Patents
Literature
9419 results about "Application layer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
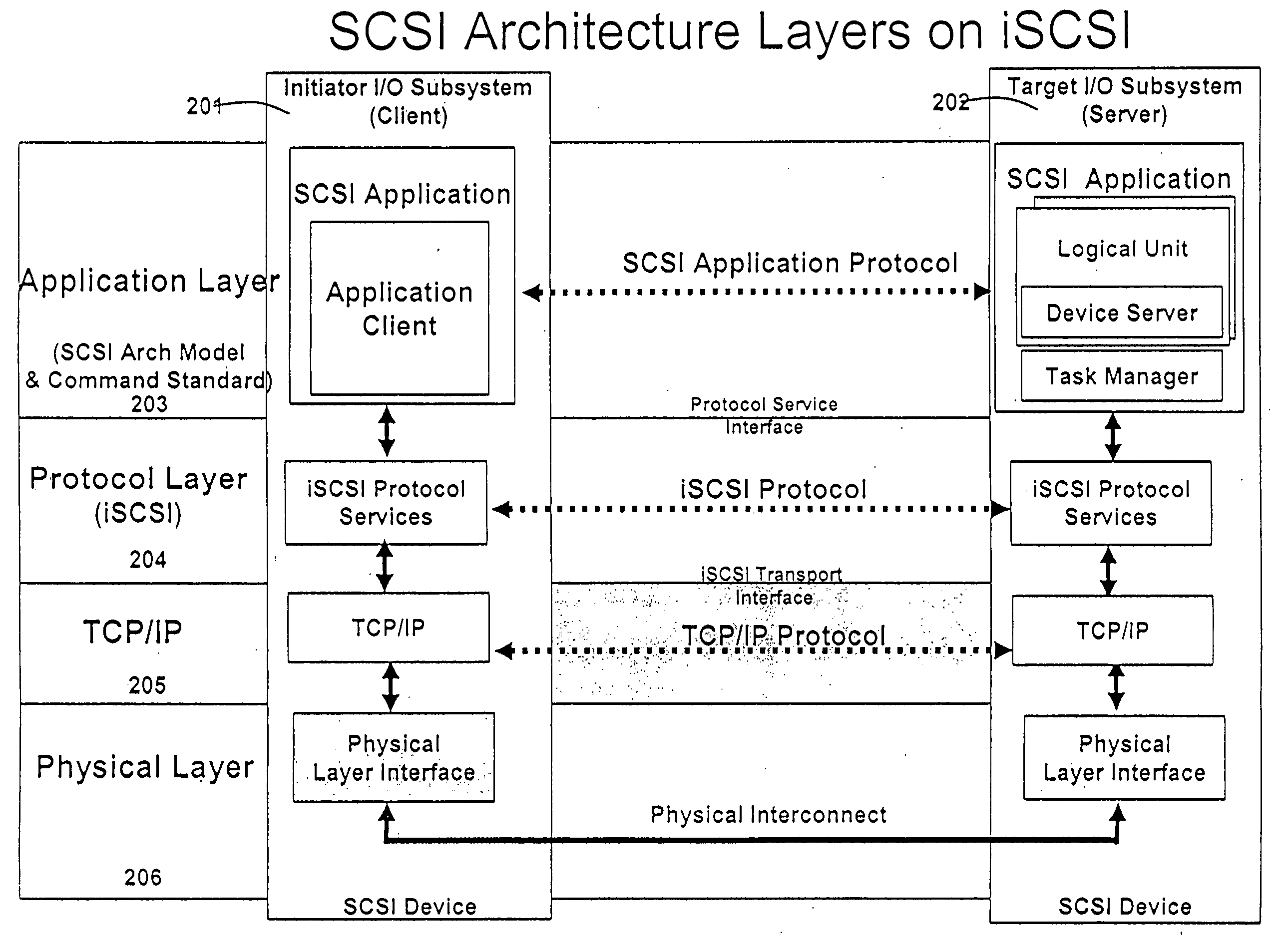
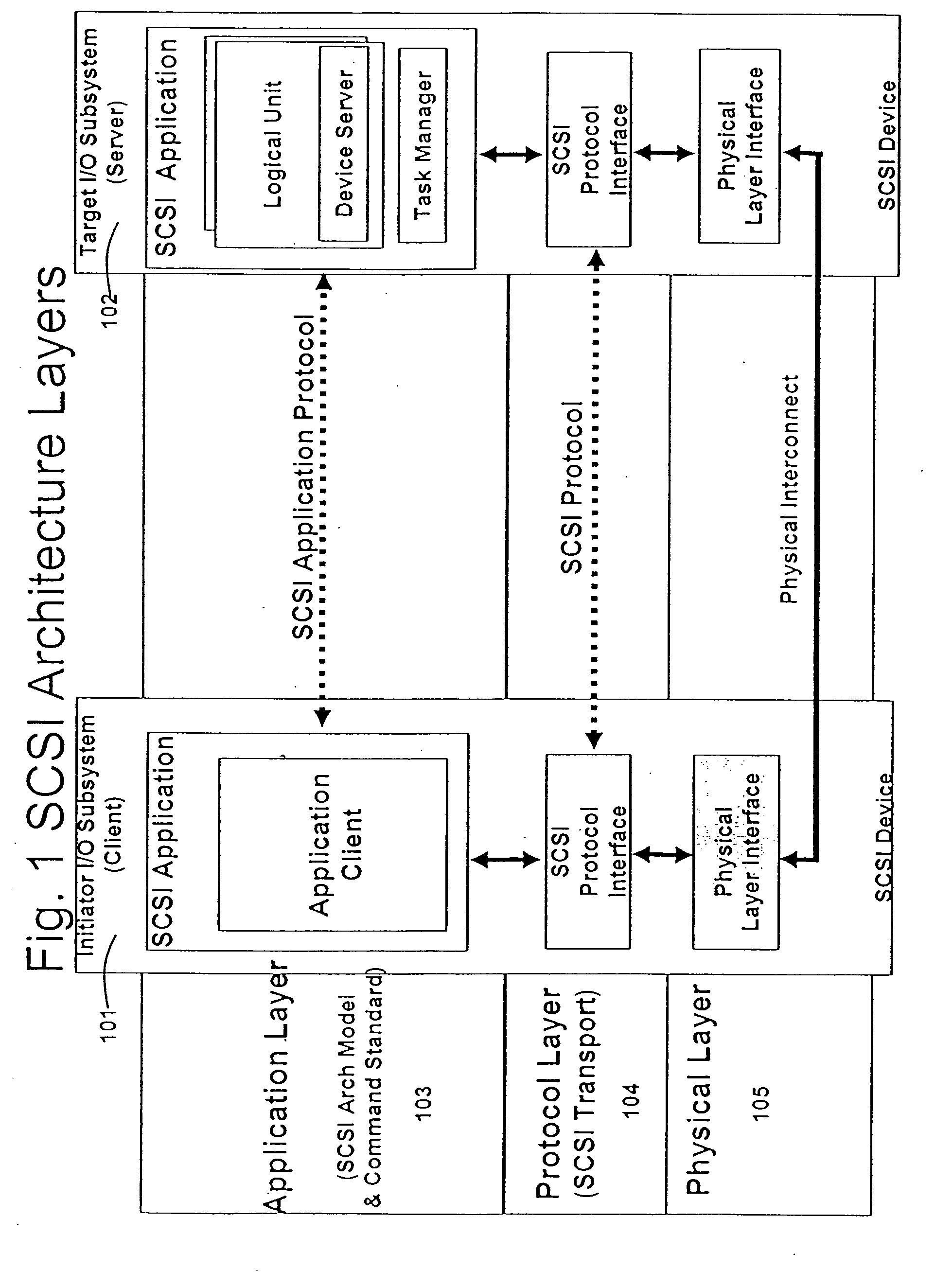
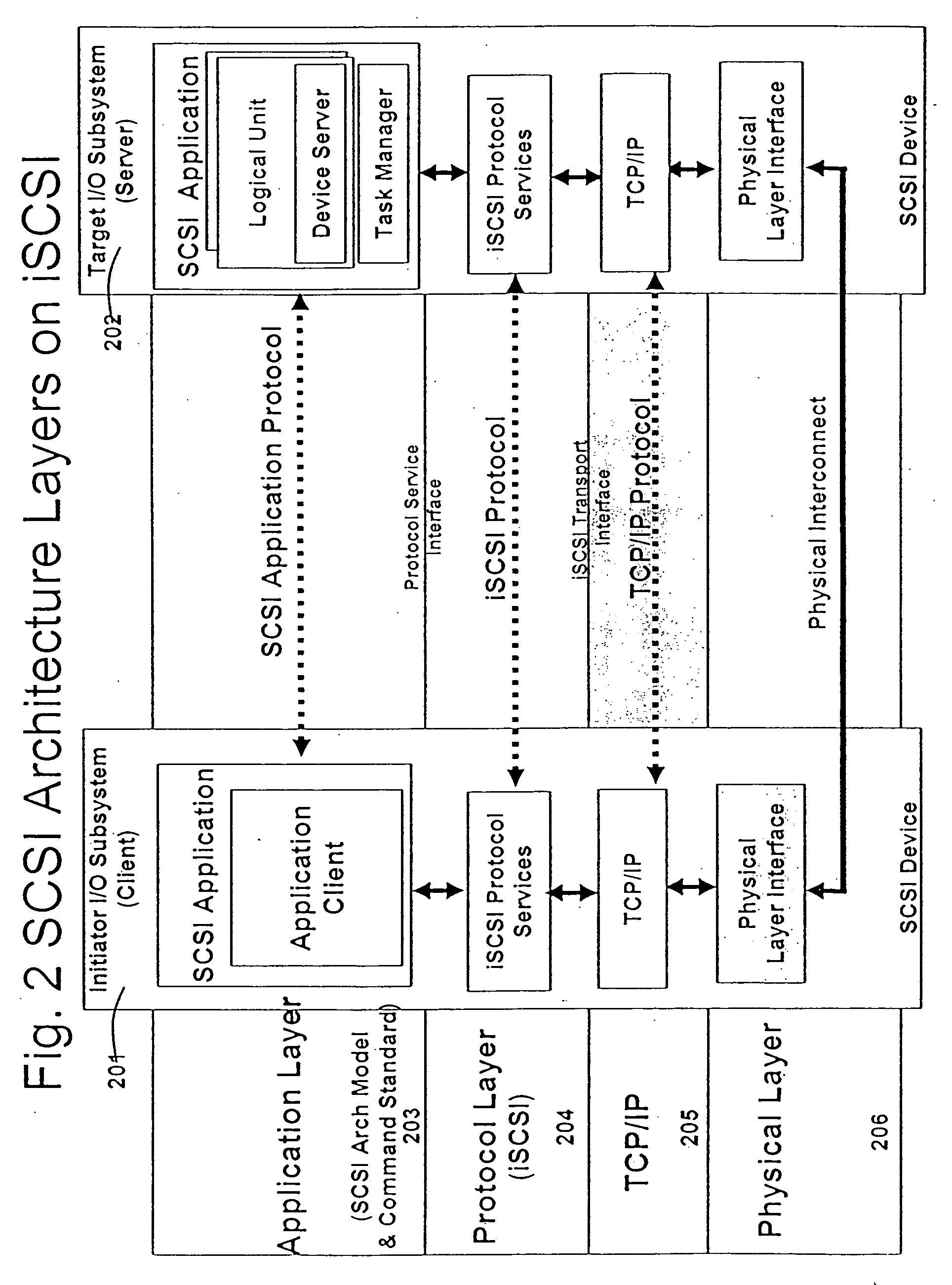
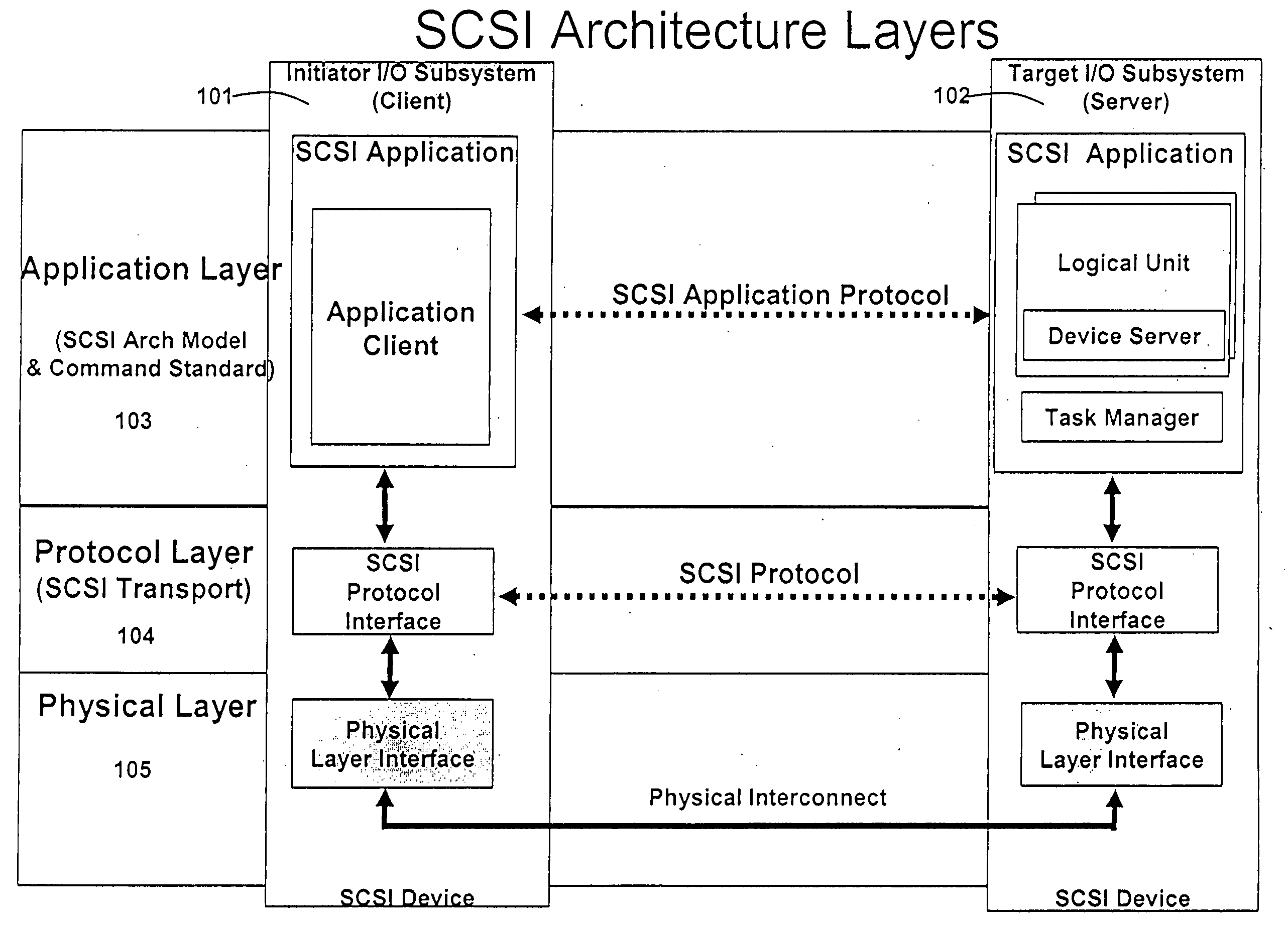
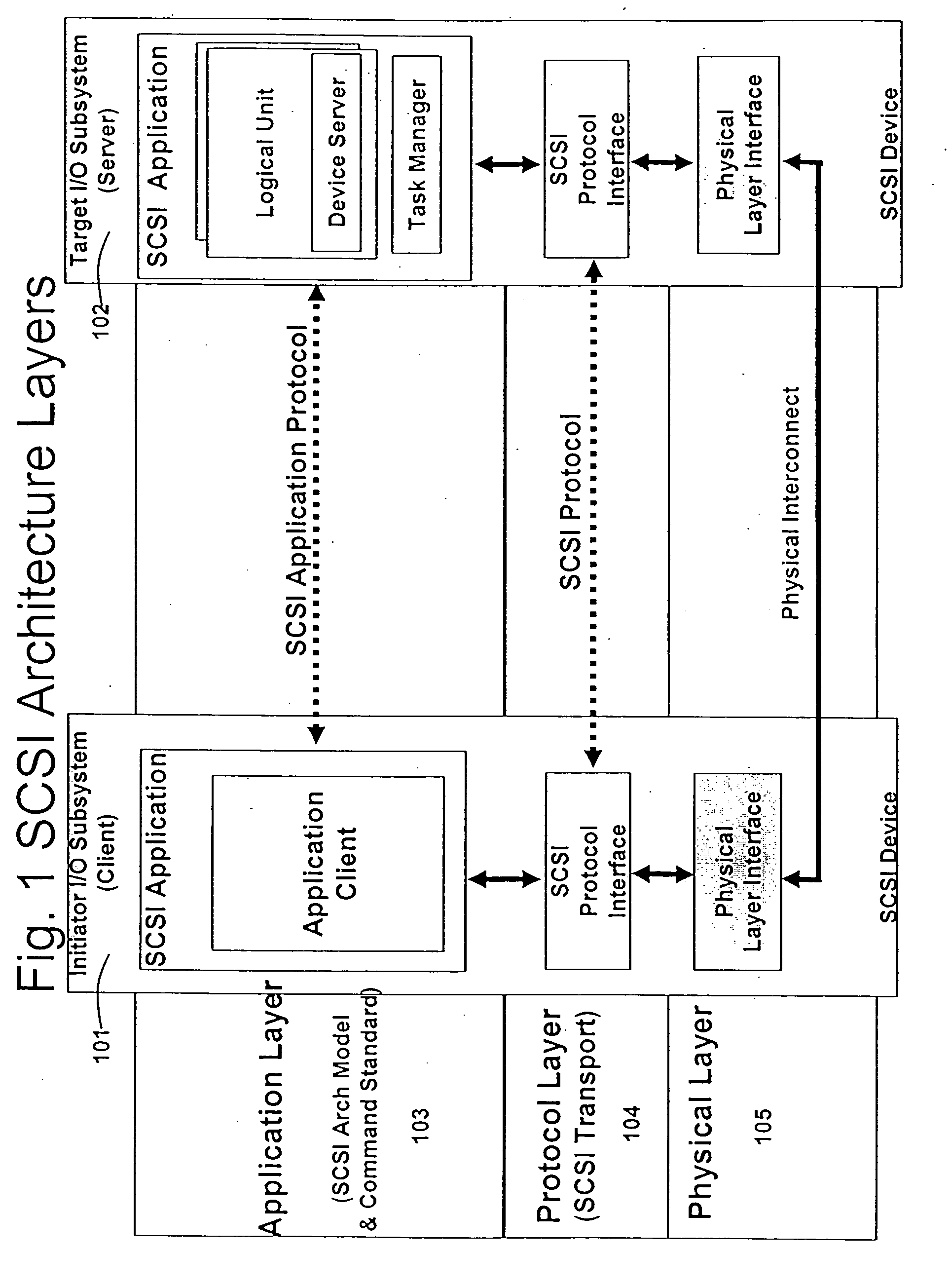
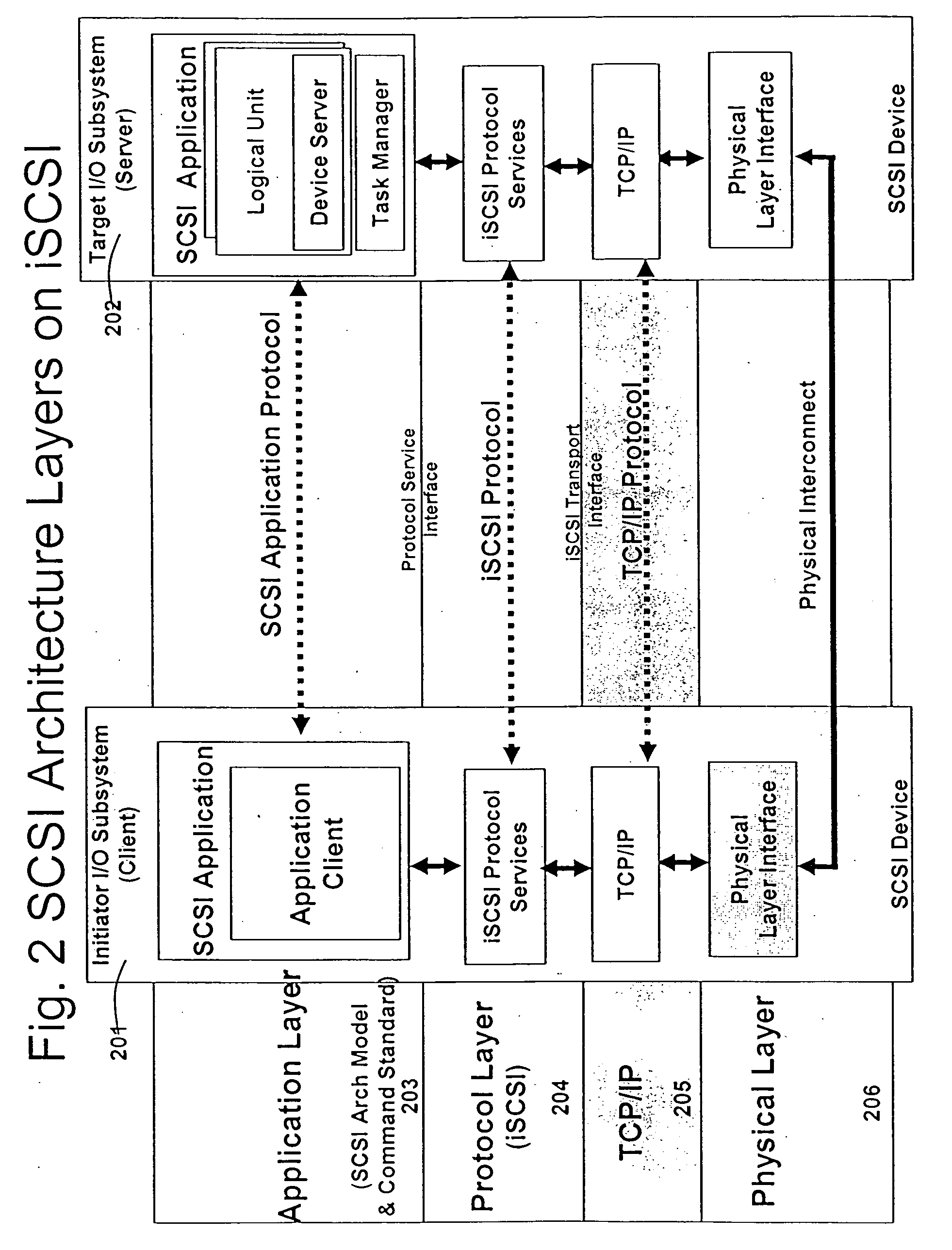
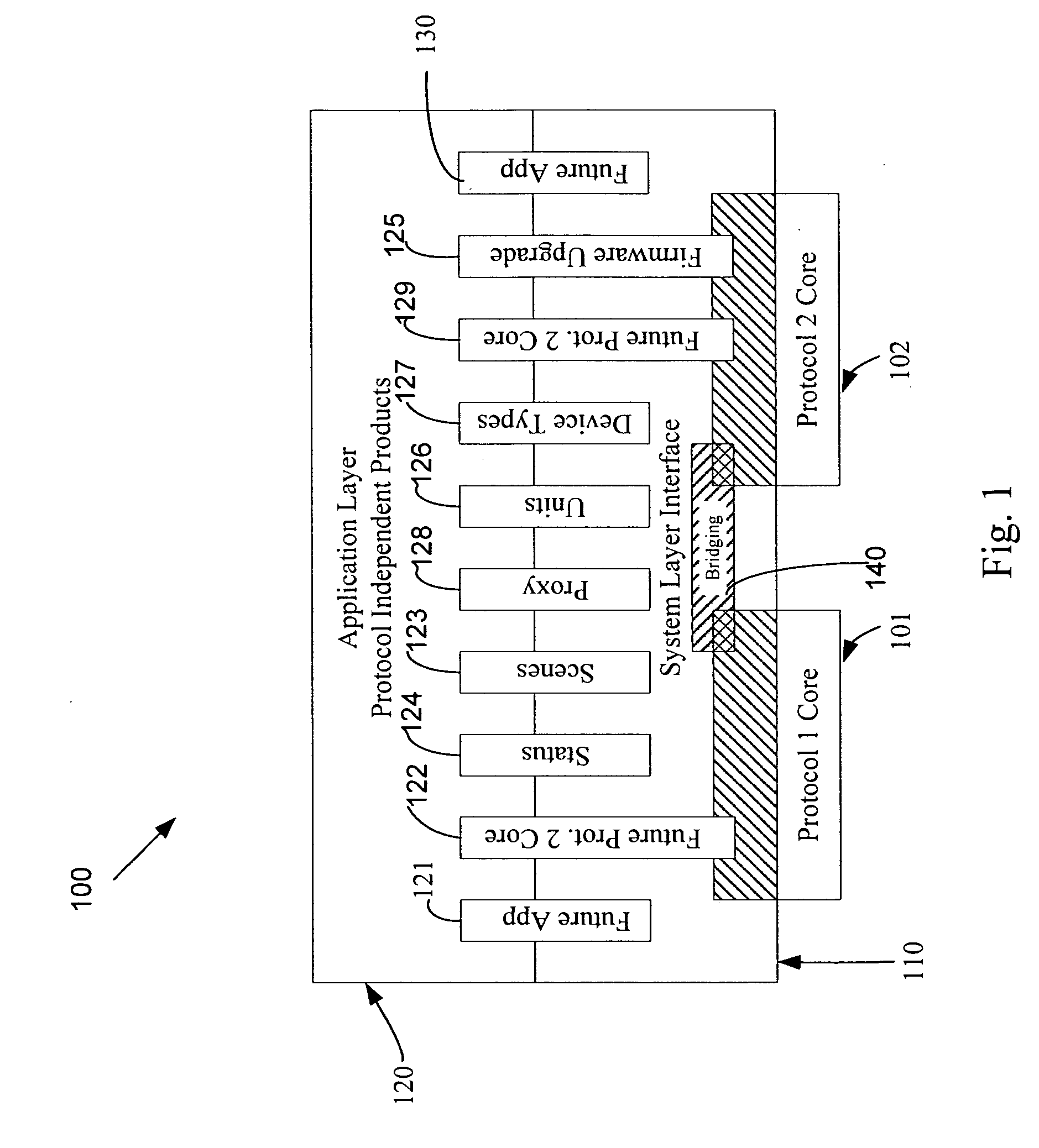
An application layer is an abstraction layer that specifies the shared communications protocols and interface methods used by hosts in a communications network. The application layer abstraction is used in both of the standard models of computer networking: the Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP) and the OSI model. Although both models use the same term for their respective highest level layer, the detailed definitions and purposes are different.
