Patents
Literature
19160 results about "Control mode" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
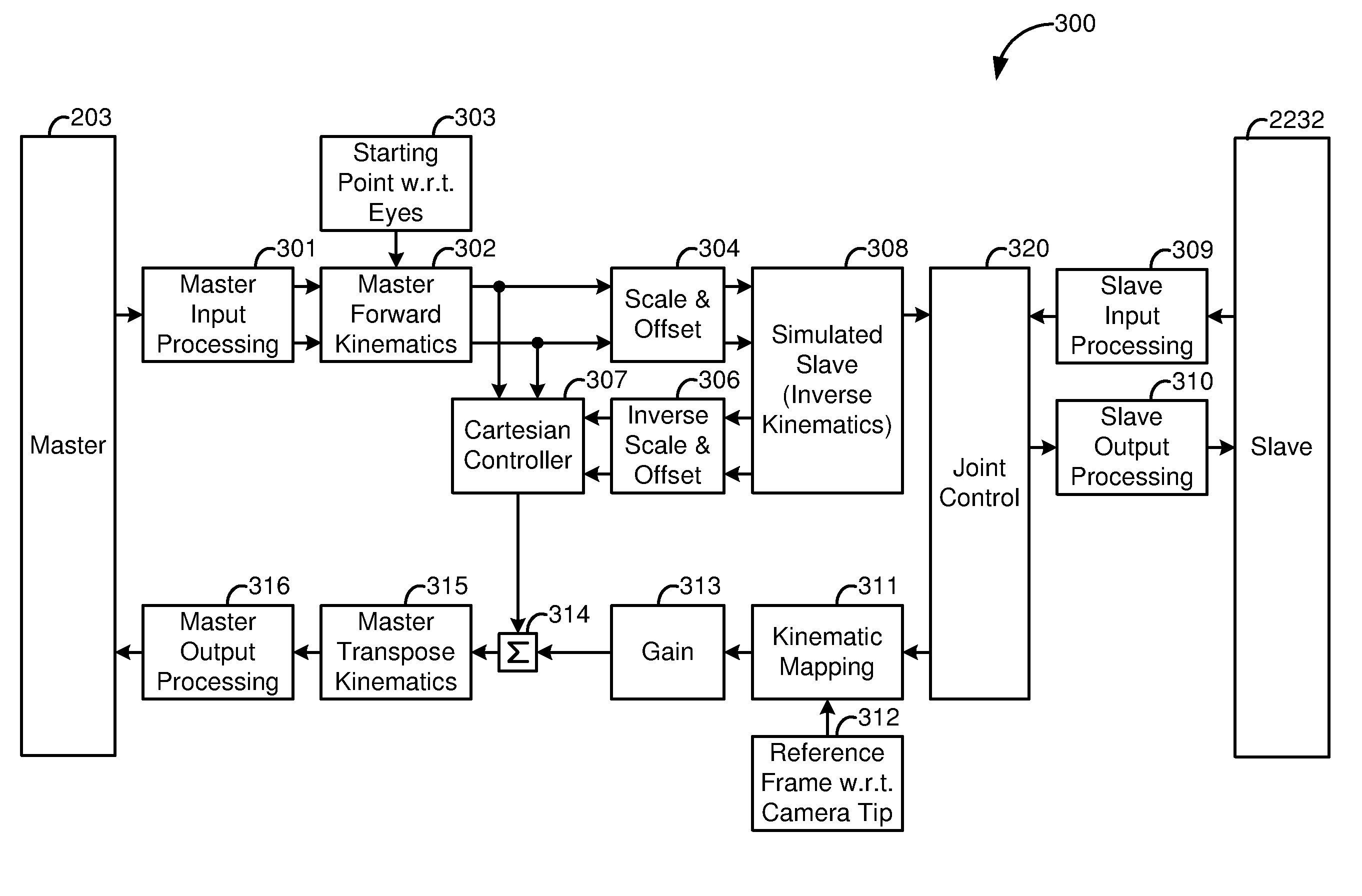
Medical robotic system with coupled control modes
In a coupled control mode, the surgeon directly controls movement of an associated slave manipulator with an input device while indirectly controlling movement of one or more non-associated slave manipulators, in response to commanded motion of the directly controlled slave manipulator, to achieve a secondary objective. By automatically performing secondary tasks through coupled control modes, the system's usability is enhanced by reducing the surgeon's need to switch to another direct mode to manually achieve the desired secondary objective. Thus, coupled control modes allow the surgeon to better focus on performing medical procedures and to pay less attention to managing the system.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Therapeutic apparatus for treating ulcers
InactiveUS7214202B1Pneumatic massageVibration massageWound dressingIntermittent pneumatic compression therapy
A method and apparatus for providing concurrent applications of intermittent pneumatic compression therapy and vacuum assisted closure therapy generally comprises a wound dressing for introduction of a negative pressure into a wound on a patient's foot and a foot wrap for application of positive, compressive forces to substantially all of the patients foot. A suction pump, having an associated vacuum sensor and first feedback mechanism, supplies negative pressure to the wound dressing. A ventable source of pressurized gas, having an associated pressure transducer and second feedback mechanism, supplies positive force to the foot wrap. At least one control system is operably associated with the suction pump and ventable source of pressurized gas for controlling the negative and positive applications of pressure to the patient's foot. Controlled modes for operation include continuous or intermittent application of one or both therapies and simultaneous or cycled application of the therapies.
Owner:KCI LICENSING INC
Medical robotic system with coupled control modes
In a coupled control mode, the surgeon directly controls movement of an associated slave manipulator with an input device while indirectly controlling movement of one or more non-associated slave manipulators, in response to commanded motion of the directly controlled slave manipulator, to achieve a secondary objective. By automatically performing secondary tasks through coupled control modes, the system's usability is enhanced by reducing the surgeon's need to switch to another direct mode to manually achieve the desired secondary objective. Thus, coupled control modes allow the surgeon to better focus on performing medical procedures and to pay less attention to managing the system.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
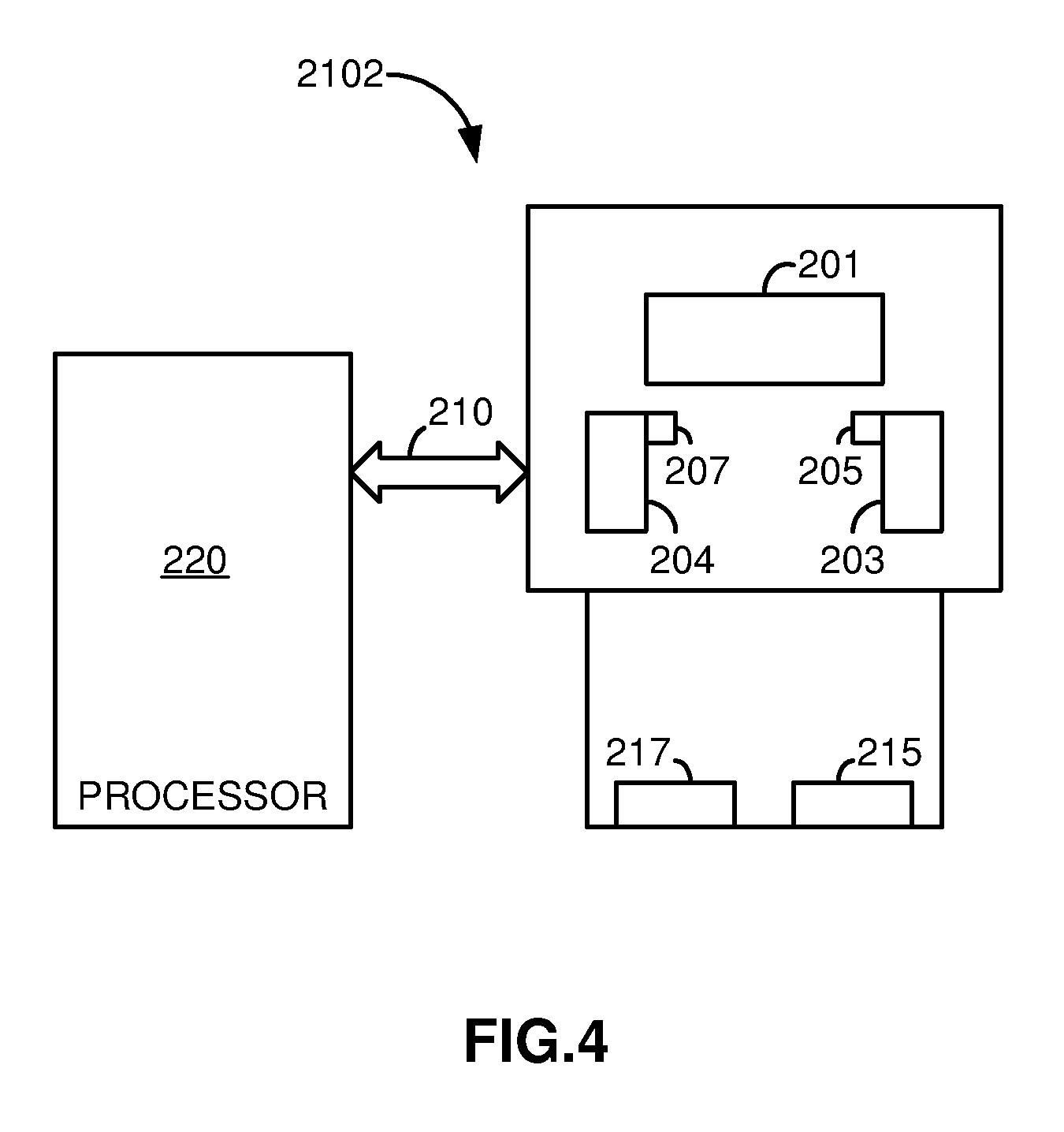
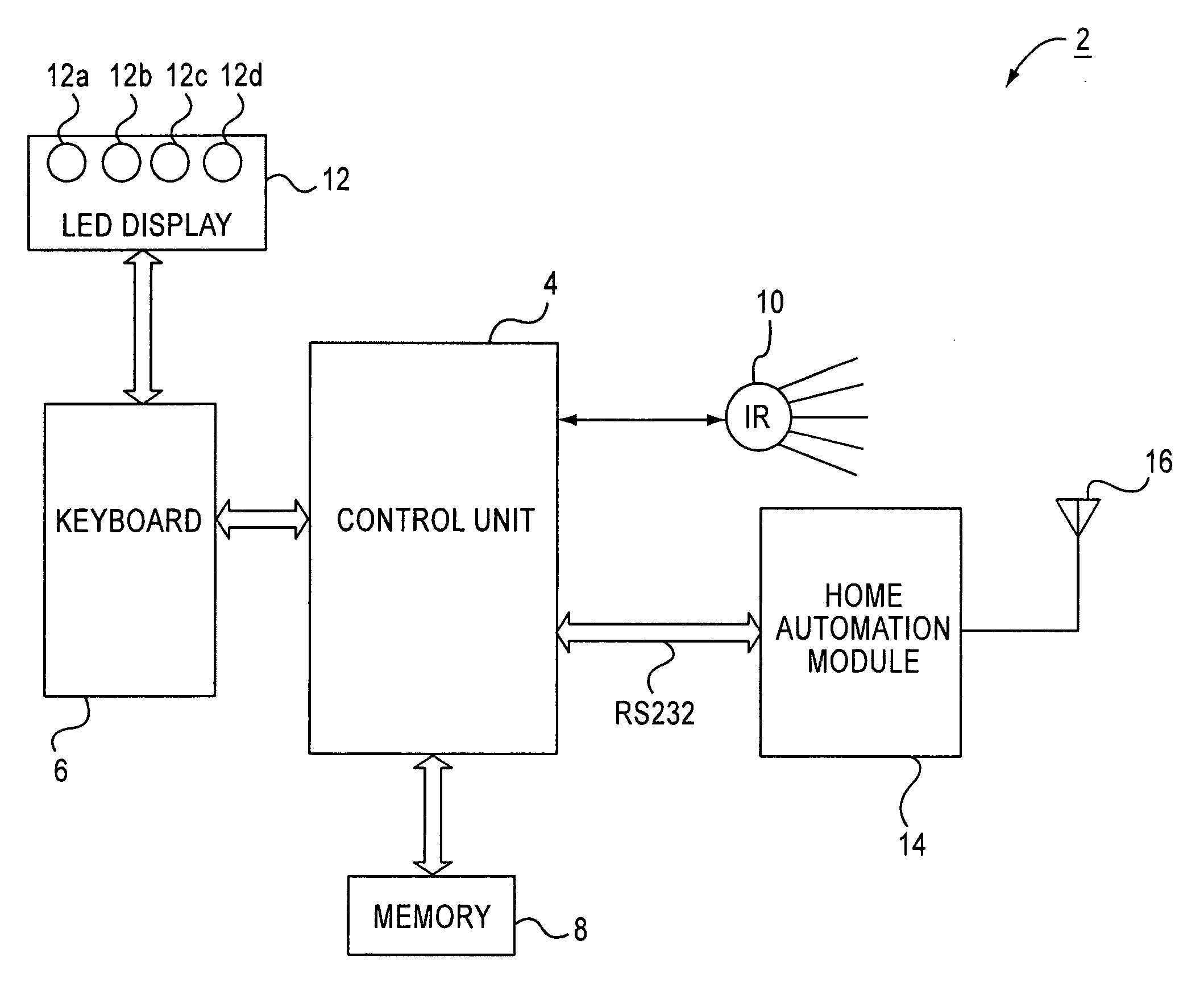
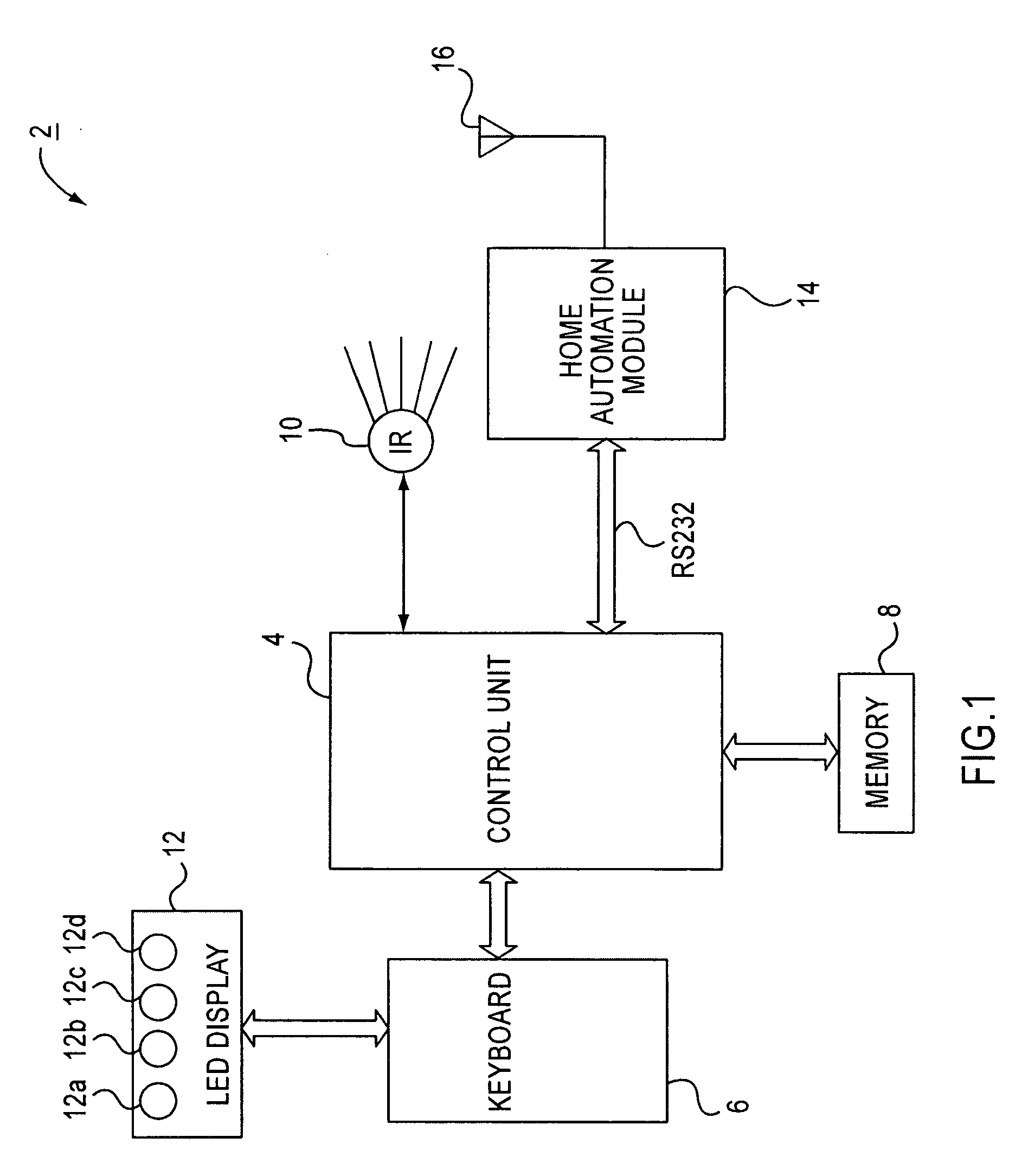
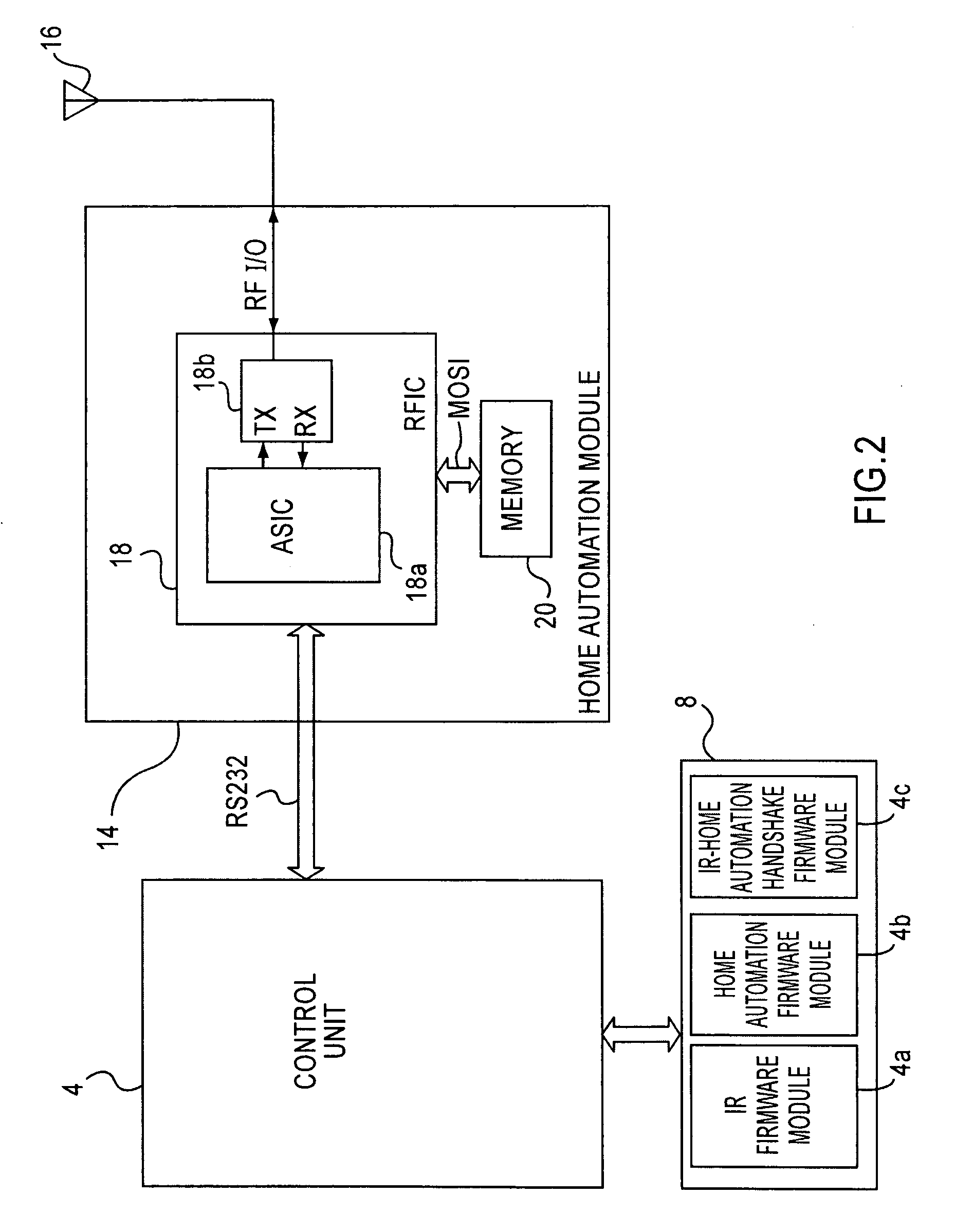
Universal remote controller having home automation function
InactiveUS20090202250A1Electric signal transmission systemsNon-electrical signal transmission systemsInfraredCommunication interface
A universal remote controller having a radio frequency (RF) control mode for generating RF signals for controlling an RF based home automation system and having an infrared (IR) control mode for controlling an infrared based electronic device using IR control signals. Control information input via a user interface is used to generate the IR control signals in the IR mode of operation and is used to generate the RF signals in the RF mode of operation. A control unit controls overall operation of the universal remote controller including the generation of IR signals to control electronic devices with the IR signals. A home automation module is connected to the control unit via a communication interface to generate RF signals to control the RF based home automation system. A display displays feedback information to the user regarding operations for controlling the home automation system.
Owner:SMK MFG
Surgical Robotic Systems with Manual and Haptic and/or Active Control Modes
ActiveUS20130006267A1Assisted movementProgramme-controlled manipulatorVehicle fittingsRobotic systemsEngineering
A surgical robotic system is disclosed that provides a combination of a programmed control, such as active control or passive control, when a high degree of accuracy is required and manual control when a high degree of accuracy is not required, such as during the removal of osteophytes, irregular bone growth and / or soft tissue. Manual resection may be completed by switching from the programmed control mode to the manual control mode and allowing the surgeon free control of the cutting tool. The manual resection may be carried out using some navigational features of the robotic system such as allowing the surgeon to visualize the position of the cutting tool thereby allowing accurate resection of osteophytes, irregular bone and tissue while having the unrestricted freedom to move the cutting tool. The programmed control mode may be reserved for procedures that require a high degree of accuracy, for example, the reaming of a bone and placement of an implant onto the bone.
