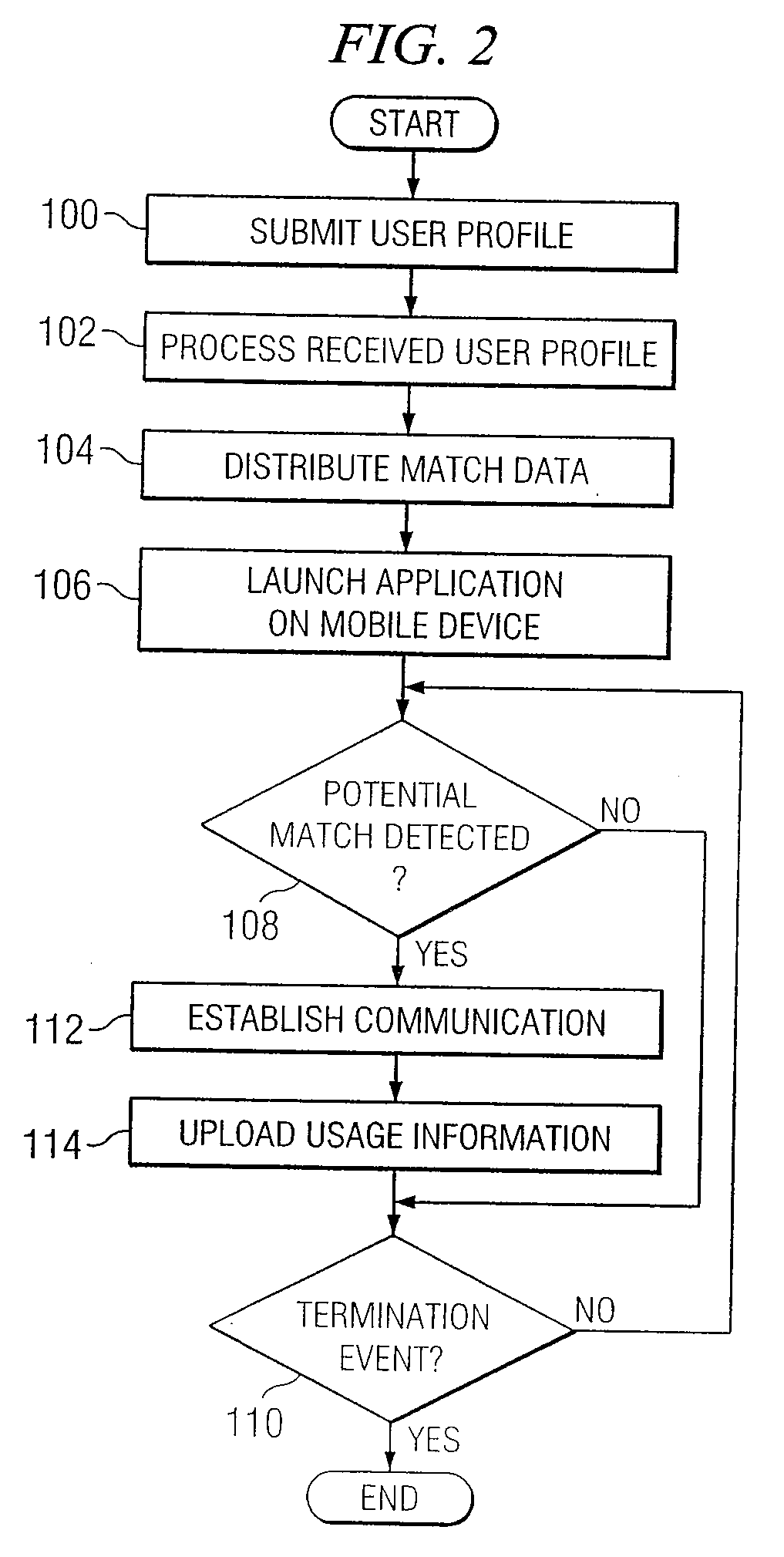
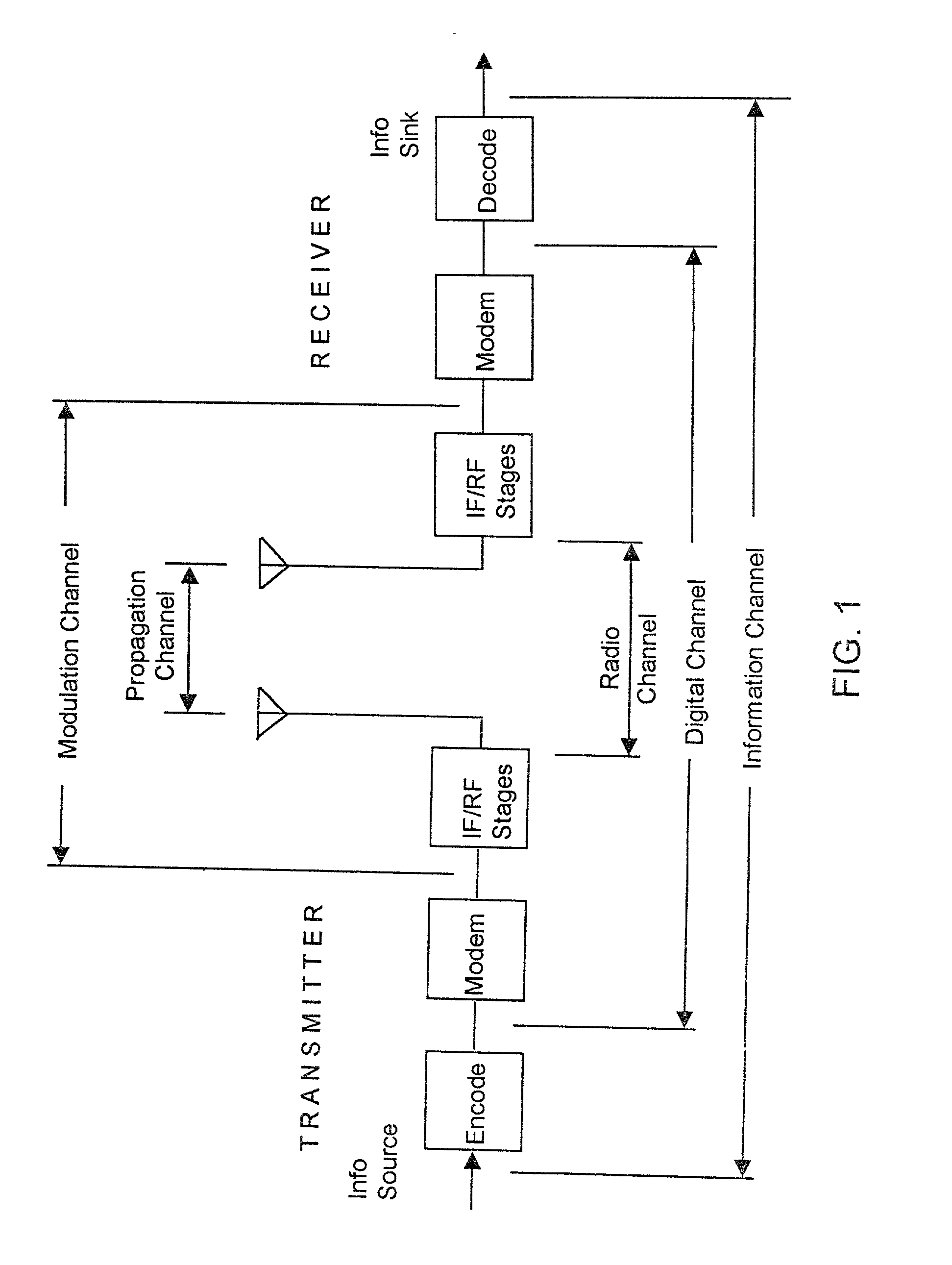
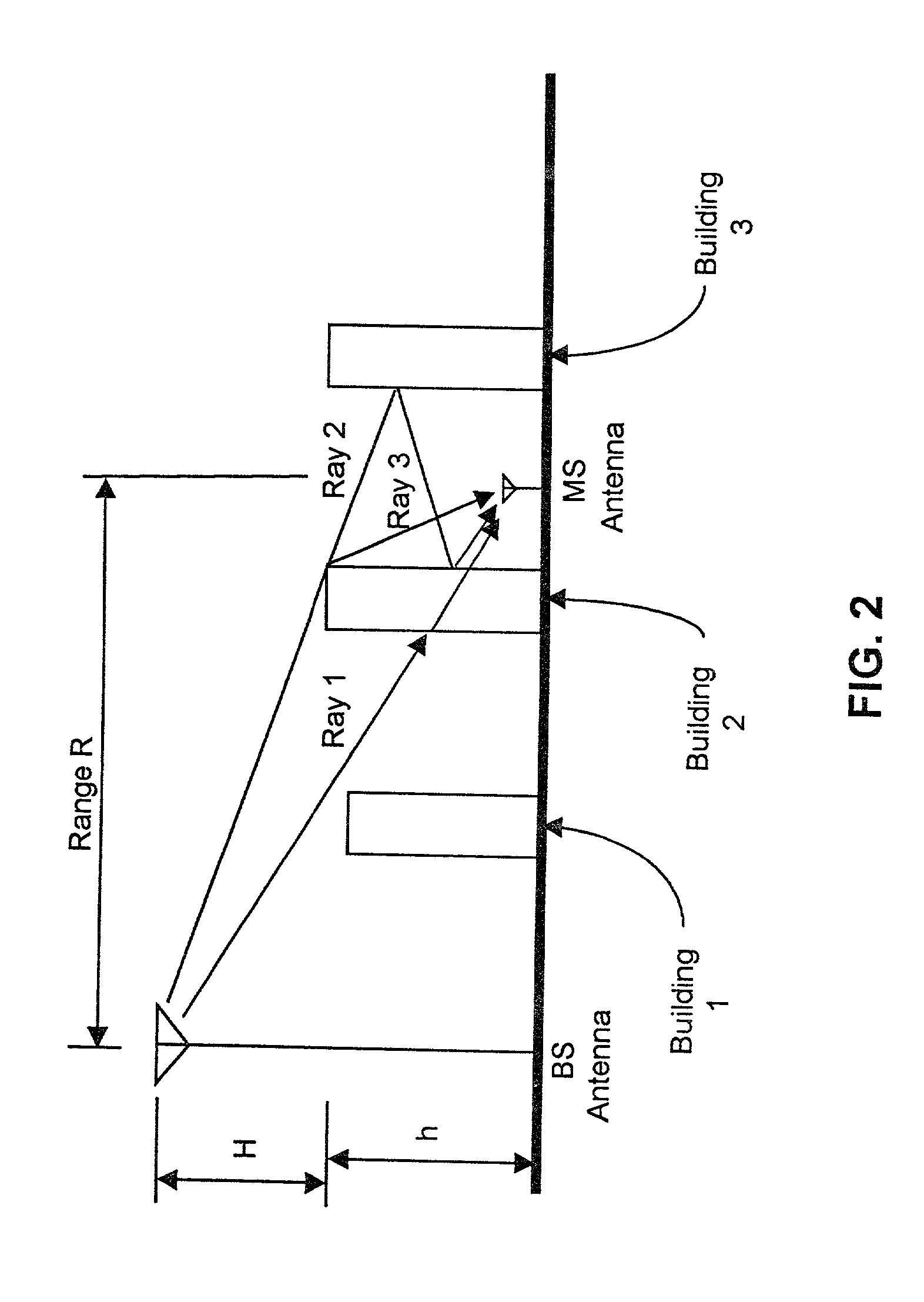
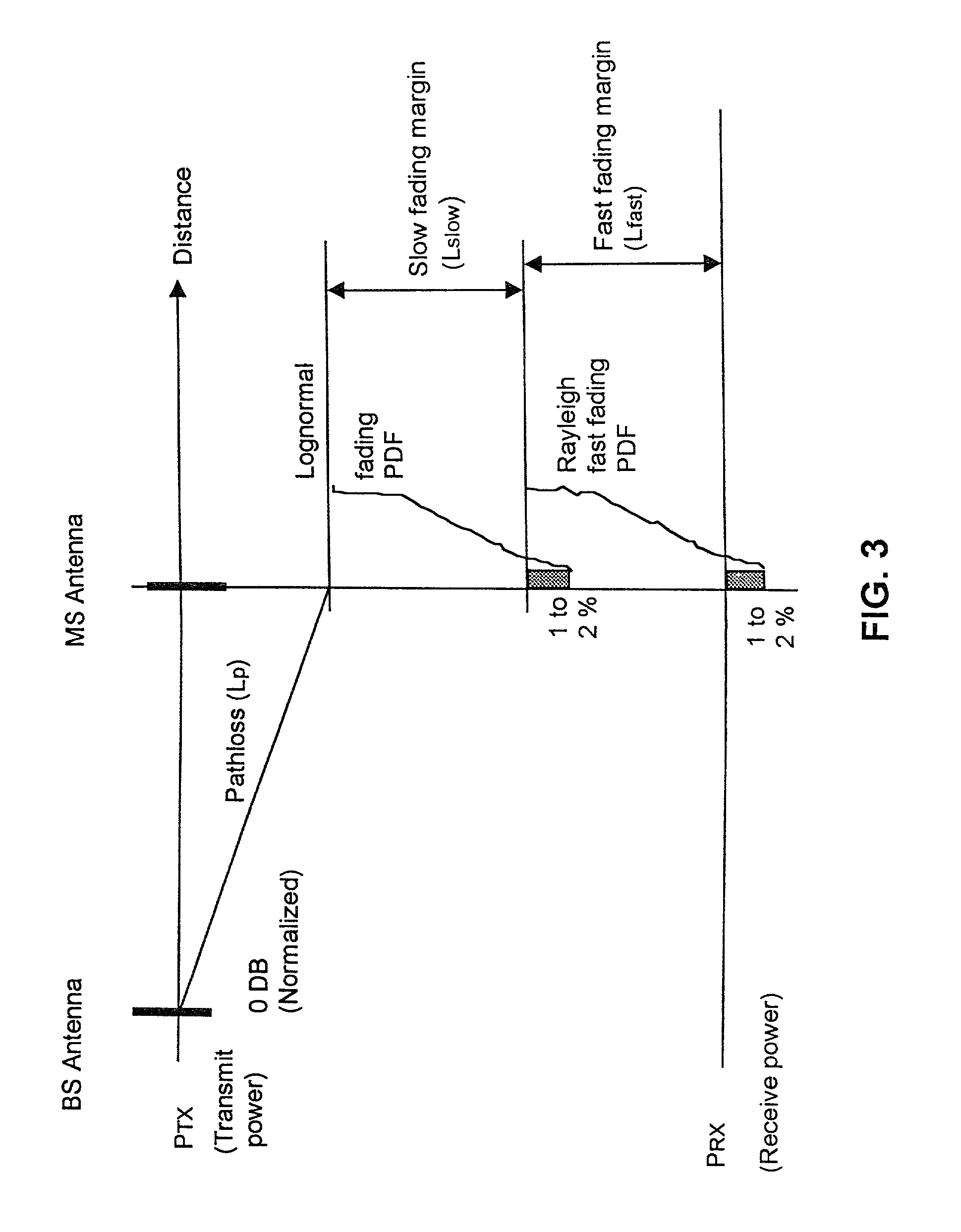
Patents
Literature
41237results about "Radio/inductive link selection arrangements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Multifactorial optimization system and method
A method for providing unequal allocation of rights among agents while operating according to fair principles, comprising assigning a hierarchal rank to each agent; providing a synthetic economic value to a first set of agents at the a high level of the hierarchy; allocating portions of the synthetic economic value by the first set of agents to a second set of agents at respectively different hierarchal rank than the first set of agents; and conducting an auction amongst agents using the synthetic economic value as the currency. A method for allocation among agents, comprising assigning a wealth generation function for generating future wealth to each of a plurality of agents, communicating subjective market information between agents, and transferring wealth generated by the secure wealth generation function between agents in consideration of a market transaction. The method may further comprise the step of transferring at least a portion of the wealth generation function between agents.
Owner:MEADWESTVACO CORP
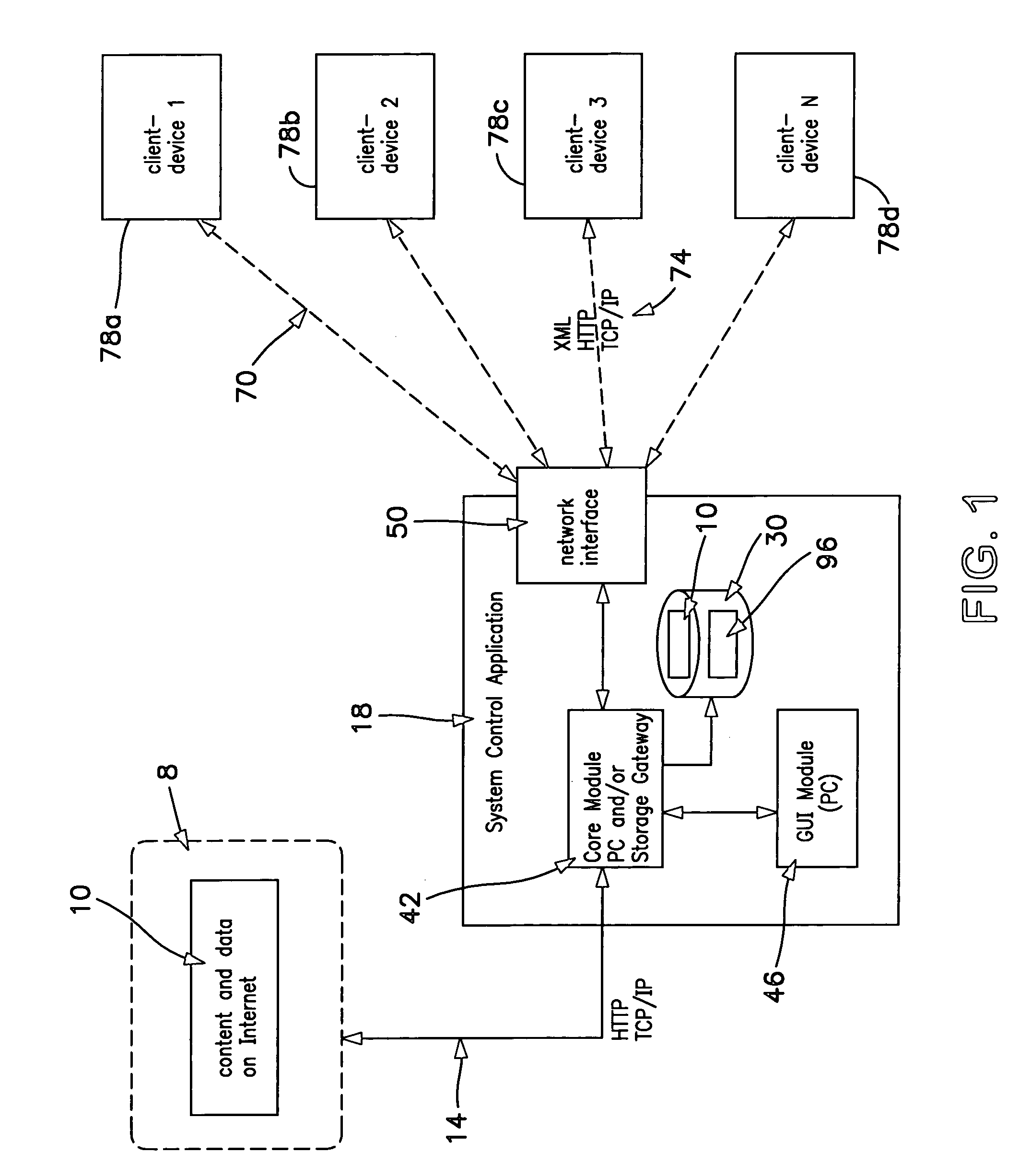
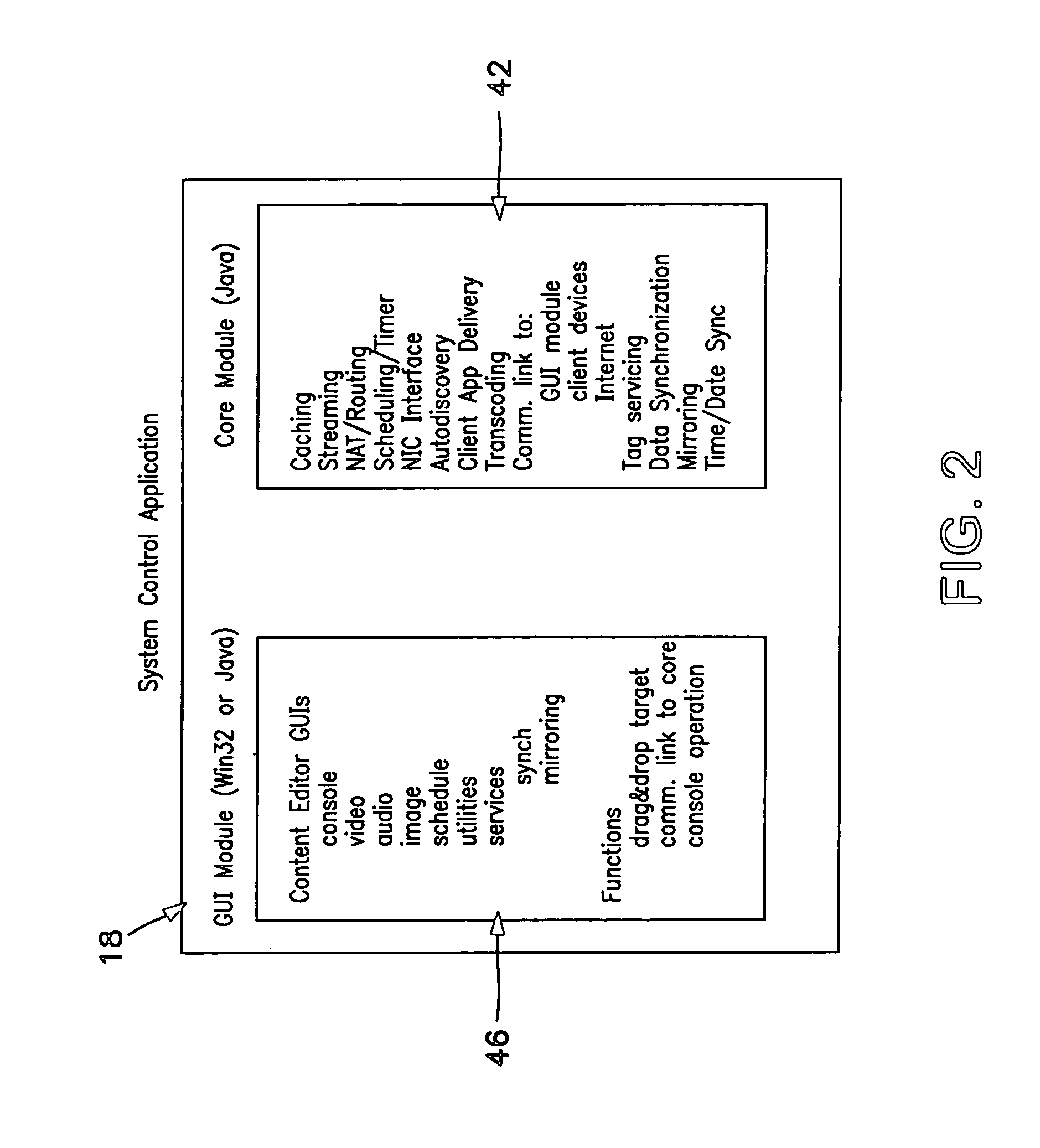
System and method for providing content, management, and interactivity for client devices
InactiveUS7130616B2Data processing applicationsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesDigital dataInternet privacy
Owner:MUSICQUBED INNOVATIONS LLC
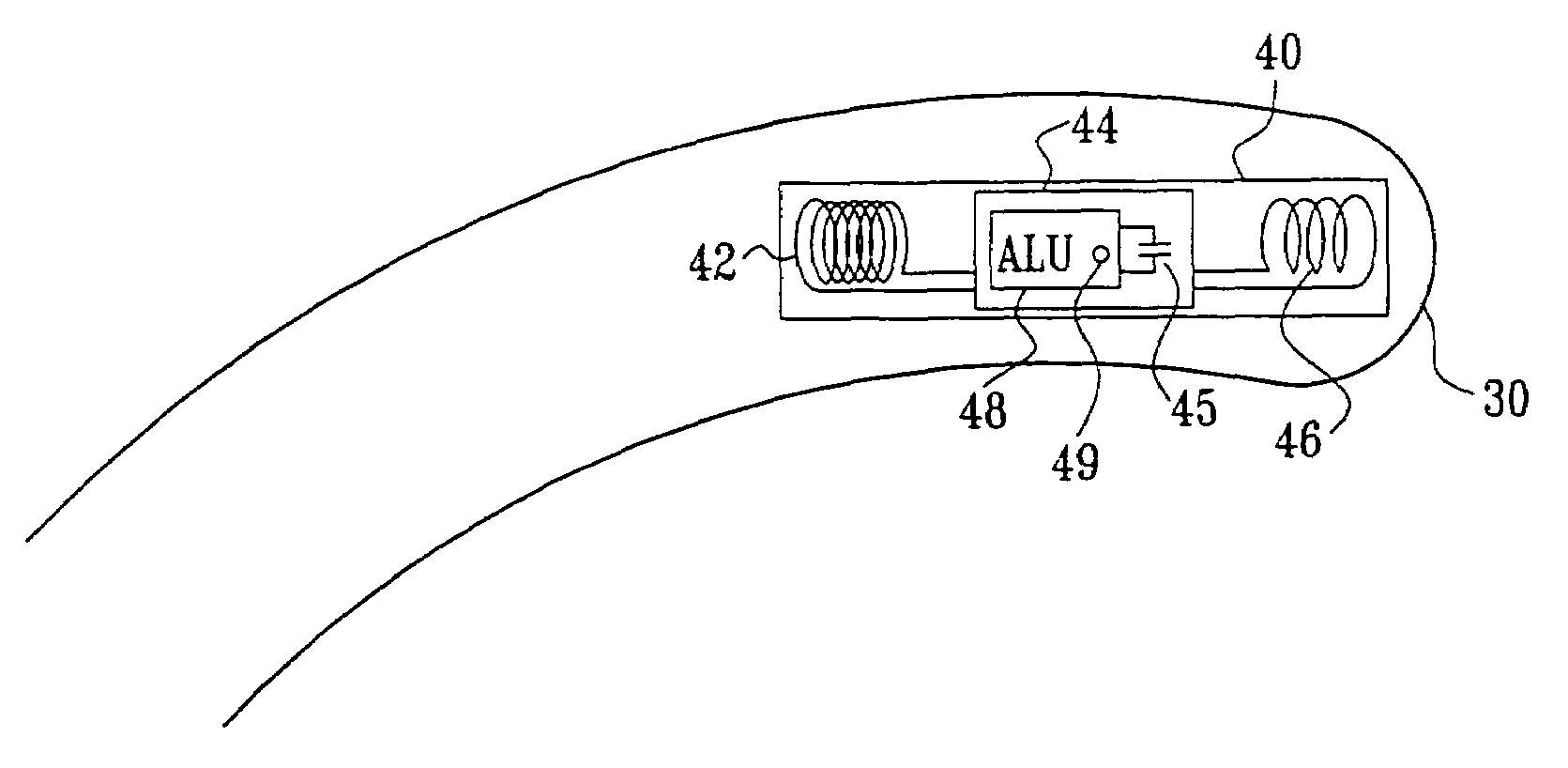
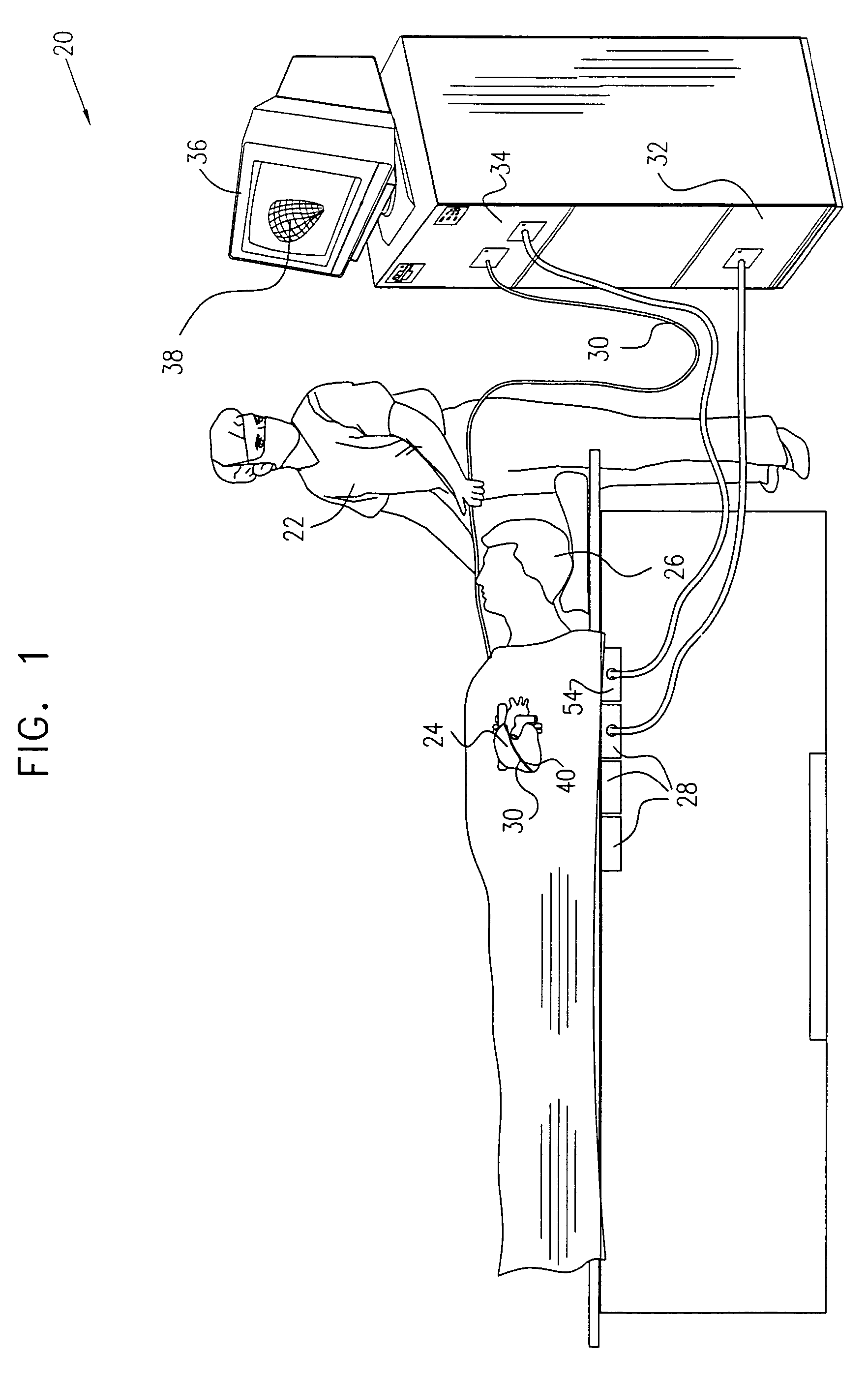
Digital wireless position sensor
ActiveUS7397364B2Fast chargingImprove signal-to-noise ratioElectric signal transmission systemsMagnetic measurementsVoltage dropEngineering
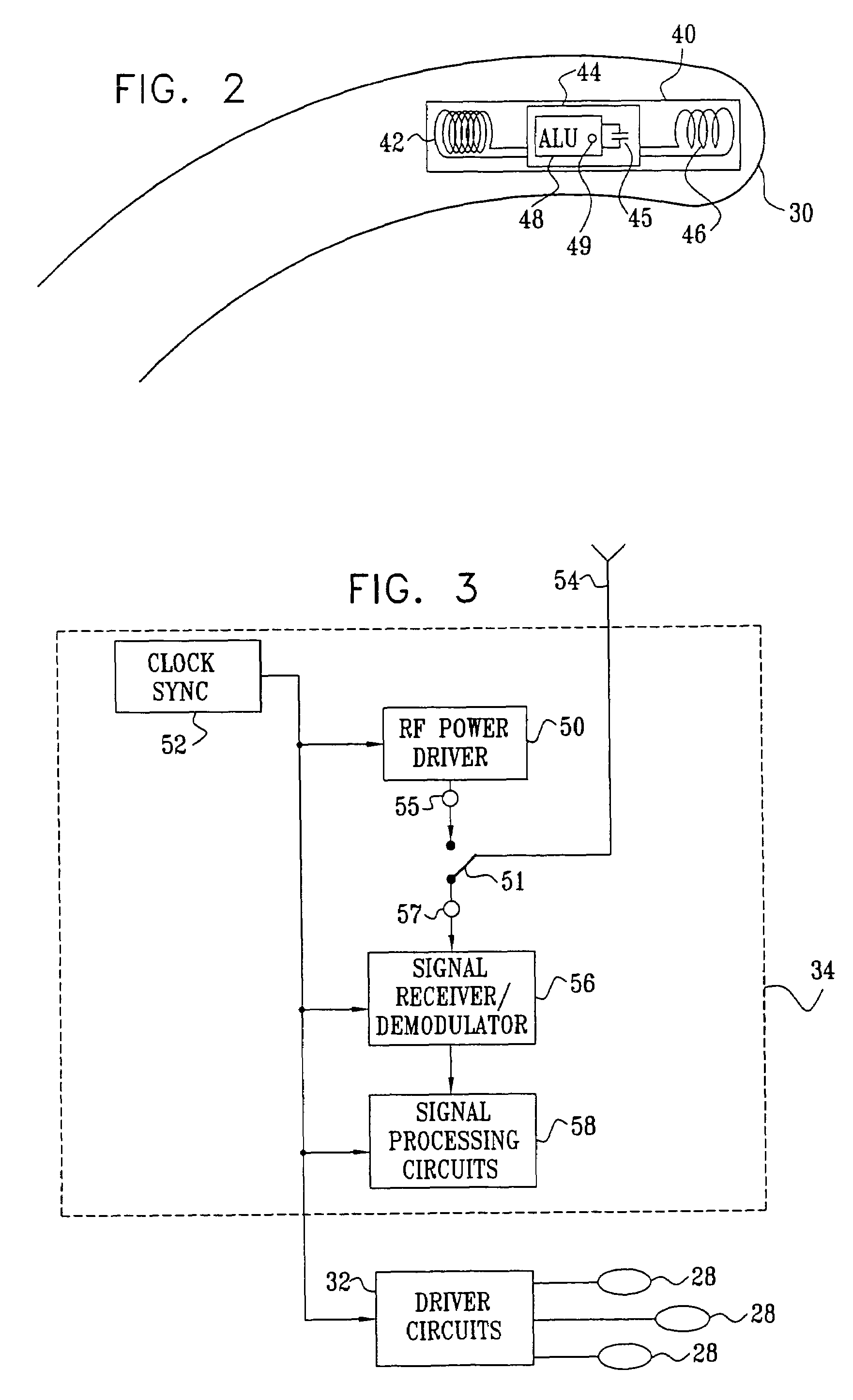
A method is provided for tracking an object, including positioning a radio frequency (RF) driver to radiate an RF driving field toward the object, and fixing to the object a wireless transponder that includes a power coil and at least one sensor coil. The method also includes receiving the RF driving field using the power coil and storing electrical energy derived therefrom. A plurality of field generators are driven to generate electromagnetic fields at respective frequencies in a vicinity of the object that induce a voltage drop across the at least one sensor coil. A digital output signal is generated at the wireless transponder indicative of the voltage drop across the sensor coil, and the generation of the digital output signal is powered using the stored electrical energy. The digital output signal is transmitted from the wireless transponder using the power coil, and the transmission of the digital output signal is powered using the stored electrical energy. The digital output signal is received and processed to determine coordinates of the object.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Wireless location using multiple location estimators
InactiveUS6249252B1Effectively and straightforwardly resolvedAmbiguity and conflictDirection finders using radio wavesBeacon systems using radio wavesTerrainHeuristic
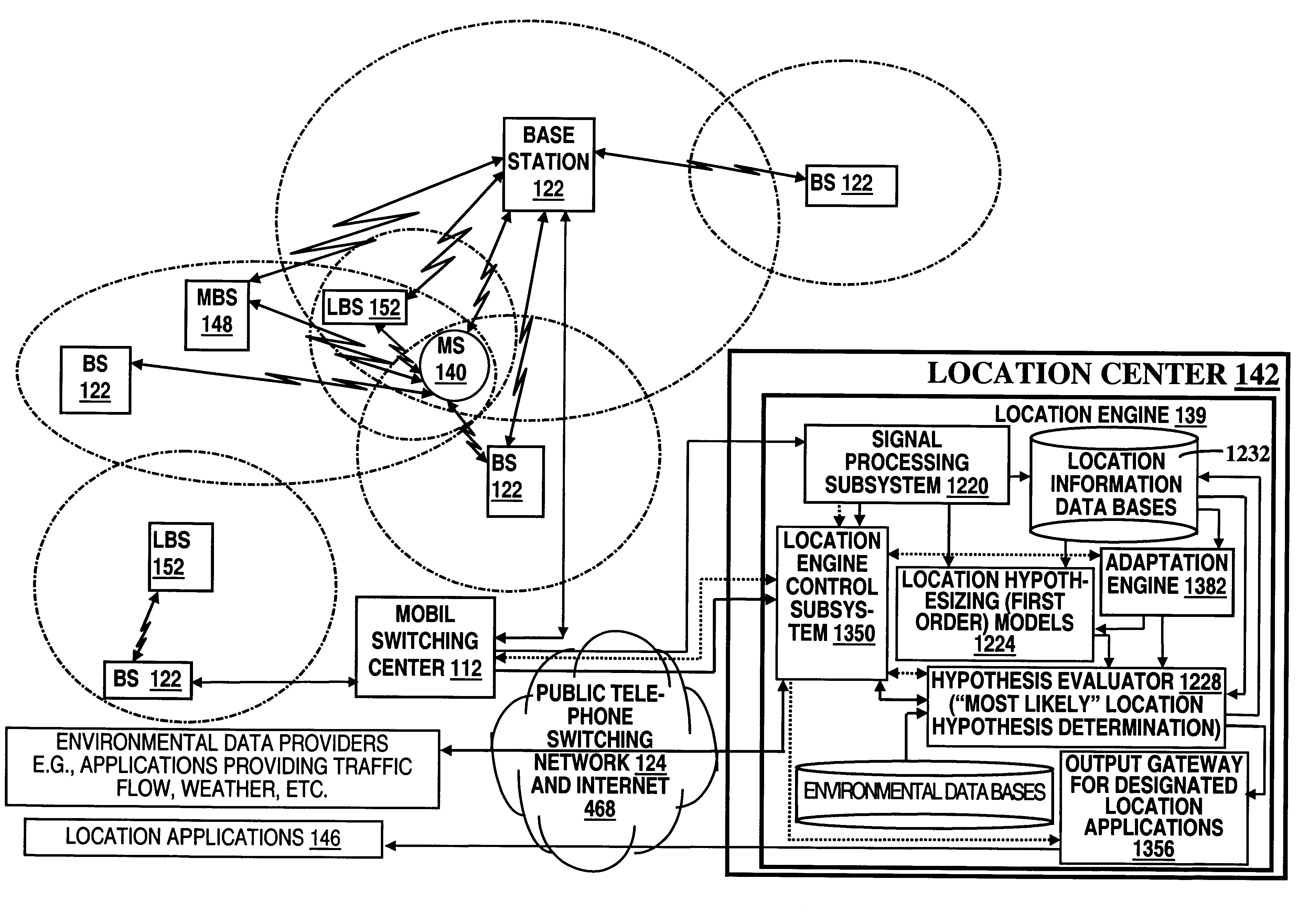
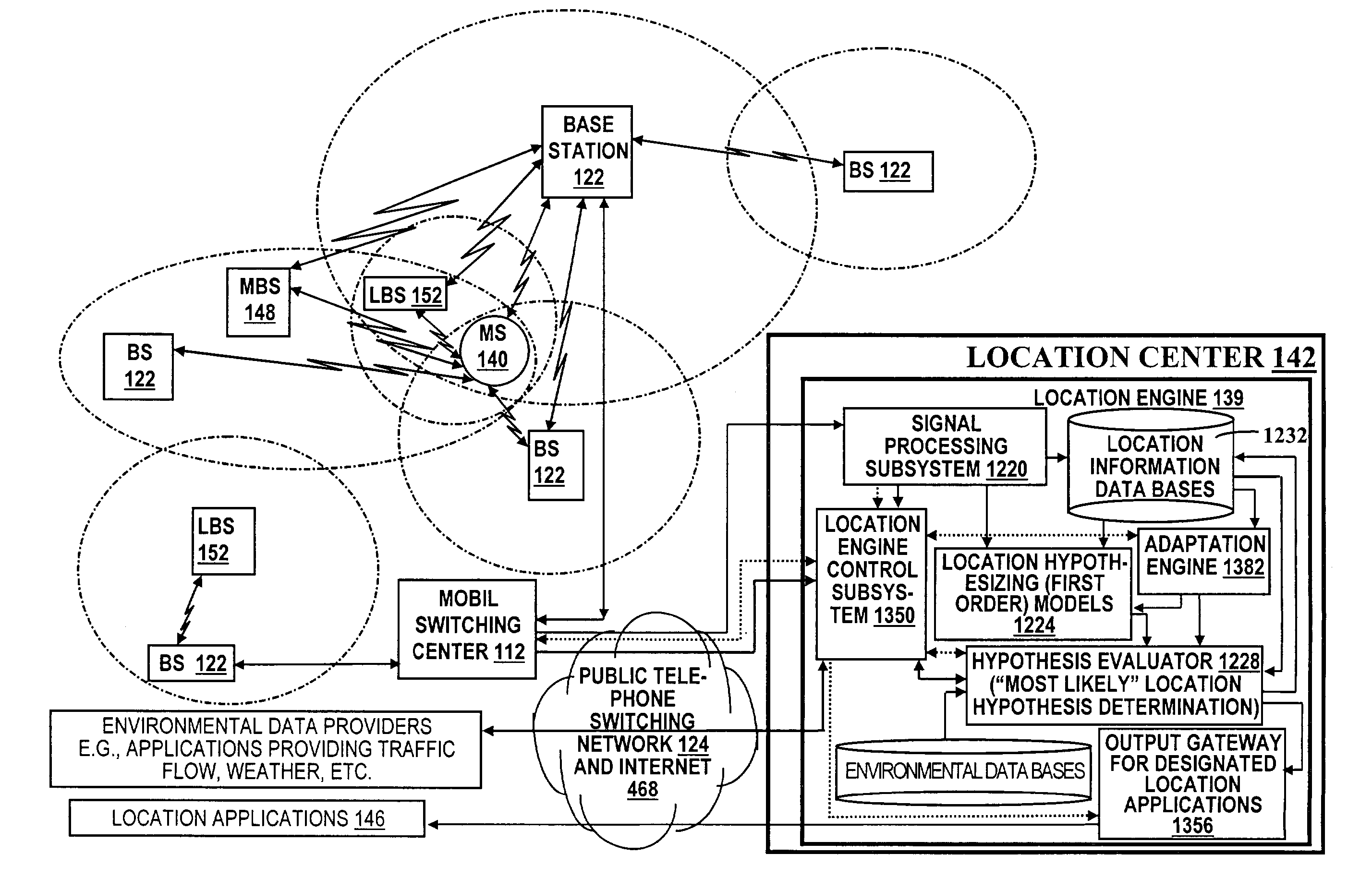
A location system is disclosed for commercial wireless telecommunication infrastructures. The system is an end-to-end solution having one or more location centers for outputting requested locations of commercially available handsets or mobile stations (MS) based on, e.g., CDMA, AMPS, NAMPS or TDMA communication standards, for processing both local MS location requests and more global MS location requests via, e.g., Internet communication between a distributed network of location centers. The system uses a plurality of MS locating technologies including those based on: (1) two-way TOA and TDOA; (2) pattern recognition; (3) distributed antenna provisioning; (5) GPS signals, (6) angle of arrival, (7) super resolution enhancements, and (8) supplemental information from various types of very low cost non-infrastructure base stations for communicating via a typical commercial wireless base station infrastructure or a public telephone switching network. Accordingly, the traditional MS location difficulties, such as multipath, poor location accuracy and poor coverage are alleviated via such technologies in combination with strategies for: (a) automatically adapting and calibrating system performance according to environmental and geographical changes; (b) automatically capturing location signal data for continual enhancement of a self-maintaining historical data base retaining predictive location signal data; (c) evaluating MS locations according to both heuristics and constraints related to, e.g., terrain, MS velocity and MS path extrapolation from tracking and (d) adjusting likely MS locations adaptively and statistically so that the system becomes progressively more comprehensive and accurate. Further, the system can be modularly configured for use in location signing environments ranging from urban, dense urban, suburban, rural, mountain to low traffic or isolated roadways. Accordingly, the system is useful for 911 emergency calls, tracking, routing, people and animal location including applications for confinement to and exclusion from certain areas.