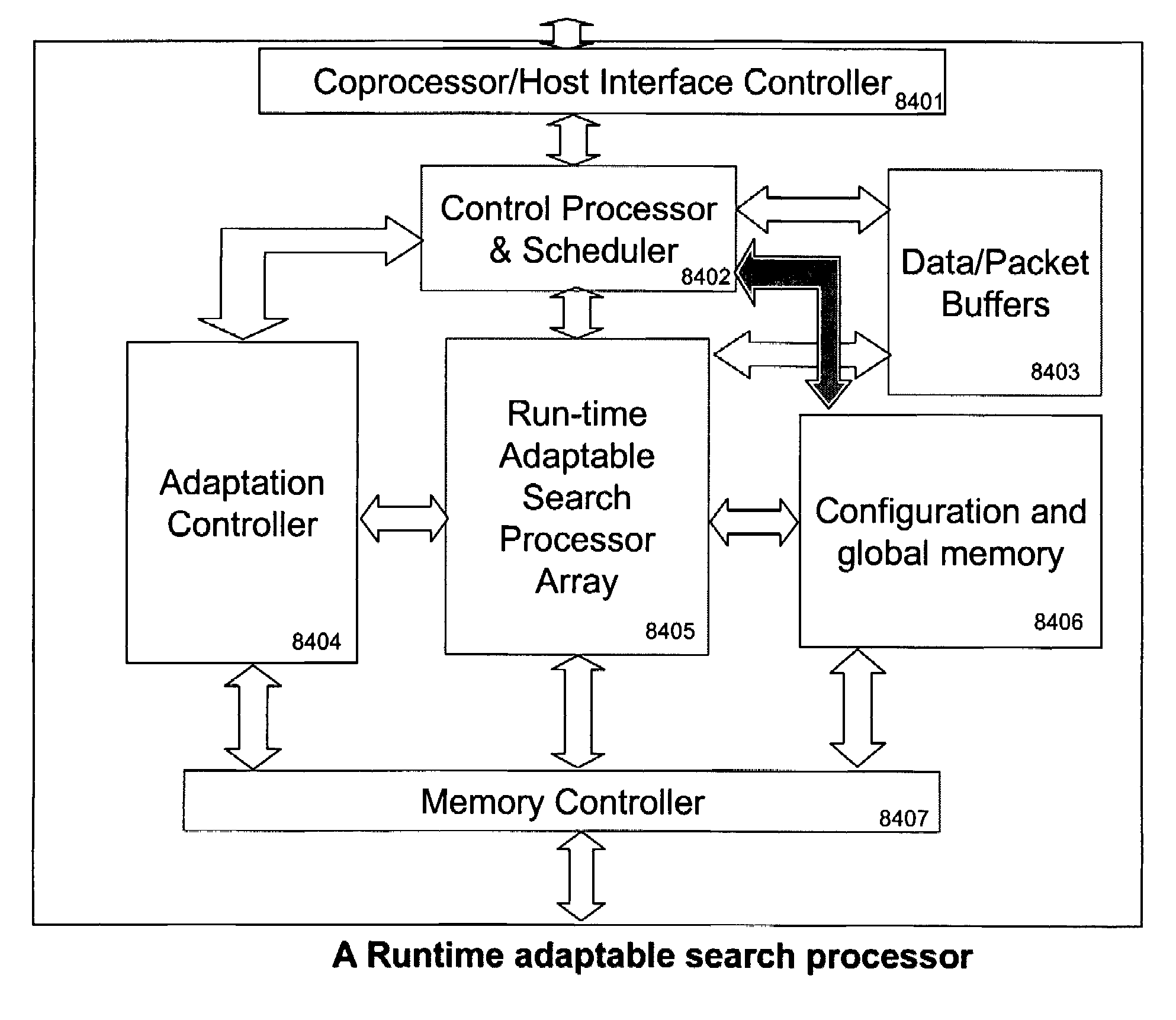
Runtime adaptable search processor
ActiveUS20060136570A1Reduce stacking processImproving host CPU performanceWeb data indexingMultiple digital computer combinationsData packInternal memory
A runtime adaptable search processor is disclosed. The search processor provides high speed content search capability to meet the performance need of network line rates growing to 1 Gbps, 10 Gbps and higher. he search processor provides a unique combination of NFA and DFA based search engines that can process incoming data in parallel to perform the search against the specific rules programmed in the search engines. The processor architecture also provides capabilities to transport and process Internet Protocol (IP) packets from Layer 2 through transport protocol layer and may also provide packet inspection through Layer 7. Further, a runtime adaptable processor is coupled to the protocol processing hardware and may be dynamically adapted to perform hardware tasks as per the needs of the network traffic being sent or received and / or the policies programmed or services or applications being supported. A set of engines may perform pass-through packet classification, policy processing and / or security processing enabling packet streaming through the architecture at nearly the full line rate. A high performance content search and rules processing security processor is disclosed which may be used for application layer and network layer security. scheduler schedules packets to packet processors for processing. An internal memory or local session database cache stores a session information database for a certain number of active sessions. The session information that is not in the internal memory is stored and retrieved to / from an additional memory. An application running on an initiator or target can in certain instantiations register a region of memory, which is made available to its peer(s) for access directly without substantial host intervention through RDMA data transfer. A security system is also disclosed that enables a new way of implementing security capabilities inside enterprise networks in a distributed manner using a protocol processing hardware with appropriate security features.
Owner:MEMORY ACCESS TECH LLC
Method, system and computer program product for detecting at least one of security threats and undesirable computer files
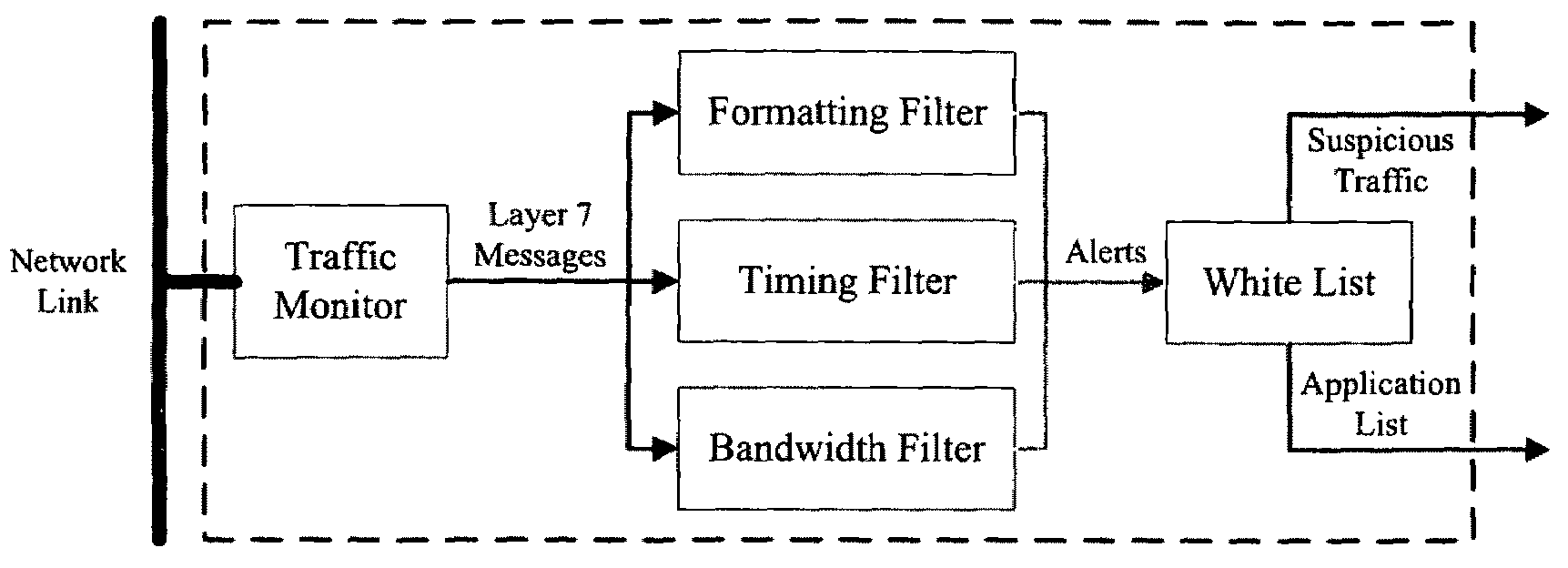
Method, system and computer program product for detecting at least one of security threats and undesirable computer files are provided. A first method includes receiving a data stream which represents outbound, application layer messages from a first computer process to at least one second computer process. The computer processes are implemented on one or more computers. The method further includes monitoring the data stream to detect a security threat based on a whitelist having entries which contain metadata. The whitelist describes legitimate application layer messages based on a set of heuristics. The method still further includes generating a signal if a security threat is detected. A second method includes comparing a set of computer files with a whitelist which characterizes all legitimate computer files. The whitelist contains one or more entries. Each of the entries describe a plurality of legitimate computer files.
Owner:SYROWIK DAVID R
Internet database system
InactiveUS6523036B1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsApplication serverHash function
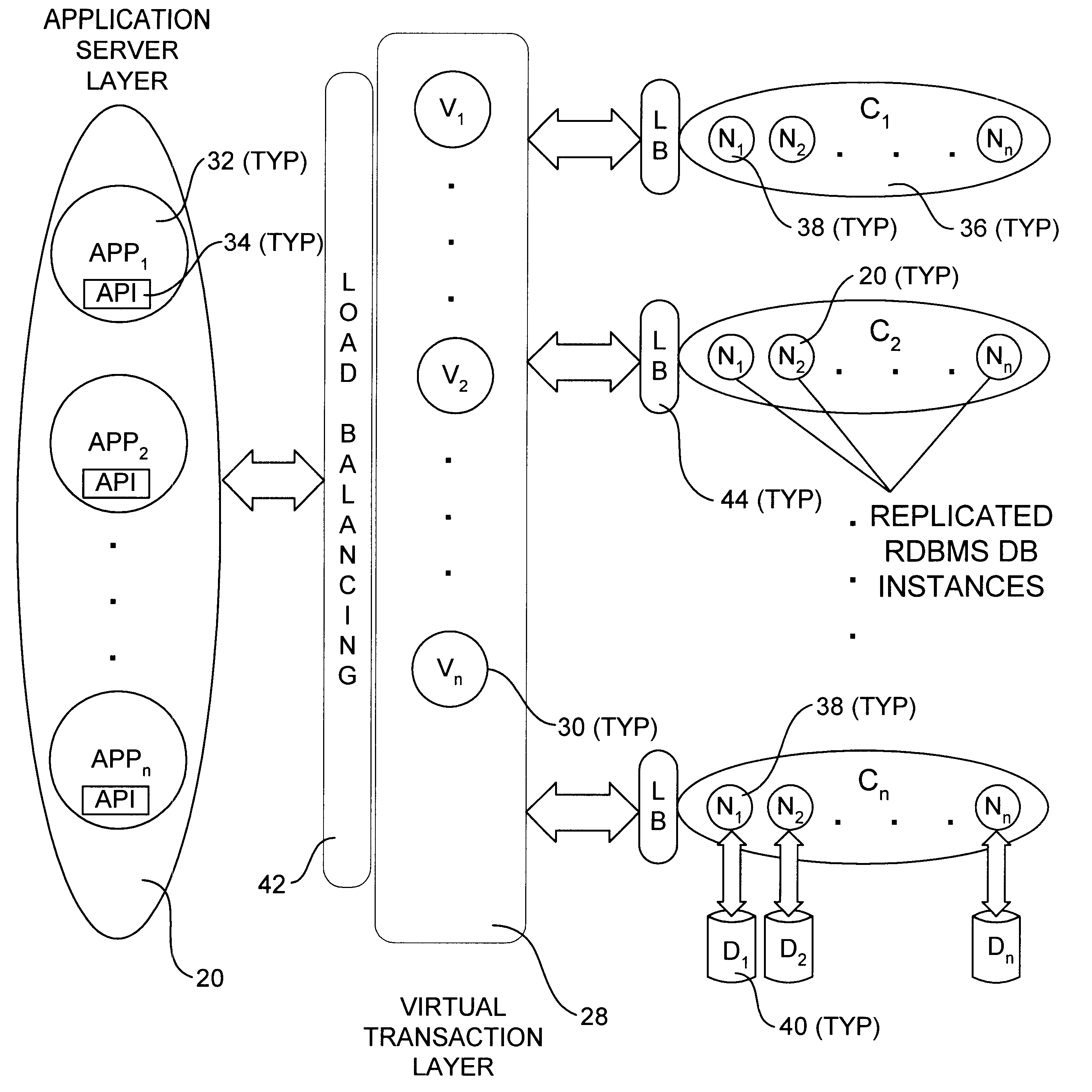
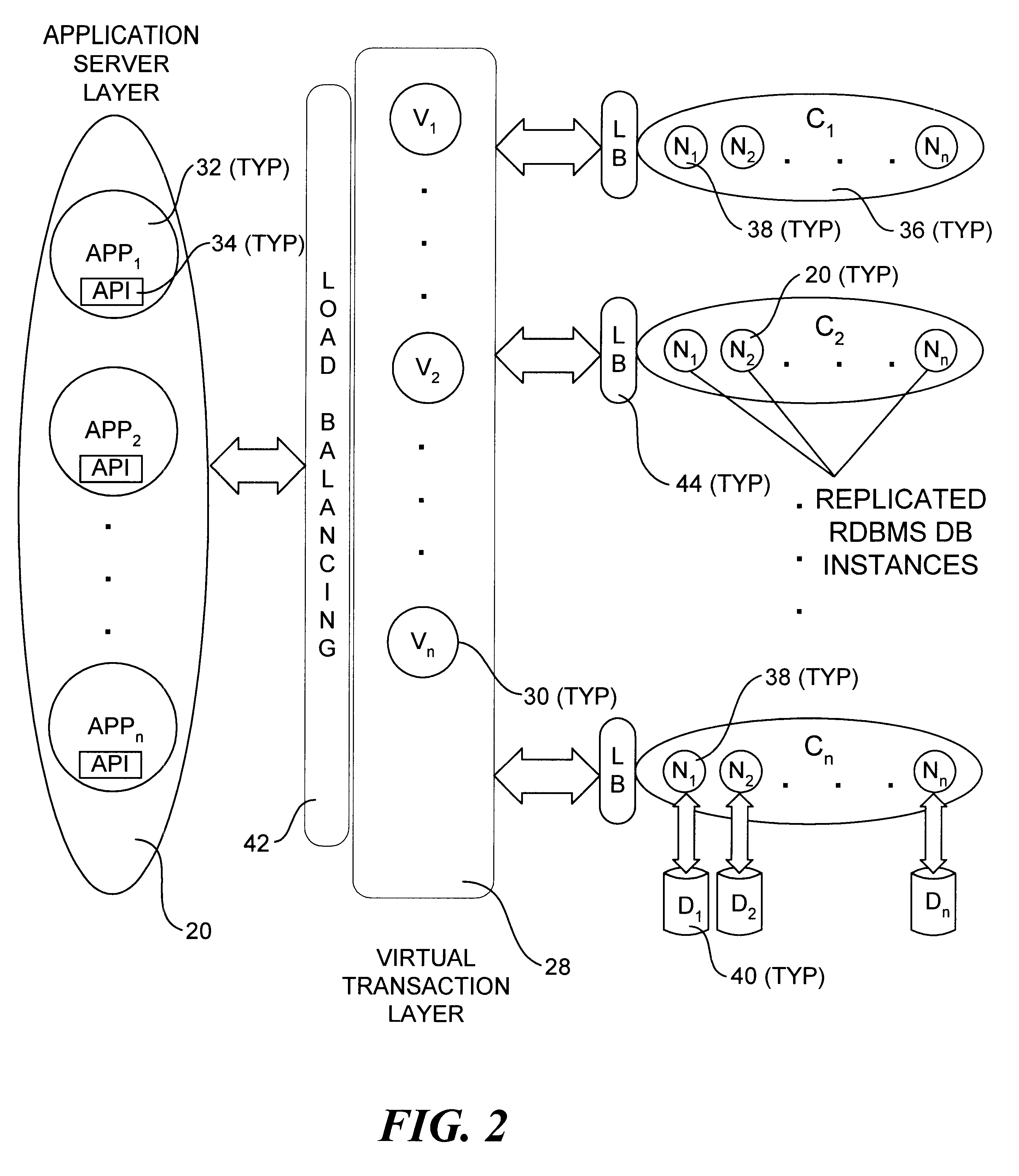
An incrementally-scalable database system and method. The system architecture enables database servers to be scaled by adding resources, such as additional servers, without requiring that the system be taken offline. Such scaling includes both adding one or more computer servers to a given server cluster, which enables an increase in database read transaction throughput, and adding one or more server clusters to the system configuration, which provides for increased read and write transaction throughput. The system also provides for load balancing read transactions across each server cluster, and load balancing write transactions across a plurality of server clusters. The system architecture includes an application server layer including one or more computers on which an application program(s) is running, a database server layer comprising two or more server clusters that each include two or more computer servers with replicated data, and an intermediate "virtual transaction" layer that includes at least two computers that facilitate database transactions with one or more databases operating in the database server layer. Data in the database(s) are evenly distributed across the server clusters in fragmented mutually exclusive subsets of data based on a hashing function. An application program interface is provided so as to enable application programs to perform a full range of database transactions without regard for where data is stored, or what database(s) is operating in the database server layer.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Runtime adaptable search processor
ActiveUS7685254B2Improve application performanceLarge capacityWeb data indexingMemory adressing/allocation/relocationPacket schedulingSchema for Object-Oriented XML
A runtime adaptable search processor is disclosed. The search processor provides high speed content search capability to meet the performance need of network line rates growing to 1 Gbps, 10 Gbps and higher. The search processor provides a unique combination of NFA and DFA based search engines that can process incoming data in parallel to perform the search against the specific rules programmed in the search engines. The processor architecture also provides capabilities to transport and process Internet Protocol (IP) packets from Layer 2 through transport protocol layer and may also provide packet inspection through Layer 7. Further, a runtime adaptable processor is coupled to the protocol processing hardware and may be dynamically adapted to perform hardware tasks as per the needs of the network traffic being sent or received and / or the policies programmed or services or applications being supported. A set of engines may perform pass-through packet classification, policy processing and / or security processing enabling packet streaming through the architecture at nearly the full line rate. A high performance content search and rules processing security processor is disclosed which may be used for application layer and network layer security. Scheduler schedules packets to packet processors for processing. An internal memory or local session database cache stores a session information database for a certain number of active sessions. The session information that is not in the internal memory is stored and retrieved to / from an additional memory. An application running on an initiator or target can in certain instantiations register a region of memory, which is made available to its peer(s) for access directly without substantial host intervention through RDMA data transfer. A security system is also disclosed that enables a new way of implementing security capabilities inside enterprise networks in a distributed manner using a protocol processing hardware with appropriate security features.
Owner:MEMORY ACCESS TECH LLC
Runtime adaptable security processor
InactiveUS20050108518A1Improve performanceReduce overheadSecuring communicationInternal memoryPacket scheduling
A runtime adaptable security processor is disclosed. The processor architecture provides capabilities to transport and process Internet Protocol (IP) packets from Layer 2 through transport protocol layer and may also provide packet inspection through Layer 7. Further, a runtime adaptable processor is coupled to the protocol processing hardware and may be dynamically adapted to perform hardware tasks as per the needs of the network traffic being sent or received and / or the policies programmed or services or applications being supported. A set of engines may perform pass-through packet classification, policy processing and / or security processing enabling packet streaming through the architecture at nearly the full line rate. A high performance content search and rules processing security processor is disclosed which may be used for application layer and network layer security. A scheduler schedules packets to packet processors for processing. An internal memory or local session database cache stores a session information database for a certain number of active sessions. The session information that is not in the internal memory is stored and retrieved to / from an additional memory. An application running on an initiator or target can in certain instantiations register a region of memory, which is made available to its peer(s) for access directly without substantial host intervention through RDMA data transfer. A security system is also disclosed that enables a new way of implementing security capabilities inside enterprise networks in a distributed manner using a protocol processing hardware with appropriate security features.
Owner:MEMORY ACCESS TECH LLC
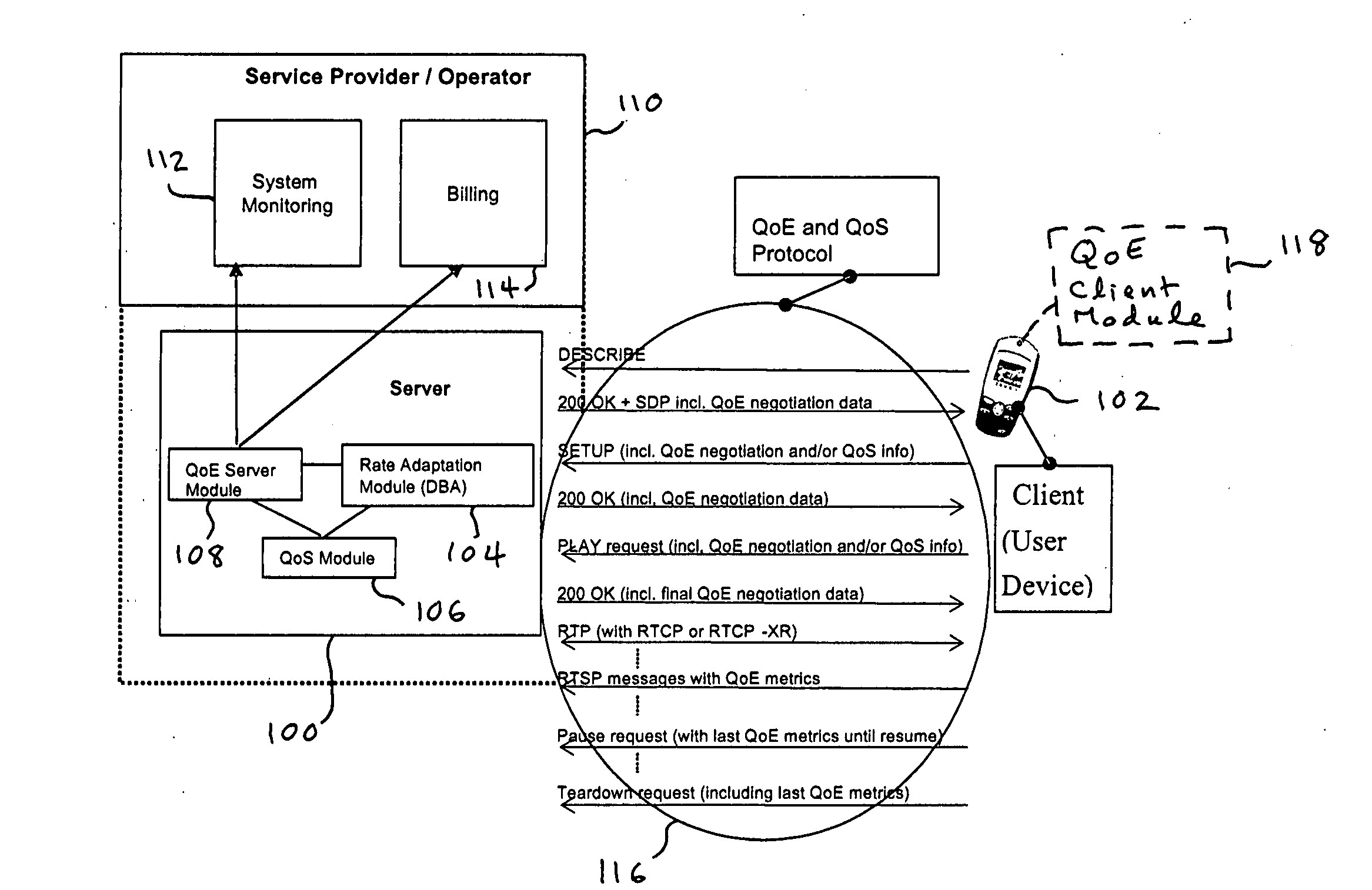
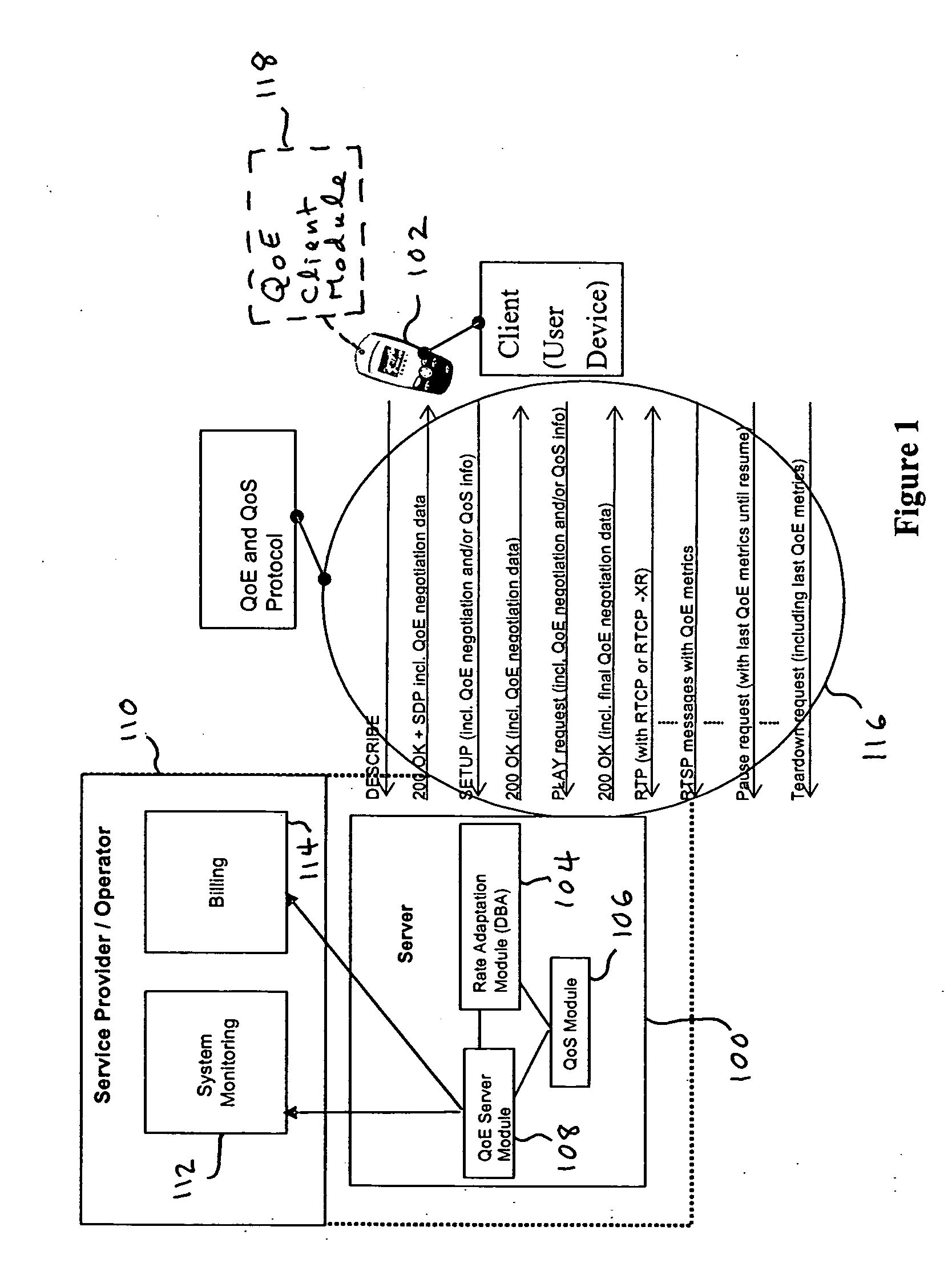
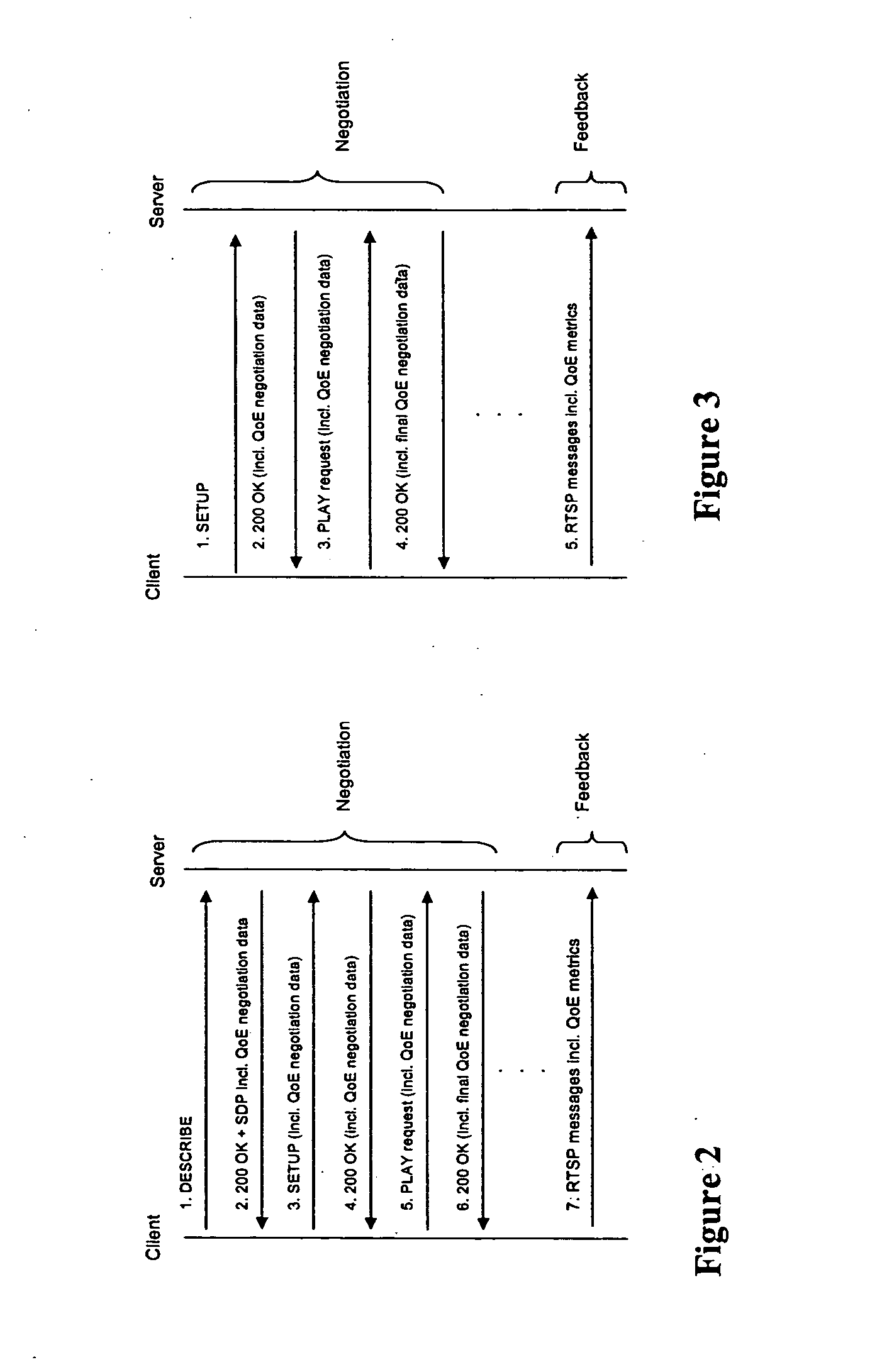
Quality of experience (QOE) method and apparatus for wireless communication networks
A Quality of Experience (QoE) framework provides a technique to assess the end user experience in a mobile wireless communication environment, such as 2.5G or 3G networks, or in any other wireless or hardwired communication environment. The framework is usable in conjunction with media streaming applications and enables a combination of network layer, transport layer, codec layer, and application layer measurements in extracting results. The extracted results can be used to monitor and improve, if necessary, the end user experience over severely variable network conditions.
