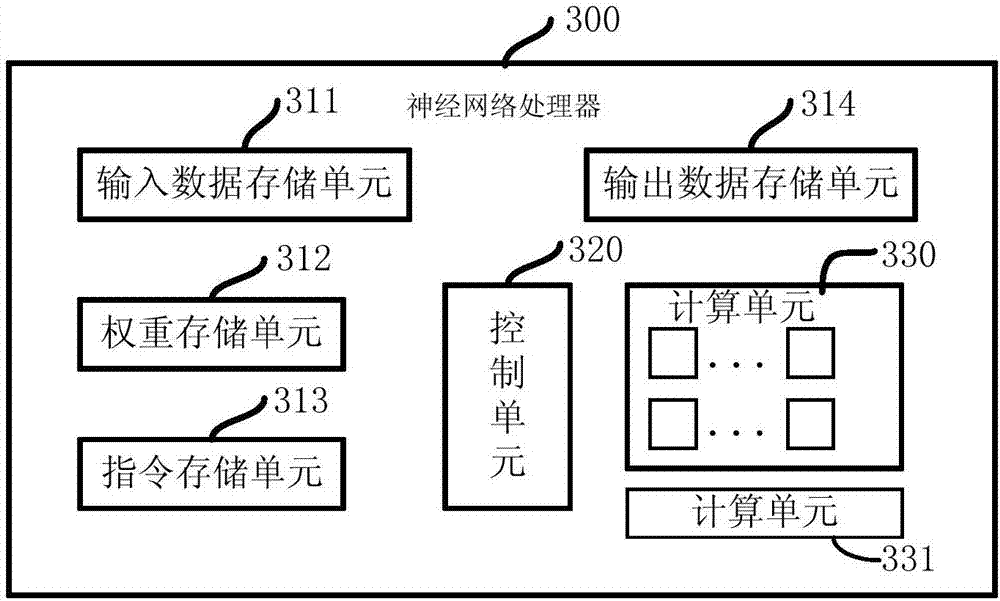
Patents
Literature
195 results about "Systolic array" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In parallel computer architectures, a systolic array is a homogeneous network of tightly coupled data processing units (DPUs) called cells or nodes. Each node or DPU independently computes a partial result as a function of the data received from its upstream neighbors, stores the result within itself and passes it downstream. Systolic arrays were invented by H. T. Kung and Charles Leiserson who described arrays for many dense linear algebra computations (matrix product, solving systems of linear equations, LU decomposition, etc.) for banded matrices. Early applications include computing greatest common divisors of integers and polynomials. They are sometimes classified as multiple-instruction single-data (MISD) architectures under Flynn's taxonomy, but this classification is questionable because a strong argument can be made to distinguish systolic arrays from any of Flynn's four categories: SISD, SIMD, MISD, MIMD, as discussed later in this article.
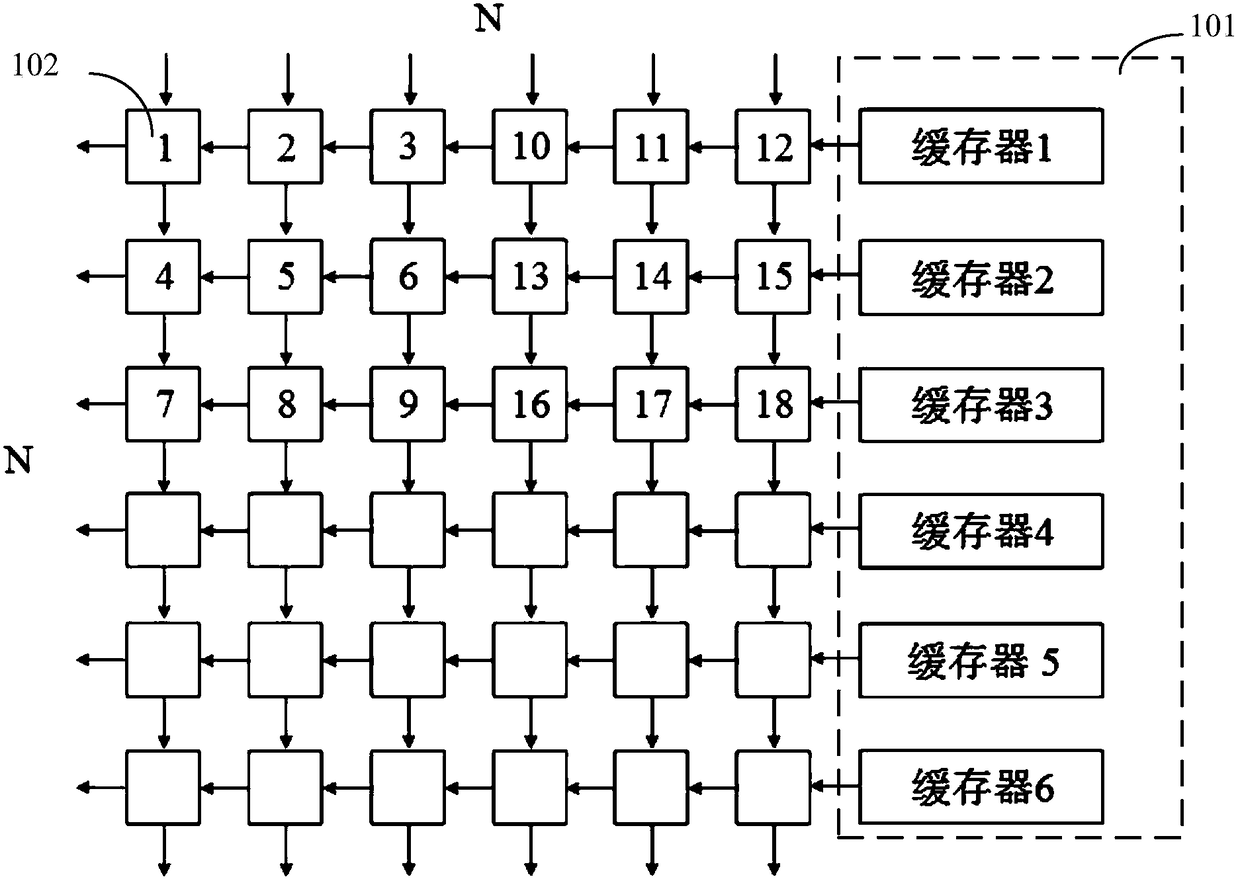
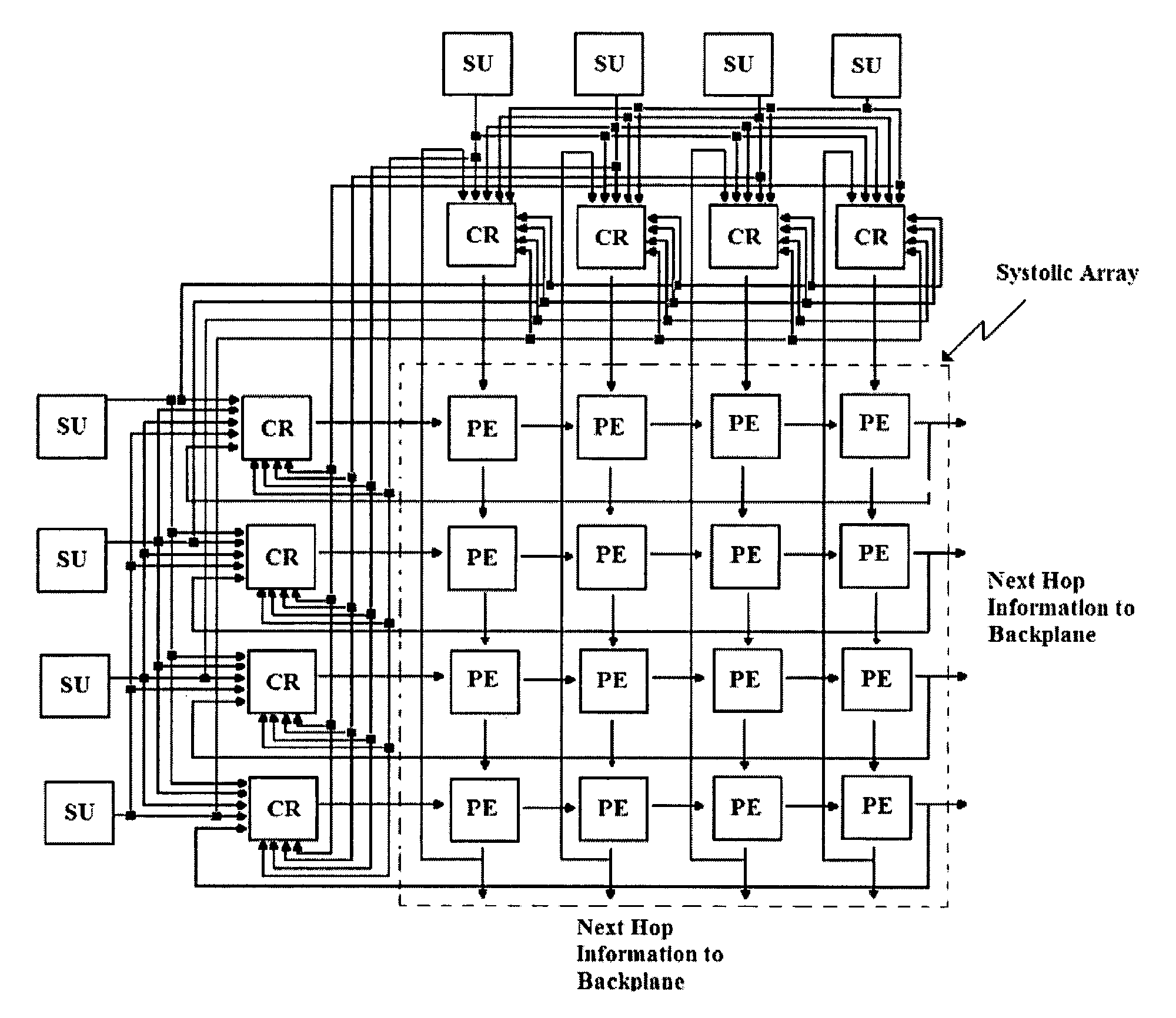
System and method for systolic array sorting of information segments
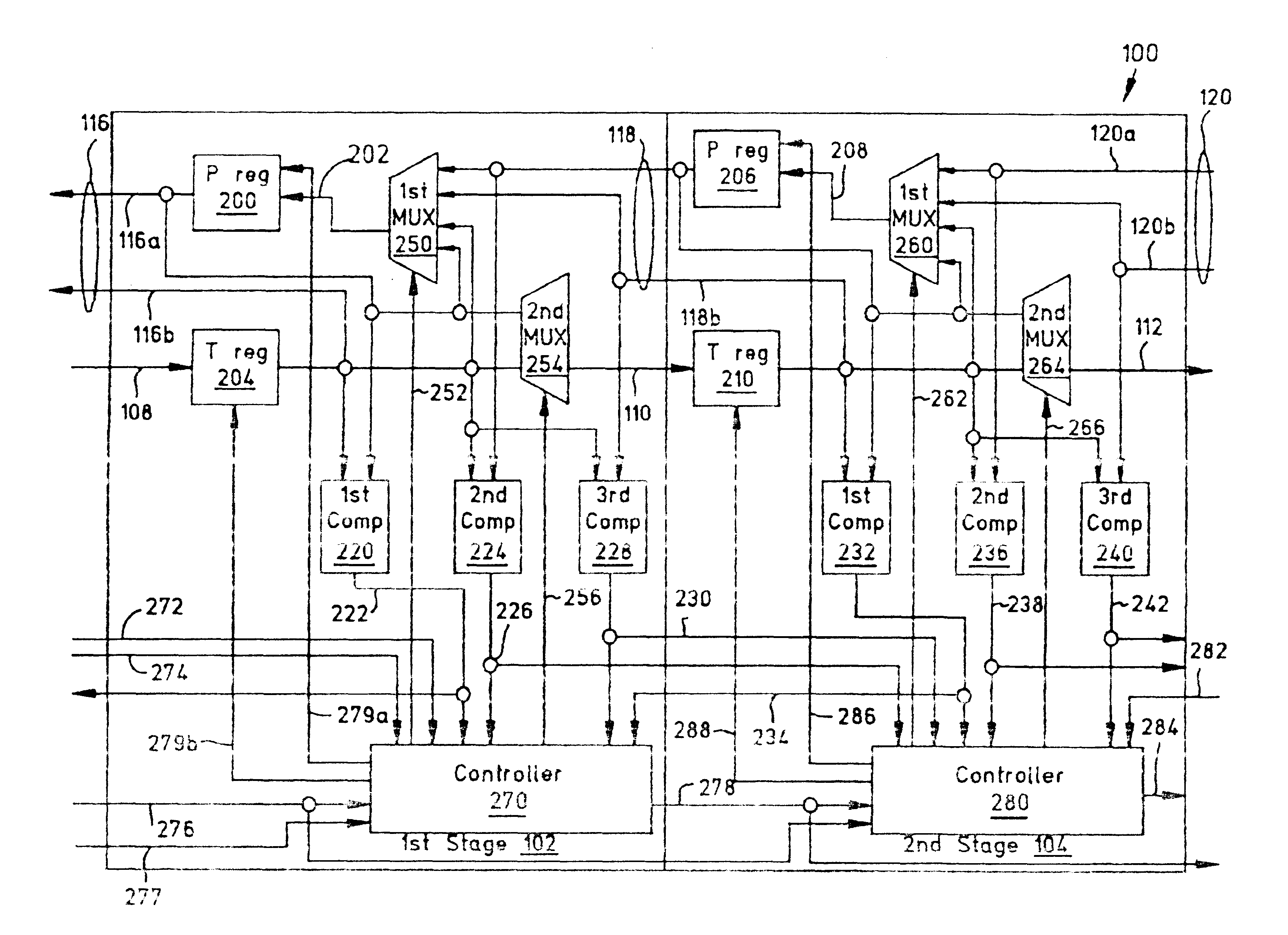
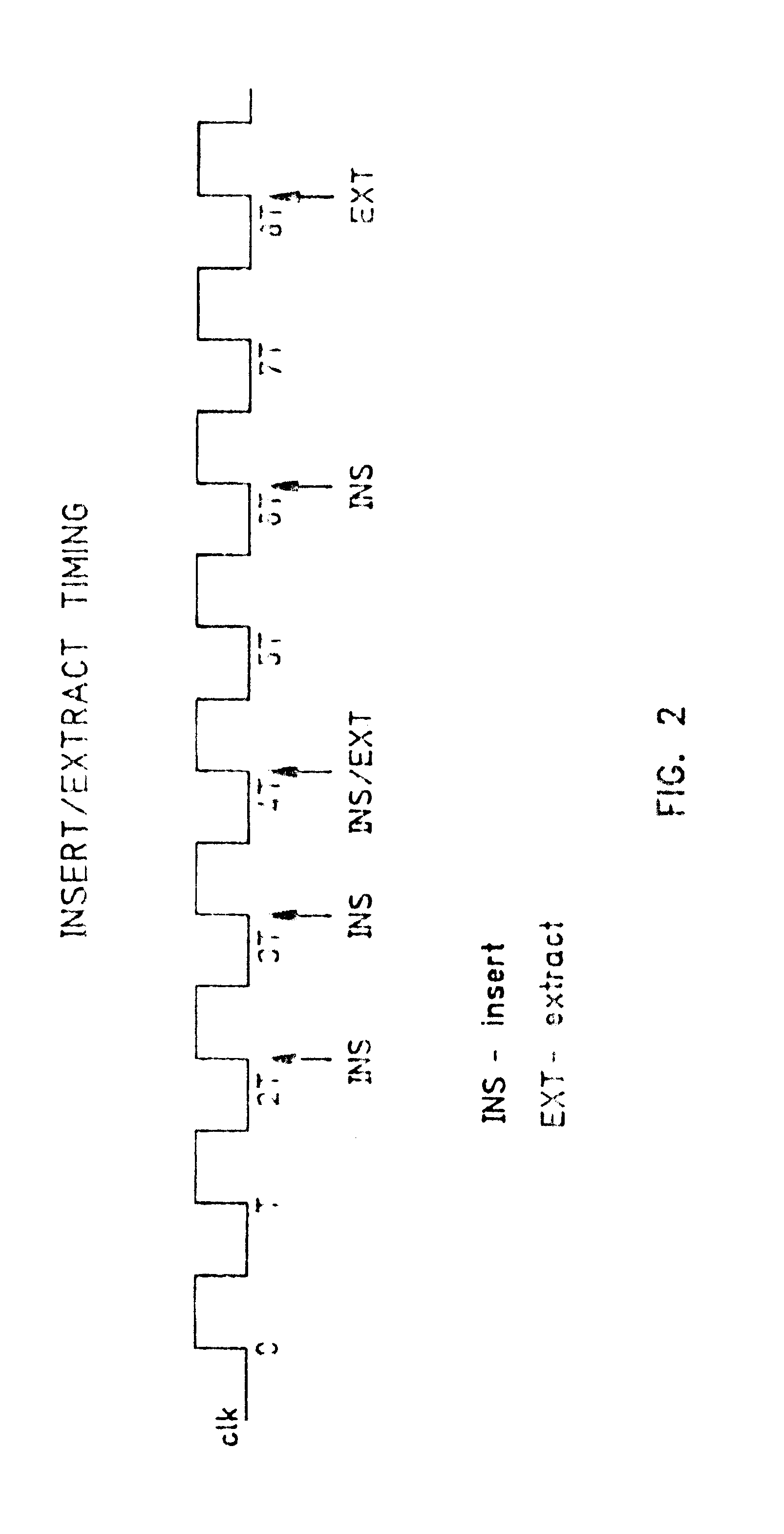
A system and method have been provided for sorting information segments in a packet / cell earliest deadline first queue circuit. The invention permits information segments to be inserted at a rate that is twice as fast as the maximum extraction rate. Pairs of permanent and temporary registers are organized into a hierarchical sequence of stages. Generally, information segments with lower field ranks move systolically through the stages to temporary registers in higher sequence stages. Information segments with higher field ranks move systolically through the stages to permanent registers lower in the sequence of stages. The invention permits the highest rank information segments to be sorted and extracted with great efficiency.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
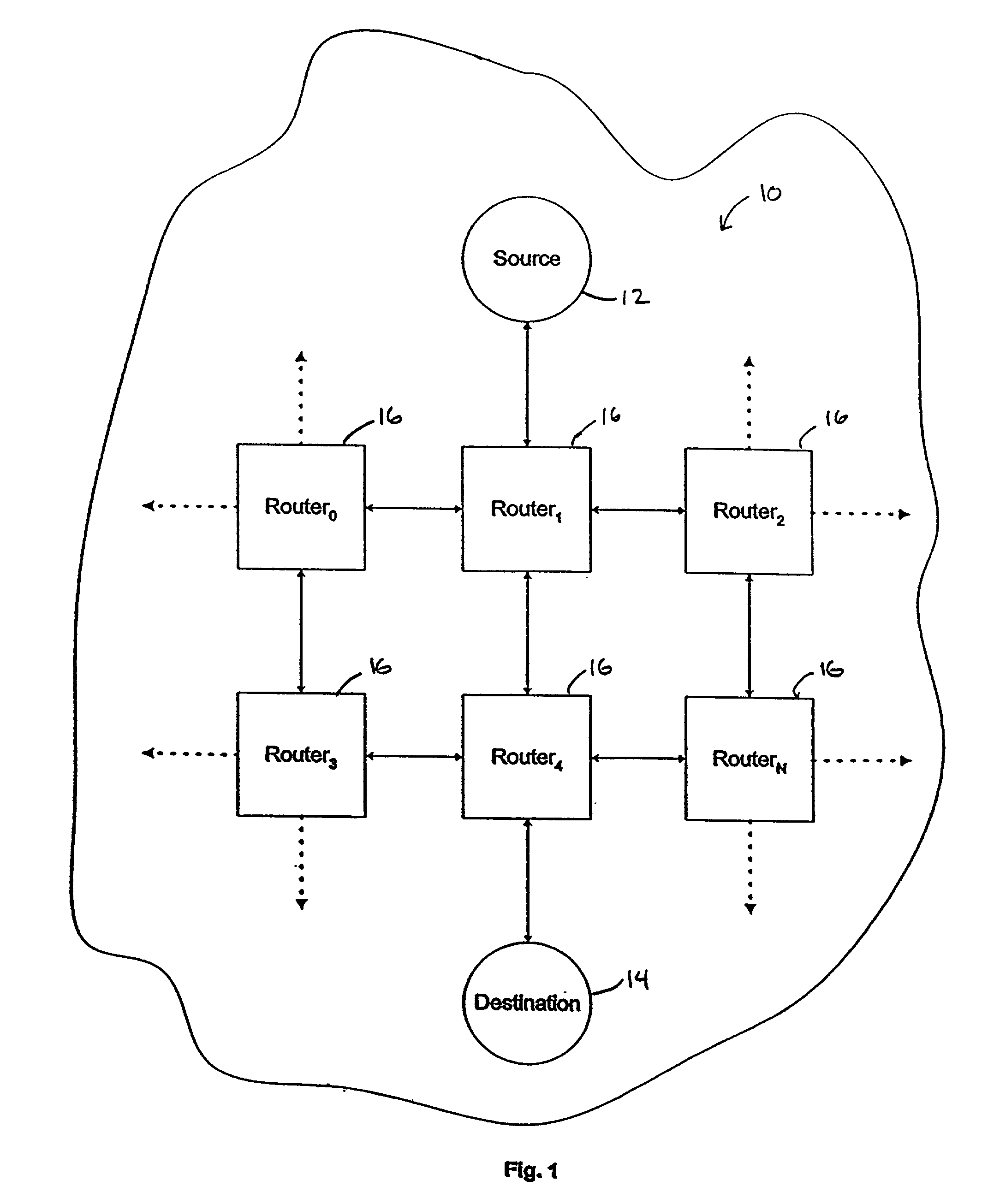
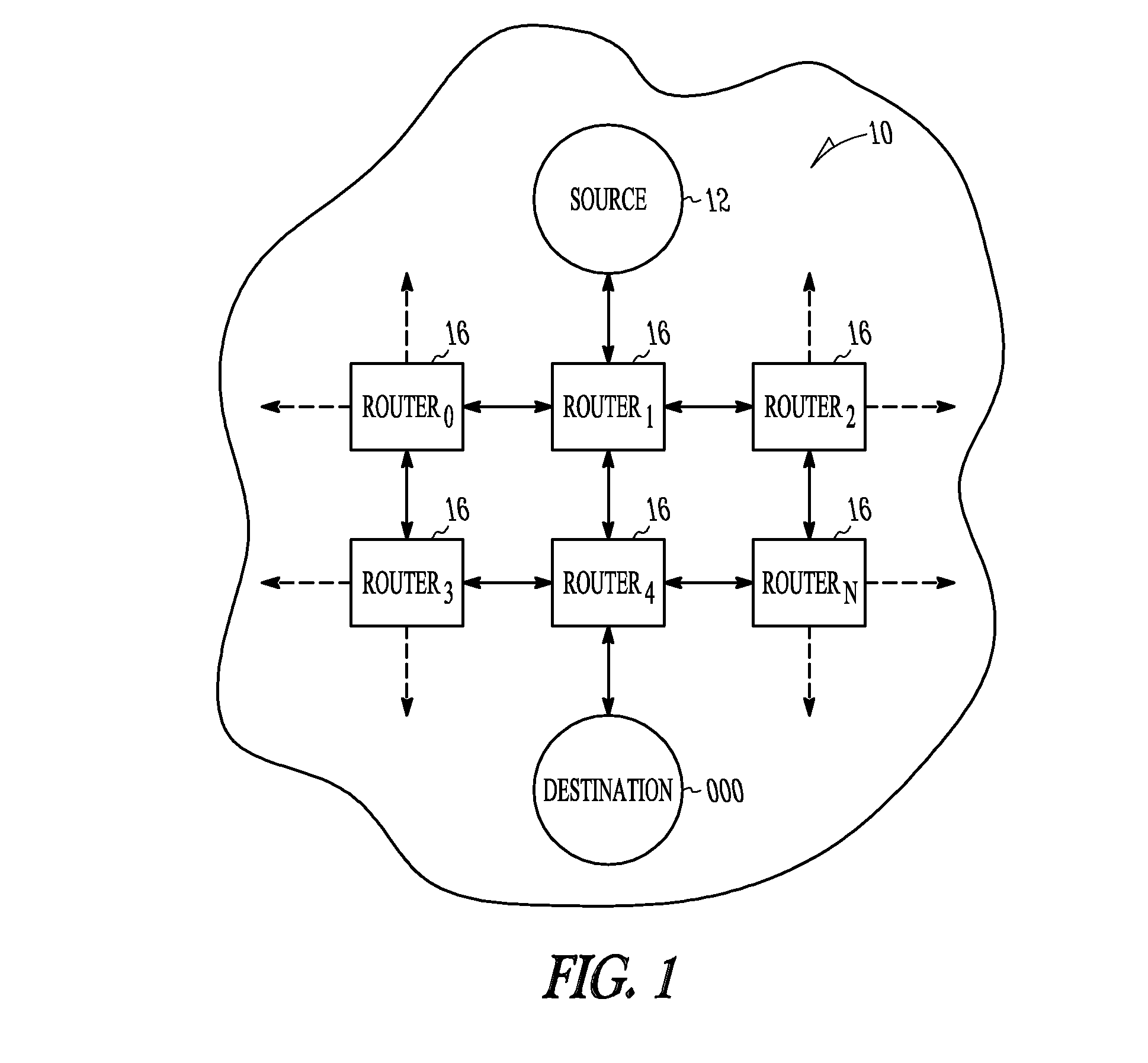
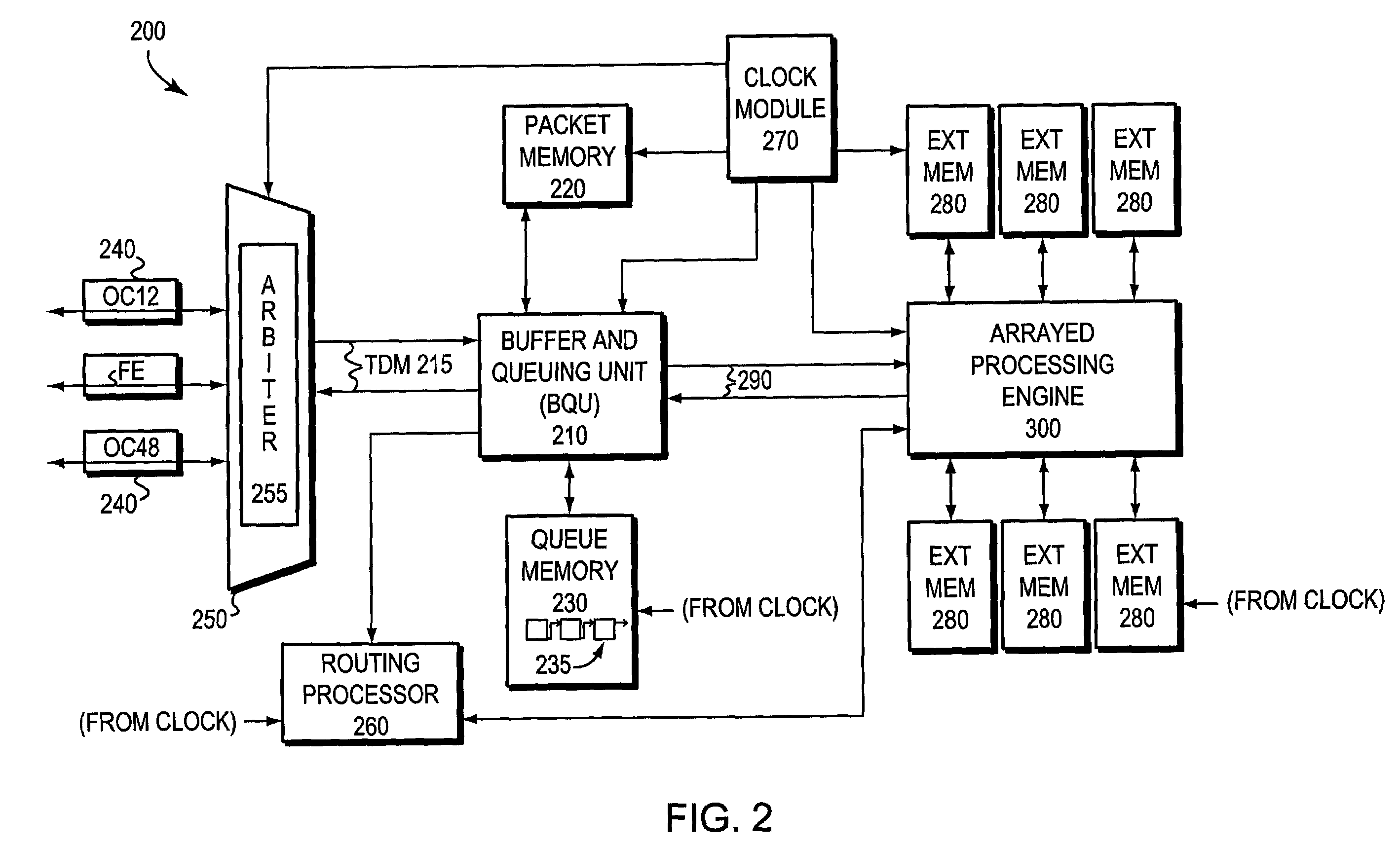
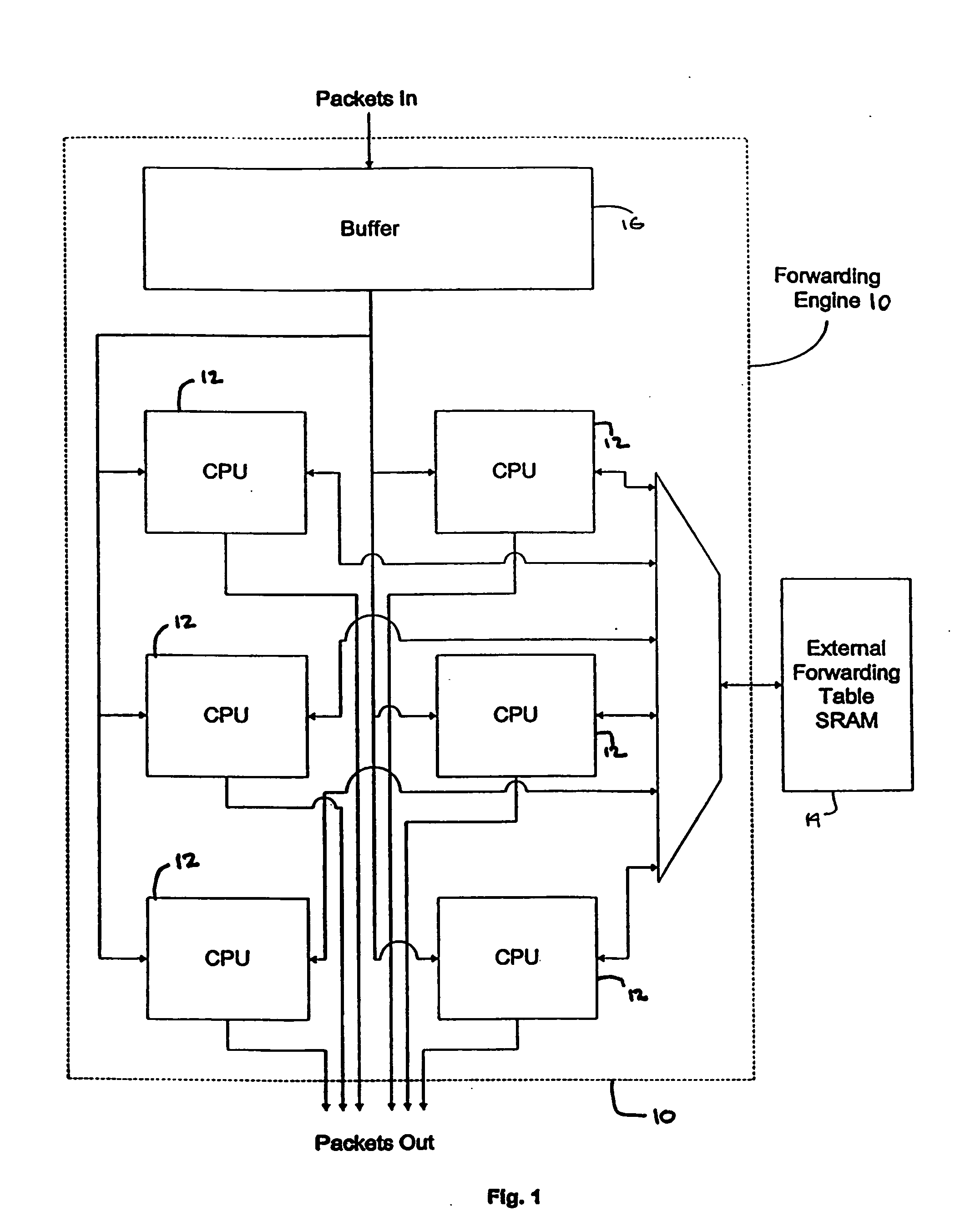
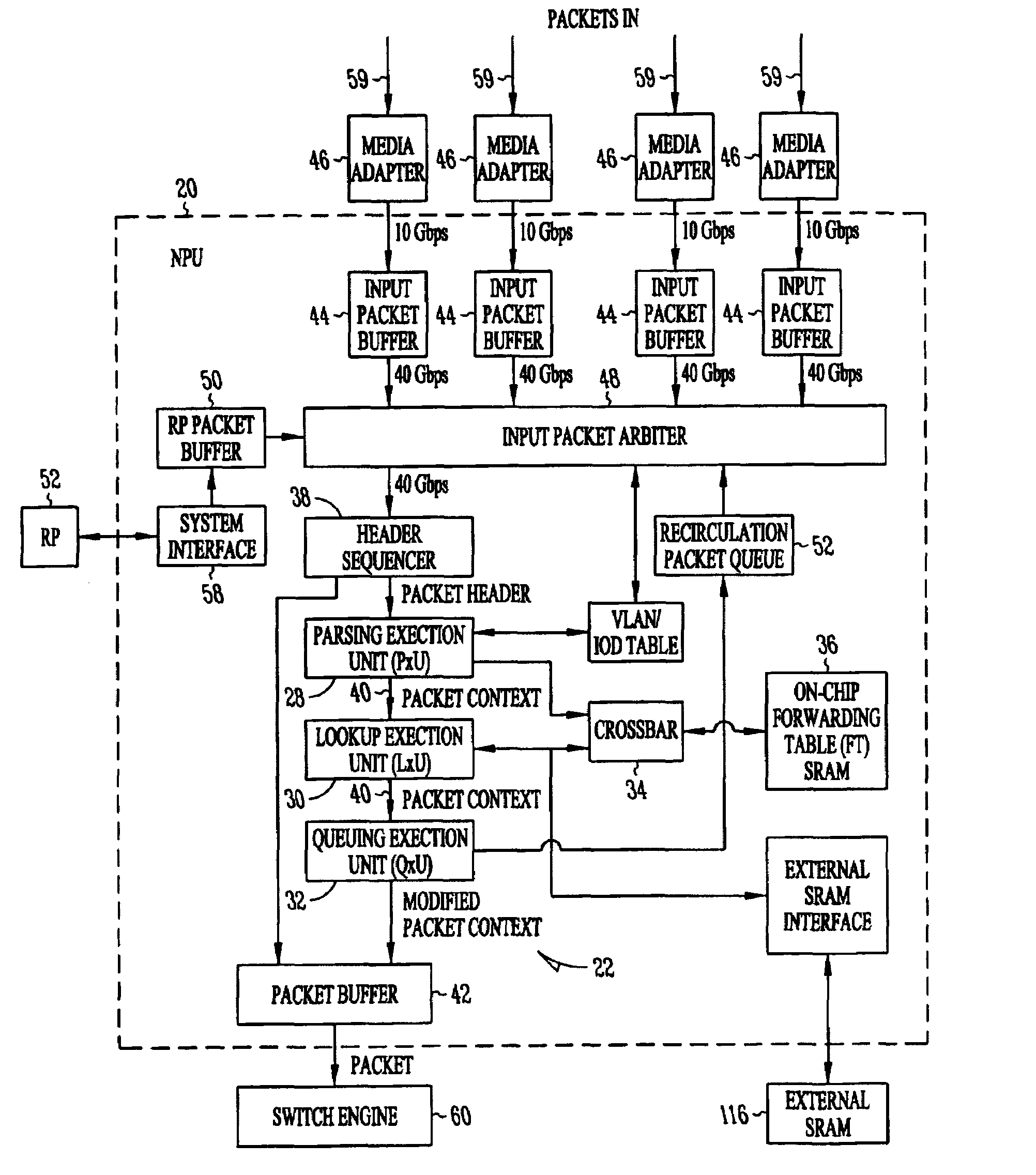
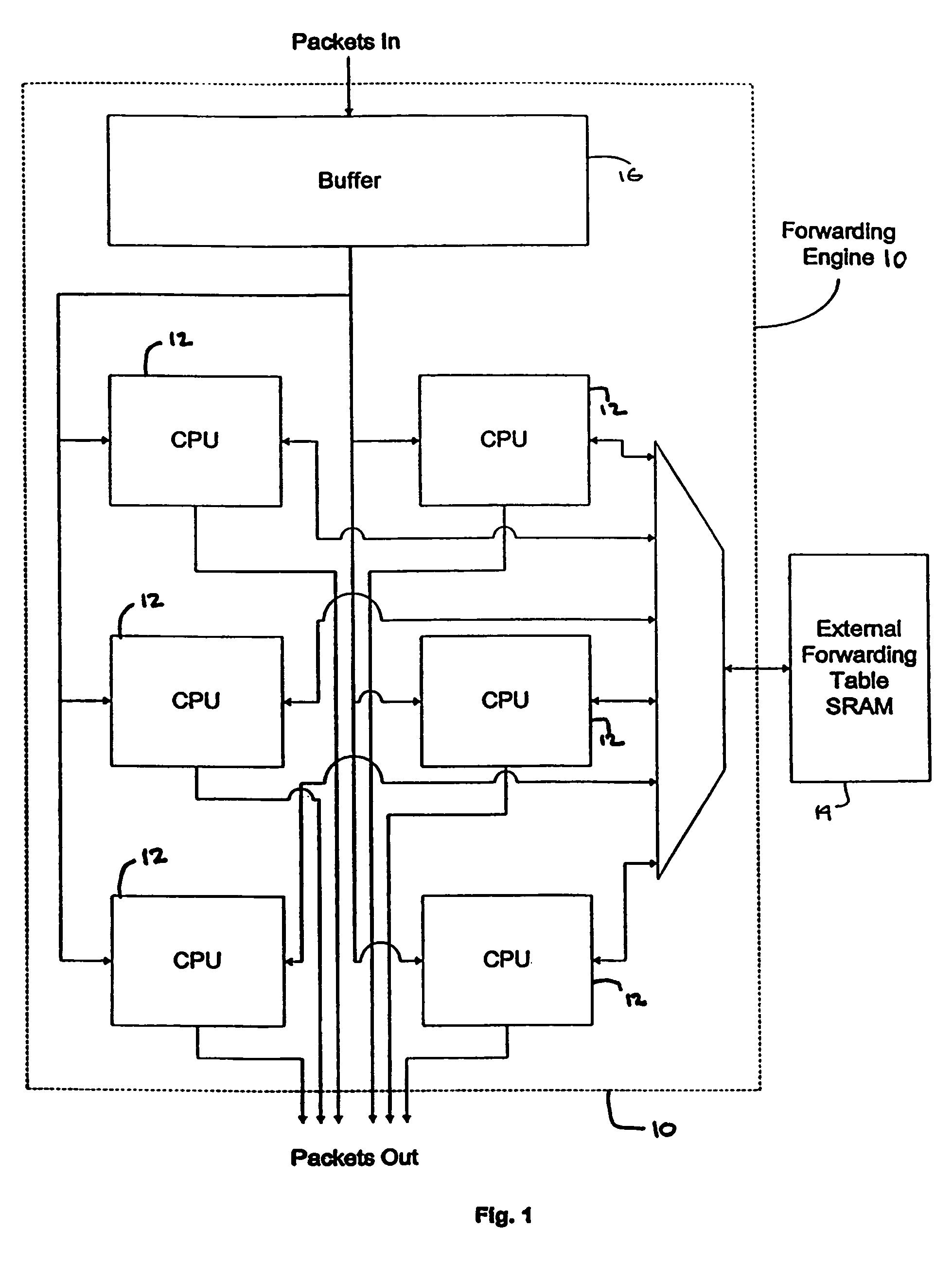
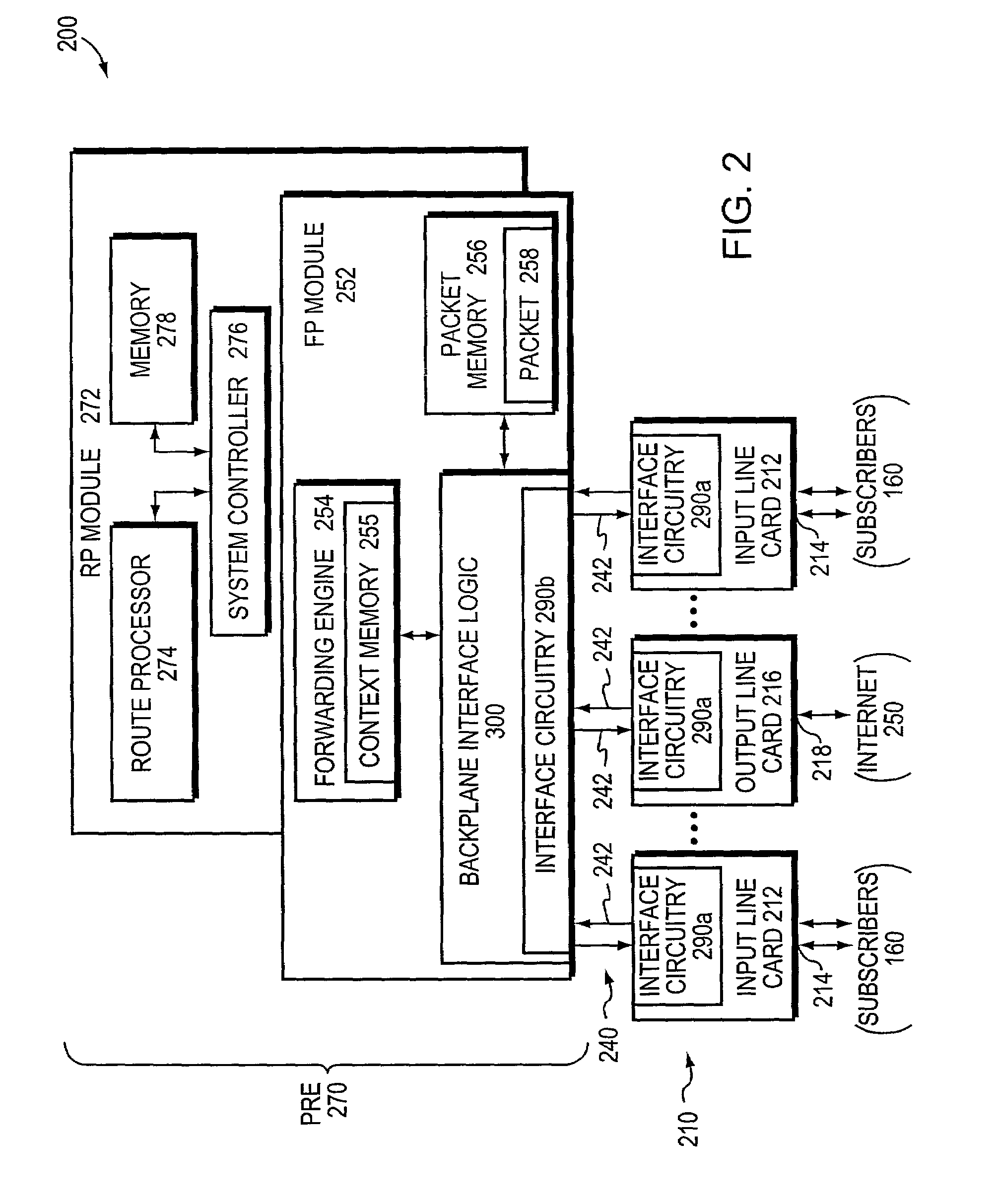
Packet routing and switching device
