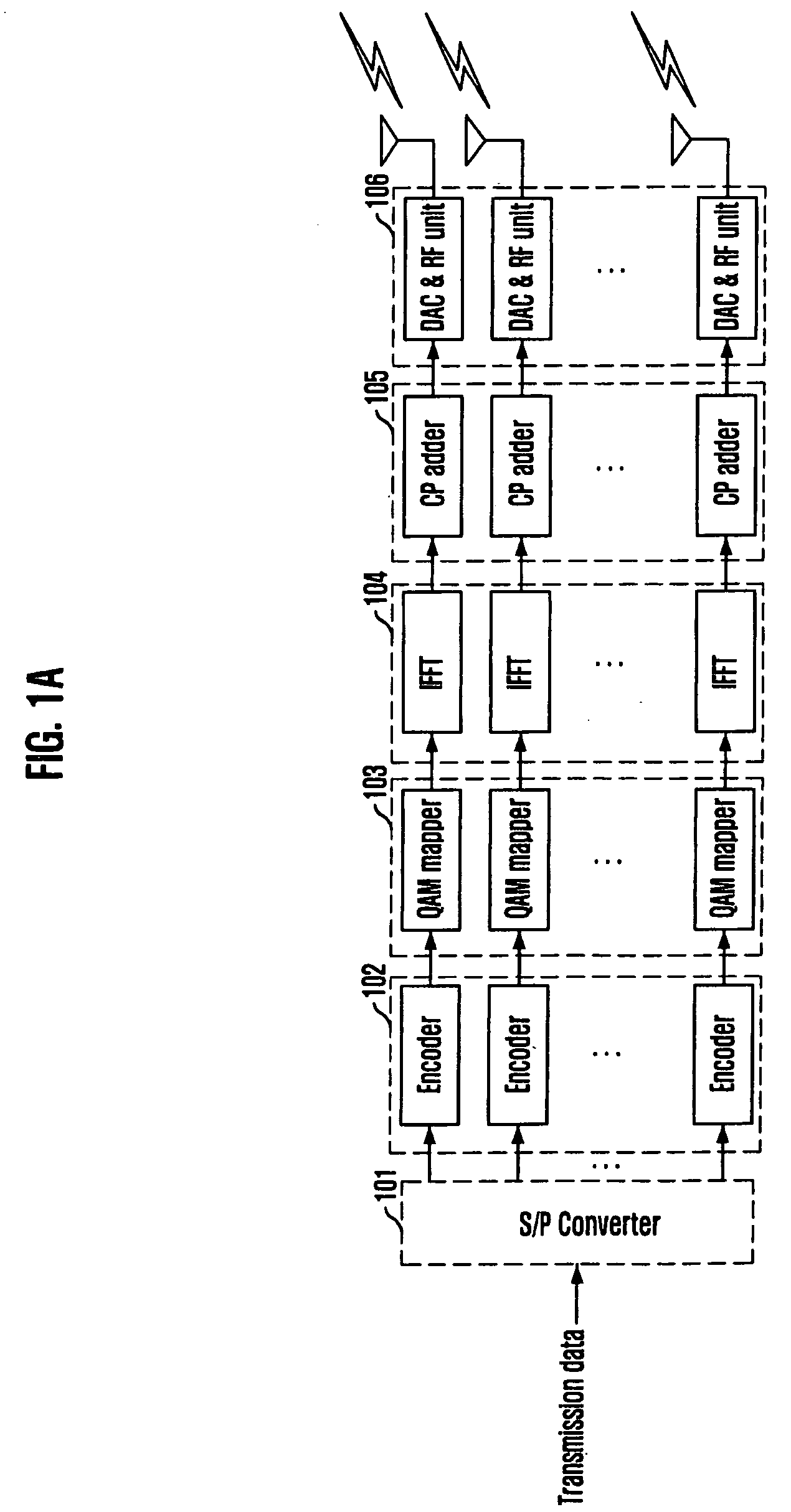
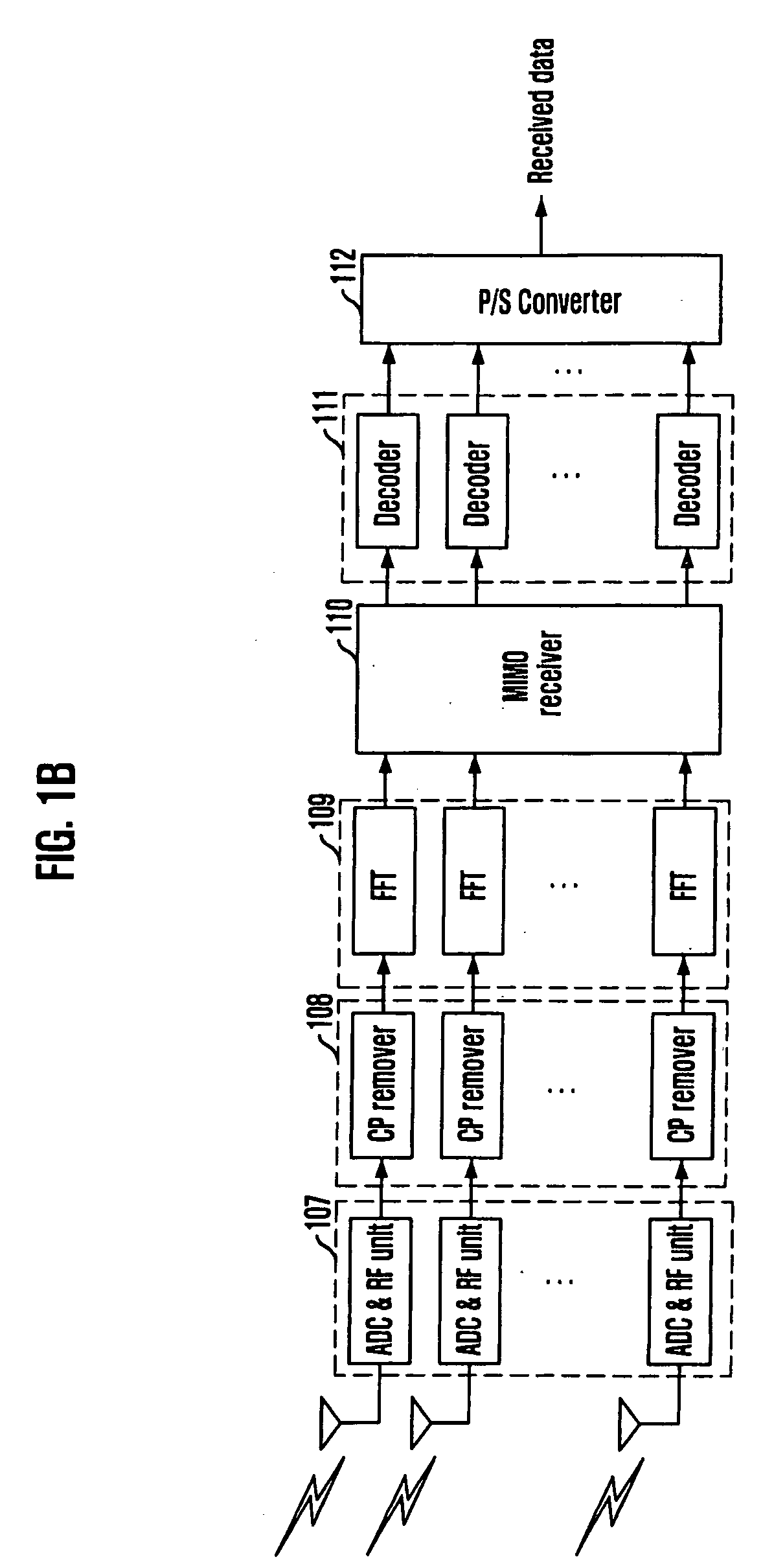
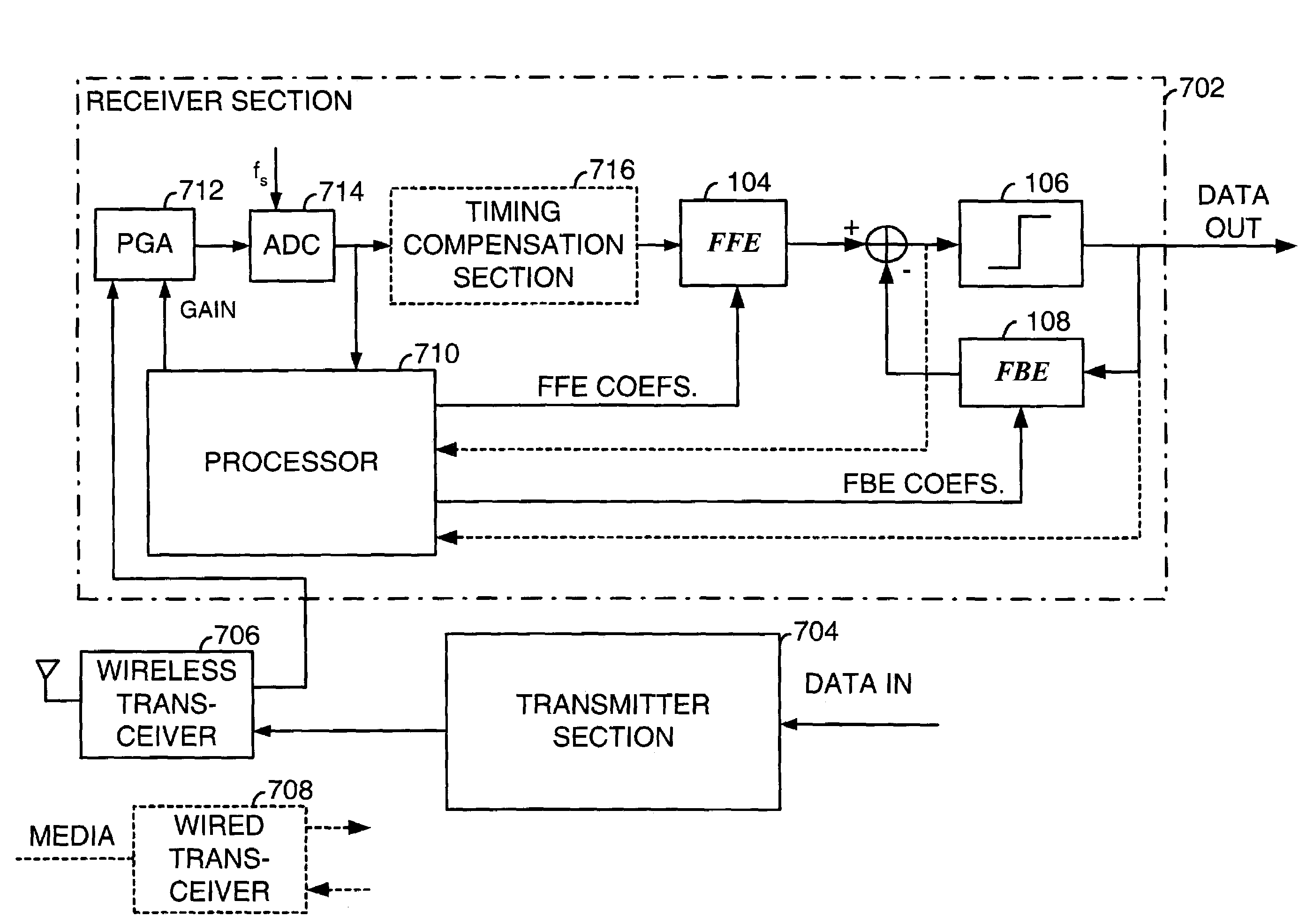
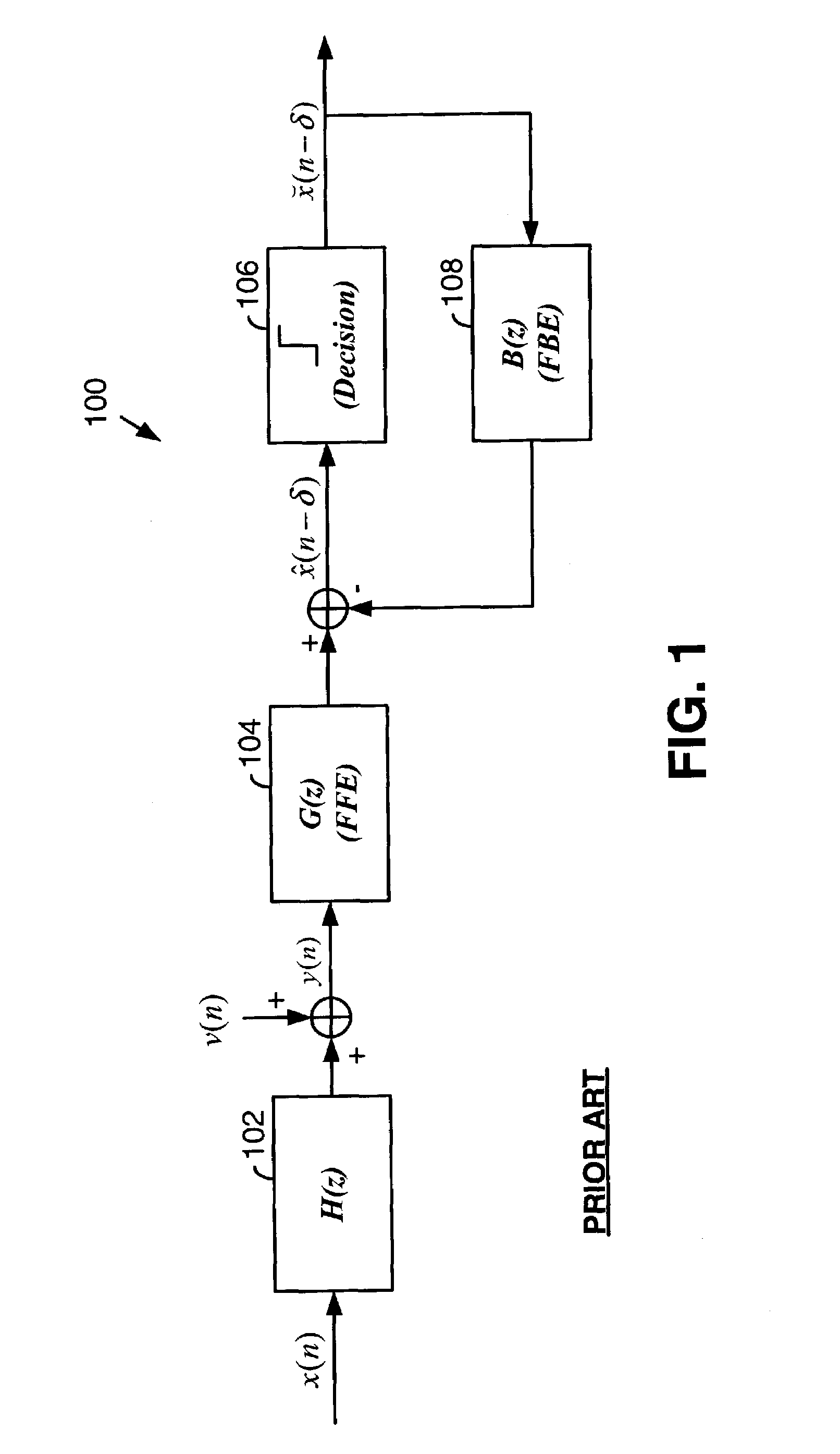
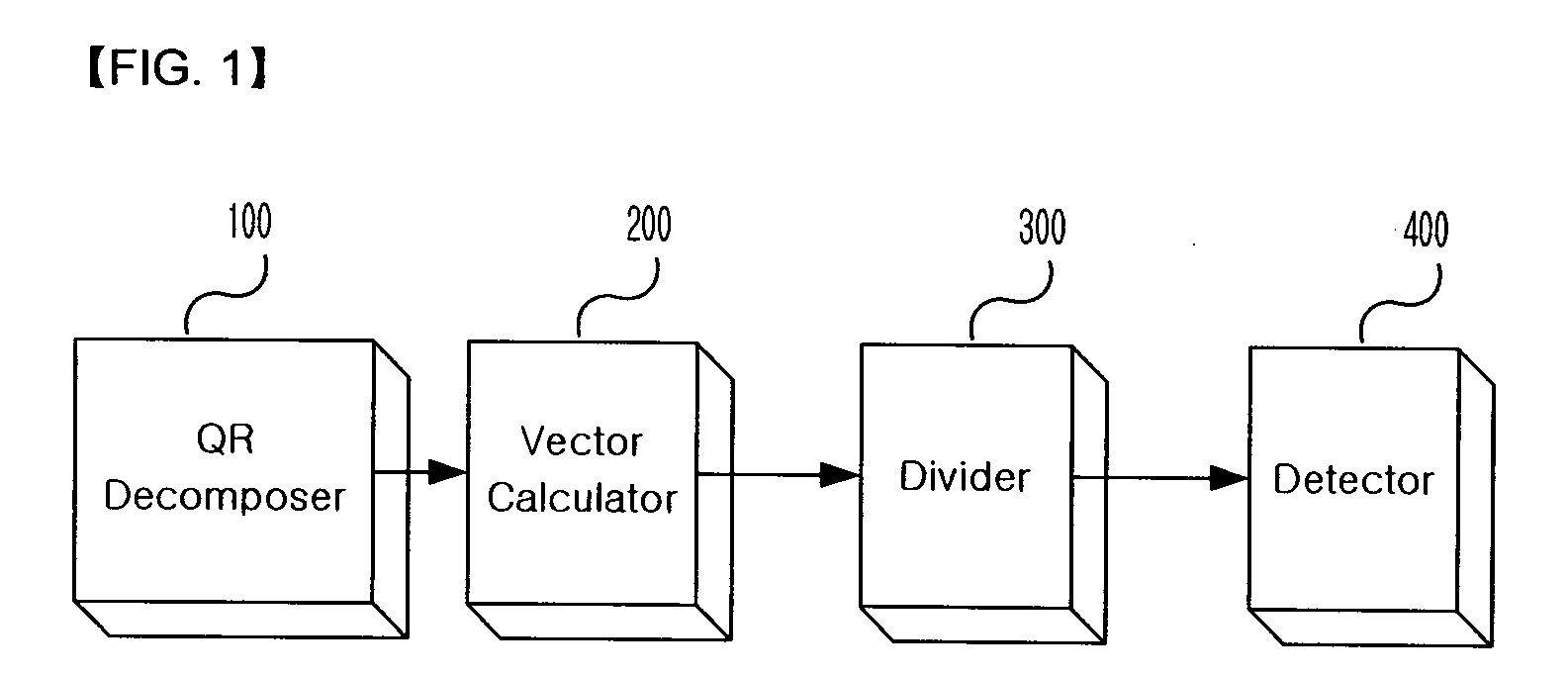
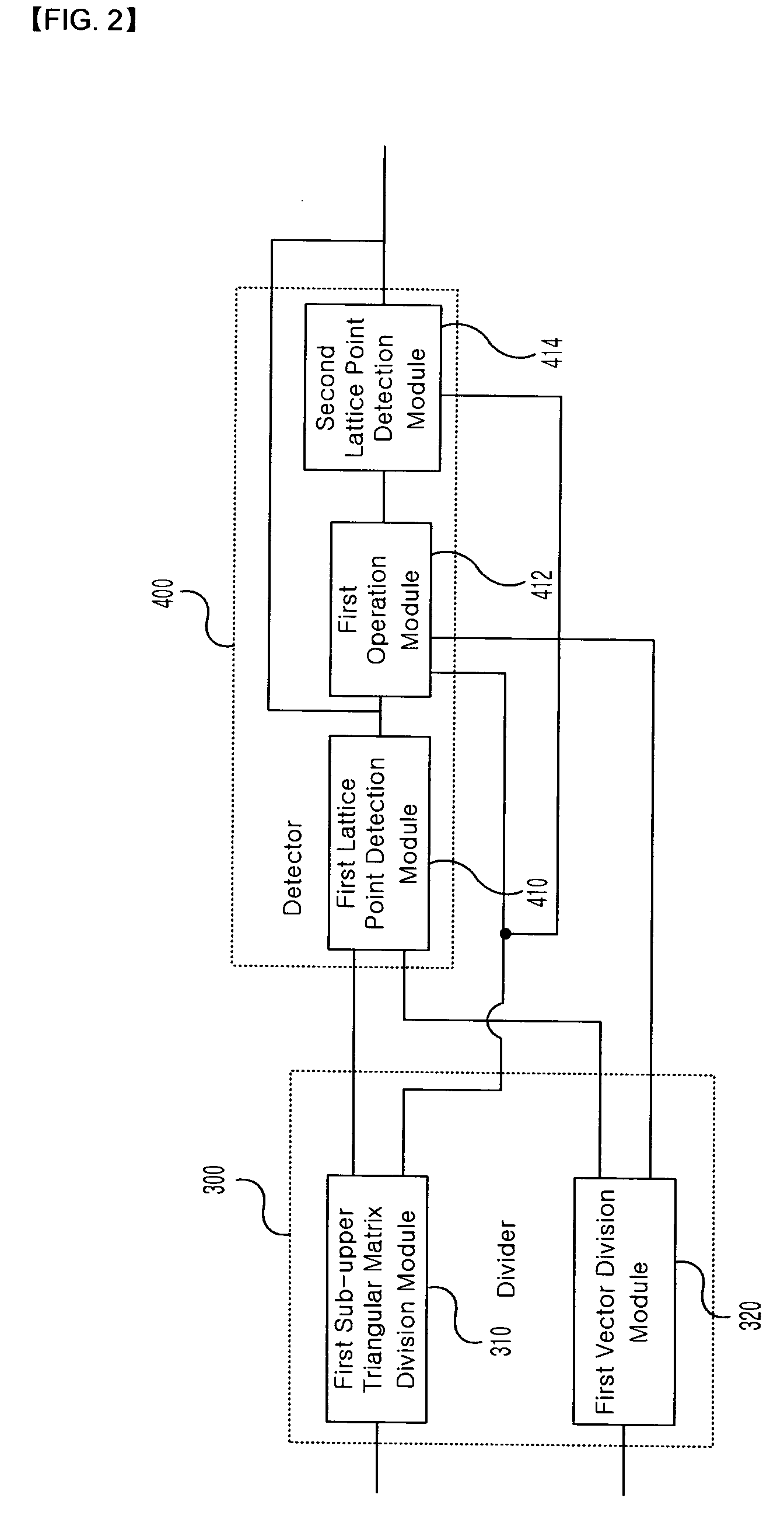
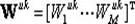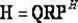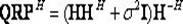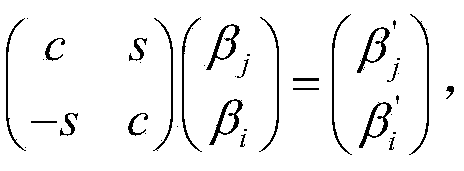Patents
Literature
372 results about "Triangular matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
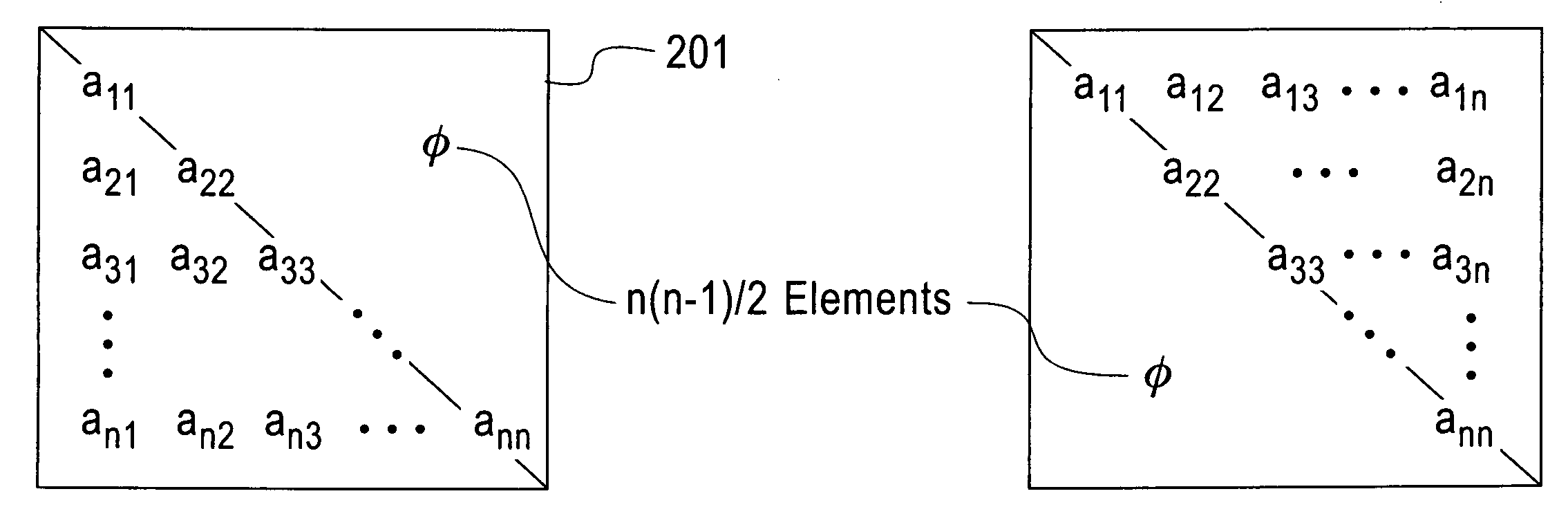
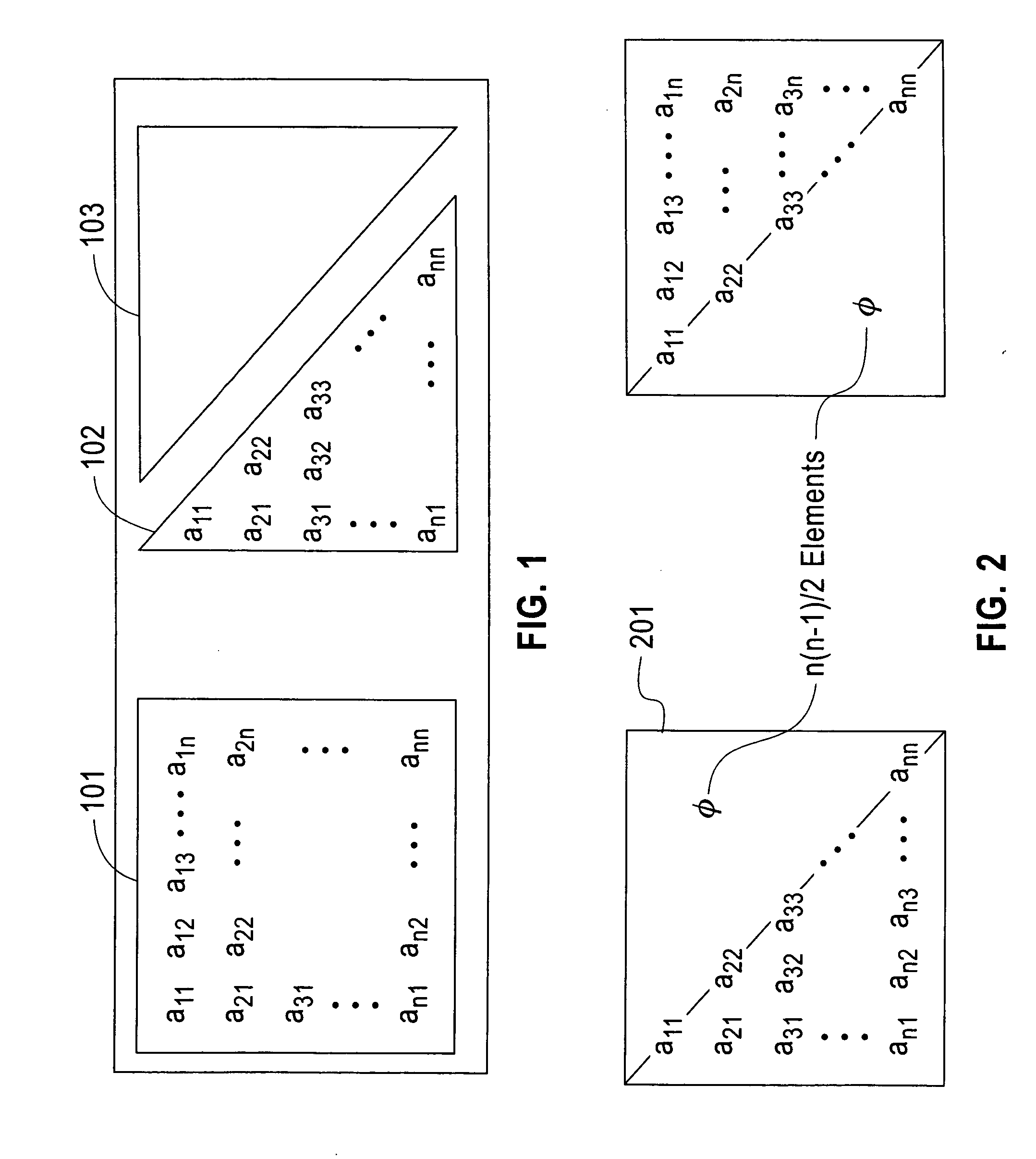
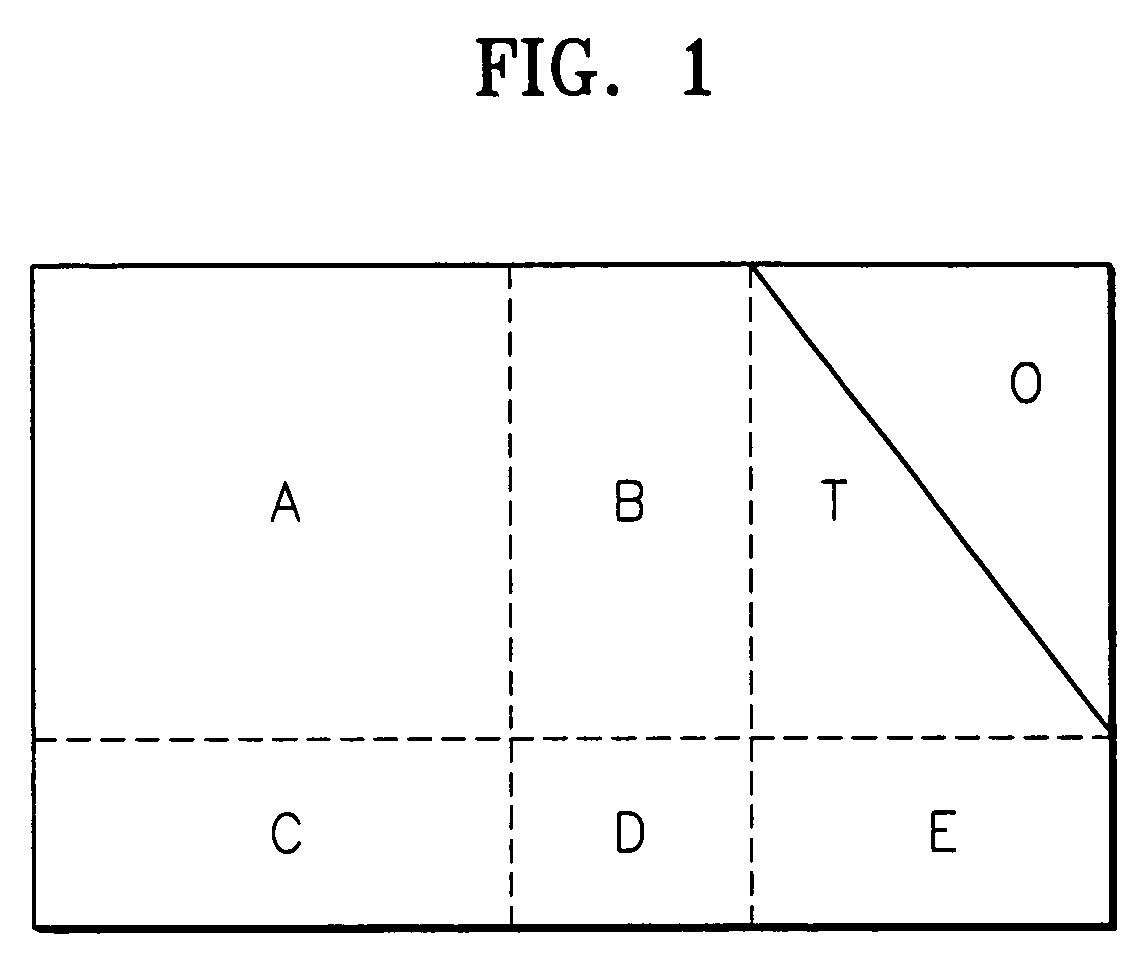
In the mathematical discipline of linear algebra, a triangular matrix is a special kind of square matrix. A square matrix is called lower triangular if all the entries above the main diagonal are zero. Similarly, a square matrix is called upper triangular if all the entries below the main diagonal are zero. A triangular matrix is one that is either lower triangular or upper triangular. A matrix that is both upper and lower triangular is called a diagonal matrix.
