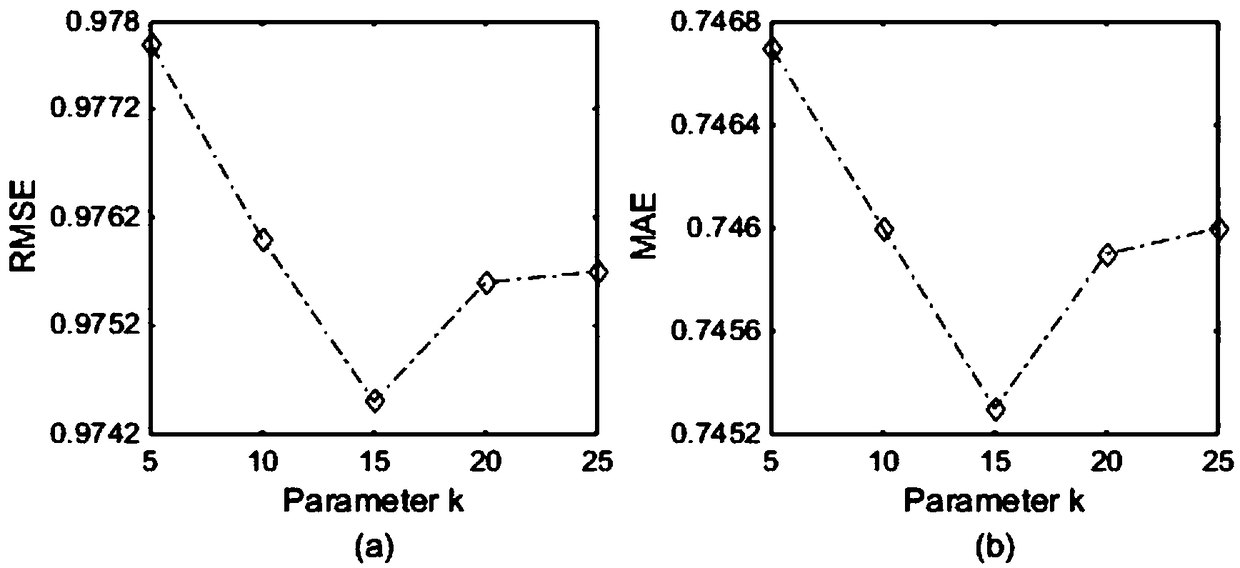
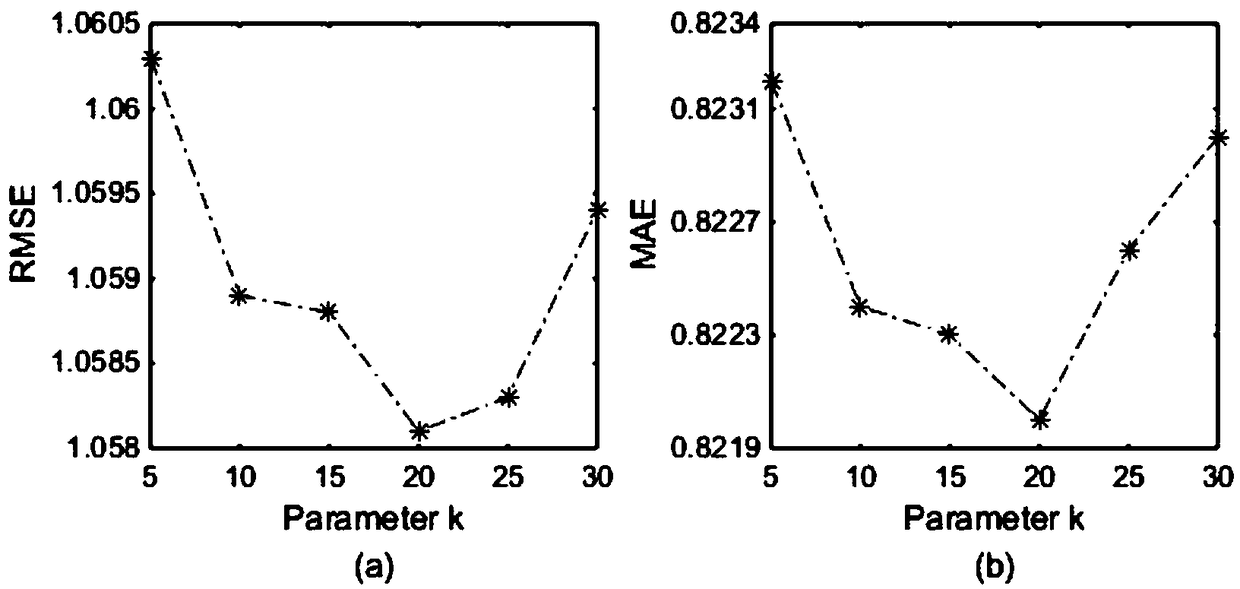
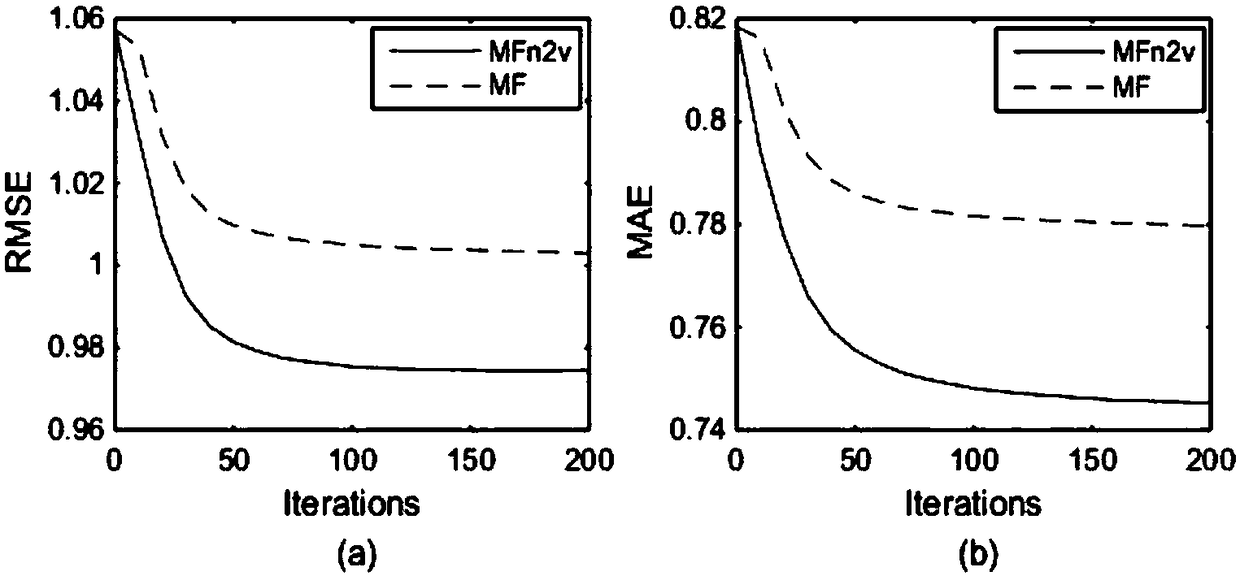
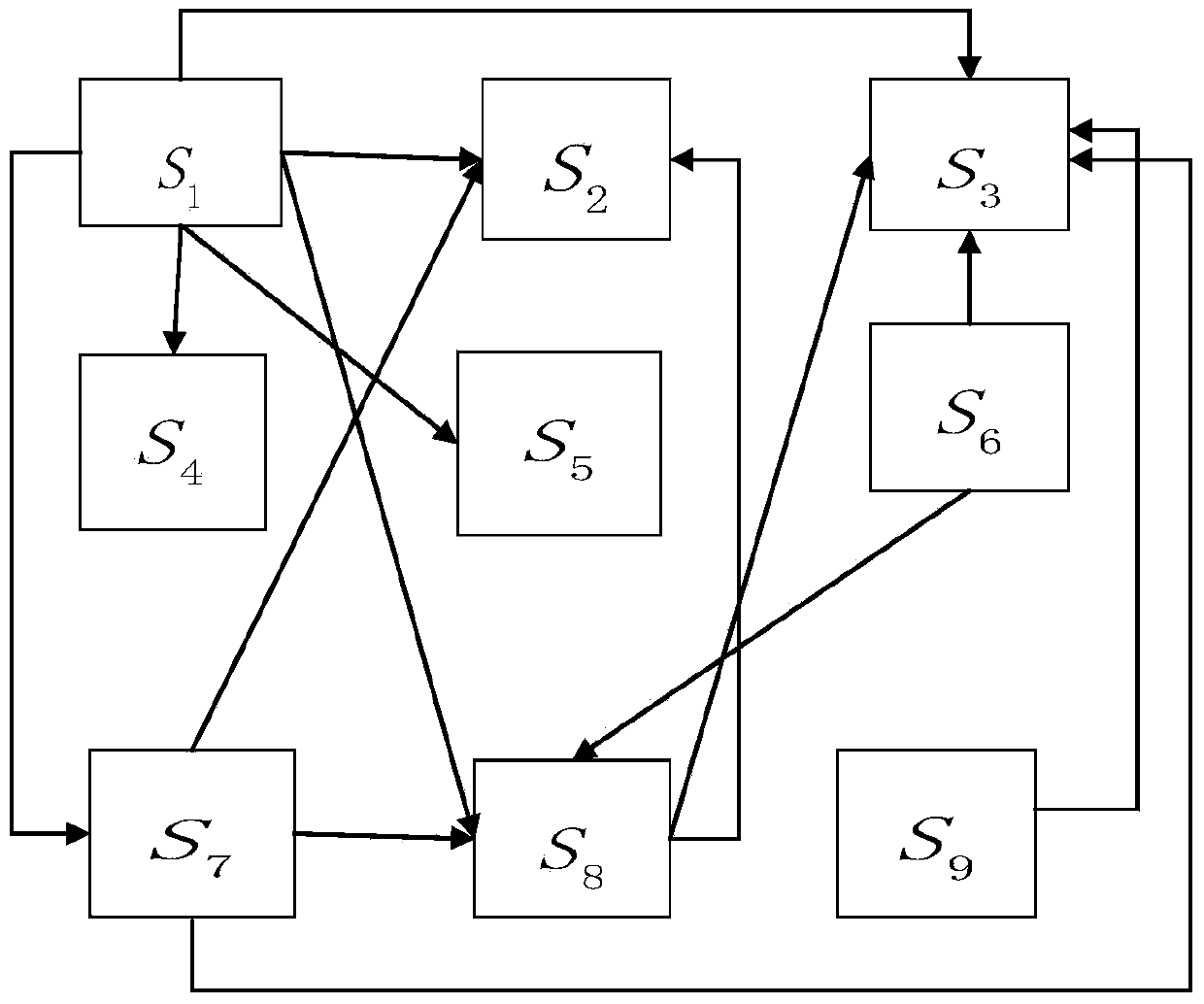
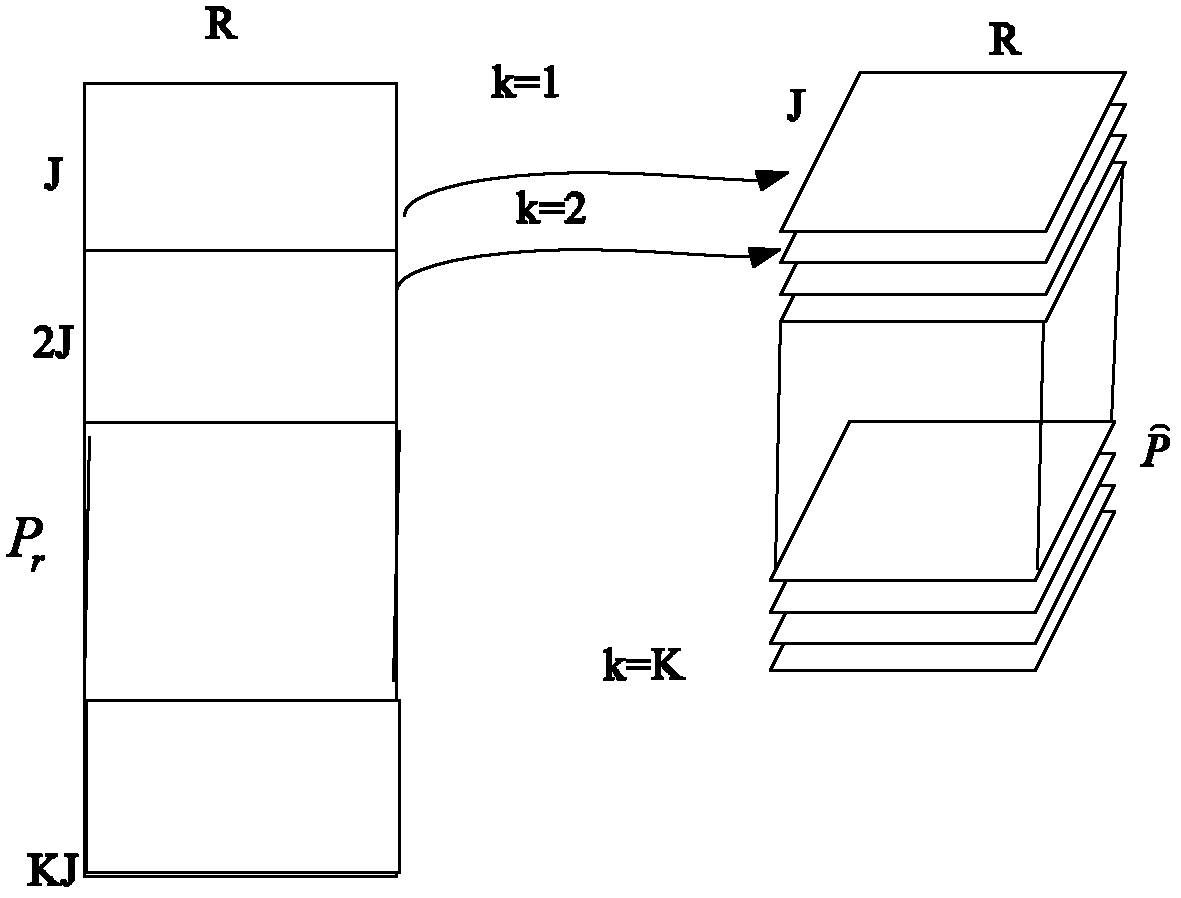
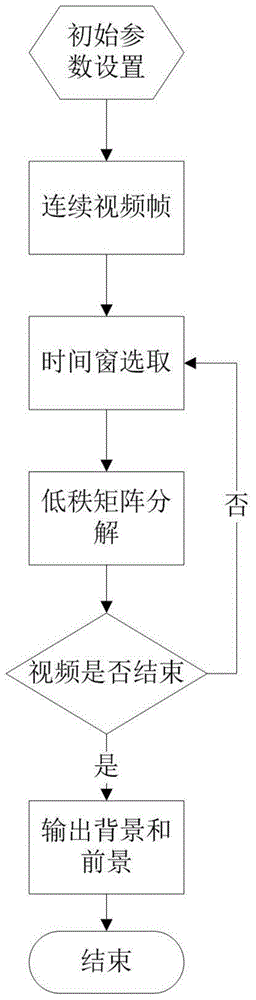
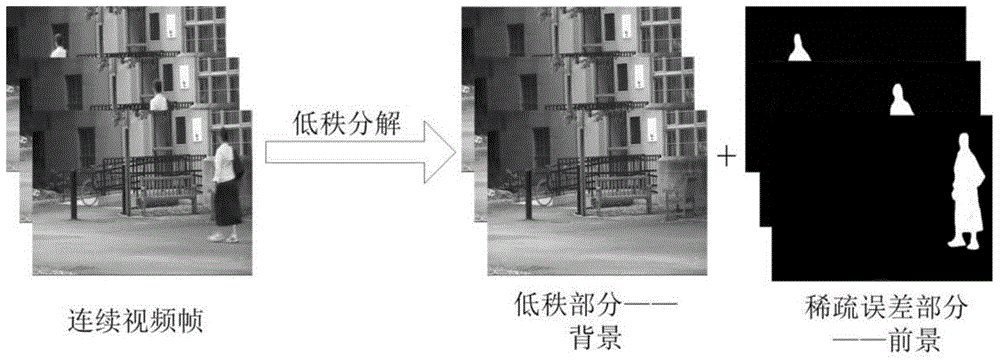
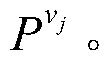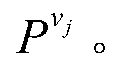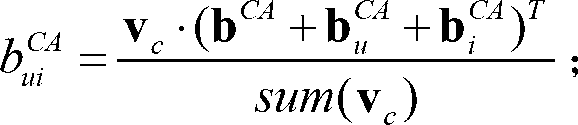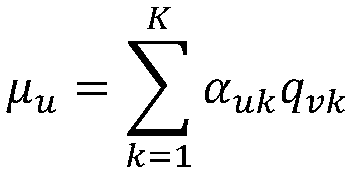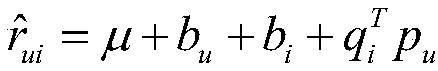Patents
Literature
712 results about "Matrix decomposition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In the mathematical discipline of linear algebra, a matrix decomposition or matrix factorization is a factorization of a matrix into a product of matrices. There are many different matrix decompositions; each finds use among a particular class of problems.