Owner:TRACBEAM
Applications for a wireless location gateway
InactiveUS20040198386A1Easy to implementEffectively and straightforwardly resolvedPosition fixationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTerrainInternet communication
A location system is disclosed for commercial wireless telecommunication infrastructures. The system is an end-to-end solution having one or more location centers for outputting requested locations of commercially available handsets or mobile stations (MS) based on, e.g., CDMA, AMPS, NAMPS or TDMA communication standards, for processing both local MS location requests and more global MS location requests via, e.g., Internet communication between a distributed network of location centers. The system uses a plurality of MS locating technologies including those based on: (1) two-way TOA and TDOA; (2) pattern recognition; (3) distributed antenna provisioning; (5) GPS signals, (6) angle of arrival, (7) super resolution enhancements, and (8) supplemental information from various types of very low cost non-infrastructure base stations for communicating via a typical commercial wireless base station infrastructure or a public telephone switching network. Accordingly, the traditional MS location difficulties, such as multipath, poor location accuracy and poor coverage are alleviated via such technologies in combination with strategies for: (a) automatically adapting and calibrating system performance according to environmental and geographical changes; (b) automatically capturing location signal data for continual enhancement of a self-maintaining historical data base retaining predictive location signal data; (c) evaluating MS locations according to both heuristics and constraints related to, e.g., terrain, MS velocity and MS path extrapolation from tracking and (d) adjusting likely MS locations adaptively and statistically so that the system becomes progressively more comprehensive and accurate. Further, the system can be modularly configured for use in location signaling environments ranging from urban, dense urban, suburban, rural, mountain to low traffic or isolated roadways. Accordingly, the system is useful for 911 emergency calls, tracking, routing, people and animal location including applications for confinement to and exclusion from certain areas.
Owner:DUPRAY DENNIS J
Systems and Methods to Target Predictive Location Based Content and Track Conversions
ActiveUS20080248815A1Particular environment based servicesDevices with GPS signal receiverCommunications systemMobile device
Methods and systems that record the location of a user and transmit targeted content to a user based upon their current and past location information. A network is configured to include a server programmed with a database of targeted content, a database of location information, a database of user information, a database searching algorithm, and a wireless communication system capable of communicating with the user's mobile device. The location of the mobile device is ascertained and recorded. The location information is analyzed to determine the routes taken by the user, businesses visited by the user, and other behaviors of the user. Targeted content is sent to the mobile device of the user and whether the user visits the physical locations associated with the targeted content is monitored. Payment systems, phone exchange systems, and other features may also be integrated to provide detailed conversion tracking to producers of targeted content and business owners.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
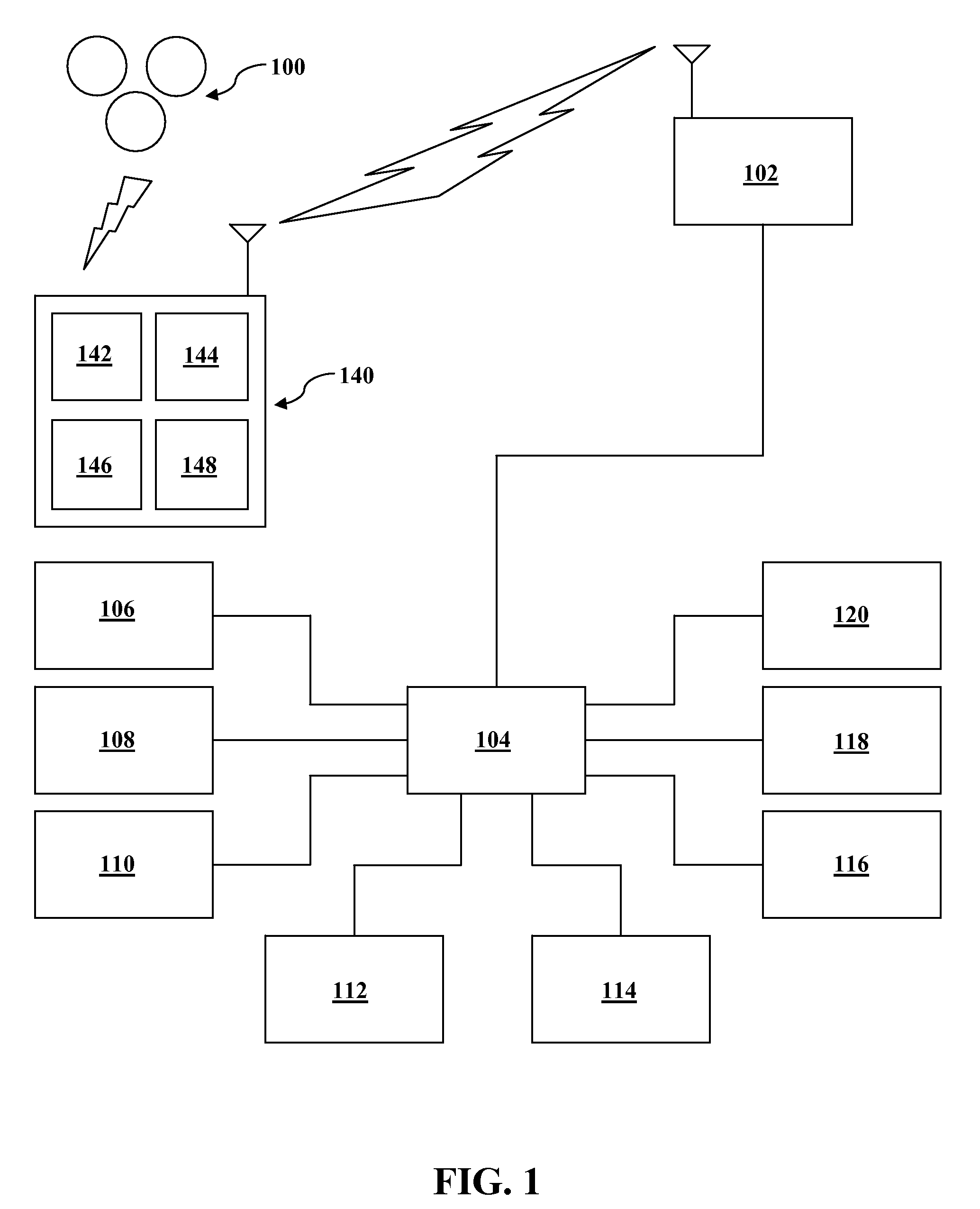
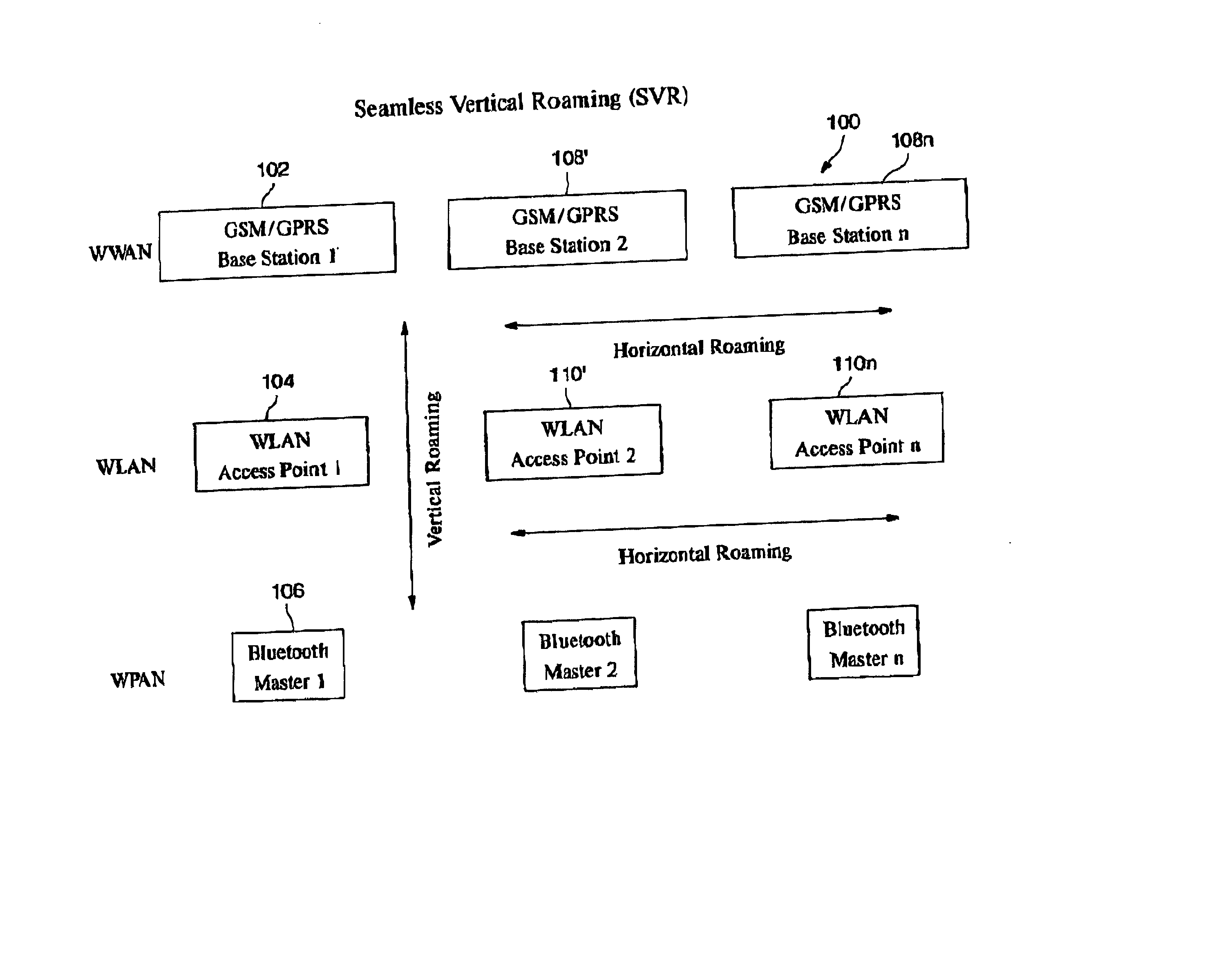
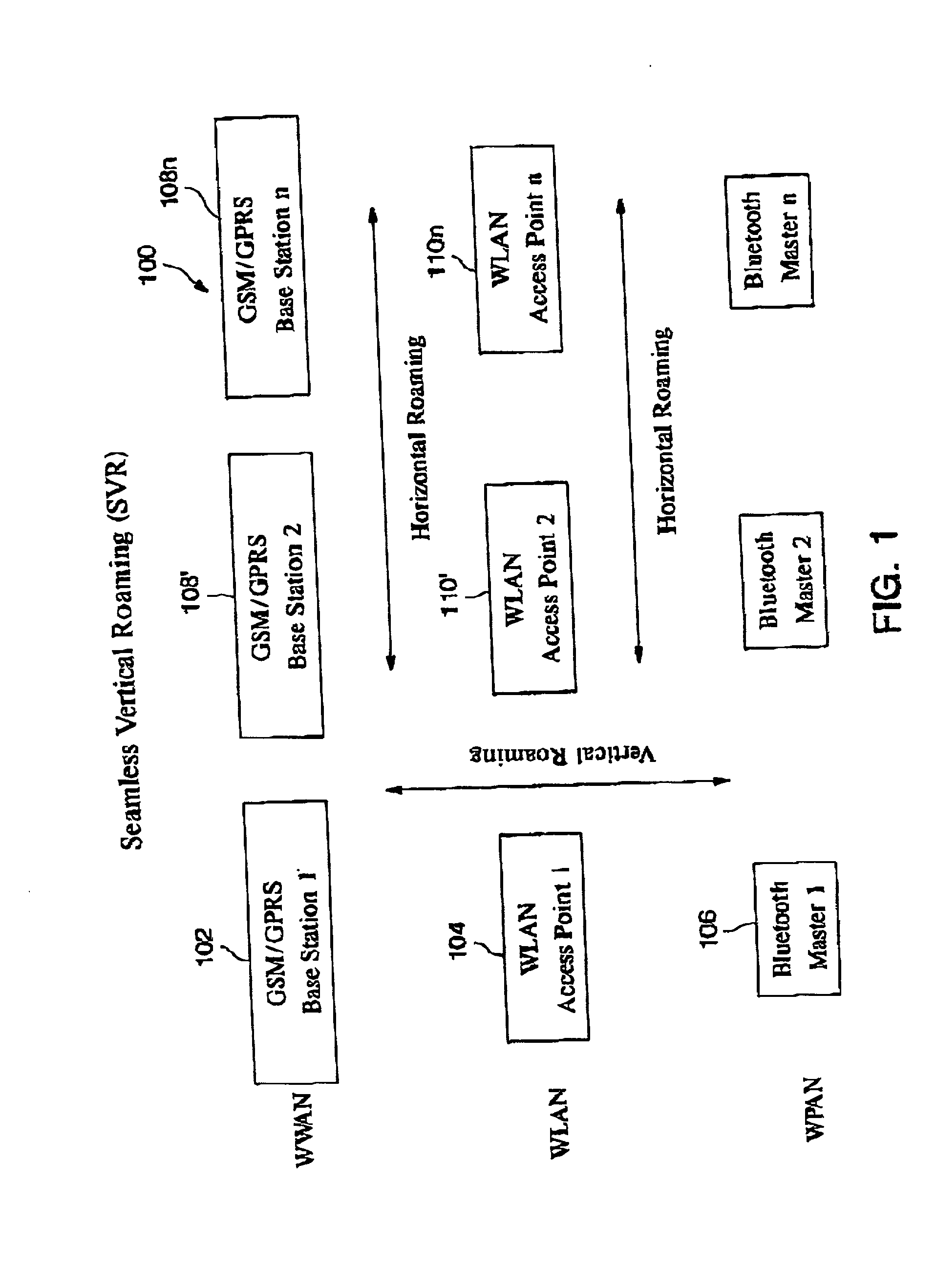
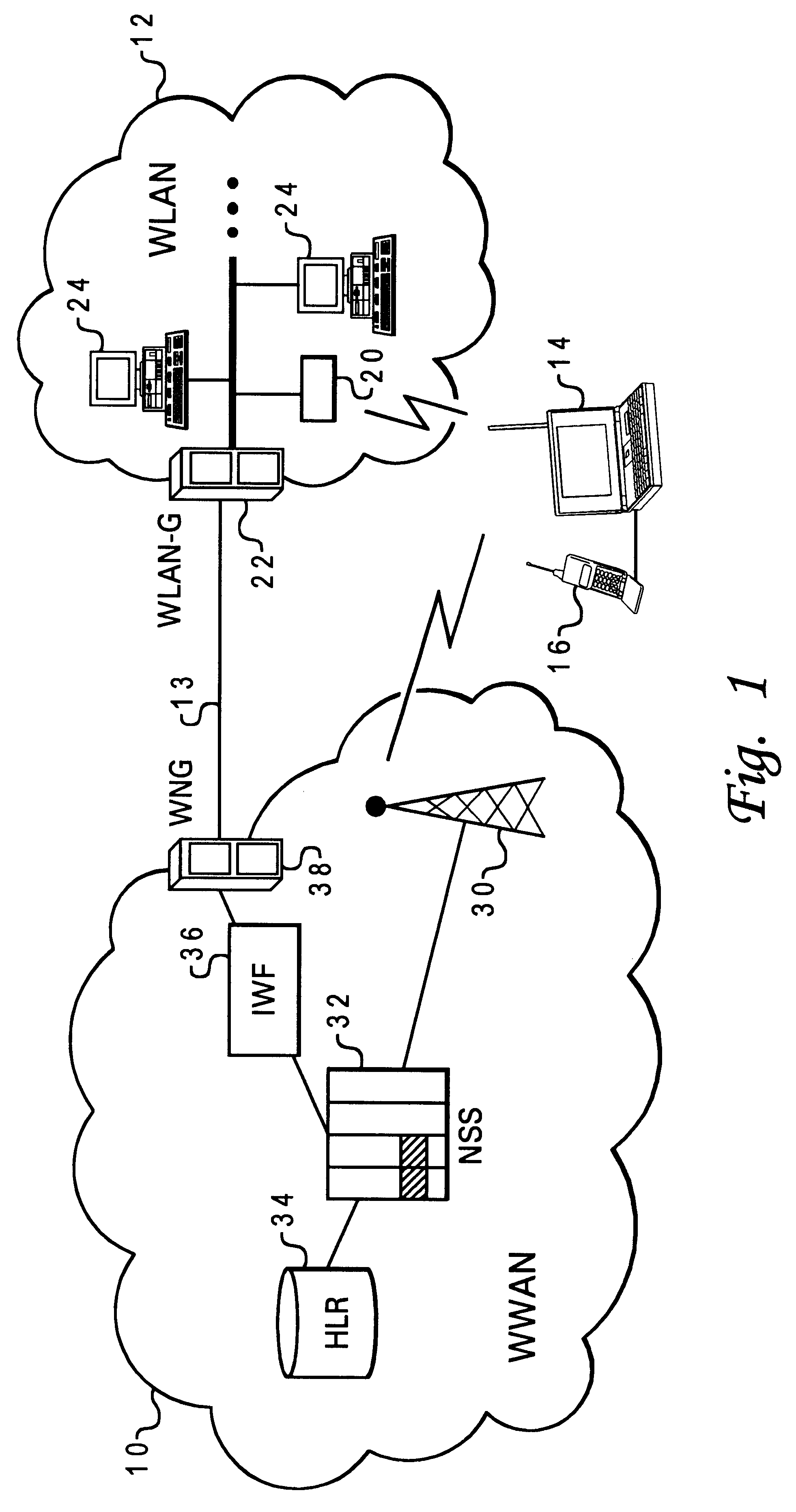
Automatic and seamless vertical roaming between wireless local area network (WLAN) and wireless wide area network (WWAN) while maintaining an active voice or streaming data connection: systems, methods and program products
ActiveUS20020085516A1Data switching by path configurationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsData connectionUser verification
A Mobile Station (MS) is able to vertically roam in either direction between two different network, i.e. WWAN and WLAN. The MS is equipped with a dual mode Radio for WWAN and WLAN transmissions. The WLAN Radio is linked to a WLAN Enterprise Gateway Controller (EGC) via a first air link and the WWAN Radio is linked to a WWAN Base Transceiver Station (BTS) via a second air link. The EGC is connected to a Mobile Switching Center (MSC) which is in turn connected to the BTS. An outgoing VoIP call from the WLAN Radio to a remote party on the WWAN will transition or seamlessly switch over to a WWAN connection when the MS detects packet error rates, frequent scale back or consistent signal degradation. Upon such conditions, the WLAN Radio requests the EGC to request an Explicit Call Transfer via the MSC to the MS integrated WWAN Radio portion which automatically accepts the call based on referenced information stored in the user's subscriber identification module (SIM). Once the WWAN Radio is confirmed connected to the remote party on the WWAN, the WLAN Radio drops the WLAN connection. An incoming call between the MS and a remote user via the WWAN will transition to the WLAN Radio when the MS enters WLAN coverage. The MS issues an ECT to the WLAN. After user verification by the WLAN Radio and the EGC signals acceptance of the call, the WWAN Radio connection is dropped and the call is now established between the WLAN Radio and the remote party on the WWAN.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for optimization of wireless multipoint electromagnetic communication networks
