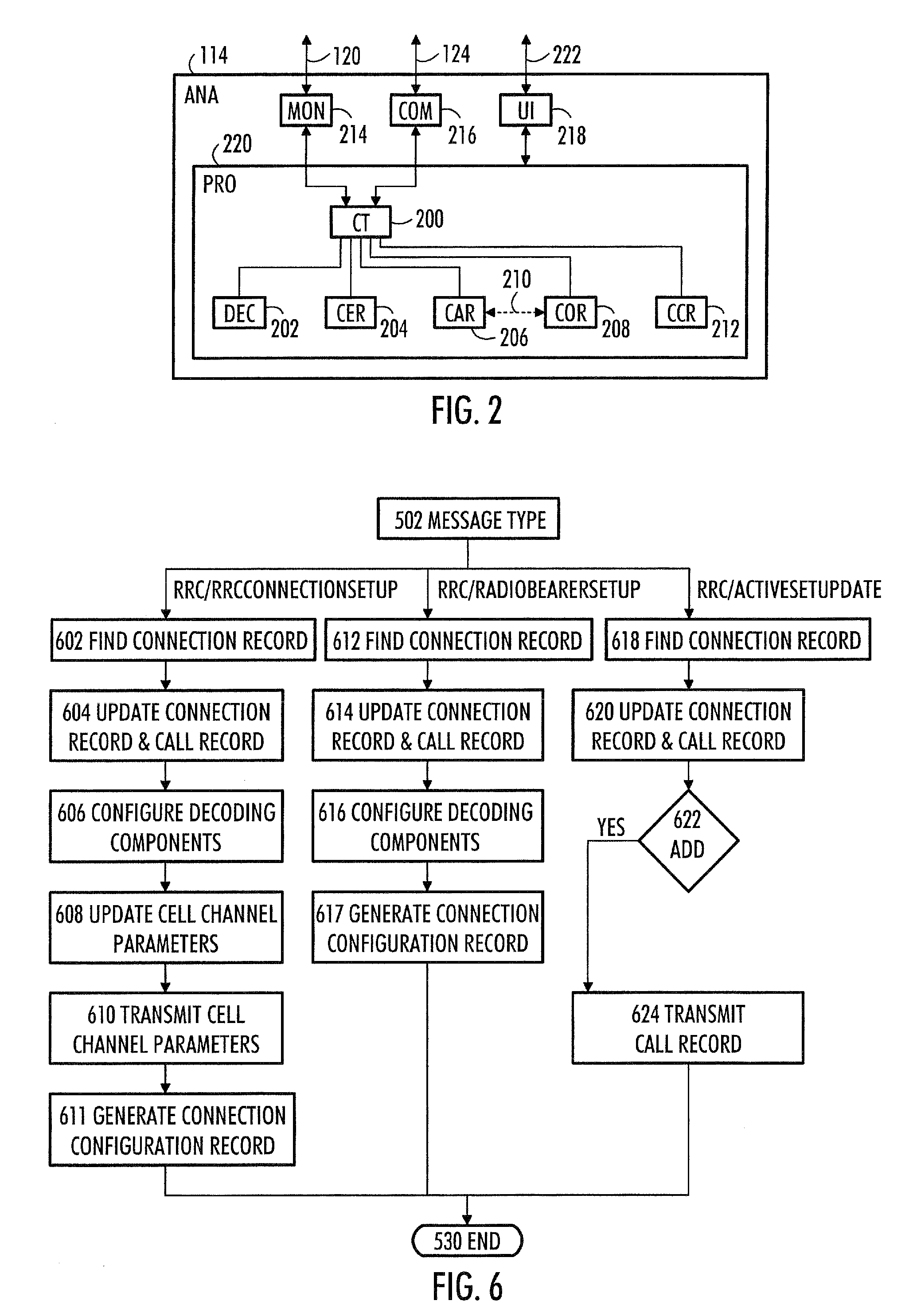
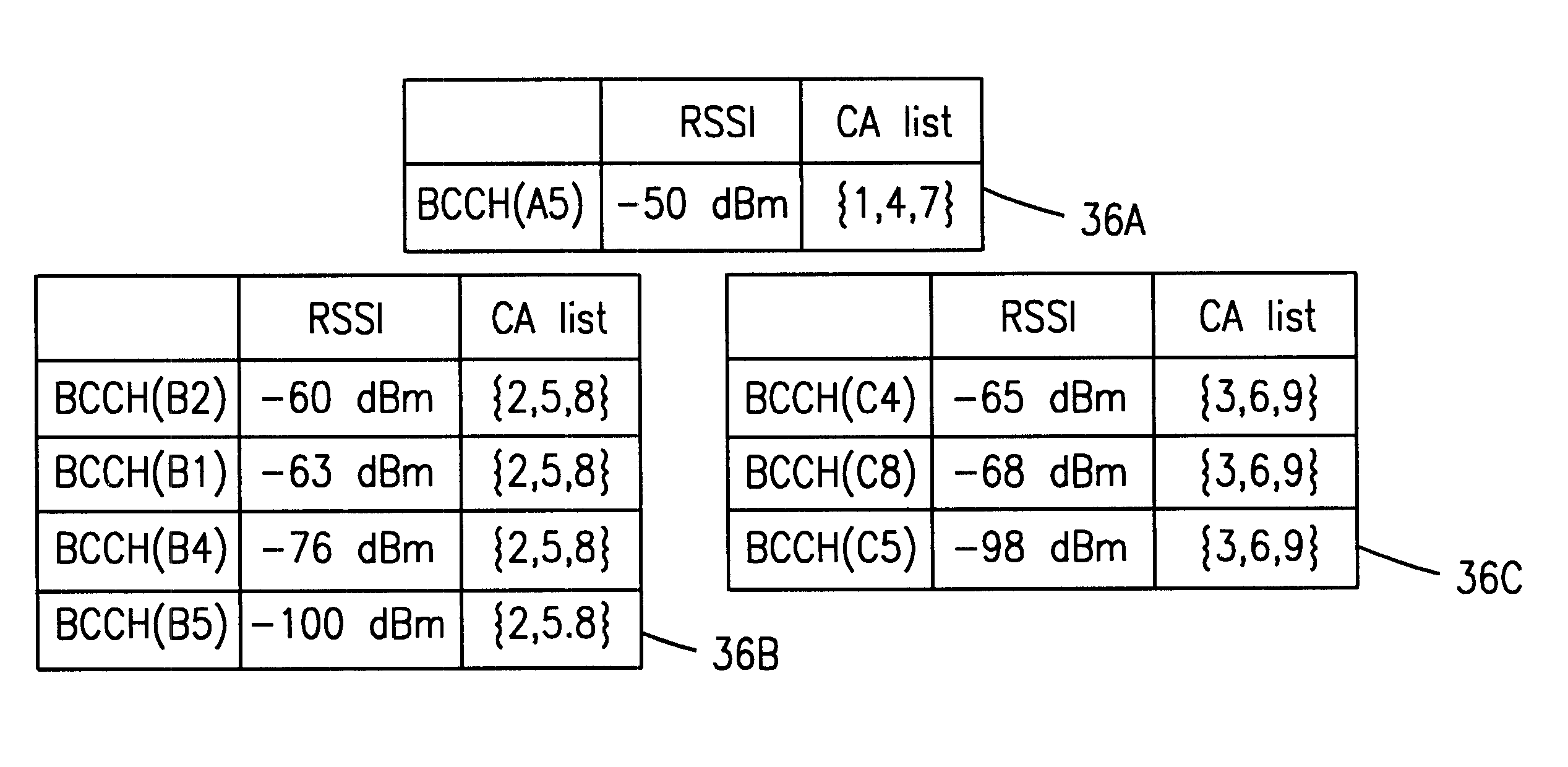
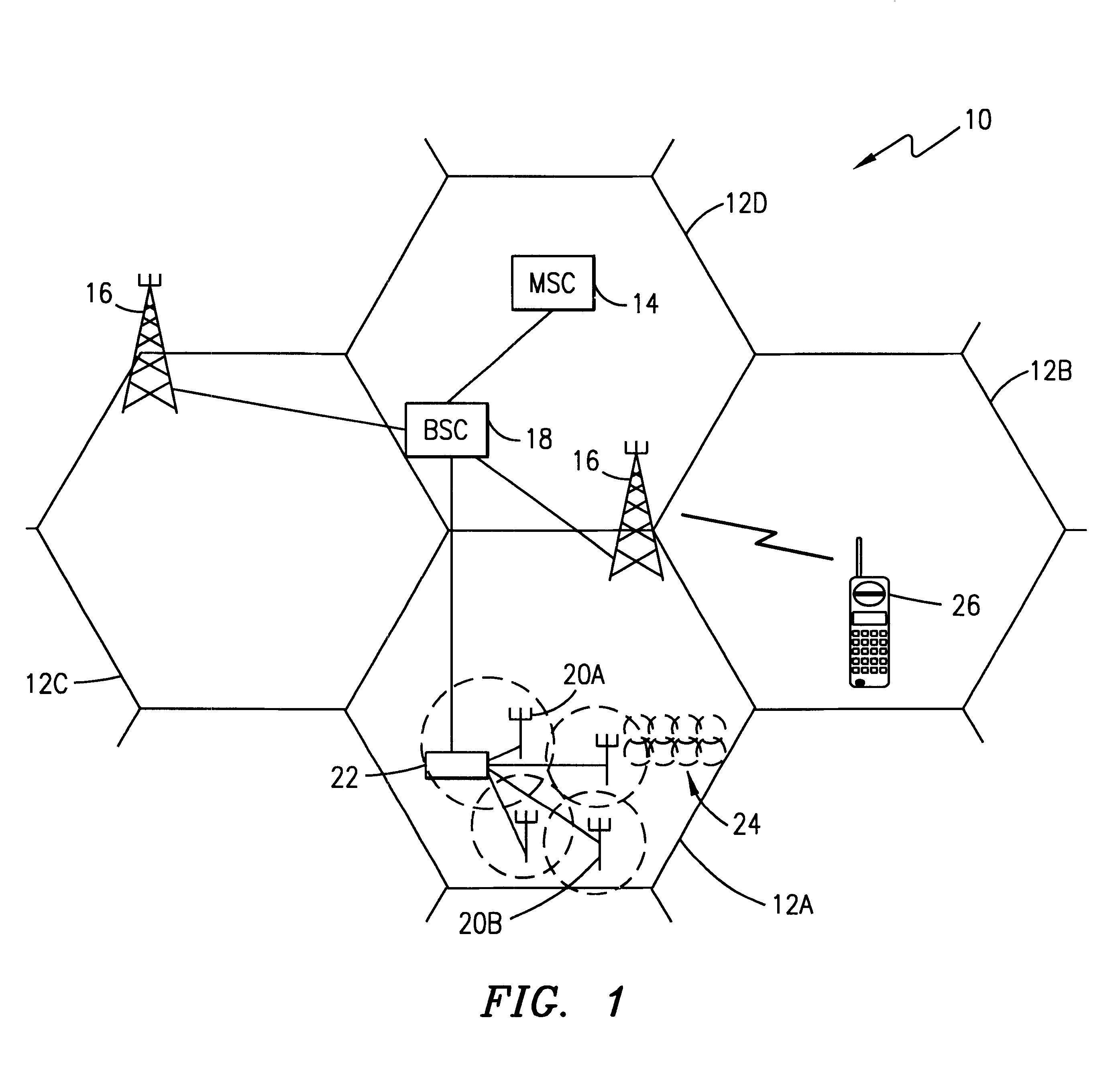
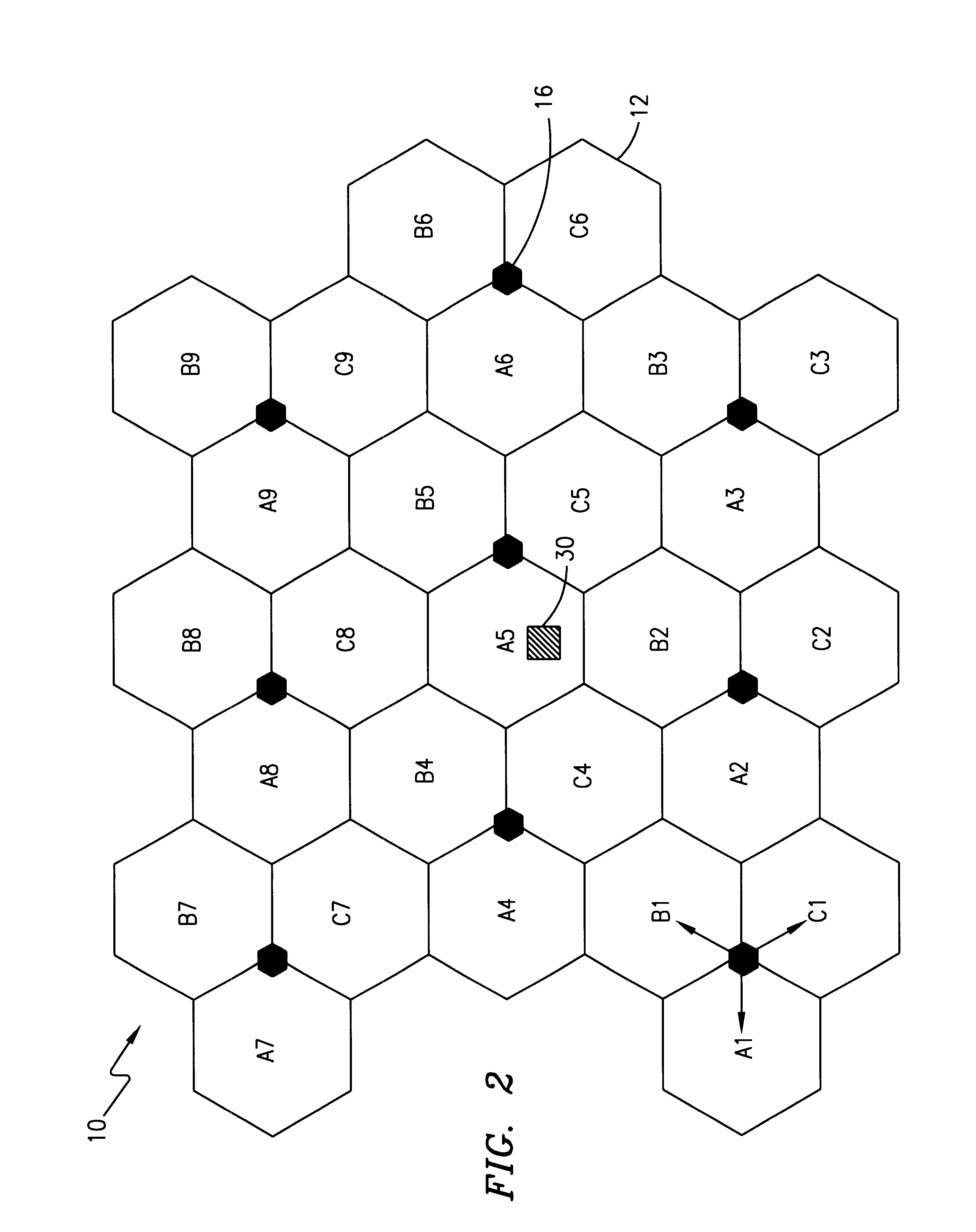
Patents
Literature
701 results about "Cellular radio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cellular radio. n. (Broadcasting) radio communication based on a network of transmitters each serving a small area known as a cell: used in personal communications systems in which the mobile receiver switches frequencies automatically as it passes from one cell to another.
Multi-beam antenna system for cellular radio base stations
InactiveUS6167286ASpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityCellular radioSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A base transceiver station operating a sectorized cell of a cellular radio system operates a plurality of narrow uplink main receive beams, and one or a plurality of uplink diversity received beams. A scanning means scans each of the uplink main receive beams to locate a communications channel on the main uplink beams. A diversity receiver receives a diverse beam signal from the diverse beam(s), which is compared with a beam signal received from a main uplink beam, and the main beam signal from the main beam, or a diverse beam signal from the diversity antenna is selected, depending on the comparative signal to noise ratio and signal strength of the main beam signal and diversity beam signal.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Cellular radio communications system
InactiveUS6748021B1Reduce bit error rateTime-division multiplexPhase-modulated carrier systemsCellular radioCommunications system
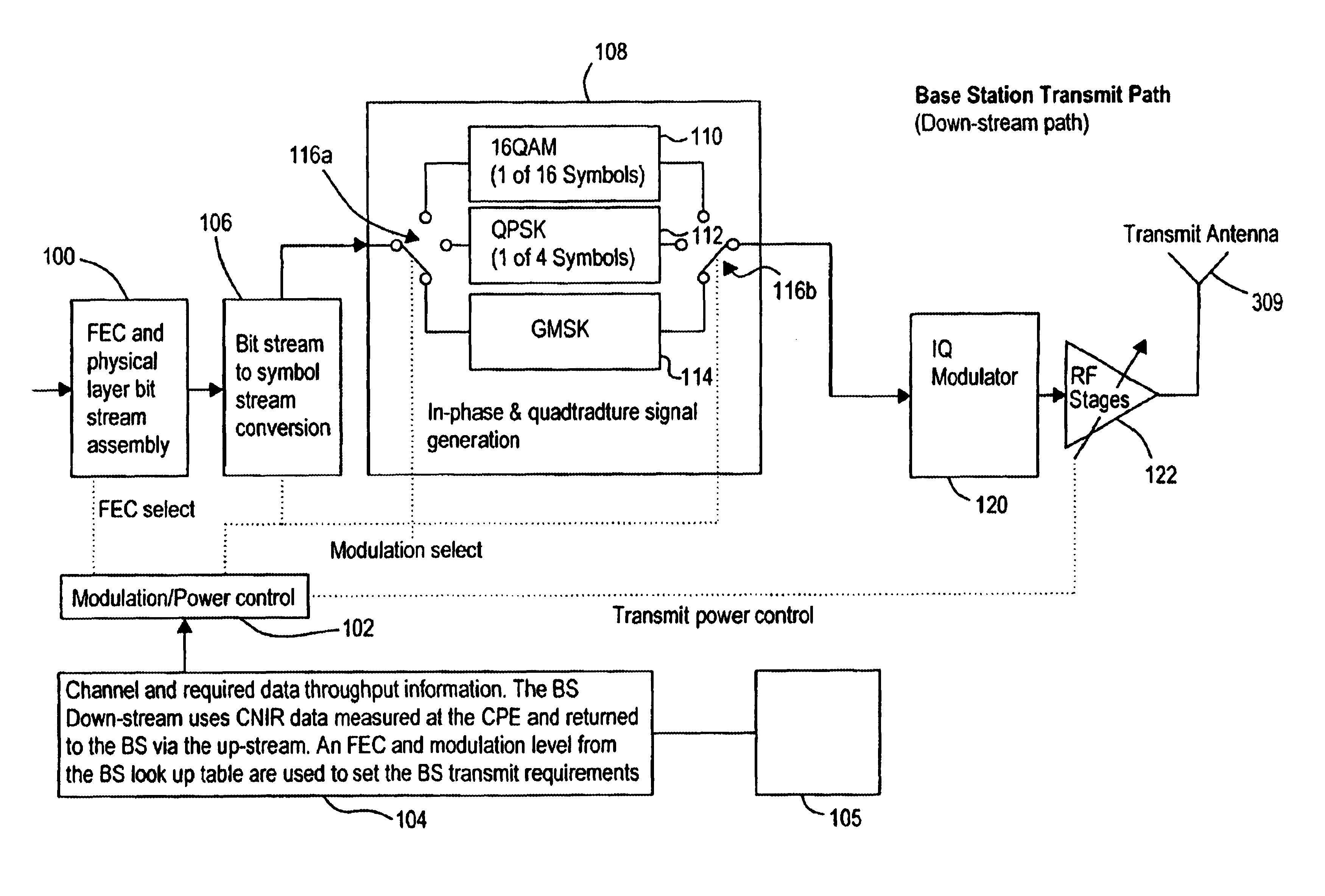
A cellular radio communication system is provided for transmitting data over a plurality of transmission links. The system includes means for generating a modulated signal by applying a constant amplitude envelope modulation scheme to data to be transmitted across poor quality transmission links and amplifier means for non-linearly amplifying the modulated signal. The system can additionally include means for generating a second modulated signal by applying an amplitude dependent modulation scheme to data to be transmitted across higher quality transmission links and amplifier means for linearly amplifying the second modulated signal. Using a constant amplitude envelope modulation scheme, such as GMSK or MLCAM for poorer quality links means that for these links signals can be amplifier non-linearly at higher gains.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Reuse of a physical control channel in a distributed cellular radio communication system
InactiveUS6108550AReduce generationIncrease capacityTransmission control/equalisingRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCellular radioCommunications system
The present invention relates to the reuse of a control channel in a distributed cellular radio communication system. At least one physical channel, the so called physical control channel, in the radio communication system is used for transferring logical control channels. According to the present invention the physical uplink control channel can be reused with respect to logical control channels comprising an access request. The physical downlink control channel can be reused with respect to logical control channels comprising a message that access is granted to a mobile station or a message that someone requests contact with a mobile station. According to the invention the physical uplink control channel and / or the physical downlink control channel is reused. This means that more connections per time unit may be established in the radio communication system.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
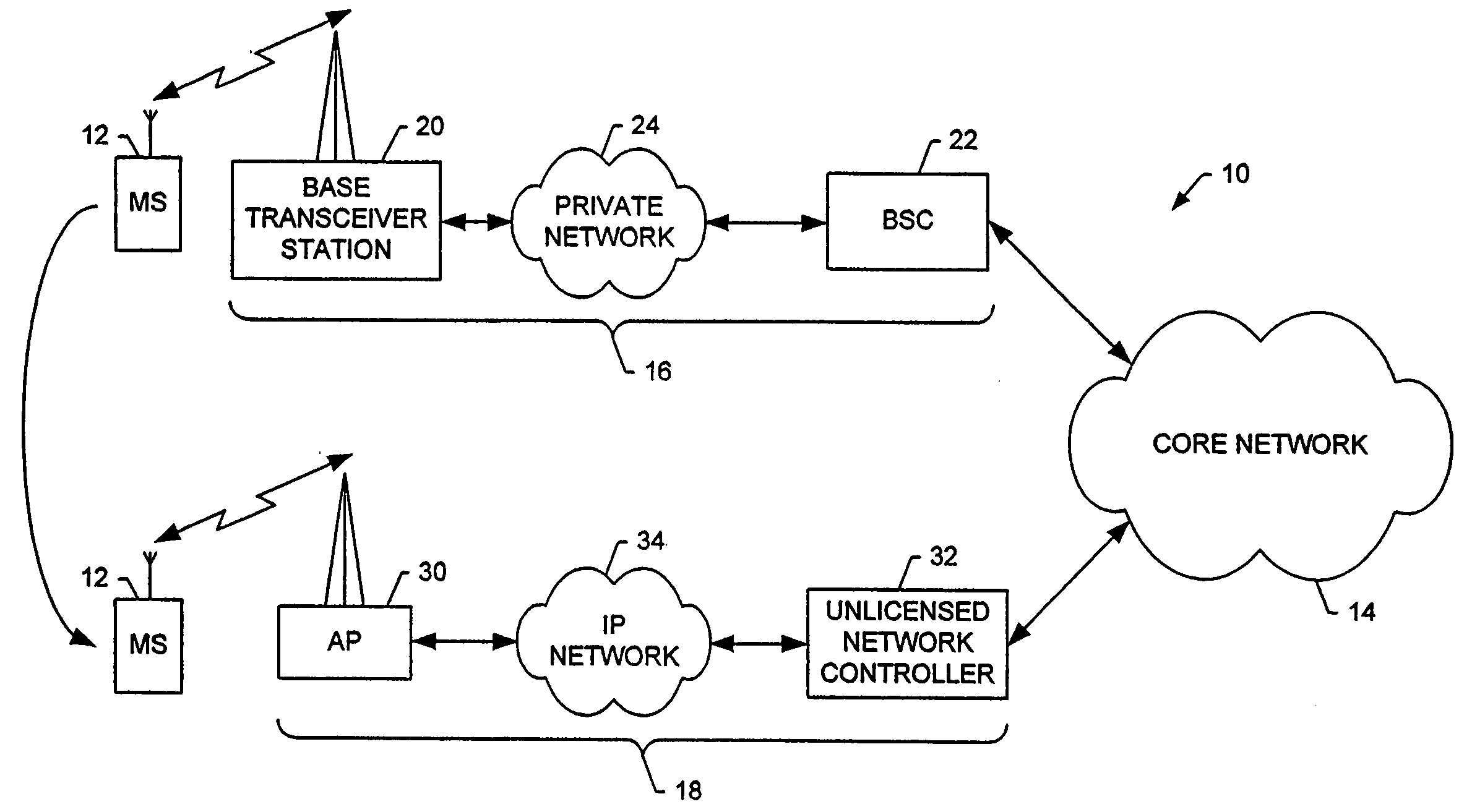
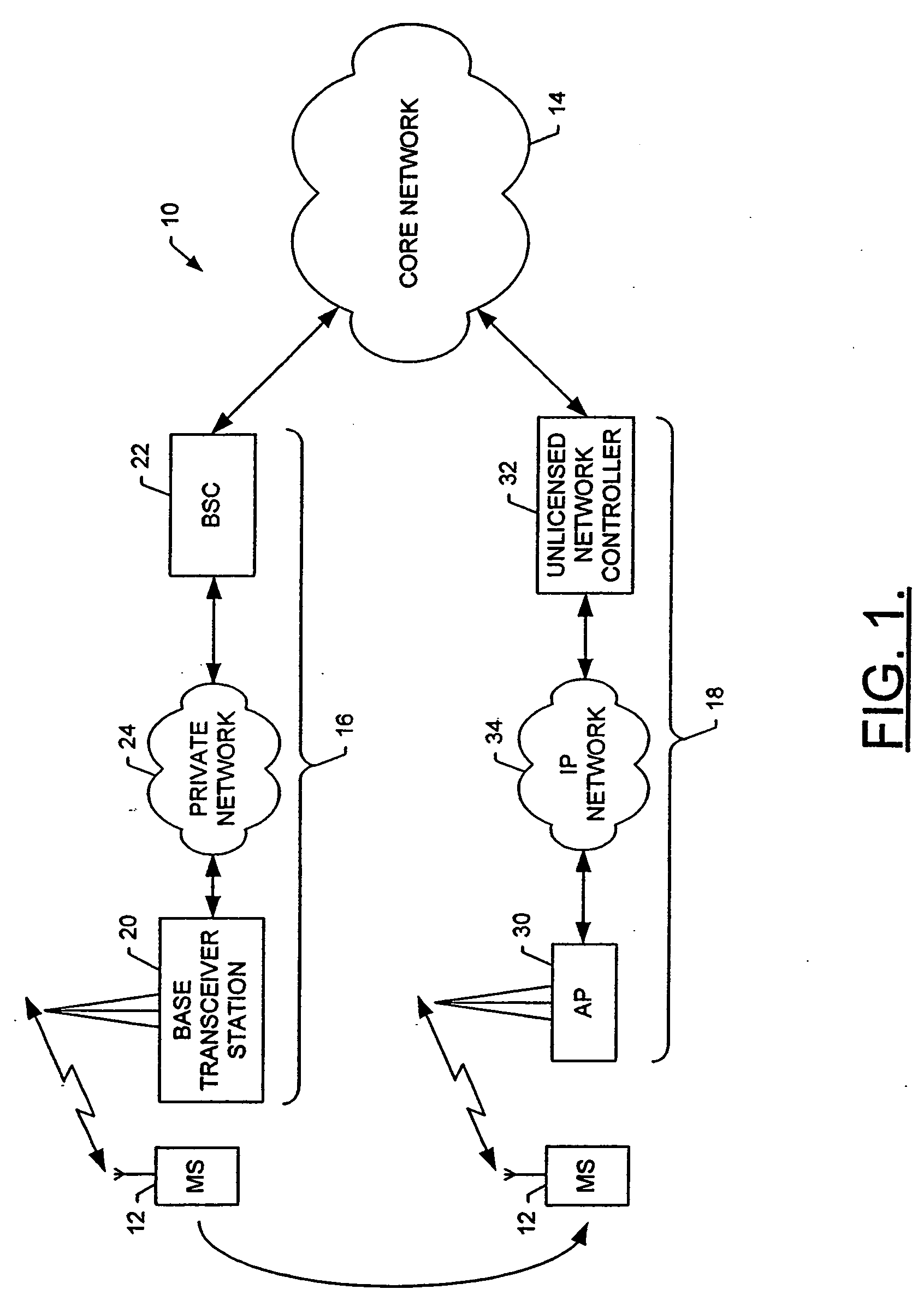
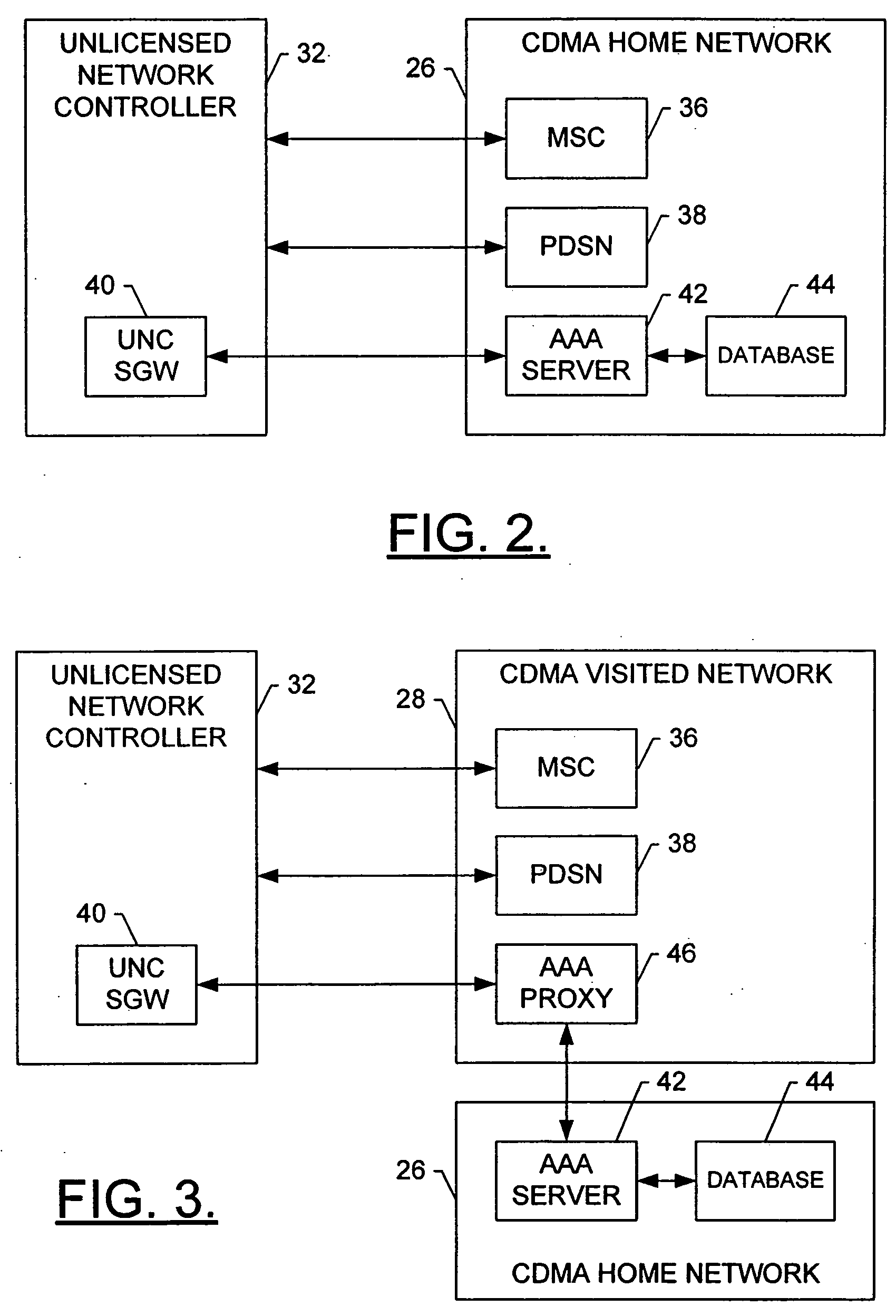
Method, system and mobile station for handing off communications from a cellular radio access network to an unlicensed mobile access network
