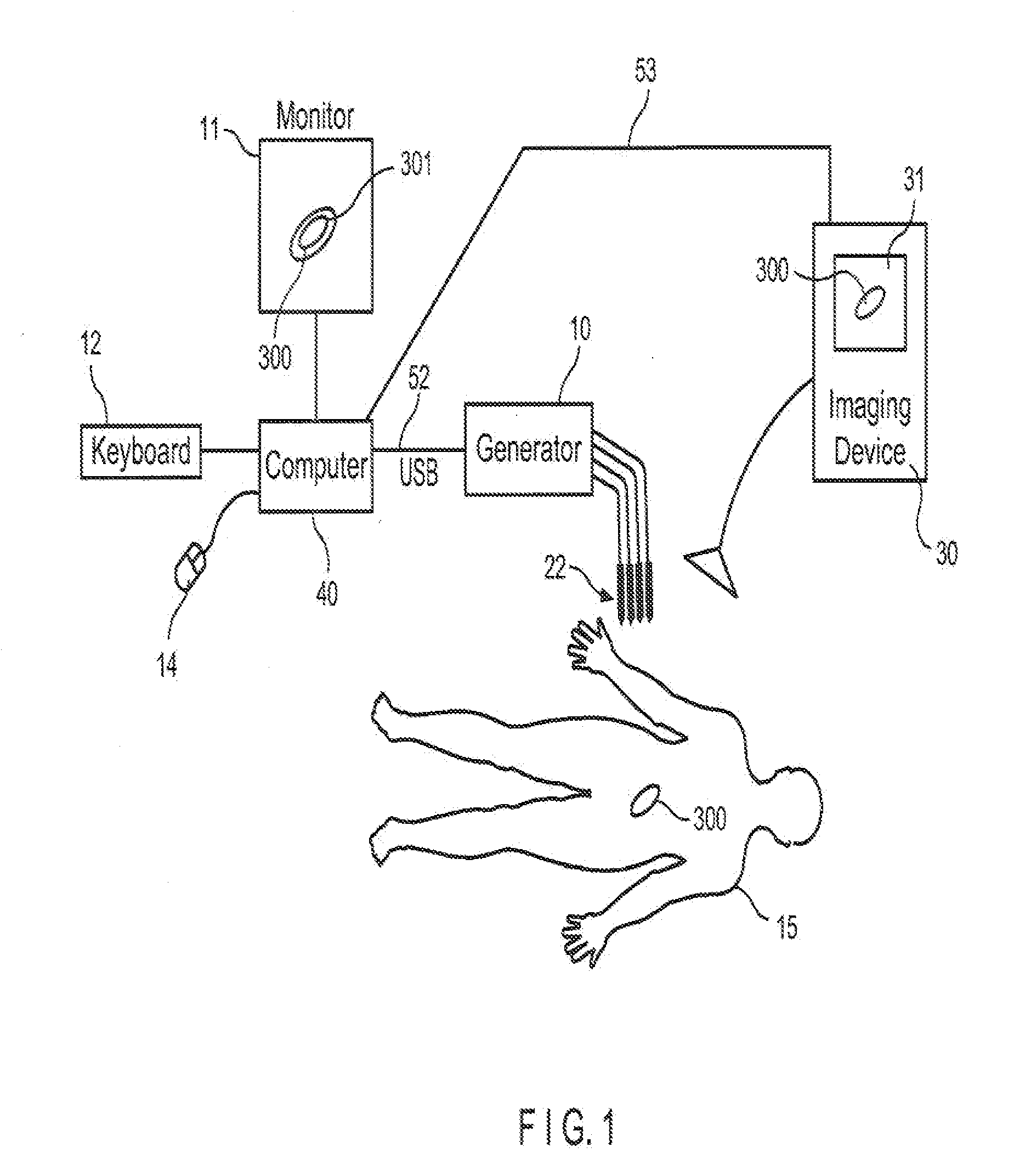
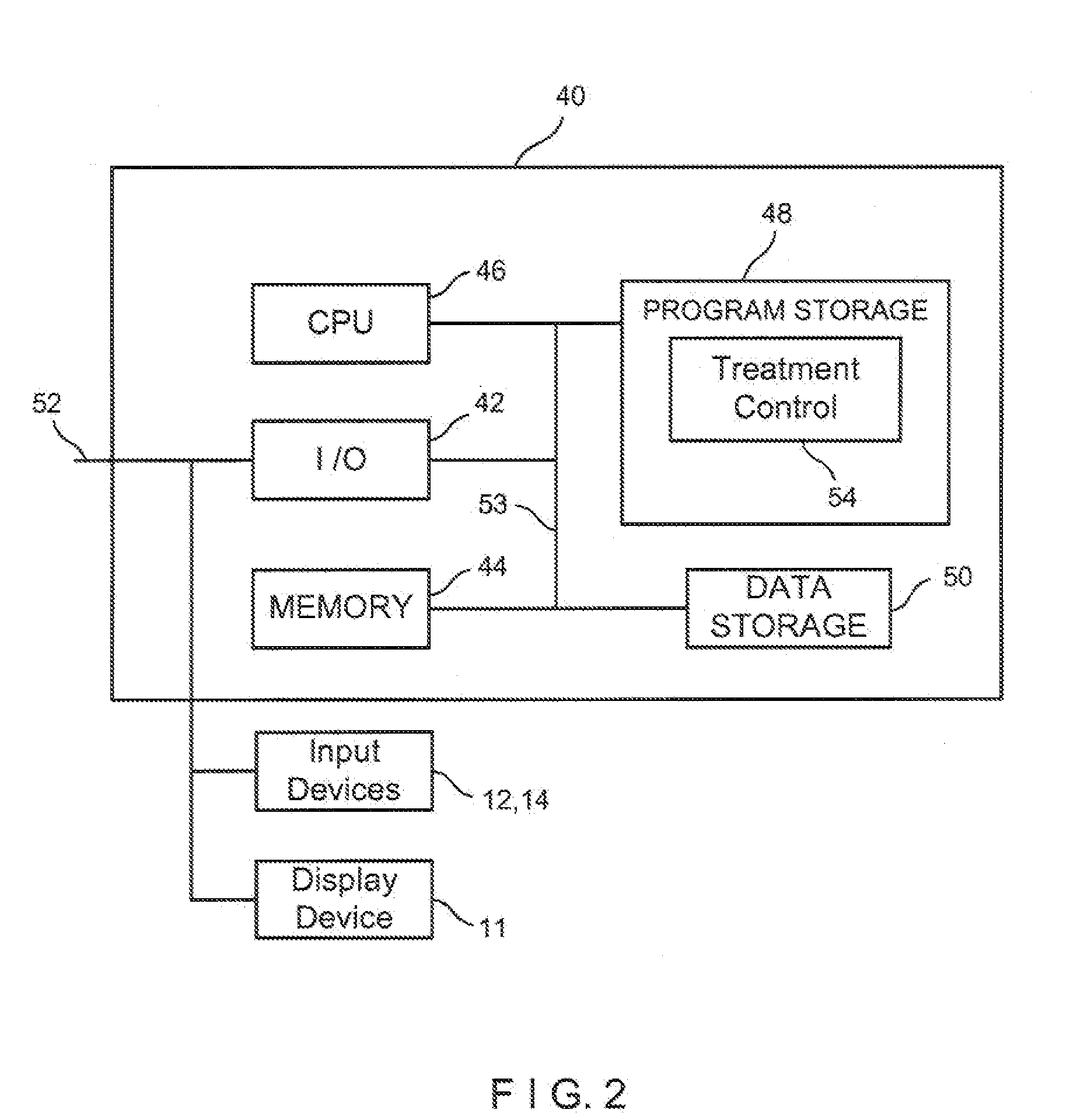
System and method for increasing a target zone for electrical ablation
System for increasing a target zone for electrical ablation includes a treatment control module executable by a processor. The control module directs a pulse generator to apply pre-conditioning pulses to subject tissue cells in a pre-conditioning zone to electroporation, the pre-conditioning zone being smaller than a target ablation zone. After the pre-conditioning pulses have been applied, the control module directs the pulse generator to apply treatment pulses to electrically ablate the tissue cells in the target ablation zone. The pre-conditioning pulses cause the pre-conditioning zone to have a much higher conductivity so that the zone acts as a larger electrode area when the treatment pulses are applied, which results in a much larger target ablation zone than otherwise possible.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
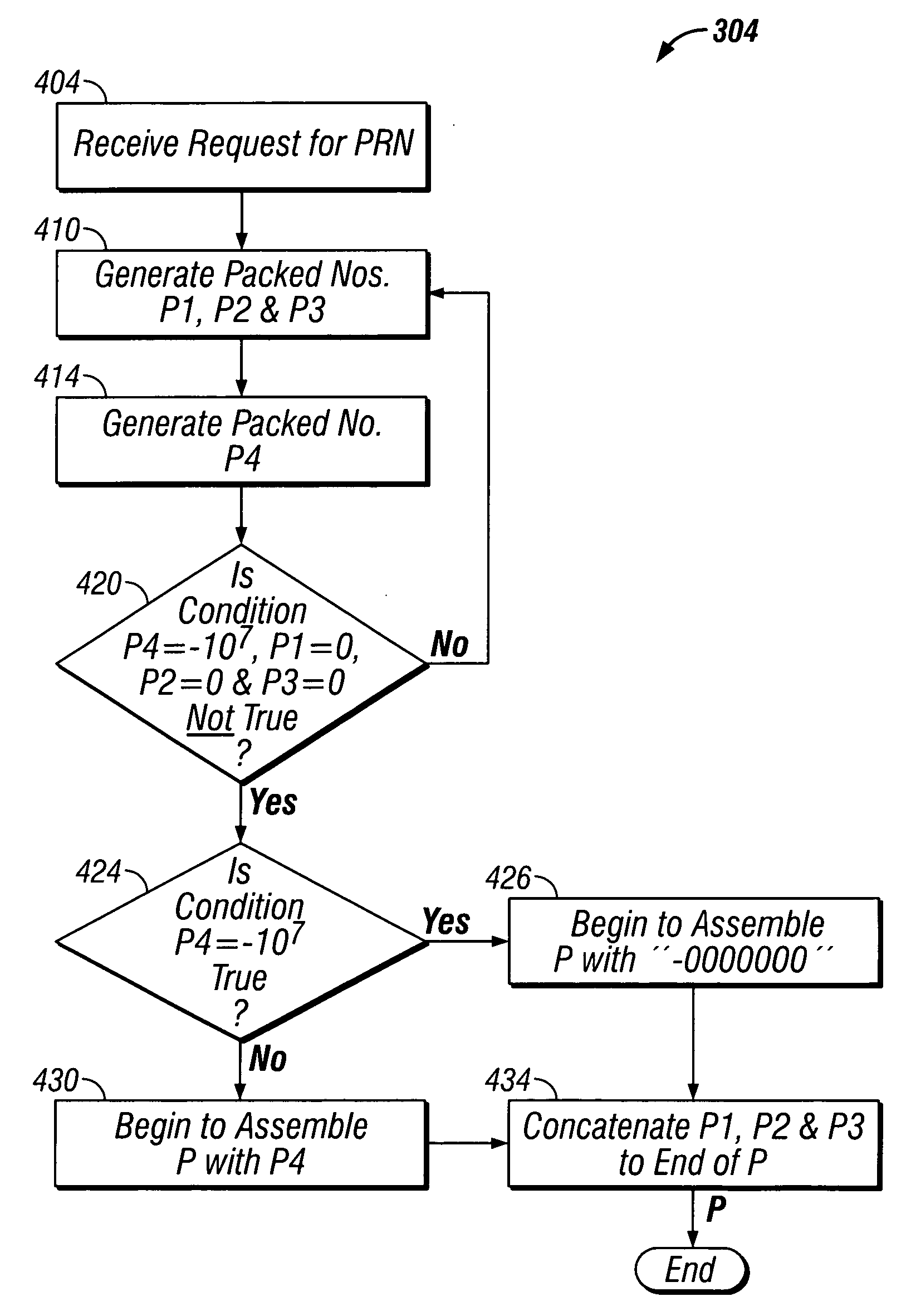
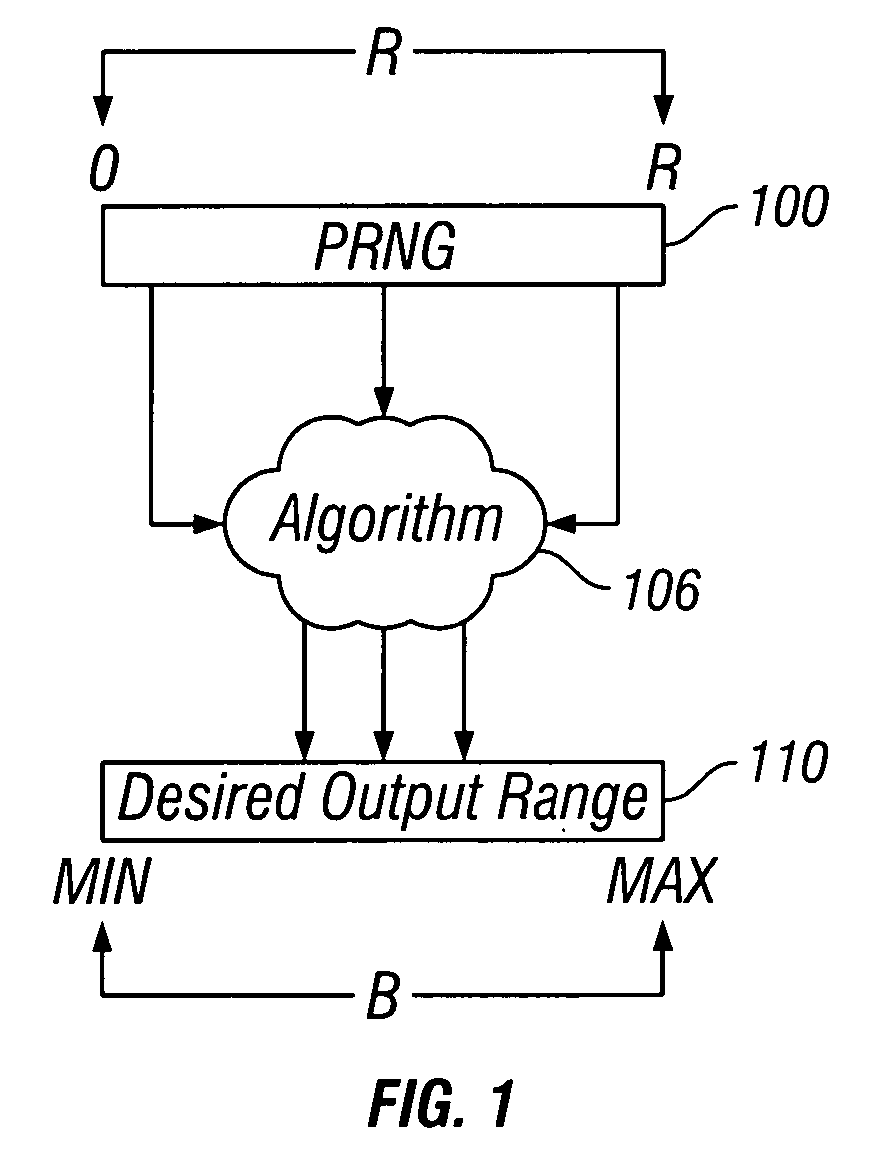
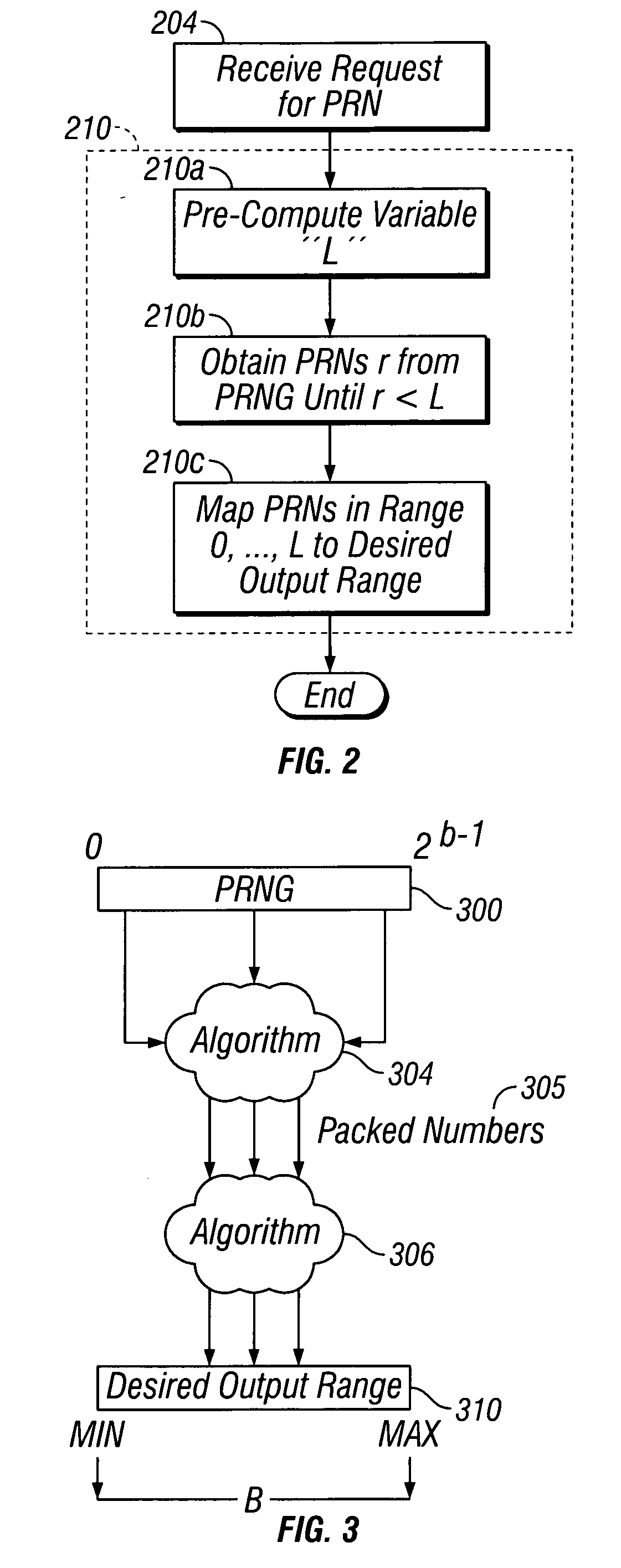
Mapping pseudo-random numbers to predefined number ranges
ActiveUS20050050121A1Low costDiminish pseudo randomnessRandom number generatorsDigital function generatorsSmall targetComputer science
Pseudo-random numbers (PRNs) generated by a PRN generator are mapped to predefined number ranges or target ranges. The target range may be smaller or larger than the range of the PRN generator. Mapping to a smaller target range may include generating PRNs (e.g., integers) from a particular bit-input stream (e.g., 32-bit) having a uniform distribution across the range of numbers; selecting an optimal subset of the generated PRNs to map; and mapping the selected PRNs to a corresponding number in a target range such that the mapped numbers are uniformly distributed across the target range. Mapping to a larger target range may include generating uniformly distributed PRNs; applying a generation function to the PRNs to generate uniformly distributed packed numbers; and applying a mapping function to map selected packed numbers to the target range such that the mapped numbers are uniformly distributed.
