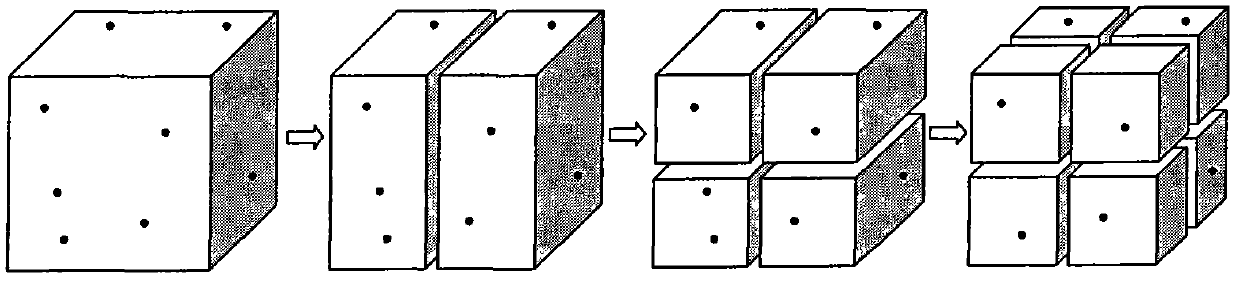
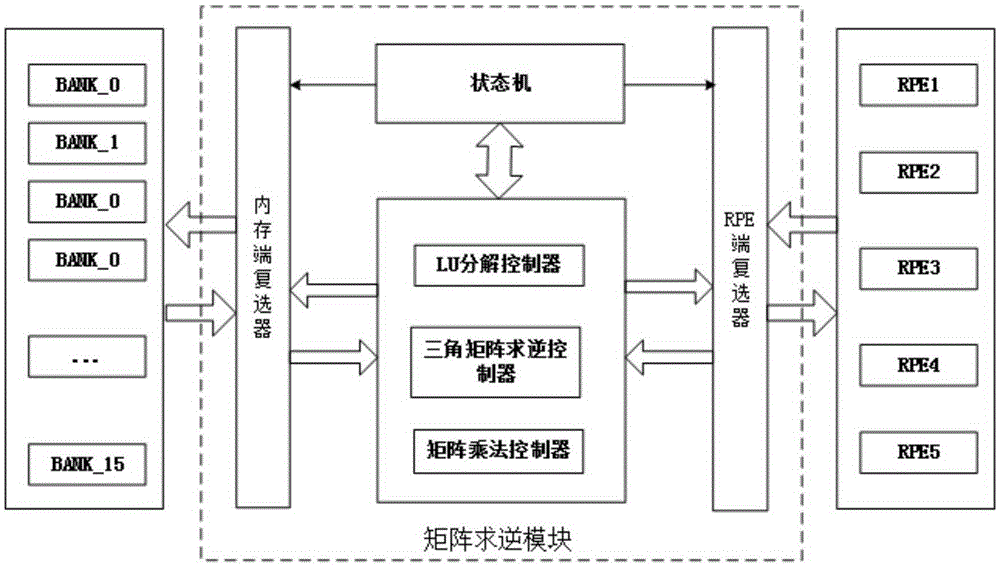
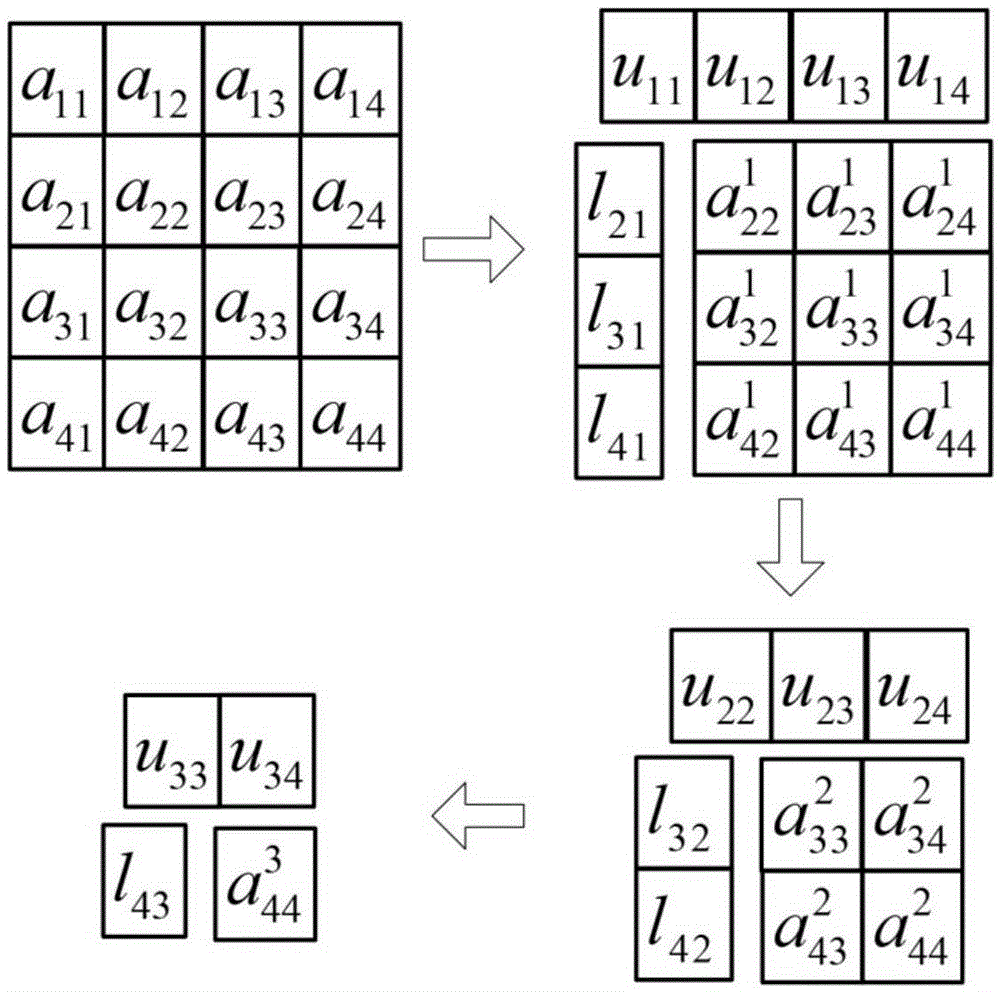
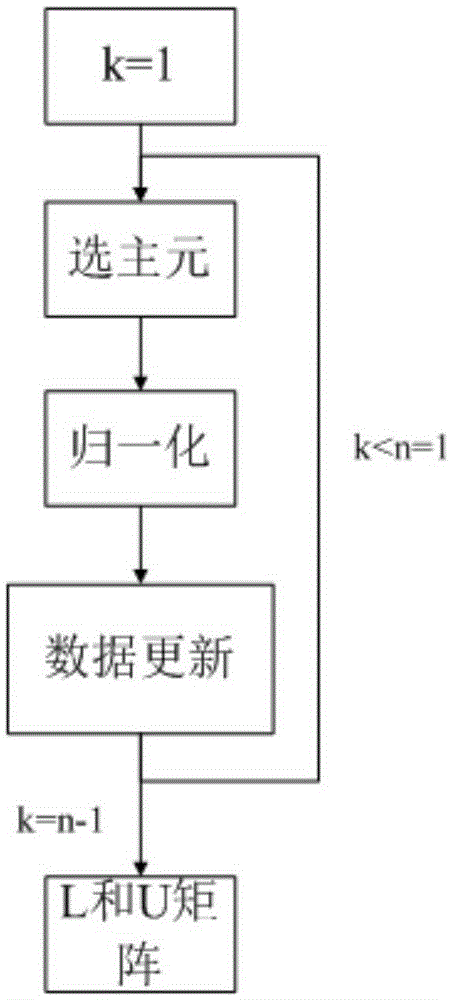
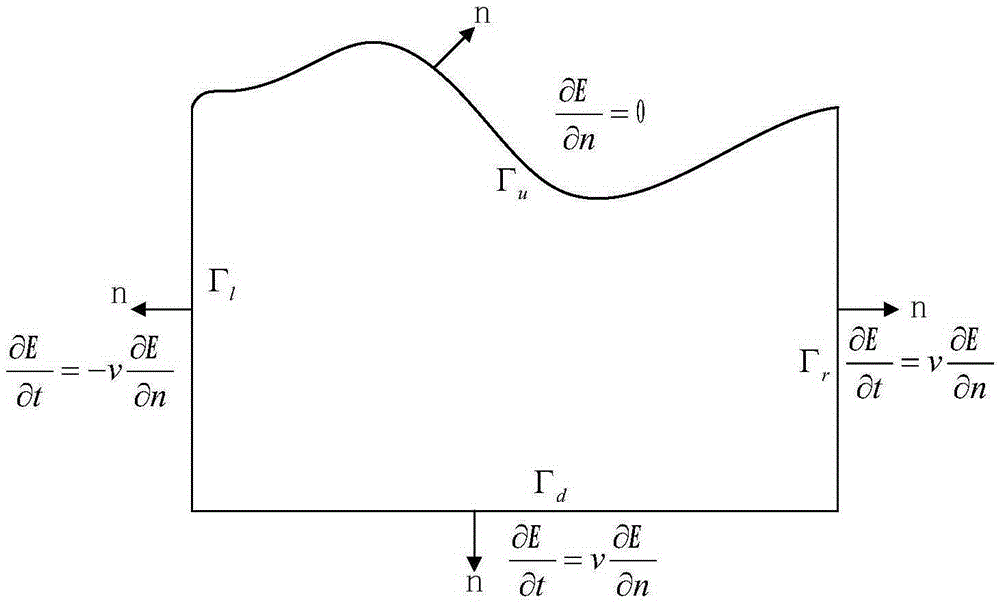
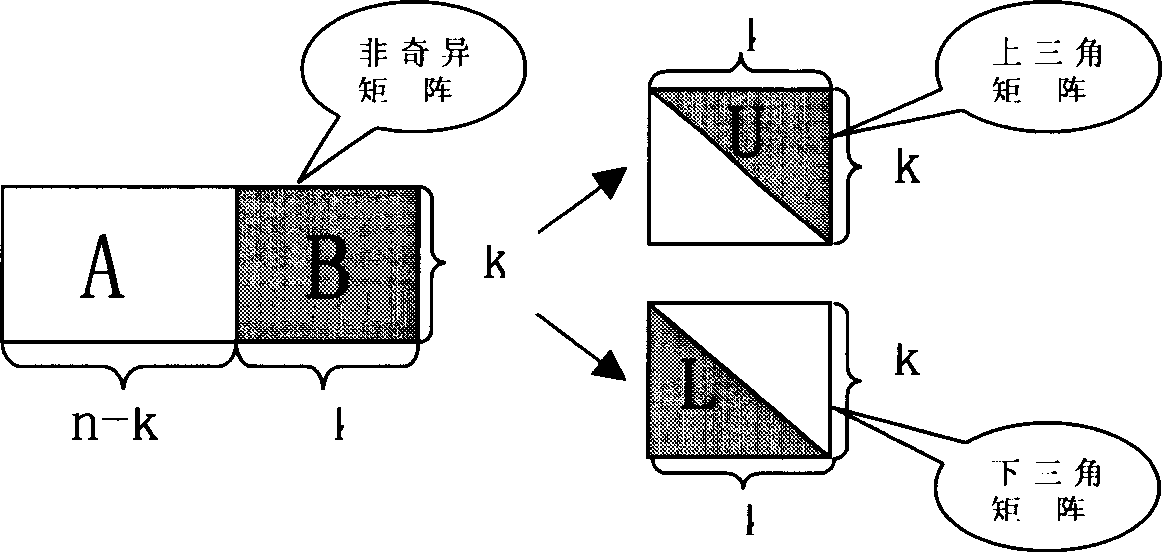
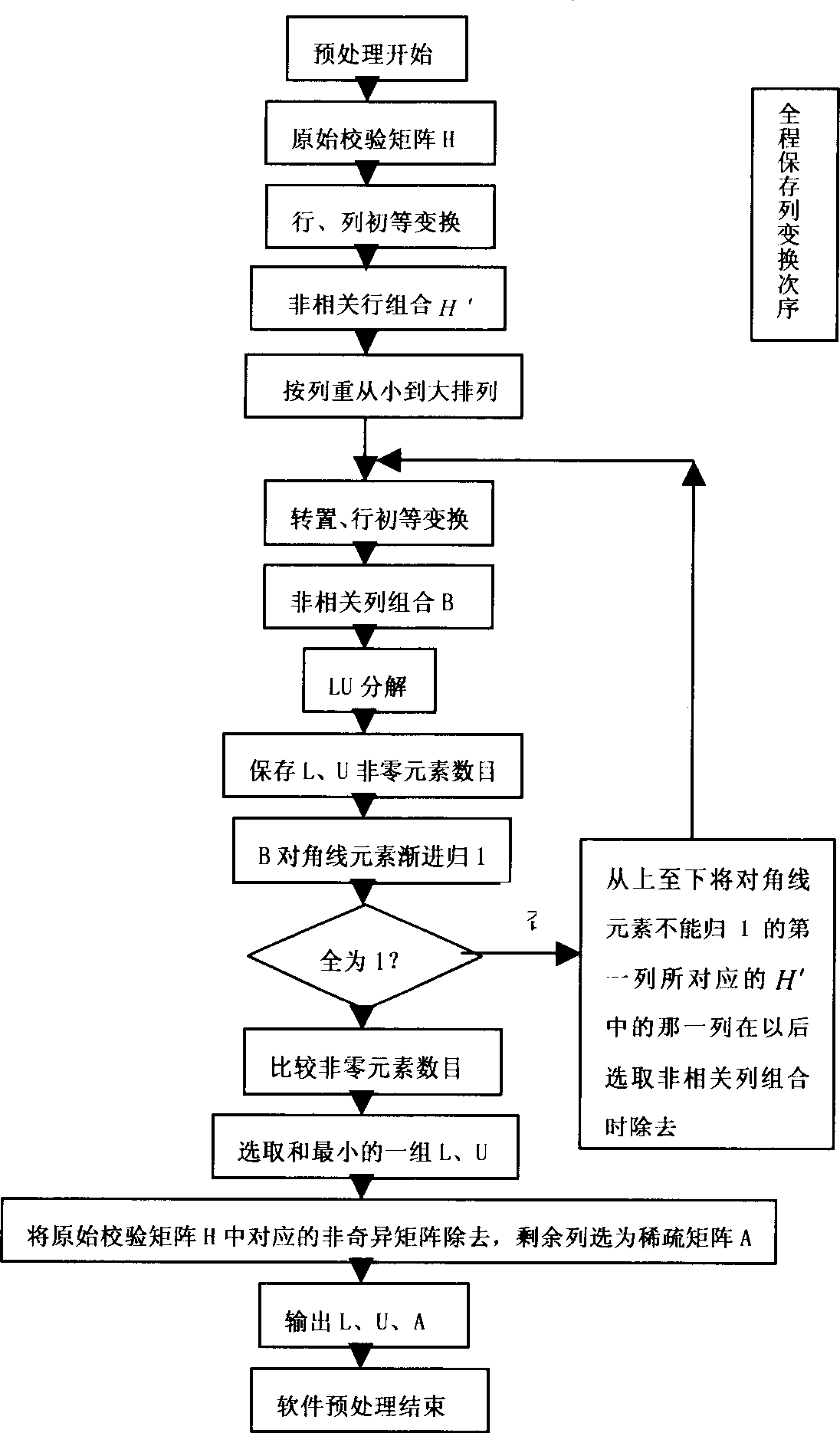
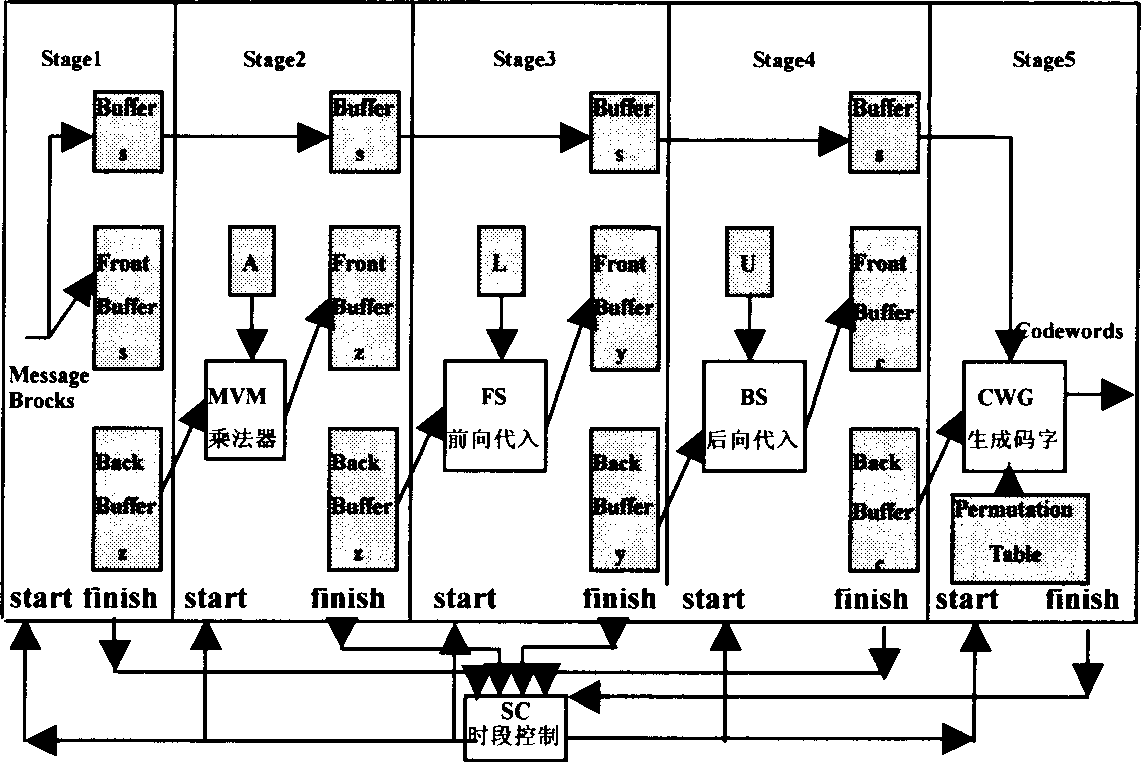
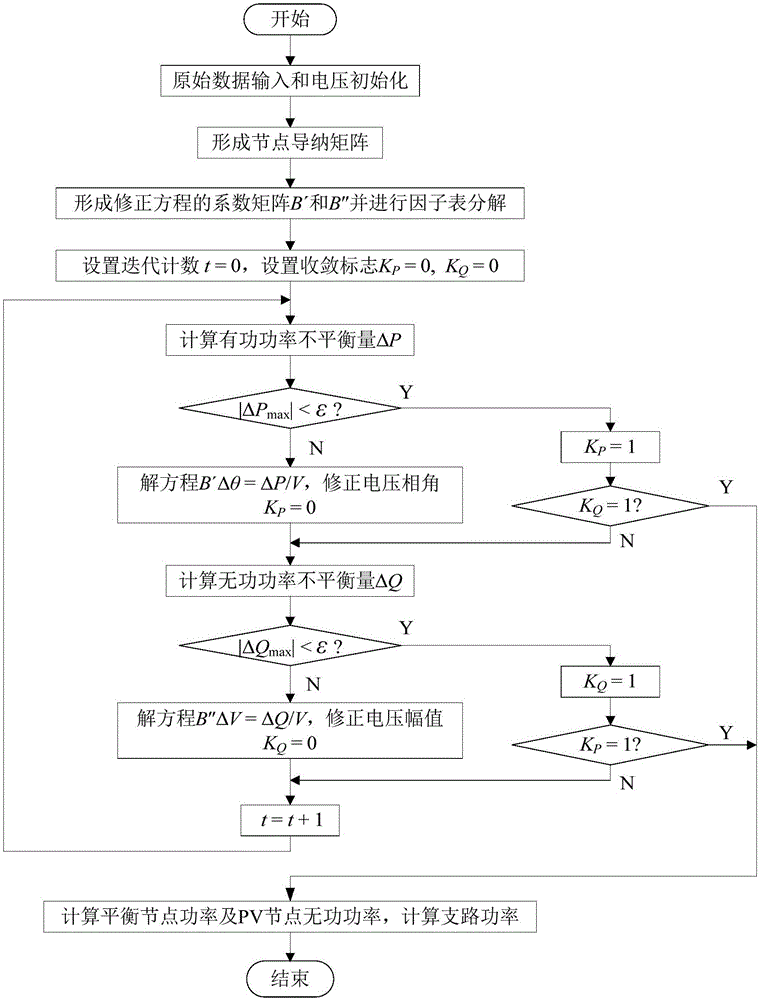
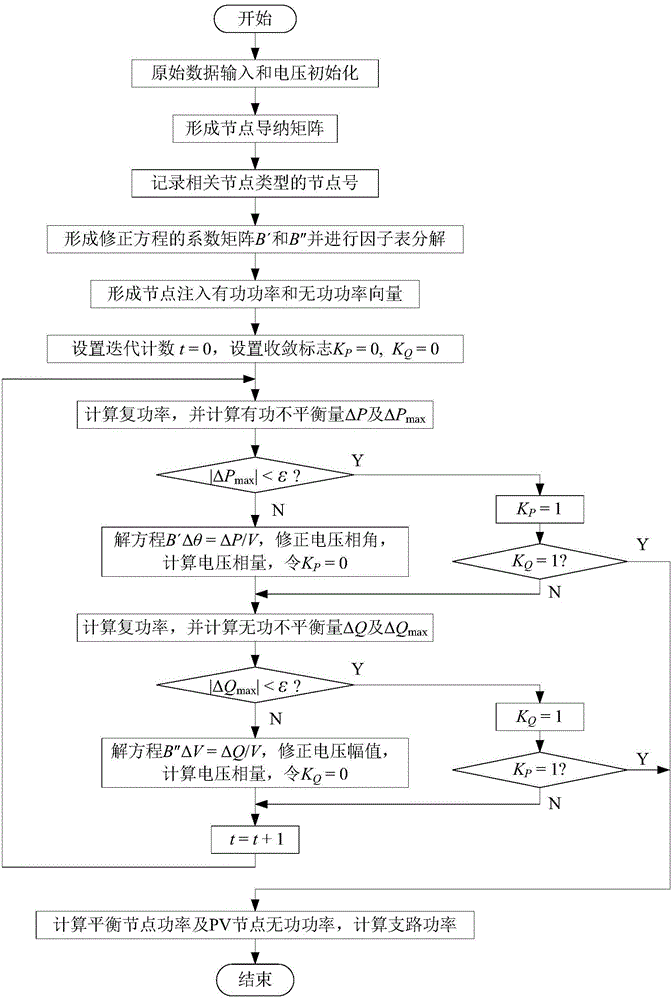
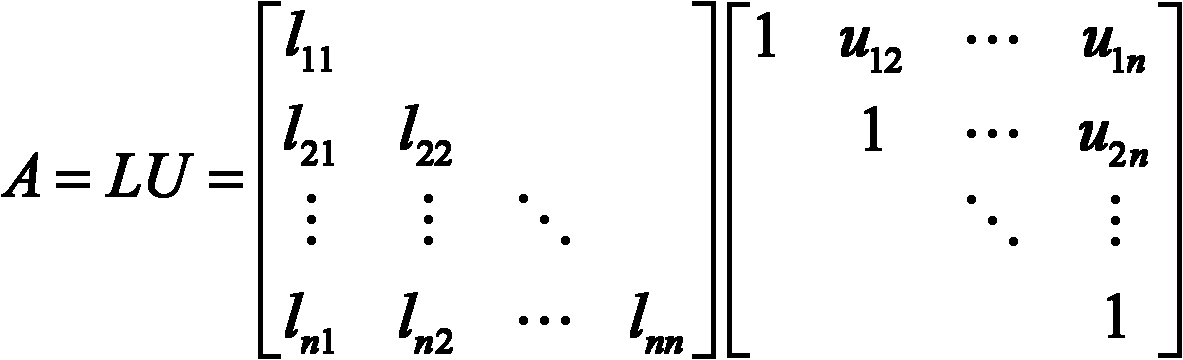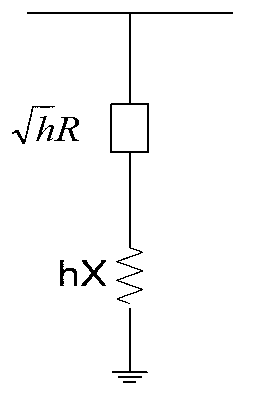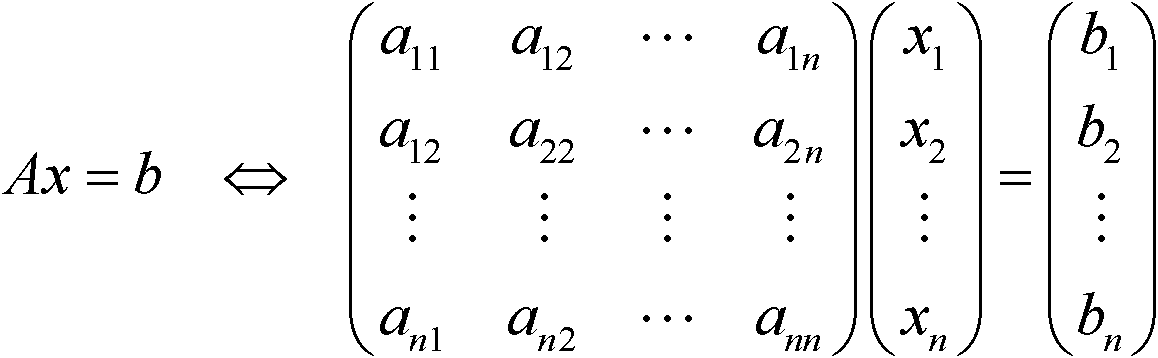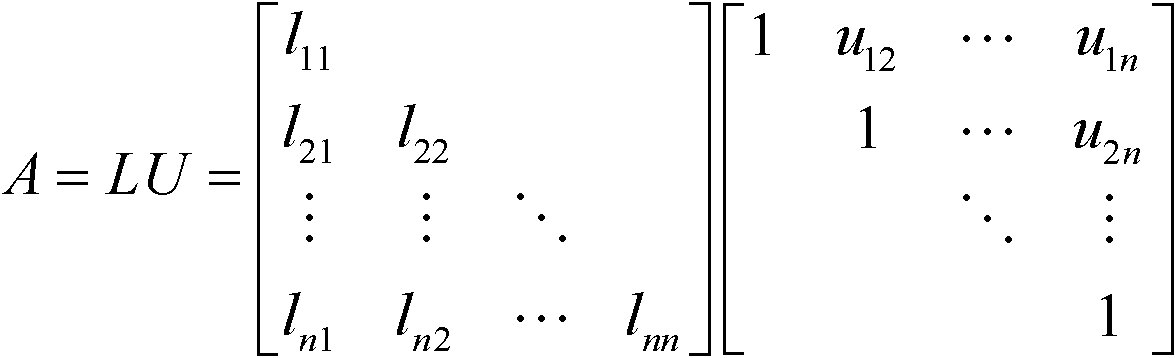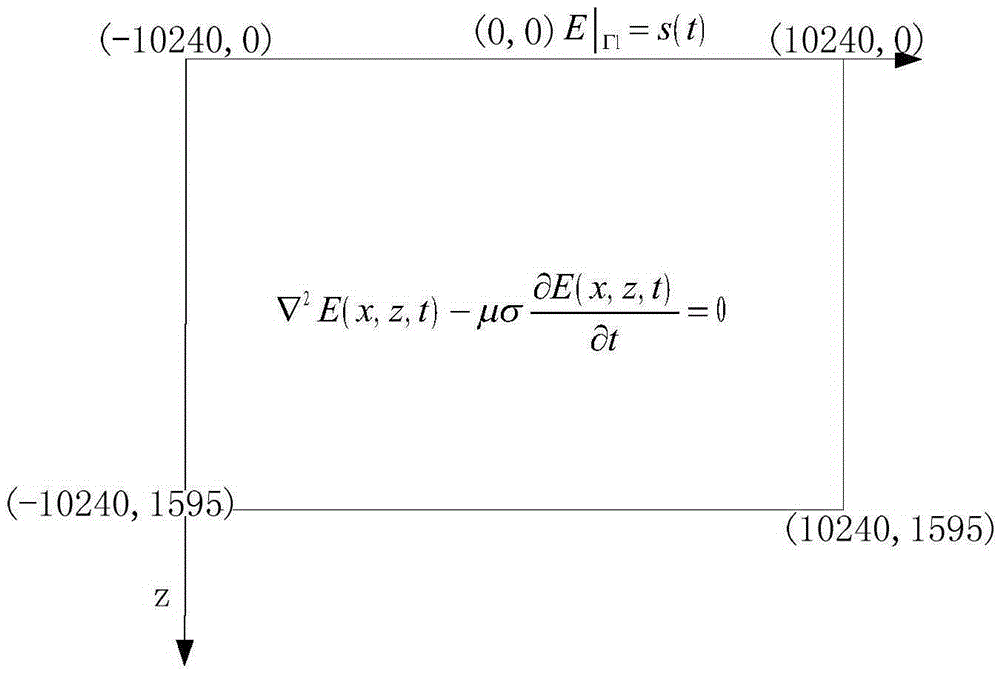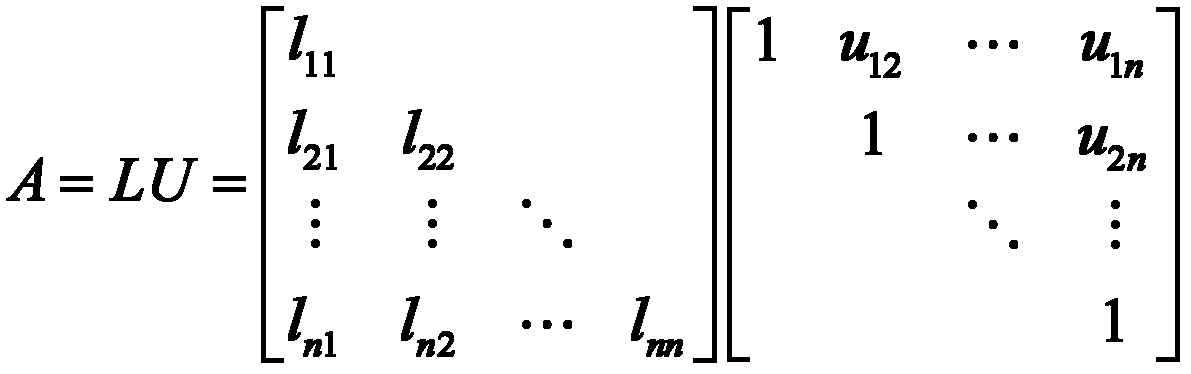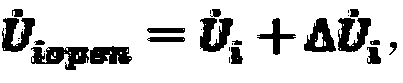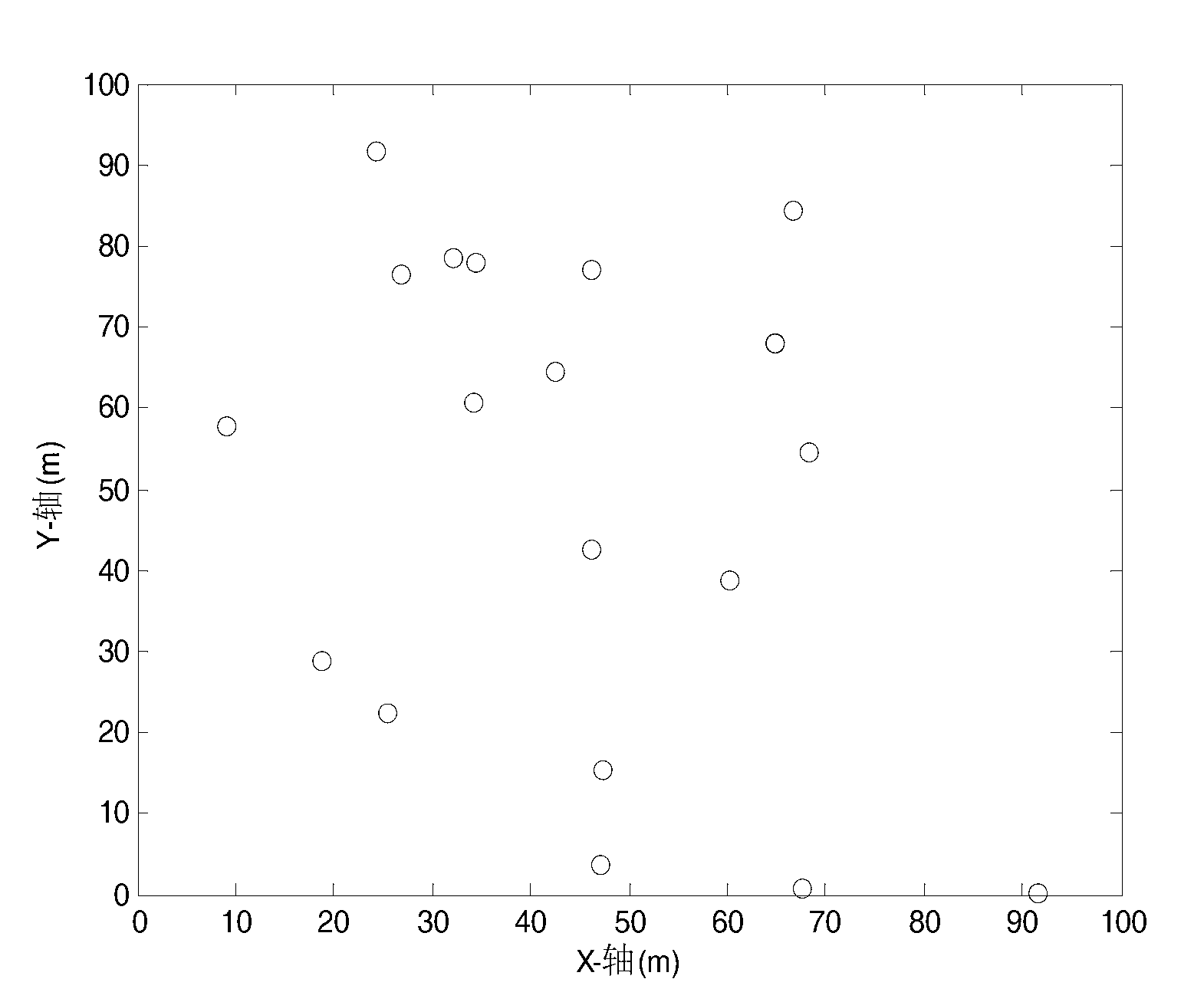Patents
Literature
101 results about "LU decomposition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In numerical analysis and linear algebra, lower–upper (LU) decomposition or factorization factors a matrix as the product of a lower triangular matrix and an upper triangular matrix. The product sometimes includes a permutation matrix as well. LU decomposition can be viewed as the matrix form of Gaussian elimination. Computers usually solve square systems of linear equations using LU decomposition, and it is also a key step when inverting a matrix or computing the determinant of a matrix. LU decomposition was introduced by mathematician Tadeusz Banachiewicz in 1938.