InactiveUS7382787B1Quick extractionTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationNetwork processing unitSystolic array
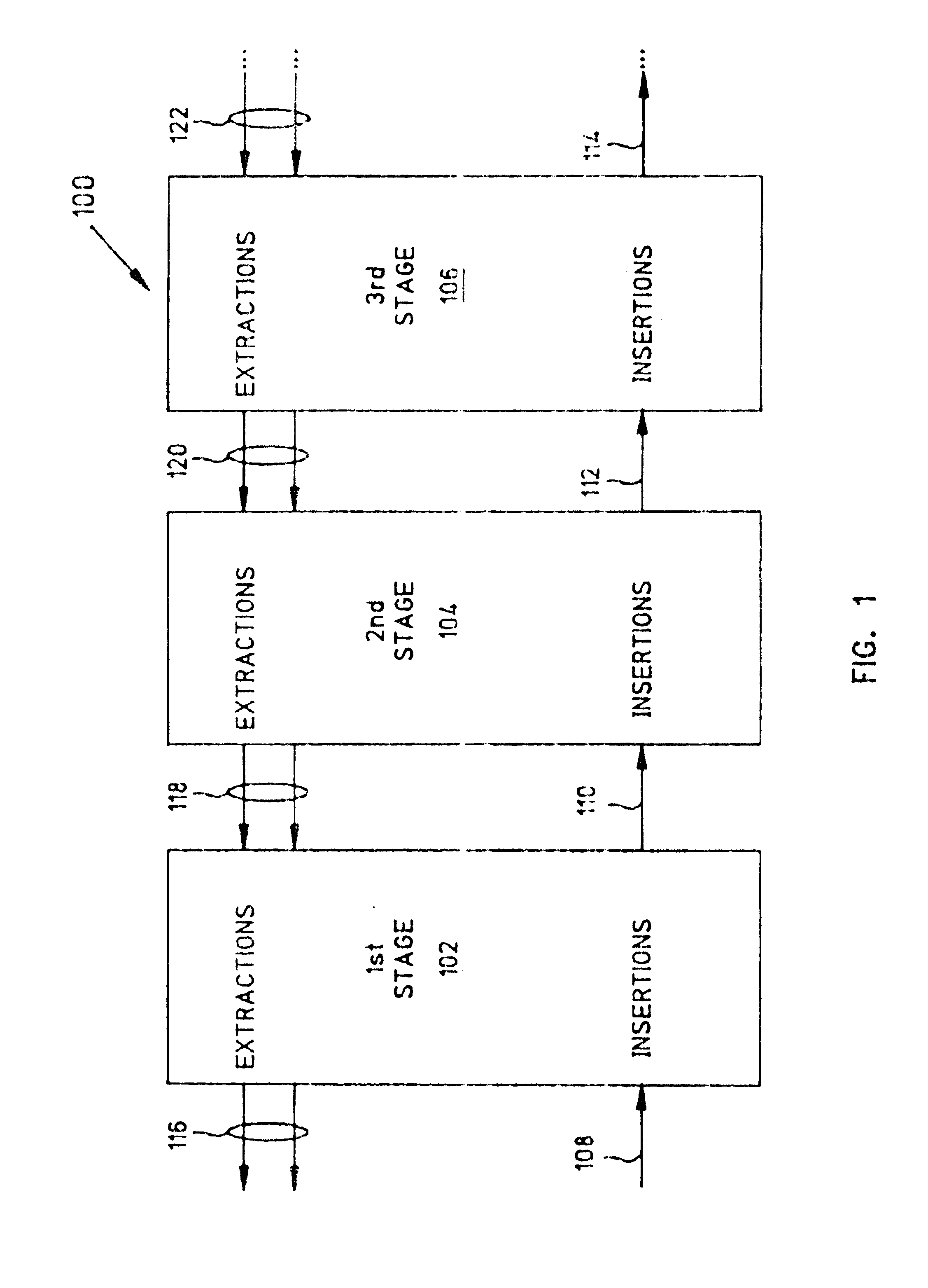
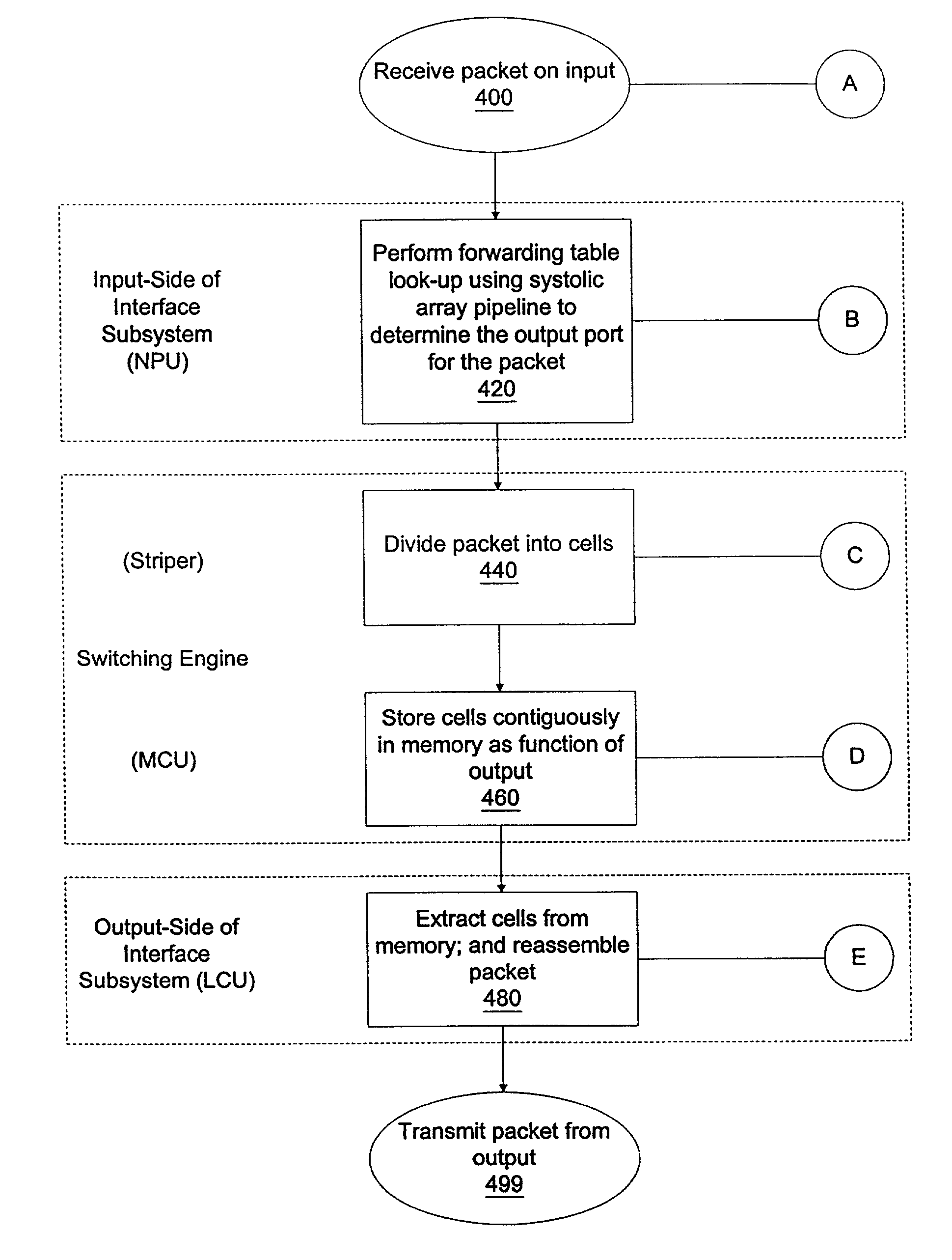
A method for routing and switching data packets from one or more incoming links to one or more outgoing links of a router. The method comprises receiving a data packet from the incoming link, assigning at least one outgoing link to the data packet based on the destination address of the data packet, and after the assigning operation, storing the data packet in a switching memory based on the assigned outgoing link. The data packet extracted from the switching memory, and transmitted along the assigned outgoing link. The router may include a network processing unit having one or more systolic array pipelines for performing the assigning operation.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Packet routing and switching device
ActiveUS8270401B1Quick extractionData switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsNetwork processing unitPacket routing
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
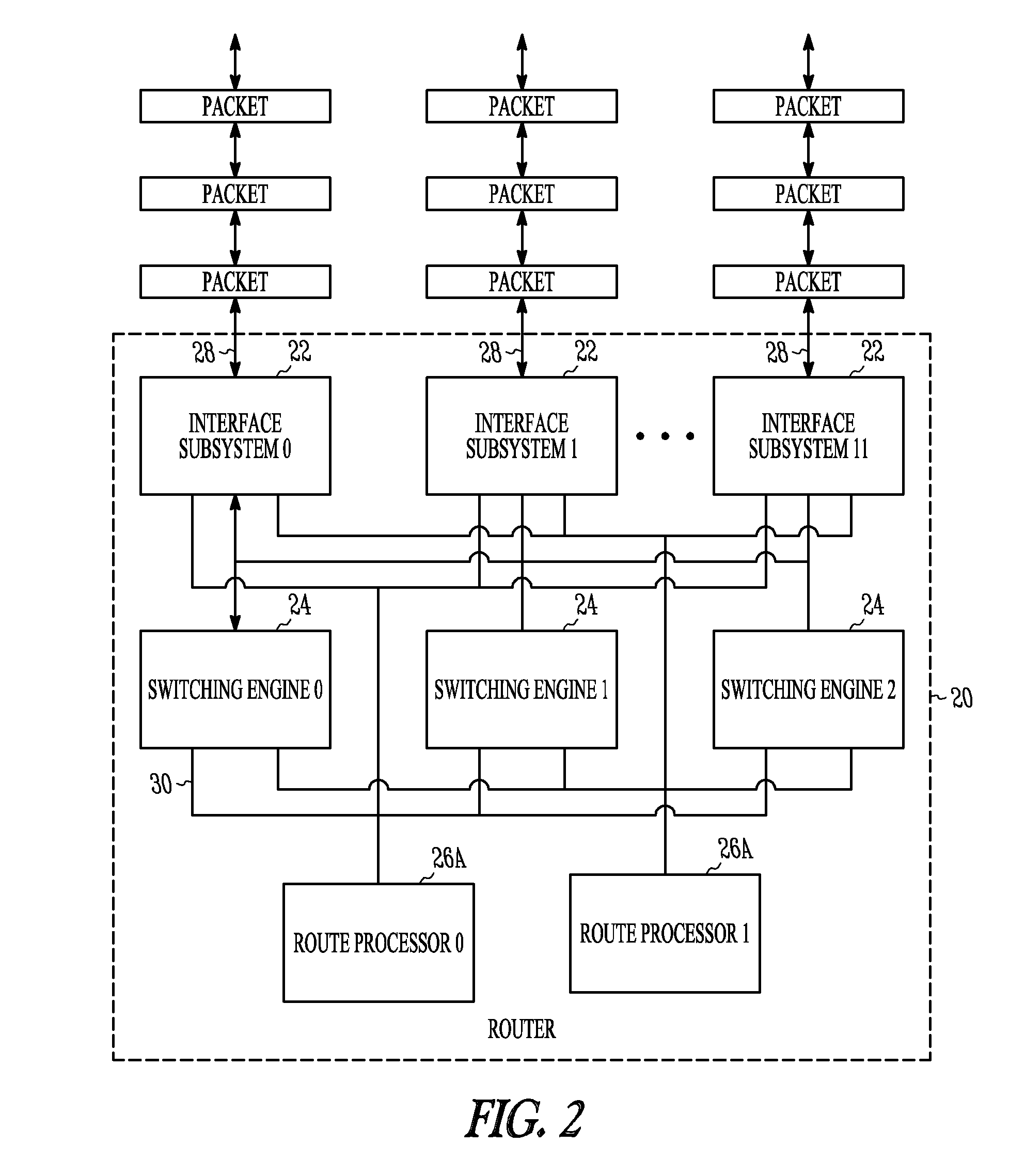
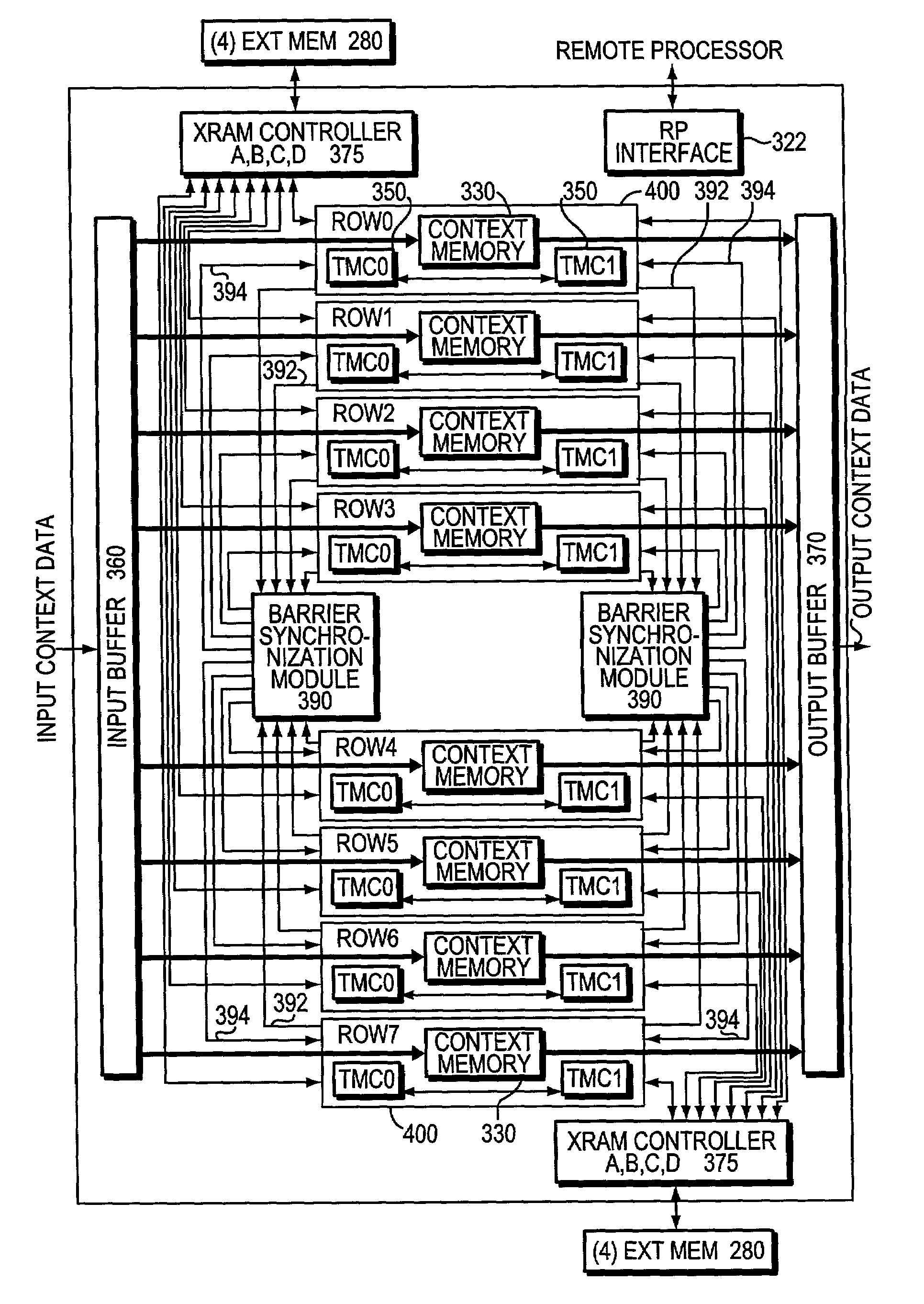
Barrier synchronization mechanism for processors of a systolic array
InactiveUS7100021B1Without consuming substantial memory resourceImprove latencyProgram synchronisationGeneral purpose stored program computerSystolic arrayCommon point
A mechanism synchronizes among processors of a processing engine in an intermediate network station. The processing engine is configured as a systolic array having a plurality of processors arrayed as rows and columns. The mechanism comprises a barrier synchronization mechanism that enables synchronization among processors of a column (i.e., different rows) of the systolic array. That is, the barrier synchronization function allows all participating processors within a column to reach a common point within their instruction code sequences before any of the processors proceed.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
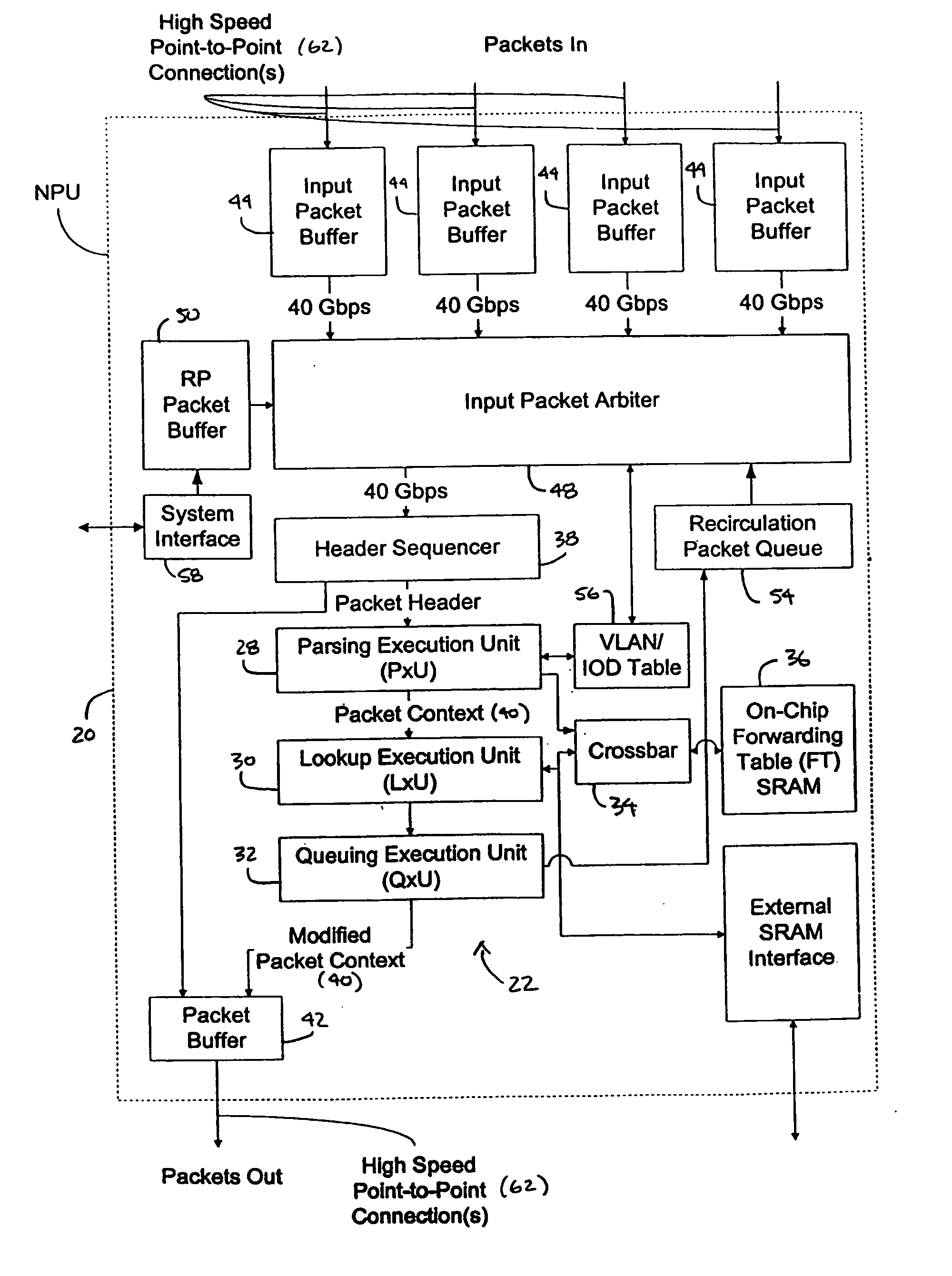
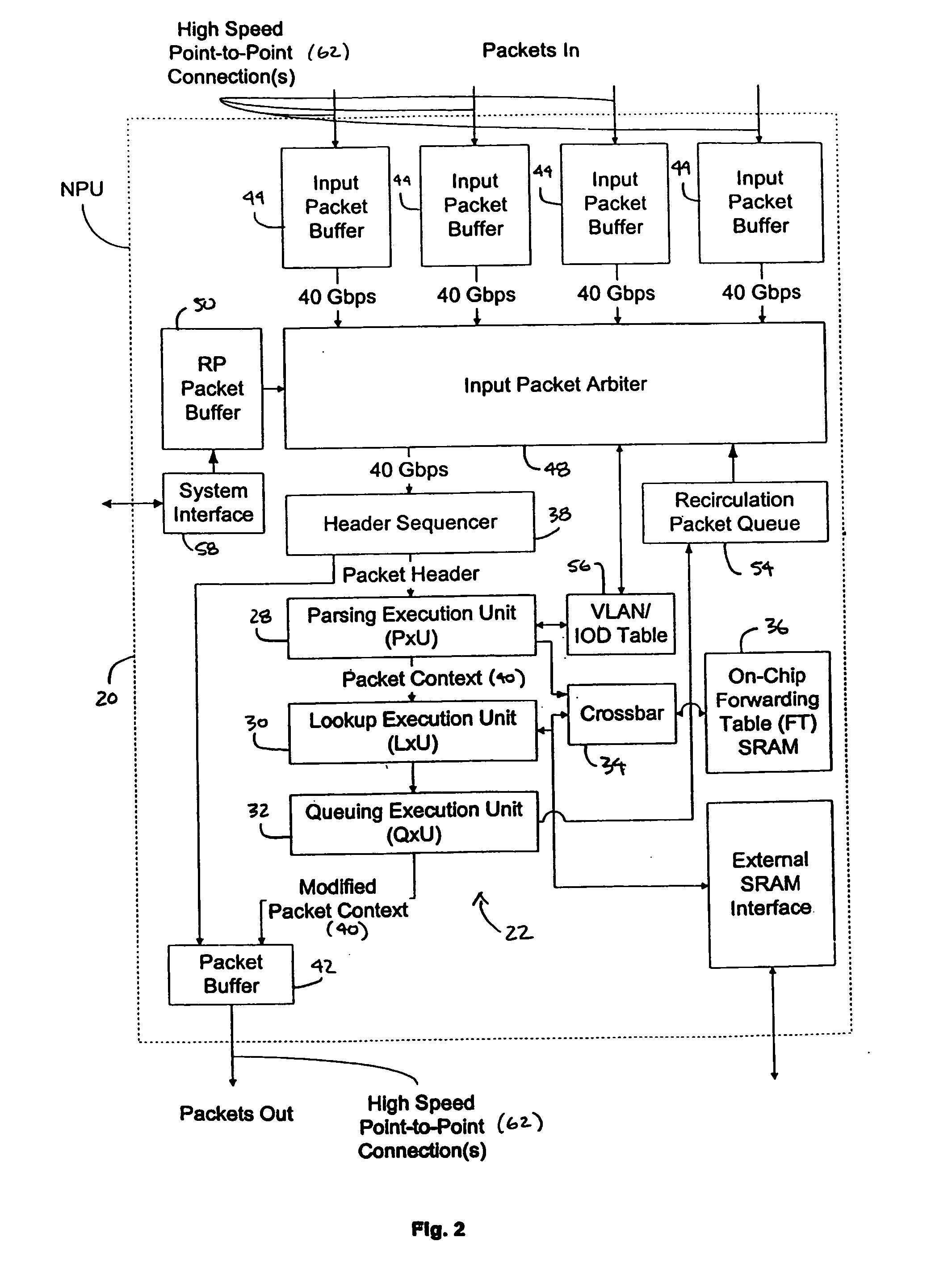
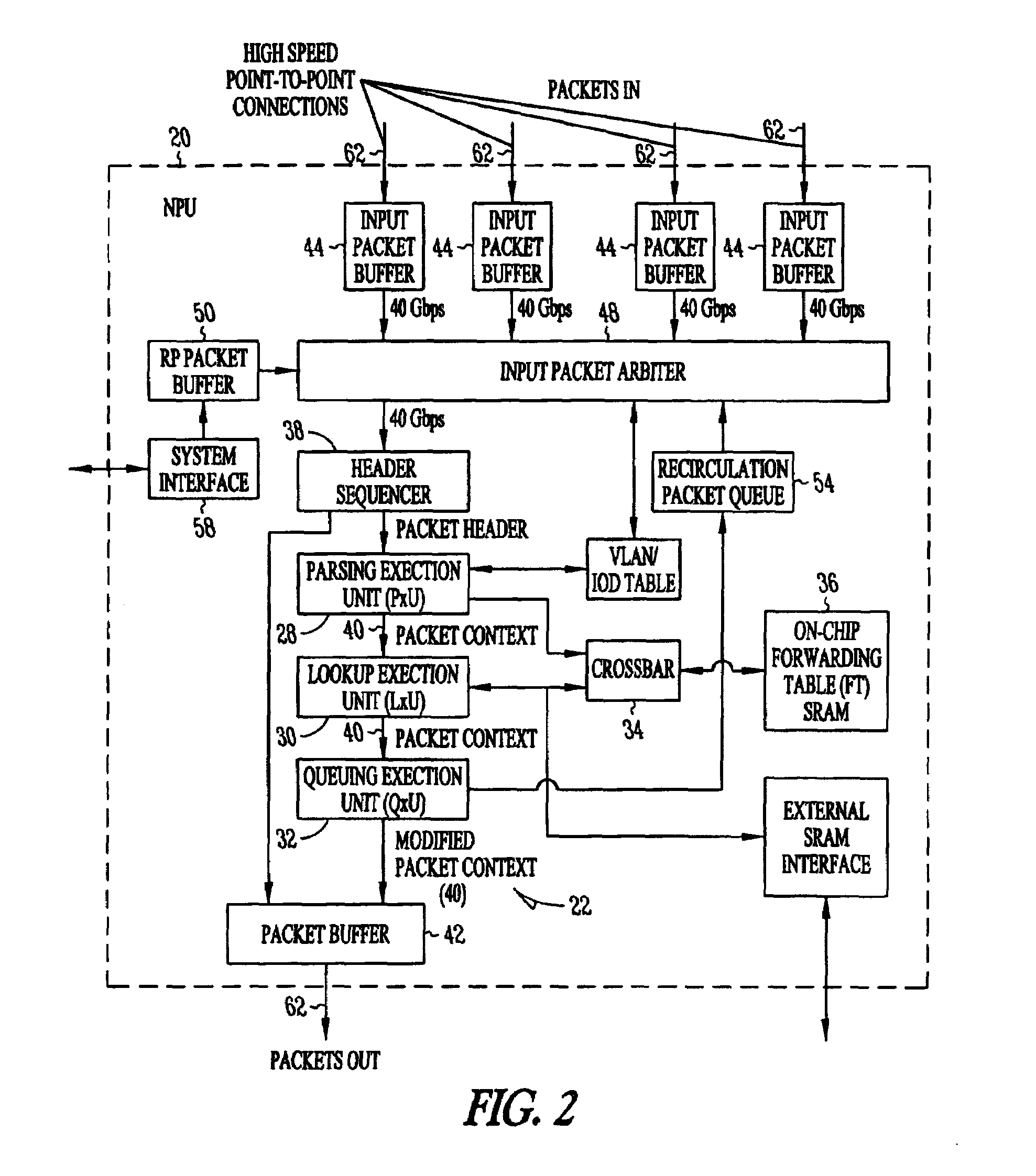
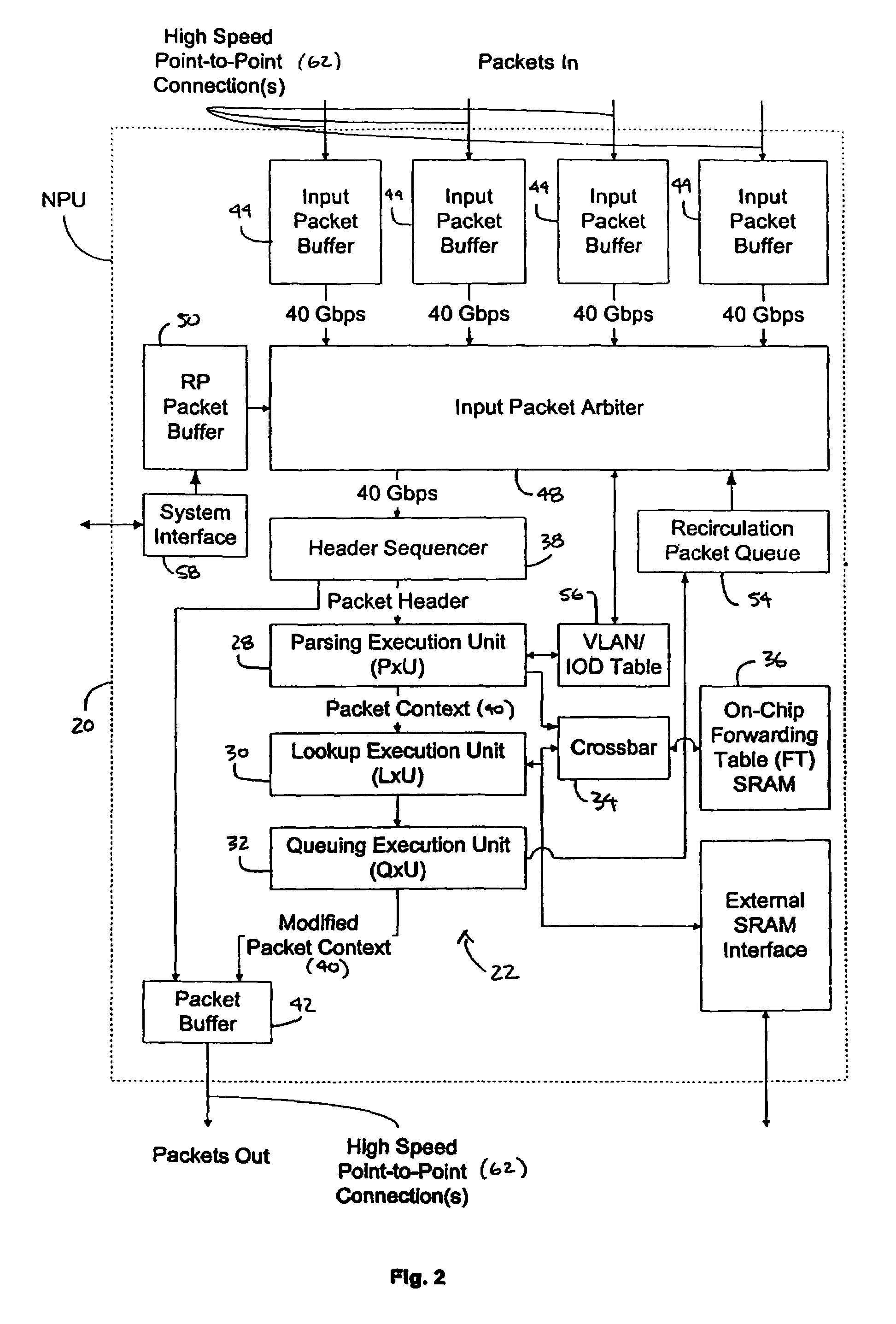
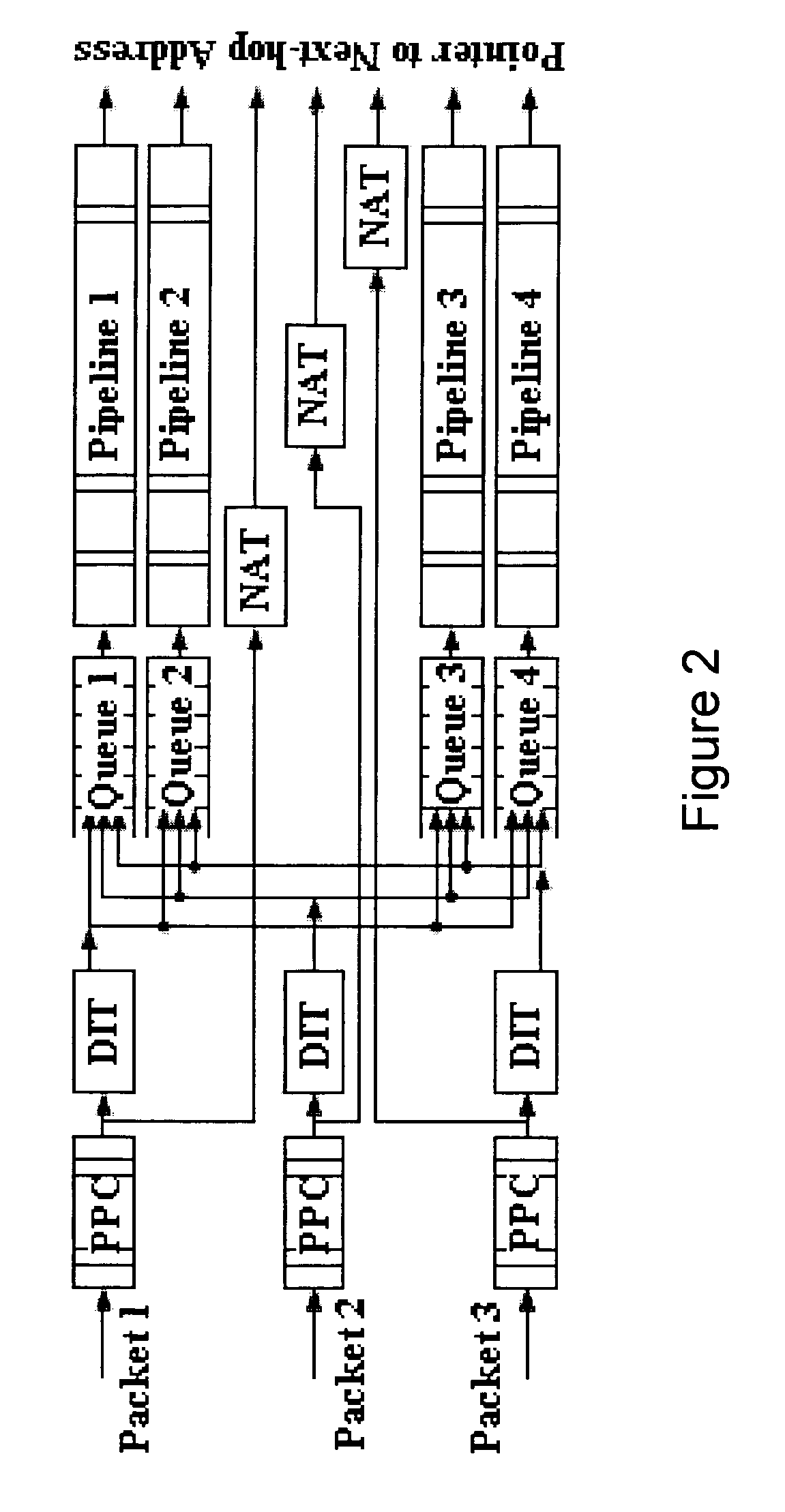
Processing unit for efficiently determining a packet's destination in a packet-switched network