Owner:SAP AG
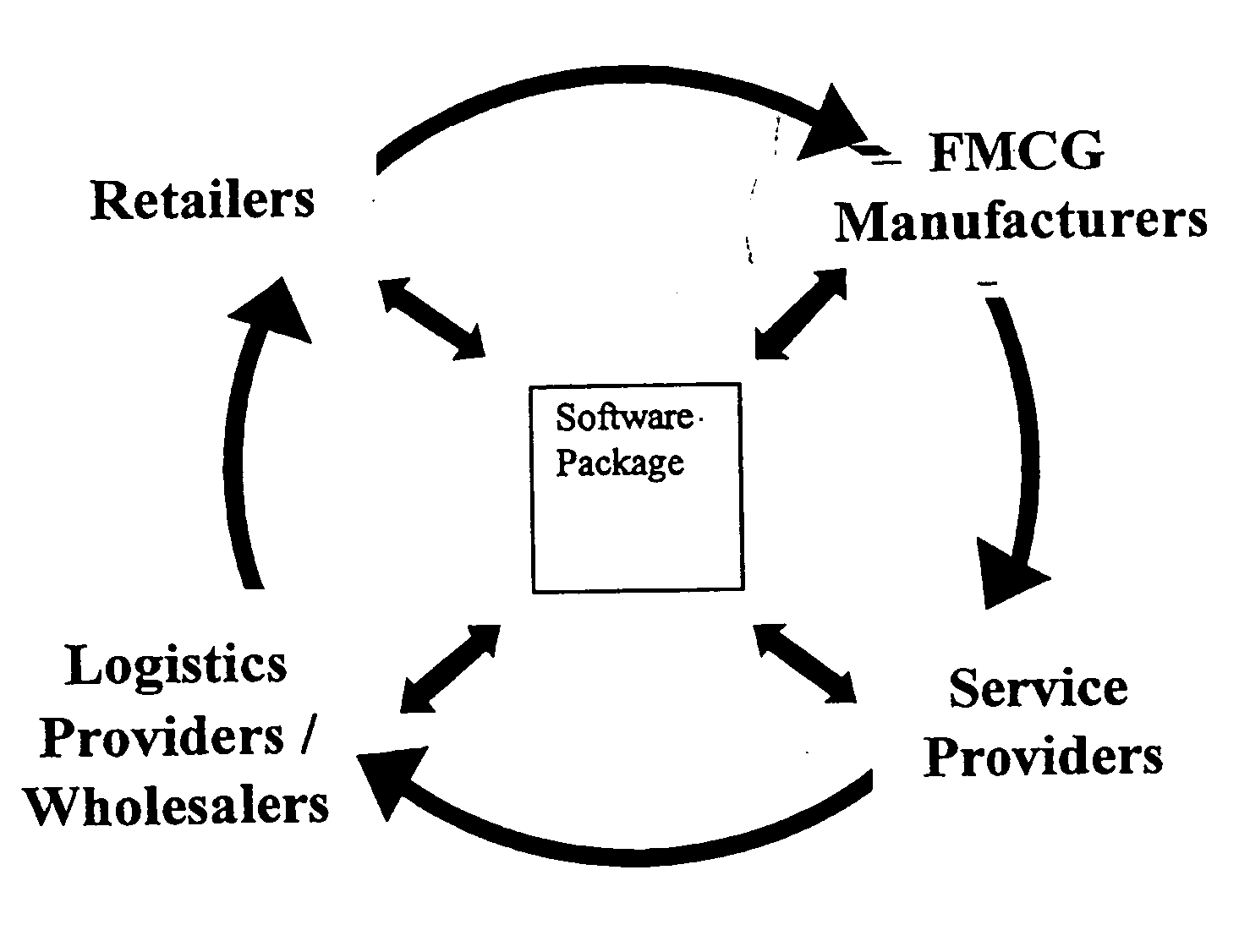
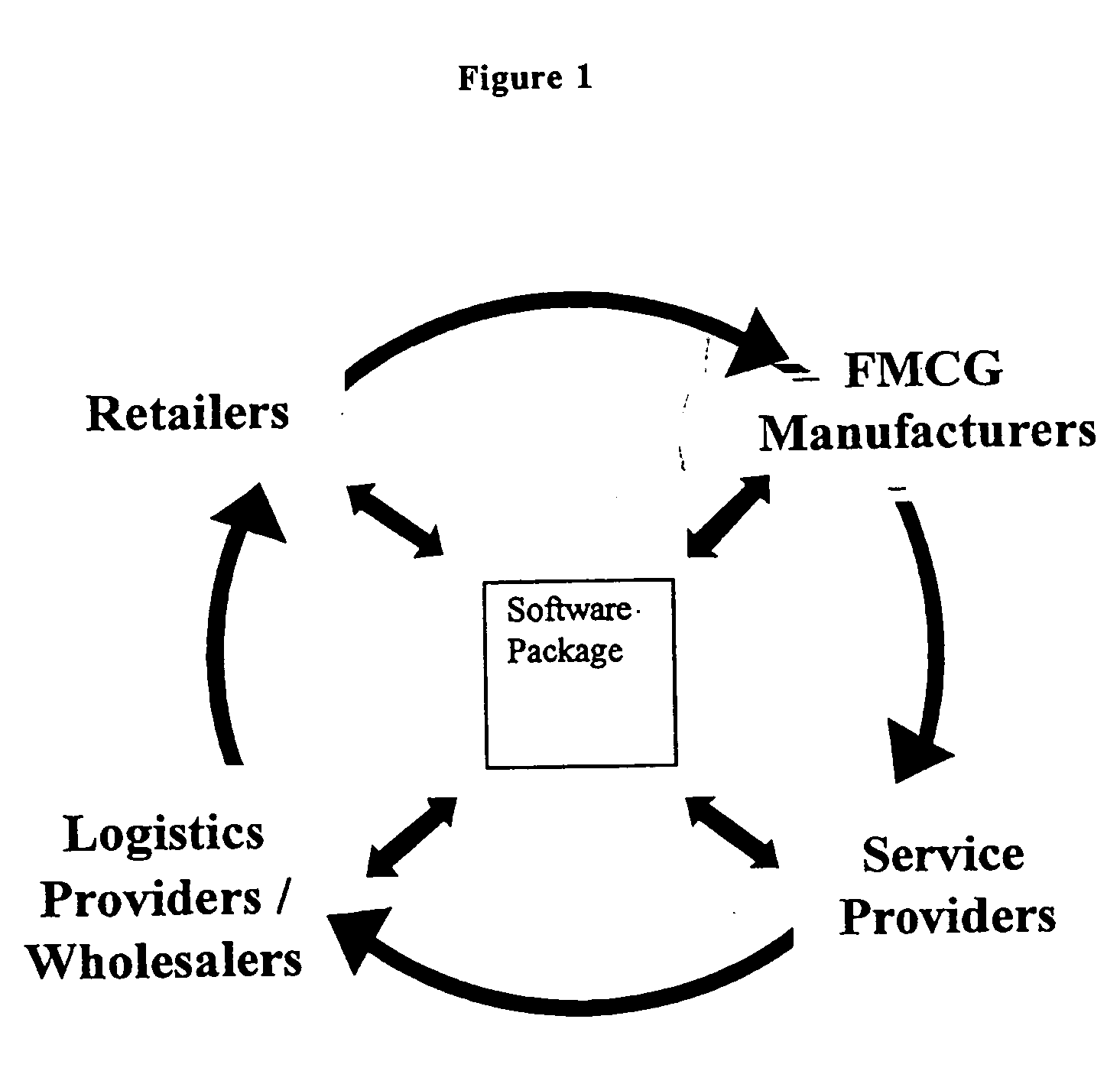
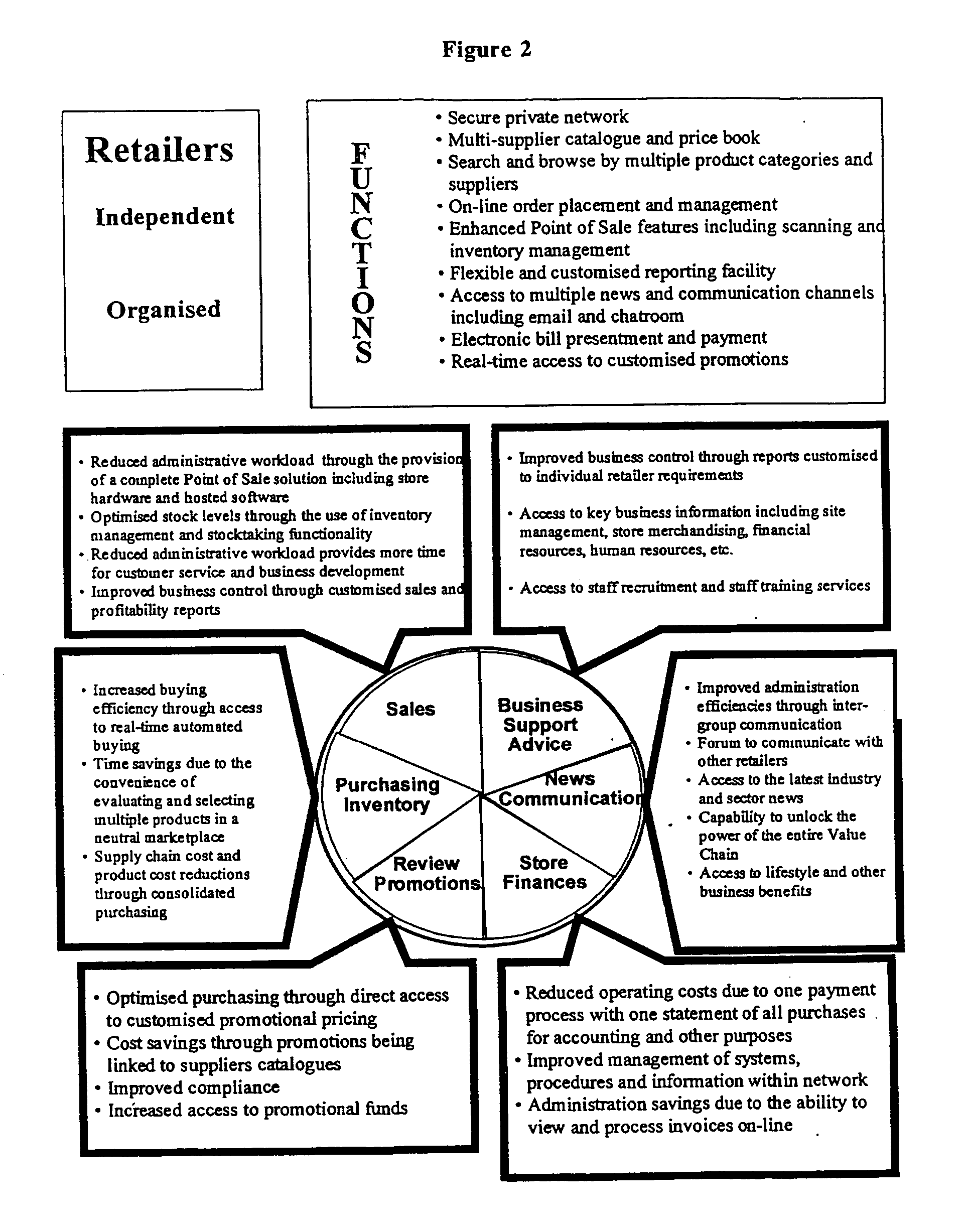
Network based business to business portal for the retail convenience marketplace
Broadly, the invention provides an Electronic Marketplace Solution (EMS) which may be embodied, in part or in whole, as a method, system or computer readable medium of instructions. The invention provides a business to business Internet portal serving companies operating within the convenience marketplace. In one embodiment, the invention is an Internet portal which assists: Independent Convenience Retailers through the provision of a single system to sell, buy and pay for goods / services and manage their business more effectively; Organised Convenience Groups, by providing them access to improved network management, the ability to ensure compliance and the ability to reduce costs; FMCG Manufacturers in the areas of secondary supply chain efficiencies, by improved business intelligence and direct access to Convenience Retailers; Wholesalers / Logistics Providers, for reduced costs and improved efficiency and enabling them to expand their customer base; and / or Service Providers, by enabling them to more efficiently reach a large target market.
Owner:BRITISH AMERICAN TOBACCO AUSTRALASIA
Method for detecting image significance
ActiveCN102722891AImprove scalabilityRemove background noiseImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImaging processing
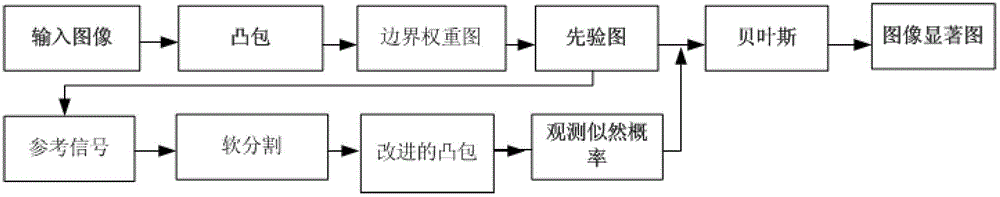
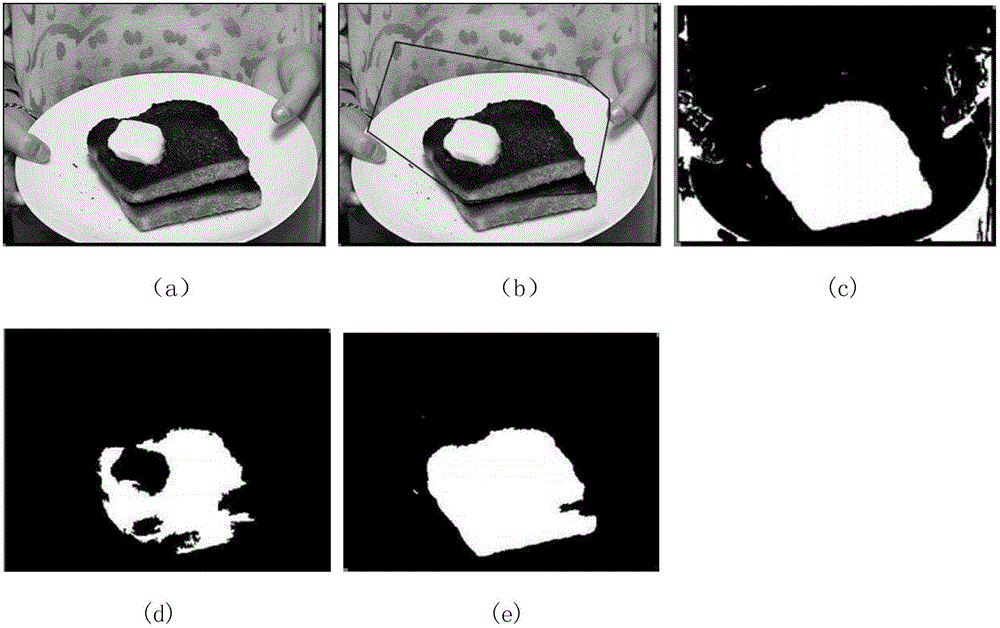
The invention belongs to the technical field of detection of image significance, which is characterized in that the significance target of any image can be detected, and relates to relevant knowledge of image processing. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, over-segmenting an image into super pixels, and performing Harris interest point detection to form a convex hall; secondly, performing edge detection on the image and calculating the edge weight map of the image; thirdly, measuring color space information by using the edge weight image to obtain a prior image; fourthly, performing soft segmentation based on the prior image to obtain an observation likelihood probability; and lastly, combining the prior image with the observation likelihood probability by using a Bayesian framework to obtain a significance detection result. The method has the beneficial effects that background noise can be well eliminated, a high-brightness image target is smoothened, the situations of target color and background similarity, large targets and complex backgrounds which are always difficult to solve in significance detection can be handled, and the method can be well applied to ordinary images.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
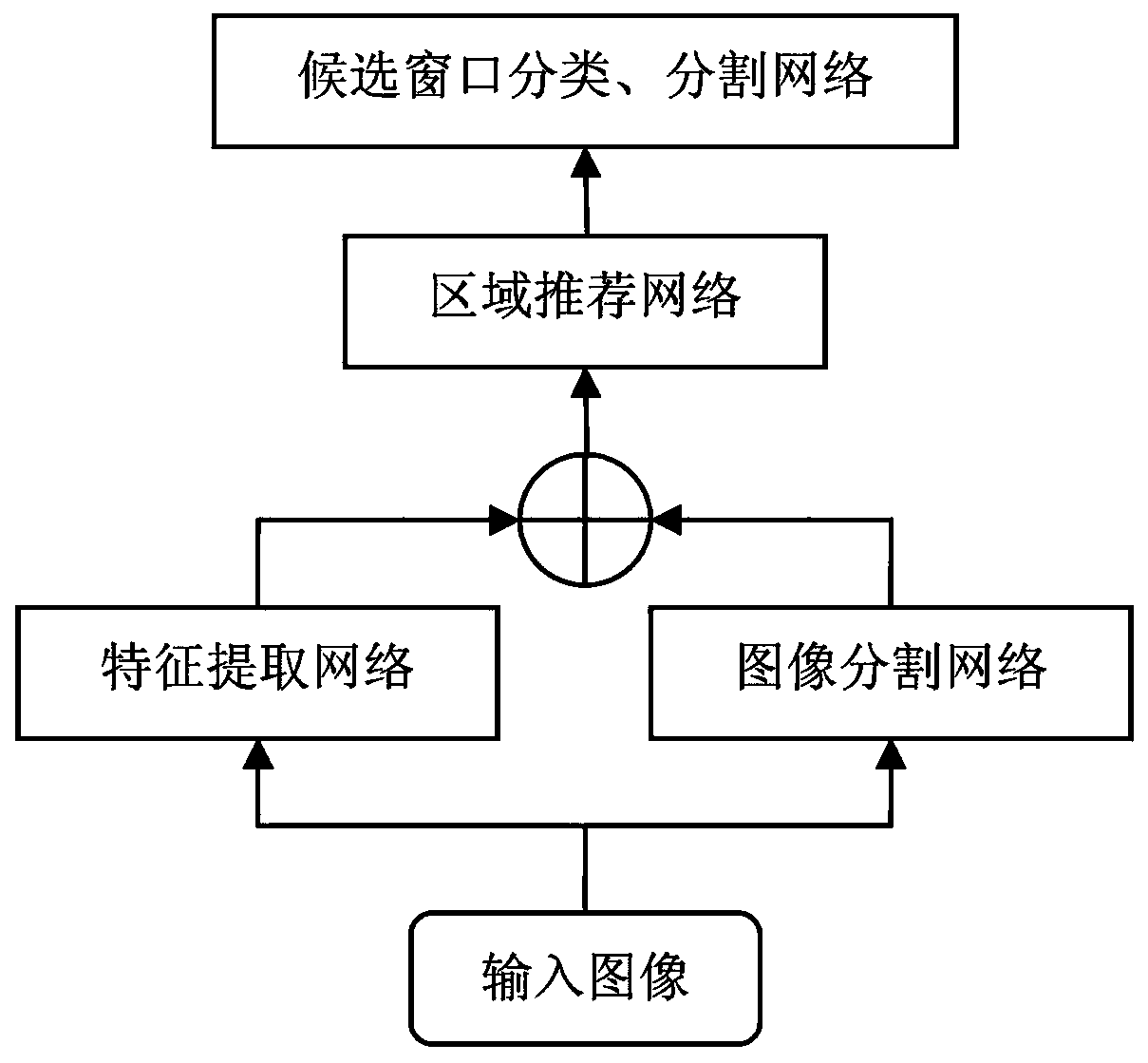
Object detection network design method based on image segmentation feature fusion
InactiveCN109145769AGreat effect on large targetsImage analysisBiometric pattern recognitionImage segmentation algorithmImage segmentation
The invention discloses a design method of a target detection network based on fused image segmentation features, which is effective for large-scale targets. Based on the general target detection framework Mask RCNN and image segmentation feature fusion, the target segmentation feature and a ResNet-101 convolutional network are integrated into the rpn module, an RoI Pooling module and an RoI Alignmodule, the experiments show that the method is effective for large targets, and the image segmentation algorithm for small targets can be improved completely if the image segmentation effect is ideal.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
System and Method for Increasing a Target Zone for Electrical Ablation
System for increasing a target zone for electrical ablation includes a treatment control module executable by a processor. The control module directs a pulse generator to apply pre-conditioning pulses to subject tissue cells in a pre-conditioning zone to electroporation, the pre-conditioning zone being smaller than a target ablation zone. After the pre-conditioning pulses have been applied, the control module directs the pulse generator to apply treatment pulses to electrically ablate the tissue cells in the target ablation zone. The pre-conditioning pulses cause the pre-conditioning zone to have a much higher conductivity so that the zone acts as a larger electrode area when the treatment pulses are applied, which results in a much larger target ablation zone than otherwise possible.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
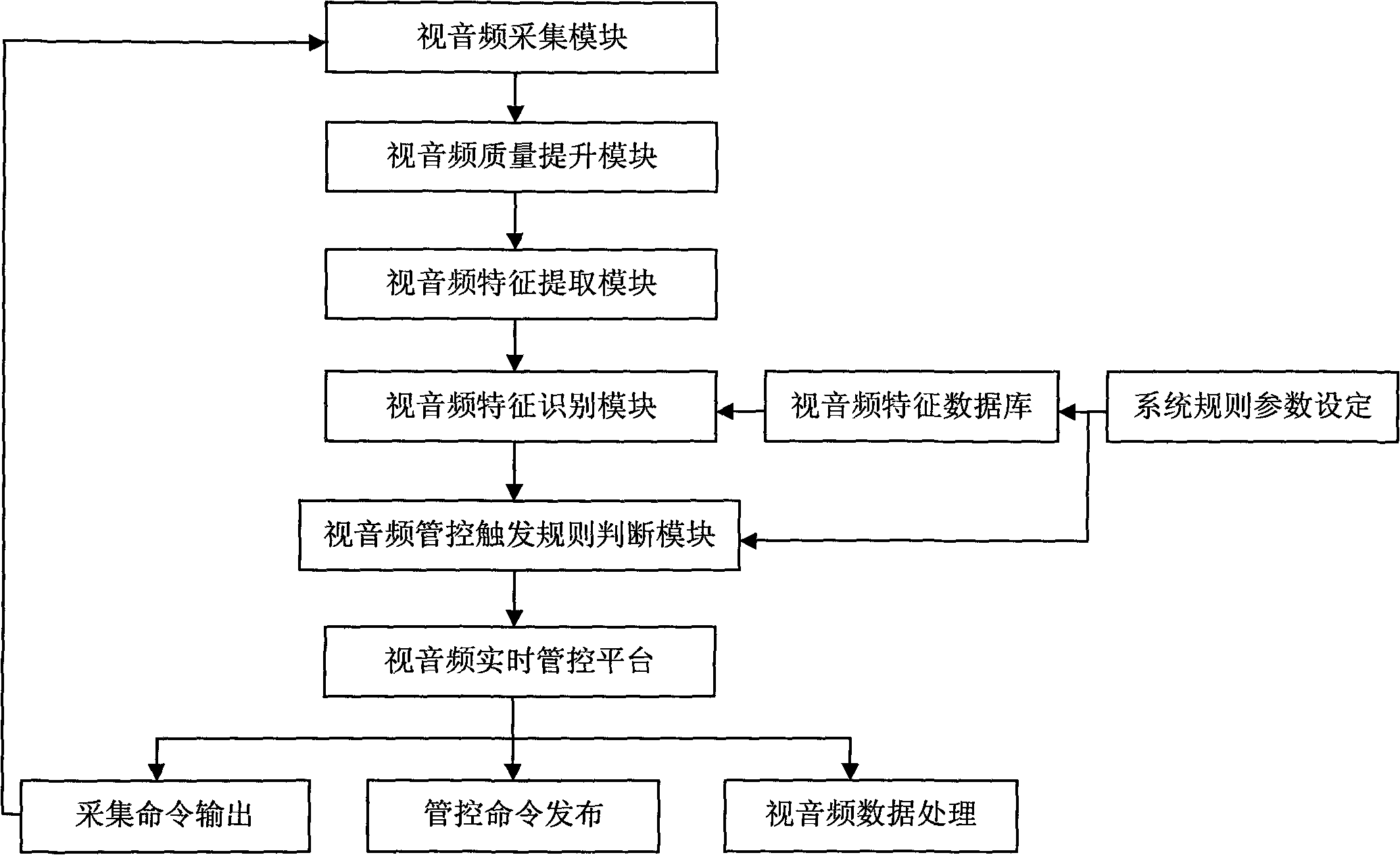
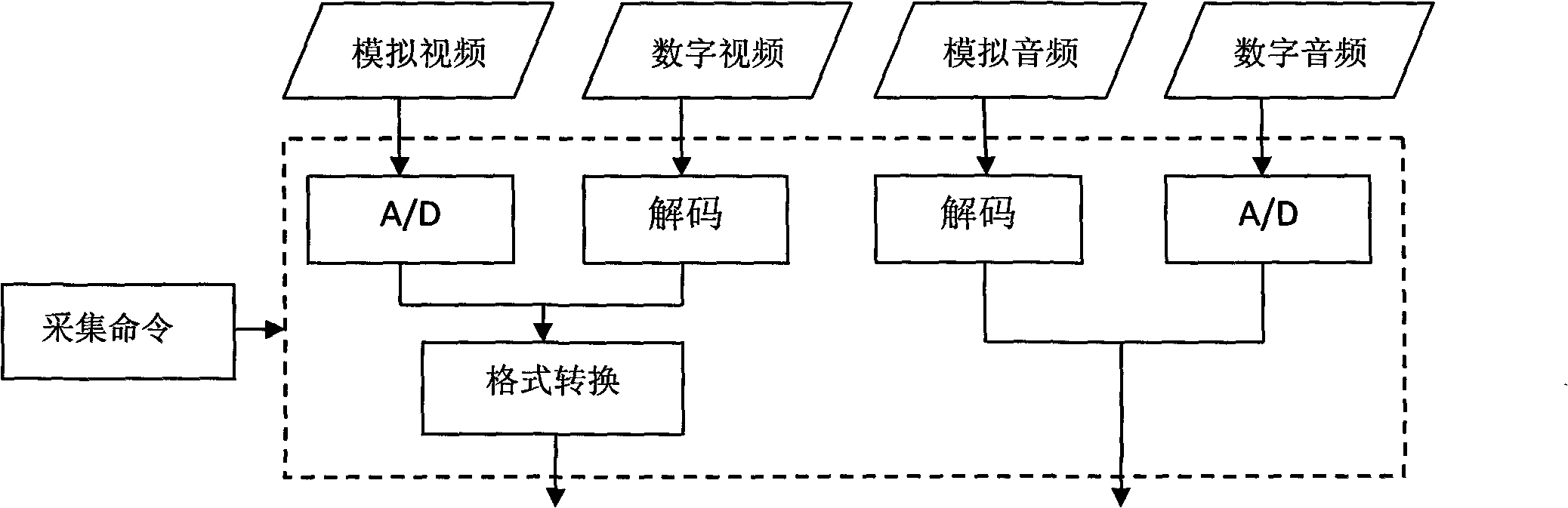
Video/audio intelligent analysis management control system
InactiveCN101799876AGood auxiliary effectEliminate false positivesCharacter and pattern recognitionClosed circuit television systemsFeature extractionControl system
The invention relates to the fields of computer vision and artificial intelligence, in particular to the field of intelligent video analysis, and provides a video / audio intelligent analysis management control system. The invention aims to solve the problems of the existing intelligent video analysis system of high misinformation rate, high report missing rate, low accuracy, single working mode, failure of realizing transmission and storage as required, and the like. The system comprises a video / audio feature database, a video / audio acquisition module, a video / audio quality improvement module, a video / audio feature extraction module, a video / audio feature recognition module, a video / audio management control trigger rule judgment module and a video / audio real-time management control platform. The system has three working modes: front-end analysis, back-end analysis and distributed analysis. The system combines voice information and image information for intelligent analysis, thereby effectively reduces the misinformation rate and report missing rate of the intelligent video analysis system. The invention enhances the quality of the video / audio information and establishes a large target and behavior feature database, thereby enhancing the system accuracy and realizing management control as required.