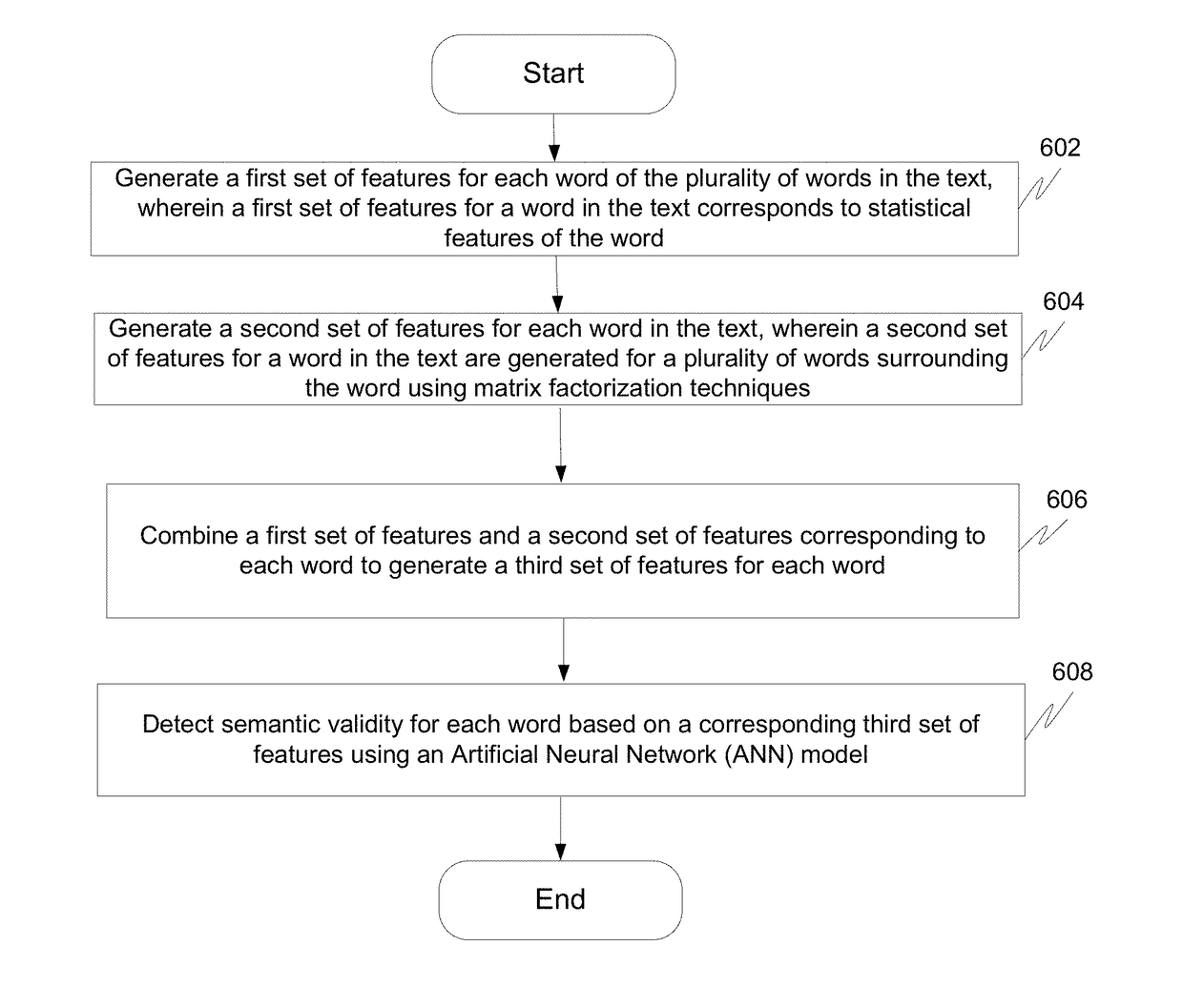
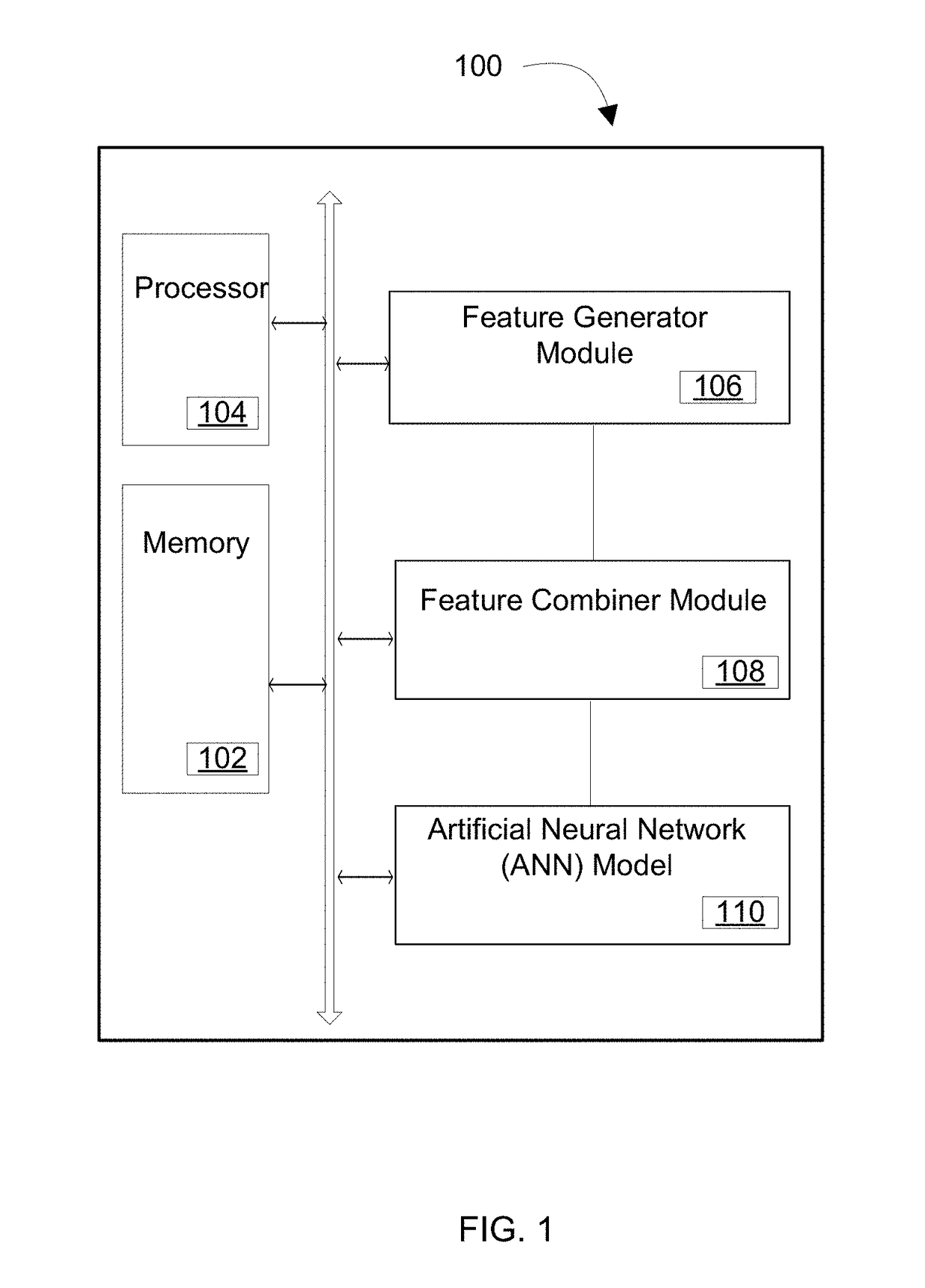
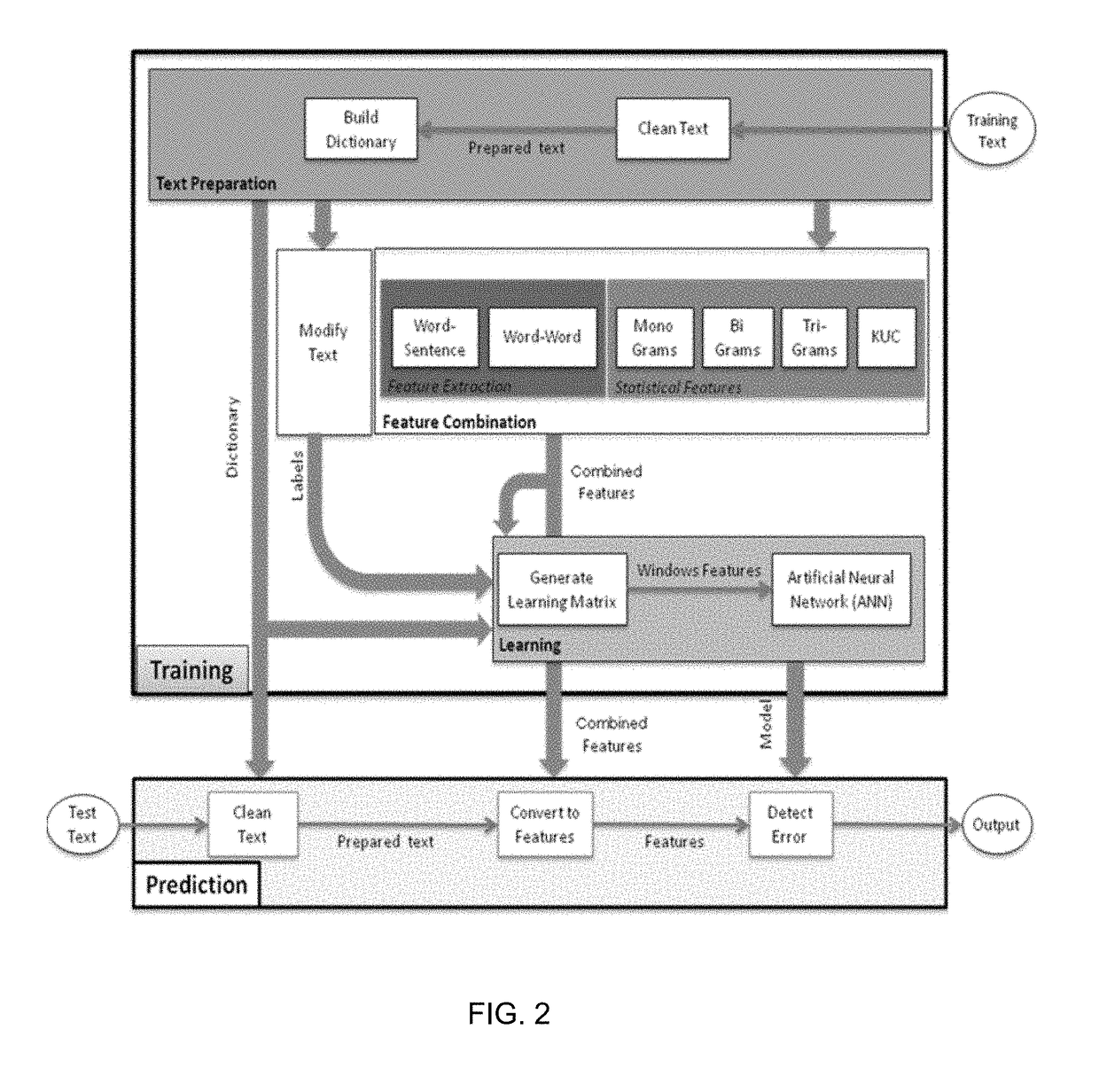
Method and system for detecting semantic errors in a text using artificial neural networks
The invention provides a method and system for automatically detecting semantic errors in a text. In order to detect the semantic errors in the text, the method generates a first set of features and a second set of features corresponding to each word in the text. A first set of features corresponds to statistical features of a word and a second set of features for a word corresponds to the features generated for a plurality of words surrounding the word in the text using matrix factorization techniques. The method, then, combines a first set of features and a second set of features to generate a third set of features corresponding to each word in the text. Thereafter, the method utilizes an Artificial Neural Network (ANN) model to detect semantic validity of each word based on a corresponding third set of features.
Owner:KING ABDULAZIZ CITY FOR SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
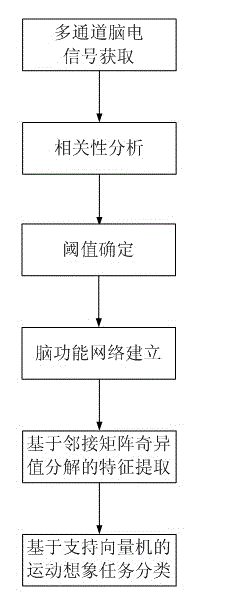
Electroencephalogram feature extracting method based on brain function network adjacent matrix decomposition
InactiveCN102722727AIgnore the relationshipIgnore coordinationCharacter and pattern recognitionMatrix decompositionSingular value decomposition
The invention relates to an electroencephalogram feature extracting method based on brain function network adjacent matrix decomposition. The current motion image electroencephalogram signal feature extraction algorithm mostly focuses on partially activating the qualitative and quantitative analysis of brain areas, and ignores the interrelation of the bran areas and the overall coordination. In light of a brain function network, and on the basis of complex brain network theory based on atlas analysis, the method comprises the steps of: firstly, establishing the brain function network through a multi-channel motion image electroencephalogram signal, secondly, carrying out singular value decomposition on the network adjacent matrix, thirdly, identifying a group of feature parameters based on the singular value obtained by the decomposition for showing the feature vector of the electroencephalogram signal, and fourthly, inputting the feature vector into a classifier of a supporting vector machine to complete the classification and identification of various motion image tasks. The method has a wide application prospect in the identification of a motion image task in the field of brain-machine interfaces.
Owner:启东晟涵医疗科技有限公司
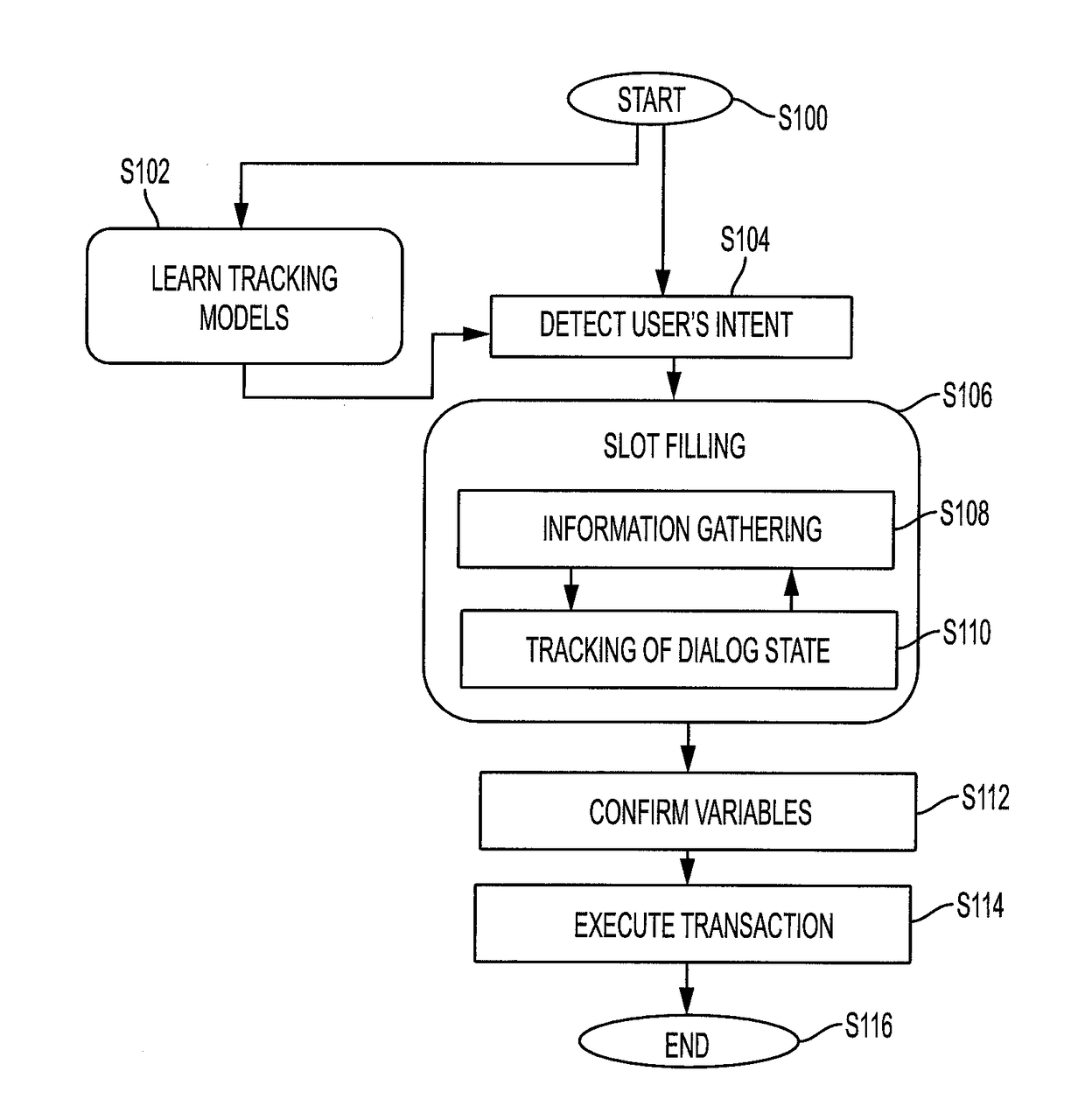
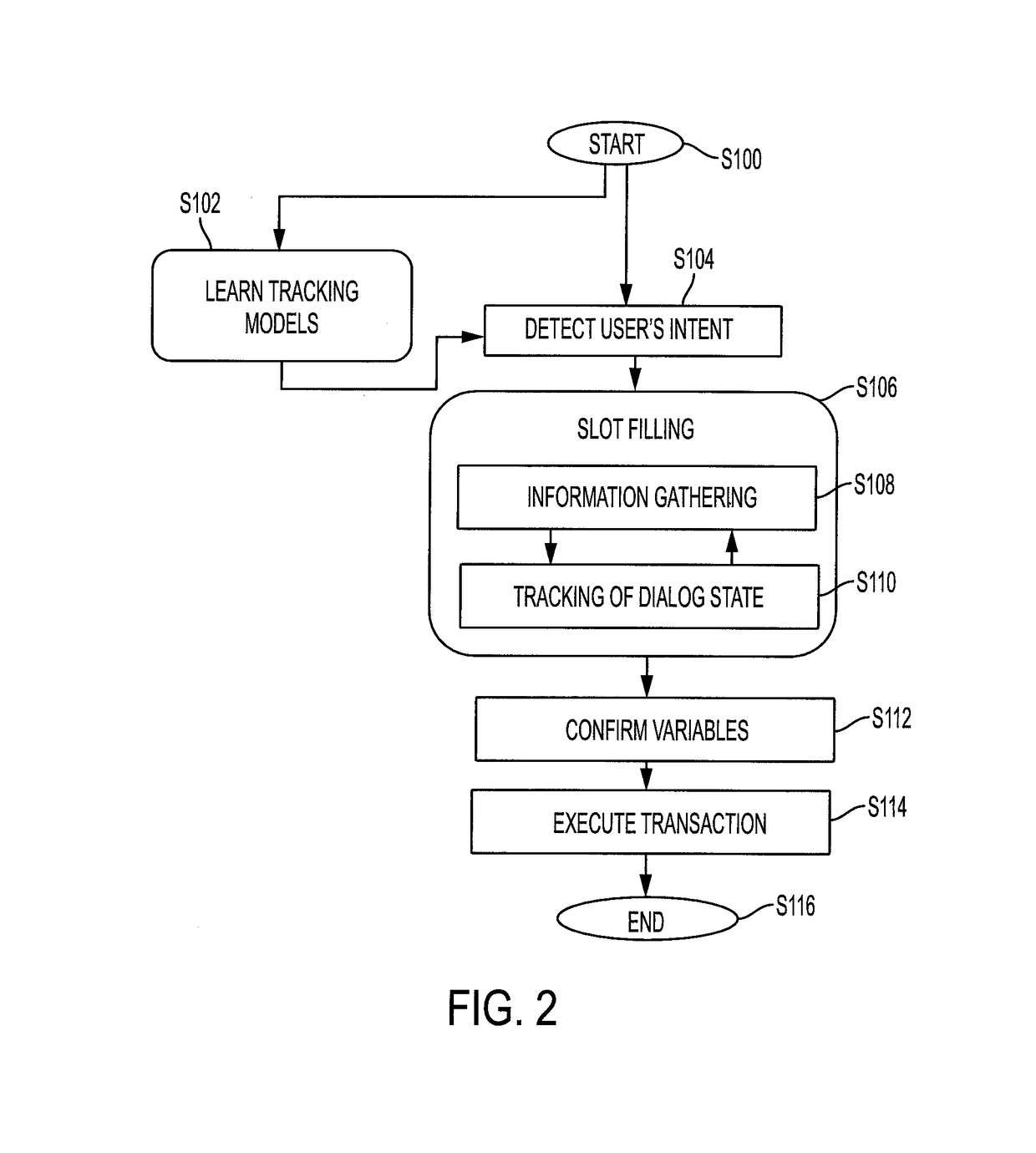
Generative discriminative approach for transactional dialog state tracking via collective matrix factorization
ActiveUS20170091171A1Natural language data processingSpeech recognitionPattern recognitionMatrix decomposition
A computer-implemented method for dialog state tracking employs first and second latent variable models which have been learned by reconstructing a decompositional model generated from annotated training dialogues. The decompositional model includes, for each of a plurality of dialog state transitions corresponding to a respective turn of one of the training dialogues, state descriptors for initial and final states of the transition and a respective representation of the dialogue for that turn. The first latent variable model includes embeddings of the plurality of state transitions, and the second latent variable model includes embeddings of features of the state descriptors and embeddings of features of the dialogue representations. Data for a new dialog state transition is received, including a state descriptor for the initial time and a respective dialogue representation. A state descriptor for the final state of the new dialog state transition is predicted using the learned latent variable models.
