Patents
Literature
10208 results about "Video processing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
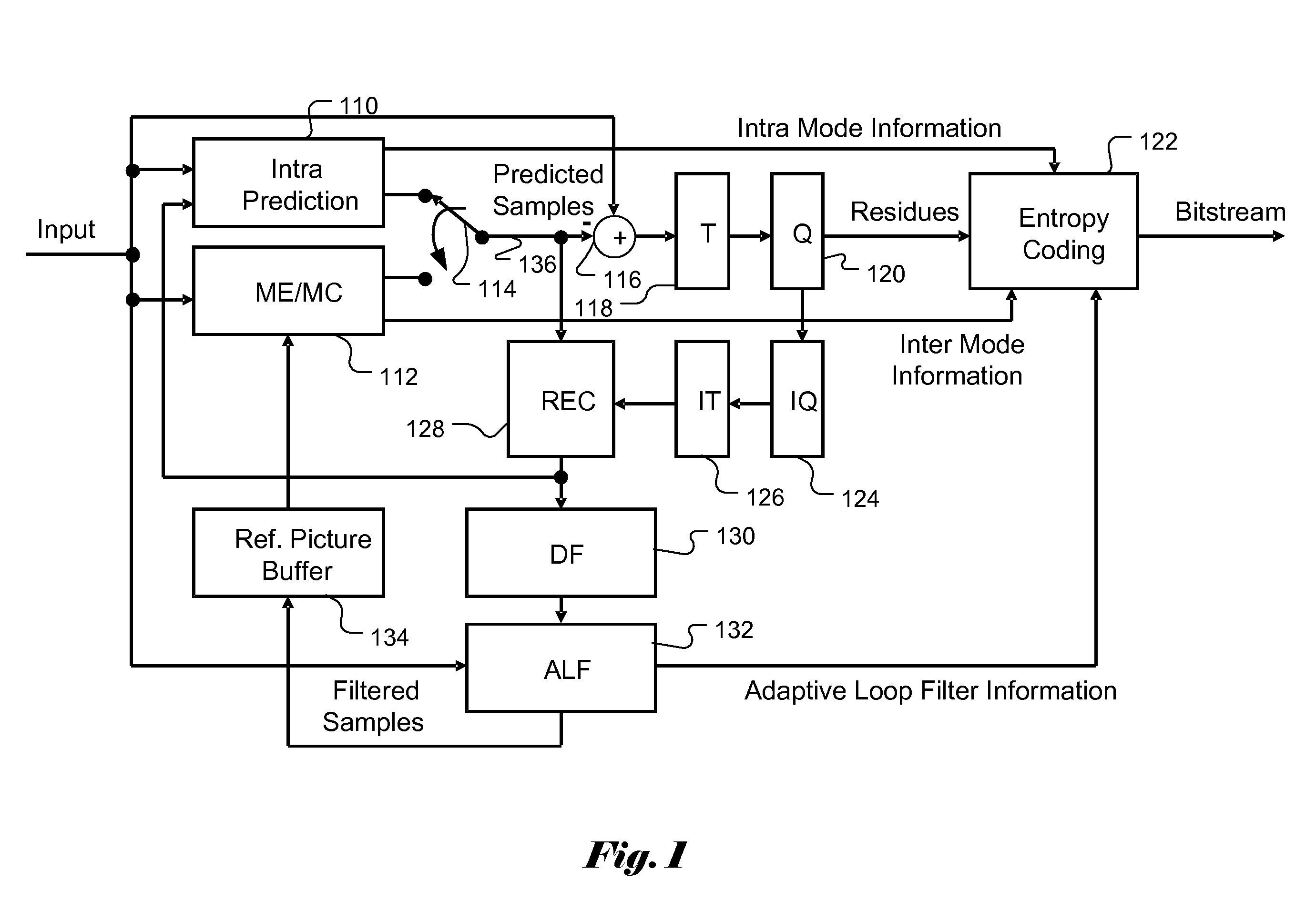
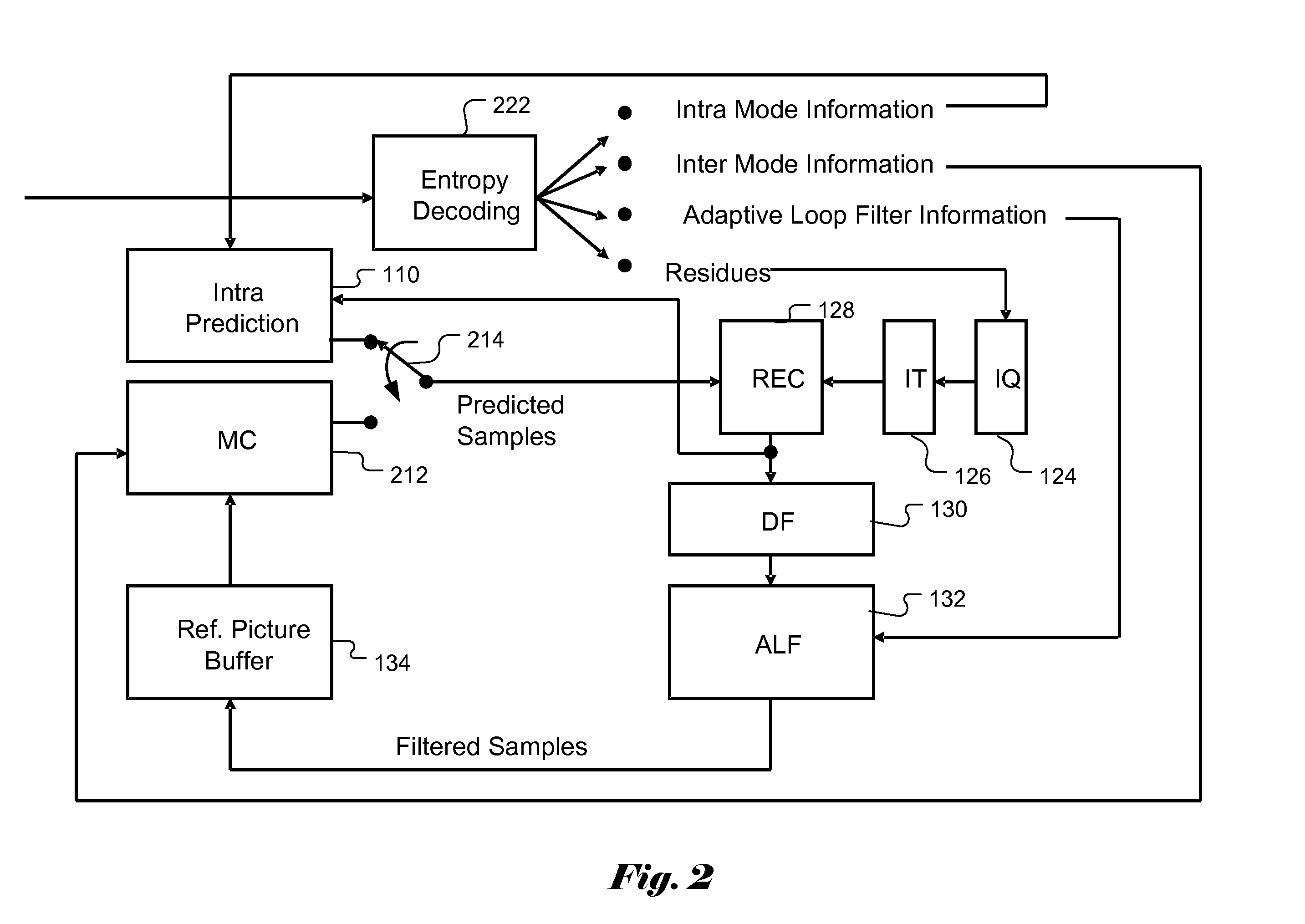
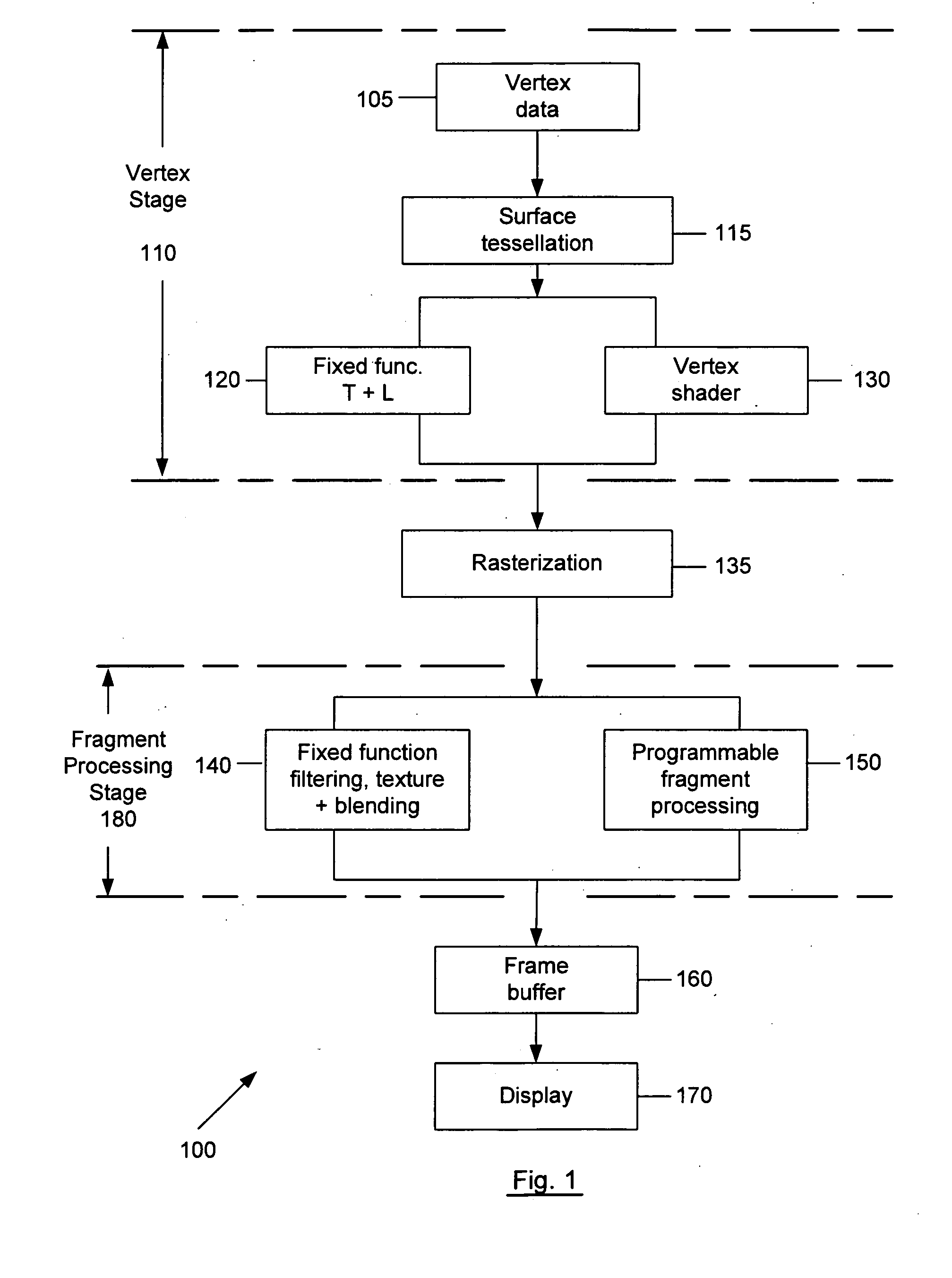
In electronics engineering, video processing is a particular case of signal processing, in particular image processing, which often employs video filters and where the input and output signals are video files or video streams. Video processing techniques are used in television sets, VCRs, DVDs, video codecs, video players, video scalers and other devices. For example—commonly only design and video processing is different in TV sets of different manufactures.
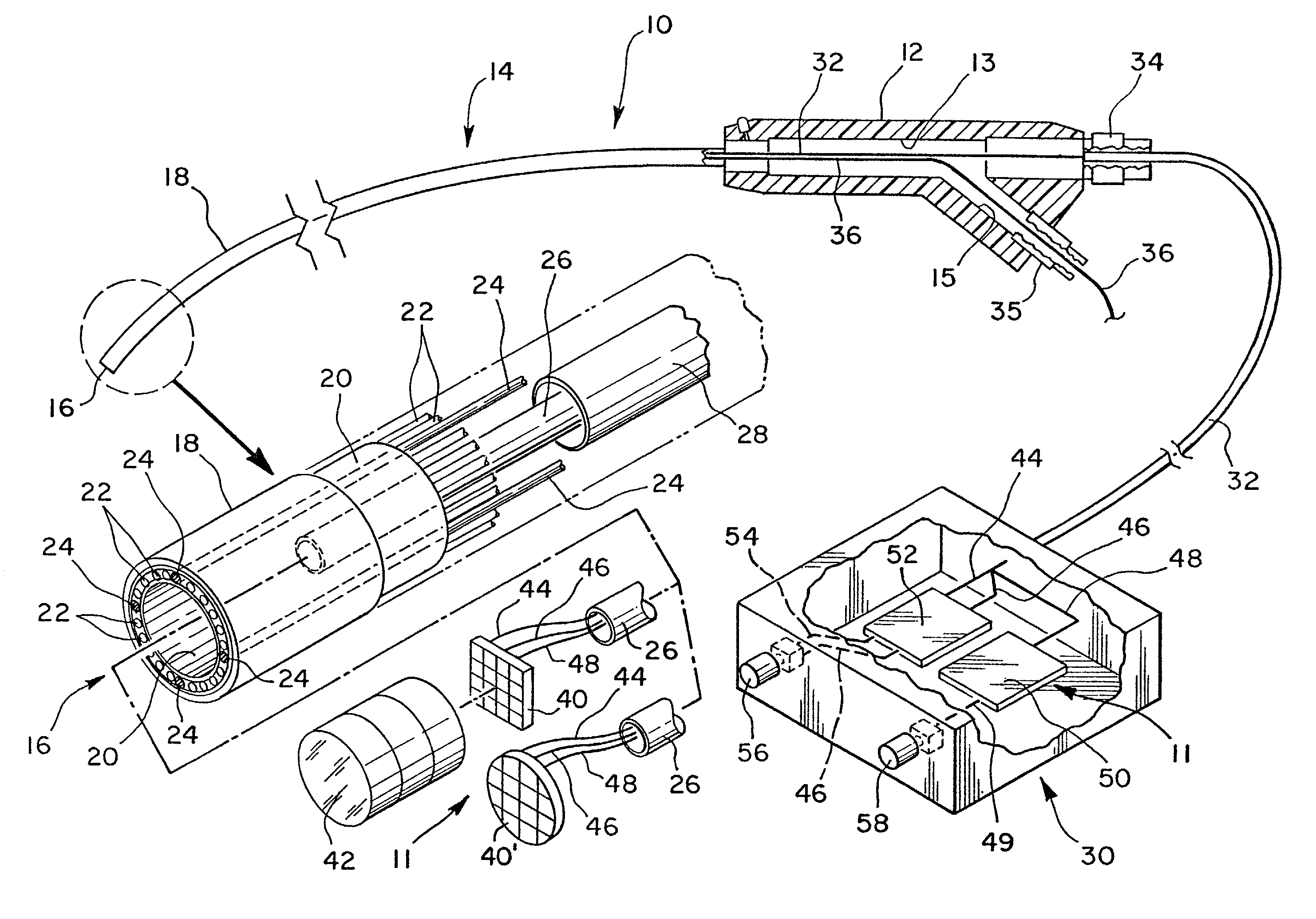
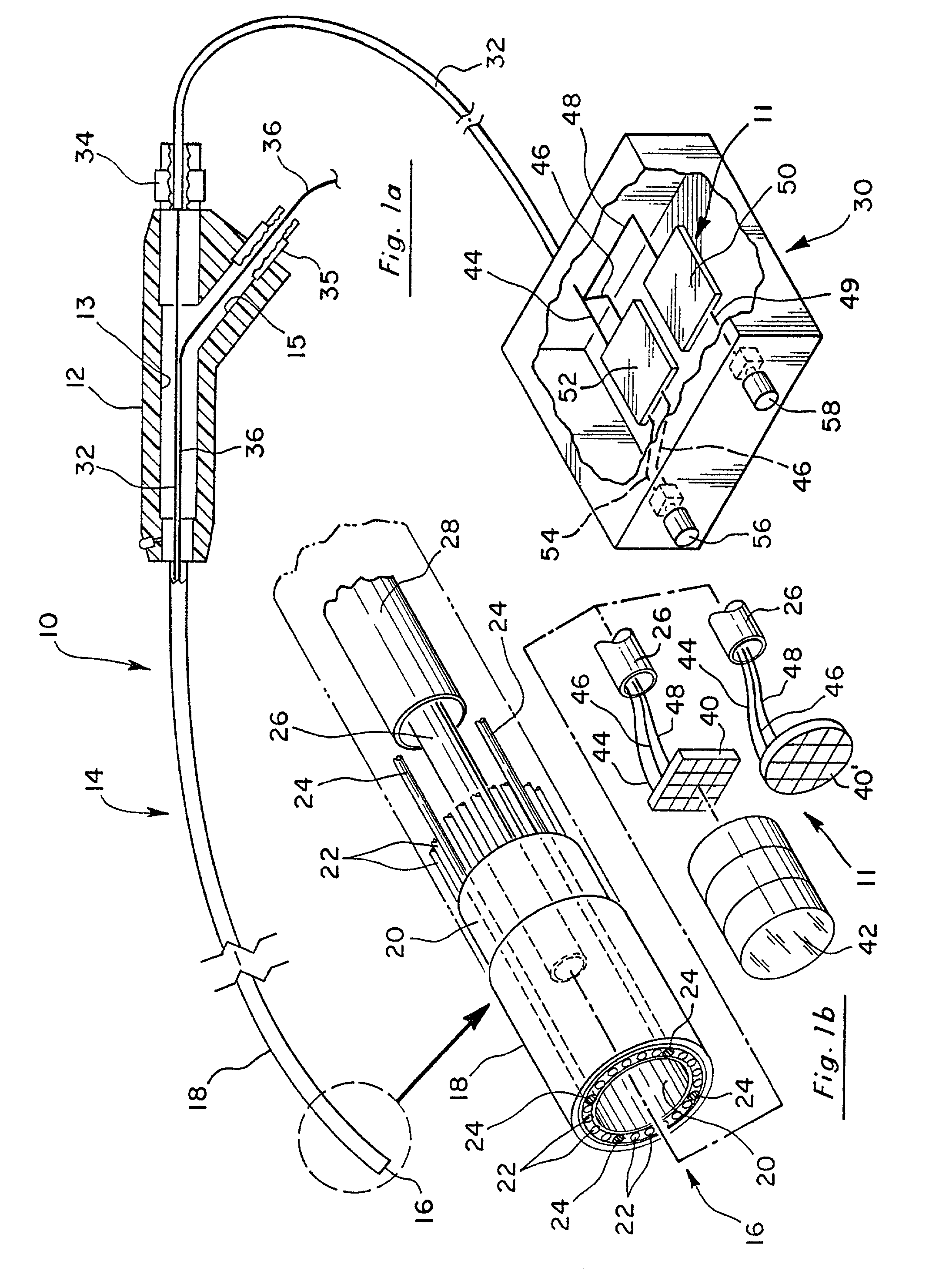
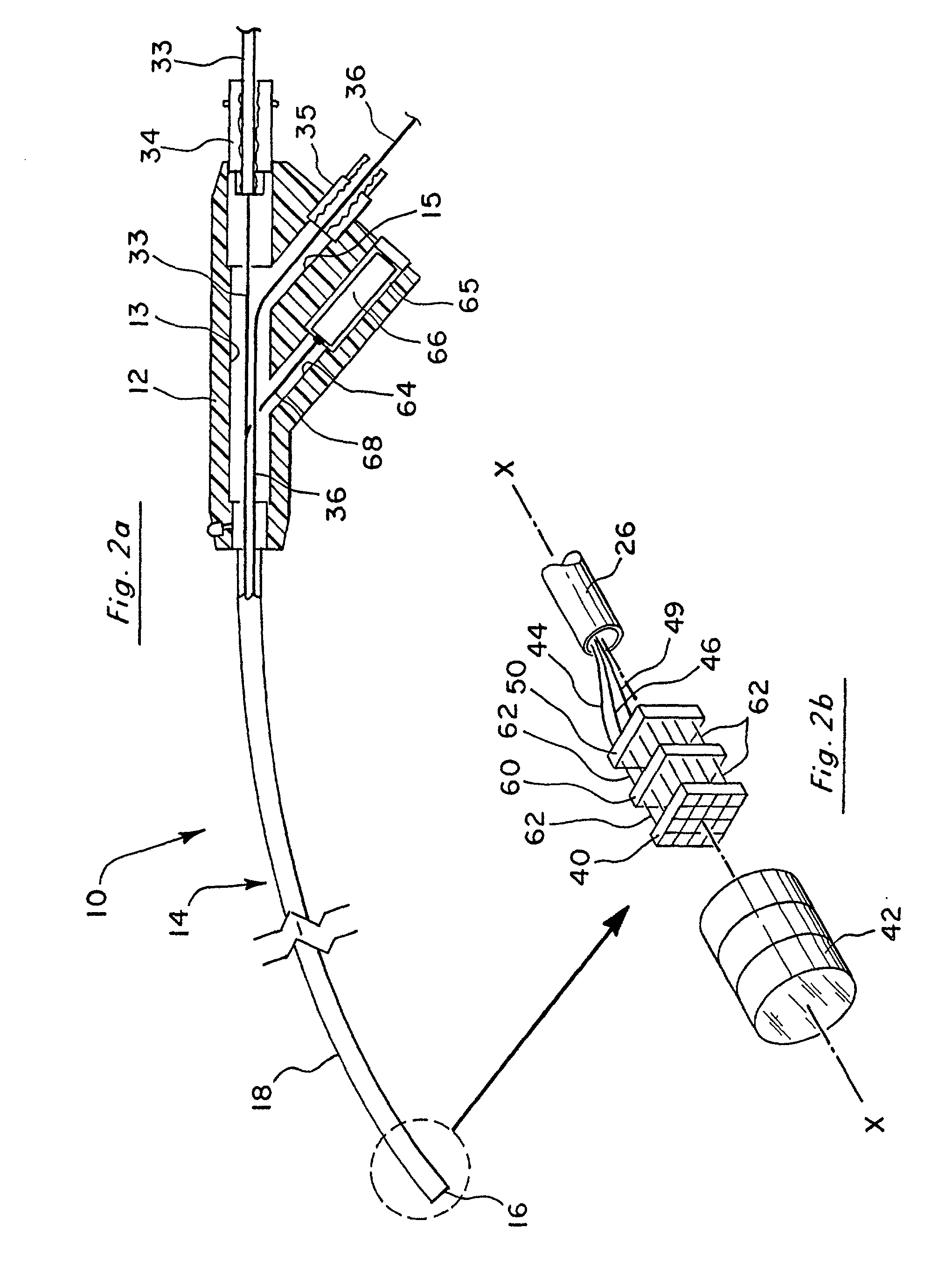
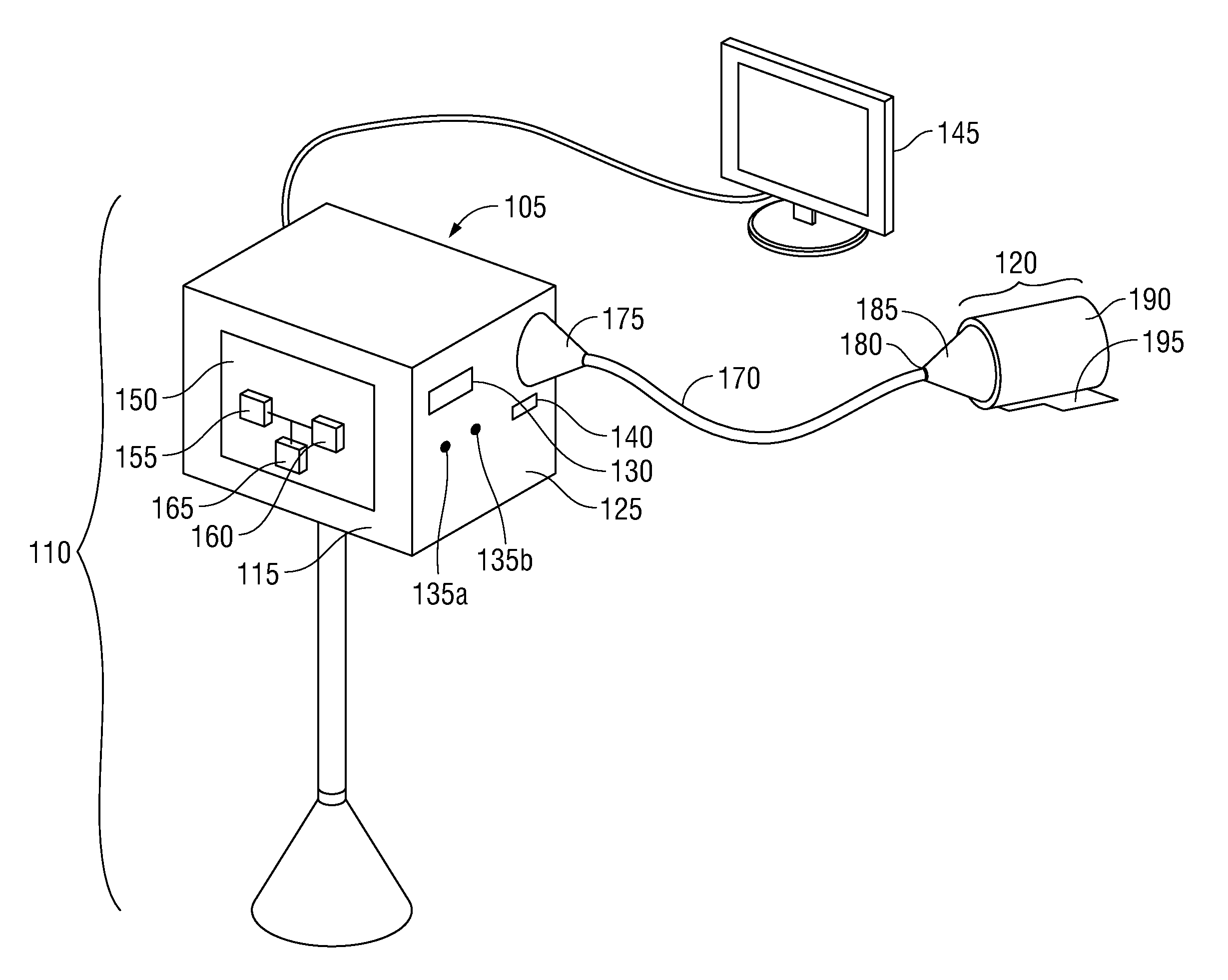
Reduced area imaging device incorporated within wireless endoscopic devices
InactiveUS7030904B2Improve usabilityImprove mobilityTelevision system detailsDigital data processing detailsDental instrumentsWireless transmission
A reduced area imaging device is provided for use in medical or dental instruments such as an endoscope. In a first embodiment of the endoscope, connections between imaging device elements and between a video display is achieved by hard-wired connections. In a second embodiment of the endoscope, wireless transmission is used for communications between imaging device components, and / or for transferring video ready signals to a video display. In one configuration of the imaging device, the image sensor is placed remote from the remaining circuitry. In another configuration, all of the circuitry to include the image sensor is placed in a stacked fashion at the same location. The entire imaging device can be placed at the distal tip of an endoscope. Alternatively, the image sensor can be placed remote from the remaining circuitry according to the first configuration, and control box is used which communicates with the image sensor and is placed remotely from the endoscope. Further alternatively, the imaging device can be incorporated in the housing of a standard medical camera which is adapted for use with traditional rod lens endoscopes. In any of the configurations or arrangements, the image sensor may be placed alone on a first circuit board, or timing and control circuits may be included on the first circuit board containing the image sensor. The timing and control circuits and one or more video processing boards can be placed adjacent the image sensor in a tubular portion of the endoscope, in other areas within the endoscope, in the control box, or in combinations of these location.
Owner:MICRO IMAGING SOLUTIONS
Surgical imaging device
A surgical imaging device includes at least one light source for illuminating an object, at least two image sensors configured to generate image data corresponding to the object in the form of an image frame, and a video processor configured to receive from each image sensor the image data corresponding to the image frames and to process the image data so as to generate a composite image. The video processor may be configured to normalize, stabilize, orient and / or stitch the image data received from each image sensor so as to generate the composite image. Preferably, the video processor stitches the image data received from each image sensor by processing a portion of image data received from one image sensor that overlaps with a portion of image data received from another image sensor. Alternatively, the surgical device may be, e.g., a circular stapler, that includes a first part, e.g., a DLU portion, having an image sensor a second part, e.g., an anvil portion, that is moveable relative to the first part. The second part includes an arrangement, e.g., a bore extending therethrough, for conveying the image to the image sensor. The arrangement enables the image to be received by the image sensor without removing the surgical device from the surgical site.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
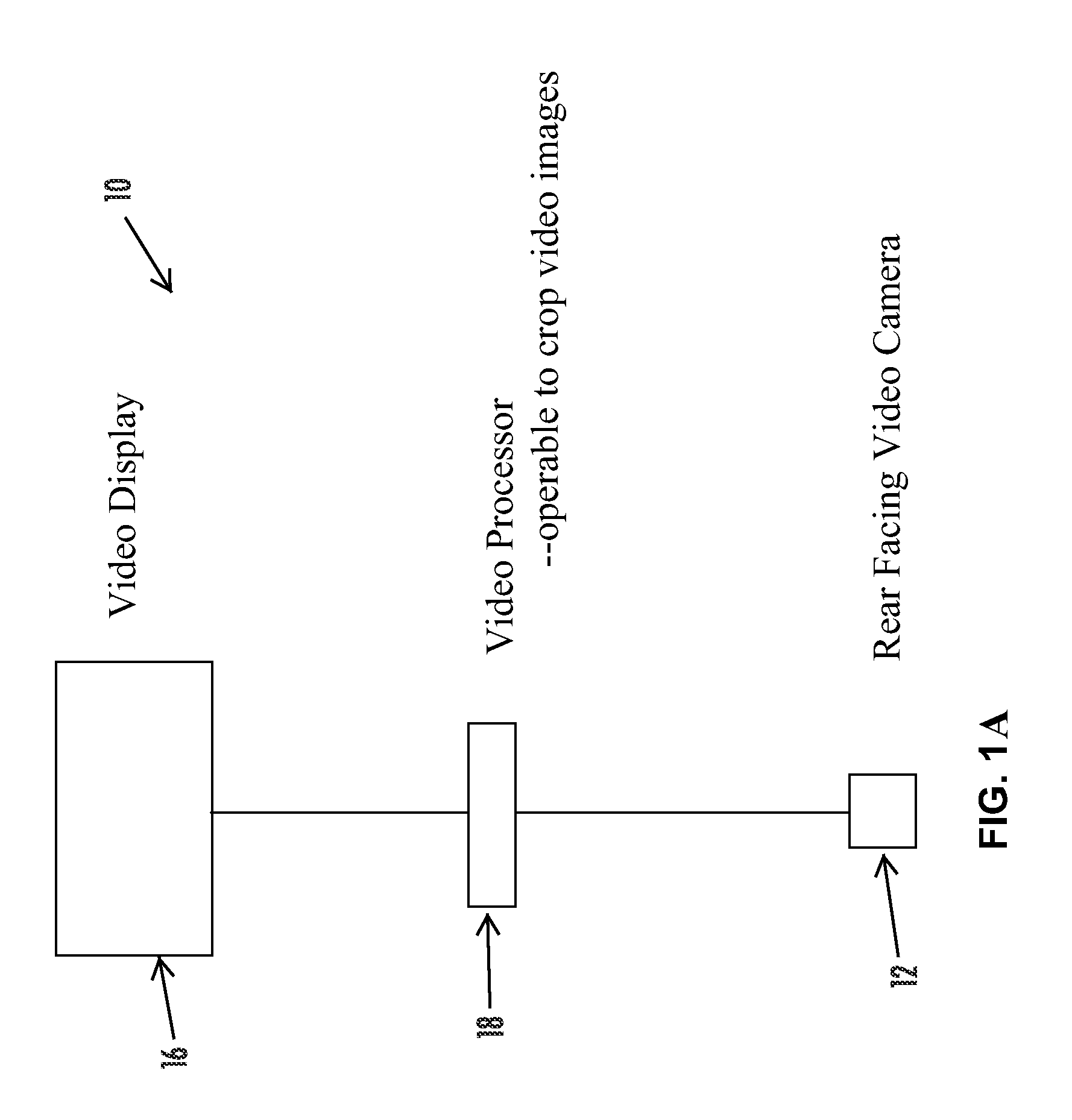
Imaging and display system for vehicle
ActiveUS20120154591A1Enhanced Situational AwarenessIncrease awarenessRoad vehicles traffic controlColor television detailsLane departure warning systemVideo processing
A vehicular imaging and display system includes a rear backup camera at a rear portion of a vehicle, a video processor for processing image data captured by the rear camera, and a video display screen responsive to the video processor to display video images. During a reversing maneuver of the equipped vehicle, the video display screen displays video images captured by the rear camera. During forward travel of the equipped vehicle, the video display screen is operable to display images representative of a portion of the field of view of the rear camera to display images representative of an area sideward of the equipped vehicle responsive to at least one of (a) actuation of a turn signal indicator of the vehicle, (b) detection of a vehicle in a side lane adjacent to the equipped vehicle and (c) a lane departure warning system of the vehicle.