Owner:VIDIATOR ENTERPRISES INC
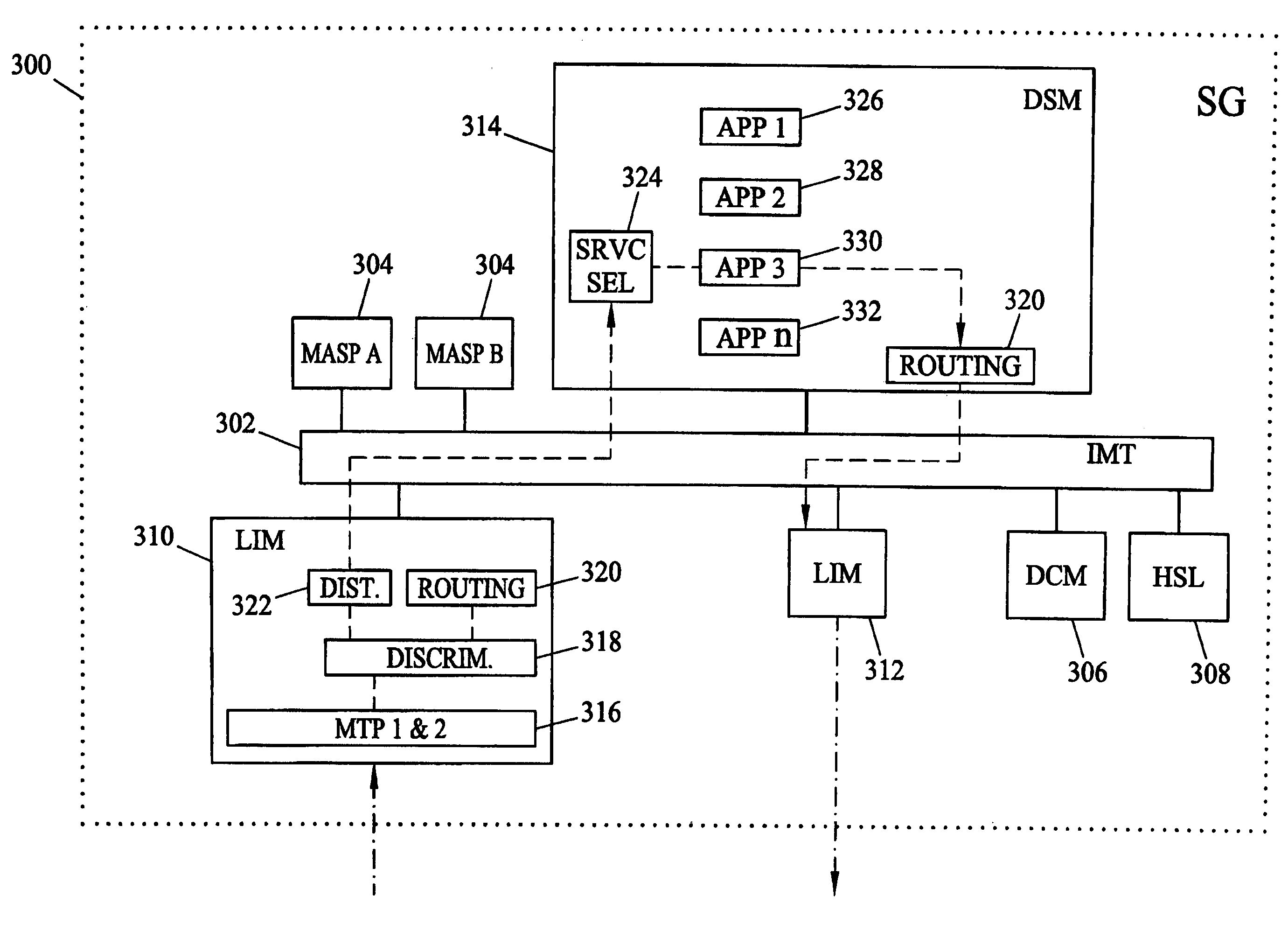
Methods and systems for universal, automatic service selection in a telecommunications signaling network
InactiveUS7092505B2Raise the possibilityRobust solutionInterconnection arrangementsTime-division multiplexMessage typeSignaling network
Methods and systems for universal, automatic service selection are disclosed. A method for universal, automatic service selection includes receiving signaling messages and identifying signaling connection control part (SCCP) messages from the signaling messages. The SCCP messages are decoded to extract SCCP parameters and application layer parameters from the messages. A routing address translation service is selected for each of the SCCP messages based on application identifiers that identify application layer message types alone or in combination with other parameters. Selecting the routing address translation service in this manner makes the service selection more robust and universally applicable, especially in networks where different or non-standard selector parameters are utilized.
Owner:TEKELEC
Service notification on a low bluetooth layer
InactiveUS7151764B1Fast contentFast processingAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesPointing deviceProtocol Application
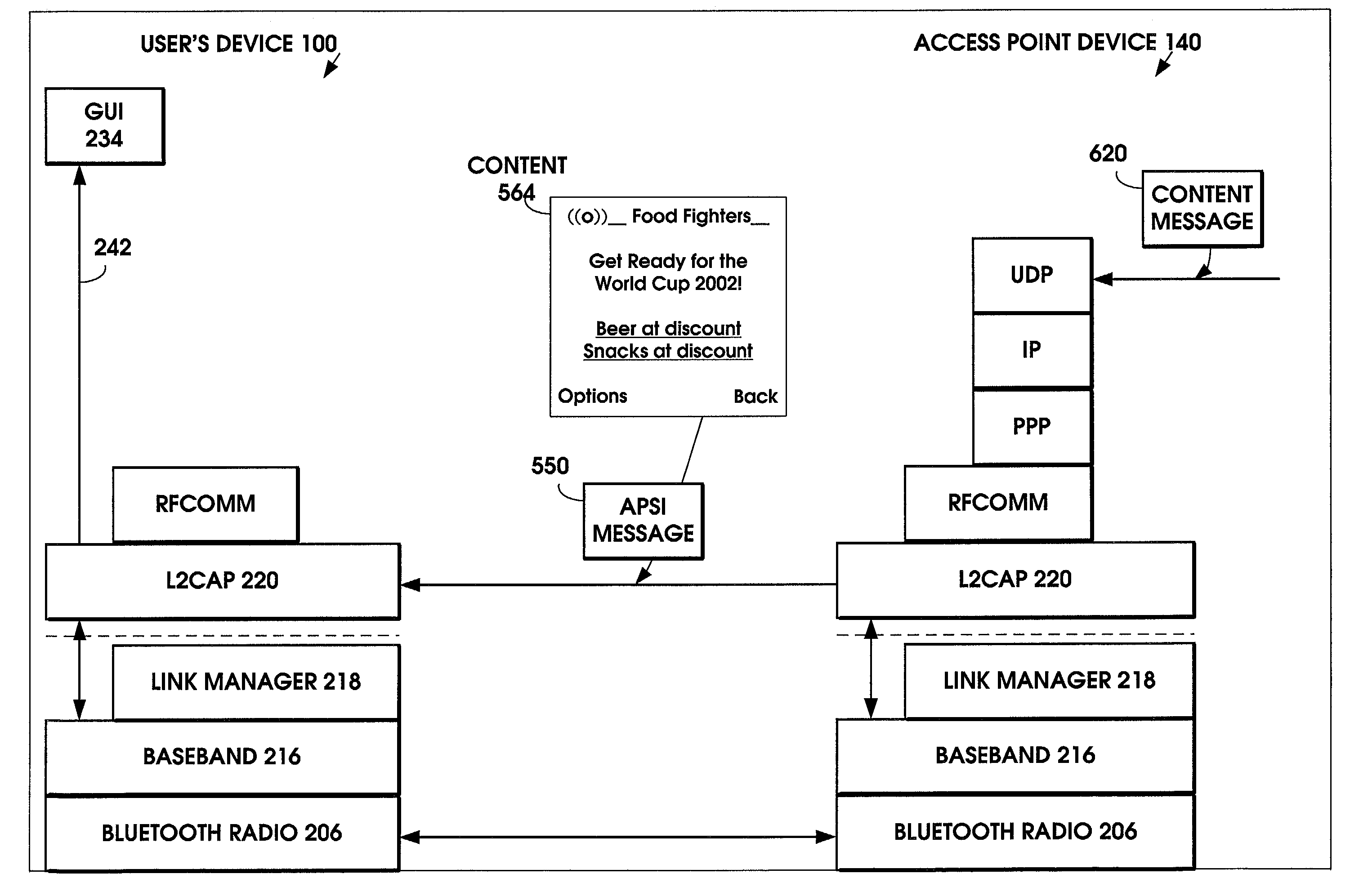
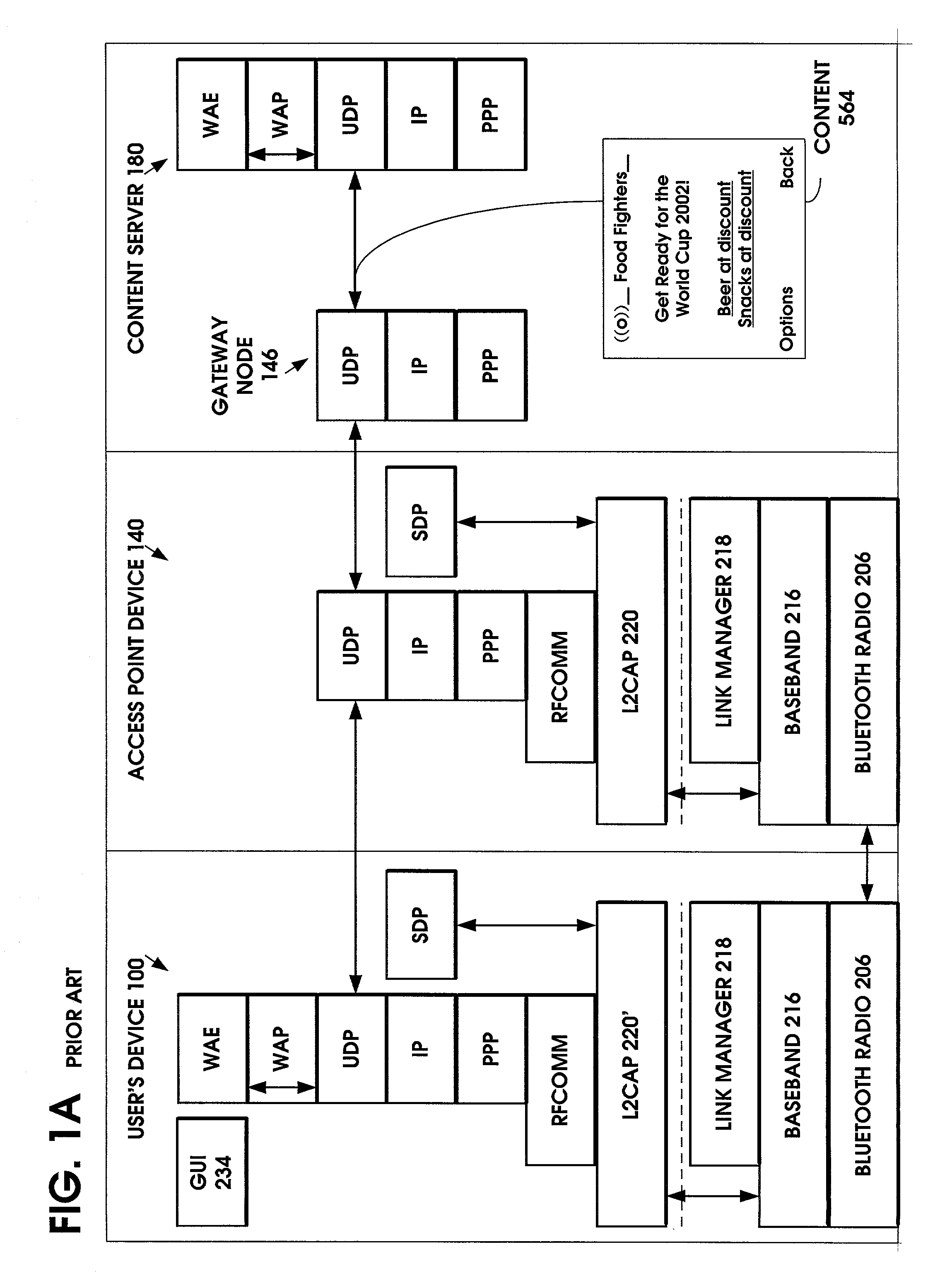
A method is provided to minimize the protocol stacks needed for a short range wireless access point to rapidly communicate a message to a short range wireless mobile device and display it to the user. The short range wireless access point device stores an Access Point Service Indicator (APSI) message characterizing the service platform offerings. The APSI message has a unique message ID in its header. The user device's transport protocol layer is modified to detect the unique message ID and load it into an APSI message buffer. The transport protocol layer passes the APSI message directly to the application layer, bypassing the middleware protocol layers. The method can be applied to communications between various types of wireless devices to enable rapid communication, such as between two mobile devices, between fixed and mobile devices, between short range devices or between long range devices.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
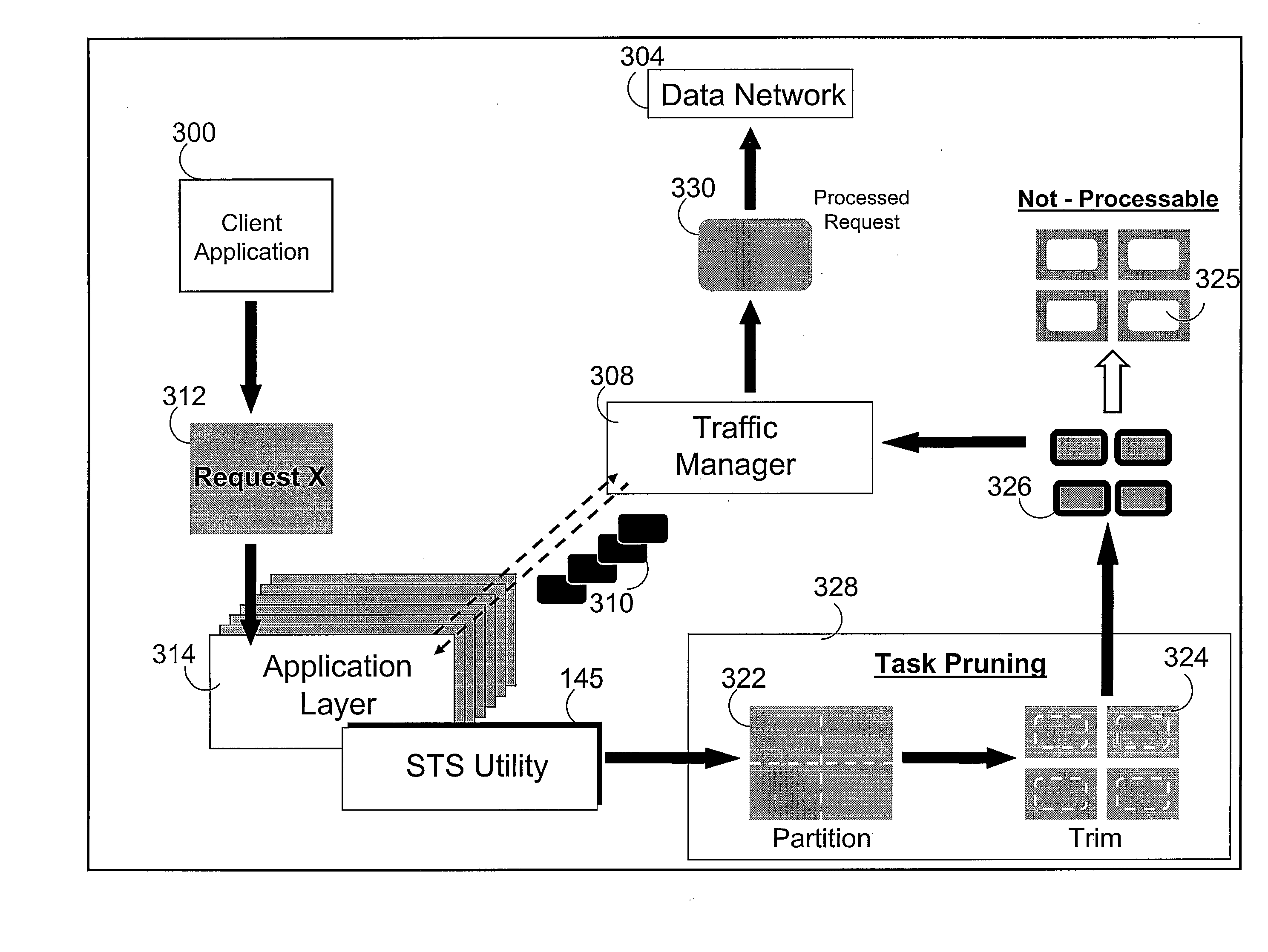
Method for application layer synchronous traffic shaping
InactiveUS20080212470A1Avoid network congestionError preventionTransmission systemsProtocol ApplicationDistributed computing
A method, a system, and a computer program product implements traffic shaping by processing as a synchronous request, tasks representing one or more units of work contained within the request. Before a request is sent through the network, the request is inspected in order to derive the amount of work that the request would generate in the network. A traffic manager queries the amount of work in that request compared to the amount of work that the network can support and generates a number of traffic envelopes. Based on the results of this query, “task pruning” may be implemented to break the request into smaller manageable task that fit into the traffic envelopes. Task pruning may also enable only a subset of the work to be performed. Thus, a measure of the amount of work, rather than the amount of data, within a request is considered when scheduling the request.
Owner:IBM CORP
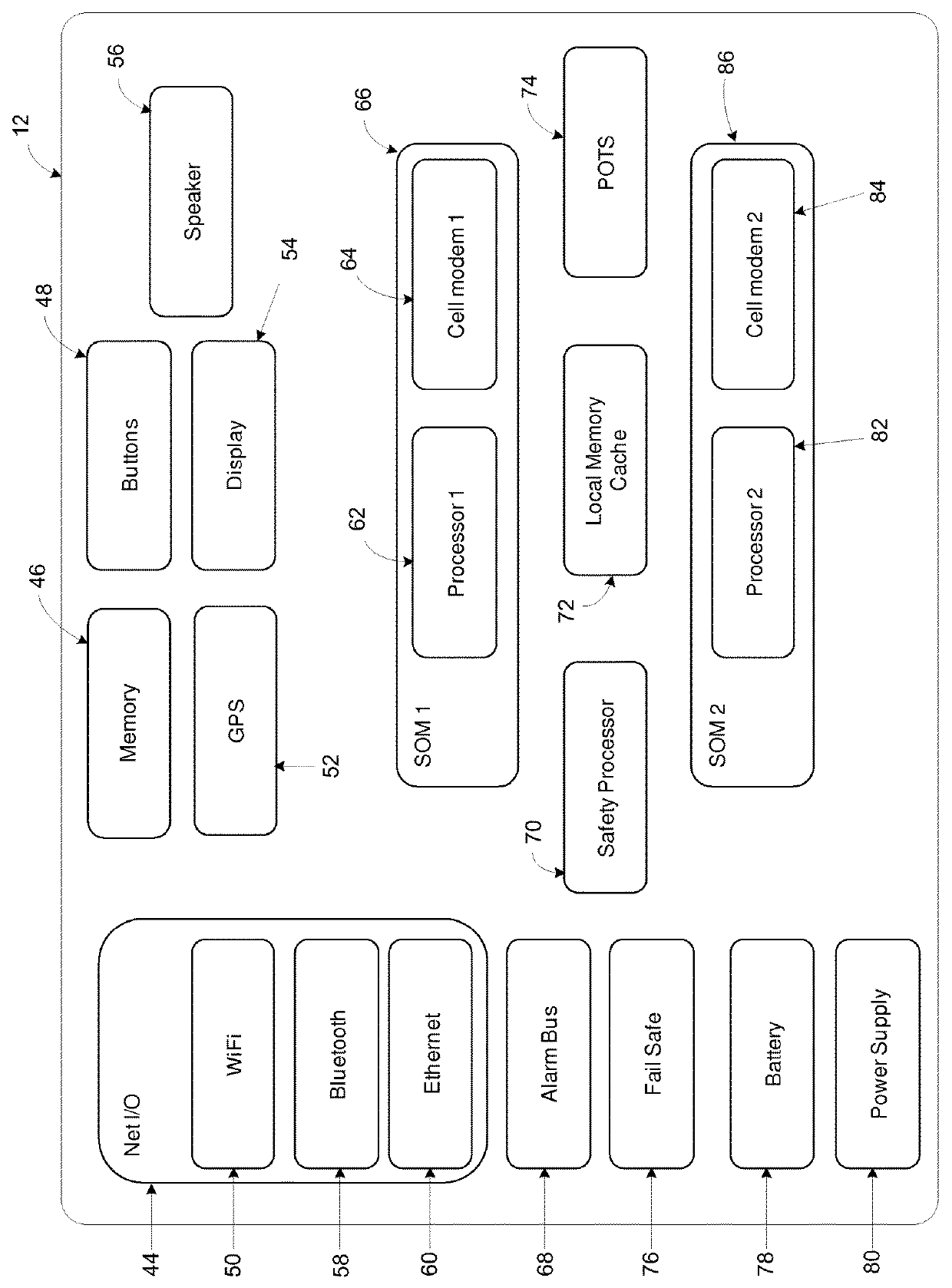
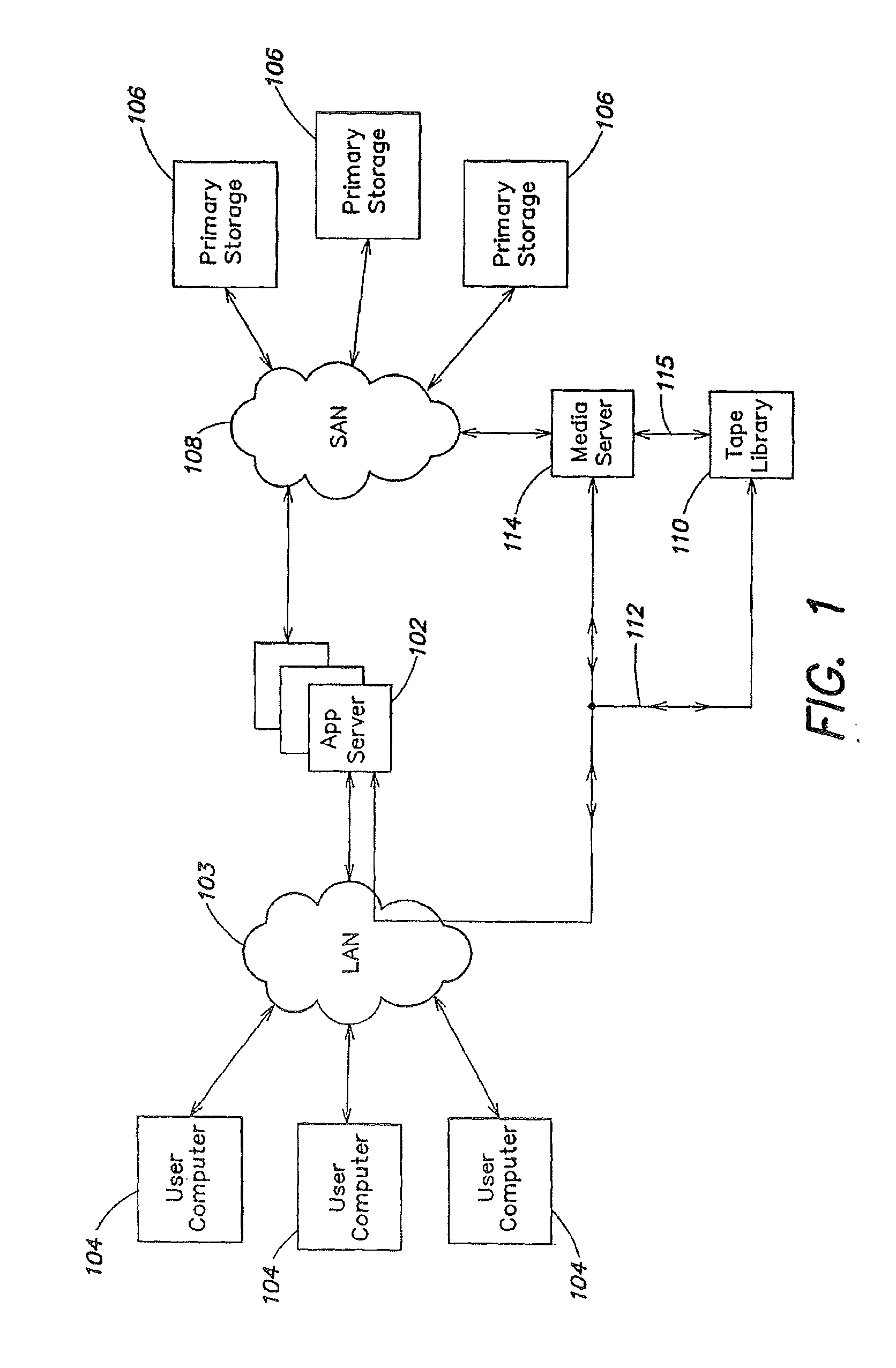
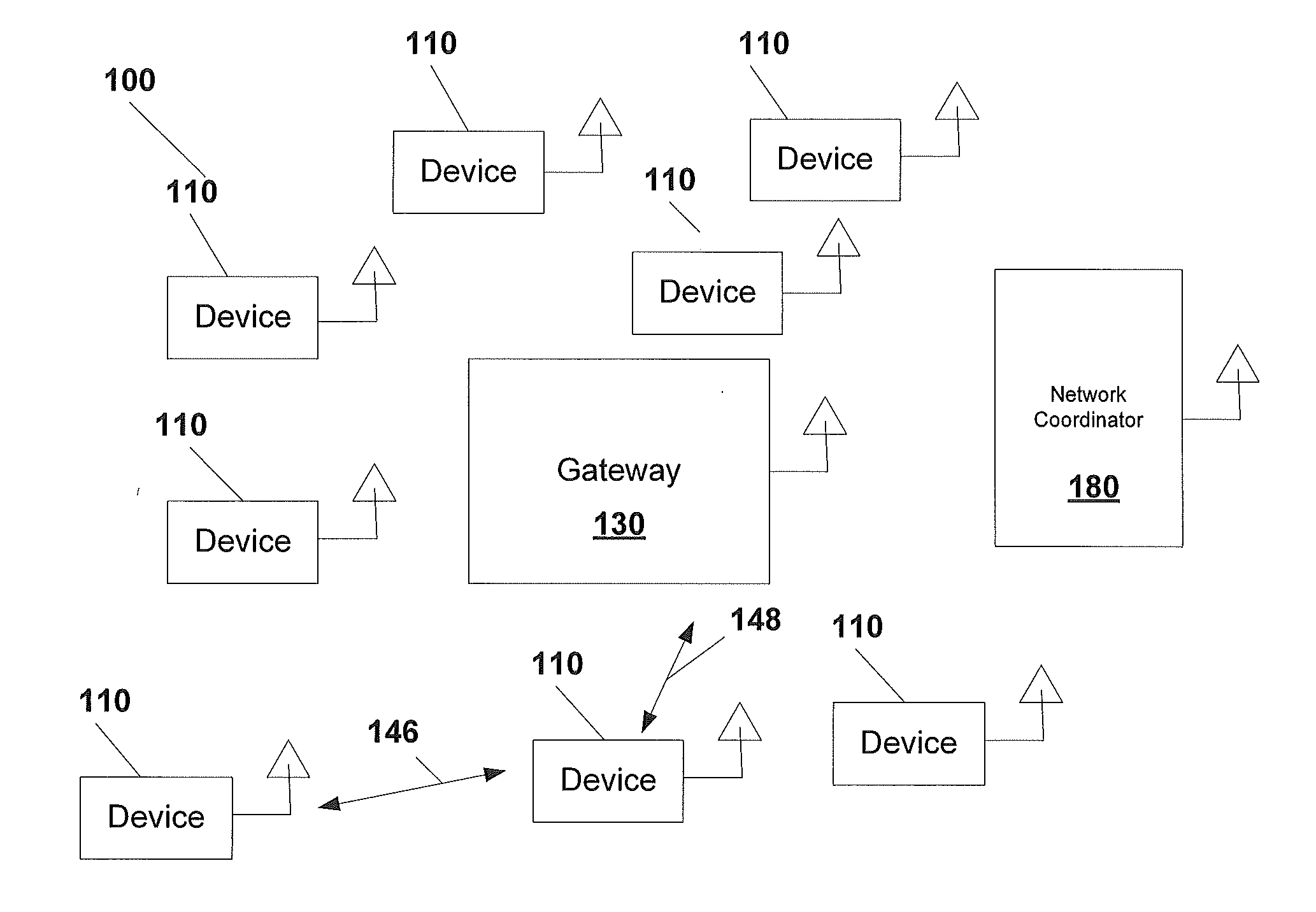
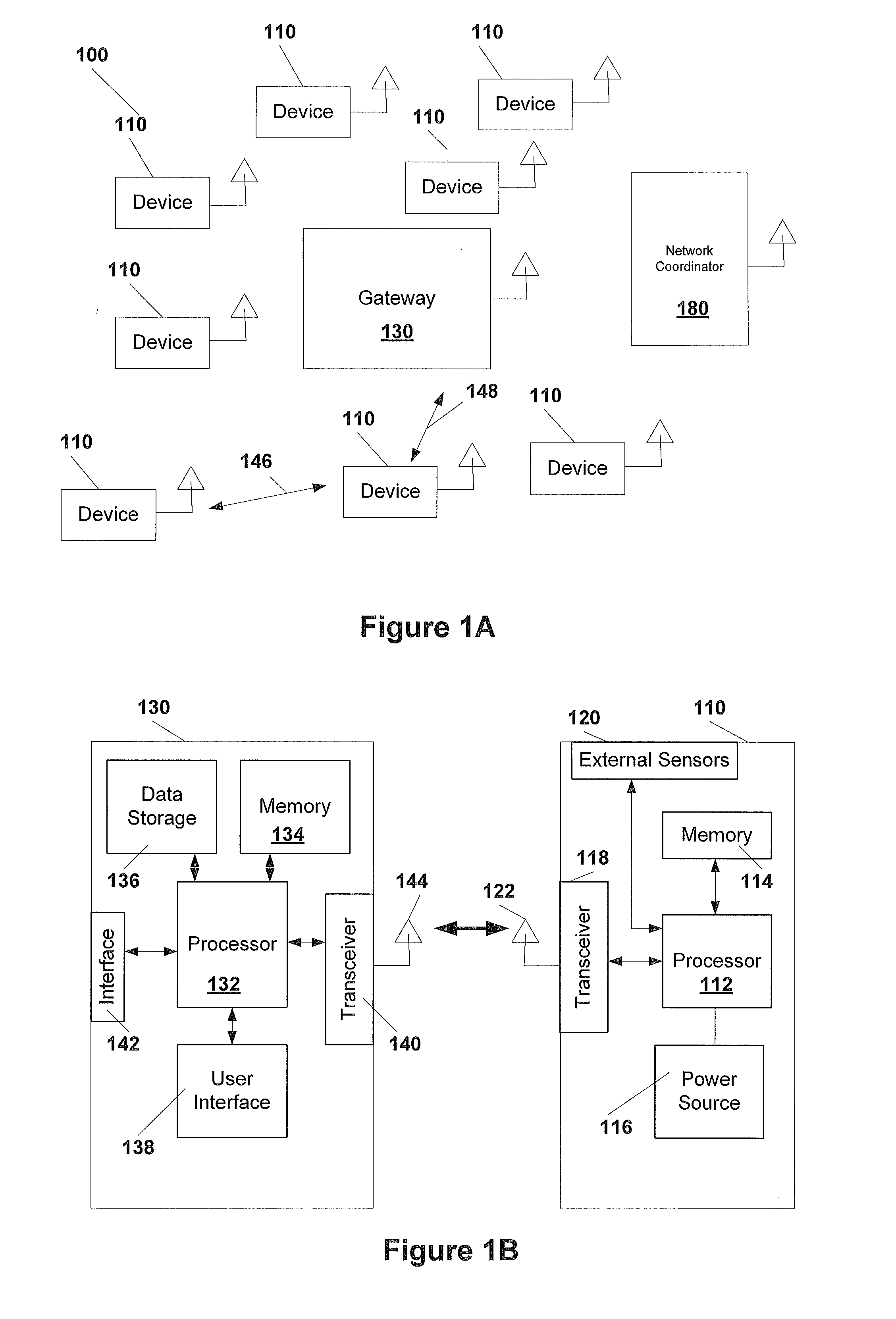
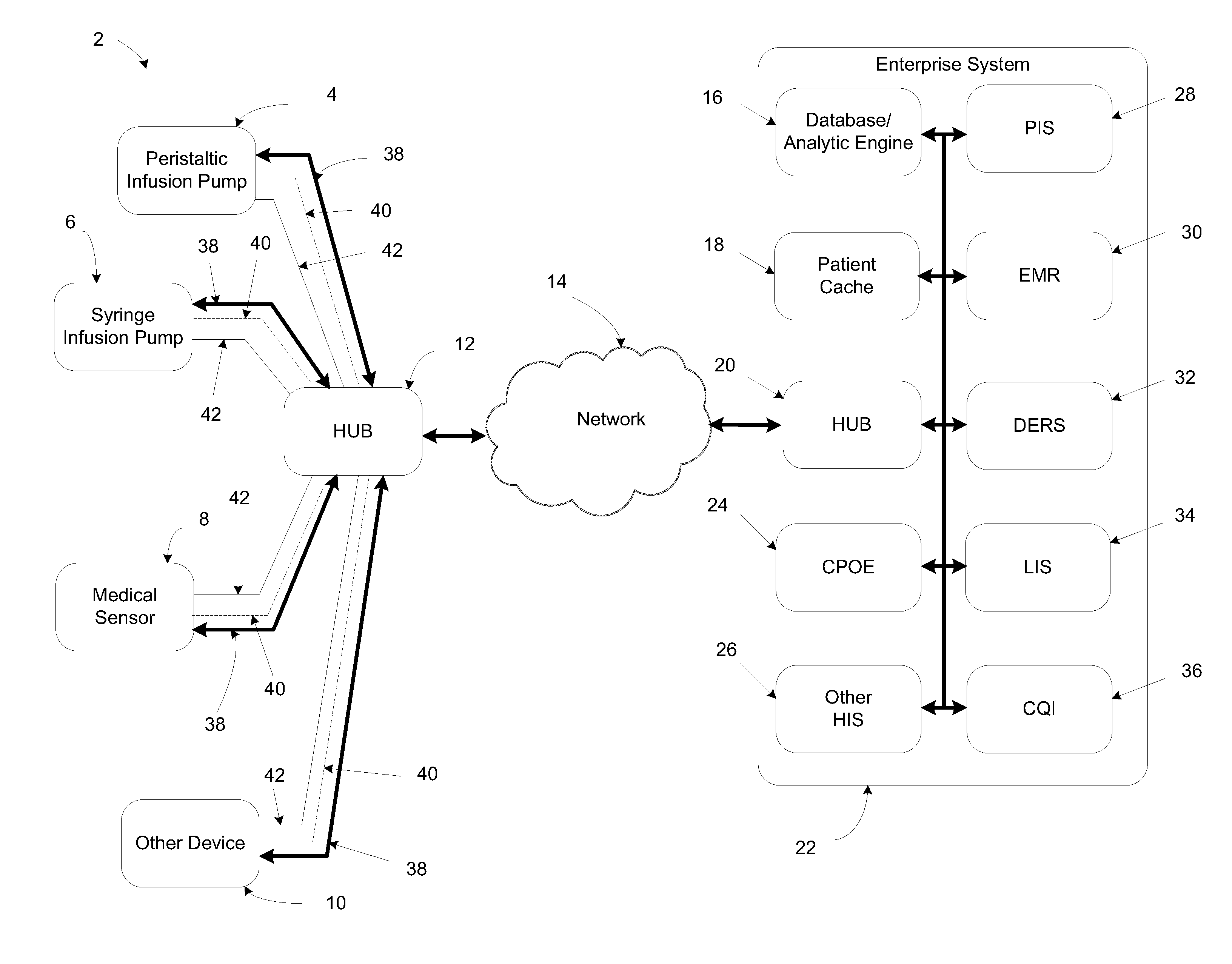
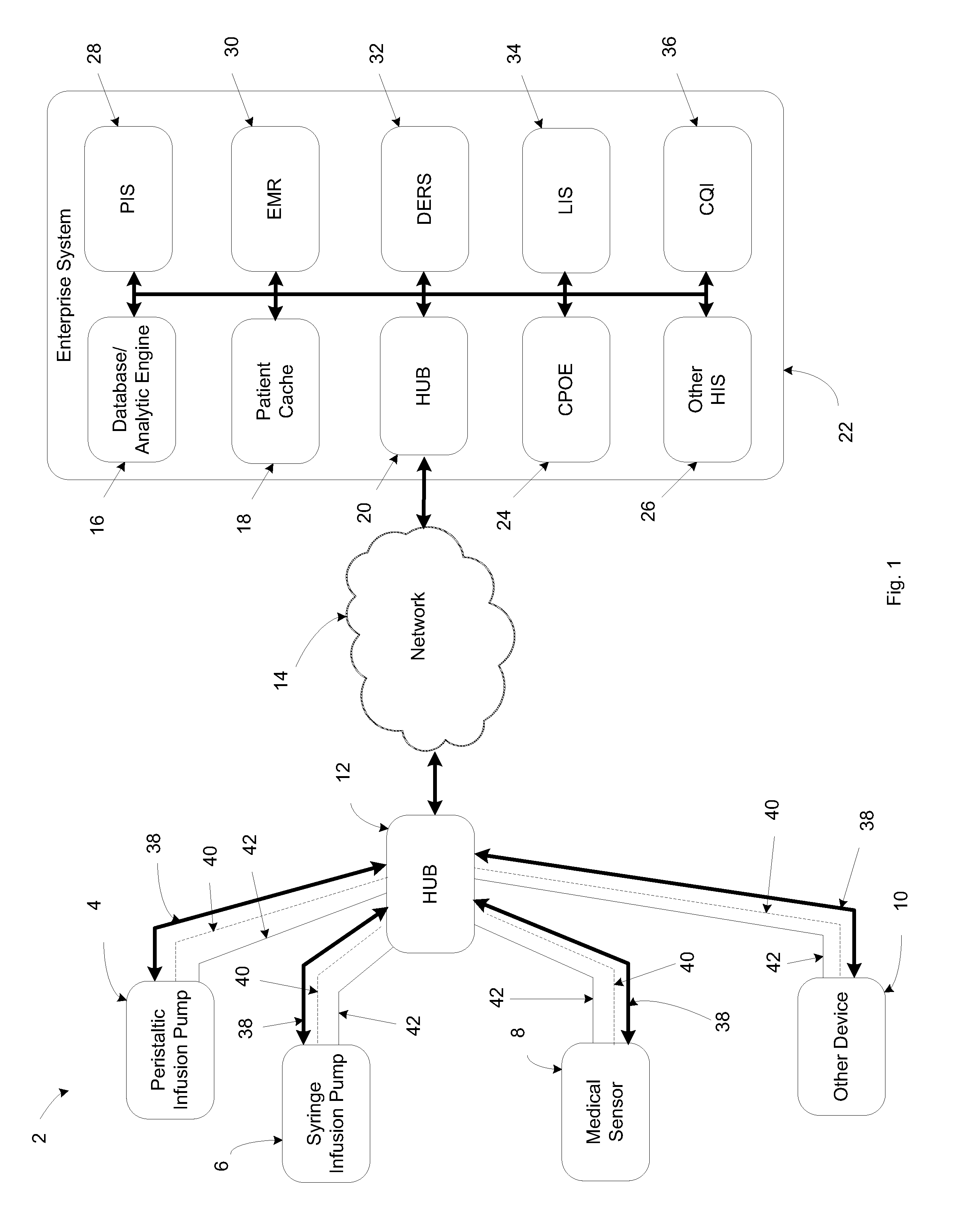
System, method, and apparatus for communicating data
A system includes first and second hubs. The first hub is configured to communicate data with a medical device through a Local Area Network and package the data into at least one application-layer packet. The second hub is configured to receive the at least one application-layer packet from the first hub operatively through at least one cellular network.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
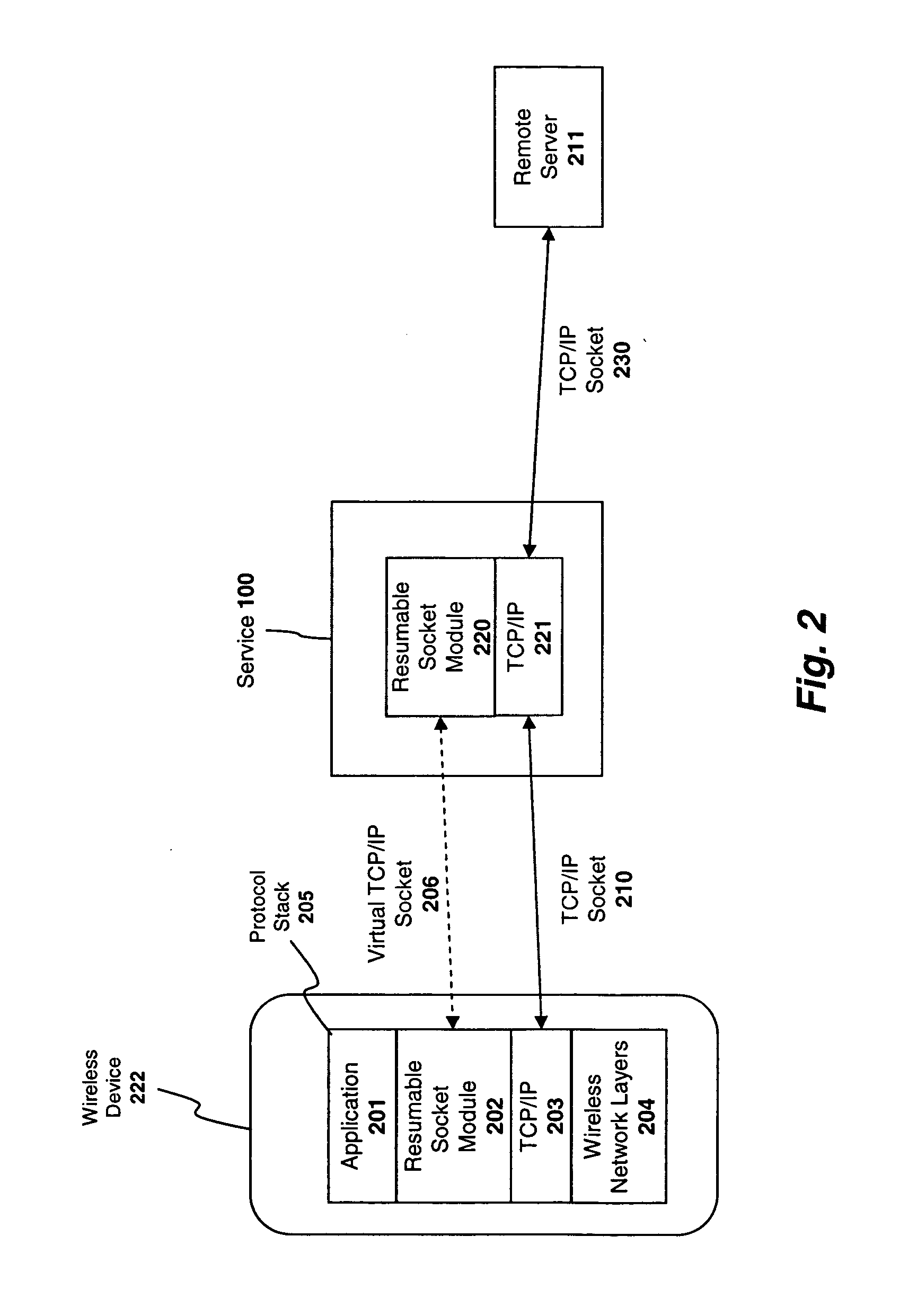
