Patents
Literature
519 results about "Packet routing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
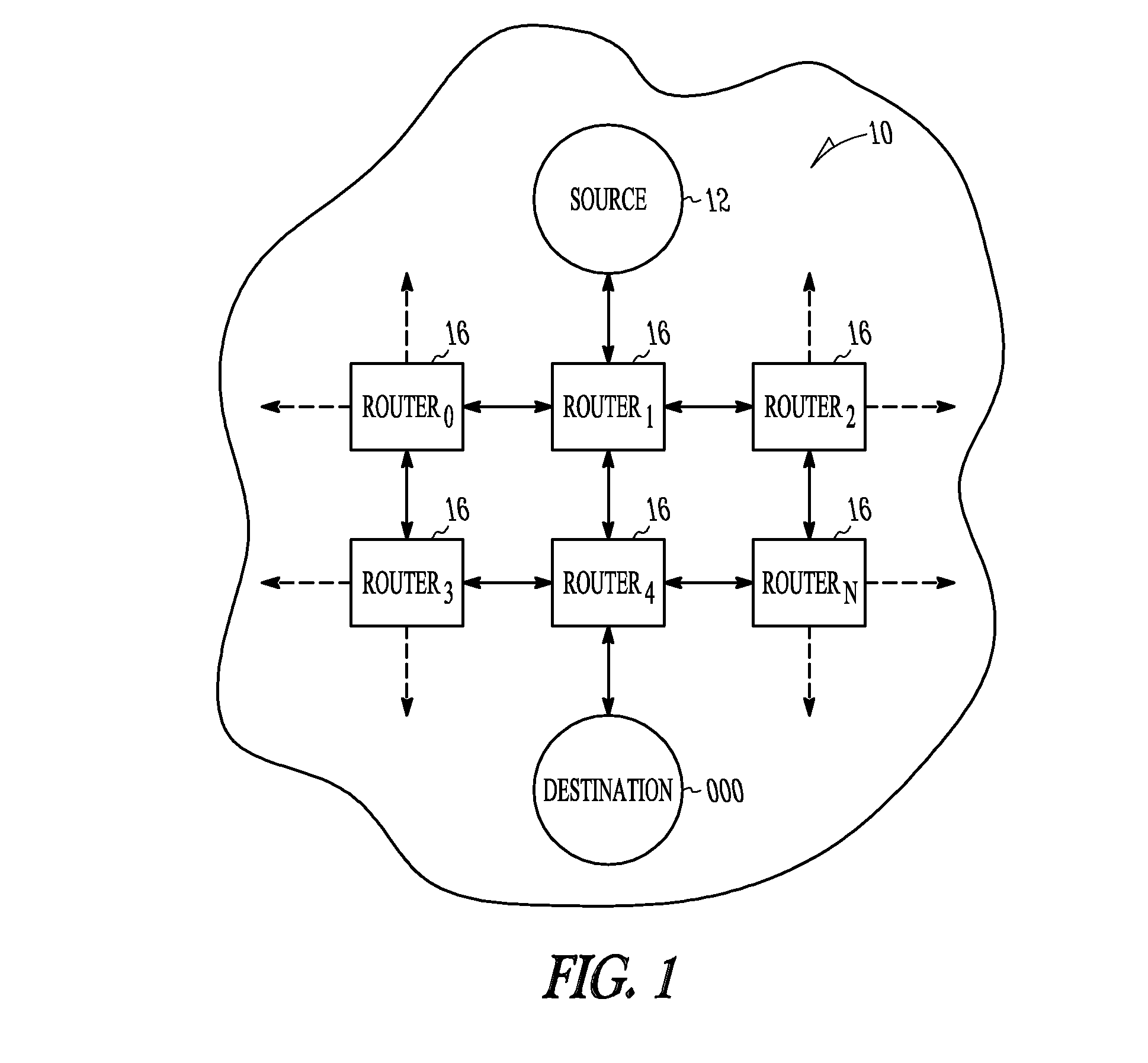
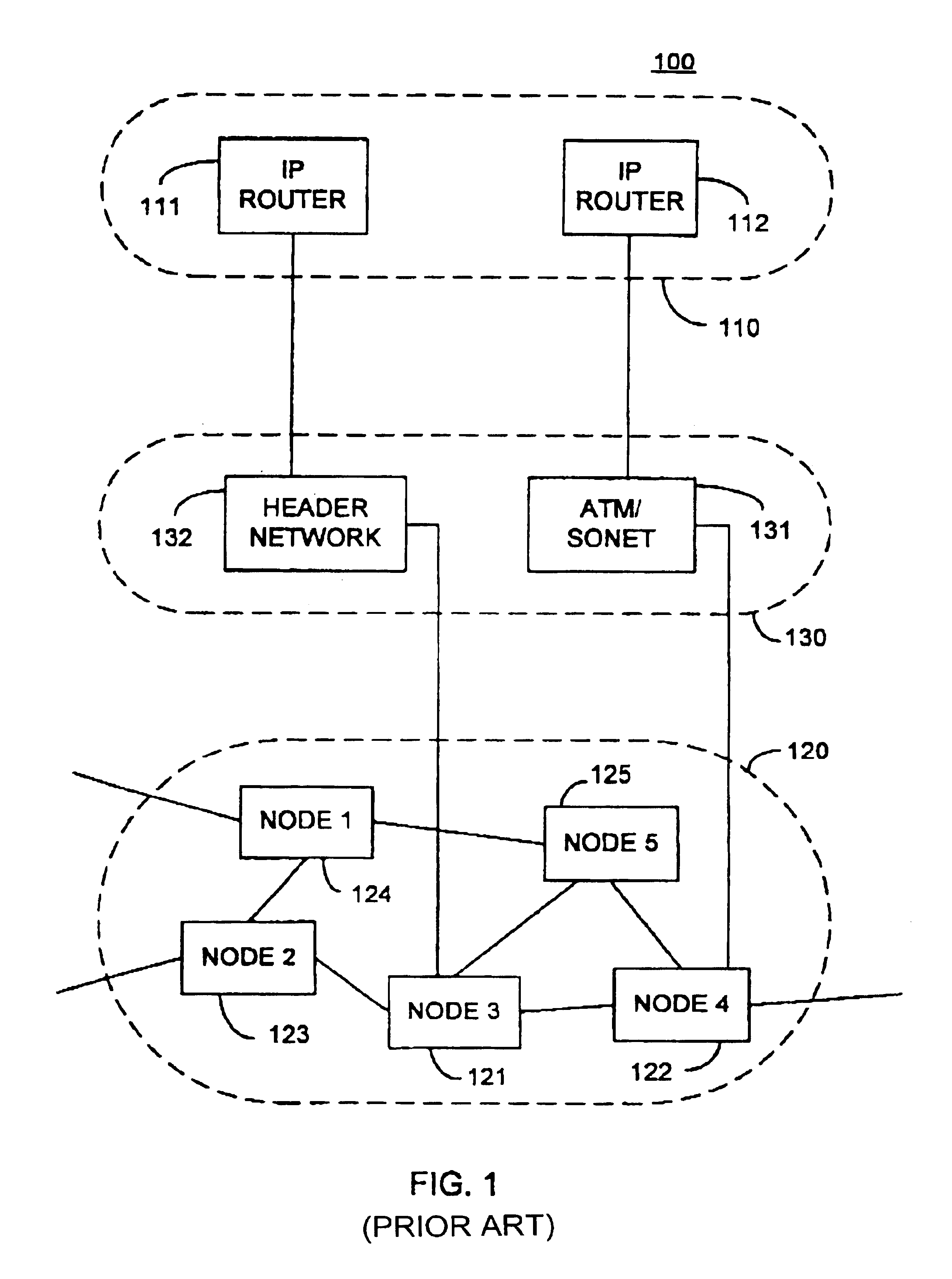
Packet routing is the forwarding of logically addressed packets from their source toward their ultimate destination through intermediate nodes.
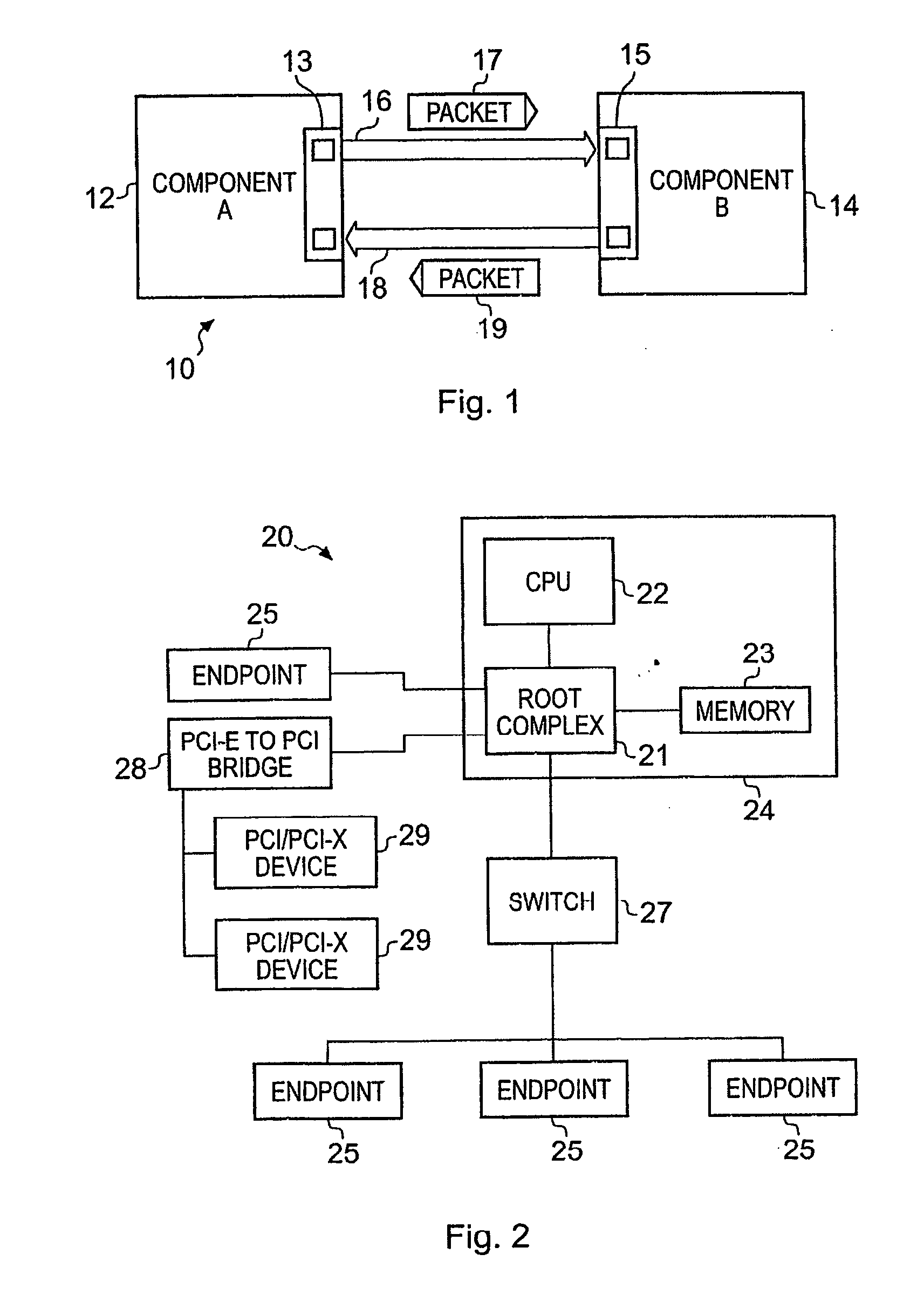
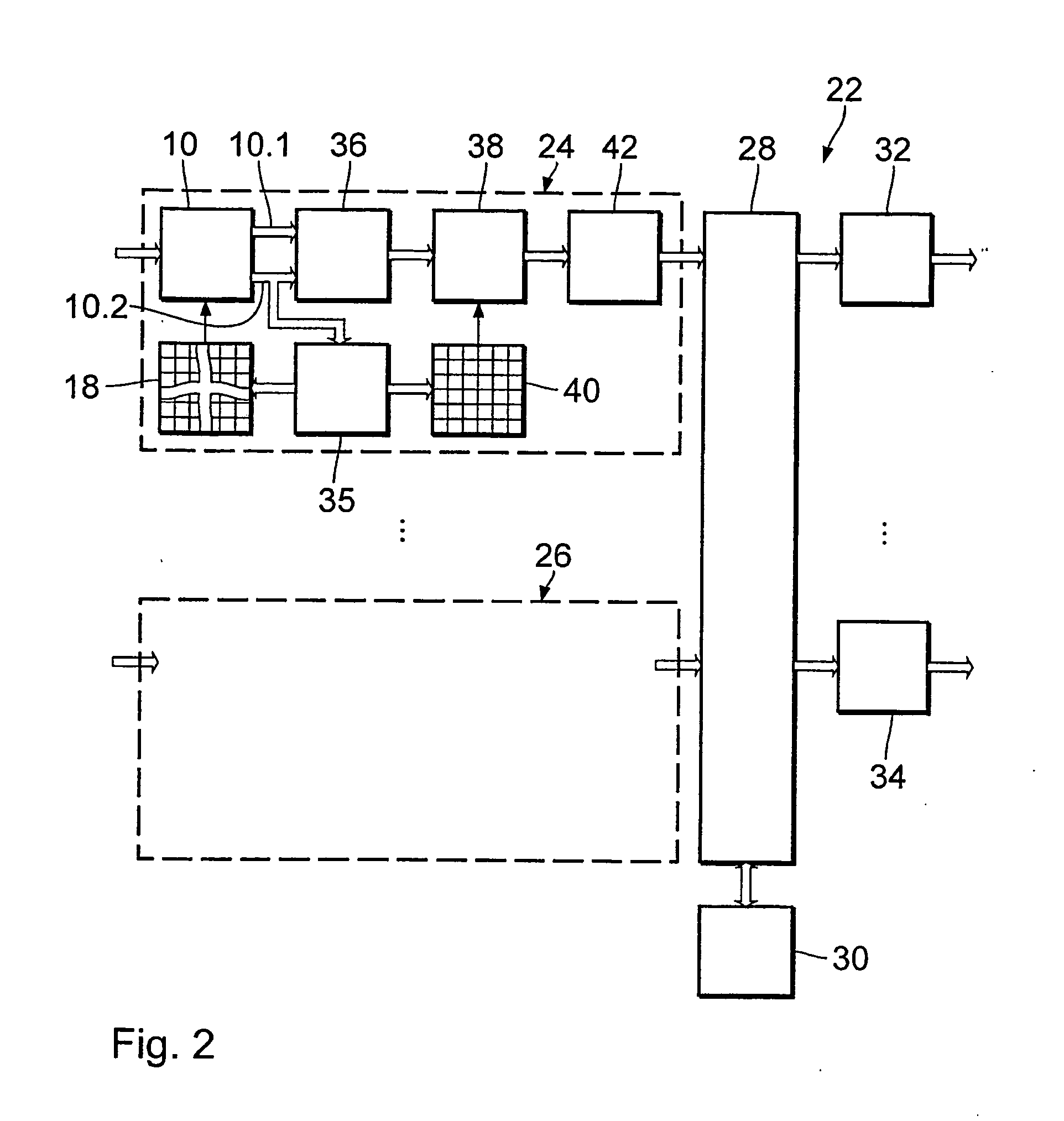
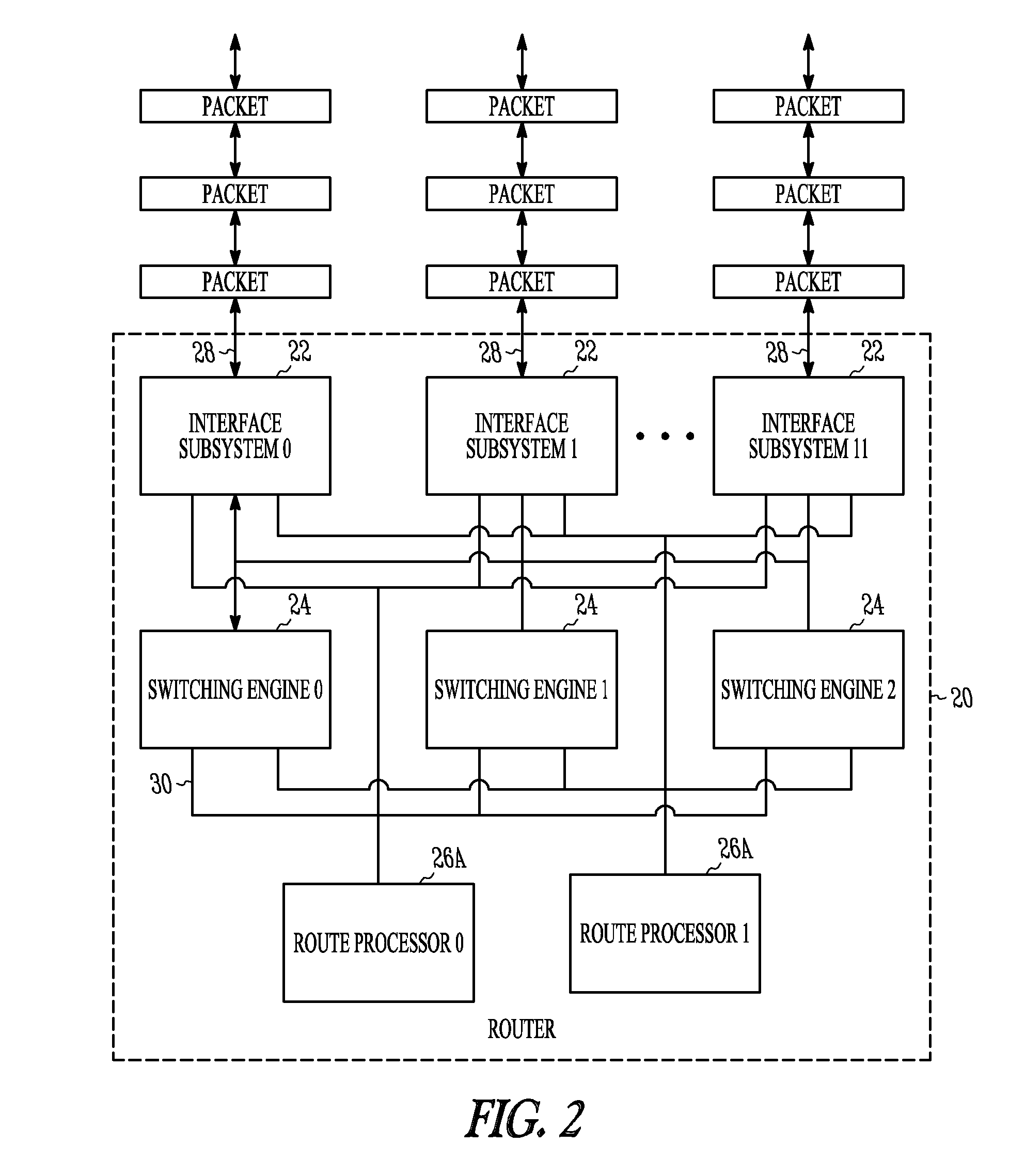
Packet routing and switching device
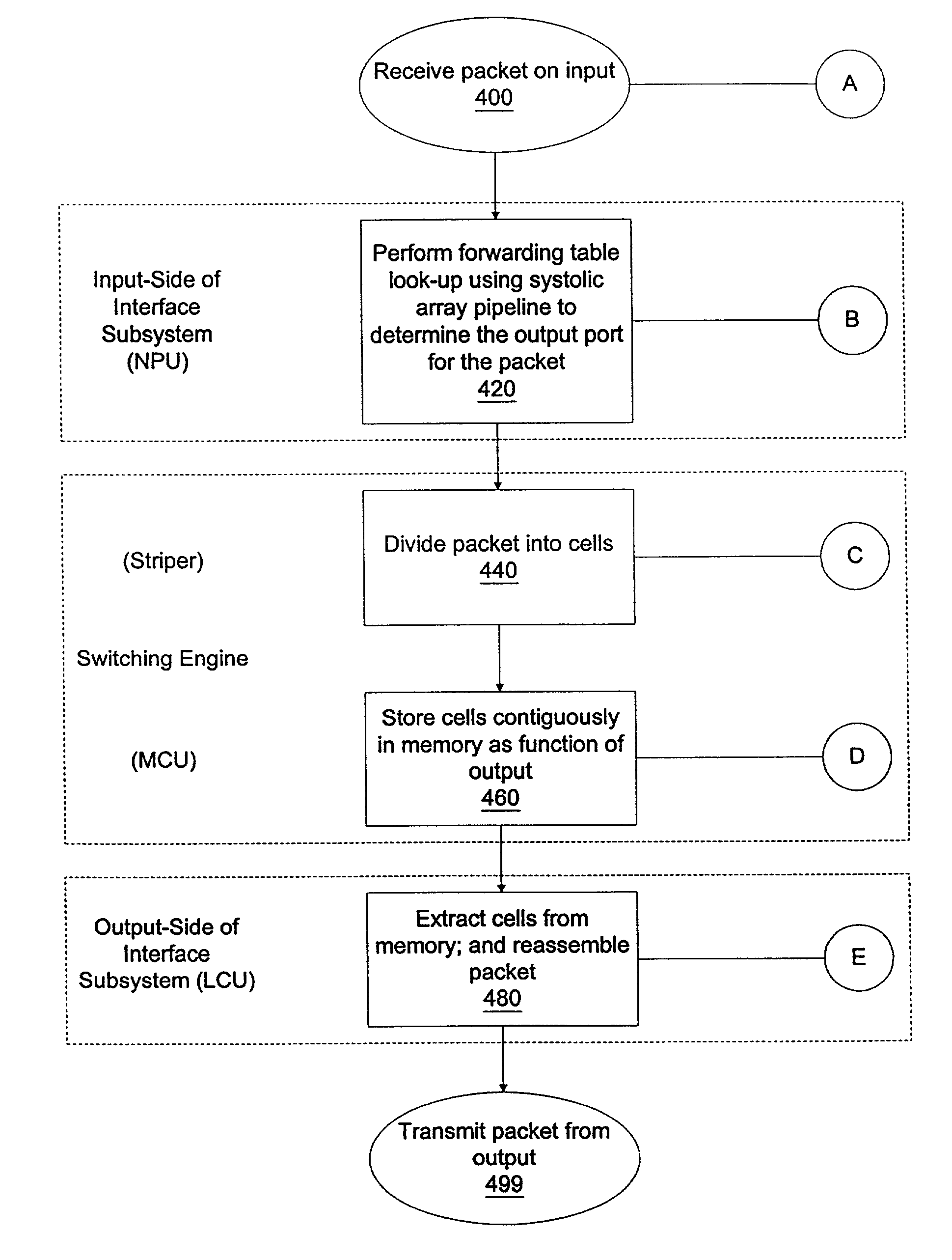
InactiveUS7382787B1Quick extractionTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationNetwork processing unitSystolic array
A method for routing and switching data packets from one or more incoming links to one or more outgoing links of a router. The method comprises receiving a data packet from the incoming link, assigning at least one outgoing link to the data packet based on the destination address of the data packet, and after the assigning operation, storing the data packet in a switching memory based on the assigned outgoing link. The data packet extracted from the switching memory, and transmitted along the assigned outgoing link. The router may include a network processing unit having one or more systolic array pipelines for performing the assigning operation.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
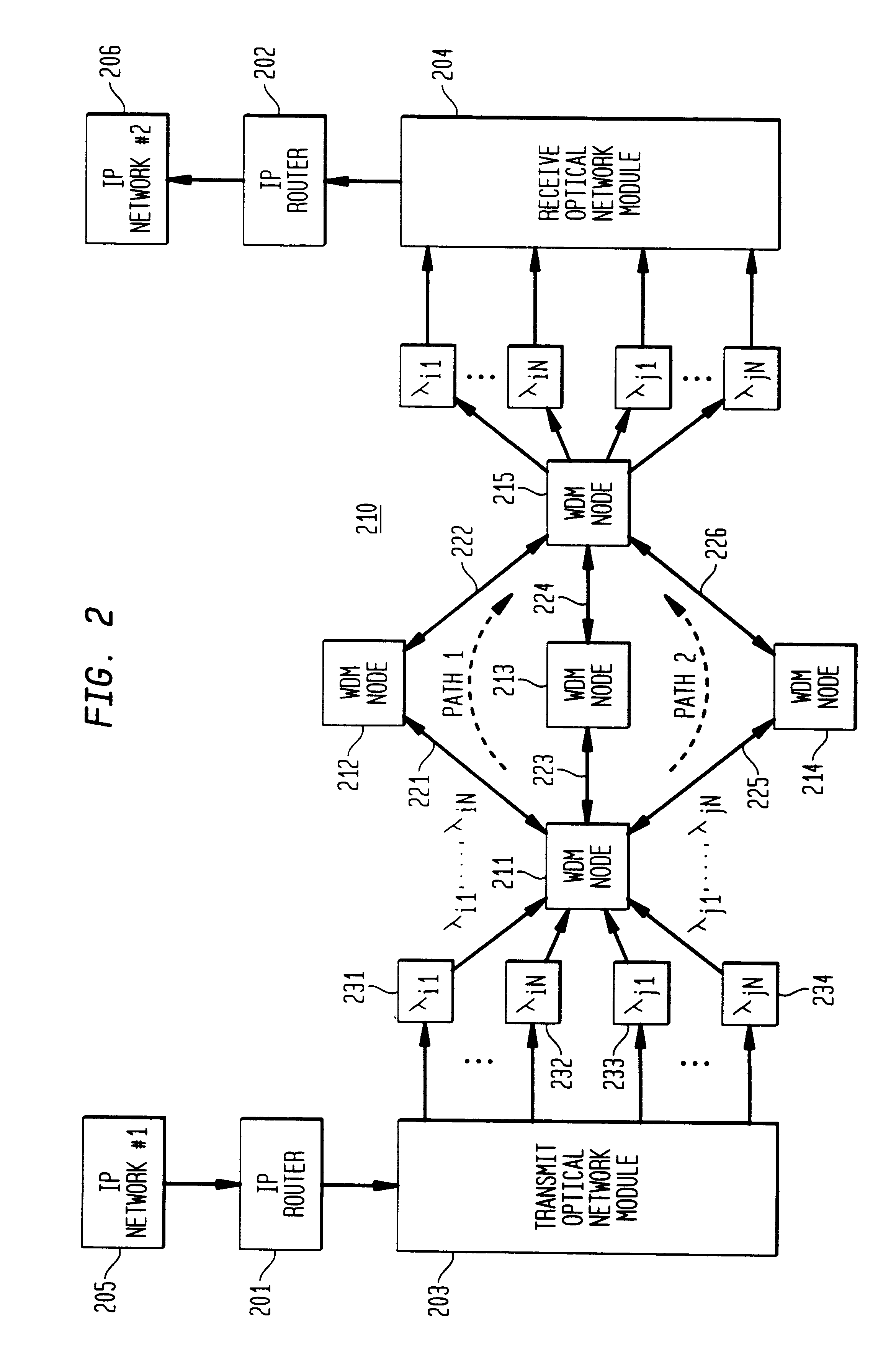
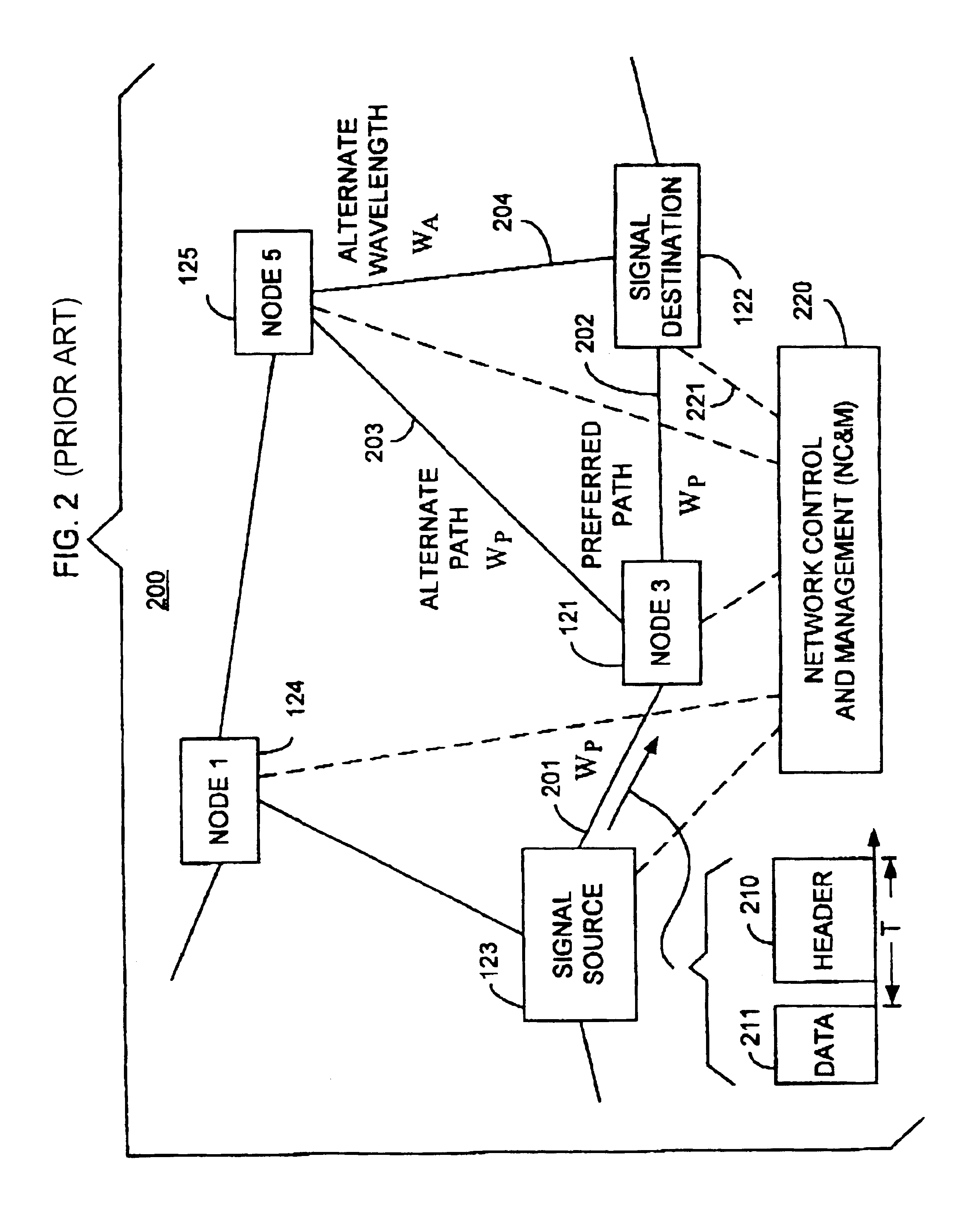
High-throughput, low-latency next generation internet networks using optical tag switching
InactiveUS6111673AEfficient comprehensive utilizationSignificant overheadMultiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsSignal routingInternet network
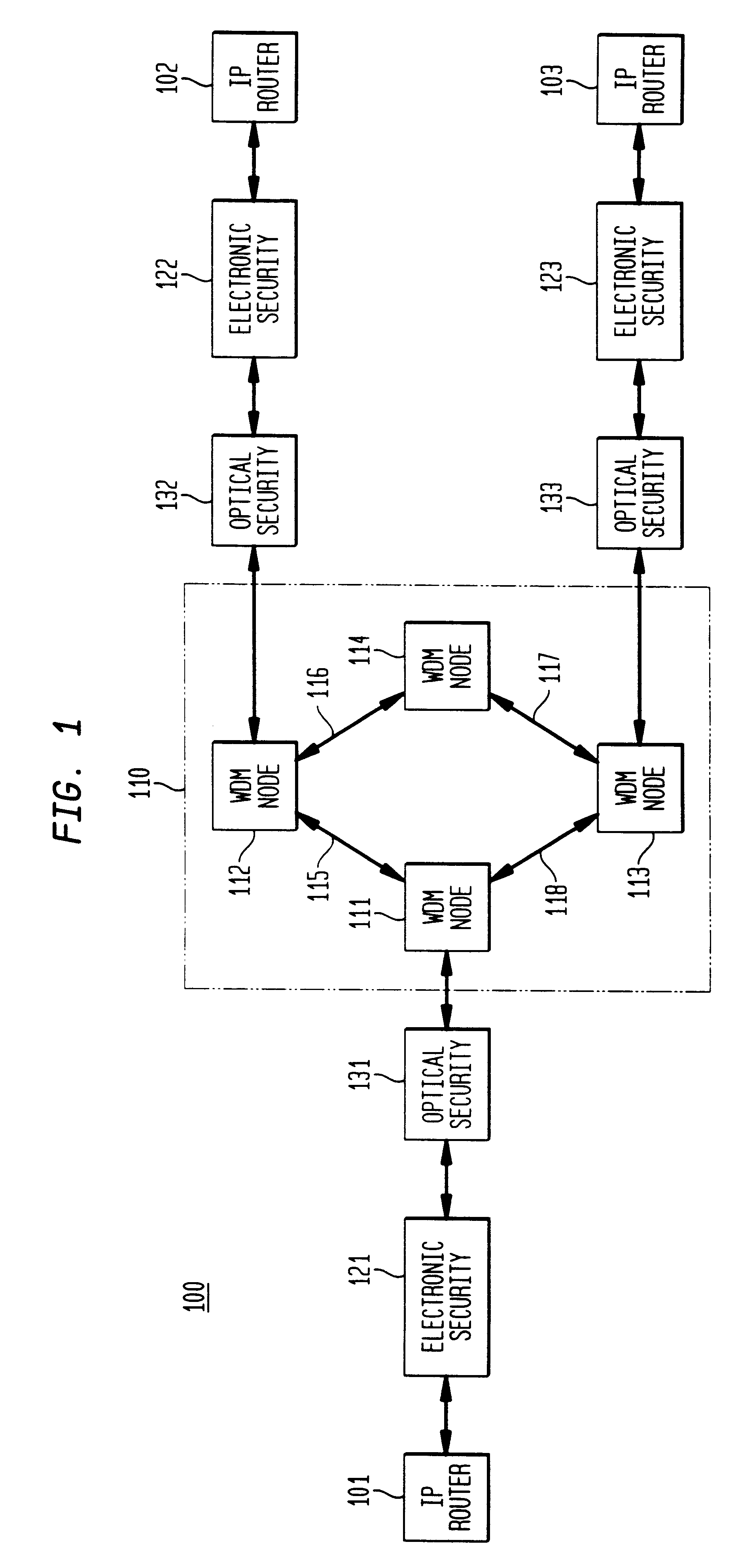
An optical signaling header technique applicable to optical networks wherein packet routing information is embedded in the same channel or wavelength as the data payload so that both the header and data payload propagate through network elements with the same path and the associated delays. The header routing information has sufficiently different characteristics from the data payload so that the signaling header can be detected without being affected by the data payload, and that the signaling header can also be removed without affecting the data payload. The signal routing technique can be overlaid onto the conventional network elements in a modular manner using two types of applique modules. The first type effects header encoding and decoding at the entry and exit points of the data payload into and out of the network; the second type effects header detection at each of the network elements.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Optical layer survivability and security system using optical label switching and high-speed optical header generation and detection
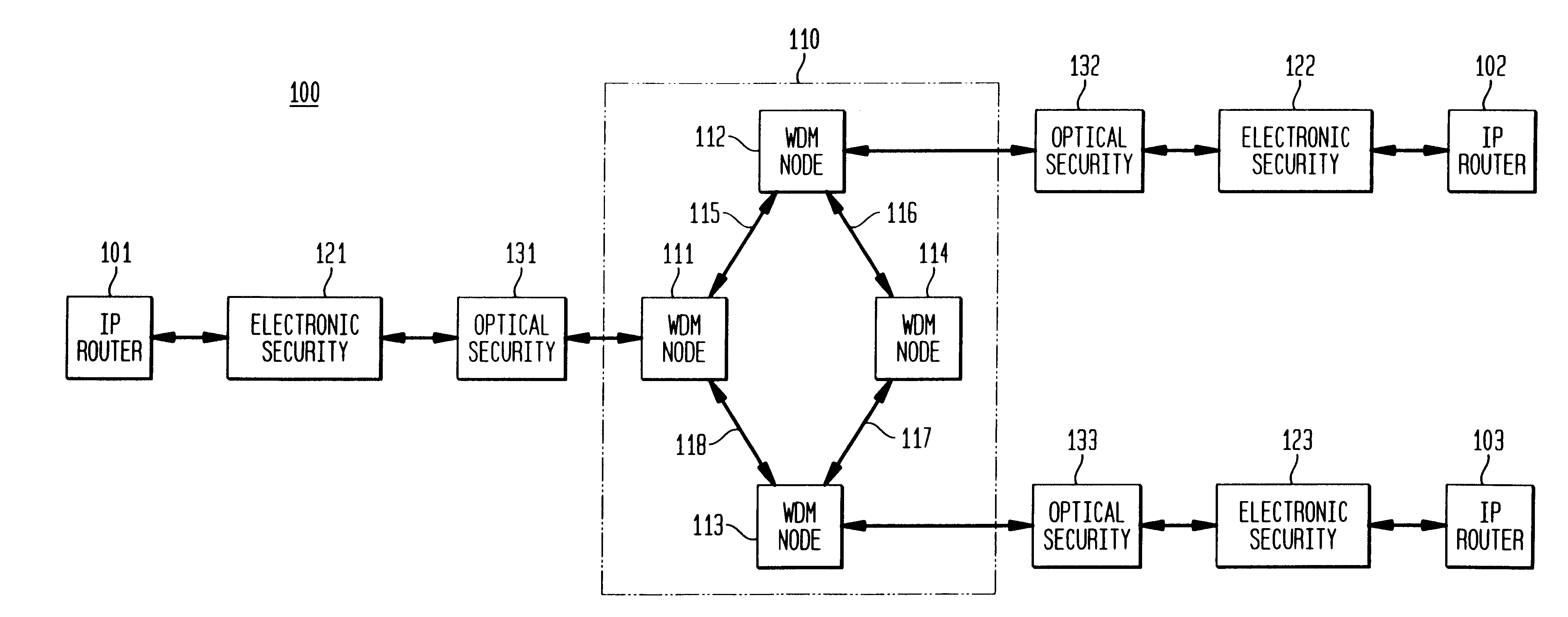
InactiveUS6271946B1Increase probabilityIncrease optical powerMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsSurvivabilityOptical burst switching
