Patents
Literature
316results about How to "Disadvantages can be reduced eliminated" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
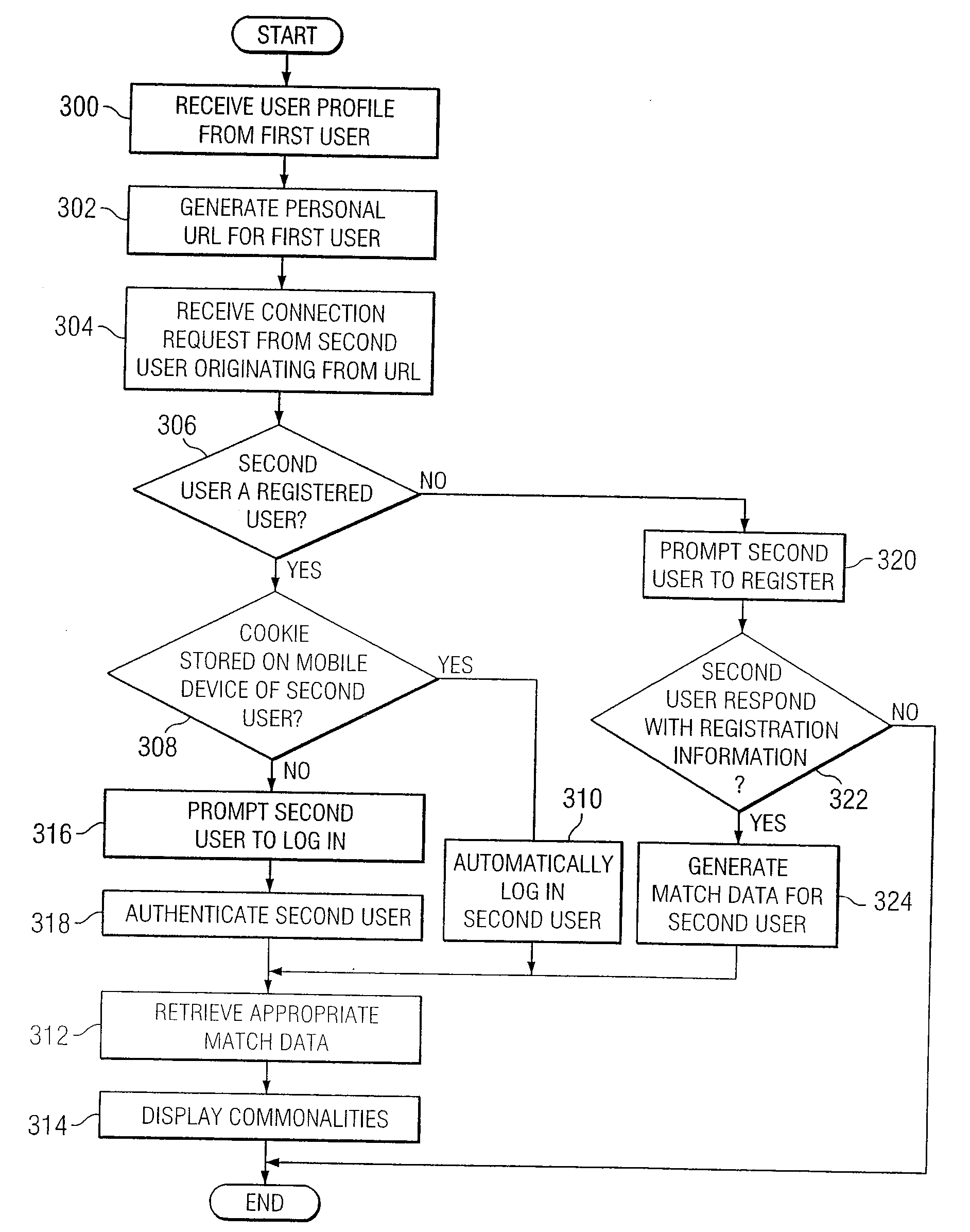
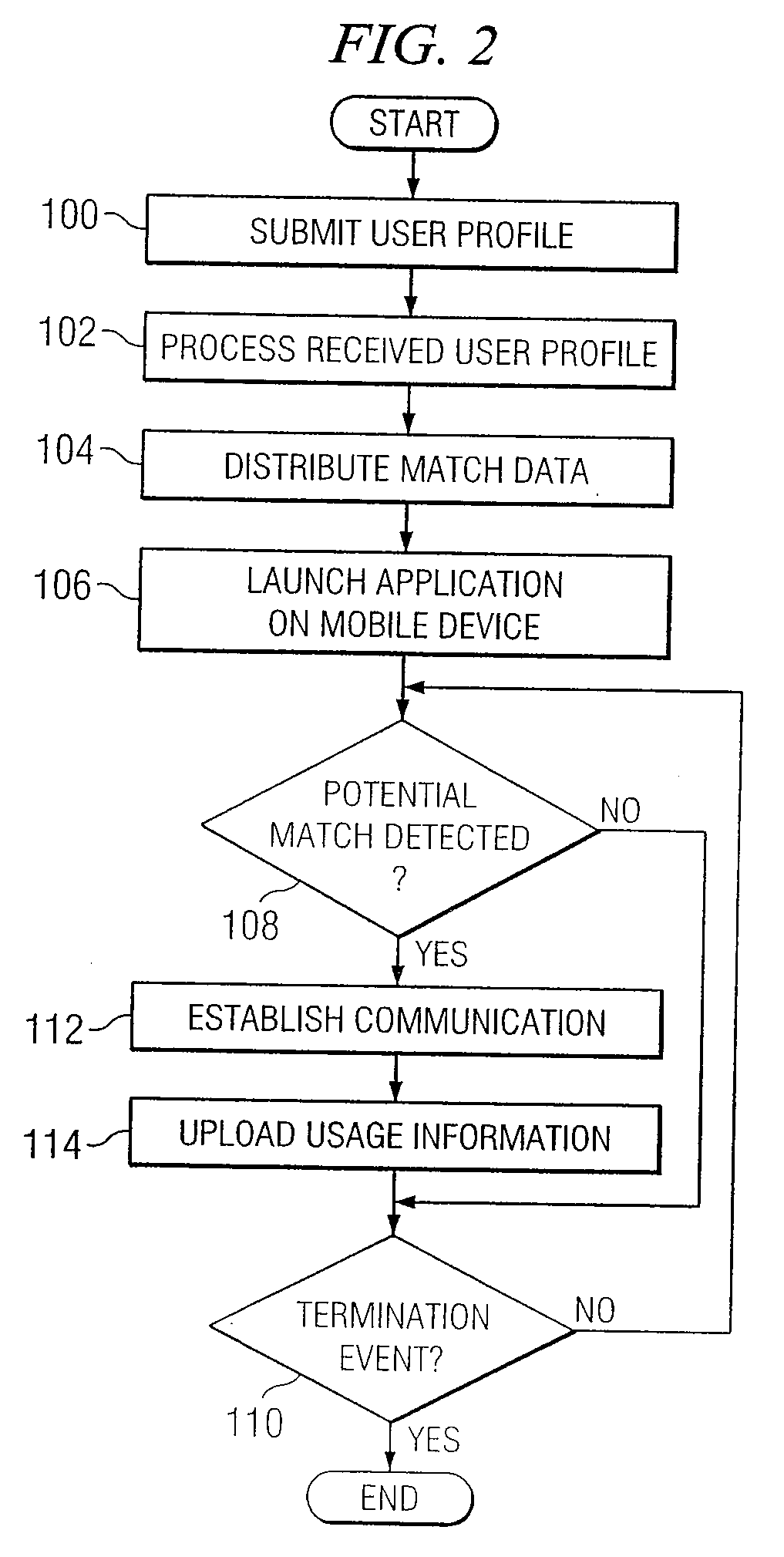
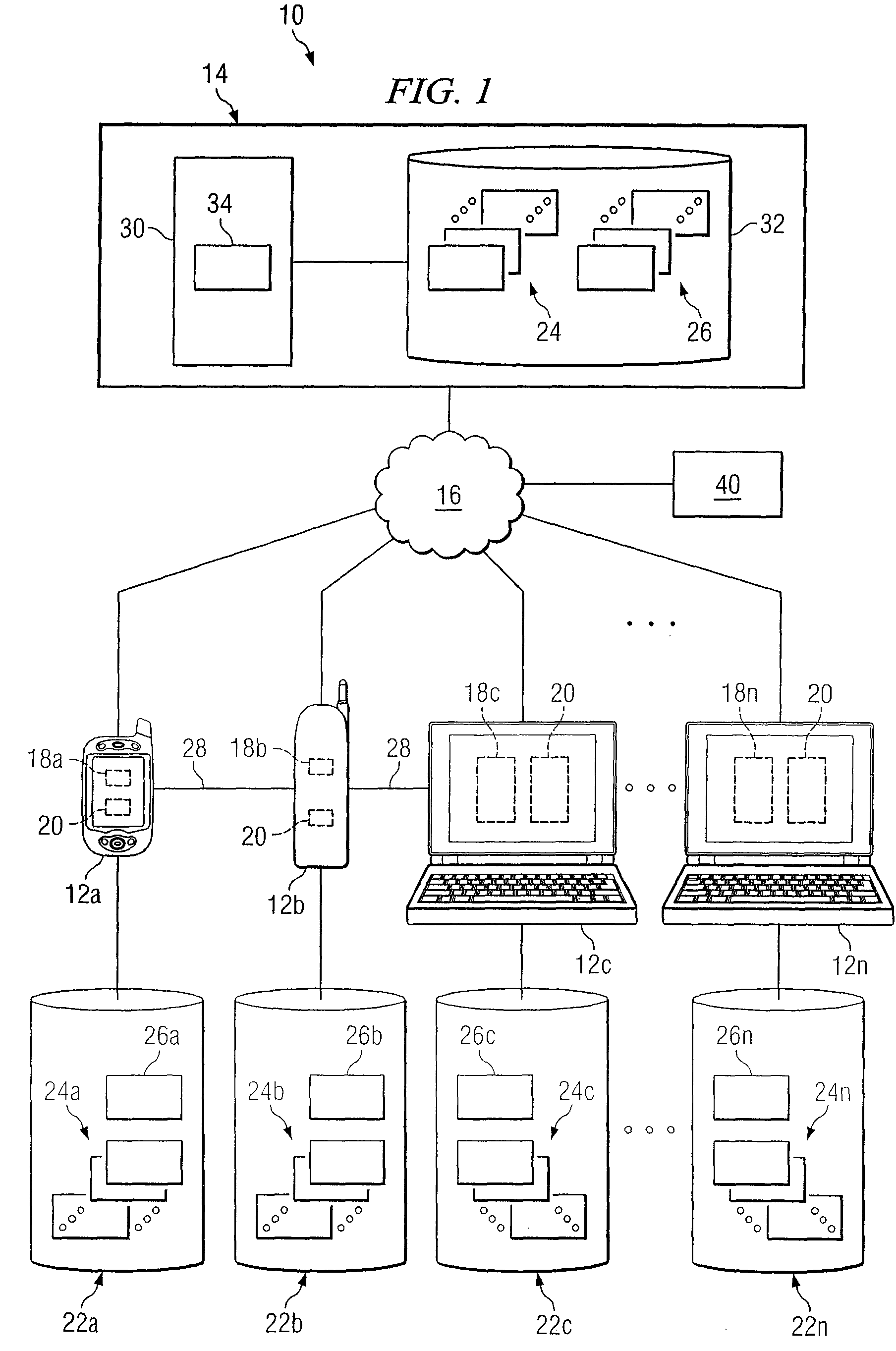
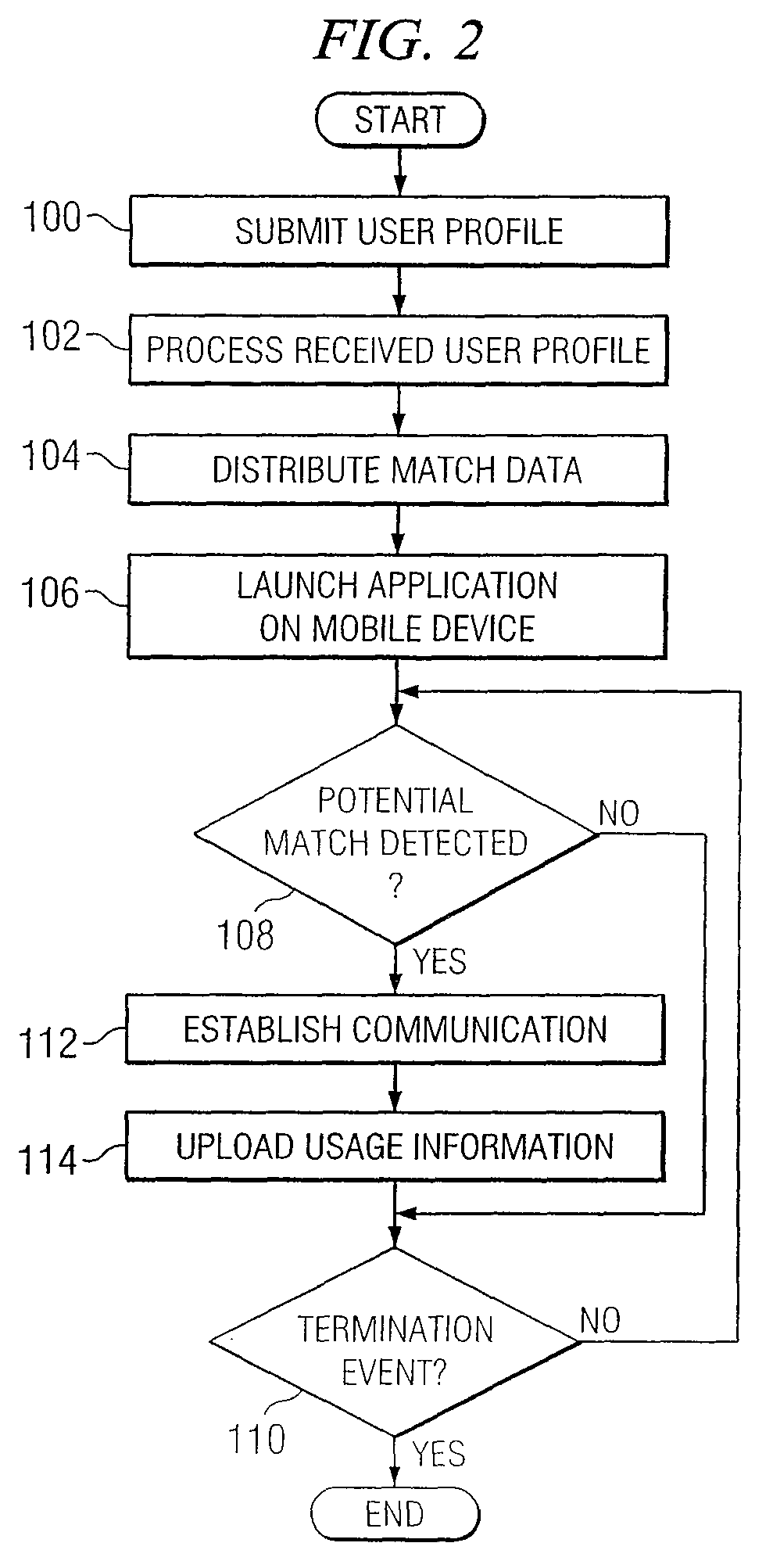
System and method for providing communication services to mobile device users incorporating proximity determination
InactiveUS20070030824A1Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedWeb data retrievalTelephonic communicationComputer networkMobile device
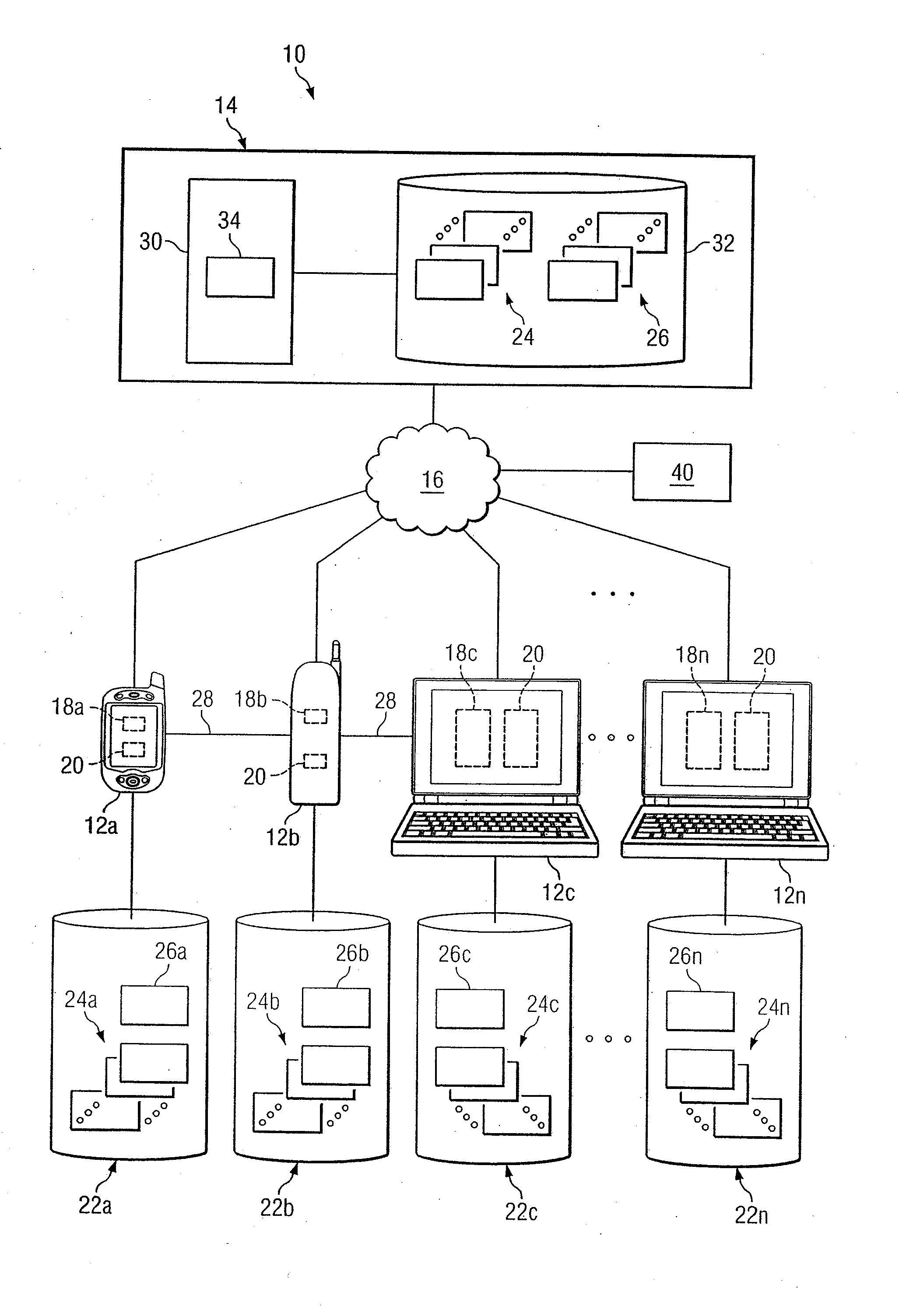
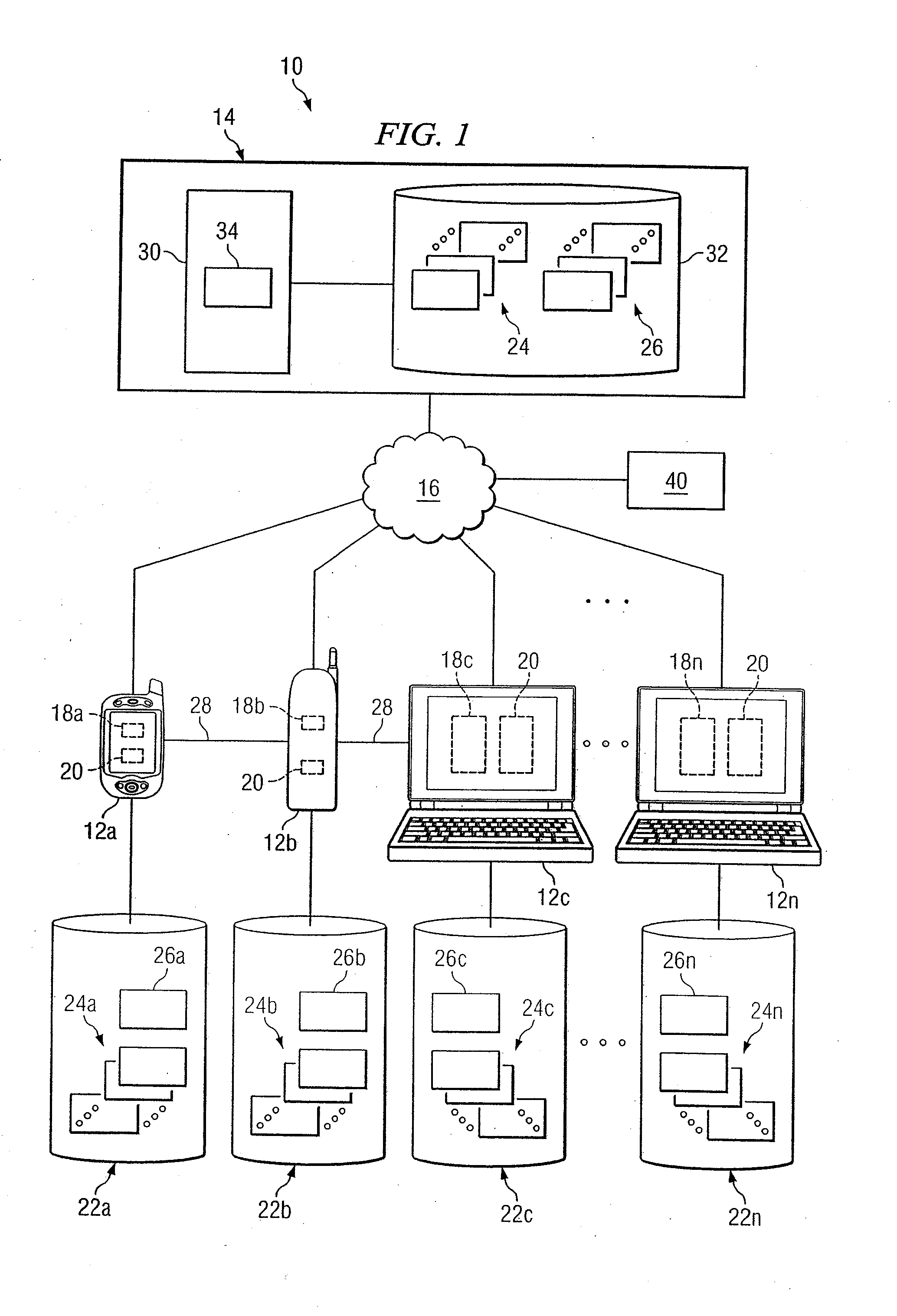
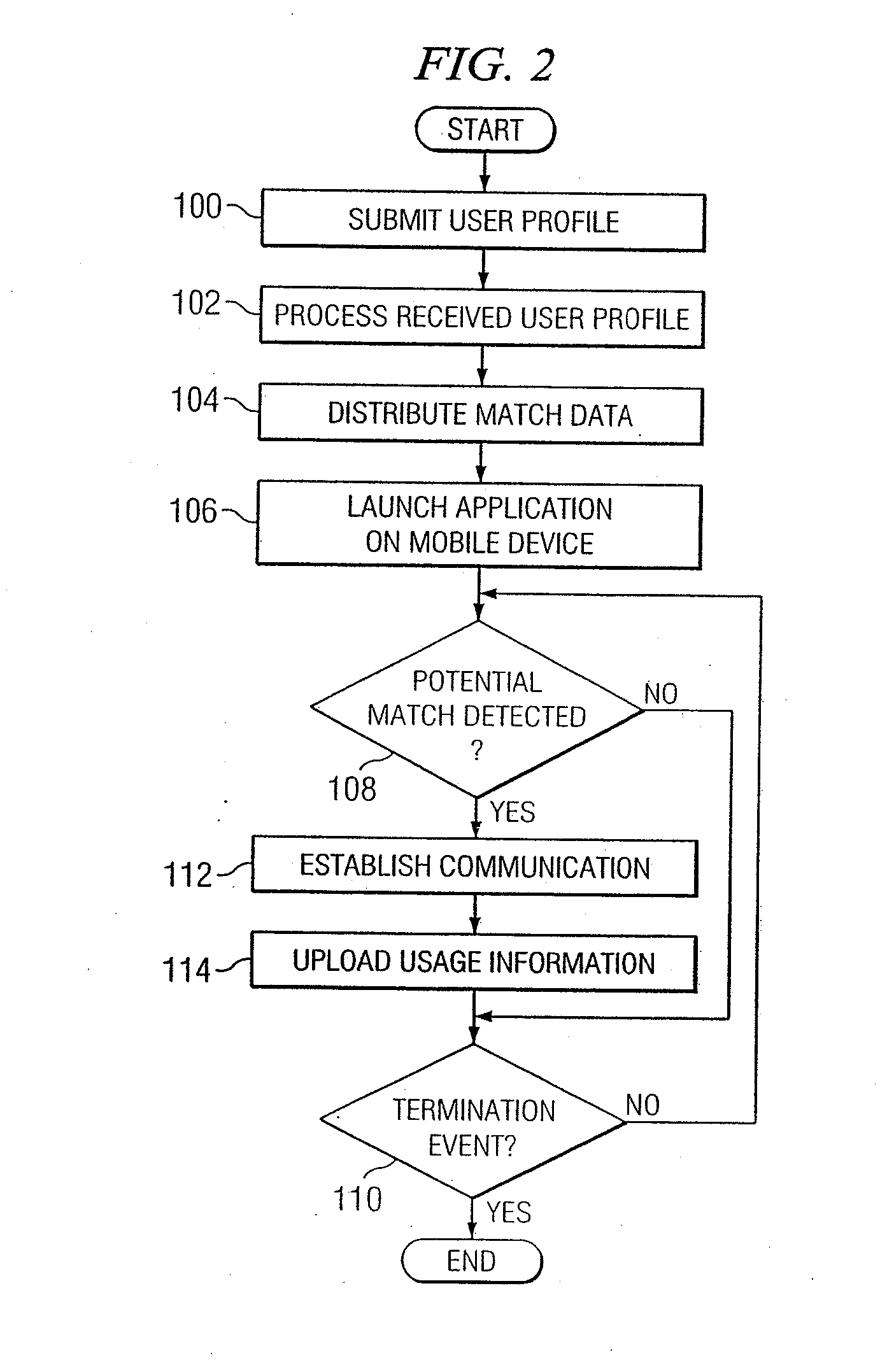
In certain embodiments, a method for proximity determination includes receiving one or more network identifiers, each associated with a corresponding network, from a first mobile device. The method further includes receiving one or more network identifiers, each associated with a corresponding network, from a second mobile device. The method further includes processing the network identifiers received from the first and second mobile devices to determine whether the first mobile device and the second mobile device are in proximity to one another.
Owner:JAMBO NETWORKS
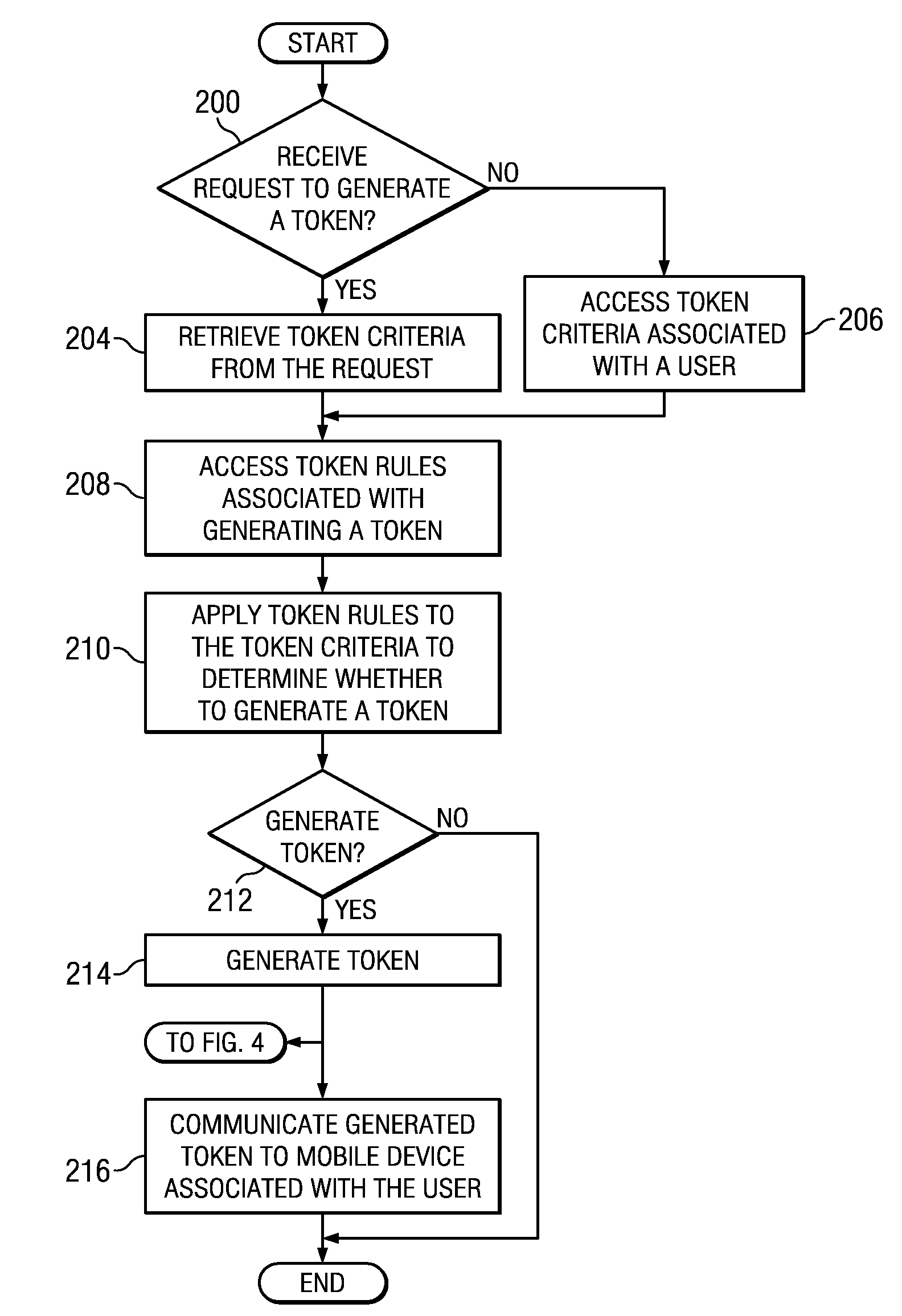
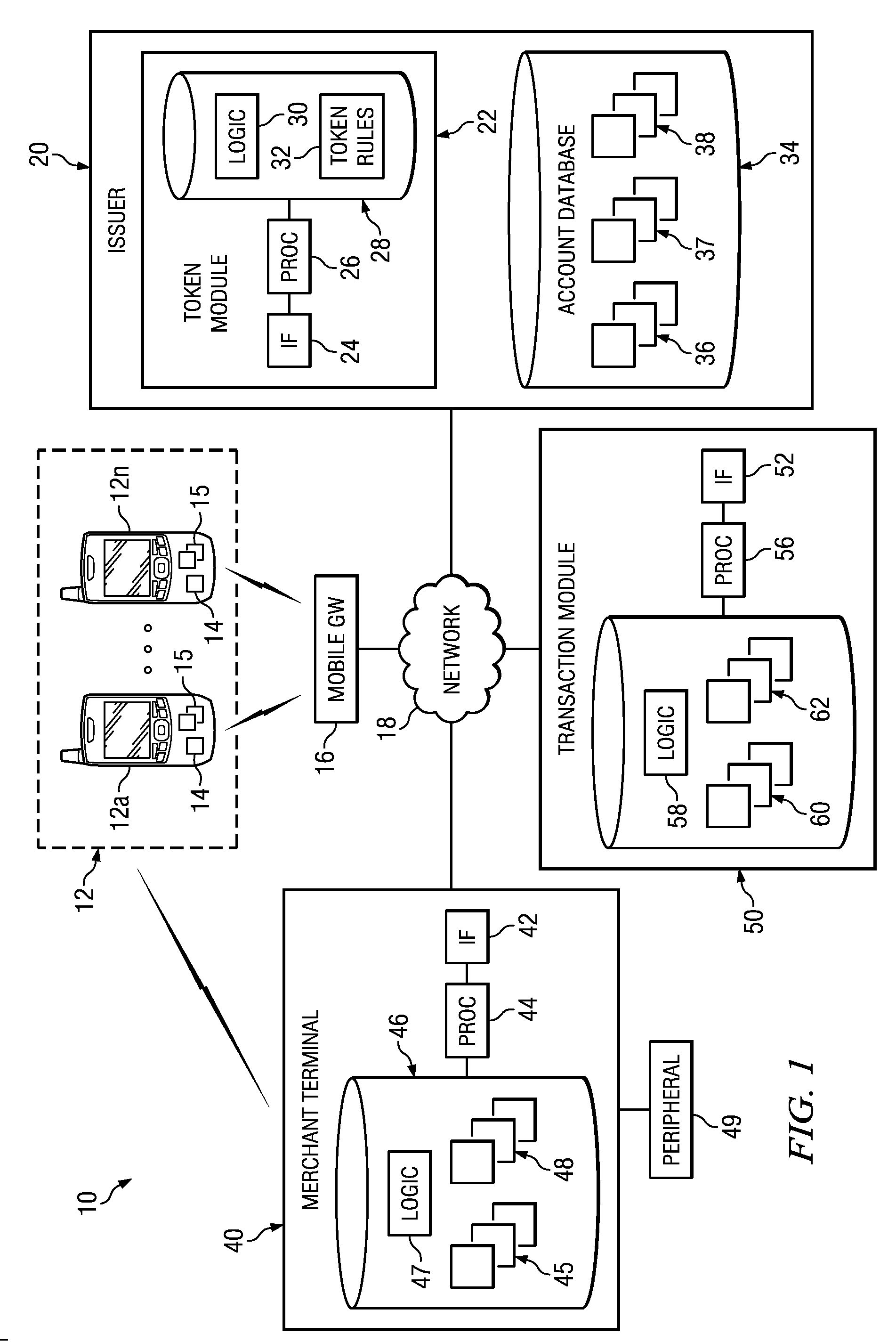
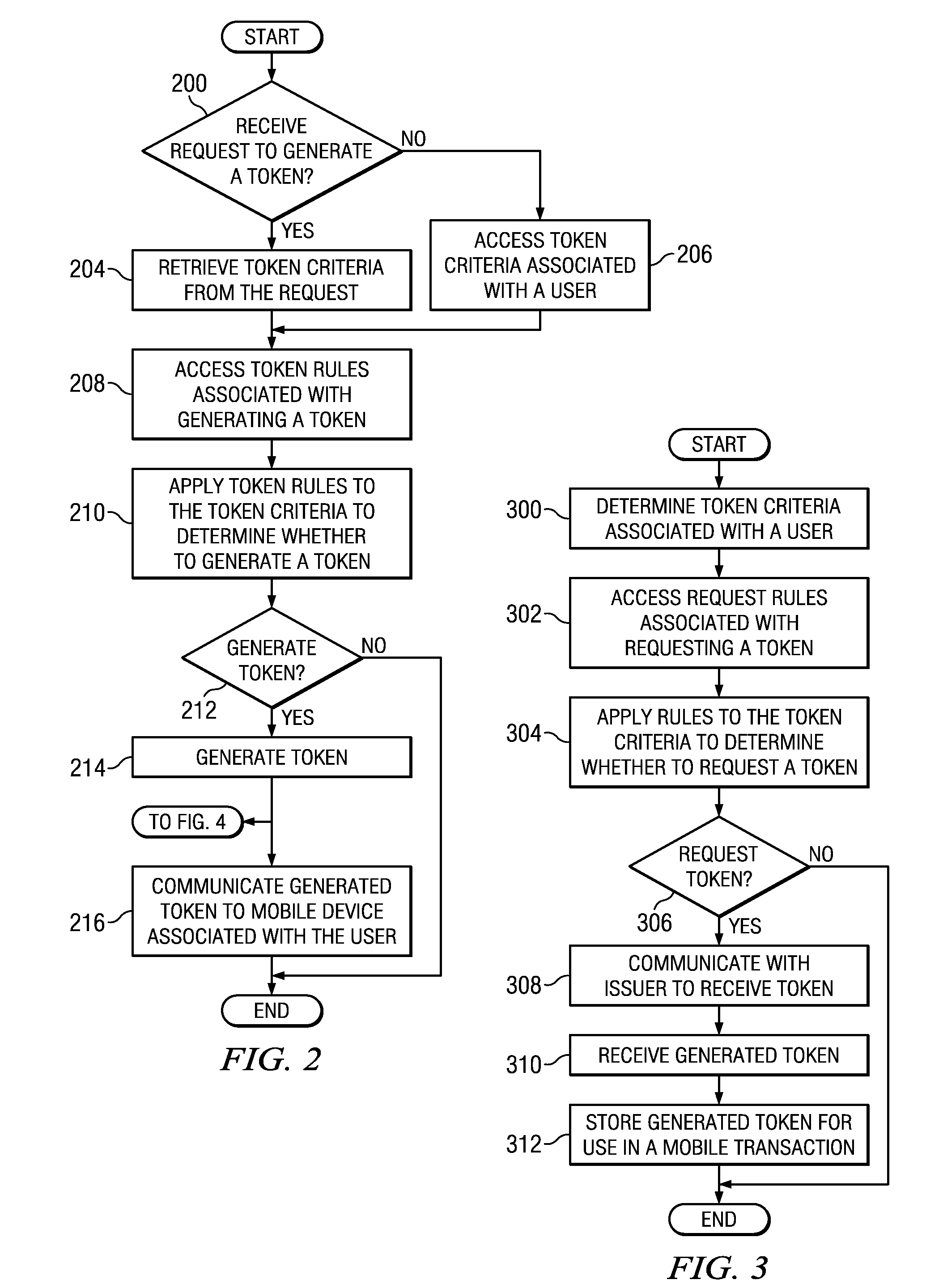
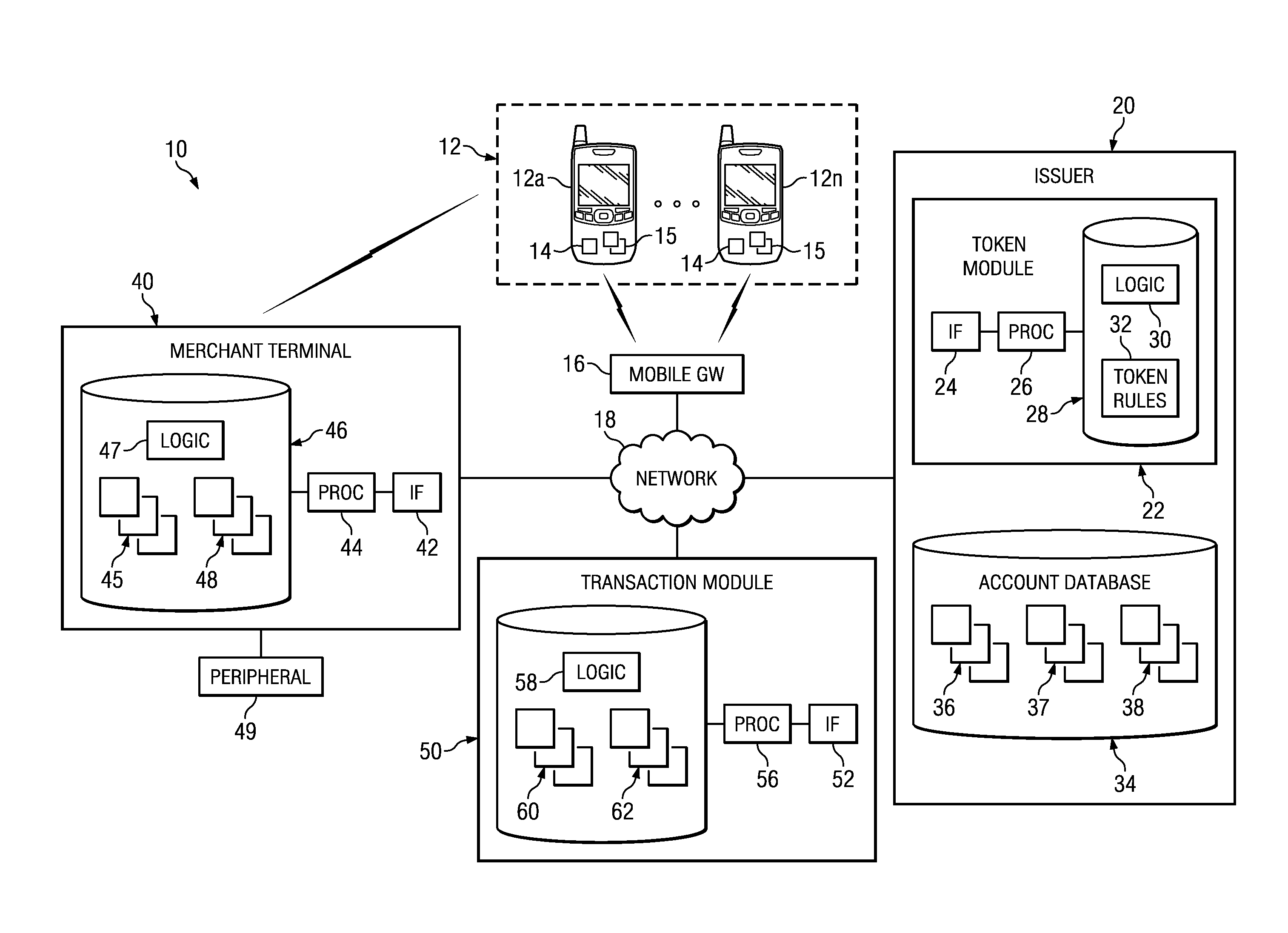
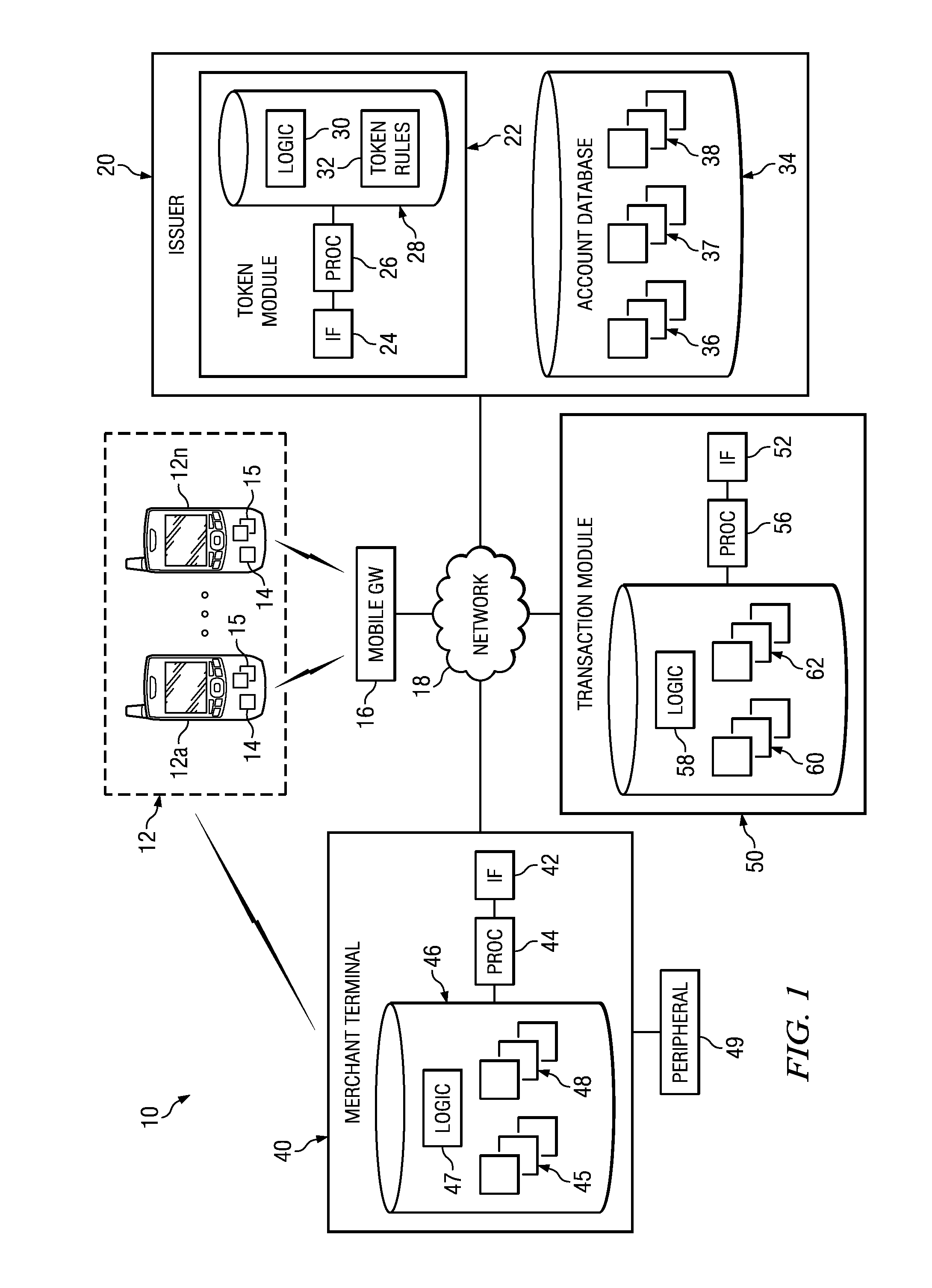
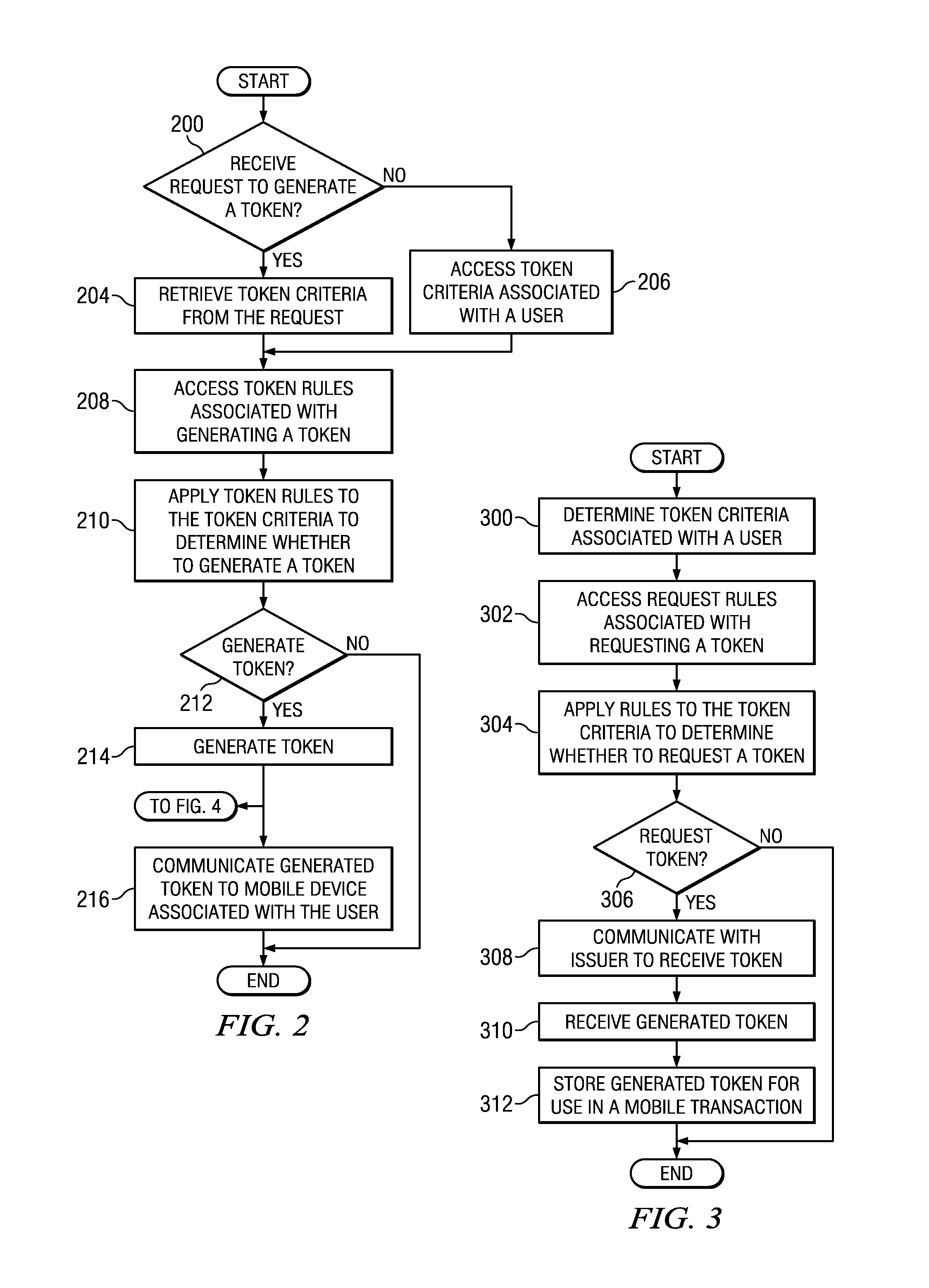
Implementing security measures for authorized tokens used in mobile transactions
ActiveUS20140025958A1Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedTransactions be reduced eliminatedUnauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringSecurity MeasureMobile transaction
Security measures for tokens comprise storing security rules associated with a generated token in a memory. A processor, communicatively coupled to the memory, accesses the security rules associated with the generated token and determines whether to encrypt the generated token by applying at least a portion of the security rules to the generated token. The processor encrypts the generated token. An interface, communicatively coupled to the processor, communicates the encrypted token to a mobile device associated with a user.
