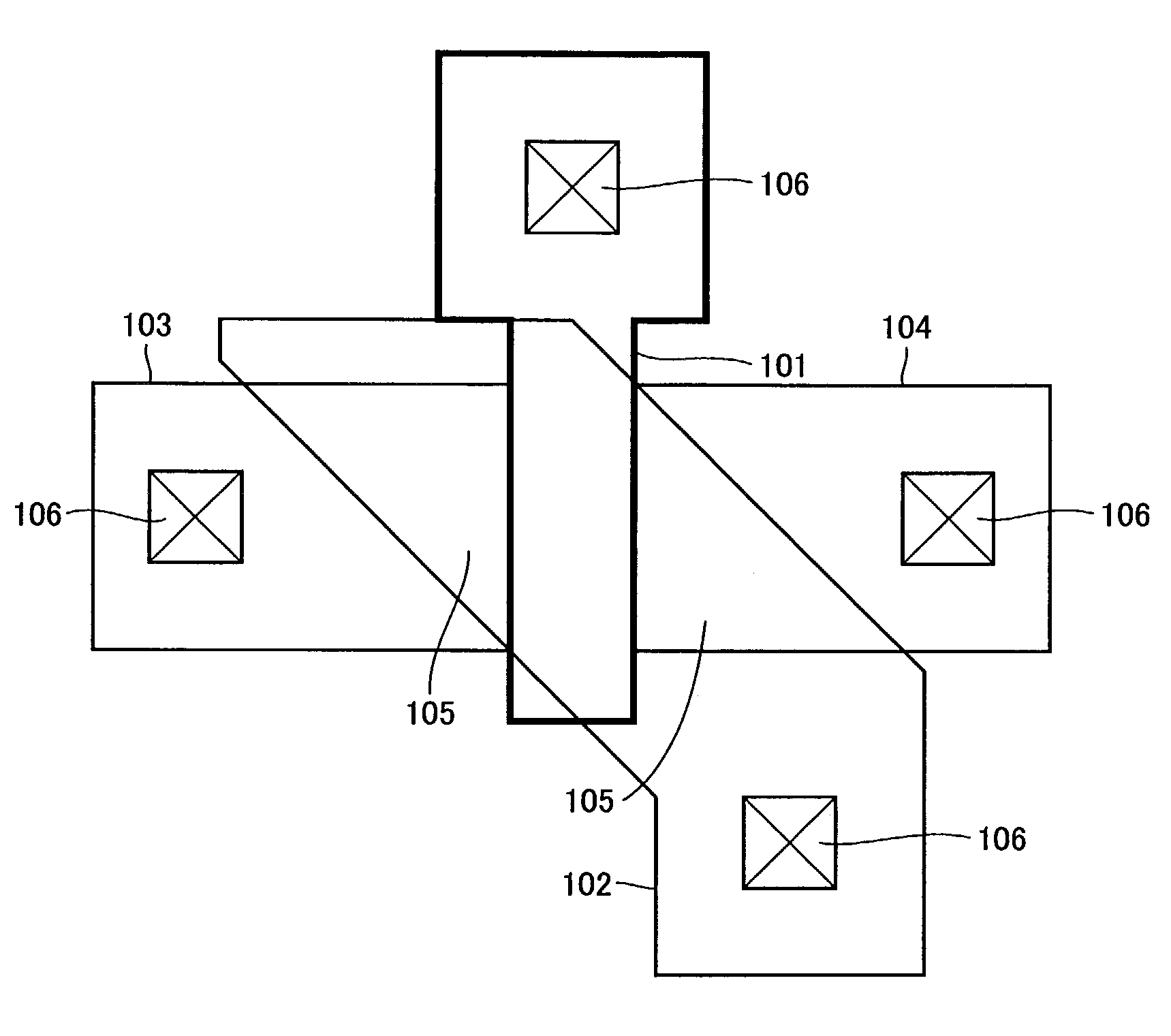
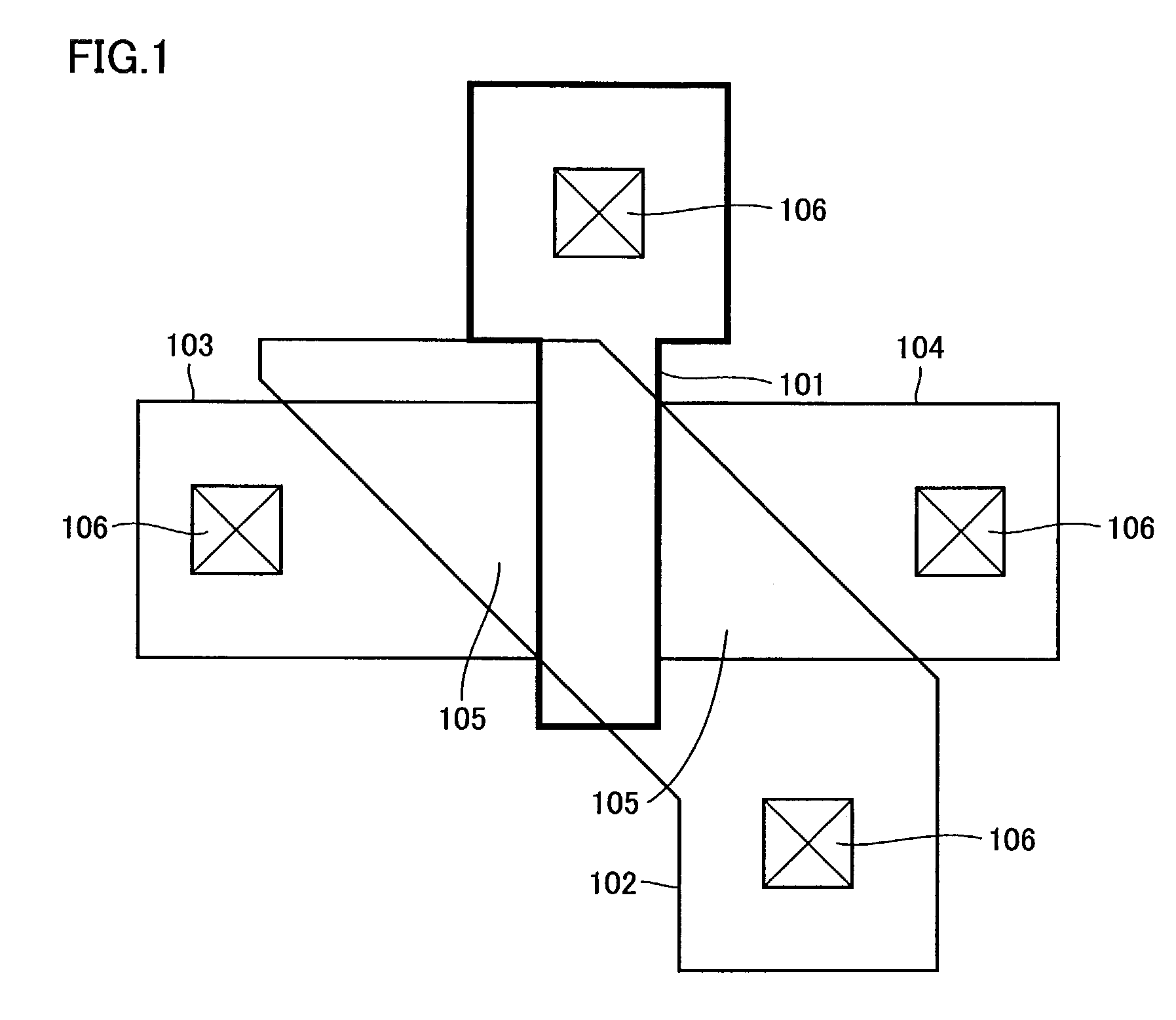
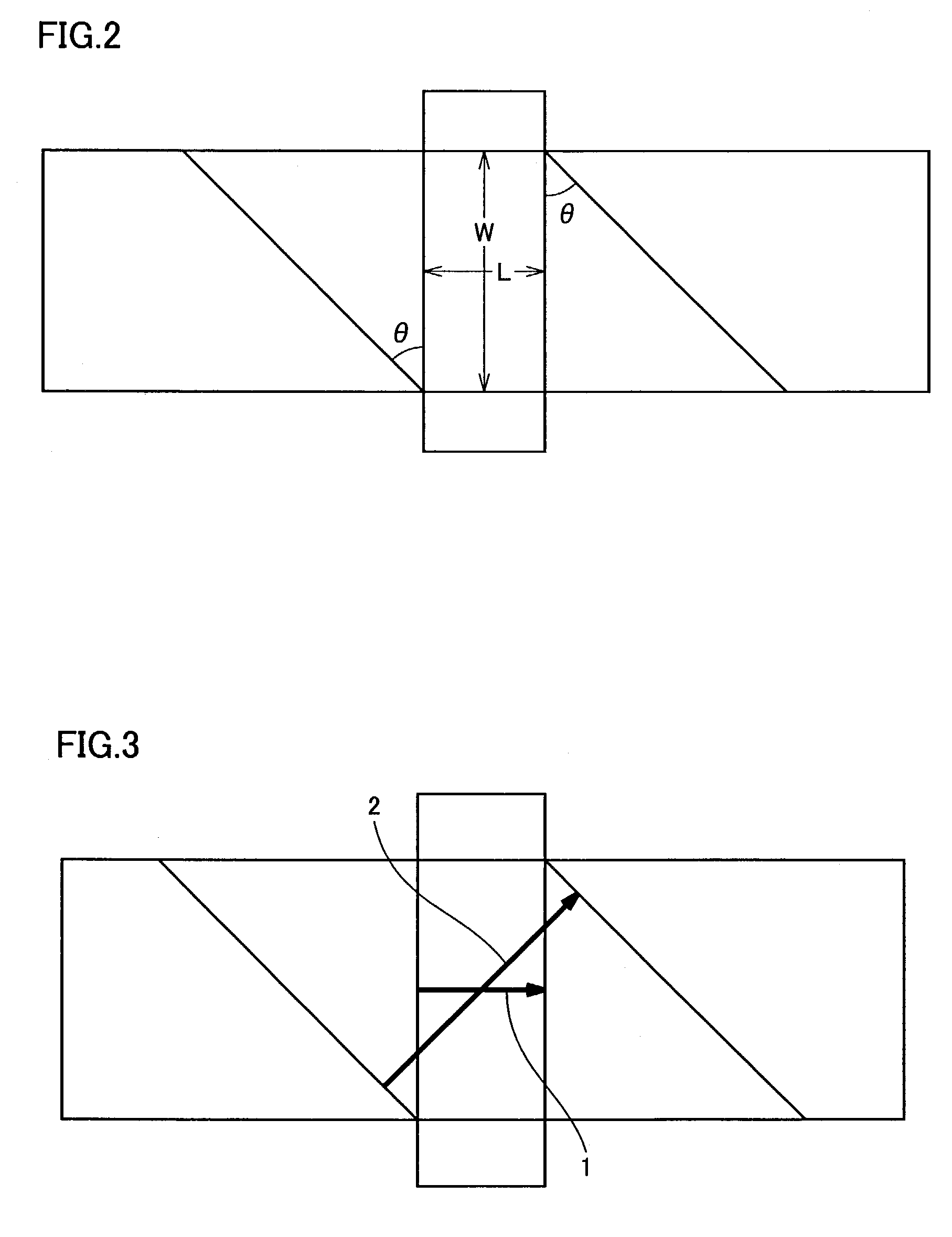
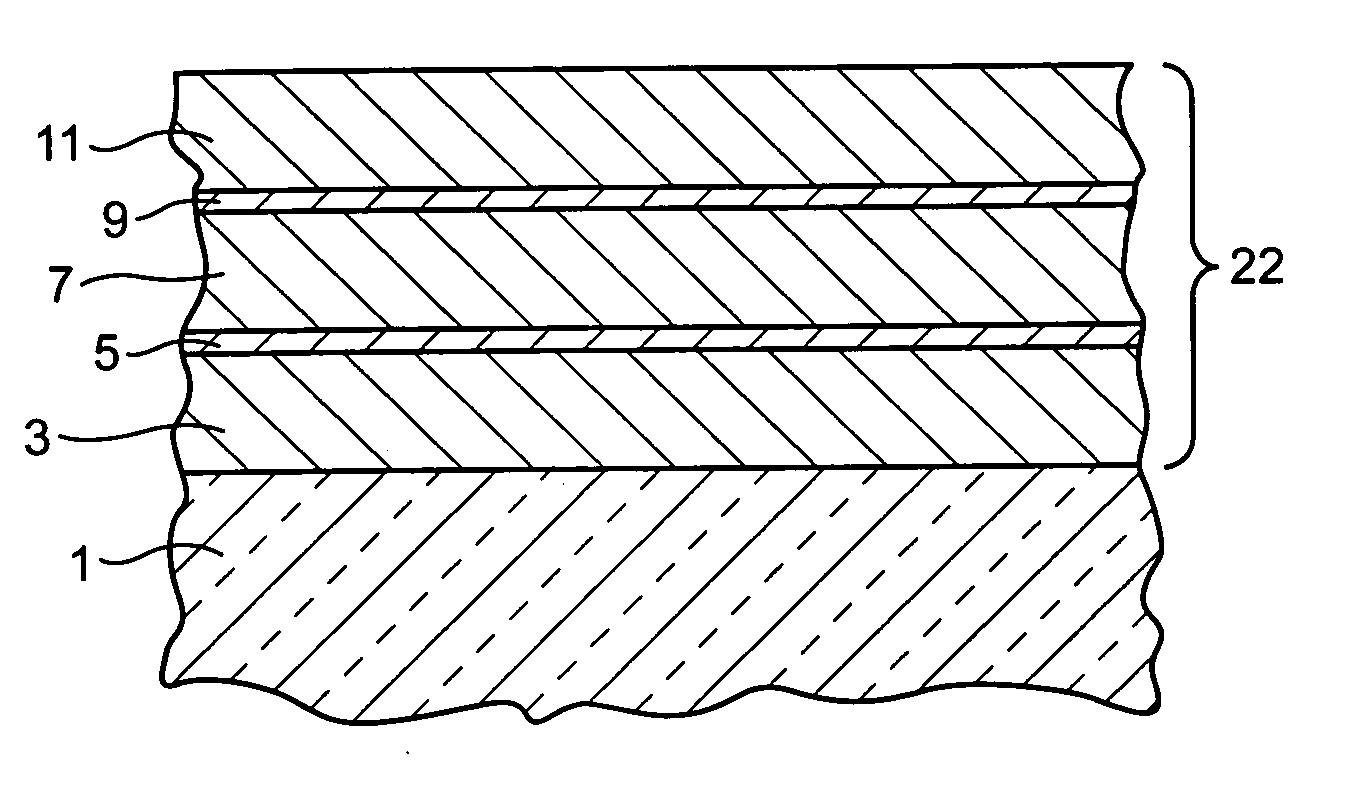
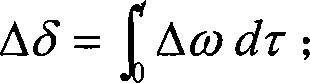Patents
Literature
594 results about "Gain coefficient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The gain coefficient describes how the density of photons, u n(z), changes as they propagate along the z-direction. The definition implicitly used before was. u n(z) dz. =. g n · u n(z) The physical process for the change of the photon density was stimulated emission (increasing the density) and fundamental absorption (decreasing the density).
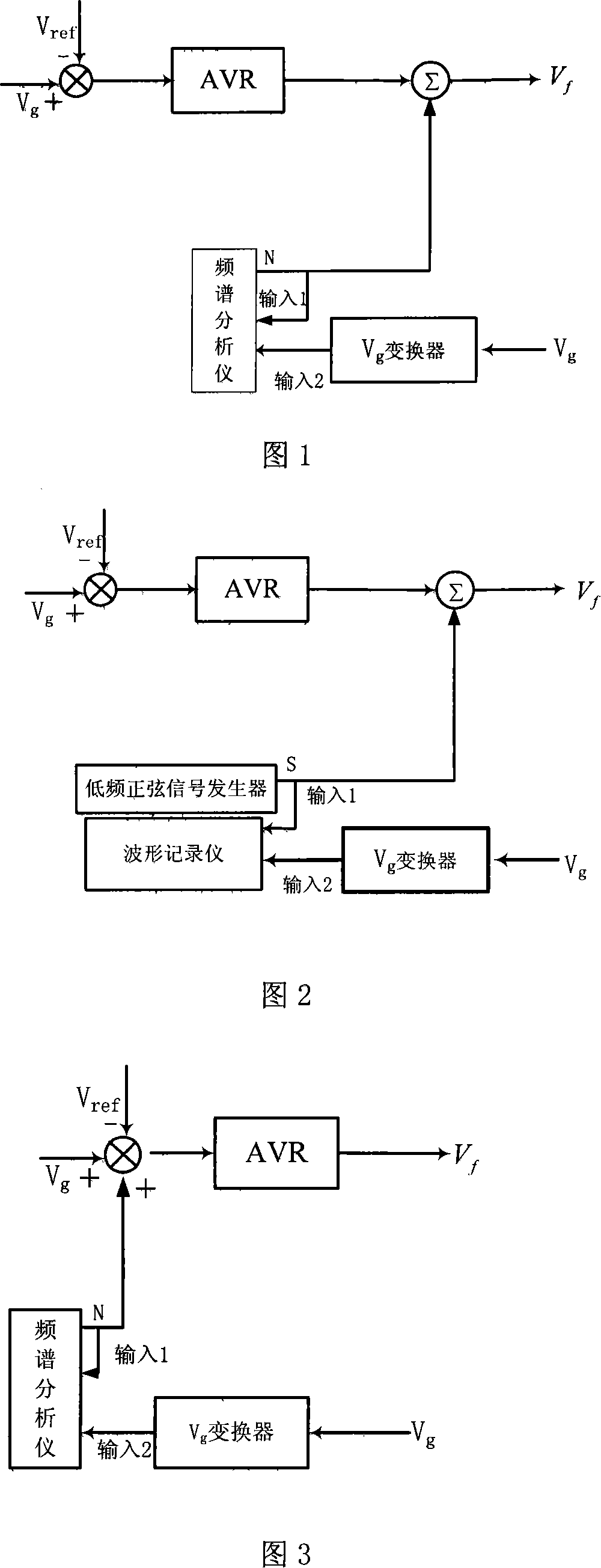
Delta-sigma A/D converter
InactiveUS6271782B1Without compromising the modulator's stabilityTo overcome the large delayElectric signal transmission systemsDifferential modulationLoop filterAnalog feedback
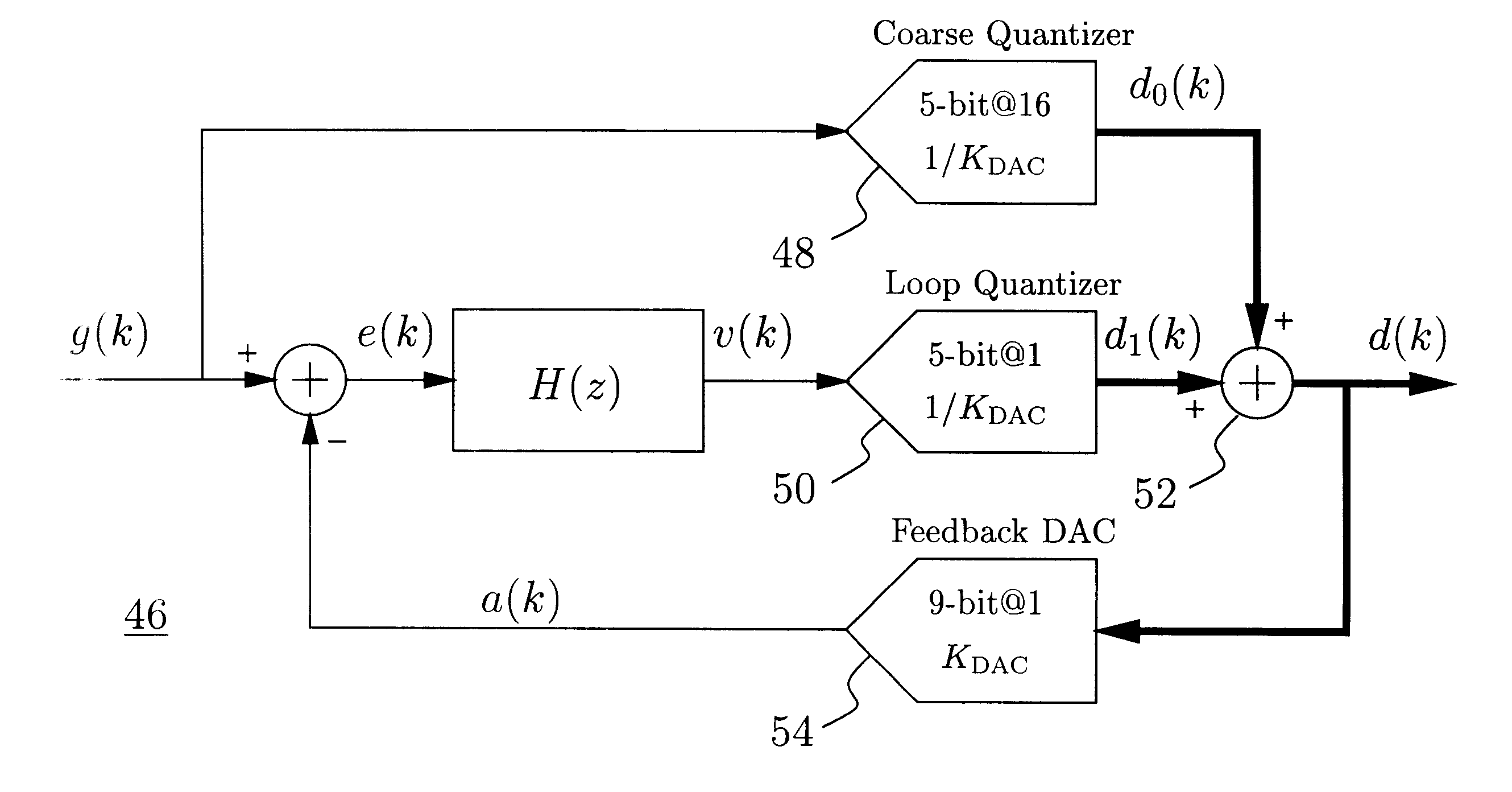
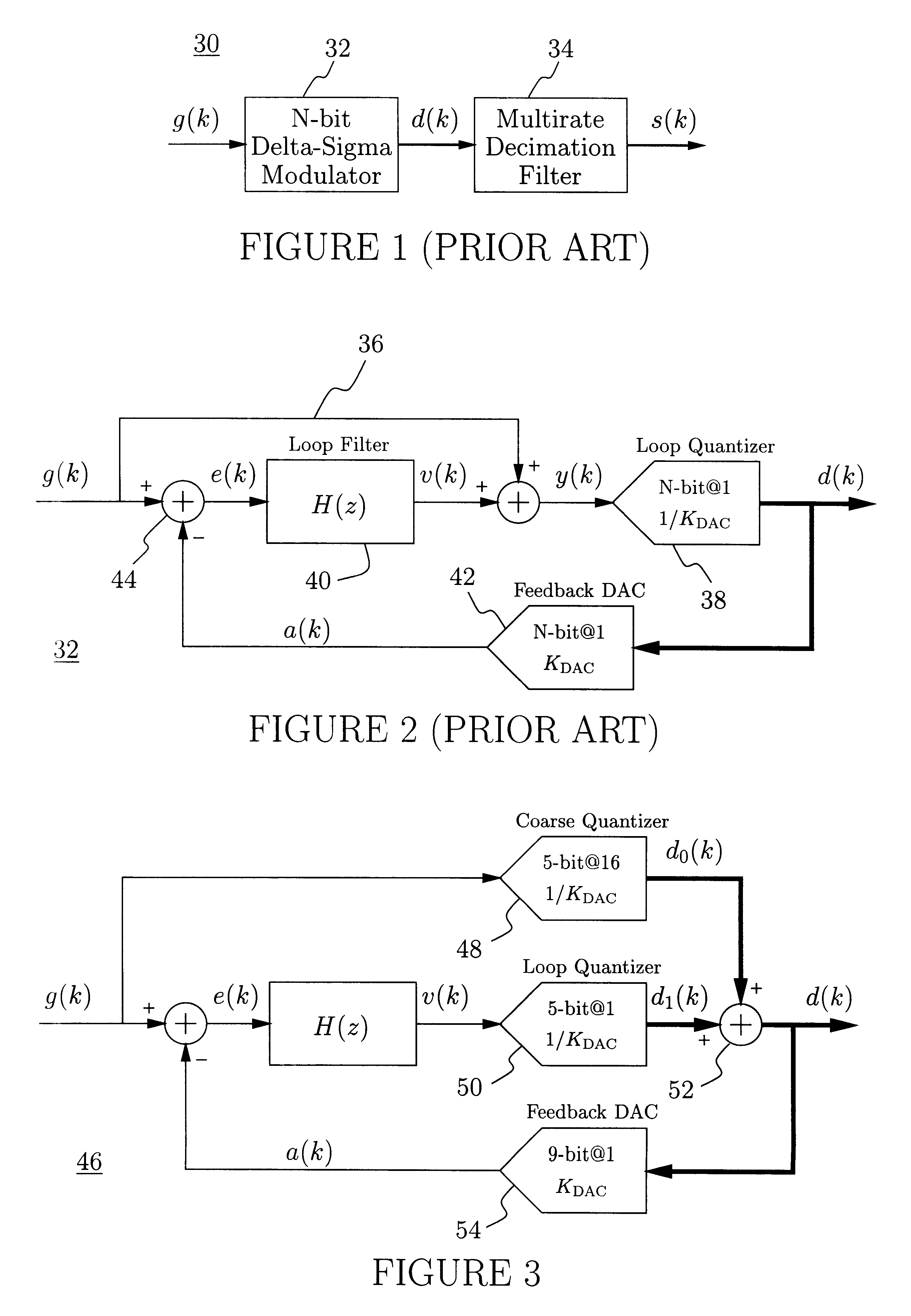
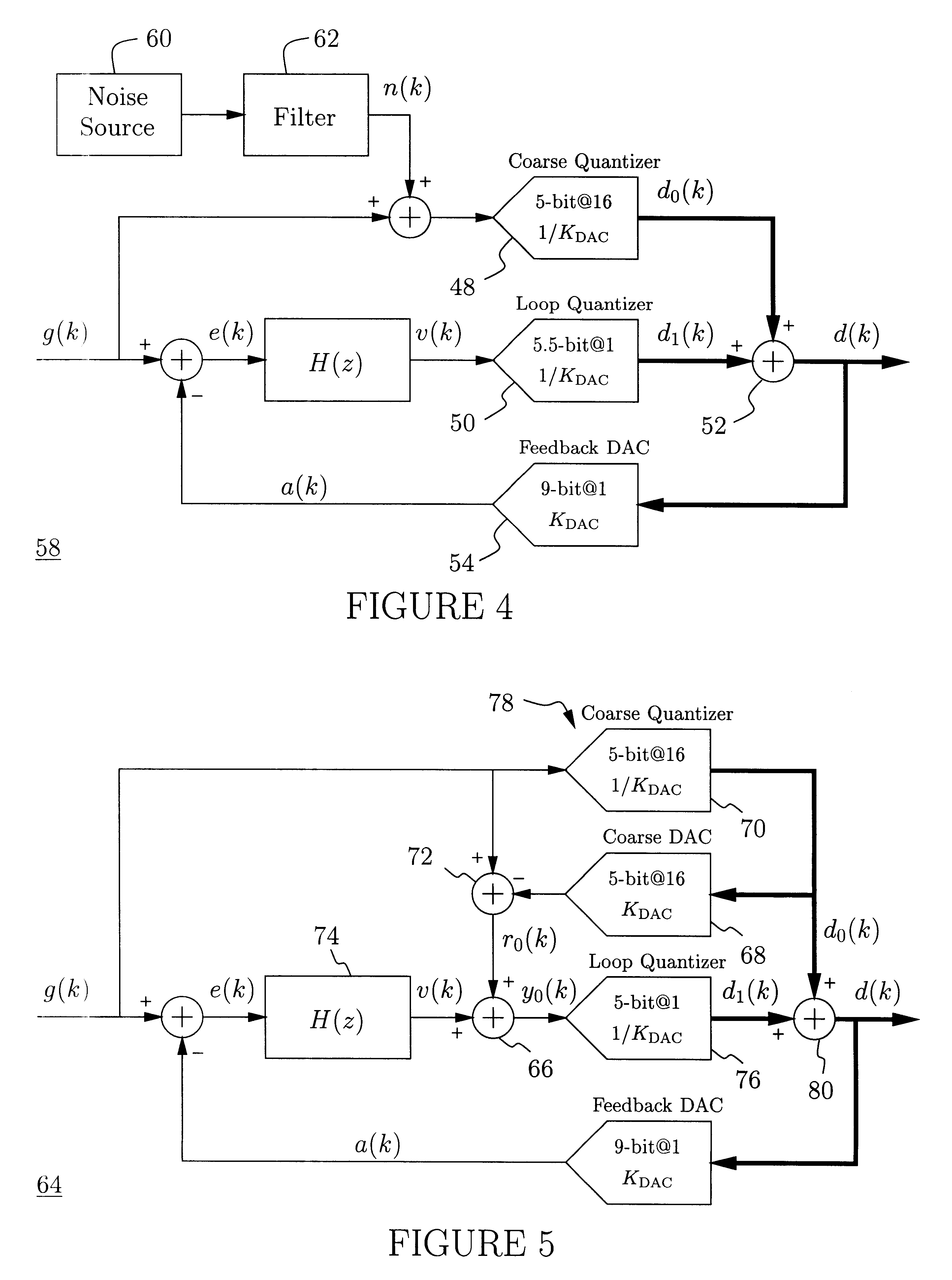
A delta-sigma modulator comprising a first quantizer providing a first digital signal d0(k) representing the input signal g(t); a loop filter with input signal paths; a loop quantizer providing a corrective digital signal d1(k) representing the loop filter's output signal y(t); an array of feedback DACs D / A converting