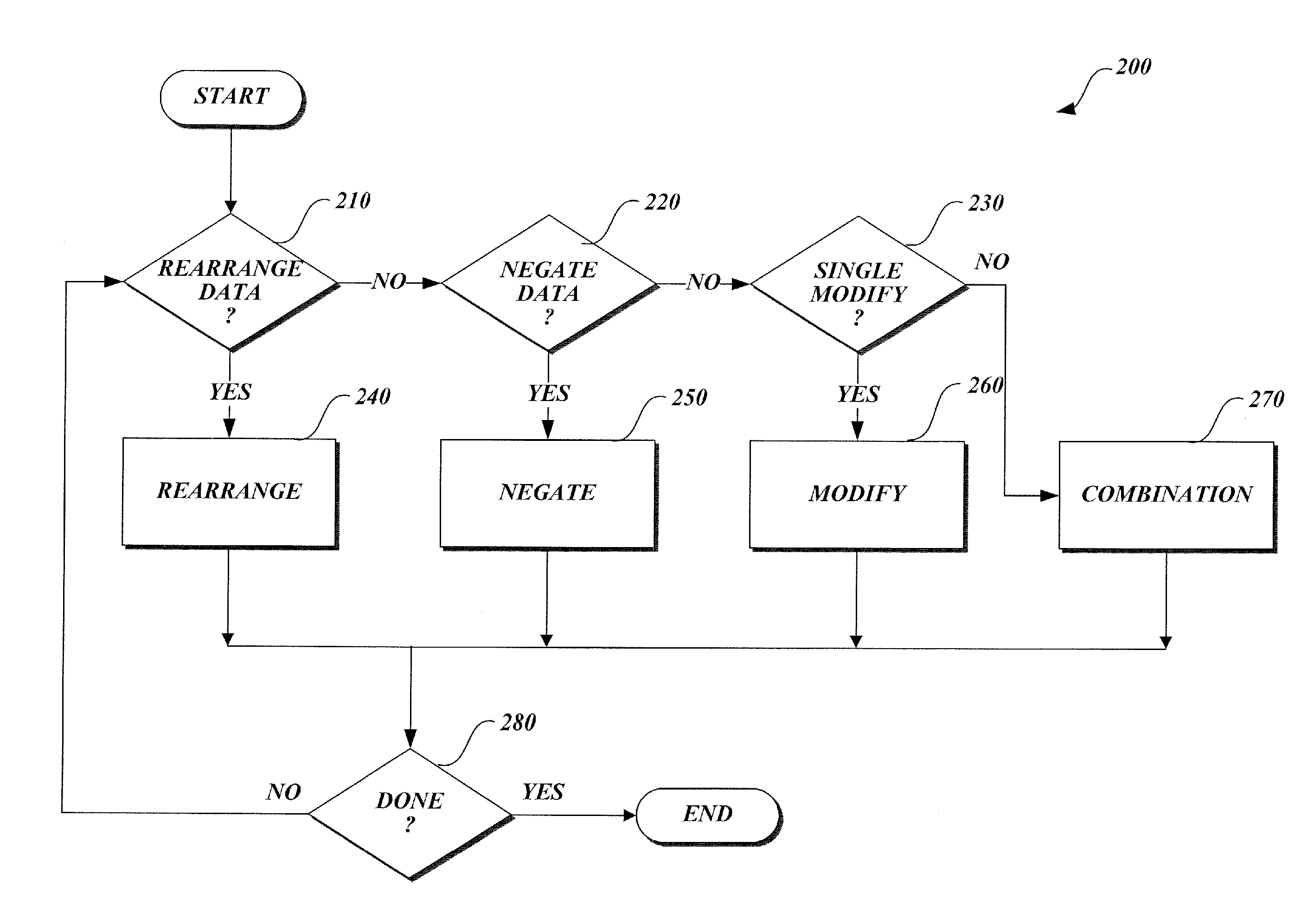
Method of generating matrix factors for a finite-dimensional linear transform
InactiveUS20070211952A1Character and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationPartition of unityLU decomposition
A method of generating matrix factors for a finite-dimensional linear transform using a computer. The linear transform is represented by data values stored in a linear transformation matrix having a nonzero determinant. In one aspect, a first LU-decomposition is applied to the linear transformation matrix. Four matrices are generated from the LU-decomposition, including a first permutation matrix, a second permutation matrix, a lower triangular matrix having a unit diagonal, and a first upper triangular matrix. Additional elements include a third matrix Â, a signed permutation matrix Π such that A=ΠÂ, a permuted linear transformation matrix A′, a second upper triangular matrix U1, wherein the second upper triangular matrix satisfies the relationship Â=U1A′. The permuted linear transformation matrix is factored into a product including a lower triangular matrix L and an upper triangular matrix U. The linear transformation matrix is expressed as a product of the matrix factors.