Owner:王巍
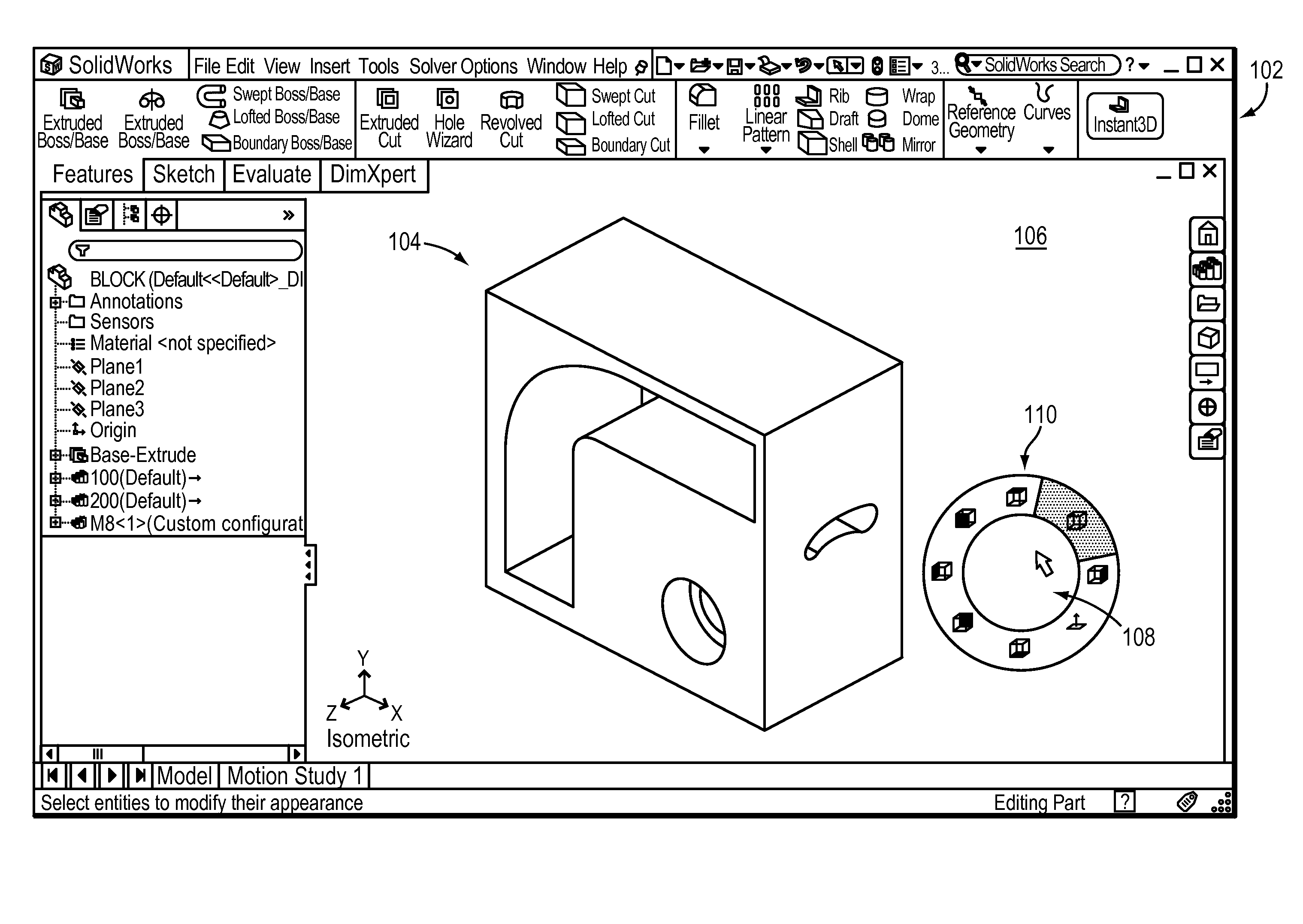
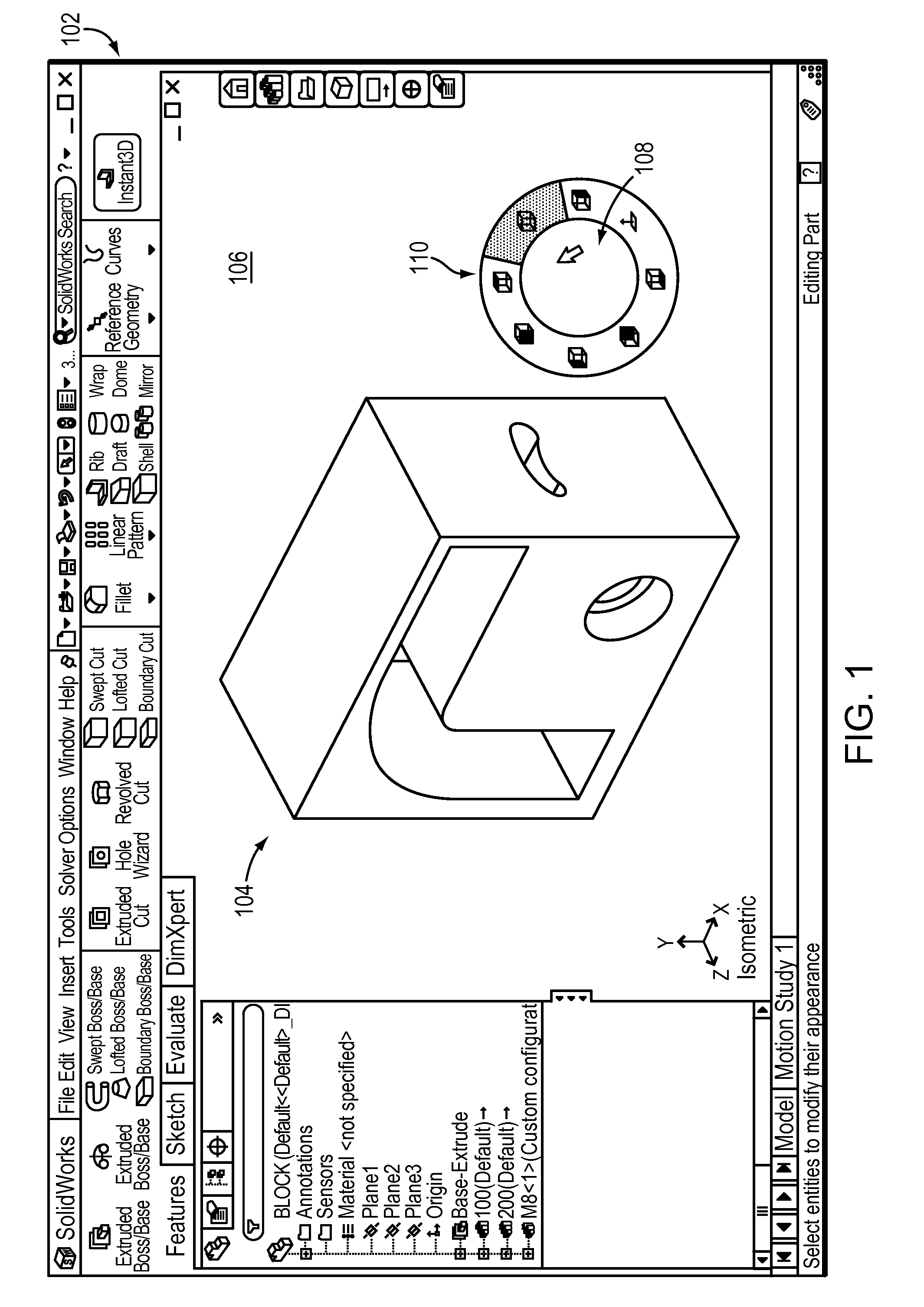
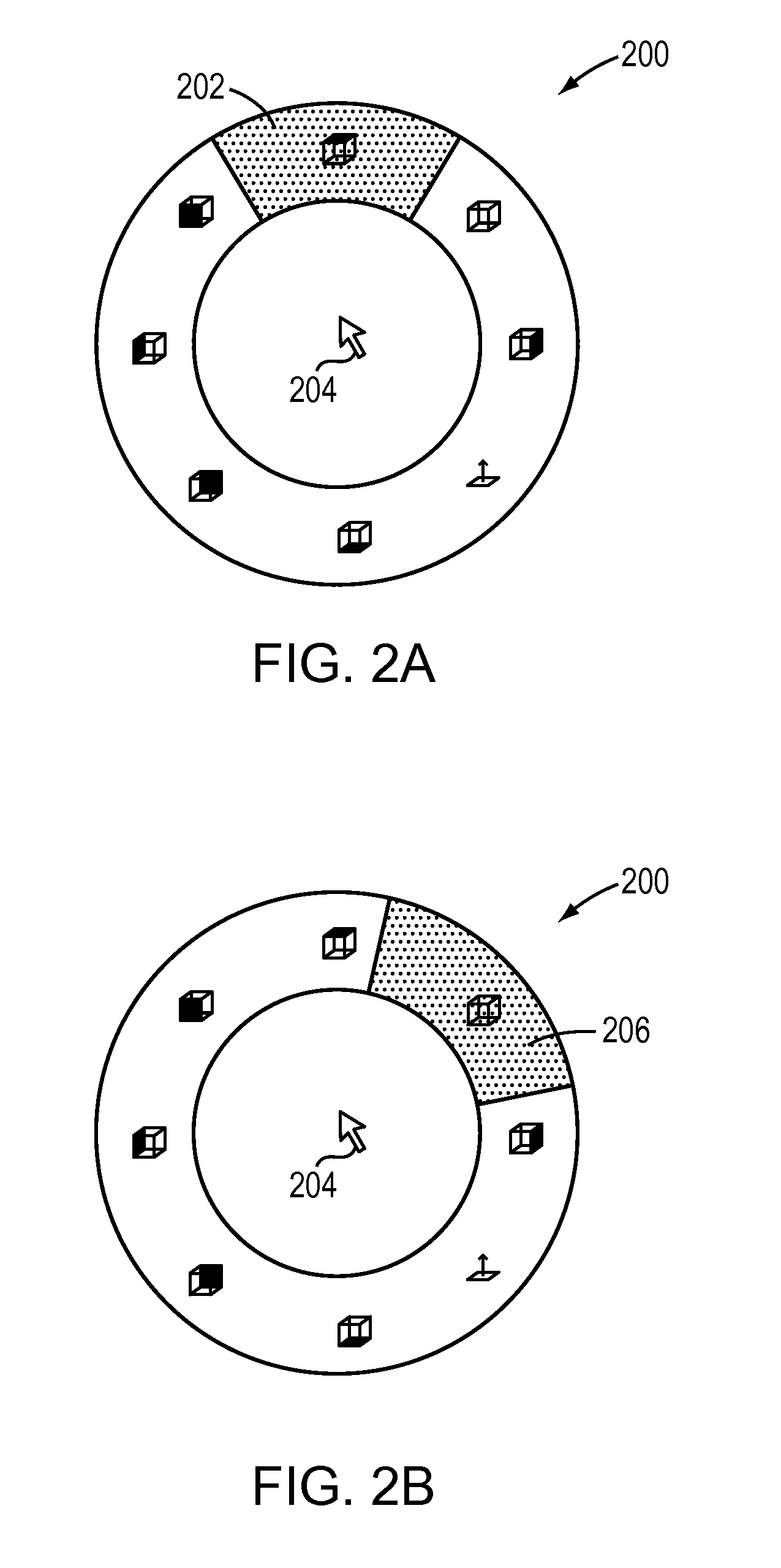
Predictive target enlargement
ActiveUS20110138324A1Facilitates user selectionInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsGraphical user interface
Techniques for aiding user input with a graphical user interface (GUI) are disclosed. A target object among various command regions of the GUI is predicted, e.g., substantially before the cursor reaches any of the regions. The command region corresponding to the predicted target object is enlarged to facilitate user selection of the predicted target object. Enlarging the predicted target object may cause the target object to overlap and / or occlude nearby command regions. After a first target object is predicted, the prediction may be changed based on updated cursor movements. By using predictive target enlargement, users are given early visual feedback about the target, and are given a larger target to acquire, thereby allowing them to be faster and less precise (their mouse direction can wander) yet still acquire their desired result.