System and method for preserving socket connections over a wireless network
InactiveUS20090103515A1Time-division multiplexWireless commuication servicesNetworking protocolService provision
A system, apparatus, and method for maintaining a socket connection over a wireless network. For example, one embodiment of the invention is a wireless data processing device for emulating a socket connection comprising: a wireless radio for establishing a wireless communication channel with a wireless service provider over a wireless network; a network protocol stack including at least one layer configured to establish a socket connection with a remote server over the wireless network, the network protocol stack further including an application layer for executing applications capable of transmitting and receiving data over the socket connection; and a resumable socket module configured to emulate an open socket connection transparently to applications within the application layer, even when the wireless communication channel is temporarily lost, the resumable socket module counting a number of bytes transmitted or to be transmitted to the remote server and maintaining a buffer containing the bytes transmitted or to be transmitted.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
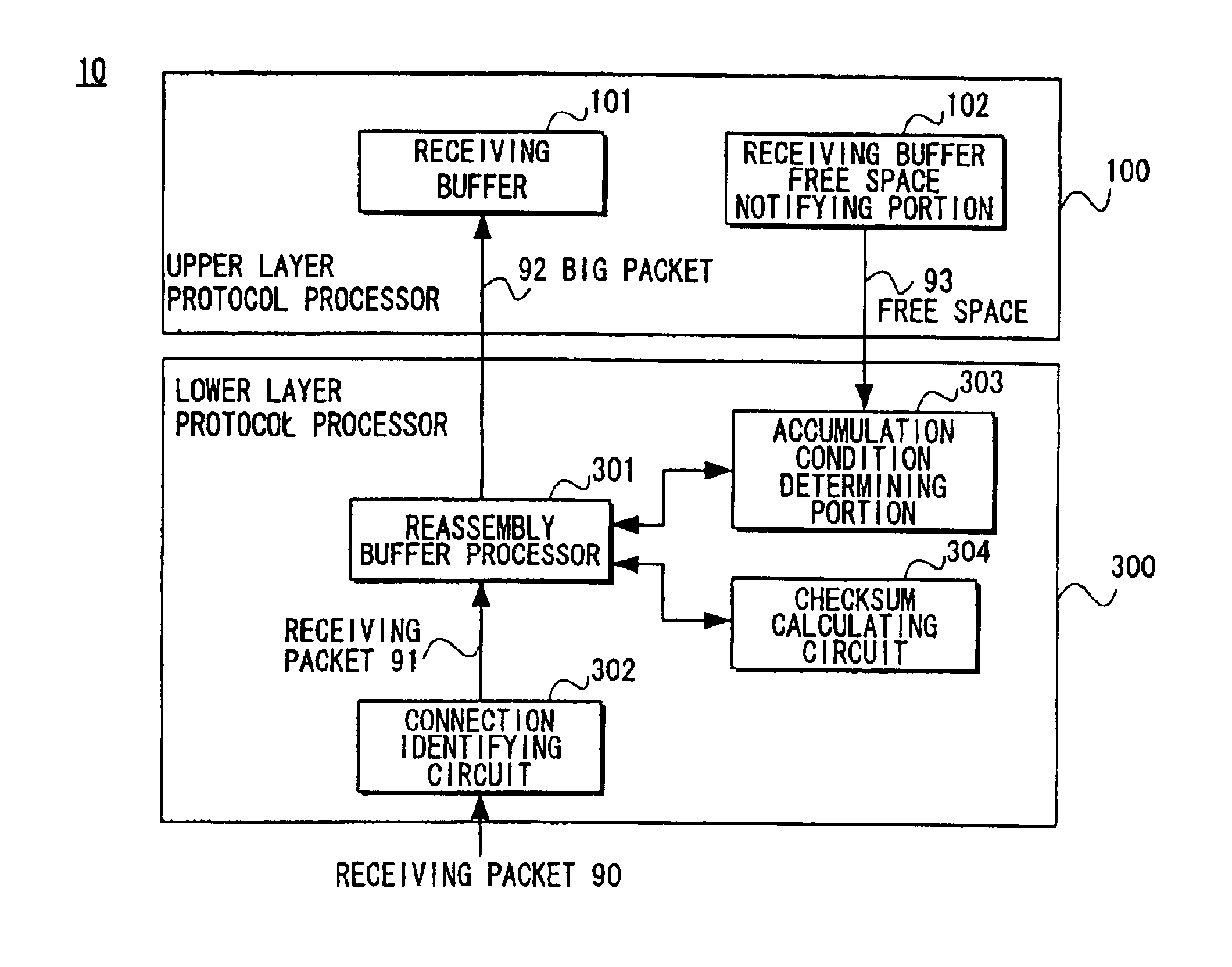
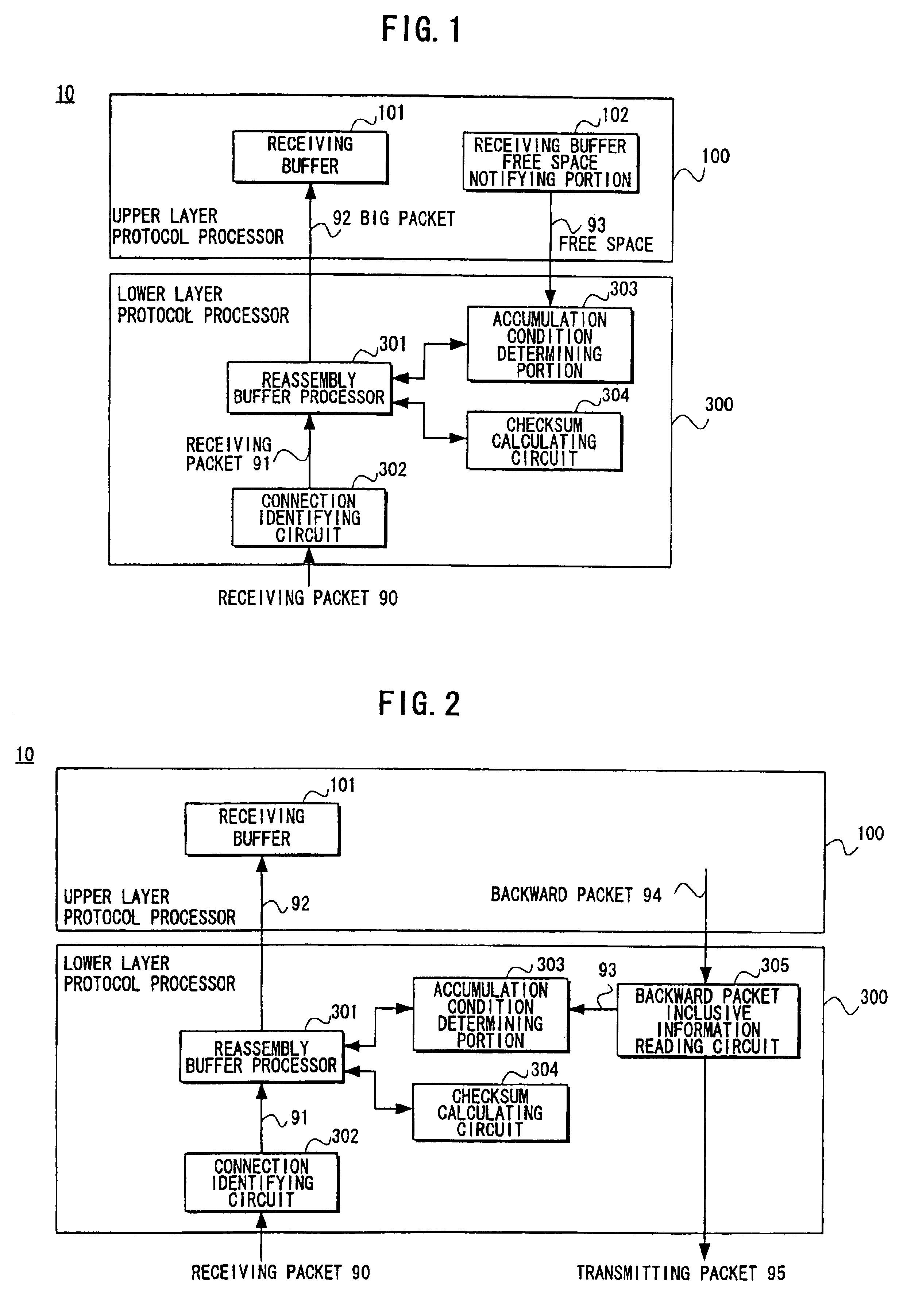
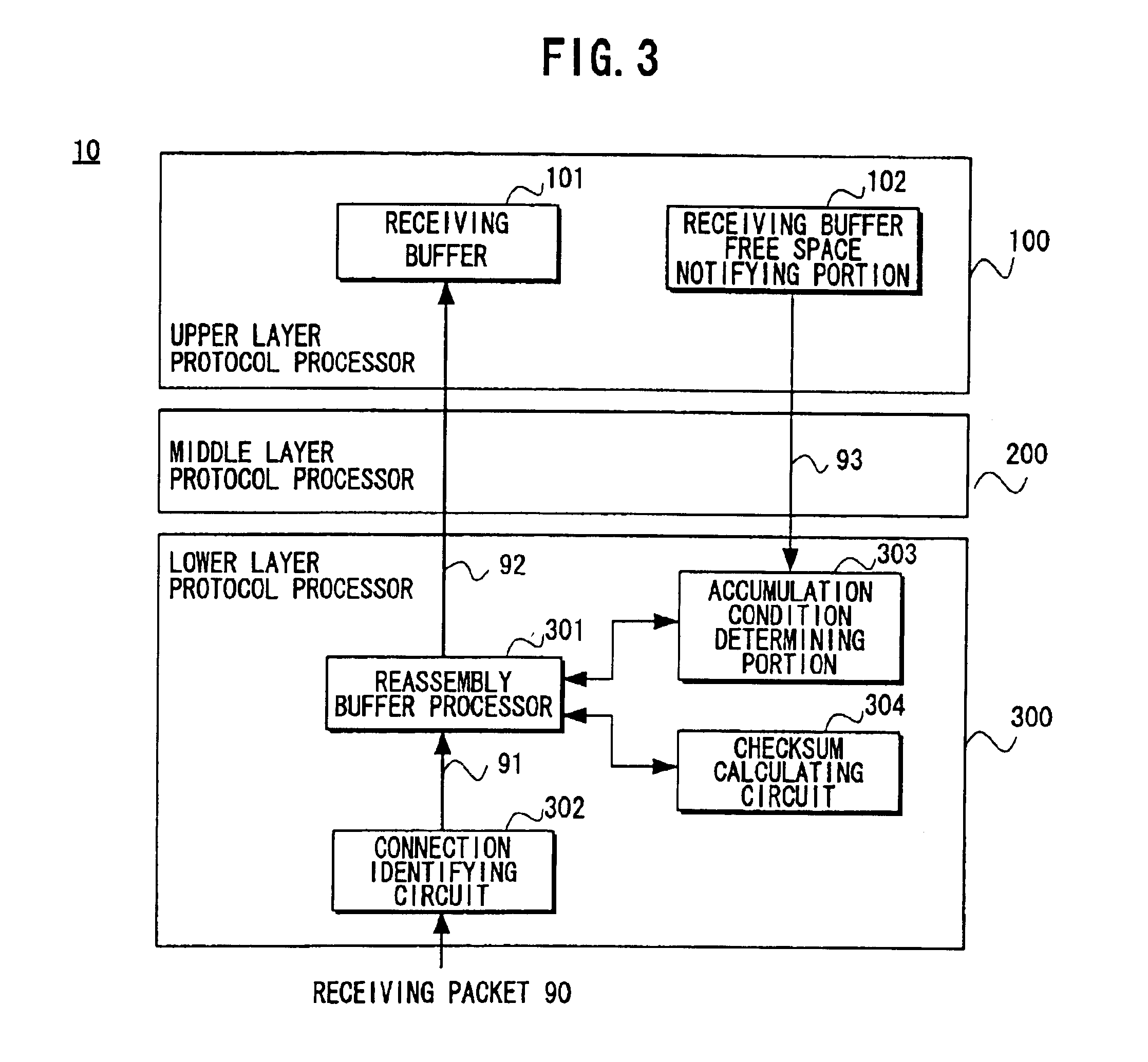
Packet processing device
InactiveUS6907042B1Reduce the number of processesEliminate overheadError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransport layerProtocol Application
A packet processing device in which a receiving buffer free space notifying portion notifies a free space of a receiving buffer, an accumulation condition determining portion determines a size of a big packet based on the free space, and a reassembly buffer processor reassembles a plurality of receiving packets into a single big packet to be transmitted to the receiving buffer. A backward packet inclusive information reading circuit for detecting the free space based on information within a backward packet from the upper layer may be used as the receiving buffer free space notifying portion. Also, an application layer may be used as the upper layer so that the big packet is transmitted not through a buffer of a transport layer but directly to the receiving buffer.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method and system for handoff between wireless networks
ActiveUS8184590B2Time-division multiplexWireless network protocolsSession Initiation ProtocolWireless mesh network
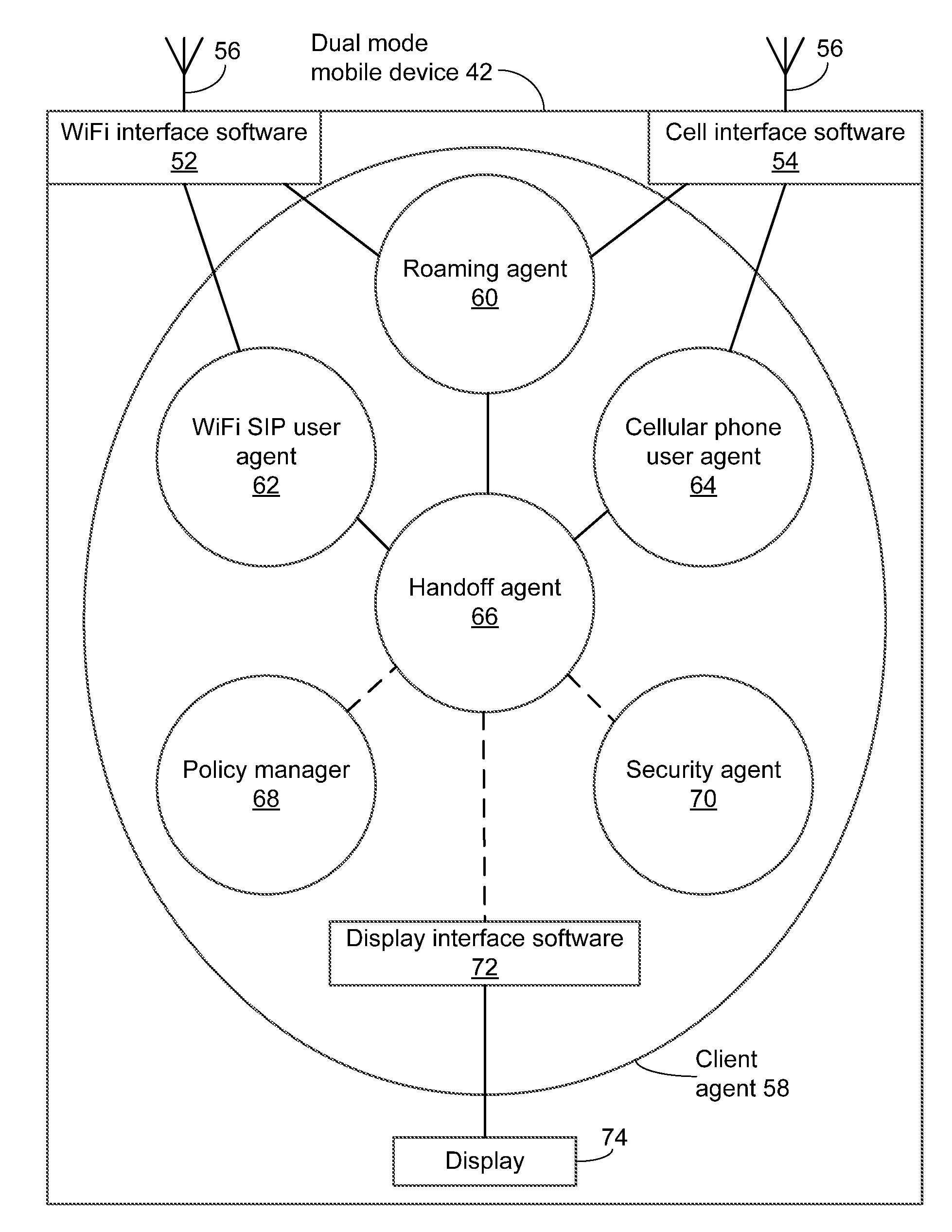
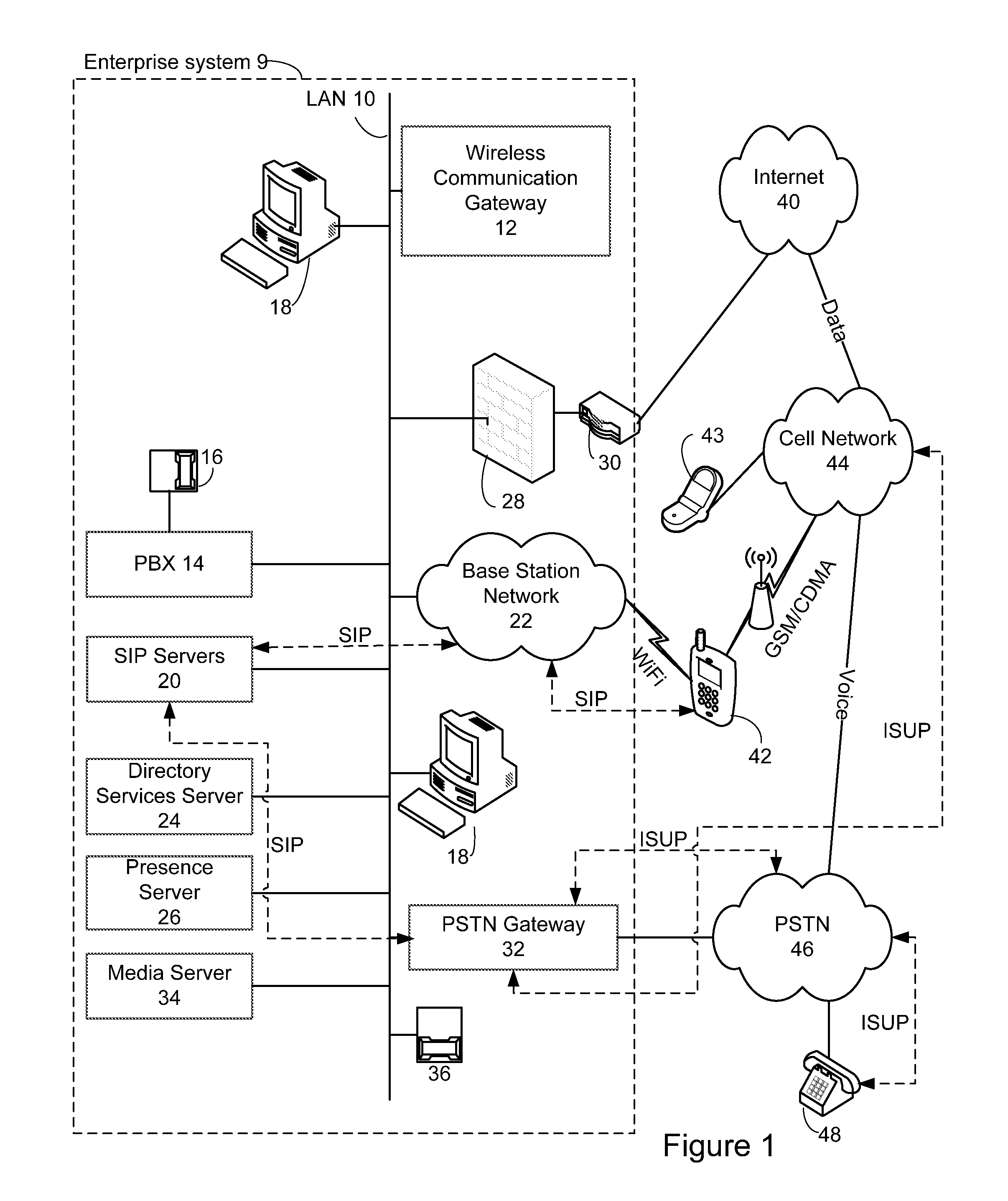
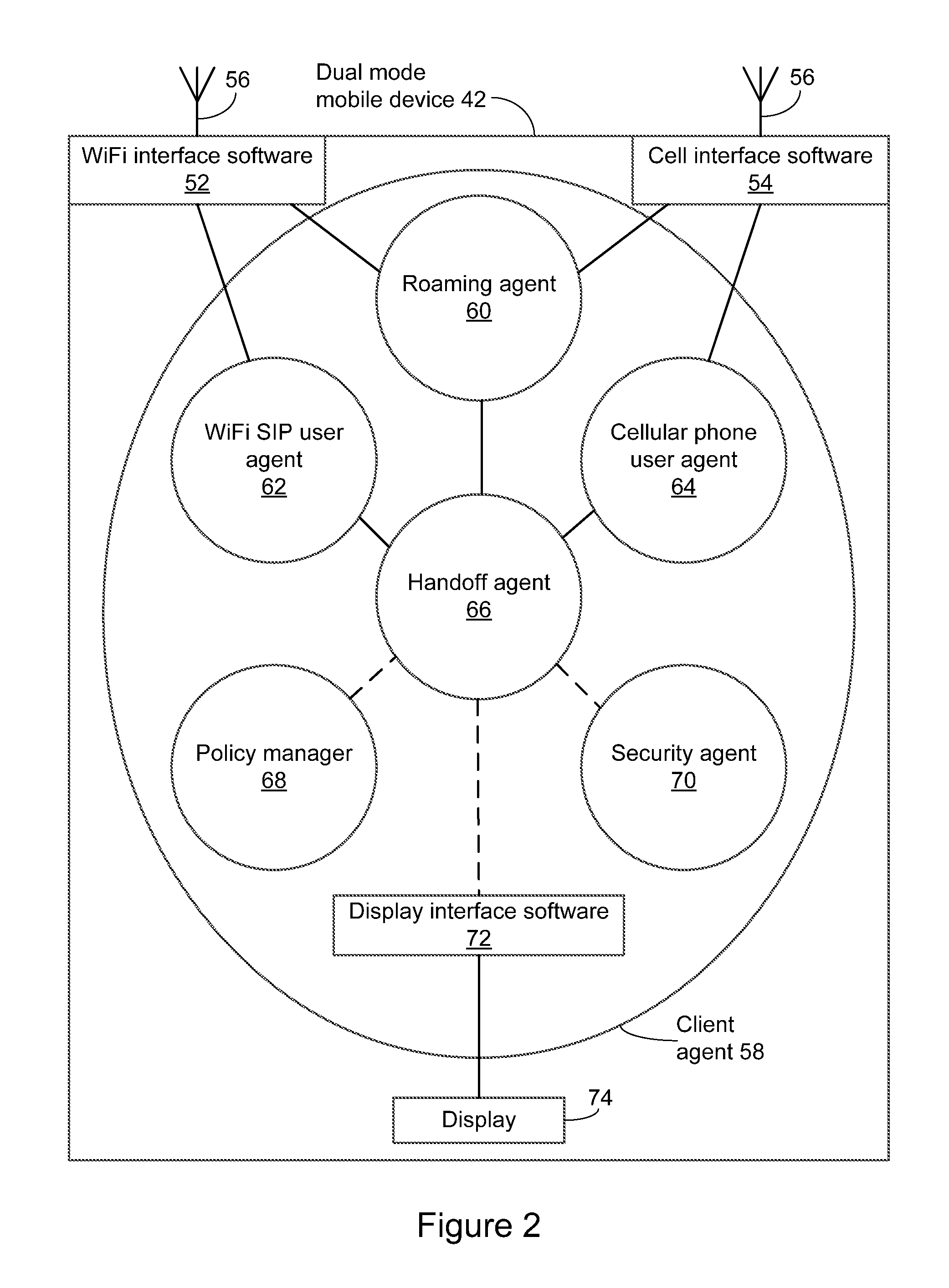
A method and system for operating a standalone client in a dual-mode mobile communications device to hand off a call between first and second wireless networks operating under different communications protocols, using Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) and ISDN User Part (ISUP) signalling. The standalone client-side application, or handoff agent, directly controls handoff of the call to the second wireless network until at least one new media stream to connect the dual-mode mobile communications device to the second device is established over the second wireless network. The standalone client-side application solely originates and controls an exchange of messages at the application layer, the exchange of messages modifying the communications channel.
Owner:ALIANZA INC
Method And System For Network Intrusion Detection, Related Network And Computer Program Product
ActiveUS20070214504A1Easy to detectMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionData streamProtocol Application
A system for providing intrusion detection in a network wherein data flows are exchanged using associated network ports and application layer protocols. The system includes a monitoring module configured for monitoring data flows in the network, a protocol identification engine configured for detecting information on the application layer protocols involved in the monitored data flows, and an intrusion detection module configured for operating based on the information on application layer protocols detected. Intrusion detection is thus provided independently of any predefined association between the network ports and the application layer protocols.