the sum d(k)=df(k)=d0(k)+d1(k) of the first and the corrective digital signals and injecting feedback signals into the loop filter.The loop filter's input node is applied the difference of the input signal g(t) and the global analog feedback signal a3(t). The global feedback signal a3(t) is delayed several clock cycles with respect to the digital output signal d(k). The delay is used to carry out mismatch-shaping and deglitching algorithms in the feedback DACs. The feedback DACs' different delays and gain coefficients are designed such that the modulator is stable. The filter's input signal paths and the compensating DAC are designed such that the gain from the input signal g(t) to the loop quantizer is small, ideally zero. Thus, the loop quantizer's resolving range can be a fraction of the first quantizer's resolving range, whereby the output signal's d(k) resolution can be much higher than the individual resolutions of d0(k) and d1(k).The delta-sigma modulator is well suited for the implementation of high-resolution wide-bandwidth A / D converters. Important applications include digital communication systems.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES BV
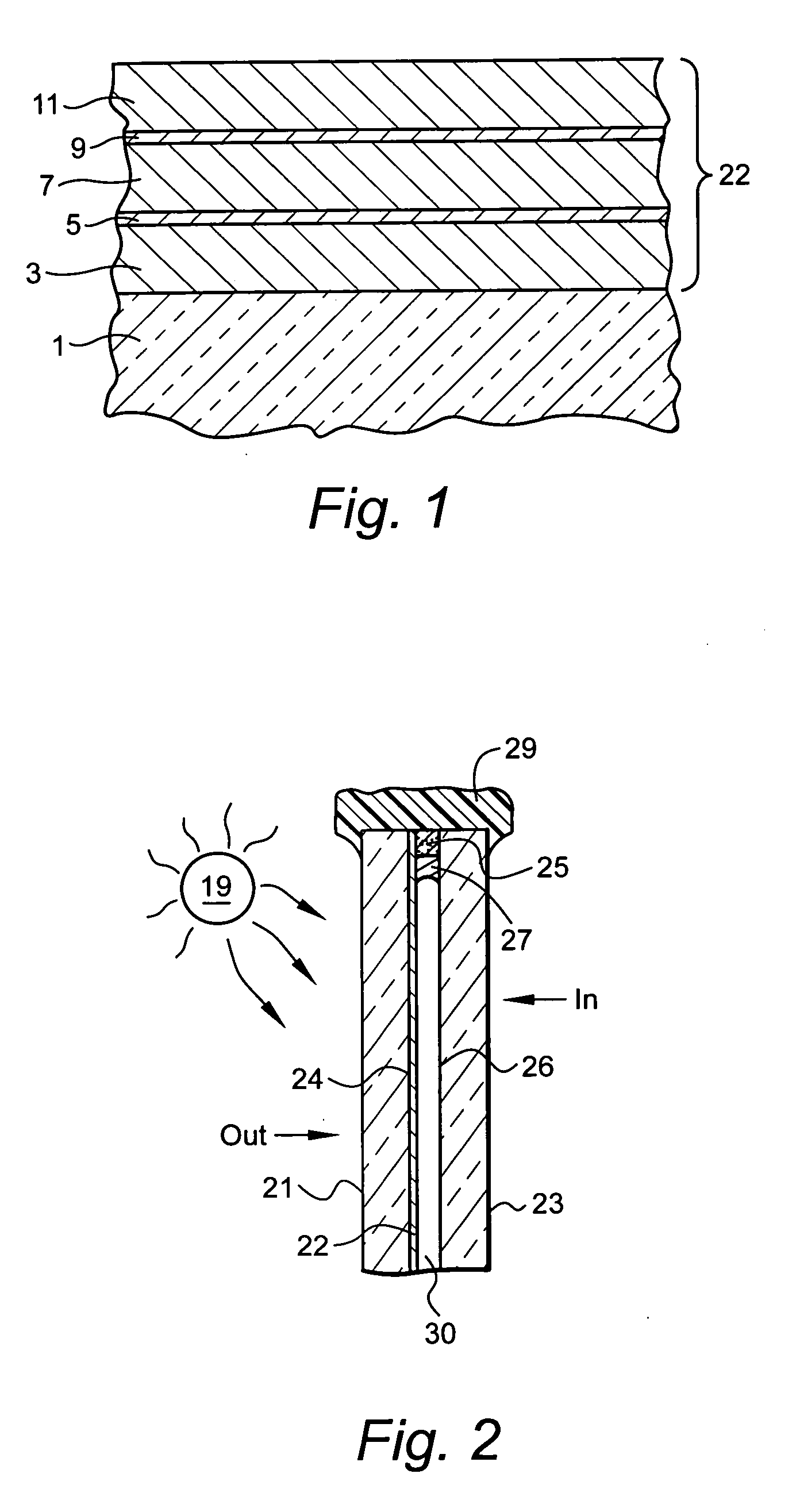
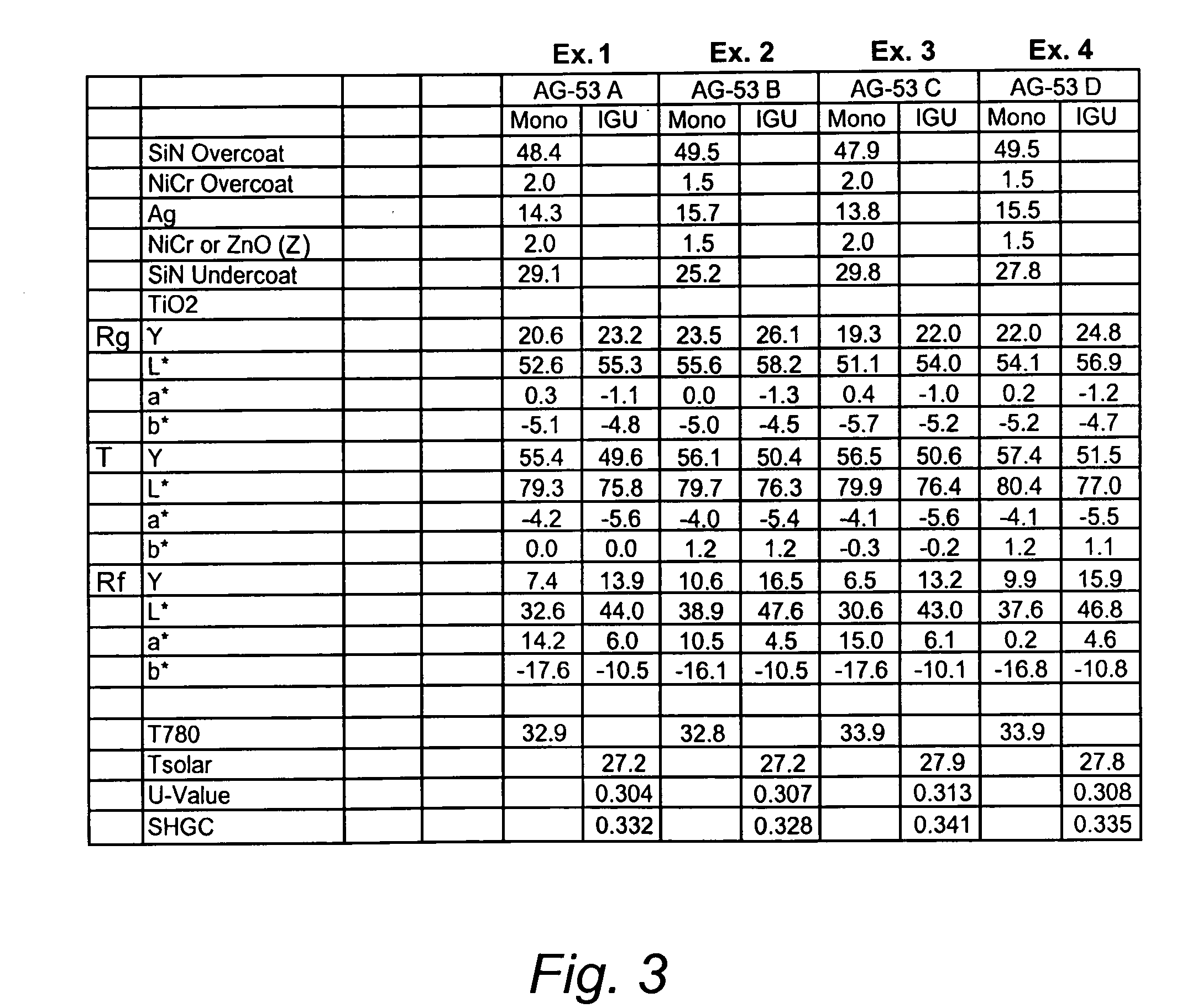
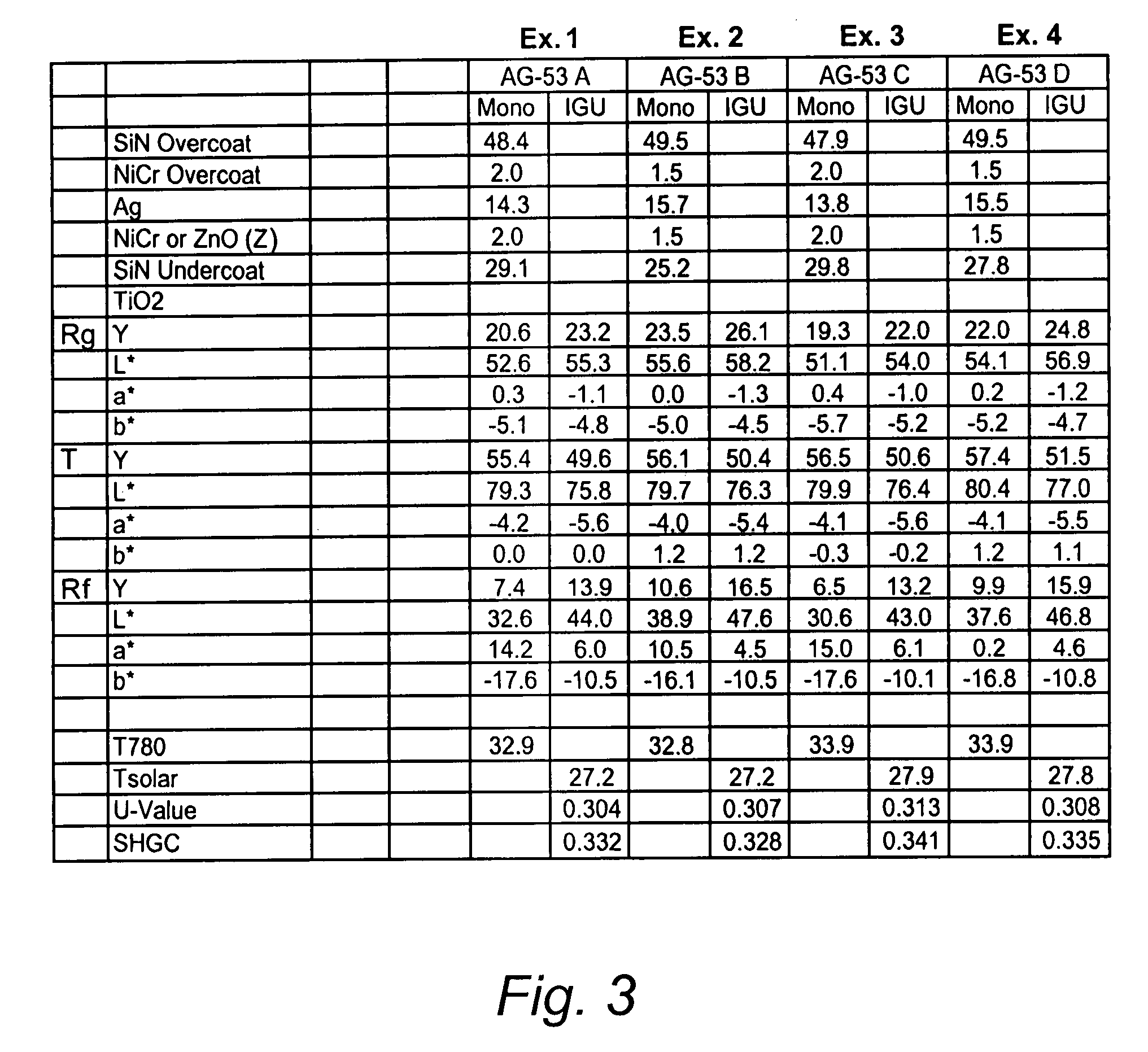