Owner:BANK OF AMERICA CORP
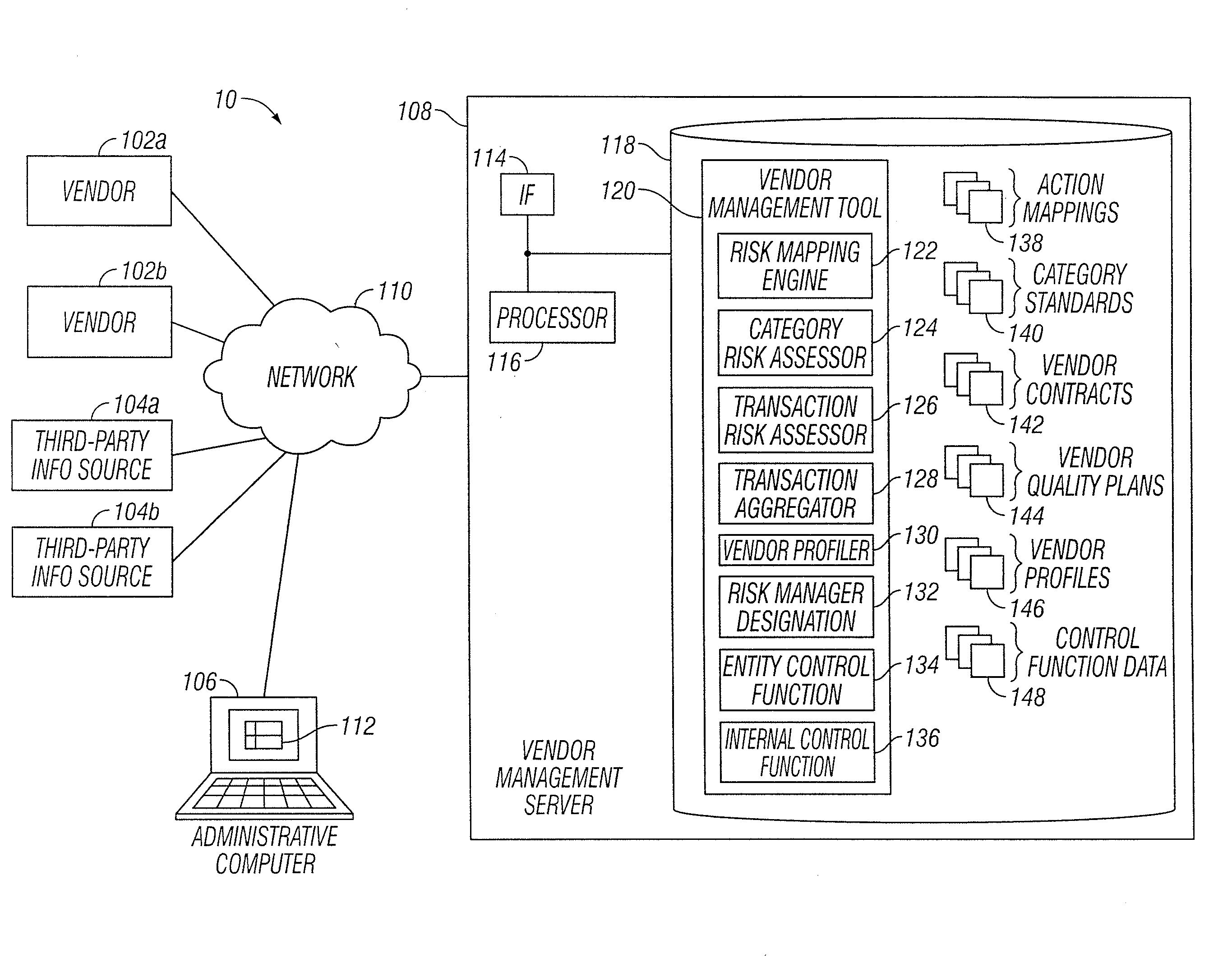
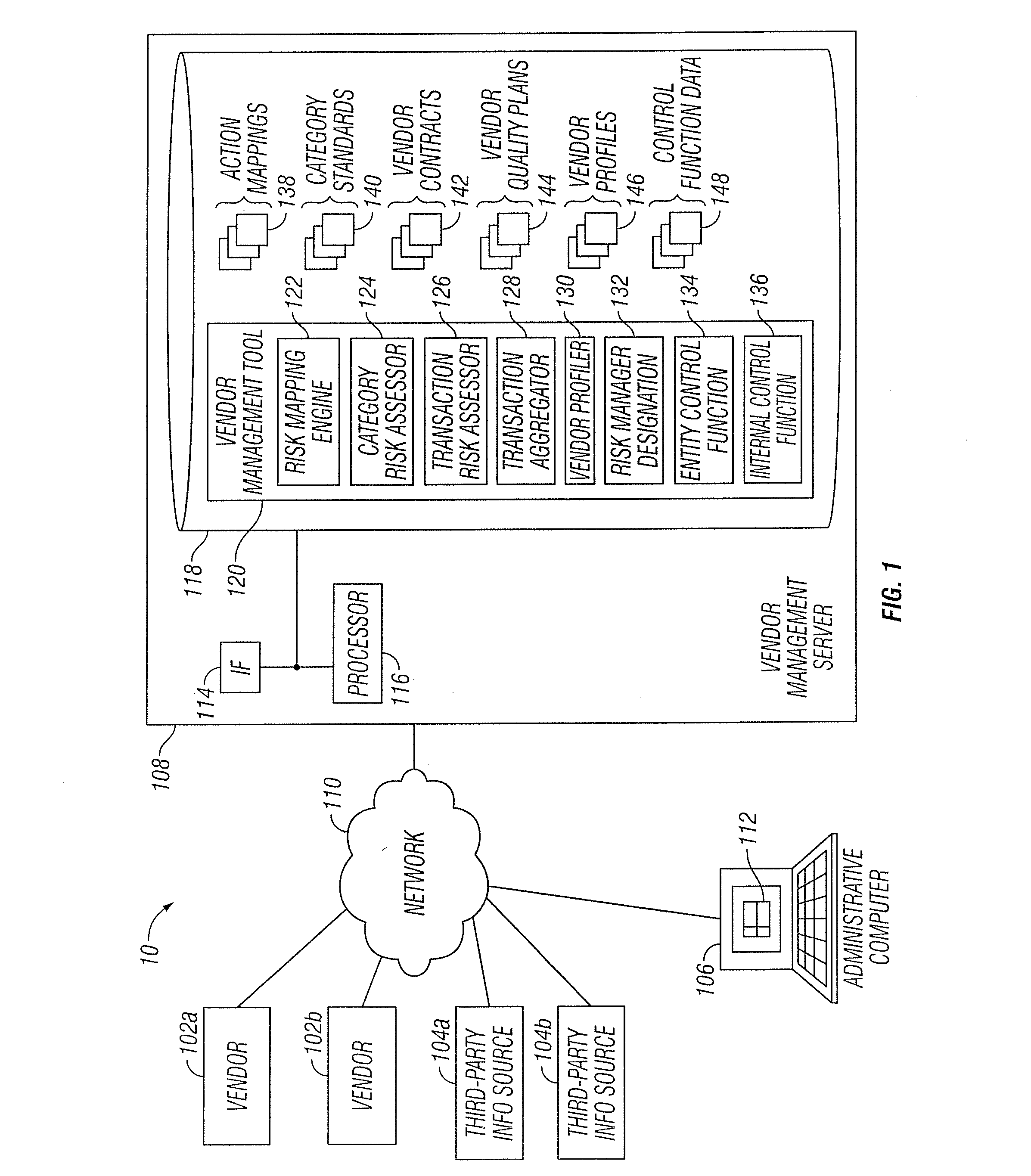
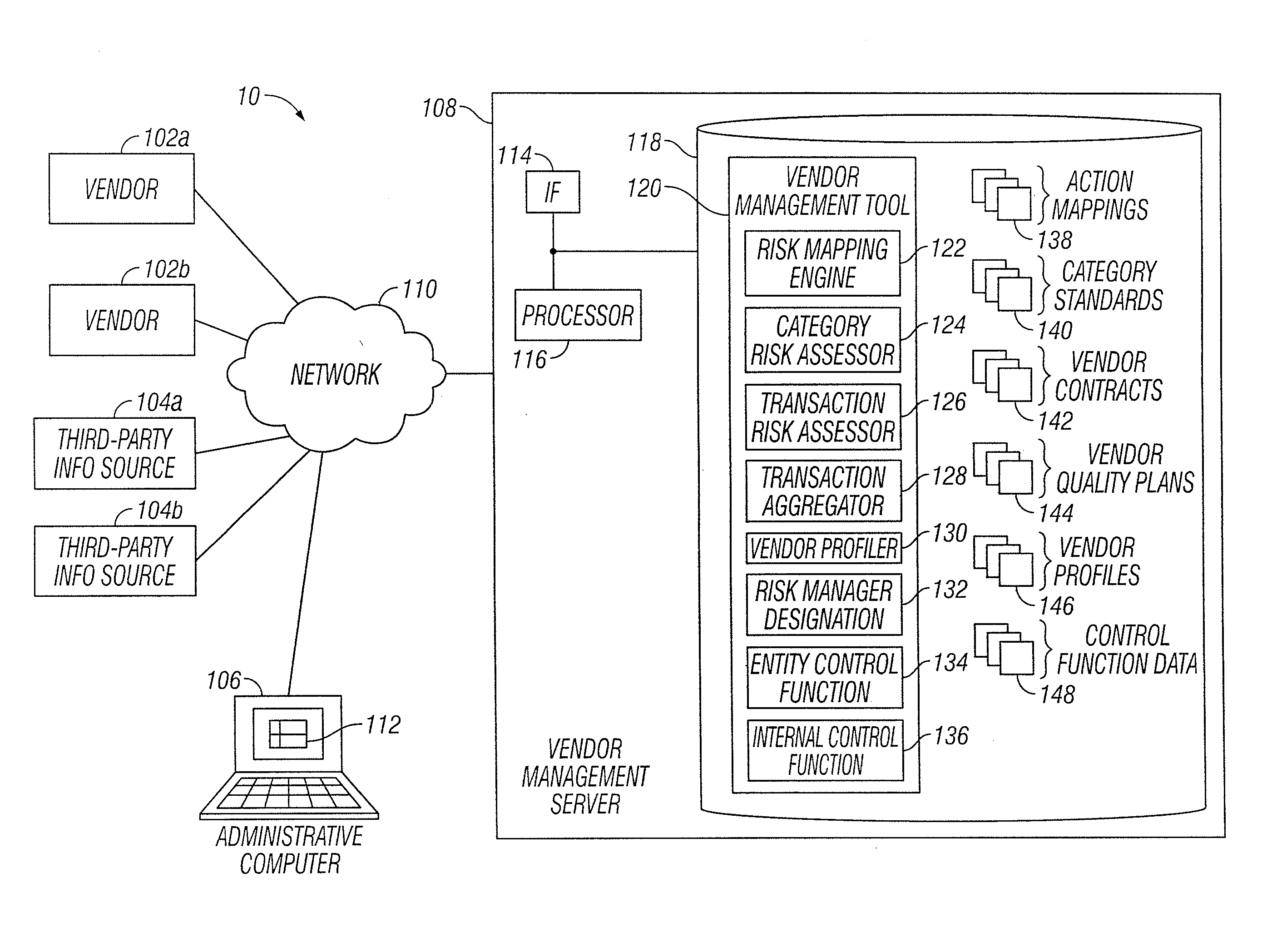
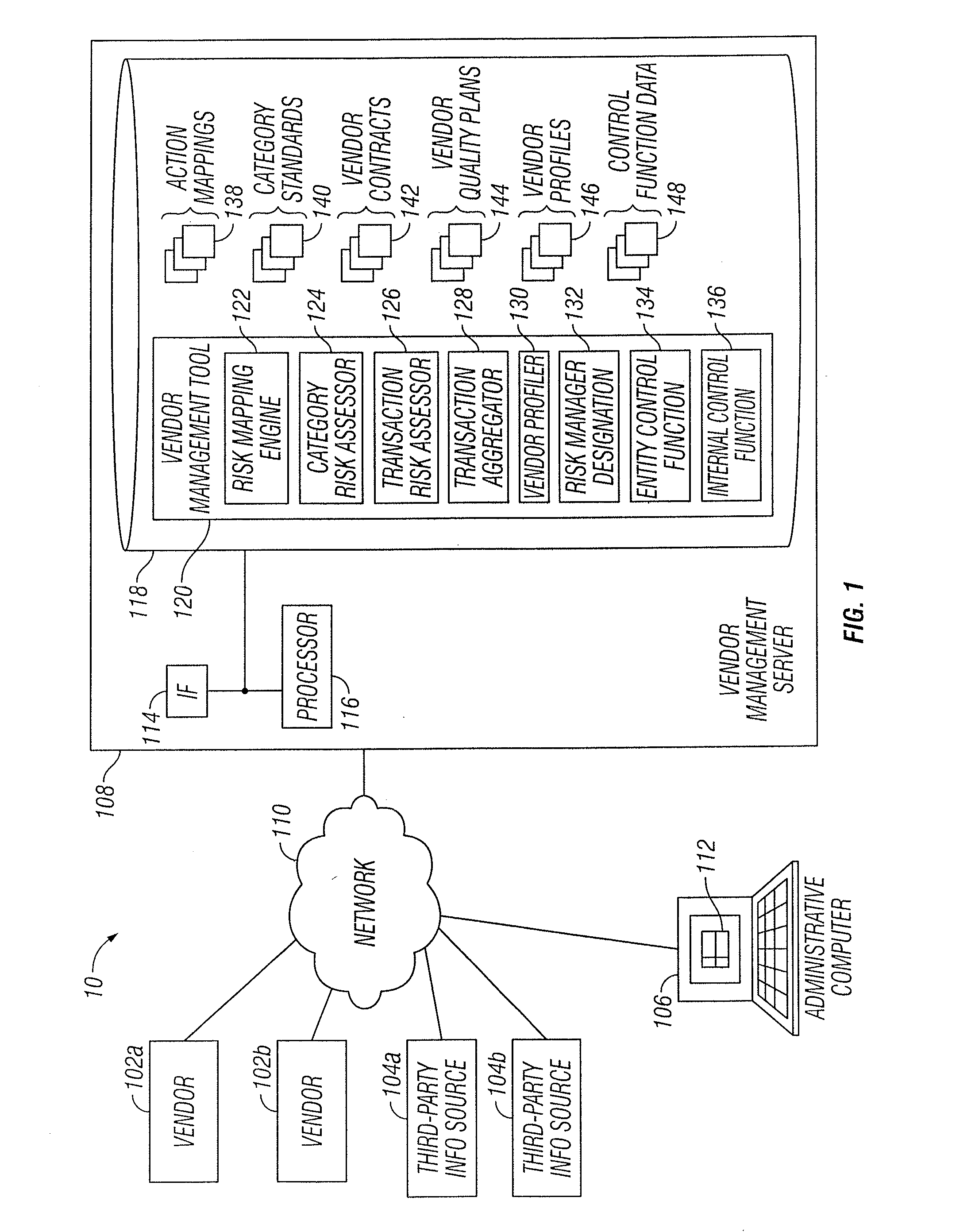
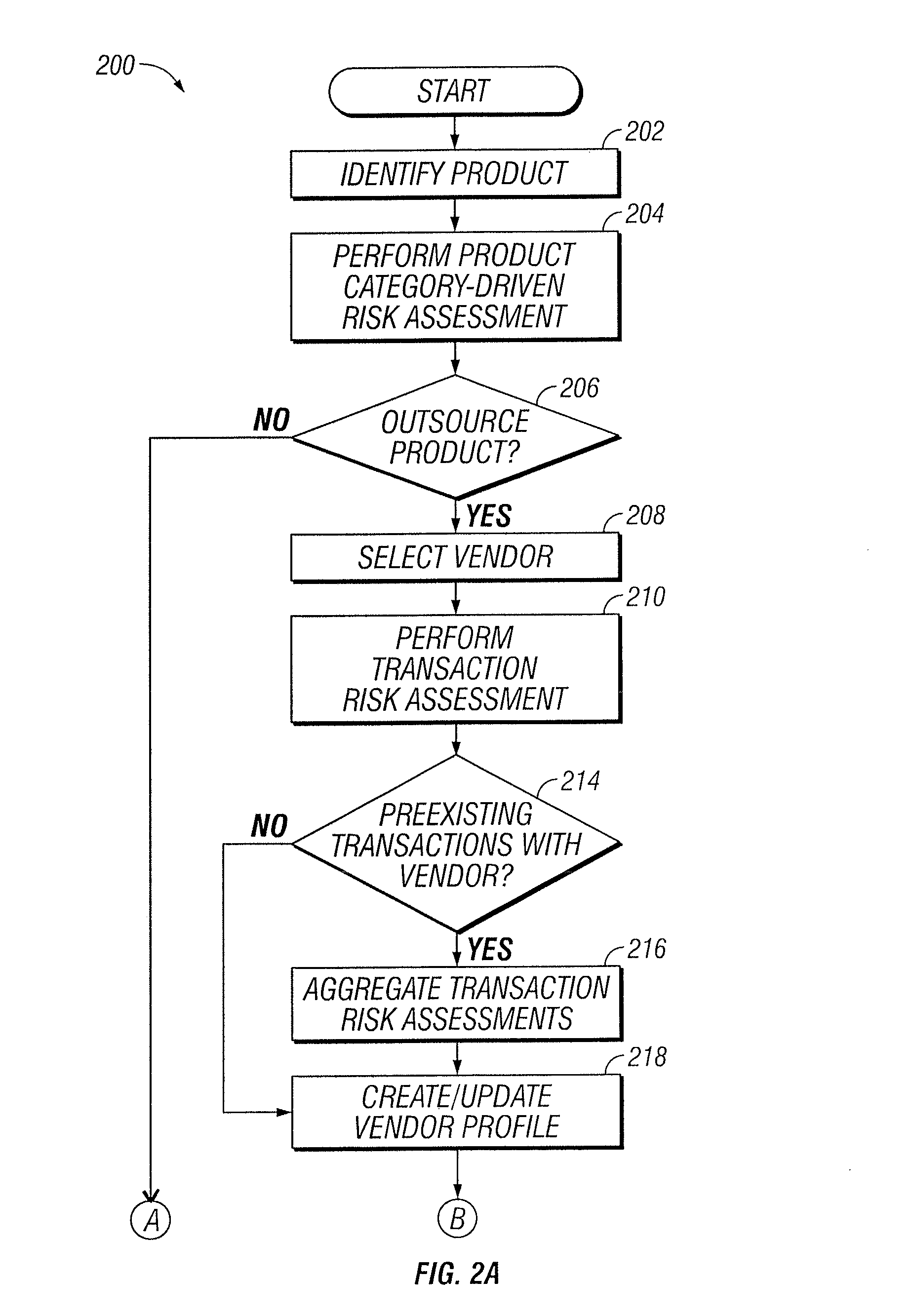
Vendor Management System
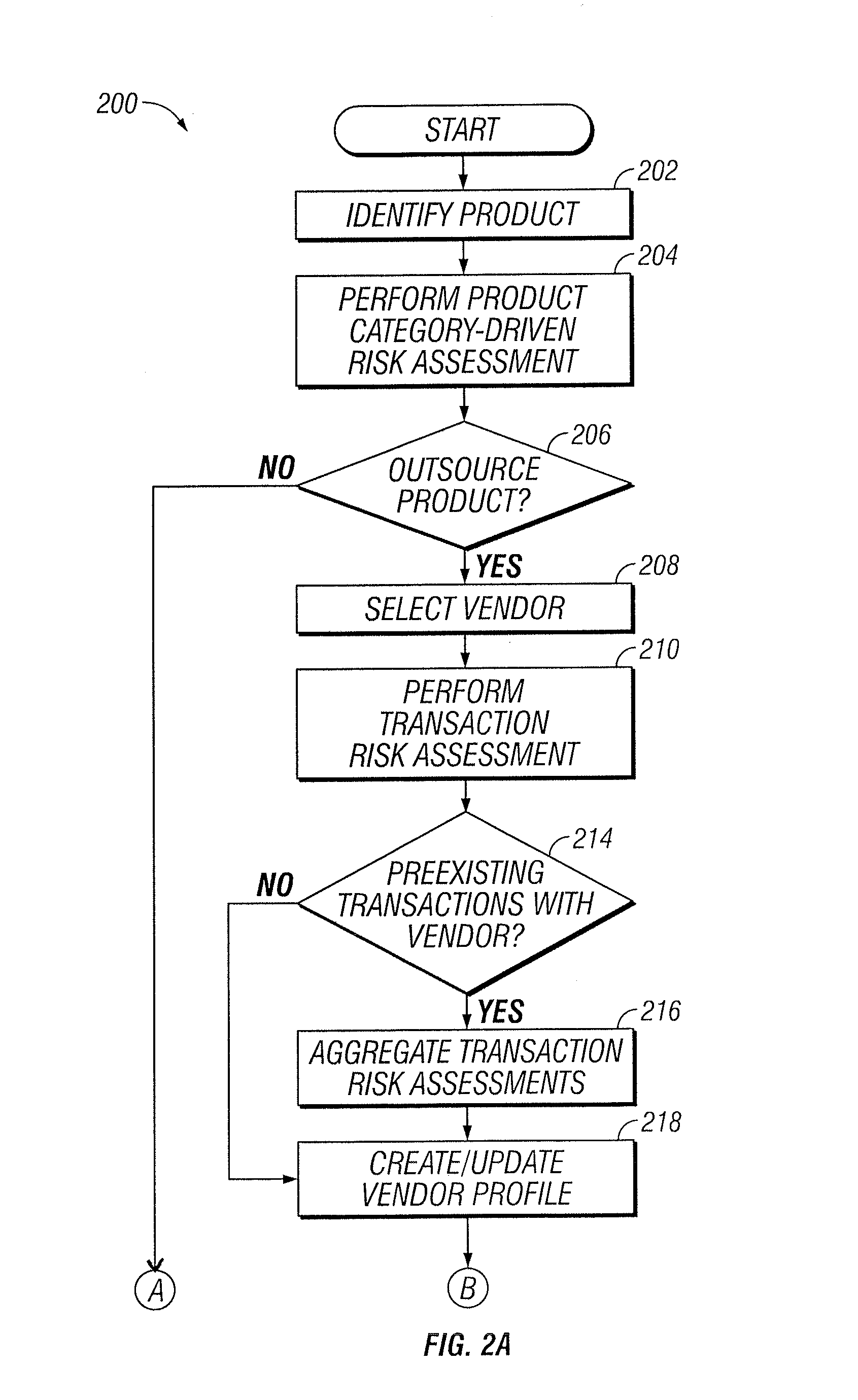
InactiveUS20150242778A1Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedProblems be reduced eliminatedFinanceResourcesDriving riskEngineering
Managing a vendor may comprise identifying a product to be supplied to an entity. Risk elements associated with the product may be determined by performing a product category-driven risk assessment. A transaction level risk assessment is performed for one or more vendors proposed to supply the product to the entity. At least one management action is determined for reducing risk for a risk element of the plurality of risk elements associated with supplying the product to the entity by a selected vendor from a group comprising the one or more vendors proposed to the supply the product to the entity, wherein the at least one management action is determined according to results of the product category-driven risk assessment and the transaction level risk assessment for the selected entity. A vendor level quality plan for the selected vendor is created that comprises the at least one management action.
Owner:BANK OF AMERICA CORP
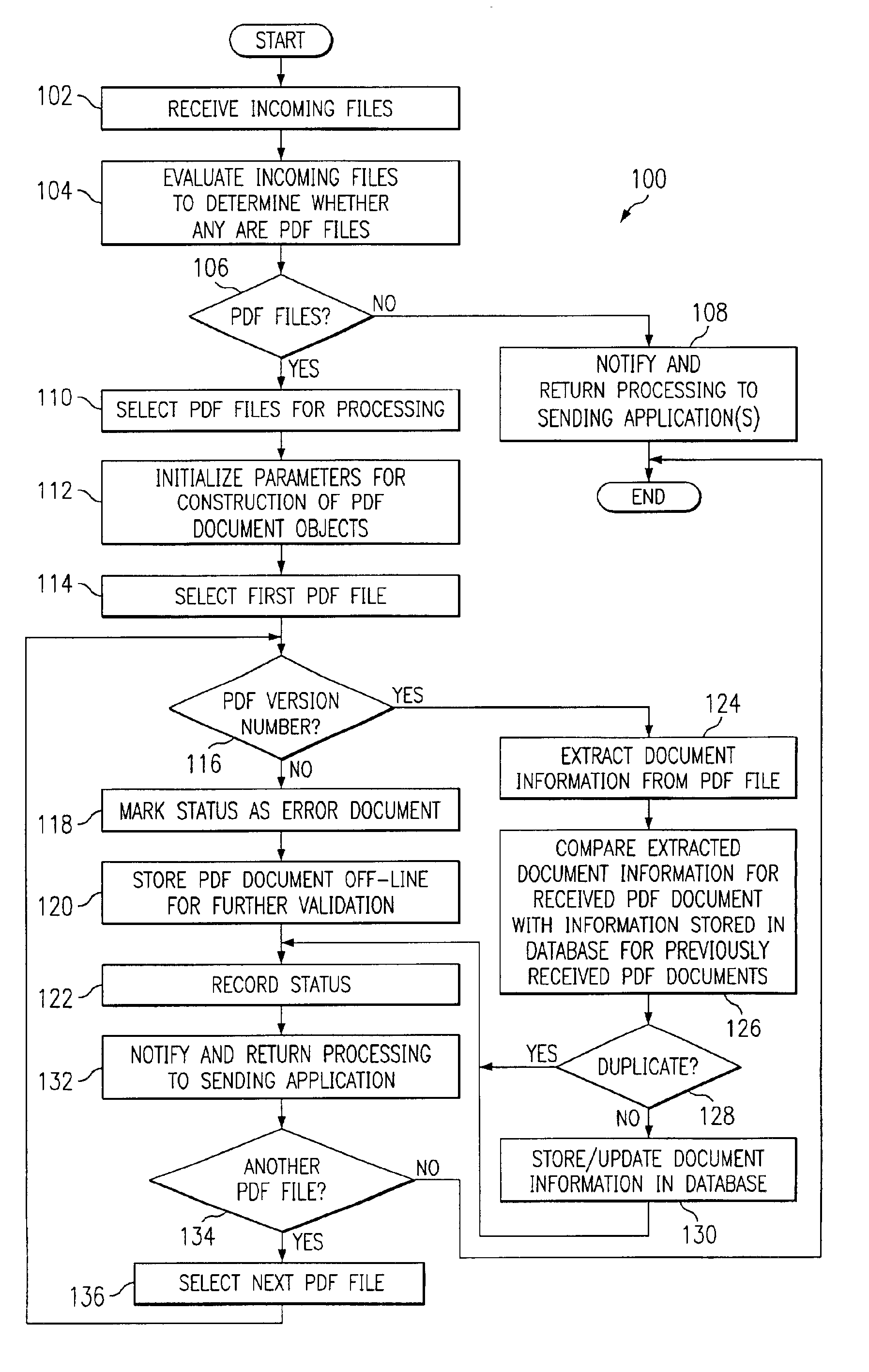
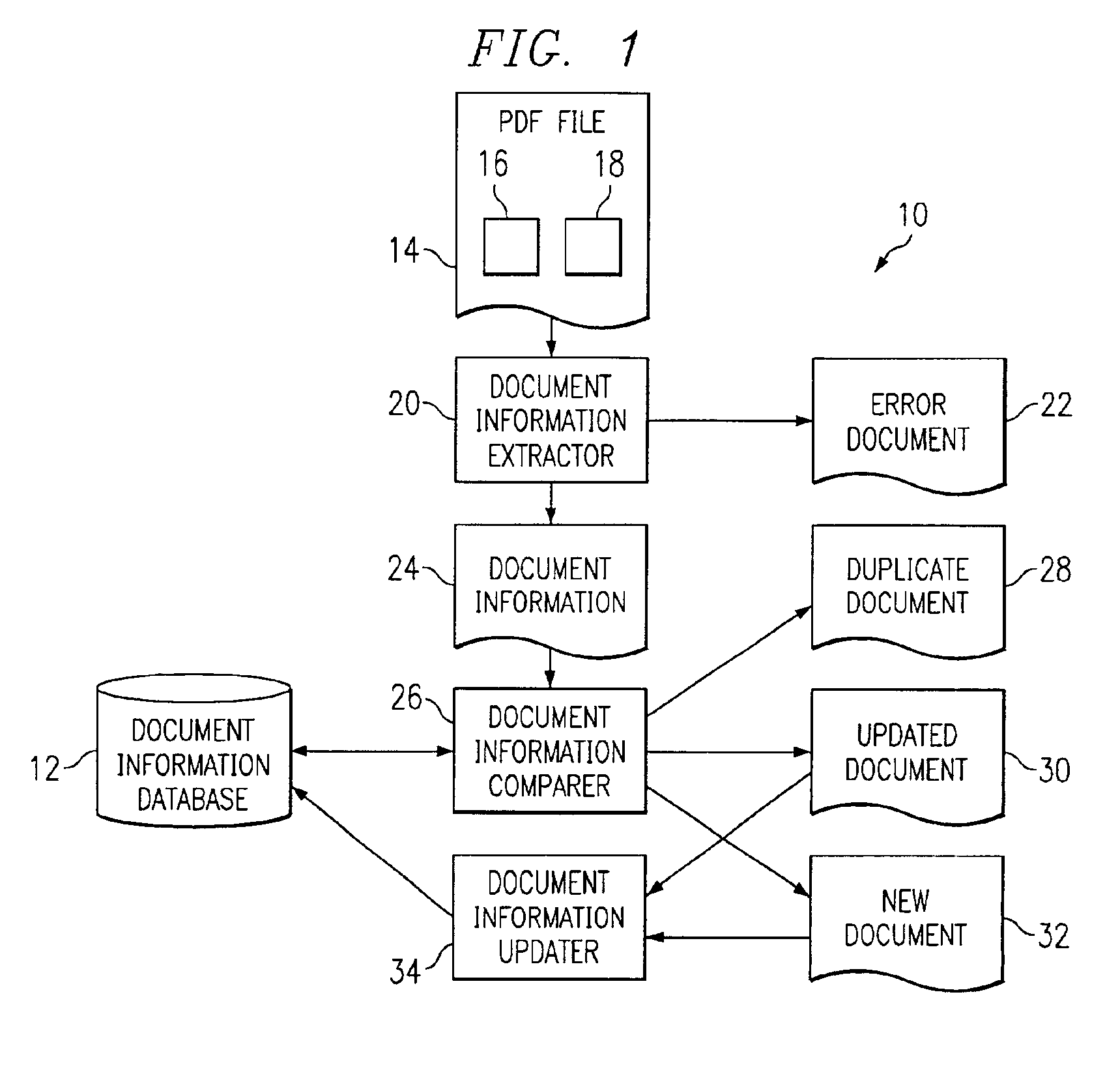
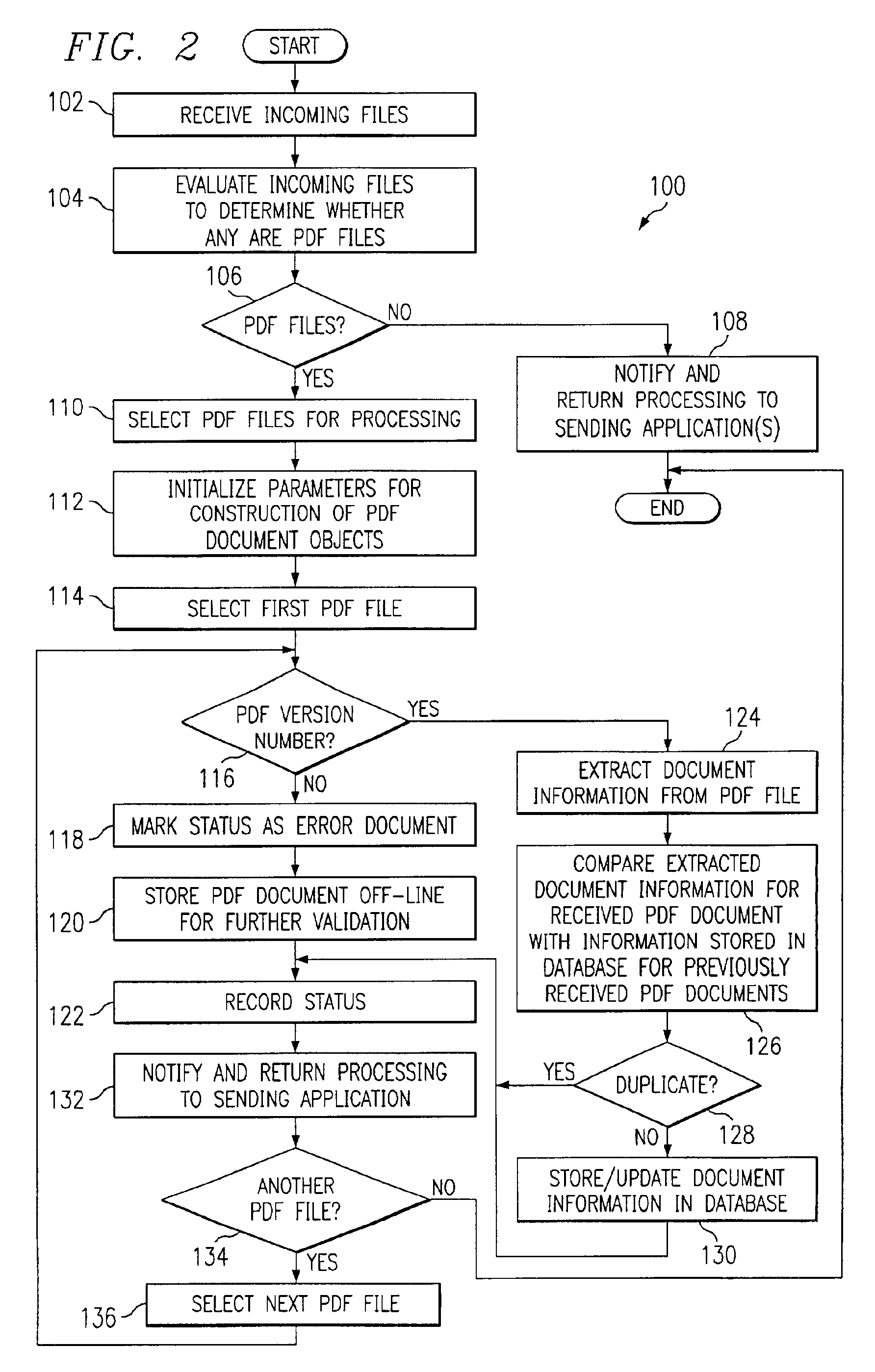
Computer-implemented PDF document management
InactiveUS6895550B2Shorten the timeReduce effortDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsExternal applicationDocument preparation
A PDF file is received from an external application and key information from the PDF file, concerning a PDF document contained in the PDF file, is extracted. The extracted key information is compared with analogous reference information stored for previously received PDF documents to determine a status for the received PDF document, which is provided to the external application from which the PDF file was received. The received PDF document is a duplicate if all the extracted key information matches analogous reference information, is an updated document if certain but not all the extracted key information matches analogous reference information, or is a new document if at least certain extracted key information does not match analogous reference information. If the PDF document is a duplicate document, processing of the PDF file is returned to the application without storing any extracted key information as reference information. If the PDF document is an updated document, certain extracted key information is stored to update the reference information and processing of the PDF file is returned to the application. If the PDF document is new, all extracted key information is stored as reference information and processing of the PDF file is returned to the application.