Owner:DASSAULT SYST SOLIDWORKS CORP
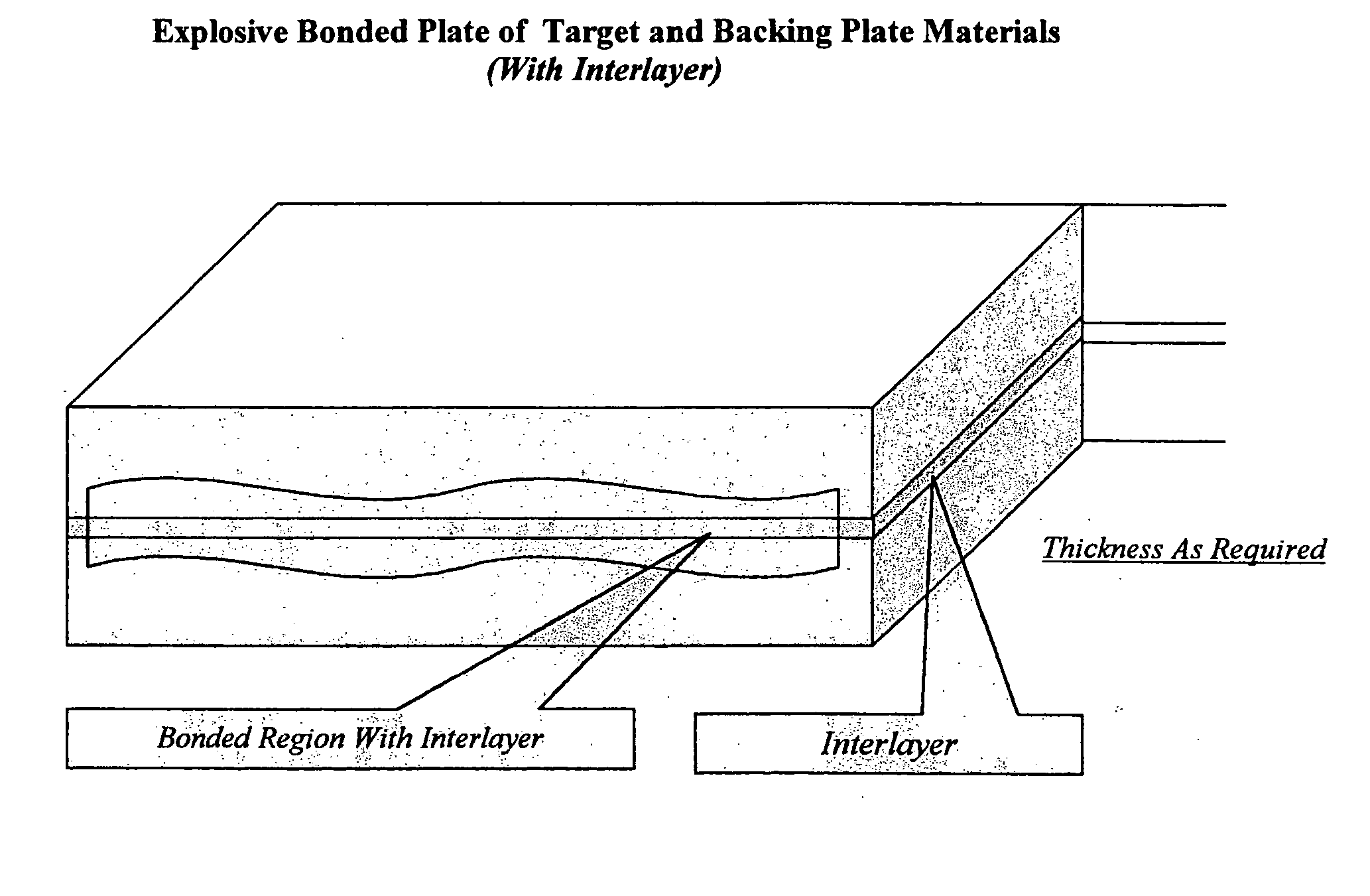
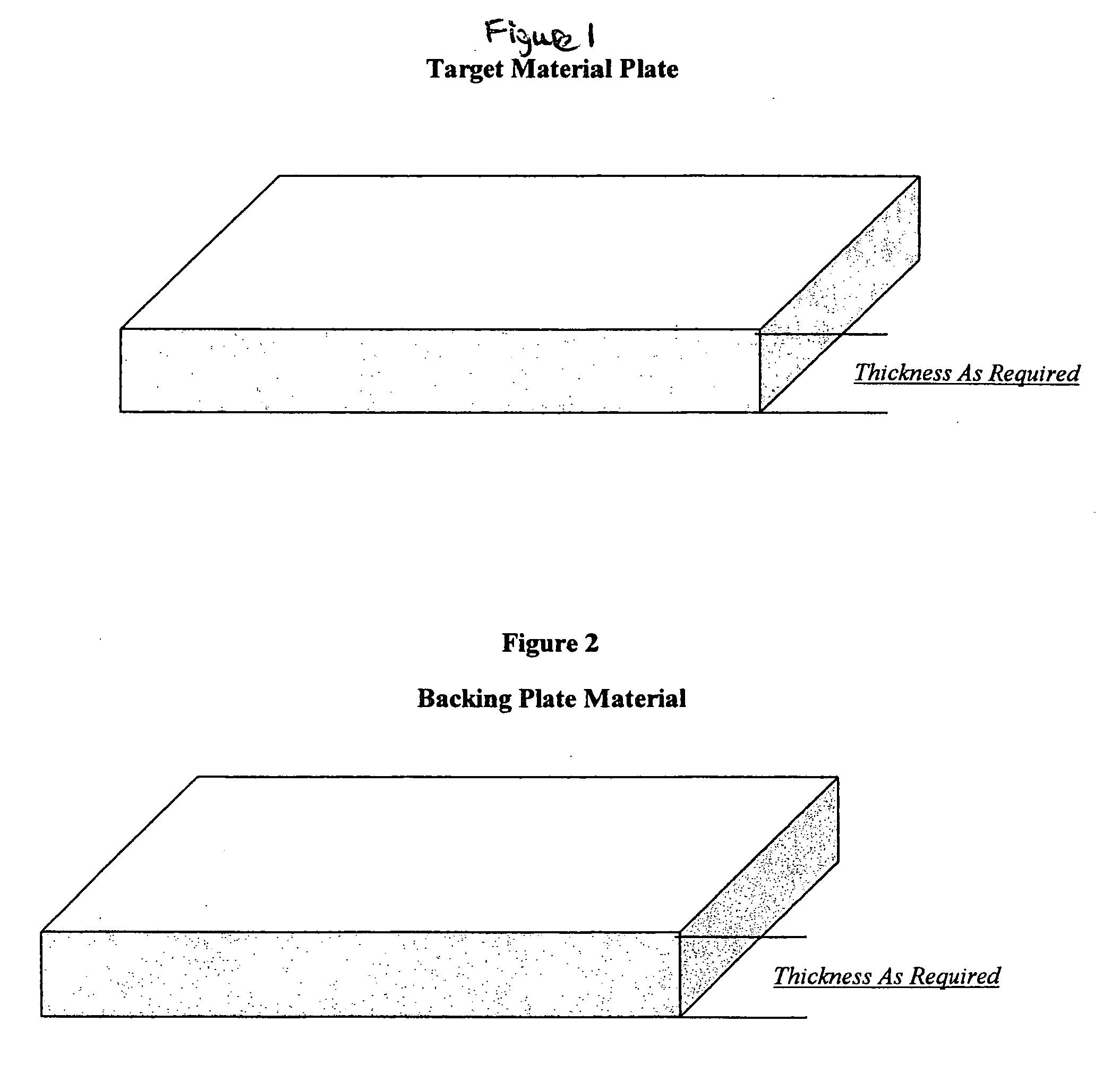
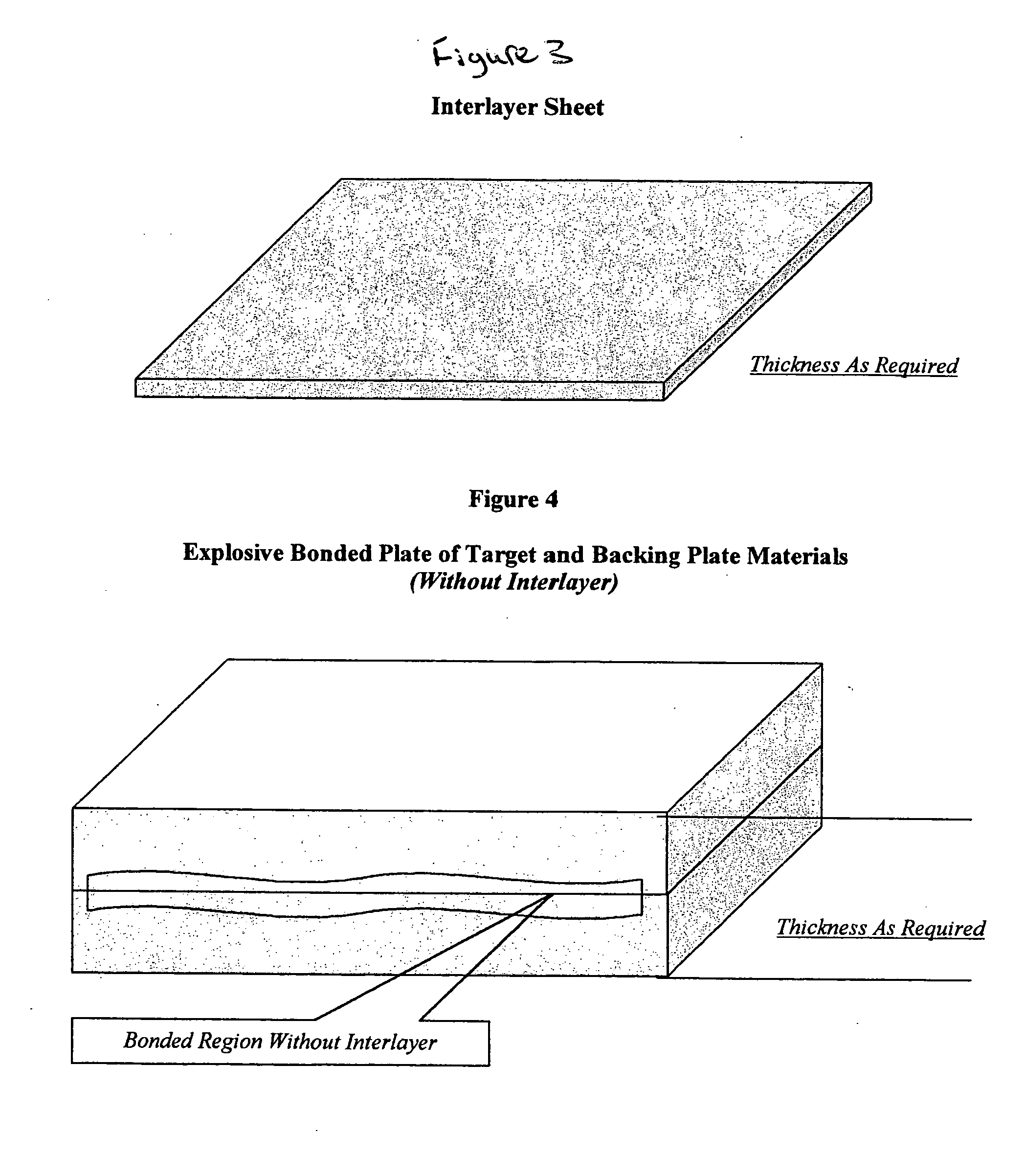
Method of forming sputtering target assembly and assemblies made therefrom
A method of forming a sputtering target assembly is described that involves explosively bonding a target grade plate and a backing plate member to form a bonded preform having dimensions such that a large target or several target assemblies can be obtained. The method includes optionally partitioning the bonded preform into a plurality of sputtering target assemblies. An interlayer can optionally be disposed between the target grade plate and the backing plate member before bonding. A bond quality test sample can be produced by the method. The sputtering target assemblies, the bonded preform, and the bond quality test sample are further described.
Owner:CABOT CORP
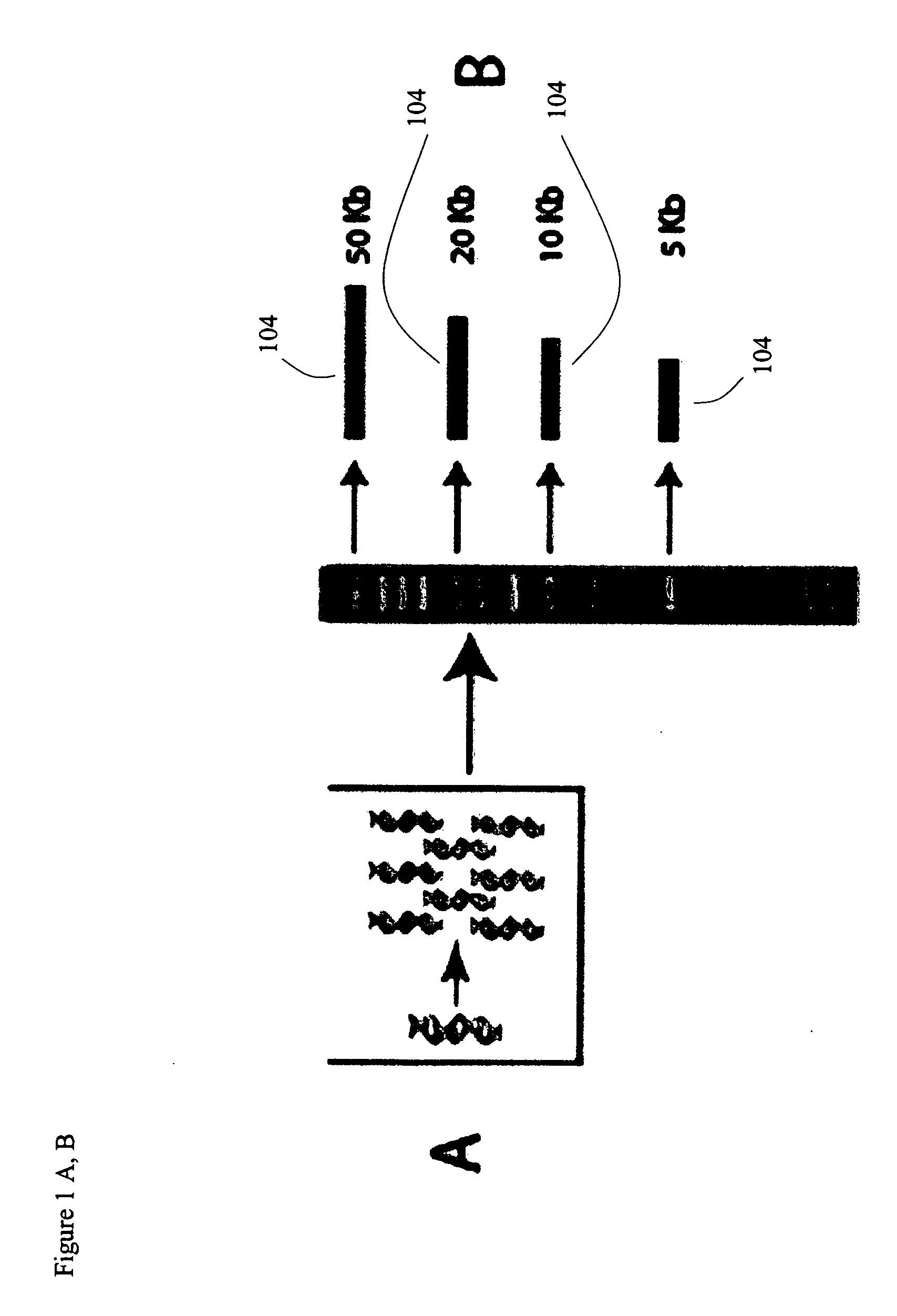
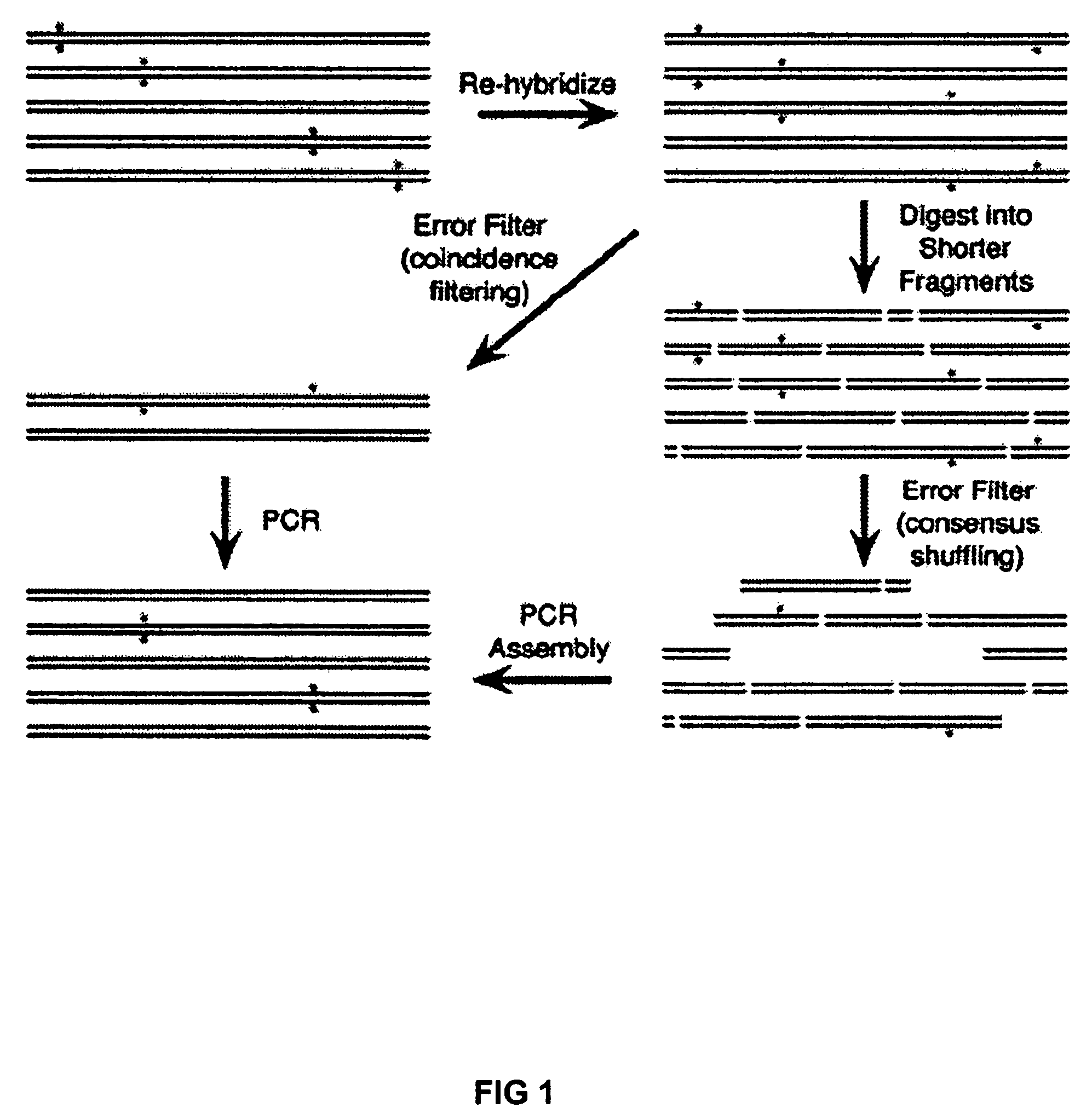
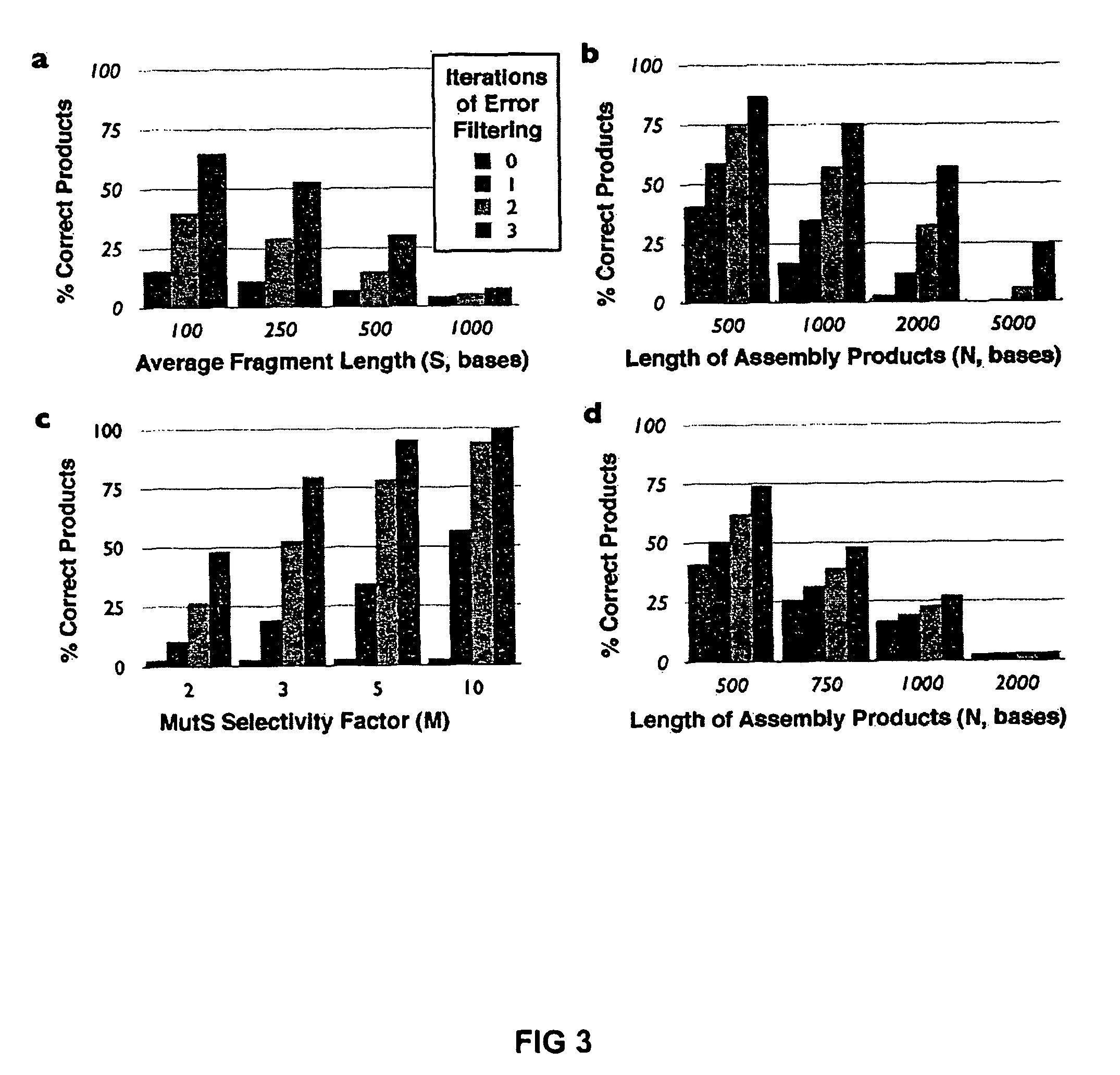
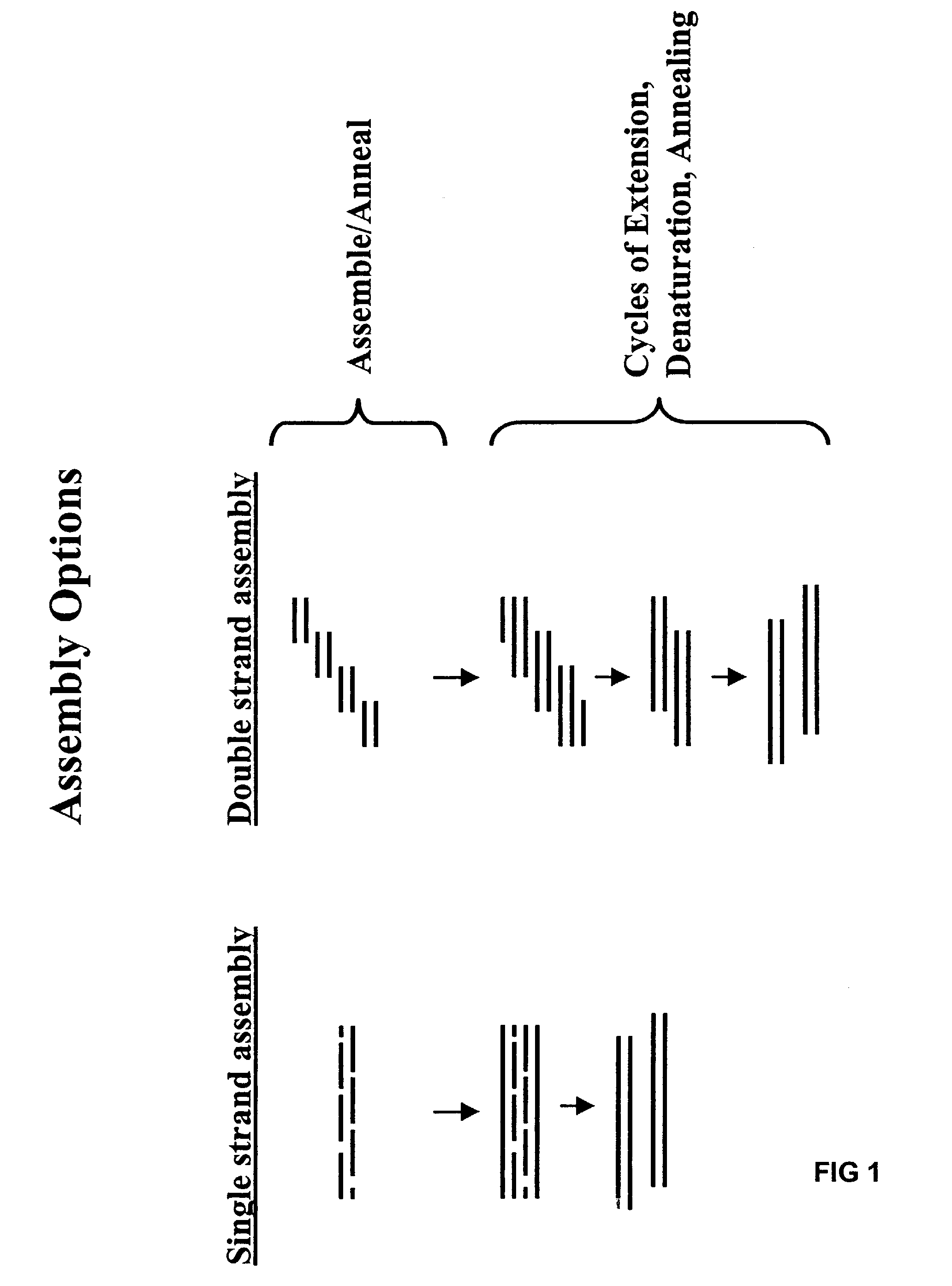
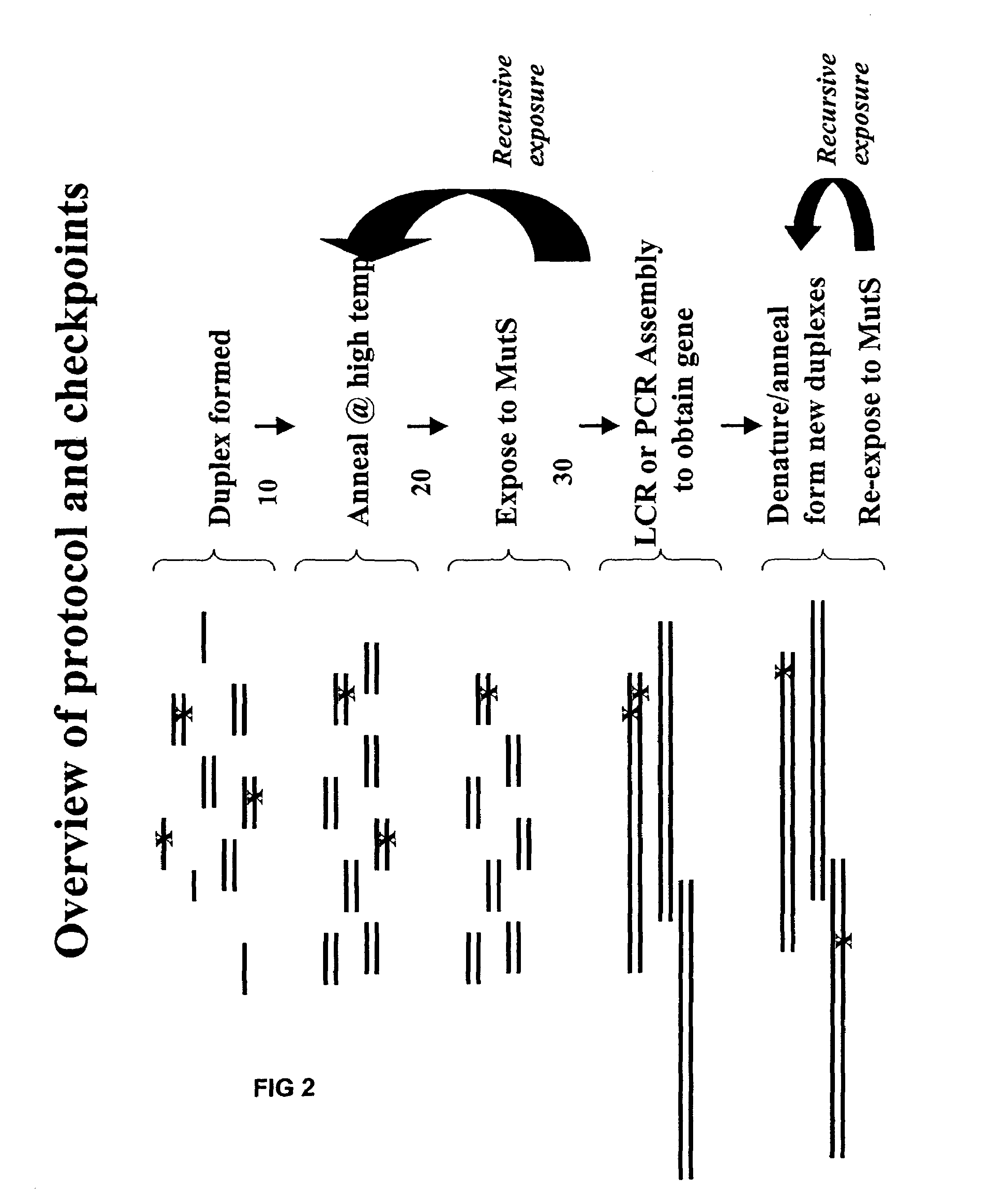
Method of error reduction in nucleic acid populations
A method is disclosed for the direct synthesis of double stranded DNA molecules of a variety of sizes and with any desired sequence. The DNA molecule to be synthesis is logically broken up into smaller overlapping DNA segments. A maskless microarray synthesizer is used to make a DNA microarray on a substrate in which each element or feature of the array is populated by DNA of a one of the overlapping DNA segments. The complement of each segment is also made in the microarray. The DNA segments are released from the substrate and held under conditions favoring hybridization of DNA, under which conditions the segments will hybridize to form duplexes. The duplexes are then separated using a DNA binding agent which binds to improperly formed DNA helixes to remove errors from the set of DNA molecules. The segments can then be hybridized to each other to assemble the larger target DNA sequence.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
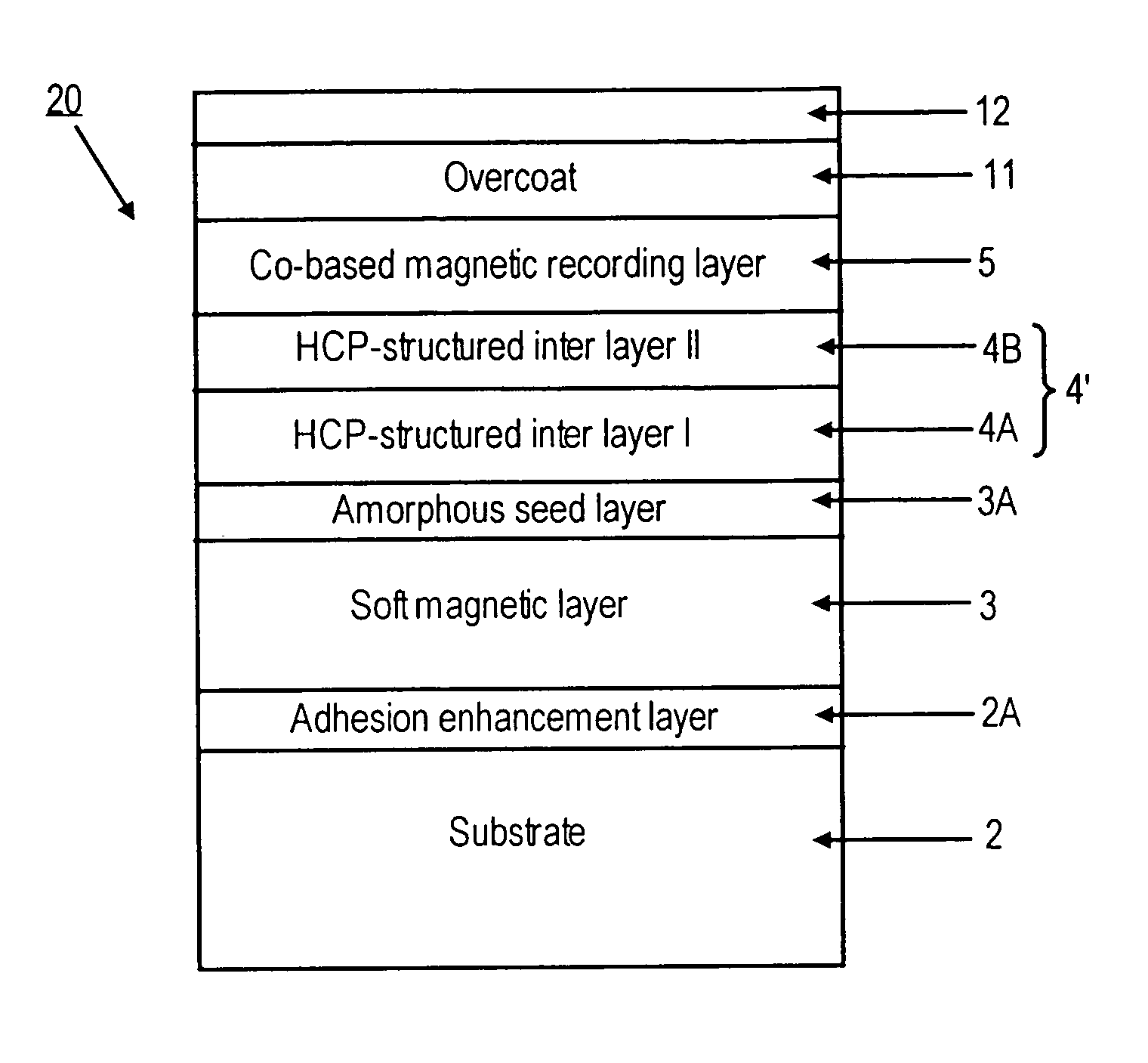
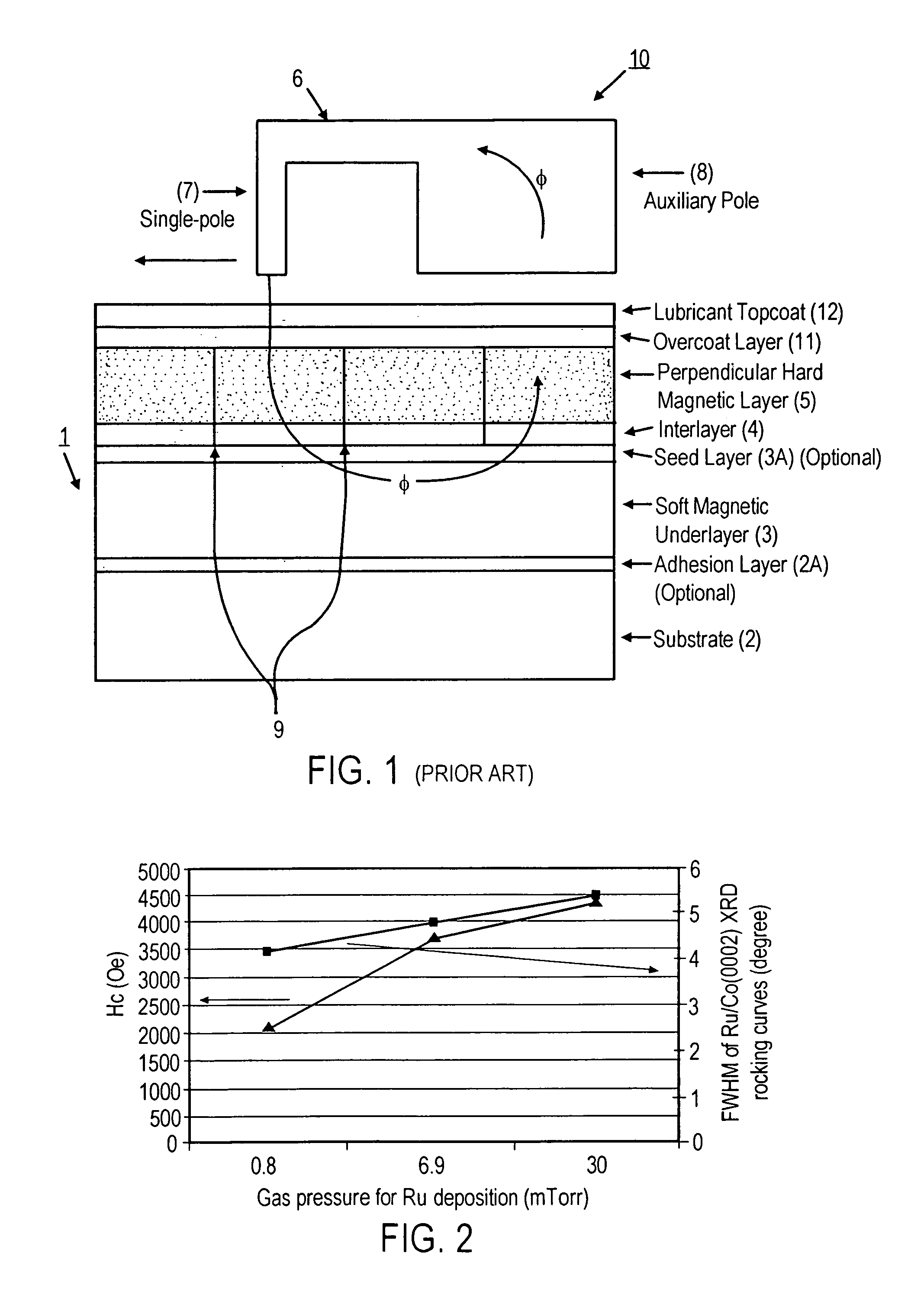
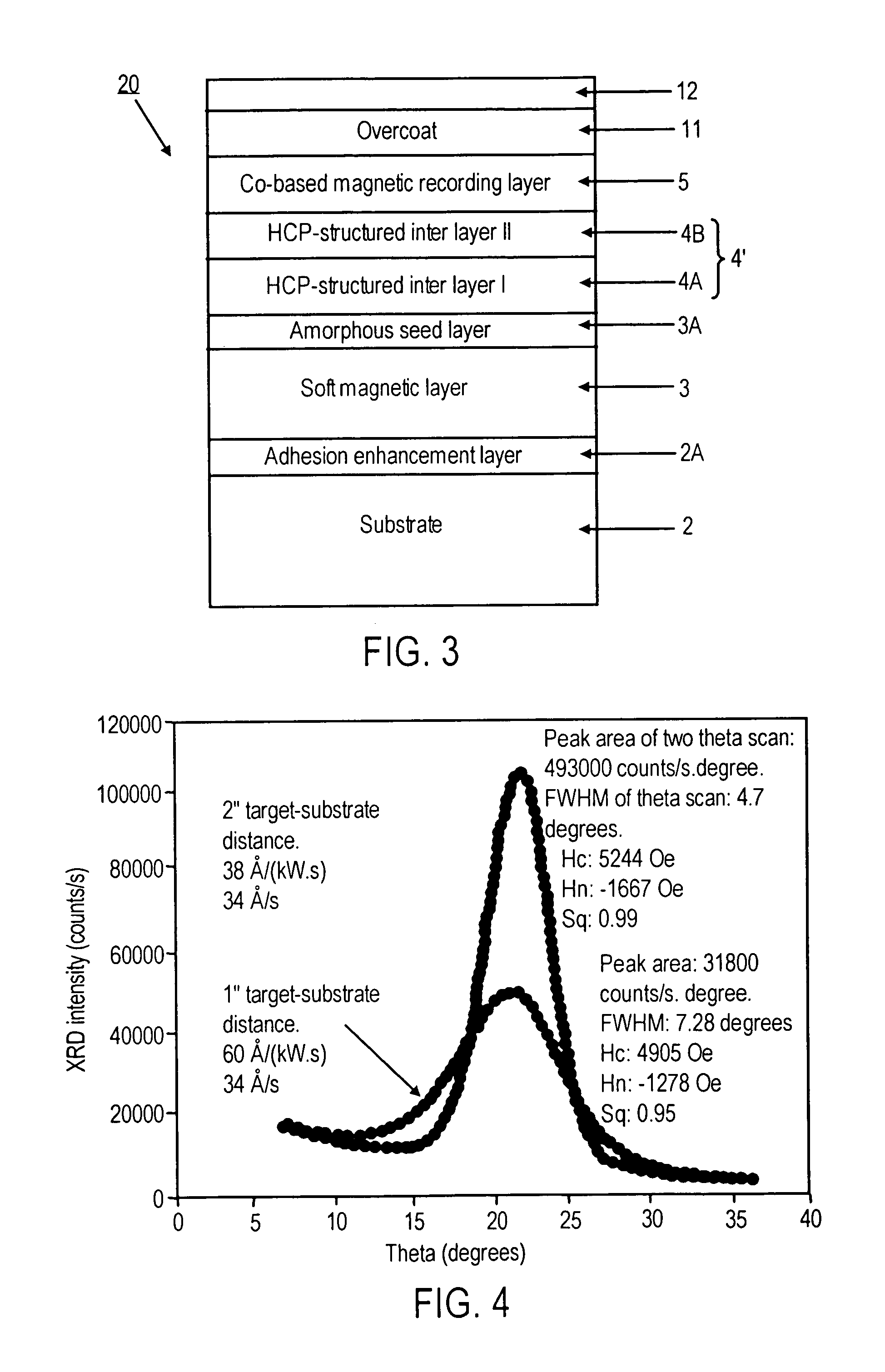