Owner:CELARTEM
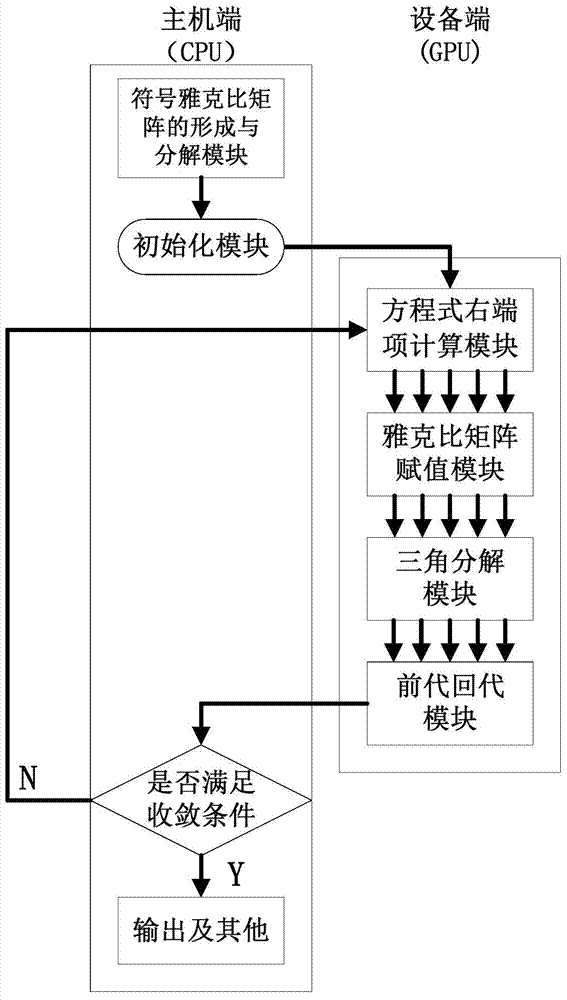
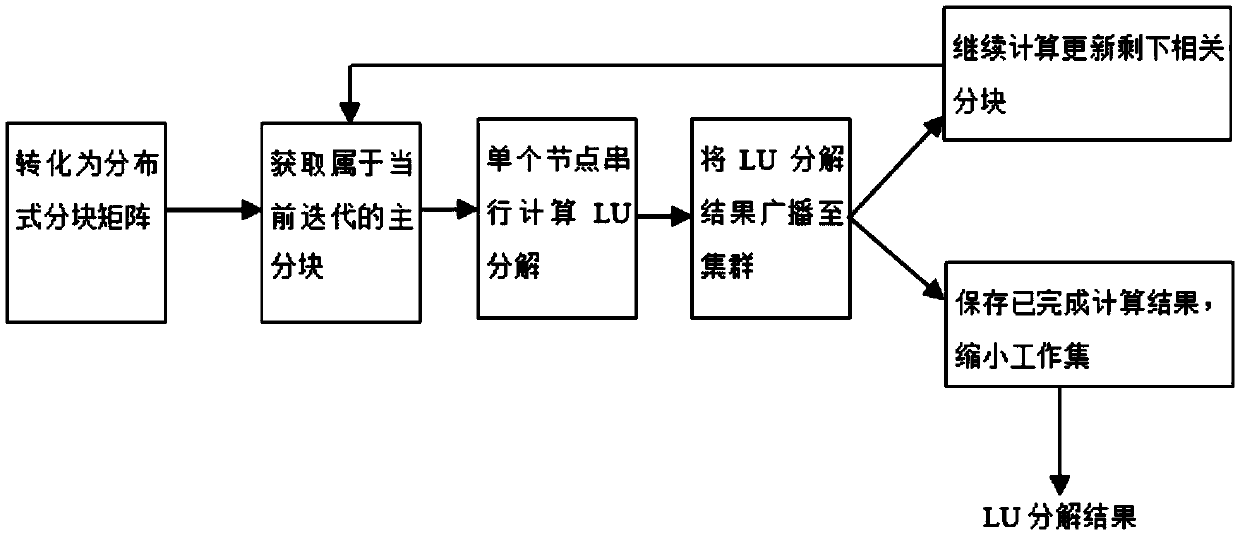
GPU (graphic processing unit) based parallel power flow calculation system and method for large-scale power system
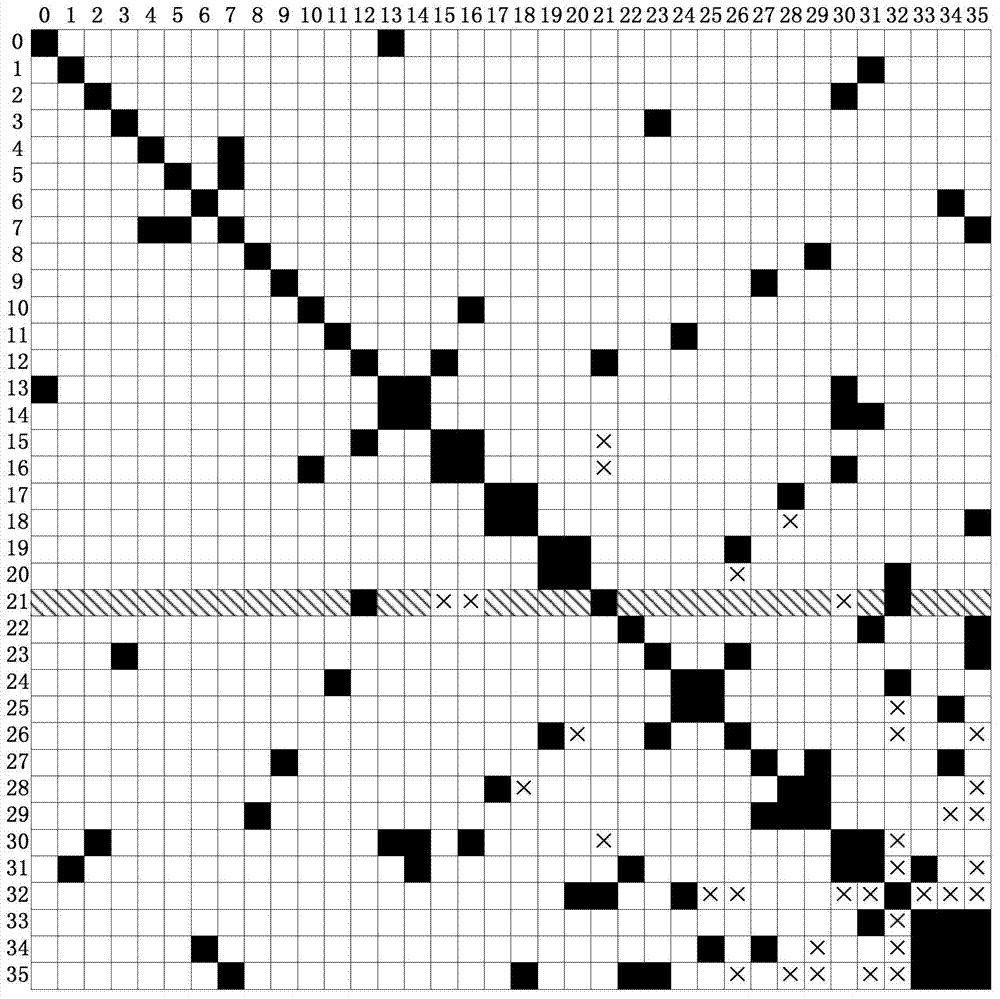
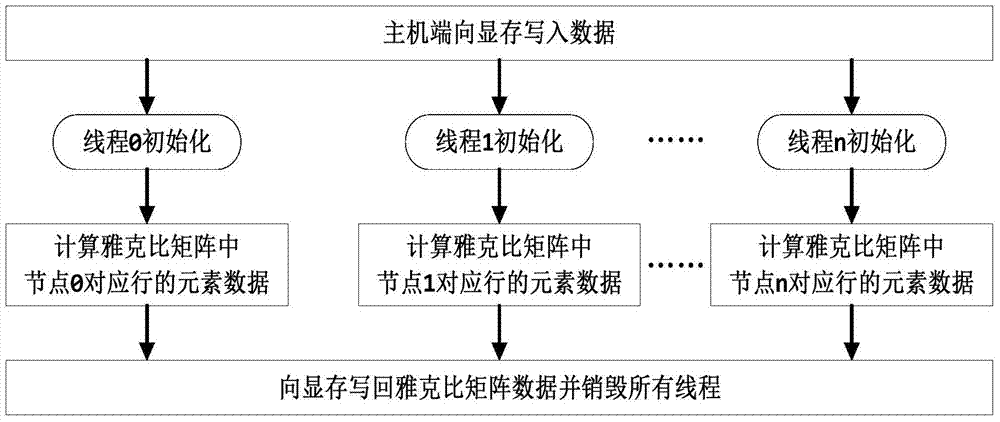
ActiveCN103617150ARealize the loop iterative processImplement parallel build methodsComplex mathematical operationsMain processing unitArithmetic processing unit
The invention relates to a GPU (graphic processing unit) based parallel power flow calculation system and method for a large-scale power system. The system comprises a symbol Jacobian matrix forming and decomposing module, an initialization module, a power flow equation right-hand side calculation module, a jacobian matrix assignment module, an LU decomposing module and a forward and backward substitution module; the symbol Jacobian matrix forming and decomposing module is located on a host side, and the host side transmits calculating data to an equipment side; the power flow equation right-hand side calculation module, the jacobian matrix assignment module, the LU decomposing module and the forward and backward substitution module are sequentially connected on the equipment side. The method includes (1) transmitting data needed by calculation to the host side entirely; (2) generating a symbol Jacobian matrix and performing symbol composition on the symbol Jacobian matrix; (3) transmitting a decomposition result by the host side to the equipment side; (4) executing power flow equation right-hand side calculation; (5) executing Jacobian matrix assignment; (6) executing LU decomposition; (7) executing forward and backward substitution.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
High-efficiency time domain electromagnetic simulation method based on H matrix algorithm
InactiveCN102033985AQuick solveDiscrete Fit ExactSpecial data processing applicationsComputation complexityDecomposition
The invention discloses a high-efficiency time domain electromagnetic simulation method based on an H matrix algorithm, which can realize electromagnetic simulation on a large three-dimensional target. In the method, a time domain finite element method (TDFEM) is used as a background, a low-rank compression technique is used as a core, and a tree structure is used as a basis for carrying out logical unit (LU) decomposition on a sparse matrix generated by the TDFEM by a four arithmetic algorithm corresponding to the H matrix. The acquired upper and lower triangular factors have low-rank compressible characteristics, and the compressed matrix equation can realize quick solution of high-efficiency time domain electromagnetic simulation by the H matrix algorithm. The high-efficiency time domain electromagnetic simulation method has the advantages of fast computation speed, low memory consumption, controllable computation accuracy, good stability and the like, can reduce the complexity of computation to O(Nlog<2>N) and reduce the memory consumption to O(NlogN), can be widely applied to the solution of a large sparse linear system of equations during high-efficiency time domain electromagnetic simulation, and can provide important reference for analyzing the electromagnetic property of the large three-dimensional target.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
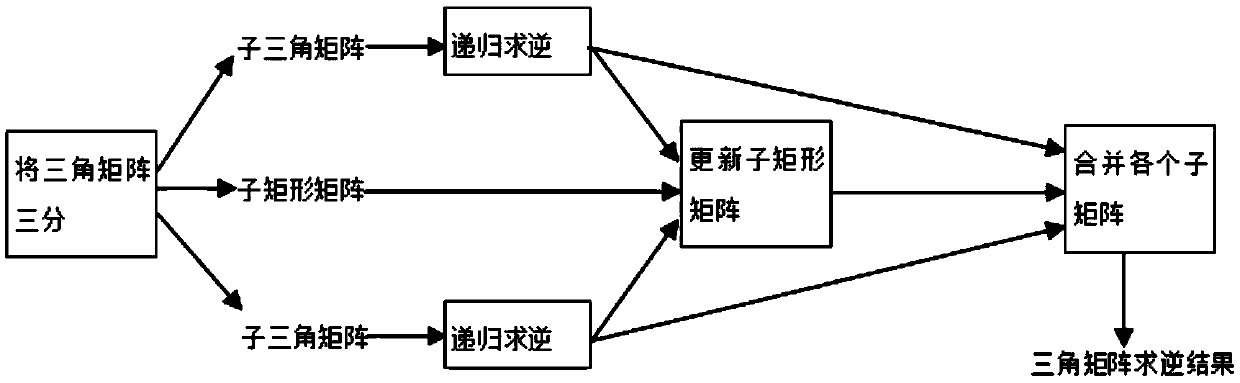
Matrix inverse operation method
InactiveCN105426345AImplement the inverse operationMeet performance needsComplex mathematical operationsMatrix inverseLU decomposition
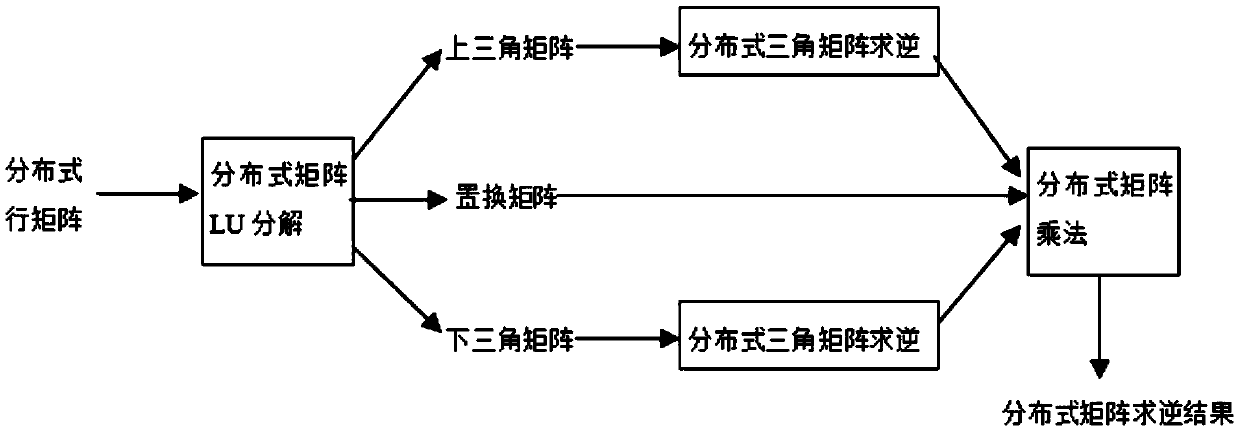
The invention relates to a matrix inverse operation method. The method comprises the steps of 1, conducting column pivoting LU decomposition, wherein a source matrix A is decomposed into a unit lower triangular matrix L, an upper triangular matrix U and a permutation matrix P according to the formula PA=LU; 2, conducting triangular matrix inversion, wherein the inverse matrix L-1 of the matrix L is obtained through matrix inversion, and matrix inversion is conducted on the transposed matrix of the matrix U and then transposition is conducted to obtain U-1; 3, finally conducting matrix multiplication, wherein the matrix U-1 and the matrix L-1 are multiplied, and column transformation is conducted on the matrix multiplication result according to the permutation matrix P to obtain a source matrix A-1. The method has the advantages that by using the column pivoting LU decomposition algorithm, the time complexity of the matrix inversion algorithm is effectively reduced, parallelizability of matrix inversion operation is improved, time for matrix inversion operation is shortened, matrix inversion operation of any order can be conducted, and the number of hardware resources can be increased or reduced according to count requirements of operation so that practical application requirements can be better met.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
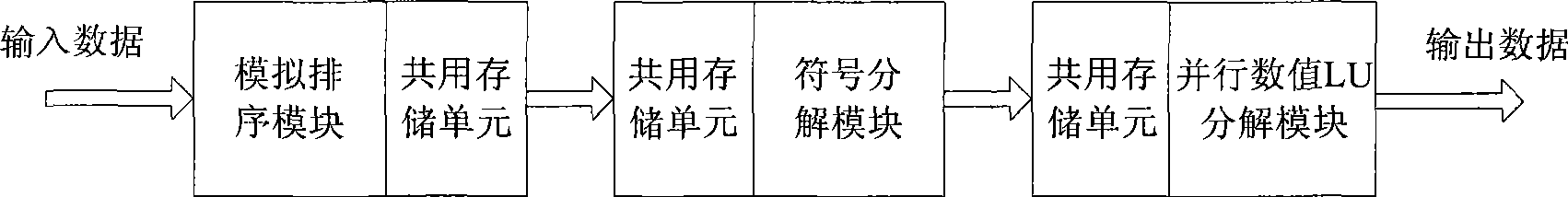
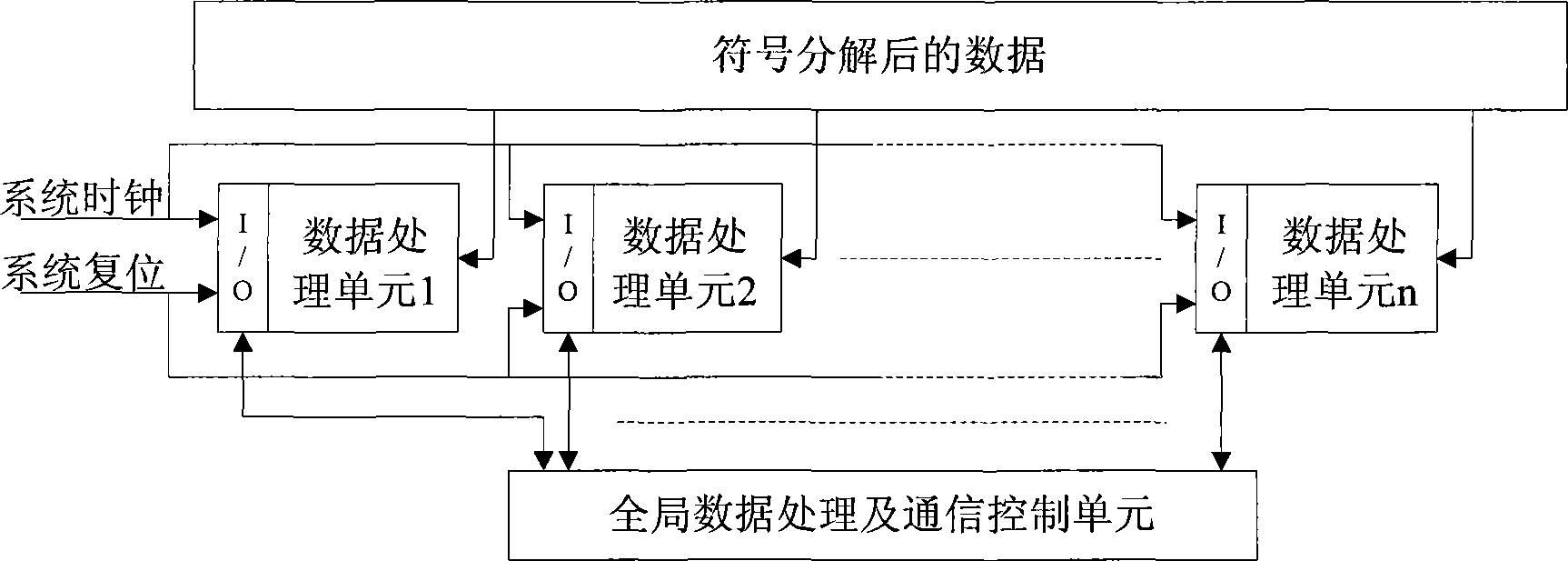
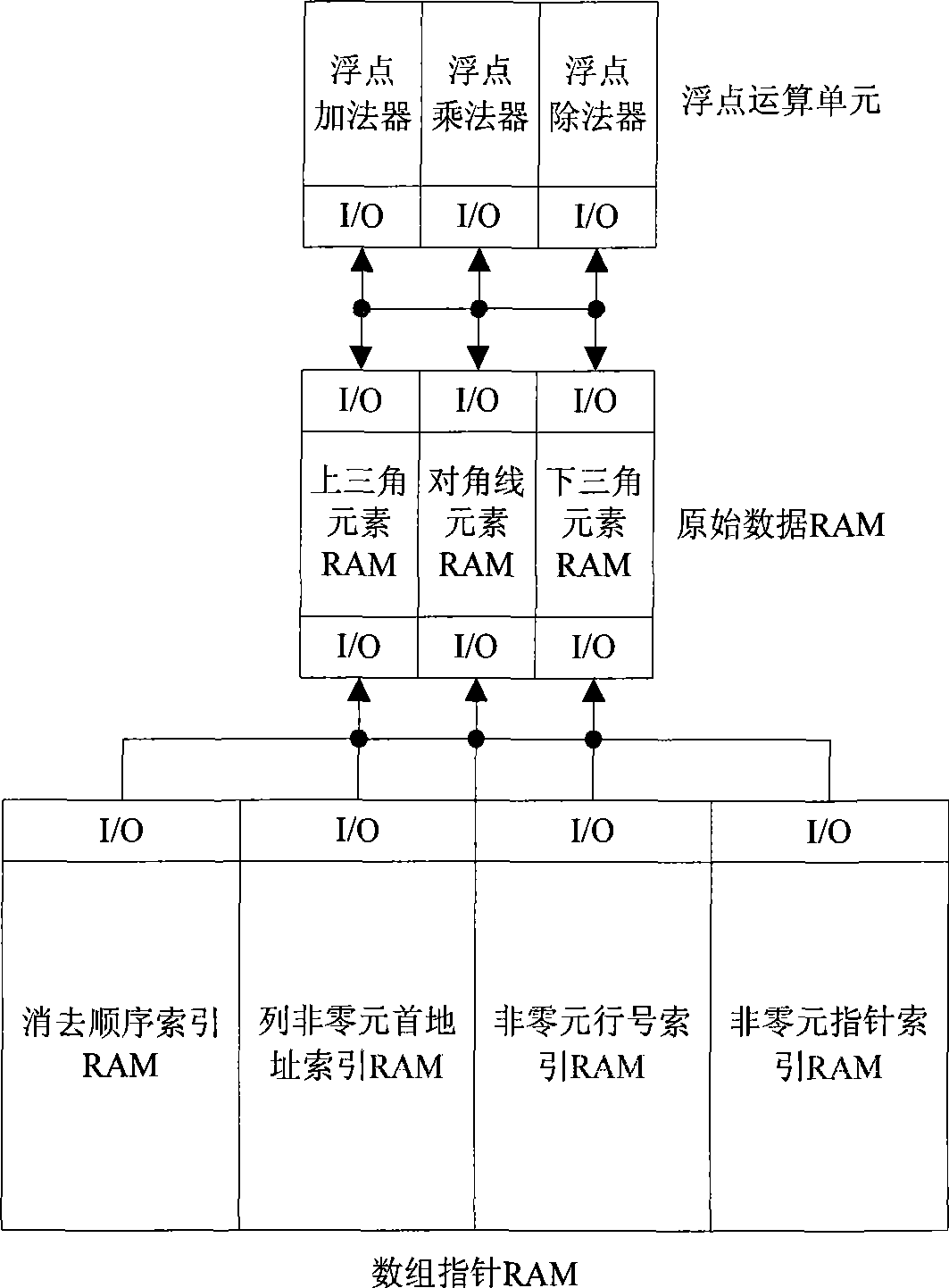
Parallel LU decomposition for corner sparse matrix based on FPGA