InactiveUS20060094431A1Convenient handoverEasy transitionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesAccess networkCellular radio
A method, system and mobile station for handing off communications from a cellular radio access network, such as a code division multiple access (CDMA) radio access network, to an unlicensed mobile access network (UMAN) are provided. The handoff may be effected by a signaling sequence between the mobile station, an unlicensed network controller of the UMAN, a base station controller of the cellular radio access network and the core network. In this signaling sequence, the UMAN may be identified in various manners, such as by means of an otherwise unassigned pilot PN offset or by means of a band class and an invalid frequency.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
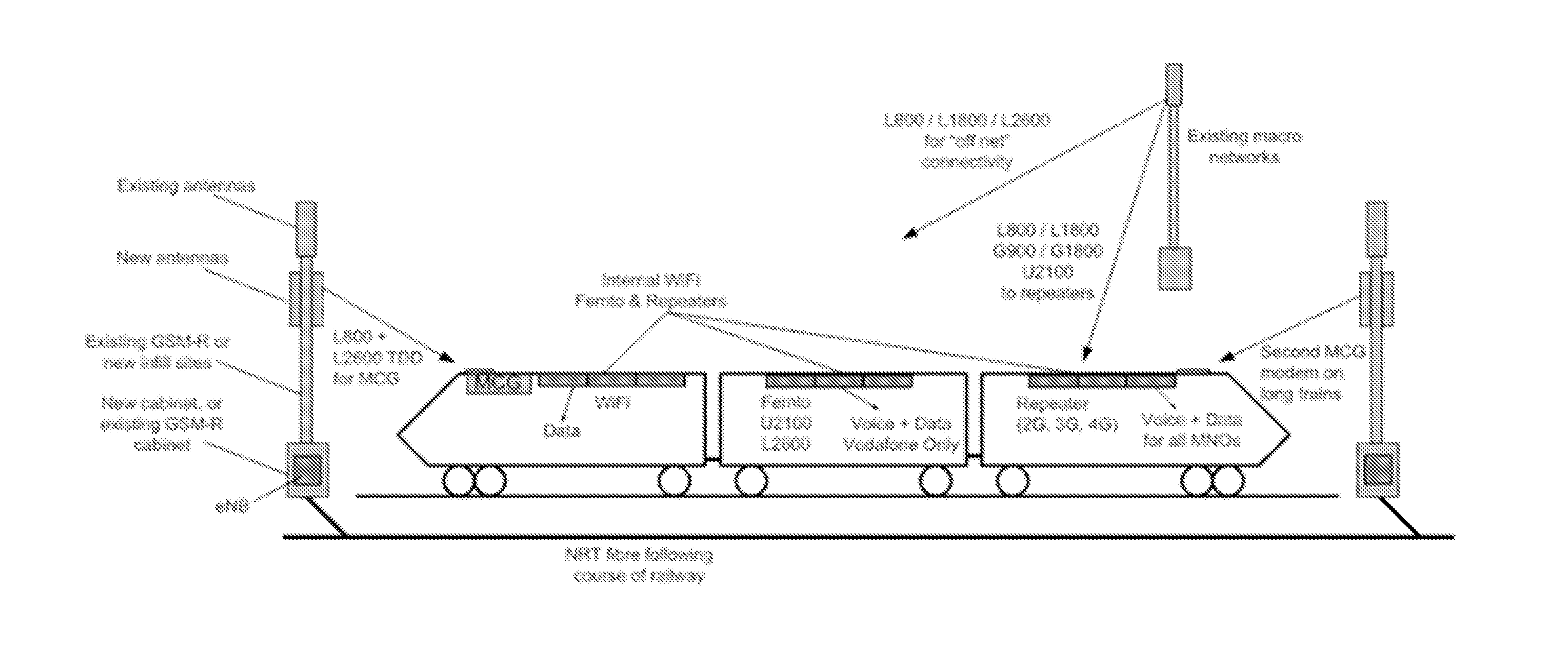
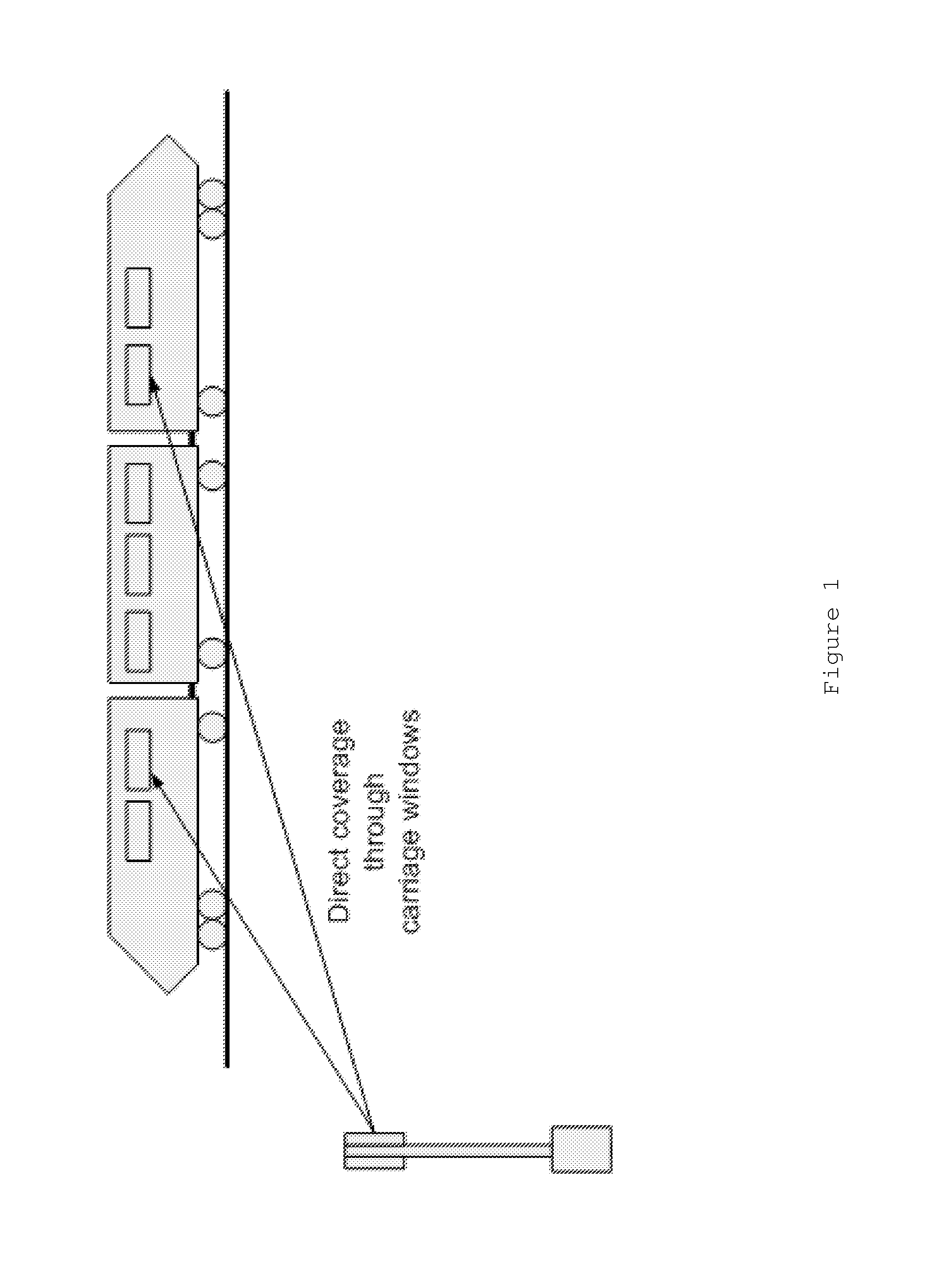
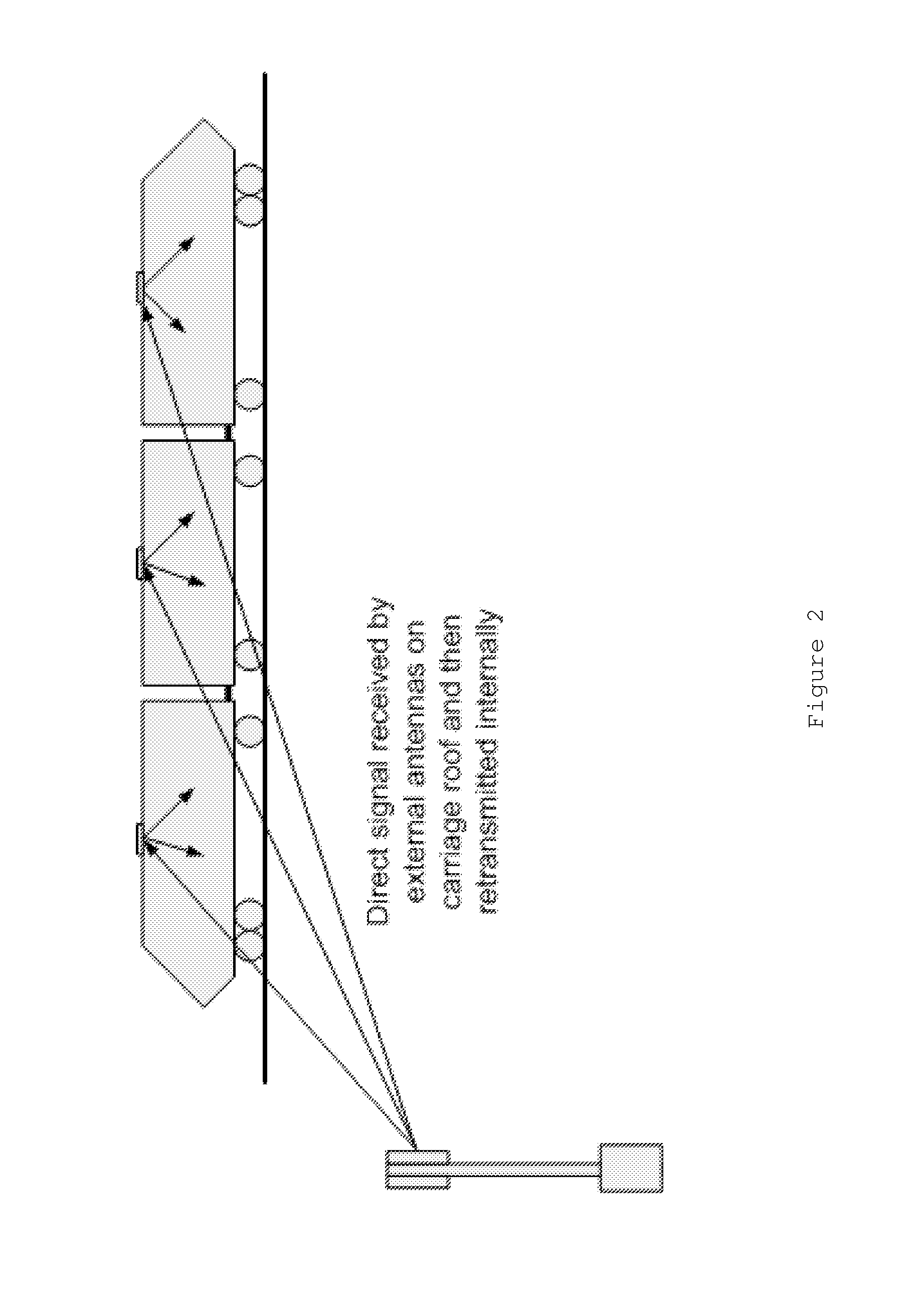
Providing broadband service to trains
InactiveUS20160249233A1Improve communication performanceSimple procedureSpatial transmit diversityNetwork topologiesCellular radioRadio networks
A cellular radio network system and method for communicating with at least one vehicle-based mobile gateway terminal is provided. The at least one mobile gateway terminal is configured to communicate a network service for one or more user mobile terminals on-board the vehicle. A plurality of network cells provide cellular radio network coverage along a route of the vehicle. Each network cell is dedicated for communication with the at least one vehicle-based mobile gateway terminal so as to allow communication between the at least one vehicle-based mobile gateway terminal and a core network of the cellular radio network.
Owner:VODAFONE IP LICENSING
Integration of wireless LAN and cellular distributed antenna
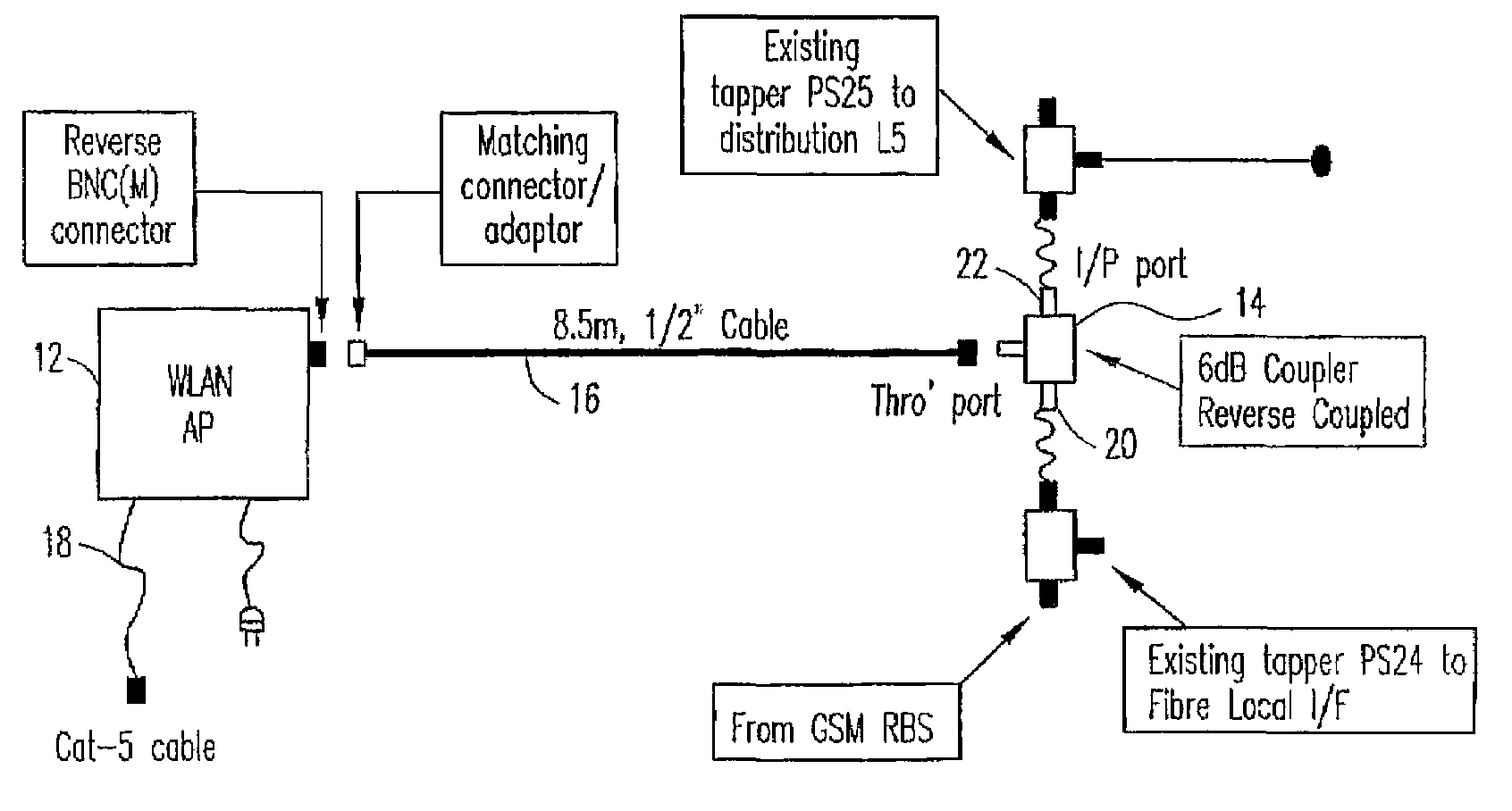
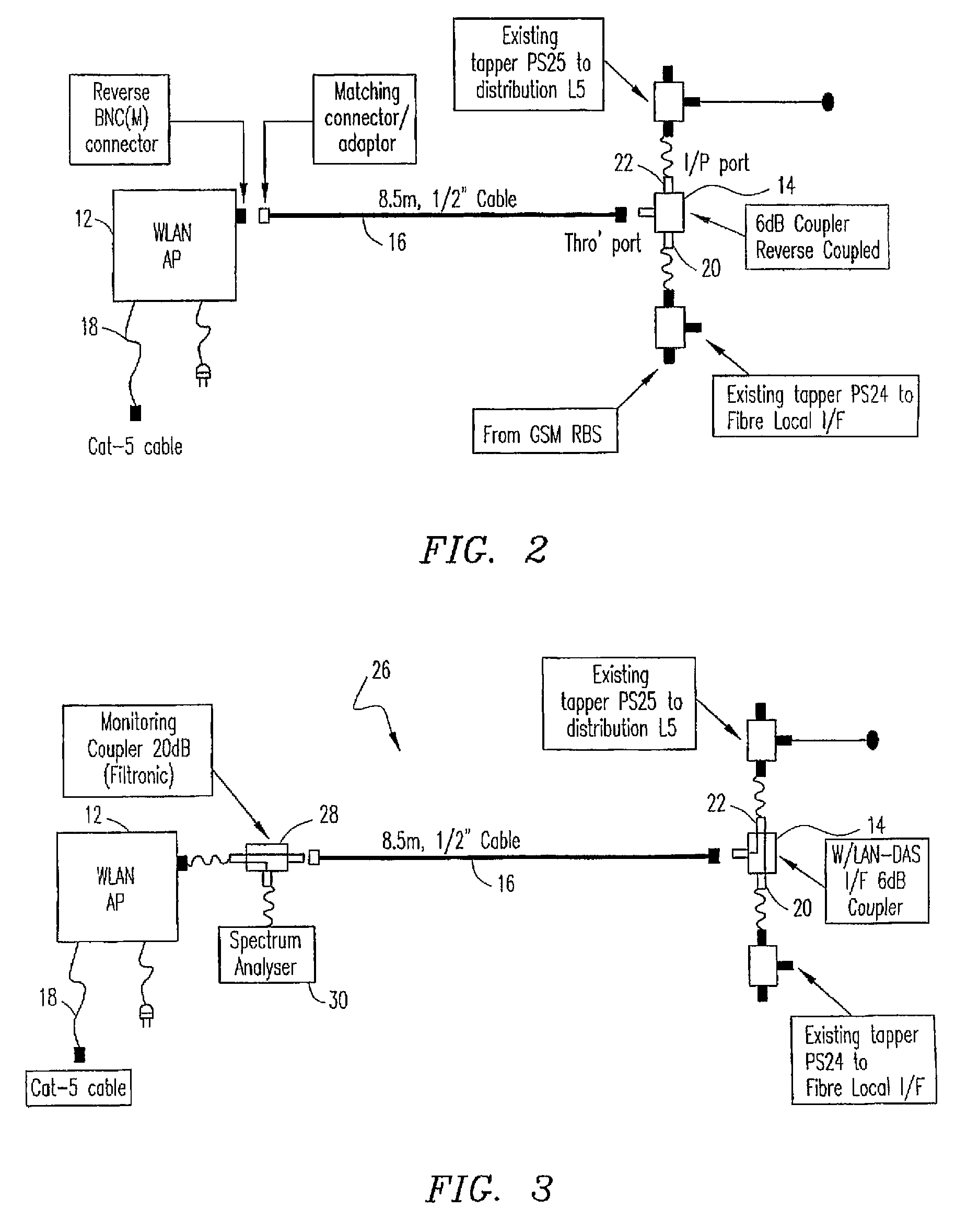
InactiveUS7082320B2Data switching by path configurationSubstation equipmentCellular radioDistributed antenna system
A system and method for supporting wireless in-building communications uses a wireless local area network access point, a cellular distributed antenna system, and a cellular radio base station coupled to the cellular distributed antenna system. The cellular radio base station provides cellular communication service via the cellular distributed antenna system. A coupler couples the wireless local area network access point to the cellular distributed antenna system in reverse mode, such that the wireless local area network access point provides wireless local area network service via the cellular distributed antenna system.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
System access method and apparatus of a narrowband terminal in a wireless communication system supporting wideband and narrowband terminals
ActiveUS20130077582A1Synchronisation arrangementWireless commuication servicesCellular radioAccess method
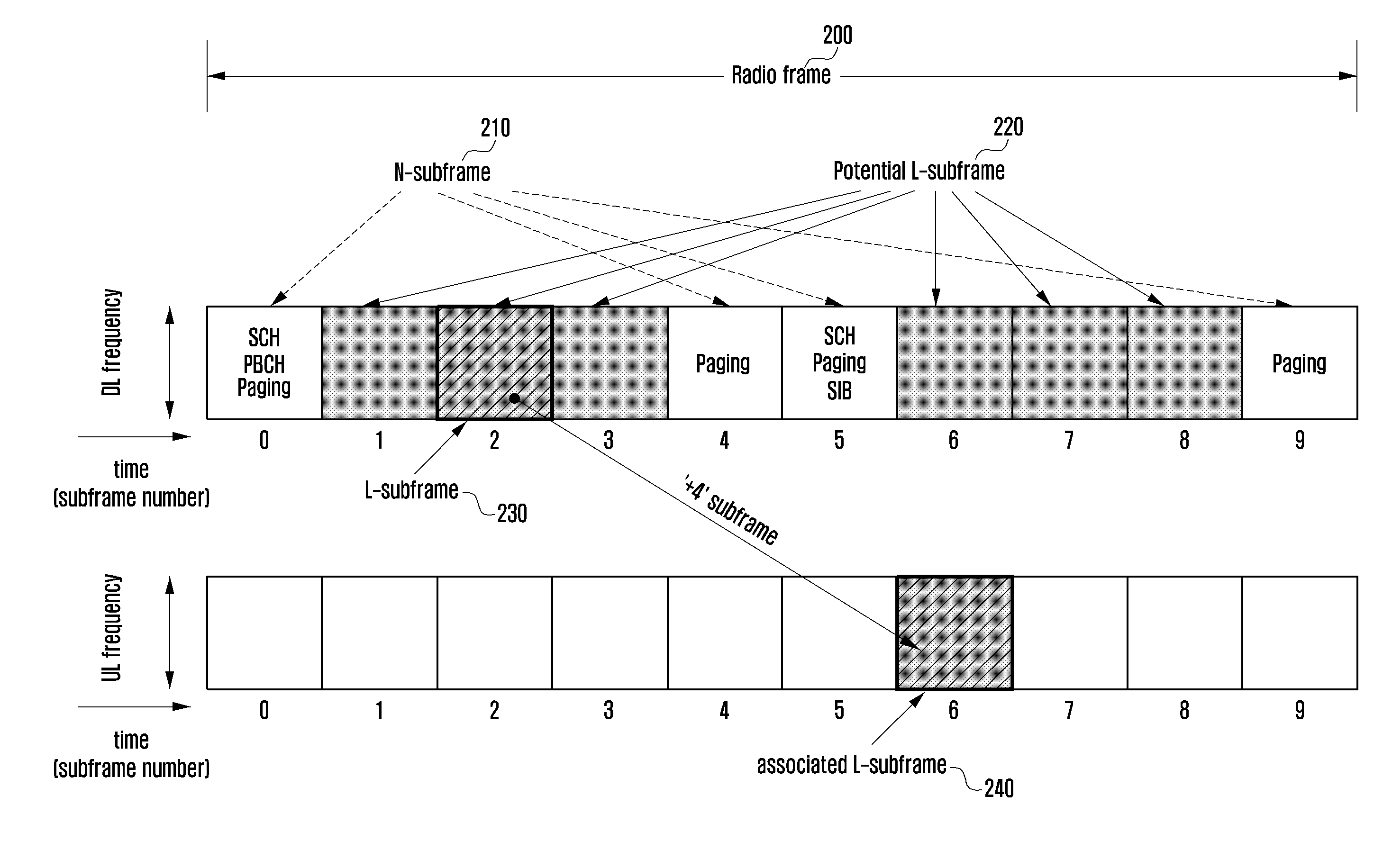
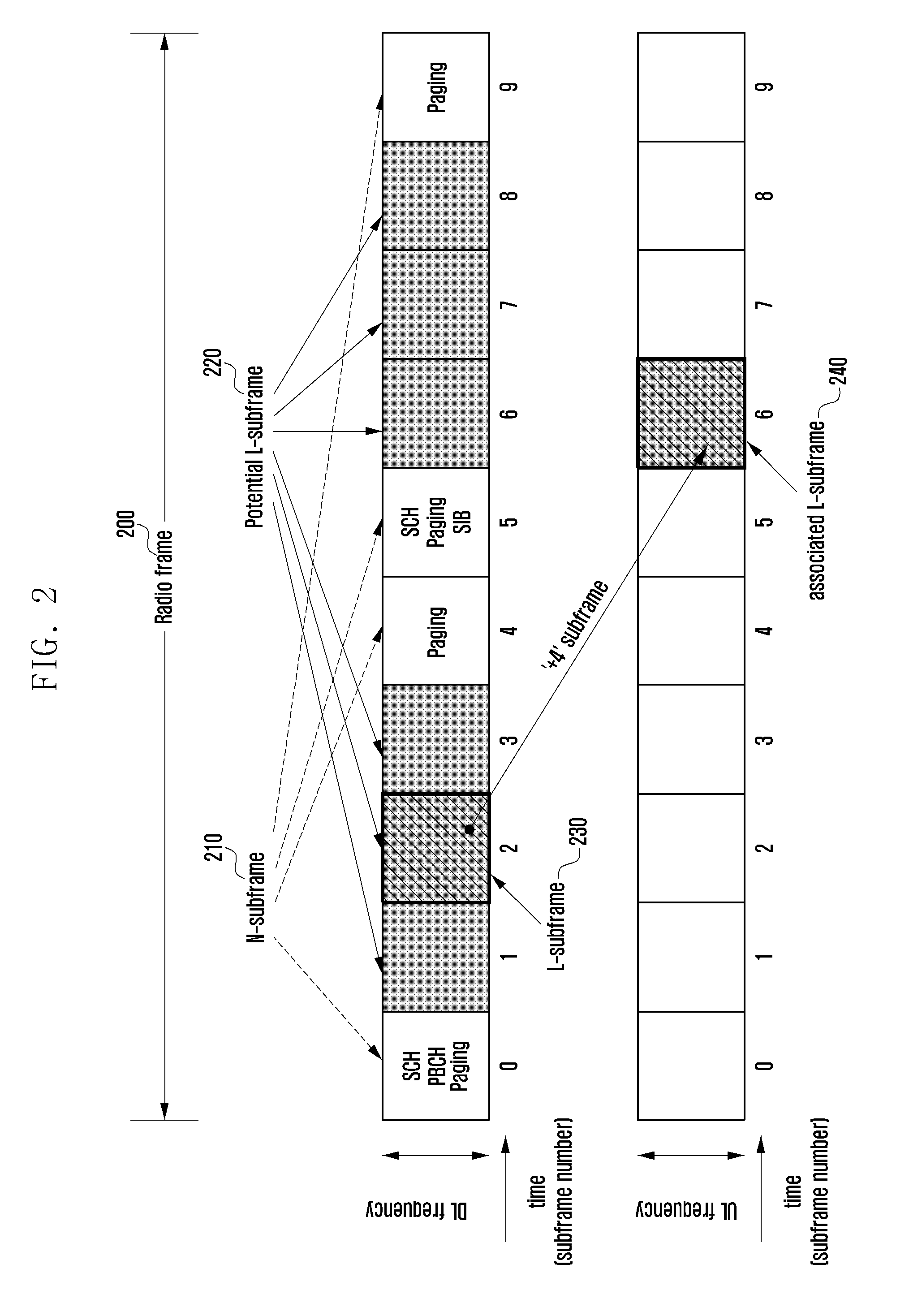
A system access method of a narrowband terminal is provided for supporting both wideband and narrowband terminals in a cellular radio communication system. The method includes broadcasting a Shared CHannel (SCH) for a terminal to acquire system synchronization; transmitting a Low-end Master Information Block (L-MIB) including control information on an L-subframe configuration for supporting a second type terminal and a sub-band configuration of the L-subframe; transmitting a Low-end System Information Block (L-SIB) including information on downlink reception and uplink transmission of the second type terminal; and performing a random access procedure, when an attach request is received from one of the first type terminals and the second type terminals.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
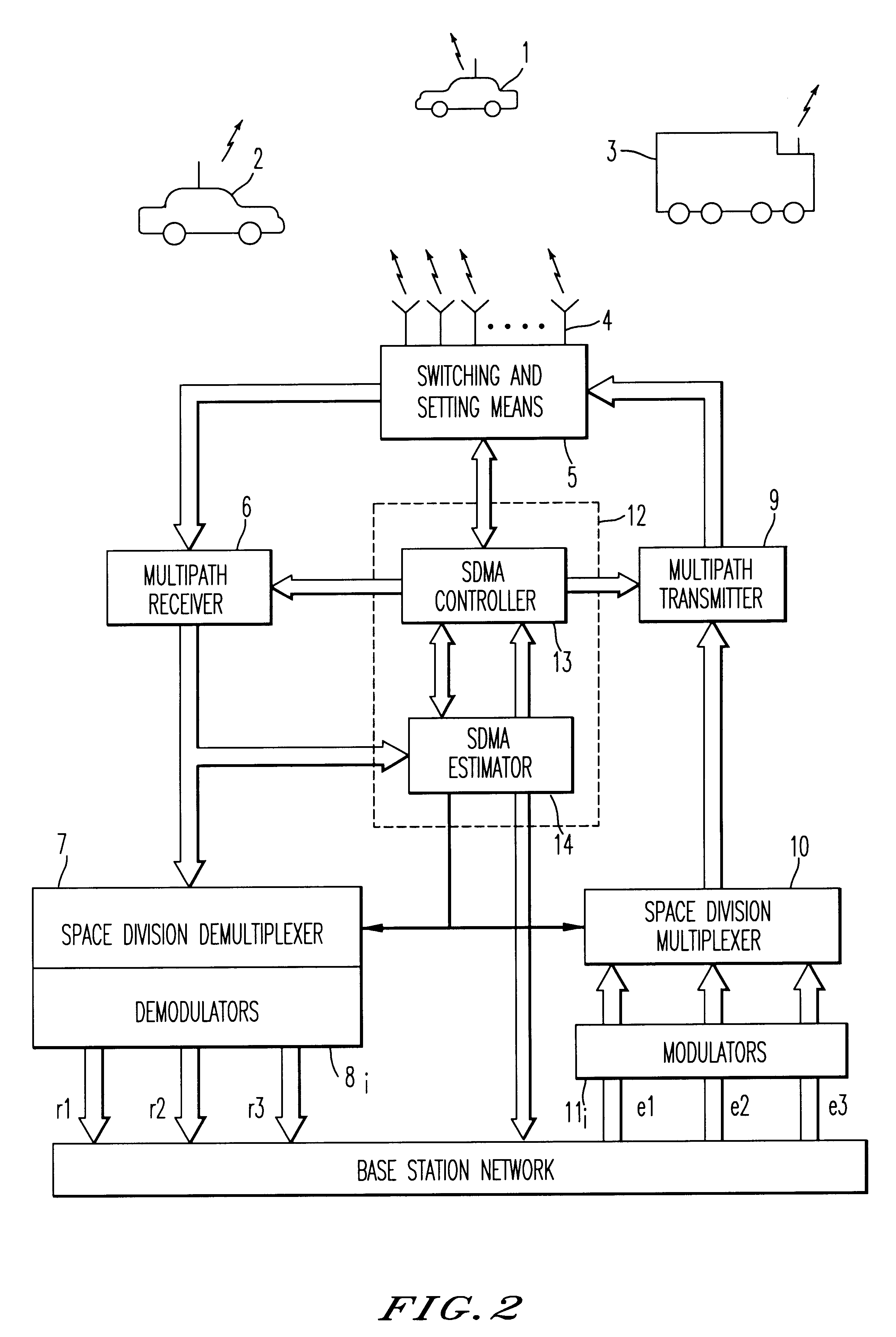
Method and device for space division multiplexing of radio signals transmitted in cellular radio communications