Owner:JDA SOFTWARE GROUP
Mobile transactions using authorized tokens
InactiveUS20140025581A1Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedTransactions be reduced eliminatedPayment protocolsComputer securityMobile station
Conducting mobile transactions comprises determining, using a processor, whether a network is available to facilitate a mobile transaction. An interface, communicatively coupled to the processor, receives an encrypted token from a mobile device without using the network if the network is not available. The processor is further operable to process the encrypted token to complete the mobile transaction.
Owner:BANK OF AMERICA CORP
Risk Assessment On A Transaction Level
InactiveUS20150242858A1Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedRisk be reduced eliminatedFinanceBuying/selling/leasing transactionsData scienceHealth risk assessment
Assessing risk associated with a transaction may comprise identifying a potential vendor for supplying a product to an entity in a transaction. A response to one or more of a first plurality of questions for measuring risk to the entity associated with engaging the potential vendor to supply the product in the transaction is determined. Responsive to determining the response to the one or more of the first plurality of questions, a dynamically-triggered question for measuring risk to the entity associated with engaging the potential vendor to supply the product in the transaction is identified. A response to the dynamically-triggered question is determined. A provision for insertion into a contract associated with the transaction is determined according to at least one of the response determined for the one or more of the first plurality of questions and the response determined for the dynamically-triggered question.
Owner:BANK OF AMERICA CORP
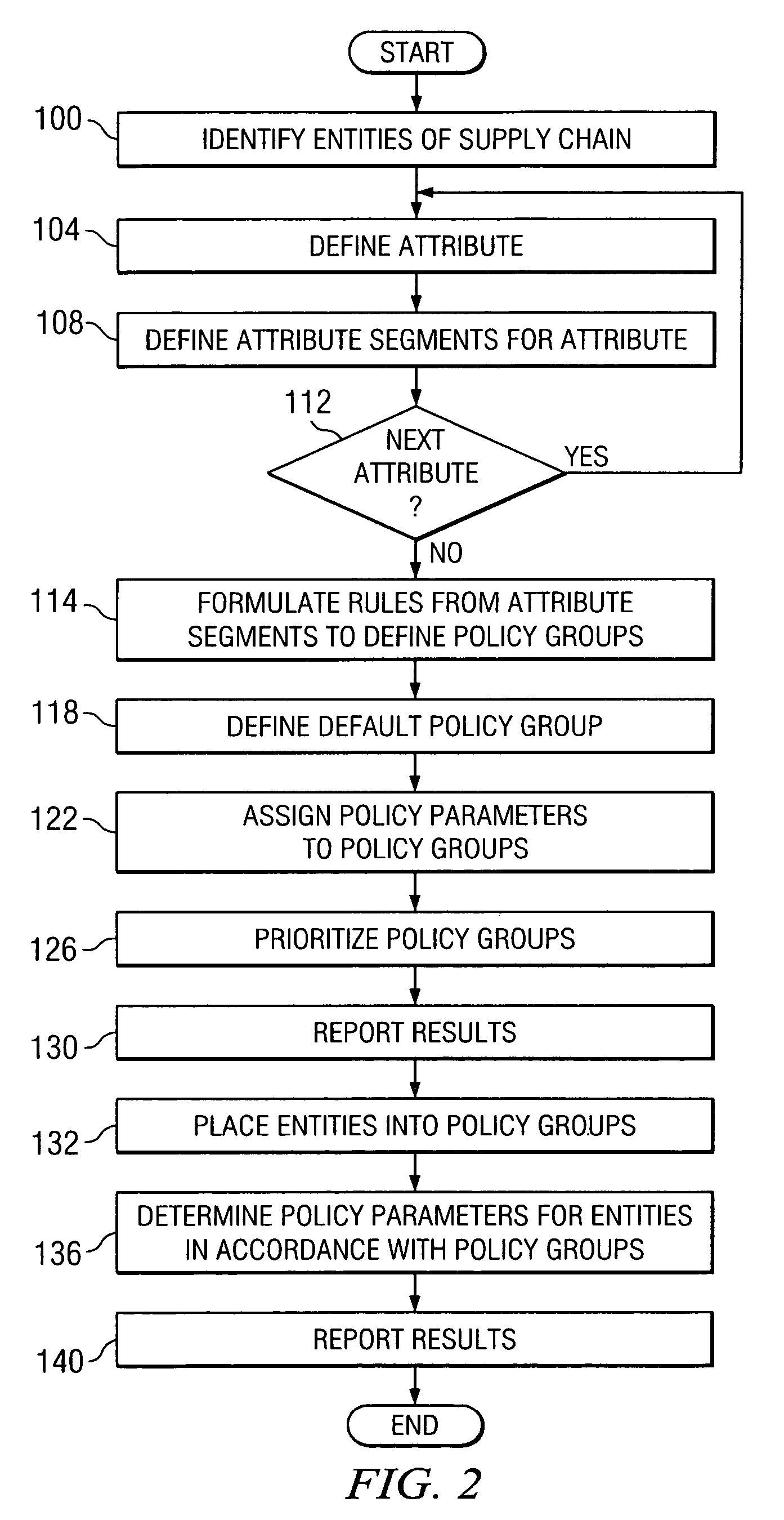
Determining a policy parameter for an entity of a supply chain
InactiveUS7523483B2Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedEffective and efficient selectionComputer security arrangementsResourcesData mining
Owner:BLUE YONDER GRP INC
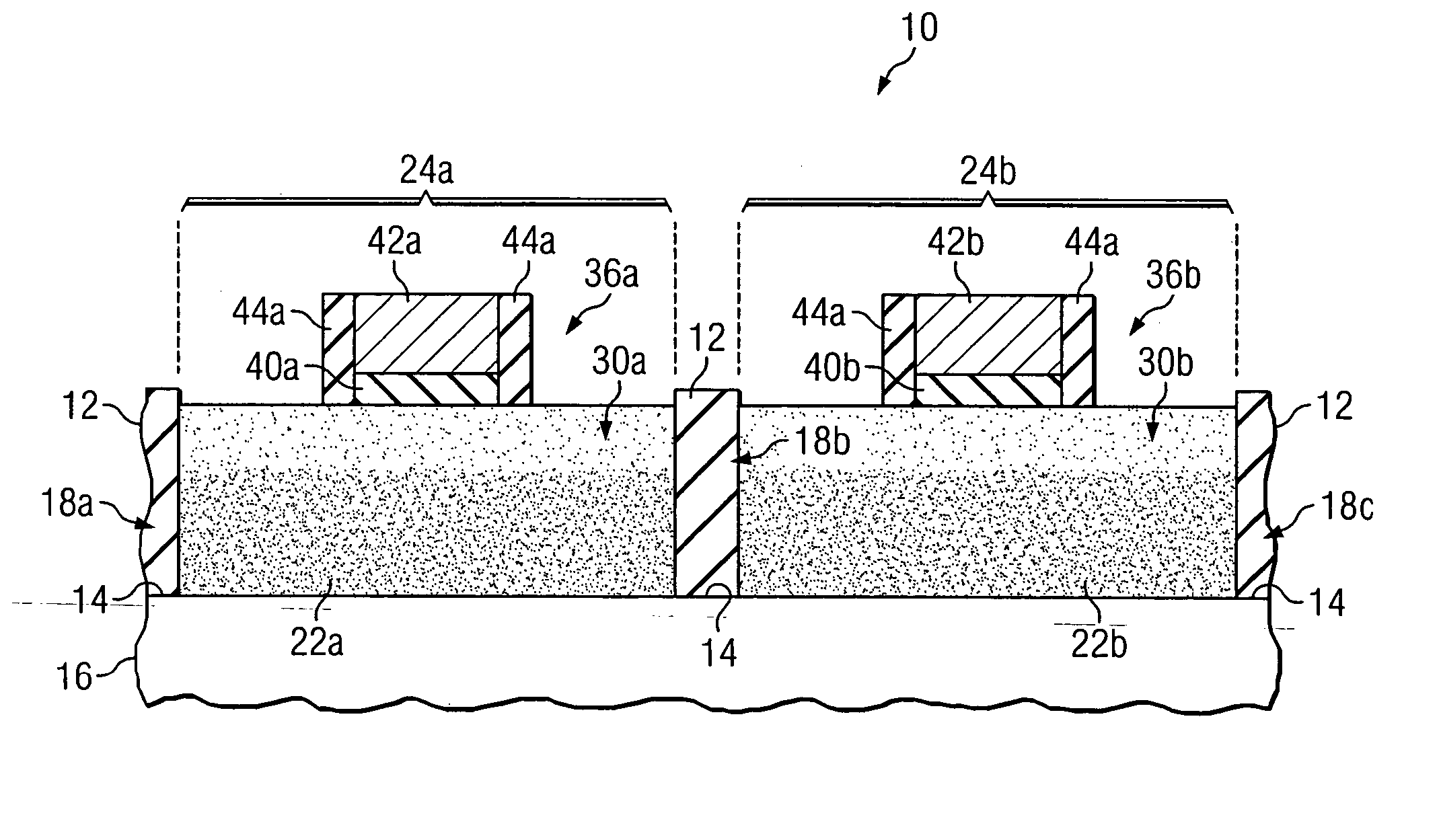
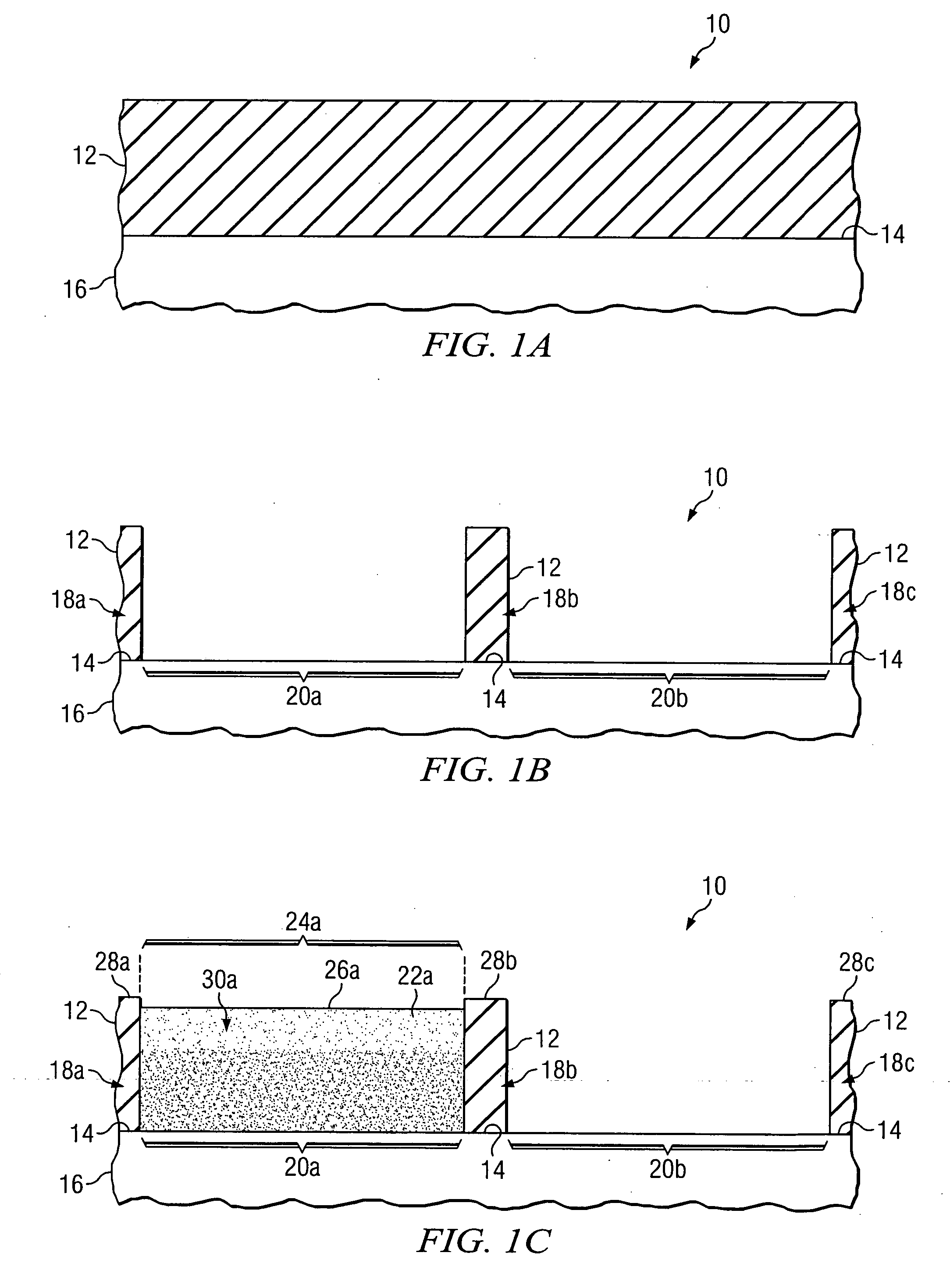
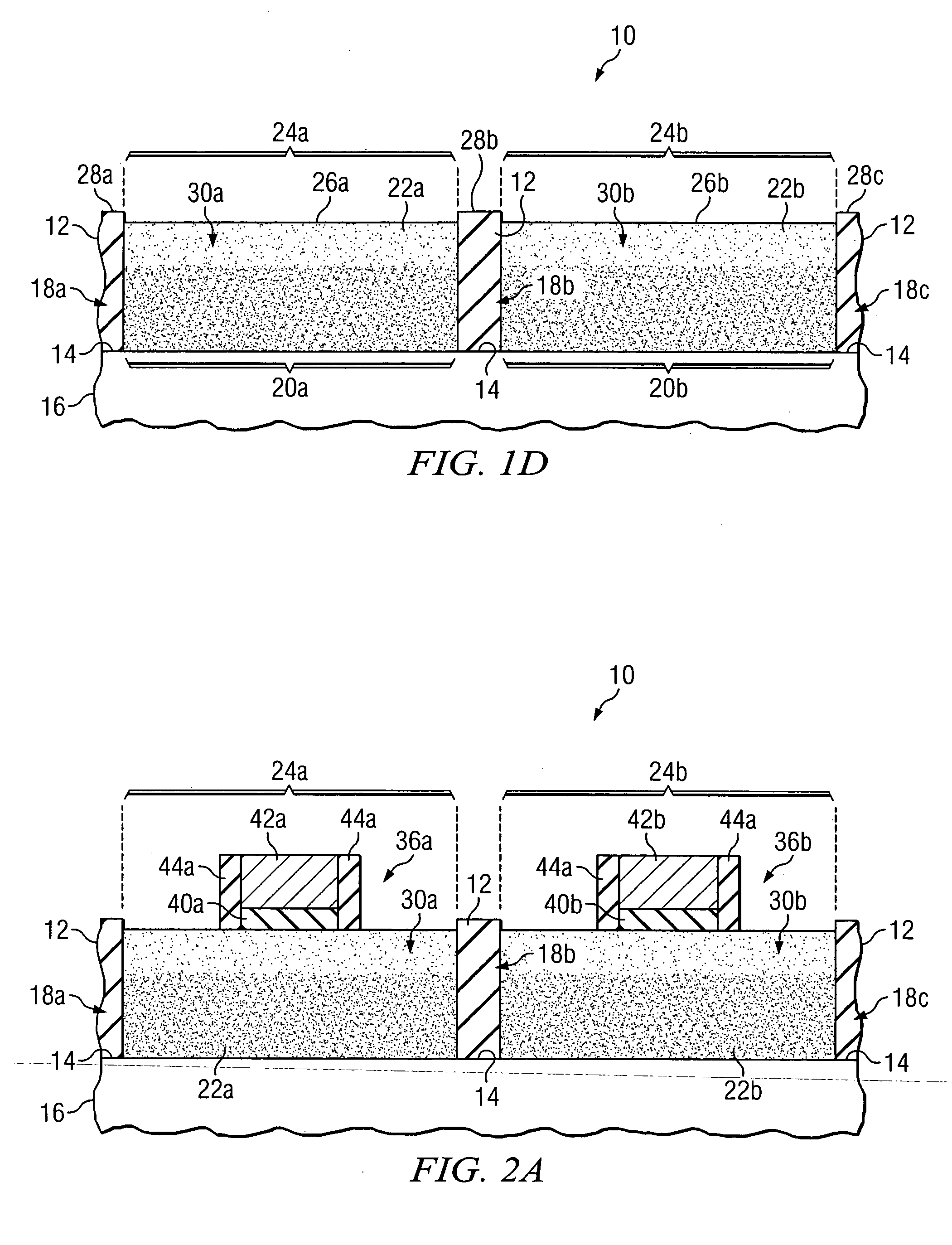
Forming a semiconductor structure in manufacturing a semiconductor device using one or more epitaxial growth processes
InactiveUS20050104156A1Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedReducing and eliminating need for implant and anneal stepSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialSemiconductor structure
In one embodiment, a semiconductor structure used in manufacturing a semiconductor device includes a substrate layer. The structure also includes first and second isolation regions formed by etching an oxide layer provided on the substrate layer to define an epitaxial growth surface of the substrate layer for epitaxial growth of a substrate material on the epitaxial growth surface between the first and second isolation regions. The structure also includes an active region that includes the epitaxially-grown substrate material between the first and second isolation regions, the active region formed by epitaxially growing the substrate material on the epitaxial growth surface of the substrate layer.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
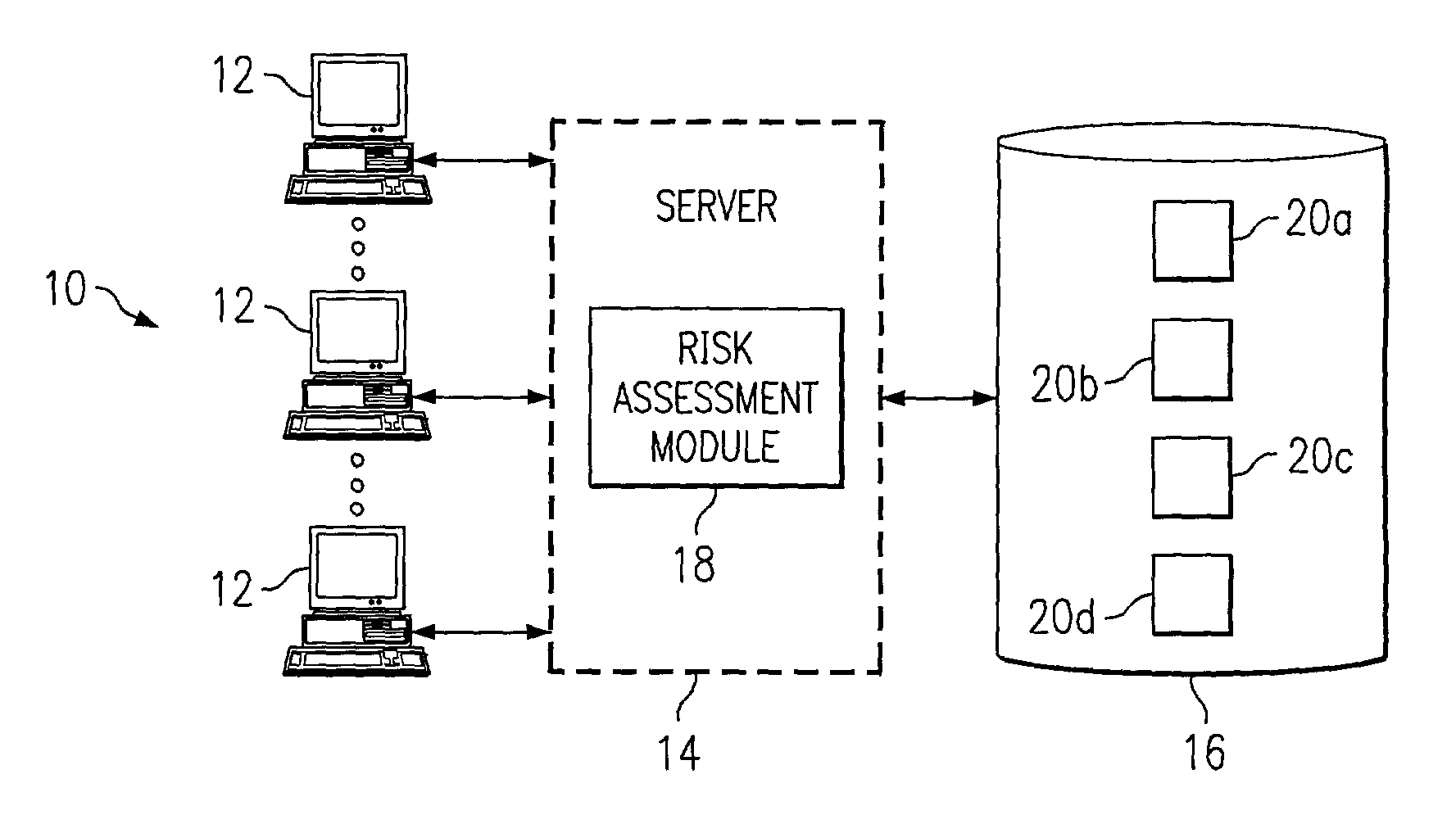
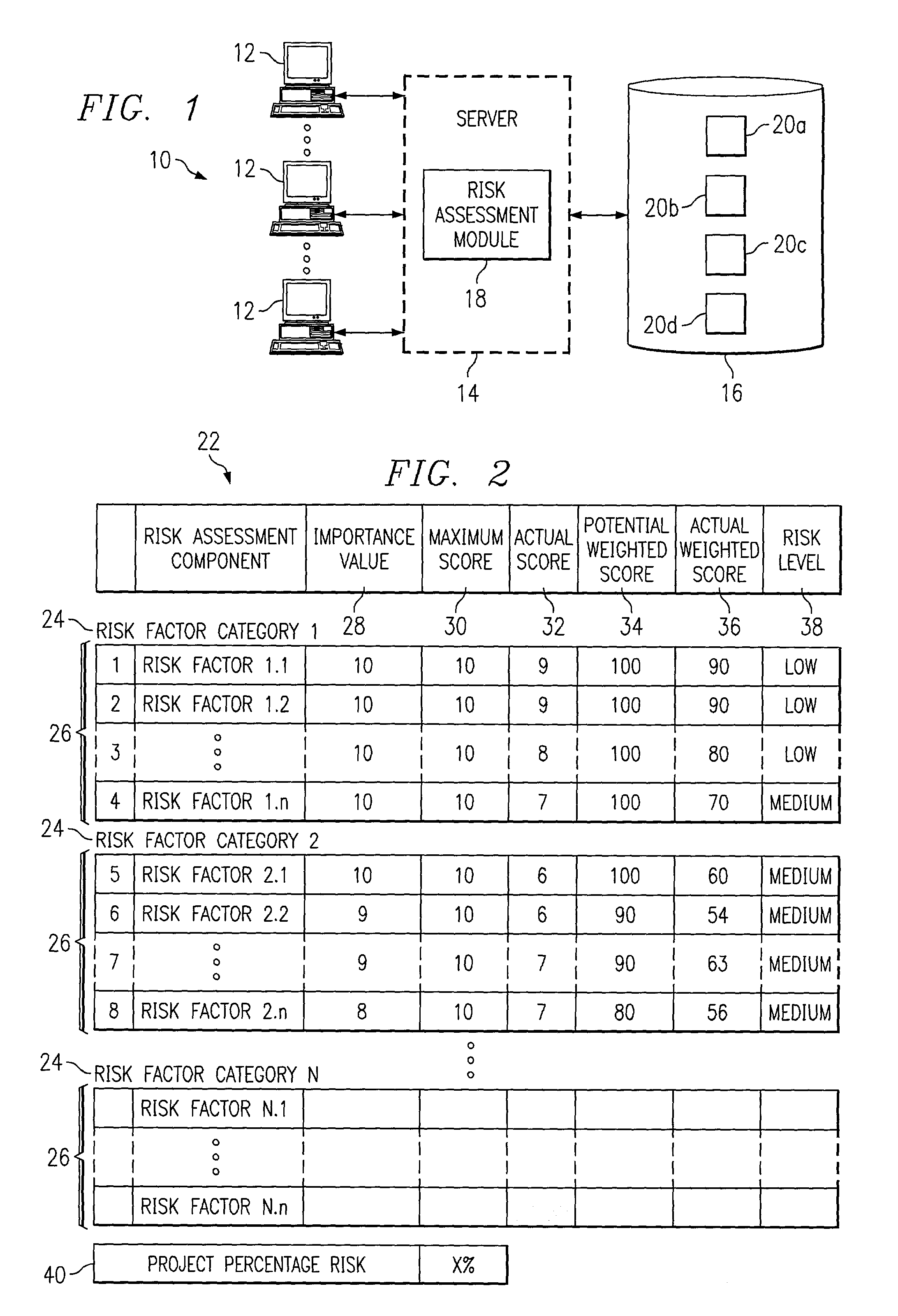
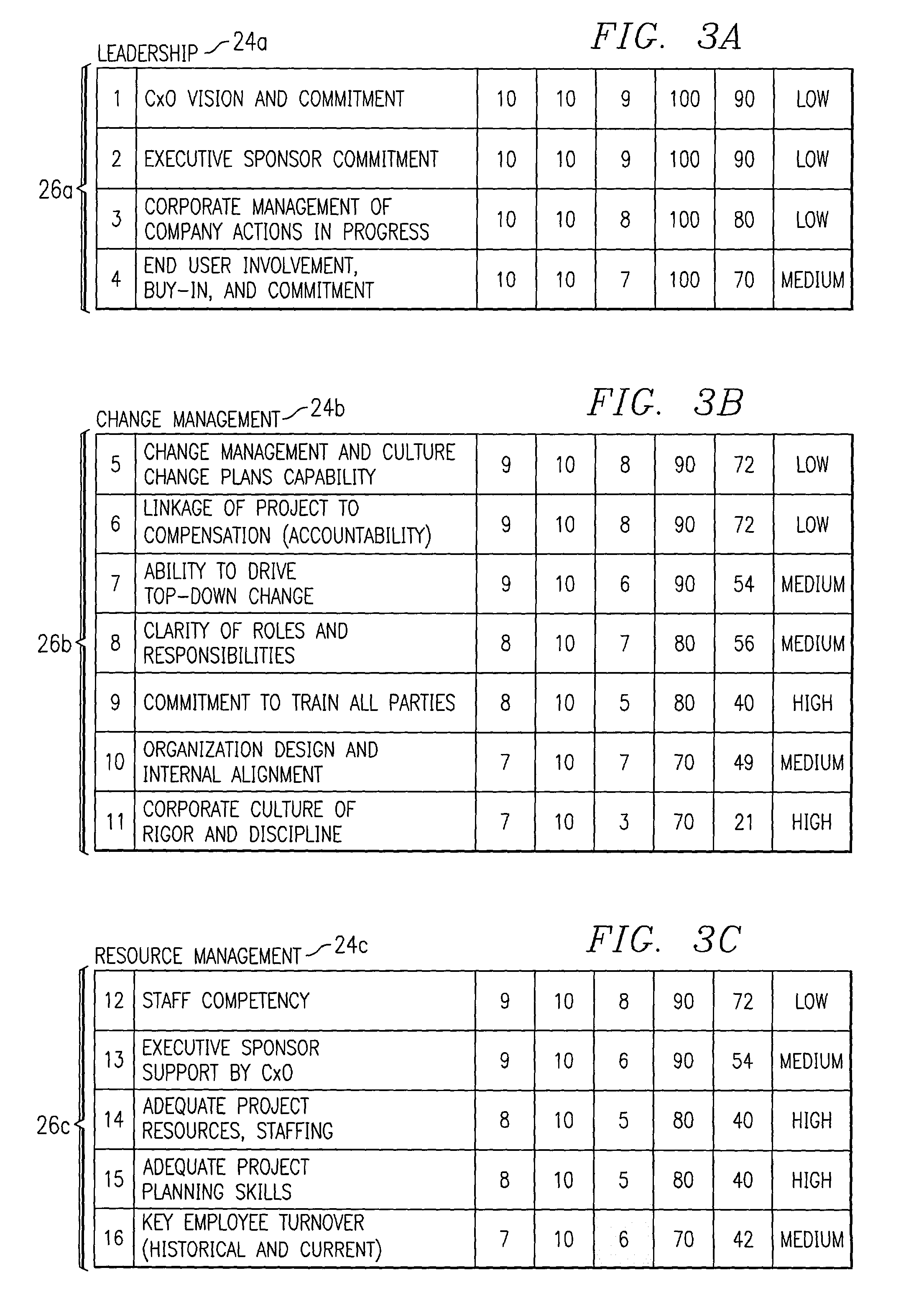
Generating a risk assessment regarding a software implementation project
InactiveUS7359865B1Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedImplementation be reduced eliminatedFinanceResourcesRisk levelItem generation
A computer-implemented method for generating a risk assessment regarding a software implementation project includes accessing a previously specified importance value and maximum score for each of a multiple of risk factors. The importance value for each risk factor reflects experience of an implementing entity regarding the extent to which the factor may negatively impact a software implementation project if the factor is not adequately addressed, the importance value and maximum score for each factor being multiplied to define a potential weighted score for the factor. An actual score for a particular software implementation project is received for each factor based on an analysis specific to the particular project. An actual weighted score for the particular project is generated for each factor by multiplying the importance value and actual score for the factor, and a relationship between the potential weighted score and actual weighted score for each factor. A risk level for the particular project is assigned to each factor according to the relationship between the potential weighted score and the actual weighted score for the factor. The risk level for each factor represents an assessment regarding the extent to which the factor may negatively impact the particular project if the factor is not adequately addressed. A risk assessment is generated for the particular project including one or more of the assigned risk levels for the particular project for one or more corresponding factors.