Owner:III HLDG 1
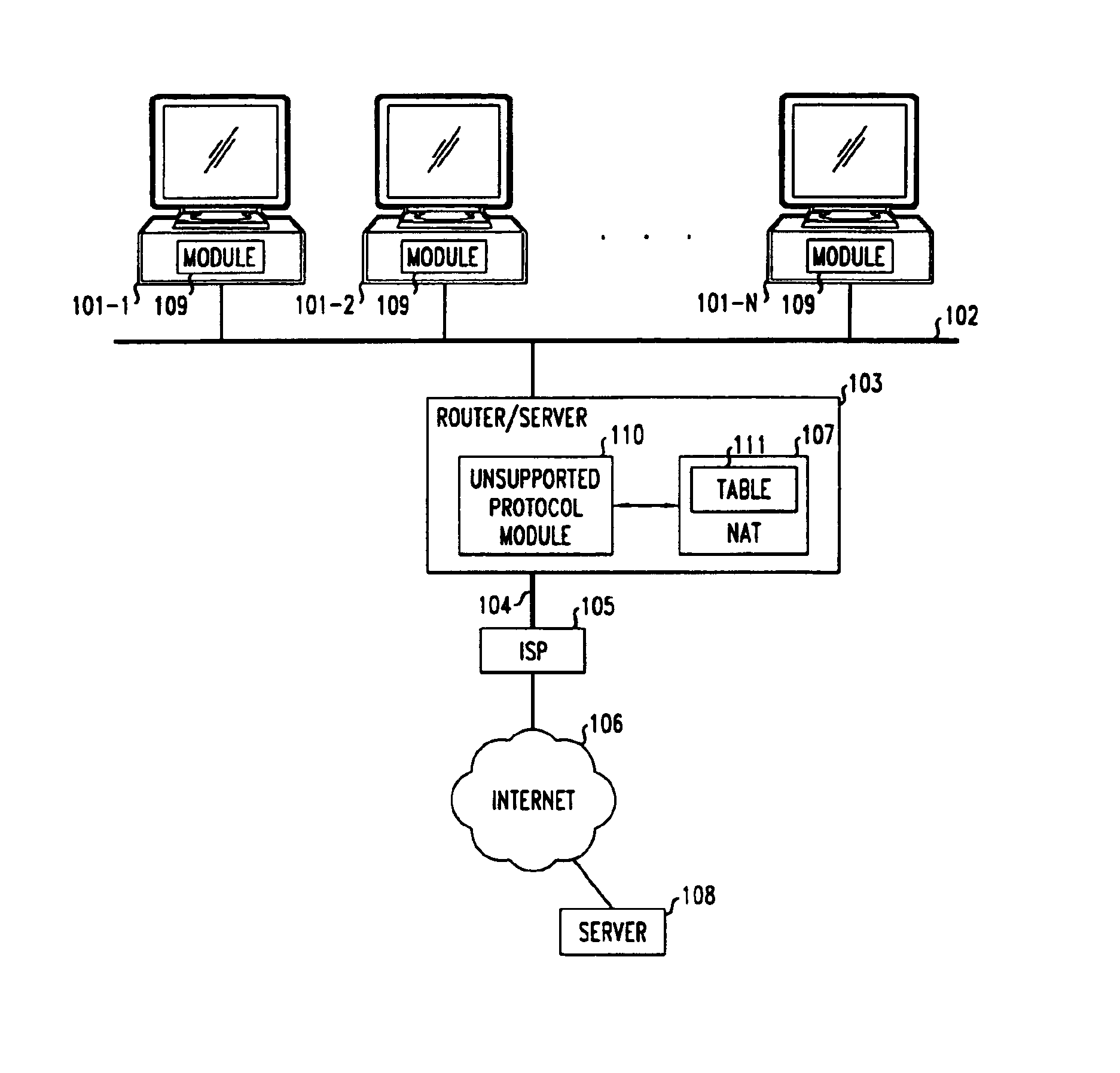
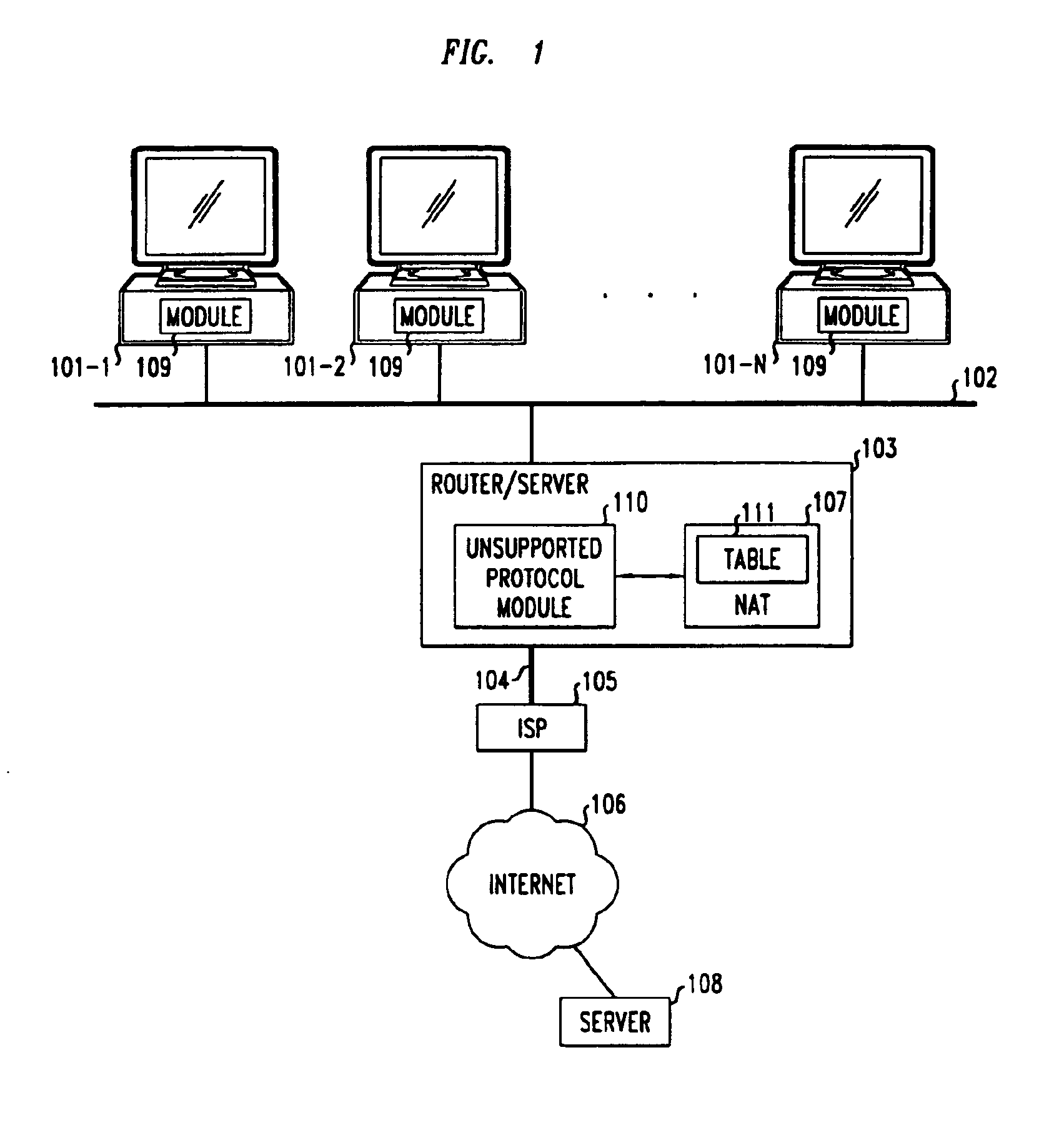
Method and apparatus for extending network address translation for unsupported protocols
InactiveUS6886103B1Ensure safetyMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlExpiration TimeIp address
Clients that are connected on a private network and which are assigned a private IP address that is not routable on the Internet can connect to the Internet through a router / server that includes a network address translator (NAT). For outgoing packets, the NAT translates the client's private source IP address and generalized port number (GPN) to the NAT's global IP address and GPN. For incoming packets sent to the NAT's global IP address and GPN, the NAT translates the global destination IP address and GPN to the client's private IP address and GPN. For protocols which cannot be directly supported by the NAT, such as those in the IPSec security protocol suite, the NAT is extended by creating in the NAT's translation table an entry that associates, for a specific unsupported protocol, a client's private IP address and GPN, the NAT's global IP address and GPN, and a foreign address on the Internet, that is valid until a specified or default expiration time. Outgoing packets from the client to that foreign address and incoming packets from that foreign address to the NAT's global IP address and GPN are translated according to the entry until the entry expires. In associations with these translations to outgoing and incoming packets, the client implements any Application Layer Gateway (ALG) that would otherwise be implemented at the NAT. Further, at the client, outgoing packets are modified before being transmitted so as to pre-compensate for the effects of the translations. Incoming packets at the client from the NAT are similarly modified so as to post-compensate for the effects of the translations. For the IPSec protocol, these modification include adjusting the checksum in the TCP or UDP header to account for IP address and TCP or UDP port number translations.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
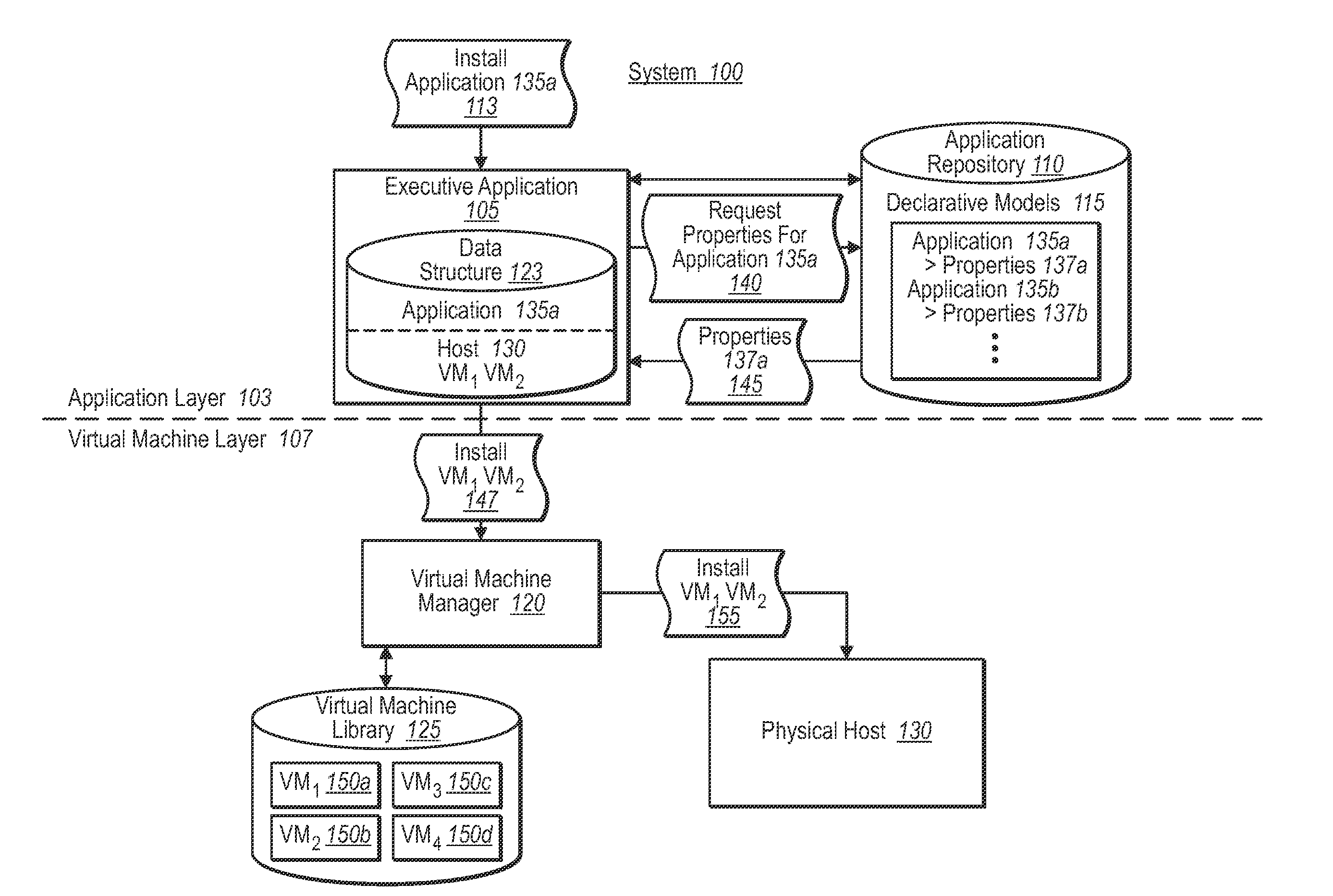
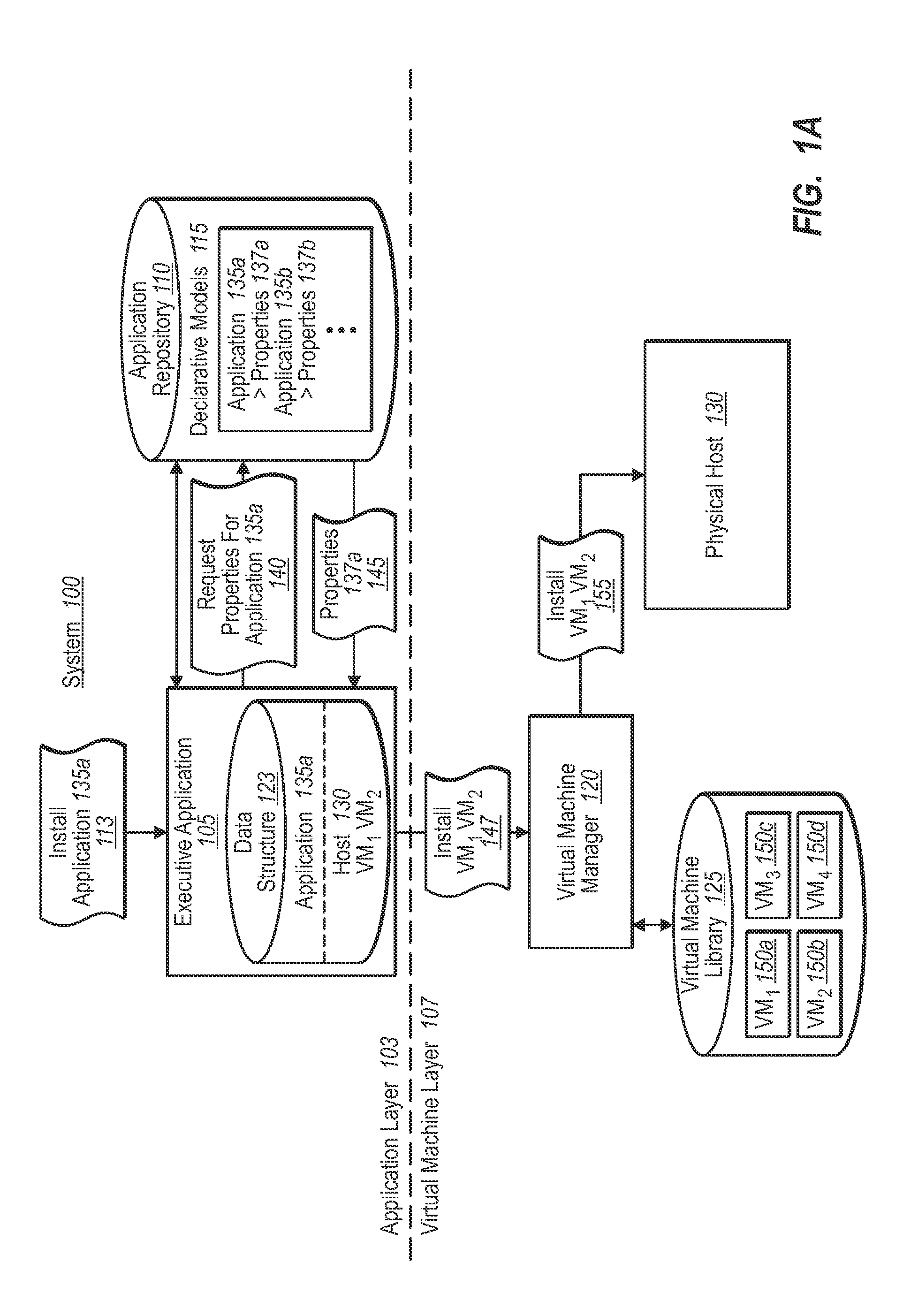
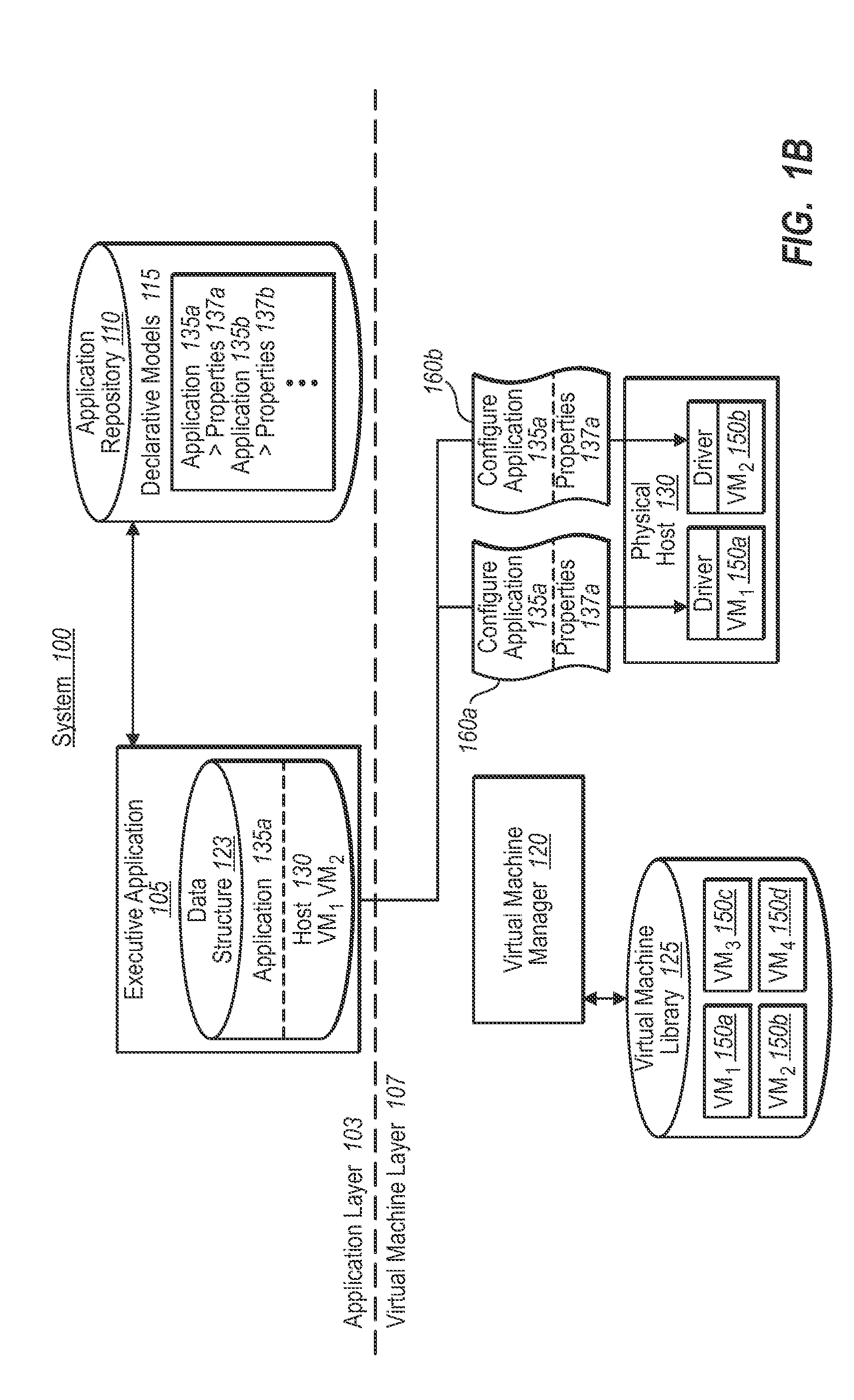
Synchronizing virtual machine and application life cycles
ActiveUS20090313620A1Create efficientlyGuaranteed uptimeProgram loading/initiatingSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationApplication softwareProtocol Application
A virtual environment can be configured to coordinate life cycles of virtual machines and application programs executing therein. In one implementation, the virtual environment includes an application layer and a virtual machine layer. The application layer communicates with the virtual machine layer to coordinate and directs virtual machine creation and deletion in a coordinated fashion with application programs. For example, the application layer receives a request to initiate an application program. The application layer determines from associated application properties the type and / or number of virtual machines to be created. The application layer then directs creation of the appropriate virtual machines (through the virtual machine layer), and further directs installation of the requested application programs therein. When detecting removal of the application program from the created virtual machines, the application layer can automatically direct removal or decommissioning of the corresponding virtual machine.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Systems and Methods of Symmetric Transport Control Protocol Compression
ActiveUS20080046616A1Reduce network latencyImprove experienceNetwork traffic/resource managementWireless network protocolsTraffic capacityData compression
