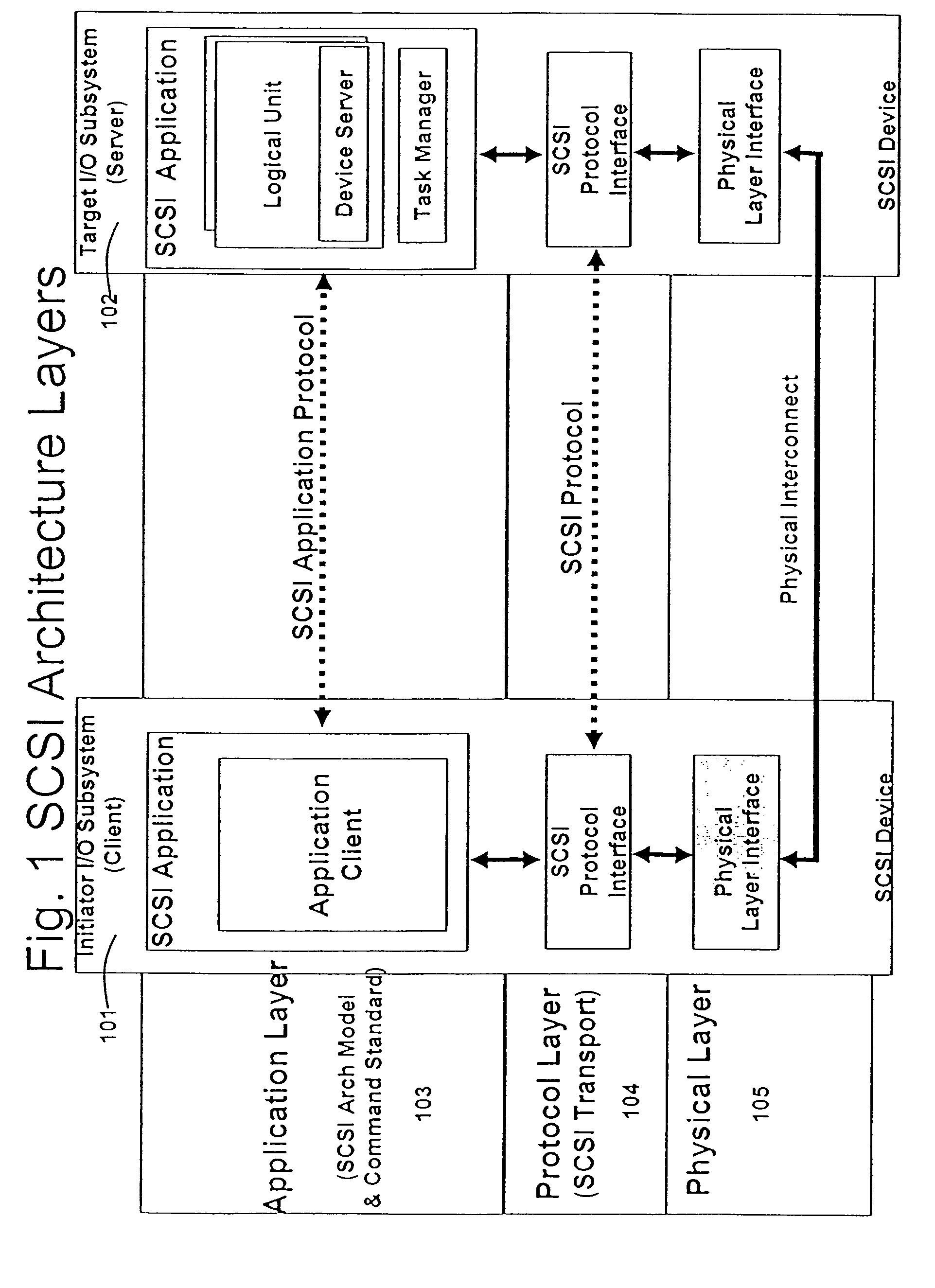
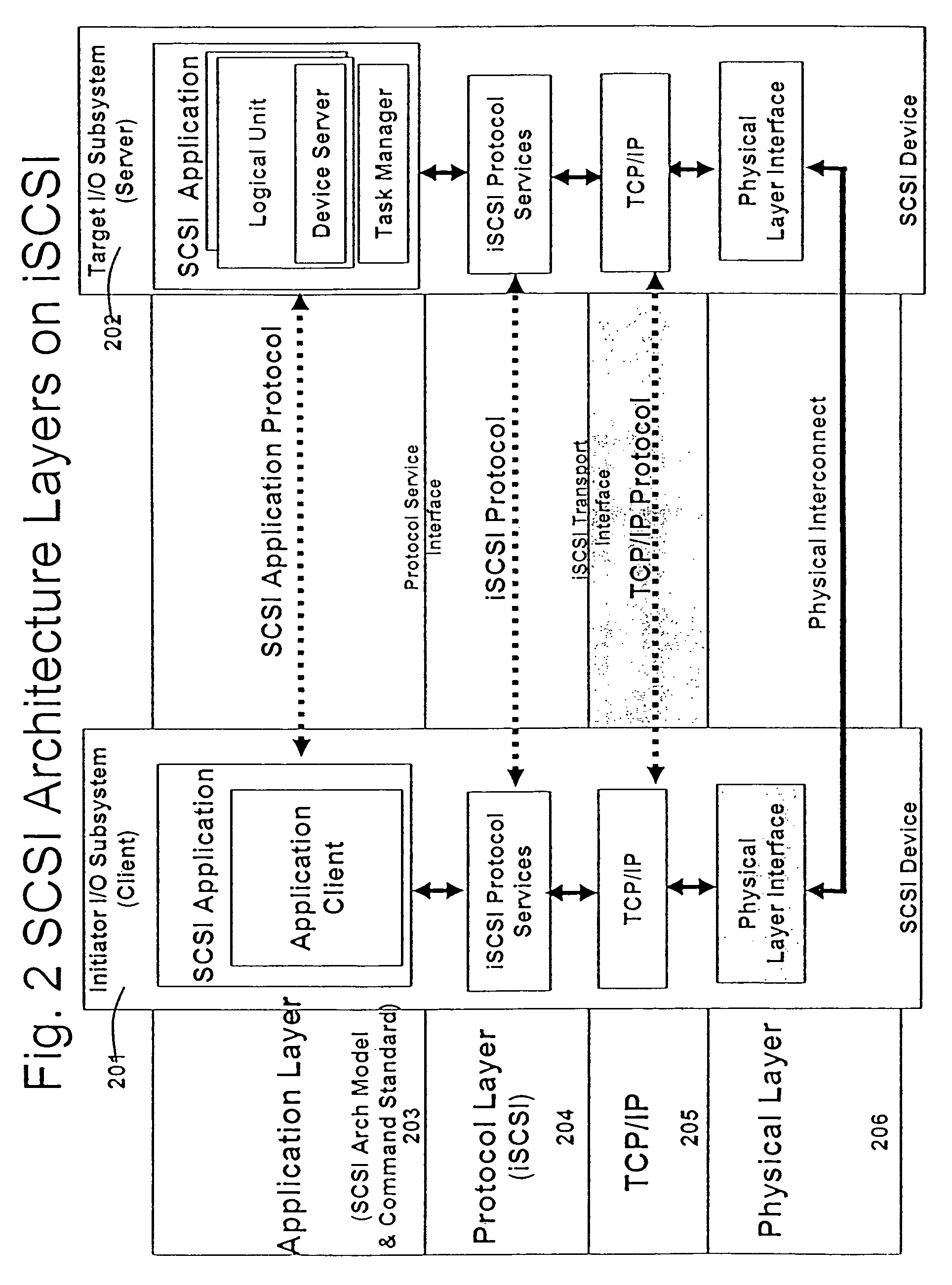
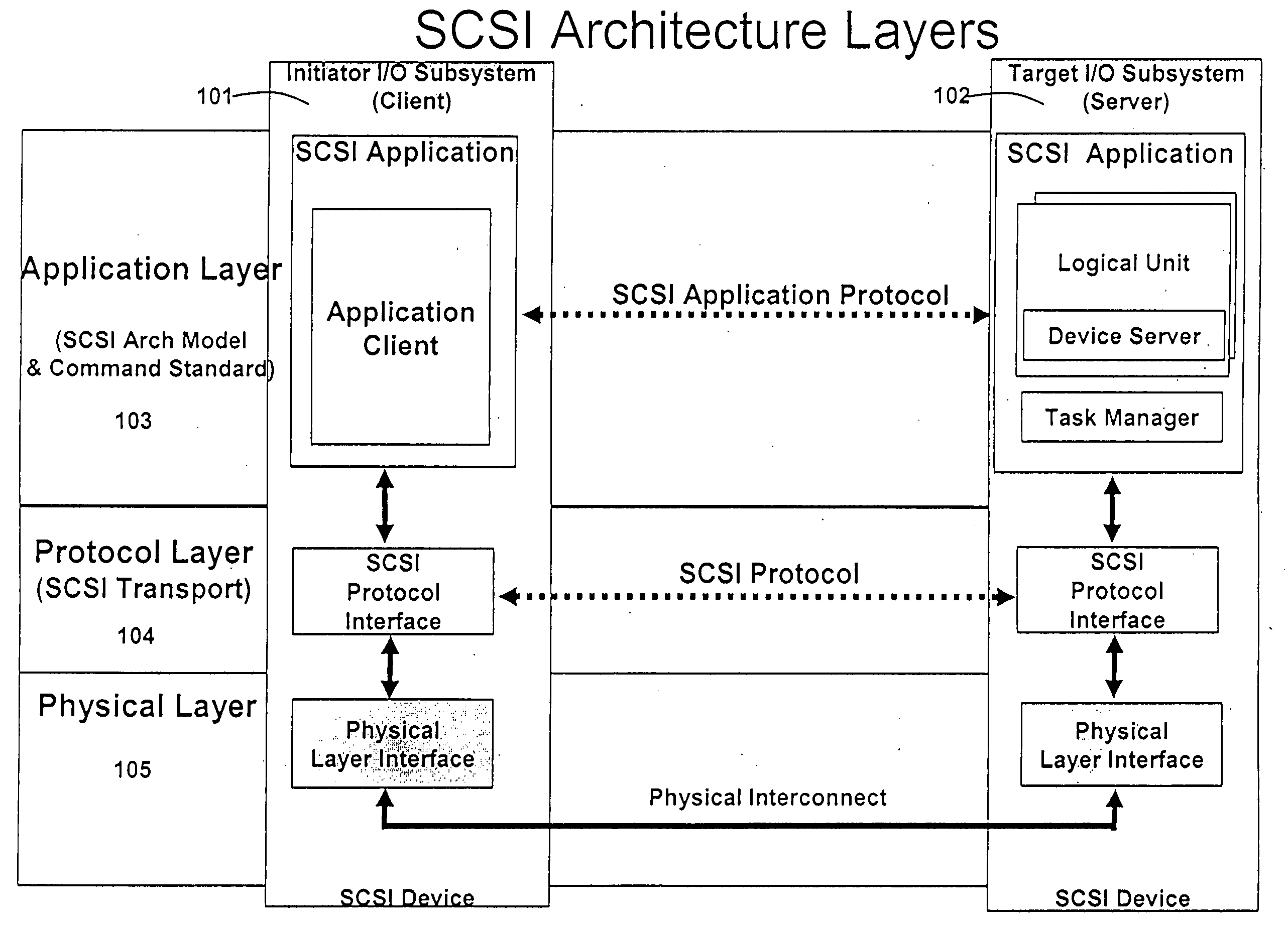
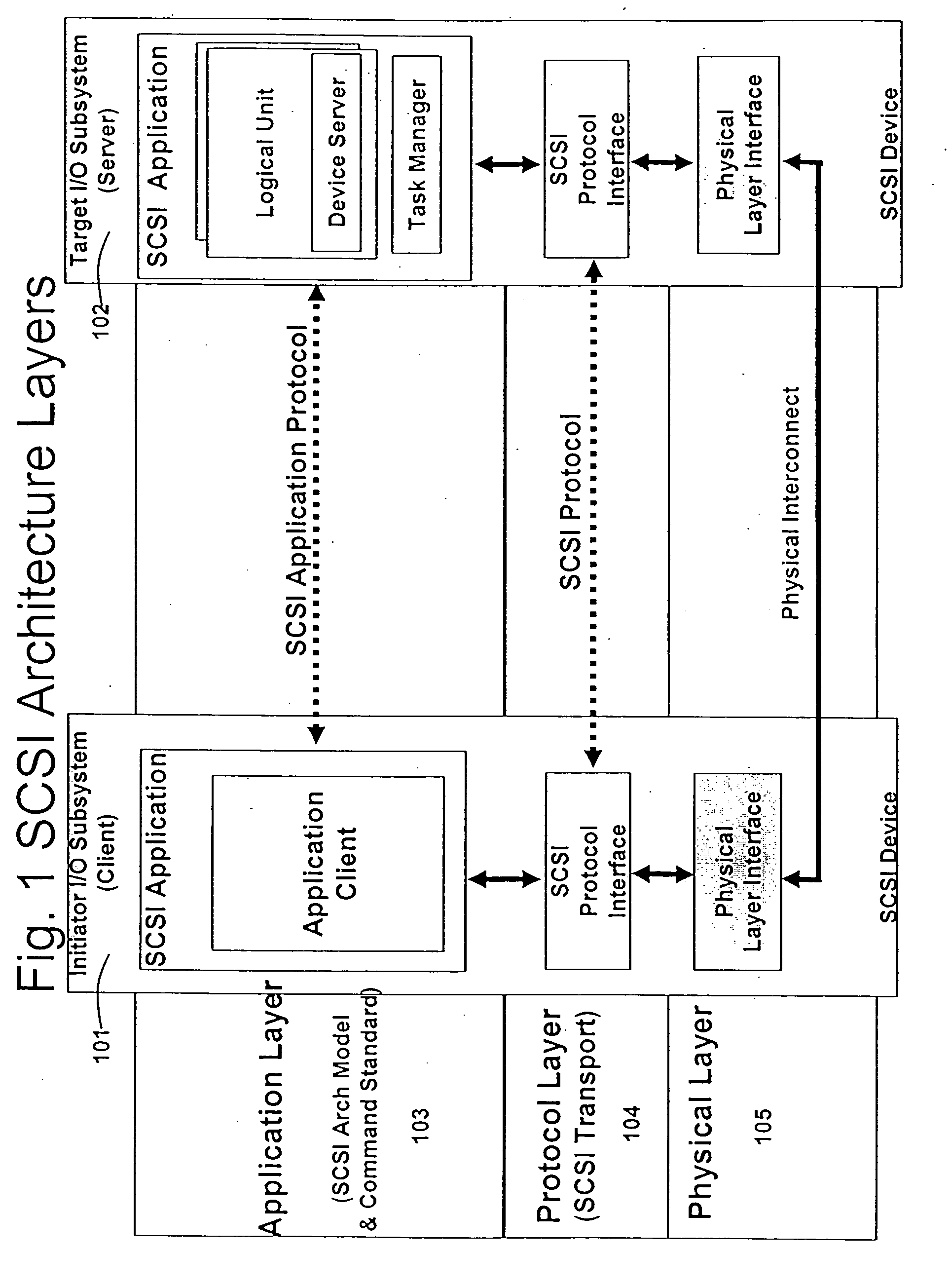
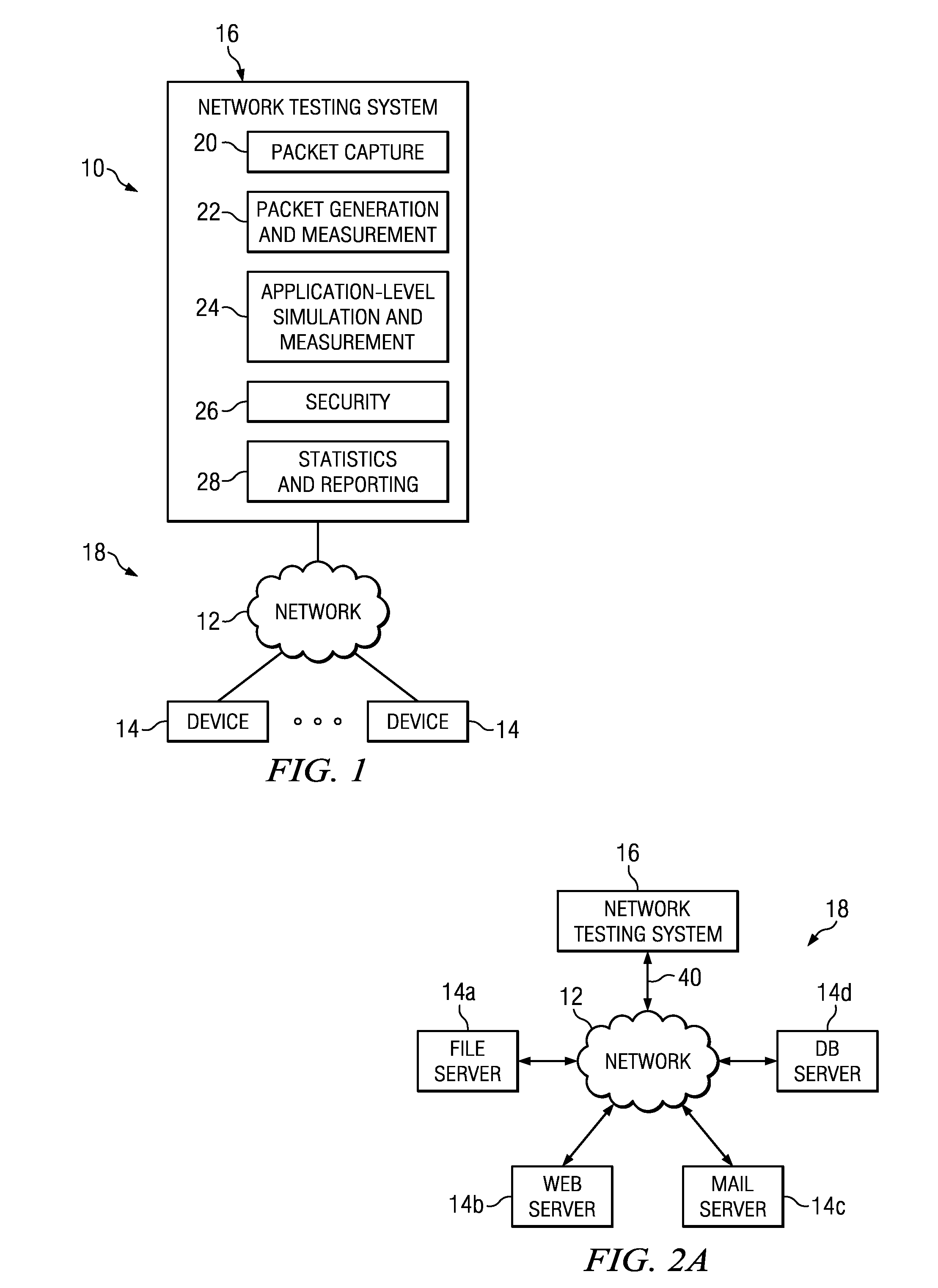
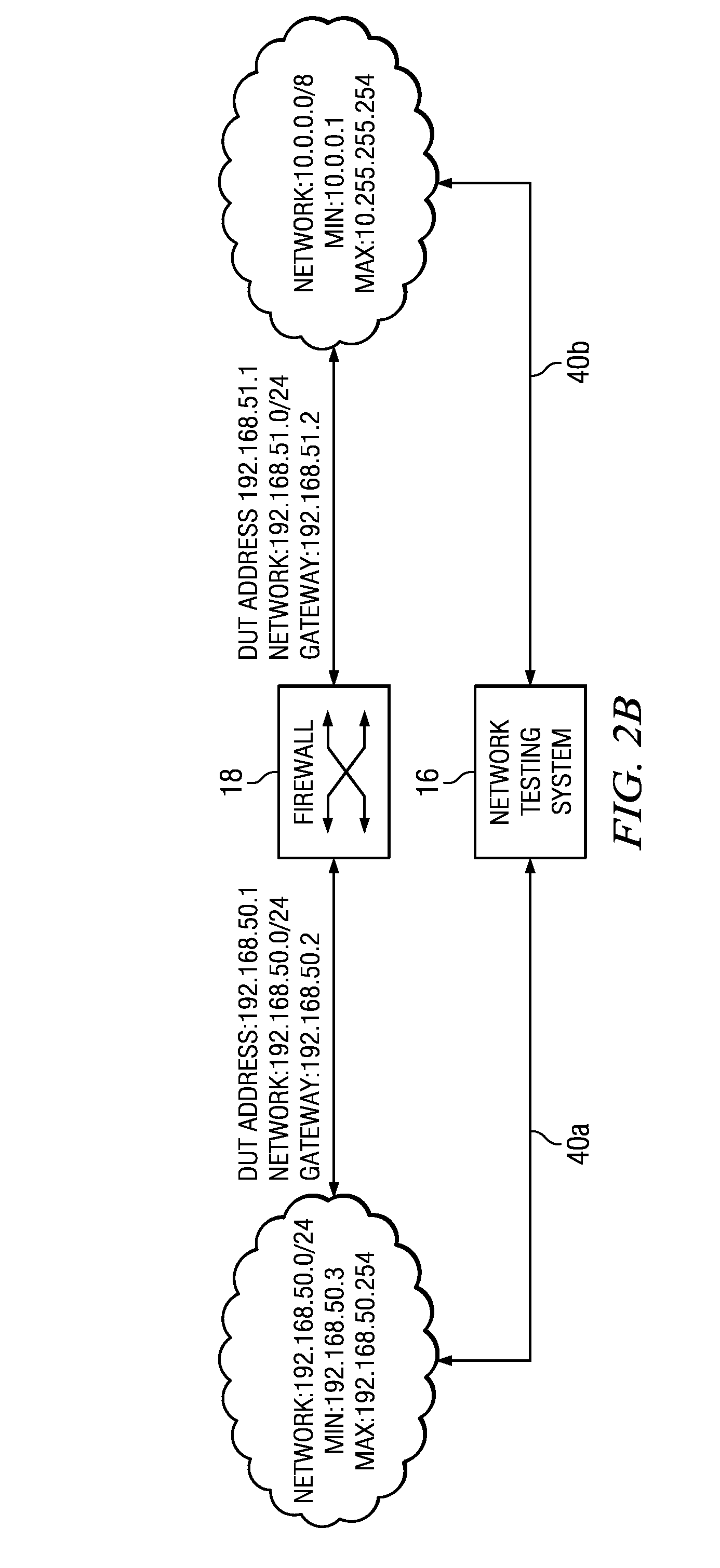
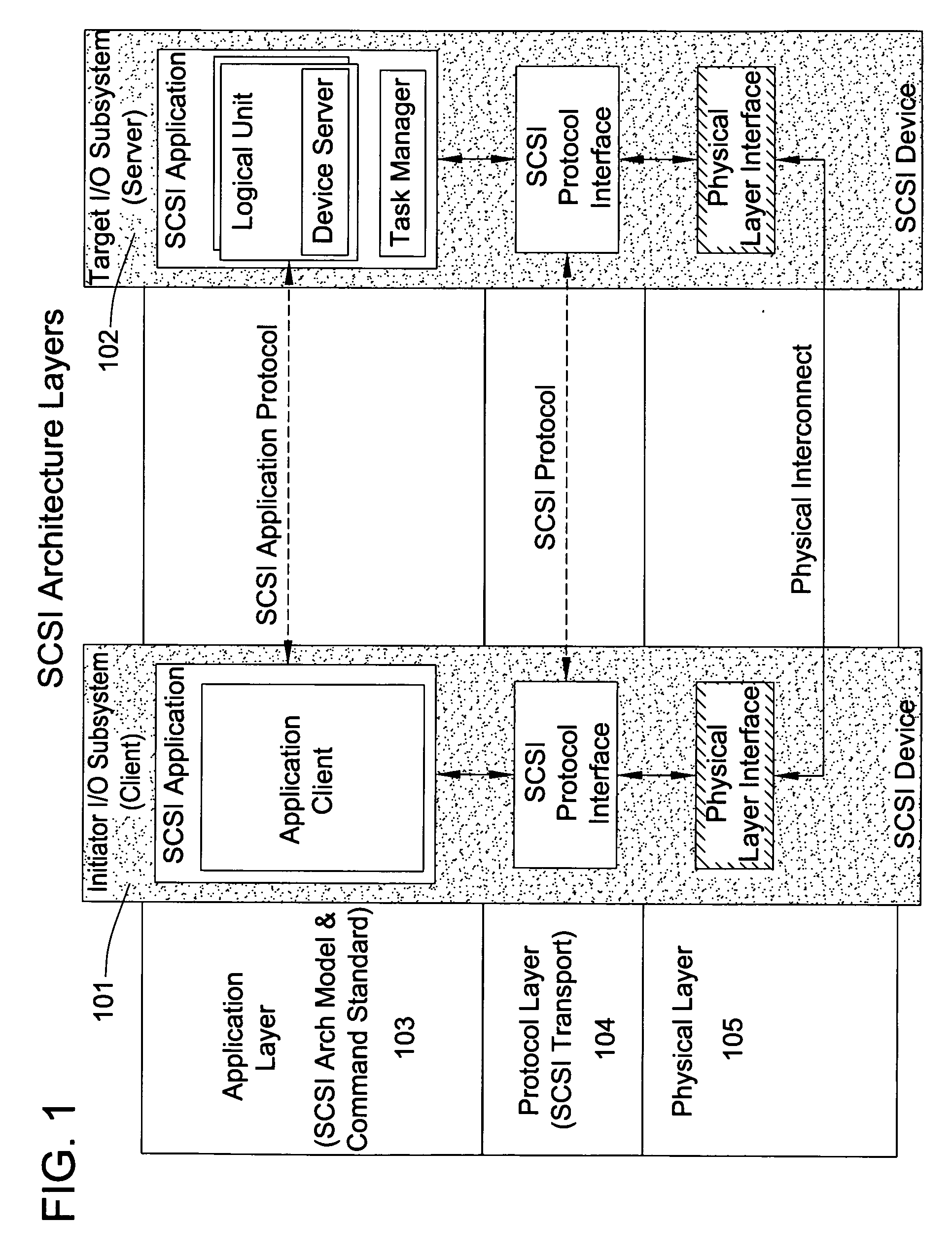
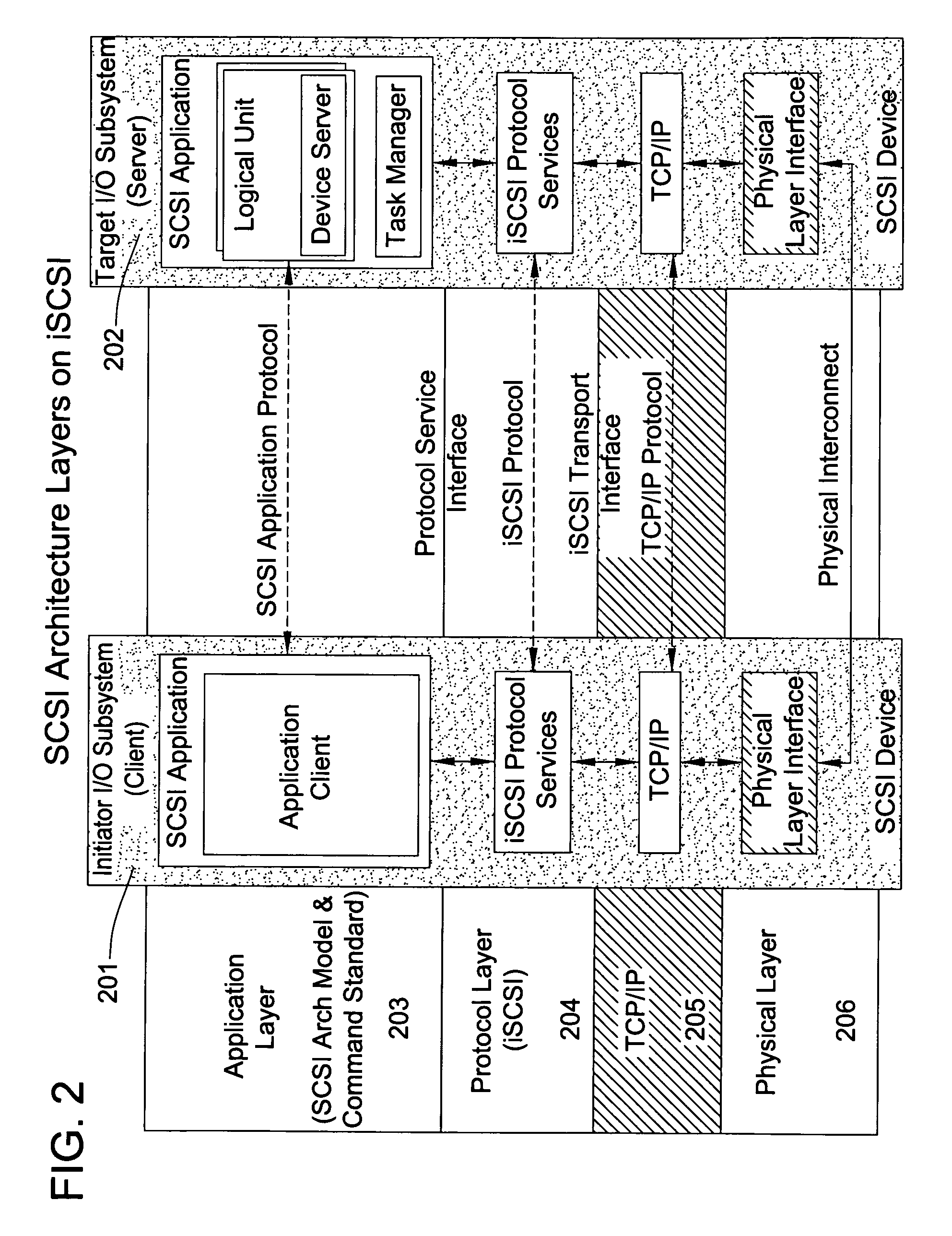
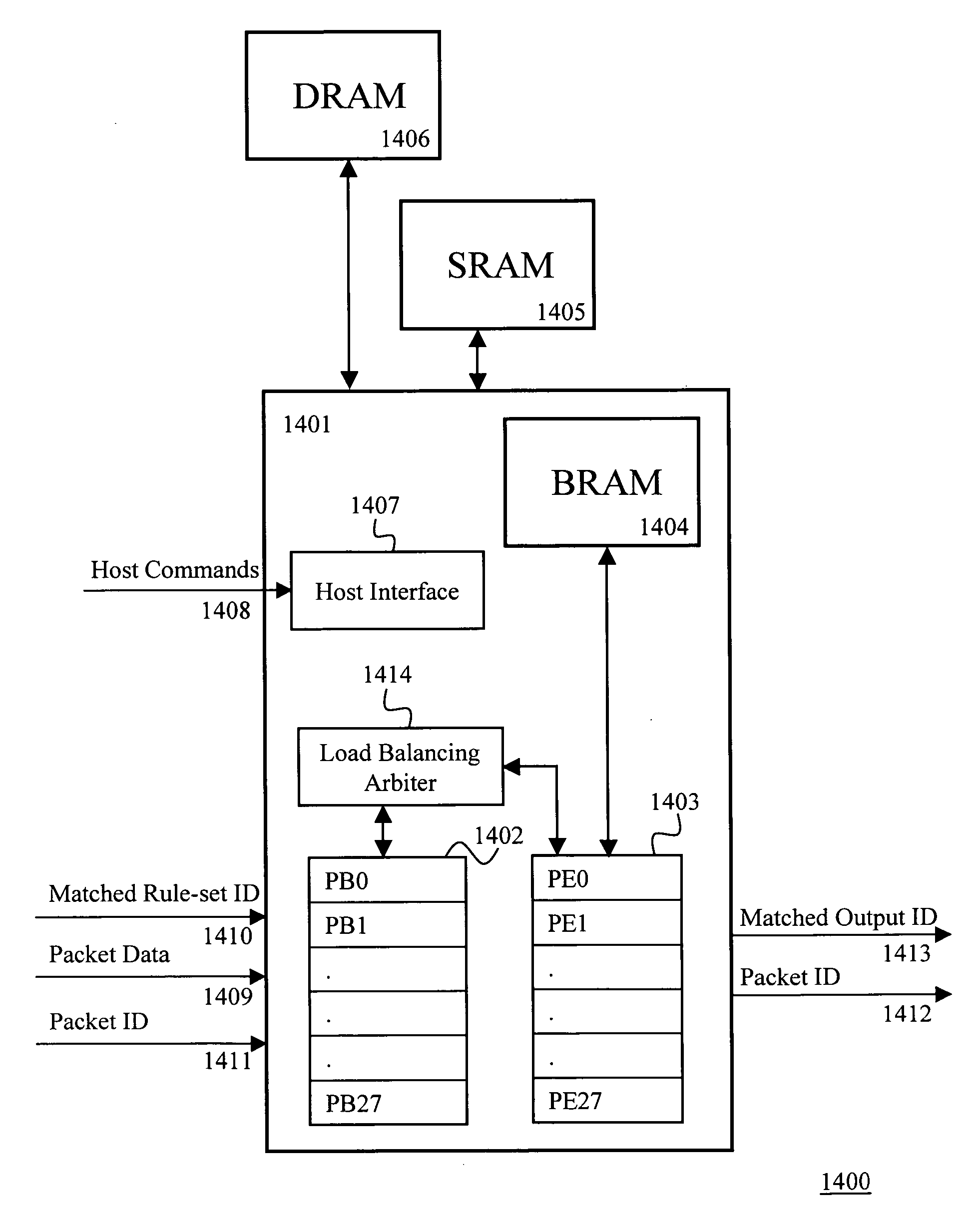
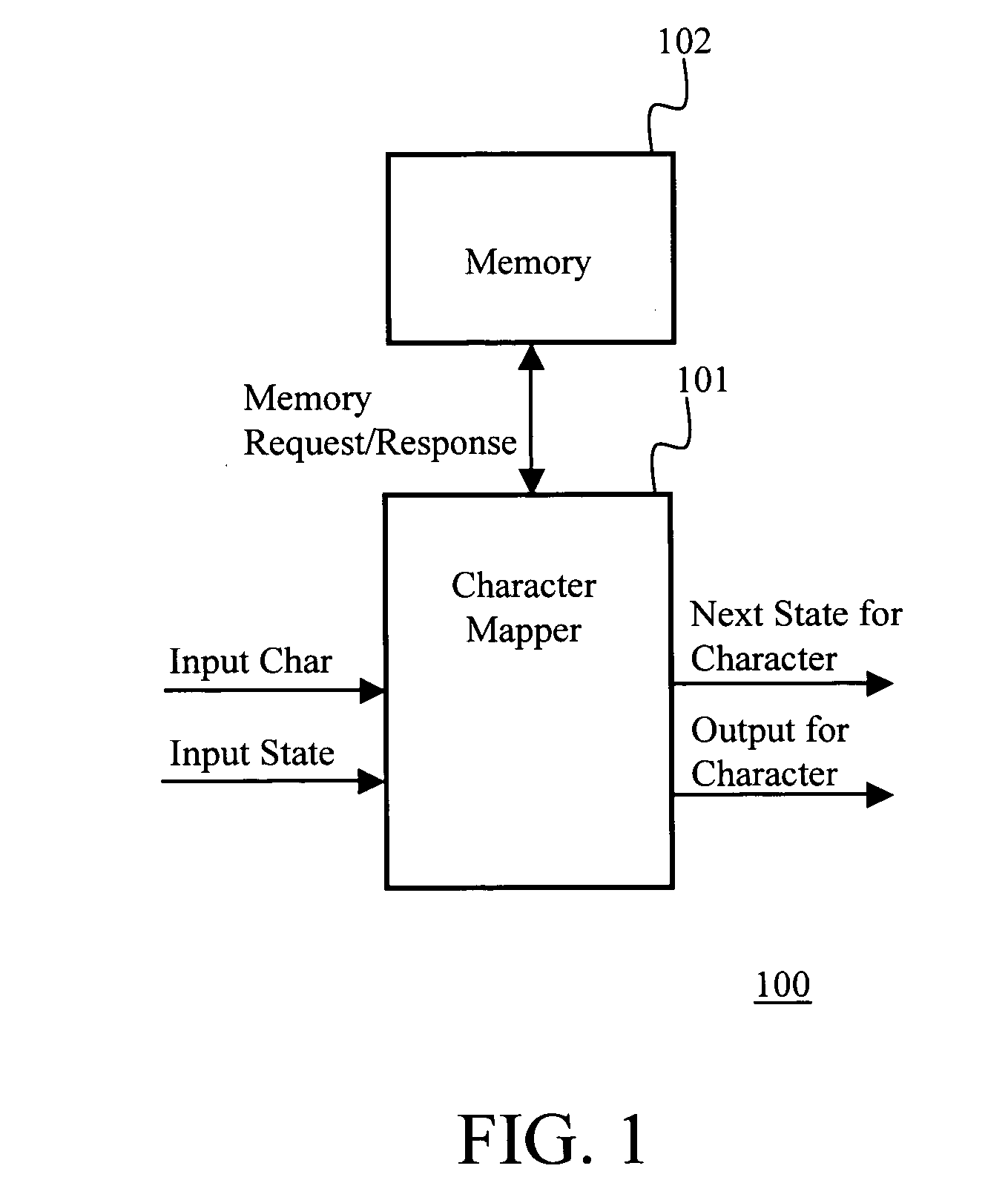
Patents
Literature
178 results about "Line rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
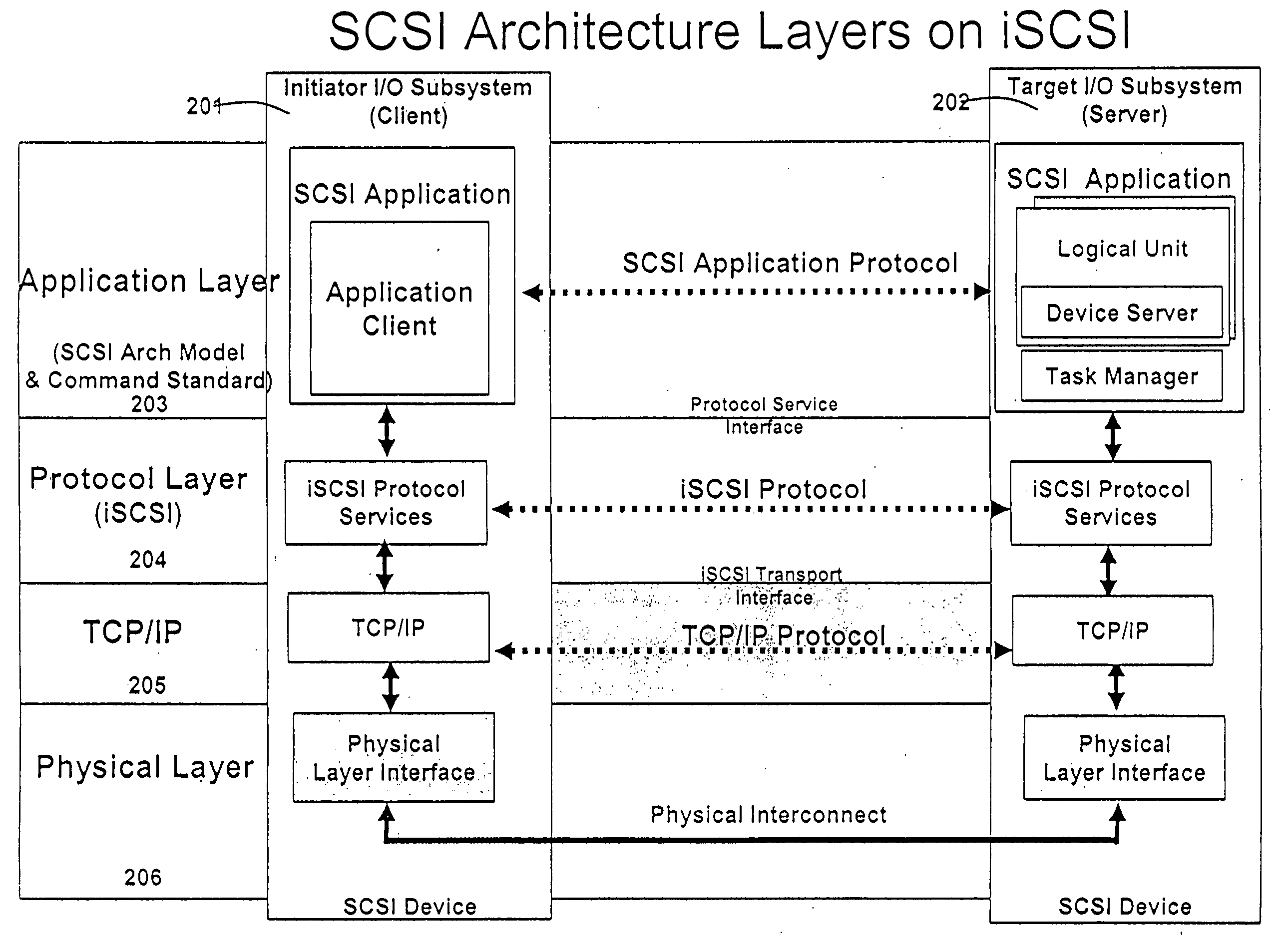
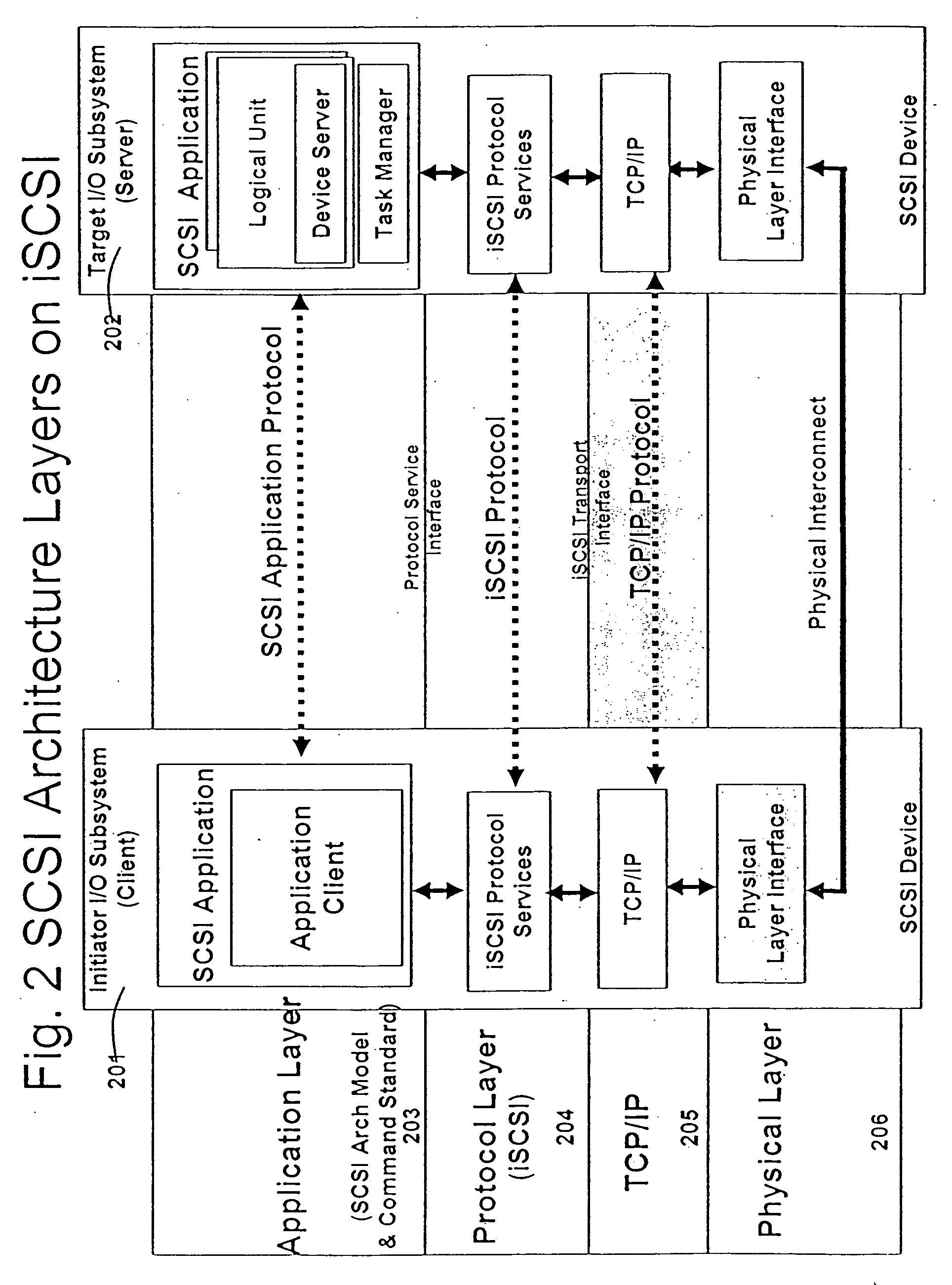
Line rate is physical (sync) speed at which you router communicates with the equipment directly connected to the other end of the telephone line in the exchange.
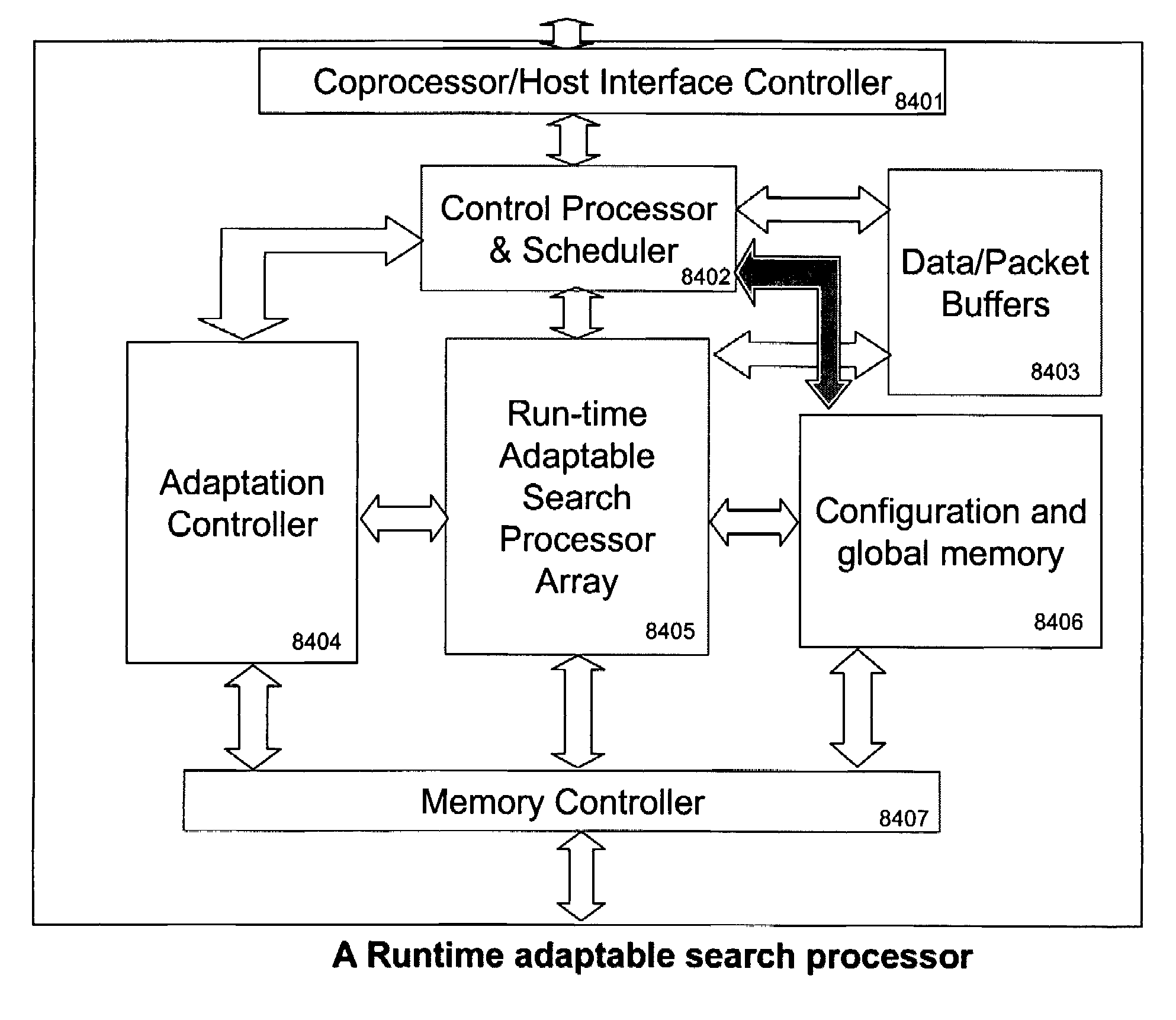
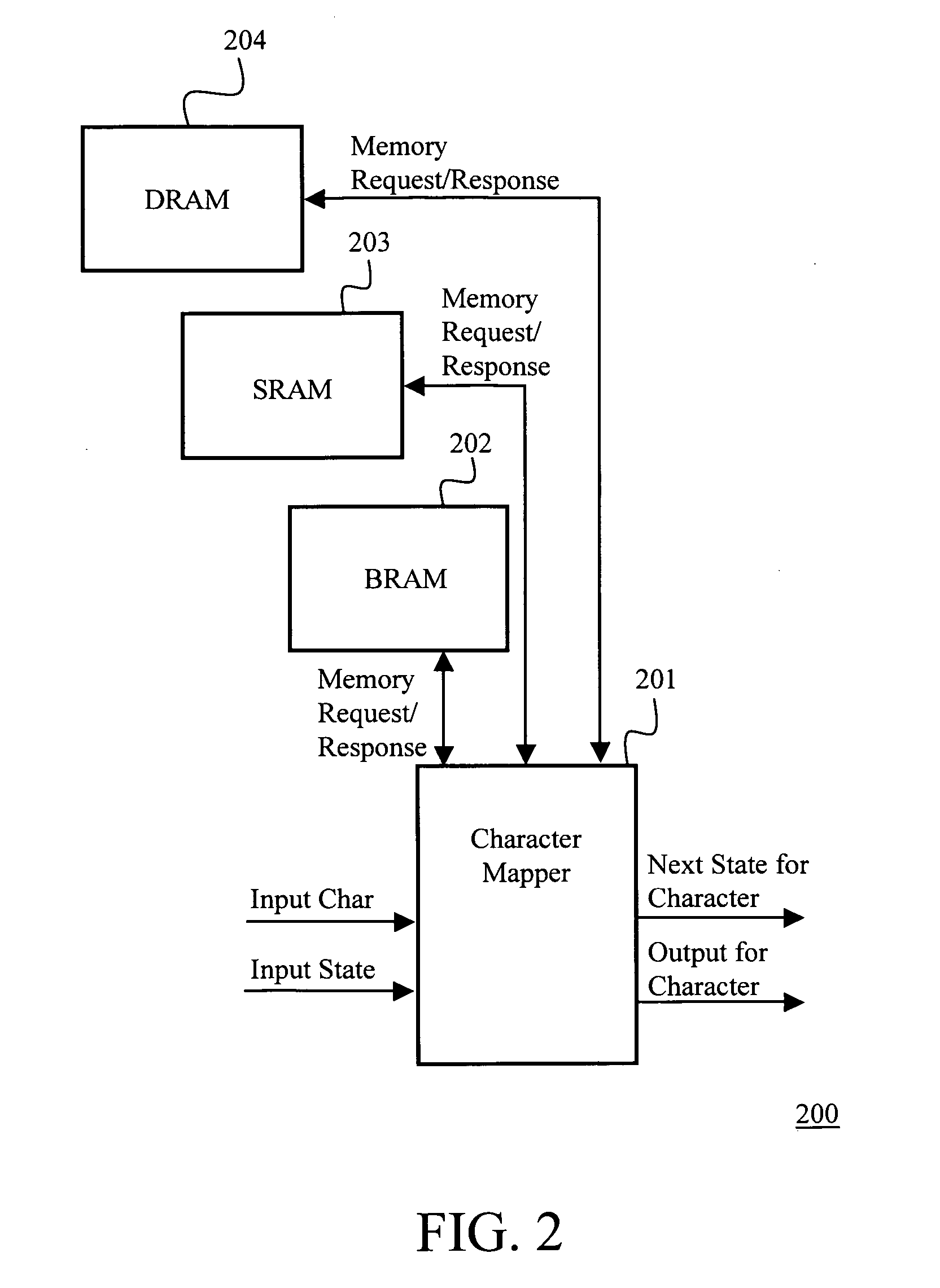
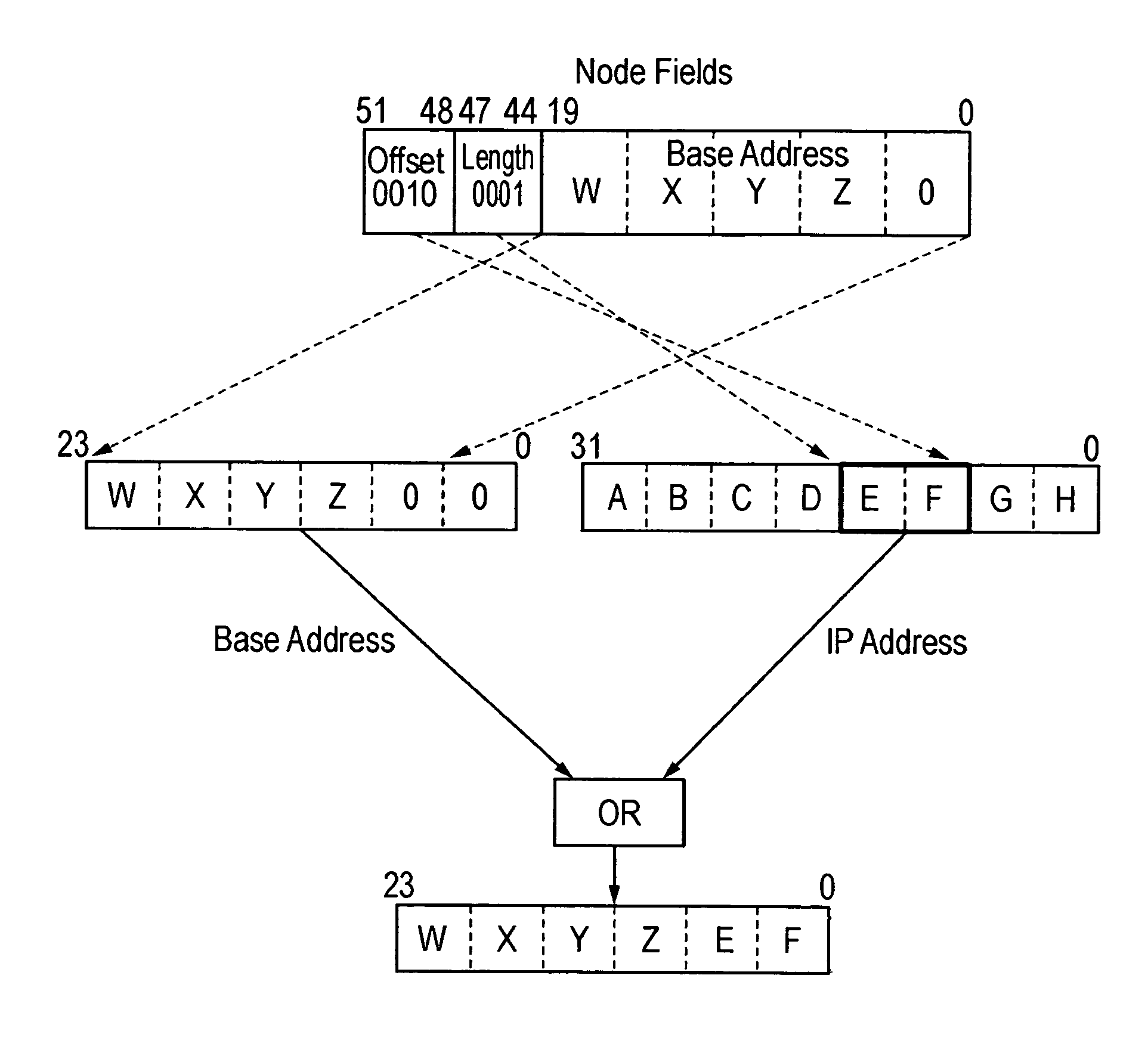
Runtime adaptable search processor
ActiveUS20060136570A1Reduce stacking processImproving host CPU performanceWeb data indexingMultiple digital computer combinationsData packInternal memory
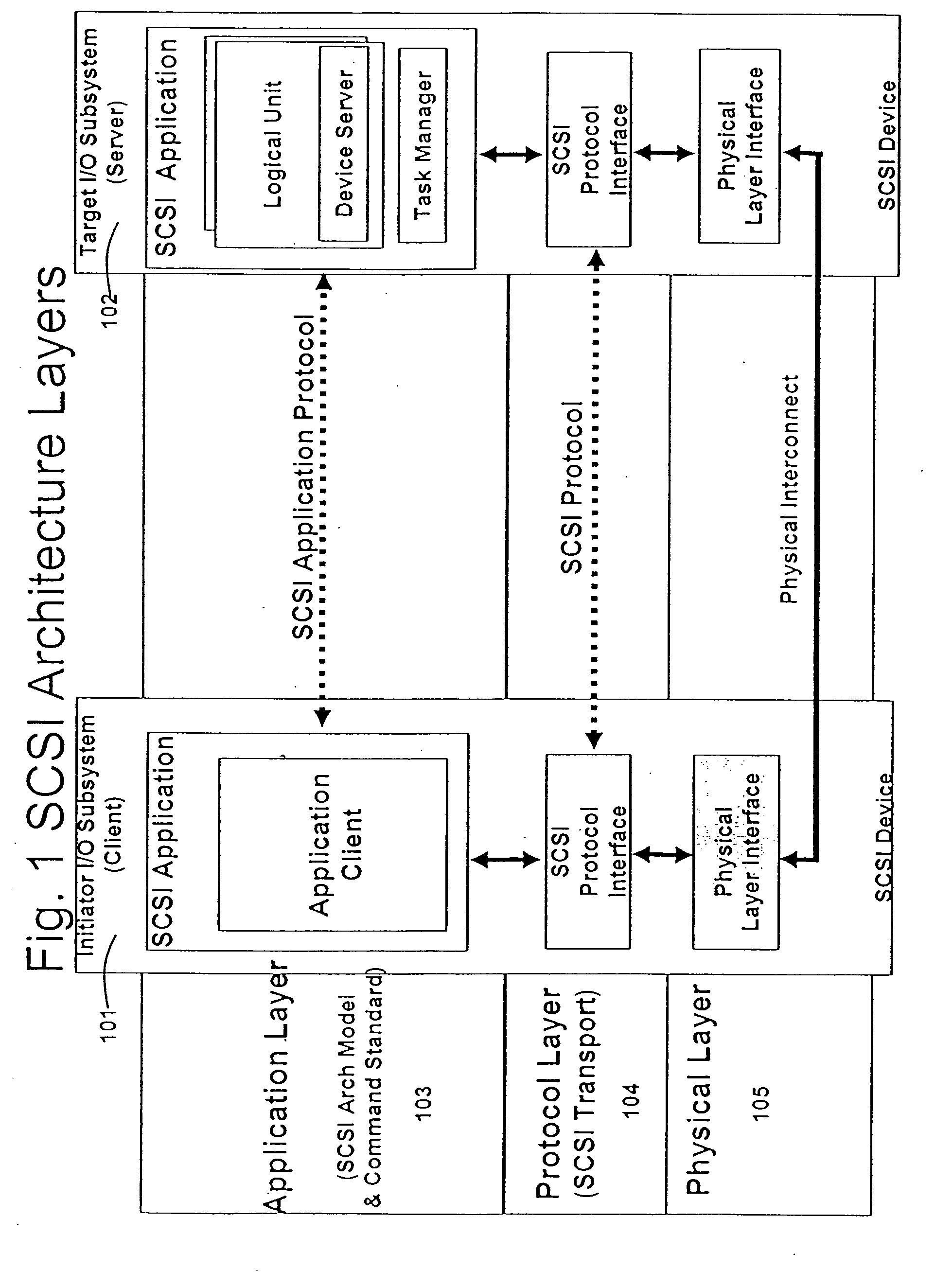
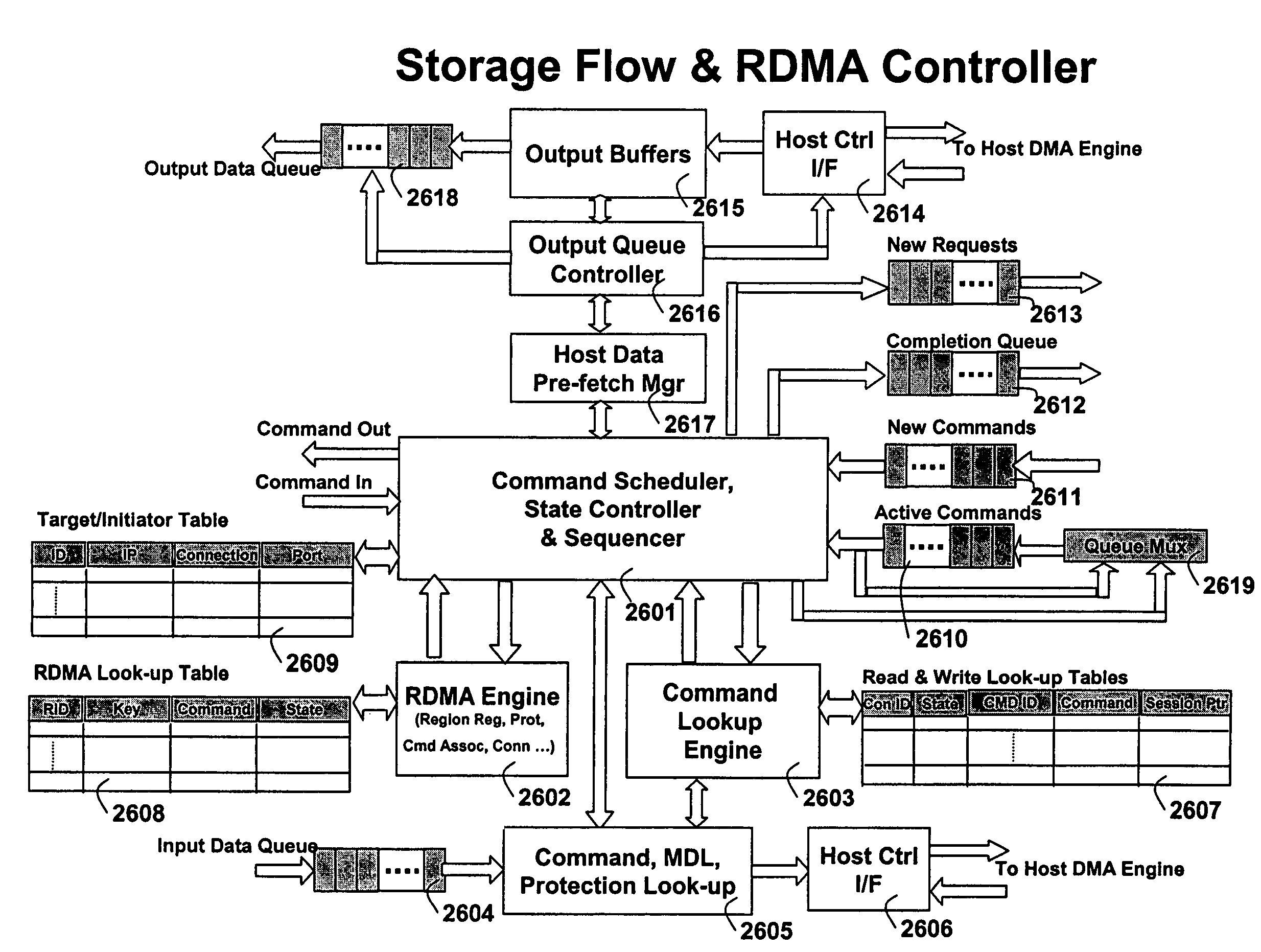
A runtime adaptable search processor is disclosed. The search processor provides high speed content search capability to meet the performance need of network line rates growing to 1 Gbps, 10 Gbps and higher. he search processor provides a unique combination of NFA and DFA based search engines that can process incoming data in parallel to perform the search against the specific rules programmed in the search engines. The processor architecture also provides capabilities to transport and process Internet Protocol (IP) packets from Layer 2 through transport protocol layer and may also provide packet inspection through Layer 7. Further, a runtime adaptable processor is coupled to the protocol processing hardware and may be dynamically adapted to perform hardware tasks as per the needs of the network traffic being sent or received and / or the policies programmed or services or applications being supported. A set of engines may perform pass-through packet classification, policy processing and / or security processing enabling packet streaming through the architecture at nearly the full line rate. A high performance content search and rules processing security processor is disclosed which may be used for application layer and network layer security. scheduler schedules packets to packet processors for processing. An internal memory or local session database cache stores a session information database for a certain number of active sessions. The session information that is not in the internal memory is stored and retrieved to / from an additional memory. An application running on an initiator or target can in certain instantiations register a region of memory, which is made available to its peer(s) for access directly without substantial host intervention through RDMA data transfer. A security system is also disclosed that enables a new way of implementing security capabilities inside enterprise networks in a distributed manner using a protocol processing hardware with appropriate security features.