Perpendicular magnetic recording media with improved crystallographic orientations and method of manufacturing same
InactiveUS7175925B2Easy to optimizeImproved perpendicular magnetic recording mediaBase layers for recording layersVacuum evaporation coatingAtomic force microscopySurface roughness
A perpendicular magnetic recording medium, comprising:(a) a non-magnetic substrate having a surface; and(b) a layer stack formed over the substrate surface, comprising in overlying sequence from the substrate surface:(i) a magnetically soft underlayer;(ii) an interlayer structure for crystallographically orienting a layer of a perpendicular magnetic recording material formed thereon; and(iii) at least one crystallographically oriented magnetically hard perpendicular recording layer;wherein the magnetically soft underlayer is sputter-deposited at a sufficiently large target-to-substrate spacing and at a sufficiently low gas pressure selected to provide the underlayer with a smooth surface having a low average surface roughness Ra below about 0.3 nm, as measured by Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM).
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Plunge slitter with clam style anvil rollers
InactiveUS6837135B2Compensation for wearGuide fencesCross-cut reciprocating sawsOrder formPaperboard
An apparatus for slitting a running paperboard web includes a thin high speed rotary slitting blade that is plunged through the moving web and into a slot between a pair of anvil rollers supporting the web on the opposite side. Because the slitting blade and the anvil rollers are vertically separated and pre-positioned before order change, an adjustment apparatus is provided to spread the anvil rollers axially apart to provide an open gap with a large target for blade edge when it is plunged through the web and into the slot. The anvil rollers are then closed against the opposite faces of the blade for running operation. Preferably, the anvil rollers are mounted on brackets hinged together below the rollers to move the opposite upper edges of the rollers between the opened and closed position in the manner of a clam shell. The anvil roller assembly is also adjustable in the machine direction to compensate for reduction in rotary slitting blade diameter with blade wear.