Method of generating matrix factors for a finite-dimensional linear transform
InactiveUS20070211952A1Character and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationPartition of unityLU decomposition
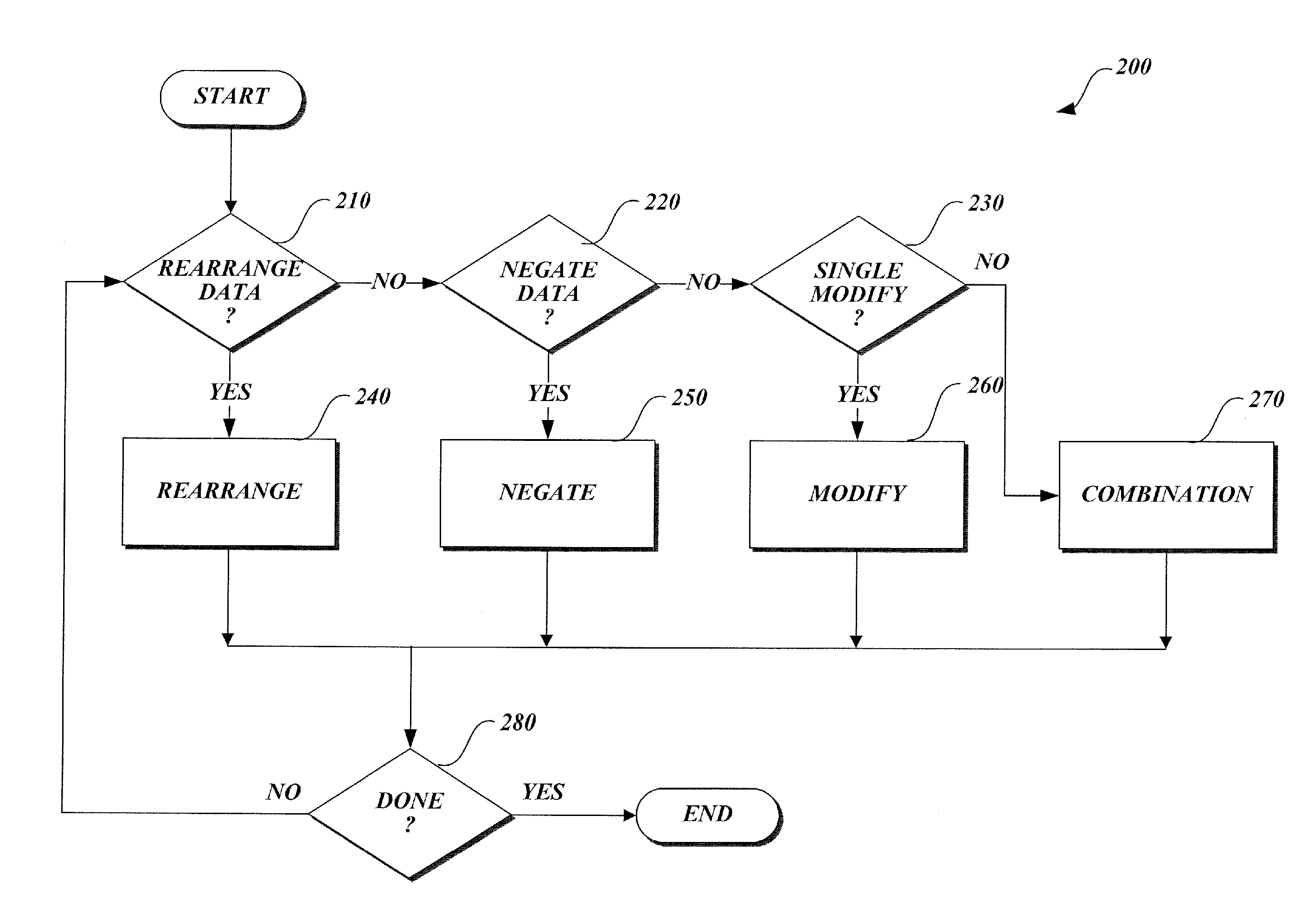
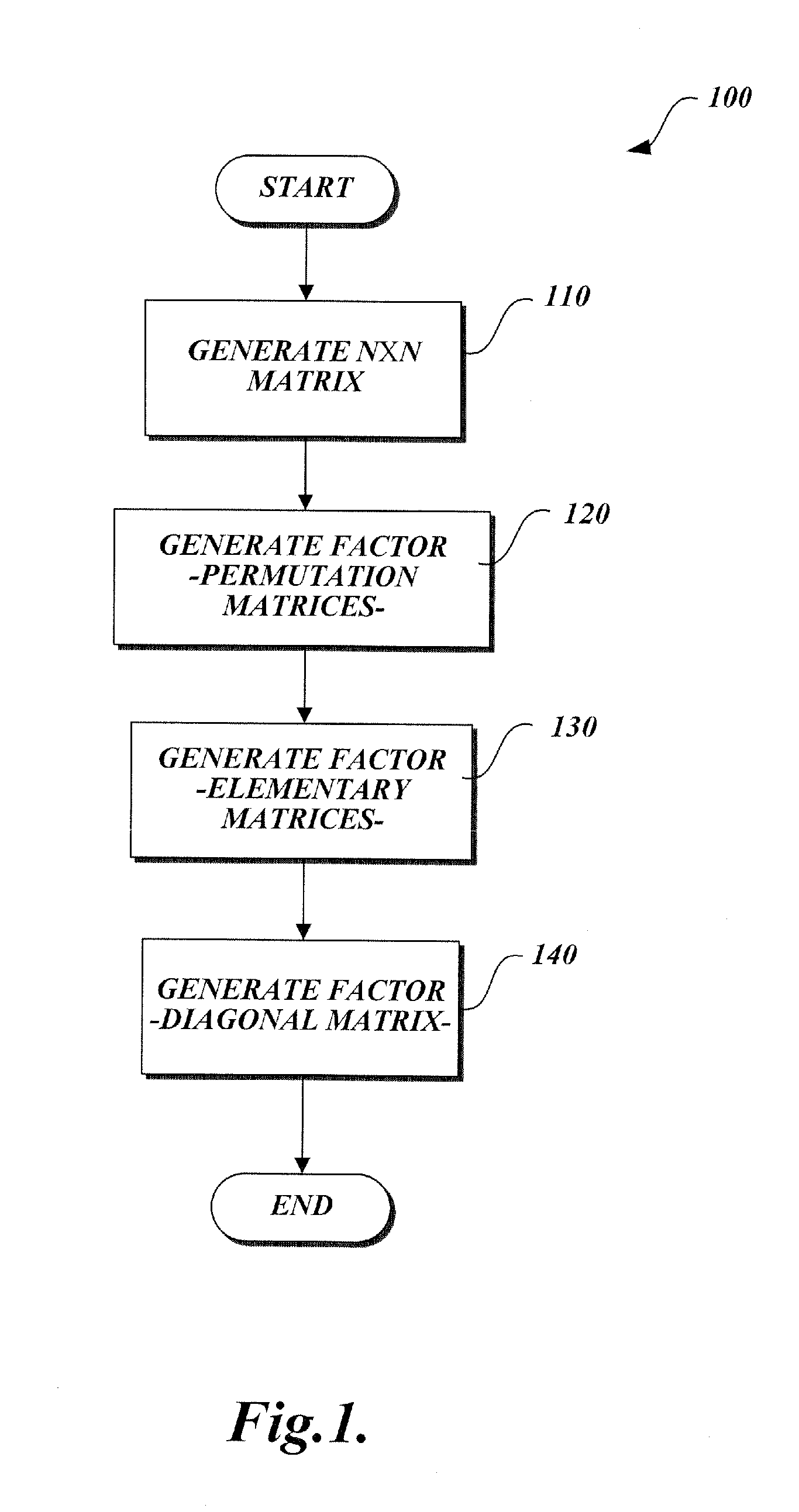
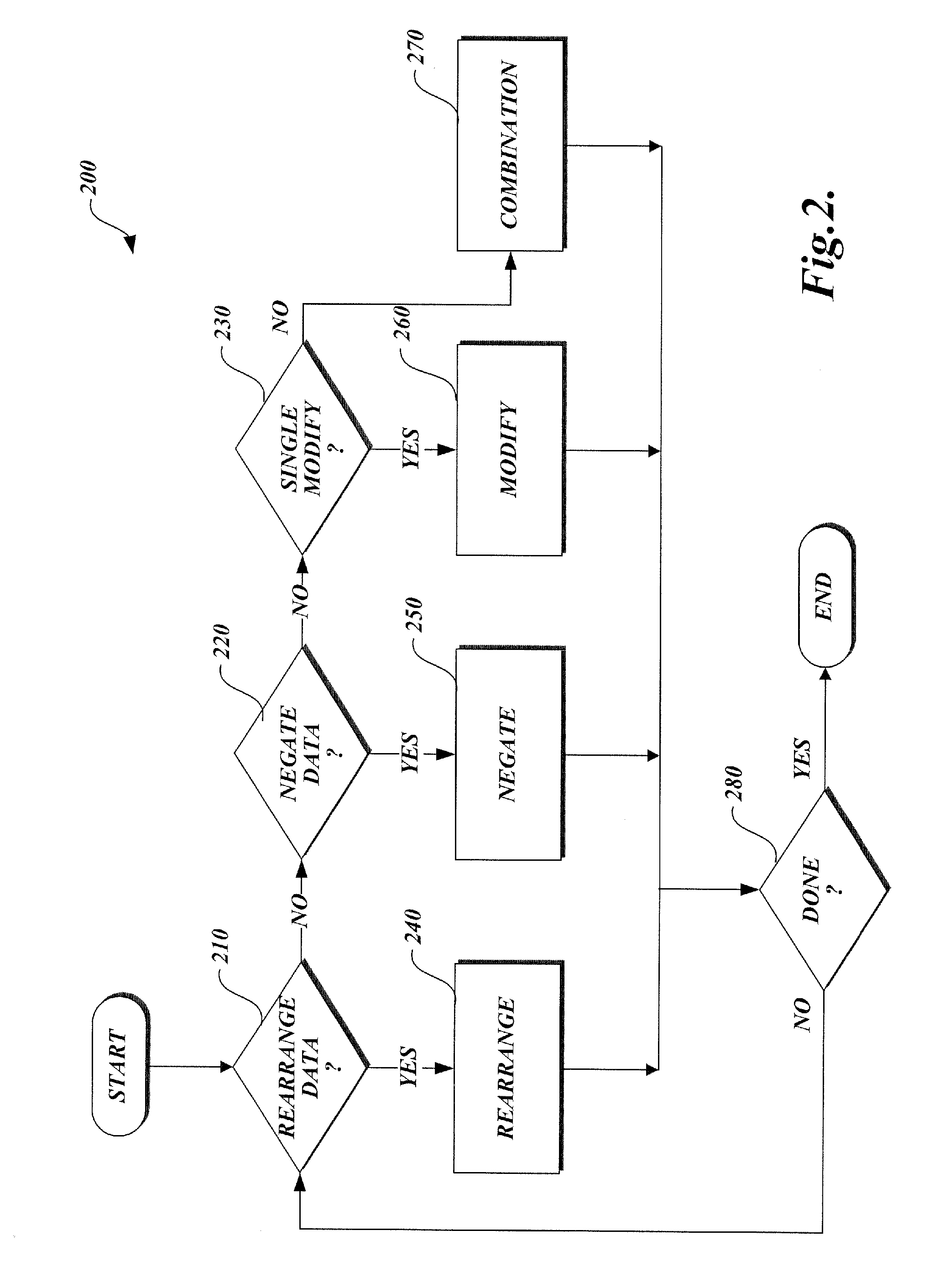
A method of generating matrix factors for a finite-dimensional linear transform using a computer. The linear transform is represented by data values stored in a linear transformation matrix having a nonzero determinant. In one aspect, a first LU-decomposition is applied to the linear transformation matrix. Four matrices are generated from the LU-decomposition, including a first permutation matrix, a second permutation matrix, a lower triangular matrix having a unit diagonal, and a first upper triangular matrix. Additional elements include a third matrix Â, a signed permutation matrix Π such that A=ΠÂ, a permuted linear transformation matrix A′, a second upper triangular matrix U1, wherein the second upper triangular matrix satisfies the relationship Â=U1A′. The permuted linear transformation matrix is factored into a product including a lower triangular matrix L and an upper triangular matrix U. The linear transformation matrix is expressed as a product of the matrix factors.
Owner:CELARTEM
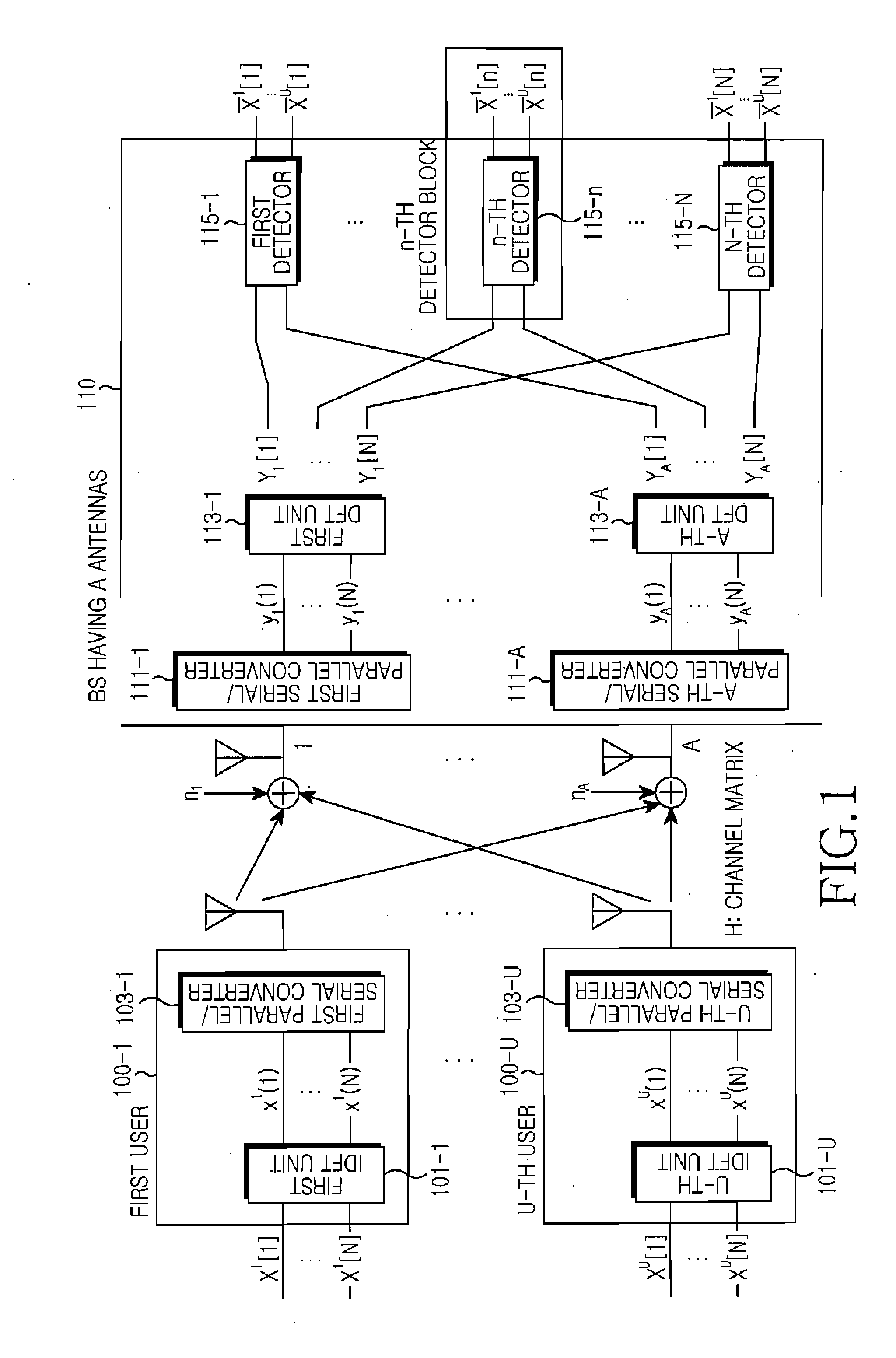
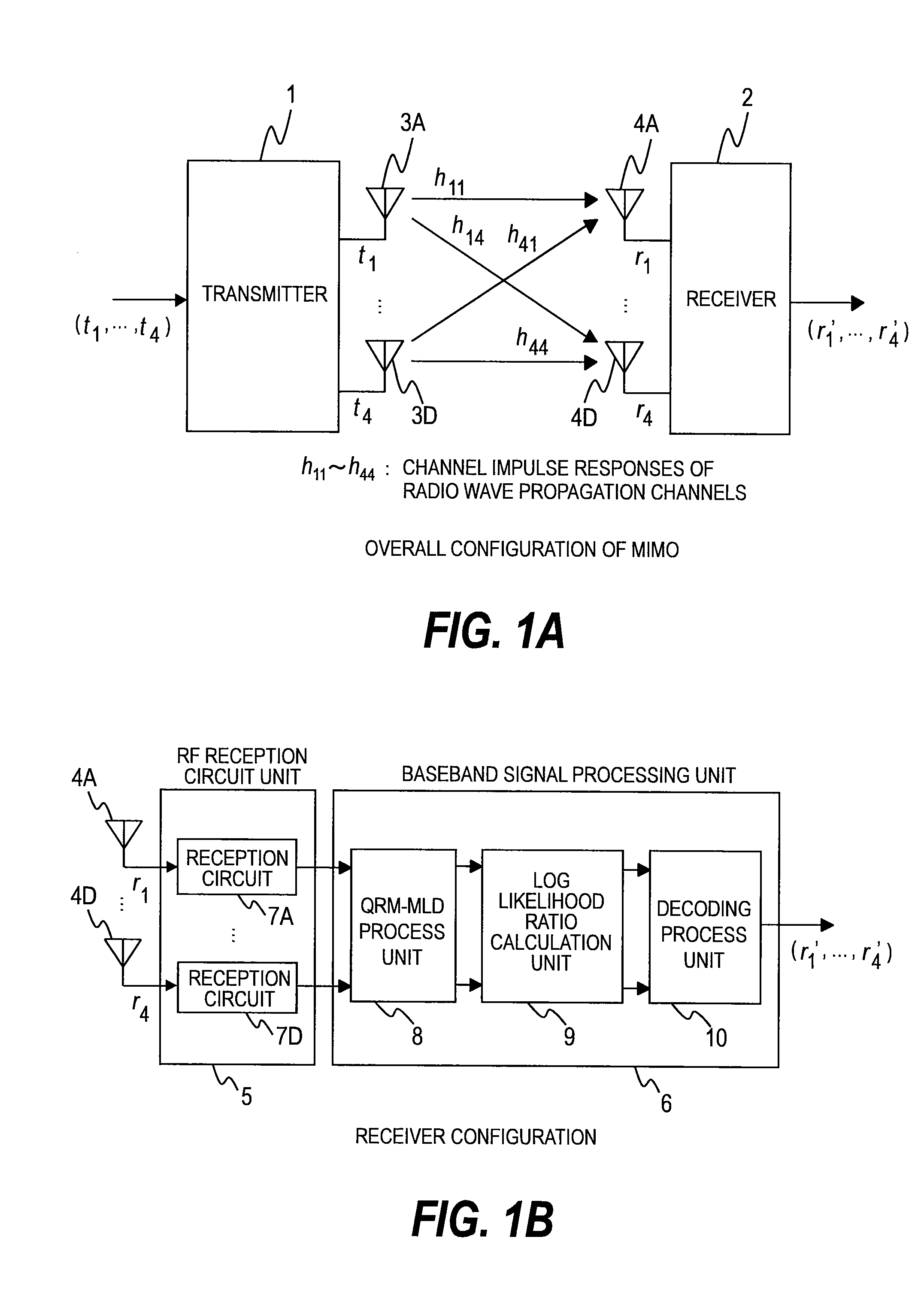
Multi-dimensional detector for receiver of MIMO system
InactiveUS20090154604A1Reduce hardware complexityImprove performanceSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityQR decompositionMulti dimensional
Provided are a multi-dimensional detector for a receiver of an MIMO system and a method thereof. The multi-dimensional detector includes a first symbol detecting unit for calculating symbol distance values using an upper triangular matrix (R) obtained from QR decomposition to detect an mth symbol; a symbol deciding unit for deciding a symbol having a minimum distance value among the calculated symbol distance values from the first symbol detecting unit; and a second symbol detecting unit for calculating symbol distance values using an updated received signal y and the upper triangular matrix R to detect a (m−1)th symbol.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
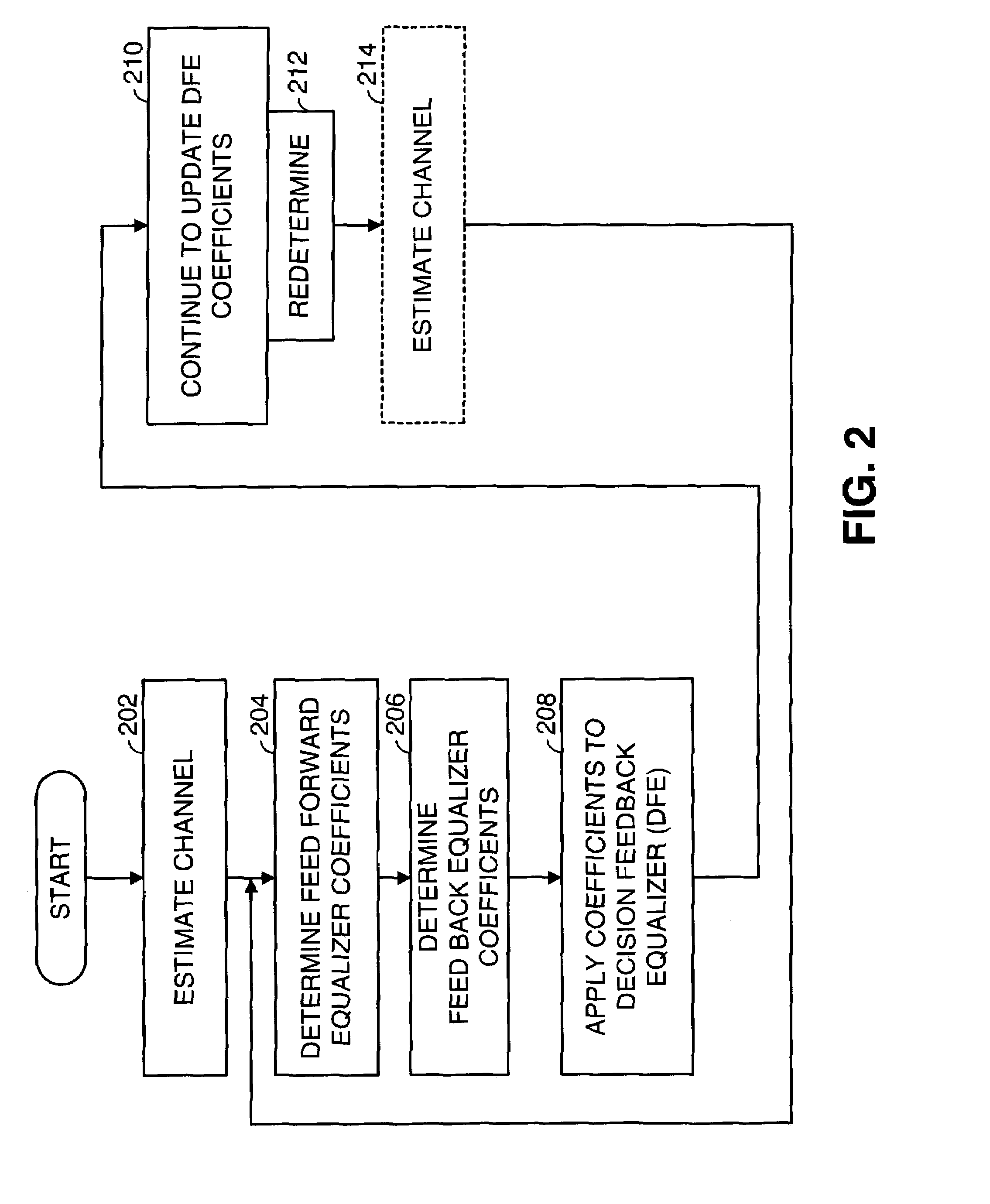
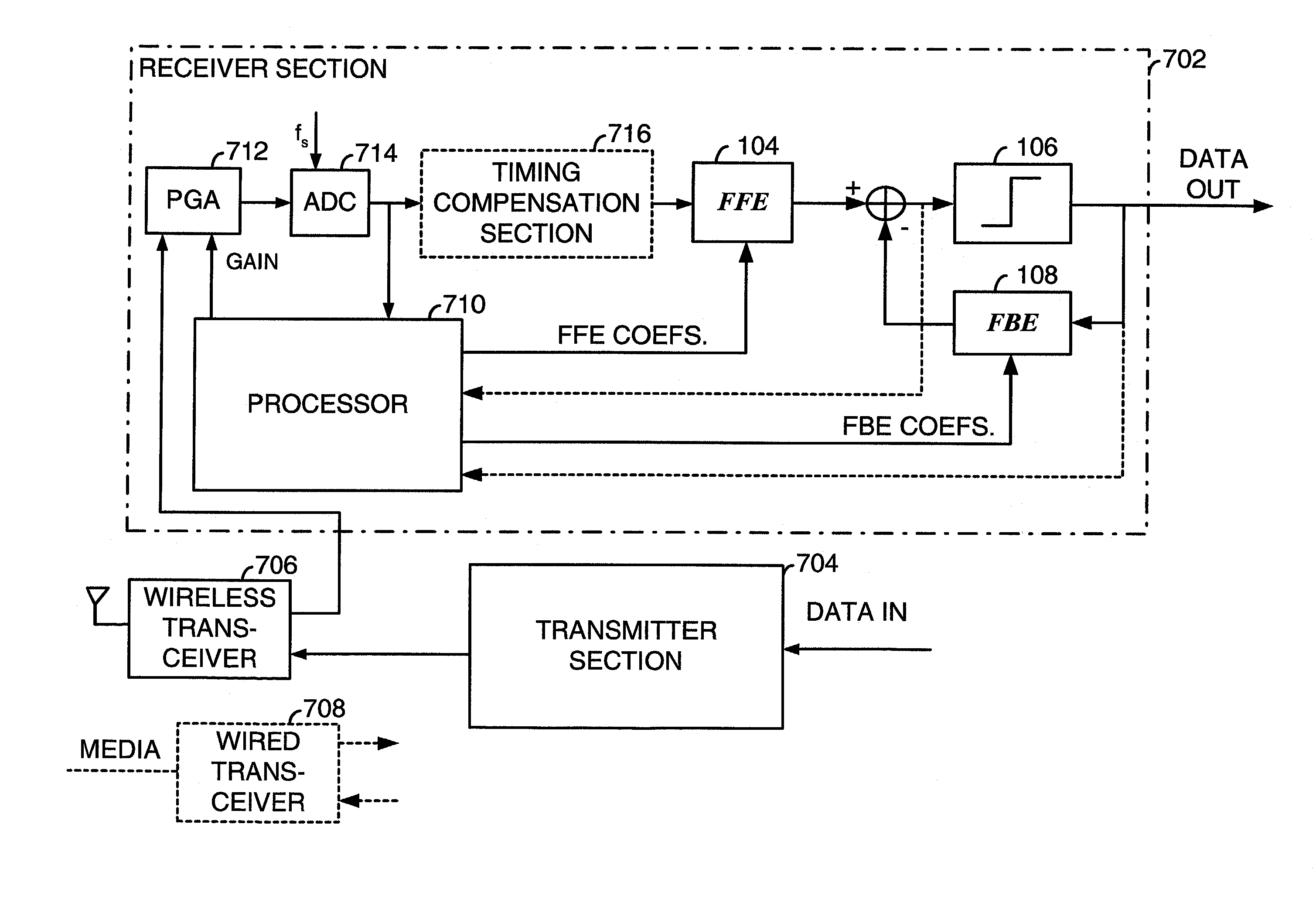
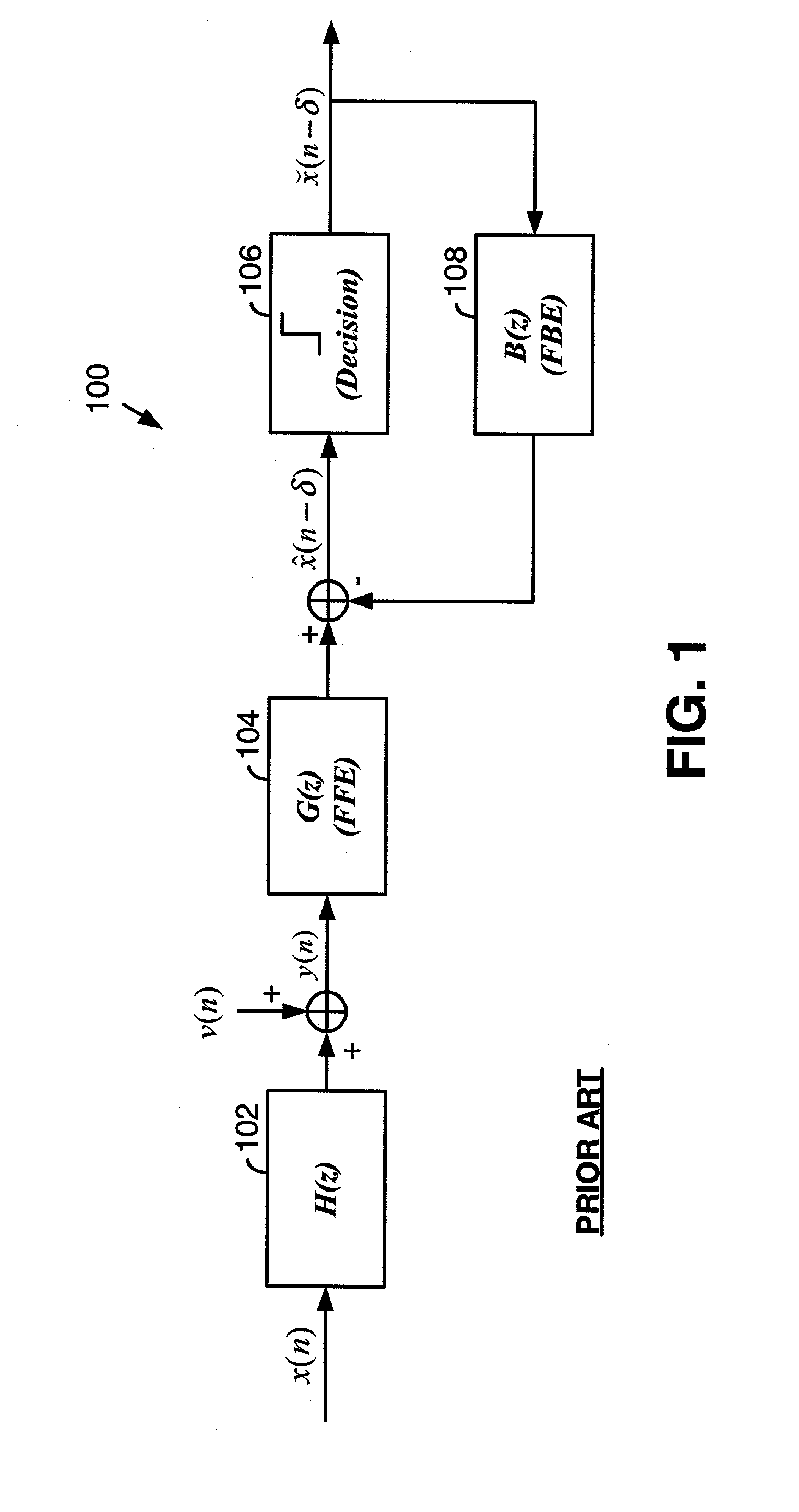
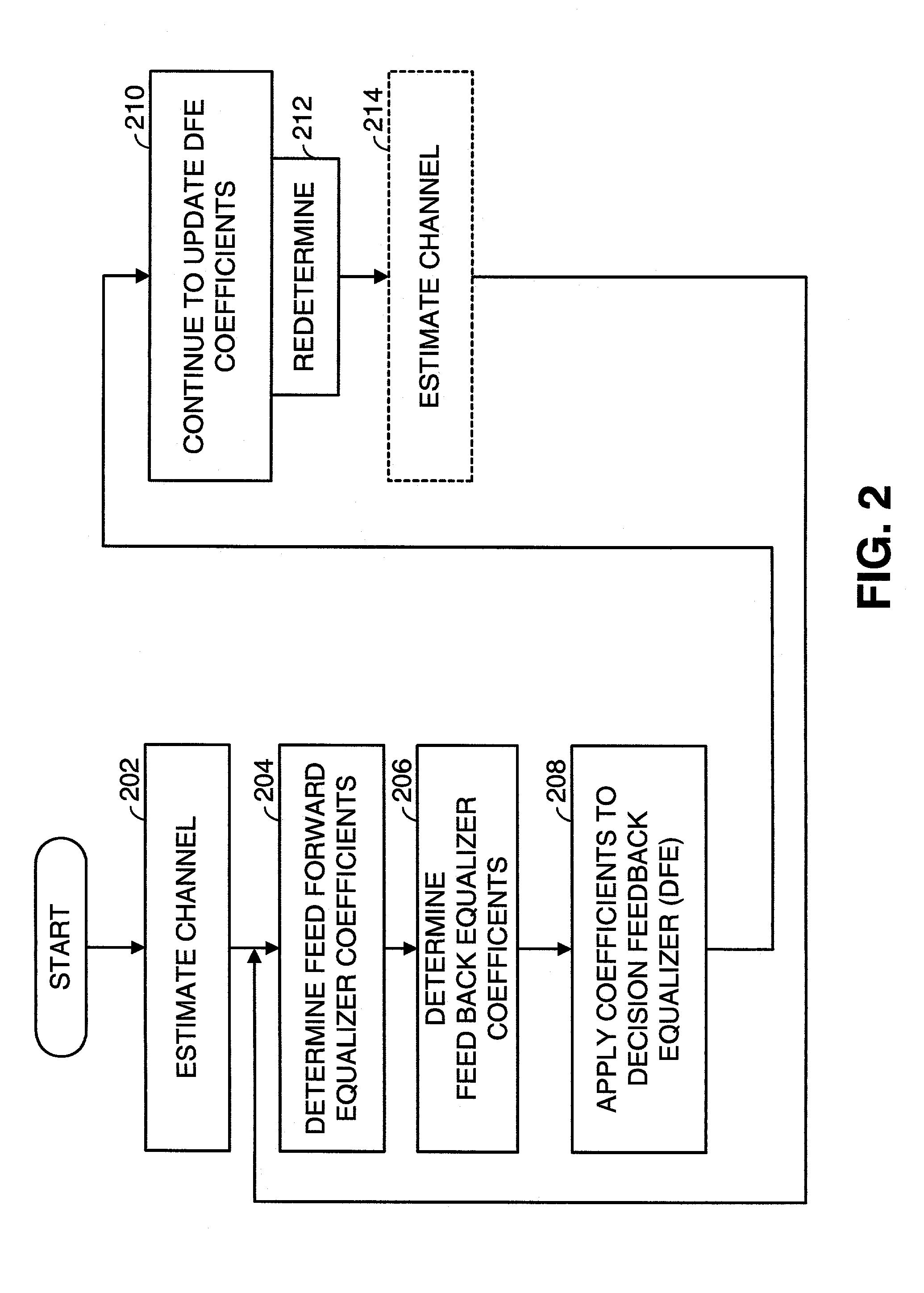
Fast computation of coefficients for a variable delay decision feedback equalizer
InactiveUS7263123B2Reduce computational complexityIncrease computing speedMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsOptimal decisionComputational problem
Optimal Decision Feedback Equalizer (DFE) coefficients are determined from a channel estimate by casting the DFE coefficient problem as a standard recursive least squares (RLS) problem and solving the RLS problem. In one embodiment, a fast recursive method, e.g., fast transversal filter (FTF) technique, is used to compute the Kalman gain of the RLS problem, which is then directly used to compute MIMO Feed Forward Equalizer (FFE) coefficients. The FBE coefficients are computed by convolving the FFE coefficients with the channel impulse response. Complexity of a conventional FTF algorithm may be reduced to one third of its original complexity by selecting a DFE delay to force the FTF algorithm to use a lower triangular matrix. The length of the DFE may be selected to minimize the tap energy in the FBE coefficients or to ensure that the tap energy in the FBE coefficients meets a threshold.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
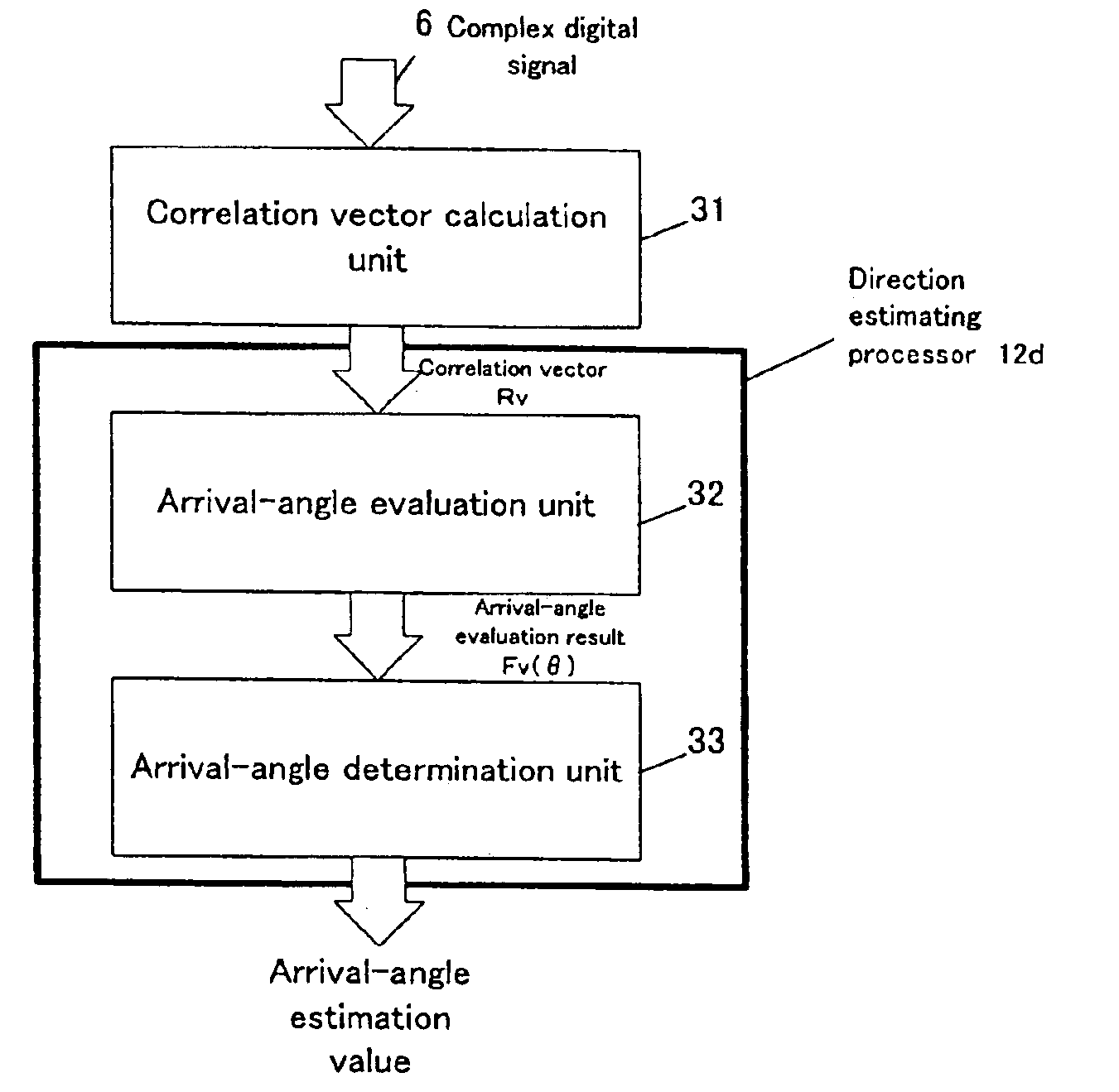
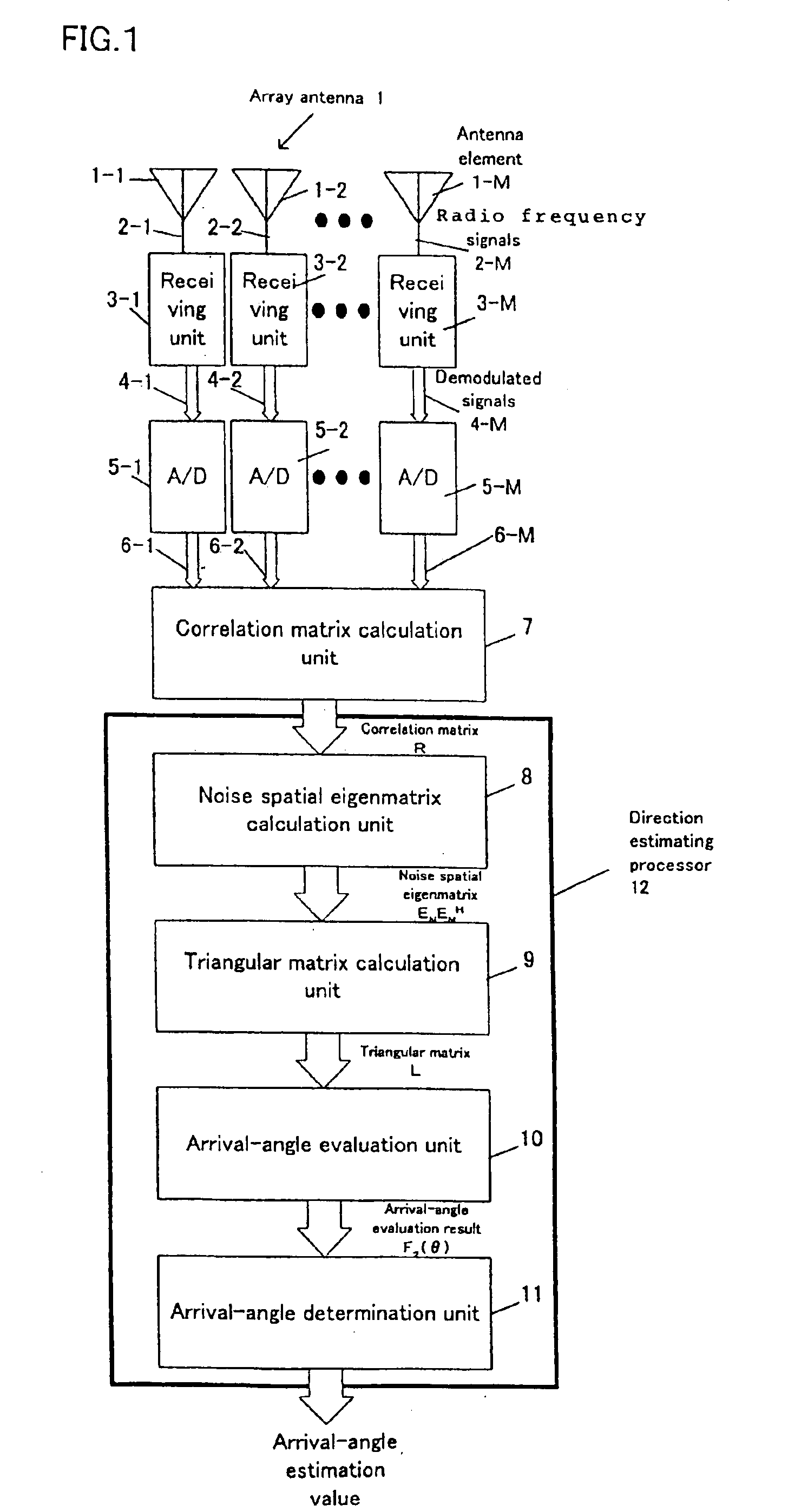
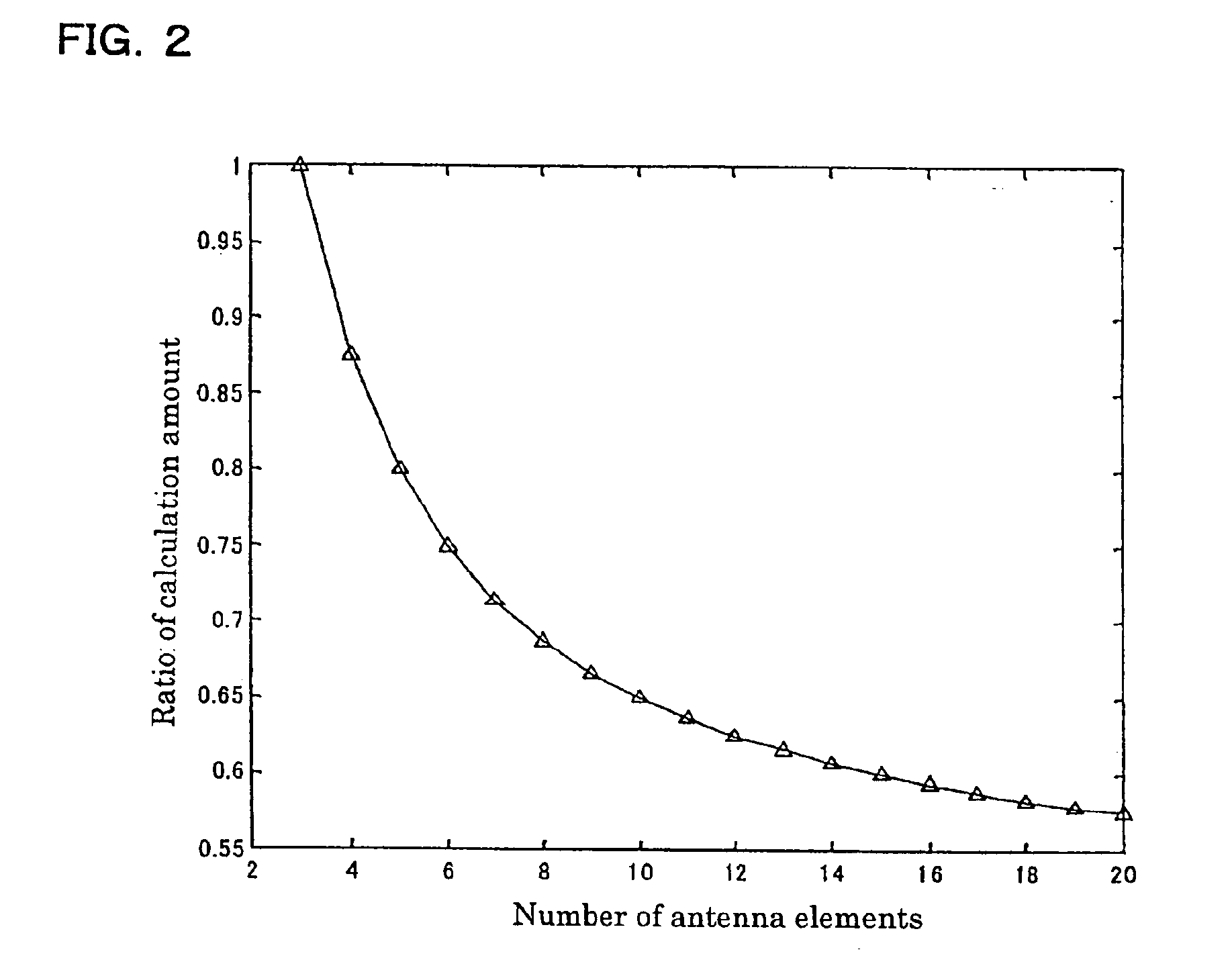
Radio-wave arrival-direction estimating apparatus and directional variable transceiver
InactiveUS6897807B2Quality improvementReduce the amount of calculationMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesPosition fixationAngular scanMatrix decomposition
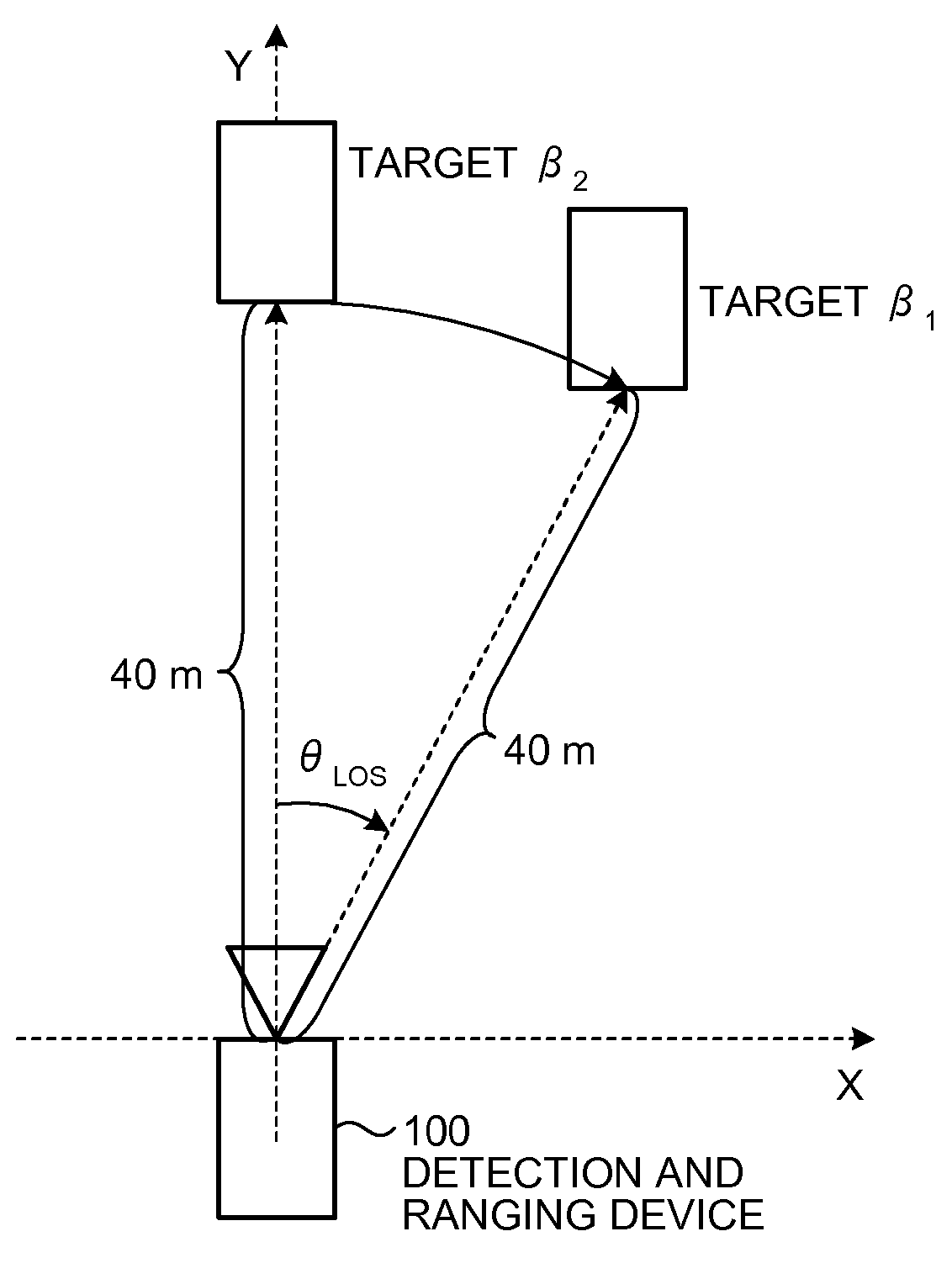