InactiveUS20060117126A1Input is hugeEliminate needTransmissionElectric digital data processingMain processing unitSingle stage
A processor for use in a router, the processor having a systolic array pipeline for processing data packets to determine to which output port of the router the data packet should be routed. In one embodiment, the systolic array pipeline includes a plurality of programmable functional units and register files arranged sequentially as stages, for processing packet contexts (which contain the packet's destination address) to perform operations, under programmatic control, to determine the destination port of the router for the packet. A single stage of the systolic array may contain a register file and one or more functional units such as adders, shifters, logical units, etc., for performing, in one example, very long instruction word (vliw) operations. The processor may also include a forwarding table memory, on-chip, for storing routing information, and a cross bar selectively connecting the stages of the systolic array with the forwarding table memory.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
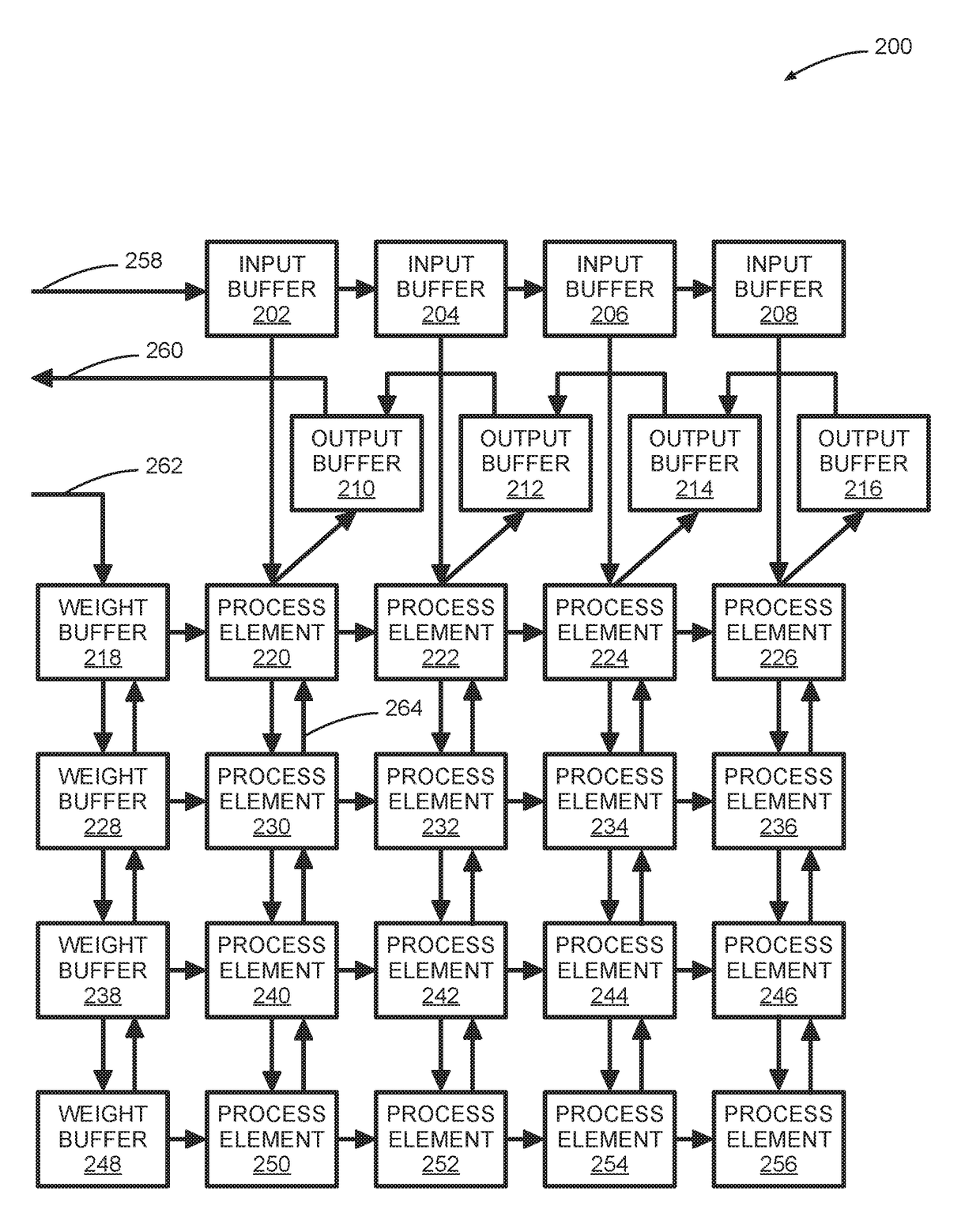
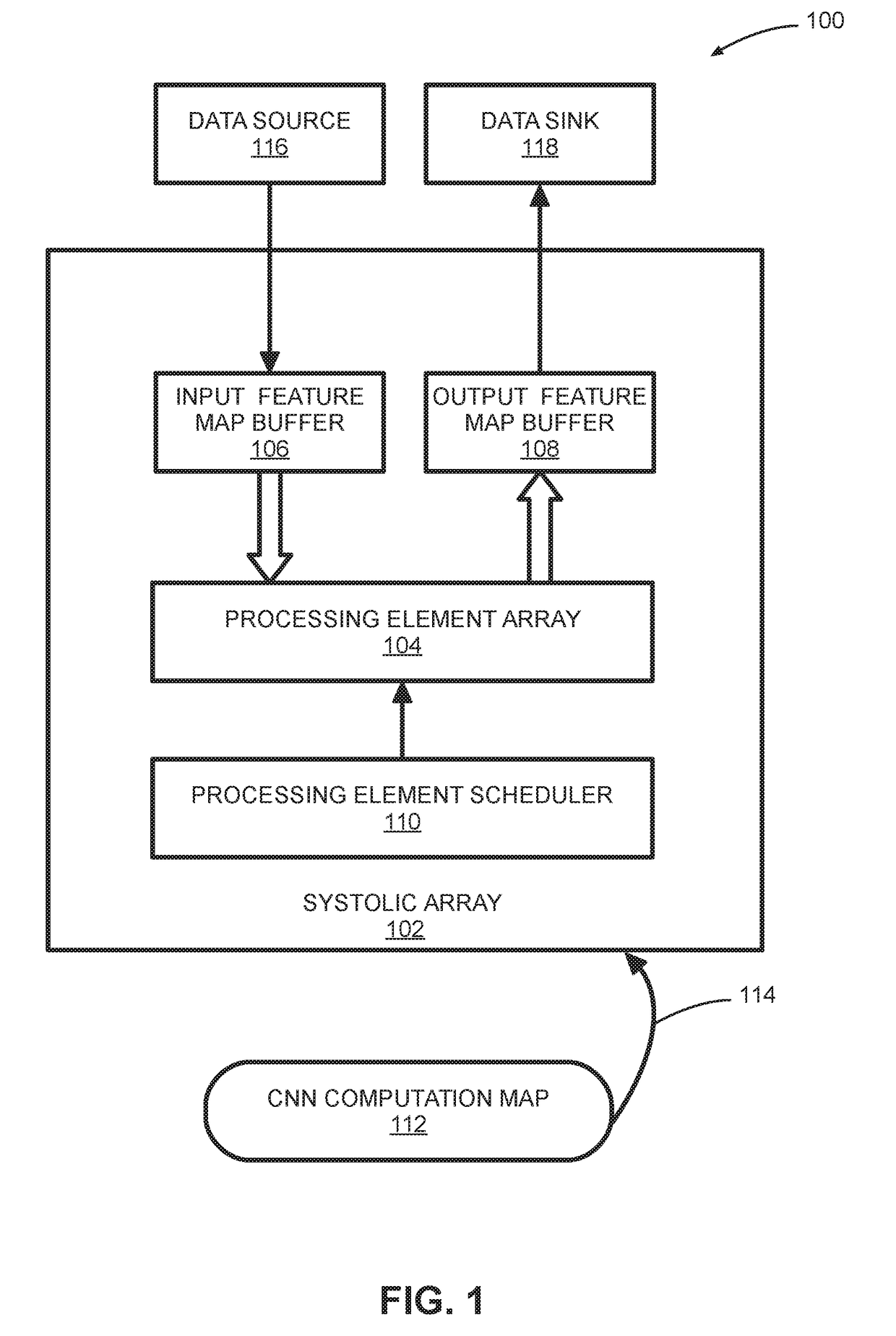
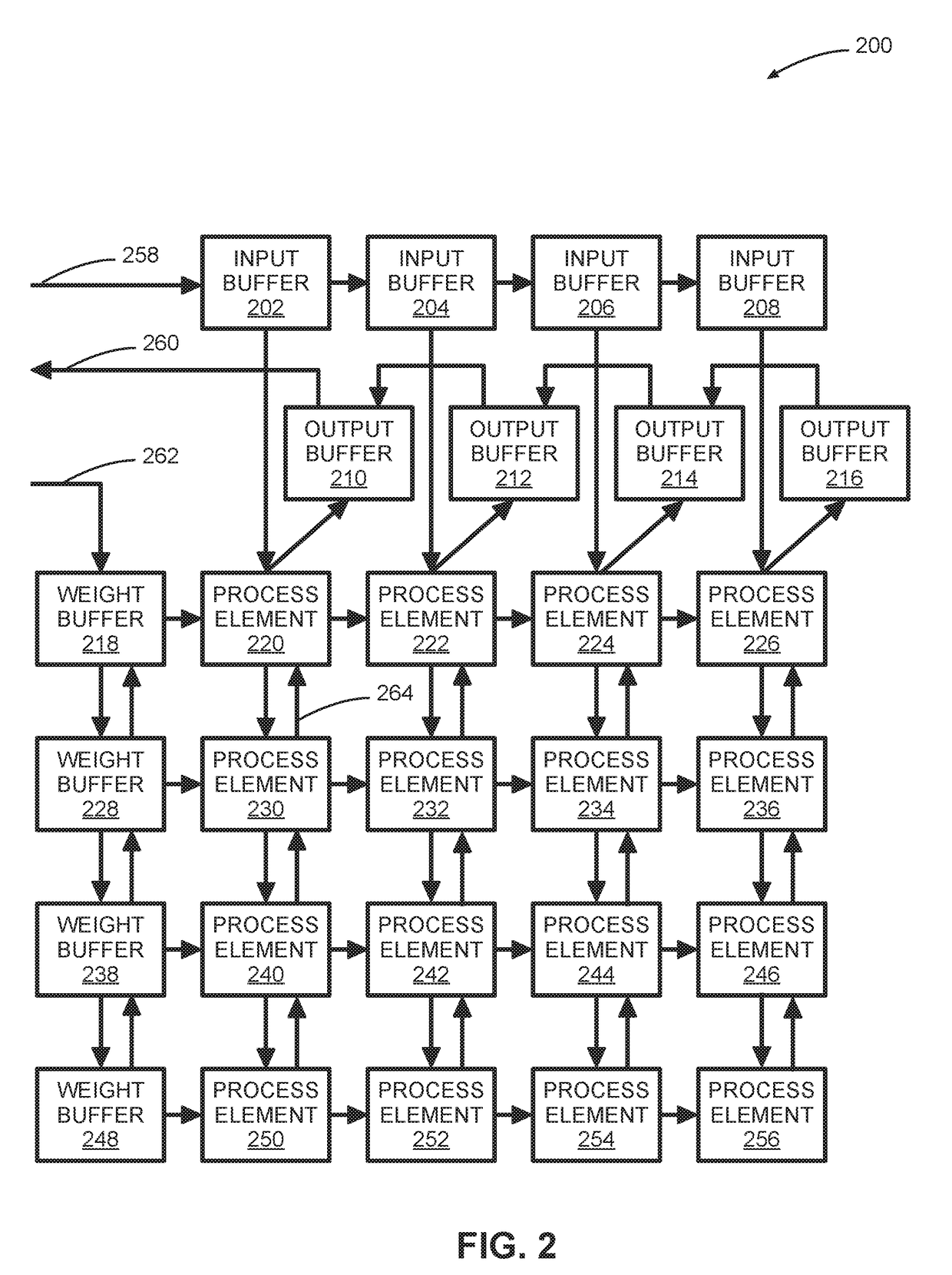
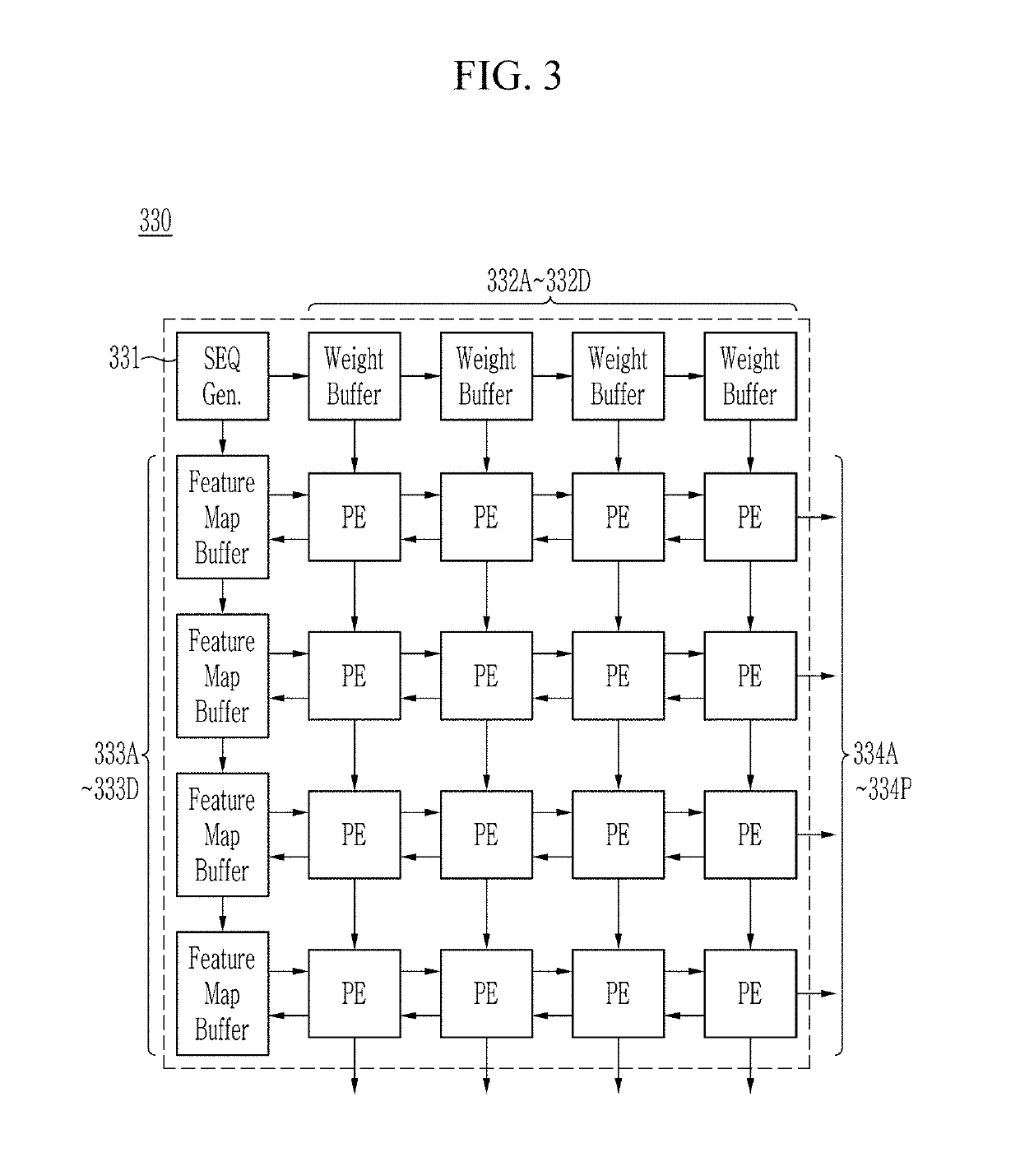
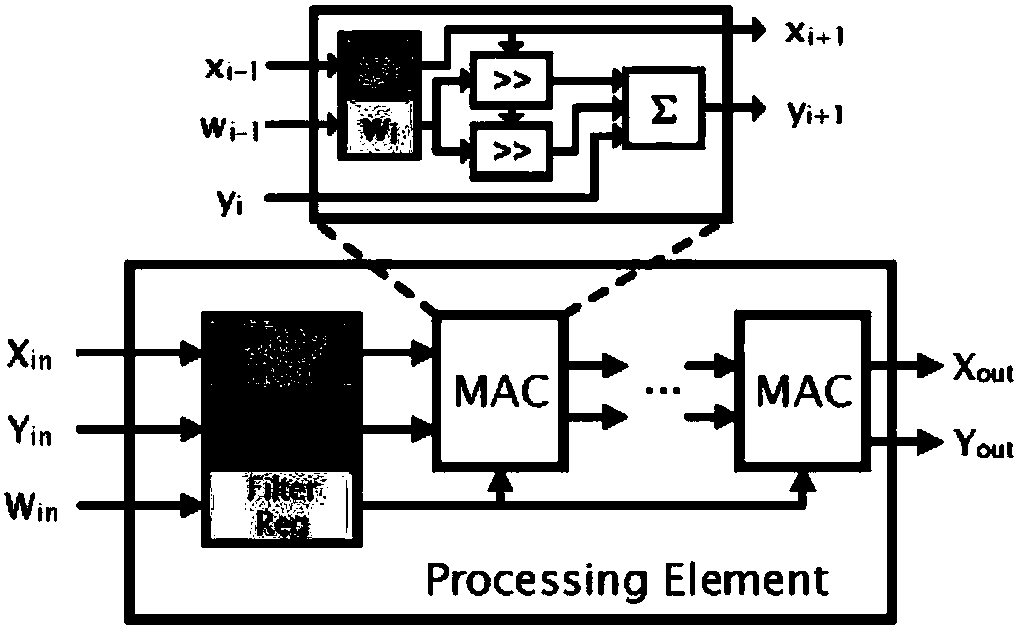
Systems And Methods For Systolic Array Design From A High-Level Program
ActiveUS20180314671A1Improve design throughputSingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsSystolic arraysParallel computingProcessing element
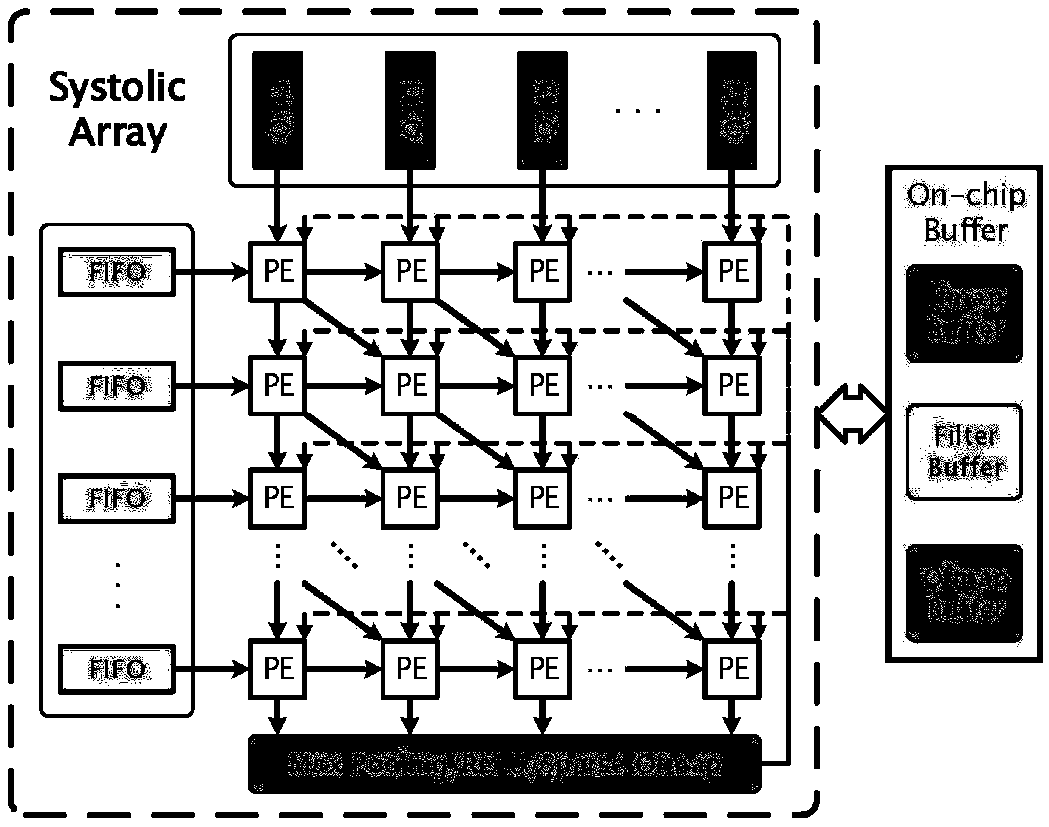
Systems and methods for automated systolic array design from a high-level program are disclosed. One implementation of a systolic array design supporting a convolutional neural network includes a two-dimensional array of reconfigurable processing elements arranged in rows and columns. Each processing element has an associated SIMD vector and is connected through a local connection to at least one other processing element. An input feature map buffer having a double buffer is configured to store input feature maps, and an interconnect system is configured to pass data to neighboring processing elements in accordance with a processing element scheduler. A CNN computation is mapped onto the two-dimensional array of reconfigurable processing elements using an automated system configured to determine suitable reconfigurable processing element parameters.