Low emissivity coating with low solar heat gain coefficient, enhanced chemical and mechanical properties and method of making the same
ActiveUS20070281171A1Equal and good chemical and durabilityEqual and good and mechanical durabilityGlass/slag layered productsCoatingsLow emissivityGain coefficient
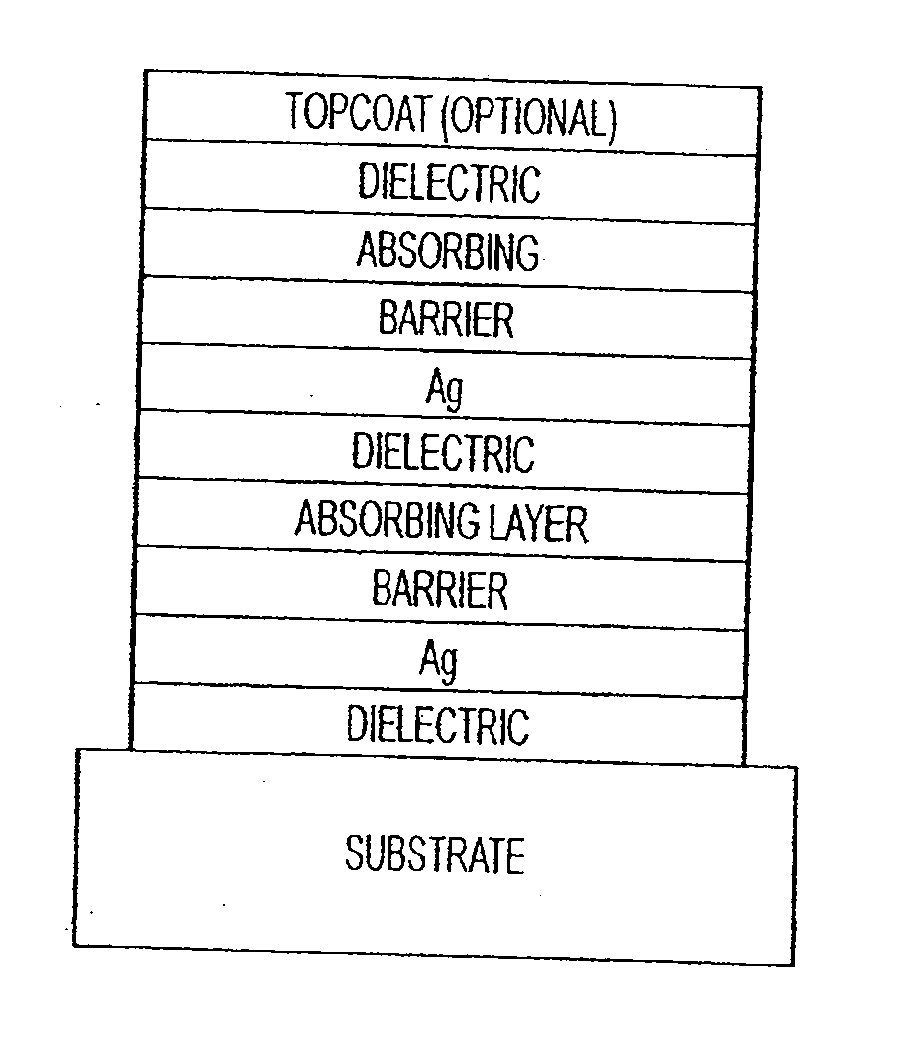
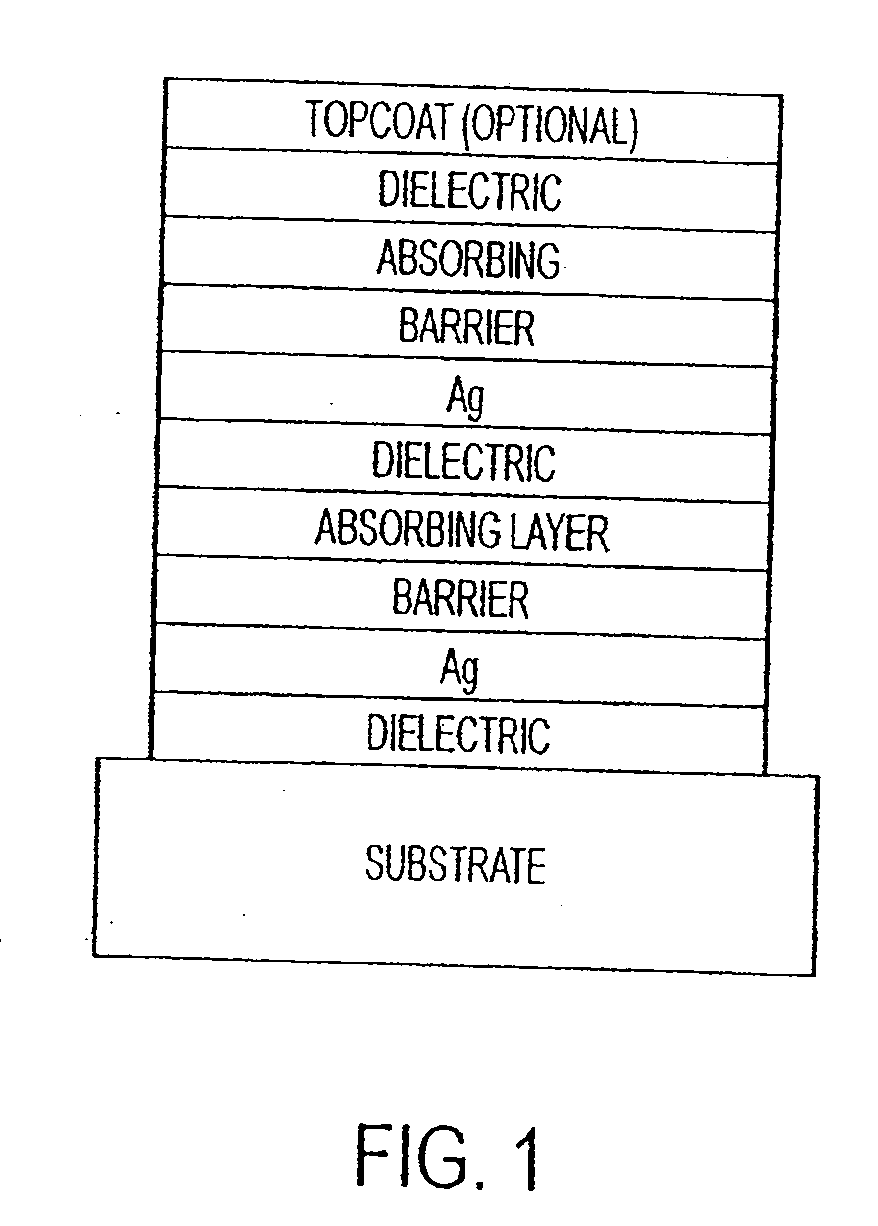
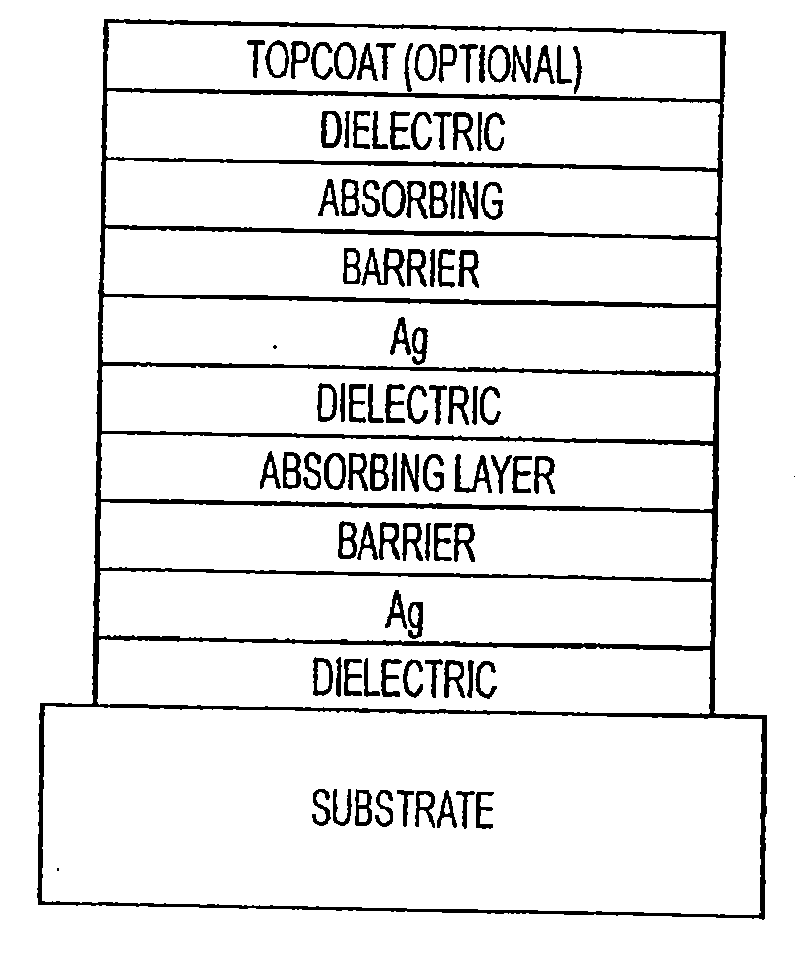
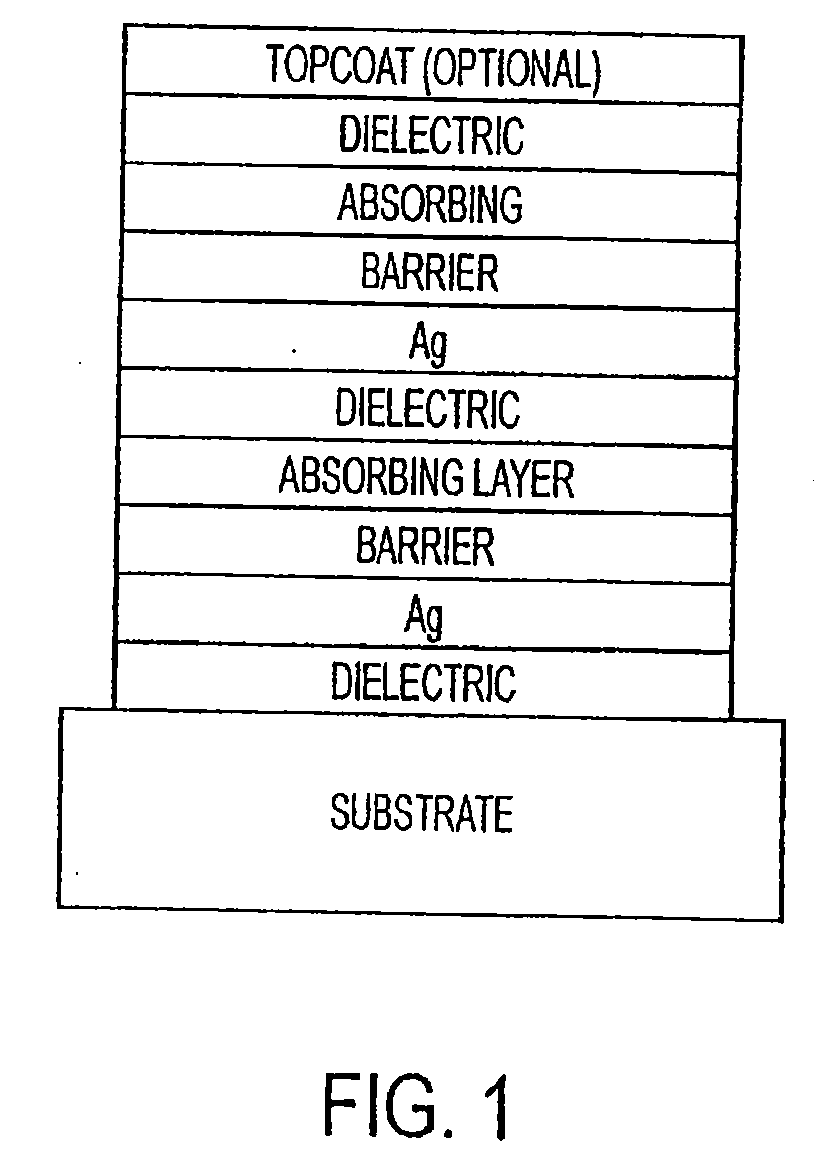
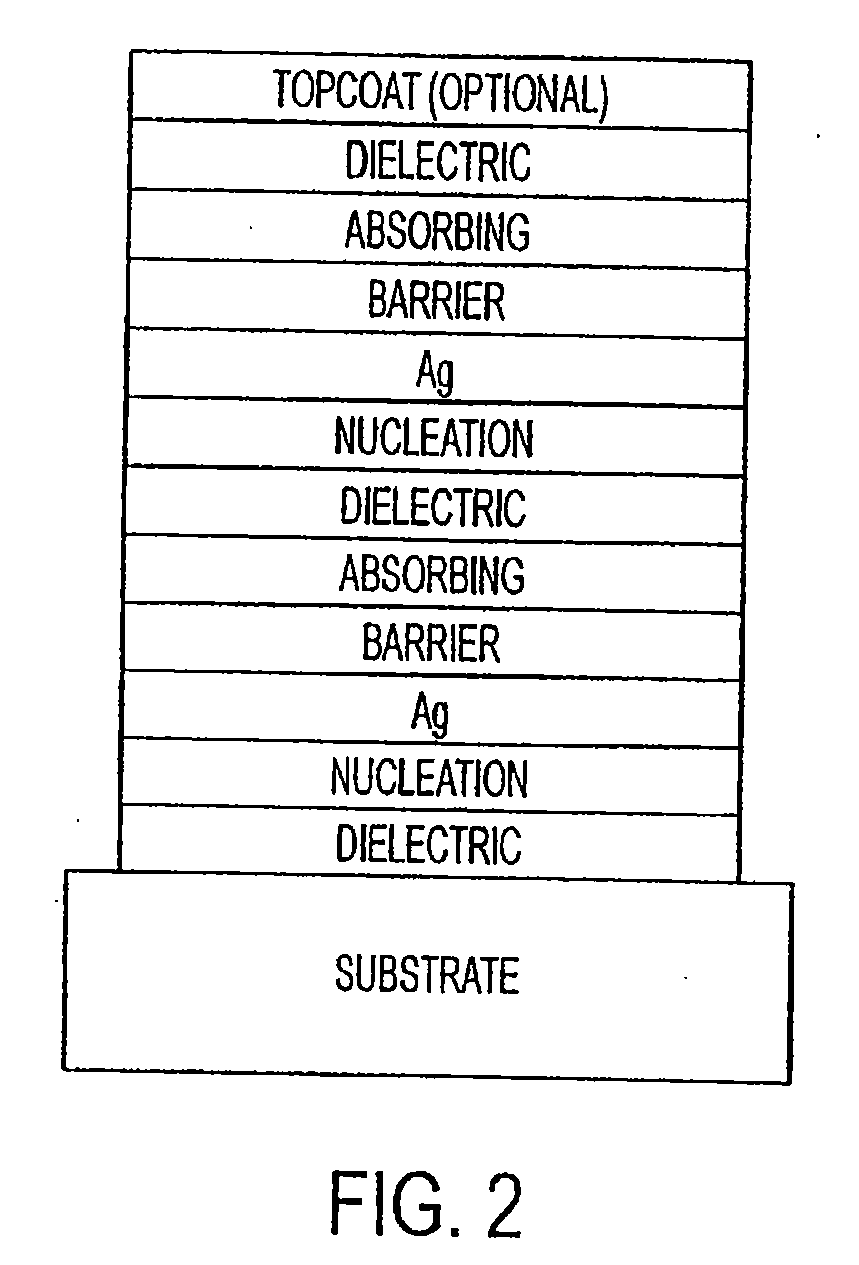
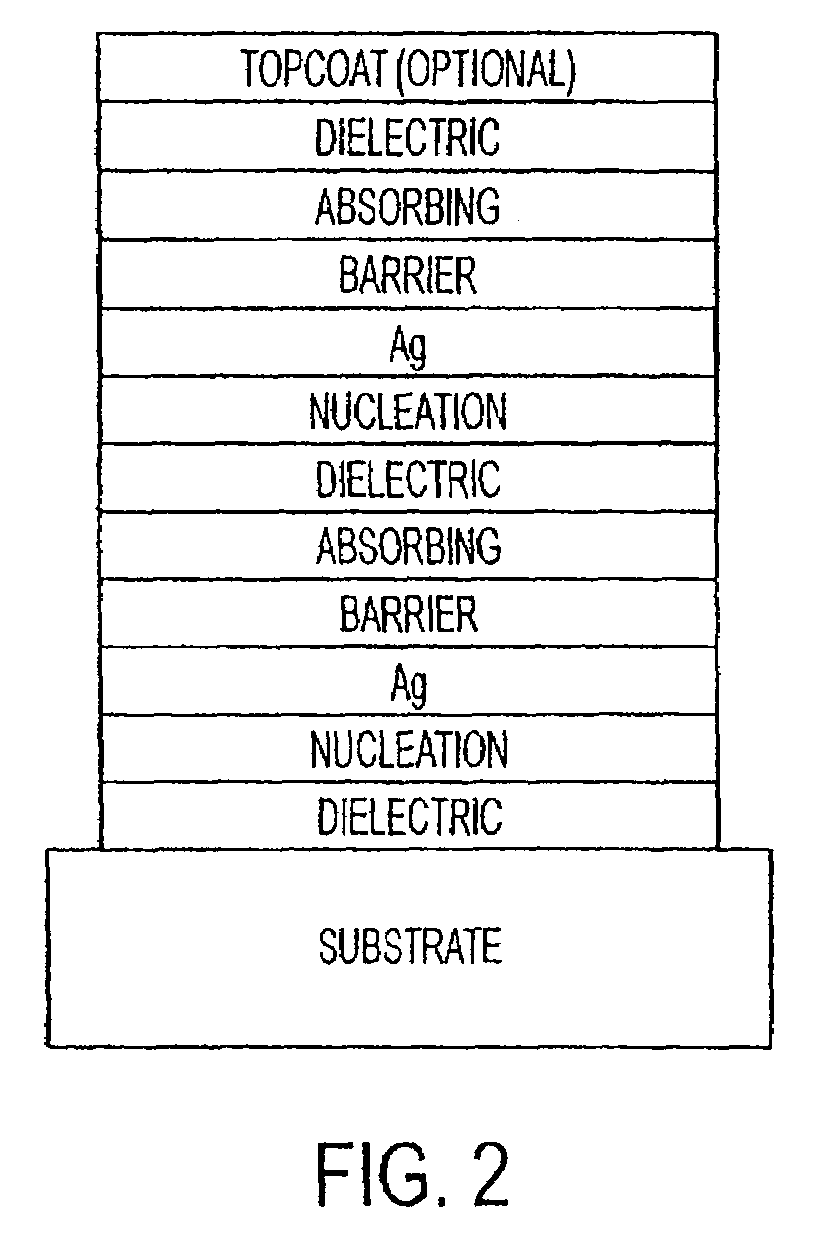
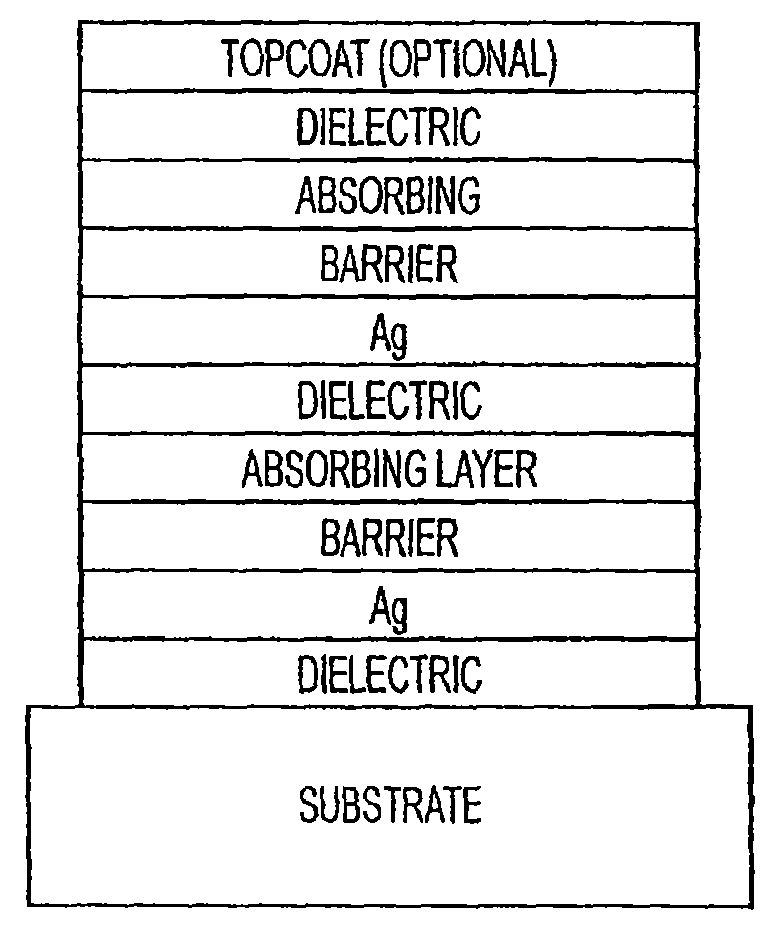
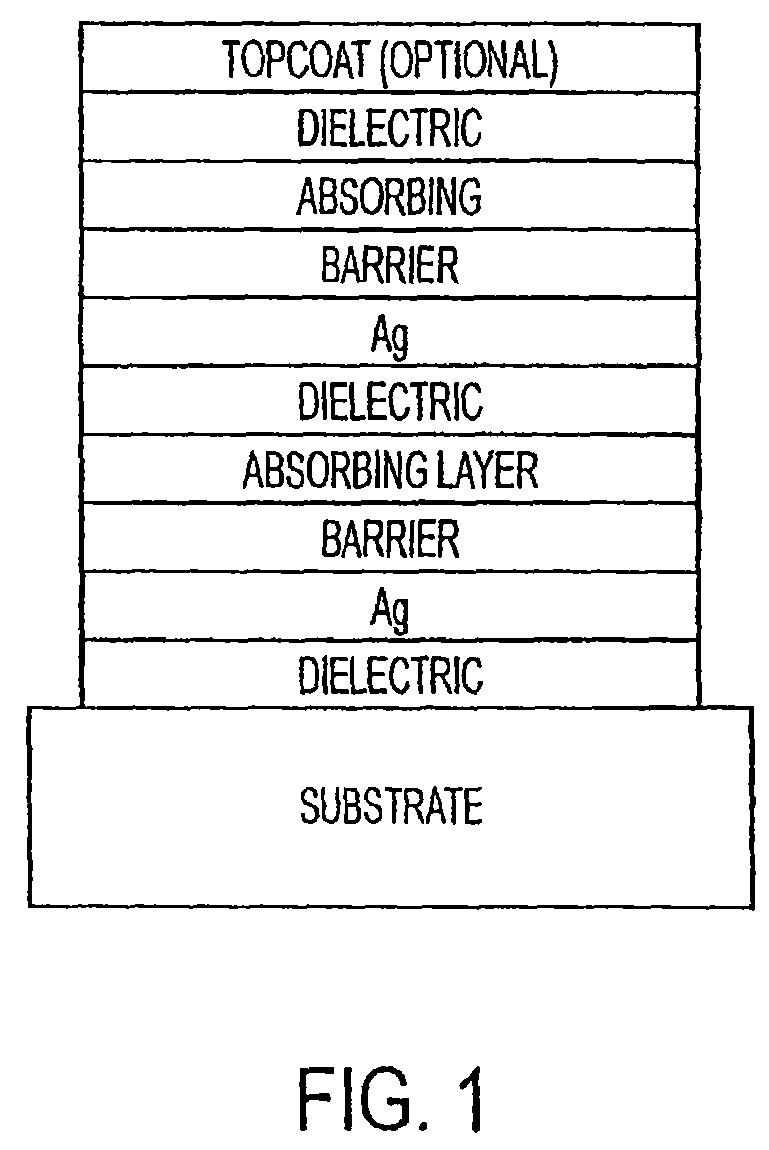
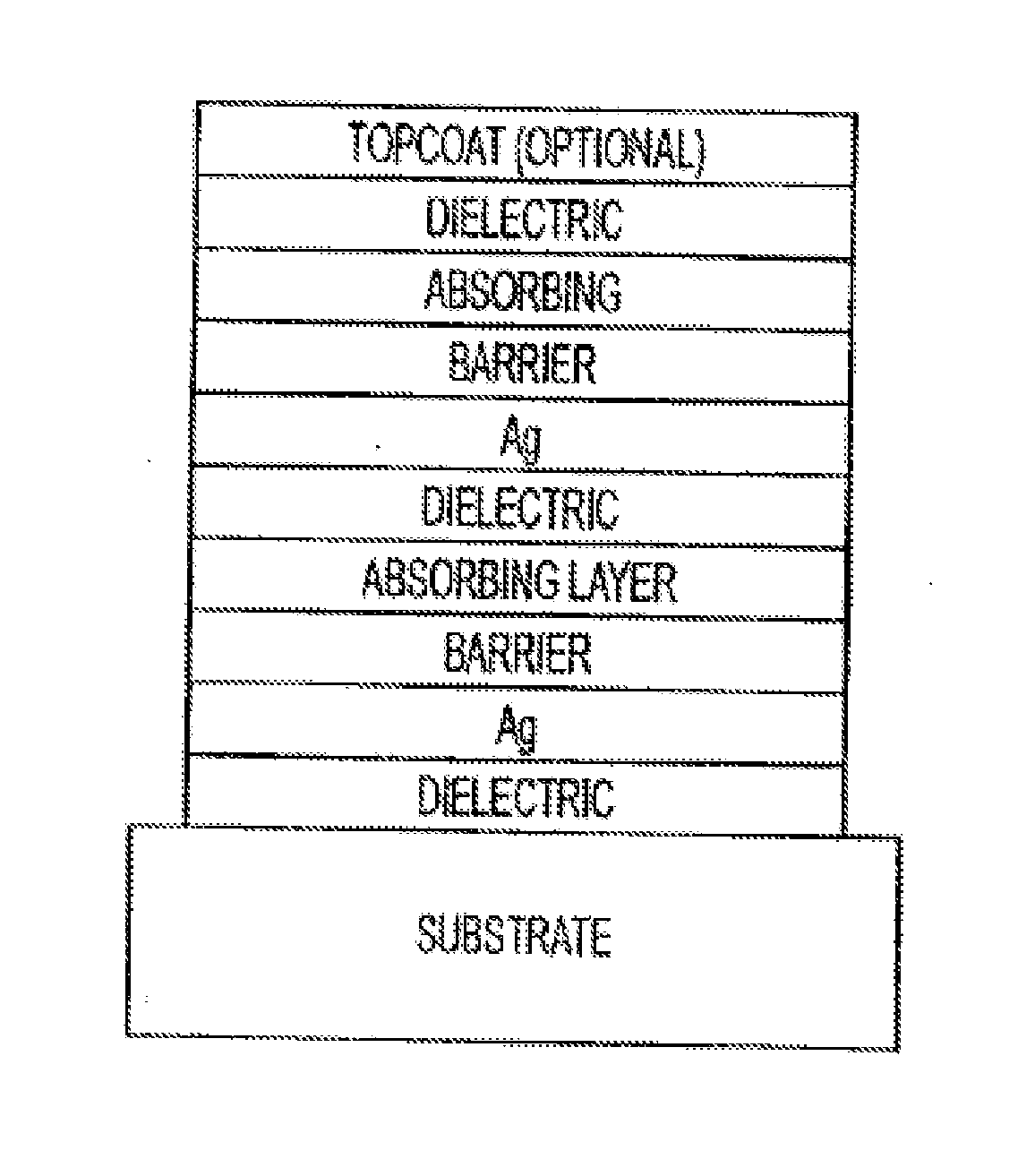
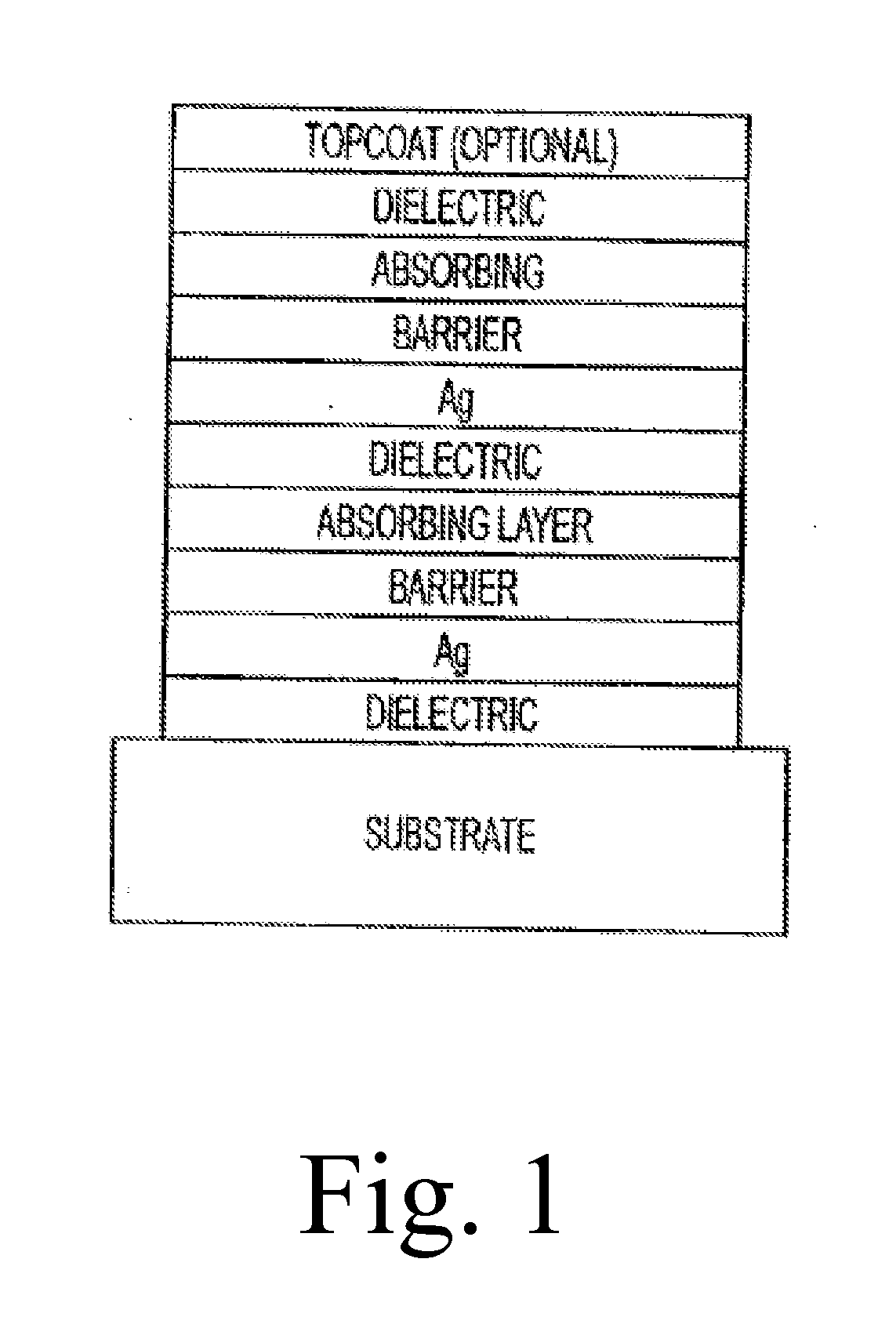
The invention provides low-emissivity stacks comprising at least one absorbing layer, said stacks being characterized by a low solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC), enhanced aesthetics, mechanical and chemical durability, and a tolerance for tempering or heat strengthening. The invention moreover provides low-emissivity coatings comprising, in order outward from the substrate a first dielectric layer, a first Ag layer; a first barrier layer; a first absorbing layer; a second dielectric layer; a second Ag layer; a second absorbing layer; a third dielectric layer; and optionally, a topcoat layer, and methods for depositing such coatings on substrates.