A radio-wave arrival-direction apparatus calculates a correlation matrix of received signals by correlation calculation between antenna elements, and calculates a noise spatial eigenmatrix, of which each row or column is an eigenvector belonging to a noise eigen-space, by eigenvalue factorization of the correlation matrix. The apparatus also factorizes a matrix including a product of the noise spatial eigenmatrix and a conjugated and transposed matrix of it to an upper or lower triangular matrix, using cholesky factorization. The apparatus calculates an angle evaluation value in a predetermined angle range of an arrival-angle evaluation function using the derived upper or lower triangular matrix, and determines an arrival angle based on the calculation result. A calculation amount in a variable angle range can be thus reduced without causing accuracy degradation of arrival direction, in an algorism requiring all angle sweep for arrival angle estimation of MUSIC method or the like.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Fast computation of multi-input-multi-output decision feedback equalizer coefficients
InactiveUS7113540B2Lower requirementRapid productionMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsMulti inputOptimal decision
Multi-Input-Multi-Output (MIMO) Optimal Decision Feedback Equalizer (DFE) coefficients are determined from a channel estimate h by casting the MIMO DFE coefficient problem as a standard recursive least squares (RLS) problem and solving the RLS problem. In one embodiment, a fast recursive method, e.g., fast transversal filter (FTF) technique, then used to compute the Kalman gain of the RLS problem, which is then directly used to compute MIMO Feed Forward Equalizer (FFE) coefficients gopt. The complexity of a conventional FTF algorithm is reduced to one third of its original complexity by choosing the length of a MIMO Feed Back Equalizer (FBE) coefficients bopt (of the DFE) to force the FTF algorithm to use a lower triangular matrix. The MIMO FBE coefficients bop are computed by convolving the MIMO FFE coefficients gopt with the channel impulse response h. In performing this operation, a convolution matrix that characterizes the channel impulse response h extended to a bigger circulant matrix. With the extended circulant matrix structure, the convolution of the MIMO FFE coefficients gopt with the channel impulse response h may be performed easily performed in the frequency domain.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and structure for improving processing efficiency in parallel processing machines for rectangular and triangular matrix routines
InactiveUS20060265445A1Reduce storageImprove efficiencyData mergingComplex mathematical operationsDistributed memoryData preparation
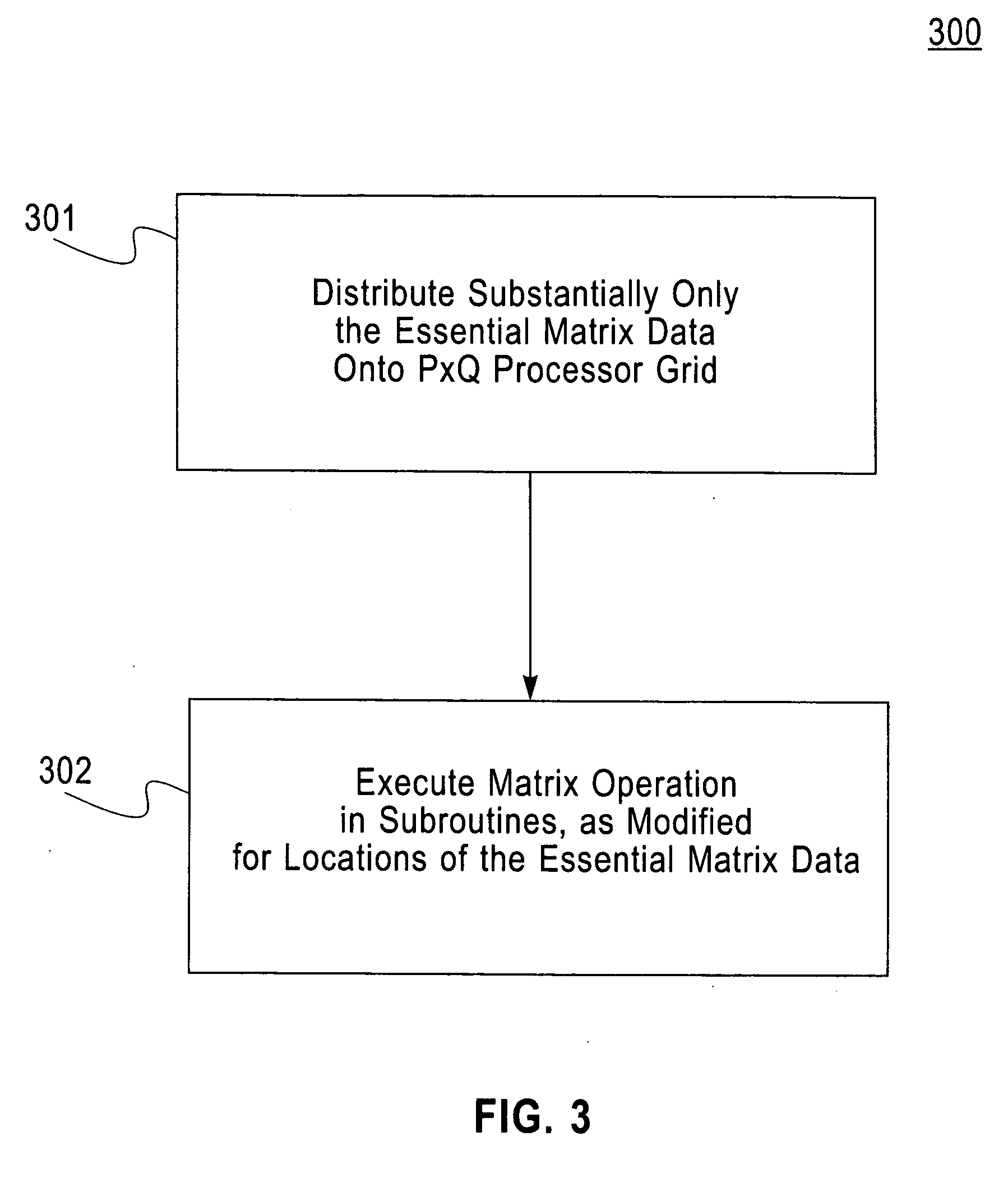
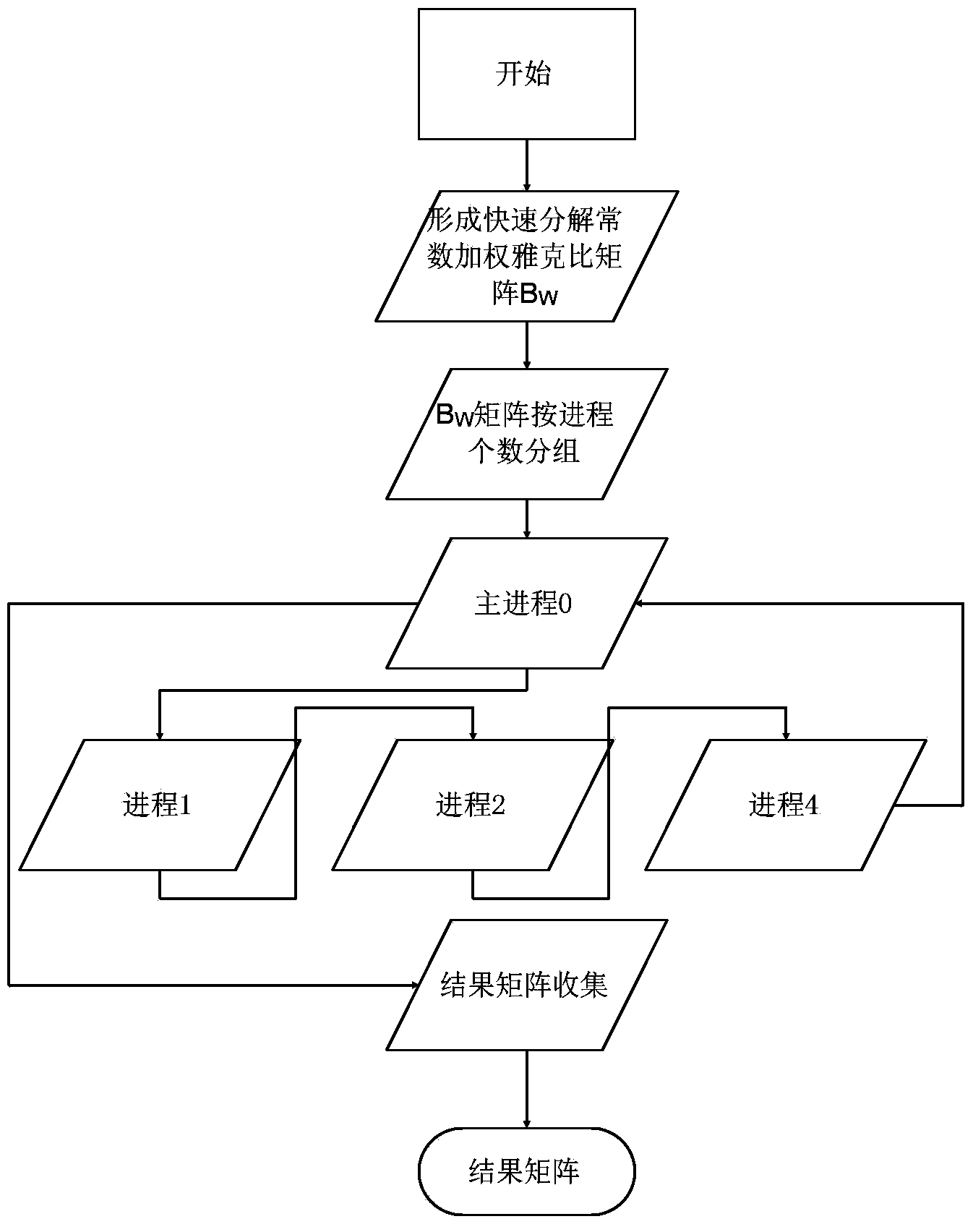
A computerized method (and structure) of linear algebra processing on a computer having a plurality of processors for parallel processing, includes, for a matrix having elements originally stored in a memory in a rectangular matrix AR or especially of one of a triangular matrix AT format and a symmetric matrix AS format, distributing data of the rectangular AR or triangular or symmetric matrix (AT, AS) from the memory to the plurality of processors in such a manner that keeps all submatrices of AR or substantially only essential data of the triangular matrix AT or symmetric matrix AS is represented in the distributed memories of the processors as contiguous atomic units for the processing. The linear algebra processing done on the processors with distributed memories requires that submatrices be sent and received as contiguous atomic units based on the prescribed block cyclic data layouts of the linear algebra processing. This computerized method (and structure) defines all of its submatrices as these contiguous atomic units, thereby avoiding extra data preparation before each send and after each receive. The essential data or AT or AS is that data of the triangular or symmetric matrix that is minimally necessary for maintaining the full information content of the triangular AT or symmetric matrix AS.