Owner:XILINX INC
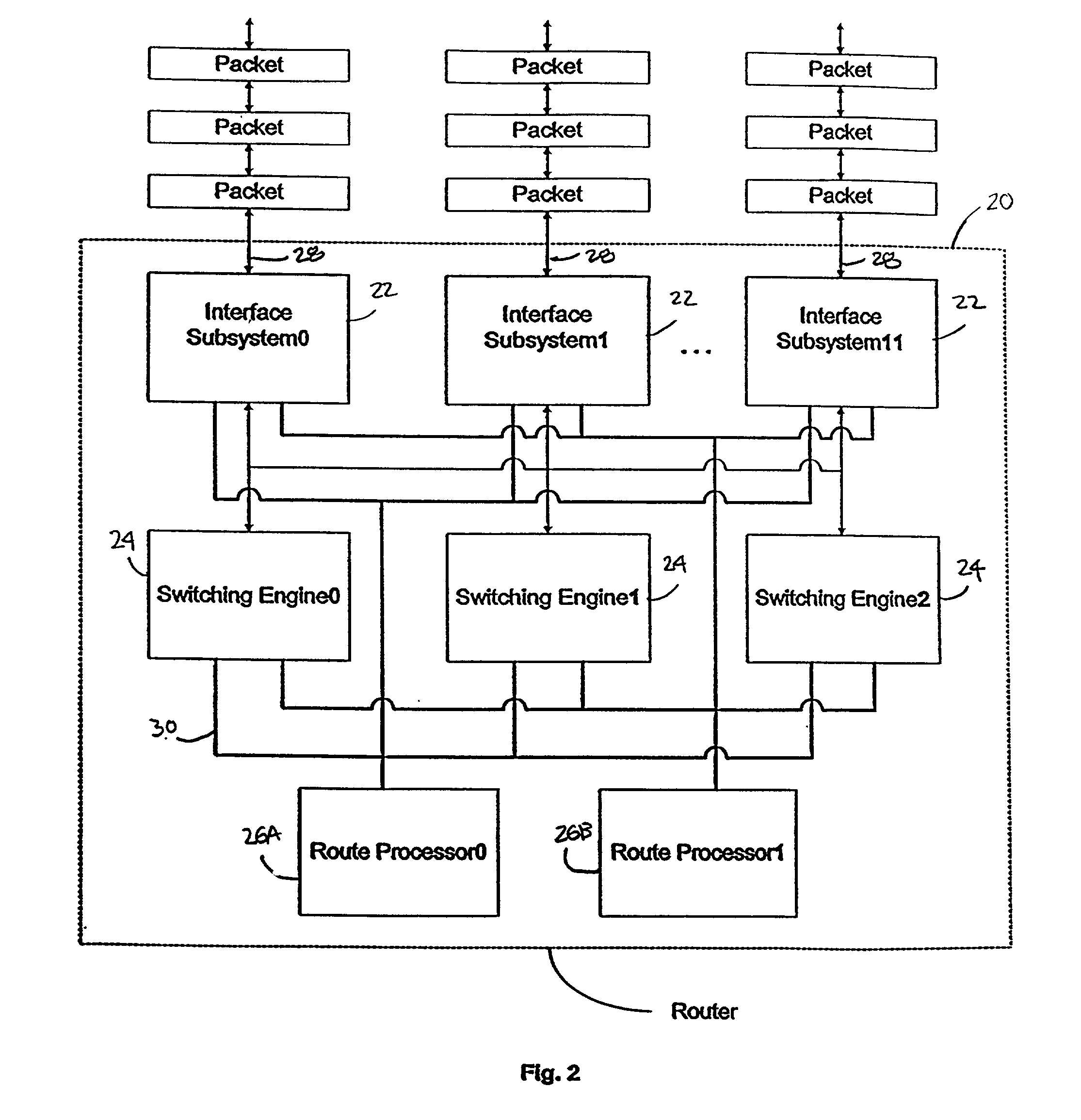
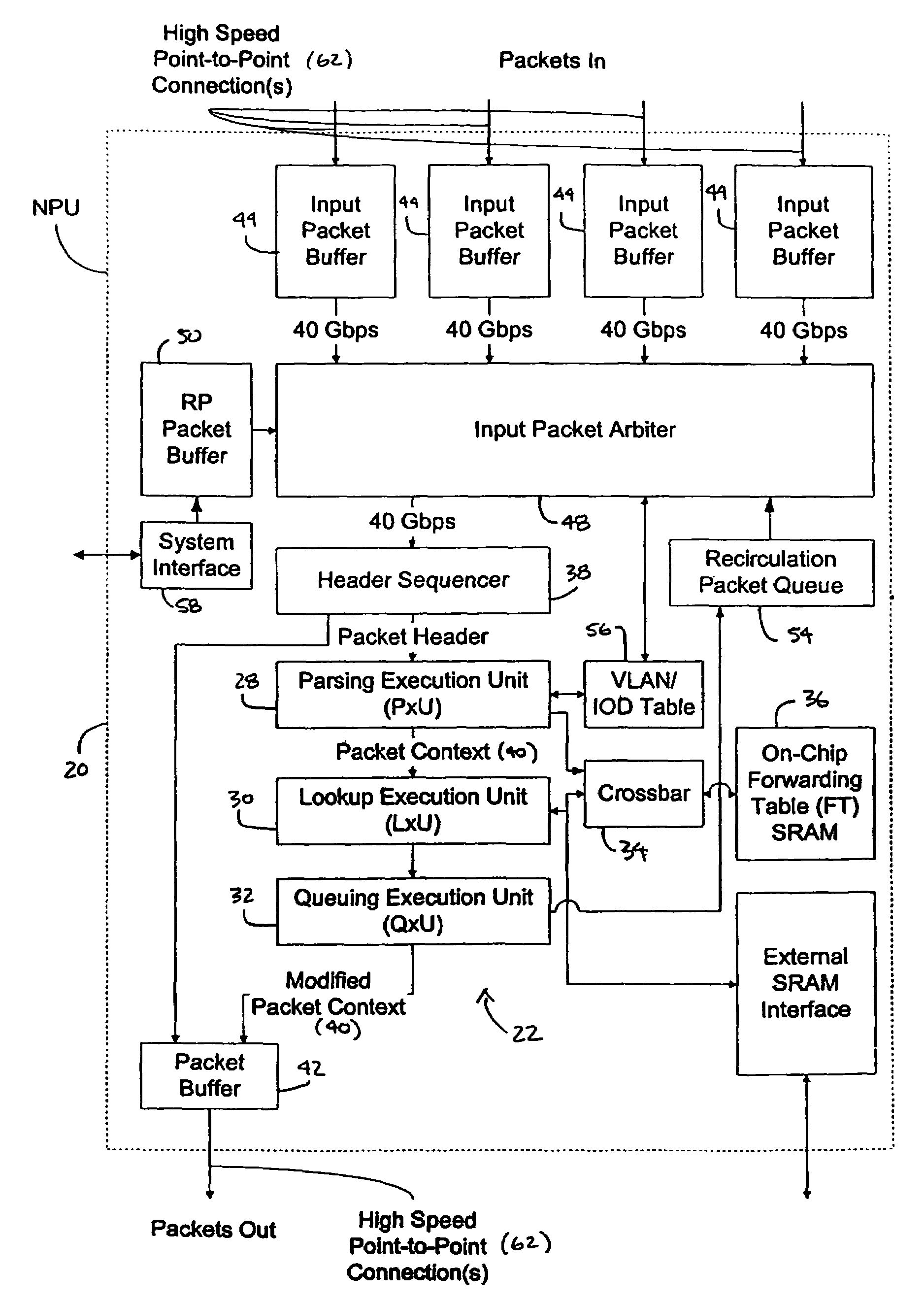
Processor having systolic array pipeline for processing data packets
InactiveUS7069372B1Input is hugeEliminate needSystolic arraysDigital data processing detailsSingle stageProcessor register
A processor for use in a router, the processor having a systolic array pipeline for processing data packets to determine to which output port of the router the data packet should be routed. In one embodiment, the systolic array pipeline includes a plurality of programmable functional units and register files arranged sequentially as stages, for processing packet contexts (which contain the packet's destination address) to perform operations, under programmatic control, to determine the destination port of the router for the packet. A single stage of the systolic array may contain a register file and one or more functional units such as adders, shifters, logical units, etc., for performing, in one example, very long instruction word (vliw) operations. The processor may also include a forwarding table memory, on-chip, for storing routing information, and a cross bar selectively connecting the stages of the systolic array with the forwarding table memory.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
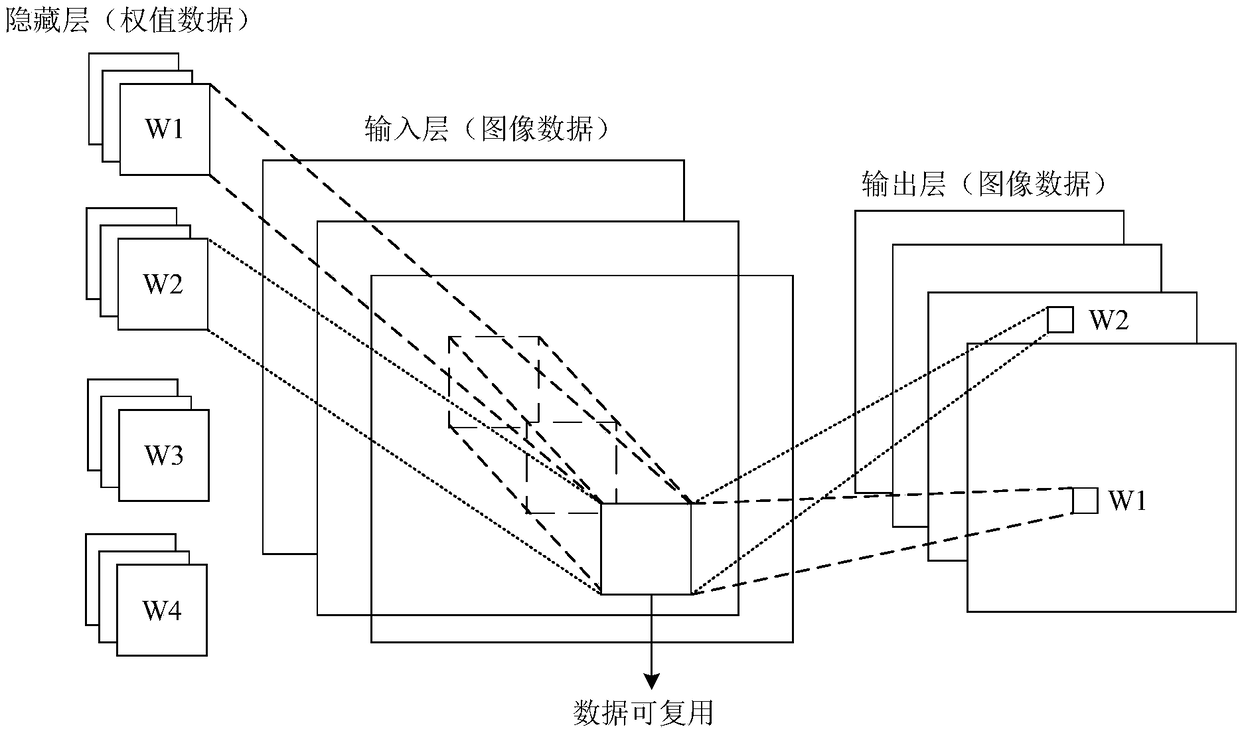
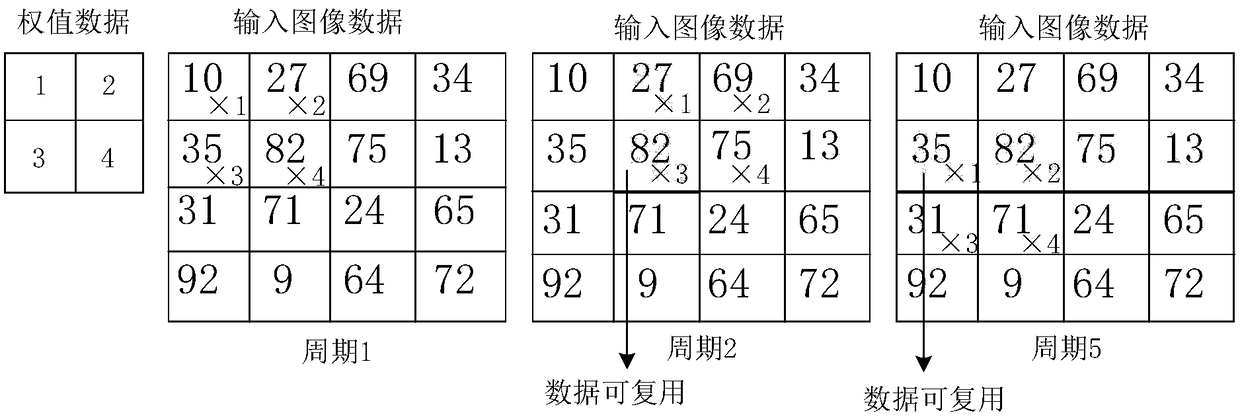
Convolutional neural network inference accelerator and method
ActiveCN108182471AImprove loading efficiencyImprove addition efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesAlgorithmReusability
The invention discloses a convolutional neural network inference accelerator and method. The accelerator comprises an input image buffer module which comprises N buffers for loading input image data,and N*N operation units which are connected to an input image buffer module and are used for performing convolution operations, wherein each of the buffers stores data of one row corresponding to an image, the N*N operation units support a pulsating form of the image data transmitted between adjacent operation units and are connected to the operation units in the buffers to read image data from the buffer, and remaining operation units read the image data from an adjacent operation unit. According to the convolutional neural network inference accelerator and the method, a bidirectional pulsation array is designed for data reusability brought by a convolutional neural network, the loading efficiency of the data is improved, and thus the convolutional neural network is accelerated.
Owner:上海岳芯电子科技有限公司
A universal convolutional neural network accelerator based on a one-dimensional pulsation array
ActiveCN109934339AGuaranteed uptimeRealize data reuseNeural architecturesEnergy efficient computingParallel computingBus interface
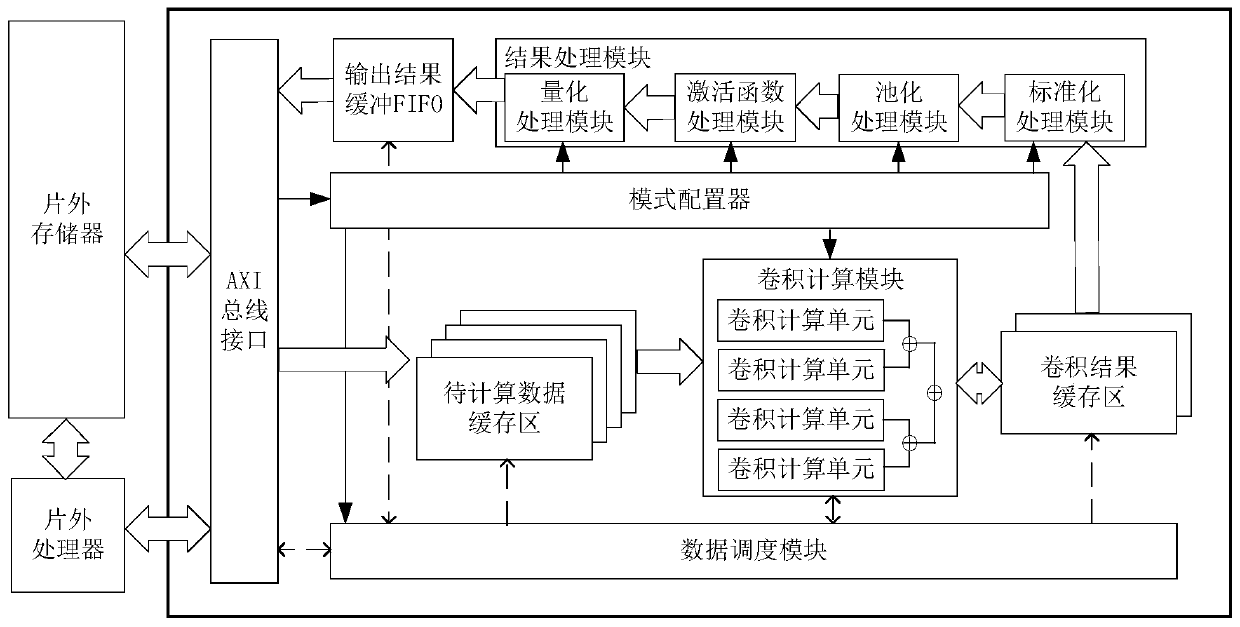
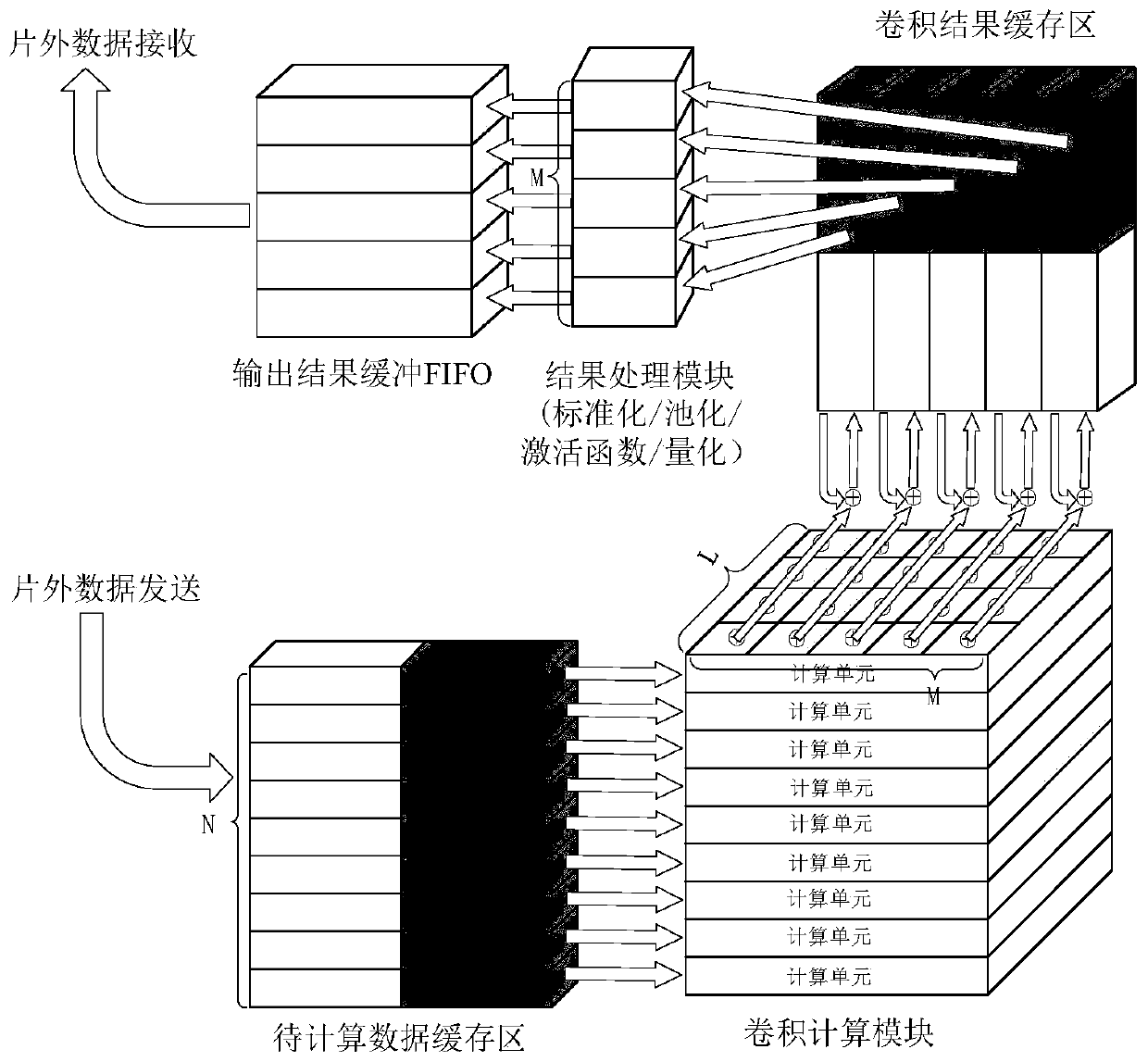
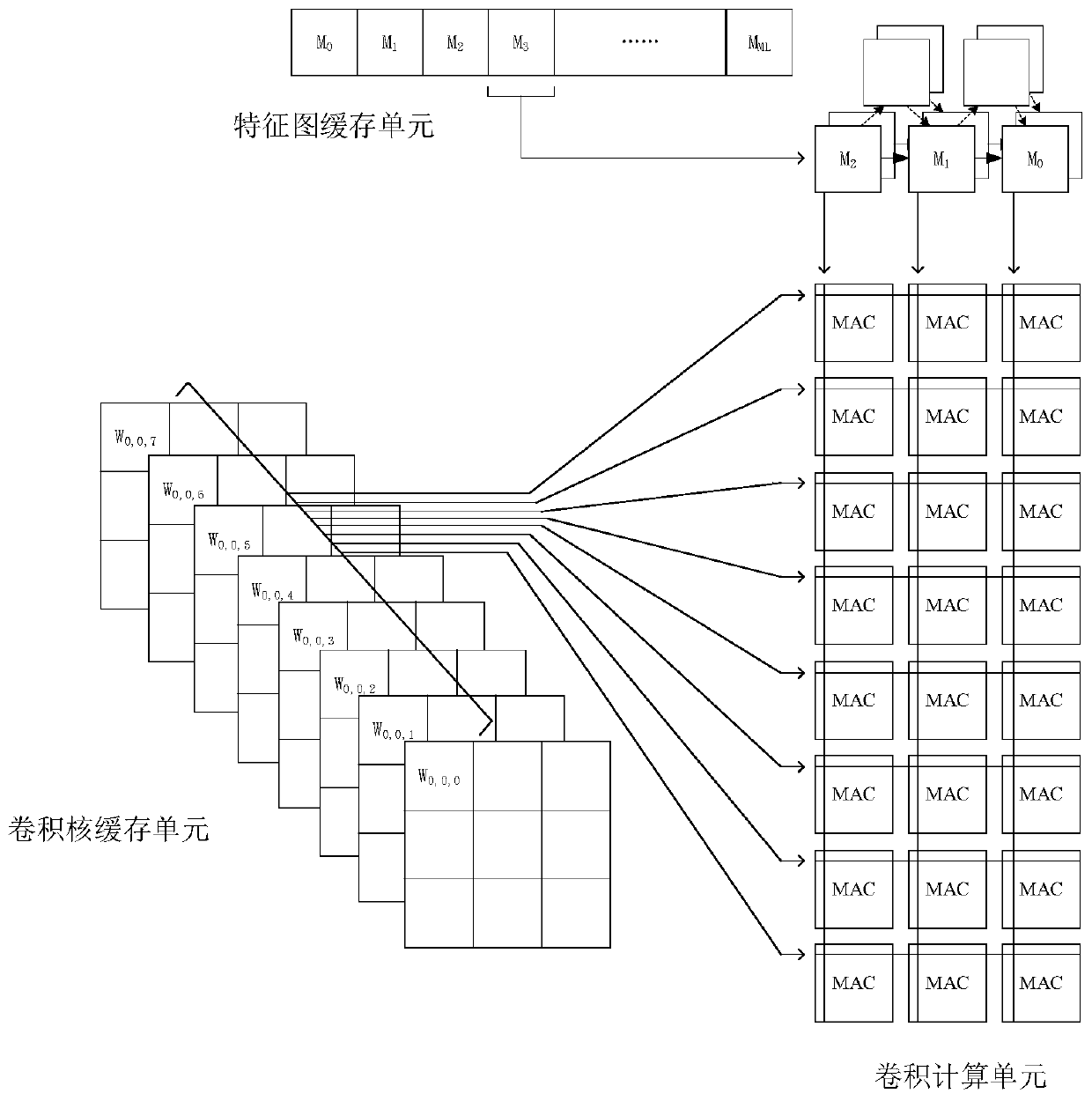
The invention discloses a universal convolutional neural network accelerator based on a one-dimensional pulsation array. An AXI4 bus interface is used for realizing loading of a mode configuration instruction, reading of to-be-calculated data and batch sending of result data. The mode configurator configures each functional module as a corresponding working type through the mode configuration instruction; The data scheduling module can concurrently perform tasks of caching data to be calculated, reading calculation data, caching convolution results, processing the convolution results and outputting the convolution results; The convolution calculation module adopts a one-dimensional pulsation array mode to carry out convolution calculation; The to-be-calculated data cache region, the convolution result cache region and the output result buffer FIFO are used for caching corresponding data; And the result processing module carries out common result processing operation in the convolutional neural network. The accelerator can be compatible with different calculation types in a convolutional neural network, high-parallelism calculation is carried out to effectively accelerate, and onlya lower off-chip memory access bandwidth requirement and a small amount of on-chip memory resources are needed.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV +1
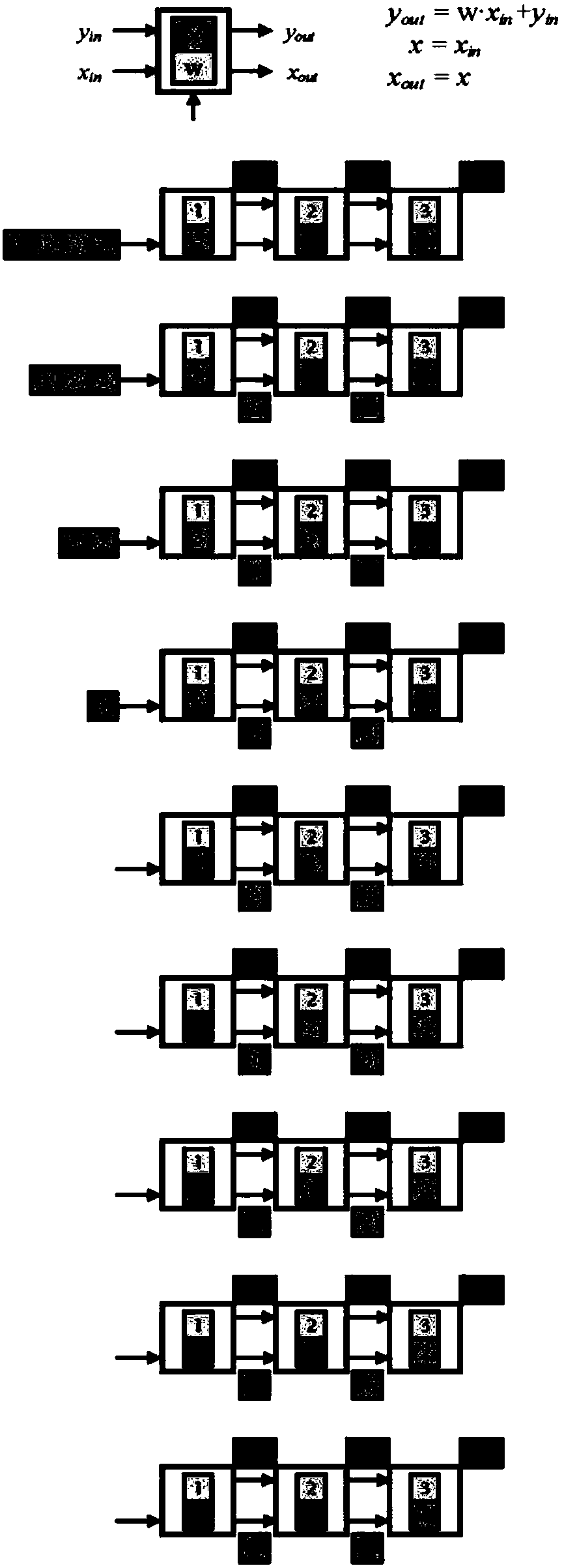
Method and apparatus for an adaptive systolic array structure
ActiveUS8184696B1Minimizes local memory storage usageUse minimizedColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionProcessing elementSelf adaptive
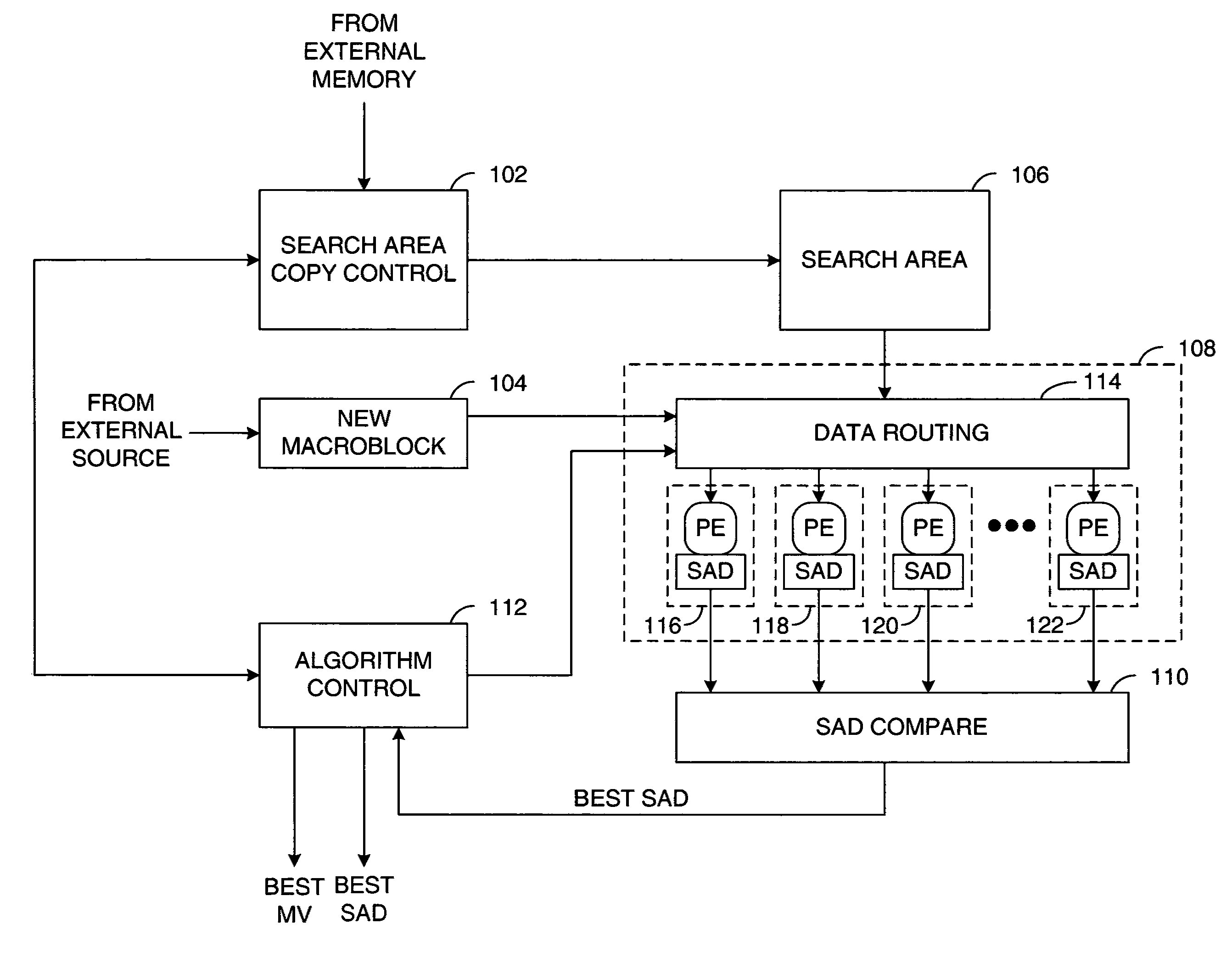
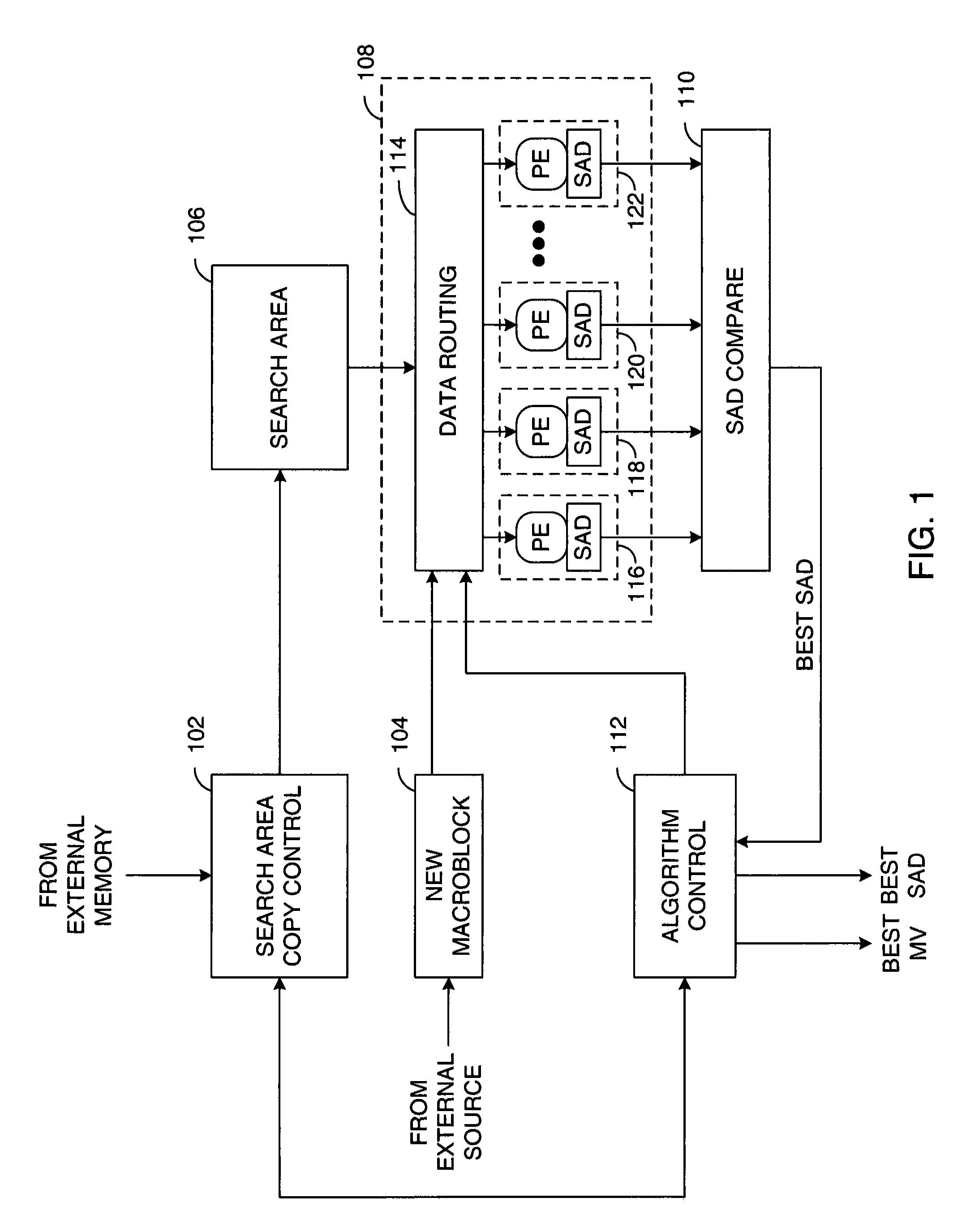
A method and apparatus for an adaptive systolic array structure is initially configured for motion estimation calculations and optionally reconfigured as the motion estimation algorithm progresses. A scheduling map of the processing element (PE) calculations for a given motion estimation algorithm is generated. A systolic array structure may then be generated from the scheduling map, whereby the size and shape of a processing element array is configured to generate the search pattern that is to be used during the search. In addition, delay elements may be implemented within the systolic array structure, so as to preserve the pixels of a current macroblock that are reused in accordance with the scheduling map. The systolic array structure may also be adapted by the motion estimation algorithm during subsequent search stages to accommodate refinements required by the search strategy.