InactiveUS20040095907A1Improve signal qualityReduce interference energyPower managementSpatial transmit diversityGlobal optimizationDiversity scheme
Exploiting the substantive reciprocity of internode channel responses through dynamic, adaptive modification of receive and transmit weights, enables locally enabled global optimization of a multipoint, wireless electromagnetic communications network of communication nodes. Each diversity-channel-capable node uses computationally efficient exploitation of pilot tone data and diversity-adaptive signal processing of the weightings and the signal to further convey optimization and channel information which promote local and thereby network-global efficiency. The preferred embodiment performs complex digital signal manipulation that includes a linear combining and linear distribution of the transmit and receive weights, the generation of piloting signals containing origination and destination node information, as well as interference-avoiding pseudorandom delay timing, and both symbol and multitione encoding, to gain the benefit of substantive orthogonality at the physical level without requiring actual substantive orthogonality at the physical level.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM LLC
Portable communications device and method of use
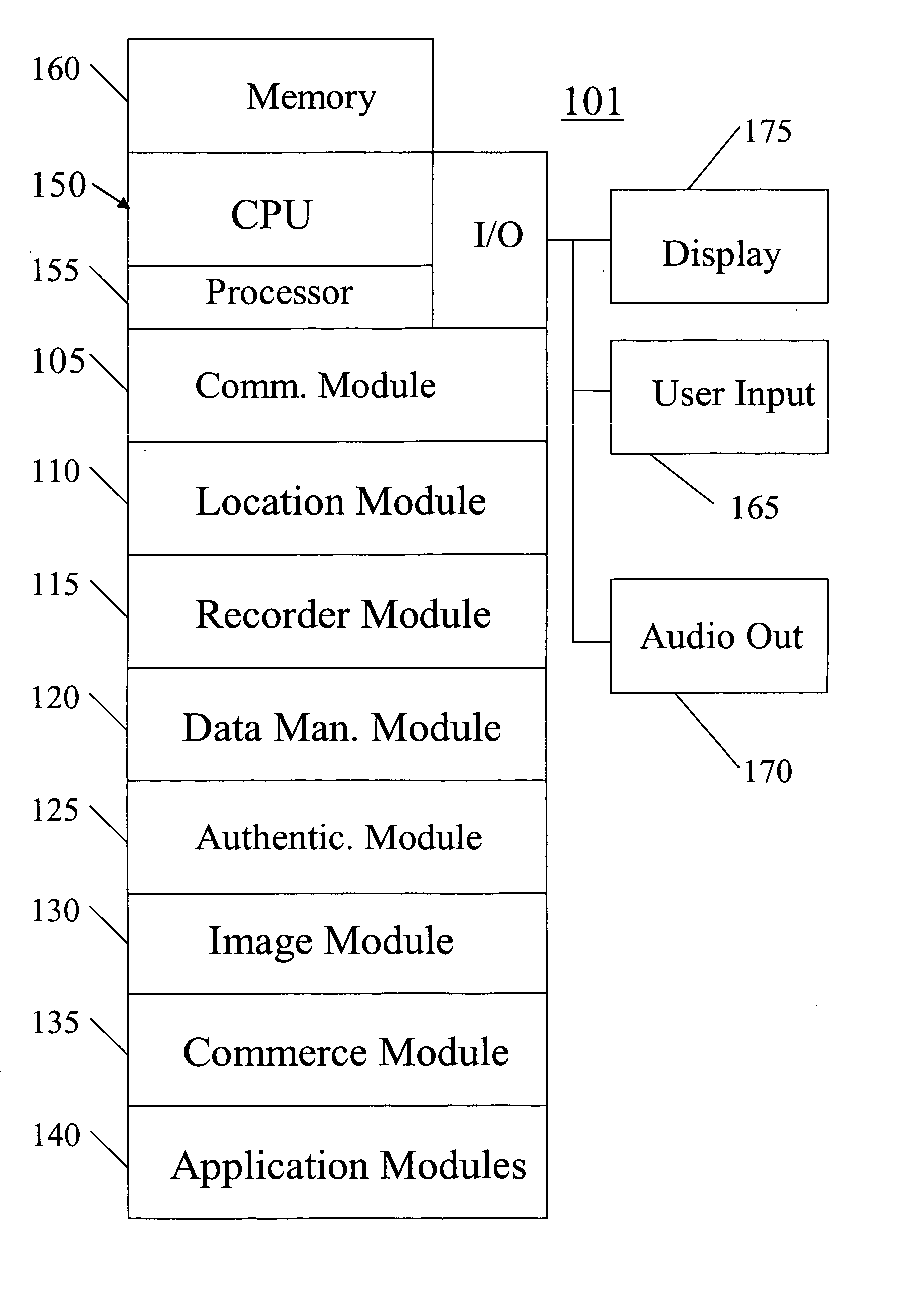
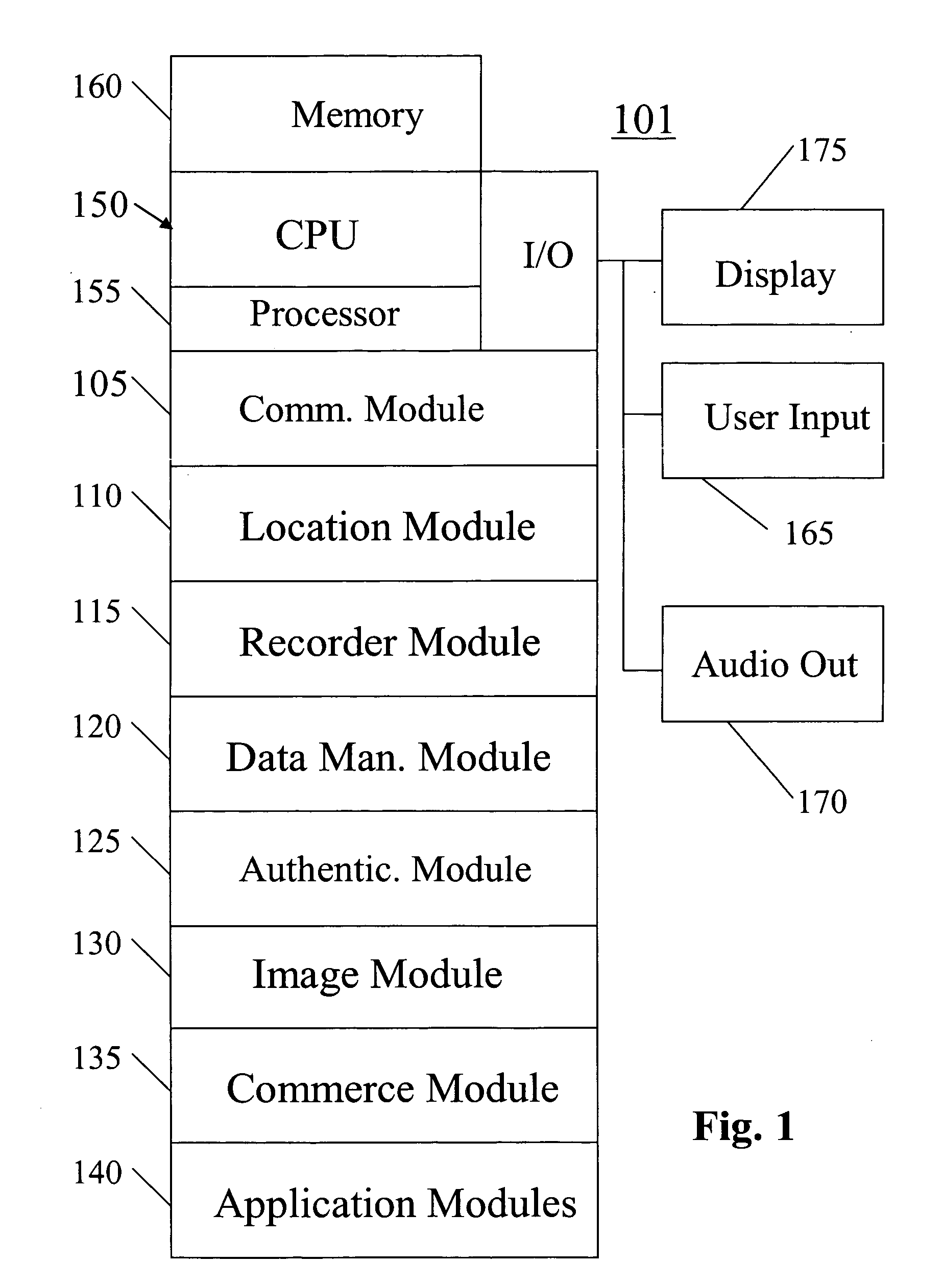
A system, method, apparatus and computer program product for providing location based functions and mobile e-commerce comprising a central processing unit including a processor, a storage device, and programming stored in the storage device, a display device, an audio input device, an audio output device, a communications module, a commerce module, an image module, and a location module. The programming controls the operation of the present invention to provide functions based on location data, to facilitate commercial exchanges by wirelessly exchanging payment and product information with venders, to identify services such as venders meeting selection criteria, to wirelessly exchange select information with other users and systems, to restrict and / or monitor the use of the device based on authorized user parameters, to select one of a plurality networks through which to communicate, to detect a trigger for performing an action based on a change in location and sensed data, to store a voice annotation with a computer data file, to determine service providers and associated communication parameters, to contemporaneously maintain a wireless voice and data link, to provide a system for selecting mobile advertisements, and many other functions and services that are described herein.
Owner:WOUNDER
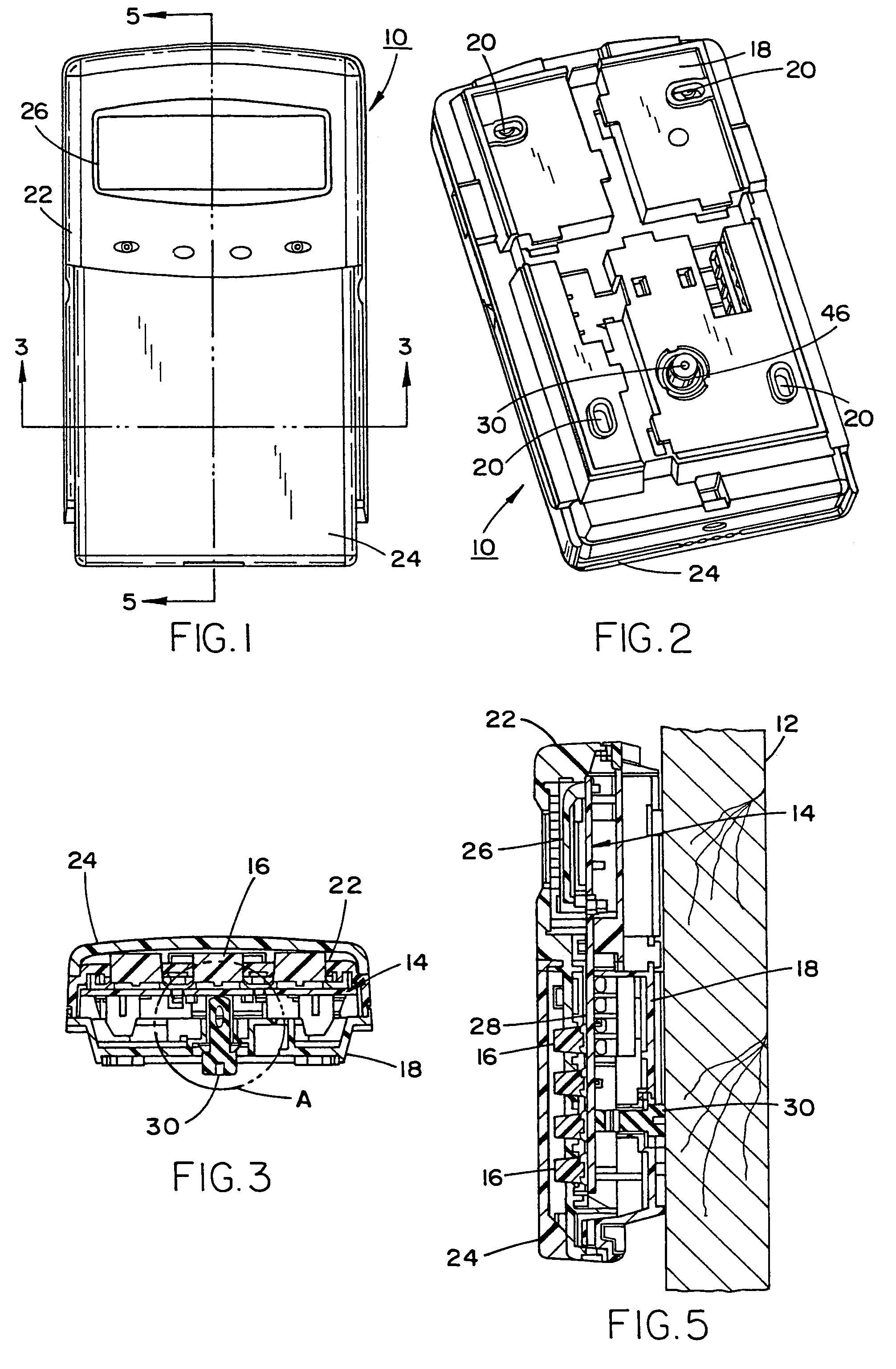
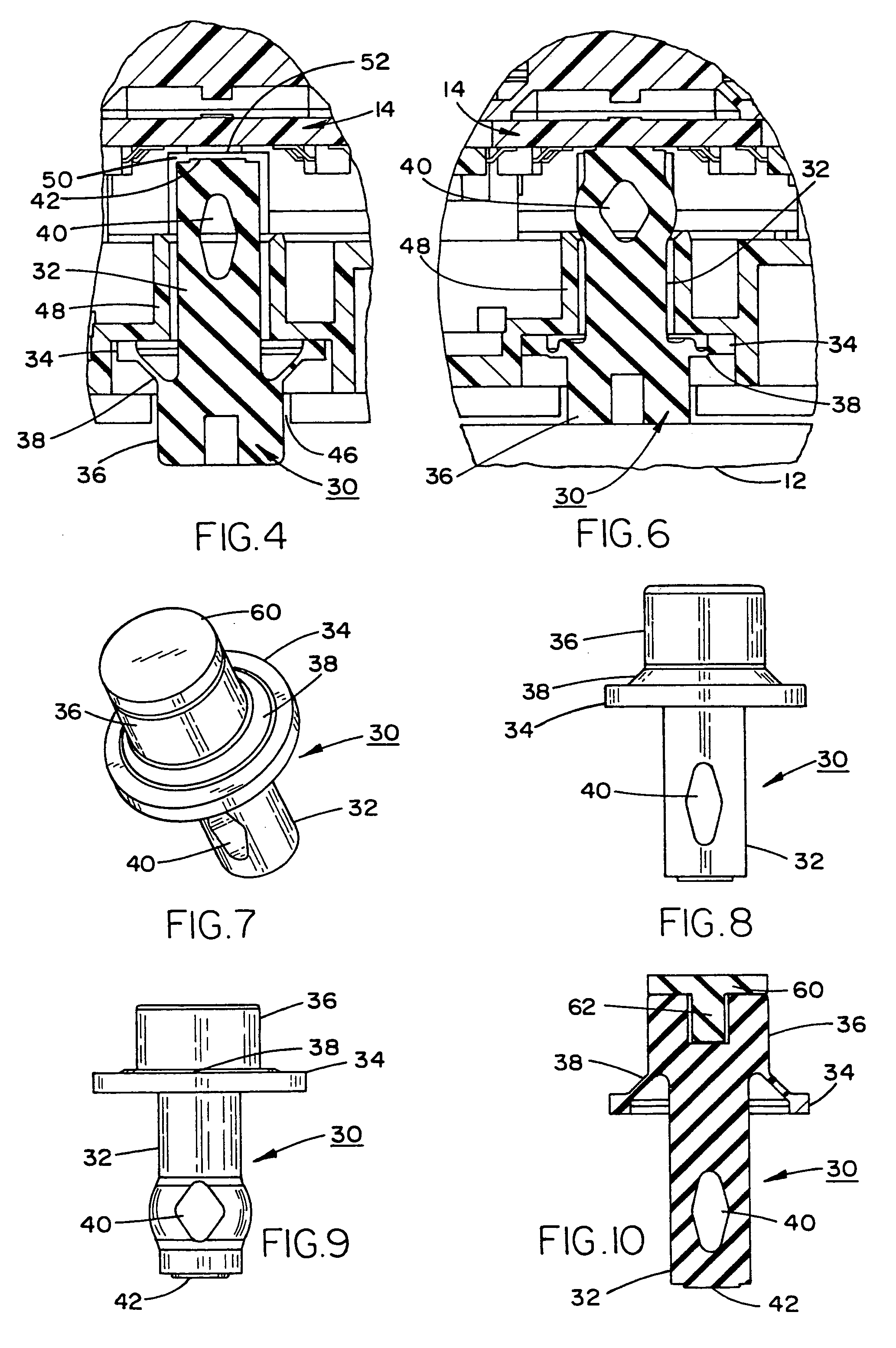
Conductive tamper switch for security devices
InactiveUS7388484B2Highly efficient and reliable in operationCost-effectively mountedInternal/peripheral component protectionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsMonitoring siteFire alarm system
A tamper switch mechanism utilized in security interface devices such as keypad installations to render them tamper-resistant, wherein the devices are generally connected to burglar alarm and fire alarm systems. More particularly, provided is a conductive tamper switch which is installed in a security interface device, such as a keypad, which upon an unauthorized attempt to dislodge the device or keypad from a wall or surface on which it is mounted, will trigger an alarm or generate a warning signal at a monitoring site indicative that an effort at tampering with the device has been effected. Also disclosed is a method of providing the tamper switch mechanism in a security interface device, such as a keypad installation.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
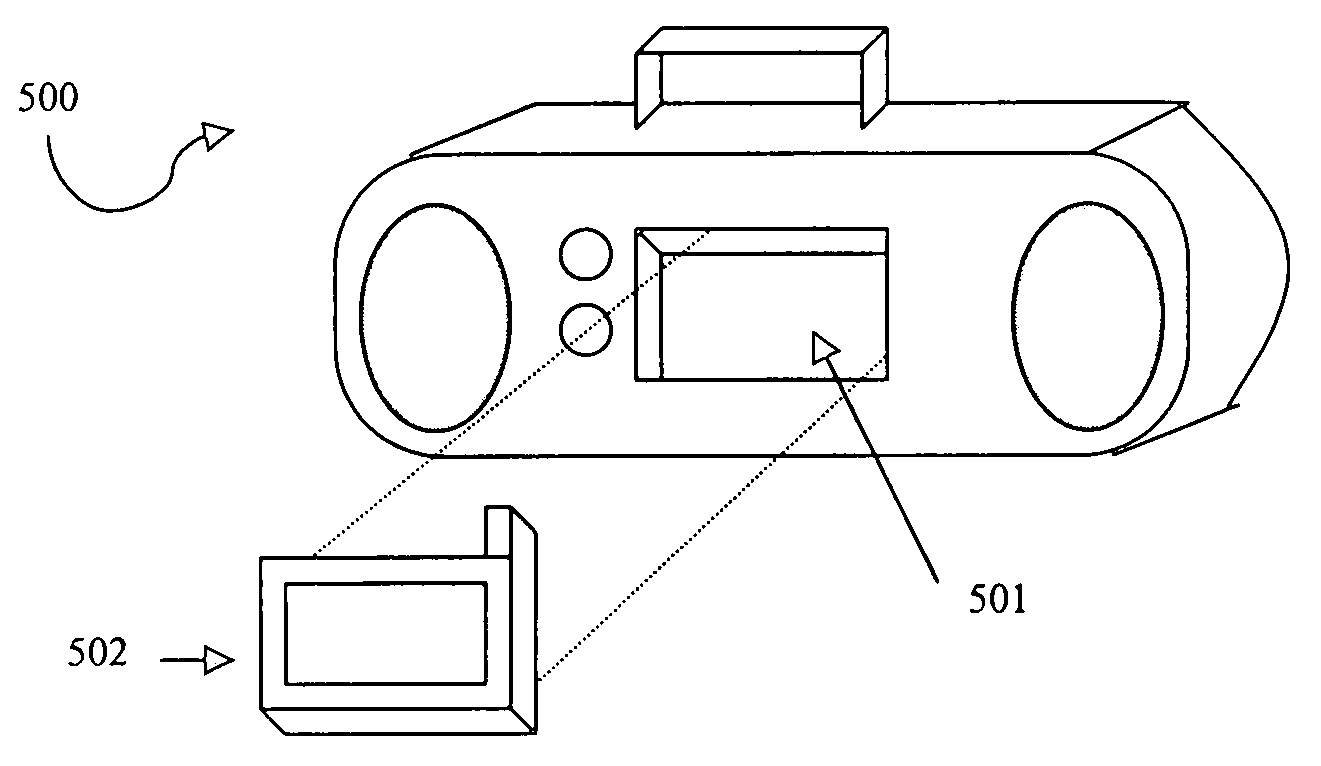
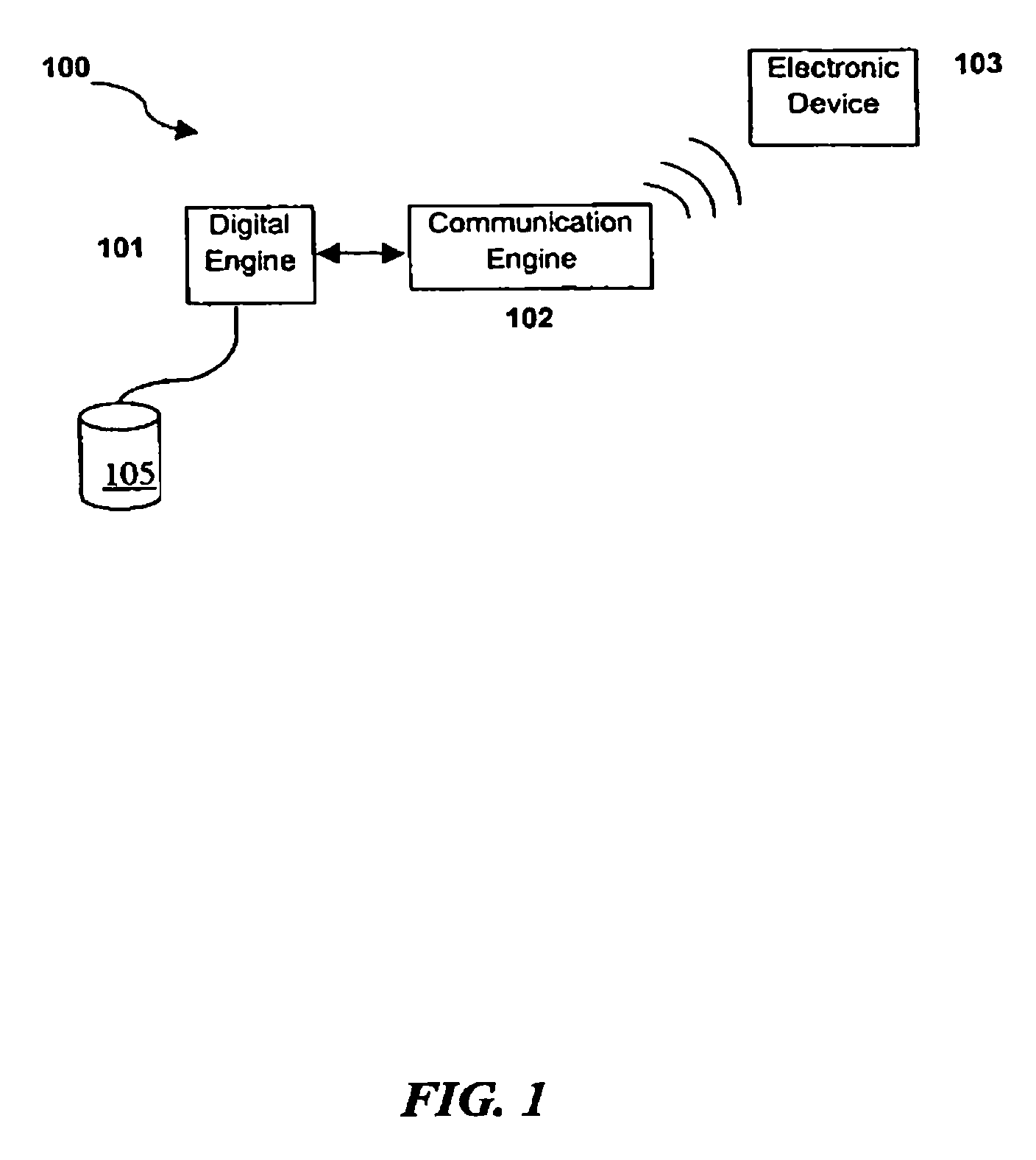
System and method for communicating selected information to an electronic device
InactiveUS7187947B1Sound qualityBig advantageNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesGraphical user interfaceEngineering
Disclosed are a system and method for communicating selected information to an electronic device. The disclosed system may include a digital engine operable to maintain data representing the selected information in a digital format. In some embodiments, the digital engine may be communicatively coupled to a graphical user interface that allows a user to identify the selected information. The system may also include a communication engine communicatively coupled to the digital engine, the communication engine may be operable to wirelessly communicate the data representing the selected information to an electronic device.