Owner:CONDUENT BUSINESS SERVICES LLC
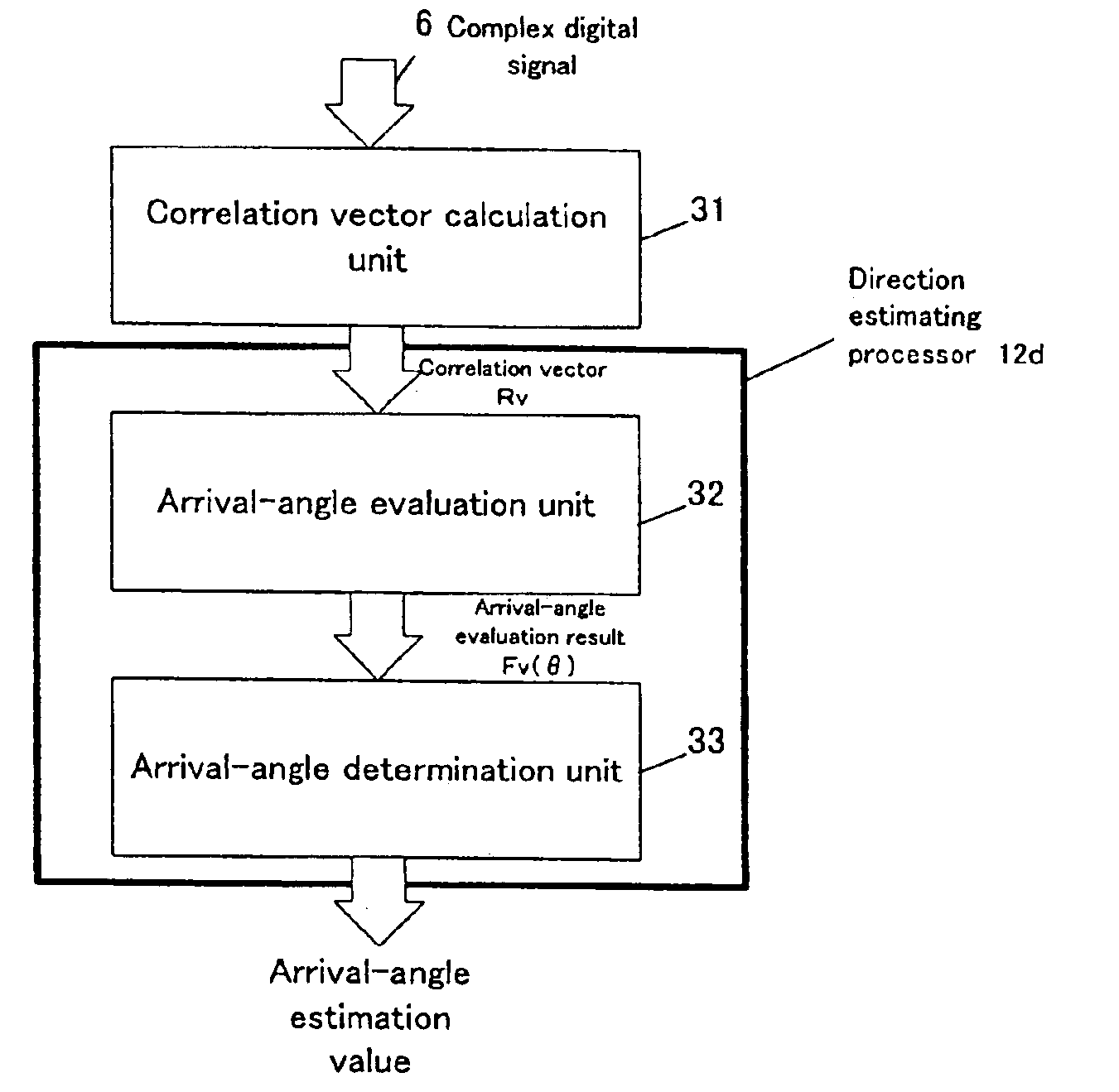
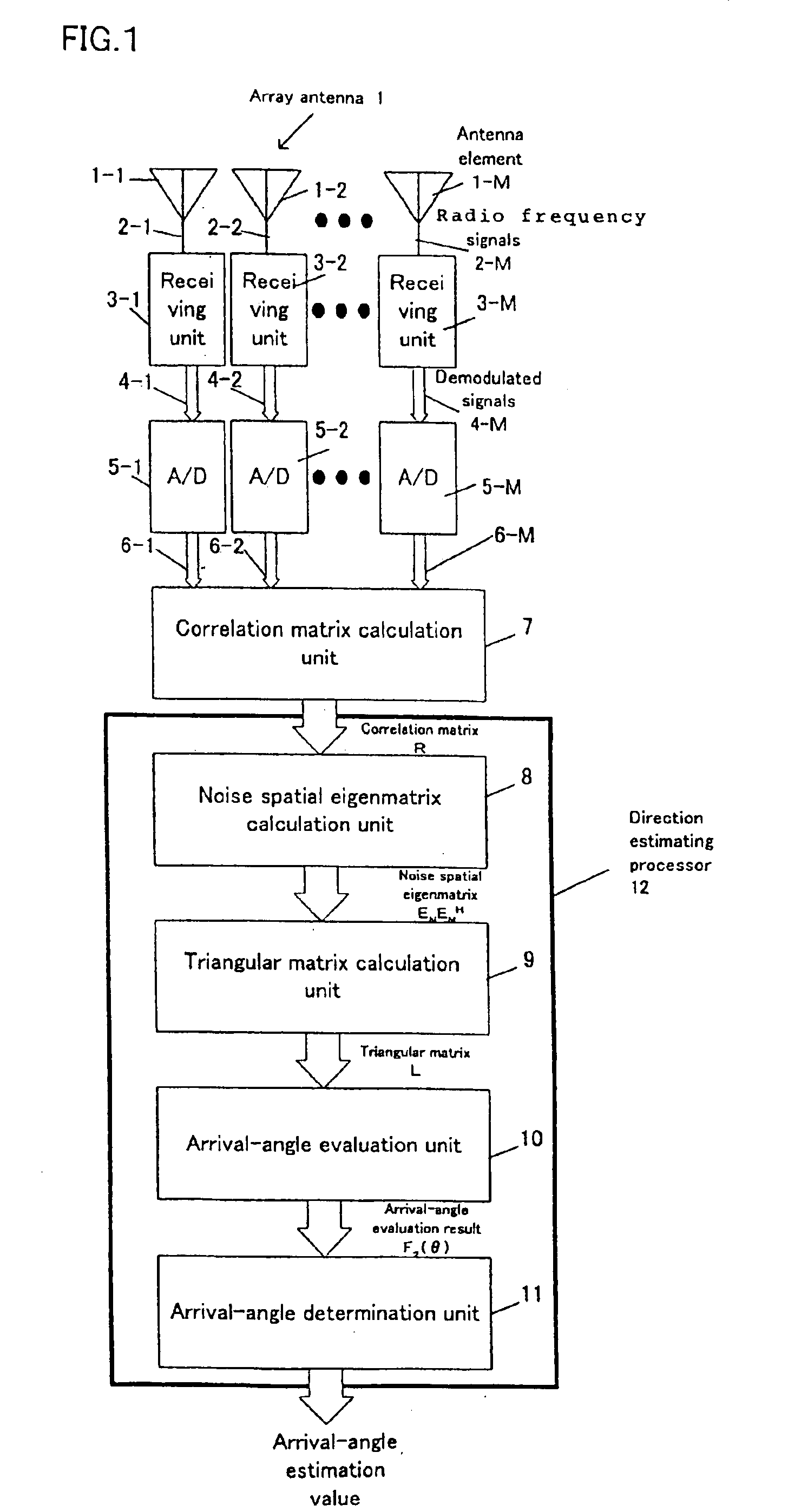
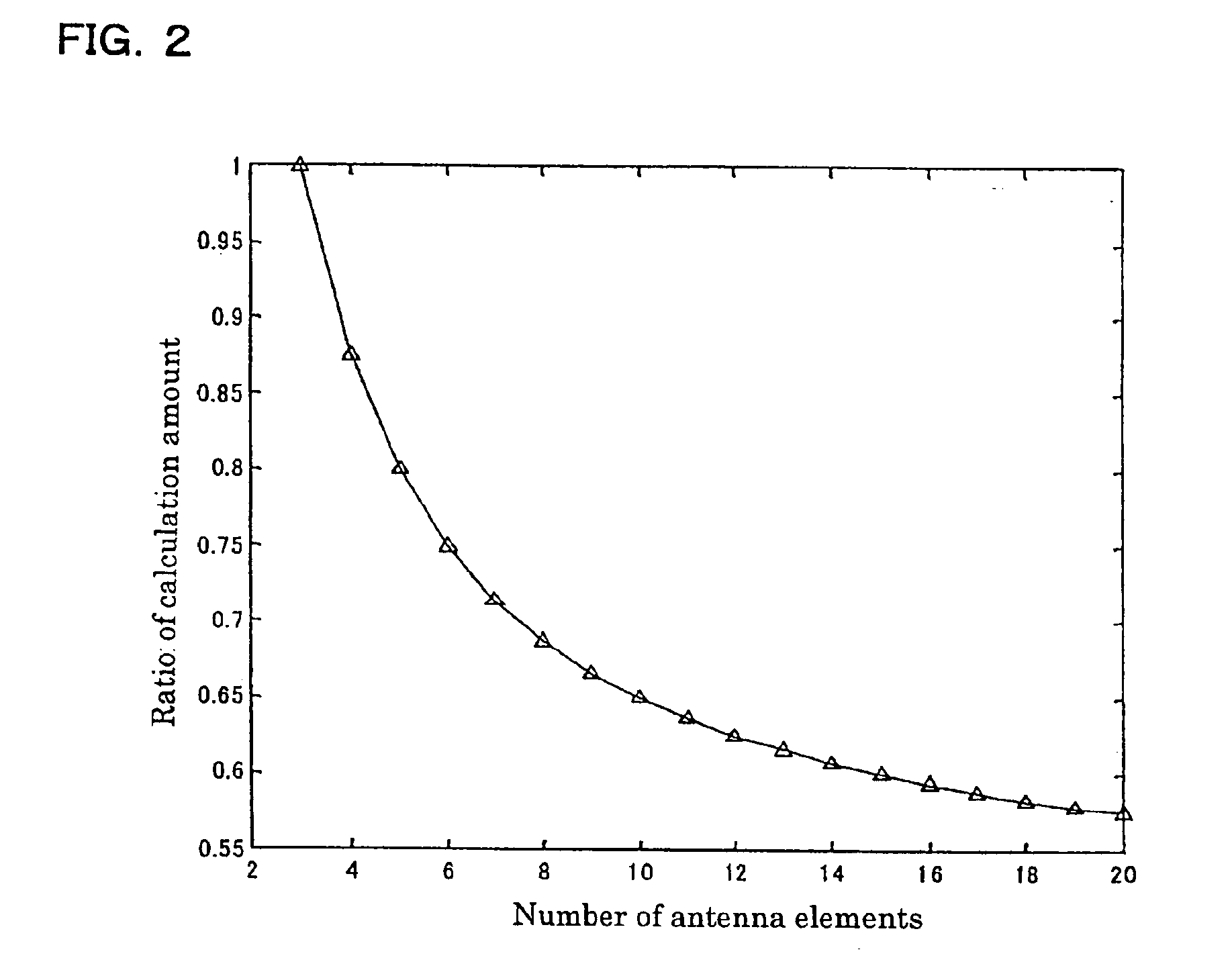
Radio-wave arrival-direction estimating apparatus and directional variable transceiver
InactiveUS6897807B2Quality improvementReduce the amount of calculationMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesPosition fixationAngular scanMatrix decomposition
A radio-wave arrival-direction apparatus calculates a correlation matrix of received signals by correlation calculation between antenna elements, and calculates a noise spatial eigenmatrix, of which each row or column is an eigenvector belonging to a noise eigen-space, by eigenvalue factorization of the correlation matrix. The apparatus also factorizes a matrix including a product of the noise spatial eigenmatrix and a conjugated and transposed matrix of it to an upper or lower triangular matrix, using cholesky factorization. The apparatus calculates an angle evaluation value in a predetermined angle range of an arrival-angle evaluation function using the derived upper or lower triangular matrix, and determines an arrival angle based on the calculation result. A calculation amount in a variable angle range can be thus reduced without causing accuracy degradation of arrival direction, in an algorism requiring all angle sweep for arrival angle estimation of MUSIC method or the like.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Efficient image rendering method based on modeling
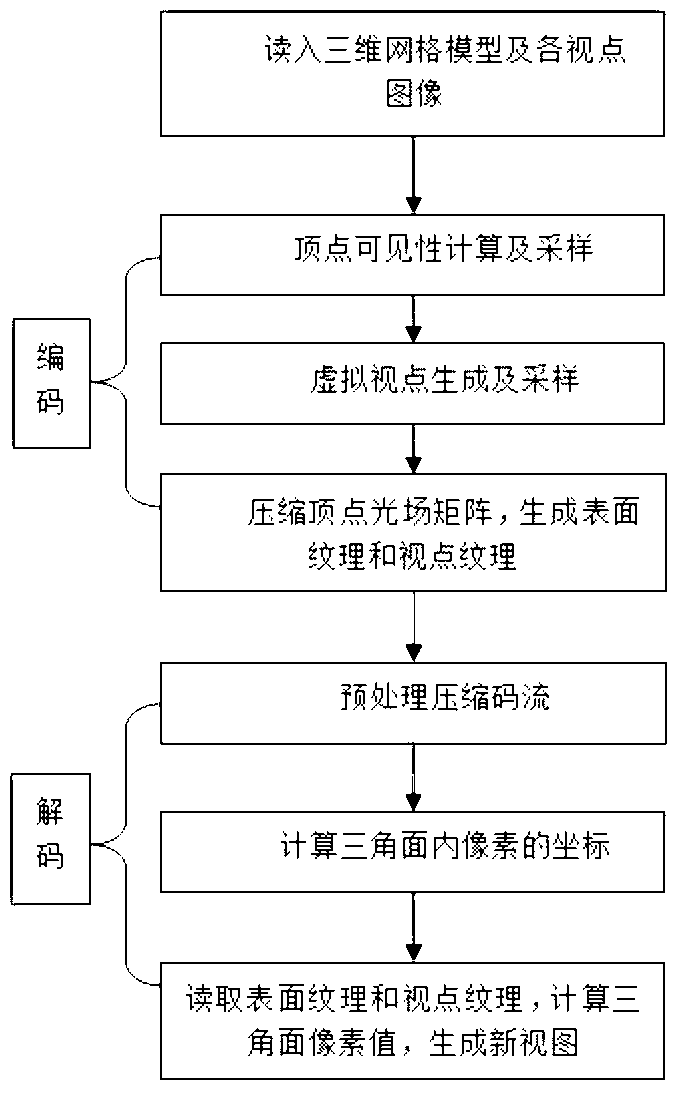
ActiveCN103345771AUniform transitionEliminate texture seams3D-image renderingMatrix decompositionComputer graphics (images)
The invention provides an efficient image rendering method based on modeling. With the method, a target image under free points view points can be generated. A light field model is adopted for recording surface information of a target; on the premise that that a three-dimensional grid model of the target and an appropriate amount of view point surrounding images of the target, through determining of a visible view point list of every vertex, the view points under which sampling is performed are determined; a triangular face ring of every vertex is selected as a sampling unit, virtual view points are generated with the triangulation method, and sampling information under the virtual view points is generated according to weight interpolations; sampling matrixes of all the vertexes are compressed with a matrix decomposition and compression method to facilitate transmission of the sampling information; in order to generate the target under the free view points, the three-dimensional grid model just needs to be projected to a screen coordinate system of new view points, and then a view under the new view points can be generated through reading of the sampling information. The method not only considers the problem of handling of a lapped seam phenomenon in texture mapping, but also reduces storage space for texture information and simplifies the rendering process.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Gaussian ranking using matrix factorization
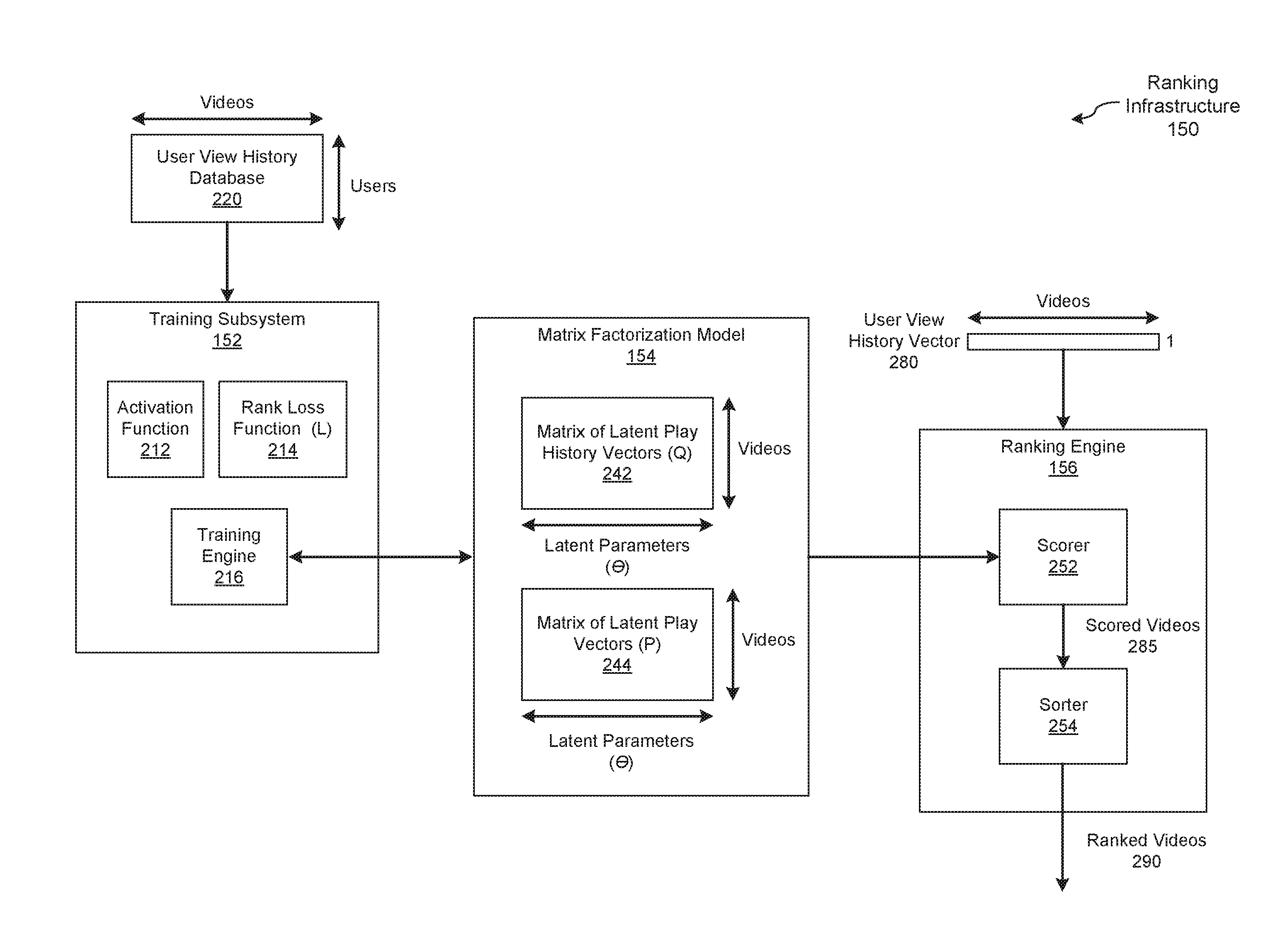
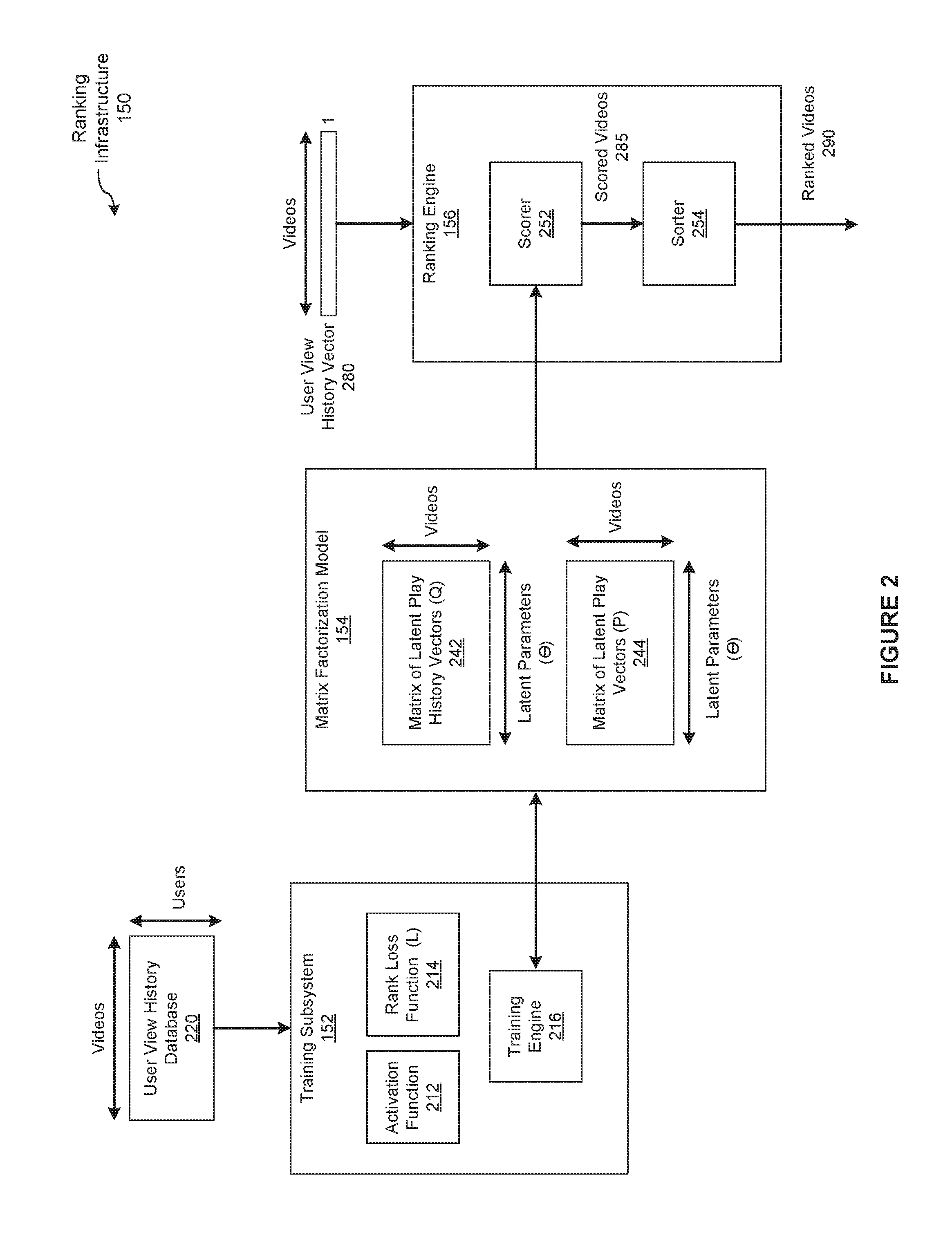
ActiveUS20170024391A1Efficiently and accurately trainMathematical modelsDigital data information retrievalMatrix decompositionActivation function
In one embodiment of the present invention, a training engine teaches a matrix factorization model to rank items for users based on implicit feedback data and a rank loss function. In operation, the training engine approximates a distribution of scores to corresponding ranks as an approximately Gaussian distribution. Based on this distribution, the training engine selects an activation function that smoothly maps between scores and ranks. To train the matrix factorization model, the training engine directly optimizes the rank loss function based on the activation function and implicit feedback data. By contrast, conventional training engines that optimize approximations of the rank loss function are typically less efficient and produce less accurate ranking models.
Owner:NETFLIX
Color unmixing and region of interest detection in tissue samples
InactiveUS20070053573A1Acquiring/recognising microscopic objectsImage data processingMatrix decompositionTissue sample
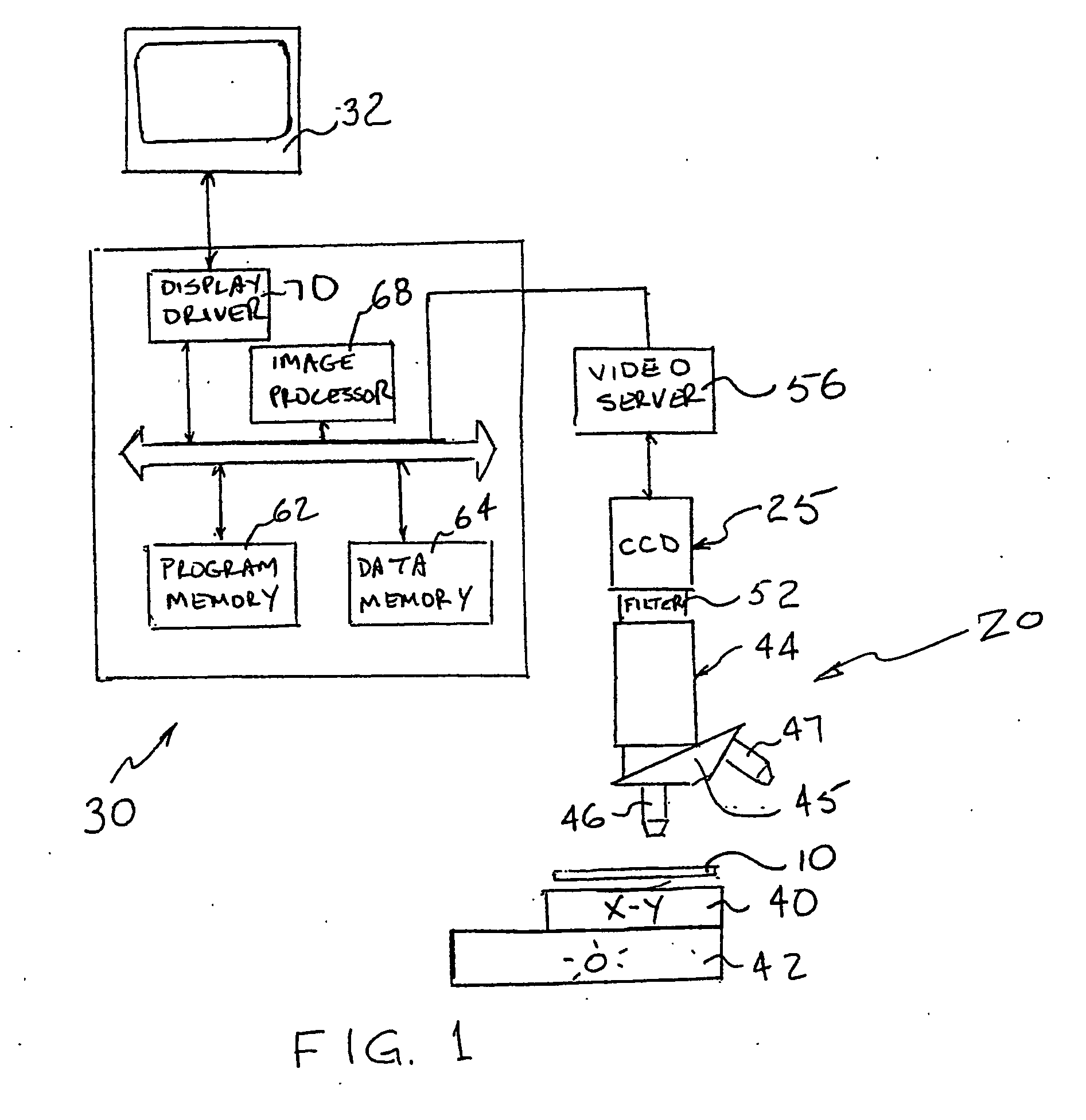
In a method and system and machine-readable medium, colors in an image (200) are unmixed (202) using a matrix X=AS, where A is a ns×nd matrix of spectral definitions, where s is the number of spectral components and d is the number of dyes into which the image is decomposed, and where S is a ns×l matrix of amounts of each dye at every pixel, where l is the number of pixels; the matrix X is constrained for solution by an unsupervised matrix decomposition method having constraints consistent with properties of an additive color model; and nd is determined. A texture is determined to identify areas of interest. Further processing may automatically measure cell dye concentration in the determined regions of interest.