InactiveUS6240098B1Space can be allowedImprove performanceRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsSpatial transmit diversityEngineeringTime-division multiplexing
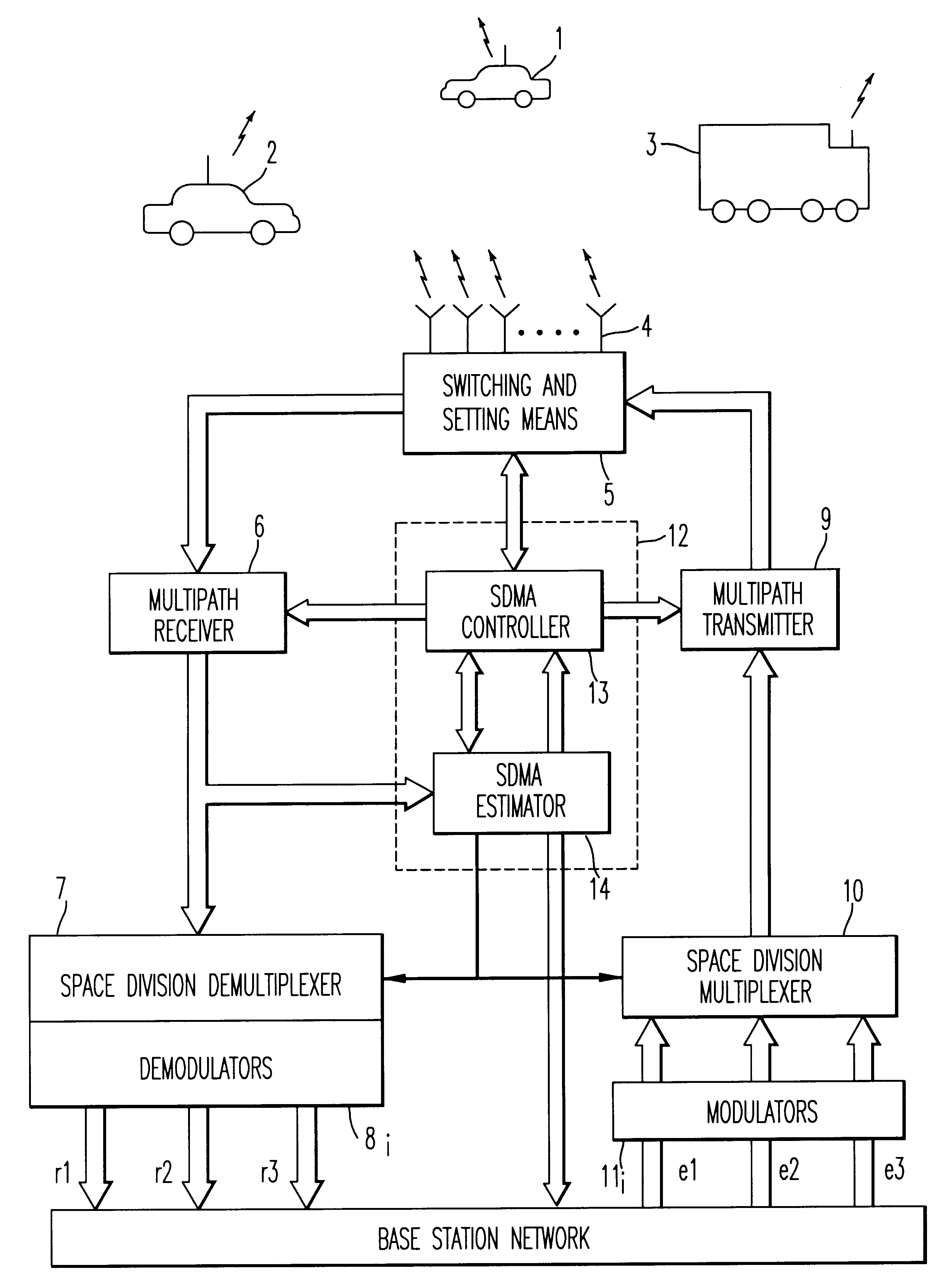
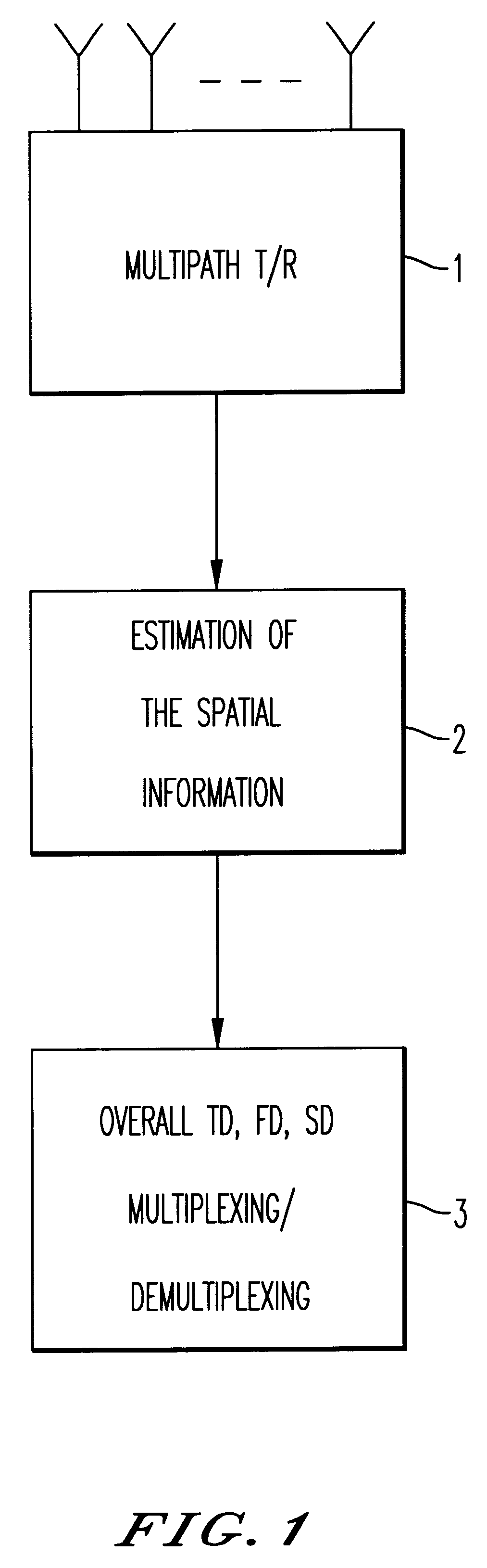
A method and apparatus for spatial multiplexing and demultiplexing of radio signals. A multichannel transmitter and receiver is integrated in a base station and coupled to an antenna array. Using digital radio signals containing previously known or non-Gaussian sequences and arranged in frames, the spatial information about each mobile unit is estimated on the basis of the signal received by the receiver for the reception and transmission frequencies. This is done by known sequences or by blind source separation methods. The respective paths of each mobile unit with the power above a predetermined threshold is isolated by spatial filtering in the presence of multiple channel paths in order to provide spatial demultiplexing. Simultaneously, the intended signal is transmitted in the direction of the main path of each mobile unit while protecting each mobile unit from signals transmitted in the direction of other mobile units by spatial filtering with cancelling constraints in order to provide spatial multiplexing.
Owner:THOMSON CSF SA
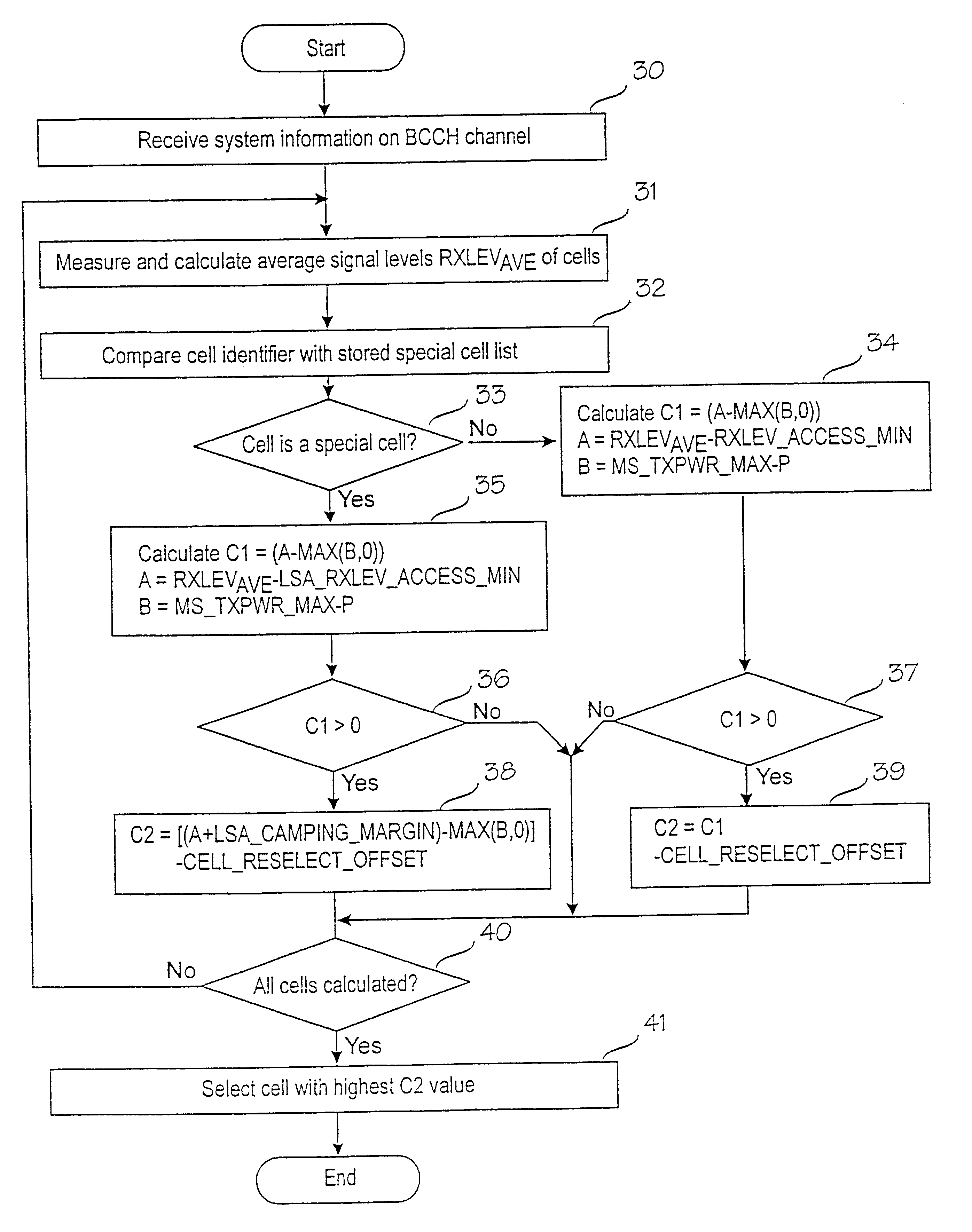
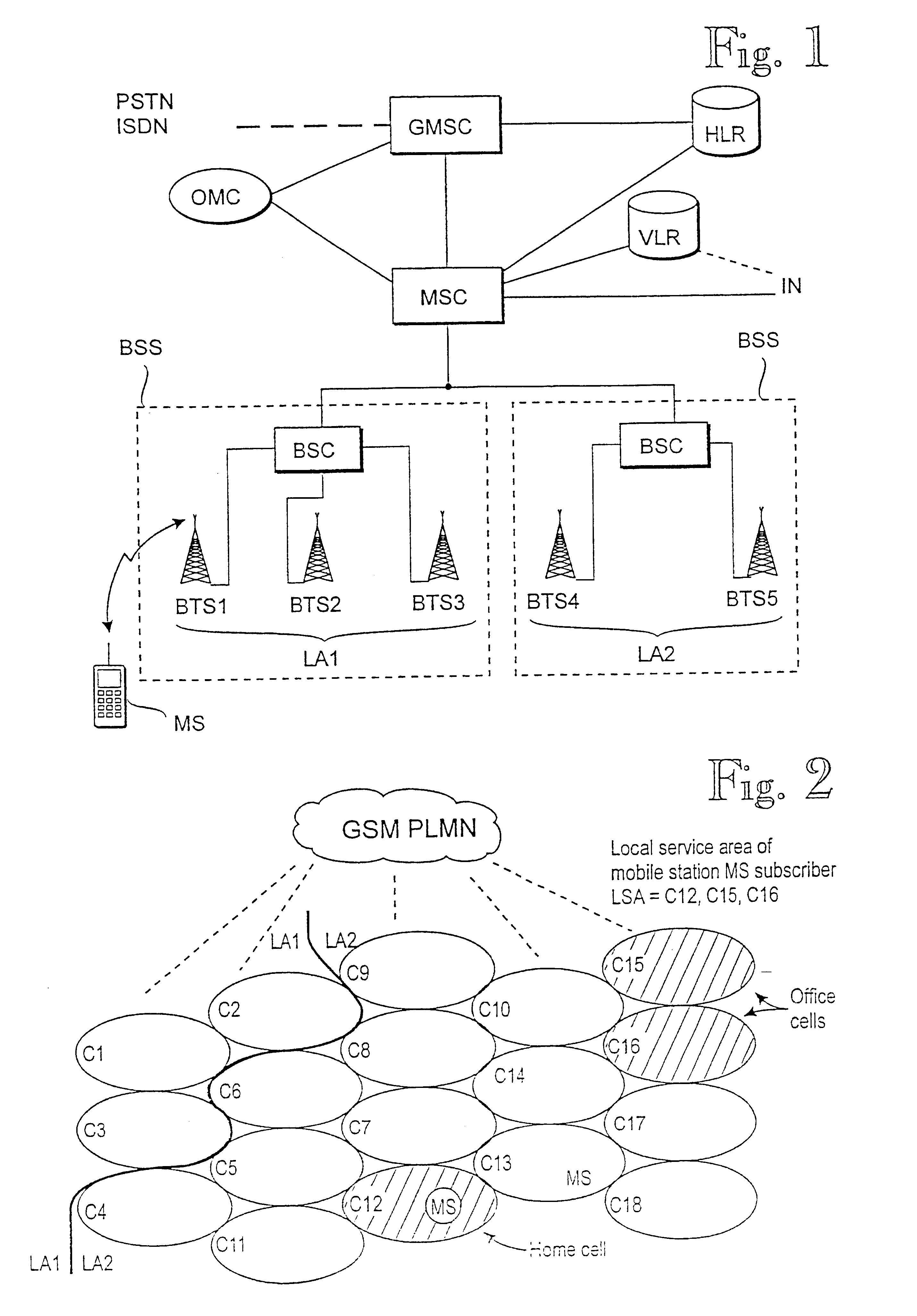
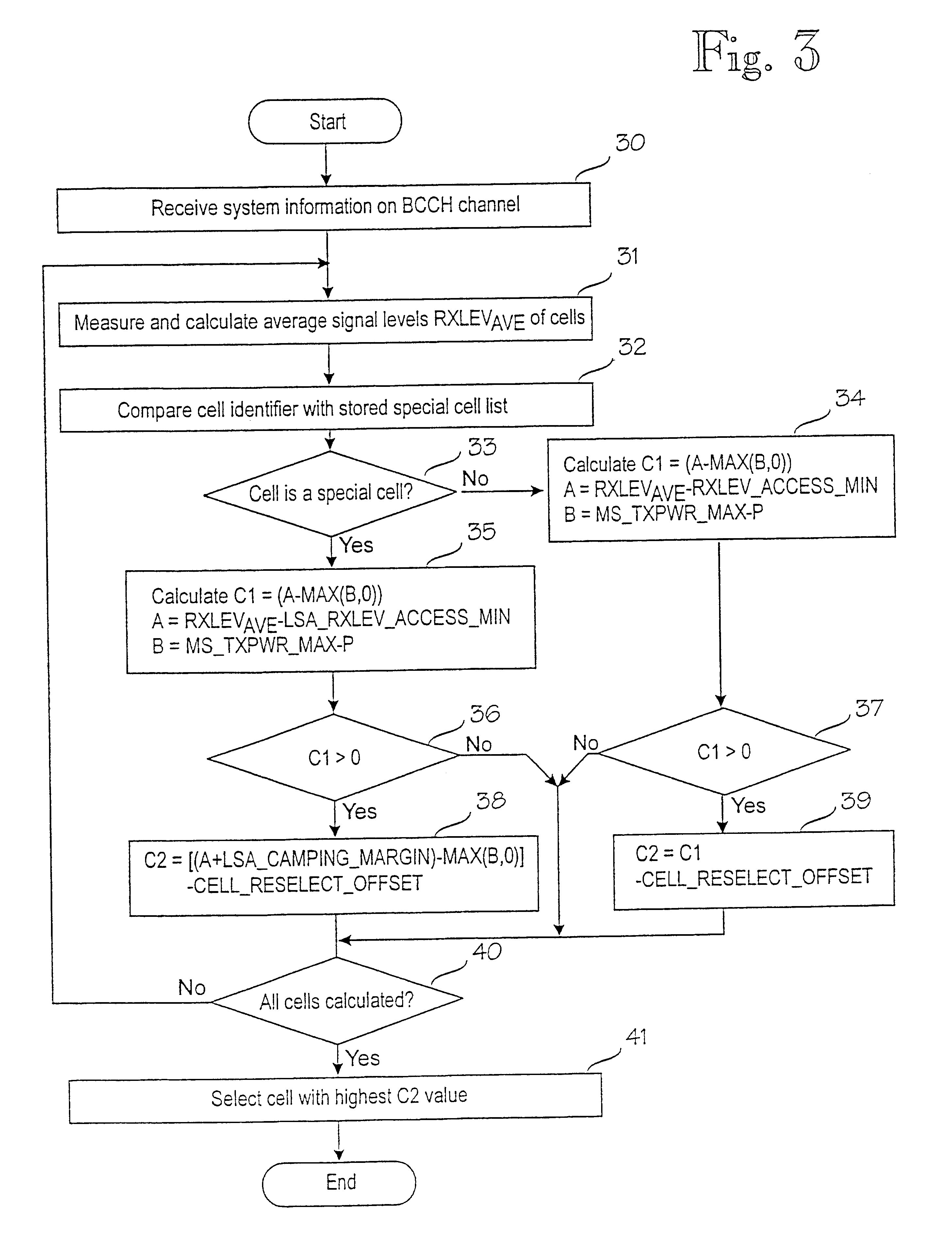
Method for selecting cell in cellular network
InactiveUS6434389B1Enhance cell selectionExpand selectionAssess restrictionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCellular radioRadio networks
The present invention relates to prioritizing special cells in cell selection in a cellular radio network. In a cellular radio network one or more cells provide a subscriber with special services or tariffs not offered to all subscribers. These cells are called subscriber's special cells. The mobile station measures an average reception level and calculates by means of them cell selection parameters on the basis of which the best cell is selected. In accordance with the invention, when the mobile station detects that the cell is one of cells of a special cell list stored in a memory, it checks first if the cell fulfils a minimum requirement of cell selection on the basis of the measured signal level. If the minimum requirement is fulfilled, the mobile station manipulates the calculation of the cell selection parameter of a special cell to the effect that the selection probability of a special cell is improved with respect to a normal cell. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, the manipulation of the calculation comprises a step of adding a predetermined margin to the measured signal level of a special cell before the cell selection parameter is calculated. This will minimize the possibility that the mobile station would accidentally be camped on a normal cell when it is within the area of a special cell.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Communication system
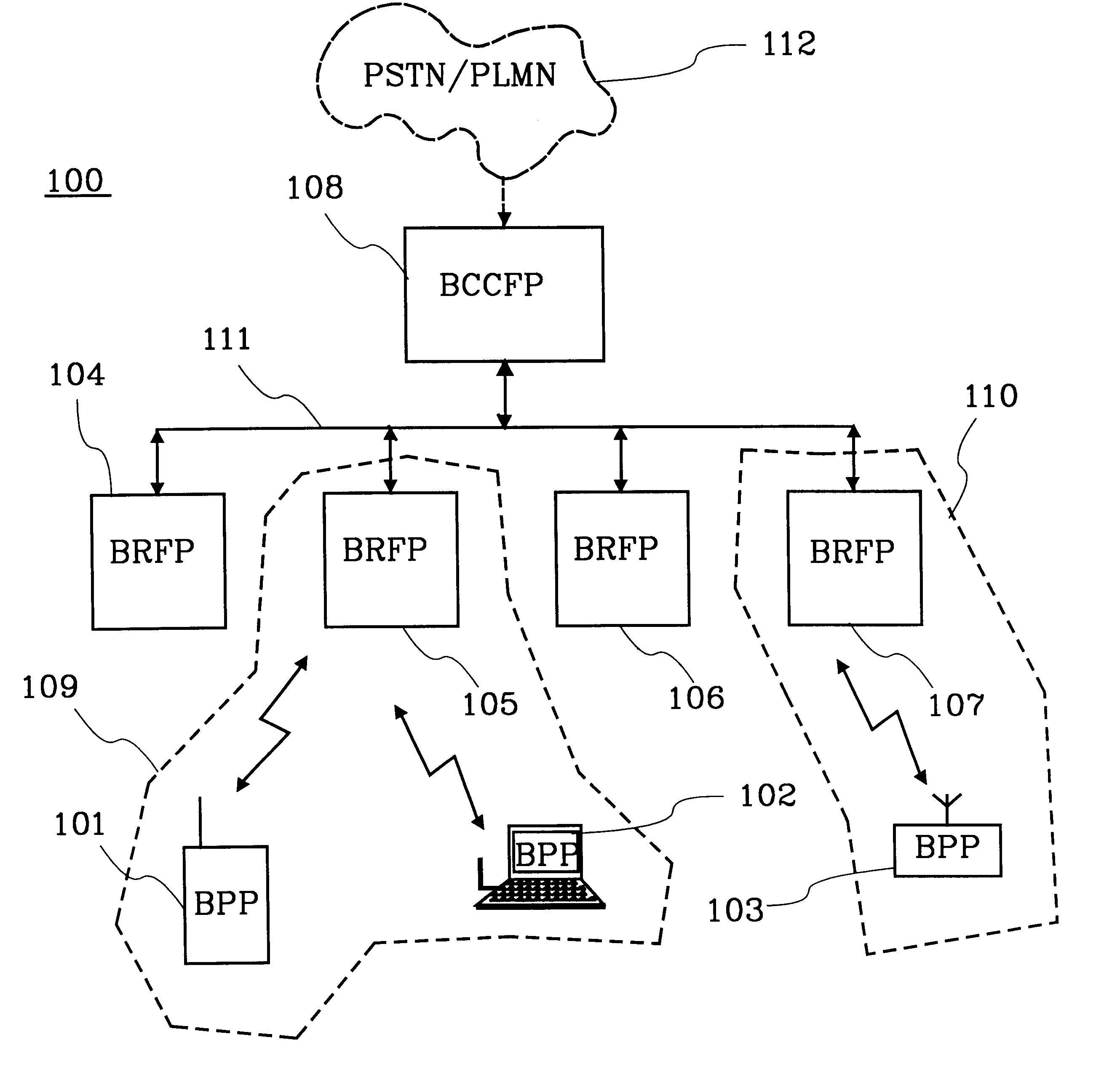
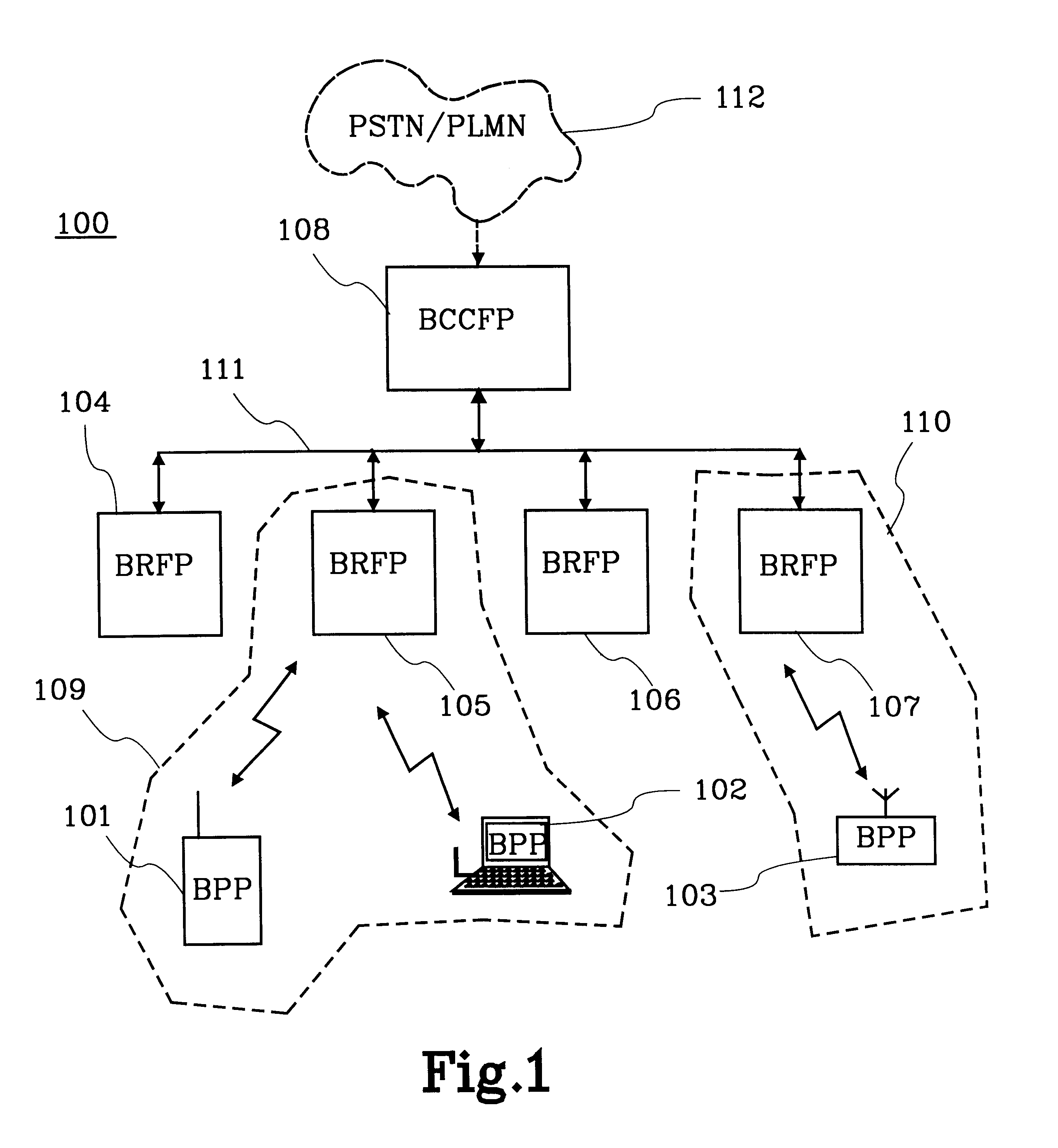
InactiveUS6788656B1Keep trackNetwork topologiesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsBroadcast channelsCellular radio
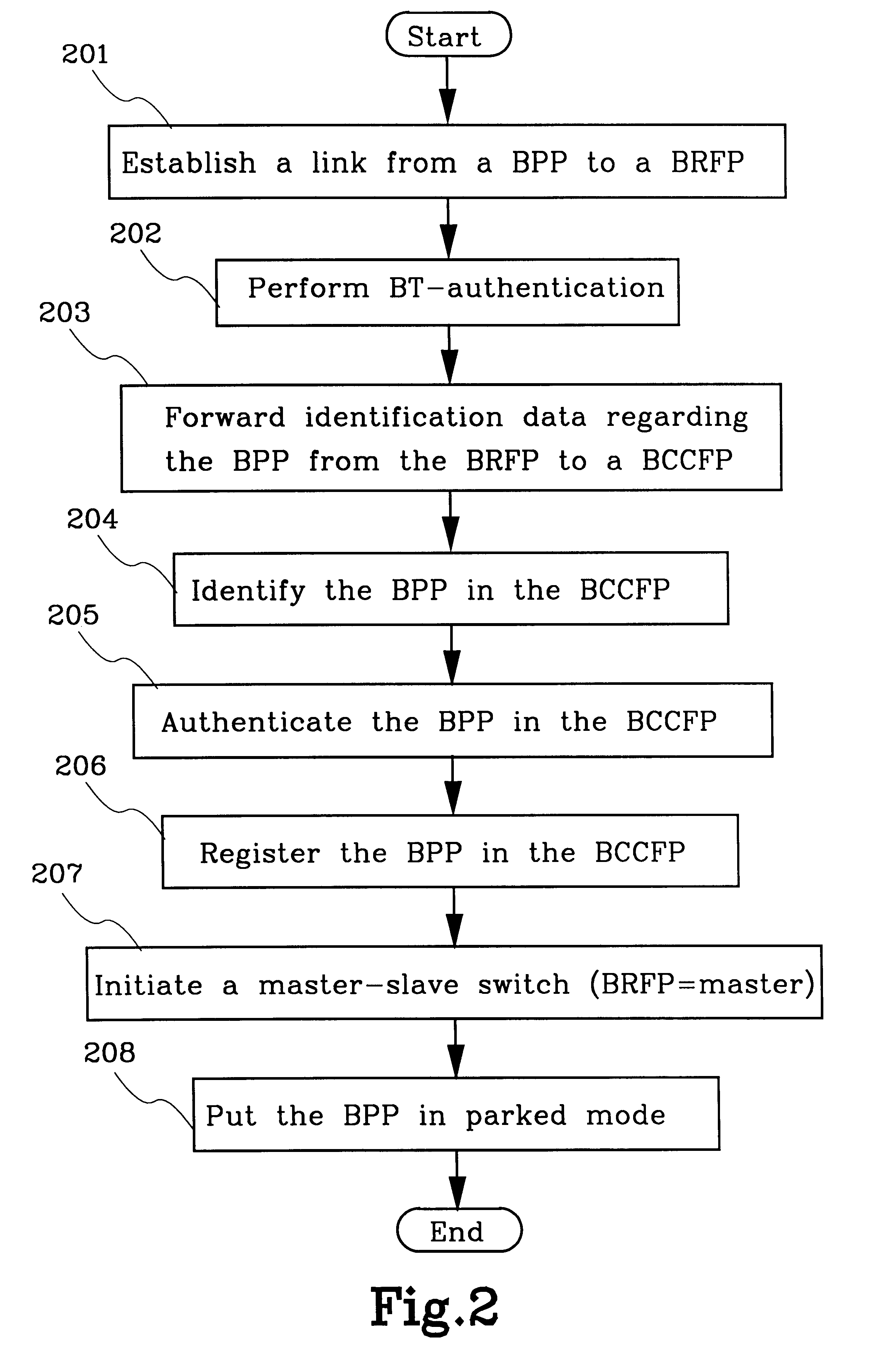
The present invention relates to methods and means for creating a cellular radio communication system (100) out of a number of local radio networks (109, 110), e.g. piconets. The local radio networks (109,110) are unsynchronised with each other and uses a radio interface that has no broadcast channel, e.g. the Bluetooth radio interface. A control unit (108) is connected to each local radio network to provide the basic means and methods for a cellular radio communication system (100). Radio units (101-103) can attach and retain a connection to the control unit (108) via their respective radio node (104-107). The radio units (101-103) can also perform roaming, handover, measurments and fast connection set-ups in the system (100).