Owner:CARDINAL CG
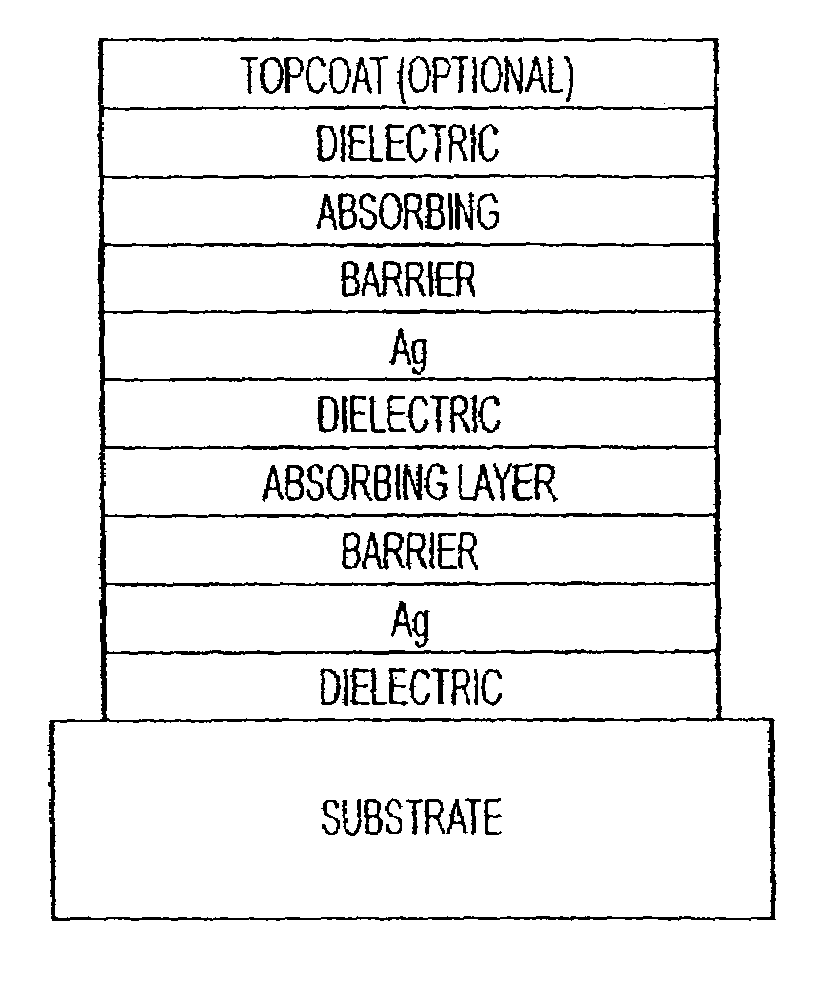
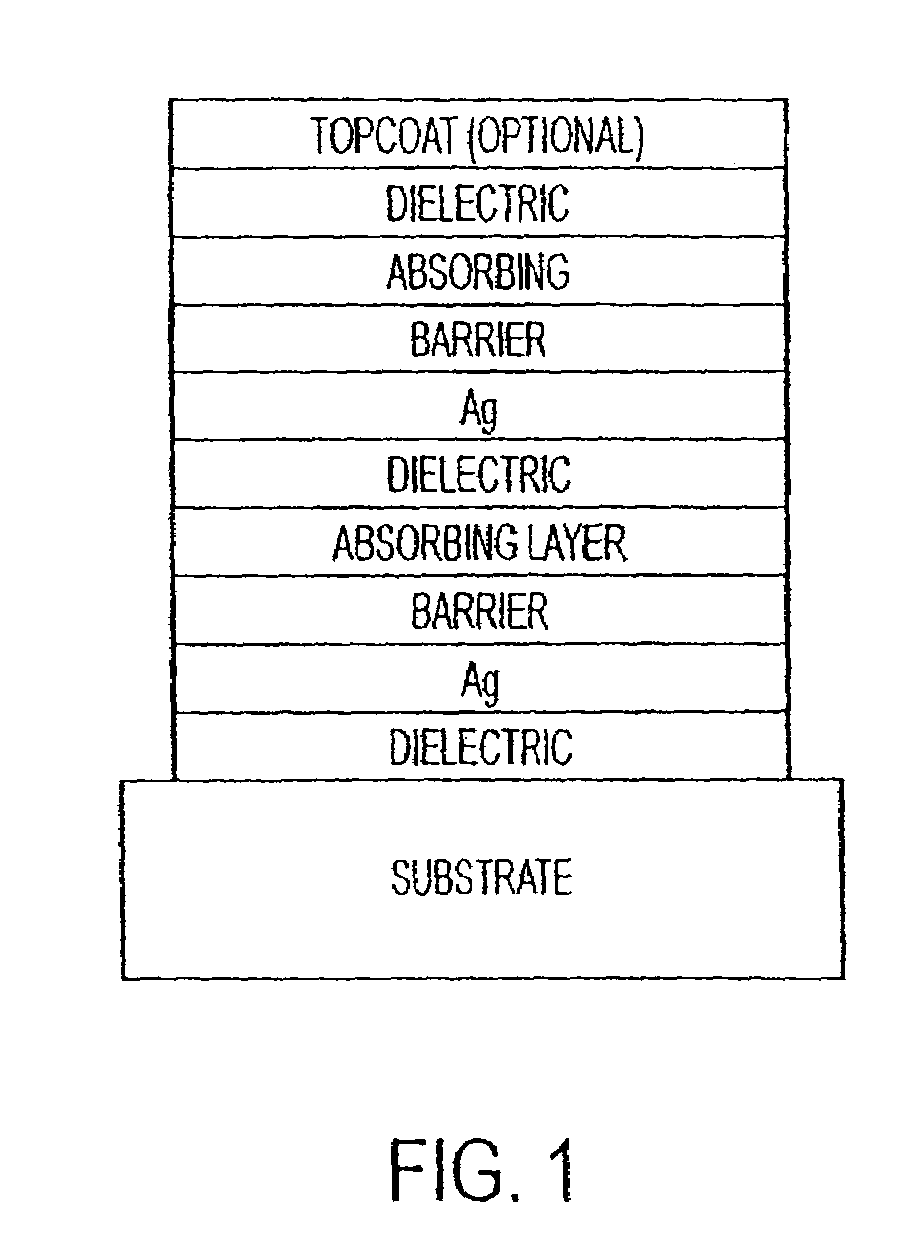
Low emissivity coating with low solar heat gain coefficient, enhanced chemical and mechanical properties and method of making the same
ActiveUS20090136765A1Equal and good chemical and durabilityEqual and good and mechanical durabilityGlass/slag layered productsElectrostatic spraying apparatusRadianceLow emissivity
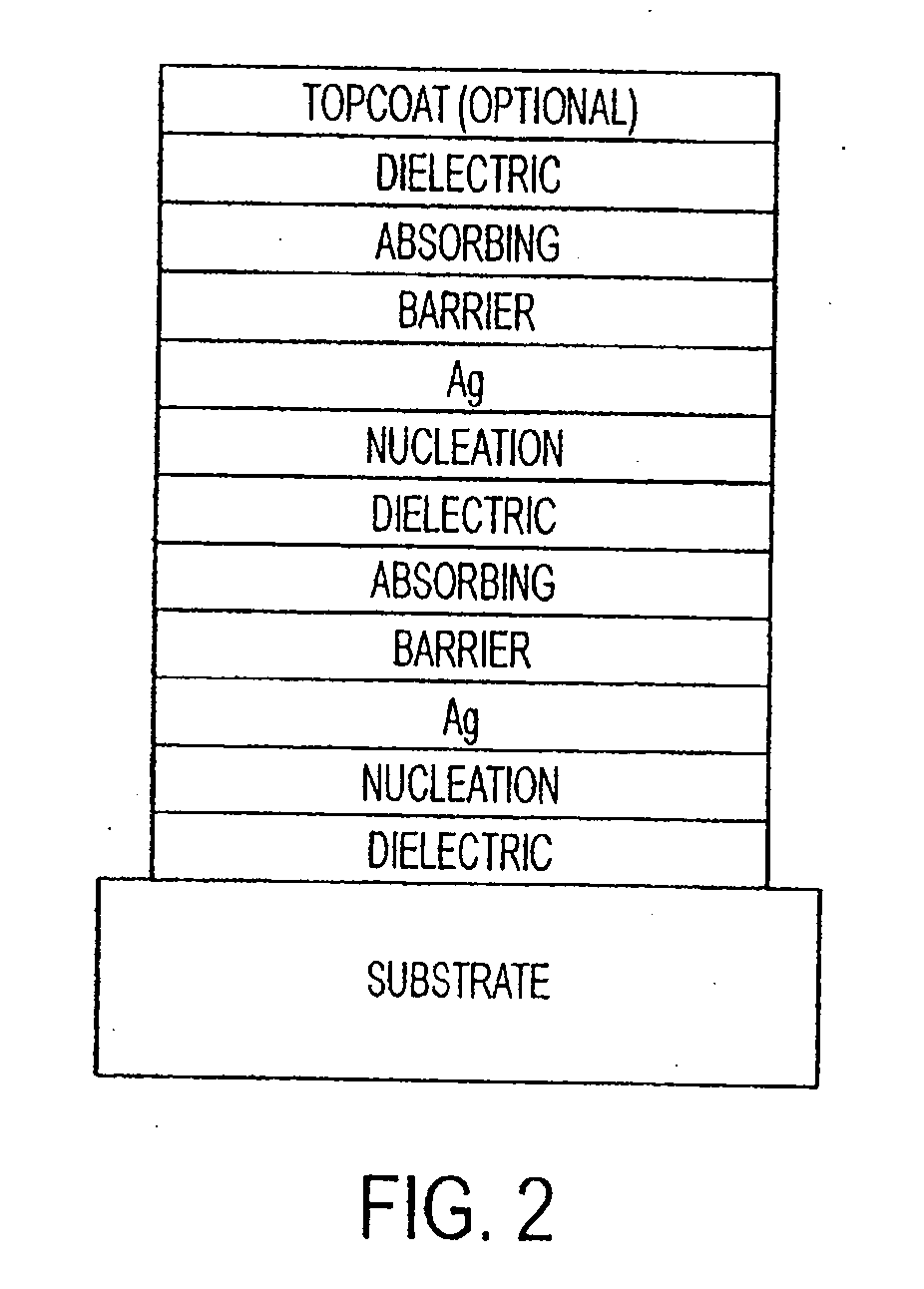
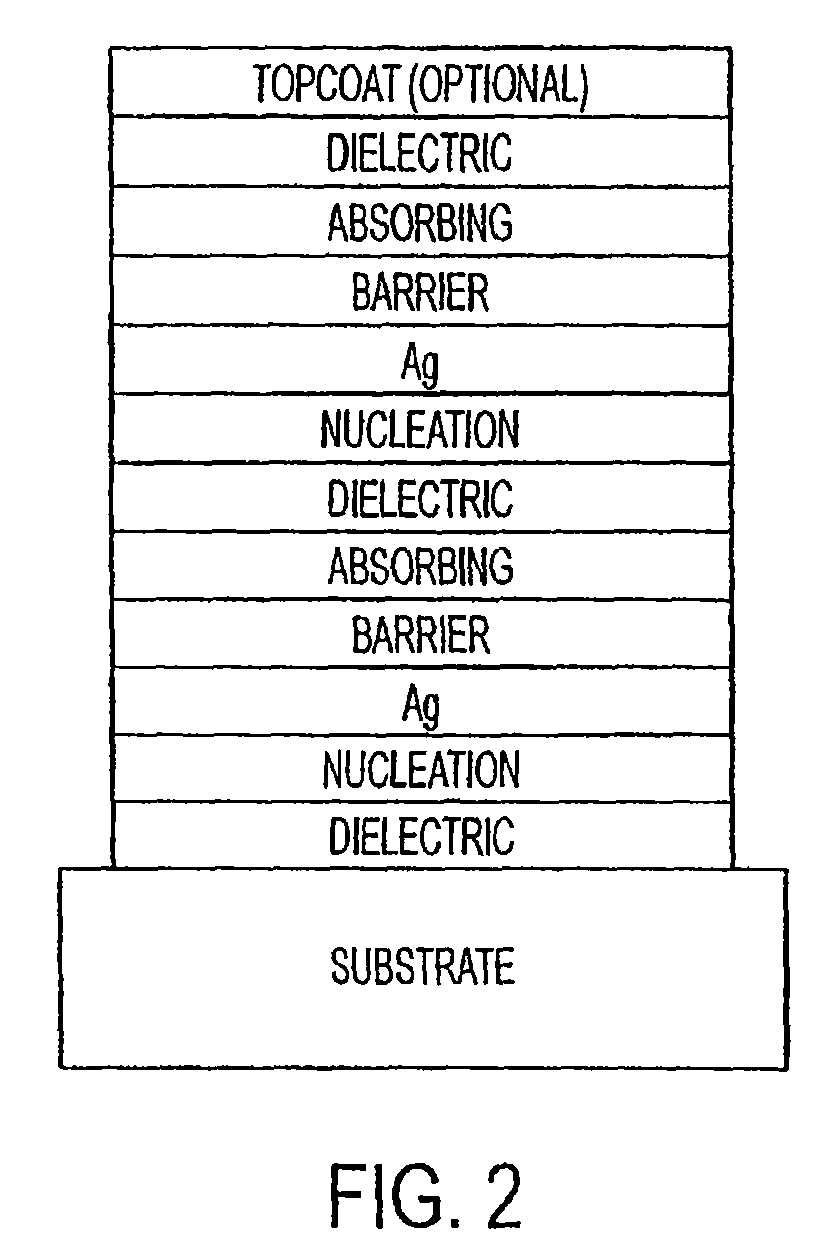
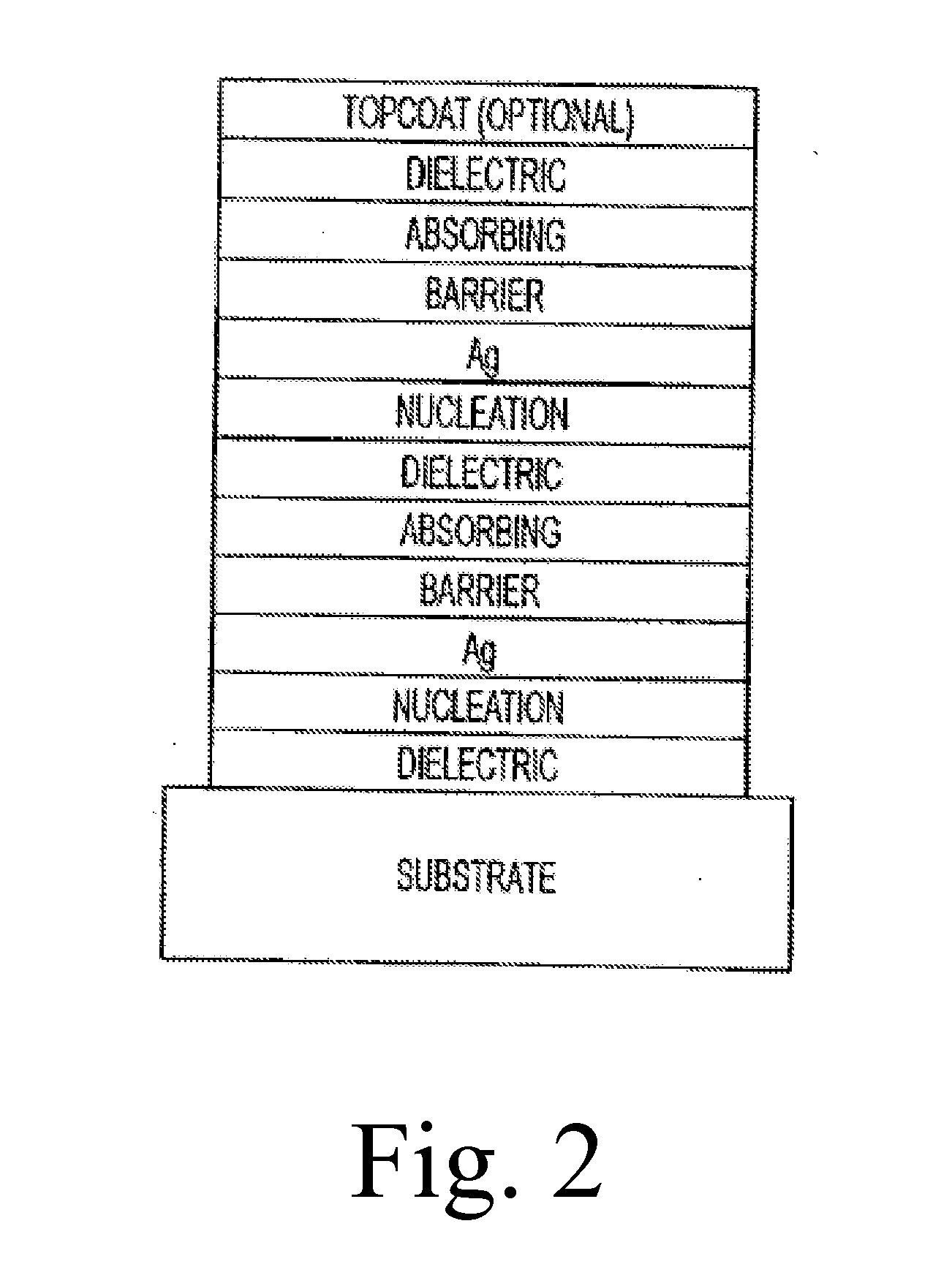
The invention provides low-emissivity stacks being characterized by a low solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC), enhanced aesthetics, mechanical and chemical durability, and a tolerance for tempering or heat strengthening. The invention moreover provides low-emissivity coatings comprising, in order outward from the substrate a first dielectric layer; a first nucleation layer; a first Ag layer; a first barrier layer; a second dielectric layer; a second nucleation layer; a second Ag layer; a second barrier layer; a third dielectric layer; and optionally, a topcoat layer, and methods for depositing such coatings on substrates.
Owner:CARDINAL CG
Efficient configurable frequency domain parameter stereo-sound and multi-sound channel coding and decoding method and system
InactiveCN101067931AImprove compression efficiencyEnsure consistencySpeech analysisDecoding methodsFrequency conversion
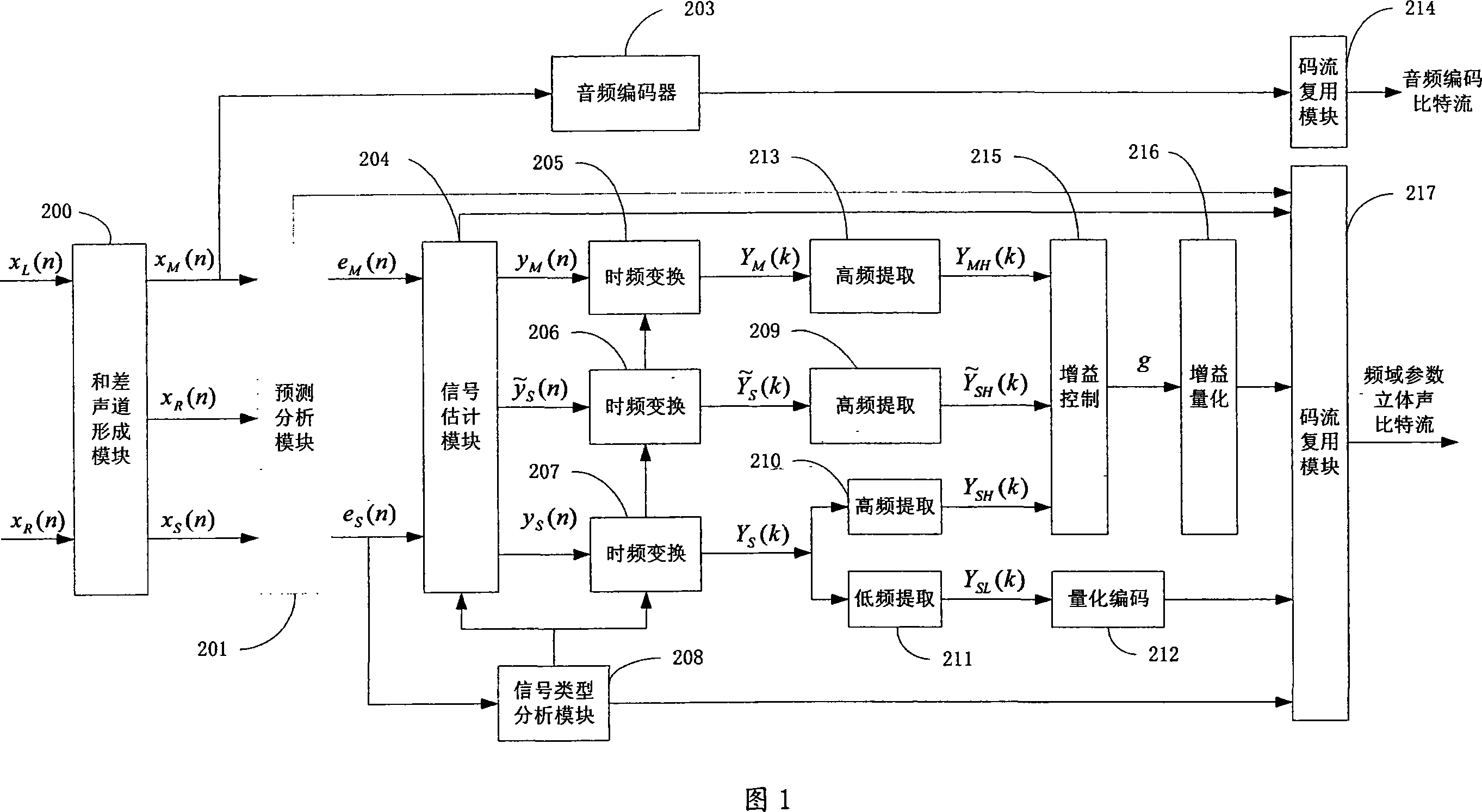
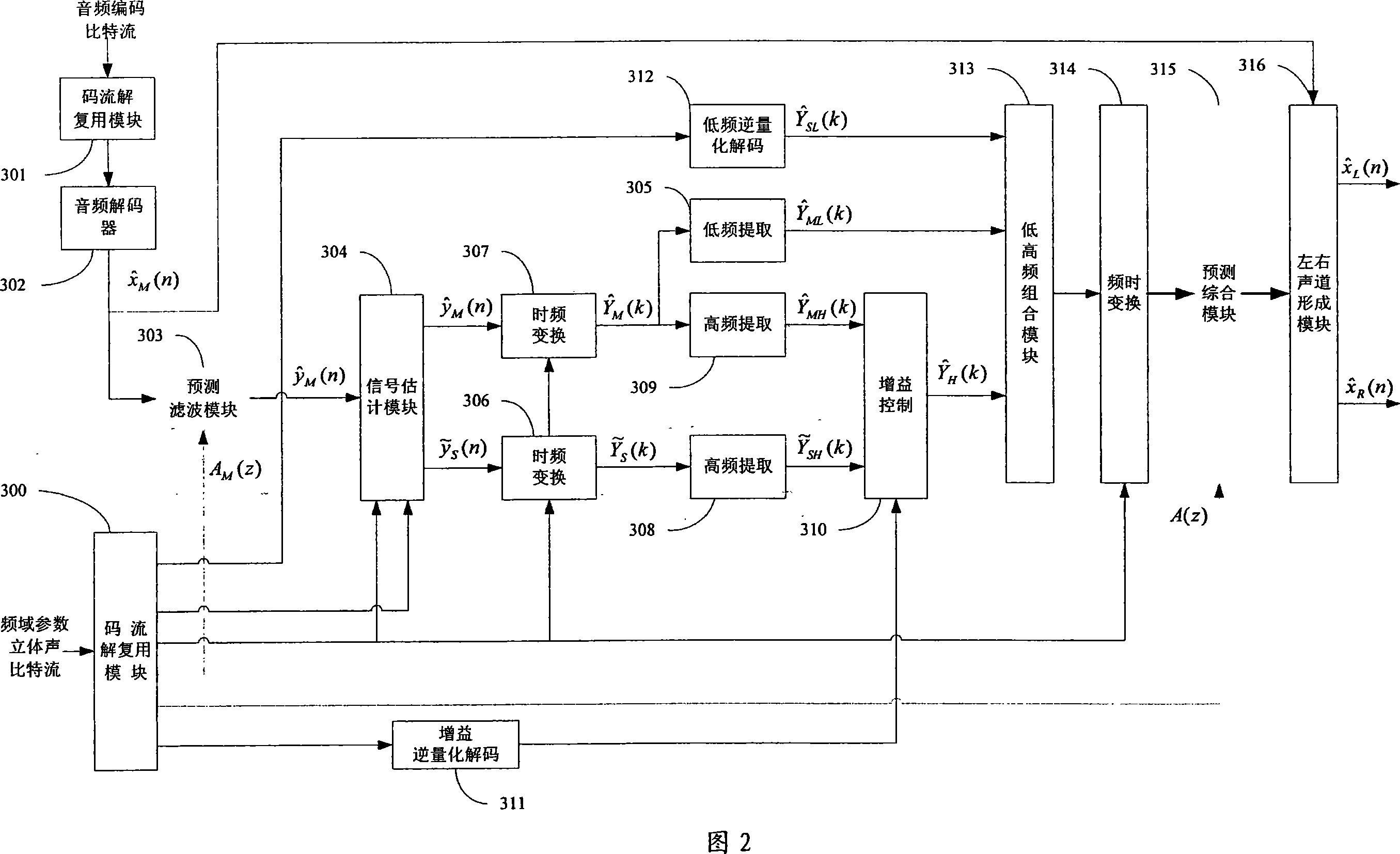
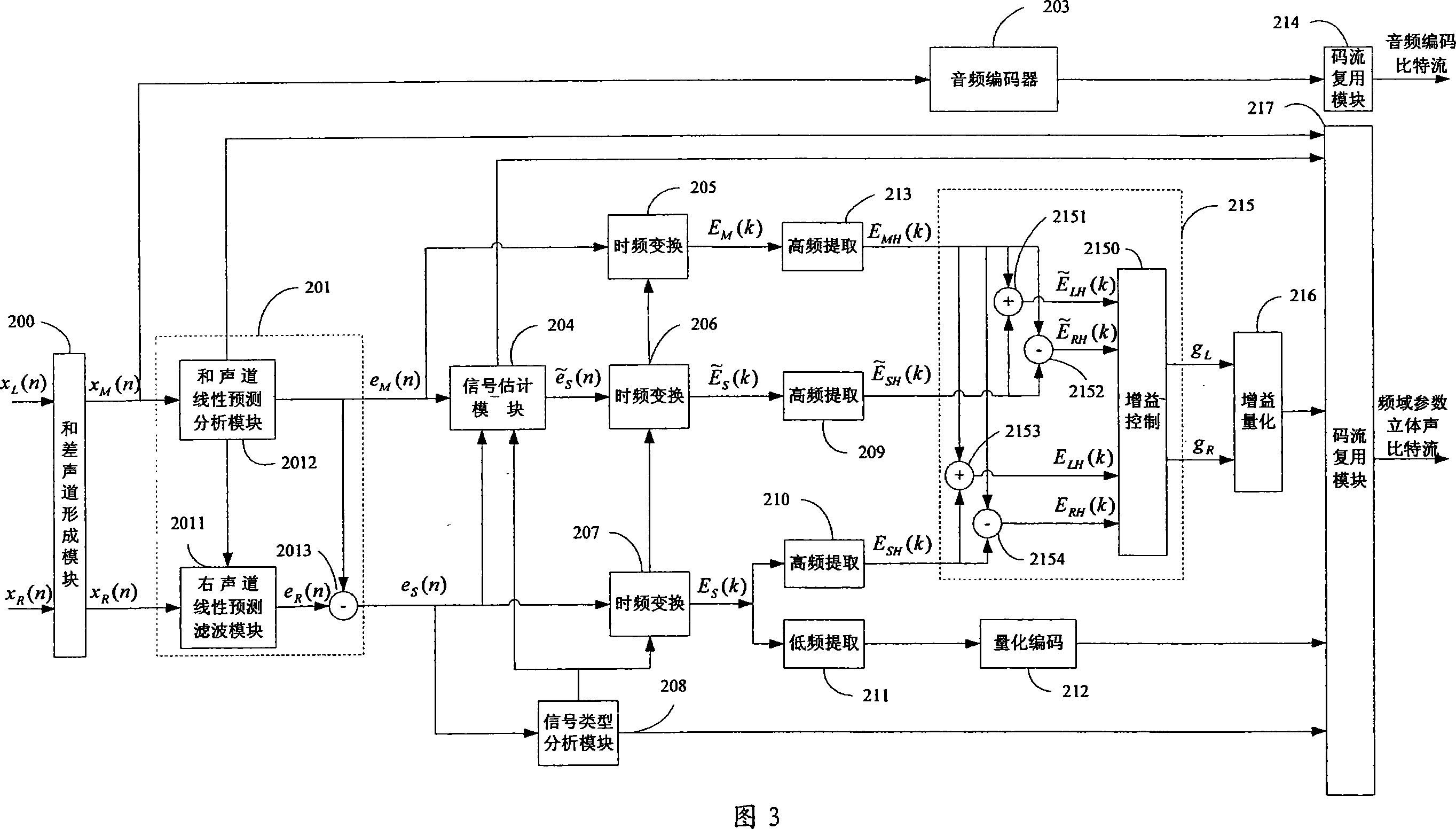
This invention provides a method and a system for coding / decoding frequency domain parameter stereos and multiple tracks, which converts signals of right and left tracks to a residual signal of a sum-difference tack and a residual signal of an estimated difference track, carries out time frequency conversion to residual signals of the estimated difference track, the original difference track and the original sum track to pick up the HF component and low frequency component of the residual signal of the original difference track, which is coded in quantization to utilize the HF component to get estimated residual RF component of the right and left tracks and gets the original residual RF component of the right and left tracks to be controlled in gain to get a gain coefficient of the difference of the two tracks and coded in quantization and finally multiplexes the coded data and edge information to get a frequency domain parameter stereo bit stream.