Owner:MAKO SURGICAL CORP
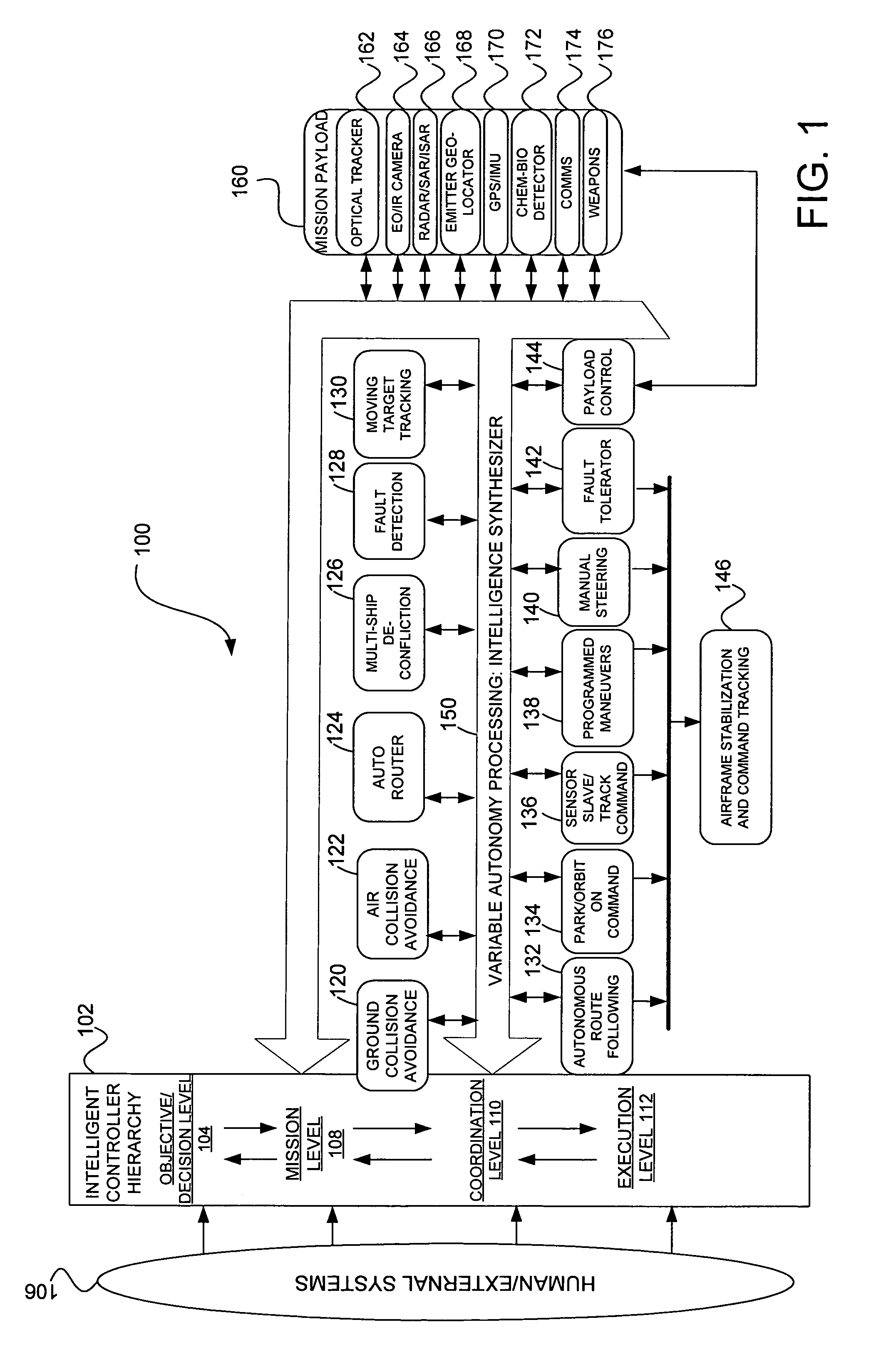
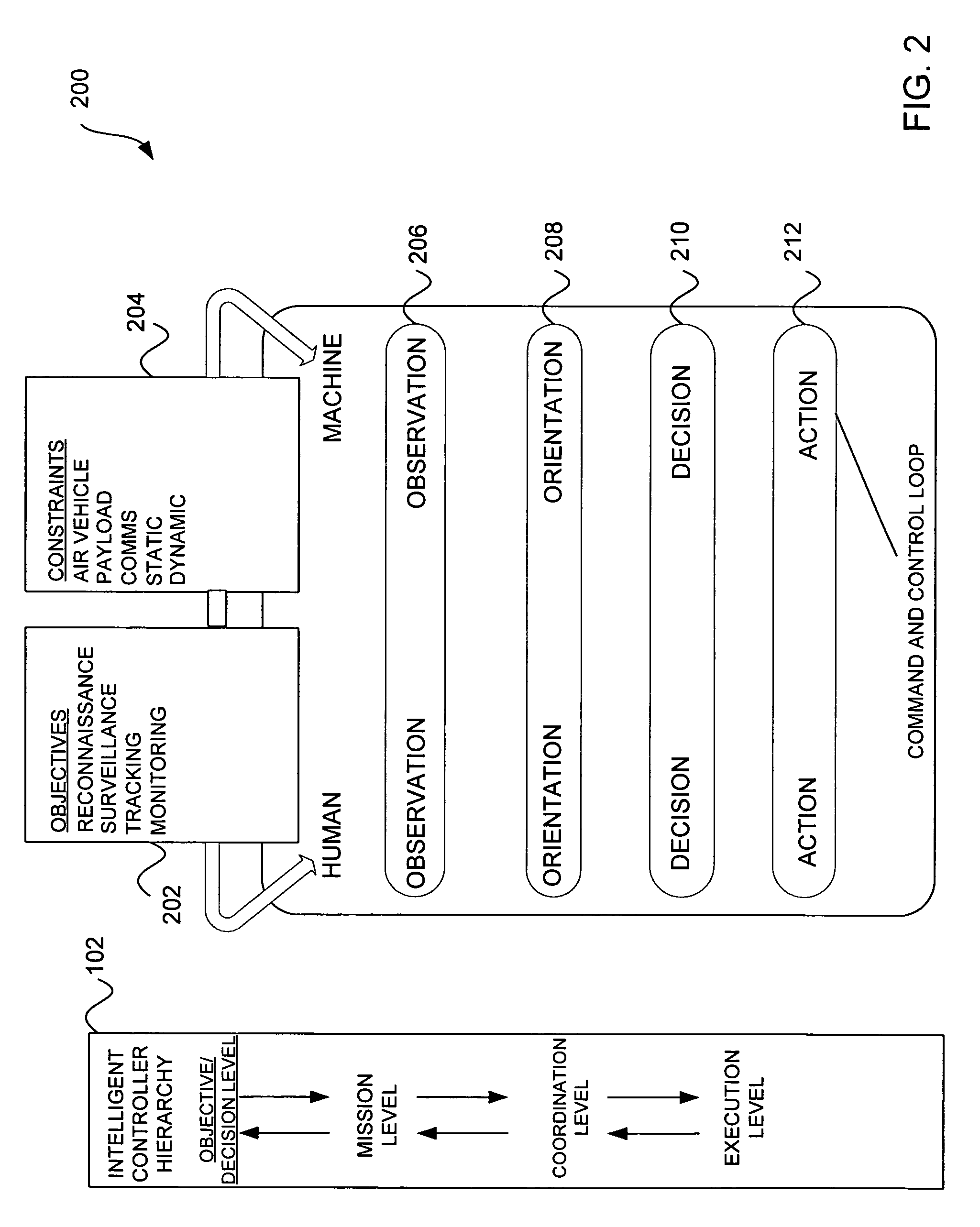
Vehicle control system including related methods and components
ActiveUS7343232B2Conveniently updatedConveniently upgradedAutonomous decision making processCosmonautic vehiclesControl systemOperation mode
Embodiments are disclosed for a vehicle control system and related sub-components that together provide an operator with a plurality of specific modes of operation, wherein various modes of operation incorporate different levels of autonomous control. Through a control user interface, an operator can move between certain modes of control even after vehicle deployment. Specialized autopilot system components and methods are employed to ensure smooth transitions between control modes. Empowered by the multi-modal control system, an operator can even manage multiple vehicles simultaneously.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
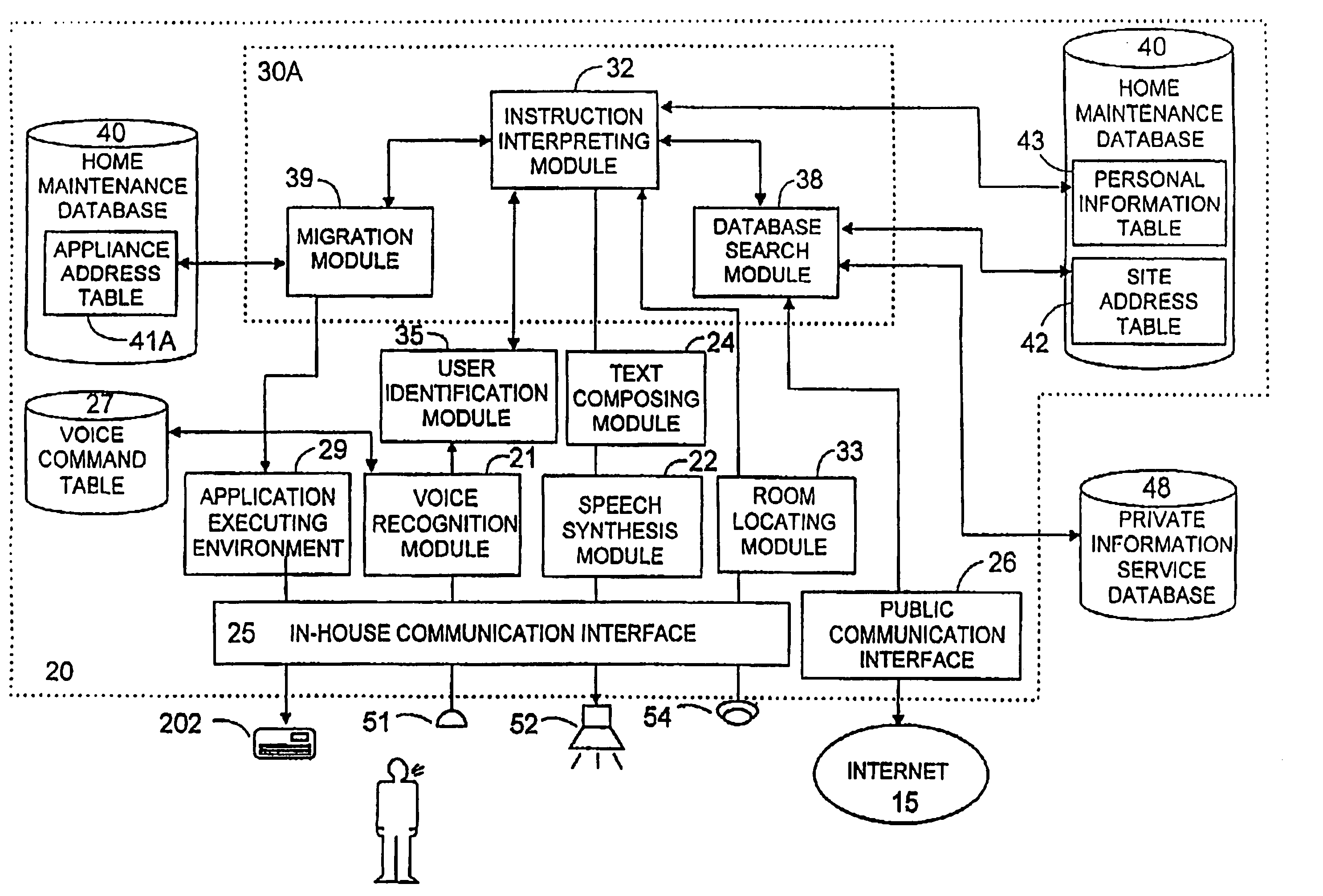
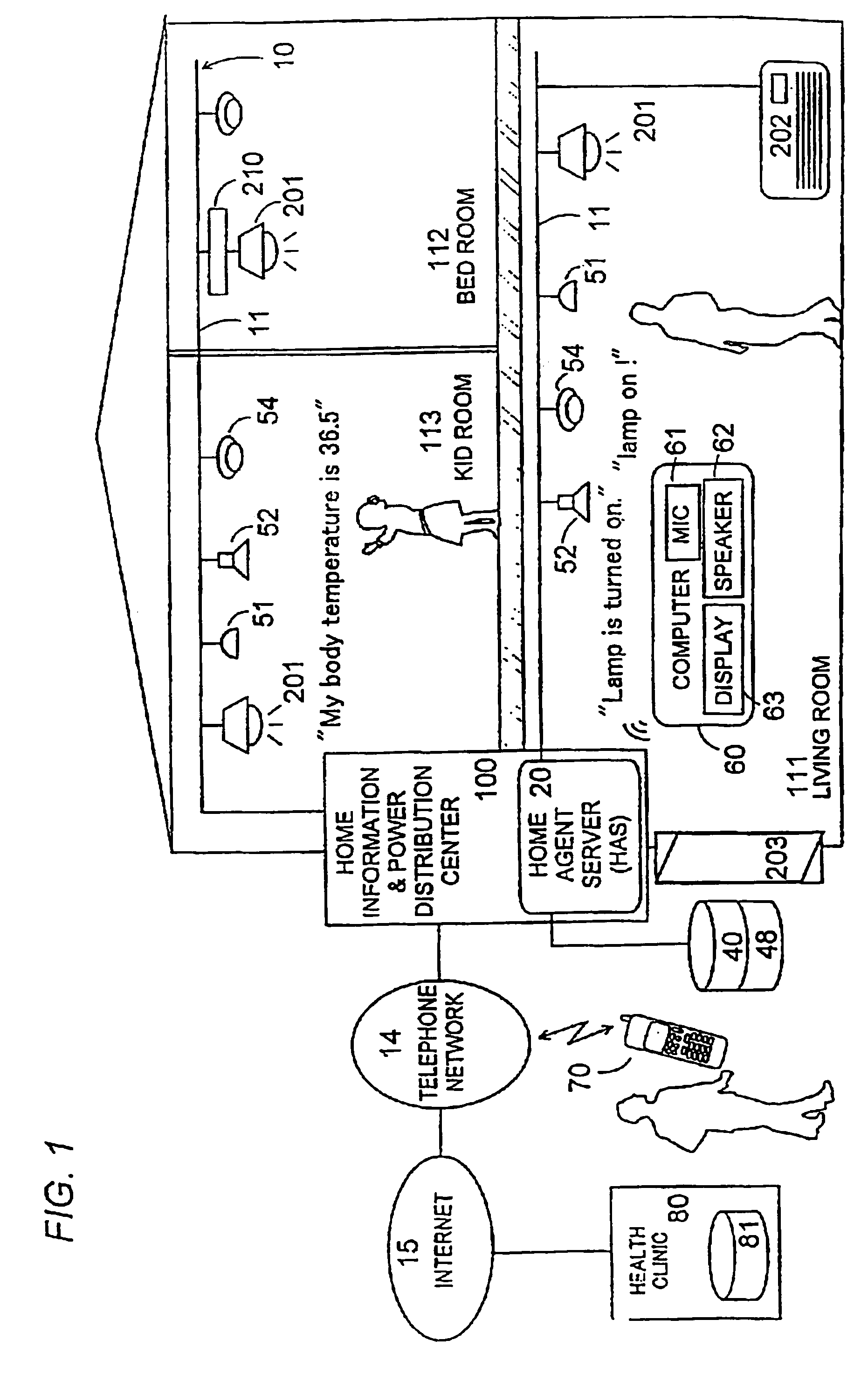
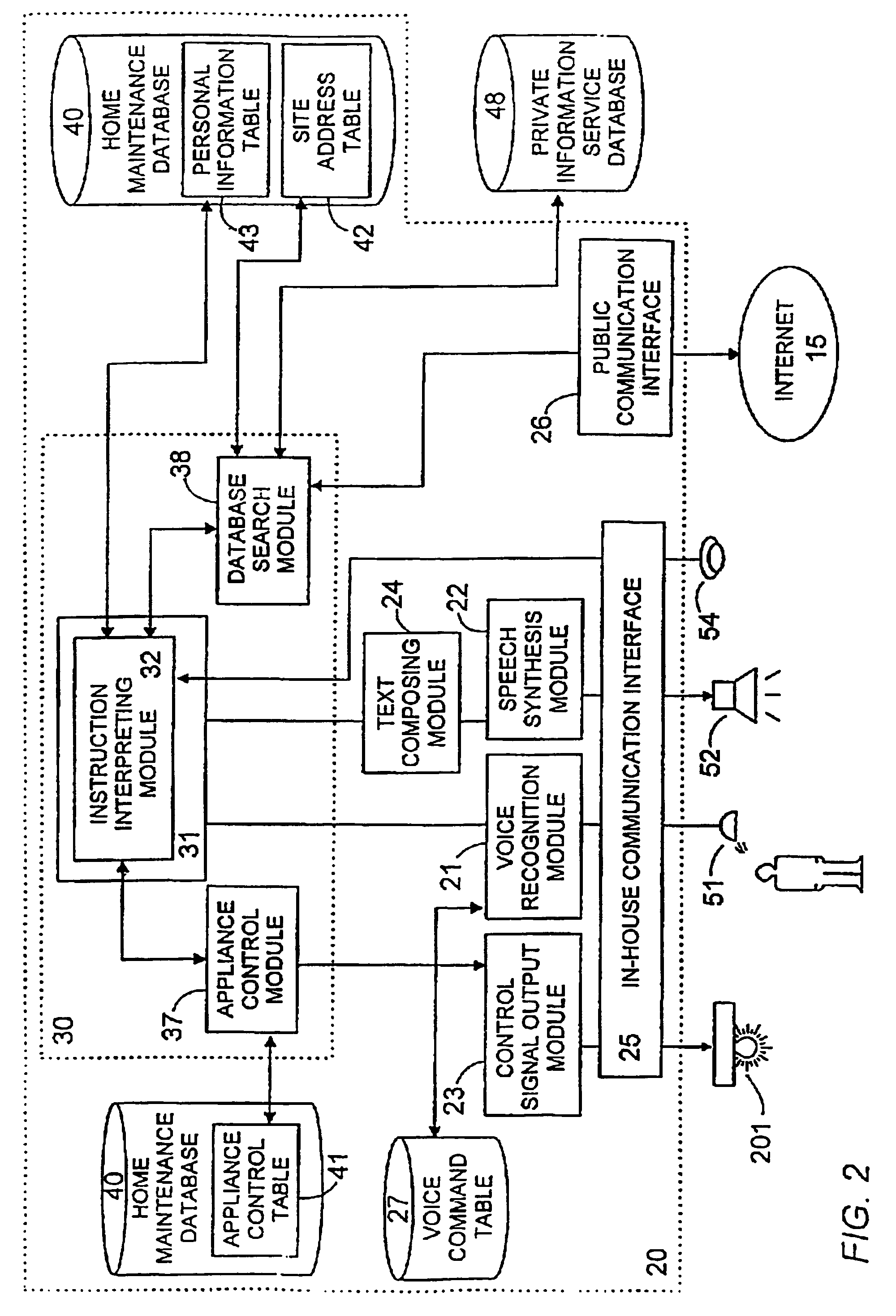
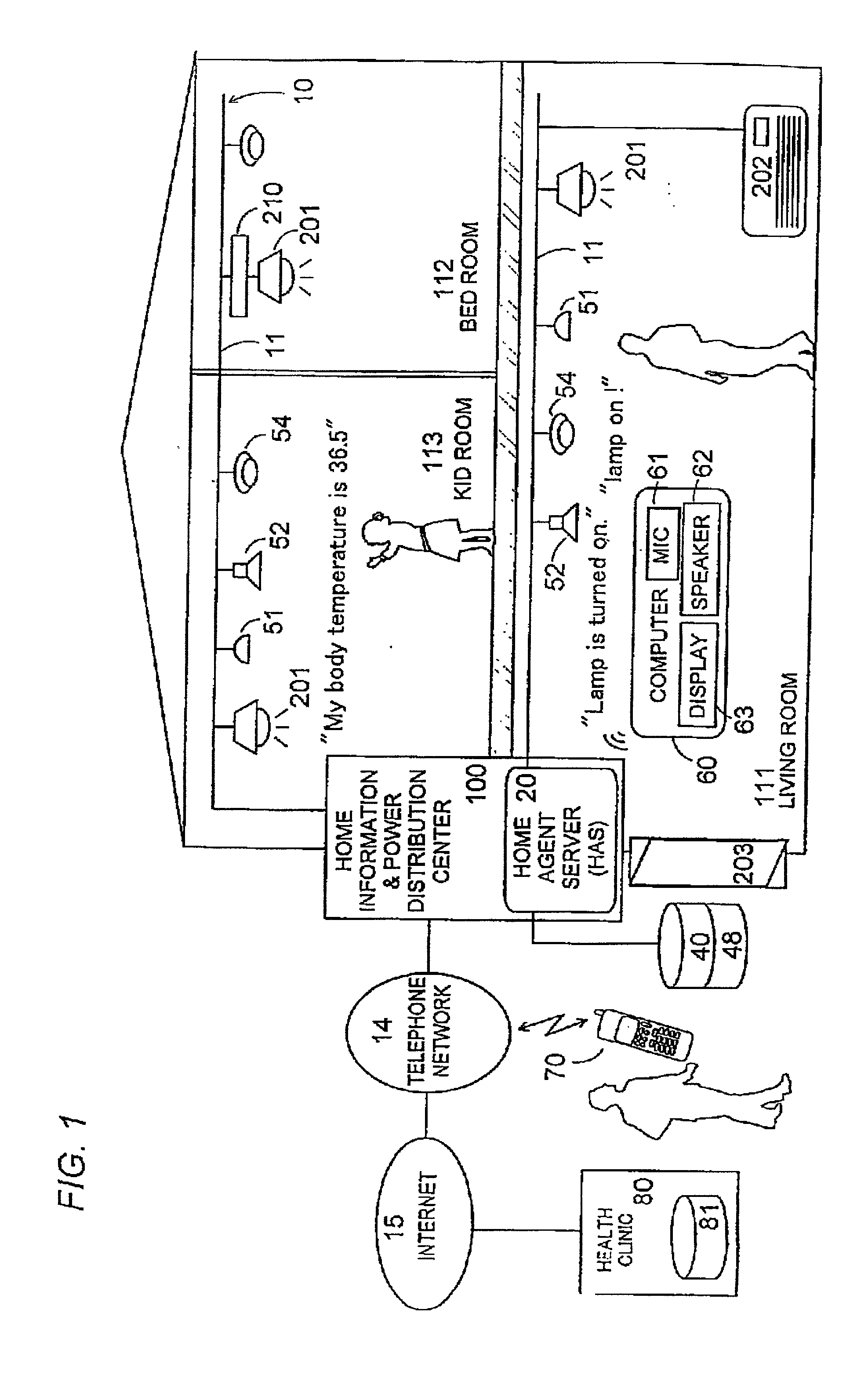
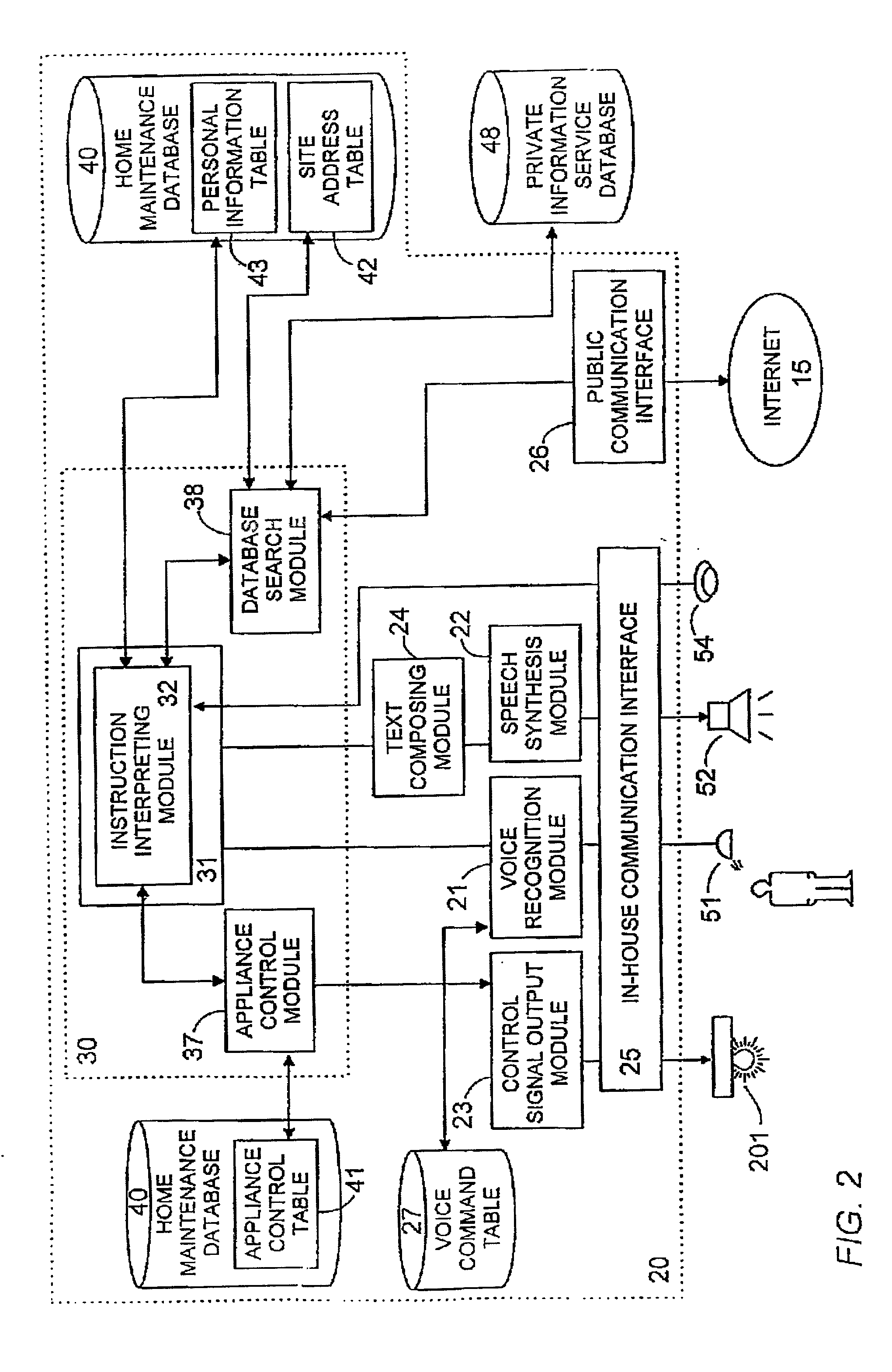
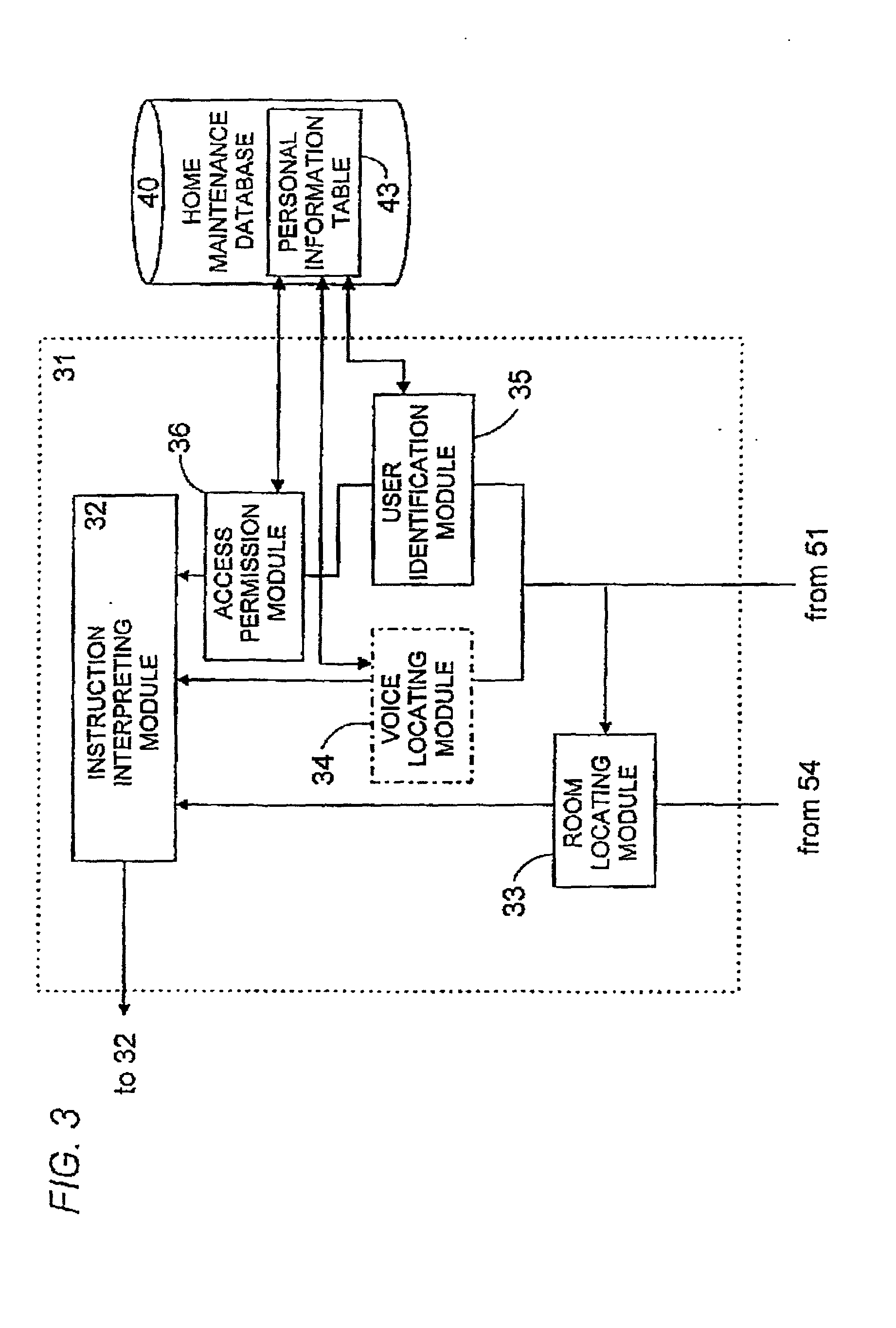
Voice control system for operating home electrical appliances
InactiveUS6988070B2Easy to operateEasy to manageTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsData processing applicationsControl systemControl manner
A voice control system for managing home electrical appliances includes a home agent server (HAS) connected to the home electrical appliances, a microphone and a speaker linked to the agent server through an in-house network. An transaction processing (TP) program runs on HAS and interprets the user's voice request to find a destined appliance and a manner of control the same, and performs the requested control to the destined appliance. The result is notified to the user by means of a voice message.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Voice control system for operating home electrical appliances
InactiveUS20010041982A1Avoid controlSafety managementData processing applicationsTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsControl mannerControl system
A voice control system for managing home electrical appliances includes a home agent server (HAS) connected to the home electrical appliances, a microphone and a speaker linked to the agent server through an in-house network. An transaction processing (TP) program runs on HAS and interprets the user's voice request to find a destined appliance and a manner of control the same, and performs the requested control to the destined appliance. The result is notified to the user by means of a voice message.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