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
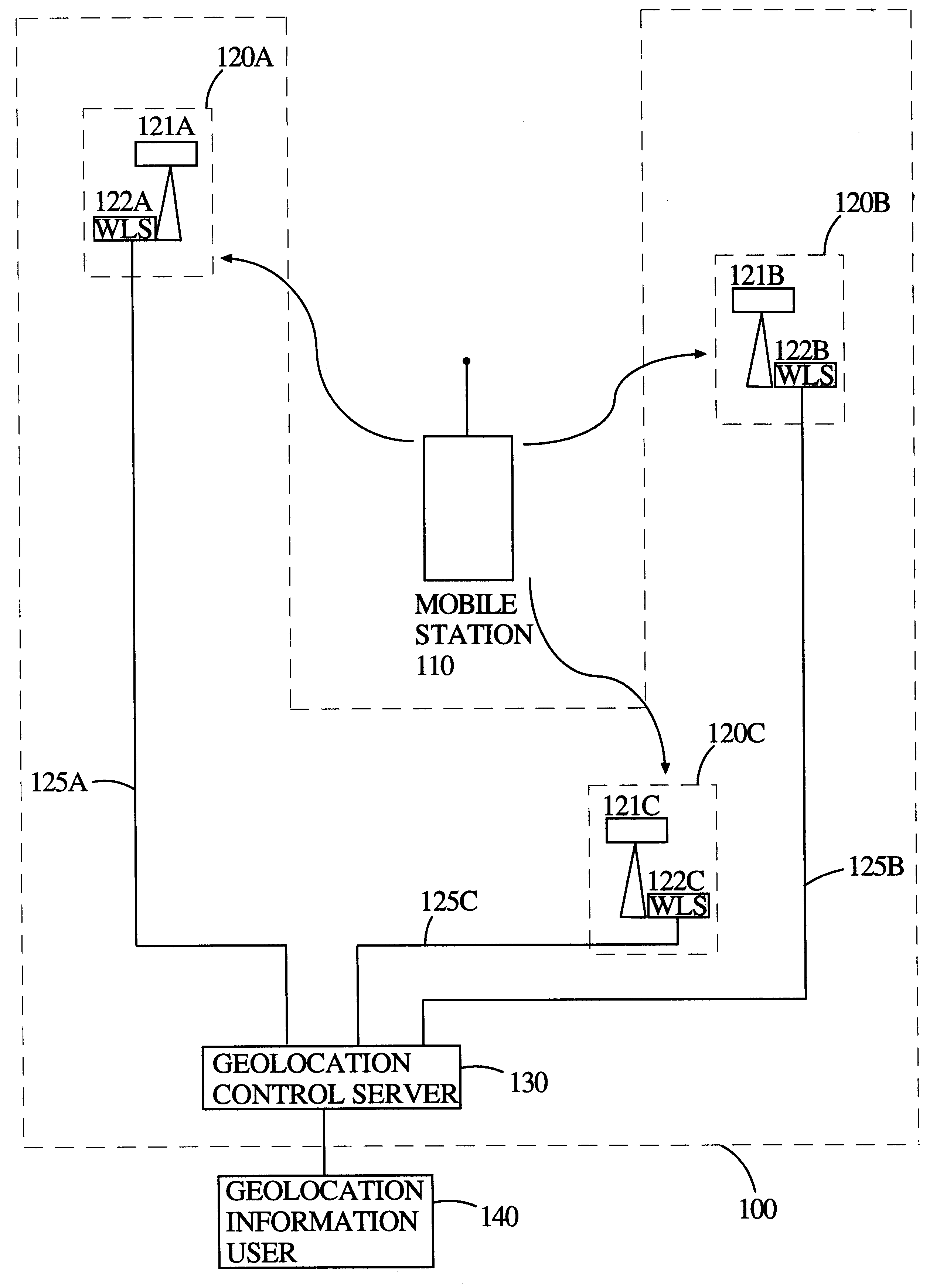
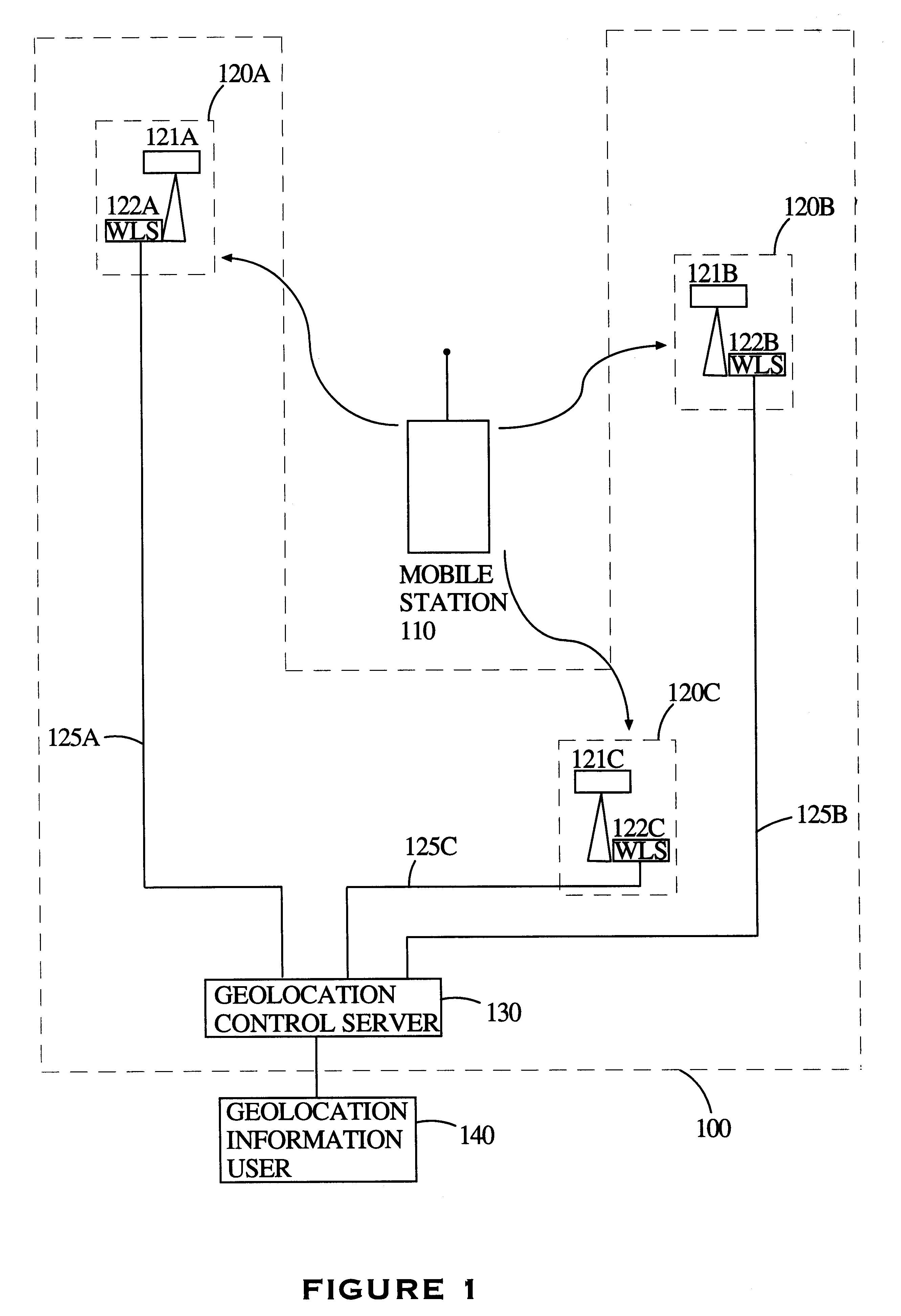
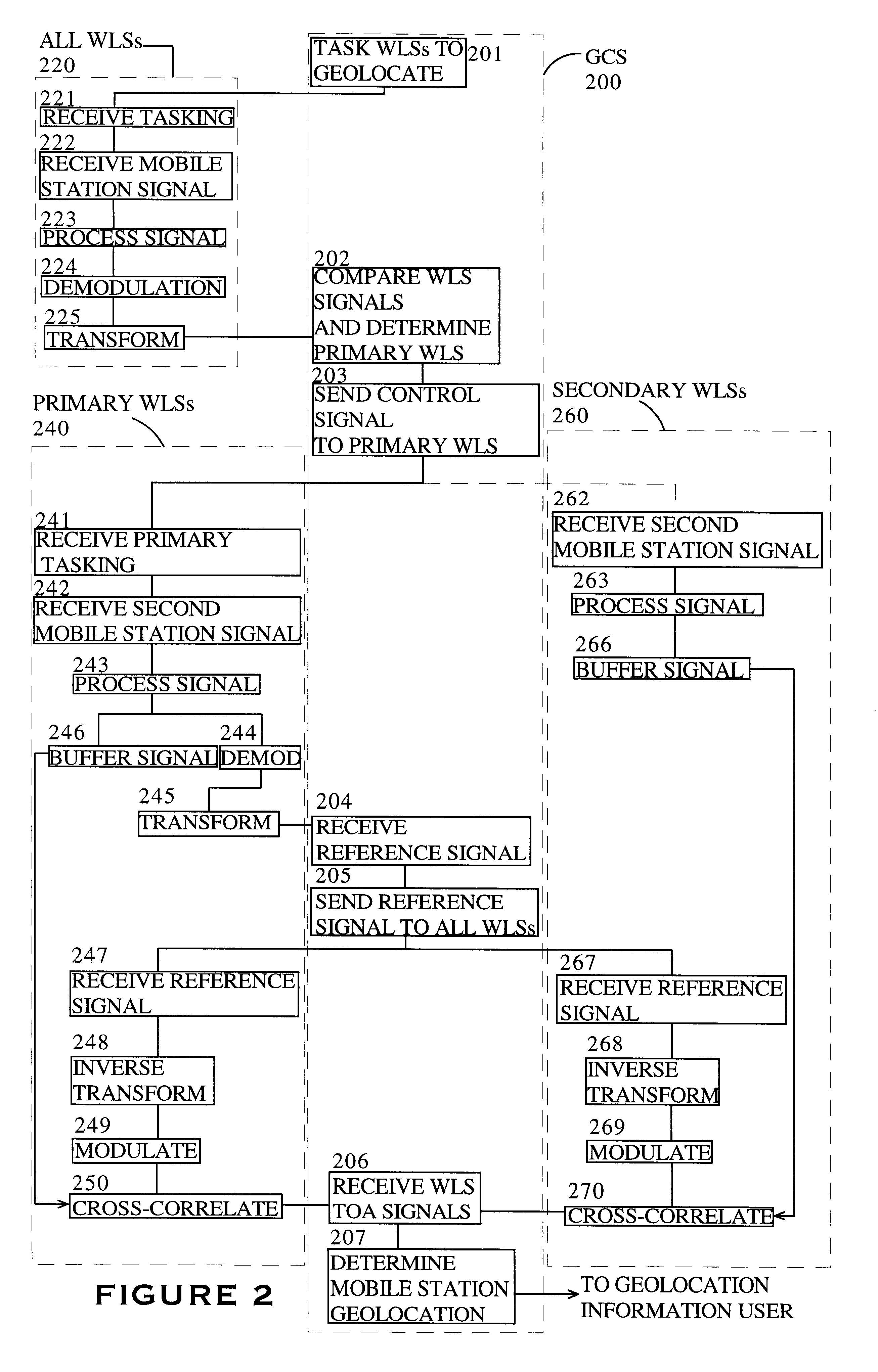
Geolocation of a mobile terminal in a CDMA communication system
InactiveUS6898197B1Small impactEasy to useTime-division multiplexCode division multiplexGeolocationCarrier signal
A cellular radio system in which a base station receiver can receive, on the reverse link, data from a mobile terminal in one of four control modes. In the first mode, the mobile terminal sends an independent user pilot, not synchronized with the base station, on the reverse link and the user data channel is synchronized to this independent user pilot. In the second mode, the mobile terminal slaves its user pilot to the pilot it receives from the base station and the user data channel is synchronized with this slaved user pilot. This second mode allows the user terminal to receive round trip delay information for purposes of geolocation and rapid reacquisition. In the third mode, the mobile terminal slaves its user pilot to the incoming base station pilot, as in the case of mode two, but the user data channel operates in the orthogonal mode using the ranging information received from the base station. The phase relationship between the user pilot channel and the user data channel is calibrated. The user pilot carrier is also the carrier for the user data channel and can be used as the carrier reference for detecting the user data channel. In the fourth mode, the slaved pilot implementation of mode three is used for acquisition but, after acquisition, the user pilot code is phase shifted to be synchronous with the user data channel, thus also making it an orthogonal channel. In this mode, the pilots no longer contribute interference to the user data channels, within the cell, and can be transmitted at higher power levels.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Method, apparatus and computer program product for monitoring data transmission connections
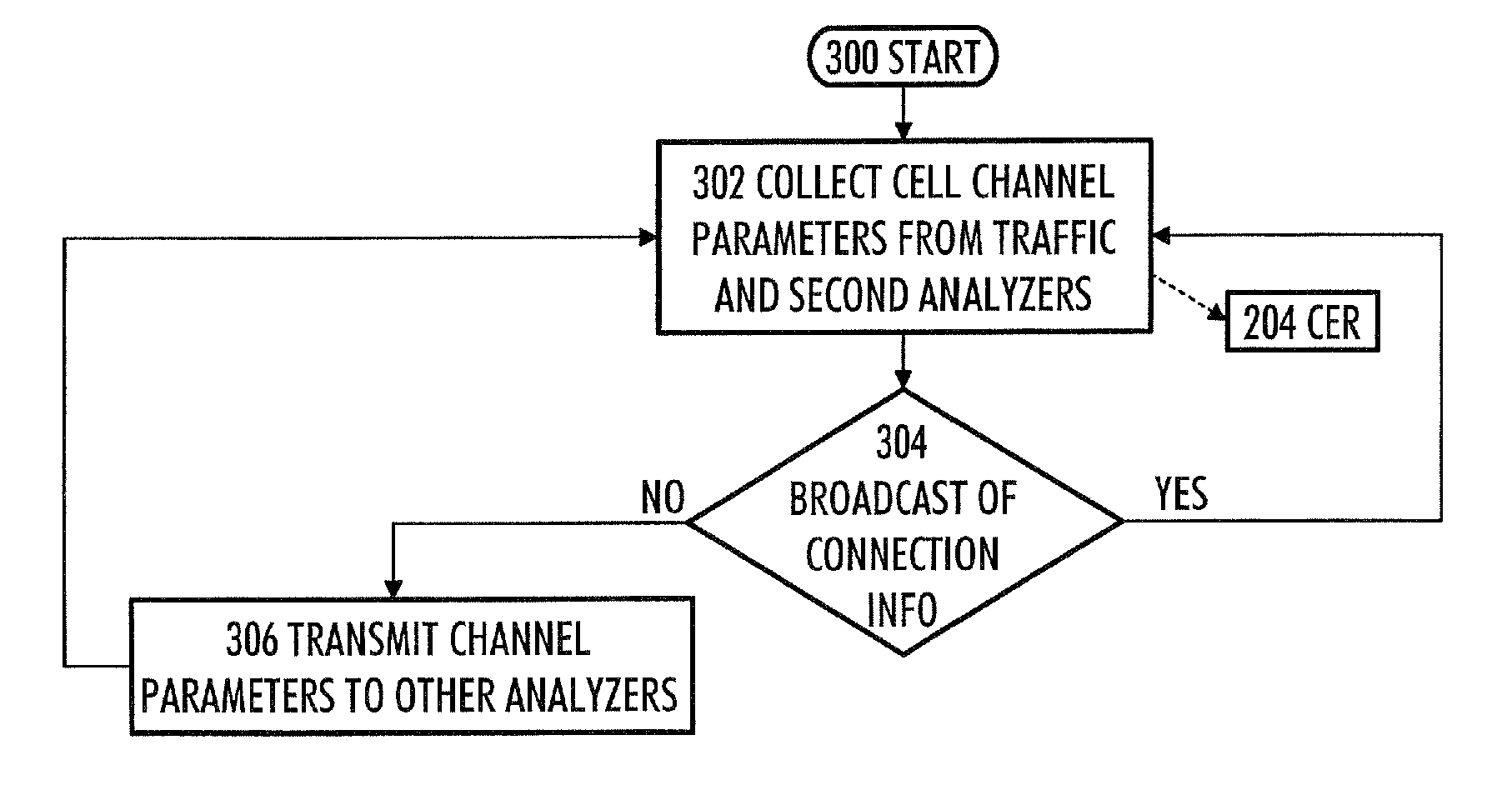
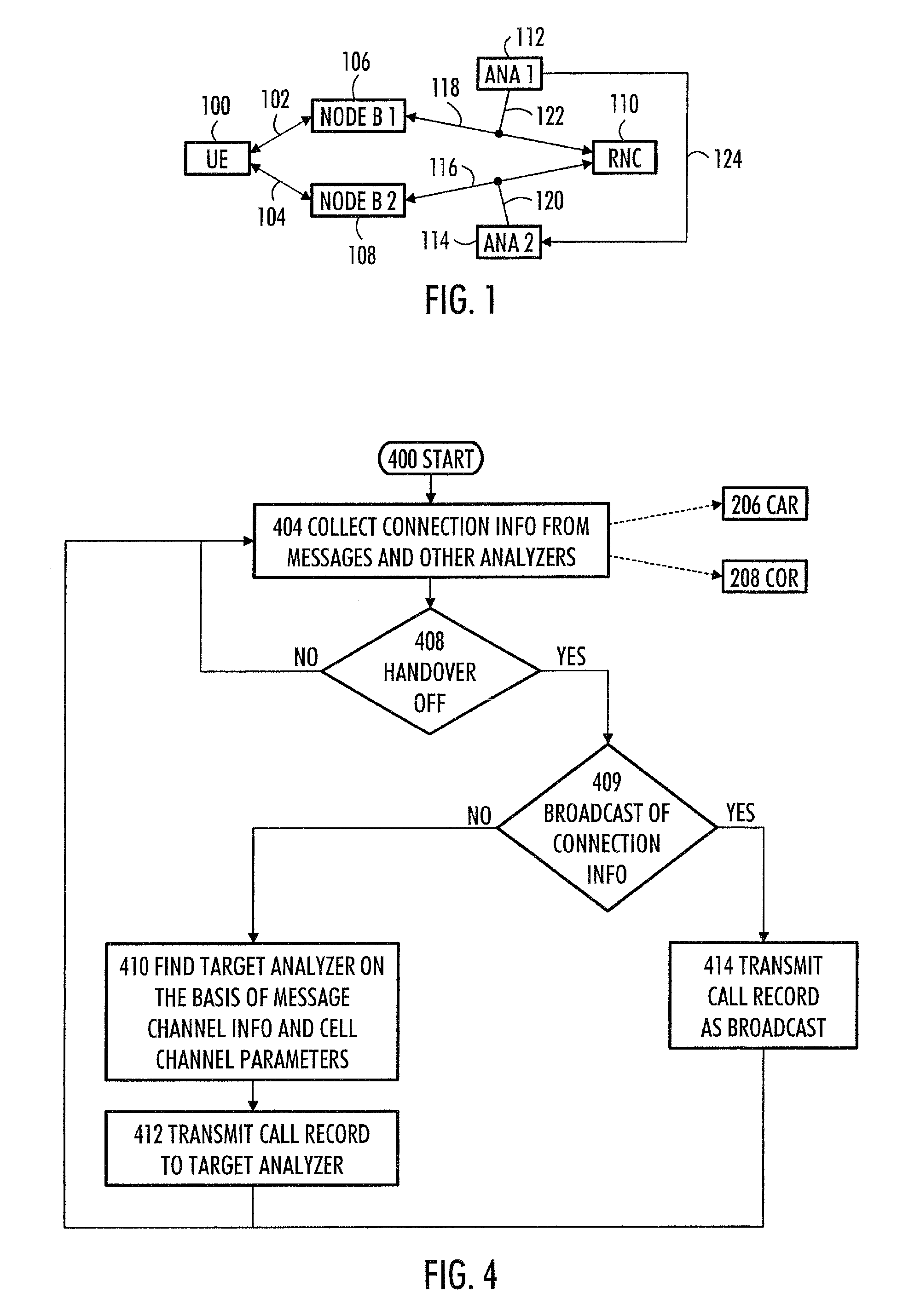
ActiveUS8032168B2Easy to implementEasy to doTelephonic communicationRadio transmissionCellular radioCombined use
A method, device and computer program product for monitoring data transmission connections. The method comprises monitoring data transmission connections between a cellular radio network and a subscriber terminal with two analyzers. With the first analyzer, first connection information is collected on a first data transmission connection of the subscriber terminal to a first cell. With the second analyzer, second connection information is collected on a second data transmission connection of the subscriber terminal to a second cell. The first connection information is transferred from the first analyzer to the second analyzer. In the second analyzer, the first connection information is used combined with the second connection information for analyzing the second data transmission connection.