An optical signaling header technique applicable to optical networks wherein packet routing information is embedded in the same channel or wavelength as the data payload so that both the header and data payload propagate through network elements with the same path and the associated delays. The technique effects survivability and security of the optical networks by encompassing conventional electronic security with an optical security layer by generating replicated versions of the input data payload at the input node, and the transmission of each of the replicated versions over a corresponding one of the plurality of links. Moreover, each of the links is composed of multiple wavelengths to propagate optical signals or optical packets, and each of the replicated versions of the data payload may be propagated over a selected one of the wavelengths in each corresponding one of the plurality of links.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
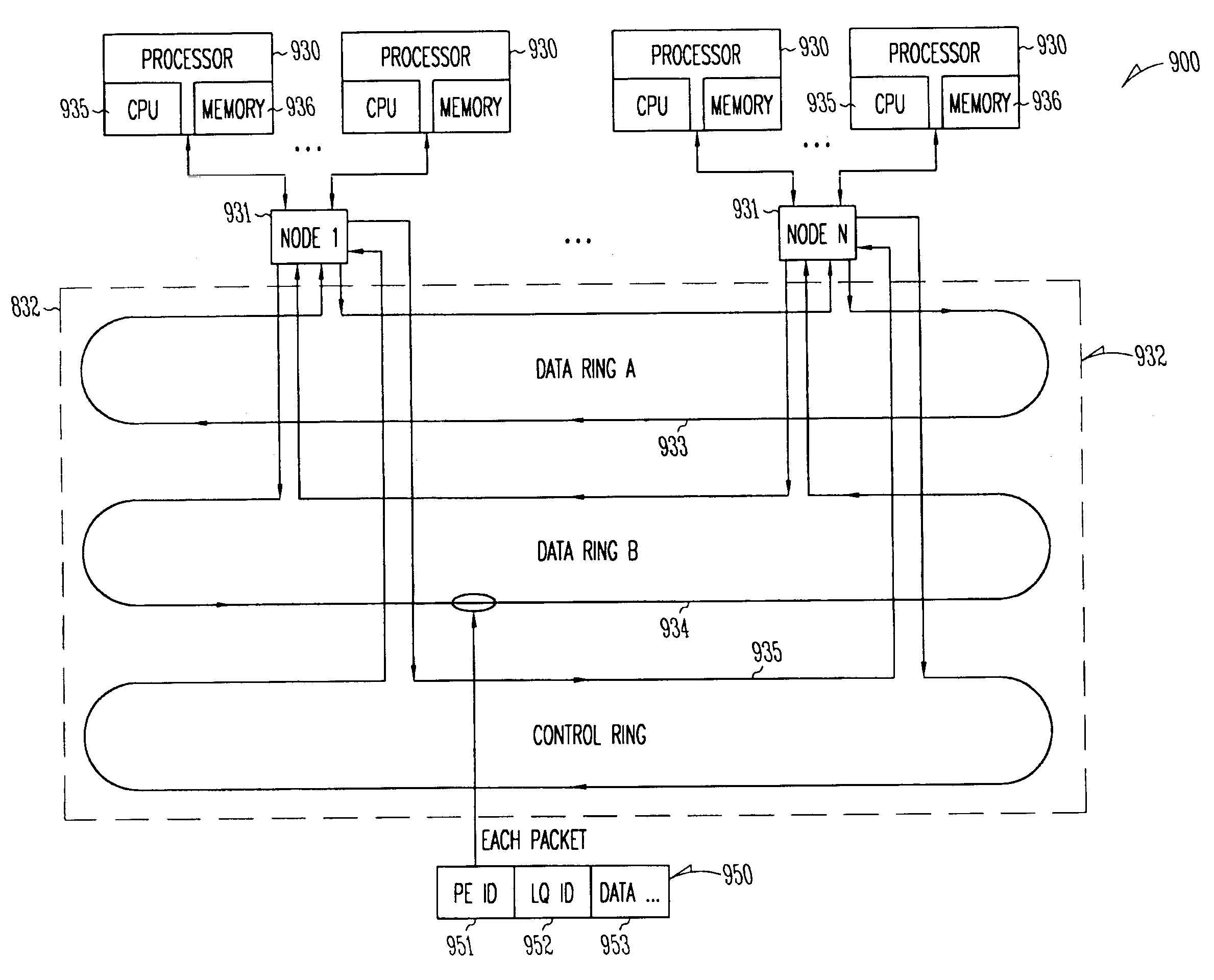
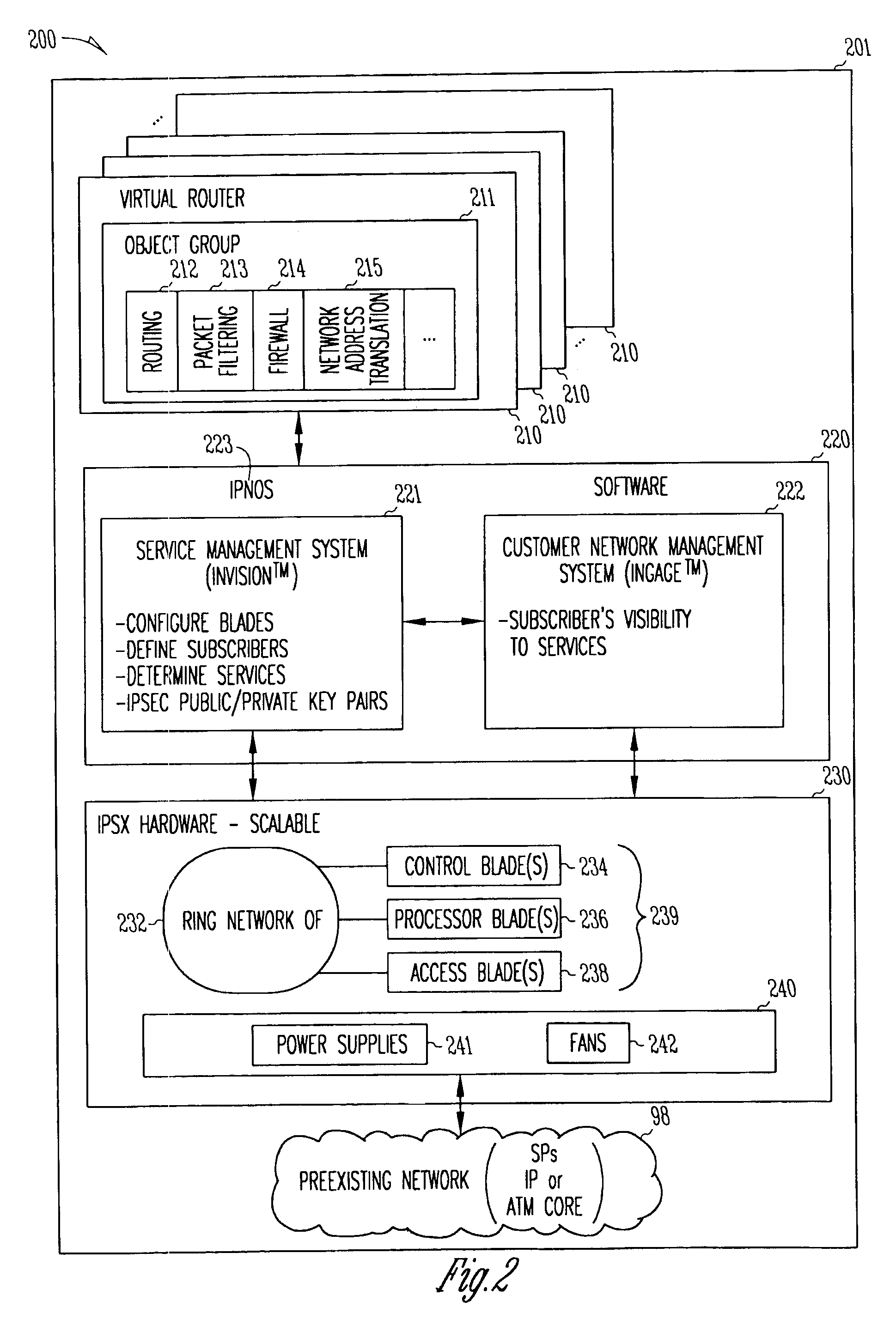
Packet routing system and method
InactiveUS7111072B1Multiple digital computer combinationsLoop networksComputer hardwarePrivate network
A flexible, scalable hardware and software platform that allows a service provider to easily provide internet services, virtual private network services, firewall services, etc., to a plurality of customers. One aspect provides a method and system for delivering security services. This includes connecting a plurality of processors in a ring configuration within a first processing system, establishing a secure connection between the processors in the ring configuration across an internet protocol (IP) connection to a second processing system to form a tunnel, and providing both router services and host services for a customer using the plurality of processors in the ring configuration and using the second processing system. a packet routing system and method is described that includes a processor identifier in each packet to route the packets to a physical processor, and a logical queue identifier to route the packets to the destination object within that processor.
Owner:FORTINET
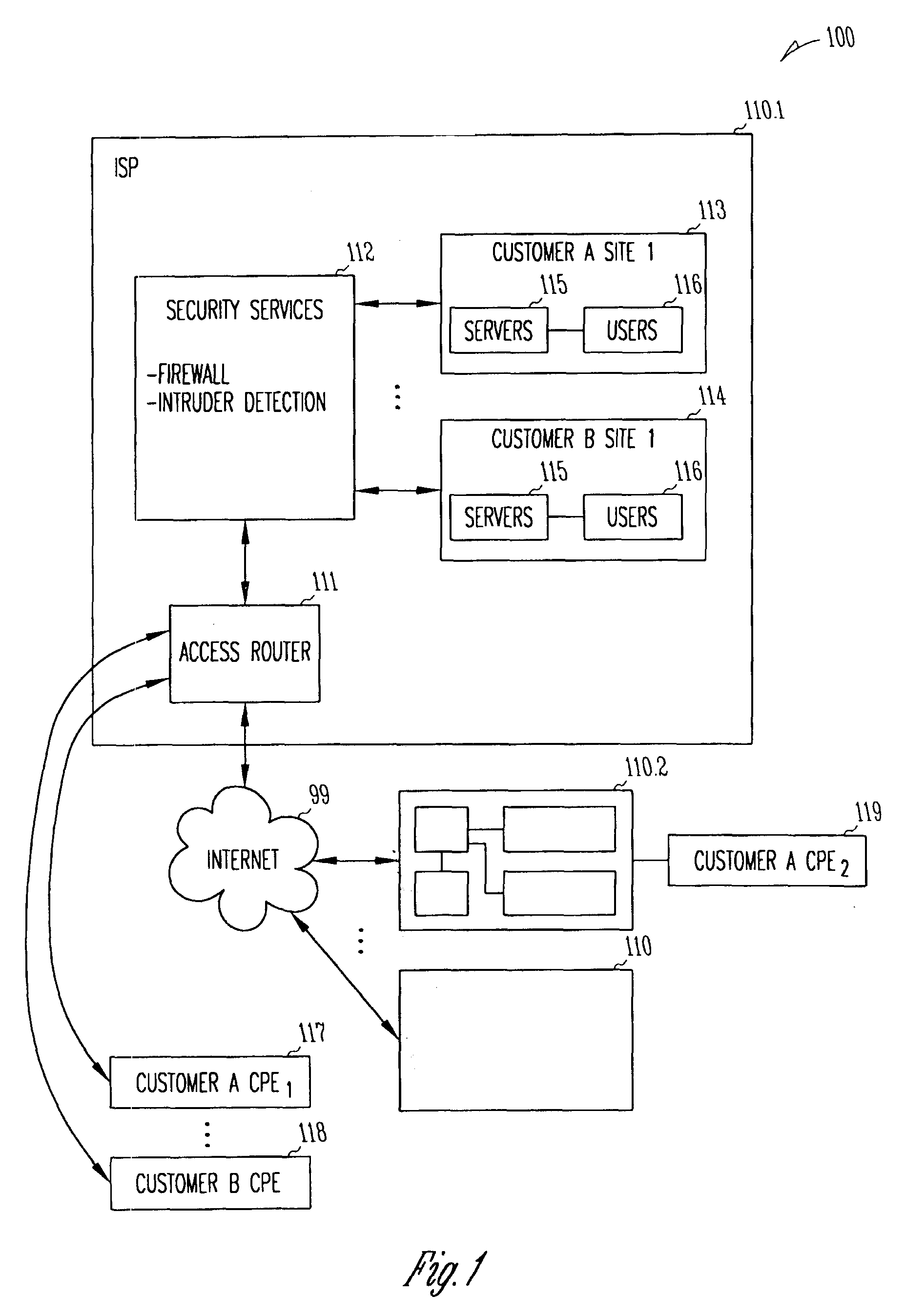
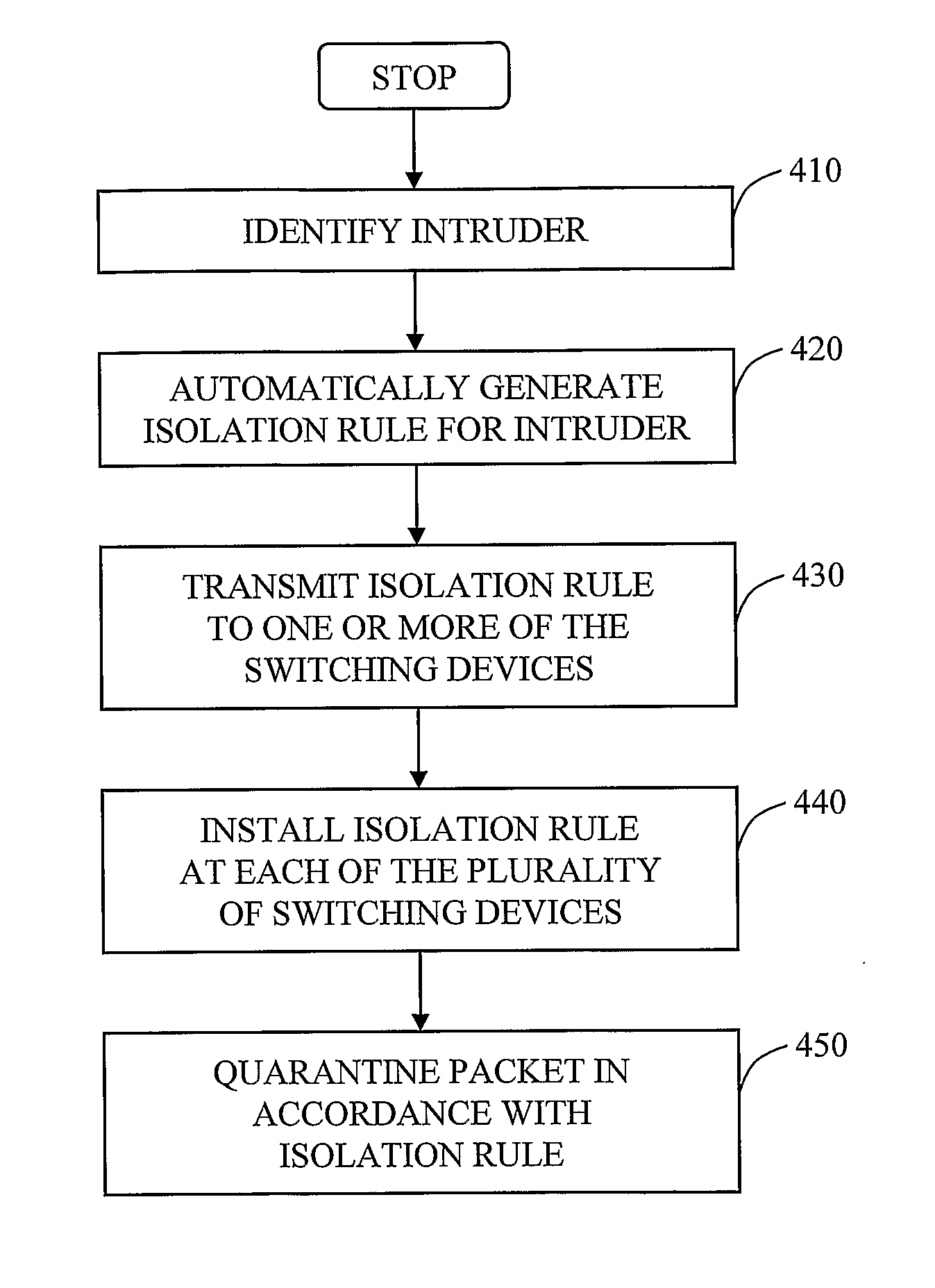
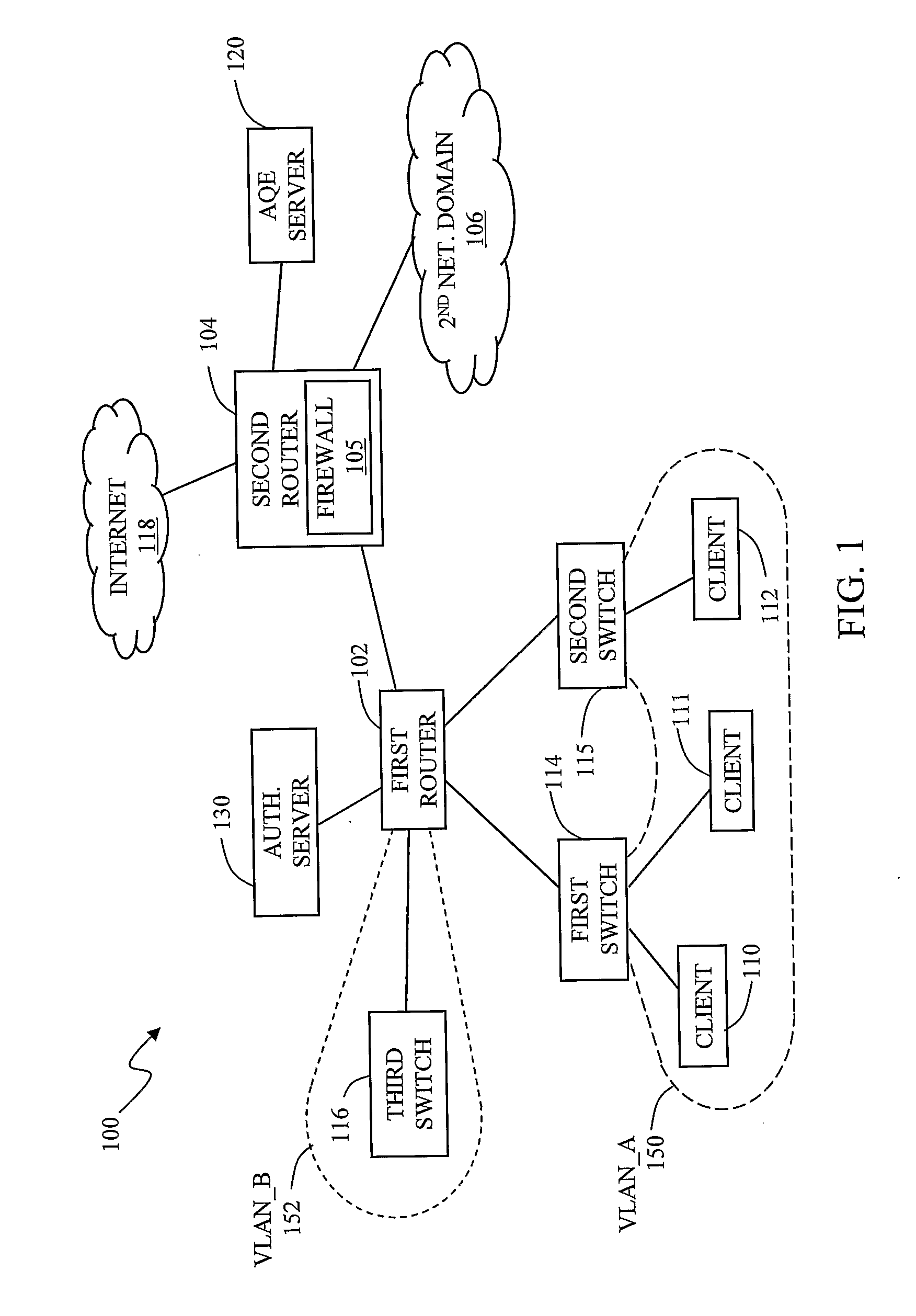
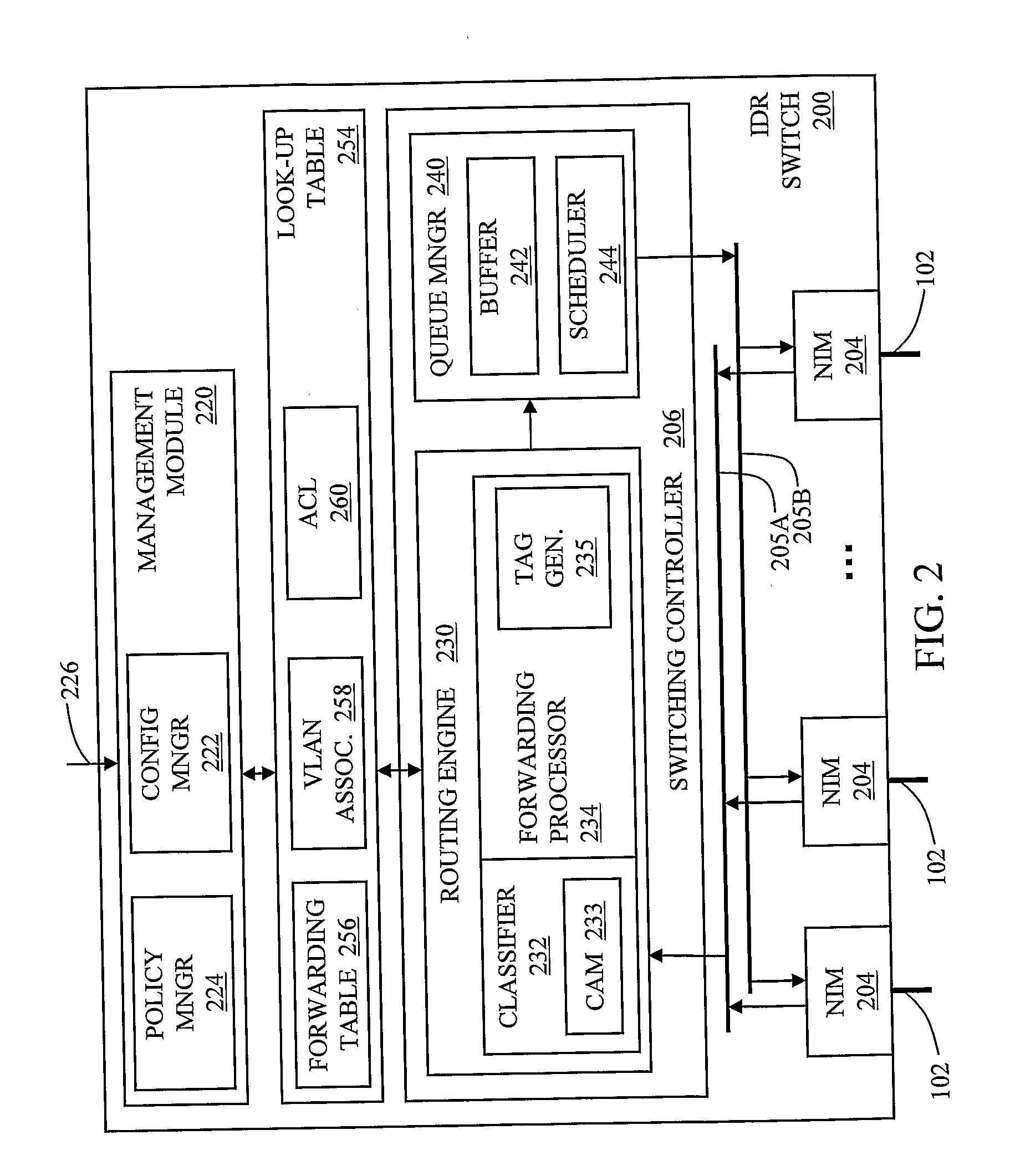
Automated containment of network intruder
InactiveUS20070192862A1Network degradationLow costMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionAutomatic controlVirtual LAN
The invention in the preferred embodiment features a system (200) and method for automatically segregating harmful traffic from other traffic at a plurality of network nodes including switches and routers. In the preferred embodiment, the system (200) comprises an intrusion detection system (105) to determine the identity of an intruder and a server (130) adapted to automatically install an isolation rule on the one or more network nodes (114, 115, 116) to quarantine packets from the intruder. The isolation rule in the preferred embodiment is a virtual local area network (VLAN) rule or access control list (ACL) rule that causes the network node to route any packets from the intruder into a quarantine VLAN or otherwise isolate the traffic from other network traffic. In large networks, the isolation rule may be installed on a select plurality of network nodes under the gateway router (104) associated with the node at which the intruder first entered the network (100).