Owner:MAGNA ELECTRONICS
Dynamic target tracking and positioning method of unmanned plane based on vision
The invention discloses a dynamic target tracking and positioning method of an unmanned plane based on vision, and belongs to the navigation field of the unmanned planes. The dynamic target tracking and positioning method comprises the following steps of: carrying out video processing, dynamic target detecting and image tracking; carrying out cloud deck servo control; establishing a corresponding relationship between a target in the image and a target in the real environment, and further measuring the distance between a camera and a dynamic target to complete precise positioning of the dynamic target; and enabling an unmanned plane control system to fly by automatically tracking the dynamic target on the ground. The dynamic target tracking and positioning method of the unmanned plane based on the vision can automatically realize the movement target detecting, image tracking and optical axis automatic deflecting without the full participation of the people, so that the dynamic target is always displayed at the center of an image-forming plane; and the distance between the unmanned plane and the dynamic target is measured in real time according to an established model on the basis of obtaining the height information of the unmanned plane. Therefore, the positioning of the dynamic target is realized; closed-loop control is formed by using the positioned dynamic target as a feedback signal, so that the tracking flight of the unmanned plane is guided.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
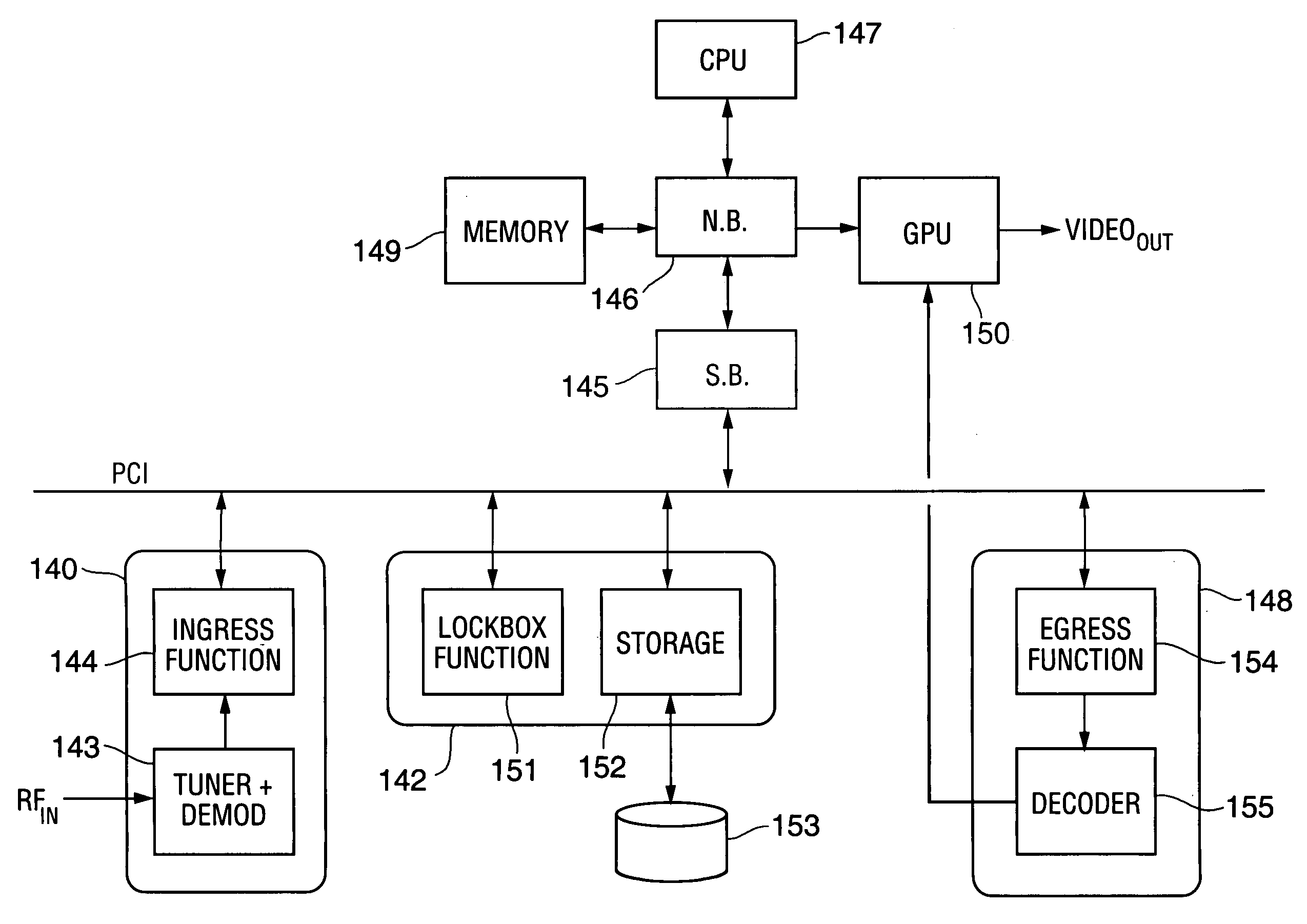
Method and apparatus for content protection in a personal digital network environment
InactiveUS20050144468A1Easy to disassembleReliable lockingTelevision system detailsUser identity/authority verificationGraphicsVideo processing
In some embodiments, the invention is a personal digital network (“PDN”) including hardware (sometimes referred to as Ingress circuitry) configured to transcrypt encrypted content that enters the PDN. Typically, the transcryption (decryption followed by re-encryption) is performed in hardware within the Ingress circuitry and the re-encryption occurs before the decrypted content is accessible by hardware or software external to the Ingress circuitry. Typically, transcrypted content that leaves the Ingress circuitry remains in re-encrypted form within the PDN whenever it is transferred between integrated circuits or is otherwise easily accessible by software, until it is decrypted within hardware (sometimes referred to as Egress circuitry) for display or playback or output from the PDN. Typically, the PDN is implemented so that no secret in Ingress or Egress circuitry (for use or transfer by the Ingress or Egress circuitry) is accessible in unencrypted form to software or firmware within the PDN or to any entity external to the PDN. Other aspects of the invention are methods for protecting content in a PDN (e.g., an open computing system) and devices (e.g., multimedia graphics cards, set top boxes, or video processors) for use in a PDN.
Owner:OPTIMUM CONTENT PROTECTION
Multi-Level Video Processing Within A Vehicular Communication Network
InactiveUS20120105637A1Registering/indicating working of vehiclesDigital data processing detailsVideo processingVideo decoder
A system for performing multi-level video processing within a vehicle includes a pre-processing module for determining an encoding mode and enabling one or more levels of encoding based on the encoding mode. The pre-processing module further receives a video stream from a camera attached to the vehicle via a vehicular communication network and encodes the video stream based on the encoding mode to produce a packet stream output. The system further includes a video decoder for receiving the packet stream output and decoding the packet stream output in accordance with the encoding mode to produce a decoded video output.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Apparatus and method for processing video data
ActiveUS7158680B2Increases robustness and applicabilityReduce non-linearityImage enhancementImage analysisFeature extractionComputer graphics (images)
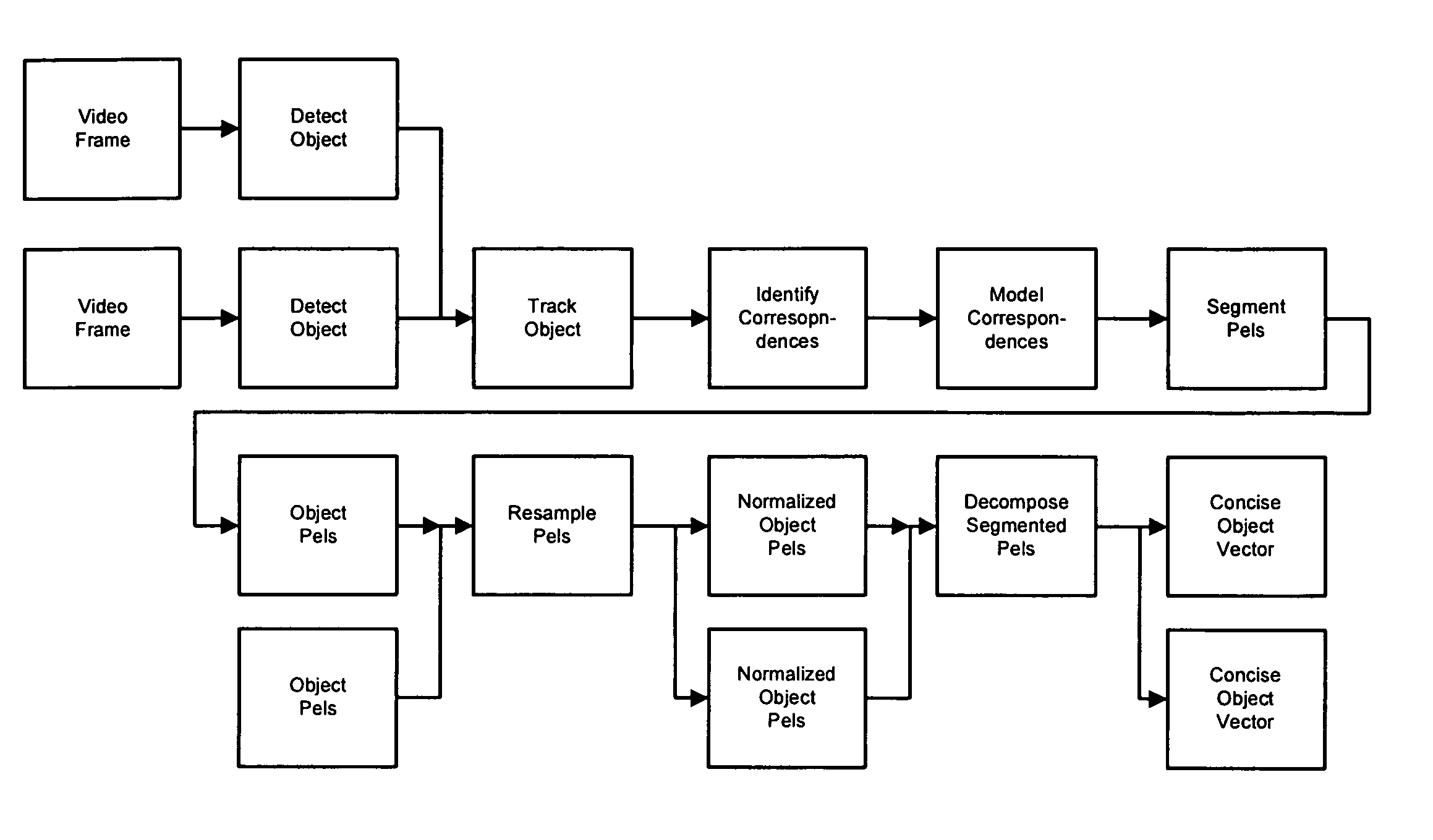
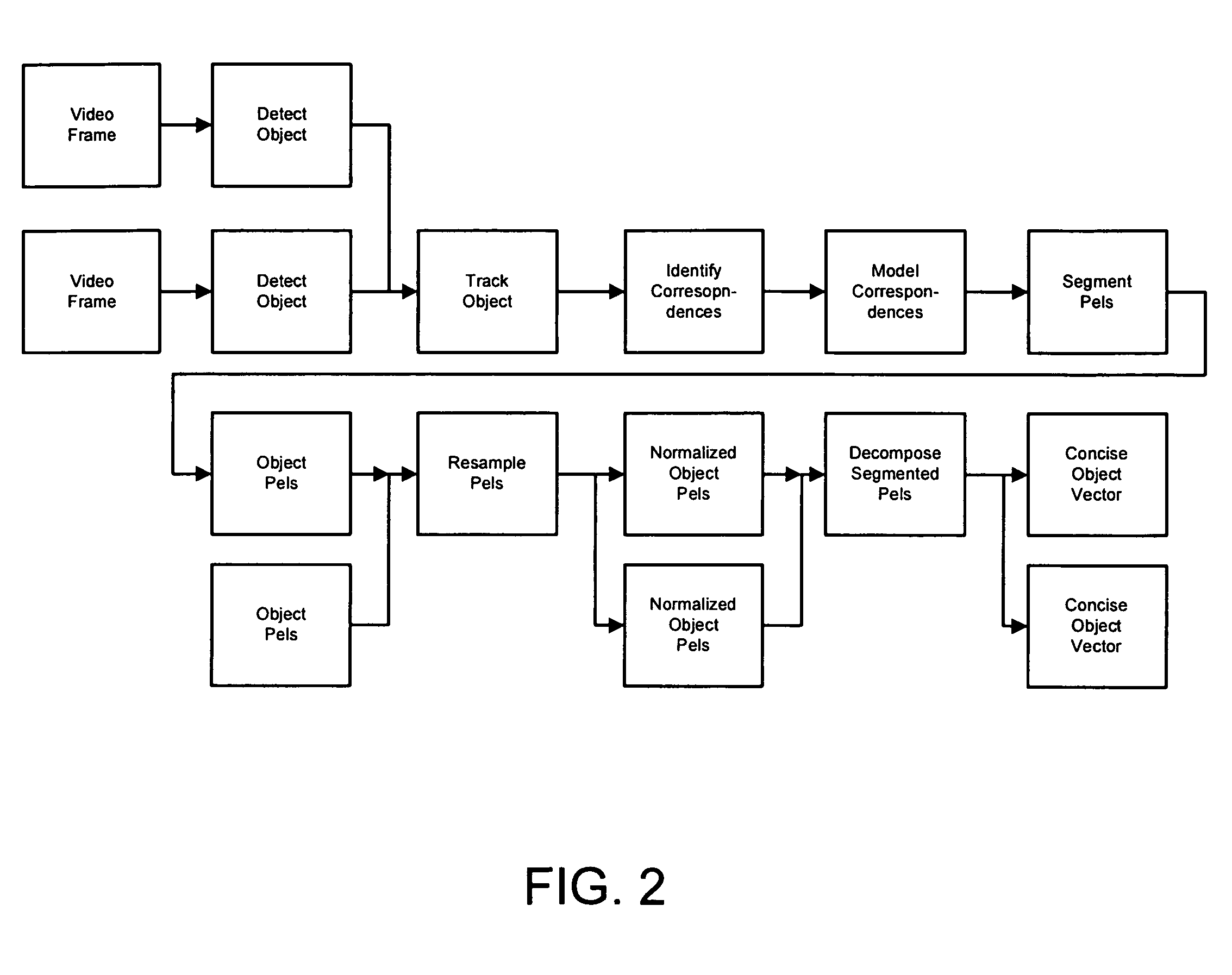
An apparatus and methods for processing video data are described. The invention provides a representation of video data that can be used to assess agreement between the data and a fitting model for a particular parameterization of the data. This allows the comparison of different parameterization techniques and the selection of the optimum one for continued video processing of the particular data. The representation can be utilized in intermediate form as part of a larger process or as a feedback mechanism for processing video data. When utilized in its intermediate form, the invention can be used in processes for storage, enhancement, refinement, feature extraction, compression, coding, and transmission of video data. The invention serves to extract salient information in a robust and efficient manner while addressing the problems typically associated with video data sources
Owner:EUCLID DISCOVERIES LLC
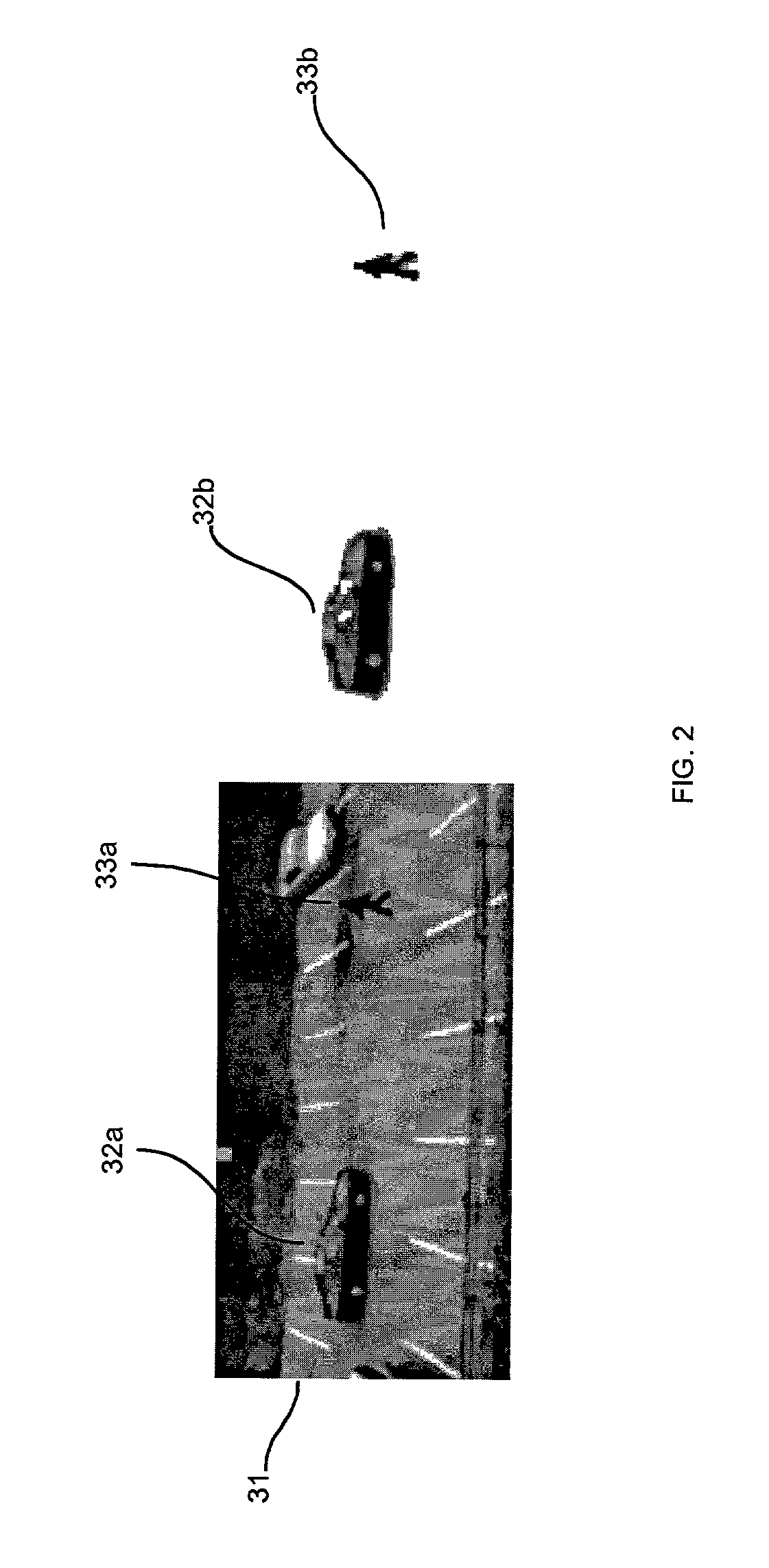
Target detection and tracking from video streams
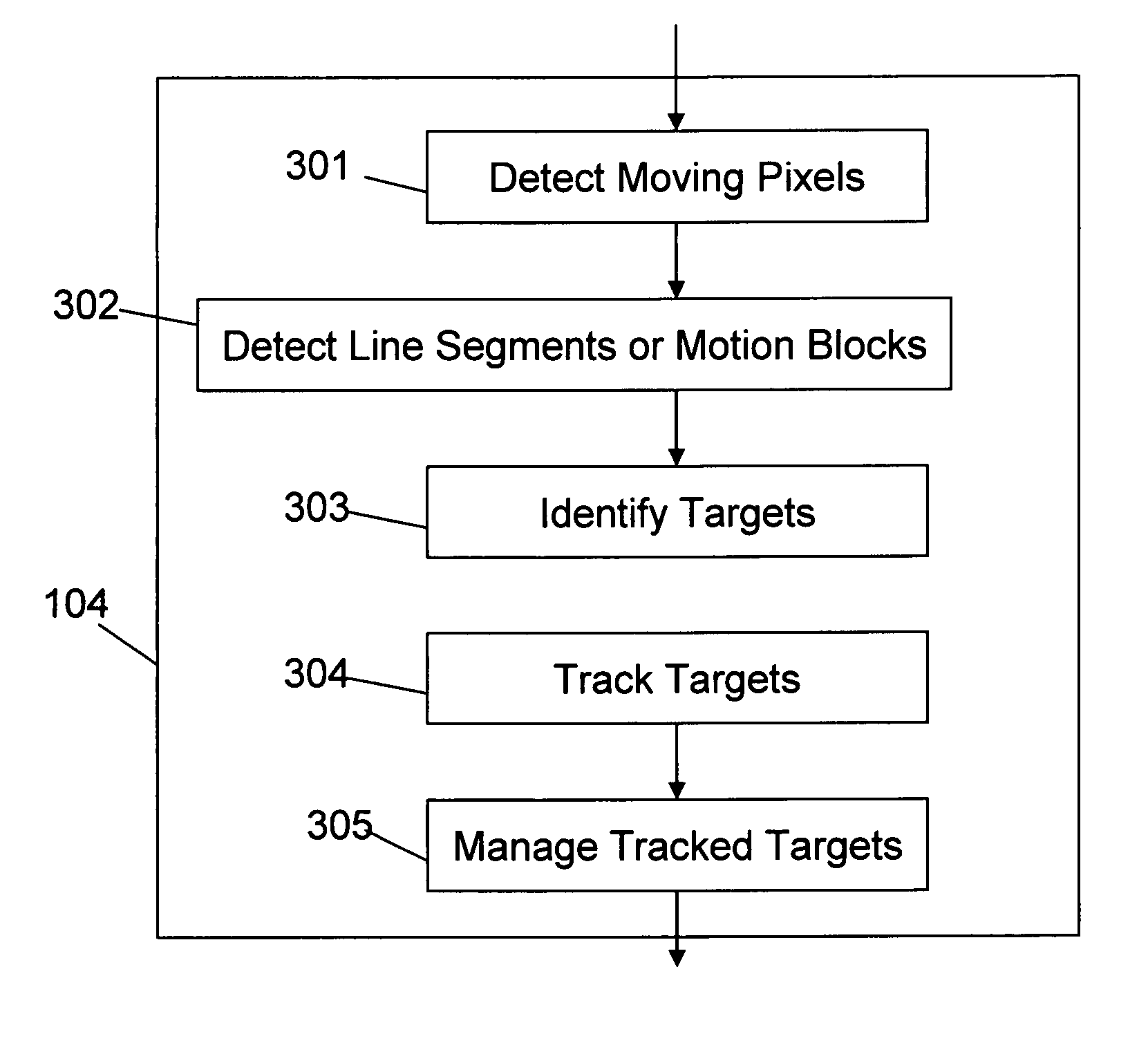
A technique for video processing includes: receiving video from a scene; detecting moving pixels in the video; detecting line segments or motion blocks in the video based on the detected moving pixels; identifying targets in the video based on the detected line segments or motion blocks; tracking targets in the video based on the identified targets; and managing the tracked targets in the video.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
Modular parallel-pipelined vision system for real-time video processing
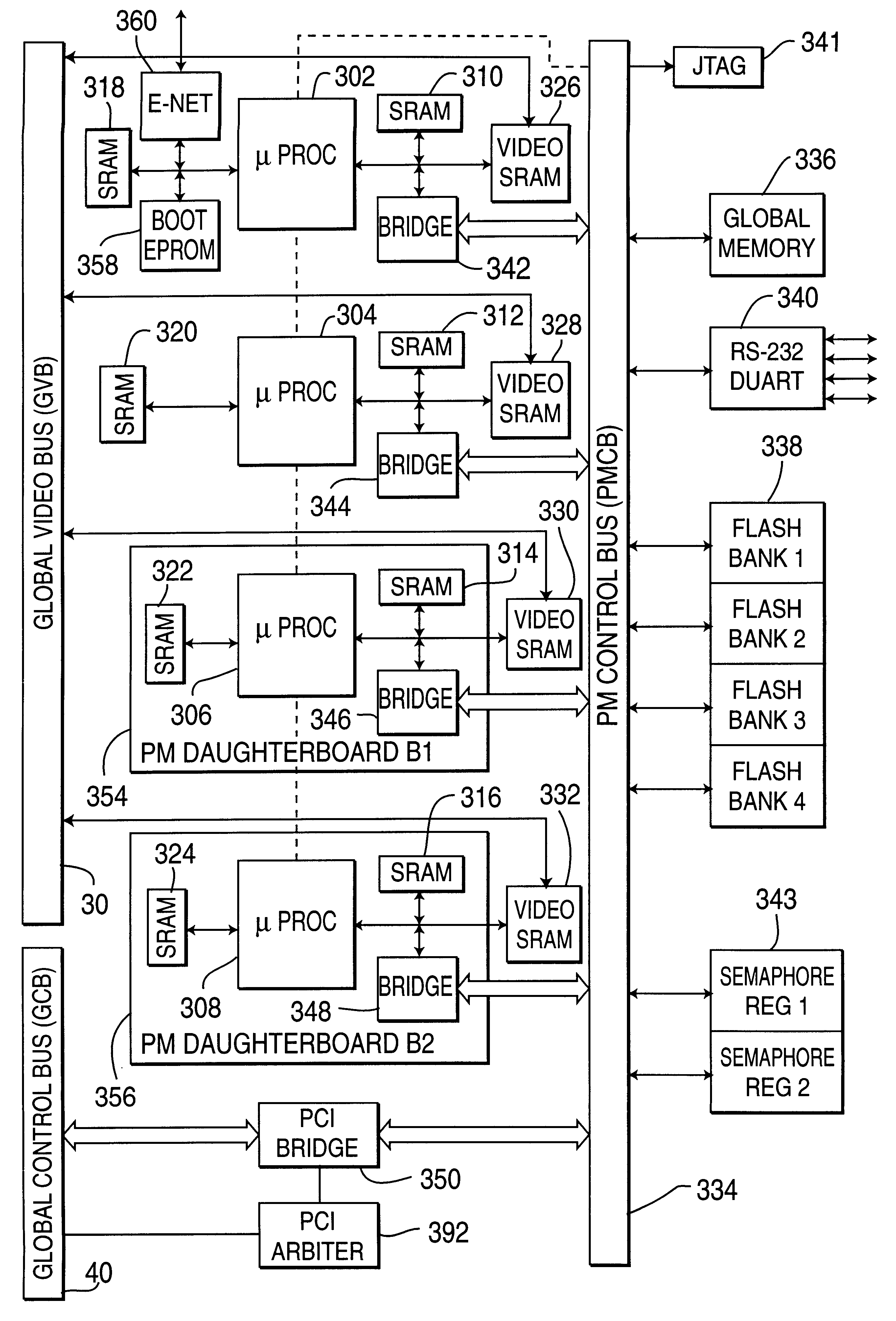
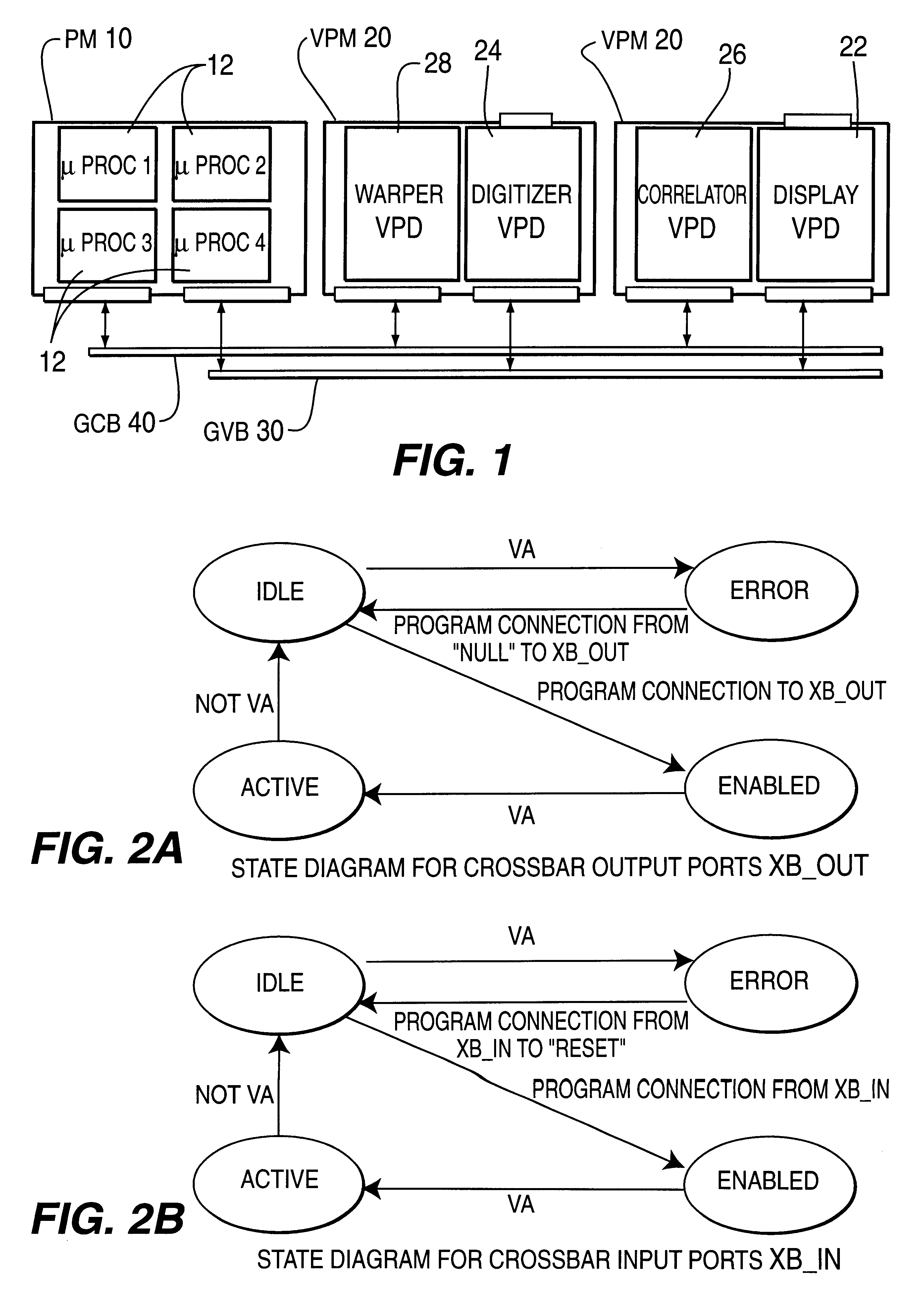
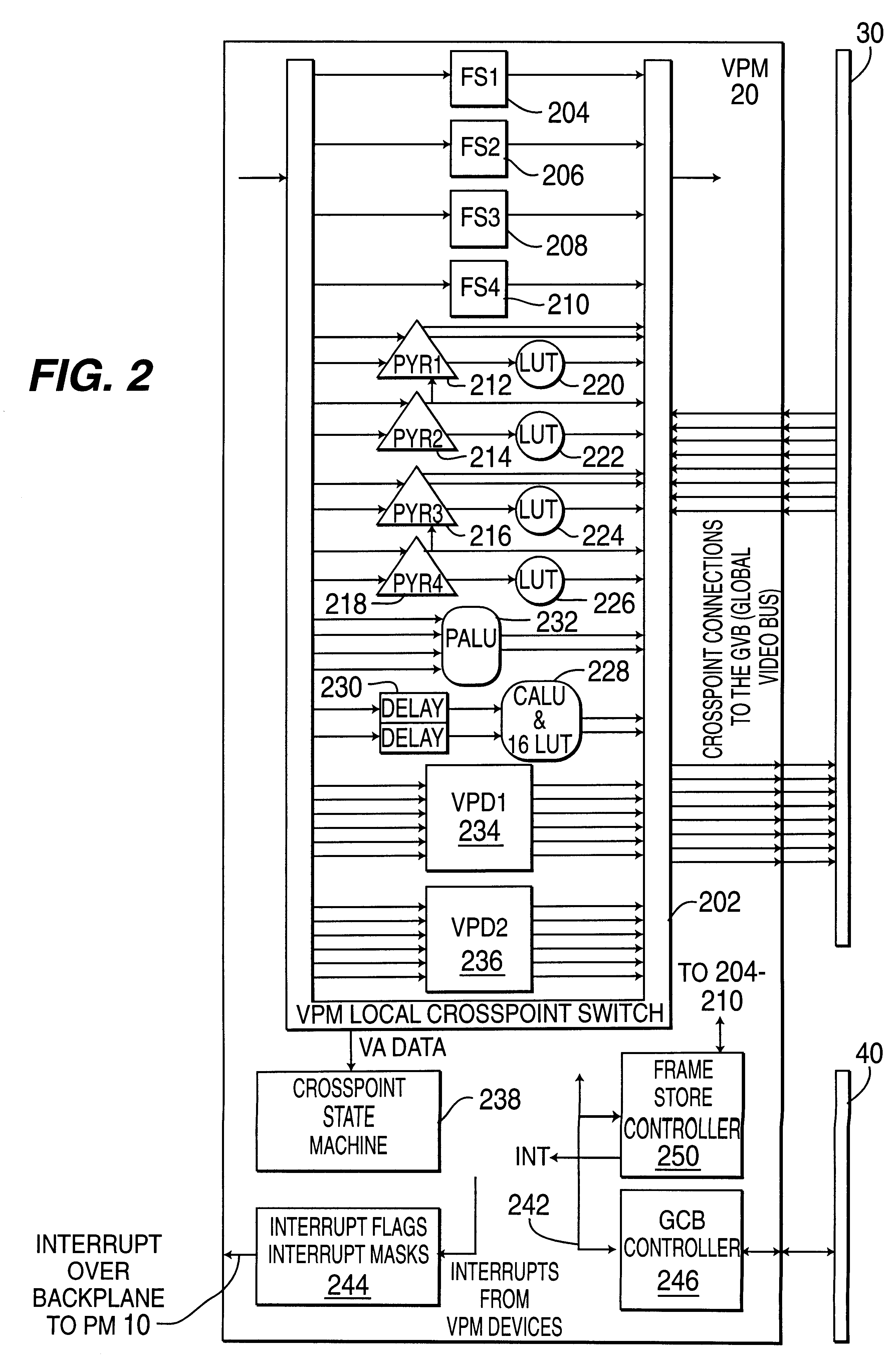
InactiveUS6188381B1Easy to operateReduce control overheadTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsProcess moduleHandling system
A real-time modular video processing system (VPS) which can be scaled smoothly from relatively small systems with modest amounts of hardware to very large, very powerful systems with significantly more hardware. The modular video processing system includes a processing module containing at least one general purpose microprocessor which controls hardware and software operation of the video processing system using control data and which also facilitates communications with external devices. One or more video processing modules are also provided, each containing parallel pipelined video hardware which is programmable by the control data to provide different video processing operations on an input stream of video data. Each video processing module also contains one or more connections for accepting one or more daughterboards which each perform a particular image processing task. A global video bus routes video data between the processing module and each video processing module and between respective processing modules, while a global control bus provides the control data to / from the processing module from / to the video processing modules separate from the video data on the global video bus. A hardware control library loaded on the processing module provides an application programming interface including high level C-callable functions which allow programming of the video hardware as components are added and subtracted from the video processing system for different applications.