Owner:凯为半导体科技(上海)有限公司
Pixel selective white balancing
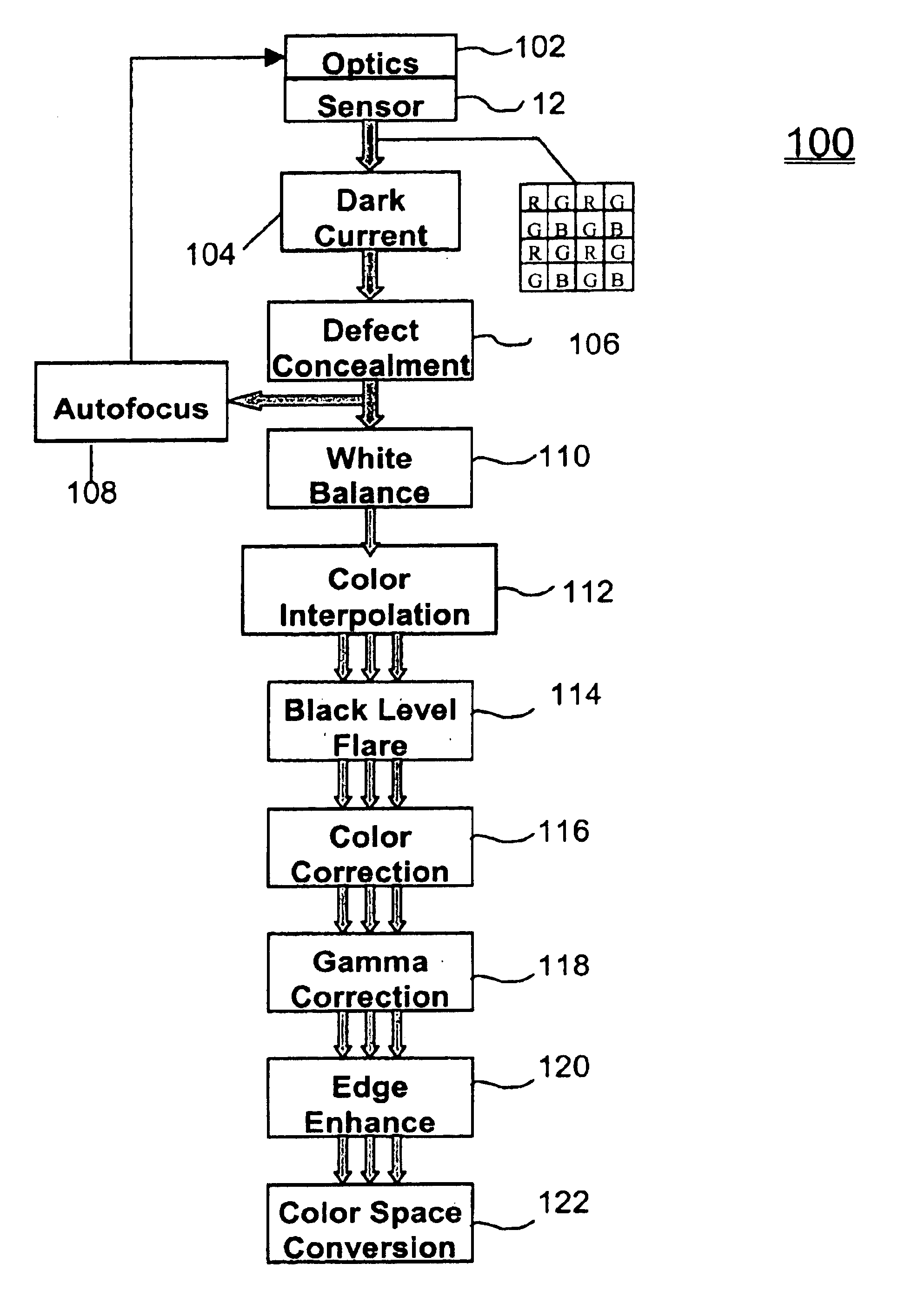
InactiveUS6876384B1Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsColor imageGain coefficient
A system and method for processing data representative of a color image is disclosed. Image data represents an intensity of photoexposure of an imaging array at specific locations in the imaging array and in distinct spectral regions corresponding to color channels. A process identifies “white” regions in the color image by comparing the intensities of photoexposure of groups of associated pixels which are responsive to photon energy in different spectral regions. If the intensities of photoexposure of the pixels in the group of associated pixels are proportionally equivalent, these pixels are determined to be in a white region of the image. White balancing gain coefficients are then based upon the pixel intensity values at pixel locations in the white regions of the image.
Owner:BIOMORPHIC VLSI
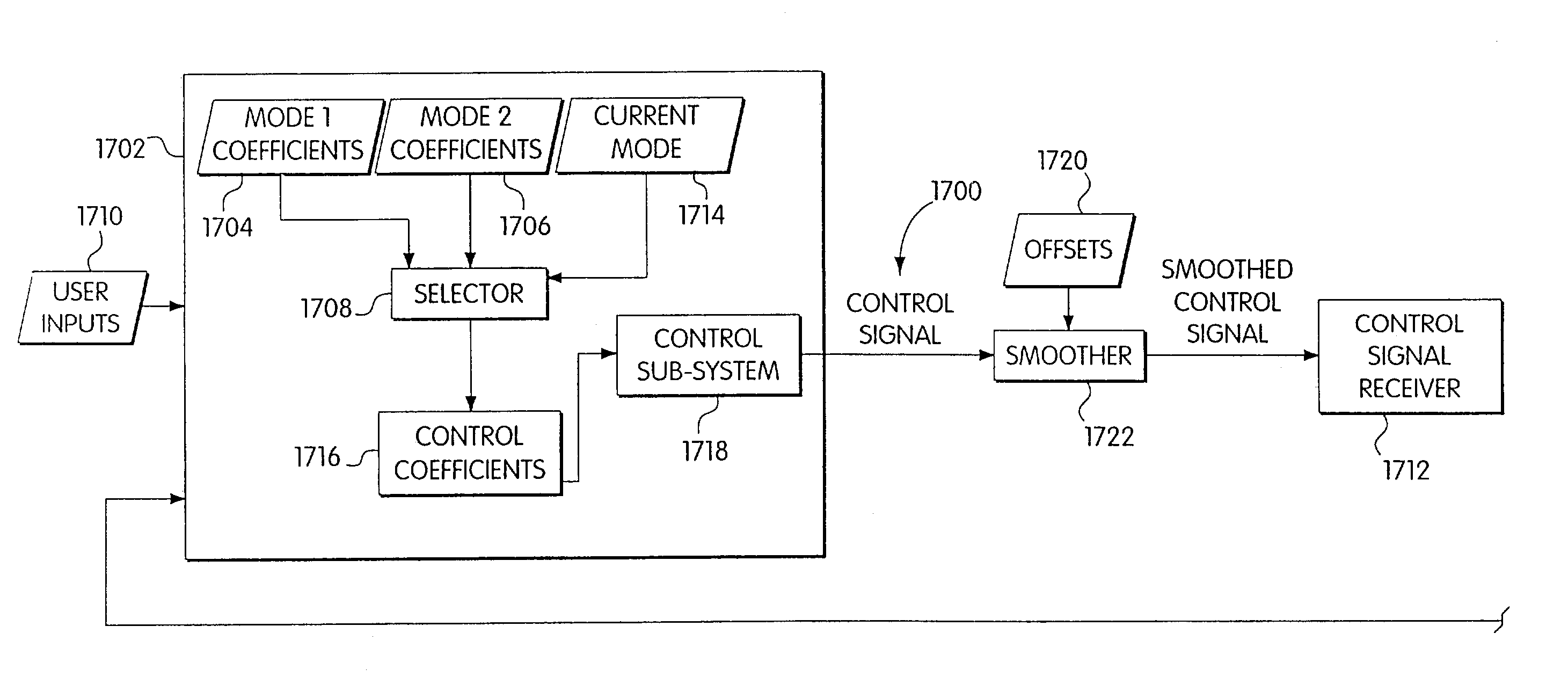
System and method for control scheduling
A system and method for controlling a device such that device operates in a smooth manner. The system may switch between control architectures or vary gain coefficients used in a control loop to control the device. As the architecture or gains are switched, the control signal may be smoothed so that the device does not experience an abrupt change in the control signal it receives. In one embodiment, the control signal may be smoothed by adding a decaying offset value to the control signal to create a smoothed control signal that is applied to the device.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
Low-emissivity coatings having high visible transmission and low solar heat gain coefficient
Low-emissivity coatings that are highly reflective to infrared radiation. The coating includes three infrared-reflection film regions, which may each include silver.
Owner:CARDINAL CG
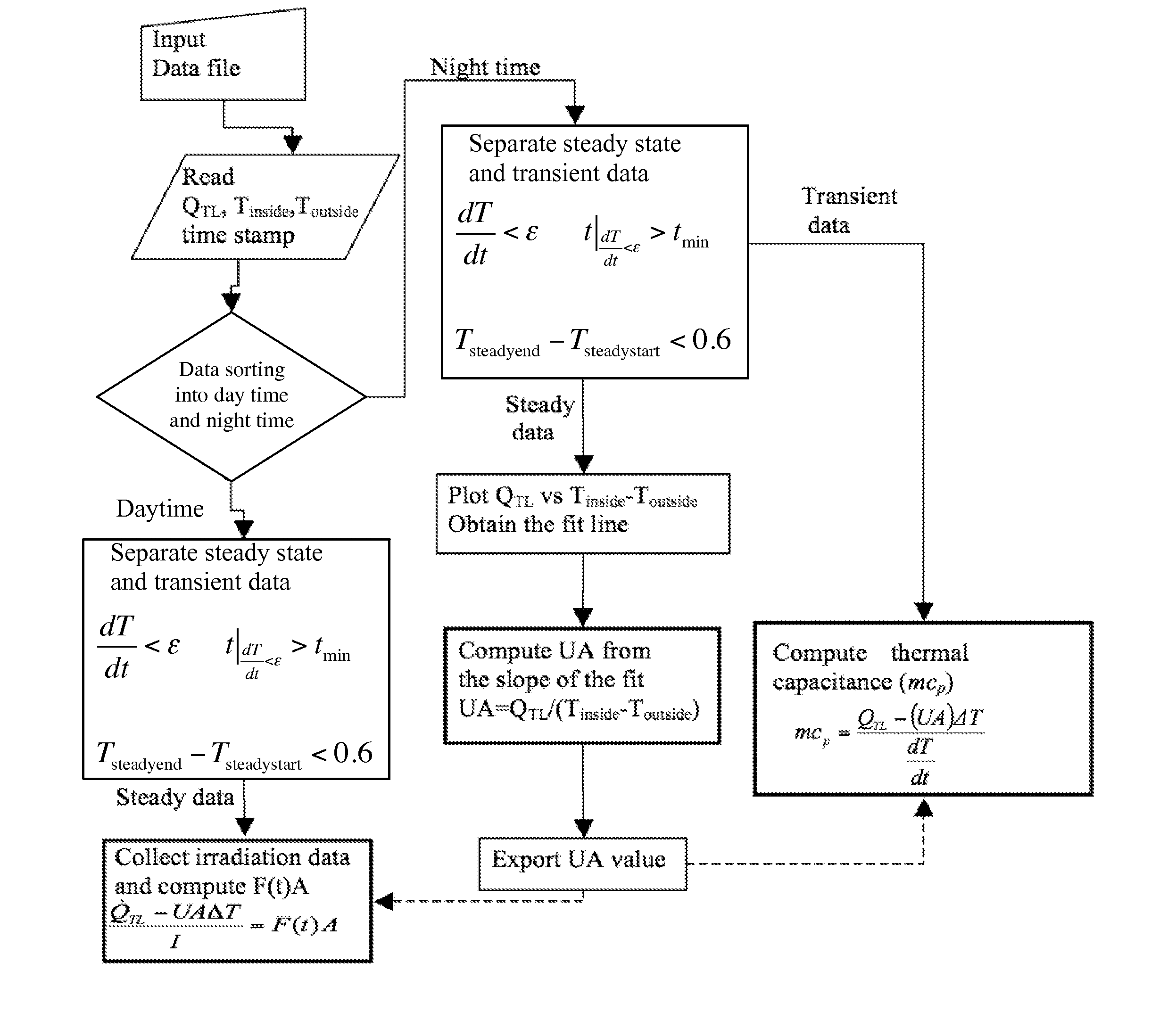
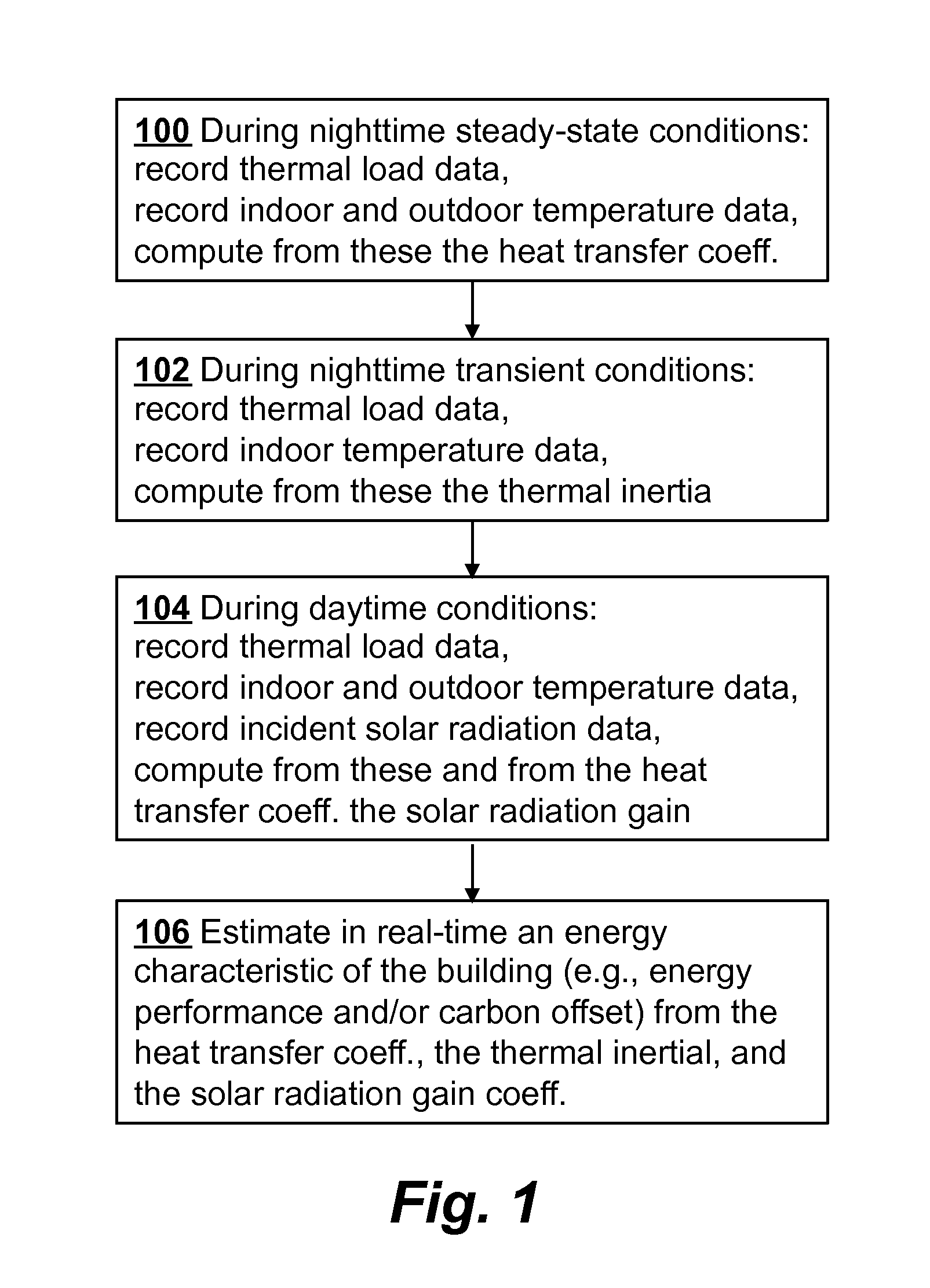
Estimating energy savings and carbon offsets for buildings in real-time
InactiveUS20130060471A1Easy to implementLow costDigital computer detailsSpecial data processing applicationsGain coefficientEngineering
Real-time monitoring of an energy characteristic of a building such as an energy performance of the building or a carbon offset of the building is performed by first computing a heat transfer coefficient of the building from nighttime steady-state thermal load data of the building and from nighttime steady-state indoor and outdoor temperature data of the building. A thermal inertia of the building is then computed from nighttime transient indoor temperature data of the building and nighttime transient thermal load data of the building. During daytime, a solar radiation gain coefficient is computed from daytime thermal load data, daytime indoor and outdoor temperature data, incident solar radiation data, and the heat transfer coefficient. The energy characteristic of the building is then estimated in real time from the heat transfer coefficient, the thermal inertia, and the solar radiation gain coefficient.
Owner:SANTA CLARA UNIVERSITY
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS7187016B2Improve performanceEasy to produceTransistorSolid-state devicesCMOSGain coefficient
In a semiconductor device an electric field is controlled in direction or angle relative to a gate, or a channel to adjust a gain coefficient of a transistor. In some embodiments, there are provided a first gate forming a channel region in a rectangle or a parallelogram, and a second gate forming a channel region substantially containing a triangle between the channel region formed by the first gate and each of a source region and a drain region. In some embodiments, there is included a channel region formed by the first gate that is sandwiched by the channel region formed by the second gate, all the channel regions together substantially forming a rectangle or a parallelogram. As such, a semiconductor device allowing a gain coefficient β of an MOS transistor to be modulated by voltage in an analog manner can readily be produced by conventional processing technology and incorporated into any conventional LSIs configured by a CMOS circuit.
Owner:EXPL OF NEXT GENERATION
Low-E coated articles and methods of making same
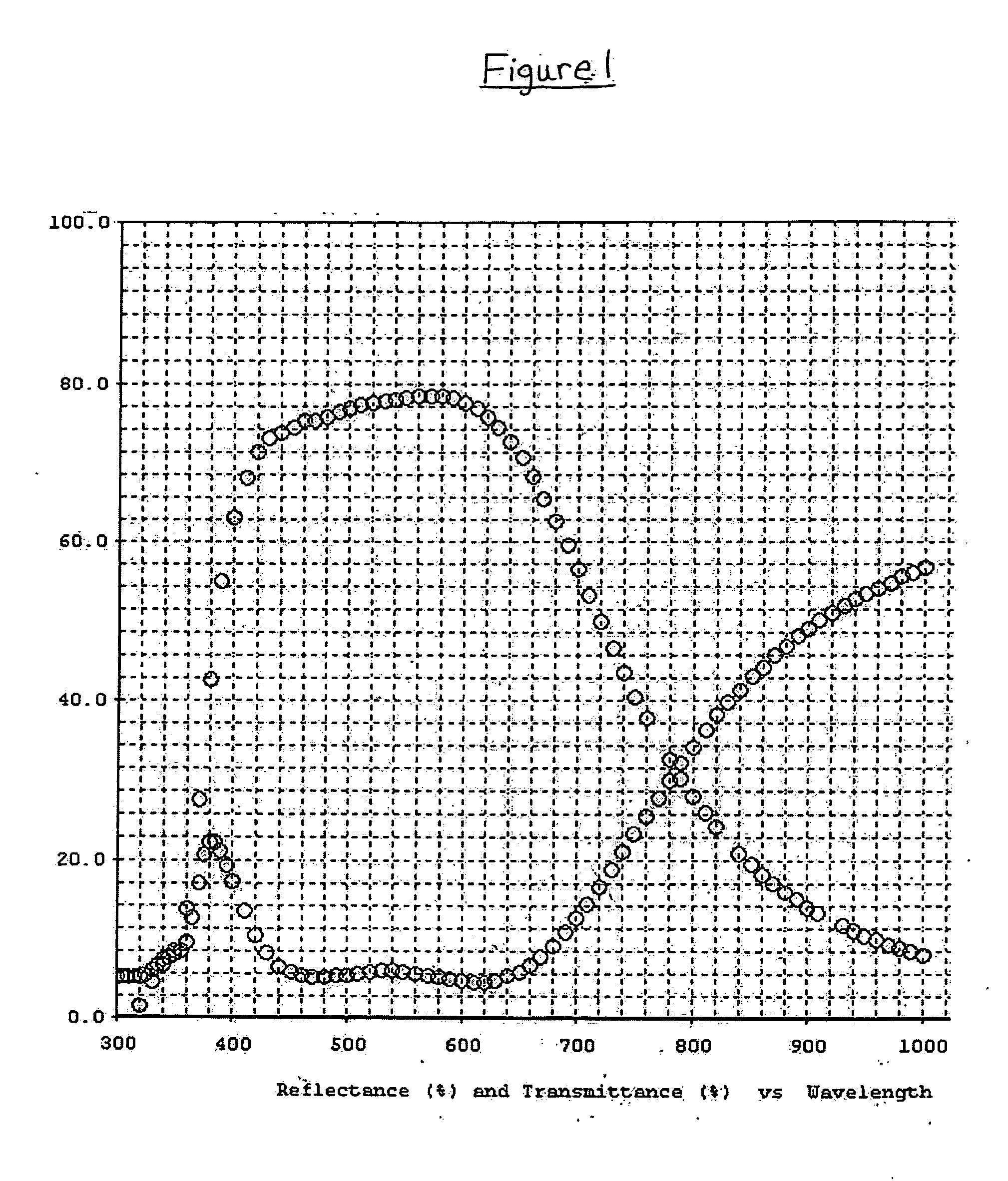
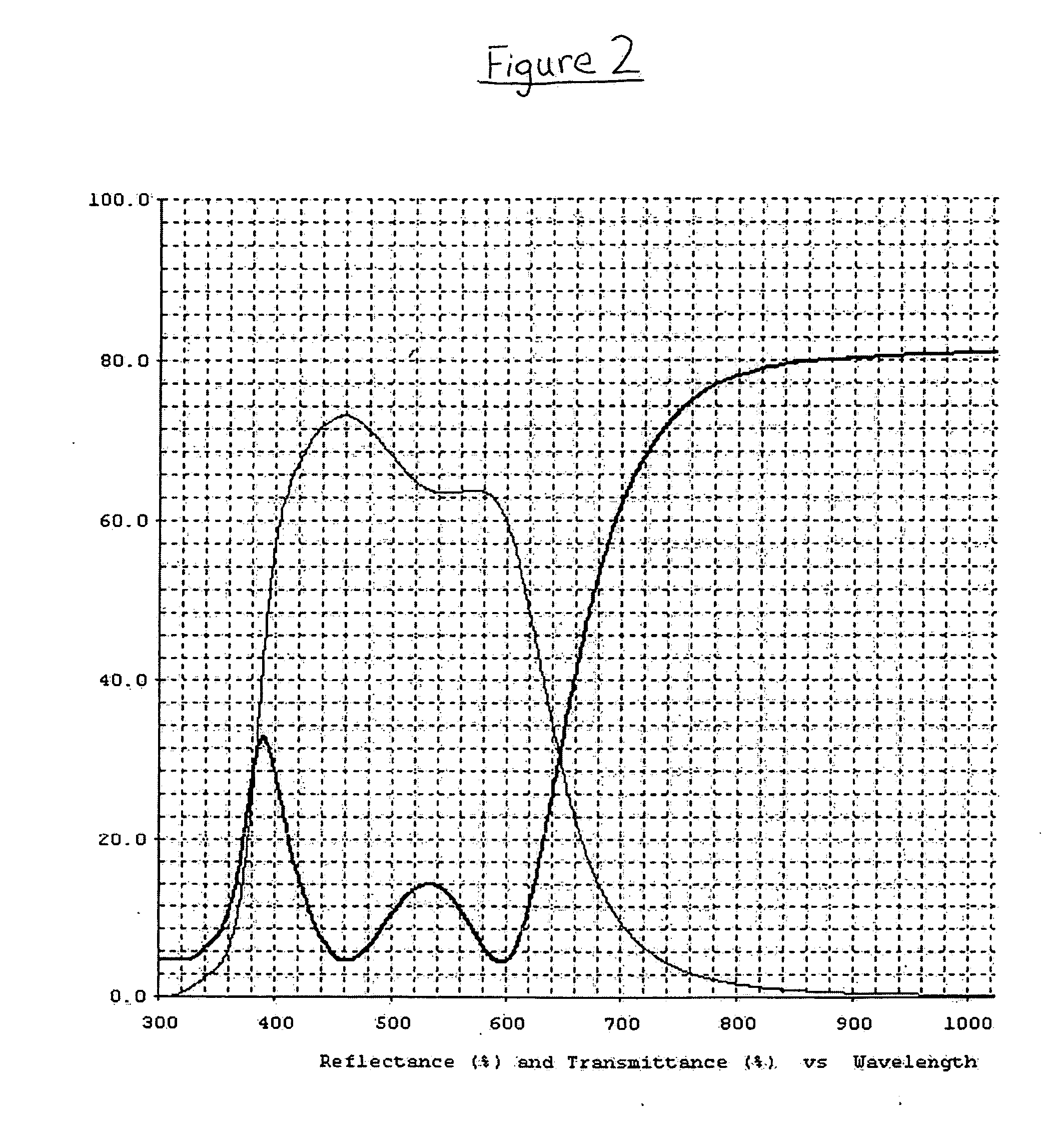
In certain example embodiments, low-E coated articles may be designed so as to realize a combination of good visible transmission (Tvis) and an excellent solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC), thereby realizing an improved (i.e., higher) Tvis / SHGC ratio. In certain example embodiments of this invention, if heat treated (HT), the low-E coated articles may have approximately the same color characteristics as viewed by the naked eye both before and after heat treatment (i.e., a low ΔE* value) in certain example instances. Such coated articles may be used in insulating glass (IG) units, windows, and / or other suitable applications.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Low emissivity coating with low solar heat gain coefficient, enhanced chemical and mechanical properties and method of making the same
ActiveUS7659002B2Improve the overall coefficientIncreased durabilityGlass/slag layered productsCoatingsLow emissivityGain coefficient
Owner:CARDINAL CG
Low-emissivity coatings having high visible transmission and low solar heat gain coefficient
The invention provides low-emissivity coatings that are highly reflective of infrared radiation. The coating includes three infrared-reflection film regions, which may each comprise silver.
Owner:CARDINAL CG
Low emissivity coating with low solar heat gain coefficient, enhanced chemical and mechanical properties and method of making the same
ActiveUS7901781B2Improve the overall coefficientIncreased durabilityGlass/slag layered productsSpecial surfacesRadianceLow emissivity
The invention provides low-emissivity stacks being characterized by a low solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC), enhanced aesthetics, mechanical and chemical durability, and a tolerance for tempering or heat strengthening. The invention moreover provides low-emissivity coatings comprising, in order outward from the substrate a first dielectric layer; a first nucleation layer; a first Ag layer; a first barrier layer; a second dielectric layer; a second nucleation layer; a second Ag layer; a second barrier layer; a third dielectric layer; and optionally, a topcoat layer, and methods for depositing such coatings on substrates.
Owner:CARDINAL CG
Low emissivity coating with low solar heat gain coefficient, enhanced chemical and mechanical properties and method of making the same
InactiveUS20110135955A1Improve the overall coefficientIncreased durabilityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingLow emissivityGain coefficient
The invention provides low-emissivity stacks being characterized by a low solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC), enhanced aesthetics, mechanical and chemical durability, and a tolerance for tempering or heat strengthening. The invention moreover provides low-emissivity coatings comprising, in order outward from the substrate a first dielectric layer; a first nucleation layer; a first Ag layer; a first barrier layer; a second dielectric layer; a second nucleation layer; a second Ag layer; a second barrier layer; a third dielectric layer; and optionally, a topcoat layer, and methods for depositing such coatings on substrates.