InactiveCN101533387AParallel processing high speedData speedSpatial transmit diversityBaseband system detailsSorting algorithmDecomposition
Aiming at the characteristics that corner-block sparse matrix is capable of parallel computing, the invention provides a parallel LU decomposition for corner sparse matrix based on FPGA. a simulating-sorting module, a symbol resolution module and a parallel numerical LU decomposition module form a three-layer processing platform structure consisting of, wherein the parallel numerical LU decomposition module is used for executing the parallel LU decomposition to matrix data and is positioned at the tail end of a whole processing structure; the symbol decomposition module is used for marking the position of an element to be modified in the matrix and is positioned at the middle end of the whole processing structure; and the simulating-sorting algorithm module is used for determining the elimination order of the matrix and is positioned at the foremost end of the whole processing structure; and the three modules are connected through a shared memory unit. The decomposition has the advantage of executing parallel LU decomposition to the corner sparse matrix in real time, can greatly save development cost as compared with the prior art using parallel computers and distributed computers, and can be applied to the field of real-time electrical network analysis.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
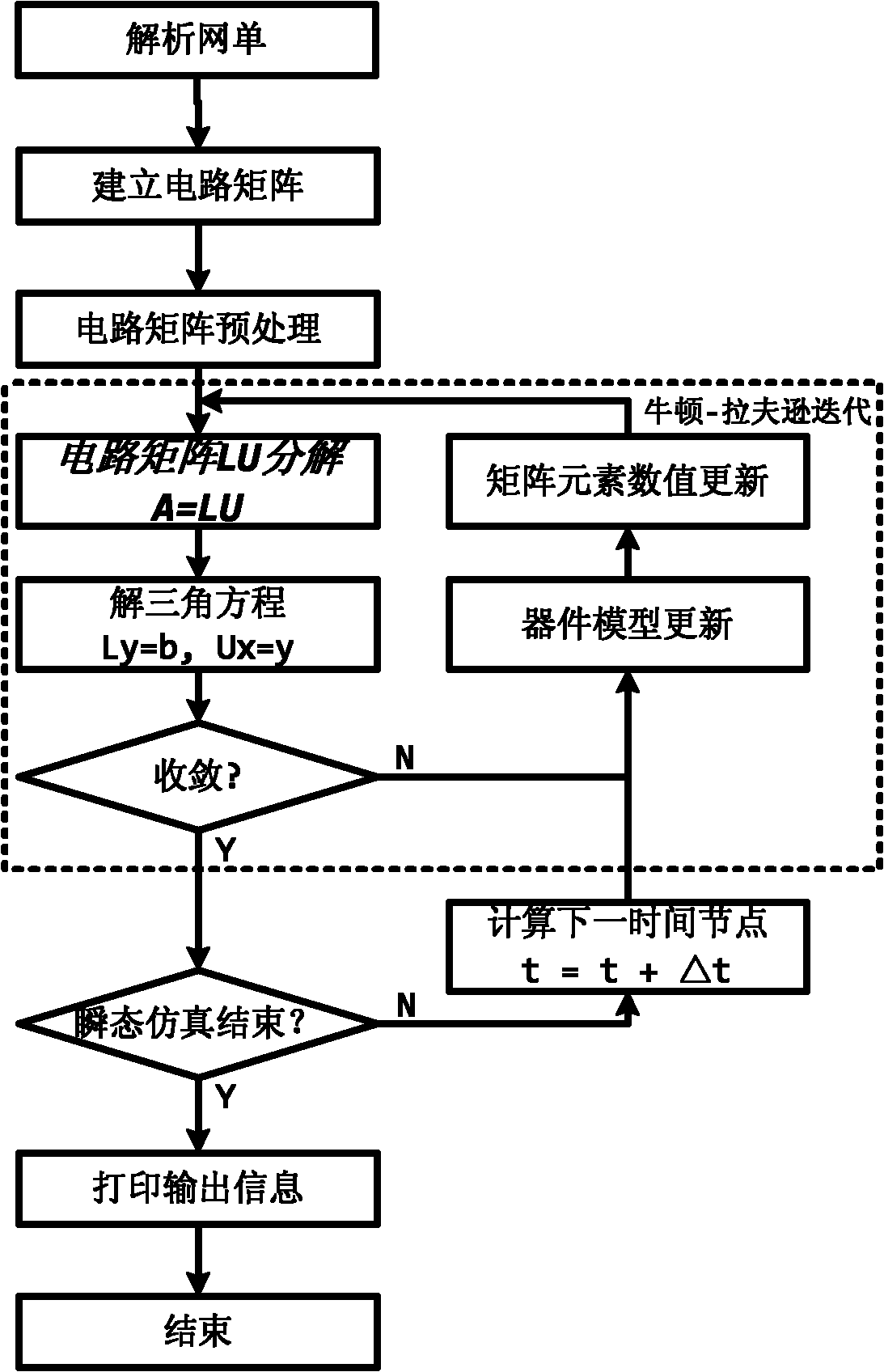
Quick LU factorization method for circuit sparse matrix in circuit simulation
ActiveCN102142052ASpeed up decompositionShorten the timeSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmLU decomposition
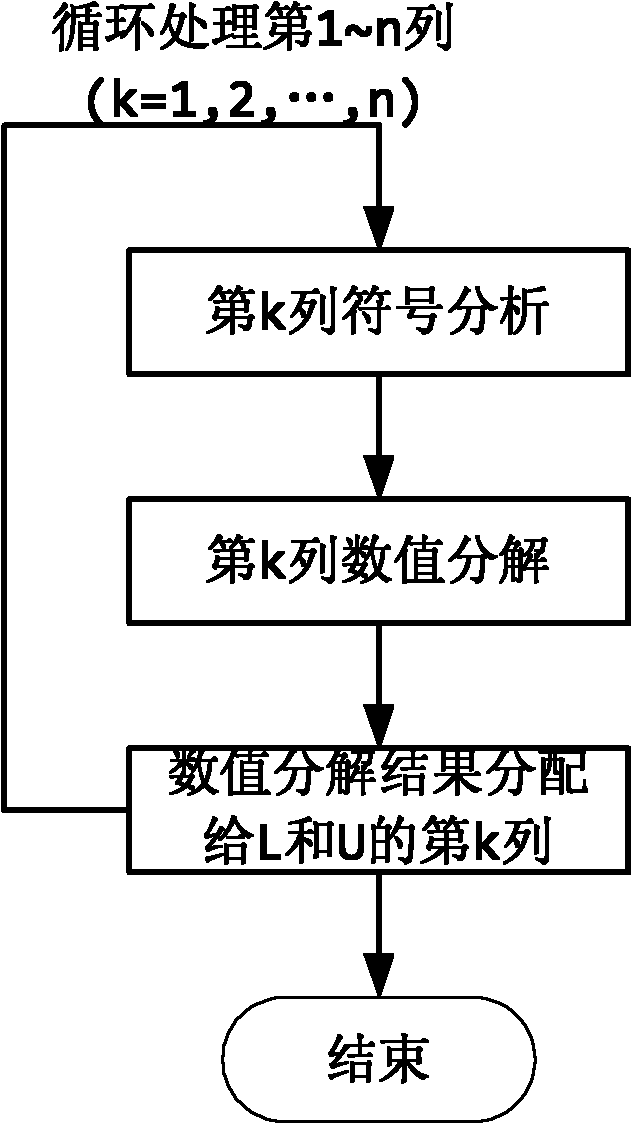
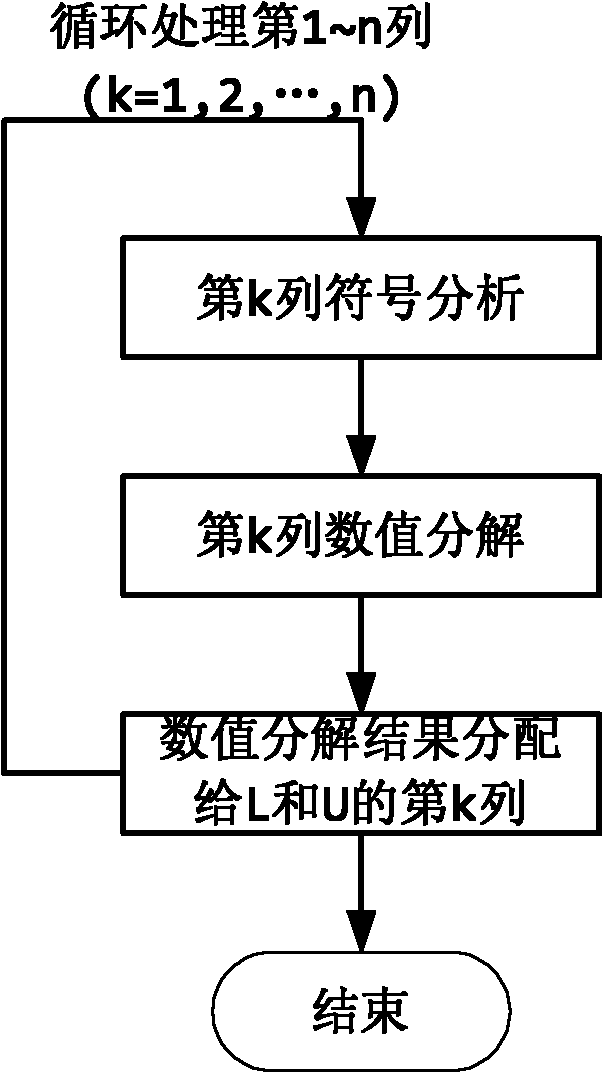
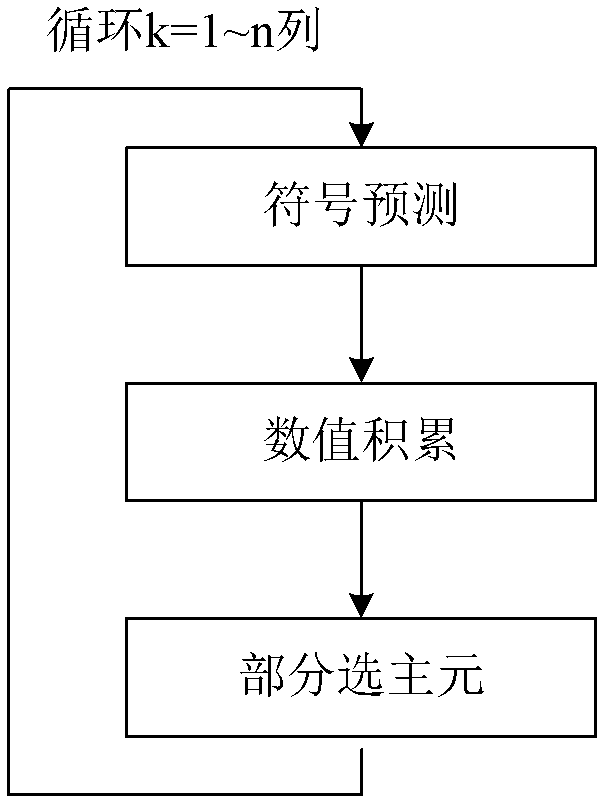
The invention relates to a quick LU factorization method for a circuit sparse matrix in circuit simulation, and belongs to the technical field of electronic design automation (EDA). The method comprises the following steps of: symbolic analysis and the calculation of LU factorization, wherein in the step of the symbolic analysis, a preprocessed matrix is analyzed to forecast each row of a non-zero structure of matrixes L and U formed after the matrix is subjected to the LU factorization; and in the step of the calculation of the LU factorization, based on the non-zero structures, obtained by the symbolic analysis, of the matrixes L and U, each row of the matrix is subjected to numerical solving and numerical distribution to obtain the matrixes L and U after the LU factorization. The method is characterized in that the symbolic analysis is separated from the circulation of the LU factorization, and the symbolic analysis is executed beyond the circulation of Newton-Raphson iteration in the process of the circuit simulation, namely is executed once, so the complexity of the circuit simulation can be reduced effectively, and the speed of the LU factorization can be improved to accelerate the integral circuit simulation.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
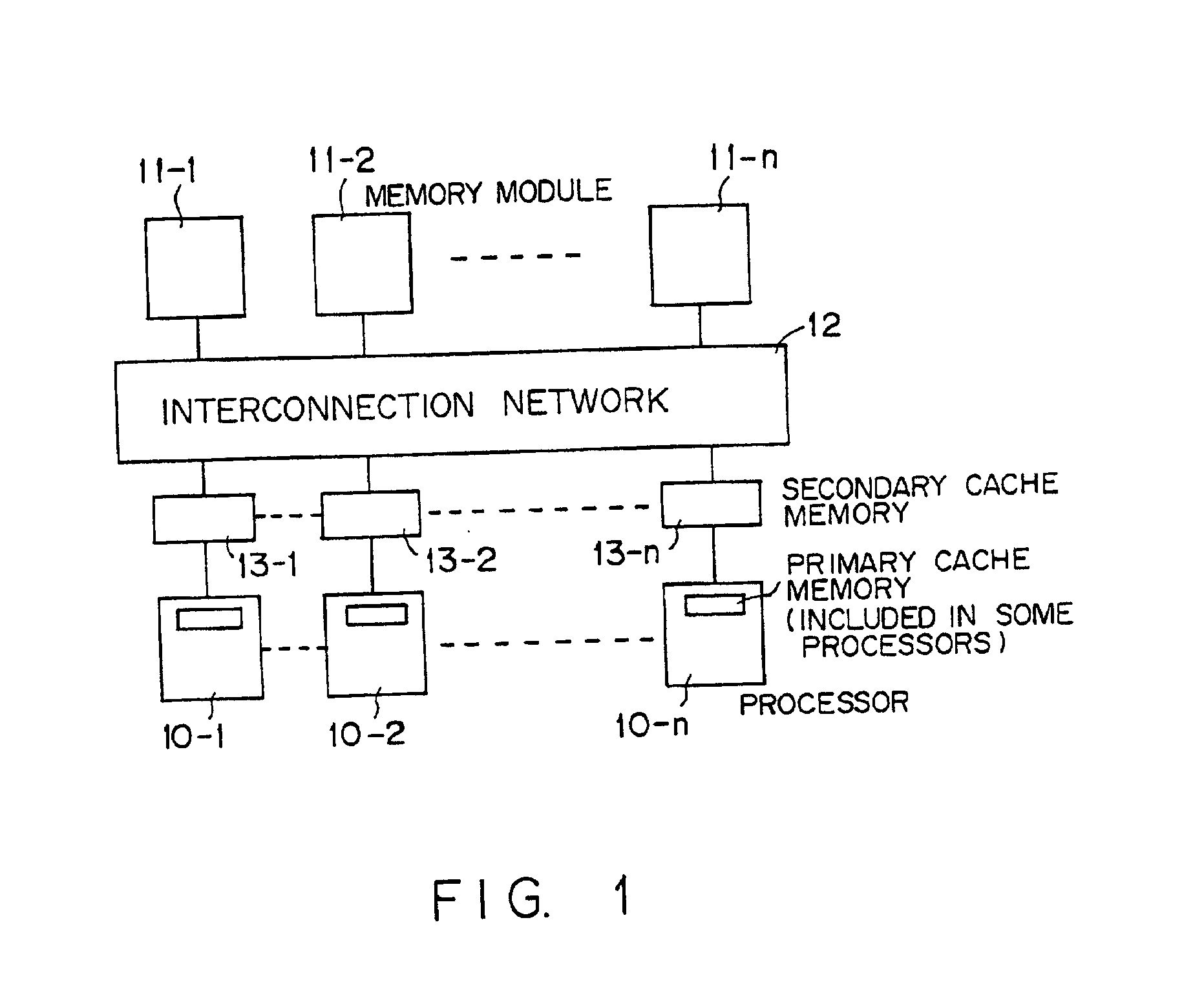
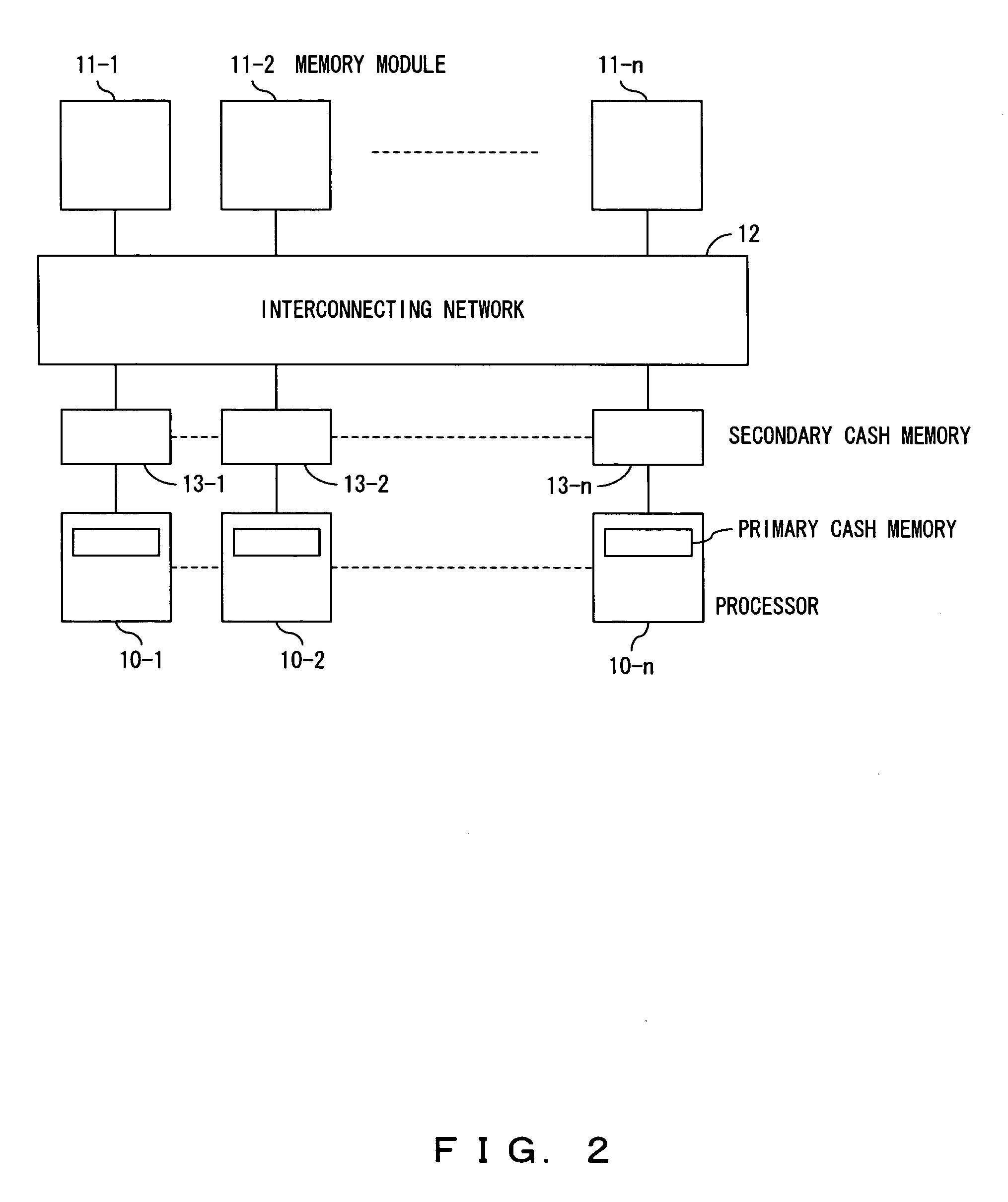
Matrix processing method of shared-memory scalar parallel-processing computer and recording medium
InactiveUS6907513B2Improve efficiencyUtilization areaGeneral purpose stored program computerConcurrent instruction executionLU decompositionDiagonal
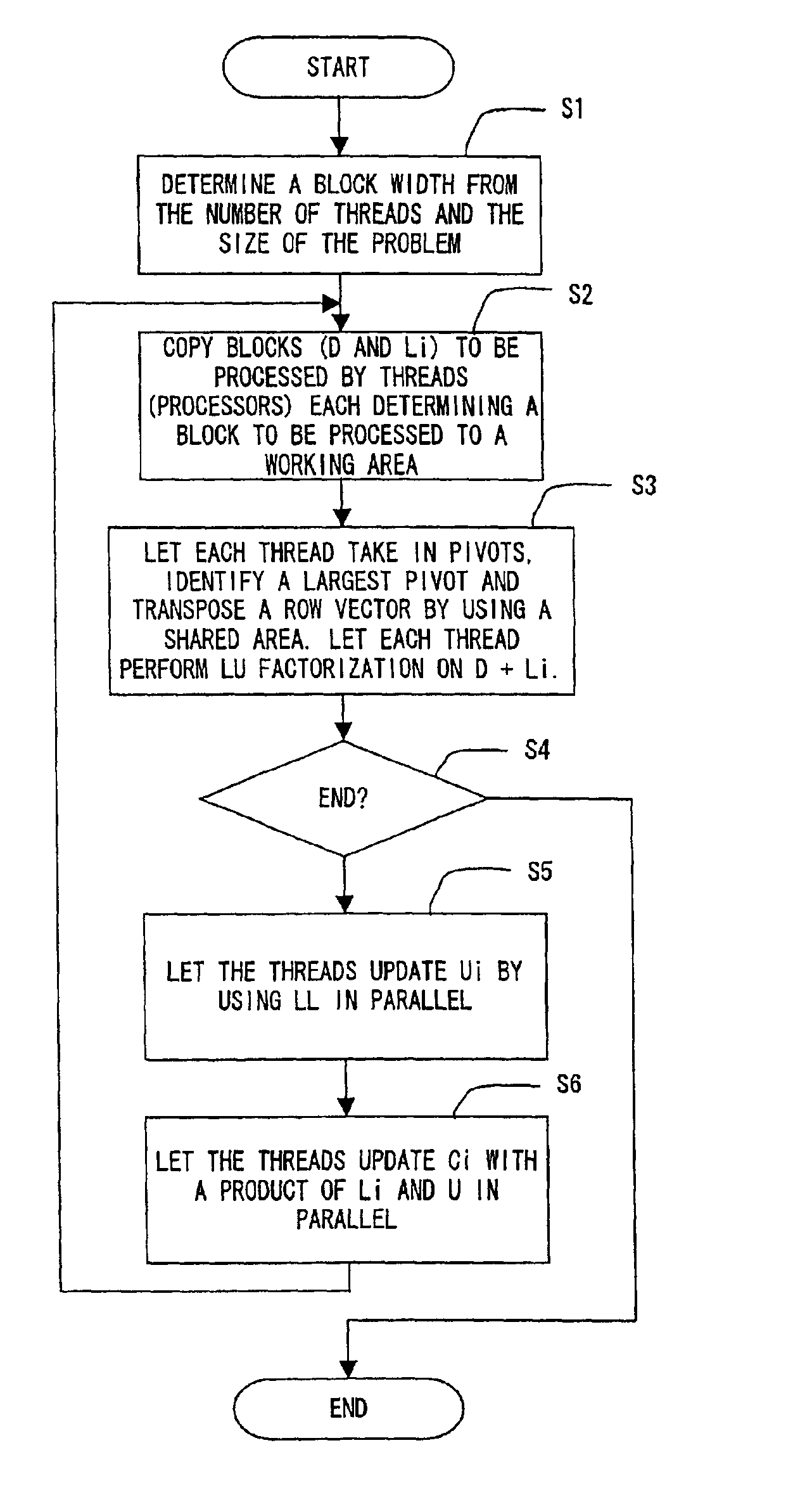
In accordance with a parallel matrix processing method adopted in a shared-memory scalar computer, a matrix to be subjected to LU factorization is divided into a block D of the diagonal portion and blocks beneath the D diagonal block such as L1, L2 and L3. Then, D+L1, D+L2 and D+L3 are assigned to 3 processors respectively for processing them in parallel. Next, a block U is updated by adopting an LU-factorization method and C1 to C3 are updated with L1 to L3 and U. By carrying out this processing on the inner side gradually decreasing in size as blocks, finally, a portion corresponding to the D diagonal block remains to be processed. By applying the LU factorization to this D portion, the LU factorization for the entire matrix can be completed.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
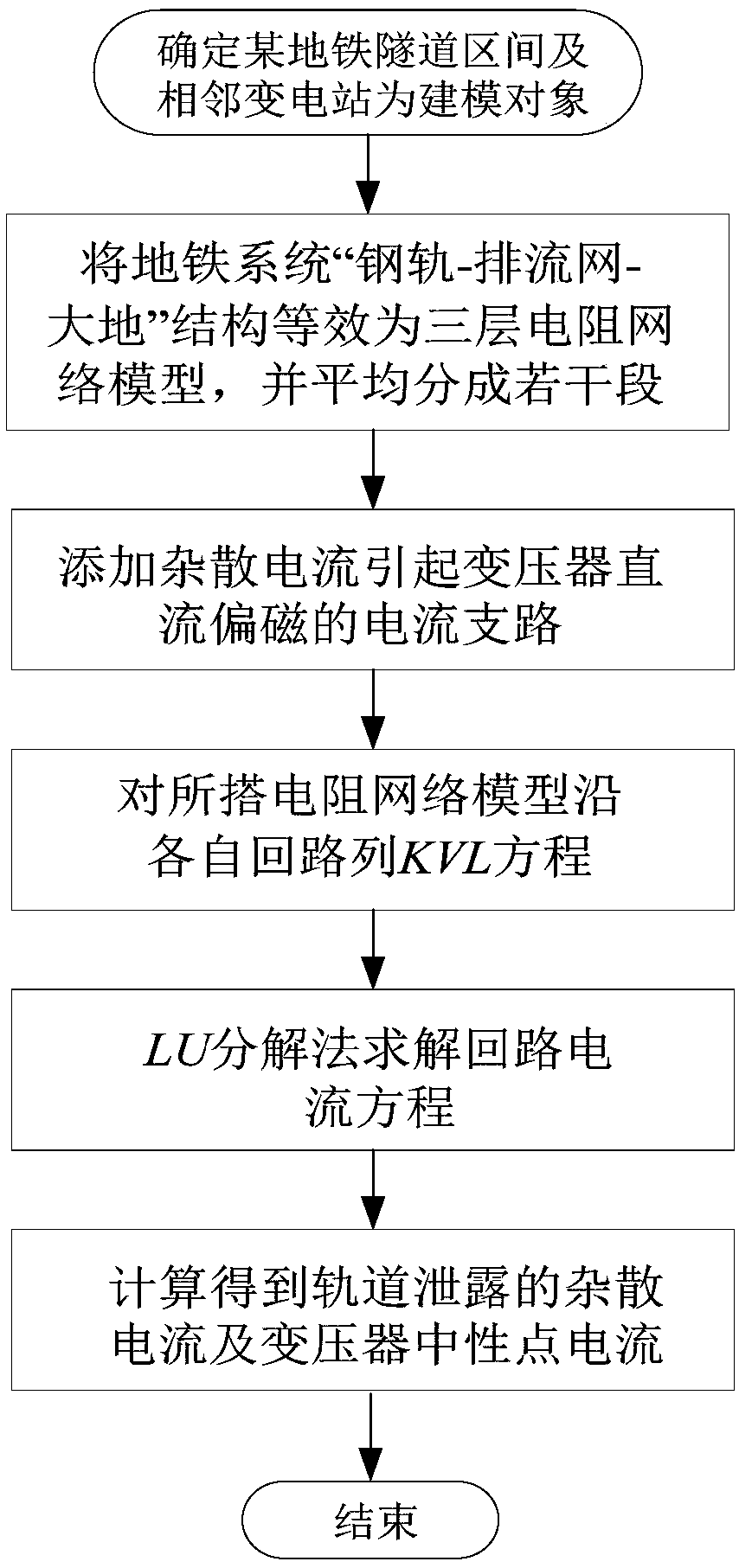
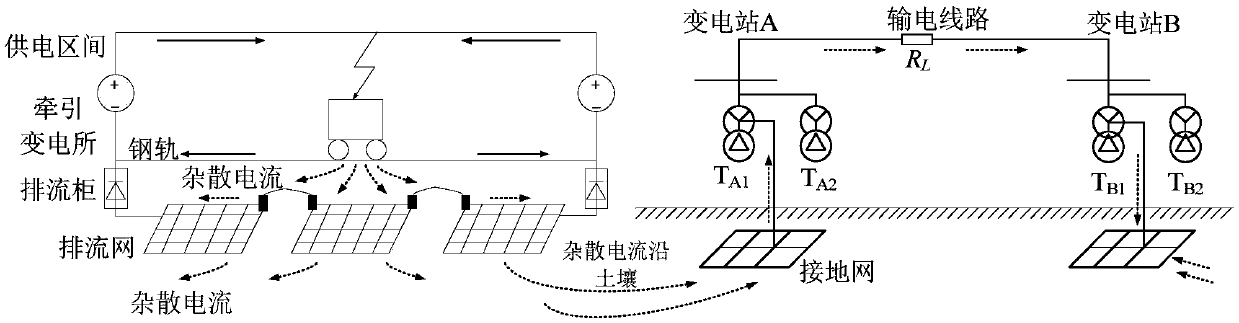
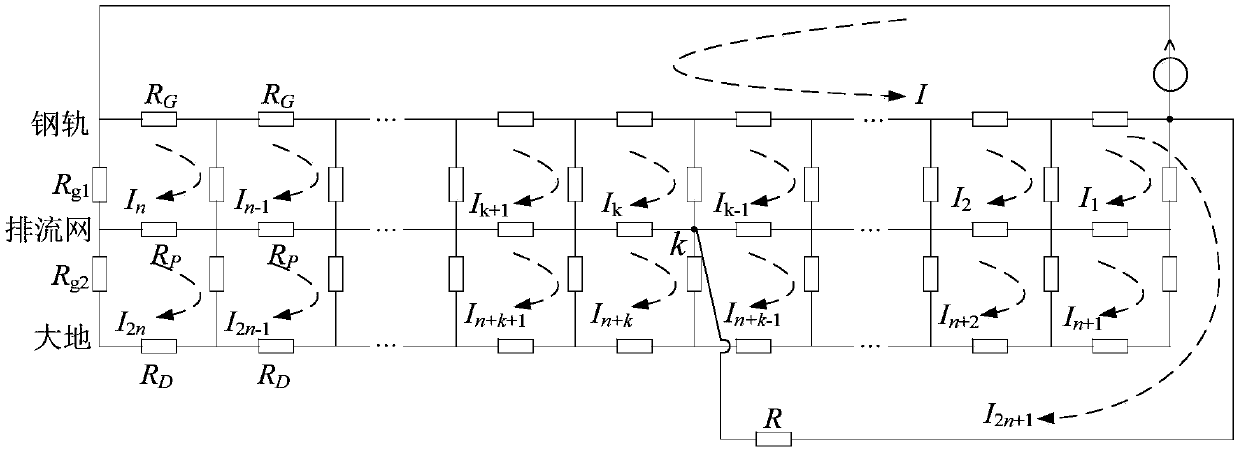
Calculation method of stray current and neutral point dc current of transformer caused by stray current in metro
ActiveCN109256771ARealize Numerical ComputationFast iterationAc network circuit arrangementsTransformerDc current