Owner:MEMORY ACCESS TECH LLC
Runtime adaptable search processor
ActiveUS7685254B2Improve application performanceLarge capacityWeb data indexingMemory adressing/allocation/relocationPacket schedulingSchema for Object-Oriented XML
A runtime adaptable search processor is disclosed. The search processor provides high speed content search capability to meet the performance need of network line rates growing to 1 Gbps, 10 Gbps and higher. The search processor provides a unique combination of NFA and DFA based search engines that can process incoming data in parallel to perform the search against the specific rules programmed in the search engines. The processor architecture also provides capabilities to transport and process Internet Protocol (IP) packets from Layer 2 through transport protocol layer and may also provide packet inspection through Layer 7. Further, a runtime adaptable processor is coupled to the protocol processing hardware and may be dynamically adapted to perform hardware tasks as per the needs of the network traffic being sent or received and / or the policies programmed or services or applications being supported. A set of engines may perform pass-through packet classification, policy processing and / or security processing enabling packet streaming through the architecture at nearly the full line rate. A high performance content search and rules processing security processor is disclosed which may be used for application layer and network layer security. Scheduler schedules packets to packet processors for processing. An internal memory or local session database cache stores a session information database for a certain number of active sessions. The session information that is not in the internal memory is stored and retrieved to / from an additional memory. An application running on an initiator or target can in certain instantiations register a region of memory, which is made available to its peer(s) for access directly without substantial host intervention through RDMA data transfer. A security system is also disclosed that enables a new way of implementing security capabilities inside enterprise networks in a distributed manner using a protocol processing hardware with appropriate security features.
Owner:MEMORY ACCESS TECH LLC
Runtime adaptable security processor
InactiveUS20050108518A1Improve performanceReduce overheadSecuring communicationInternal memoryPacket scheduling
A runtime adaptable security processor is disclosed. The processor architecture provides capabilities to transport and process Internet Protocol (IP) packets from Layer 2 through transport protocol layer and may also provide packet inspection through Layer 7. Further, a runtime adaptable processor is coupled to the protocol processing hardware and may be dynamically adapted to perform hardware tasks as per the needs of the network traffic being sent or received and / or the policies programmed or services or applications being supported. A set of engines may perform pass-through packet classification, policy processing and / or security processing enabling packet streaming through the architecture at nearly the full line rate. A high performance content search and rules processing security processor is disclosed which may be used for application layer and network layer security. A scheduler schedules packets to packet processors for processing. An internal memory or local session database cache stores a session information database for a certain number of active sessions. The session information that is not in the internal memory is stored and retrieved to / from an additional memory. An application running on an initiator or target can in certain instantiations register a region of memory, which is made available to its peer(s) for access directly without substantial host intervention through RDMA data transfer. A security system is also disclosed that enables a new way of implementing security capabilities inside enterprise networks in a distributed manner using a protocol processing hardware with appropriate security features.
Owner:MEMORY ACCESS TECH LLC
Method of and system for physically distributed, logically shared, and data slice-synchronized shared memory switching
An improved data networking technique and apparatus using a novel physically distributed but logically shared and data-sliced synchronized shared memory switching datapath architecture integrated with a novel distributed data control path architecture to provide ideal output-buffered switching of data in networking systems, such as routers and switches, to support the increasing port densities and line rates with maximized network utilization and with per flow bit-rate latency and jitter guarantees, all while maintaining optimal throughput and quality of services under all data traffic scenarios, and with features of scalability in terms of number of data queues, ports and line rates, particularly for requirements ranging from network edge routers to the core of the network, thereby to eliminate both the need for the complication of centralized control for gathering system-wide information and for processing the same for egress traffic management functions and the need for a centralized scheduler, and eliminating also the need for buffering other than in the actual shared memory itself,—all with complete non-blocking data switching between ingress and egress ports, under all circumstances and scenarios.
Owner:QOS LOGIX
TCP/IP processor and engine using RDMA
ActiveUS7376755B2Sharply reduces TCP/IP protocol stack overheadImprove performanceMultiplex system selection arrangementsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationTransmission protocolInternal memory
A TCP / IP processor and data processing engines for use in the TCP / IP processor is disclosed. The TCP / IP processor can transport data payloads of Internet Protocol (IP) data packets using an architecture that provides capabilities to transport and process Internet Protocol (IP) packets from Layer 2 through transport protocol layer and may also provide packet inspection through Layer 7. The engines may perform pass-through packet classification, policy processing and / or security processing enabling packet streaming through the architecture at nearly the full line rate. A scheduler schedules packets to packet processors for processing. An internal memory or local session database cache stores a TCP / IP session information database and may also store a storage information session database for a certain number of active sessions. The session information that is not in the internal memory is stored and retrieved to / from an additional memory. An application running on an initiator or target can in certain instantiations register a region of memory, which is made available to its peer(s) for access directly without substantial host intervention through RDMA data transfer.
Owner:MEMORY ACCESS TECH LLC
Systems and methods of data processing using an fpga-implemented hash function
InactiveUS20130343181A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsComputer hardwareHash function
A method for processing data packets in a computer system may include receiving a data packet at a configurable logic device (e.g., an FPGA), each packet including header information regarding the data packet, the configurable logic device automatically identifying particular information elements in the header information of the data packet, the configurable logic device automatically executing a hash function programmed on the configurable logic device to calculate a hash value for the data packet based on the particular information elements, and processing the data packet based on the calculated hash value for the data packet. The calculate hash value may be used for various purposes, e.g., routing and / or load balancing of traffic across multiple interfaces. The configurable logic device may be able to execute the hash function at line rate, thus freeing up processor cycles in one or more related processors.
Owner:BREAKINGPOINT SYST
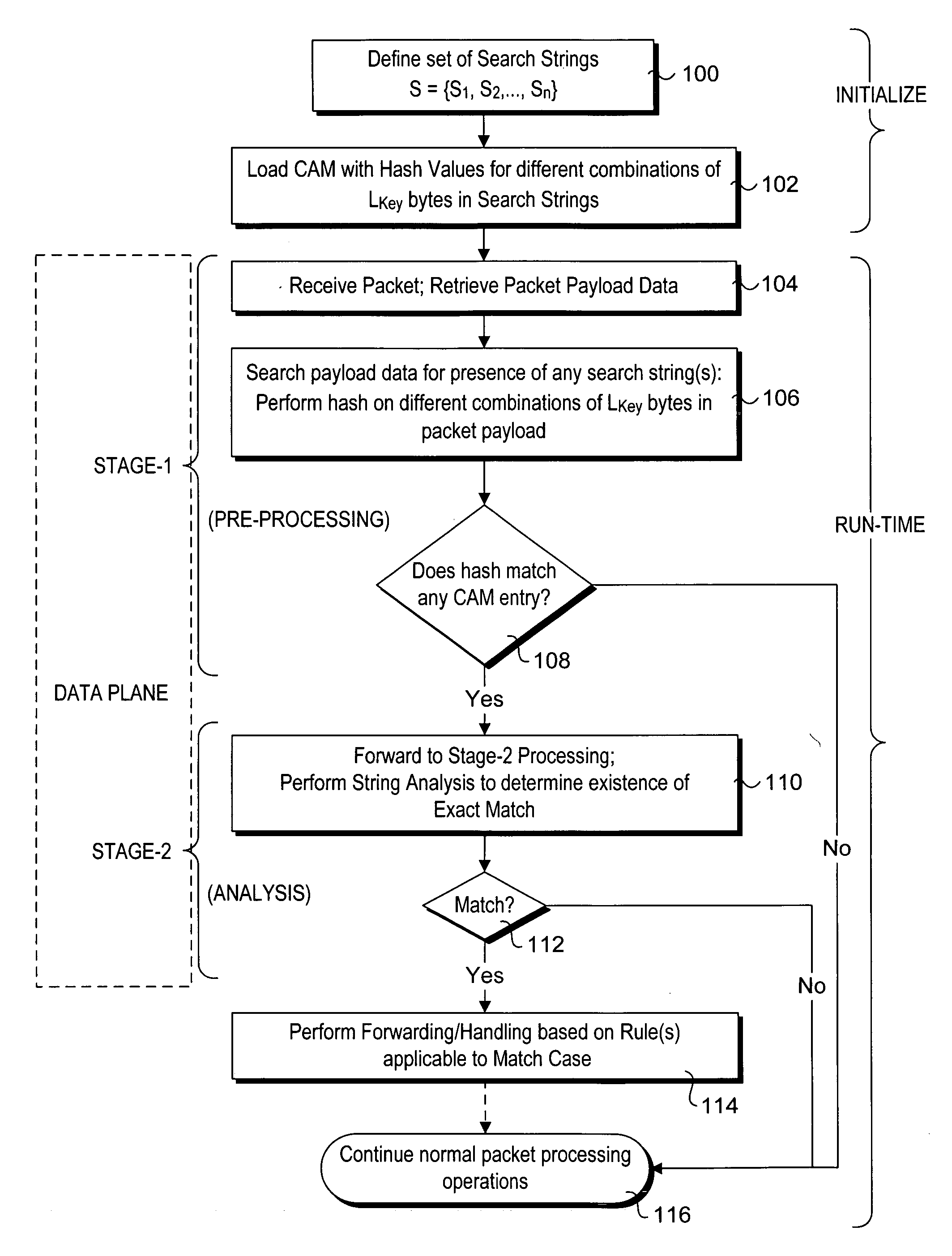
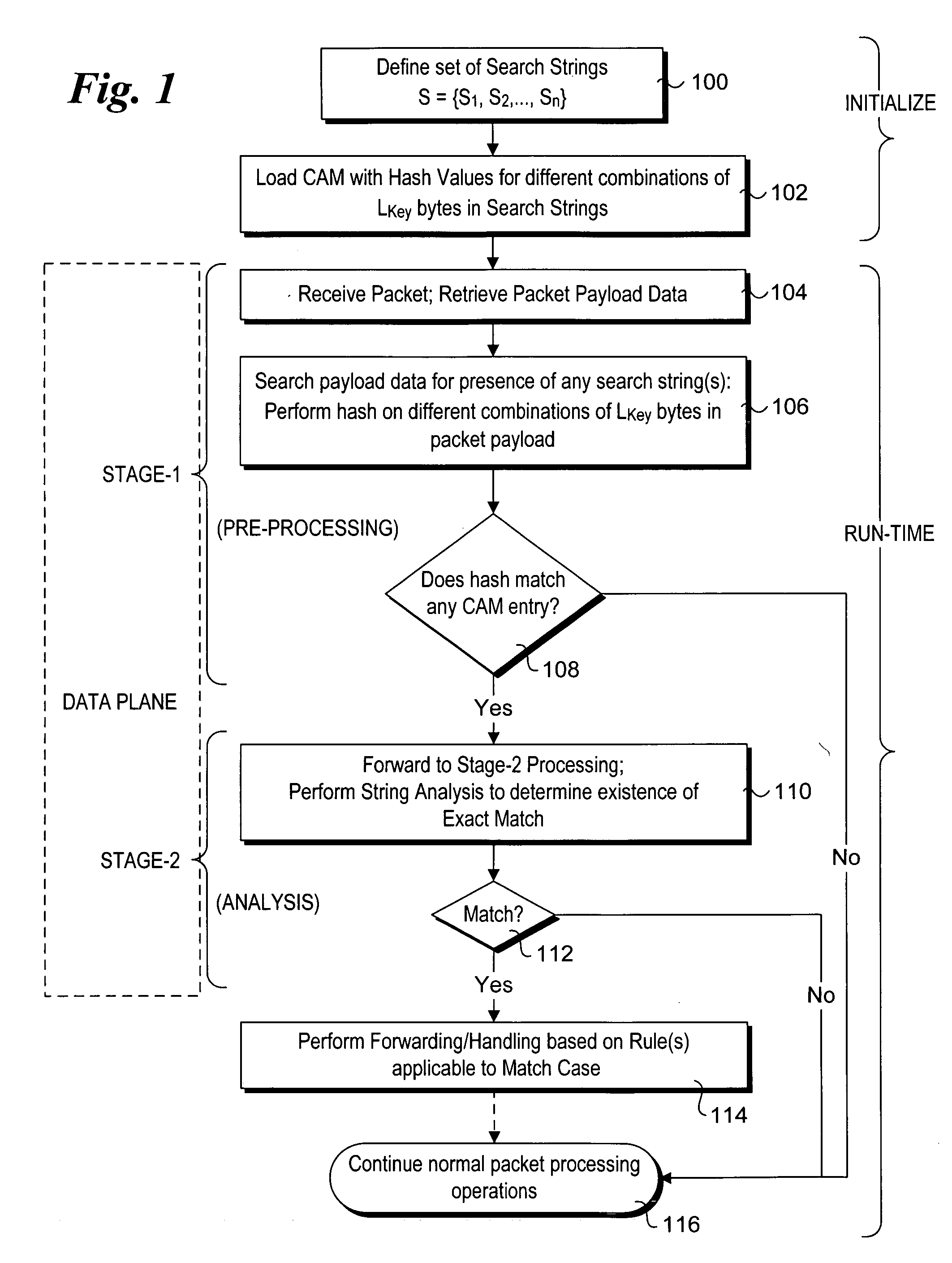
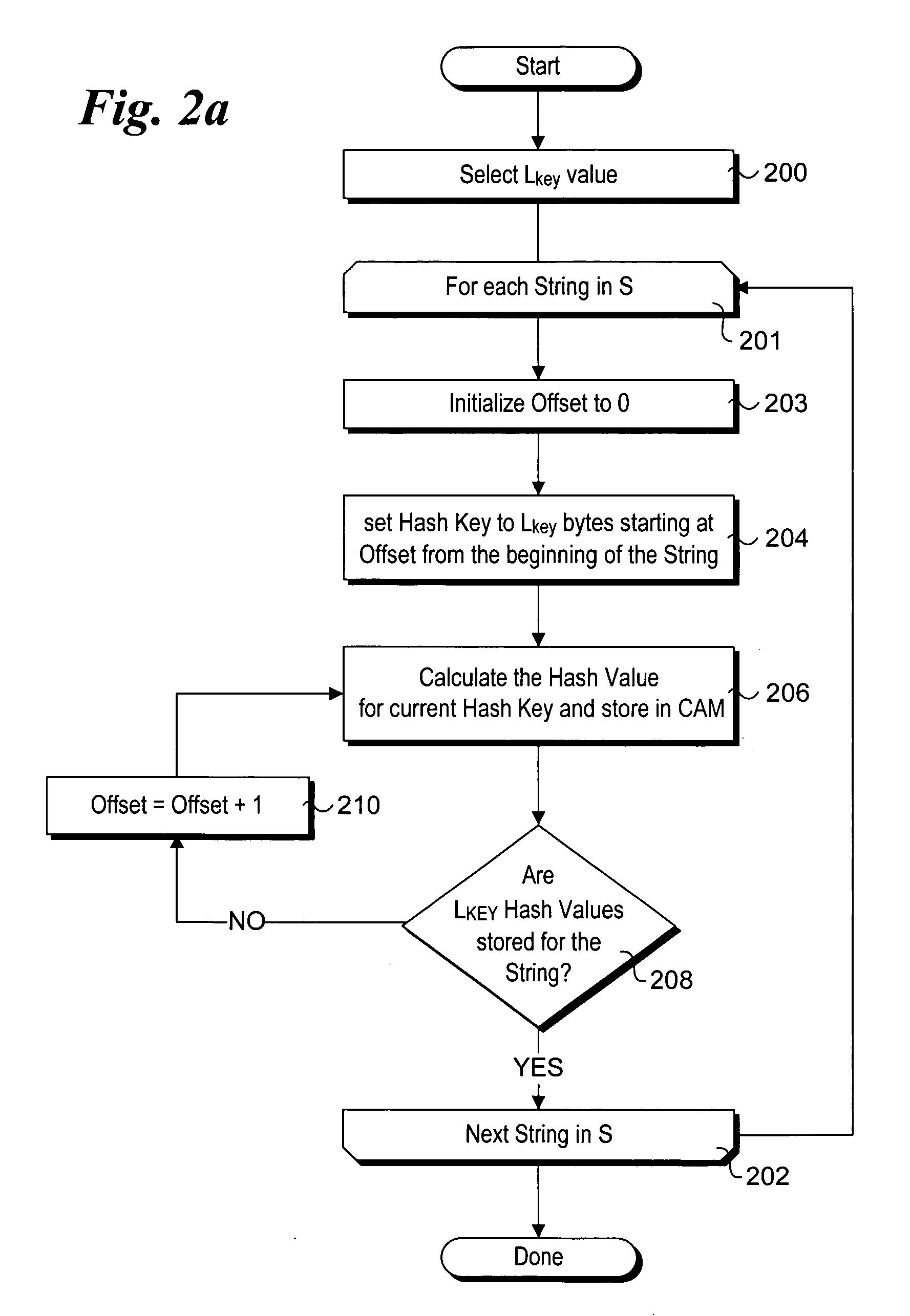
Method to perform exact string match in the data plane of a network processor
InactiveUS20070115986A1Digital computer detailsData switching by path configurationData packLine rate
Methods for performing exact search string matches in the data plane of a network processor. The methods employ a two-stage string search mechanism to identify the existence of a search string from a set S in a packet payload. A first pre-processing stage identifies a potential search string match and a second analysis stage determines whether the first stage match corresponds to an exact string match. The first stage is implemented using hash values derived from at least one of search strings in set S or sub-strings of those search strings. In one embodiment, a plurality of Bloom filters are used to perform the first pre-processing stage, while in other embodiments various CAM-based technique are used. Various TCAM-based schemes are disclosed for performing the second analysis stage. The methods enable packet payloads to be searched for search strings at line-rate speeds.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Runtime adaptable protocol processor
ActiveUS7631107B2Sharply reduces TCP/IP protocol stack overheadImprove performanceComputer controlTime-division multiplexInternal memoryData pack
A runtime adaptable protocol processor is disclosed. The processor architecture provides capabilities to transport and process Internet Protocol (IP) packets from Layer 2 through transport protocol layer and may also provide packet inspection through Layer 7. Further, a runtime adaptable processor is coupled to the protocol processing hardware and may be dynamically adapted to perform hardware tasks as per the needs of the network traffic being sent or received and / or the policies programmed or services or applications being supported. A set of engines may perform pass-through packet classification, policy processing and / or security processing enabling packet streaming through the architecture at nearly the full line rate. A scheduler schedules packets to packet processors for processing. An internal memory or local session database cache stores a session information database for a certain number of active sessions. The session information that is not in the internal memory is stored and retrieved to / from an additional memory. An application running on an initiator or target can in certain instantiations register a region of memory, which is made available to its peer(s) for access directly without substantial host intervention through RDMA data transfer. A security system is also disclosed that enables a new way of implementing security capabilities inside enterprise networks in a distributed manner using a protocol processing hardware with appropriate security features.
Owner:MEMORY ACCESS TECH LLC
Real-time network monitoring and security
ActiveUS20050108573A1Easy programmingEasy maintenanceWeb data indexingMemory loss protectionHigh bandwidthWire speed
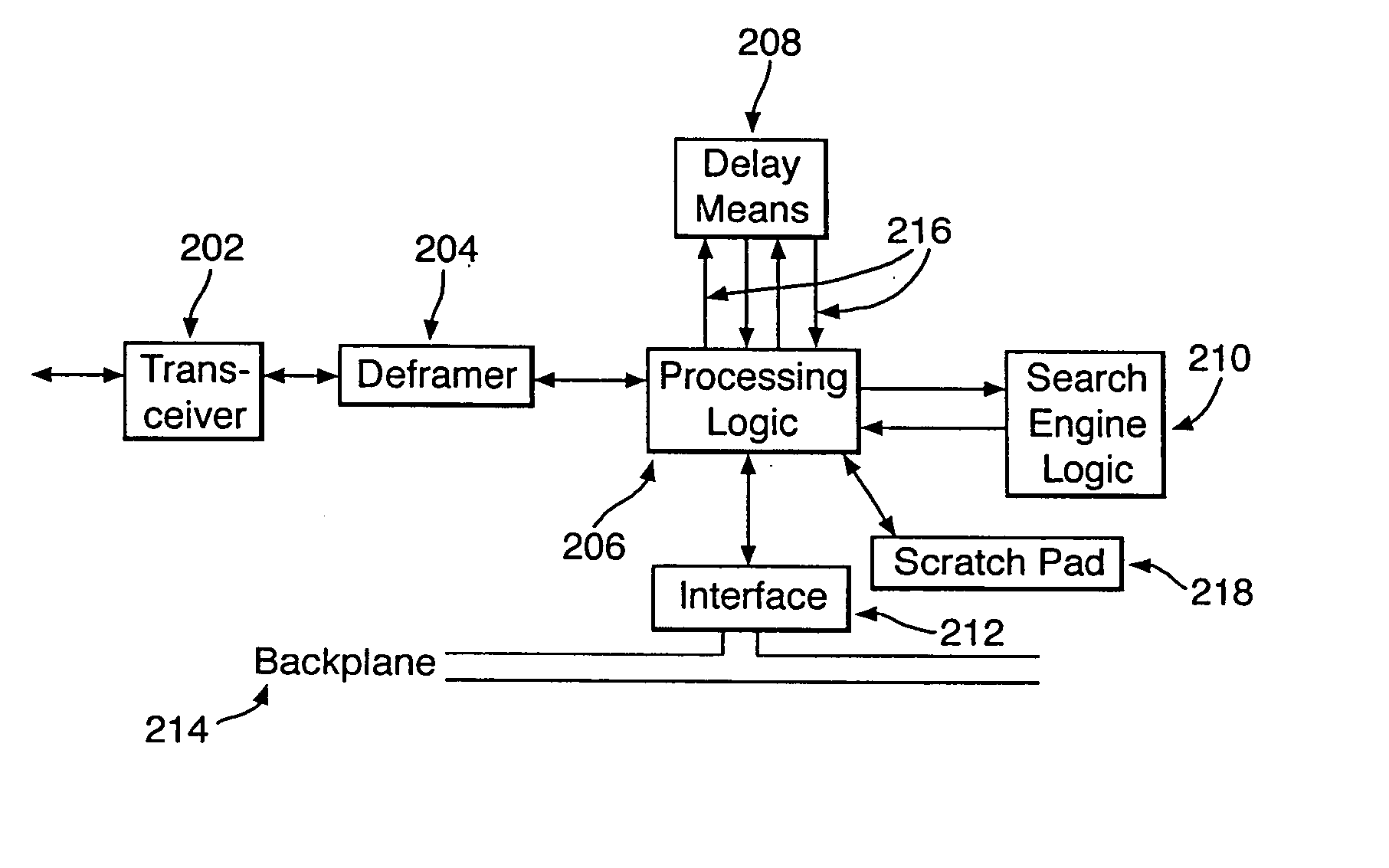
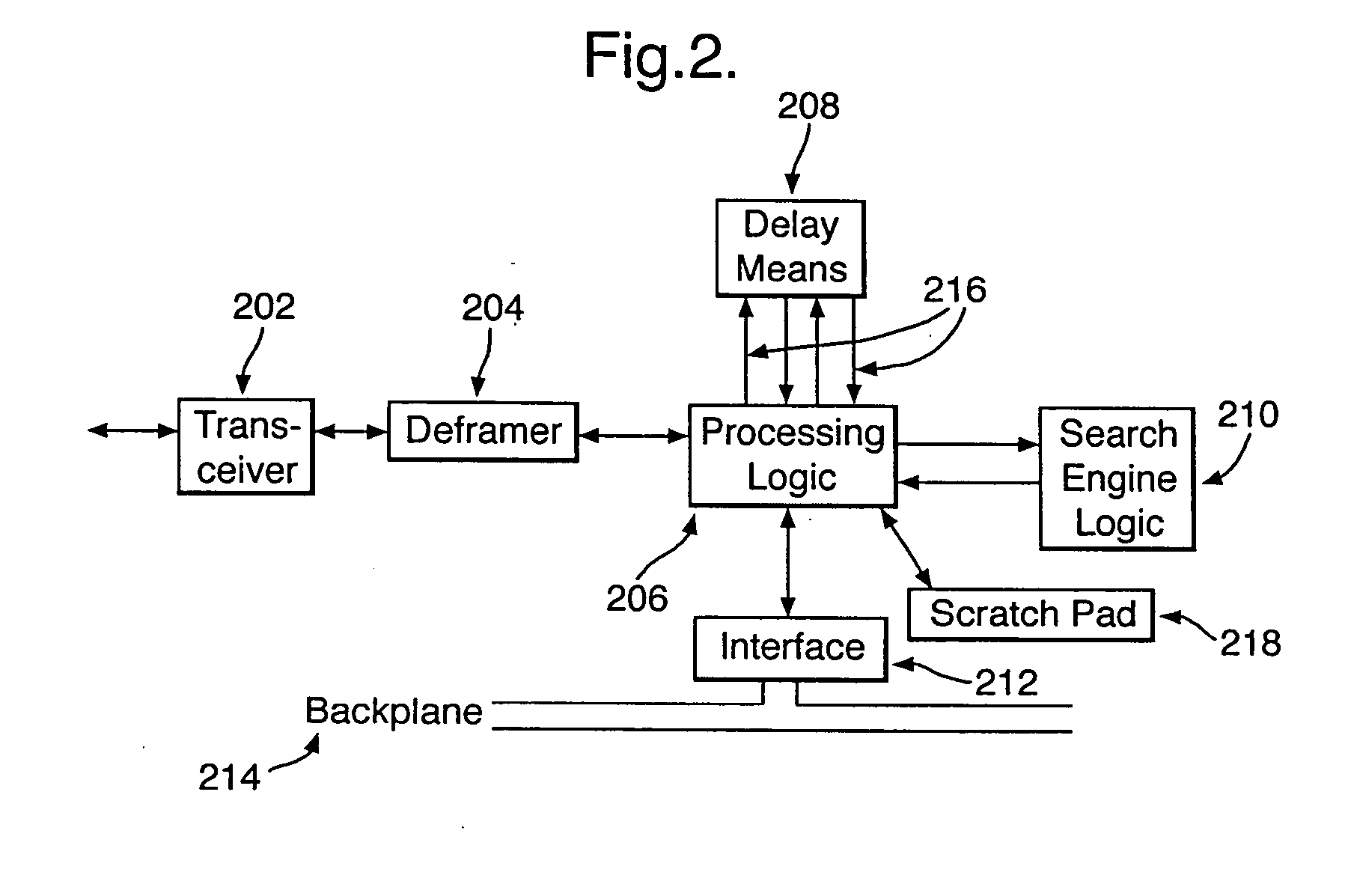
There is provided a hardware device for monitoring and intercepting data packetized data traffic at full line rate. In preferred high bandwidth embodiments, full line rate corresponds to rates that exceed 100 Mbytes / s and in some cases 1000 Mbytes / s. Monitoring and intercepting software, alone, is not able to operate on such volumes of data in real-time. A preferred embodiment comprises: a data delay buffer (208) with multiple delay outputs (216); a search engine logic (210) for implementing a set of basic search tools that operate in real-time on the data traffic; a programmable gate array (206); an interface (212) for passing data quickly to software sub-systems; and control means for implementing software control of the operation of the search tools. The programmable gate array (206) inserts the data packets into the delay buffer (208), extracts them for searching at the delay outputs and formats and schedules the operation of the search engine logic (210). One preferred embodiment uses an IP co-processor as the search engine logic.
Owner:BAE SYSTEMS PLC
Tcp/ip processor and engine using rdma
InactiveUS20080253395A1Sharply reduces TCP/IP protocol stack overheadImprove performanceDigital computer detailsTime-division multiplexInternal memoryTransmission protocol
A TCP / IP processor and data processing engines for use in the TCP / IP processor is disclosed. The TCP / IP processor can transport data payloads of Internet Protocol (IP) data packets using an architecture that provides capabilities to transport and process Internet Protocol (IP) packets from Layer 2 through transport protocol layer and may also provide packet inspection through Layer 7. The engines may perform pass-through packet classification, policy processing and / or security processing enabling packet streaming through the architecture at nearly the full line rate. A scheduler schedules packets to packet processors for processing. An internal memory or local session database cache stores a TCP / IP session information database and may also store a storage information session database for a certain number of active sessions. The session information that is not in the internal memory is stored and retrieved to / from an additional memory. An application running on an initiator or target can in certain instantiations register a region of memory, which is made available to its peer(s) for access directly without substantial host intervention through RDMA data transfer.