Owner:RPX CORP
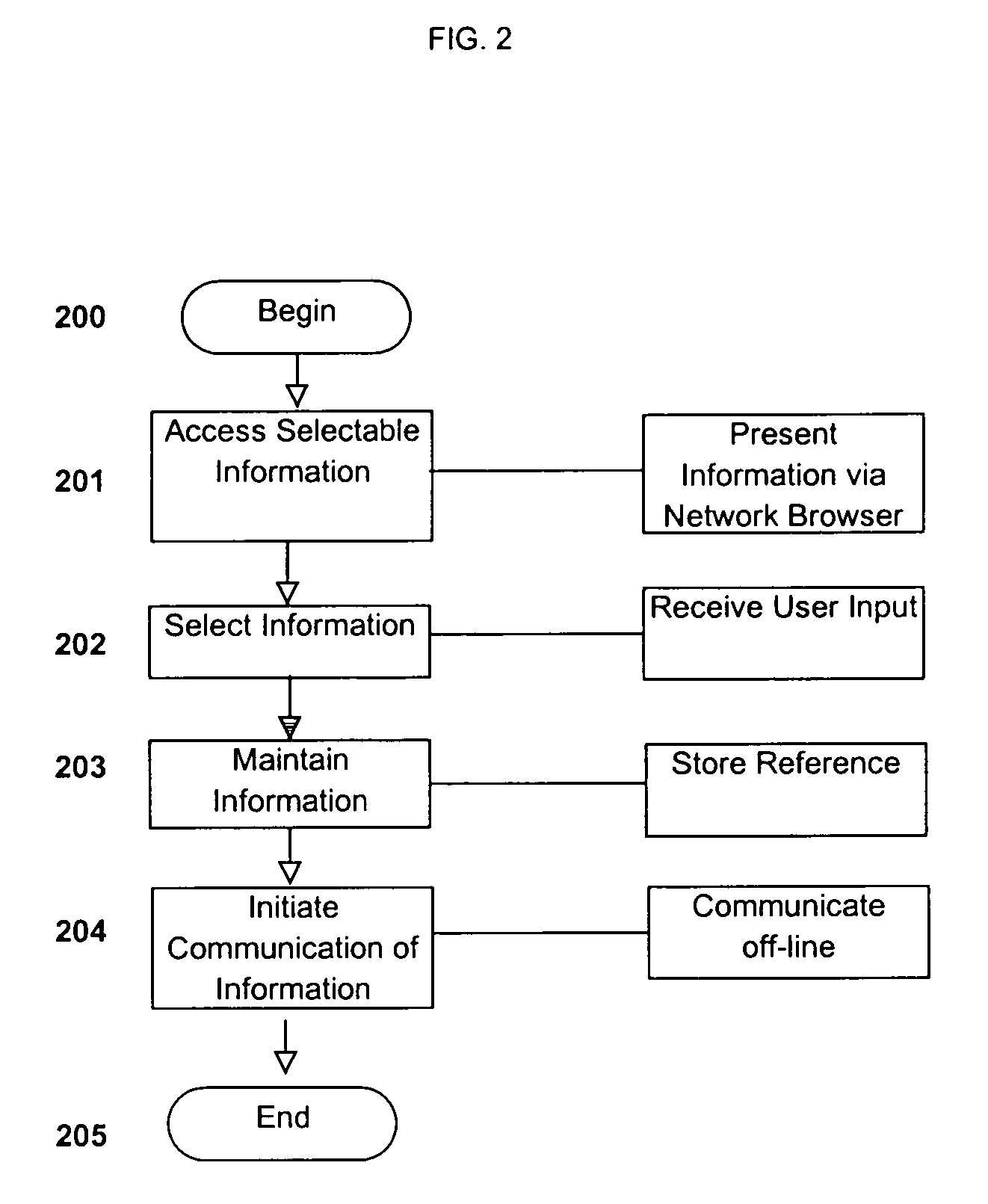
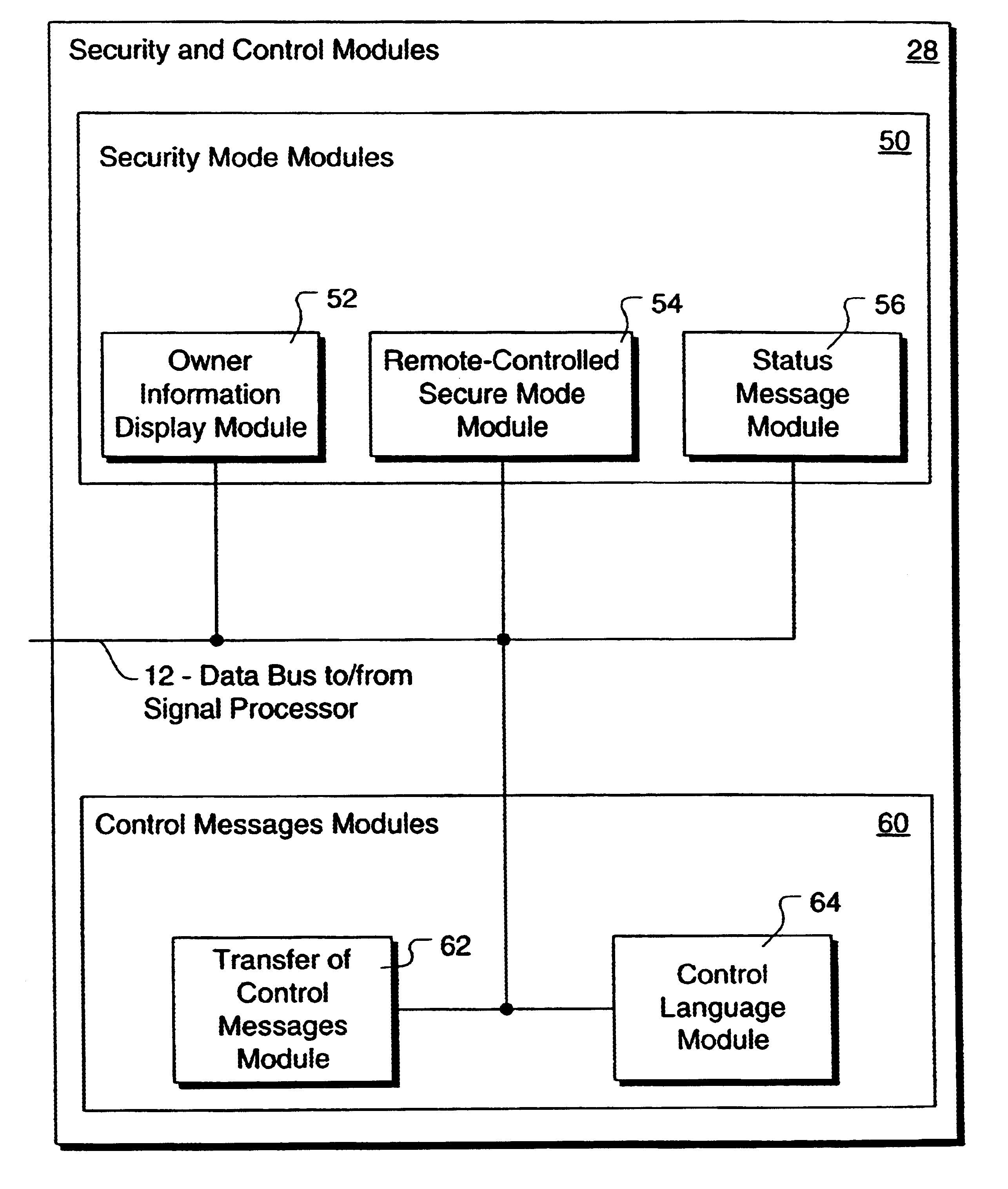
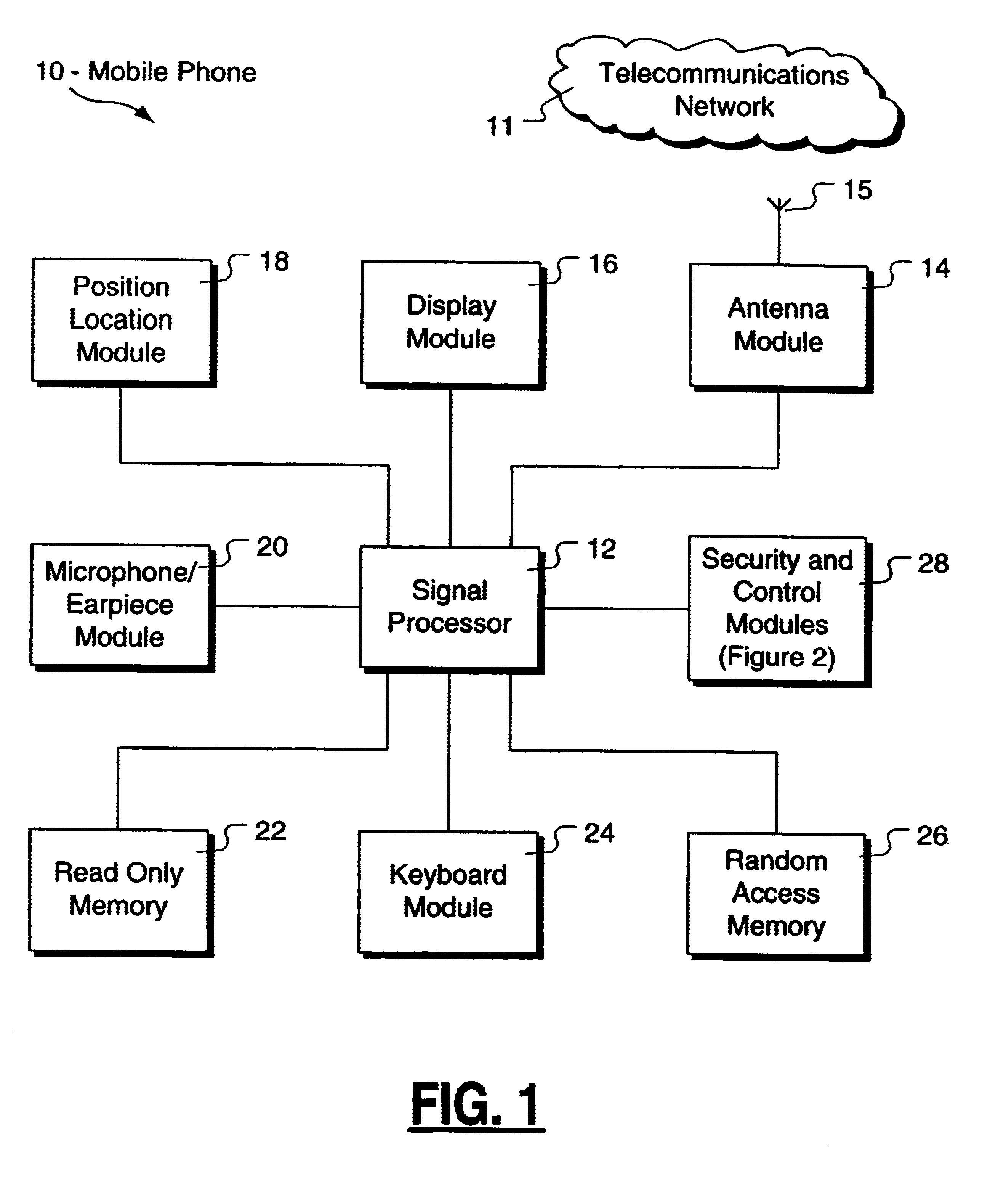
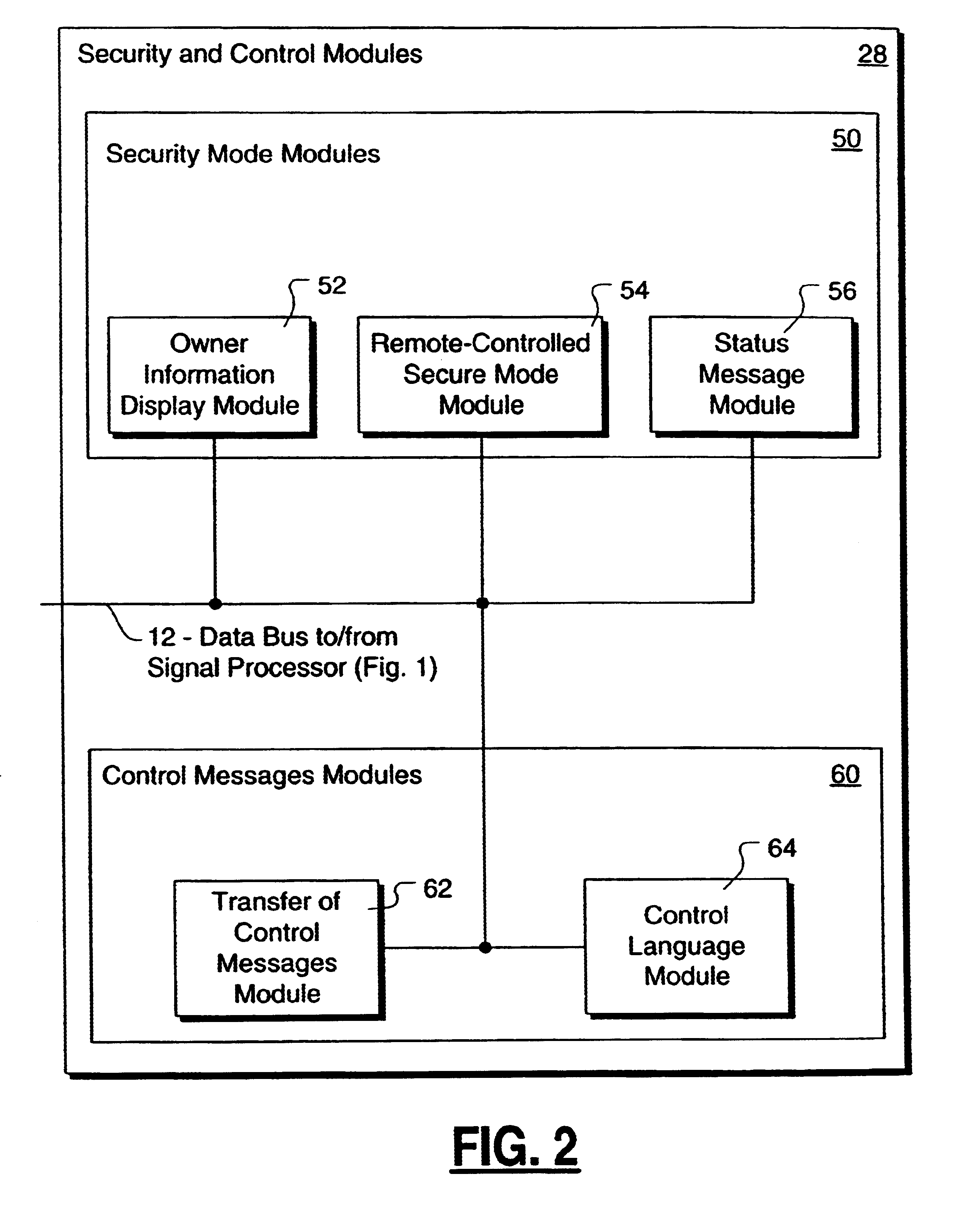
Method and apparatus for controlling and securing mobile phones that are lost, stolen or misused
InactiveUS6662023B1Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsSecure stateStart up
A method and apparatus is provided for controlling a mobile phone when it has been lost or stolen in order to prevent its use except to help the owner find it. Controlling the phone remotely may be implemented via a known Short Messaging System, for example. The security features provided are as follows: (1) Displaying contact information (phone number) of the owner on screen when the mobile phone can not start up normally, for example, due to an incorrect security code entry; (2) Setting the mobile phone in a secure state where it can only be used to call one number (Emergency calls are of course always possible.); and (3) Commanding the mobile phone to send information about its location and usage via SMS to a given number.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
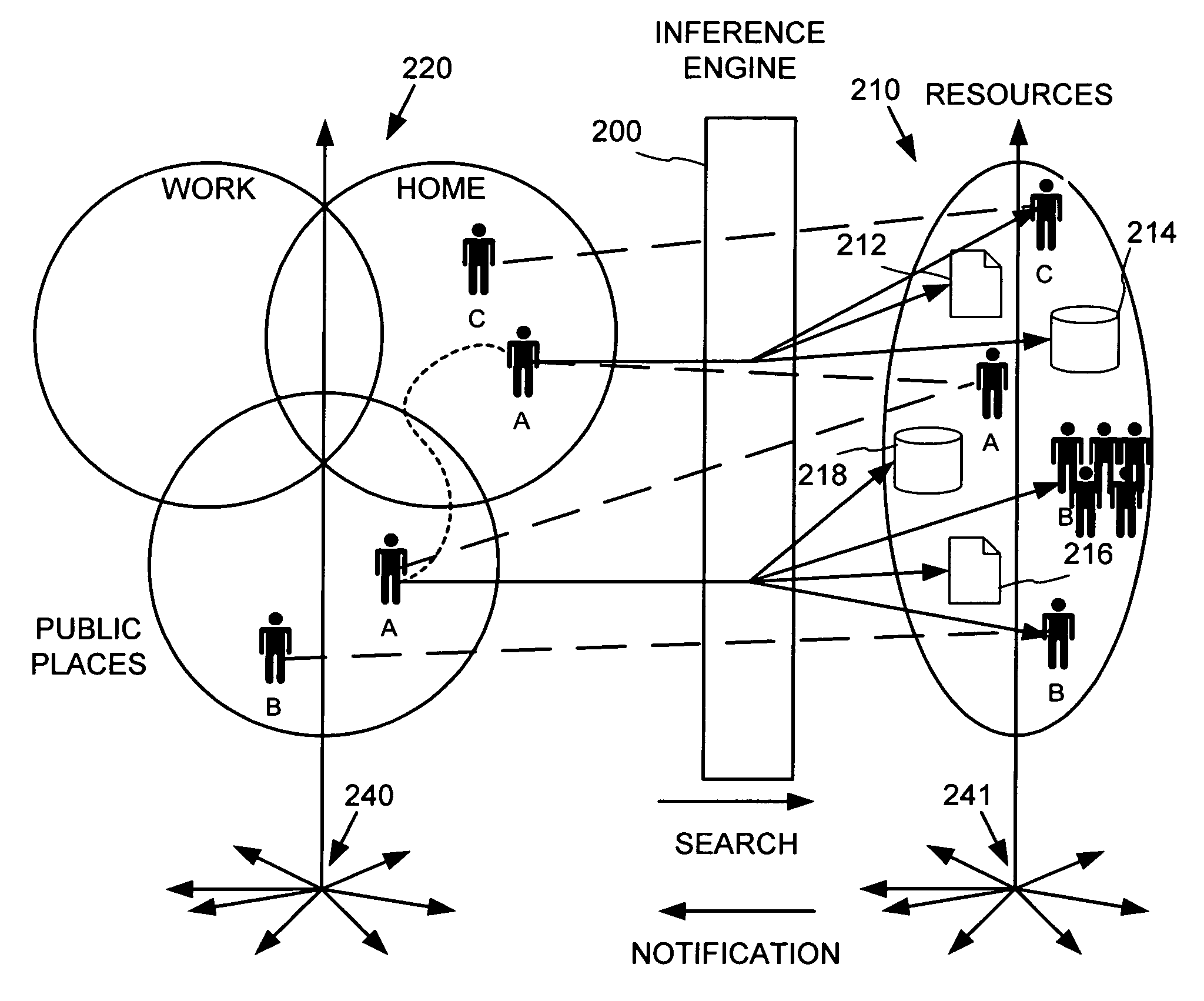
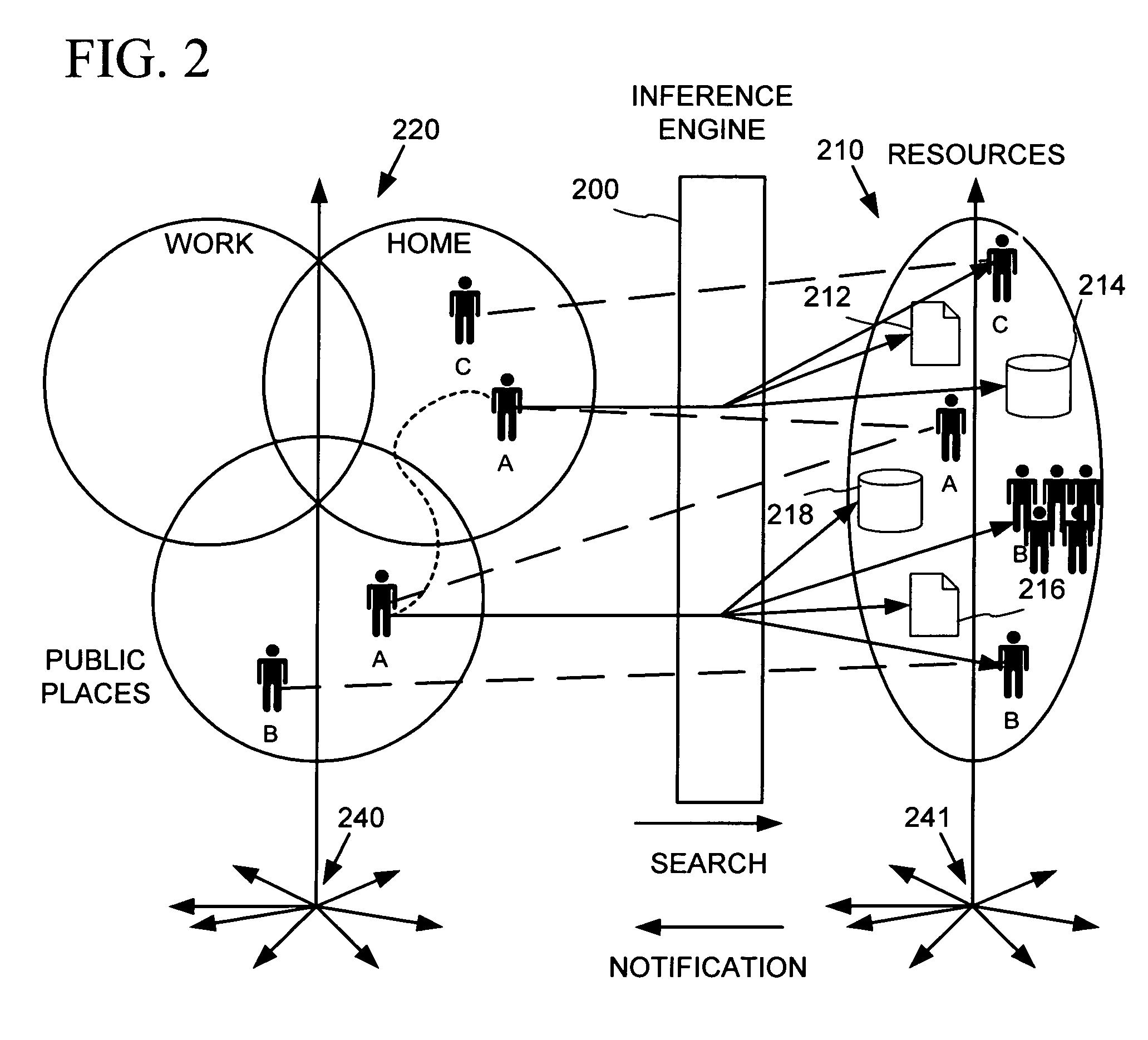
Place specific buddy list services
InactiveUS6968179B1Information formatSpecial service for subscribersWorld Wide WebPositioning equipment
An information service provides search and notifications to inform when certain people (e.g., friends, family, business contacts, etc.) are nearby so as to facilitate communications with those people. Users may define lists of people whose locations may be tracked by positioning equipment based on personal communications / computing devices carried by the people. The information service processes this people and place data to identify those of the listed people that are in the user's vicinity, and provide notifications and user-initiated search results informing the user such as via the user's personal communications / computing device.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Location-based services
ActiveUS20060270421A1Change frequencyExtend battery lifeRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsMessaging/mailboxes/announcementsLocation based informationMobile device
Provided herein are methods and systems relating to location-based services such as social networking, providing demographic information, tracking mobile devices, providing business information, providing an adaptable user interface, remotely effecting a change on a portable electronic device, providing a geofence, outputting location-based information on a mobile device, varying transmissions to and from a mobile device, providing location-based alerts, verifying transactions and tailoring information to the behavior of a user.
Owner:PAYPAL INC
System for providing mobile VoIP
ActiveUS20050286466A1Preserve battery lifeLow power capabilityPower managementNetwork topologiesMobile deviceHandover
A system for providing handoff for a mobile devices comprising a mobile phone programmed to automatically handover between differing data bearers and to optimally detect those bearers in a roaming environment keeping power consumption to a minimum. Repeating means for these mobile devices to extend the range of coverage and the protocol for that coverage.