The invention discloses a method for calculating stray current and neutral point direct current of transformer caused by stray current in a metro. The method comprises the following steps: 1. The structure of rail-drain network-earth in metro system is equivalent to a three-layer resistance network model, and the resistance network is divided into several sections equally; 2, that flow path of theDC bias magnetic field of the transformer caused by stray current is analyzed, and a current branch of the DC bias magnetic field of the transformer caused by stray current is added into the resistance network model; 3, KVL equations along respective loop are arranged to obtain loop current equations for that built resistance network model; 4, a loop current equation is resolved by using the LU decomposition method, and the stray current of the rail leakage and the neutral point current of the transformer is calculated. This method can be used to calculate the distribution curves of neutral current and stray current of transformer under subway operation, which provides a theoretical basis for evaluating the influence of stray current on DC magnetic bias of transformer.
Owner:STATE GRID HUNAN ELECTRIC POWER +2
Sparse matrix LU decomposition method based on GPU
InactiveCN103399841AGuaranteed to work togetherReduced simulation timeComplex mathematical operationsAlgorithmDecomposition
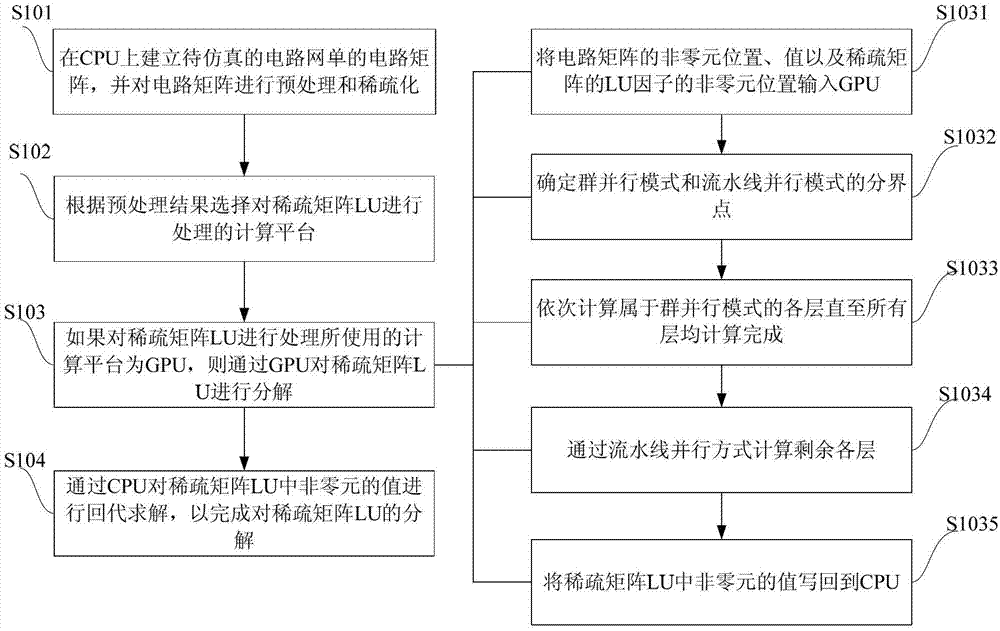
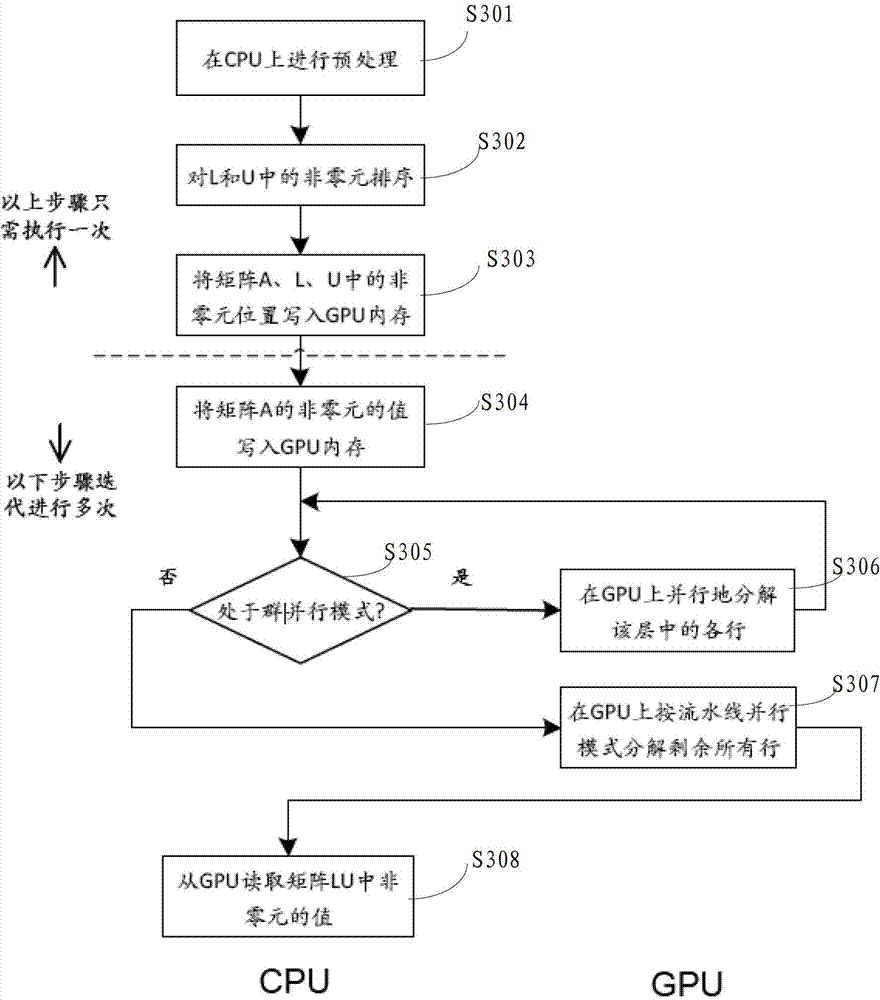
The invention provides a sparse matrix LU decomposition method based on a GPU. The sparse matrix LU decomposition method includes the following steps: A, building a to-be-simulated circuit matrix of a circuit network on a CPU, and performing preprocessing and rarefaction on the circuit matrix; B, selecting a computing platform for processing a sparse matrix LU according to preprocessing results; C, performing decomposition on the sparse matrix LU through the GPU if the computing platform which is used is the GPU; D, performing back substitution solution on values of non-zero elements in the sparse matrix LU through the CPU so as to complete decomposition of the sparse matrix LU. According to the sparse matrix LU decomposition method, the computing platform can be selected automatically according to the number of floating-point operation times in decomposition, the task on the CPU and the task on the GPU can be distributed reasonably, coordinated operation of a plurality of threads on the GPU is guaranteed, and therefore the computing speed is improved and circuit simulation time is shortened.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
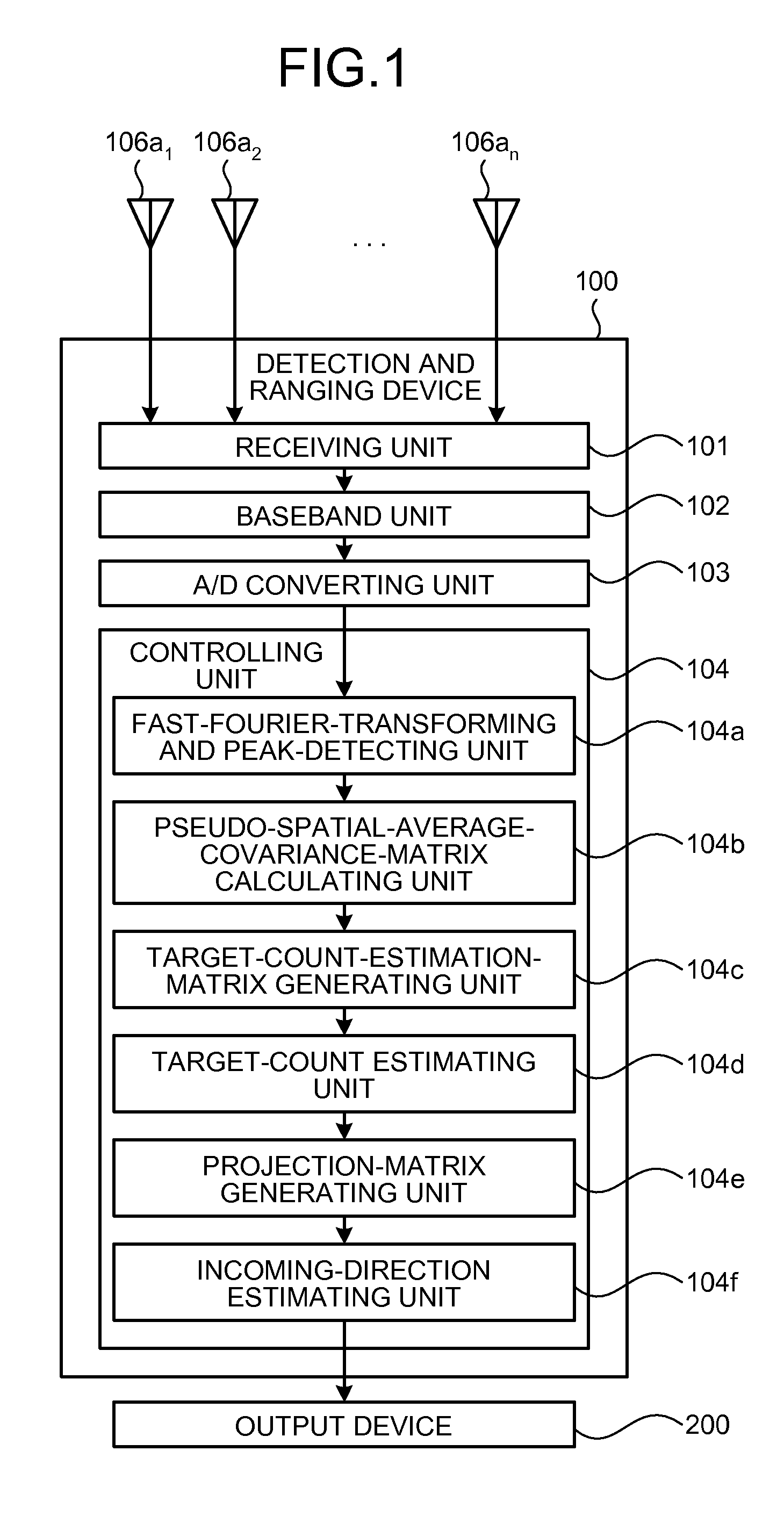
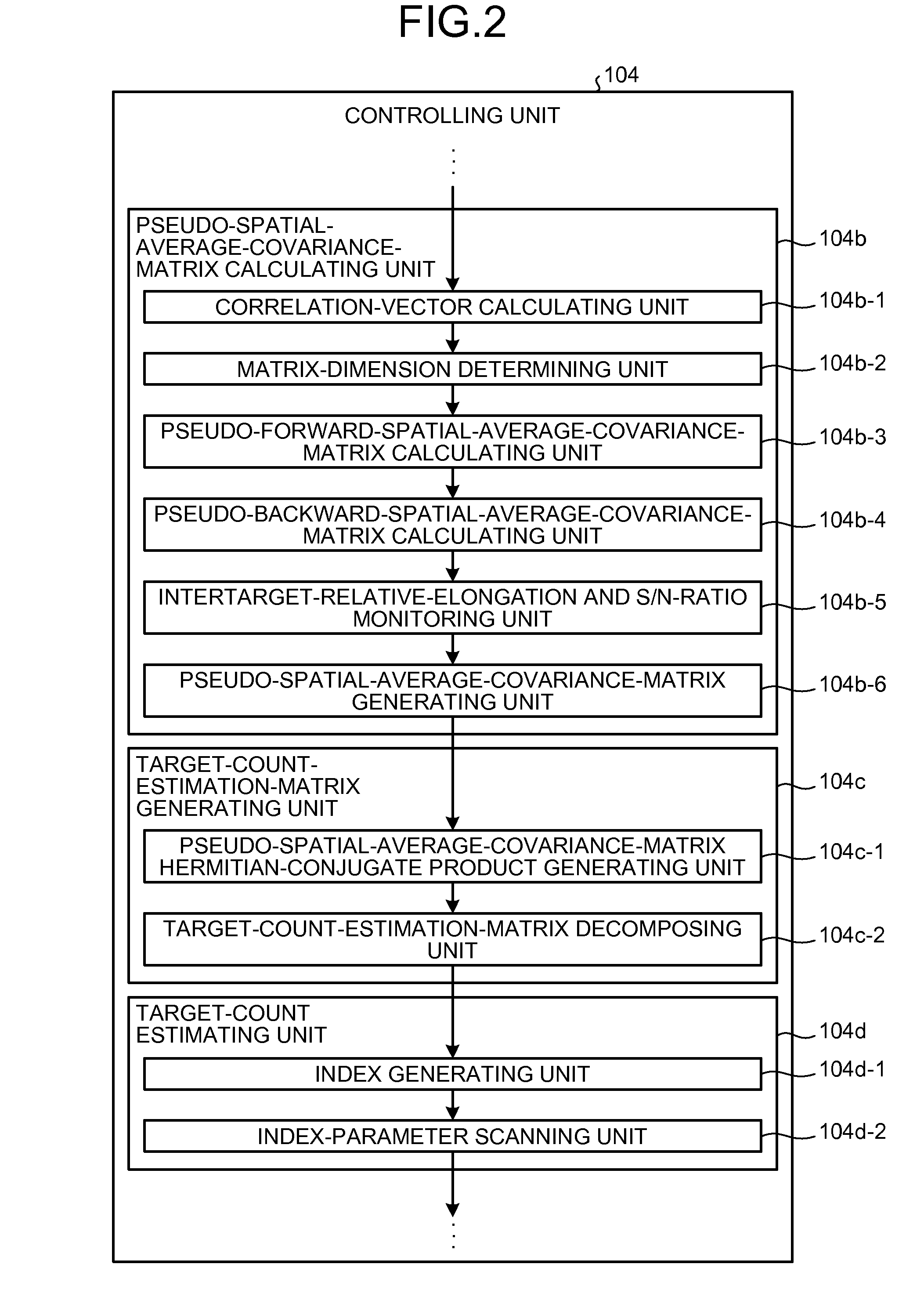
Detection and Ranging Device and Detection and Ranging Method
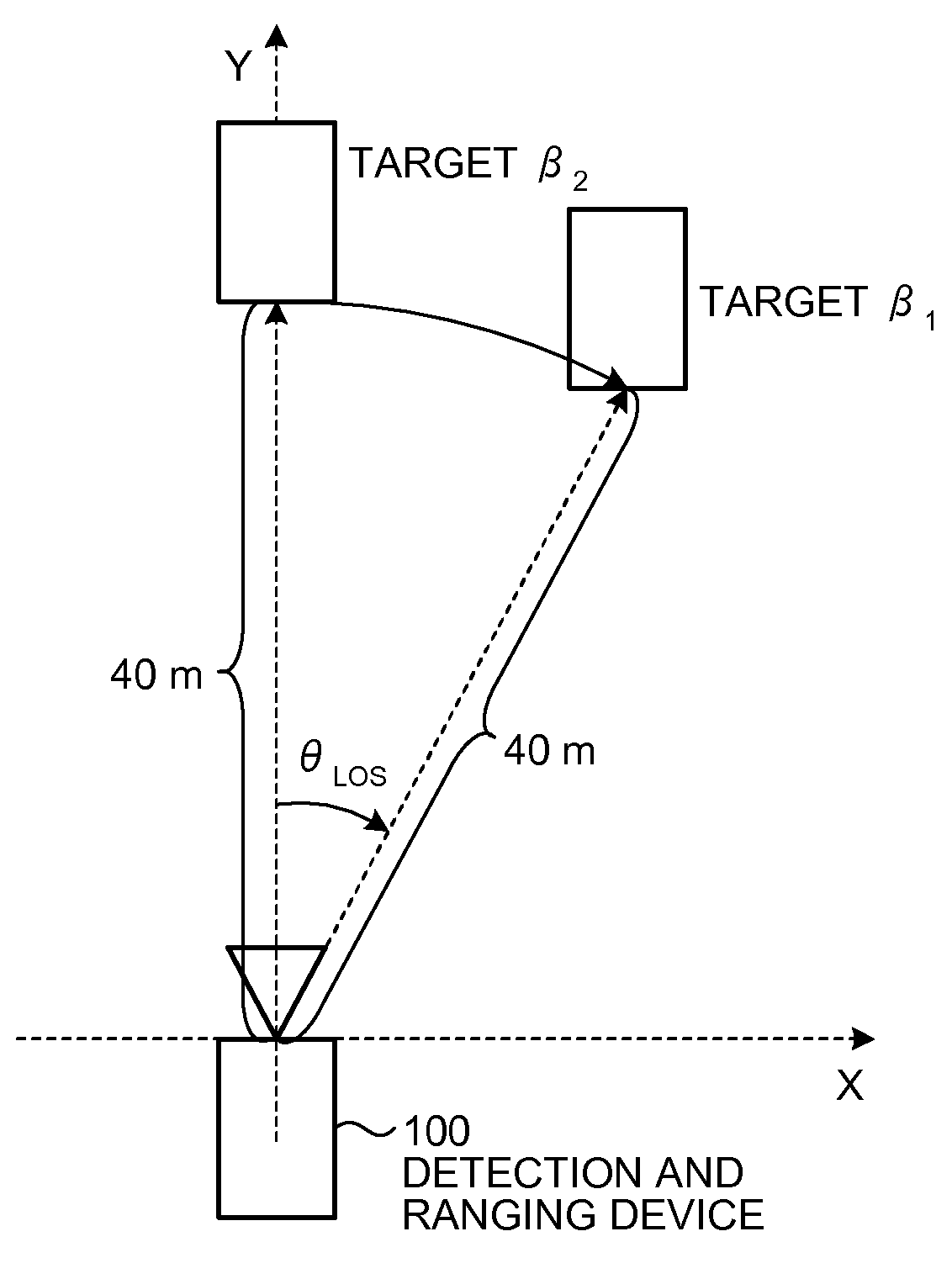
InactiveUS20090224978A1Solve problemsBeacon systems using radio wavesMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesSpatial averageLU decomposition
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
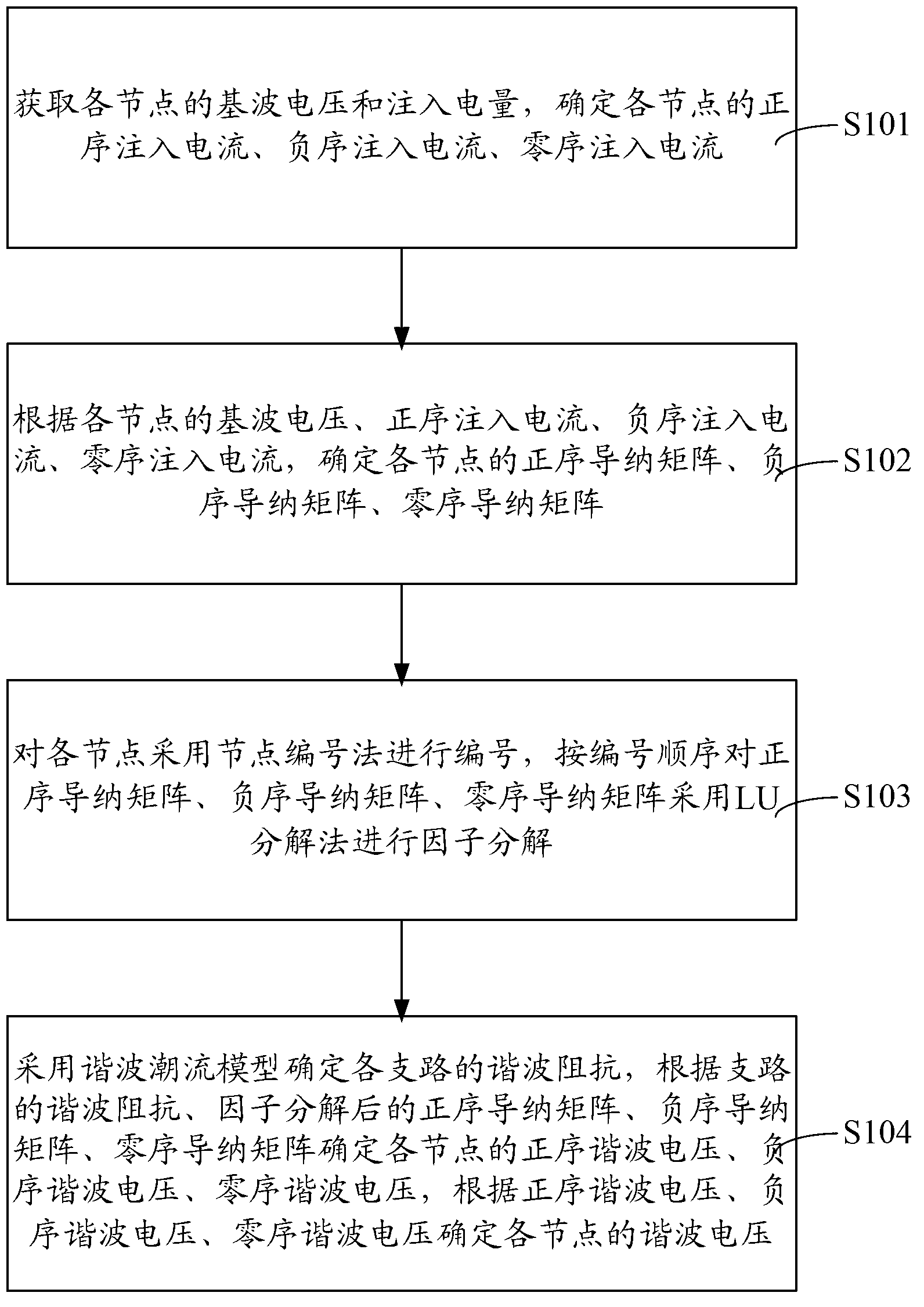
Method and system for determining harmonic voltage
ActiveCN103018534ASimplify calculation stepsImprove calculation accuracySpectral/fourier analysisCurrent/voltage measurementPower flowLU decomposition
A method for determining harmonic voltage comprises the steps of obtaining the fundamental wave voltage and the injection electric quantity of each of the nodes, and determining positive-sequence, negative-sequence and zero-sequence current of each of the nodes; according to the fundamental wave voltage and positive-sequence, negative-sequence and zero-sequence current of each of the nodes, determining positive-sequence, negative-sequence and zero-sequence admittance matrixes of each of the nodes; numbering each of the nodes with a node numbering method, and conducting factorization on positive-sequence, negative-sequence and zero-sequence admittance matrixes with an LU decomposition according to the numbering sequence; and using harmonic power flow models to determine harmonic impedance of each of the branches, determining positive-sequence harmonic voltage, negative-sequence harmonic voltage and zero-sequence harmonic voltage of each of the nodes according to the harmonic impedance of branches and positive-sequence, negative-sequence and zero-sequence admittance matrixes after factorization, and determining the harmonic voltage of each of the node according to the positive-sequence harmonic voltage, the negative-sequence harmonic voltage and the zero-sequence harmonic voltage. The invention also provides a corresponding system. By the aid of the method and the system, the calculation precision can be improved, and the calculation can be simplified.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID
Solution program recording media for simultaneous linear equations having band coefficient matrix
InactiveUS20060064452A1Improve parallel efficiencySpeed up the processComputation using non-contact making devicesDigital computer detailsArray data structureBand shape
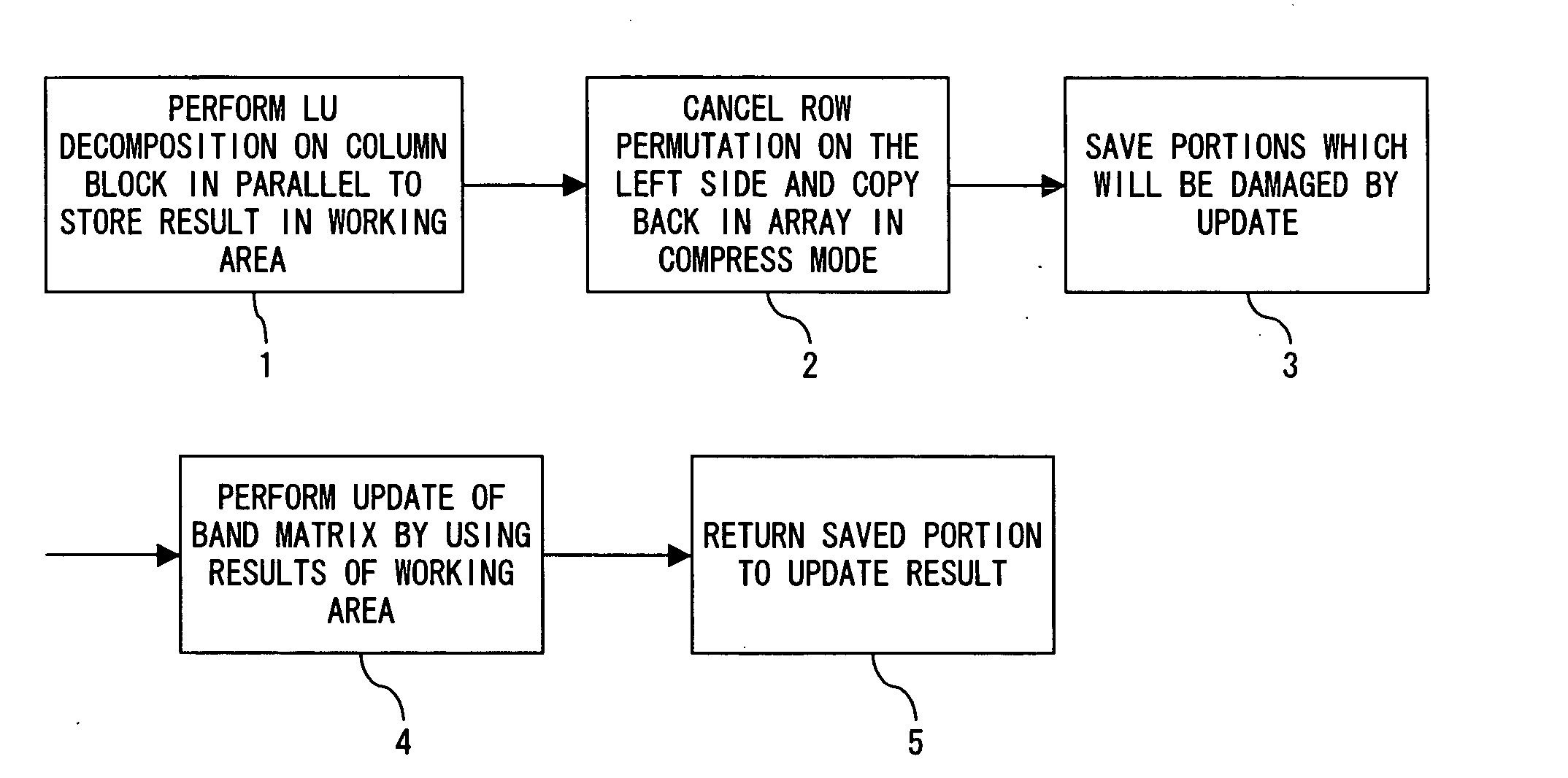
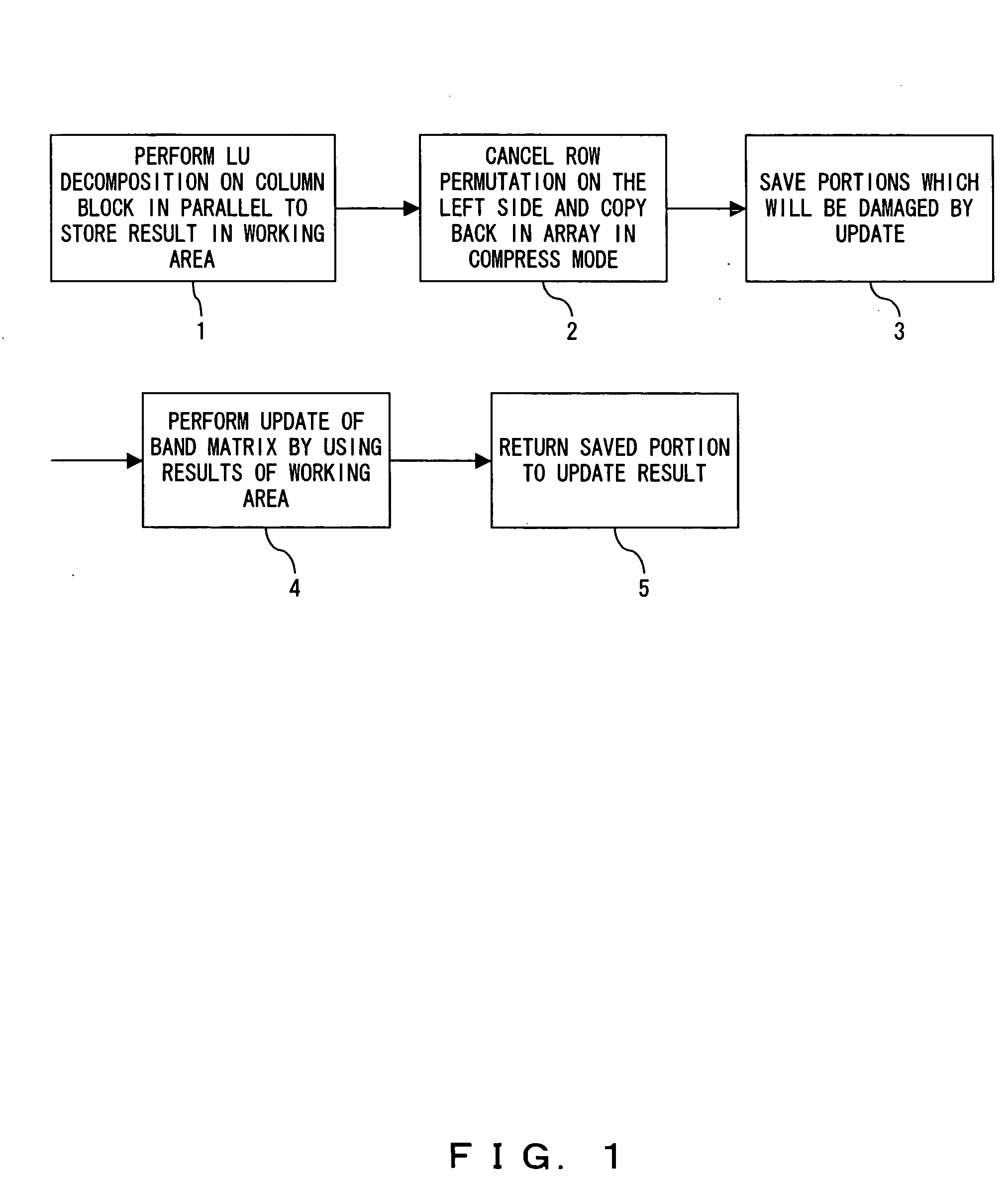
The solution program causes a computer to execute step 1 for performing, in parallel, the LU decomposition on the column block comprising a plurality of columns and for storing the result in the working area; step 2 for canceling the row permutation on the left of each column to the result in step 1 and for copying back the result in the array in compress mode; step 3 for saving the portion which may be damaged by updating the band matrix corresponding to the result in step 1; step 4 for updating the band matrix in parallel by using the result in step 1; and step 5 for returning the saved portion in step 3 to the result in step 4.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Deleted graph-based parallel decomposition method for circuit sparse matrix in circuit simulation