Owner:BLUE YONDER GRP INC
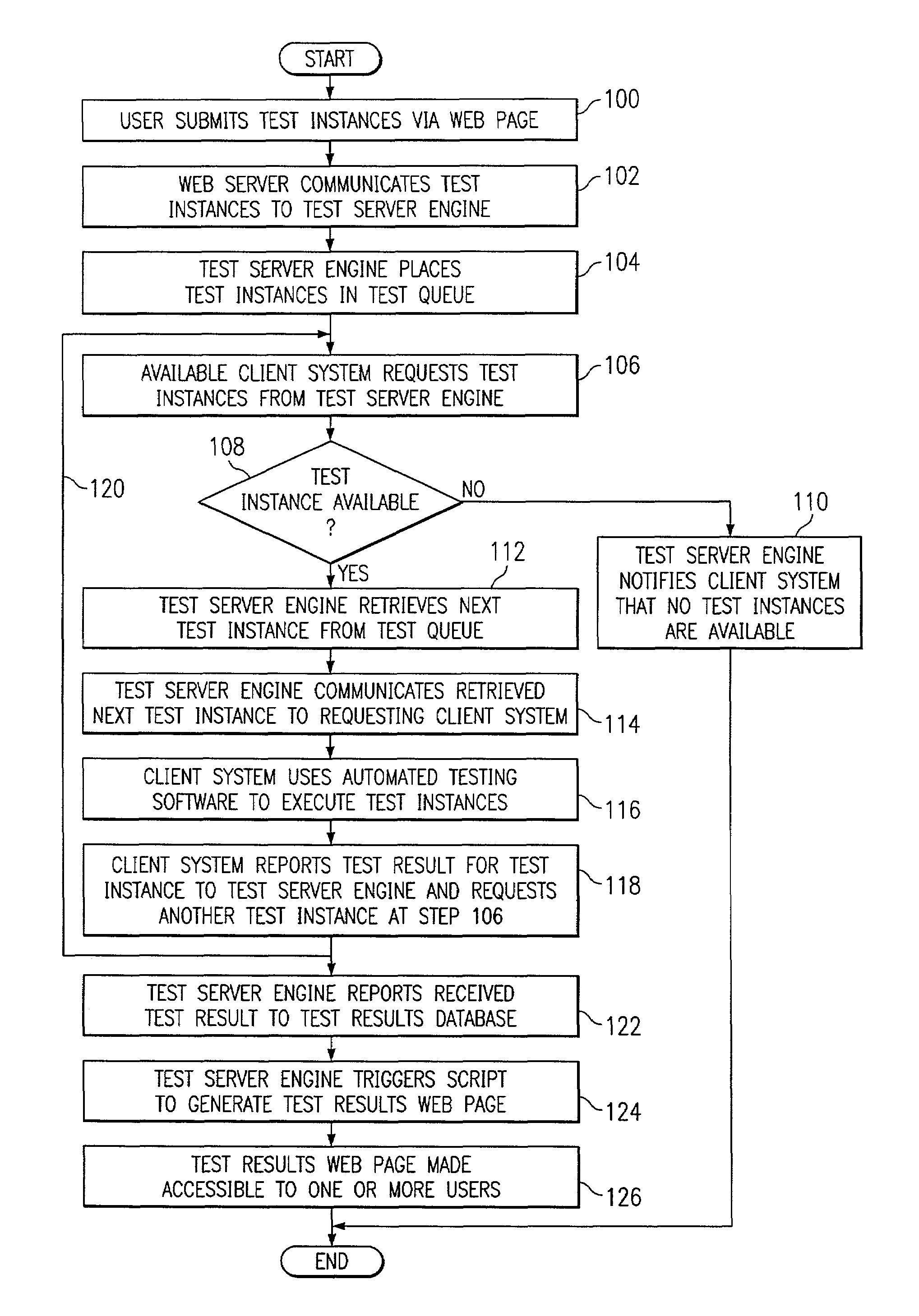
Distributed automated software graphical user interface (GUI) testing
InactiveUS7055137B2Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedEfficient managementSoftware testing/debuggingSpecific program execution arrangementsGraphicsComputer hardware
Owner:JDA SOFTWARE GROUP
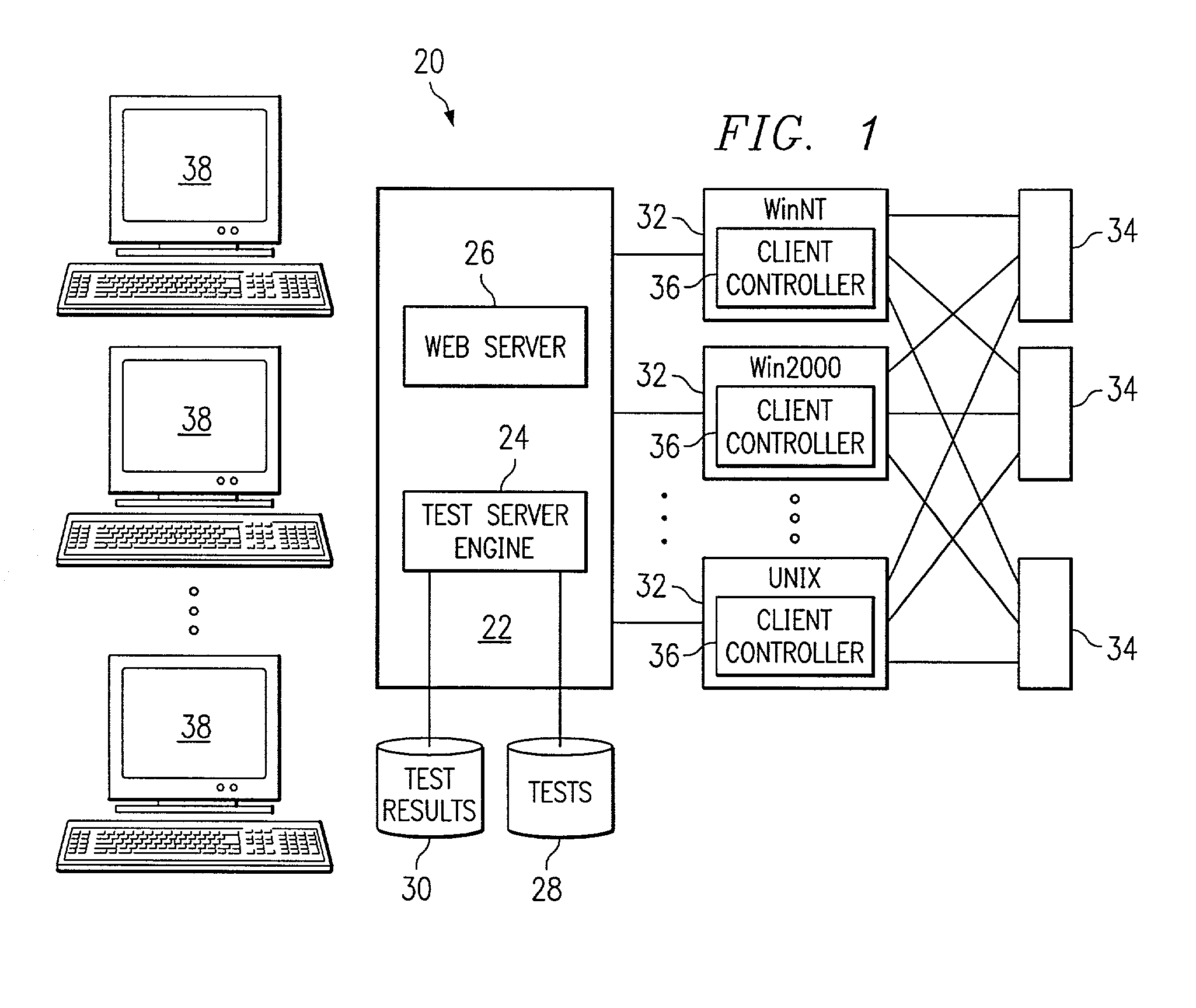
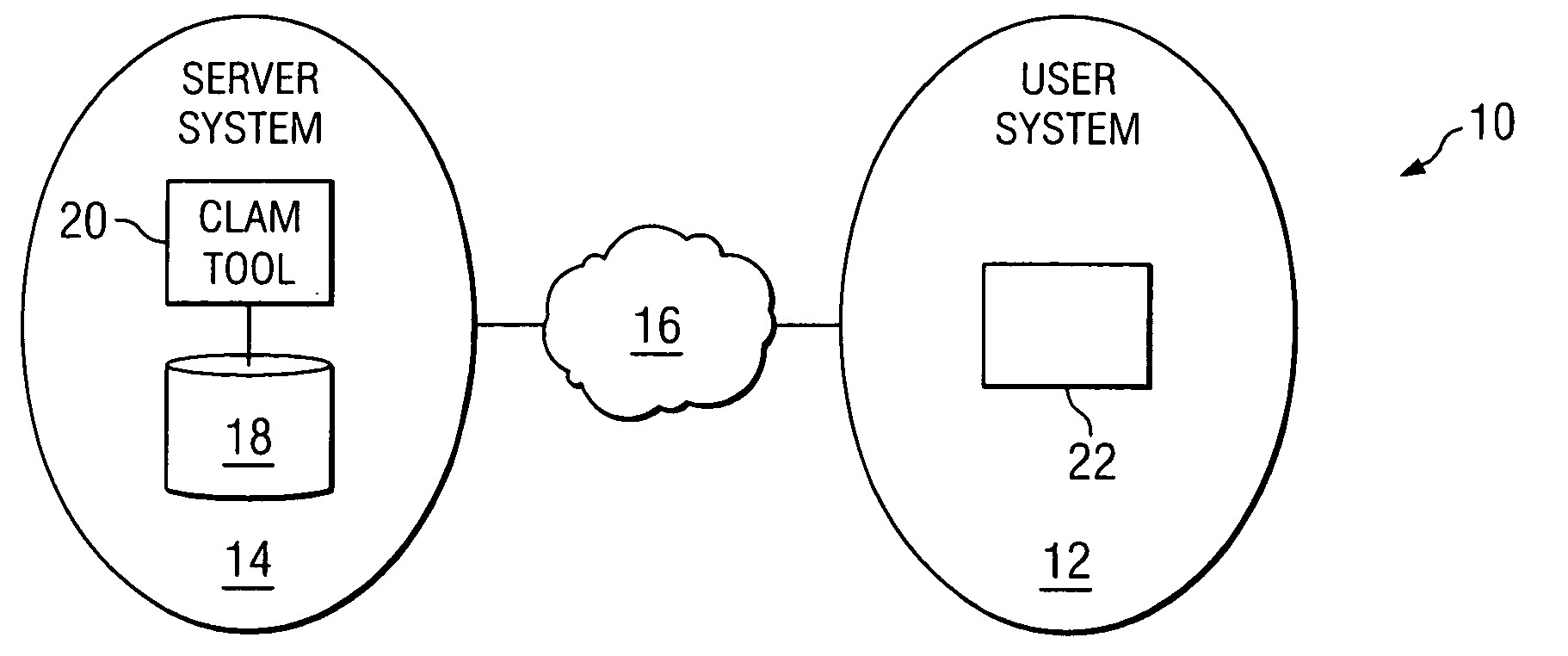
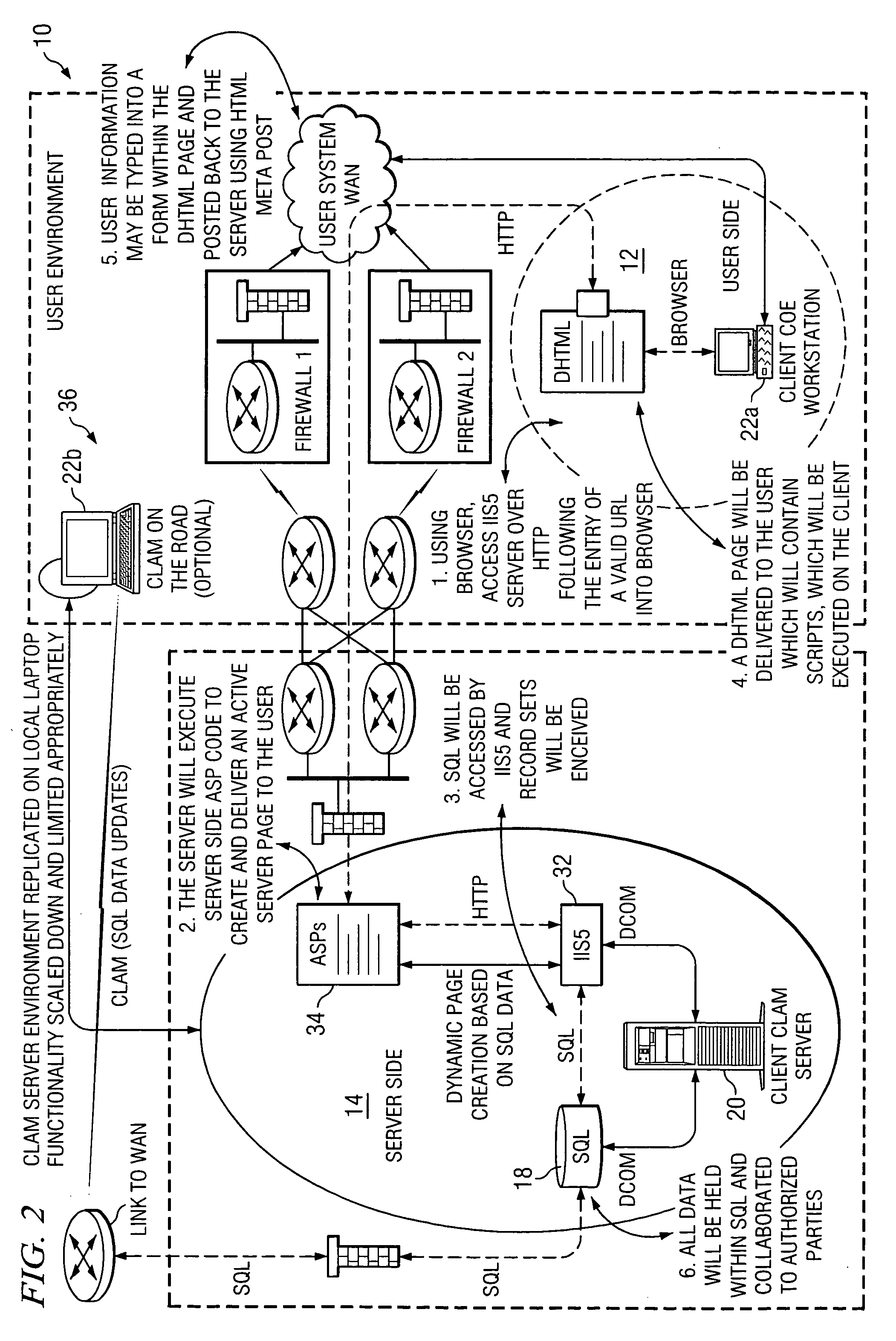
Managing information technology (IT) infrastructure of an enterprise using a centralized logistics and management (CLAM) tool
InactiveUS20050159969A1Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedReducing and eliminating ambiguity and misunderstandingSpecial data processing applicationsLogistics managementKnowledge management
In one embodiment, a process for managing information technology (IT) infrastructure of an enterprise includes: (1) capturing and storing IT infrastructure information regarding the IT infrastructure of the enterprise; (2) defining a plurality of roles within the enterprise, each role specifying a particular job function within the enterprise; (3) associating items of IT infrastructure with roles within the enterprise such that each role is associated with one or more predetermined items of IT infrastructure; (4) assigning roles to one or more employees of the enterprise such that each of the one or more employees is associated with one or more roles and is assigned the one or more predetermined items of IT infrastructure associated with each of these one or more roles; (5) automatically modeling a change in the IT infrastructure for one or more impacted employees; and (6) automatically initiating deployment of one or more IT infrastructure assets for the one or more impacted employees by organizing delivery of the one or more IT infrastructure assets to the one or more impacted employees to implement the change modeled.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
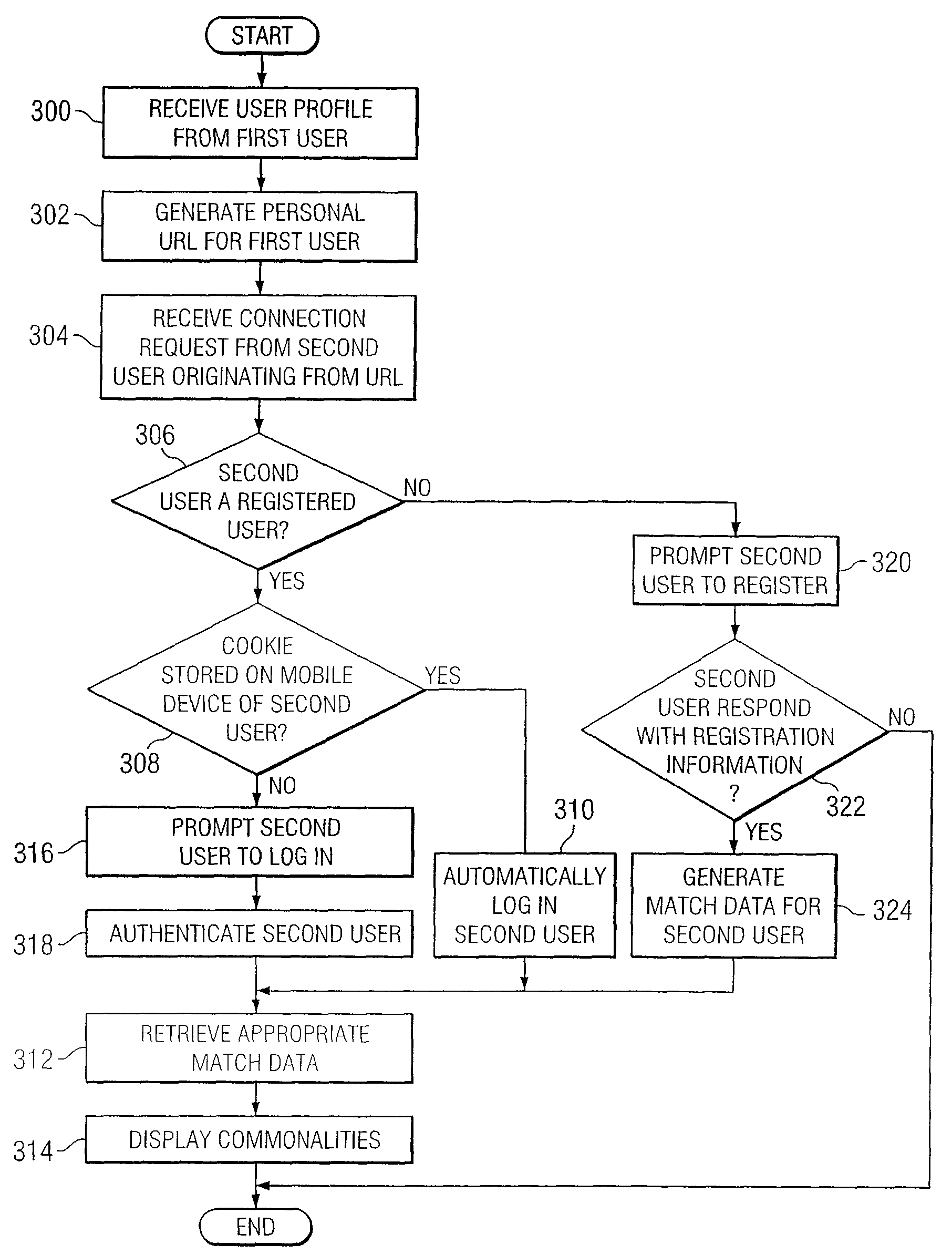
System and method for a directory secured user account
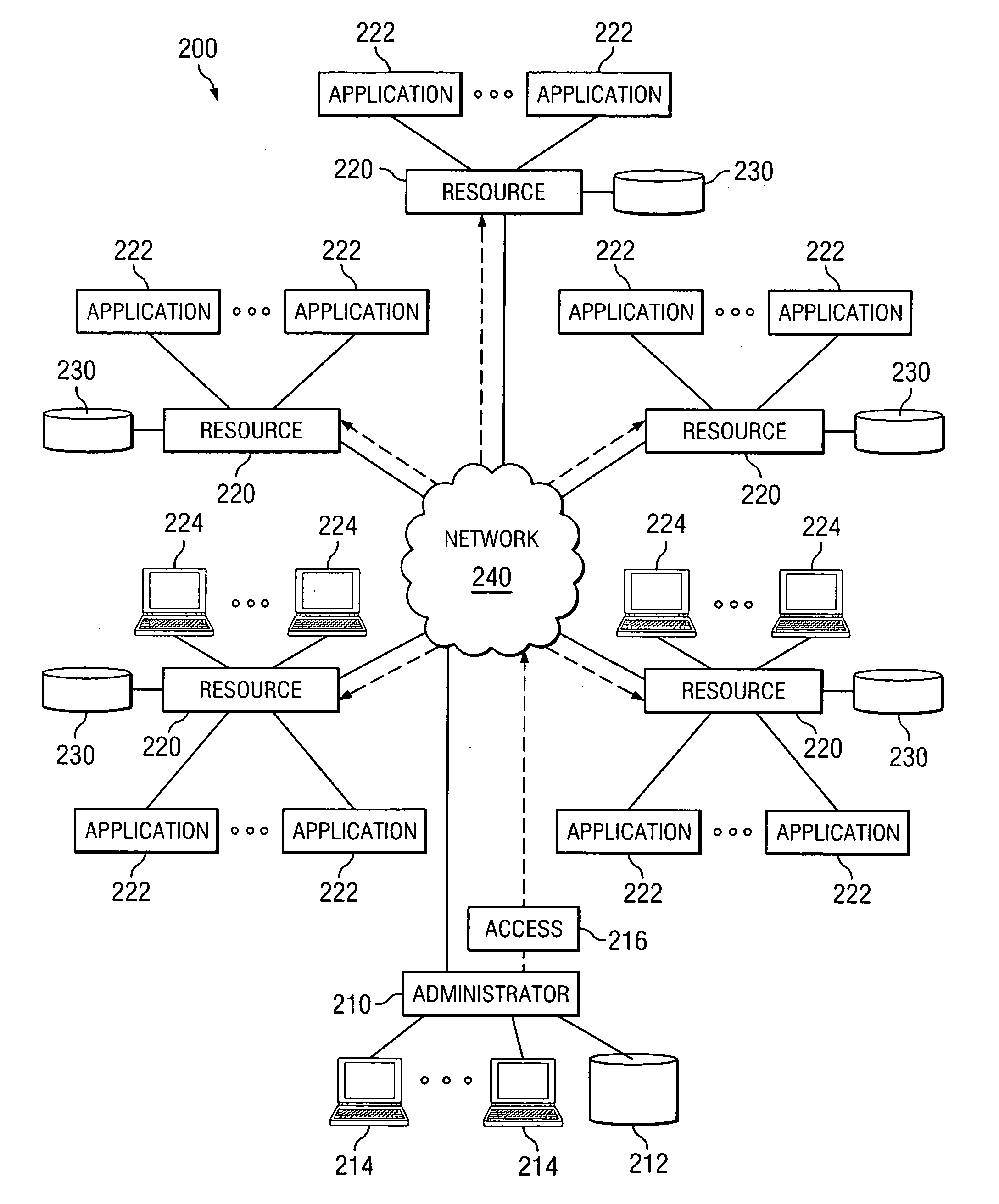
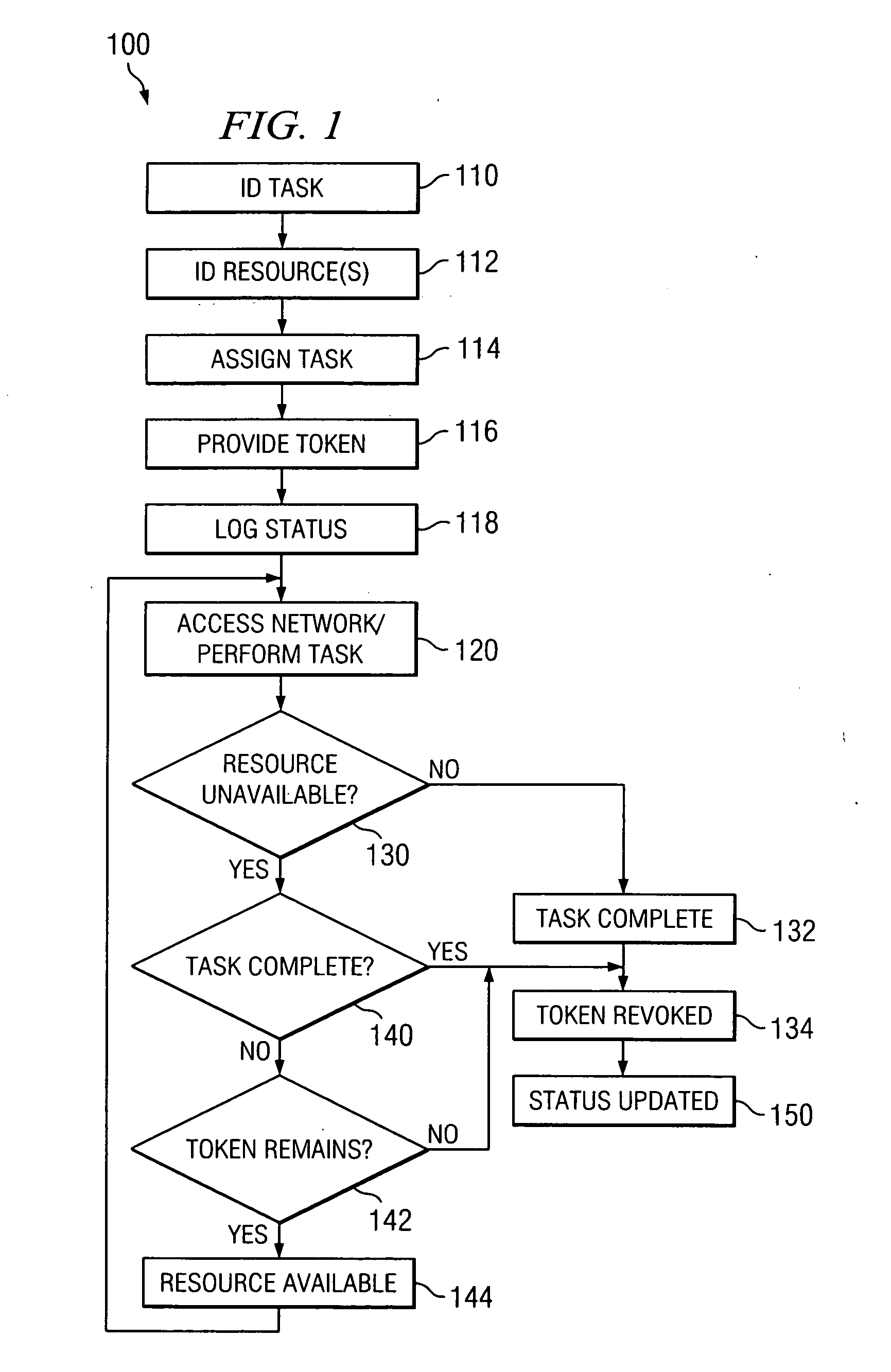
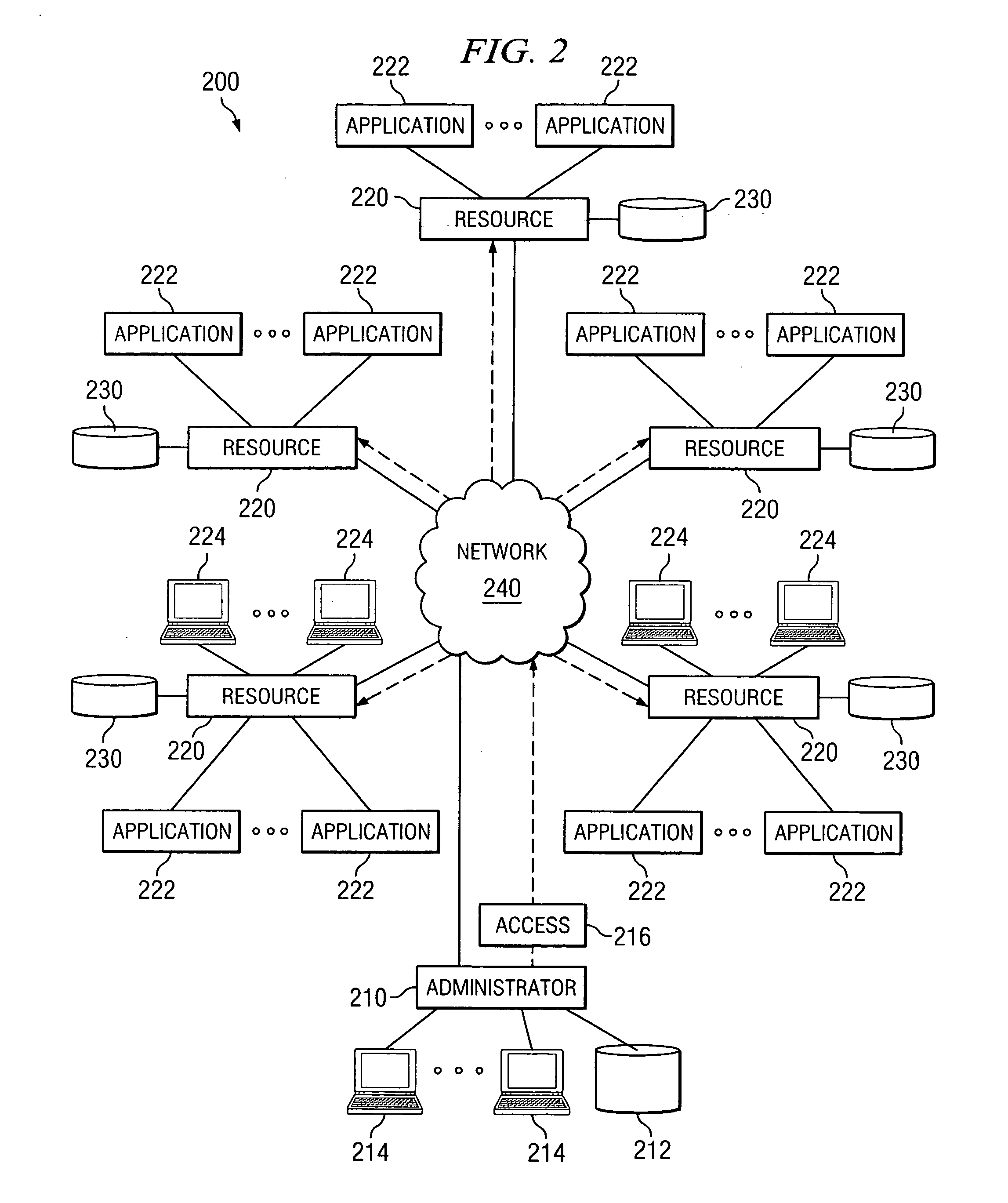
InactiveUS20050160276A1Access be reduced eliminatedDisadvantages can be reduced eliminatedComputer security arrangementsSecret communicationComputer networkAccess token
A system and method for providing network access includes identifying an available network resource, providing an access token to the available network resource, tracking the access token, and terminating the access token.
Owner:CAPITAL ONE FINANCIAL
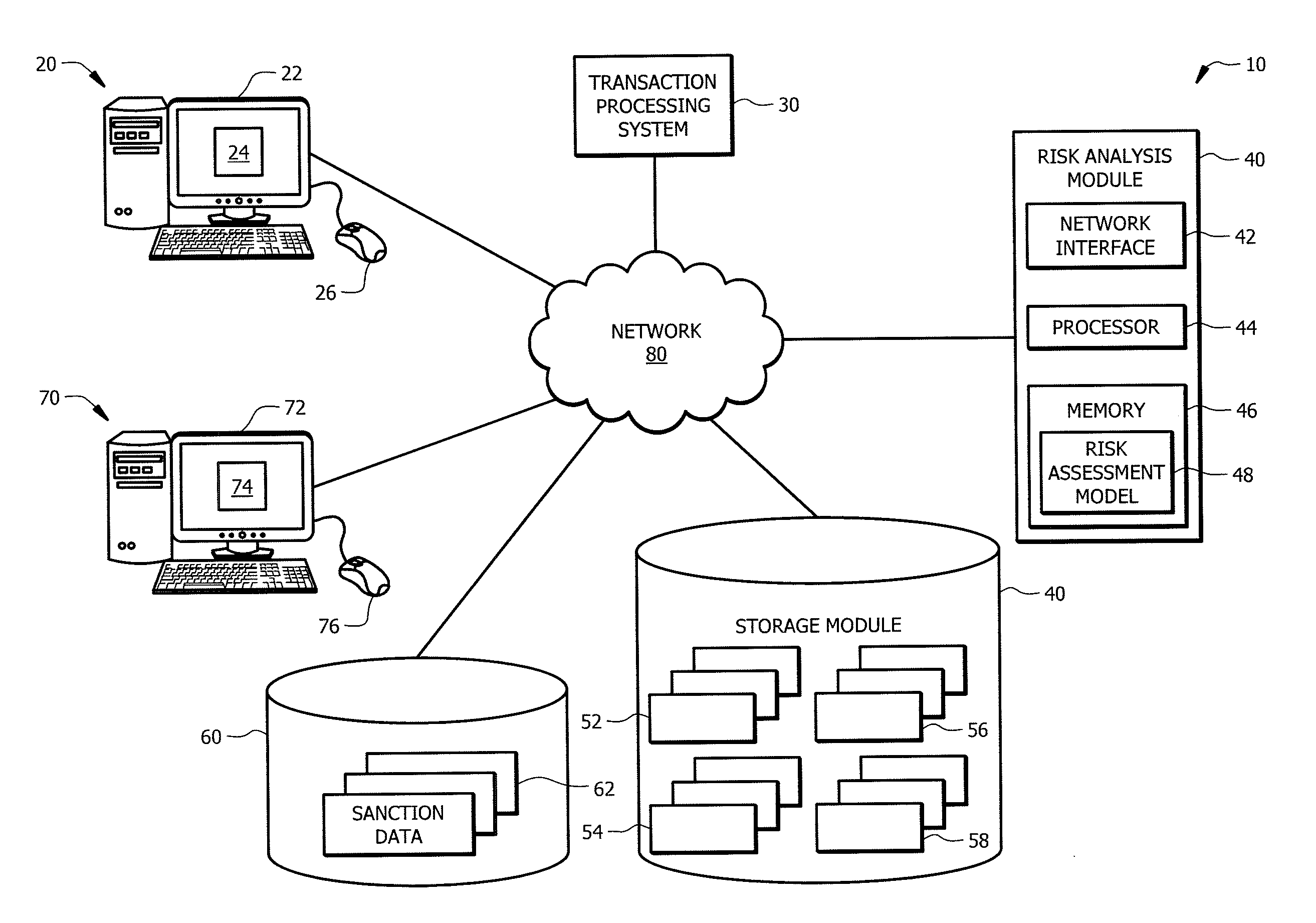
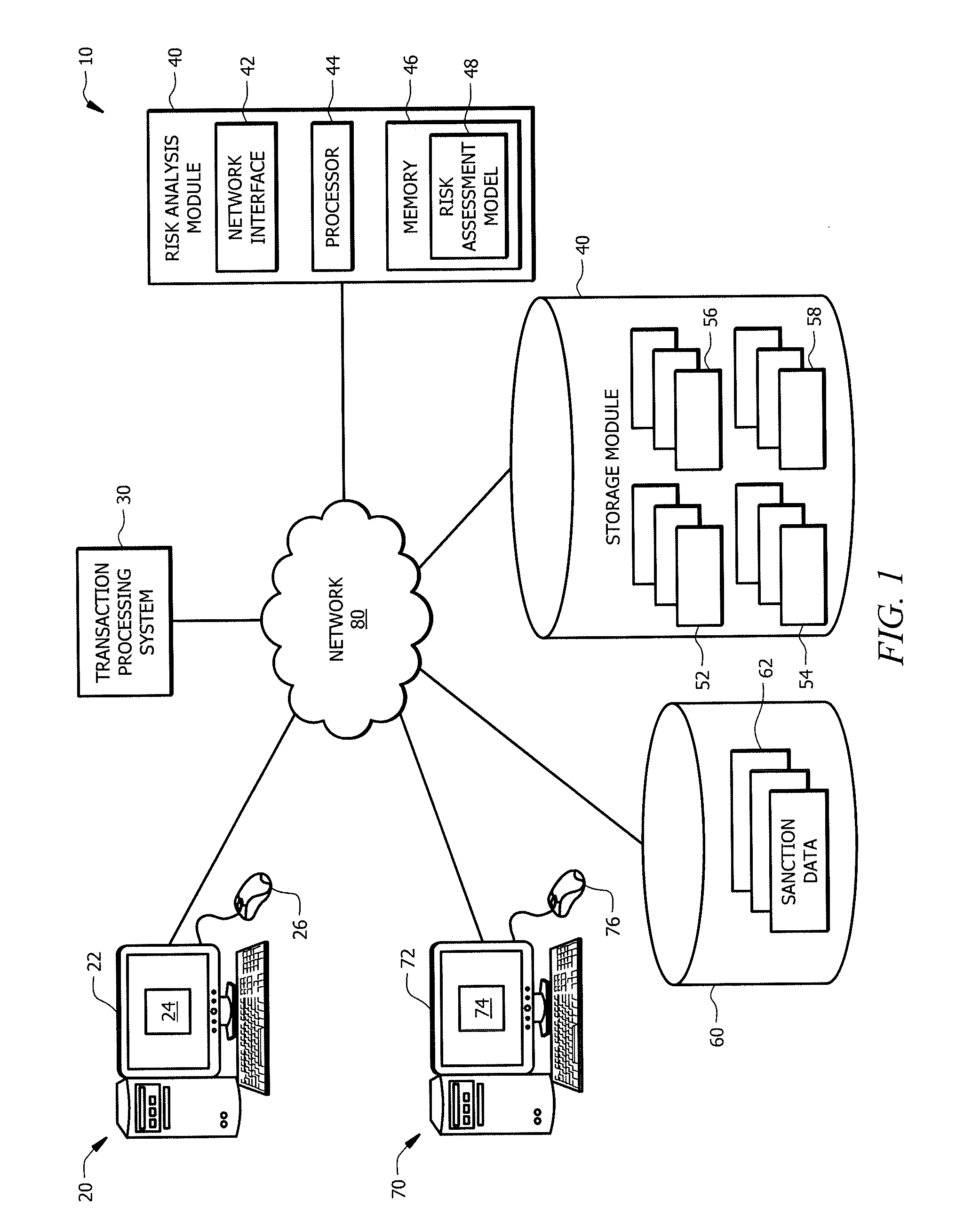
ldentifying Potentially Risky Transactions
ActiveUS20160104163A1Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedTransactions be reduced eliminatedFinanceWeb data indexingComputer scienceRisk assessment
In certain embodiments, a computer-implemented method includes determining, by a processor, characteristics of a new transaction and processing, by the processor, the characteristics of the new transaction using a risk assessment model. The risk assessment model is generated using an iterative training process that processes, over time, historical transactions to train the risk assessment model based on characteristics of historical transactions and associated risk assessment analysis of the historical transactions. The method includes generating, by the processor, a risk assessment indicator for the new transaction based on processing the characteristics of the new transaction using the risk assessment model. The risk assessment indicator indicates a degree of risk of the new transaction.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
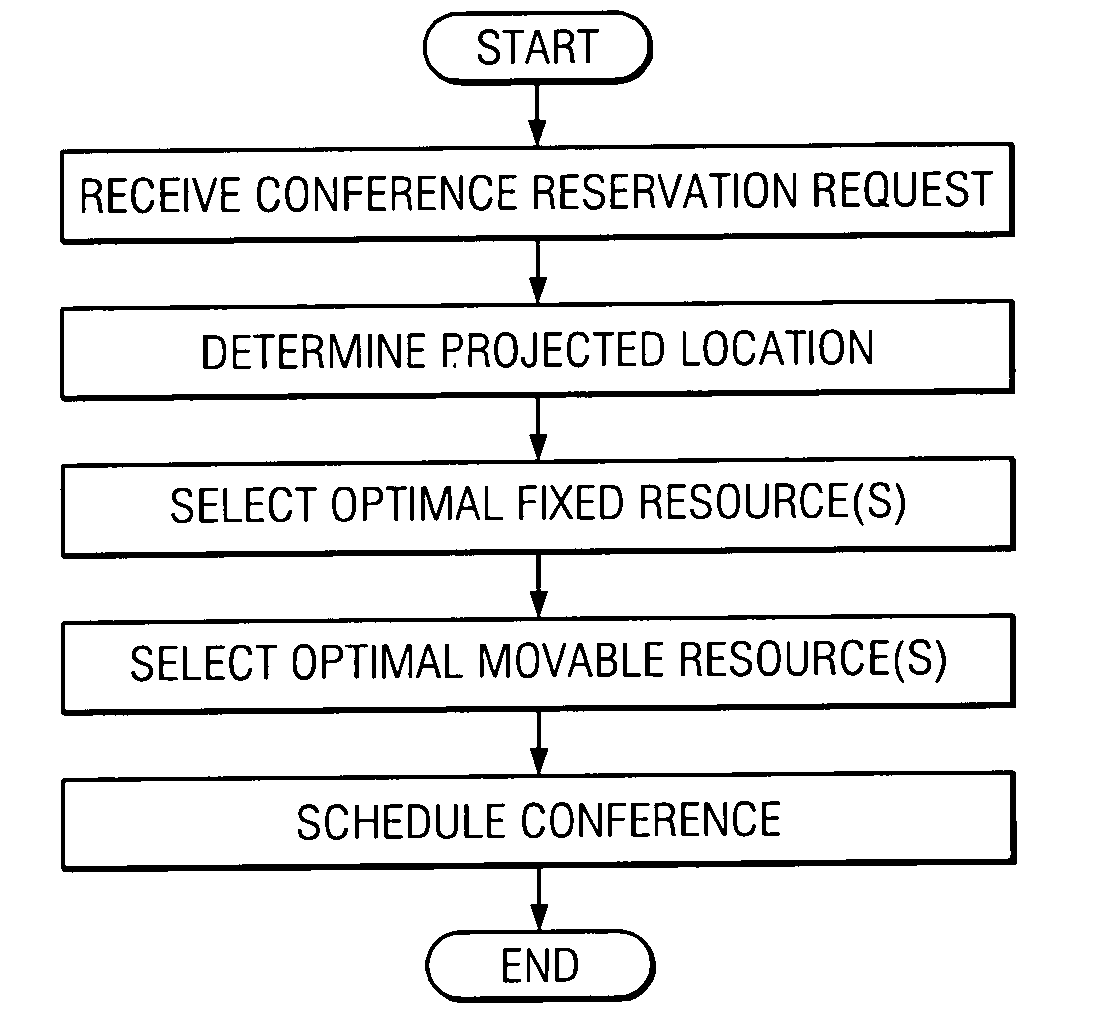
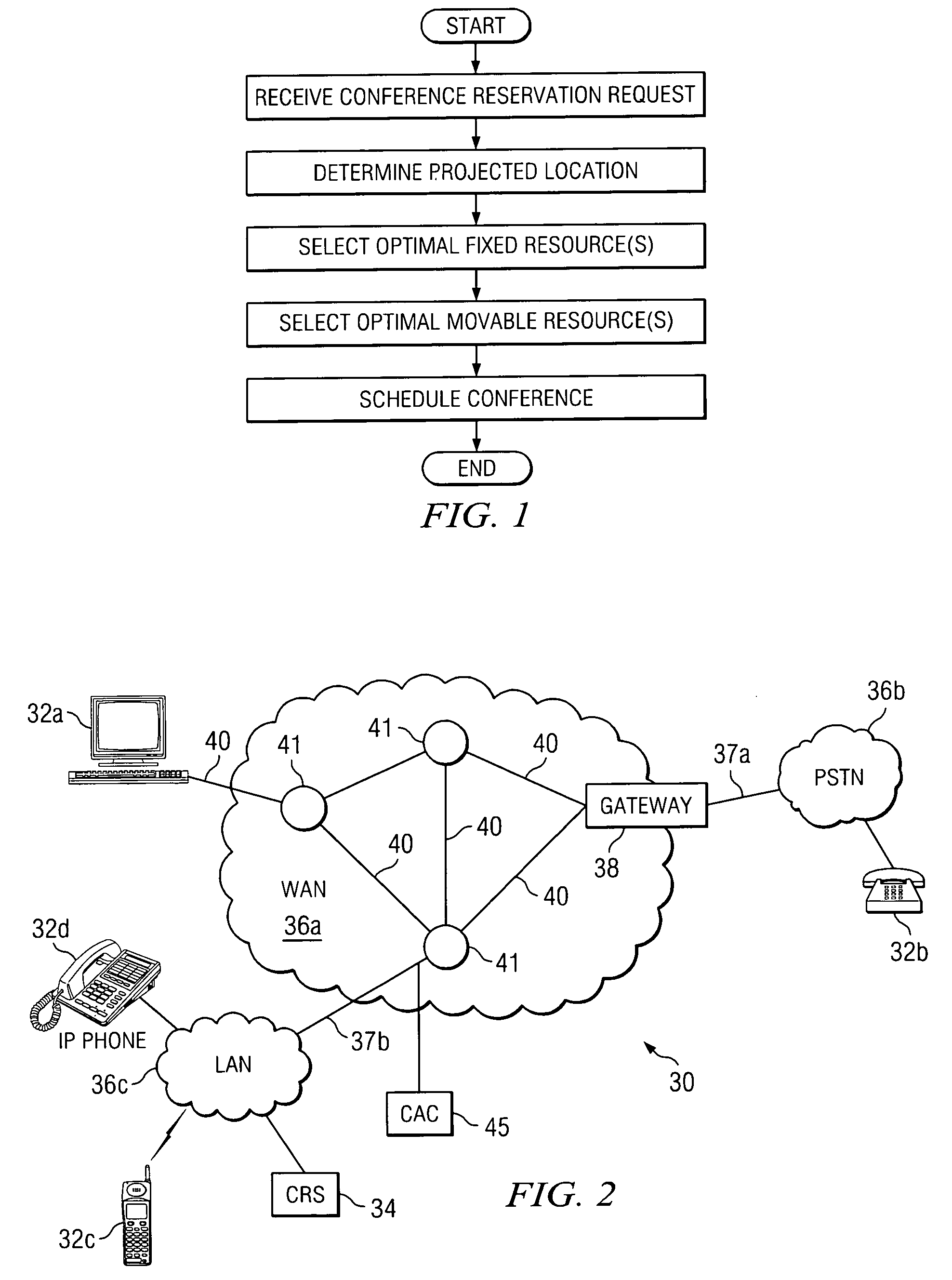
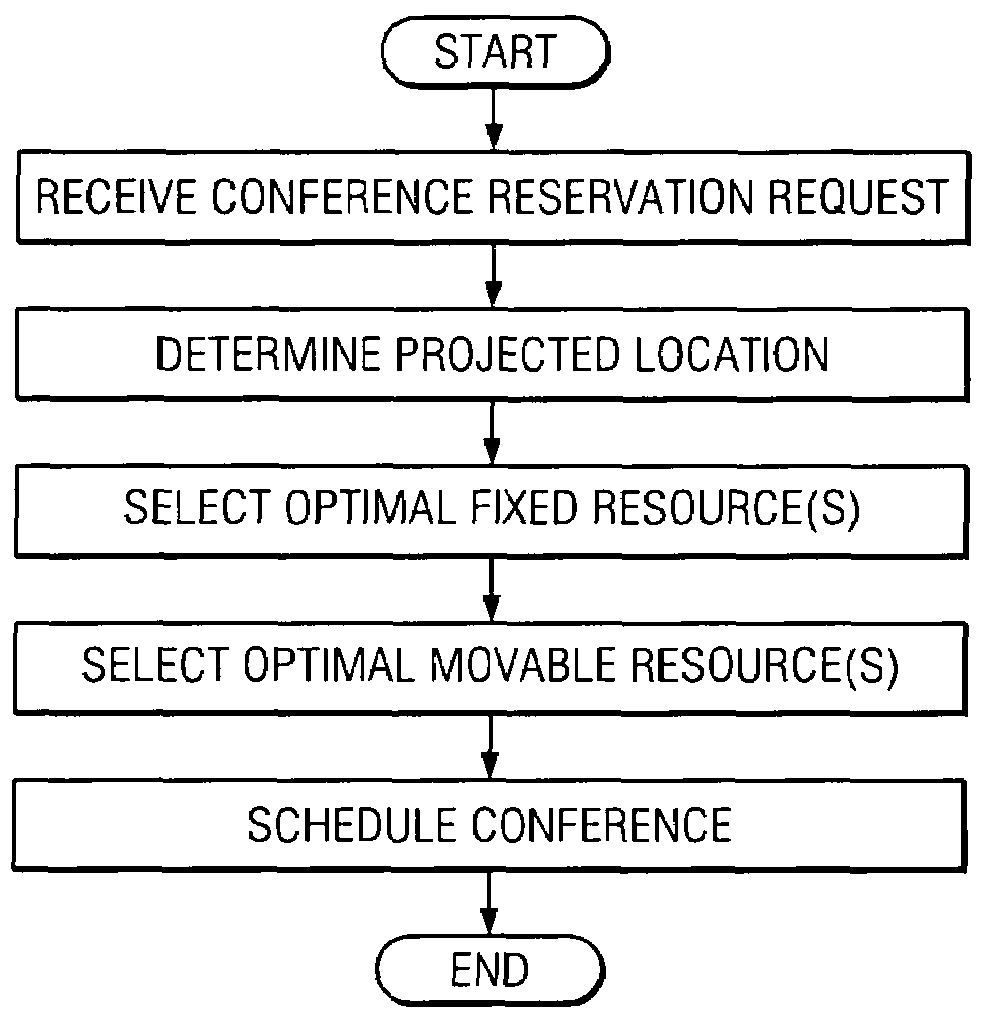
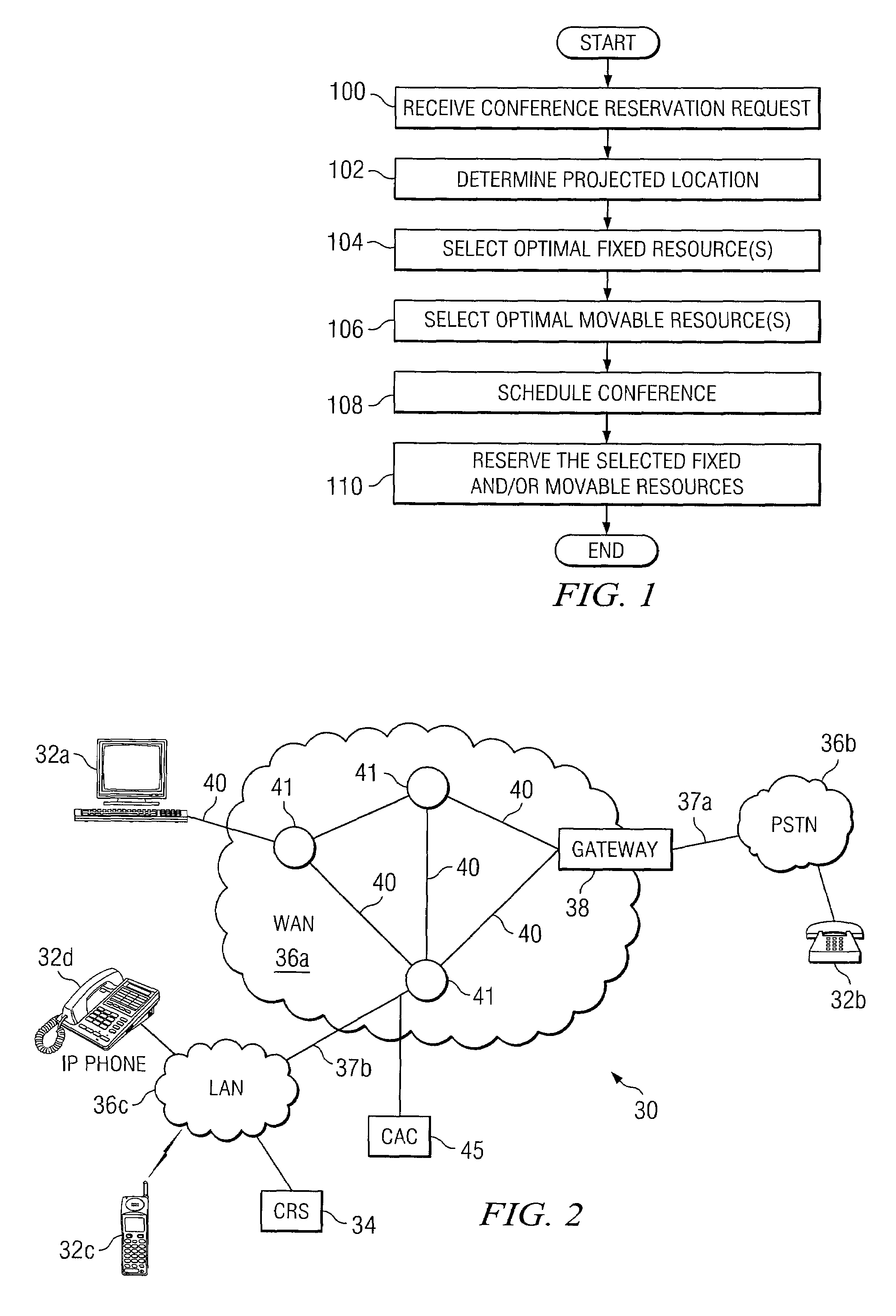
System and method for scheduling conference resources
InactiveUS20060062367A1Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedResources be reduced eliminatedMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationStart timeReal-time computing
A method for scheduling conference resources is provided, that includes receiving a request for a conference reservation. The request may include the identities of a plurality of proposed participants, a proposed start time, and at least one fixed resource criterion. In accordance with a particular embodiment of the present invention, a projected location of at least one of the proposed participants is automatically calculated. The projected location may be a location at which the at least one of the proposed participants is expected to be at approximately the proposed start time. The method may also include automatically calculating a projected location of at least one invitee of the conference. In accordance with this embodiment, the projected location of the at least one invitee may be used to select an optimal one of a plurality of fixed resources, that match the at least one fixed resource criterion.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