Owner:AGC FLAT GLASS NORTH AMERICA INC
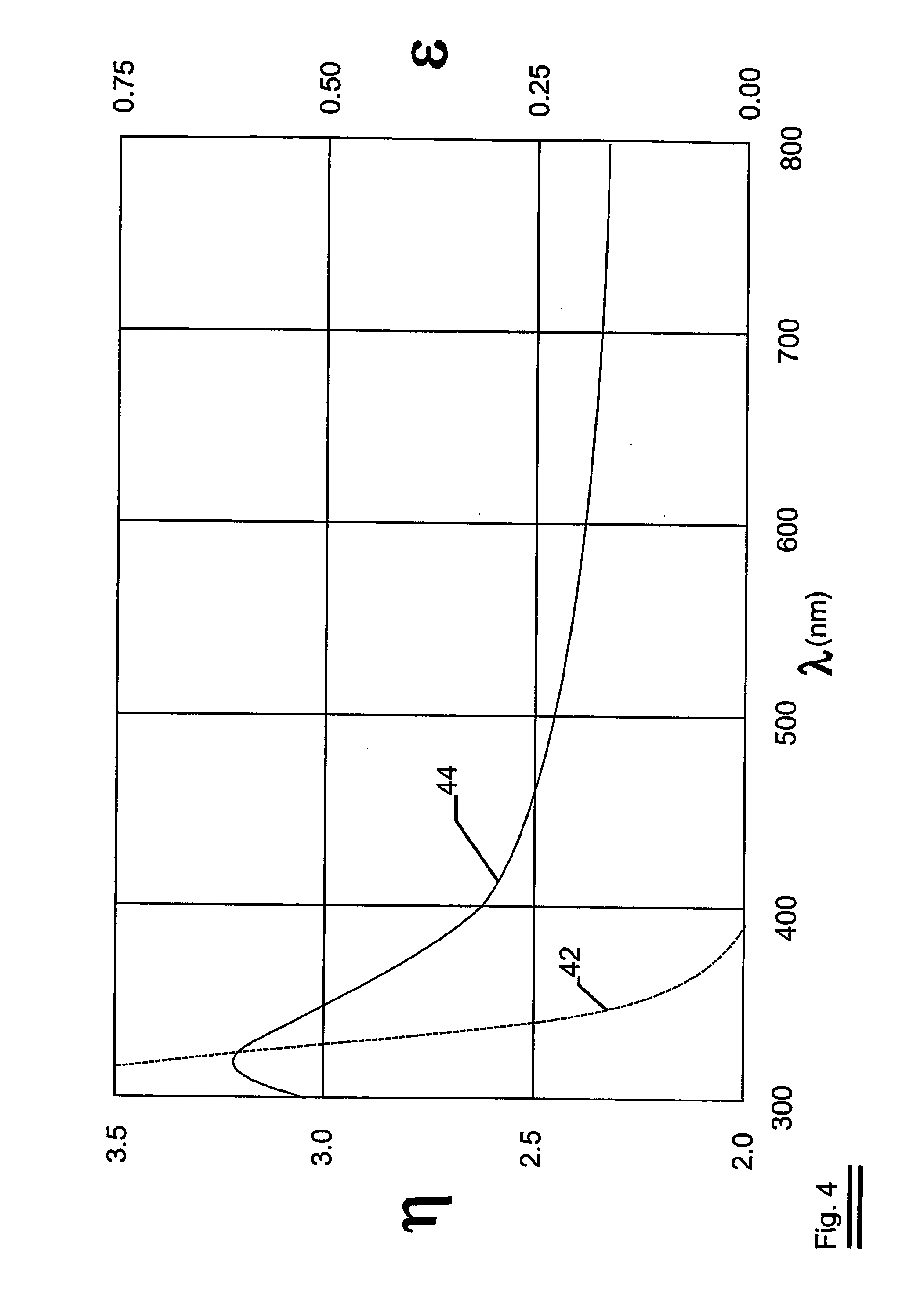
Infra-red reflecting layered structure
ActiveUS7709095B2Good visible light transmittanceLow solar heat gain coefficientElectric discharge tubesMagnetic/electric field screeningGain coefficientRefractive index
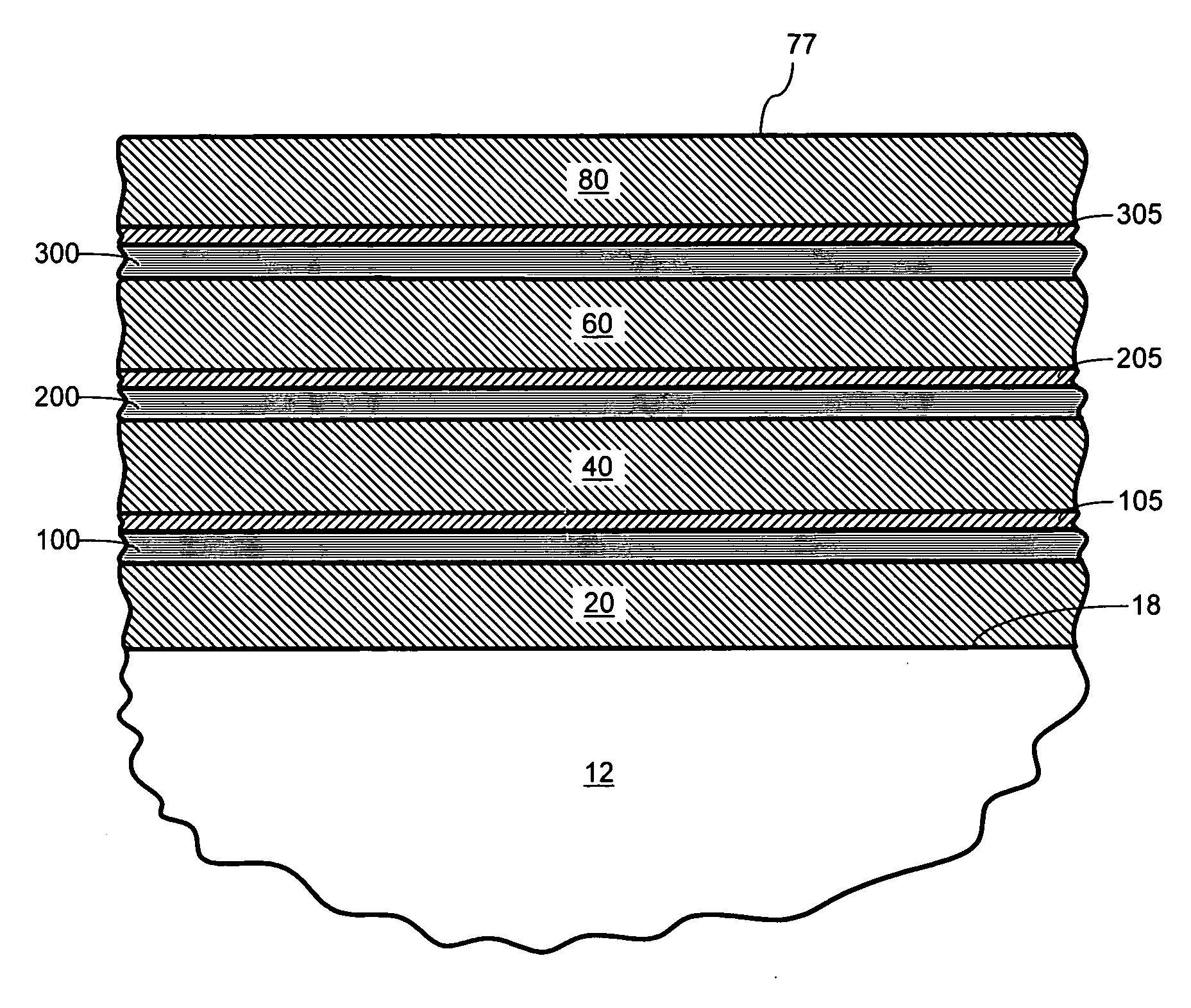
The invention relates to an infra-red reflecting layered structure comprising a transparent substrate layer; a first metal oxide layer; a first silver containing layer, a second metal oxide layer; a second silver containing layer and a third metal oxide layer. The first, second and third metal oxide layer have a refractive index of at least 2.40 at a wavelength of 500 nm. The layered structure according to the present invention laminated on glass has a visual light transmittance (VLT) higher than 70% and a solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC) lower than 0.44. The invention further relates to the use of a layered structure as a transparent heat-mirror.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN PERFORMANCE PLASTICS CHAINEUX
Low shading coefficient and low emissivity coatings and coated articles
InactiveUS20070009747A1Acceptable aestheticImprove reflectivityGlass/slag layered productsCoatingsOrganic filmLow emissivity
The present invention is directed to a low emissivity, low shading coefficient, multi-layer coating and coated article having a luminous transmission of less than about 70 percent, a shading coefficient less than about 0.44 and a solar heat gain coefficient of less than about 0.38 and a ratio of luminous transmittance to solar heat gain coefficient of greater than about 1.85. The coated article, e.g. an IG unit, has a substrate with at least one antireflective layer deposited over the substrate. At least one infrared reflective layer is deposited over the antireflective layer and at least one primer layer is deposited over the infrared reflective layer. Optionally a second antireflective layer is deposited over the first primer layer and optionally a second infrared reflective layer is deposited over the second antireflective layer. Optionally a second primer layer is deposited over the second infrared reflective layer and optionally a third antireflective layer is deposited over the second primer layer, such that the coated article can have the aforementioned optical properties. Also an optional protective overcoat, e.g. an oxide or oxynitride of titanium or silicon, and / or solvent soluble organic film former may be deposited over the uppermost antireflective layer.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Low-E coated articles and methods of making same
In certain example embodiments, low-E coated articles may be designed so as to realize a combination of good visible transmission (Tvis) and an excellent solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC), thereby realizing an improved (i.e., higher) Tvis / SHGC ratio. In certain example embodiments of this invention, if heat treated (HT), the low-E coated articles may have approximately the same color characteristics as viewed by the naked eye both before and after heat treatment (i.e., a low ΔE* value) in certain example instances. Such coated articles may be used in insulating glass (IG) units, windows, and / or other suitable applications.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Infra-red reflecting layered structure
ActiveUS20060057399A1Good visible light transmittanceLow solar heat gain coefficientElectric discharge tubesMagnetic/electric field screeningInfraredRefractive index
The invention relates to an infra-red reflecting layered structure comprising a transparent substrate layer; a first metal oxide layer; a first silver containing layer, a second metal oxide layer; a second silver containing layer and a third metal oxide layer. The first, second and third metal oxide layer have a refractive index of at least 2.40 at a wavelength of 500 nm. The layered structure according to the present invention laminated on glass has a visual light transmittance (VLT) higher than 70% and a solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC) lower than 0.44. The invention further relates to the use of a layered structure as a transparent heat-mirror.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN PERFORMANCE PLASTICS CHAINEUX
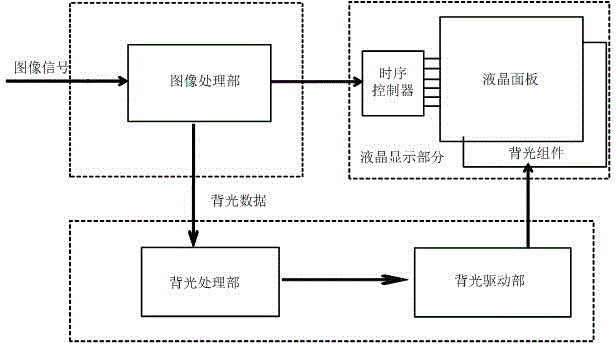
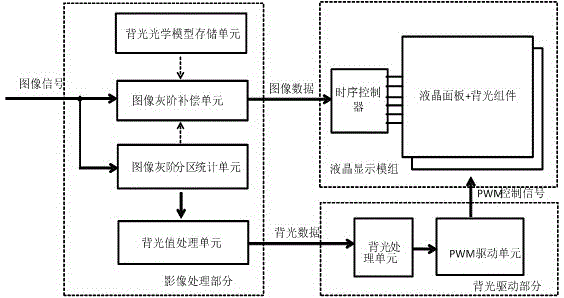
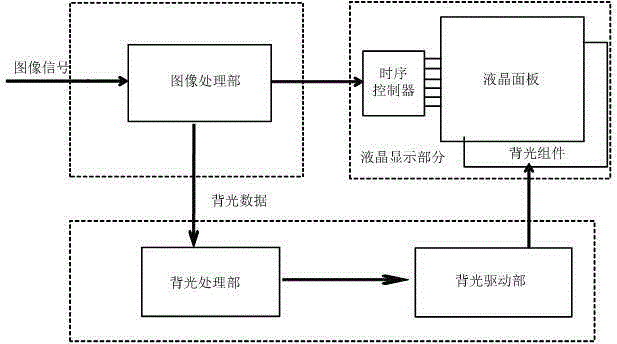
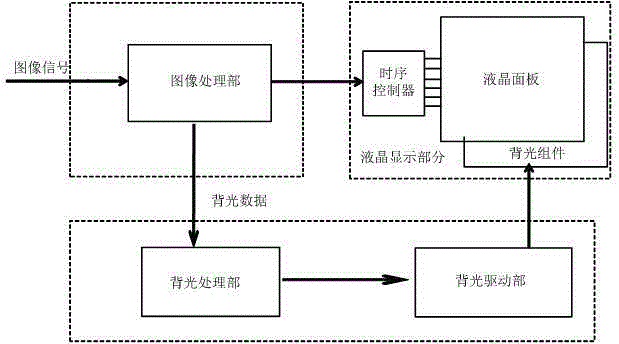
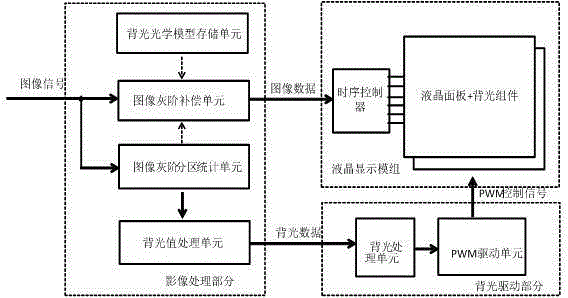
Liquid crystal display brightness control method and device and liquid crystal display equipment
ActiveCN105047142AEnhance layeringImprove the level of display brightnessCathode-ray tube indicatorsLiquid-crystal displayImaging quality
The invention provides a liquid crystal display brightness control method and device and liquid crystal display equipment, and belongs to the technical field of liquid crystal display. An image gray-scale value in a partition image data block is confirmed based on the preset rules according to the received image signals, and a partition backlight value corresponding to the partition image data is pre-extracted according to the image gray-scale value; the preset backlight value gain coefficient and the pre-extracted partition backlight value are multiplied so that the partition backlight value of the backlight partition after gain is obtained, wherein the preset backlight value gain coefficient is greater than 1; and each partition backlight value after gain is mapped to the driving circuit of a backlight source in the corresponding backlight partition so as to control backlight source brightness of the corresponding backlight partition through driving. The contrast image quality effect of a liquid crystal display frame can be improved.
Owner:HISENSE VISUAL TECH CO LTD
Method for regulating frequency domain based nonlinear power system stabilizer parameter
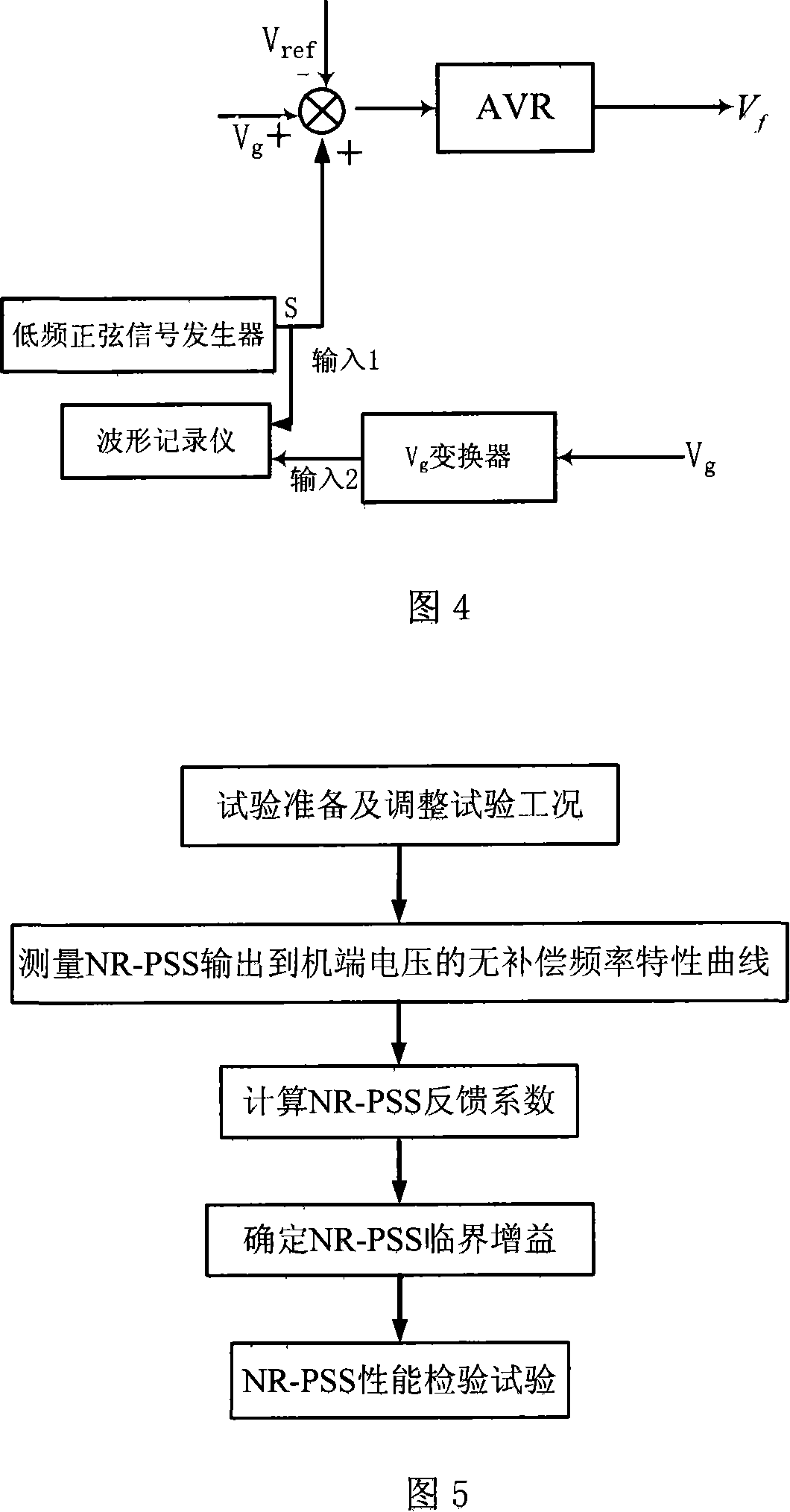
ActiveCN101119094AClear thinkingSimple stepsFrequency analysisDynamo-electric machine testingGain coefficientEngineering
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
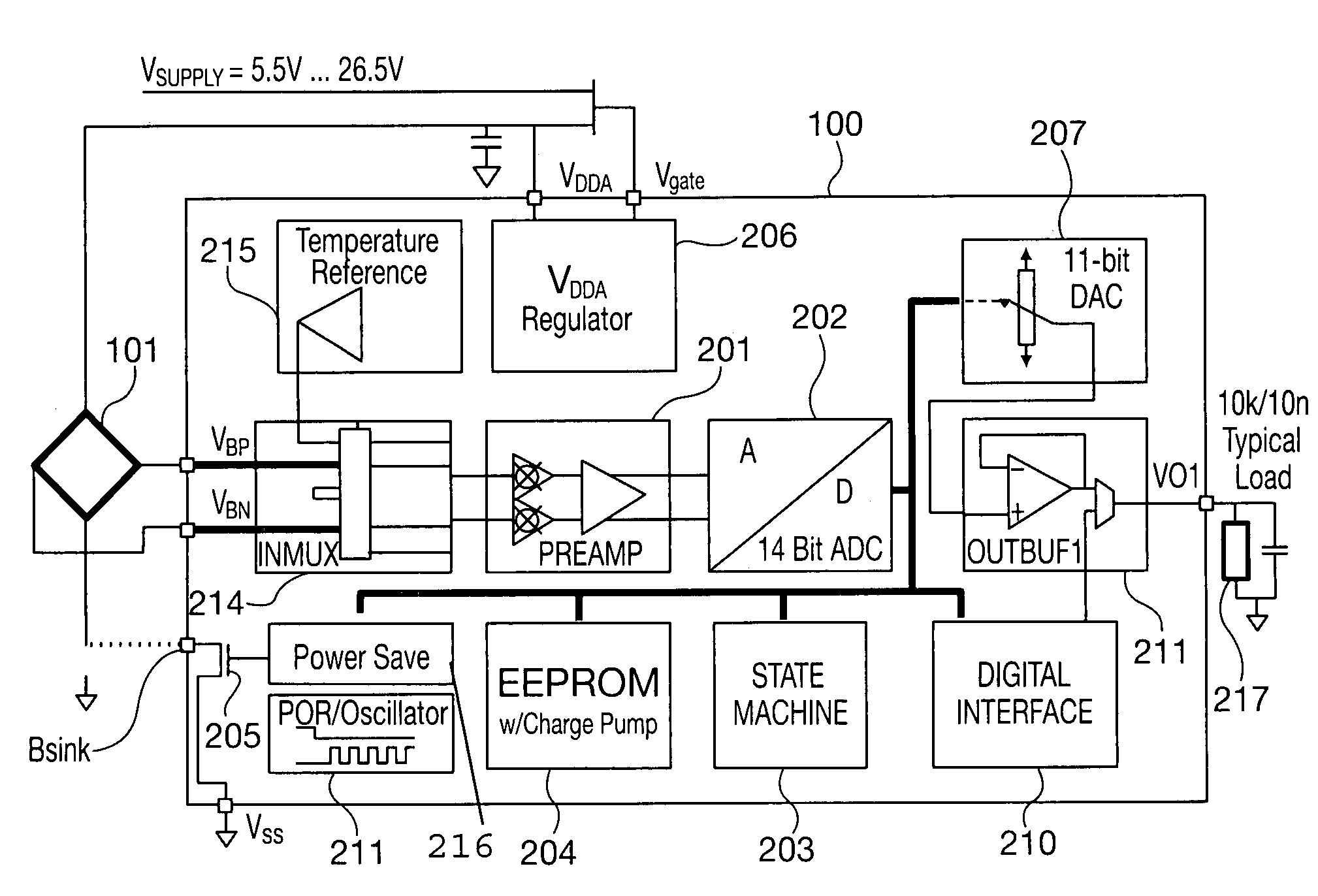
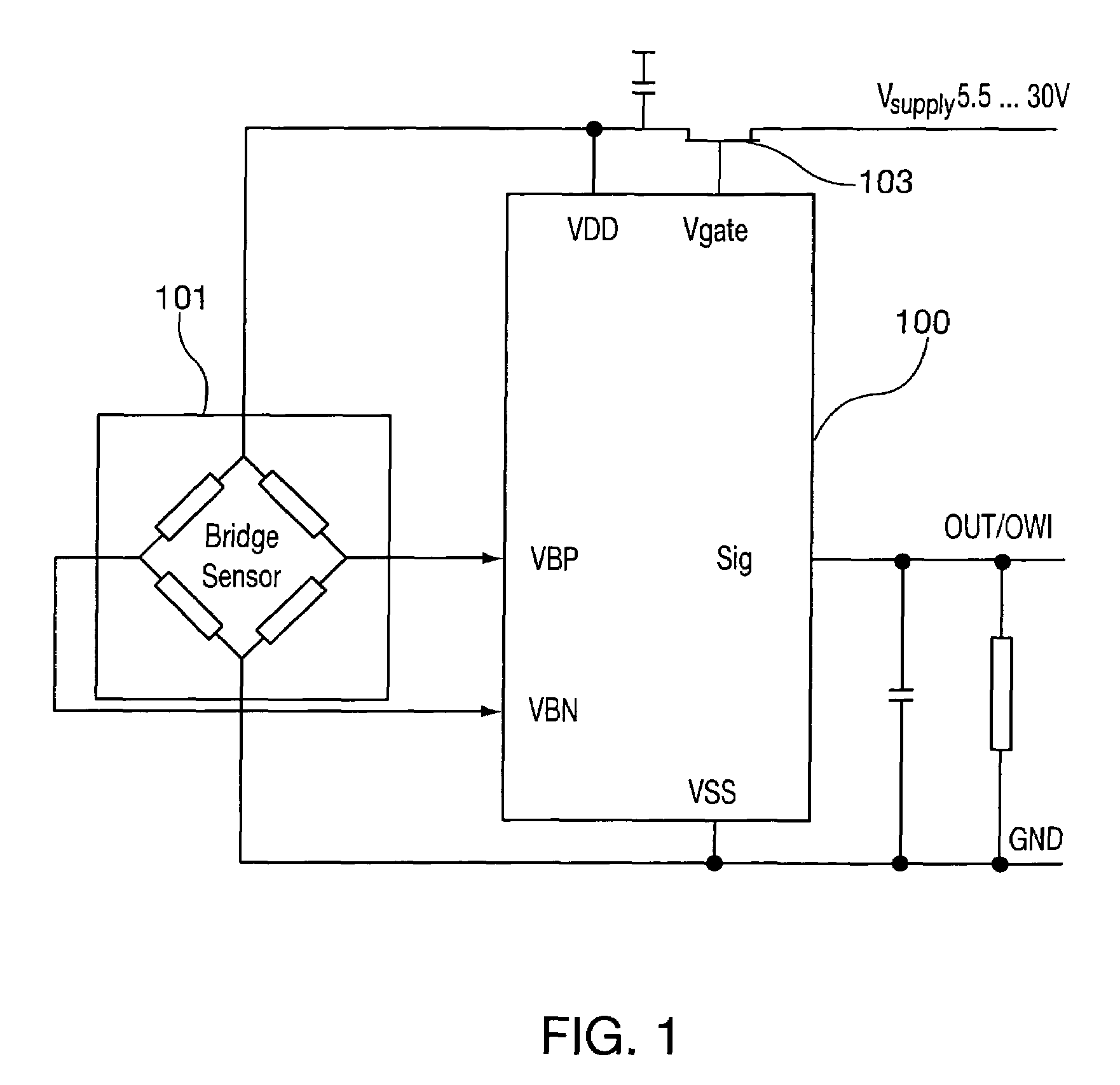
Sensor interface and sensor calibration technique
InactiveUS7577539B2Fluid pressure measurementSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGain coefficientLinearity
Owner:ZMD AMERICA
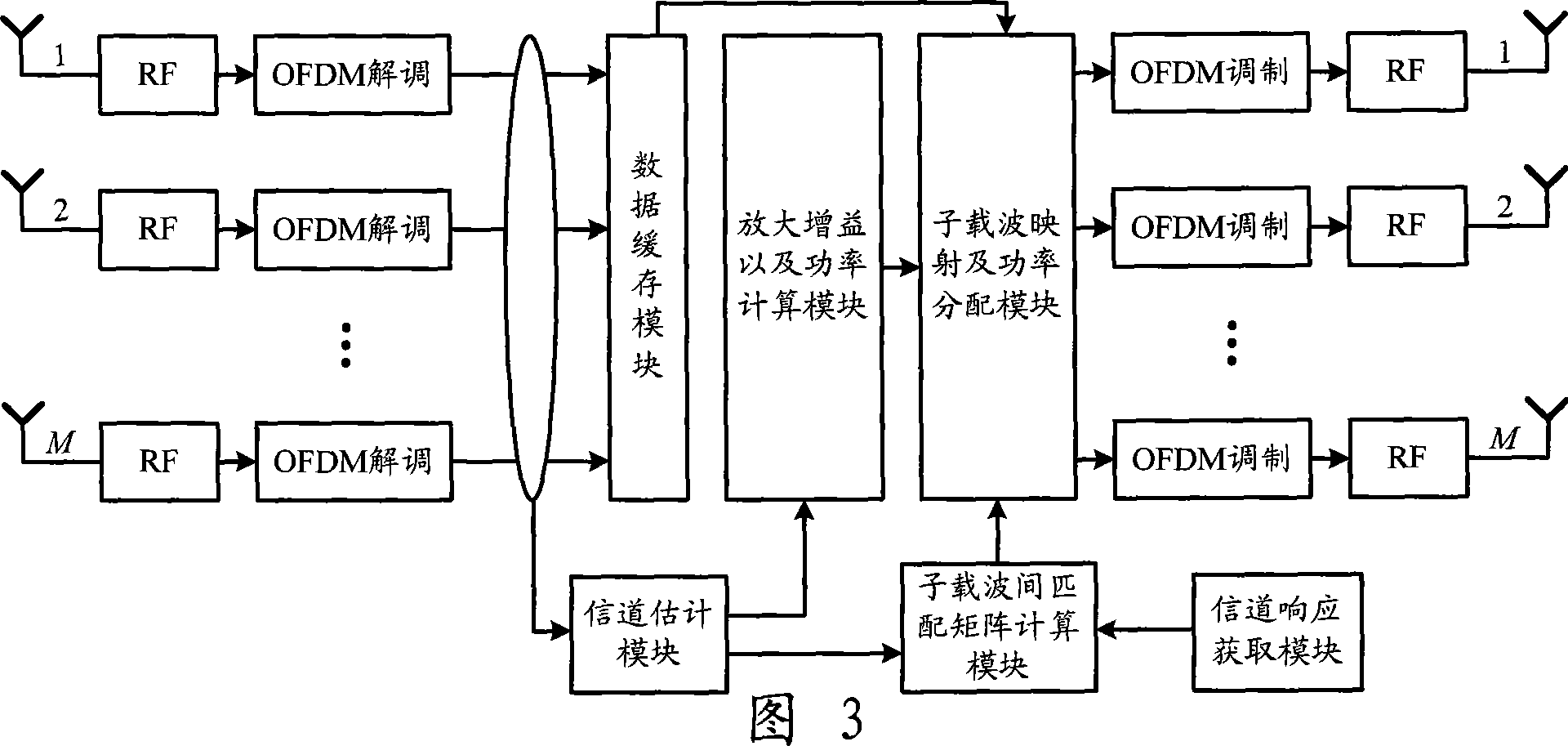
MIMO-OFDM system channel estimation method based on compressed sensing
ActiveCN104052691AImproved channel estimation resultsSmall distribution intervalBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsEstimation methodsGain coefficient
The invention provides an MIMO-OFDM system channel estimation method based on compressed sensing. The MIMO-OFDM system channel estimation method based on compressed sensing is mainly applied to channel estimation when a receiving terminal is provided with a two-dimensional antenna array. According to the MIMO-OFDM system channel estimation method based on compressed sensing, the time delay, incidence angle and gain of each path of a space channel are estimated in sequence, and channel estimation accuracy can be improved effectively. The MIMO-OFDM system channel estimation method based on compressed sensing comprises the following steps that 1, an initially-estimated value of a channel frequency domain response vector of each pilot frequency sub-carrier is obtained according to the least square criterion; 2, by means of the sparsity of the channel frequency domain response vectors in a time delay domain, the time delay of each path of the channel and an estimated value of a channel time domain response vector of each path of the channel are estimated on the basis of the compressed sensing theory; 3, by means of the sparsity of the channel time domain response vectors in a two-dimensional angle domain, the incidence angle of each path of the channel is estimated on the basis of the compressed sensing theory; 4, the gain coefficient of each path of the channel is estimated according to the least square criterion; 5, estimated values of channel frequency domain responses of all the sub-carriers and antennas are obtained.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Rack end protection method of electric power steering system