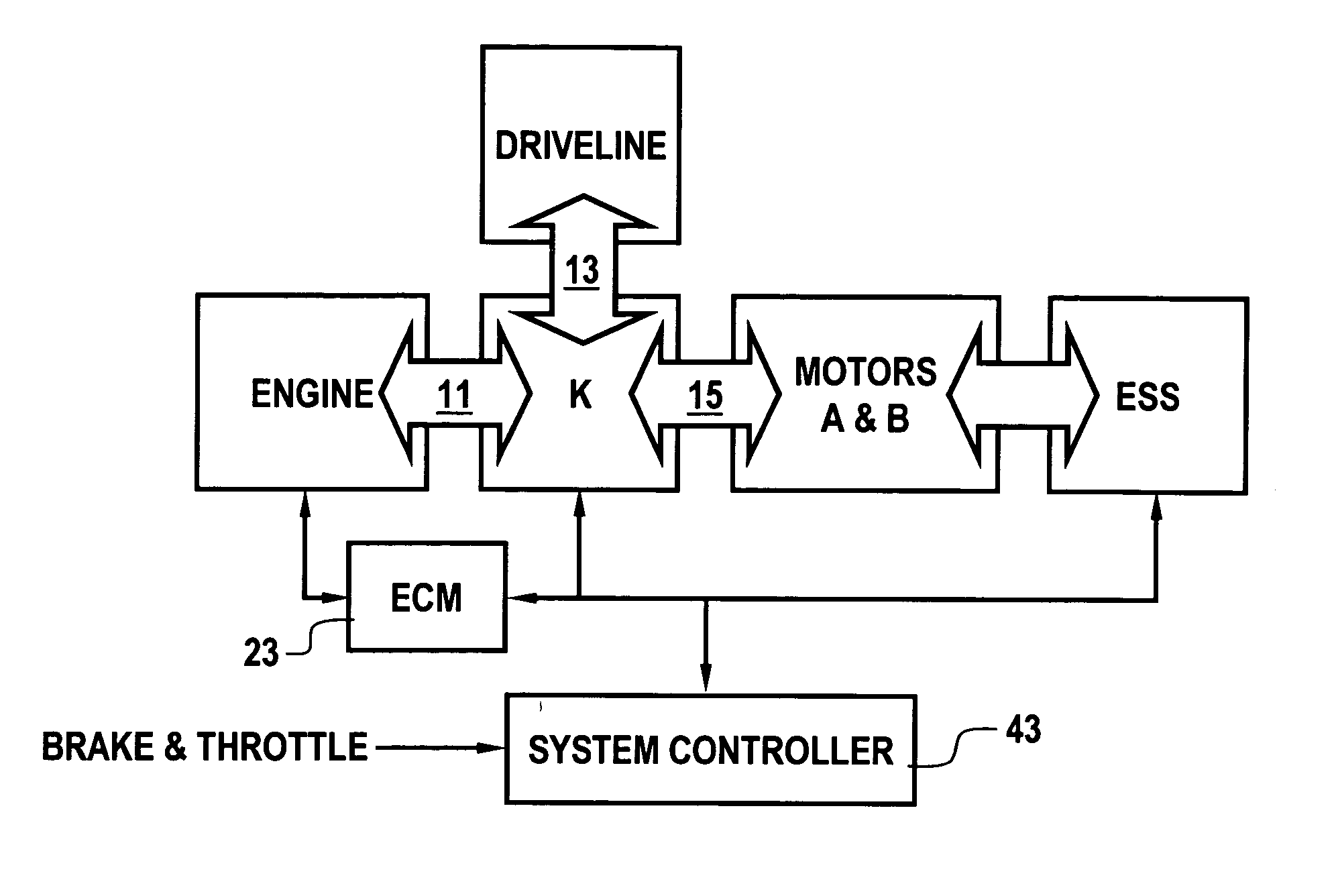
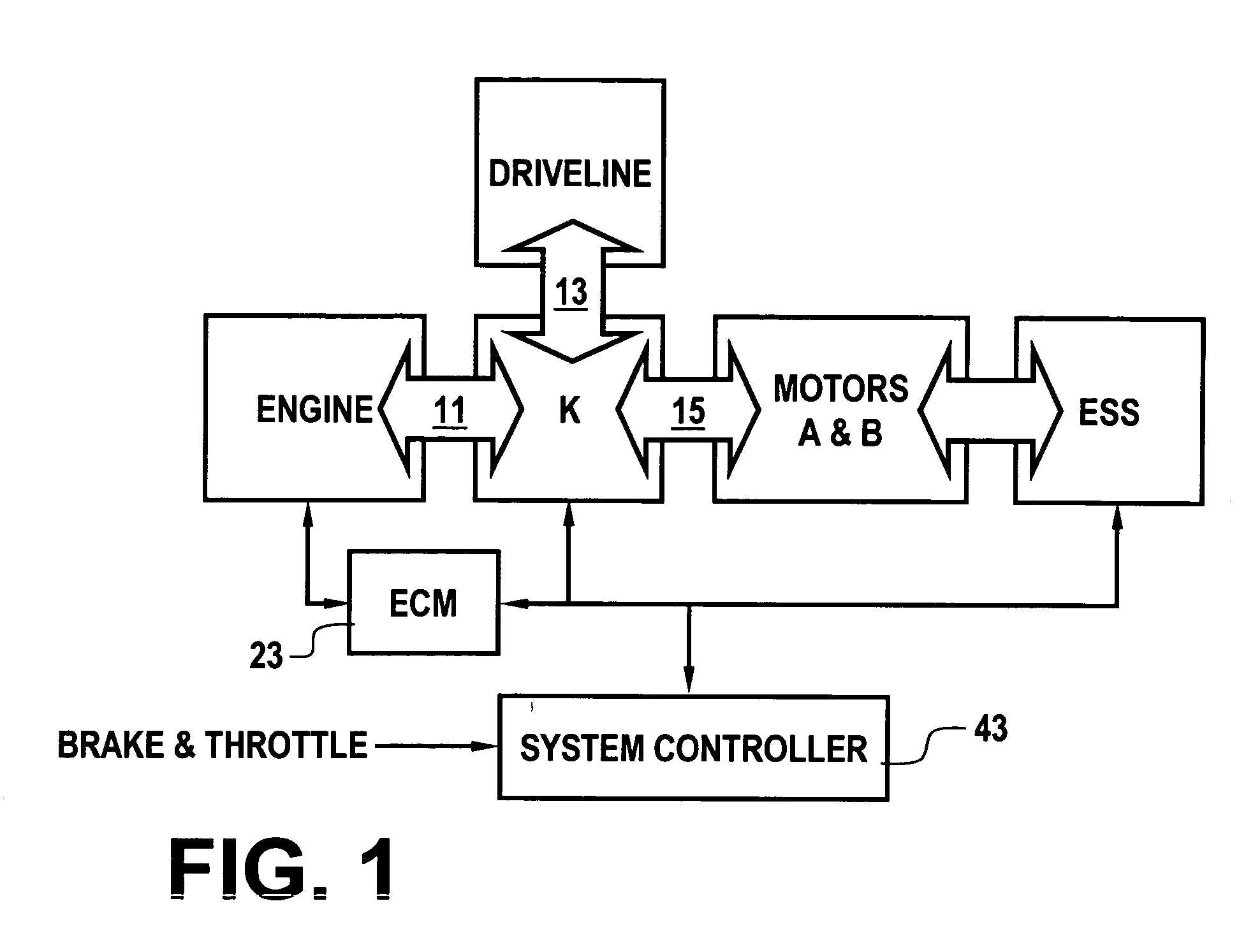
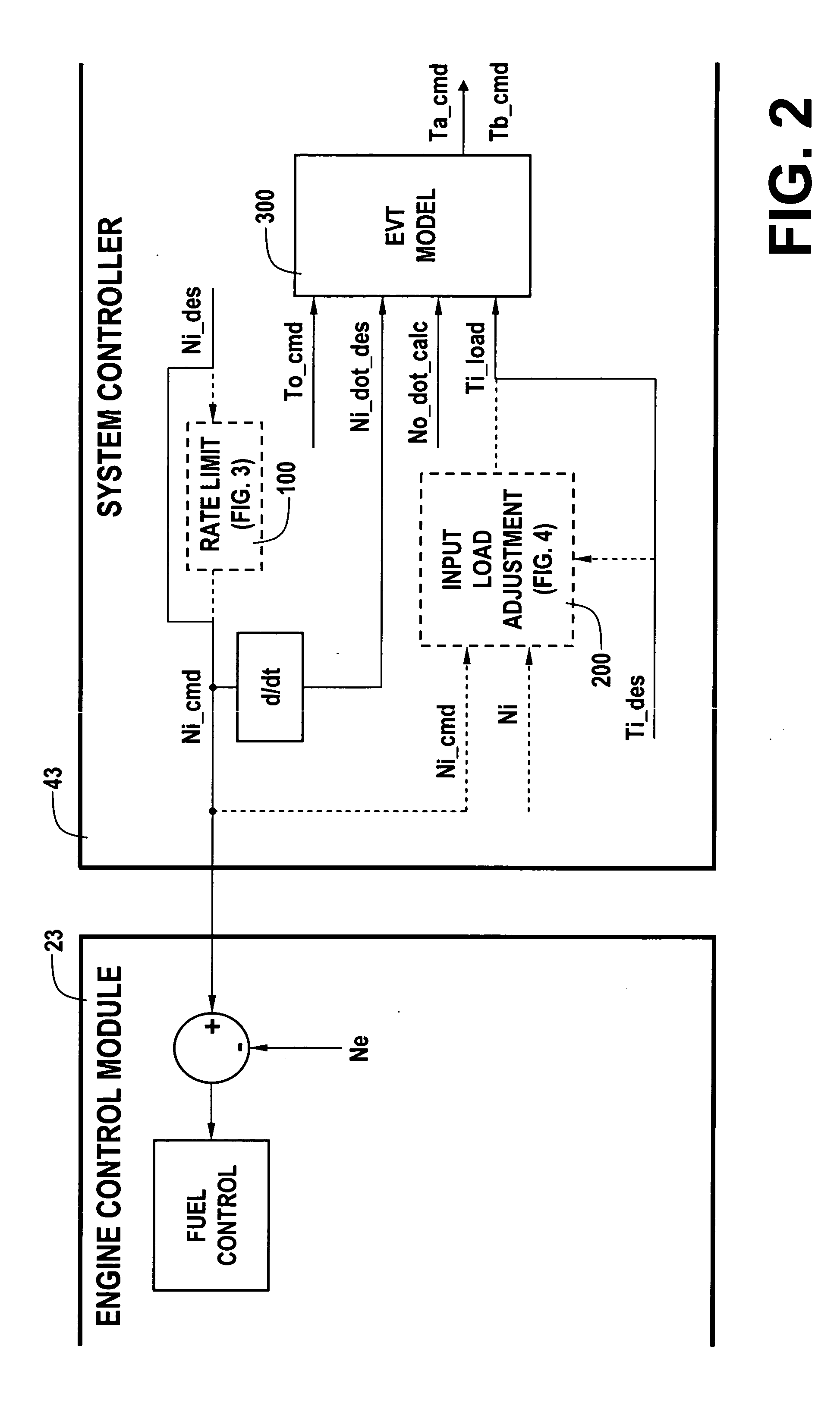
Single motor recovery for an electrically variable transmission
A vehicular powertrain includes operatively coupled engine, electrically variable transmission and driveline. During normal operation when all motors are operating as expected, the engine is operated in a torque control mode in accordance with a torque command provided by a system controller to an engine controller and engine speed is controlled by the motors. During operation when all motors are not operating as expected, the engine is operated in a speed control mode in accordance with a speed command provided by the system controller to the engine controller and engine load torque is controlled by the operative motors.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
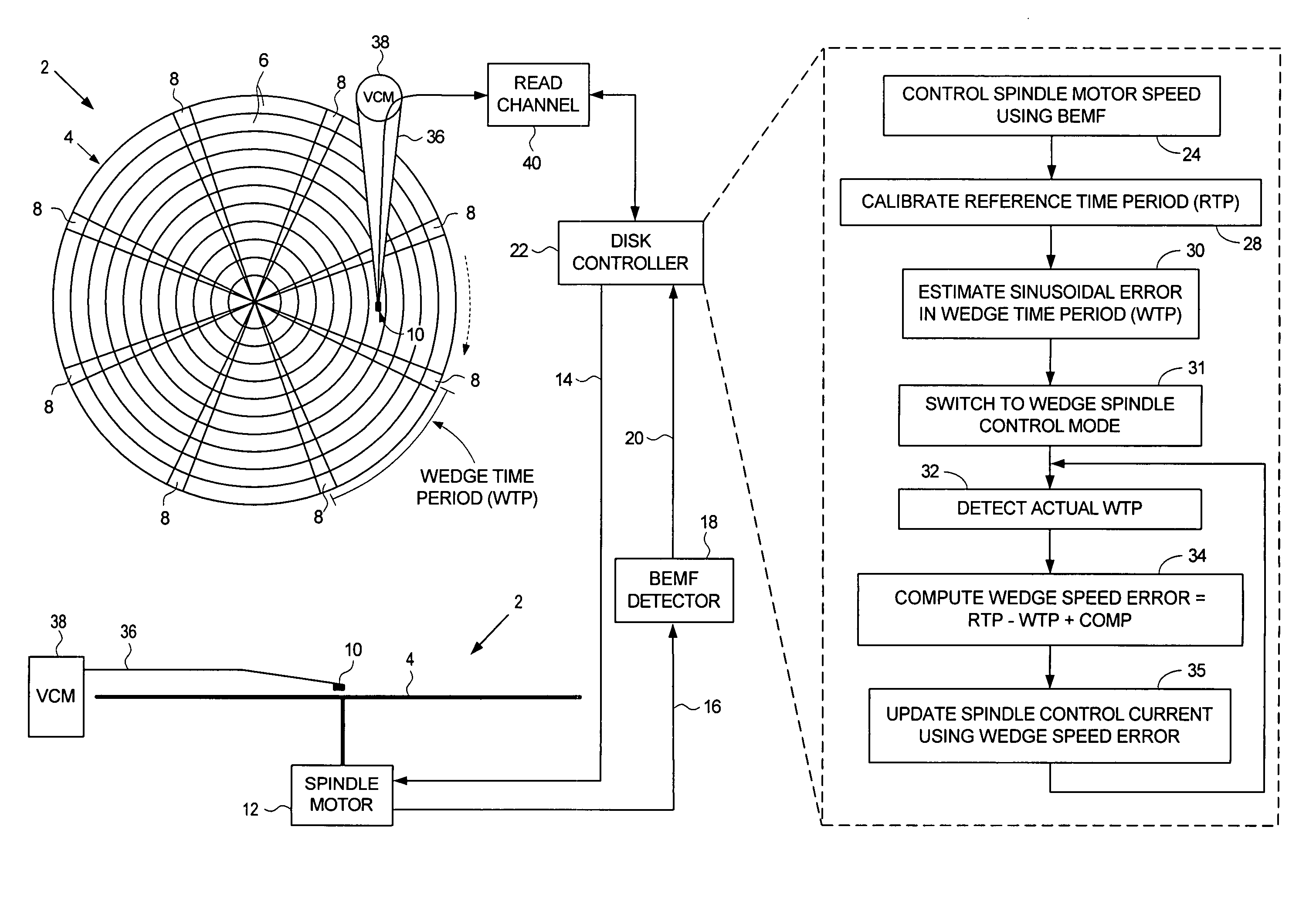
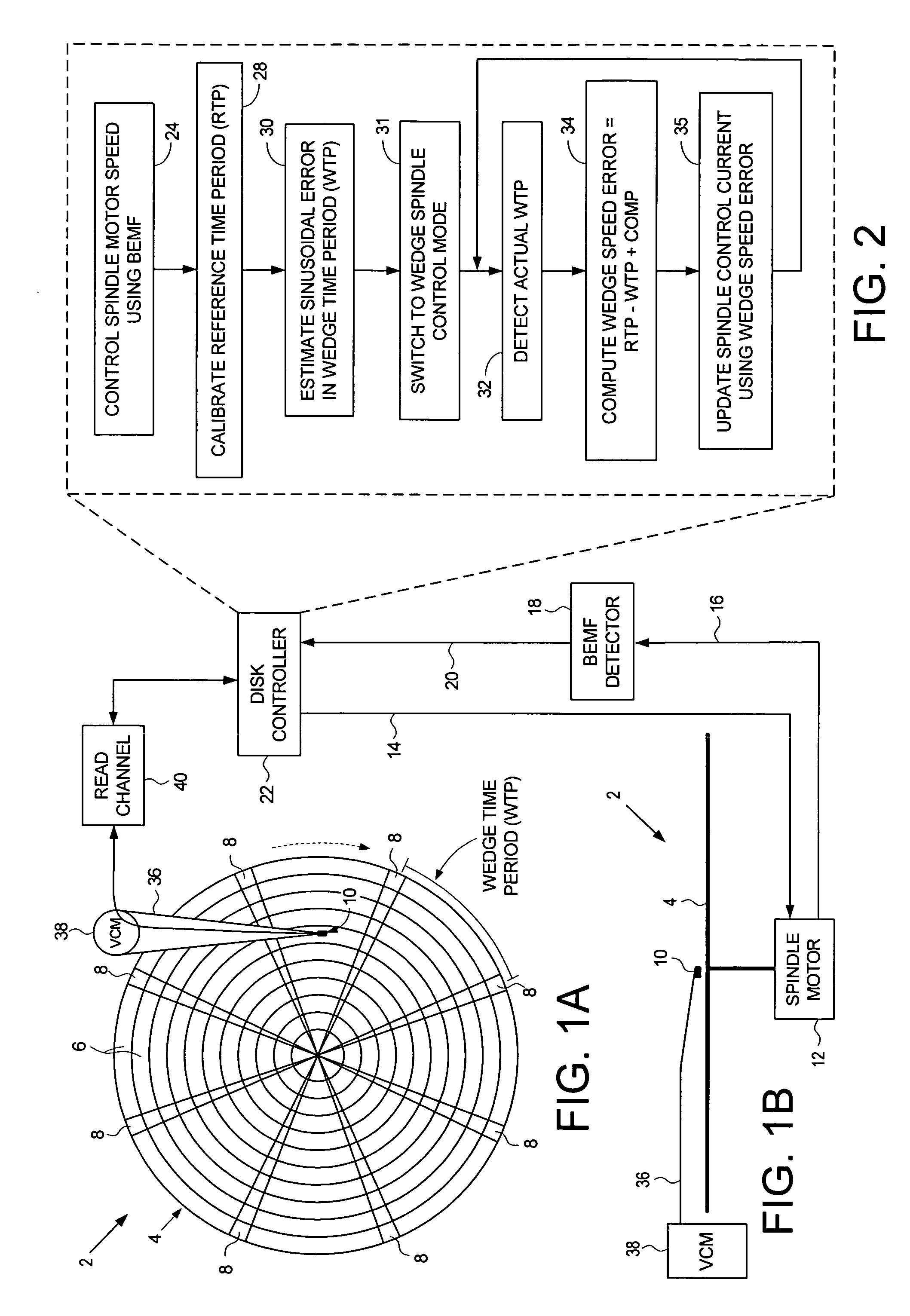
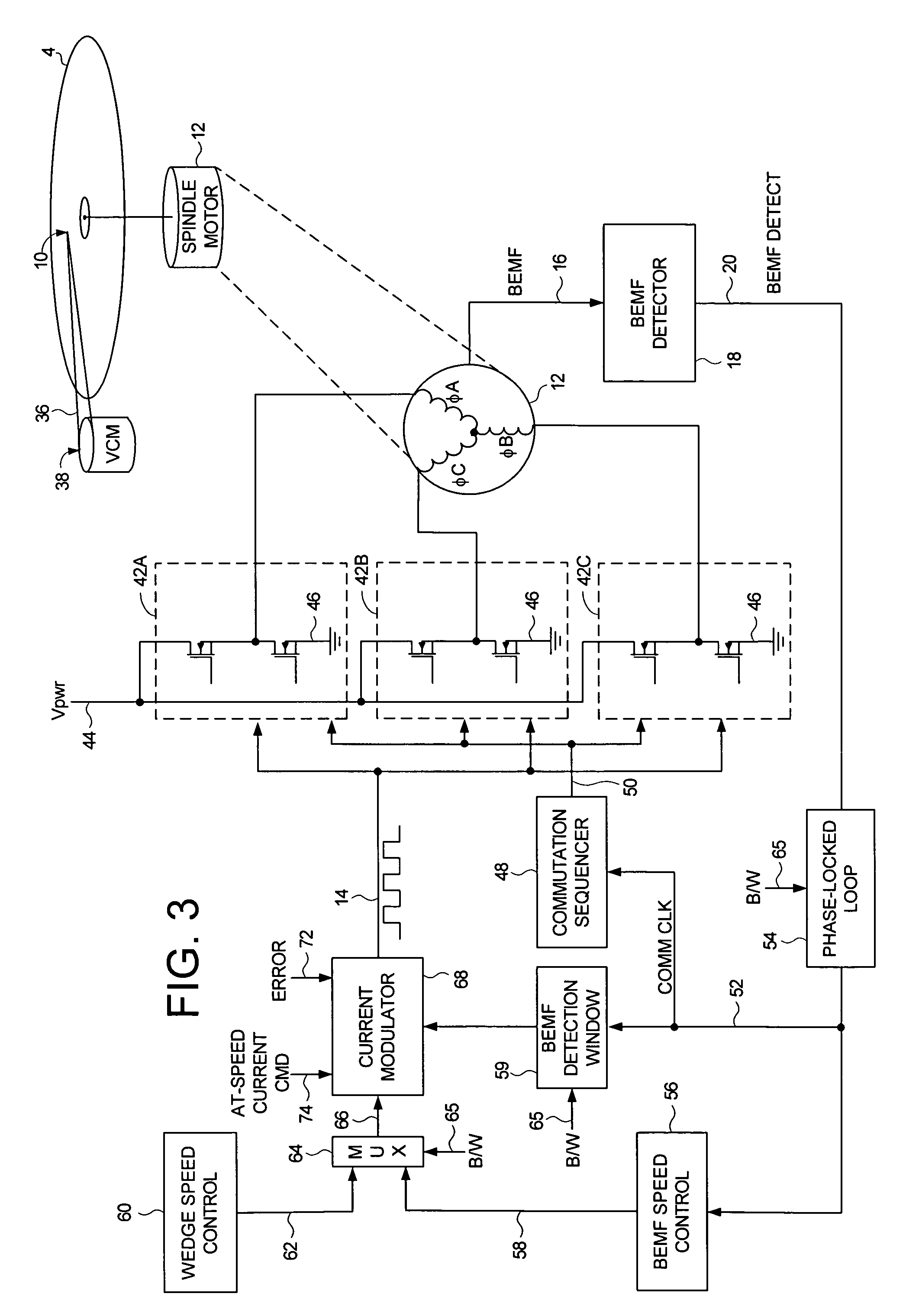
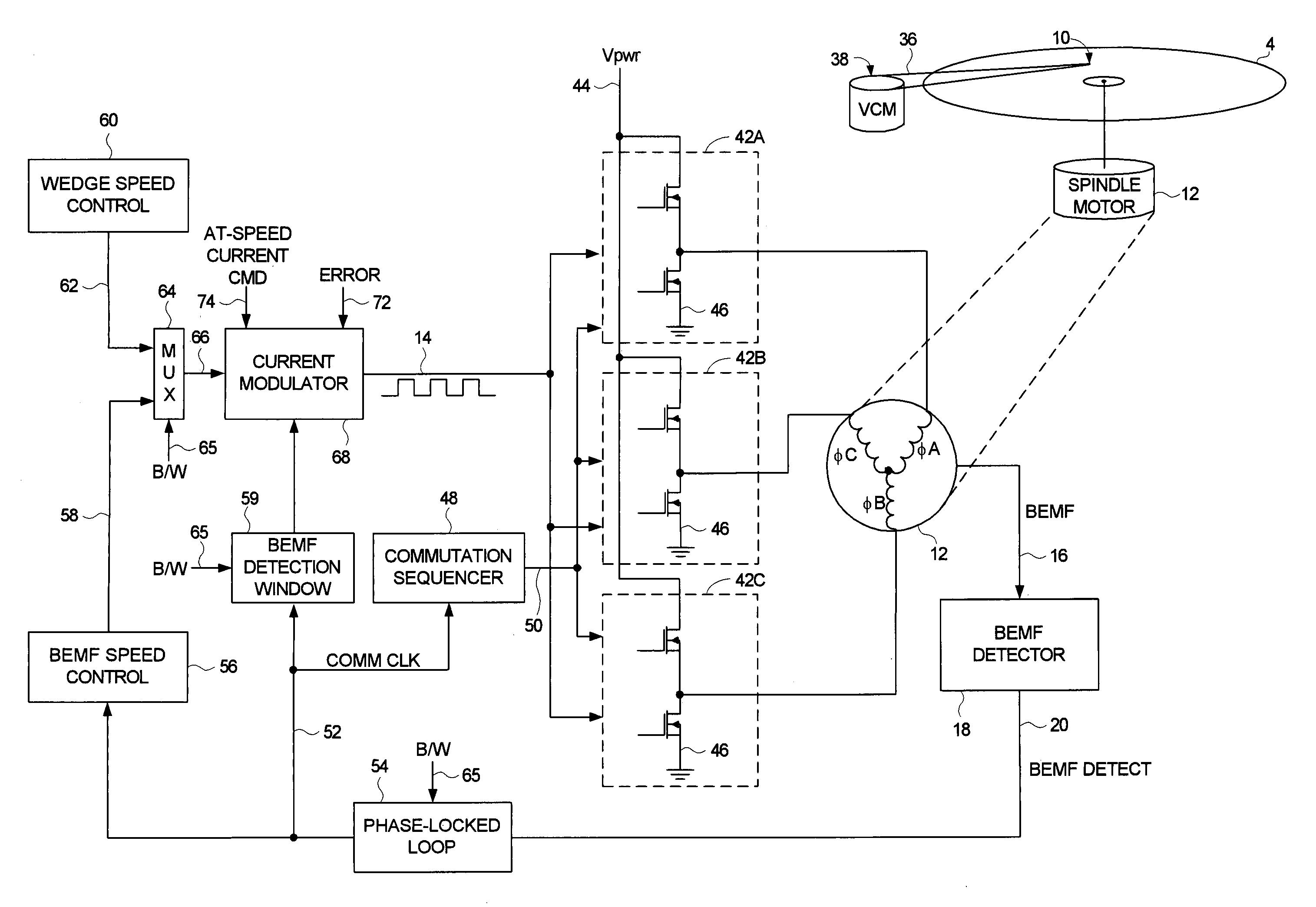
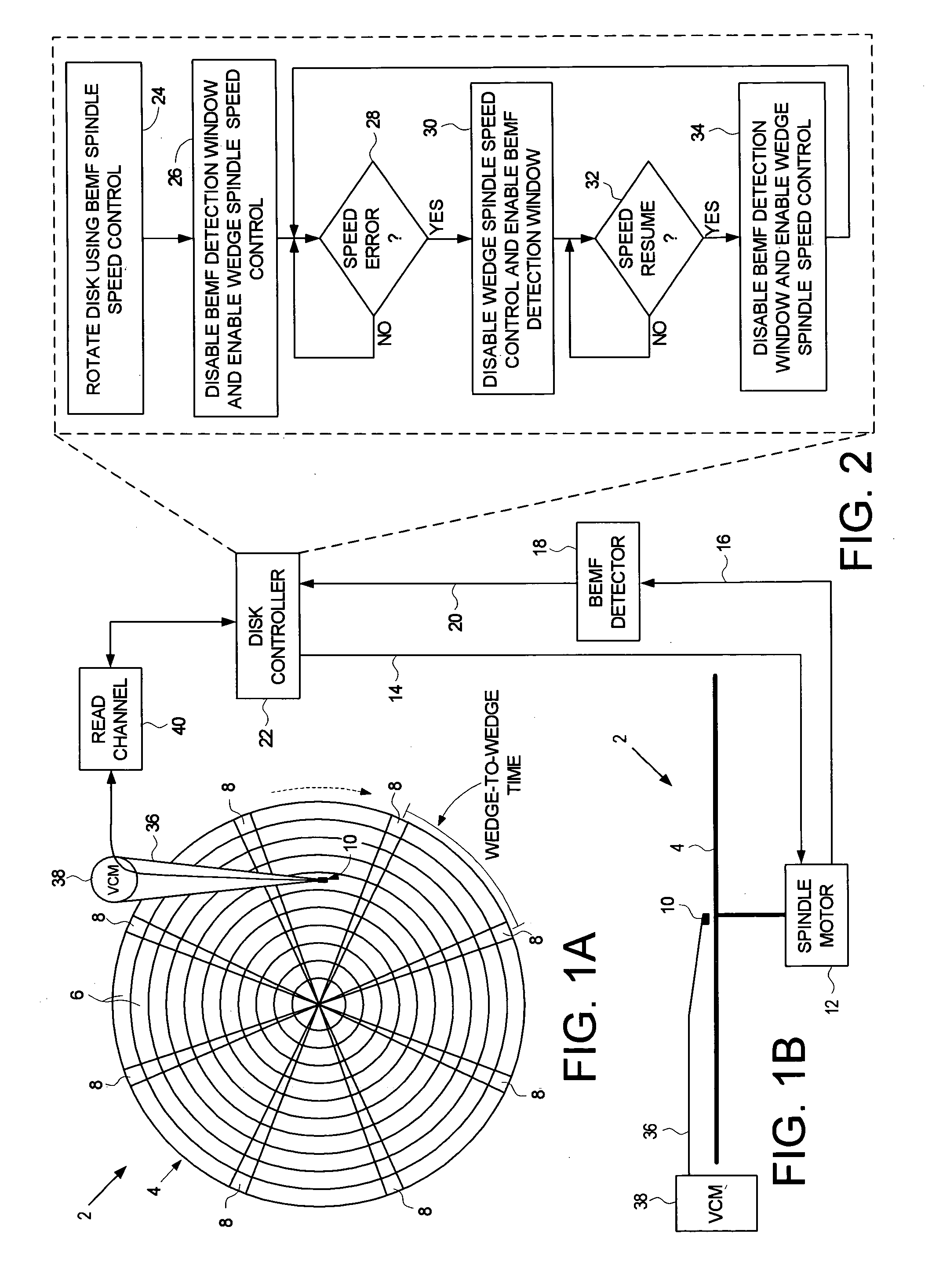
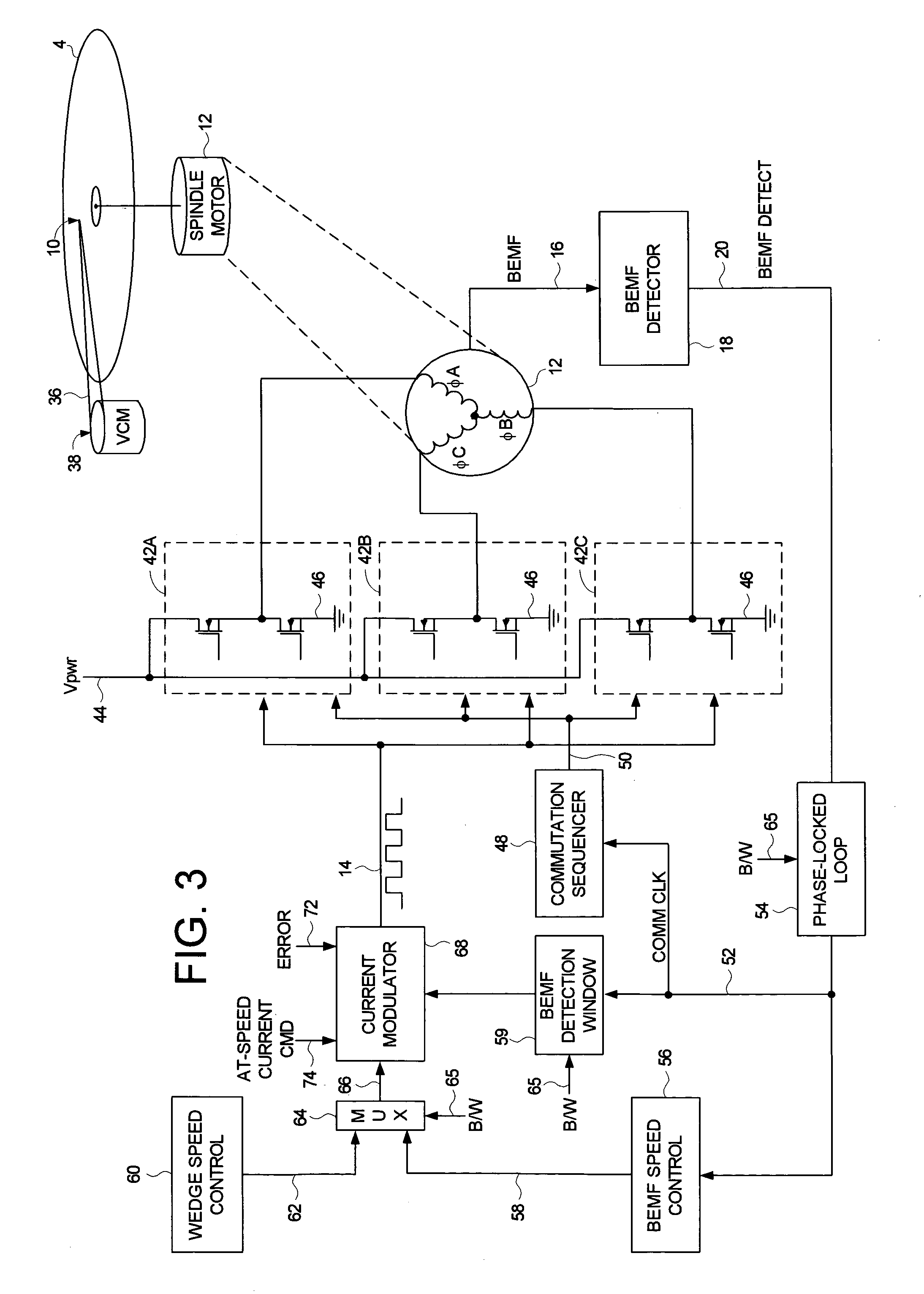
Disk drive employing wedge spindle speed control with eccentricity compensation
A disk drive is disclosed wherein a BEMF speed error is measured during a BEMF spindle speed control mode, and a spindle control current is updated in response to the BEMF speed error to drive the disk at an operating speed. A reference time period (RTP) is calibrated, and a sinusoidal error in a wedge time period (WTP) due to eccentricity in the disk rotating is estimated to generate an eccentricity compensation value. After switching to a wedge spindle speed control mode, an actual WTP is detected and a wedge speed error is generated in response to the RTP, the detected actual WTP, and the eccentricity compensation value. The disk is then maintained at the operating speed by updating the spindle control current in response to the wedge speed error.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Active matrix light emitting device display pixel circuit and drive method
InactiveUS7589707B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingActive matrixDisplay device
Display pixel circuits and a drive scheme utilizing a switching element operating in reverse direction in a data scan period to provide voltage reference are provided. Preferred embodiments and operation method leading to three-transistor solutions in current-control mode, common-cathode, and n-channel transistor drive configuration for light emitting device display are described.
