Patents
Literature
545 results about "Pixel intensity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
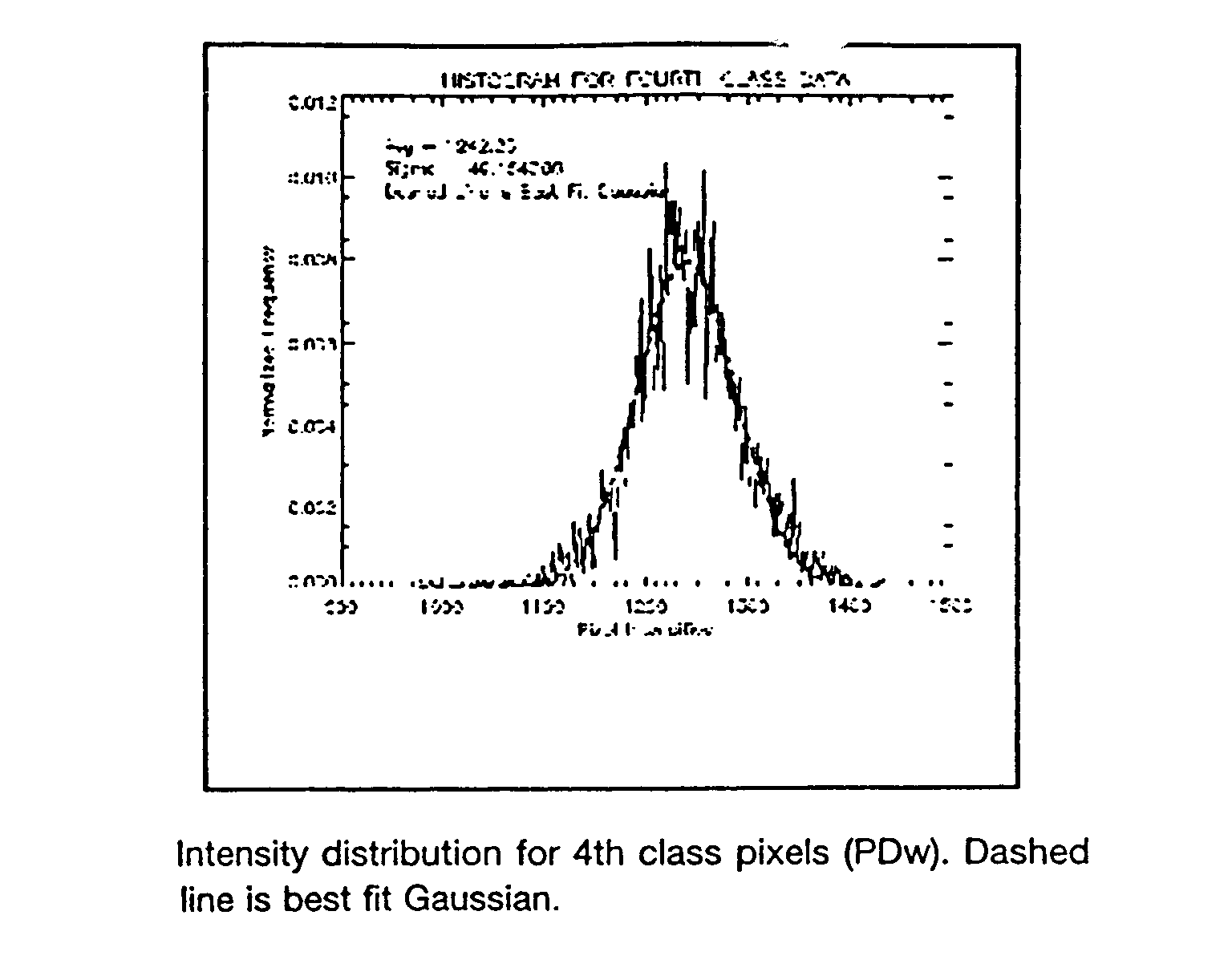
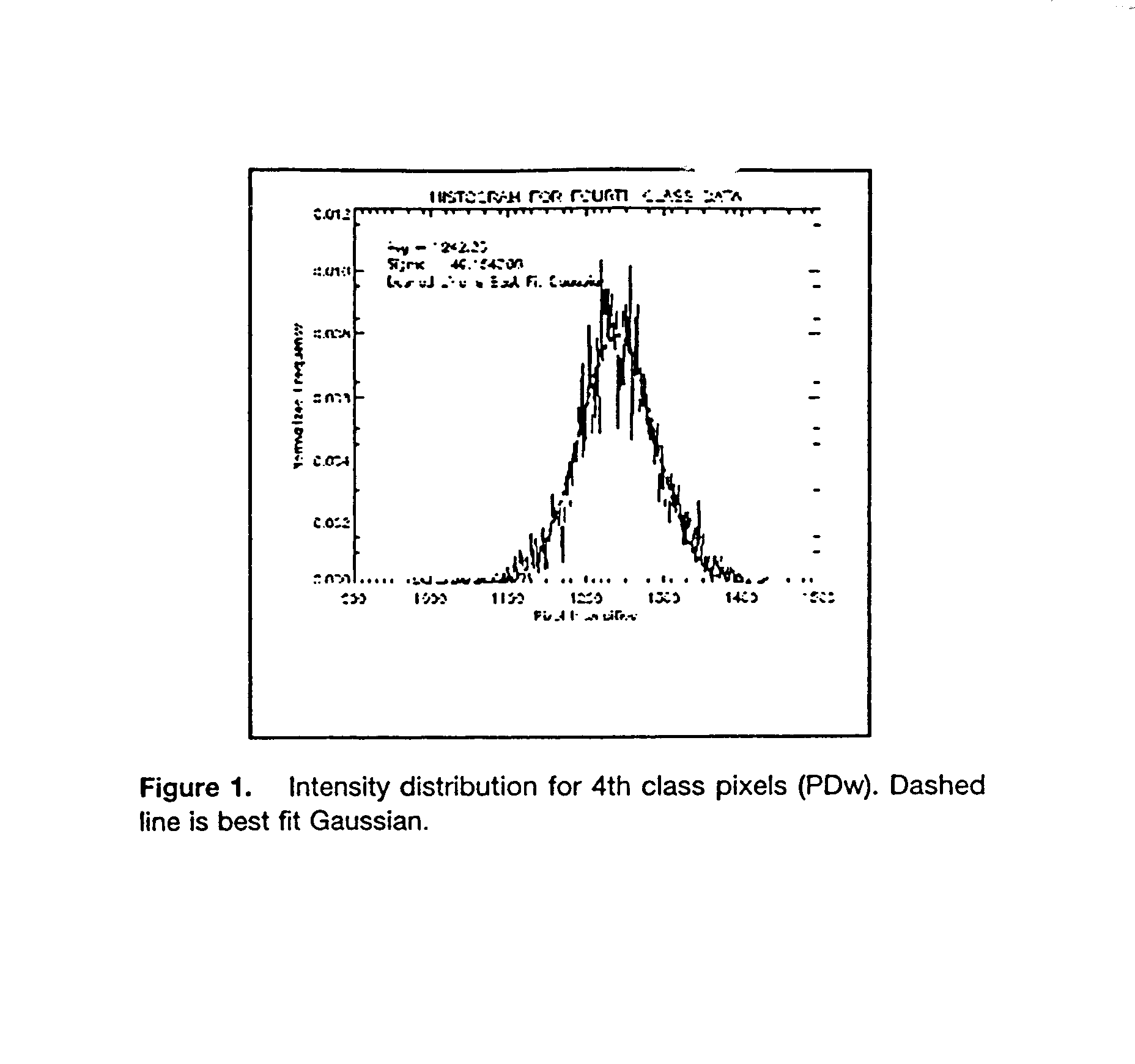
(to quote a line from "Independence Day"). A pixel's intensity is its brightness (I won't get into how that is calculated, but as a rule of thumb this will do). The histogram shows you how many pixels are at a given intensity level as compared to the others in the image.
Method and system for knowledge guided hyperintensity detection and volumetric measurement
InactiveUS6430430B1High sensitivityHigh detectionImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresTissues types
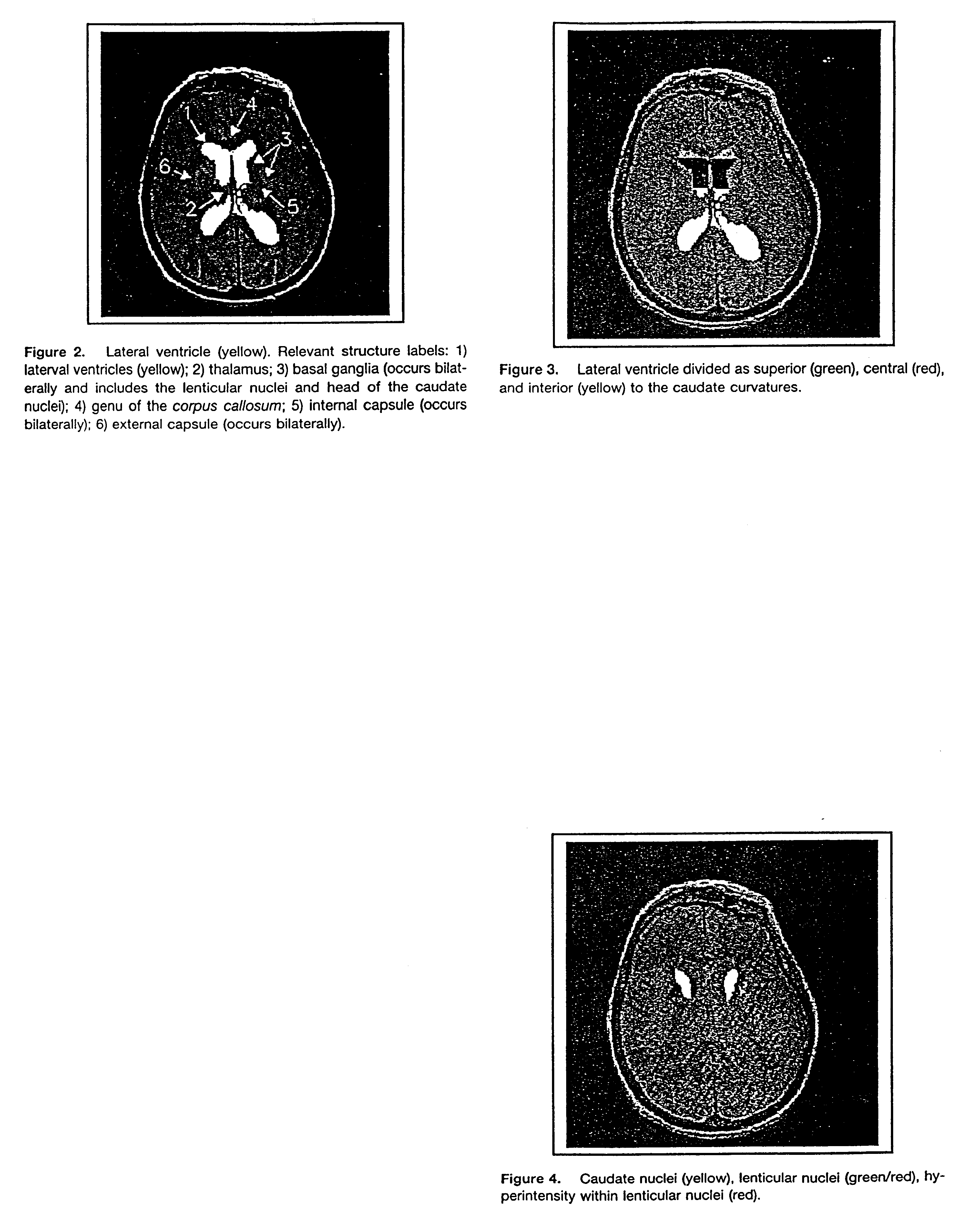
An automated method and / or system for identifying suspected lesions in a brain is provided. A processor (a) provides a magnetic resonance image (MRI) of a patient's head, including a plurality of slices of the patient's head, which MRI comprises a multispectral data set that can be displayed as an image of varying pixel intensities. The processor (b) identifies a brain area within each slice to provide a plurality of masked images of intracranial tissue. The processor (c) applies a segmentation technique to at least one of the masked images to classify the varying pixel intensities into separate groupings, which potentially correspond to different tissue types. The processor (d) refines the initial segmentation into the separate groupings of at least the first masked image obtained from step (c) using one or more knowledge rules that combine pixel intensities with spatial relationships of anatomical structures to locate one or more anatomical regions of the brain. The processor (e) identifies, if present, the one or more anatomical regions of the brain located in step (d) in other masked images obtained from step (c). The processor (f) further refines the resulting knowledge rule-refined images from steps (d) and (e) to locate suspected lesions in the brain.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Arbitrary fractional pixel movement
ActiveUS20100060646A1Continuous appearancePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningComputer graphics (images)Source image
A technique is provided for displaying pixels of an image at arbitrary subpixel positions. In accordance with aspects of this technique, interpolated intensity values for the pixels of the image are derived based on the arbitrary subpixel location and an intensity distribution or profile. Reference to the intensity distribution provides appropriate multipliers for the source image. Based on these multipliers, the image may be rendered at respective physical pixel locations such that the pixel intensities are summed with each rendering, resulting in a destination image having suitable interpolated pixel intensities for the arbitrary subpixel position.
Owner:APPLE INC
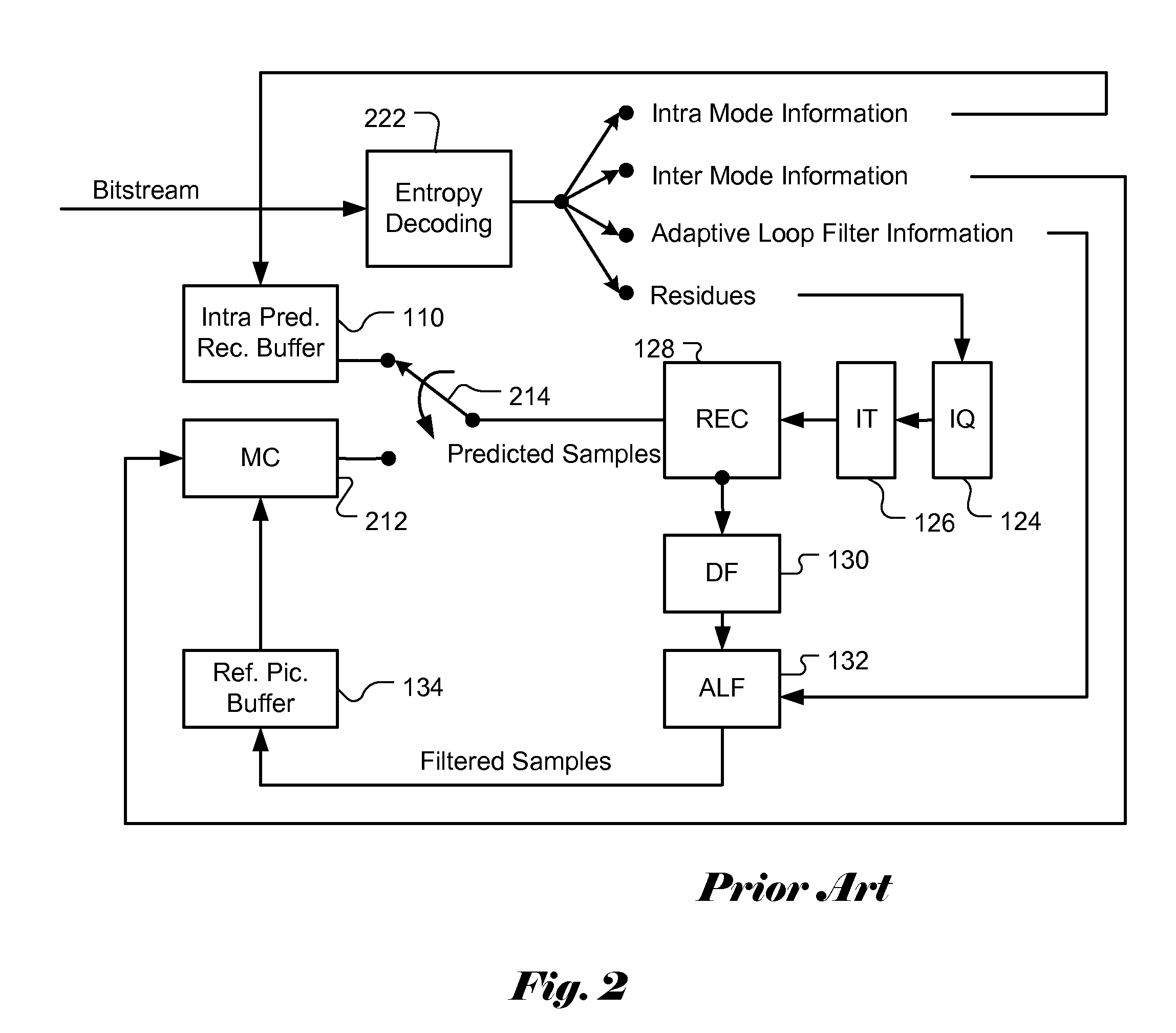
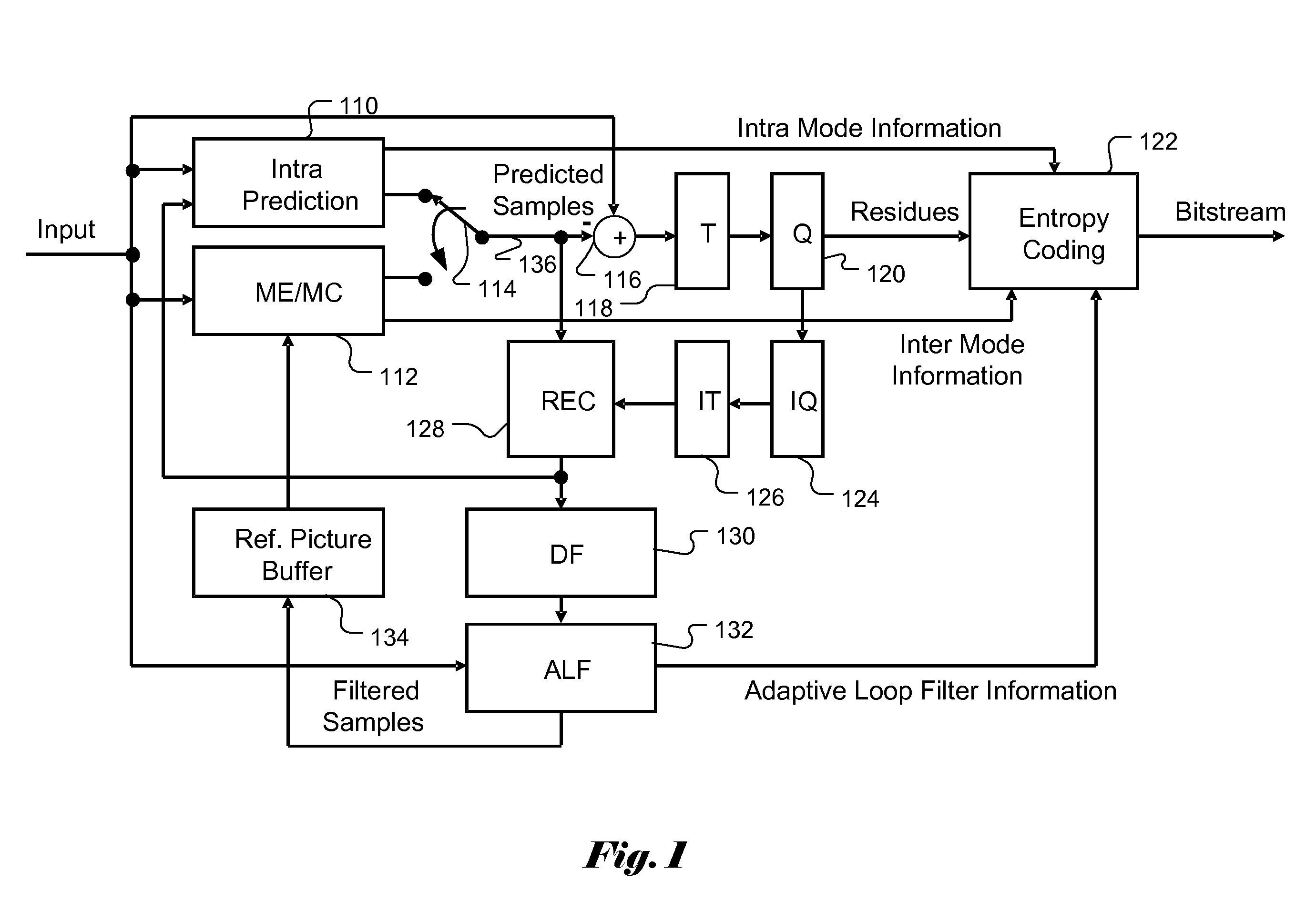
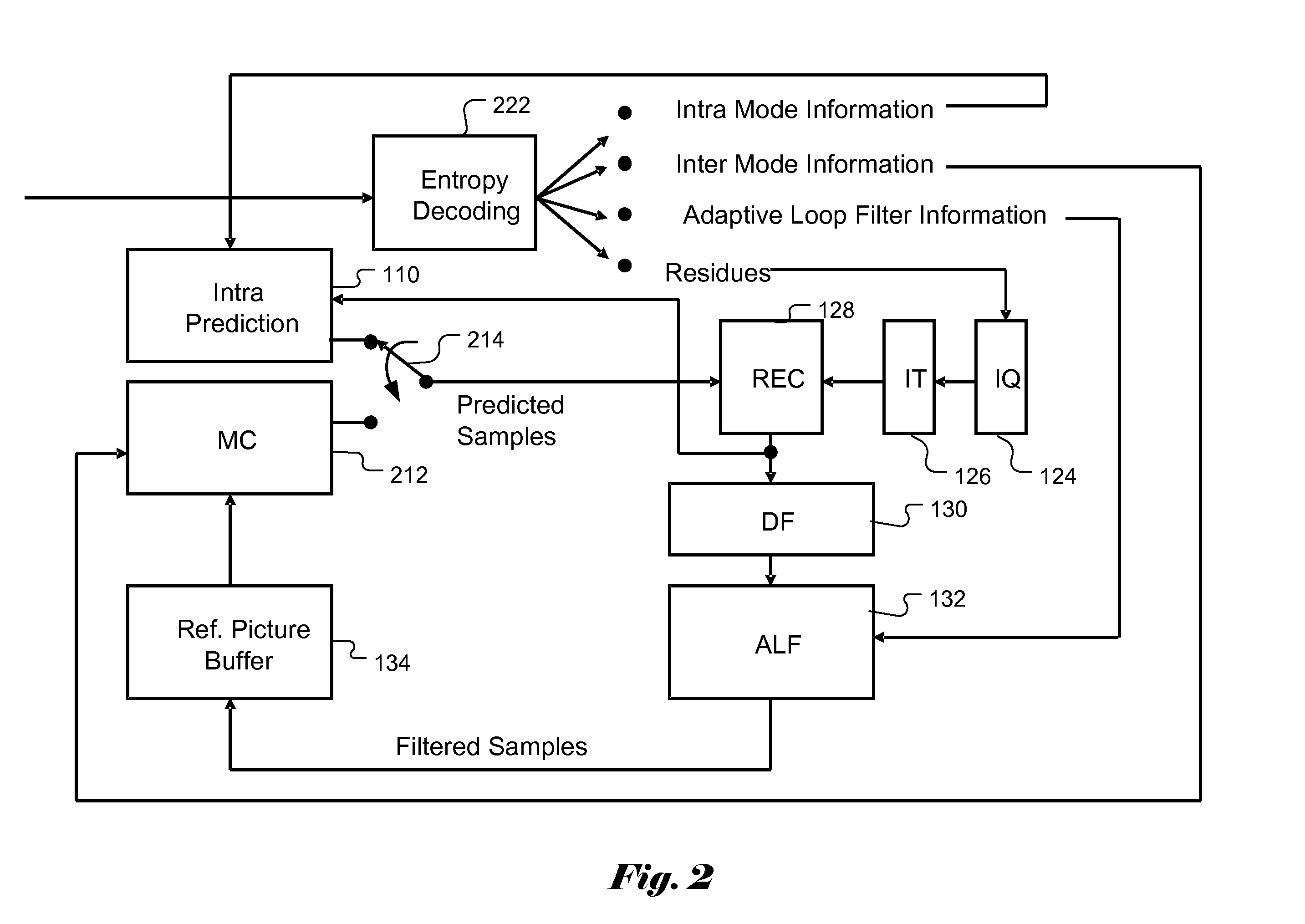
Apparatus and Method of Sample Adaptive Offset for Video Coding
ActiveUS20120177107A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer graphics (images)Self adaptive
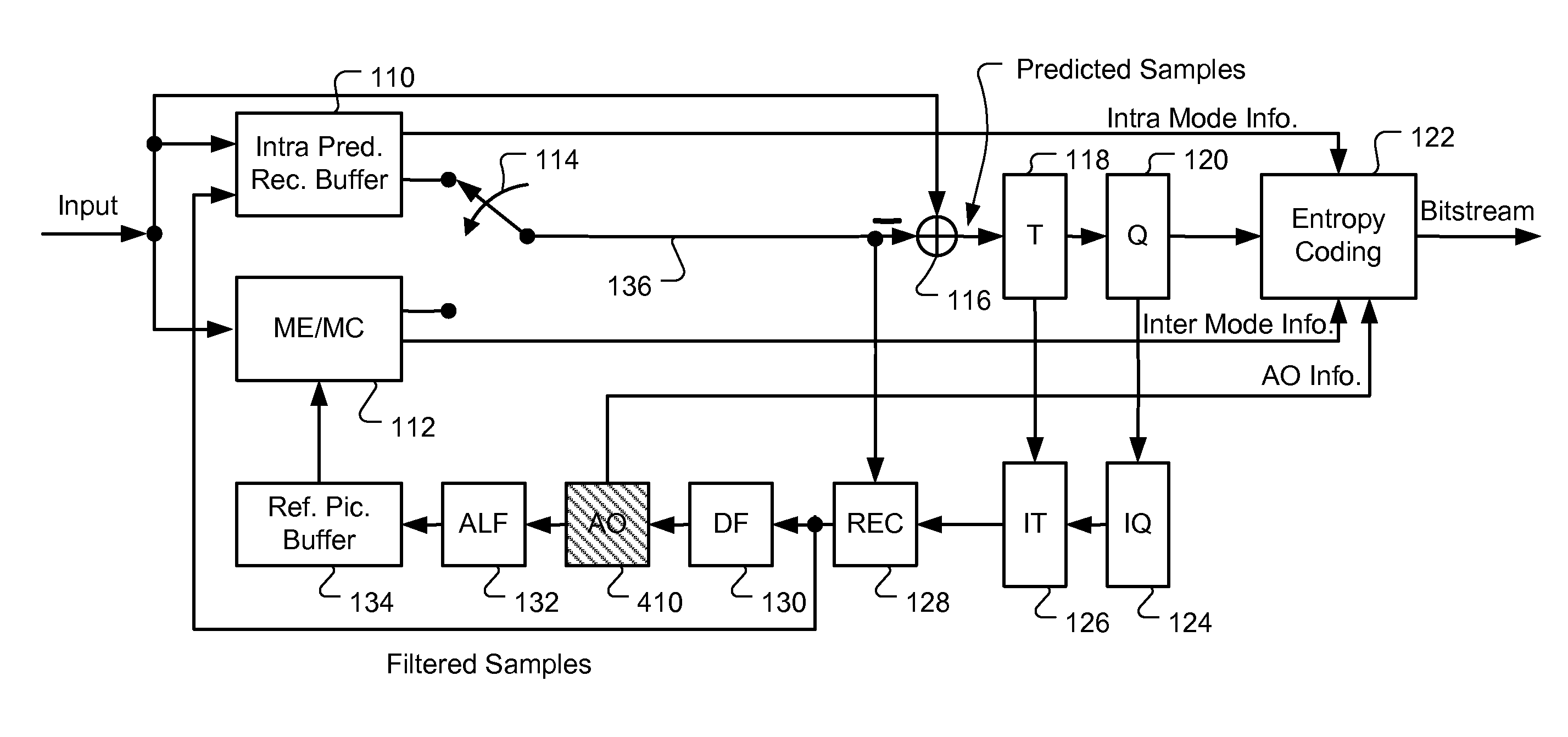
An apparatus and method for sample adaptive offset to restore intensity shift of processed video data are described. In a video coding system, the video data are subject to various processing such as prediction, transformation, quantization, deblocking, and adaptive loop filtering. Along the processing path in the video coding system, certain characteristics of the processed video data may be altered from the original video data due to the operations applied to video data. For example, the mean value of the processed video may be shifted. Therefore, the pixel intensity shift has to be carefully compensated or restored to alleviate the artifacts. Accordingly a sample adaptive offset scheme is disclosed that can take into consideration of the dynamic characteristics within a frame using a region partition scheme. Furthermore, the sample adaptive offset scheme also supports multiple SAO types that can be tailored to the characteristics of processed video data and achieve better quality.