Owner:VERMEULEN VINCENT +1
Reliable, high-throughput, high-performance transport and routing mechanism for arbitrary data flows
ActiveUS20070153782A1Minimum delayImprove performanceTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationData streamEdge node
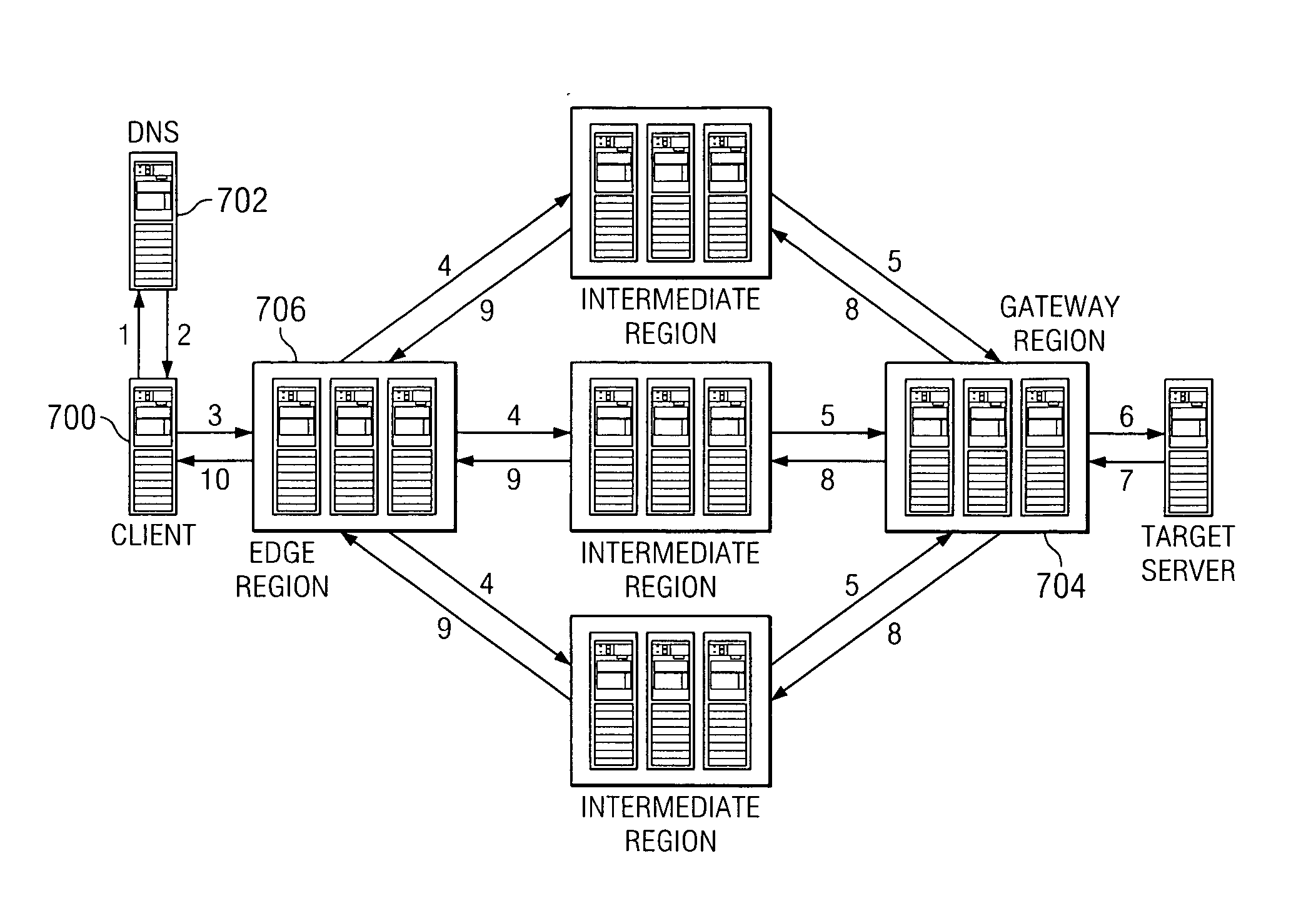
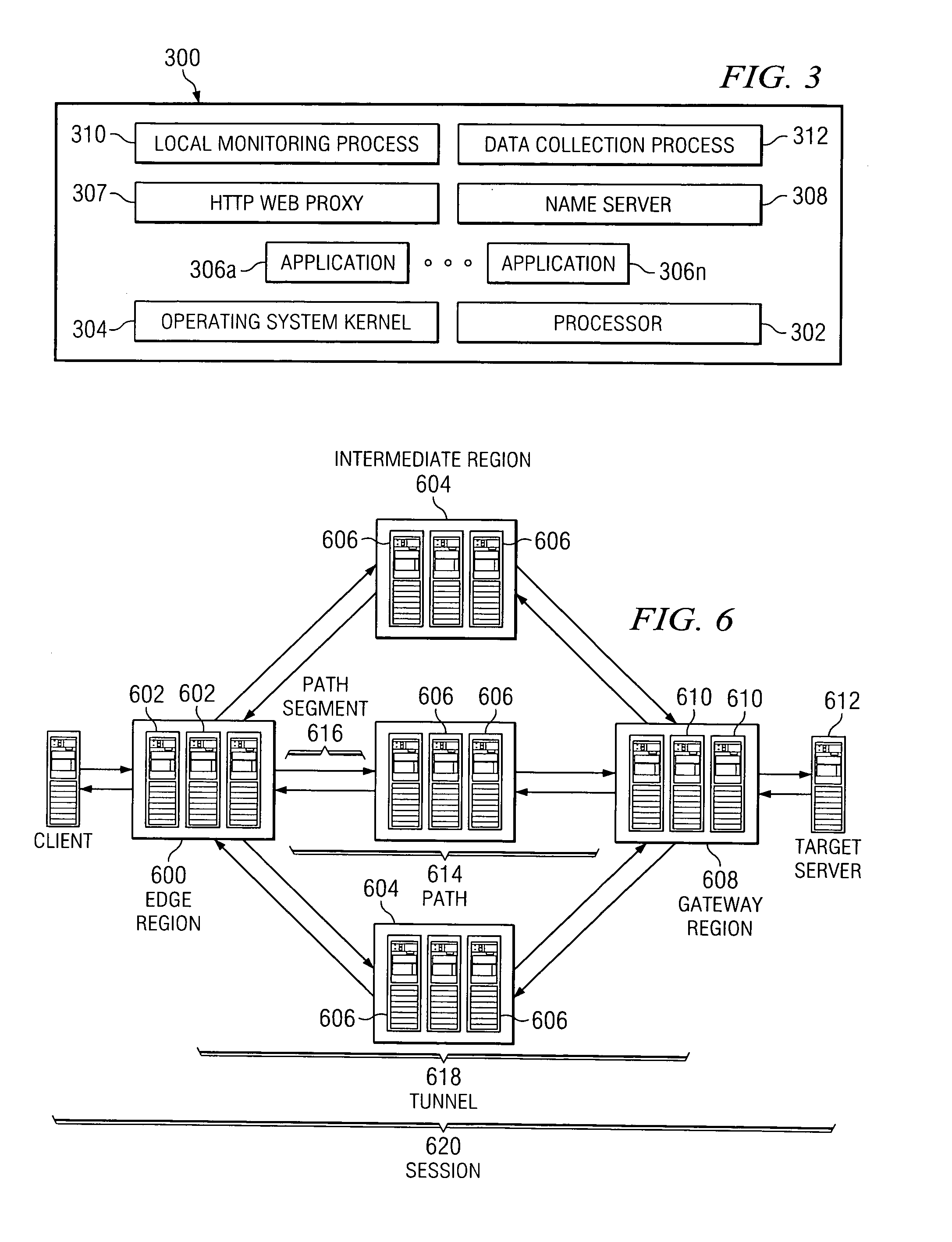
The present invention leverages an existing content delivery network infrastructure to provide a system that enhances performance for any application that uses the Internet Protocol (IP) as its underlying transport mechanism. An overlay network comprises a set of edge nodes, intermediate nodes, and gateway nodes. This network provides optimized routing of IP packets. Internet application users can use the overlay to obtain improved performance during normal network conditions, to obtain or maintain good performance where normal default BGP routing would otherwise force the user over congested or poorly performing paths, or to enable the user to maintain communications to a target server application even during network outages.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
Caching with selective multicasting in a publish-subscribe network
ActiveUS7672275B2Efficient routingOvercome disadvantagesData switching by path configurationWireless commuication servicesRouting decisionEncapsulated data
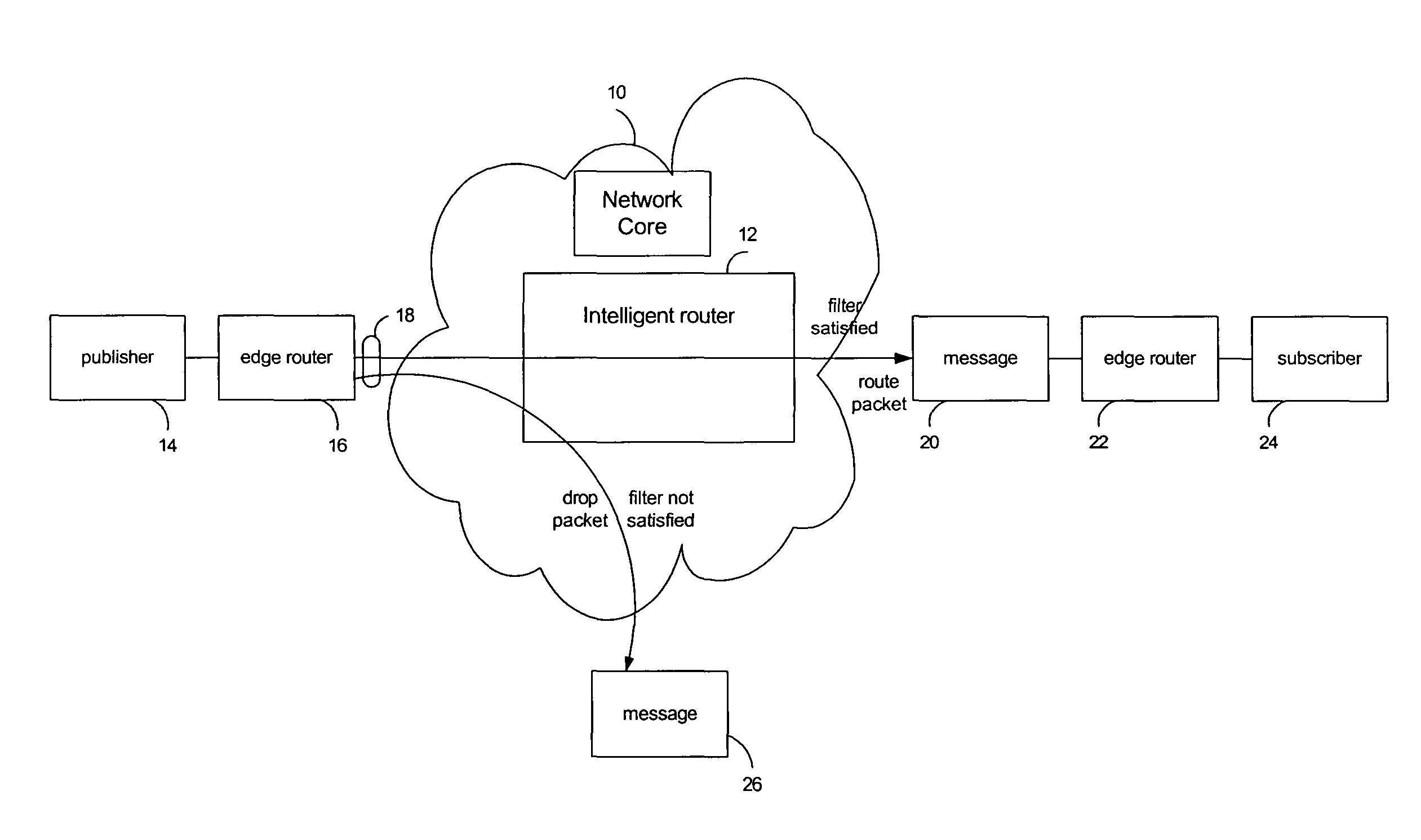
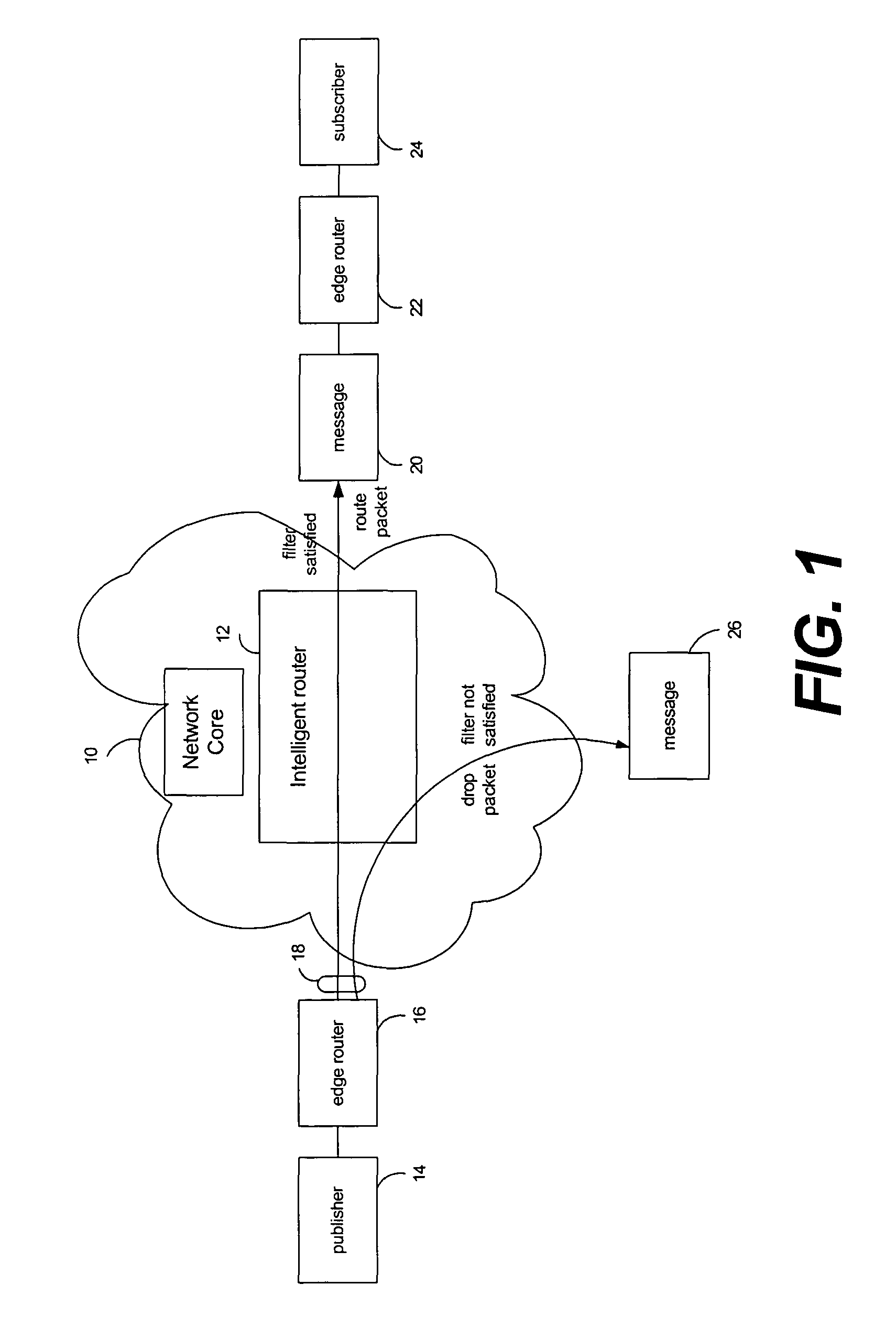
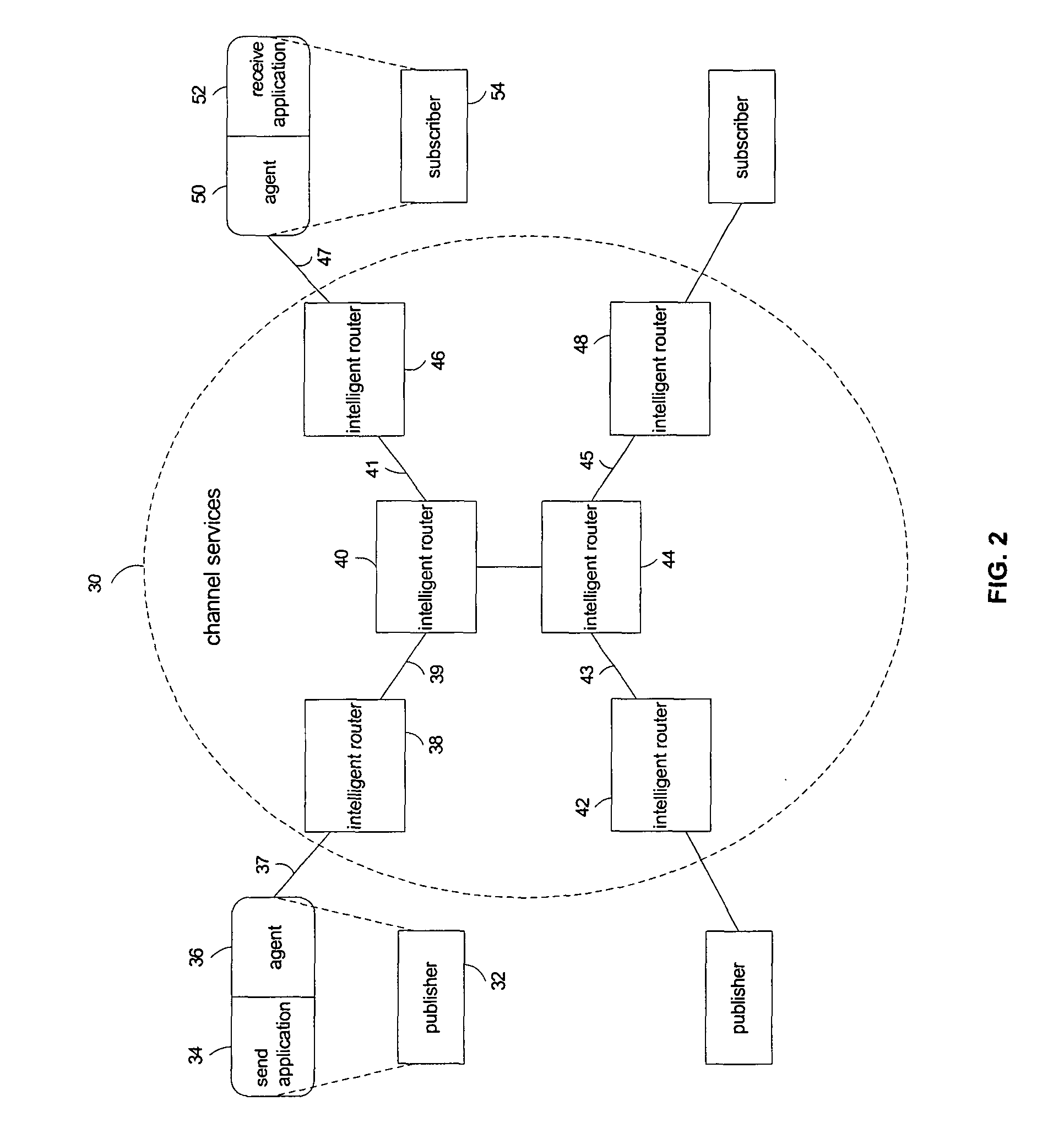
Packet routing via payload inspection at routers in a core of a distributed network. Packets include subjects and attributes in addition to routing information. The subjects correspond with particular types of content for subscriptions, and the attributes encapsulate the data or content. The routers store filters corresponding with subscriptions to content. Upon receiving a packet, a router inspects the payload section of the packet containing the attributes in order to retrieve the attributes and apply them to the filters for the subscriptions. If an attribute satisfies a filter, the packet is routed to the next link. If the attributes do not satisfy the filters, the router discards the packet. These routing decisions are distributed among routers in the network core. The router locally caches the data in the network core.