Owner:EXFO
Method and system for autonomously allocating frequencies to a radio system sharing frequencies with an overlapping macro radio system
InactiveUS6405048B1Avoid co-channel interferenceMaximize radio spectrum usageAssess restrictionFrequency-division multiplexCellular radioCommunications system
A system and a method to automatically select a frequency set in a low-tier radio communication system, sharing frequencies with an overlapping high-tier cellular radio system, that minimally interferes with the high-tier system employing frequency hopping is described. The present invention makes use of the broadcast information that is transmitted by the high-tier radio base stations on their broadcast control channels (BCCH), which contains not only the BCCH carrier frequencies of surrounding cells, but also information regarding the frequencies applied in the considered cell for frequency hopping traffic channels. With this broadcast information, the low-tier system can derive the frequency planning of the high-tier system, and can then derive a frequency set for low-tier usage that minimally interferes with the overlapping high-tier system. The advantage with this technique is that only measurements on BCCH carriers have to be performed, which are non-hopping, have a constant transmit power, and have a continuous (non-bursty) signal.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Cellular telecommunications systems having selectively associatable usage parameters
InactiveUS6253074B1Accounting/billing servicesSpecial service for subscribersCellular radioProcessor register
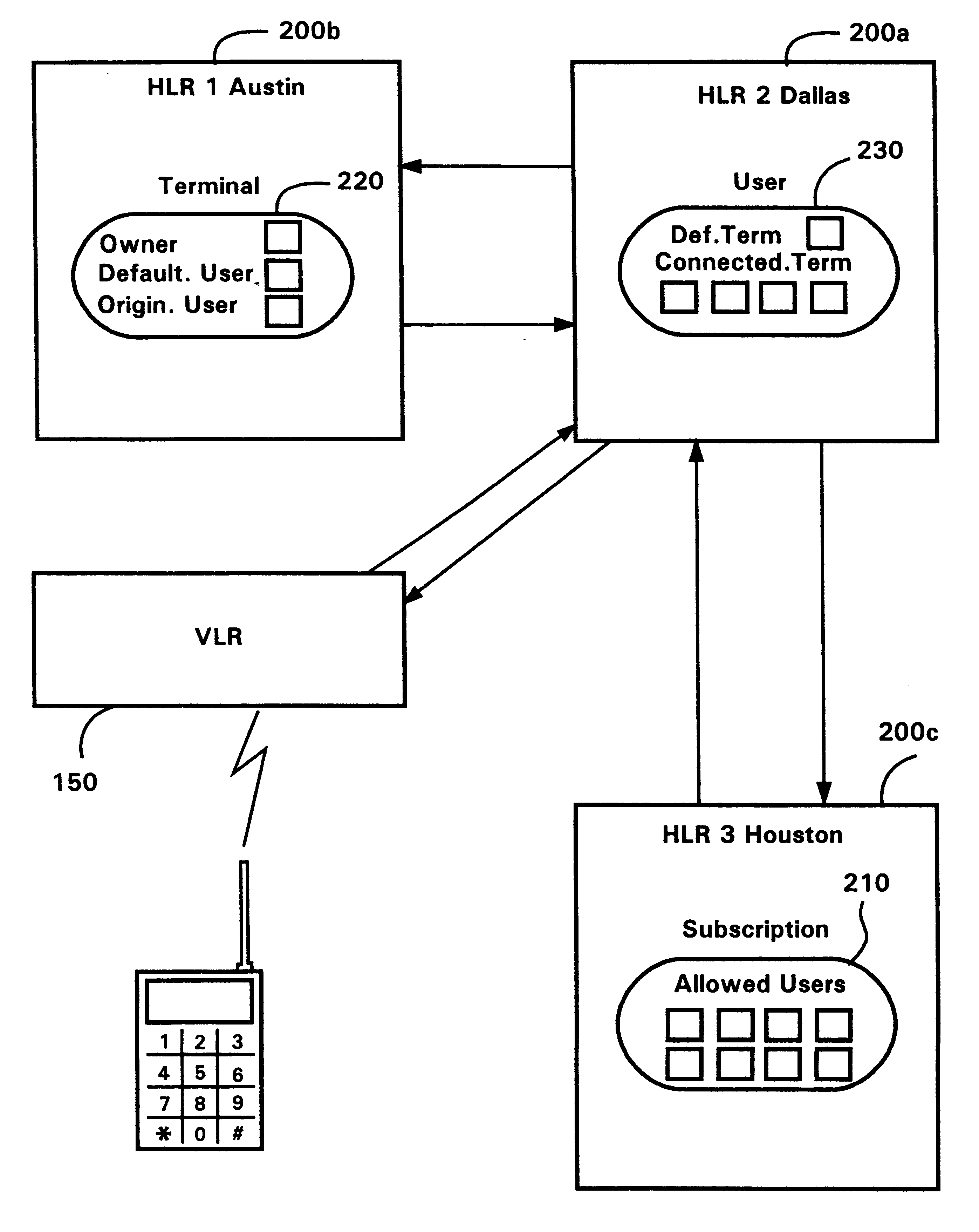
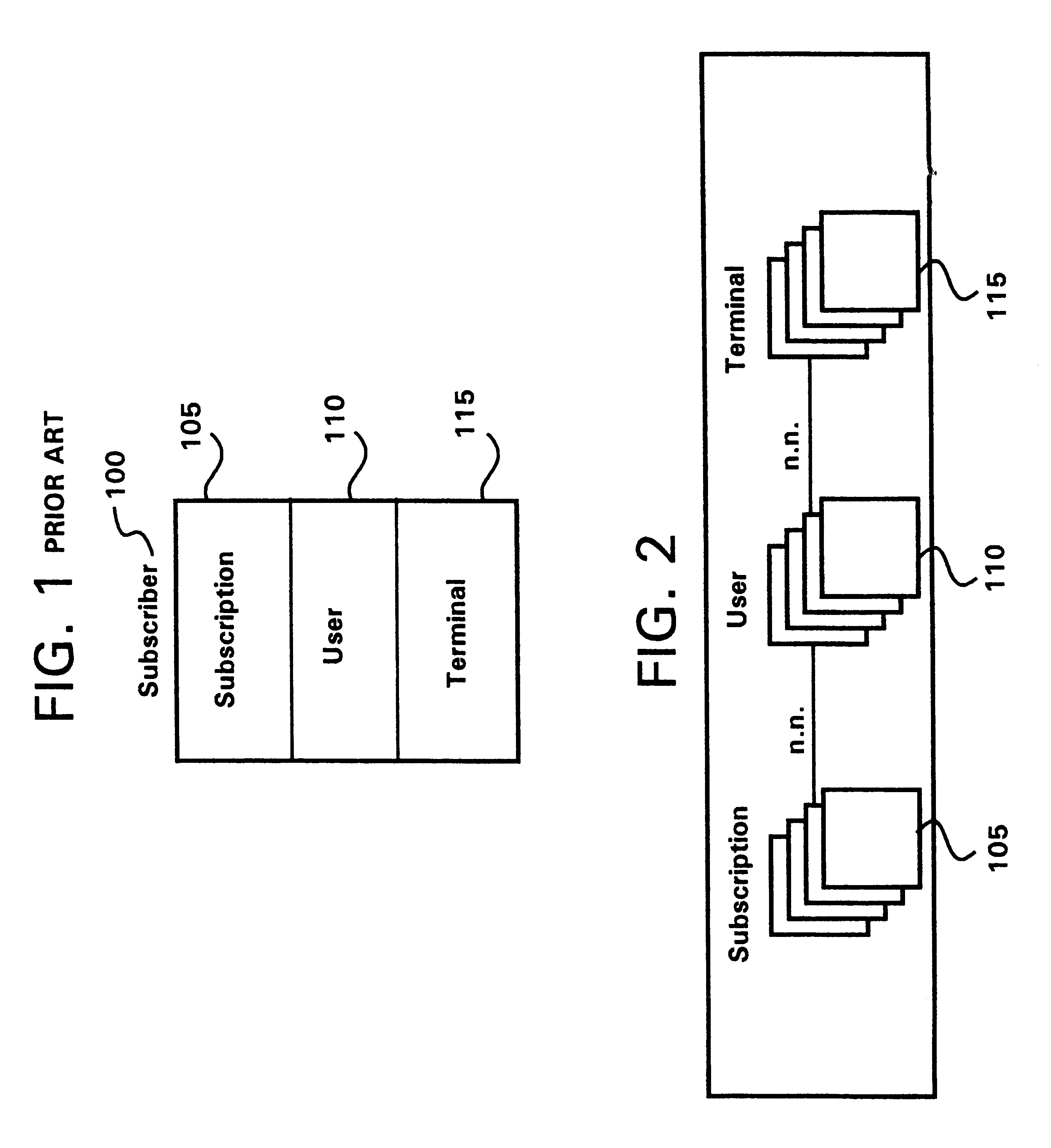
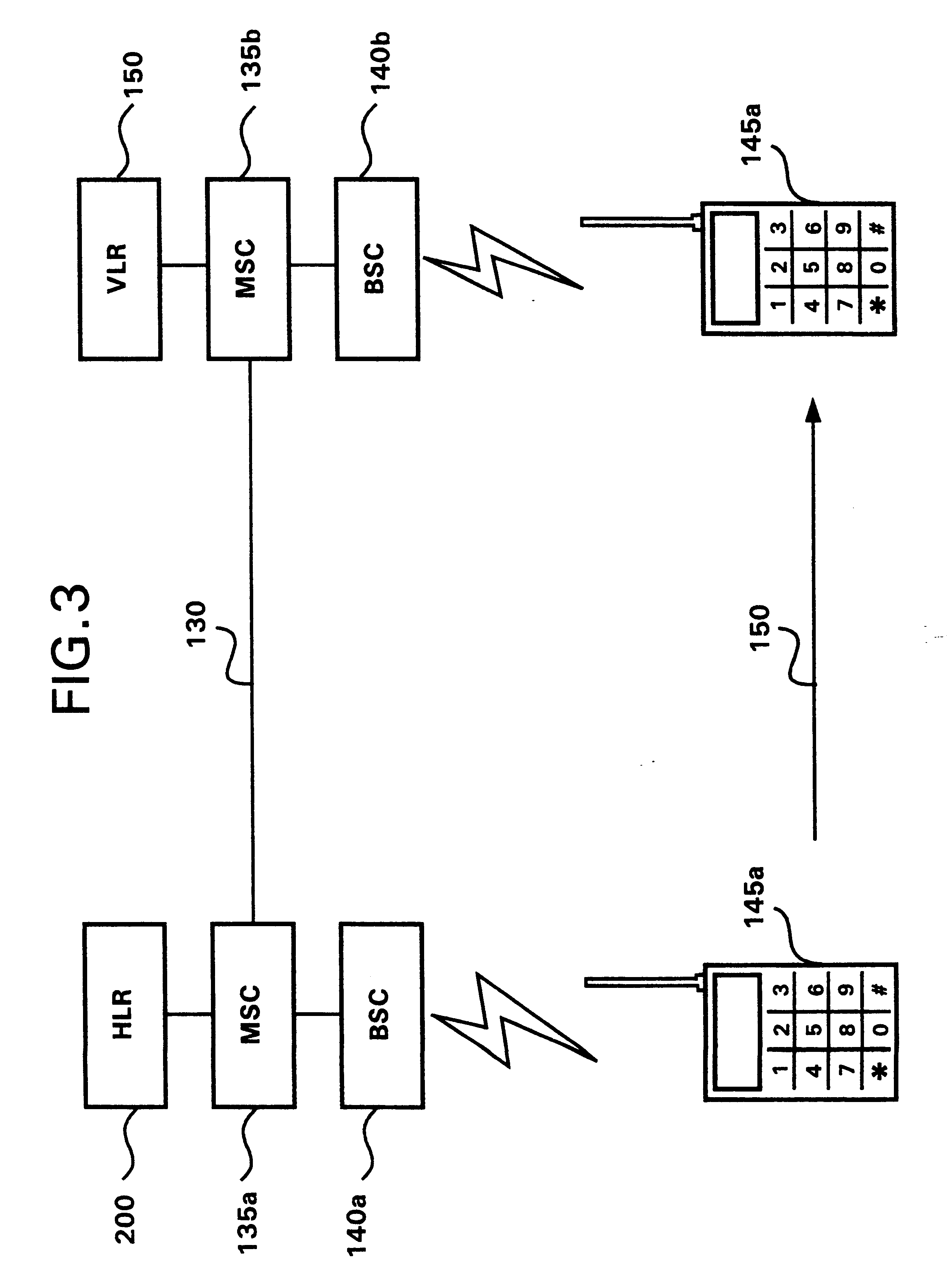
A telecommunication system is architecturally sub-divided into the concepts of user, subscription and terminal. A database within a cellular radio telecommunication system is provided with separate and independent storage registers for storing information relating to each of user, subscription and terminal. An user register is provided for user information, a terminal register is provided for terminal information and a subscription register is provided for subscription information. The use of three separate registers within the system allow several terminals to be associated with one user, several users to be associated with one terminal, several subscriptions to be associated with one user, and several users to be selectively associated with one subscription.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
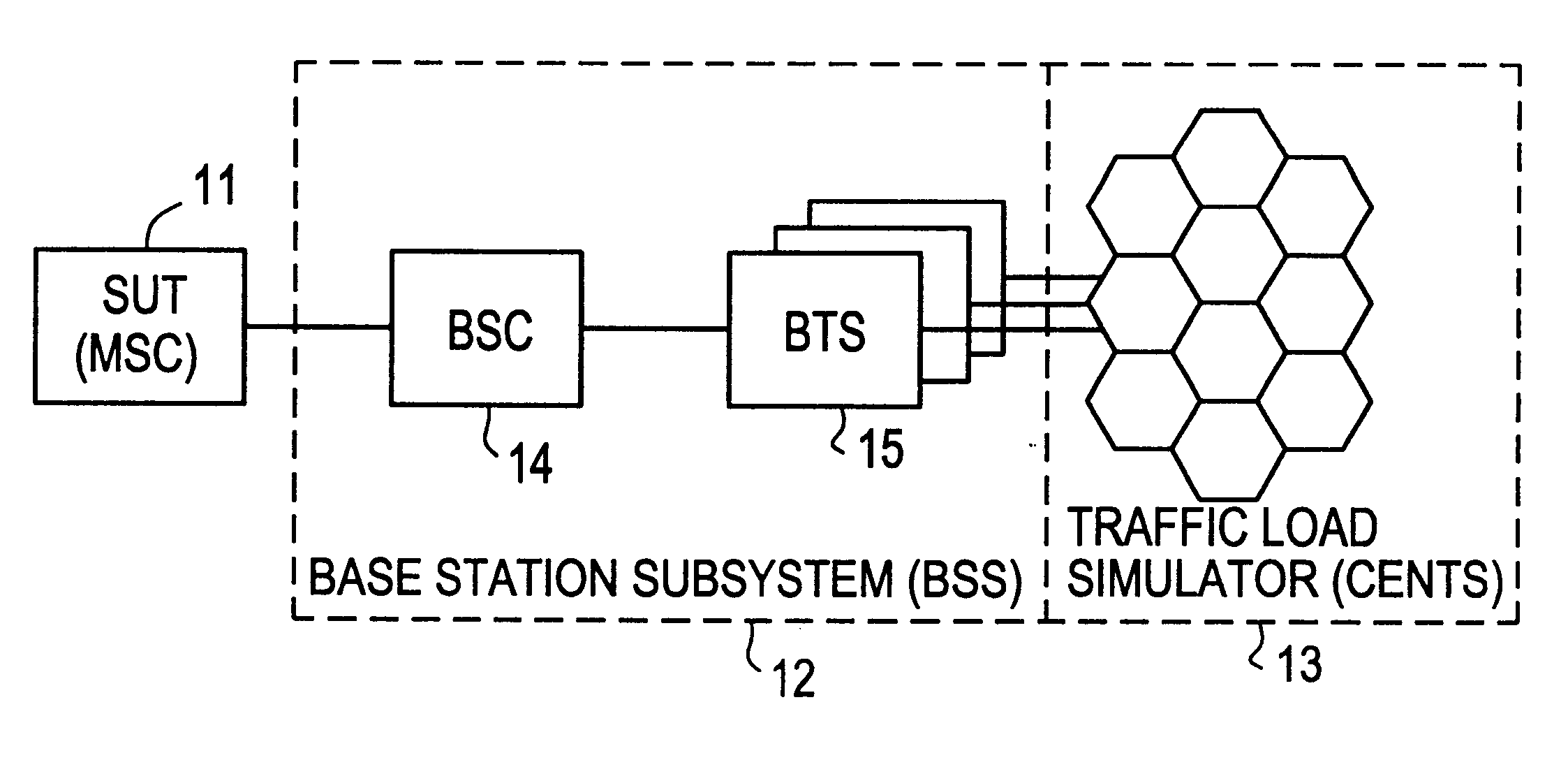
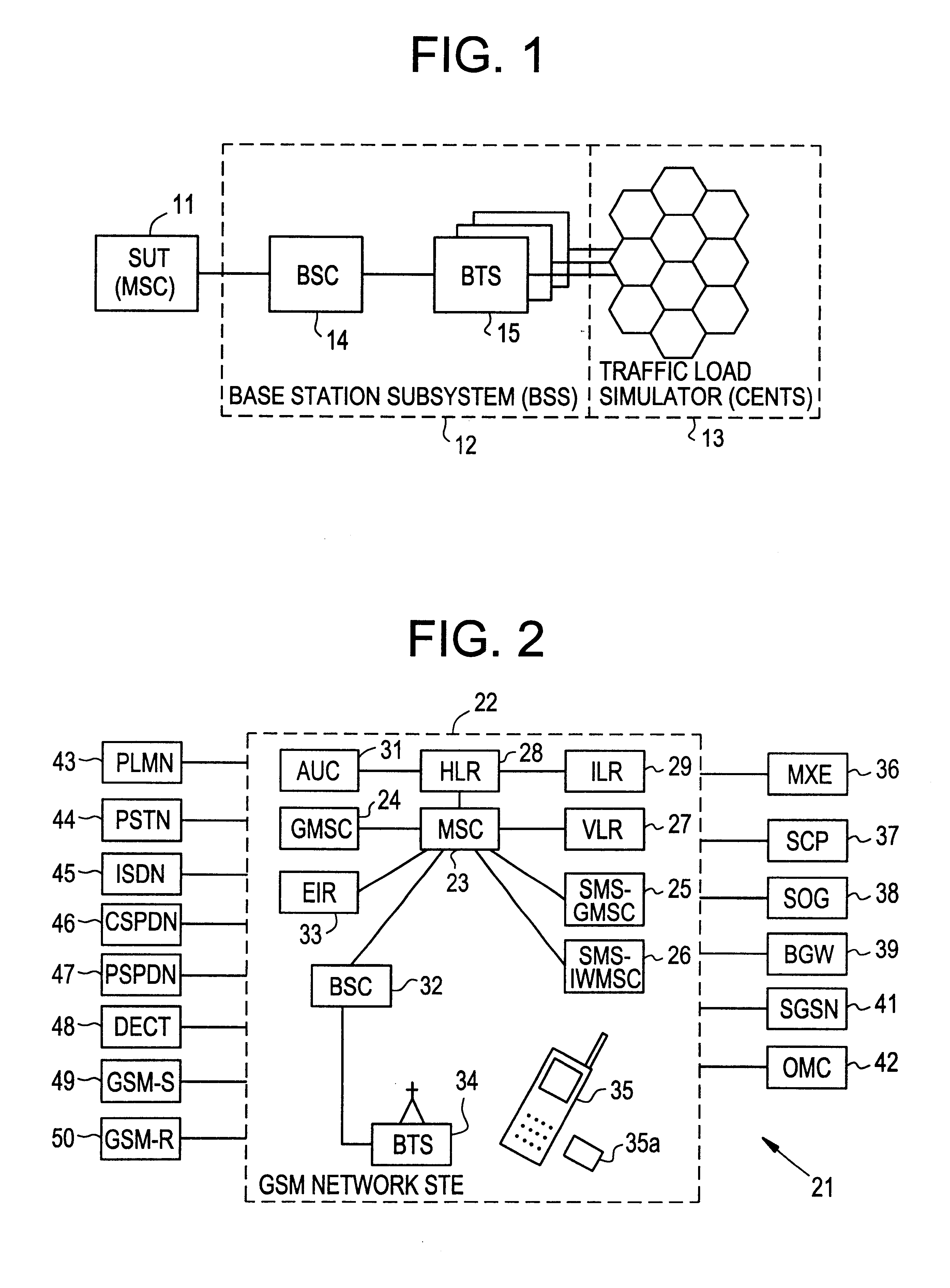
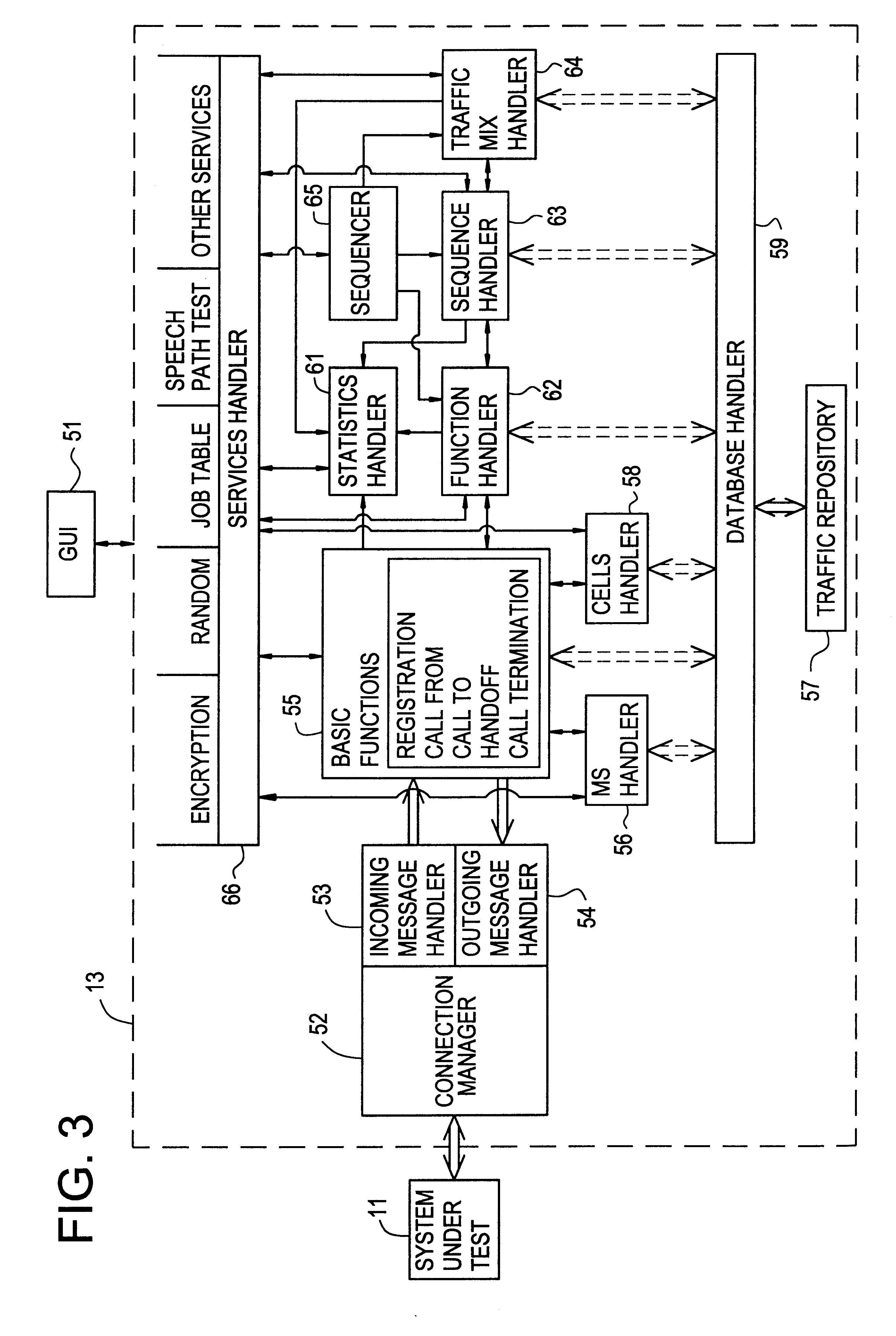
Cellular network traffic simulator (cents)
A traffic simulator for a cellular radio telecommunications network. The traffic simulator includes a function handler which generates a plurality of basic call functions performed by mobile stations (MSs) over an air interface link with the network. A sequence handler utilizes the basic functions to generate a plurality of call sequences, and a traffic mix handler utilizes the plurality of call sequences to generate an overall traffic mix. A MS handler includes a plurality of MS state machines for different types of MSs and a database of MS properties. The MS handler interfaces with the basic functions to generate realistic inputs to the sequence handler. A cells handler includes a database of cells in the network and parameters relating to radio conditions. The cells handler also interfaces with the basic functions to generate realistic inputs to the sequence handler. A traffic repository may inject recorded real mobile station traffic into the traffic mix. A connection manager sends the traffic mix to external network components, and a graphical user interface (GUI) enables an operator to interface with the traffic simulator and generate specified traffic scenarios.
Owner:INFOVISTA
Managing uplink resources in a cellular radio communications system
ActiveUS20090225709A1Increase data rateEasy to handleNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationCellular radioCommunications system
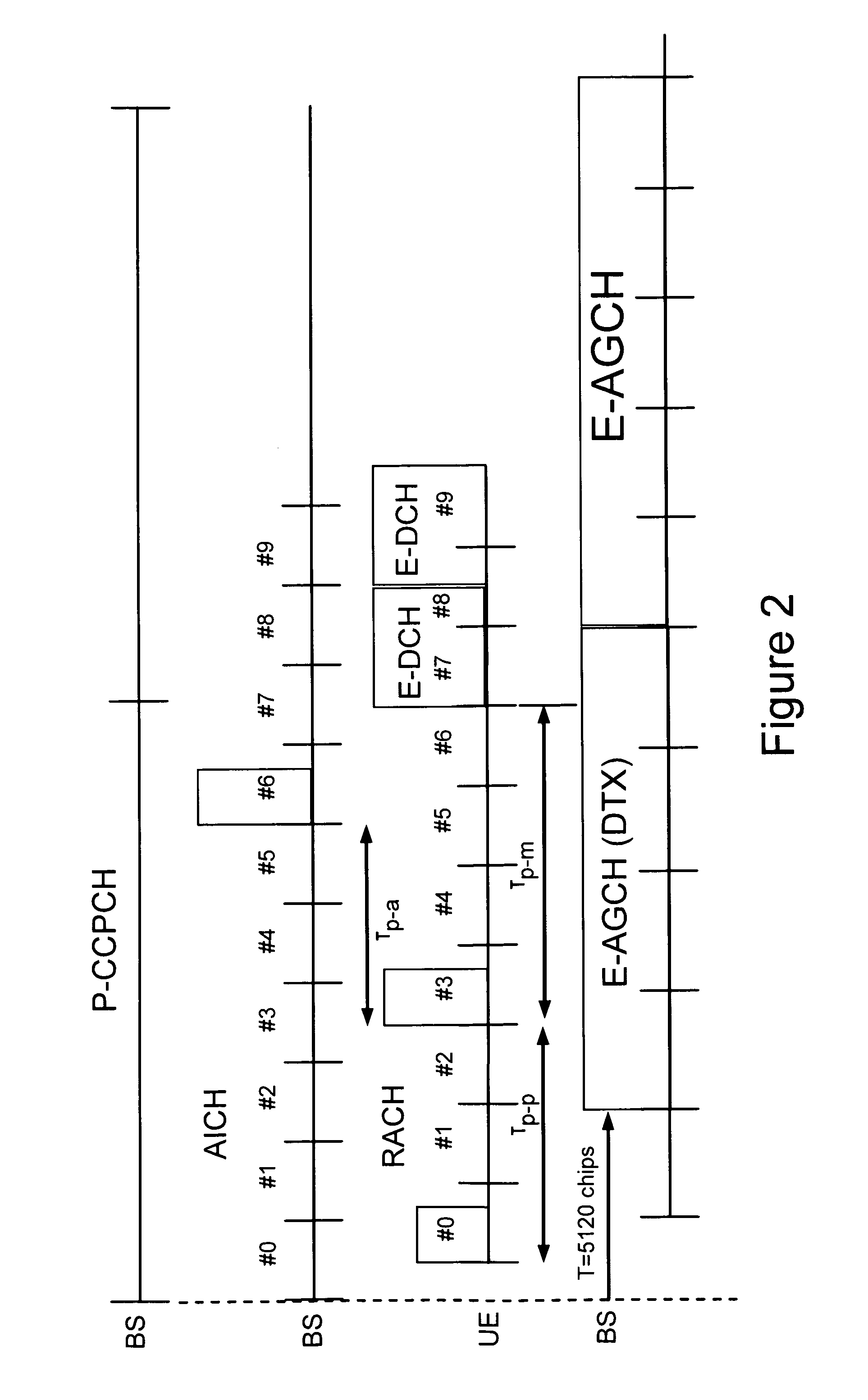
The technology in this application provides a method and apparatus for efficiently using common uplink radio resources, e.g. a common uplink enhanced-dedicated physical channel (E-DCH) resource. A UE releases a common E-DCH resource very quickly after a completed transmission. In addition or alternatively, a base station may release a common E-DCH resource configuration from the network side to free up common E-DCH resources for use by other UEs. A low overhead signaling scheme for quickly and effectively releasing of common E-DCH resources between a UE and a base station is also described. For example, existing signaling fields on protocol layer 2 (L2) or layer 1 (L1) may be used. In one preferred example embodiment, signaling fields already in use in a CELL_DCH service state are given a different meaning for UEs in a CELL_FACH service state so that common E-DCH resources are quickly and effectively released.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
System and method for analog cellular radio geolocation
InactiveUS6845240B2Reduce data volumeEfficiently and accurately geolocatingSpatial transmit diversityDirection finders using radio wavesFourier transform on finite groupsGeolocation
A system and method for determining the geolocation of autonomous mobile appliances emitting analog waveforms is disclosed. More specifically, the inventive system and method is used to geolocate FM analog signals such as those used in the AMPS cellular radio air standard by using a time difference of arrival (“TDOA”) approach. The inventive system and method uses a novel approach to minimize the amount of data sent between location sensors and the central location processor comprising adaptive signal combining from N channel to a single channel, FM demodulation to reduce bandwidth, Fourier transformation for signal compression, and segmentation of the location sensors into primary and secondary modes to allow for parallel processing to ease the computational burden on the central location processor.
Owner:ANDREW CORP +1
Method and device for selecting parameters for a cellular radio communication network based on occurrence frequencies
InactiveUS20040259565A1Increase the number ofRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesCellular radioRadio resource
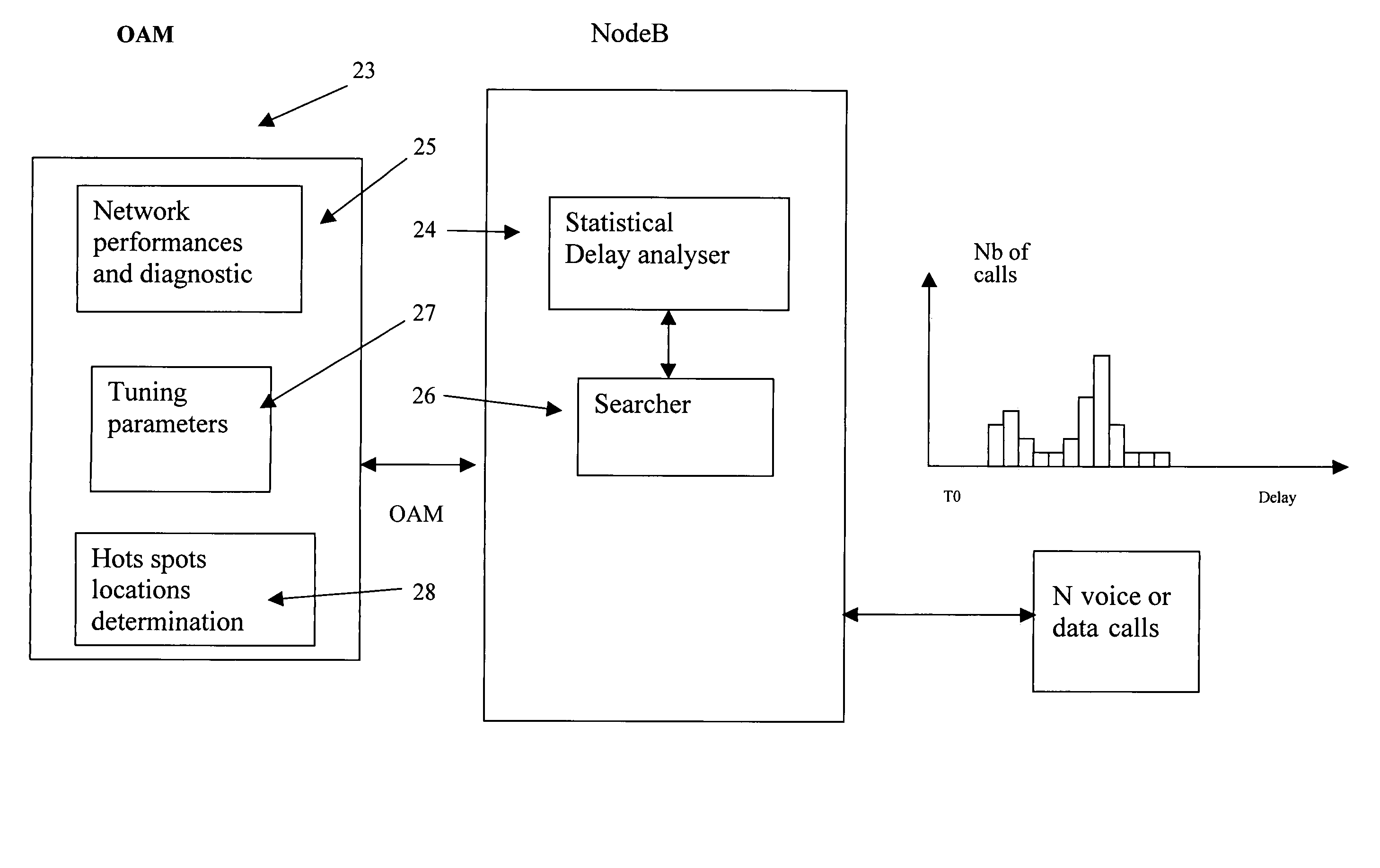
A method and apparatus for selecting a value of at least one network operating parameter, cell operating parameter, radio resource management parameter or dimensioning parameter for a cellular radio communications network having a base station and mobile units communicating therewith is described. A statistic is maintained of estimated mobile unit occurrence densities or estimated changes of mobile unit occurrence densities at locations in a cell. The selection of the value of the at least one network operating parameter, cell operating parameter, radio resource management parameter or a dimensioning parameter is made in accordance with an occurrence frequency density stored in the statistic. The apparatus and method are particularly suited for detection and remediation of hot spots.