A method for compressing a stream of application layer network traffic communicated over a transport layer connection of a virtual private network connection between a client and a server using an appliance. The appliance intercepts one or more transport layer packets of a stream of application network traffic communicated via a transport layer connection of a virtual private network connection between a client and a server. The appliance accumulates data from a payload of the intercepted transport layer packets, determines data accumulated for transmission should be compressed based on one or more compression trigger, and compresses the accumulated data into a self-contained compression block for transmission.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
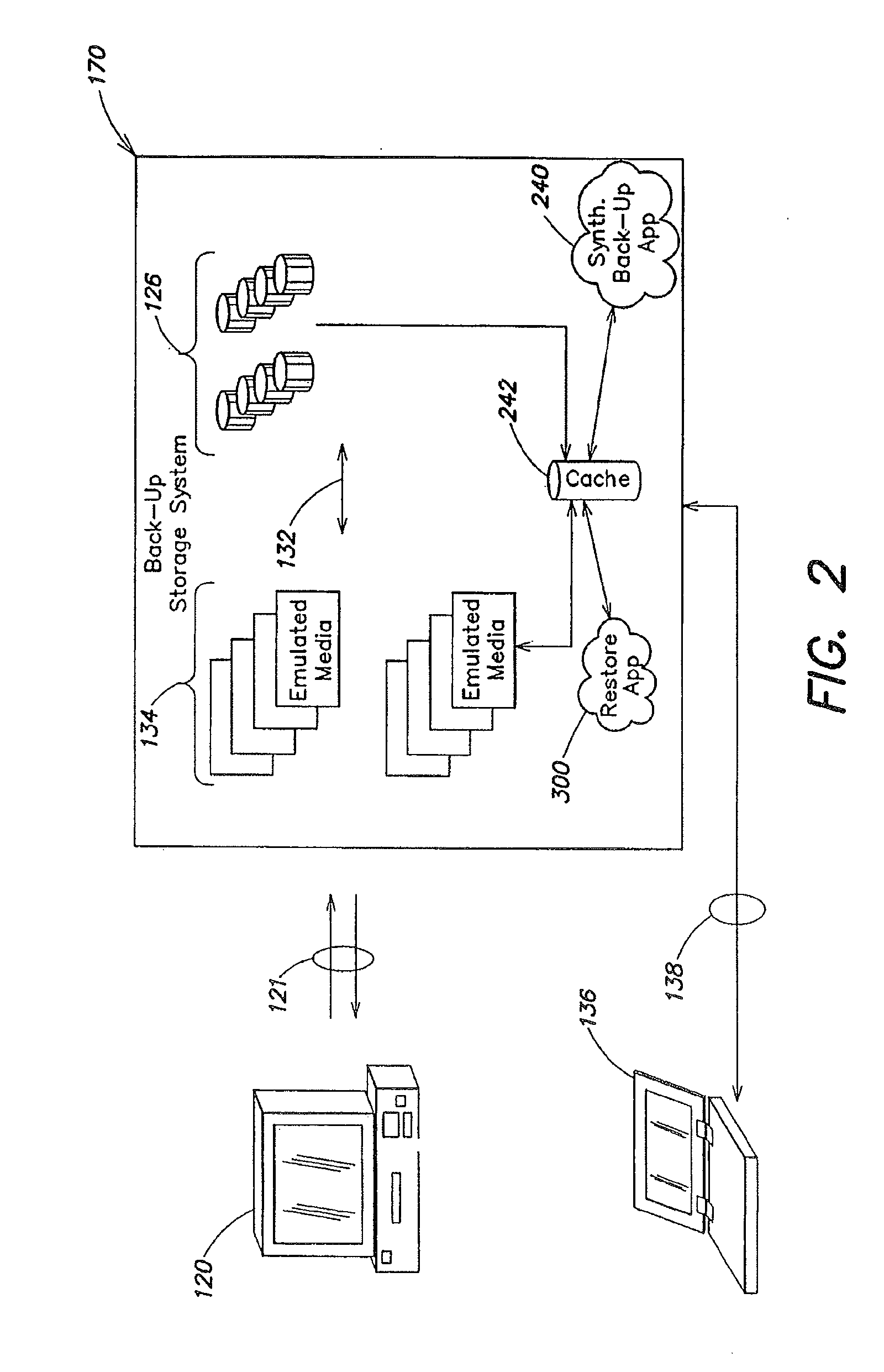
Scalable de-duplication mechanism
ActiveUS20090182789A1Improve efficacyImprove scalabilityDigital data processing detailsError detection/correctionProtocol ApplicationData deduplication
A method for removing redundant data from a backup storage system is presented. In one example, the method may include receiving the application layer data object, selecting a de-duplication domain from a plurality of de-duplication domains based at least in part on a data object characteristic associated with the de-duplication domain, determining that the application layer data object has the characteristic and directing the application layer data object to the de-duplication domain.
Owner:HITACHI VANTARA LLC
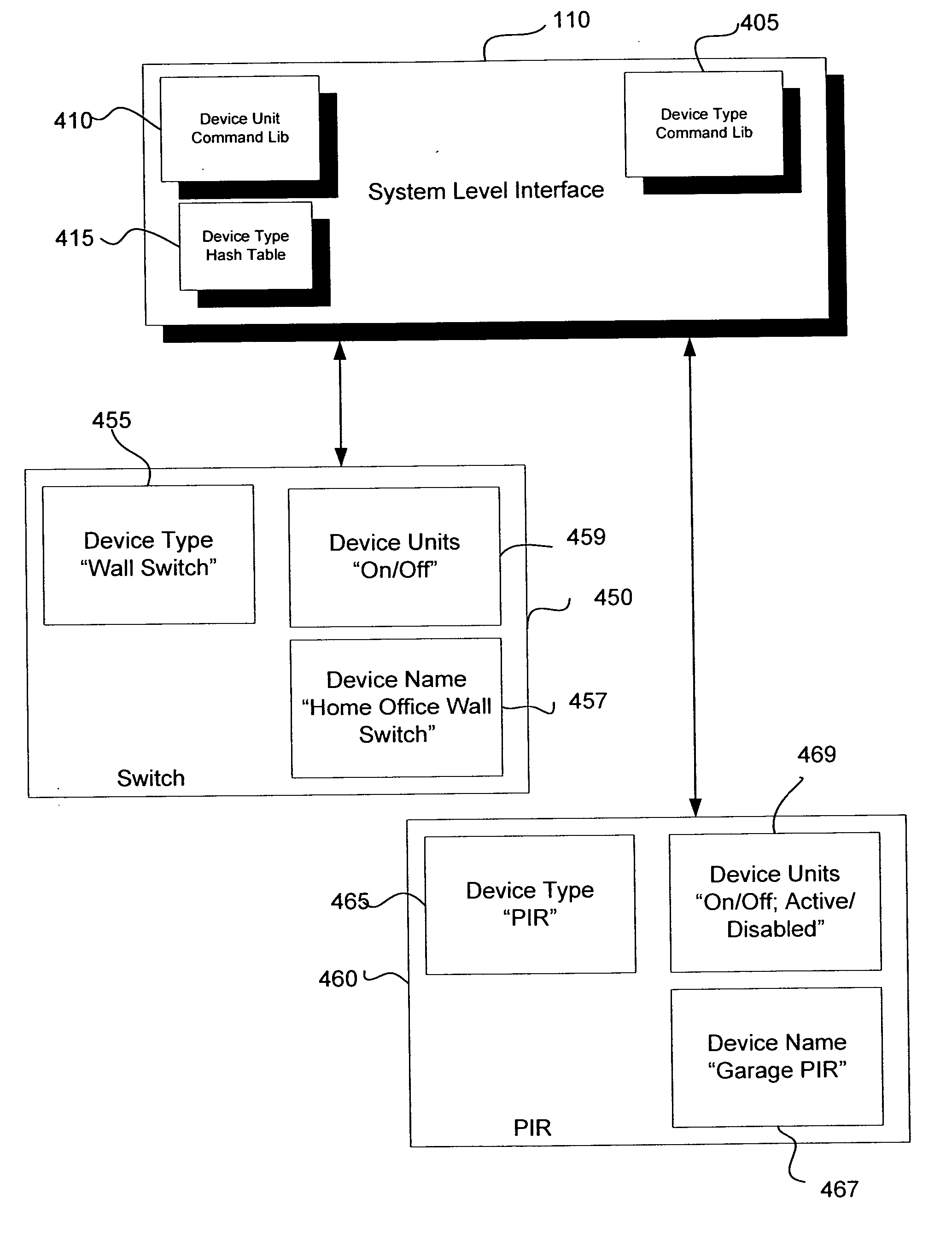
Application updating in a home automation data transfer system
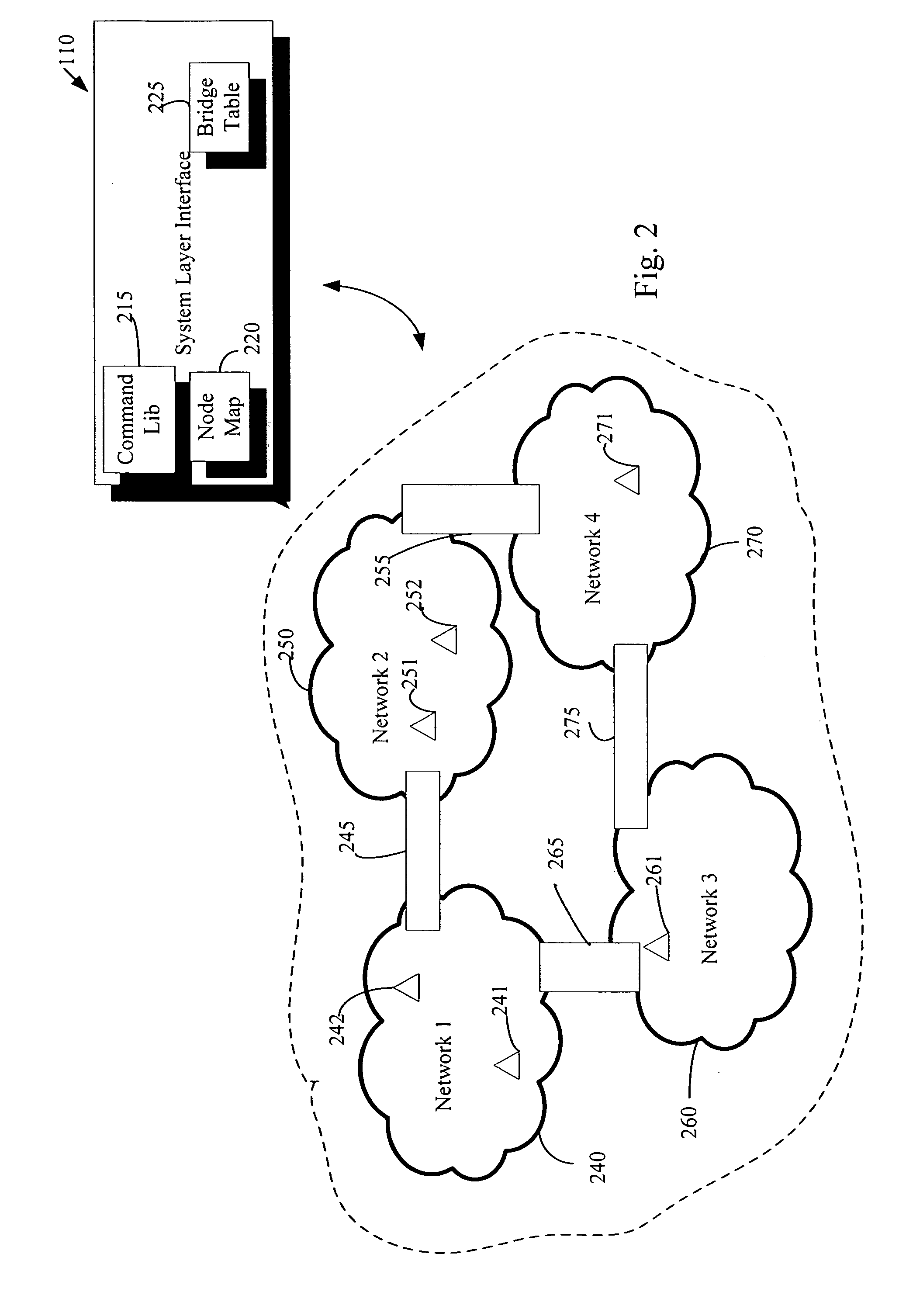
InactiveUS20070143440A1Simple interfaceEfficient upgradeMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksData packTransport layer
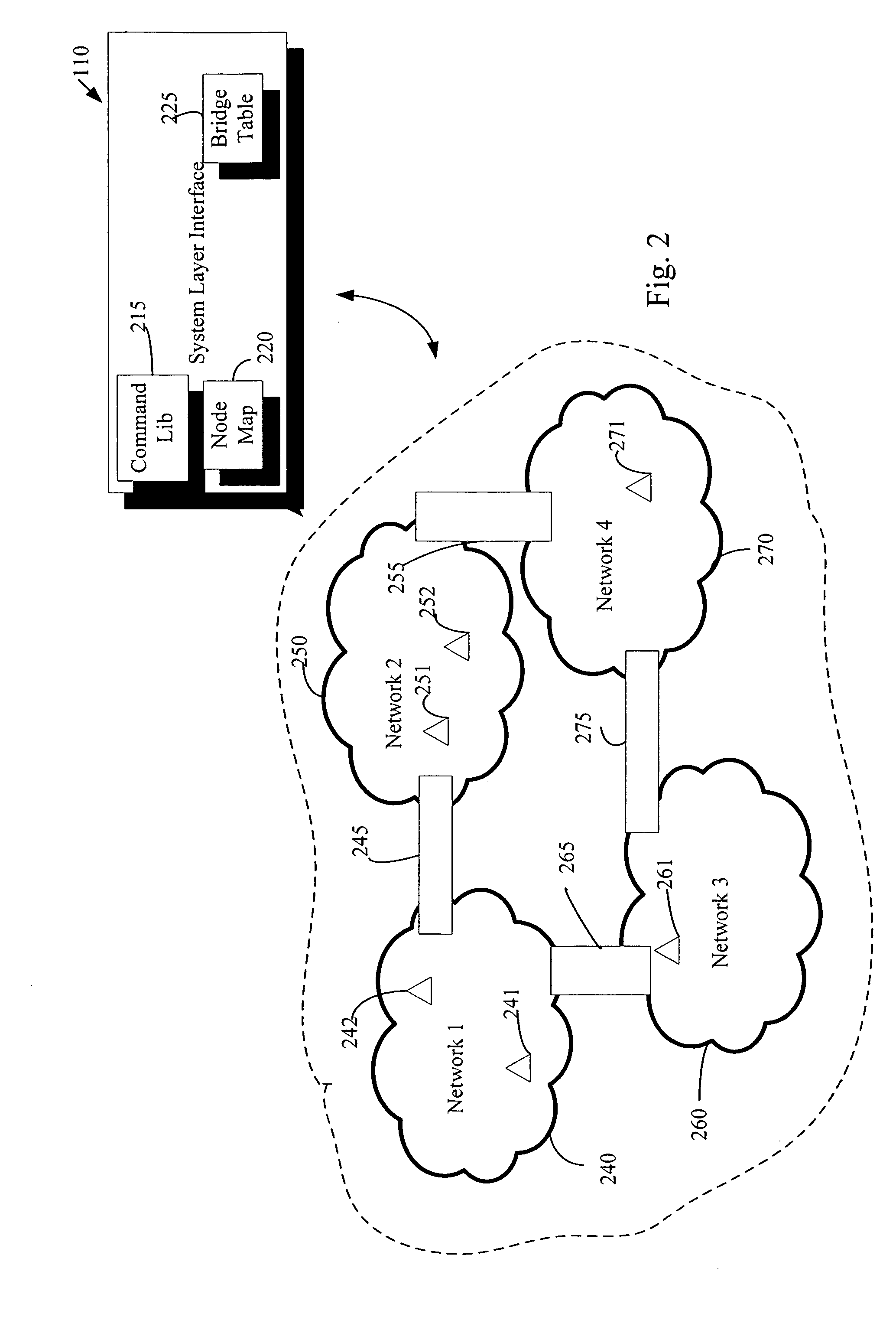
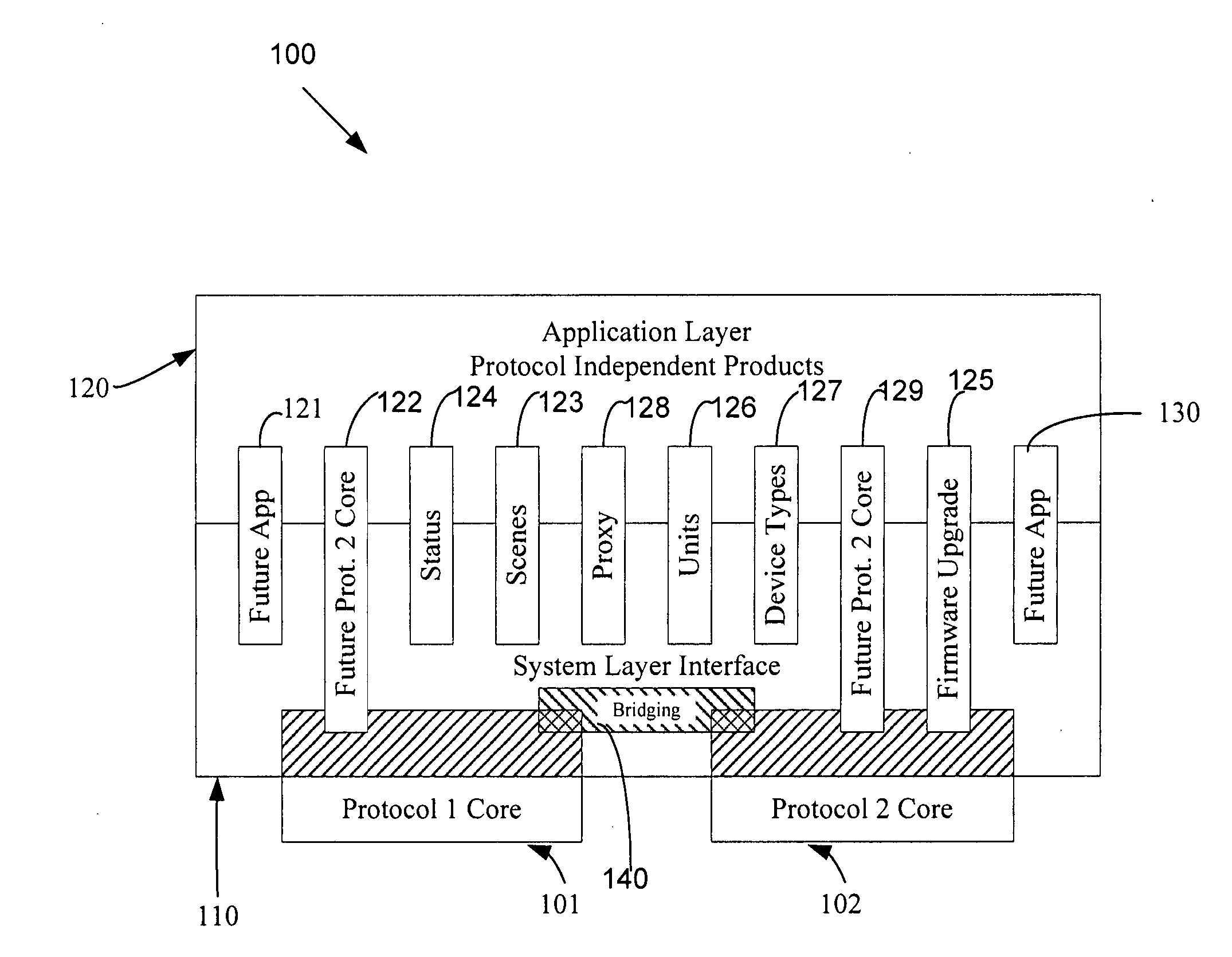
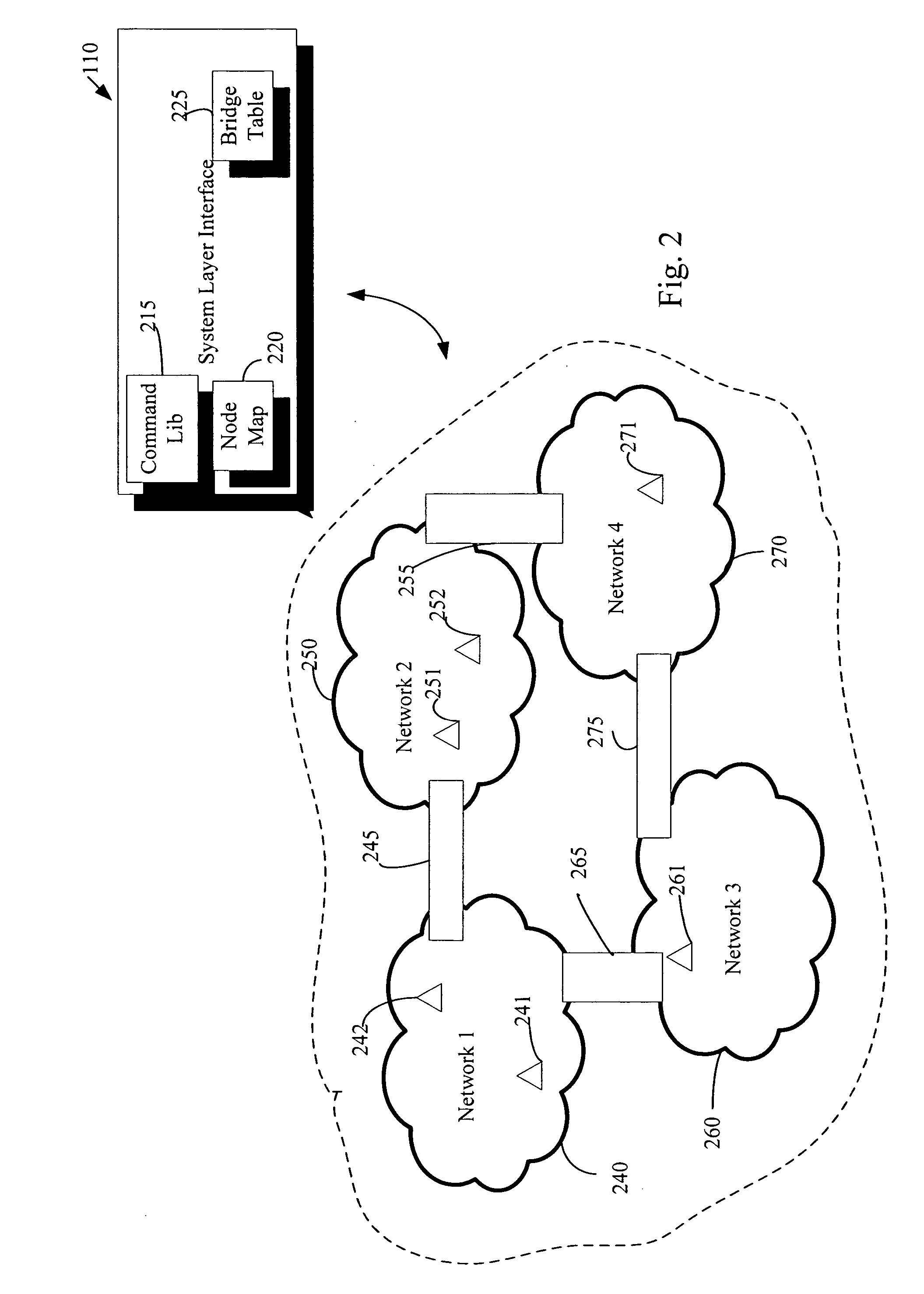
An automation network includes automation network devices connected to the network and a system level interface that interfaces with a transport layer and an application layer of the automation network. A method is disclosed that programs an automation network device in communication with an automation network, where the automation network includes an access point coupled with an external network. The method includes receiving application upgrade data at the access point, where the application upgrade data includes upgrade data associated with a target automation network device in communication with the automation network. Application upgrade data is transmitted through the home to the target automation network device. A next application upgrade data packet to be transmitted across the automation network is requested from the target automation network device. An application stored in the target automation network device is programmed, using an application upgrade data command transmitted to the target home automation network device.
Owner:INTERMATIC
Systems and Methods for Tracking Application Layer Flow Via a Multi-Connection Intermediary Device
ActiveUS20130041934A1Energy efficient ICTMultiple digital computer combinationsGranularityTemplate based
The present disclosure is directed towards tracking application layer flow via a multi-connection intermediary. Transaction level or application layer information may be tracked via the intermediary, including one or more of: (i) the request method; (ii) response codes; (iii) URLs; (iv) HTTP cookies; (v) RTT of both ends of the transaction in a quad flow arrangement; (vi) server time to provide first byte of a communication; (vii) server time to provide the last byte of a communication; (viii) flow flags; or any other type and form of transaction level data may be captured, exported, and analyzed. The application layer flow or transaction level information may be provided in an IPFIX-compliant data record. This may be done to provide template-based data record definition, as well as providing data on an application or transaction level of granularity.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
RFID applications
An RFID device is disclosed. The RFID device can include a transceiver; and a processor coupled to the transceiver. The processor can operate a Physical (PHY) layer with the transceiver, a Media Access Control (MAC) layer over the PHY layer, and an RFID application layer over the MAC layer. The MAC layer and the PHY layer can operate according to a non-RFID wireless protocol.