Owner:TRUPHONE
Software fault management system
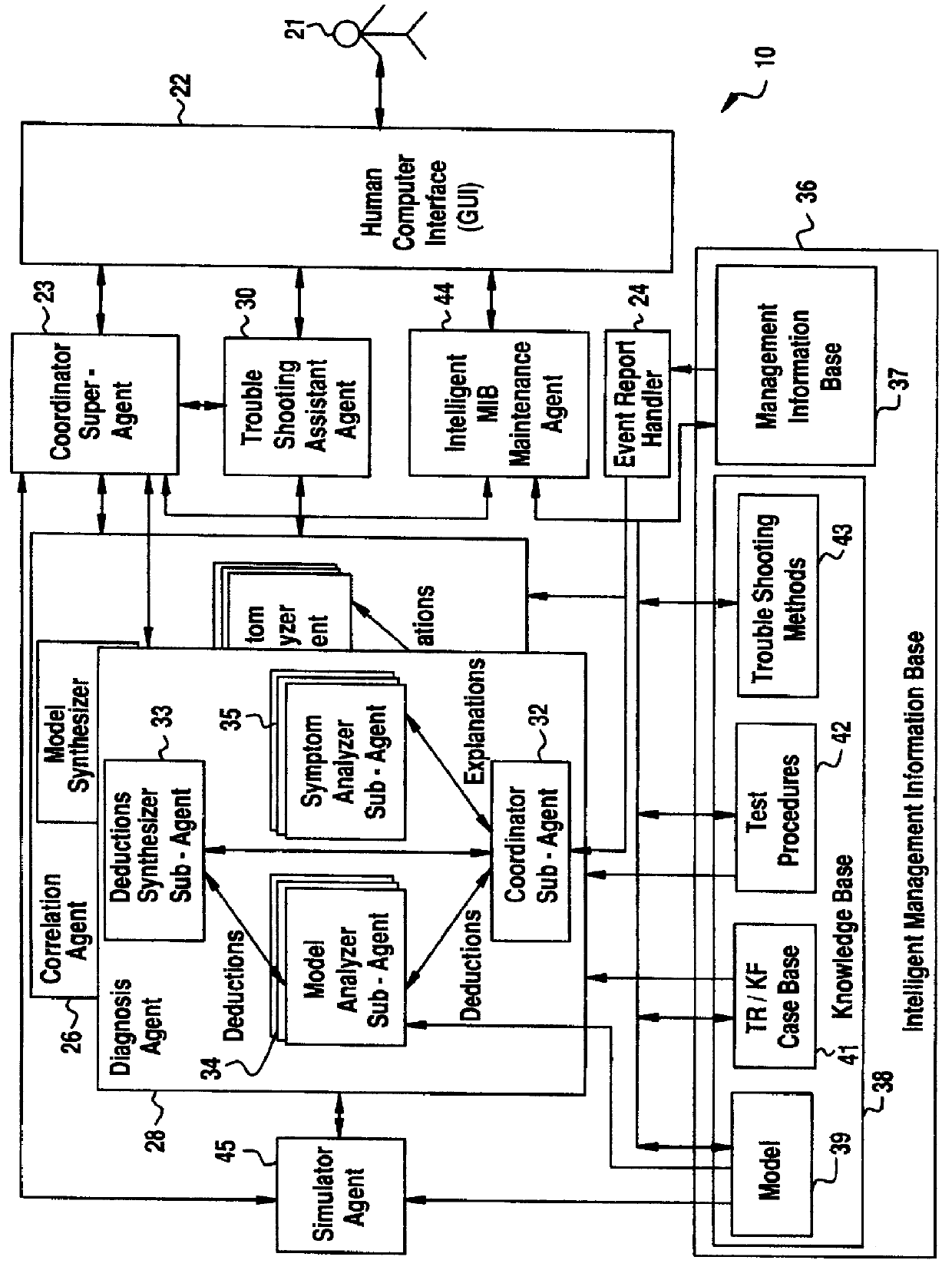
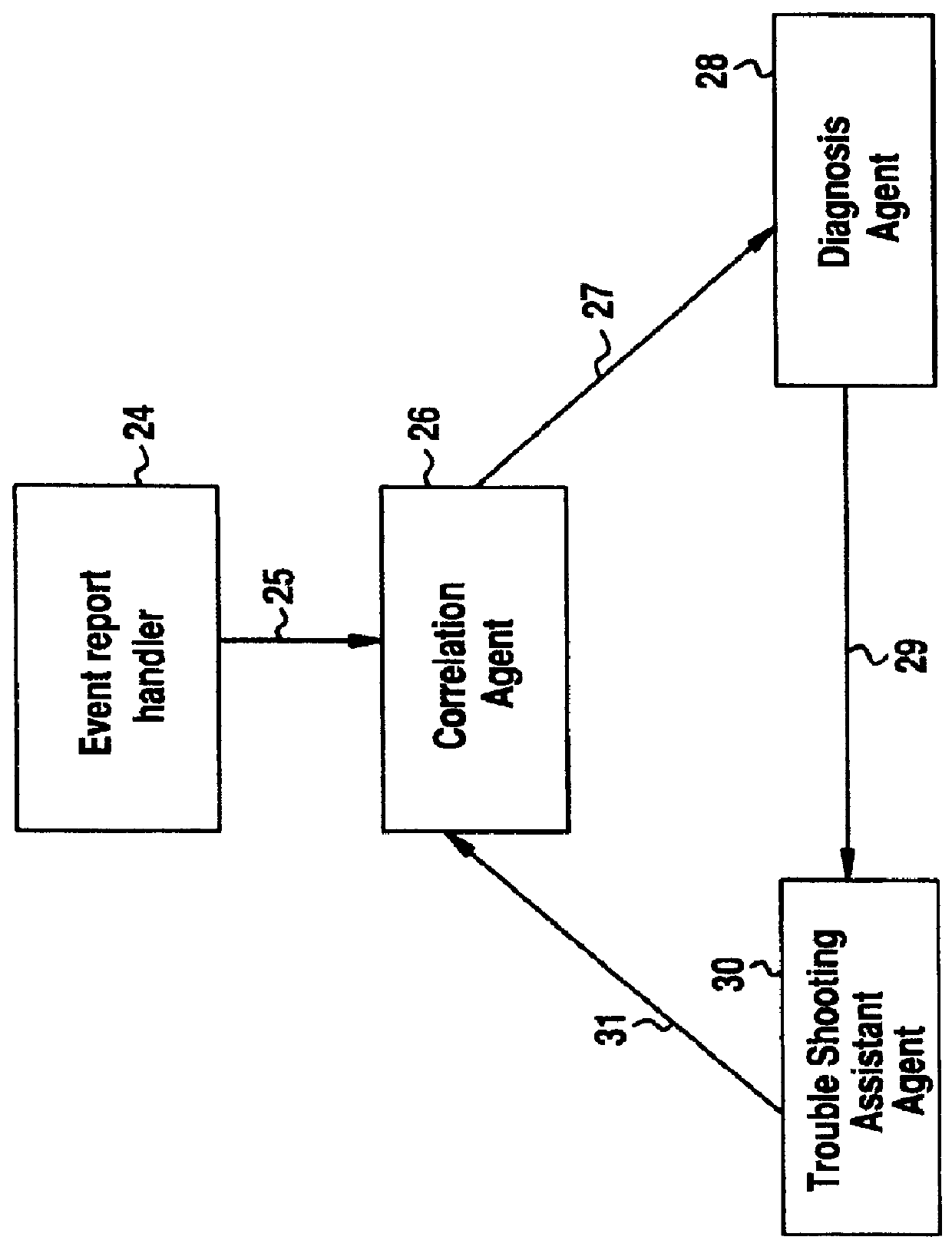
InactiveUS6012152ASupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsInformation repositoryManagement information systems
A Software Fault Management (SFM) system for managing software faults in a managed mobile telecommunications network. The SFM system includes an Intelligent Management Information Base (I-MIB) comprising a Management Information Base (MIB) and a Knowledge Base (KB) having a functional model of the managed network and a trouble report / known faults (TR / KF) case base. The SFM system also includes an intelligent multi-agent portion having a plurality of agents which process the software faults utilizing the functional model from the I-MIB, case-based information, and other management information. The I-MIB and the intelligent multi-agent portion are compliant with Telecomunications Management Network (TMN) principles and framework. Fault management is both proactive and reactive. The SFM system is made independent of technology-specific implementations by representing the underlying switch design knowledge in a modular and changeable form which is then interpreted by the intelligent multi-agent portion. A clear separation is maintained between the generic procedural inference mechanisms and agents, and the specific and explicit models of the different network elements of a mobile telecommunications network.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method and system for seamless roaming between wireless communication networks with a mobile terminal
A mobile computer system capable of seamless roaming between wireless communication networks includes data processing resources for executing software, a plurality of wireless interfaces that supports simultaneous wireless connections with first and second wireless communication networks, and a network access arbitrator that routes data communicated between the software executed by the data processing resources and the first and second wireless communication networks. To permit seamless roaming, the network access arbitrator routes the data to the first wireless communication network via a first wireless interface and then seamlessly reroutes the data to a second wireless communication network via a second wireless interface. According to one embodiment, the network access arbitrator reroutes the data in response to the data bandwidths of the connections with the first and second wireless communication networks.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
System and method for providing communication services to mobile device users incorporating proximity determination
InactiveUS20070030824A1Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedWeb data retrievalTelephonic communicationComputer networkMobile device
In certain embodiments, a method for proximity determination includes receiving one or more network identifiers, each associated with a corresponding network, from a first mobile device. The method further includes receiving one or more network identifiers, each associated with a corresponding network, from a second mobile device. The method further includes processing the network identifiers received from the first and second mobile devices to determine whether the first mobile device and the second mobile device are in proximity to one another.
Owner:JAMBO NETWORKS
Wireless location using signal fingerprinting
InactiveUS20010022558A1Low costSpectrum efficiencyDirection finders using radio wavesBeacon systems using radio wavesInternet communicationCall tracing
A location system is disclosed for commercial wireless telecommunication infrastructures. The system is an end-to-end solution having one or more location centers for outputting requested locations of commercially available handsets or mobile stations (MS) based on, e.g., CDMA, AMPS, NAMPS or TDMA communication standards, for processing both local MS location requests and more global MS location requests via, e.g., Internet communication between a distributed network of location centers. The system uses a plurality of MS locating technologies including those based on: (1) two-way TOA and TDOA; (2) pattern recognition; (3) distributed antenna provisioning; and (4) supplemental information from various types of very low cost non-infrastructure base stations for communicating via a typical commercial wireless base station infrastructure or a public telephone switching network. Accordingly, the traditional MS location difficulties, such as multipath, poor location accuracy and poor coverage are alleviated via such technologies in combination with strategies for: (a) automatically adapting and calibrating system performance according to environmental and geographical changes; (b) automatically capturing location signal data for continual enhancement of a self-maintaining historical data base retaining predictive location signal data; (c) evaluating MS locations according to both heuristics and constraints related to, e.g., terrain, MS velocity and MS path extrapolation from tracking and (d) adjusting likely MS locations adaptively and statistically so that the system becomes progressively more comprehensive and accurate. Further, the system can be modularly configured for use in location signaling environments ranging from urban, dense urban, suburban, rural, mountain to low traffic or isolated roadways. Accordingly, the system is useful for 911 emergency calls, tracking, routing, people and animal location including applications for confinement to and exclusion from certain areas.
Owner:TRACBEAM
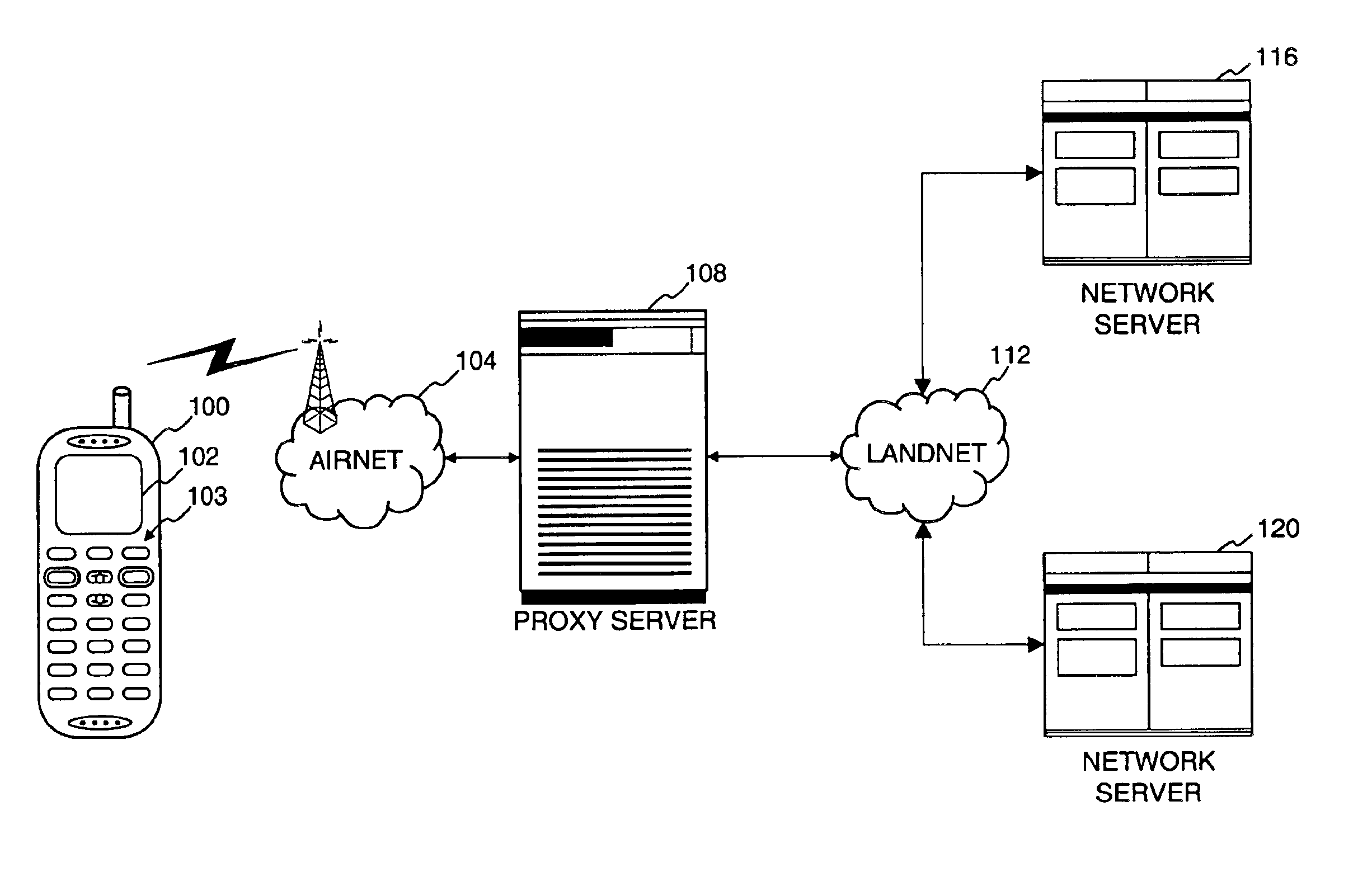
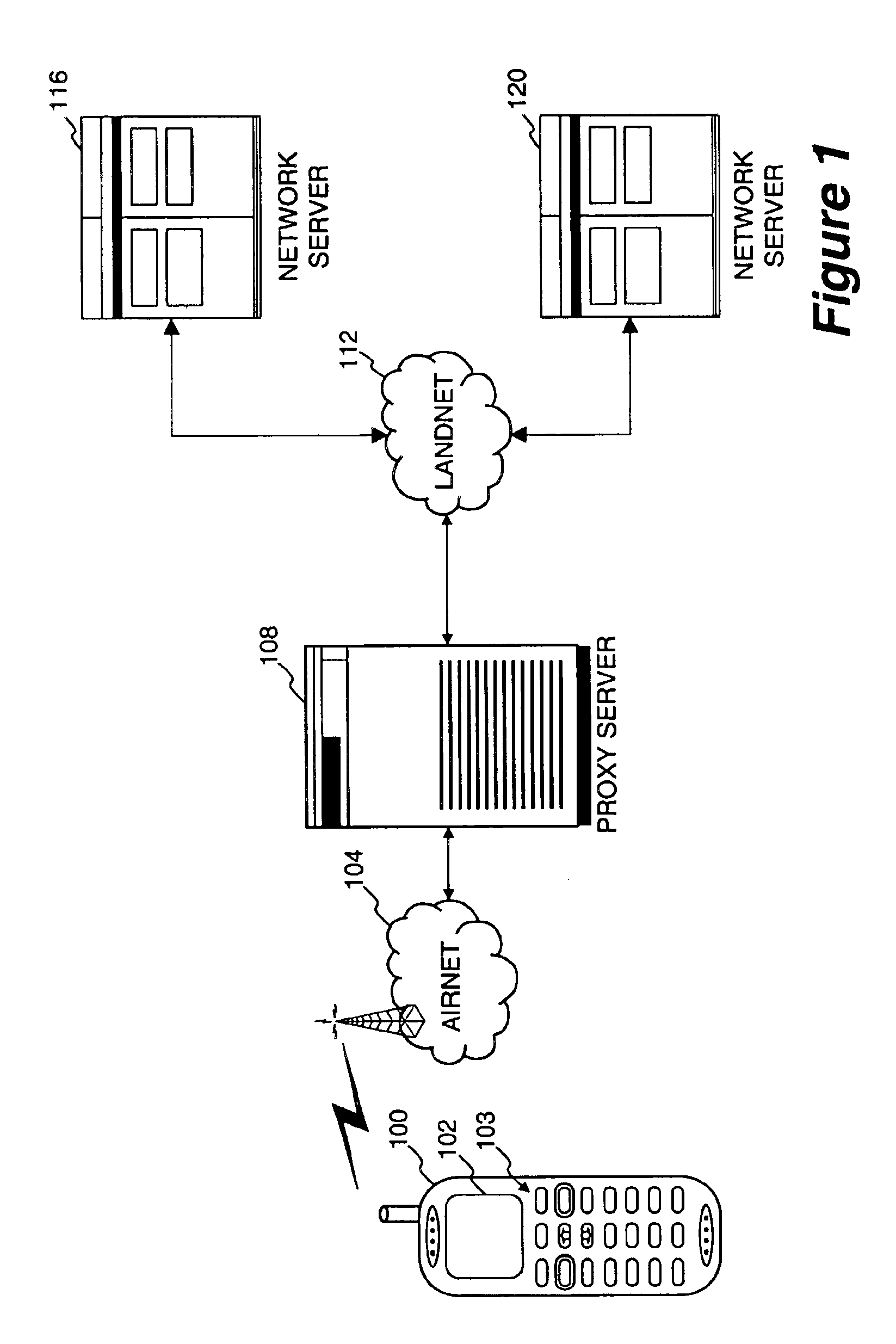
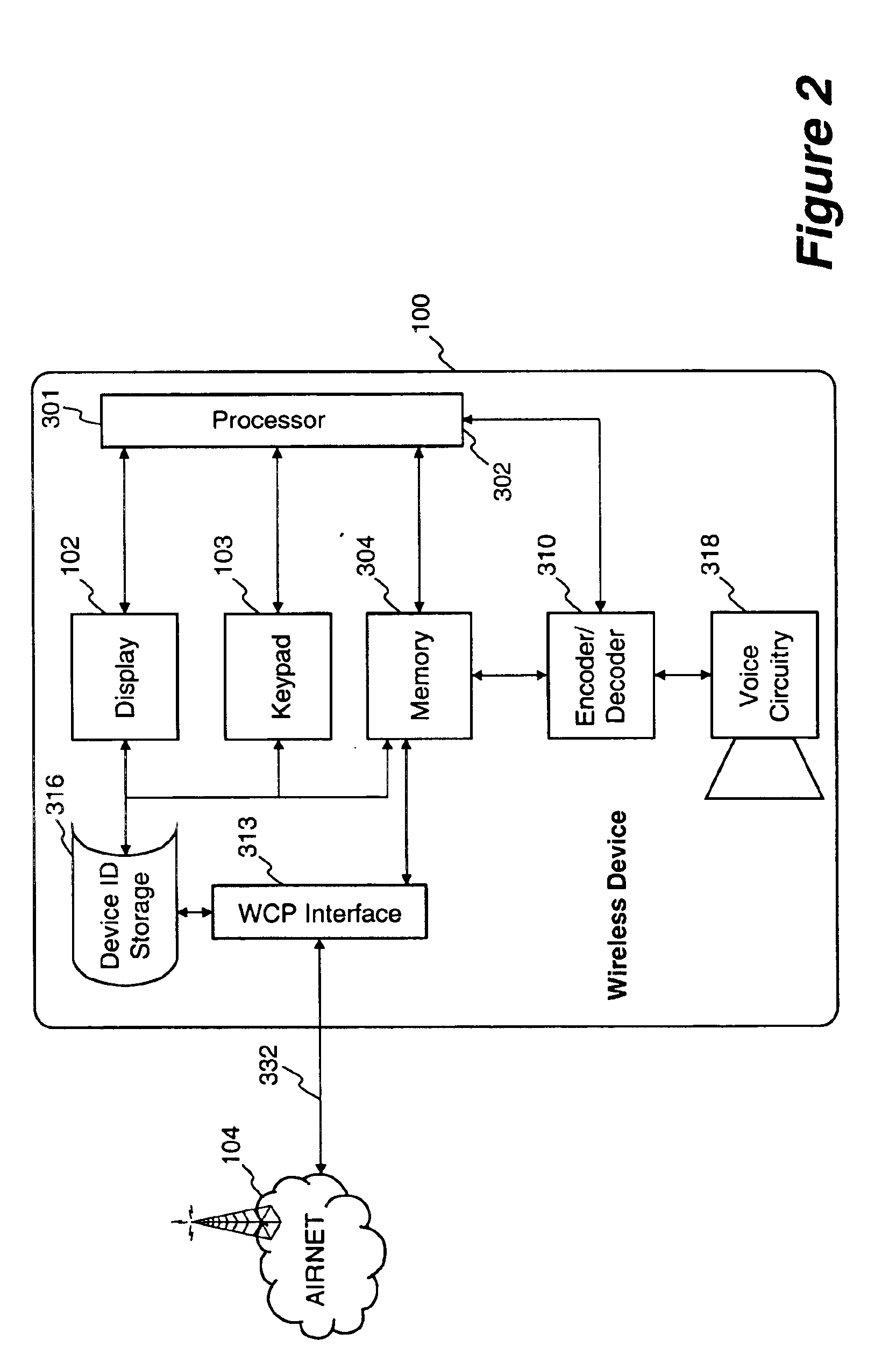
Method and apparatus for providing internet content to SMS-based wireless devices
A method and apparatus for providing hypermedia content maintained remotely on a network to a wireless device without a browser are described. A Short Message Service (SMS) request for Internet-based content is received from the wireless device at a proxy server, via an SMS Center (SMSC). The SMS request is transmitted to the SMSC on a wireless network. The proxy server transcodes the SMS request from a character set of the SMSC to a character set of an application and extracts a keyword from the trancoded request. The proxy server maintains a mapping of keywords to URLs. The proxy server looks up the extracted keyword in the keyword-to-URL mapping to identify the URL of an application associated with the keyword. The proxy server constructs an HTTP POST operation containing the keyword and the URL, and submits the HTTP POST operation to the application over a wireline network such as the Internet. Upon receiving an HTTP response containing the requested content from the application in response to the POST operation, the proxy server extracts the content from the HTTP response. The proxy server then translates the content from the content-type used by the application to the content-type used by the SMSC and transcodes the content from the character set used by the application to the character set used by the SMSC. The proxy server then sends the translated and transcoded content in an SMS response to the SMSC, for subsequent delivery to wireless device as an SMS message.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
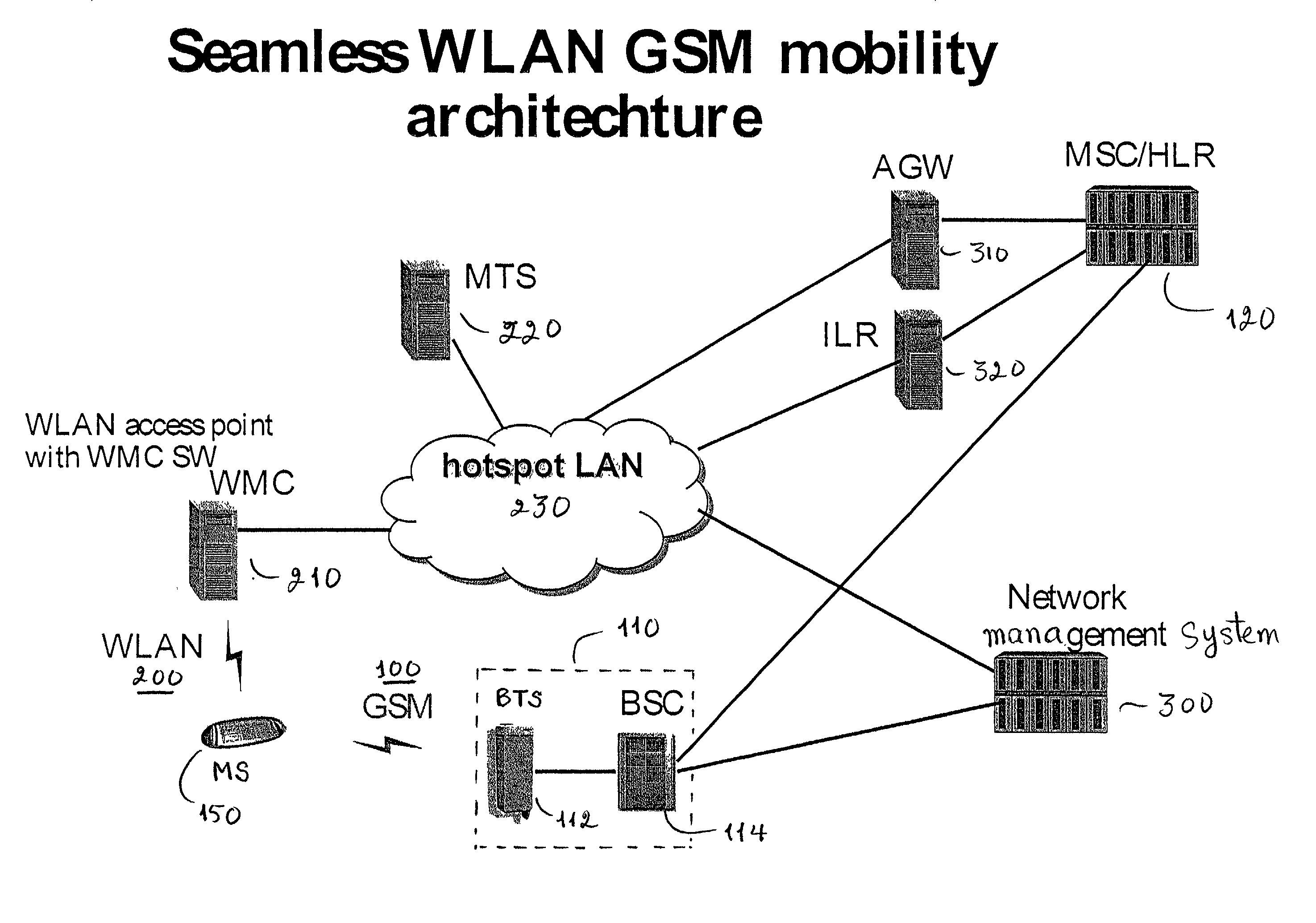
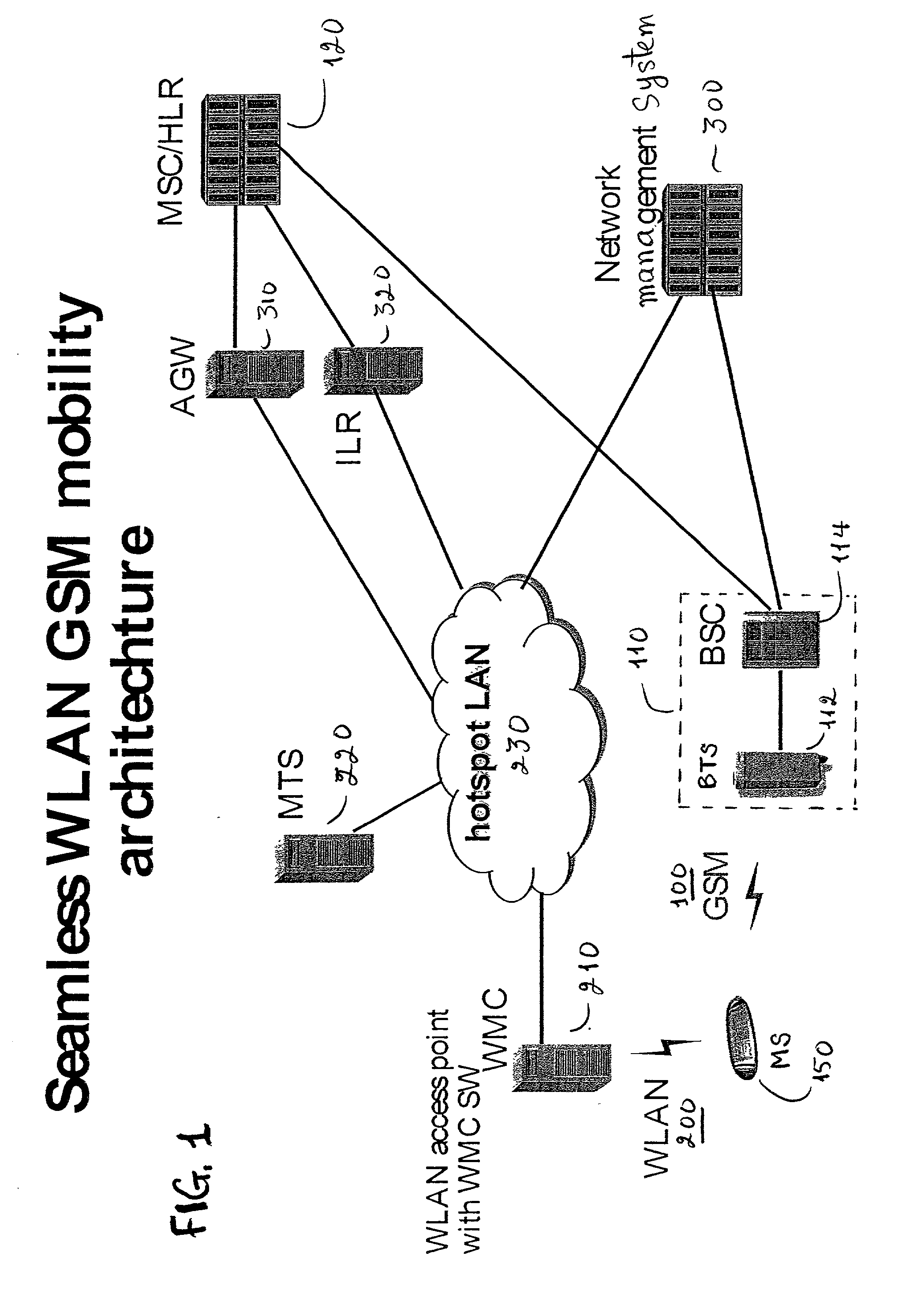
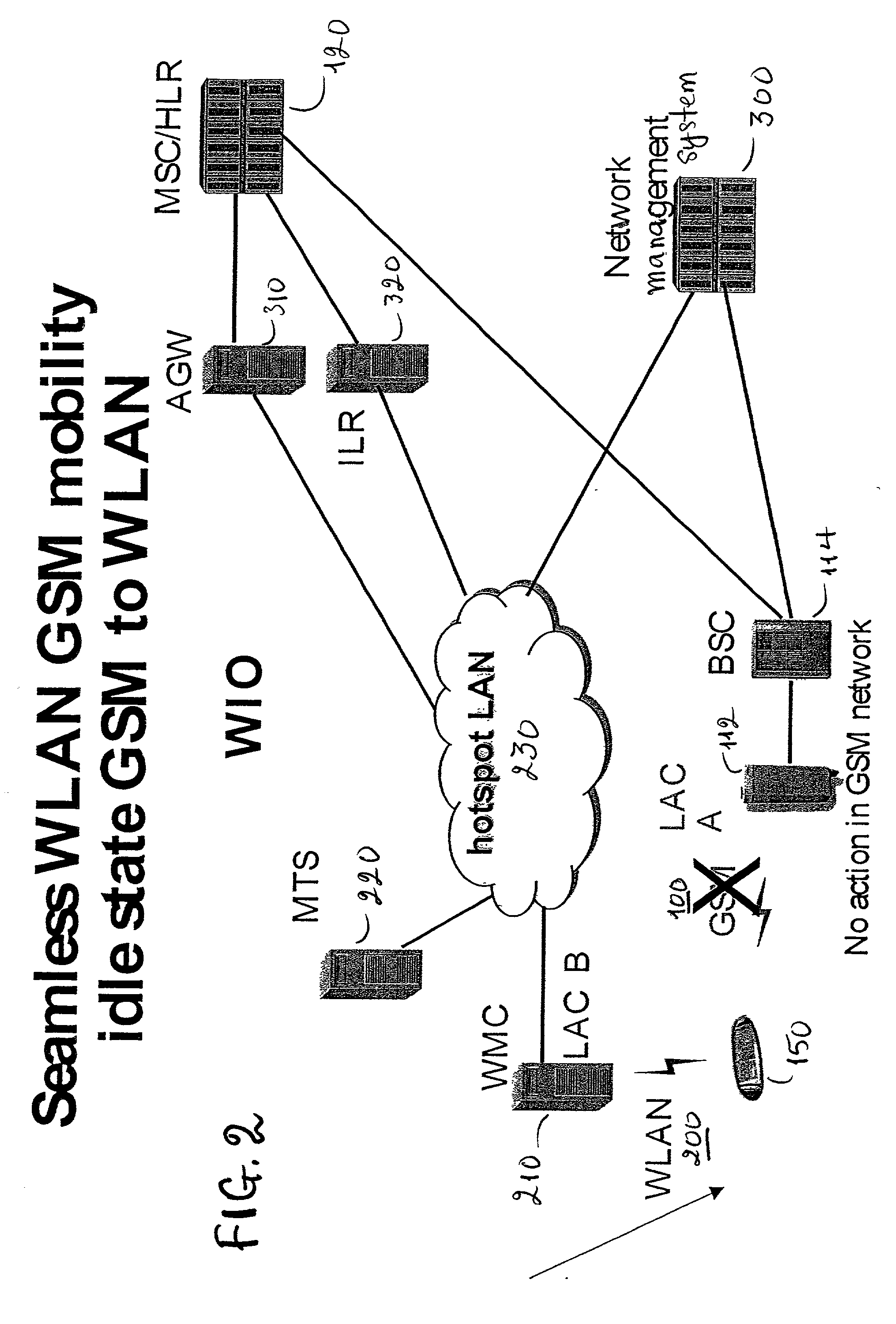
GSM Networks and solutions for providing seamless mobility between GSM Networks and different radio networks
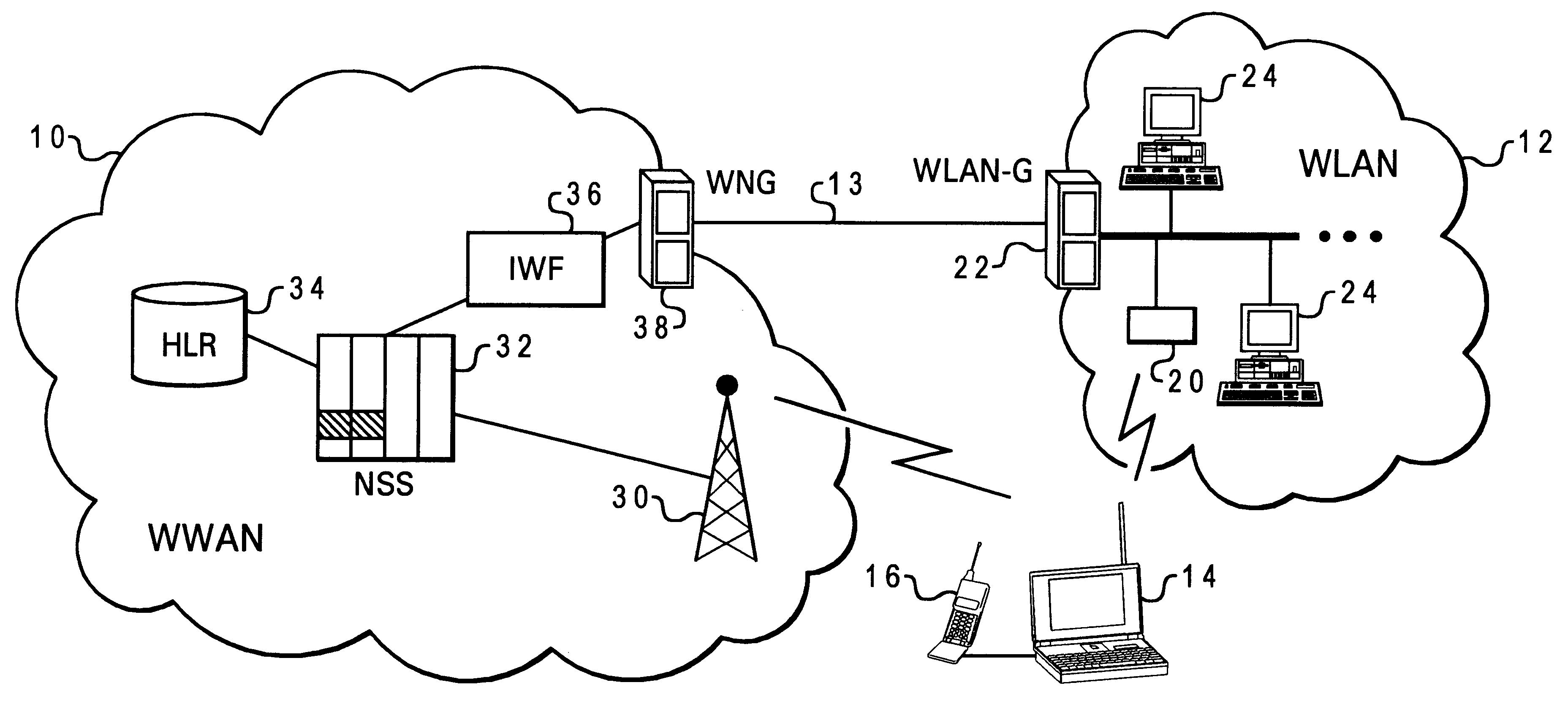
InactiveUS20020147008A1Data switching by path configurationSubstation equipmentRadio networksDual mode
A network architecture for Wireless Intranet Office (WIO) applications including a local radio network such as a wireless local area network (WLAN) which comprises a Wireless Mobile Center (WMC) arranged to serve as a WLAN access point; a GSM network which comprises a Mobile Station (MS) in a form of a dual-mode cellular phone to access both WLAN and GSM radio technologies, a Base Station (BS) arranged to convert a radio signal from the Mobile Station (MS) for communication, a Mobile Switching Center (MSC) arranged to establish call connection; and a Handover Module implemented in either the Mobile Station (MS) or the Wireless Mobile Center (WMC) for providing seamless mobility between the GSM network and the wireless LAN, when the Mobile Station (MS) roams between the GSM network and the wireless LAN.