Owner:HFI INNOVATION INC
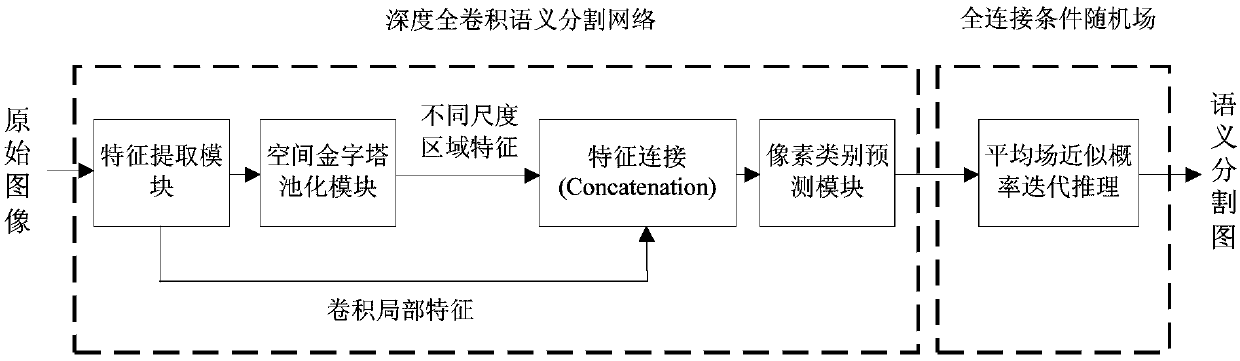
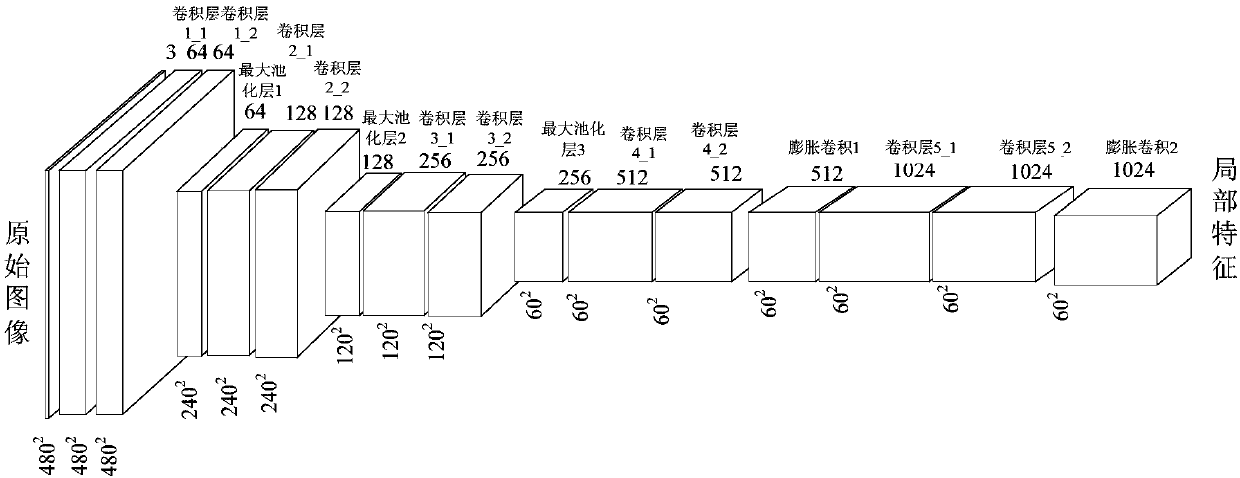
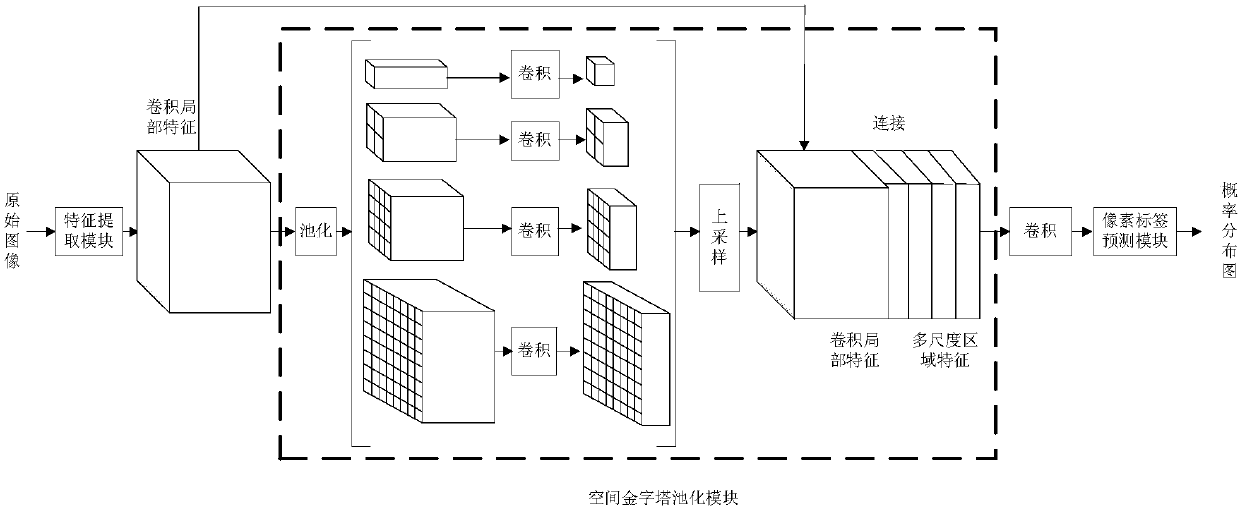
Image semantic division method based on depth full convolution network and condition random field
InactiveCN108062756ADoes not reduce dimensionalityHigh-resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisConditional random fieldImage resolution
The invention provides an image semantic division method based on a depth full convolution network and a condition random field. The image semantic division method comprises the following steps: establishing a depth full convolution semantic division network model; carrying out structured prediction based on a pixel label of a full connection condition random field, and carrying out model training, parameter learning and image semantic division. According to the image semantic division method provided by the invention, expansion convolution and a spatial pyramid pooling module are introduced into the depth full convolution network, and a label predication pattern output by the depth full convolution network is further revised by utilizing the condition random field; the expansion convolution is used for enlarging a receptive field and ensures that the resolution ratio of a feature pattern is not changed; the spatial pyramid pooling module is used for extracting contextual features of different scale regions from a convolution local feature pattern, and a mutual relation between different objects and connection between the objects and features of regions with different scales are provided for the label predication; the full connection condition random field is used for further optimizing the pixel label according to feature similarity of pixel strength and positions, so that a semantic division pattern with a high resolution ratio, an accurate boundary and good space continuity is generated.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
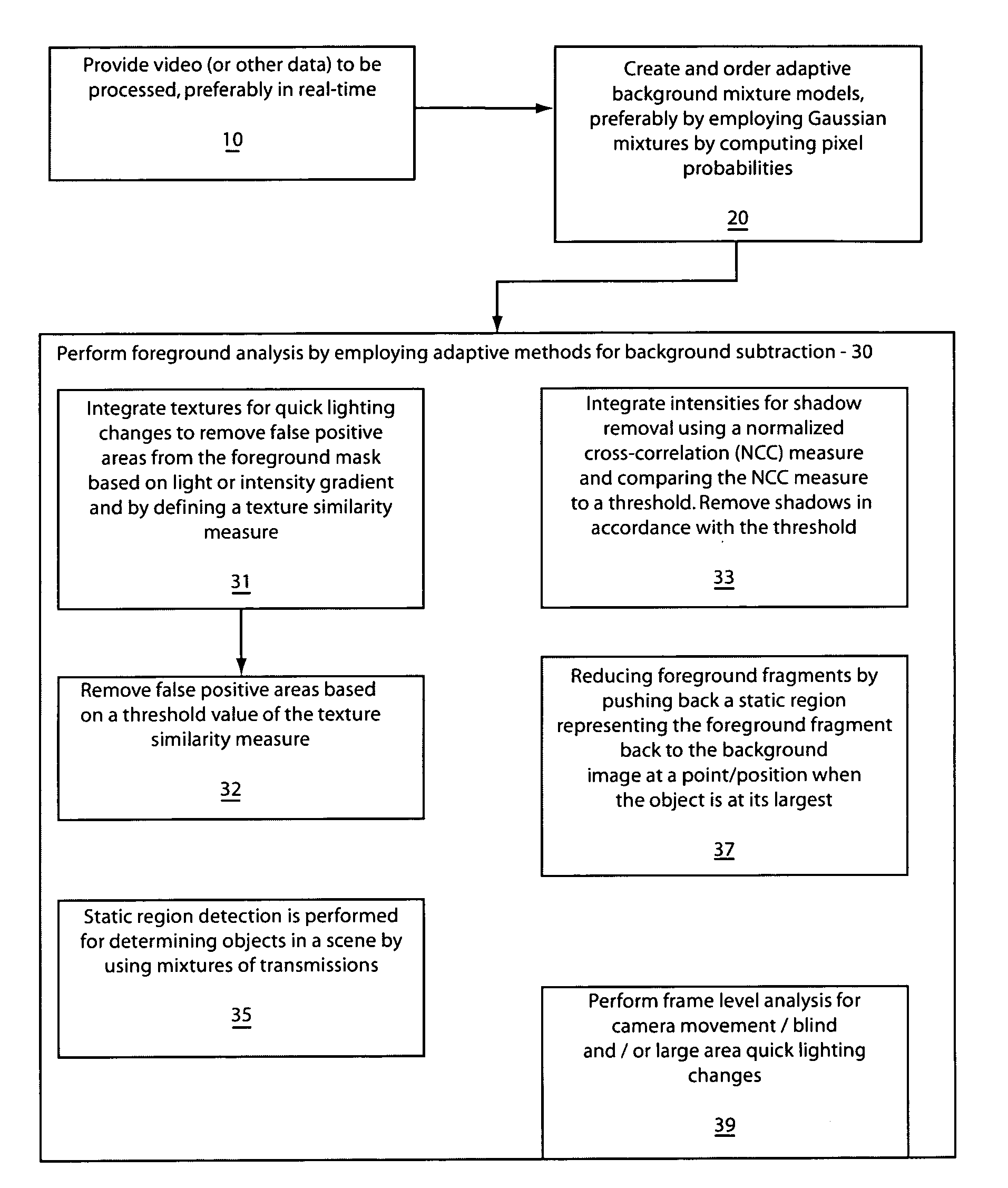
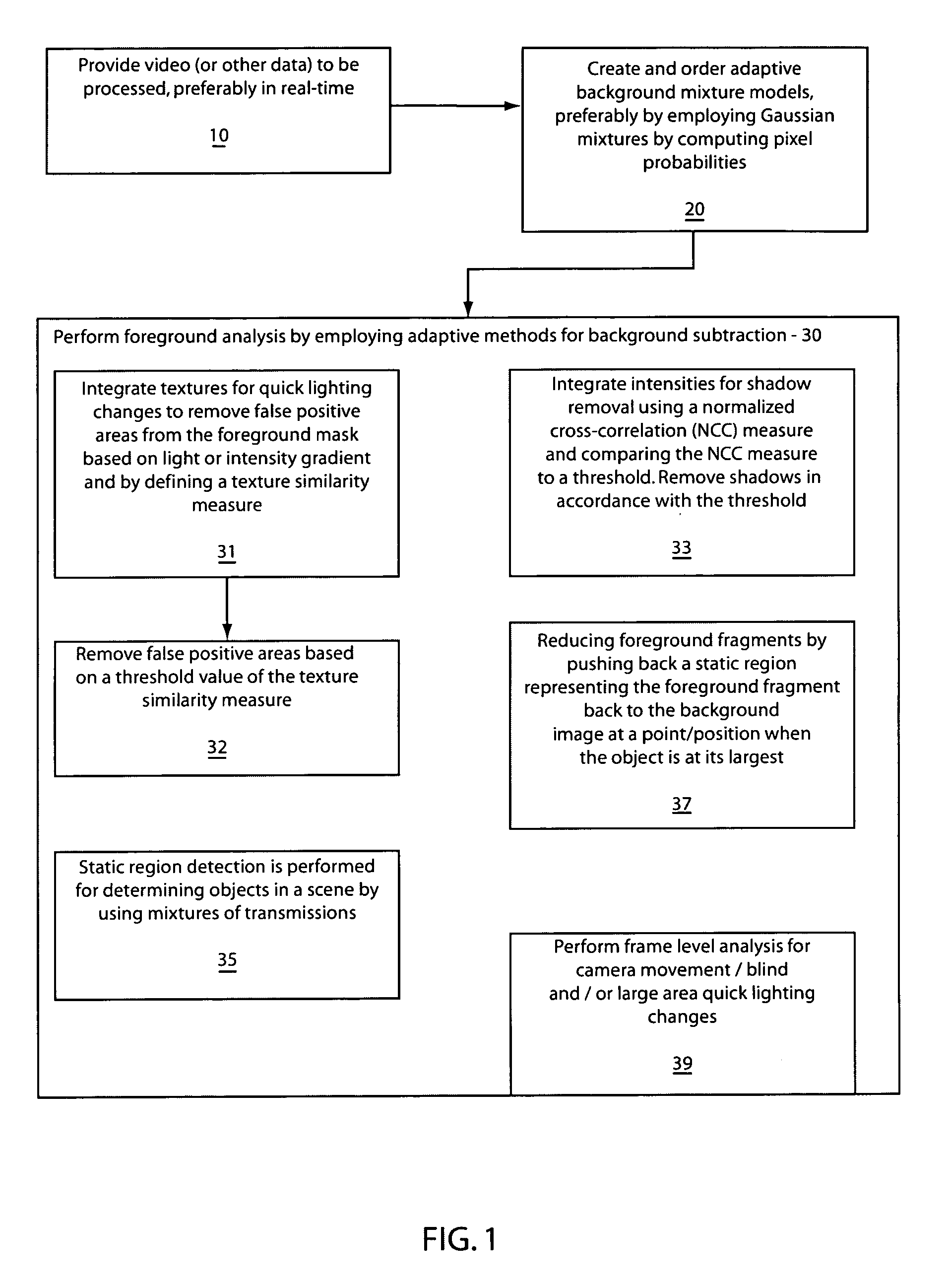
Robust and efficient foreground analysis for real-time video surveillance
Systems and methods for foreground analysis in real-time video include background subtraction and foreground detection, shadow removal, quick lighting change adaptation, static foreground region detection, foreground fragment reduction, and frame level change detection. Processes include background image extraction and foreground detection, integrating texture information of the background image and a current frame to remove false positive foreground areas resulting from lighting changes, integrating pixel intensity information by determining a cross-correlation of intensities between a current frame and the background image for each pixel in a foreground mask to remove image shadows. Static foreground region detection and fragment reduction are also included.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatus and method of adaptive offset for video coding
ActiveUS20110305274A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionOriginal dataVideo encoding
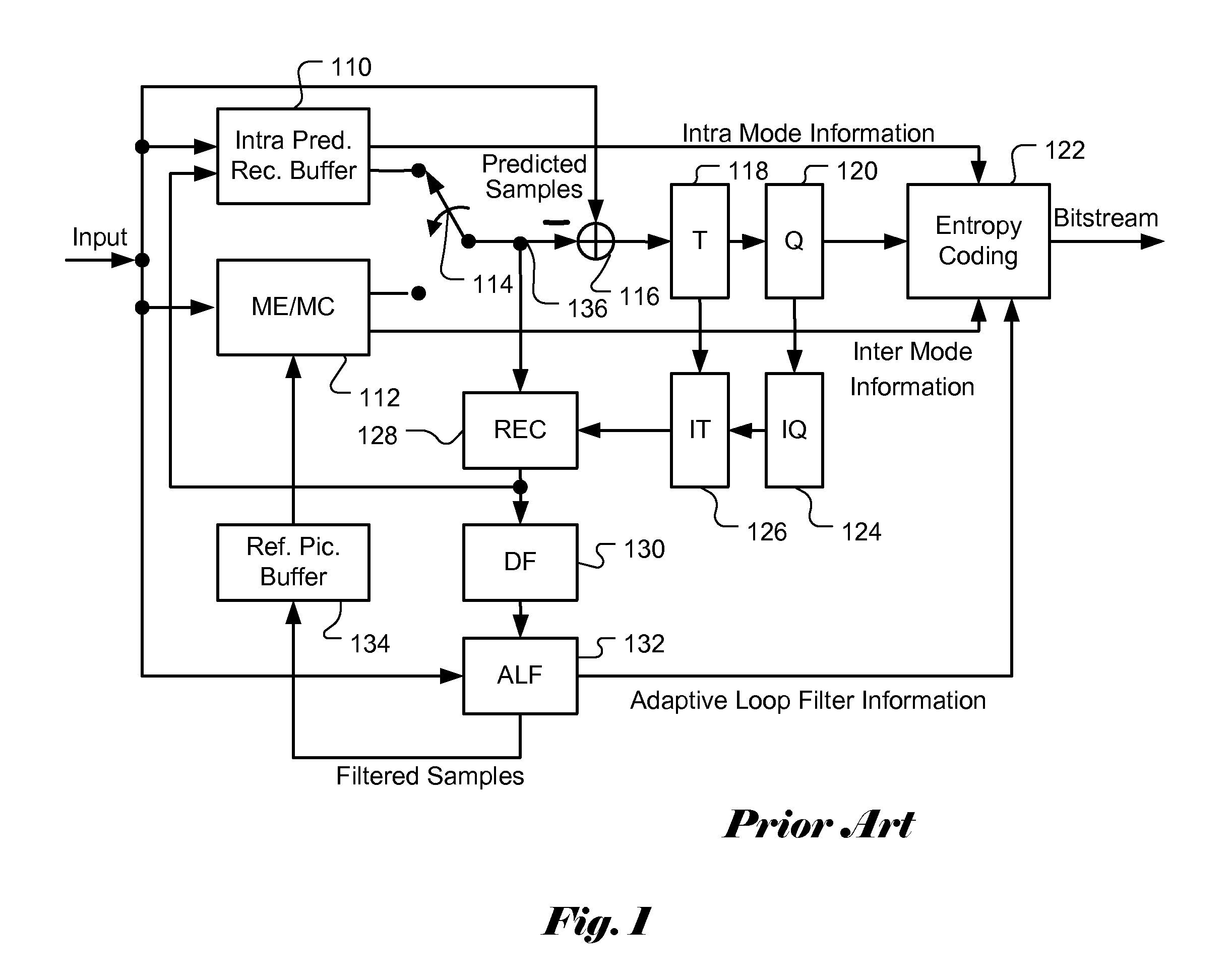
An apparatus and method for content adaptive offset restoration are described. In video processing system, due to various mathematic operations applied to the data, the mean intensity of the processed video data may be shifted from mean intensity of original data. The intensity offset will result in noticeable artifacts. Accordingly adaptive offset restoration is disclosed which derives intensity offset for a region of a picture based on the dynamic characteristics of underlying pixels. According to the characteristics measurement of underlying pixels, the pixels in each region are classified into classes and an intensity offset is determined for each class. The characteristics measurement may be based on pixel patterns at an underlying pixel and the characteristics may be related to edge, peak and valley at the underlying pixel. Alternatively, the characteristics measurement may be based on pixel intensity of an underlying pixel and the pixel intensity is partitioned into multiple bands for classification.
Owner:HFI INNOVATION INC
Interactive Display System
InactiveUS20110227827A1Reduce human perceptibilityPositioning can be rapidly and efficientlyInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay deviceConsecutive frame
An interactive display system including a wireless pointing device including a camera or other video capture system. The pointing device captures images displayed by the computer, including one or more human-imperceptible positioning targets. The positioning targets are presented as patterned modulation of the intensity (e.g., variation in pixel intensity) in a display frame of the visual payload, followed by the opposite modulation in a successive frame. At least two captured image frames are subtracted from one another to recover the positioning target in the captured visual data and to remove the displayed image payload. The location, size, and orientation of the recovered positioning target identify the aiming point of the remote pointing device relative to the display. Another embodiment uses temporal sequencing of positioning targets (either human-perceptible or human-imperceptible) to position the pointing device.
Owner:INTERPHASE CORP
Devices and methods for reducing artefacts in display devices by the use of overdrive
ActiveUS20100207960A1Reducing imaging artefactReduce artefactCathode-ray tube indicatorsControl signalDisplay device
The invention relates to a method for reducing imaging artefacts during a frame-changeover from a current frame to a following frame displayed by a display device comprising a plurality of pixels, wherein the artefacts are reduced by overdriving at least one control signal for controlling the pixel intensity of the related pixel during the frame-changeover, wherein the overdrive is carried out in dependence of the magnitude of an intensity step between a designated start intensity value of the pixel within the current frame and a designated target intensity value of the pixel within the following frame.
Owner:BARCO NV
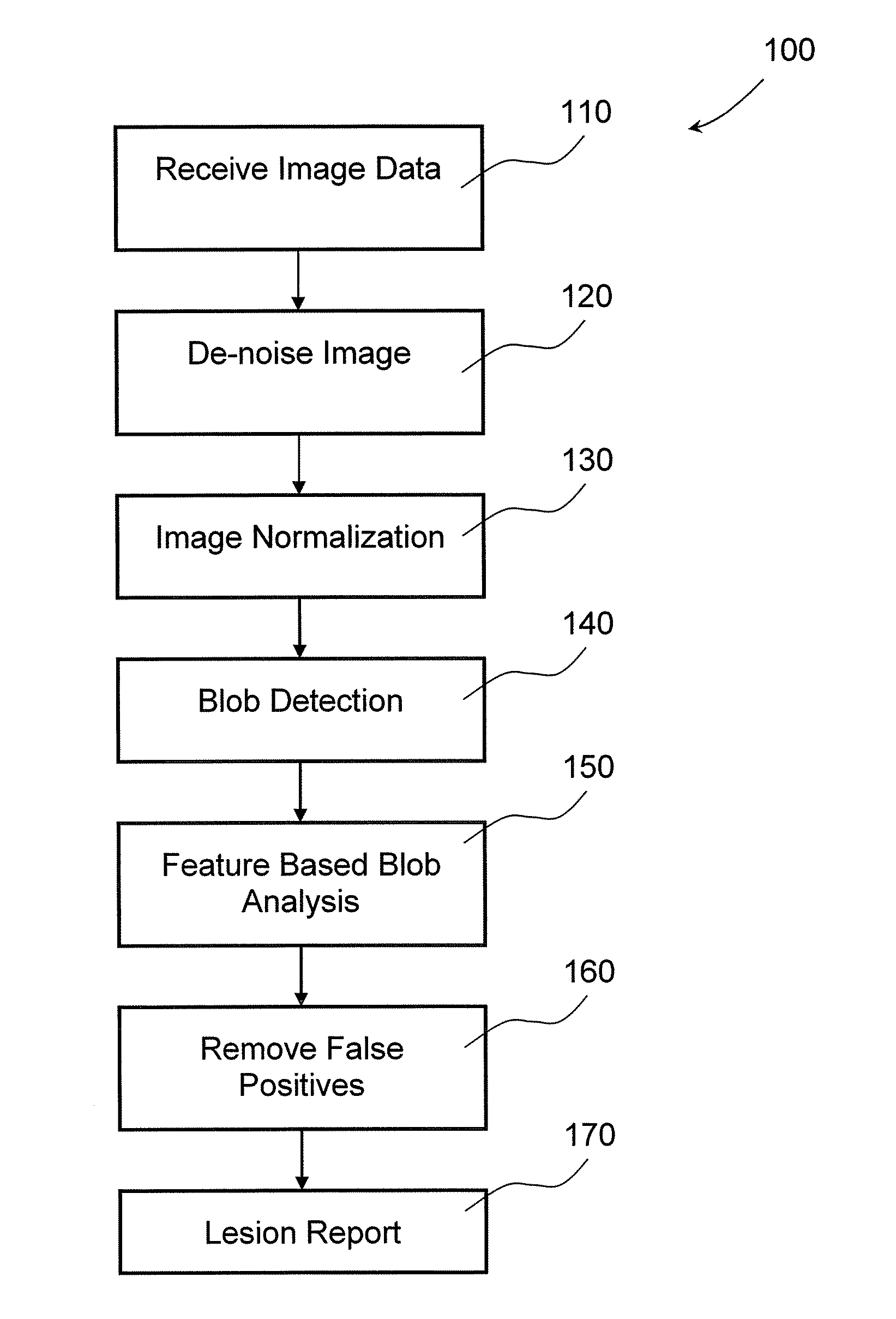
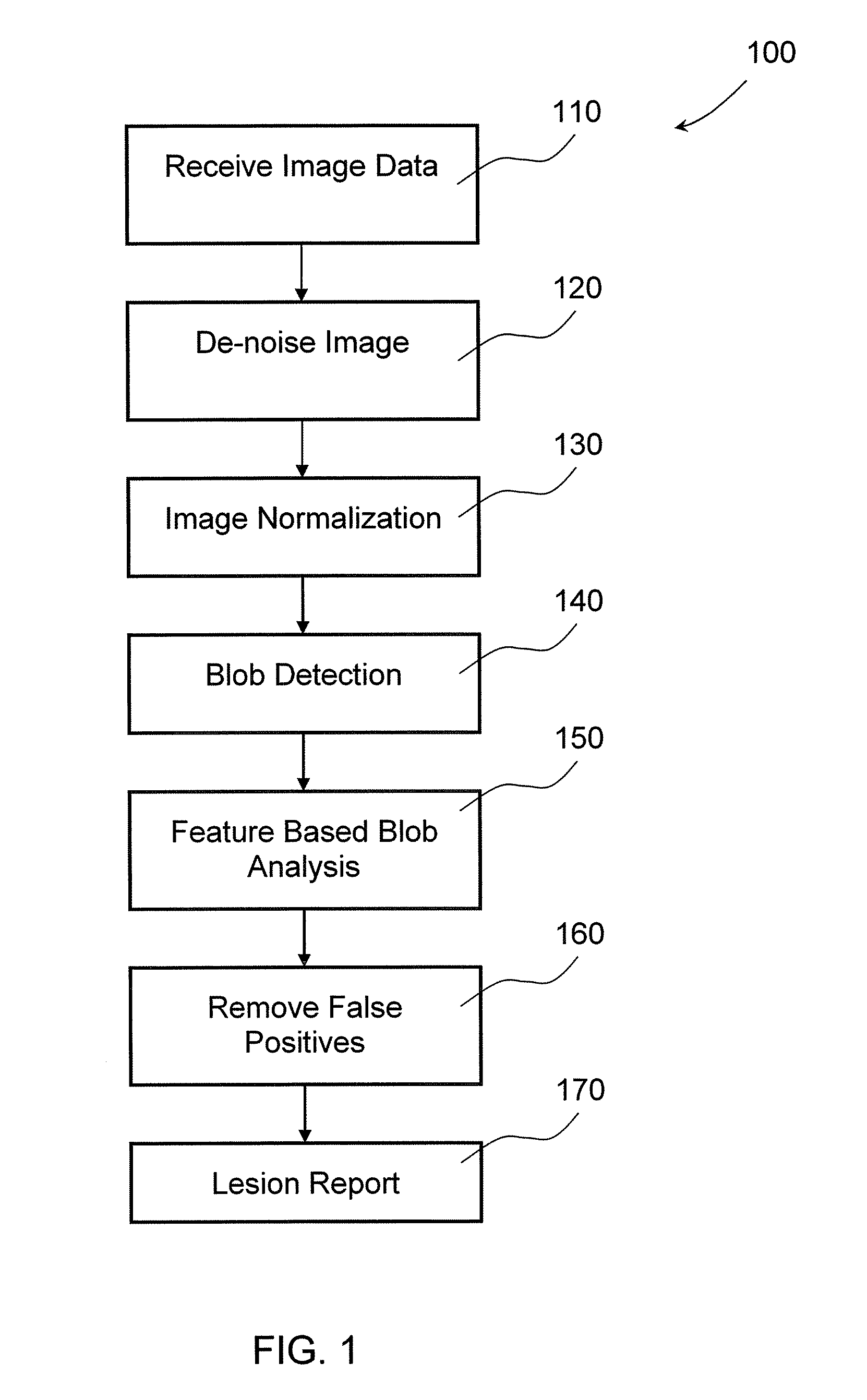
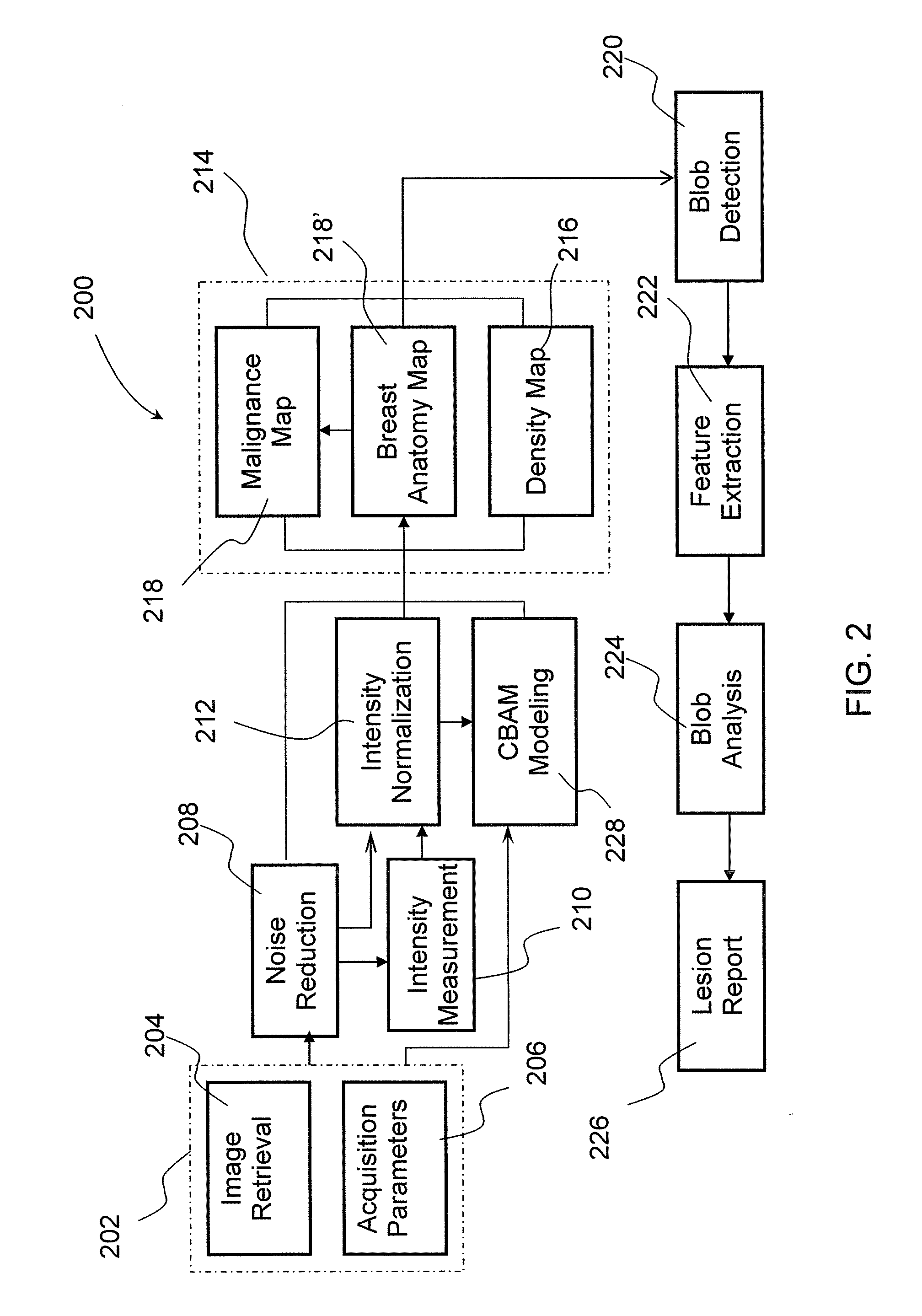
Method and system of automated detection of lesions in medical images
InactiveUS20100158332A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementNon malignantComputer vision
The invention provides a system and method for processing medical images. Input medical images are normalized first, utilizing pixel intensities of control point tissues, including subcutaneous fat. Clustered density map and malignance probability map are generated from a normalized image and further analyzed to identify regions of common internal characteristics, or blobs, that may represent lesions. These blobs are analyzed and classified to differentiate possible true lesions from other types of non-malignant masses often seen in medical images.