Owner:IBM CORP
Quickening method utilizing cooperative work of CPU and GPU to solve triangular linear equation set
InactiveCN101751376ASpeed up the solutionImplement overlapping computingComplex mathematical operationsCooperative workComputer science
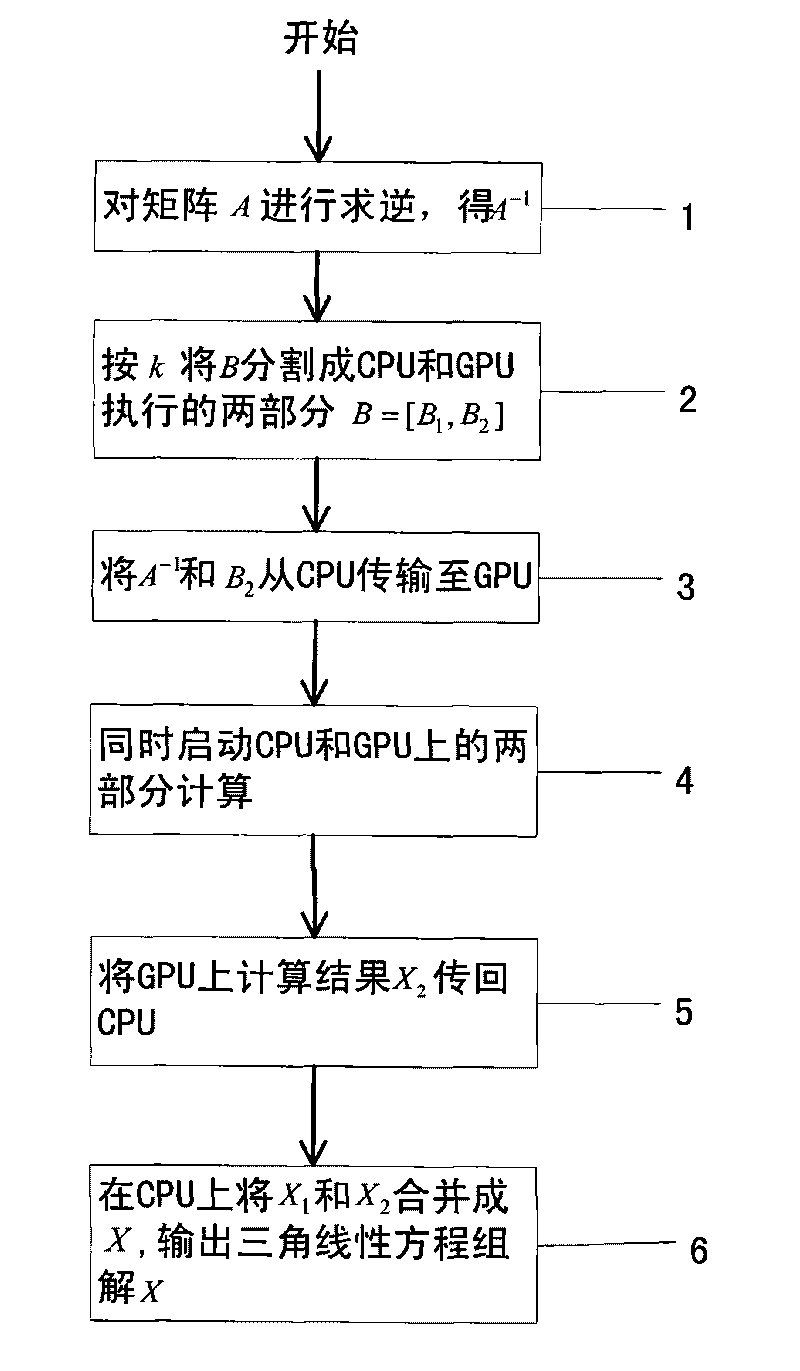
The invention discloses a quickening method utilizing cooperative work of a CPU and a GPU to solve a triangular linear equation set, aiming at providing the quickening method so as to lead a solving method based on a CPU platform for the triangular linear equation set to be quickened on a heterogeneous platform of the CPU plus the GPU. The technical scheme of the quickening method is as follows: first, the CPU is utilized to carry out matrix inversion so as to obtain an inverse matrix A-1 of a triangular matrix A; second, a matrix B is divided into two matrixes B1 and B2; third, two calculations of A-1*B1 and A-1*B2 are executed on the CPU and the GPU in a collateral manner so as to achieve load balance of the CPU and the GPU, and the results of A-1*B1 and A-1*B2 are respectively X1 and X2; finally, the X2 is returned to the CPU, and the X1 and the X2 are merged into one matrix X for output. The quickening method realizes overlapping calculation of the CPU and the GPU, achieves good effect of load balance, and quickens the solving of the triangular linear equation set.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
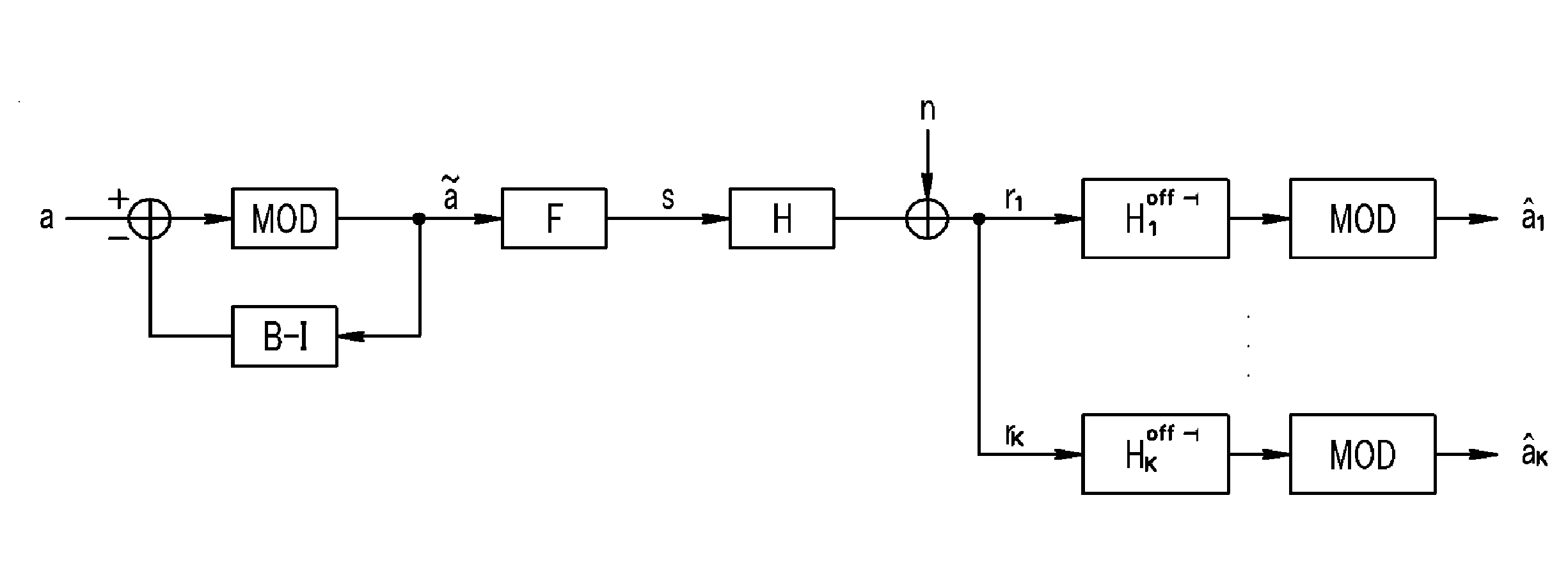
Mitigation of Interference and Crosstalk in Communications Systems
InactiveUS20080239937A1Effectively competeSubstations coupling interface circuitsInterconnection arrangementsMulti inputDecomposition
Signals in a multi-channel, impaired communication system are post-processed at the receiver. A triangular matrix Decision Feedback Demodulator (DFD) at the receiver extracts channels without requiring delivery of receiver parameters to the transmitter. Multi-Input Multi-Output (MIMO) processing matrices and DFD parameters are computed by first applying matrix transformations to diagonalize the noise covariance matrix of the multiple channels received at the receiver. QR decompositions (i.e., decompositions into orthogonal and triangular matrices) are then applied to the main channels to obtain triangular channel matrices. The noise-diagonalizing transformations and QR decompositions are then combined to form the MIMO postprocessing matrices and DFD parameters. MIMO postprocessing matrices and DFD parameters are computed from training data and then adapted during live data transmission.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Apparatus and method for detecting signal in multi-input multi-output system
InactiveUS20070291882A1Low computing complexityImprove performancePolarisation/directional diversityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsMulti inputMatrix decomposition
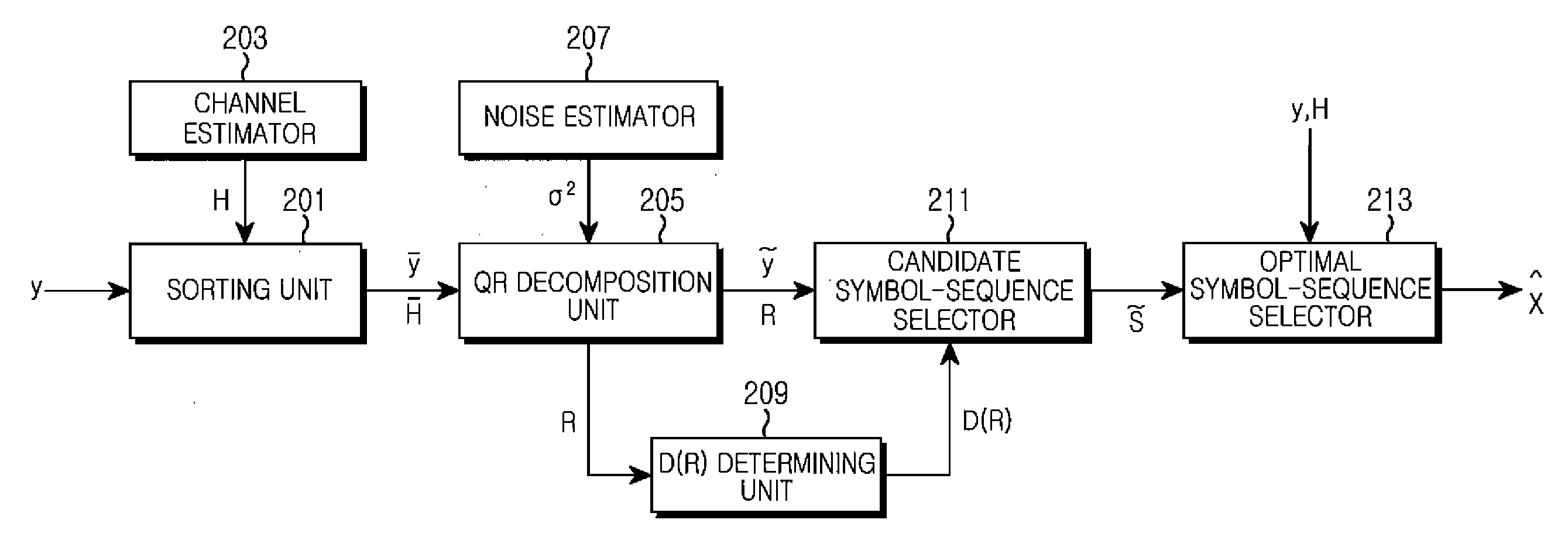
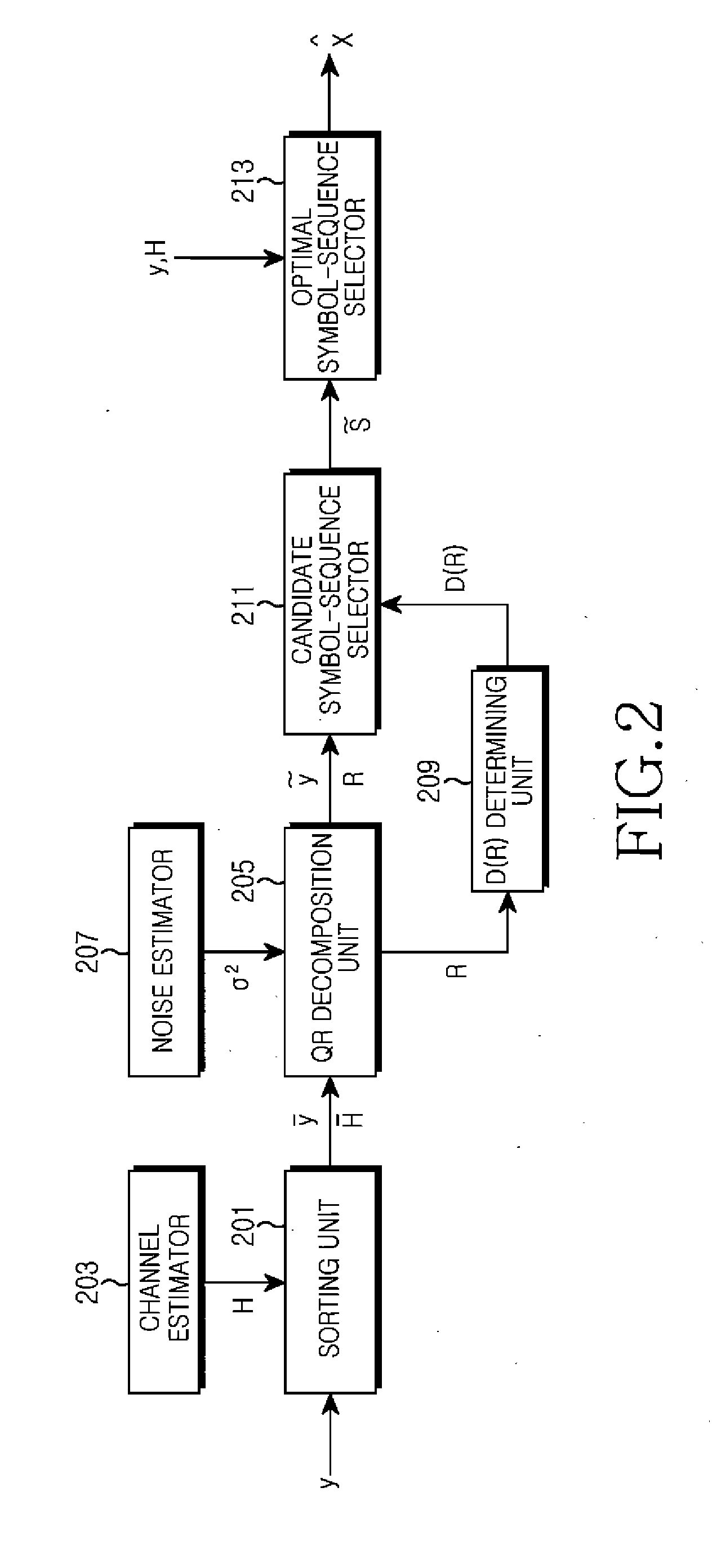
A signal detection apparatus and method using a modified stack algorithm in a Multi-Input Multi-Output (MIMO) system are provided. The signal detection method includes sorting signals received via antennas and channel coefficients for respective users in descending order, decomposing a channel matrix composed of the sorted channel coefficients into a unitary matrix and an upper-triangular matrix, determining the number of candidate symbol-sequences using the decomposed upper-triangular matrix, obtaining a signal vector for the antennas by using the sorted signals received via respective antennas and the unitary matrix, wherein the signal vector is proportional to the upper-triangular matrix, and detecting the determined number of candidate symbol-sequences by using a modified stack algorithm while expanding a stack structure for the obtained signal vector.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Method and device for detecting transmission signal with division detection
InactiveUS20100042666A1Reduce complexityComputation using non-contact making devicesDigital computer detailsQR decompositionAlgorithm
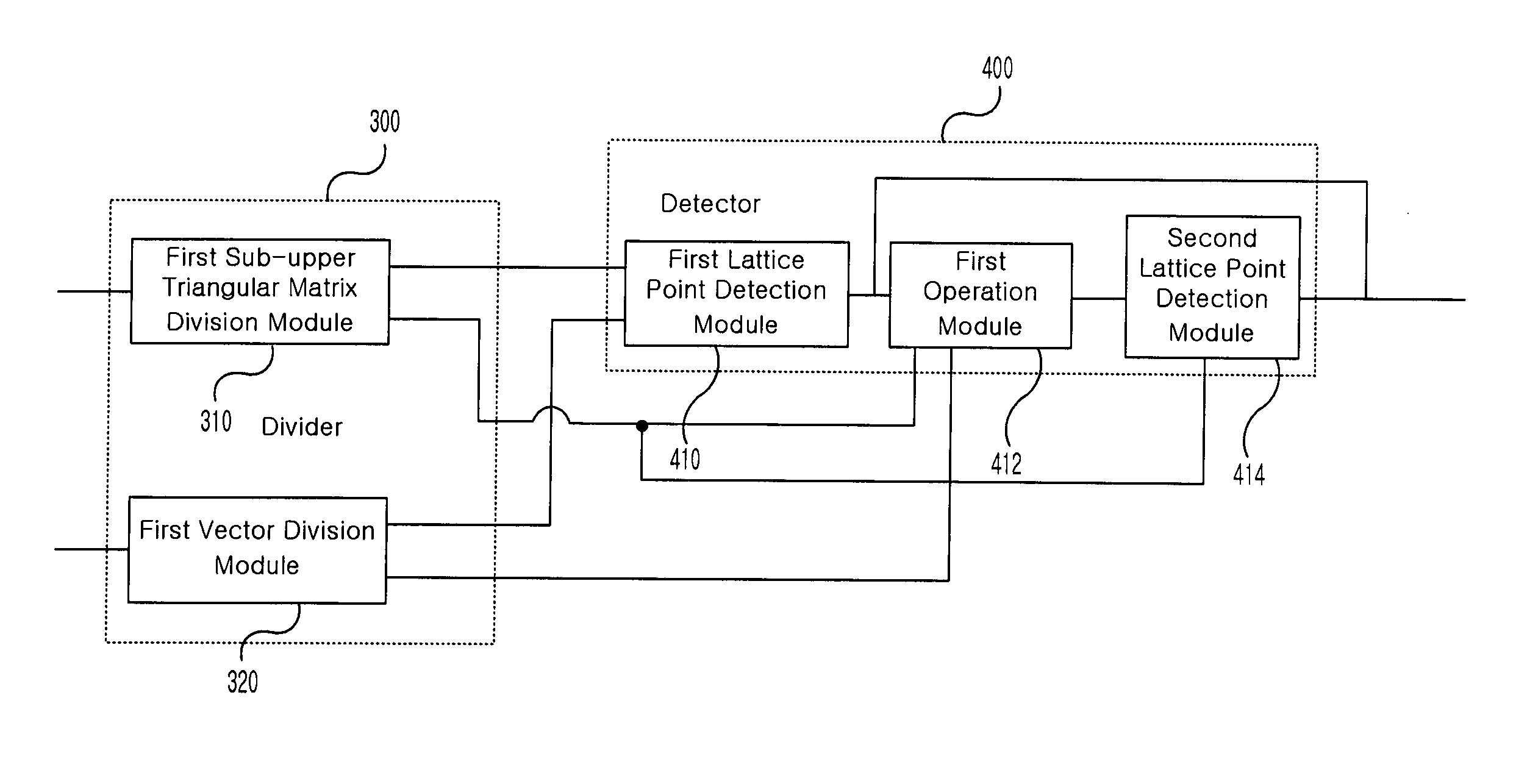
The present invention relates to a method and device for detecting a transmission signal on the basis of a received signal by applying a division and detection algorithm. An embodiment of the invention provides a method of detecting a transmission signal including: obtaining a unitary matrix and an upper triangular matrix by performing a sorted QR-decomposition algorithm with respect to a matrix indicating a channel state; calculating a vector y by multiplying a transpose matrix of the unitary matrix by the received signal Y; dividing the upper triangular matrix R into a plurality of sub-upper triangular matrices and dividing the calculated vector y into a plurality of sub-vectors so as to correspond to the divided plurality of sub-upper triangular matrices; and detecting a lattice point corresponding to each of the divided sub-vectors using the divided plurality of sub-upper triangular matrices.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Maximum likelihood detection for MIMO receivers
InactiveUS20070077969A1Spatial transmit diversitySubstation equipmentMaximum likelihood detectionSystem transformation
Maximum likelihood detection of signals in a MIMO receiver. A system transformation is obtained by selecting a weighting matrix that when linearly transforming a channel utilized for wireless communication, results in a particular transformed triangular matrix. The weighting matrix is then used to provide a transformed vector for a received signal that allows a search in one constellation. In searching the constellation recursion values are used to calculate the Euclidean distances between set points of the constellation and the location on the constellation corresponding to the received signal for both bit values 0 and 1. Minimum Euclidean distances are determined for bit values 0 and 1 and the difference of the minimum Euclidean distances is used to compute the maximum likelihood value for bits contained in the received signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
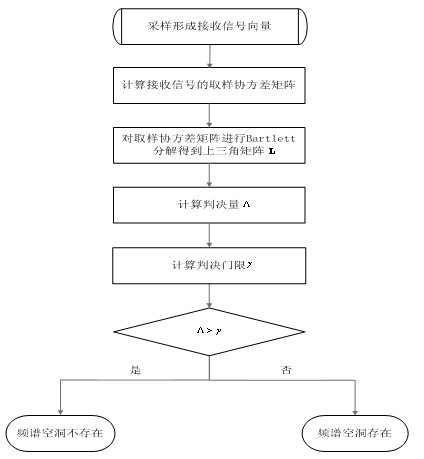
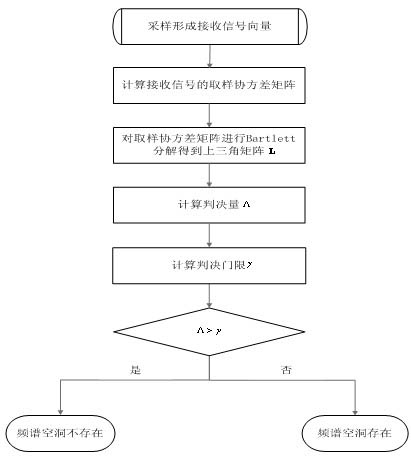
Frequency spectrum blind sensing method based on covariance matrix decomposition
InactiveCN102118201AMake sure it's simple and preciseOvercoming the "Noise Uncertainty" ProblemTransmission monitoringFrequency spectrumAlgorithm
A frequency spectrum blind sensing method based on covariance matrix decomposition relates to a method used in wireless communication for secondary users to detect frequency spectrum holes. The method comprises the following steps: conducting Bartlett decomposition on a sampling covariance matrix receiving signal vector to obtain an upper triangular matrix; utilizing the quadratic sum of off-diagonal elements in the matrix and the quotient of the quadratic sum diagonal elements as statistical decision amount for detecting frequency spectrum holes; and judging the inexistence of frequency spectrum holes when the decision amount is higher than a threshold value, or else, judging the existence of frequency spectrum holes. In the sensing method disclosed by the invention, theoretical decisionthreshold has a simple close manner, so as to be precisely calculated out, and the theoretical decision threshold is suitable for sensing scenes having different sampling scales; and on the other hand, as a novel fully-blind sensing method, the method does not need the participation of the statistical characteristics of master user's signals and channel, as well as noise in the implementation of frequency spectrum sensing, and can effectively solve the problem of noise uncertainty encountered during the adoption of a classical energy detection method.