Owner:SAVI TECH INC
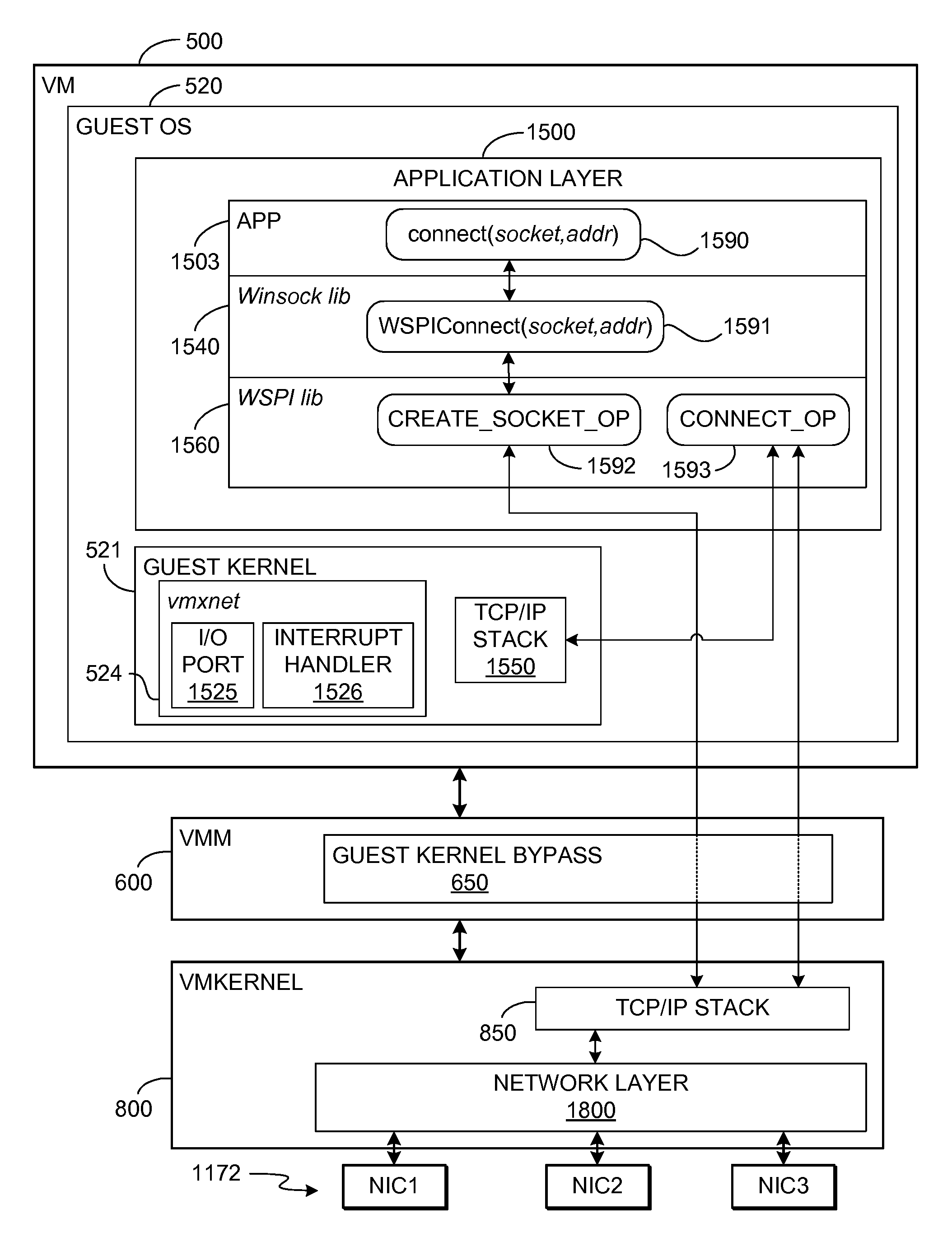
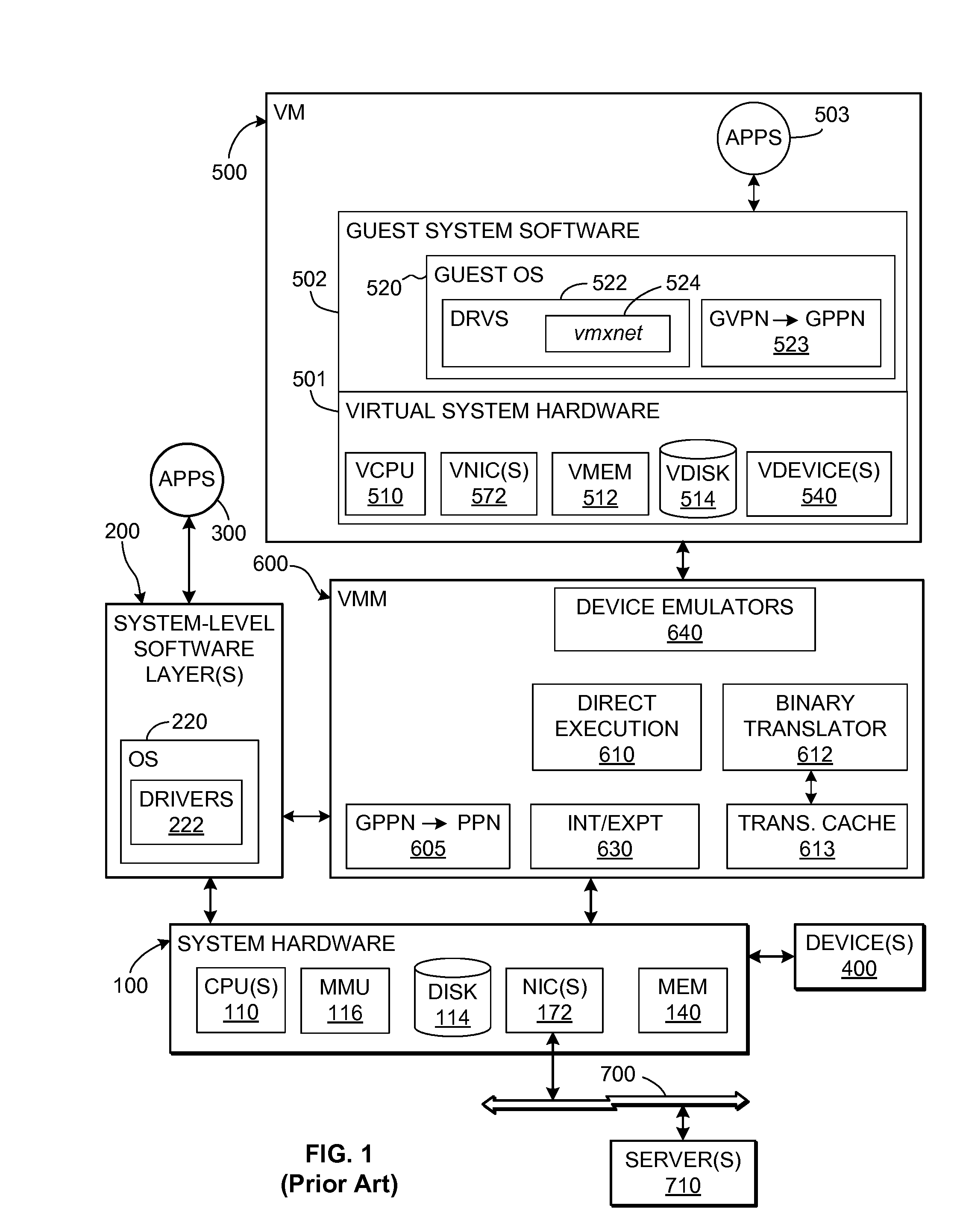
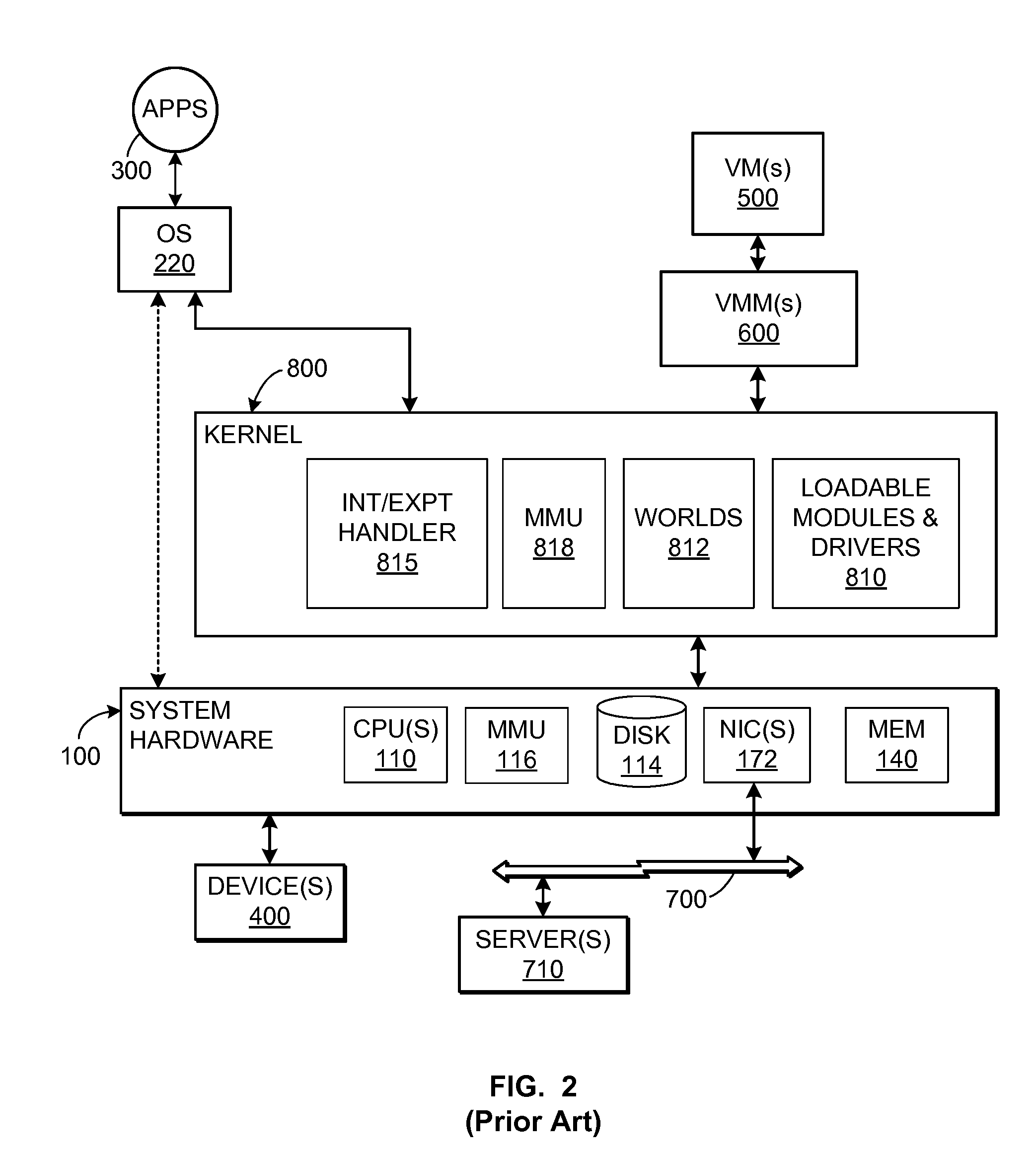
TCP/IP offloading for virtual machines
An engine (TOE) is provided in a virtualized computer system for offloading I / O tasks using any defined protocol such as TCP / IP. The system includes a virtual machine (VM), which has a guest operating system (OS) that runs via a virtual machine monitor (VMM) on a system-level software platform (vmkernel), which also forms the software interface layer to at least one physical network connection device. A TCP / IP stack is included in vmkernel. During normal I / O operation, for sockets associated with TOE, processes in an application layer in the guest OS are able to communicate directly with vmkernel's TCP / IP stack, thereby bypassing the guest OS kernel.
Owner:VMWARE INC
Remote device management in a home automation data transfer system
An automation network includes automation network devices connected to the network and a system layer interface that interfaces with a transport layer and an application layer of the home automation network. The system layer interface includes command libraries configured to upgrade a remote network device. The automation network queries the network devices to determine if there are lost network devices or newly added network devices. The automation network may update a new remote device with scene information related to any lost network devices.
Owner:INTERMATIC
System and Method of Fraud and Misuse Detection Using Event Logs
InactiveUS20070073519A1Nuclear monitoringDigital computer detailsRelevant informationMisuse detection
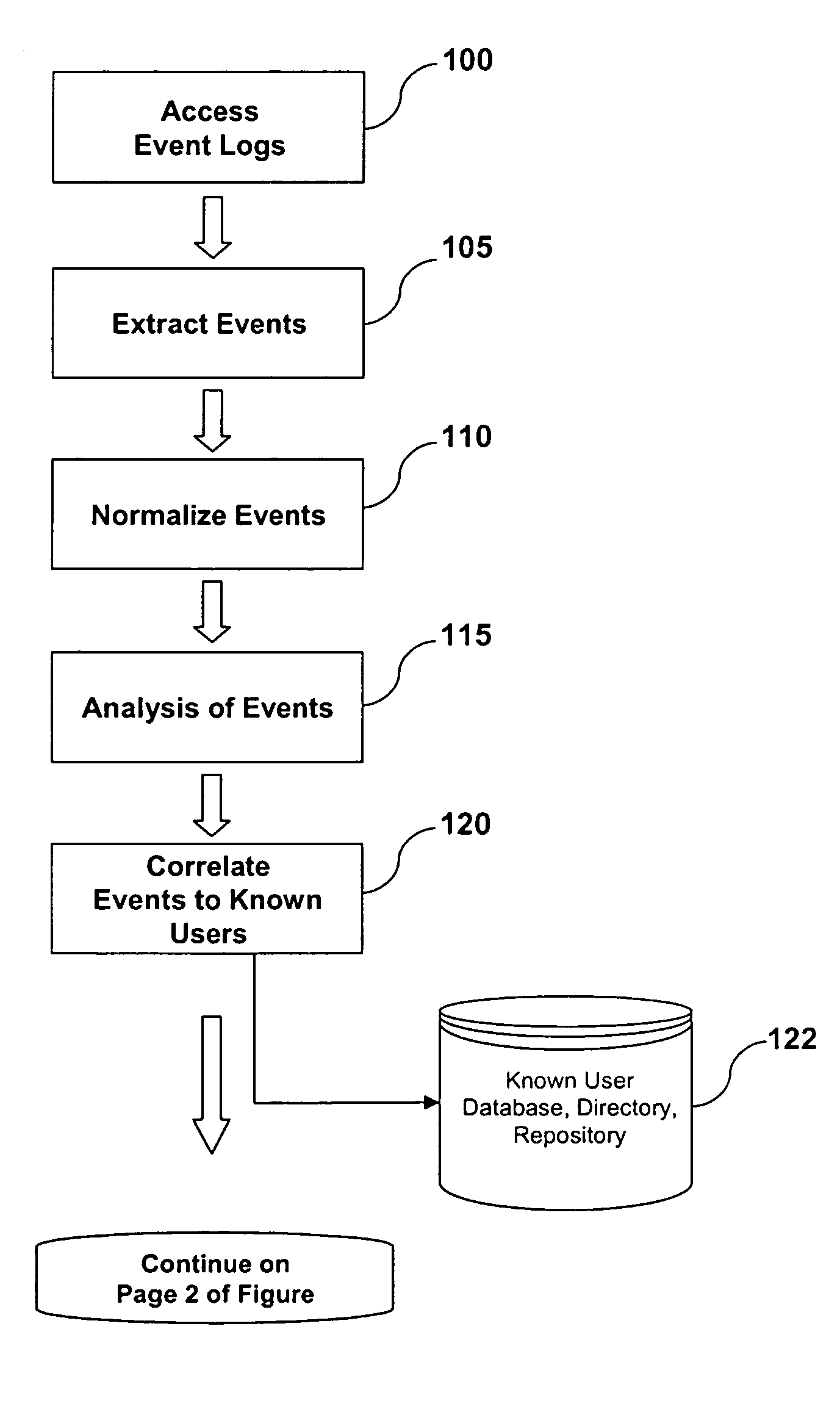
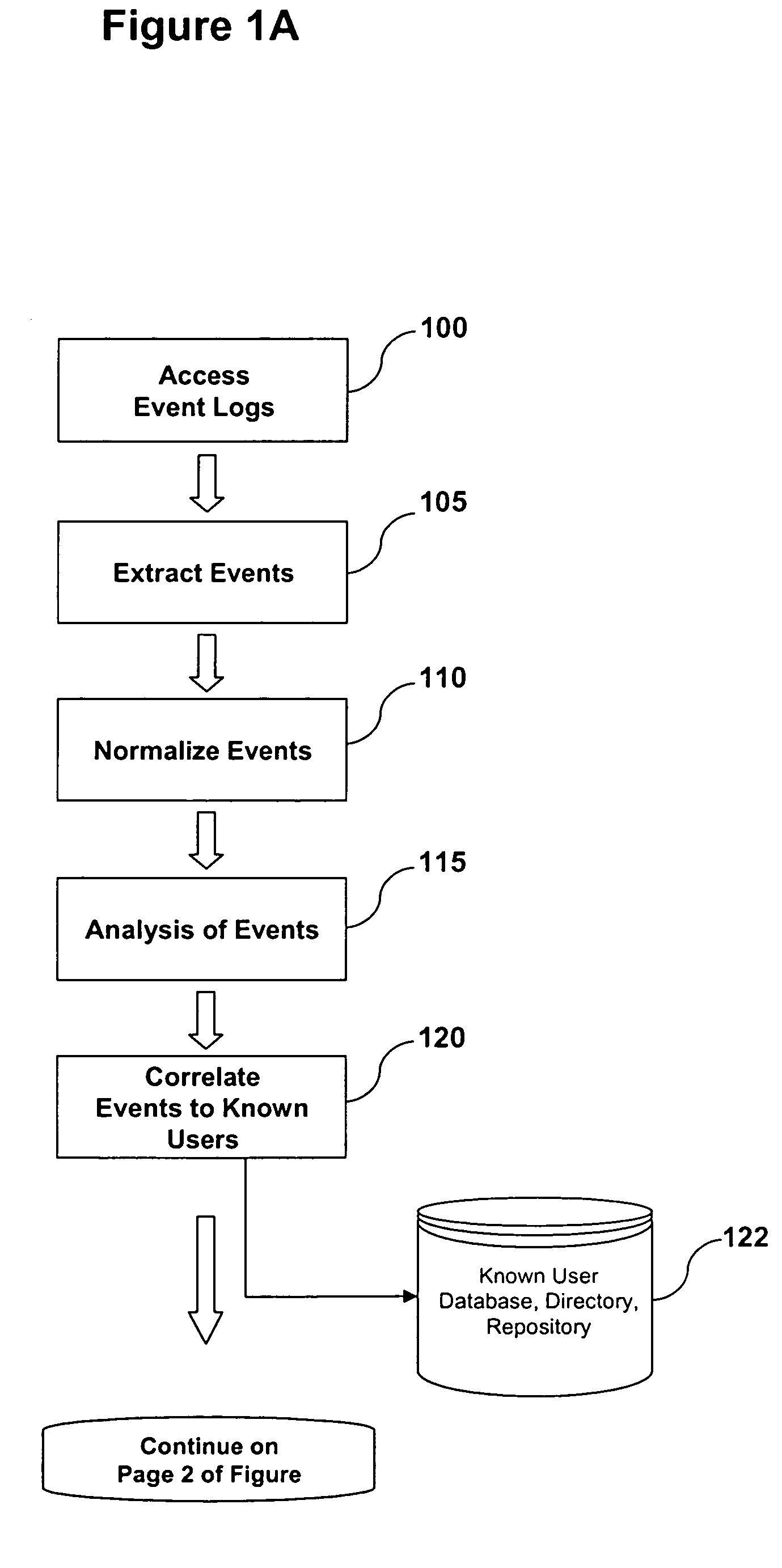
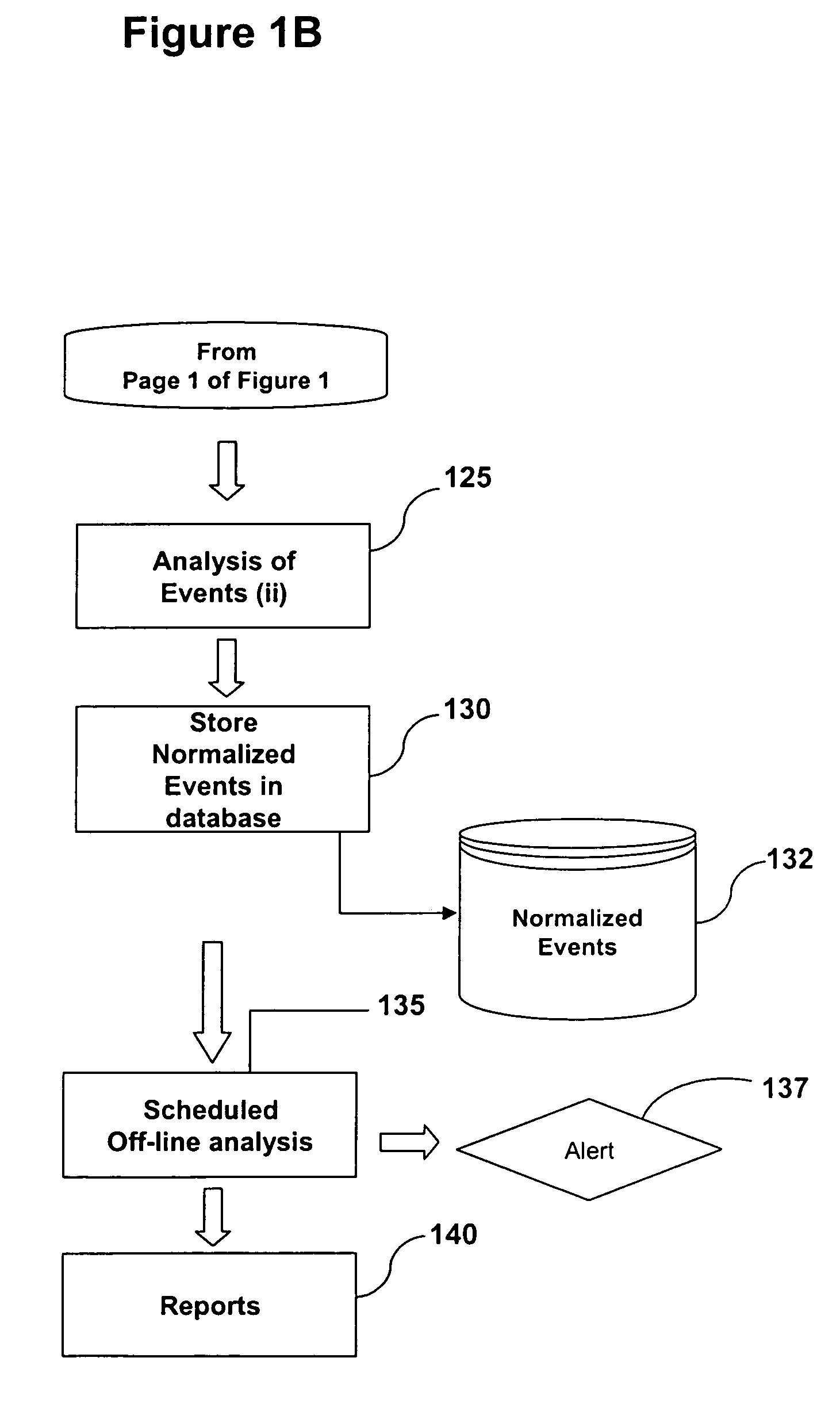
A system and method are provided for detecting fraud and / or misuse in a computer environment through tracking users activities at the application layer for known users. Application layer data and other data are normalized and records are created. The normalized data is correlated to user identities to produce correlated information that is analyzed against modeling information. The modeling information is generated using rules, algorithms, and / or database queries to define fraud scenarios and misuse scenarios. Reports and / or alerts may be generated if fraud and / or misuse are detected.
Owner:LONG KURT
Proxy commands and devices for a home automation data transfer system
InactiveUS20070255856A1Simple interfaceMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksTransport layerTransfer system
An automation network includes automation network devices connected to the network and a system level interface that interfaces with a transport layer and an application layer of the automation network. The system level interface includes proxy command libraries configured to designate a proxy device from the automation network devices. The proxy device accepts commands or messages to be transmitted to another automation network device.