Owner:THE MEDIPATTERN CORP
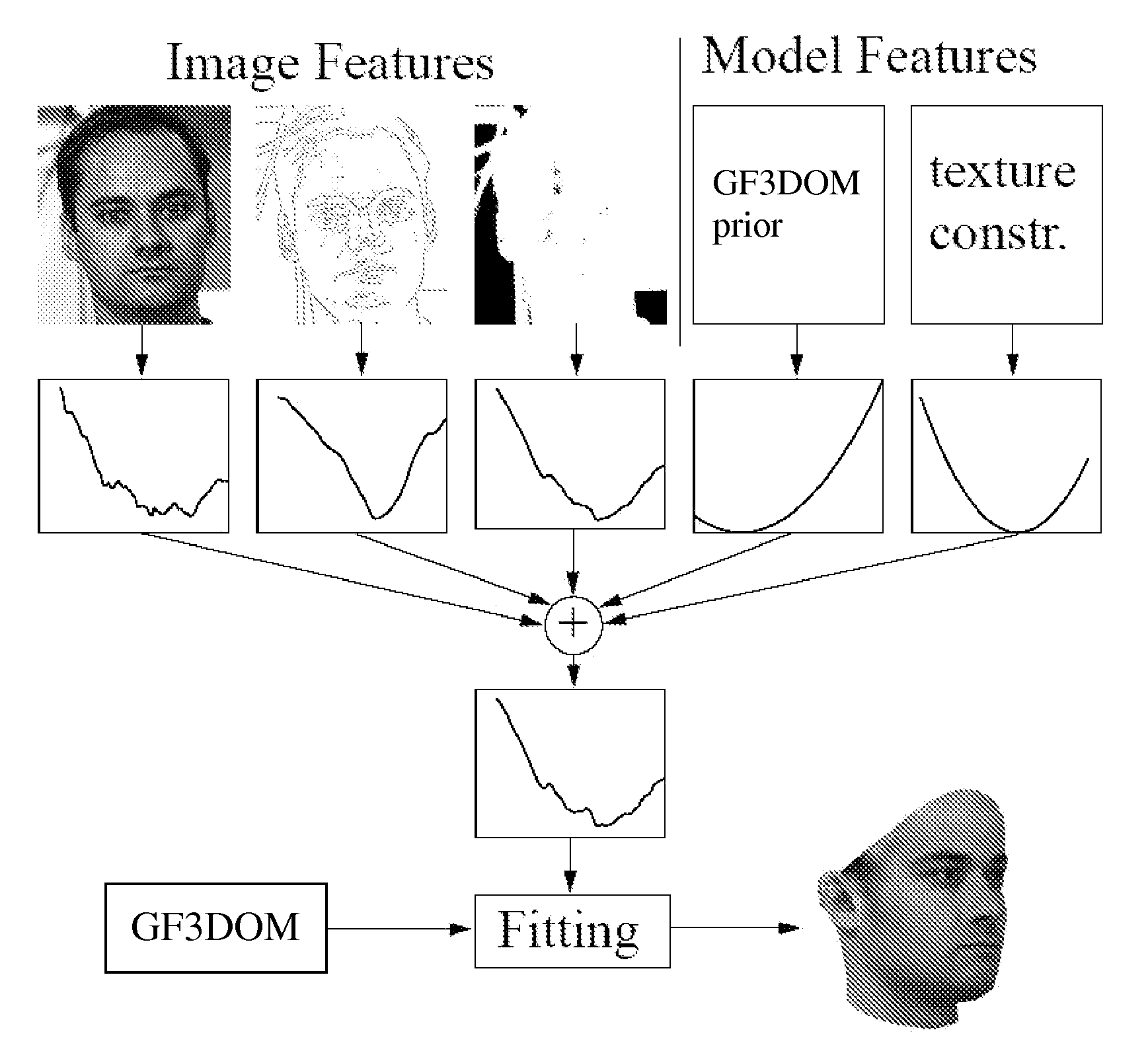
Estimating 3D shape and texture of a 3D object based on a 2d image of the 3D object
InactiveUS20070031028A1Maximizing posterior probabilityPerformance maximizationAdditive manufacturing apparatusDrawing from basic elements3d shapesObject based
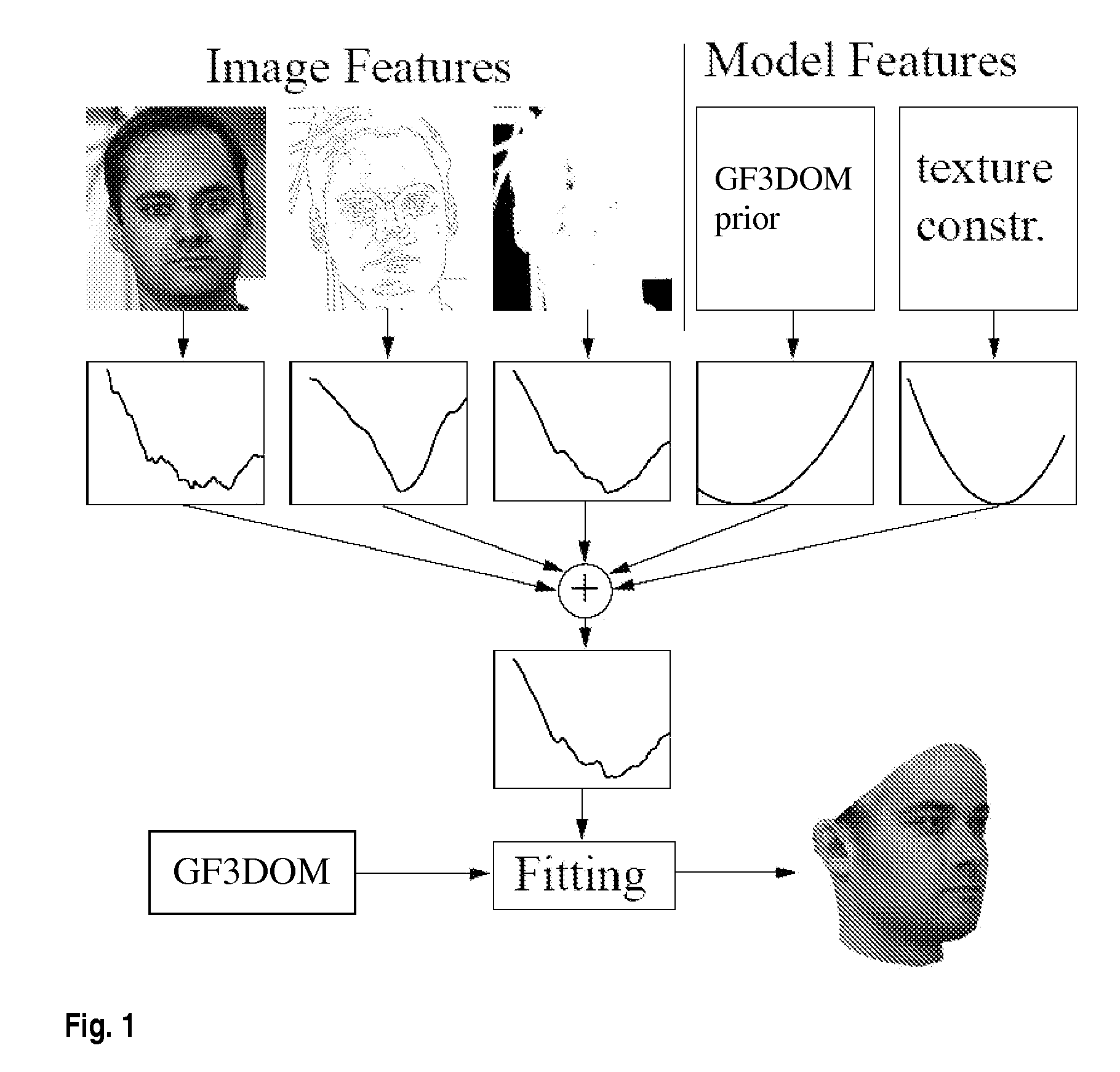
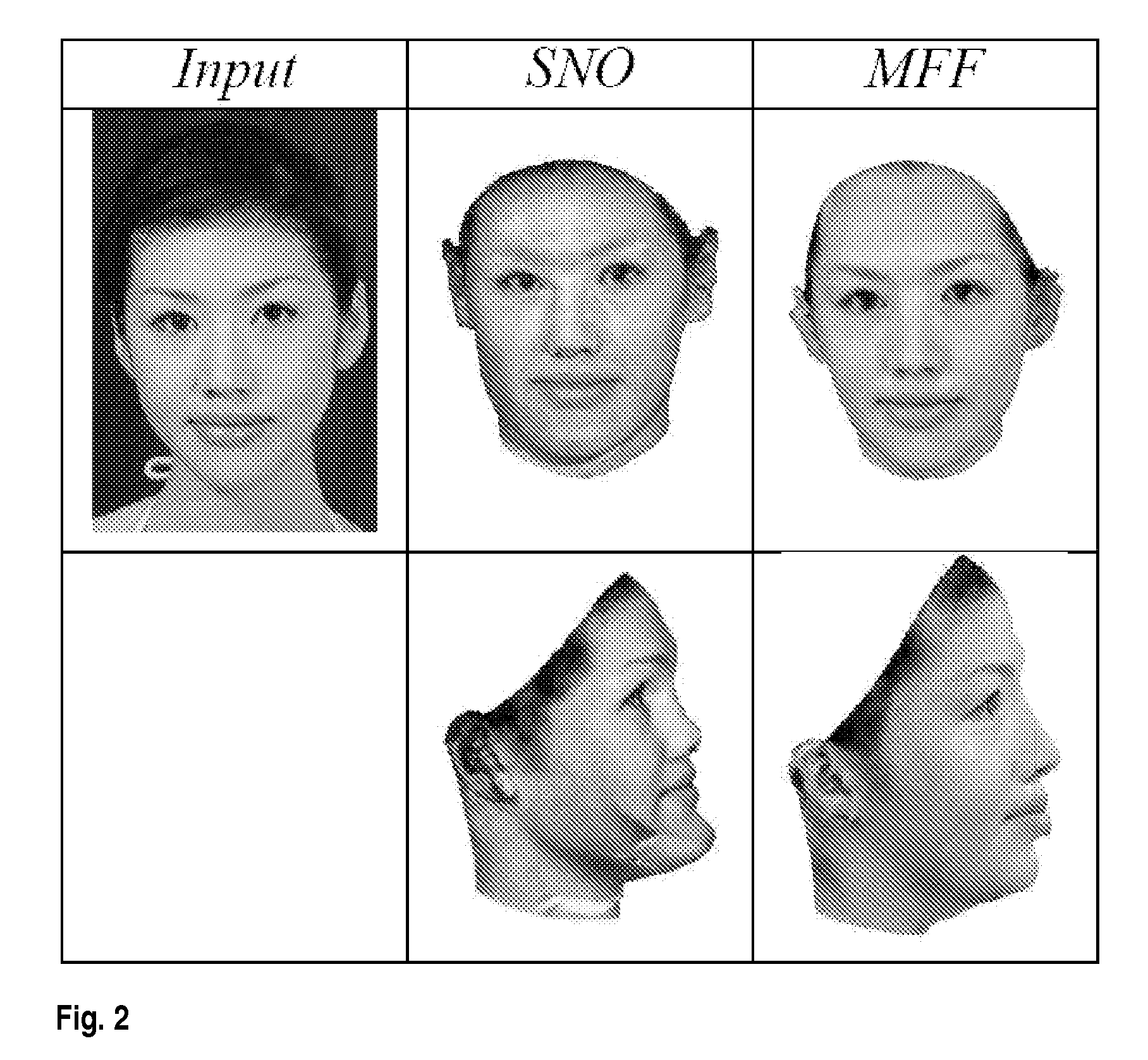
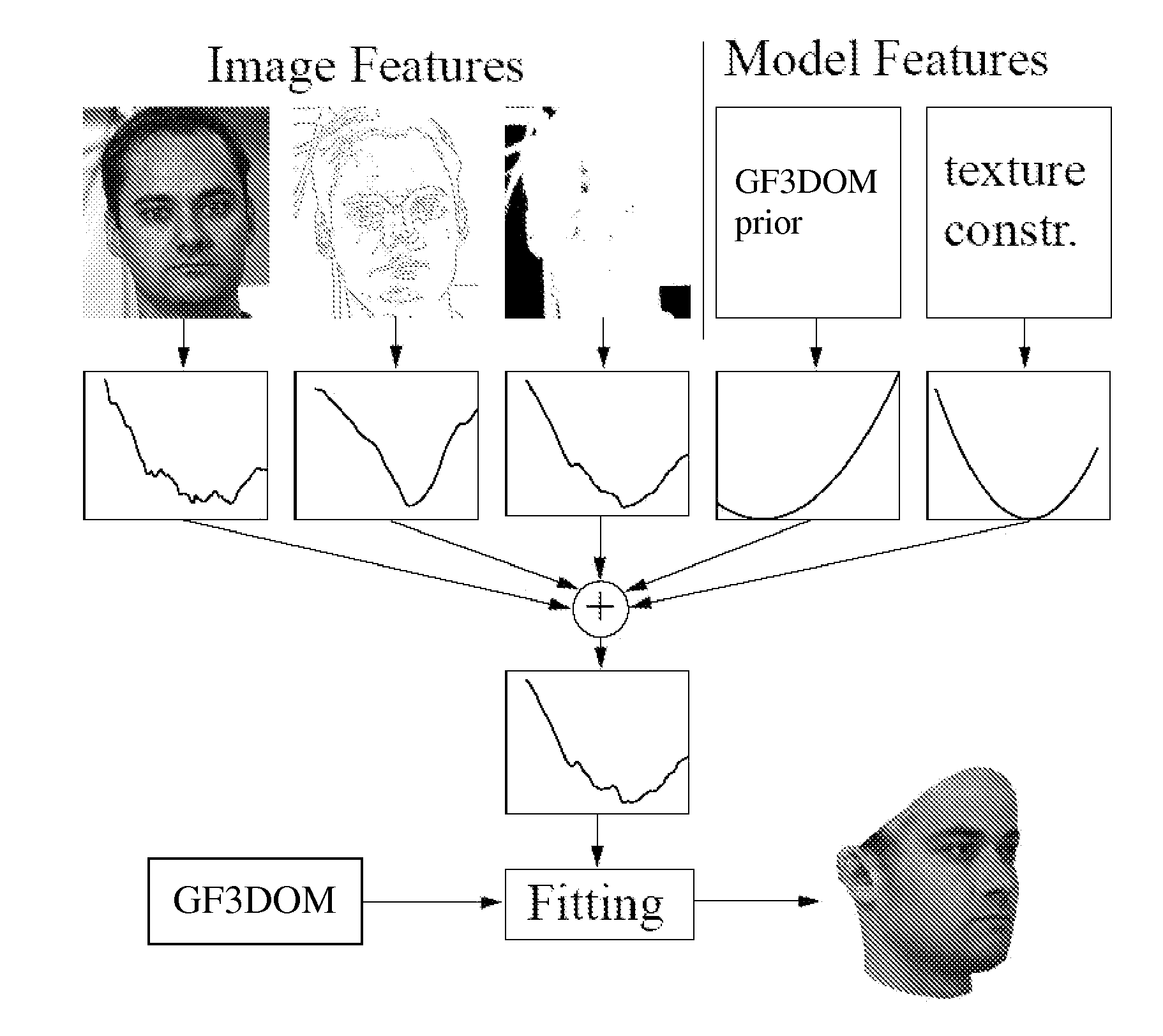
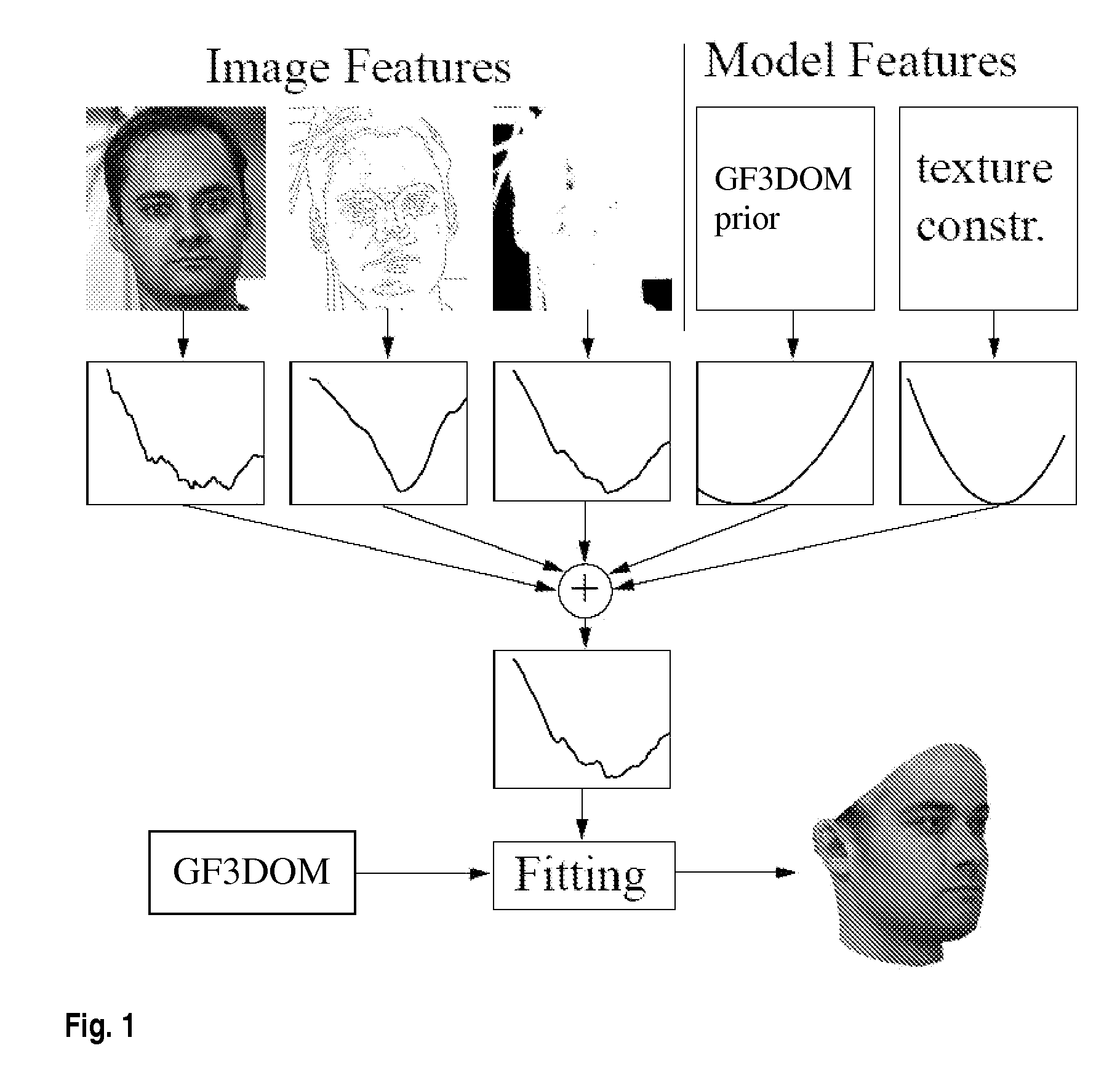
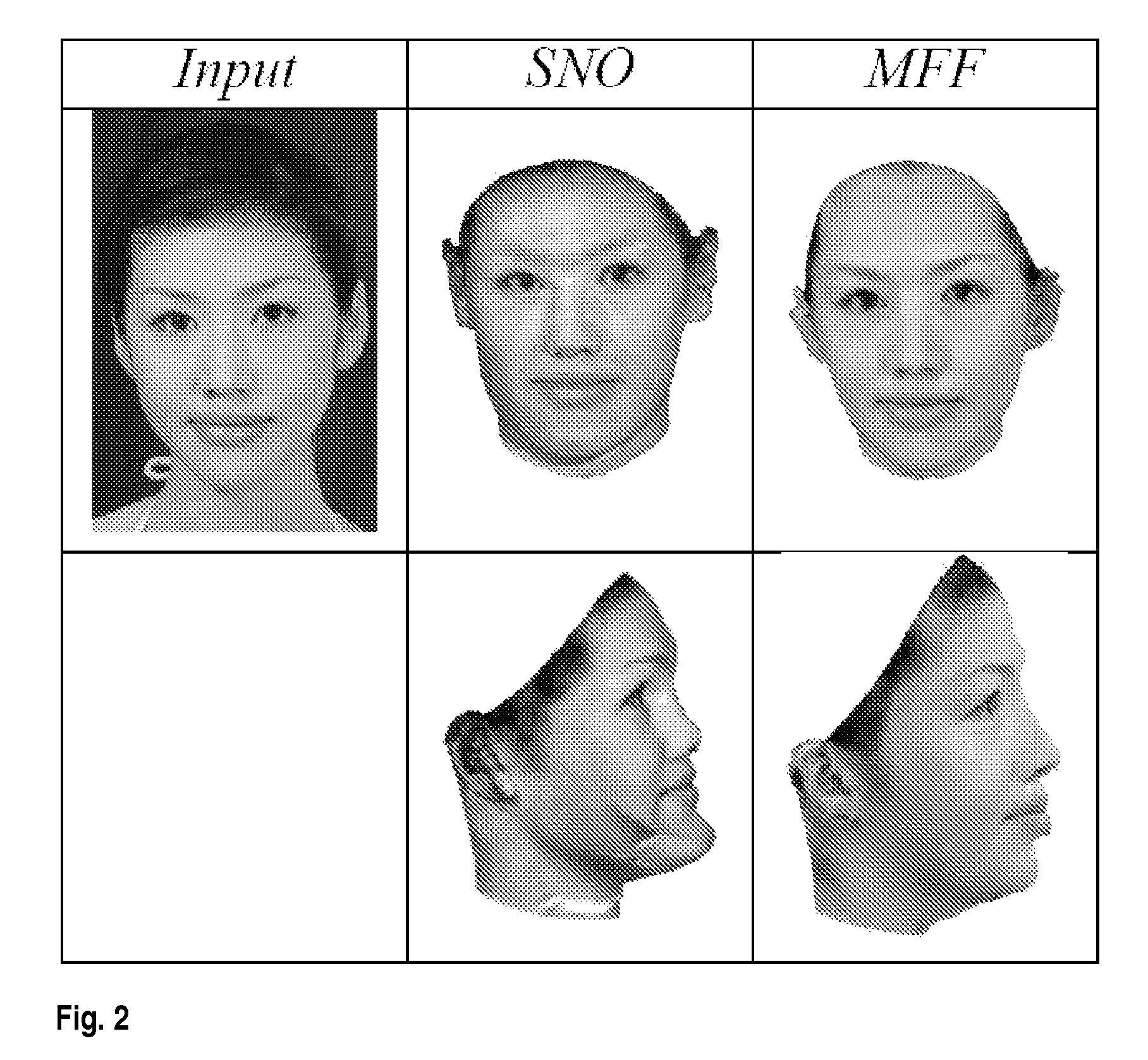
Disclosed is an improved algorithm for estimating the 3D shape of a 3-dimensional object, such as a human face, based on information retrieved from a single photograph by recovering parameters of a 3-dimensional model and methods and systems using the same. Beside the pixel intensity, the invention uses various image features in a multi-features fitting algorithm (MFF) that has a wider radius of convergence and a higher level of precision and provides thereby better results.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF BASEL
Processing a video for vascular pattern detection and cardiac function analysis
InactiveUS20130322729A1Quick discoveryEffective toolImage enhancementImage analysisPattern detectionLength wave
What is disclosed is a non-contact system and method for determining cardiac function parameters from a vascular pattern identified from RGB and IR video signals captured simultaneously of a region of exposed skin of a subject of interest. In one embodiment, a video of a region of exposed skin is captured using a video camera that captures color values for pixels over visible channels and an IR camera that measures pixel intensity values in wavelength ranges of interest. Pixel intensity values are processed to generate a vascular binary mask that indicates pixel locations corresponding to the vascular pathways. The IR images are registered with corresponding data from the camera's visible channels such that pixels that correspond to the vascular pattern can be isolated in each frame of the video of visible color data. Once processed, pixels associated with the isolated vascular patterns are analyzed to determine desired cardiac function parameters.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Copy protection for digital motion picture image data
InactiveUS7043019B2Television system detailsUser identity/authority verificationComputer graphics (images)Copy protection
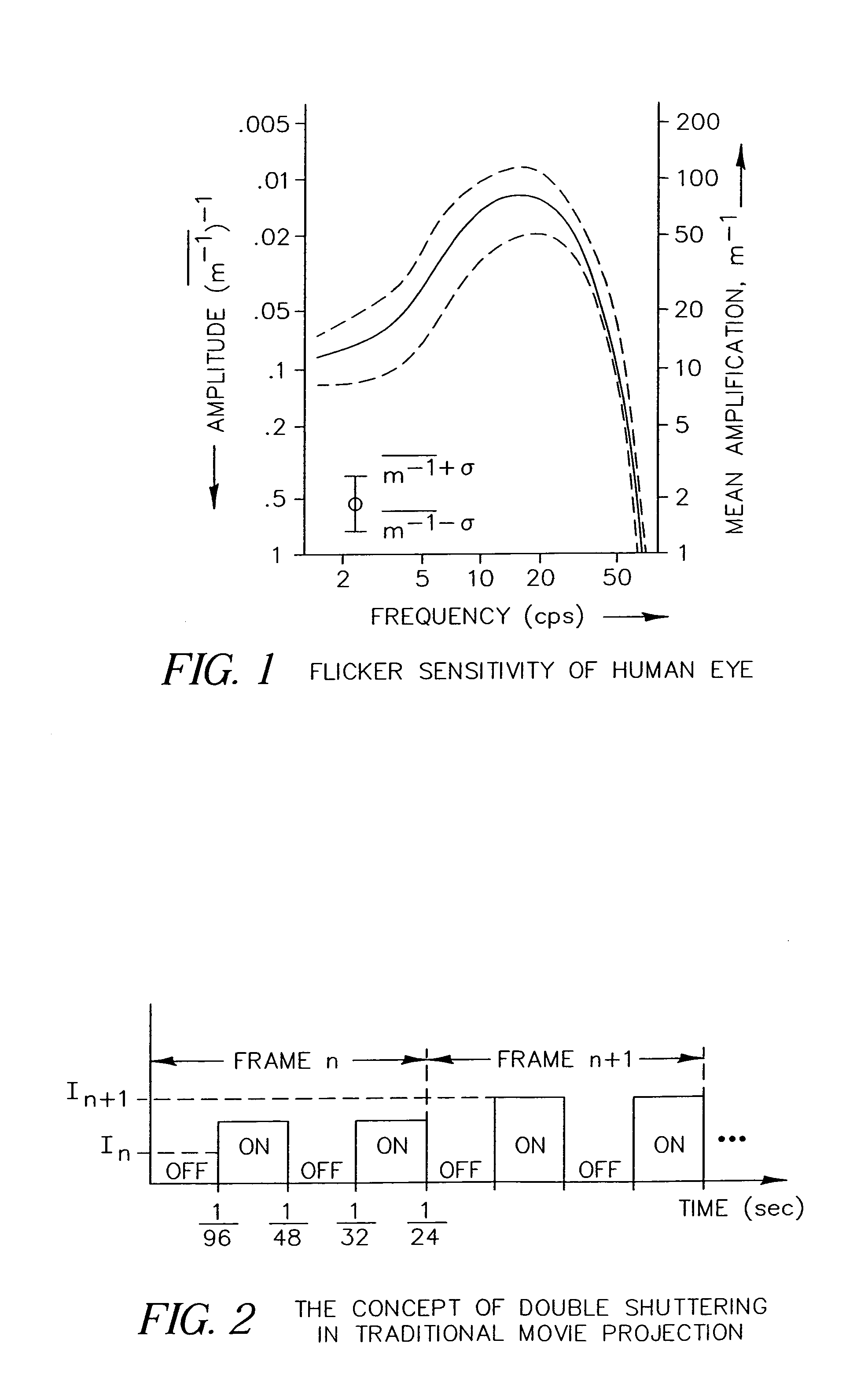
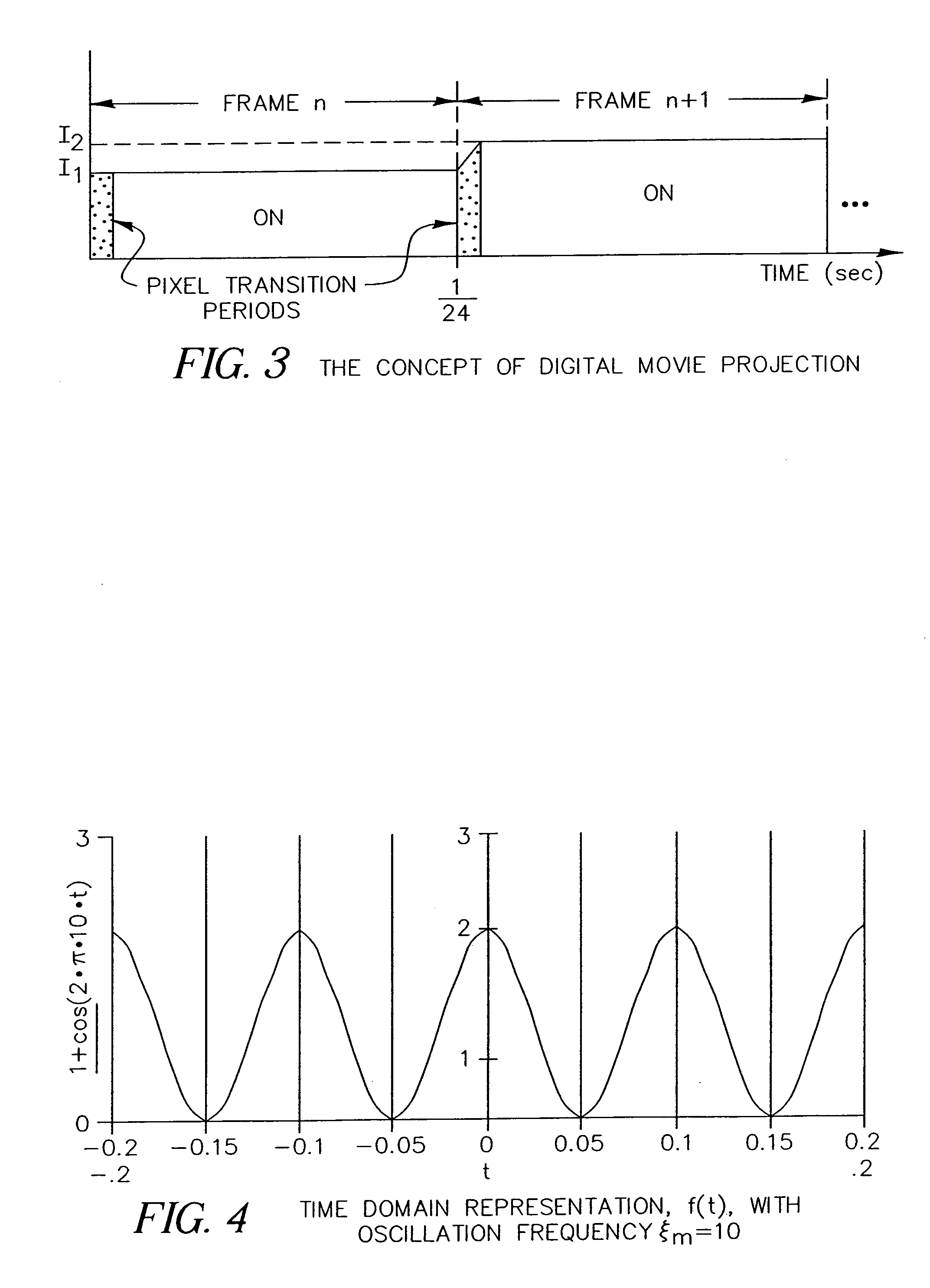
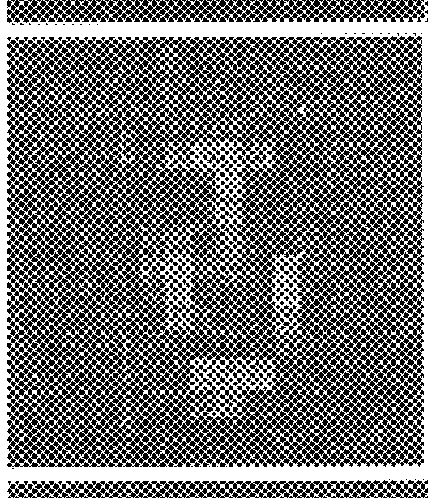
An apparatus and method for displaying a copy-deterrent pattern (104) within a digital motion picture in order to discourage recording of the motion picture using a video camera or other sampling recording device. A copy-deterrent pattern (104) could be, for example, one or more symbols, a random pattern, a digital watermark or a text message (106). The copy-deterrent pattern (104) comprises a plurality of pixels within each frame of the digital motion picture, and the displayed pixel intensities are modulated at a temporal frequency using modulation characteristics deliberately selected to be imperceptible to human observers while simultaneously producing objectionable aliasing in any copy made using a video camera.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Multiresolutional critical point filter and image matching using the same
A multiresolutional filter called a critical point filter is introduced. This filter extracts a maximum, a minimum, and two types of saddle points of pixel intensity for every 2x2 (horizontal x vertical) pixels so that an image of a lower level of resolution is newly generated for every type of a critical point. Using this multiresolutional filter, a source image and a destination image are hierarchized, and source hierarchical images and destination hierarchical images are matched using image characteristics recognized through a filtering operation.