Owner:CHOU CHEN JEAN
Geolocation of a mobile terminal in a CDMA communication system
InactiveUS6898197B1Small impactEasy to useTime-division multiplexCode division multiplexGeolocationCarrier signal
A cellular radio system in which a base station receiver can receive, on the reverse link, data from a mobile terminal in one of four control modes. In the first mode, the mobile terminal sends an independent user pilot, not synchronized with the base station, on the reverse link and the user data channel is synchronized to this independent user pilot. In the second mode, the mobile terminal slaves its user pilot to the pilot it receives from the base station and the user data channel is synchronized with this slaved user pilot. This second mode allows the user terminal to receive round trip delay information for purposes of geolocation and rapid reacquisition. In the third mode, the mobile terminal slaves its user pilot to the incoming base station pilot, as in the case of mode two, but the user data channel operates in the orthogonal mode using the ranging information received from the base station. The phase relationship between the user pilot channel and the user data channel is calibrated. The user pilot carrier is also the carrier for the user data channel and can be used as the carrier reference for detecting the user data channel. In the fourth mode, the slaved pilot implementation of mode three is used for acquisition but, after acquisition, the user pilot code is phase shifted to be synchronous with the user data channel, thus also making it an orthogonal channel. In this mode, the pilots no longer contribute interference to the user data channels, within the cell, and can be transmitted at higher power levels.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
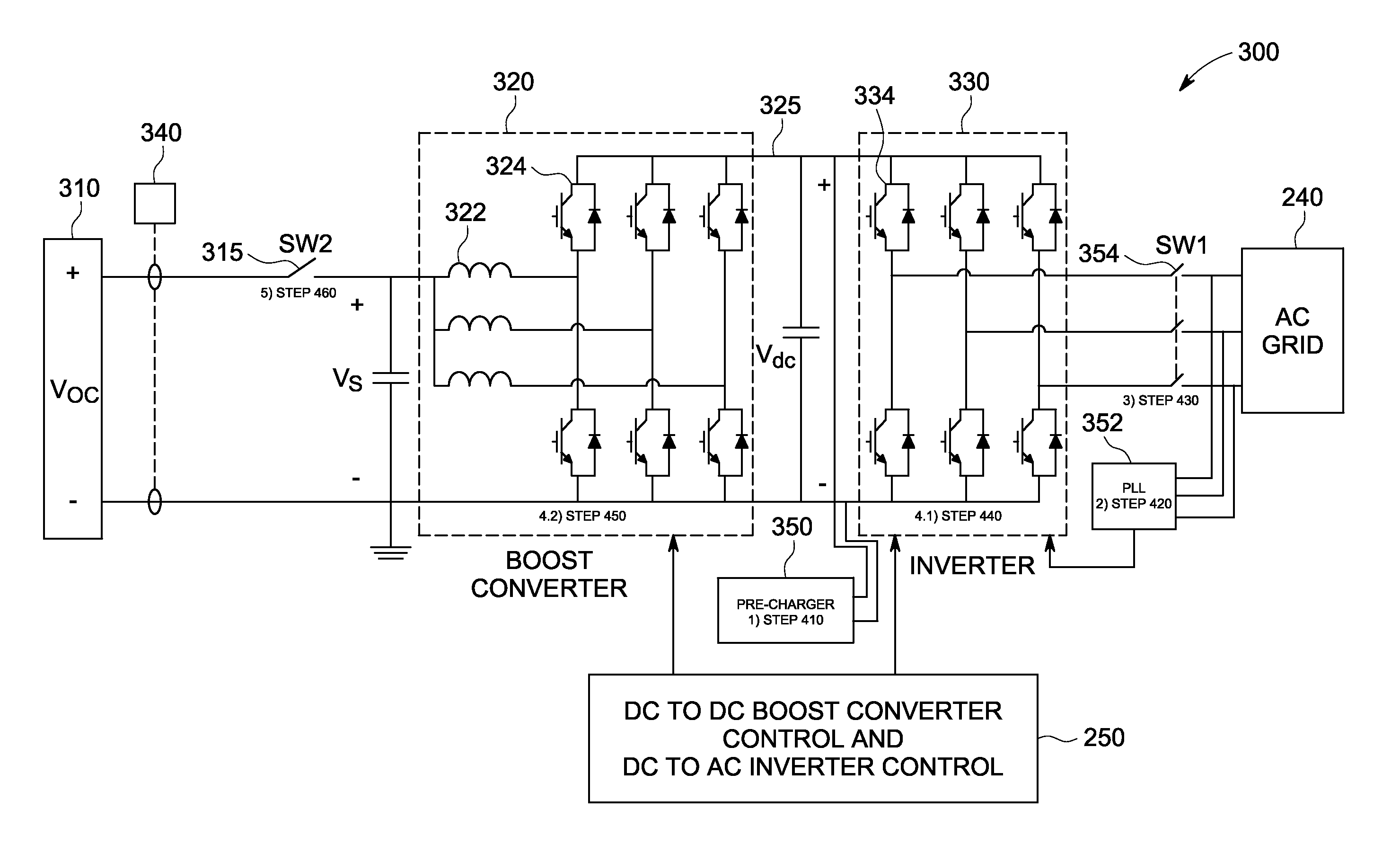
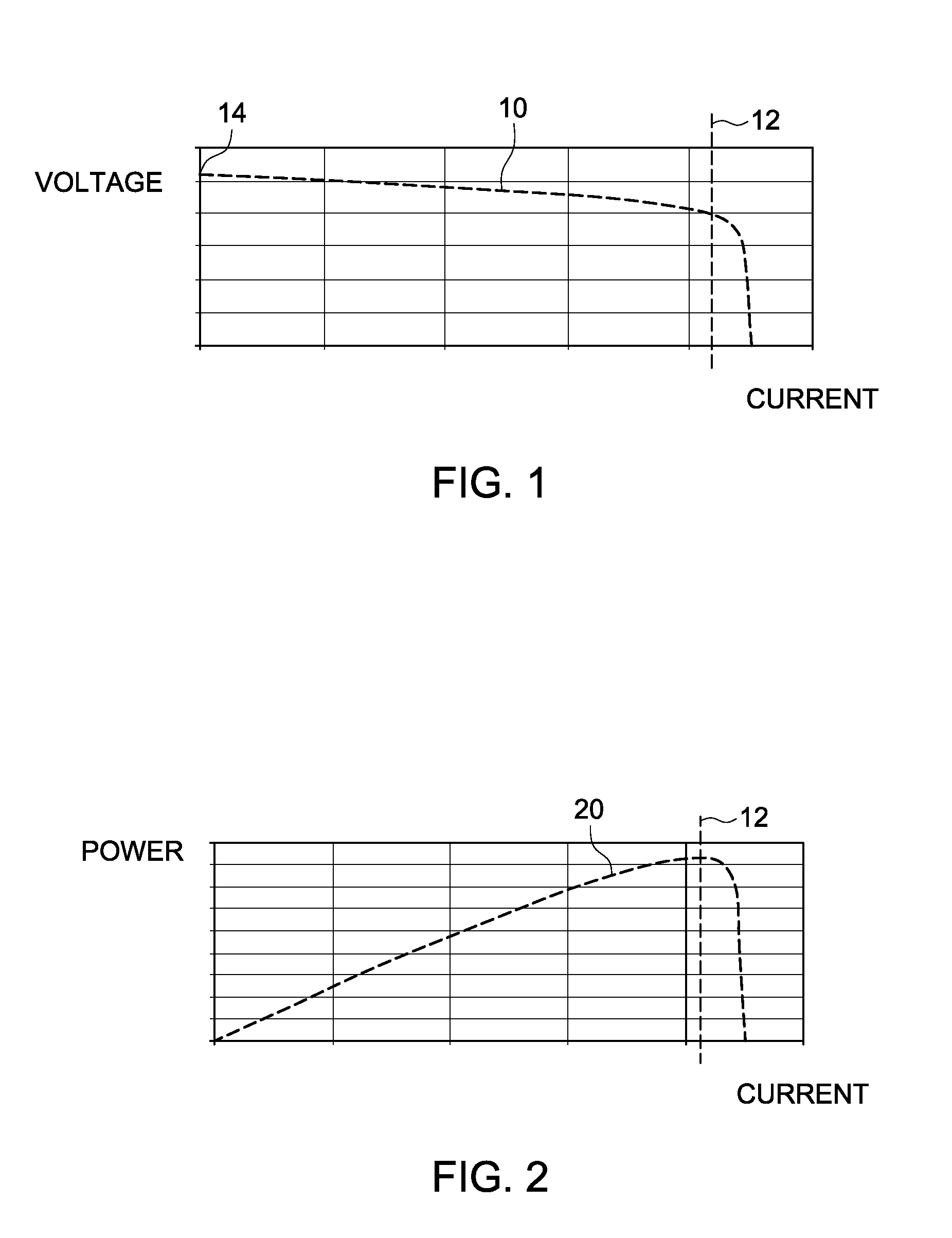
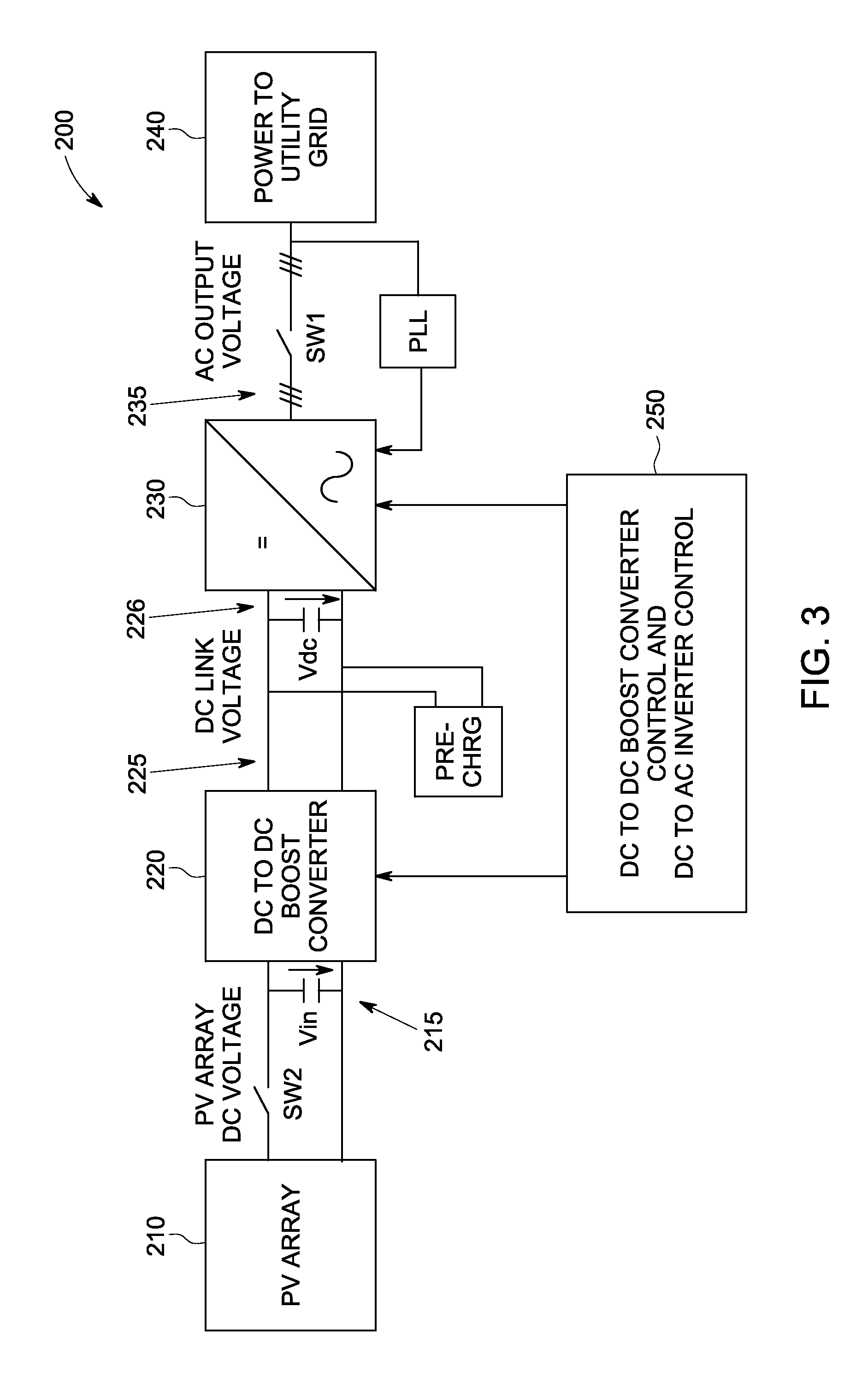
Photovoltaic inverter system and method of starting same at high open-circuit voltage
ActiveUS20120026769A1Dc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPre-chargeEngineering
A power inverter system includes a DC to AC inverter configured to convert DC voltage from a DC power source to AC voltage. A DC link couples the DC power source and the inverter. An inverter pre-charger operates to pre-charge the inverter to achieve a desired DC link voltage prior to connecting the power inverter system to an AC power grid. A phased lock loop synchronizes the pre-charged inverter to the AC power grid prior to connecting the power inverter system to the AC power grid. The pre-charged inverter regulates the DC link voltage to about the minimum voltage level that allows control of AC grid currents via the inverter subsequent to connecting the power inverter system to the AC grid. The inverter operates in a maximum power point tracking control mode only subsequent to a first voltage transient caused by connecting the DC power source to energize the power inverter system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
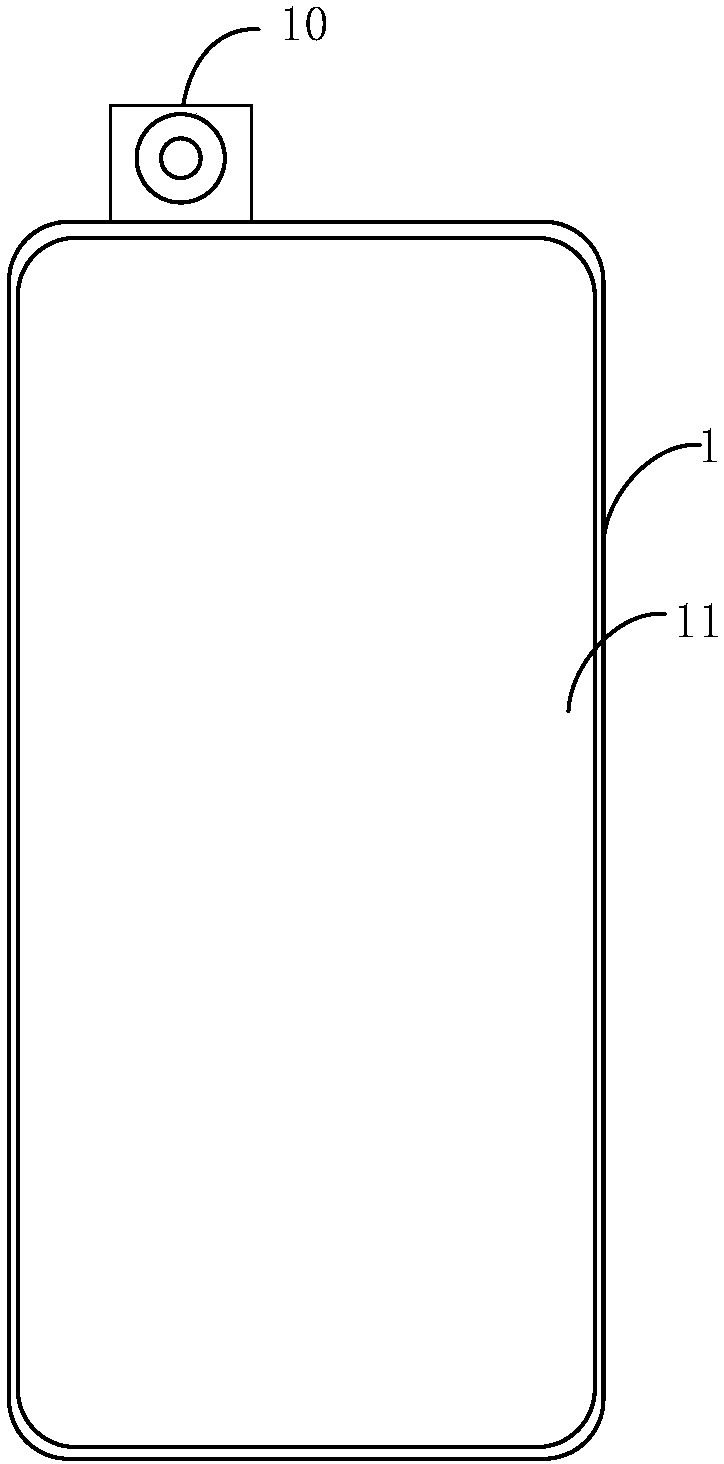
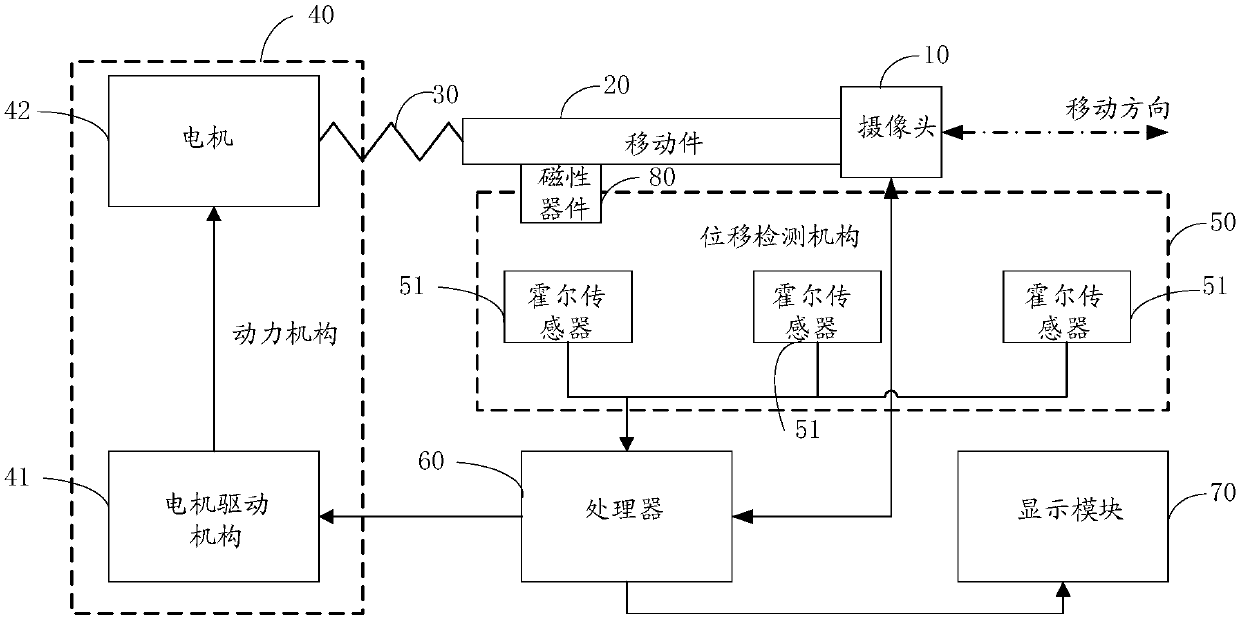
Camera control method and mobile terminal
ActiveCN107819907AControl movementVarious control methodsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsControl modeCamera control
The invention provides a camera control method and a mobile terminal. The method is applied to the mobile terminal, the mobile terminal is provided with an accommodating space for accommodating a retractable camera component, the retractable camera component includes a camera and a motor, and the motor is connected to the camera through an elastic transmission structure for driving the camera to move. The method includes the following steps: if a trigger operation for the camera is detected, identifying the current state of the camera, wherein the trigger operation includes a pressing operation or a stretching operation, and the state of the camera includes a contraction state, an extension state, a contraction process or an extension process; and controlling the movement of the camera according to the trigger operation and the current state of the camera. According to the camera control method provided by the invention, the control modes of the camera of the retractable camera component can be increased.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
Dc-dc converter
InactiveUS20100066328A1Increase currentReduce switching frequencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDc dc converterEngineering
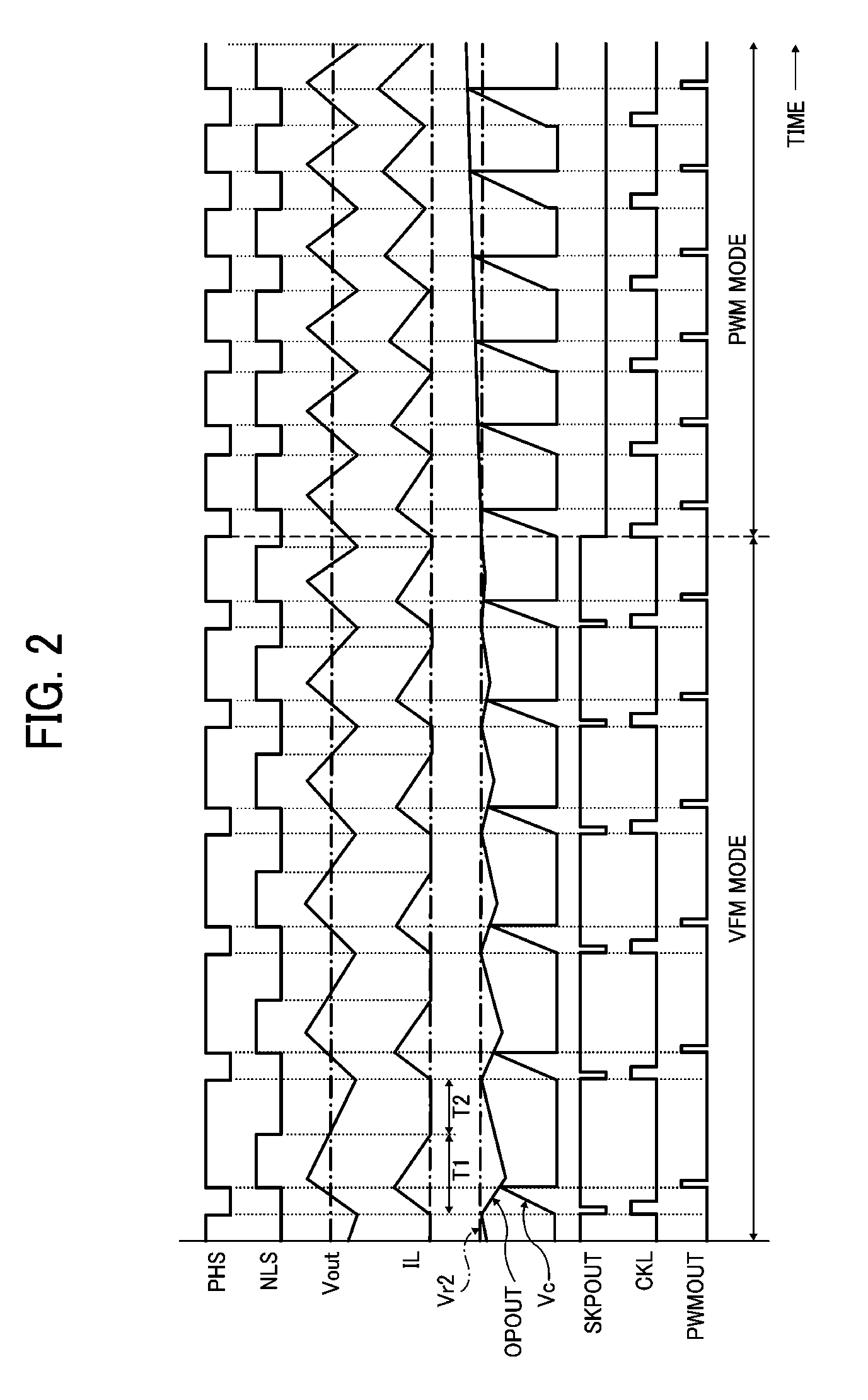
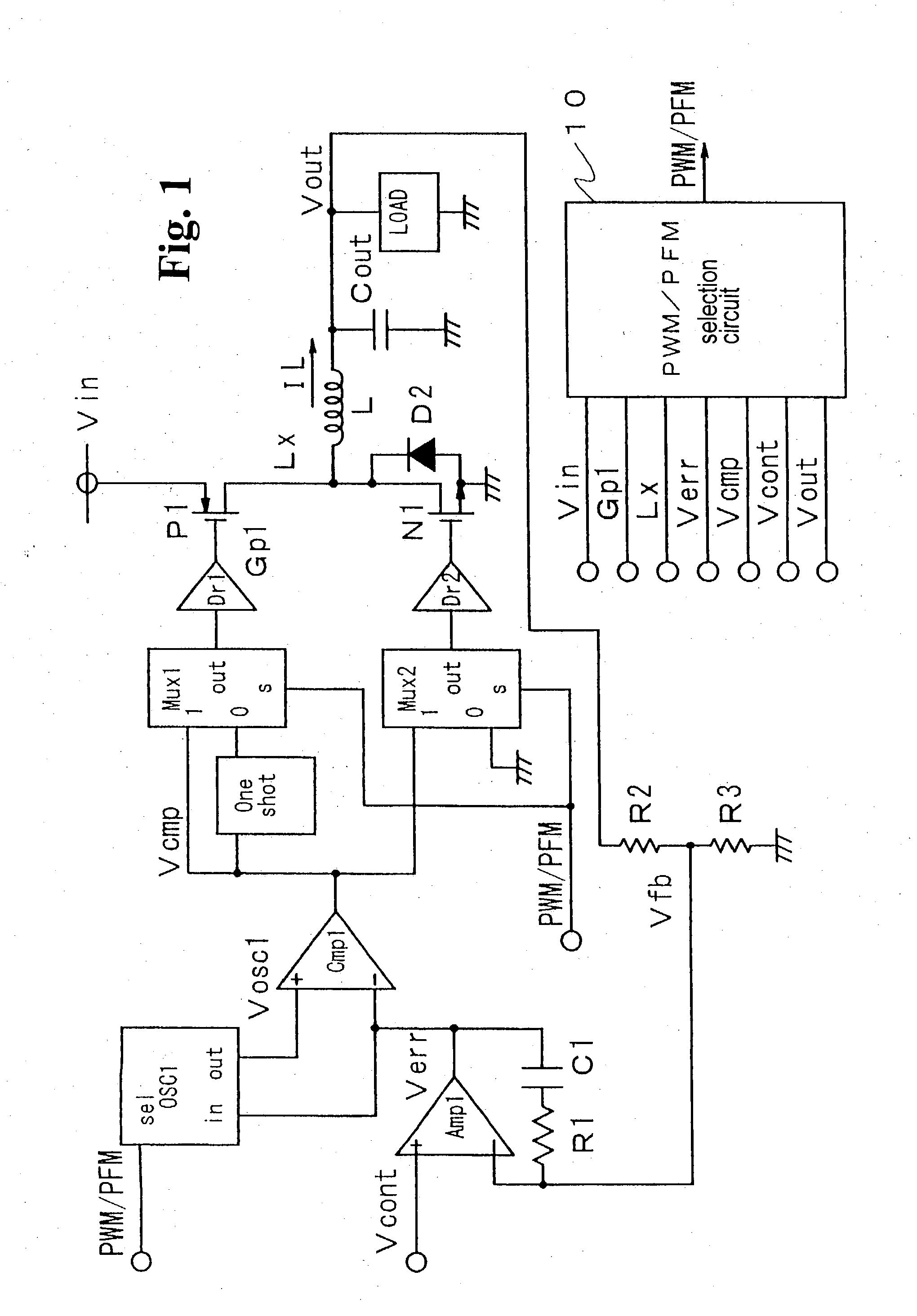
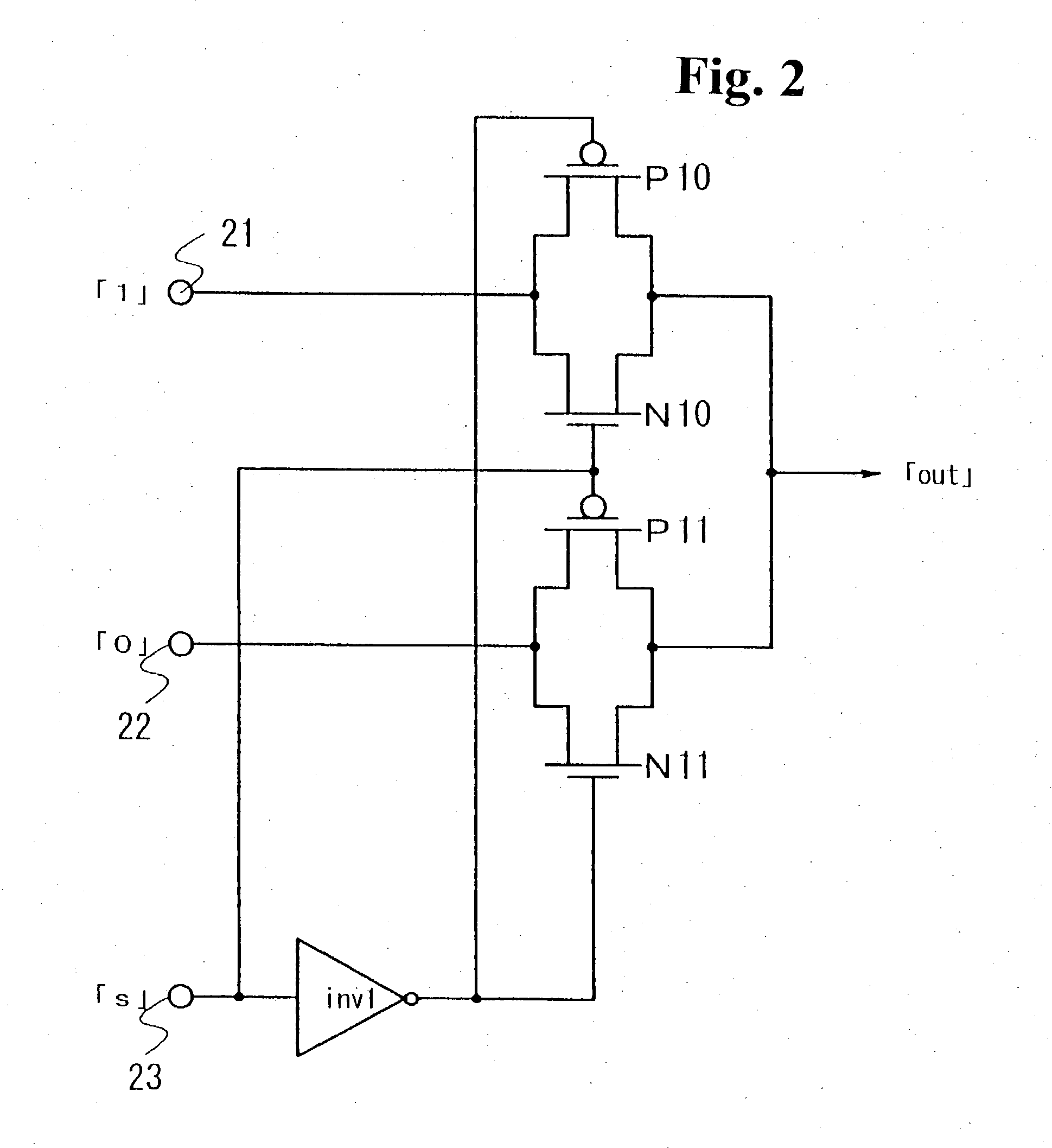
A non-isolated DC-DC converter that converts a voltage input to an input terminal to output a constant output voltage to a load terminal while switching control mode between a PWM mode and a VFM mode depending on a current output to the load terminal. The DC-DC converter includes an inductor, a switching circuit, and a control circuit. The inductor stores electric energy for supply to the load terminal. The switching circuit switches on and off current flow at a switching frequency to alternately charge and discharge the inductor. The control circuit increases an electric current flowing to the load terminal through the inductor per one operational cycle as the switching frequency decreases during VFM control mode operation.