Owner:RABINOVICH ANDREW M
Surface light field decomposition using non-negative factorization
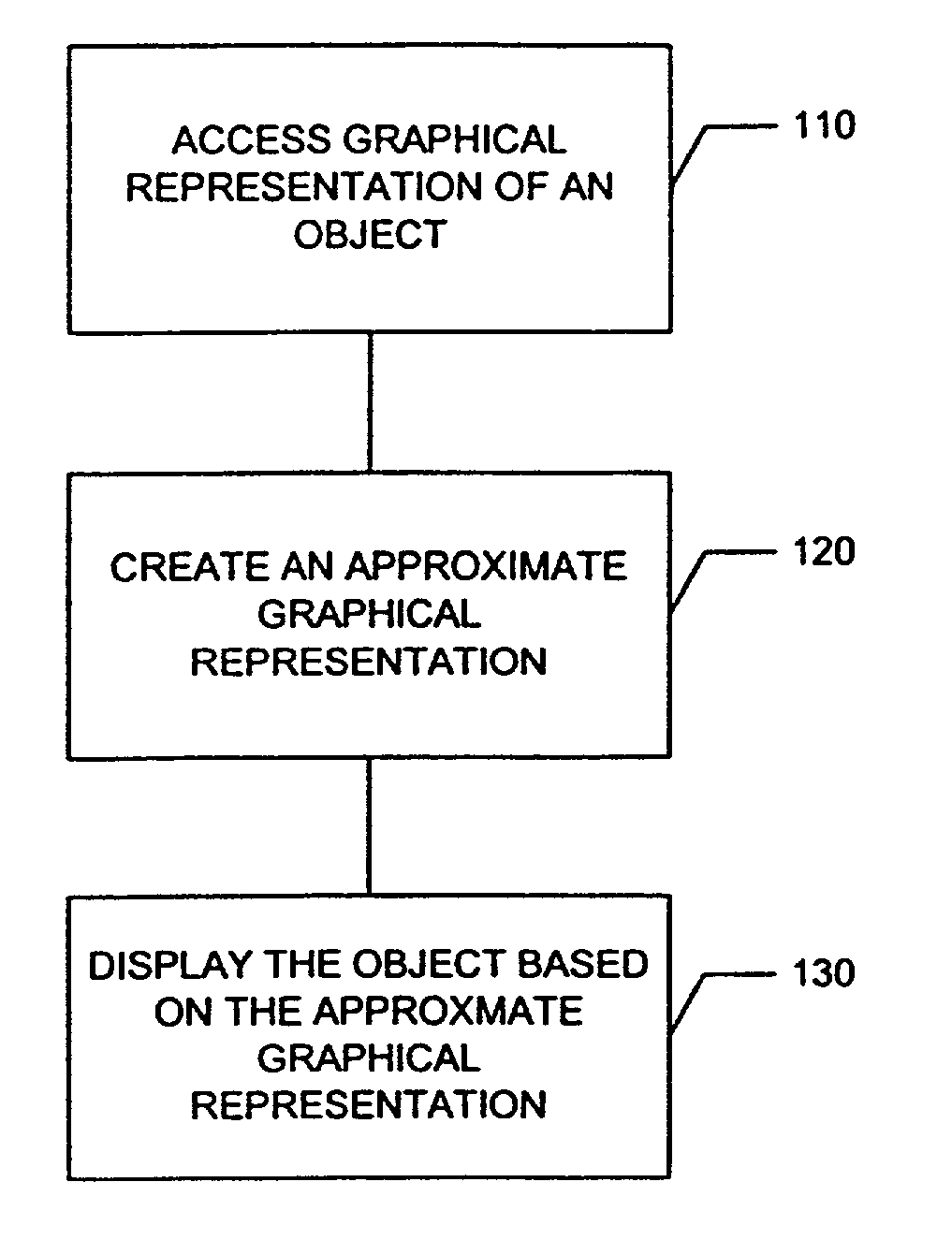
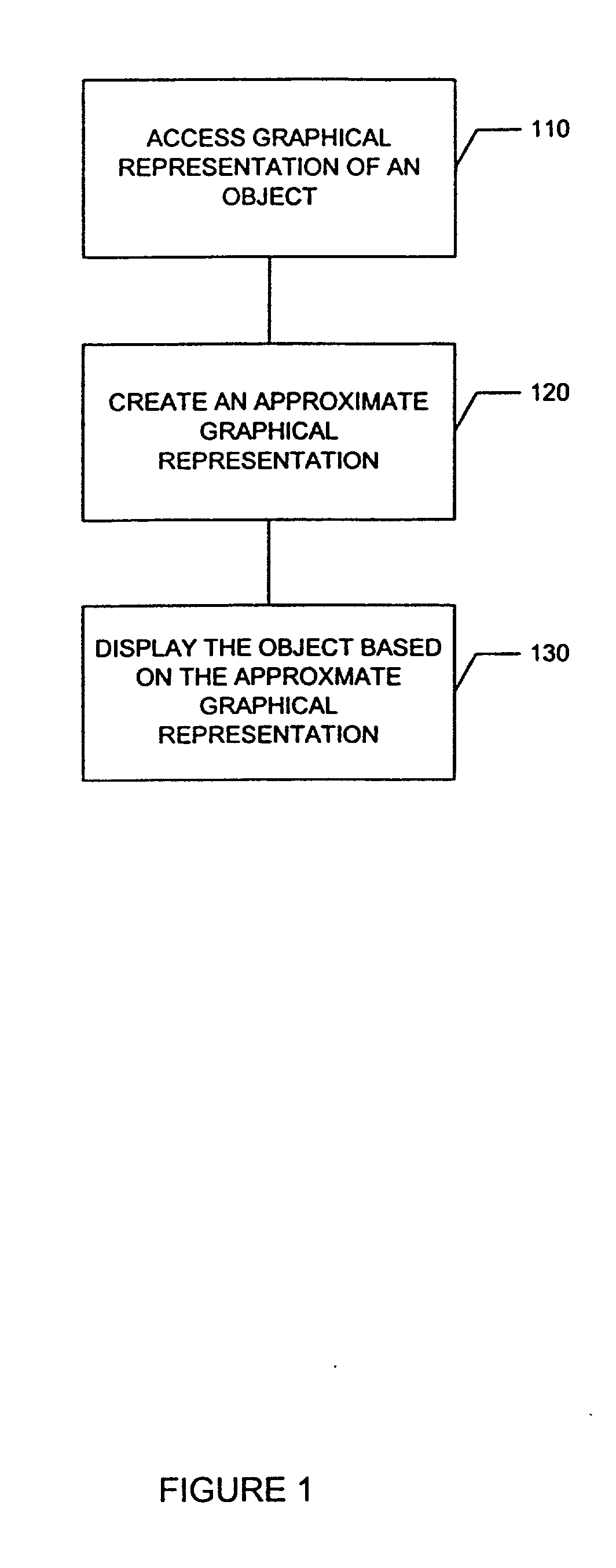
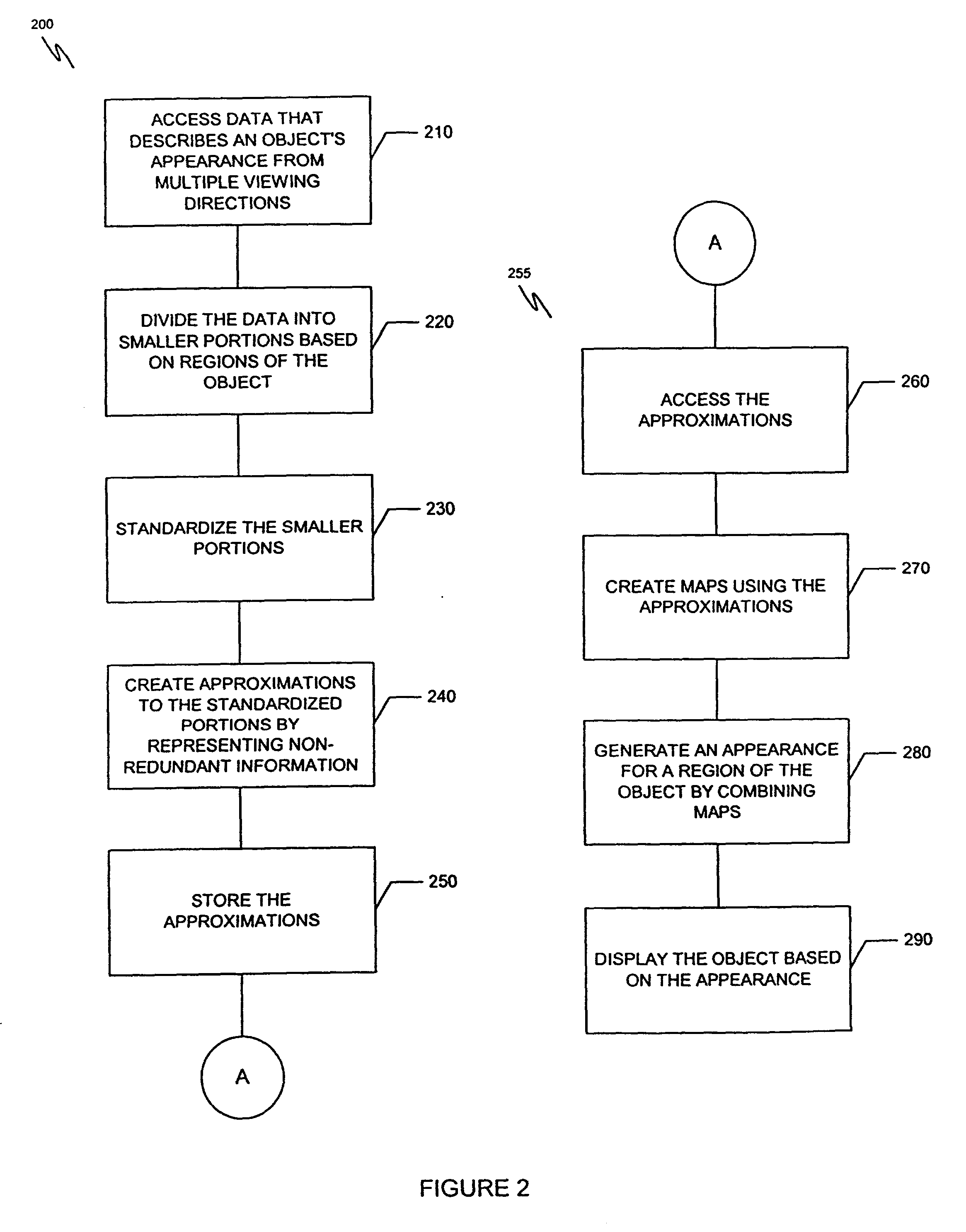
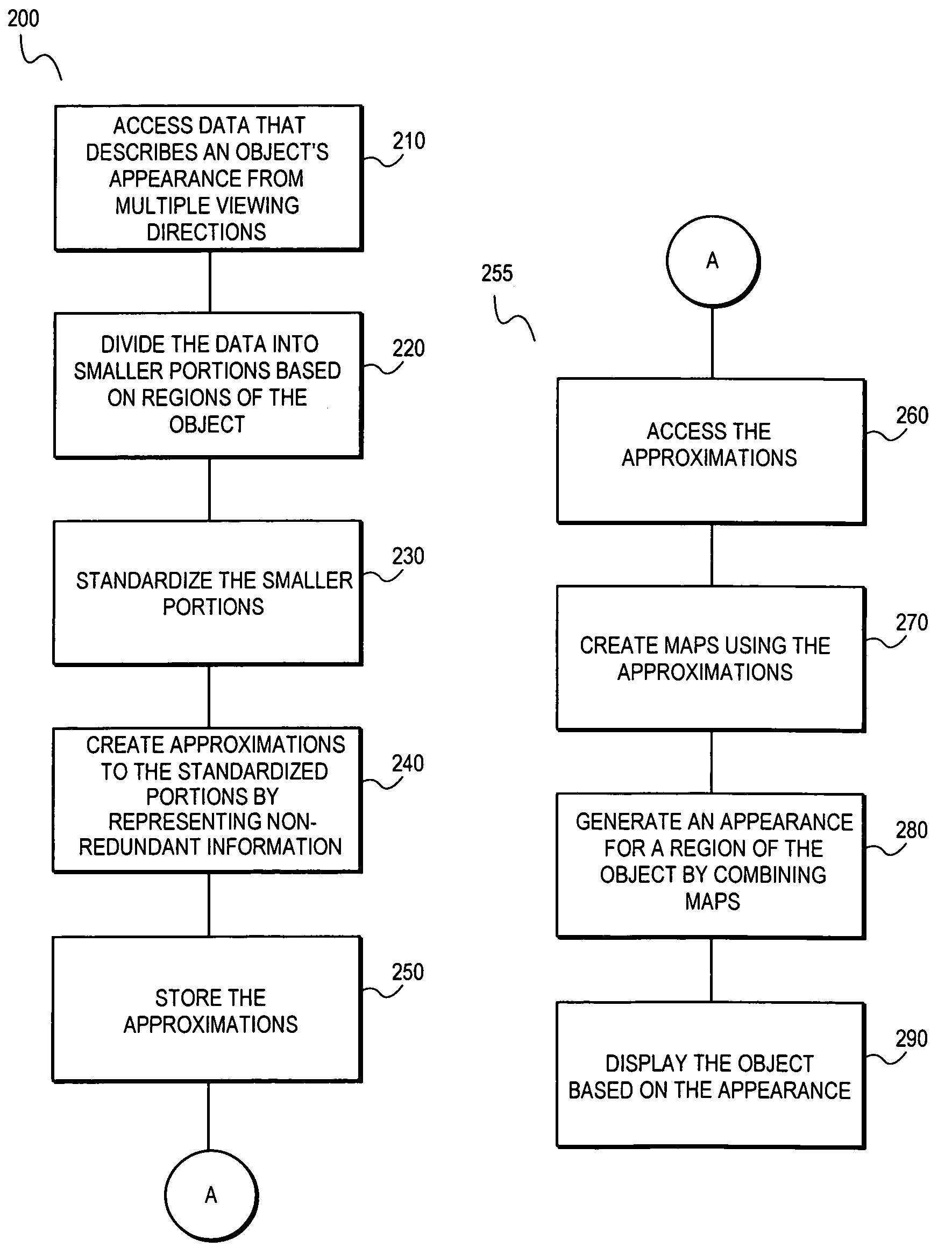
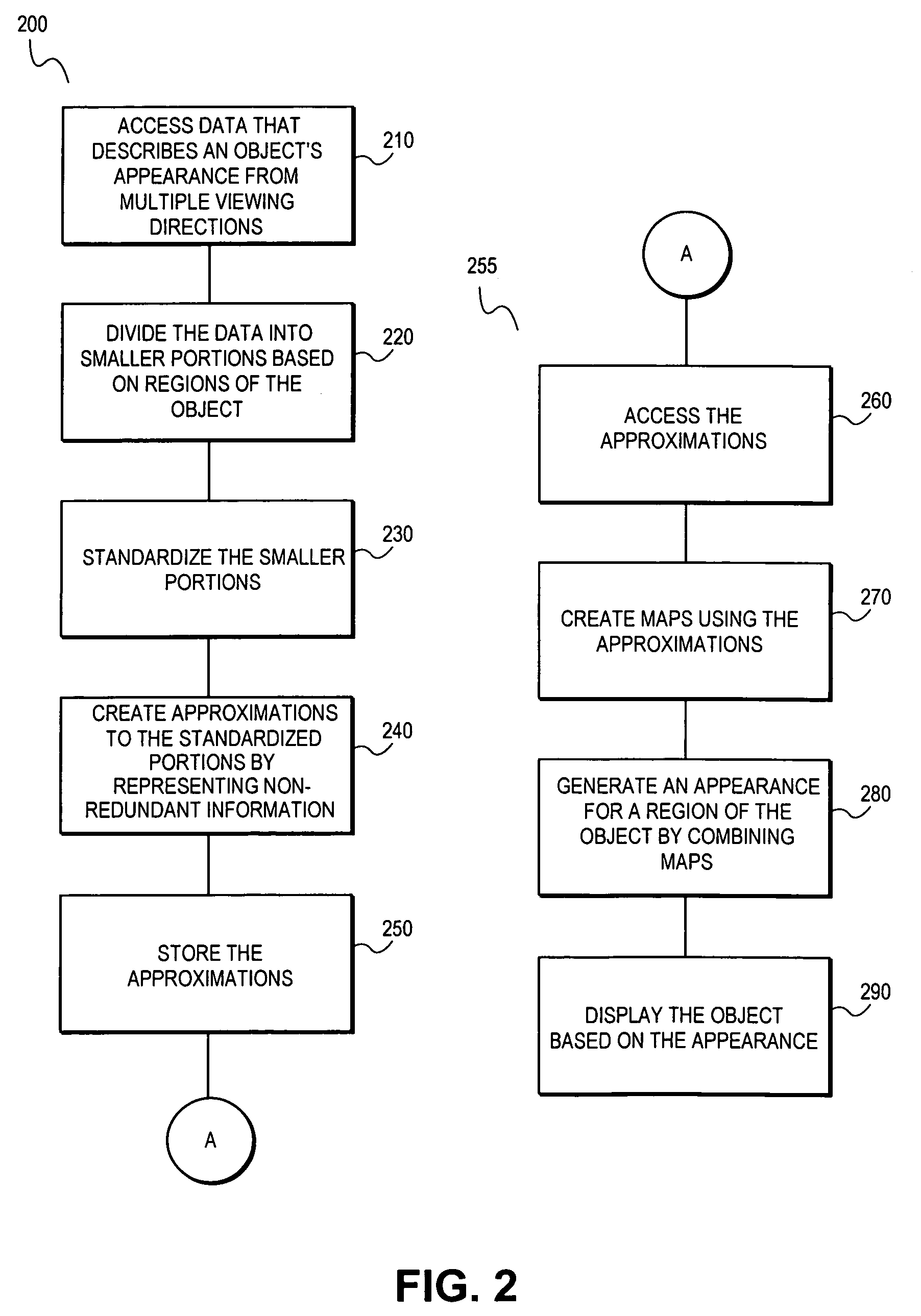
A system and method are provided for compressing a graphical representation that describes the appearance of an object from a plurality of viewing directions. Compressing includes accessing the graphical representation, removing redundant descriptive information from the graphical representation using sign consistent matrix factorization and approximation techniques, and representing the remaining information for efficient rendering, such as rendering with hardware-assisted computation.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Recommendation system optimization method with information of user and item and context attribute integrated
ActiveCN102982107AImprove recommendation accuracyImprove rating prediction accuracyComplex mathematical operationsPersonalizationMatrix decomposition
The invention discloses a recommendation system optimization method with information of a user and an item and a context attribute integrated. According to the method, the information of the user, the item and the context attribute is integrated in a matrix decomposition model, and recommendation accuracy is improved in a personalized recommendation system. The recommendation system optimization method with the information of the user, the item and the context attribute integrated is characterized in that different influences of the information of the user, the item and the context attribute on overall scores, user interests and item scores are considered, and is applied to calculation of an original matrix decomposition model. The influences of the user, the item and the context attribute on the scores are considered at the same time, and therefore the recommendation accuracy is obviously higher than that of the rectangular decomposition model which only adopts user program two-dimensional score matrix information.