Owner:JISHOU UNIVERSITY
Mobile communication system, receiving device, and method
InactiveUS20100329393A1Improve signal detection accuracyAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsRadio transmissionQR decompositionFourier transform on finite groups
A transmitting device Fourier-transforms symbols in a transmission symbol sequence, maps the Fourier-transformed symbols to subcarriers, inverse-Fourier-transforms the mapped symbols, and transmits the inverse-Fourier-transformed symbols from multiple transmitting antennas. A receiving device Fourier-transforms received signals, extracts signal components mapped to the subcarriers, and estimates the symbols transmitted via the subcarriers by applying a QR decomposition algorithm to the extracted signal components. The receiving device obtains a unitary matrix QH such that the product of the unitary matrix QH, a weight matrix W determining a correspondence between the transmission symbol sequence and the subcarriers, and a channel matrix H becomes a triangular matrix R, and estimates candidates of the symbols transmitted from the transmitting antennas based on the unitary matrix QH and the triangular matrix R.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
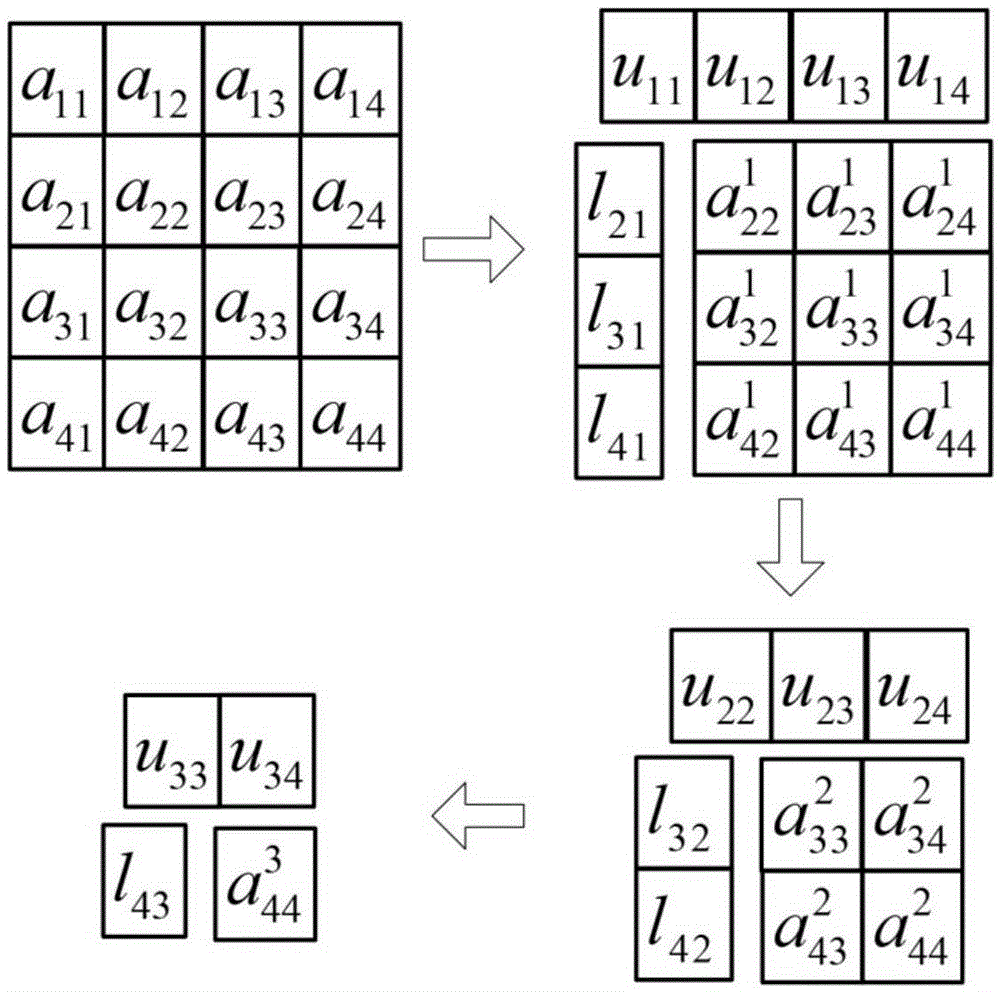
Matrix inverse operation method
InactiveCN105426345AImplement the inverse operationMeet performance needsComplex mathematical operationsMatrix inverseLU decomposition
The invention relates to a matrix inverse operation method. The method comprises the steps of 1, conducting column pivoting LU decomposition, wherein a source matrix A is decomposed into a unit lower triangular matrix L, an upper triangular matrix U and a permutation matrix P according to the formula PA=LU; 2, conducting triangular matrix inversion, wherein the inverse matrix L-1 of the matrix L is obtained through matrix inversion, and matrix inversion is conducted on the transposed matrix of the matrix U and then transposition is conducted to obtain U-1; 3, finally conducting matrix multiplication, wherein the matrix U-1 and the matrix L-1 are multiplied, and column transformation is conducted on the matrix multiplication result according to the permutation matrix P to obtain a source matrix A-1. The method has the advantages that by using the column pivoting LU decomposition algorithm, the time complexity of the matrix inversion algorithm is effectively reduced, parallelizability of matrix inversion operation is improved, time for matrix inversion operation is shortened, matrix inversion operation of any order can be conducted, and the number of hardware resources can be increased or reduced according to count requirements of operation so that practical application requirements can be better met.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
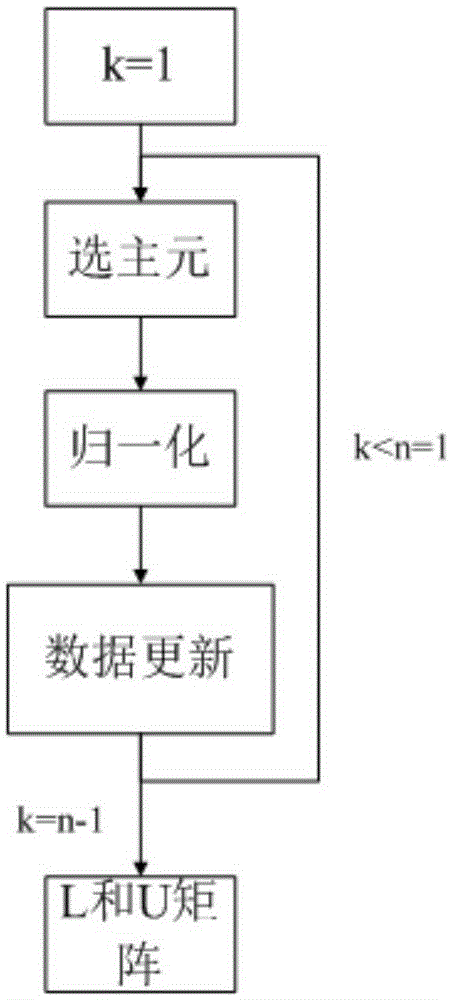
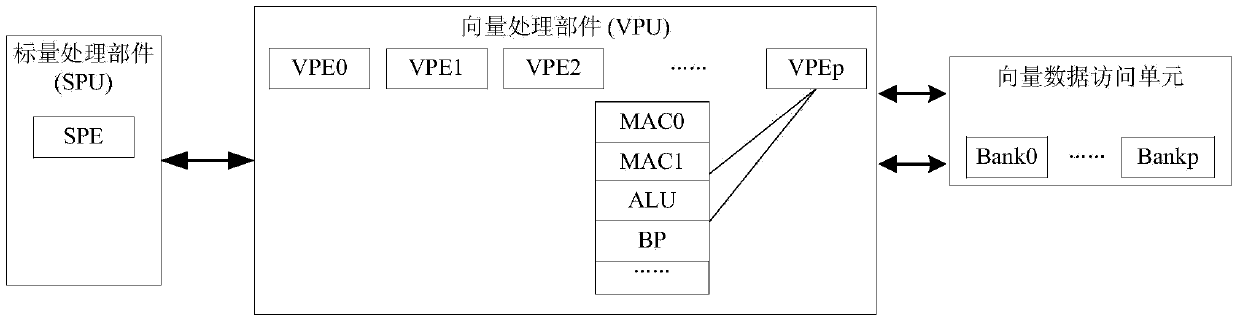
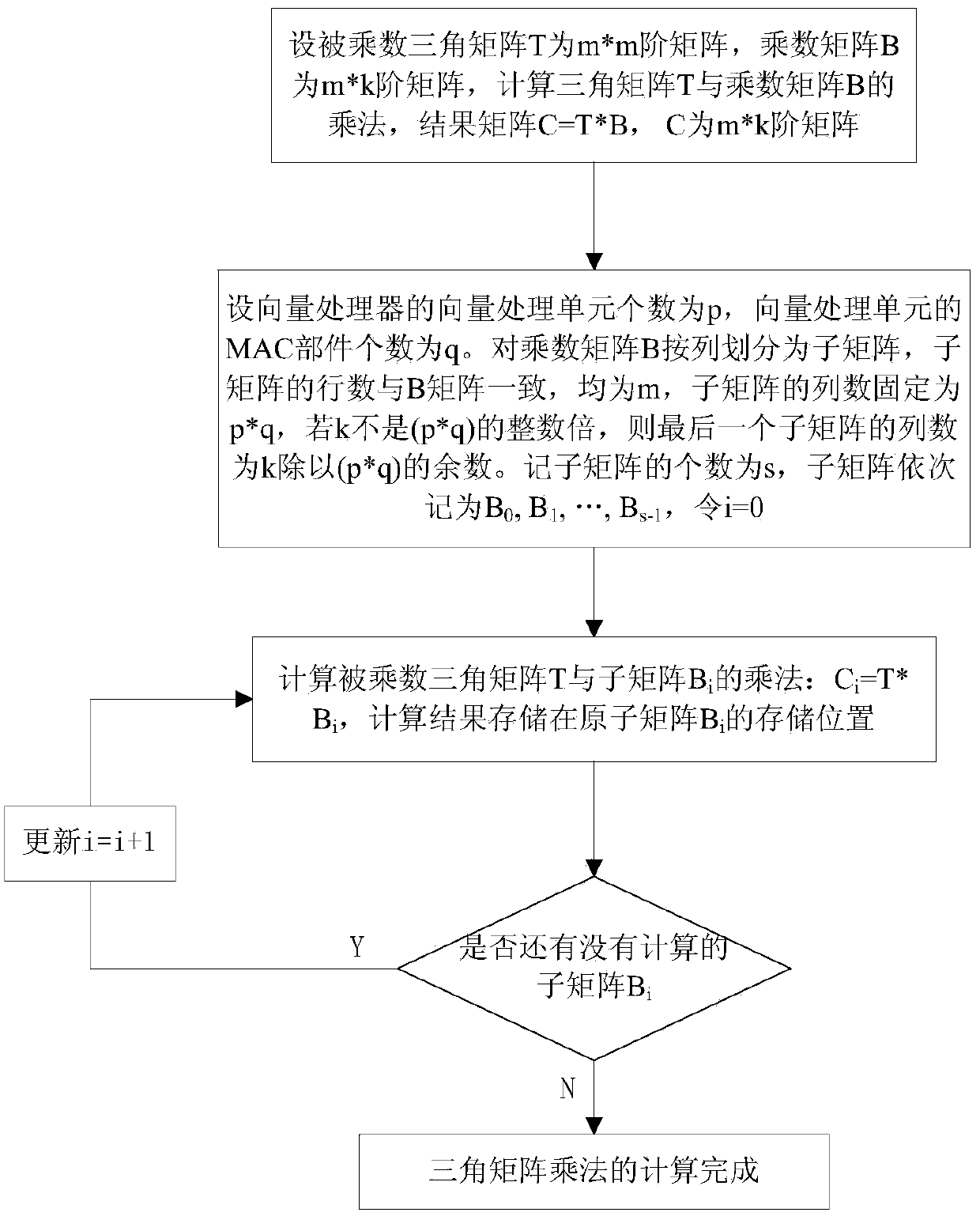
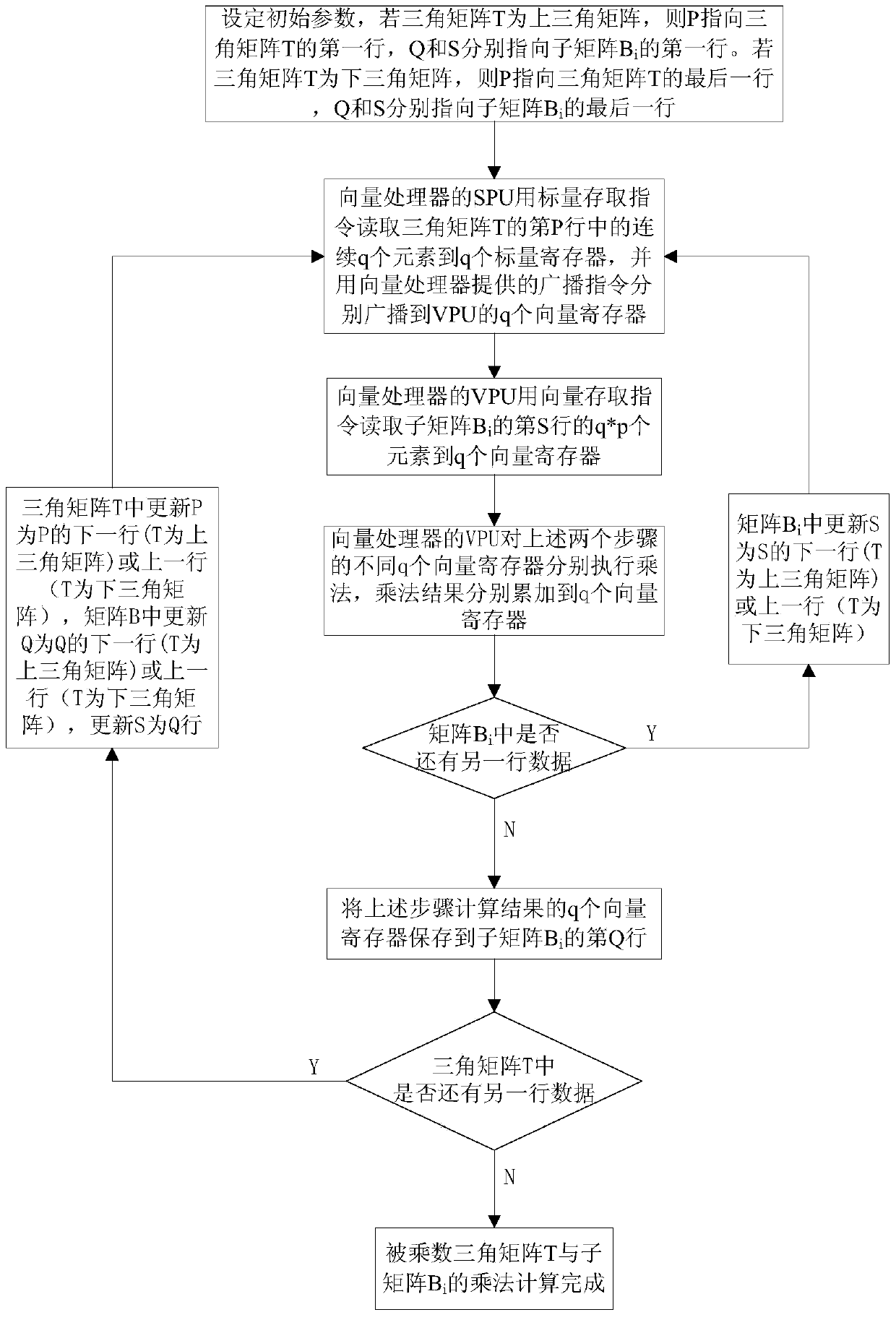
Triangular matrix multiplication vectorization method of vector processor
ActiveCN103440121ASmall amount of calculationRealize in-situ computingConcurrent instruction executionVector processorTriangular matrix
The invention discloses a triangular matrix multiplication vectorization method of a vector processor. The triangular matrix multiplication vectorization method of the vector processor comprises the steps that (1) triangular matrix elements in a multiplicand triangular matrix T are stored continuously by row; (2) a multiplier matrix B is divided into a plurality of sub-matrixes Bi by row according to the number of vector processing units of the vector processor and the number of MAC parts of the vector processing units; (3) the sub-matrixes Bi are multiplied by the multiplicand triangular matrix T in sequence and then the results are stored on storage positions of the original sub-matrixes Bi; (4) the sub-matrixes Bi of the multiplier matrix are traversed and then the fact that whether sub-matrixes Bi which are not multiplied by the multiplicand triangular matrix exist is judged, the I is updated according to the formula i=i+1 and the steps are repeated from the step (3) if sub-matrixes Bi which are not multiplied by the multiplicand triangular matrix exist, and step (5) is executed if sub-matrixes Bi which are not multiplied by the multiplicand triangular matrix do not exist; (5) triangular matrix multiplication is accomplished. The triangular matrix multiplication vectorization method of the vector processor has the advantages that the principle is simple, operation is easy and convenient, and the calculation efficiency of the vector processor can be fully performed.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
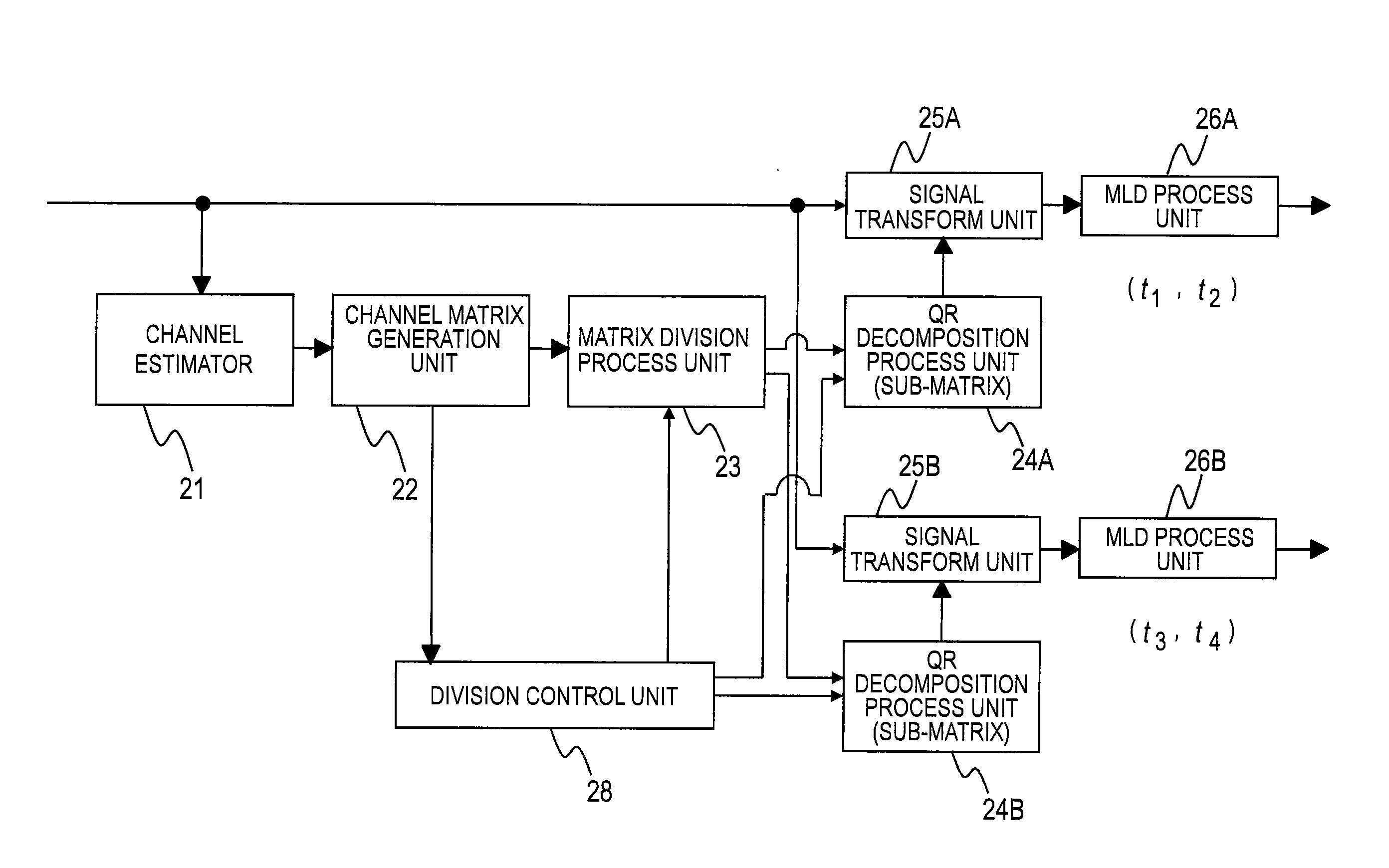
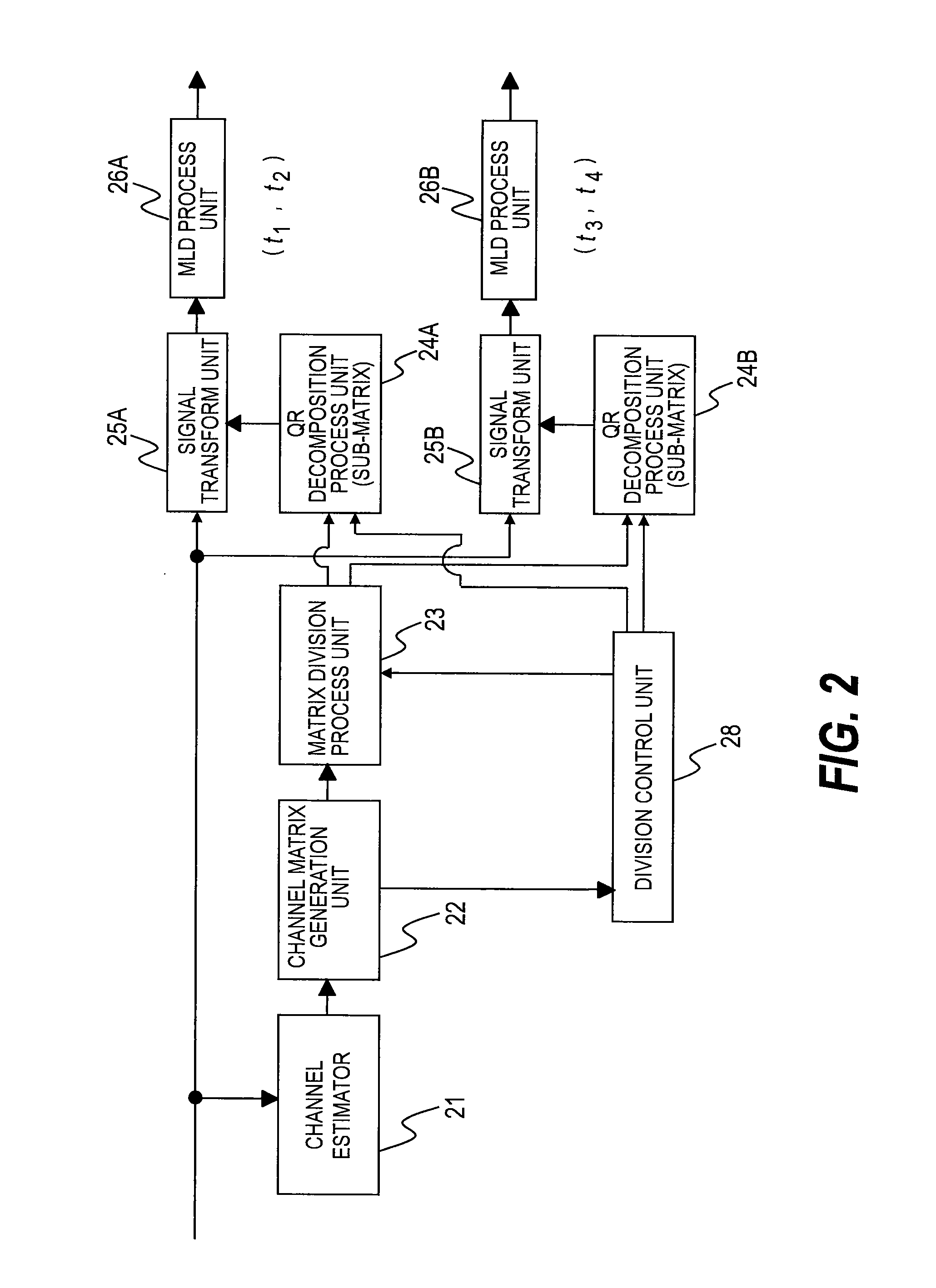
Maximum likelihood decoding method, equipment, and receiver
InactiveUS20090103641A1Quality improvementReduce complexityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSecret communicationQR decompositionDecoding methods
Provided is a maximum likelihood decoding method of separating and estimating multiple transmitted signals transmitted by multiple transmitter antennas from multiple received signals received by multiple receiver antennas, comprising: a first step of generating a channel matrix based on channel impulse responses corresponding to the received signals; a second step of dividing the generated channel matrix into multiple sub-matrices, of identifying parts of the received signals corresponding to the sub-matrices obtained through the division, and of transforming the sub-matrices obtained through the division, by using inverse matrices of the sub-matrices obtained through the division; a third step of applying QR decomposition to the transformed sub-matrices to obtain triangular matrices, and of transforming the received signals of the parts by using the obtained triangular matrices; and a fourth step of determining one combination candidate for the parts of the transmitted signals corresponding to the transformed received signals.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
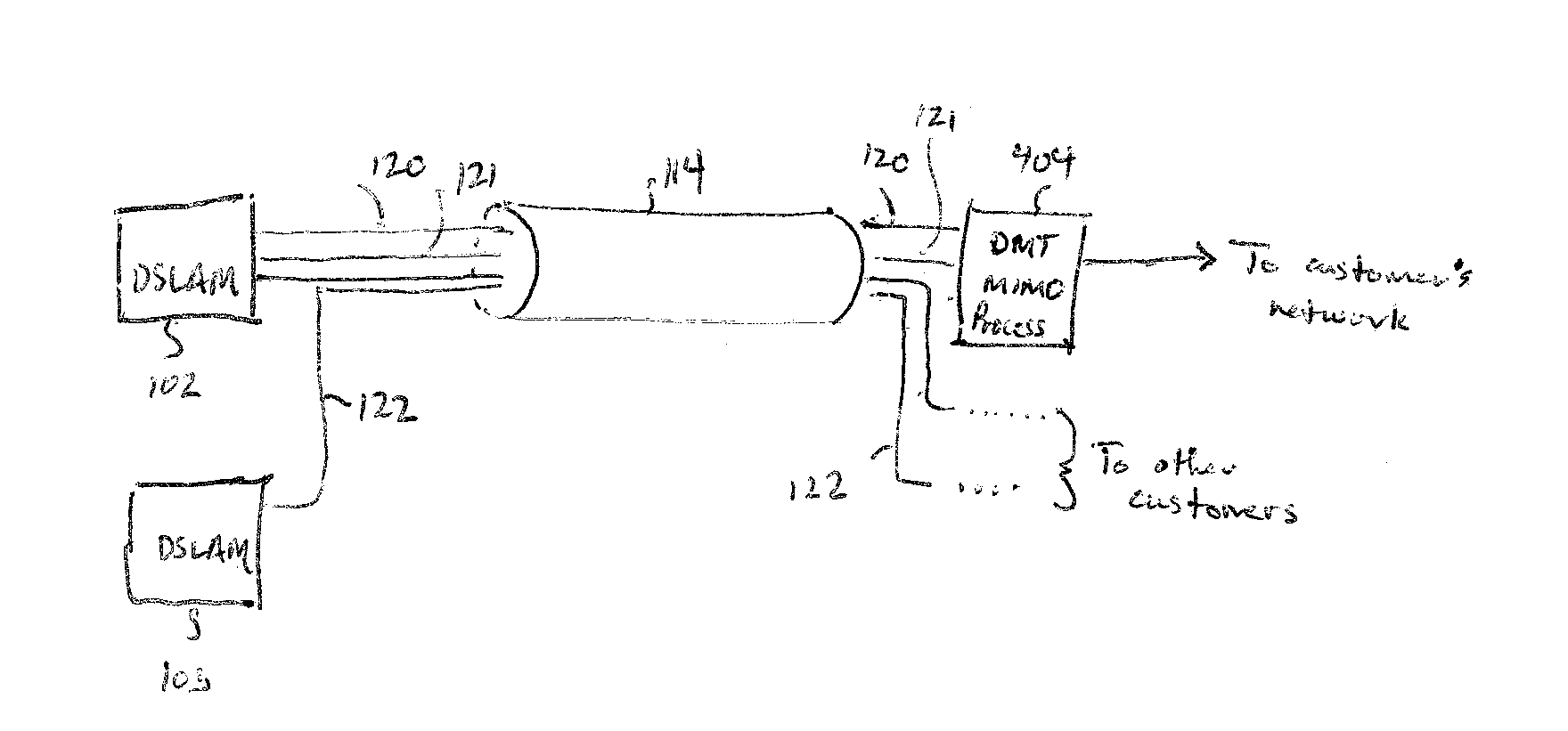
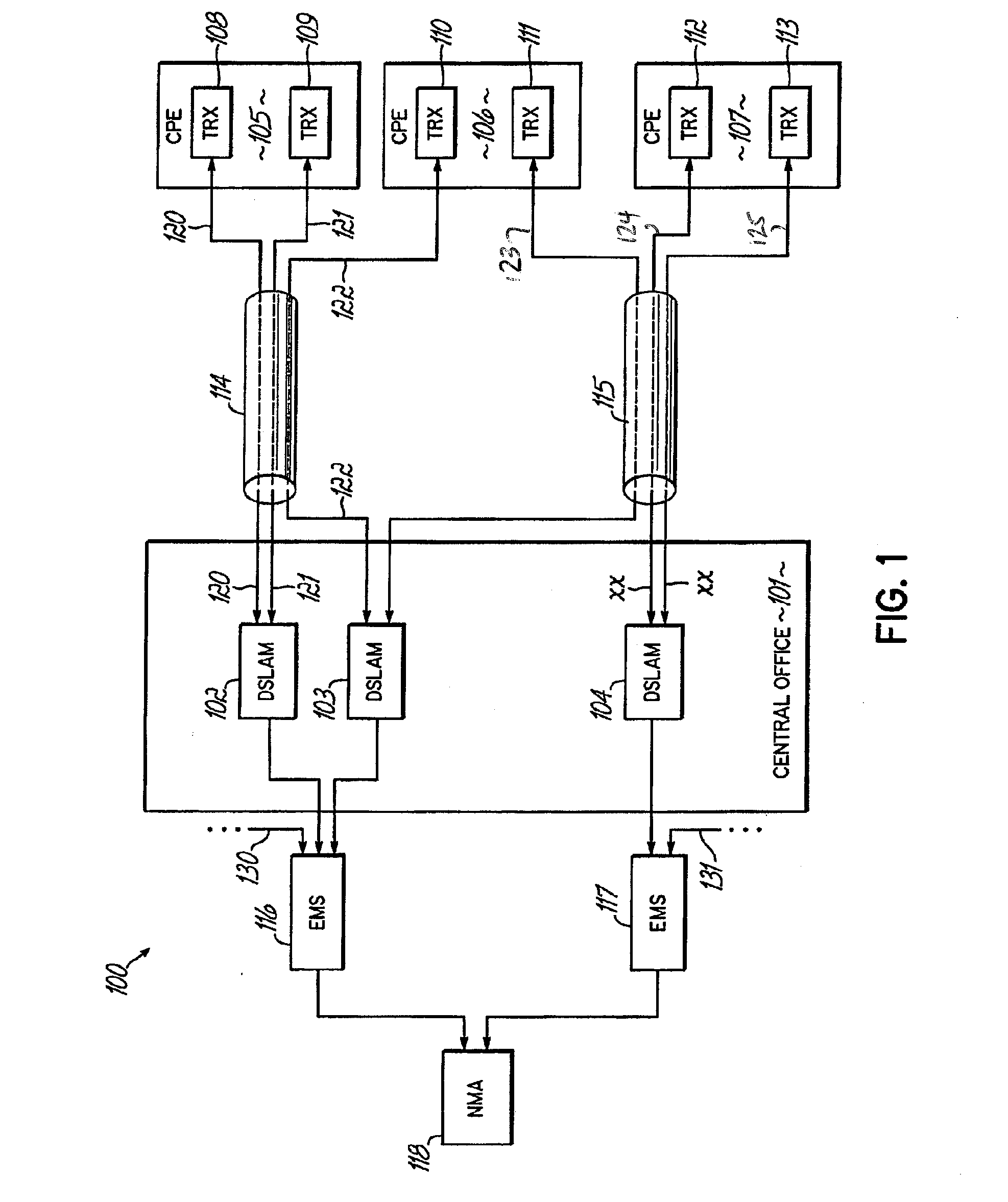
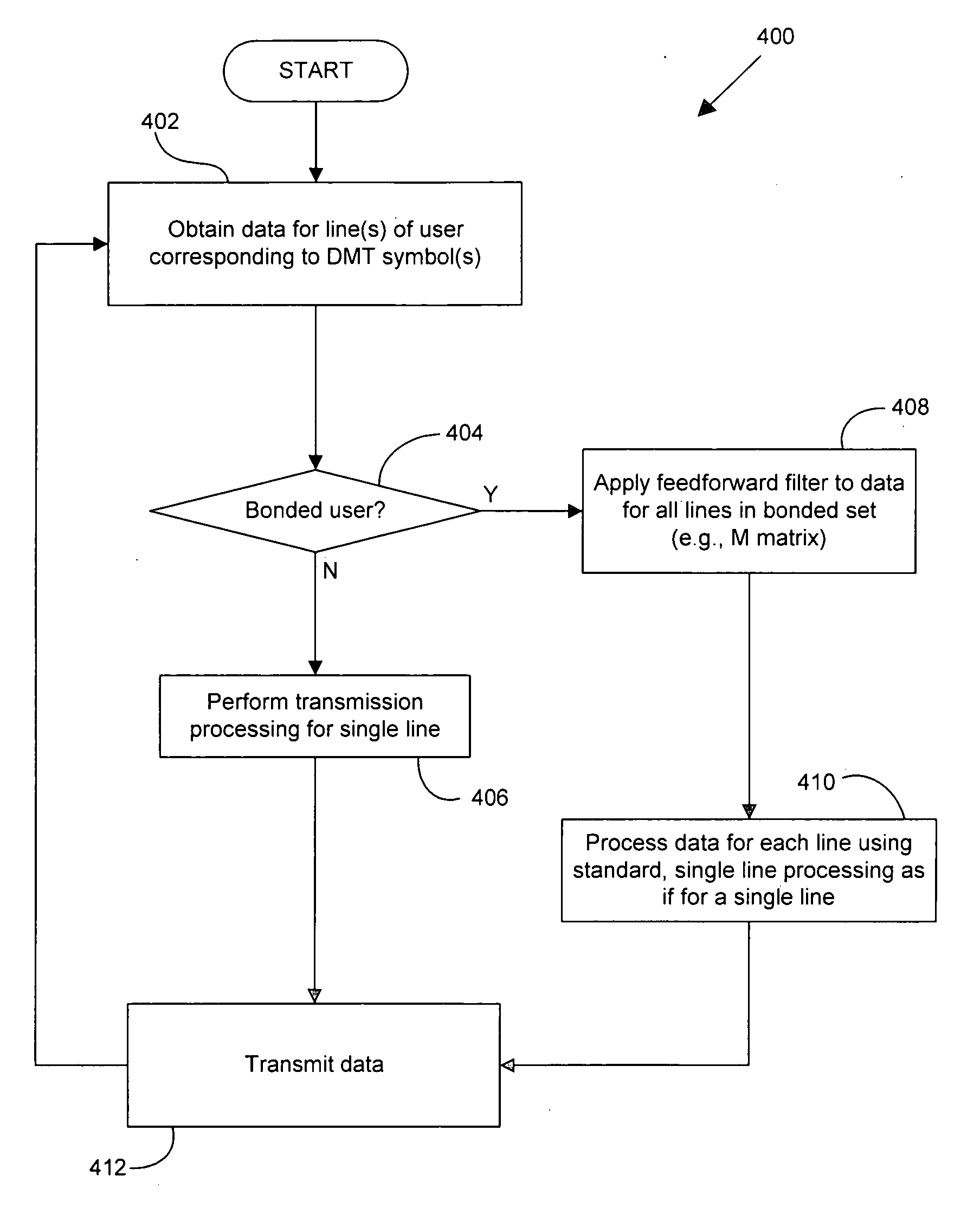
Vectored DSL nesting
InactiveUS20060280238A1Improve performanceMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsComputer scienceBond line
Methods, apparatus, systems and computer program products address one-sided vectoring systems that include a bonded-line set having two or more bonded DSL lines within a vectored group wherein other techniques such as precoding, tonal predictive GDFEs, tonal rotors and ordering techniques can be implemented. The performance of lines within a bonded set for a single customer can be improved for both upstream and downstream by nesting a vector coding system within, for example, GDFE and / or precoder architectures. The DSL lines within such a bonded group can have rotors applied at both transmit and receive side to achieve higher performance for these lines. The triangular matrix used by the GDFE and the precoder systems of the above-referenced applications can be modified in this context.