Owner:RICOH ELECTRONIC DEVICES CO LTD
Controlled mode conversion connector for reduced alien crosstalk
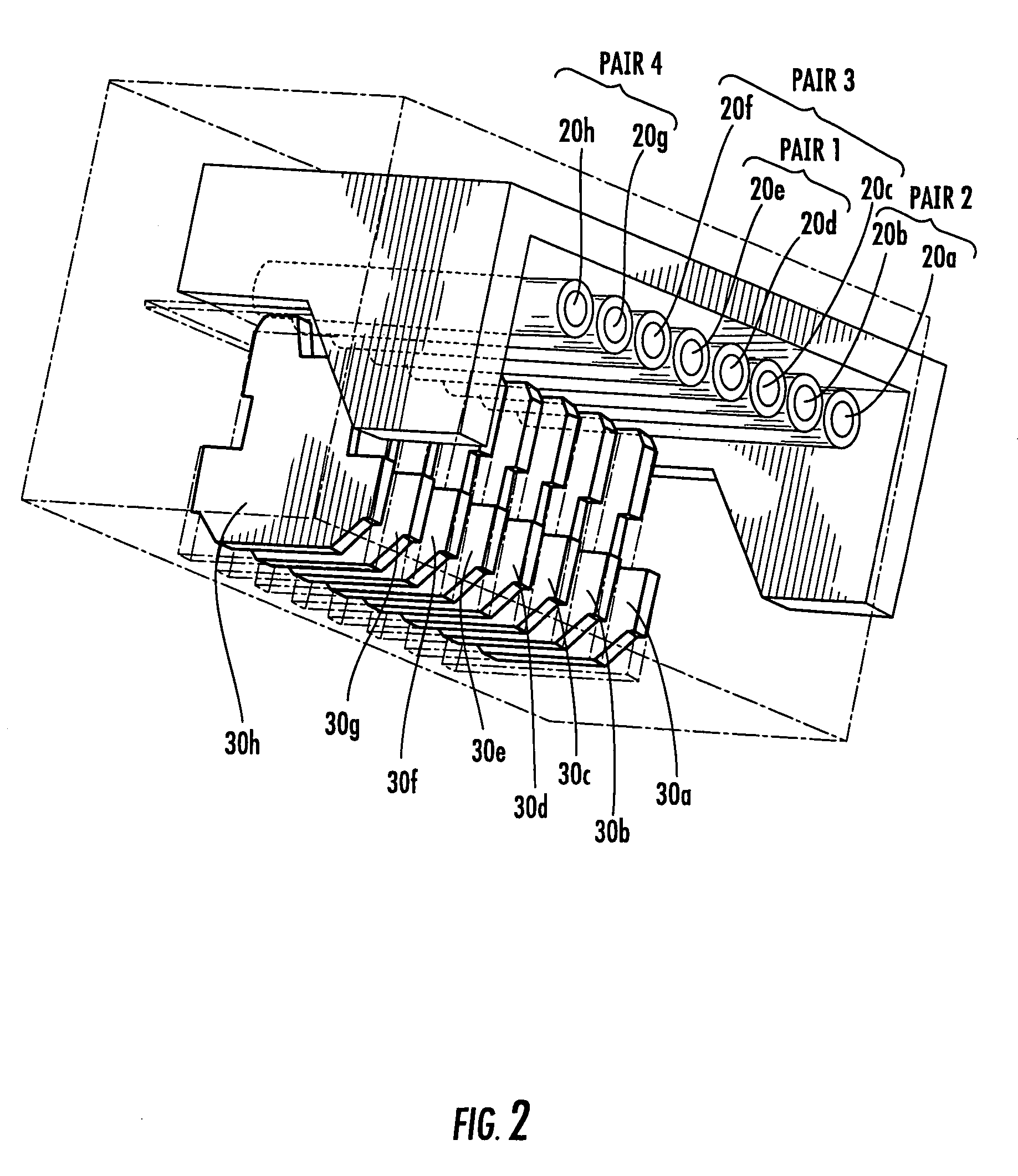
ActiveUS7201618B2Reduce alien crosstalkCoupling device detailsTwo-part coupling devicesElectrical conductorElectrical polarity
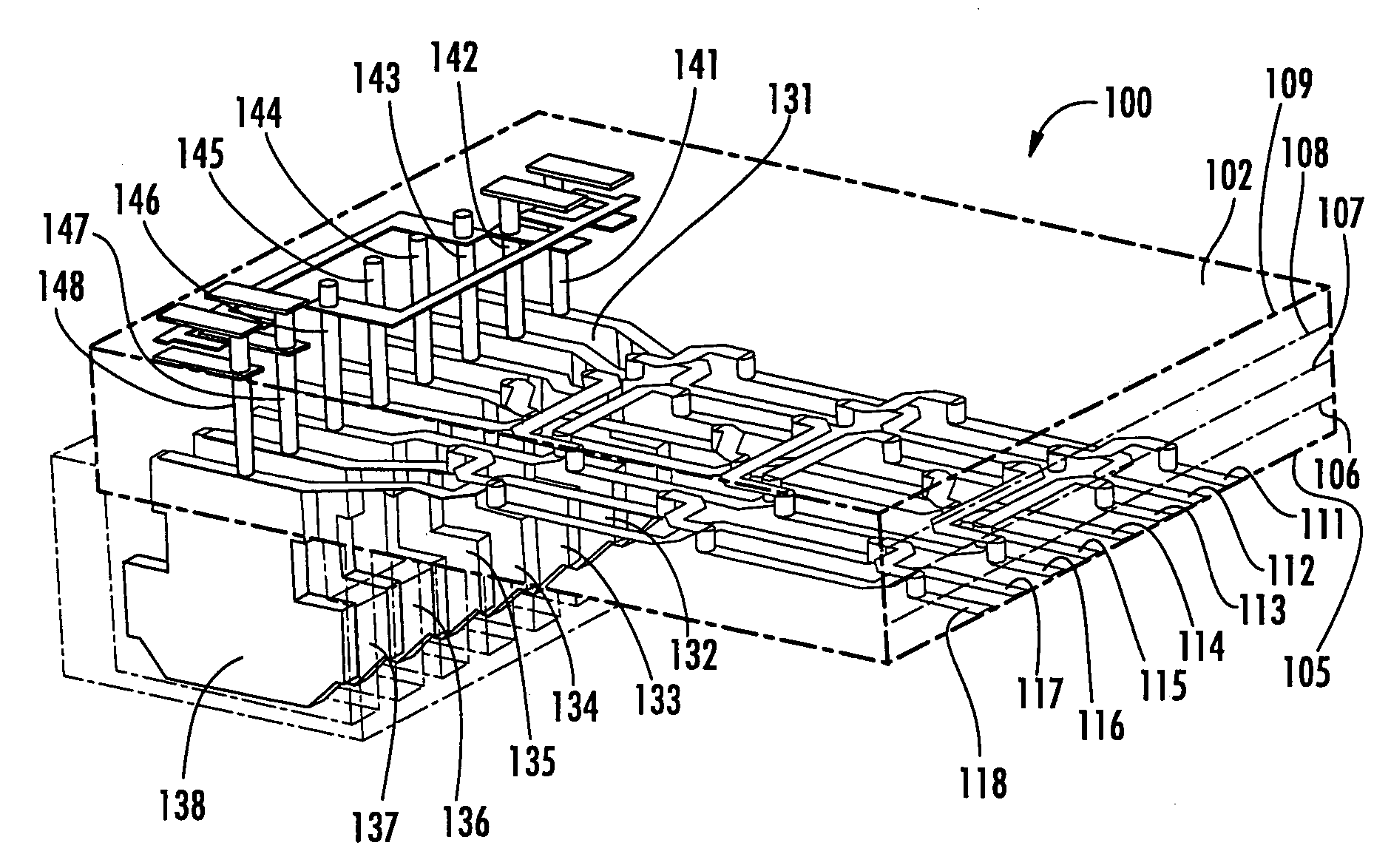
A telecommunications connector includes first and second pairs of electrical conductors. The first and second pairs of conductors are arranged in one region of the connector such that one conductor of the first pair is selectively positioned to be closer to both of the conductors of the second pair than is the other conductor of the first pair, and such that the one conductor of the first pair couples a common mode signal of a first polarity onto the conductors of the second pair. In another region of the connector the other conductor of the first pair is selectively positioned to be closer to both of the conductors of the second pair to asymmetrically couple a common mode signal of a second polarity onto the conductors of the second pair.
Owner:COMMSCOPE INC
Method for controlling touch control module and electronic device thereof
InactiveUS20110134032A1Convenient for userCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDisplay deviceHuman–computer interaction
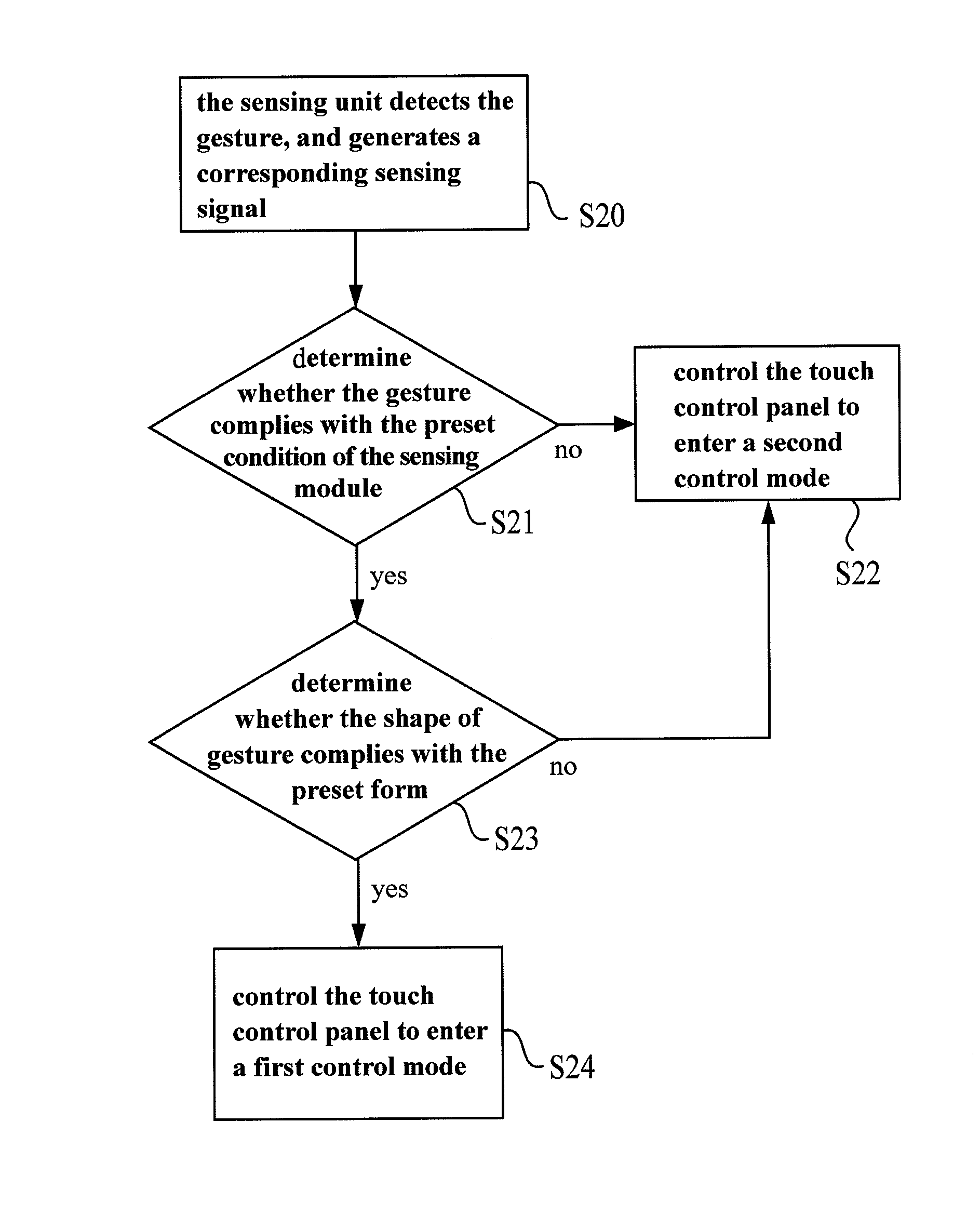
A method for controlling a touch control module and an electronic device are provides. The electronic device includes a display and a host. The host includes a sensing module, a touch control module and a control unit. The sensing module includes a sensing unit for detecting the gesture and generating the corresponding sensing signal. The control unit determines whether the gesture complies with a preset condition according to the sensing signal. When the determining result is yes, the control unit controls the touch control module to enter the first control mode. On the contrary, if the determining result is no, the control unit controls the touch control module to enter the second control mode.
Owner:ASUSTEK COMPUTER INC
Disk drive disabling BEMF detection window to reduce acoustic noise while using wedge spindle speed control
InactiveUS6954324B1Reduce noiseRecord information storageCarrier speed control/regulation/indicationAcoustic noise reductionElectric machine
A disk drive is disclosed employing either back electromotive force (BEMF) spindle speed control mode or wedge spindle speed control mode. A BEMF detector monitors the BEMF voltage generated by the windings of the spindle motor to generate a BEMF speed error. The BEMF spindle speed control mode is used to spin up the disk to an operating speed, and the wedge spindle speed control to maintain the disk at the operating speed. While in the wedge spindle speed control mode, a BEMF detection window is disabled to reduce acoustic noise.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Electronic device and method of controlling mode thereof and mobile communication terminal
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
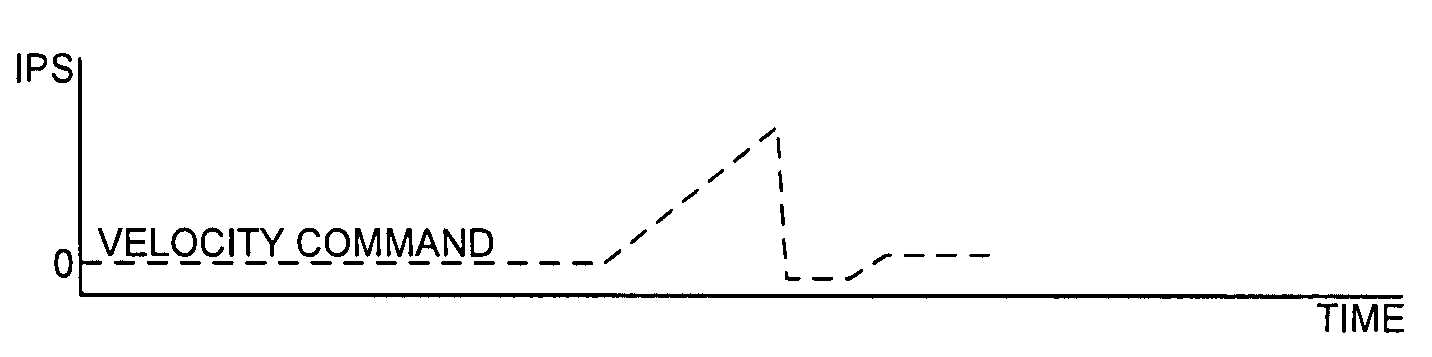
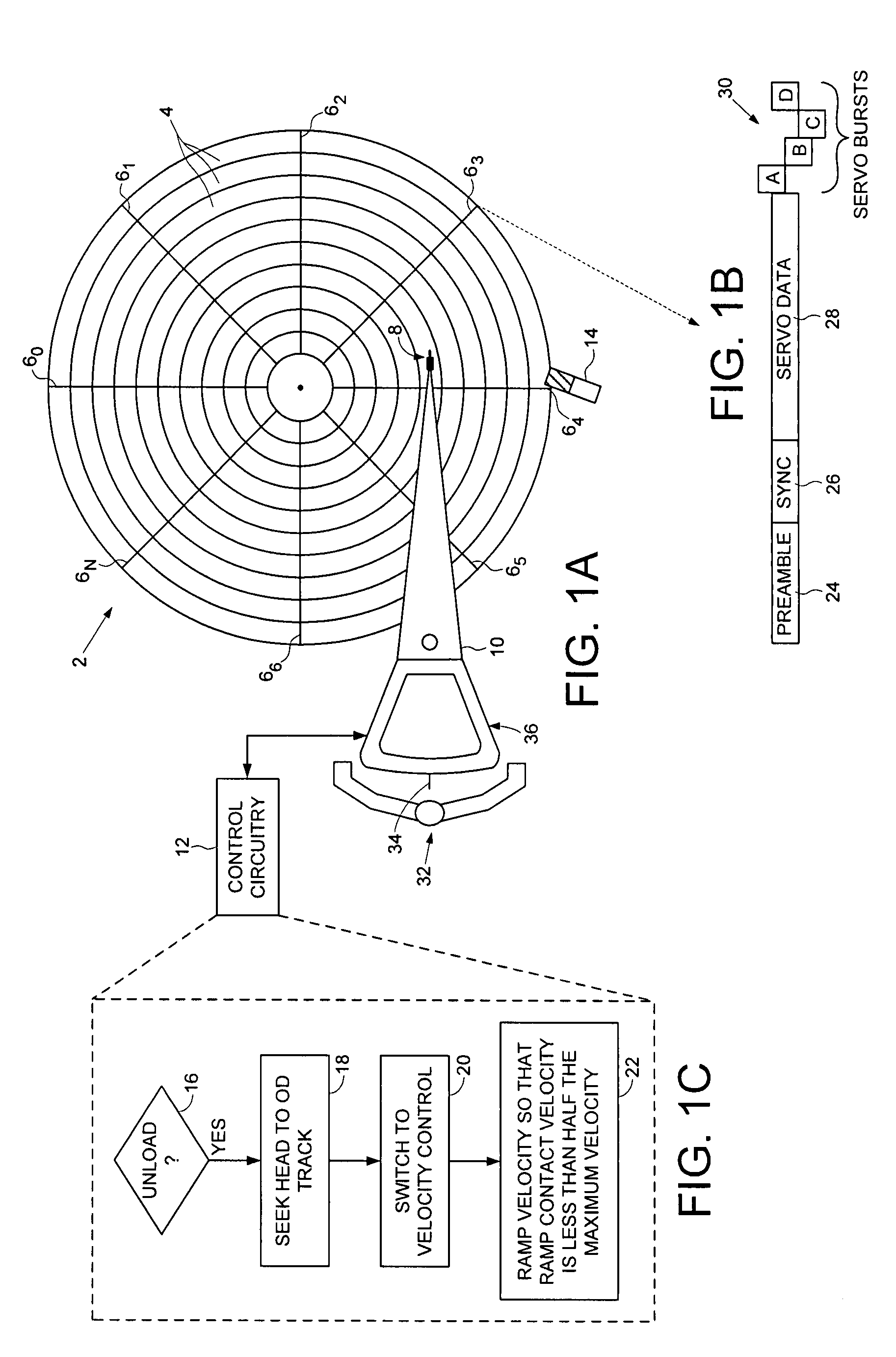
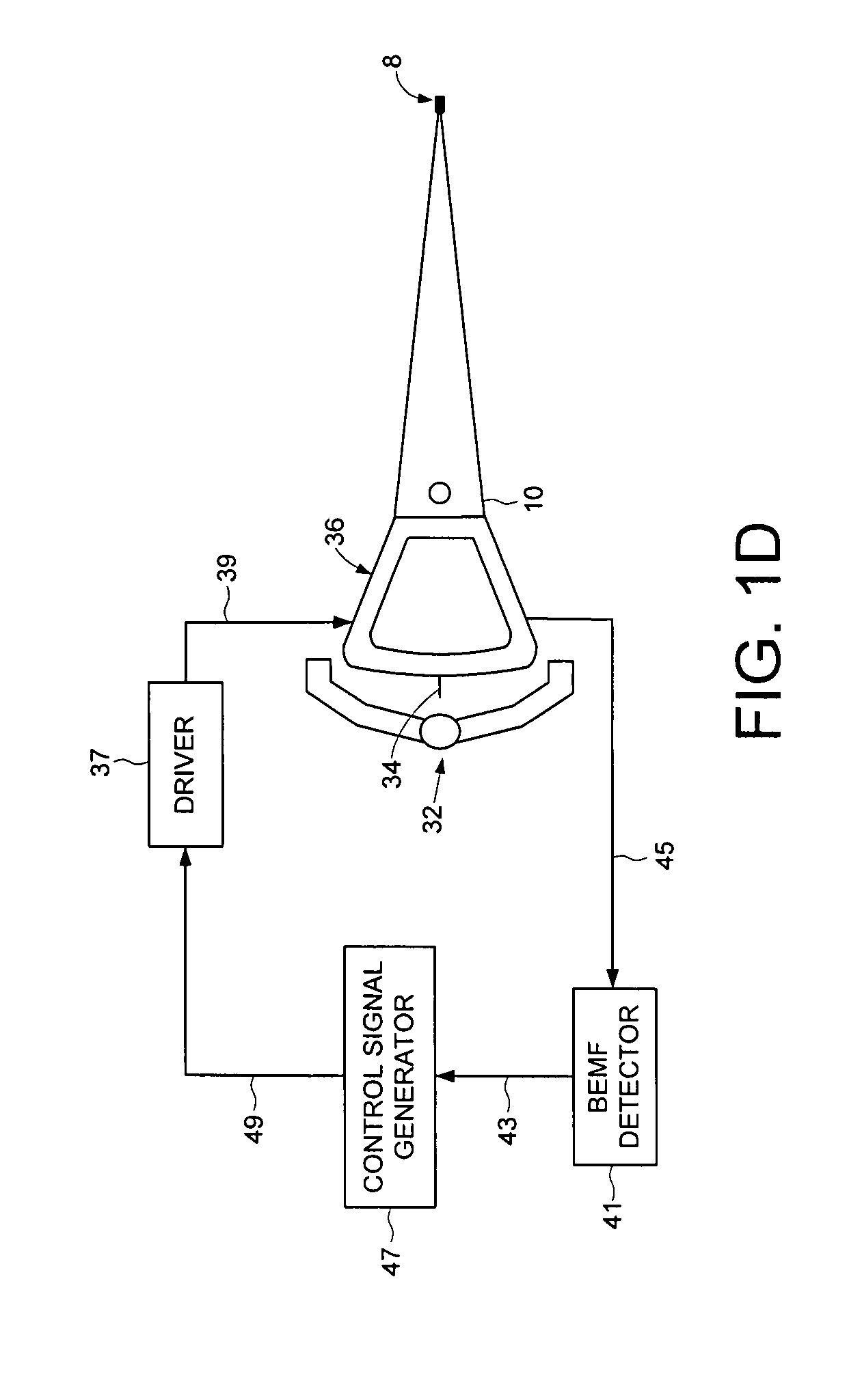
Disk drive seeking to OD track and then ramping velocity to implement fast unload
InactiveUS7573670B1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageCounter-electromotive forceActuator
A disk drive is disclosed including a disk having a plurality of tracks, wherein each track comprises a plurality of embedded servo sectors. A head connected to a distal end of an actuator arm is rotated about a pivot by a voice coil motor (VCM) in order to actuate the head radially over the disk. The actuator arm is unloaded onto a ramp by seeking the head to a track near an outer diameter of the disk in response to the embedded servo sectors, switching to a velocity control mode to unload the actuator arm onto the ramp at a controlled unload velocity in response to a back electromotive force voltage generated by the VCM, and ramping a velocity command so that the velocity of the actuator arm when contacting the ramp is less than half the maximum unload velocity while traveling along the ramp.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