Owner:JBF PARTNERS
Pixel selective white balancing
InactiveUS6876384B1Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsColor imageGain coefficient
A system and method for processing data representative of a color image is disclosed. Image data represents an intensity of photoexposure of an imaging array at specific locations in the imaging array and in distinct spectral regions corresponding to color channels. A process identifies “white” regions in the color image by comparing the intensities of photoexposure of groups of associated pixels which are responsive to photon energy in different spectral regions. If the intensities of photoexposure of the pixels in the group of associated pixels are proportionally equivalent, these pixels are determined to be in a white region of the image. White balancing gain coefficients are then based upon the pixel intensity values at pixel locations in the white regions of the image.
Owner:BIOMORPHIC VLSI
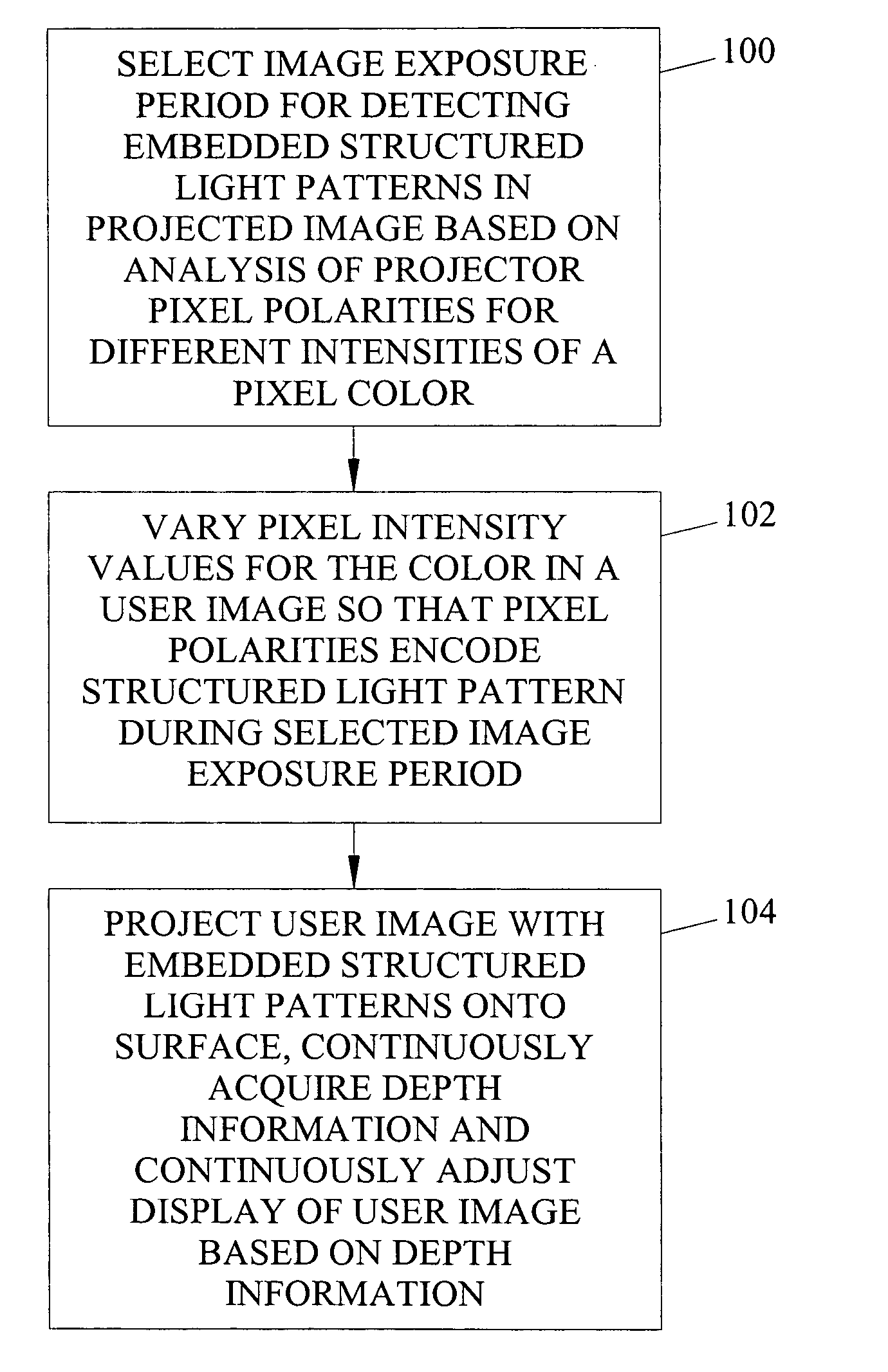
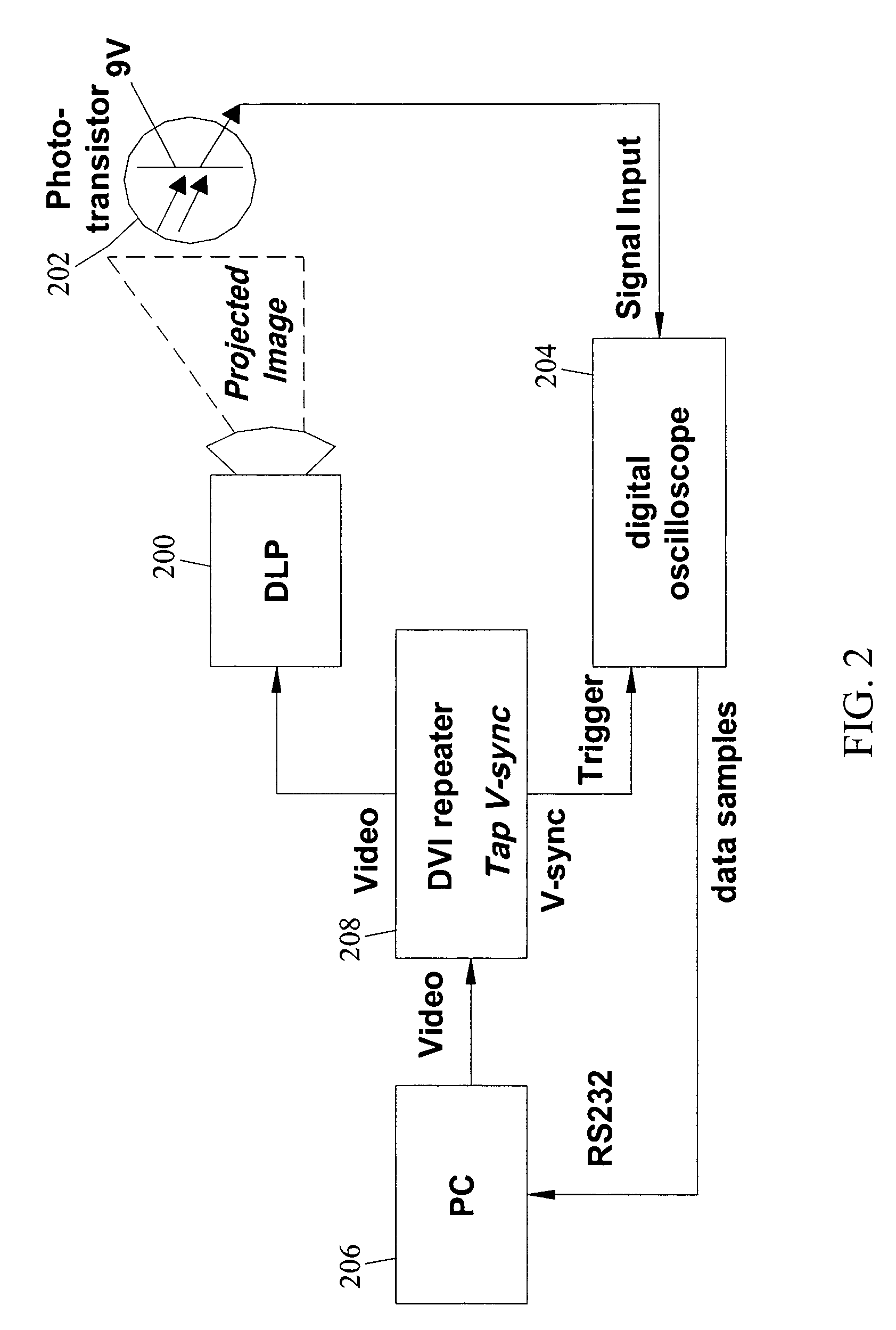
Methods, systems, and computer program products for imperceptibly embedding structured light patterns in projected color images for display on planar and non-planar surfaces
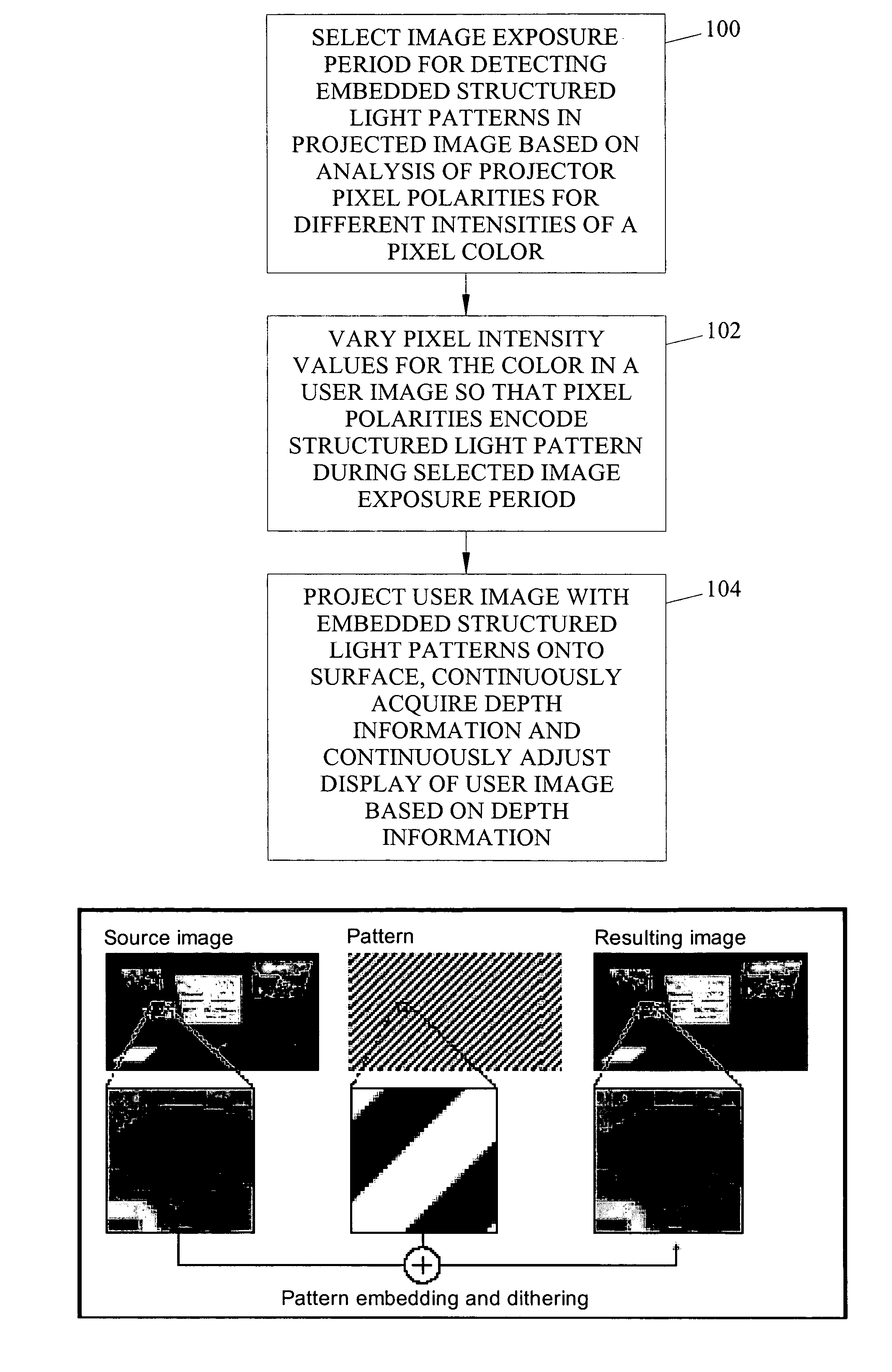
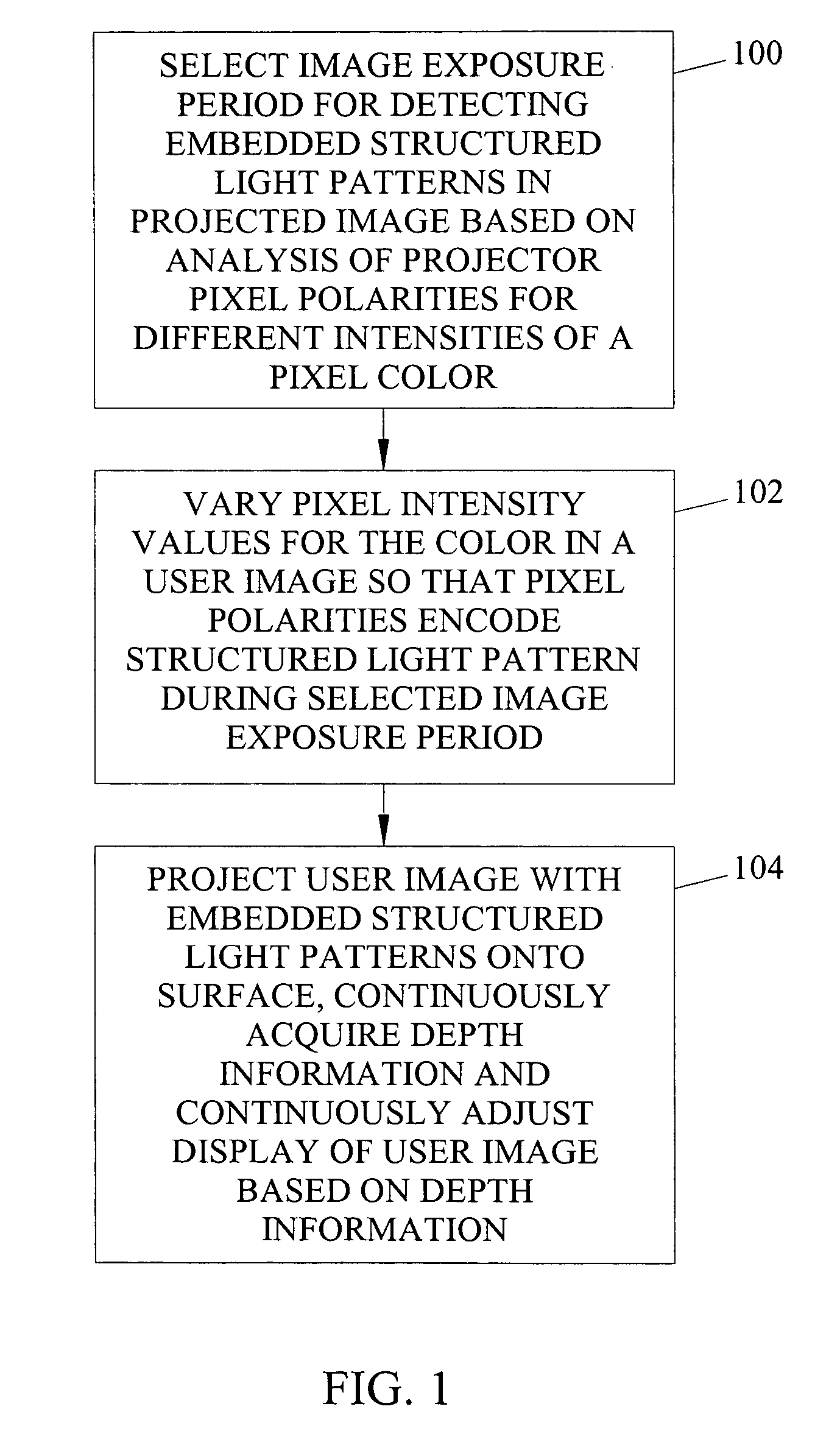
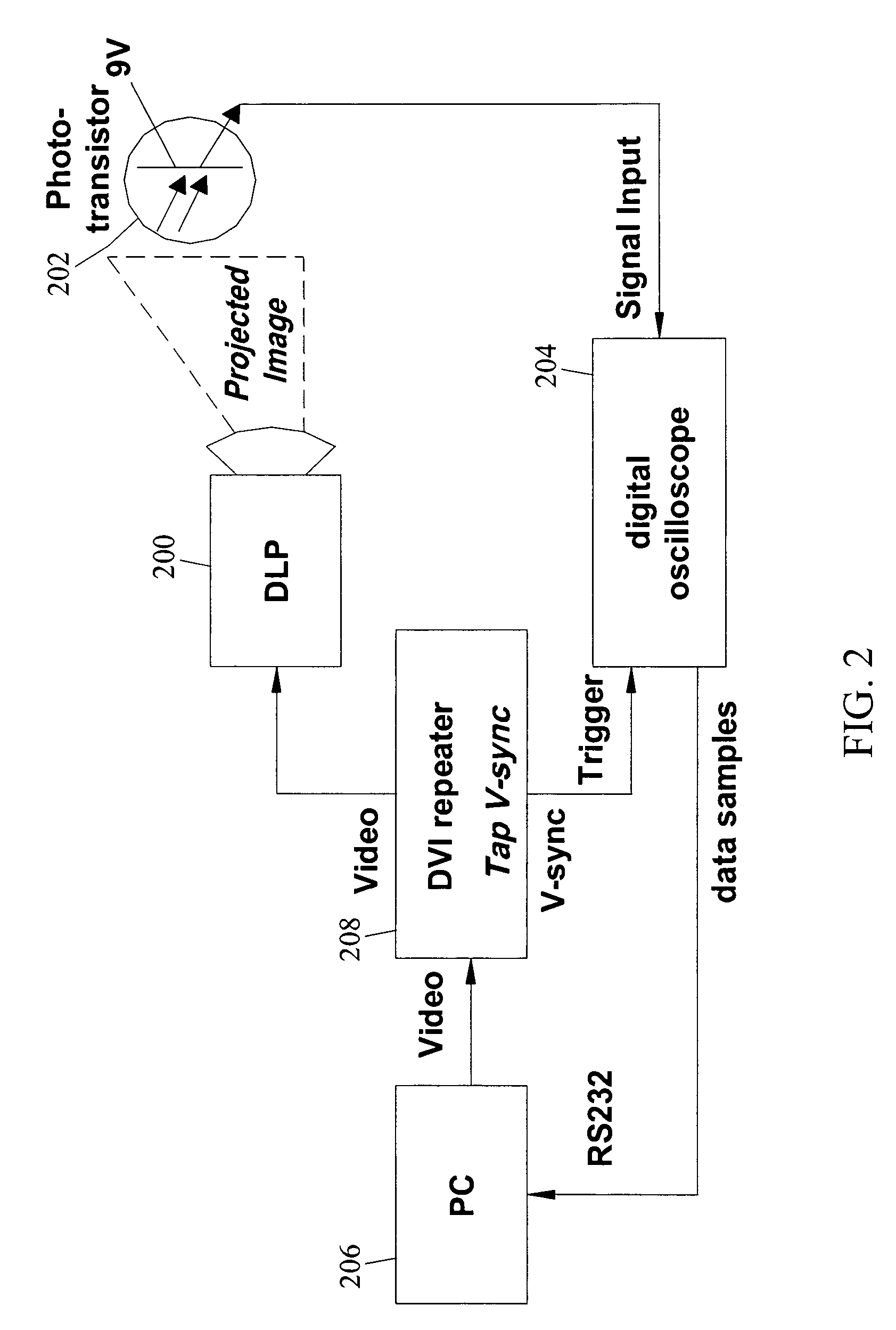
Methods, systems, and computer program products for imperceptibly embedding structured light patterns in projected color images for display on planar and non-planar surfaces are disclosed. According to one method, an image exposure period for detecting an embedded structured light patterns in a projected image is selected based on analysis of pixel polarities for different pixel intensities of a pixel color. Pixel intensities for the color are varied in the user image so that pixel polarities encode the structured light patterns during image exposure period. The user image is projected with the structured light patterns onto the surface. Depth information is continuously acquired and used to adjust display of the user image.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
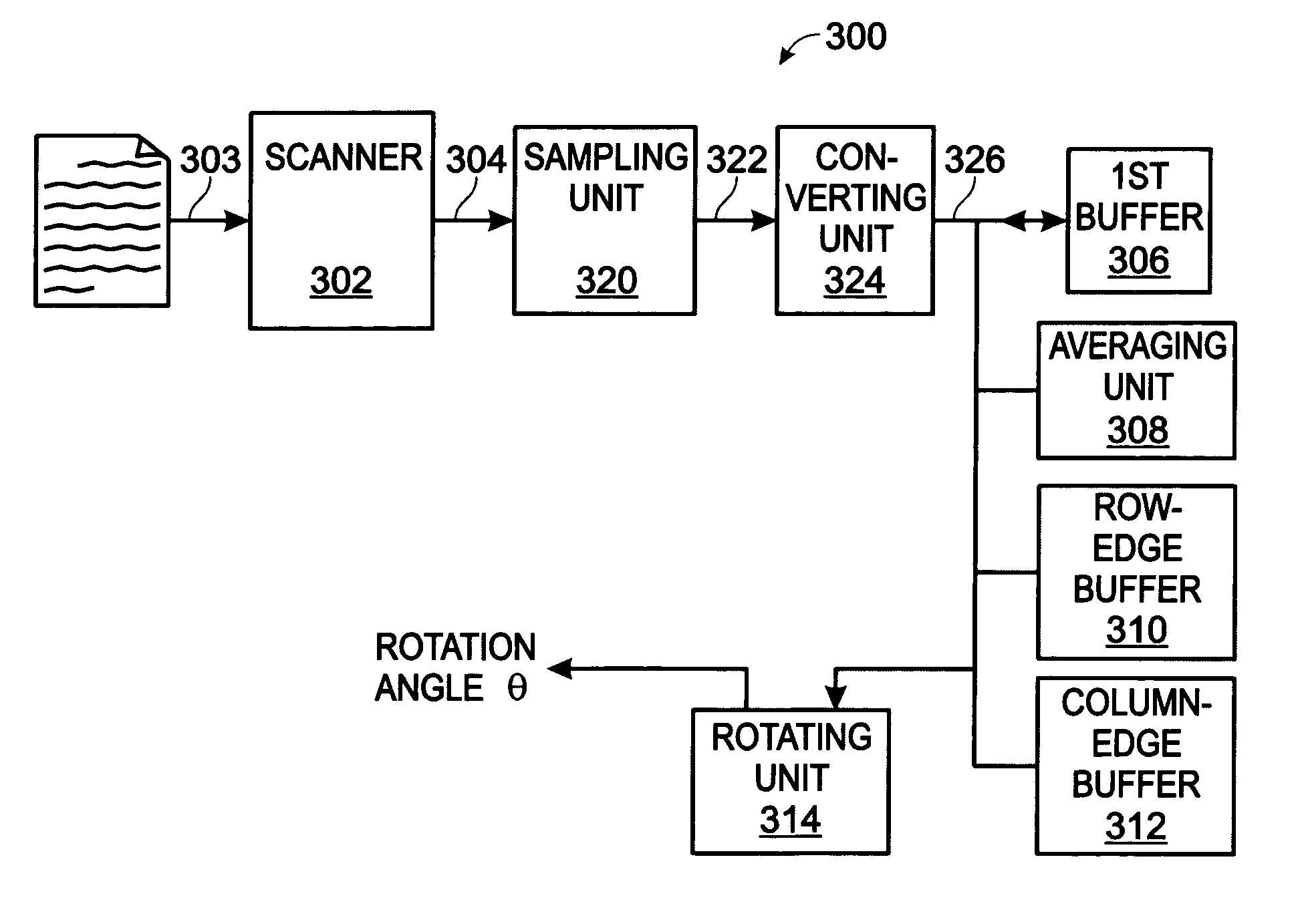
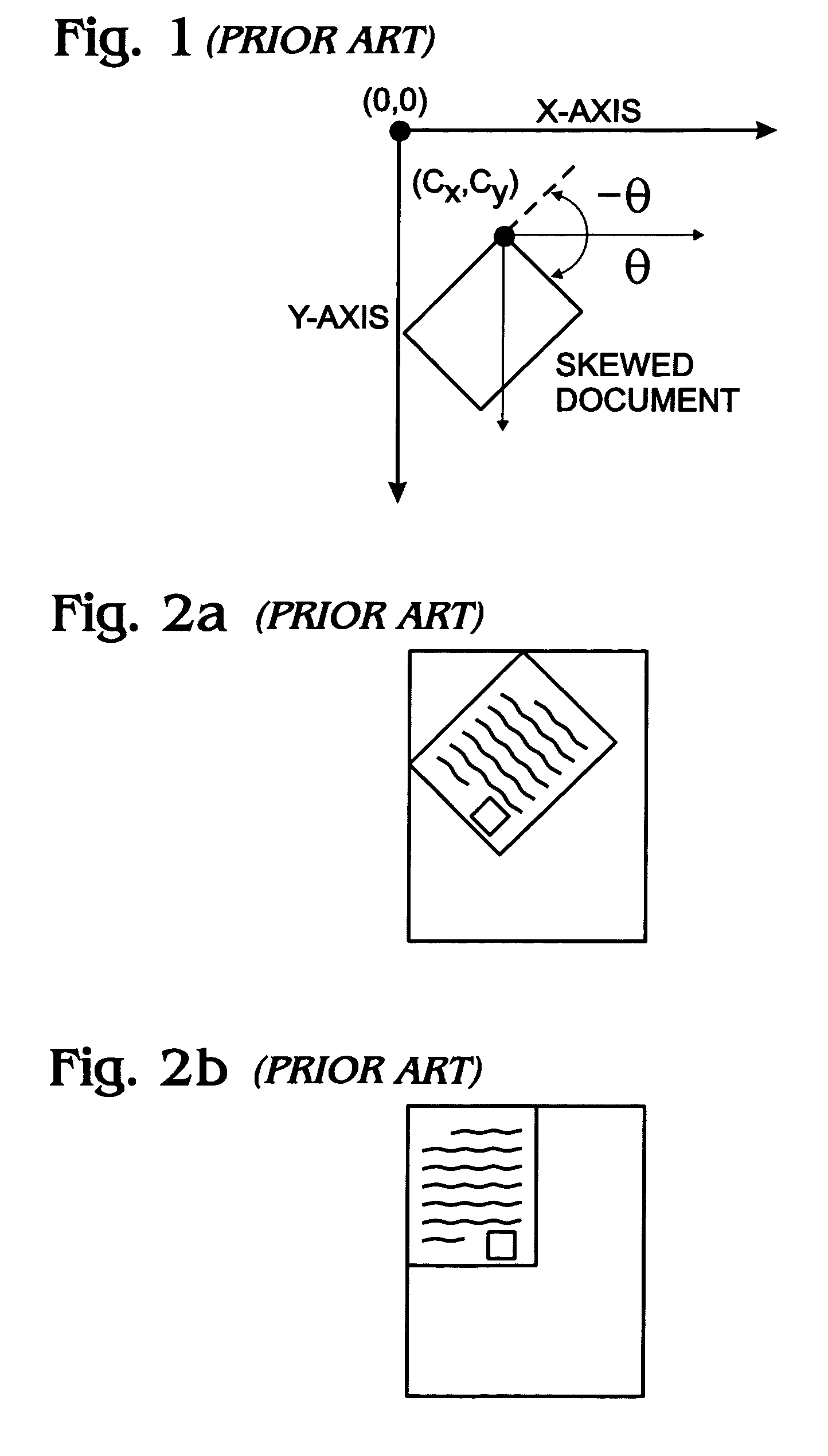
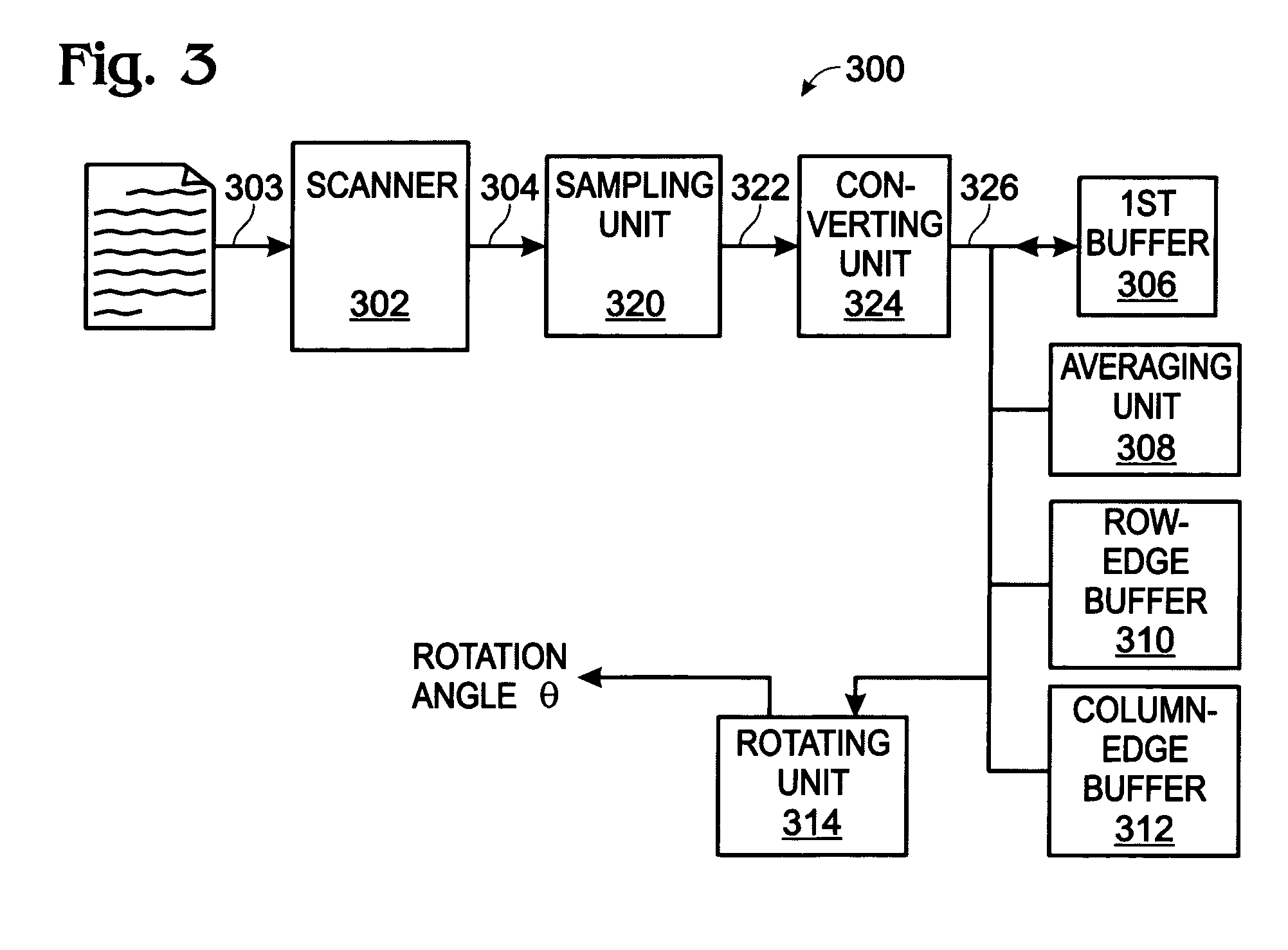
System and method for digital document alignment
A system and method are provided for aligning a scanned document in a digital scanner. The method comprises: scanning a document to create a matrix of pixel information; averaging pixel intensity information into a first plurality of row-mean buffer elements, where each row strip includes information from a second plurality of column elements; and, averaging pixel information into a third plurality of column-mean buffer elements, where each column strip includes information from a fourth plurality of row elements; comparing adjacent elements of matrix row information to generate a first set of edge positions; comparing adjacent elements of matrix column information to generate a second set of edge positions; generating a rotation angle in response to analyzing the first and second edge positions; and, rotating the scanned document by the rotation angle.