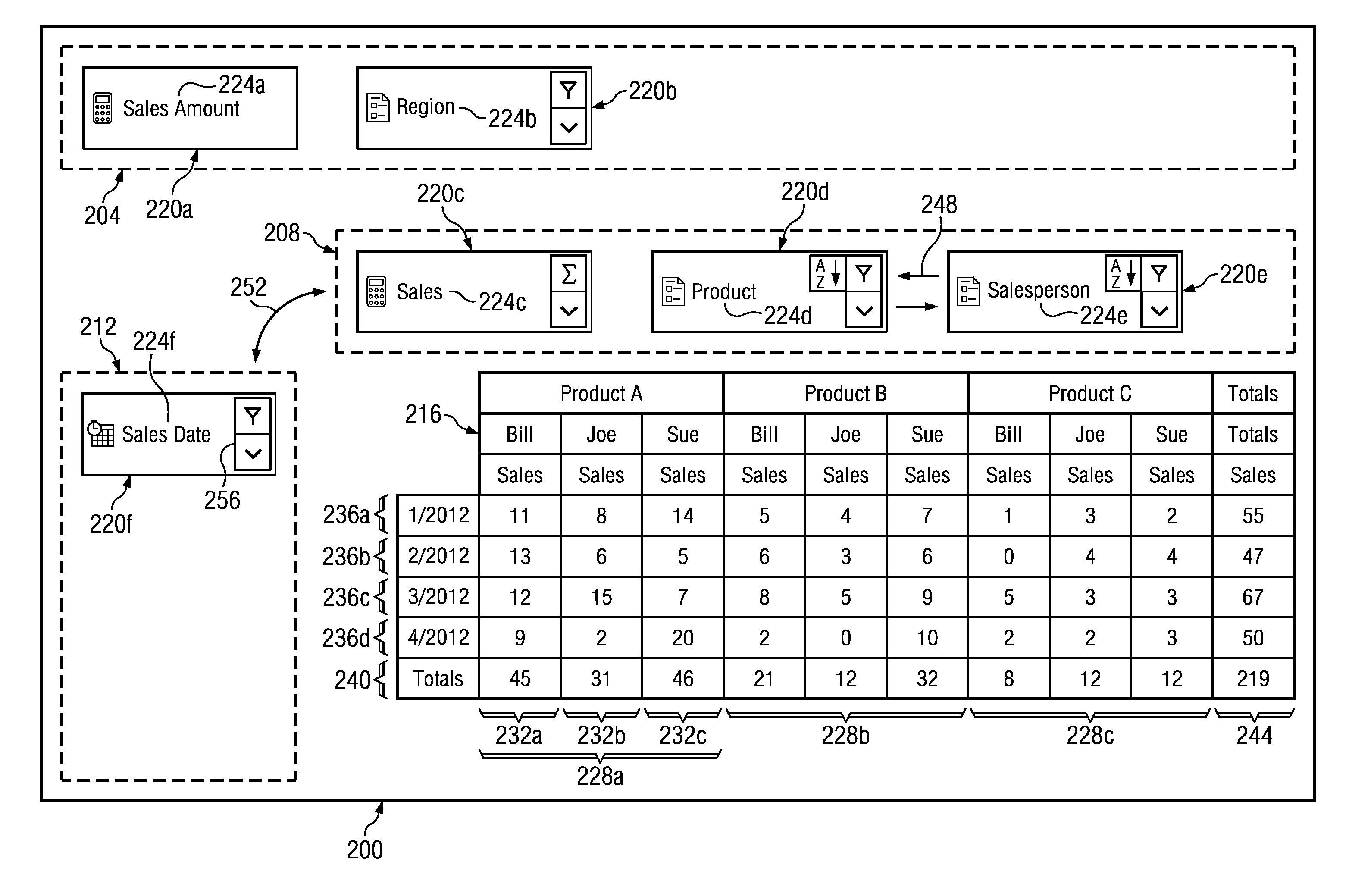
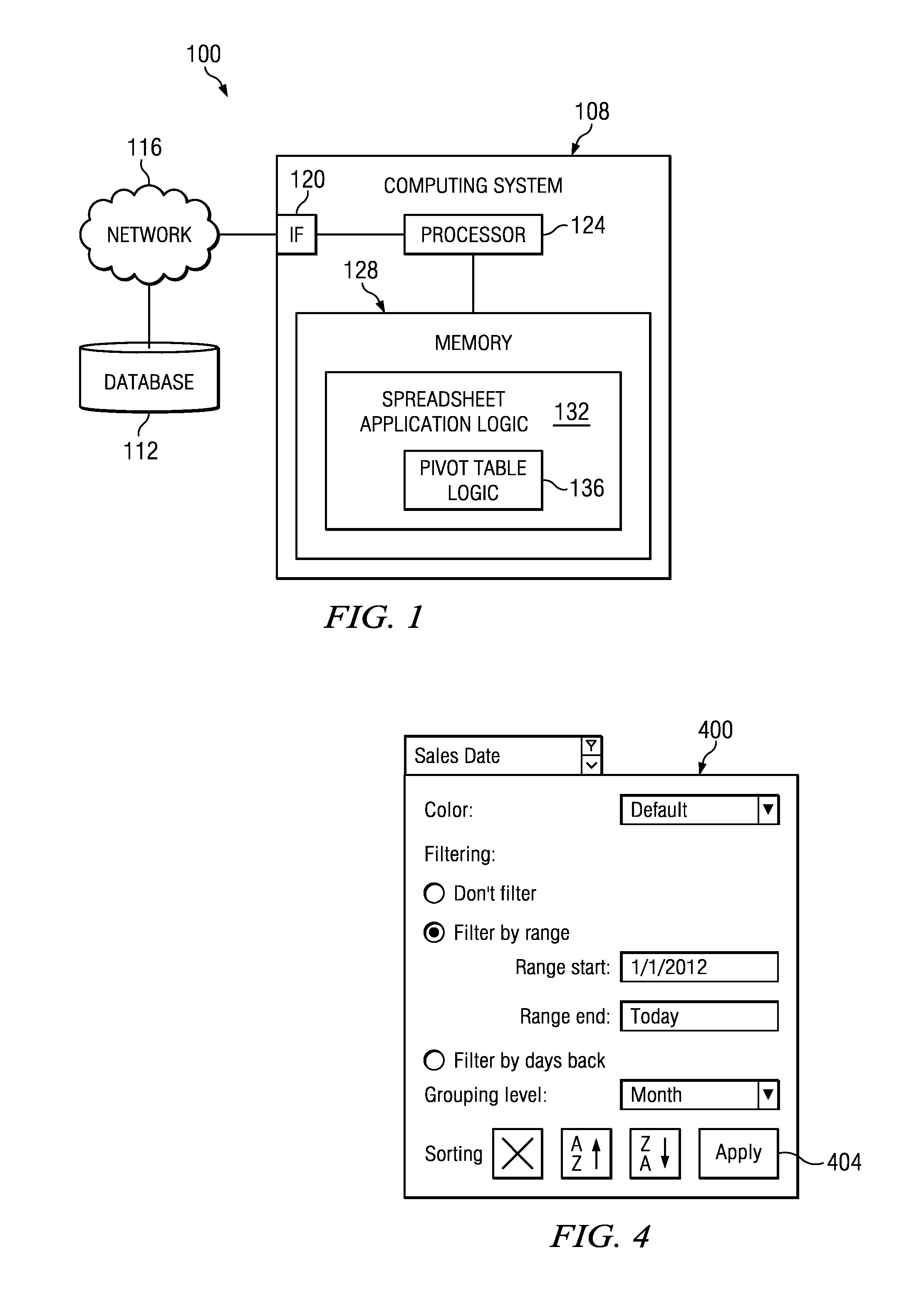
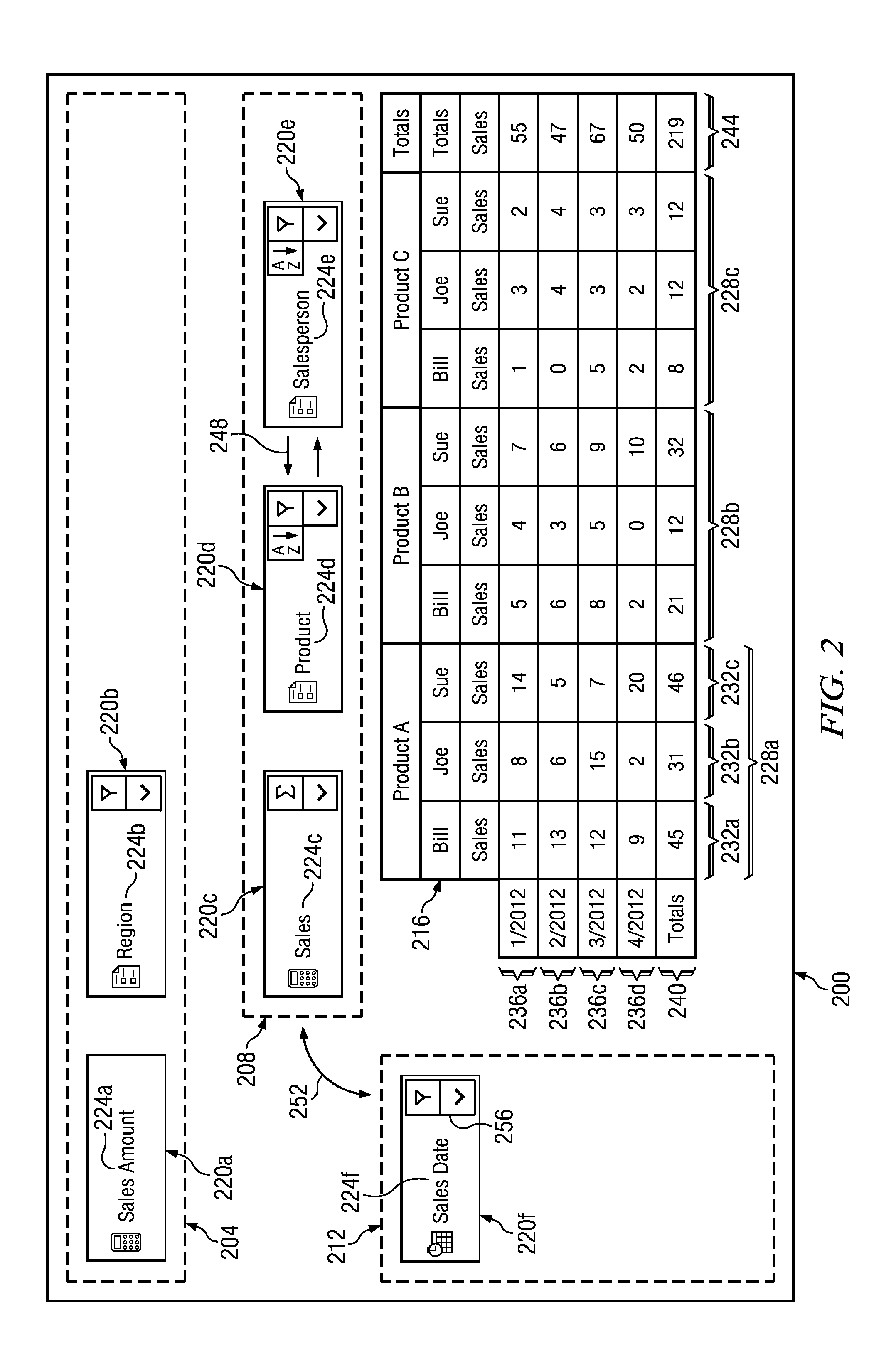
Dynamic Pivot Table Creation and Modification
InactiveUS20140019842A1Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedProblems be reduced eliminatedText processingSpecial data processing applicationsData setComputer science
In an exemplary embodiment, a method includes determining a plurality of field identifiers of a data set. A plurality of field cells that each correspond to a field identifier of the plurality of field identifiers are generated and displayed within an available fields region. A column field region and a row field region are displayed. A first field cell of the plurality of field cells is moved from the available fields region to the column field region or the row field region in response to a first input from a user. The pivot table is updated to include one or more rows or columns corresponding to the first field cell upon detection of the movement of the first field cell to the column field region or the row field region.
Owner:BANK OF AMERICA CORP
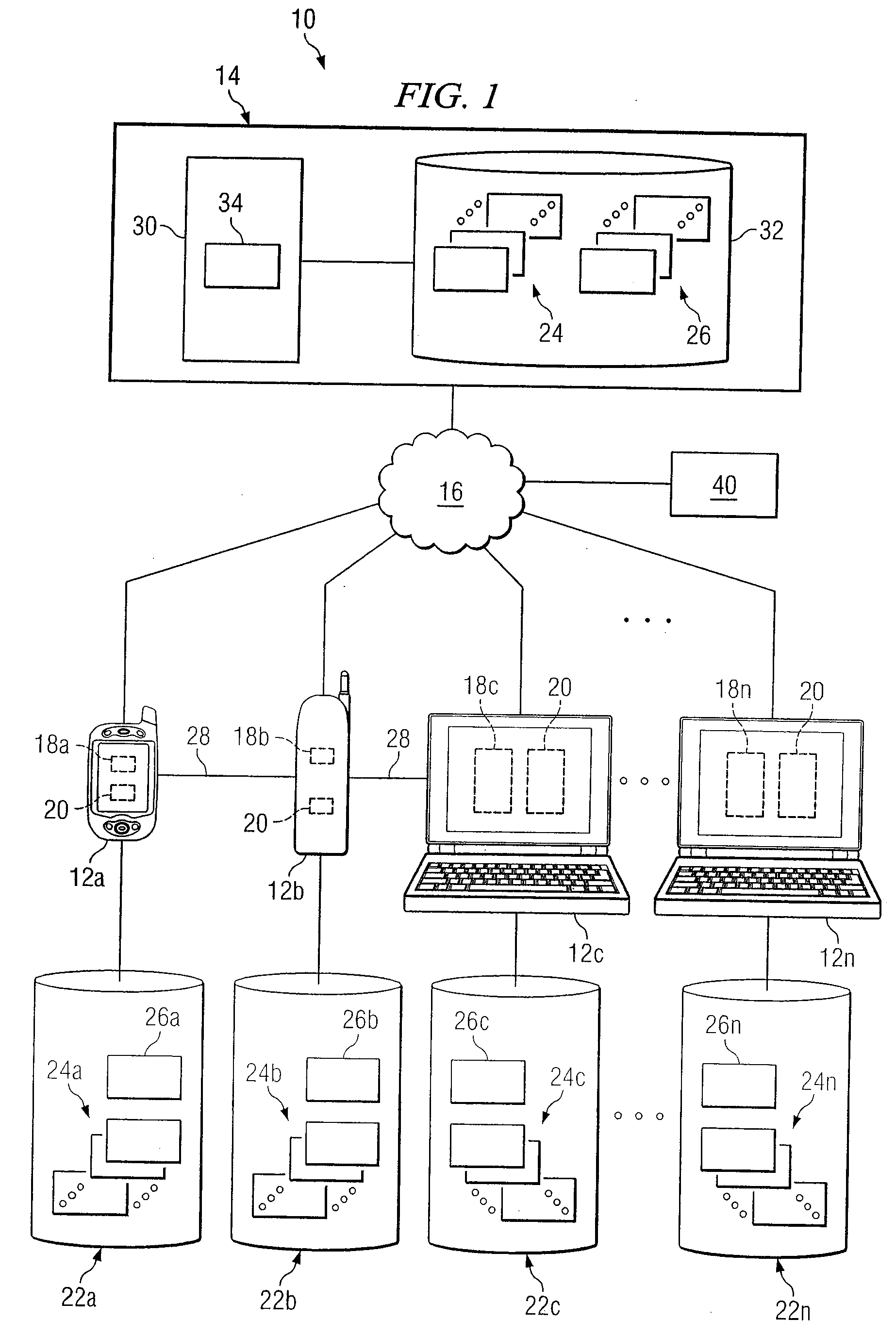
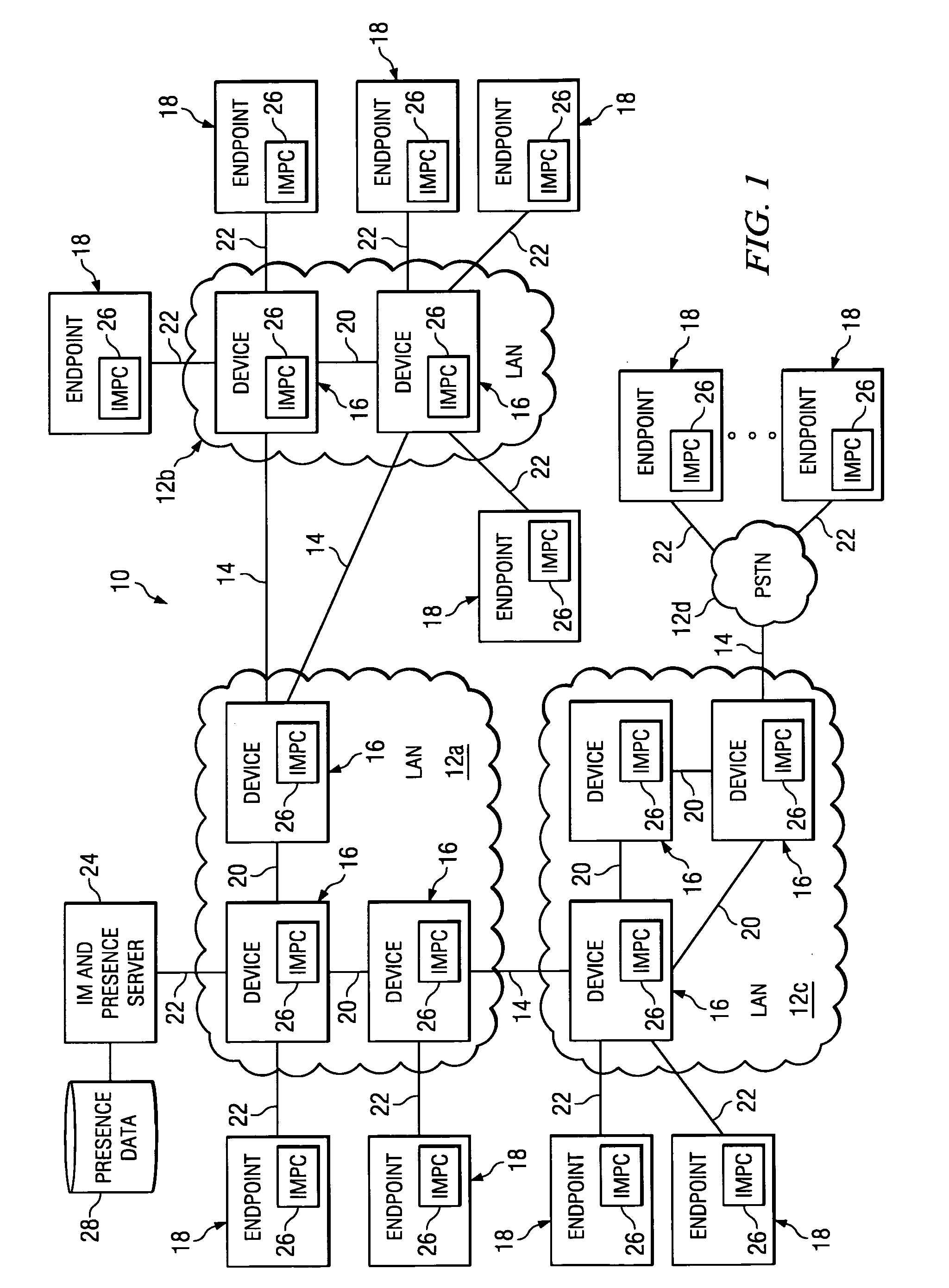
System and method for providing communication services to mobile device users incorporating proximity determination
InactiveUS8150416B2Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedWeb data retrievalPosition fixationComputer networkMobile device
In certain embodiments, a method for proximity determination includes receiving one or more network identifiers, each associated with a corresponding network, from a first mobile device. The method further includes receiving one or more network identifiers, each associated with a corresponding network, from a second mobile device. The method further includes processing the network identifiers received from the first and second mobile devices to determine whether the first mobile device and the second mobile device are in proximity to one another.
Owner:JAMBO NETWORKS
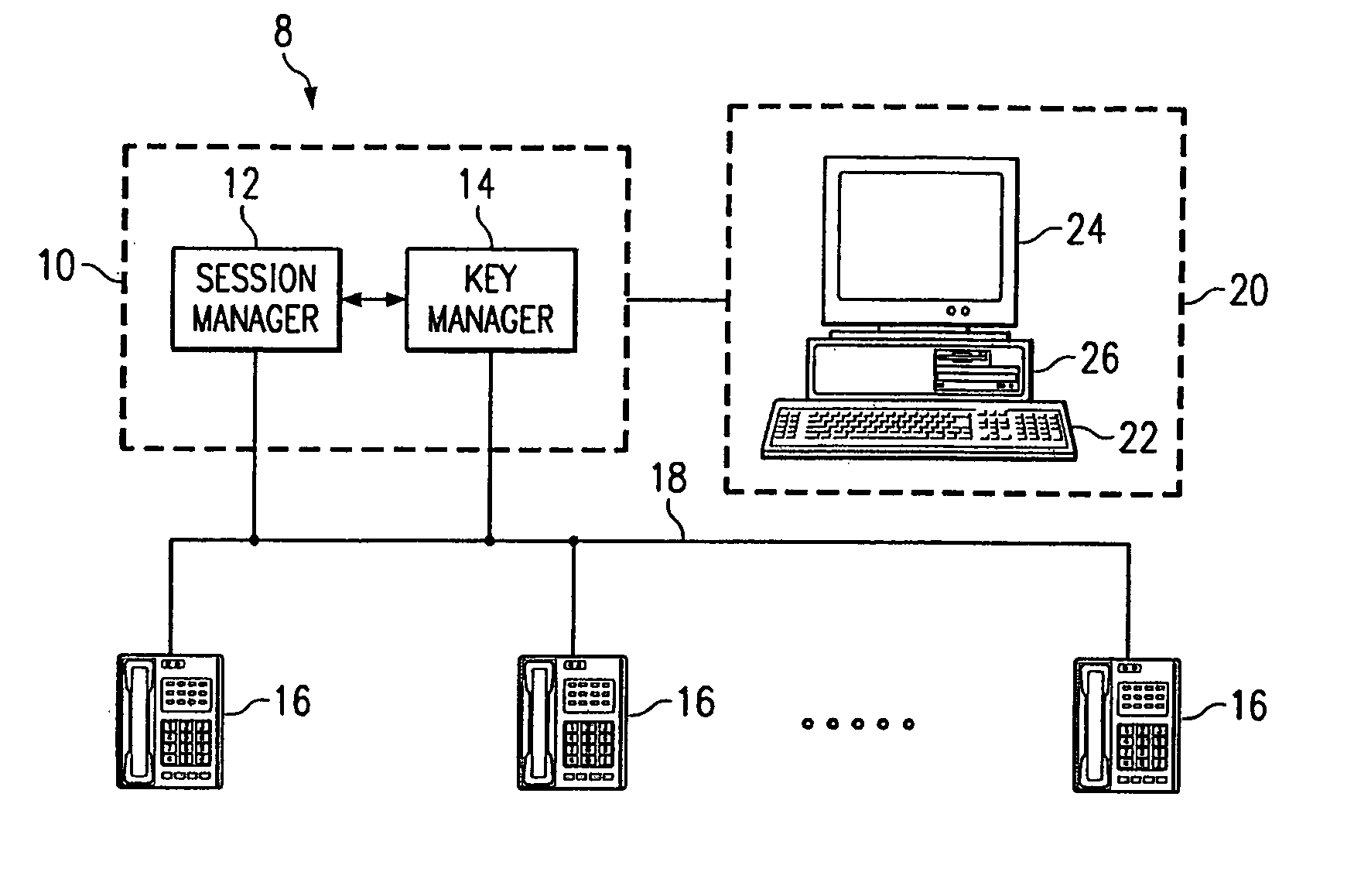
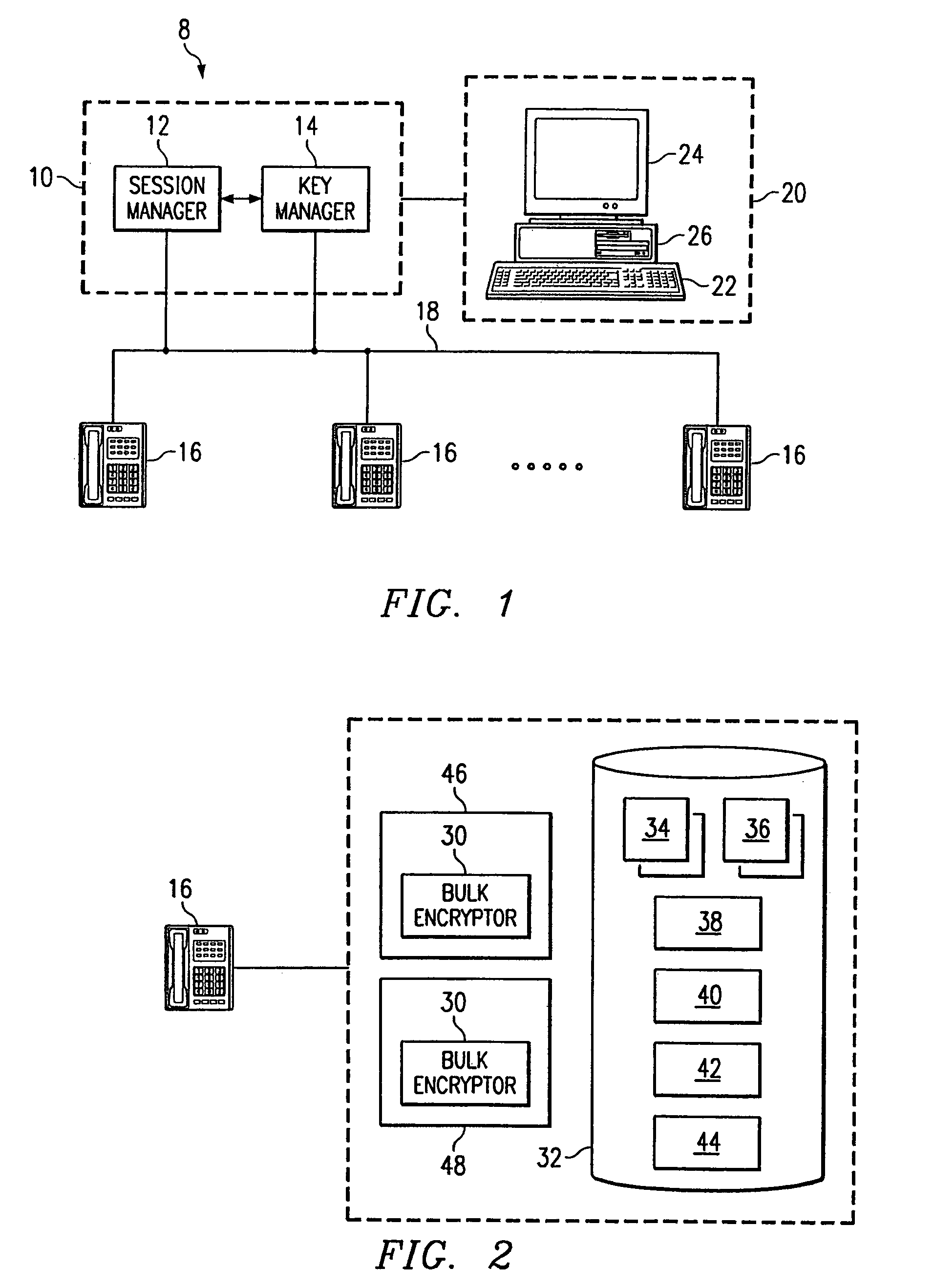
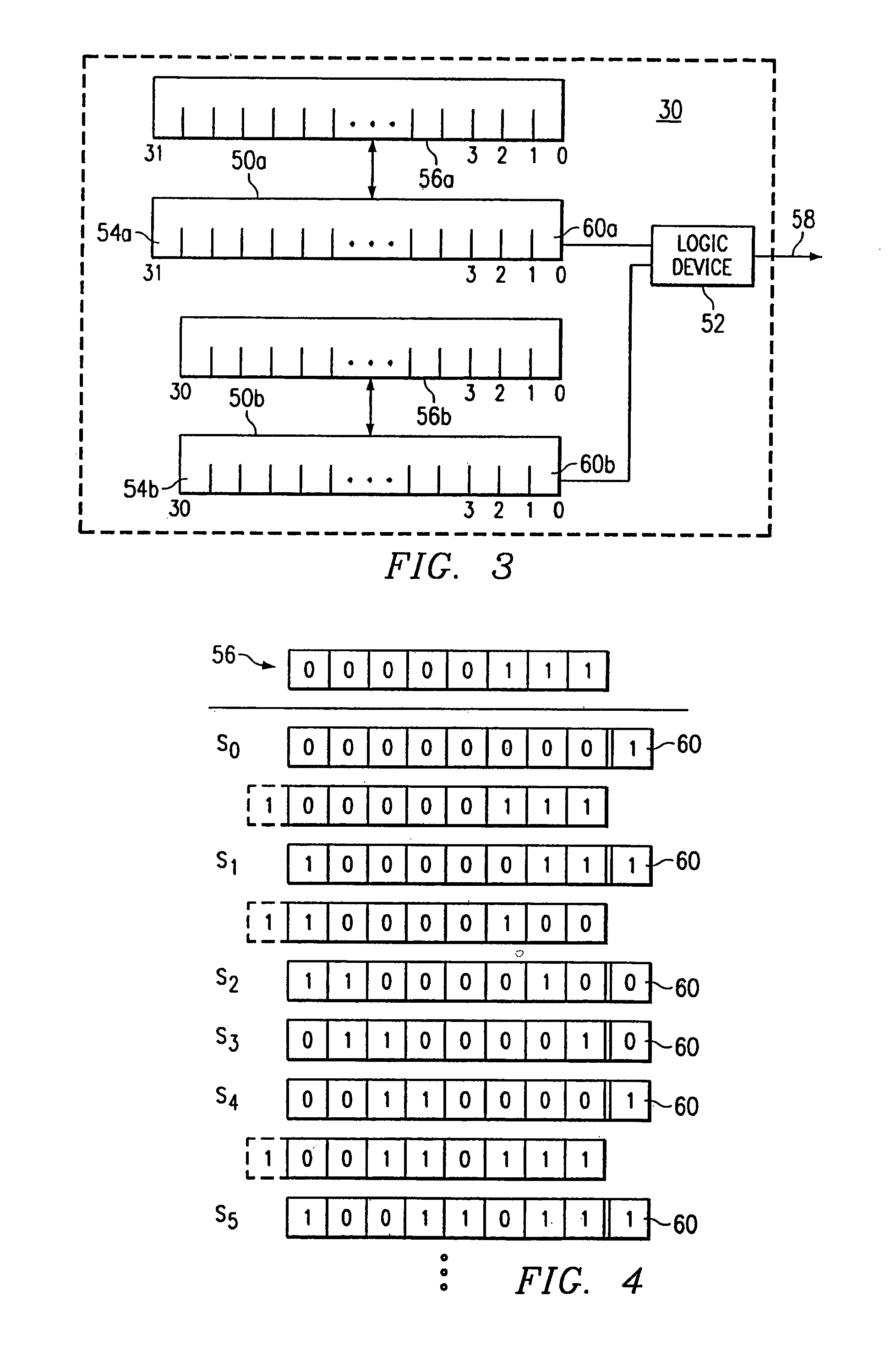
Encrypting information in a communications network
InactiveUS7171552B1Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedNetwork be reduced eliminatedKey distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesComputer terminalComputer science
According to one embodiment, an end station is provided for coupling to a communications network and participation in a communications session with another end station using the network. The end station includes encryption circuitry including a first linear feedback shift register (LFSR) and an associated first interconnect mask. The encryption circuitry is operable to generate an output sequence using the first LFSR and the first interconnect mask. A first table contains a plurality of polynomials each corresponding to an available interconnect mask. The end station is operable to receive a key specifying the first interconnect mask and to use the output sequence of the encryption circuitry to encrypt an information stream.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
System And Method For Distributed Processing
ActiveUS20120197596A1Few latency delayDisadvantages can be reduced eliminatedDigital data information retrievalError detection/correctionOperating systemData set
In one embodiment, a first portion and a second portion of a data set are identified. The first portion of the data set is sent to a first node that stores it in a first primary storage. The first primary storage is configured such that a first processor of the first node accesses information stored in the first primary storage without accessing another storage device. The second portion of the data set is sent to a second node that stores it in a second primary storage. The second primary storage is configured such that a second processor of the second node accesses information stored in the second primary storage without accessing another storage device. The first node generates a first set of results by processing the first portion of the data set. The second node generates a second set of results by processing the second portion of the data set.