Owner:XILINX INC
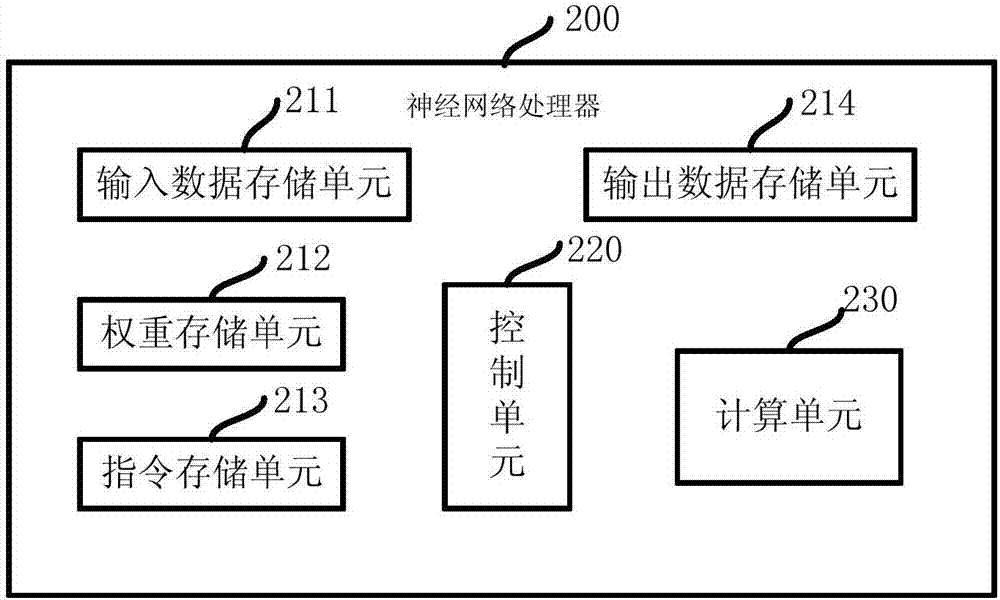
Neural network processor based on systolic array
ActiveCN107578098AImprove computing efficiencyAlleviate bandwidth requirementsPhysical realisationNetwork processorNeural network nn
The invention provides a neural network processor which comprises a control unit, a calculation unit, a data storage unit and a weight storage unit. The calculation unit controlled by the control unitacquires data and weights from the data storage unit and the weight storage unit to perform operation related to a neural network. The calculation unit comprises an array controller and a plurality of processing units connected in a systolic array mode, the data and the weights are input to a systolic array formed by the processing units in different directions, and the processing units simultaneously and parallelly process the data flowing through the processing units. The neural network processor can reach high processing speed, and the input data are repeatedly reused, so that high operation throughput rate can be realized under the condition of consuming small memory access bandwidth.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
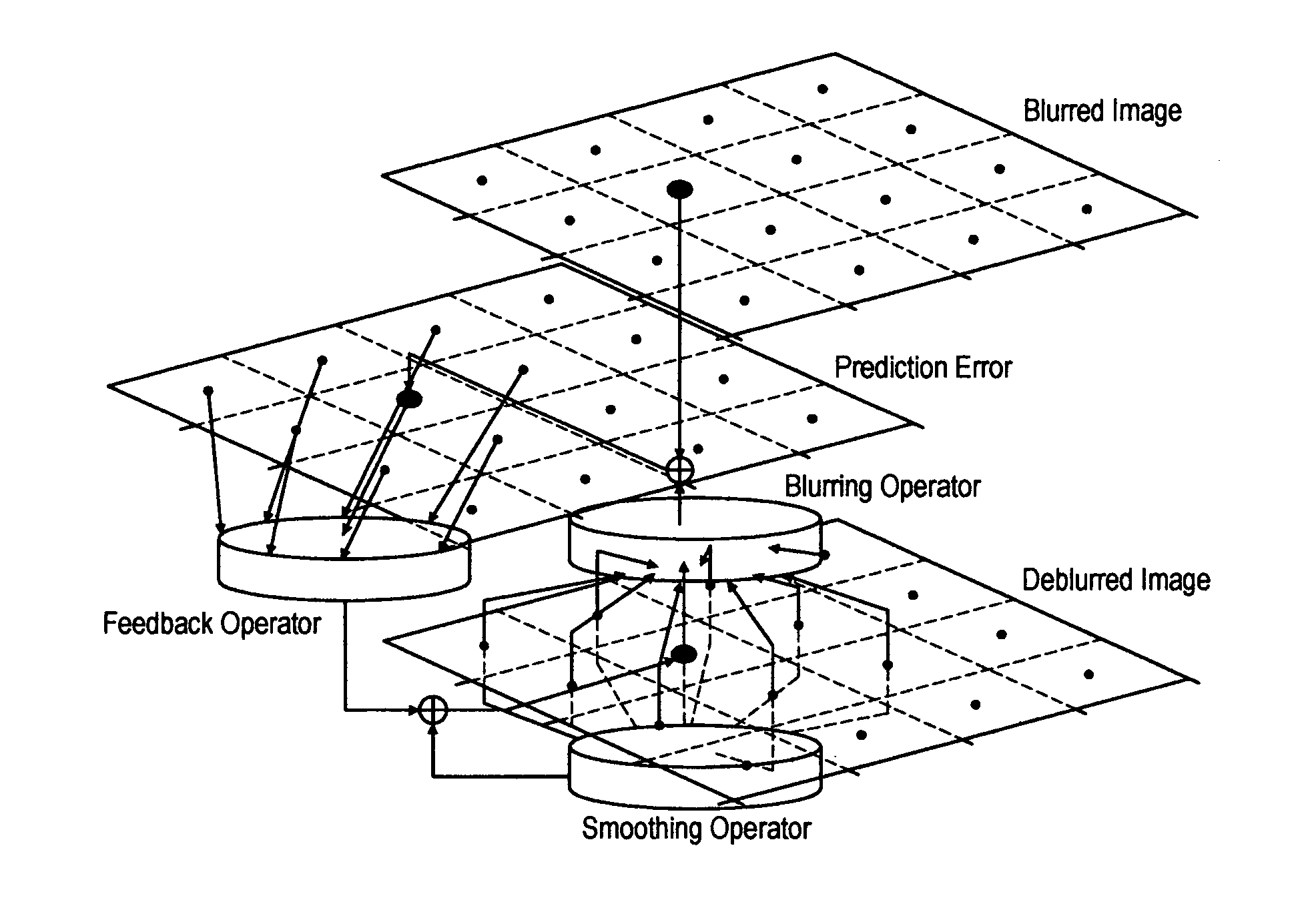
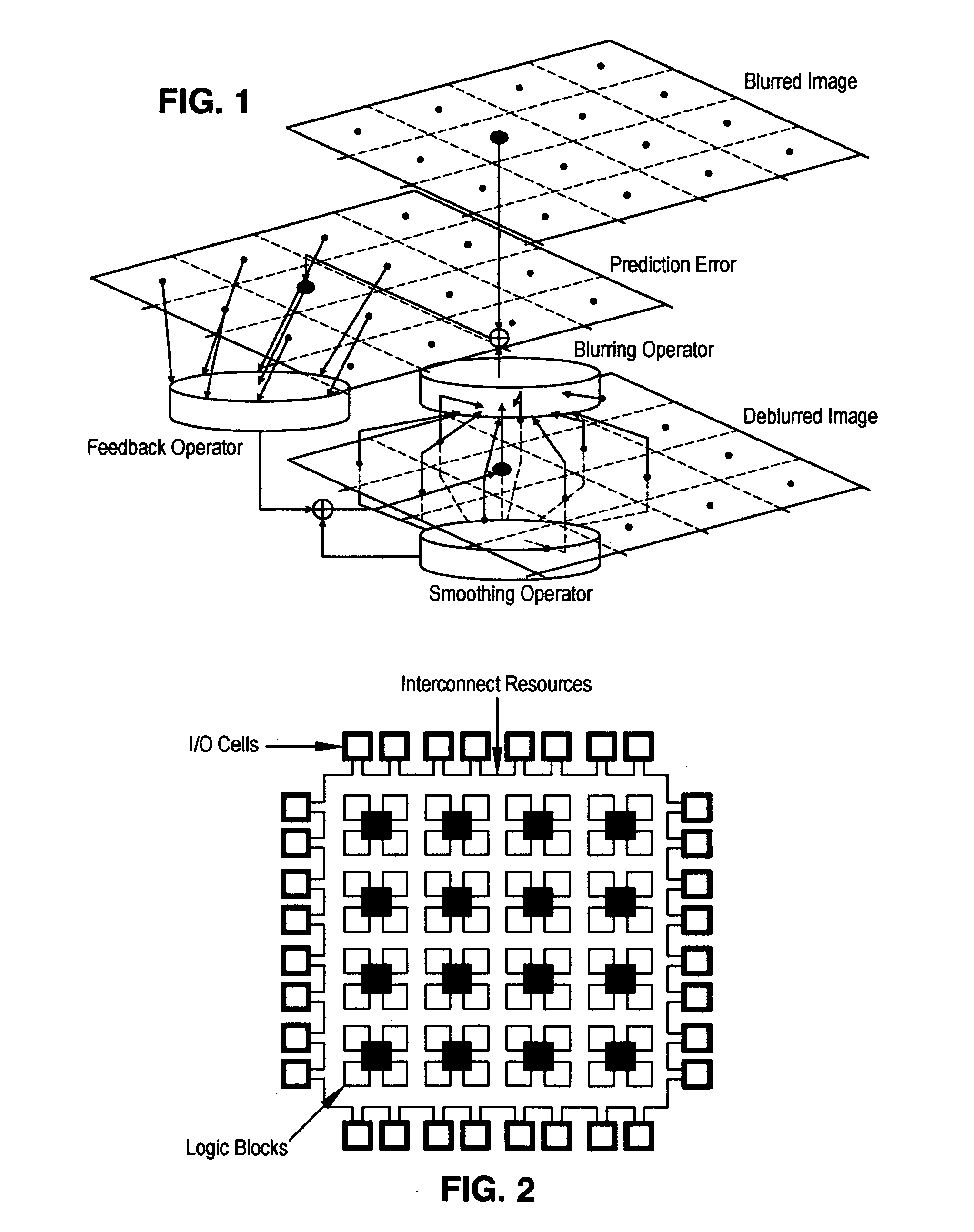
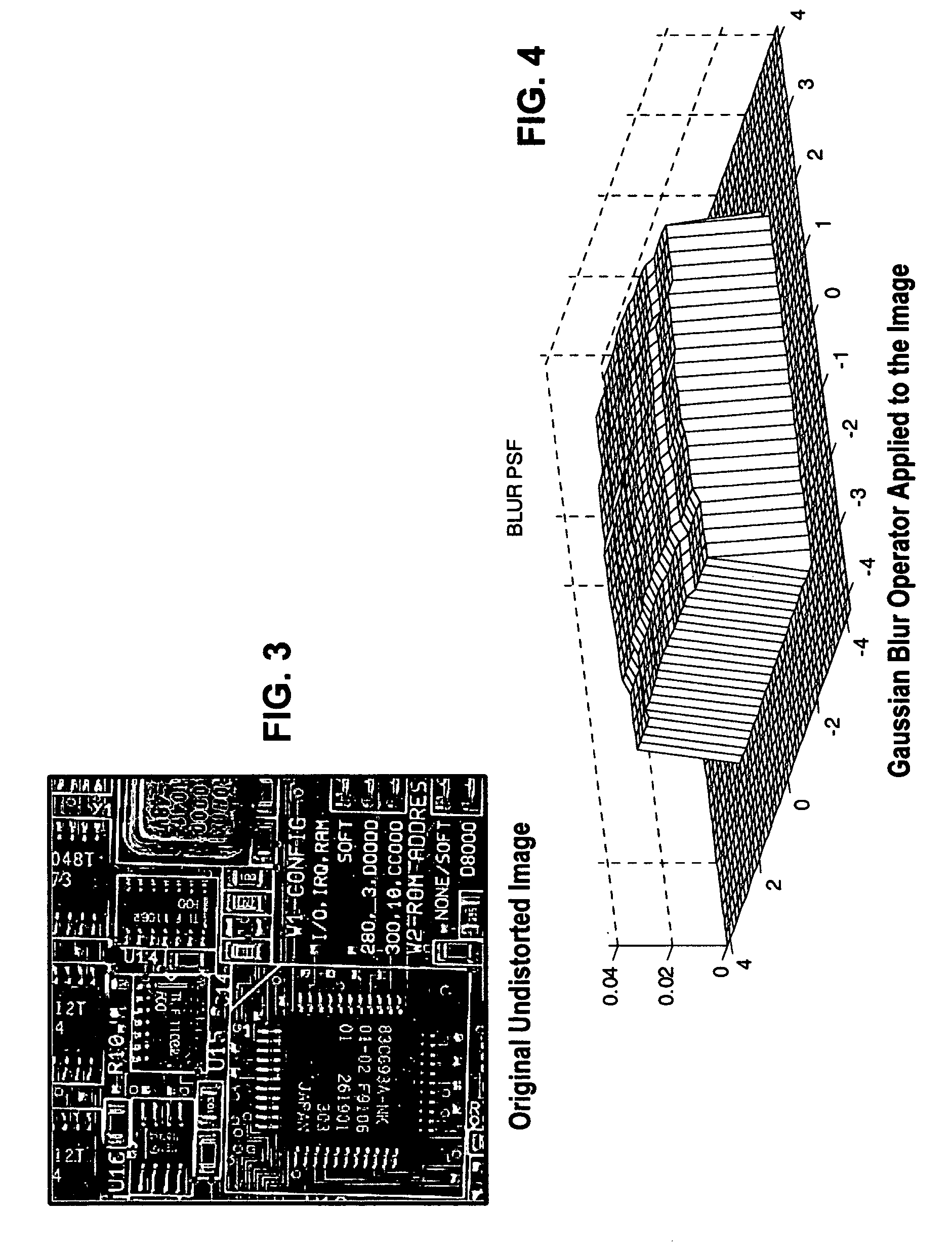
Image deblurring with a systolic array processor
InactiveUS20050147313A1Simple multiplicationSimple addition operationImage enhancementGeneral purpose stored program computerSystolic arrayImage prediction
A method and device for deblurring an image having pixels. A blurred image is downloaded into a systolic array processor having an array of processing logic blocks such that each pixel arrives in a respective processing logic block of one pixel or small groups of pixels. Data is sequentially exchanged between processing logic blocks by interconnecting each processing logic block with a predefined number of adjacent processing logic blocks, followed by uploading the deblurred image. The processing logic blocks provide an iterative update of the blurred image by (i) providing feedback of the blurred image prediction error using the deblurred image and (ii) providing feedback of the past deblurred image estimate. The iterative update is implemented in the processing logic blocks by u(n+1)=u(n)−K*(H*u(n)−yb)−S*u(n).
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Affine transformation analysis system and method for image matching
InactiveUS20040175057A1Minimize the differenceImprove accuracyImage analysisGeneral purpose stored program computerRadio frequencyVisual perception
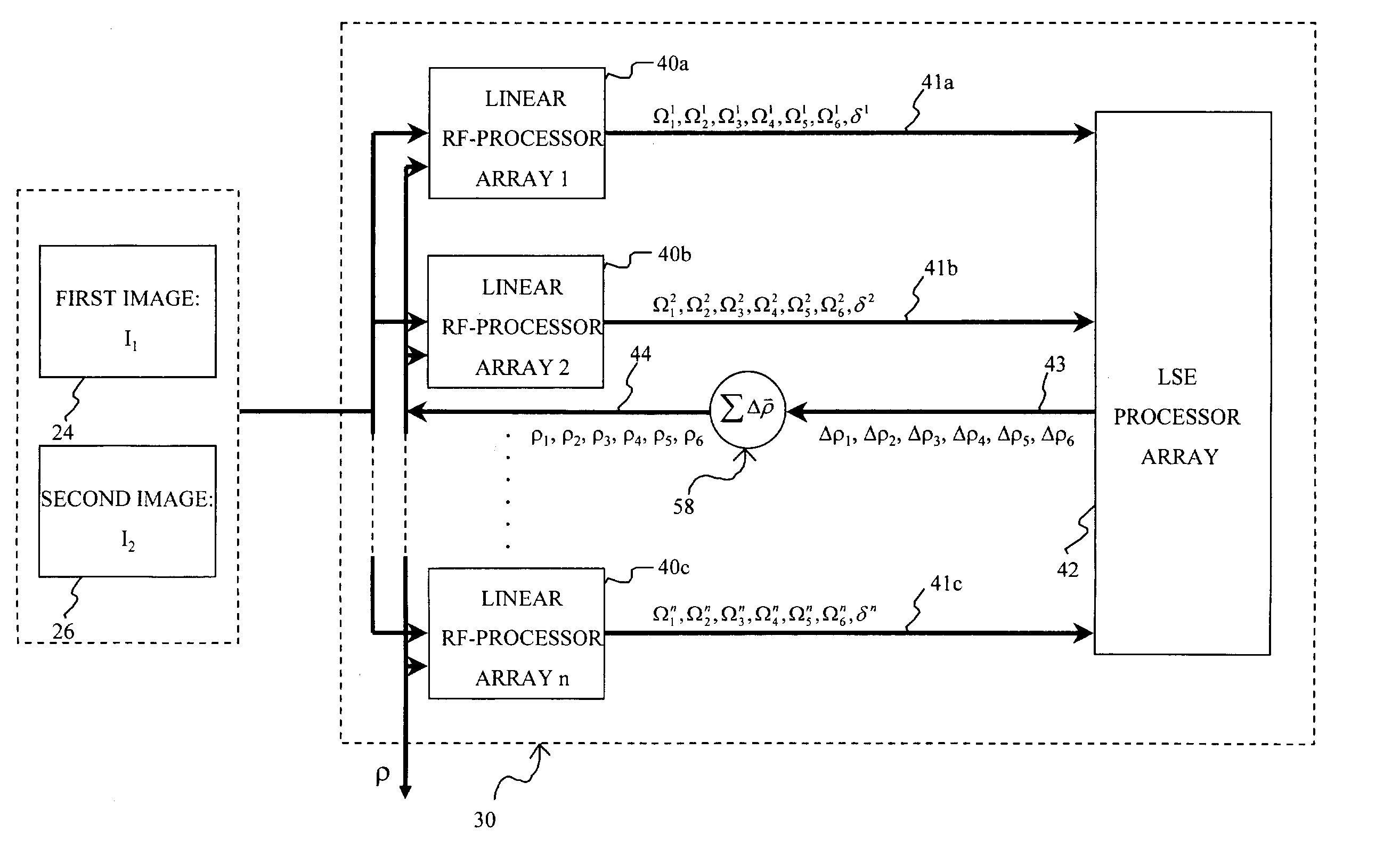
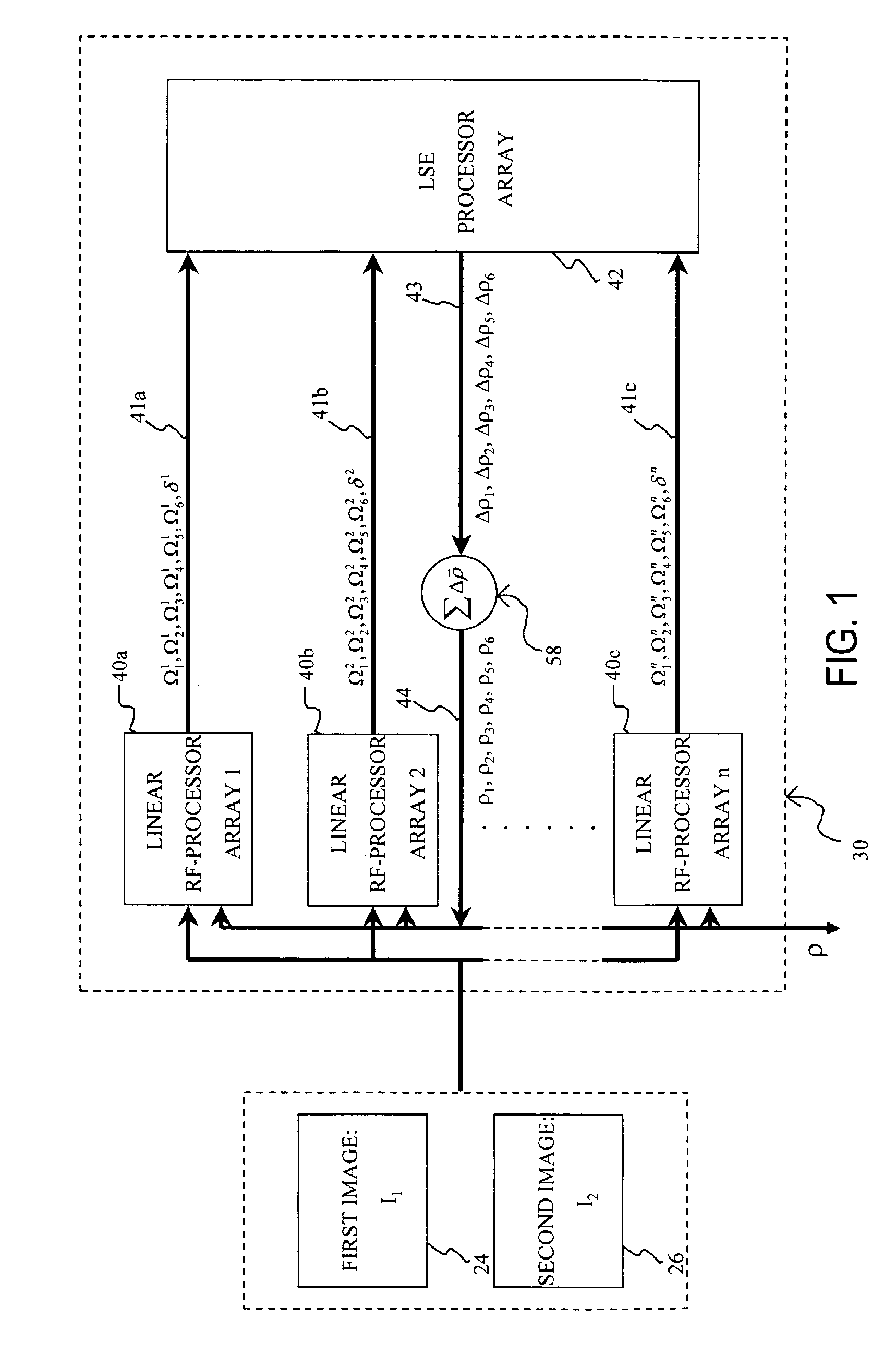
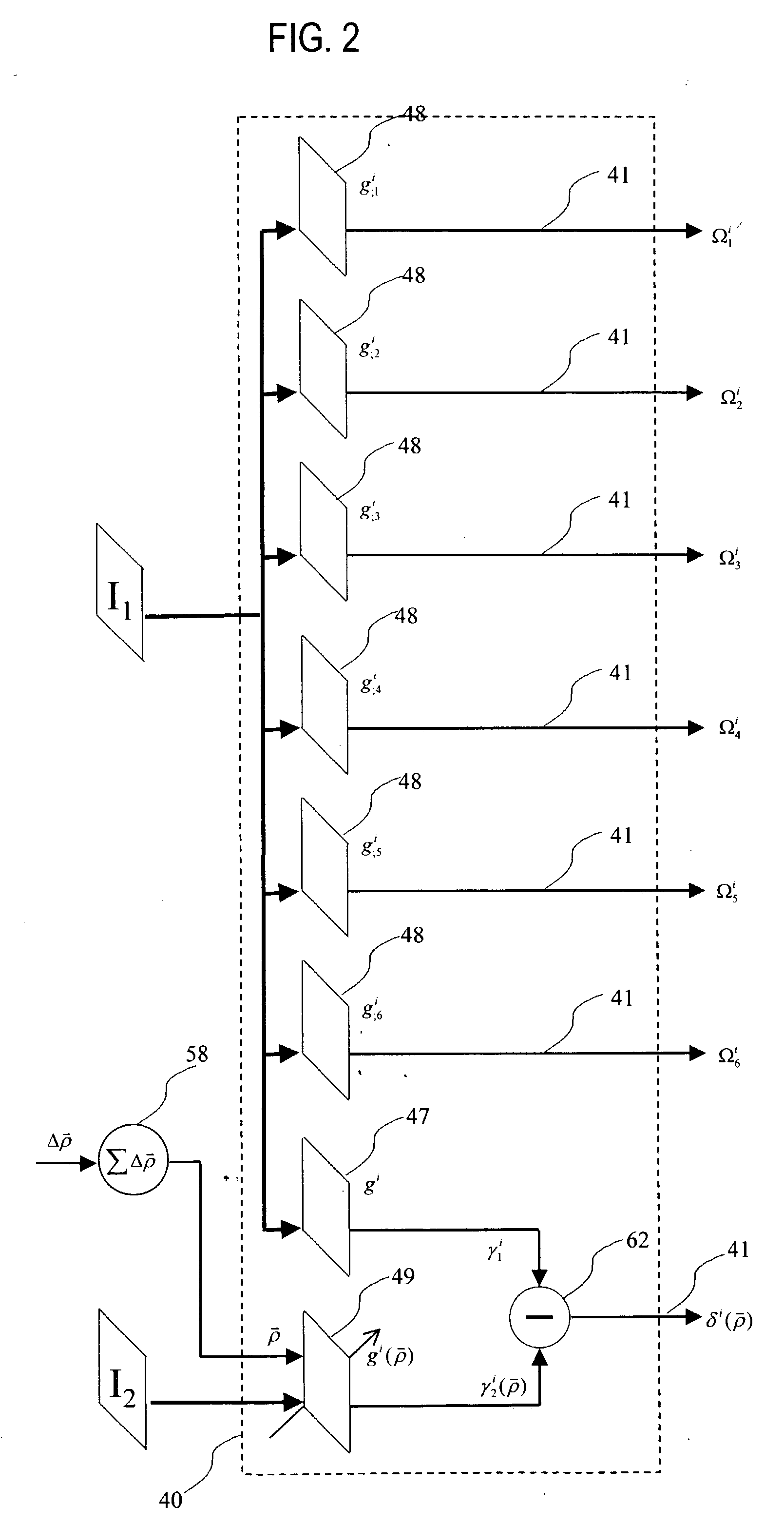
An affine transformation analysis system and method is provided for matching two images. The novel systolic array image affine transformation analysis system comprising a linear rf-processing means, an affine parameter incremental updating means, and a least square error fitting means is based on a Lie transformation group model of cortical visual motion and stereo processing. Image data is provided to a plurality of component linear rf-processing means each comprising a Gabor receptive field, a dynamical Gabor receptive field, and six Lie germs. The Gabor coefficients of images and affine Lie derivatives are extracted from responses of linear receptive fields, respectively. The differences and affine Lie-derivatives of these Gabor coefficients obtained from each parallel pipelined linear rf-processing components are then input to a least square error fitting means, a systolic array comprising a QR decomposition means and a backward substitution means. The output signal from the least square error fitting means then be used to updating of the affine parameters until the difference signals between the Gabor coefficients from the static and dynamical Gabor receptive fields are substantially reduced.