Owner:RPX CORP
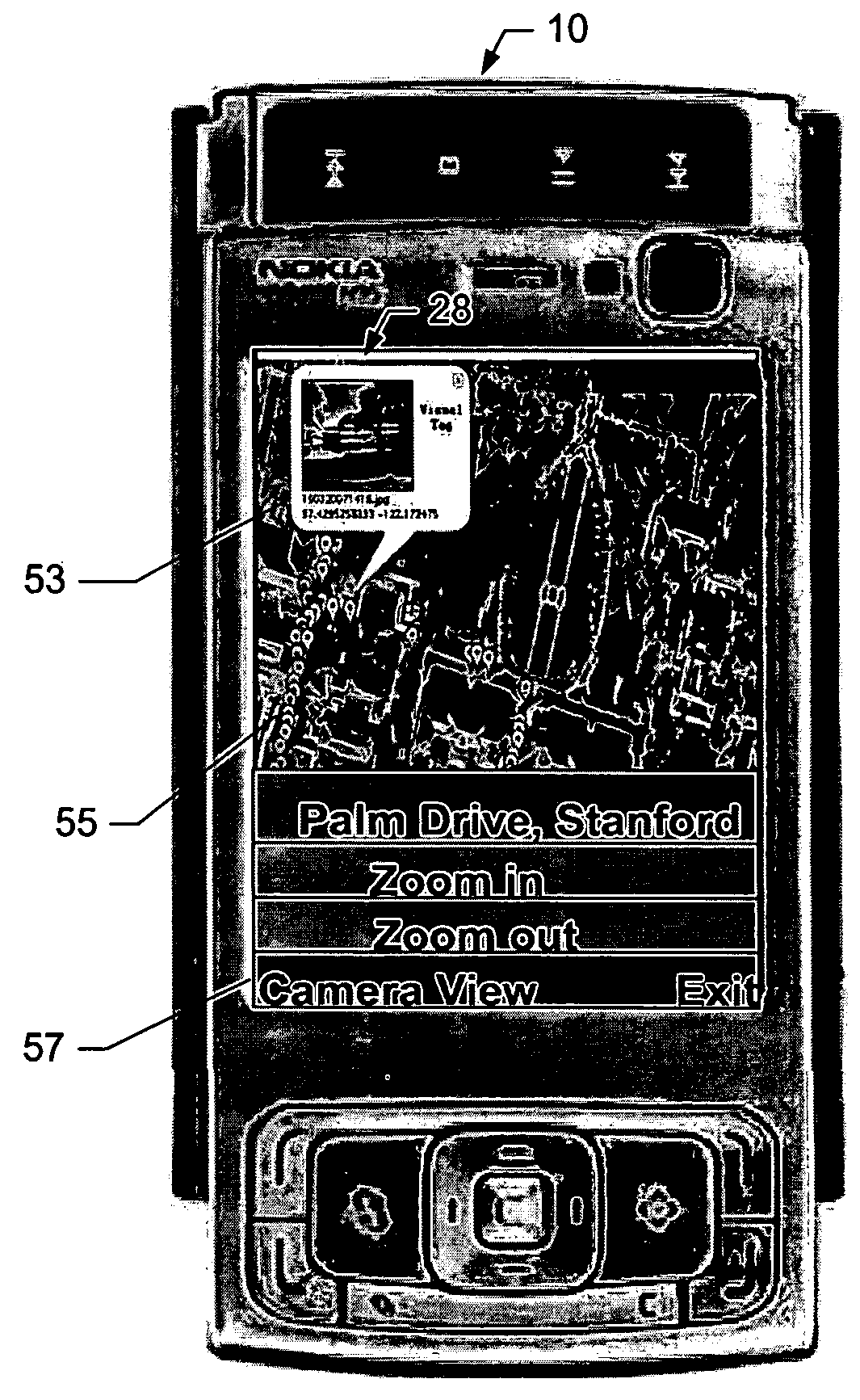
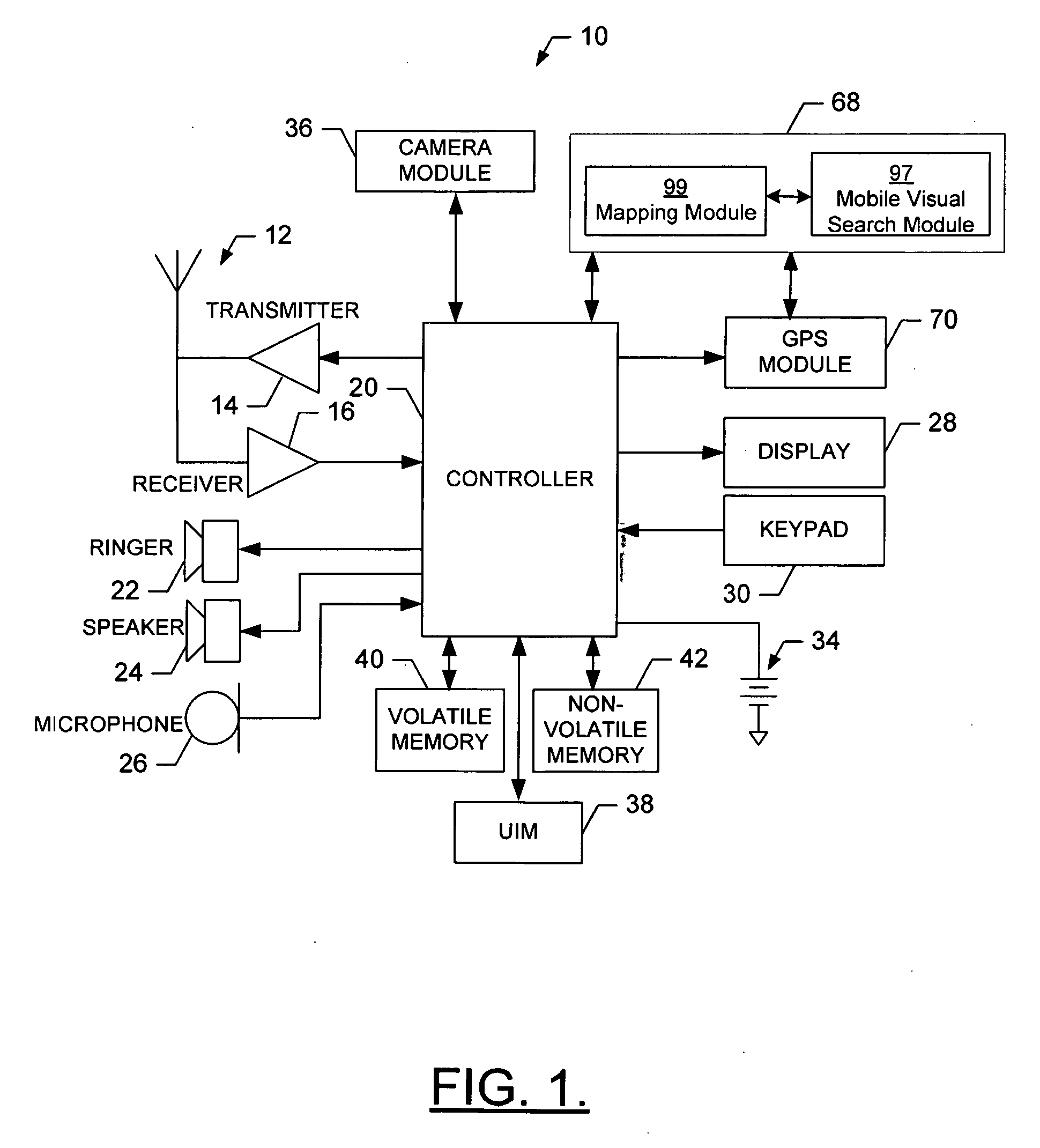
Method, Device, Mobile Terminal, and Computer Program Product for a Point of Interest Based Scheme for Improving Mobile Visual Searching Functionalities
InactiveUS20080268876A1Easy accessImprove experienceSubstation equipmentRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsInformation resourceMobile vision
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Cordless device system
InactiveUS20050130682A1Fast chargingSolution to short lifeBatteries circuit arrangementsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsEngineeringControl circuit
A cordless instrument (20, 40) detachable from a charger (10, 30, 31) is attached to the charger (10, 30, 31), and is charged. A first storage part (12, 33) chargeable from a direct current source (11, 32) included in the charger (10, 30, 31), a first charge and discharge control circuit (13, 50) to control charge and discharge of the first storage part (12, 33), a second storage part (21, 43) included in the cordless instrument (20, 40), and a second charge and discharge control circuit (22, 45) to control charge and discharge of the second storage part (21, 43) are provided. Further, a third storage part (28) chargeable from the direct current source (11, 32) may be provided. Also to the cordless instrument (20, 40), a fourth storage part (44) may be provided. Upon attaching the cordless instrument, the second storage part (21, 43) is charged at least from the first storage part (12, 33). In comparison with charging time to conventional secondary batteries, it is capable of rapid charge, long life use, resulting in such merits as to realize the compact size of a charger and low cost.
Owner:SUN BRIDGE CORP
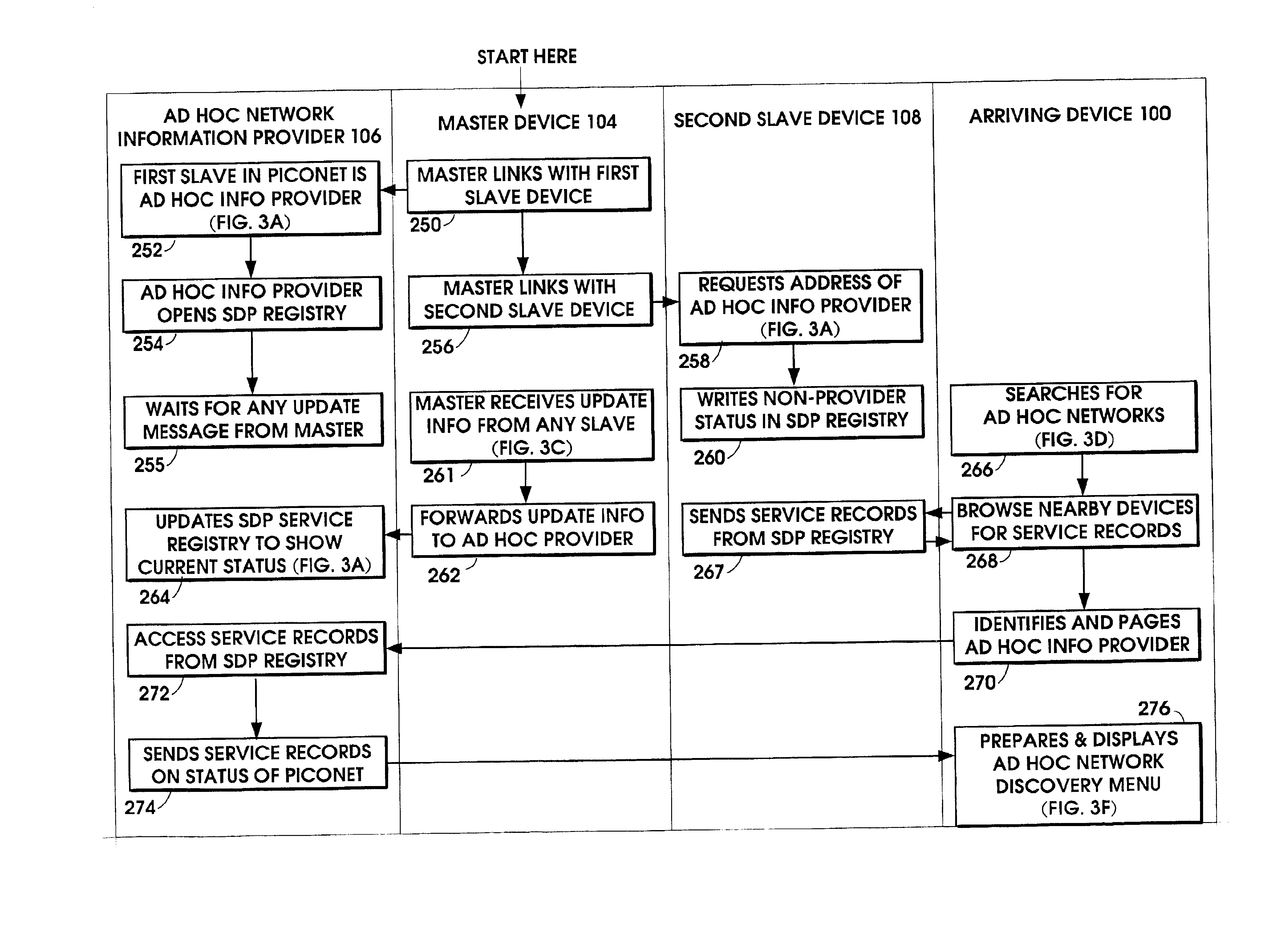
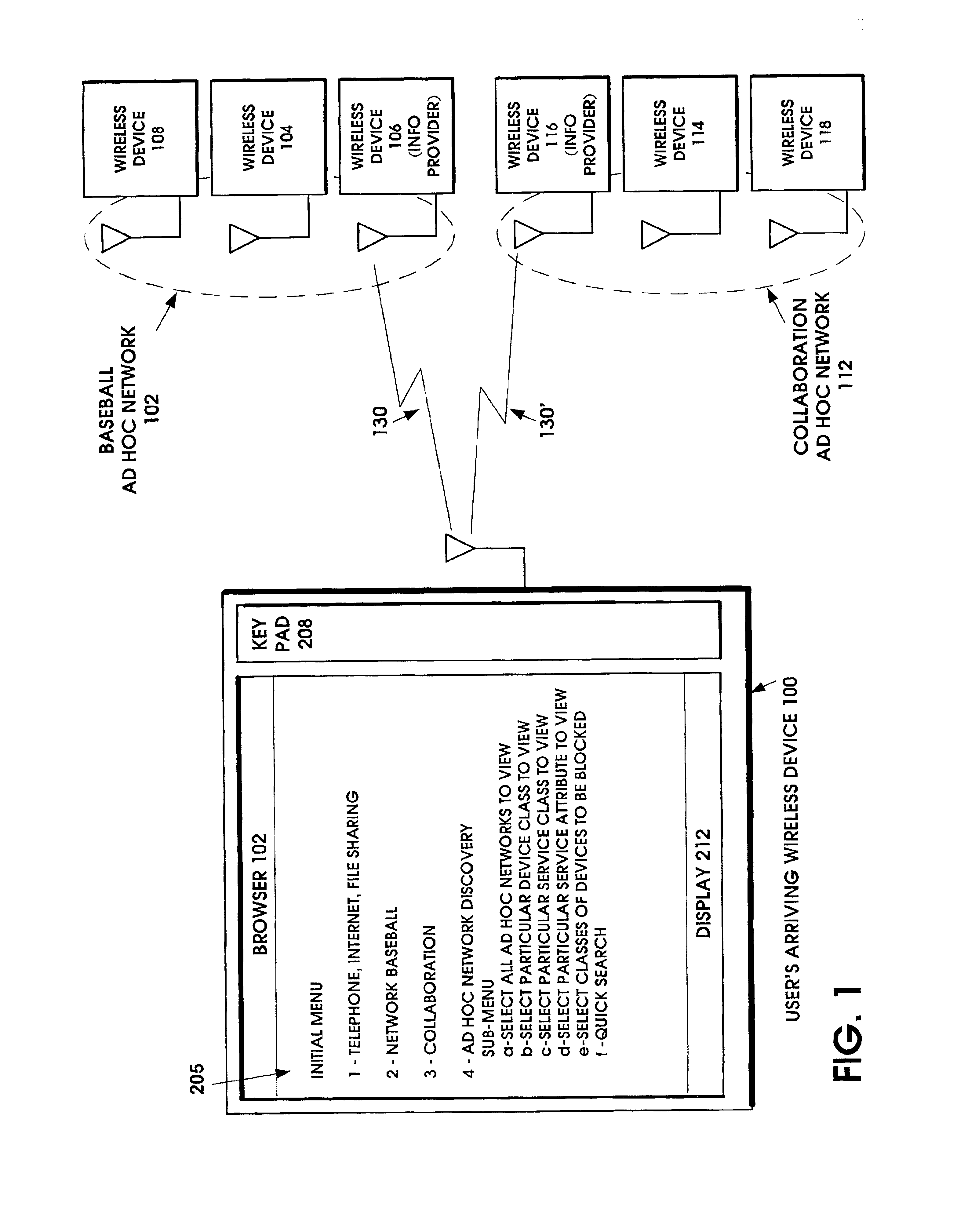
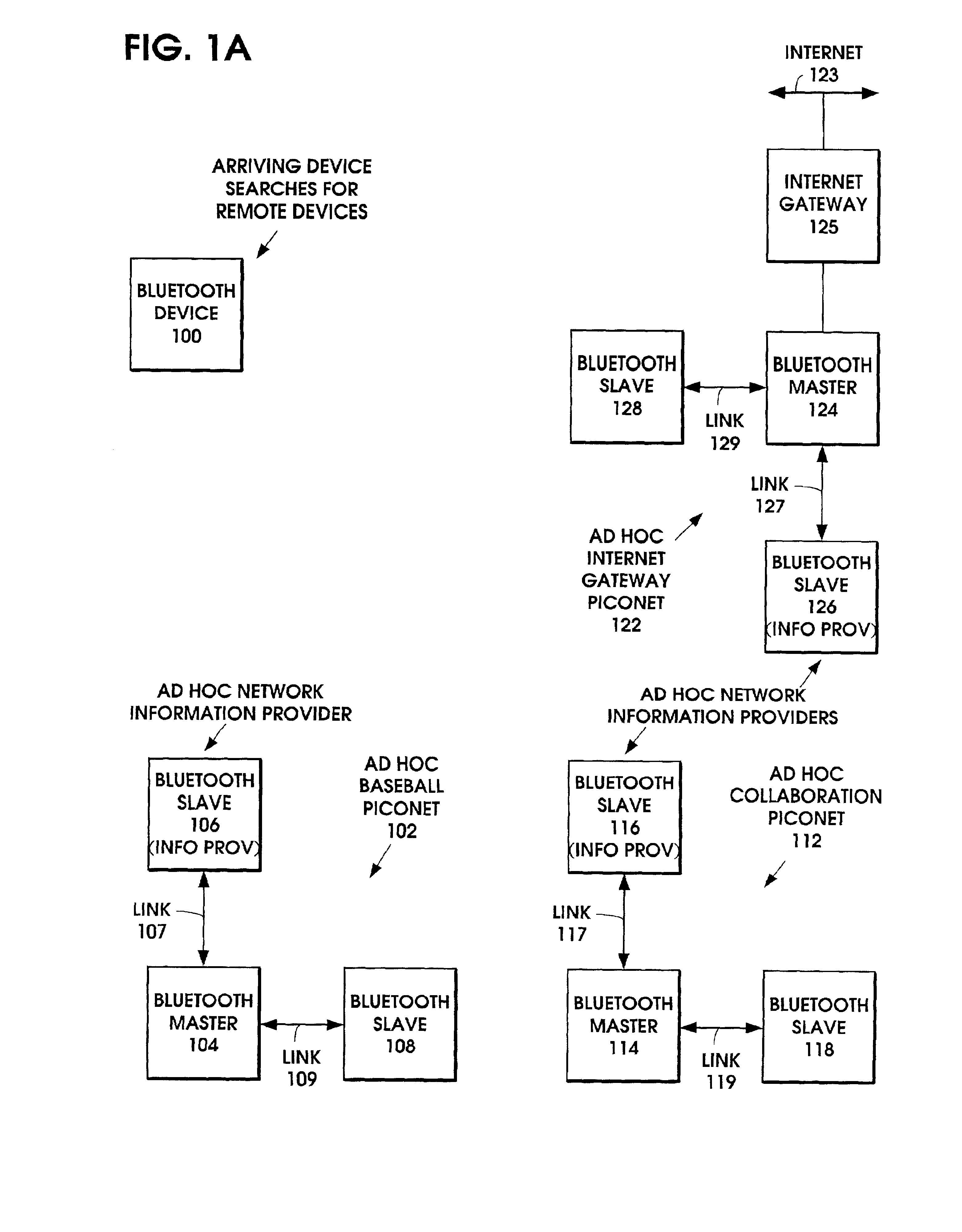
Ad hoc network discovery menu
When an ad hoc network is formed between short range wireless devices, at least one device assumes the role of an ad hoc network information provider for the new piconet. In this role, the device allocates a browsing hierarchy of service classes in its service registry. The service classes will provide a record to characterize the ad hoc network. When a new wireless device arrives within the communication range of any member of the ad hoc network, its inquiry signals are answered by the first member detecting the inquiry. If that first member is an ad hoc network information provider, it responds with information accessed from its service registry characterizing the ad hoc network. If, instead, an ordinary device in the ad hoc network is the first to respond to the inquiry signals of the arriving device, the device responds with the address of the ad hoc network information provider. The arriving device then pages the ad hoc network information provider to obtain information characterizing the ad hoc network.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
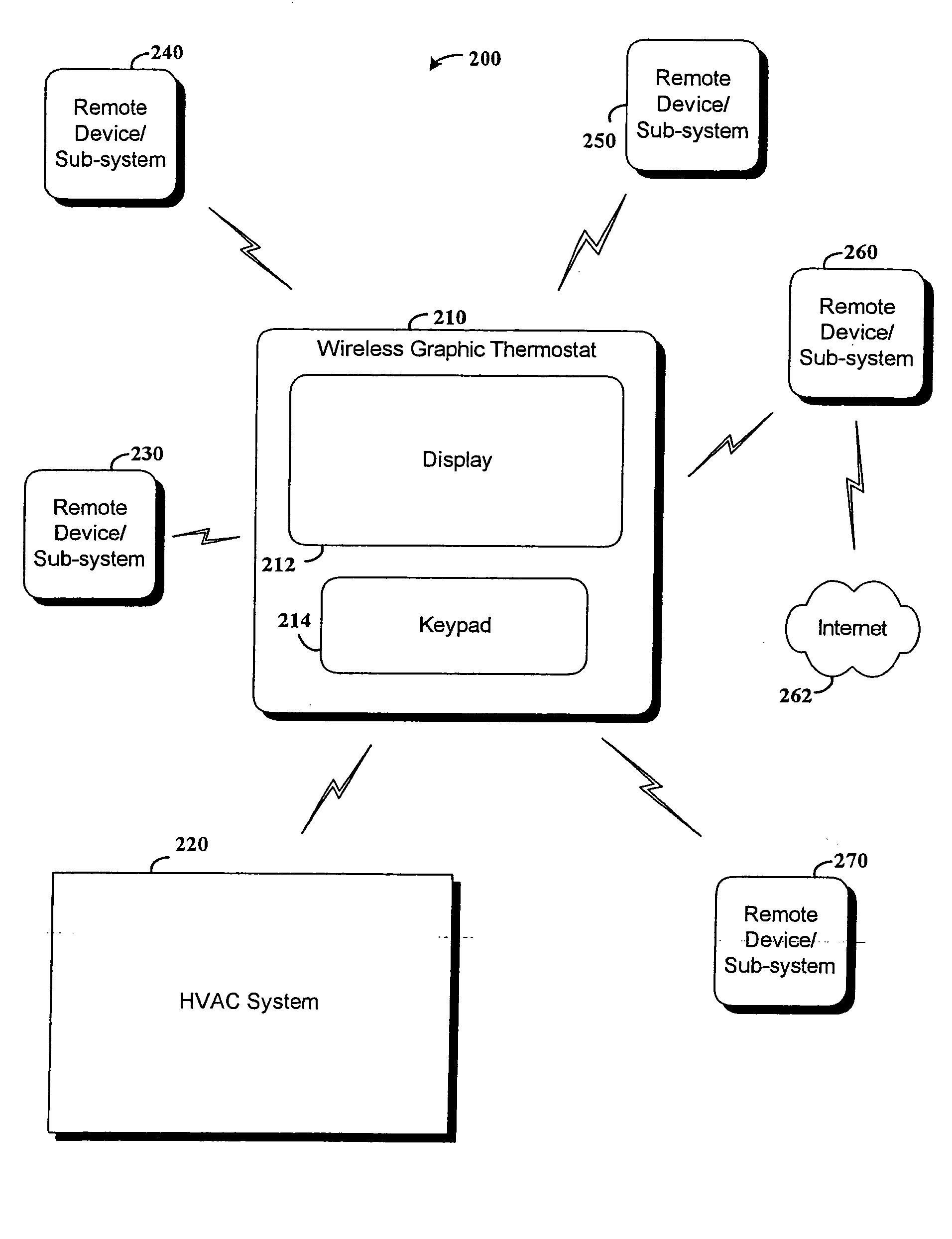
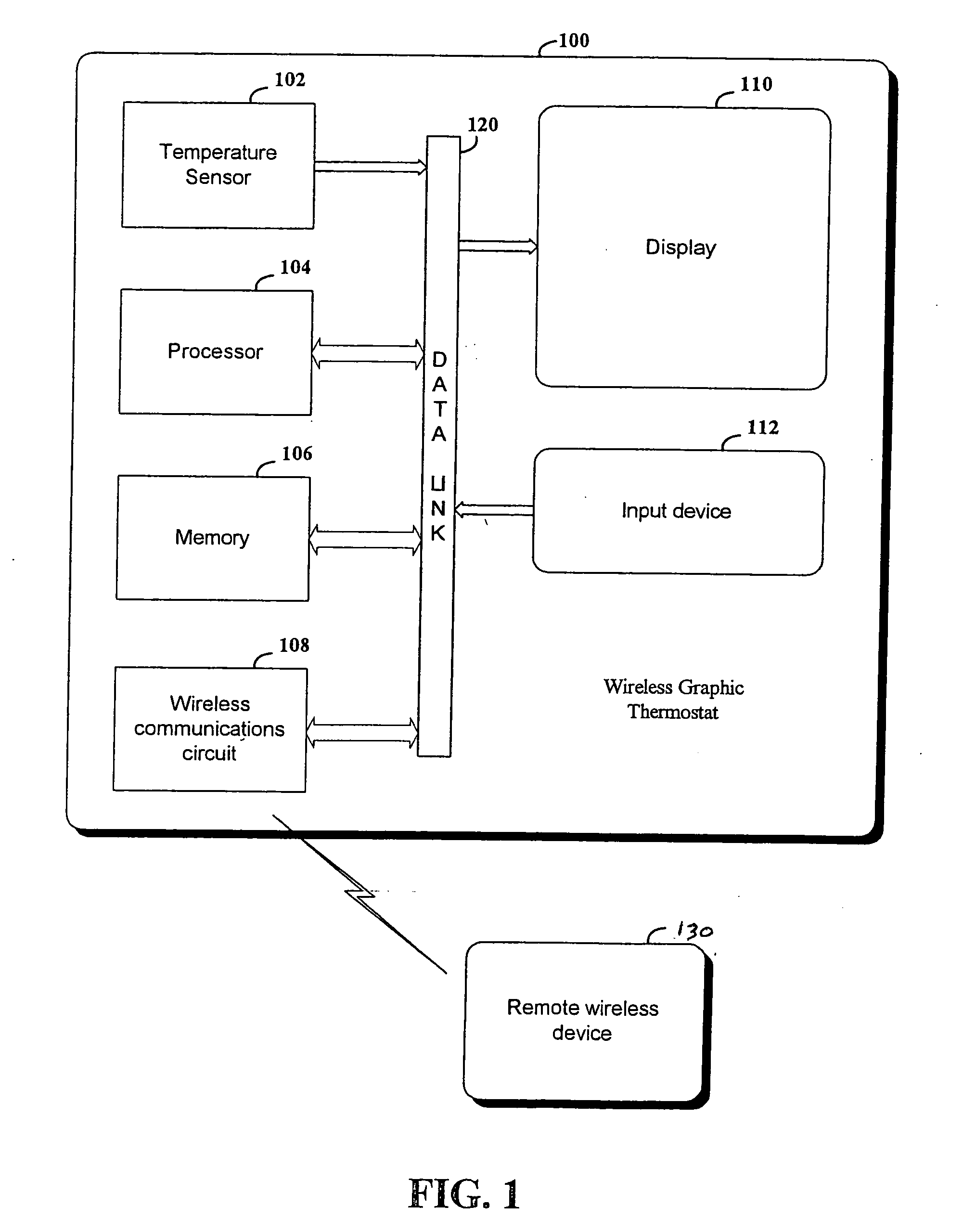