Owner:ASSIA SPE LLC CO THE CORP TRUST CO
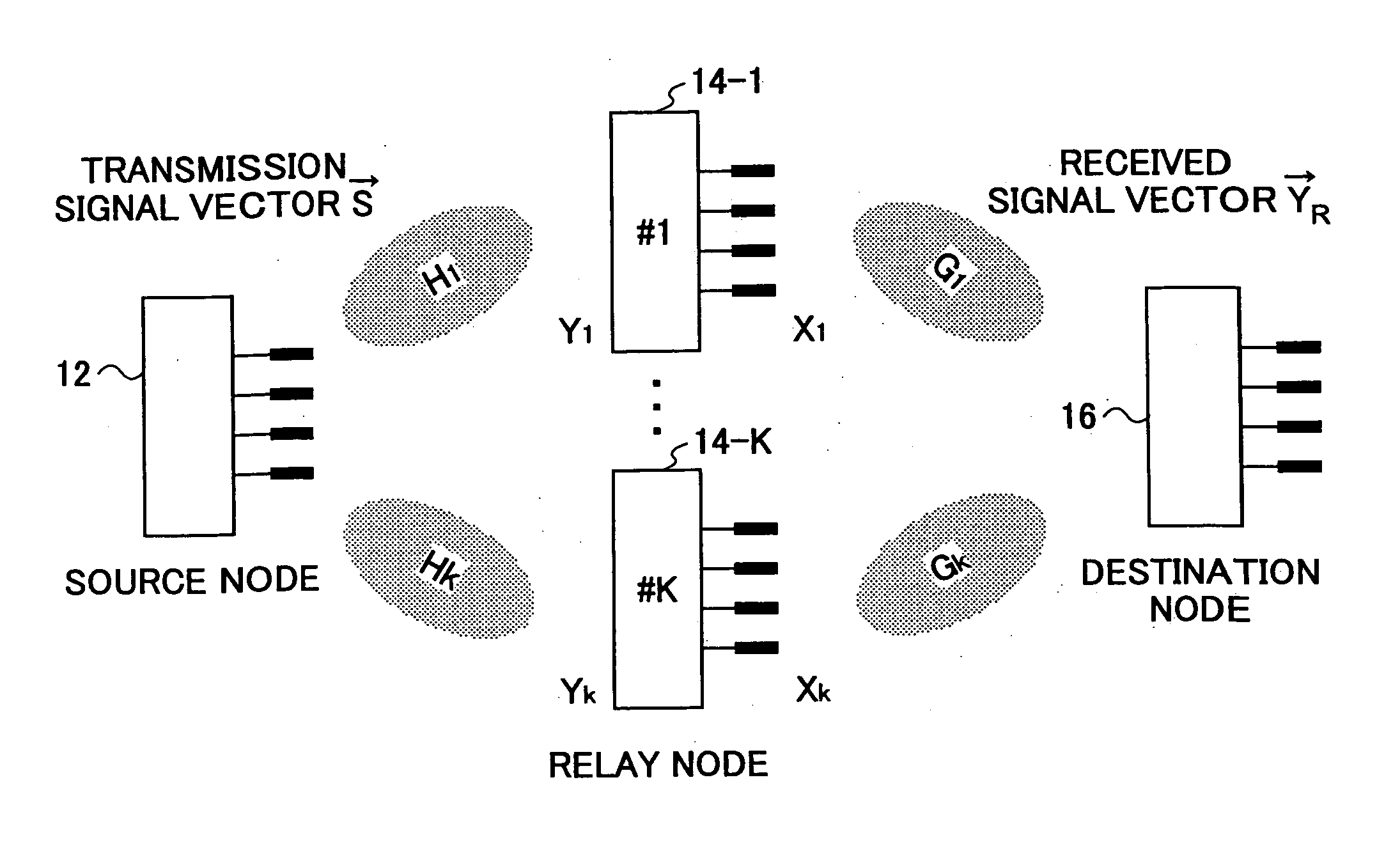
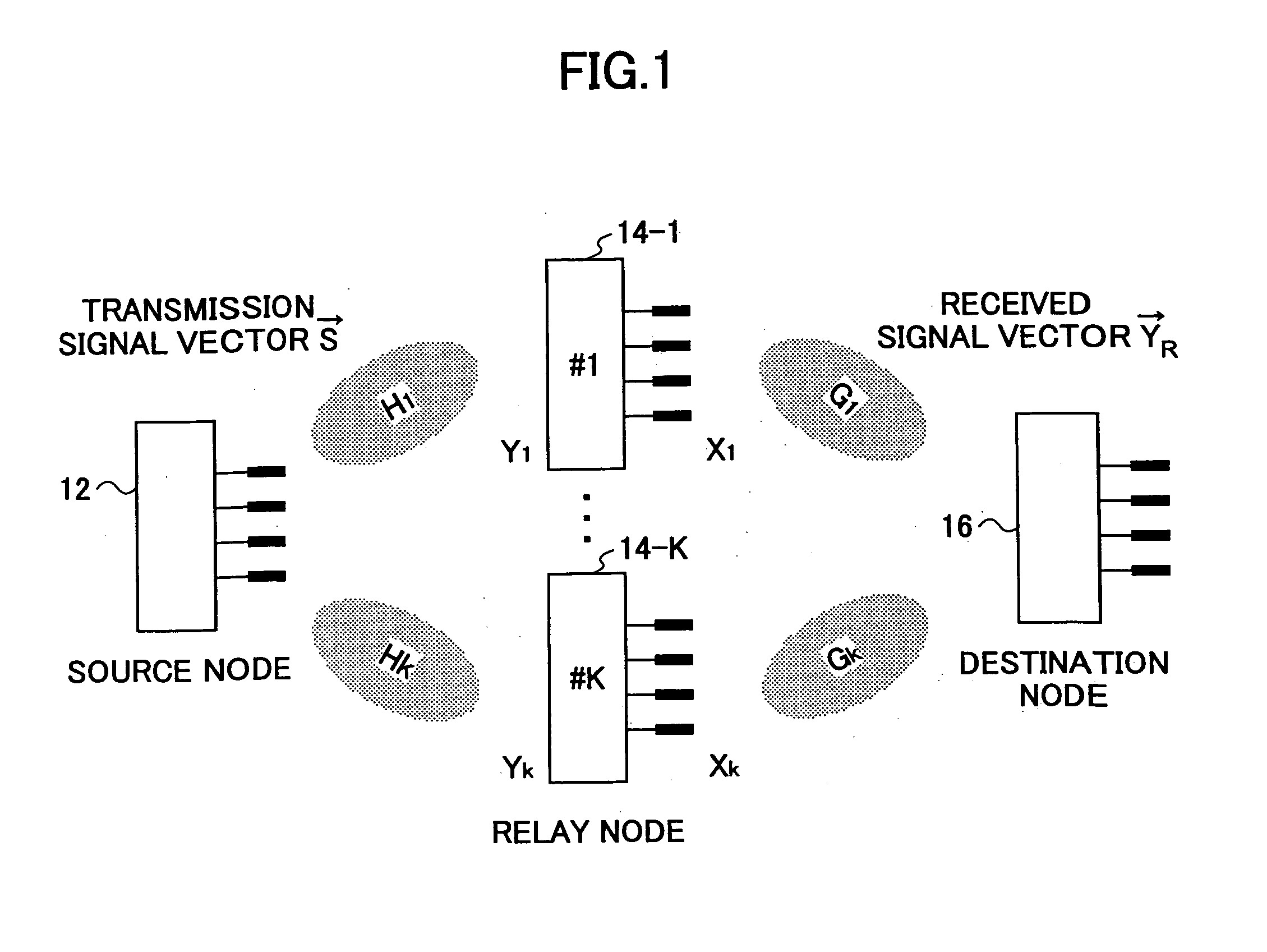
Communication system and method using a relay node
InactiveUS20060050655A1Quality improvementAvoid degradationPower managementSite diversityQR decompositionCommunications system
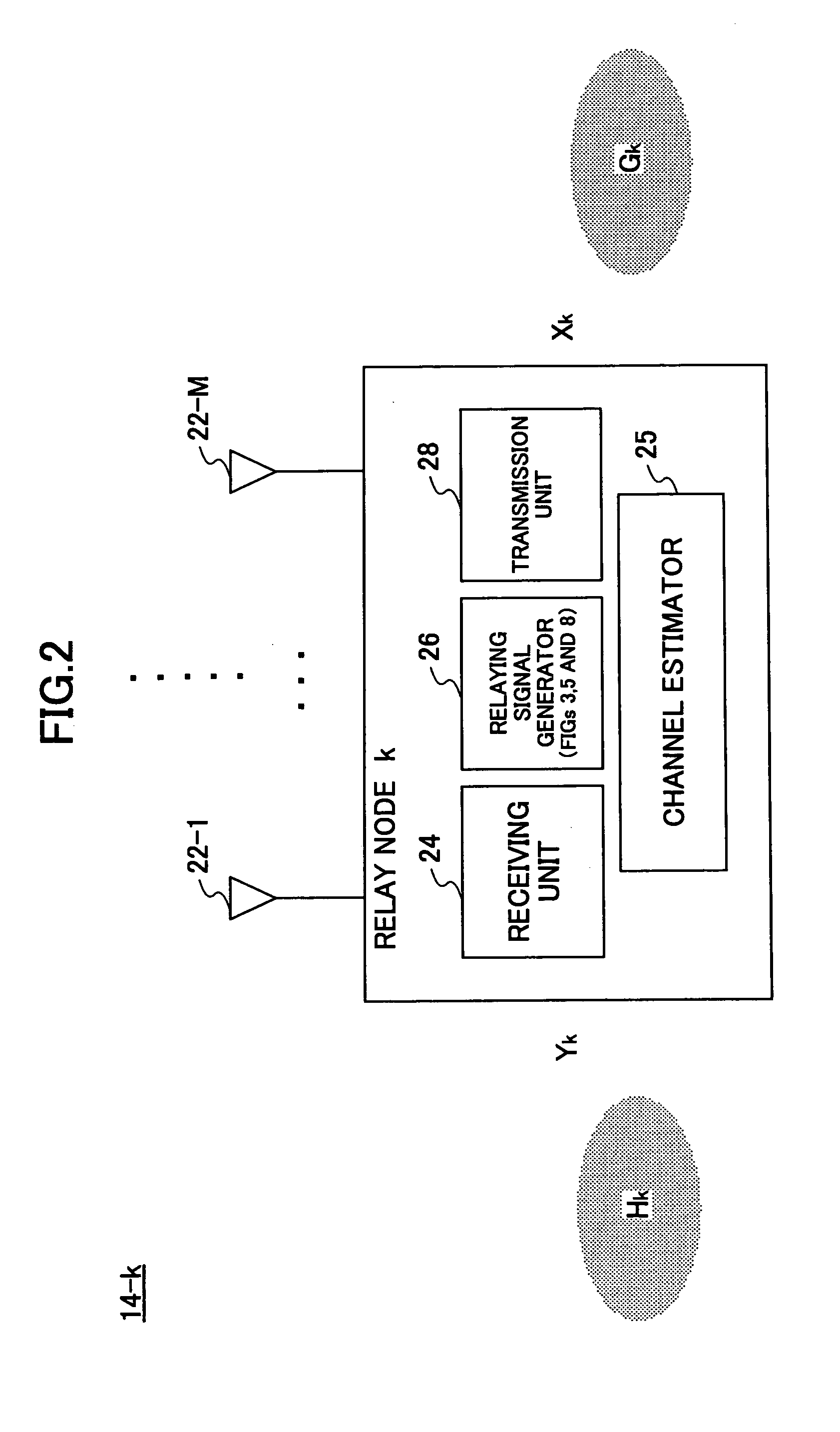
A communication node that relays signals between a source node and a destination node includes (a) a first unitary matrix calculation unit configured to calculate a first unitary matrix based on a first channel between the source node and the relay node, (b) a second unitary matrix calculation unit configured to calculate a second unitary matrix based on a second channel between the relay node and the destination node, (c) a transformation matrix estimation unit configured to estimate a transformation matrix based on a triangular matrix derived from QR decomposition of the first and / or second channel matrix, (d) a relaying signal generator configured to generates a relaying signal by multiplying a received signal by at least one of the first unitary matrix, the second unitary matrix, and the transformation matrix, and (e) a transmission unit configured to transmit the relaying signal to the destination node.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Incoming wave number estimation method, incoming wave number estimation device, and radio device
InactiveUS7450067B2Accurate estimateSmall amount of calculationRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceQR decompositionEstimation methods
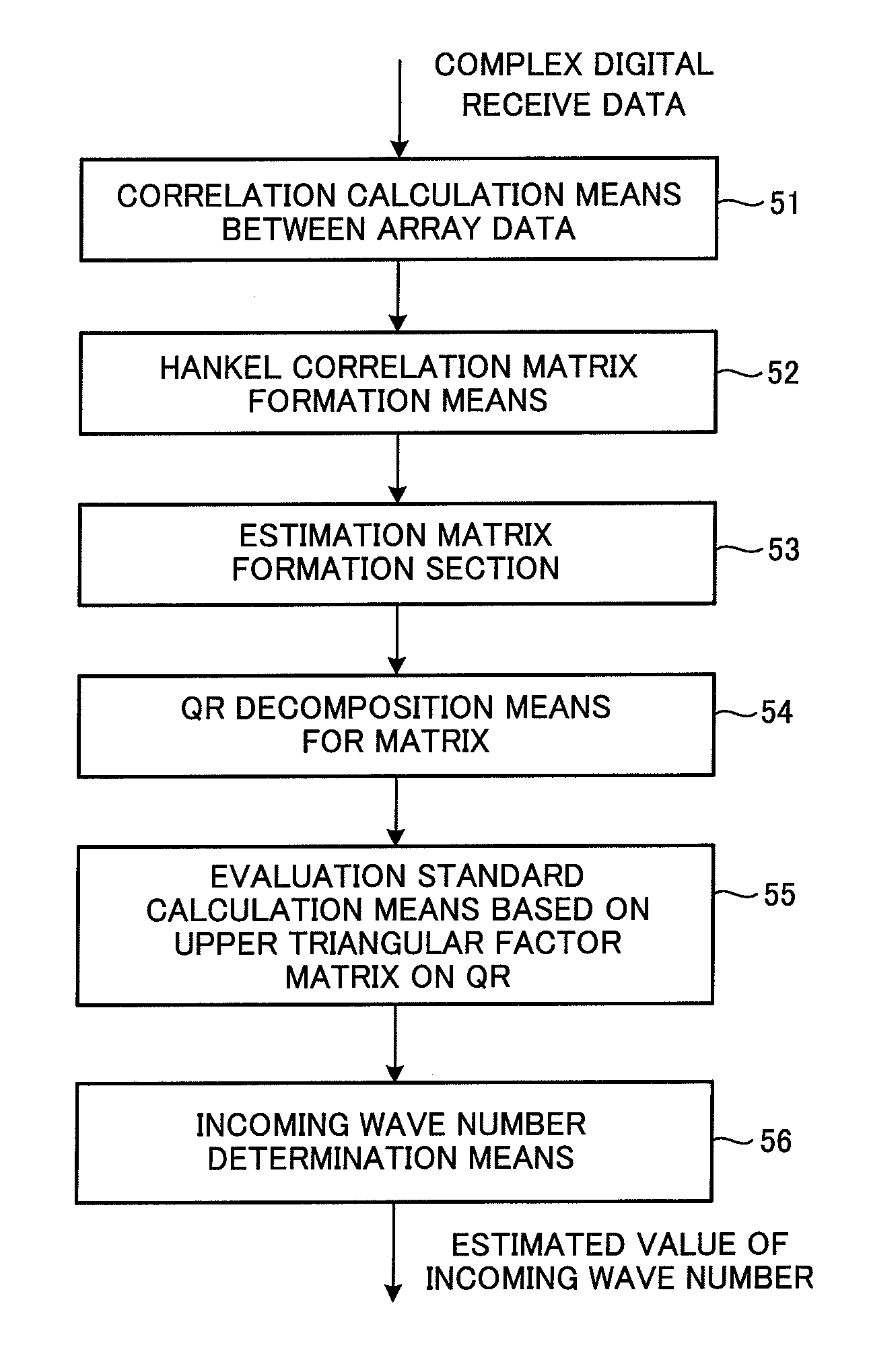
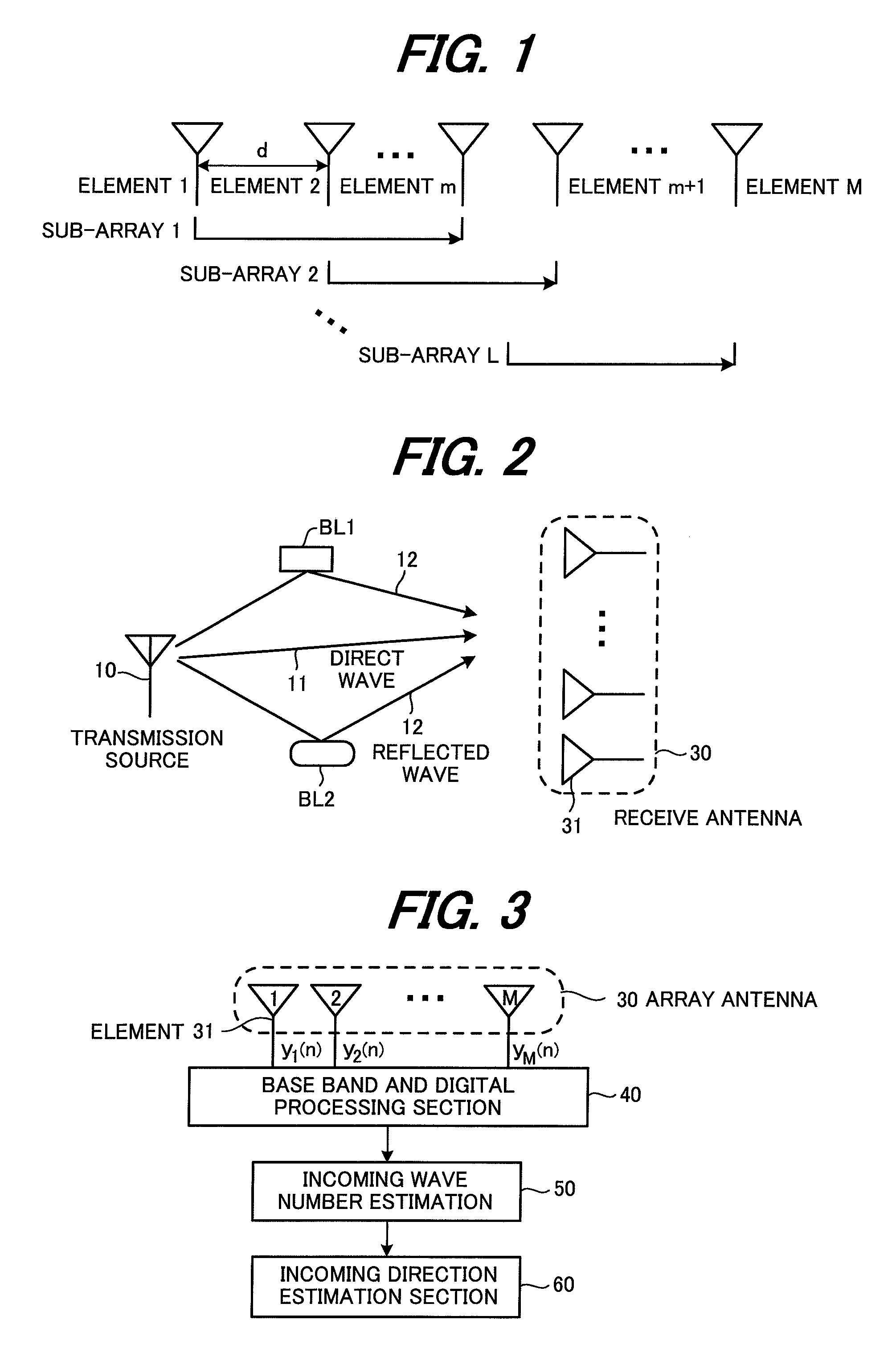
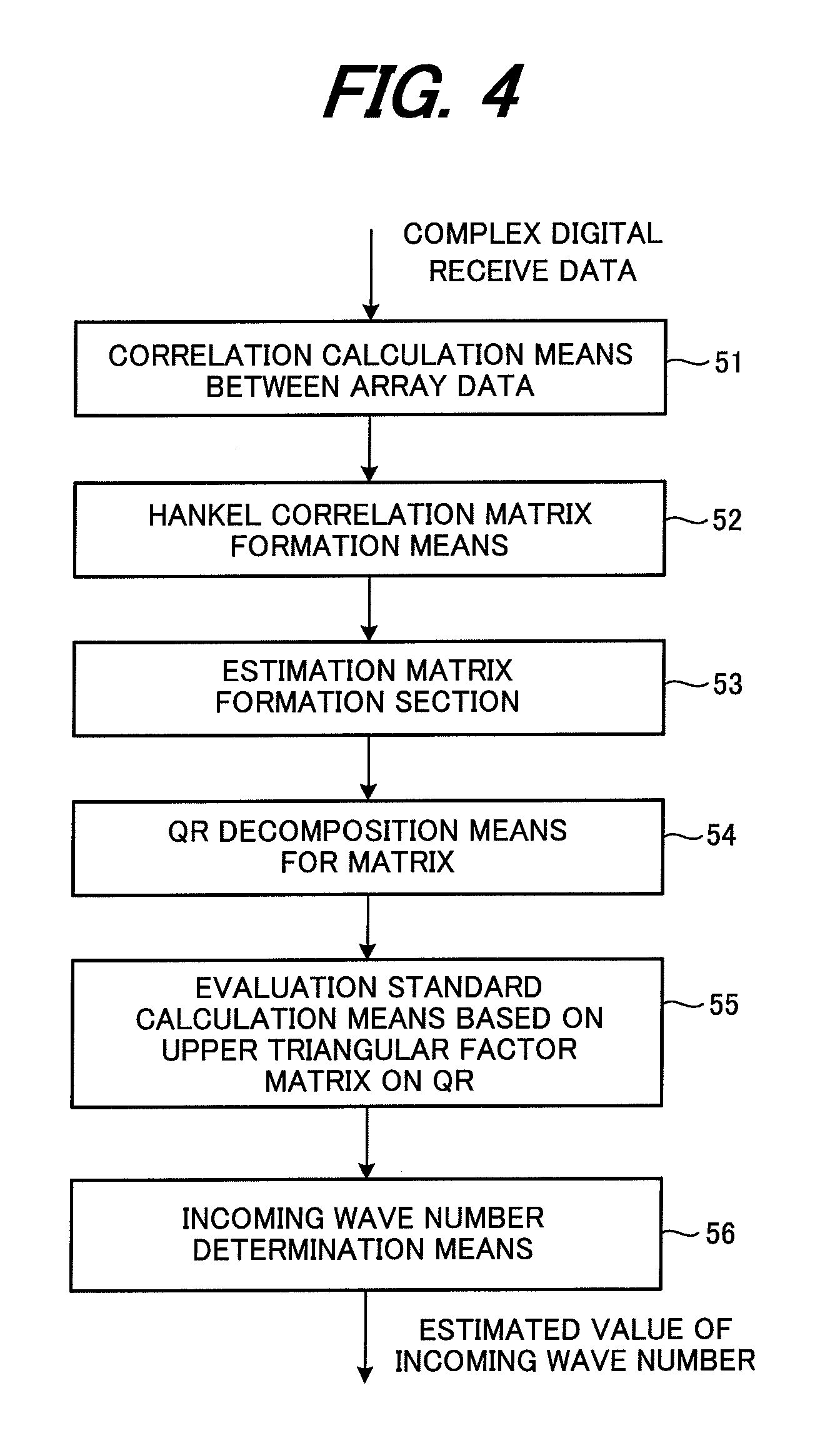
An incoming wave number estimation device for receiving incoming radio waves by an array antenna in which a plurality (=M) of antenna elements are linearly arrayed with a same element spacing, and estimating the number of the incoming radio waves, including: a correlation matrix creation section for removing a diagonal element from a predetermined row or column constituting an M×M array covariance matrix, and creating a correlation matrix by extracting a predetermined p number of correlations from (M−1) number of correlations after the diagonal element is removed while sequentially shifting one element at a time, and arraying the p number correlations in a matrix; an estimation matrix creation section for creating an estimation matrix for estimating the incoming wave number using the correlation matrix; a QR decomposition section for performing QR decomposition on the estimation matrix; and an incoming wave number determination section for determining the number of incoming radio waves based on each row element of an upper triangular matrix factor obtained by the QR decomposition.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Layered space-time nonlinear precoding method in multi-carrier code division multiple access (MC-CDMA) system
InactiveCN101854328AReduce complexityElimination of false layer transfer effectsError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsTelecommunicationsCarrier signal
The invention relates to a layered space-time nonlinear precoding method in a multi-carrier code division multiple access (MC-CDMA) system. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, establishing a precoding system; adopting geometric mean resolution on feedback channel information in the system to form a product of a unitary matrix and an upper triangular matrix to obtain a precoding matrix with the same equivalent noise gain; carrying out nonlinear modular algebra precoding (THP, Tomlinson-Harashima Precoding) among MC-CDMA subcarrier channels at the transmitting end; multiplying all subcarrier signals after carrying out THP and the unitary matrix obtained by channel geometric mean resolution and then transmitting from a corresponding antenna; and processing at the receiving end by adopting a Zero Forcing (ZF) criterion or a minimum mean-squared error (MMSE) criterion. The method effectively eliminates the layer mistaking transmission effect of a layered space-time code, improves the code mistaking performance of the system, reduces the complexity of a downlink receiver and can effectively resist the selective fading of channel frequency, thereby improving the transmission performance of the system.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
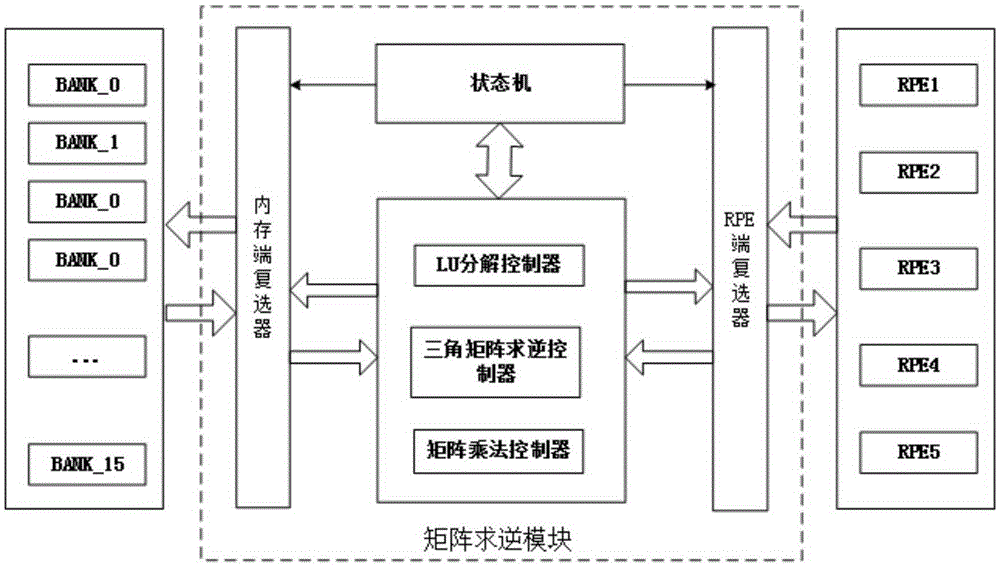
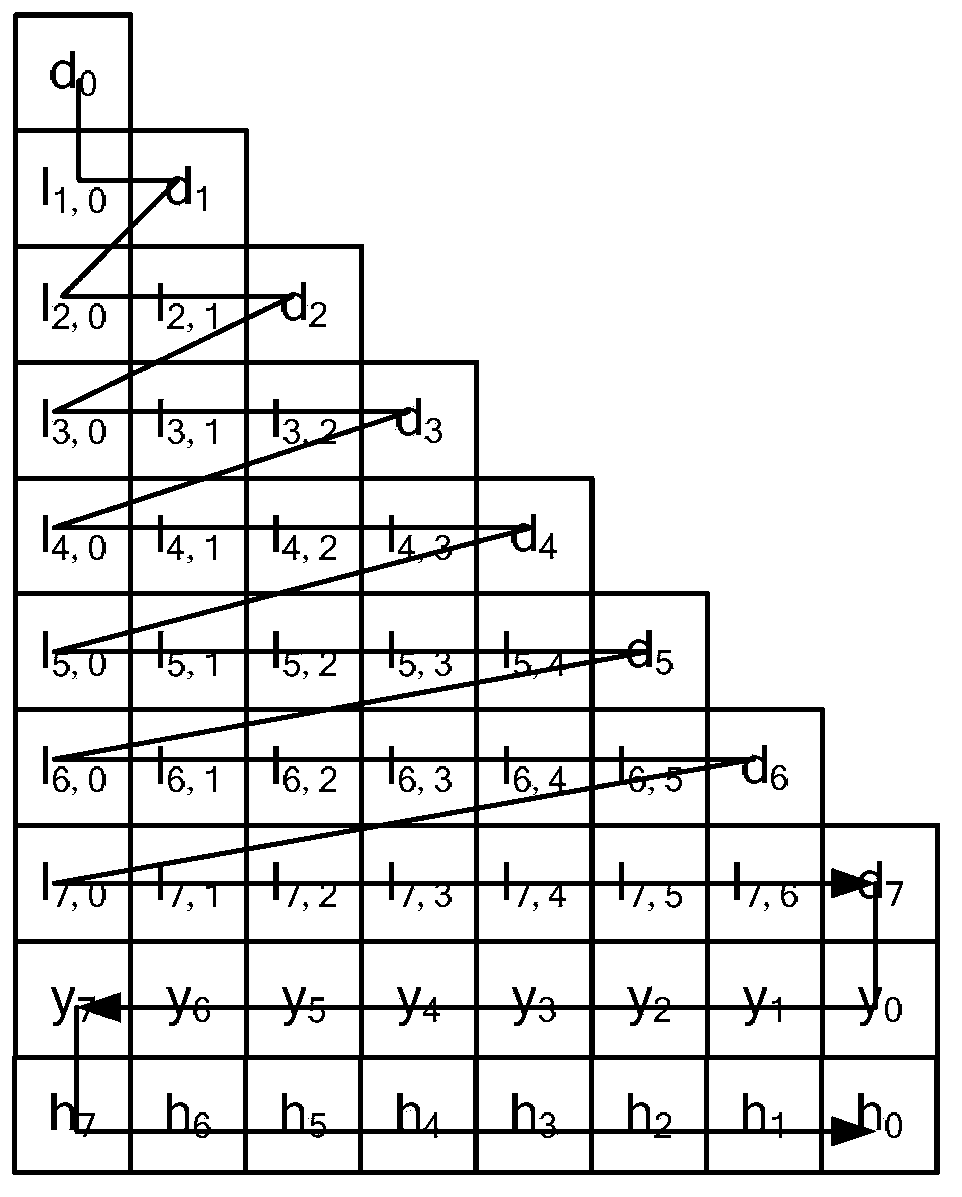
Low-complexity quick parallel matrix inversion method
ActiveCN104298649AImprove efficiencyReduce complexityTransmitter/receiver shaping networksComplex mathematical operationsSubstitution methodSignal processing
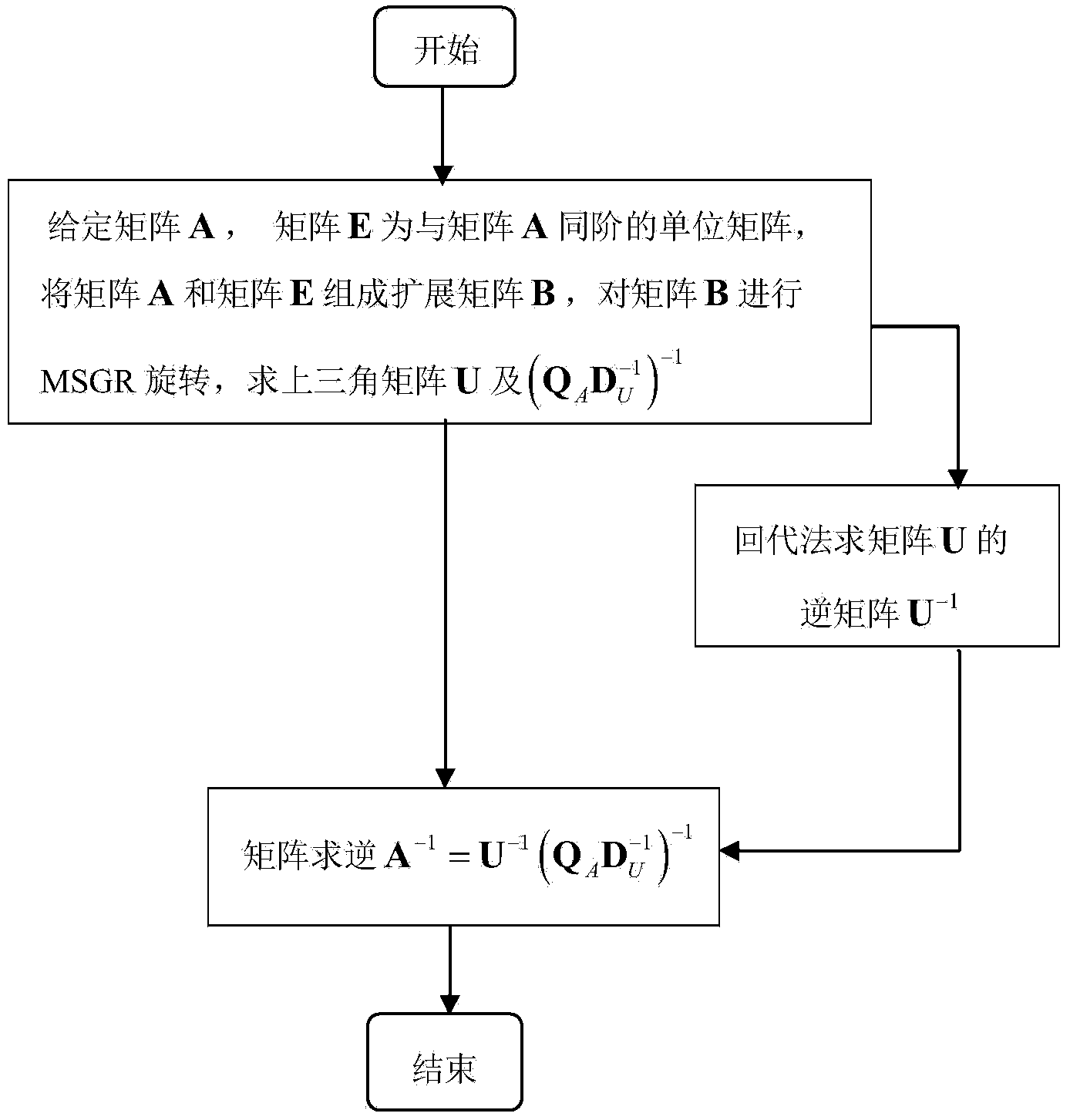
The invention discloses a low-complexity quick parallel matrix inversion method. The method comprises the following steps that first, a matrix A is given, a matrix E is made to be a unit matrix with the same order as the matrix A, the matrix A and the matrix E form an expanding matrix B, modified Givens rotation (MSGR, Modified Square Givens Rotations) is carried out on the matrix B, an upper triangular matrix U and , wherein according to the define of the matrix U and , an SGR (Squared Givens Rotations) method is used for deforming the QR division of the matrix A according to the equation, and the relation between the QR division and original QR division meets the equations , , , and ; according to the MSRG method, the square root operation in the process of Givens rotation can be omitted while division operation is reduced, and algorithm complexity is obviously reduced; second, a back substitution method is used for working out the inverse matrix U-1 of the upper triangular matrix U; third, matrix inversion is carried out according to the equation . According to the low-complexity quick parallel matrix inversion method, a large amount of division operation and a large amount of square root operation are omitted, algorithm complexity is reduced, and the method can be used for matrix inversion of the fields of wireless communication, signal processing and numerical calculation.