Owner:PRECACHE
Small group multicast in a computer network
InactiveUS7016351B1RelievingBroadcast transmission systemsTime-division multiplexRouting tableMulticast packets
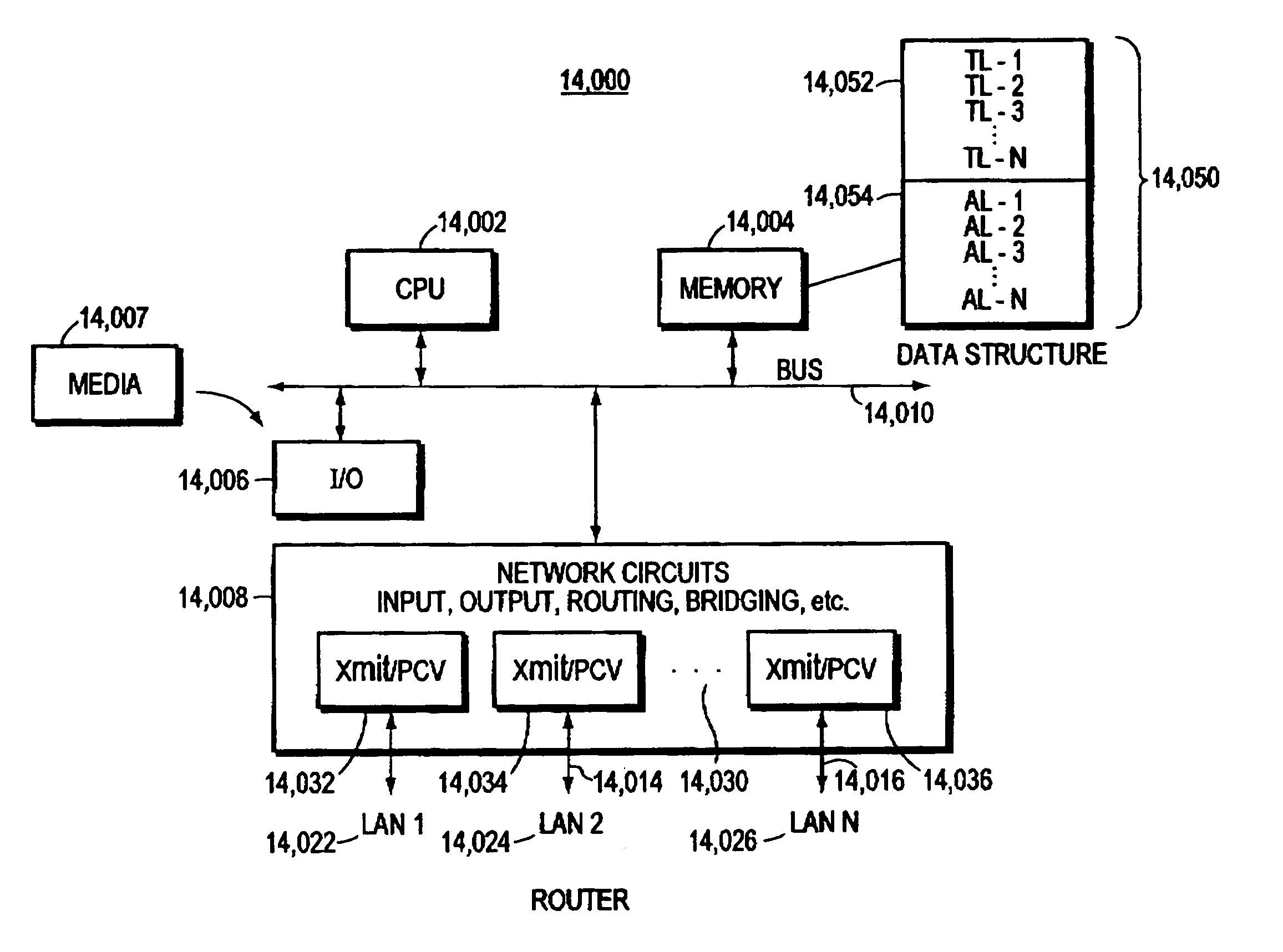
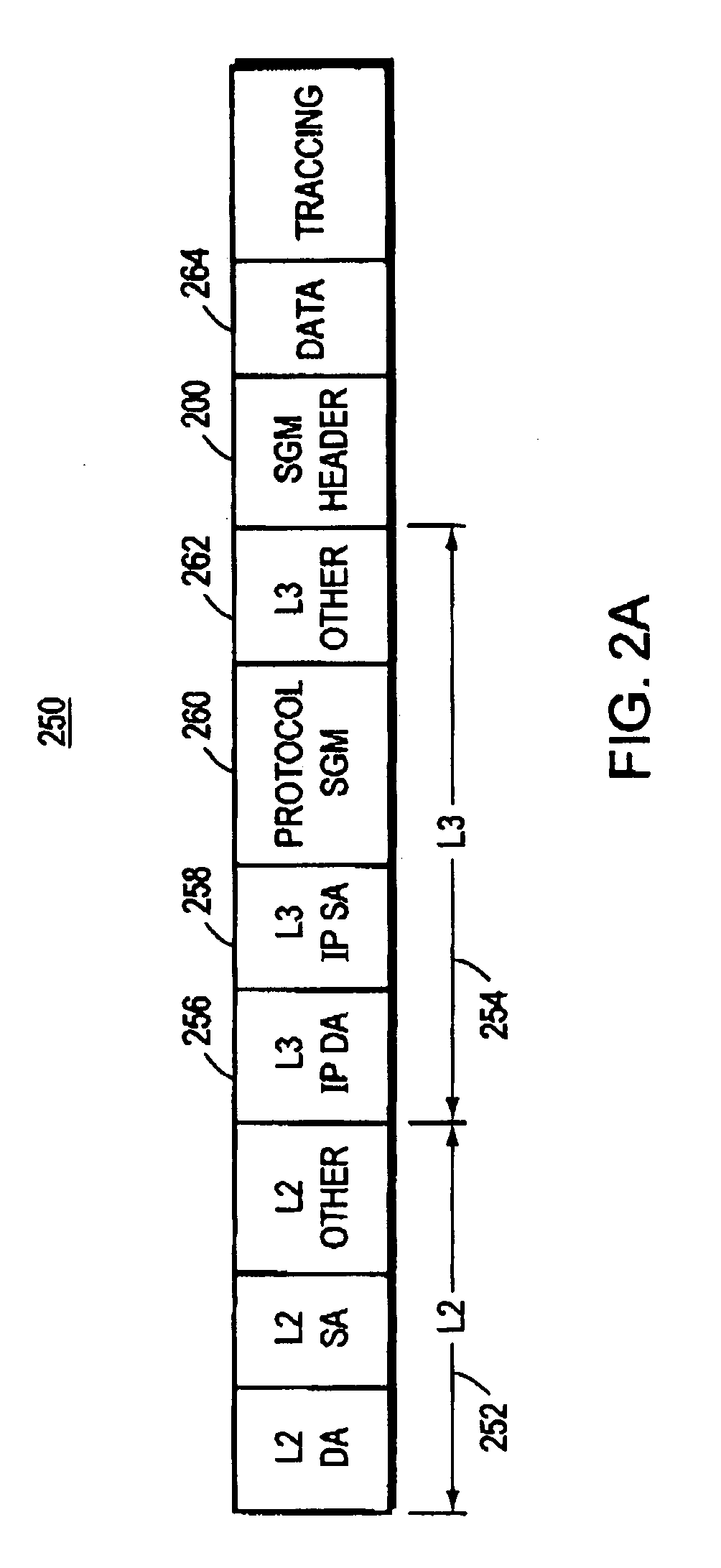
The invention solves the problem of overloading intermediate routers with state information as the number of multicast groups increases to millions of groups. The invention places multicast delivery tree information in the header of an encapsulated multicast packet, thereby relieving the routers from maintaining any state information about the multicast groups. The encapsulated packet is referred to as a small group multicast packet, or SGM packet. Routers which are neither branch points of the delivery tree nor destination routers will also need to do no additional forwarding processing other than that needed for standard unicast forwarding. A protocol designation field in the Layer 3 header informs the router that the packet is a SGM packet, and that the router is therefore instructed to parse the packet for route information. The router parses the SGM packet header and determines the next hop address of routers in the multicast delivery tree. The standard unicast forwarding tables are then consulted to determine the next packet destination addresses, and the router then rewrites the SGM packet and routes it to the next hop router. The routing tables also instruct the router as to which outbound port to route the packet.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Enabling Co-Existence of Hosts or Virtual Machines with Identical Addresses
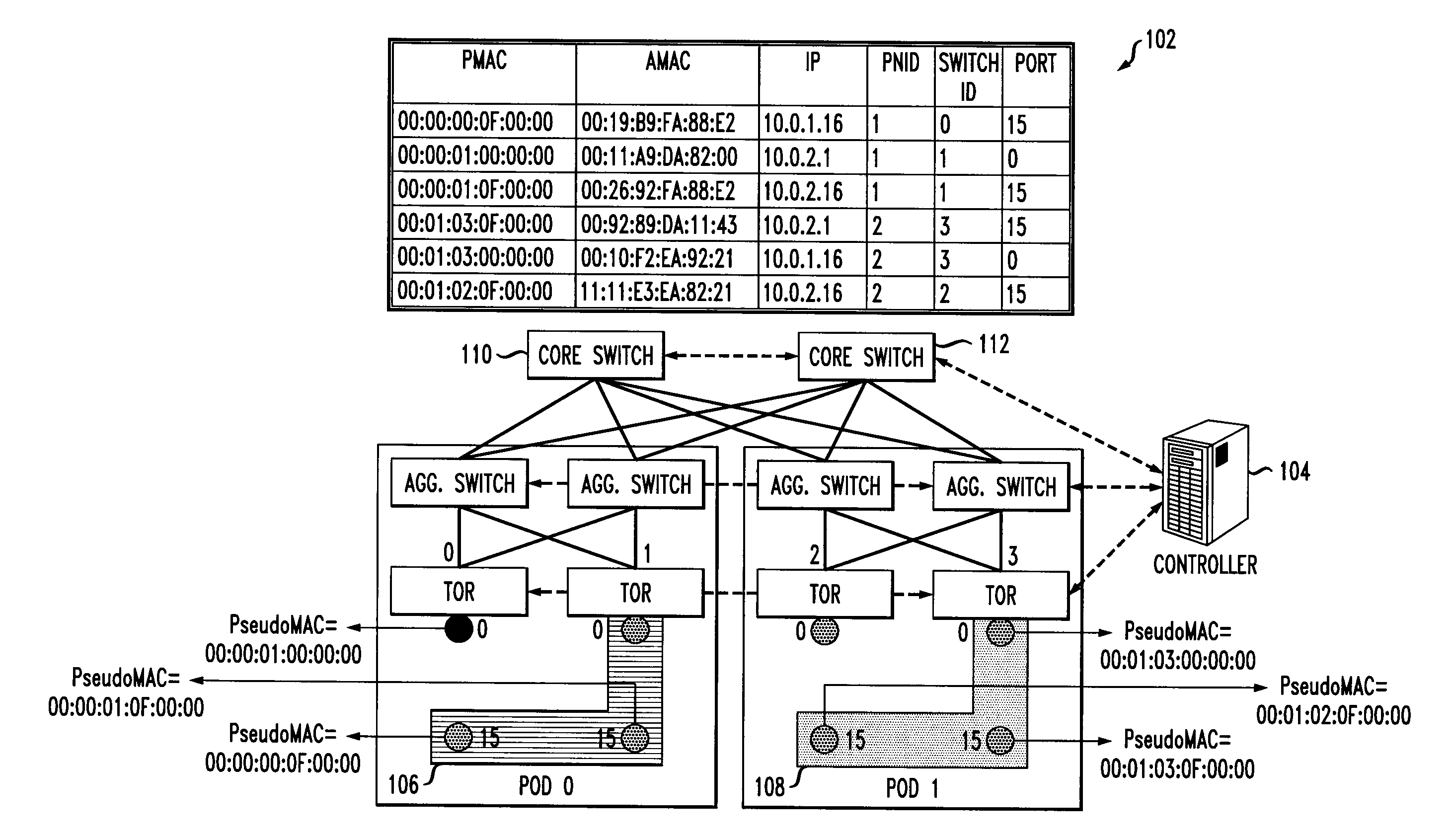
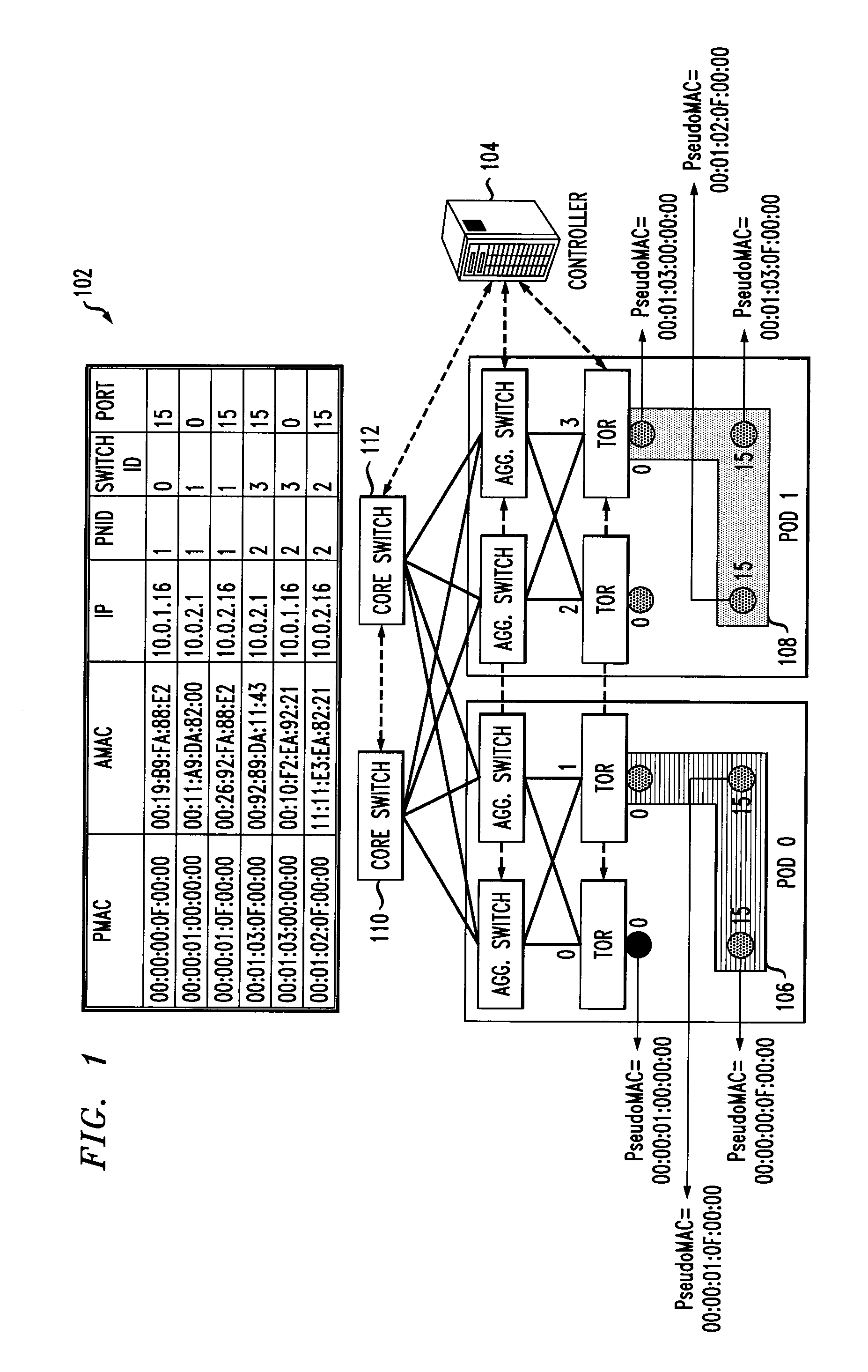
A method for enabling co-existence of multiple machines with identical addresses within a single data center network. The method includes assigning a unique pseudo identifier to each machine in the network that can be used for routing a packet to a destination machine, replacing a sender media access control address on an address resolution protocol request with a pseudo identifier of the sender at an edge network switch, retrieving a private network identifier from a mapping table based on the sender pseudo identifier and returning a pseudo identifier for the destination address based on the private network identifier, and replacing the pseudo identifier of the destination address with an actual identifier at a destination edge network switch for routing the packet to the destination machine.
Owner:IBM CORP
Adding packet routing information without ECRC recalculation
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Routing data packets in a compressed-header domain
InactiveUS20060075134A1Reduce loadReduce processing loadDigital computer detailsData switching networksData packReal-time computing
The invention concerns routing of data packets in a header-compressed domain. According to the method described, routing a data packet with a compressed header section and an uncompressed payload section comprises steps of receiving the data packet at an ingress interface, routing the data packet to an egress interface, and forwarding the data packet to the egress interface. According to this method, the compressed header section remains unchanged between the ingress interface and the egress interface. Various implementations of this method are described, including the use of the header compression context identifier (HCCID) by for routing the packets to the correct egress interface. Accordingly, a decompressor and a router are also disclosed.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
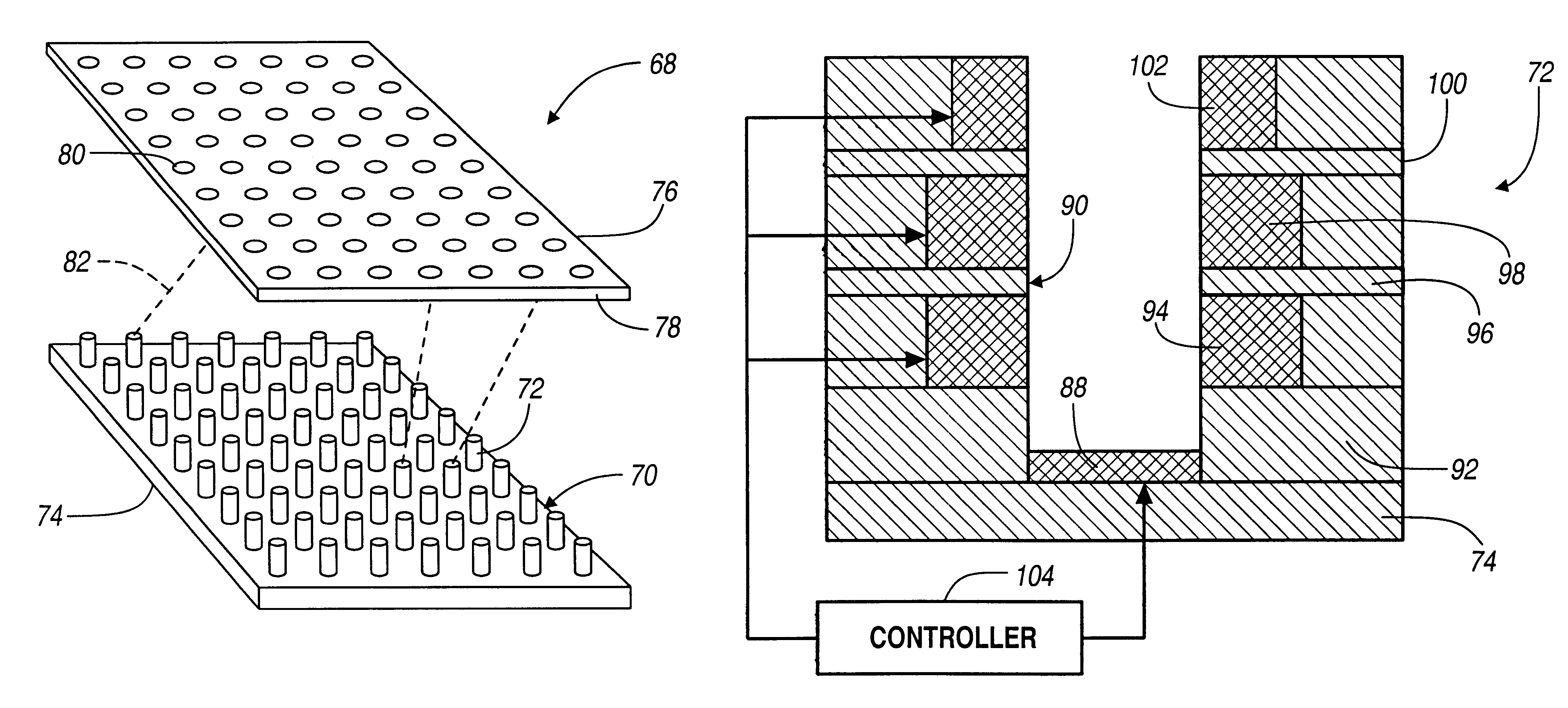
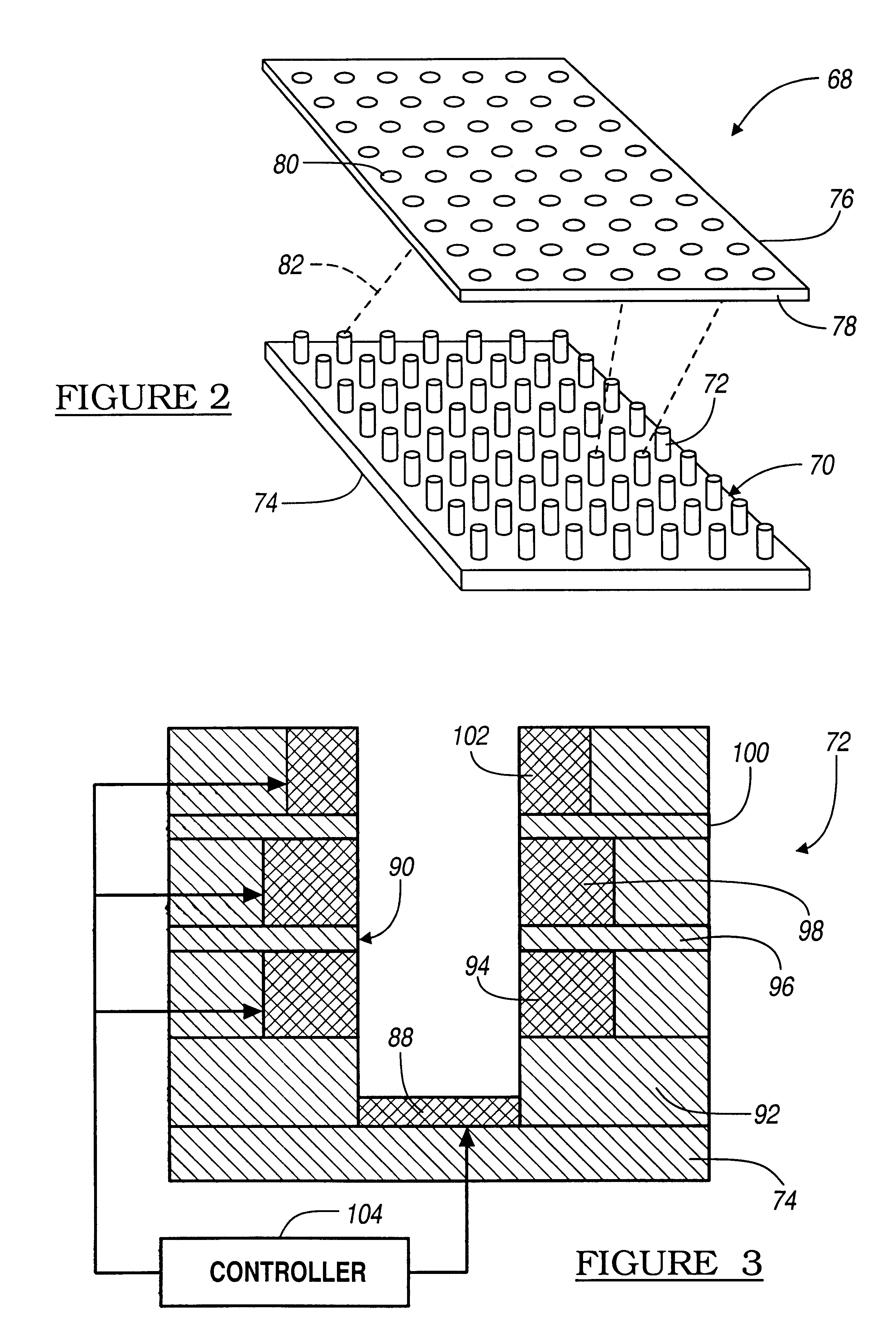
Use of a free space electron switch in a telecommunications network
InactiveUS6545425B2Laser detailsStatic indicating devicesTelecommunications linkTelecommunications network
A communications system that includes one or more free space electron switches. The free space electron switch employs an array of electron emitters, where each emitter is responsive to an RF or optical input signal on an input channel. Each emitter includes a cathode that emits electrons in response to the input signal. Each emitter further includes a focussing / accelerating electrode for collecting and accelerating the emitted electrons into an electron beam. Each emitter further includes an aiming anode that directs the beam of electrons to a desired detector within an array of detectors that converts the beam of electrons to a representative RF or optical signal on an output channel. Each emitter may include a modulating electrode that generates an electric field to modulate data onto the beam of electrons. The communications systems employing the switch can be an ISDN, DSLAM networks, packet routing systems, ADSL networks, PBX systems, local exchange systems, etc.