Owner:MEMORY ACCESS TECH LLC
Layered memory architecture for deterministic finite automaton based string matching useful in network intrusion detection and prevention systems and apparatuses
ActiveUS20060101195A1Reduce decreaseTransmissionMemory systemsLine rateDeterministic finite automaton
Owner:FORTINET
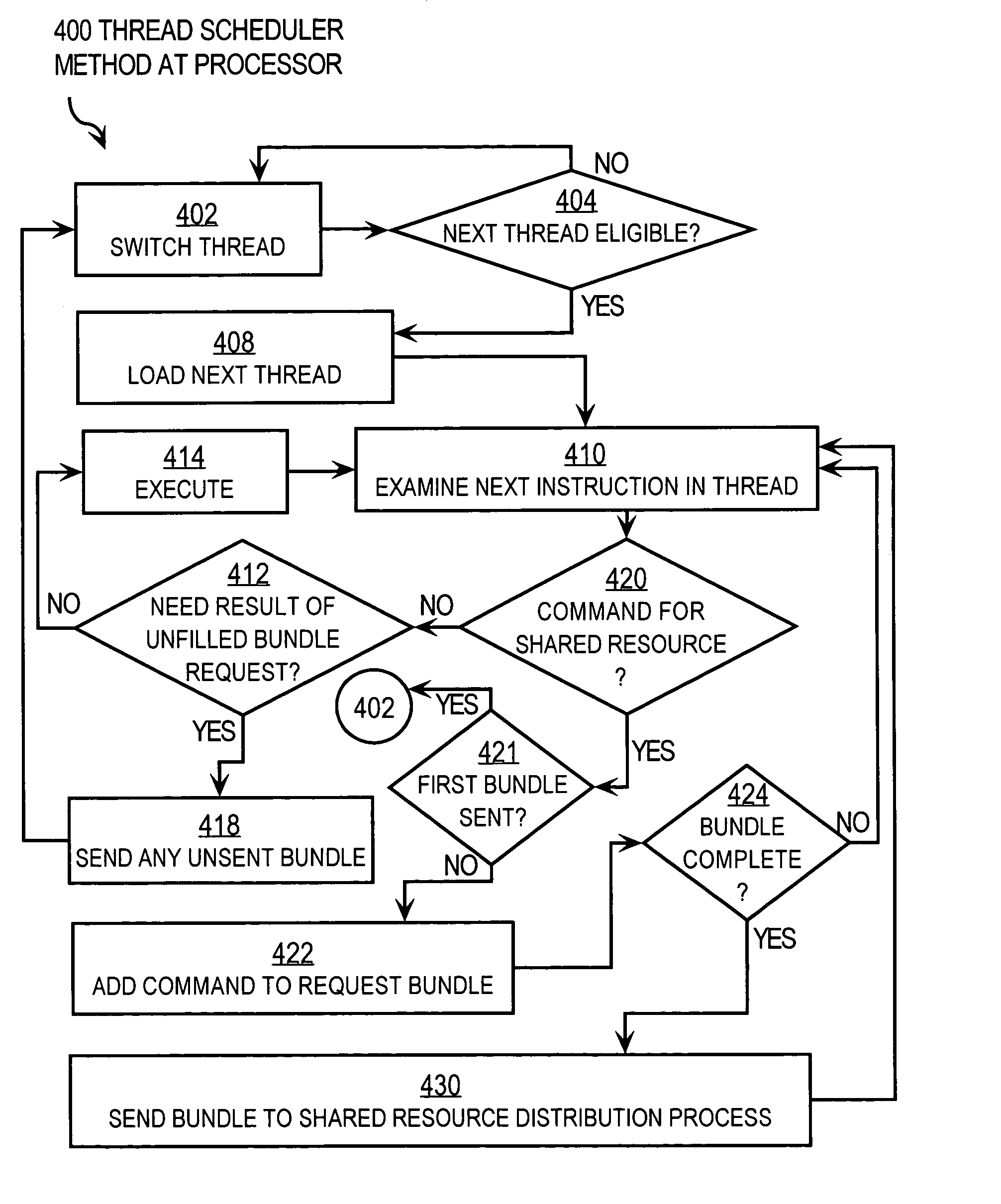
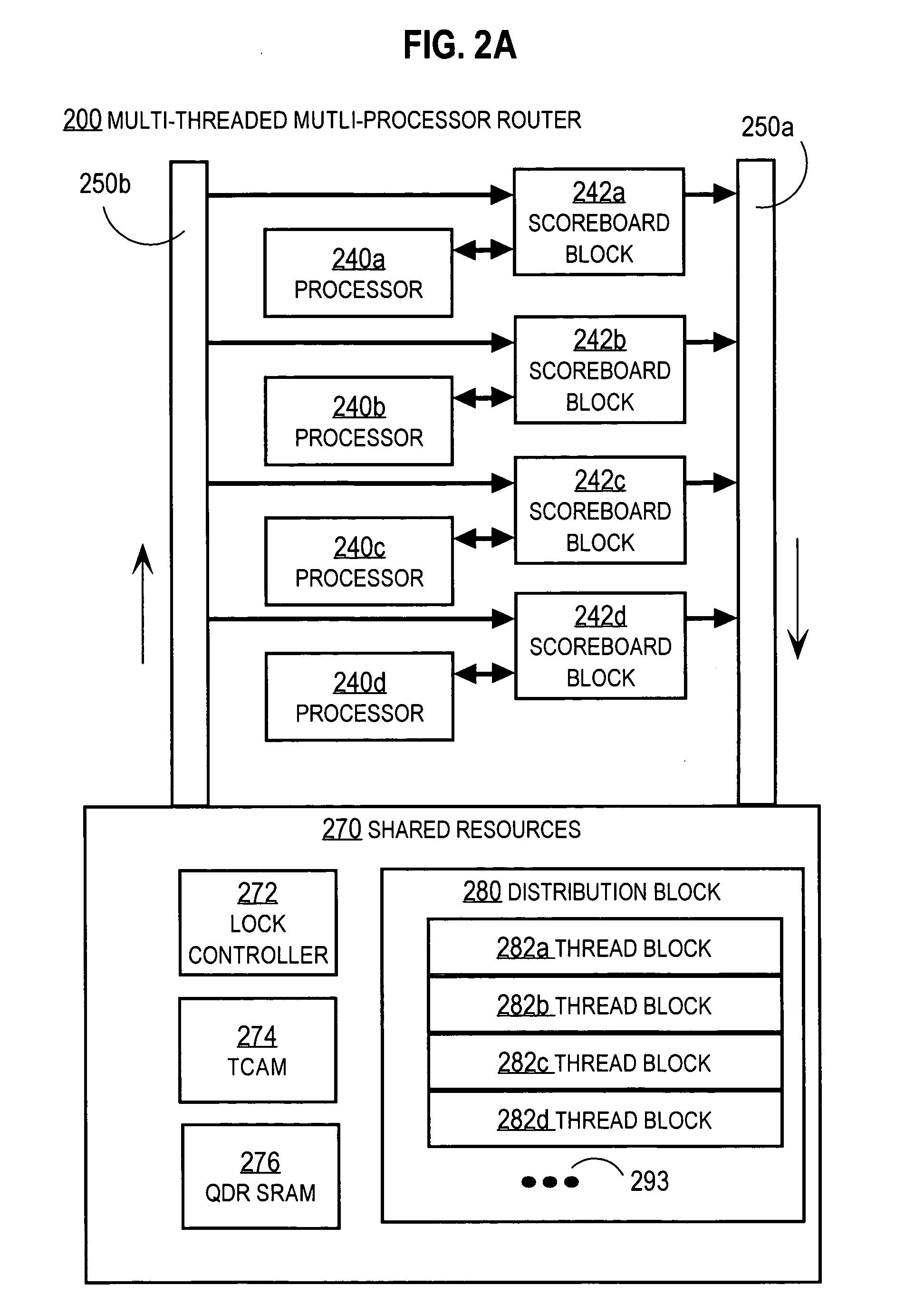
Techniques for reducing thread overhead for systems with multiple multi-theaded processors
Techniques for processing requests from a processing thread for a shared resource shared among threads on one or more processors include receiving a bundle of requests from a portion of a thread that is executed during a single wake interval on a particular processor. The bundle includes multiple commands for one or more shared resources. The bundle is processed at the shared resource(s) to produce a bundle result. The bundle result is sent to the particular processor. The thread undergoes no more than one wake interval to sleep interval cycle while the bundle commands are processed at the shared resource(s). These techniques allow a lock for shared resource(s) to be obtained, used and released all while the particular thread is sleeping, so that locks are held for shorter times than in conventional approaches. Using these techniques, line rate packet processing is more readily achieved in routers with multiple multi-threaded processors.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
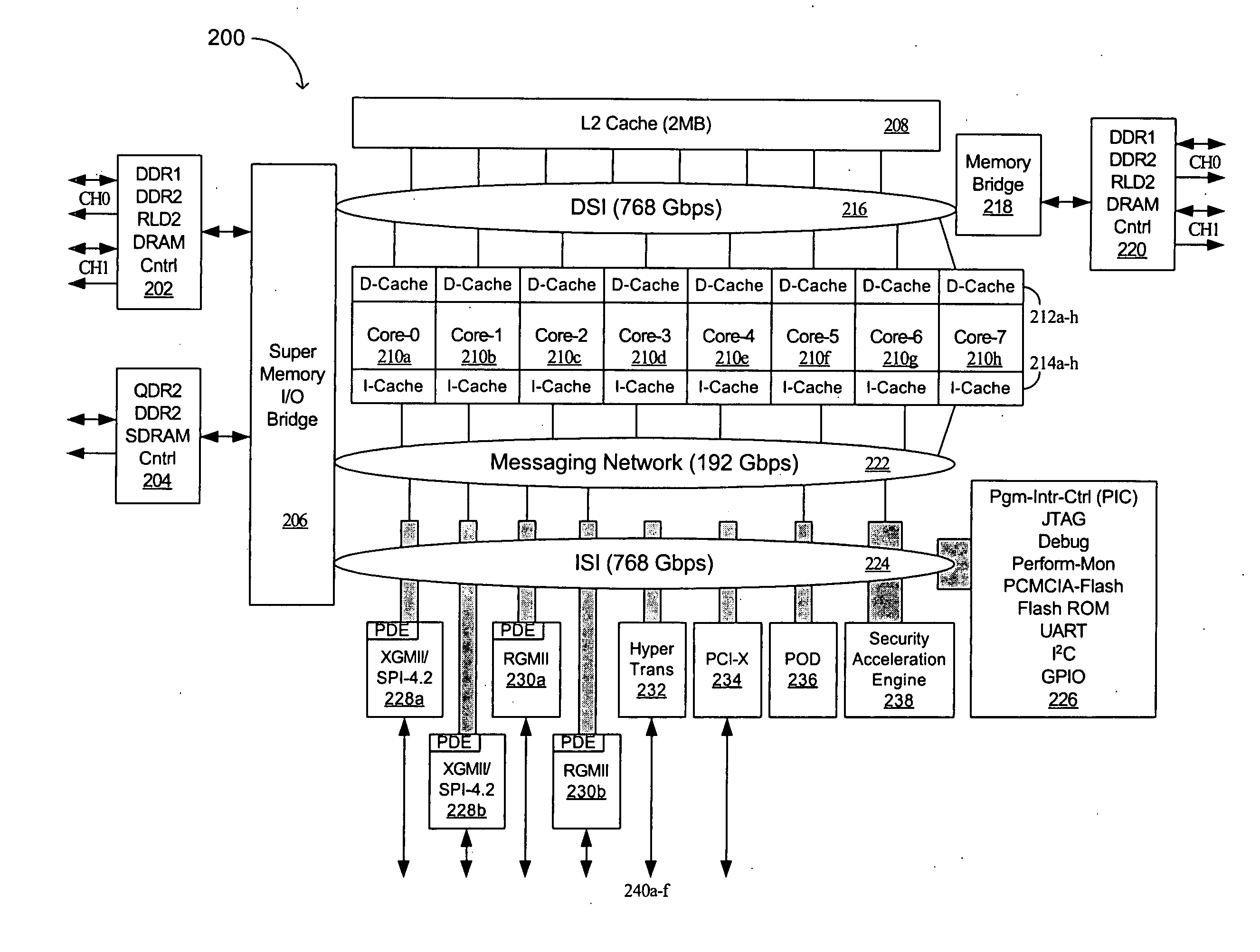
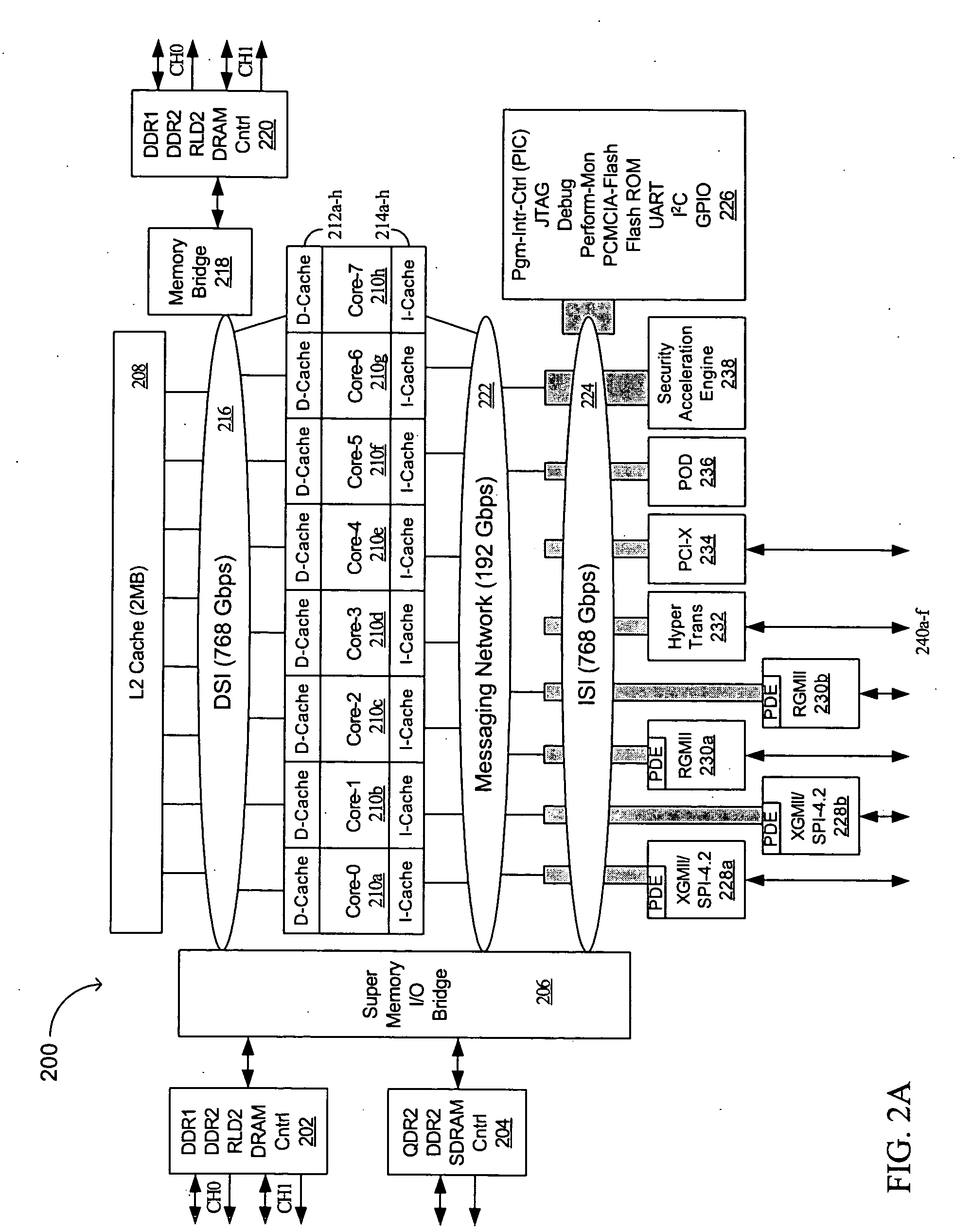
Advanced processor with mechanism for packet distribution at high line rate
InactiveUS20050027793A1High bandwidth communicationEfficient and cost-effectiveMemory adressing/allocation/relocationGeneral purpose stored program computerHigh bandwidthWire speed
An advanced processor comprises a plurality of multithreaded processor cores each having a data cache and instruction cache. A data switch interconnect is coupled to each of the processor cores and configured to pass information among the processor cores. A messaging network is coupled to each of the processor cores and a plurality of communication ports. In one aspect of an embodiment of the invention, the data switch interconnect is coupled to each of the processor cores by its respective data cache, and the messaging network is coupled to each of the processor cores by its respective message station. Advantages of the invention include the ability to provide high bandwidth communications between computer systems and memory in an efficient and cost-effective manner.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
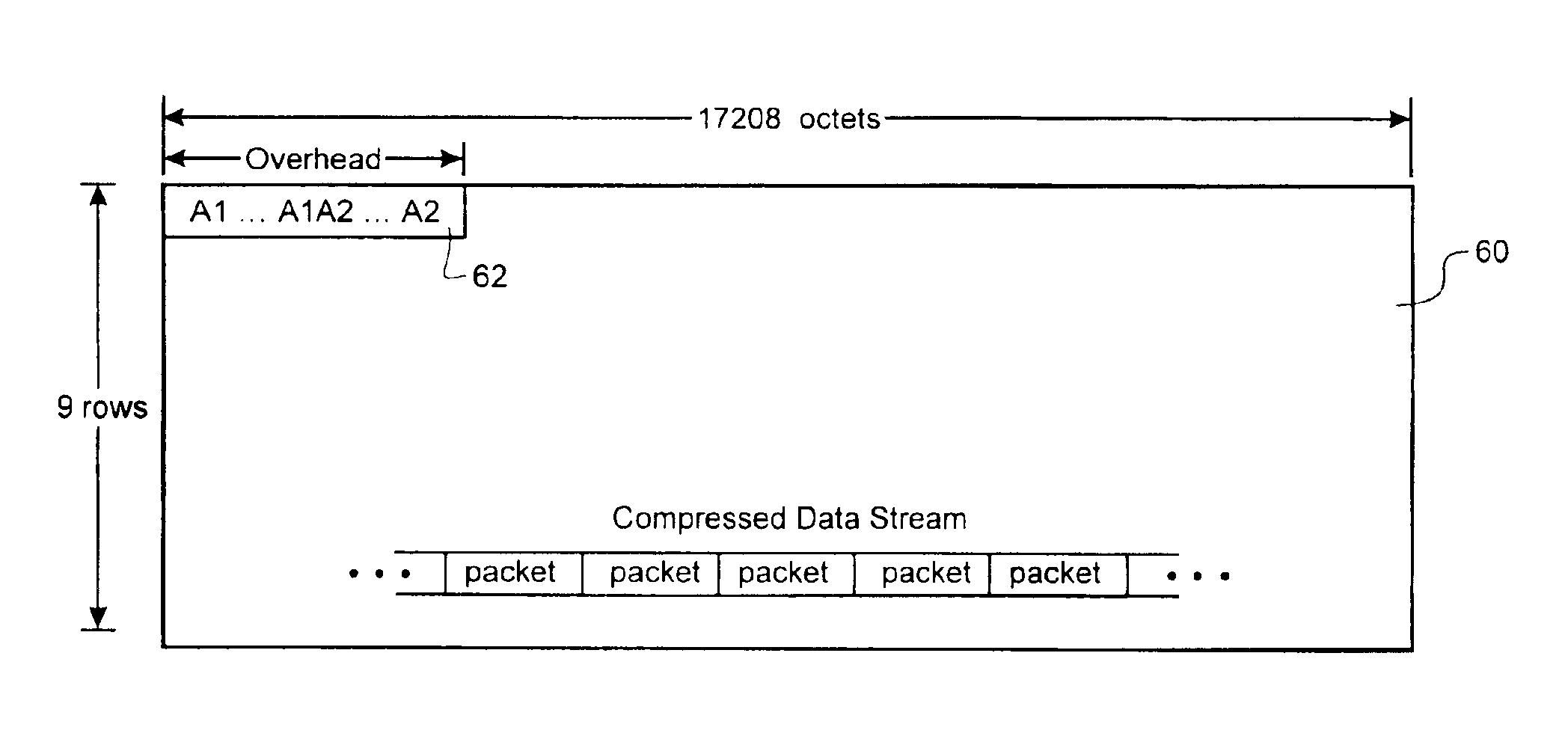
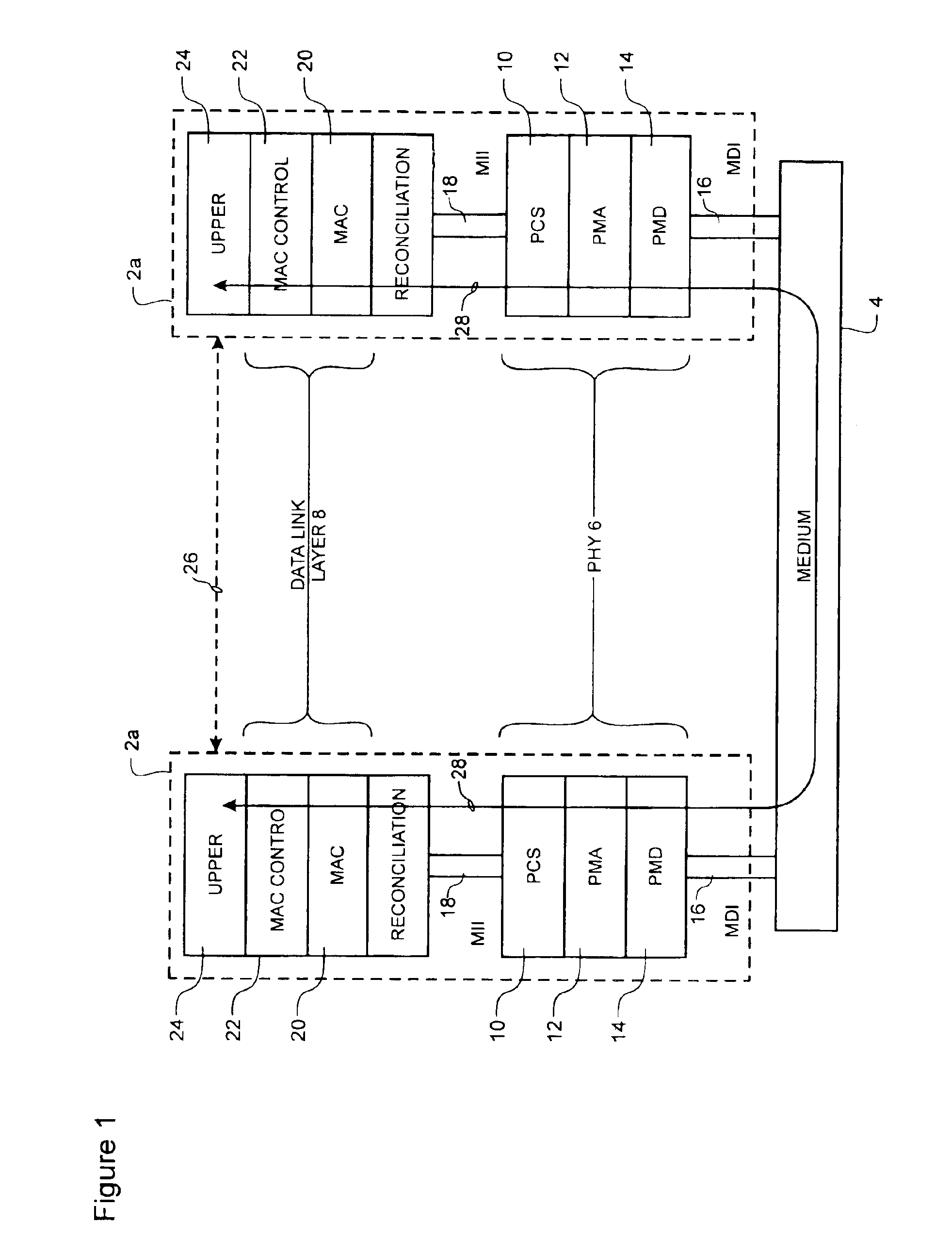
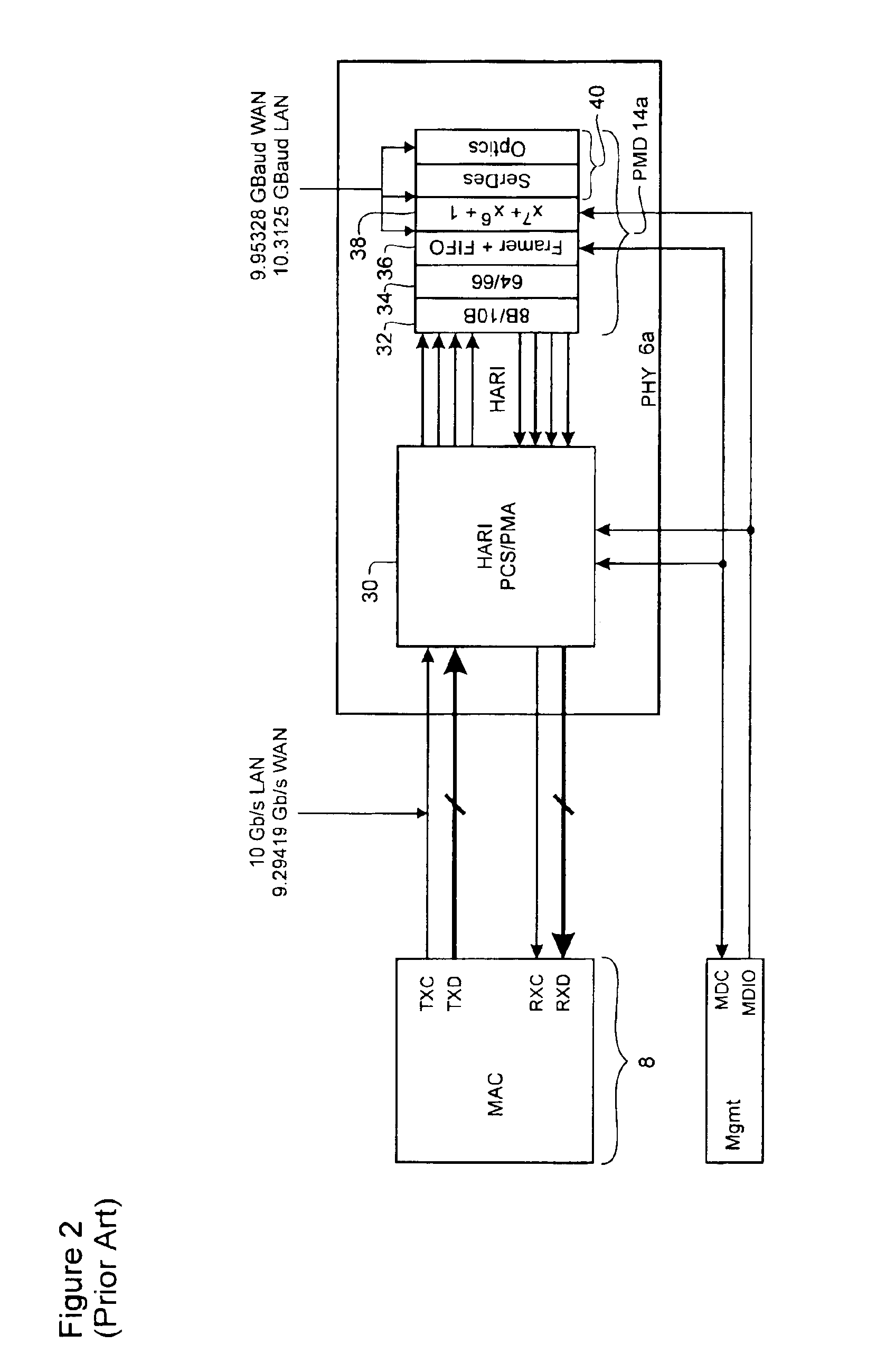
10 Gigabit ethernet mappings for a common LAN/WAN PMD interface with a simple universal physical medium dependent interface
An Ethernet mapping enables high speed Ethernet data streams having a data rate of 10 Gb / s to be transported across a synchronous packet switched network fabric having a standard SONET OC-192 line rate of 9.953280 Gbaud. The 10 Gb / s Ethernet data stream is compressed by removing interframe gaps between successive MAC frames to produce a compressed data stream, which is then mapped to a synchronous container. The synchronous container is then launched across the synchronous packet switched network fabric at a standard SONET OC-192 line rate of 9.953280 Gbaud. The synchronous container is preferably provided as a stripped STS-192c frame having only A1 and A2 octets of the Transport Overhead (TOH). The compressed data stream is mapped directly to the synchronous container, starting at the first octet following the A1 and A2 octets, without first being inserted into a conventional STS-192c SPE, so that most of the space normally used for TOH and Path overhead (POH) within a conventional STS-192c frame is freed-up for carrying the compressed data stream. At a receiving interface, the compressed data stream is extracted from received synchronous containers and decompressed, by insertion of interframe gaps between successive MAC frames, to generate a recovered 10 Gb / s Ethernet data stream. The starting bit of each successive MAC frame can be identified by examination of the length field of the immediately previous MAC frame.