Owner:TSAO THOMAS +1
Processor having systolic array pipeline for processing data packets
InactiveUS7418536B2Input is hugeEliminate needGeneral purpose stored program computerTransmissionSingle stageLogic cell
A processor for use in a router, the processor having a systolic array pipeline for processing data packets to determine to which output port of the router the data packet should be routed. In one embodiment, the systolic array pipeline includes a plurality of programmable functional units and register files arranged sequentially as stages, for processing packet contexts (which contain the packet's destination address) to perform operations, under programmatic control, to determine the destination port of the router for the packet. A single stage of the systolic array may contain a register file and one or more functional units such as adders, shifters, logical units, etc., for performing, in one example, very long instruction word (vliw) operations. The processor may also include a forwarding table memory, on-chip, for storing routing information, and a cross bar selectively connecting the stages of the systolic array with the forwarding table memory.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
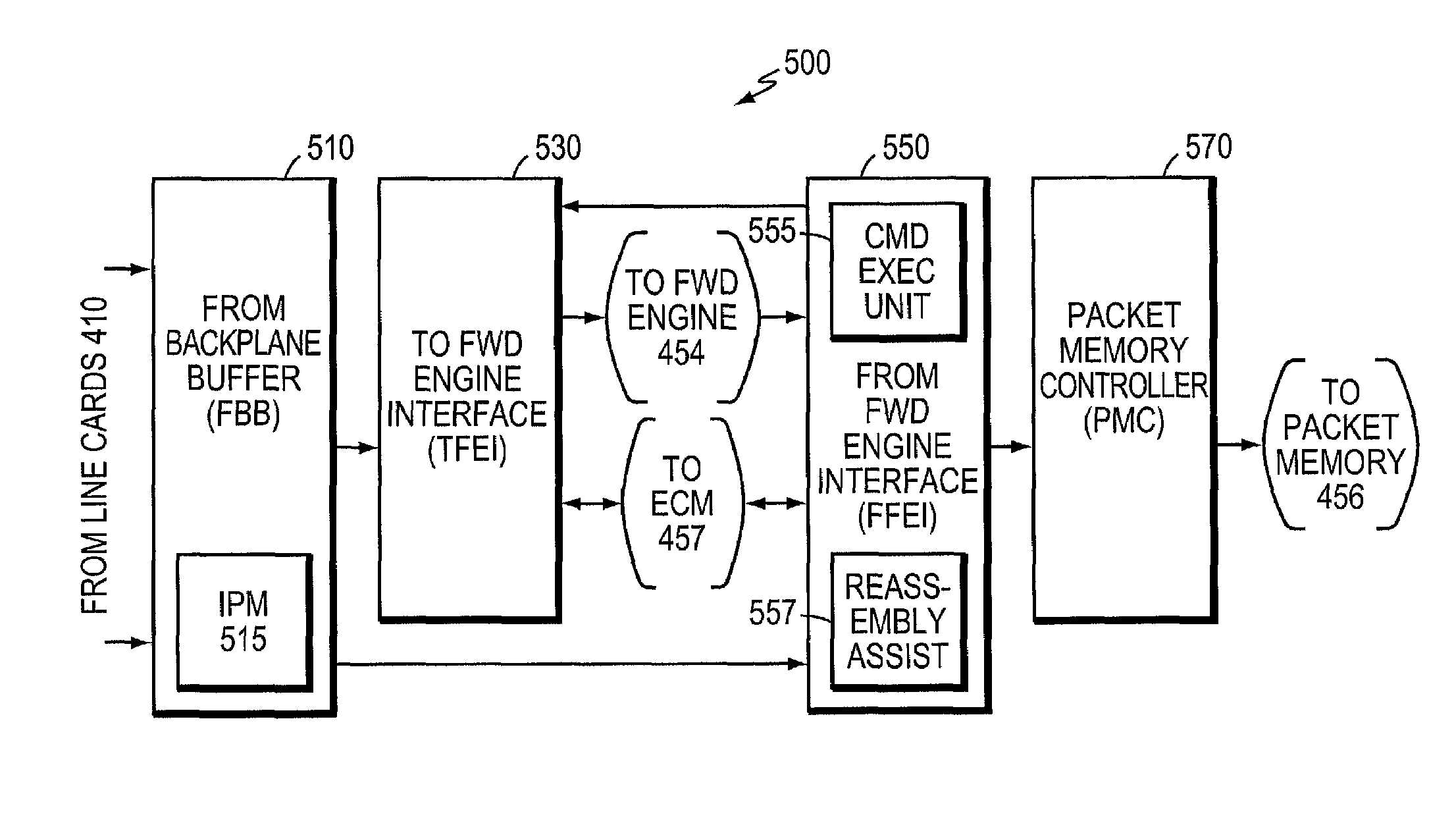
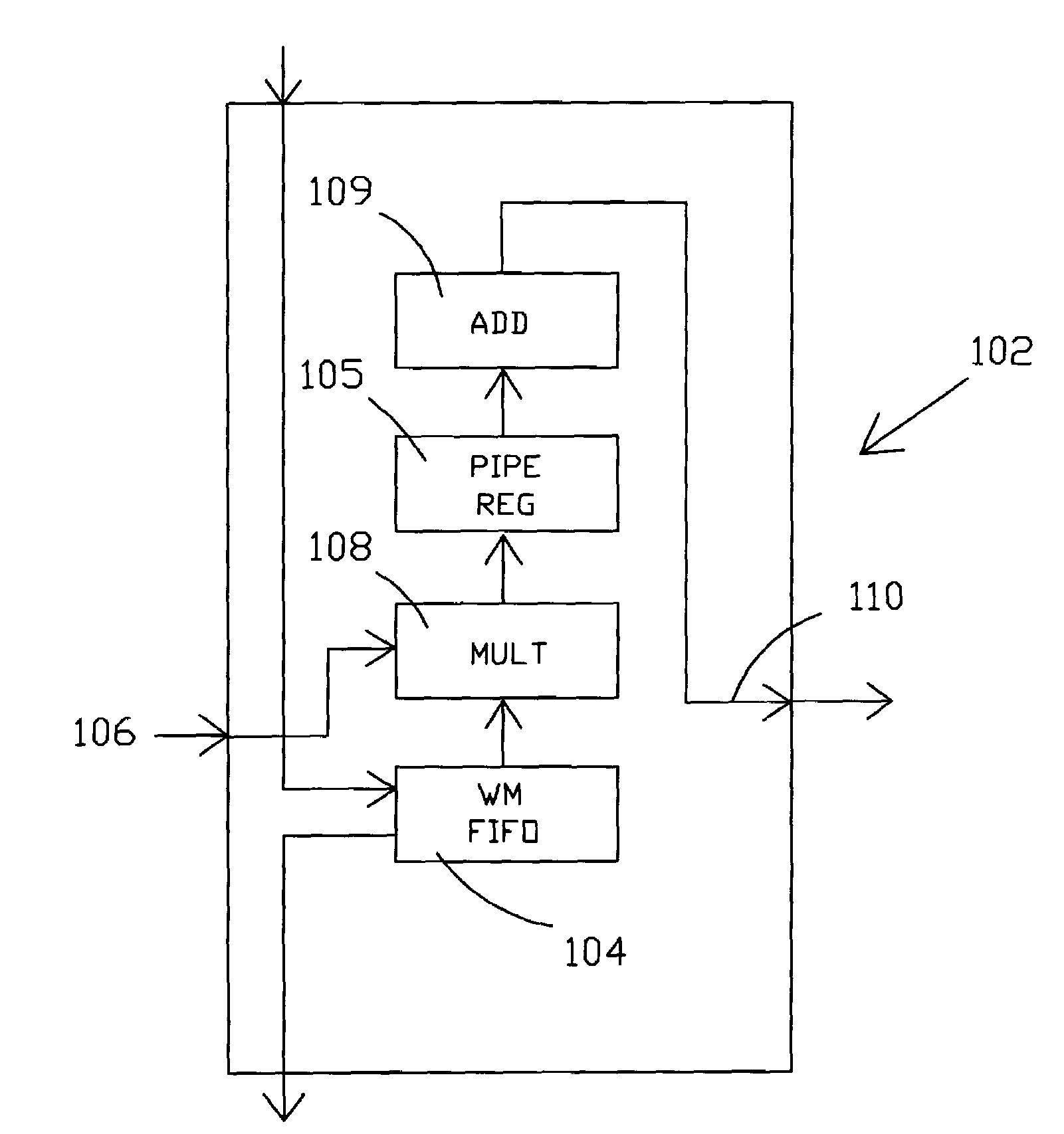
Scheduling assist for data networking packet dequeuing in a parallel 1-D systolic array system
ActiveUS7085229B1Rapid positioningStay flexibleError preventionTransmission systemsNetwork packetNetwork data
The present invention comprises a scheduling assist function (scheduling assist) that enables a processor to schedule events and be notified when these events expire. In addition, the present invention includes features that enable a processor to associate these events with output channels and enable the processor to quickly locate output channels (links) that are available and ready to be serviced. The invention takes advantage of the fact that the scheduling assist can be dedicated exclusively to scanning tables in its own dedicated memories looking for events that have expired and / or output channels that are available and not involve the processor in the search for output channels that are available and ready to be serviced.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
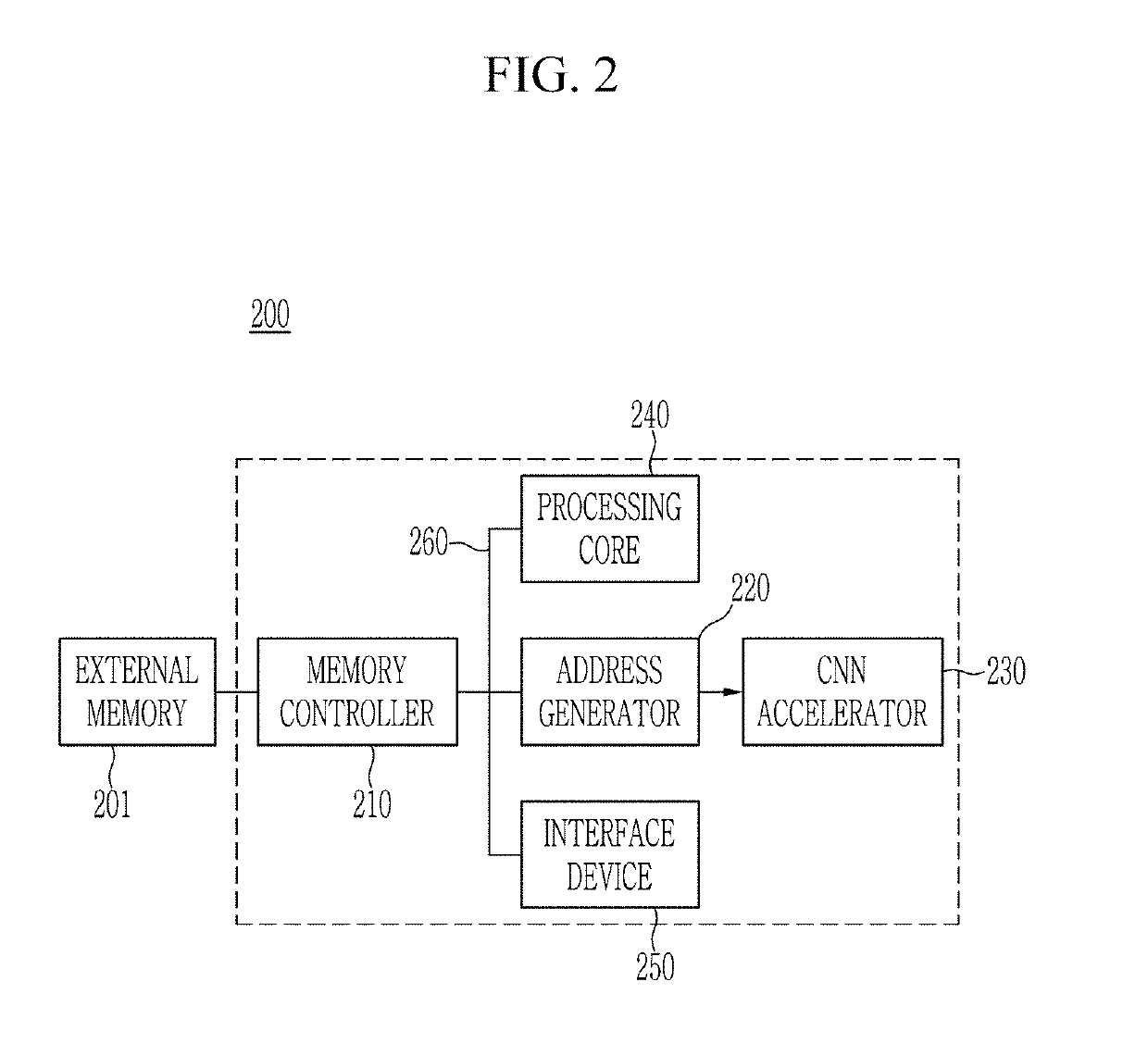
Apparatus for processing convolutional neural network using systolic array and method thereof
InactiveUS20190164037A1Efficient storageEasy to useSystolic arraysNeural architecturesAddress generatorFeature mapping
In the present invention, by providing an apparatus for processing a convolutional neural network (CNN), including a weight memory configured to store a first weight group of a first layer, a feature map memory configured to store an input feature map where the first weight group is to be applied, an address generator configured to determine a second position spaced from a first position of a first input pixel of the input feature map based on a size of the first weight group, and determine a plurality of adjacent pixels adjacent to the second position; and a processor configured to apply the first weight group to the plurality of adjacent pixels to obtain a first output pixel corresponding to the first position, a memory space may be efficiently used by saving the memory space.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
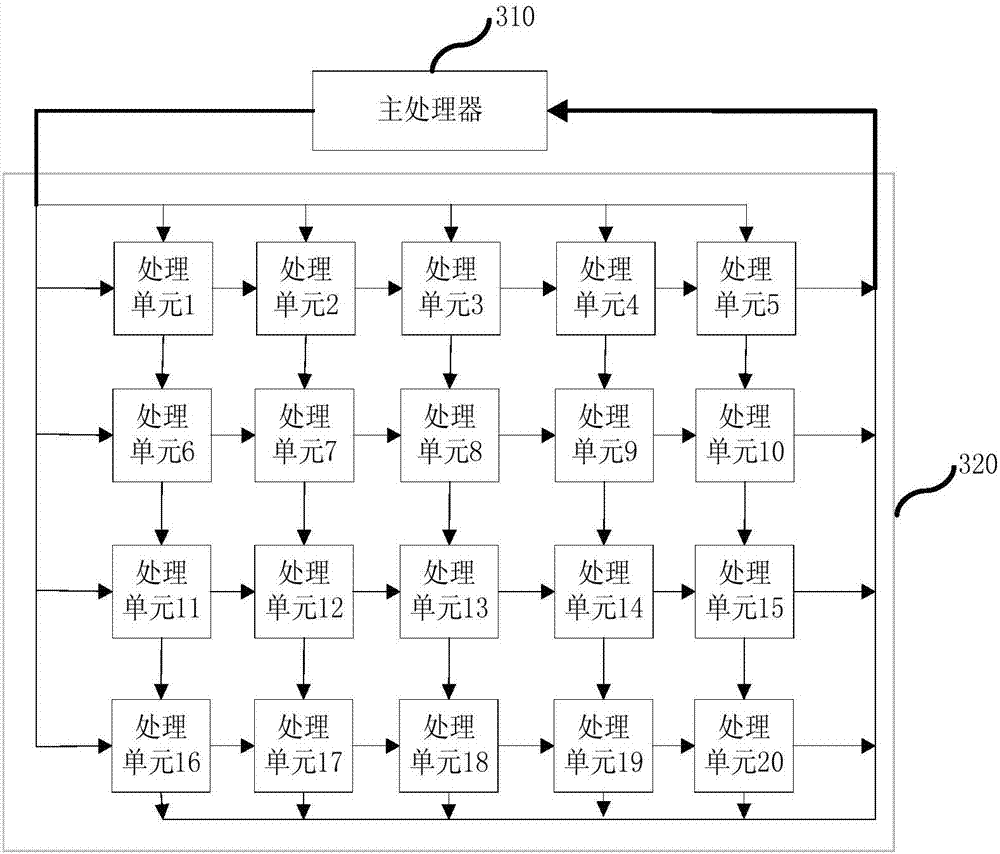
Neural network computing device and processor comprising same
ActiveCN107578095AImprove computing efficiencyReduce bandwidth requirementsPhysical realisationParallel computingMaster processor
The invention provides a neural network computing device and a processor comprising the same, wherein the computing device comprises a pulsating array processing unit and a main processor. The main processor is used for controlling the loading of computational elements in a neural network to the pulsating array processing unit and the transmitting in the pulsating array processing unit; the pulsating array processing unit is composed of a plurality of processing units; each processing unit performs calculations on received computational elements and / or passes the received computational elements to the next processing unit, wherein the computational elements include neuron data and corresponding weight values. The computing device of the invention is capable of speeding up the computational speed of the neural network and reducing the demand for bandwidth in the computing process.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Image data processing method and device, computer equipment and storage medium
PendingCN111897579AAvoid CatonImprove processing efficiencyImage memory managementConcurrent instruction executionData packOccurrence data
The invention relates to an image data processing method, which comprises the steps of obtaining image data of N to-be-processed images, and the image data of each to-be-processed image comprising C parts of image channel data; storing the image data into C storage areas of a local memory, wherein N storage units in each storage area store one piece of image channel data of N to-be-processed images respectively; when a data reading instruction occurs, determining a historical address according to a current address carried by the data reading instruction, thereby reading target image channel data from a local memory based on the storage address; arranging the read target image channel data in the form of a two-dimensional matrix, enabling the data corresponding to the same channel to be inthe same matrix row, and enabling the data corresponding to the same to-be-processed image in the adjacent matrix rows to be distributed in two adjacent matrix columns; and sequentially transmitting each column of data arranged in a two-dimensional matrix form to the pulsation array according to a time sequence for operation to obtain an operation result. By adopting the method, the data processing efficiency can be improved.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Systolic-array based systems and methods for performing block matching in motion compensation
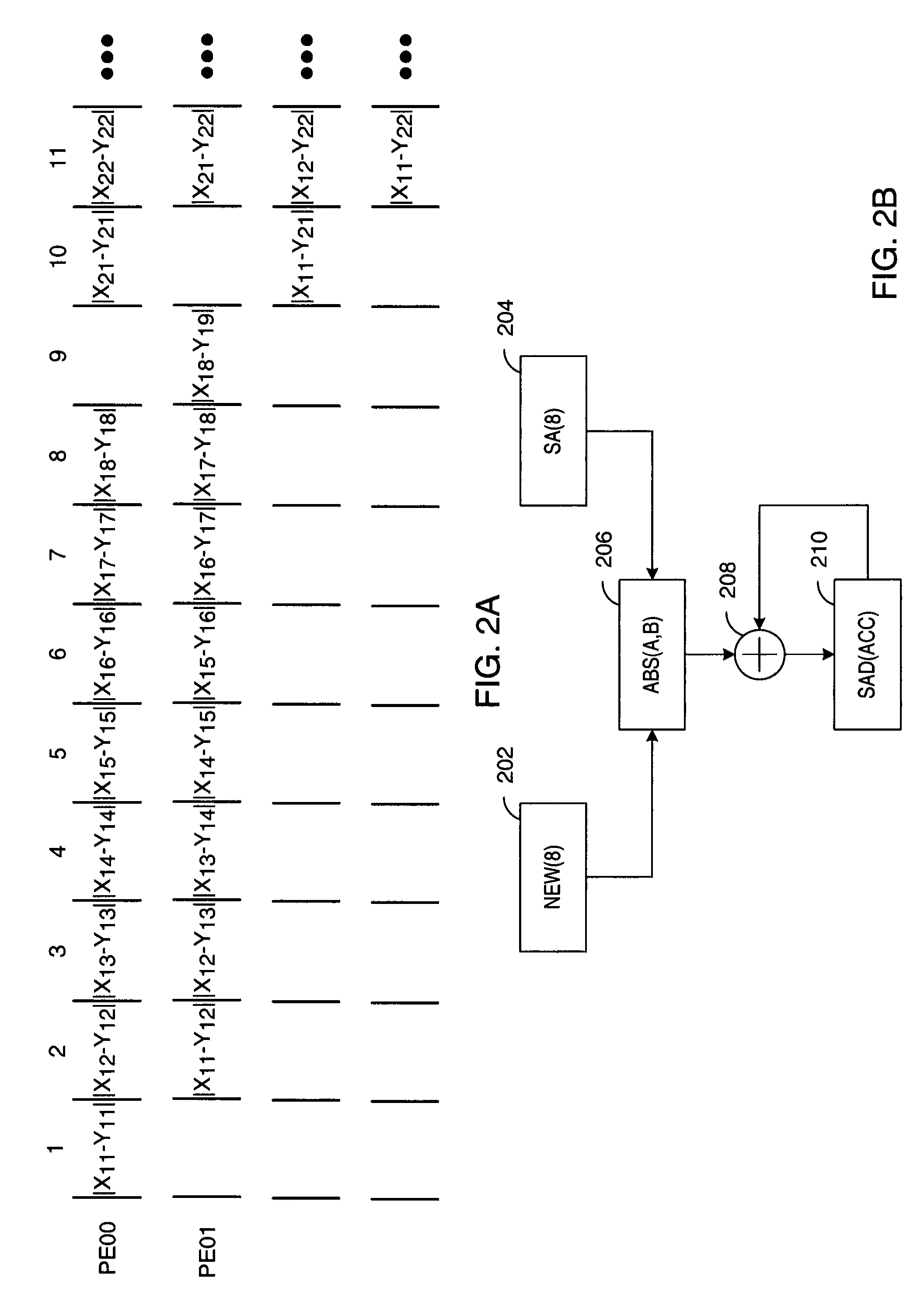
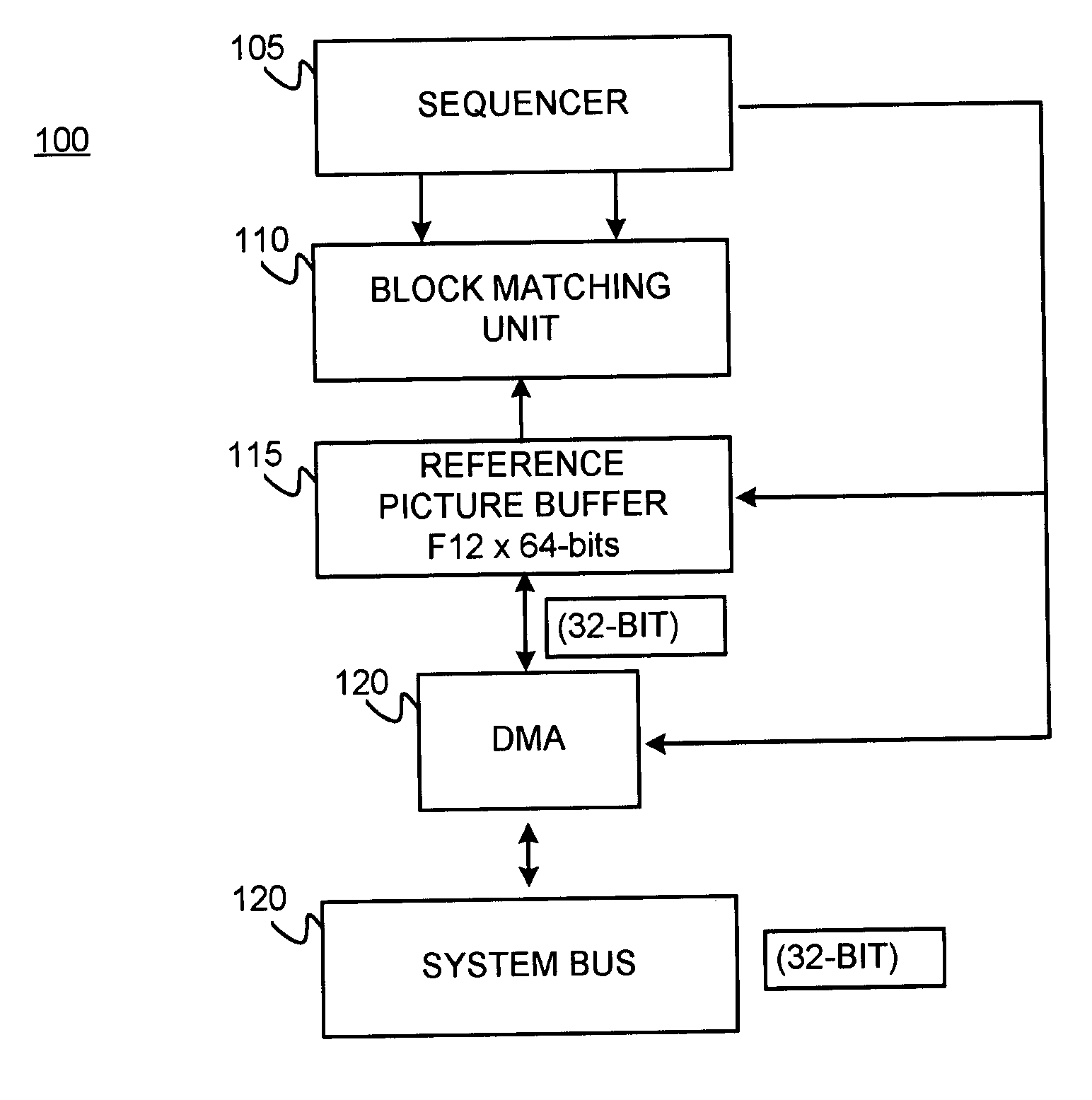
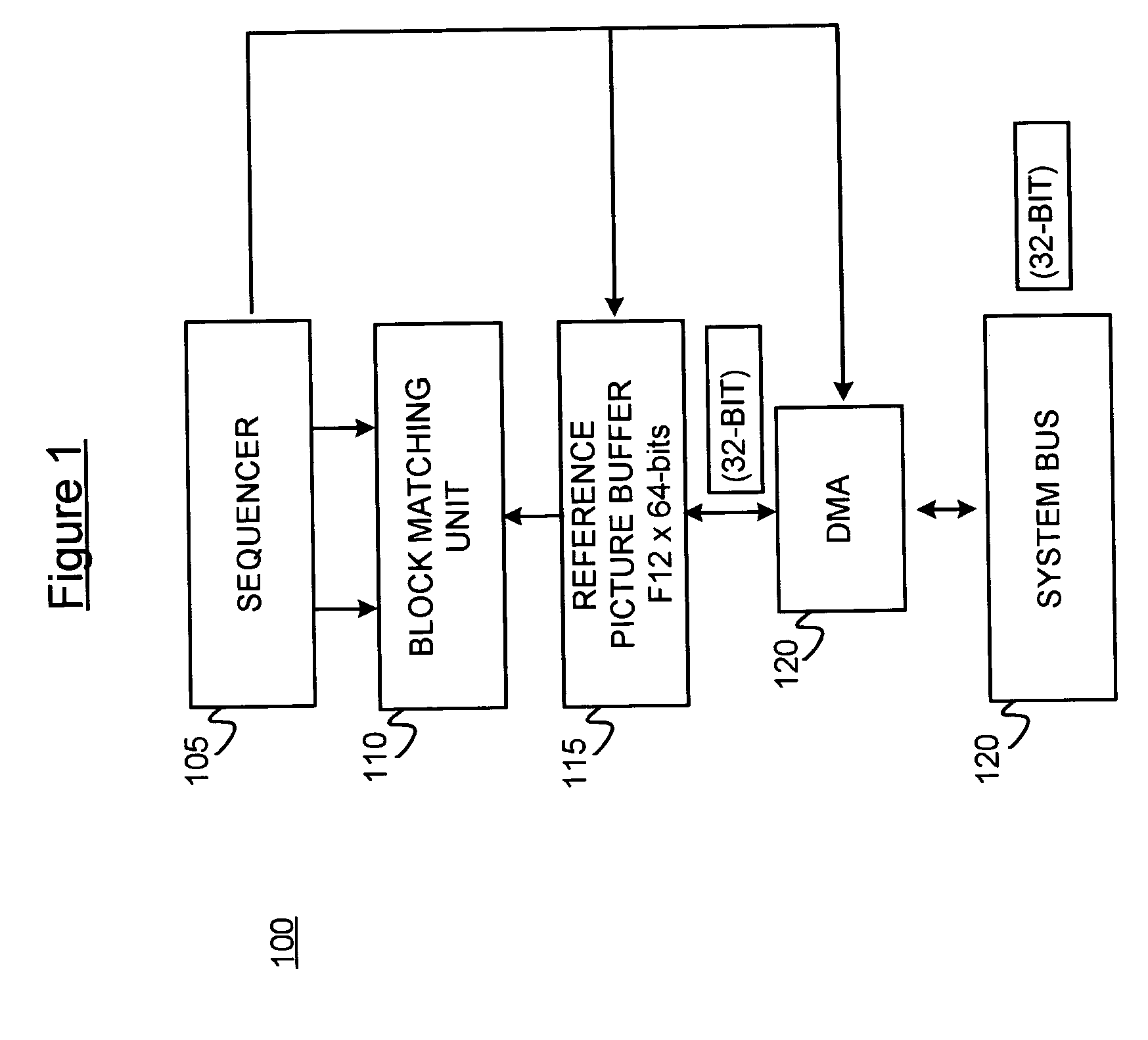
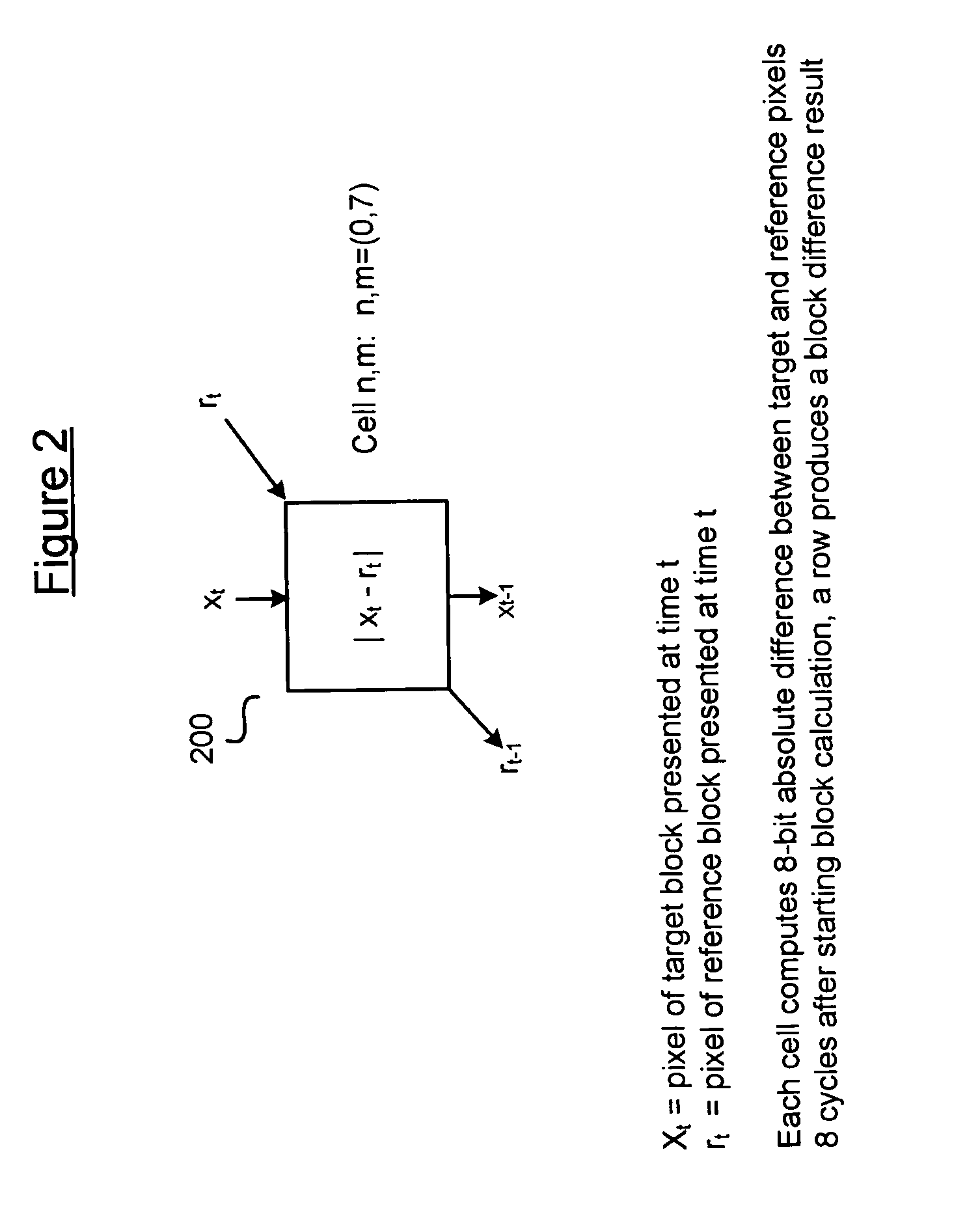
ActiveUS20070071101A1Geometric image transformationPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesReference spaceMotion vector
Systolic array-based systems and methods for performing block matching in motion compensation. A target pixel block is loaded into a systolic array. A matching sized block of a reference search space is loaded into the array, row by row. A sum of absolute difference (SOAD) is computed for each row and stored. After each row has been loaded, the reference space is incremented to the next column. After the entire reference space has been searched, the reference block with the smallest SOAD is taken as the motion vector for the target pixel block.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
FPGA device for matrix QR decomposition
InactiveCN102111350AAdd depthReduce usageBaseband system detailsMatrix decompositionComputer science
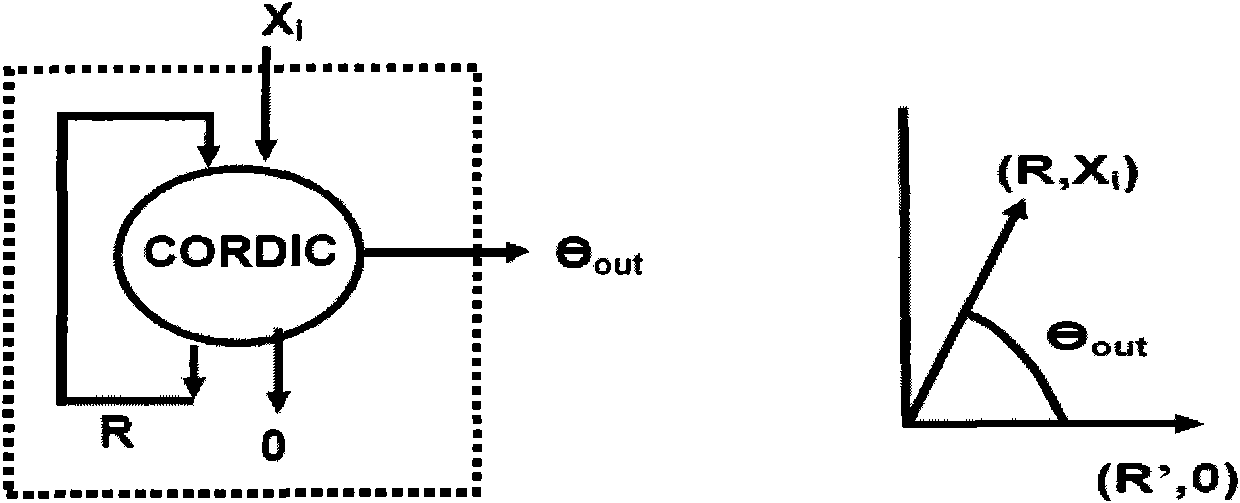
The invention discloses an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) device for matrix QR decomposition, which greatly speeds up matrix QR decomposition. The technical scheme is that the FPGA device for matrix QR decomposition transmits data and corresponding control information to a processing unit by the aid of a dispatcher, is in charge of the processing sequence of systolic array and adopts the systolic array to achieve Givens rotation through the processing unit, and each element in the systolic array adopts the CORDIC (Coordinated Rotation Digital Computer) technology, so as to achieve coordinated rotation of both real and complex numbers.