Owner:EXACONNECT
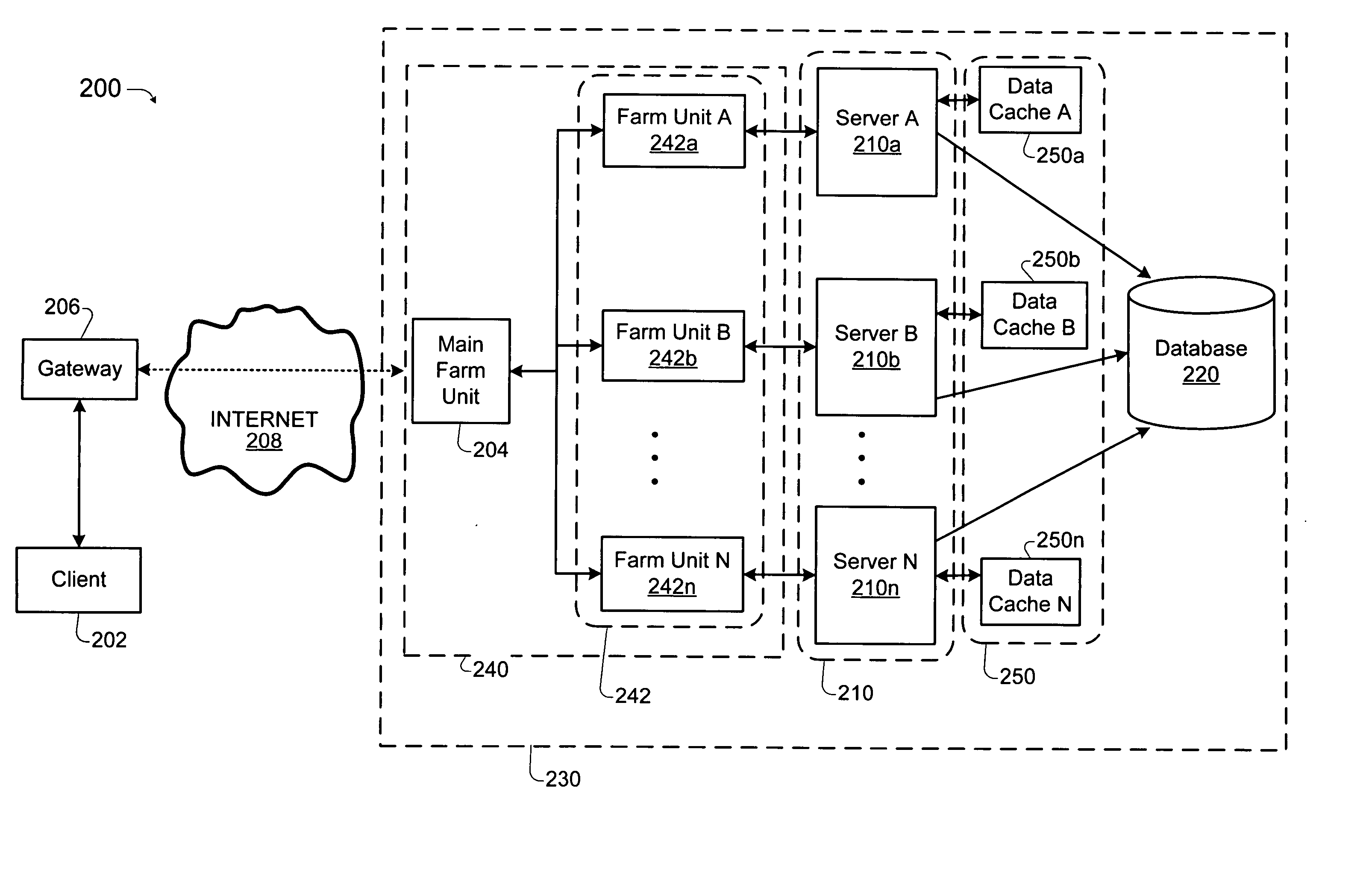
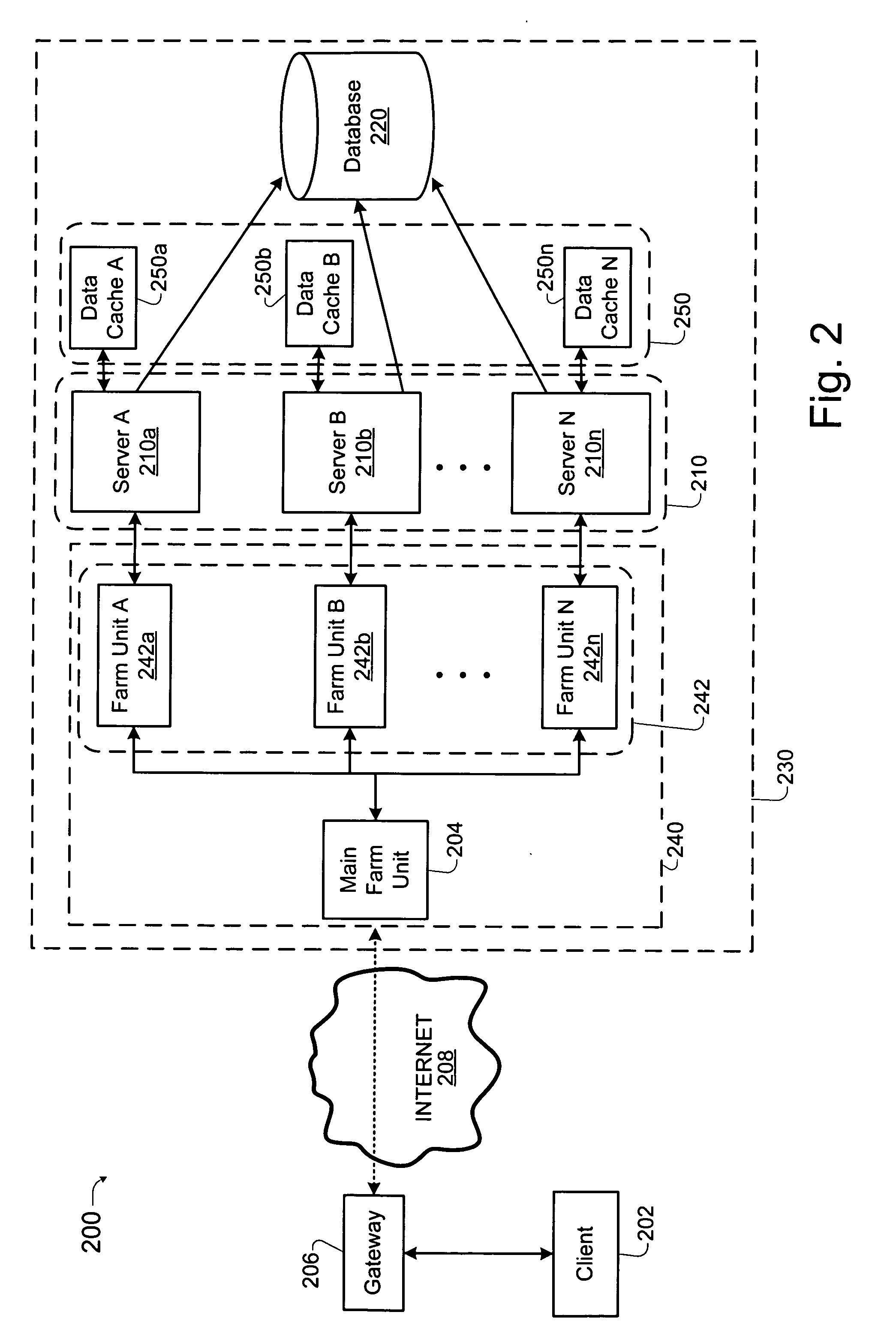
Load balancing technique implemented in a data network device utilizing a data cache
InactiveUS20050261985A1Easy to useDigital data information retrievalMultiprogramming arrangementsLoad SheddingData pack
Techniques for implementing a load balanced server system are described which may be used for effecting electronic commerce over a data network. The system comprises a load balancing system and a plurality of servers in communication with the load balancing system. Each of the plurality of servers may include a respective data cache for storing state information relating to client session transactions conducted between the server and a particular client. The load balancing system can be configured to select, using a load balancing protocol, an available first server from the plurality of servers to process an initial packet received from a source device such as, for example, a client machine of a customer. The load balancing system can also configured to route subsequent packets received from the source device to the first server. Before generating its response, the first server may verify that the state information relating to a specific client session stored in the data cache is up-to-date. If the first server determines that the state information stored in the data cache is not up-to-date, then the first server may be configured to retrieve the desired up-to-date state information from a database which is configured to store all state information relating to client sessions which have been initiated with the server system.
Owner:JUNE RAY
Packet routing and switching device
ActiveUS8270401B1Quick extractionData switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsNetwork processing unitPacket routing
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method to enable remote storage utilization
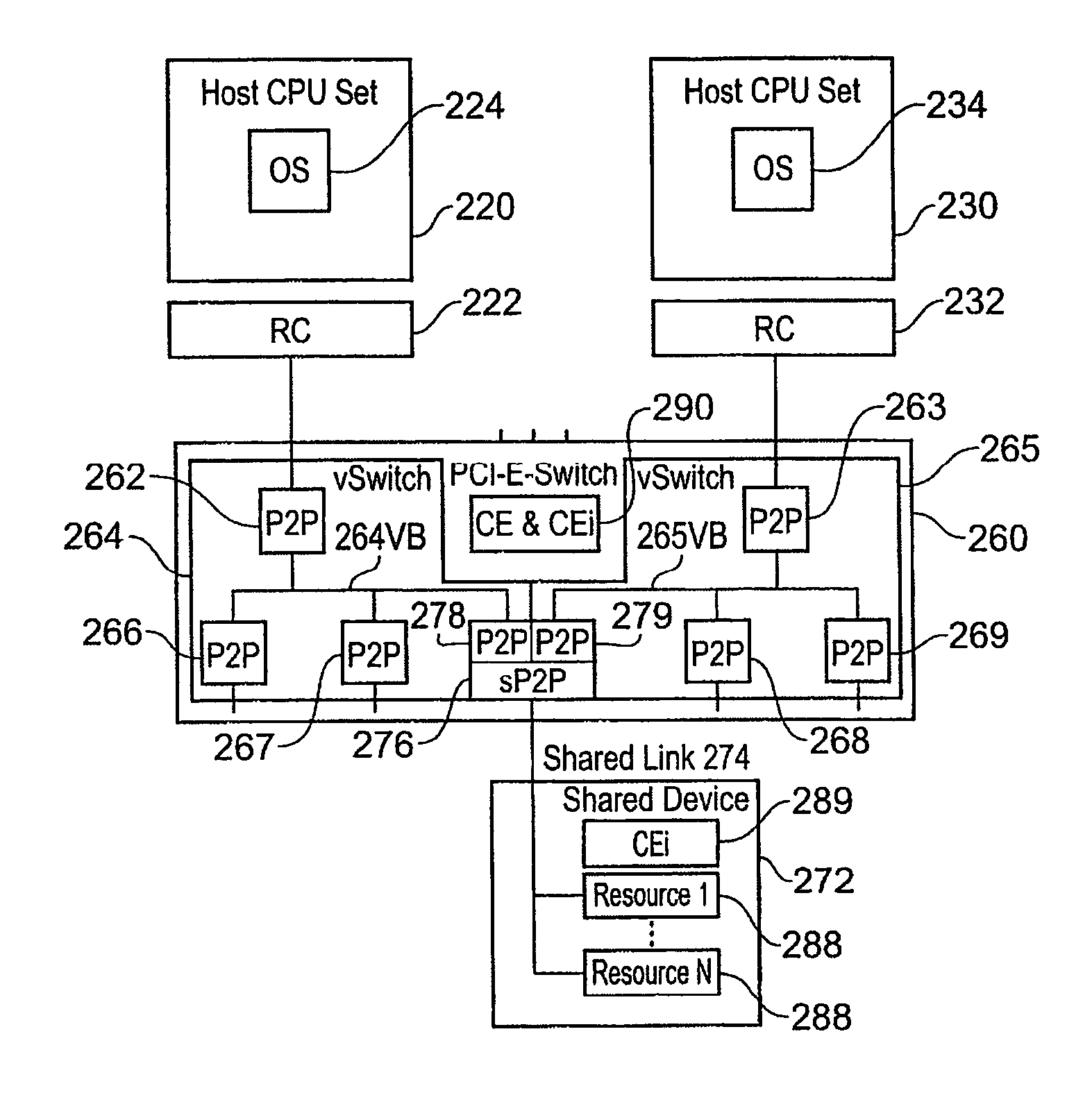
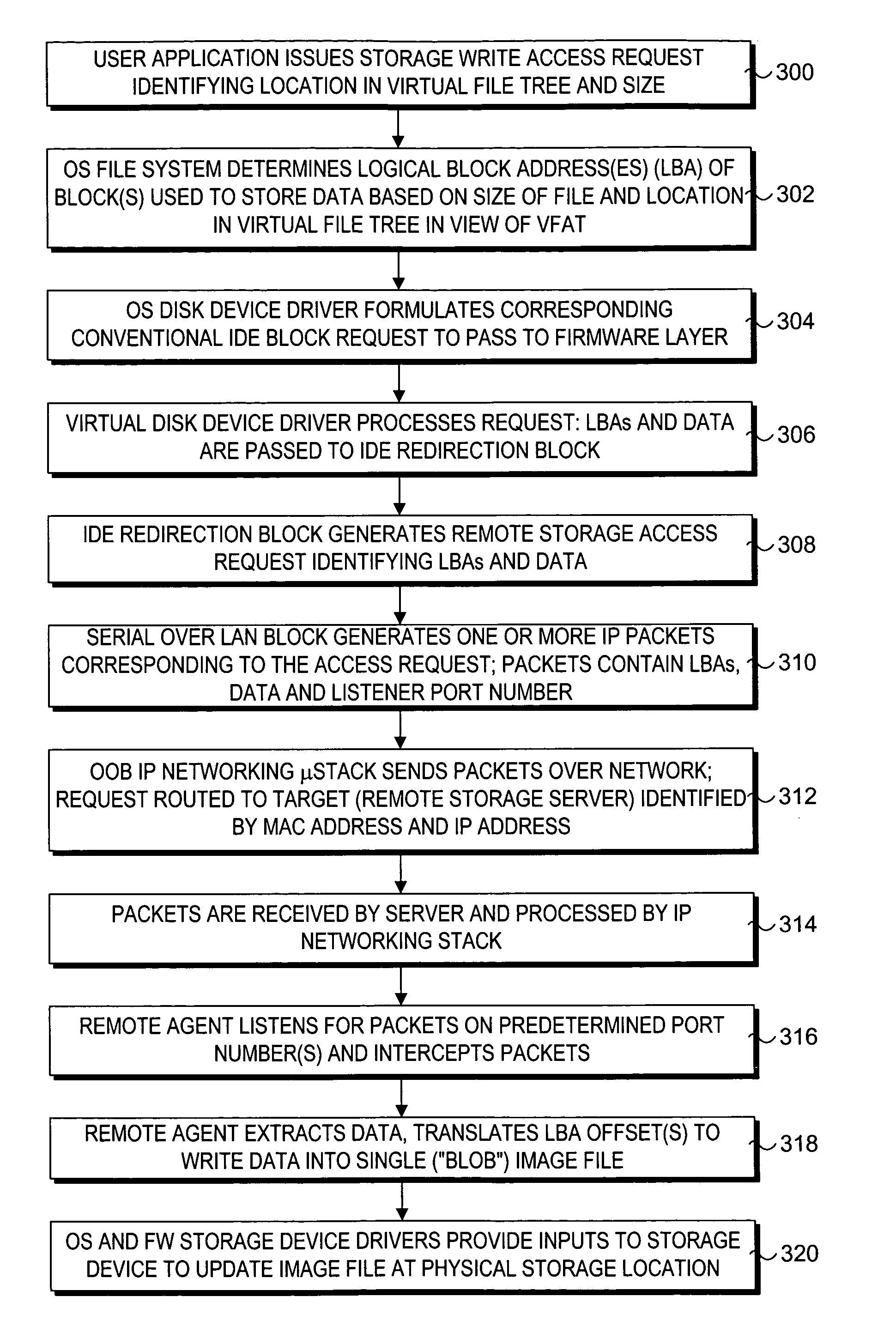
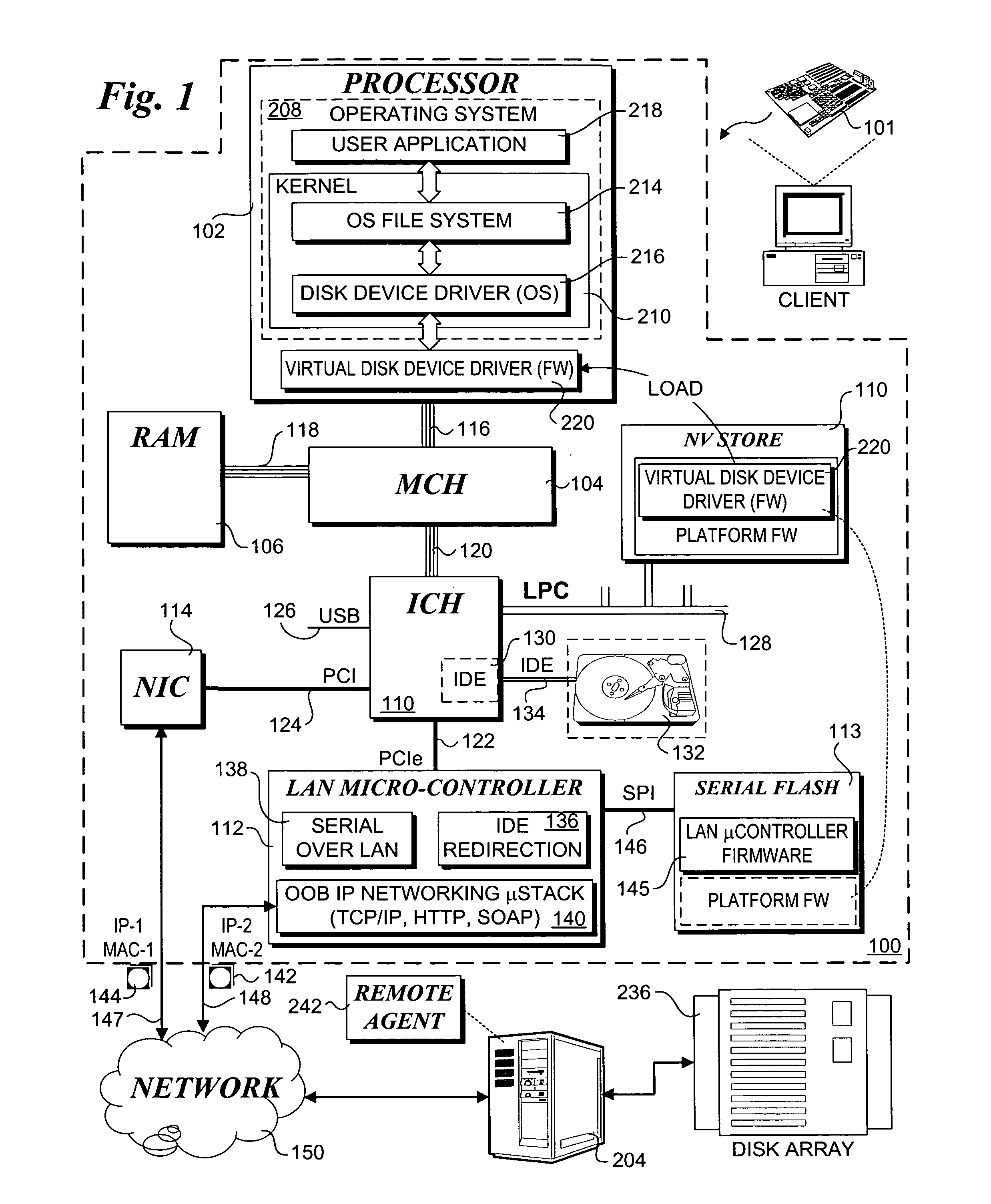
InactiveUS20050289218A1Input/output to record carriersMultiple digital computer combinationsMicrocontrollerData pack
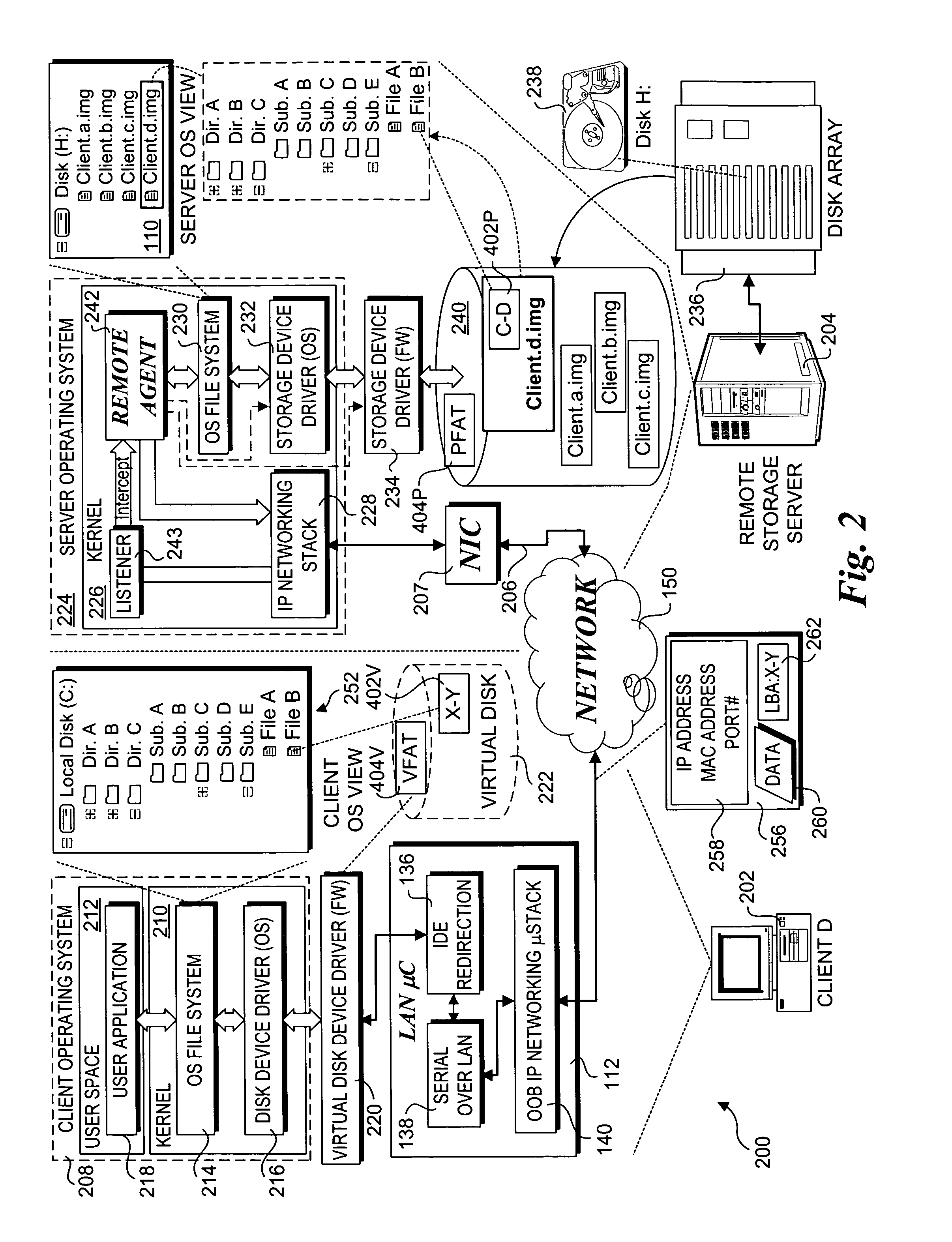
Techniques for enabling remote storage utilization as local disk resources. A virtual disk drive comprising an emulation of a non-existent local (to a client) disk drive is facilitated via out-of-band (OOB) communications with a remote storage server in a manner that is transparent to an operating system (OS) running on the client. Storage access requests are processed in a conventional manner by the client OS, being passed as a block storage request to a firmware driver. The firmware driver redirects the request to a remote agent running on the remote storage server via a LAN microcontroller on the client using an OOB channel. A listener at the remote server routes packets to the remote agent. The remote agent performs a logical-to-physical storage block translation to map the storage request to appropriate storage blocks on the server. In one embodiment, an image of the virtual disk is stored in a single file on the server. The scheme supports diskless clients, disk mirroring and remote OS provisioning.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Minimum latency cut-through switch fabric
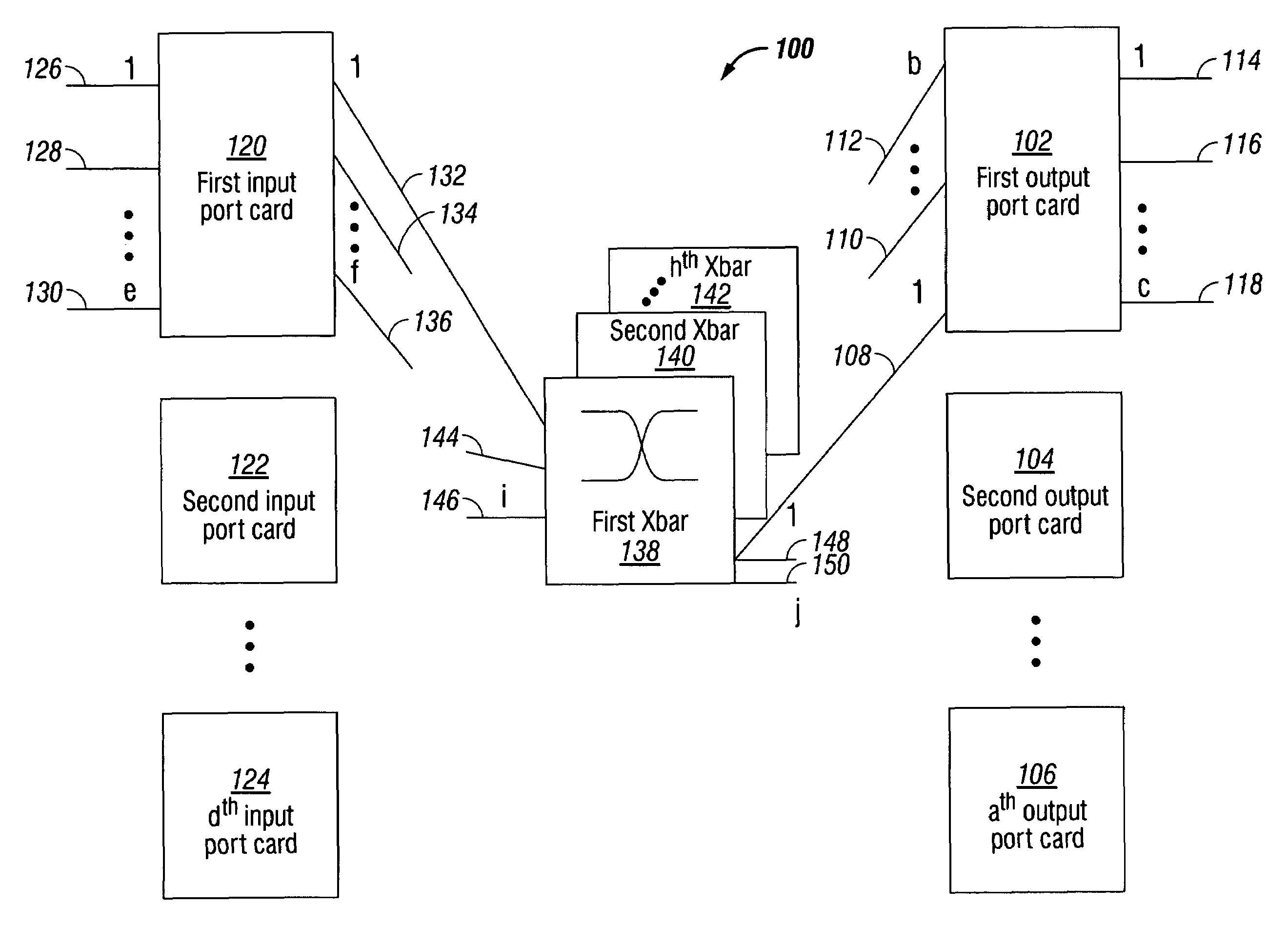
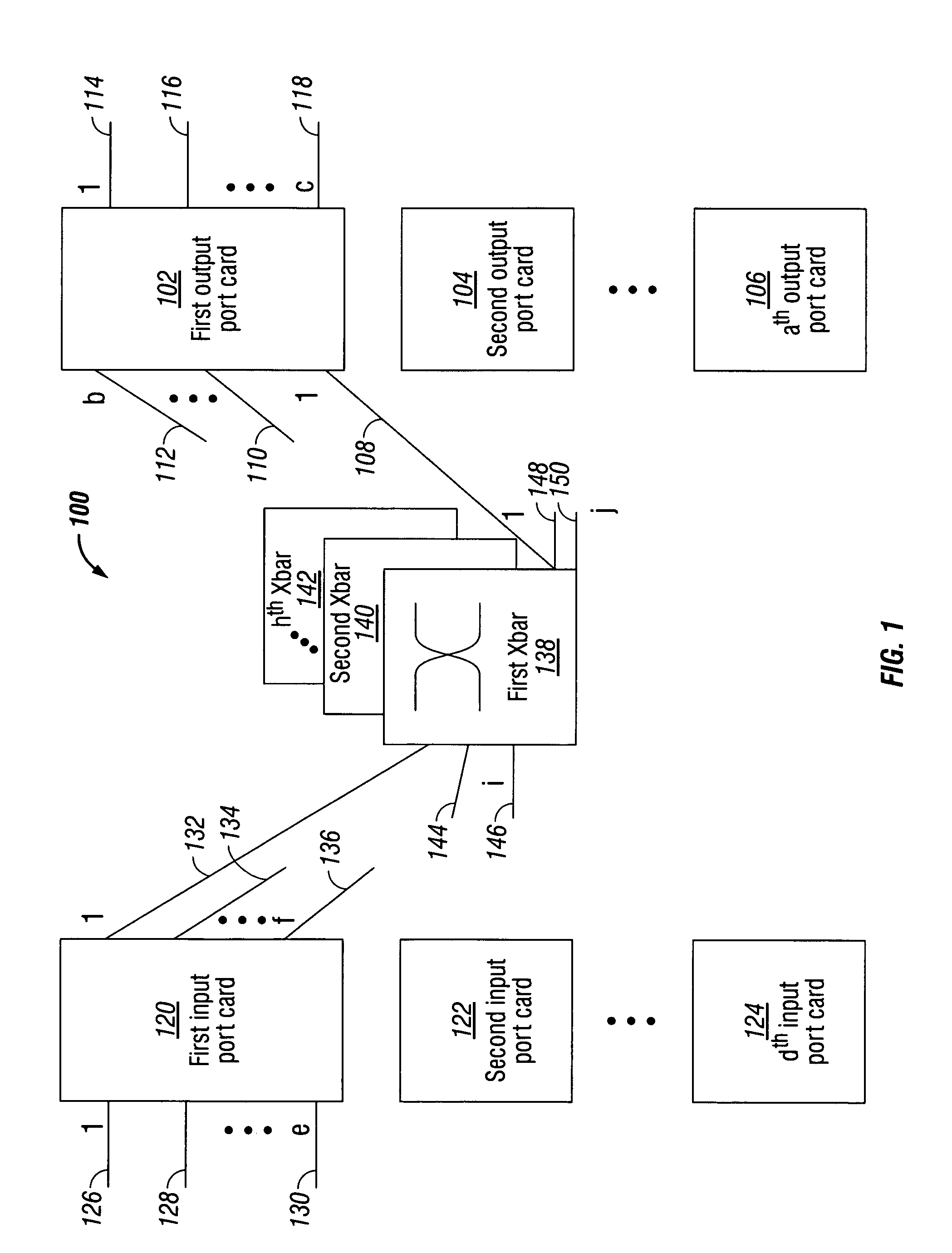
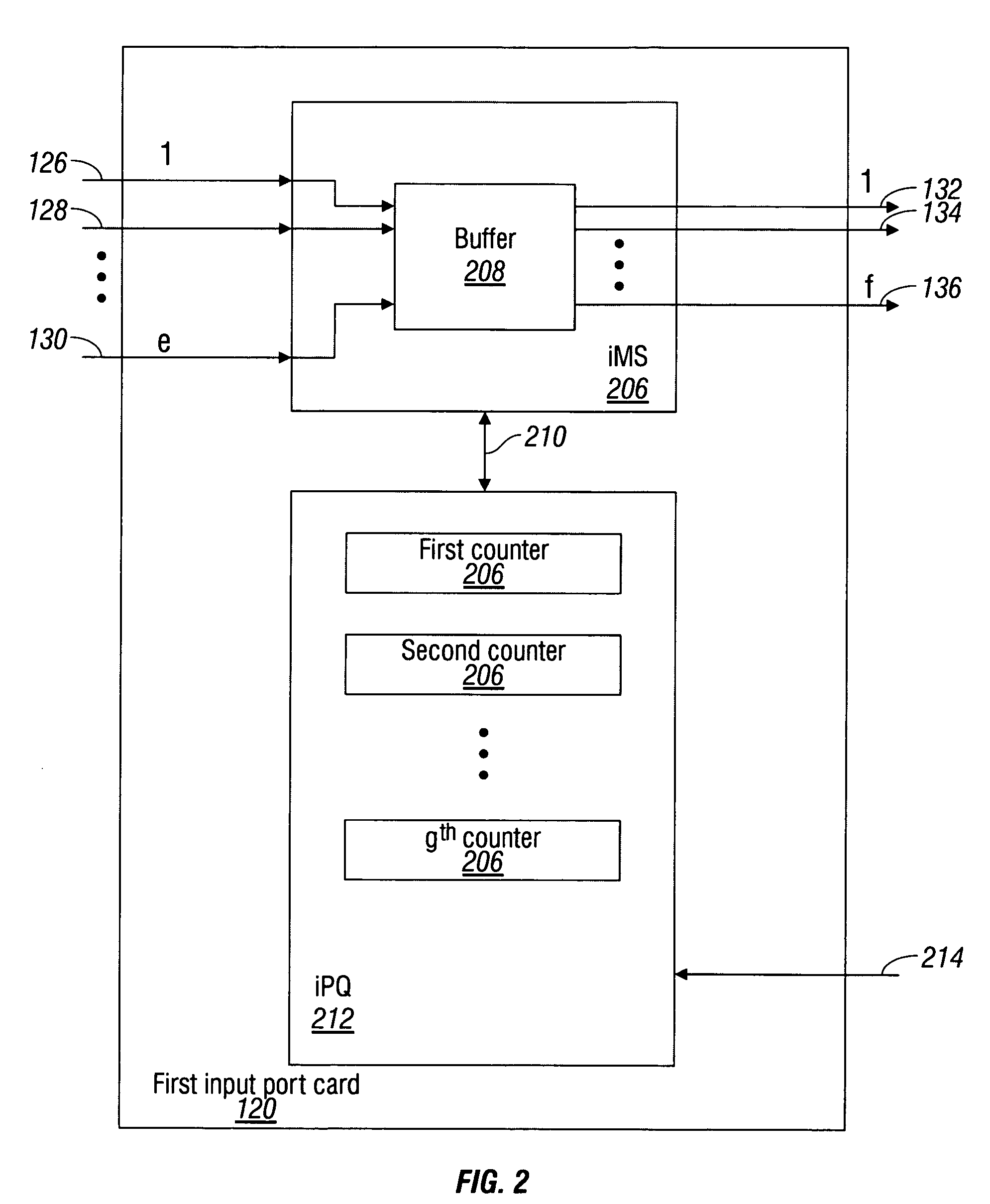
InactiveUS7230947B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationPacket communicationCut-through switching
A system and method are provided for cut-through packet routing in a packet communications switch fabric. The method comprises: accepting information packets addressed to a plurality of output port card egress ports at an input port card ingress port; routing information packets between port cards on backplane data links through an intervening crossbar; maintaining a credit counter for each port card egress destination, at the input port card; decrementing the counter in response to transmitting cells in a packet from the input port card; and, incrementing the counter in response to transmitting cells from the packet at the output port card. In some aspects of the method, accepting information includes buffering the packets in an ingress memory subsystem (iMS). Routing information includes the iMS transmitting buffered packets on a selected backplane data link. Decrementing the counter includes the iMS communicating with the iPQ in response to transmitting a cell.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
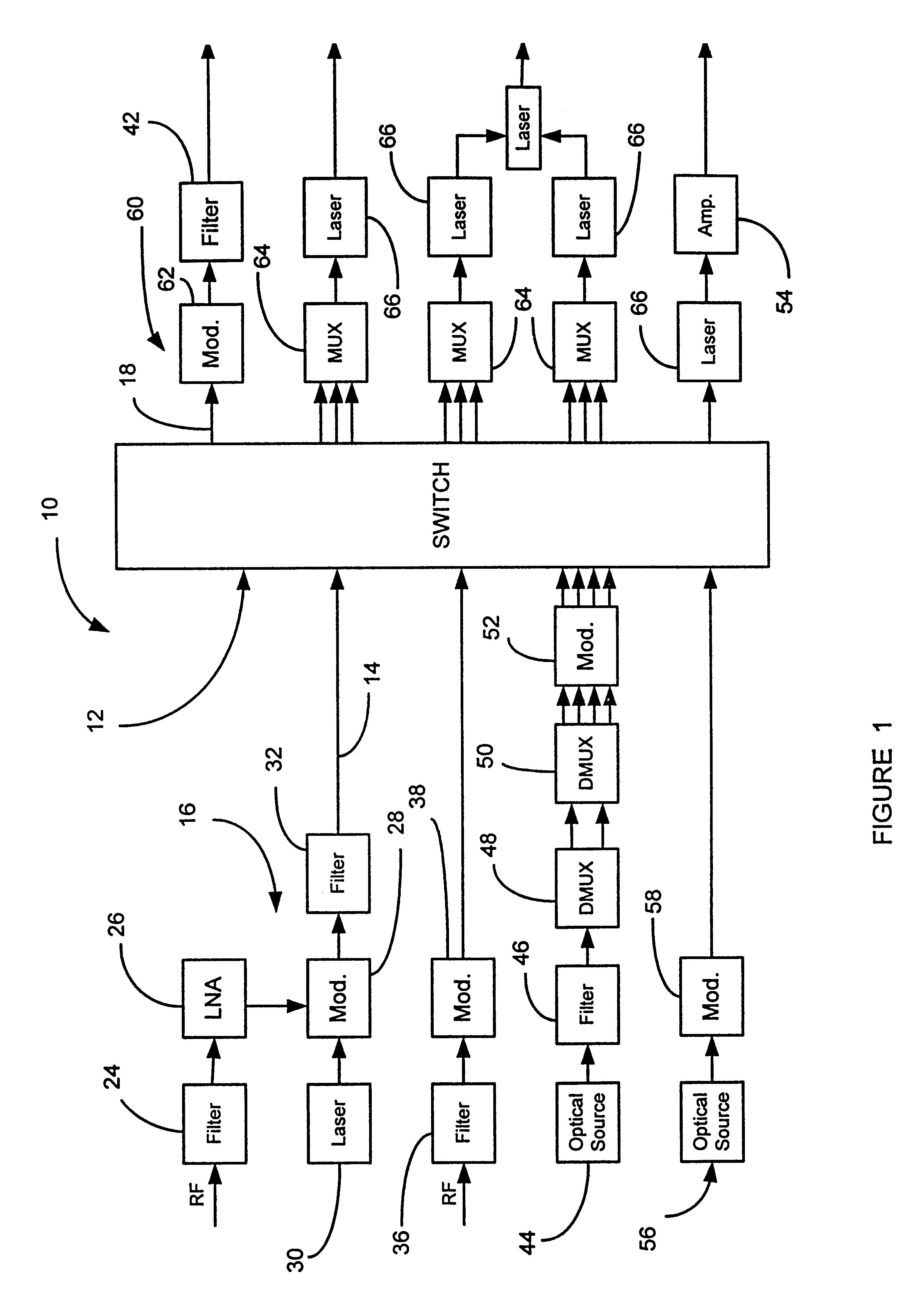
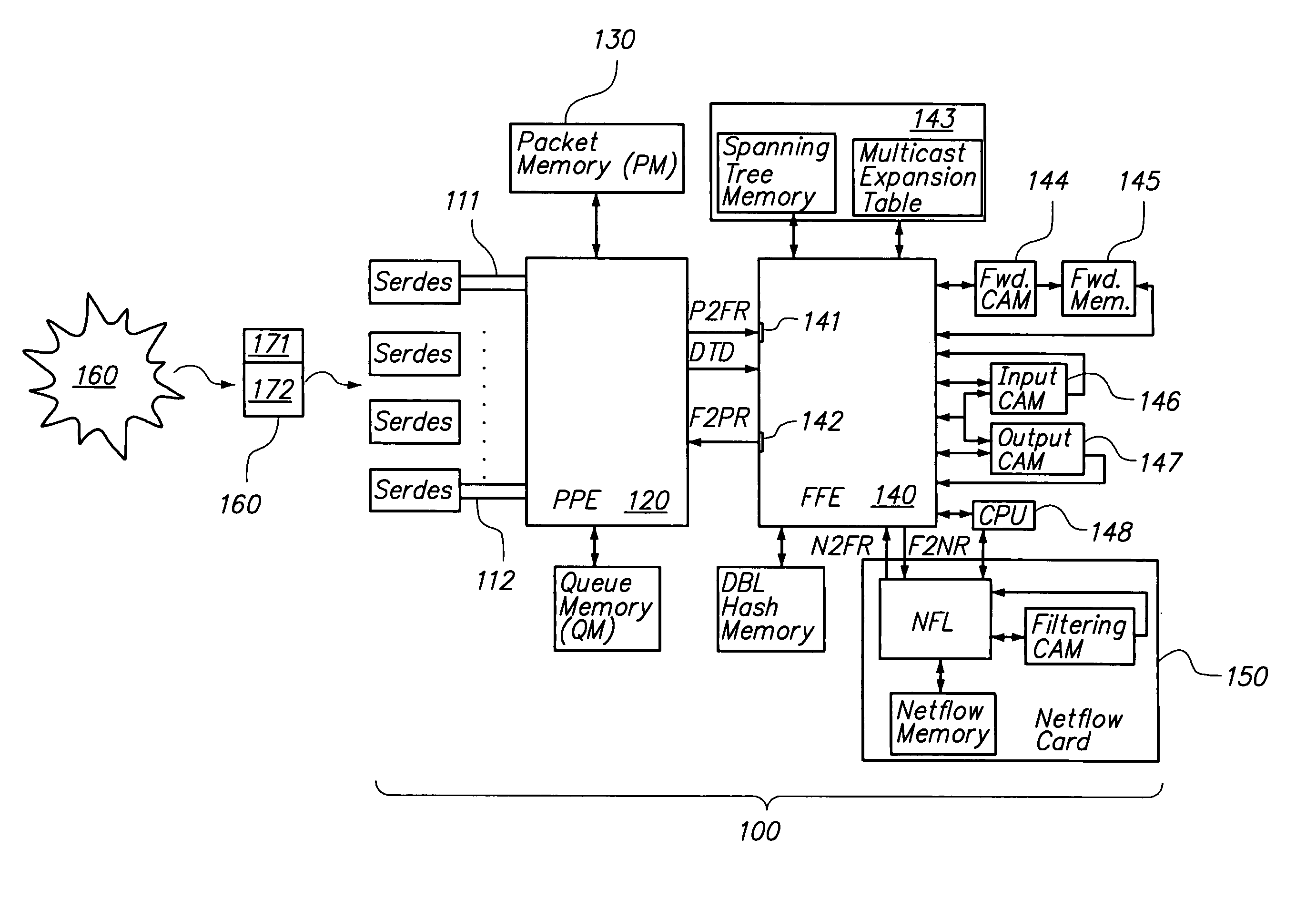
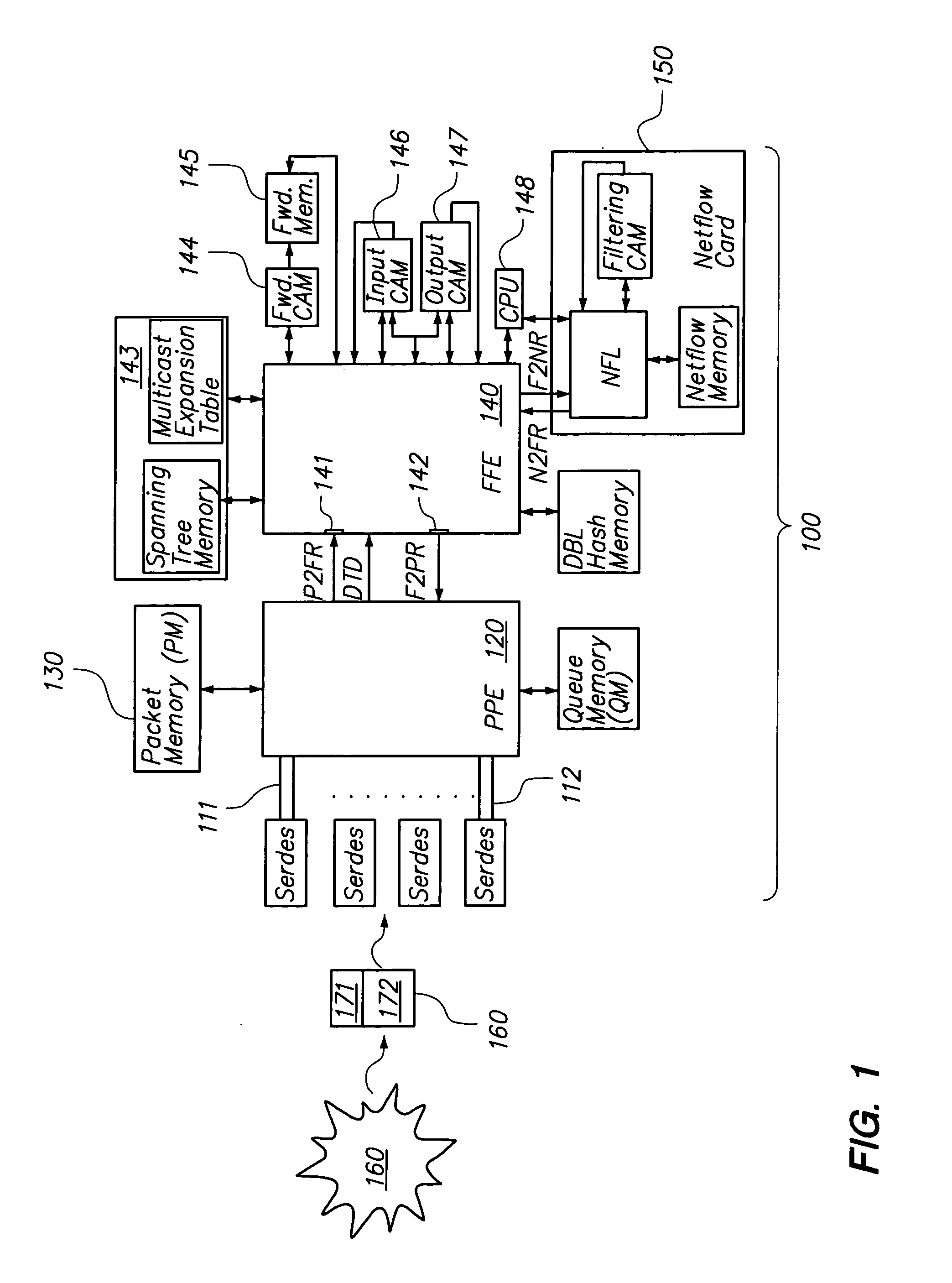