Owner:CIENA
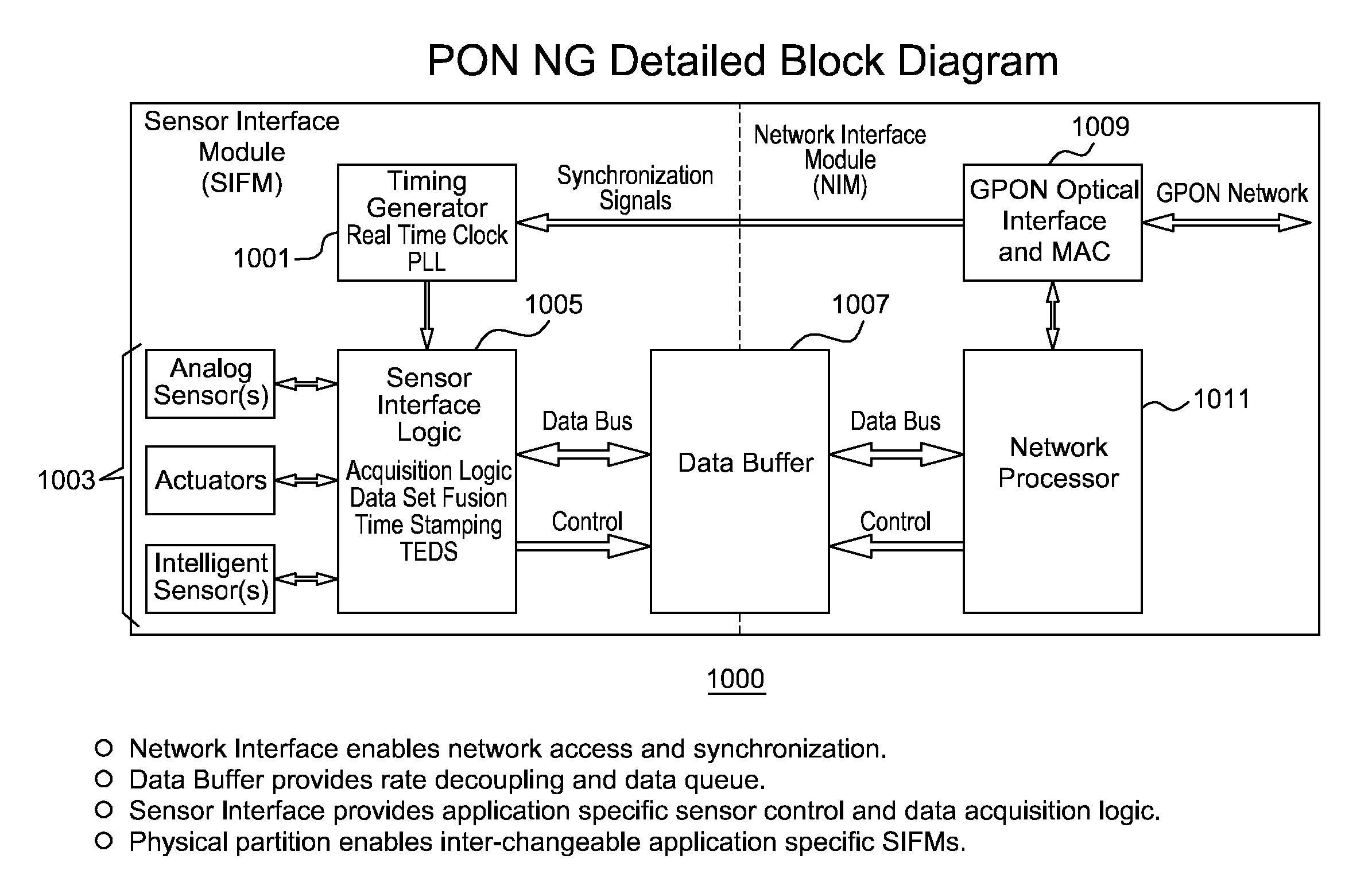
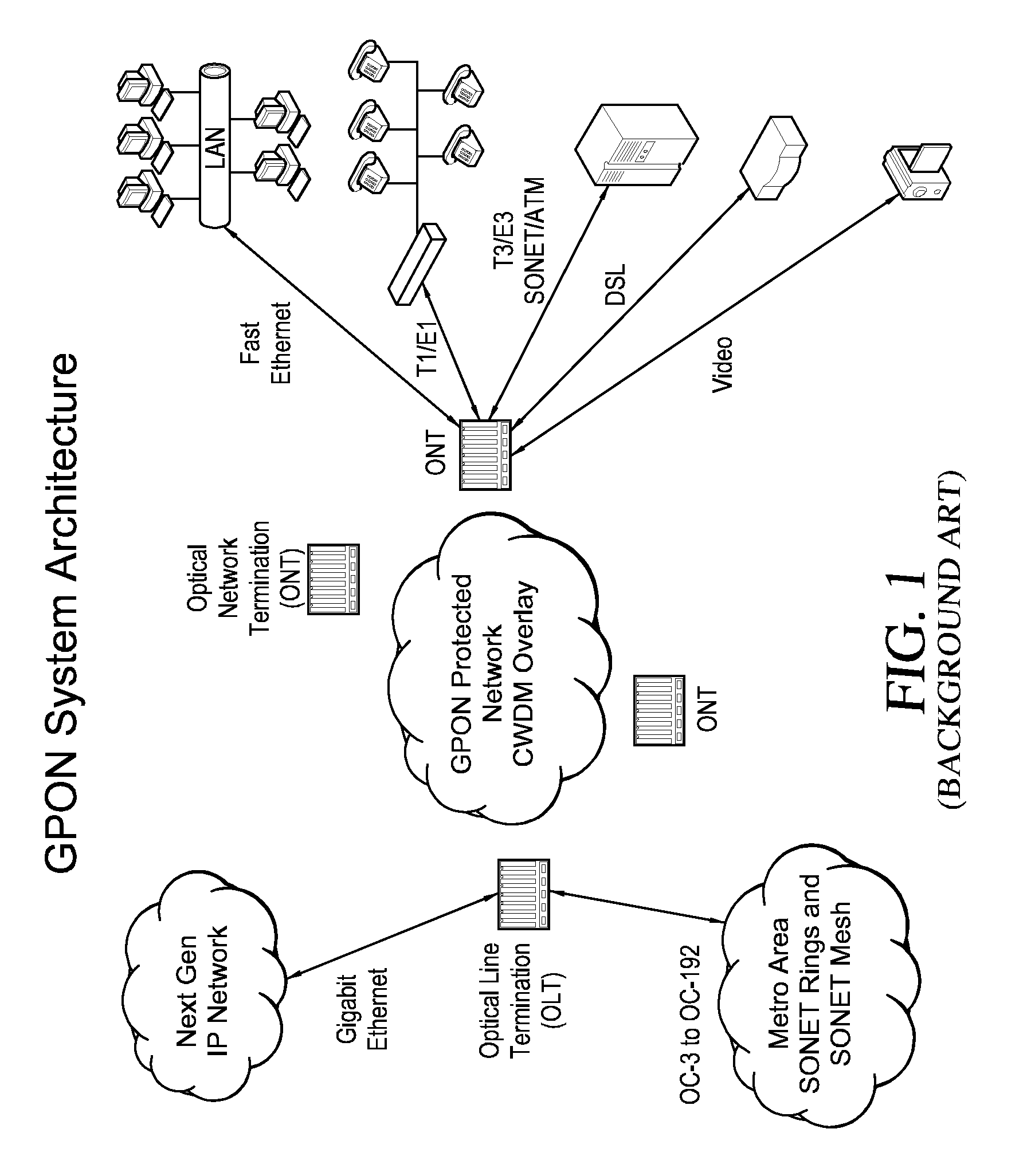
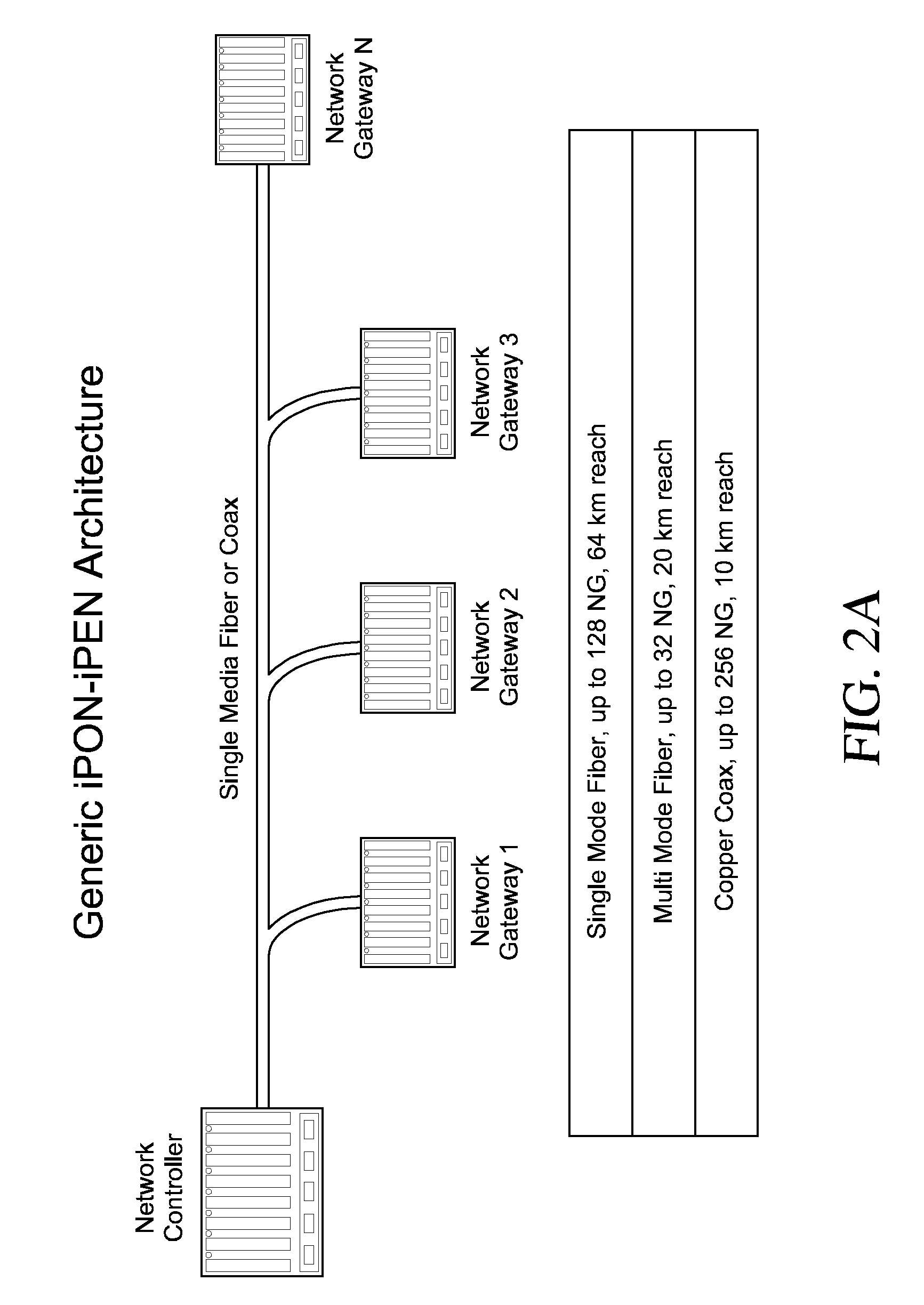
Inverted Passive Optical Network/inverted Passive Electrical Network (iPON/iPEN) Based Data Fusion and Synchronization System
InactiveUS20070291777A1Easy to integrateEasy to fuseTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationTelecommunications linkLine rate
The present invention is an apparatus, method and system for time synchronizing data from various sensor types that enables data fusion and transport. To provide this capability, the present invention utilizes an inverted Passive Optical Network (PON) approach for synchronous communication. Further, the present invention introduces an inverted Passive Electrical Network (iPEN) that extends the iPON approach. Data that are in a common format with embedded time synchronization information can easily be integrated or fused and transported over such communication links. The present invention provides the ability to merge and aggregate data from a wide range of disparate sensors and systems while maintaining close synchronization. The present invention is appropriate for synchronization of data, voice, and video onto a single network and / or multi-tiered networks and can also handle signal processing and control technologies at line rates well into the Gigabits per second (Gbps) range.
Owner:3 PHOENIX
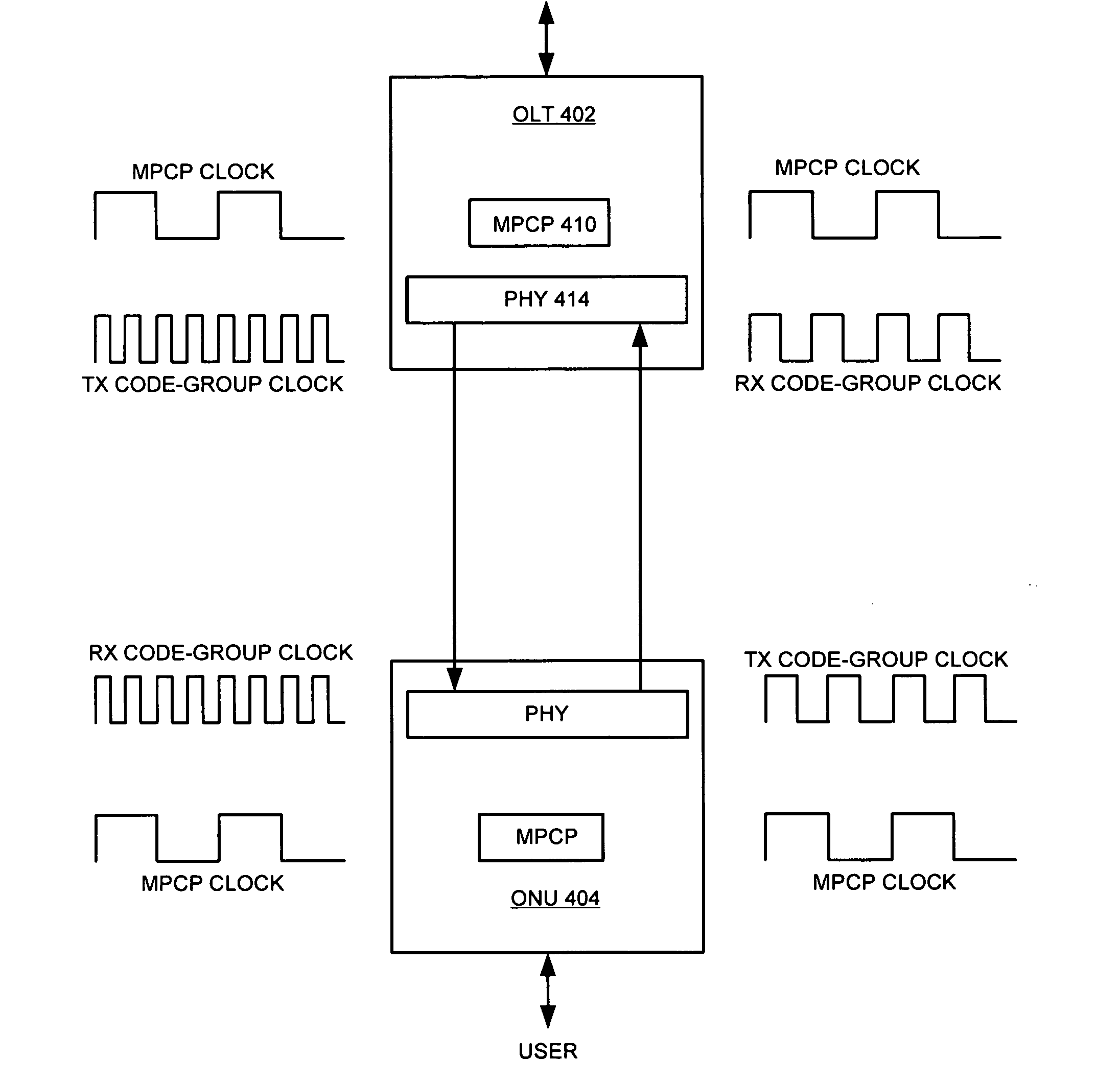
Method and apparatus for facilitating asymmetric line rates in an ethernet passive optical network
ActiveUS20070014575A1Facilitating line rateBoost rateTime-division multiplexStar/tree networksLine rateFrequency ratio
One embodiment of the present invention provides a method for facilitating asymmetric line rates in an Ethernet passive optical network (EPON) which includes a central node and at least one remote node. During operation, the system provides a downstream code-group clock, wherein each cycle thereof corresponds to a code group transmitted from the central node to a remote node. The system also provides an upstream code-group clock, wherein each cycle thereof corresponds to a code group received at the central node from a remote node. In addition, the system provides a multi-point control protocol (MPCP) clock, wherein the frequency ratio of the MPCP clock to the downstream code-group clock is different from the frequency ratio of the MPCP clock to the upstream code-group clock, thereby allowing the downstream transmission to be performed at a faster line rate than the upstream transmission line rate.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Memory management system and algorithm for network processor architecture
InactiveUS7006505B1Low costMaximize memory bandwidthData switching by path configurationMemory systemsLine rateParallel computing
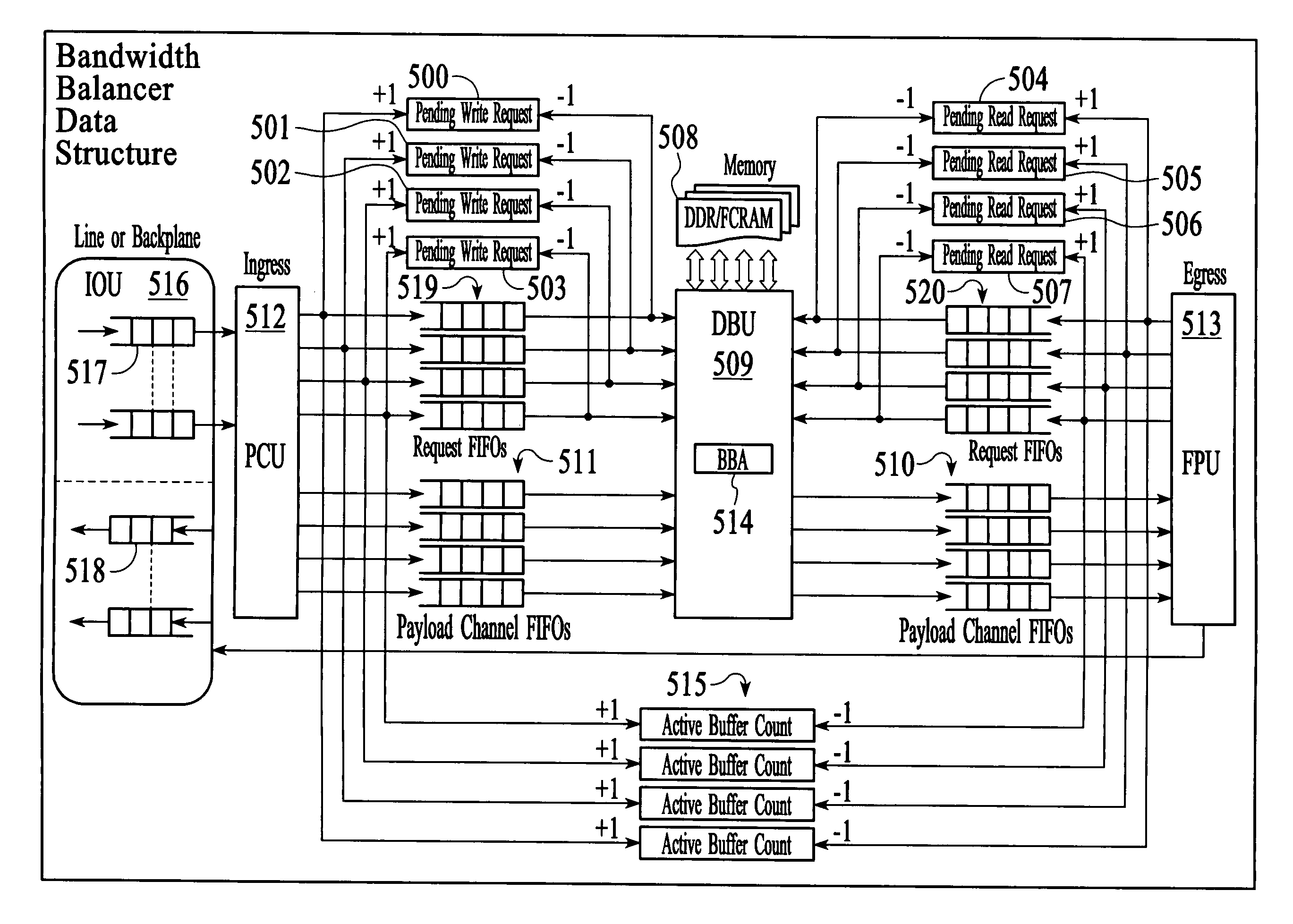
An embodiment of this invention pertains to a system and method for balancing memory accesses to a low cost memory unit in order to sustain and guarantee a desired line rate regardless of the incoming traffic pattern. The memory unit may include, for example, a group of dynamic random access memory units. The memory unit is divided into memory channels and each of the memory channels is further divided into memory lines, each of the memory lines includes one or more buffers that correspond to the memory channels. The determination as to which of one or more buffers within a memory line an incoming information element is stored is based on factors such as the number of buffers pending to be read within each of the memory channels, the number of buffers pending to be written within each of the memory channels, and the number of buffers within each of the memory channels that has data written to it and is waiting to be read.
Owner:BAY MICROSYSTEMS INC
Method for Traffic Grooming, Wavelength Assignment and Spectrum Allocation
InactiveUS20120251117A1Easy to optimizeIncrease the number ofWavelength-division multiplex systemsTraffic groomingMultiplexing
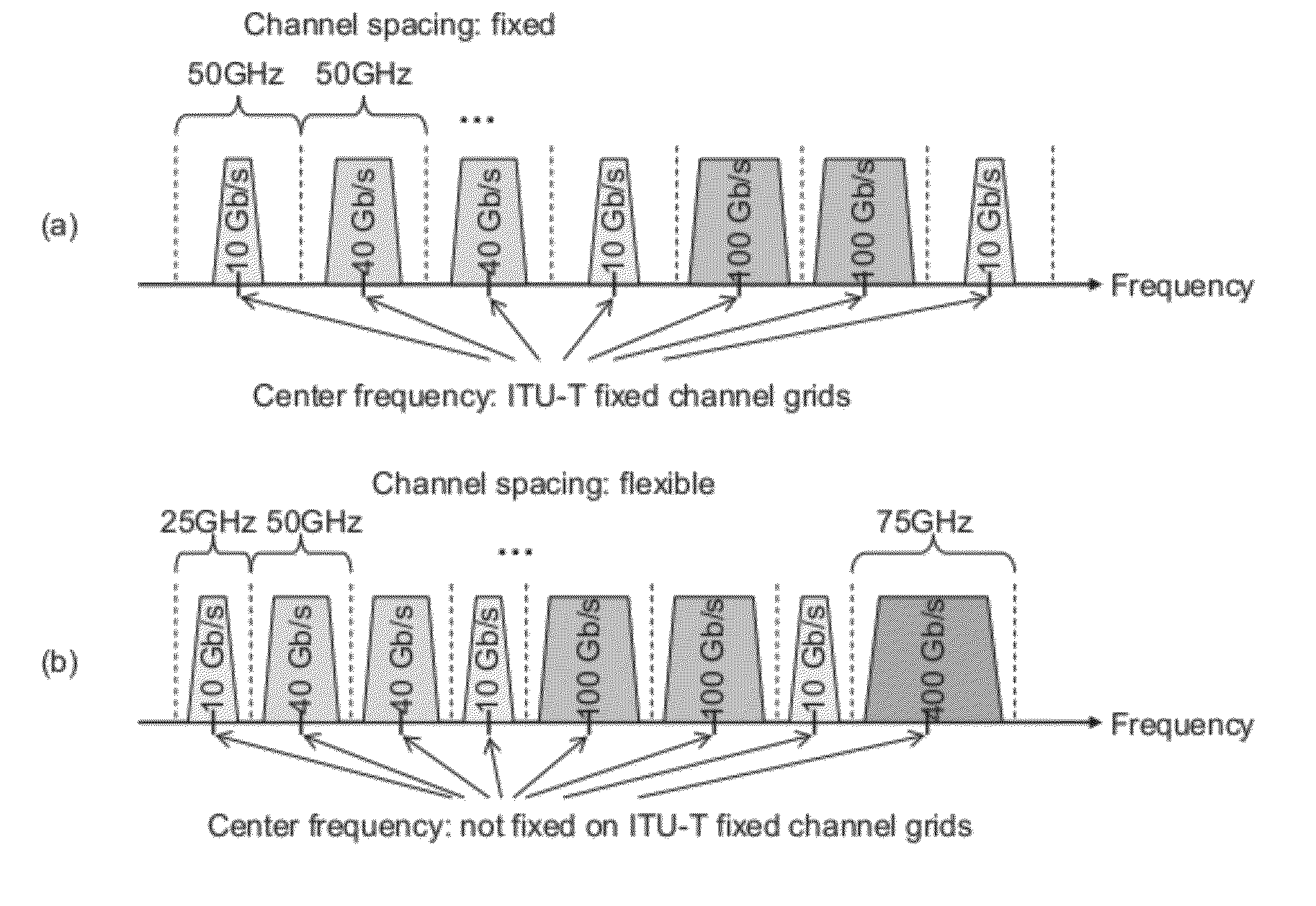
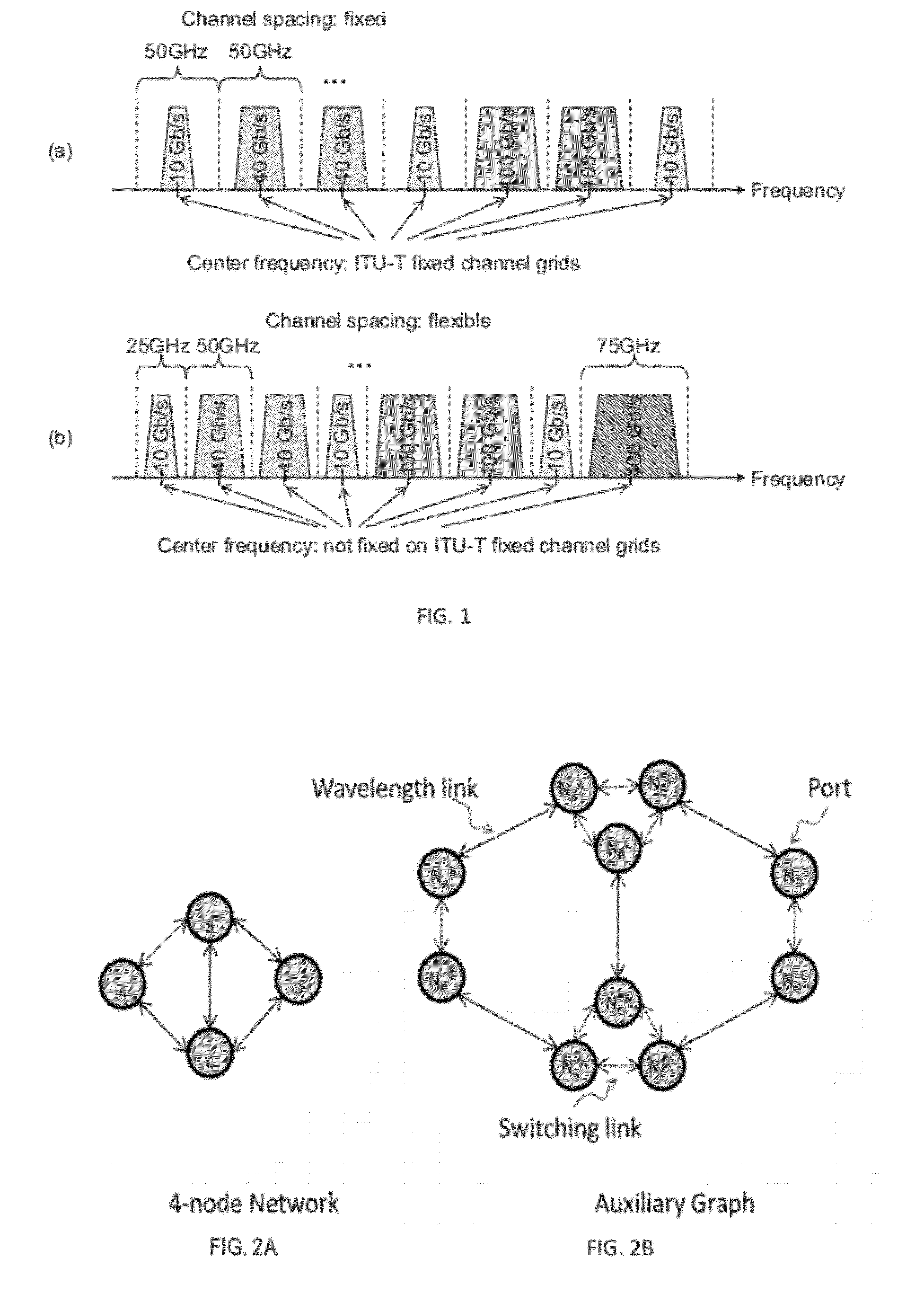
A method includes determining a line rate selection for a flexible optical wavelength-division-multiplexing WDM network, determining a traffic routing in said network, and determining simultaneously a channel routing, wavelength assignment and spectrum allocation in said network based on an auxiliary graph.
Owner:NEC CORP
Multi-rate transparent mux for optical communications networks
InactiveUS20080075113A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationLine rateData rate
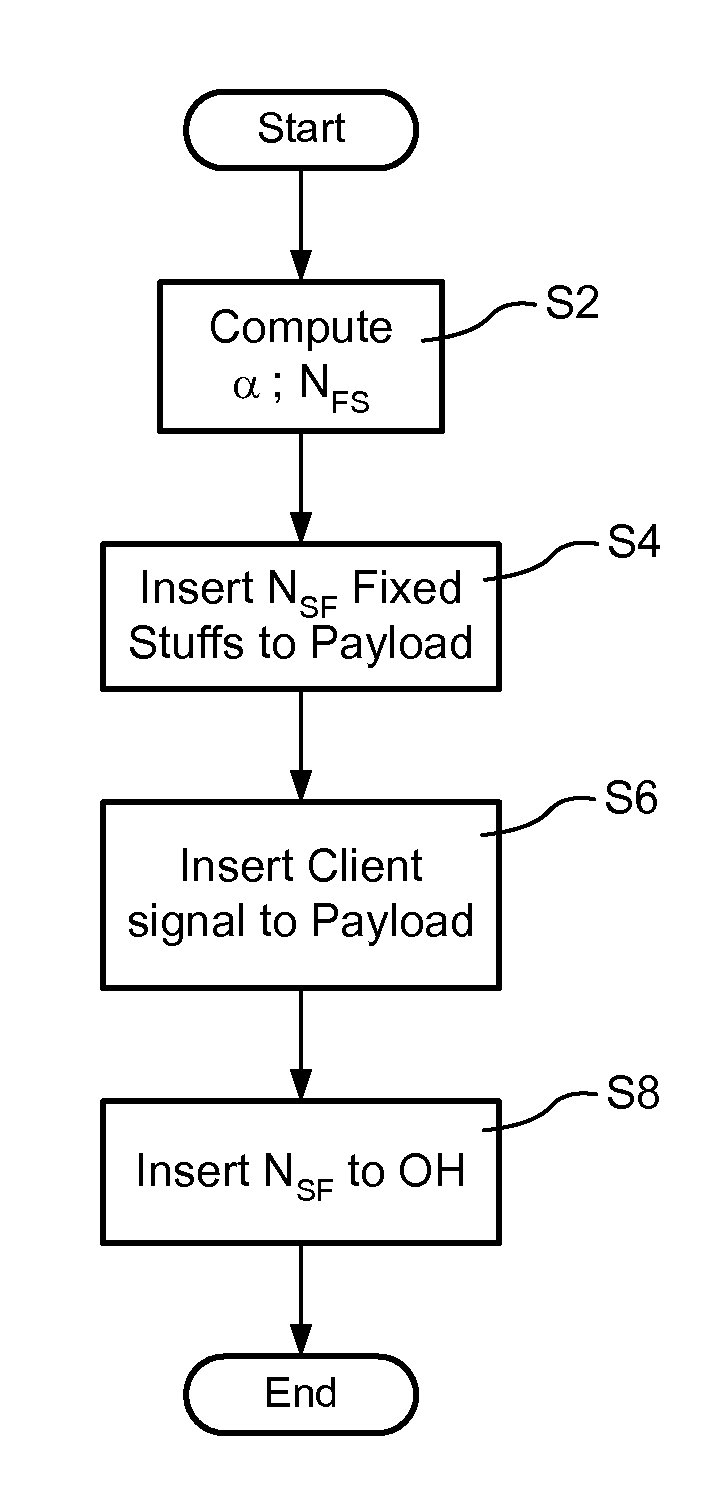
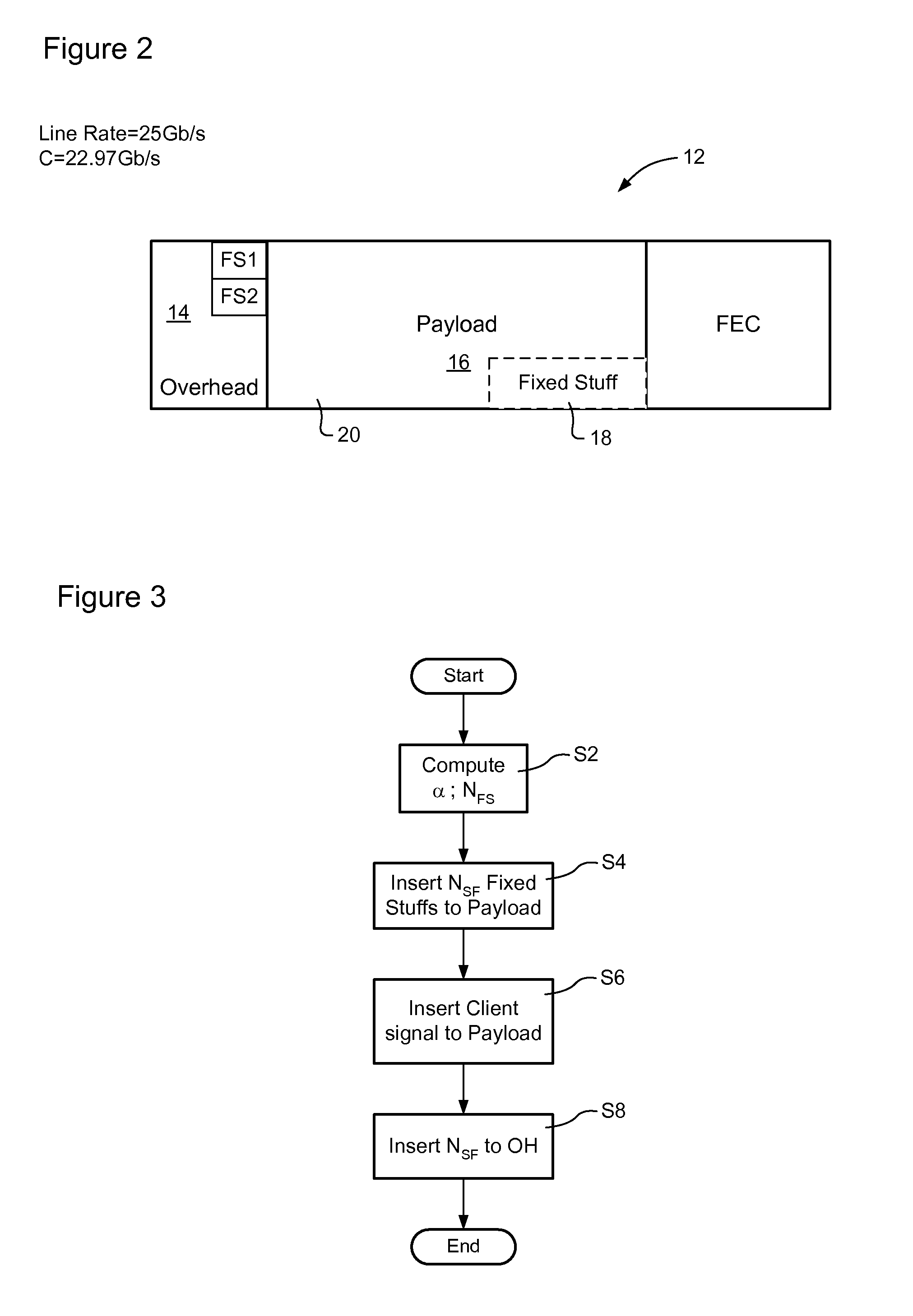
Bit-transparent muxing of an input signal for transport through an optical communications network. A fixed length container of the optical communications network is defined, which includes an overhead and a payload. A stuffing ratio (α) is based based on a line rate of the input signal and a data rate of the container. A number (NFS) of fixed stuffs is computed based on the stuffing ratio (α). The input signal and NFS fixed stuffs are inserted into the payload of the container, and the computed number NFS stored in the container's overhead. In some embodiments, the container is an overclocked OTU-3 (OTU3+) frame having a line rate of 44.6 Gb / s. This enables bit-transparent mux / demux of four nominal 10-Gig signals having line rates within a range of between 7.6 Gb / s and 10.4 Gb / s, or a single nominal 40-Gig signal having a line rate within a range of between 38.8 Gb / s and 41.6 Gb / s.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
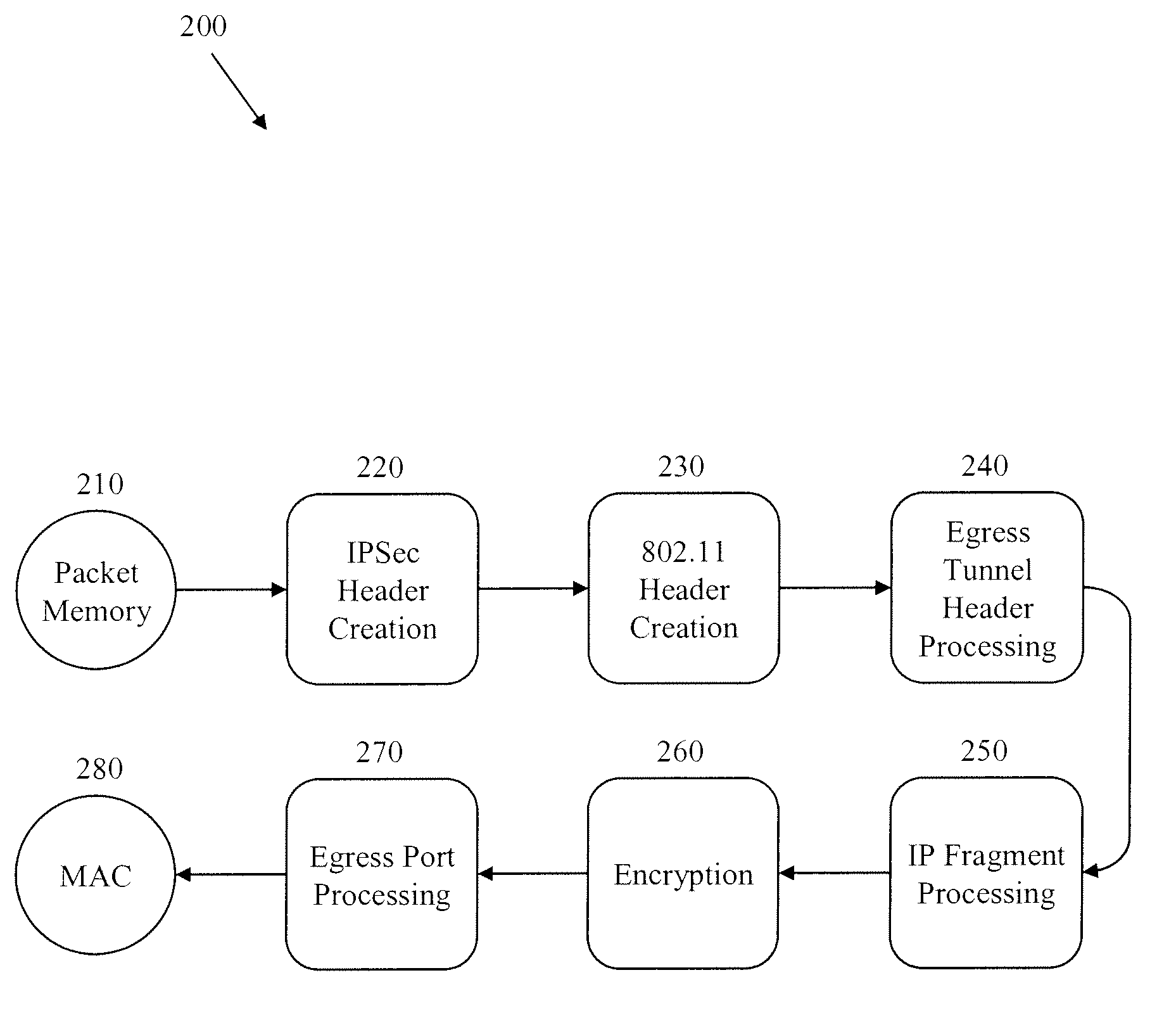
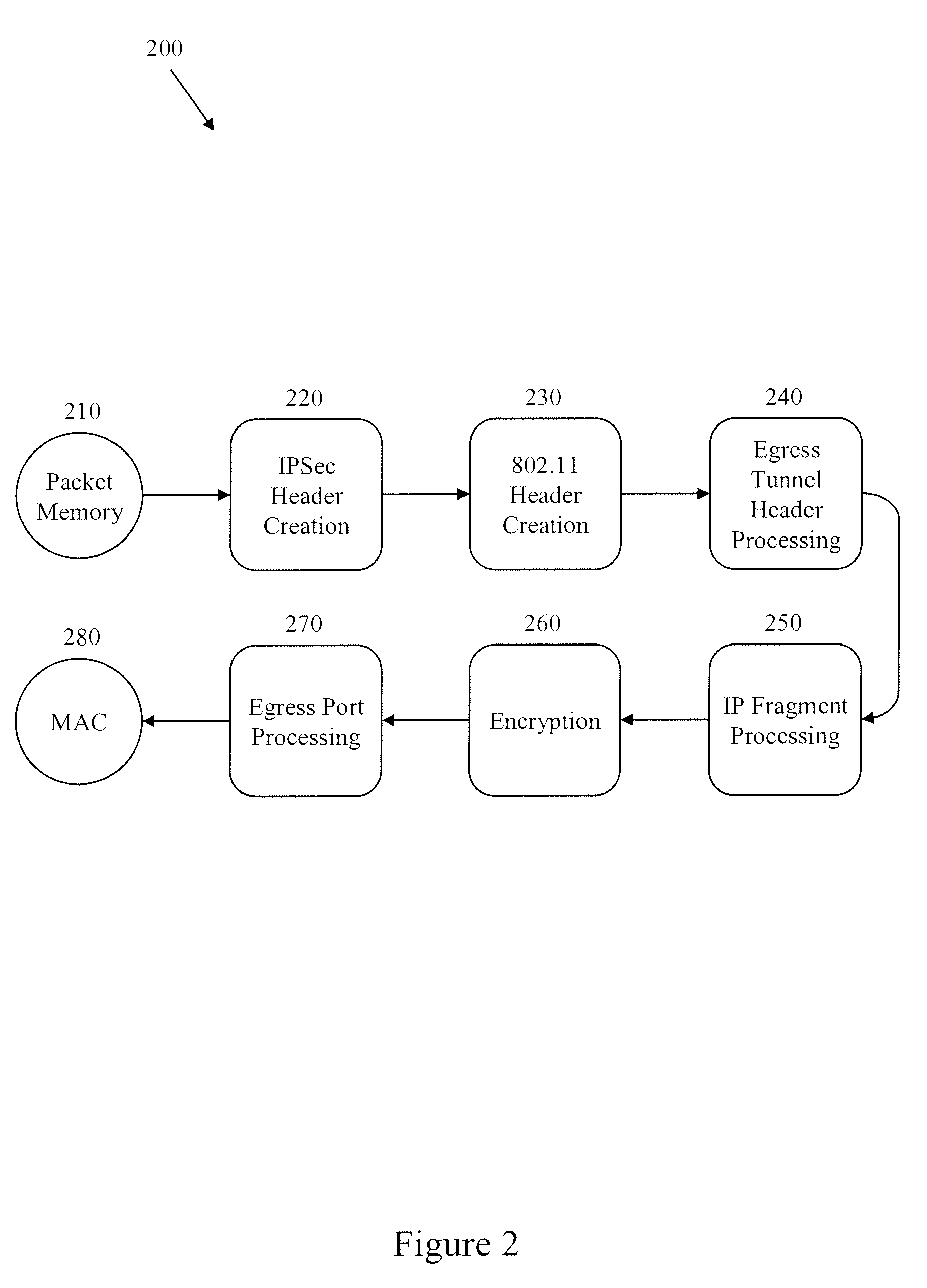
Methods and Systems for Fragmentation and Reassembly for IP Tunnels in Hardware Pipelines
A novel flow-through architecture for fragmentation and reassembly of tunnel packets in network devices is presented. The fragmentation and reassembly of tunneled packets are handled in the hardware pipeline to achieve line-rate processing of the traffic flow without the need for additional store and forward operations typically provided by a host processor or a co-processor. In addition, the hardware pipeline may perform fragmentation and reassembly of packets using encrypted tunnels by performing segment-by-segment crypto. A network device implementing fragment reassembly can include an ingress hardware pipeline that reassembles fragmented packets between a media access control (MAC) of the device and an output packet memory of the device, where the incoming fragmented packets can be encrypted and / or tunneled. A network device implementing packet fragmentation can include an egress hardware pipeline that fragments packets between an input packet memory of the device and the MAC, where the outgoing fragments can be encrypted and / or tunneled.