Owner:南京易太可通信技术有限公司
Multiple-input and multiple-output precoding method and device
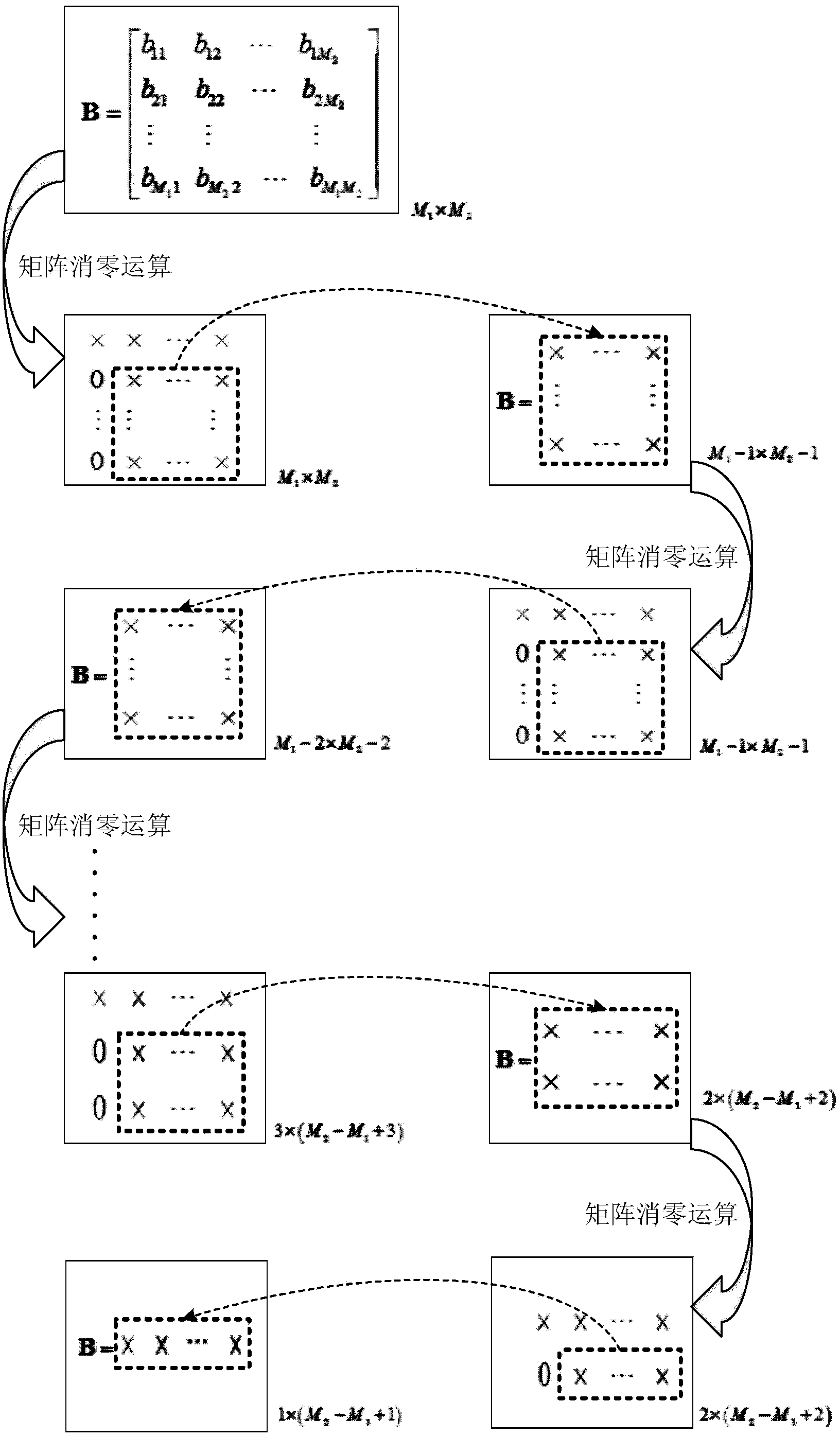
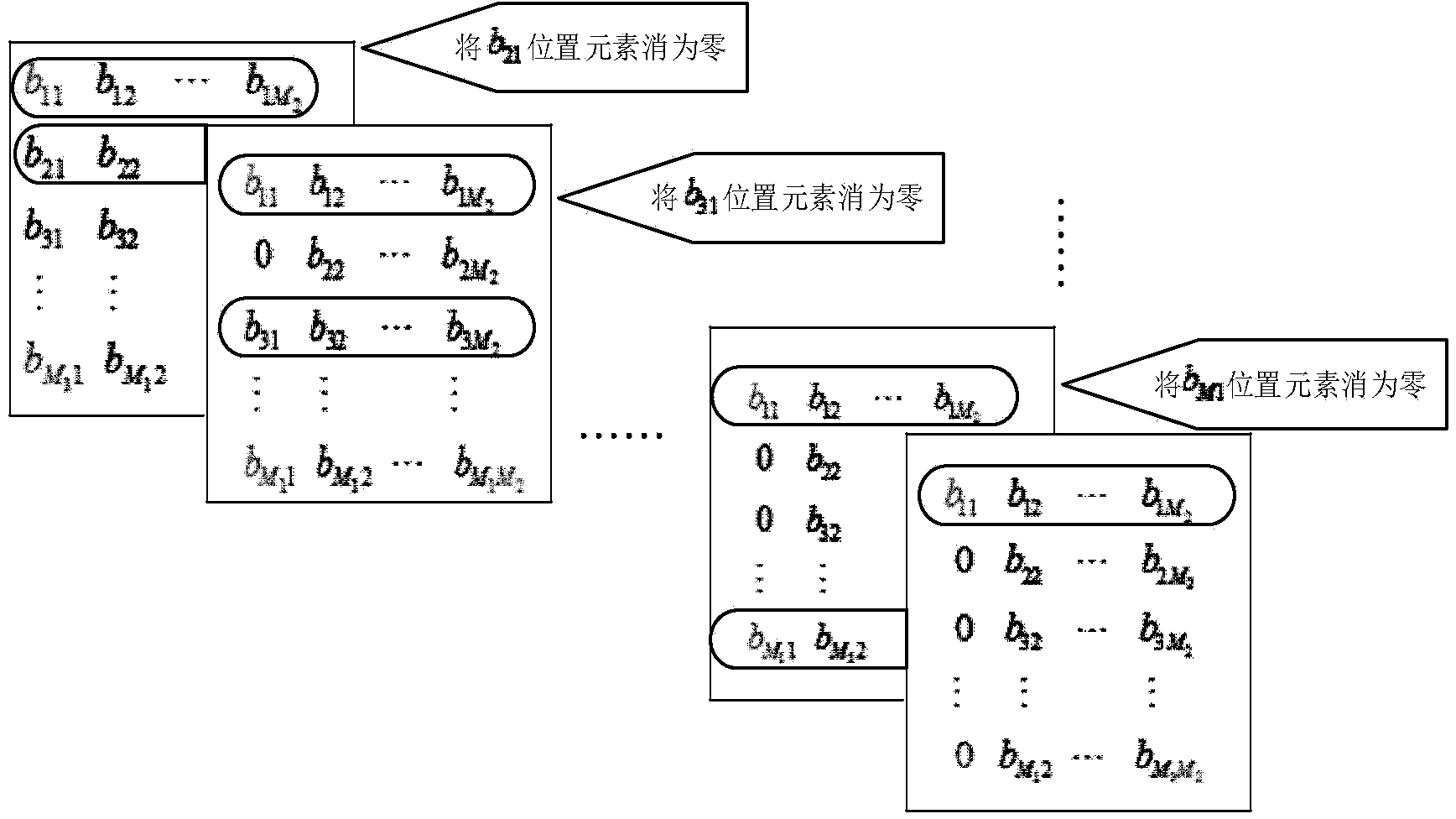
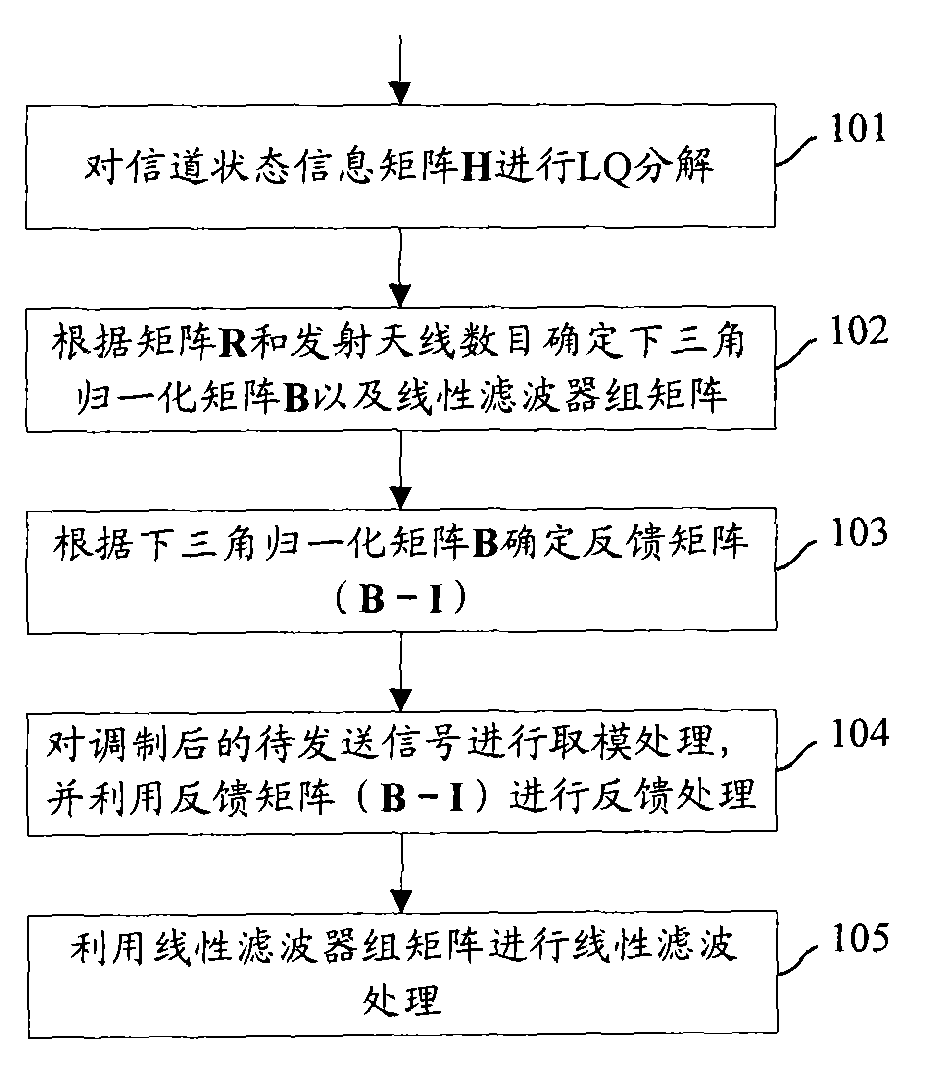
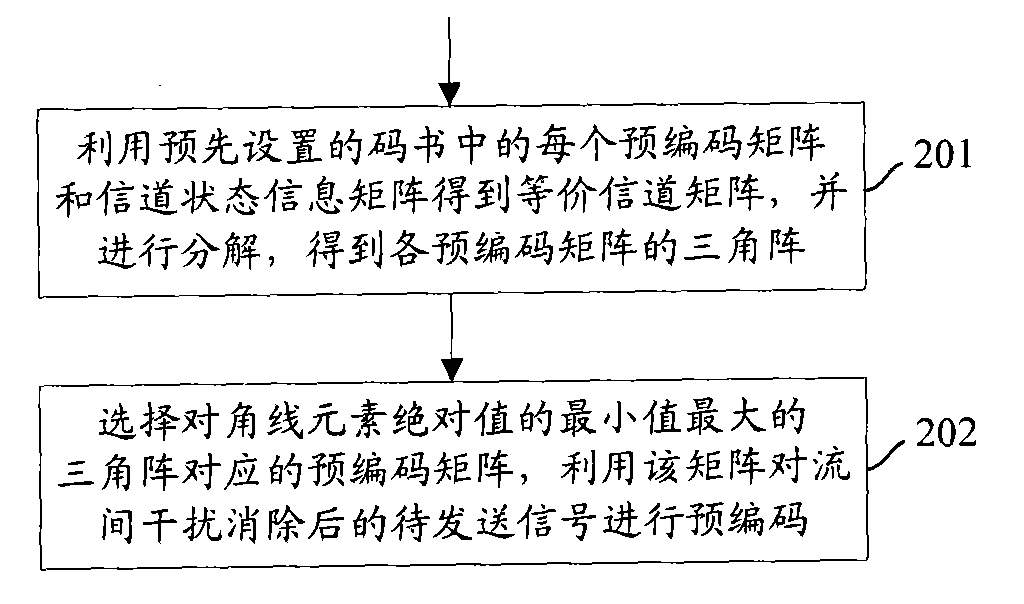
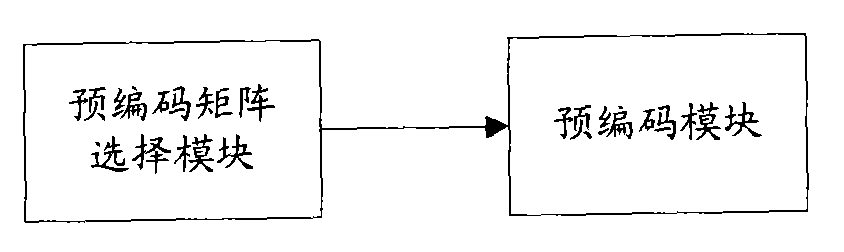
InactiveCN101552633AReduce signal to noise ratioReduce bit error rateSpatial transmit diversityTransmitter/receiver shaping networksChannel state informationTransmission quality
The invention discloses a multiple-input and multiple-output precoding method and device. In the method, an equivalent channel matrix is obtained by each precoding matrix and each channel state information matrix in a predetermined codebook; after the equivalent channel matrix is analyzed, a triangular matrix corresponding to each precoding matrix is obtained; a precoding matrix with a maximal minimum value of diagonal element absolute values is selected, and a pre-transmitting signal with eliminated inter-stream interference is precoded by using the precoding matrix. The precoding device comprises a codebook selecting module and a precoding module. The invention can effectively improve the signal transmission quality in a single-user and multi-user MIMO system.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
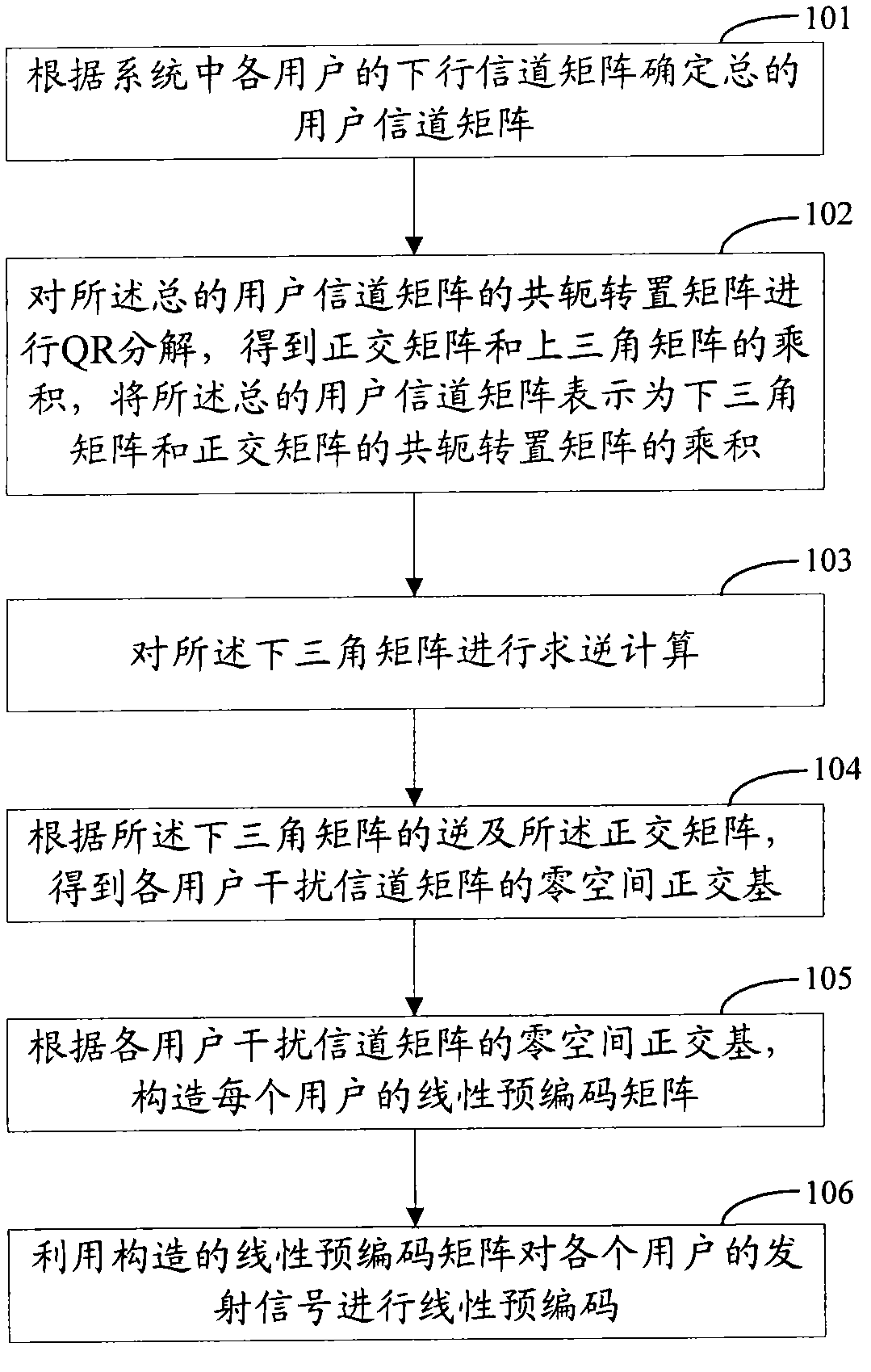
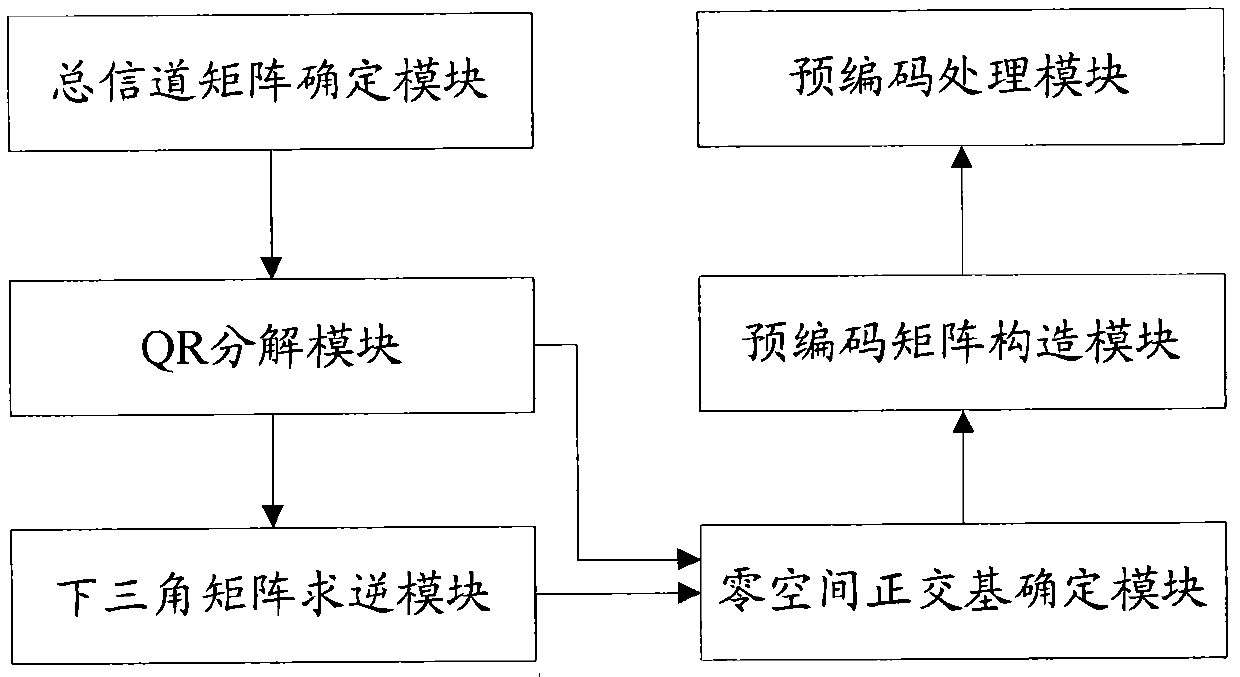
BD (block diagonalization) pre-coding method and device
InactiveCN102546088AReduce computational complexityImprove precoding efficiencySpatial transmit diversityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionQR decompositionConjugate transpose
The invention discloses a BD (block diagonalization) pre-coding method and device, wherein the method comprises the following steps: determining a total user channel matrix Hs according to a downlink channel matrix of each user in a system; carrying out QR factorization on a conjugate transpose matrix of the total user channel matrix Hs to obtain a product of an orthogonal matrix Q and an upper triangular matrix R, and expressing the total user channel matrix Hs as the product of a lower triangular matrix L and a conjugate transpose matrix QH of the orthogonal matrix Q; carrying out inverse calculation on the lower triangular matrix L to obtain L-1; according to the inversed L-1 of the lower triangular matrix L and the orthogonal matrix Q, obtaining a null space orthogonal basis of an interference channel matrix of each user; according to the null space orthogonal basis of the interference channel matrix of each user, constructing a linear pre-coding matrix of each user; and carrying out linear pre-coding on a transmitting signal of each user by utilizing the constructed linear pre-coding matrix. The technical scheme disclosed by the invention can reduce the system complexity and improve the coding efficiency.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for eliminating serial interference in multi-input multi-output system
InactiveCN101409604ASimplified Computational ComplexitySpatial transmit diversityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionPrecodingMulti input
The invention discloses a successive interference cancellation method in a multiple input and multiple output system, comprising QR ordering and decomposition are carried out on a channel transmission matrix based on householder transformation to obtain an upper triangular matrix R, and according to the matrix R, precoding successive interference cancellation is executed on all the transmit signals, or the successive interference cancellation is executed on the received signal. As the matrix R is the upper triangular matrix, the successive interference cancellation can be sequentially executed on all the transmit signals by utilizing the characteristics of the upper triangular matrix, thus avoiding determining the successive detection sequence in a way using VBLAST for matrix inverse or pseudo-inverse, and further simplifying the computational complexity of the successive interference cancellation and improving the performance of signal detection.
Owner:TD TECH COMM TECH LTD
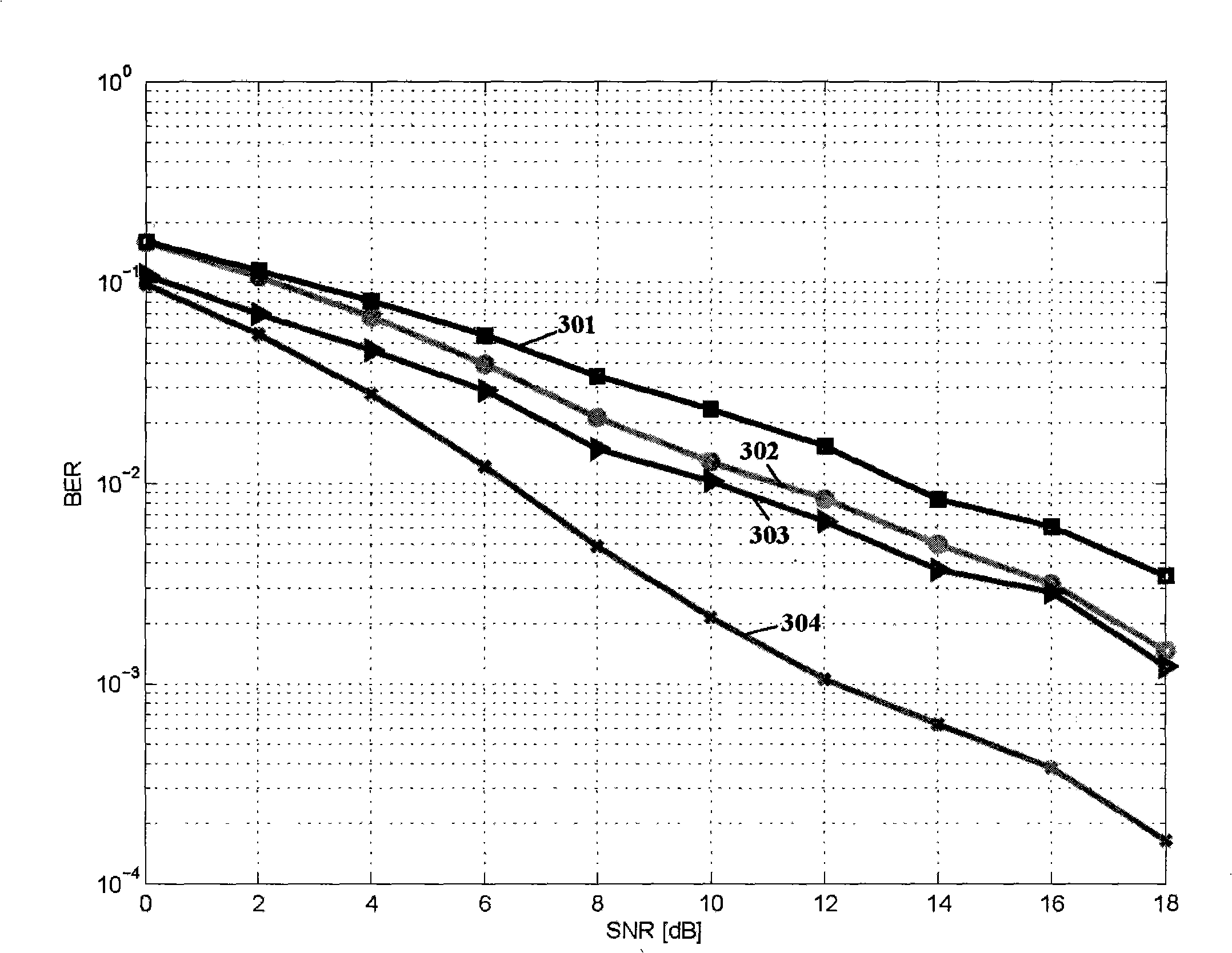
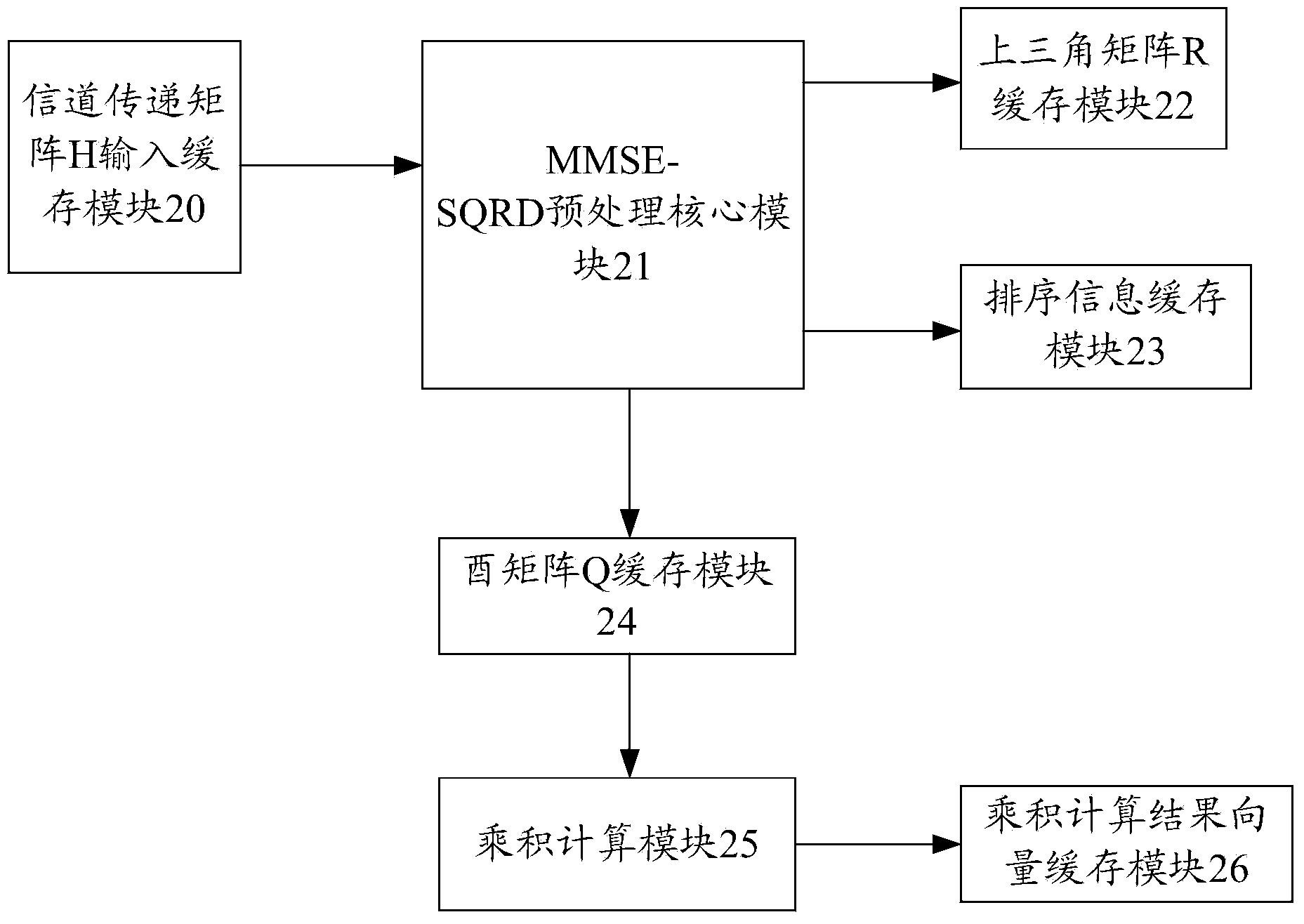
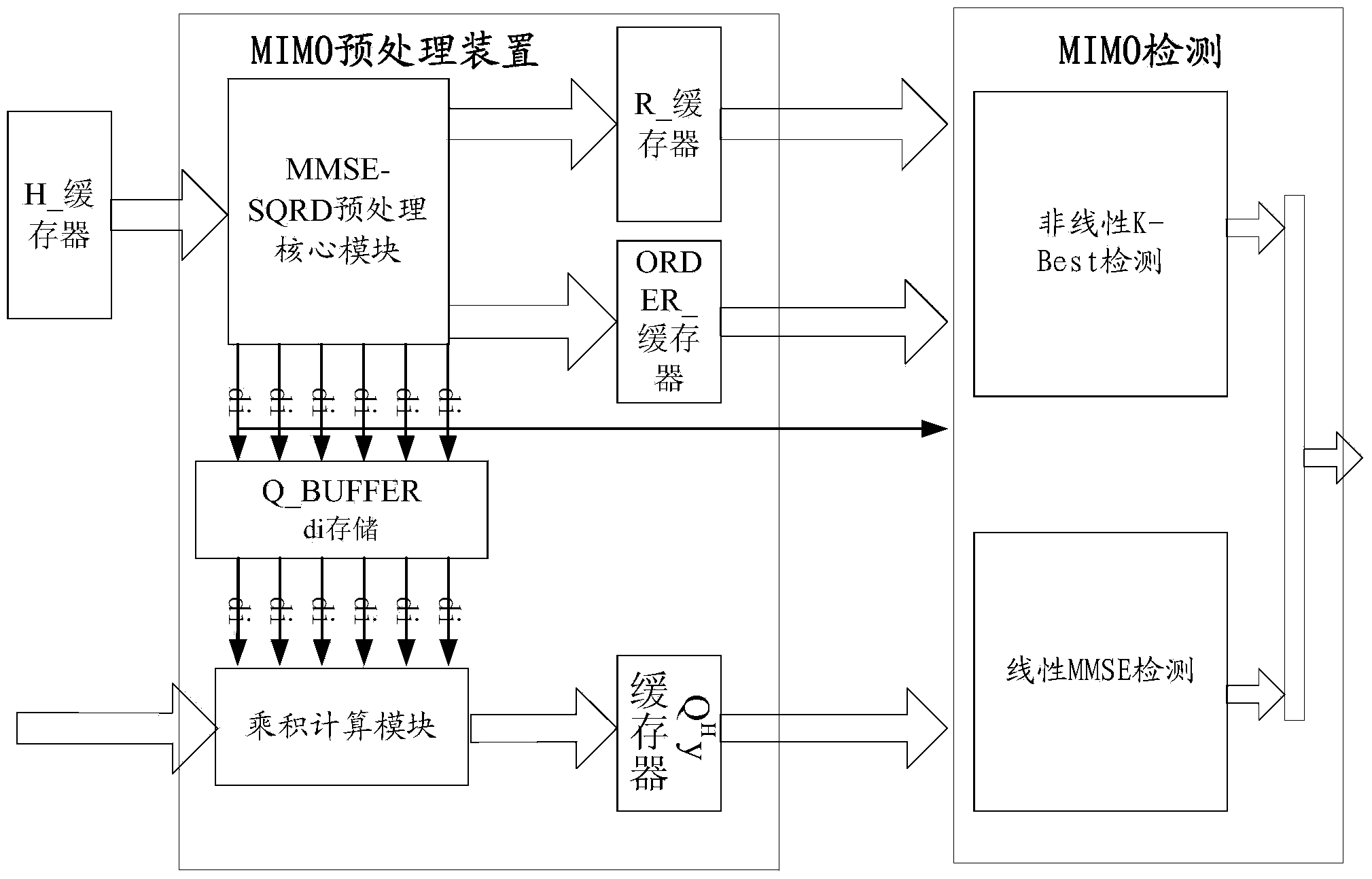
MIMO detecting preprocessing device and method
The invention discloses an MIMO detecting preprocessing device and method. The device comprises a channel transfer matrix input cache module, an MMSE-SQRD preprocessing core module, an upper triangular matrix R cache module, a sorting information cache module, a unitary matrix Q cache module, a product computing module and a product computing result cache module. According to the MIMO detecting preprocessing device and method, QR decomposition of an augmented matrix of a channel transfer matrix received by an MIMO receiving end is achieved, sorting operation is added in the matrix QR decomposition process, a unitary matrix and an upper triangular matrix after QR decomposition are obtained, the sorting information vectors of the matrixes are obtained, the device and method are suitable for fields such as MIMO detecting, and the obtained unitary matrix and the obtained upper triangular matrix after QR decomposition can be effectively reused in next-level MMSE and K-Best detecting.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
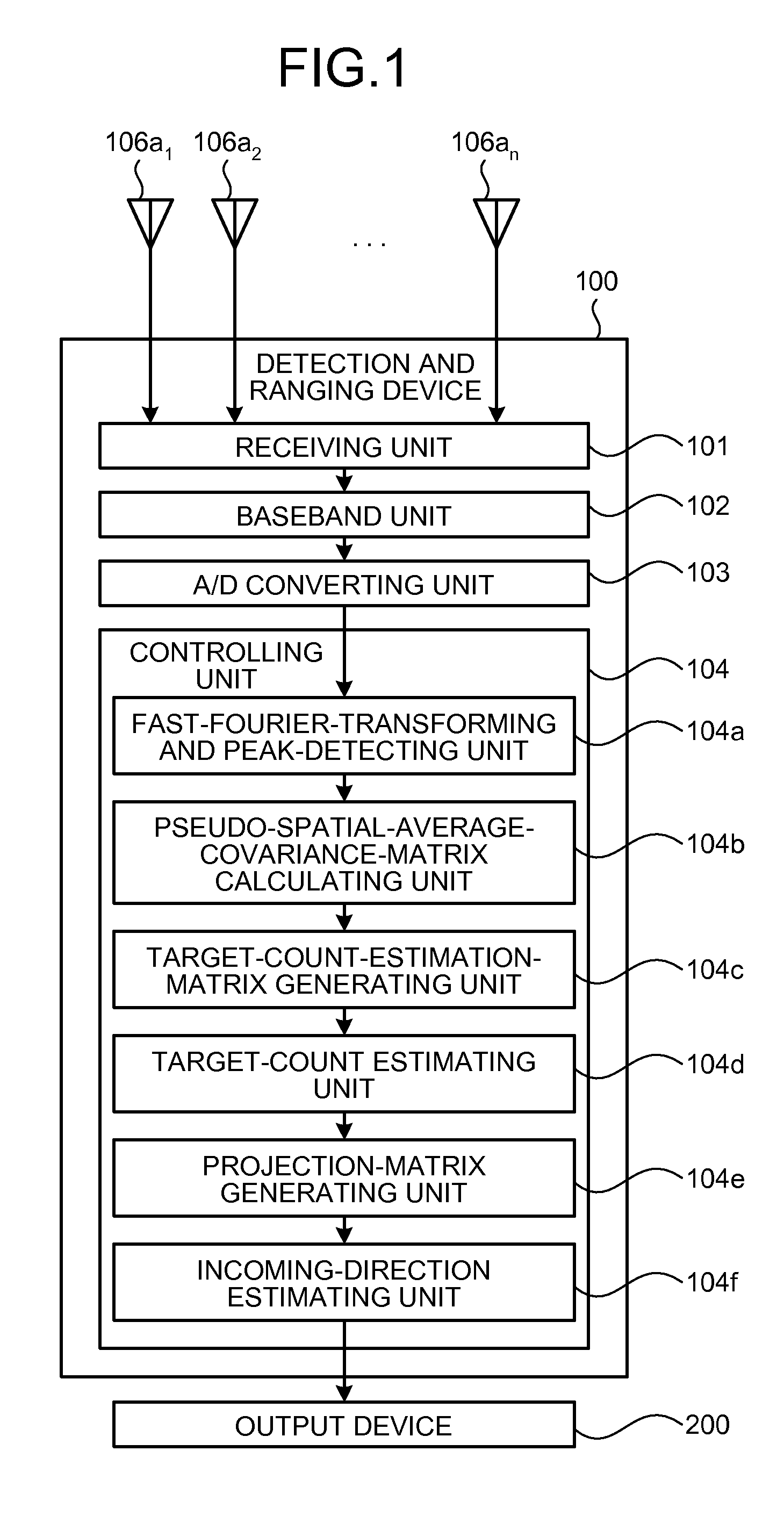
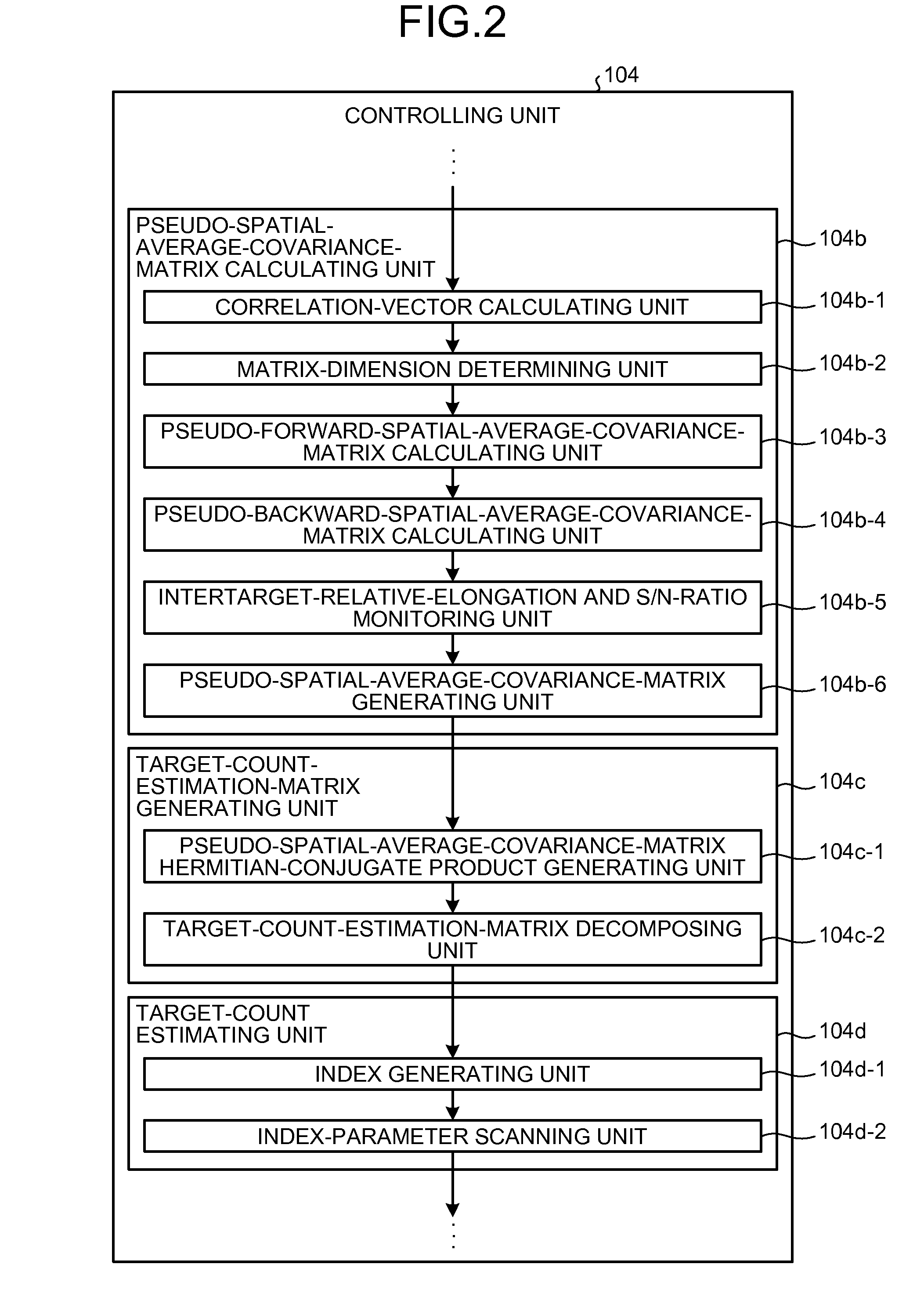
Detection and Ranging Device and Detection and Ranging Method