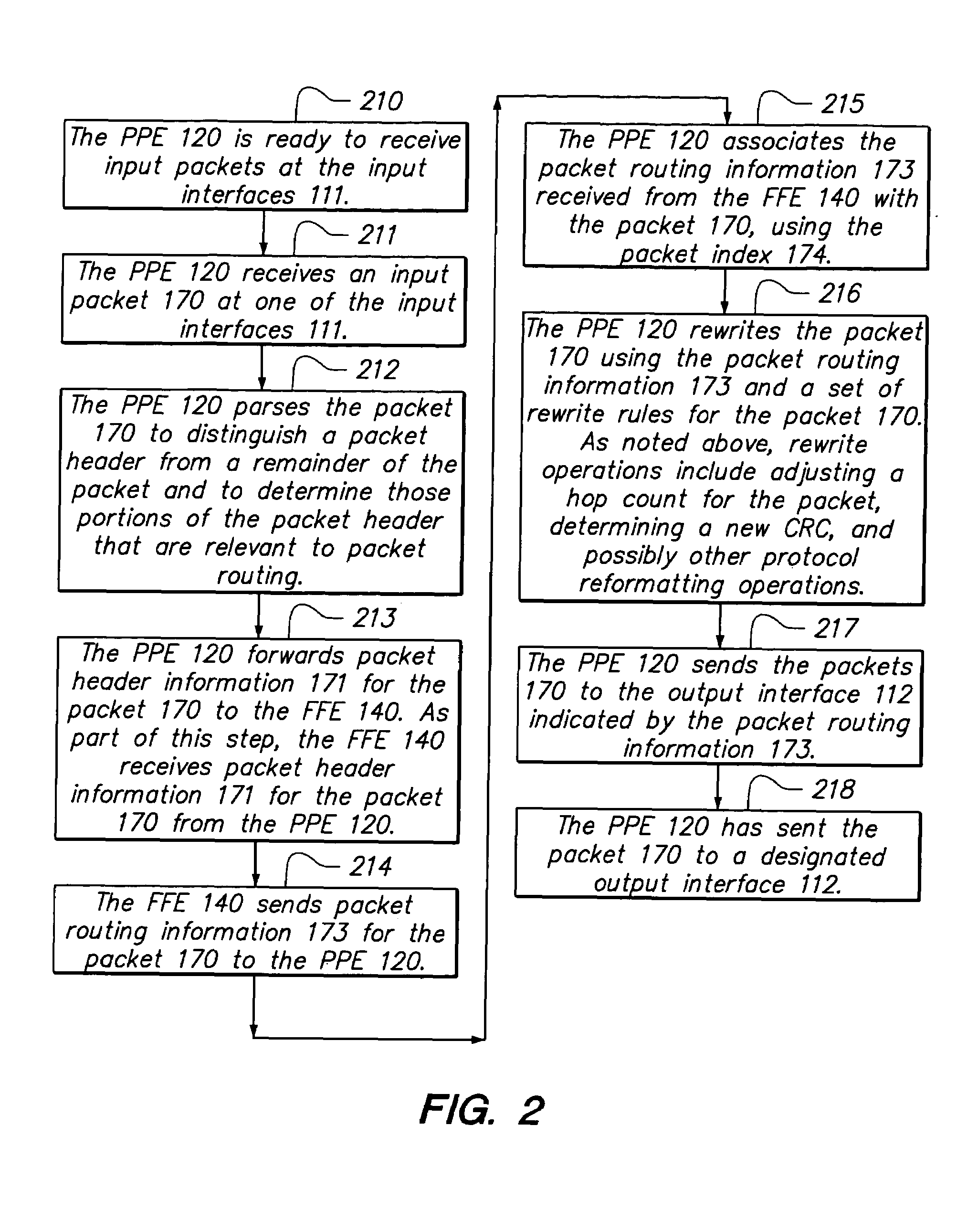
Packet processing engine architecture
InactiveUS7218632B1Reduce data volumeReduced pin countData switching by path configurationPacket routingPacket processing
The invention provides a method and system for packet processing, in which a router (or switch) is capable of quickly processing incoming packets, thus performing level 2, 3, and 4 routing and additional services, in real time. A system includes a packet processing engine (PPE), having elements for receiving packets, distinguishing header and payload information for those packets, outsourcing router decision-making to additional hardware resources such as a fast forwarding engine (FFE), and forwarding those packets. The PPE is synchronized to the FFE, so that the PPE can send and the FFE can receive packets at each one of a sequence of constant-duration time quanta. Similarly, the PPE can receive and the FFE can send packet routing information at each one of a sequence of similar time quanta. The PPE and the FFE have separate hardware so that their functions can be performed in parallel without contention for operating resources.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method of programming a co-verification system
ActiveUS20060015313A1Detecting faulty computer hardwareComputer aided designAnalog signalTerm memory
A co-verification system includes a computer programmed to act as a simulator for simulating behavior of a first portion of an electronic device under test (DUT) by acquiring, processing and generating data representing DUT signals. The co-verification system also includes emulation resources programmed to emulate a second portion of the DUT by receiving, processing and generating emulation signals representing DUT signals. The signals of the DUT are mapped to separate addresses within a memory space, and the simulator controls and reads states of emulation signals by writing data to and reading data from addresses of the memory space states mapped to the DUT signals the emulation signals represent. The computer and the emulation resources are also programmed to implement transactors communicating with one another through a packet routing network. The transactors set states of the emulation signals when the simulator writes to memory space addresses and for reading states of the emulation signals. The transactors monitor states of emulation signals and return data indicating those states to the simulator when the simulator reads memory space addresses mapped to DUT signals represented by the emulation signals.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Network routing apparatus that performs soft graceful restart
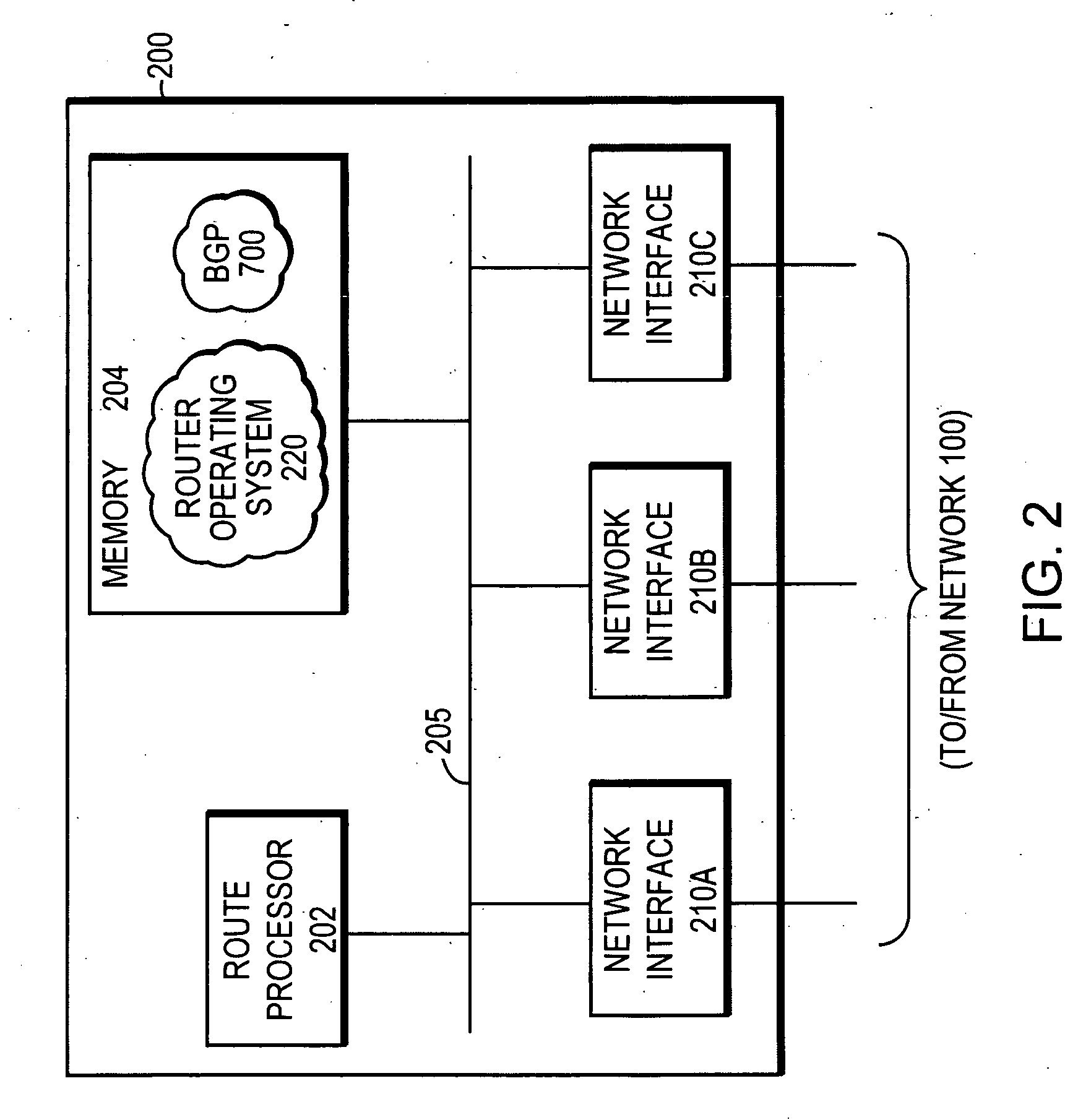
ActiveUS20060171404A1Data switching by path configurationStore-and-forward switching systemsBorder Gateway ProtocolNetwork data
A network data packet routing apparatus with BGP is configured to soft reset an AFI or SAFI, so that forwarding on routes associated with the AFI or SAFI can continue even after an event or error. One approach involves establishing a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) peering session between a first node and a second node in a packet-switched network; detecting a BGP condition requiring a reset of a BGP address family indicator (AFI) data structure or a sub-address family indicator (SAFI) data structure, wherein the BGP condition does not affect states of routes in the AFI or SAFI; preserving a BGP state and a forwarding state of the AFI or SAFI; and forwarding data on routes represented in the AFI or SAFI. Soft notification messaging and marking routes as stale facilitates the approach.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
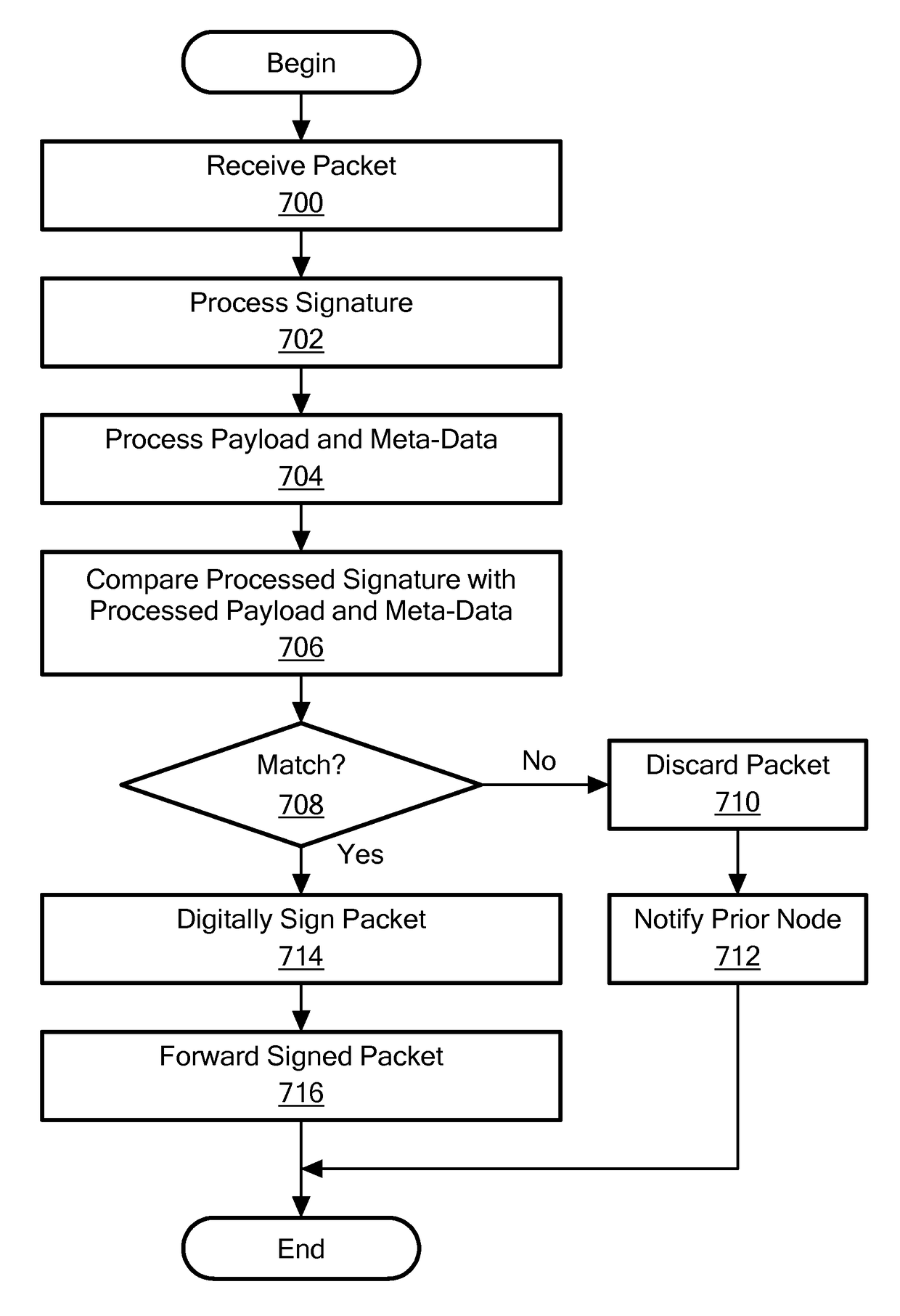
Network device and method for processing a session using a packet signature
A method processes a session having a first session packet received by a current node in an IP network having a plurality of nodes. The plurality of nodes includes a next node, and the current node that communicates with the next node using a Layer 3 protocol. The method receives the first session packet, which has a digital signature, payload data, and meta-data, at the current node. The method uses the payload data and meta-data to produce validation information, and uses the digital signature to produce a comparator digital signature. Next, the method compares the validation information with the comparator digital signature. If the validation information does not match the comparator digital signature, then the method discards the first session packet. If there is a match, then the method digitally signs the first session packet, and routes the first session packet to the next node via the IP network.