Owner:BARRY WEHMILLER PAPERSYST INC
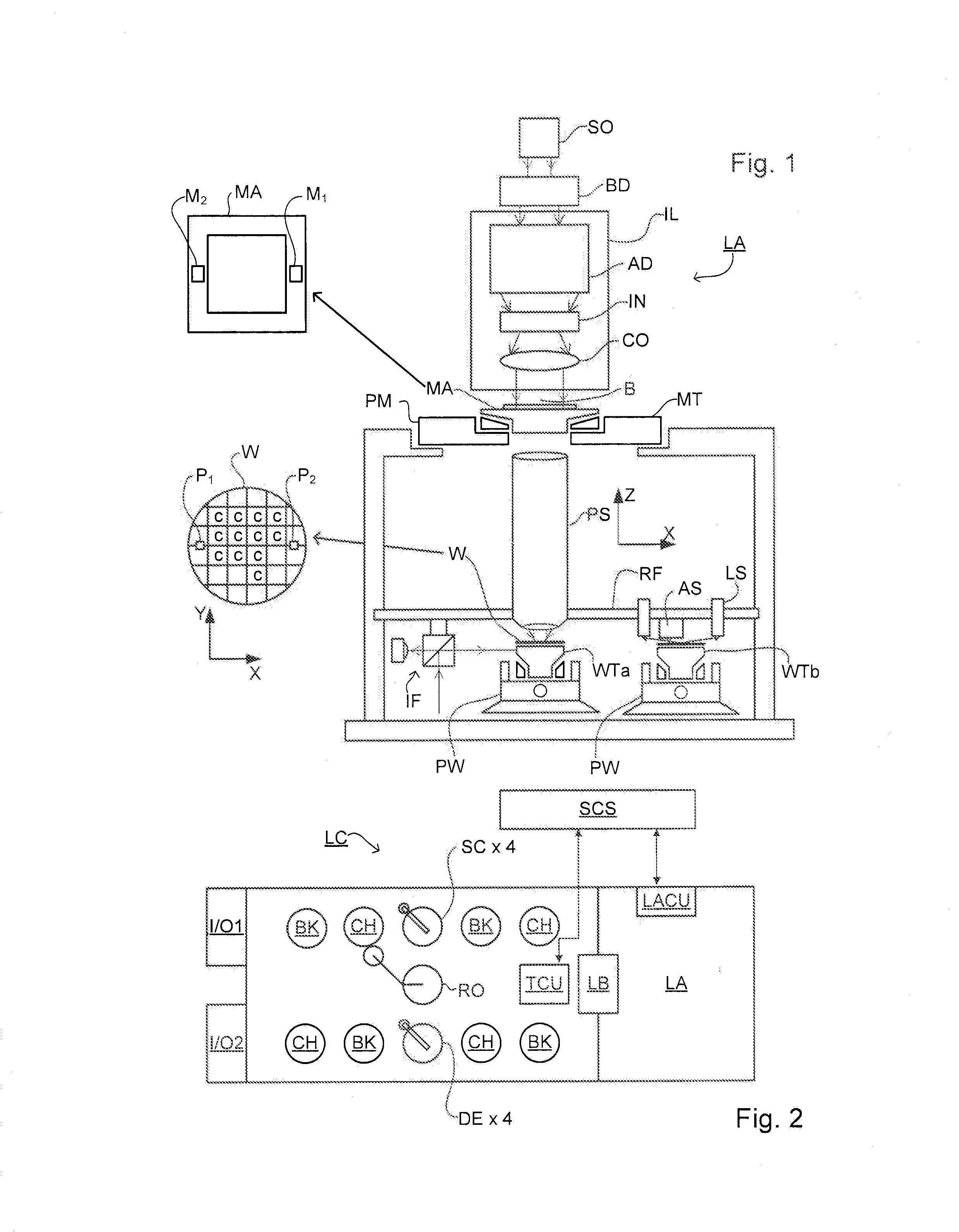
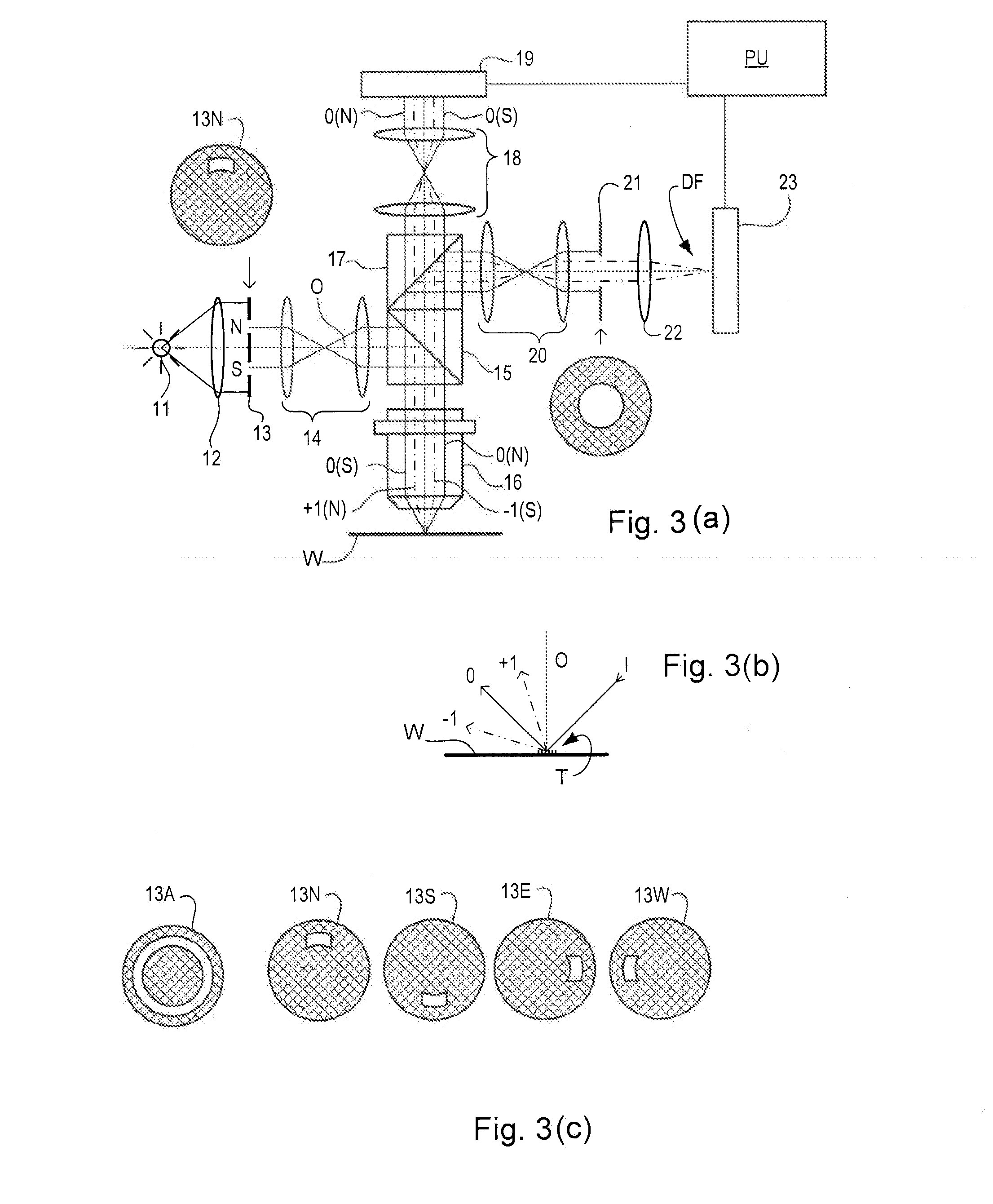
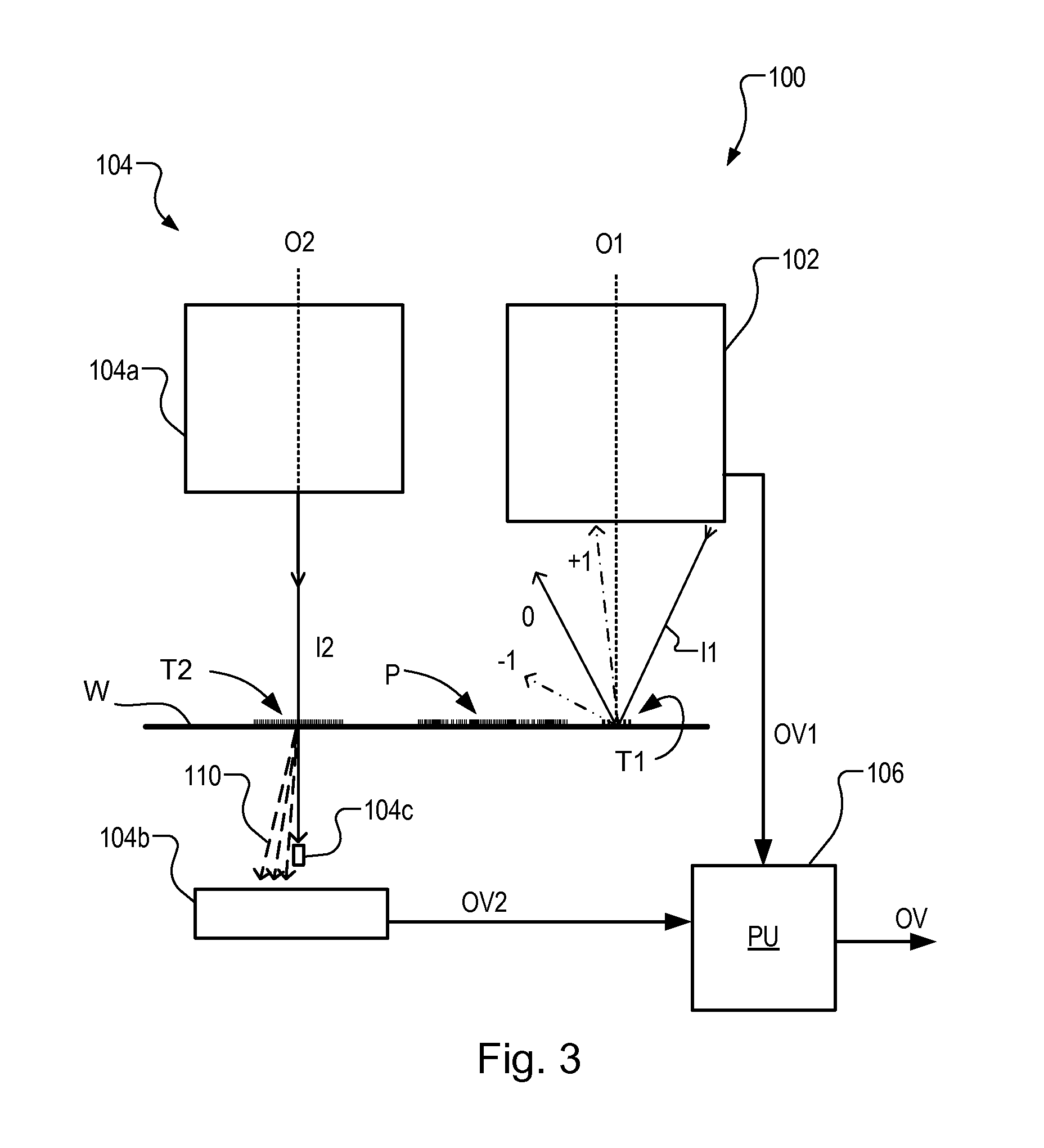
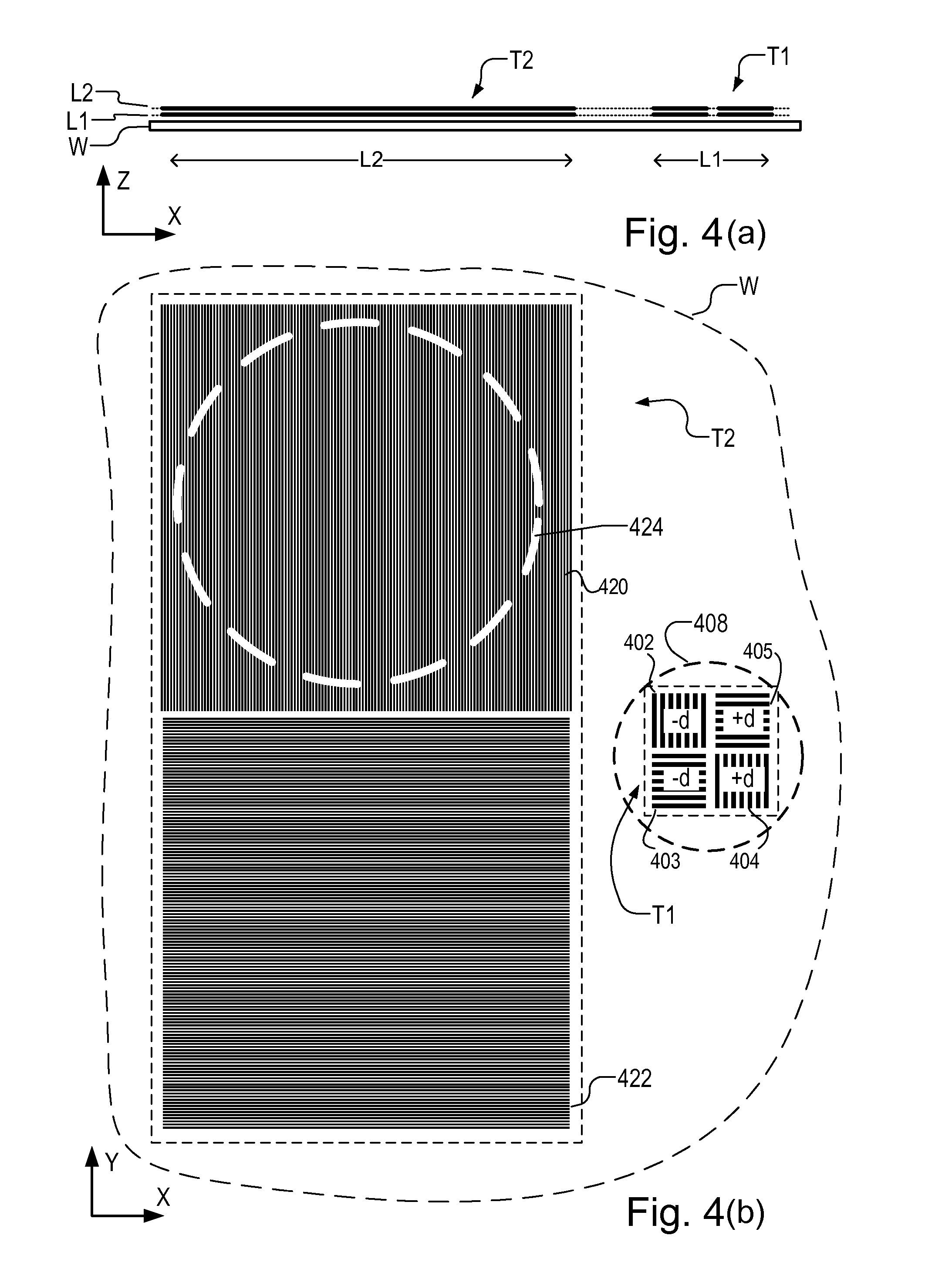
Substrate and Patterning Device for Use in Metrology, Metrology Method and Device Manufacturing Method
ActiveUS20130059240A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMetrologyTarget distribution
A pattern from a patterning device is applied to a substrate by a lithographic apparatus. The applied pattern includes product features and metrology targets. The metrology targets include large targets and small targets which are for measuring overlay. Some of the smaller targets are distributed at locations between the larger targets, while other small targets are placed at the same locations as a large target. By comparing values measured using a small target and large target at the same location, parameter values measured using all the small targets can be corrected for better accuracy. The large targets can be located primarily within scribe lanes while the small targets are distributed within product areas.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
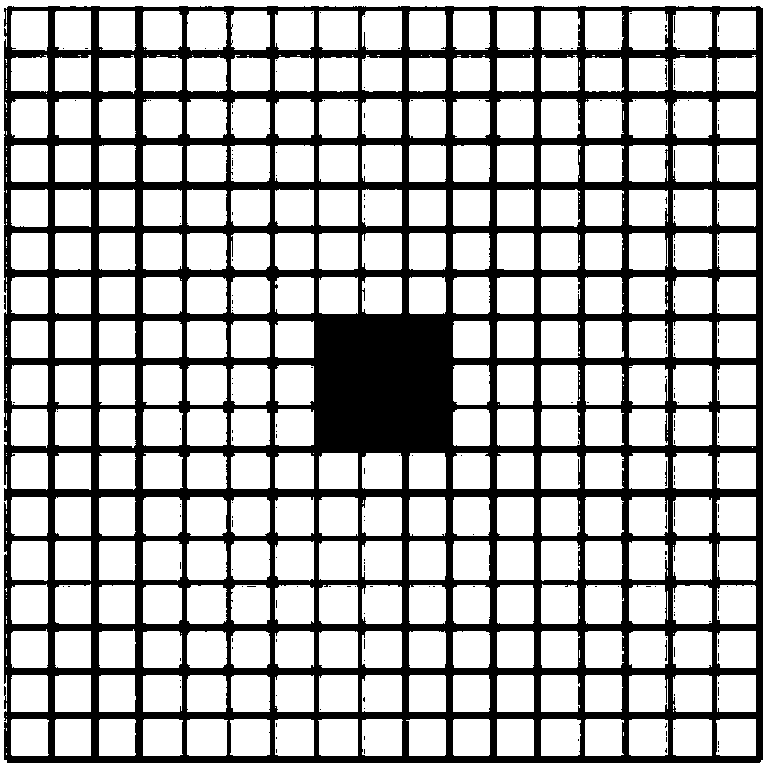
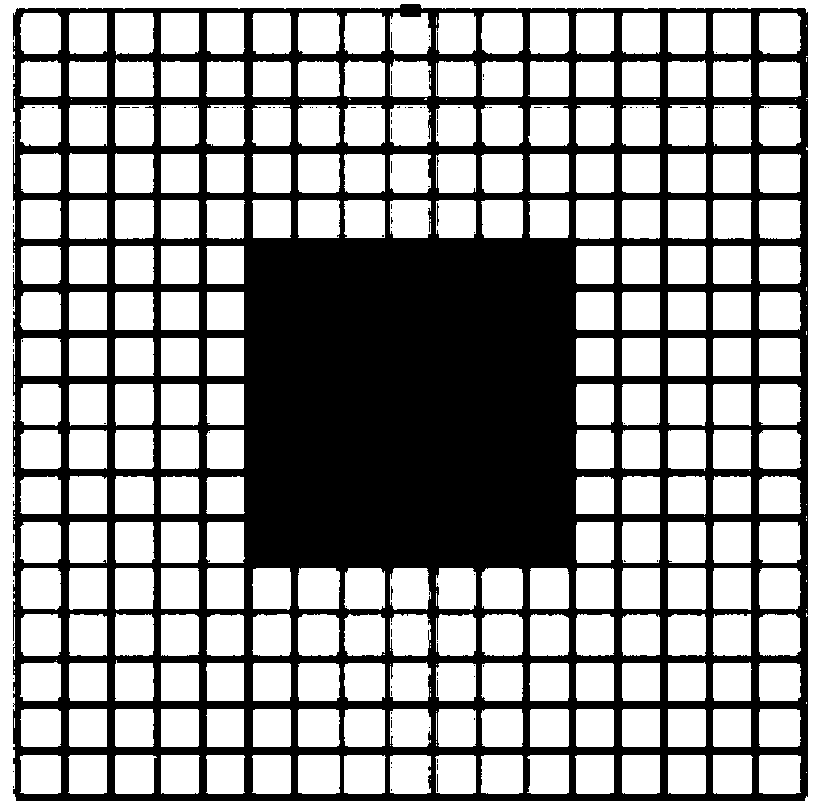
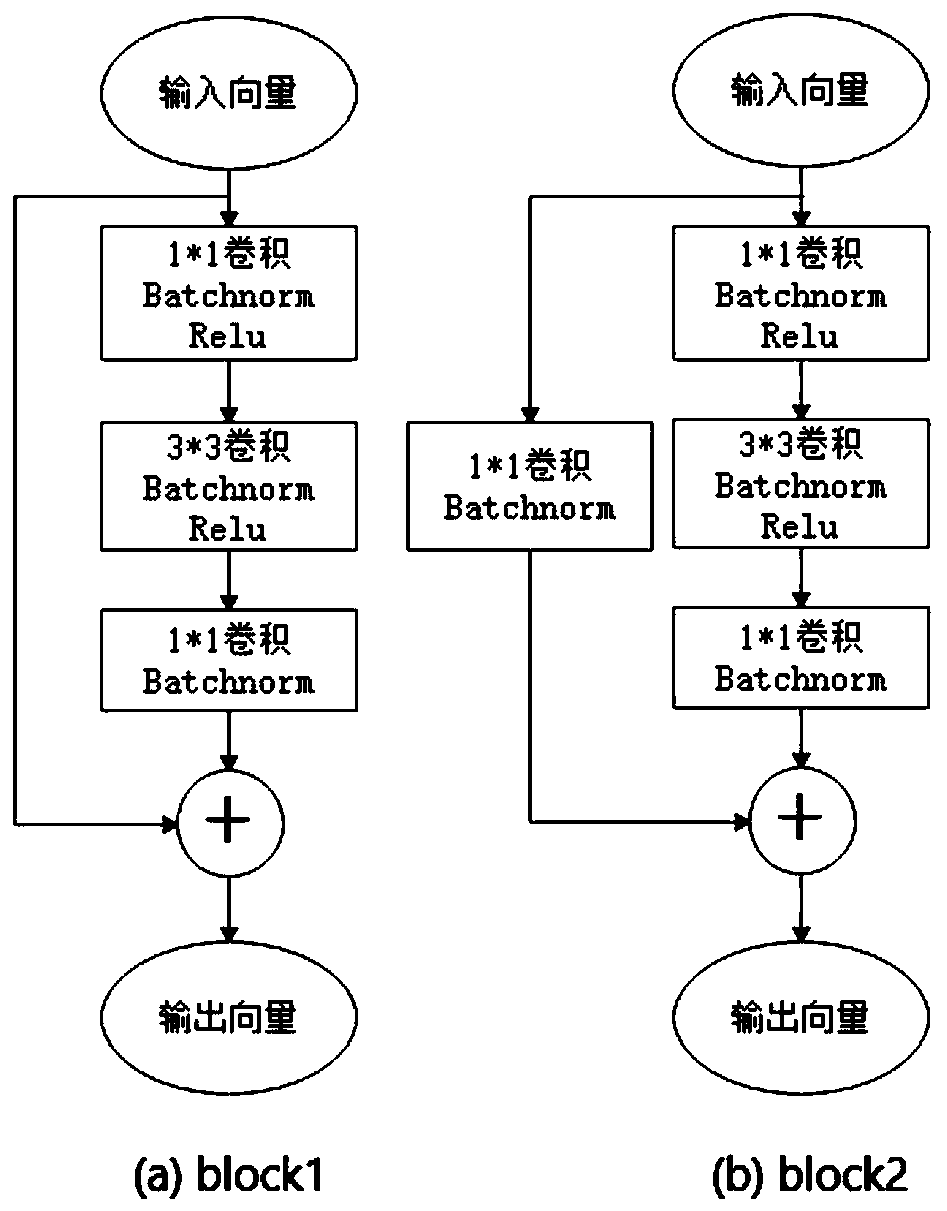
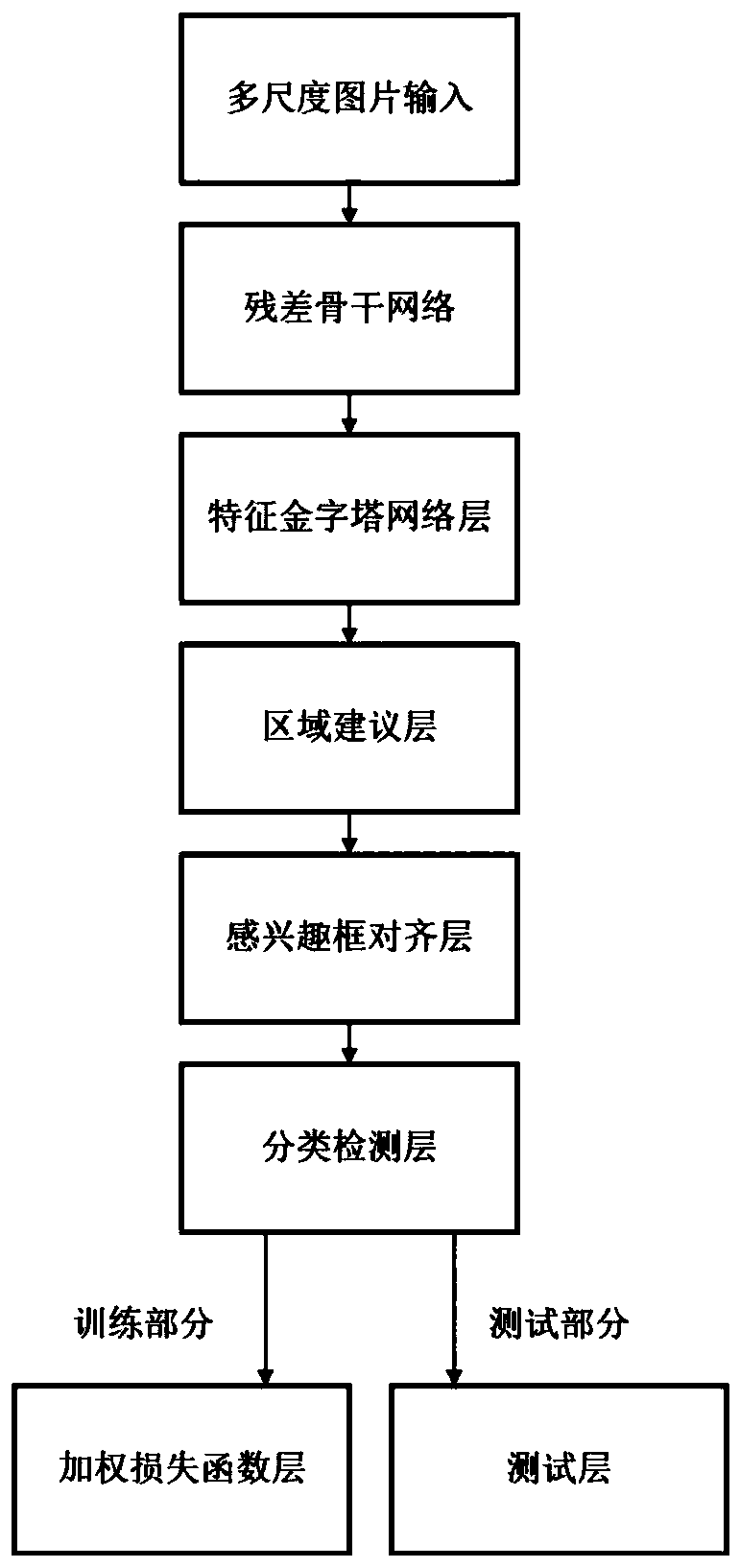
Small target detection method based on multi-scale images and weighted fusion loss
ActiveCN111461110AImprove feature extractionReduce network parametersInternal combustion piston enginesCharacter and pattern recognitionImage extractionFeature vector
The invention belongs to the field of image and video processing, and relates to a small target detection method based on multi-scale images and weighted fusion loss, and the method comprises the steps: extracting a plurality of groups of feature vectors from a plurality of different-scale images based on an improved Mask RCNN model, carrying out the fusion of the plurality of groups of feature vectors, and constructing a feature pyramid; generating a candidate detection box based on the feature pyramid and screening to obtain a suggested detection box; correspondingly returning the suggesteddetection boxes to the feature pyramid to generate feature maps of the suggested detection boxes, and performing aligned interception on the feature maps; inputting the aligned suggested detection boxes into a classifier layer to obtain category confidence coefficients and position offsets of the suggested detection boxes; in the test stage, screening a certain suggested detection box according tothe category confidence score of the suggested detection box, and performing non-maximum suppression; in the training stage, weighting the loss function calculated by detecting the small target feature layer and fusing with the loss function of detecting the large target layer and the middle target layer, thus the sensitivity of the model to the small target object is enhanced.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
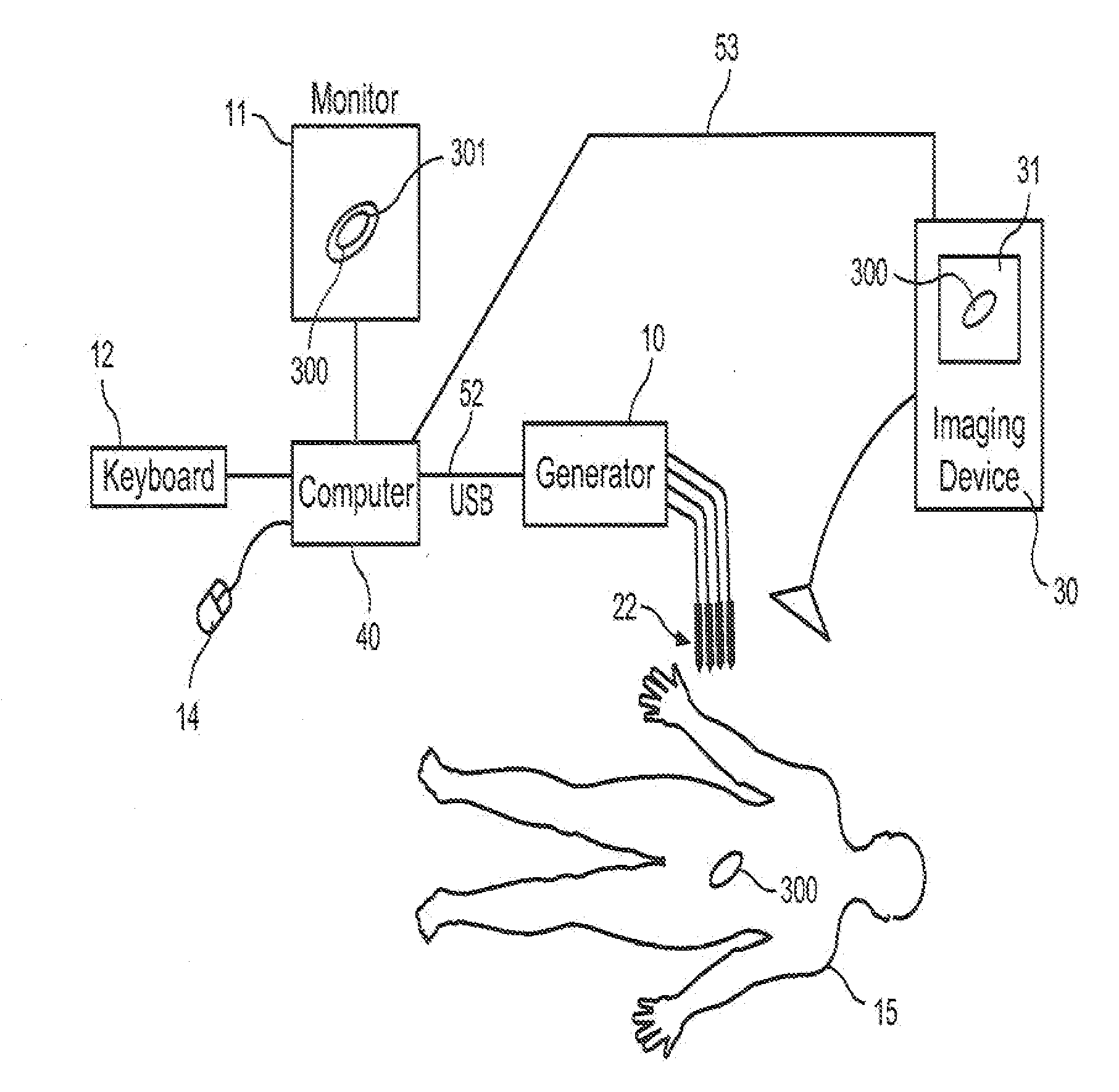
Determining intracranial pressure non-invasively by acoustic transducer
A plurality of acoustic source and / or detector elements are employed in a scanning mode to acoustically illuminate and acquire acoustic data from numerous sites within a larger target area. Based on the acoustic data collected in the scanning mode, a localised site within the target area is selected as the target site for focused acoustic illumination and / or probing. Elements of the acoustic source / detector array are focused on the selected target site in an automated fashion. Thereafter, the target area is periodically scanned and the acoustic focus repositioned, as required, to maintain the focus of the acoustic source at the desired target site.
Owner:菲西奥松尼克斯公司 +1
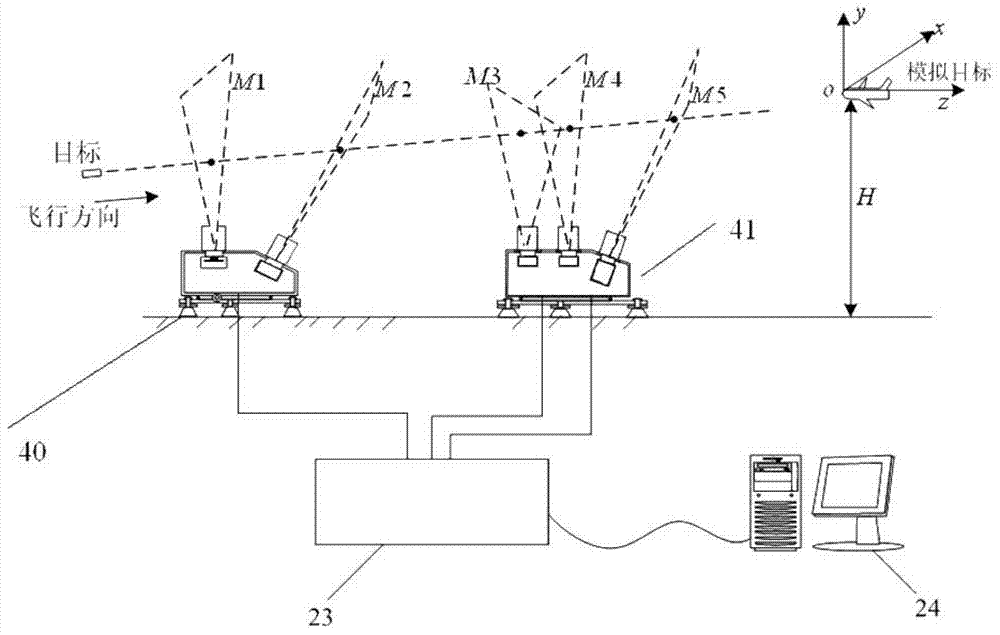
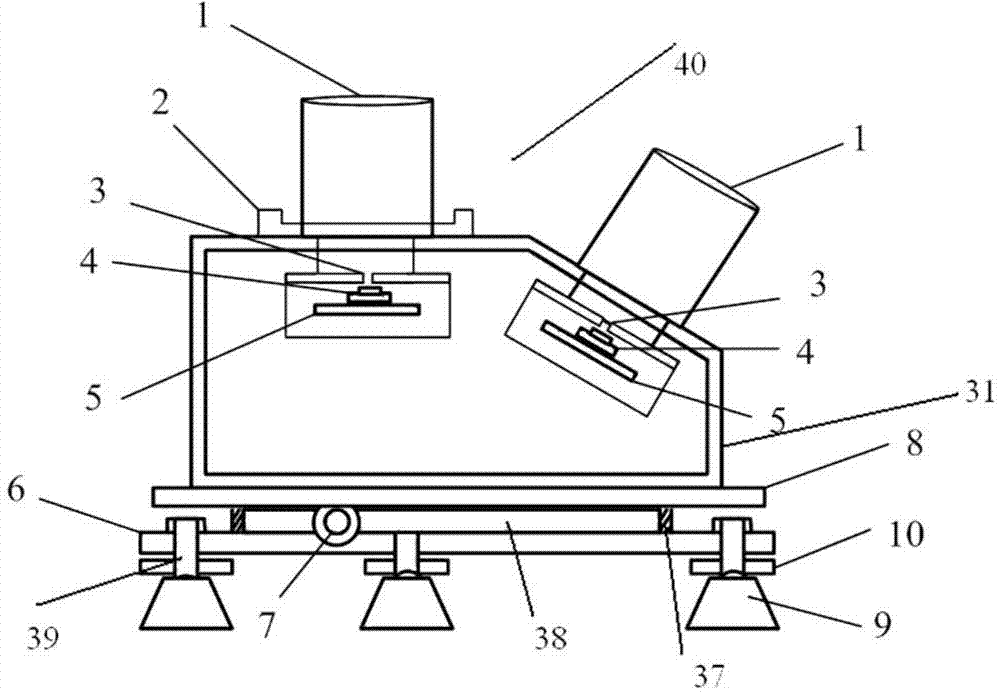
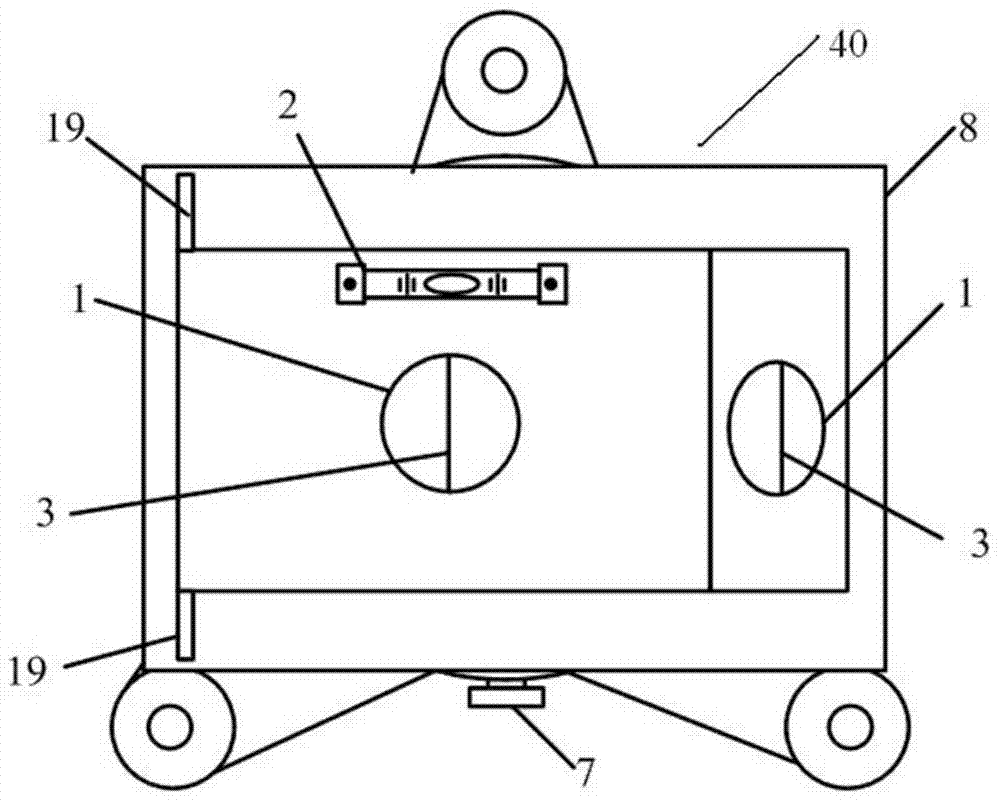
Correction and test system and method for miss distance of large target surface
The invention relates to a correction and test system for the miss distance of a large target surface. The correction and test system comprises a first photoelectric detection target, a second photoelectric detection target and a timing and image collecting instrument, wherein the first photoelectric detection target and the second photoelectric detection target are adjacently arranged on a test segment of a ballistic range in the direction of gun firing, the two photoelectric detection targets are respectively connected with the timing and image collecting instrument, and the timing and image collecting instrument is connected with a computer. Five intersection awning space geometry arrays produced by the two photoelectric detection targets are utilized for achieving measurement of target speeds, flight angle vectors and coordinates.