Owner:SHARP KK
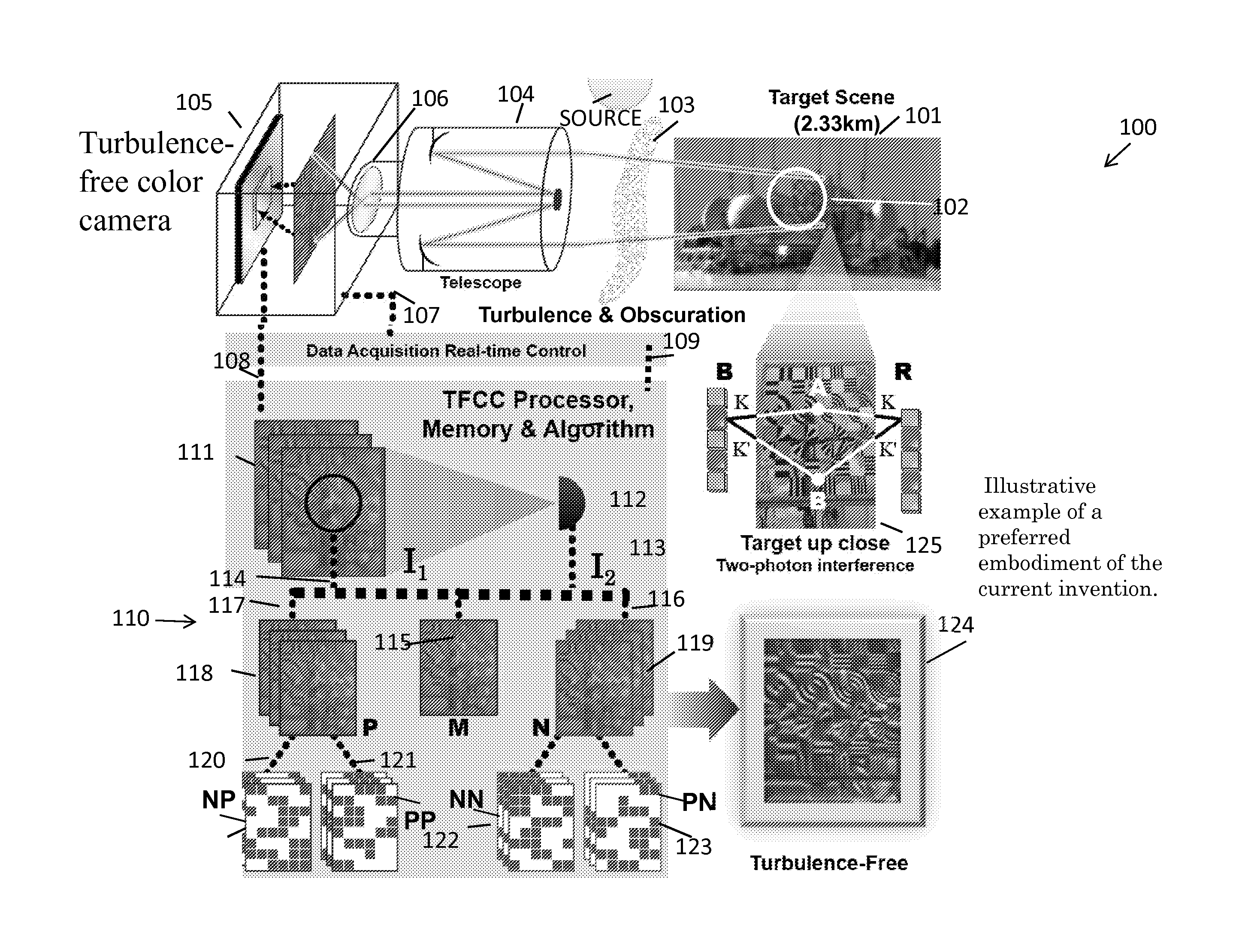
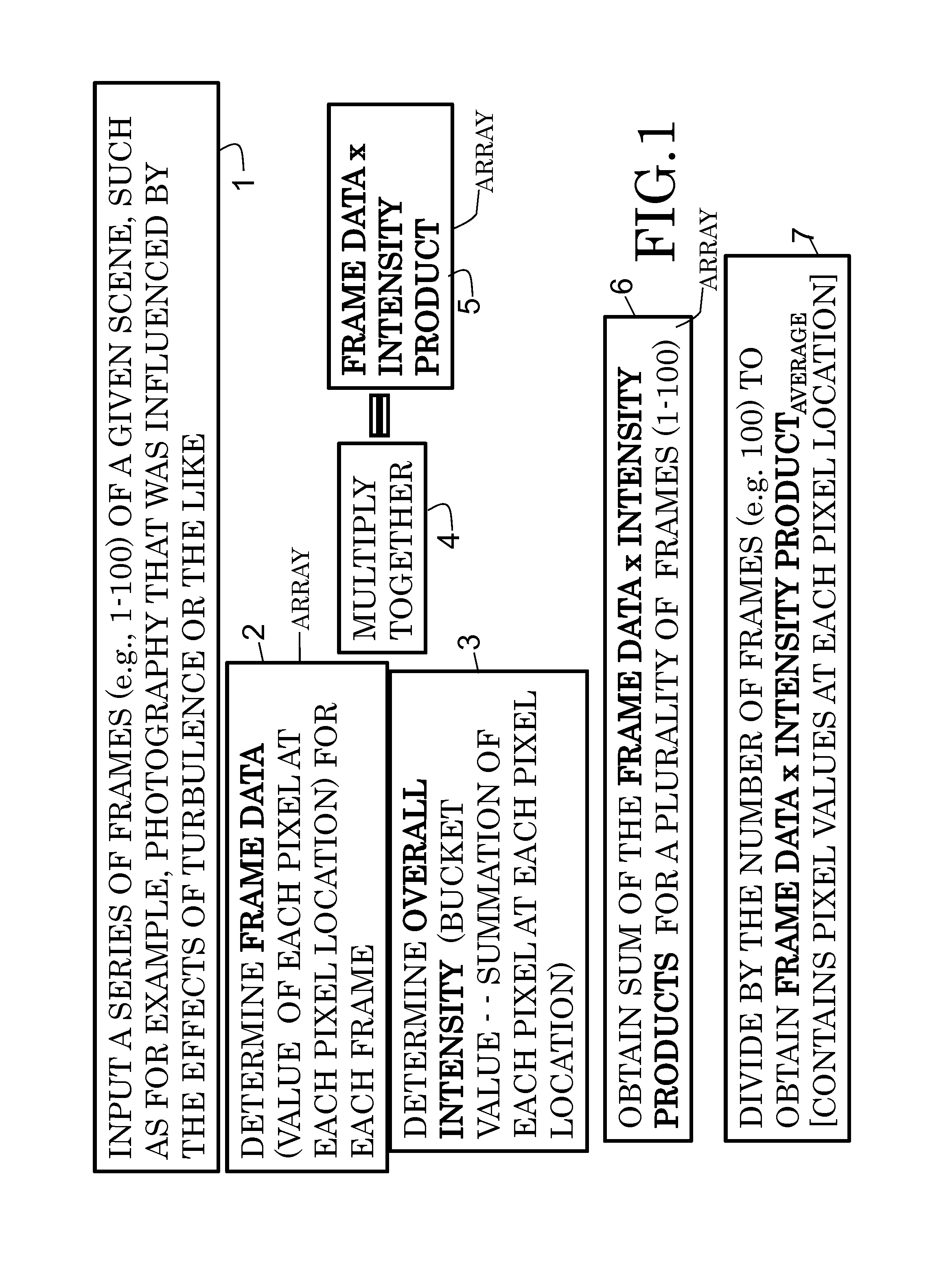
System and processor implemented method for improved image quality and generating an image of a target illuminated by quantum particles
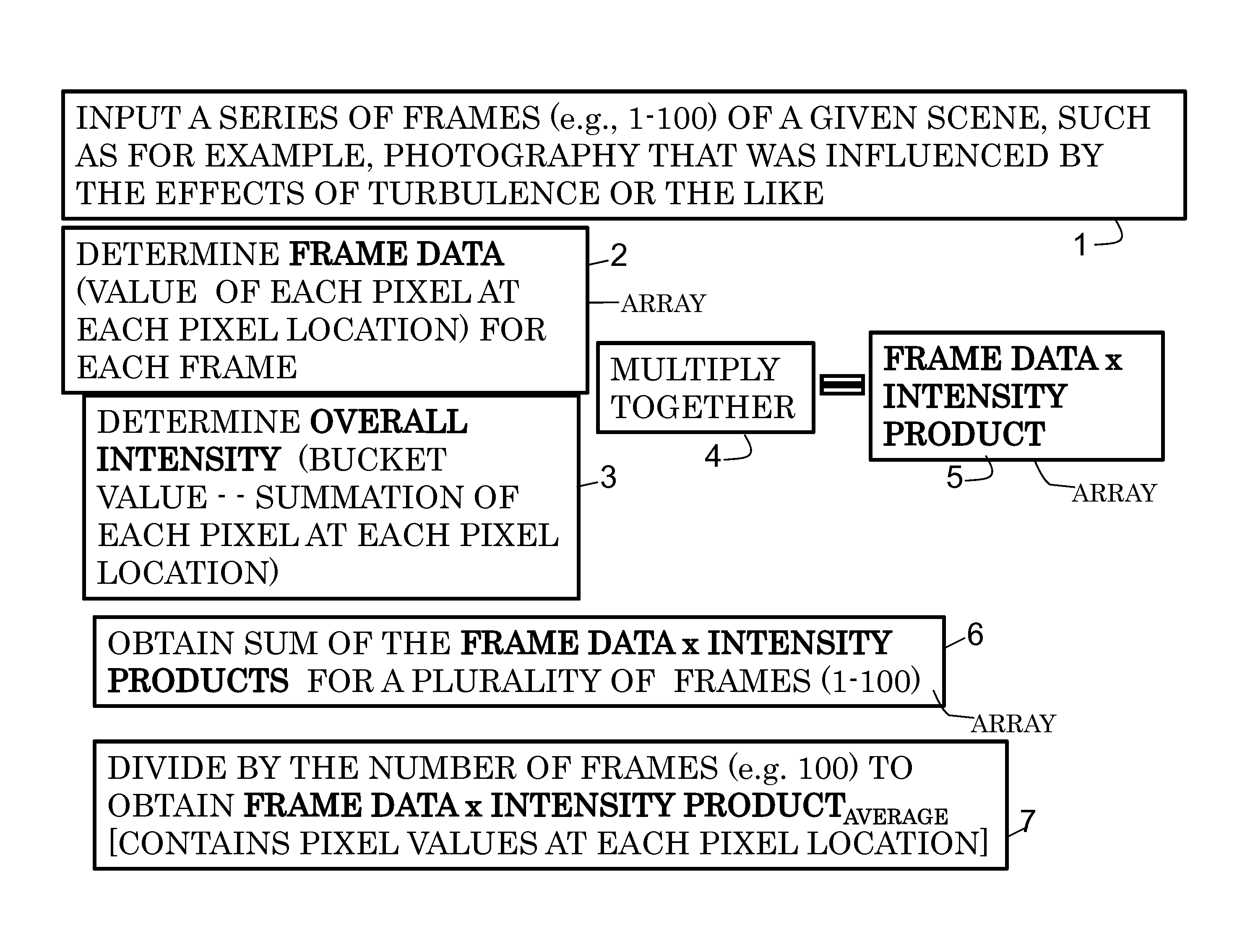
ActiveUS20140340570A1Improve generation of imageIncrease generationImage enhancementTelevision system detailsQuantum entanglementImaging quality
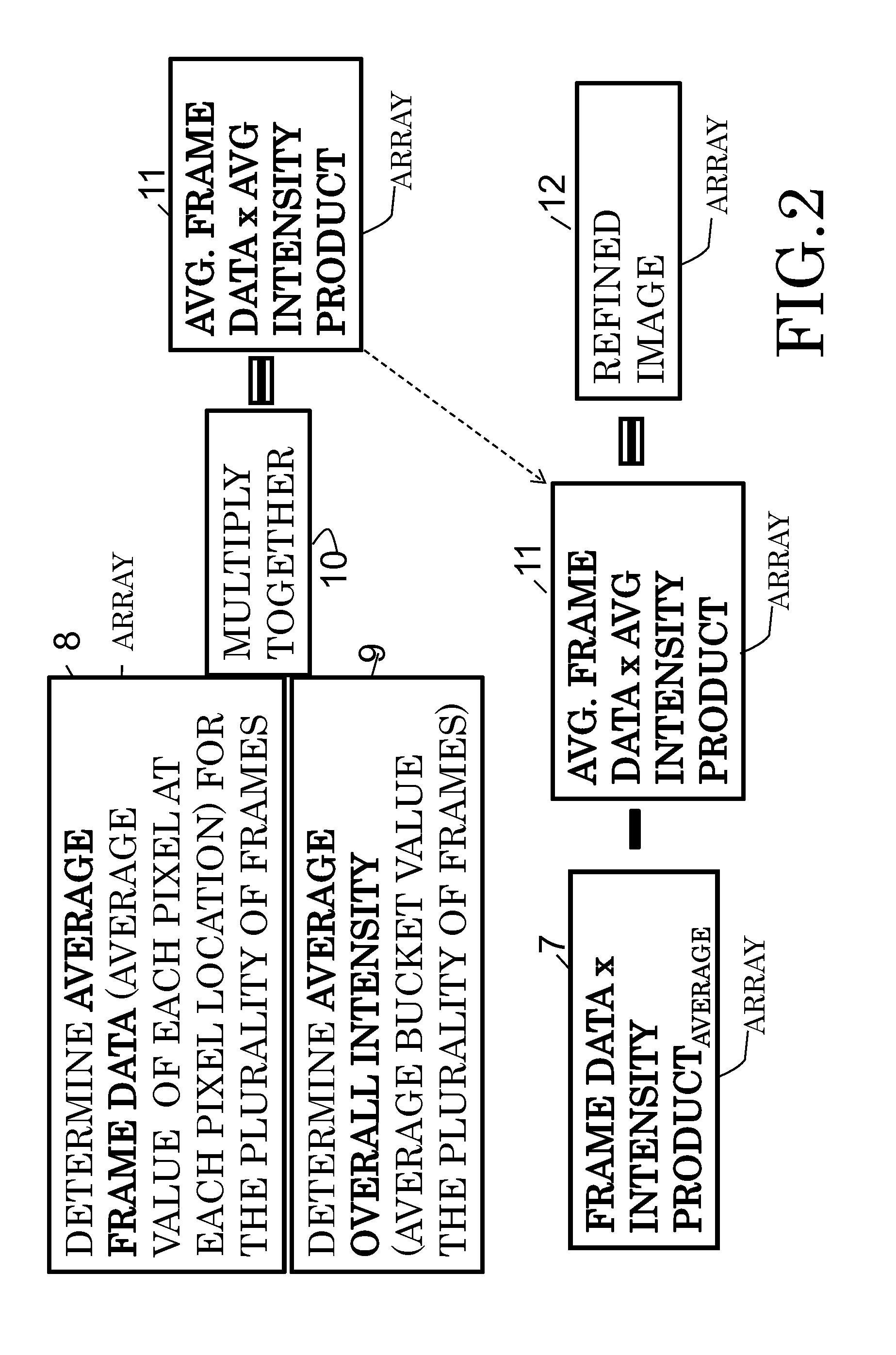
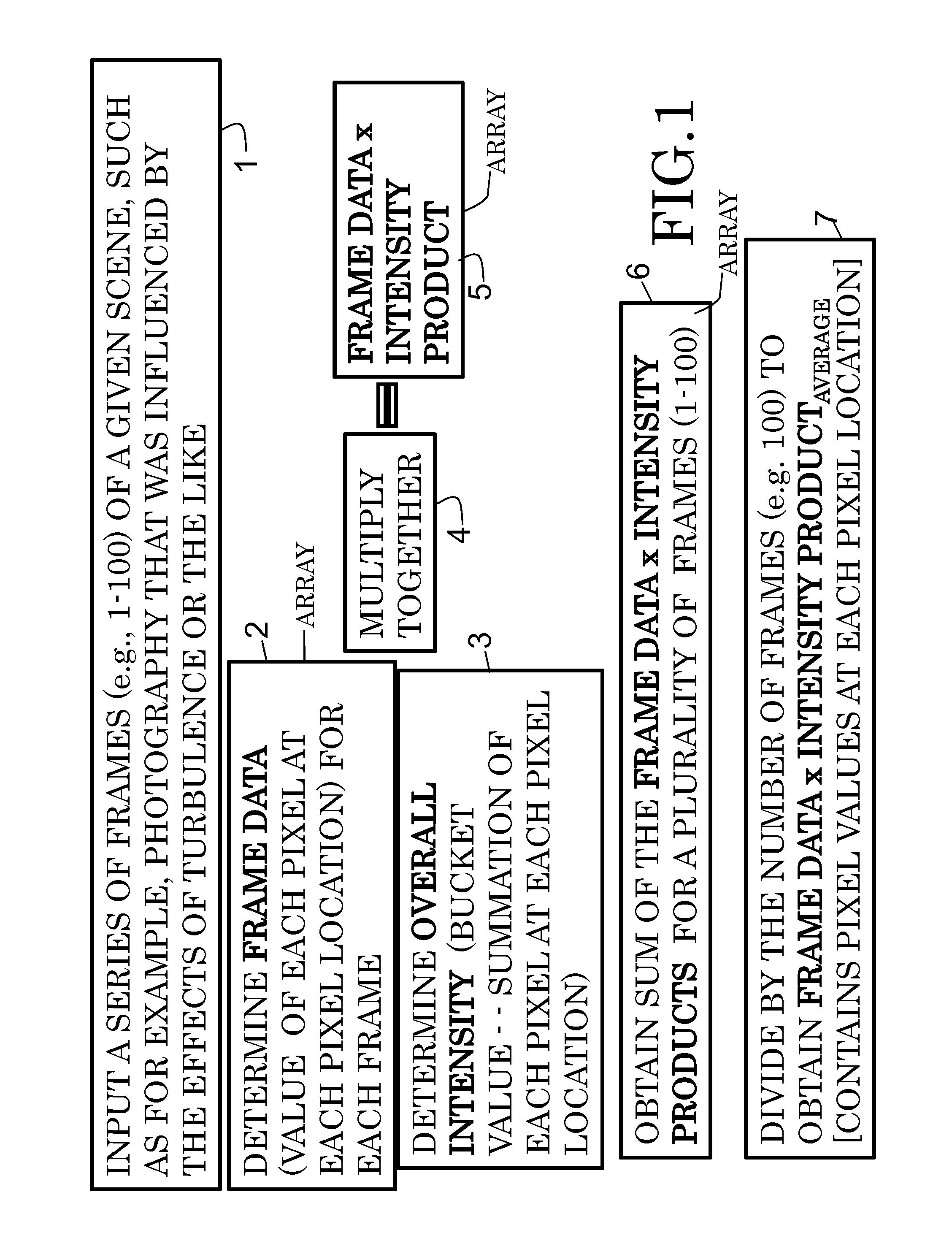
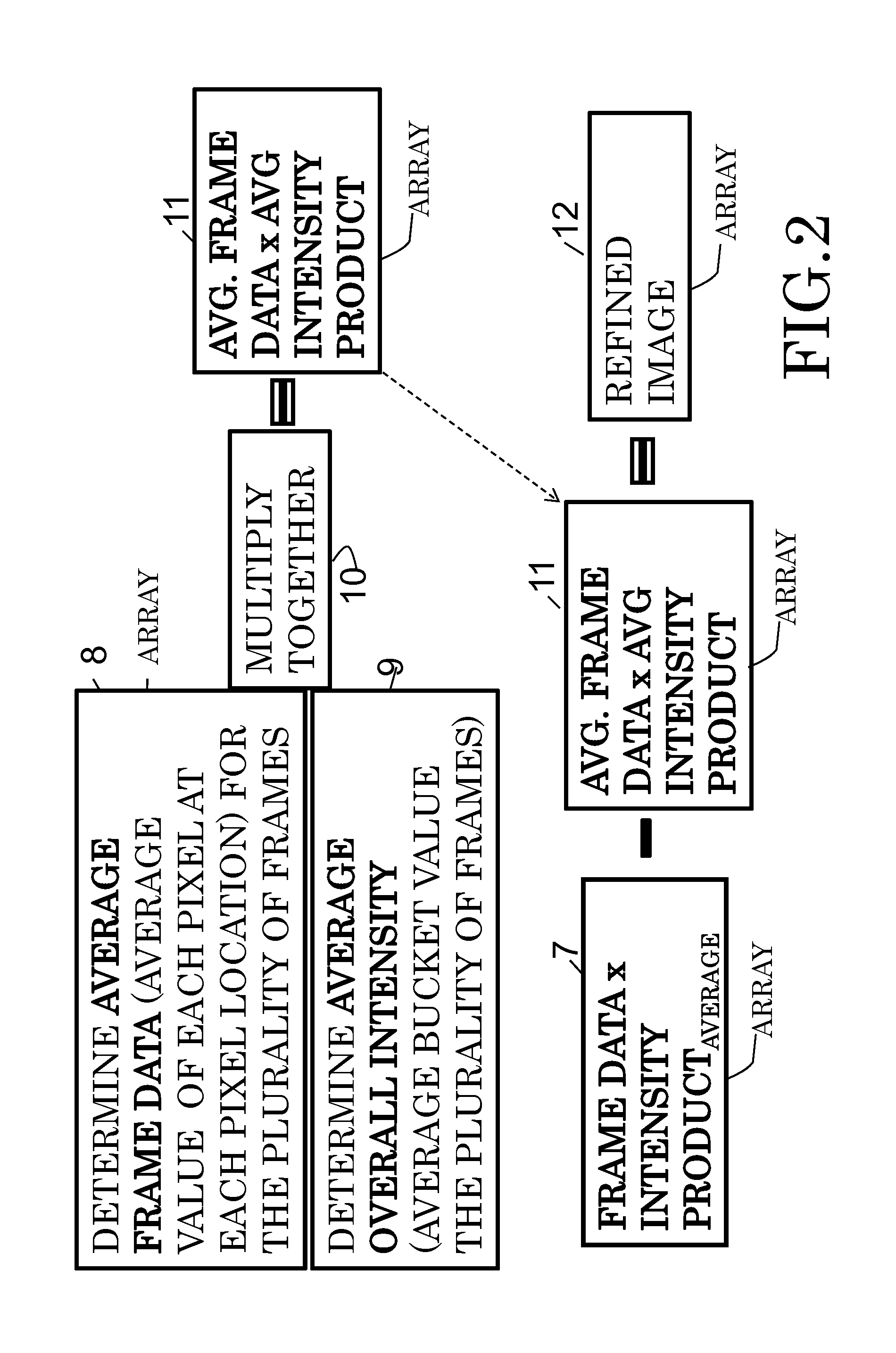
According to some embodiments, system and methods for image improvement comprise: receiving a plurality of frames of a given region of interest, the frames comprised of a plurality of pixels; determining, based on a quantum property of the frames, a normalized pixel intensity value for each pixel of each of the plurality of frames; and generating an improved image of the given region of interest based on the plurality of frames and the corresponding normalized pixel intensity values for the frames, the order of the image being two. Also embodiments for generating an image of a target illuminated by quantum entangled particles, such as, photons, are disclosed.