Owner:RPX CORP
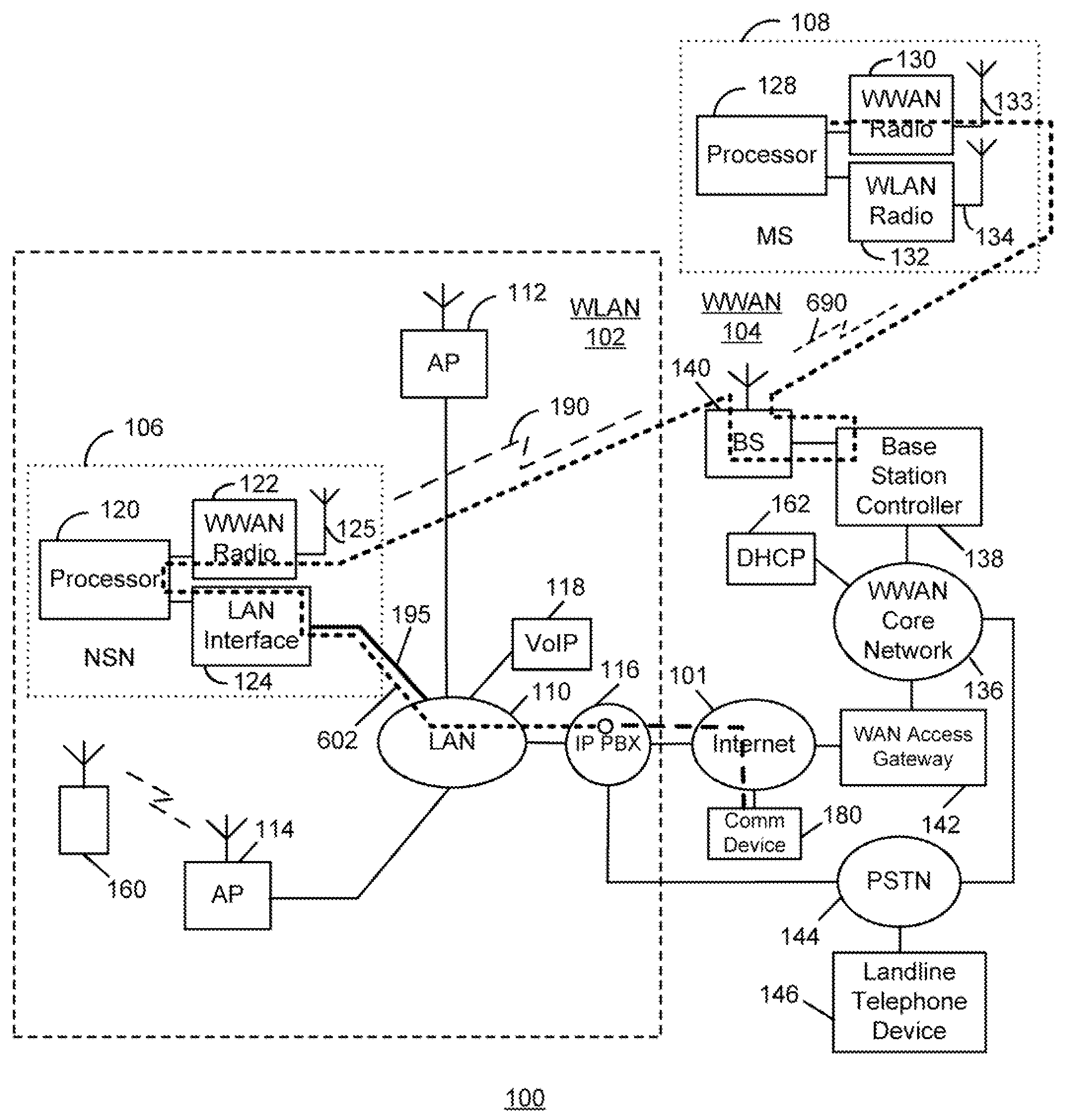
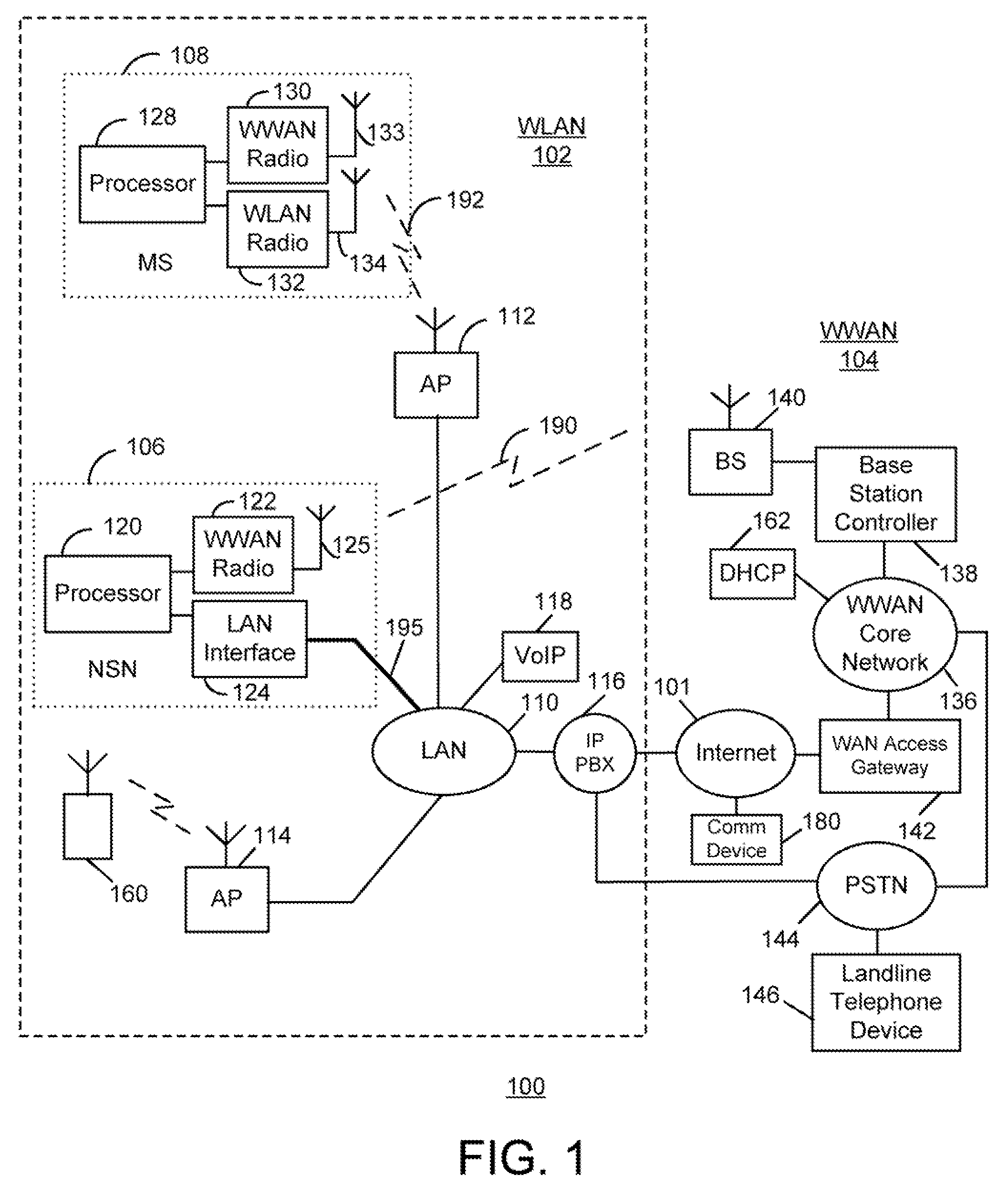
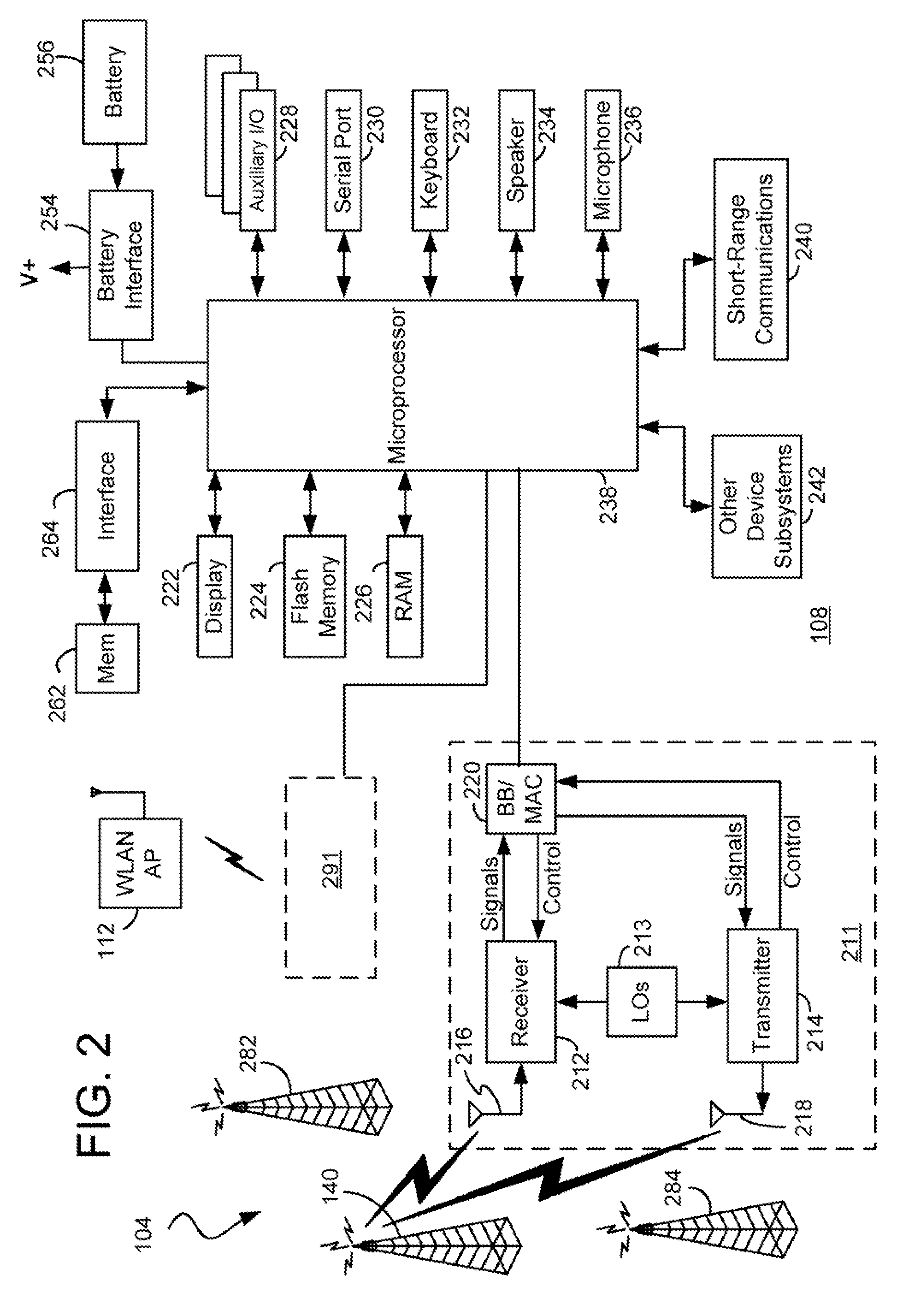
WLAN-To-WWAN Handover Methods And Apparatus Using A WLAN Support Node Having A WWAN Interface
ActiveUS20080102843A1Data switching by path configurationSubstation equipmentTelecommunications linkAir interface
Methods and apparatus for use in switching communication operations between a wireless local area network (WLAN) (e.g. an IEEE 802.11-based network) and a wireless wide area network (WWAN) (e.g. a cellular telecommunications network) for a mobile communication device are disclosed. A network support node which is utilized to facilitate such transitioning has a first communication interface (e.g. an Ethernet interface) for connection with a communication network which includes the WLAN and a second communication interface (e.g. a cellular radio air interface) for communicating with a base station of the WWAN over a wireless communication link. The mobile device initially operates in the WLAN in a communication session with another communication device. During the session, the network support node receives an indication that the mobile device is transitioning from the WLAN to the WWAN. In response to receiving the indication, the network support node causes a message to be sent which instructs a router of the communication network to communicate voice data of the session to it. In response to the message, the network support node receives voice data of the session from the router through its first communication interface. The network support node communicates the voice data with the mobile device via the WWAN through its second communication interface over the wireless communication link with the base station. These communications are performed at least while communication operations for the mobile device are being switched from the WLAN to the WWAN. Advantageously, disruption of communications during the WLAN-to-WWAN transition is reduced or eliminated.
Owner:MCMASTER UNIV
Dual band unidirectional scheme in a cellular mobile radio telecommunications system
InactiveUS20030104816A1Time-division multiplexFrequency-division multiplexCellular radioTelecommunications network
A cellular radio telecommunications system and method of operating the same is described which includes a first cellular radio telecommunications network for providing frequency division duplex radio transmissions over an air interface to one or more fixed or mobile terminals and a second cellular unidirectional radio telecommunications network which at least partly overlaps the first cellular radio telecommunications network for providing unidirectional simplex radio transmissions over an air interface to the one or more fixed or mobile terminals. At least one of access to the unidirectional second cellular network and handover of a communication supported by the unidirectional second cellular network is managed by the first cellular network. A special dedicated uplink channel may be provided in the first network for trasmitting uplink control and / or error messages of the second network.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Intra cell handover and channel allocation to reduce interference
InactiveUS6301478B1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionCellular radioMicro cell
A method of reducing interference in a cellular radio communication including performing a courtesy handover of a first call to another channel to reduce interference in a second call when the presence of the first call on the same frequency as the second call causes the interference in the second call. Also, a method of setting up a call which permits a retry to a macro cell when a channel of sufficient quality is not found in a micro cell.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
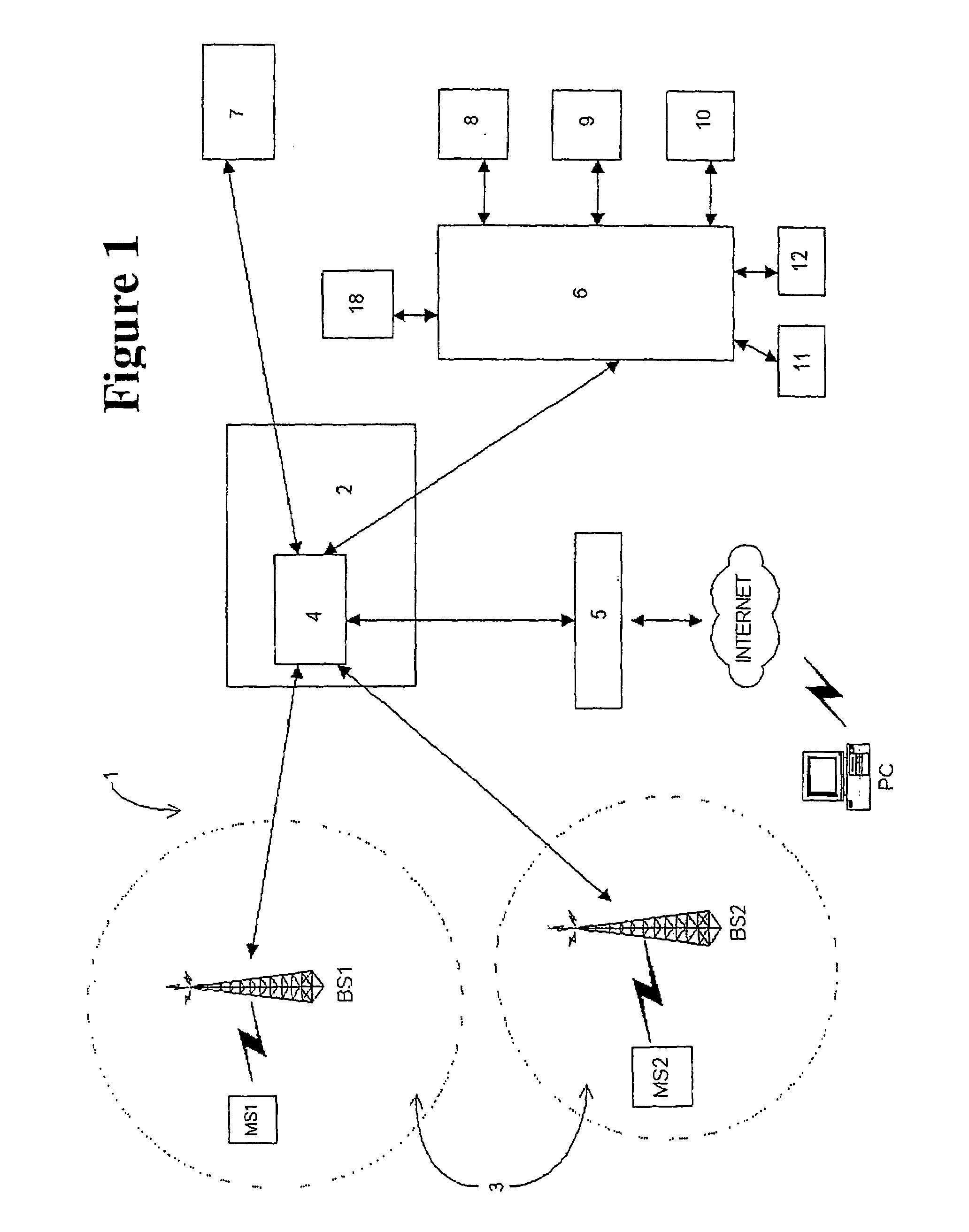
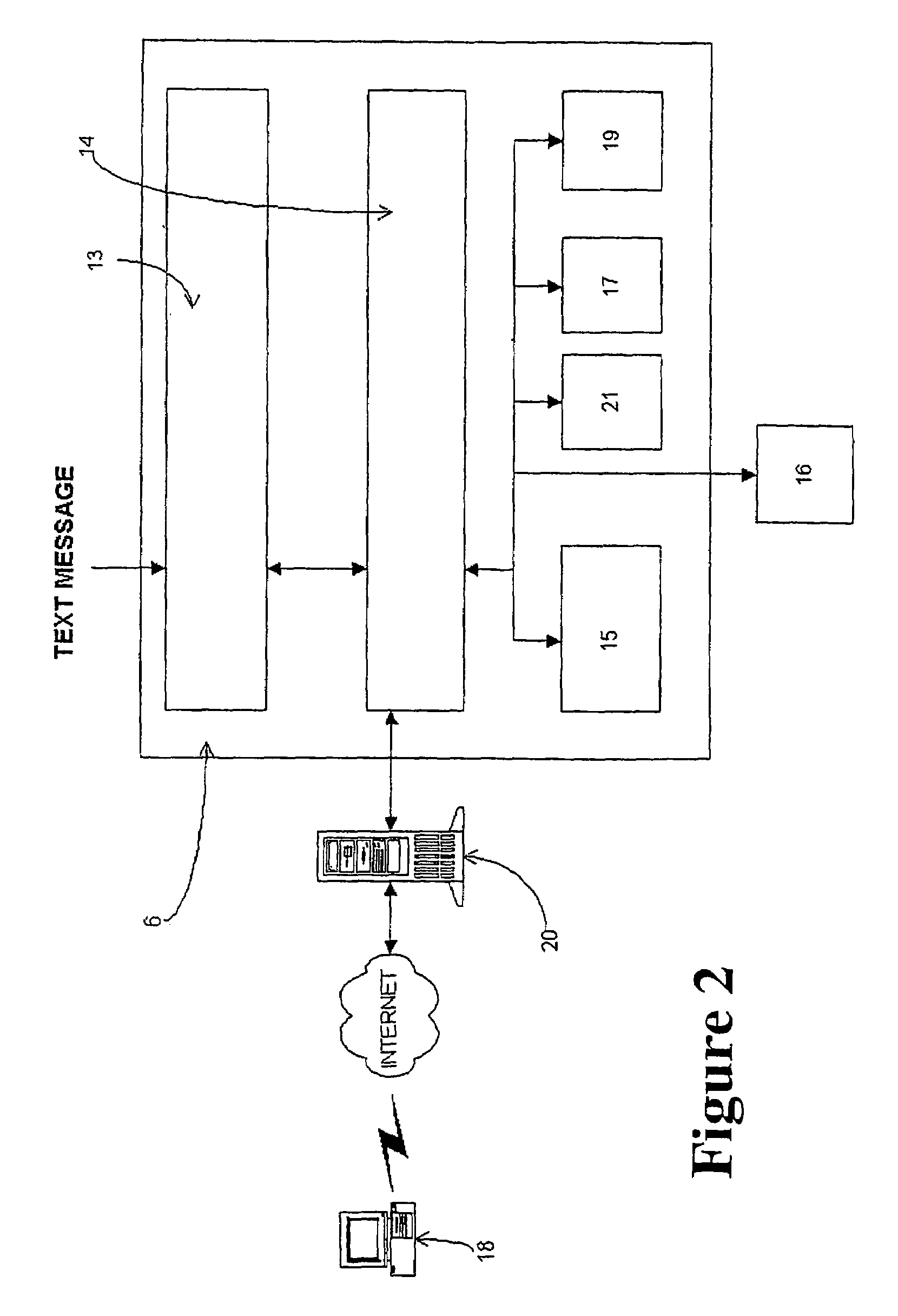
System and method for provisioning of text message services
InactiveUS7107068B2Good varietyHighly accessibleWater closetsSpecial service for subscribersCellular radioEmail address
A system (1) which allows content providers of value-added SMS services to set-up their own services comprises a Small Message Entity Agent (SMEA) (6) which is coupled to a Short Message Service Centre (4) of a cellular radio telephone network. Providers of value added services can access the SMEA to register a unique identifier in the form of an easily remembered name, which is then translated into a numerical number, which is used as part of the destination address in text messages destined for the content provider. The content provider is able to self-configure his service so that text messages delivered to the SMEA are forwarded to selected message handlers for forwarding to appropriate destinations, such as email addresses, pagers or mobile phones.
Owner:BEYOND WIRELESS
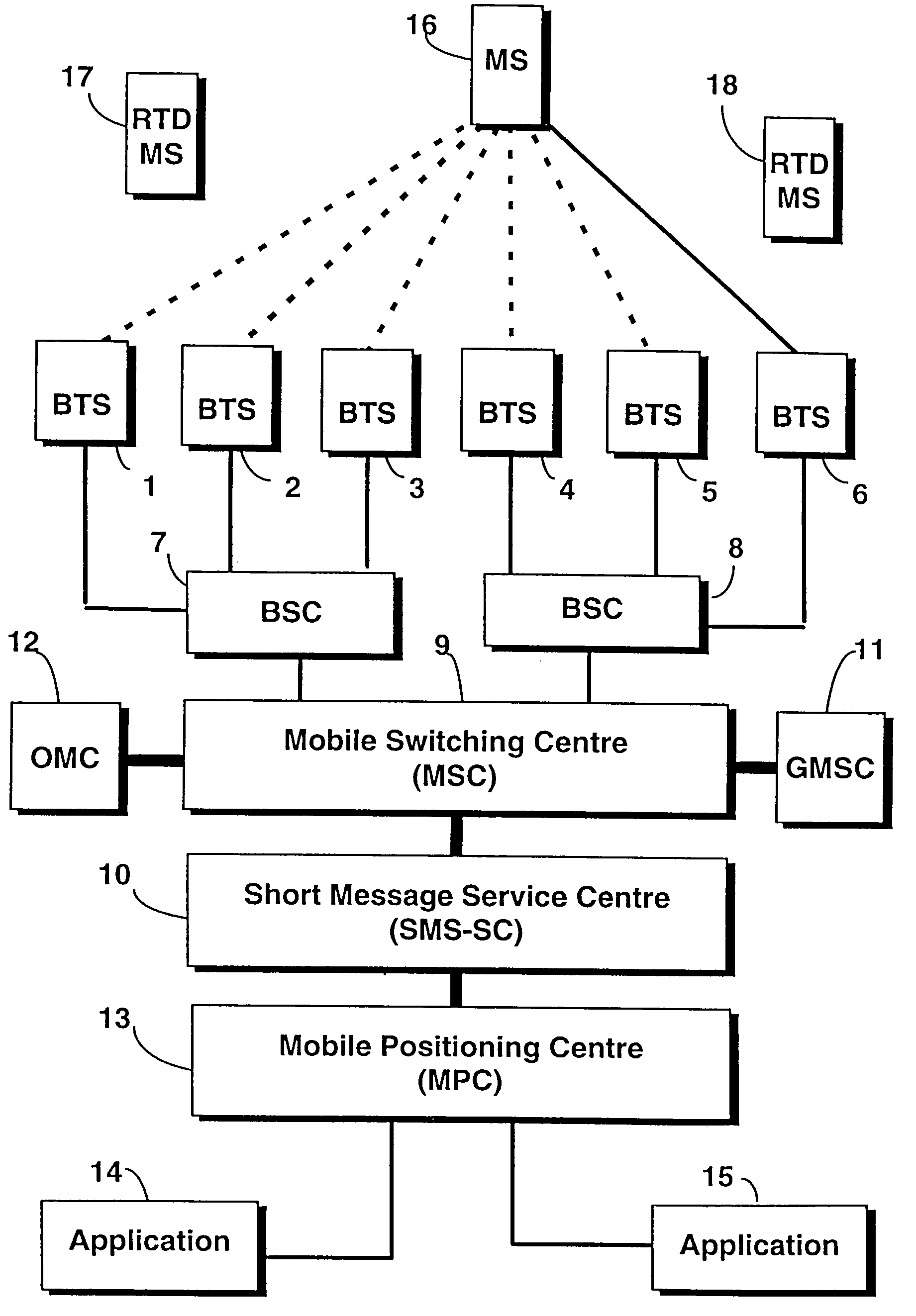
Cellular radio locator system
InactiveUS7274939B2Poor propertyReduce riskPosition fixationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCellular radioTransceiver
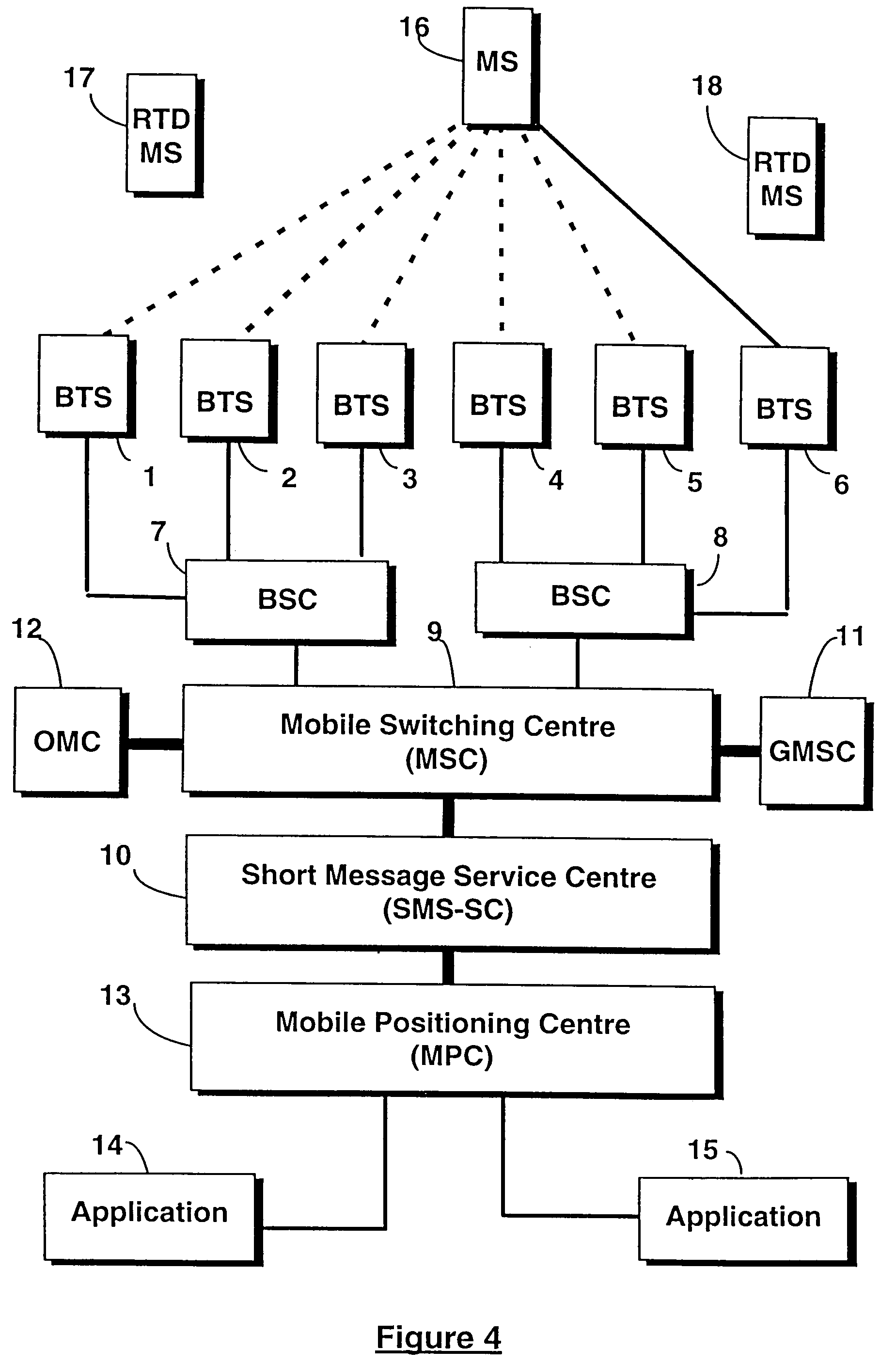
A cellular radio network based positioning system for determining the position of a mobile station (16). For each base transceiver station (1 to 5) or cell of the network, a fixed list of base transceiver stations is stored by a Mobile Positioning Centre (13). Each list identifies those base transceiver stations which enable the position of a mobile station served by the corresponding base transceiver station (6) to be optimally determined. The list is transmitted to the mobile station (16) via the serving base transceiver station (6) and the mobile station determines an observed time difference for each of the listed base transceiver stations, relative to the serving base transceiver station (6), from signals broadcast by the listed base transceiver stations. The observed time differences are transmitted from the mobile station (6) to the serving base transceiver station (6) and are used by the network to compute the position of the mobile station (16).