Owner:珠海市颢腾智胜科技有限公司
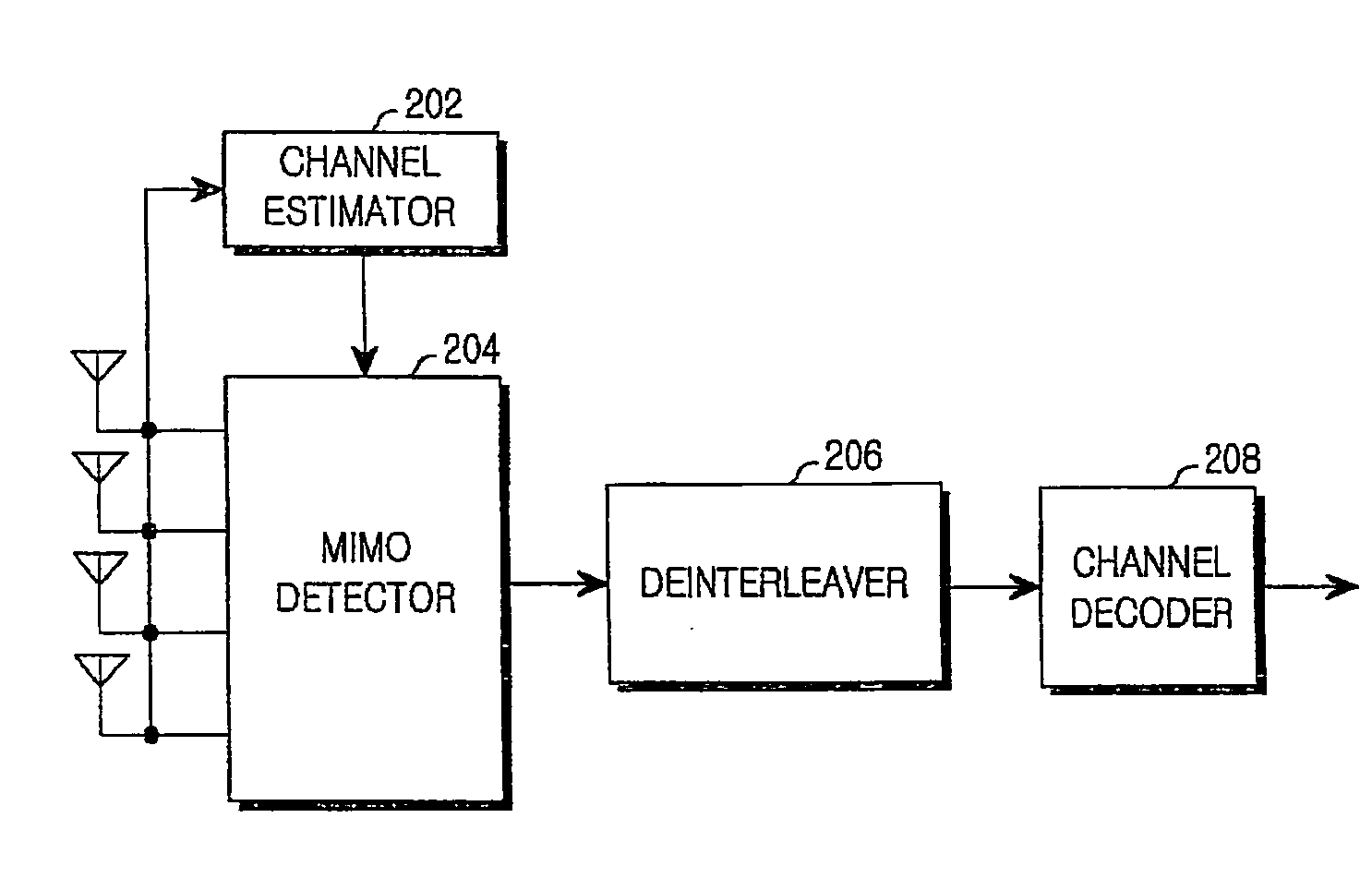
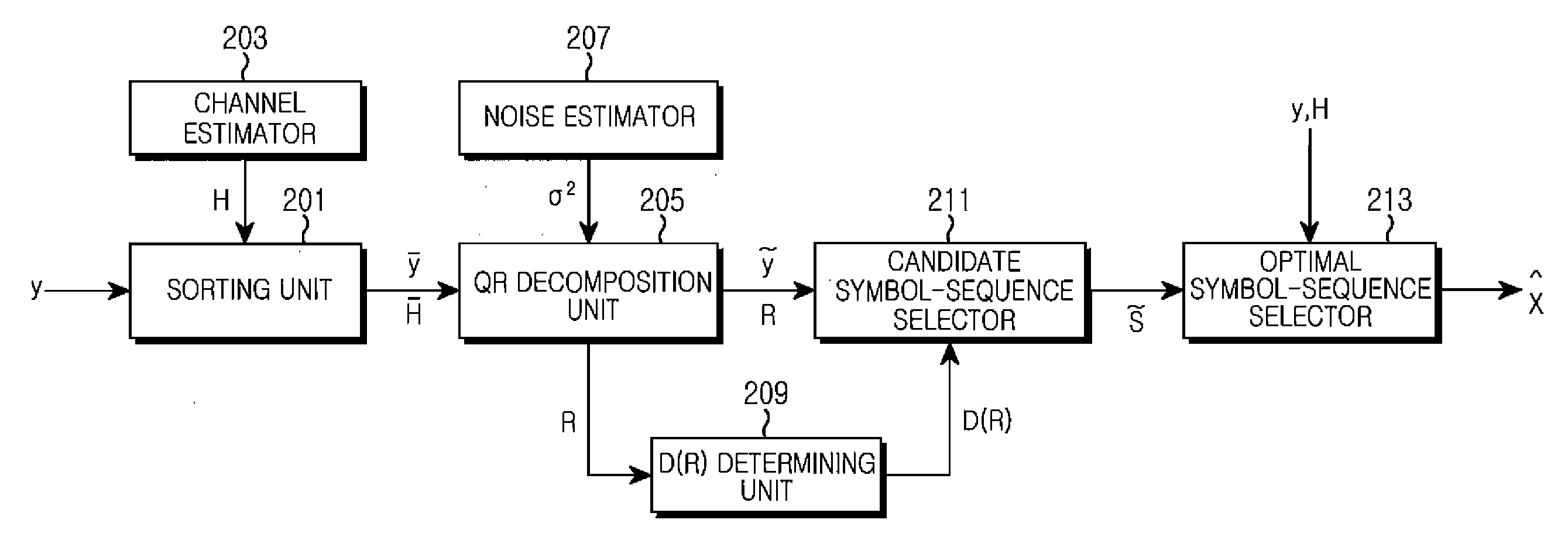
Apparatus and method for detecting signal in multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) wireless communication system
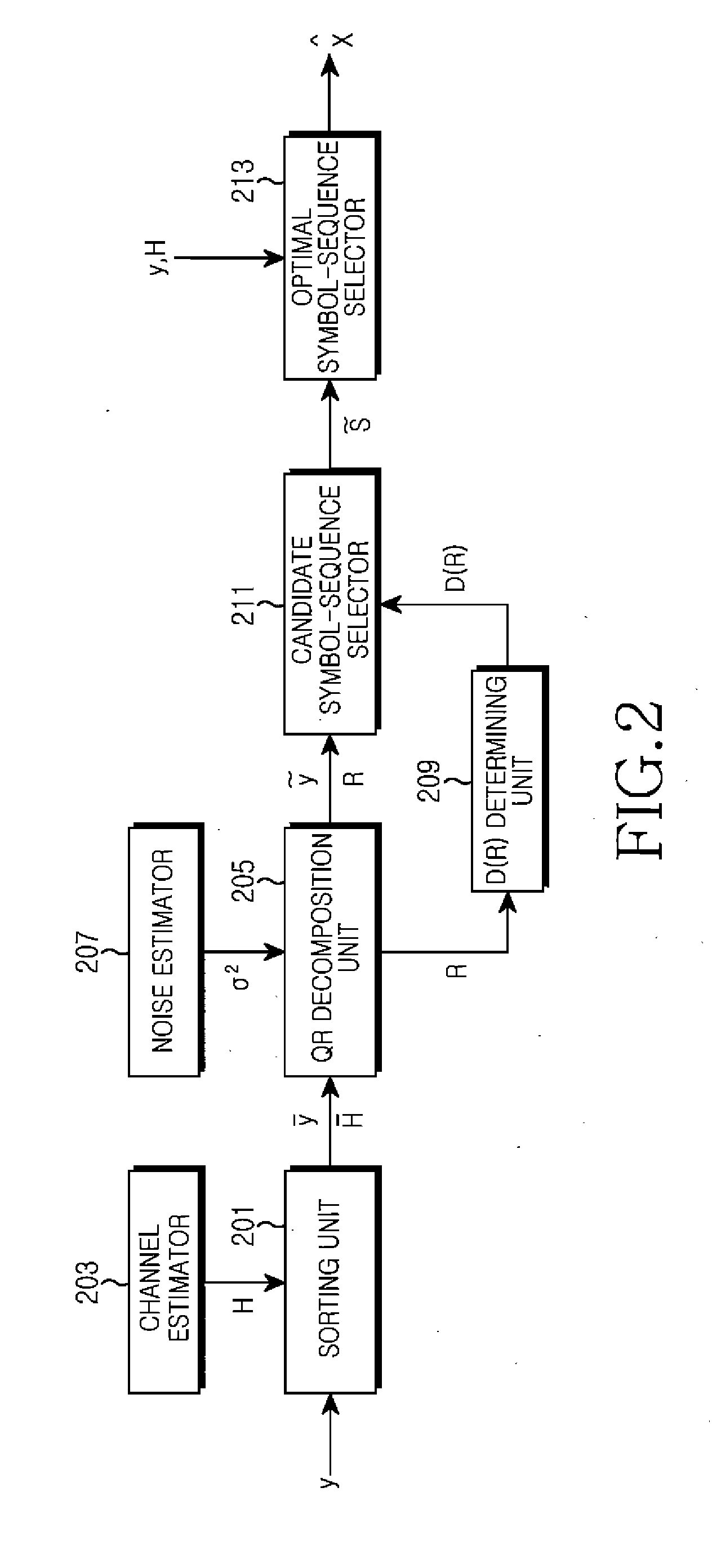
ActiveUS20080310556A1Reduce complexityGenerate efficientlyPolarisation/directional diversityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsMatrix decompositionQR decomposition
Receiving apparatus and method in a Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) wireless communication system are provided. The receiver having N-ary receive antennas includes a decomposer for decomposing a channel matrix to a matrix Q and a matrix R through a QR decomposition; a detector for determining a candidate group of an n-th phase by estimating a plurality of transmit signal vectors by substituting a plurality of transmittable symbols into symbol combinations of a candidate group of a (n−1)-th phase as an n-th symbol and detecting (n+1)-th through N-th symbols using characteristics of the matrix R; a calculator for calculating square Euclidean distance values between the transmit signal vectors and a receive signal vector; and a determiner for determining the candidate group of the n-th phase by selecting transmit signal vectors having the smallest square Euclidean distance value among the transmit signal vectors.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Surface light field decomposition using non-negative factorization
A system and method are provided for compressing a graphical representation that describes the appearance of an object from a plurality of viewing directions. Compressing includes accessing the graphical representation, removing redundant descriptive information from the graphical representation using sign consistent matrix factorization and approximation techniques, and representing the remaining information for efficient rendering, such as rendering with hardware-assisted computation.
Owner:INTEL CORP
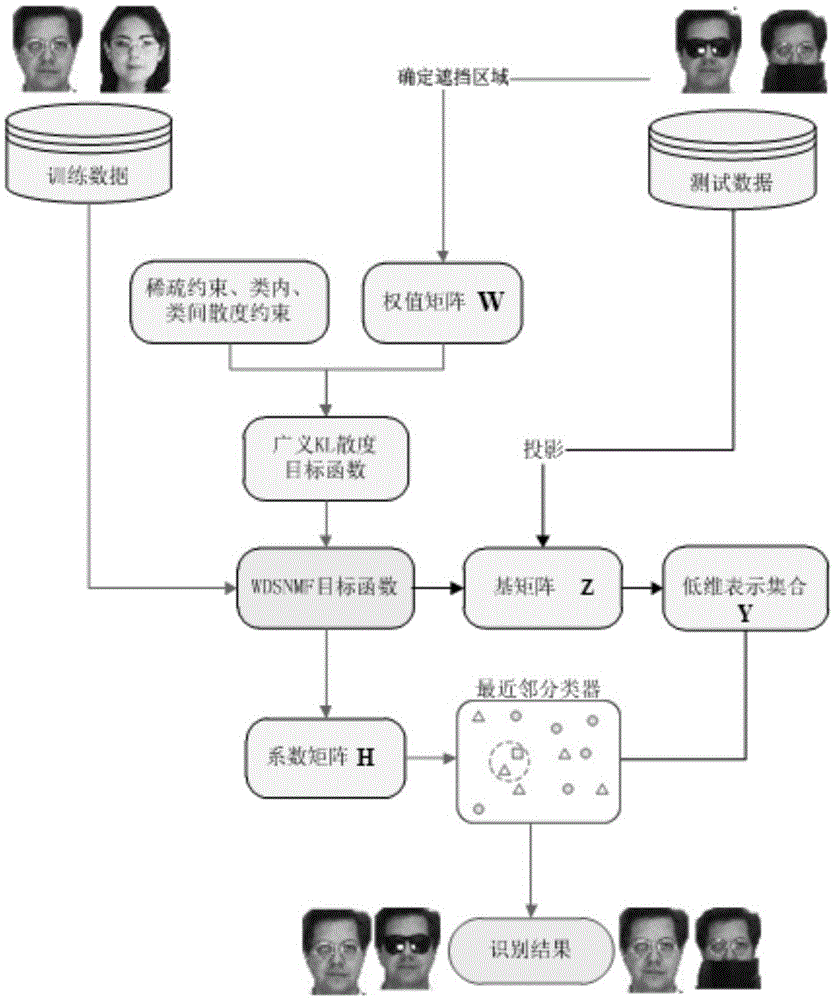
Face recognition method based on weighted diagnostic sparseness constraint nonnegative matrix decomposition
ActiveCN105469034AOvercome the problem of weak expression ability of facial featuresOvercoming the problem of poor occlusion robustnessCharacter and pattern recognitionMatrix decompositionIdentity recognition
The invention discloses a face recognition method based on weighted diagnostic sparseness constraint nonnegative matrix decomposition, and mainly aims to solve the problem that the method in the prior art is not robust to an obscured face and is of low recognition rate. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the following steps: (1) constructing a nonnegative weight matrix according to the obscured area of a test image; (2) introducing the weight matrix into a general KL divergence objective function, applying a sparseness constraint to a basis matrix, and applying intra-class and inter-class divergence constraints to a coefficient matrix to get a weighted diagnostic sparseness constraint nonnegative matrix decomposition objective function; (3) solving the objective function, and decomposition-training a data matrix to get a basis matrix and a coefficient matrix; (4) projecting a test data matrix on the basis matrix to get a corresponding low-dimensional representation set, and taking the low-dimensional representation set as final test data; and (5) using a nearest neighbor classifier to classify the test data by taking the coefficient matrix as training data, and outputting the result. By using the method, the effect of obscured face recognition is improved. The method can be used in identity recognition and information security.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
miRNA-disease association relation prediction method based on similarity and logical matrix decomposition
PendingCN107862179AImprove forecast accuracyIncrease credibilityBiostatisticsHybridisationPattern recognitionMatrix decomposition
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
A personalized test recommendation method based on user learning behavior
PendingCN109509126AAccurate graspLearning status is goodForecastingResourcesPoint correlationPersonalization
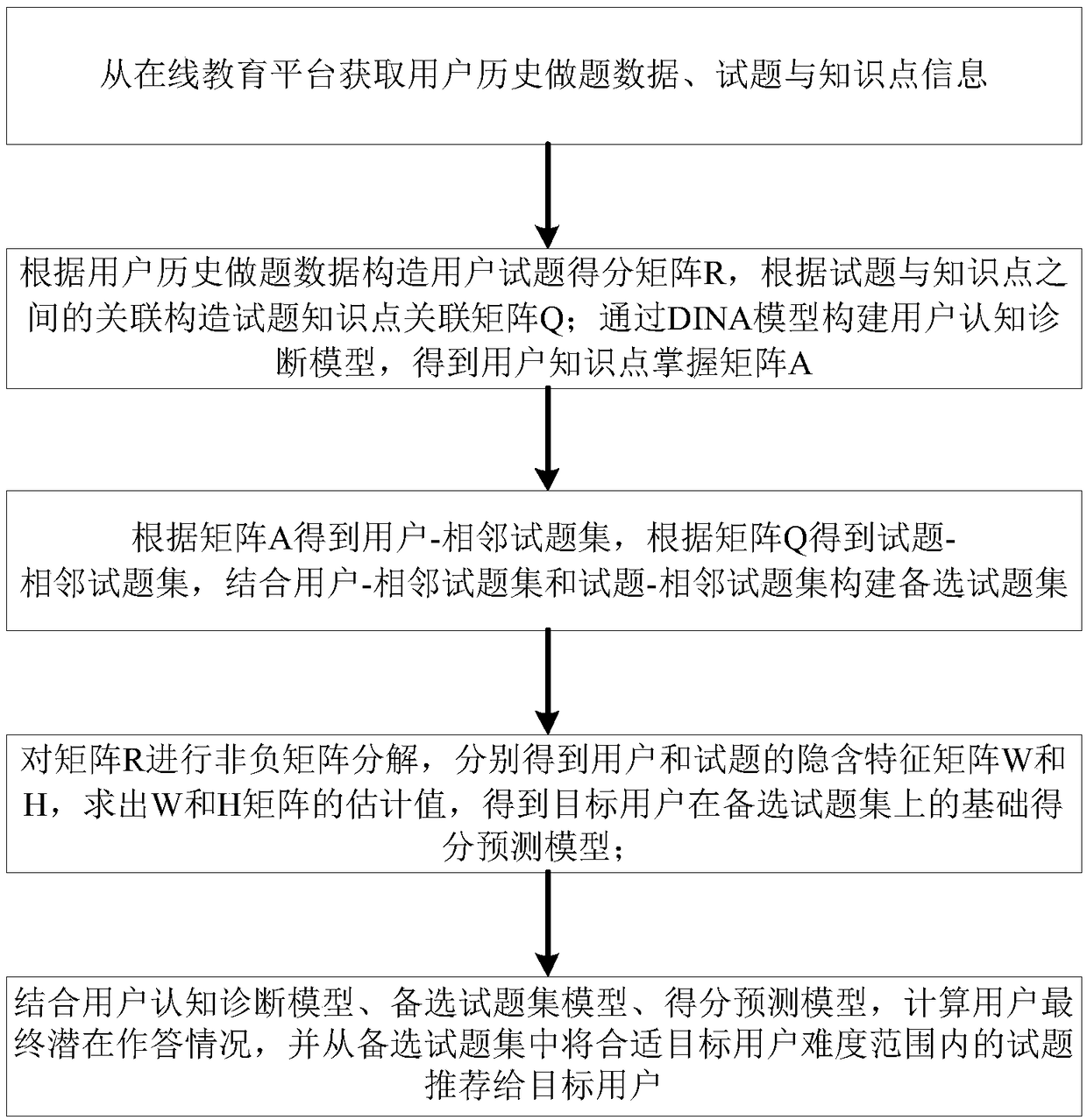
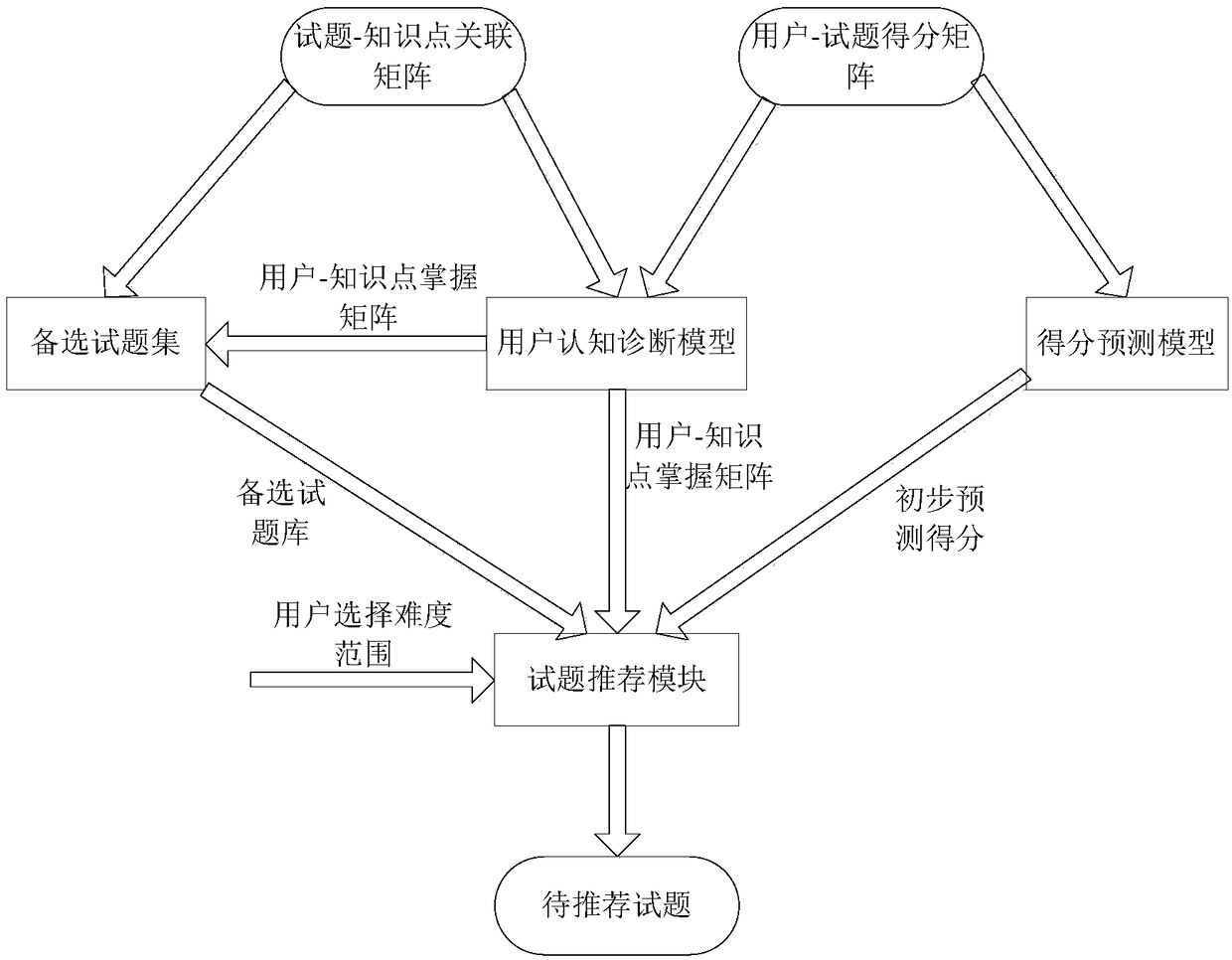