ActiveCN102156777AImprove simulation speedGuaranteed a high degree of parallelismSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmDecomposition
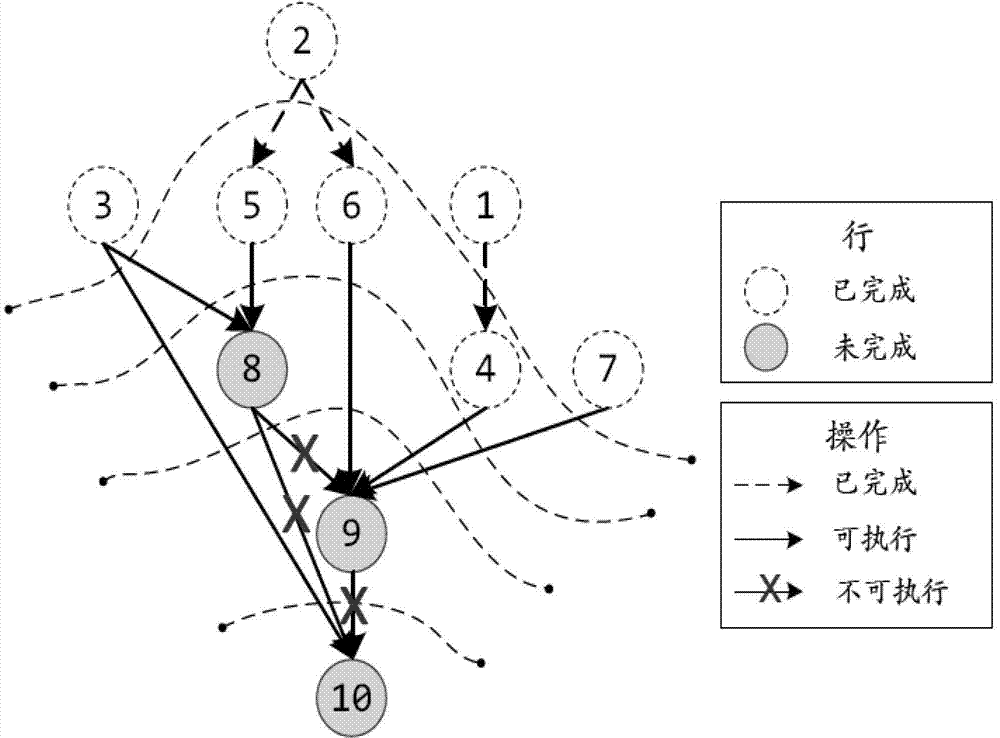
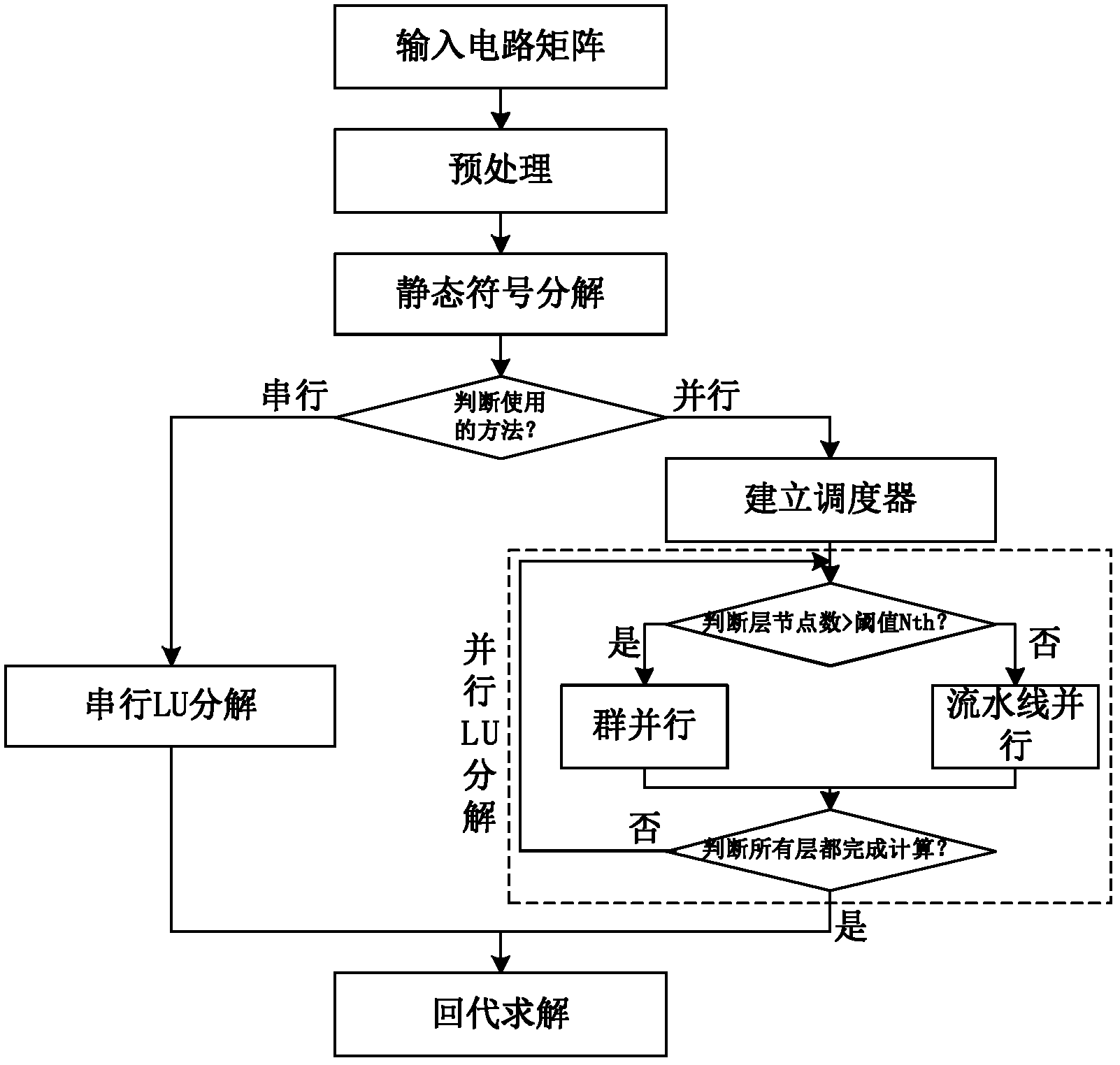
The invention provides a deleted graph-based parallel decomposition method for a circuit sparse matrix in circuit simulation, belonging to the field of electronic design automation (EDA). The method is characterized in that a deleted graph is extracted from a symbolic analysis result of a circuit matrix for representing data independence in a lower-upper (LU) decomposition process; and two different parallel methods, namely a group parallel method and stream-line parallel method, are used according to different structures of the deleted graph, so that the calculation time of LU decomposition is reduced, and the speed of circuit simulation is accelerated. Test results on a series of test circuit matrixes indicate that the LU decomposition speed according to the invention is 1.66-7.72 times faster than that of LU decomposition software KLU when the count of parallel threads is 1-8.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Line source time domain electromagnetic response numerical calculation method based on meshless method
ActiveCN105426339AGet rid of dependenceImprove smoothnessComplex mathematical operationsTerrainElectromagnetic response
The invention relates to a line source time domain electromagnetic response numerical calculation method based on meshless method, particularly a numerical simulation which can overcome dependence on mesh in the conventional numerical calculation method and is suitable for time domain electromagnetic surveying under complex terrain. In the line source time domain electromagnetic response numerical calculation method based on meshless method, based on a governing equation and a definite condition which the transient electromagnetic method satisfies, a generic function of a two-dimensional line source boundary value problem is established, essential boundary conditions are loaded through a penalty method, a paraxial approximate equation is provided to eliminate reflected waves at truncated boundaries, time discretization is carried out through a Crack-Nicolson format, and a recurrence equation is obtained. Based on an isoparametric element thought, units with regular shape in local coordinates are discretized to be irregular solving objects of which nodes are distributed at random. The recurrence equation is solved through a LU decomposition method, and finally, a field value of each node in a solving region is obtained. Calculation result shows that, with the method provided by the invention, a shape function has good smoothness, simulation precision is high, maximum error is not more than 1*10<-3>, and electromagnetic method high-accuracy numerical calculation is realized.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
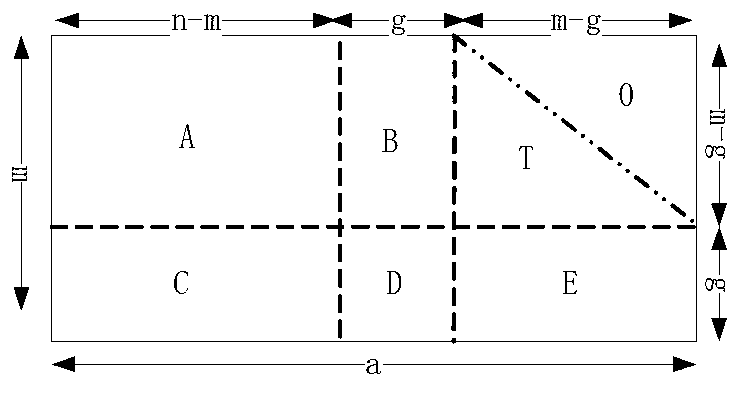
LDPC code coding method based on optimum searching matrix LU decomposition
InactiveCN1801630AReduce computationReduce its latencyError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionHardware structureDecomposition
The encoding method for LDPC code based on LU decomposition for optimized search matrix is realized by software pretreatment and hardware encoding. Wherein, eliminating correlative rows of check matrix, realigning the matrix; selecting nonsingular matrix with non-correlative column composite algorism for decomposition with simple LU algorism; optimizing search by diagonal element asymptotic one of nonsingular matrix; finally, selecting nonsingular matrix with lowest density, and reducing delay of whole coding system by time interval control parallel process hardware structure. This invention holds advantages in prior art, reduces calculation amount near Greedy algorism, and fit to any LDPC code special to abnormal code and normal node with correlative rows.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
Rapid decomposition method trend calculating method based on Matlab
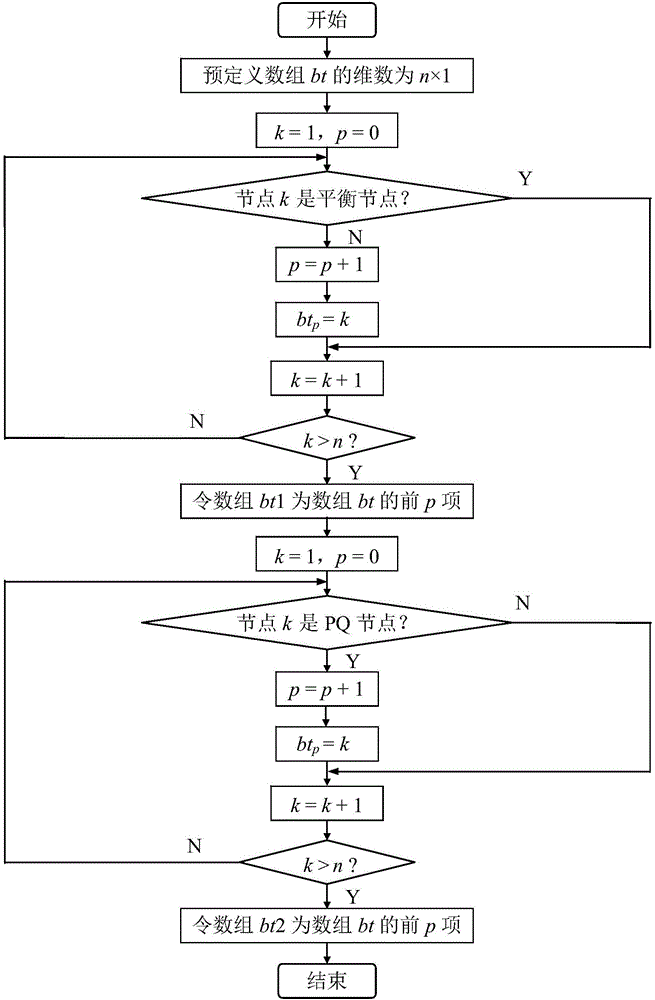
InactiveCN106602570AEasy to testEasy to analyzeAc networks with different sources same frequencyArray data structureLU decomposition