Owner:NOKIA MOBILE PHONES LTD
Band masking of self organizing cellular networks
InactiveUS8320910B2Considerable costEasy networkingRadio transmissionWireless commuication servicesCellular radioFrequency spectrum
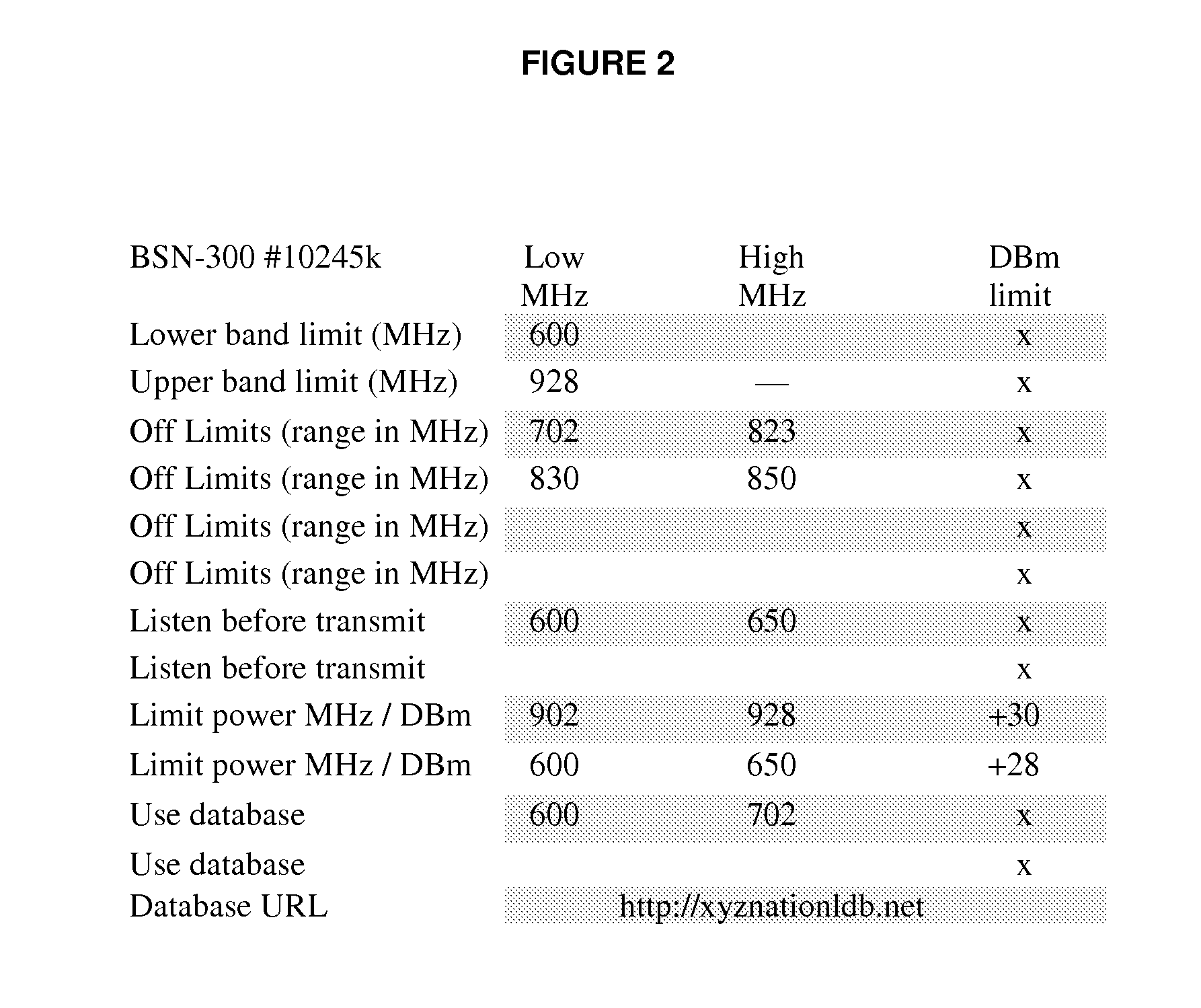
This invention addresses a method of whereby a cellular base station can scan the radio band to identify radio channels that are not in use, then claim those un-used radio channels for use to transmit and receive radio signals. A plurality of such radio base station could then comprise a cellular radio network, which channel planning and frequency re-use has become autonomous and self organizing. The present disclosure aims to further expand the utility and function of such self organizing cellular networks by including a user interface to the base station by which the operator can define the radio spectrum boundaries that the base station is authorized to operate within and to further set operational rules for the use of sub-sections of that defined spectral boundary.
Owner:VISLINK TECH INC
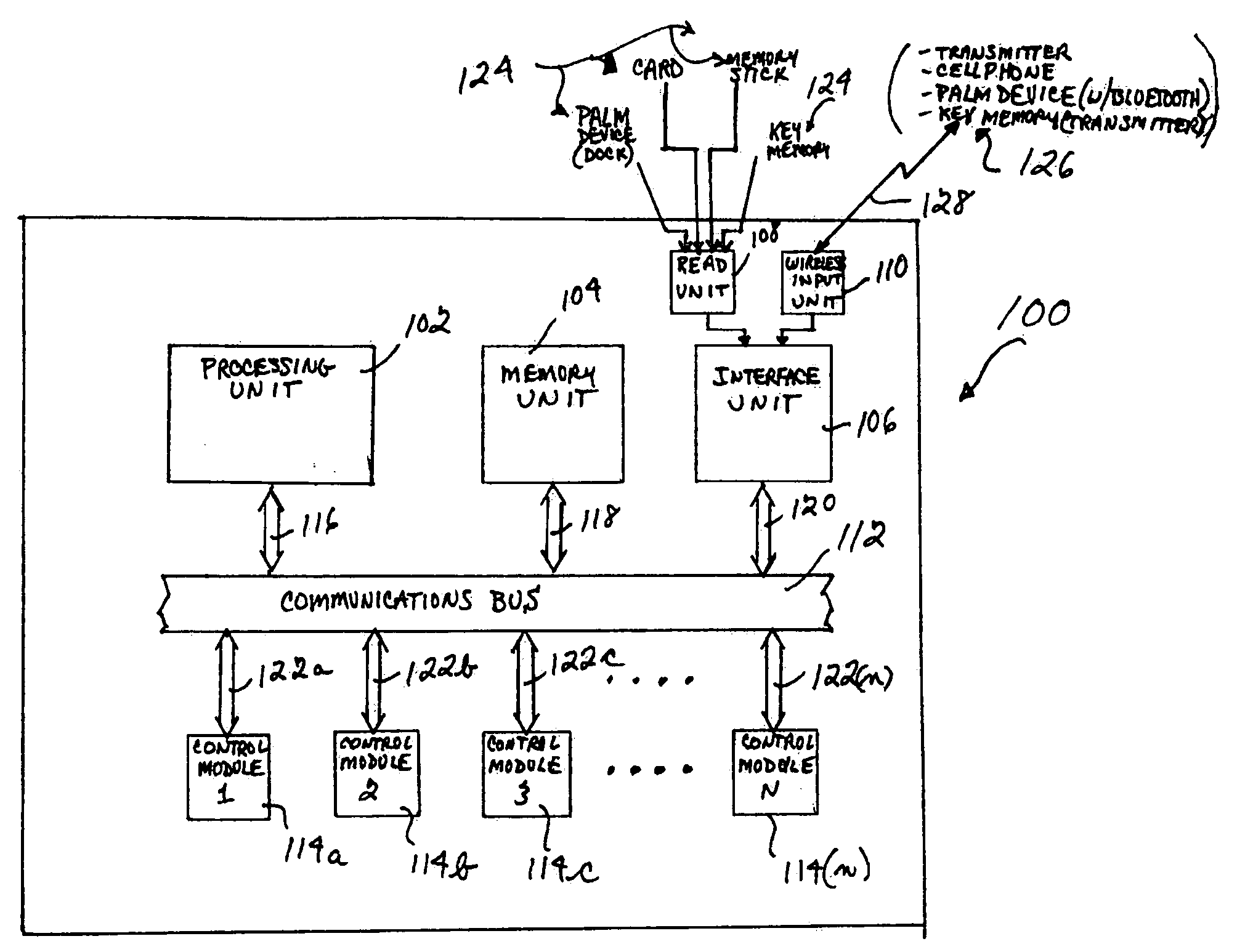
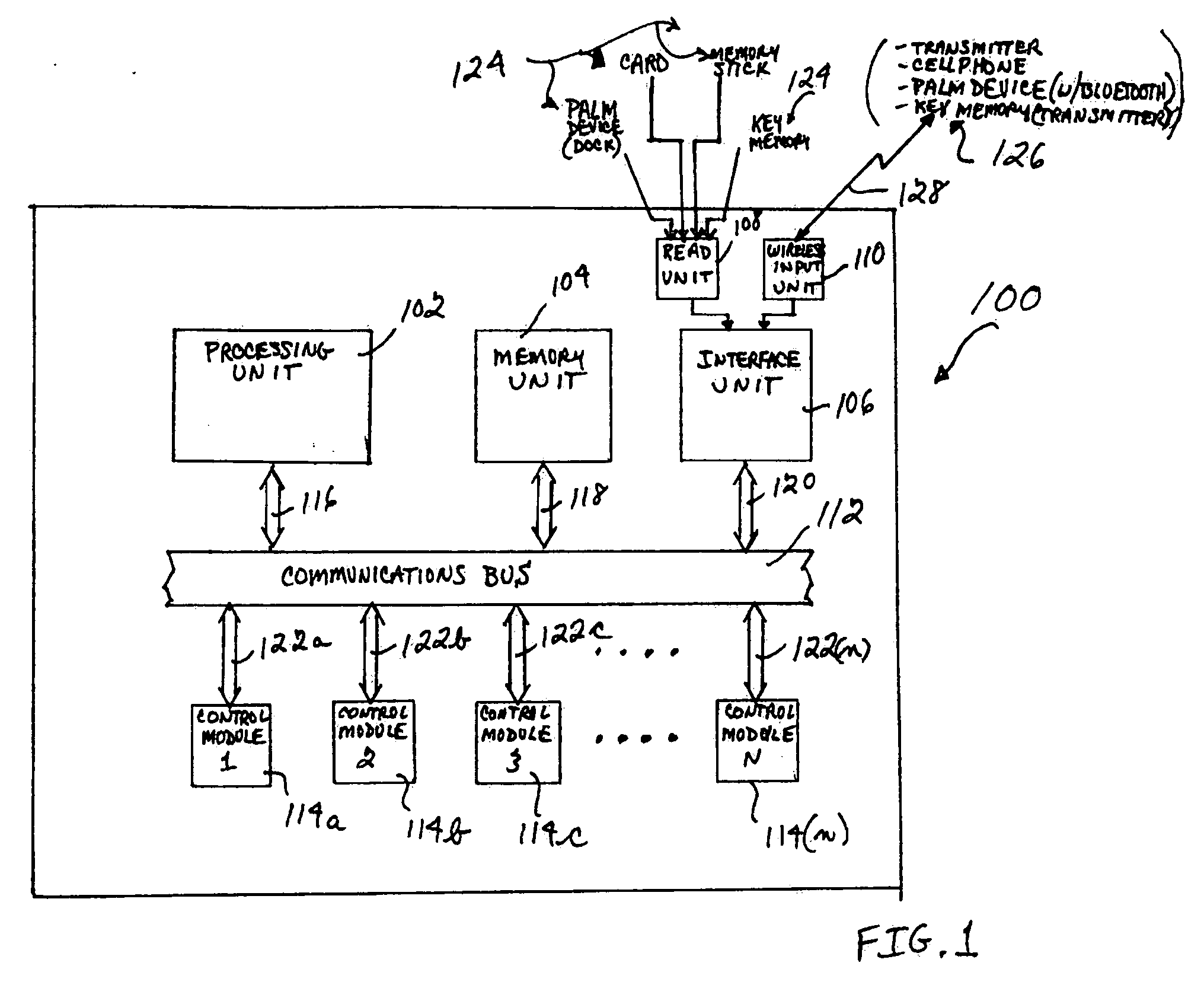
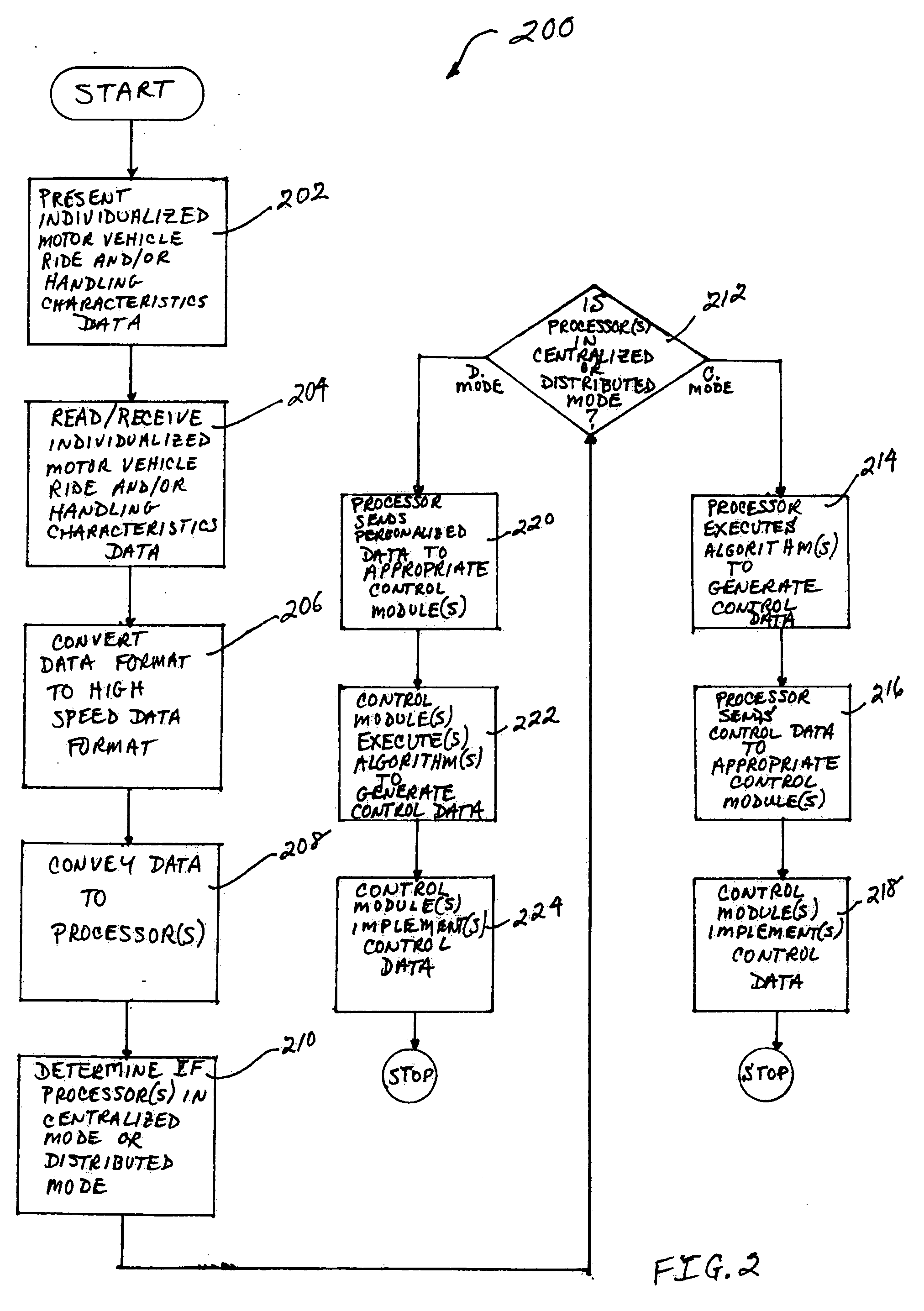
System and method for personalizing motor vehicle ride or handling characteristics
InactiveUS20070021885A1Digital data processing detailsVehicle position/course/altitude controlDocking stationPersonalization
An improved system and method for personalizing the ride and / or handling characteristics of a motor vehicle are disclosed. An example system for personalizing or individualizing the ride and / or handling characteristics of a motor vehicle is disclosed, which includes a processing unit, a memory unit, an interface unit, and a plurality of electronic control modules coupled to each other by a high speed data rate communications bus. The interface unit is also coupled to a read unit and a wireless input unit. The system can be operated in a centralized mode or a distributed mode. The read unit and wireless input unit can read in or receive, and forward to the interface unit, an individual's personal motor vehicle ride and / or handling characteristics data stored in a memory component of a device in that individual's possession. For example, an individual (e.g., driver, etc.) may carry a palm device (e.g., PDA, Palm Pilot®, etc.) including a memory component that stores that individual's personalized ride and / or handling characteristics data. The read unit can include, for example, a docking station for the palm device, which conveys the individual's personalized data from the memory component in the palm device to the interface unit. As another example, the individual may carry a cellular radiotelephone including a memory component. In this case, the wireless input unit can include, for example, a cellular radiotelephone or similar device that is compatible for operations with the individual's cellular device, and the individual can use the cellular device to transmit the individual's ride and / or handling characteristics data from the memory component to the interface unit via the wireless input unit. Thus, the processing unit and / or control modules can execute suitable algorithms for controlling the ride and / or handing characteristics of a motor vehicle, based on the individual's personalized data. Also, the use of a high speed data rate communications bus enables the system to meet future high speed data rate and processing requirements (e.g., drive-by-wire, etc.).
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
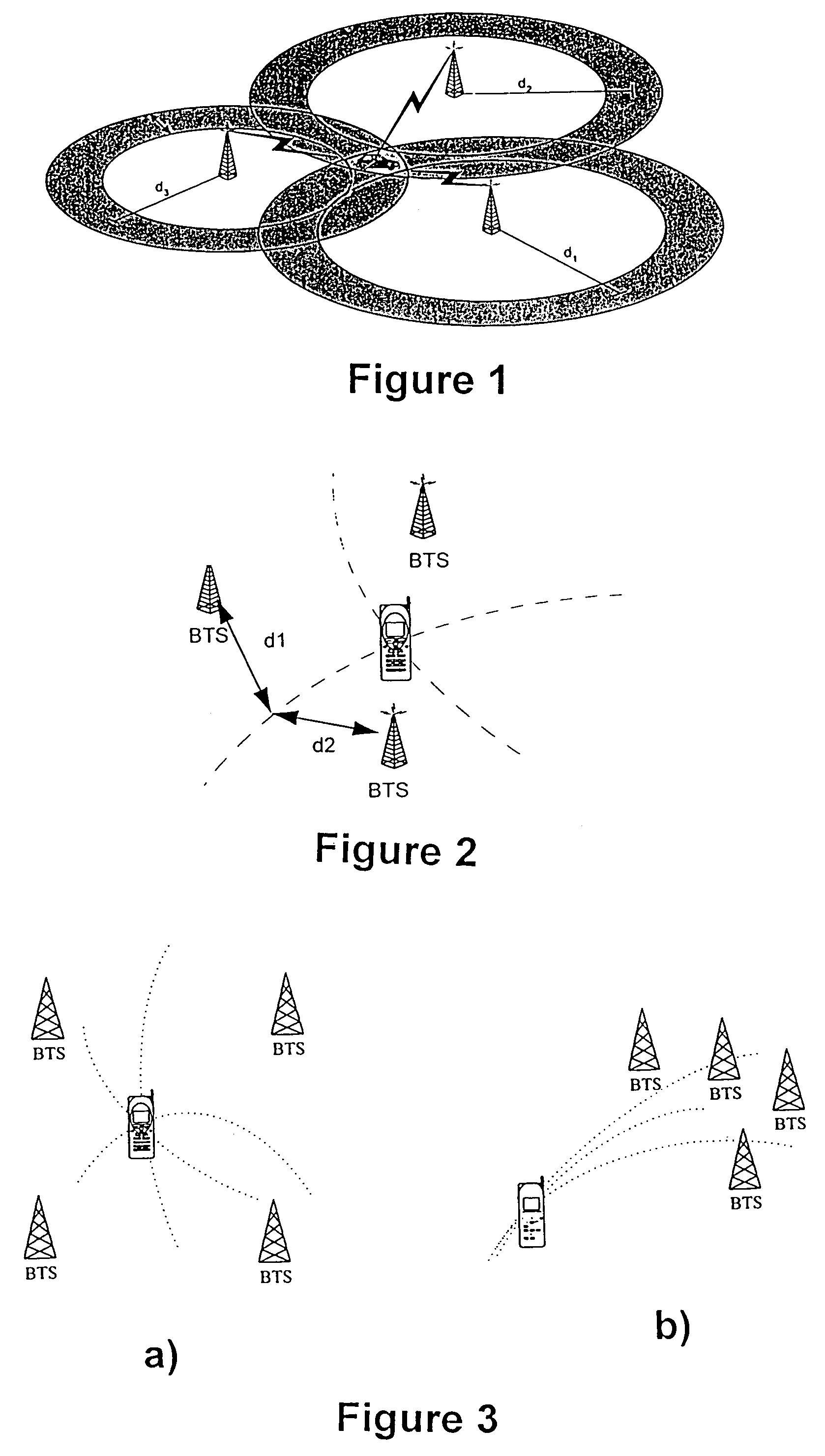
Method for determining the position of a mobile station
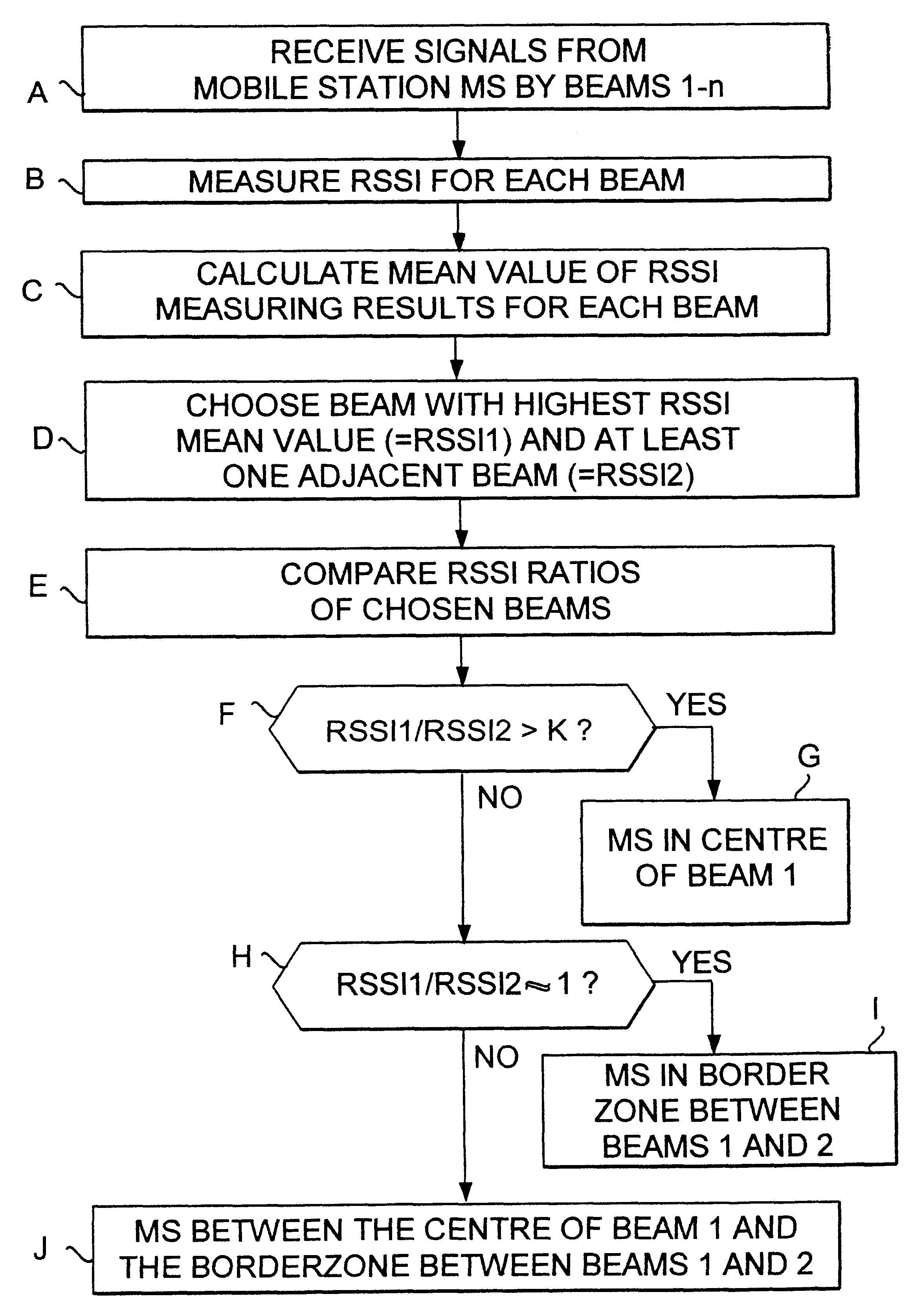
InactiveUS6850761B2Improve accuracyUnnecessary handover operationRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsPosition fixationCellular radioMobile station
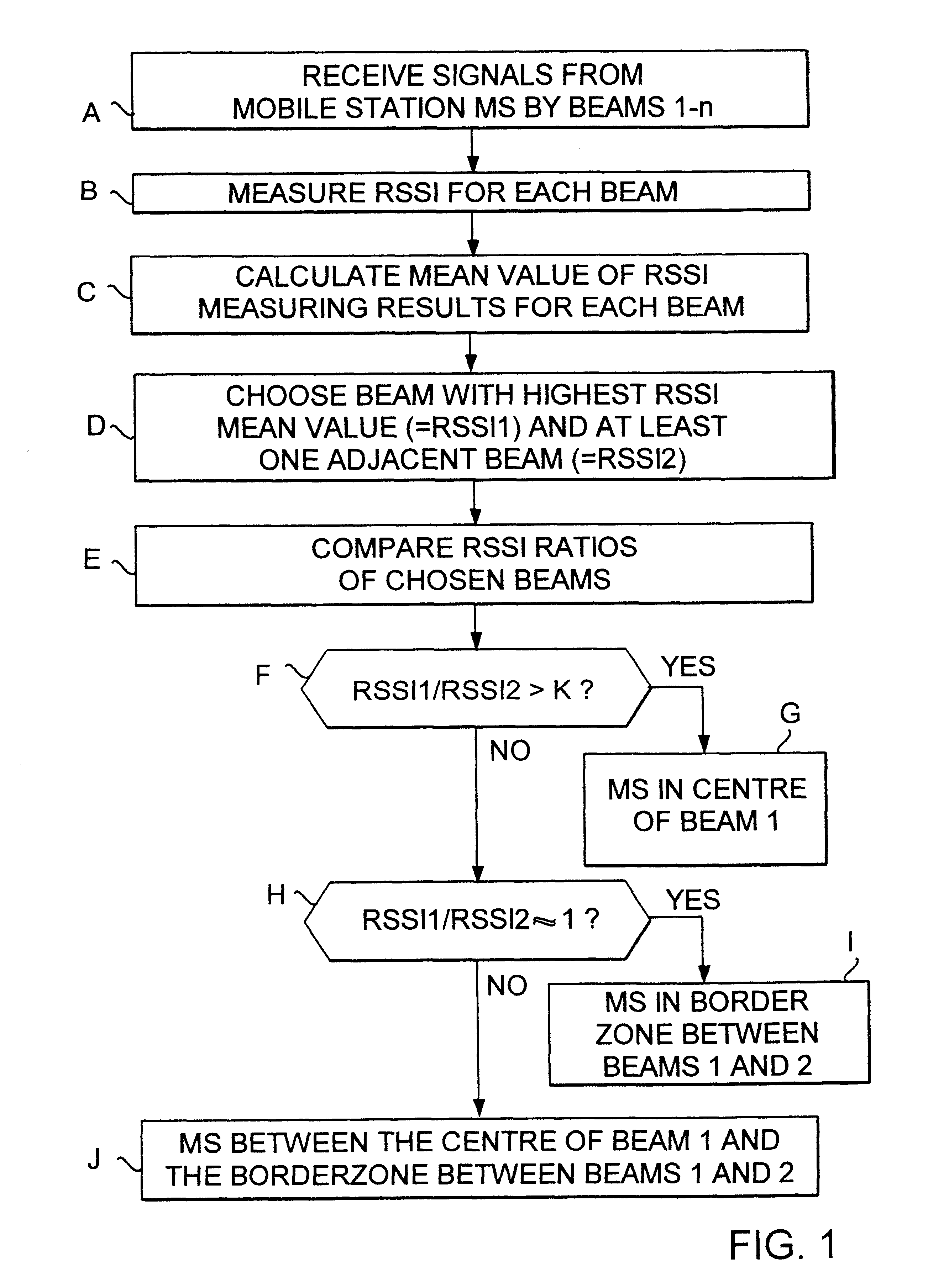
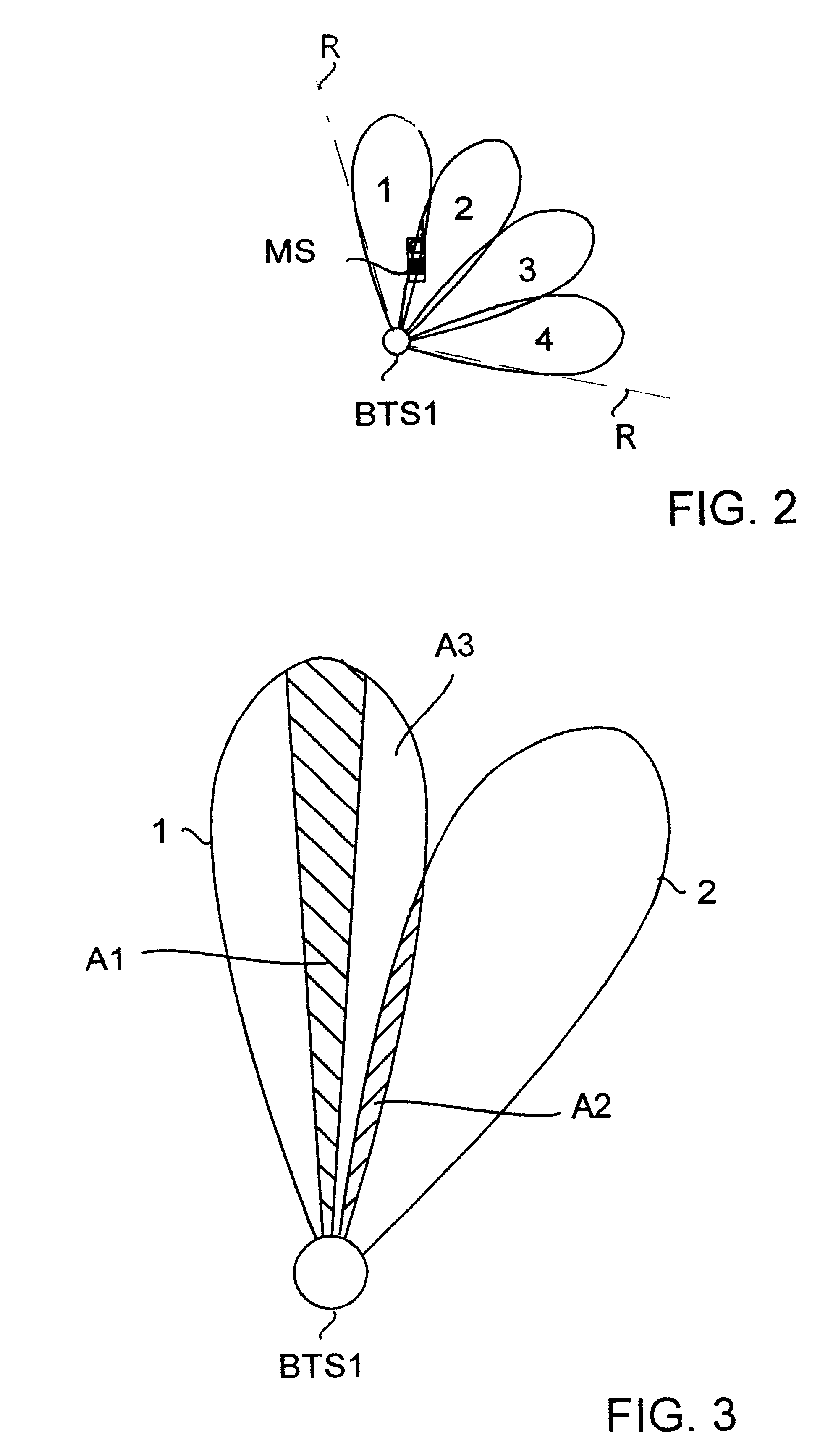
The present invention relates to a base station of a cellular radio system, which base station comprises antenna equipment for receiving signals from a certain mobile station simultaneously by at least two antenna beams directed in different directions, and measuring equipment for measuring the signal levels of the signals received by the respective antenna beans. For determining the position of the mobile station with greater accuracy the base station is provided with calculating means which are responsive to the measuring equipment to determine the direction from the base station to the mobile station by calculating the relations between the signal levels of the signals for the respective beams.