The invention discloses a personalized test question recommendation method based on user learning behavior, the method is as follows: obtaining user history problem data, test questions and knowledgepoint information from an online education platform; constructing a user based on user history data data; R, according to the relationship between the test questions and the knowledge points, constructing the test questions-Knowledge point correlation matrix Q; constructing the user cognitive diagnosis model through the DINA model, obtaining the user knowledge point mastering matrix A; obtainingthe user adjacent test set according to the matrix A, according to Matrix Q the test questions-Adjacent test sets, constructing alternative test sets; non-negative matrix decomposition of matrix R, obtaining the implicit feature matrices W and H of users and test questions, find the estimated values of W and H matrices, and get the score prediction Model; calculating the potential answering situation of the user, and recommending the test questions of the target user's own difficulty range to the target user. The invention can accurately recommend the test questions suitable for the target user to the user. The invention is applicable to the field of online education.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
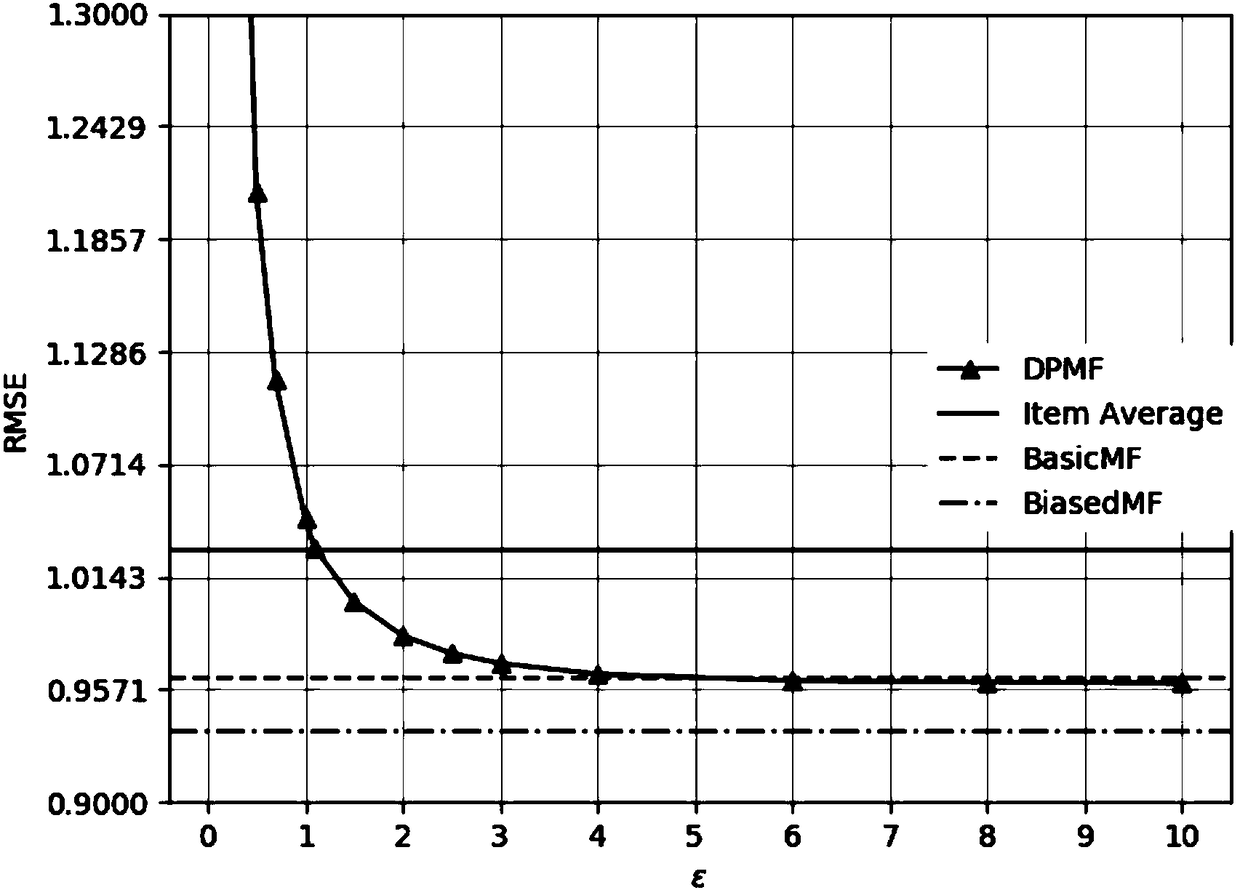
Matrix decomposition recommending method based on difference privacy protection
InactiveCN108280217AEffective protectionReduce joinDigital data protectionComplex mathematical operationsFactor matrixRating matrix
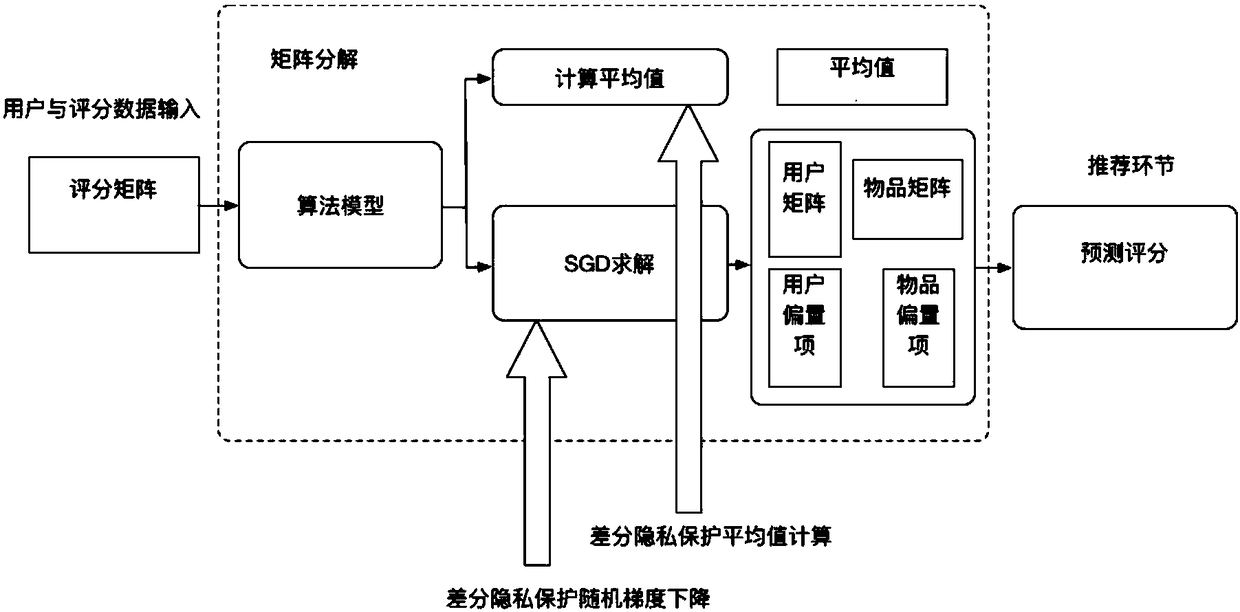
The invention discloses a matrix decomposition recommending method based on difference privacy protection. The method comprises the steps of converting the collected evaluation or preference of usersfor an object into a user-score matrix as a training set of a recommending method model; utilizing a score average value, a user factor matrix, an object factor matrix, a user bias item and an objectbias item to predict score conditions for the object by the users; through a difference privacy average value calculation method, calculating an average value of the user scores under difference privacy protection; according to a score prediction model, building a minimum square error function; through a difference privacy random gradient lowering method, training the score prediction model, adding difference privacy noise in the training process and achieving the difference privacy protection of parameters; through the score prediction model and trained difference privacy protection model parameters, predicting scores for the object by the users. When a recommending result is provided, information of the users can be subjected to the difference privacy protection, and the recommending accuracy is high.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
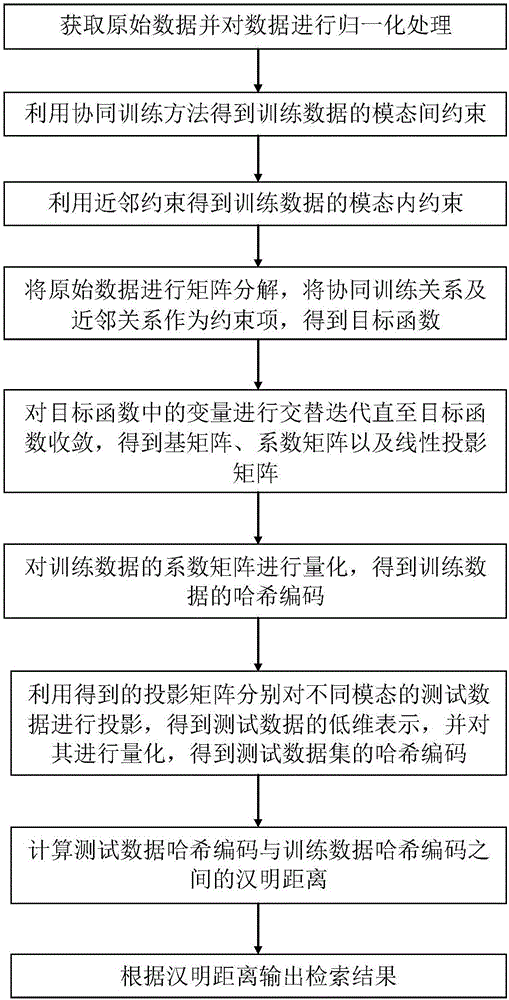
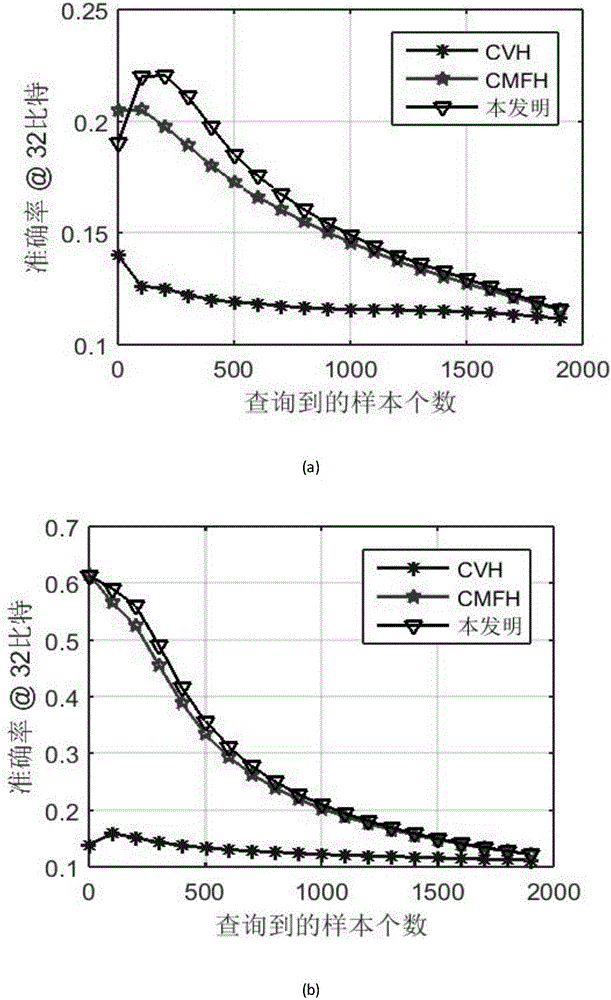
Matrix decomposition cross-model Hash retrieval method on basis of cooperative training
ActiveCN106777318AImprove mutual search performanceImprove mutual search accuracyStill image data retrievalText database queryingMatrix decompositionHat matrix
The invention discloses a cross-model Hash retrieval method on the basis of cooperative training and matrix decomposition. By the aid of the cross-model Hash retrieval method, the similarity between models and the internal similarity of the models can be effectively constrained for unlabeled cross-model data. The cross-model Hash retrieval method includes implementation steps of acquiring original data and carrying out normalization processing on the original data; carrying out cooperative training to obtain constraints between the models; acquiring internal constraints of the models by the aid of neighbor relations; decomposing training data matrixes and adding the constraints between the models and the internal constraints of the models into the training data matrixes to obtain objective functions; carrying out alternate iteration to obtain expressions of basis matrixes, coefficient matrixes and projection matrixes; carrying out quantization to obtain Hash codes of training data sets and test data sets; computing the Hamming distances between every two Hash codes of the data sets; sorting the Hamming distances to obtain retrieval results. The cross-model Hash retrieval method has the advantages that constraints on the similarity between the models of the cross-model data can be obtained by the aid of cooperative training processes, accordingly, the image and text mutual retrieval performance can be improved, and the cross-model Hash retrieval method can be used for picture and text mutual search service of mobile equipment, internets of things and electronic commerce.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