Owner:SARNOFF CORP
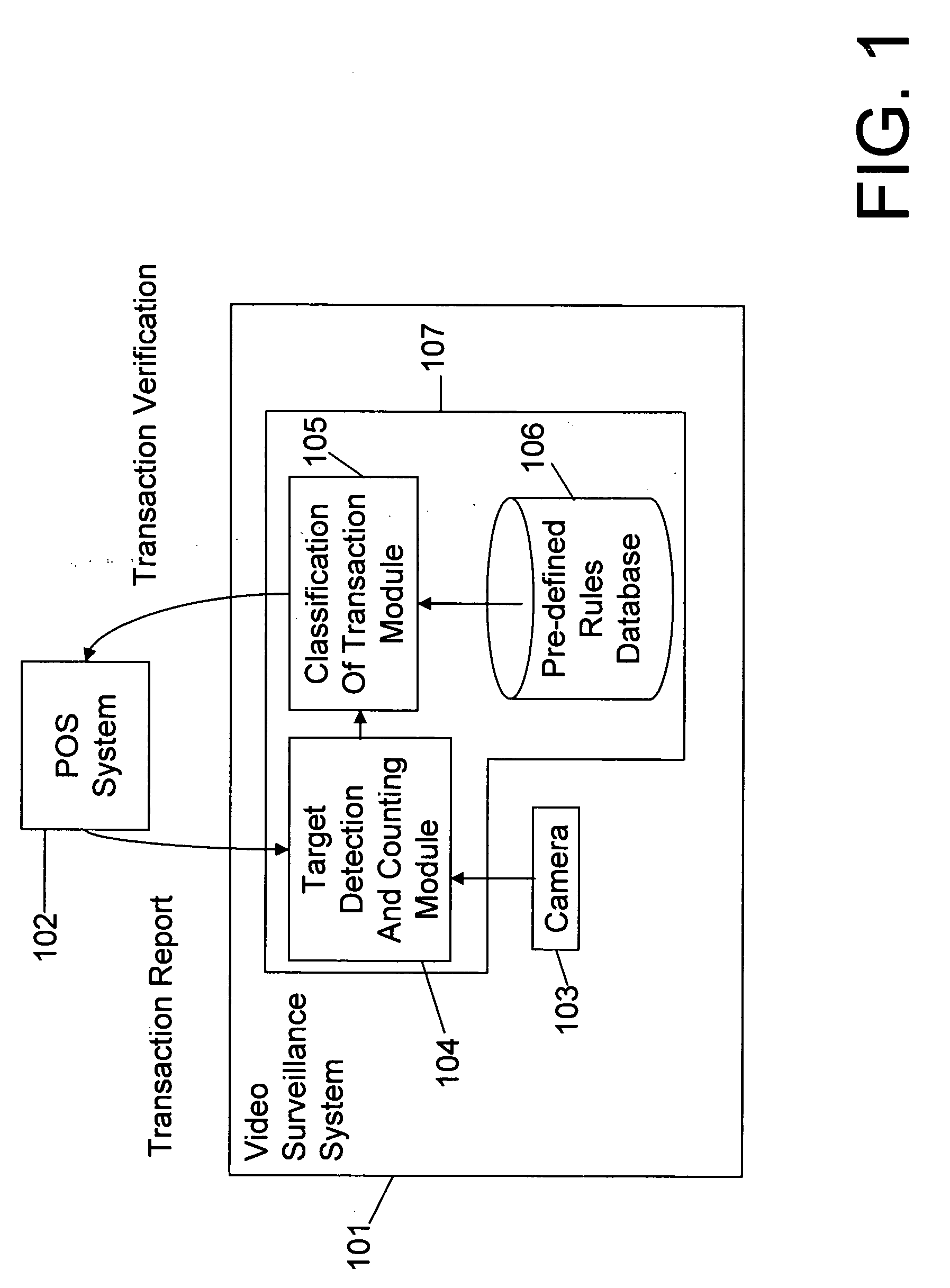
Video surveillance, storage, and alerting system having network management, hierarchical data storage, video tip processing, and vehicle plate analysis
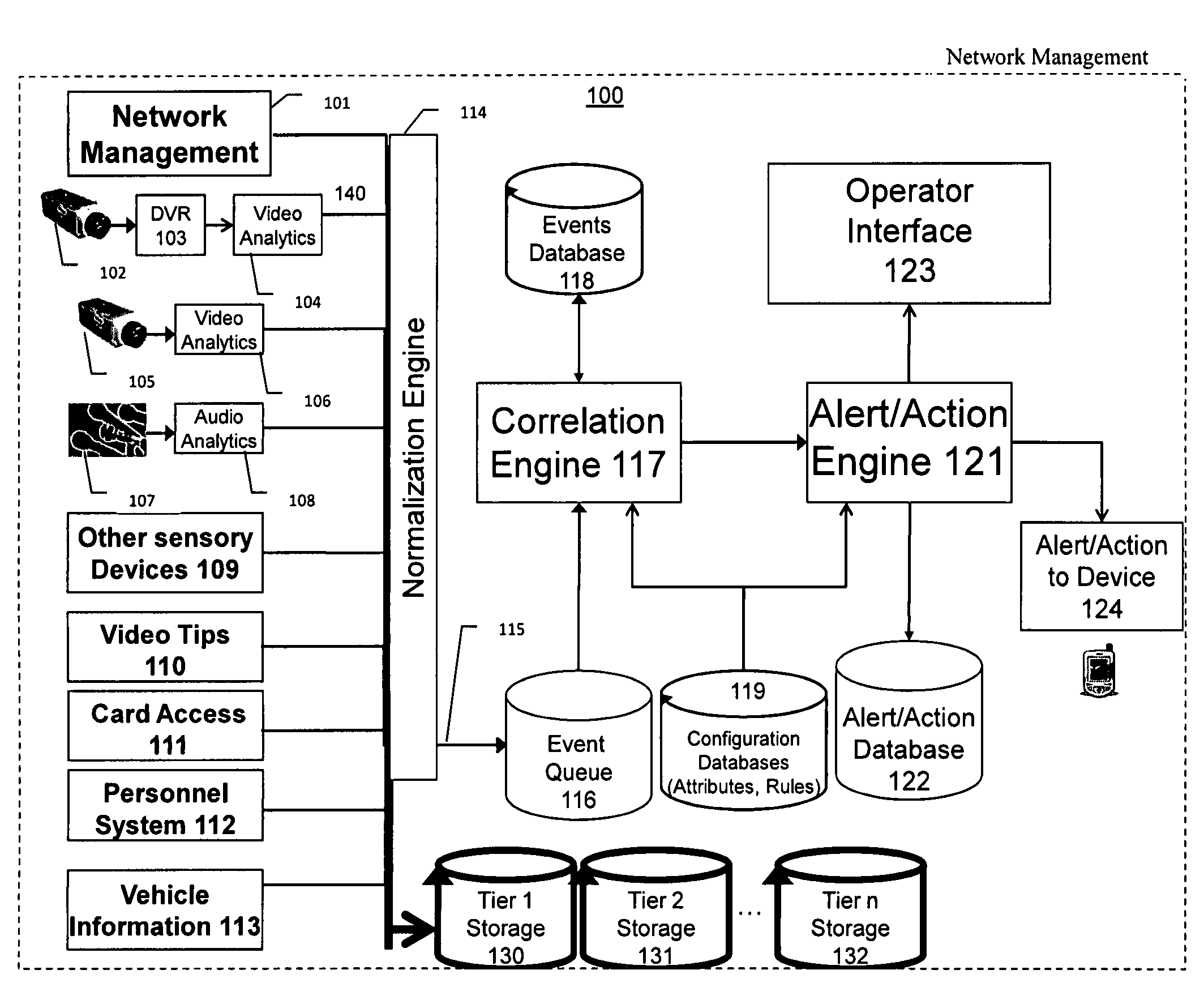
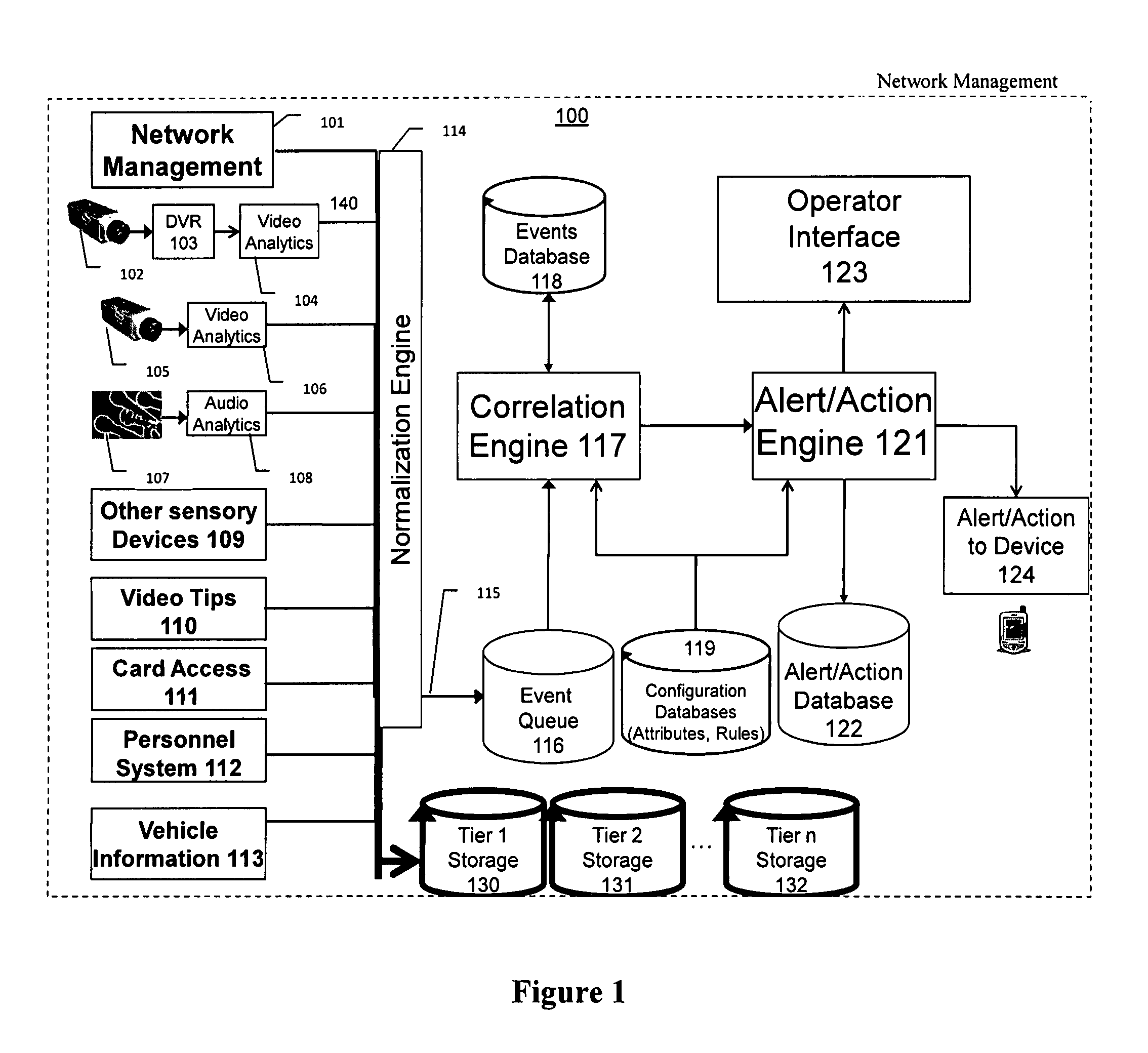
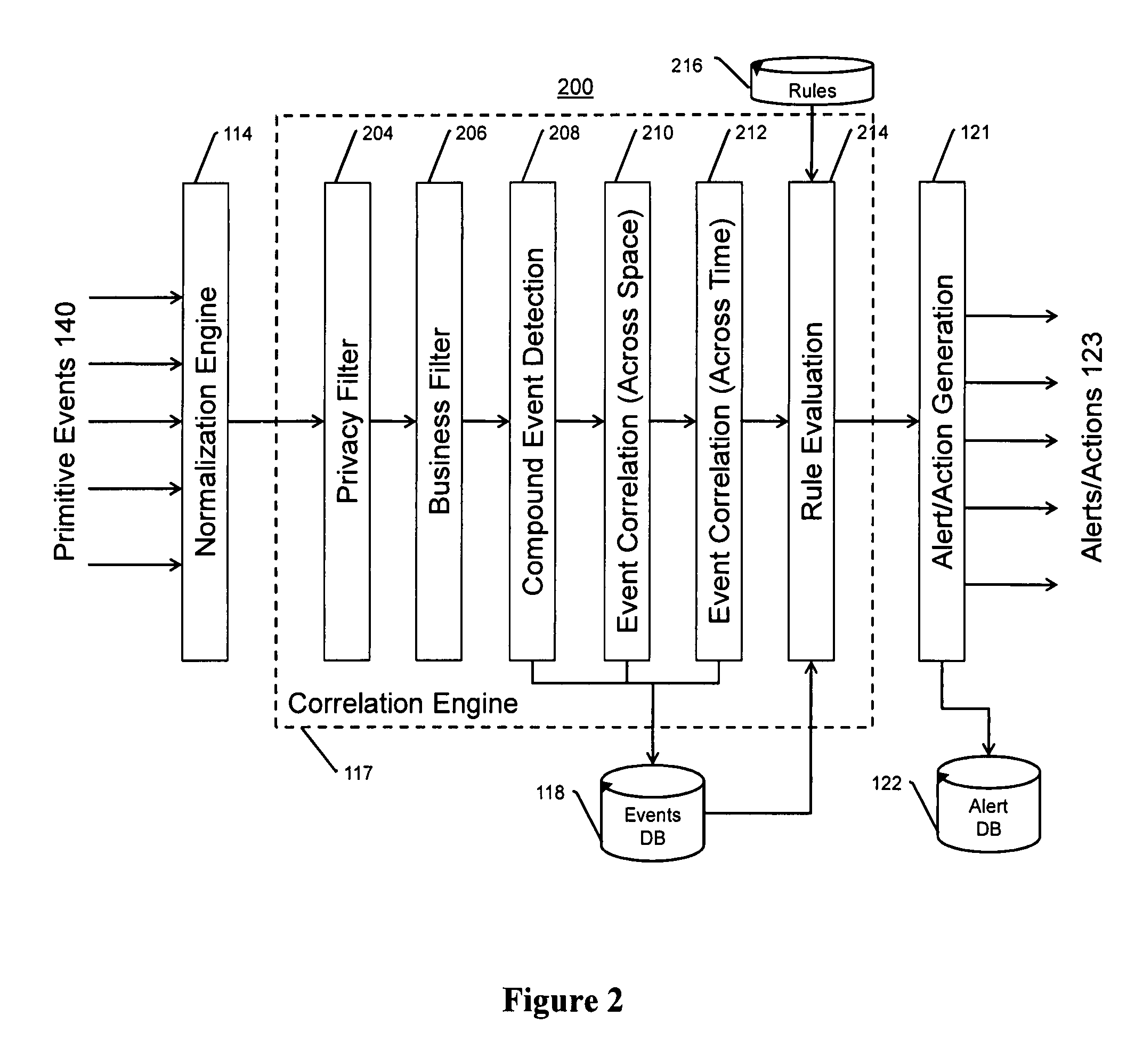
ActiveUS7382244B1Television system detailsFrequency-division multiplex detailsVideo monitoringDriver/operator
The present invention is a video surveillance, storage, and alerting system having surveillance cameras, video analytics devices, audio sensory devices, other sensory devices, and a plurality of data storage devices. A network management module monitors network status of all subsystems including cameras, servers, storage devices, etc. and shows actively monitored areas on a physical map. A vehicle information module retrieves information from a law enforcement database about vehicles detected in the video data based on the vehicle's license plate, including information about stolen vehicles, as well as warrant, wanted person, and mug shot information for registered drivers of the vehicles. Video tips are received and processed from anonymous and non-anonymous sources. A correlation engine correlates primitive events and compound events from each of the subsystems, weighted by attributes of the events, across both space and time, and an alerting engine generates alerts and performs actions based on the correlation. A hierarchical storage manager manages storage of the vast amounts of data, including video data, based on importance of the data calculated from attributes of the data. A privacy filter ensures no private data is detected, correlated, or stored.
Owner:SECURENET SOLUTIONS GRP
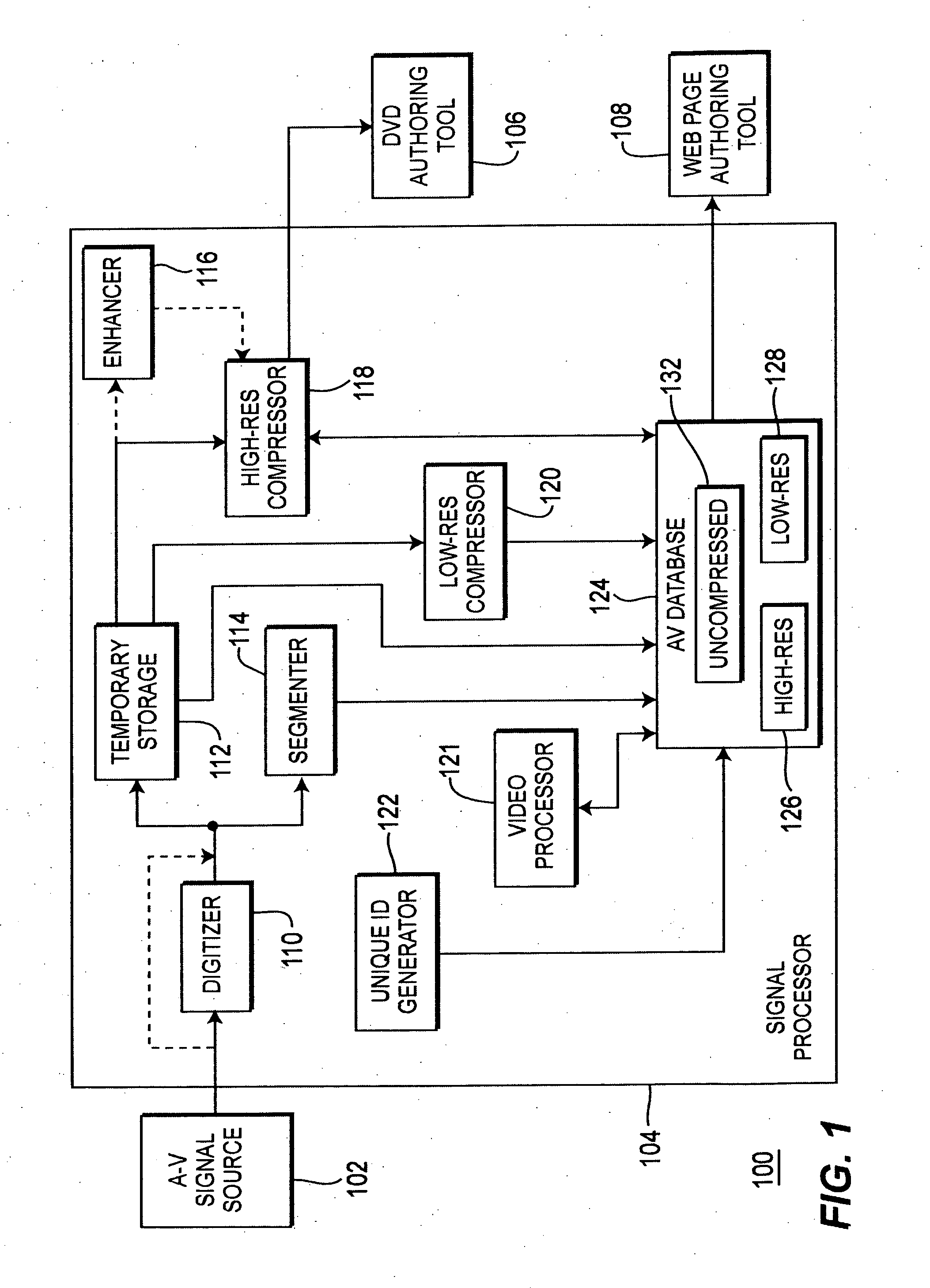
Integrated system and method for processing video
InactiveUS6476826B1Improve productivityShorten the timeElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsDigital computer detailsVideo processingEngineering
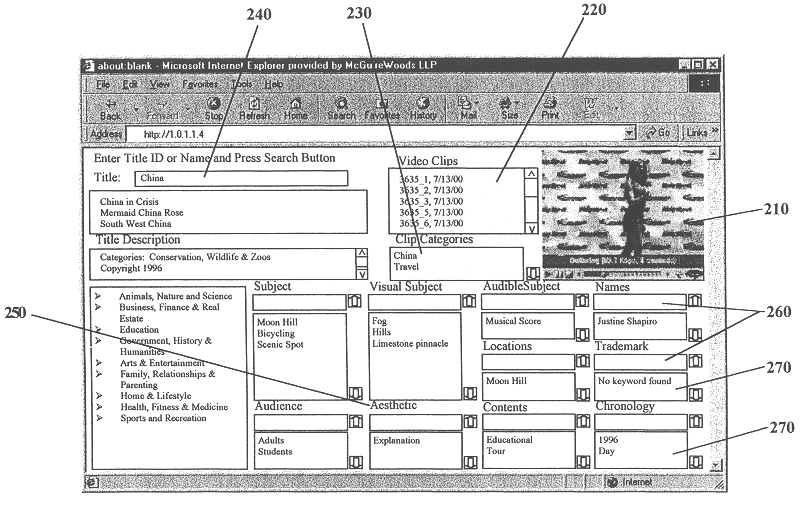
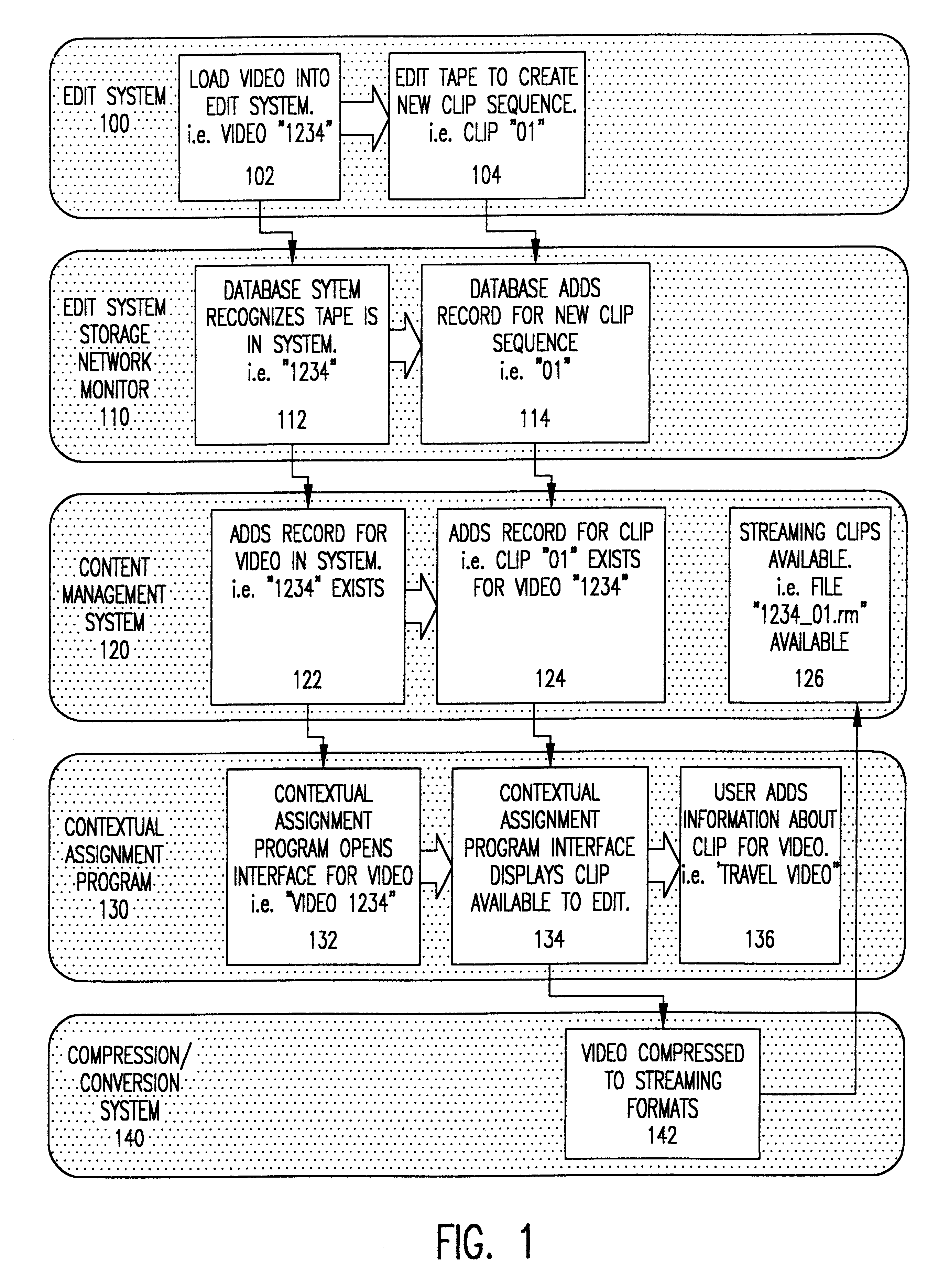
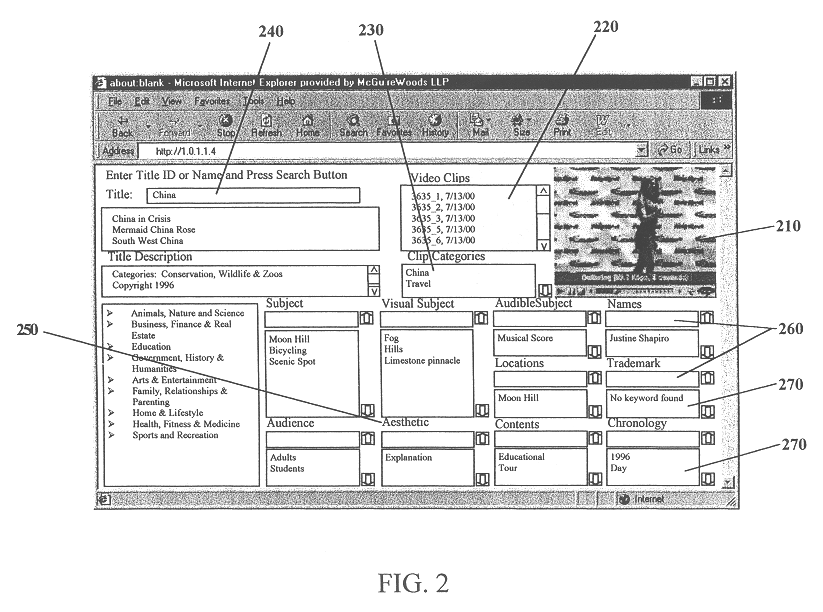
A system and method is provided that can integrate a set of video processing systems for the purpose of increasing productivity and throughput. The integrated system edits video into clips, automatically adds records corresponding to these clips in a centralized database system, adds information about the content of these clips into these records, and controls the compression or conversion of these clips for distribution. The database system is used for managing the clips as well as for the searching of the clips based primarily on the content information added in the above process. Using this process, a digital production line may be built that allows video editors to edit sections from a video tape, have these sections (or clips) be dynamically added to a database system, and provide a mechanism for the editors to apply meta-information to the newly created clips at the same time the clips have been authored. Also, this system provides for the automatic processing of the edited material into alternate formats for such purposes as Internet streaming. The combination of these processes provides significant improvement productivity in the generation of clips, such as video highlights, from complete video.