Owner:128 TECH
Packet routing with payload analysis, encapsulation and service module vectoring
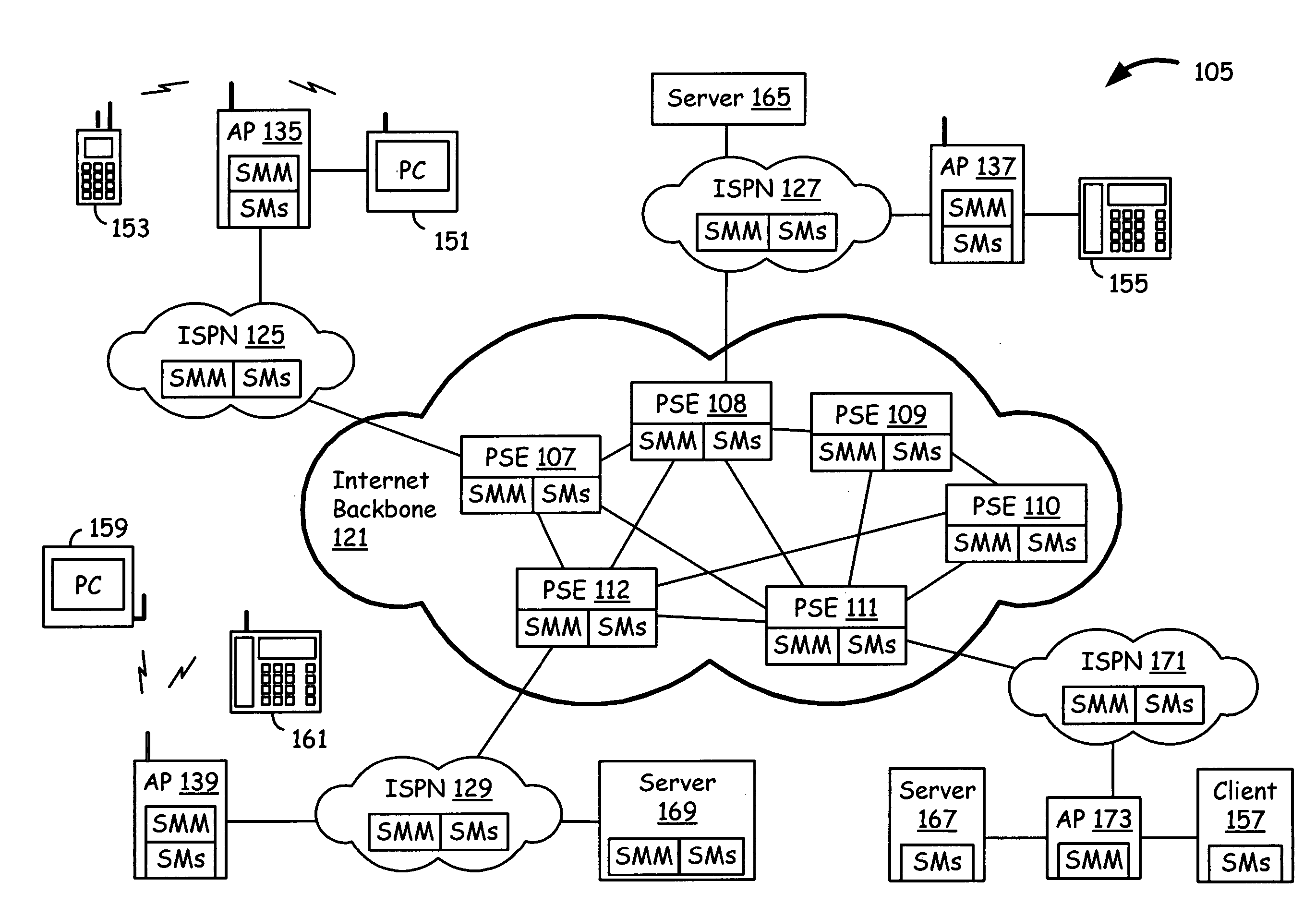
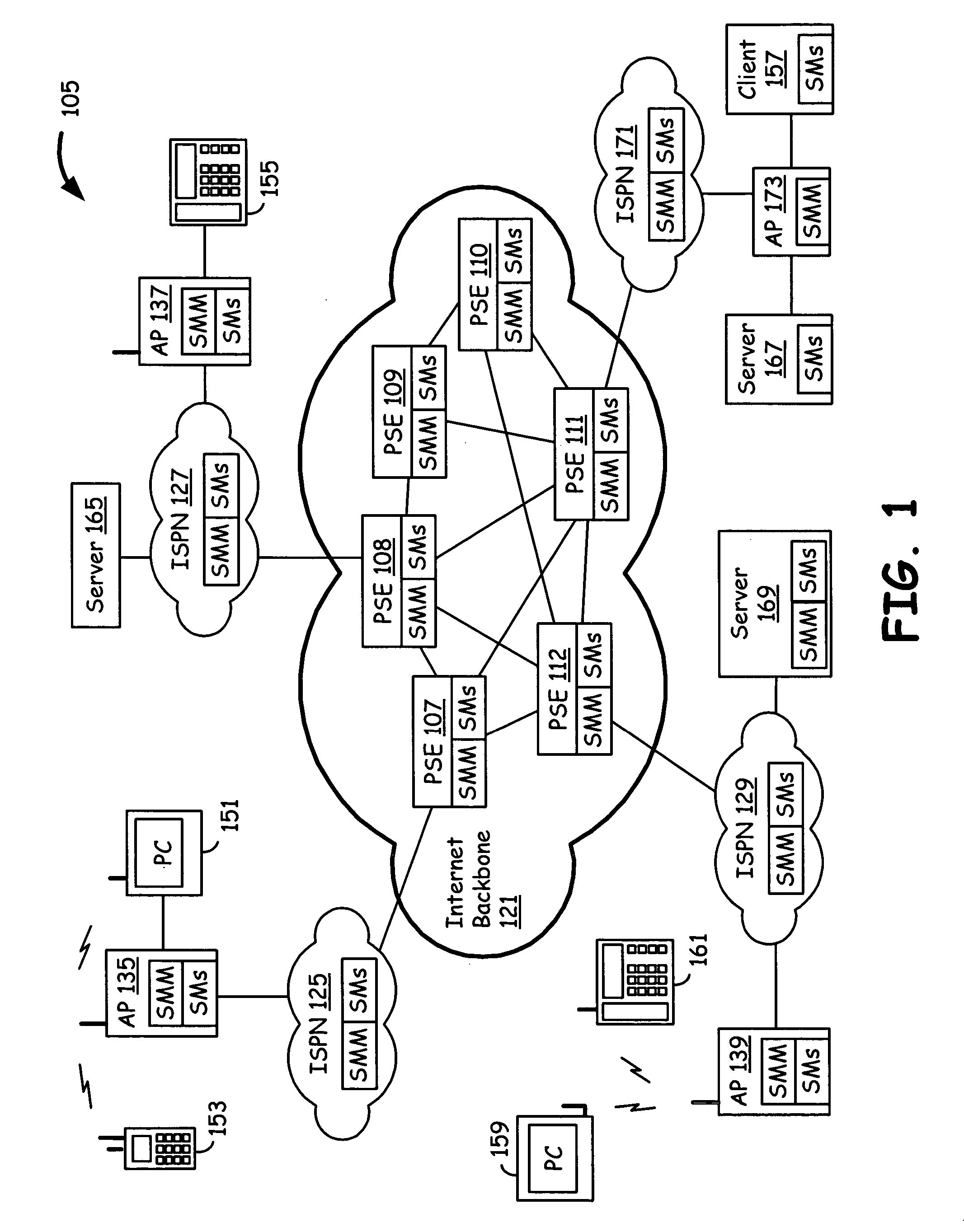
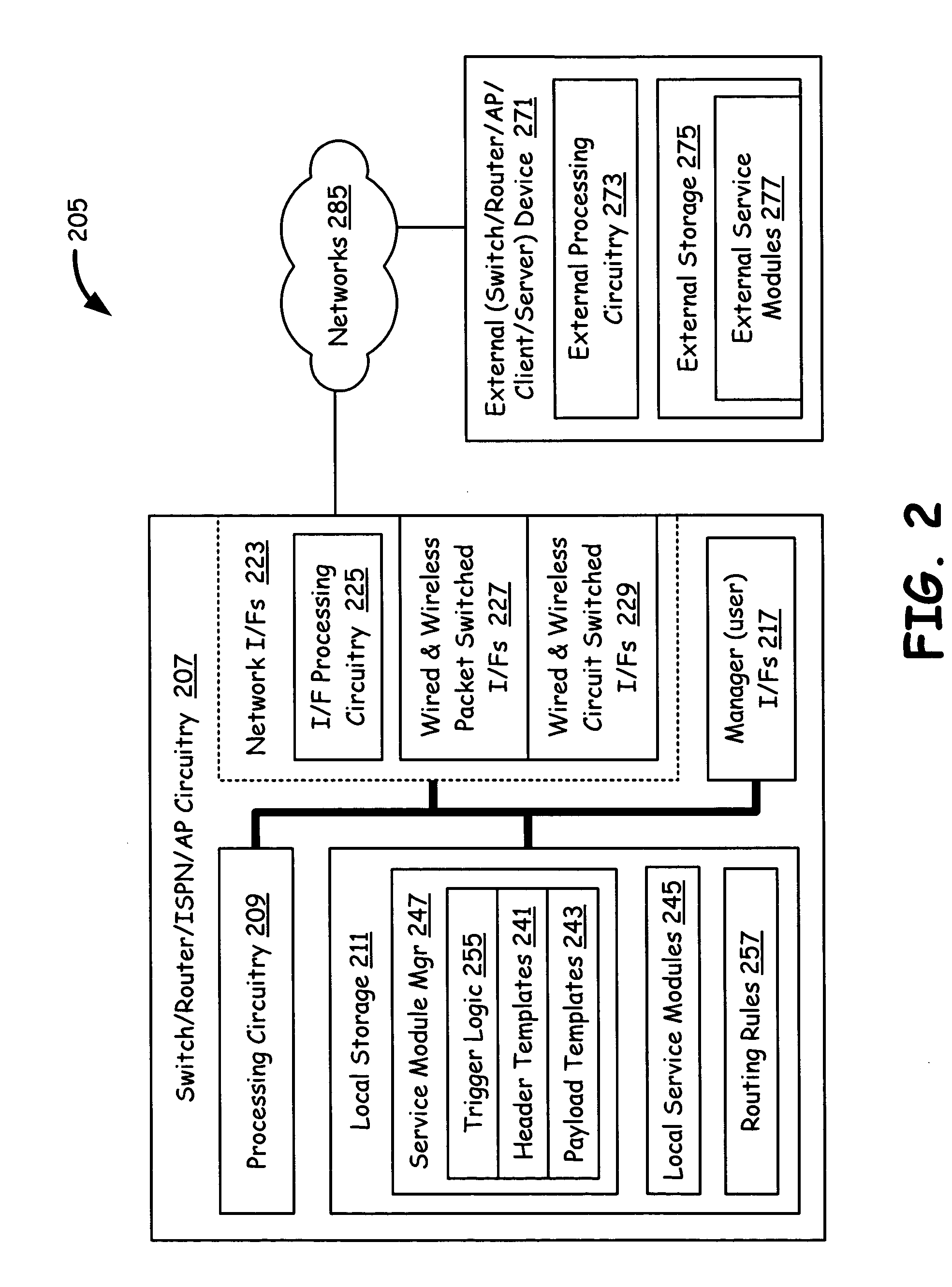
An Internet infrastructure with network devices and end point devices containing service module manager and service modules, that supports packet analysis, encapsulation and vectoring, and interleaving applications. The network device that supports packet content analysis on arriving packet, consists of a plurality of packet switched interface circuitries, user interface circuitry, local storage comprising the service module manager software and a plurality of local service modules, and processing circuitry communicatively coupled to each of the packet switched interfaces, local storage and user interface circuit. The processing circuitry executes service module manager and thus analyzes the packet content and applies one or more selected local service module processing using the packet. The processing circuitry thus takes one or more actions on the packet. A packet switching exchange that supports packet content analysis, encapsulation and vectoring on arriving packet, consisting a plurality of interconnecting switches, a plurality of line cards, general primary processing card. A client device that supports packet content analysis on arriving packet containing a plurality of network interfaces, user interface circuitry, local storage and processing circuitry communicatively coupled to each of the network interfaces, local storage and user interface circuitry.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
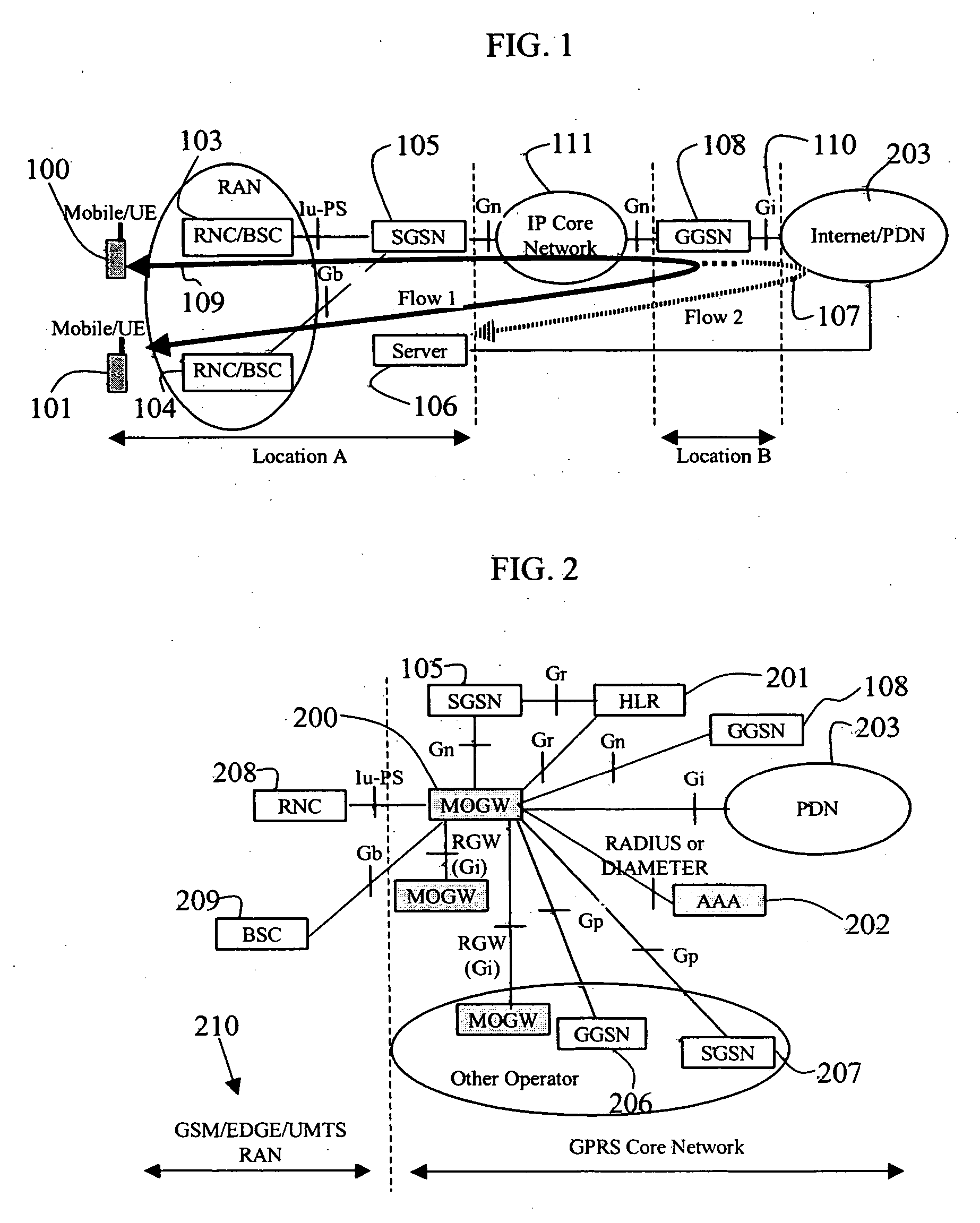
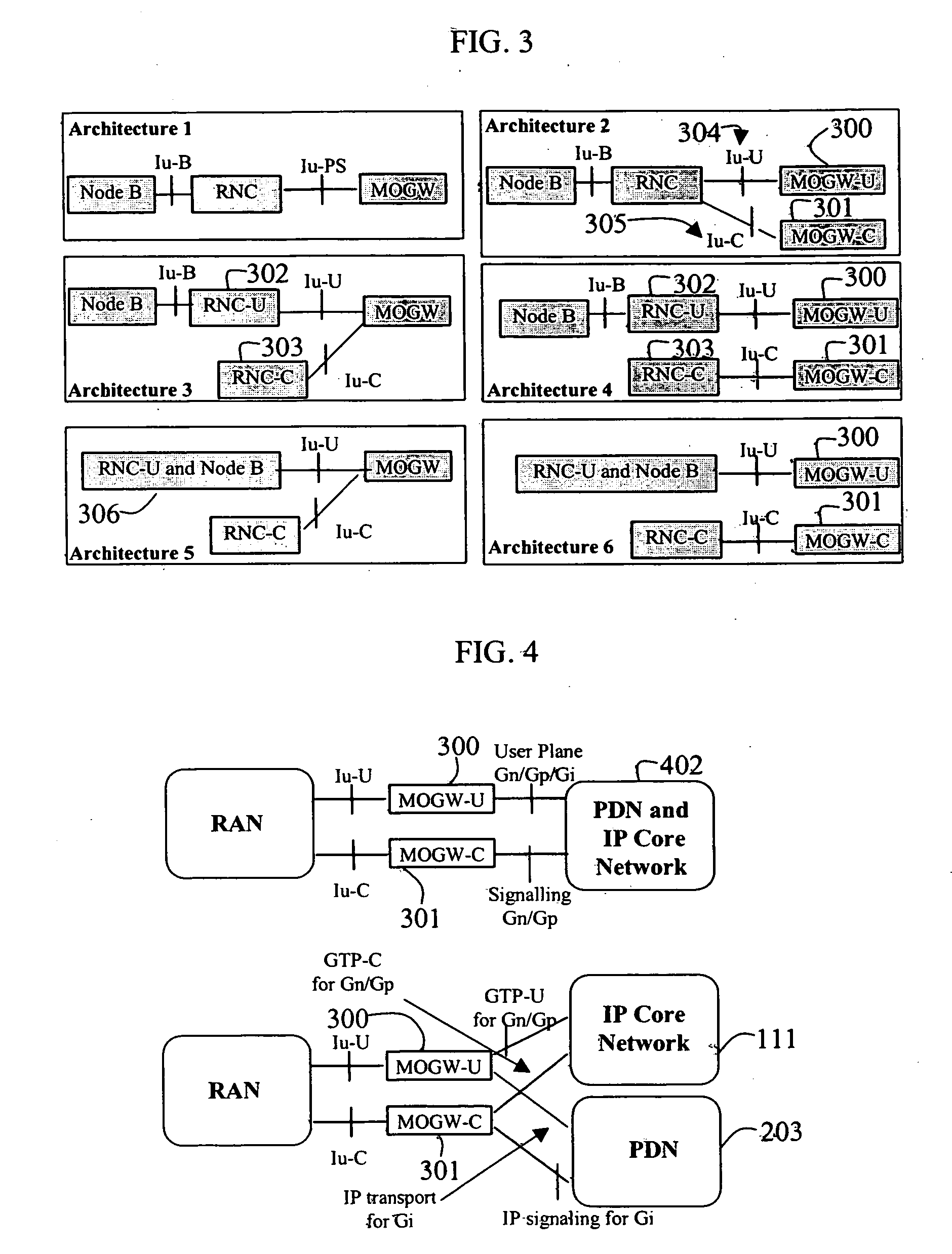
Wireless mobility gateway
ActiveUS20070091862A1Efficient forwardingEasy to moveData switching by path configurationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTelecommunicationsThe Internet
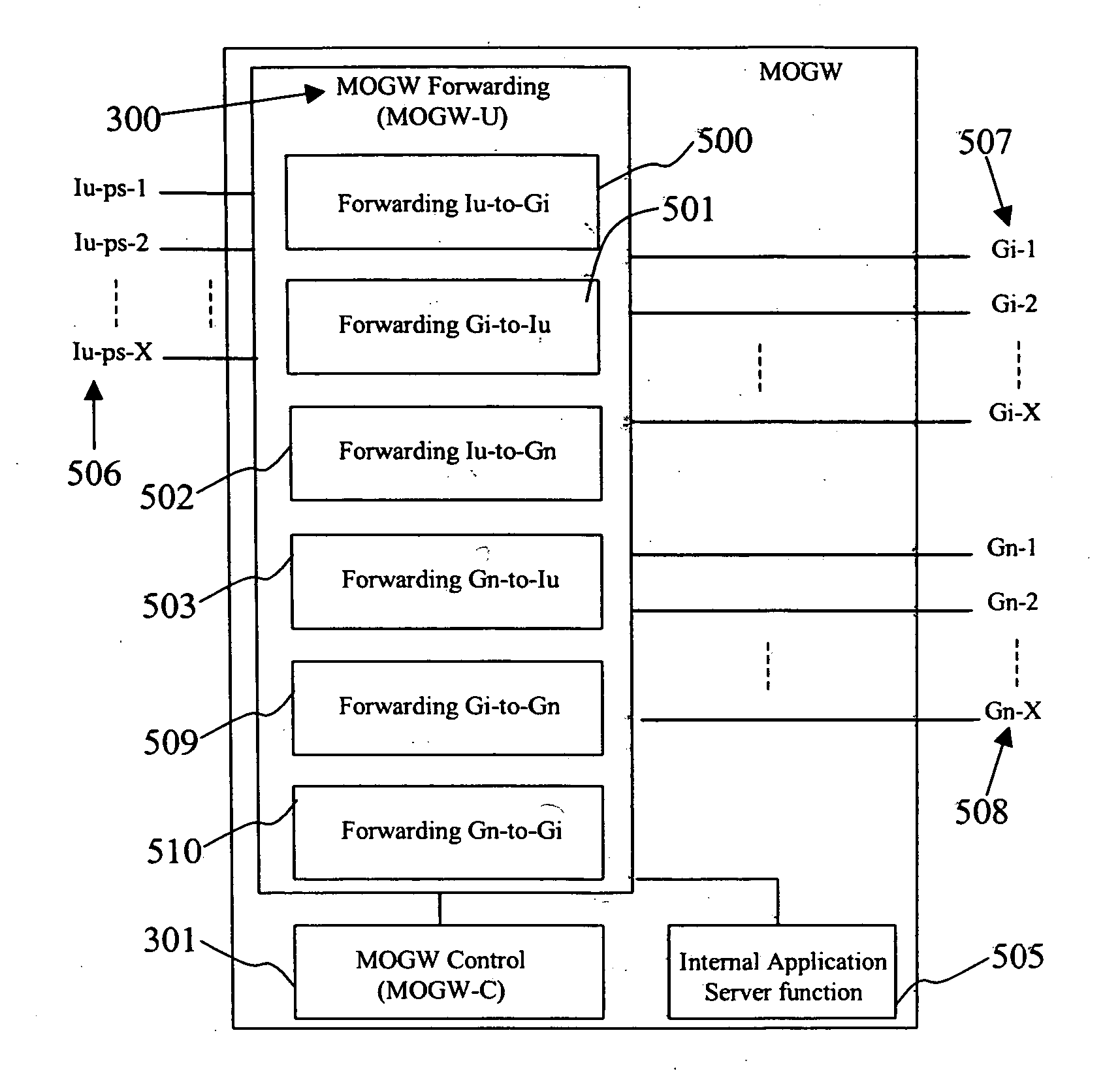
According to certain embodiments of the present invention, Wireless Mobility Gateway (MOGW) method and apparatus determines whether a wireless connection has been requested by a mobile terminal. As a consequence it performs security functions to authenticate the mobile user and grant access. If requested by the mobile user it then also creates a wireless connection to allow it to perform IP packet transmission and reception and therefore make use of mobile data services. The MOGW is able to directly route packets to Internet and Corporate Networks, thus rendering the whole mobile network more efficient and simpler to construct and manage. The MOGW generates a special tunnel identifier to identify the wireless connection that must be contained in all packets received from the RAN. The MOGW generates such a tunnel identifier by concatenating a number of values that characterize the connection. Therefore, simply by reading this tunnel identifier, the MOGW can more efficiently forward packets appropriately. The Mobility protocol and function between MOGWs allows Mobile terminals to easily move between geographical areas served by different MOGWs.