The invention discloses a rapid decomposition method trend calculating method based on a Matlab. The method comprises the following steps that matrix operation and complex number operation are used; an array bt1 is set and a node number of a non-equilibrium node is recorded, and an array bt2 is set and a node number of a PQ node is recorded; when equation set coefficient matrixes B' and B'' are formed, a node type is not considered, and then according to the arrays bt1 and bt2, a matrix element is extracted, and redundant rows and columns are removed; and before iteration, according to the arrays bt1 and bt2, node-injected active and reactive independent elements are removed. In the invention, program codes are reduced, programming is simplified, and a program is clear so that scientific research personnel can conveniently modify the program, debug and improve the program, and add a new function. In the invention, during LU decomposition, an independent element of a coefficient matrix is removed, and before iteration, node-injected active and reactive independent elements are removed; and during an iteration process, work of mentioning a correlation matrix or a vector element repeatedly can be avoided, calculating workloads are reduced and a calculating speed is increased.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Adaptive parallel LU decomposition method aiming at circuit simulation
ActiveCN102426619AImprove simulation speedReduce decomposition timeSpecial data processing applicationsQR decompositionDecomposition
The invention discloses an adaptive parallel LU decomposition method aiming at circuit simulation and belongs to the field of EDA (electronic design automation). The method is characterized in that LU decomposition is carried out on a circuit matrix by automatically selecting a serial or parallel method based on the characteristics of the circuit matrix, so that each circuit matrix can carry out LU decomposition under the optical performance. In the parallel method, data dependency is extracted from the structure of each circuit matrix, and parallel dispatching is carried out on the tasks in the LU decomposition process based on the data dependency, so as to accelerating the circuit simulation. Test results on the circuit matrixes show that the method provided by the invention can accurately determine the serial or parallel method suitable for each circuit matrix, and for the matrixes suitable for the parallel method, the decomposition speed of the method is 2.11-8.38 times that of LUdecomposition software KLU in geometric average when the number of parallel threads is 1-8.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Spark-based distributed matrix inversion parallel operation method
InactiveCN105373517AEliminate interdependenciesReduce in quantityConcurrent instruction executionComplex mathematical operationsComputational scienceFault tolerance
The invention discloses a Spark-based distributed matrix inversion parallel operation method. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out parallel LU decomposition operation on an input matrix in an iteration process; taking a distributed upper triangular matrix and a distributed lower triangular matrix obtained through the LU composition as basis so as to the inverse matrixes of the distributed upper triangular matrix and the distributed lower triangular matrix by using a recursive algorithm; and finally taking a permutation matrix and the inverse matrixes of the triangular matrixes obtained in the above two steps as basis so as to implement distributed matrix multiplication to obtain the inverse matrix of any original input matrix. According to the method, the dense matrixes with large dimensionalities can be processed, and relatively high operation efficiency as well as relatively good fault tolerance and expandability can be obtained.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
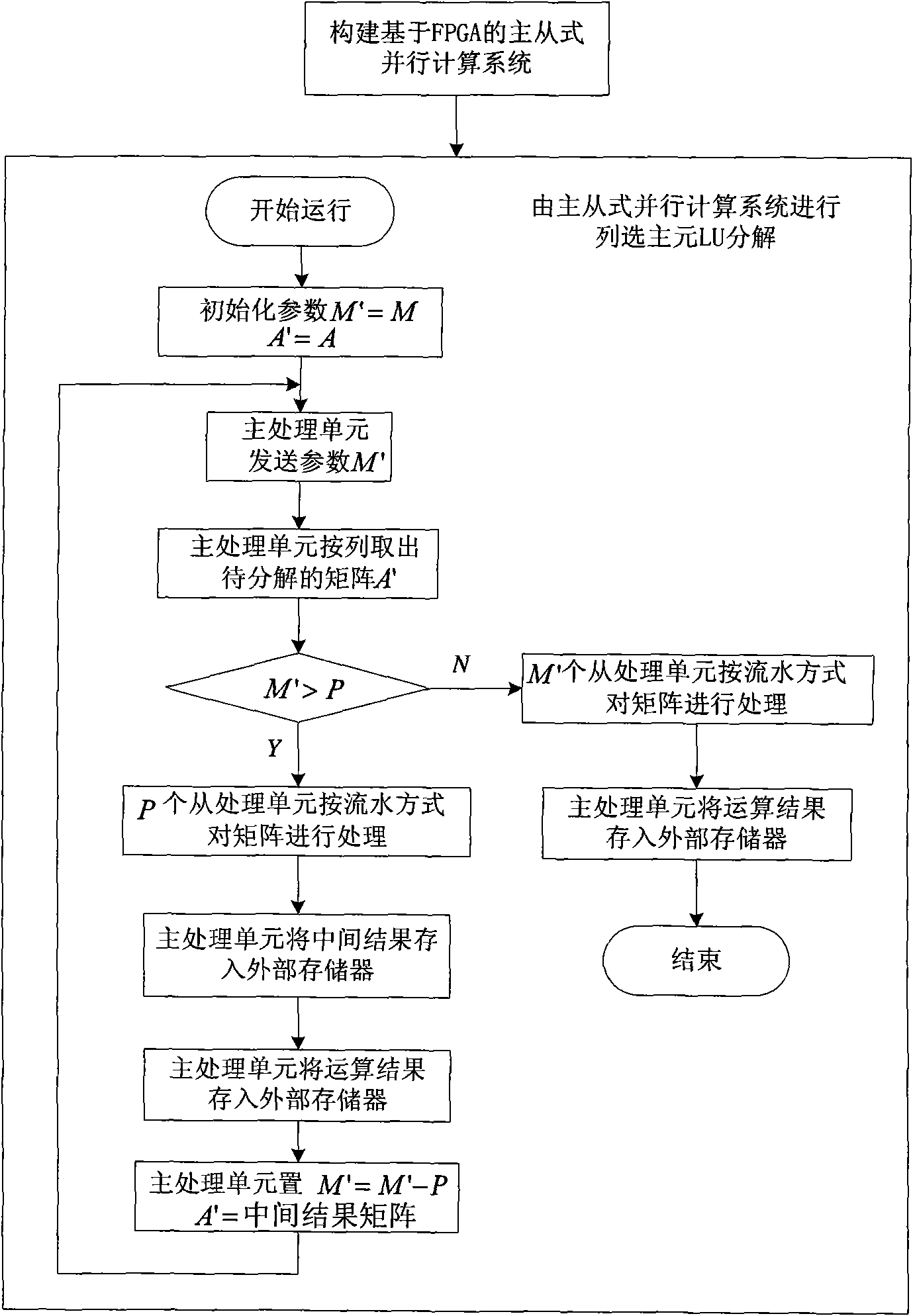
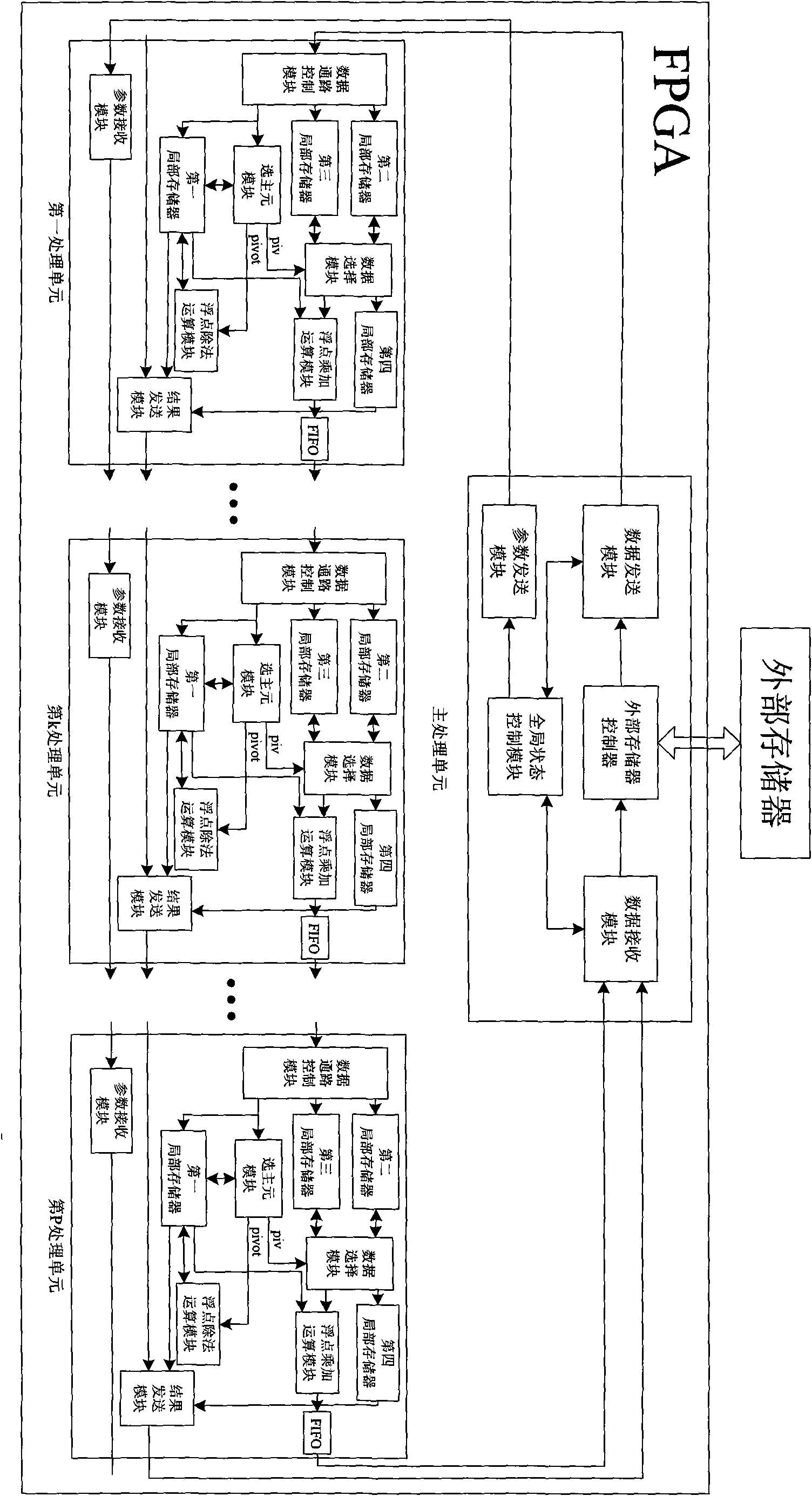
Method of column pivoting LU decomposition based on FPGA
InactiveCN101604306AImprove calculation accuracyFlexible configurationComplex mathematical operationsQR decompositionMain processing unit
The invention discloses a method of column pivoting LU decomposition based on FPGA, the technical problem to be solved is to reduce time complexity of LU decomposition and accelerate solving of dense matrix linear equation system. The technical solution comprises that: at first a FPGA-based master-slave parallel computation system composed of a master processing unit and P slave processing units is constructed, the master-slave parallel computation system carries out column pivoting LU decomposition on the matrix to be decomposed, the master processing unit sends parameters and the matrix to be decomposed to a first slave processing unit, the slave processing unit processes the matrix in a pipeline way, and the processing result is sent to the master processing unit from the P slave processing unit. Computation accuracy is dramatically improved in contrast to non-pivoting LU decomposition with the invention being used, computing speed is high, and the master-slave parallel computation system thereof has expandability.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Magnetotelluric meshless numerical simulation method for random conductive medium model
InactiveCN105354421AEasy loadingFacilitate understanding of the laws of communicationInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsCorrelation functionLU decomposition