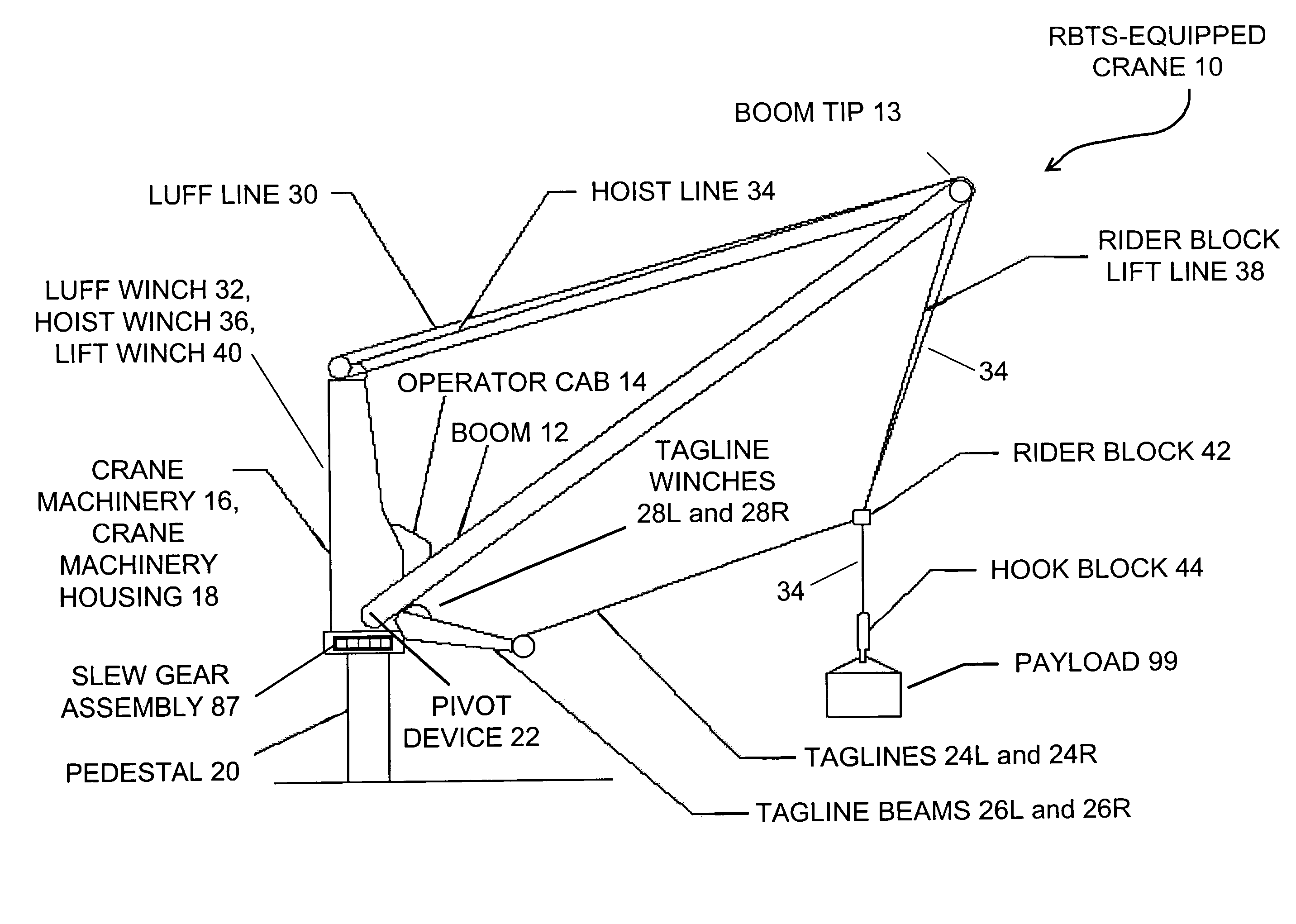
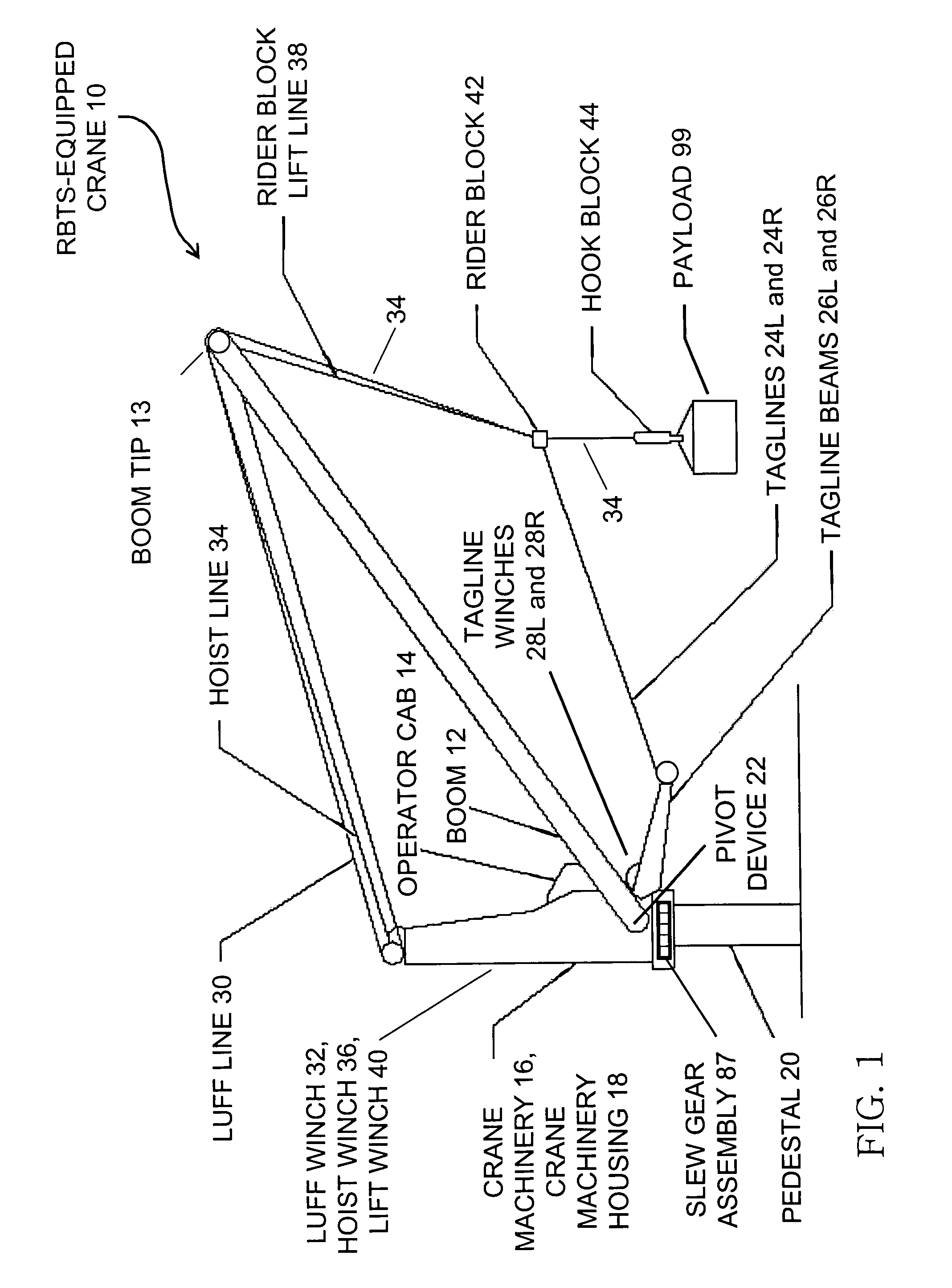
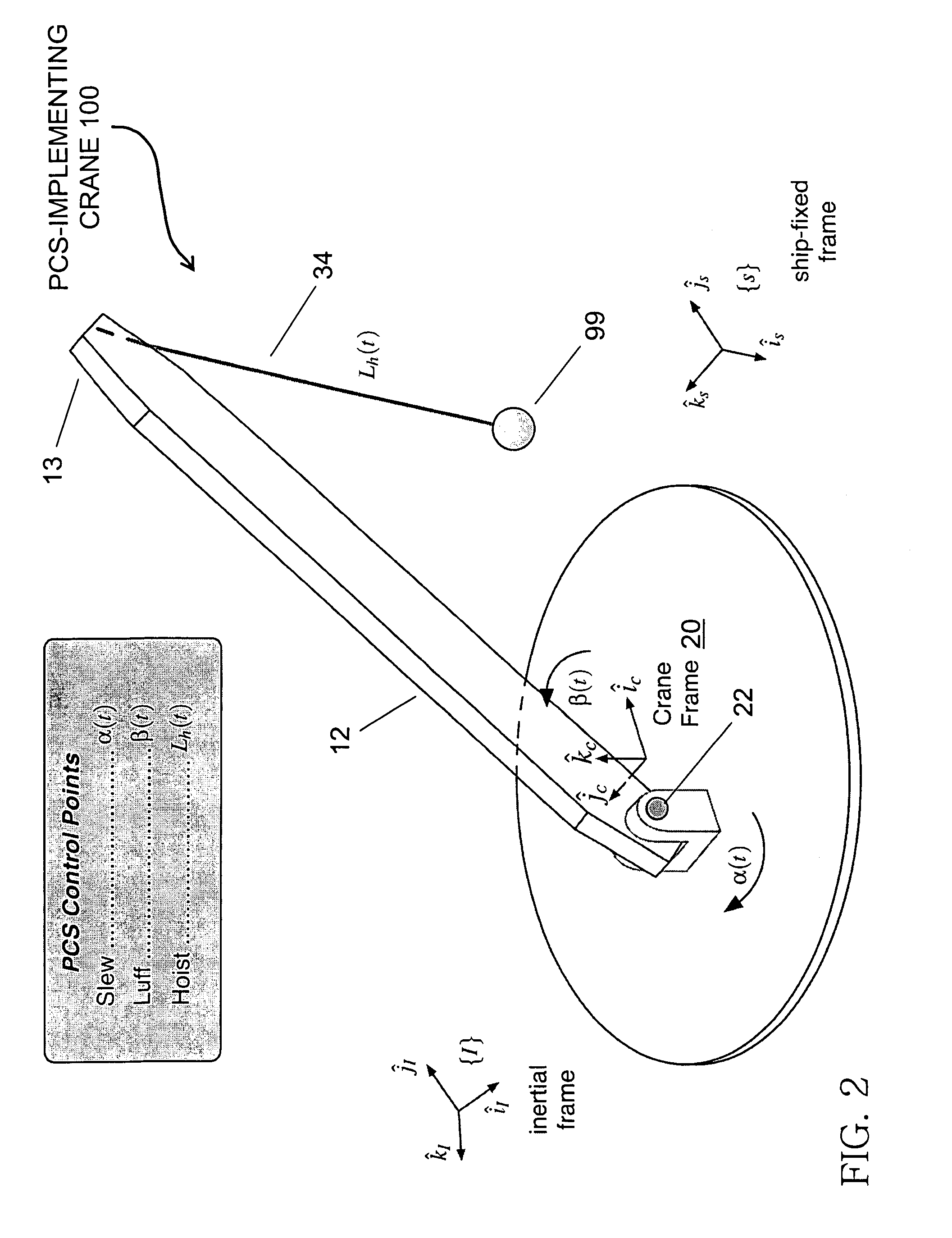
Pendulation control system with active rider block tagline system for shipboard cranes
ActiveUS7367464B1Good partitionOther workshop equipmentLoad-engaging elementsShip controlControl mode
The inventive control system, as typically embodied, includes sensing mechanisms, a computational processing unit, and an algorithm for processing inputs and generating outputs to control a rotating pedestal crane equipped with a Rider Block Tagline System (RBTS). Typical inventive embodiments uniquely feature a processing algorithm that distributes various control modes that operate not only through the crane's hoisting, luffing, and slewing mechanisms but also through the crane's RBTS; the inventive algorithm thereby effectuates motion compensation and pendulation damping with respect to the crane. This algorithmic allocation of control represents a more efficient crane anti-pendulation methodology than conventional methodologies; in particular, the inventive methodology exerts significantly greater control of the payload while exacting significantly less burden upon the hoisting, luffing, and slewing mechanisms of the crane.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
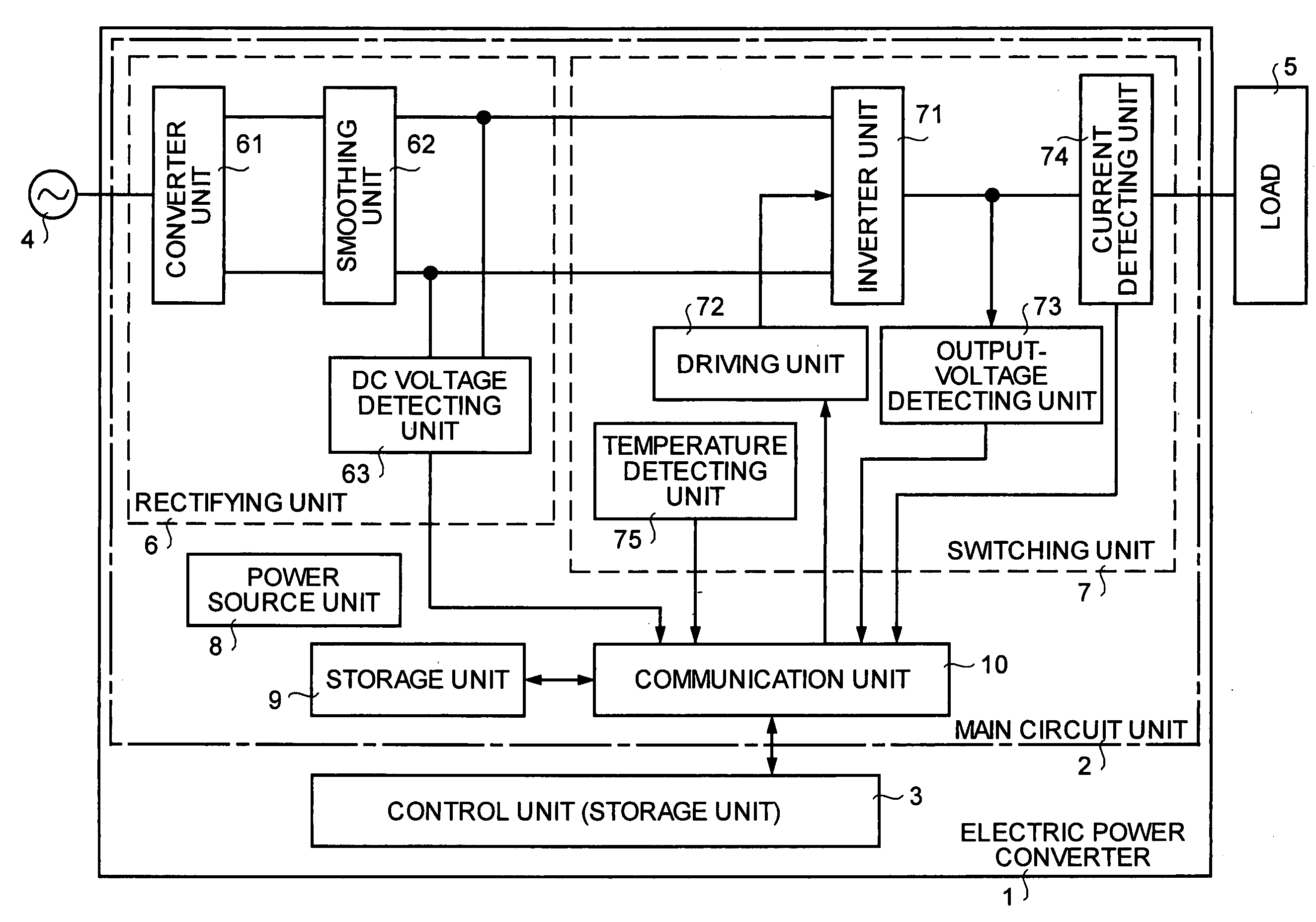
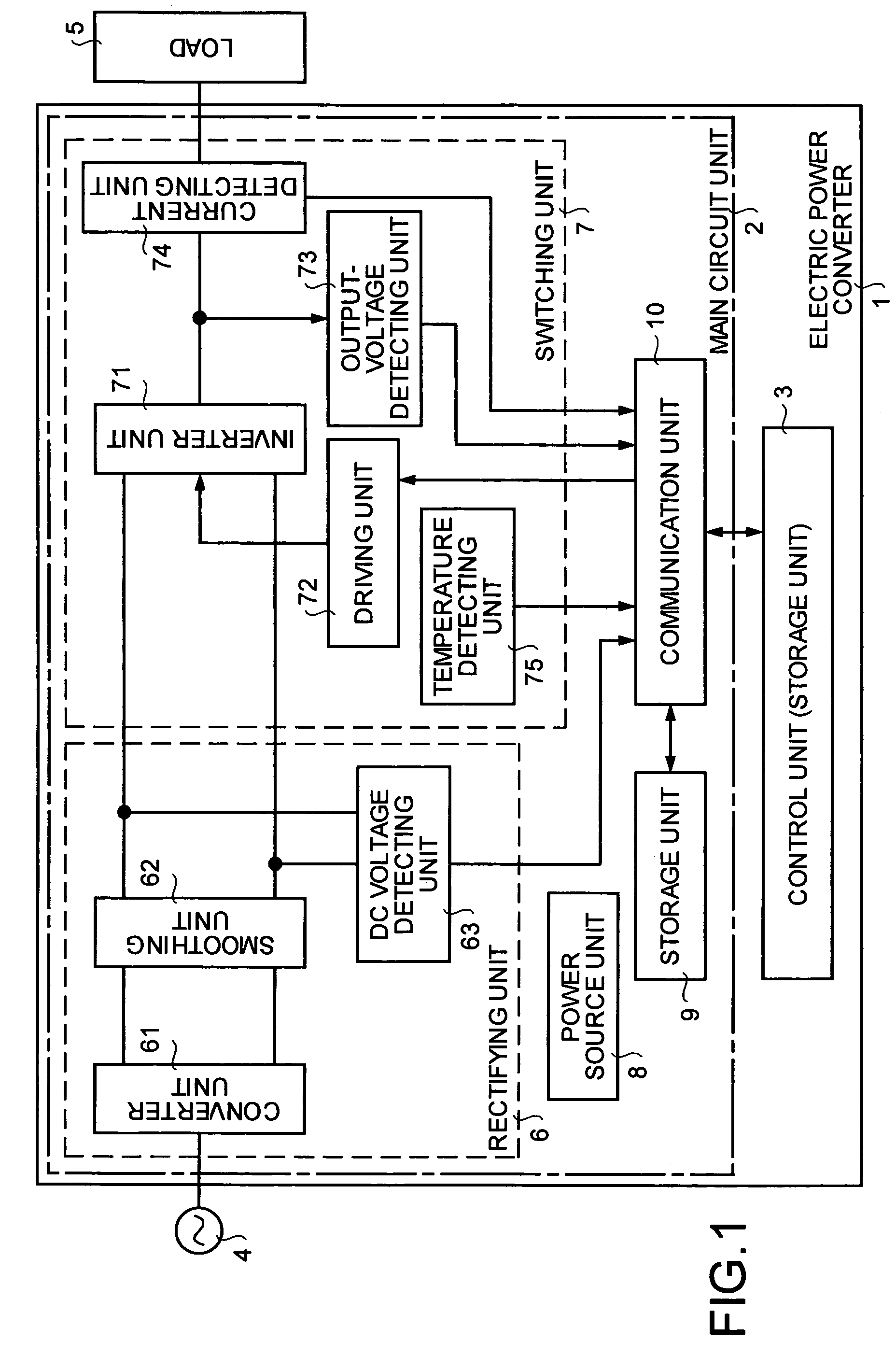
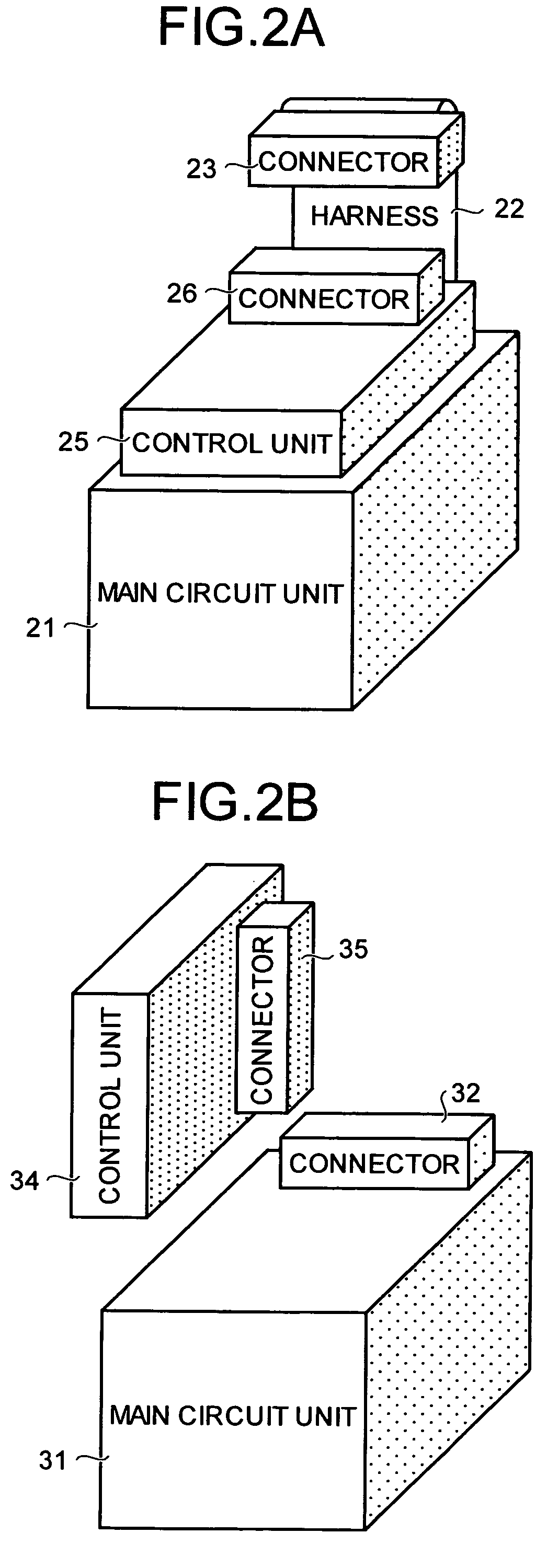
Electric power converter
ActiveUS7599200B2Easy to changeDecrease stockConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-ac conversion without reversalControl mannerEngineering
In an electric power converter, a main circuit unit and a control unit are detachably attached to each other, and another control unit differing in a control manner can be newly attached to the single main circuit unit.Moreover, the main circuit unit includes a storage unit that stores at least characteristics concerning the main circuit unit, calibration values with respect to the various detectors, a production history, an operation history, and specifications.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
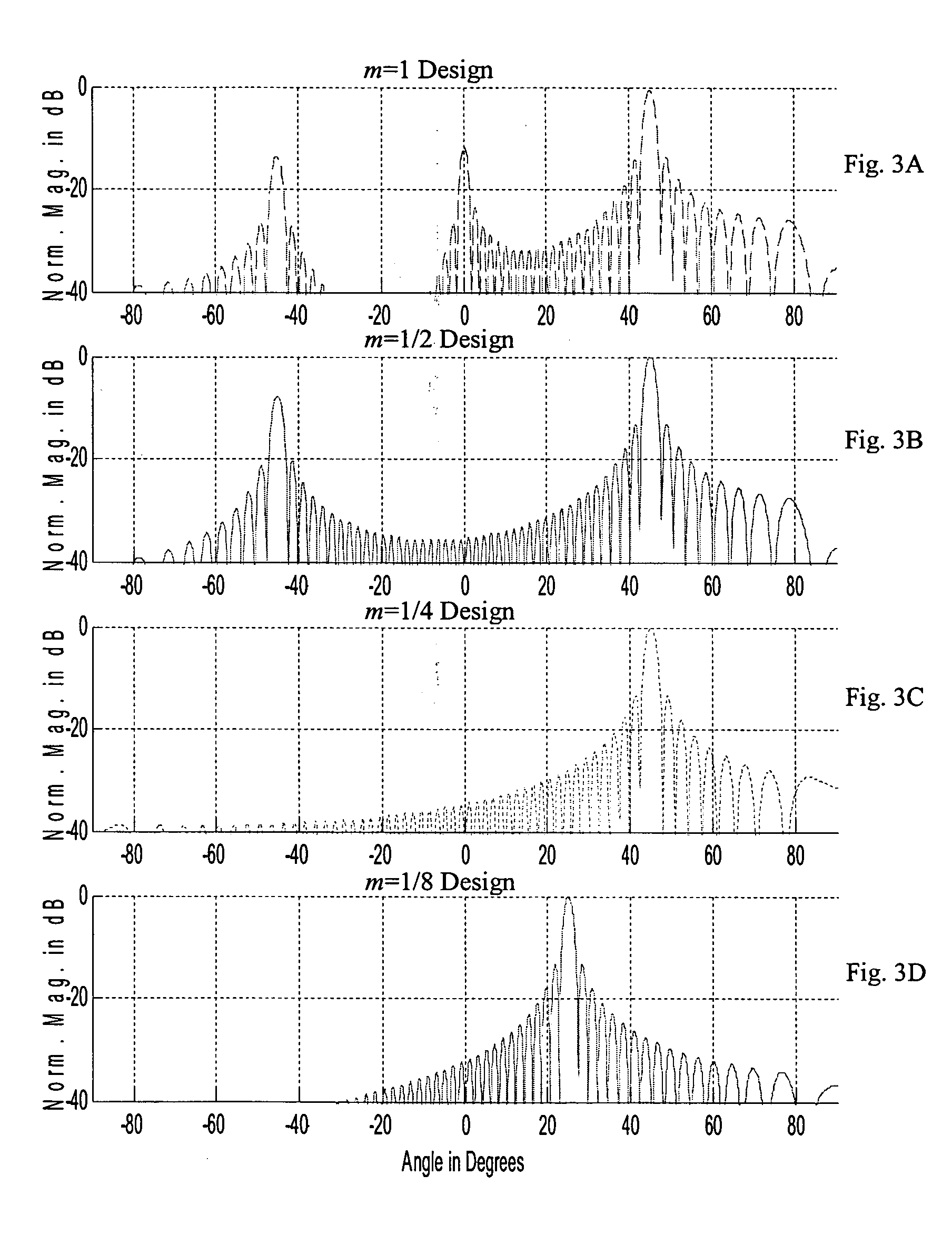
Systems and methods implementing frequency-steered acoustic arrays for 2D and 3D imaging
ActiveUS20050007882A1Improve image qualityImage can be createdSound producing devicesAcoustic wave reradiation3d imageBeam steering
Frequency-steered acoustic arrays transmitting and / or receiving multiple, angularly dispersed acoustic beams are used to generate 2D and 3D images. Input pulses to the arrays are generally non-linear, frequency-modulated pulses. Frequency-steered acoustic arrays may be provided in one-dimensional linear and two dimensional planar and curvilinear configurations, may be operated as single order or multiple order arrays, may employ periodic or non-periodic transducer element spacing, and may be mechanically scanned to generate 2D and 3D volumetric data. Multiple imaging fields of view may generated in different directions by switching the polarity of phase-shifted array transducer elements. Multiple frequency-steered arrays arranged in an X-configuration provide a wide, contiguous field of view and multiple frequency steered arrays arranged in a T-configuration provide orthogonally oriented fields of view. Methods and systems for operating acoustic arrays in a frequency-steered mode in combination a mechanical beam steering mode, electronic time-delay and phase shift beam forming modes, and phase comparison angle estimation modes are also provided.