Owner:INTERMATIC
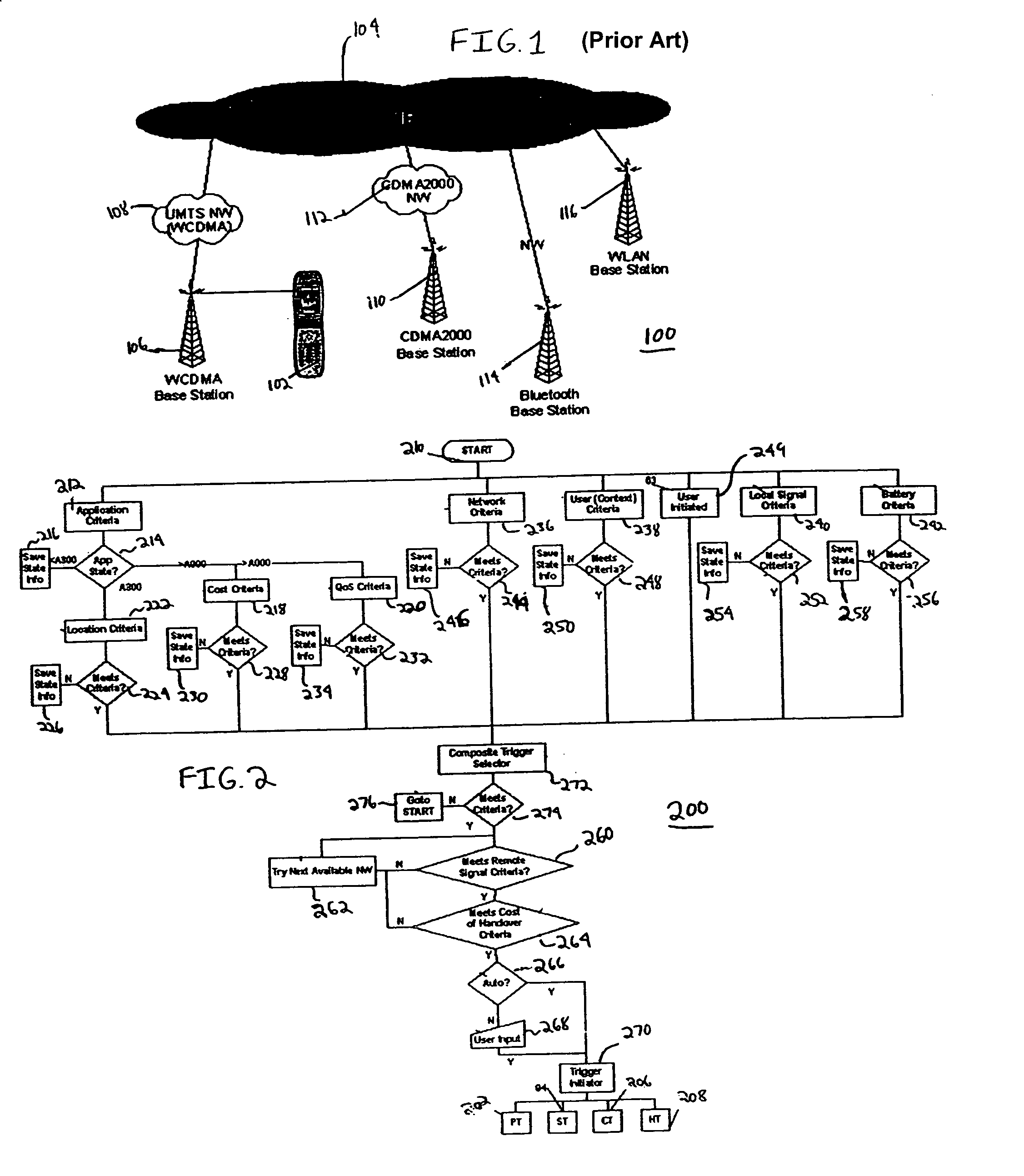
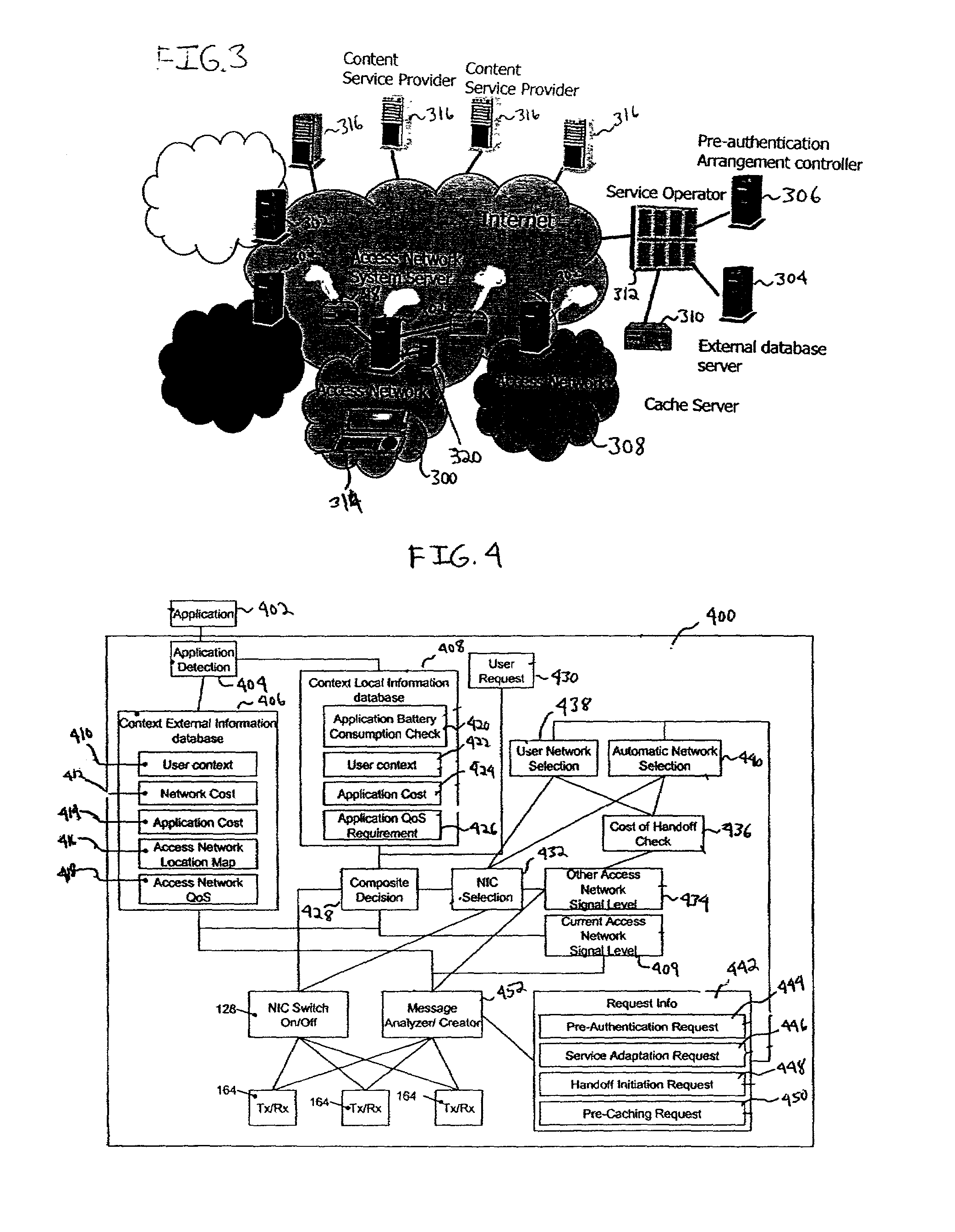
Context aware application level triggering mechanism for pre-authentication, service adaptation, pre-caching and handover in a heterogeneous network environment
ActiveUS7161914B2More experienceHuge savingsData switching by path configurationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsLevel triggerService adaptation
A network selection system that includes a mobile terminal in communication with a first network, a second network in communication with the first network and an application layer triggering mechanism that determines which one of a plurality of triggers is required in a certain set of circumstances to provide a particular application.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
System, Method, and Apparatus for Communicating Data
ActiveUS20140195639A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionProtocol ApplicationMedical device
A system includes first and second hubs. The first hub is configured to communicate data with a medical device through a Local Area Network and package the data into at least one application-layer packet. The second hub is configured to receive the at least one application-layer packet from the first hub operatively through at least one cellular network.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
Method and apparatus for content-aware web switching
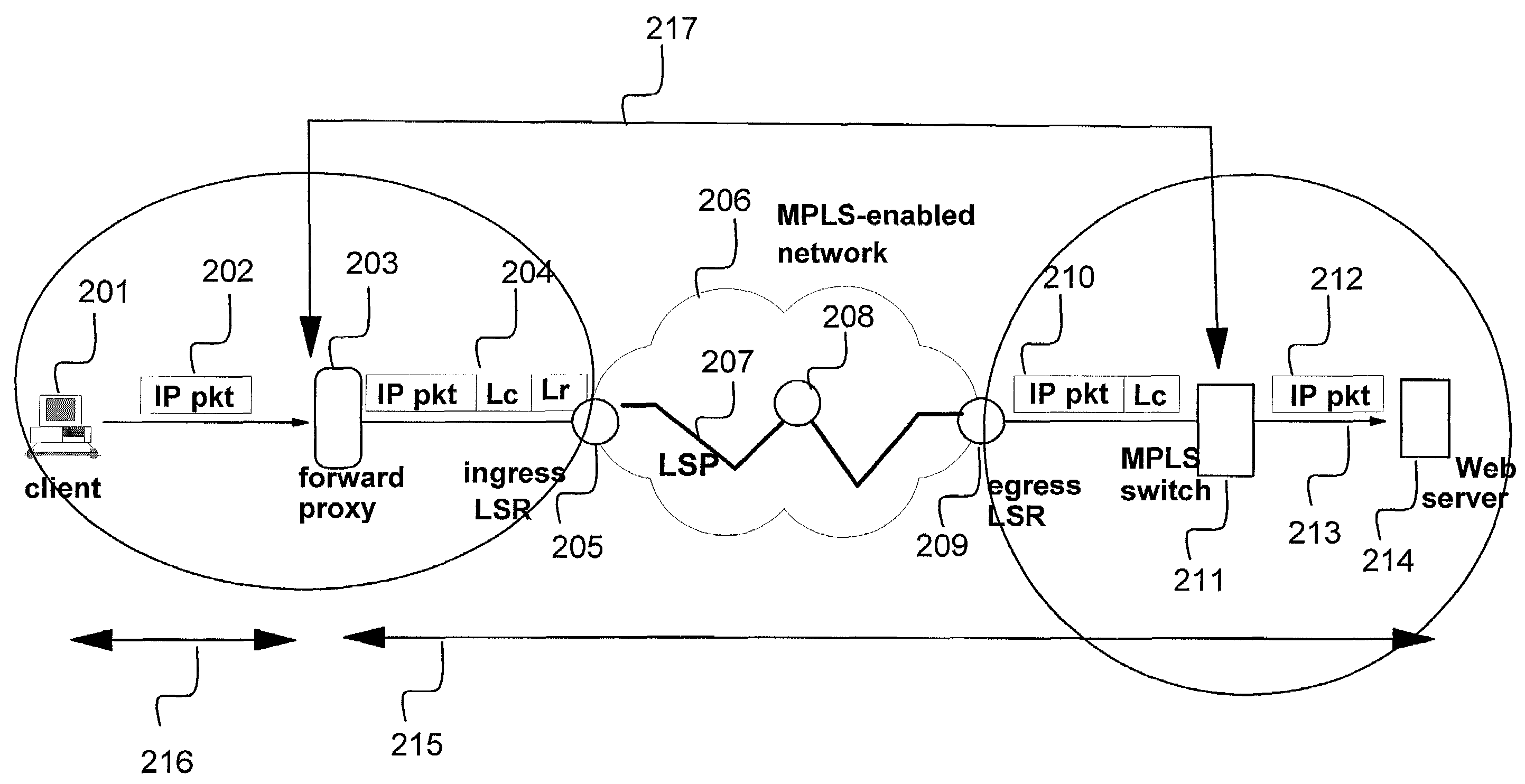
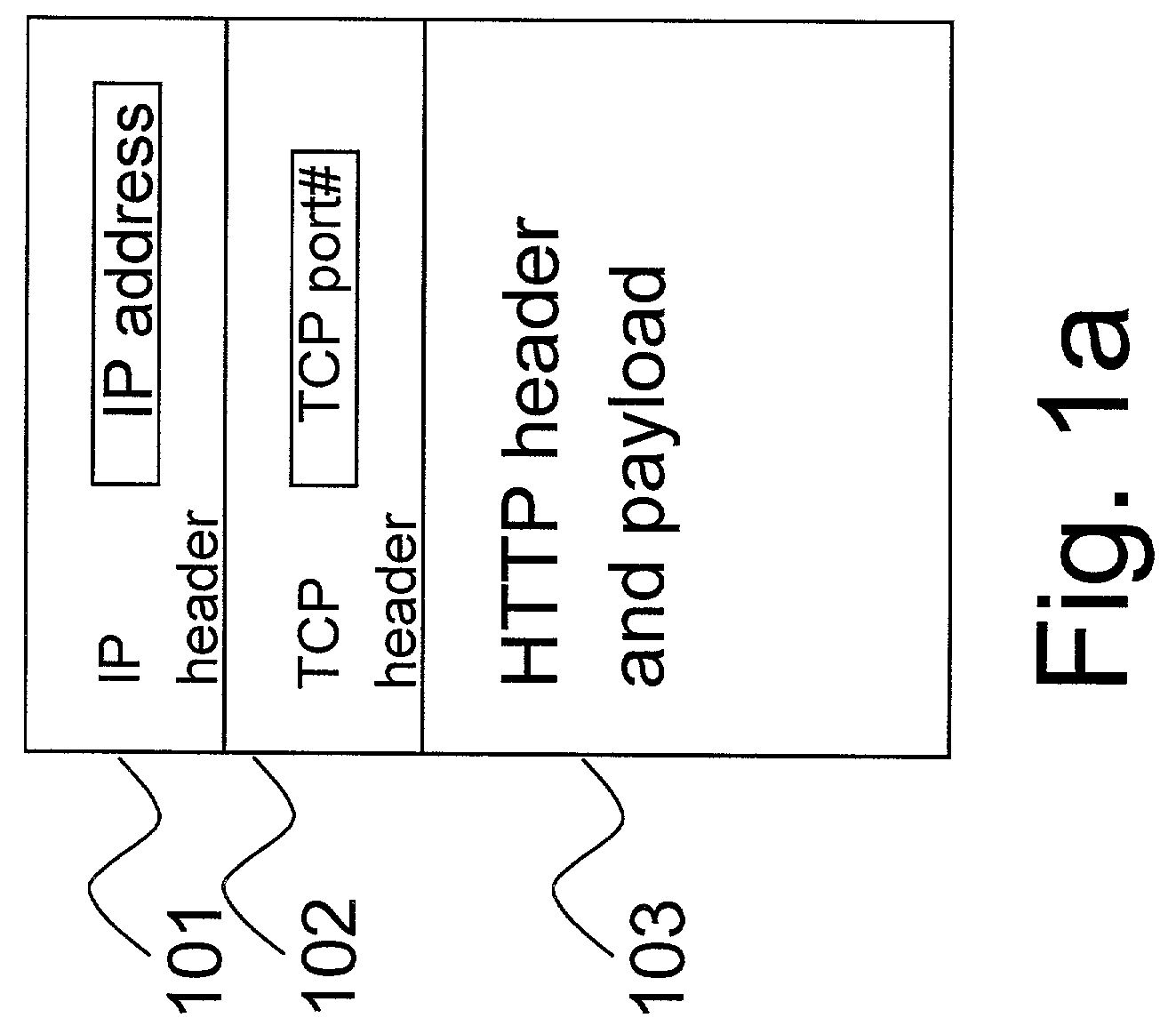
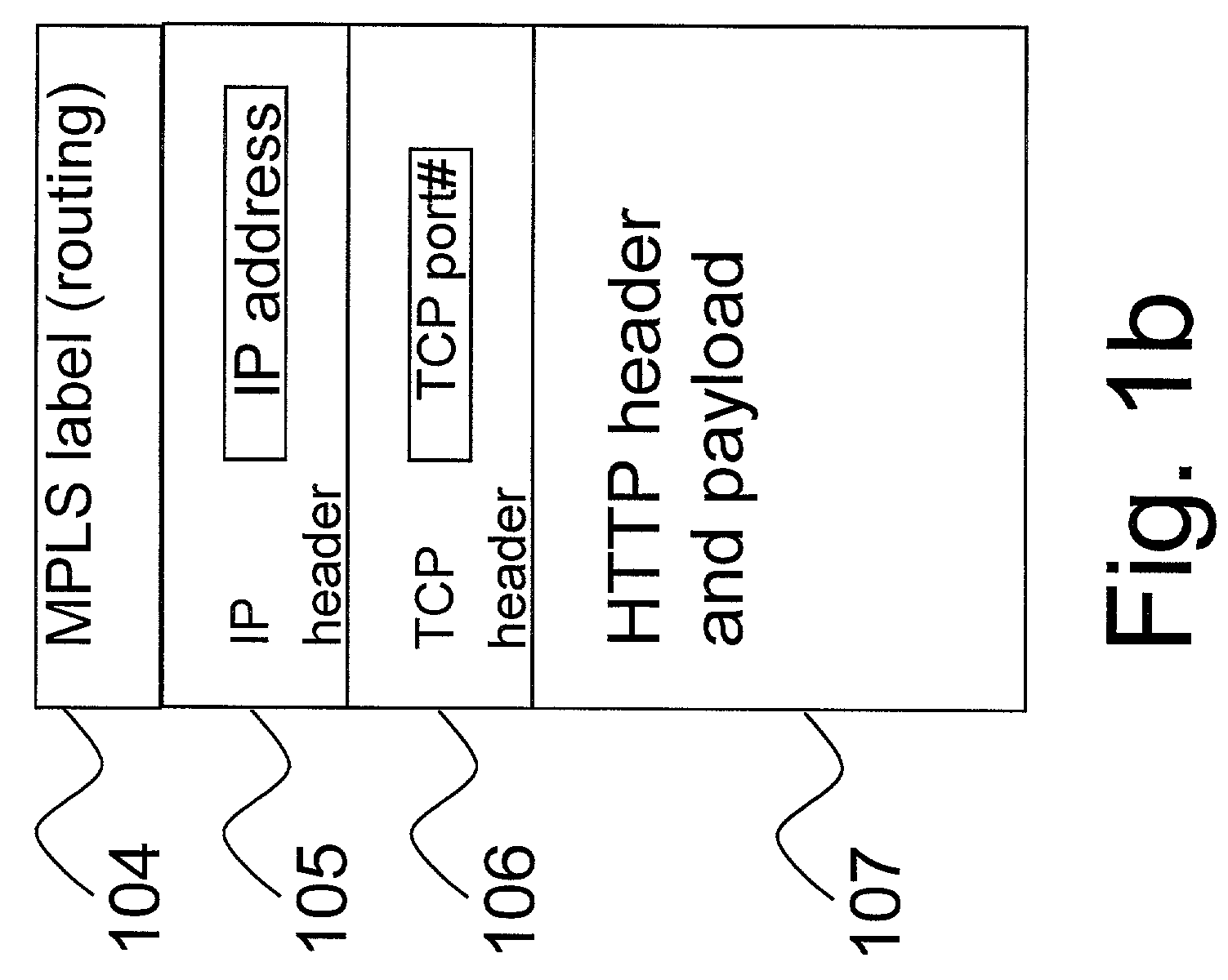
InactiveUS7209977B2High-performance Web switchingData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsIp addressWeb service
This invention provides methods and apparatus for web switching without connection termination while providing content routing functionality. Content-aware web switches terminate incoming TCP connections and inspect the HTTP header to recognize the URL (content) being requested from a web server farm. This invention maps application layer information (URLs) to MPLS labels. This allows a standard MPLS switch to provide web switching functionality without terminating TCP connections. In addition to content routing, this method is applied for client session affinity, server load balancing and service differentiation. This invention also relates to using TCP port numbers instead of MPLS labels to achieve web-switching functionality through the use of a TCP router that translates IP address and port numbers.
Owner:IBM CORP
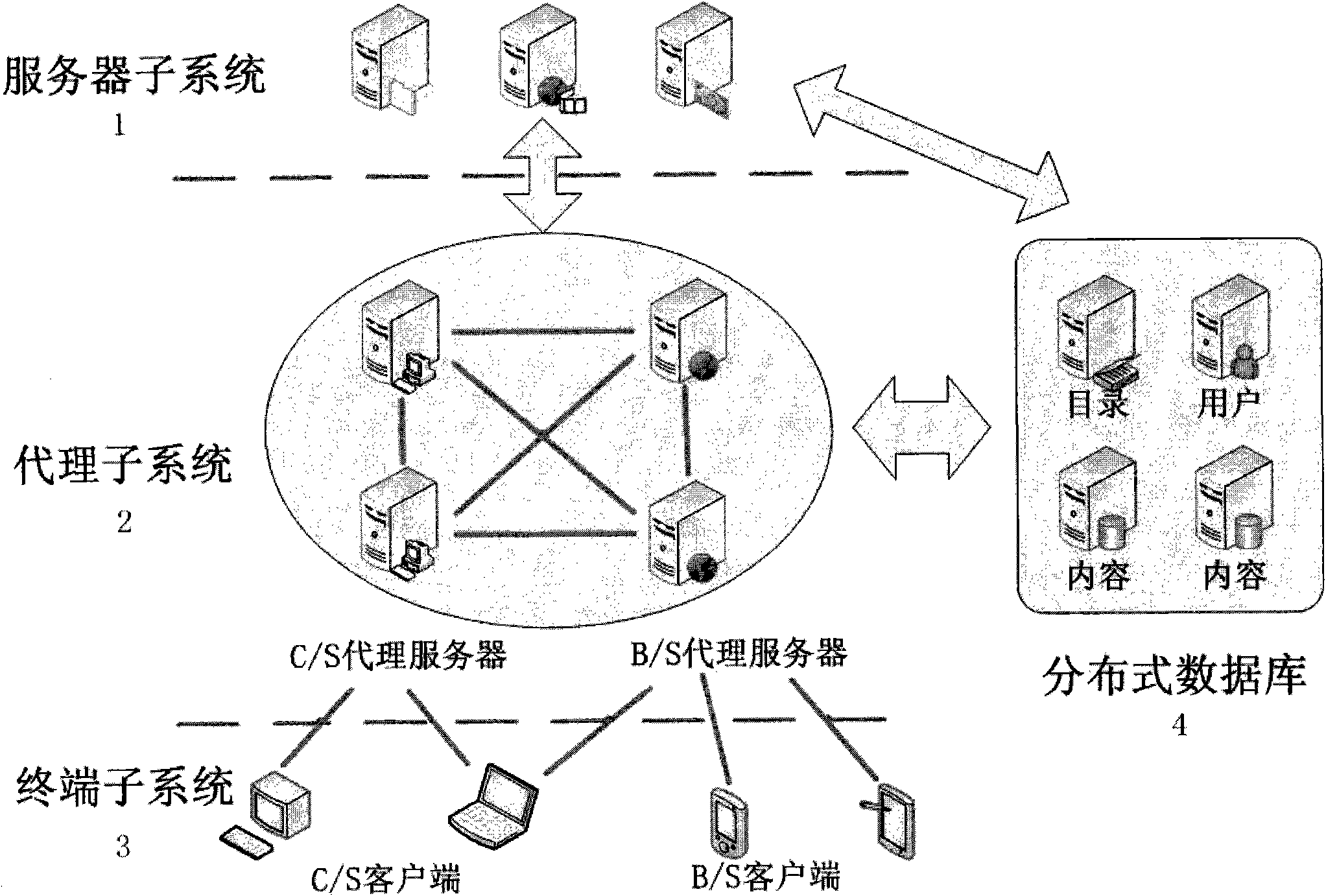
Real-time data distribution system with distributed network architecture and working method thereof
InactiveCN101848236AImplement hierarchical configurationFlexible accessData switching networksGeolocationNetwork architecture
The invention relates to a real-time data distribution system with a distributed network architecture and a working method thereof, the system adopts a publication / subscription communication mechanism to transfer information in Internet and a mobile network, and the system comprises a server sub-system, a proxy sub-system, a terminal sub-system and a distributed database, wherein, the server sub-system is used for completing the operations of topic storage, topic matching and the like; the proxy sub-system is used for completing the operations of receiving a topic from a terminal, transmitting a matching event to a subscriber, submitting the publication / subscription topic and the like; the terminal sub-system is used for completing the publication / subscription information of a user; and a distributed database which is used for storing the publication / subscription information and the system information. The system can automatically, quickly and safely provide real-time data transmission service against the subscription information of the user, provide the publication / subscription service of a variety of types of data, such as text information, streaming media, geographic position information and the like, provide up to 20 QoS control parameters, realize the QoS hierarchy configuration of an application layer and provide the convenience for function expansion of the data distribution system.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
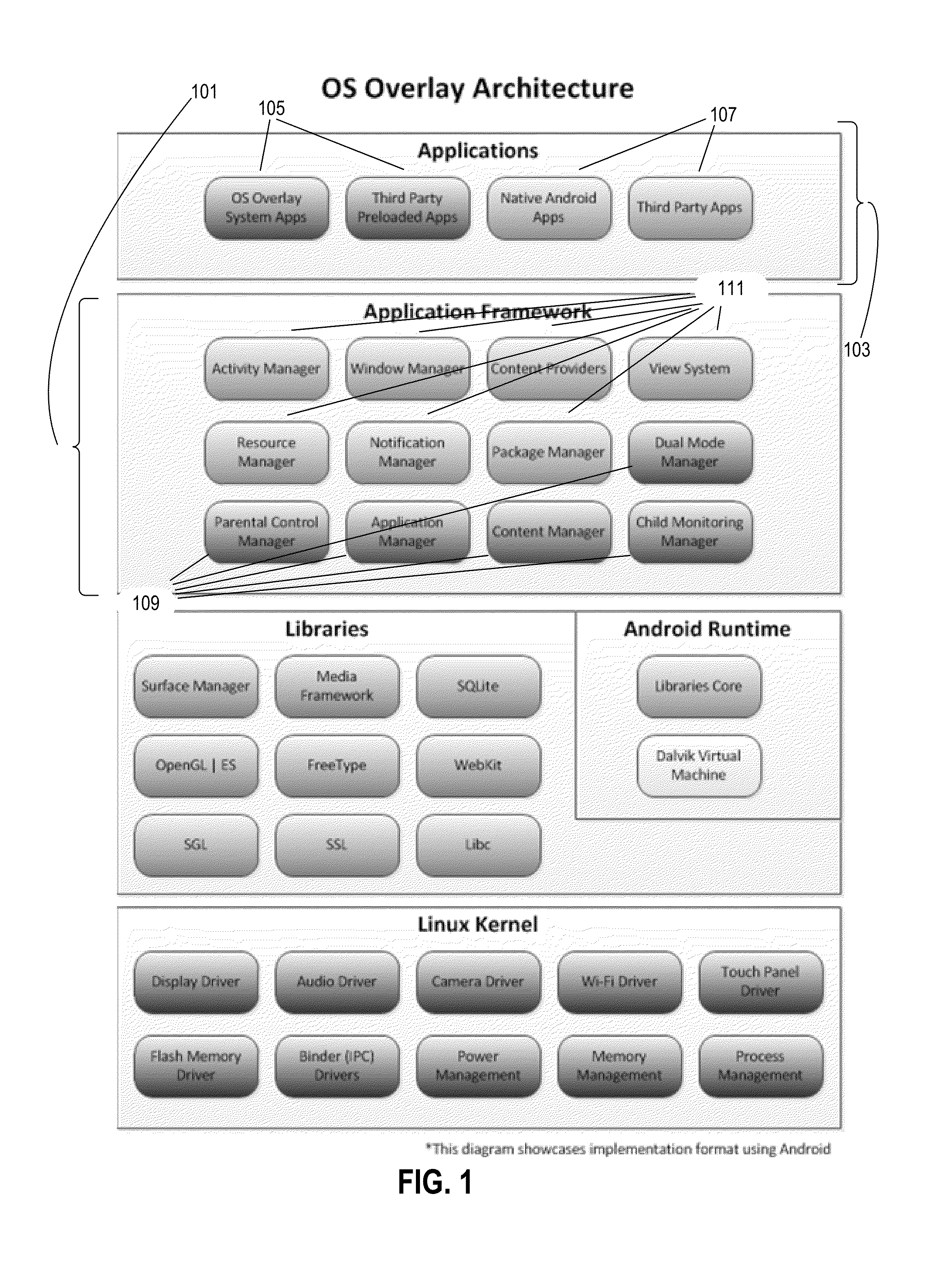
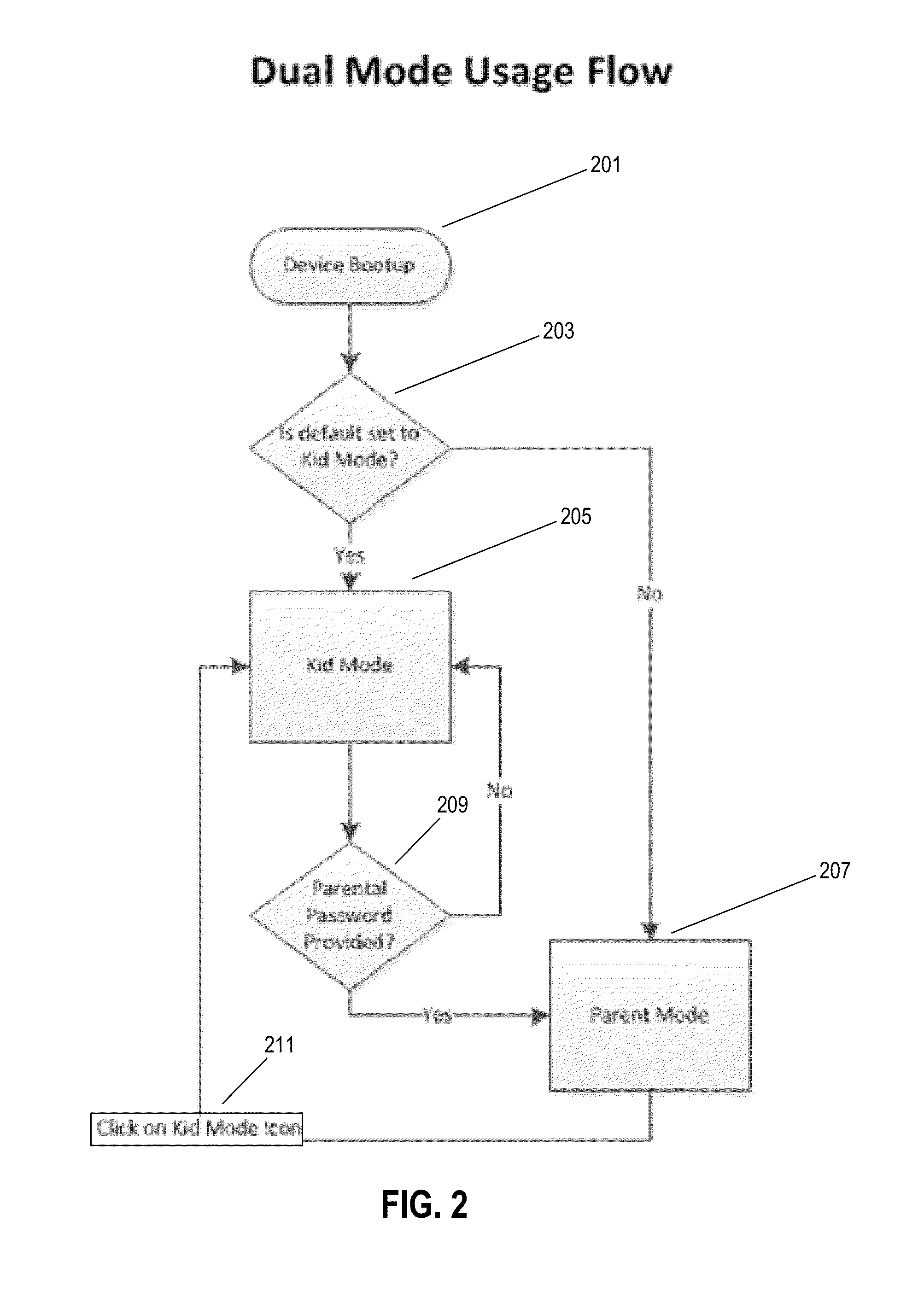
Tablet computer
A tablet computer comprises an operating system, including an application framework layer and an application layer, and an overlay system. The overlay system controls access to application programs and provides a first user interface and a second operating environment associated with a second user interface. Optionally, the overlay system provides a first operating environment associated with the first user interface. The overlay system includes an access control configured to permit or deny a request for access in the second operating environment to resources and / or data. Optionally, the overlay system is executed in the application framework layer of the operating system and may comprise a hypervisor providing an operating platform comprising the first user interface, the second operating environment, and an application space providing access to the application layer.
Owner:MATTEL INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com