InactiveUS20090224978A1Solve problemsBeacon systems using radio wavesMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesSpatial averageLU decomposition
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Transmitting/receiving method for multi-user multiple-input multiple-output system
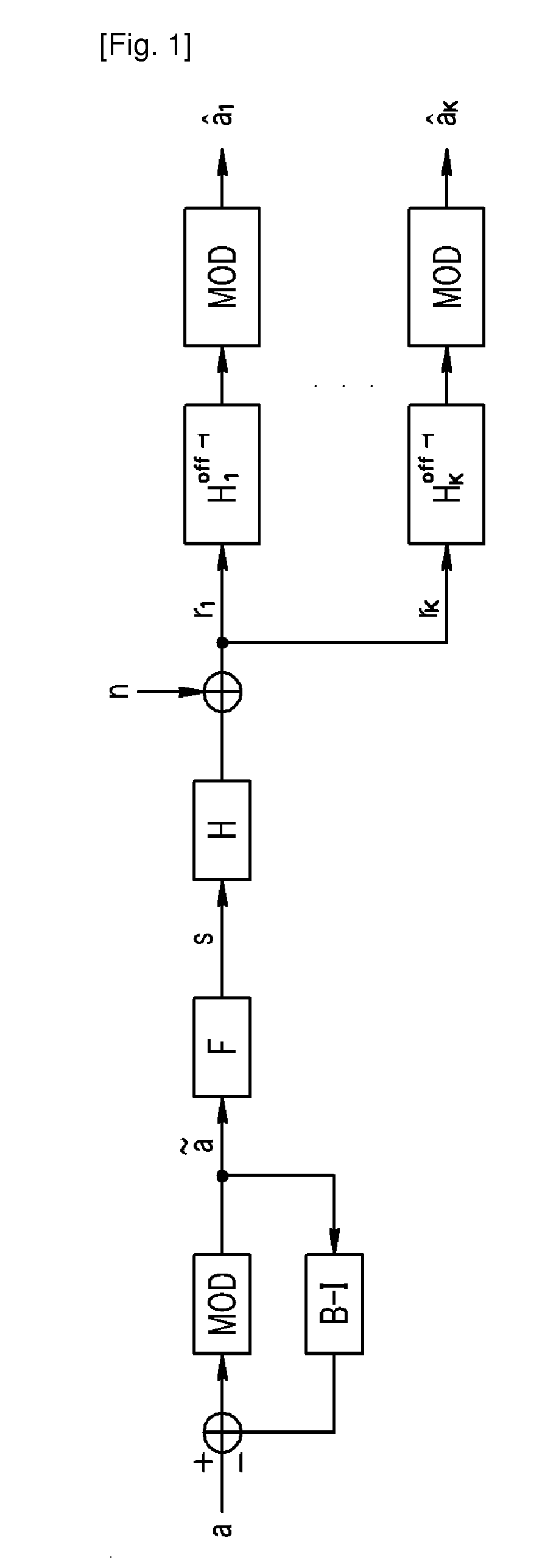
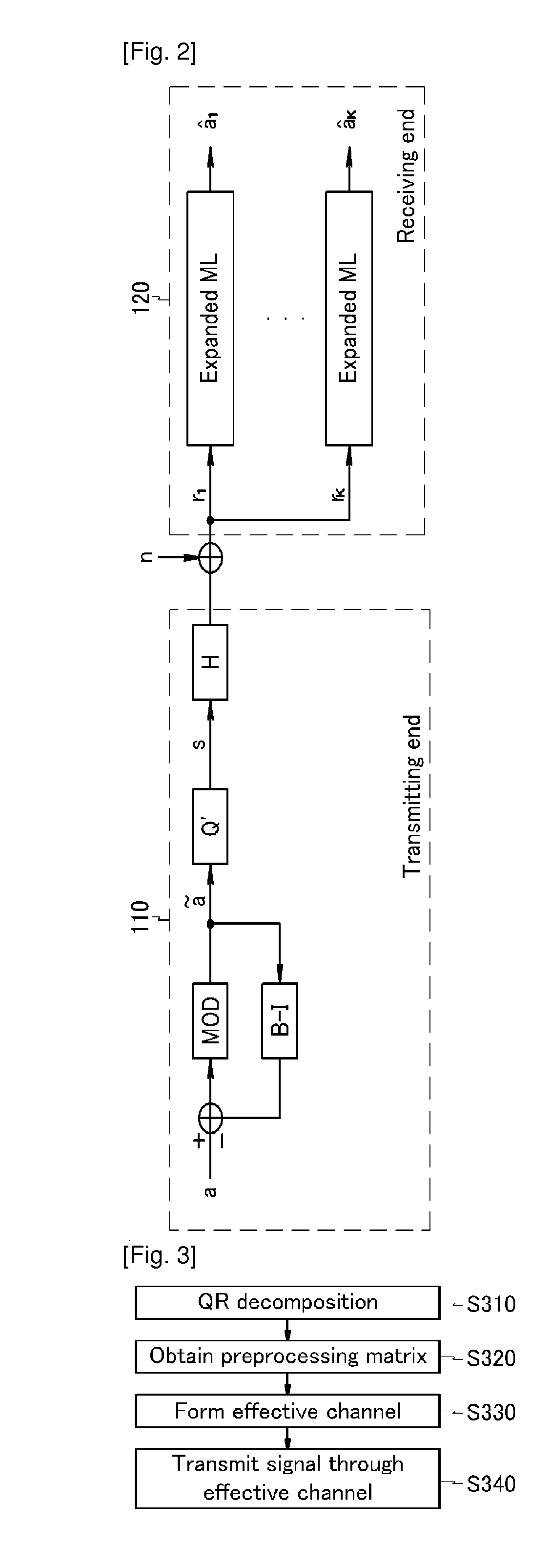
ActiveUS20100310001A1Increase data rateImprove error performanceDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationQR decompositionTriangulation
Disclosed is a transmitting / receiving method in a multi-user multiple-input multiple-output (MU-MIMO) channel. The transmitting method includes: performing QR decomposition on a Hermitian transpose matrix of a channel matrix to obtain a first matrix and a second matrix as a triangular matrix; obtaining a preprocessing matrix by using the first matrix; and forming an effective channel based on the preprocessing matrix by a block triangulation technique.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
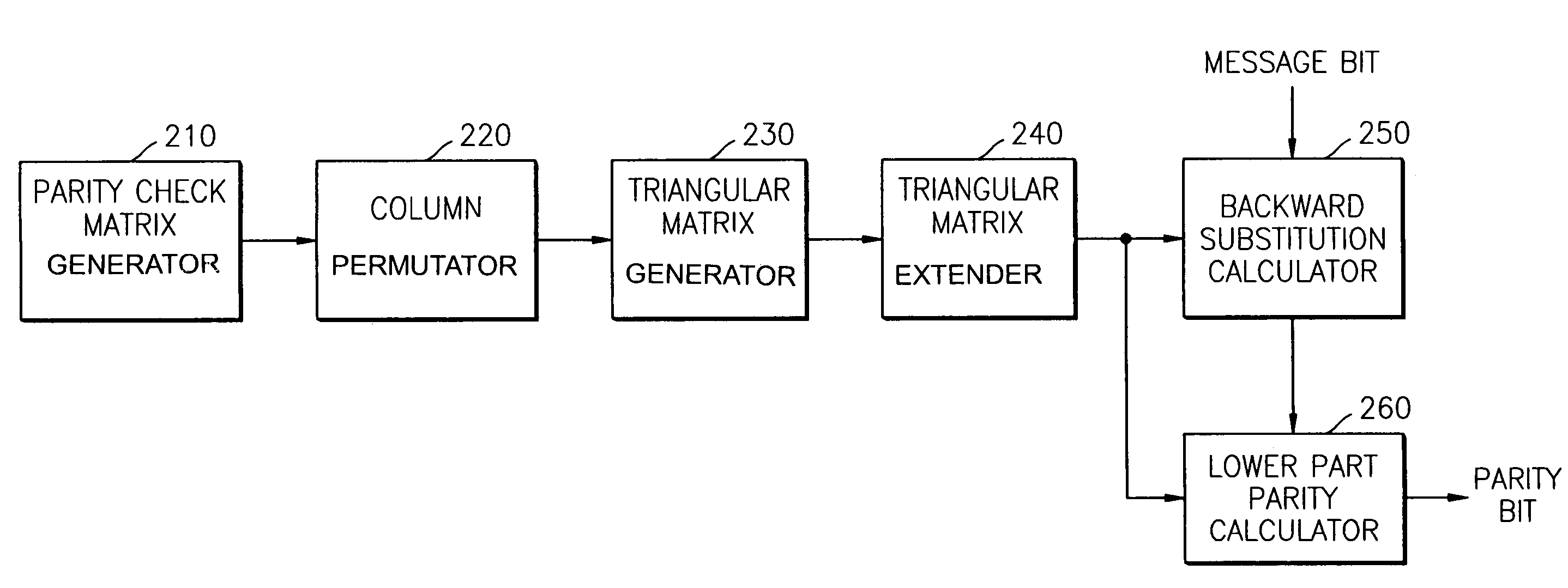
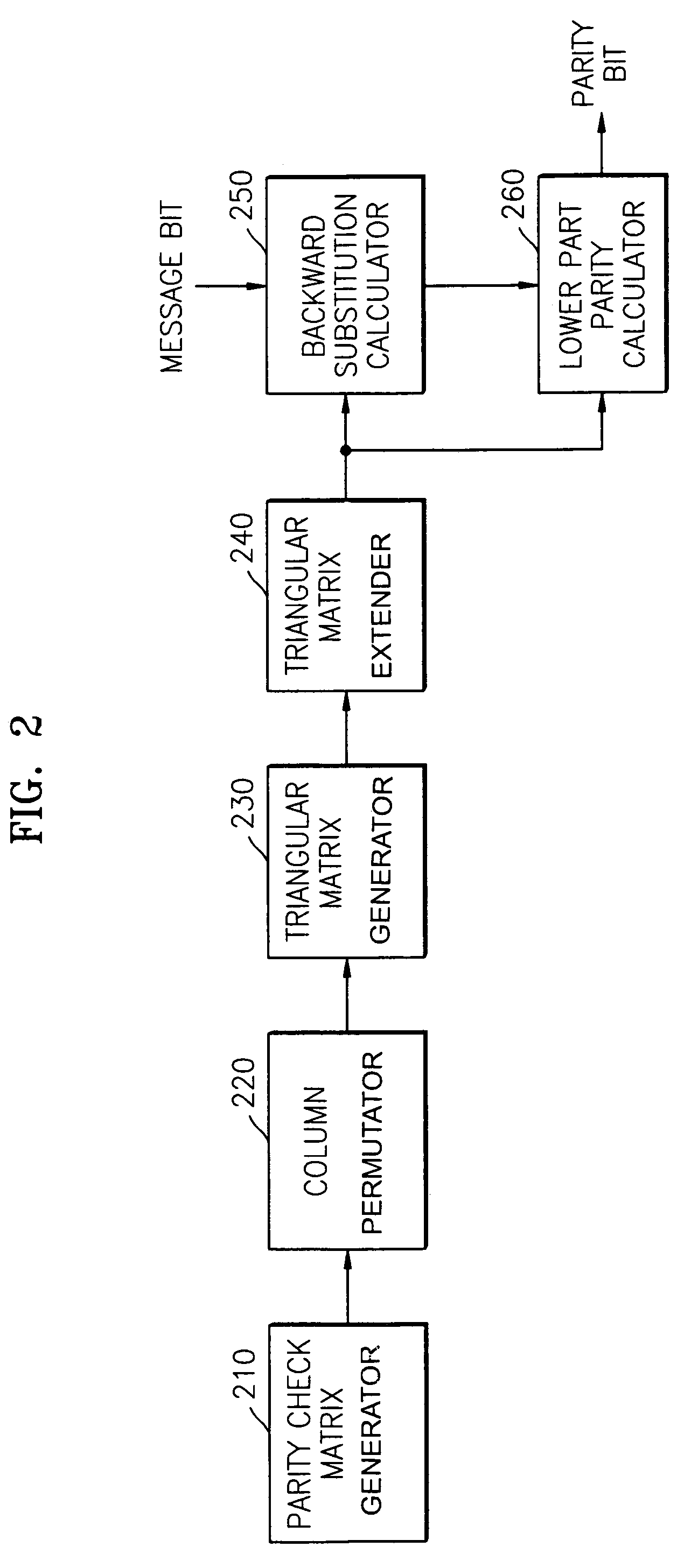
Method of generating parity data based on low-density parity check matrix and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS7278082B2Generate efficientlyError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionTheoretical computer scienceParity-check matrix
A method of generating parity data based on a low-density panty check matrix and an apparatus therefor, the method including: reordering columns of the parity check matrix based on elements in each column having values of one to generate a reordered parity check matrix; determining a cross-point between a diagonal line of a parity matrix part in the parity check matrix and a reordered diagonal line defined by a first entry of an element having a value of one in each column of the reordered parity check matrix; and performing column permutations on the reordered parity check matrix on the basis of positions of elements having a value of one in rows above a horizontal line that passes through the cross-point to generate a triangular matrix, thus reducing the computations required to generate parity data, thereby efficiently obtaining the parity data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
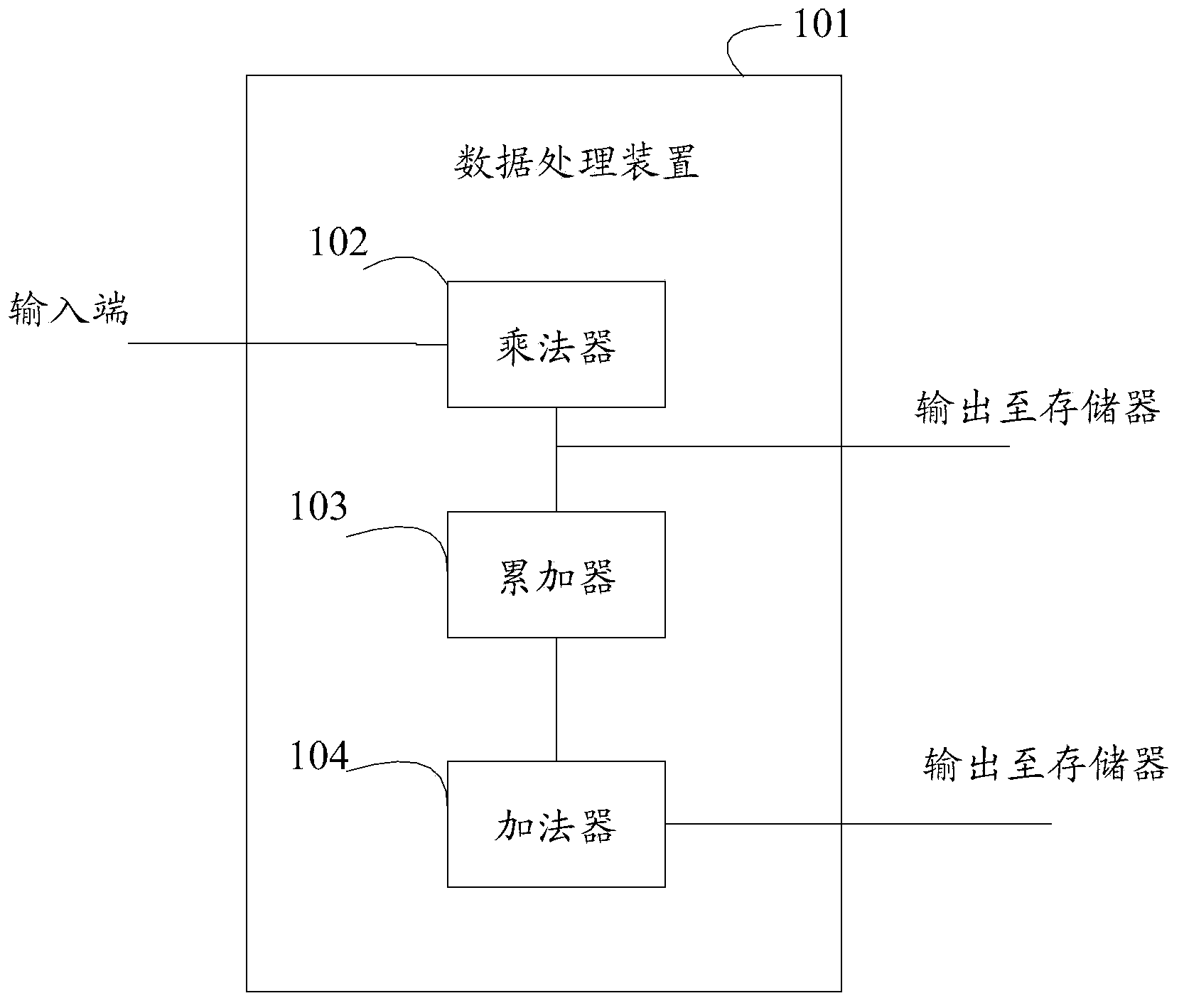
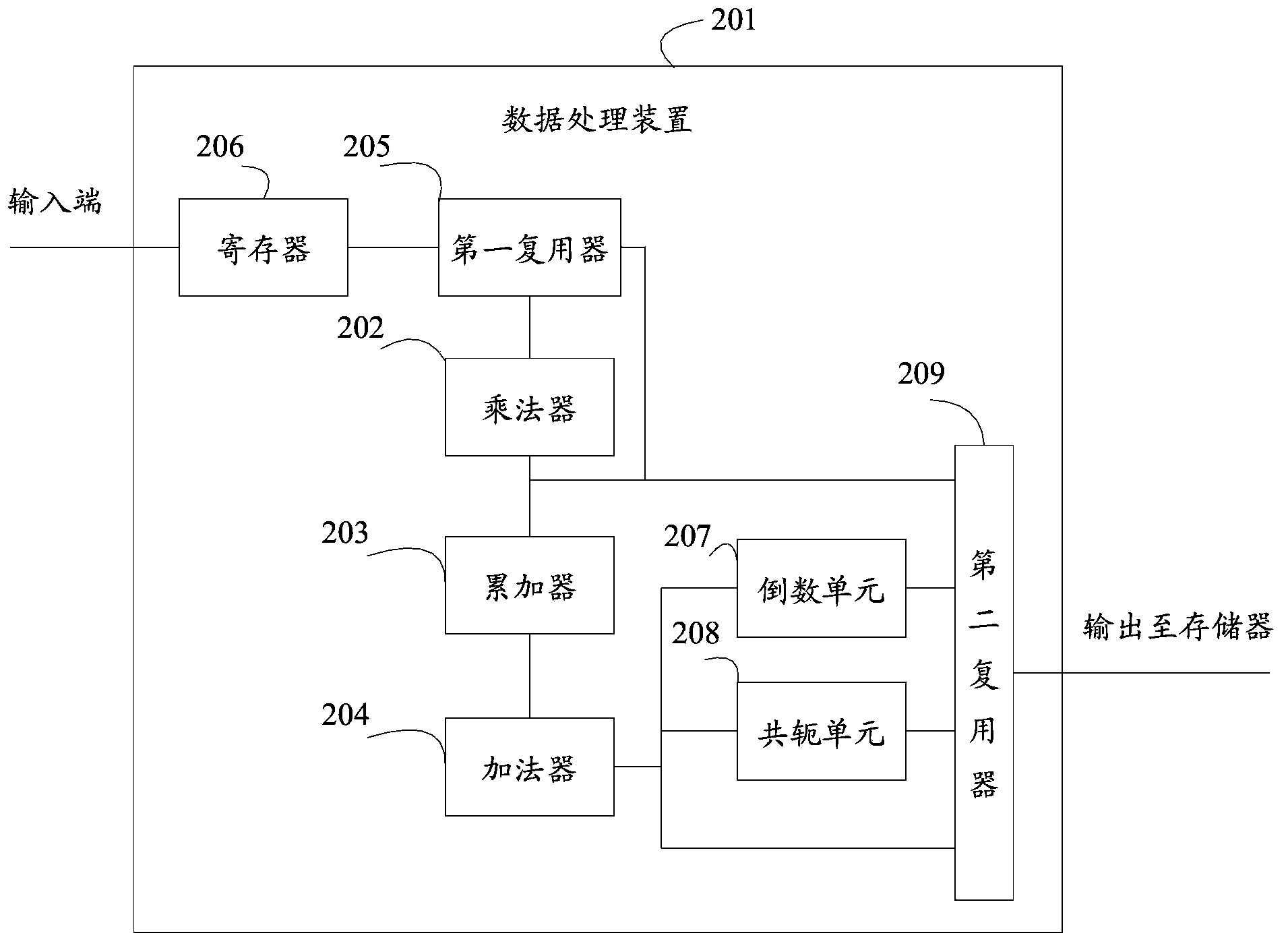
Data processing device
ActiveCN104216866AReduce operational complexitySave logic computing resourcesComplex mathematical operationsConjugate transposeDiagonal matrix
The invention discloses a data processing device. The data processing device is used for solving a lower triangular matrix L corresponding to an n*n symmetric positive definite matrix R, wherein the R is equal to LDLH, the D is a diagonal matrix, the LH is a conjugate transpose matrix of the L, and the n is an integer larger than or equal to 2. The data processing device comprises a multiplying unit, an accumulator and a summator. The input end of the data processing device is connected with the input end of the multiplying unit, the output end of the multiplying unit is connected with the input end of the accumulator, the output end of the accumulator is connected with the output end of the summator, the input end of the data processing device is also connected with the input end of the summator, the output end of the summator is used for outputting matrix data to a storage device, and the output end of the multiplying unit is also used for outputting matrix data to the storage device. By means of the data processing device, the symmetric positive definite matrix can be decomposed without a large amount of root extraction operation, operation complexity is lowered, and logical operation resources are saved.
Owner:HISILICON TECH
Robust state estimation method used for multi-voltage-class power grid model
ActiveCN104184144AEasy to identifyImprove tolerance performanceSpecial data processing applicationsAc network circuit arrangementsEstimation methodsSCADA
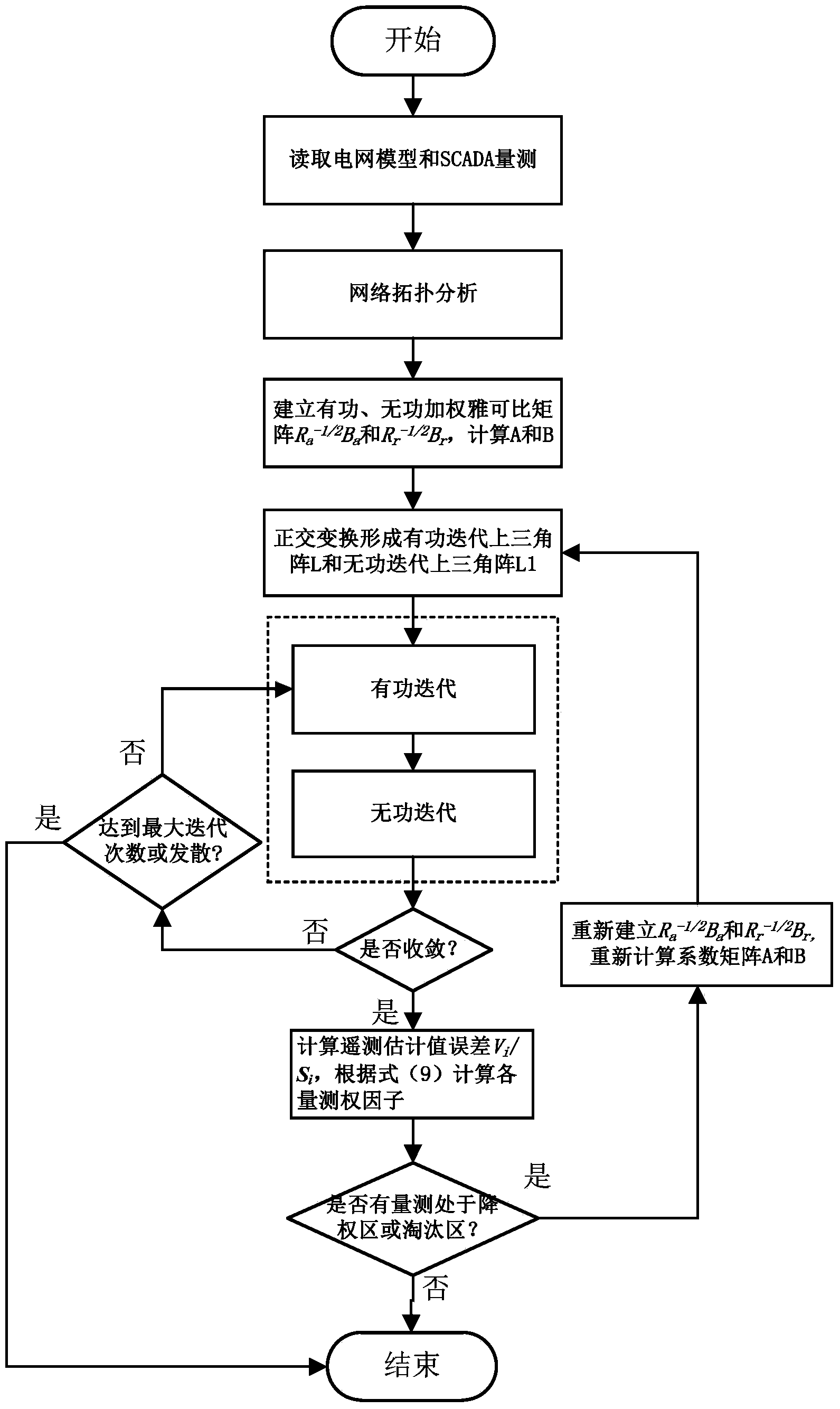
The invention relates to a robust state estimation method used for a multi-voltage-class power grid model. The method comprises the steps that the power grid model is read and SCADA measuring is conducted; network topology analysis is conducted and the physical power grid model is converted into a bus-branch calculation model; an active weighting Jacobi matrix Ra-1 / 2Ba and a reactive calculation weighting Jacobi matrix Rr-1 / 2Br are established and an active coefficient matrix A and a reactive coefficient matrix B are calculated; an upper triangular matrix L of the active coefficient matrix and an upper triangular matrix L1 of the reactive coefficient matrix are obtained through orthogonal transformation and state estimation iterative solving is conducted; the measuring residual error vi is calculated, a measuring type reference value Si is selected, and the remote measuring estimated value error |vi| / Si is calculated; a measuring weight factor is calculated, whether measuring located in a downgrading region or an elimination region exists or not is judged, and if not, state estimation calculation ends; if yes, measuring weighting matrixes Ra-1 and Rr-1 are corrected according to the measuring factor, the weighting Jacobi matrixes Ra-1 / 2Ba and Rr-1 / 2Br are regenerated, A and B are calculated and the step (4) is returned to.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com