Owner:VAST
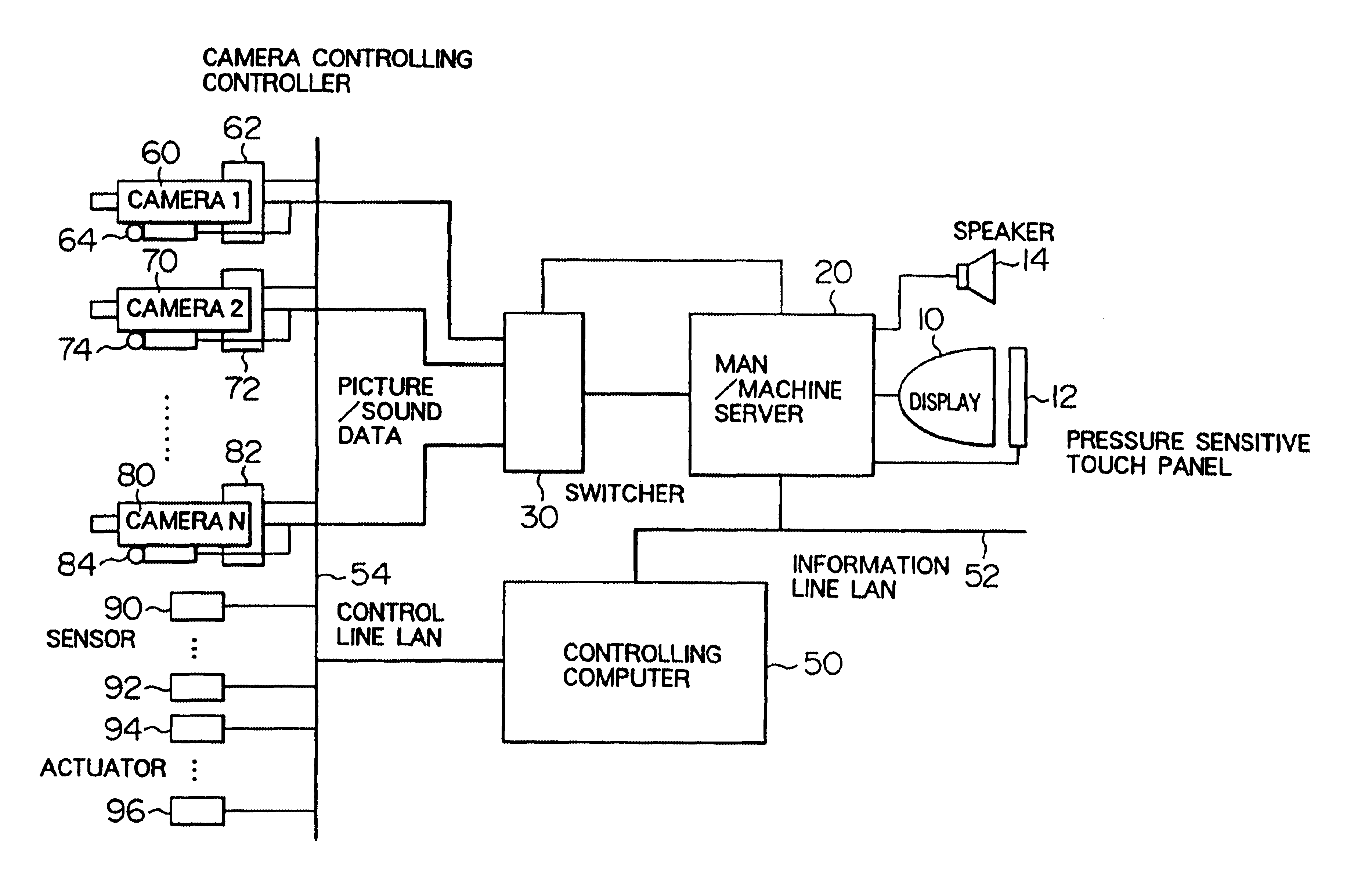
Video or information processing method and processing apparatus, and monitoring method and monitoring apparatus using the same
InactiveUS6965376B2PropagateErroneous operationComputer controlElectric testing/monitoringObject basedVideo processing
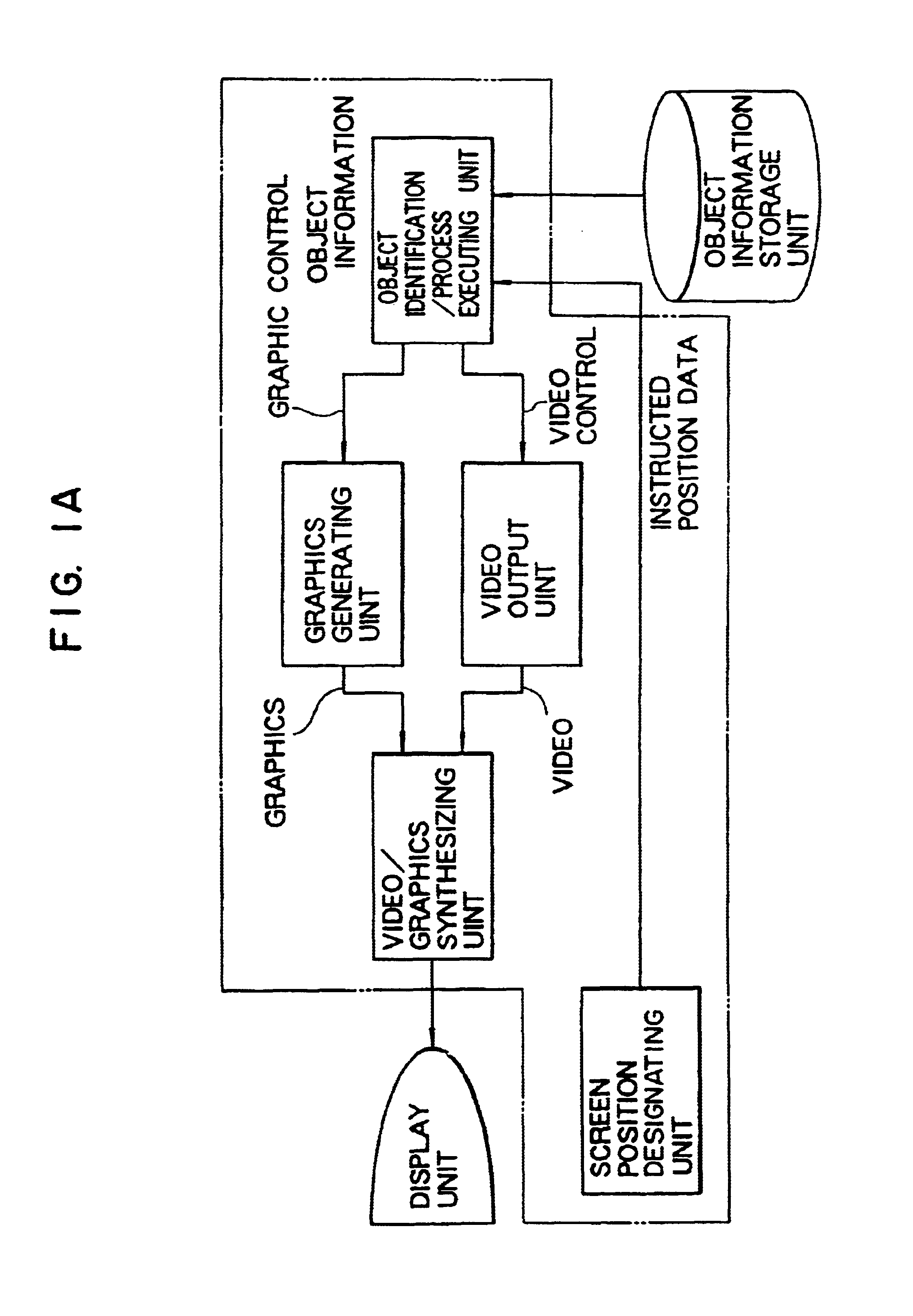
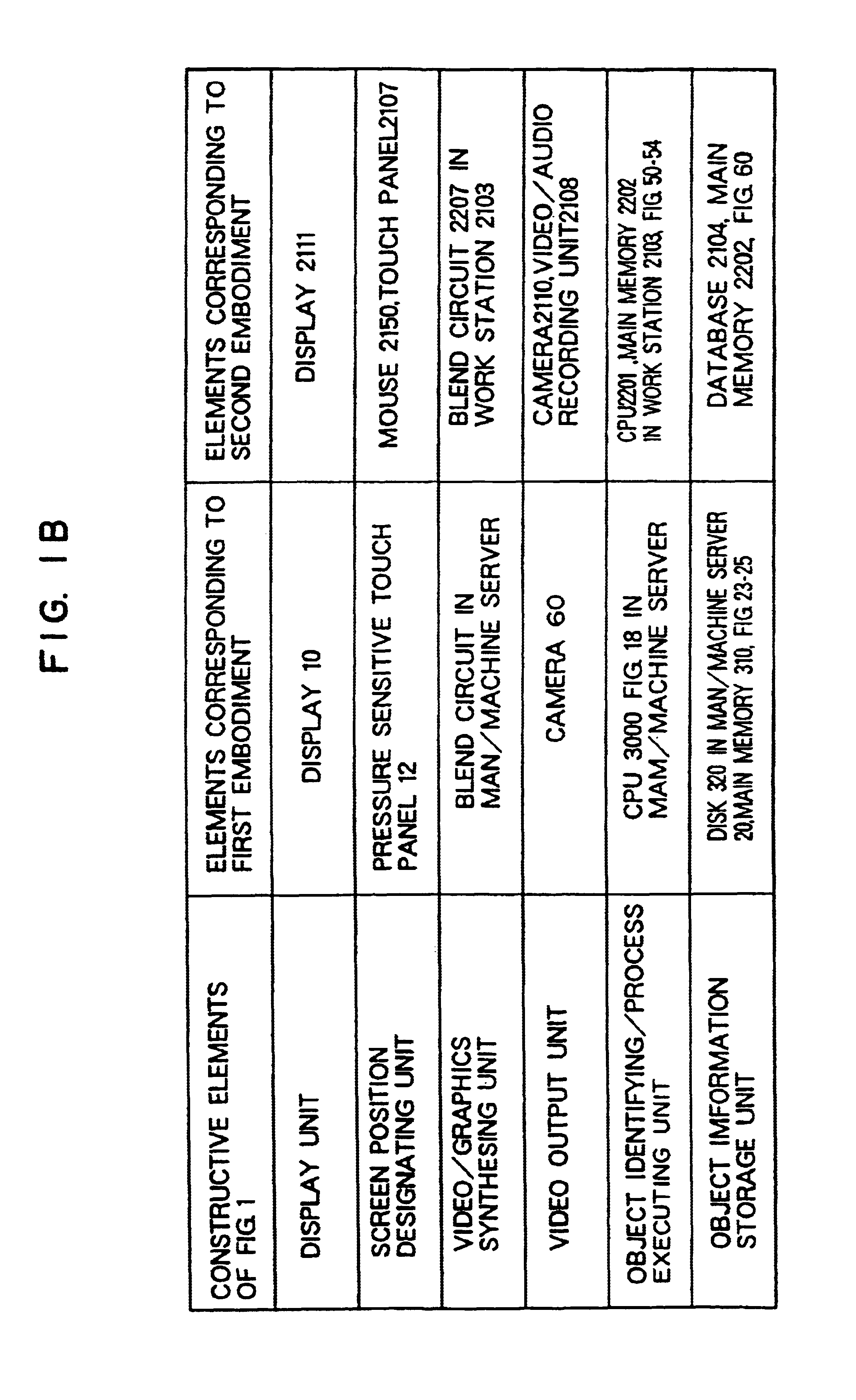
In a remote operation monitoring system and the like, it is a video processing apparatus capable of intuitively grasping an object operated by an operator and an operation result. The video processing apparatus includes a unit (310, 320, 2104, 2202) for storing information about at least one object displayed on a screen of a display unit; a unit (12, 2105) for designating information about the object; a unit (300, 2201) for searching the store unit based upon the designated information, and for obtaining information within the store unit corresponding to the designated information; and also a unit (20, 2103) for performing a process related to the object based on the obtained information. An operator can readily grasp an object to be operated and a result.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
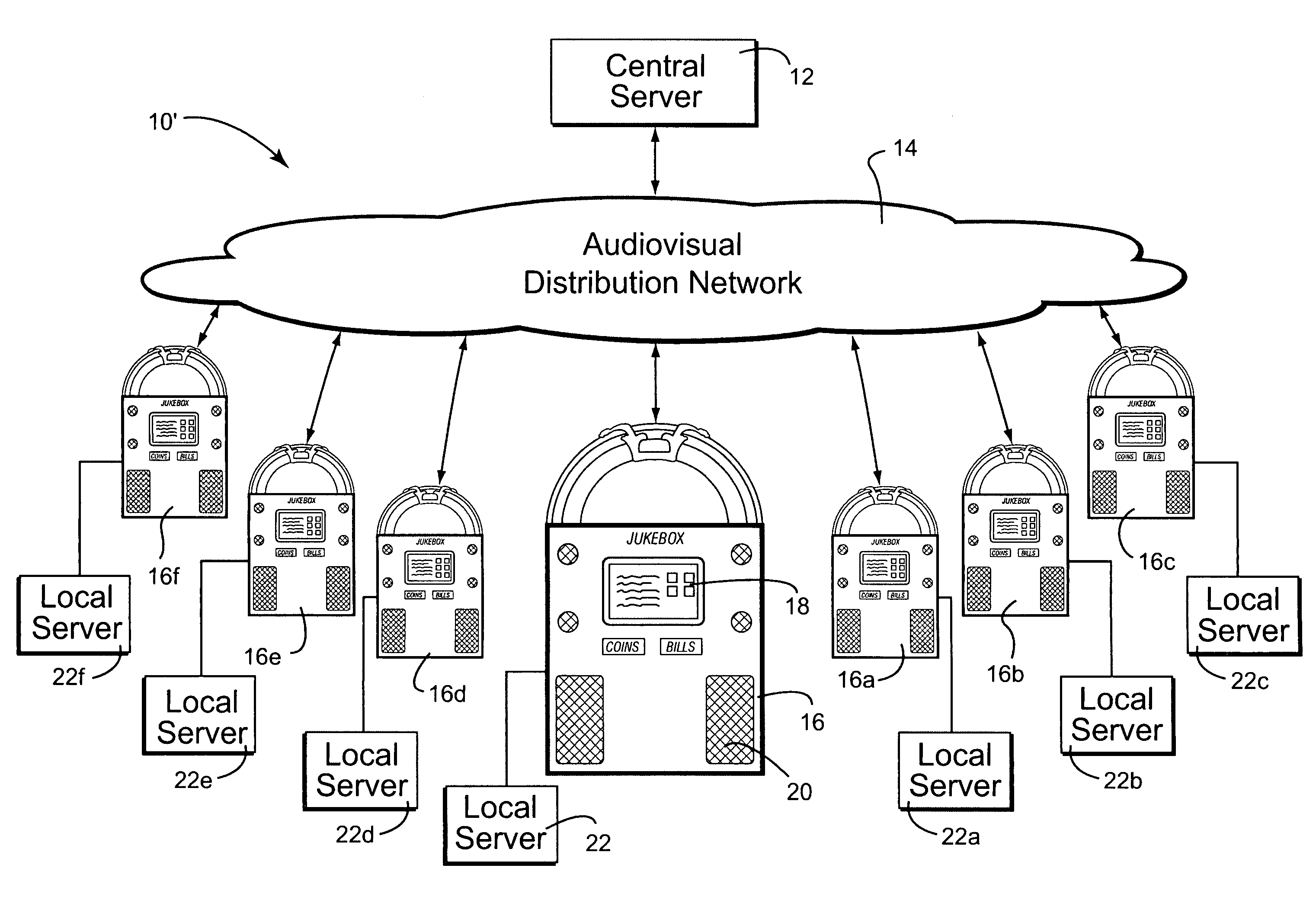
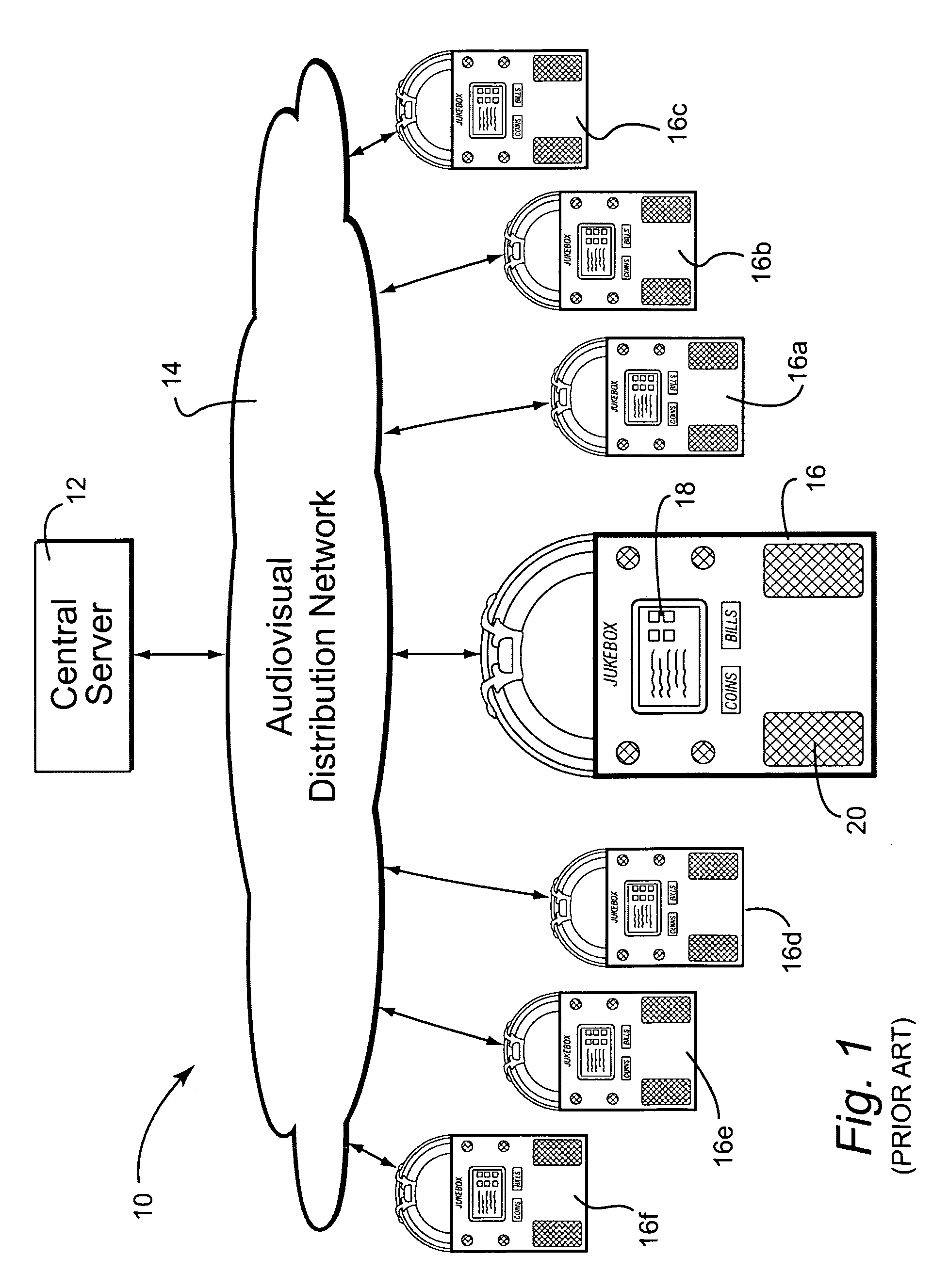
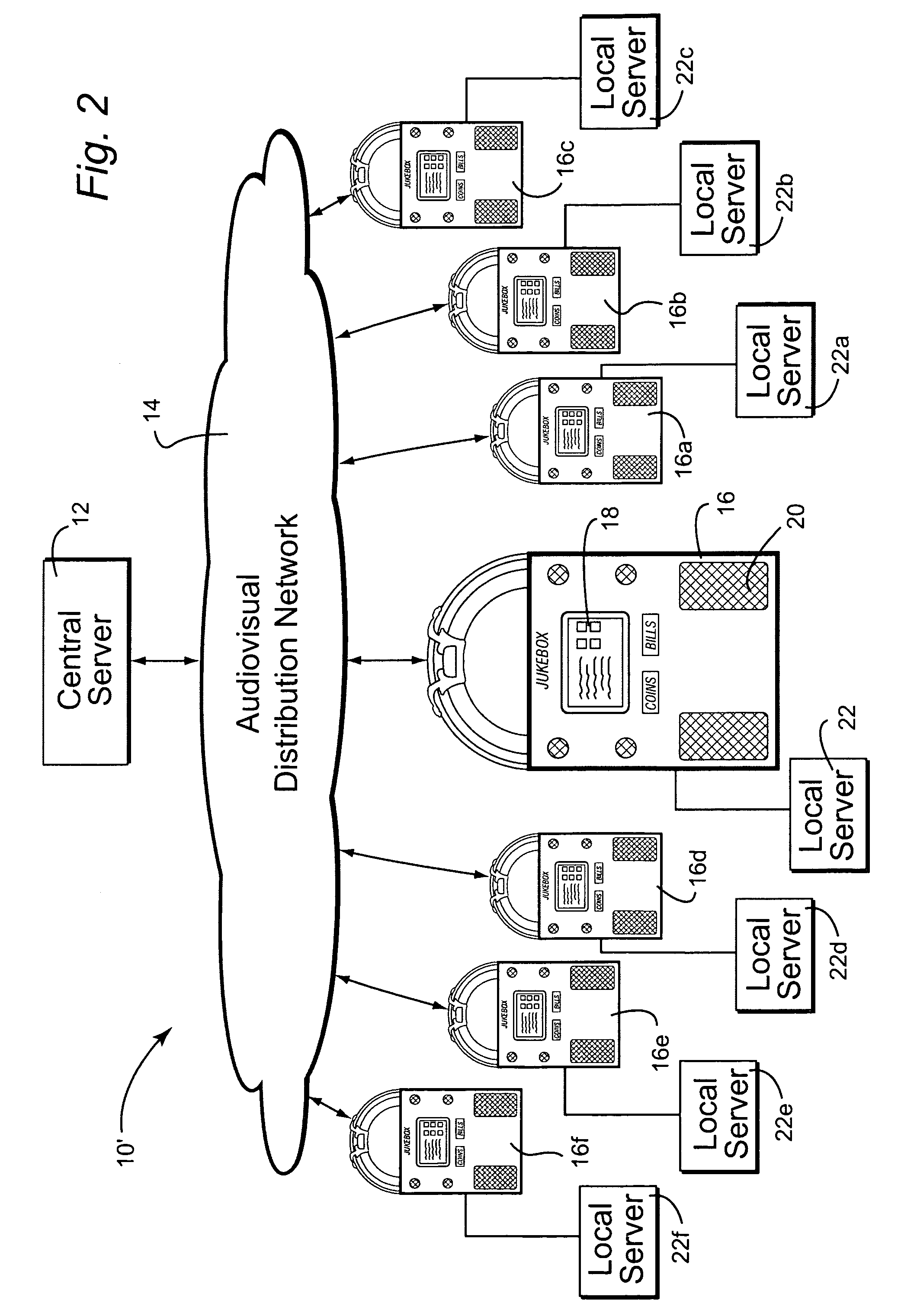
Jukebox with associated video server
ActiveUS20080239887A1Accurate and reliable processReduce needRecord information storageApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingDisplay deviceVideo processing
In certain example embodiments, jukebox systems that have associated video servers for displaying video content on one or more displays or groups of displays external to the jukebox and / or directly on the jukebox are provided. Such video servers may effectively off-load at least some of the video processing load from the jukebox device. Accordingly, video content may be provided to complement and / or further enhance the interactive experience that jukeboxes currently provide, while also enabling patrons not directly in front of the jukebox to participate in the interactive process. Content may be distributed to the jukeboxes and / or video servers via a network. In addition to creating a compelling entertainment experience for patrons, it also is possible to create new revenue opportunities for customers. For example, operators and national account customers and advertising partners may provide additional value to venues through the innovative use of managed video content.
Owner:TOUCHTUNES MUSIC CO LLC
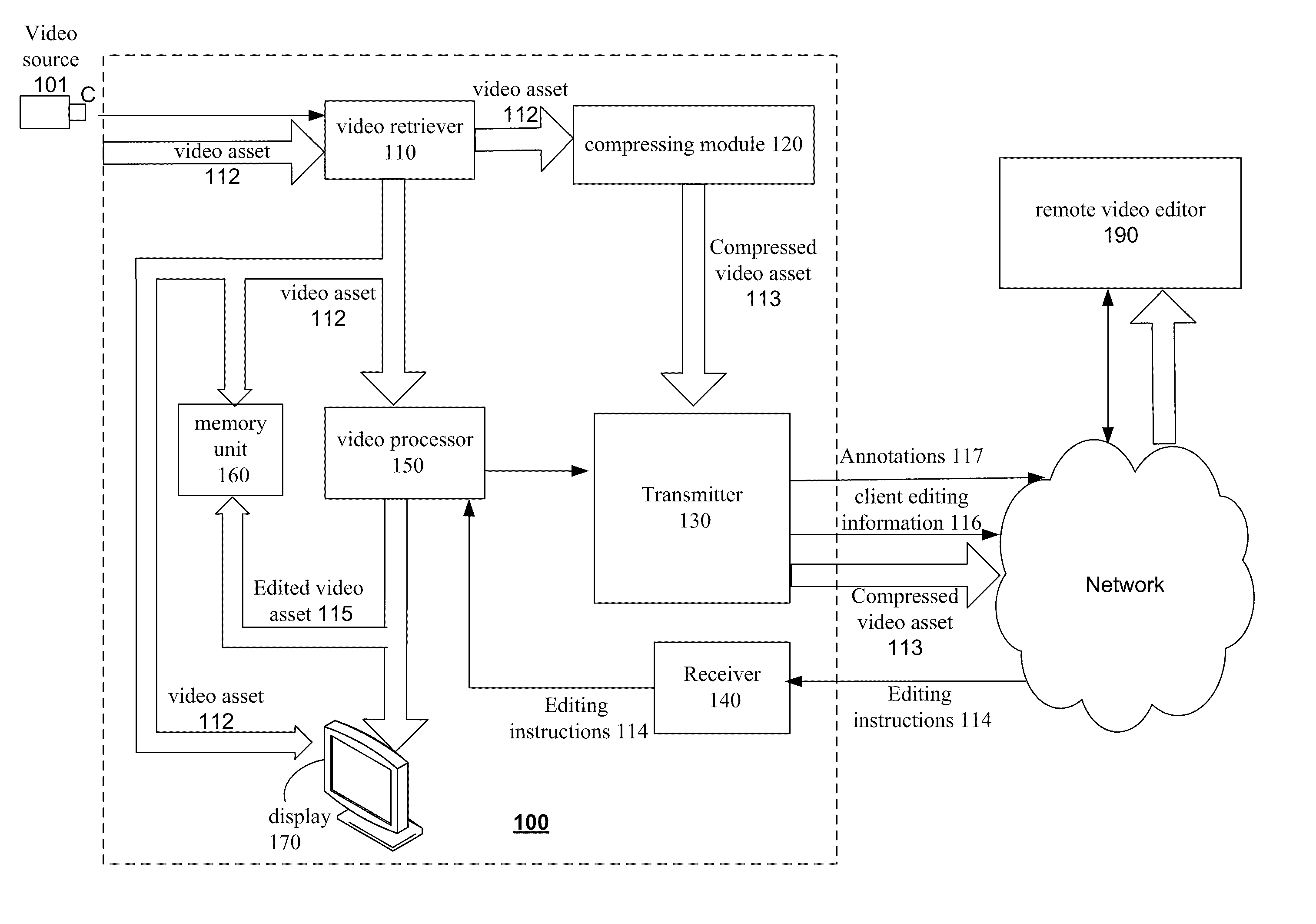
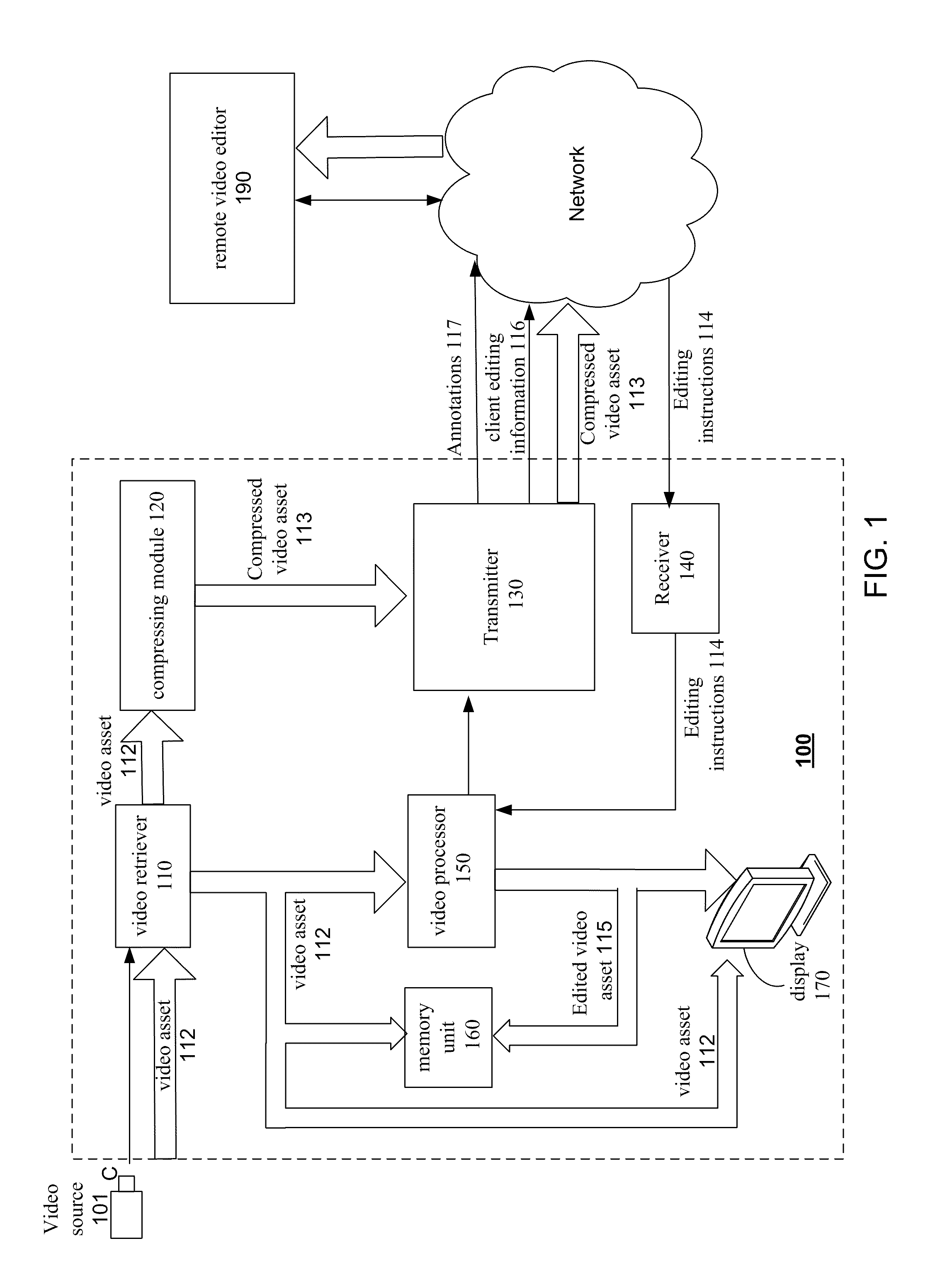
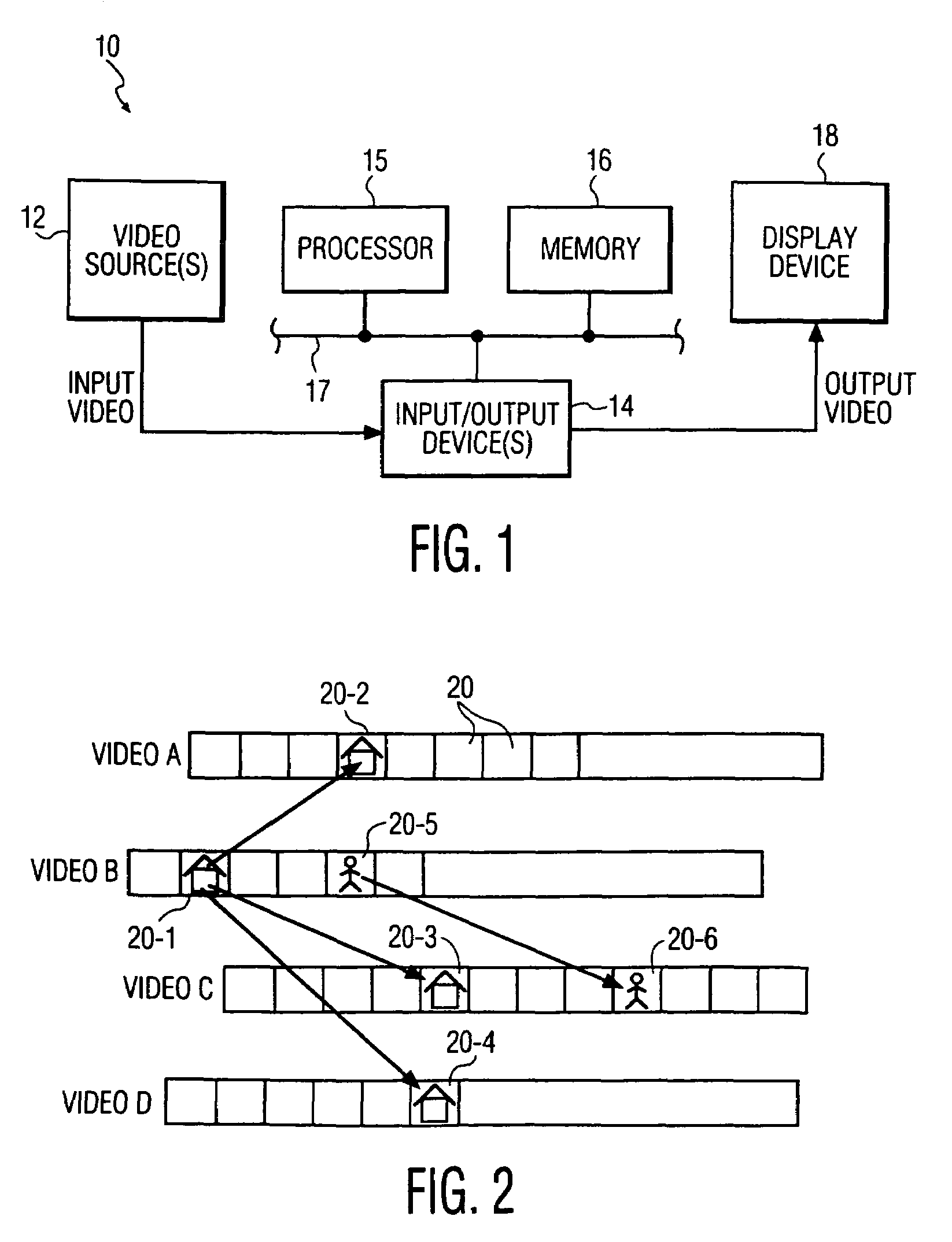
Video processing system and a method for editing a video asset
InactiveUS20110206351A1Television system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsImage resolutionVideo processing
A video processing system and a method for editing a video asset, the method includes: obtaining a video asset of a first resolution; compressing, by compressing module, a video asset to provide a compressed video asset of a second resolution that is lower than the first resolution; transmitting, by a transmitter that is a hardware component, the compressed video asset to a remote video editor; requesting the remote video editor to edit the compressed video asset; receiving editing instructions from the remote video editor, the editing instructions are generated by the remote editor when editing the compressed video asset; processing, by a video processor, the video asset based on the editing instructions to provide an edited video asset; and performing at least one of storing, displaying or publishing the edited video asset.