Owner:ARMY US SEC THE THE
Methods, systems, and computer program products for imperceptibly embedding structured light patterns in projected color images for display on planar and non-planar surfaces
Methods, systems, and computer program products for imperceptibly embedding structured light patterns in projected color images for display on planar and non-planar surfaces are disclosed. According to one method, an image exposure period for detecting an embedded structured light patterns in a projected image is selected based on analysis of pixel polarities for different pixel intensities of a pixel color. Pixel intensities for the color are varied in the user image so that pixel polarities encode the structured light patterns during image exposure period. The user image is projected with the structured light patterns onto the surface. Depth information is continuously acquired and used to adjust display of the user image.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
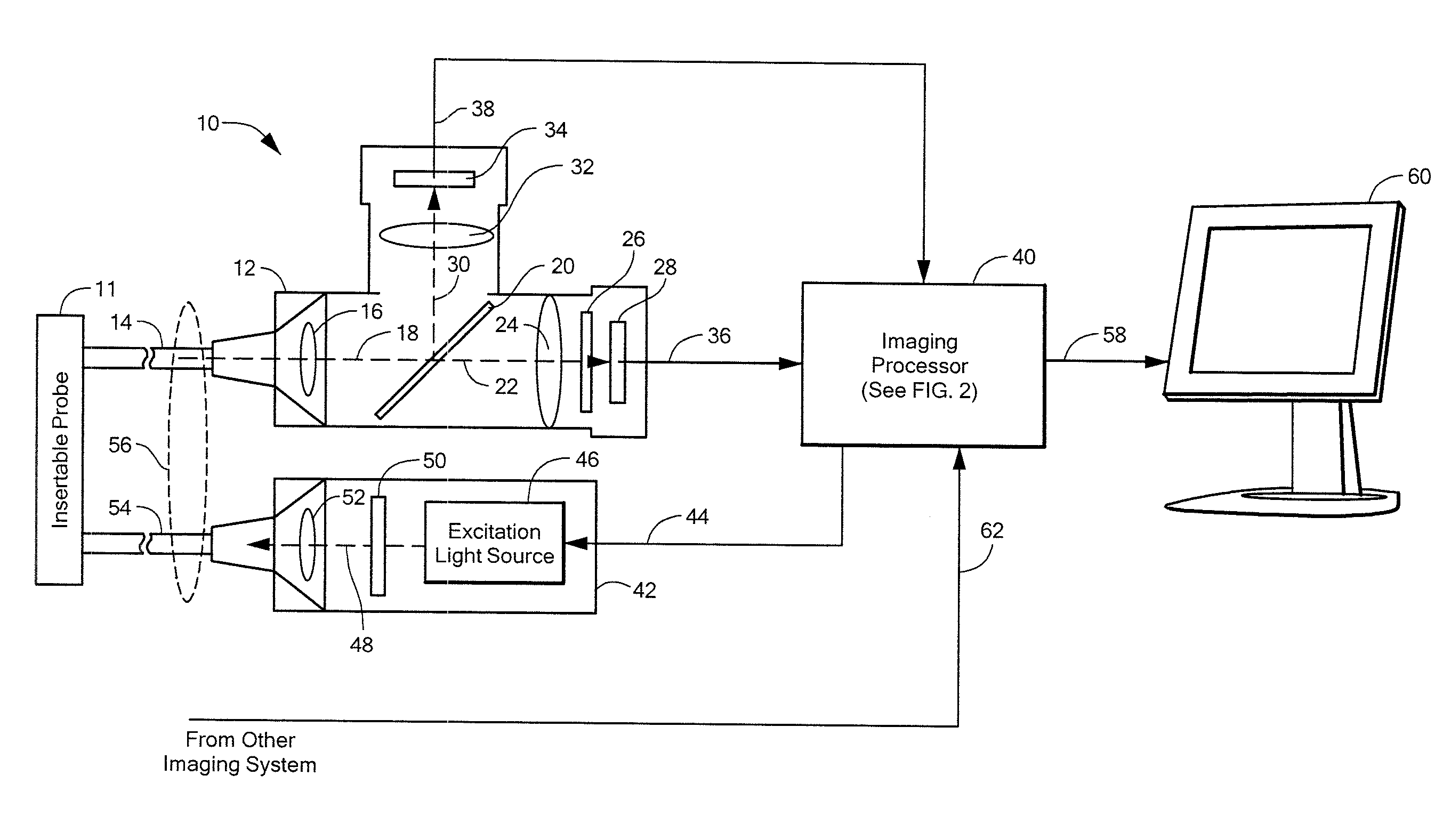
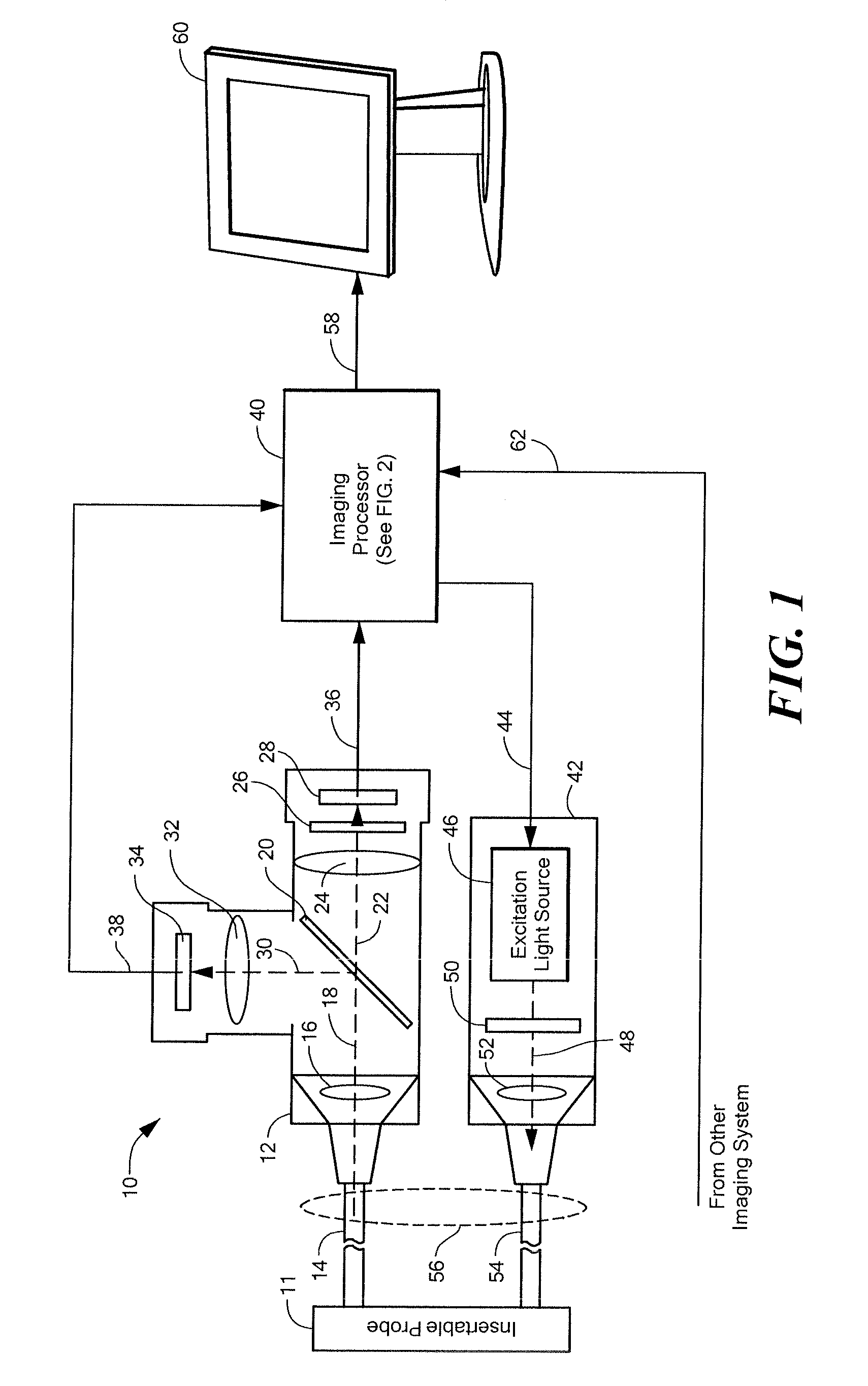
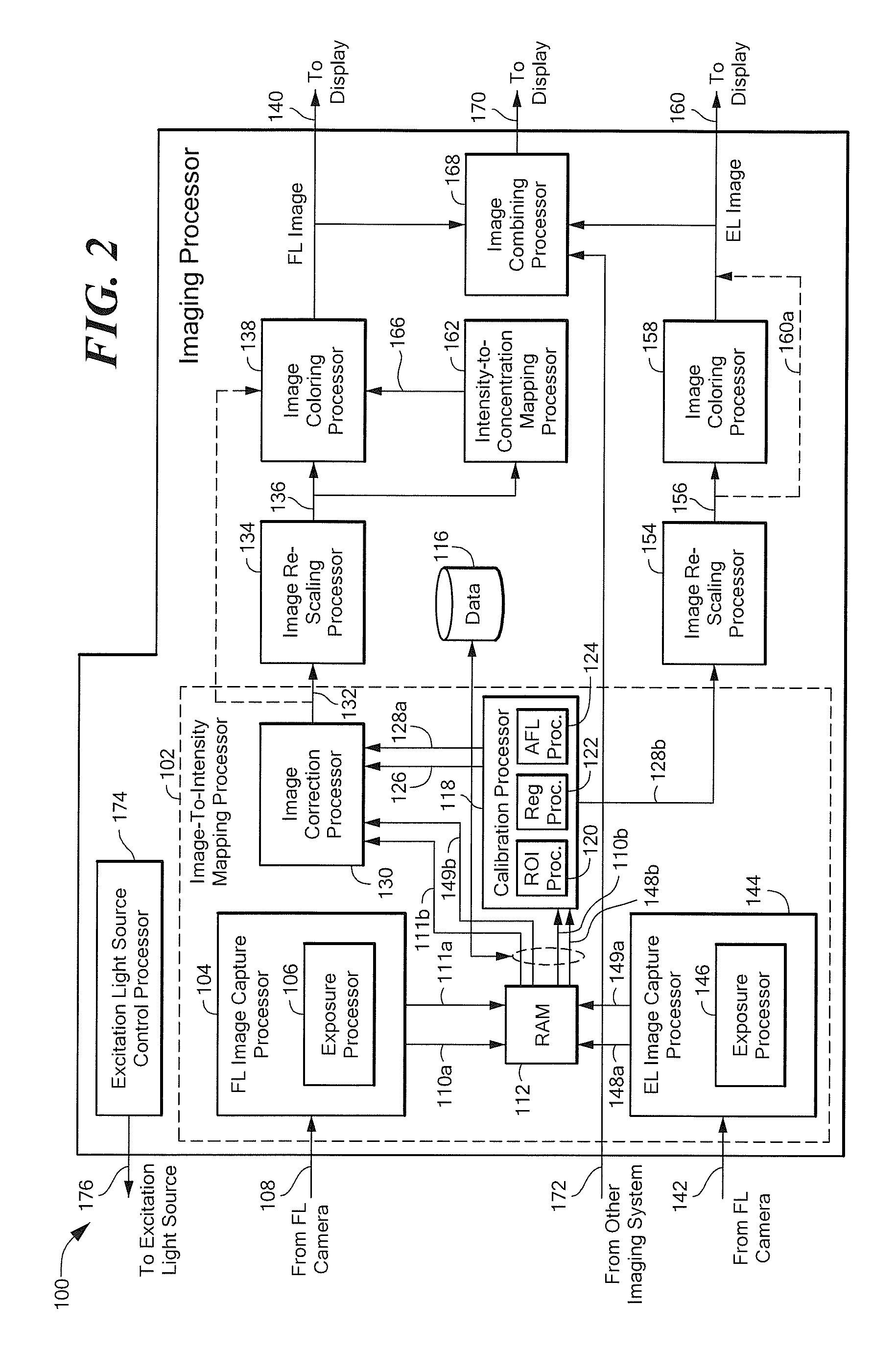
Systems and methods for generating fluorescent light images
An imaging system divides image pixels intensities by exposure time to generate image data in units of intensity per time. The imaging system divides a fluorescent light image in intensity per time units by an excitation light image in intensity per time units to provide a quantitative corrected fluorescent light image that is generally invariant to position of an imaging instrument relative to a biological tissue being imaged.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
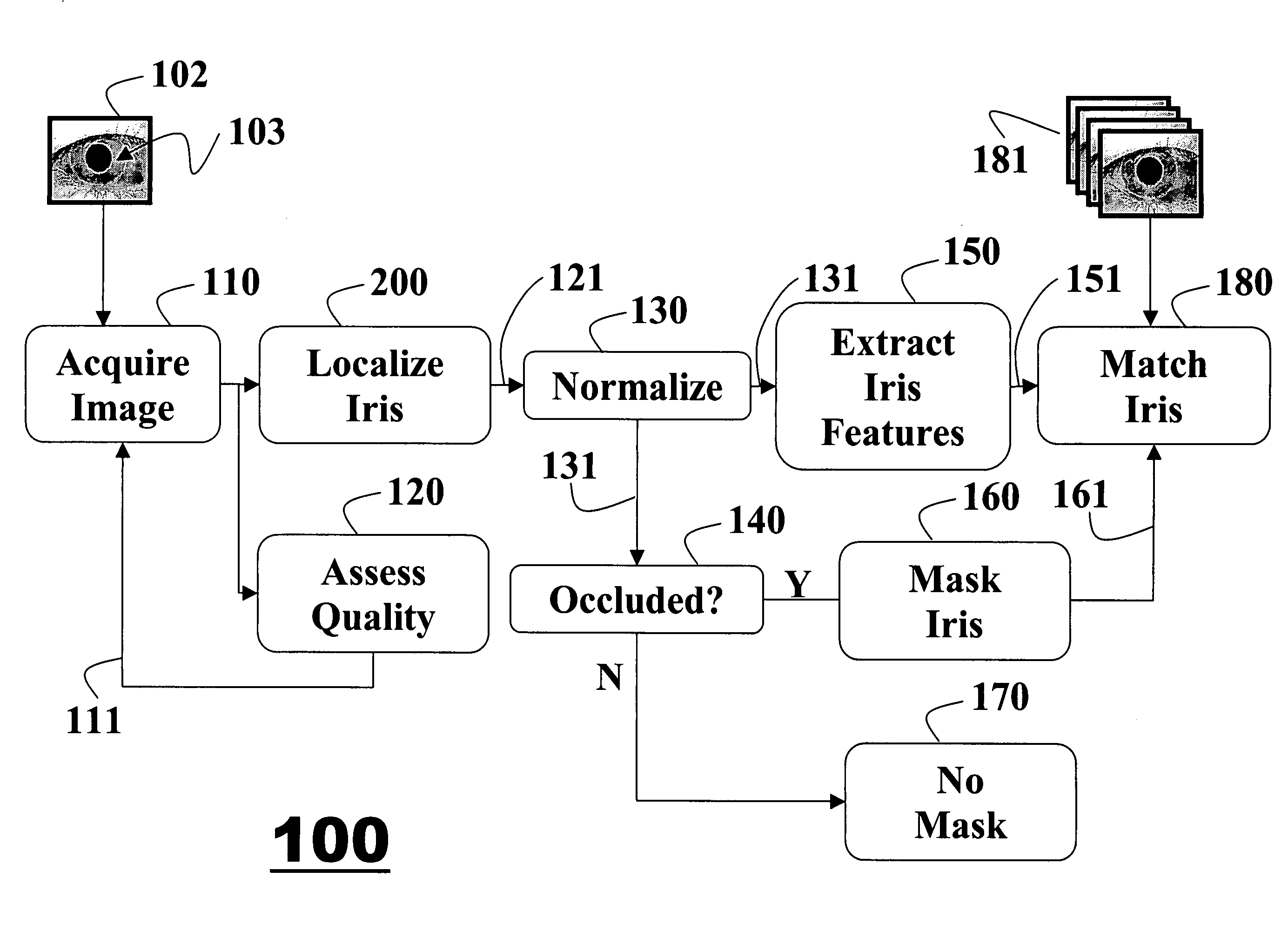
Method for extracting features of irises in images using difference of sum filters
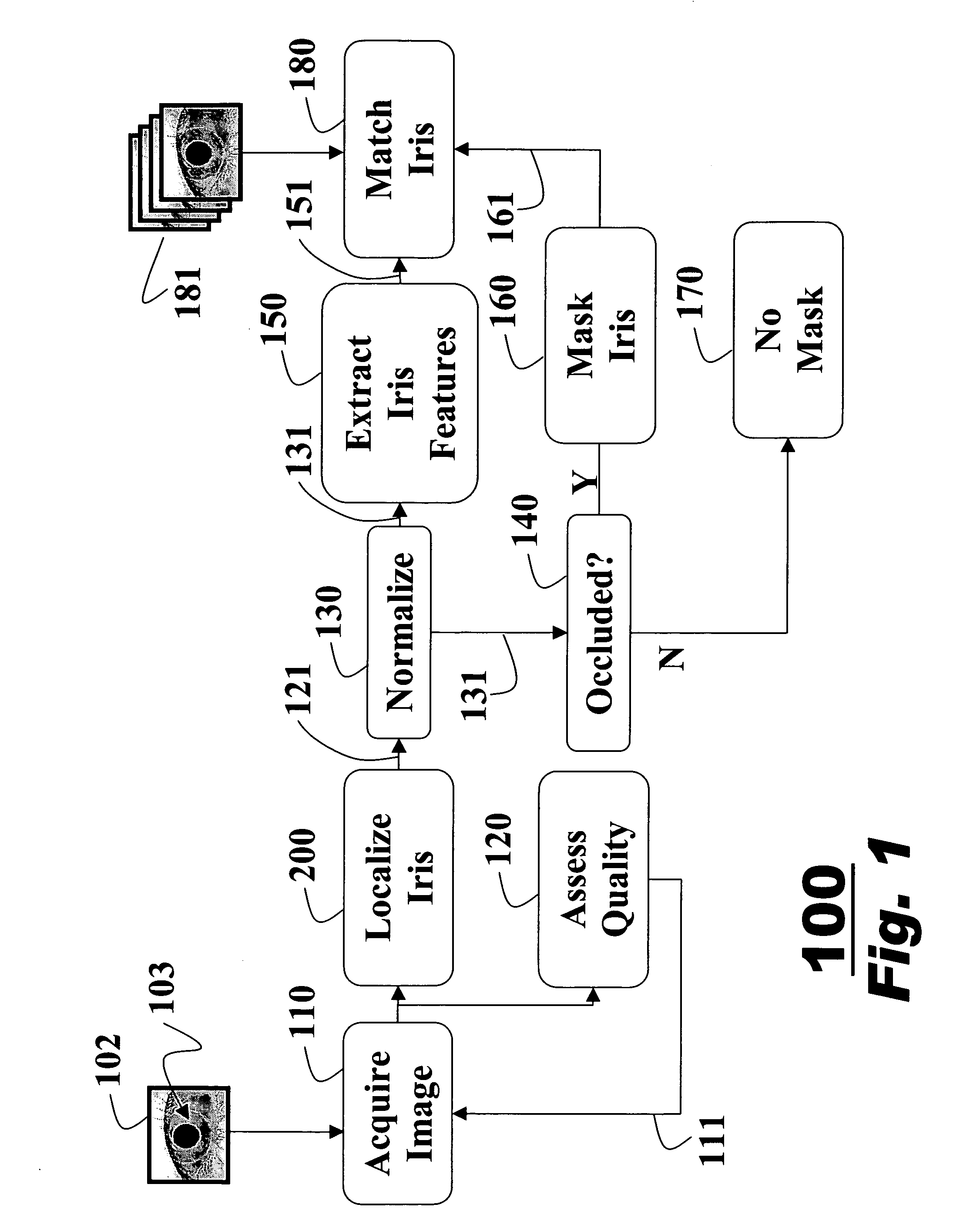
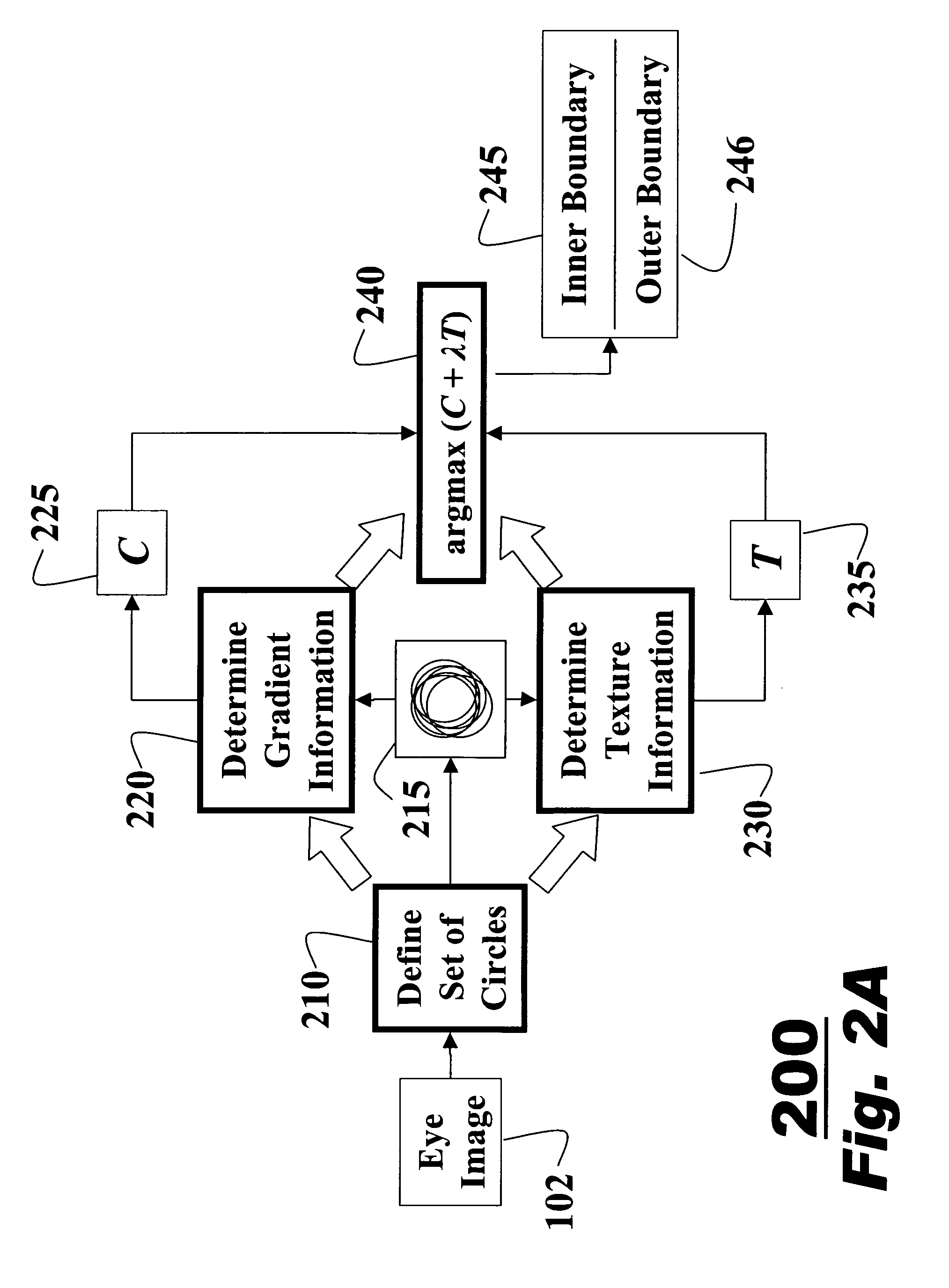
InactiveUS20070160266A1Improve accuracyAcquiring/recognising eyesPerson identificationFeature vectorIris image
A method for extracting features of an iris in an image is described. An unwrapped iris image is converted to an integral image by summations of pixel intensities. A novel bank of difference of sum filters is used to filter the integral image. The filtered output is binarized to produce an iris feature vector. The iris feature vector is used for iris matching.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
System and method for image matting
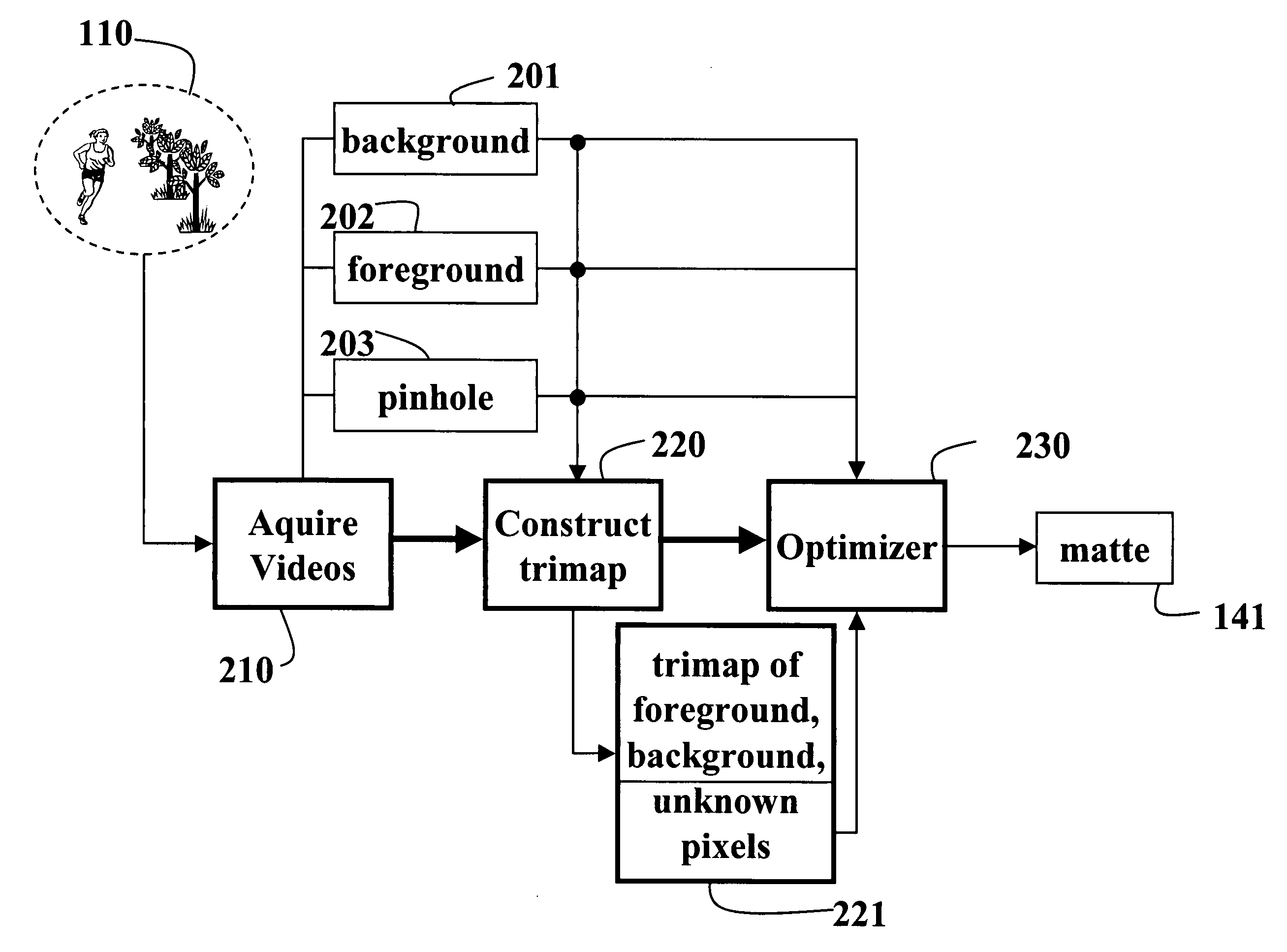
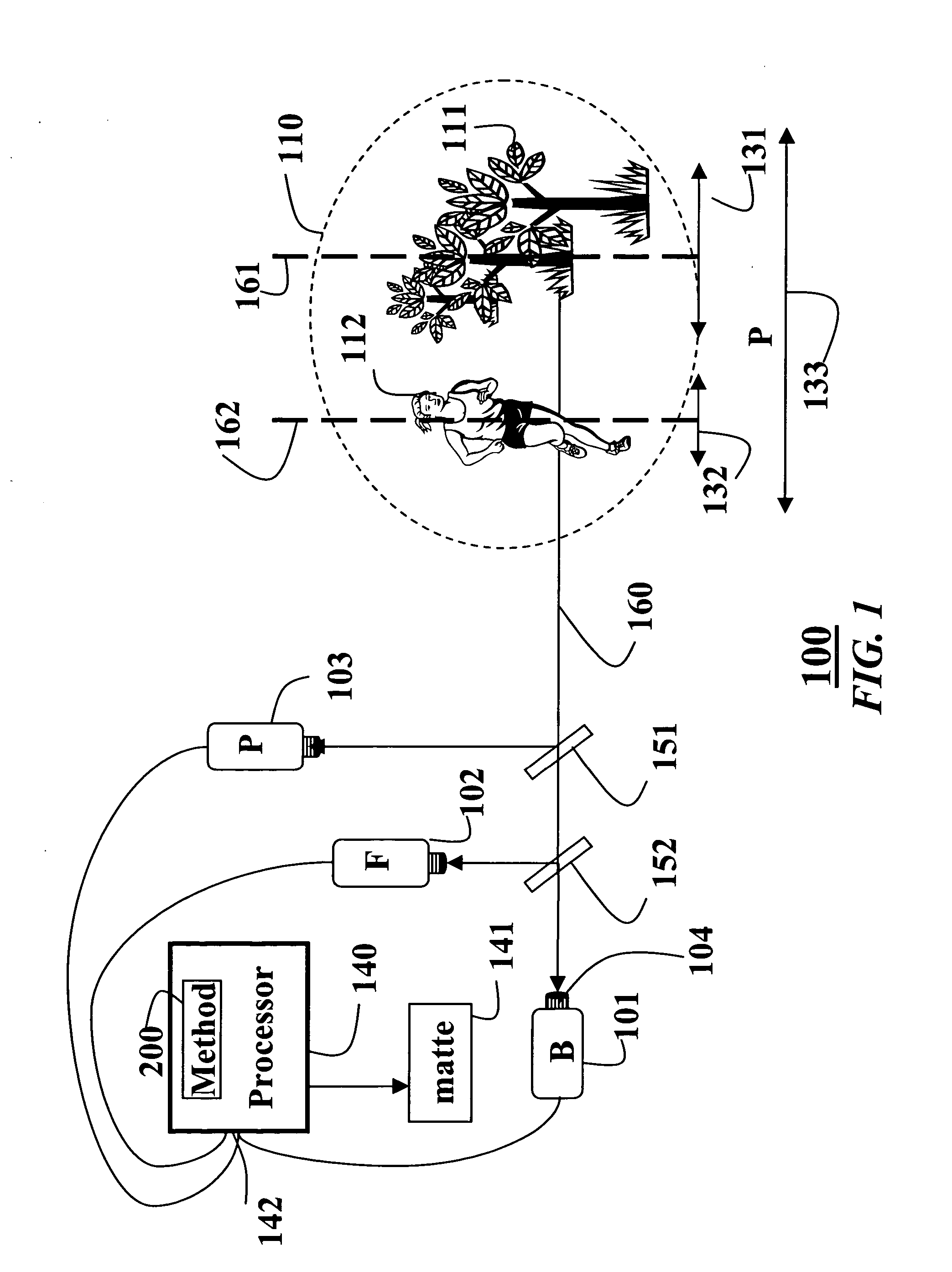
InactiveUS20060221248A1High-frequency componentSolve the real problemTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsError functionBackground image
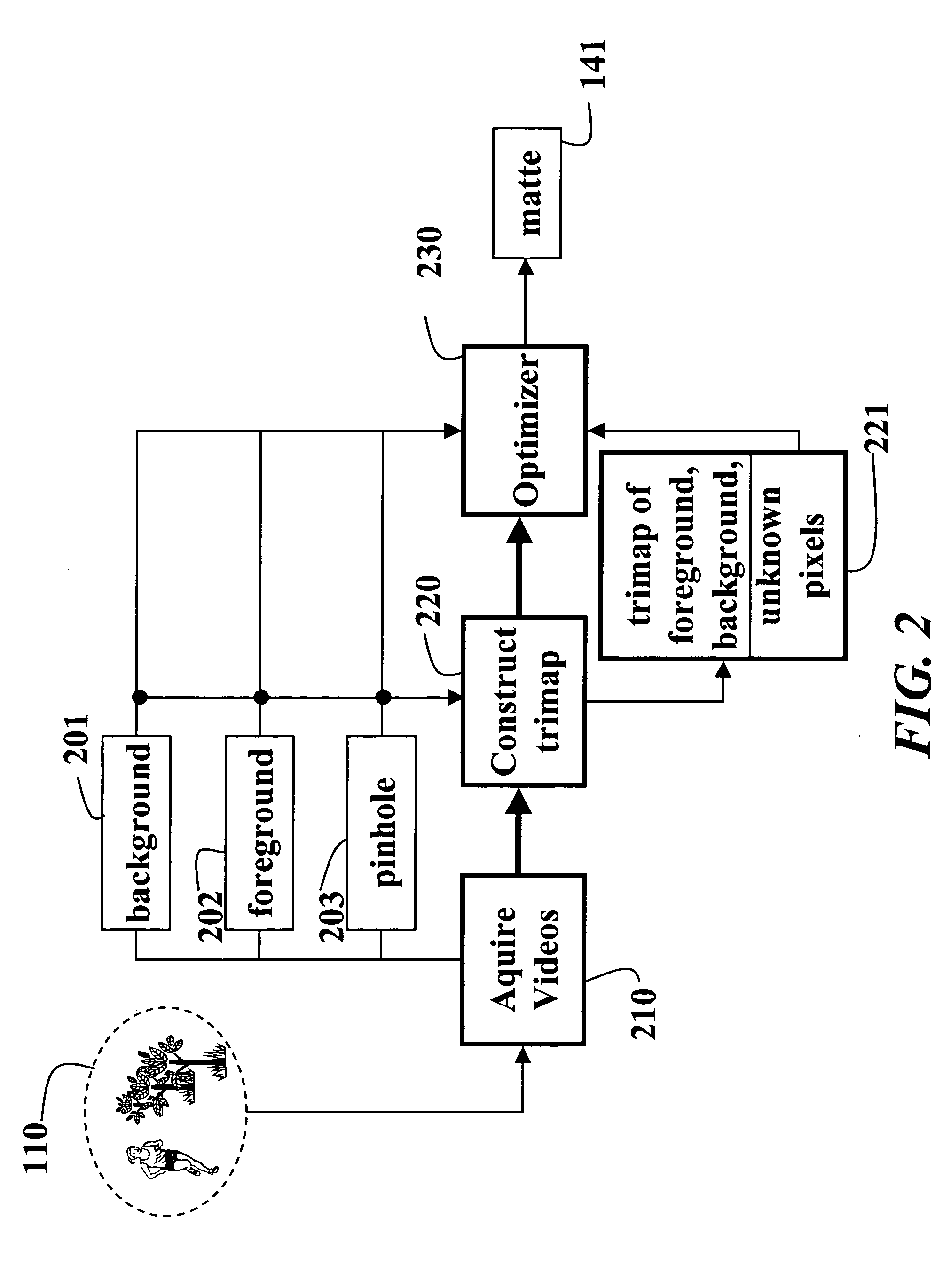
A method and system extracts a matte from images acquired of a scene. A foreground image focused at a foreground in a scene, a background image focused at a background in the scene, and a pinhole image focused on the entire scene are acquired. These three images can be acquired sequentially by a single camera, or simultaneous by three cameras. In the later case, foreground, background and pinhole sequences of images can be acquired. The pinhole image is compared to the foreground image and the background image to extract a matte representing the scene. The comparison classifies pixels in the images as foreground, background, or unknown pixels. An optimizer minimizes an error function in the form of Fourier image equations using a gradient descent method. The error function expresses pixel intensity differences.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Estimating 3D shape and texture of a 3D object based on a 2D image of the 3D object
InactiveUS7756325B2Wider radius of convergenceSmooth functionAdditive manufacturing apparatusImage analysis3d shapesObject based
Disclosed is an improved algorithm for estimating the 3D shape of a 3-dimensional object, such as a human face, based on information retrieved from a single photograph by recovering parameters of a 3-dimensional model and methods and systems using the same. Beside the pixel intensity, the invention uses various image features in a multi-features fitting algorithm (MFF) that has a wider radius of convergence and a higher level of precision and provides thereby better results.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF BASEL
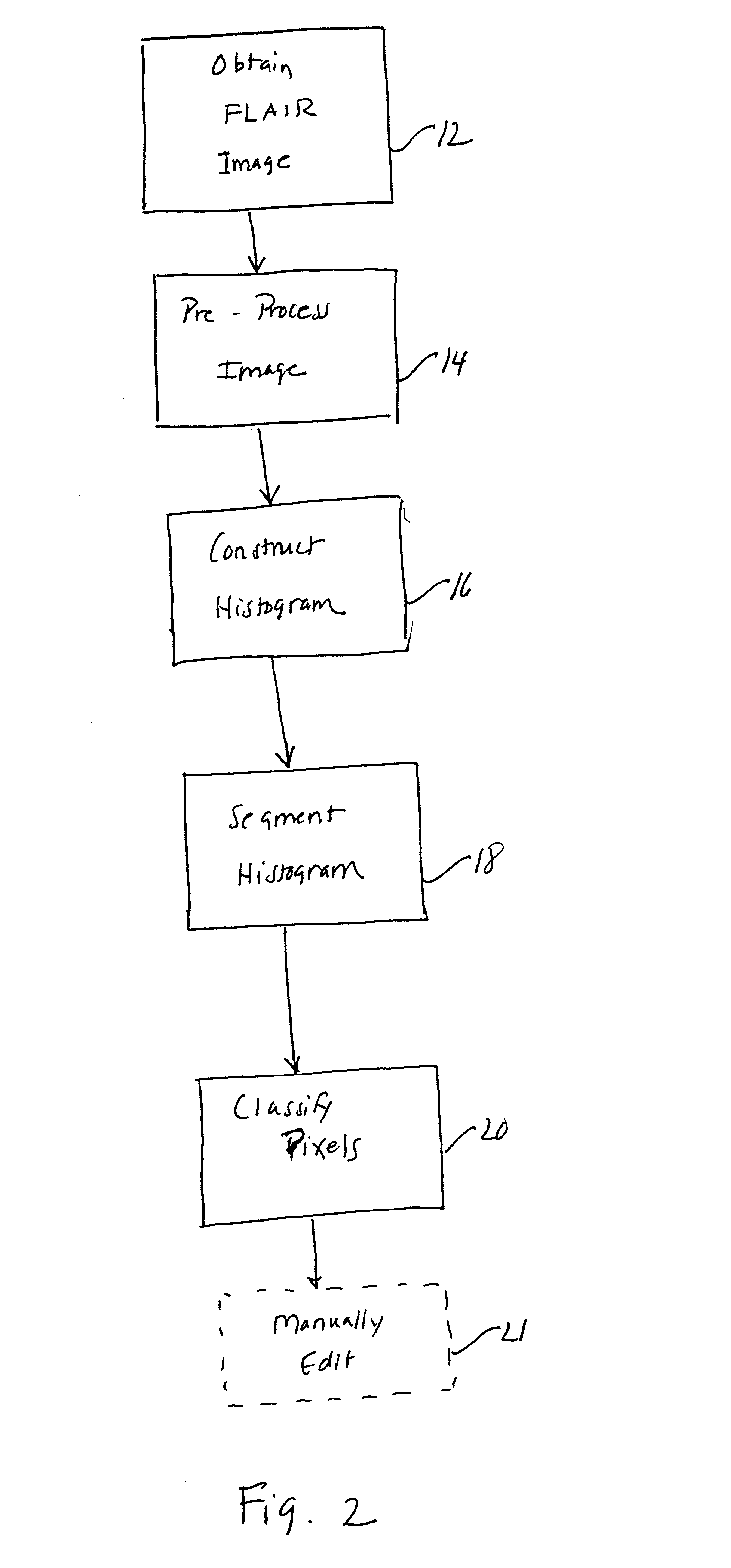
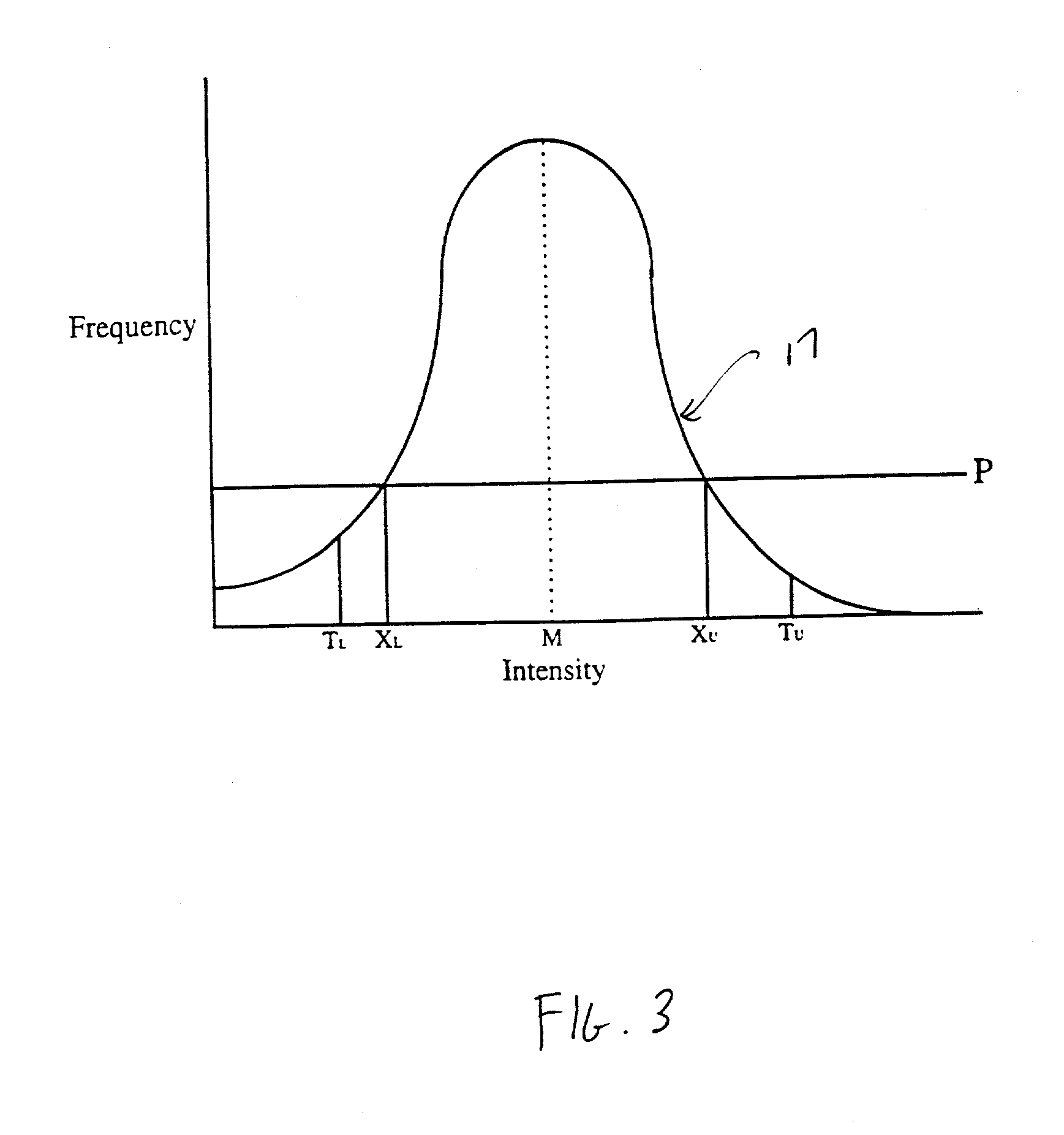
Histogram segmentation of FLAIR images
ActiveUS20030009098A1Automatically measuring the volume of tissueThe classification result is accurateImage enhancementImage analysisFluid-attenuated inversion recoveryLeukoaraiosis