Owner:TELEDYNE RESON
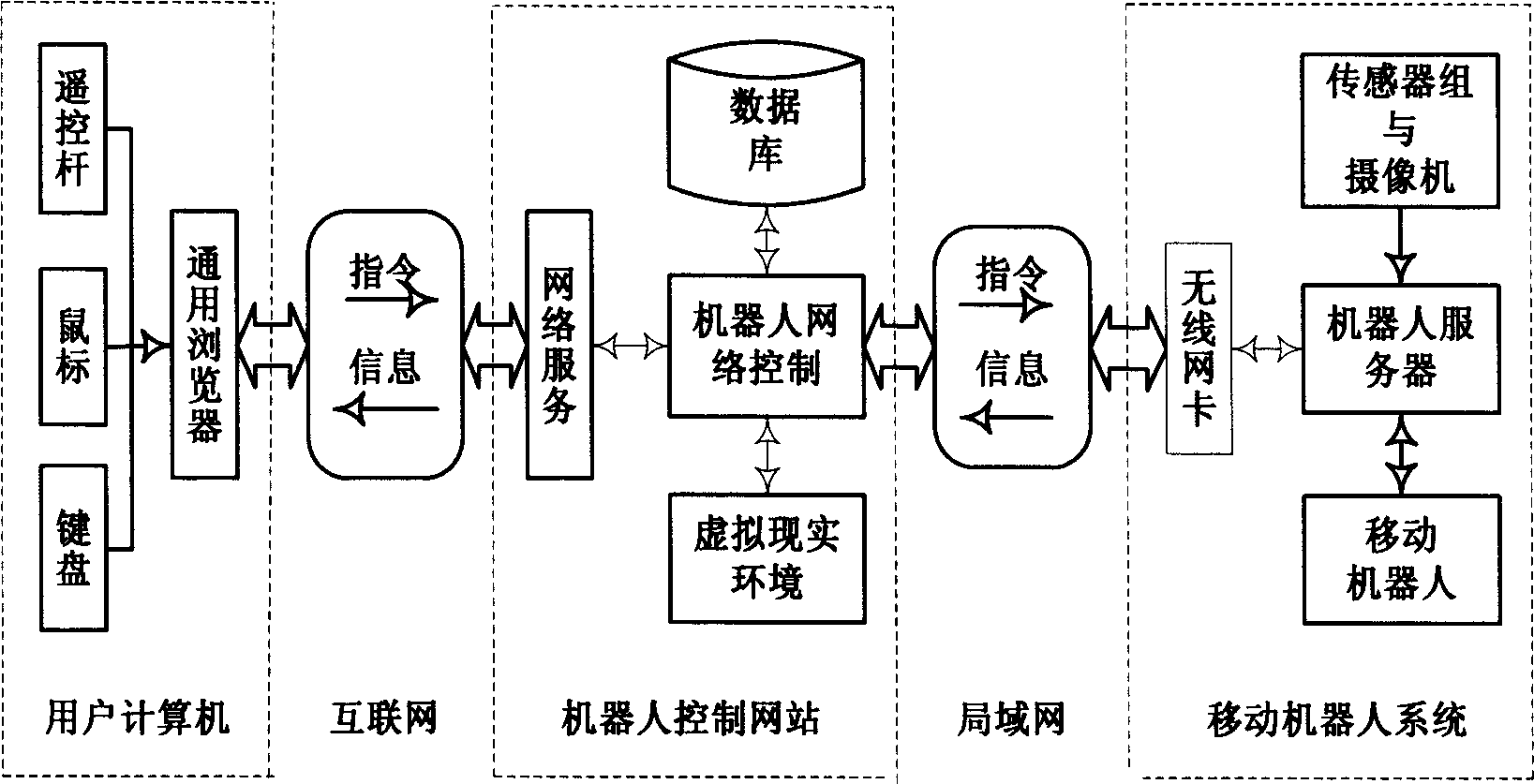
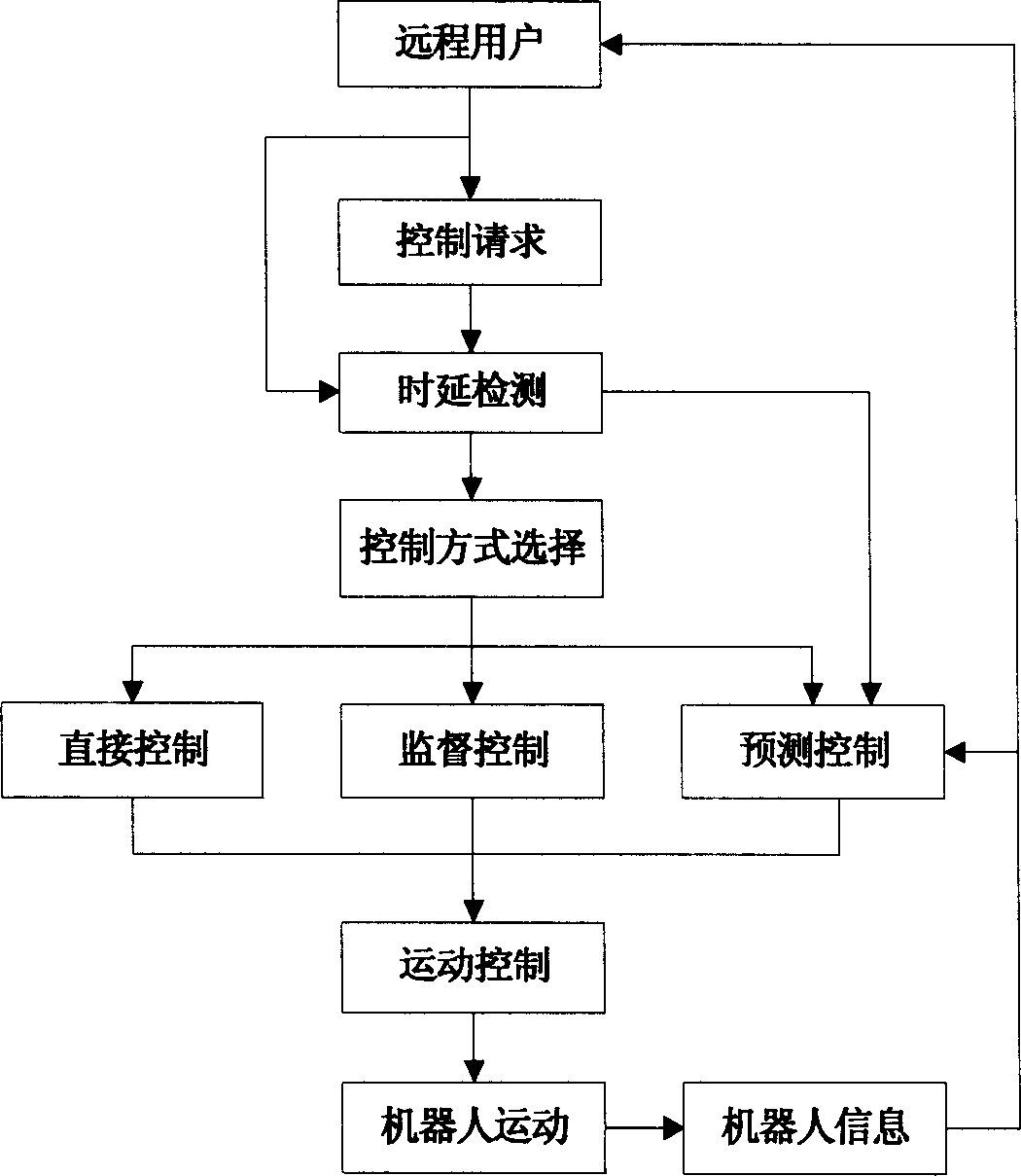
Internet-based robot long-distance control method
A robot remote control method based on Internet is disclosed. The remote user computer is connected to the robot control website through Internet, connected to the moving robot system via LAN. When the robot control website accesses in the control requirement of the remote user computer, the system detects the delay of the user by a delay-detection module, sends the result to the control selection module, provides responding control module such as direct control, prediction control or monitoring control to the user according to the delay type. The user accesses in responding control module and controls the moving of the robot through the control interface displayed on the user terminal.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
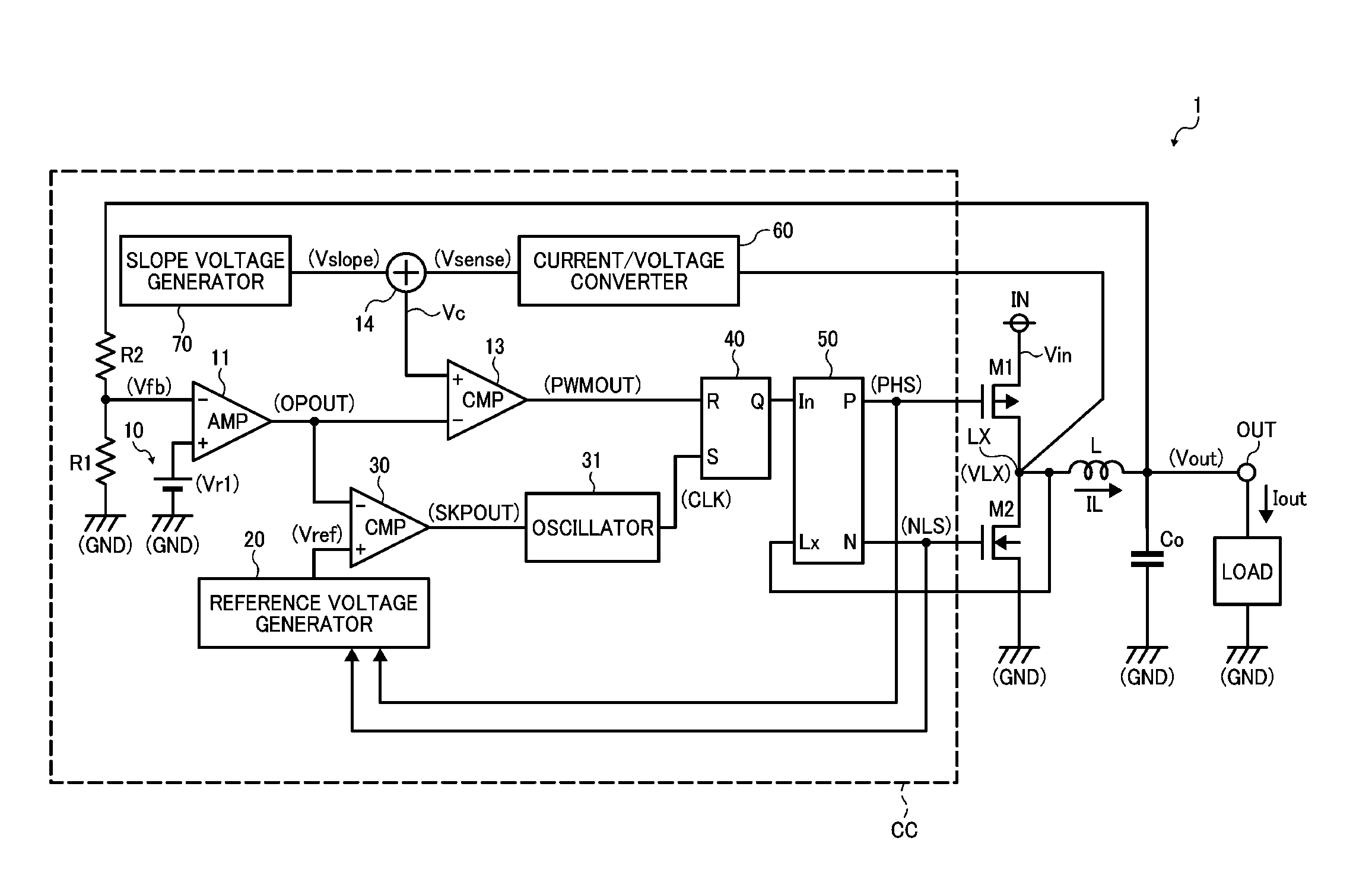
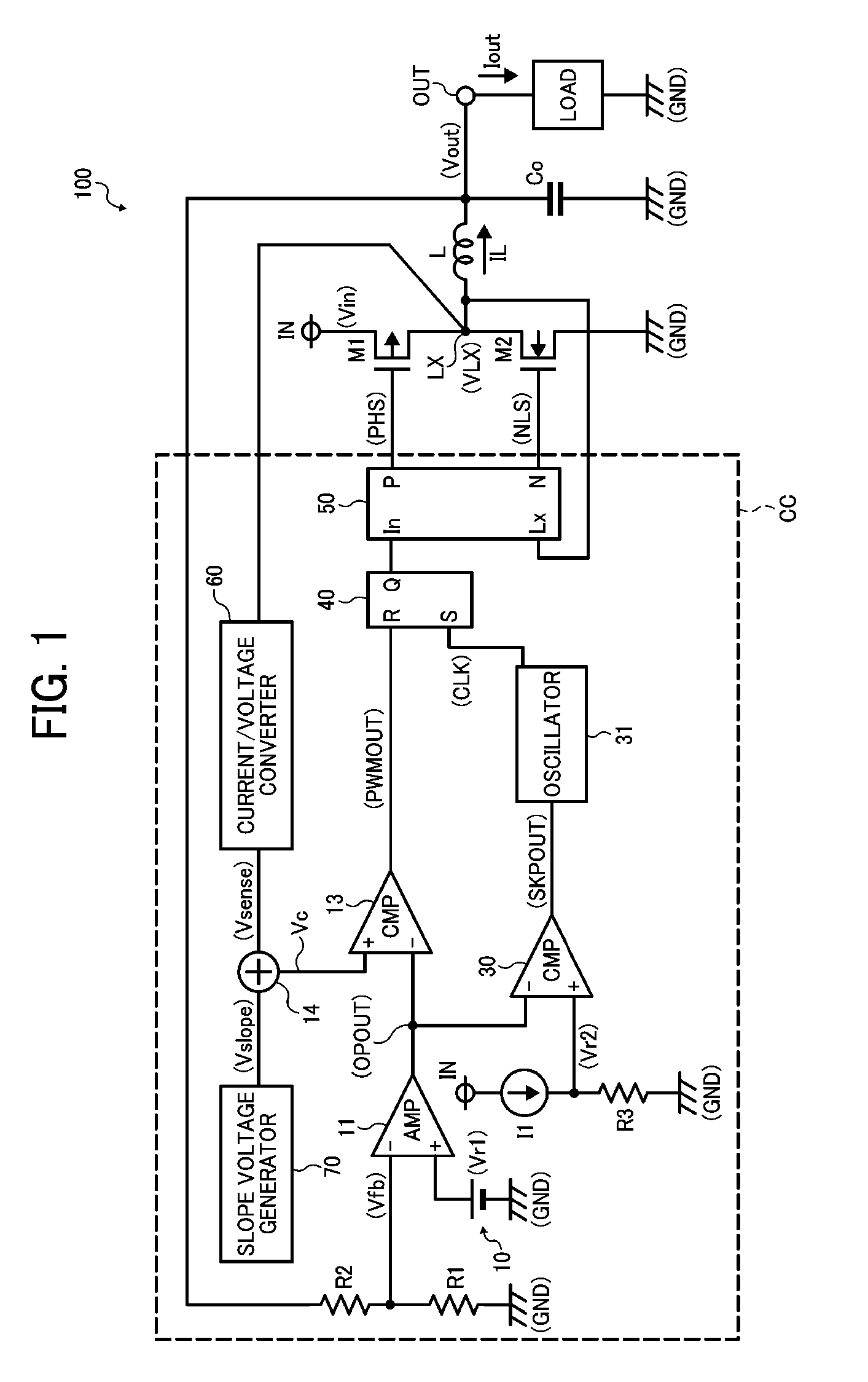
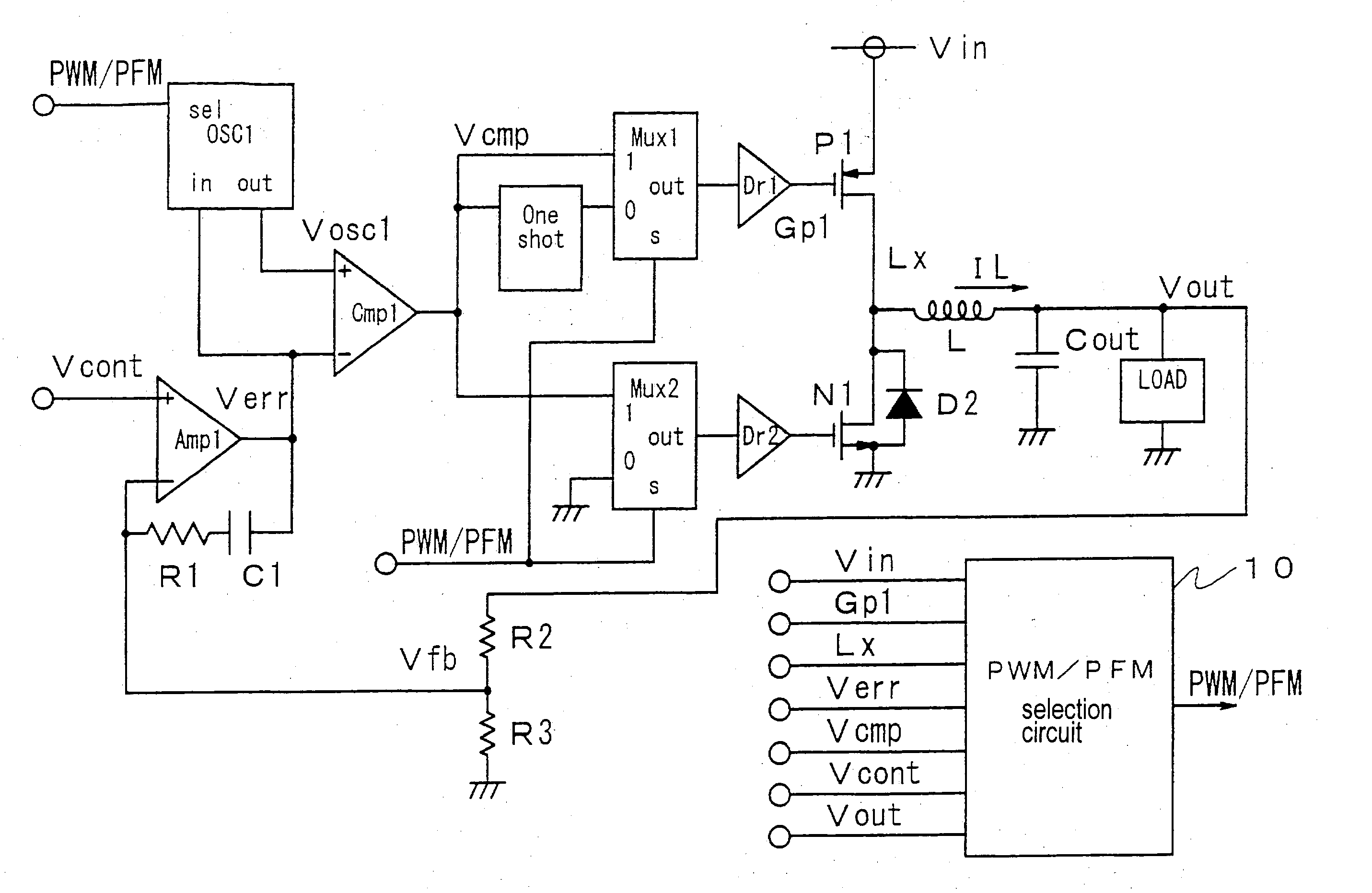
DC-DC converter
ActiveUS20050057238A1Improve efficiencyShorten the timeDc-dc conversionDc amplifiers with modulator-demodulatorDc dc converterEngineering
A DC-DC converter switches a semiconductor switch device for converting a DC voltage to a certain level and supplies the converted DC voltage to a load. The DC-DC converter is configured to be able to switch between a first feedback control mode and a second feedback control mode. The DC-DC converter selects the second feedback control mode when a load current flowing through the load is below a predetermined value. The DC-DC converter selects the first feedback control mode when a level of the DC voltage supplied to the load changes irrespective of a value of the load current.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Series resonance DC/DC converter of photovoltaic system
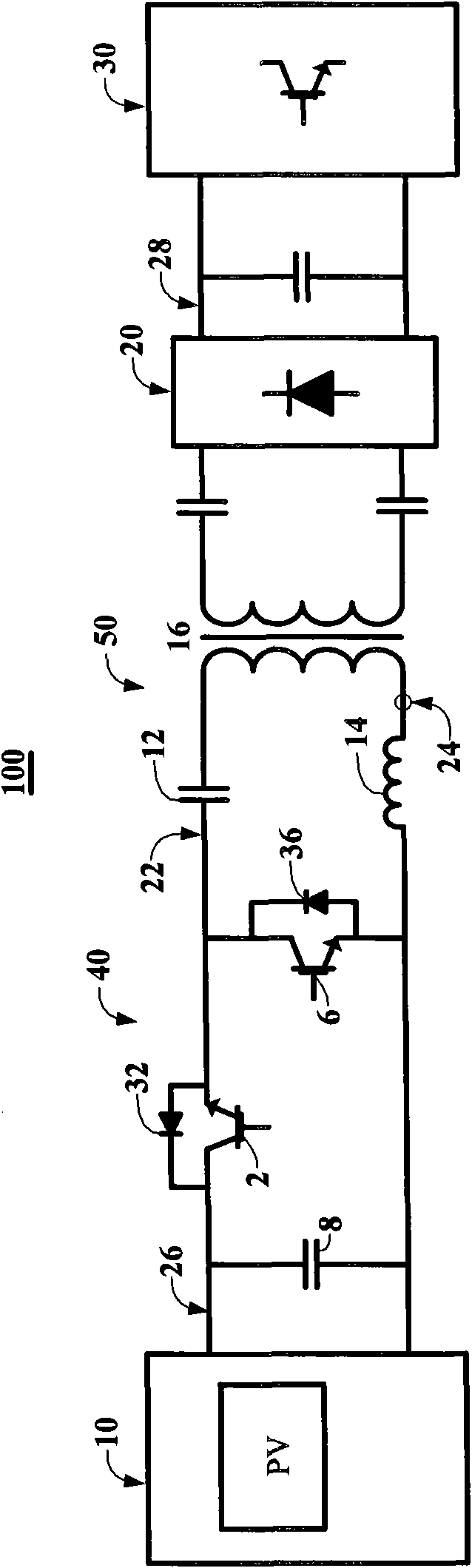
InactiveCN101976952AQuality improvementRequirements for reaching the maximum power pointEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus with intermediate ac conversionControl mannerThree phase converter
The invention relates to a series resonance DC / DC converter of a photovoltaic system, which comprises a single-pole converter (40), a series resonance circuit (50), a high-frequency isolation transformer (16) and a rapid uncontrollable rectifier (20), wherein the single-pole converter (40) is used for converting a direct voltage (26) of a photovoltaic array (10) into a single-pole pulse voltage; the series resonance circuit (50) is used for converting the single-pole pulse voltage into a sine voltage with a fixed frequency; the high-frequency isolation transformer (16) is used for boosting and isolating as well as protecting; and the rapid uncontrollable rectifier (20) is used for rectifying the high-frequency sine voltage into a stable direct current voltage (28). The converter (100) is only provided with two switching elements, has the advantages of simple control mode and no switching loss, and can be used for boosting and stabilizing the larger photovoltaic array so as to be convenient for synchronizing through a three-phase converter or charging a storage battery.
Owner:刘闯
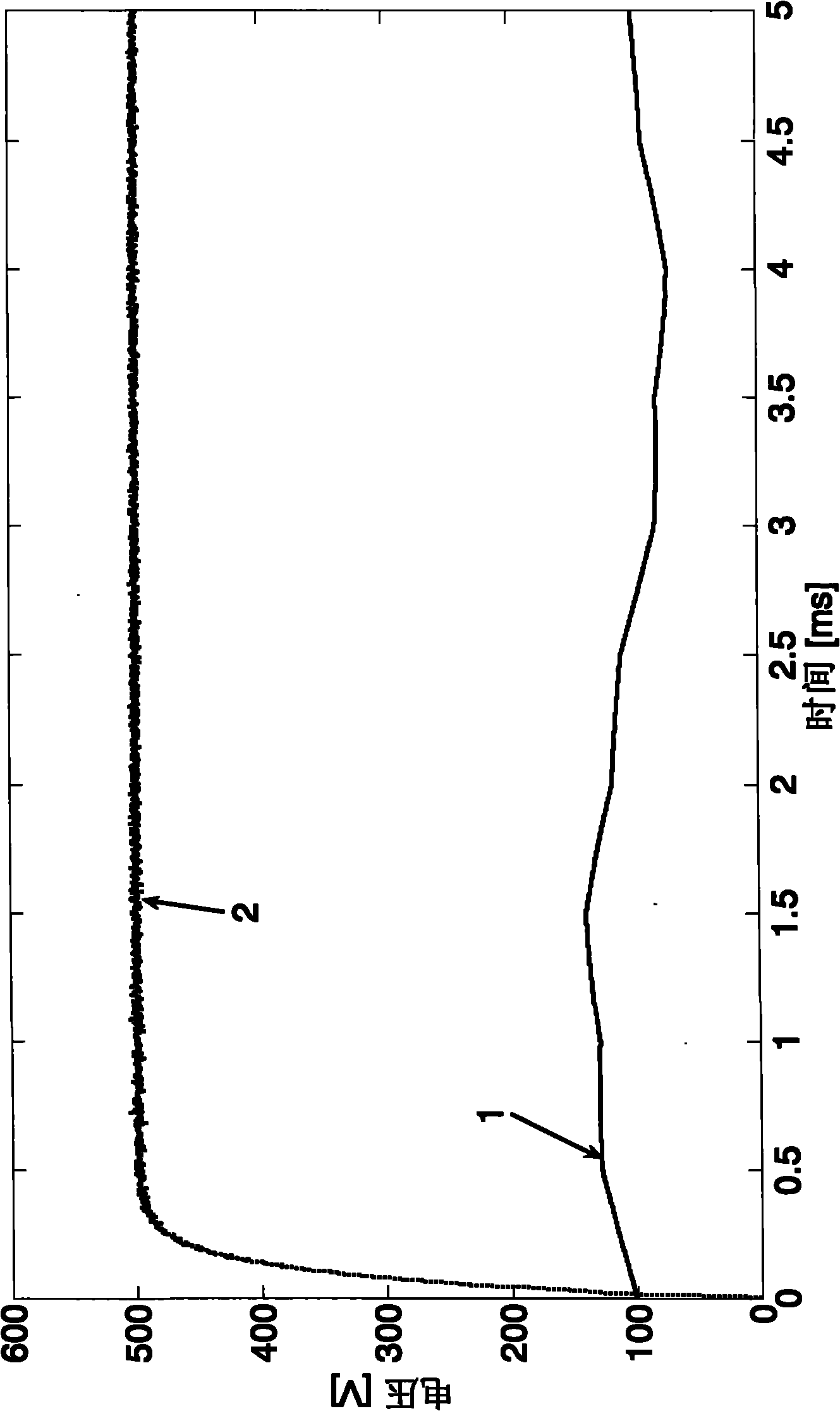
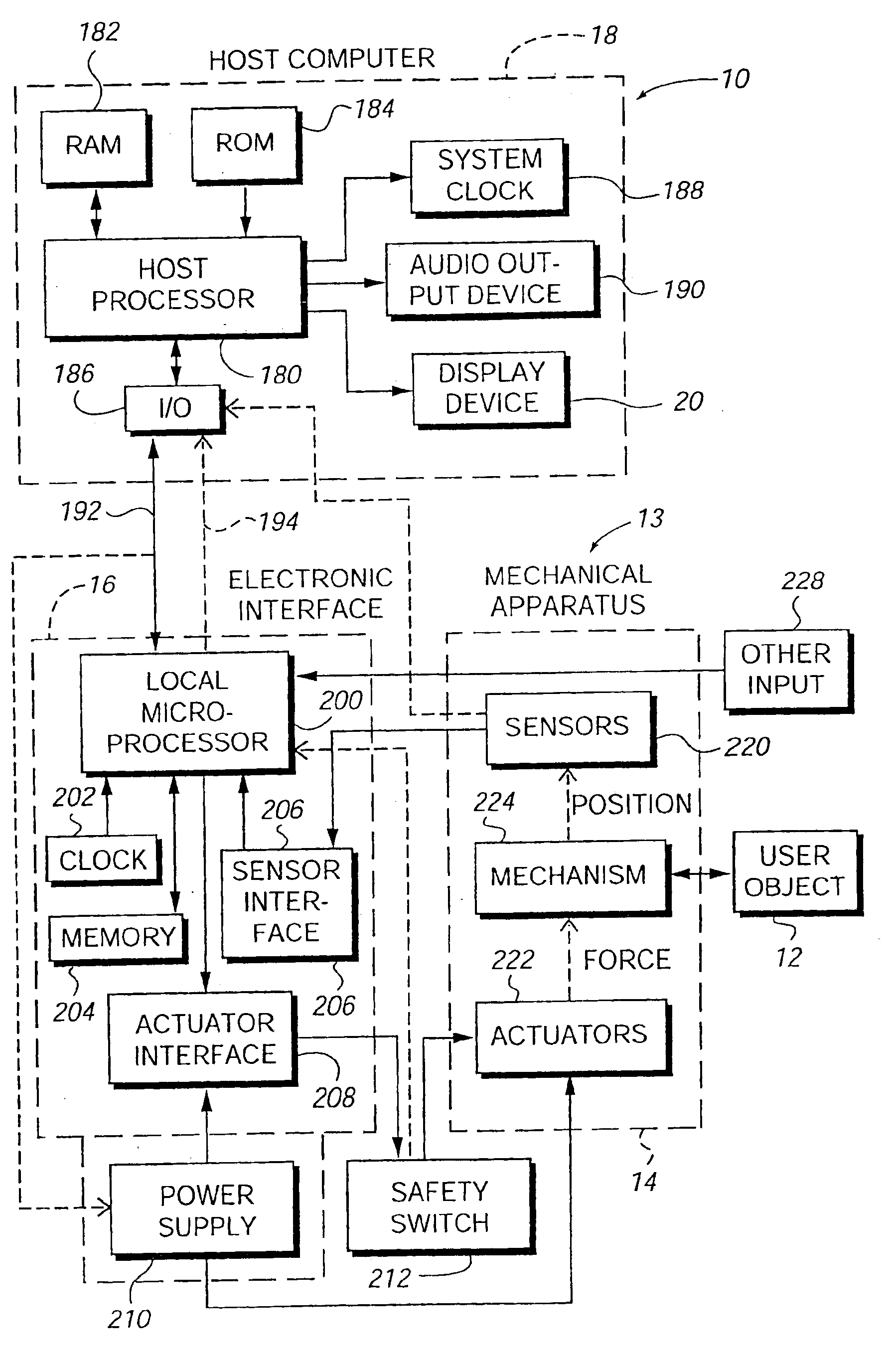
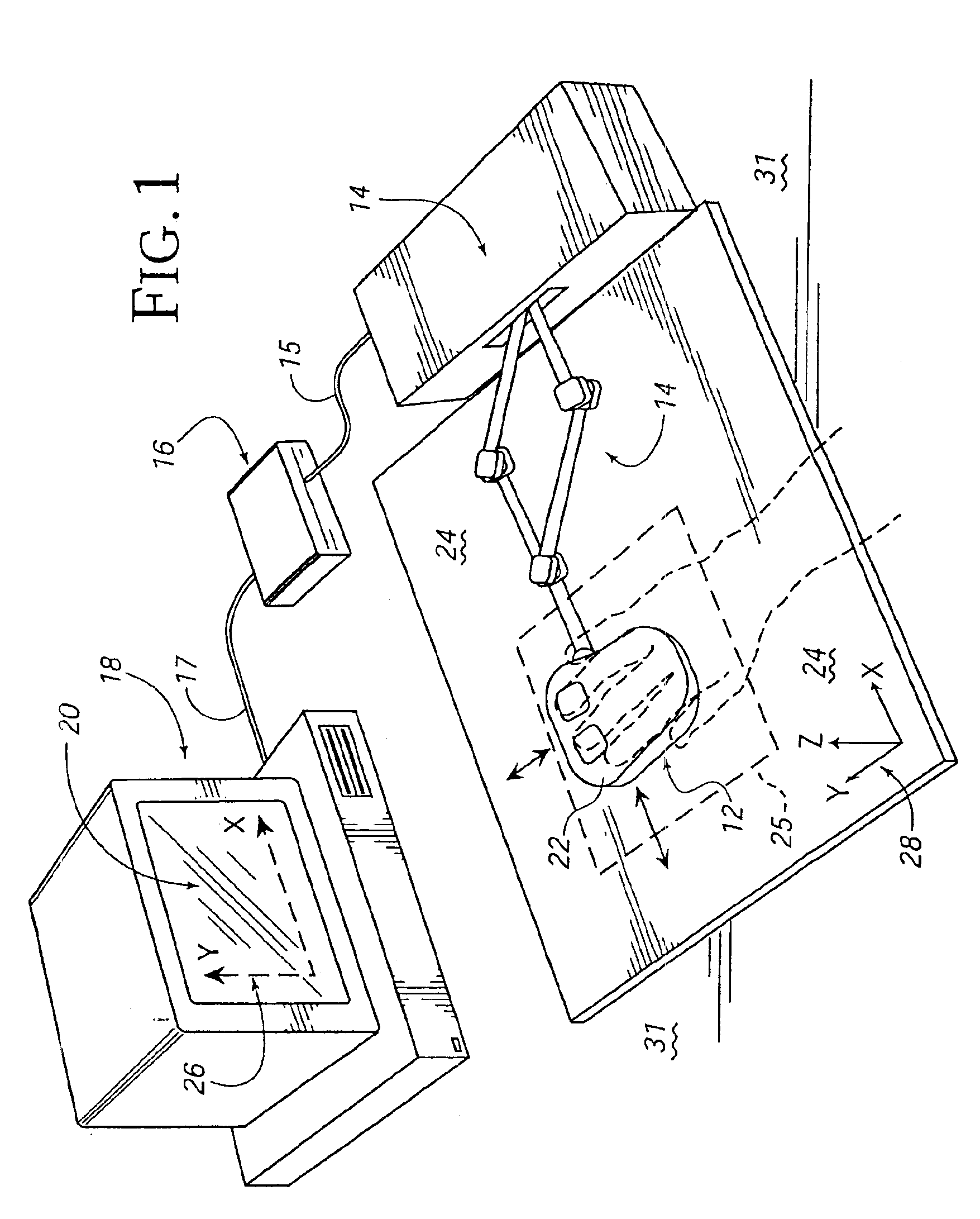
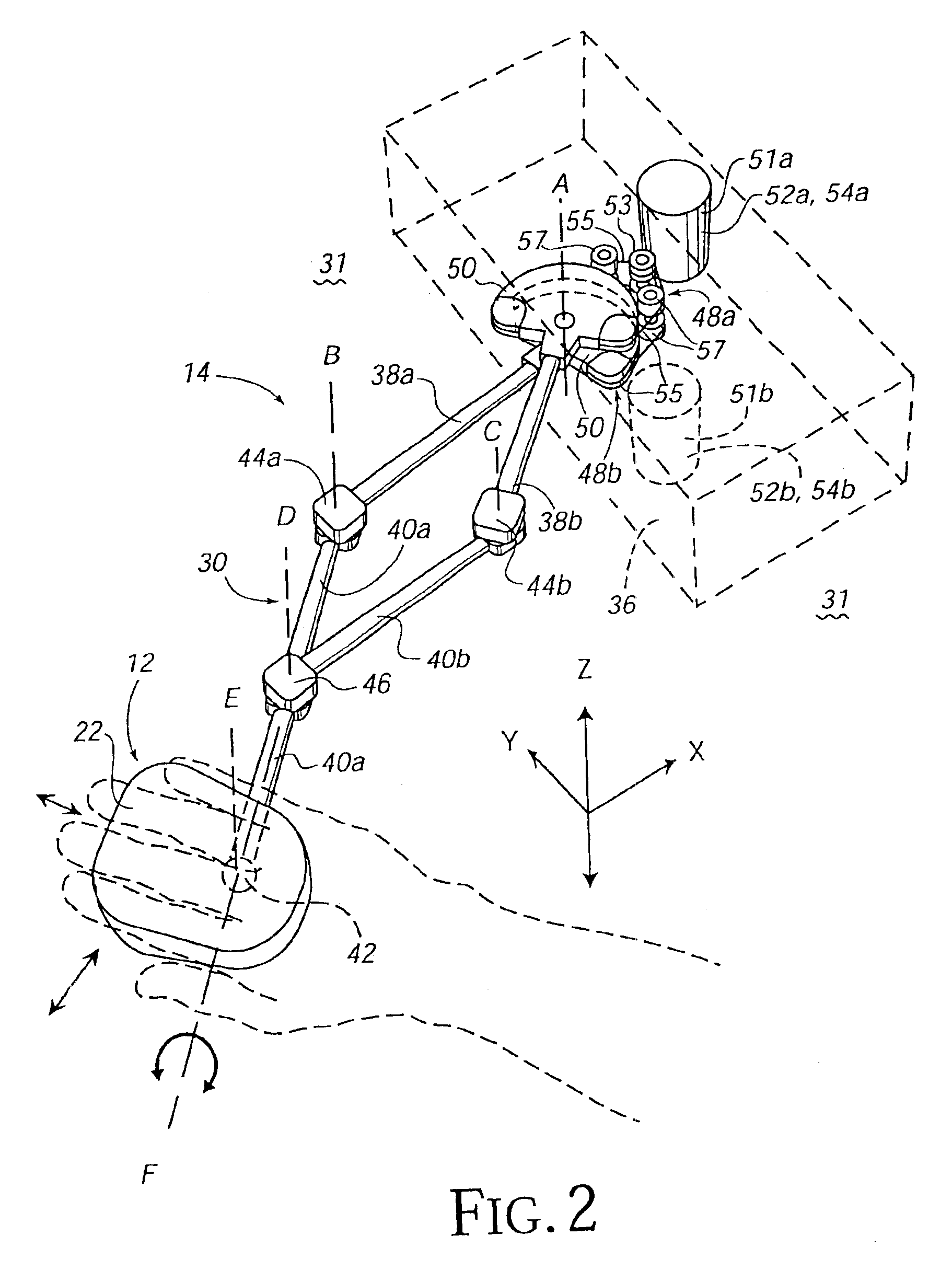
Isotonic-isometric haptic feedback interface
InactiveUS7102541B2Easily performing rate controlEasy to controlInput/output for user-computer interactionManual control with multiple controlled membersComputer basedControl mode