Owner:GIVOLI TAL
Interactive video manipulation
InactiveUS6954498B1Television system detailsImage analysisInteractive videoComputer graphics (images)
Owner:AVIGILON FORTRESS
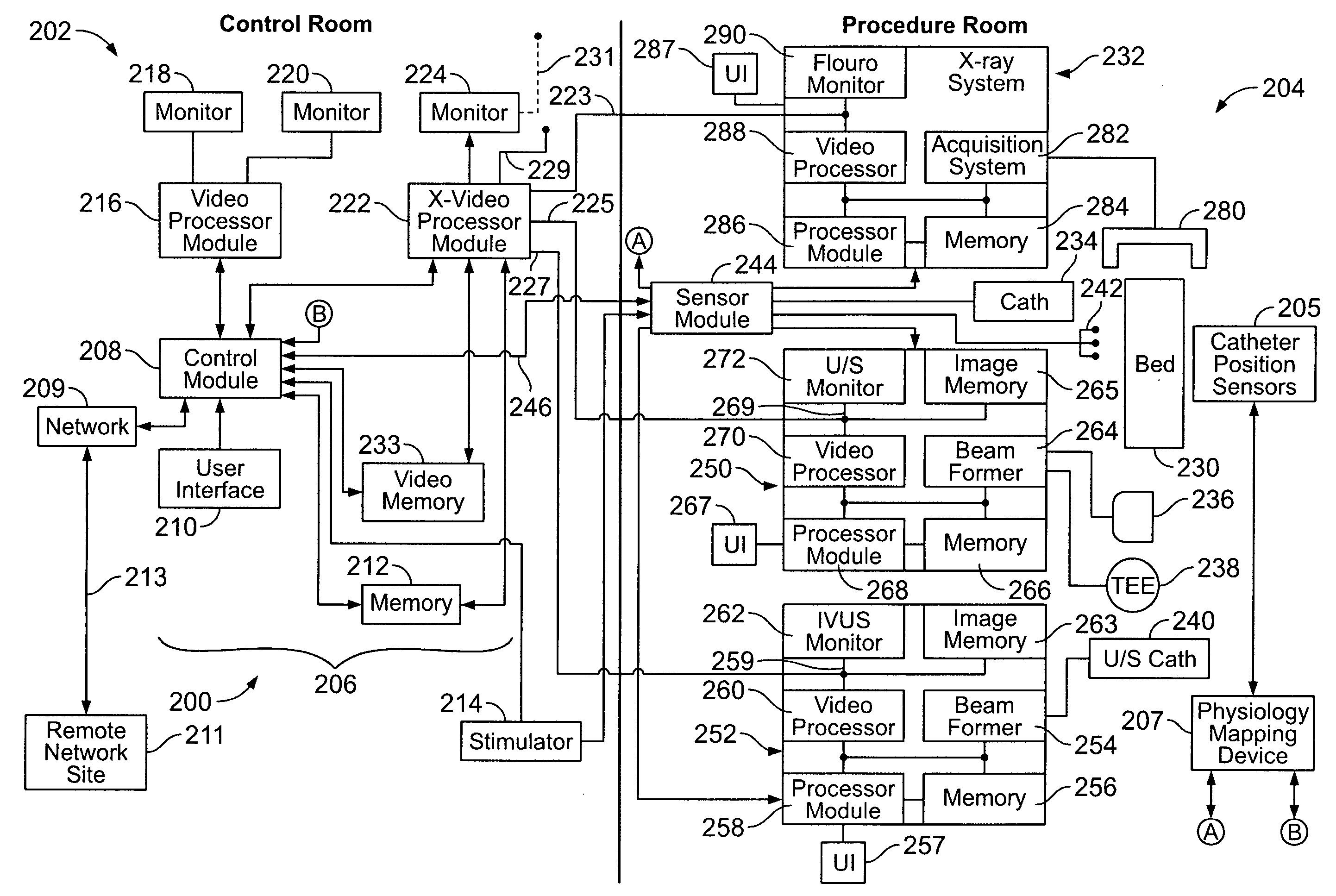
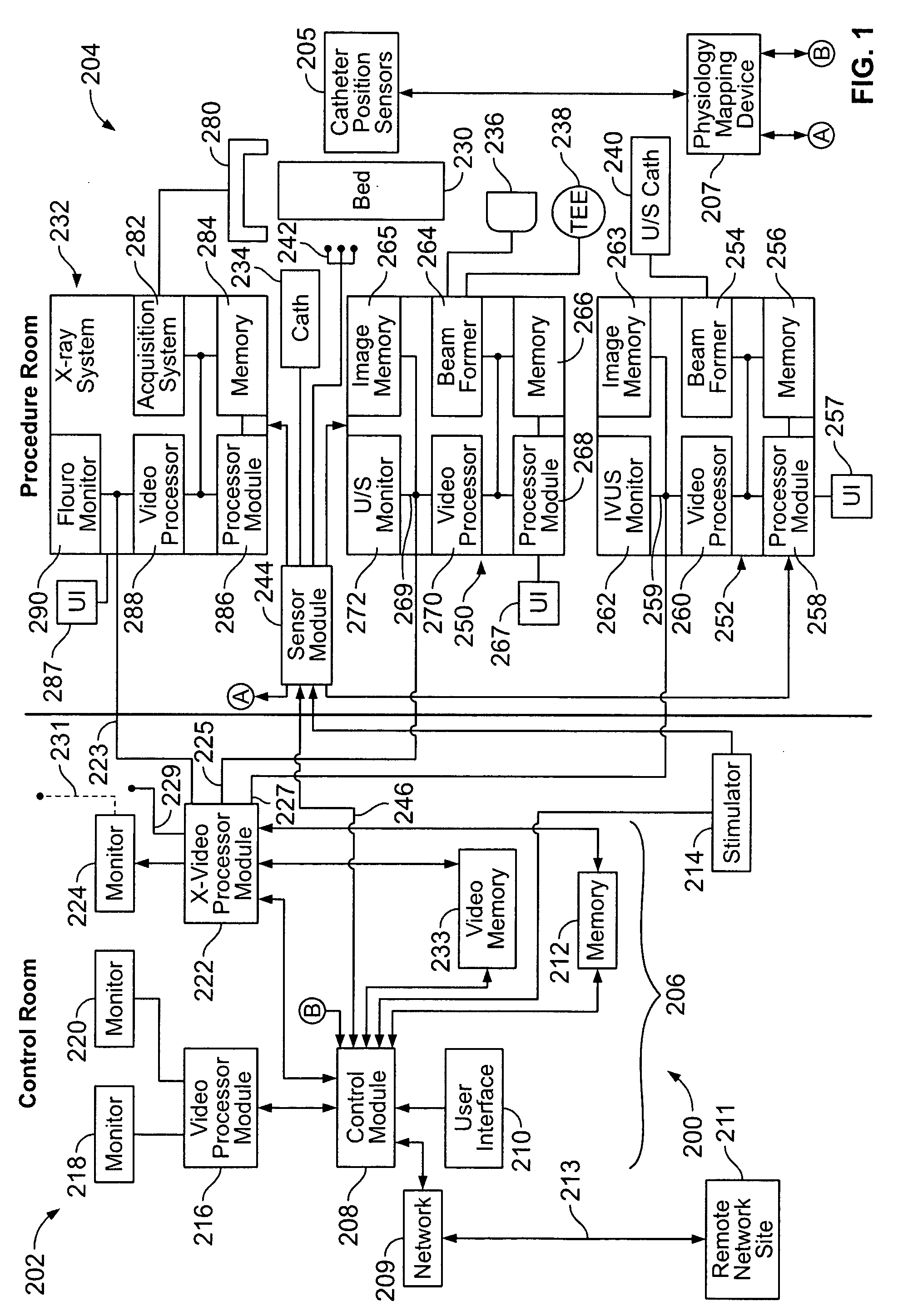
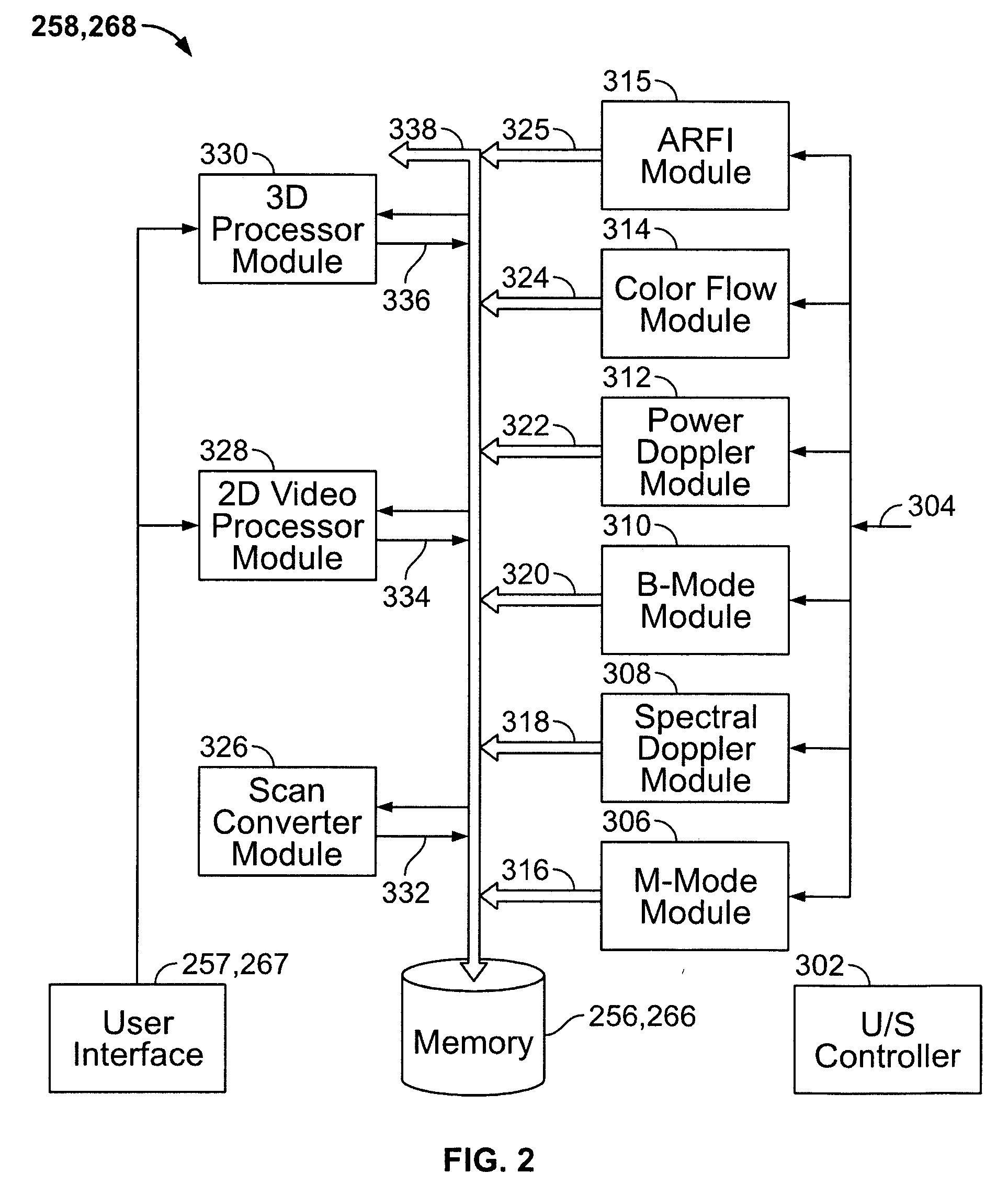
Physiology workstation with real-time fluoroscopy and ultrasound imaging
A physiology workstation is provided that comprises an physiology input configured to receive physiology signals from at least one of an intracardiac (IC) catheter inserted in a subject and surface ECG leads provided on the subject. The physiology signals are obtained during a procedure. A video input is configured to receive image frames, in real-time during the procedure. The image frames contain diagnostic information representative of data samples obtained from the subject during the procedure. A control module controls physiology operations based on user inputs. A display module is controlled by the physiology control module. The display module displays the physiology signals and the image frames simultaneously, in real-time, during the procedure. Optionally, the workstation may include a video processor module that formats the physiology signals into a display format. The video processor module may include an video processor and an external video processor that receive and control display of the physiology signals and image frames, respectively. The image frames may include at least one of ultrasound images obtained from a surface ultrasound probe, intravenous ultrasound images obtained from an ultrasound catheter and fluoroscopy images obtained from a fluoroscopy system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
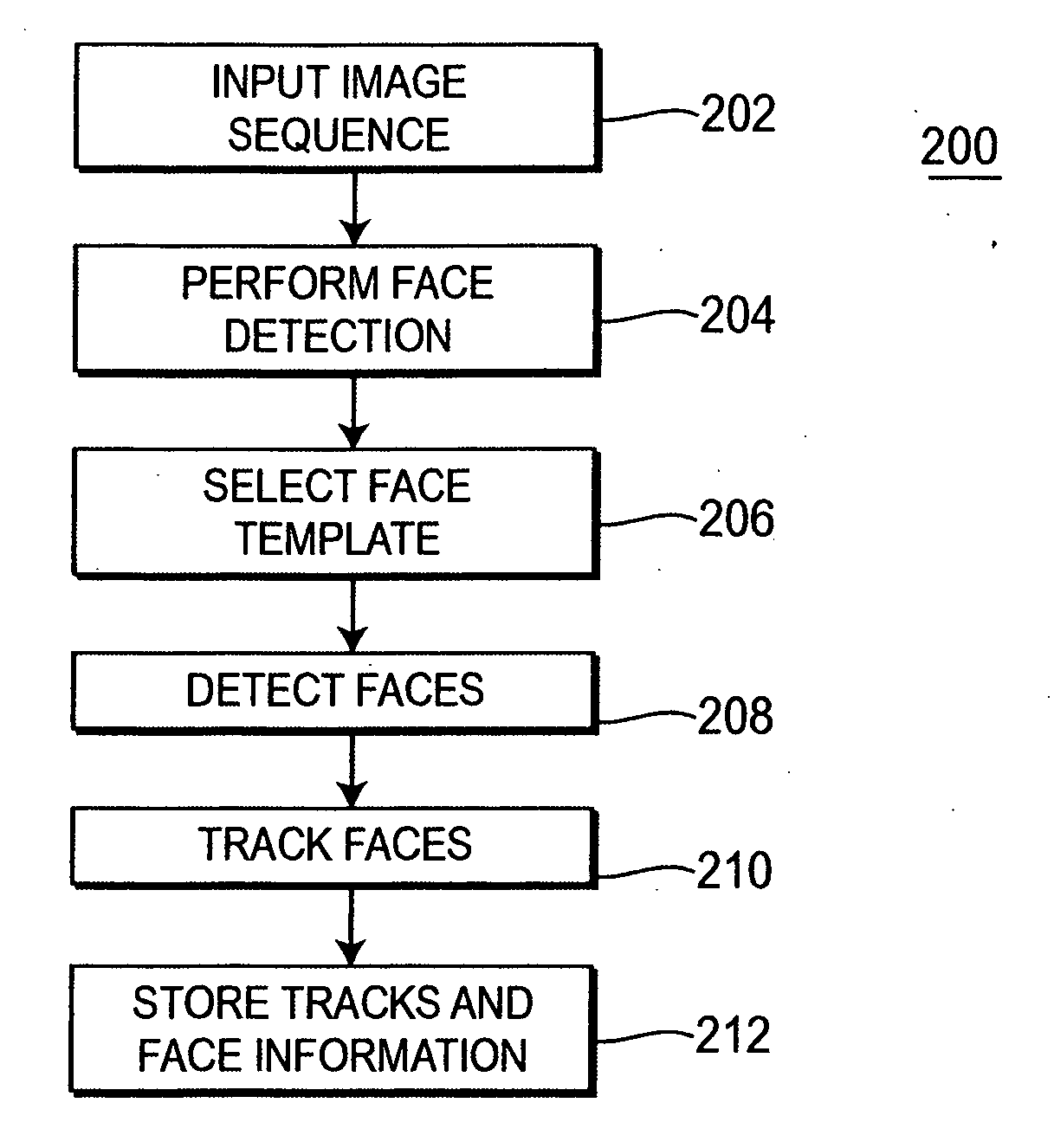
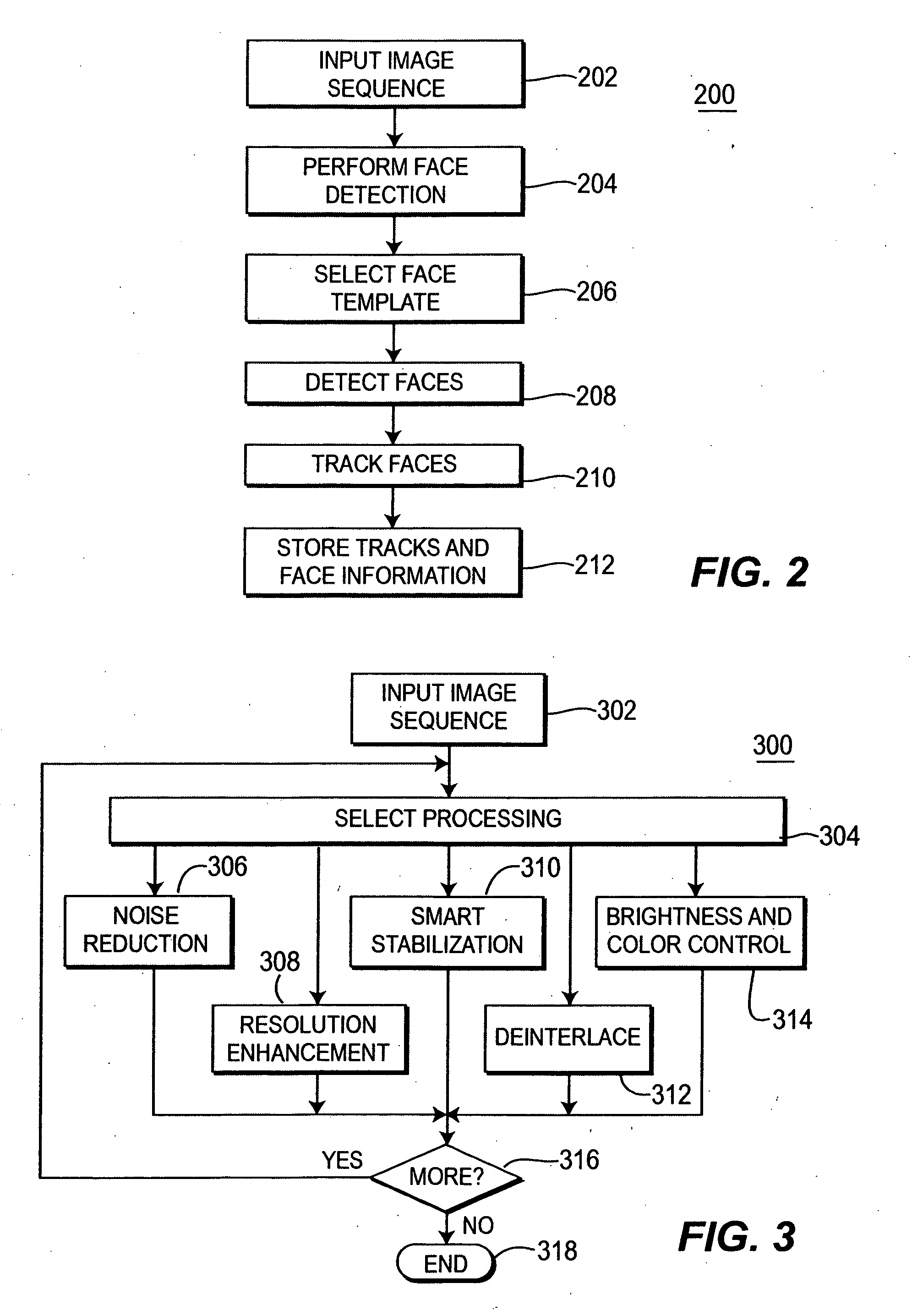
Method and apparatus for enhancing and indexing video and audio signals
InactiveUS20060008152A1Enhanced digital signalHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsRecord information storagePattern recognitionFace detection
A method and apparatus for processing a video sequence is disclosed. The apparatus may include a video processor for detecting and tracking at least one identifiable face in a video sequence. The method may include performing face detection of at least one identifiable face, selecting a face template including face features used to represent the at least one identifiable face, processing the video sequence to detect faces similar to the at least one identifiable face, and tracking the at least one identifiable face in the video sequence.
Owner:KUMAR RAKESH +2
Imaging apparatus and imaging method
InactiveUS20120026297A1Easy to adjustImprove image qualityTelevision system detailsStereoscopic photographyStereo matchingOptical axis
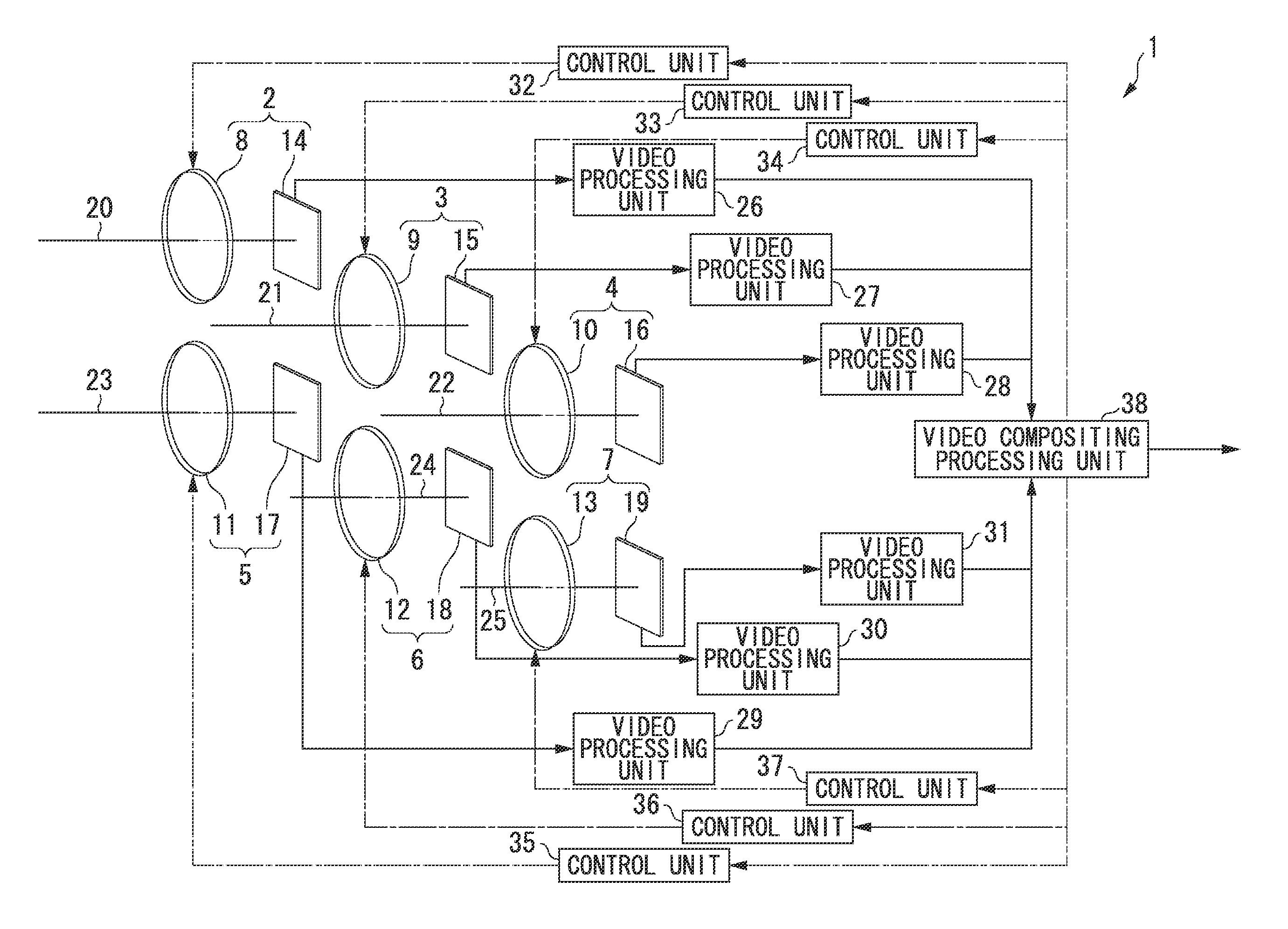
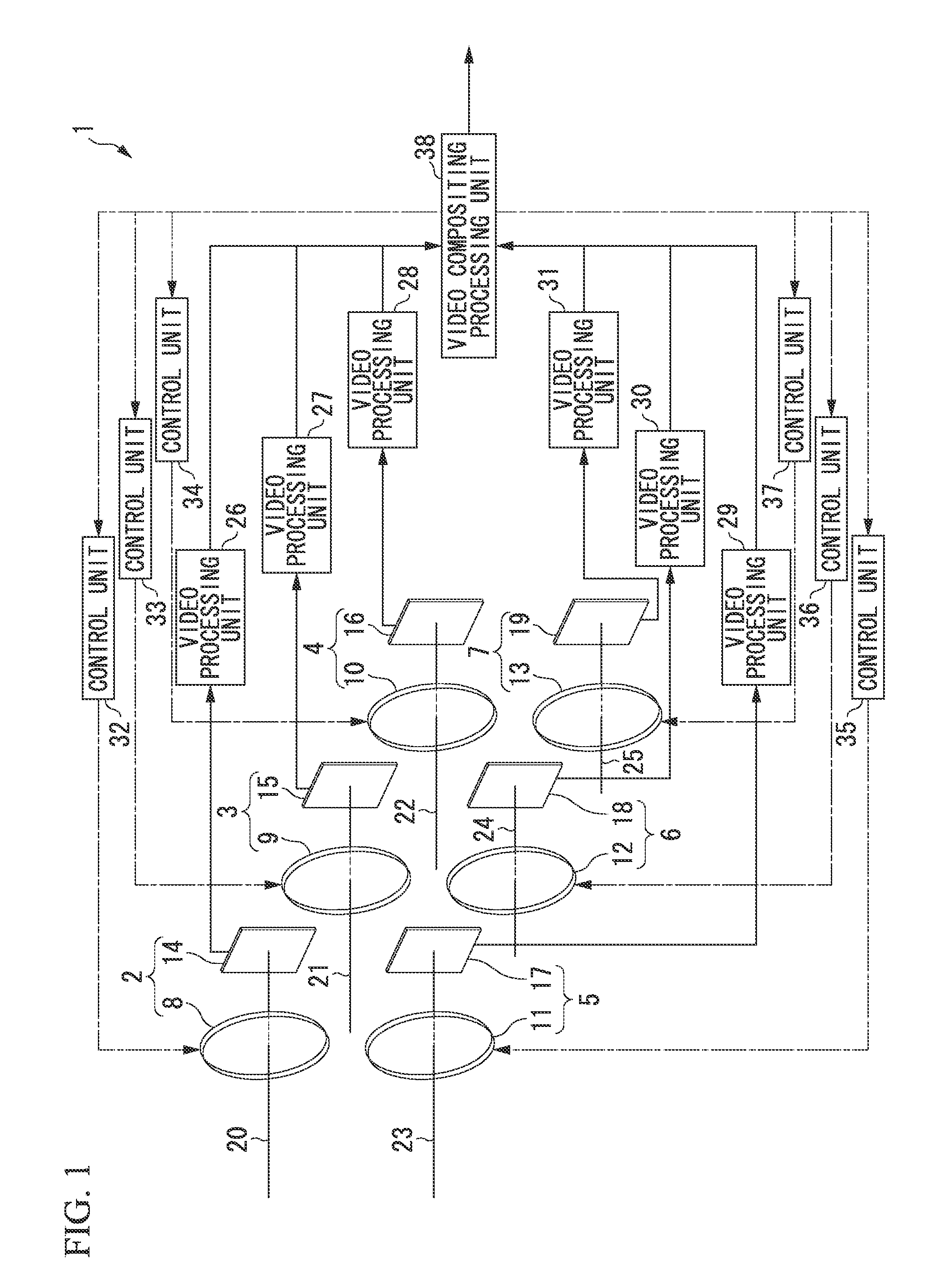
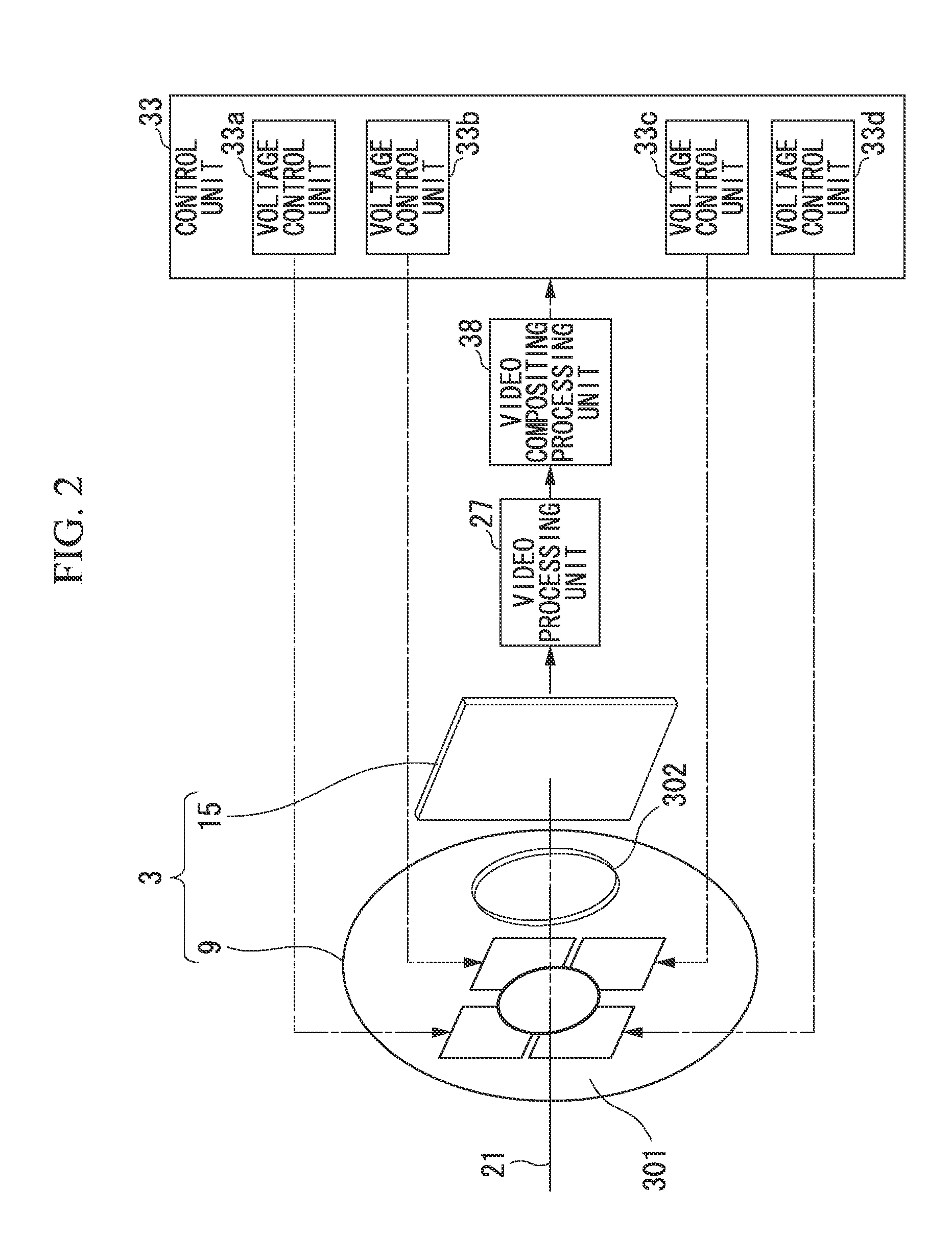
An imaging apparatus includes: a plurality of imaging elements; a plurality of solid lenses that form images on the plurality of imaging elements; a plurality of optical axis control units that control the directions of the optical axes of light that is incident to each of the plurality of imaging elements; a plurality of video processing units that convert photoelectric converted signals output from each of the plurality of imaging elements to video signals; a stereo image processing unit that, by performing stereo matching processing based on the plurality of video signals converted by the plurality of video processing units, determines the amount of shift for each pixel, and generates compositing parameters in which the shift amounts that exceed the pixel pitch of the plurality of imaging elements are normalized to the pixel pitch; and a video compositing processing unit that generates high-definition video by compositing the video signals converted by the plurality of video processing units, based on the compositing parameters generated by the stereo image processing unit.
Owner:SHARP KK
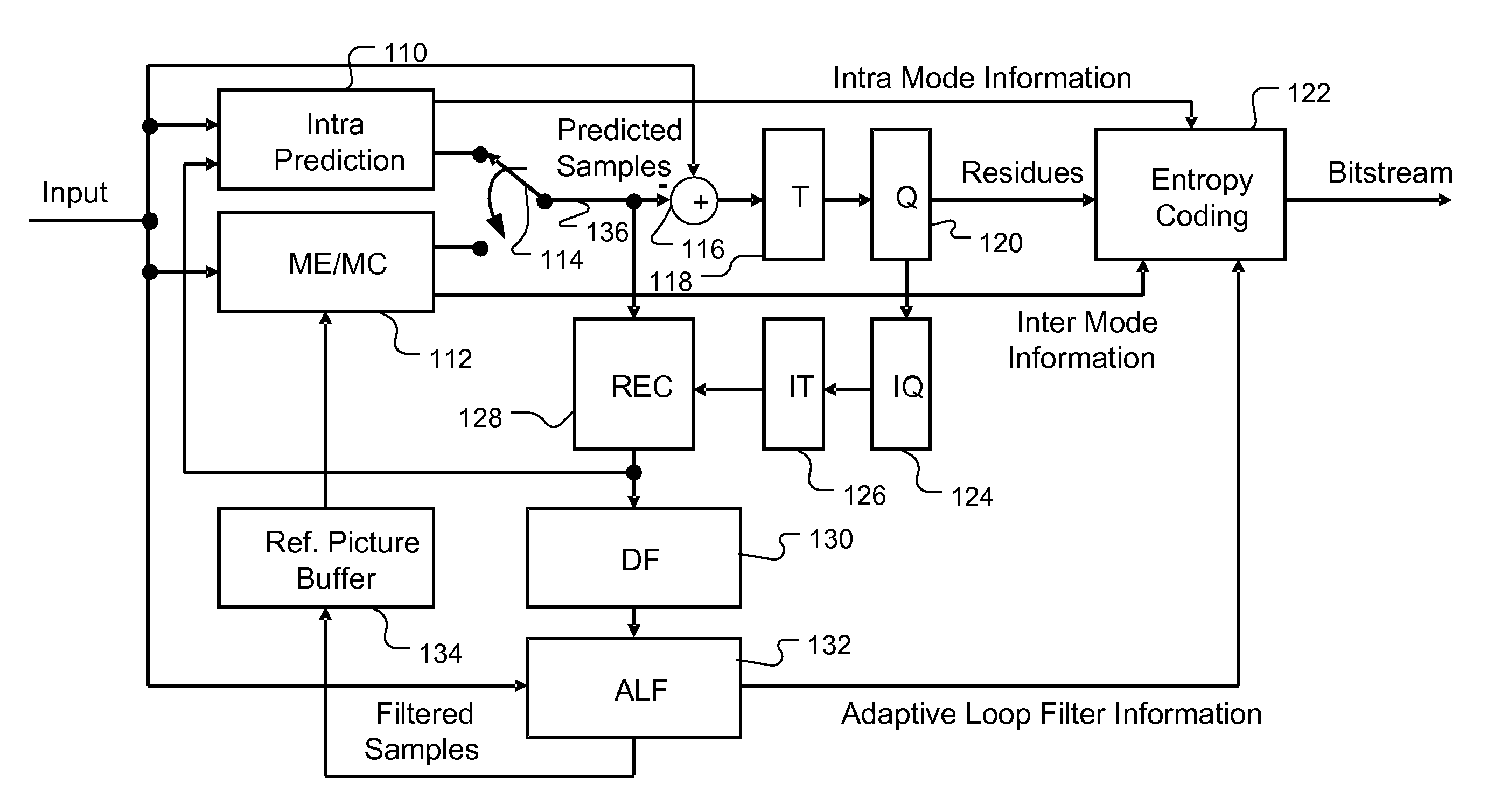
Apparatus and method of adaptive offset for video coding
ActiveUS20110305274A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionOriginal dataVideo encoding
An apparatus and method for content adaptive offset restoration are described. In video processing system, due to various mathematic operations applied to the data, the mean intensity of the processed video data may be shifted from mean intensity of original data. The intensity offset will result in noticeable artifacts. Accordingly adaptive offset restoration is disclosed which derives intensity offset for a region of a picture based on the dynamic characteristics of underlying pixels. According to the characteristics measurement of underlying pixels, the pixels in each region are classified into classes and an intensity offset is determined for each class. The characteristics measurement may be based on pixel patterns at an underlying pixel and the characteristics may be related to edge, peak and valley at the underlying pixel. Alternatively, the characteristics measurement may be based on pixel intensity of an underlying pixel and the pixel intensity is partitioned into multiple bands for classification.