Owner:NO 50 RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
Multi-link protocol reassembly assist in a parallel 1-D systolic array system
ActiveUS7245615B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationMulti linkSystolic array
The present invention comprises a technique for performing a reassembly assist function that enables a processor to perform packet reassembly in a deterministic manner. The technique employed by the present invention enables a processor to reassemble a packet without having to extend its normal processing time to reassemble a varying number of fragments into a packet. The invention takes advantage of the fact that the reassembly assist can be dedicated exclusively to reassembling a packet from a series of fragments and thereby offloading the reassembly process from the processor.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
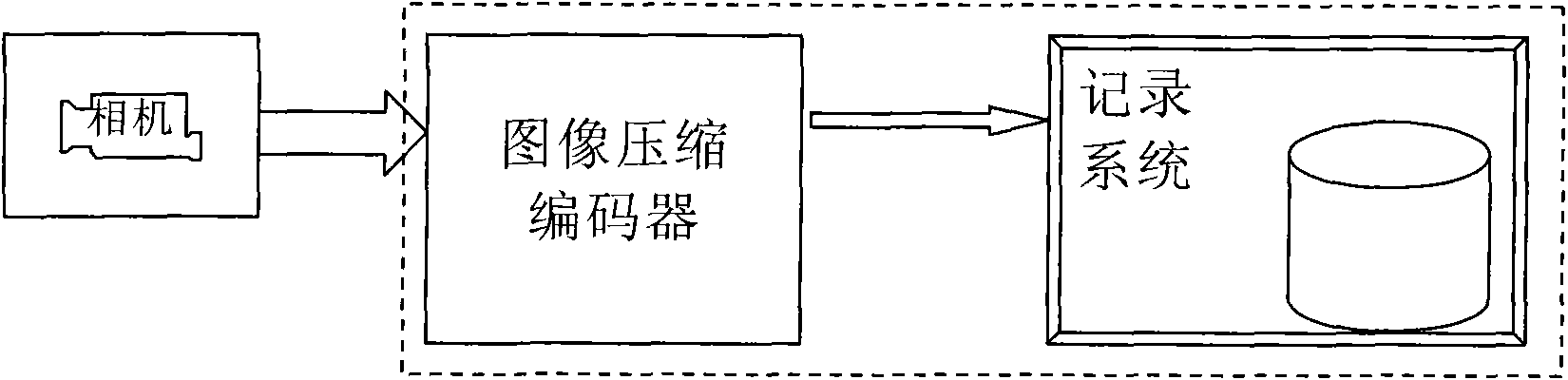
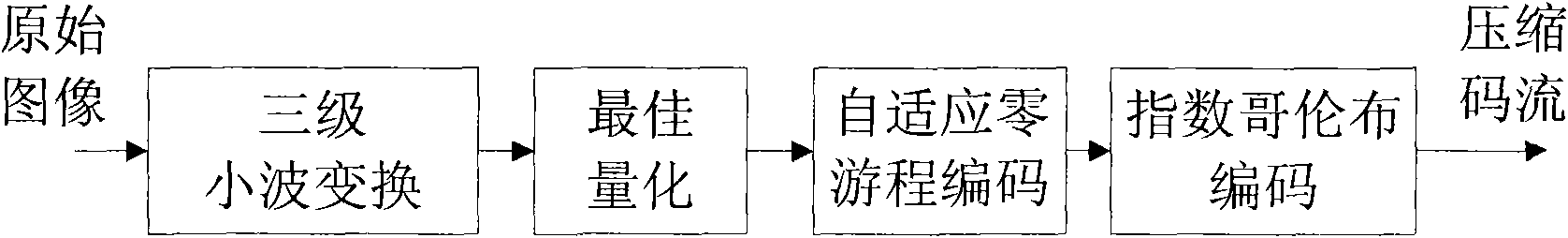
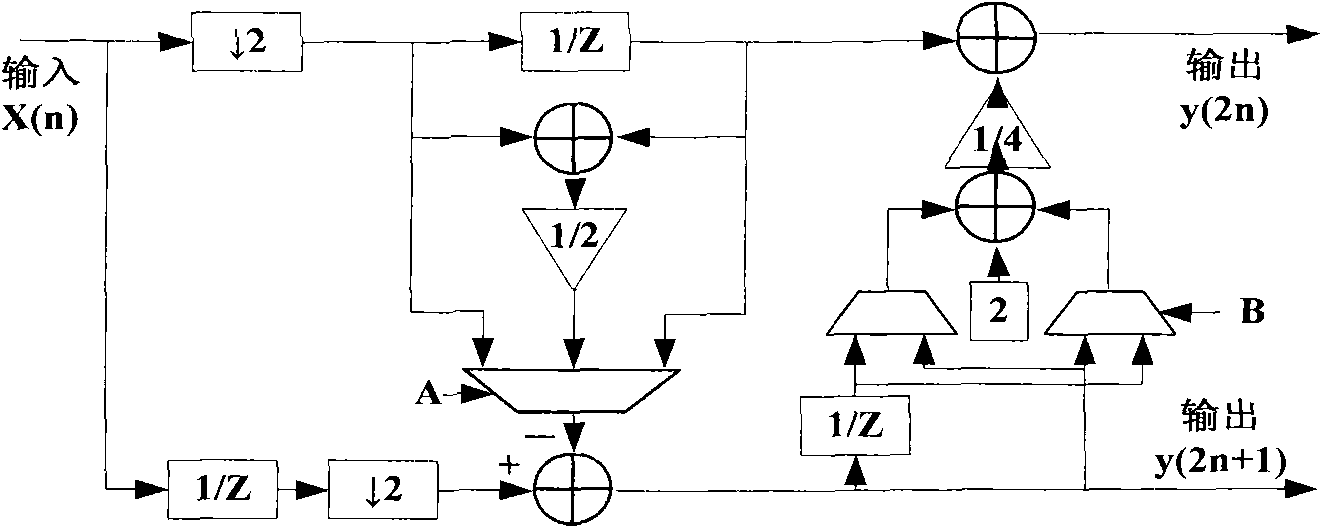
High-speed image compression VLSI coding method based on systolic array, and encoder
InactiveCN101867809AReduce complexityHigh compressibilityTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationCoding blockThree level
The invention relates to a high-speed image compression VLSI coding method based on systolic array, and an encoder. The encoder comprises an image-level controller, a code block level controller, an image segmentation partitioning device, a first, a second and a third level two-dimensional small wave converters, a QRG combined encoder and a code stream packer; the method comprises the steps of: first, using the image segmentation partitioning device to segment the image into code blocks with the size of 32*32; respectively using the first, the second and third level two-dimensional small wave converters for carrying out three-level small wave conversion on the image, then using the QRG combined encoder to read the three-level small wave conversion coefficient, carrying out best quantization, self-adaptive zero run length encoding and Exp-Golomb encoding with k=0, and obtaining code stream; and finally, using the code stream packer to pack the code stream of each code block into file according to the preset format for outputting. The invention greatly accelerates the image compression speed, effectively prolongs the recording time, and improving the transmission capability.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
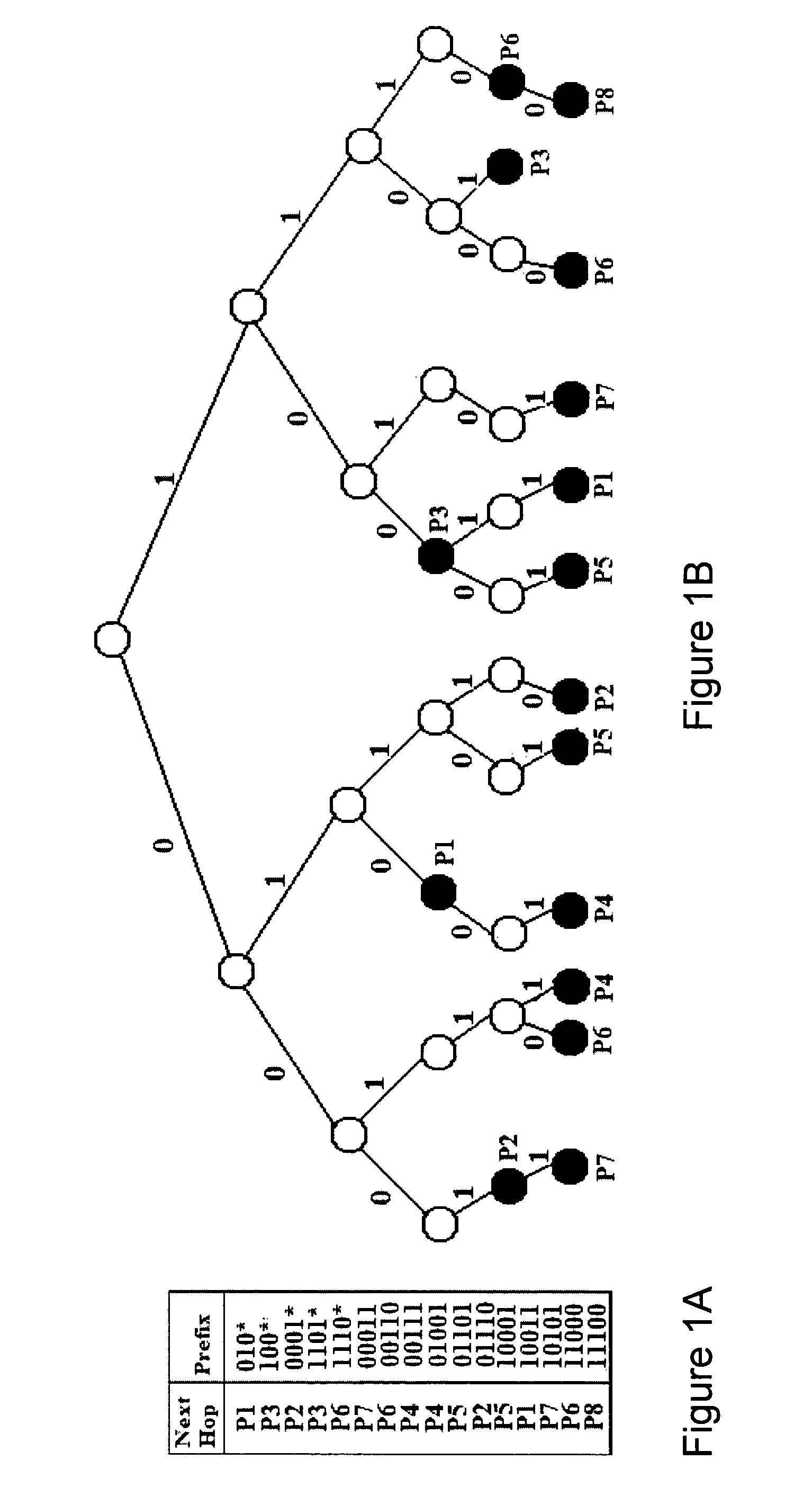
Systolic array architecture for fast IP lookup
InactiveUS8724624B2Improve performanceFast IP lookupData switching by path configurationStore-and-forward switching systemsComputer architectureParallel computing
Owner:BAZLAMACCI CUNEYT +1
Digital systolic array architecture and method for computing the discrete Fourier transform
InactiveUS7120658B2Improve throughputLower latencyDigital computer detailsComplex mathematical operationsDesign improvementFourier transform on finite groups
A more computationally efficient and scalable systolic architecture is provided for computing the discrete Fourier transform. The systolic architecture also provides a method for reducing the array area by limiting the number of complex multipliers. In one embodiment, the design improvement is achieved by taking advantage of a more efficient computation scheme based on symmetries in the Fourier transform coefficient matrix and the radix-4 butterfly. The resulting design provides an array comprised of a plurality of smaller base-4 matrices that can simply be added or removed to provide scalability of the design for applications involving different transform lengths to be calculated. In this embodiment, the systolic array size provides greater flexibility because it can be applied for use with any transform length which is an integer multiple of sixteen.
Owner:NASH JAMES G
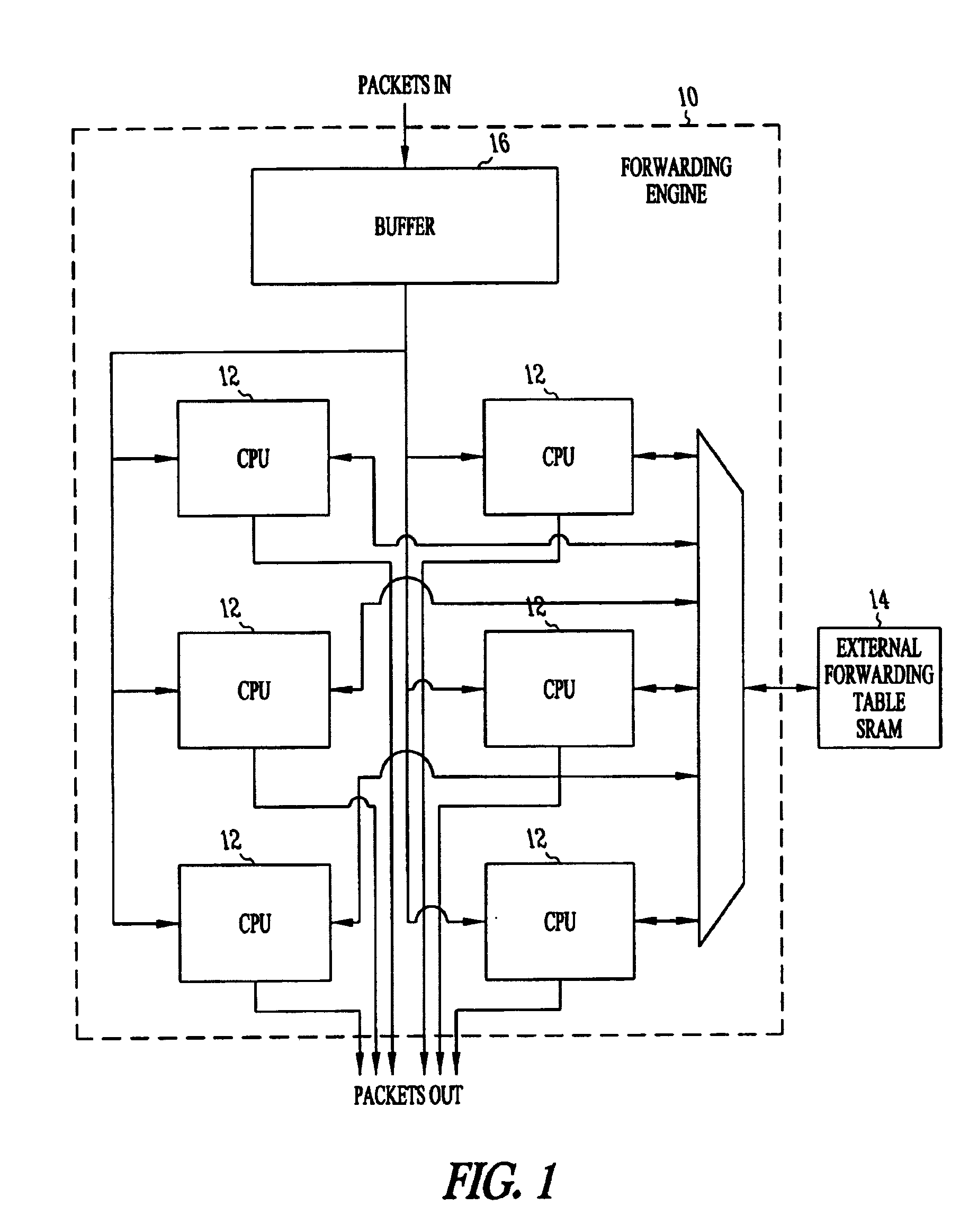
Method and apparatus for image processing
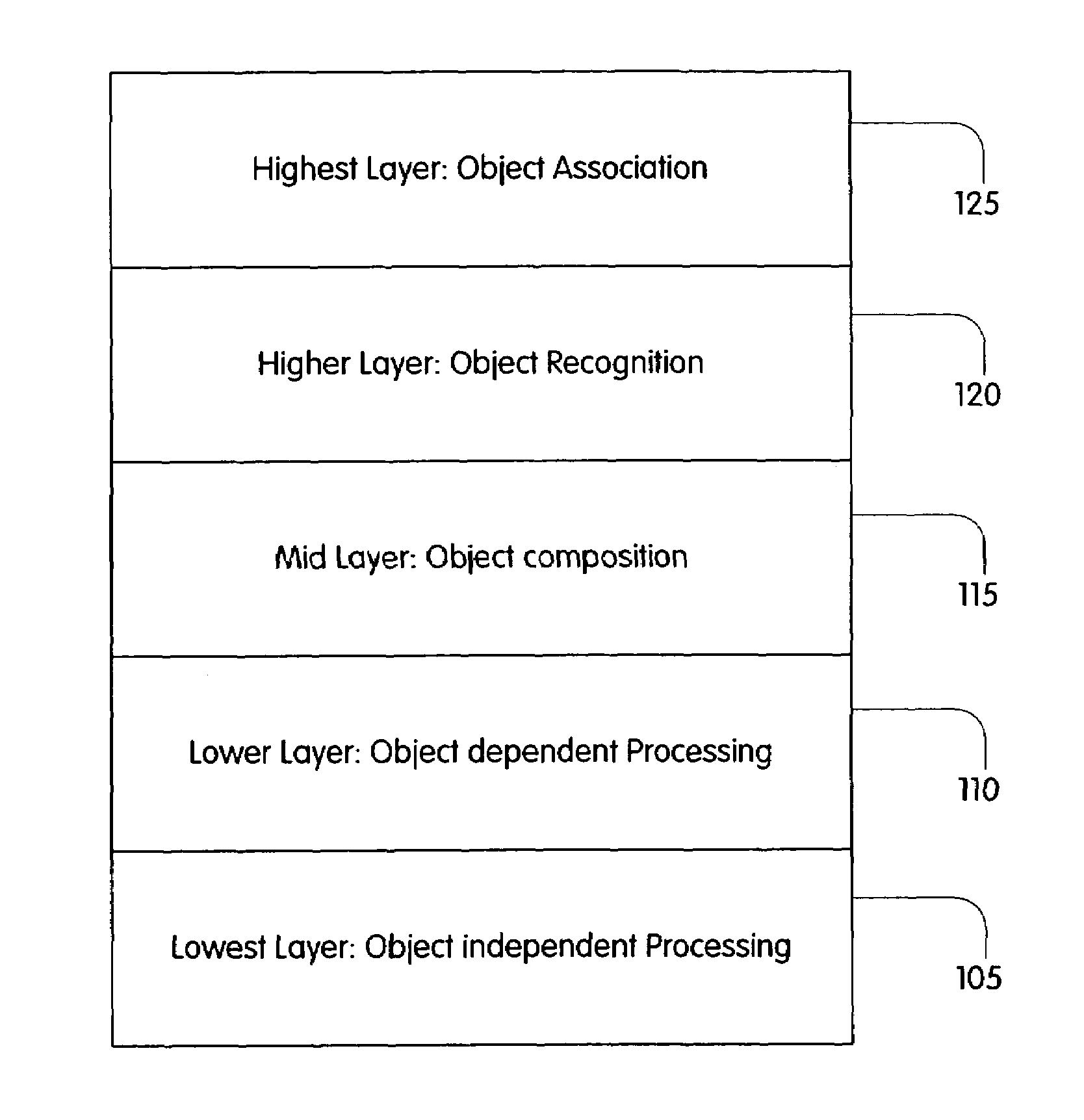
InactiveUS7489834B2General purpose stored program computerCharacter and pattern recognitionObject compositionImaging processing
An image processing system processes images via a first processing layer adapted to perform object-independent processing, a second processing layer adapted to perform object-dependent processing, and a third processing layer adapted to perform object composition, recognition and association. The image processing system performs object-independent processing using a plurality of processors each of which is associated with a different one of the pixels of the image. The image processing system performs object-independent processing using a symmetric multi-processor. The plurality of processors may form a massively parallel processor of a systolic array type and configured as a single-instruction multiple-data system. Each of the plurality of the processors is further configured to perform object-independent processing using a unified and symmetric processing of N dimensions in space and one dimension in time. The plurality of processors are formed on a semiconductor substrate different from the semiconductor substrate on which images are captured.
Owner:PARIMICS
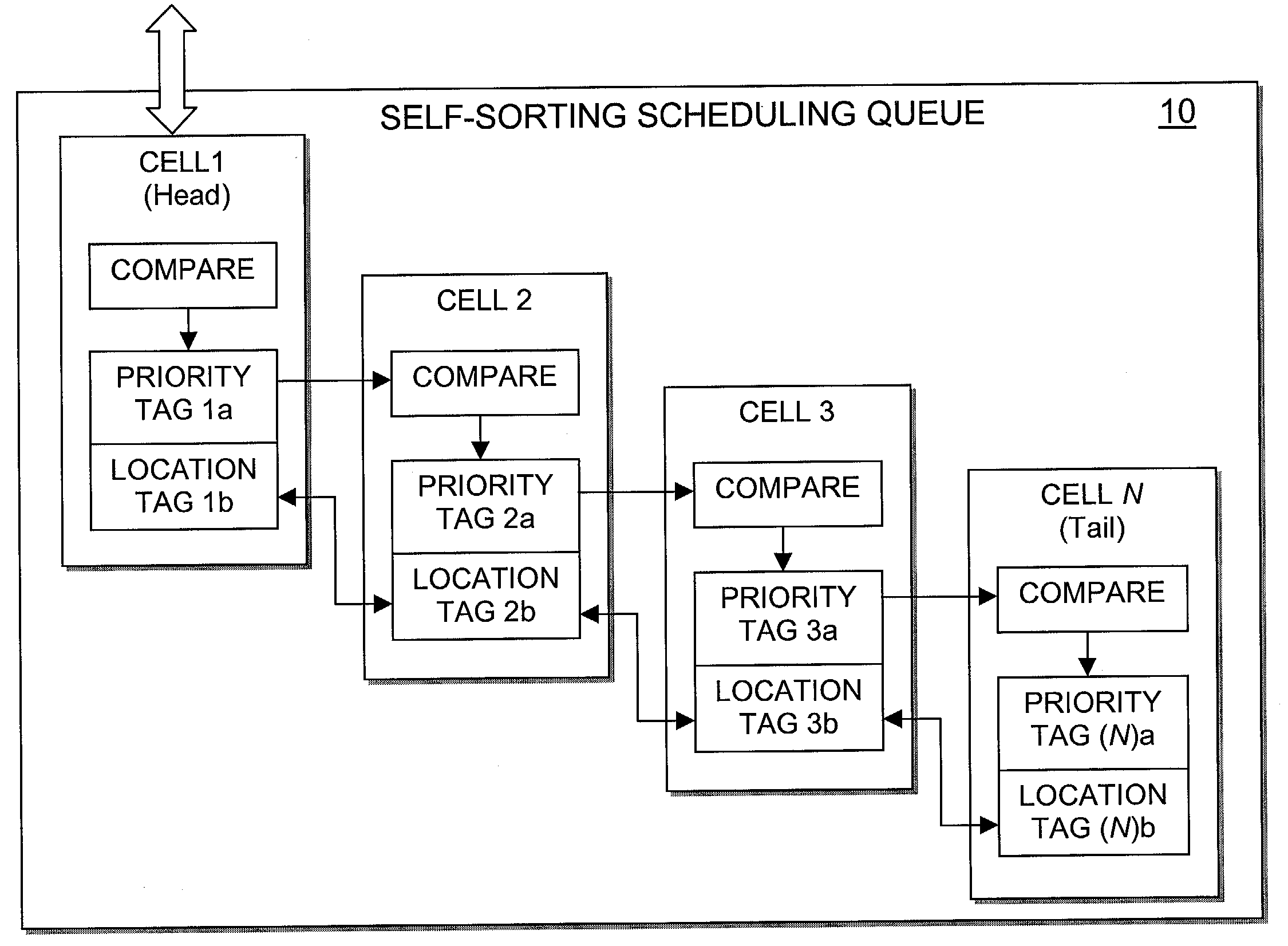
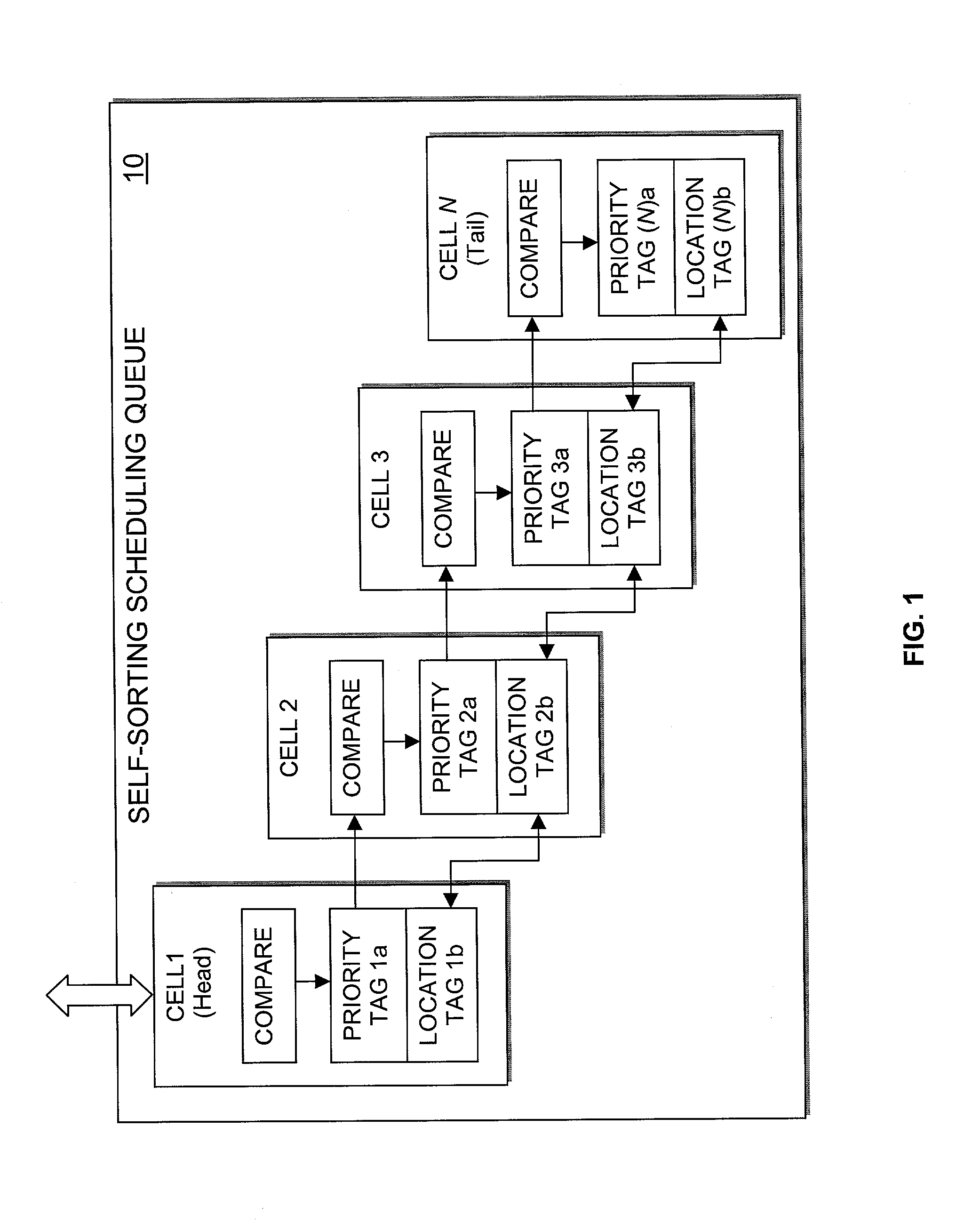
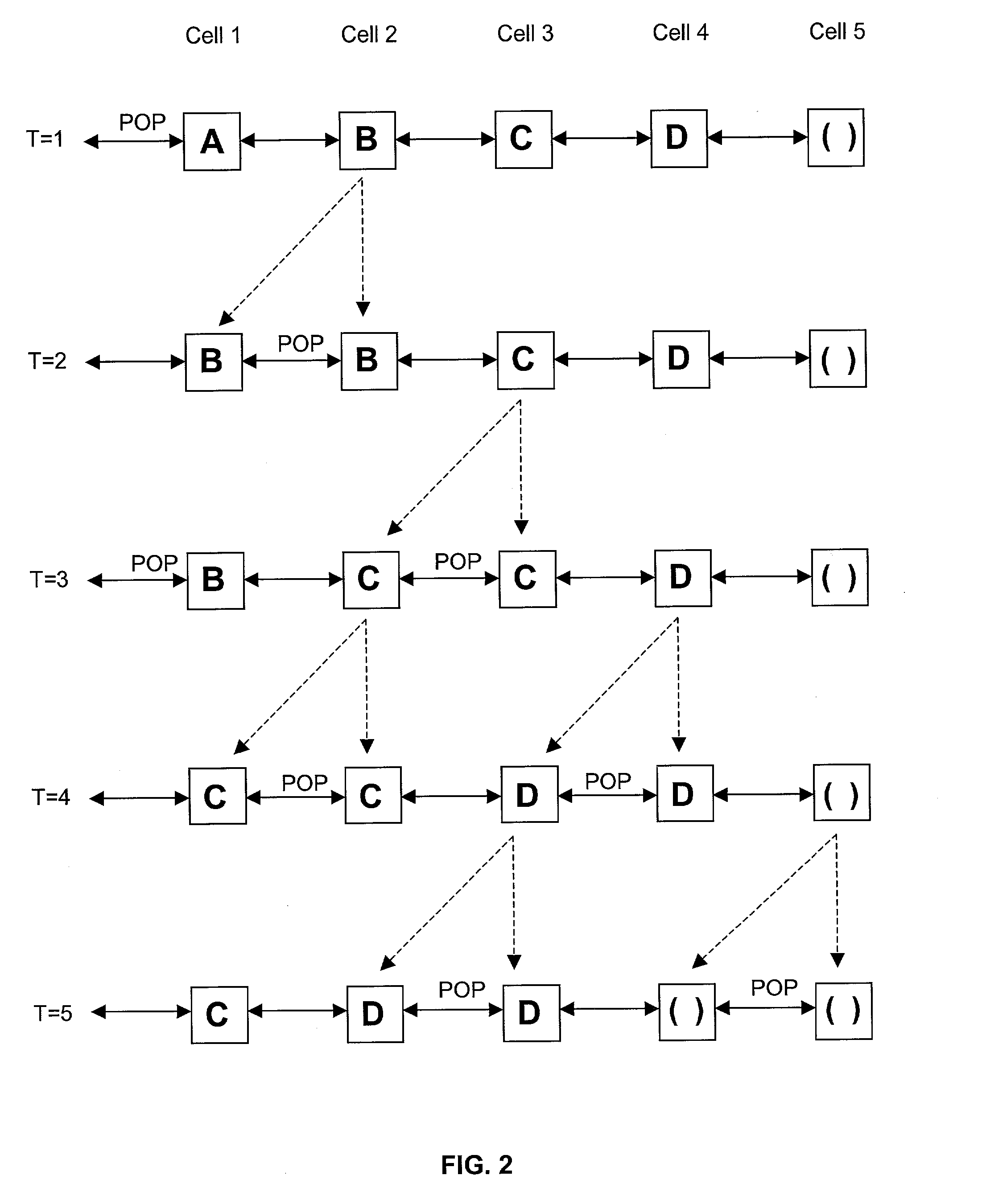
Hardware self-sorting scheduling queue
ActiveUS7113510B2Data switching by path configurationRadio transmissionDifferentiated servicesDifferentiated service
The scheduling queue of the present invention is configured as a systolic array utilizing self-sorting scheduling cells to sort information packets based upon previously assigned priorities, while at the same time yielding a small constant latency independent of the length of the queue. The scheduling queue of the present invention is effective in supporting various Quality of Service (QoS) policies and algorithms, including both Differentiated Services (DiffServ) and Integrated Services (IntServ) having an arbitrary number of flows.