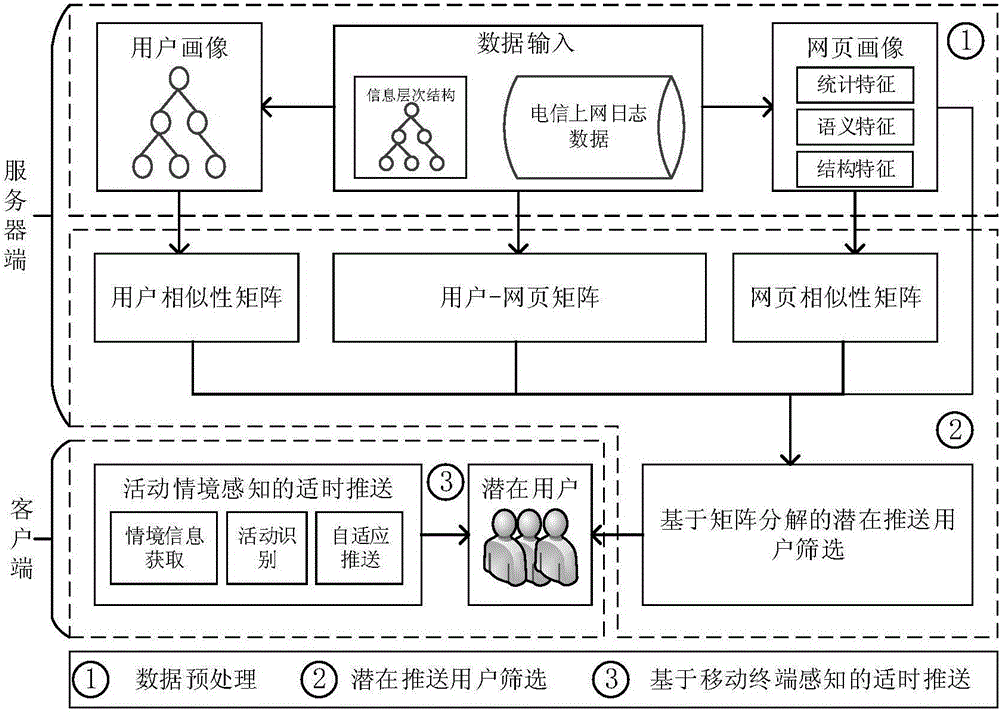
Information push method based on internet-surfing log mining and user activity recognition
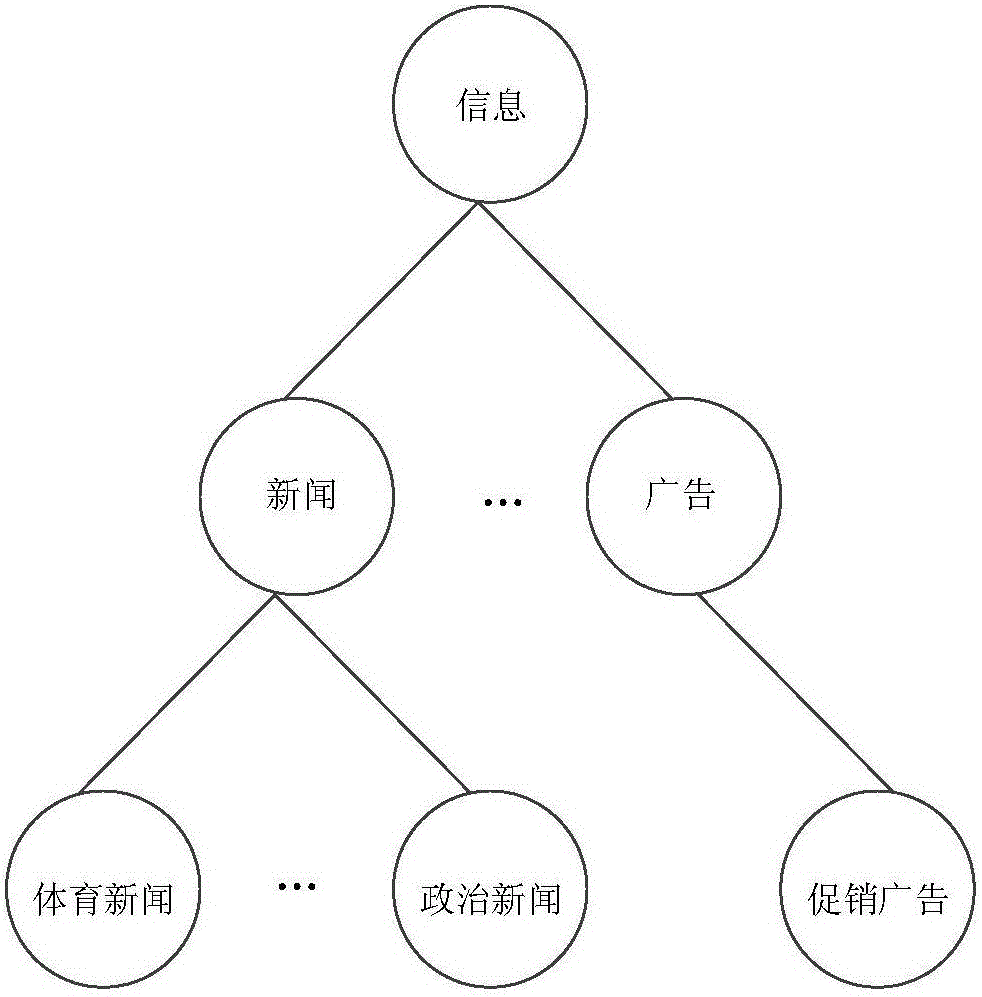
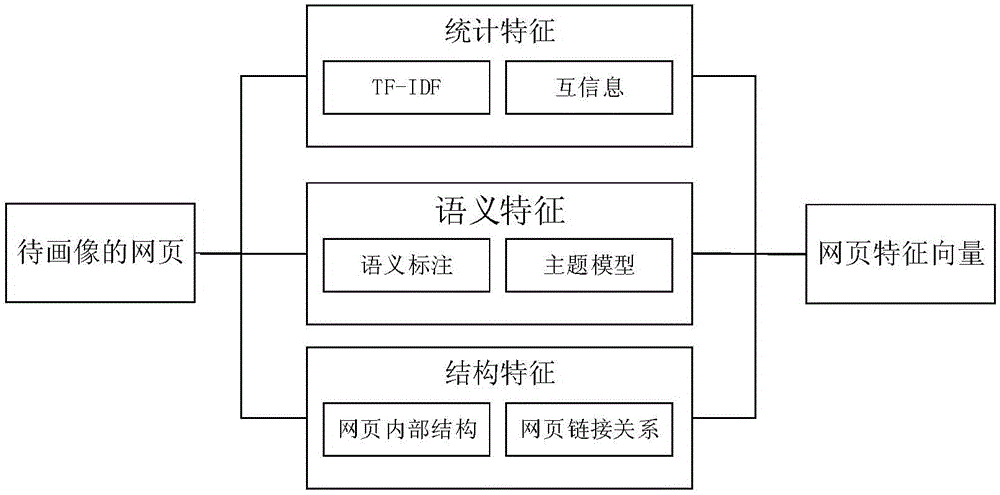
ActiveCN105718579AImprove push efficiencyAccurate portrayalSpecial data processing applicationsMatrix decompositionLog mining
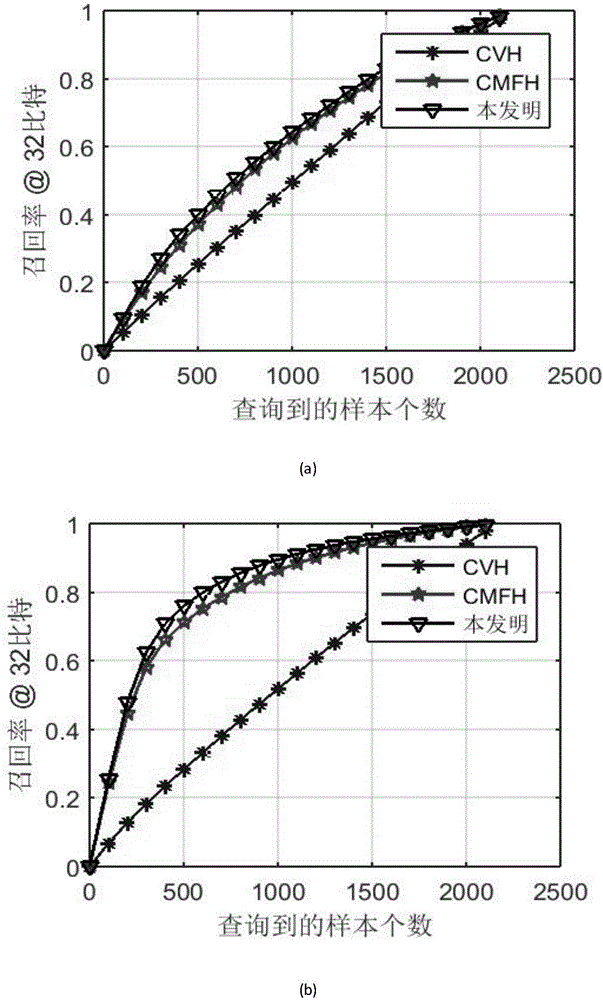
The invention discloses an information push method based on internet-surfing log mining and user activity recognition.The method includes a data preprocessing stage, a potential pushing user screening stage and a timely push stage.The data preprocessing stage comprises a webpage portrait, webpage level classification and a user portrait.In the potential pushing user screening stage, similarity between new information and historical web pages which users have access to is solved through a method based on matrix decomposition, and potential pushing users who may be interested in the new information are screened out.The timely push stage includes situational information acquisition and activity recognition based on a mobile intelligent device, and information timely pushing adaptive to the activity situation.By mining internet-surfing log data, potential users interested in information are found, when new information is generated, the new information is pushed to the potential users in good time, and therefore information push efficiency is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
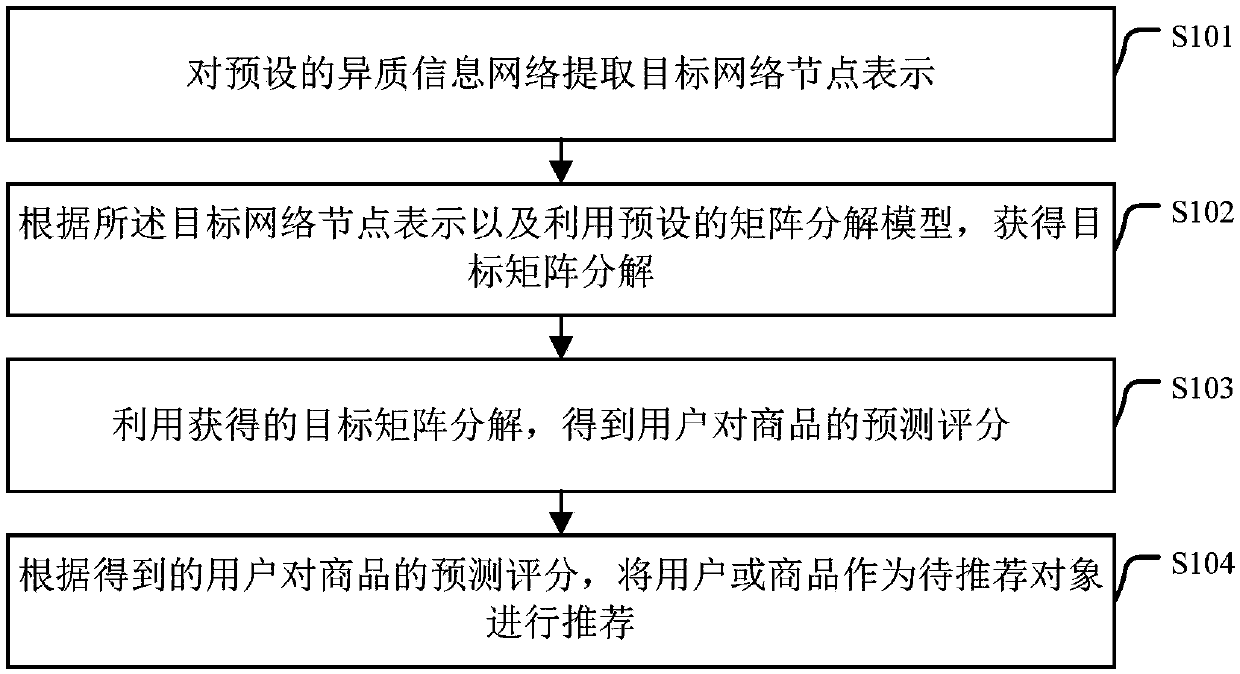
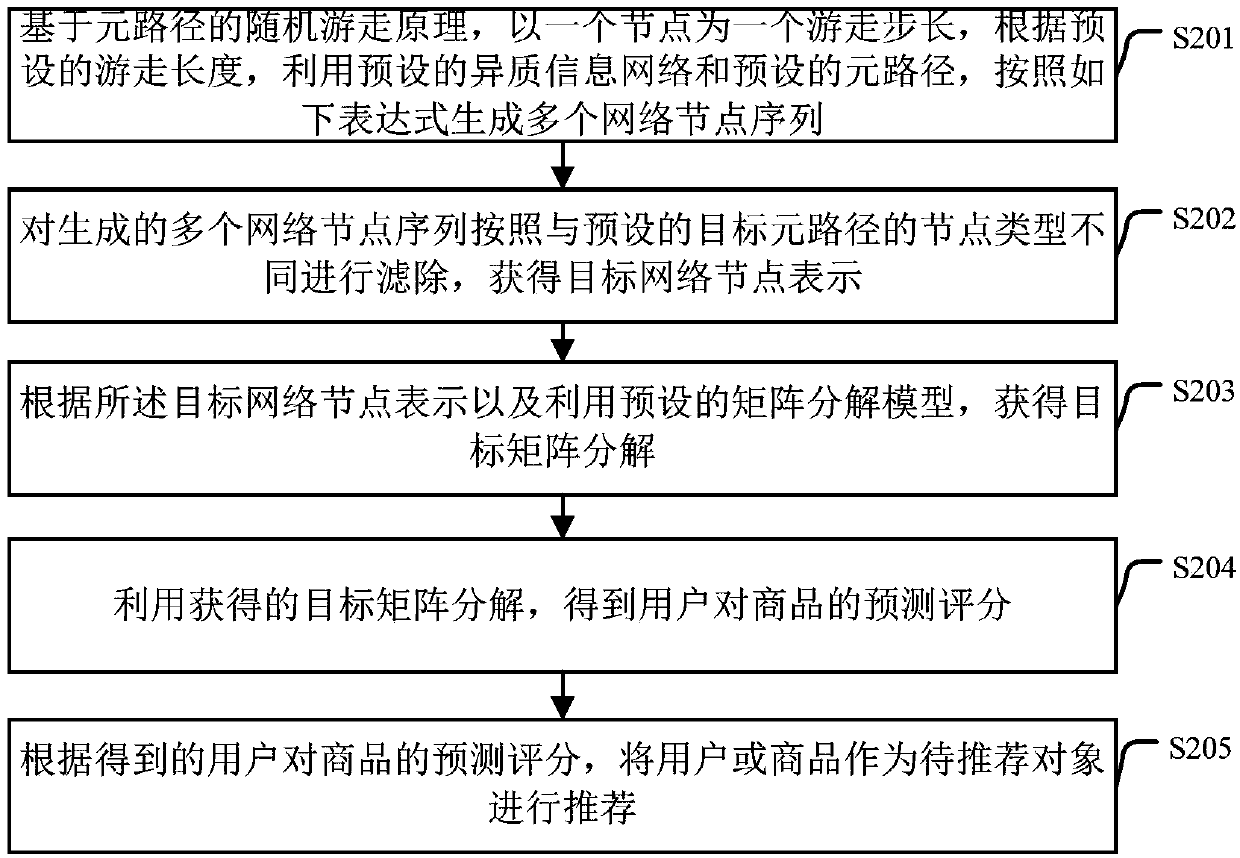
Recommendation method and apparatus based on heterogeneous information network representation
ActiveCN107944629AIncrease referral rateForecastingBuying/selling/leasing transactionsMatrix decompositionPrediction score
The embodiment of the invention provides a recommendation method and apparatus based on heterogeneous information network representation. The method includes: extracting target network node representation from a preset heterogeneous information network; acquiring target matrix decomposition according to the target network node representation and a preset matrix decomposition model; and a prediction score of a commodity by a user is obtained by using the obtained target matrix decomposition; and according to the prediction score of a commodity by the user, the user or the commodity is used as ato-be-recommended object for recommendation. Therefore, the recommendation rate is increased.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
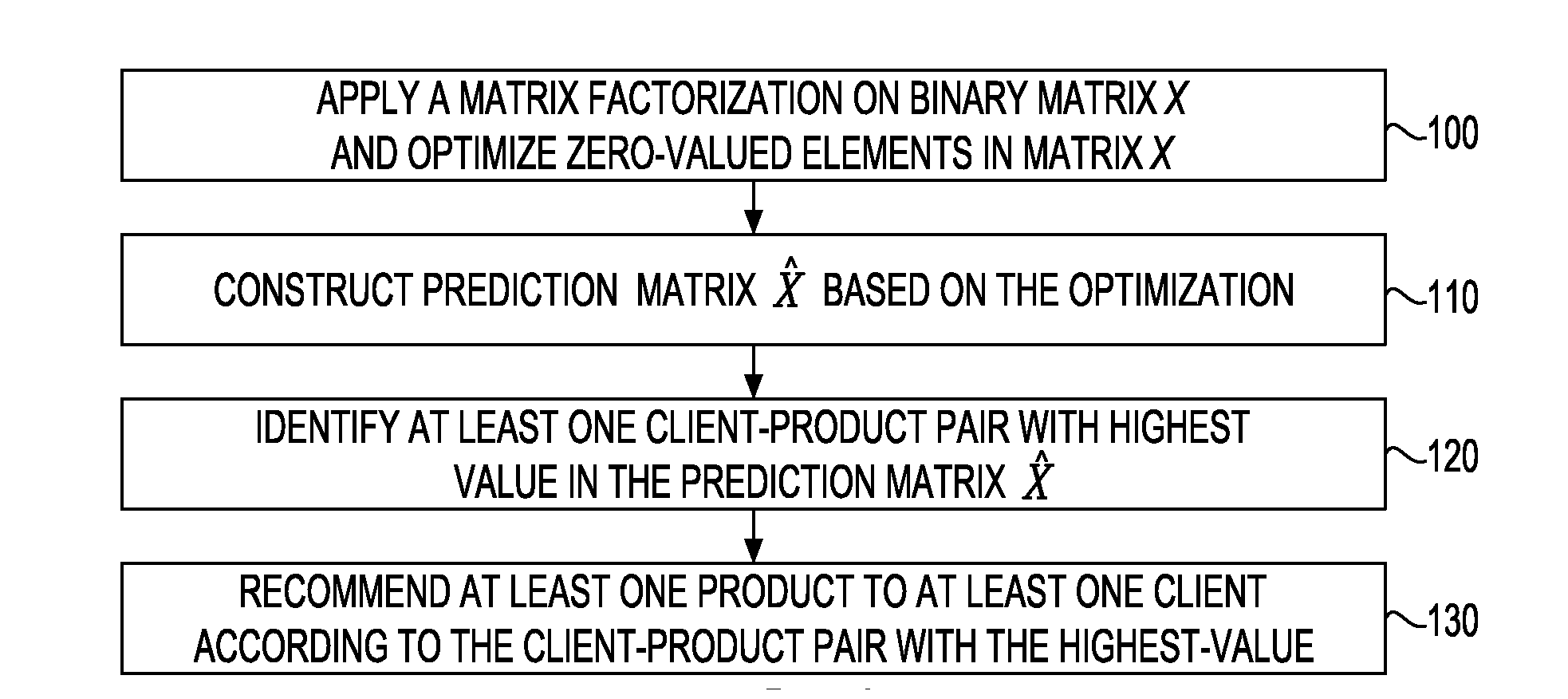
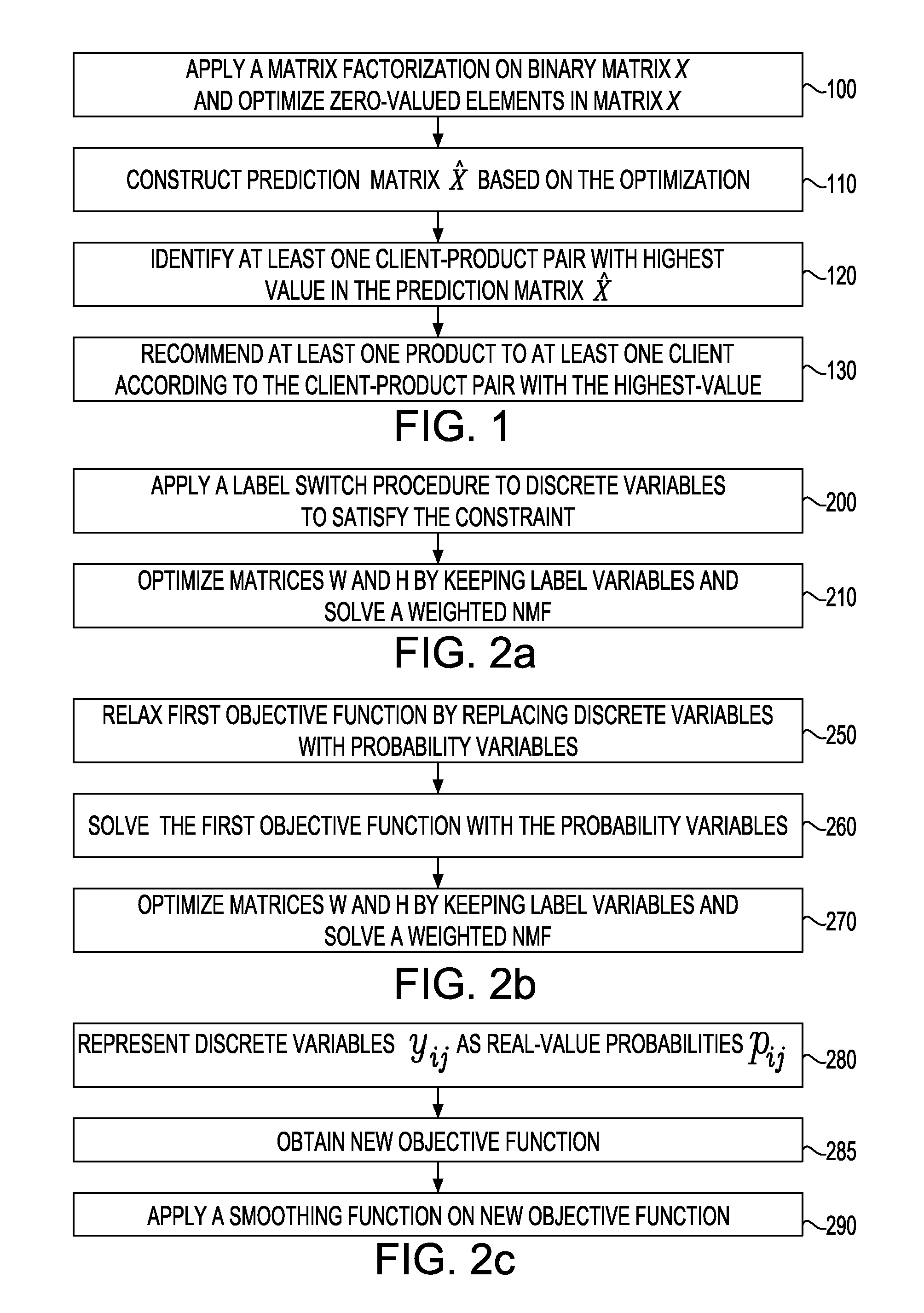
Collaborative filtering on spare datasets with matrix factorizations
A system, method and computer program product automatically present at least one product to at least one client for at least one possible purchase. The system applies a matrix factorization on a binary matrix X representing which clients purchased which products. The system optimizes zero-valued elements in the matrix X that correspond to unknown client-product affinities. The system constructs based on the optimization, a prediction matrix {circumflex over (X)} whose each element value represents a likelihood that a corresponding client purchases a corresponding product. The system identifies at least one client-product pair with the highest value in the matrix {circumflex over (X)}. The system recommends at least one product to at least one client according to the client-product pair with the highest value.
Owner:IBM CORP
Efficient and fault-tolerant distributed algorithm for learning latent factor models through matrix factorization
A method for estimating model parameters. The method comprises receiving a data set related to a plurality of users and associated content, partitioning the data set into a plurality of sub data sets in accordance with the users so that data associated with each user are not partitioned into more than one sub data set, storing each of the sub data sets in a separate one of a plurality of user data storages, each of said data storages being coupled with a separate one of a plurality of estimators, storing content associated with the plurality of users in a content storage, where the content storage is coupled to the plurality of estimators so that the content in the content storage is shared by the estimators, and estimating, asynchronously by each estimator, one or more parameters associated with a model based on data from one of the sub data sets.