Owner:HFI INNOVATION INC
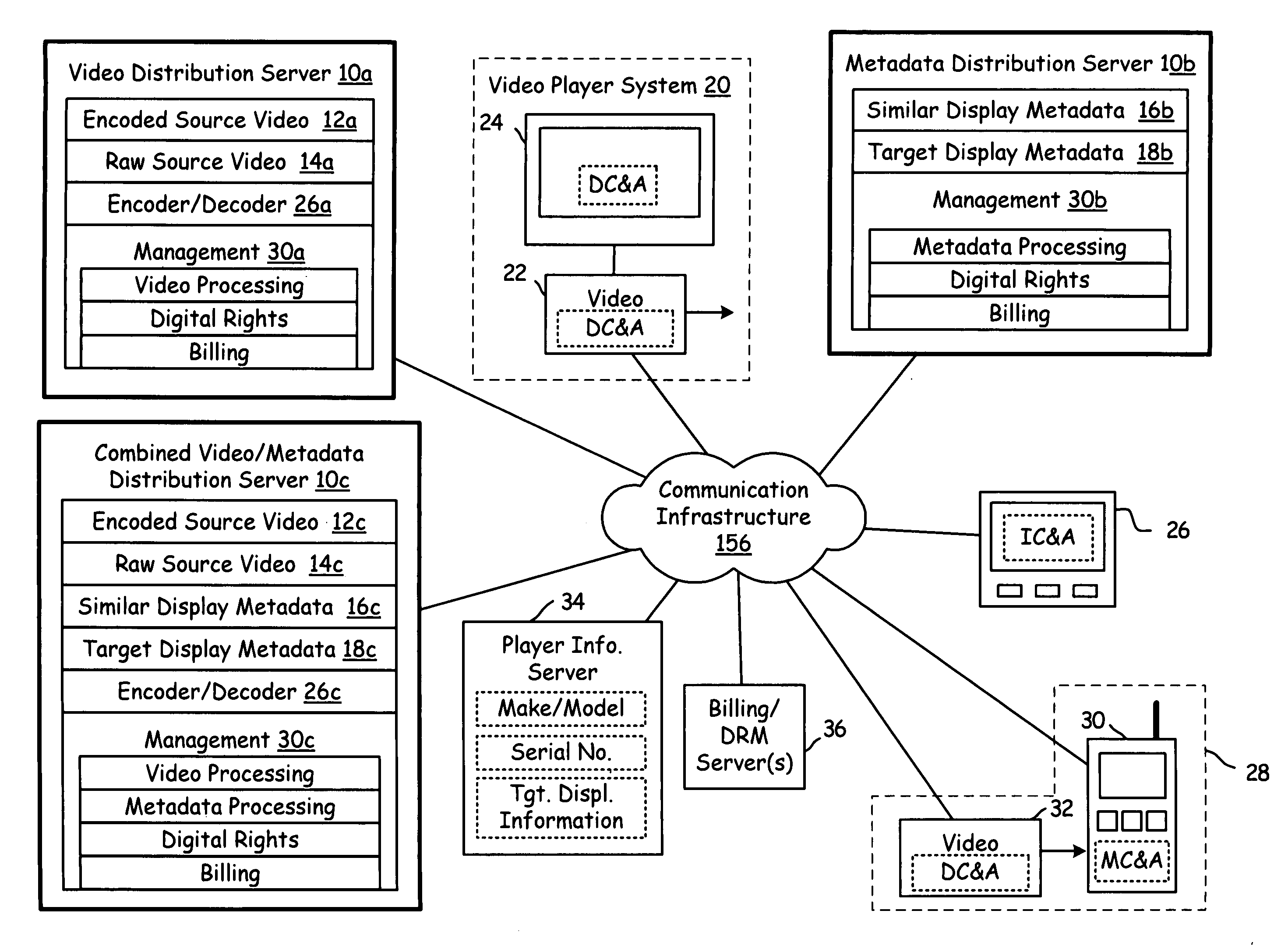
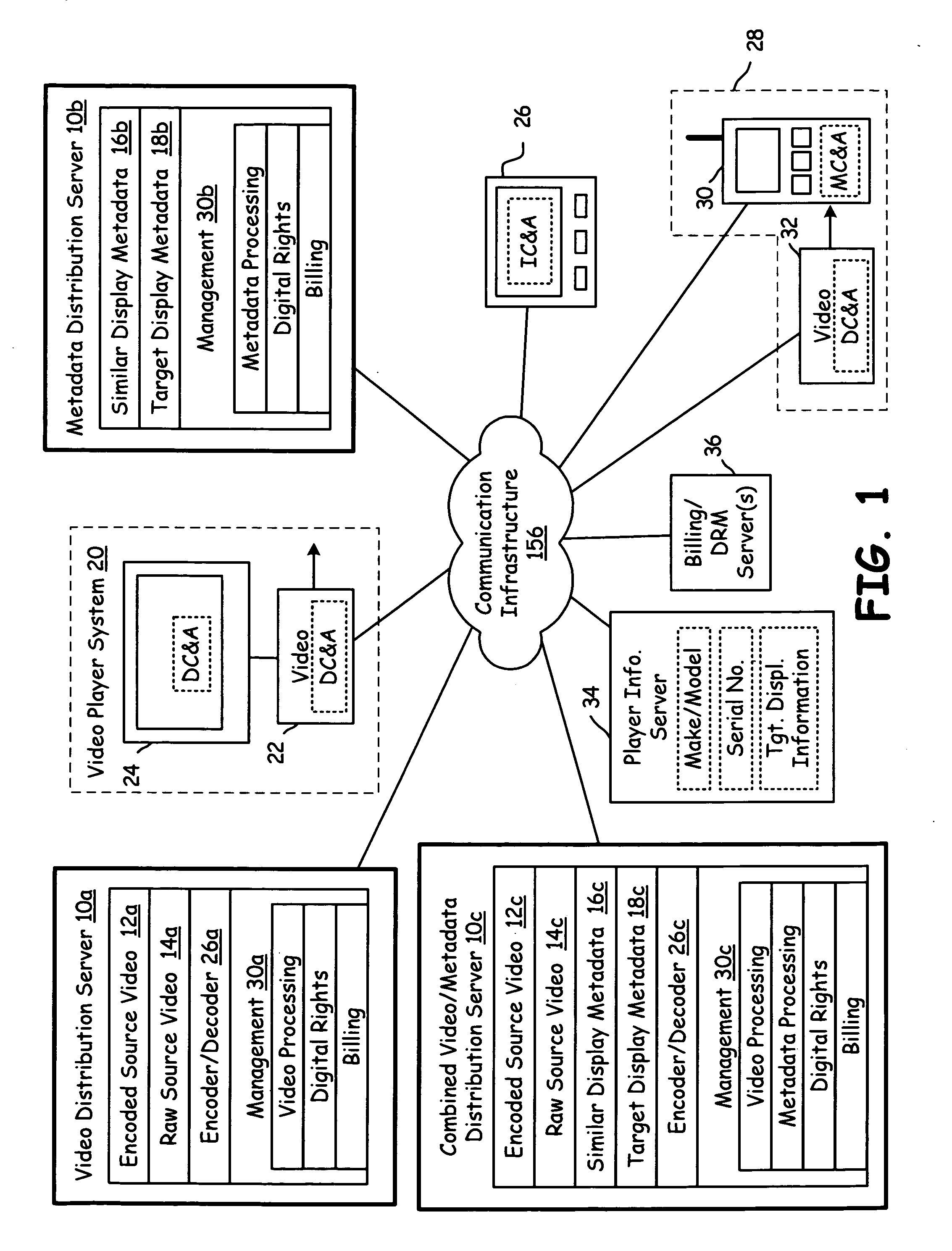
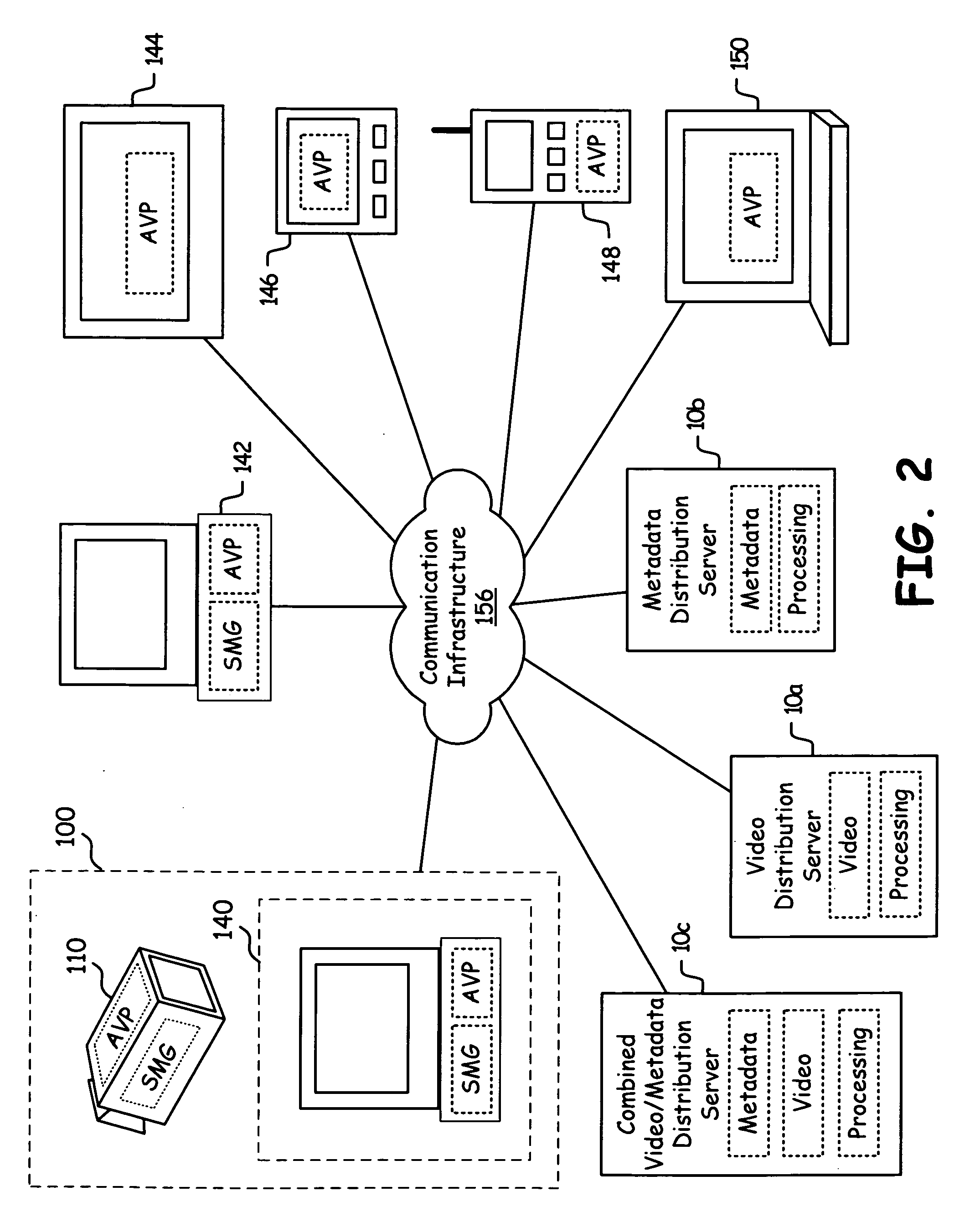
Sub-frame metadata distribution server
InactiveUS20080007651A1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningCommunication interfaceComputer graphics (images)
A distribution server includes a communication interface, storage, and processing circuitry. The processing circuitry retrieves a full screen sequence of video and sub-frame metadata relating to the full screen sequence of video. The processing circuitry sub-frame processes the sequence of full screen video using the sub-frame metadata to produce a plurality of sub-frames of video. The processing circuitry assembles the plurality of sub-frames of video to produce an output sequence for a client system. The distribution server may also receive, store, and distribute the sub-frame metadata and / or the video for subsequent use by a video processing system.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
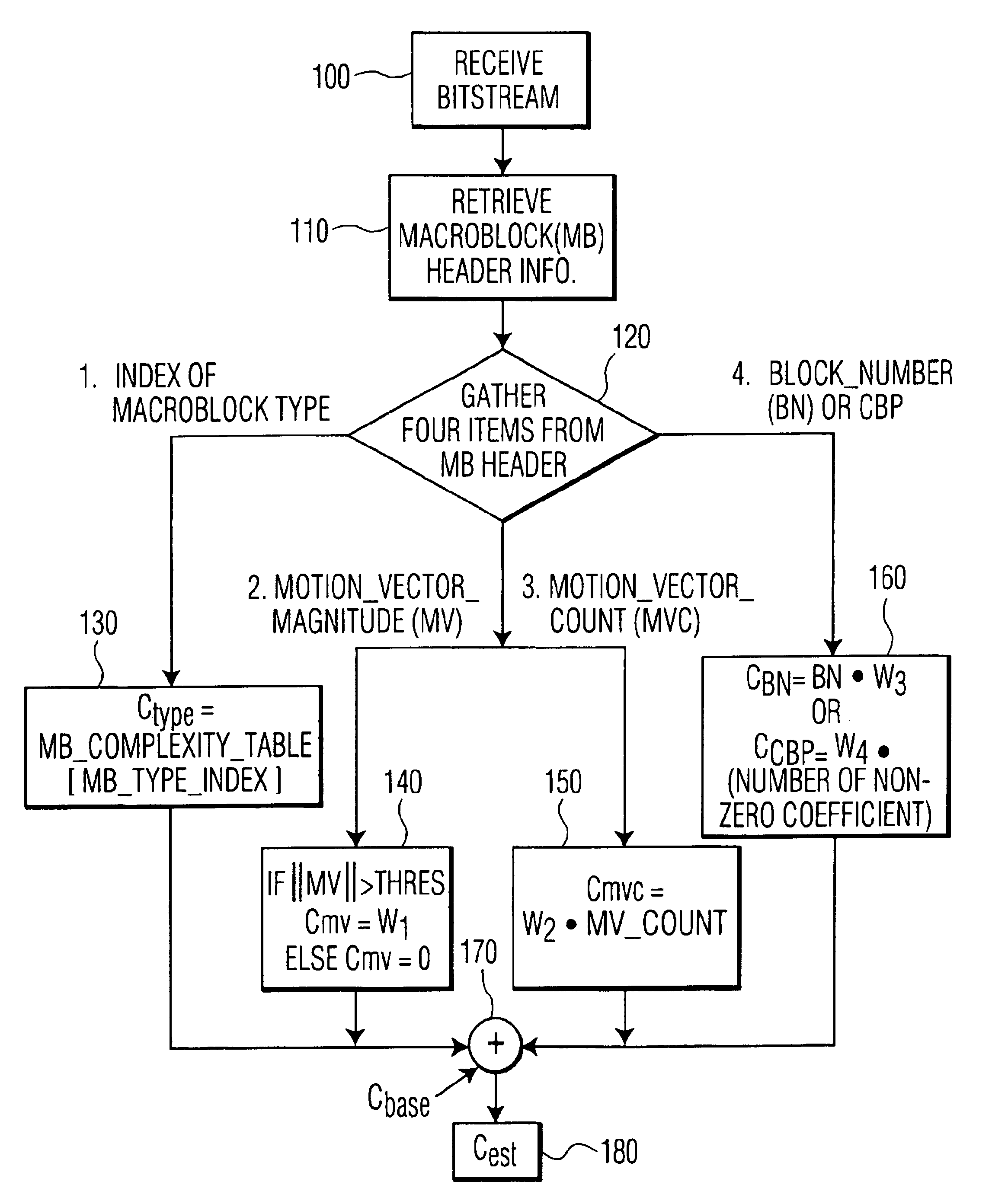
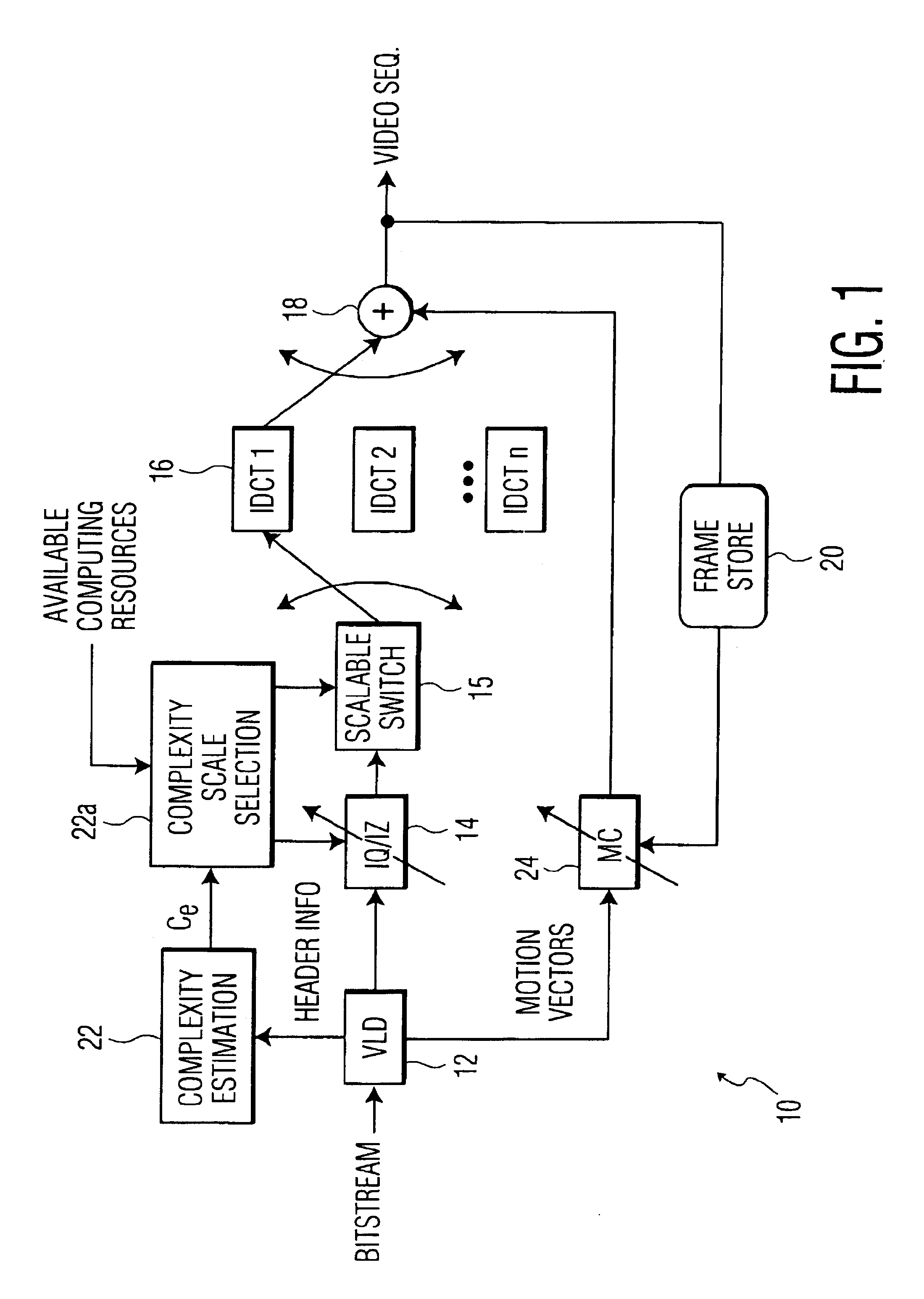
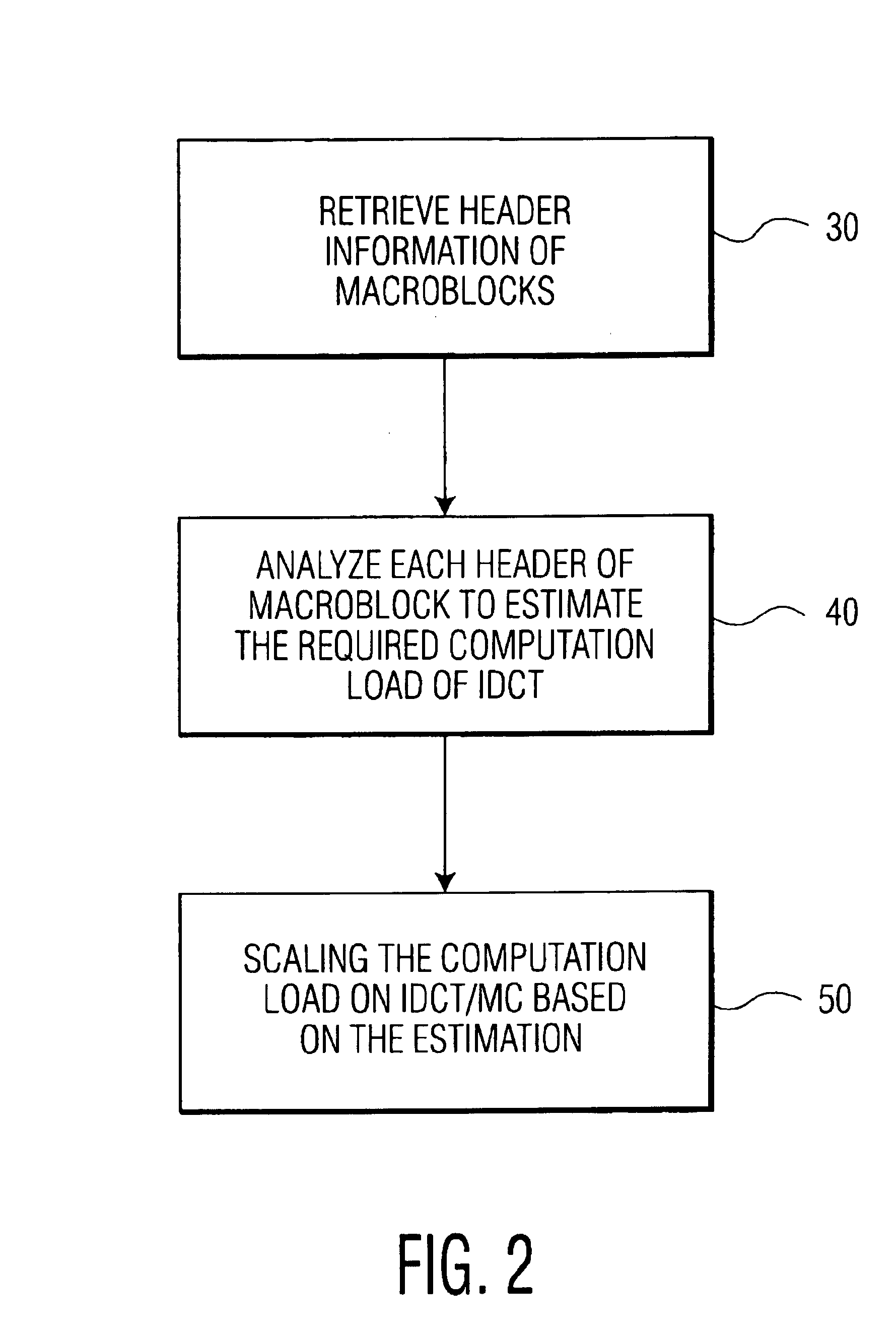
Dynamic complexity prediction and regulation of MPEG2 decoding in a media processor
InactiveUS6925126B2Improve decoding efficiencyPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesData streamMotion vector
A method and system of regulating the computation load of an MPEG decoder in a video processing system are provided. The video processing system processes the header information of a compressed video data stream including a plurality of macroblocks with a motion vector associated therewith. Then, the computation load of each functional block of the MPEG decoder is adjusted according to predetermined criteria; thus, substantial computational overhead is desirably avoided.
Owner:UNILOC 2017 LLC
Load balancing
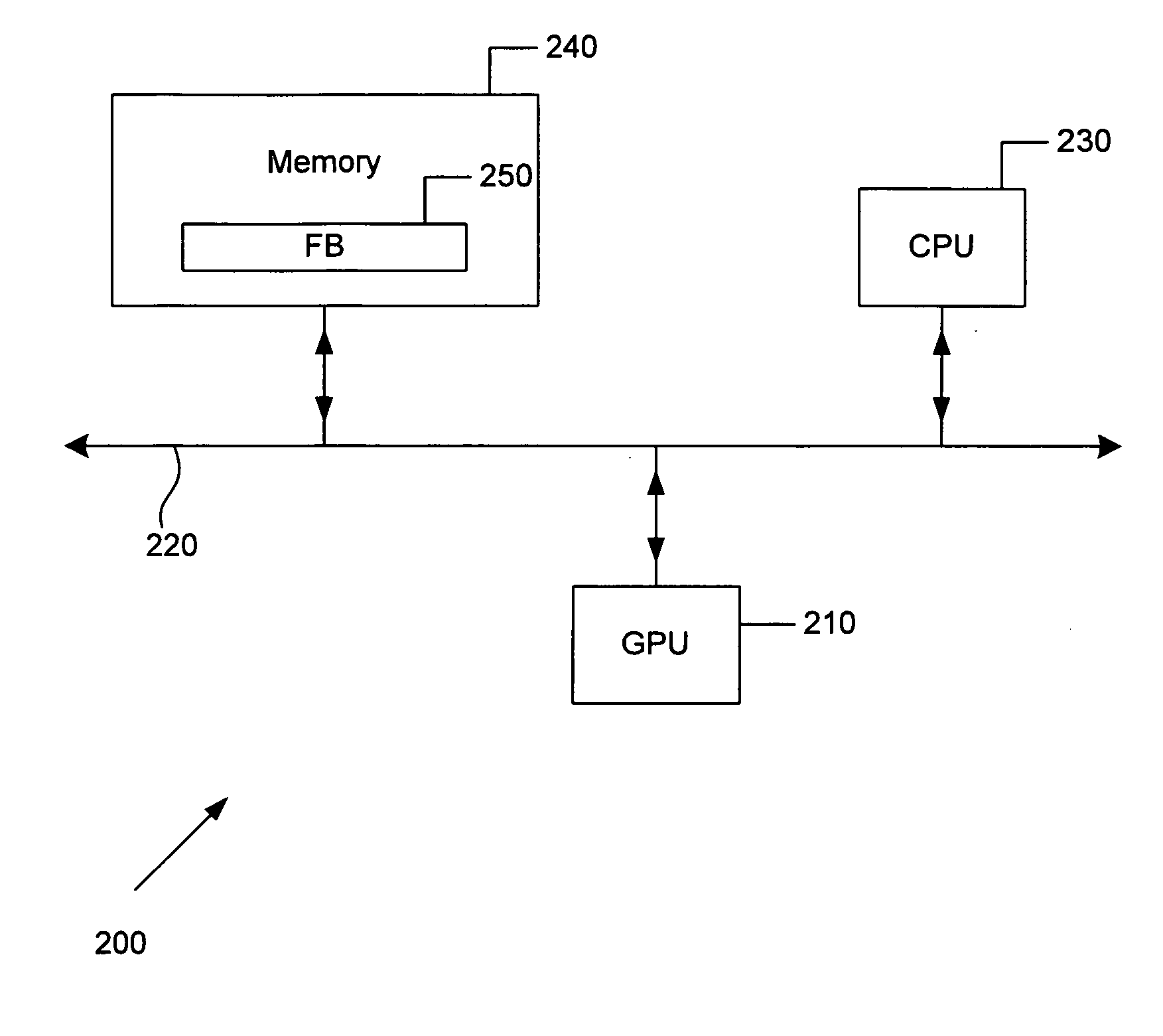
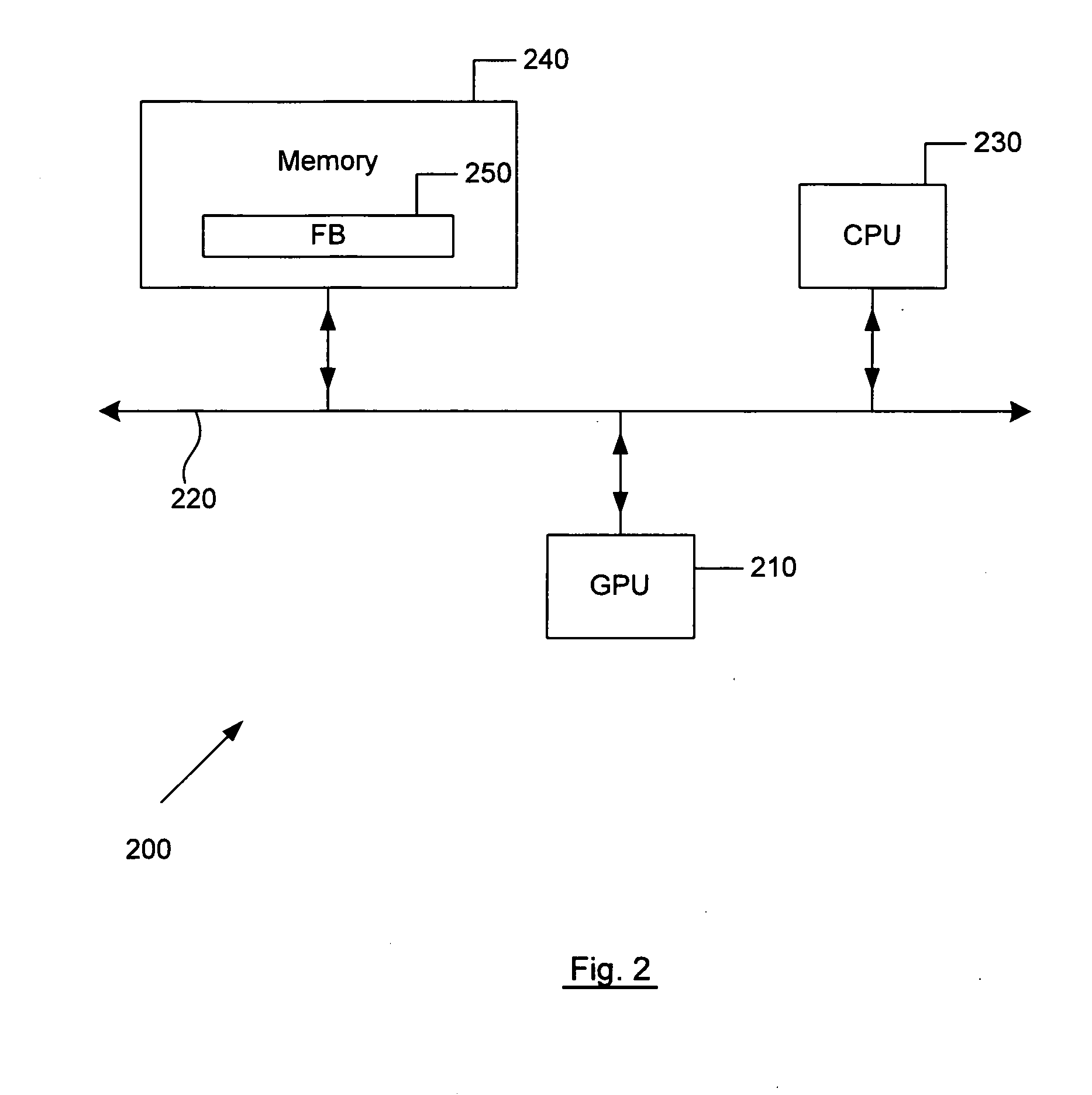
ActiveUS20060059494A1Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsComputational scienceGraphics
Embodiments of methods, apparatuses, devices, and / or systems for load balancing two processors, such as for graphics and / or video processing, for example, are described.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Reduced area imaging device incorporated within wireless endoscopic devices
InactiveUS20060022234A1Improve usabilityImprove mobilityTelevision system detailsDigital data processing detailsDental instrumentsWireless transmission
A reduced area imaging device is provided for use in medical or dental instruments such as an endoscope. In a first embodiment of the endoscope, connections between imaging device elements and between a video display is achieved by hard-wired connections. In a second embodiment of the endoscope, wireless transmission is used for communications between imaging device components, and / or for transferring video ready signals to a video display. In one configuration of the imaging device, the image sensor is placed remote from the remaining circuitry. In another configuration, all of the circuitry to include the image sensor is placed in a stacked fashion at the same location. The entire imaging device can be placed at the distal tip of an endoscope. Alternatively, the image sensor can be placed remote from the remaining circuitry according to the first configuration, and control box is used which communicates with the image sensor and is placed remotely from the endoscope. Further alternatively, the imaging device can be incorporated in the housing of a standard medical camera which is adapted for use with traditional rod lens endoscopes. In any of the configurations or arrangements, the image sensor may be placed alone on a first circuit board, or timing and control circuits may be included on the first circuit board containing the image sensor. The timing and control circuits and one or more video processing boards can be placed adjacent the image sensor in a tubular portion of the endoscope, in other areas within the endoscope, in the control box, or in combinations of these location.