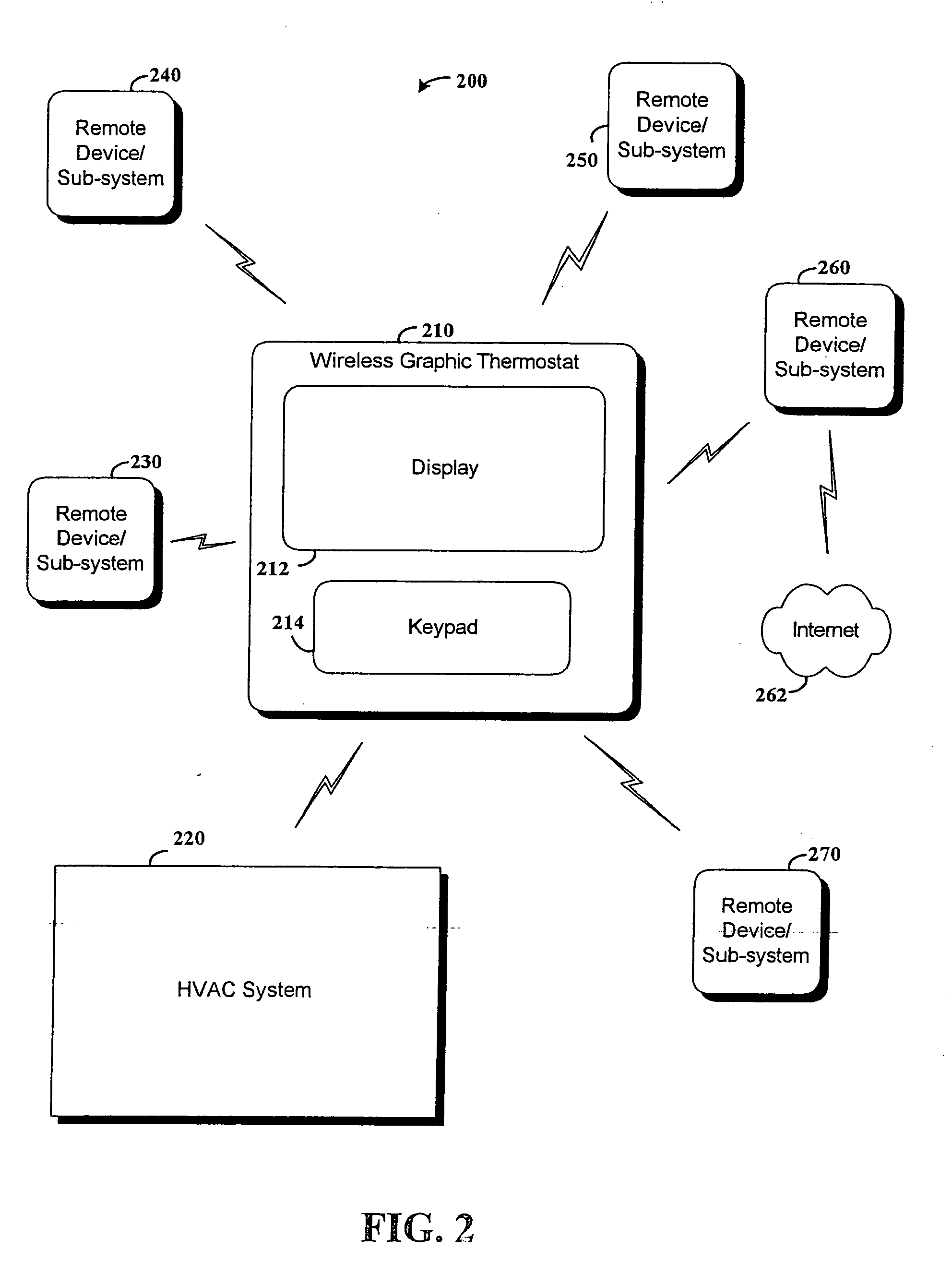
RF interconnected HVAC system and security system
InactiveUS20050270151A1Easy programmingMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsWireless controlThermostat
An interconnected wireless HVAC (heating, ventilation, air conditioning) system and wireless security system, which are interconnected and communicate with each other through the use of a common wireless technology, including the same selected frequency, modulation and a set of common protocols. The Wireless HVAC system includes wireless thermostats, which can communicate with and control both the HVAC system and the security system, and the wireless security system includes wireless controls or keypads, which can communicate with and control both the security system and the HVAC system. The universal wireless infrastructure can be expanded to provide communication or control of additional user or manufacturer installed wireless devices or systems through the universal wireless home infrastructure.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
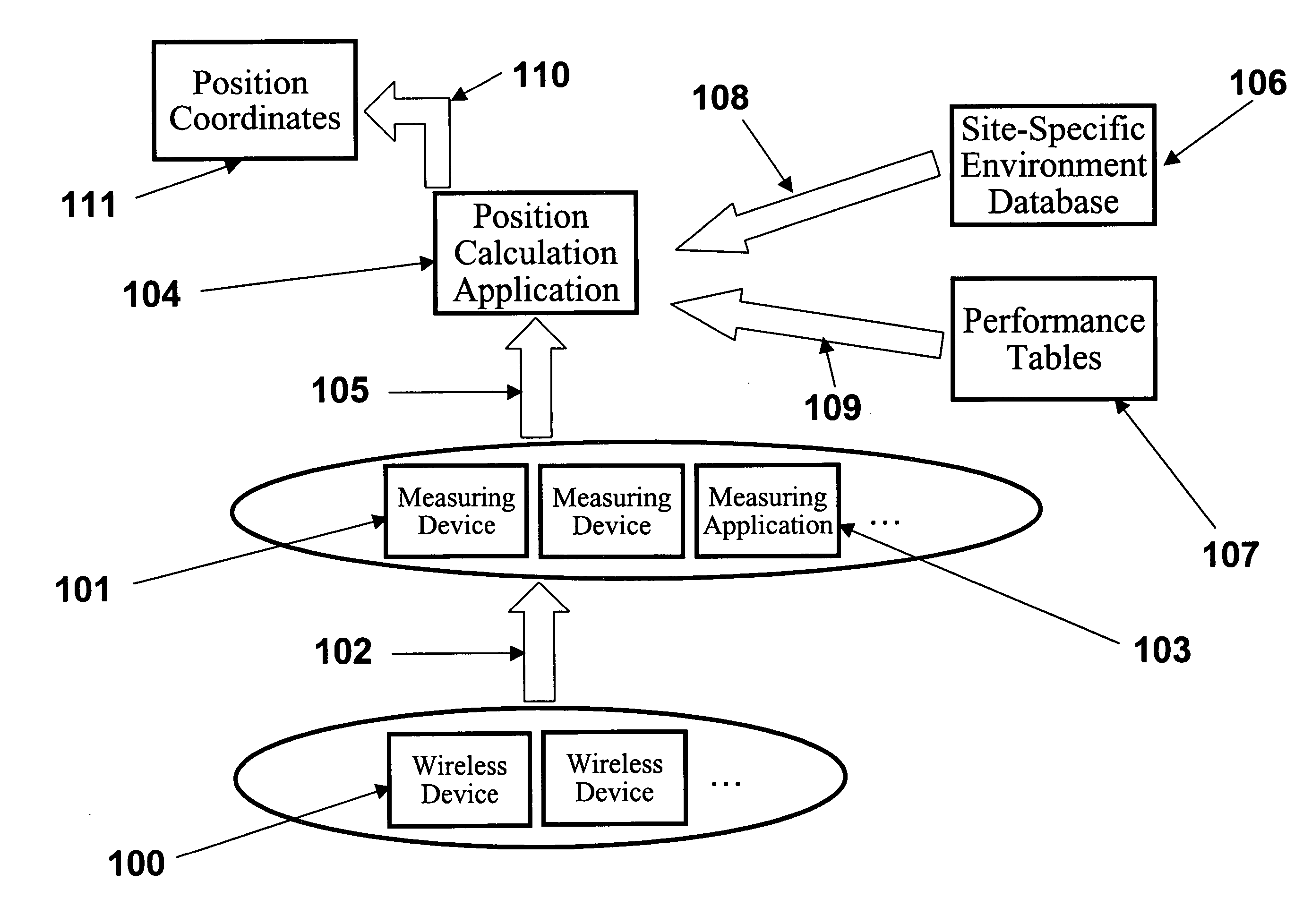
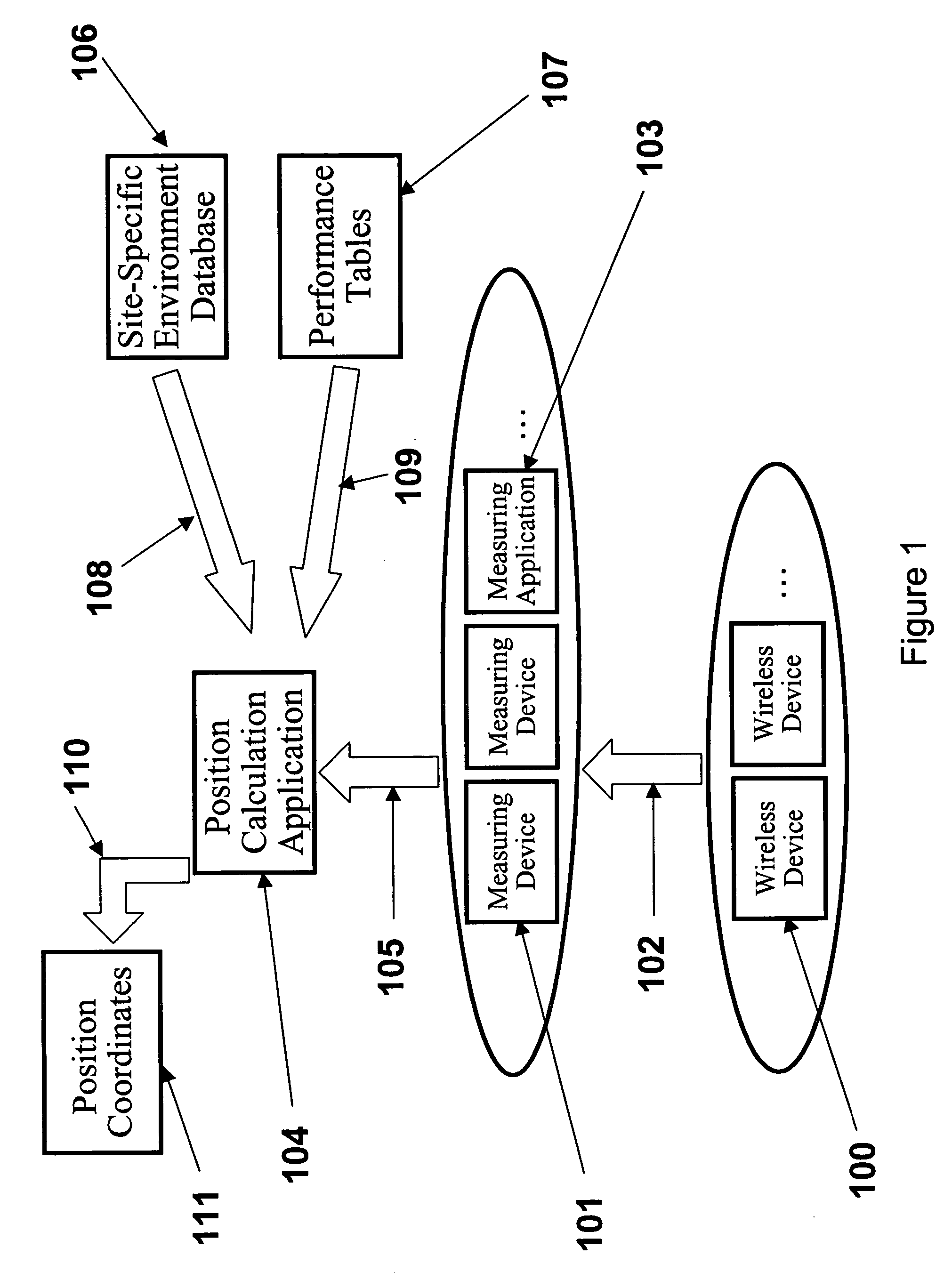
System, method, and apparatus for determining and using the position of wireless devices or infrastructure for wireless network enhancements
ActiveUS20060019679A1Increase network bandwidthHigh degreeDirection finders using radio wavesRoad vehicles traffic controlDevice typePredicting performance
A system and method for estimating the position of wireless devices within a wireless communication network combines measured RF channel characteristics for the wireless device with one or more predicted performance lookup tables, each of which correlates an RF channel characteristic to some higher order network performance metric and / or a position within an environmental model. Measured RF channel characteristics for wireless devices are compared against the performance lookup tables to determine the sent of lookup tables that most closely match the measured RF channel characteristics. The positions within the environmental model corresponding to the selected set of matching lookup tables are identified as possible locations for the wireless device. The performance lookup tables are uniquely constructed by site-specific location, technology, wireless standard, and equipment types, and / or the current operating state of the communications network.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
Location-based opportunistic recommendations
InactiveUS20090239552A1Digital data information retrievalRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSuccessful completionComputer science
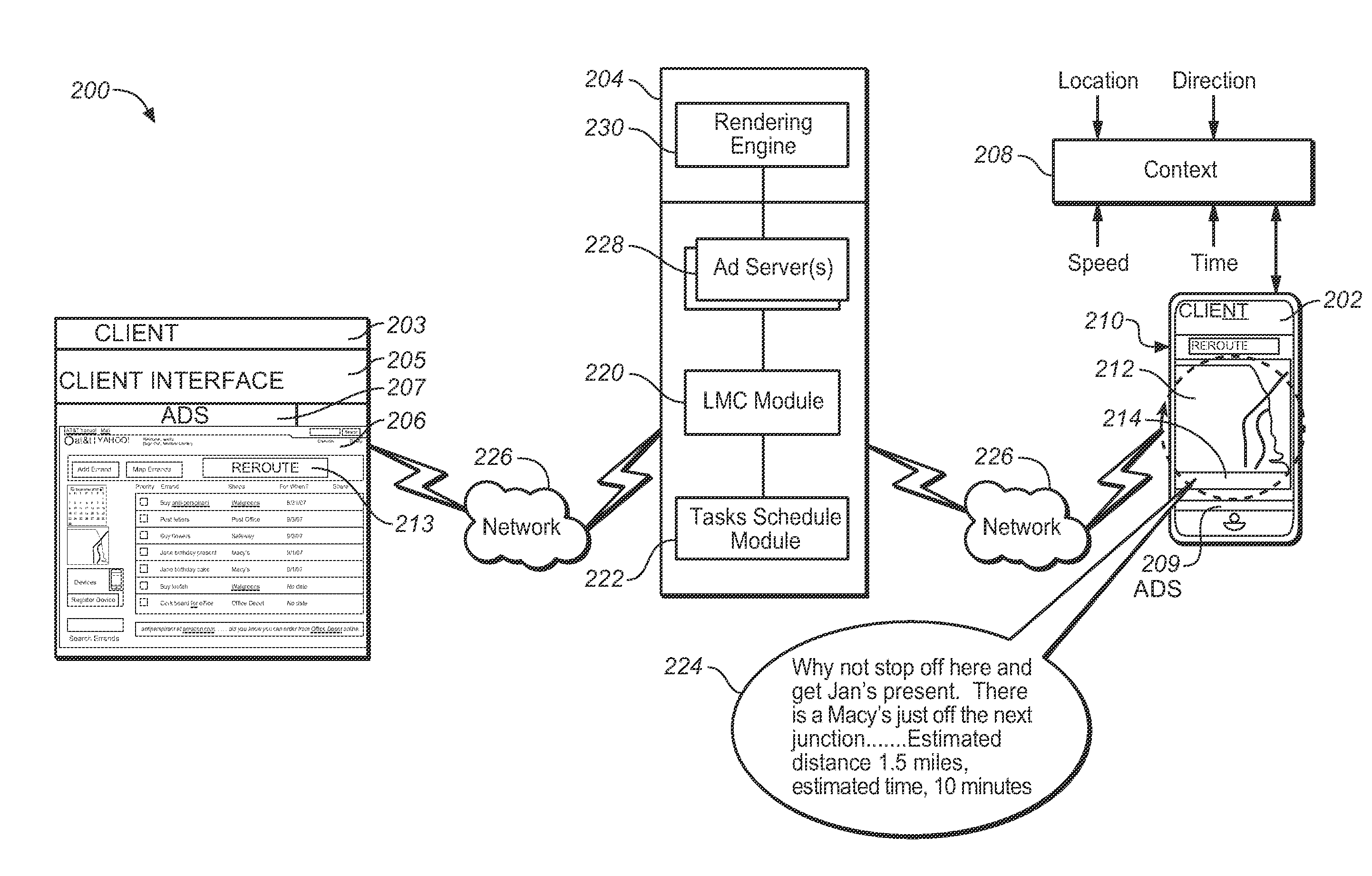
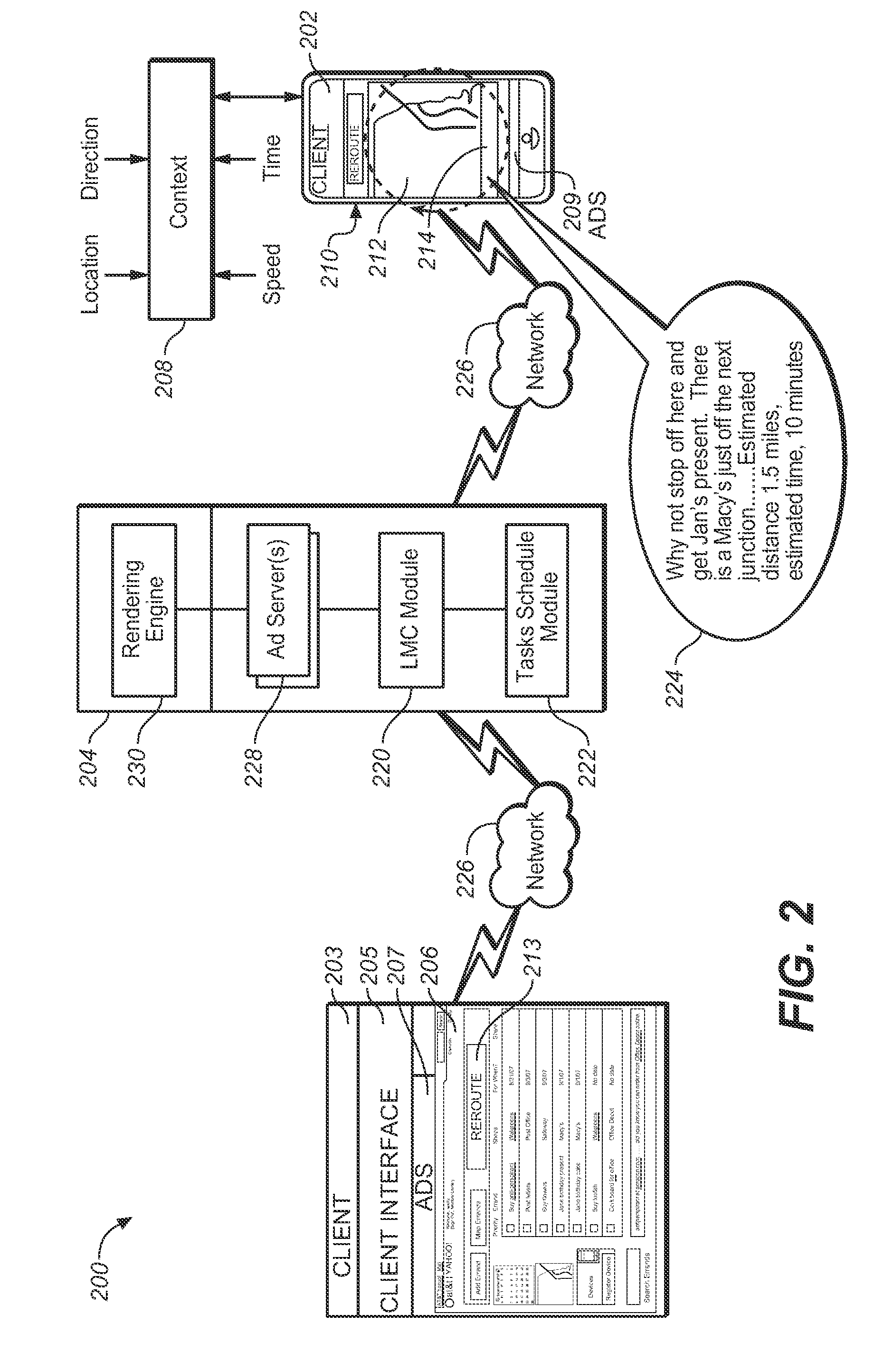
Location aware notification service technology operable to provide users with notification of opportunities to complete errands on a personal sharable list is disclosed. The location aware notification service technology provides a means for generating recommendations for users for the successful completion of errands based upon current location, time and travel context.