Owner:SINETT CORP
Line card port protection rate limiter circuitry
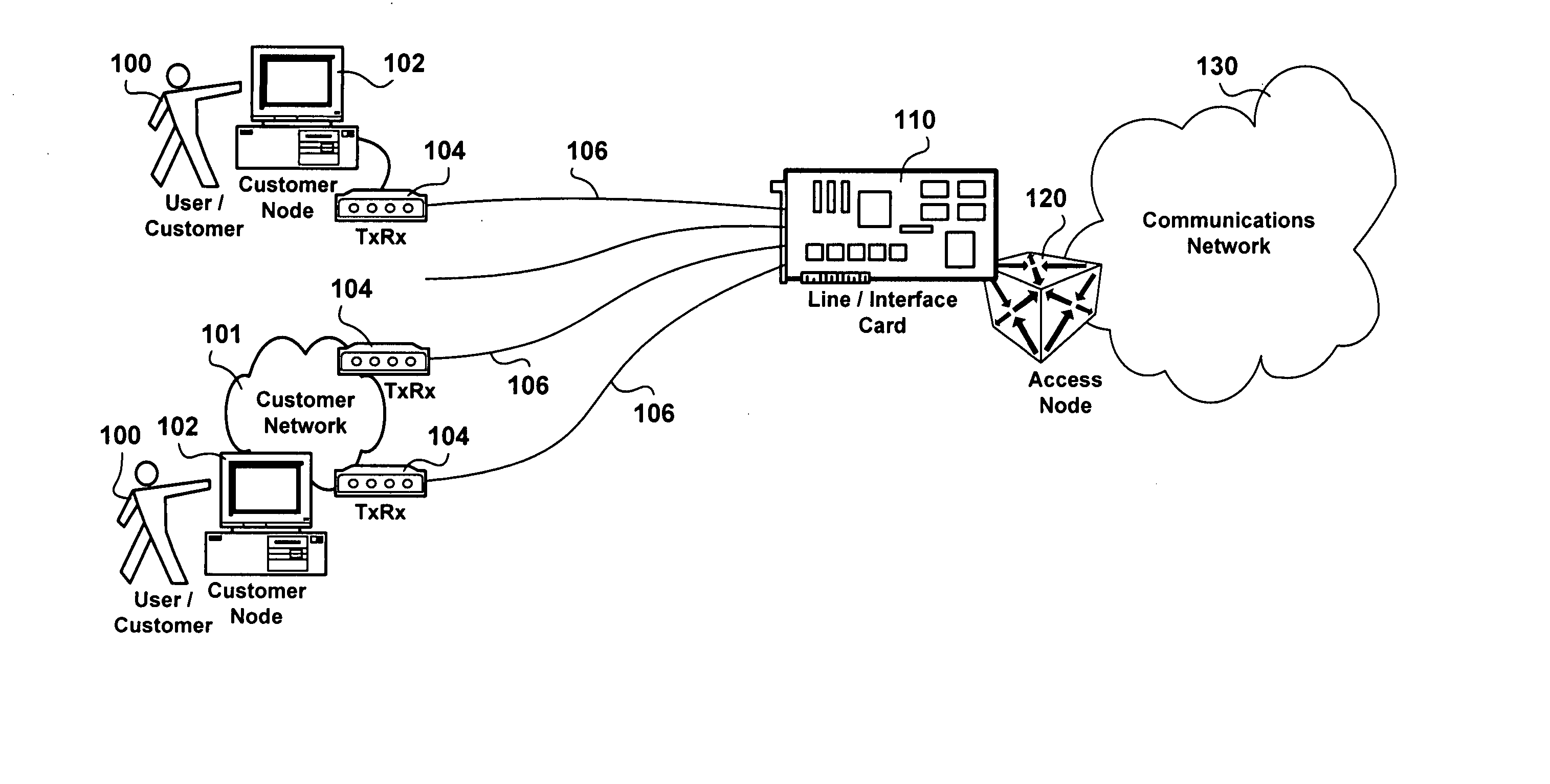
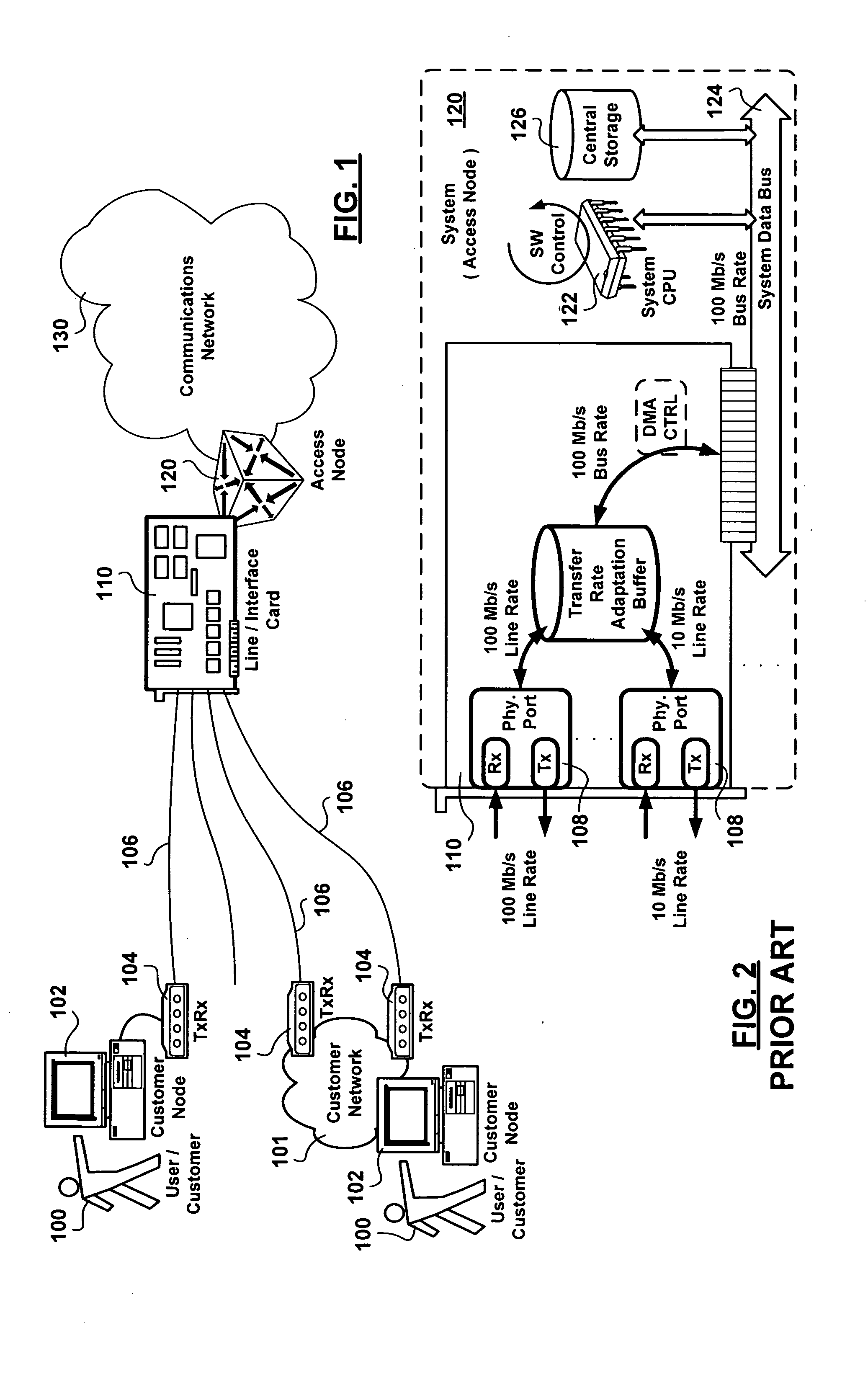
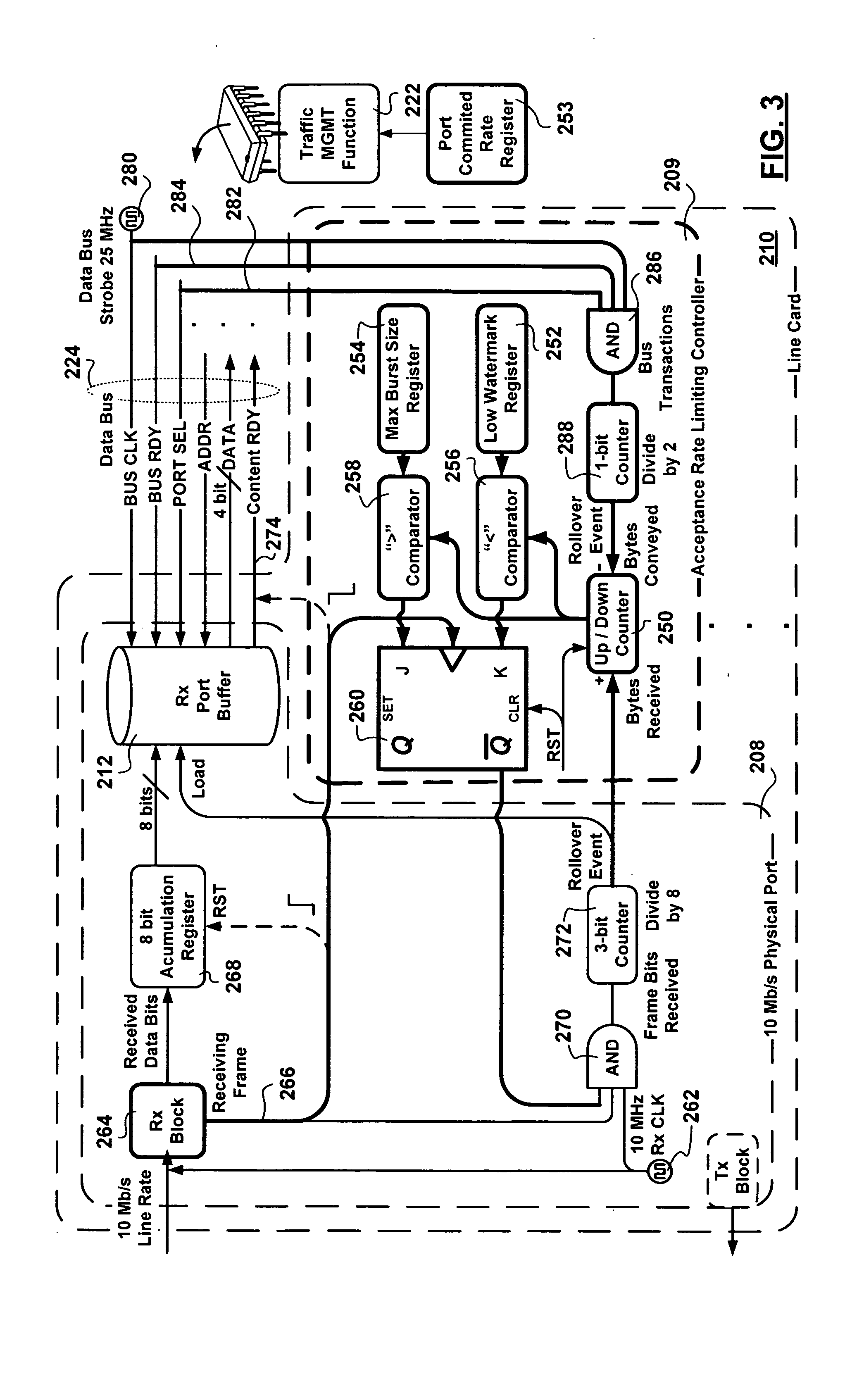
An apparatus for link layer port-based hardware implemented acceptance rate limiting control is presented. The apparatus employs a single up-down counter tracking a receive port buffer occupancy level. The single up-down counter is incremented by a receive line rate clock signal time truncated by a frame receive signal and a feedback frame acceptance control signal. The single up-down counter is decremented at an Service Level Agreement (SLA) agreed upon committed rate at which content is extracted from the receive port buffer. Outputs of comparators determining when the port receive buffer occupancy level is below a low watermark receive port buffer occupancy level, and when the receive port buffer occupancy level is above a maximum burst size, are provided to a master slave flip flop generating the frame acceptance control signal exhibiting hysteresis as the port receive buffer occupancy level transitions between the low watermark and the maximum burst size receive port buffer occupancy levels. The advantages of the link layer port-based hardware implemented acceptance rate limiting control achieved are derived from a deterministic response enforced in real time, at line rate, as content is being received employing a small number of logic gates.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
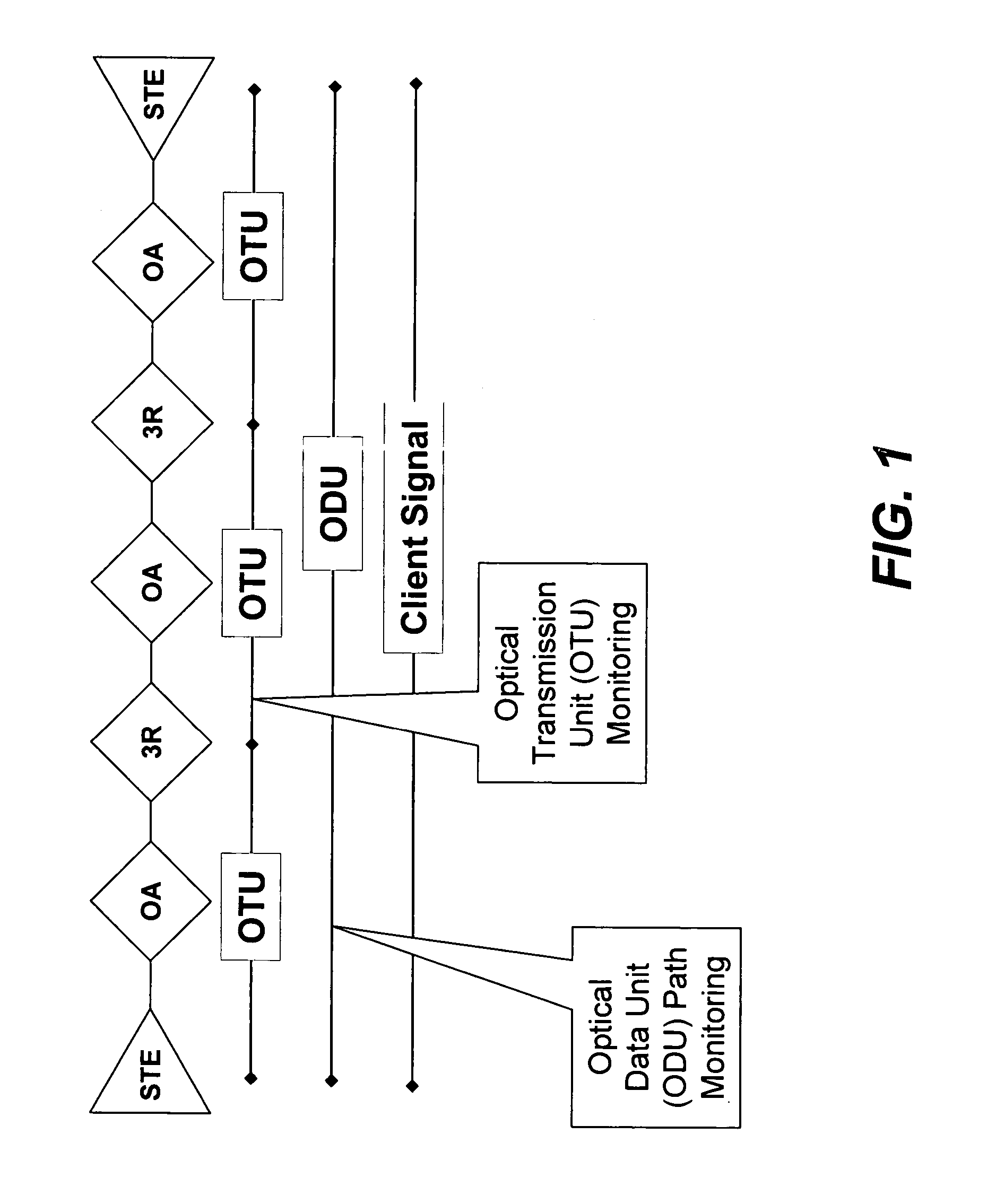
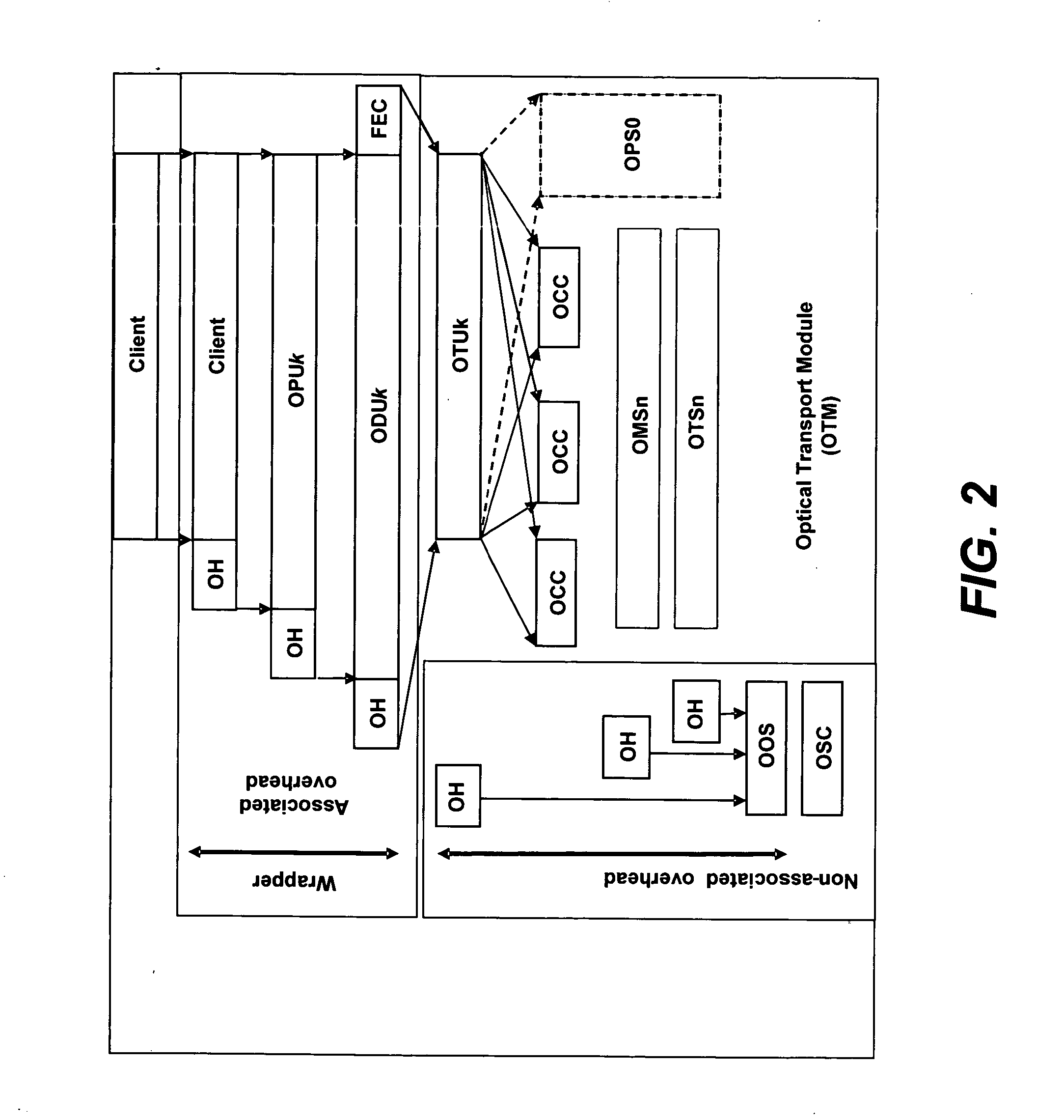
Optical transmission network with asynchronous mapping and demapping and digital wrapper frame for the same
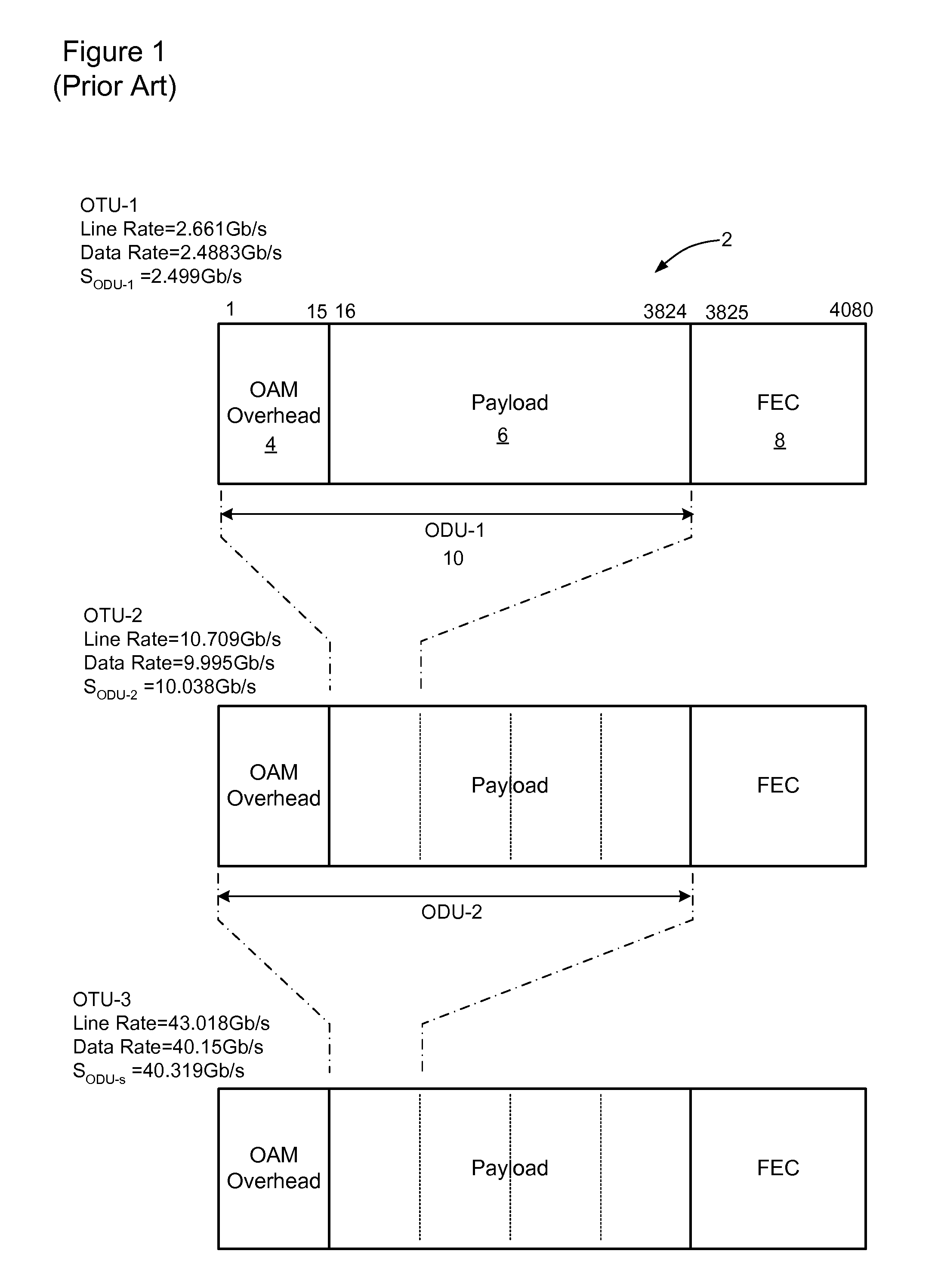
ActiveUS7286487B2Reduce manufacturing costLow costError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission protocolLine rate
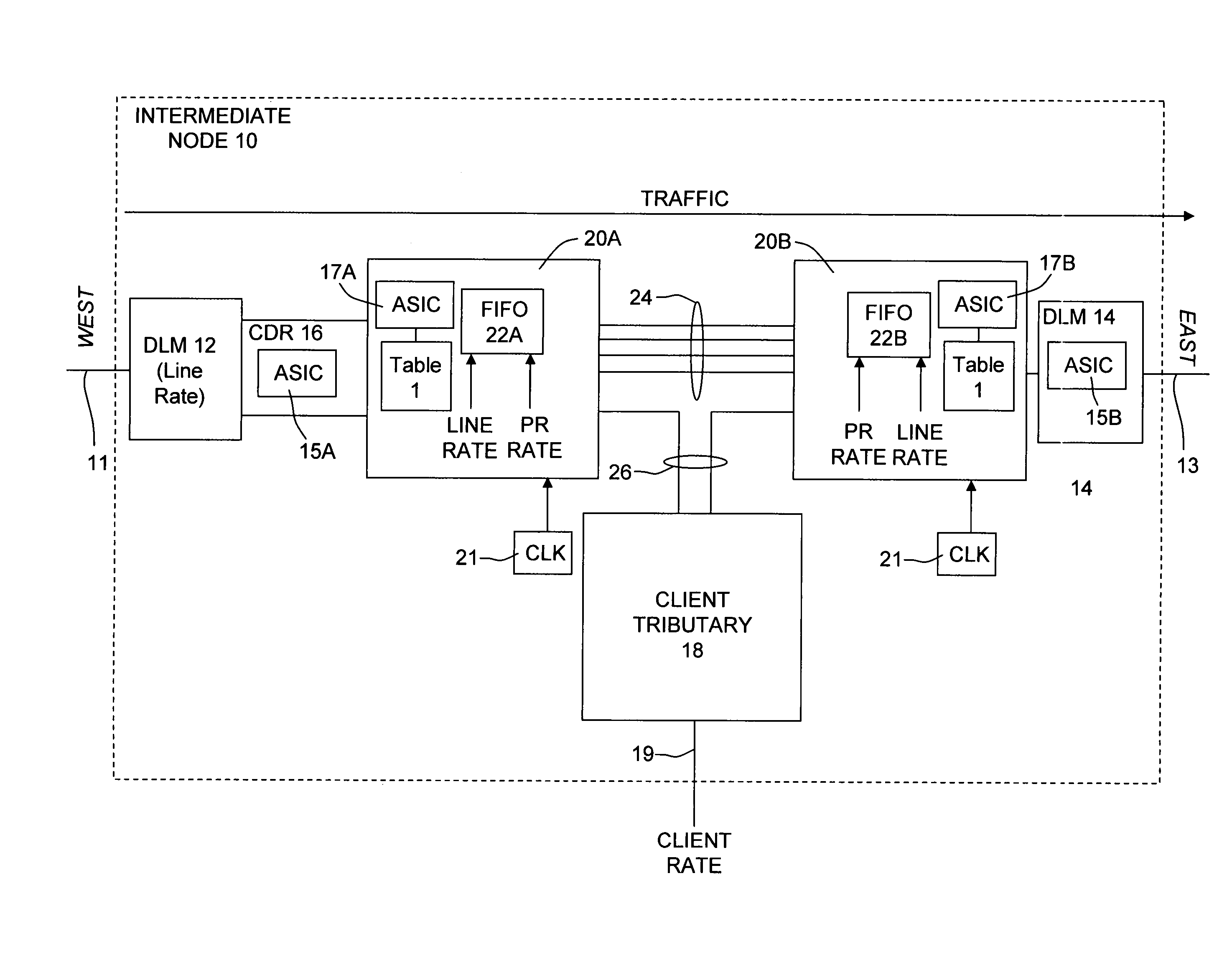
An optical transmission network is inherently asynchronous due to the utilization of a variable overhead ratio (V-OHR). The network architecture makes extensive use of OEO regeneration, i.e., deals with any electronic reconditioning to correct for transmission impairments, such as, for example, FEC encoding, decoding and re-encoding, signal reshaping, retiming as well as signal regeneration. The optical transmission network includes a plesiochronous clocking system with intermediate nodes designed to operate asynchronously with a single local frequency clock without complicated network synchronization schemes employing high cost clocking devices such as phase locked loop (PLL) control with crystal oscillators and other expensive system components. The asynchronous network operation provides for asynchronous remapping or remapping of any client signal utilizing any type of transmission protocol where the line side rate or frequency is always the same frequency for the payload signal and the local frequency at an intermediate node is set to a local reference clock in accordance with the payload type and its overhead ratio, i.e., the overhead ratio is varied to meet the desired difference between the line rate or frequency and the desired client signal payload rate or frequency for the particular client signal payload type.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Imaging engine employing planar light illumination and linear imaging
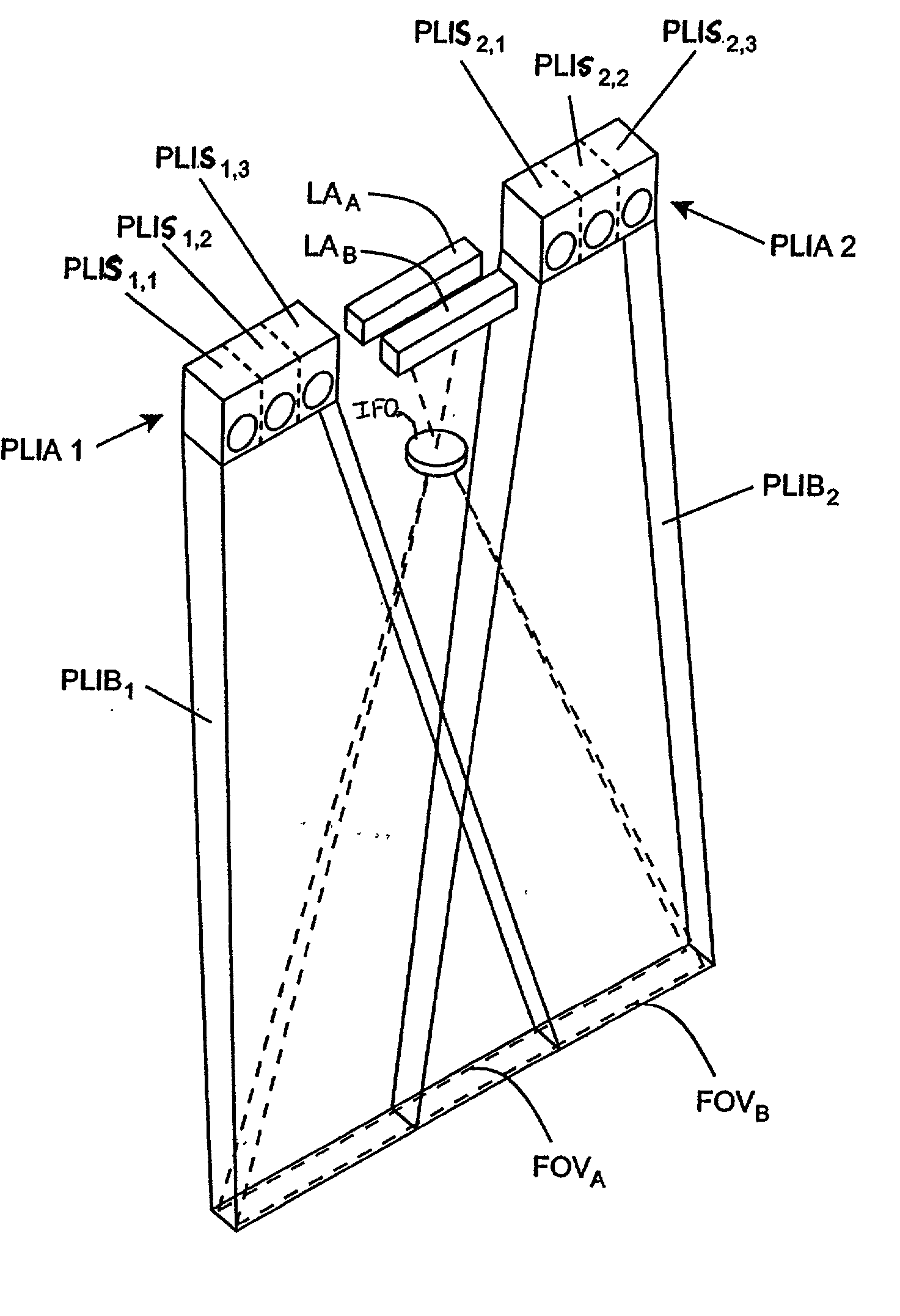
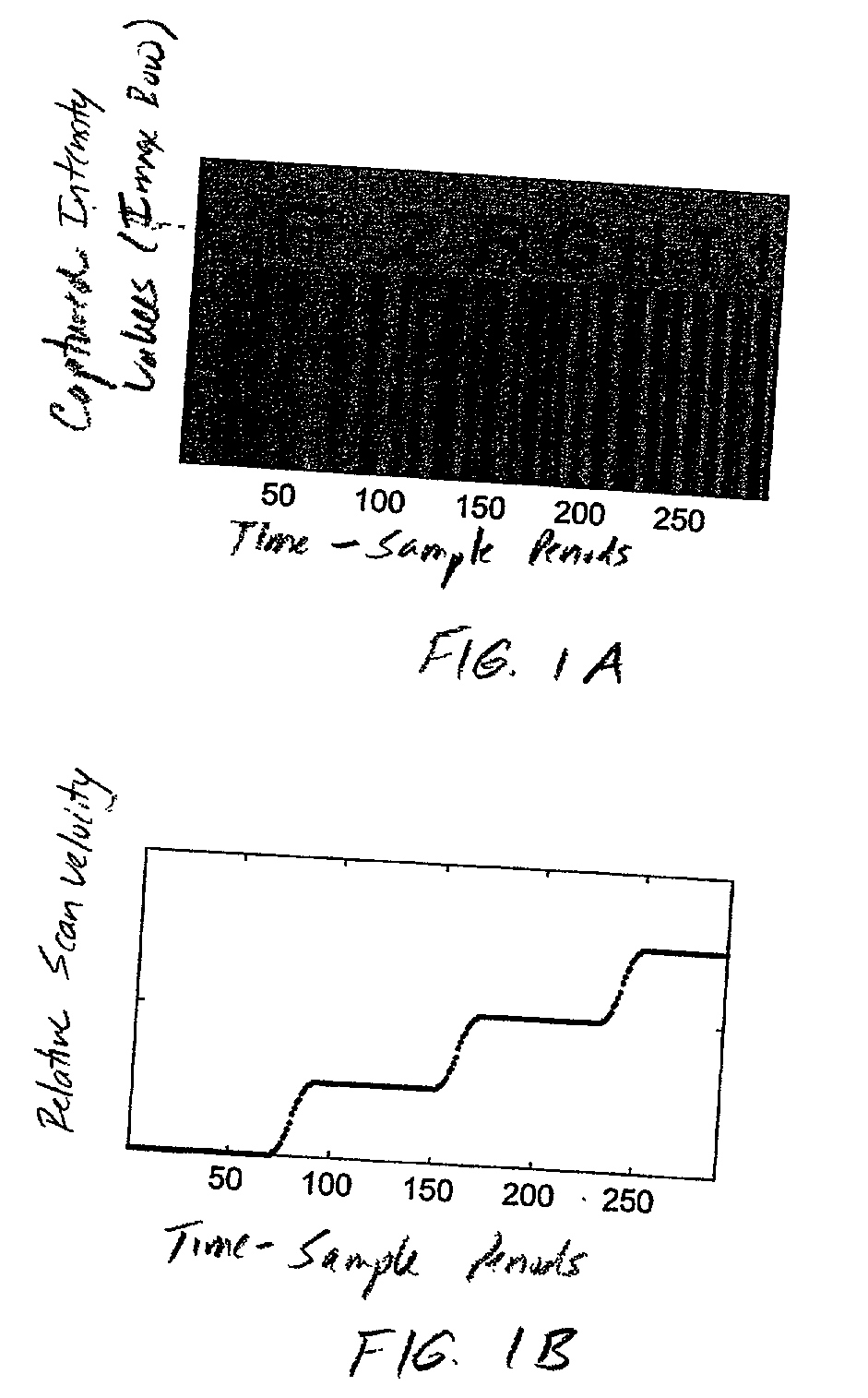
InactiveUS20030091244A1Low costReduce speckle noiseCharacter and pattern recognitionRecord carriers used with machinesTime signalImage based