Owner:MICRO IMAGING SOLUTIONS
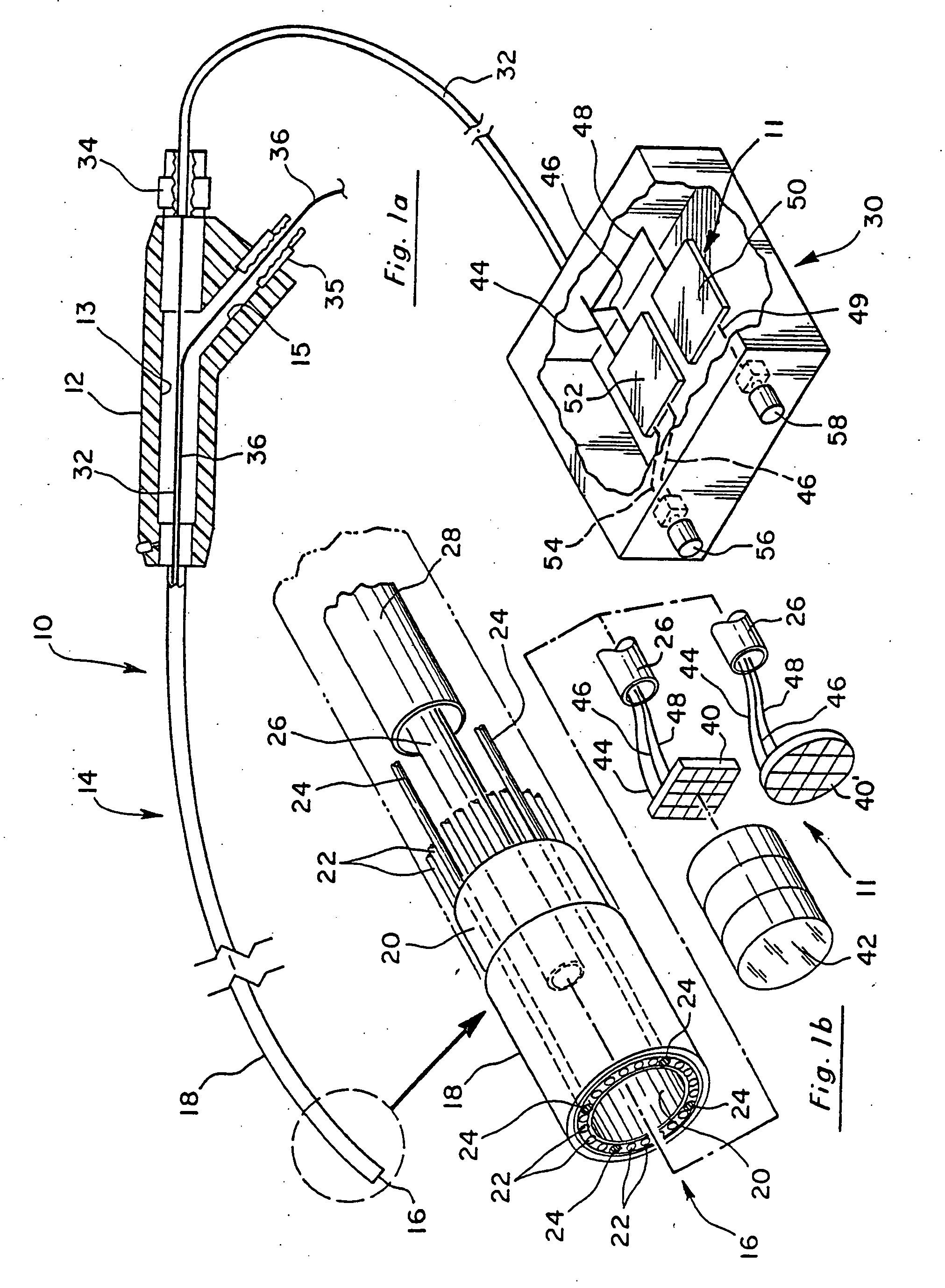
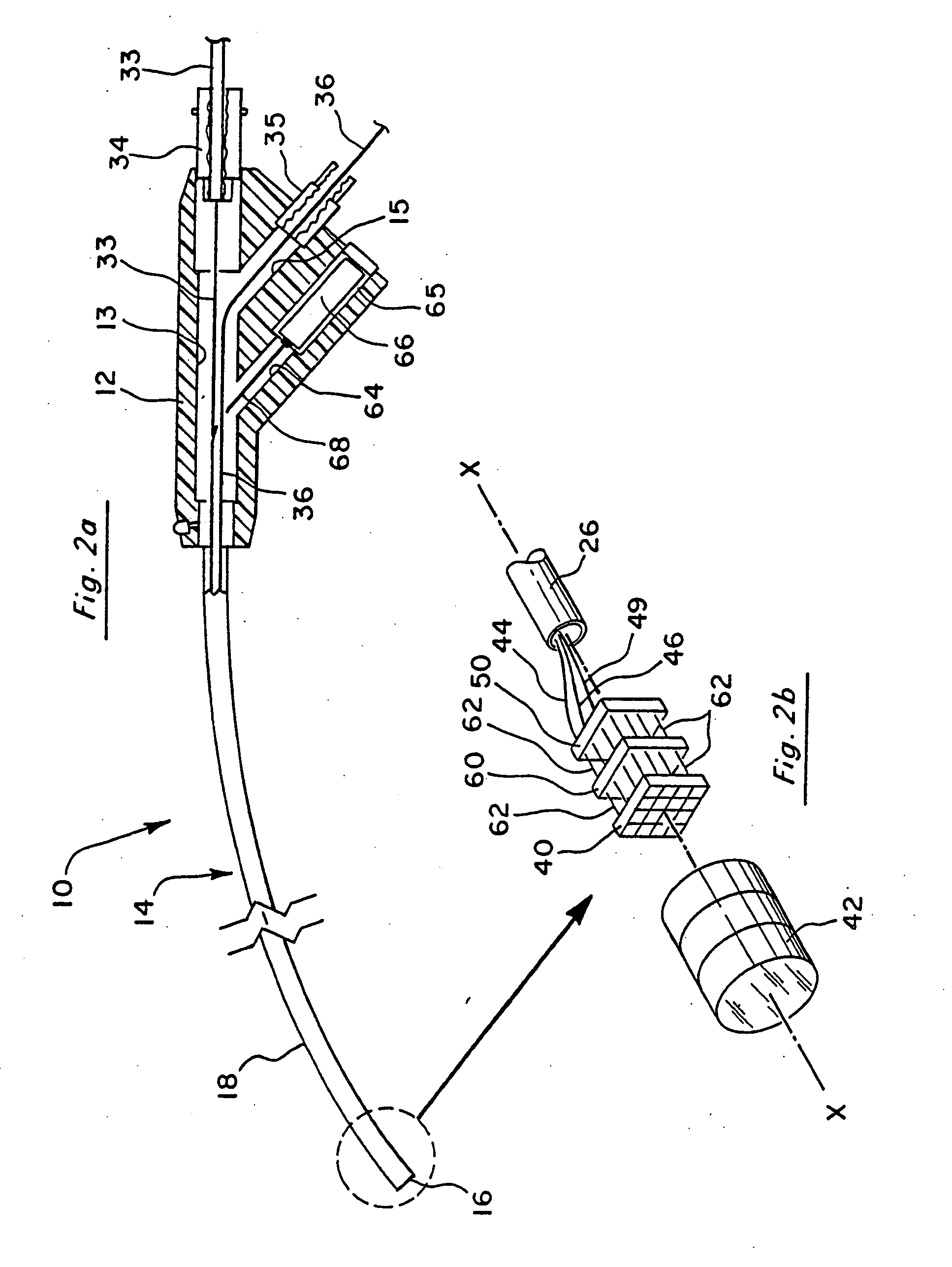
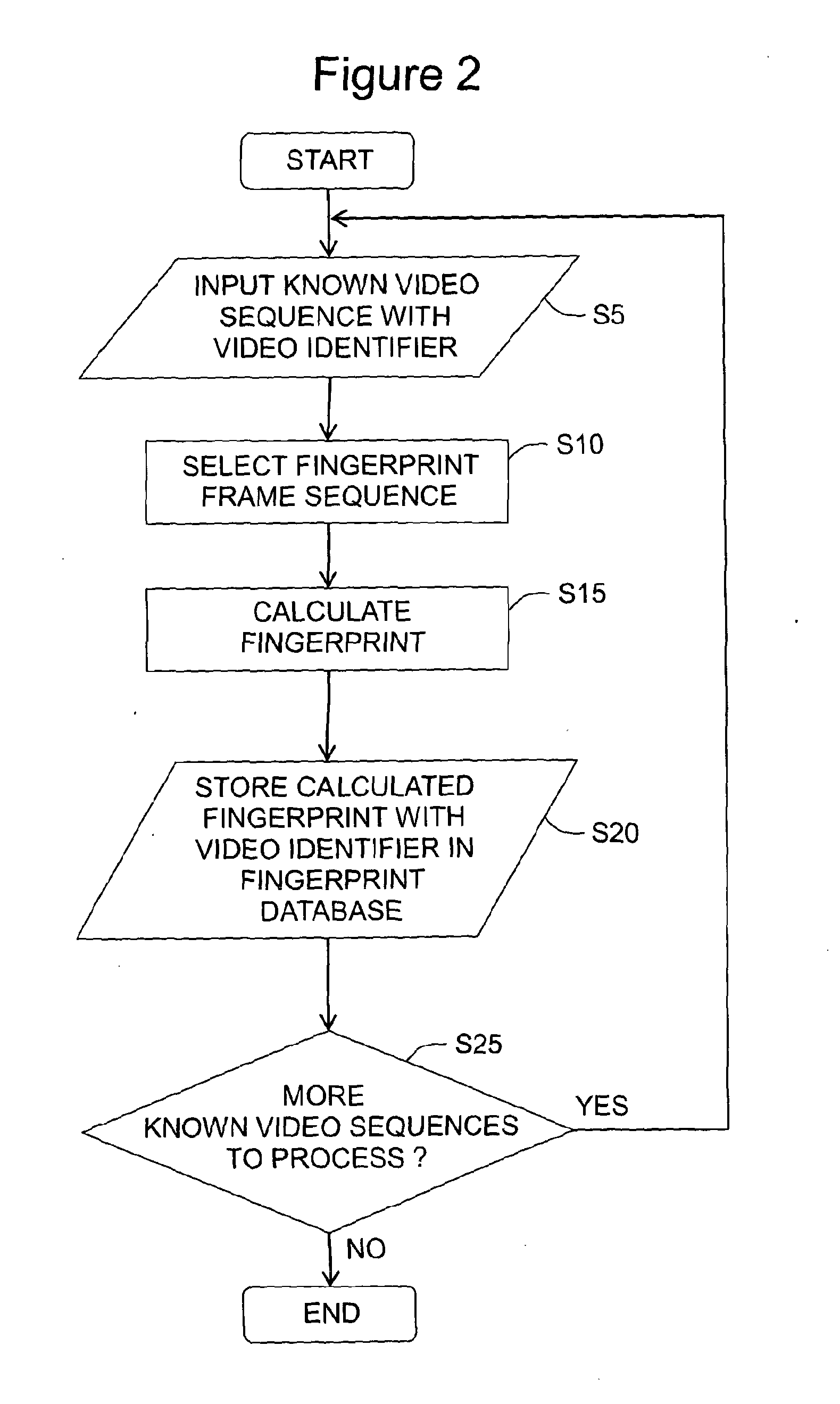
Digital video fingerprinting
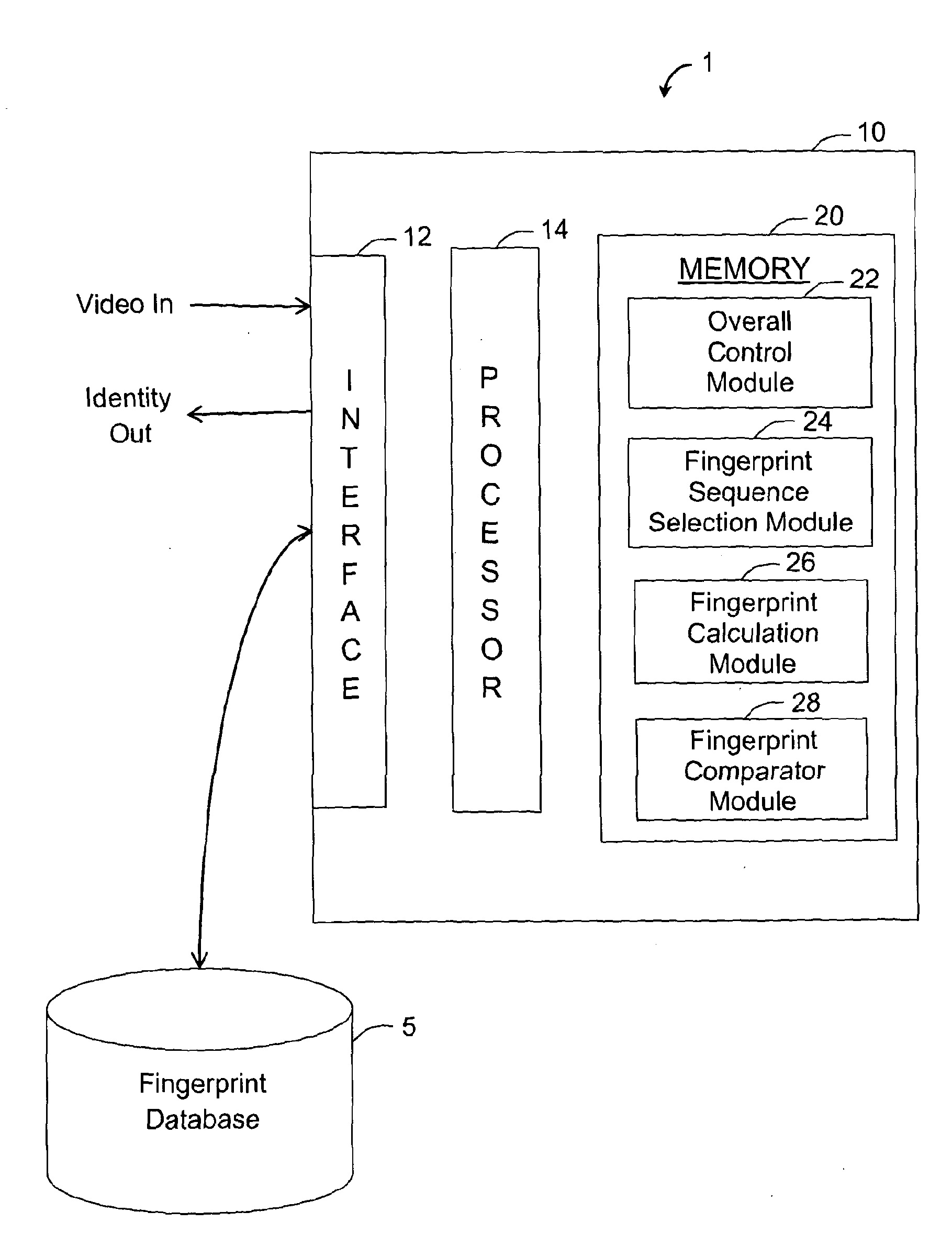
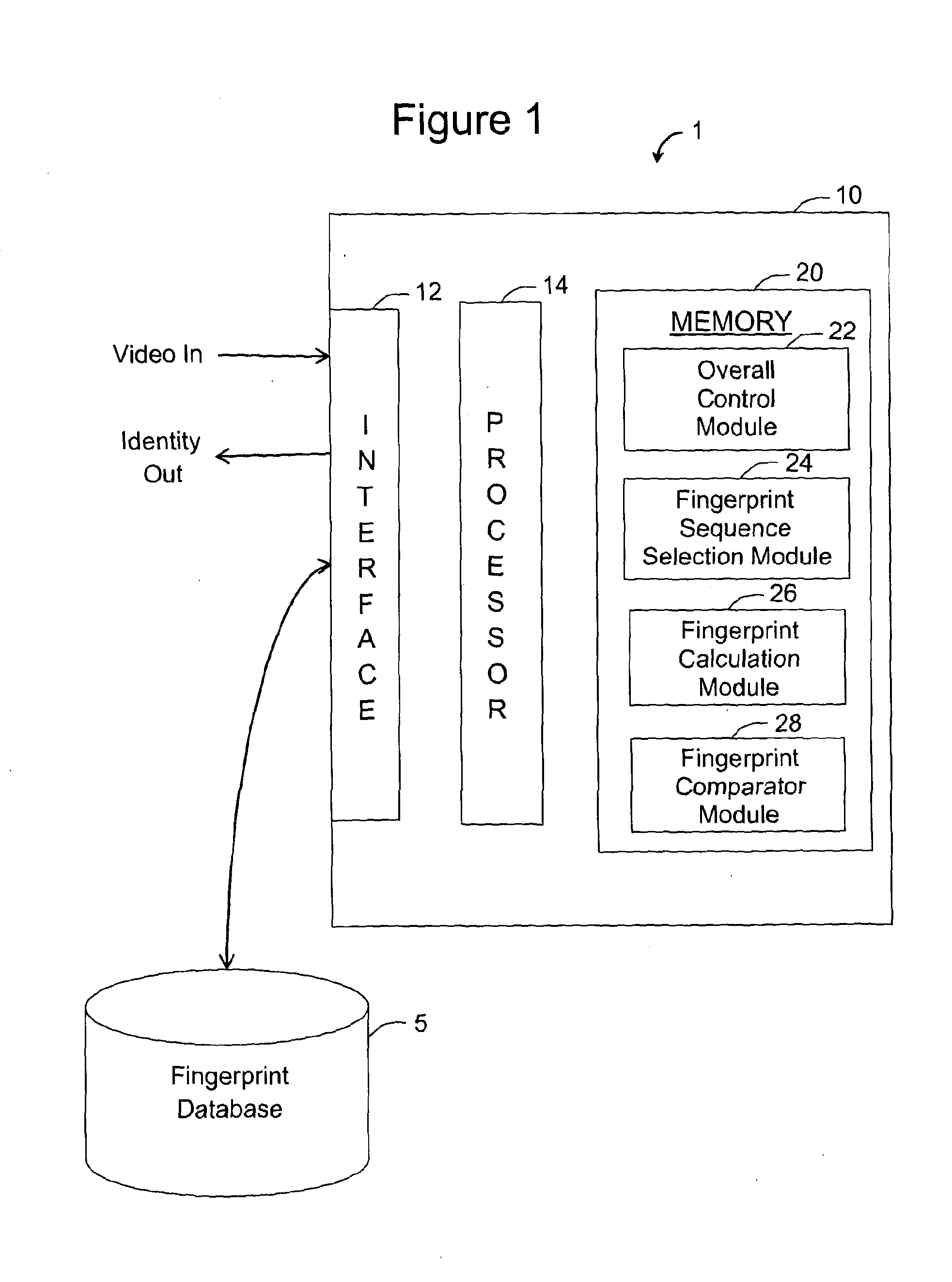
ActiveUS20130208942A1Low efficiencyHigh residual energyDigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionDigital video
A digitally encoded video fingerprinting system for generating and comparing / matching finger-prints from digitally encoded video which has been encoded according to an encoding method which involves the generation of residual macroblocks of pixels and the generation of quantized transform coefficients of the residual macroblocks, or of portions of the residual macroblocks, comprises a fingerprint database (5) and a video processing subsystem (10). The video processing subsystem (10) includes a fingerprint sequence selection module (14, 24) which is operable to select one or more sets of frames from input video content to be processed in order to generate a fingerprint; a fingerprint calculation module (14, 26) which is operable to generate a fingerprint based on a set of frames selected by the fingerprint sequence selection module; and a fingerprint comparator module (14, 28) which is operable to compare two fingerprints and to output a similarity score of the compared fingerprints. The method used by the fingerprint selection and fingerprint calculation modules includes selecting a group of frames of the encoded video content; processing the digitally encoded video content to obtain a set of quantized transform coefficients of residual macroblocks or portions of residual macroblocks associated with each of the selected frames; identifying a set of residual macroblocks per frame whose transform coefficients satisfy a threshold criterion; and generating a digital video fingerprint for the encoded video content in dependence upon the identified macroblocks or some property thereof within each of the selected frames.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
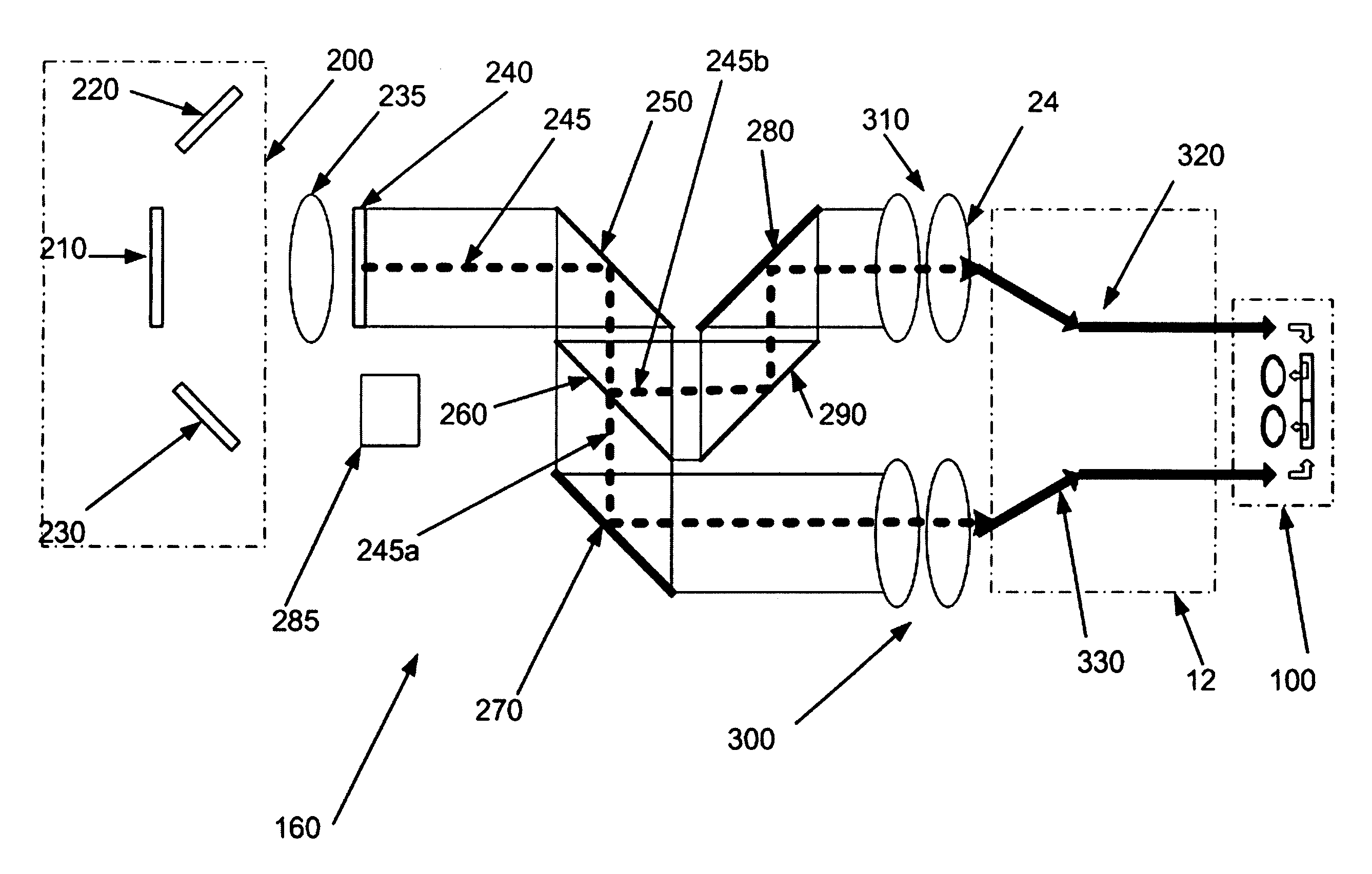
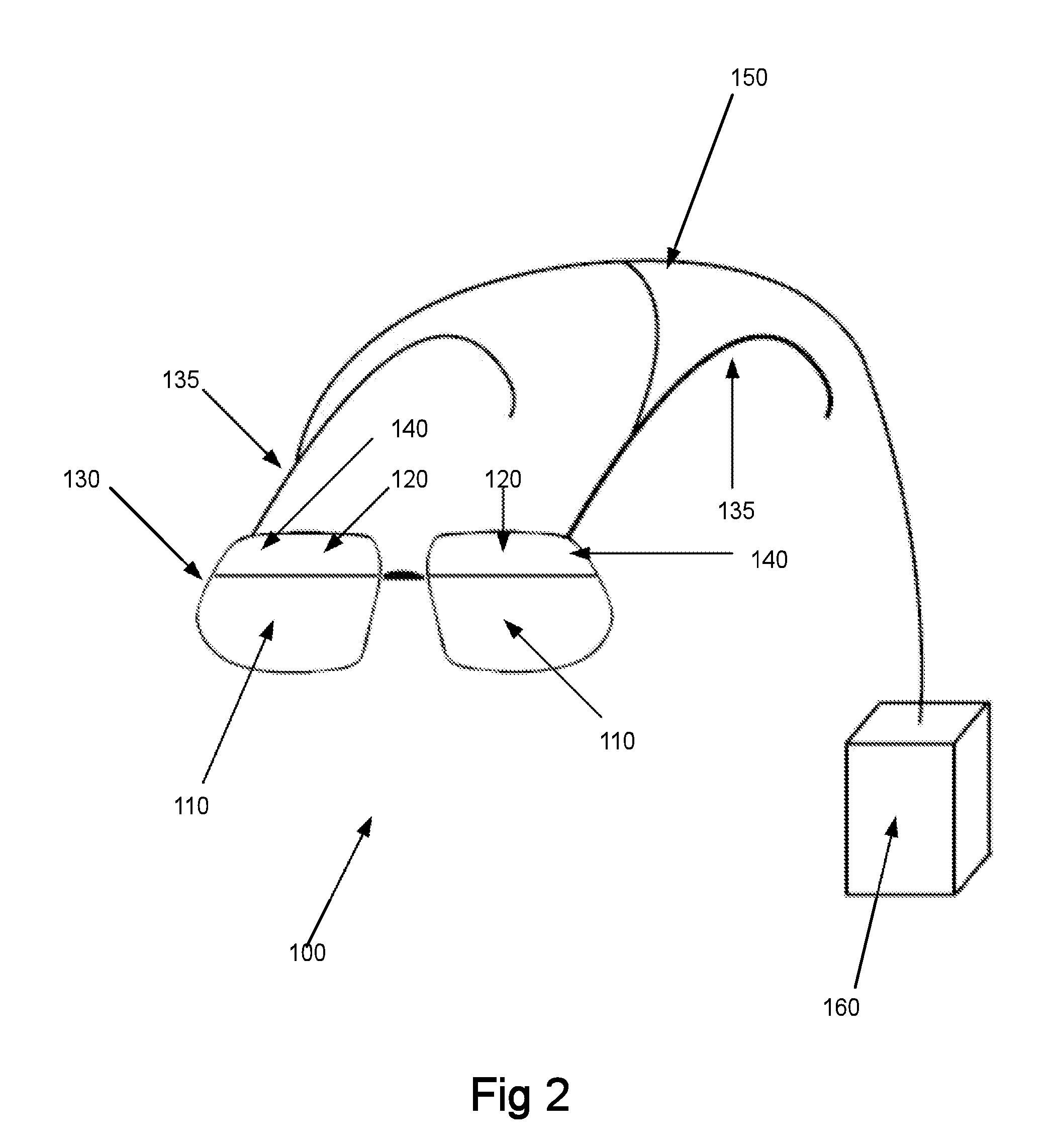
Head mountable video display
InactiveUS7436568B1Easy to adjustQuality improvementPolarising elementsOptical light guidesVideo processingEyewear
The invention comprises a distributed direct retinal display projection system that can be fabricated as an embedded, integral part of an eyeglasses frame and can be configured to address a wide range of commercial, consumer and military applications. A system is described comprising a video processing module that may worn on a belt or carried in a pocket, which transmits an image through a multi-waveform optical cable that is configured with a wave guide per pixel.
Owner:KUYKENDALL JR JACOB L
Implementing a hybrid wireless and coaxial cable network
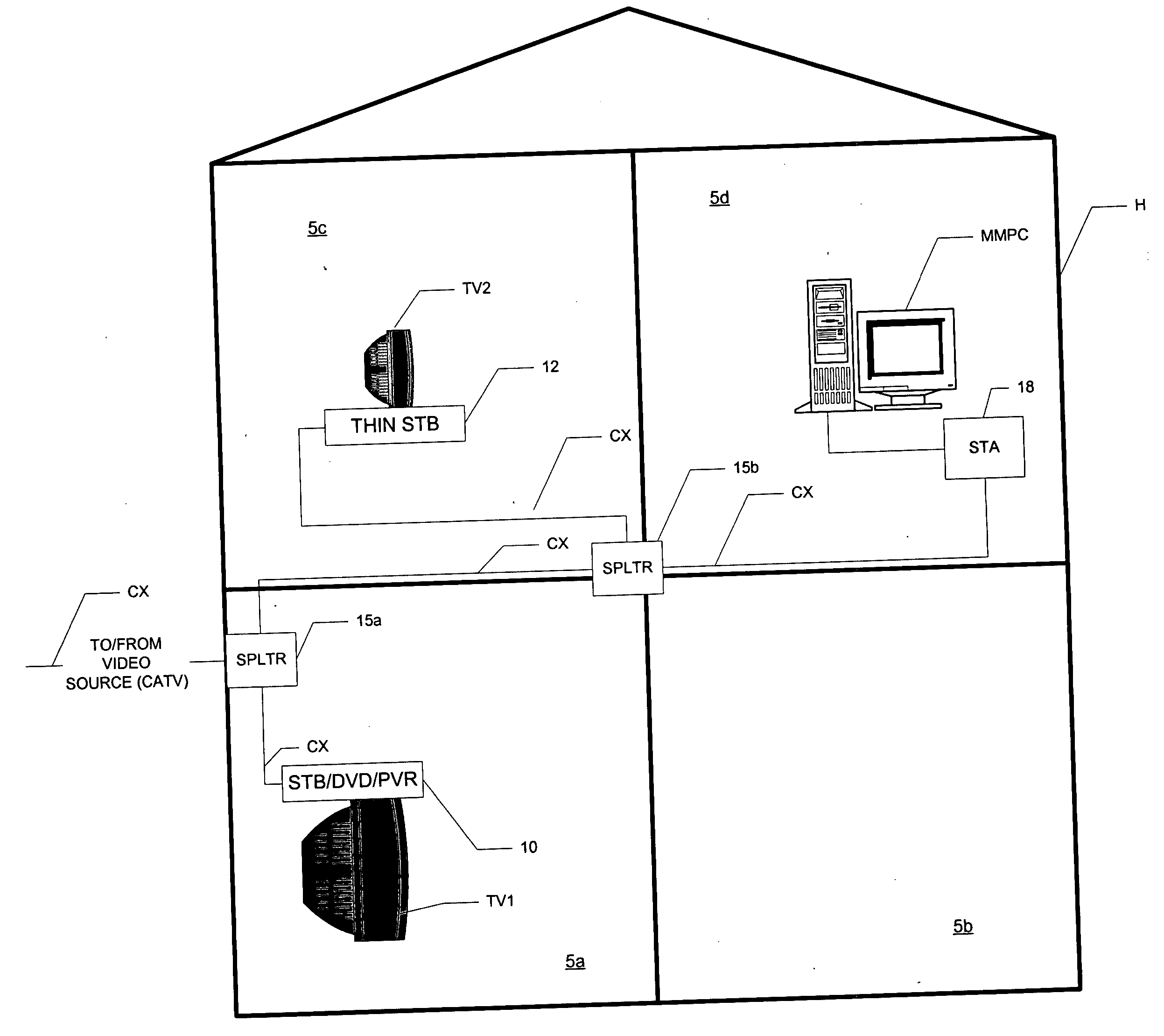
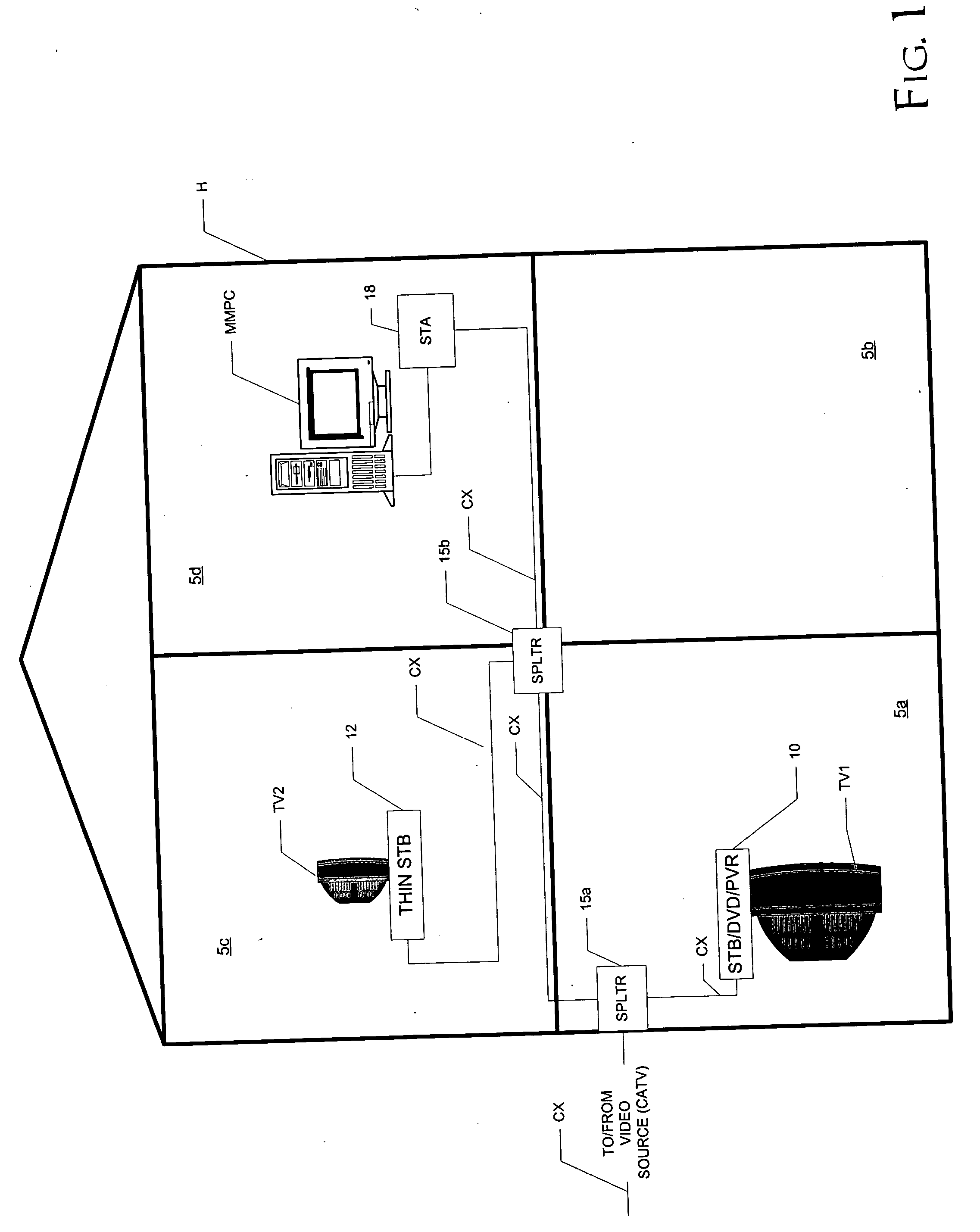
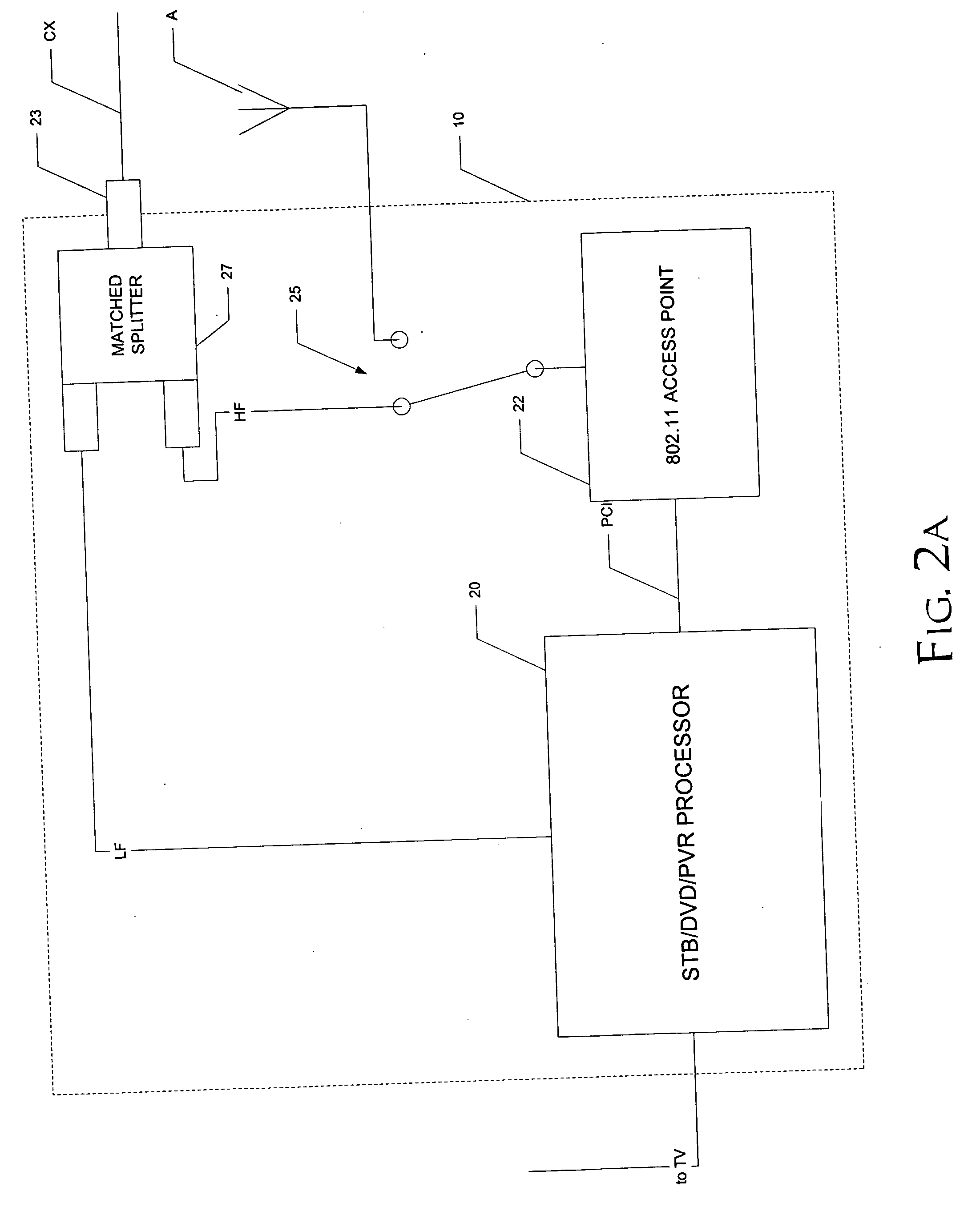
InactiveUS20050034159A1Miniaturized installationIncrease data rateBroadband local area networksClosed circuit television systemsCoaxial cableVideo processing
A home video network, and a home video and data network, utilizing wireless protocol communications over coaxial cable (CX) are disclosed. In the home video network, a main network station (10) includes video processing functionality, such as one or more of a DVD player, personal video recorder (PVR), and a set-top box (STB) for cable or satellite television reception. The main network station (10) also includes a matched splitter (27) that receives coaxial cable (CX) inputs, and provides low-pass filtered and high-pass filtered output. The low-pass filtered output (LF) corresponding to video signals is provided to the video processing functionality (20) and the high-pass filtered output (HF) corresponding to wireless protocol communications is provided to a wireless access point function (22). Other network stations and combinations of functions are also disclosed, including those that utilize a function switch (25) to switch between network communications over coaxial cable (CX) and communications over an antenna (A), in either a single BSS mode or a double BSS mode.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Video processing device and video processing method
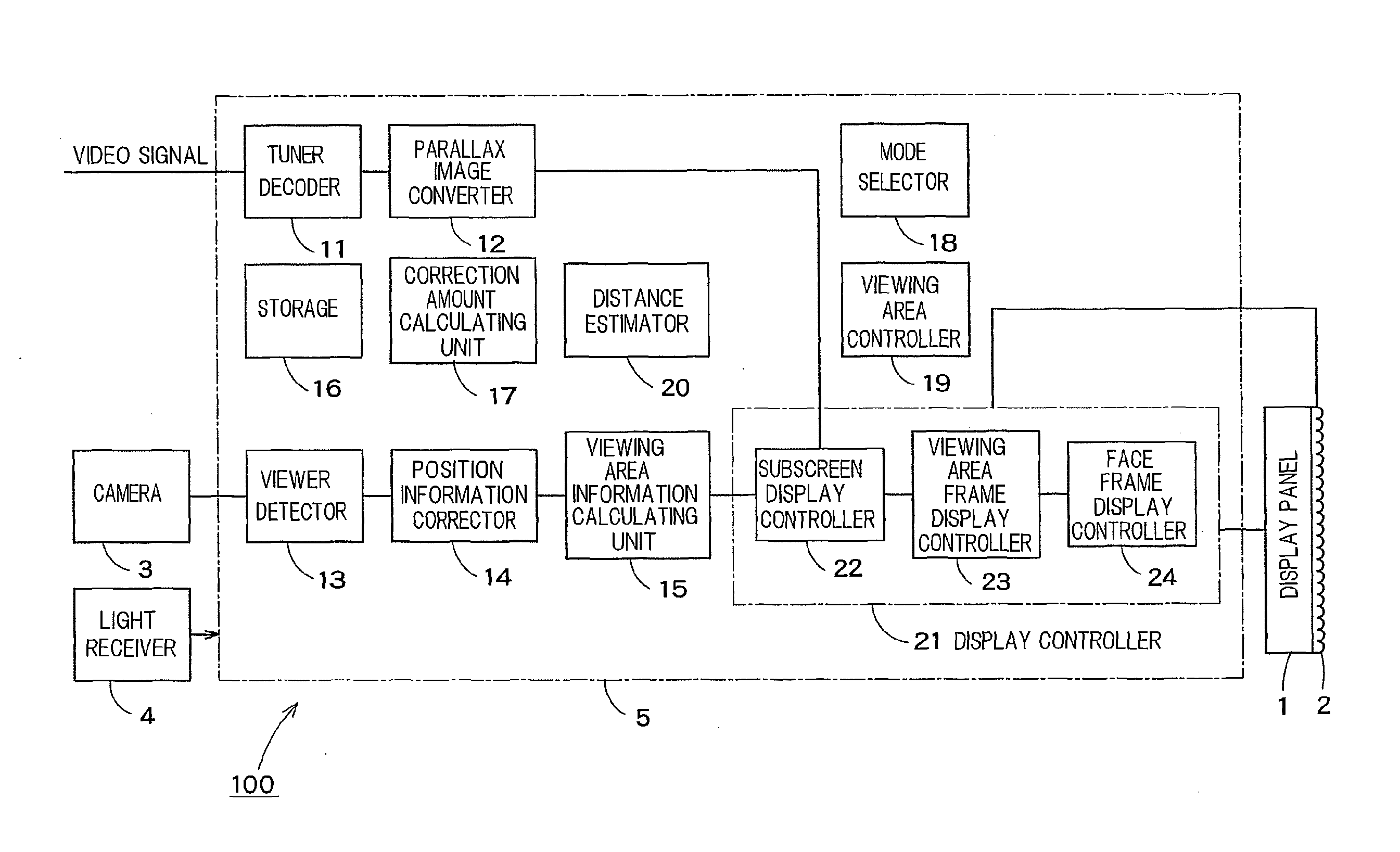