A method for classifying tissue in a magnetic resonance image. and particularly for measuring a volume of pathological tissue such as white tissue hyperintensity (leukoaraiosis) in the brain based on the segmentation of the intensity histogram of fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) images is described. A magnetic resonance image of the brain of a subject is acquired, and a pixel intensity histogram is constructed from the image. A statistically-based regression analysis is applied to the histogram to determine upper and lower threshold values, which define different types of brain tissue, particularly normal brain, cerebral spinal fluid (CSF), or lesion.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
System and processor implemented method for improved image quality and generating an image of a target illuminated by quantum particles
ActiveUS20160005154A1Improve generation of imageIncrease generationImage enhancementImage analysisQuantum entanglementImaging quality
According to some embodiments, system and methods for image improvement comprise: receiving a plurality of frames of a given region of interest, the frames comprised of a plurality of pixels; determining, based on a quantum property of the frames, a normalized pixel intensity value for each pixel of each of the plurality of frames; and generating an improved image of the given region of interest based on the plurality of frames and the corresponding normalized pixel intensity values for the frames, the order of the image being two. Also embodiments for generating an image of a target illuminated by quantum entangled particles, such as, photons, are disclosed.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
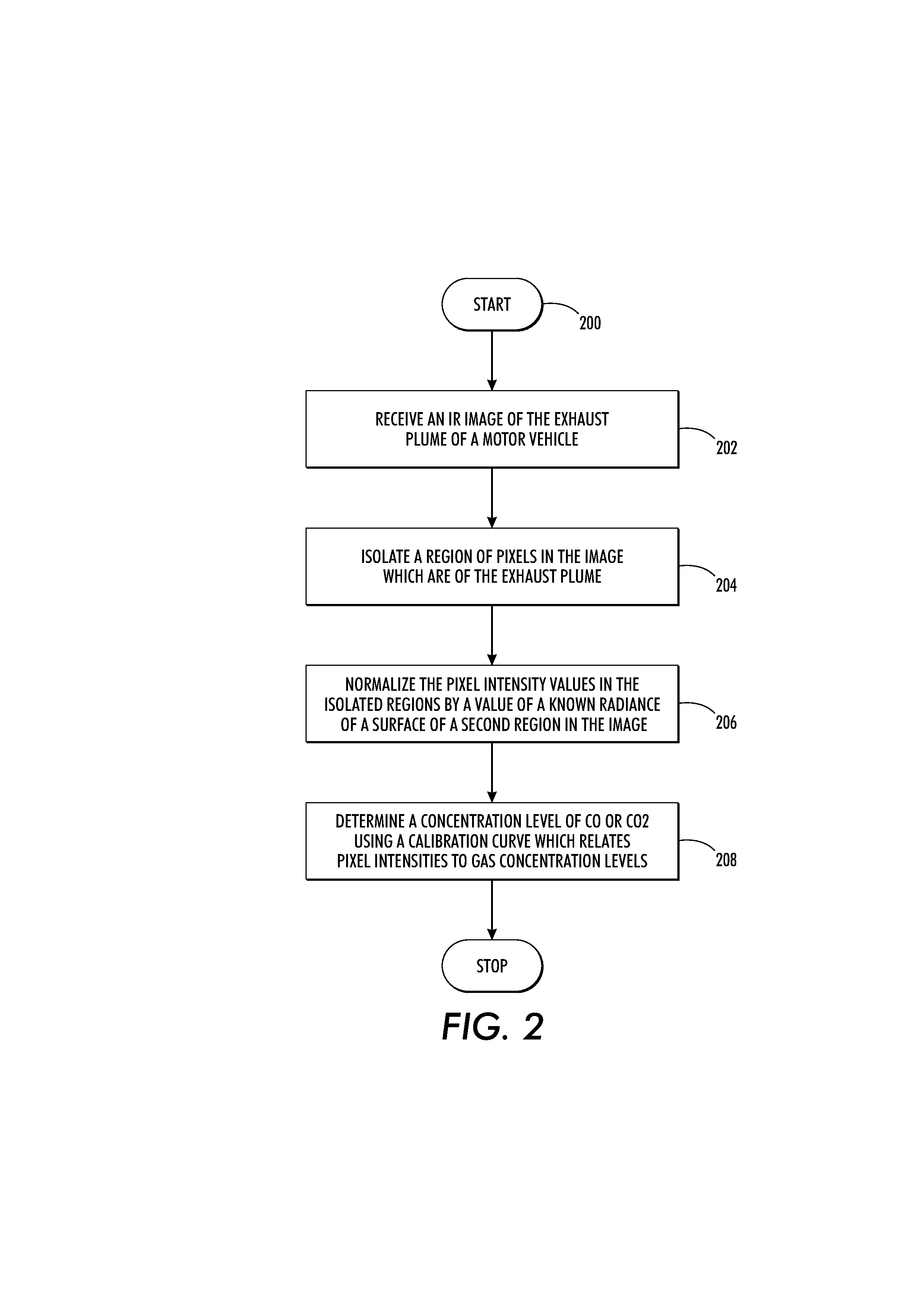
Image-based determination of co and co2 concentrations in vehicle exhaust gas emissions
ActiveUS20130181836A1Readily apparentEngine testingCharacter and pattern recognitionPresent methodEmission standard
What is disclosed is a system and method for image-based determination of concentration of CO and CO2 in a vehicle's exhaust gas in an emissions testing environment. In one embodiment, the present method involves receiving an IR image of the exhaust plume of a motor vehicle intended to be tested for CO and CO2 concentrations. The IR image has been captured using a mid-wave infrared camera with at least one optical filter tuned to the infrared absorption band of CO and CO2. The images are pre-processed to isolate pixels which contain the exhaust plume. The intensity values of pixels in those isolated regions are normalized and concentrations of CO and CO2 are determined via a calibration curve which relates pixel intensities to concentrations. The concentrations are compared to an emissions standard set for the vehicle to determine whether the vehicle is a gross polluter.
Owner:CONDUENT BUSINESS SERVICES LLC
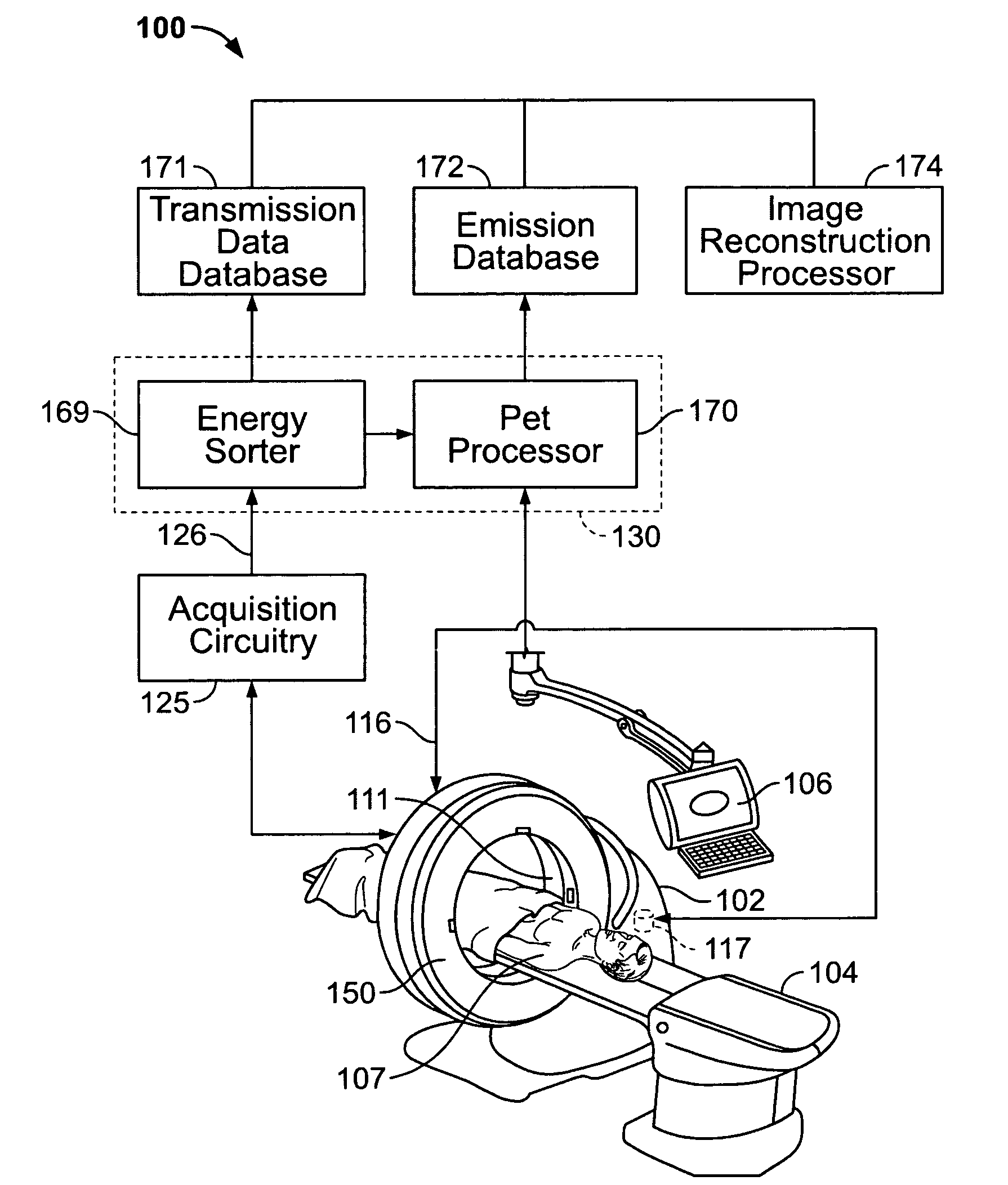
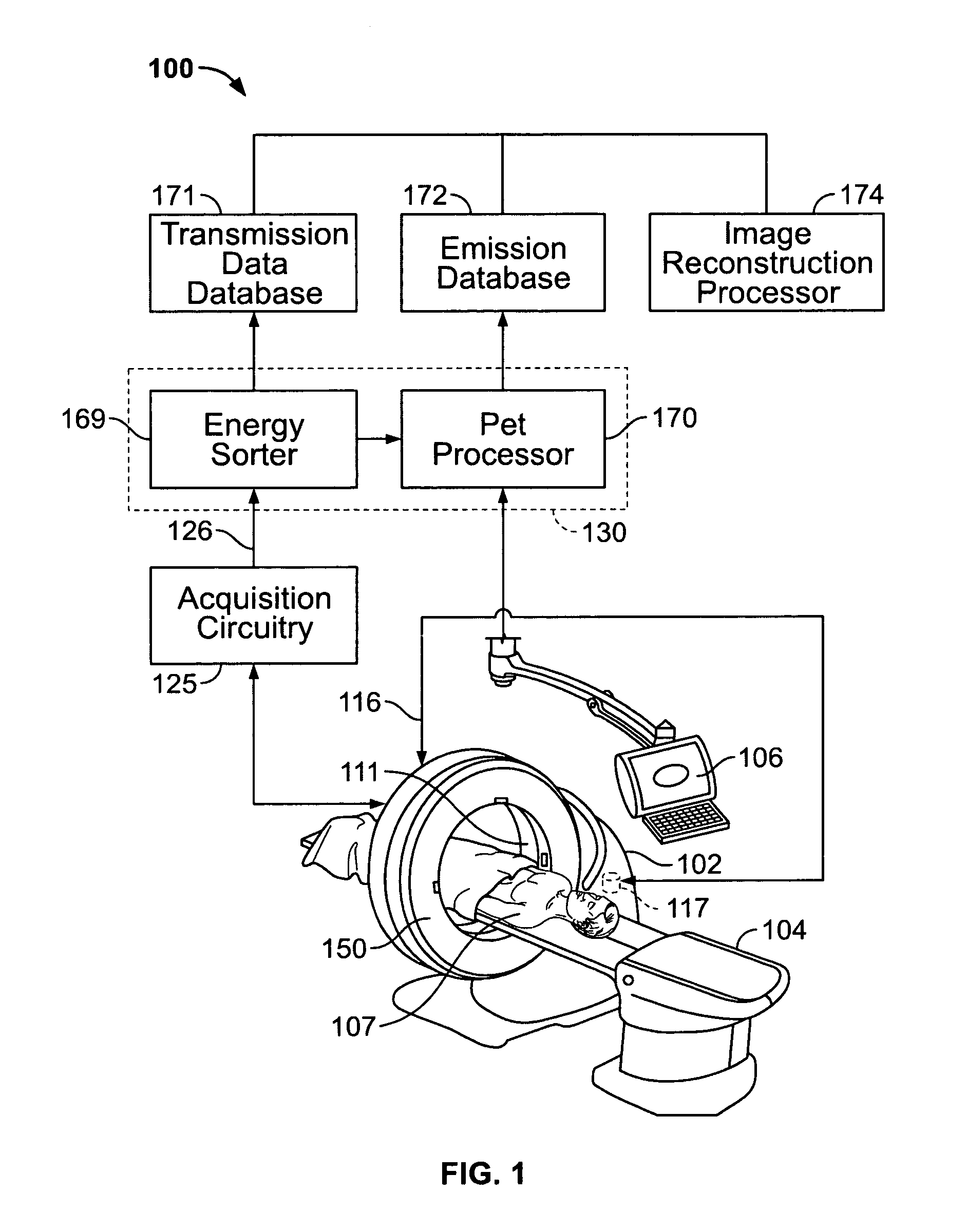
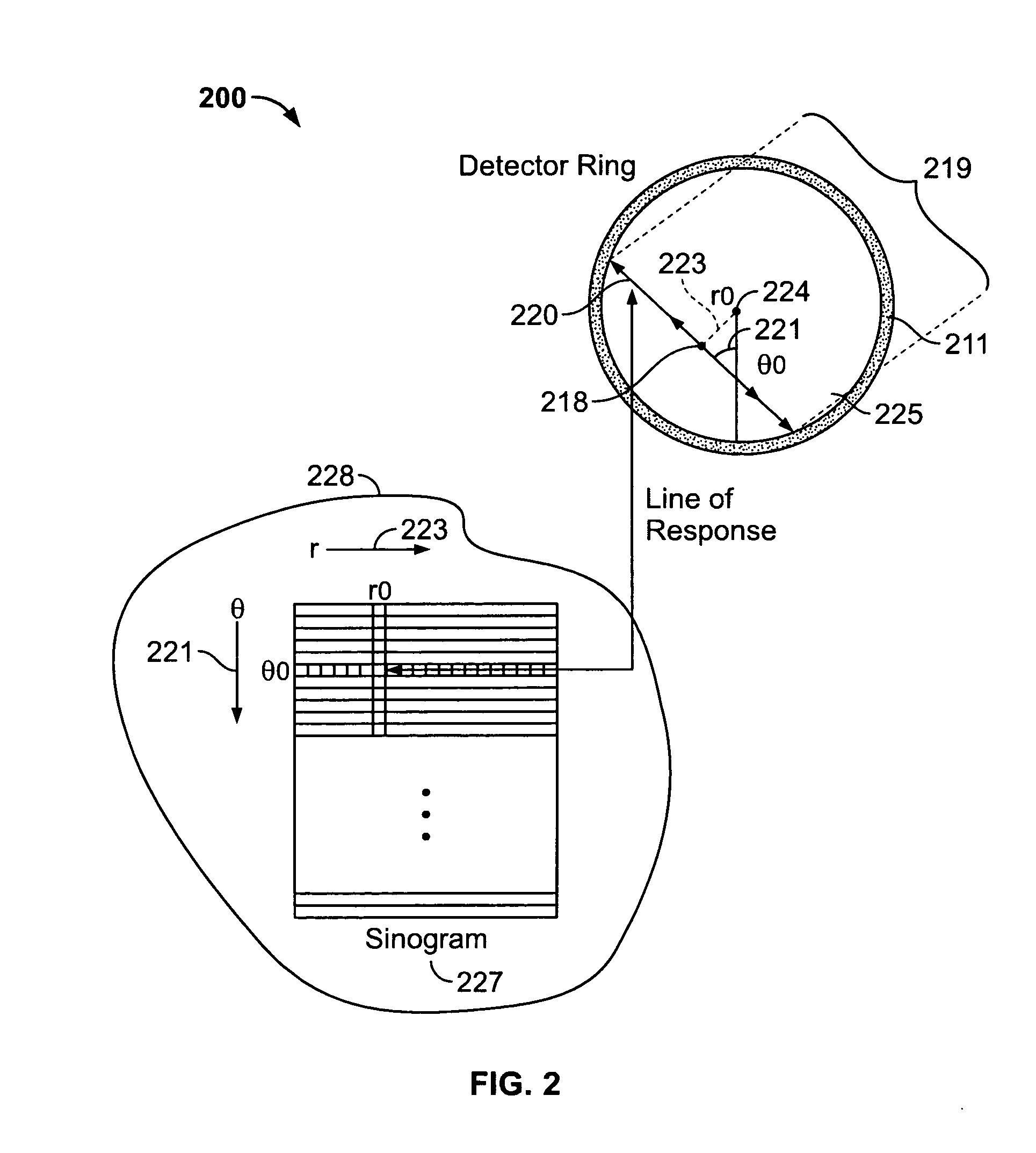
Methods and systems for attenuation correction in medical imaging
ActiveUS20080107229A1Area maximizationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingUltrasound attenuationTomography
Methods and systems for imaging a patient are provided. The method includes scanning a patient and acquiring a plurality of frames of cine computed tomography (CT) images during one complete respiratory cycle. In one embodiment, a method is provided that includes selecting an organ of interest in the cine CT data and selecting a value for each pixel in the organ of interest that represents the maximum density measurement. An attenuation corrected positron emission tomography (PET) image is constructed based on the maximization of the pixel intensity of the organ of interest in the CT attenuation correction map. Incorrect attenuation correction values for PET images can be avoided by utilizing the CT attenuation correction map.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Multiresolutional critical point filter and image matching using the same
A multiresolutional filter called a critical point filter is introduced. This filter extracts a maximum, a minimum, and two types of saddle points of pixel intensity for every 2x2 (horizontalxvertical) pixels so that an image of a lower level of resolution is newly generated for every type of a critical point. Using this multiresolutional filter, a source image and a destination image are hierarchized, and source hierarchical images and destination hierarchical images are matched using image characteristics recognized through a filtering operation.