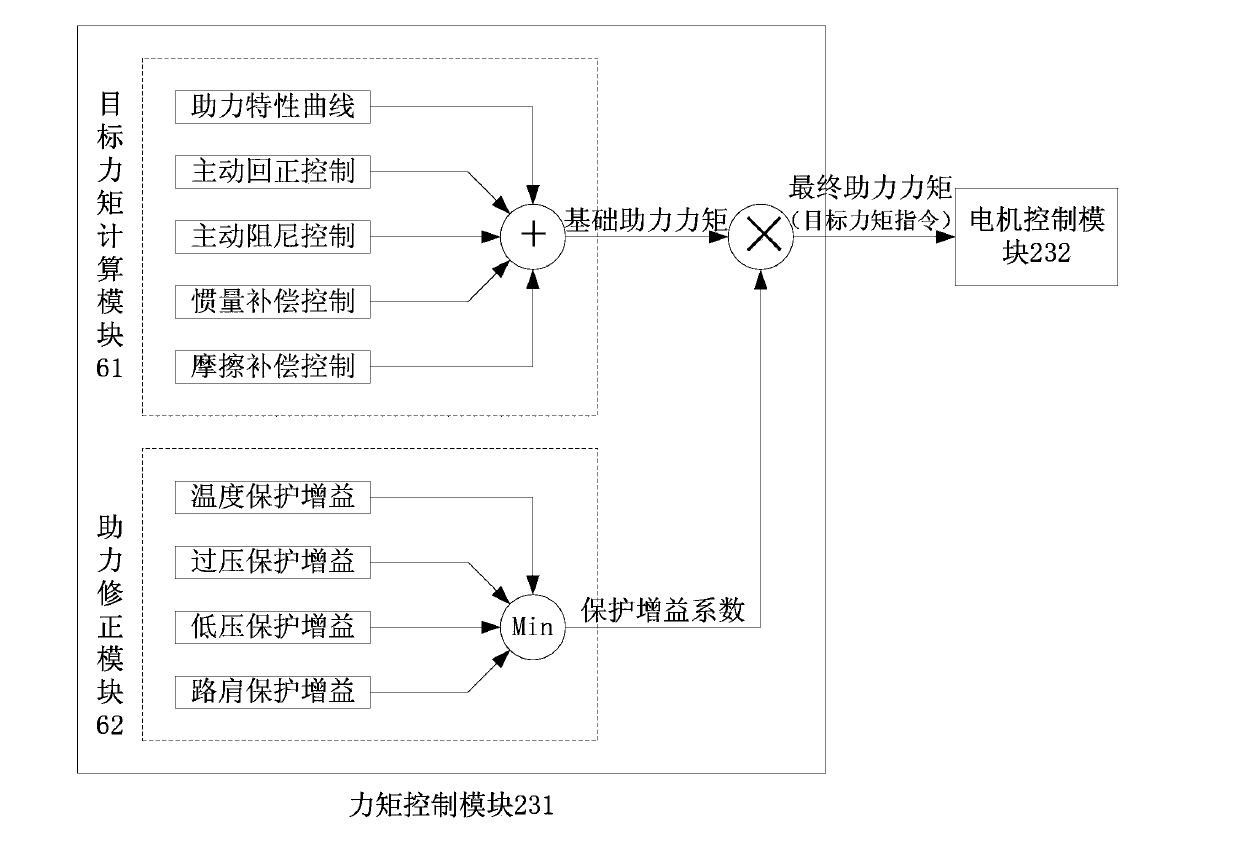
InactiveCN103863385AReduced torque outputRealize the protection functionSteering linkagesMechanical steering gearsElectric power steeringSteering wheel
The application discloses a rack end protection method of an electric power steering system. When a rack of a steering gear moves towards the end of the rack and enters a rack end protection area, an ECU (electronic control unit) of the electric power steering system takes a rotating angle of a steering wheel, the speed of the rotating angle and rotating torque as input to calculate a rack end protection gain value which serves as a multiplier during assisting torque calculation. The rack end protection gain value is the product of a basic gain coefficient, a rotating speed gain coefficient and a rotating torque gain coefficient. The basic gain coefficient decreases progressively as the absolute value of the rotating angle of the steering wheel increases. The rotating speed gain coefficient decreases progressively as the absolute value of the rotating angle of the steering wheel increases. The rotating torque gain coefficient increases progressively as the absolute value of the rotating angle of the steering wheel increases. According to the rack end protection method of the electric power steering system, during working conditions of rack ends, current output can be limited, temperature rise can be reduced and mechanical impact of the rack ends can be avoided.
Owner:LIANCHUANG AUTOMOBILE ELECTRONICS
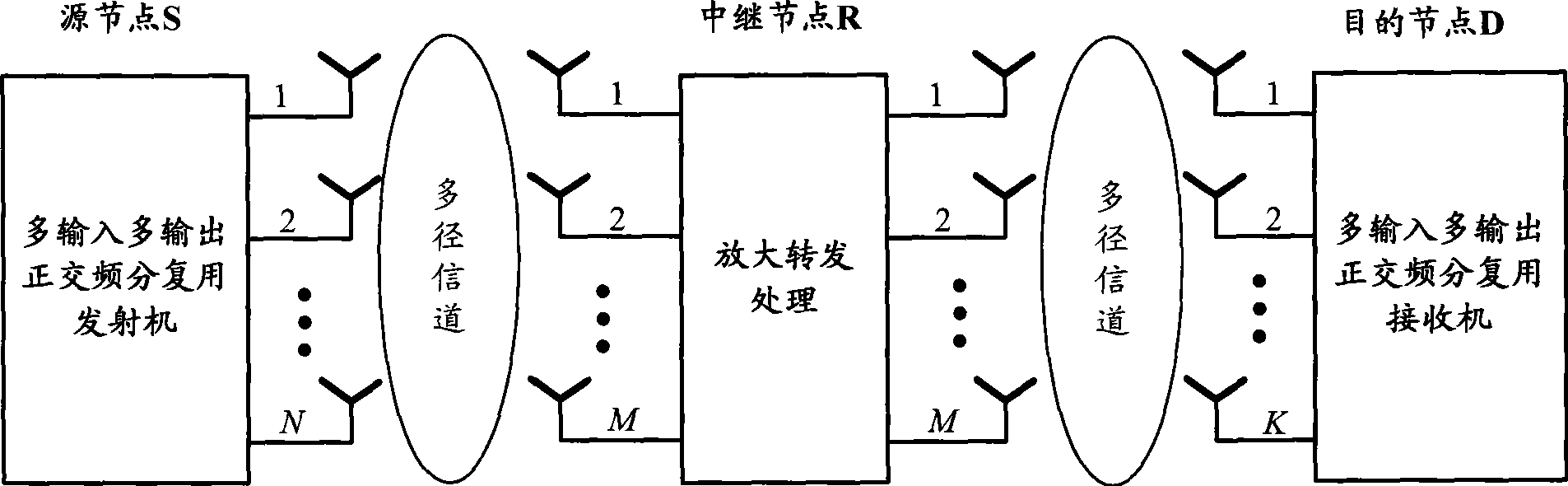
Data relaying method for OFDM system and relaying station
InactiveCN101399799AImprove performanceSpatial transmit diversityTransmission control/equalisingData informationTransmitted power
The invention discloses a data relay method of an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) system which belongs to the wireless relay technical field of a wireless mobile communication system. A relay node in the method receives signals sent by a source node, caches the data information after OFDM demodulation, estimates the channel response of the link from the source node to a relay node, and then obtains the channel response of the link from the relay node to a destination node; a relay station determines the subcarrier coupling matrix in each subcarrier group according to the channel response of the links from the source node to the relay node and from the relay node to the destination node, and simultaneously estimates gain coefficient and transmitted power; and then the relay station maps the symbol on each subcarrier in the link from the cached source node to the relay node onto corresponding subcarrier in the link from the coupled relay node to the destination node according to the coupling relation of the subcarrier, allocates the power, then carries out the OFDM modulation and finally sends the symbol to the destination node. The invention improves the performance of the entire system.
Owner:ZTE CORP
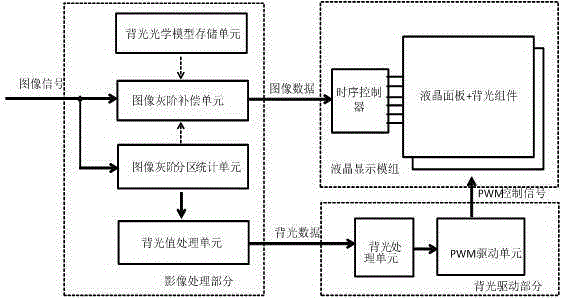
Liquid crystal display brightness control method and device and liquid crystal display device
ActiveCN105161064AImprove dynamic contrastIncrease brightnessStatic indicating devicesLiquid-crystal displayImaging quality
The invention provides a liquid crystal display brightness control method and device and a liquid crystal display device, and belongs to the technical field of liquid crystal display. The method is characterized by, determining gray-scale values of images in subregion image data blocks according to a preset rule and on the basis of the received image signals, and pre-extracting subregion backlight values corresponding to the subregion image data according to the gray-scale values of the images; multiplying a preset backlight value gain coefficient with the pre-extracted subregion backlight values to obtain subregion backlight values of backlight subregions obtained after gaining, wherein the preset backlight value gain coefficient is larger than 1; and mapping the subregion backlight values obtained after gaining to drive circuits of backlight sources of the corresponding backlight subregions respectively to drive and control the brightness of the backlight sources of the corresponding backlight subregions. Therefore, liquid crystal display frame contrast image quality effect is improved.
Owner:HISENSE VISUAL TECH CO LTD
Liquid crystal display brightness control method and device and liquid crystal display device
ActiveCN105185328AImprove contrast performanceSolve the problem of display brightness distortionStatic indicating devicesLiquid-crystal displayGray level
The invention provides a liquid crystal display brightness control method and device and a liquid crystal display device, and belongs to the technical field of liquid crystal display. The method comprises the following steps: determining image gray scale values of subregion image data blocks according to preset rules and according to received image signals, and pre-extracting subregion backlight values corresponding to subregion image data according to the image gray scale values; multiplying preset backlight valve gain coefficient with pre-extracted subregion backlight values to obtain subregion backlight values of the backlight subregions after gain, wherein the preset backlight valve gain coefficient is larger than 1; and mapping each subregion backlight value after gain to a drive circuit of a backlight source of the corresponding backlight subregion so as to drive and control the brightness of the backlight source of the corresponding backlight subregion. Therefore, contrast quality effect of liquid crystal display frame is improved.
Owner:HISENSE VISUAL TECH CO LTD
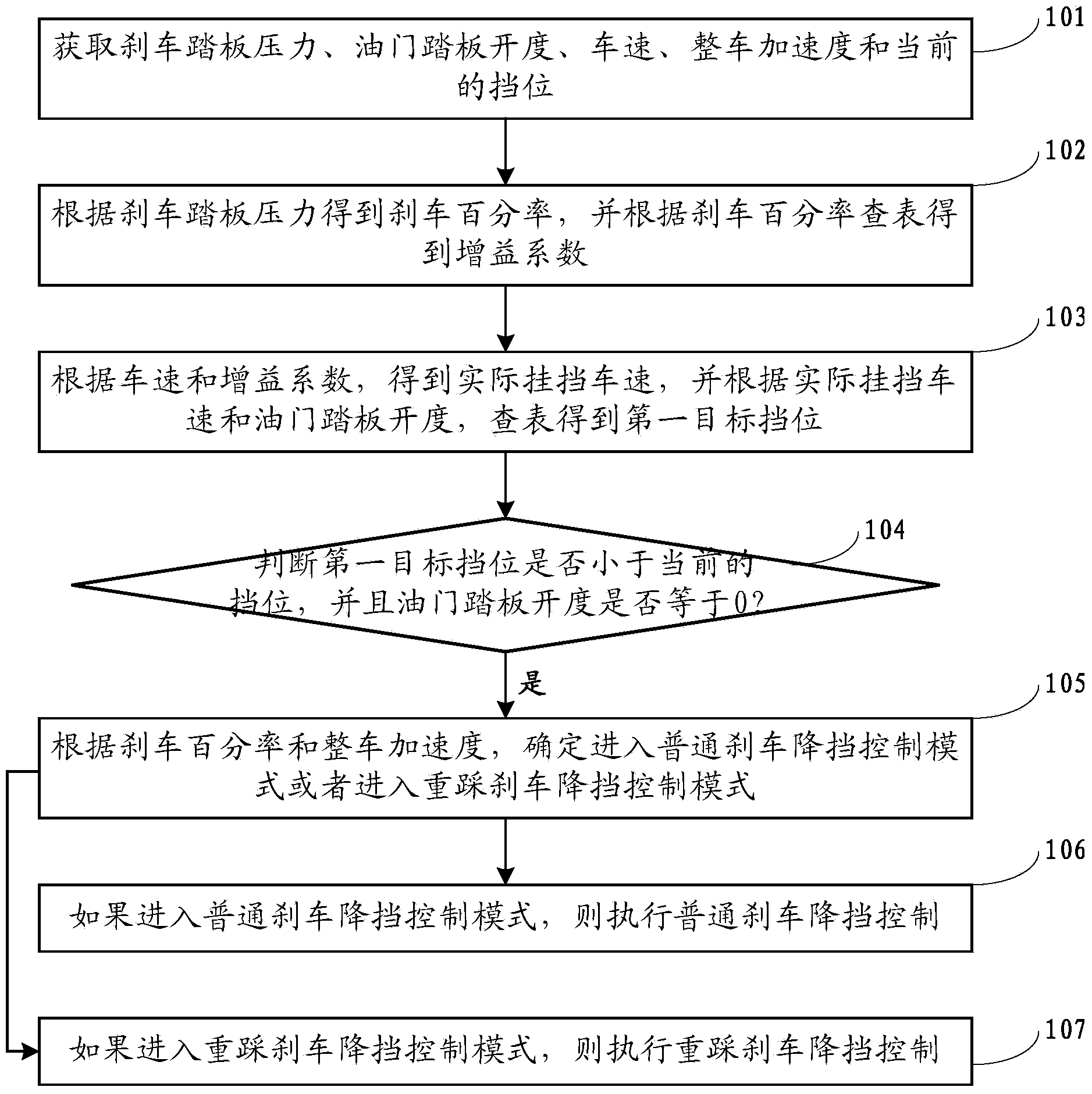
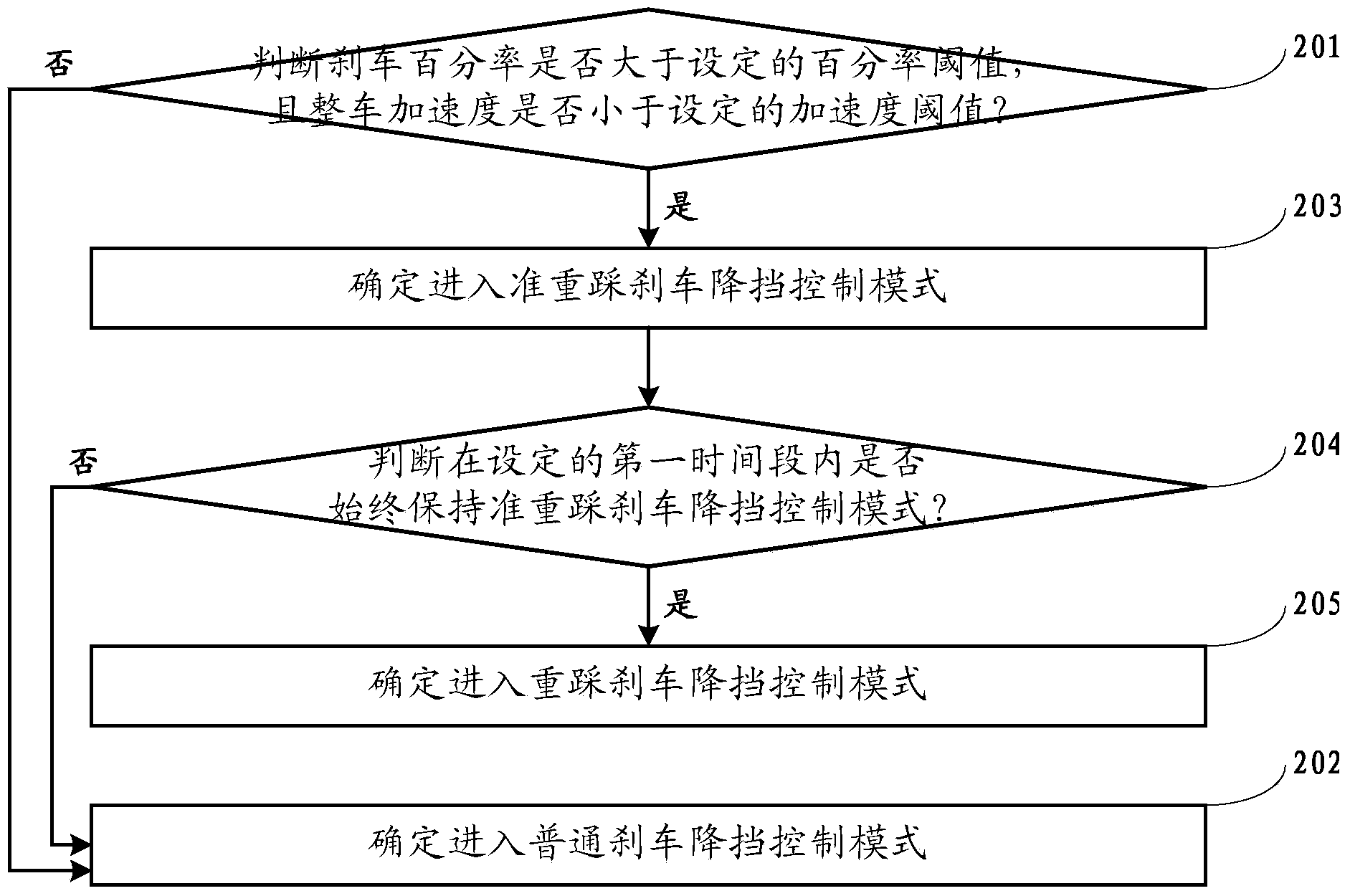
Braking kick-down control method of double clutch automatic transmission
ActiveCN103758995AAvoid overall overheatingExtend working lifeGearing controlAutomatic transmissionGain coefficient
The invention discloses a braking kick-down control method of a double clutch automatic transmission. The braking kick-down control method includes the steps that the pressure on a braking pedal, the opening degree of an accelerator pedal, the vehicle speed, the acceleration of the whole vehicle and the current gear position are acquired; the braking percentage is obtained according to the pressure on the braking pedal, and the gain coefficient is obtained by looking up a table of the braking percentage; according to the vehicle speed and the gain coefficient, the actual gear engaging vehicle speed is obtained; according to the actual gear engaging vehicle speed and the opening degree of the accelerator pedal, a first target gear position is obtained by looking up a table; whether the first target gear position is smaller than the current gear position or not is judged, and whether the opening degree of the accelerator pedal is equal to zero or not is judged; if yes, according to the braking percentage and the acceleration of the whole vehicle, it is determined that a common braking kick-down control mode is executed or a re-treading braking kick-down control mode is executed; if the common braking kick-down control mode is executed, common braking kick-down control is executed; if the re-treading braking kick-down control mode is executed, the re-treading braking kick-down control is executed. By the adoption of the method, it is guaranteed that the gear position can be fast decreased, and the driving comfort and the driving safety are improved.