Owner:CALLIDUS SOFTWARE
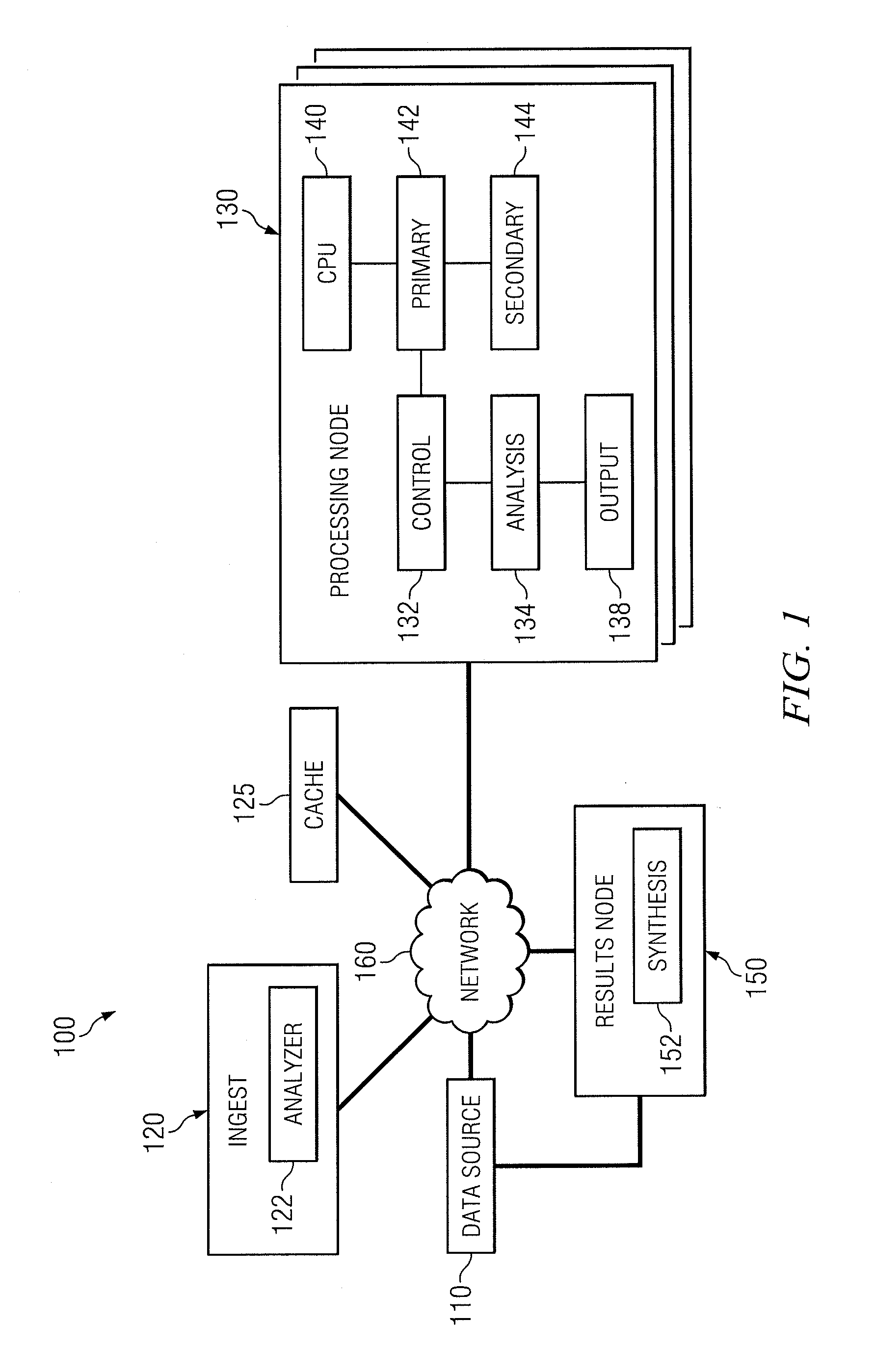
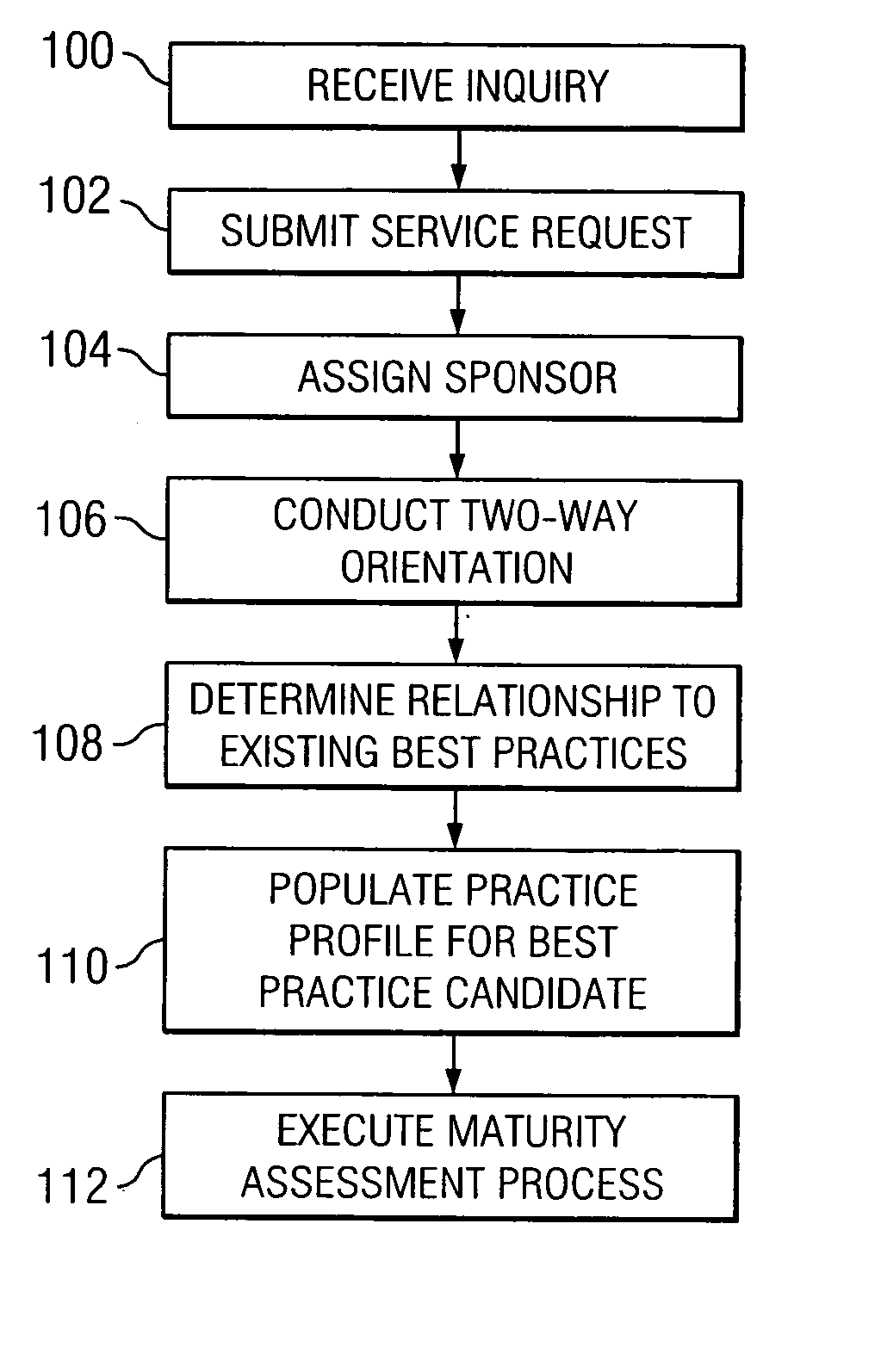
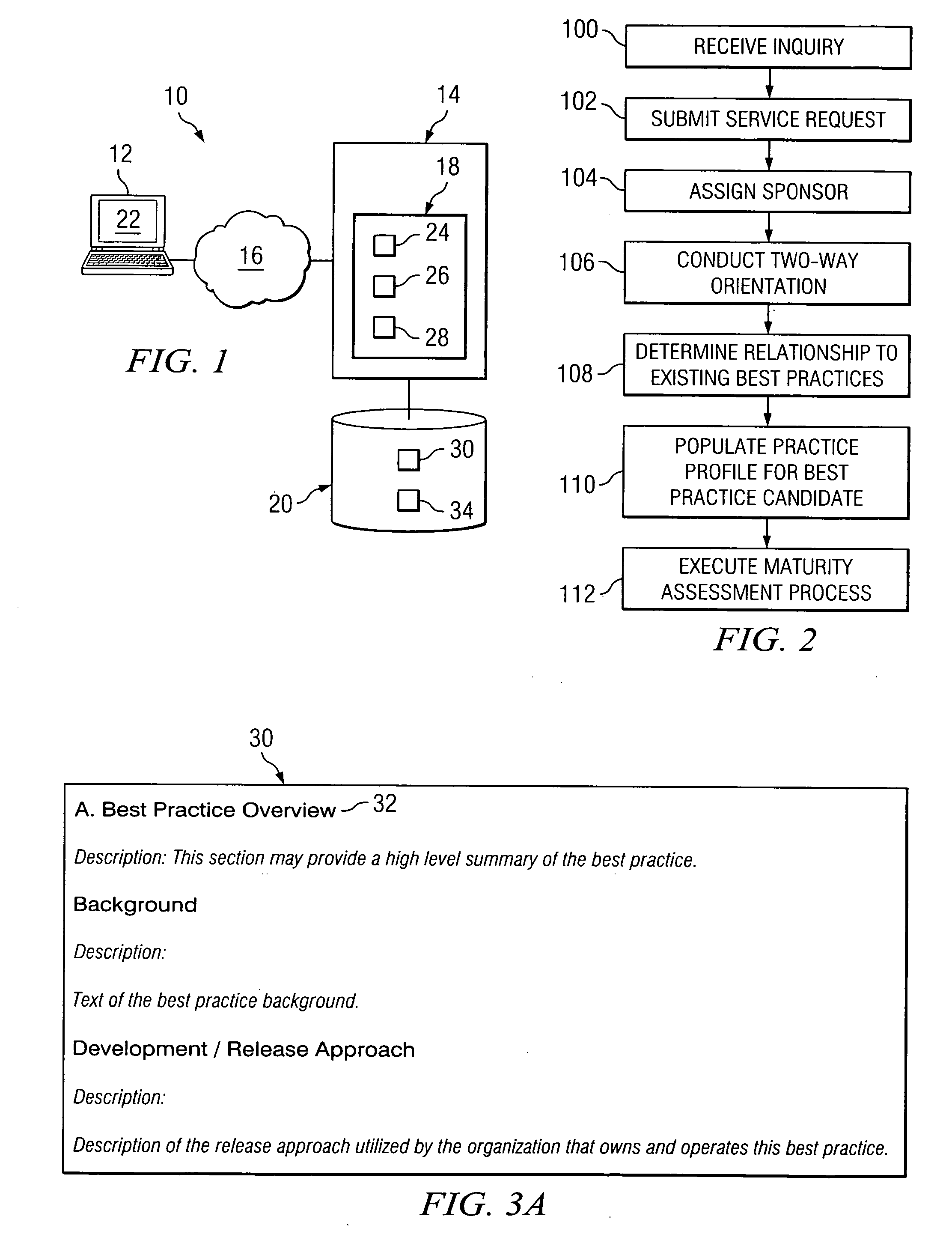
System and method for identifying and monitoring best practices of an enterprise
InactiveUS20050234767A1Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedIncrease incomeSpecial data processing applicationsGood practiceKnowledge management
In one embodiment, a process for identifying and monitoring one or more best practices of an enterprise includes defining a set of criteria for determining whether each of a plurality of practices of the enterprise qualify as a best practice of the enterprise. The process also includes receiving a practice profile of a particular practice of the enterprise, the practice profile comprising information associated with the particular practice and relating to one or more of the criteria. The process also includes performing a maturity assessment process to determine, based on a comparison between the practice profile for the particular practice and the set of criteria, whether the particular practice qualifies as a best practice of the enterprise and, if the particular practice so qualifies, assigning a best practice maturity level to the particular practice, the best practice maturity level defining to what degree the particular practice qualifies as a best practice of the enterprise.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
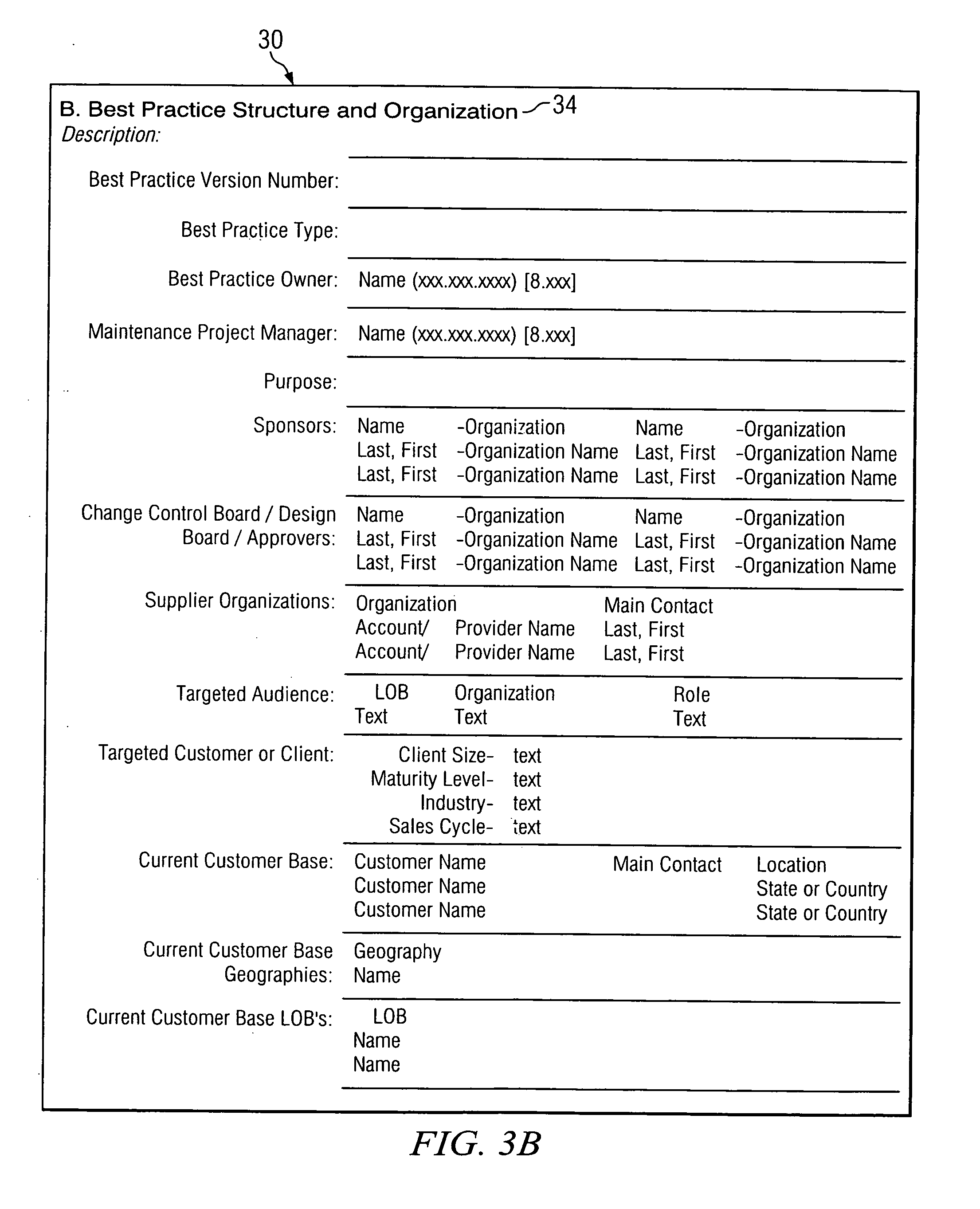
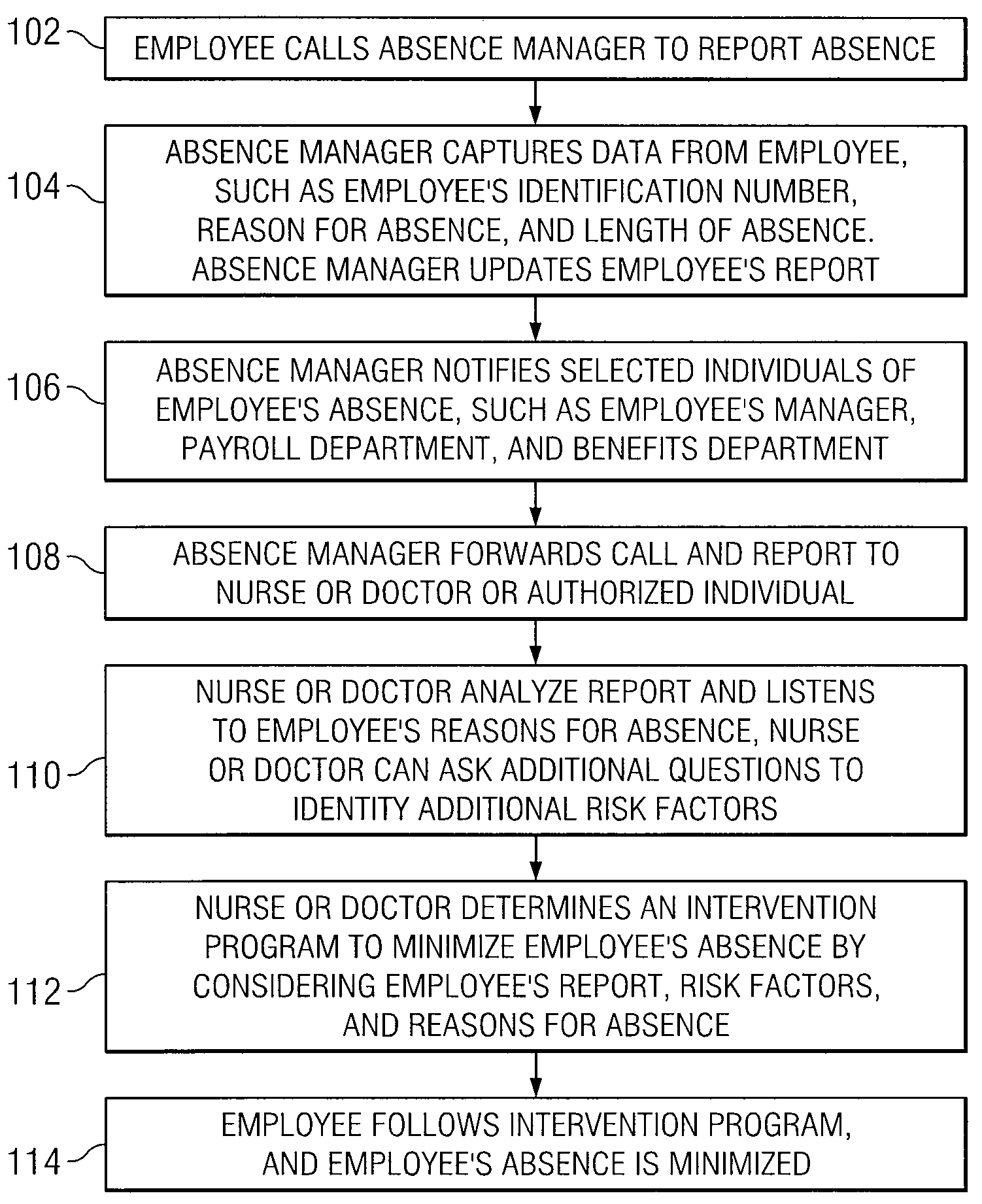
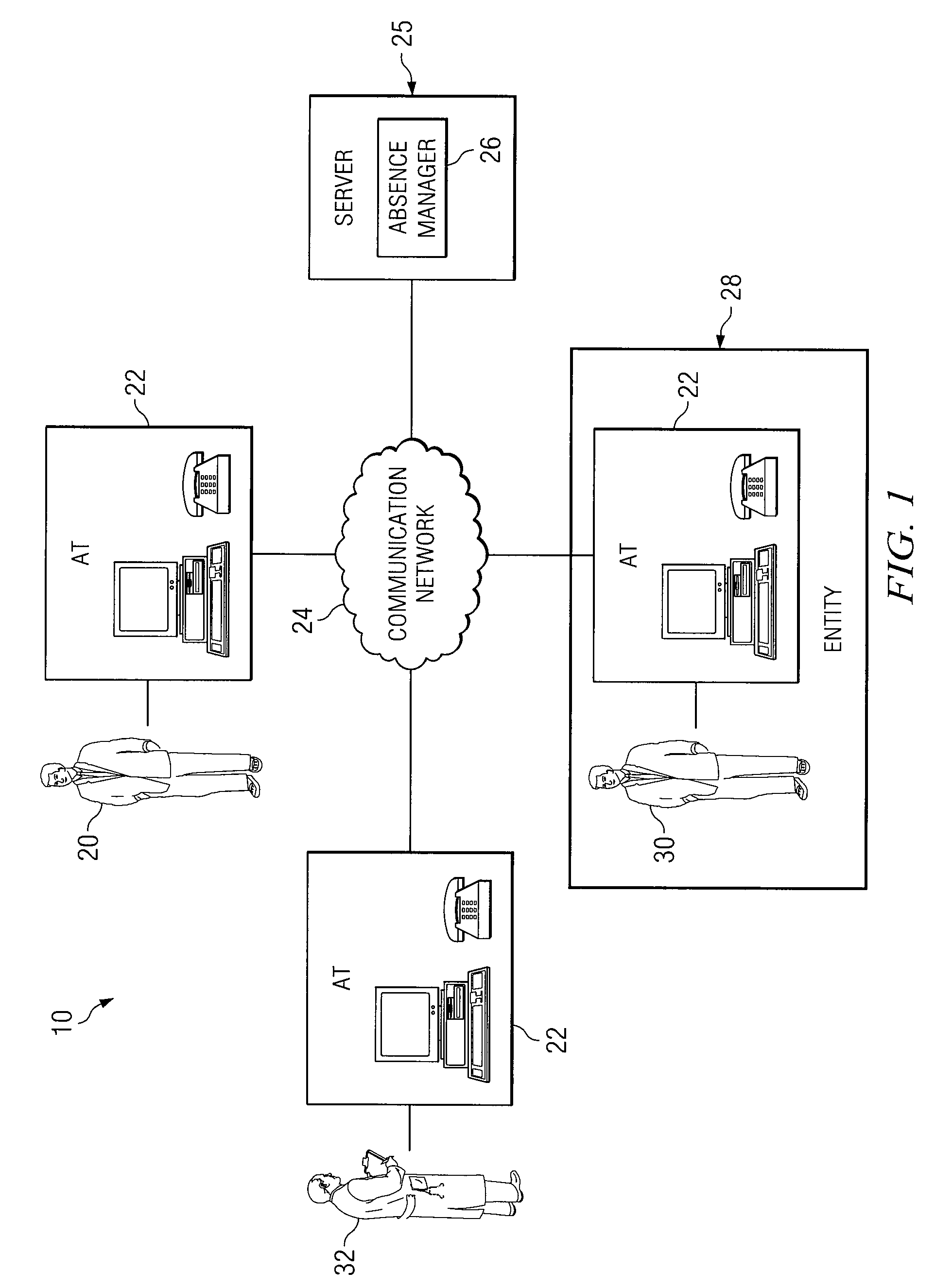
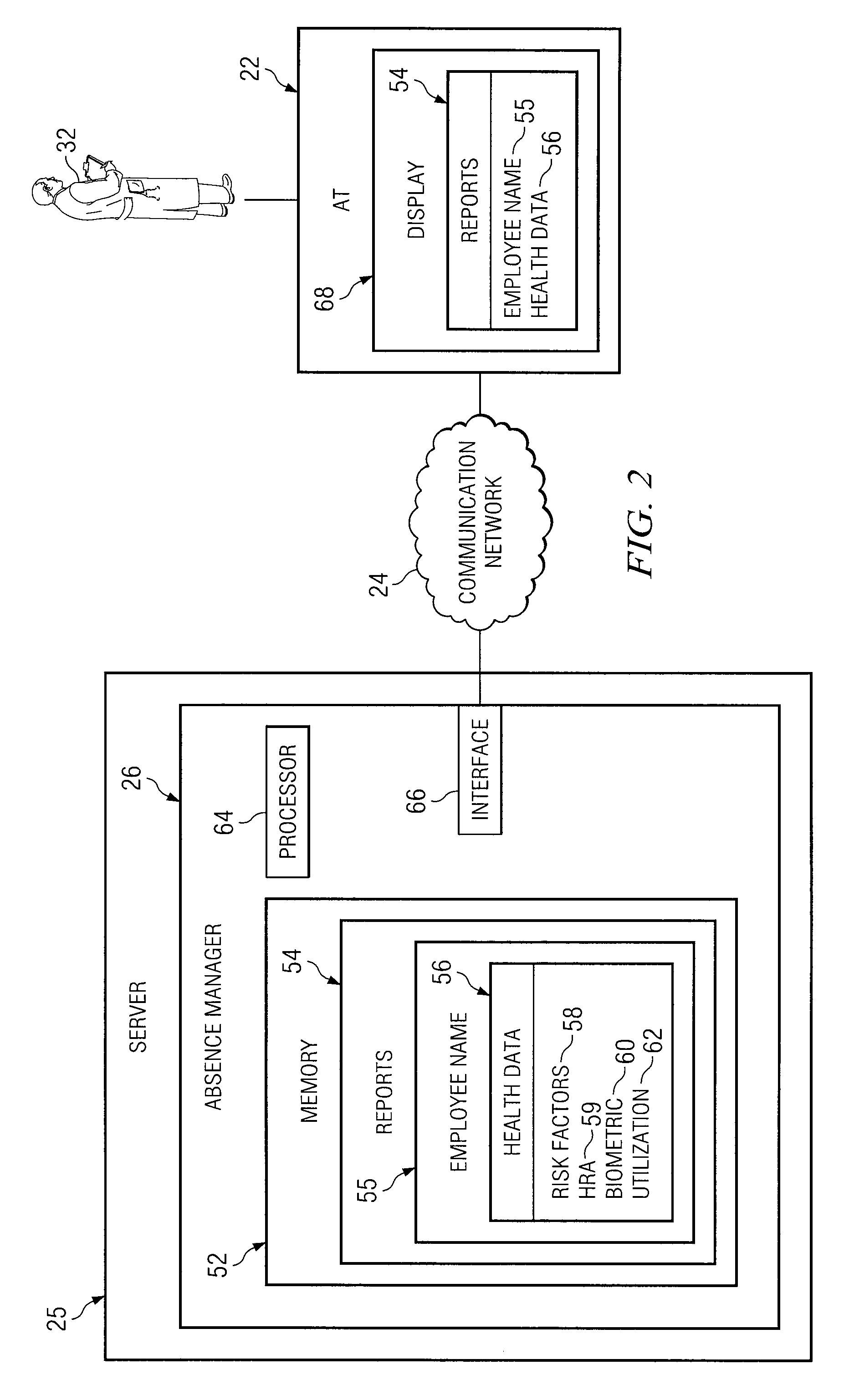
System and Method for Managing Absenteeism in an Employee Environment
InactiveUS20080306762A1Reduce medical costsDisadvantages can be reduced eliminatedHealth-index calculationForecastingProgram planningMedical education
A system for managing absenteeism includes an absence manager, employees, and healthcare individuals. Absence manager can capture health-related data associated with employee and reason for employee absence. Healthcare individuals can receive a report associated with the employee that is updated in real time as new data is captured. Healthcare individuals determine an intervention plan for the employee based on the health-related data, reason for absence, and any other relevant data. Healthcare individuals can exchange data with employee related to the intervention plan with the employee.
Owner:JAMES TERRY L
System and Method for Providing Communication Services to Mobile Device Users Incorporating Proximity Determination
InactiveUS20120329475A1Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedWeb data retrievalPosition fixationComputer networkMobile device
In certain embodiments, a method for proximity determination includes receiving one or more network identifiers, each associated with a corresponding network, from a first mobile device. The method further includes receiving one or more network identifiers, each associated with a corresponding network, from a second mobile device. The method further includes processing the network identifiers received from the first and second mobile devices to determine whether the first mobile device and the second mobile device are in proximity to one another.