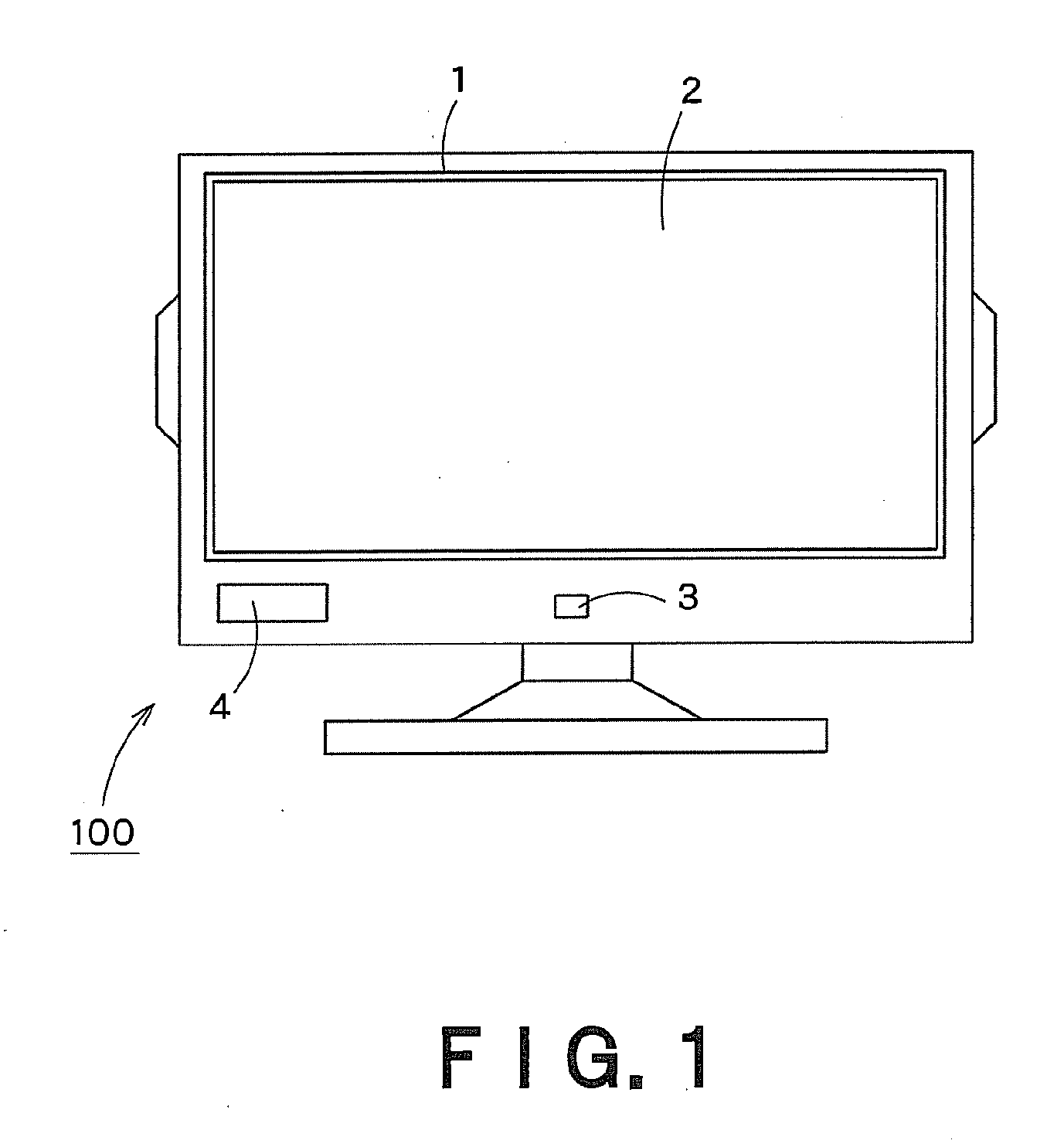
InactiveUS20130113899A1Color television detailsClosed circuit television systemsStereoscopic videoDisplay device
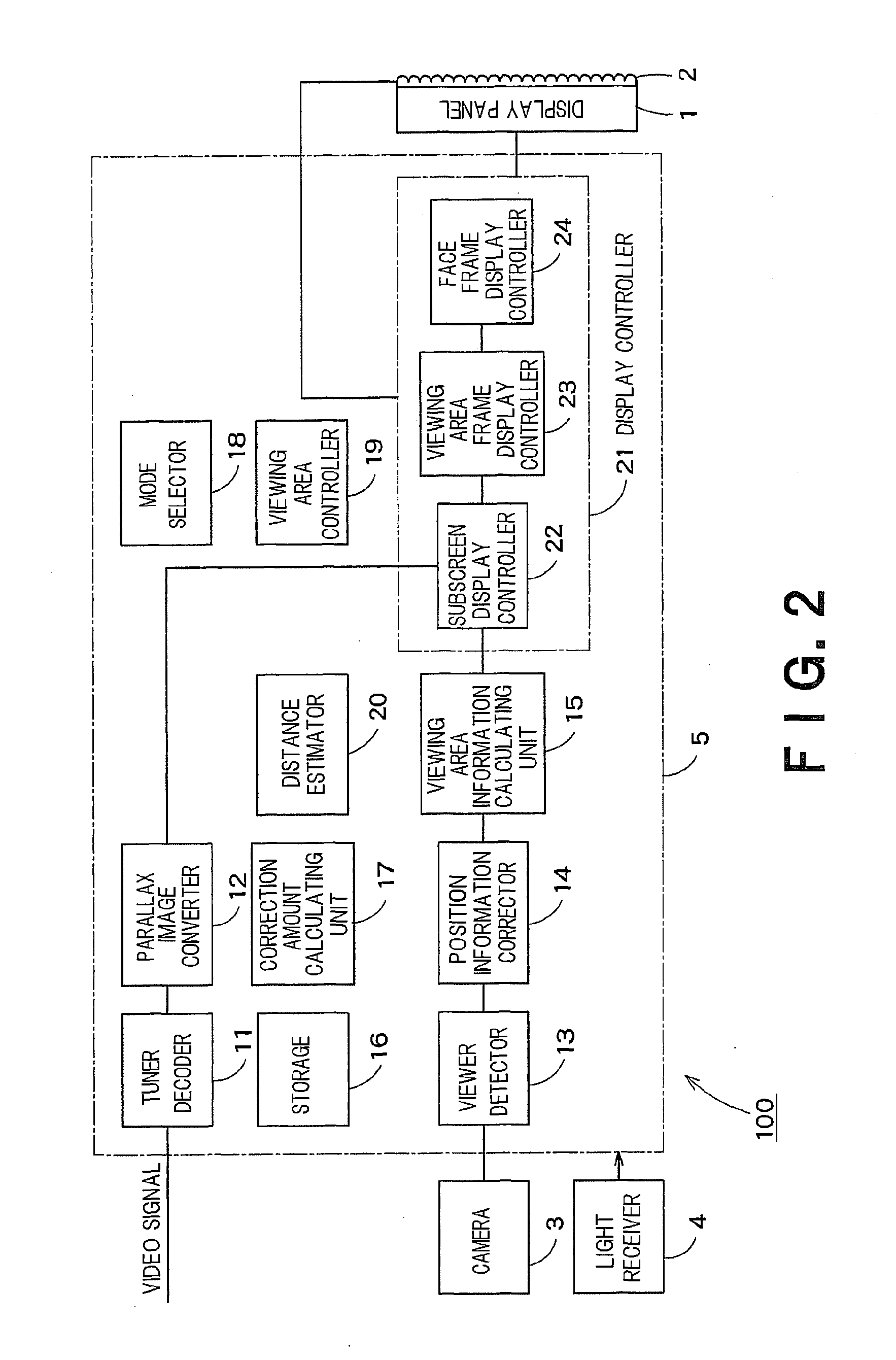
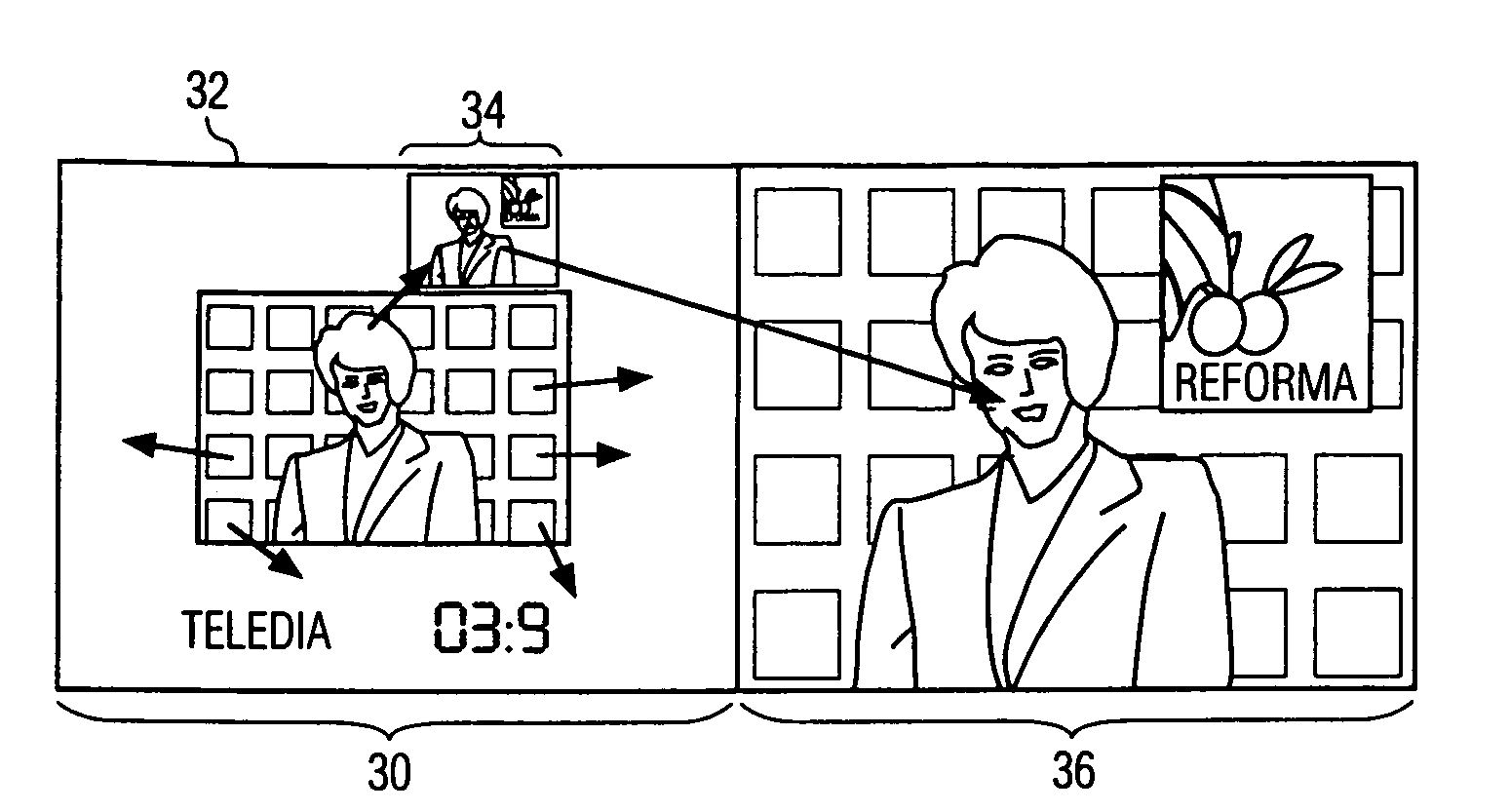
A video processing device has a viewer detector to recognize a face of a viewer using a video shot by a camera in order to acquire position information of the viewer, a subscreen display controller to superimpose a live video shot by the camera on a part of a display screen of a display device as a subscreen, a viewing area frame display controller to display, in the live video in the subscreen, a viewing area frame representing a viewing position where the viewer is viewable a stereoscopic video, and a face frame display controller to display a first face frame showing that the stereoscopic video is viewable when the viewer is located within the frame, and to display a second face frame showing that the stereoscopic video is not viewable when the viewer is located outside the frame.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method and apparatus for linking a video segment to another segment or information source
InactiveUS7356830B1Improve interactivityTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionVideo processingHandling system
A given video segment is configured to include links to one or more other video segments or information sources. The given video segment is processed in a video processing system to determine an association between an object, entity, characterization or other feature of the segment and at least one additional information source containing the same feature. The association is then utilized to access information from the additional information source, such that the accessed information can be displayed to a user in conjunction with or in place of the original video segment. A set of associations for the video segment can be stored in a database or other memory of the processing system, or incorporated into the video segment itself, e.g., in a transport stream of the video segment. The additional information source may be, e.g., an additional video segment which includes the designated feature, or a source of audio, text or other information containing the designated feature. The feature may be a video feature extracted from a frame of the video segment, e.g., an identification of a particular face, scene, event or object in the frame, an audio feature such as a music signature extraction, a speaker identification, or a transcript extraction, or a textual feature. The invention allows a user to access information by clicking on or otherwise selecting an object or other feature in a displayed video segment, thereby facilitating the retrieval of information related to that segment.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
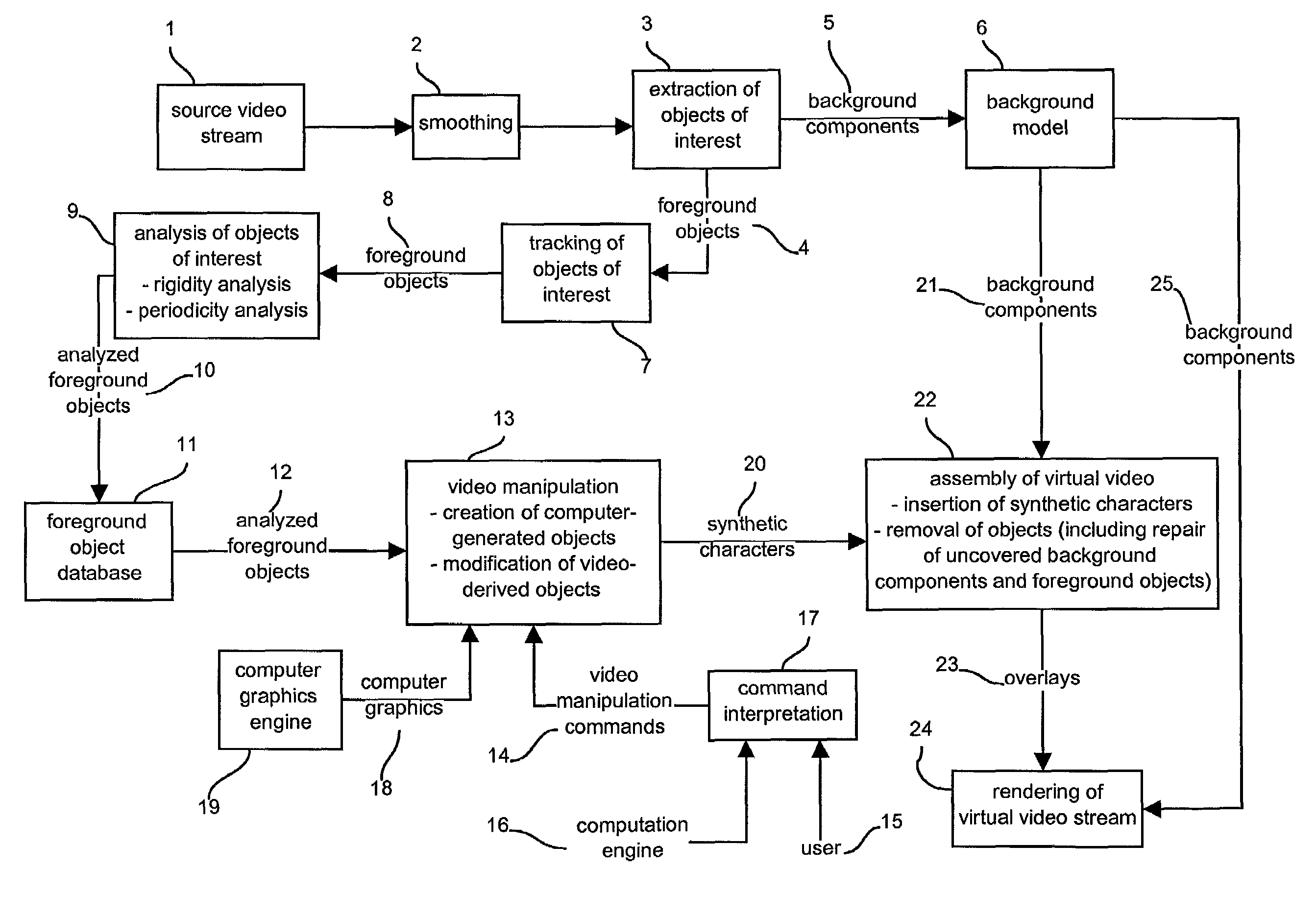
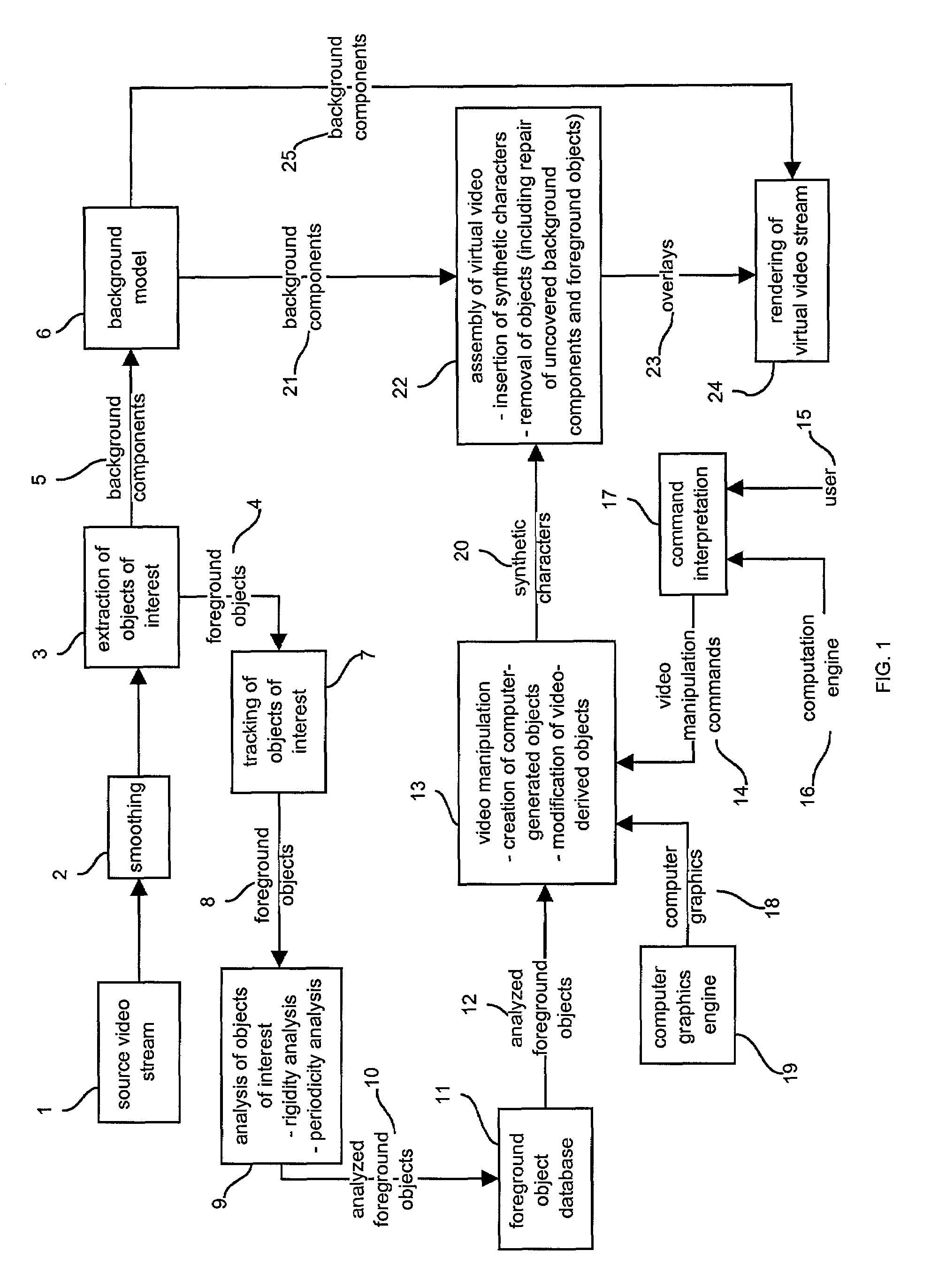
Video processing
InactiveUS20050018045A1Promote resultsImprove imaging resolutionTelevision system detailsImage analysisViewpointsComputer graphics (images)
A method for generating a desired view of a real scene from a selected desired viewpoint by identifying objects in a real image, determining the positions of the identified objects, and rendering a view of the scene from a selected viewpoint using image data from the real image to render at least some of the identified objects. Other portions of the rendered view can be rendered using other source data which may be generic or historic. Identified objects may be tracked over a period of time to determine a trajectory or path. A user interface can be provided to assist in object tracking. A number of cameras can be used to provide a number of real images, and certain cameras may be controlled using the parameters of other cameras.
Owner:BRITISH BROADCASTING CORP
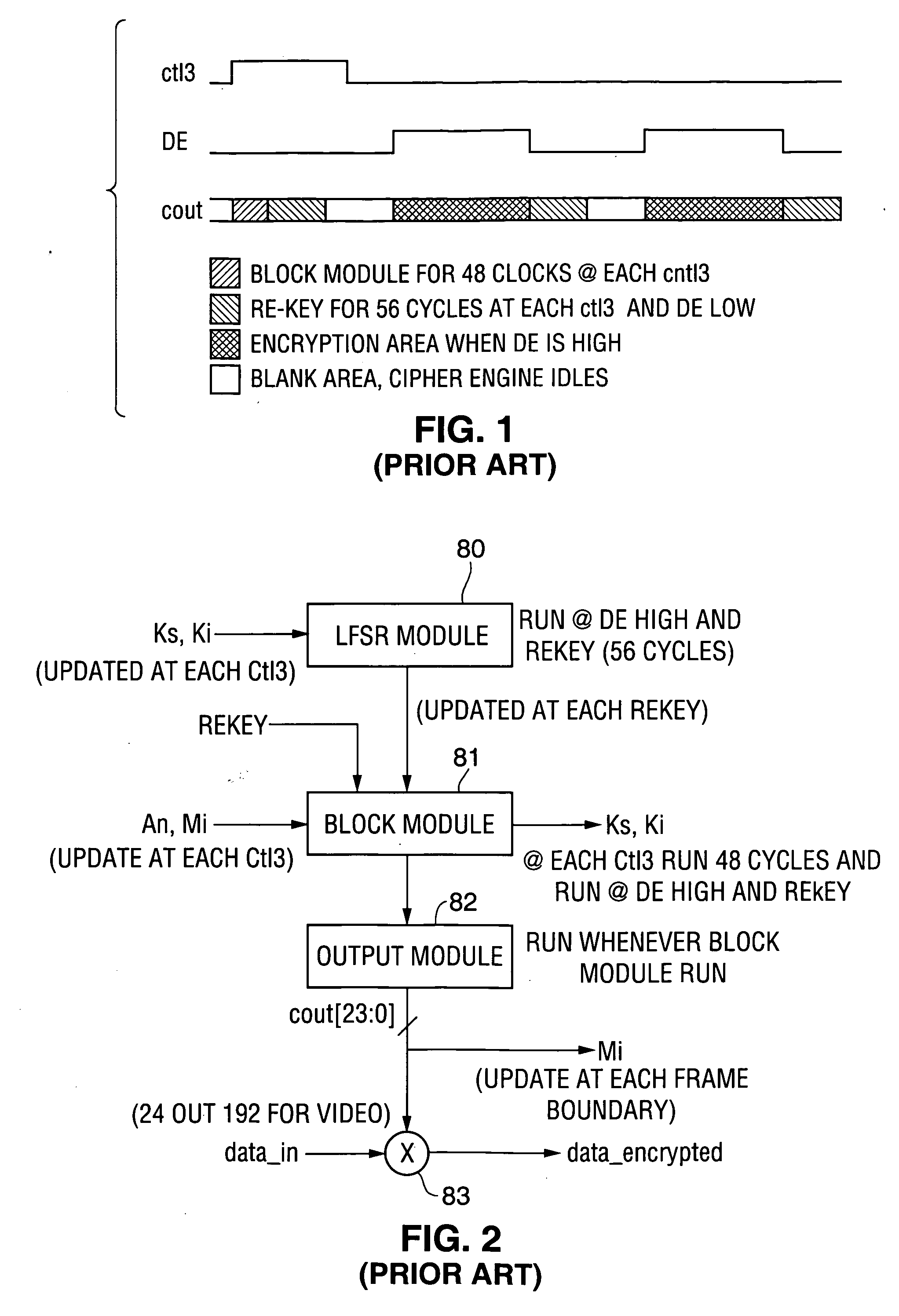
Method and apparatus for content protection in a personal digital network environment
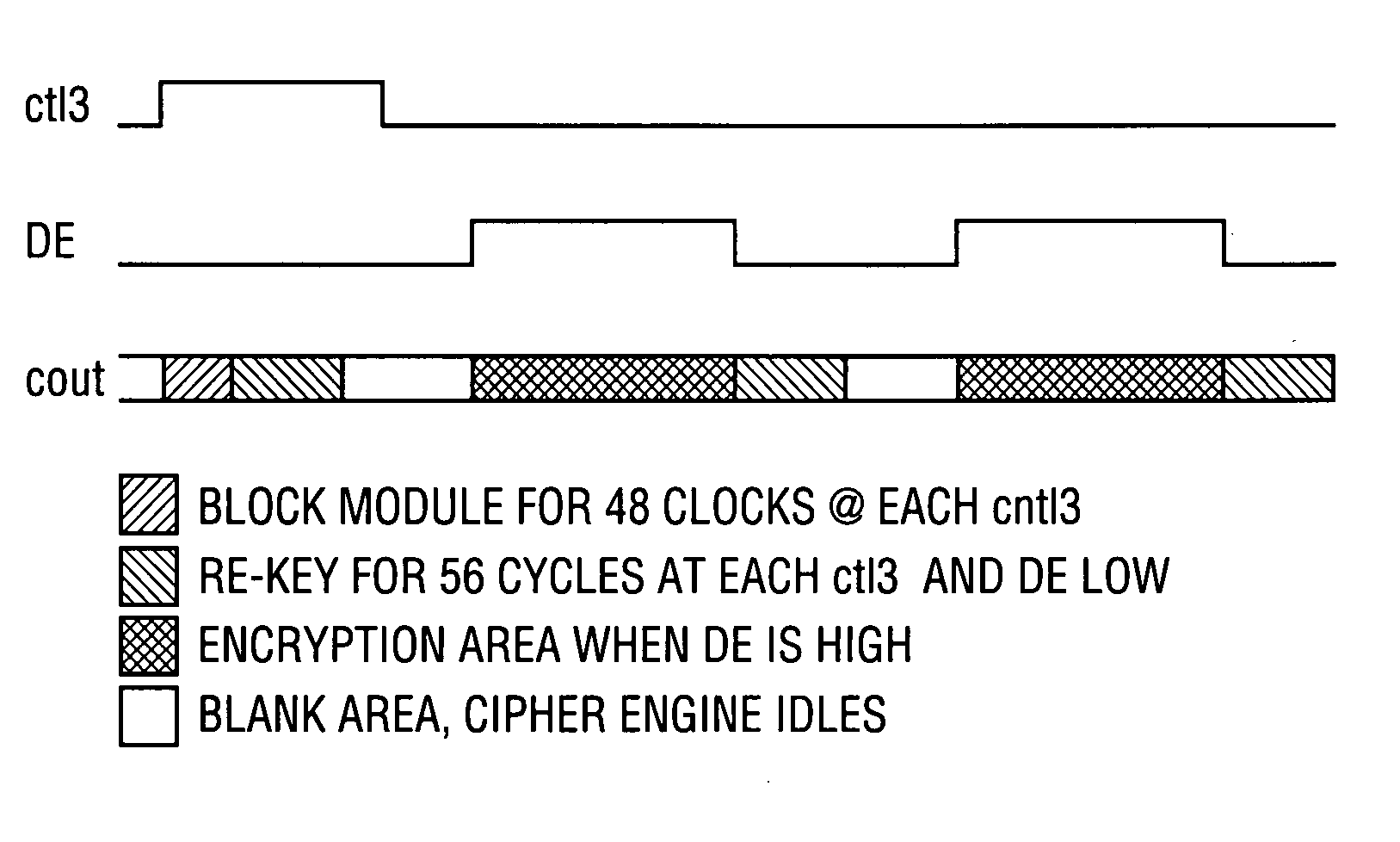
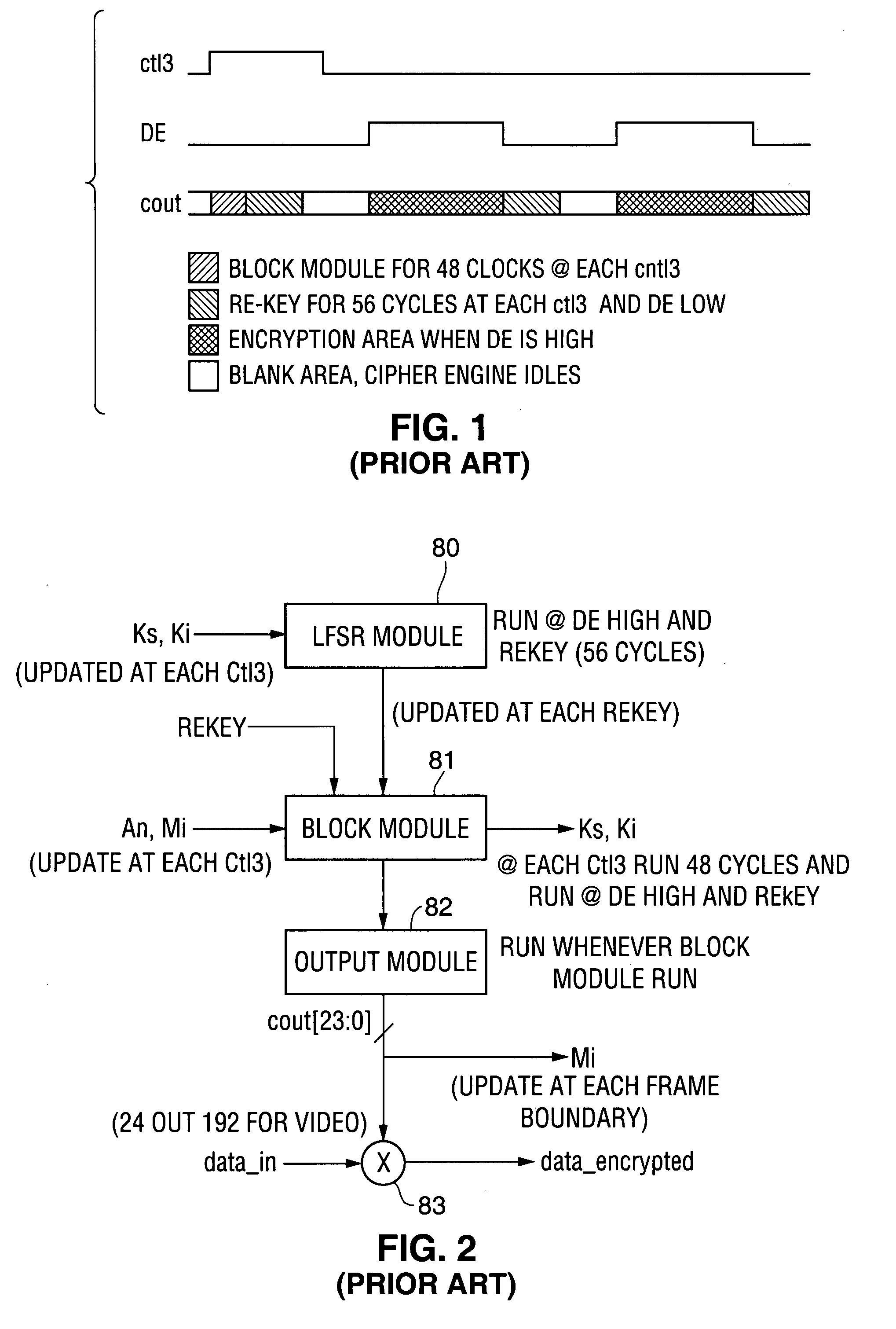
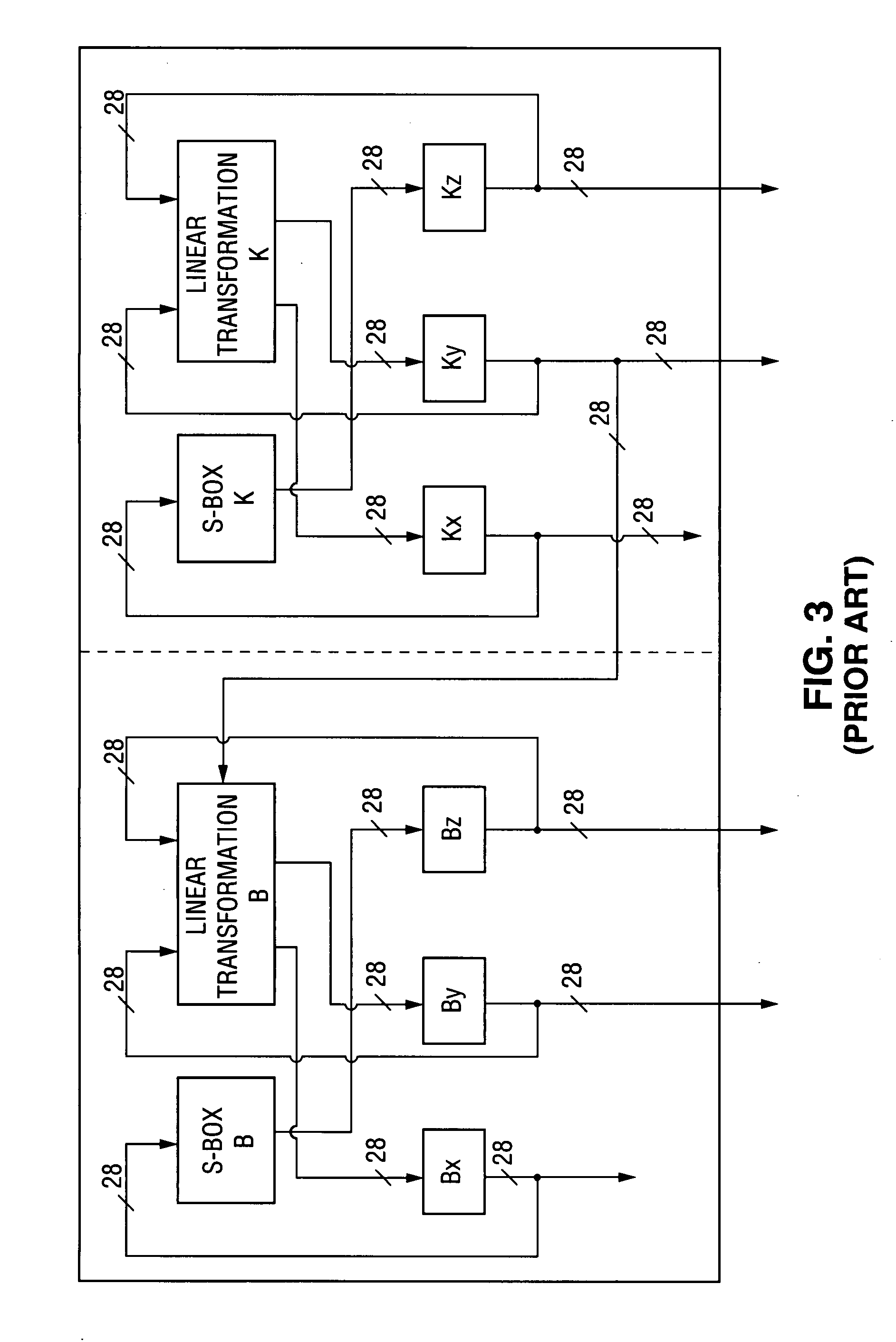
InactiveUS20070220279A1Reduce sensitivityLimit key re-useUnauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringGraphicsVideo processing
Owner:OPTIMUM CONTENT PROTECTION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com