An imaging engine includes a plurality of linear imaging arrays, image formation optics, at least one illumination module and supporting circuitry that are embodied within a modular engine housing. The plurality of linear imaging arrays and image formation optics are mounted on an optical bench (which is integral to the engine housing) and provide field of views corresponding to the plurality of linear image arrays. The at least one illumination module produces planar light illumination that substantially overlaps the field of views corresponding to the plurality of linear imaging arrays. The supporting circuitry includes: timing signal generation circuitry that supplies timing signals to the linear imaging arrays in order to read out the row image data produced by such arrays (such row image data may be read out at a constant line rate or at a variable line rate); illumination control circuitry that supplies current to the illumination sources in the at least one illumination module; analog-to-digital conversion circuitry, which optionally filters row data image signal supplied thereto (to remove unwanted noise components) and converts the row image data supplied thereto into digital form; and data buffering circuitry, for storing the digital row image data generated by the analog-to-digital conversion circuitry and communicating the row image data stored therein over a data communication bus. One linear image array (e.g., linear imaging array C) may have a variable line rate that is controlled by the timing signals supplied thereto such that the image capture operations performed by the one linear imaging array (e.g. linear imaging array C) maintain a substantially constant aspect ratio, to thereby compensate for aspect ratio distortions that result from variations in velocity of engine with respect to target object(s). The variable line rate is based upon velocity estimates derived from processing of the pixel data values of other linear imaging arrays disposed therein. The supporting circuitry may optionally include a line rate adjustment module, preferably realized as part of a programmed controller, that is operably coupled to timing signal generation circuitry and adjusts the variable line rate of the one linear image device (e.g., linear imaging array C); output illumination control module, preferably realized as part of the programmed controller, that is operably coupled to the illumination control circuitry and adjusts the optical power level and / or illumination time period for the illumination that overlaps one or more of the FOVs of the linear imaging arrays of the engine for speckle reduction / constant white levels; and / or imaging processing circuitry, operably coupled to the data buffering circuitry over the data communication bus, that realizes portions of image-based mechanisms / techniques for image velocity estimation, aspect ratio compensation, jitter estimation and compensation, bar code detection, OCR, and image lift.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
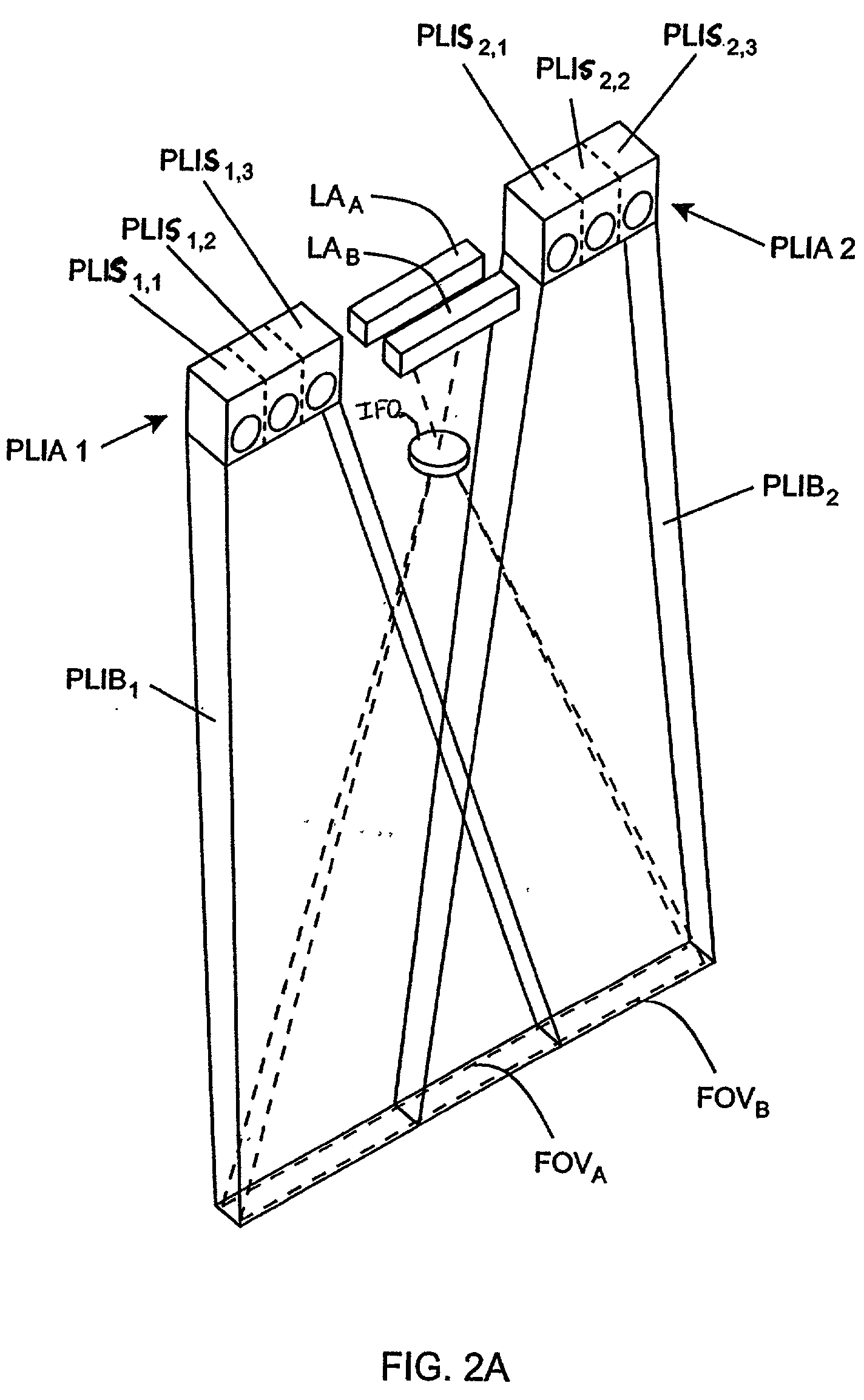
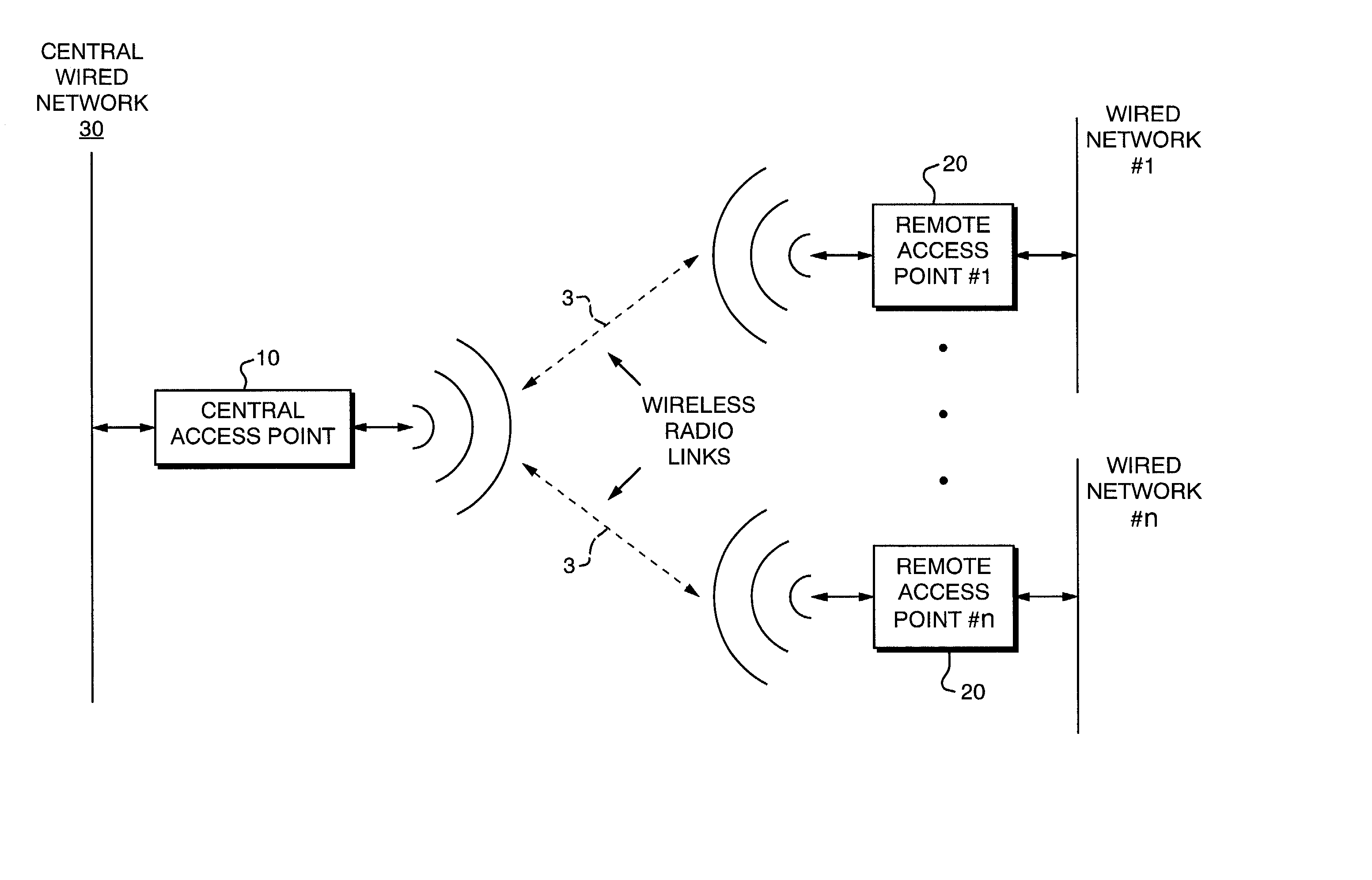
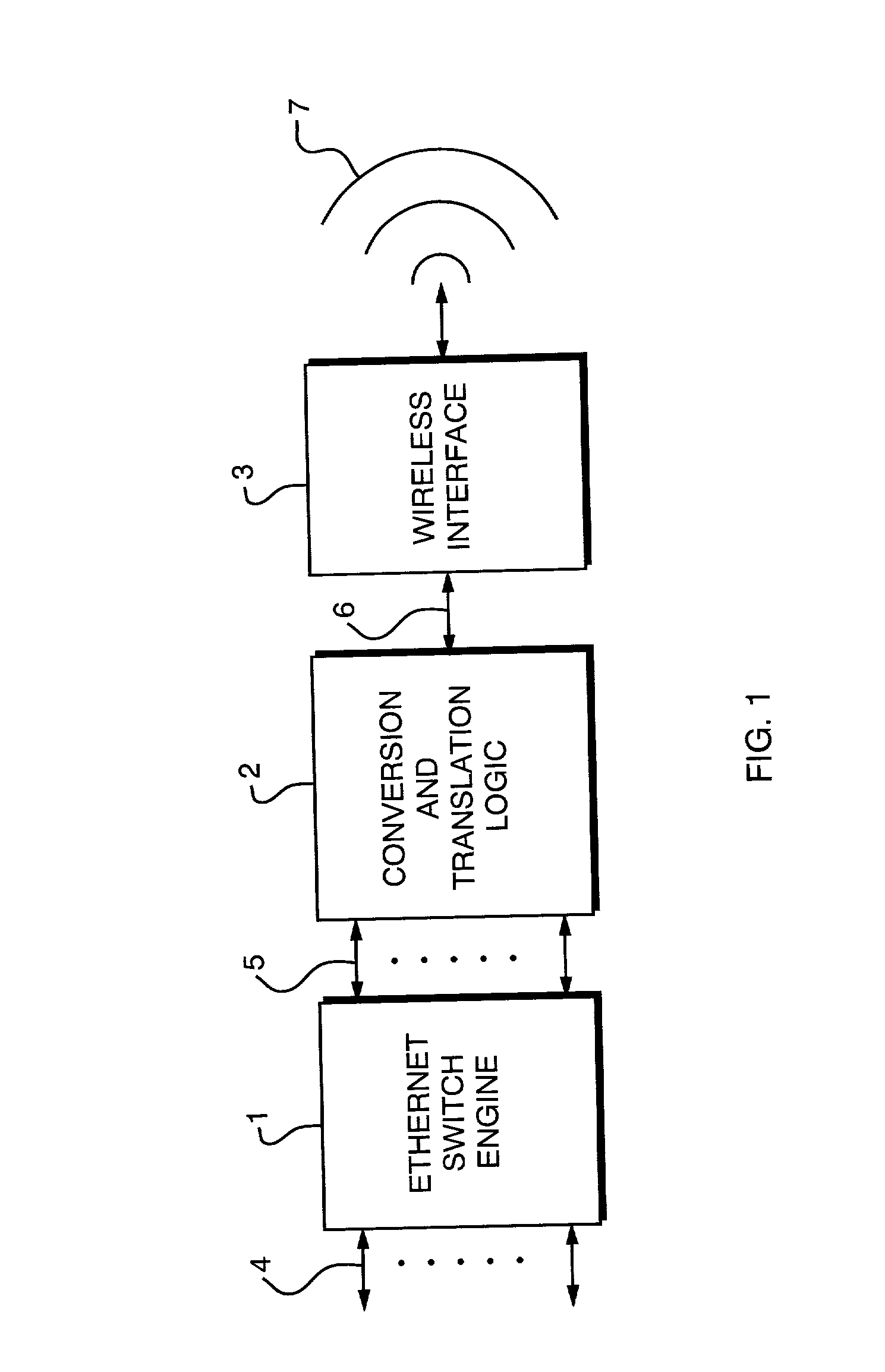
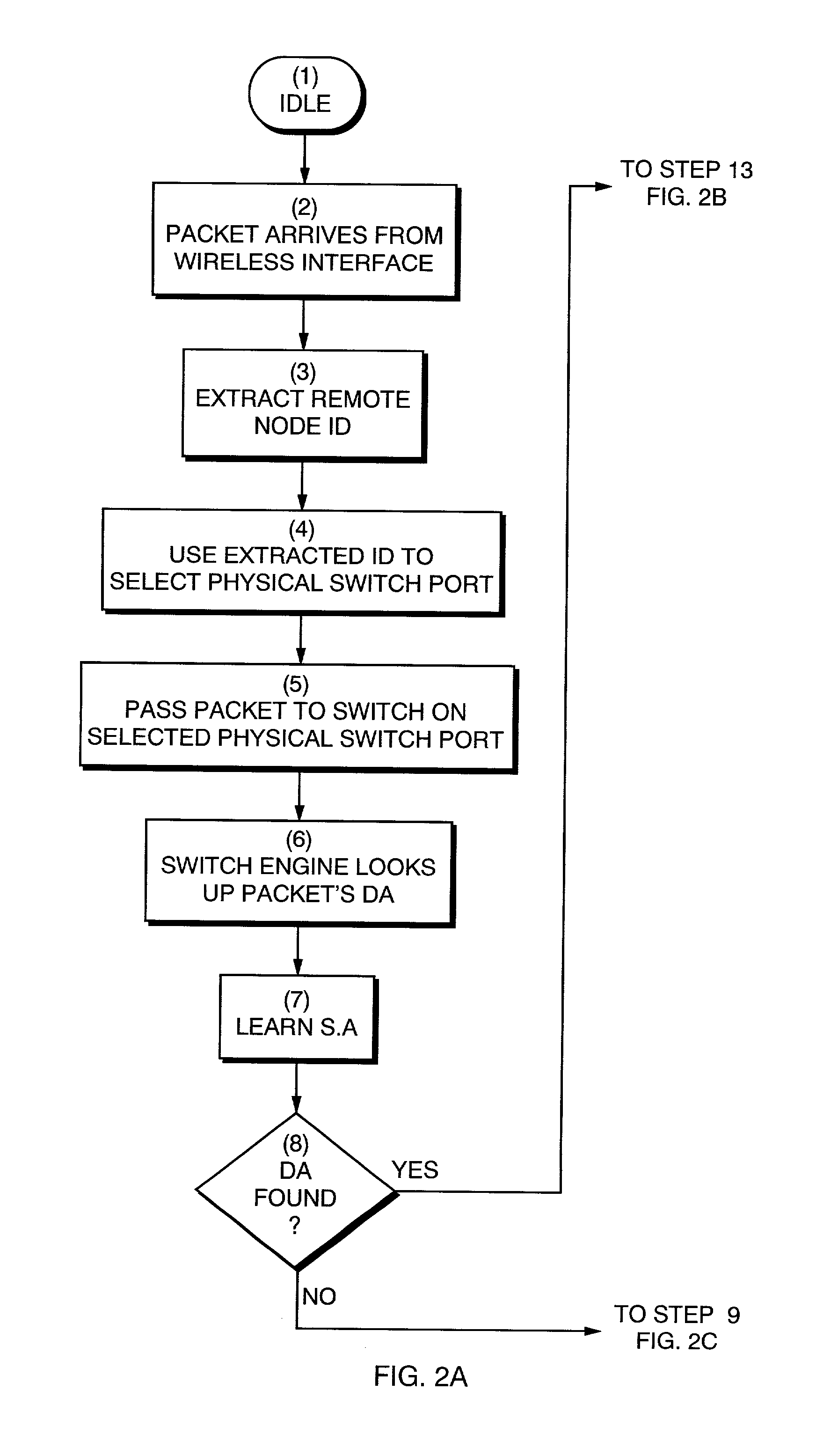
Method and apparatus for scalable, line-rate protocol-independent switching between multiple remote access points in a wireless local area network
The invention is a system and method to uniquely associate remote wireless Access Points using a switch engine. This is necessary in a multi-point wireless network where a central wireless Access Point must be able to receive packets from remote Access Points and then retransmit them, with a modified identifier, back to the wireless port from which they were received. By using available switch engine hardware this invention takes advantage of lower cost, higher performance and increased features in commodity parts. The invention resolves differences in common Ethernet switch engines that make them unsuitable for direct interface to wireless networks such as that defined by IEEE Standard 802.11 by using an aggregated set of physical ports on the switch engine. The method allows the switch engine to operate in its normal manner while satisfying the requirements for switching data packets between the Access Points in a multi-point configuration.