Owner:NOKIA NETWORKS OY
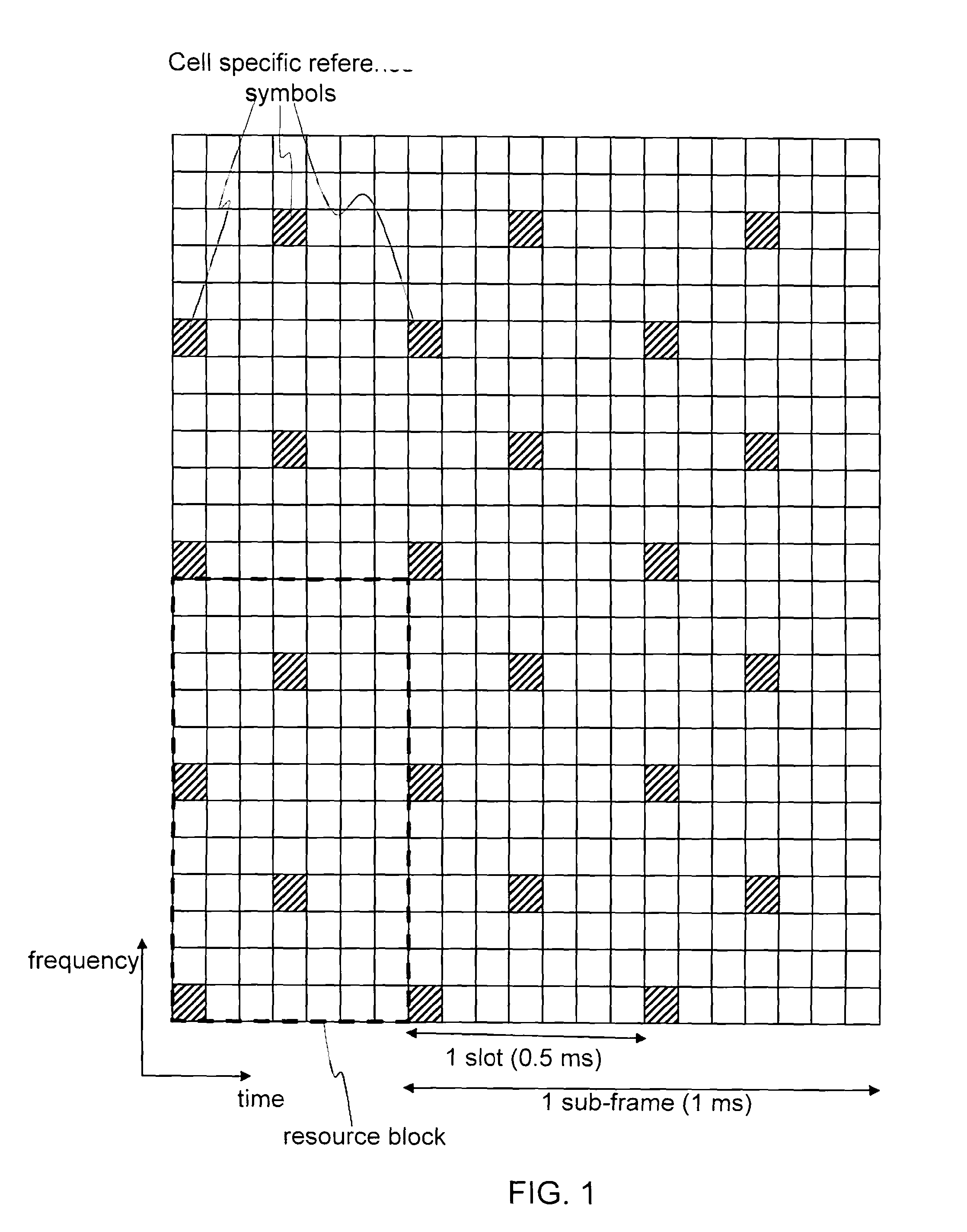
Information on Reference Signal Structure for Neighboring Cell Measurements
ActiveUS20100118706A1Accurate detectionError preventionTransmission systemsCellular radioTelecommunications
The present invention relates to cellular radio communication and in particular to providing information on neighbour cells to enable terminals to perform neighbour cell measurements. In the prior art the terminal attempts to make neighbour cell measurements in a reference signal structure that is the same in the neighbour cell as in the cell the terminal camps in. The present invention is based on the insight that the reference signal structure may differ between neighbouring cell for example in the situation of an MBSFN area that is restricted to a region of all cells of a radio network, or in the situation of TDD mode being applied there may be different regions with different allocation of sub-frames for transmission in the uplink and downlink directions. The present invention solves the problem by broadcast information in a cell indicative of the reference signal structure in neighbour cells.
Owner:OPTIS WIRELESS TECH LLC
Cellular radio communications system
InactiveUS6947490B1Improve bandwidth usageReduce the required powerChannel coding adaptationSignalling characterisationCellular radioCommunications system
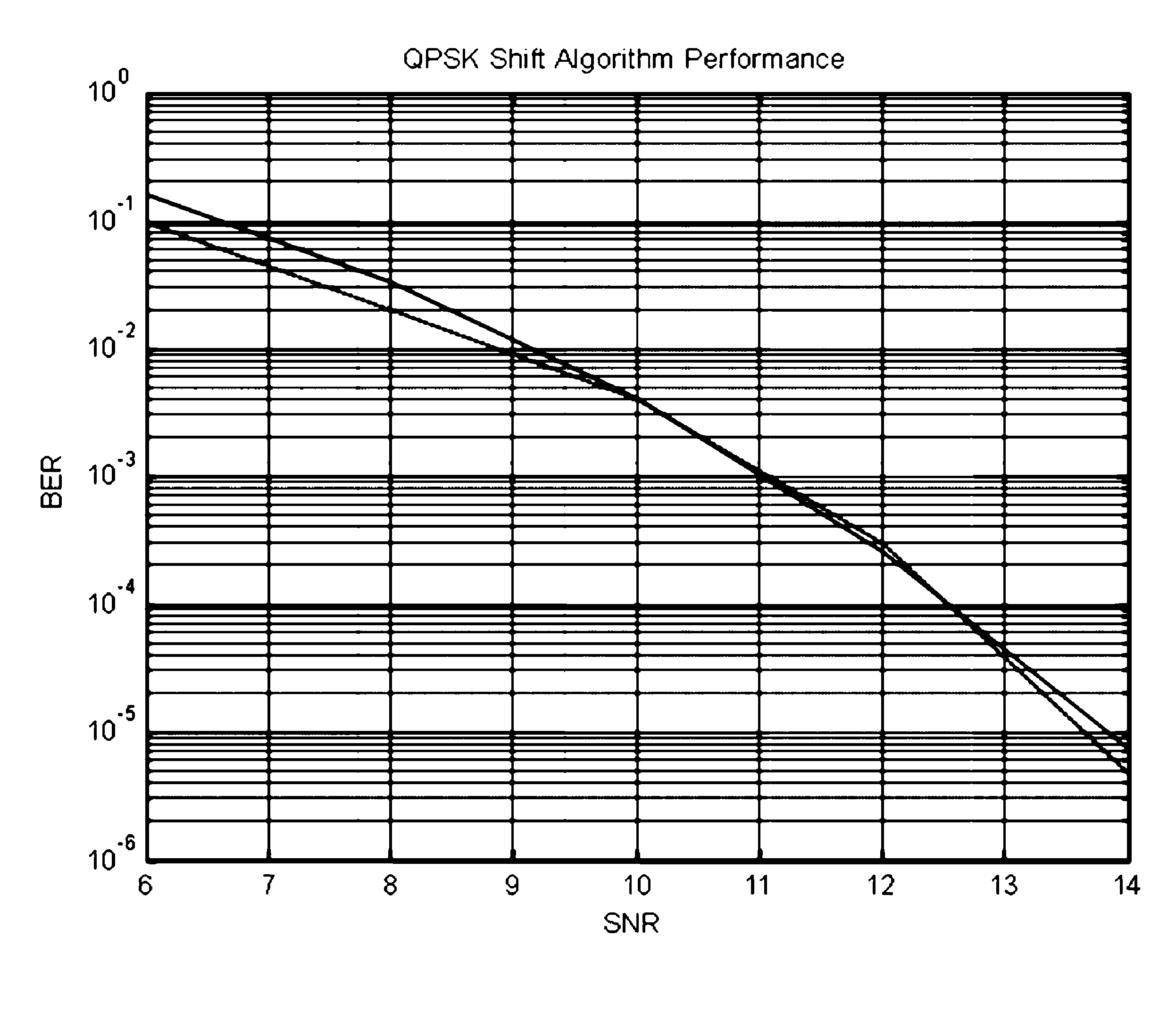
A cellular radio communication system for transmitting blocks of data over transmission links in which the quality of the transmission links are monitored. The system comprises a data storage means for storing sets of modulation scheme and forward error correction coding level pairs to give an optimum data rate at a predetermined bit error rate and a predetermined symbol rate for different quality transmission links. The database is interrogated and a modulation scheme and forward error correction coding level pair is allocated and applied to the blocks of data transmitted over a transmission link dependent on the monitored quality of the transmission link.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Download management with congestion mitigation for over the air content delivery to vehicles
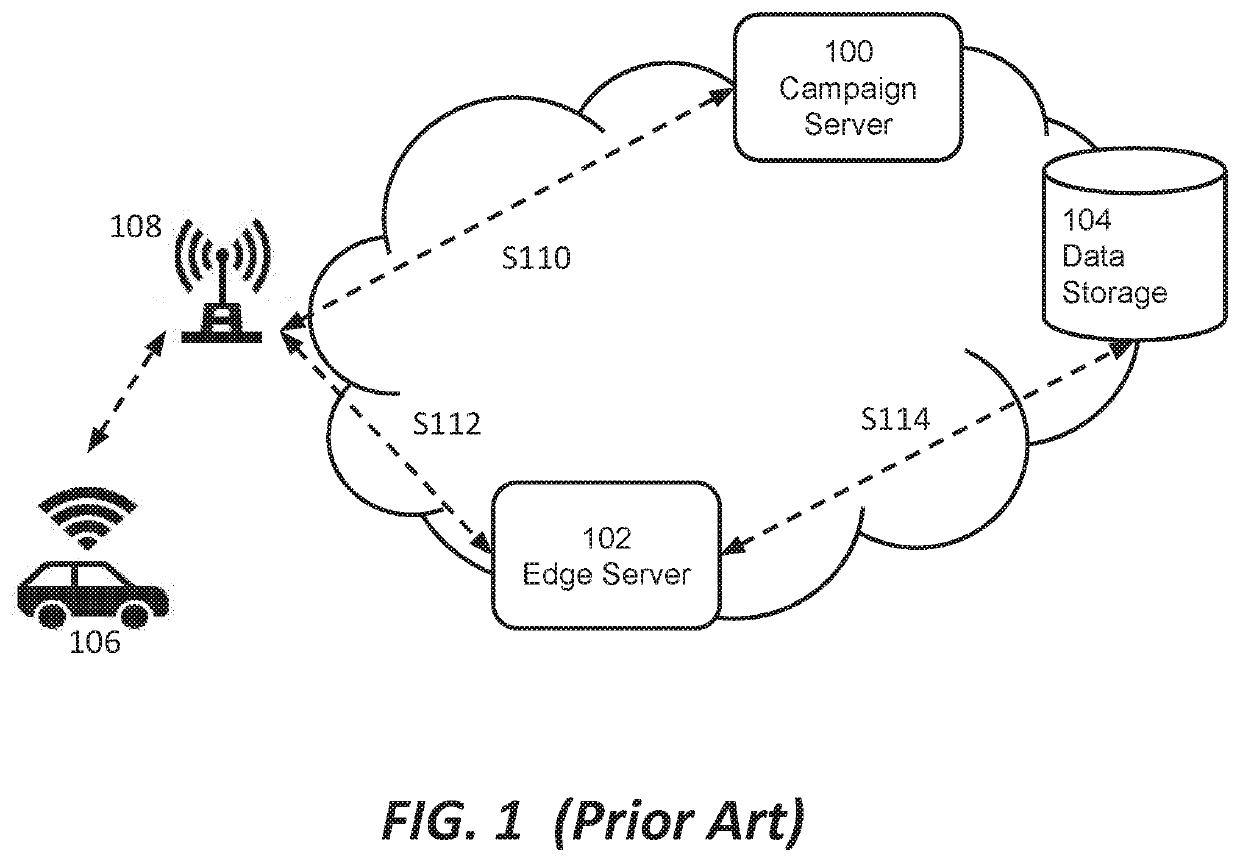
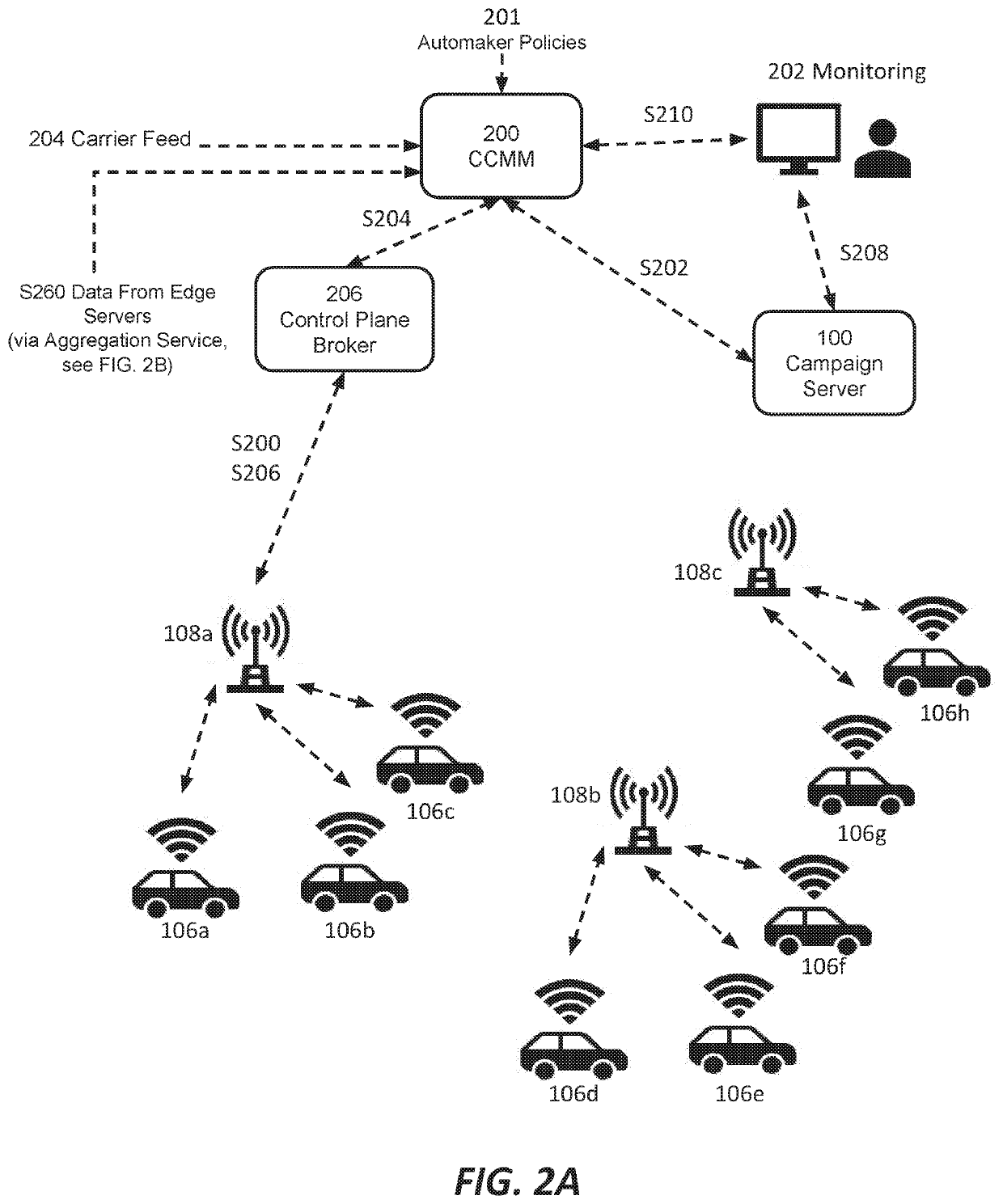
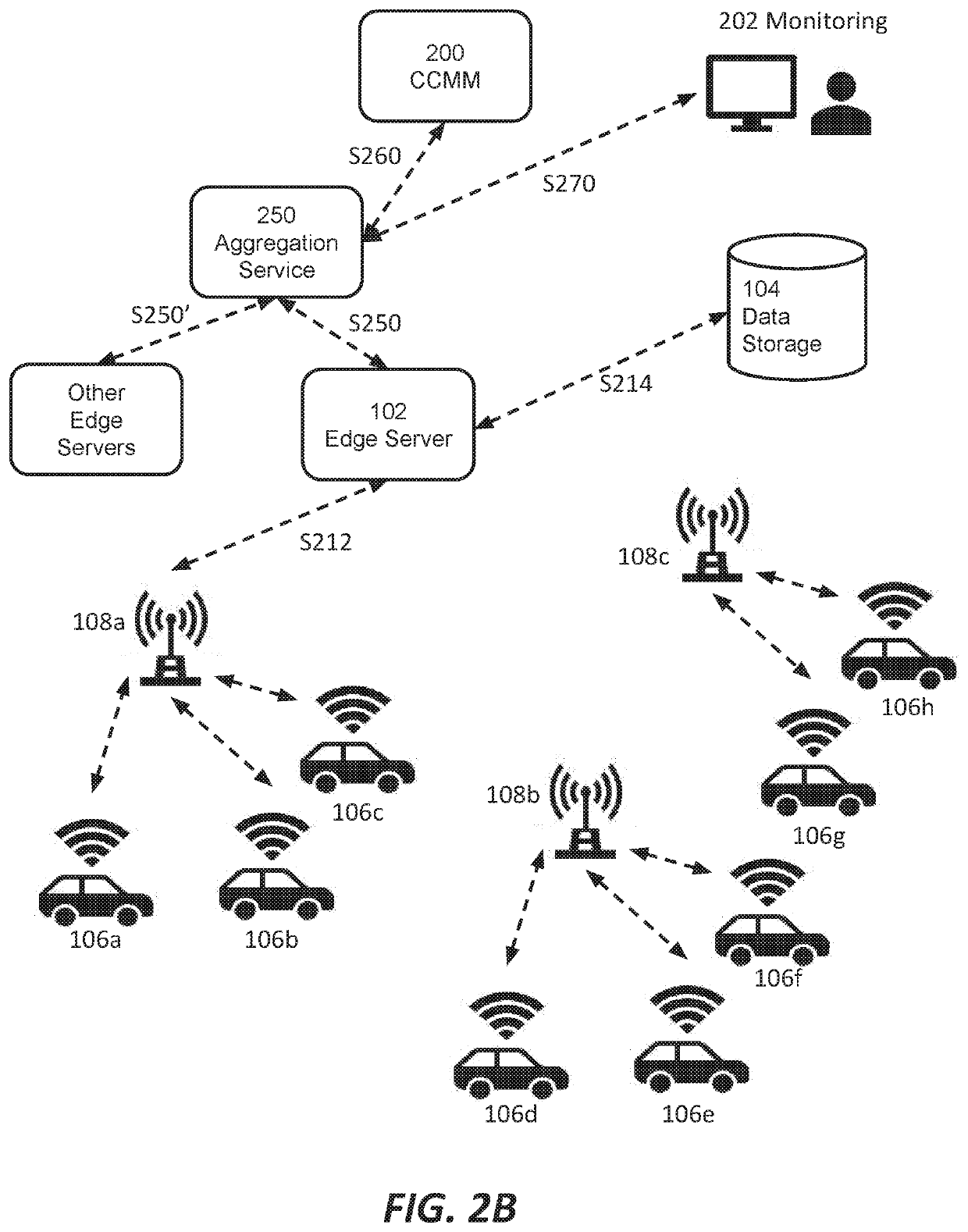
ActiveUS20190387430A1Network traffic/resource managementParticular environment based servicesCellular radioTower
Among other things, this document describes systems, devices, and methods for wireless content delivery to vehicles and in particular to vehicles in cellular radio environments. The teachings hereof can be used to deliver a vehicle manufacturer's head unit updates, firmware, configurations, and other data to a vehicle. In embodiments, downloads are managed at the control plane and / or data plane. Download management can include mitigating either current or anticipated wireless congestion at cell towers, enforcing campaign priority for firmware updates, accommodating occupant-originated data flows to and from the vehicle, and / or accounting for contractual data arrangements between vehicles makers and cellular providers, among other things.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
System and method for communicating using bandwidth on demand
ActiveUS8787873B1Increase data rateEfficient combinationNetwork traffic/resource managementTelephonic communicationCyber operationsQuality of service
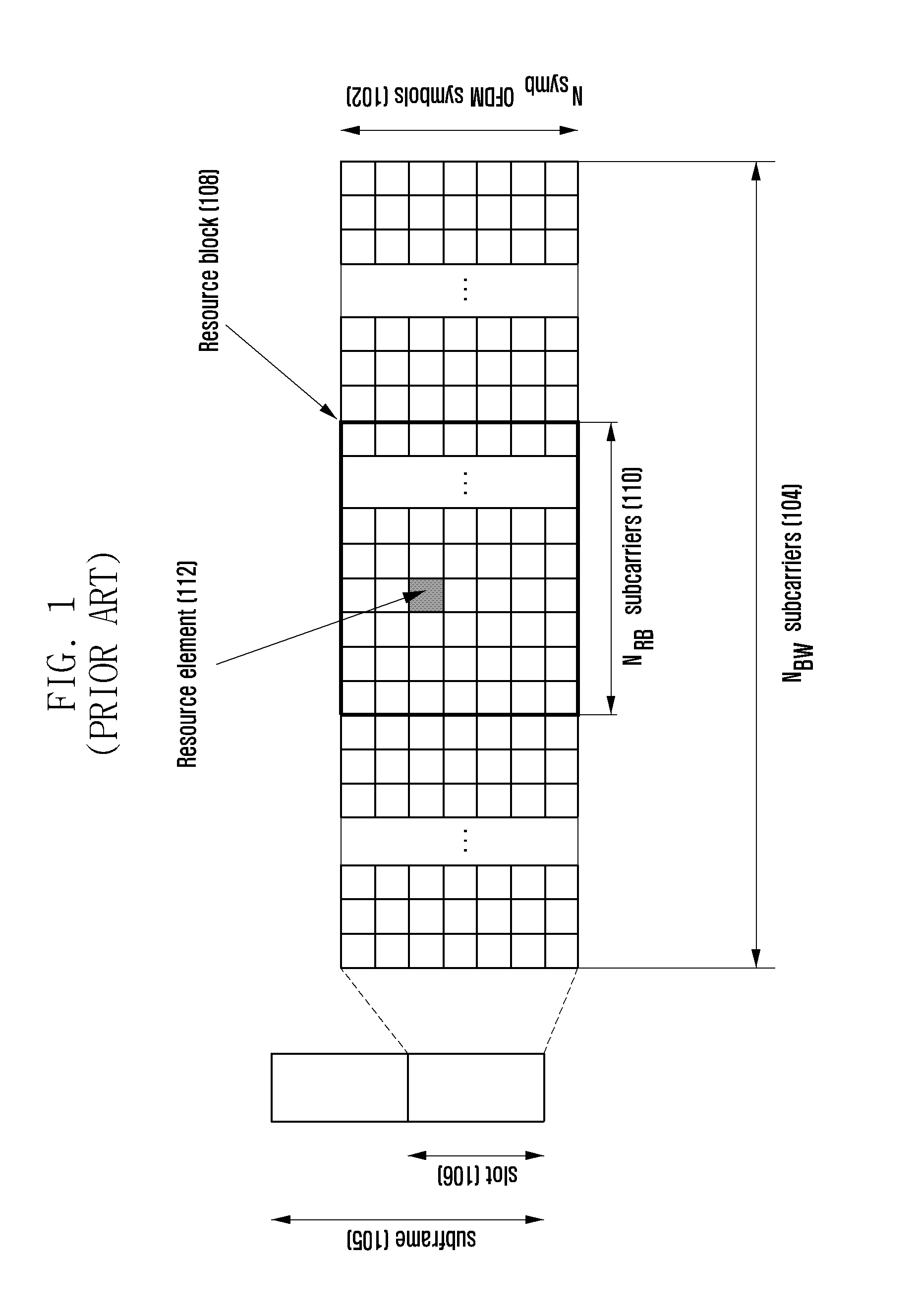
A system and method for dynamically changing the quality of service (QoS) for a subscriber of a cellular radio system. Bandwidth-on-Demand (BoD) enables the subscriber to dynamically switch to higher bandwidth and to enable a higher throughput. This may be for a limited time or amount of data, for example. The initiation may be by the subscriber, carrier, sponsor, or automatically by an application. The QoS increase may be dynamically priced in a kind of auction. The wireless device may contact the policy servers of a multiple network operator (MNO), which in turn contacts the Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA) server in the MNO's core network. The policy server contacts the scheduler on the serving basestation which then determines whether to allocate more resources (i.e. bandwidth in the form of subcarriers, resource blocks, resource elements, timeslots) to the subscriber. The initiation may start a timer or data counter.
Owner:RPX CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com