Owner:XIAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIV
Substrate and Patterning Device for Use in Metrology, Metrology Method and Device Manufacturing Method
ActiveUS20150331336A1Improve accuracyPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusMetrologyX-ray
A pattern from a patterning device is applied to a substrate by a lithographic apparatus. The applied pattern includes product features and metrology targets. The metrology targets include large targets which are for measuring overlay using X-ray scattering and small targets which are for measuring overlay by diffraction of visible radiation. Some of the smaller targets are distributed at locations between the larger targets, while other small targets are placed at the same locations as a large target. By comparing values measured using a small target and large target at the same location, parameter values measured using all the small targets can be corrected for better accuracy. The large targets can be located primarily within scribe lanes while the small targets are distributed within product areas.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
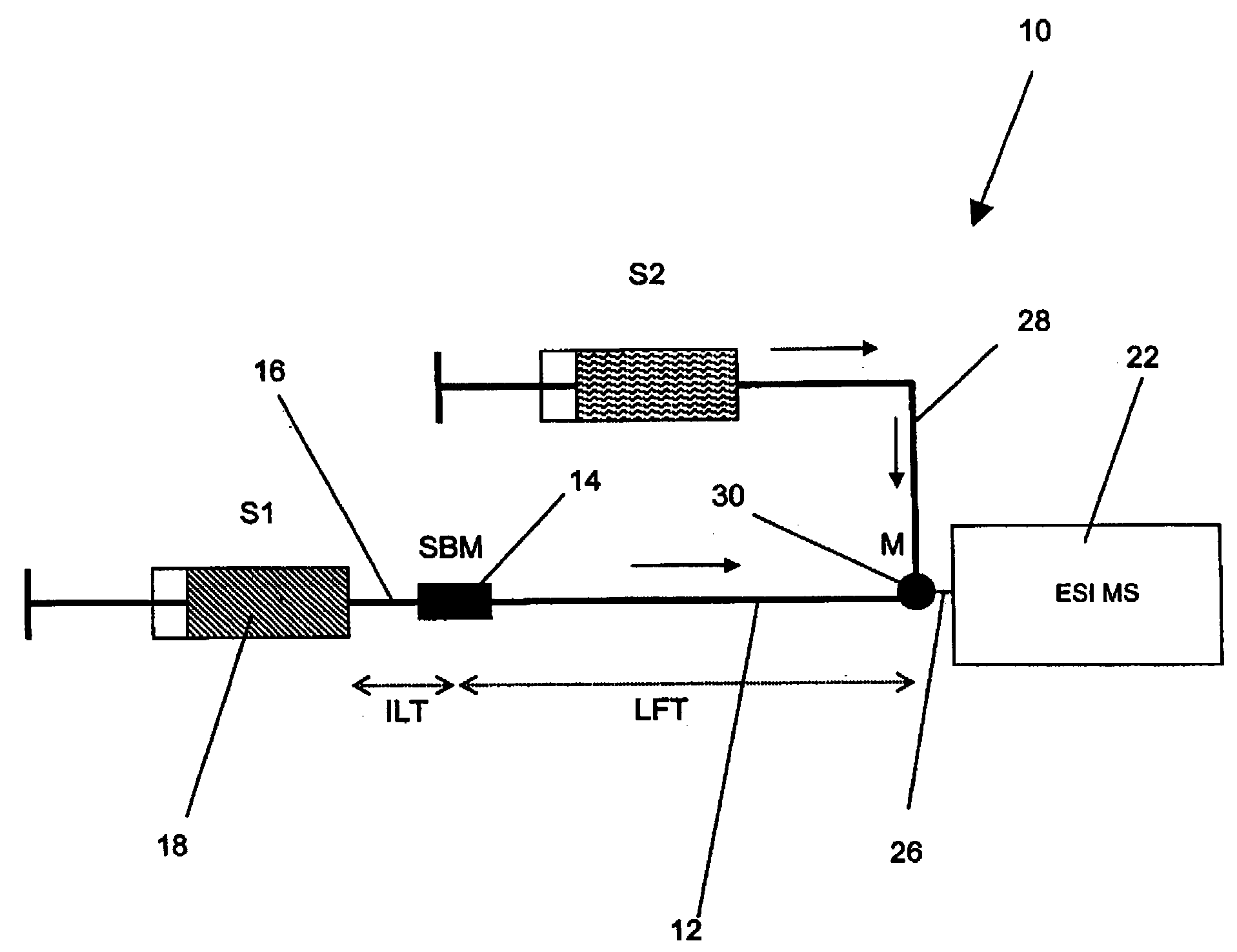
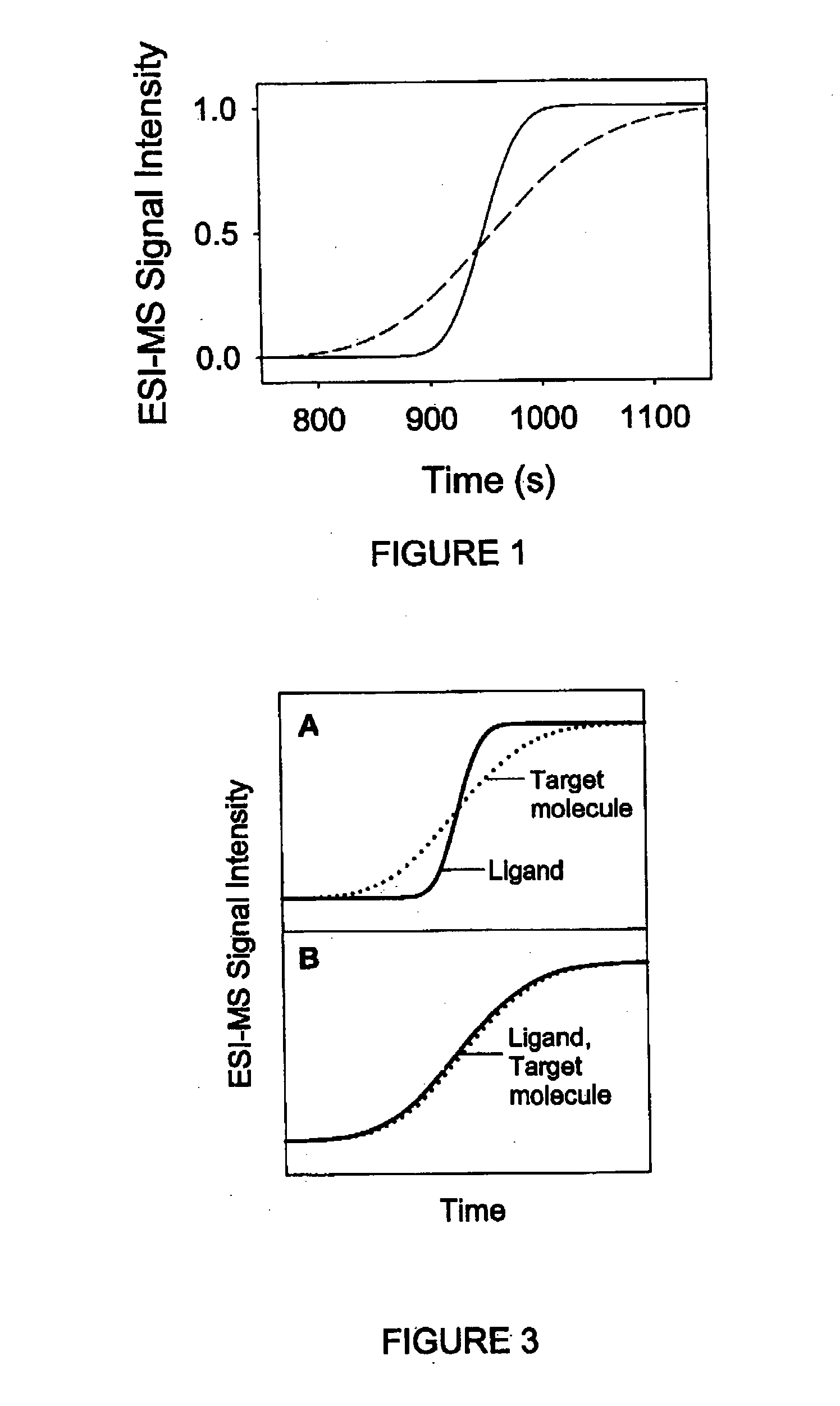
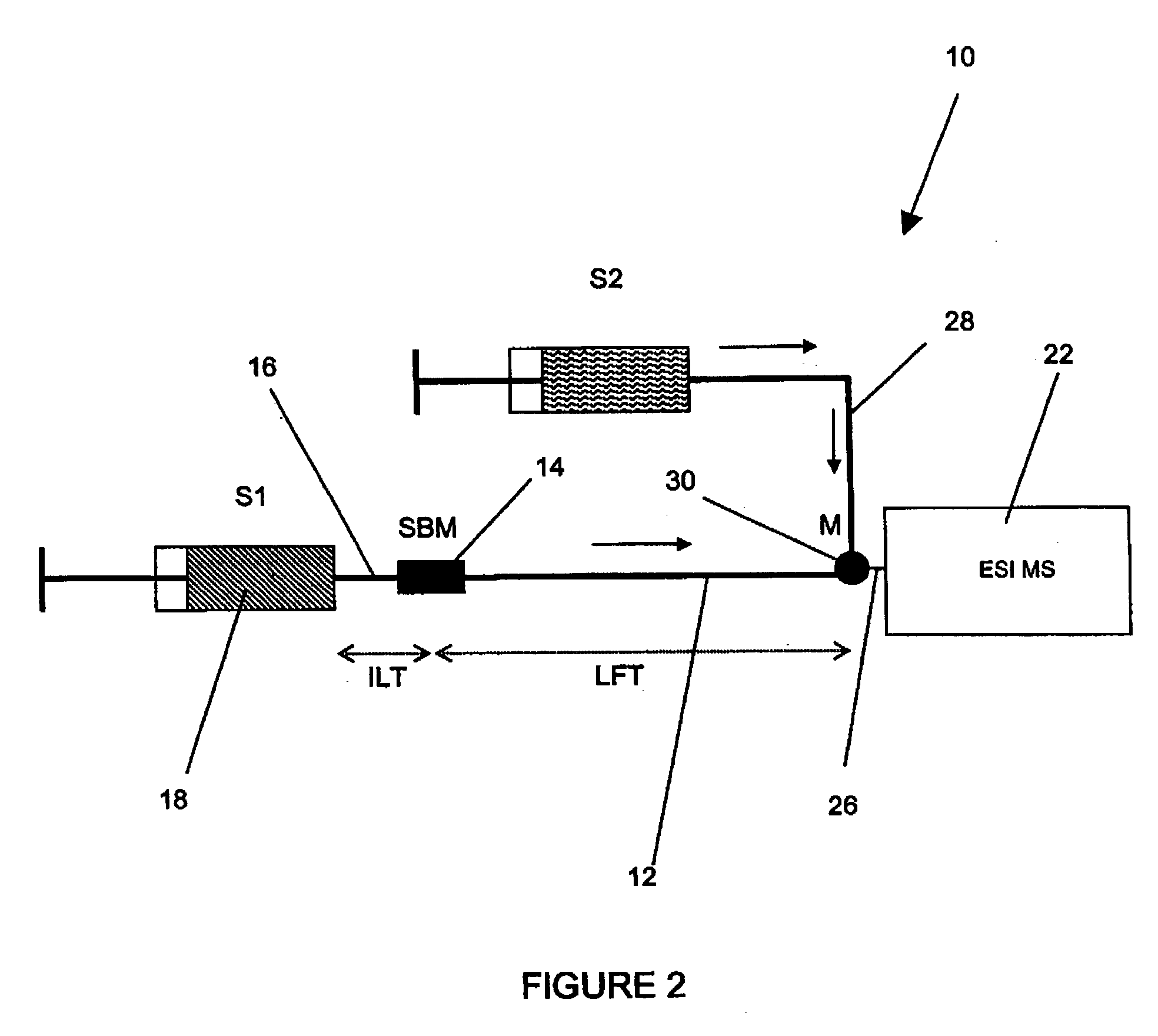
Method and apparatus for the detection of noncovalent interactions by mass spectrometry-based diffusion measurements
InactiveUS20030234356A1Accurate measurementShorten the timeSamples introduction/extractionSurface/boundary effectHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsGas phase
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for detecting the noncovalent binding of a potential ligand (such as a drug candidate) to a target, e.g. a biochemical macromolecule such as a protein. The method is based on the Taylor dispersion of an initially sharp boundary between a carrier solution, and an analyte solution that contains the potential ligand(s) and the target. Dispersion profiles of one or more potential ligands are monitored by mass spectrometry at the exit of the laminar flow tube. Potential ligands will usually be relatively small molecules that have large diffusion coefficients. In the absence of any noncovalent interactions in solution, very steep dispersion profiles are expected for these potential ligands. However, a ligand that binds to a large target in solution, will show an apparent diffusion coefficient that is significantly reduced, thus resulting in a more extended dispersion profile. Noncovalent binding can therefore be detected by monitoring dispersion profiles of potential ligands in the presence and in the absence of the target. In contrast to other mass spectrometry-based methods for detecting noncovalent interactions, this method does not rely on the preservation of specific noncovalent interactions in the gas phase. This method has an excellent sensitivity and selectivity, therefore it can be used for testing multiple potential ligands simultaneously. The method is therefore useful for the high throughput screening of compound libraries.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN ONTARIO
A traffic sign detection method in automatic driving based on a YOLOv3 network
ActiveCN109447034AFast convergenceReduce the impactCharacter and pattern recognitionTraffic sign recognitionData set
The invention discloses a traffic sign detection method in automatic driving based on a YOLOv3 network, and belongs to the field of traffic sign detection. The method solves the problems that an existing YOLOv3 network target detection algorithm is not high in detection precision and the detection speed cannot meet the real-time requirement. According to the invention, an improved loss function isprovided, so that the influence of a large target error on a small target detection effect is reduced, and the detection accuracy of a small-size target is improved. An improved activation function is provided, a negative value is reserved, meanwhile, changes and information propagated to the next layer are reduced, and the robustness of the algorithm to noise is enhanced. The real frames in thetraffic sign data set are clustered by using a K-means algorithm to realize the pre-fetching of a target frame position and accelerate convergence of the network. The detection precision mAP of the traffic sign detection model on a test set reaches 92.88%, the detection speed reaches 35FPS, and the requirement for real-time performance is completely met. The method can be applied to the field of traffic sign detection.