Owner:JAMBO NETWORKS
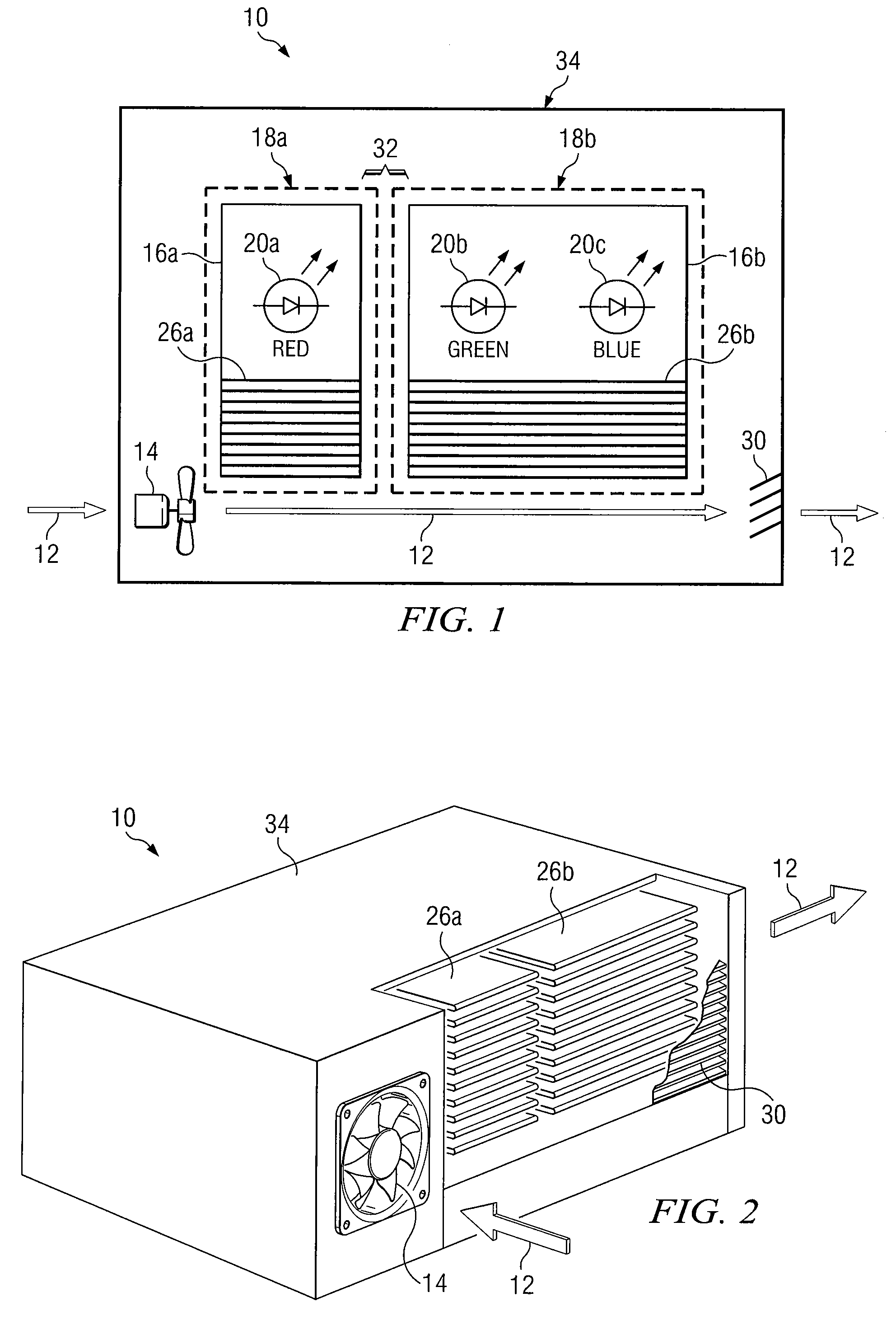
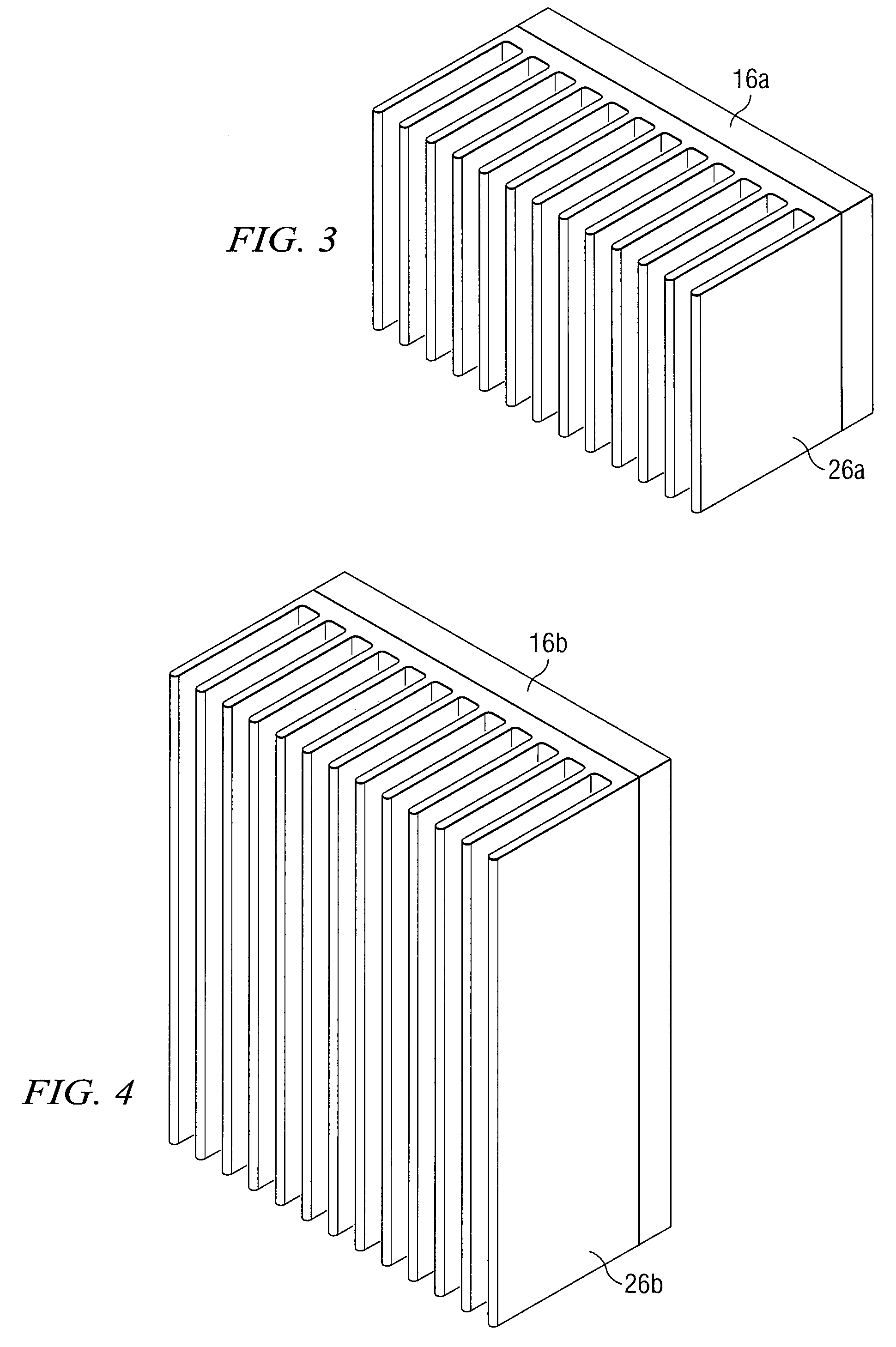
Heat Sinks for Cooling LEDS in Projectors
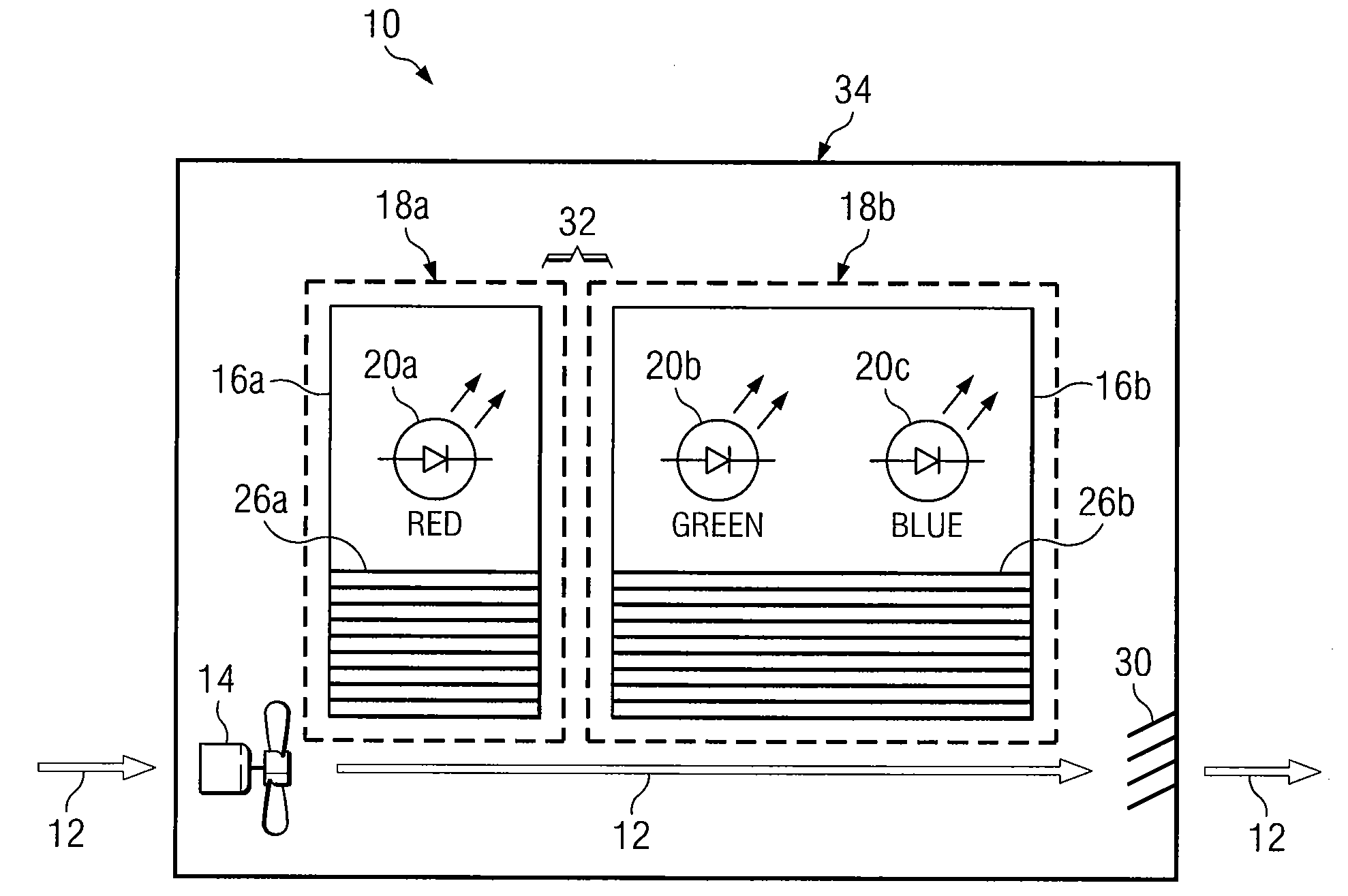
ActiveUS20090059582A1Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedProblems can be reduced eliminatedLighting elementsLighting heating/cooling arrangementsJunction temperatureEngineering
According to certain embodiments, an apparatus for cooling light emitting diodes (LEDs) in projectors includes one or more first LEDs, one or more first heat sinks, one or more second LEDs, and one or more second heat sinks. The first LEDs are configured to generate light, and each first LED has a first desired junction temperature. The first heat sinks are configured to dissipate heat generated by the first LEDs. The second LEDs are configured to generate light, and each second LED has a second desired junction temperature that is higher than the first desired junction temperature. The second heat sinks are configured to dissipate heat generated by the one or more second LEDs. A cooling fan directs air flow over the first heat sinks and the second heat sinks, and an exhaust vent enables the air flow over the first heat sinks and the second heat sinks.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
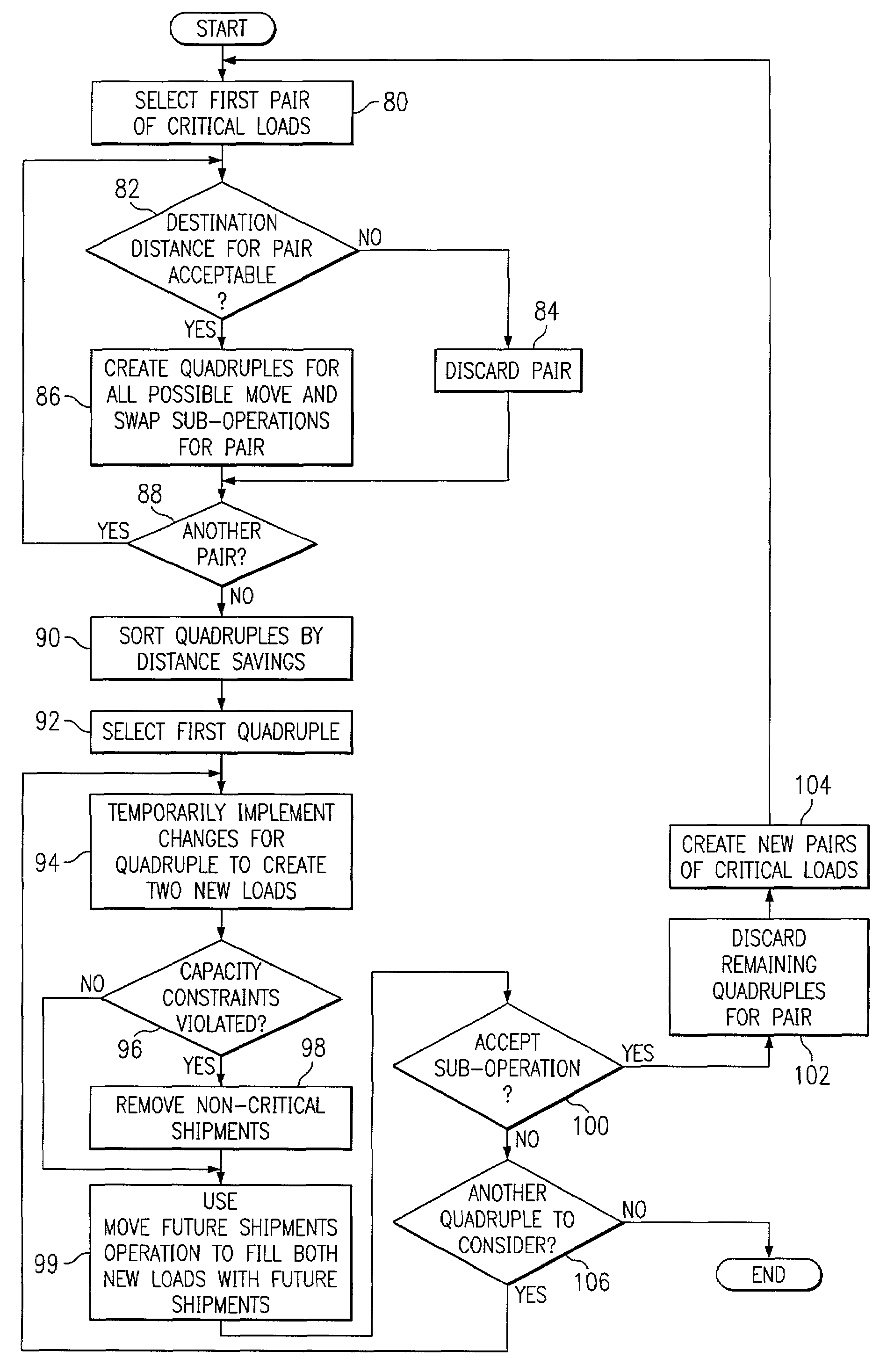
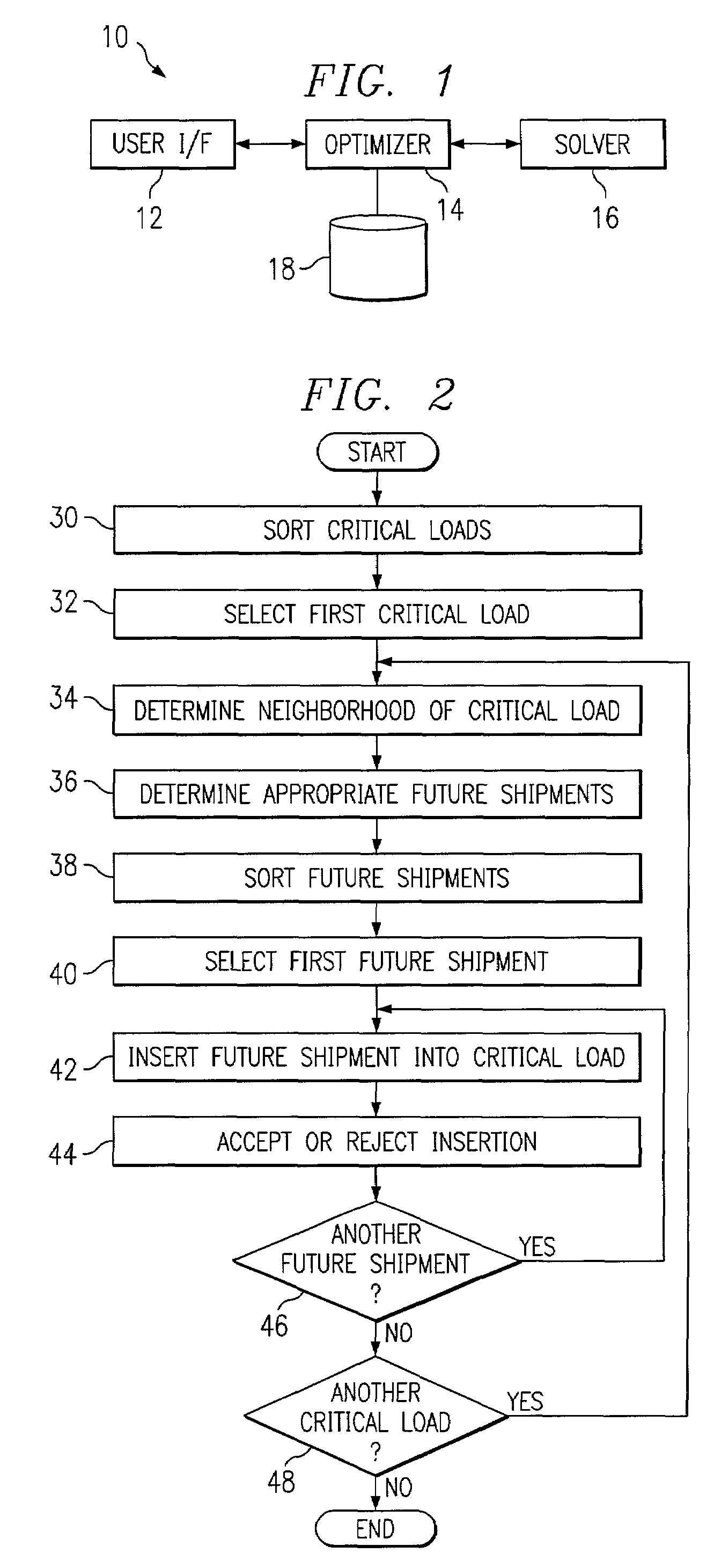
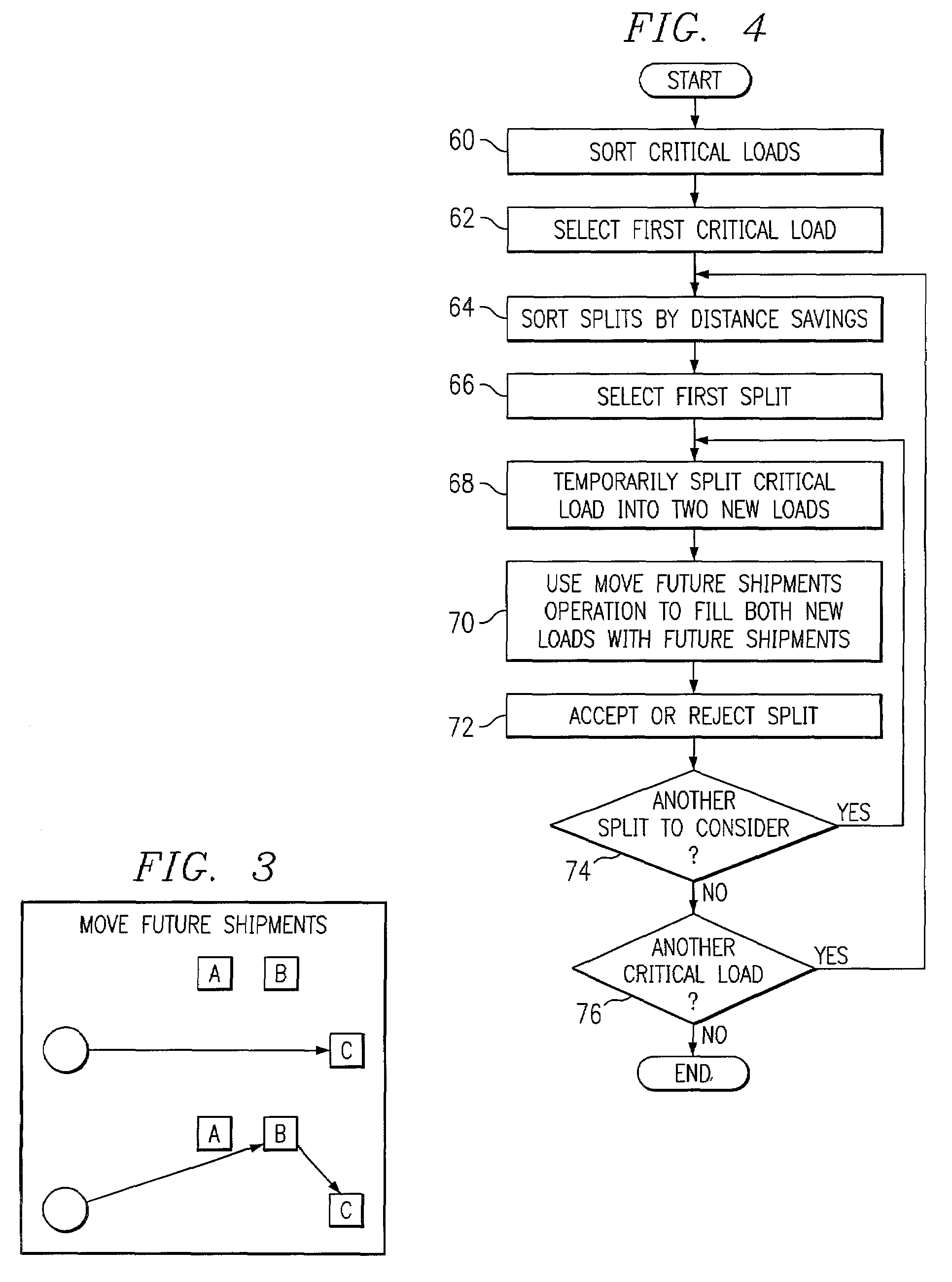
Routing shipments according to criticality
InactiveUS6980885B2Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedSimple and flexible and effectiveAcutation objectsDigital data processing detailsCritical loadParallel computing
A computer-implemented method for routing shipments according to criticality includes accessing an initial solution to an optimization problem of routing multiple shipments to multiple locations using multiple vehicles, the initial solution including multiple loads such that each shipment is routed within exactly one load and a global cost across all loads is minimized, the initial solution being generated independent of the criticality of the shipments. Into each of one or more critical loads in a current solution, one or more non-critical shipments are inserted that are within a neighborhood of the critical load, a critical load being a load containing at least one critical shipment. One or more local search operations are executed to improve the initial solution, the operations including at least one of: (a) splitting each of one or more selected critical loads in a current solution into two new critical loads; (b) for each of one or more selected critical load pairs in a current solution, move a sequence of stops from one critical load in the pair to the other critical load in the pair and / or swap two sequences of stops between the critical loads in the pair; and (c) for each of one or more selected critical loads in a current solution that are indirect critical loads having at least one in-transit stop, break up the indirect critical load into a plurality of new direct critical loads having no in-transit stops and execute operation (b) on each of one or more selected critical load pairs, each selected critical load pair including at least one new direct critical load.
Owner:BLUE YONDER GRP INC
System and method for scheduling conference resources
InactiveUS7693734B2Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedResources be reduced eliminatedMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationStart timeReal-time computing
A method for scheduling conference resources is provided, that includes receiving a request for a conference reservation. The request may include the identities of a plurality of proposed participants, a proposed start time, and at least one fixed resource criterion. In accordance with a particular embodiment of the present invention, a projected location of at least one of the proposed participants is automatically calculated. The projected location may be a location at which the at least one of the proposed participants is expected to be at approximately the proposed start time. The method may also include automatically calculating a projected location of at least one invitee of the conference. In accordance with this embodiment, the projected location of the at least one invitee may be used to select an optimal one of a plurality of fixed resources, that match the at least one fixed resource criterion.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
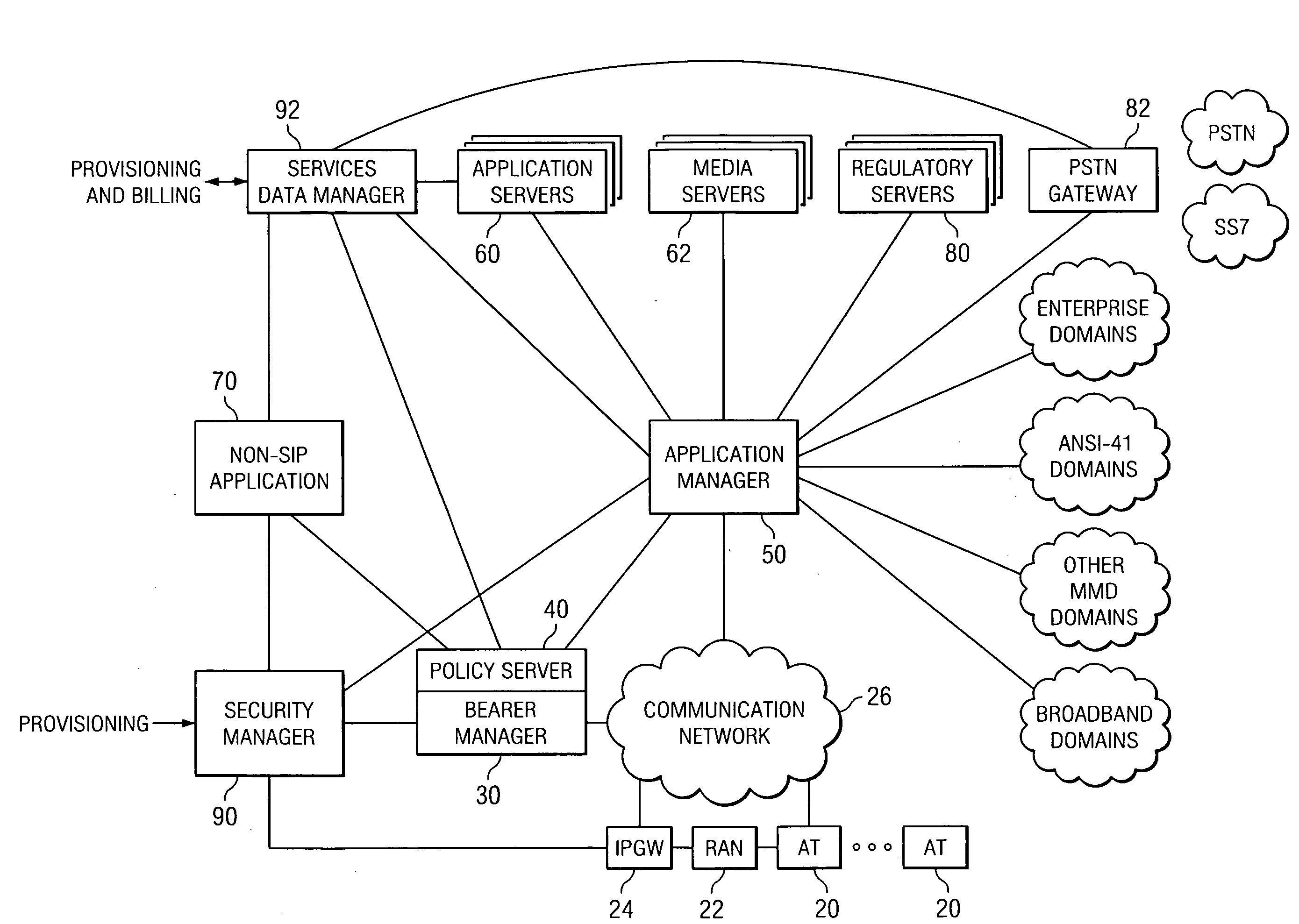
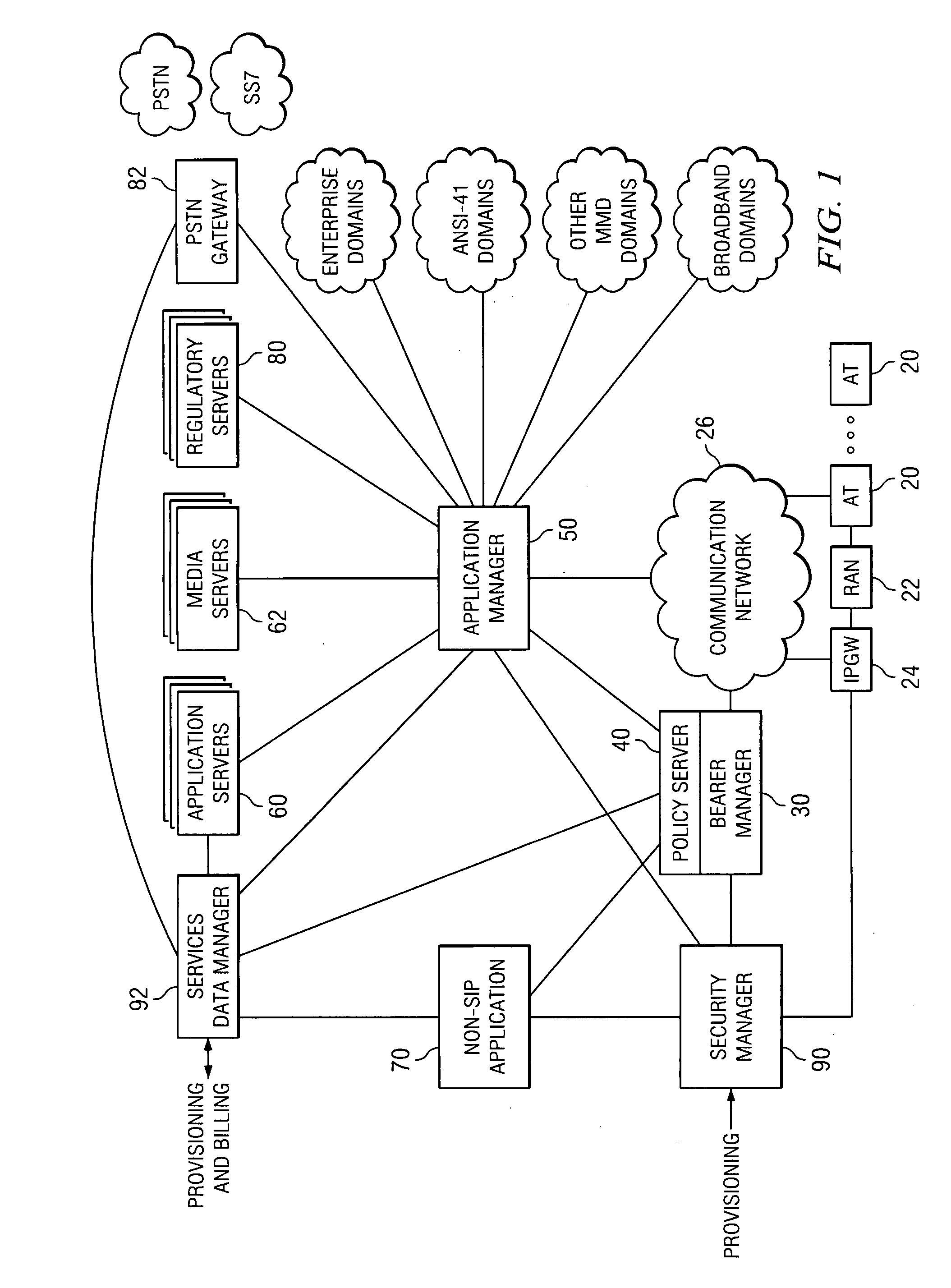
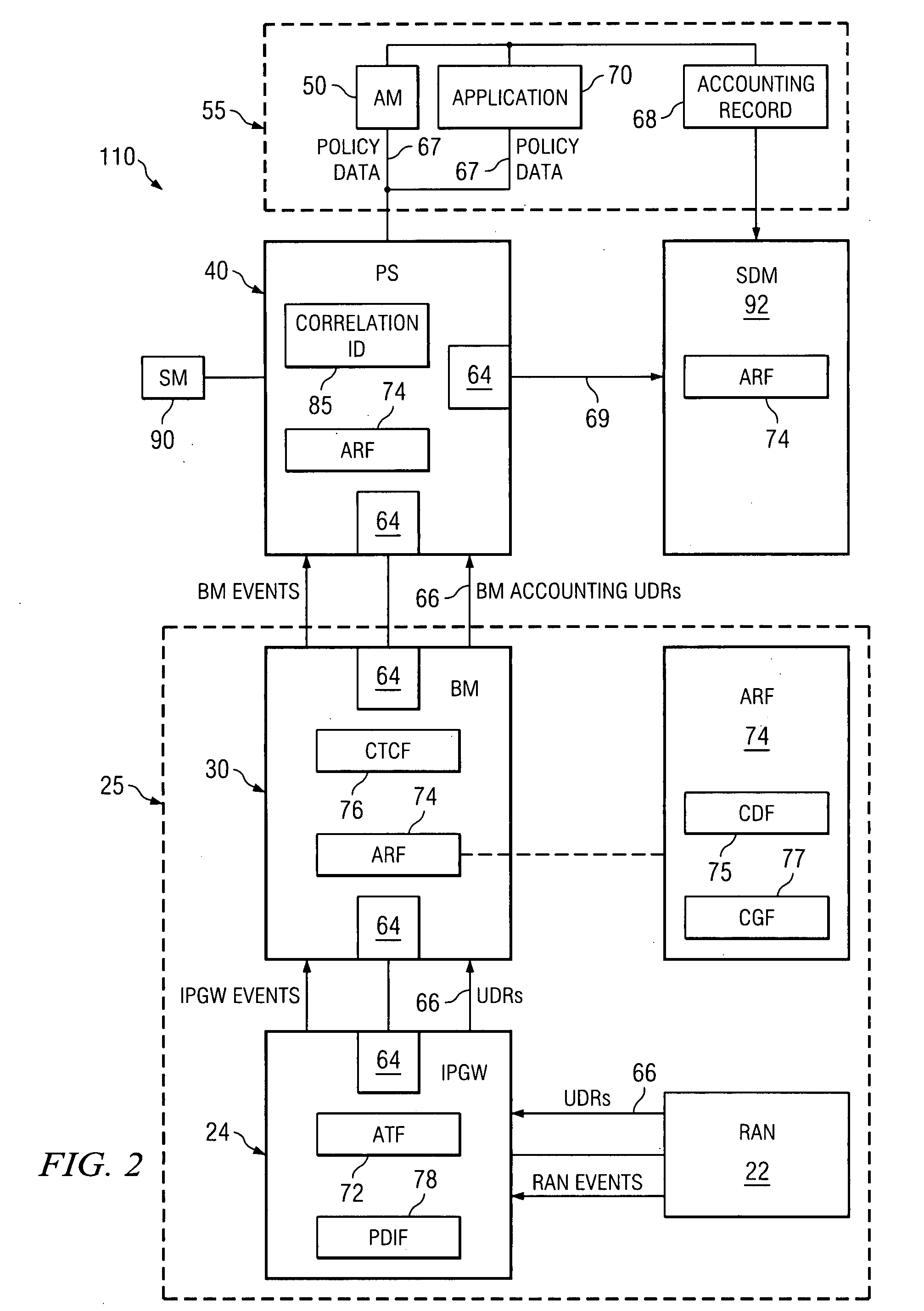
System and method for generating a unified accounting record for a communication session
ActiveUS20070206515A1Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedEasily introducedMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsNetwork traffic/resource managementProtocol ApplicationDatabase
A method for creating an accounting record in a policy server in a communication network. The method also includes receiving policy data from one or more application layer elements. The method includes receiving accounting data from one or more lower layer elements, such that the accounting data is associated with the policy data. The method also includes consolidating the accounting data and the policy data received.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
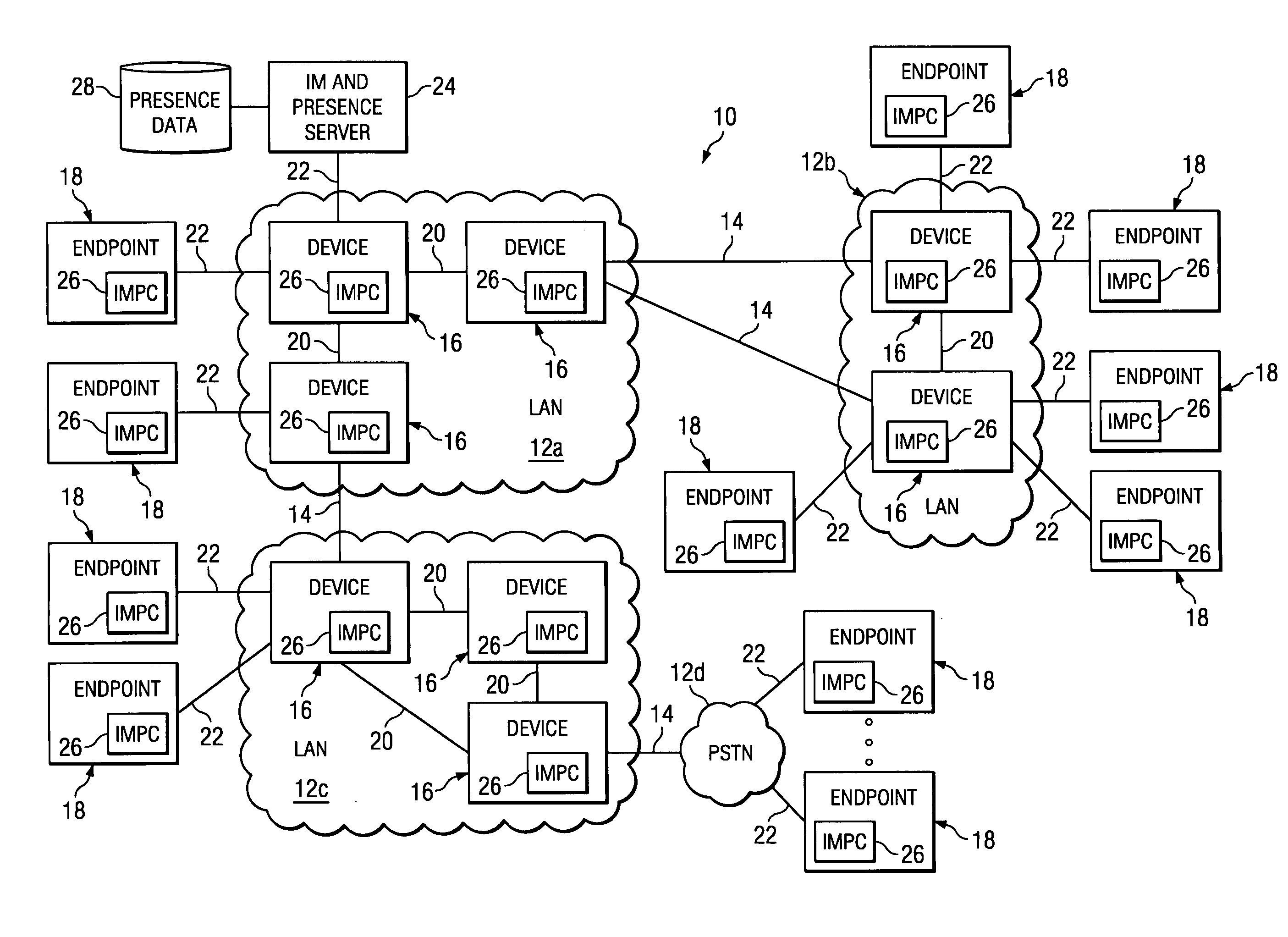
Presence-based management in a communication network
InactiveUS20050213563A1Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedNetwork be reduced eliminatedData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsDistributed computing
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
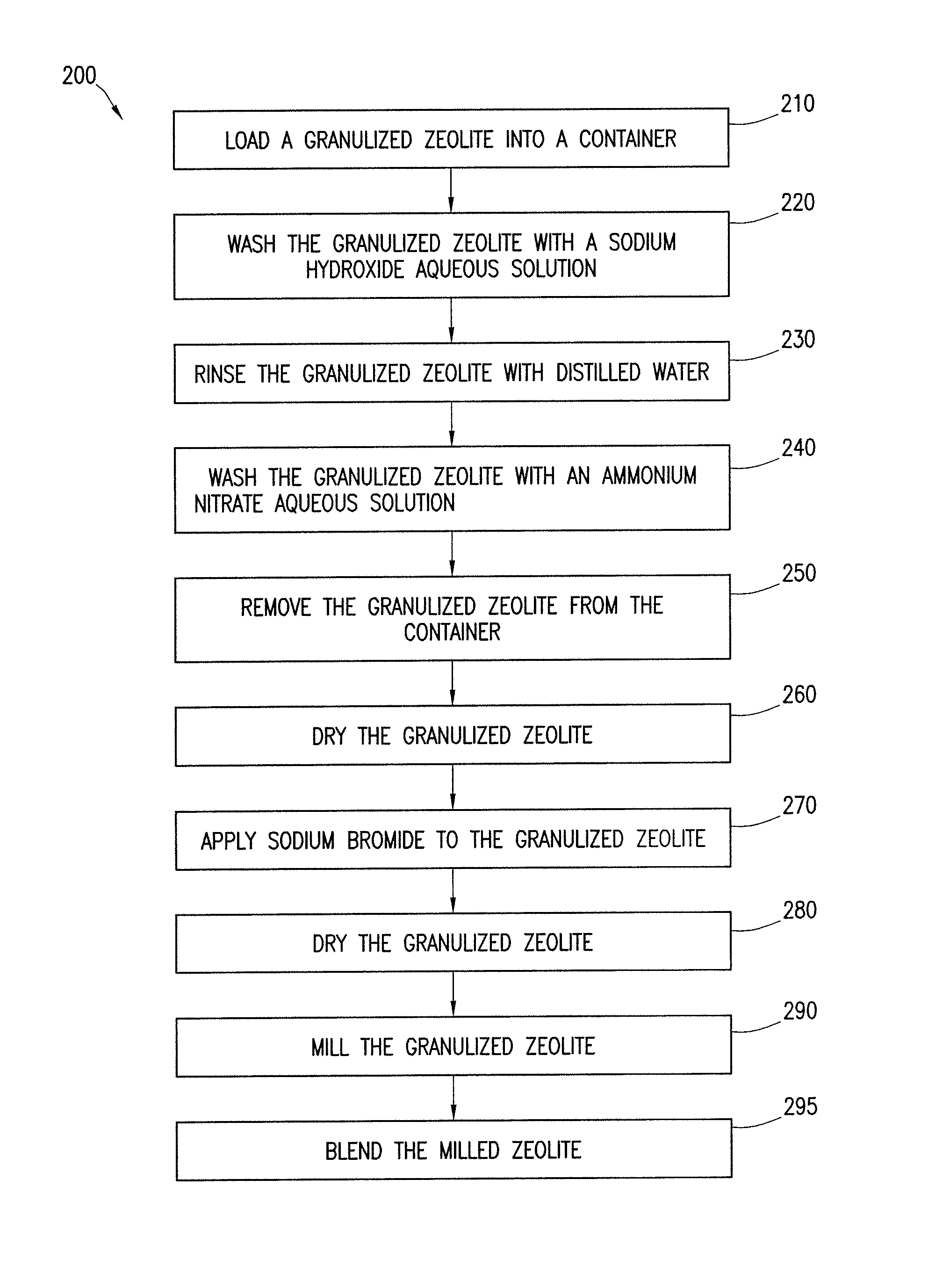
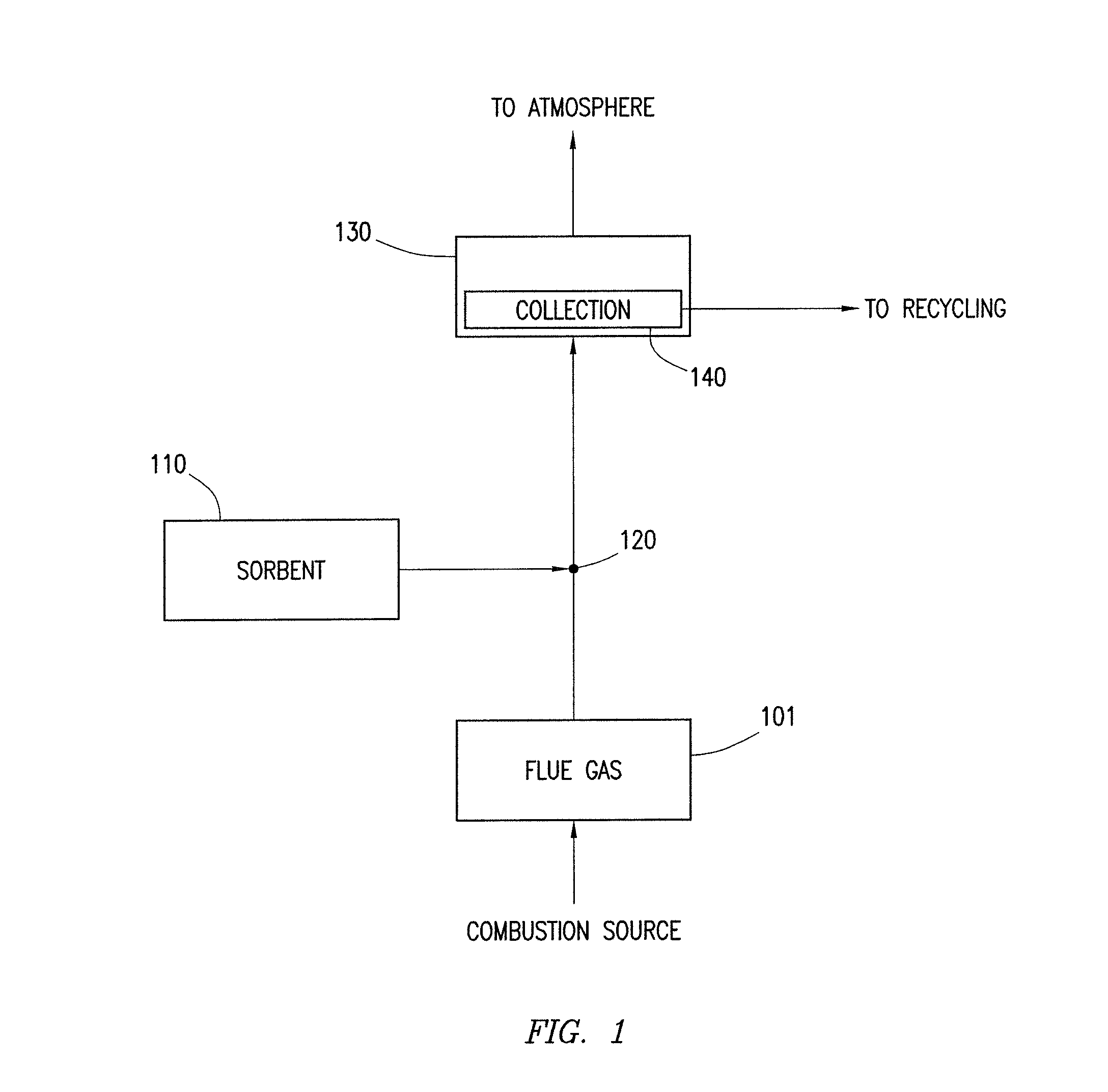
Mercury removal from flue gas streams using treated sorbents
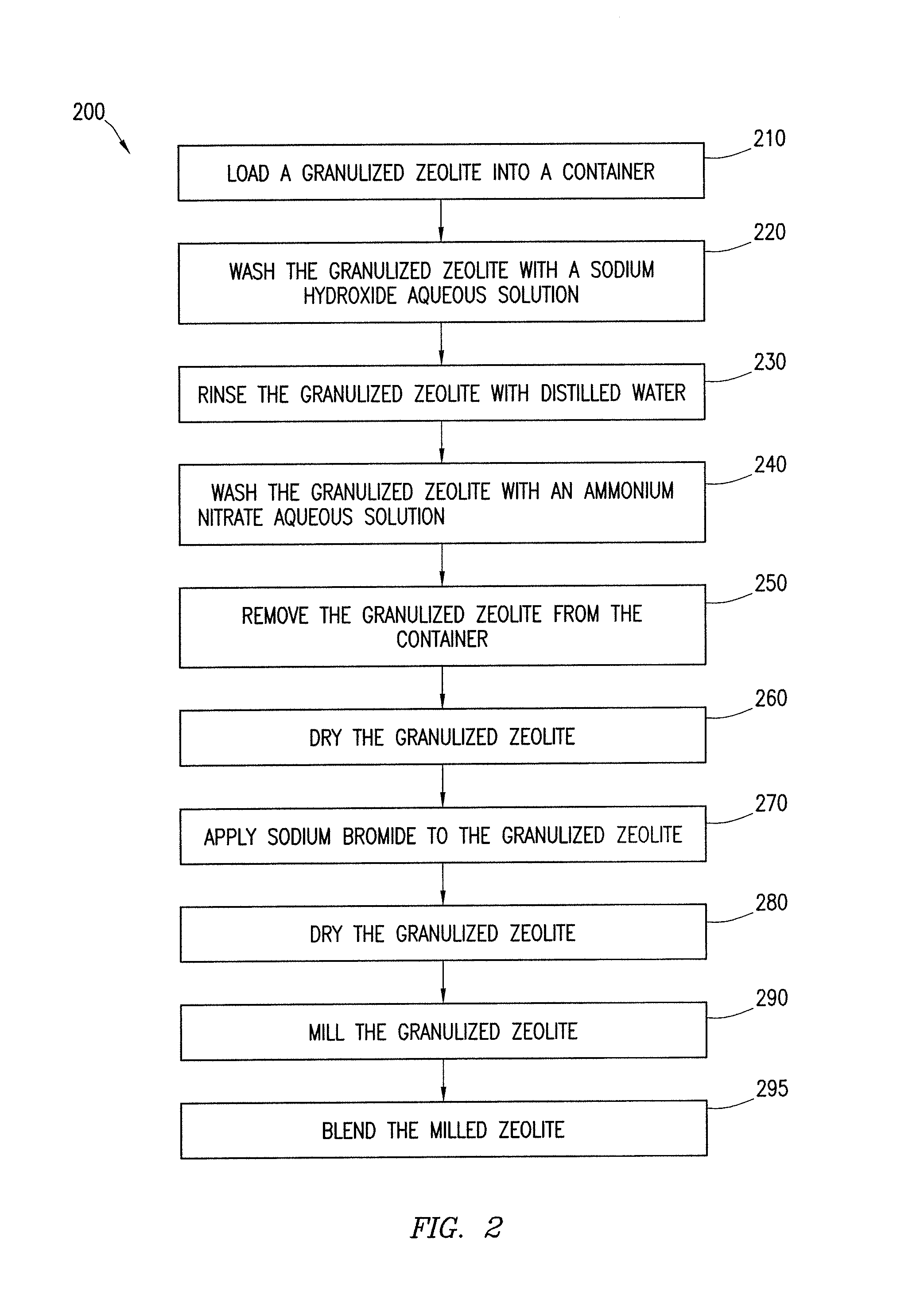
ActiveUS8551431B1Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedProblems can be reduced eliminatedGas treatmentMolecular sieve catalystsHalogenFlue gas
A method for modifying the properties of a sorbent comprising washing a sorbent with a washing solution so as to achieve an exchange of ions between the sorbent and the washing solution, and applying a halogen compound to the sorbent that has been washed with the washing solution to achieve a predetermined concentration of the halogen on the sorbent.