Owner:JBF PARTNERS
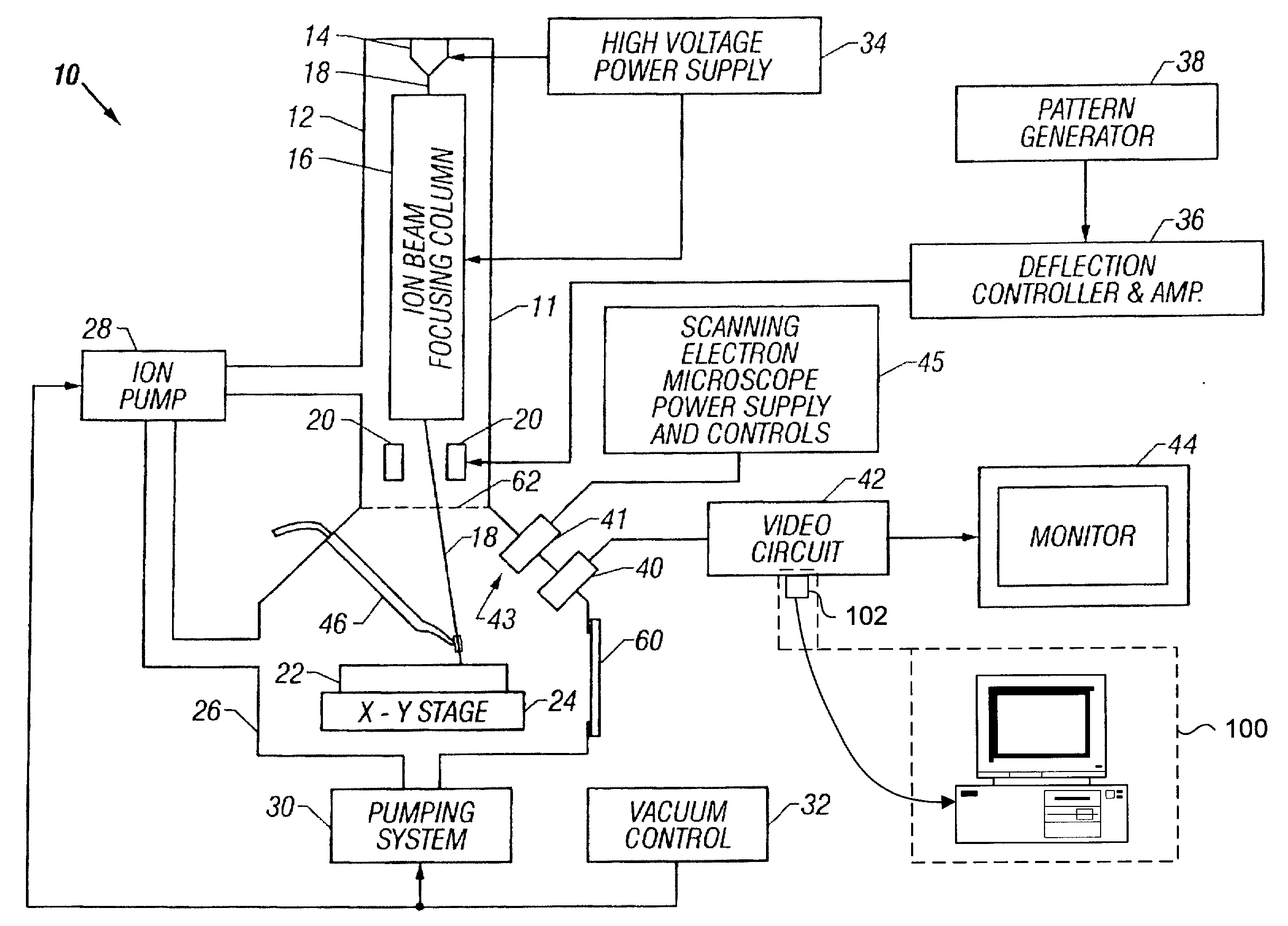
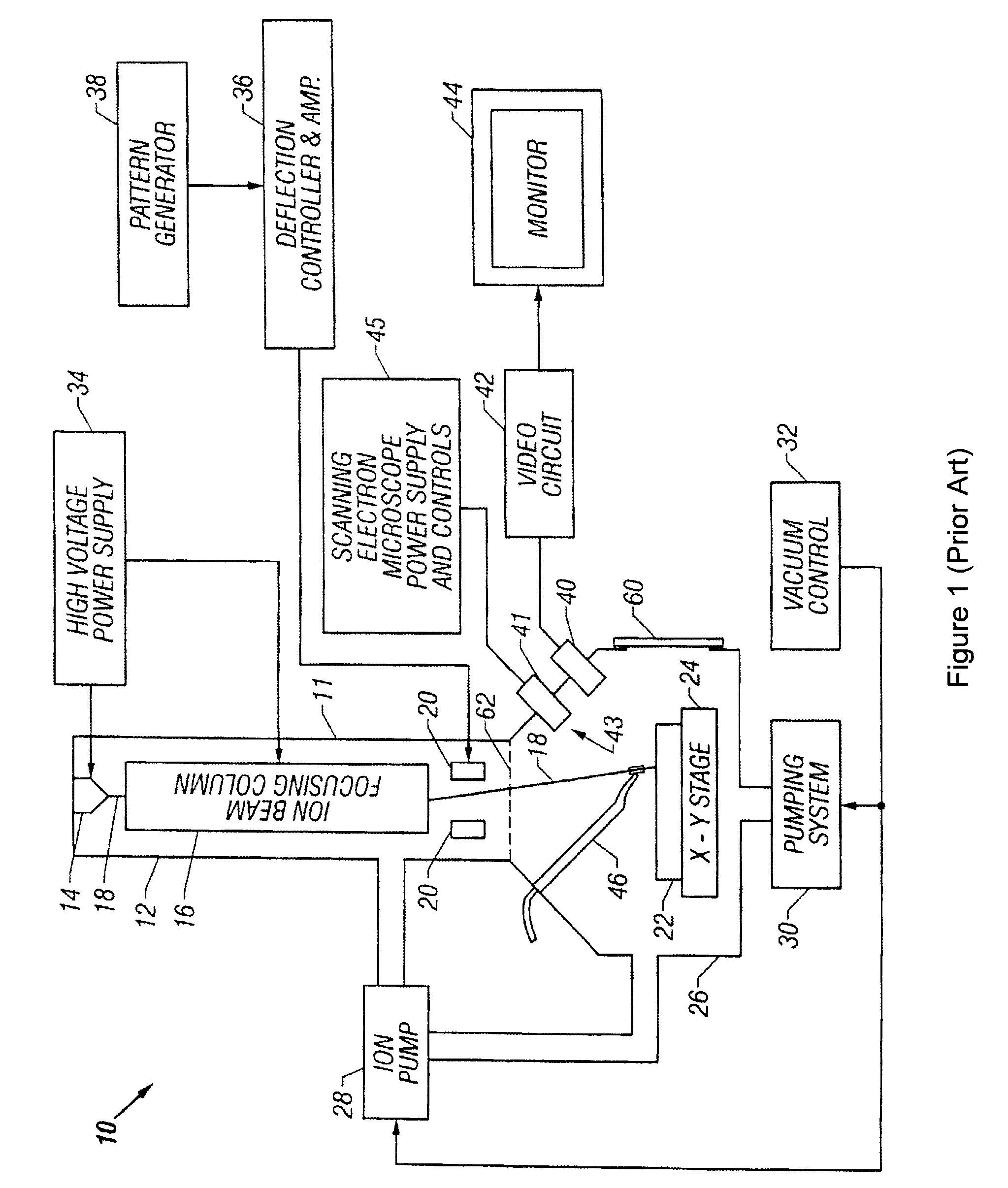
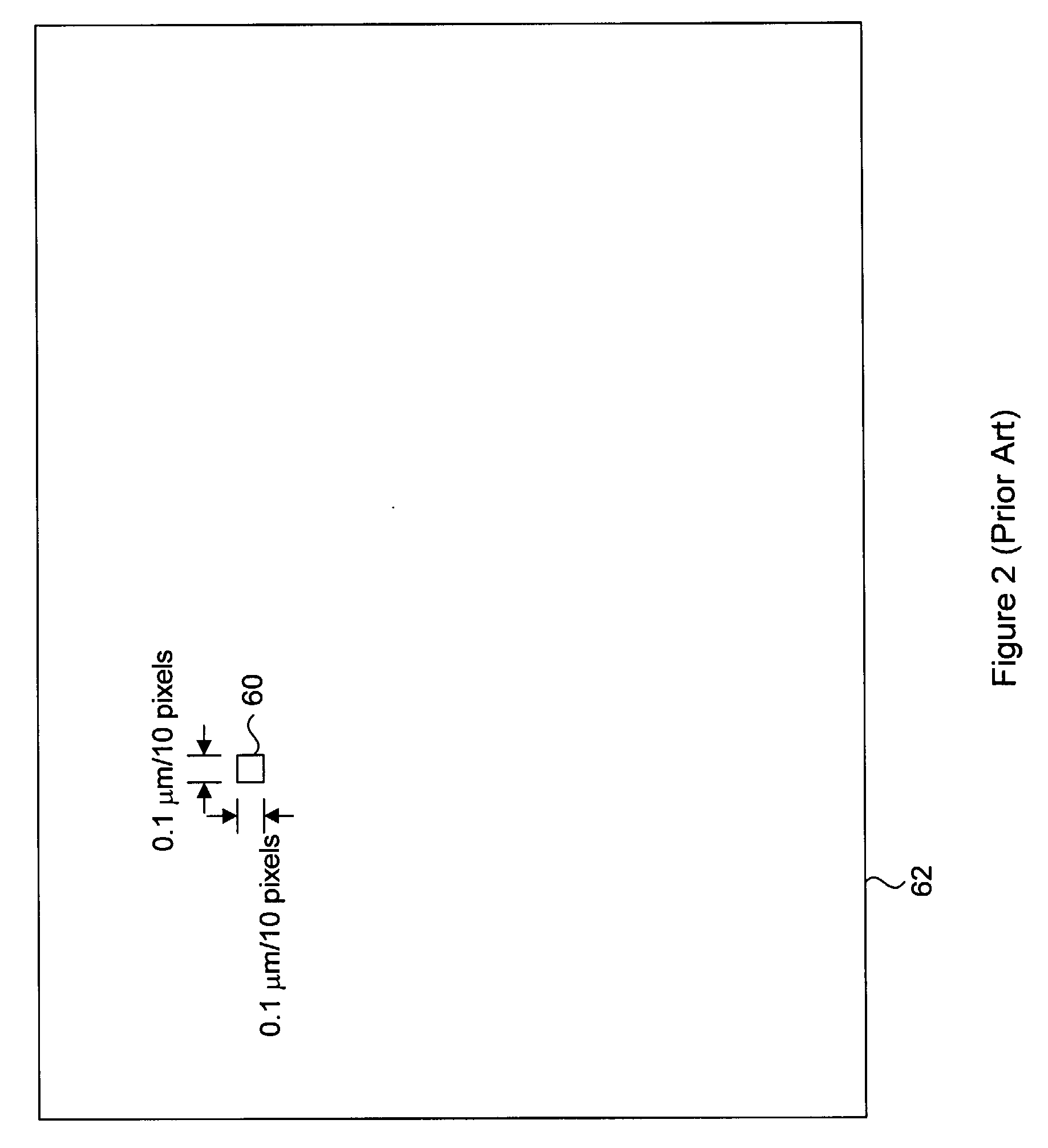
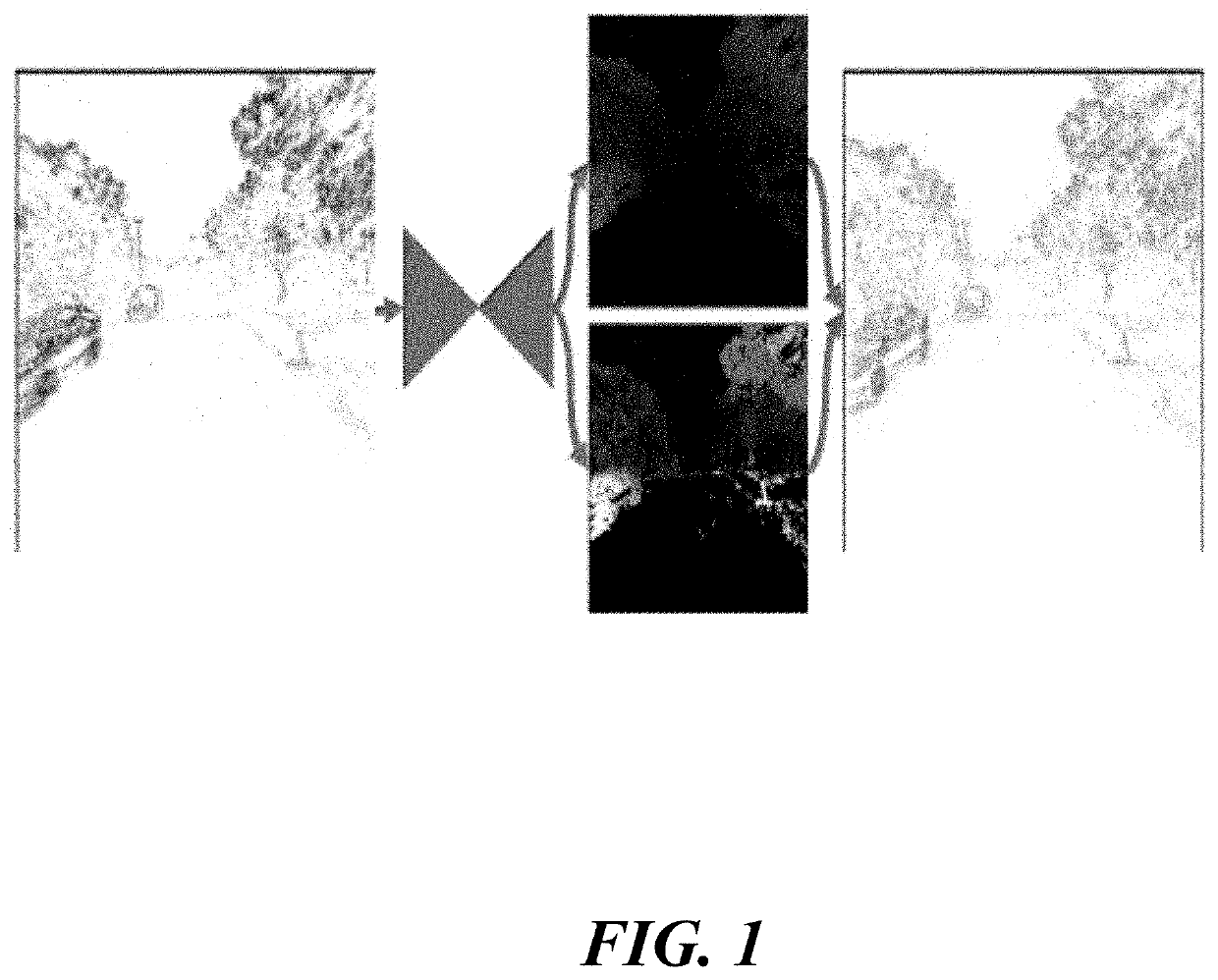
System and Method for Focused Ion Beam Data Analysis
ActiveUS20090135240A1Increase changeFacilitate cognitionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSamplingGraphicsIon beam
A system and method for improving FIB milling endpointing operations. The methods involve generating real-time images of the area being milled and real-time graphical plots of pixel intensities with an increased sensitivity over native FIB system generated images and plots. The images and plots are generated with raw signal data obtained from the native FIB system. More specifically, the raw signal data is processed according to specific algorithms for generating images and corresponding intensity graphs which can be reliably used for accurate endpointing. In particular, the displayed images will display more visual information regarding changes in milled material, while the intensity graphs will plot aggregate pixel intensity data on a dynamically adjusting scale to dramatically highlight relative changes in milled material.
Owner:DCG SYST
Methods, systems, and computer readable media for estimation of optical flow, depth, and egomotion using neural network trained using event-based learning
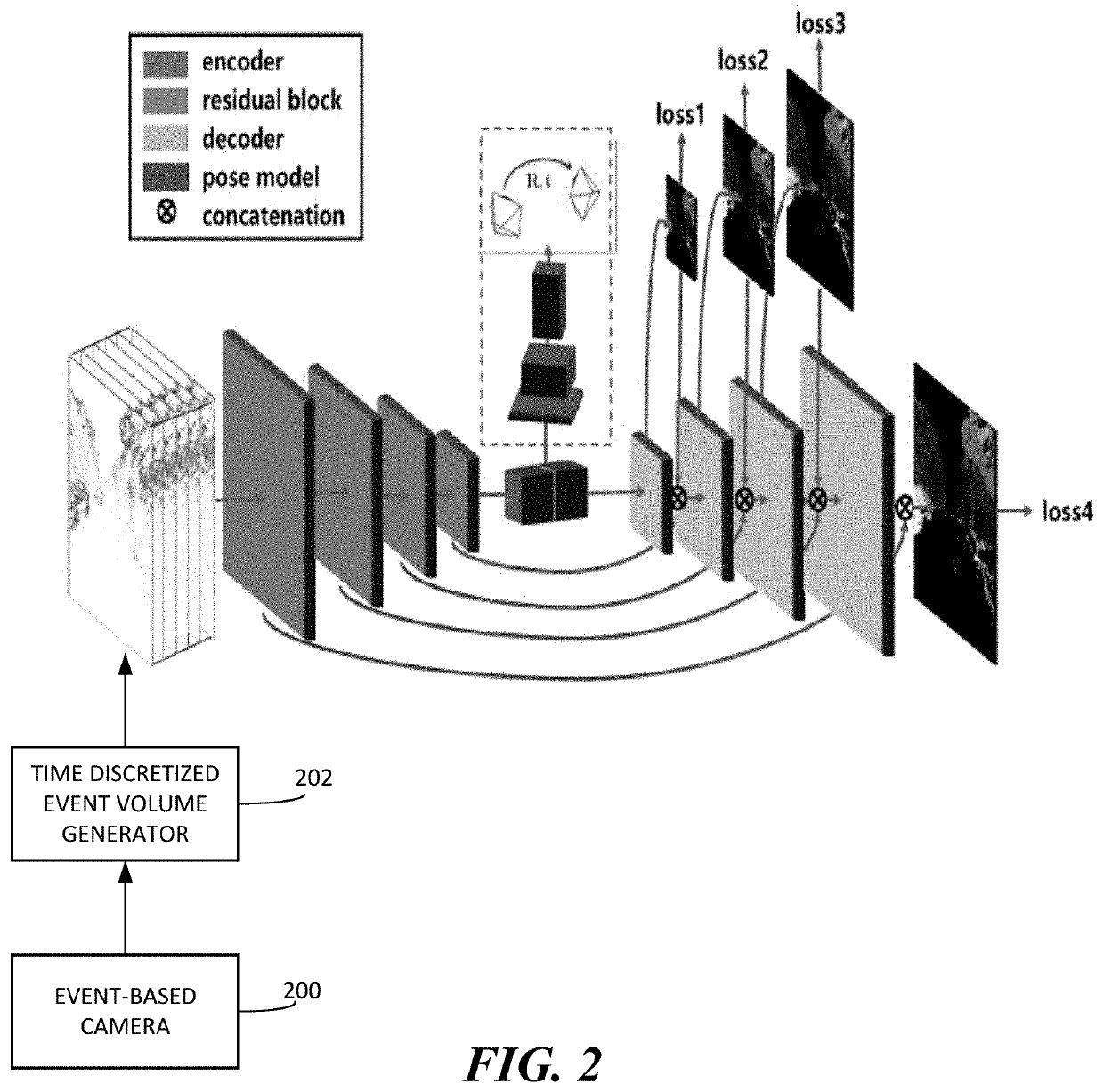
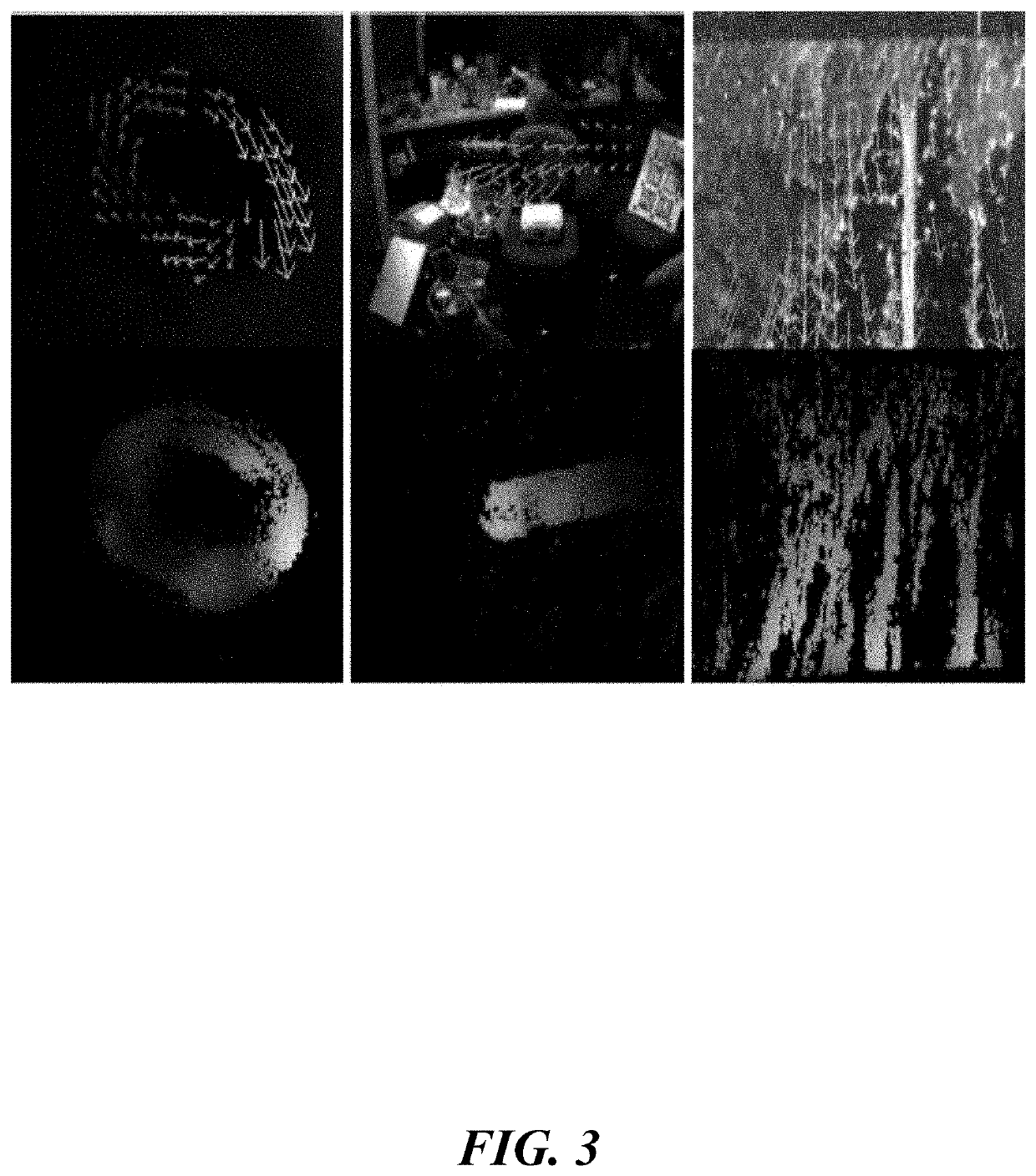
A method for prediction of an indication of motion using input from an event-based camera includes receiving events captured by an event-based camera, wherein each of the events represents a location of a change in pixel intensity, a polarity of the change, and a time. The method further includes discretizing the events into time discretized event volumes, each of which contain events that occur within a specified time range. The method further includes providing the time discretized event volumes as input to an encoder-decoder neural network trained to predict an indication of motion using a loss function that measures quality of image deblurring; generating, using the neural network, a prediction of the indication of motion. The method further includes using the prediction of the indication of motion in a machine vision application.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
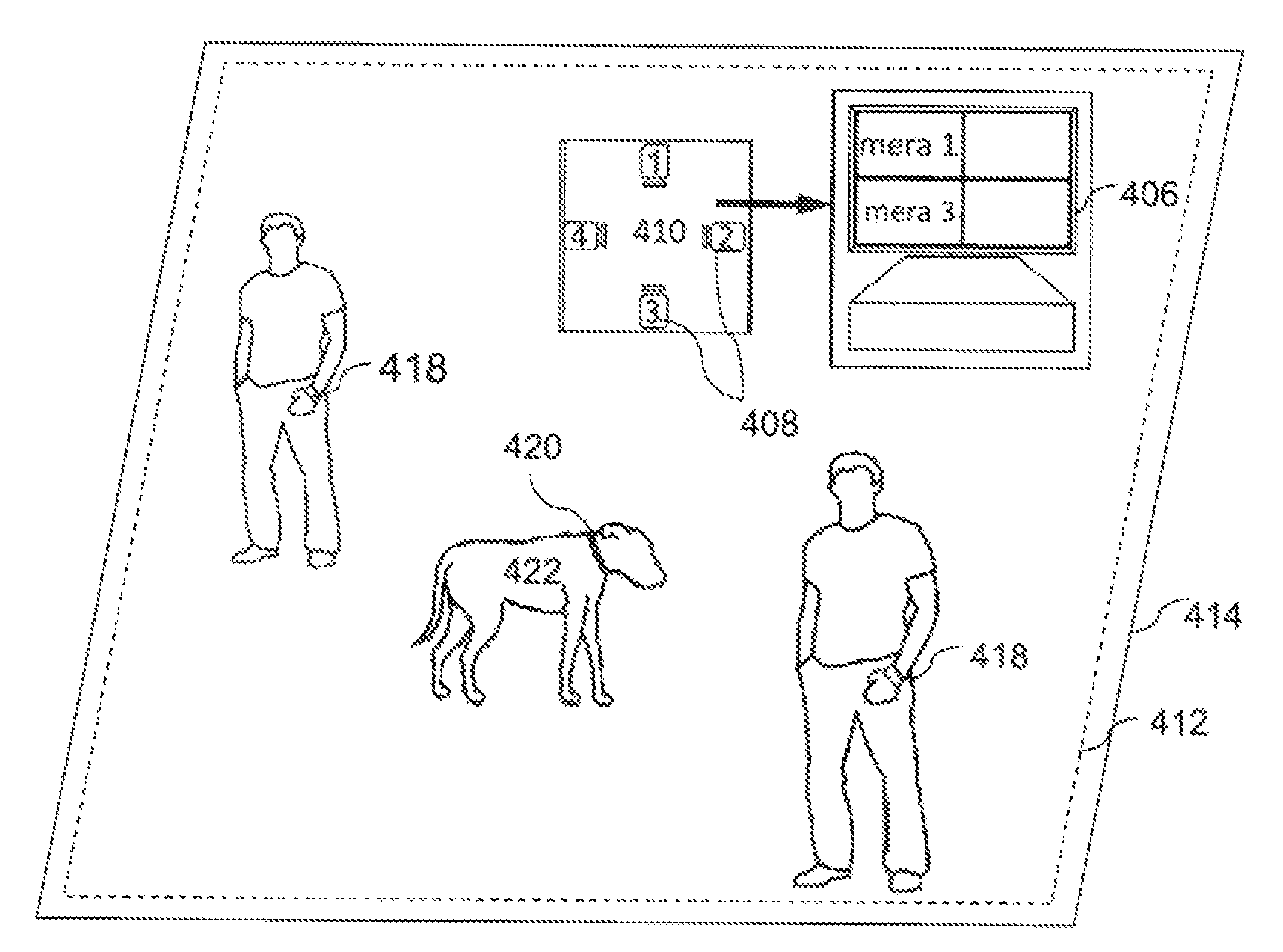
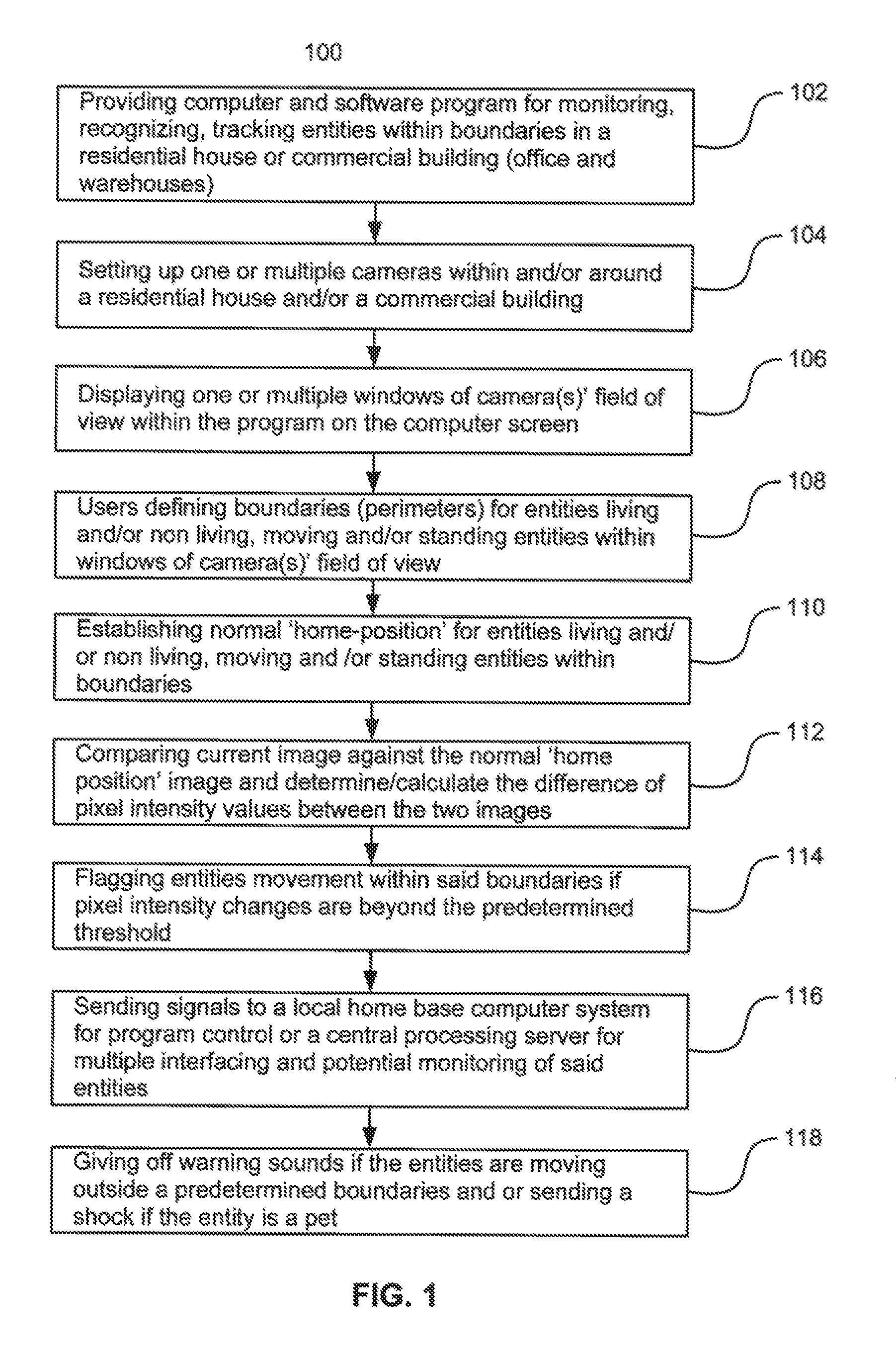
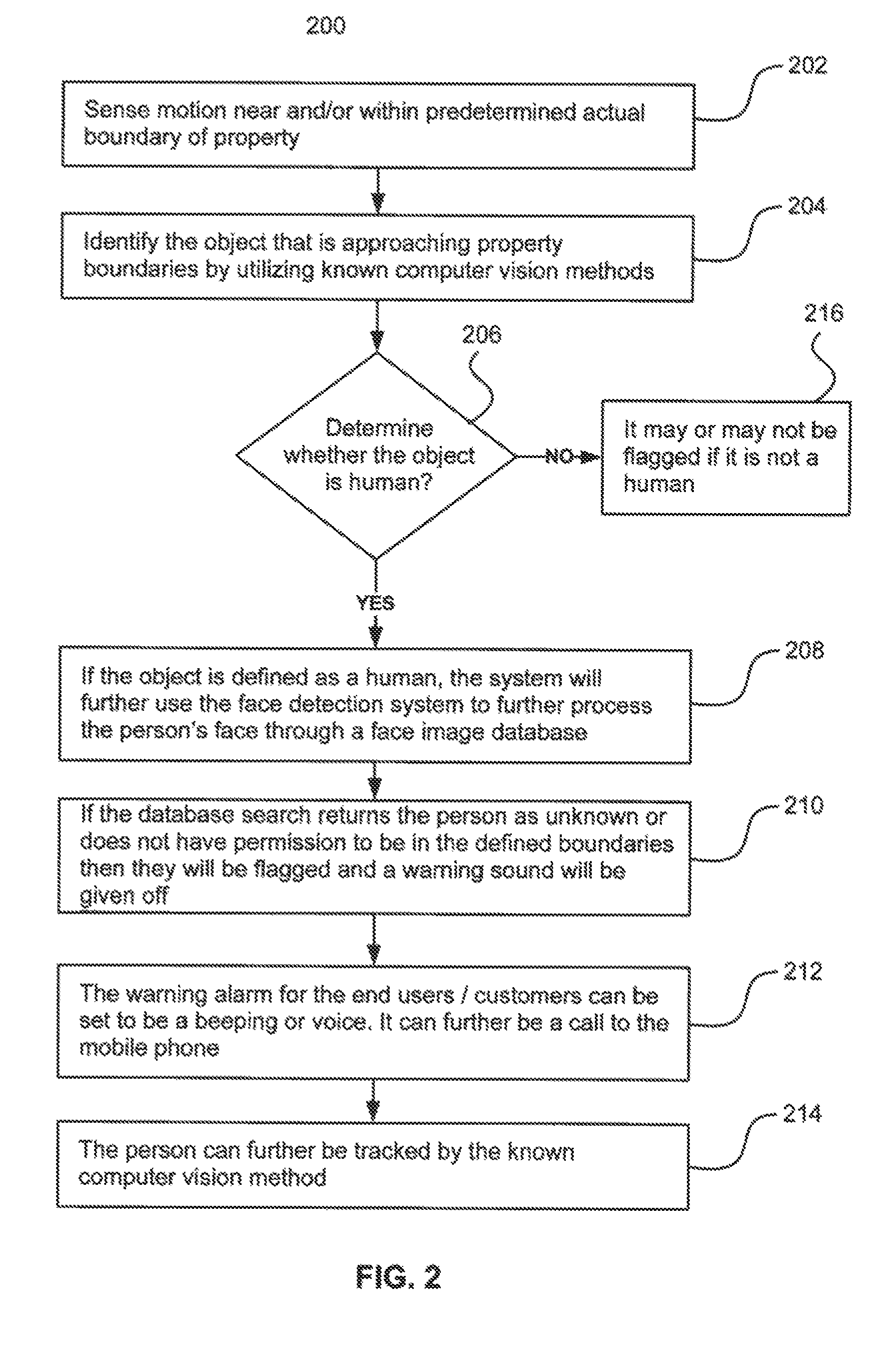
Surveillance systems and methods to monitor, recognize, track objects and unusual activities in real time within user defined boundaries in an area
InactiveUS8908034B2Color television detailsClosed circuit television systemsNon real timeMonitoring system
A surveillance system and method that utilize computer vision technology and background subtraction to monitor, recognize, and track objects or unusual activities within user specified boundaries. The system and method comprises at least one camera and at least one computer with a software program showing one or multiple windows of camera's field of views in real time. The program allows users to define one or multiple boundaries within any window. The program further utilizes background subtraction technique to establish normal “home-position” of objects within defined boundaries. The program compares current image of the objects against the normal “home-position” to determine / calculate the difference of pixel intensity values. If the difference is beyond the predetermine threshold, the program will flag the movement of the object and give off alert.
Owner:BORDONARO JAMES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com