Owner:ANHUI JIANGHUAI AUTOMOBILE GRP CORP LTD
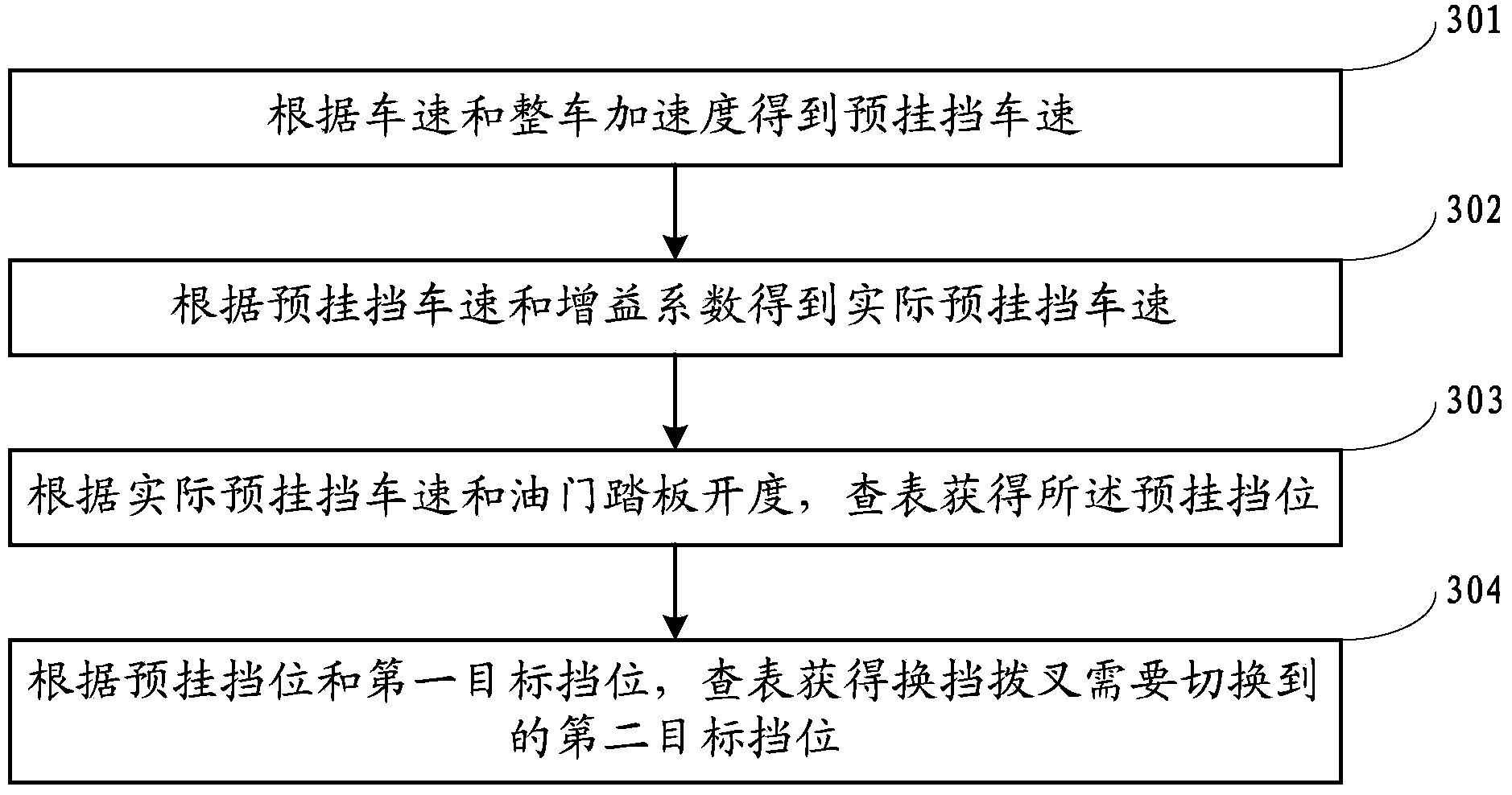
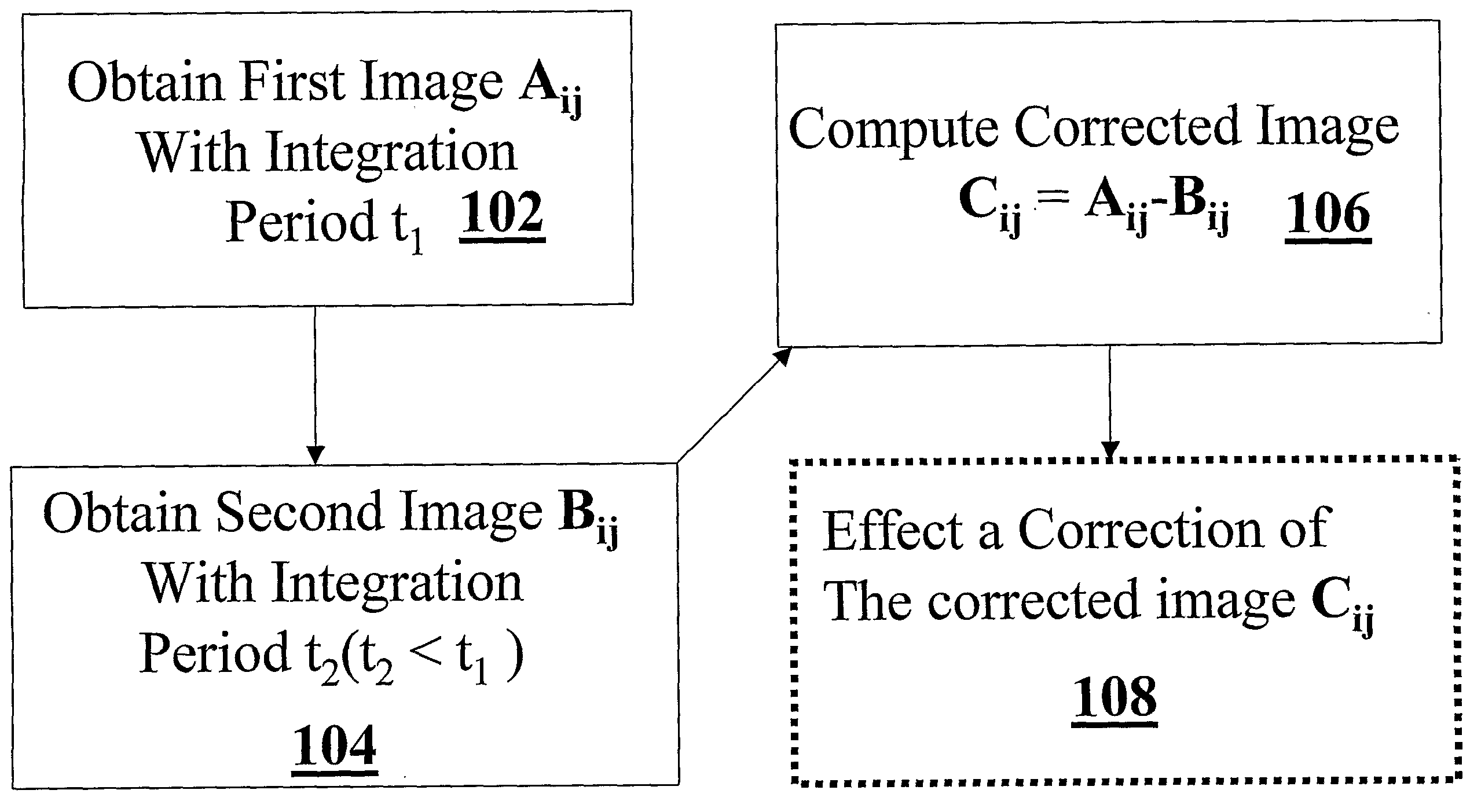
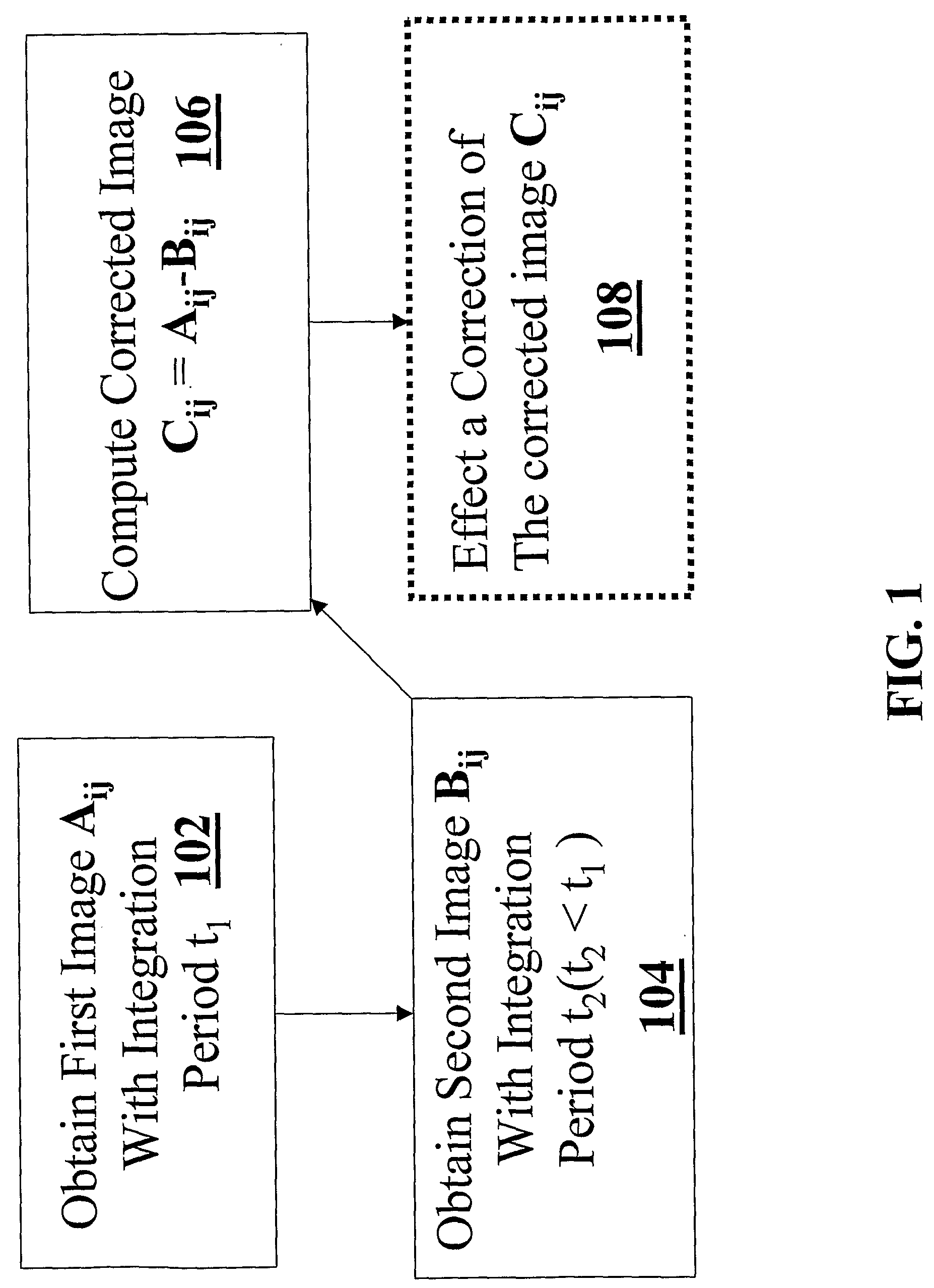
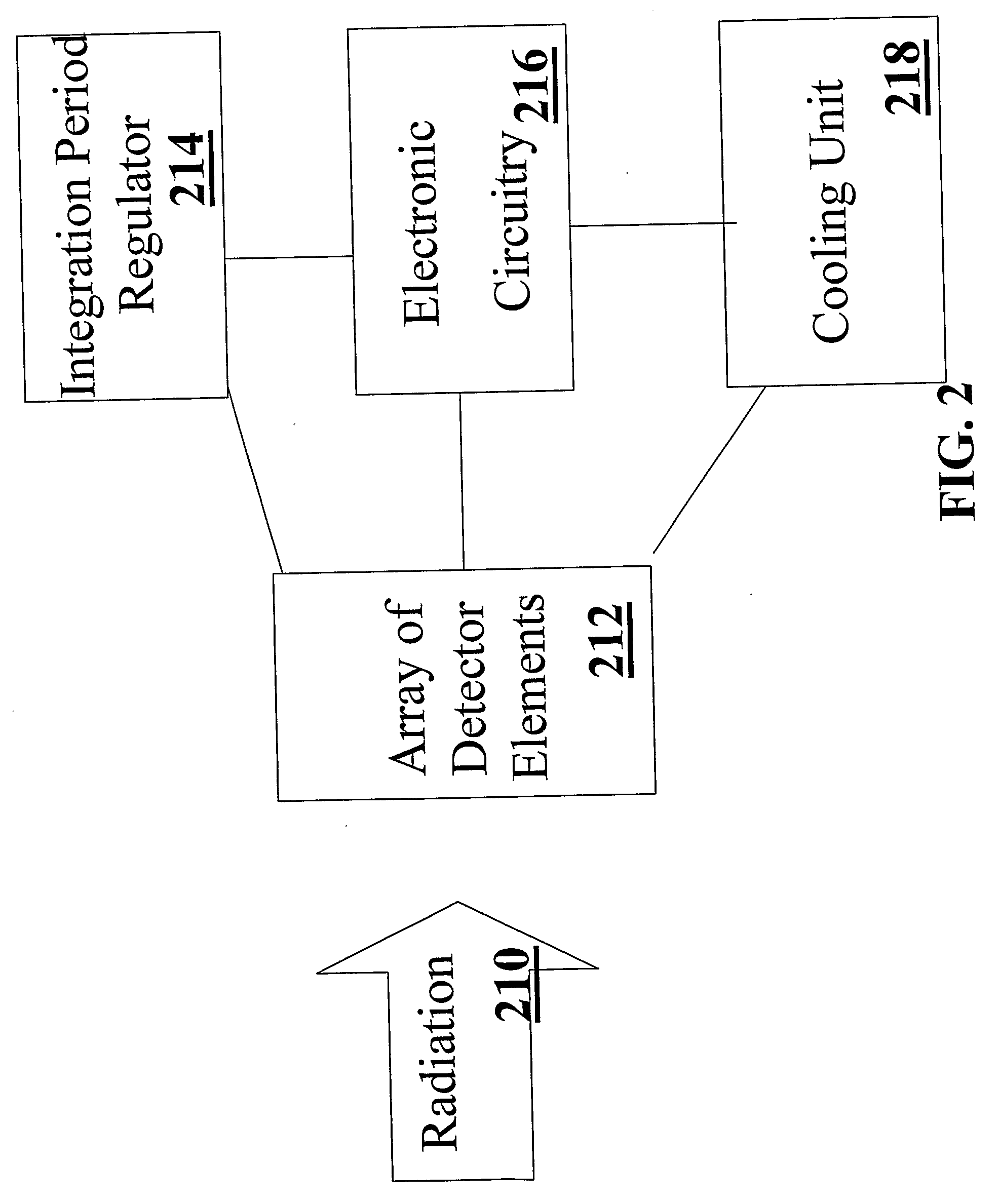
Non-uniformity correction of images generated by focal plane arrays of photodetectors
ActiveUS20090079854A1Reduce residual non-uniformityEliminate unevennessImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
Methods and apparatus for effecting a non-uniformity correction of images of a scene obtained with an array of detector elements are disclosed. A first image of the scene having a first integration period is acquired using the array of detector elements. A second image of the scene having a different integration period is acquired, and a corrected image of the scene is generated by computing a difference of the images. In some embodiments, the first and second images are images of substantially identical scenes. According to some embodiments, the images are infrared images. Optionally, the corrected image is subjected to further correction using pixel dependent correction coefficients, such as gain coefficients. Exemplary image detection elements include but are not limited to InSb detector elements and ternary detector elements, such as InAlSb, MCT (Mercury Cadmium Telluride), and QWIP technology (Quantum Well Infrared Photodiodes). In some embodiments, the detector elements are cooled to a temperature substantially equal to an atmospheric boiling point of liquid nitrogen. Alternatively, the detector elements are cooled to a temperature below an atmospheric boiling point of liquid nitrogen, or any other operating temperature.
Owner:RAFAEL ADVANCED DEFENSE SYSTEMS
Multifunctional static or semi-static photovoltaic skylight and/or methods of making the same
InactiveUS20140090687A1Dominate costLess materialPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energySemiconductor materialsEffect light
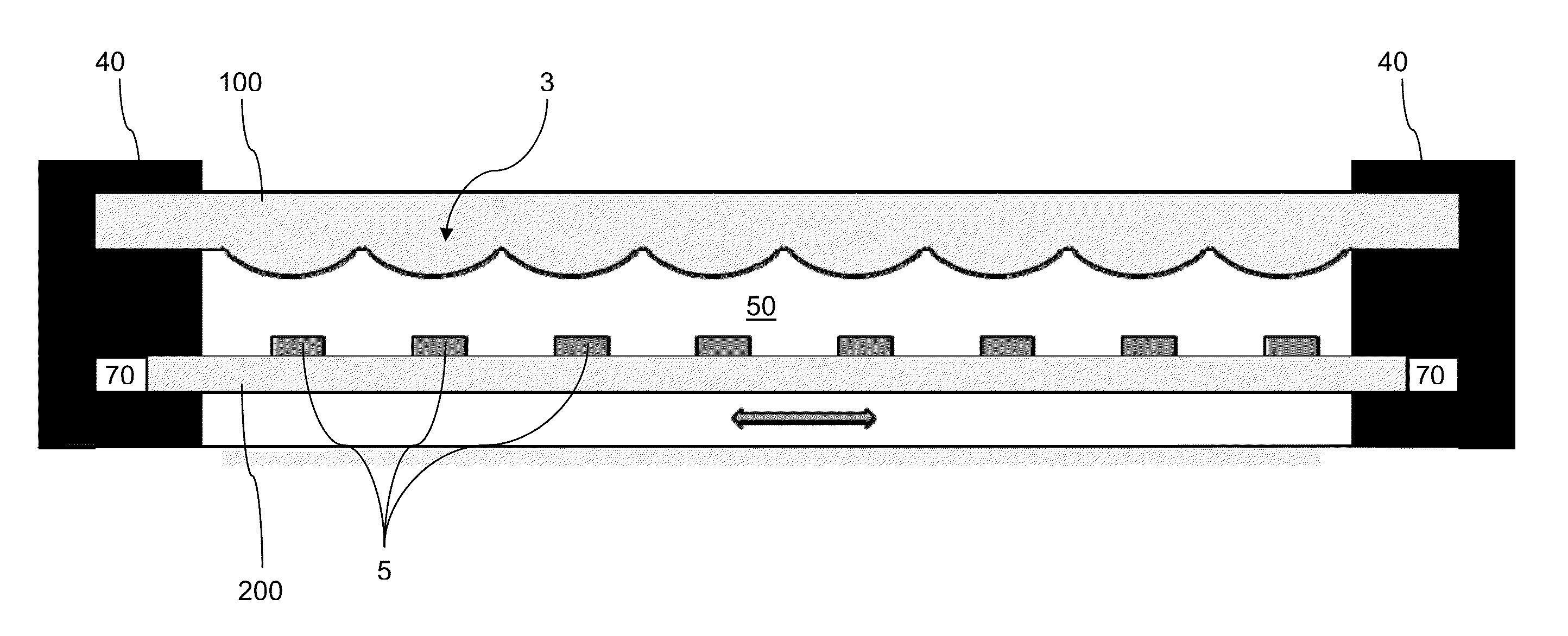
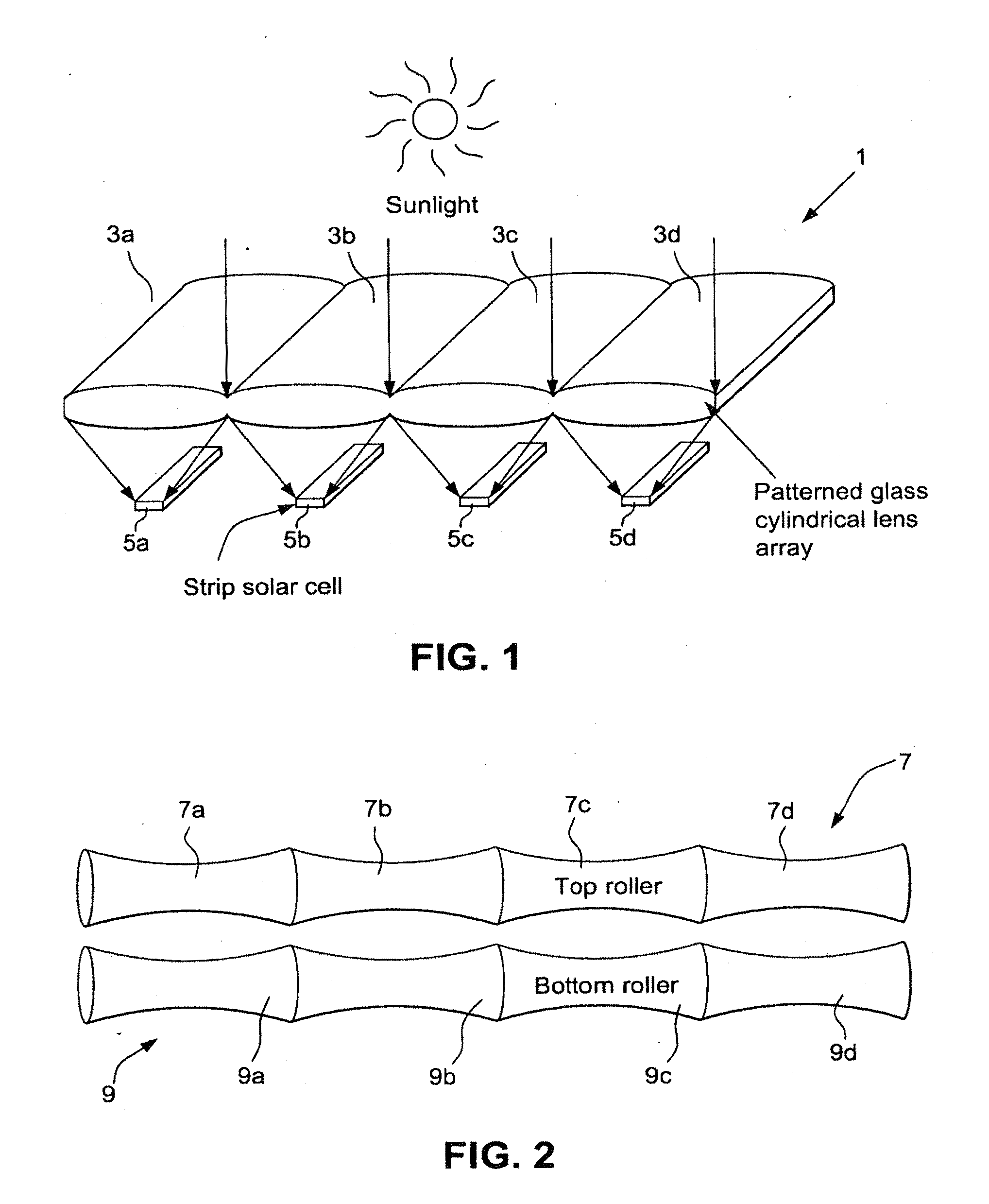
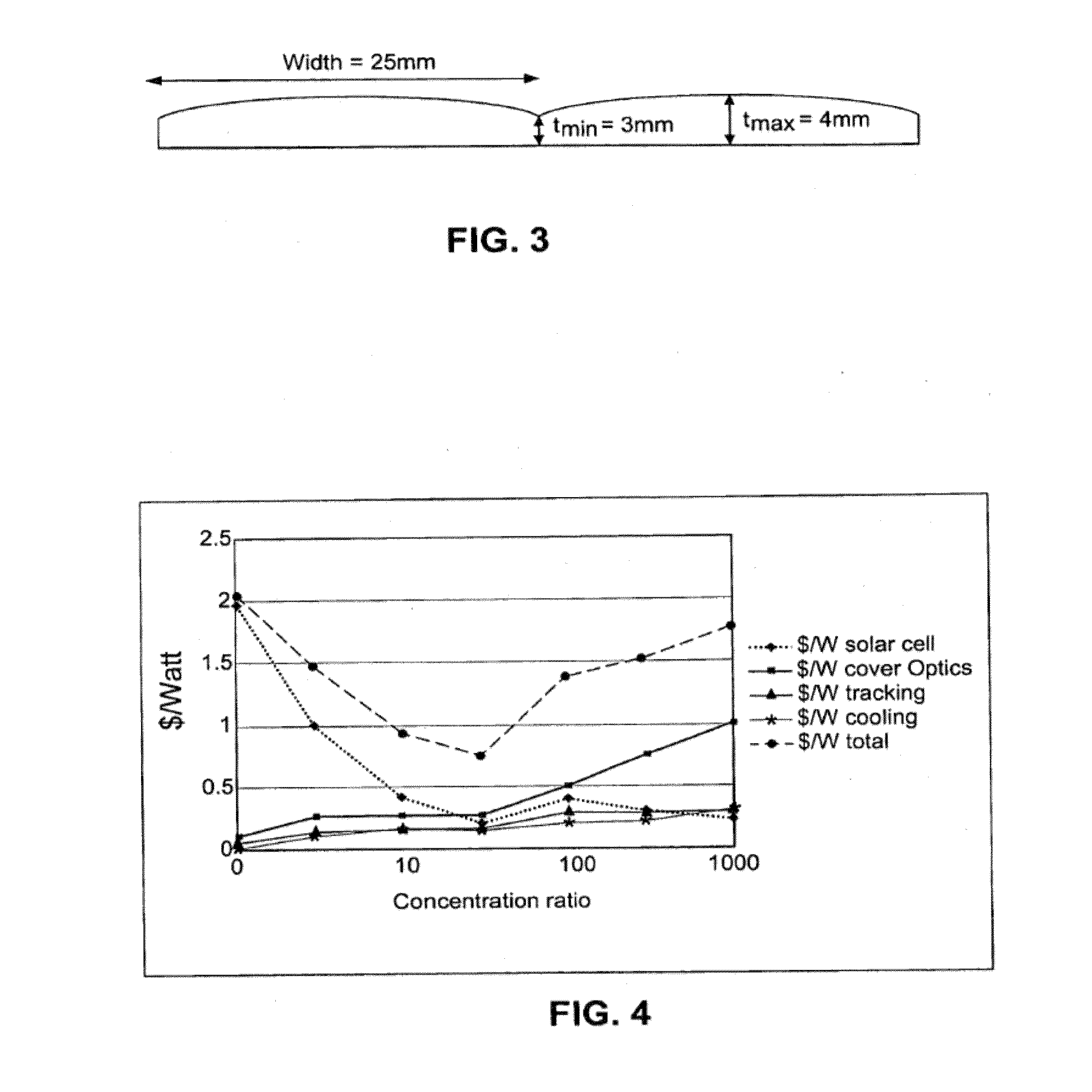
Improved building-integrated photovoltaic systems according to certain example embodiments may include concentrated photovoltaic skylights or other windows having a cylindrical lens array. The skylight may include an insulated glass unit, which may improve the Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC). The photovoltaic skylight and lens arrays may be used in combination with strip solar cells. Arrangements that involve lateral displacement tracking systems, or static systems (e.g., that are fixed at one, two, or more predefined positions) are contemplated herein. Such techniques may advantageously help to reduce cost per watt related, in part, to the potentially reduced amount of semiconductor material to be used for such example embodiments. A photovoltaic skylight may permit diffuse daylight to pass through into an interior of a building so as to provide lighting inside the building, while the strip solar cells absorb the direct sunlight and convert it to electricity, providing for SHGC tuning.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Low solar absorbing blue glass, solar reflecting coated blue glass, and insulating unit having a low solar heat gain
An insulating unit having a neutral grey color and a solar heat gain coefficient less than 0.40 includes a clear glass sheet spaced from a coated glass sheet. The coated glass sheet includes a colored glass substrate having a solar infrared reflective coating. The composition of the coated substrate includes a base glass portion and a glass colorant portion, the glass colorant portion including total iron in the range of 0.04 to less than 0.28 weight percent; CoO in the range of 32 to 90 parts per million, and Se in the range of greater than 0 to less than 5.5 parts per million. In one non-limiting embodiment of the invention the glass substrate at a thickness of 0.223 inches has a* chromaticity coordinates of −3.5 to +2.5 and b* chromaticity coordinates of −1 to −15, and a visible light transmittance of 40 to 80%.
Owner:VITRO FLAT GLASS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com