Owner:CABOT NORIT AMERICAS
Multilevel Authentication
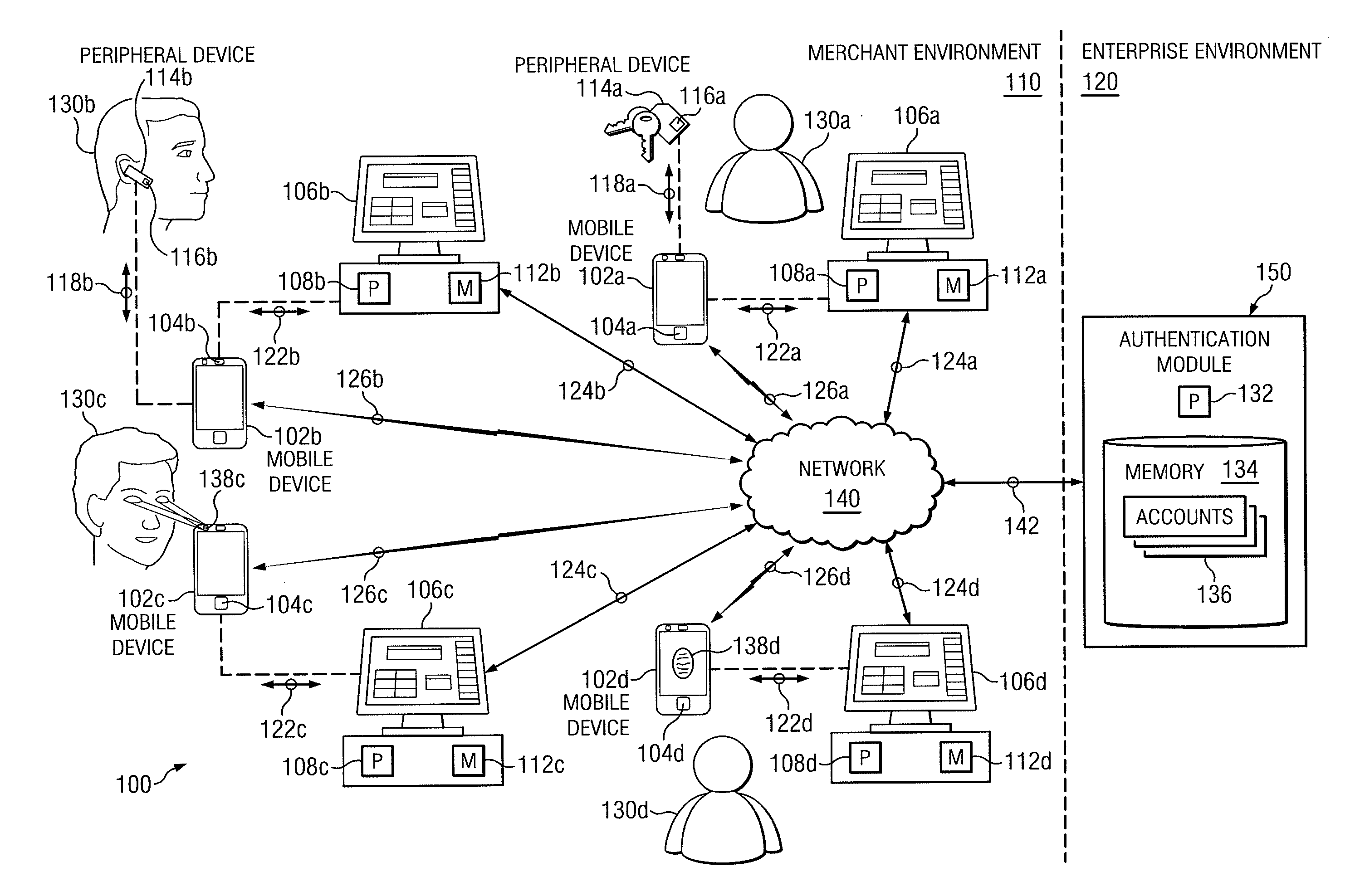
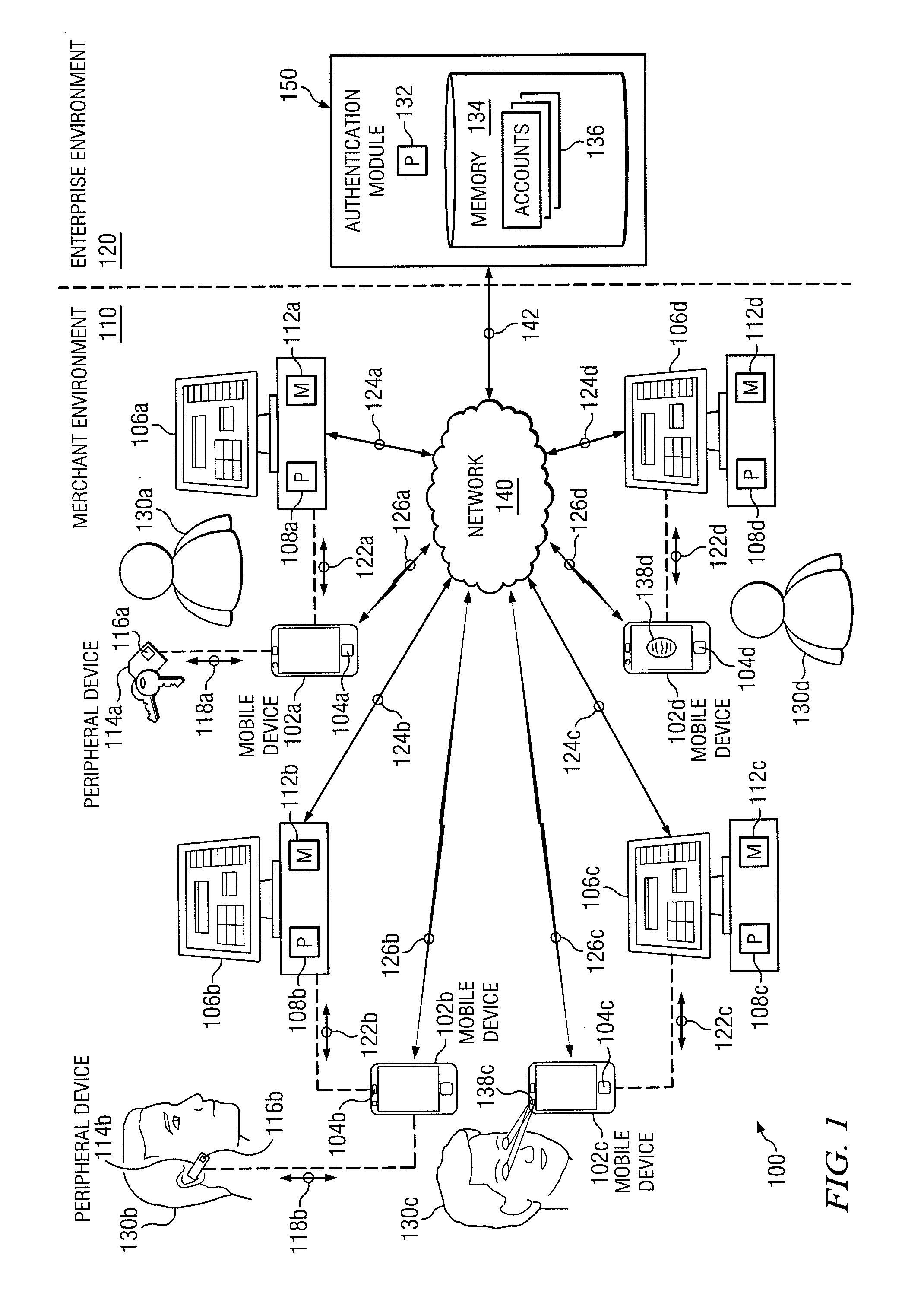
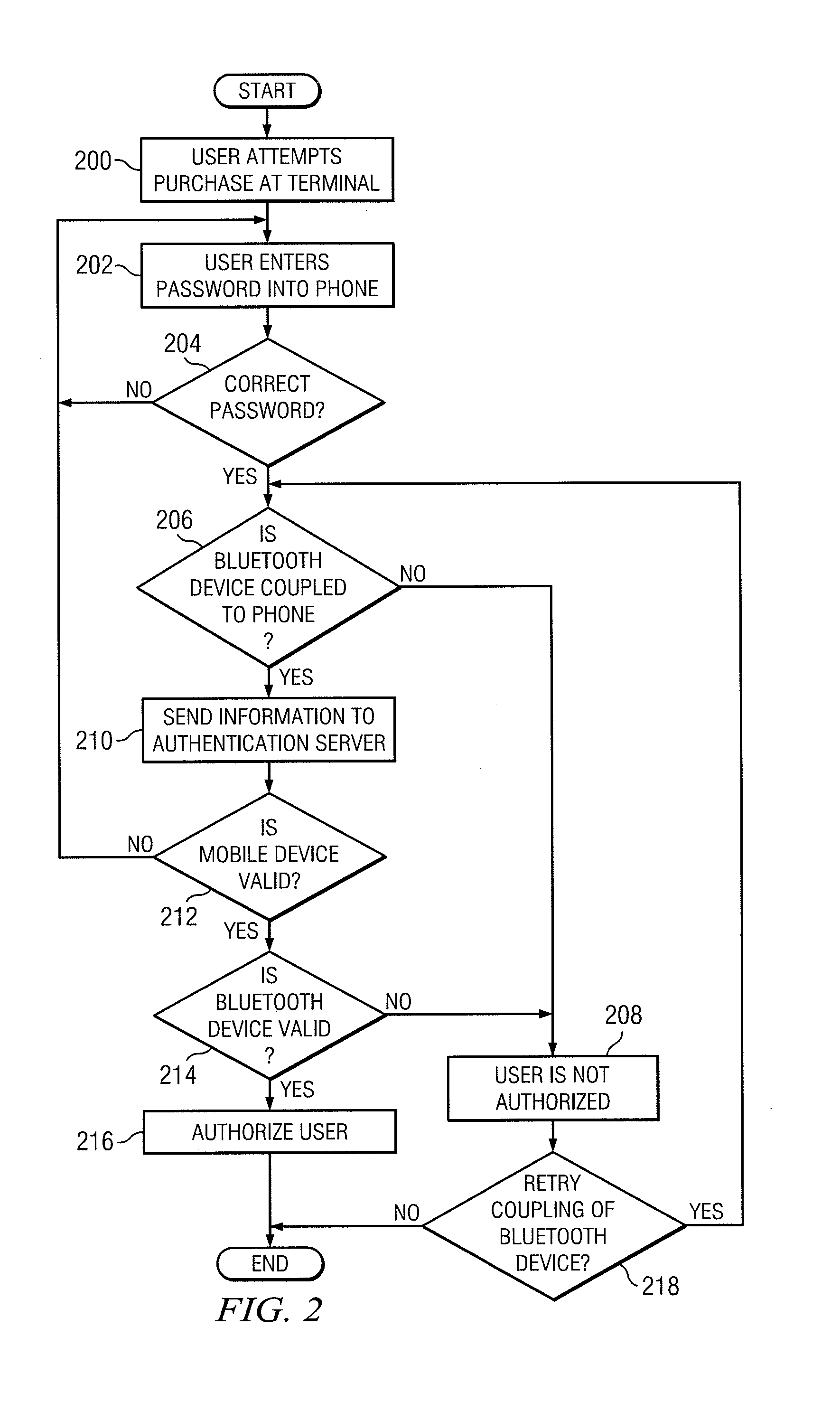
ActiveUS20130067551A1Authentication be reduced eliminatedDisadvantages can be reduced eliminatedDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationInternet privacyUser input
In an exemplary embodiment, a system includes a memory operable to store a user account identifier associated with a user account and a mobile device identifier associated with a mobile device. The memory is also operable to store a first user credential and a second user credential, the second user credential, wherein the second user credential comprises user input data captured by a sensor. The system includes a network interface operable to receive a request to authenticate a requesting user. The system also includes a processor operable to determine information included in the request to facilitate authentication of the requesting user and whether the information included in the request matches the information associated with the user account. The processor is further operable to authenticate the requesting user if the request is associated with the user account and information included in the request matches the information associated with the user account.
Owner:BANK OF AMERICA CORP
Enhanced call pickup
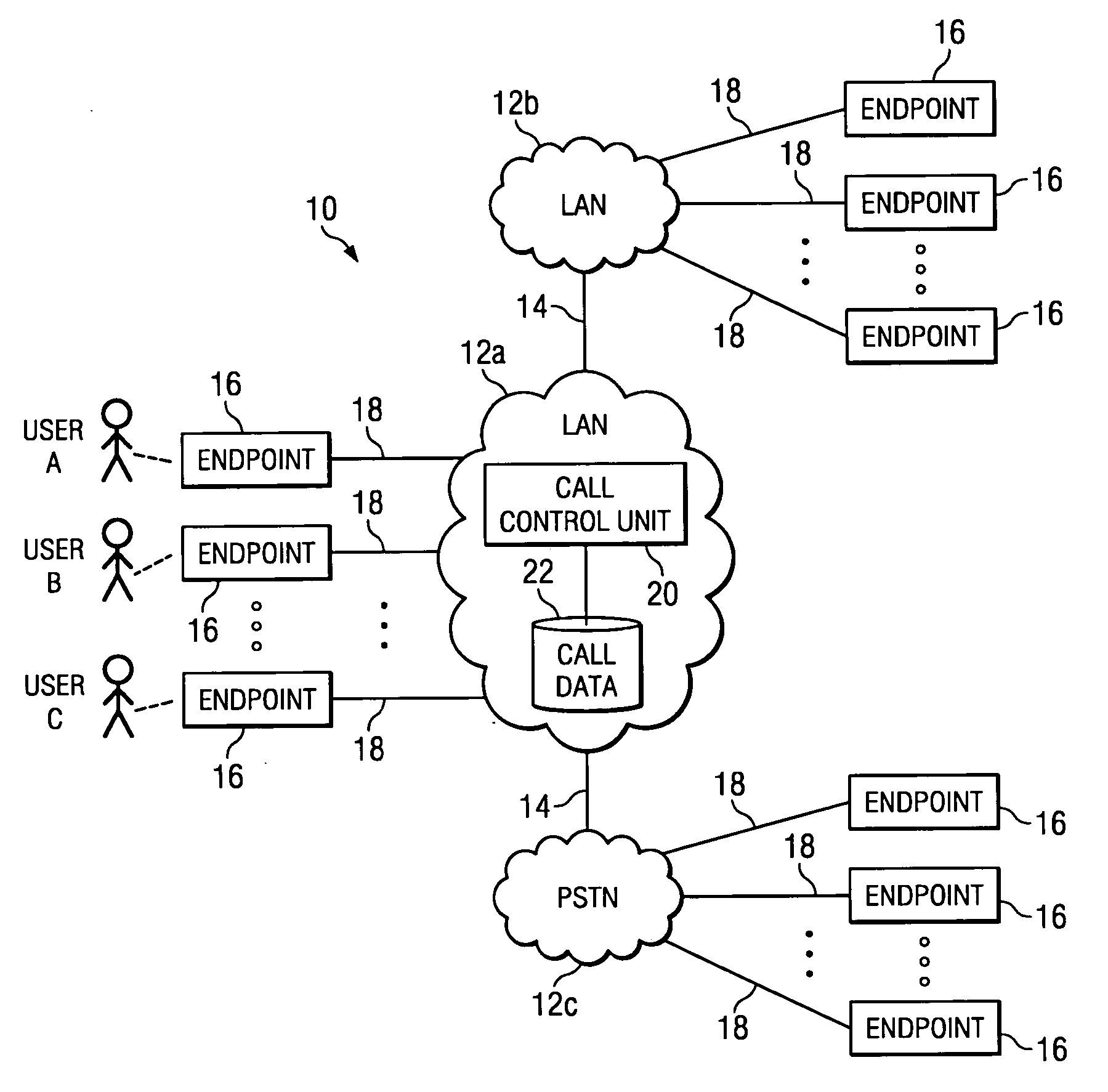
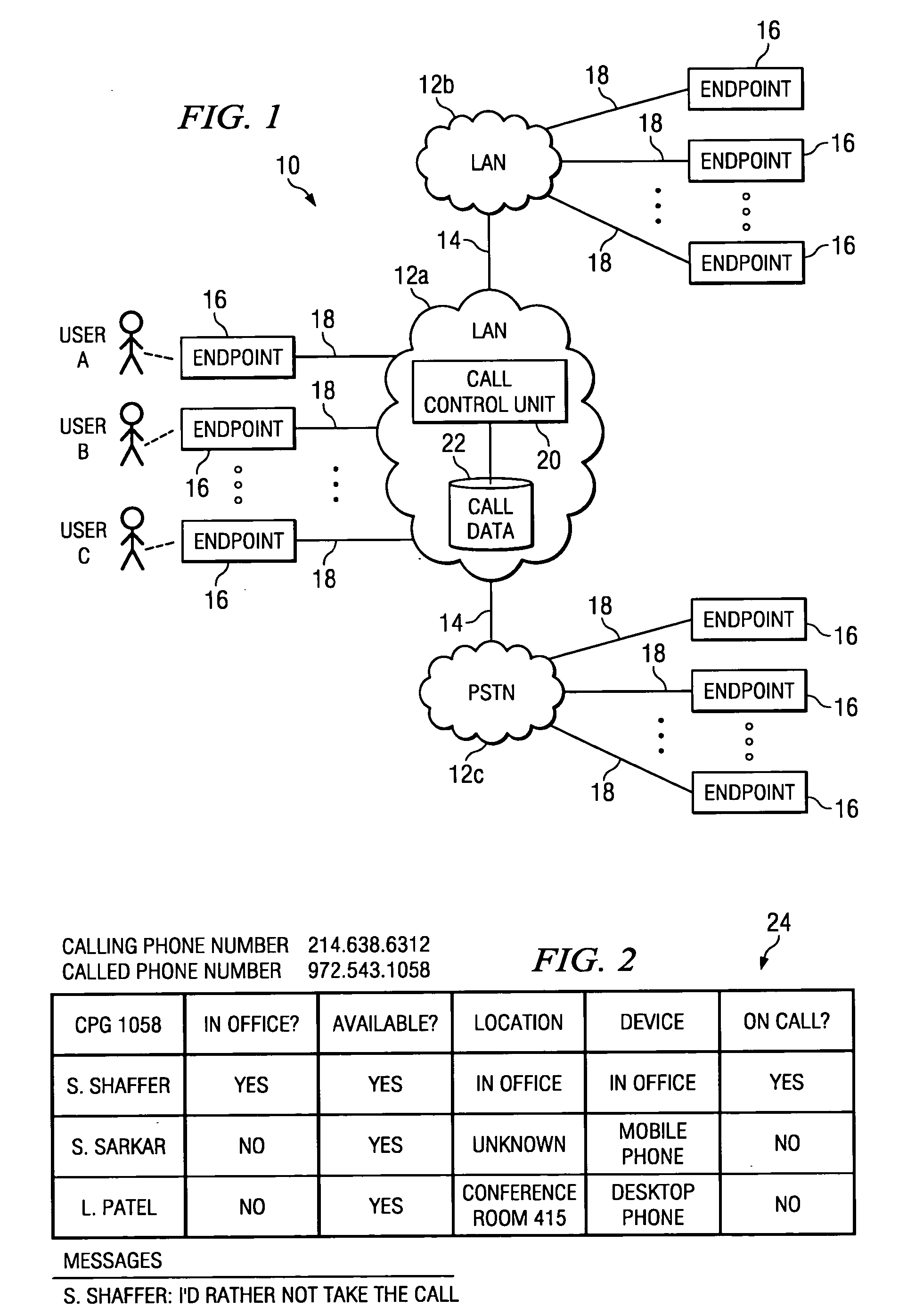
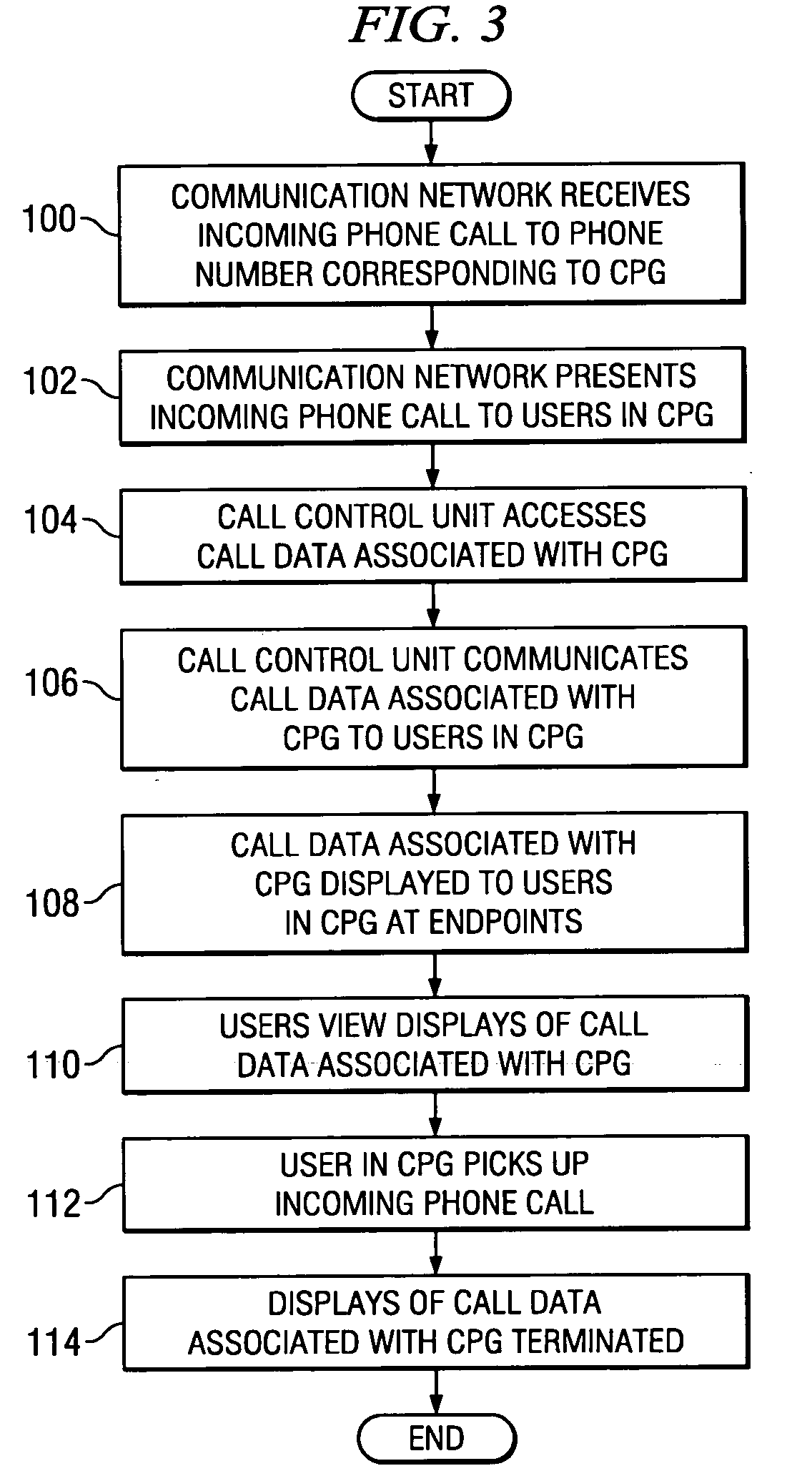
InactiveUS20050238157A1Enhanced call pickupFacilitate decision-makingInterconnection arrangementsSpecial service for subscribersWorld Wide WebTelephony
In one embodiment, a method for enhanced call pickup includes accessing data indicating a current status of each of one or more users in a call pickup group (CPG) with respect to an incoming phone call to a phone number corresponding to the CPG and communicating the data to one or more endpoints of one or more users in the CPG for display to one or more users in the CPG. A display of the data to a first user in the CPG facilitates the first user determining a current status of each of one or more second users in the CPG to facilitate a decision by the first user regarding whether to pick up the incoming phone call.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Interactive approach for managing risk and transparency
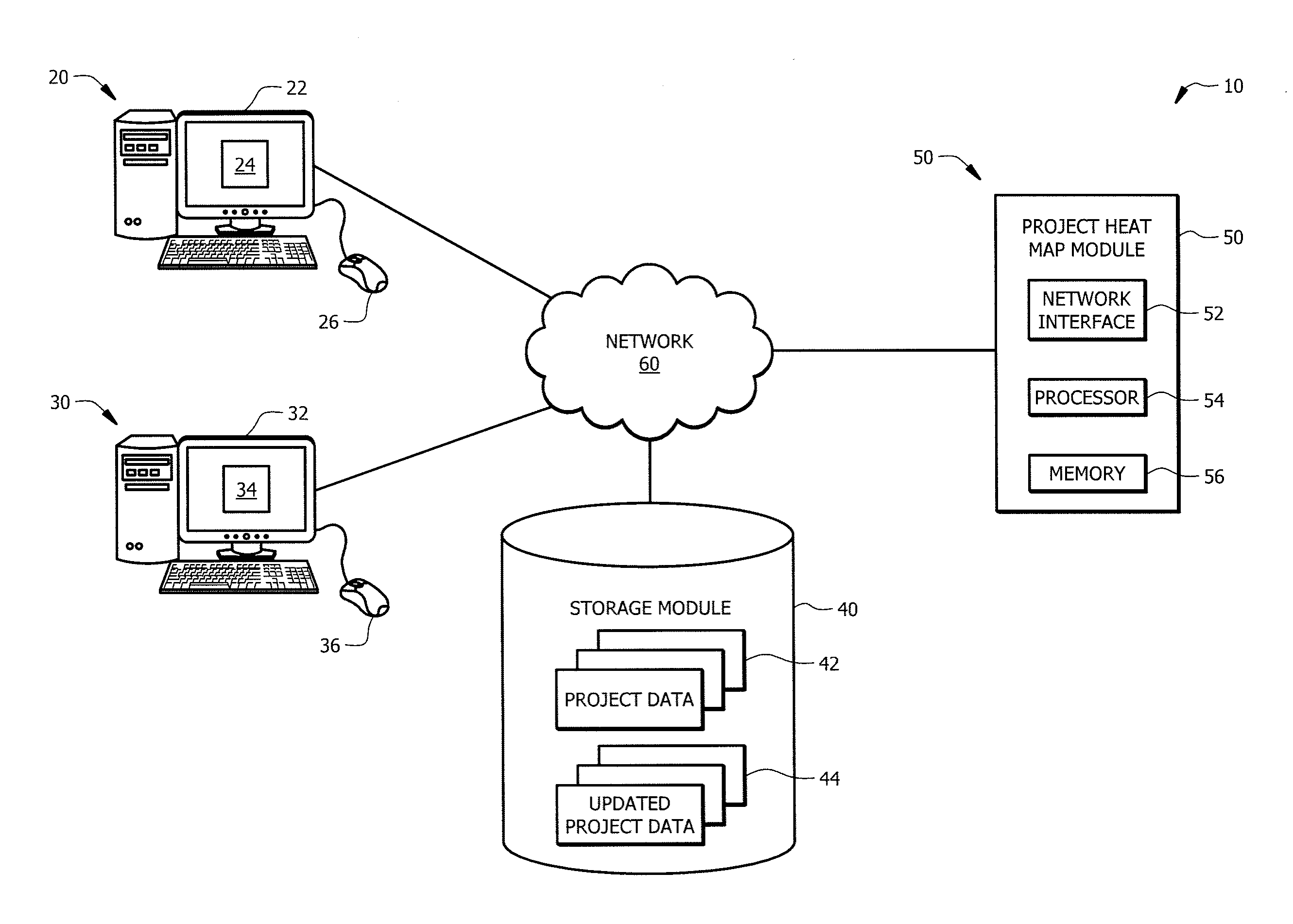
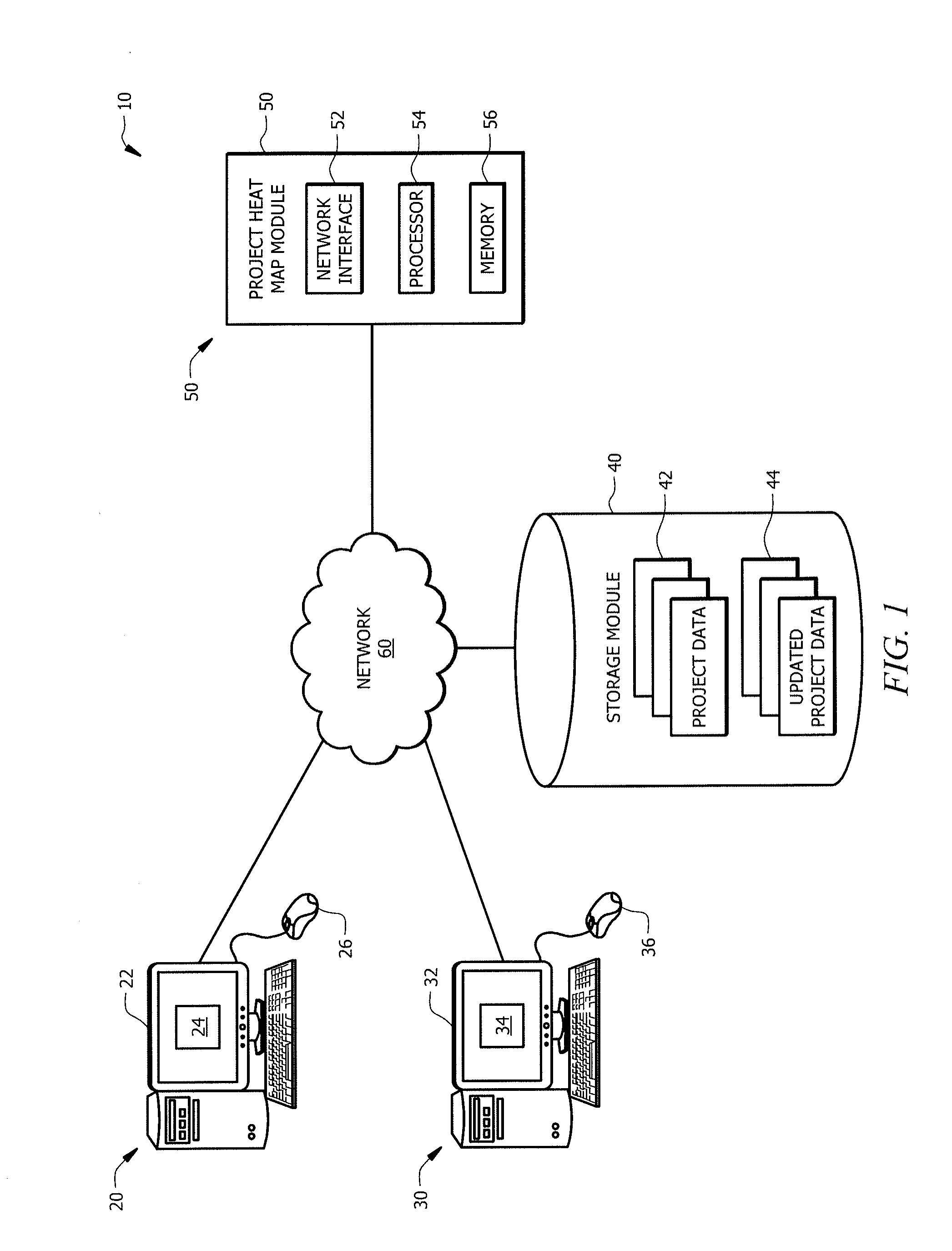
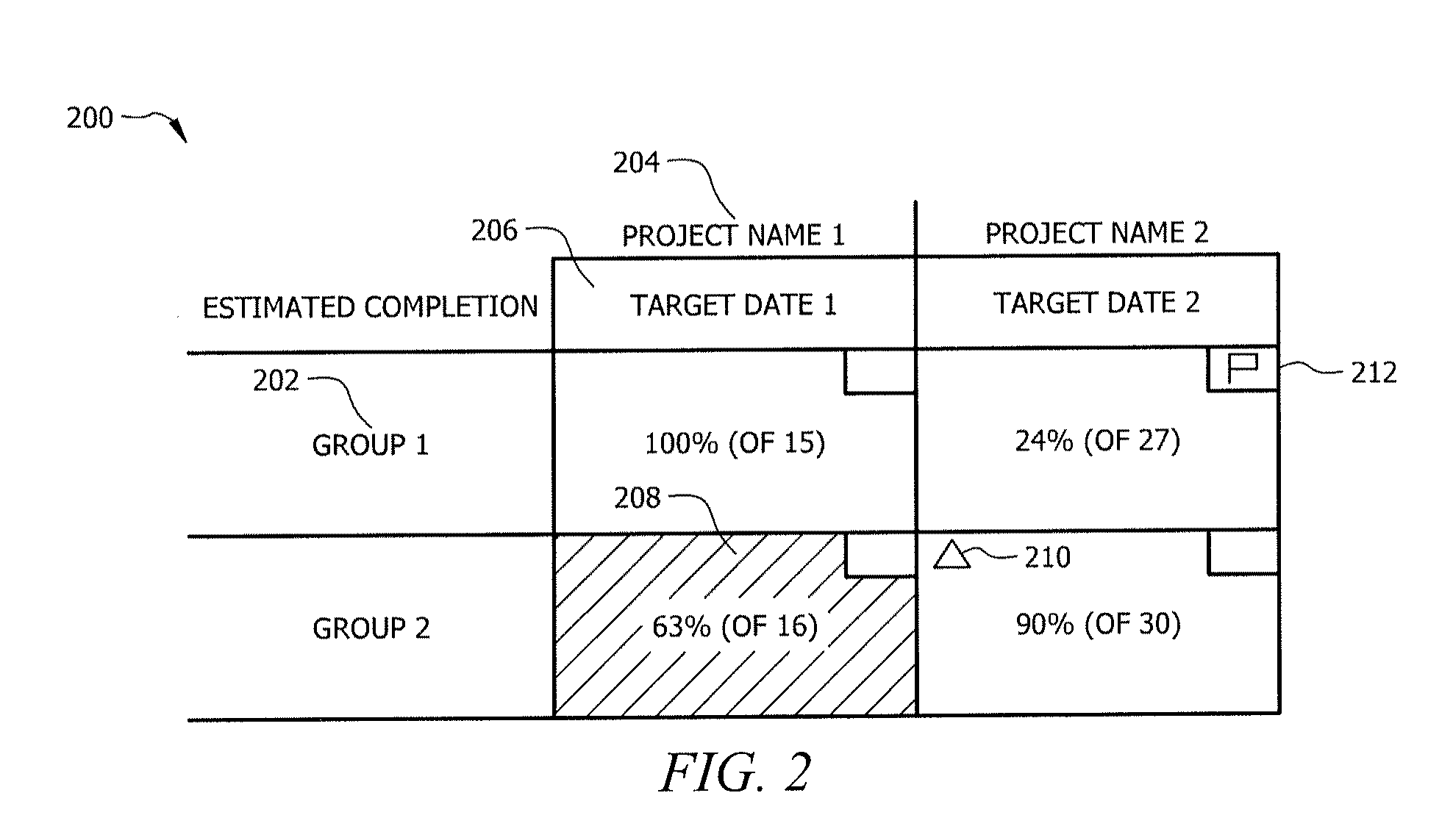
ActiveUS20170061342A1Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedHeat be reduced eliminatedResourcesNetwork interfaceProject assessment
A network interface accesses project data, wherein the project data comprises a metric for a project. A processor determines a project completeness based on the project data. The network interface receives a project assessment and also accesses updated project data, wherein the updated project data comprises an updated metric for the project. The processor then determines an updated completeness of the project, and determines a change in the completeness of the project. When the change in the completeness of the project is over a threshold, the processor sets a material change flag. The processor also determines a low-granularity project status. The processor then generates a project heat map. The project heat map is displayed in a tabular format. The project heat map presents the completeness of the project, material change flag, and the low-granularity project status for the project simultaneously.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com