A force feedback interface having isotonic and isometric control capability coupled to a host computer that displays a graphical environment such as a GUI. The interface includes a user manipulatable physical object movable in physical space, such as a mouse or puck. A sensor detects the object's movement and an actuator applies output force on the physical object. A mode selector selects isotonic and isometric control modes of the interface from an input device such as a physical button or from an interaction between graphical objects. Isotonic mode provides input to the host computer based on a position of the physical object and updates a position of a cursor, and force sensations can be applied to the physical object based on movement of the cursor. Isometric mode provides input to the host computer based on an input force applied by the user to the physical object, where the input force is determined from a sensed deviation of the physical object in space. The input force opposes an output force applied by the actuator and is used to control a function of an application program, such as scrolling a document or panning or zooming a displayed view. An overlay force, such as a jolt or vibration, can be added to the output force in isometric mode to indicate an event or condition in the graphical environment.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
LED-switching controller and LED-switching control method
ActiveUS20050104542A1Efficient switchingBoosting circuit can be rapidly increasedElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesLow voltageAnalog signal
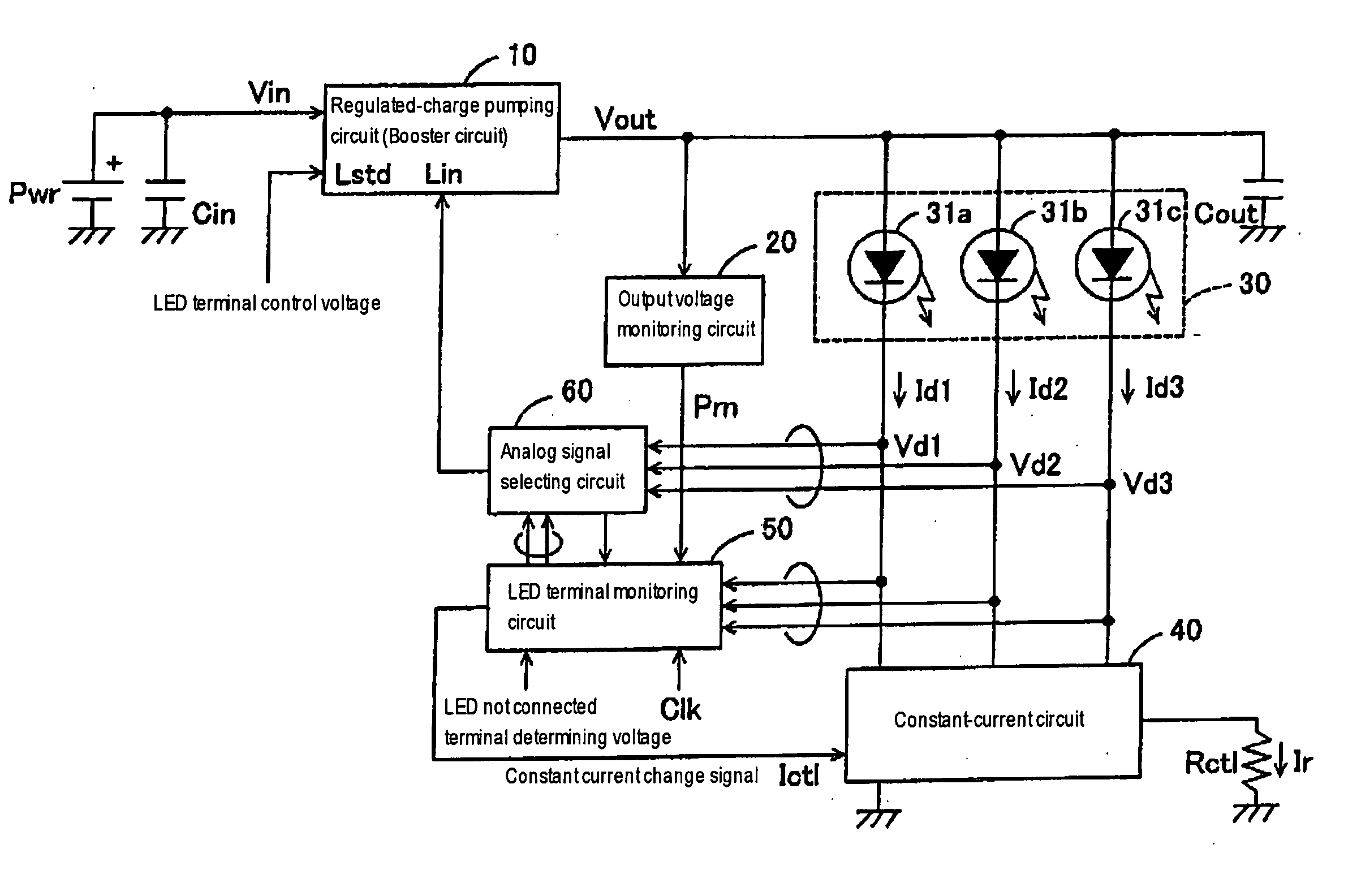
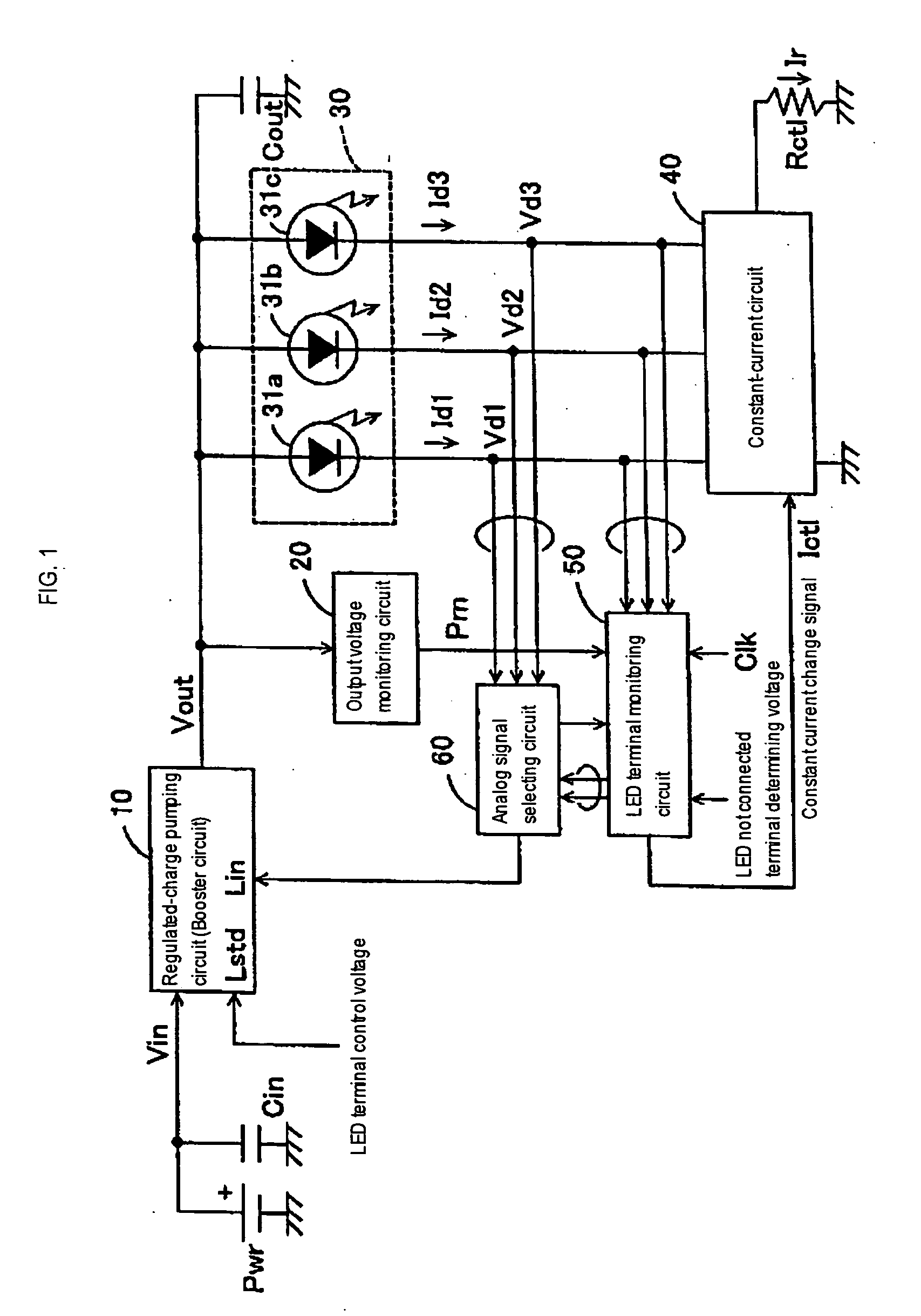
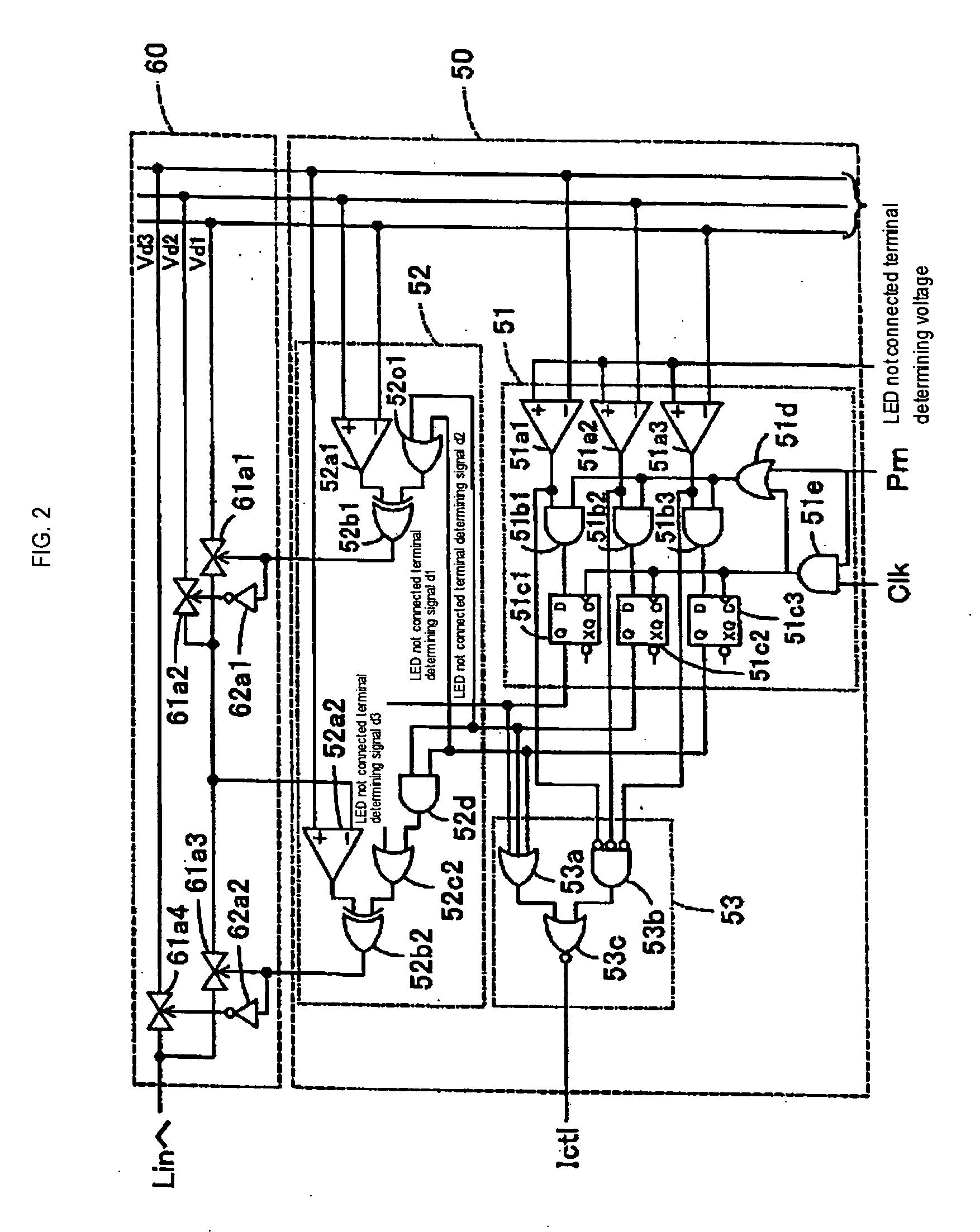
An LED terminal monitoring circuit detects an LED at the lowest potential among a plurality of parallel-connected LEDs. An analog signal selecting circuit gives a signal indicating the voltage of the detected LED to a boosting circuit. The boosting circuit performs a boosting operation on the basis of the condition of the detected LED at the lowest voltage and, consequently, a voltage sufficient for driving the LEDs in a current-control mode can be applied to all the LEDs. Signal lines not connected to LEDs are excluded from objects of a LED-switching control operation.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
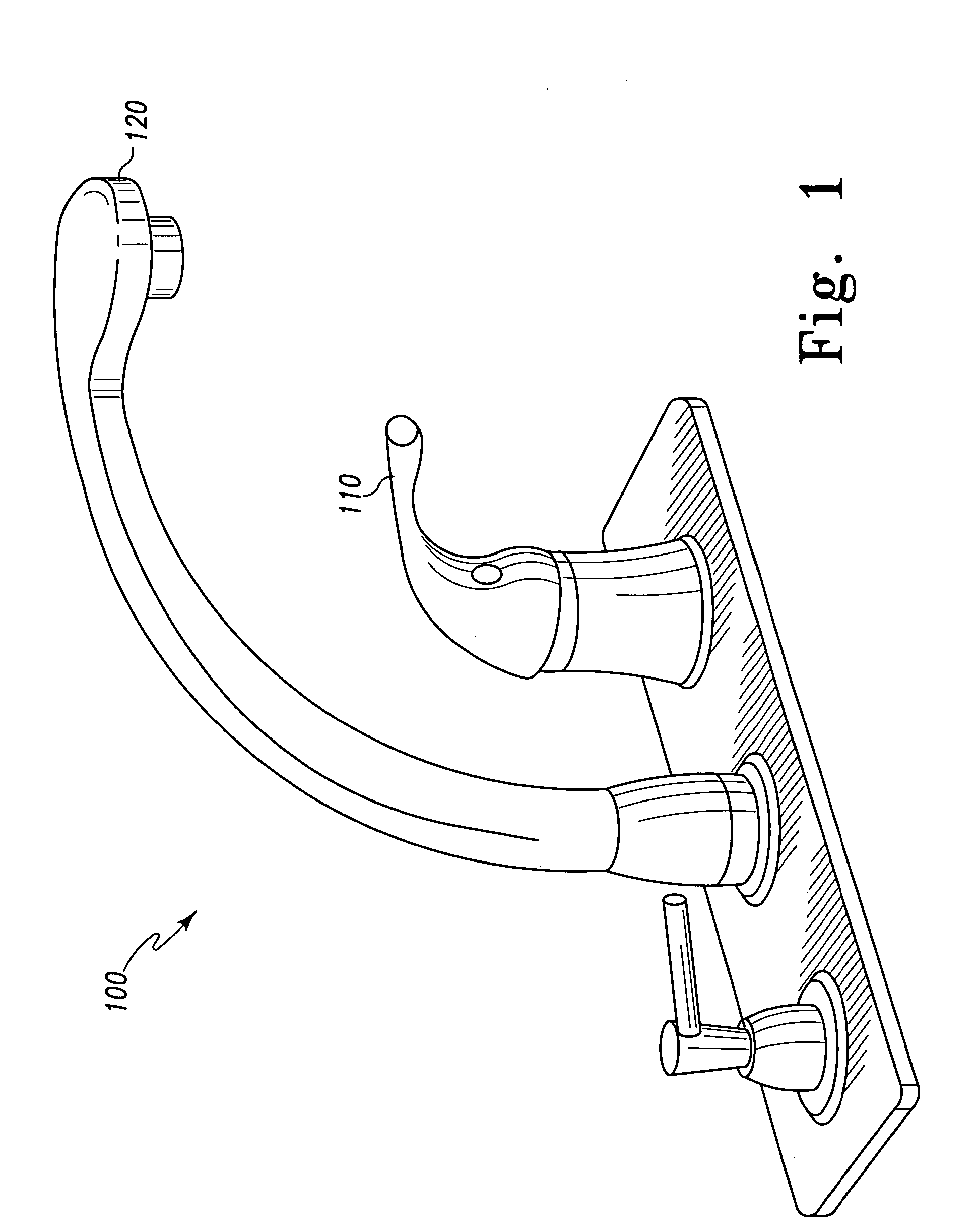
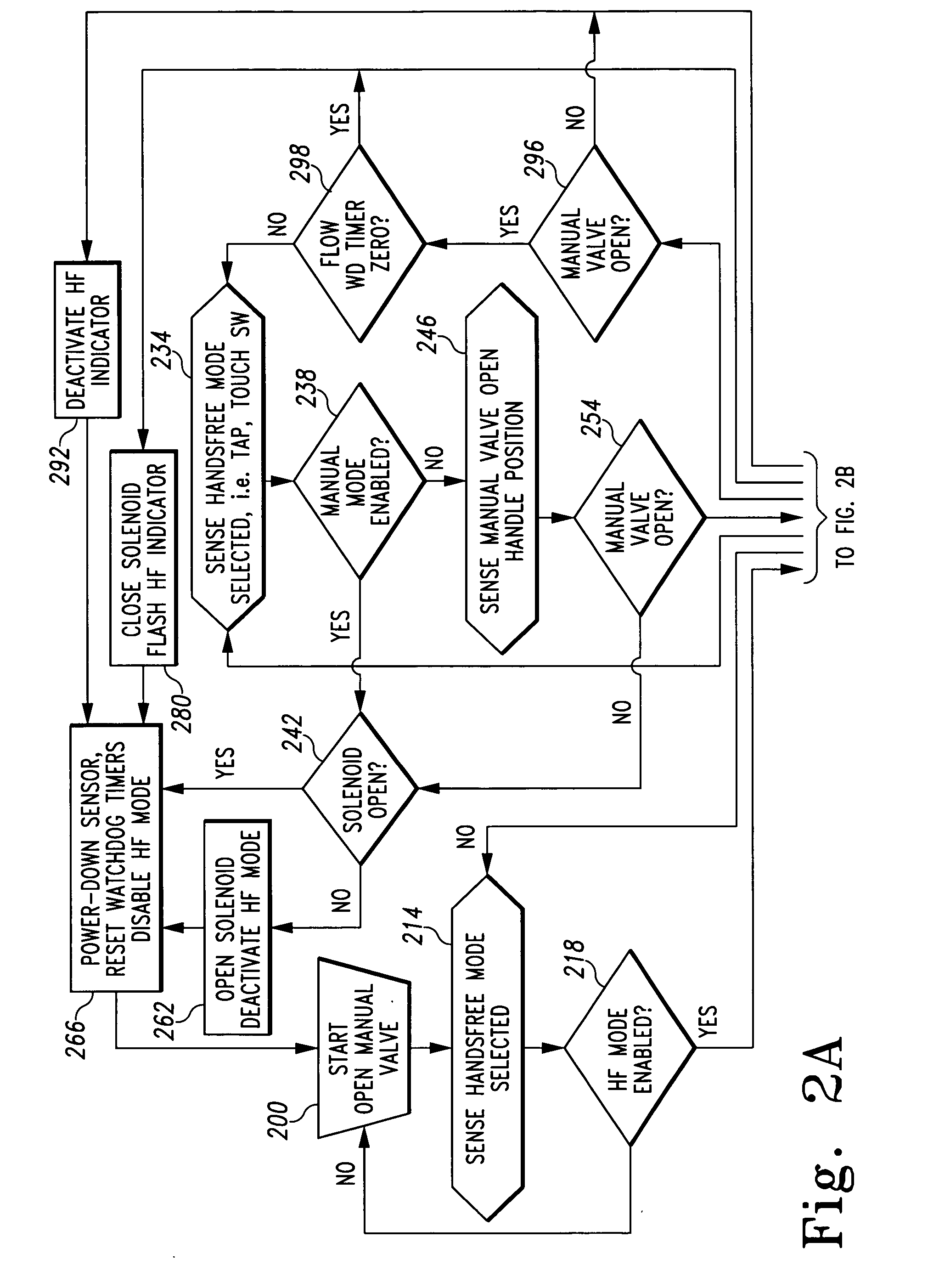
Multi-mode hands free automatic faucet
A hands-free faucet comprises a proximity sensor, a logical control, a handle including a first touch control, a second touch control, and a mode indicator. The logical control has a manual mode (wherein the proximity sensor is inactive, and water flow is toggled on and off by positioning the handle) and a hands-free mode (wherein water flow is toggled on and off in response to the proximity sensor). The first touch control puts the faucet in the hands-free mode when touched by a user. The second touch control toggles the logical control between the hands-free mode and the manual mode when touched by a user. The mode indicator indicates which mode the faucet is presently in. The water flow has a temperature and a flow rate that are determined by the position of the handle.
Owner:DELTA FAUCET COMPANY
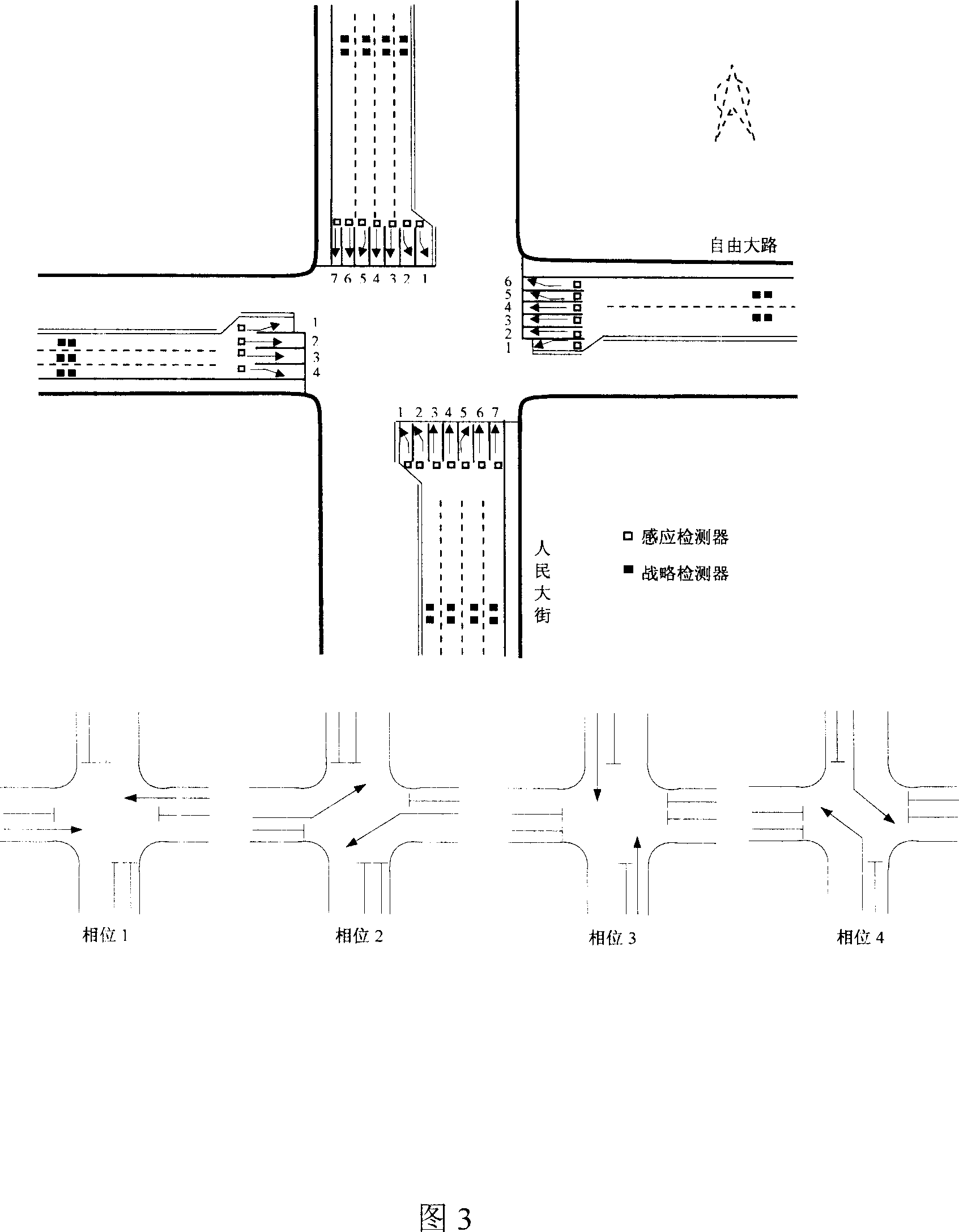
Control method for single crossing mixed traffic signal
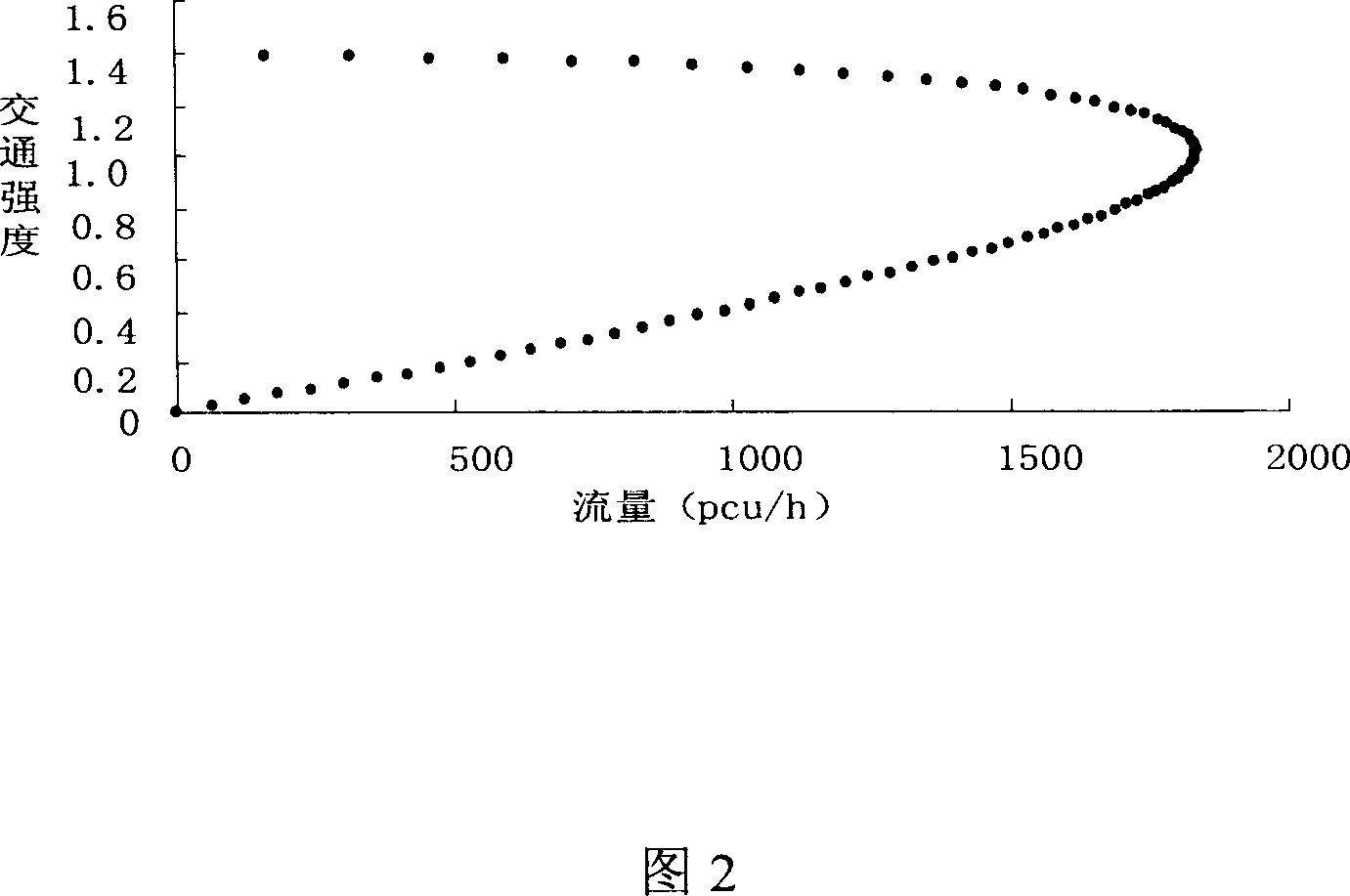
InactiveCN101042805ASolve the real problemImprove statistical accuracyControlling traffic signalsTraffic signalControl manner
This invention relates to one single cross mixture traffic signal control method by use of computer program, which comprises the following steps: summing up the automobile car number relative to standard car number by use of the computer program of the formula method and for the number of bicycle number; summing up each channel traffic flow standard car number per hour by use of data process program; signal machine judges and selects whether for single point time control type or signal sense control type or single optimization type for each type signal optimization scheme.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com