Owner:ATHONET
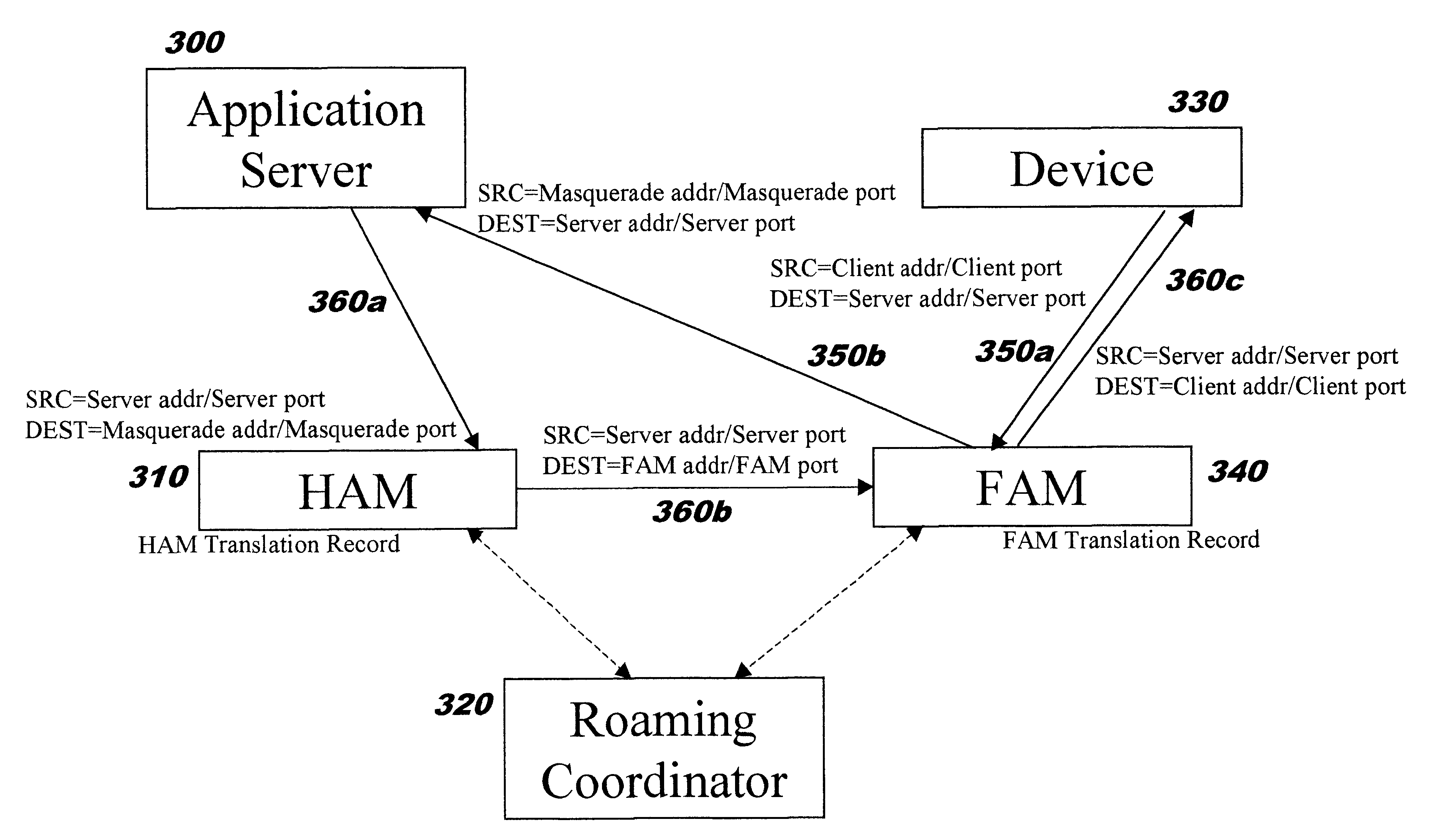
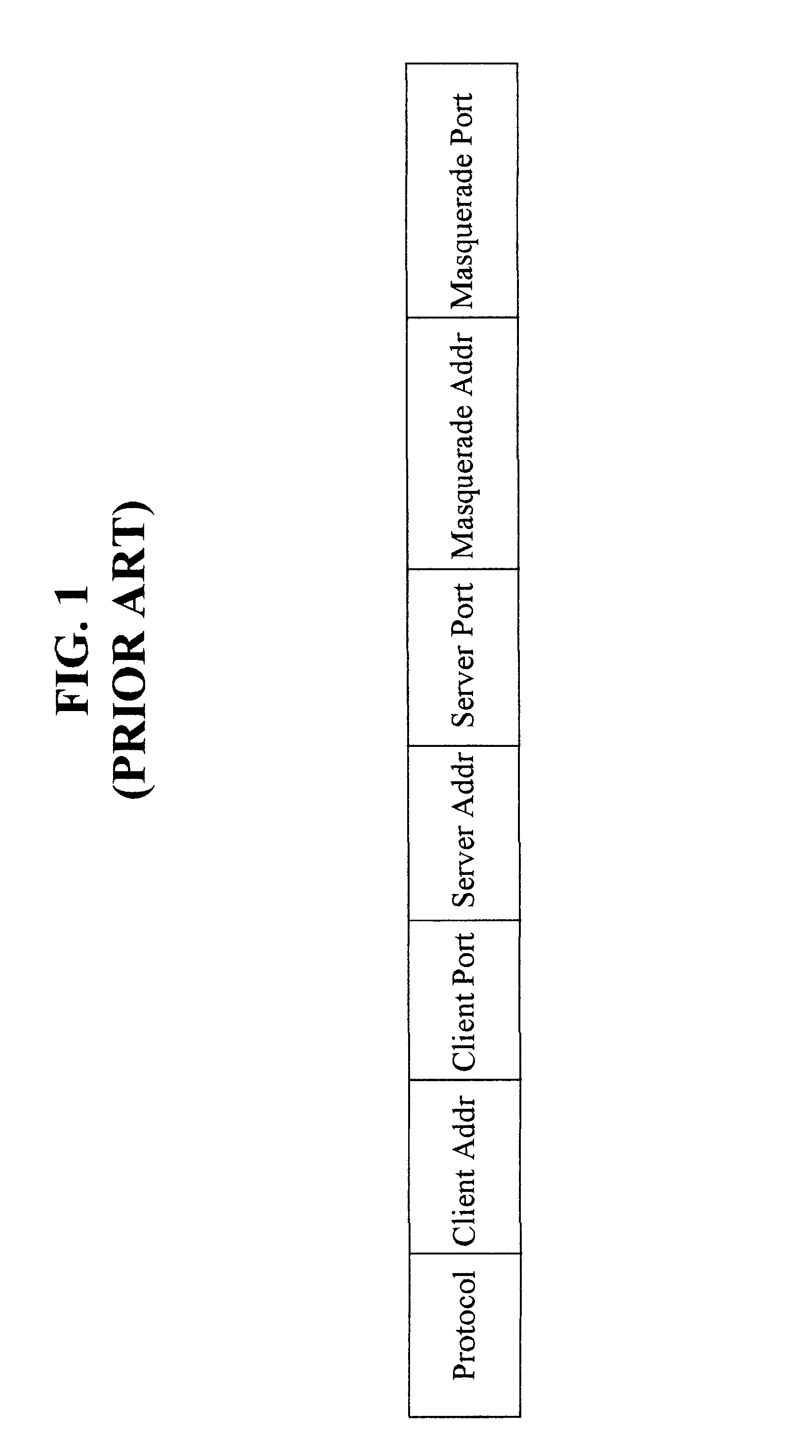
Providing secure network access for short-range wireless computing devices
InactiveUS6851050B2Improve system performanceImprove scalabilityKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationEncrypted functionClient-side
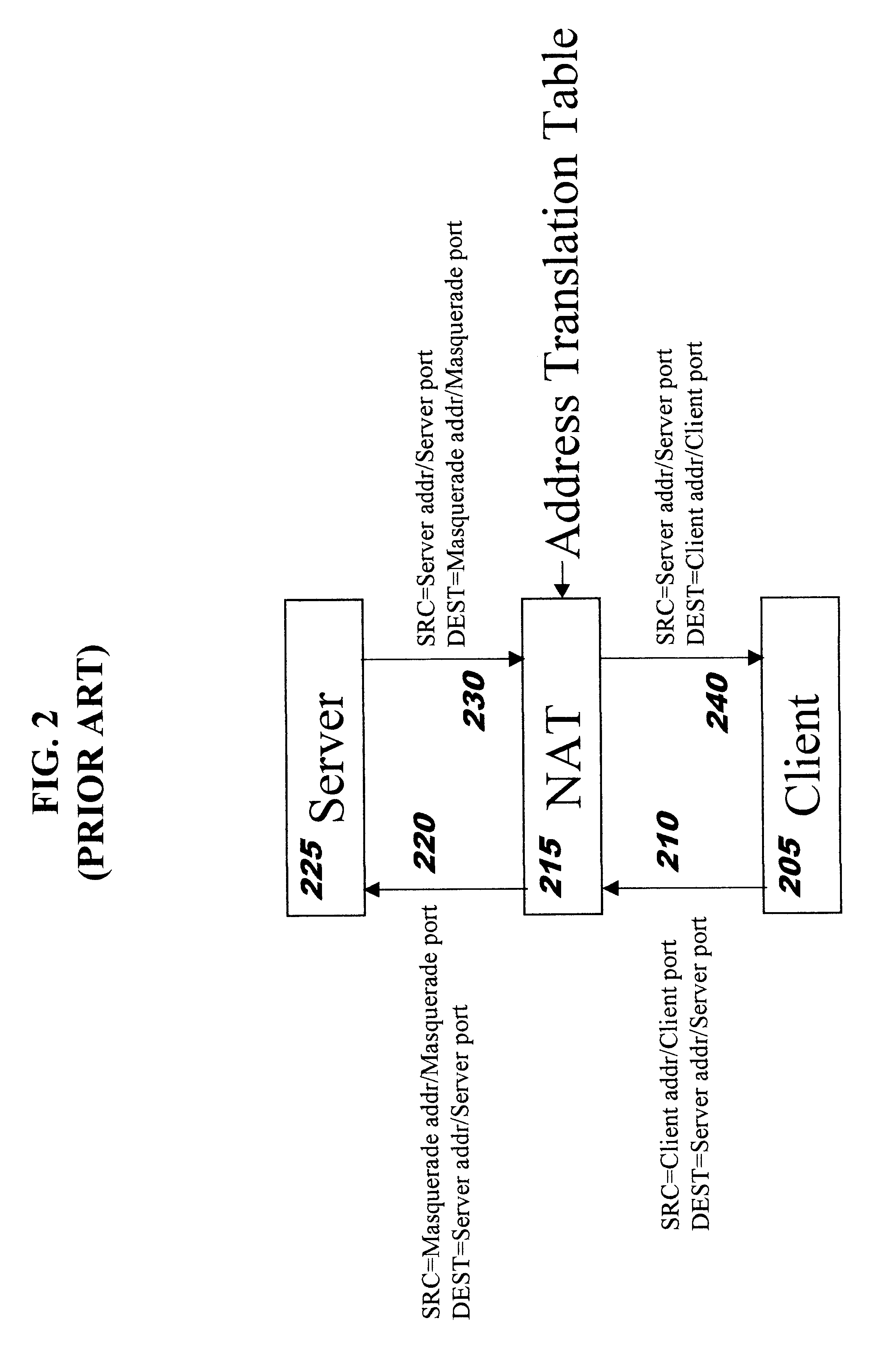
The present invention provides methods, systems, and computer program instructions for providing location-independent packet routing and secure access in a wireless networking environment (such as that encountered within a building), enabling client devices to travel seamlessly within the environment. Each client device uses a constant address. An address translation process that is transparent to the client and server is automatically performed as the device roams through the environment, enabling efficient client migration from one supporting access point to another. The secure access techniques provide user-centric authentication and allow policy-driven packet filtering, while taking advantage of encryption capabilities that are built in to the hardware at each endpoint.
Owner:REEFEDGE
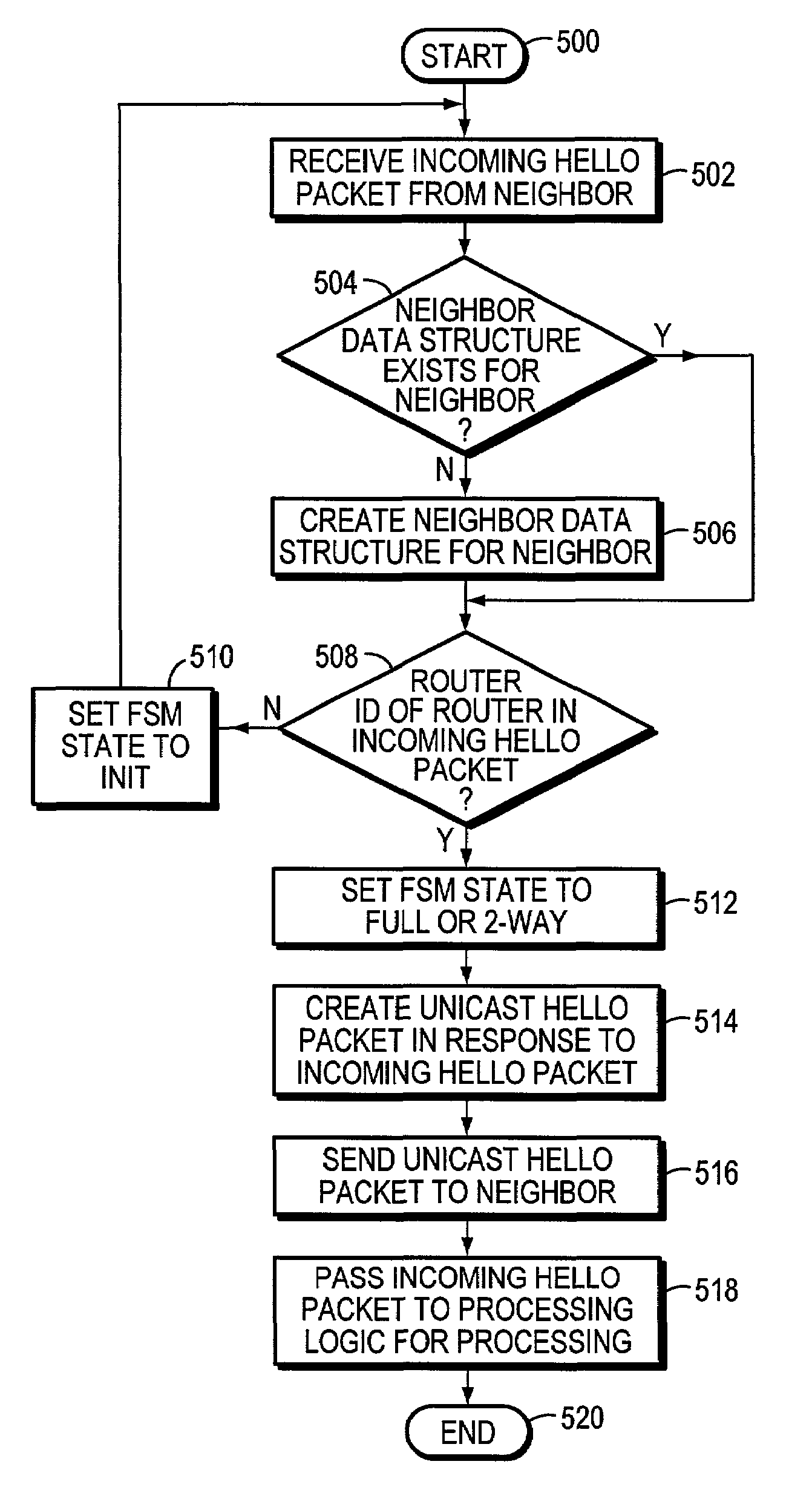
Technique for restoring adjacencies in OSPF in a non-stop forwarding intermediate node of a computer network
InactiveUS7065059B1Broadcast transmission systemsDigital computer detailsNetwork packetProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
A technique restores adjacencies between a non-stop forwarding (NSF) router and its neighboring routers during reload of routing protocol software on the NSF router within a computer network. When a new instance of the routing protocol software is re-loaded, each interface of the NSF router is placed in a special state that enables it to receive incoming Hello packets from its neighboring routers. When placed in the special state, the interface passively “listens” for incoming Hello packets from the neighbors to determine which neighbors send the packets. The router thereafter promptly creates and sends a unicast Hello packet to each neighbor from whom it has received an incoming Hello packet and creates associated neighbor data structures.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Stateful load balancing in a stateless network
A packet routing method for directing packets of a session in an IP network causes an intermediate node to obtain a lead packet of a plurality of packets in a given session. The intermediate node has an electronic interface in communication with the IP network and obtains the lead packet through that same interface. The method maintains, in a routing database, state information relating to a plurality of sessions in the IP network. Each session includes a single stateful session path formed by an ordered plurality of nodes in the IP network, and the state information includes information about the ordered plurality of nodes in the sessions. The method further accesses the routing database to determine the state of a plurality of sessions, and forms a stateful given path for packets of the given session across the IP network as a function of the state information in the routing database.
Owner:128 TECH
Optical layer multicasting
InactiveUS6873797B2Special service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsOptical packetEngineering
An optical signaling header technique applicable to optical networks wherein packet routing information is embedded in the same channel or wavelength as the data payload so that both the header and data payload propagate through network elements with the same path and the associated delays. The technique effects survivability and security of the optical networks by encompassing conventional electronic security with an optical security layer by generating replicated versions of the input data payload at the input node, and the transmission of each of the replicated versions over a corresponding one of the plurality of links. Moreover, each of the links is composed of multiple wavelengths to propagate optical signals or optical packets, and each of the replicated versions of the data payload may be propagated over a selected one of the wavelengths in each corresponding one of the plurality of links.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC +1
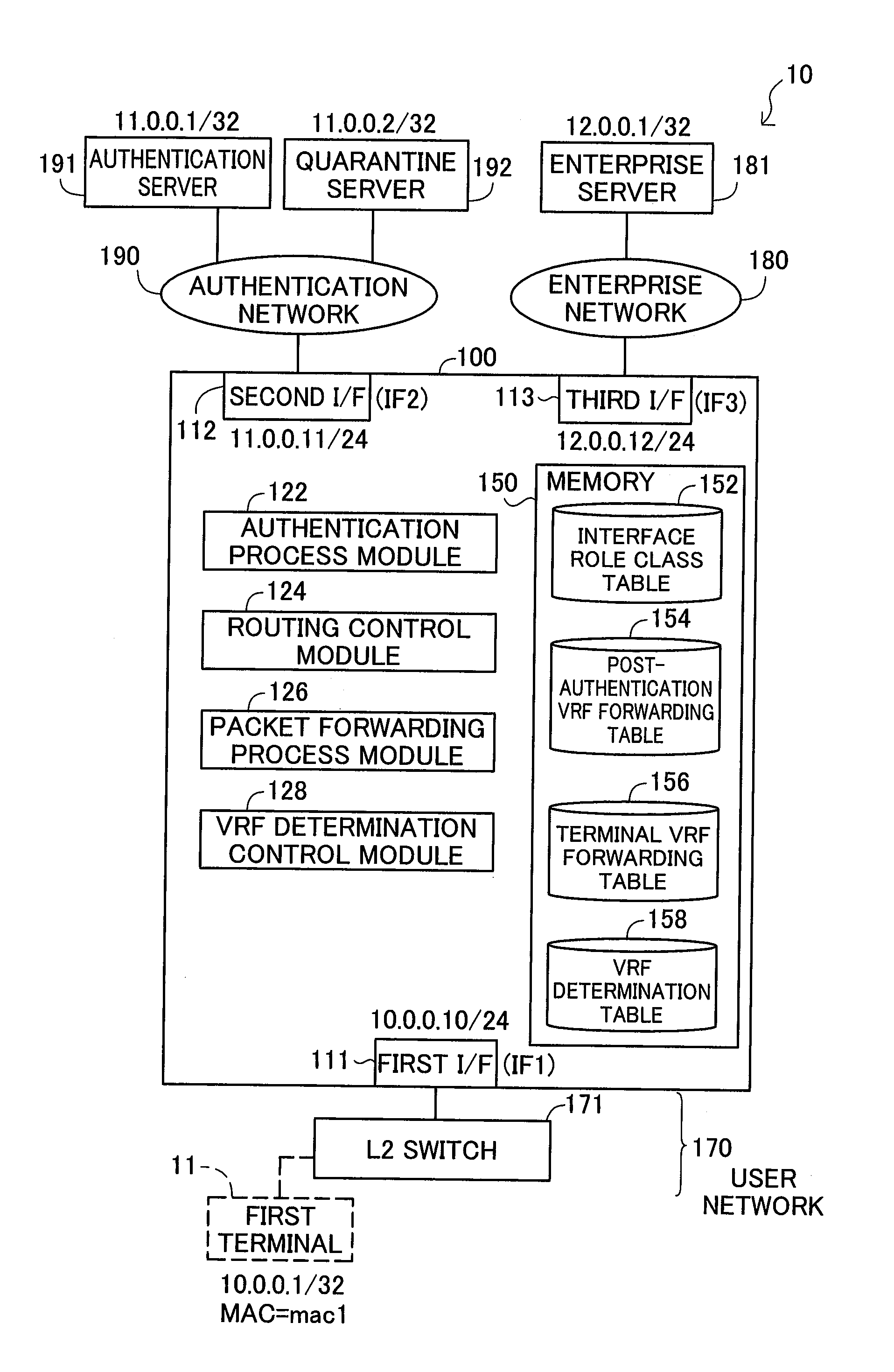
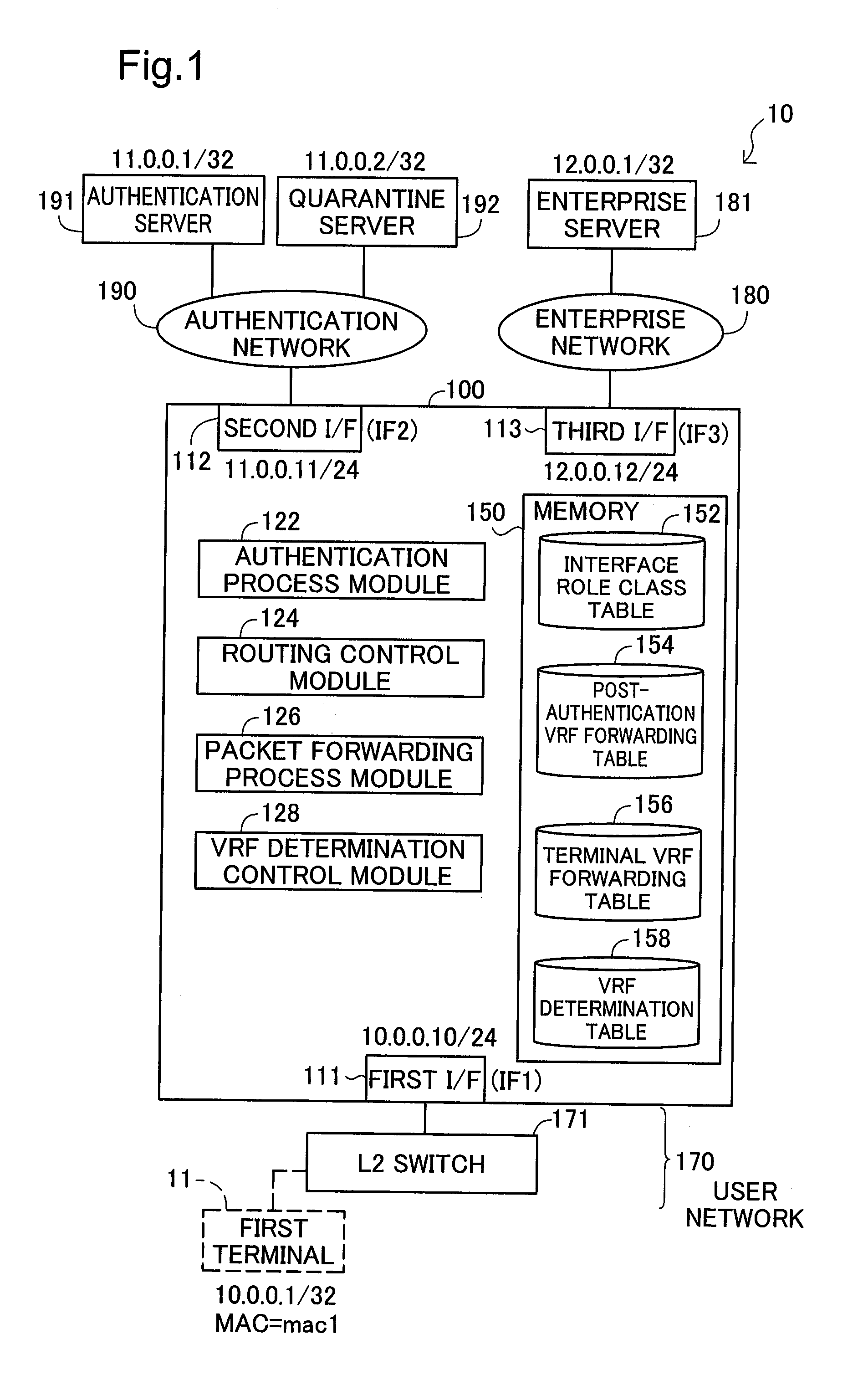
Network system, packet forwarding apparatus, and method of forwarding packets
InactiveUS20110032939A1Address utilization efficiencyAvoid forwardingDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsRouting tableNetworked system
A network system includes: a first network; an authentication server; a second network; a network; and a packet forwarding apparatus, wherein the packet forwarding apparatus includes: a forwarding route table storage storing a first forwarding route table containing packet routing information to the second network, and a second forwarding route table containing packet routing information to the second network and the third network; and a forwarding route table selector that, prior to determination of successful authentication for the terminal apparatus, selects the first forwarding route table as a search forwarding route table, and that upon receipt of determination of successful authentication for the terminal apparatus, selects the second forwarding route table as the search forwarding route table.
Owner:ALAXALA NETWORKS
Use of a free space electron switch in a telecommunications network
InactiveUS20040080285A1Tubes with more than two output electrodesImage/pattern display tubesTelecommunications linkTelecommunications network
A communications system that includes one or more free space electron switches. The free space electron switch employs an array of electron emitters, where each emitter is responsive to an RF or optical input signal on an input channel. Each emitter includes a cathode that emits electrons in response to the input signal. Each emitter further includes a focussing / accelerating electrode for collecting and accelerating the emitted electrons into an electron beam. Each emitter further includes an aiming anode that directs the beam of electrons to a desired detector within an array of detectors that converts the beam of electrons to a representative RF or optical signal on an output channel. Each emitter may include a modulating electrode that generates an electric field to modulate data onto the beam of electrons. The communications systems employing the switch can be an ISDN, DSLAM networks, packet routing systems, ADSL networks, PBX systems, local exchange systems, etc.
Owner:EXACONNECT
Multicast wireless ad hoc packet routing
A wireless LAN communications system capable of supporting communications within a multidisciplinary group or team of individuals, comprising a plurality of LAN radios that transmit, receive and route messages. Radios that are within range of each other send messages directly to each other. Radios that are within two hops of each other extract route information from the specific roles within the group and periodic update messages sent by the LAN radios. Radios that are more than two hops from each other use modified ad hoc multicast routing protocols.
Owner:RECEPTREXX LLC
Next generation network for providing diverse data types
InactiveUS20070104096A1Medium convergenceError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of serviceData pack
A data-processing network based on a new Internet protocol features a modified addressing system, a novel routing method, resolution of congestion problems in the routers, differentiated transport of data, real-time videos and communications, a multicast system to distribute real-time videos, and data transport with quality of services. The network uses homogeneous network protocol to transport multi-cast, real-time stream, and file data over the same network and to provide multiple qualities of service. Multi-packets may be unpacked at any node for predictive and reactive congestion control and dynamic packet routing. Specifically, a network node updating adjacent nodes with its congestion status, so that each node dynamically routes data away from any congested nodes and prioritizes higher quality of service traffic. In routing data, paths not stored in data packets, but instead, paths are dynamically recomputed around congestion or failed nodes and multicast data is routed using bread crumb trail techniques.
Owner:LGA PARTNERSHIP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com