Owner:PINTEREST
Social information recommendation algorithm and system based on deep network embedding feature
InactiveCN108596774AReduce test errorImprove accuracyBuying/selling/leasing transactionsResourcesMatrix decompositionDeep level
The invention discloses a social information recommendation algorithm and system based on a deep network embedding feature. A network embedding model is trained on the social network of a user in advance to extract network feature representation of the user, the extracted network feature is integrated into a matrix decomposition model; and a final generated model is used for score prediction and project recommendation. The social information recommendation algorithm and system based on the deep network embedding feature in the invention can not only make in-depth use of the social network information, but also can use a collaborative filtering model for recommendation as well as have better information recommendation accuracy and convergence.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Failure analysis method for numerically-controlled machine tool
InactiveCN103870659AFault transfer relationship is intuitive and profoundVarious methodsSpecial data processing applicationsNumerical controlMatrix decomposition
The invention discloses a failure analysis method for a numerically-controlled machine tool. The failure analysis method overcomes the defects that in the prior art, failure relevance is not considered in machine tool failure analysis. A DEMATEL-ISM method is integrated, related failure statistics data are combined, failure correlation between subsystems is taken into consideration, a digraph and matrix operations are applied to obtain a comprehensive influence matrix between the subsystems and relevancy, an overall influence matrix and a reachable matrix are obtained through the comprehensive influence matrix between the subsystems, and the reachable matrix is decomposed so that a multilevel hierarchical structure model can be obtained. The relevancy and the multilevel hierarchical structure model are synthesized to obtain a numerically-controlled machine tool key subsystem; possible failure modes of components of the key subsystem and influences of the failure modes on operation of a numerically-controlled machine tool are determined by means of FMECA technical analysis, a single point of failure is found, and perniciousness of the failure modes is determined according to the severe degree of the failure modes and the probability of occurrence of the failure modes.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
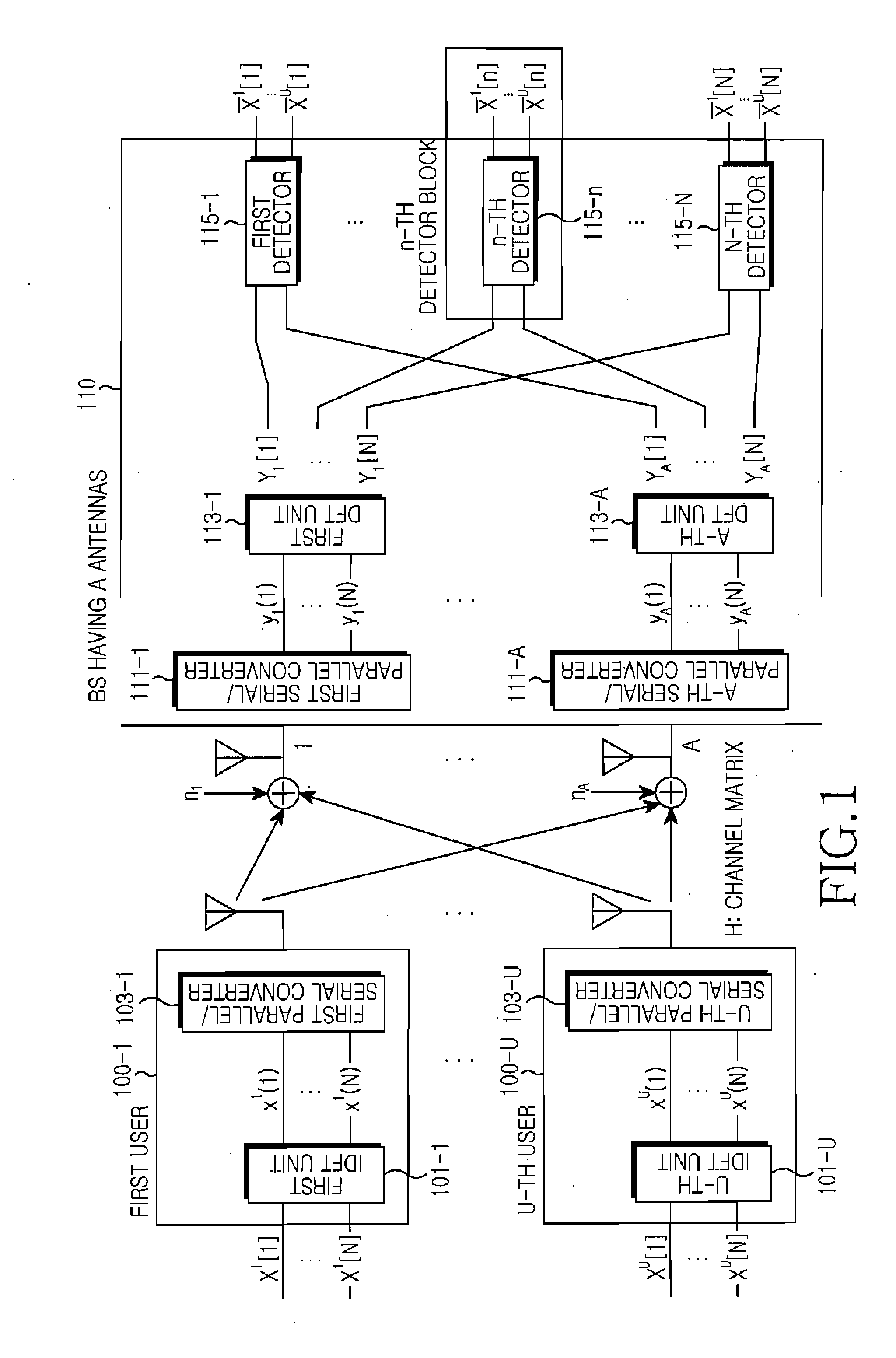
Apparatus and method for detecting signal in multi-input multi-output system
InactiveUS20070291882A1Low computing complexityImprove performancePolarisation/directional diversityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsMulti inputMatrix decomposition
A signal detection apparatus and method using a modified stack algorithm in a Multi-Input Multi-Output (MIMO) system are provided. The signal detection method includes sorting signals received via antennas and channel coefficients for respective users in descending order, decomposing a channel matrix composed of the sorted channel coefficients into a unitary matrix and an upper-triangular matrix, determining the number of candidate symbol-sequences using the decomposed upper-triangular matrix, obtaining a signal vector for the antennas by using the sorted signals received via respective antennas and the unitary matrix, wherein the signal vector is proportional to the upper-triangular matrix, and detecting the determined number of candidate symbol-sequences by using a modified stack algorithm while expanding a stack structure for the obtained signal vector.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Smooth symmetrical surface rebuilding method based on single image
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
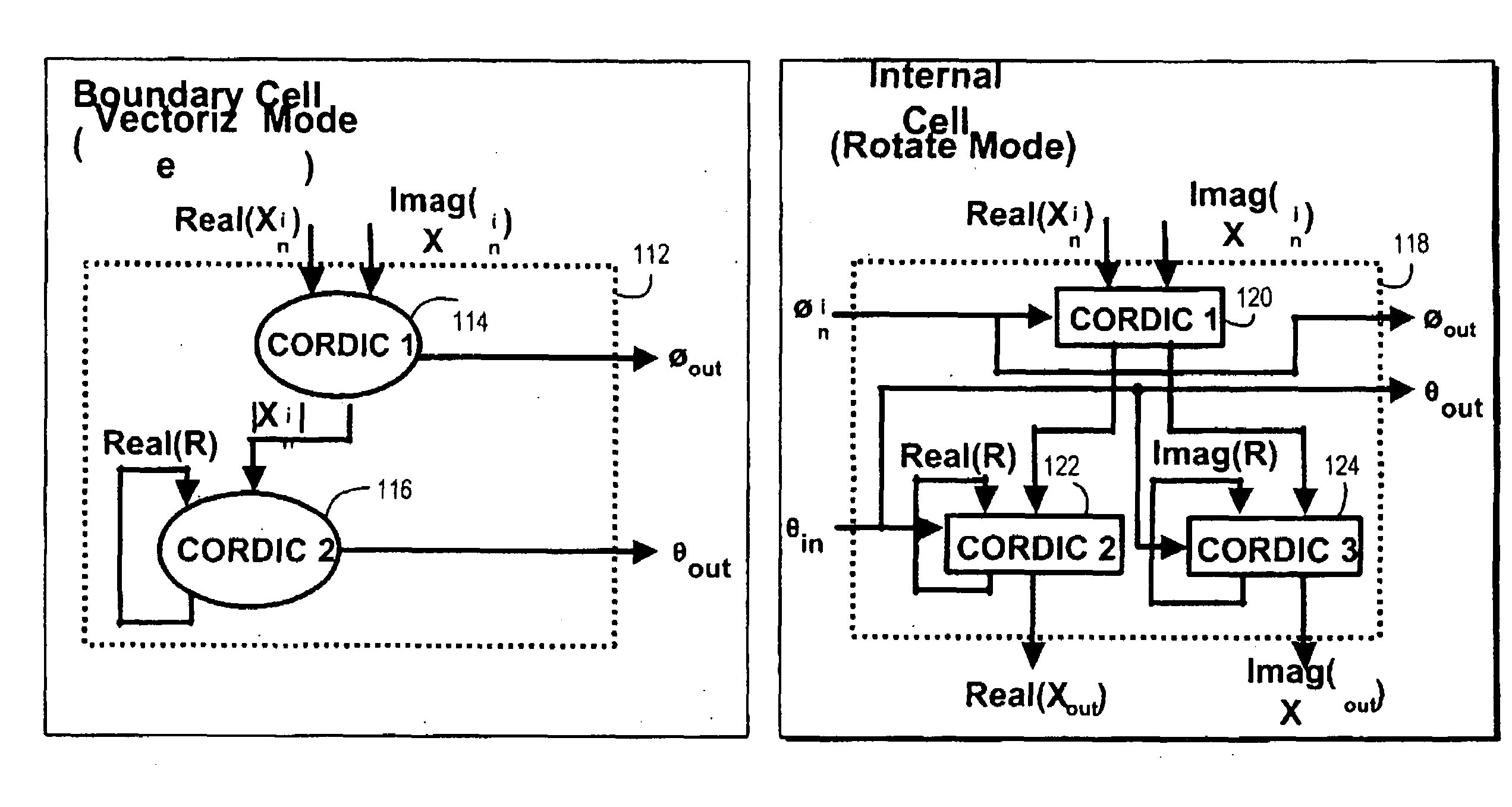
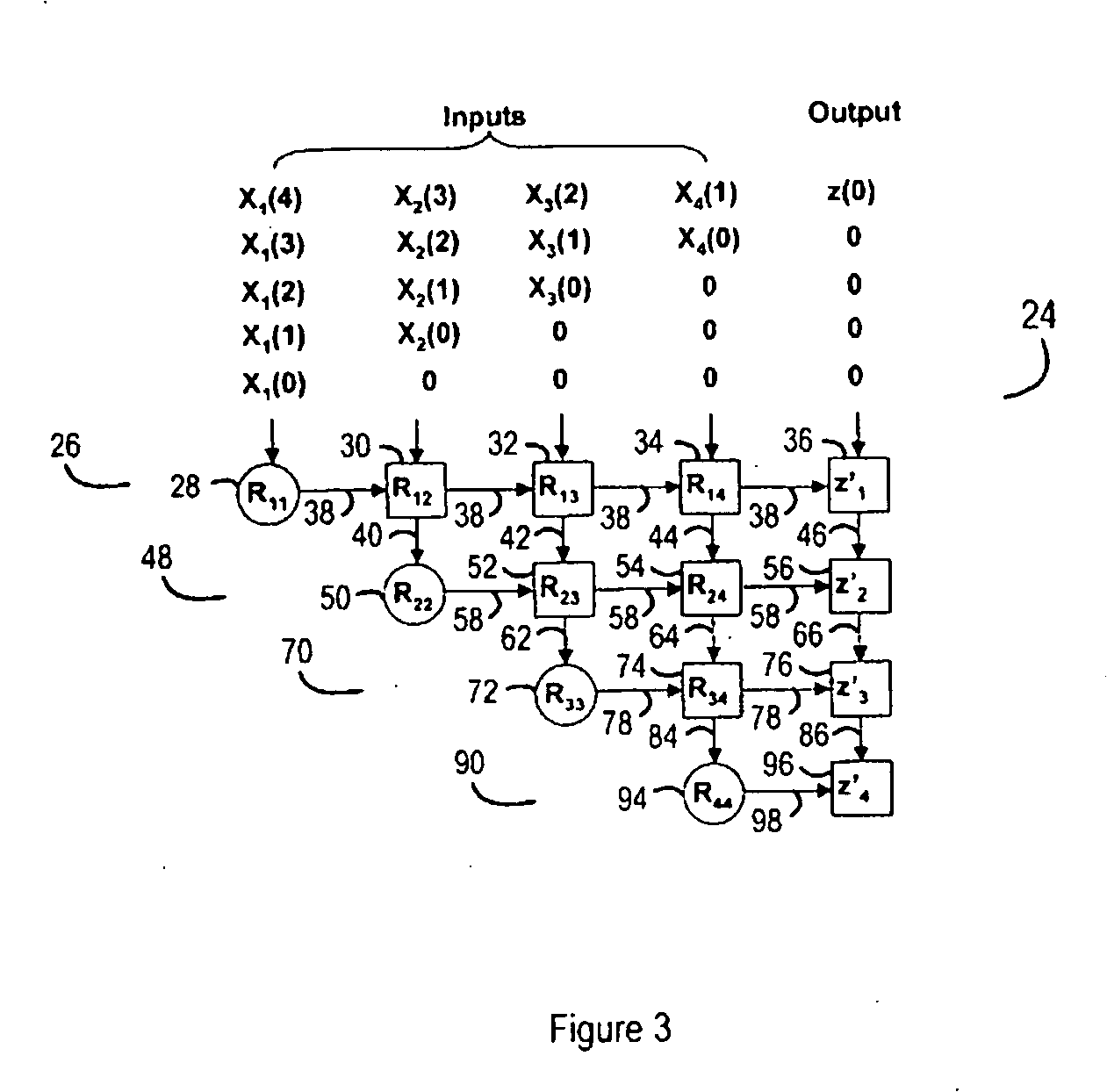
Method and apparatus for matrix decomposition in programmable logic devices
InactiveUS20090240917A1Program control using stored programsGeneral purpose stored program computerMatrix decompositionQR decomposition
A processor is adapted for performing a QR-decomposition. The processor has a program memory, a program controller, connected to the program memory to receive program instructions, and at least one processing unit. The processing unit includes a CORDIC calculation block, and has a distributed memory structure, with separate memory blocks for storing respective parameter values.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
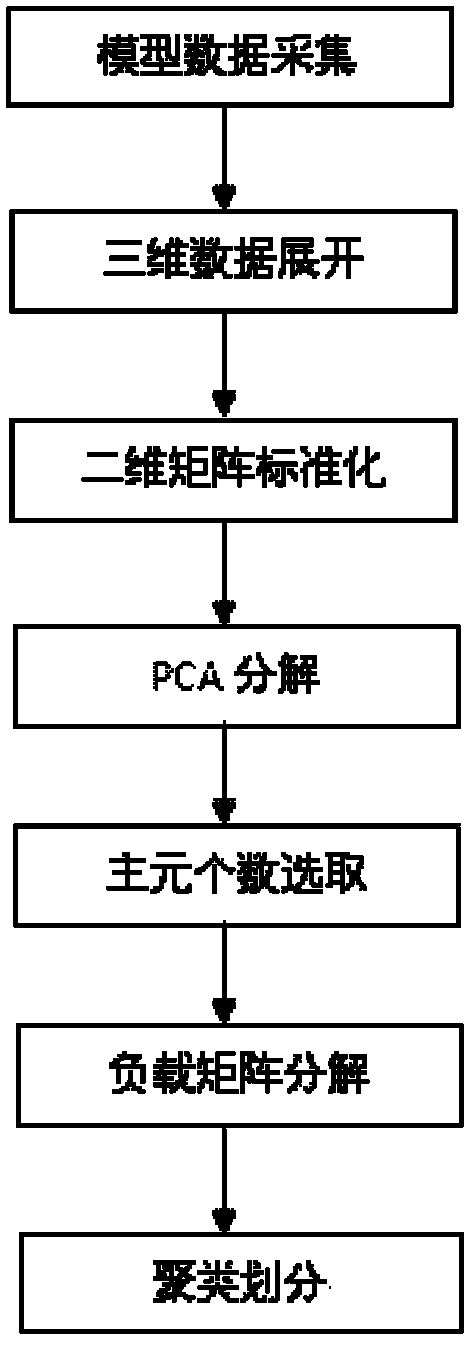
Multi-phase batch process phase dividing method based on multiway principal component analysis method
The invention relates to a multi-phase batch process phase dividing method based on a multiway principal component analysis method, which comprises the following steps: model data acquisition, three dimensional data expansion, two dimension matrix standardization, PCA decomposition, principal component number selection, load matrix decomposition and K-means cluster analysis. The method firstly uses a load matrix of a multiway principal component analytical method model to identify process phase according to timeslice sequence through decomposition deformation, thereby the misunderstanding that the multiway principal component analytical method is not suitable for the multi-phase batch process modeling in the traditional theory is solved. The method not only extracts cross correlation of variable on each timeslice, and simultaneously extracts the self dynamic change characteristic of measure variable in the whole batch at each sampling time for identifying the phase, thereby improving the monitoring efficiency during monitoring process and the accuracy of fault diagnosis result, and providing a new possibility for multi-phase process phase dividing under the condition without process prior knowledge.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HKUST FOK YING TUNG RES INST
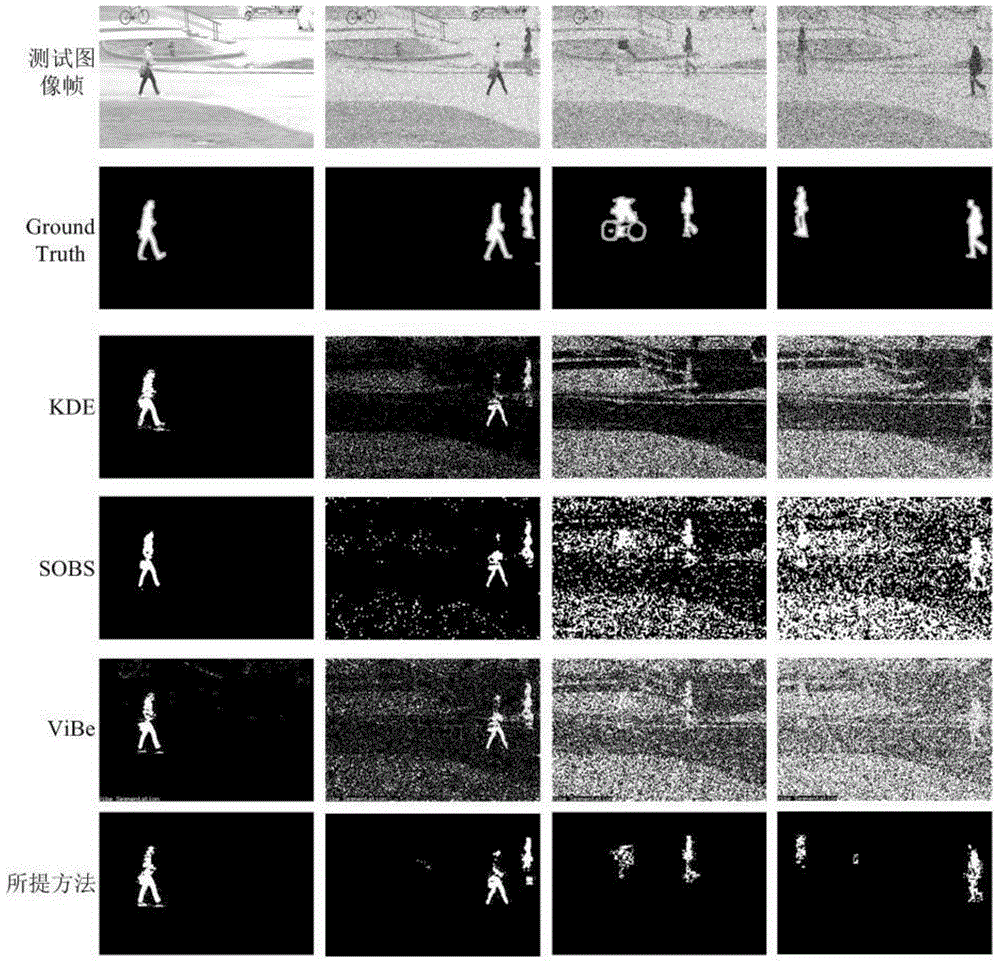
Noise-resistant moving target detection algorithm based on low rank matrix
ActiveCN104599292AImprove robustnessProven Noise ImmunityImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionMatrix decomposition
The invention relates to the field of digital image processing, in particular to an algorithm for utilizing similarity of a continuous video frame to conduct matrix decomposition under low rank restraint to obtain a noise robustness foreground detection result under the condition that an image sequence is polluted by noise signals. By means of the similarity of the continuous image frame in the video, the low rank features of the video matrix are obtained. A convex optimizing method is utilized to excavate the low rank features in the video matrix, and the low rank structure and the sparse error structure of the original video matrix are acquired gradually through iteration optimization. The low rank structure corresponds to a background model in the moving target detection problem, and the sparse error portion corresponds to the moving foreground in the moving target detection problem.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Color unmixing and region of interest detection in tissue samples
InactiveUS7689023B2Acquiring/recognising microscopic objectsImage data processingPattern recognitionMatrix decomposition
In a method and system and machine-readable medium, colors in an image (200) are unmixed (202) using a matrix X=AS, where A is a ns. ×nd matrix of spectral definitions, where ns is the number of spectral components and nd is the number of dyes into which the image is decomposed, and where S is a nd×l matrix of amounts of each dye at every pixel, where l is the number of pixels; the matrix X is constrained for solution by an unsupervised matrix decomposition method having constraints consistent with properties of an additive color model; and nd is determined. A texture is determined to identify areas of interest. Further processing may automatically measure cell dye concentration in the determined regions of interest.
Owner:RABINOVICH ANDREW M
Cross-modal retrieval method based on collaborative matrix decomposition
ActiveCN108334574AGuaranteed SimilarityEasy to calculateSpecial data processing applicationsPattern recognitionMatrix decomposition
The invention discloses a cross-modal retrieval method based on collaborative matrix decomposition. Keeping local geometric manifold structure for an original spatial sample pair is considered; intramodal and intermodal restraints are added via graphic regular items; mAP (mean average precision) that is commonly used is used as a performance evaluation index. The intramodal similarity of samples is considered, and the intermodal similarity of the sample pair is also considered; accuracy in text-based graph retrieval and graph-based retrieval is guaranteed. The collaborative matrix decomposition technique and hash function are utilized, graphic regular items to keep intramodal and intermodal similarity are added, mutual retrieving performance is improved for text-based graph retrieval and graph-based retrieval, and the method is widely applicable to image-text mutual retrieval services in mobile devices, the internet and e-commerce.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Tonal rotors
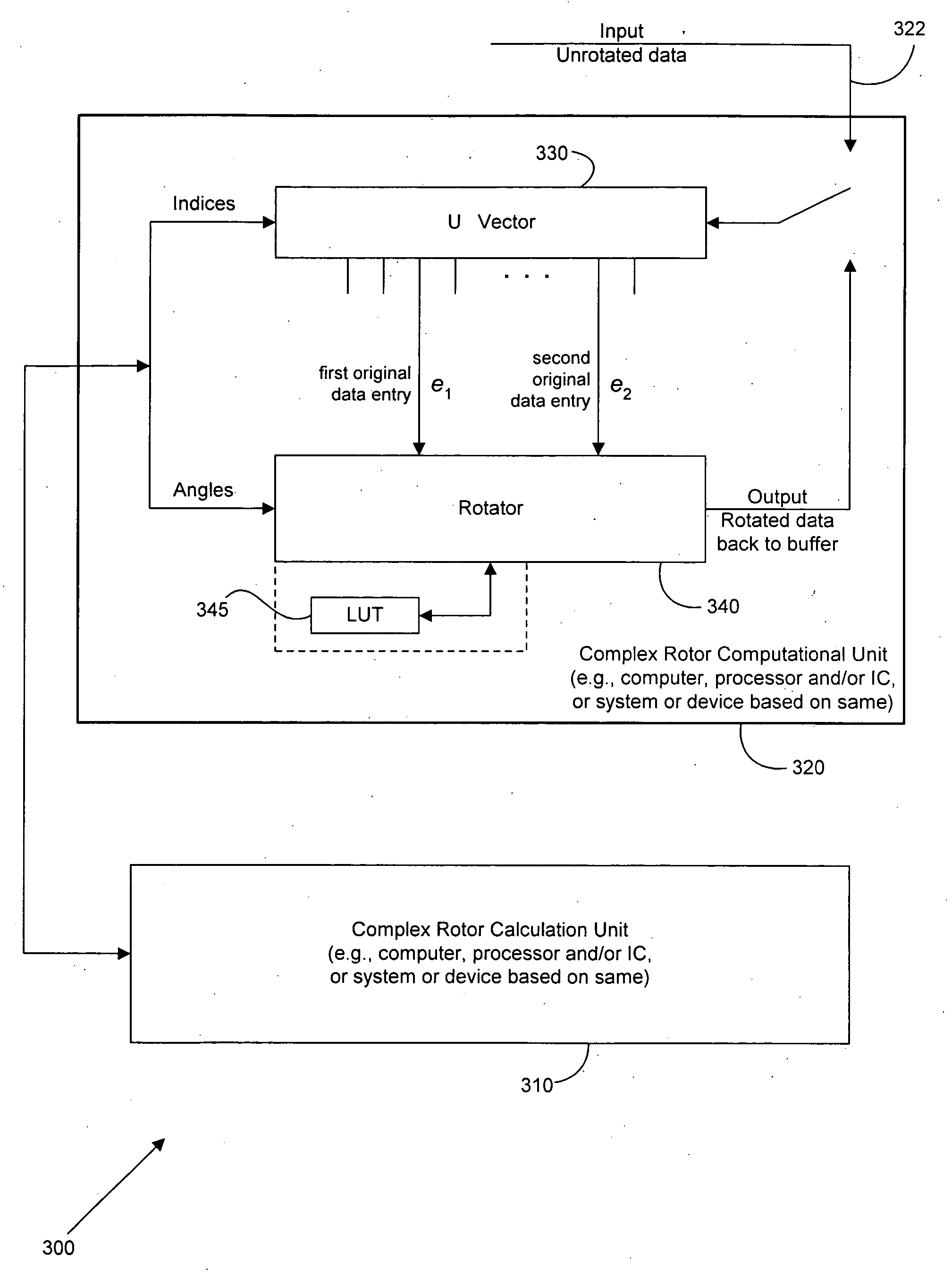
InactiveUS20060259535A1Efficient implementationSave computational complexityError preventionMultiplex communicationMatrix decompositionQ-matrix
A set of complex rotations are used to implement a unitary “Q” matrix that can arise in various transmitters and / or receivers in communication line vectoring. Each complex rotation is a set of real rotations, where the minimum number of real rotations to perform the complex rotation is three, and where the minimum number of angles to characterize the real rotations is two. An order of rotations is also provided. The invention assists in the efficient implementation of any unitary “Q” matrix in a QR or other sophisticated matrix factorization. A complex form of the so-called “Givens” implementation of the Q matrix is characterized in terms of a sequence of complex rotations that can implemented using a complex rotor computational unit that accepts a minimum of two real angles and a pair of integer indices for each of a set of successive complex rotor calculations and then implements the complex rotation as a series of a minimum of three real rotations with one real angle used twice and the other real angle used once, providing two complex outputs (that is, two rotated data entries from a data vector comprising indexed communication data) for two complex inputs (two original data entries from a data vector comprising indexed communication data). The index-angle sets for each successive rotation can be provided by a complex rotor calculation unit, which may be collocated with the complex rotor computational unit, located in a controller such as a DSL optimizer, or located in any other suitable device or apparatus that has performed the QR factorization upon supplied matrix MIMO transfer functions for the vectored channel.
Owner:ASSIA SPE LLC CO THE CORP TRUST CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com