Owner:ENTERASYS NETWORKS
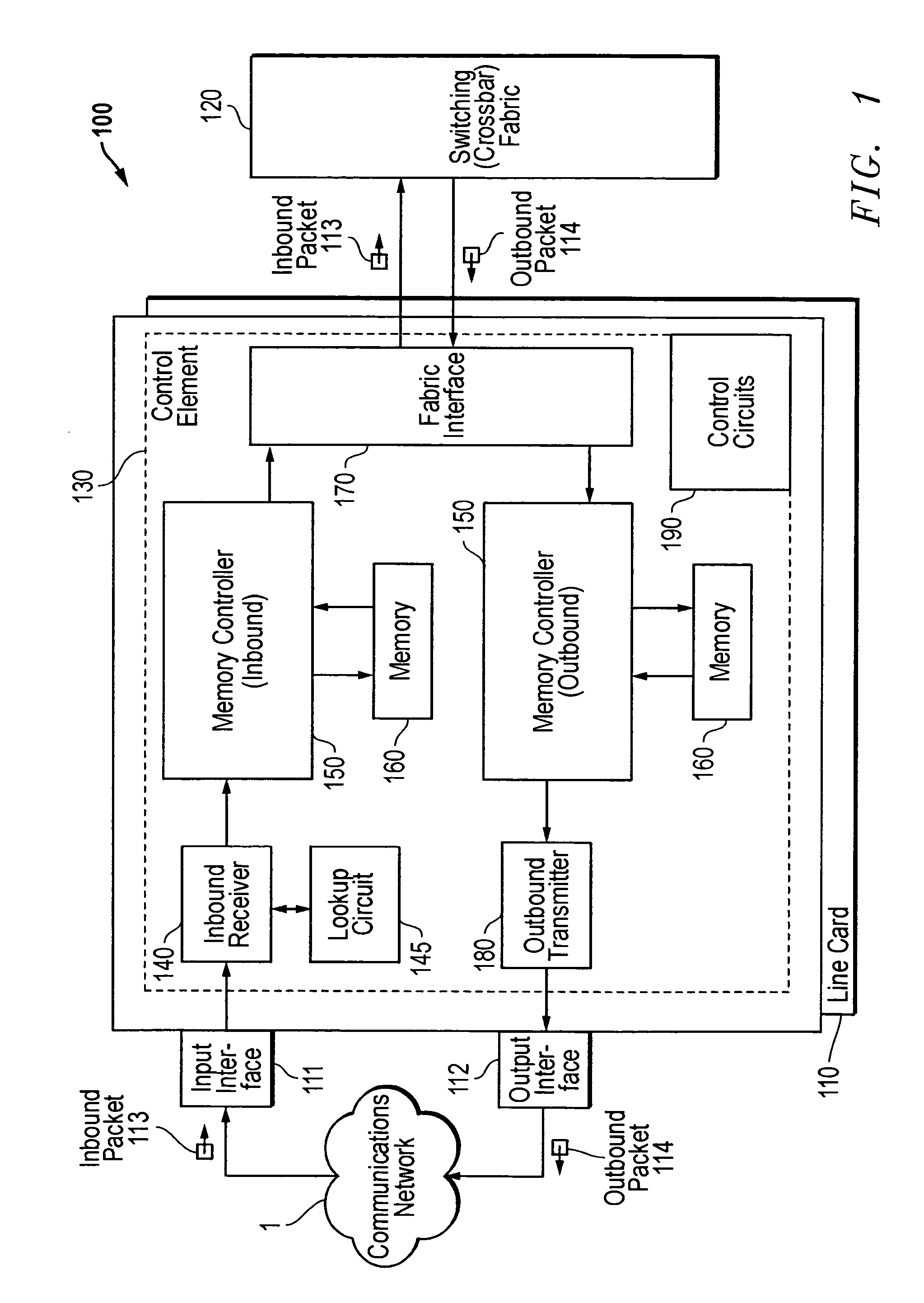
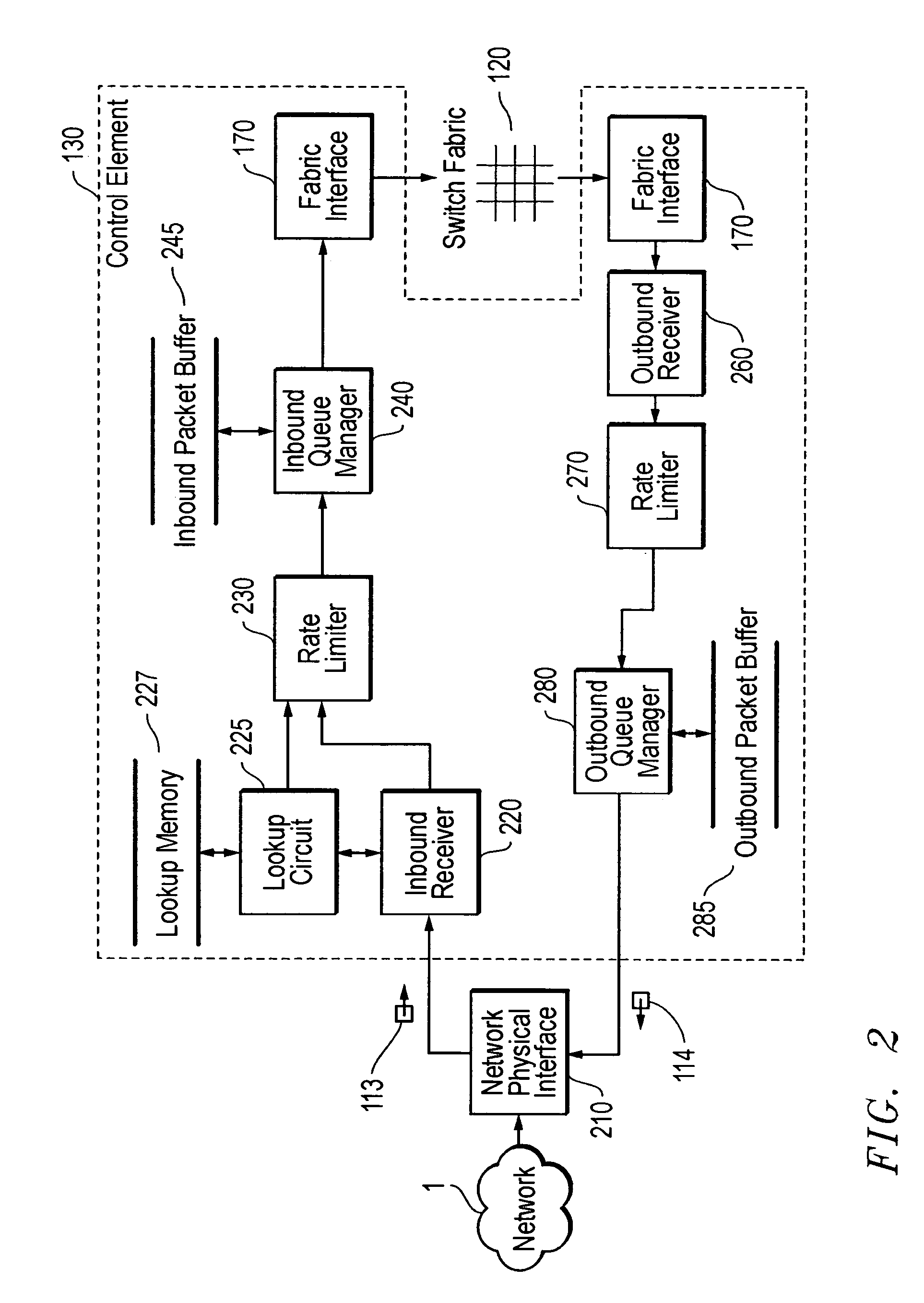
Architecture for high speed class of service enabled linecard
InactiveUS7558270B1High speed routingMinimal packet delaySpecial service provision for substationData switching by path configurationWire speedData stream
A linecard architecture for high speed routing of data in a communications device. This architecture provides low latency routing based on packet priority: packet routing and processing occurs at line rate (wire speed) for most operations. A packet data stream is input to the inbound receiver, which uses a small packet FIFO to rapidly accumulate packet bytes. Once the header portion of the packet is received, the header alone is used to perform a high speed routing lookup and packet header modification. The queue manager then uses the class of service information in the packet header to enqueue the packet according to the required priority. Enqueued packets are buffered in a large memory space holding multiple packets prior to transmission across the device's switch fabric to the outbound linecard. On arrival at the outbound linecard, the packet is enqueued in the outbound transmitter portion of the linecard architecture. Another large, multi-packet memory structure, as employed in the inbound queue manager, provides buffering prior to transmission onto the network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
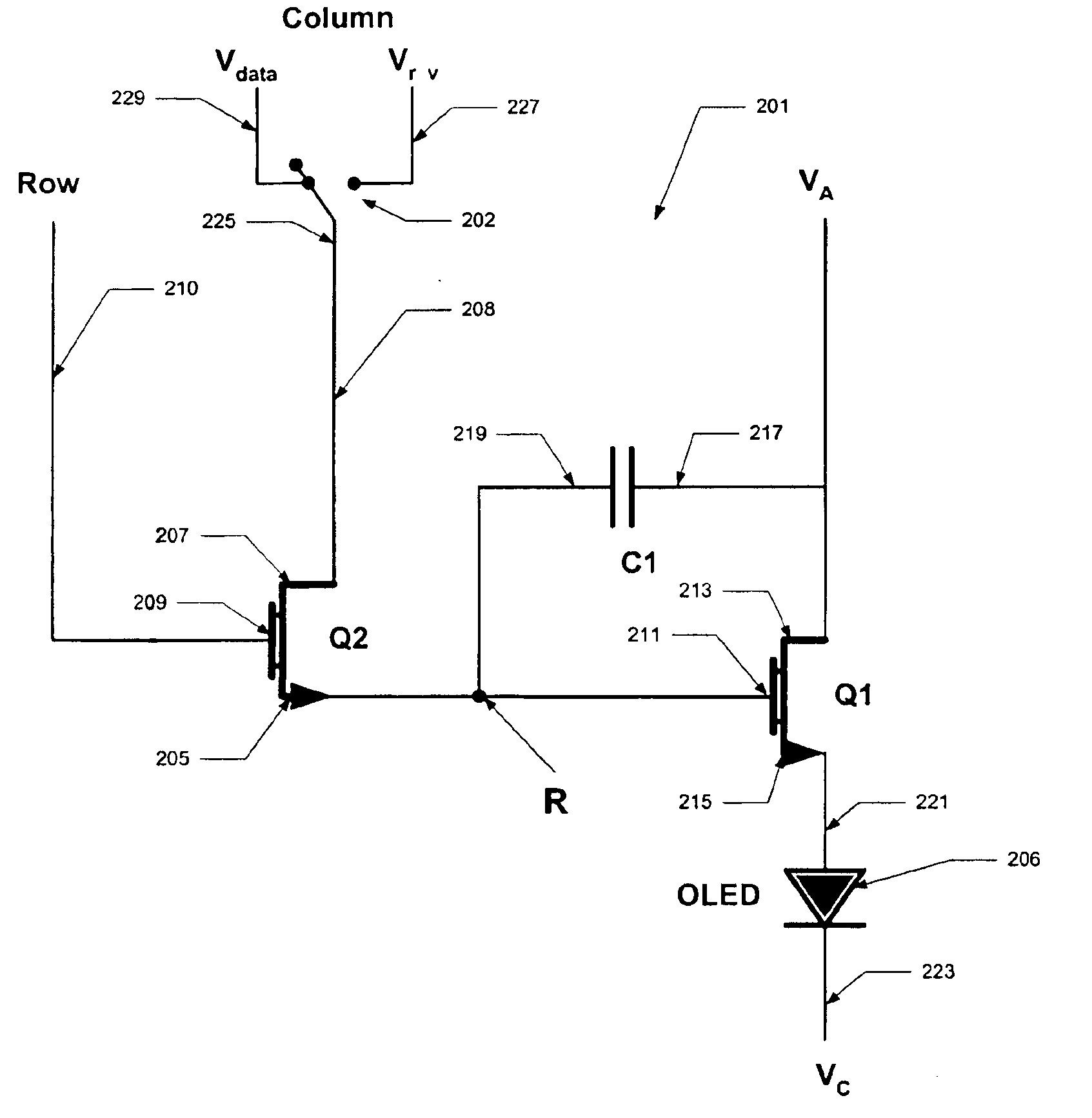
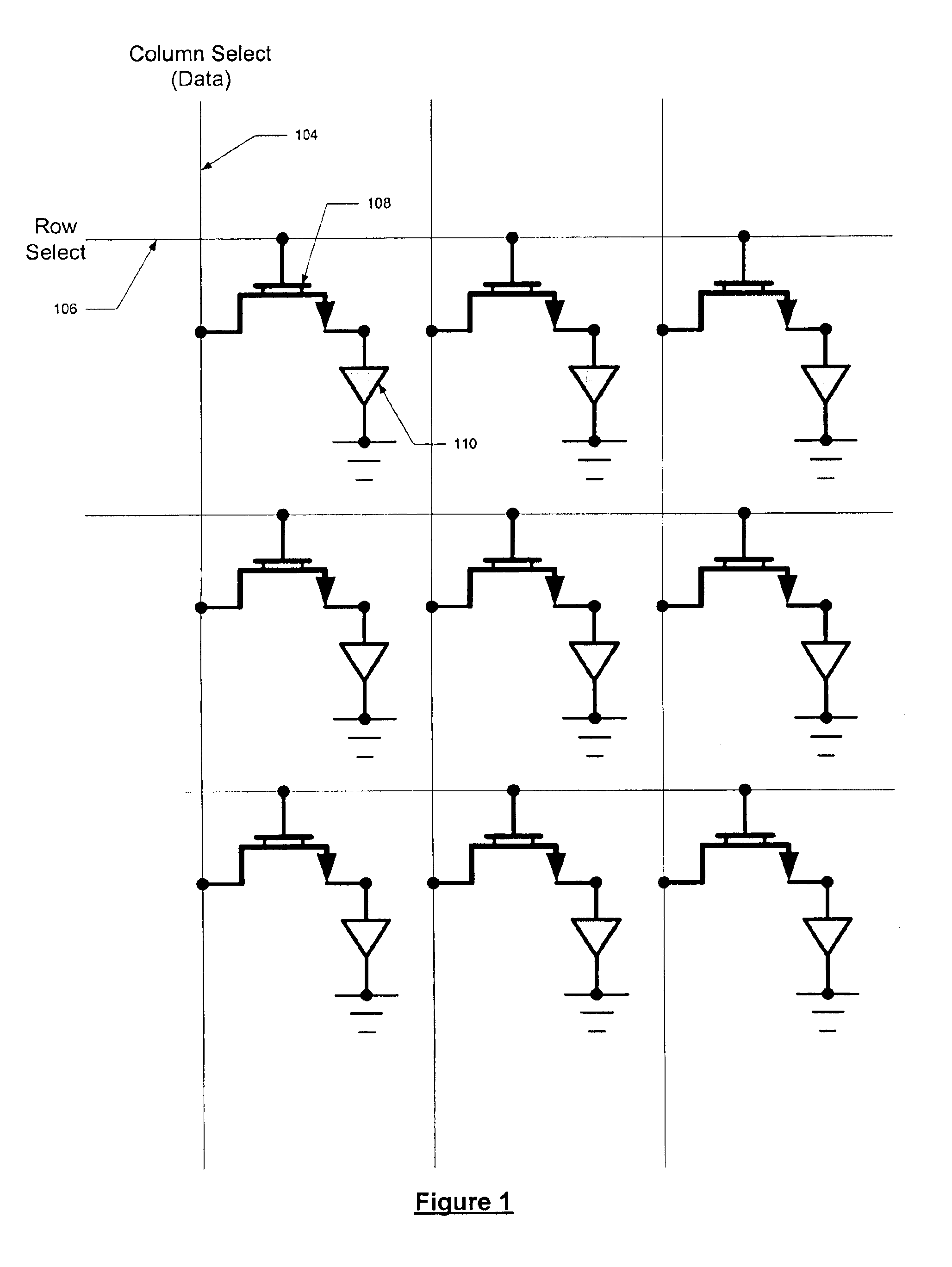
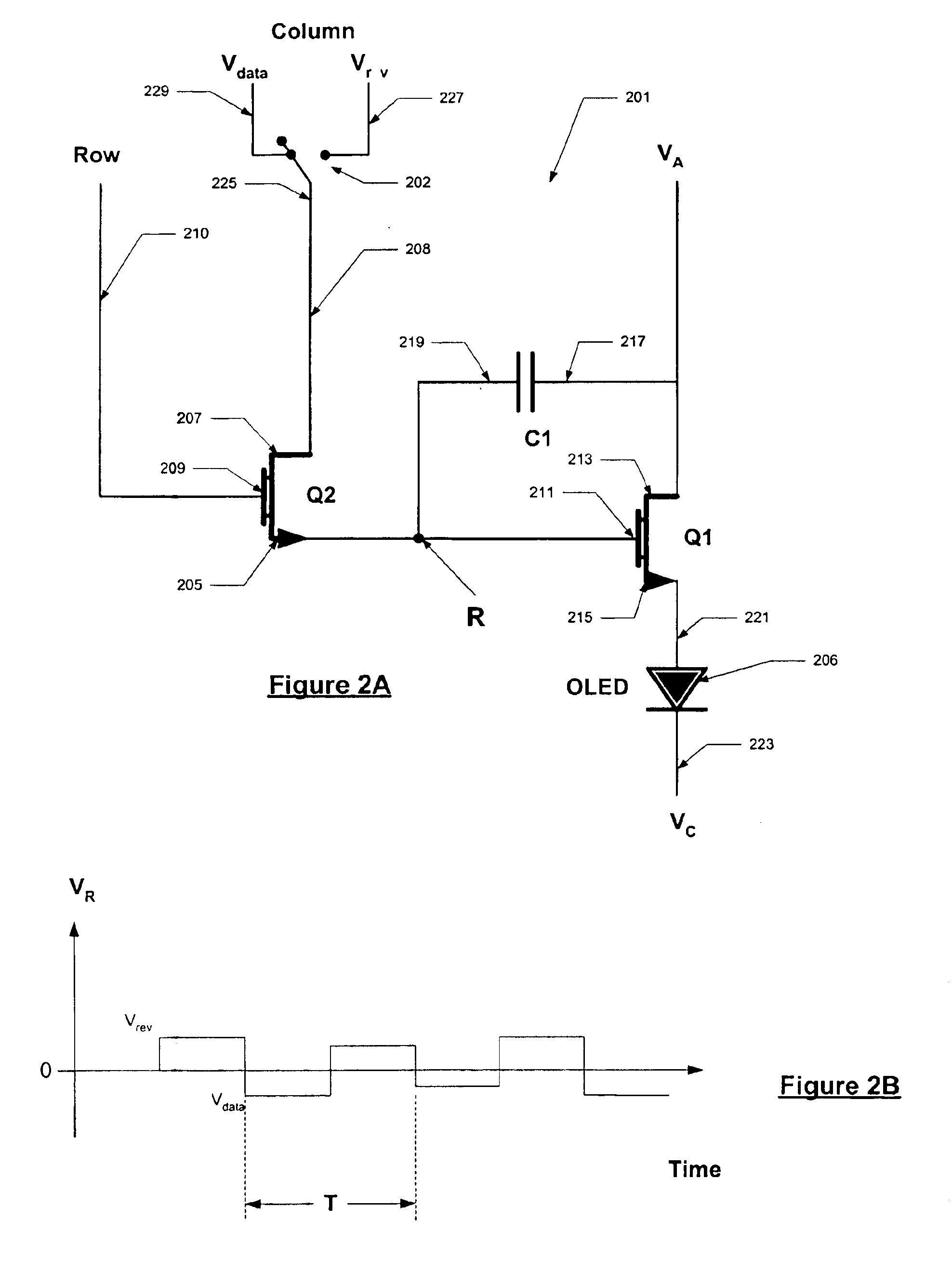
Method and system for stabilizing thin film transistors in AMOLED displays
InactiveUS6858989B2Reduce the impactReduce impactCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingControl signalActive matrix
An active matrix OLED display includes current driving TFT transistors to provide current to corresponding OLEDs. The control signals to each TFT gate include a data signal that is proportional to the desired luminance output for the OLED and a reverse data signal that is used to reverse bias the TFT to prevent threshold drift in the TFT. The data signal alteration is preformed either at a frame rate or at a line rate.
Owner:EMAGIN CORP
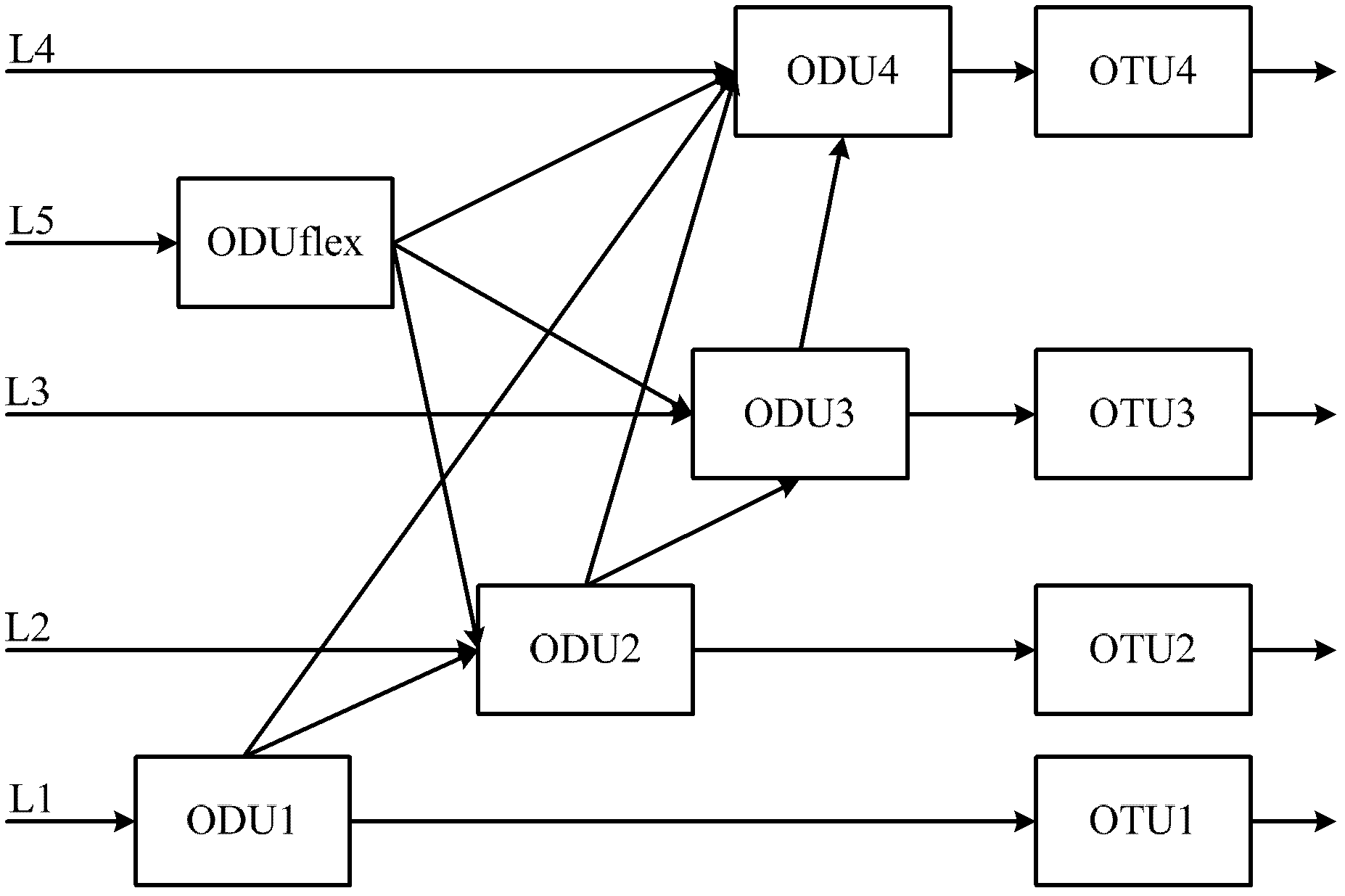
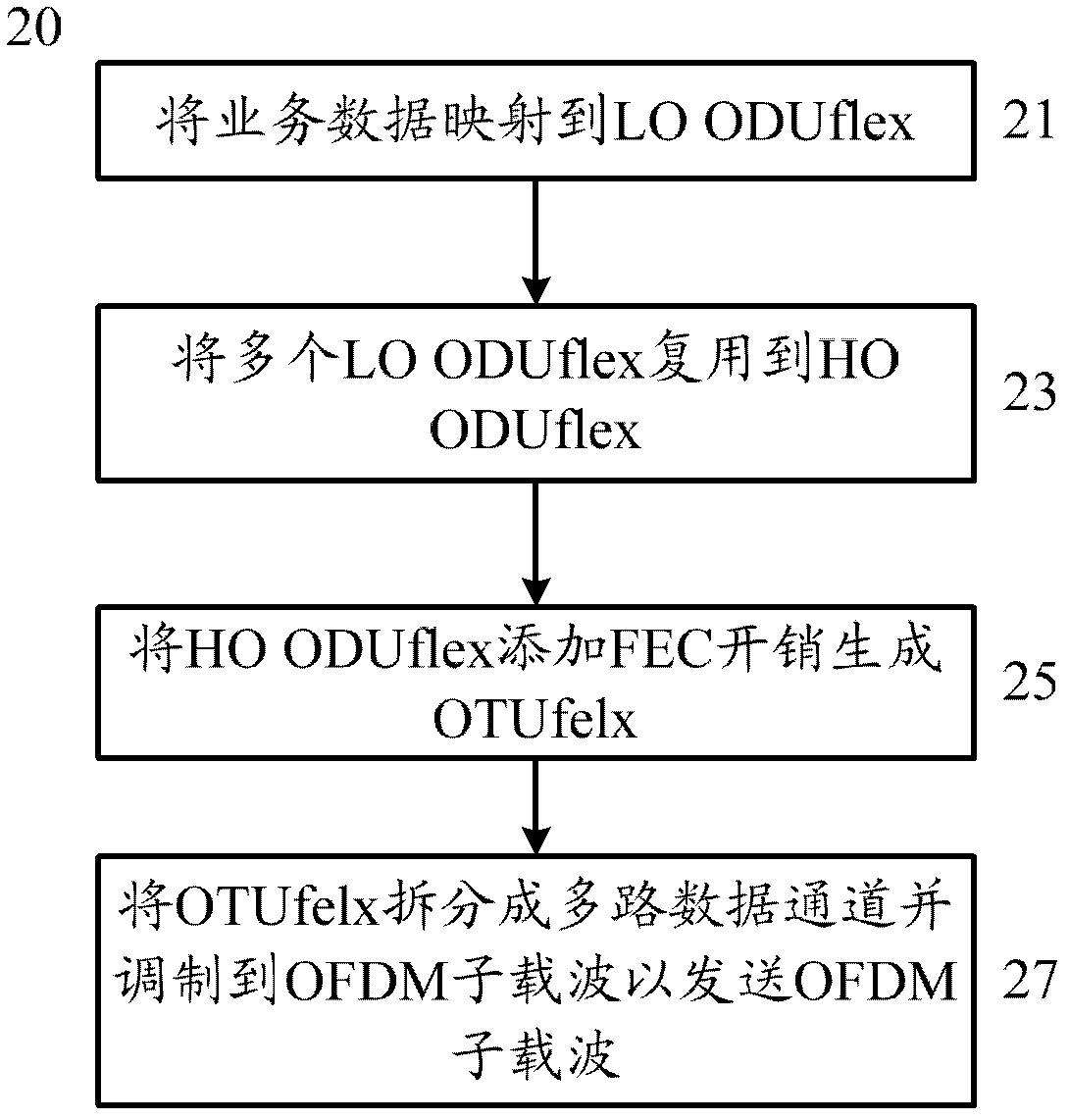
Method, device and system for transmitting business data on optical transmission network
The present invention provides a method, device and system for transmitting business data on optical transmission network, wherein the method comprises: the business data is mapped as a low order and flexible optical channel data unit,a plurality of low order and flexible optical channel data units are multiplexed as the high orderand flexible optical channel data units which are added with FEC expenditure so as to generate the flexible optical channel transmission units,and the flexible optical channel transmission units are divided into multi-channel data channel signals and are modulated to an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing sub carrier to send the orthogonal frequency division multiplexing sub carrier. The technical scheme can provide flexible optical channel transmission units so as to make the network adapt the business data as flexible and changable optical transmission network line rate through the network, and can realize the requirements for transmitting the business data with various rates so as to adapt the optical transmission network to the higher rate.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
High Performance, High Bandwidth Network Operating System
InactiveUS20120039336A1Reduce memory usageReduce context switchingData switching by path configurationProgram controlNetwork operating systemOperational system
The present subject matter relates to computer operating systems, network interface cards and drivers, CPUs, random access memory and high bandwidth speeds. More specifically, a Linux operating system has specially-designed stream buffers, polling systems interfacing with network interface cards and multiple threads to deliver high performance, high bandwidth packets through the kernel to applications. A system and method are provided for capturing, aggregating, pre- analyzing and delivering packets to user space within a kernel to be primarily used by intrusion detection systems at multi-gigabit line rate speeds.
Owner:RICHMOND ALFRED +2
Systems and methods for implementing host-based security in a computer network
An architecture for implementing host-based security such that data security may be applied whenever the confidential data leaves a host computer or a networked device. The improved method and architecture may be implemented in a single integrated circuit for speed, power consumption, and space-utilization reasons. Within the integrated circuit, a combination of hardware-implemented, network processor-implemented, and software-implemented functions may be provided. The innovative host-based security architecture may offer line-rate IPSec acceleration, TCP acceleration, or both.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
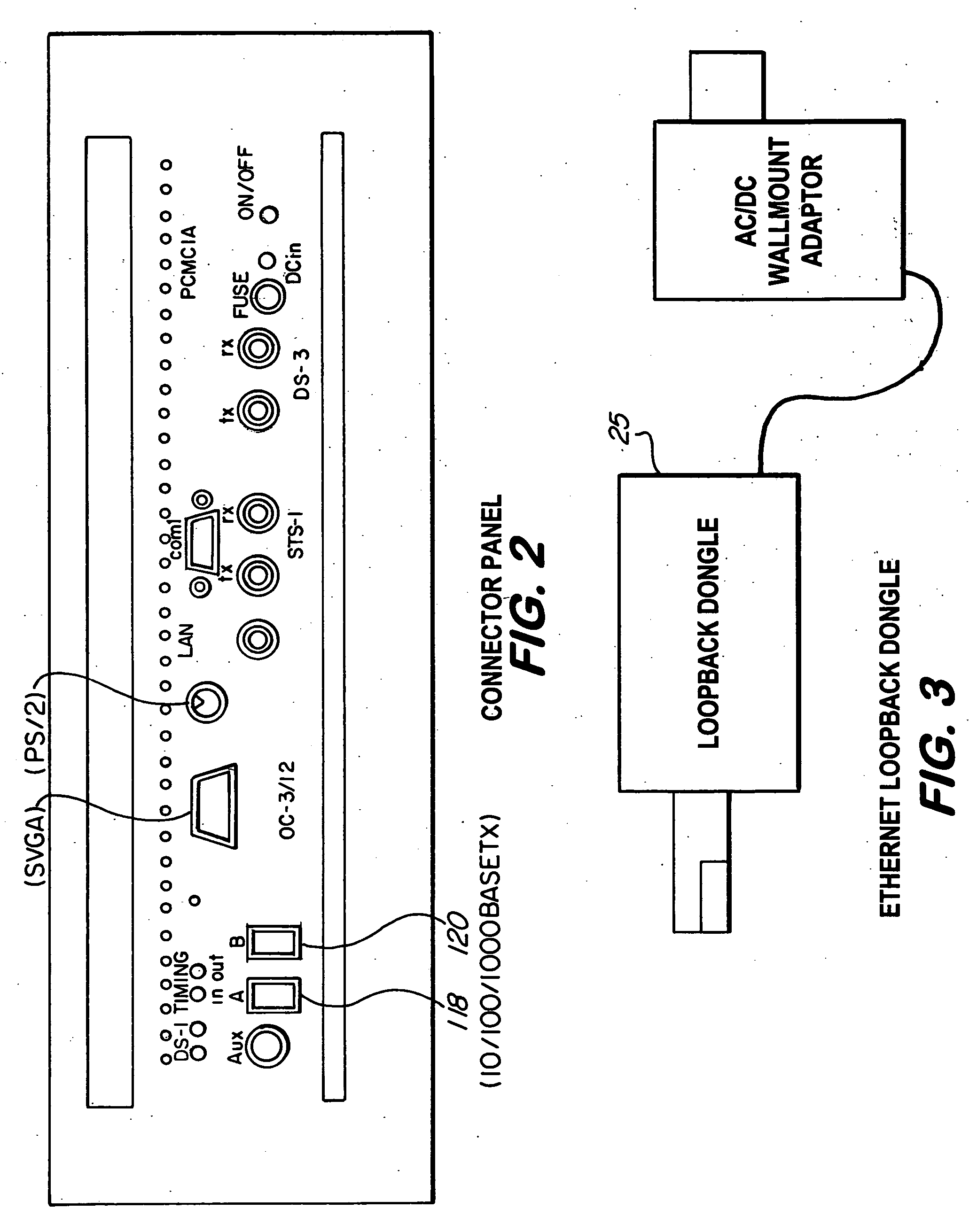
Hand-held electronic tester for telecommunications networks
InactiveUS20050135259A1Accurate countError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPacket communicationHand held
The present invention concerns a portable, field-oriented test gear which permits validation of both digital circuit (TOM) and packet based communications. The test set includes a method and graphical user interface for configuring OSI, 0S3, SONET and packet communication based tests, a method and system that allows testing an Ethernet WAN link by using a Pseudo-Random Bit Sequence (PRBS) pattern, as well as a method and system to remotely validate full-duplex 10 / 100 / 1 000BaseTX WAN communication at full line rate (1 Gbps) using a single test gear and a low cost accessory included with the test gear.
Owner:YAZDI SAMI +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com