Owner:OATH INC
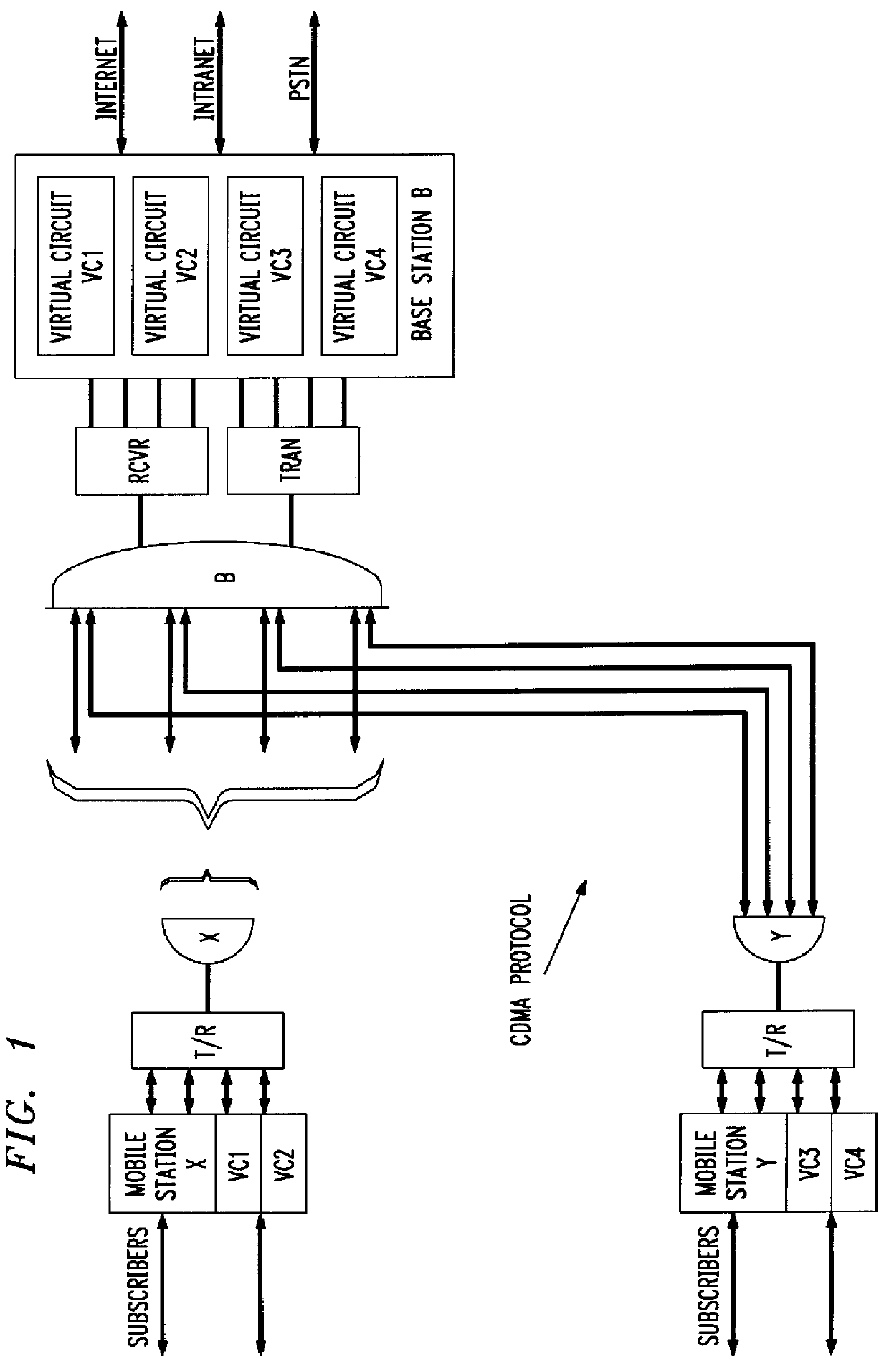
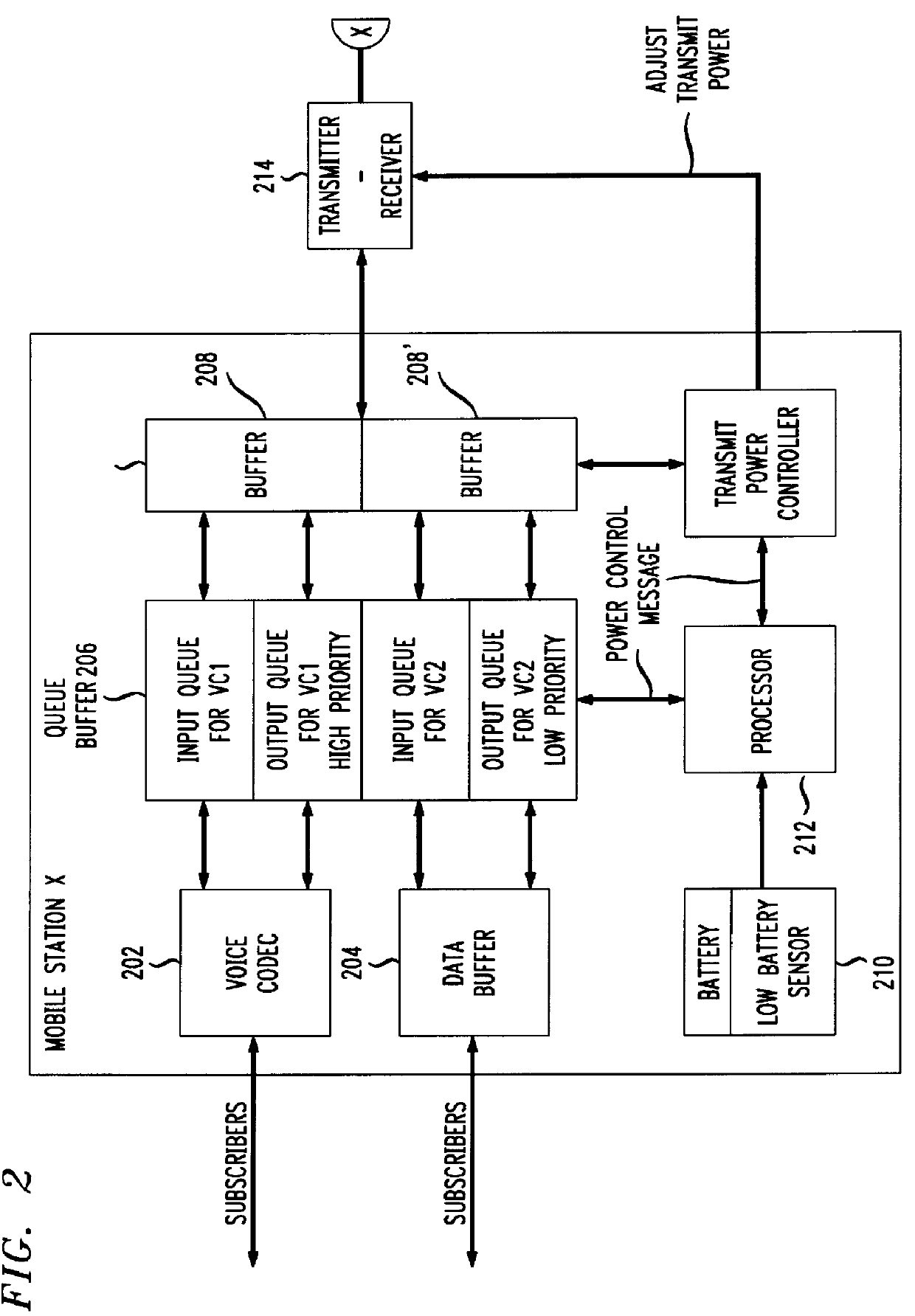
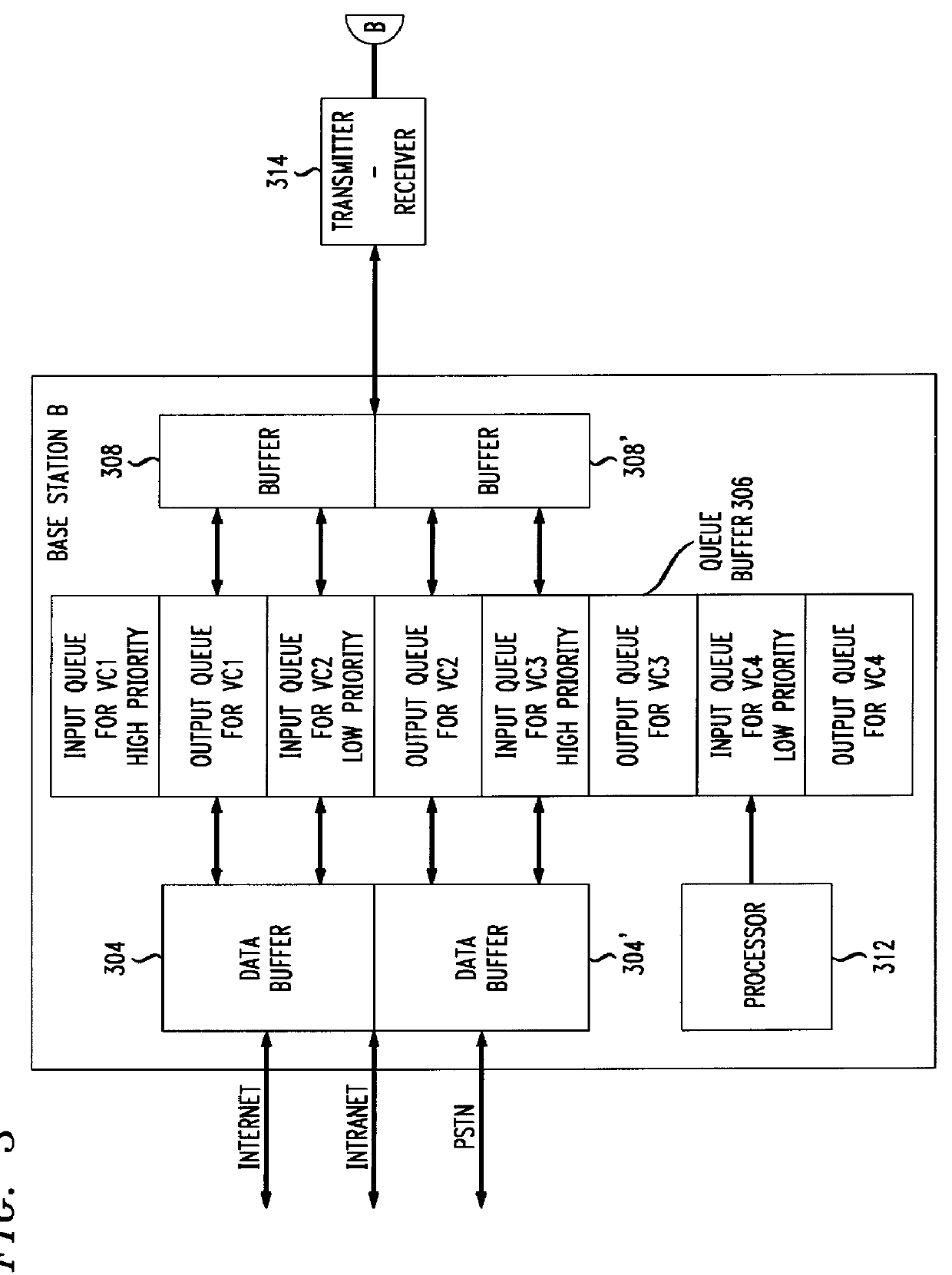
CDMA mobile station wireless transmission power management with adaptive scheduling priorities based on battery power level
InactiveUS6072784ASave battery powerOptimally conserve battery powerPower managementEnergy efficient ICTWireless transmissionCommunications system
A method adapts scheduling priorities in a CDMA wireless communications system to conserve battery power in mobile terminals operating within the system. A base station, within the system, receives battery power level information and other setup information from mobile terminals operating within the service area of the base station during call setup procedures. Based on the battery power level information and other setup information, the base station adapts scheduling priorities for the mobile terminals to expedite wireless transmissions from those mobile terminals reporting low battery power levels. The base station schedules the transmissions from low battery power mobile stations to be clustered together in a low-power time slot which is separate in time from the scheduled transmissions from high battery power mobile stations. The base station transmits a power control message to the low battery power mobile stations, to reduce the transmission power required for those mobile stations during the low-power time slot.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
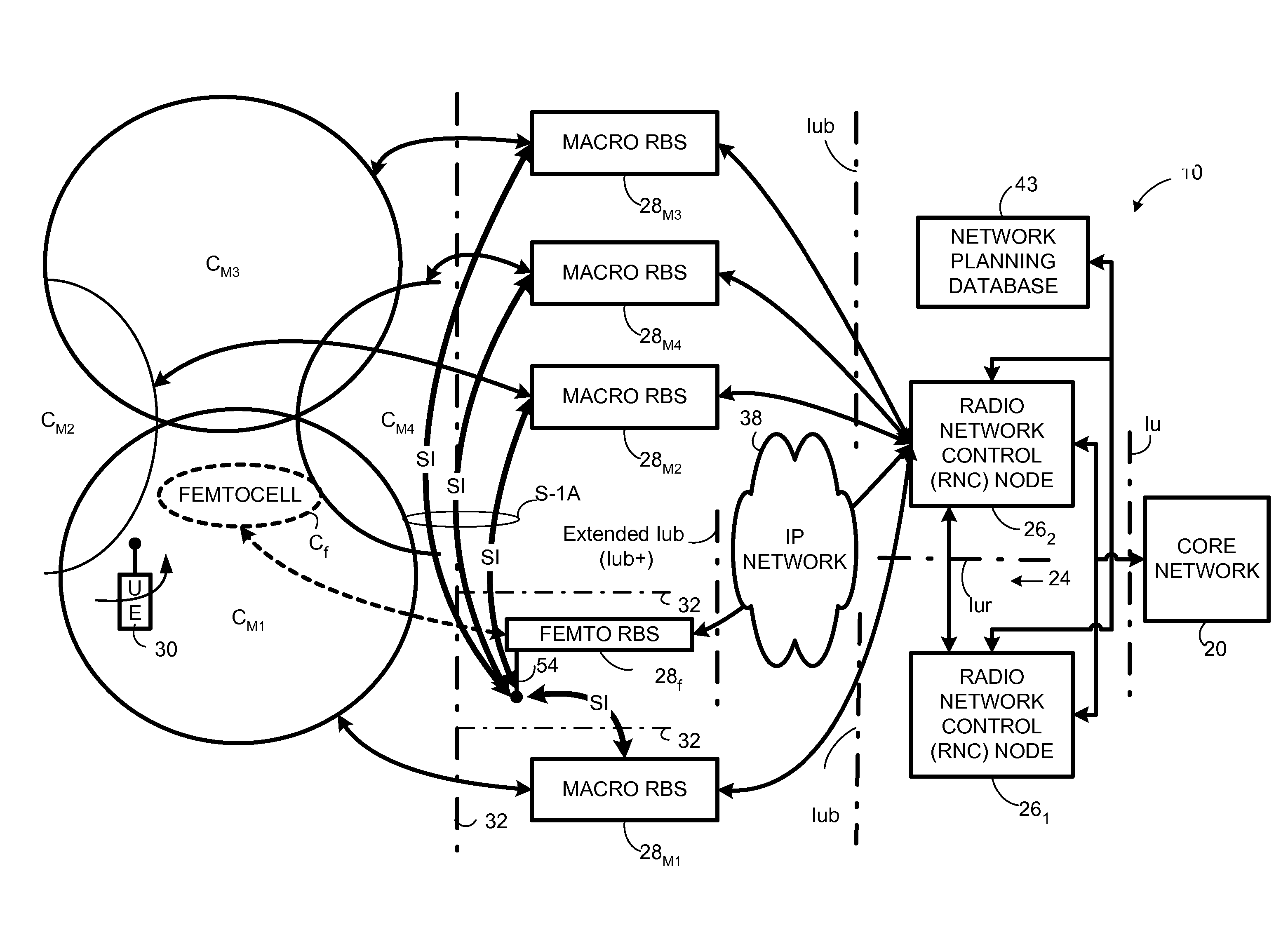
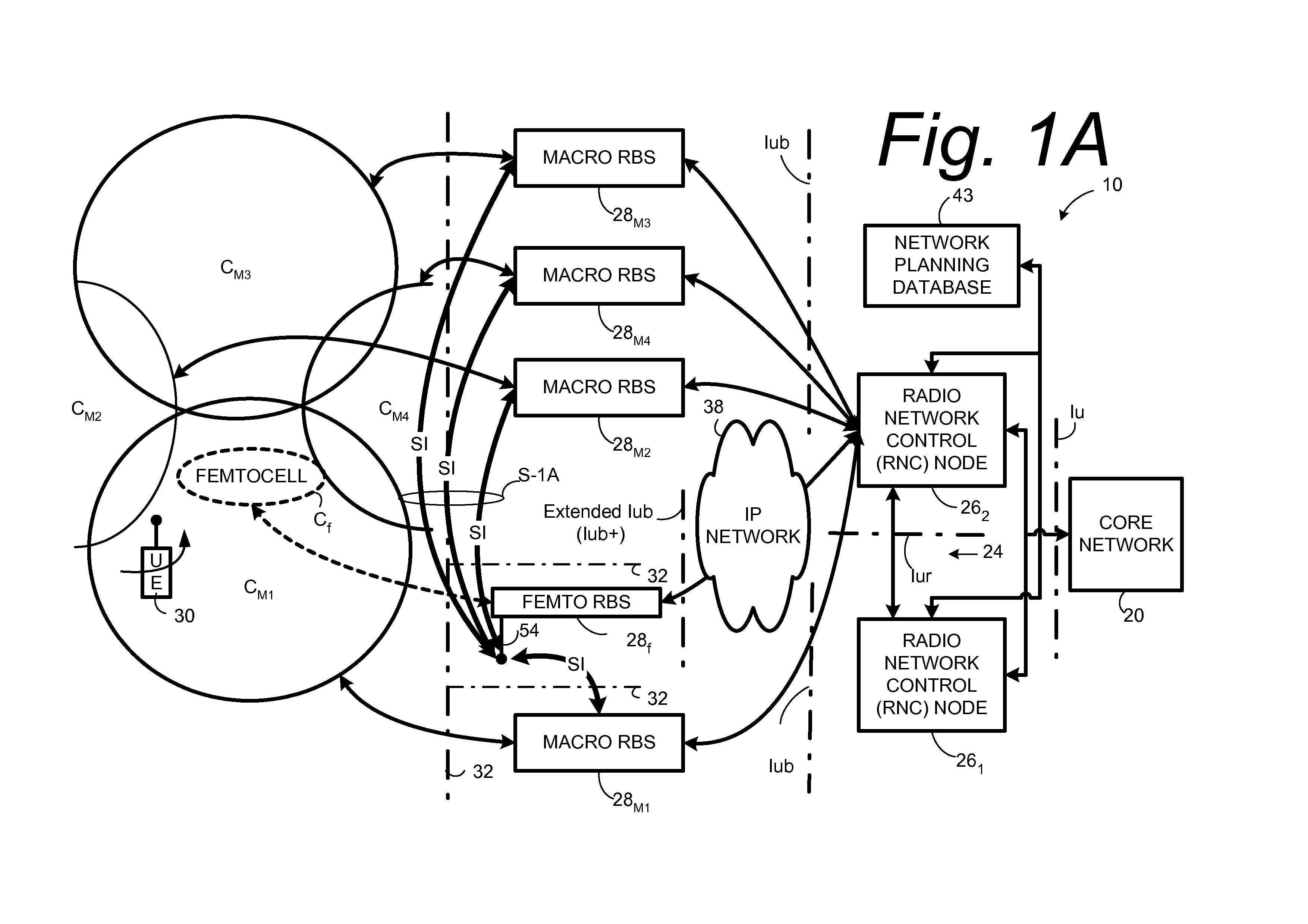
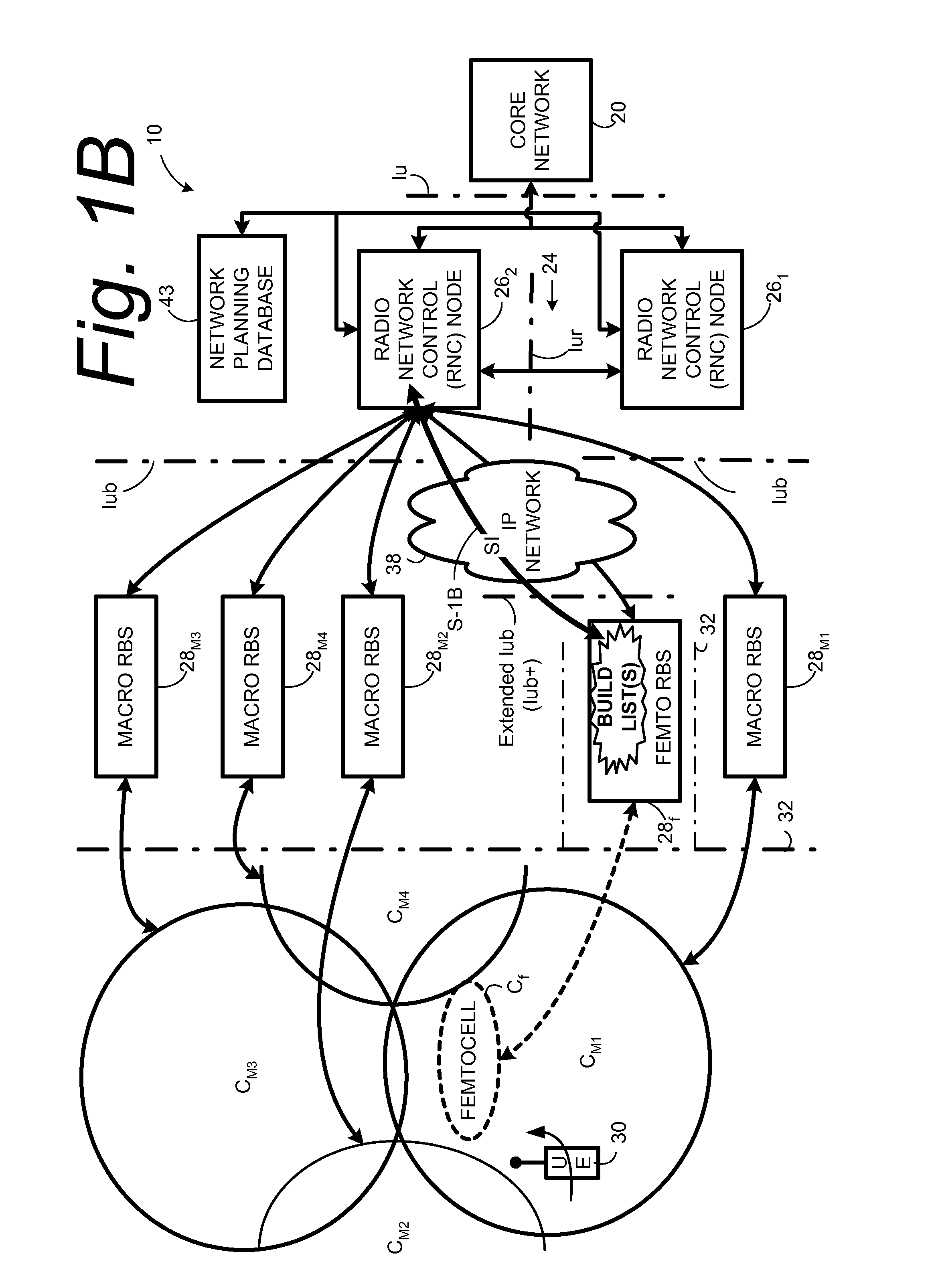
Automatic configuration of pico radio base station
Methods and apparatus configure a femto radio base station ( 28 f). A macro receiver of the femto radio base station ( 28 f) is used to acquire detected coverage information of a radio access network ( 24 ). The detected coverage information is used to determine an operation parameter for use by the macro transceiver ( 52 ) of the femto radio base station ( 28 f). In one embodiment, the detected coverage information is transmitted to a control node ( 26 ) of the radio access network. The control node ( 26 ) determines the operation parameter and communicates the operation parameter to the femto radio base station ( 28 f). The femto radio base station ( 28 f) is accordingly configured using the operation parameter for further operation towards UEs ( 30 ) accessing the femto radio base station ( 28 f).
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
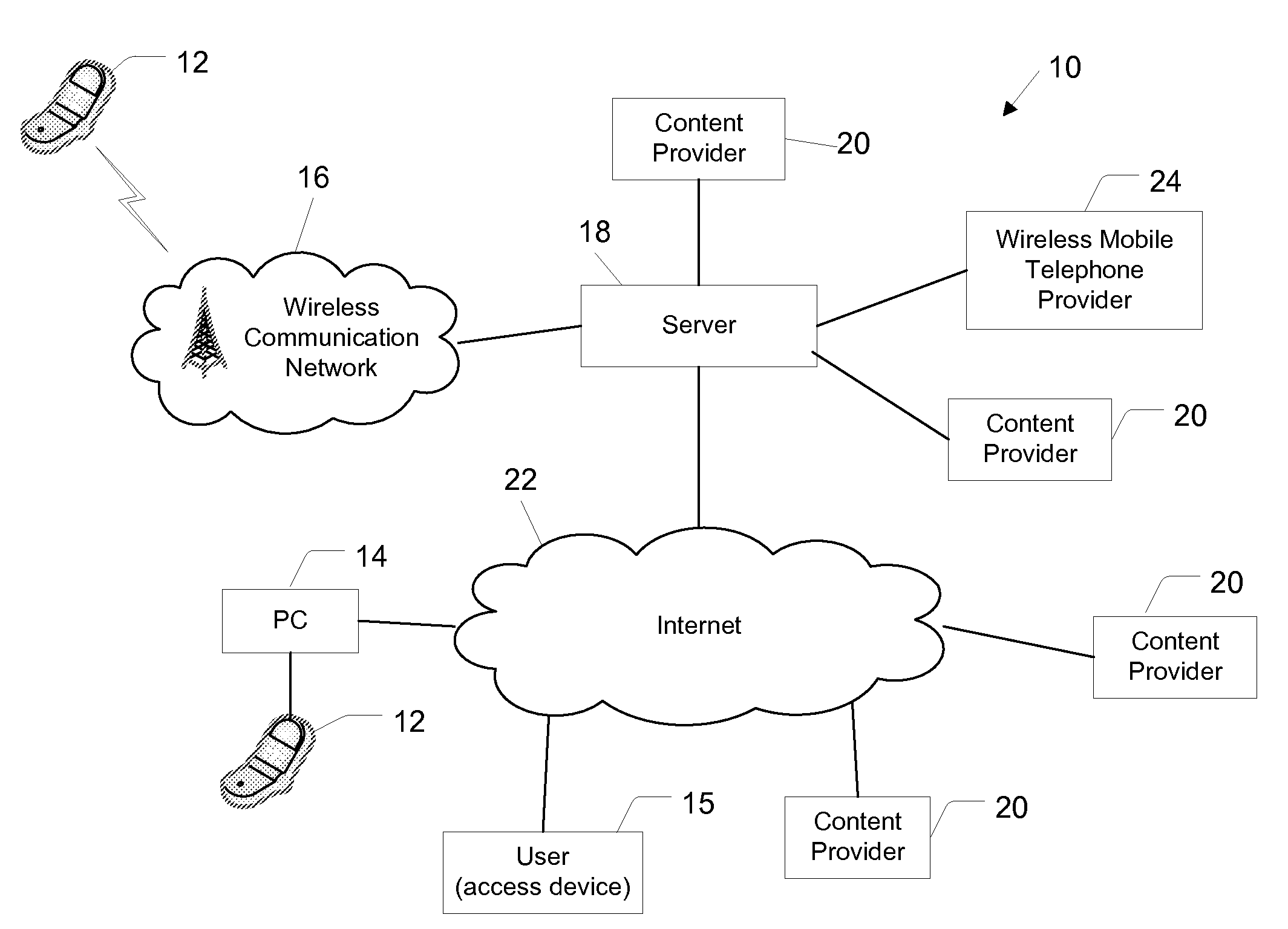
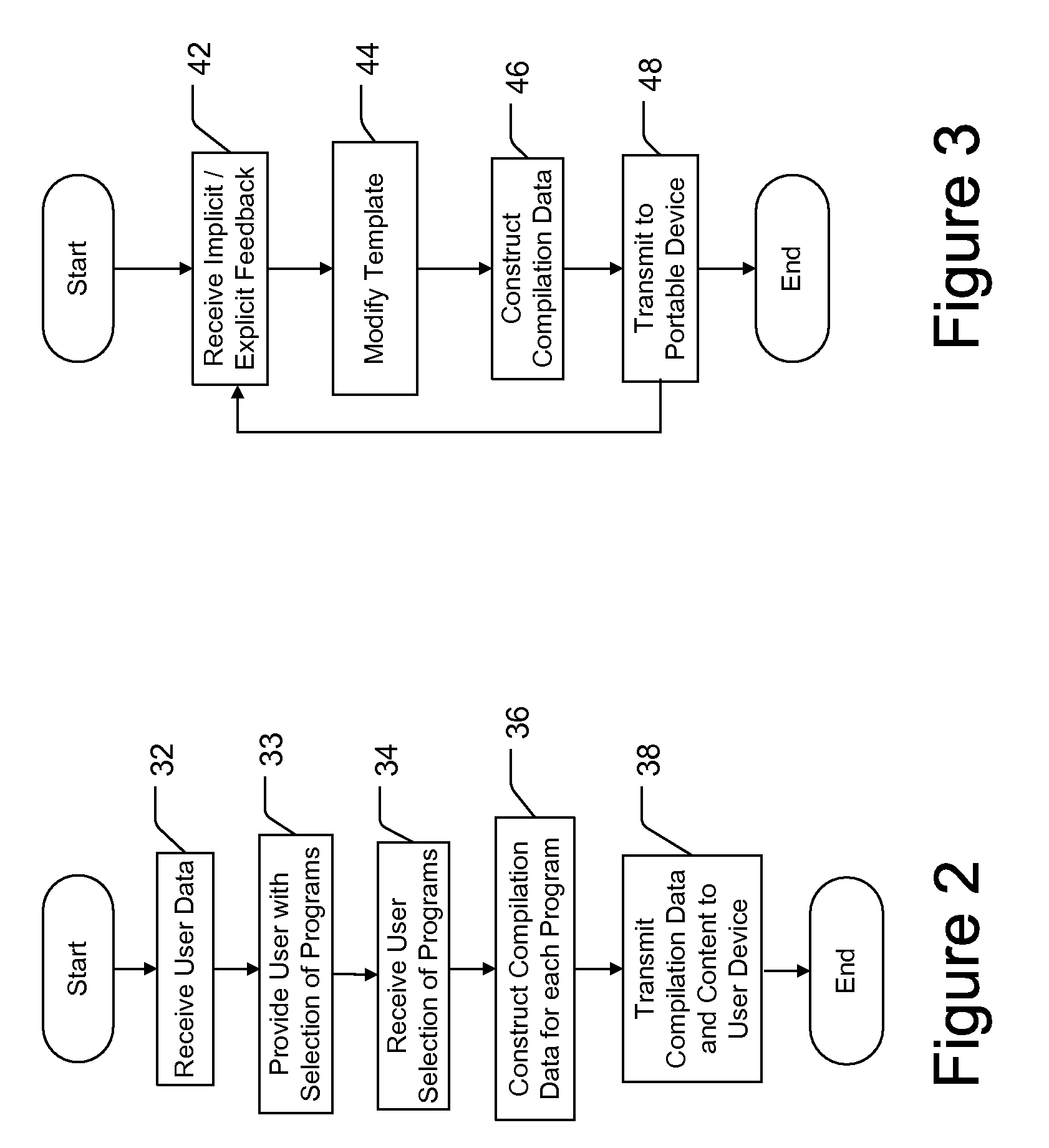
Content Delivery System and Method
ActiveUS20080242280A1Special service for subscribersAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsTelecommunications linkWireless data
A method and system for delivering content to a plurality of devices is provided. In one embodiment, the method may be for delivering content elements of one or more presentations to a device configured to communicate via a wireless data network, wherein the content elements include static content elements, dynamic content elements, and on-demand content elements. The method may comprise delivering to the device, data, such as compilation data, of the content elements included in the one or more presentations; delivering the static content elements to the device via the wireless data network during one or more time periods of increased available wireless data network capacity; delivering the dynamic content elements to the device via the wireless data network substantially according to a schedule; and delivering the on-demand content elements to the device via the wireless data network substantially immediately after a user request for an on-demand content element. In addition, the method may comprise determining that the device is accessible via a communication link, such as a wireless local area network, that does not include the wireless data network and delivering one or more content elements to the device via the communication link. Further, the method may comprise determining that the device is communicatively coupled to an internet access device and delivering one or more content elements to the device via the internet access device.
Owner:IOCAST
Popular searches
Payment schemes/models Network planning Protocol authorisation Market data gathering Picture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanning Picture reproducers using projection devices Picture reproducers using solid-state color display Television systems Color motion picture films scanning Selective content distribution
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com