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION SCI & TECH UNIV
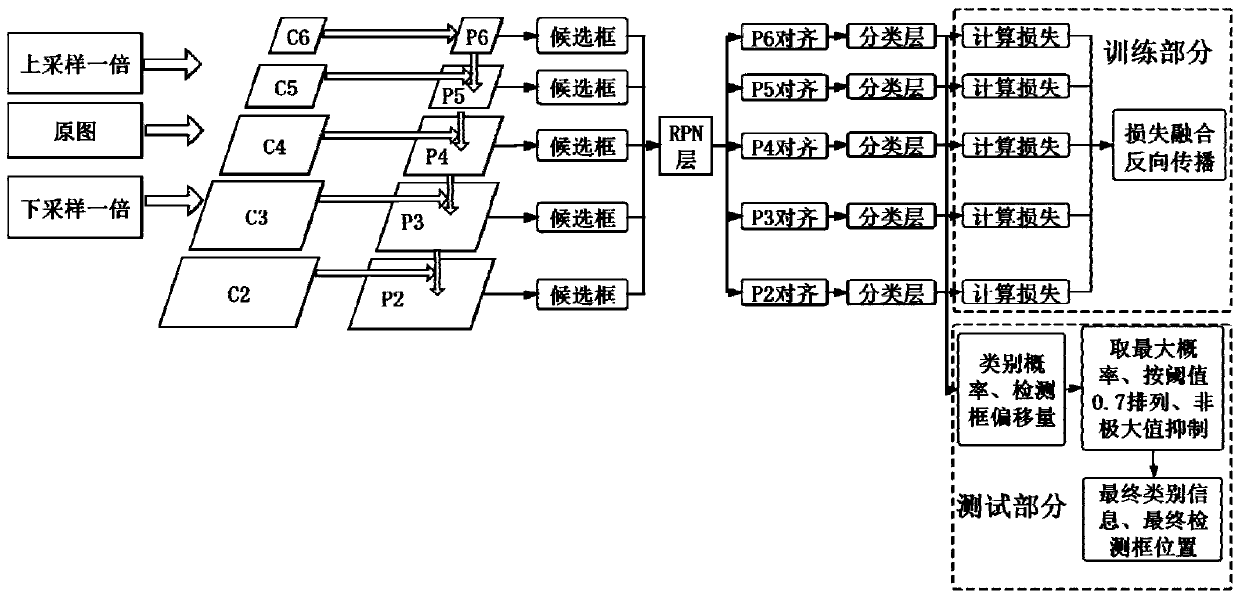
An image small target detection method based on combination of two-stage detection
PendingCN109598290AFully excavatedReduce the problem of false detection and missed detection of small targetsCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionNetwork model
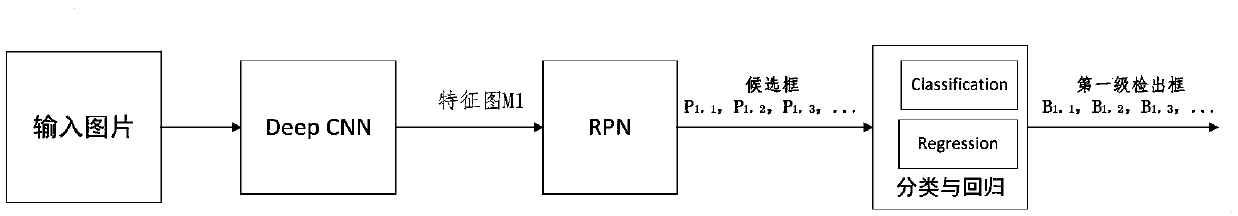
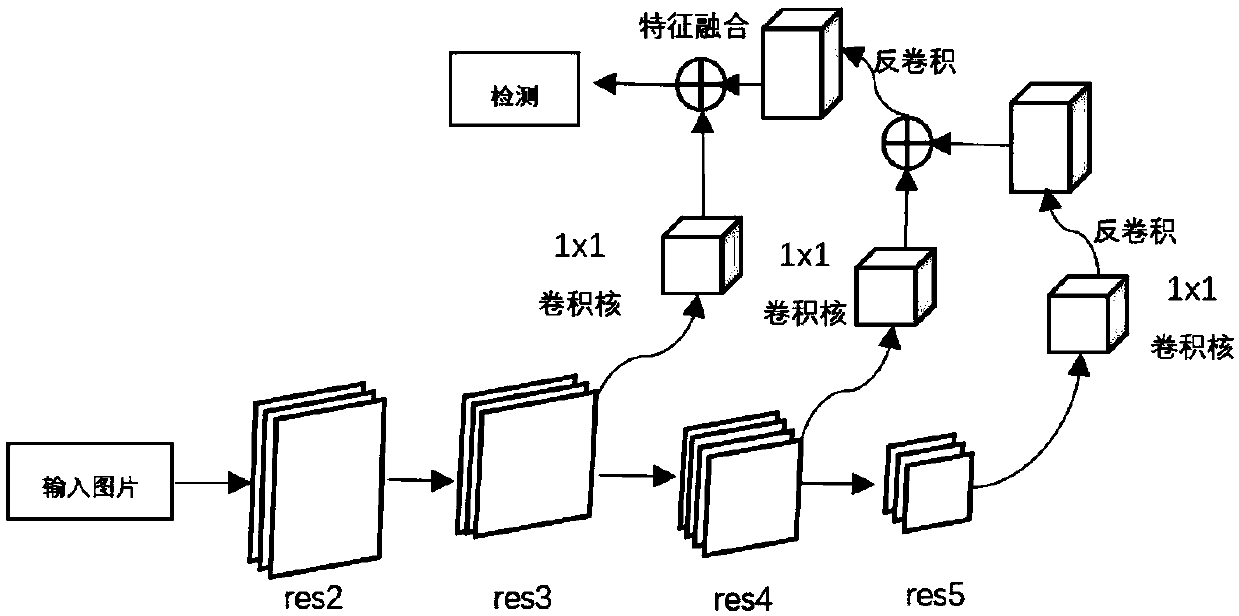
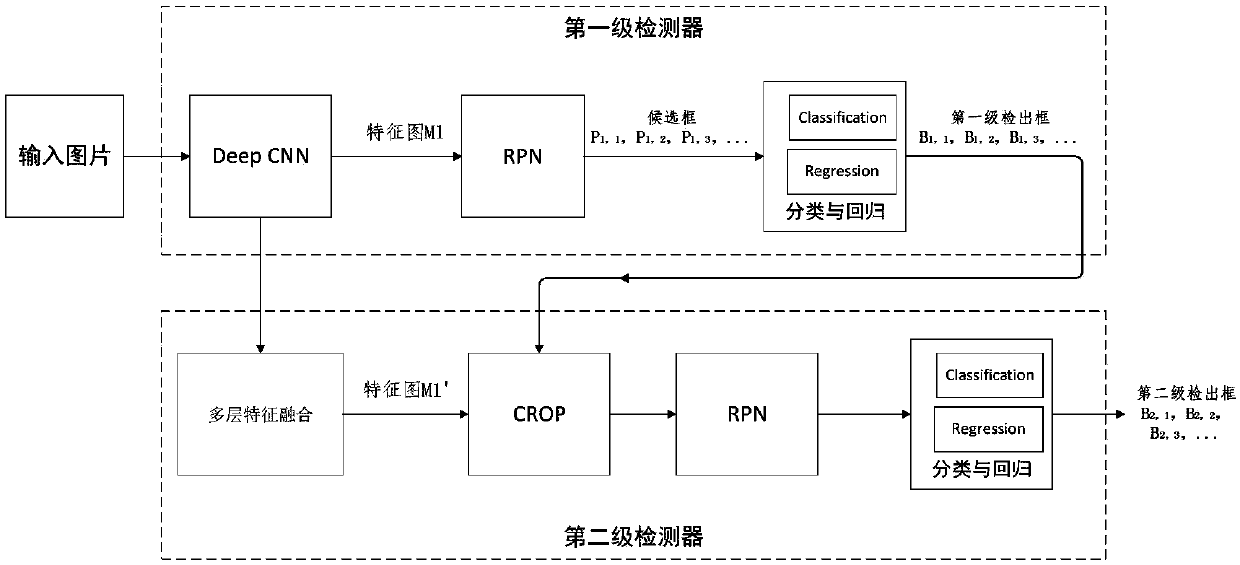
The invention discloses a small target detection method based on combination of two-stage detection. The method includes: Sending the original image into a first detector to detect a first-stage target B1; Fusing the output features of the shallow CNN and the output features of the deep CNN to obtain M1 ', and selecting a corresponding feature map M2 from the M1' by using B1; taking the M2 as an input feature map and sending the M2 to an RPN module and a classification and regression module of a second-stage detector for detection and positioning of a second-stage target; And adding d loss obtained from two-stage detection as the total Loss of the whole network to obtain an end-to-end detection network model. According to the invention, a two-stage detection network is constructed; A largetarget is accurately detected firstly, then a small target is detected in a large target area, and a detection frame of the small target is limited in a local area which is most possible and most easily detected, namely the area where the large target is located, so that complex background interference is effectively removed, the false detection probability is reduced, and the detection precisionof the small target and the small target in the image is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
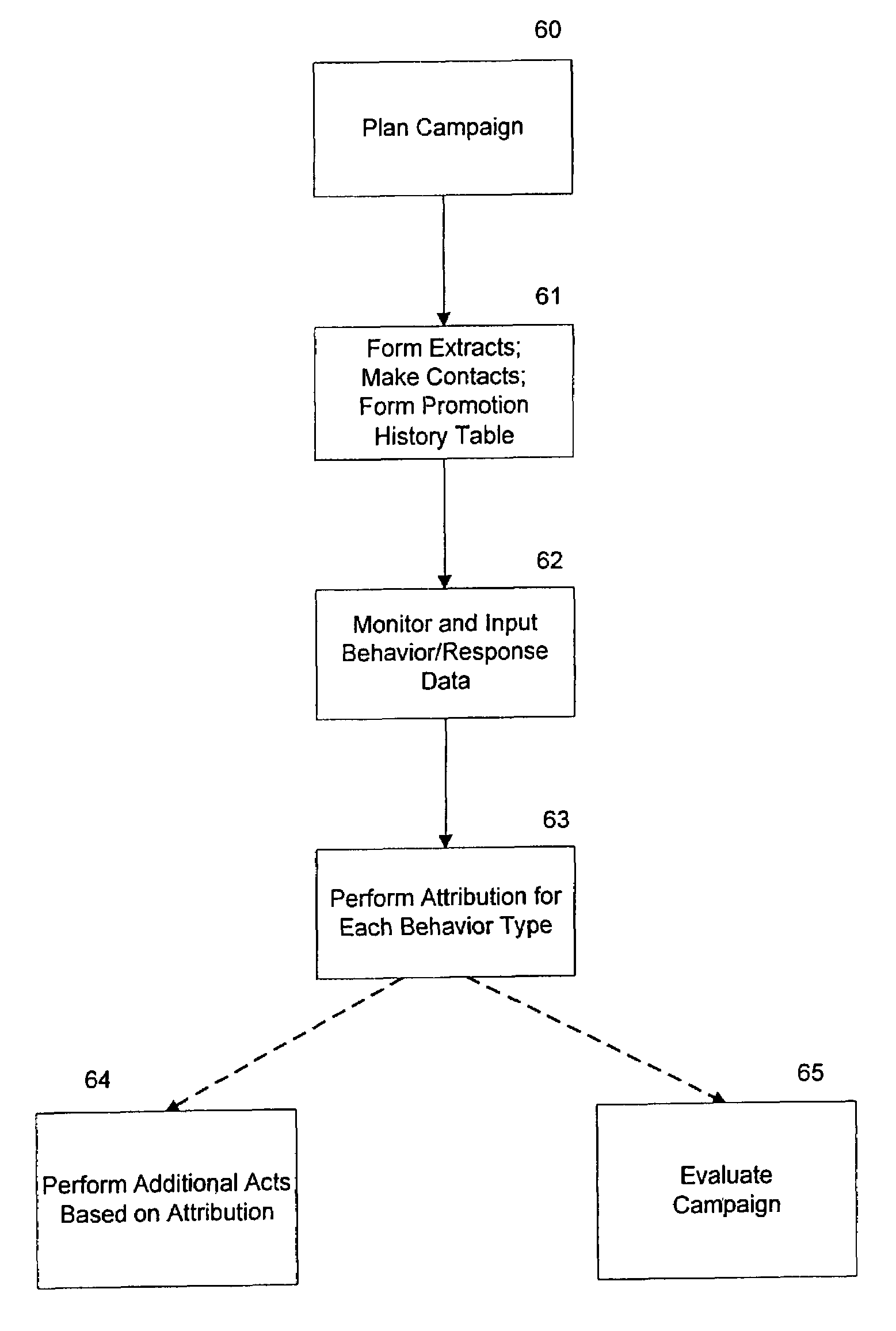
Method and apparatus for implied attribution of responses to promotional contacts
Method and apparatus for performing automatic implied attribution is described, and in particular implied attribution in connection with a campaign. The campaign can be a marketing campaign in which actions (offer cells) are aimed at a contact group and behaviors are monitored within a defined evaluation period. By this method, the behaviors of the contact group can be attributed to the offer cells The method allows the monitoring of multiple behaviors for any number of offer cells for any number of contact groups. Contact groups can be obtained by any query process. The behaviors of a larger target group can also be implied where a link can be established between the contact group and the target group. Also described is a system for performing implied attribution, where the system can be software running on a general purpose computer.
Owner:AMDOCS SOFTWARE SYST +1
Method of error reduction in nucleic acid populations
InactiveUS7303872B2Minimum errorSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA microarrayError reduction
A method is disclosed for the direct synthesis of double stranded DNA molecules of a variety of sizes and with any desired sequence. The DNA molecule to be synthesis is logically broken up into smaller overlapping DNA segments. A maskless microarray synthesizer is used to make a DNA microarray on a substrate in which each element or feature of the array is populated by DNA of a one of the overlapping DNA segments. The complement of each segment is also made in the microarray. The DNA segments are released from the substrate and held under conditions favoring hybridization of DNA, under which conditions the segments will hybridize to form duplexes. The duplexes are then separated using a DNA binding agent which binds to improperly formed DNA helixes to remove errors from the set of DNA molecules. The segments can then be hybridized to each other to assemble the larger target DNA sequence.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com