Owner:XYLON LLC
Low-bit efficient deep convolutional neural network hardware acceleration design method based on logarithm quantization, and module and system
ActiveCN108491926AAchieve accelerationAccelerated design method is simpleNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsNerve networkProcess module
The present invention discloses a low-bit efficient deep convolutional neural network hardware acceleration design method based on logarithm quantization. The method comprises the following steps: S1:implementing non-uniform fixed-point quantization of low-bit high-precision based on the logarithmic domain, and using multiple quantization codebooks to quantize the full-precision pre-trained neural network model; and S2: controlling the qualified range by introducing the offset shift parameter, and in the case of extremely low bit non-uniform quantization, adaptively searching the algorithm ofthe optimal quantization strategy to compensate for the quantization error. The present invention also discloses a one-dimensional and two-dimensional pulsation arrays processing module and system byusing the method. According to the technical scheme of the present invention, hardware complexity and power consumption can be effectively reduced.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method and circuit of accelerated operation of pooling layer of neural network
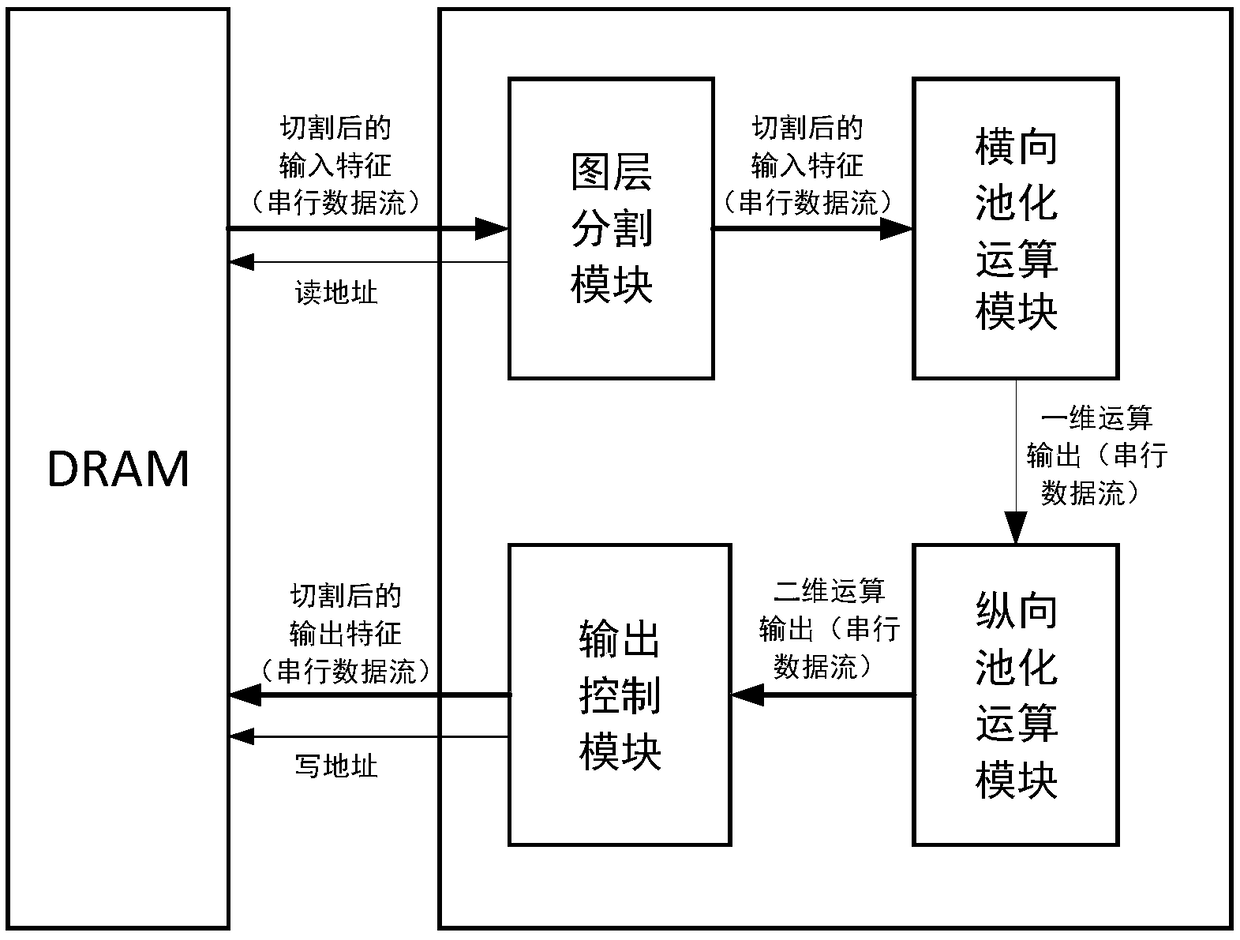
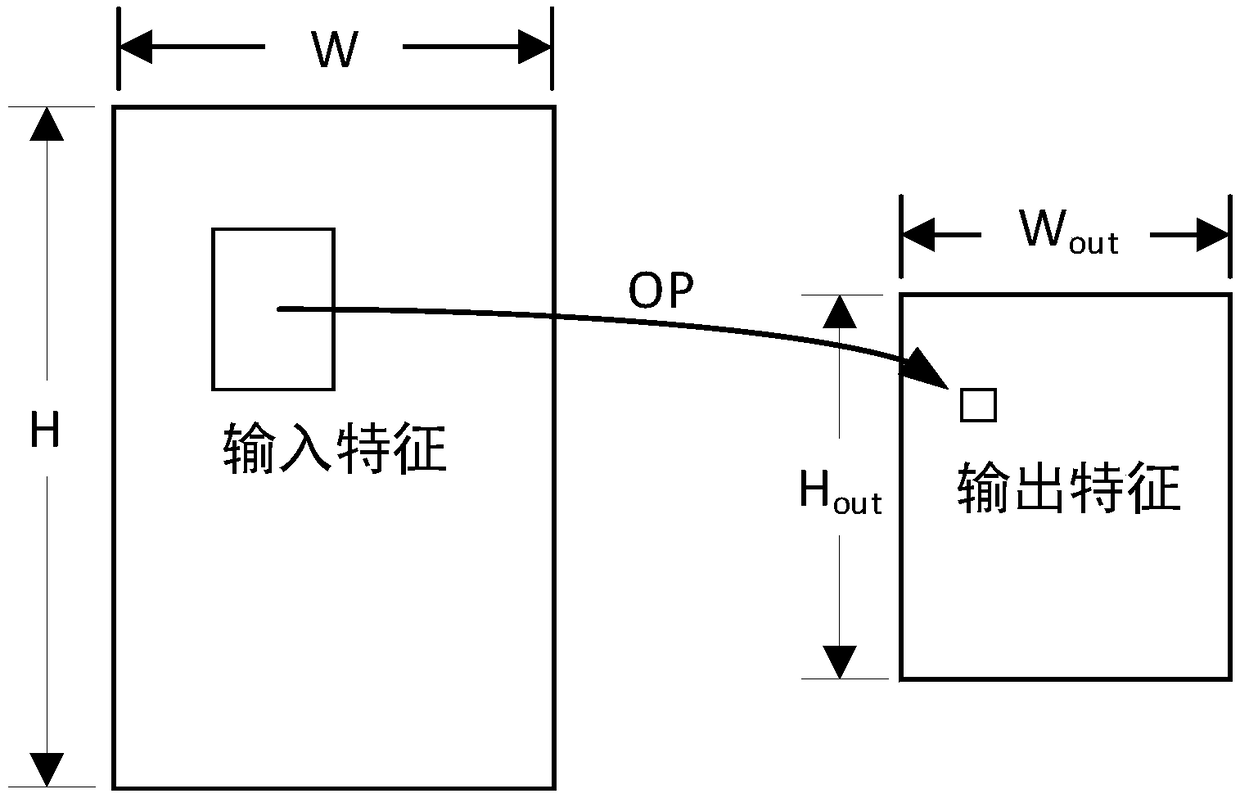
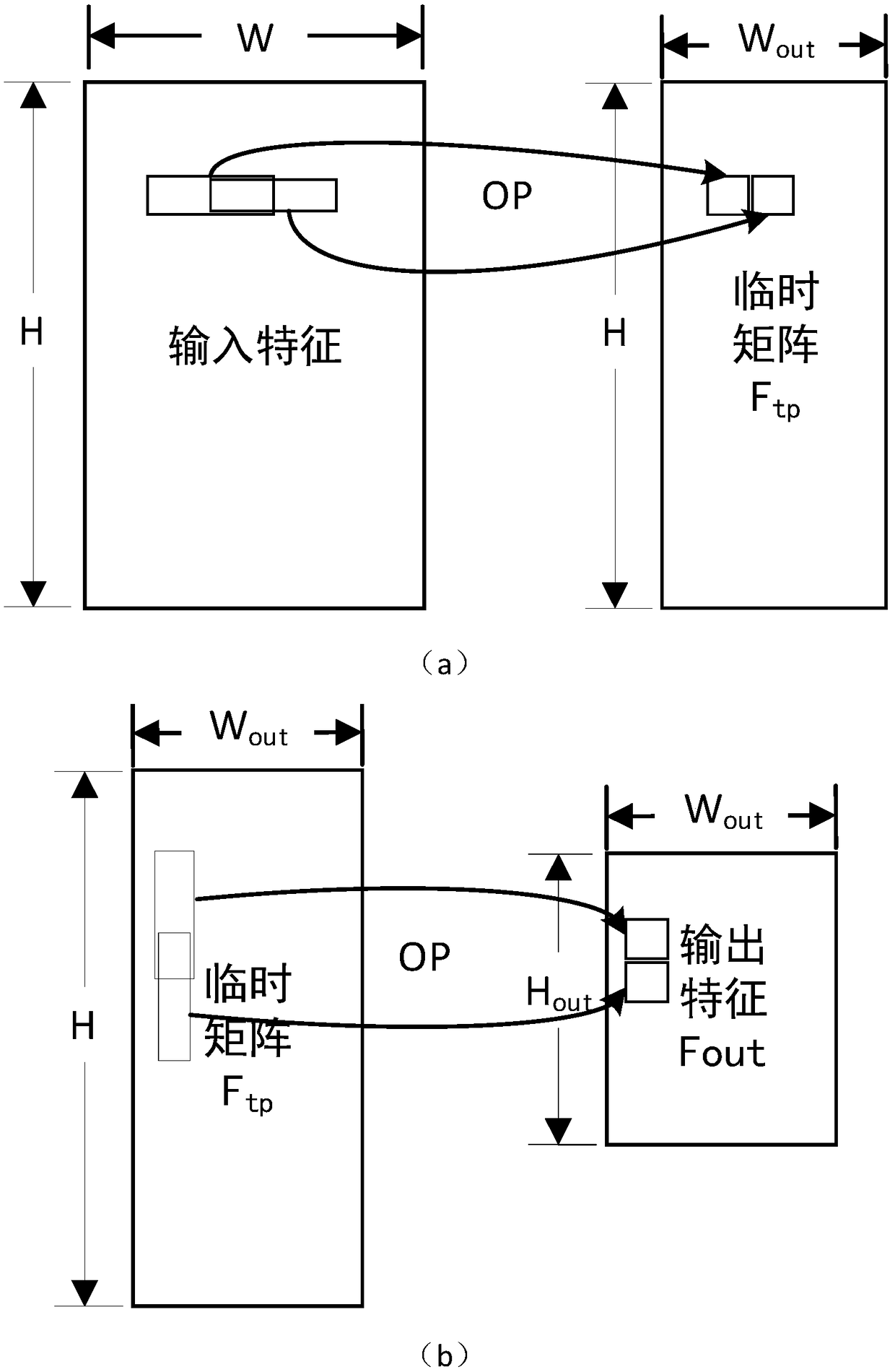
ActiveCN108763612AAvoid complexityAvoid the problem of redundant operationsBiological neural network modelsCAD circuit designNerve networkData stream
The invention belongs to the technical field of integrated-circuit design, and particularly relates to a method and a circuit of accelerated operation of a pooling layer of a neural network. The method is to decompose two-dimensional pooling operation into two times of one-dimensional pooling operation of one-dimensional pooling operation of a width direction and one-dimensional pooling operationof a height direction. A circuit structure includes five parts including a graph layer segmentation module used for graph layer segmentation and data reading, a horizontal-pooling-operation module used for pooling operation of the width direction, a vertical-pooling-operation module used for pooling operation of the height direction and an output control module responsible for data writing-back. Compared with traditional methods, the method of the invention reduces calculation quantity; all modules in the circuit process data stream, thus too many on-chip buffers are not needed for storing temporary results, and chip areas are saved; and at the same time, the circuit uses a systolic array structure, all hardware units in each clock cycle are enabled to be all in a working state, a hardwareunit use rate is increased, and thus working efficiency of the circuit is improved.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Systolic equalizer and method of using same
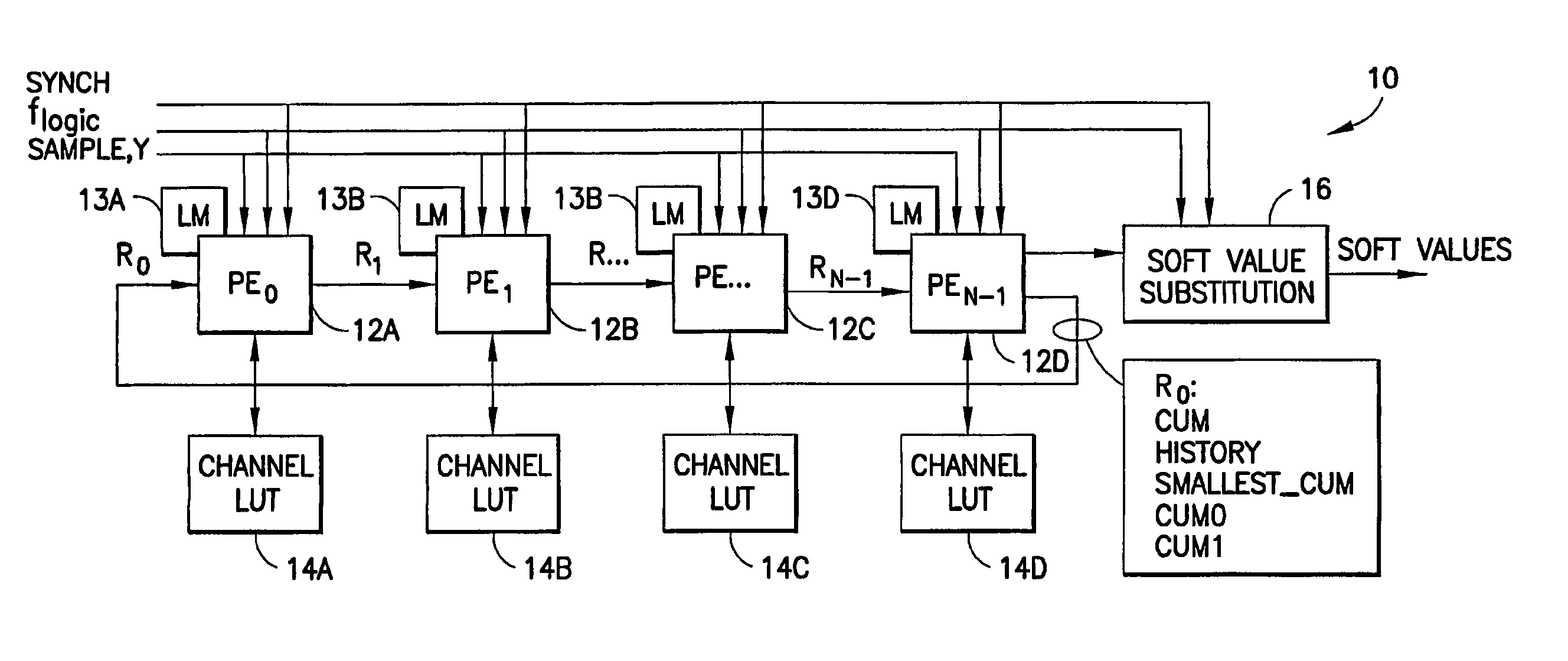
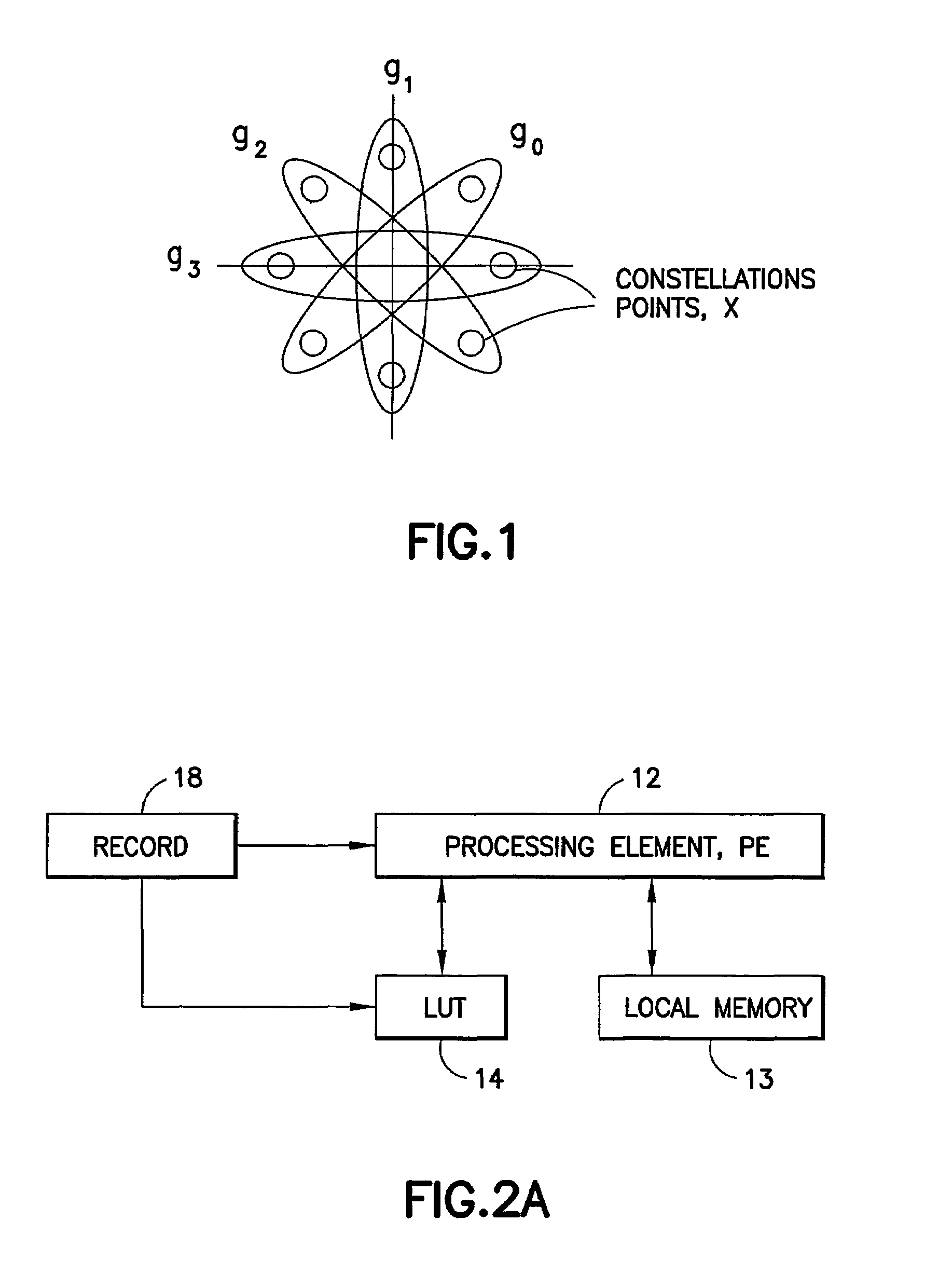
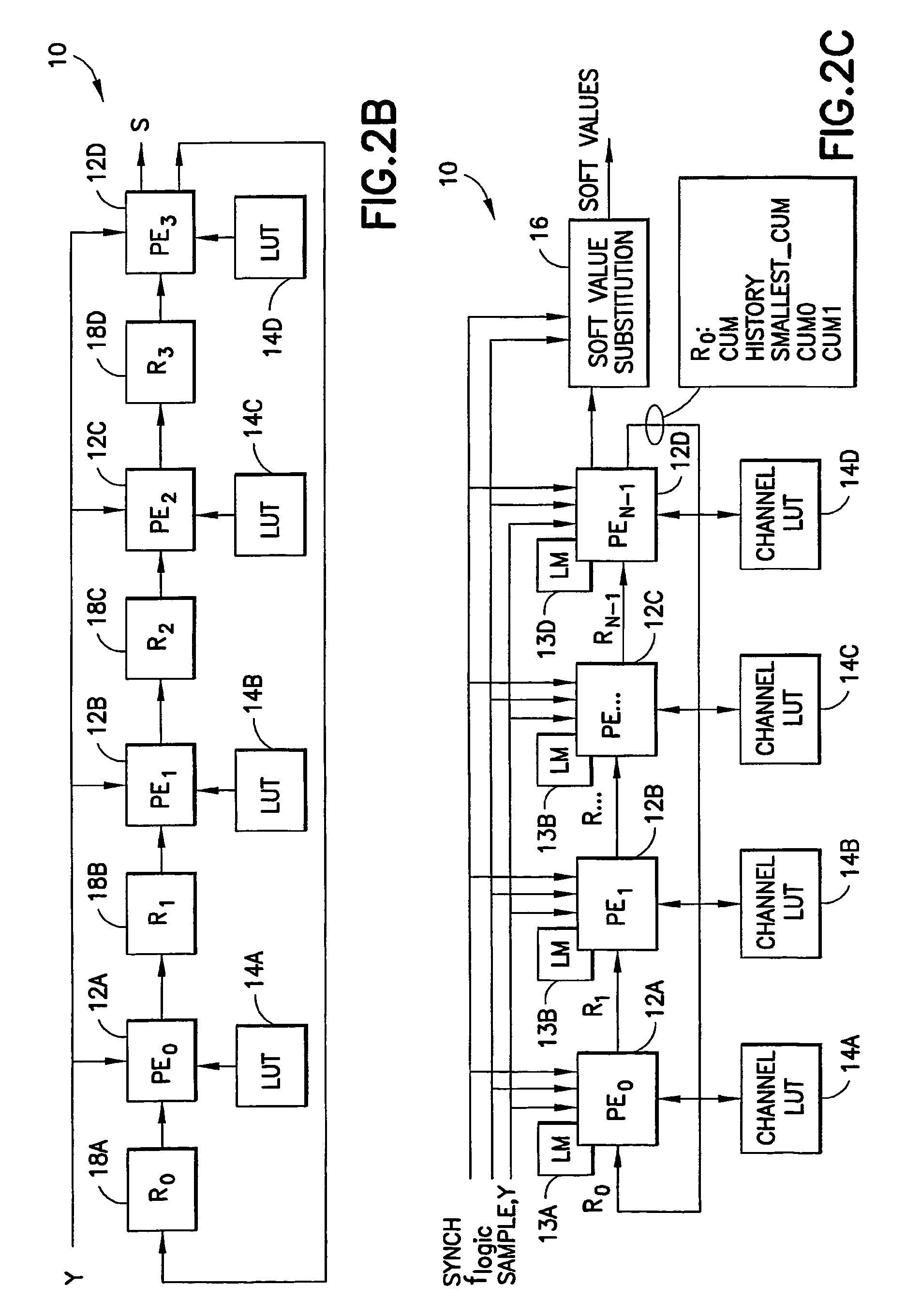
A method and apparatus provide a systolic equalizer for Viterbi equalization of an 8-PSK signal distorted by passage through a communication channel. The systolic equalizer architecture is scalable to process, as examples, four, eight and 16 state received signals. An equalizer in accordance with this invention includes a logical arrangement of a plurality of instantiations of locally coupled processing elements forming a systolic array for processing in common received signal samples having distortion induced by passage through a communication channel. The equalizer outputs soft values for input to a decoder, the soft values representing an approximation of maximum a posteriori (MAP) probabilities. A trellis search procedure is employed to reconstruct estimates of a received signal sequence based on a reduced number of states. The reduced number of states is represented by a plurality of groups determined by partitioning a symbol constellation such that there are fewer groups than possible symbols.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Systolic array
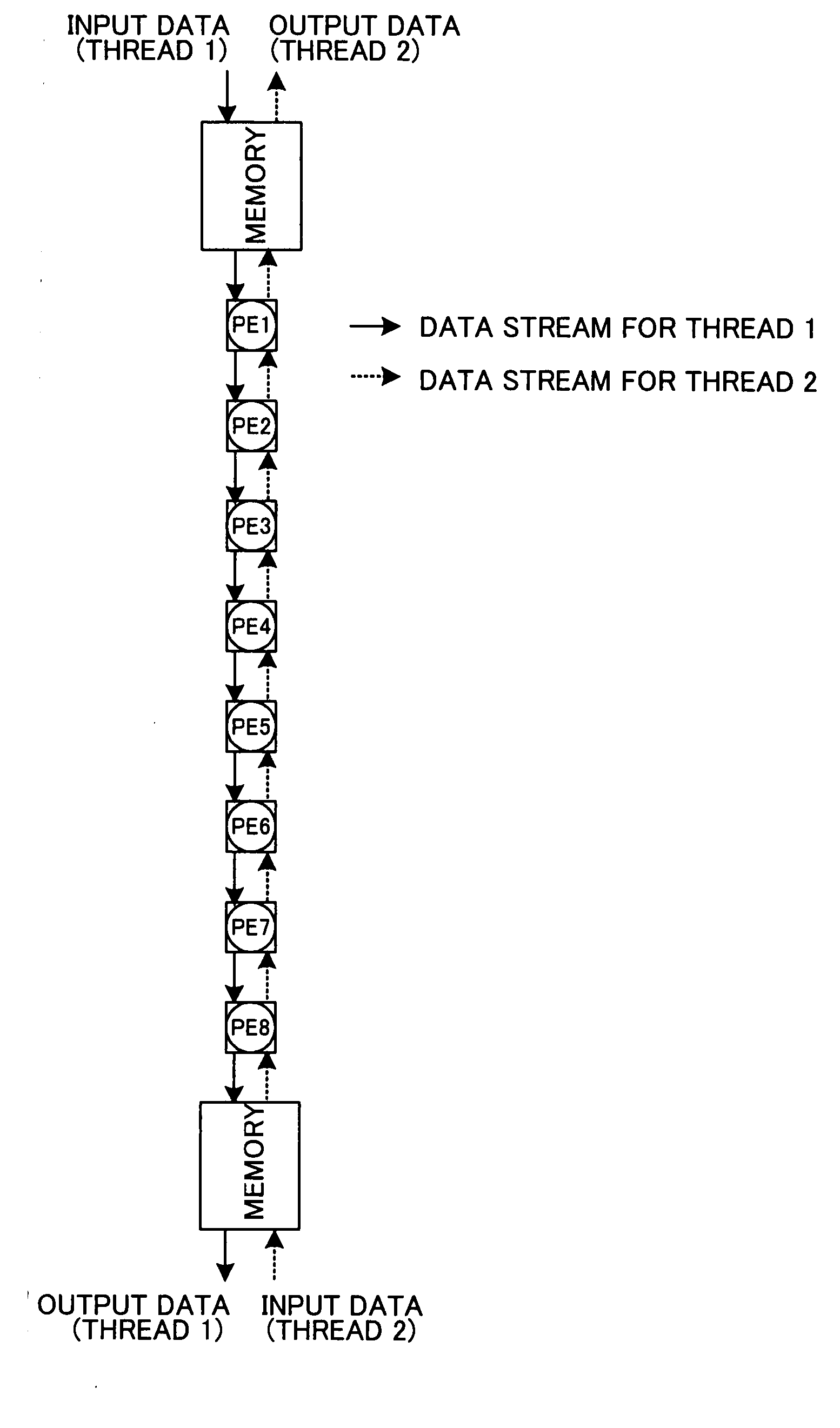
InactiveUS20080028015A1Low efficiencySolve complex processData mergingComplex mathematical operationsParallel computingSystolic array
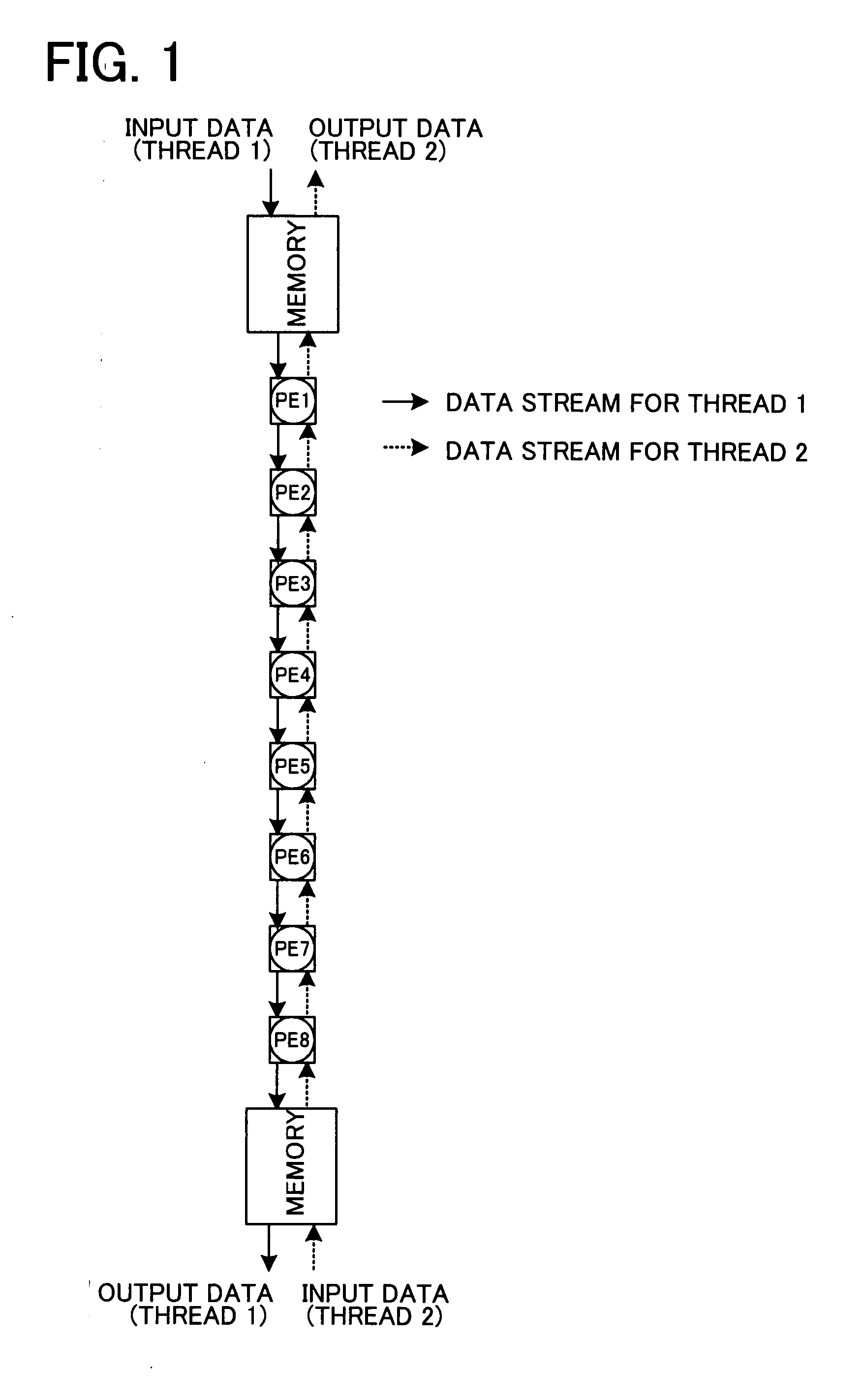
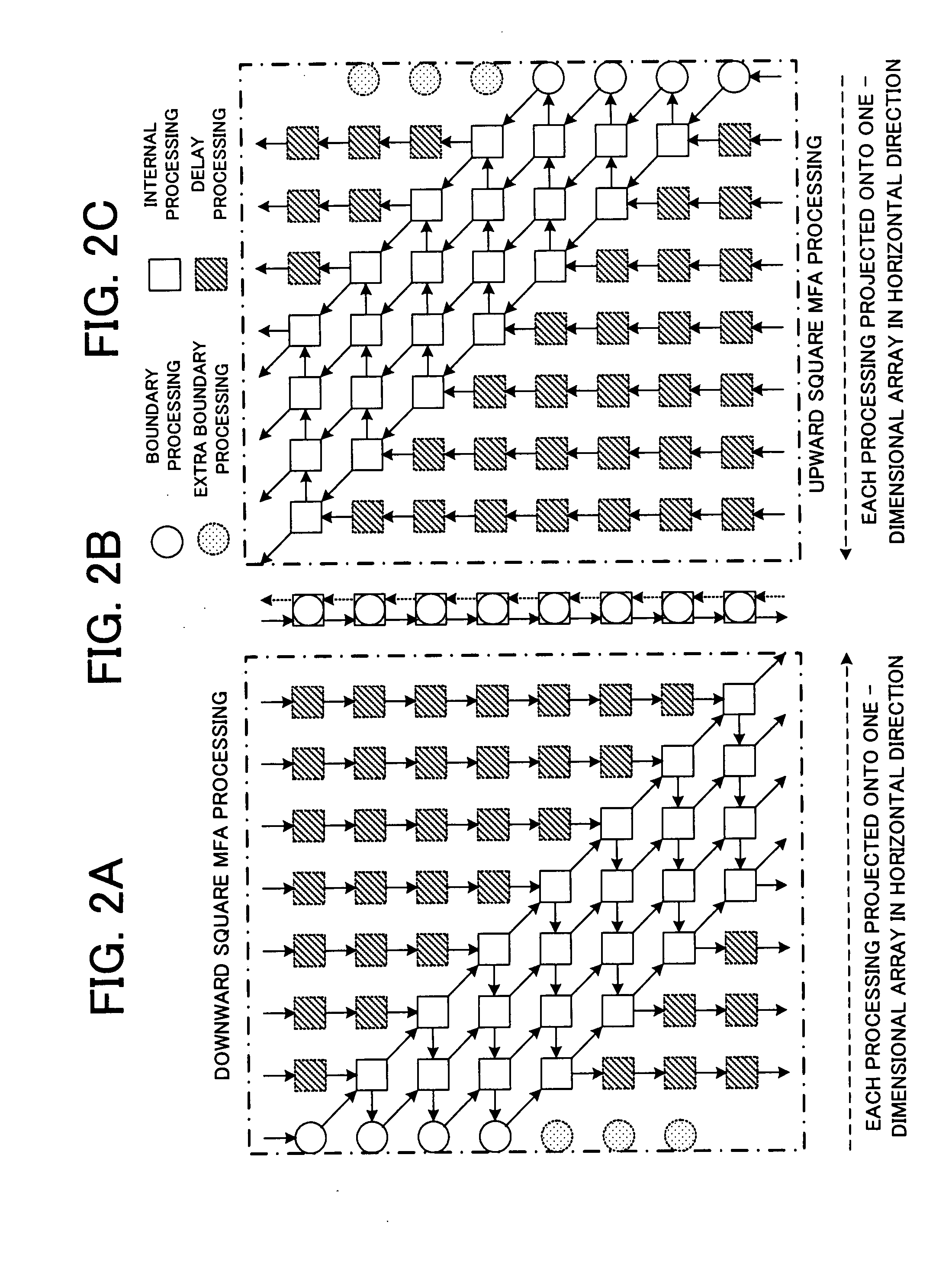
Disclosed is a one-dimensional MFA systolic array for matrix computation using an MFA (modified Faddeeva algorithm), in which downward square MFA array processing and upward square MFA array processing are mapped to a one-dimensional array in horizontal directions, respectively. In each PE in the one-dimensional array, downward and upward MFA matrix calculations for two threads are executed. An input and an output are provided for each of PEs at both ends of the one-dimensional array.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com