The present invention proposes a magnetotelluric meshless numerical simulation method for a random conductive medium model. The method is for heterogeneity of underground space, and according to the method, a shape function is constructed based on discrete nodes, and dependence on a mesh no longer exists. The method provided by the present invention comprises: using the spectral decomposition theory and the hybrid autocorrelation function theory of the stochastic modeling process to construct a random conductive medium model of underground space; establishing a function of the magnetotelluric corresponding boundary value problem; establishing a shape function of a meshless method by using a least squares method; using the Lagrange multipliers method to load essential boundary conditions; resolving linear equations by using the biconjugate gradient stabilized (BICGSTAB) algorithm of incomplete LU decomposition preprocessing, to obtain a field value of each node in the region; and using the field values to calculate the apparent resistivity and phase of each point, thereby completing the whole numerical simulation calculation process. The section calculated according to values of the random conductive medium model better complies with the actual situation, and is more advantageous for the interpretation and processing work of the magnetotelluric data.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
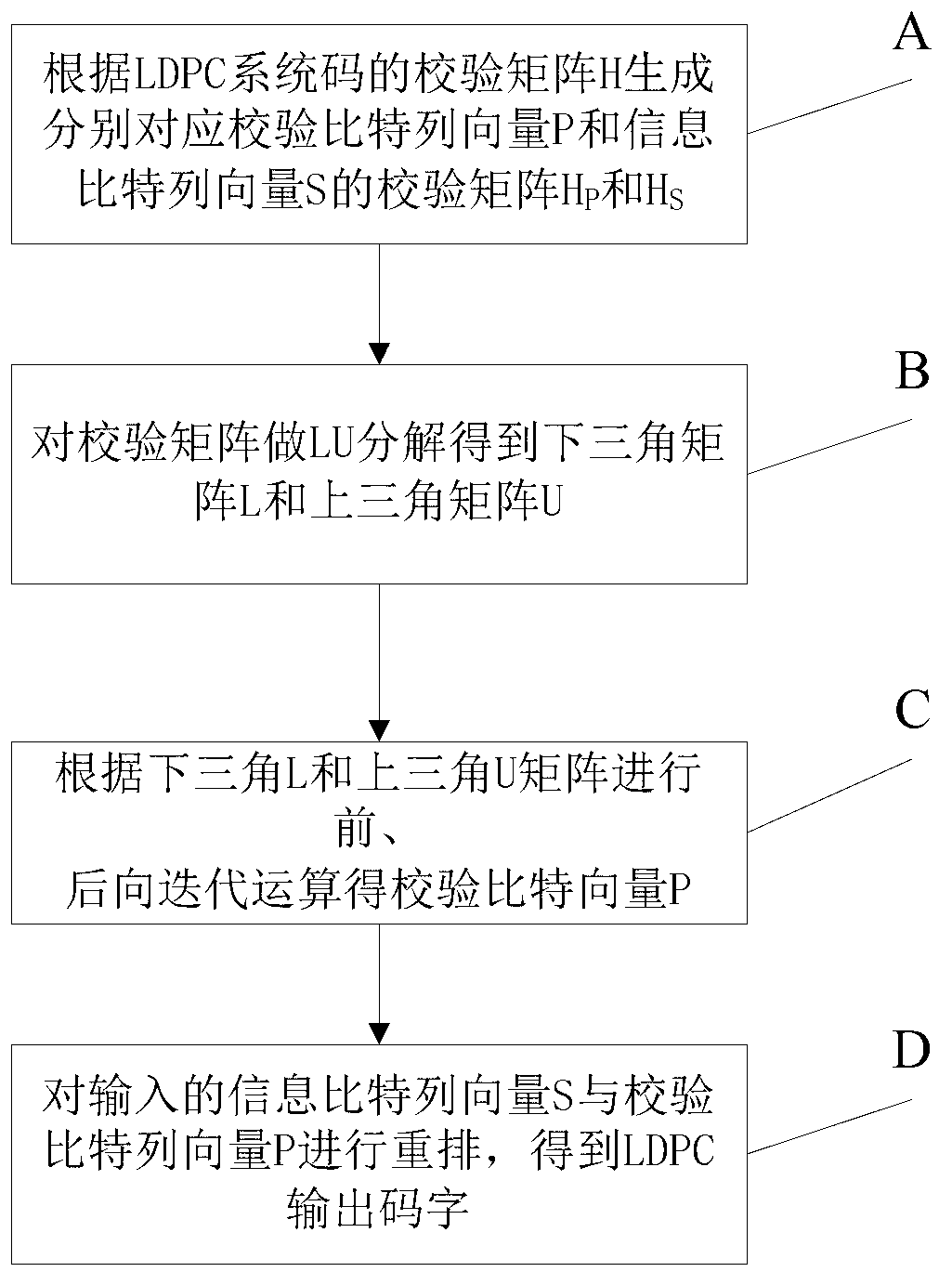
LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) encoding method based on FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) and used in CMMB (China Mobile Multimedia Broadcasting) exciter
InactiveCN102739259AAvoid the problem of large storage resource requirementsReduce computational complexityError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsComputer architectureDecomposition
The invention discloses an LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) encoding method based on FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) and used in CMMB (China Mobile Multimedia Broadcasting) exciter. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, processing a verification matrix H of an LDPC system code on an MATLAB (Matrix Laboratory) platform, so as to generate verification matrixes Hp and Hs which correspond to a verification bit column vector P and an information bit column vector S; carrying out LU (Logical Unit) decomposition to the verification matrixes so as to obtain a lower triangular matrix L and an upper triangular matrix U; and realizing the LDPC encoding on the FPGA platform, which mainly involves the storage of a large matrix, matrix multiplication, forward iteration and backward iteration. According to the encoding method, an encoding mode based on a LU decomposition verification matrix is adopted; the logic calculation that large matrixes are multiplied is avoided; and the problem of large requirement on FPGA internal storage resource caused by large data quantity storage is solved, thereby simplifying the logic calculation operation, saving the storage space, and being beneficial for the realization of the LDPC encoding of the CMMB system.
Owner:ALLWIN TELECOMM
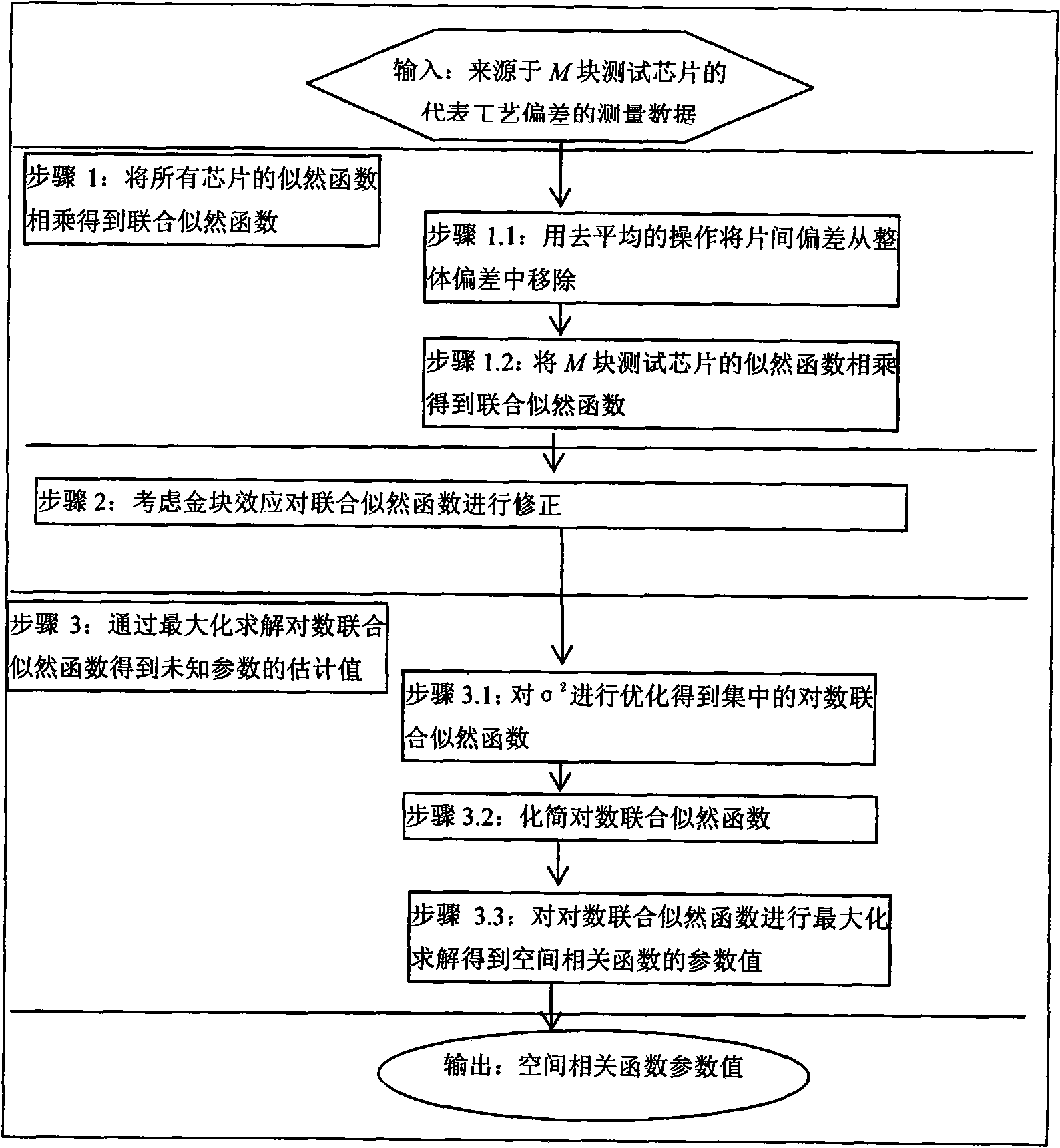
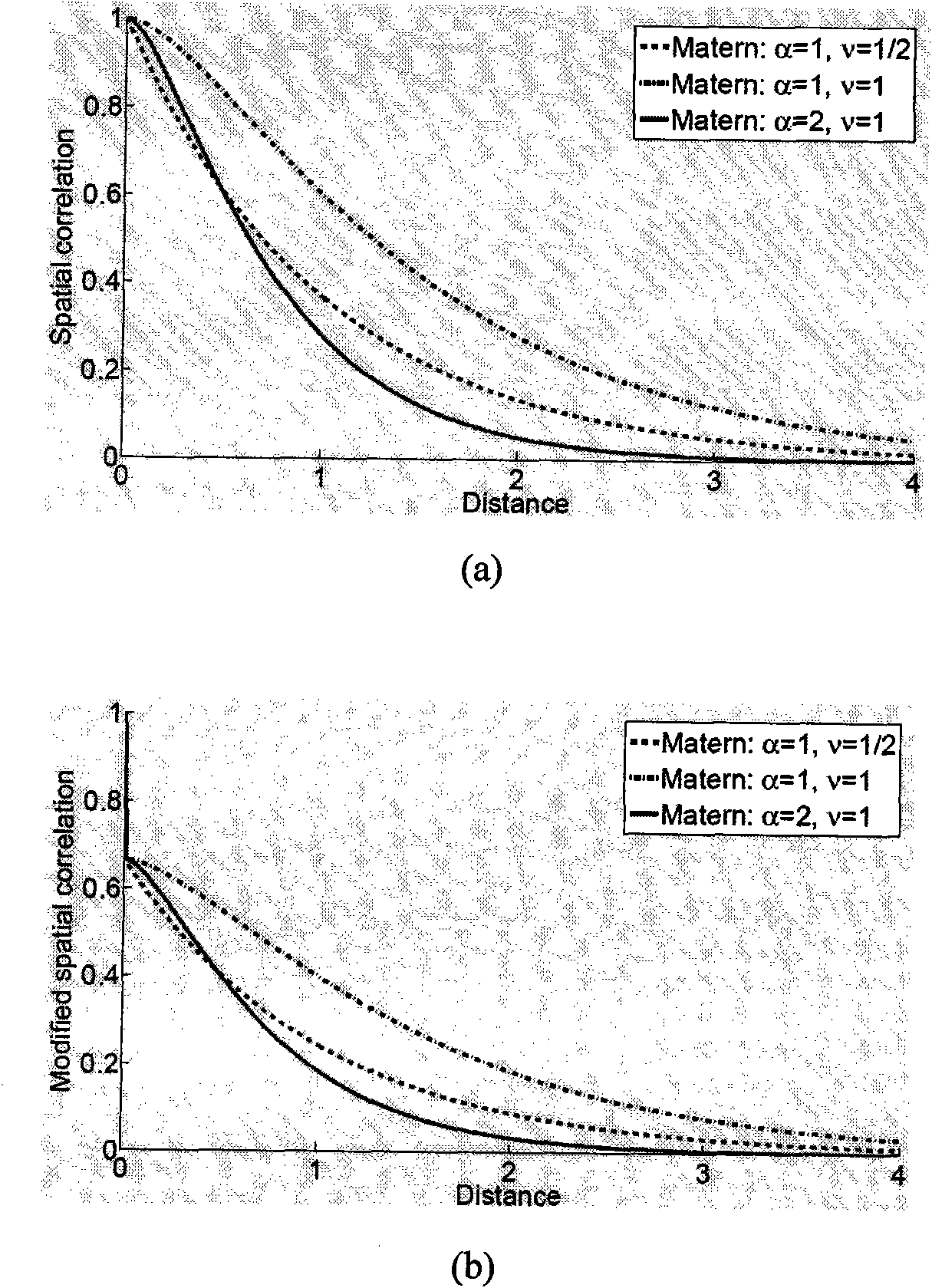
Method for establishing space correlation model of technical error in integrated circuit chip
ActiveCN101996266APracticalHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsObservational errorProcess deviations
The invention belongs to the field of integrated circuits, relating to a method for establishing a space correlation model of technical errors in an integrated circuit chip. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting an unknown parameter of a space correlation function by utilizing the maximum likelihood estimation of a multi-test chip, and establishing the space correlation model ofthe errors in the chip; and multiplying a likelihood function of all test chips to obtain a joint likelihood function, solving through maximizing the joint likelihood function to obtain the space correlation function which is determined by a parameter value and can be directly used for circuit analysis design of the technical errors. The influence of pure random part of the error in the chip and the measurement error can be processed in the extraction process of the space correlation function, and the precision of an extracted result is remarkably improved. Determinant logarithms of symmetrical positive definite matrixes in the joint likelihood function are calculated by utilizing an LU (Logic Unit), and the problem of unstable number value occurring in direct calculation is solved.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
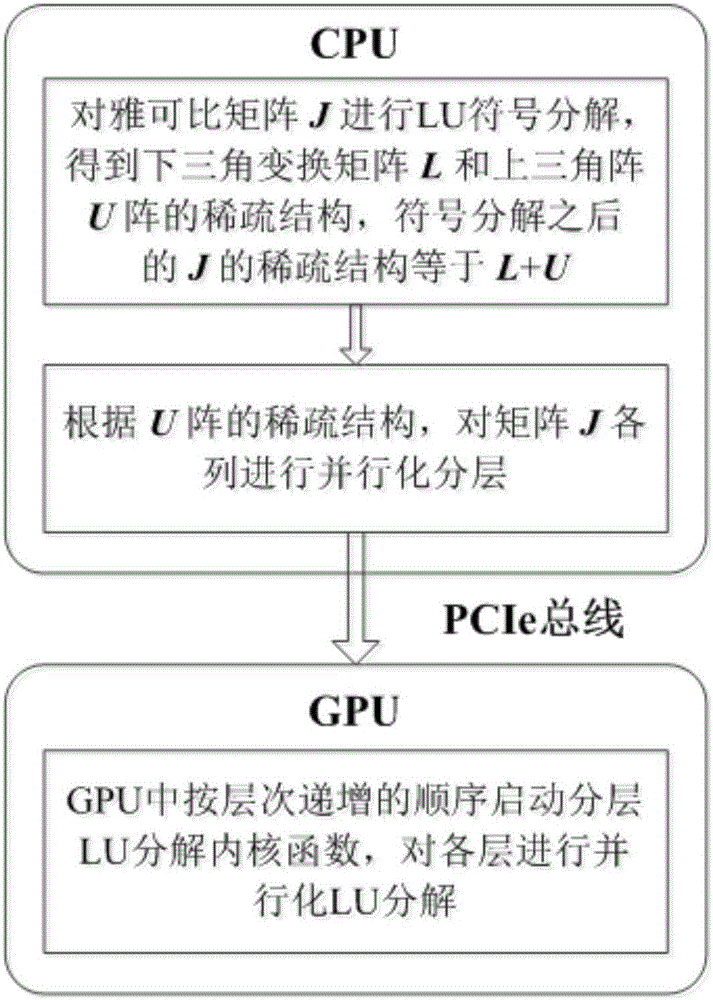
GPU accelerated power flow jacobian matrix LU decomposition method
ActiveCN106157176AImprove decomposition efficiencyReduce floating point calculationsData processing applicationsResource allocationDecompositionLU decomposition
The invention discloses a GPU accelerated power flow jacobian matrix LU decomposition method. The method includes the steps that LU symbol decomposition is carried out on a jacobian matrix J in a CPU to obtain sparse structures of a lower triangle transformation matrix L and an upper triangle matrix U, and the sparse structure of J is equal to L+U after symbol decomposition; according to the sparse structure of the matrix U, all columns of the matrix J are layered in a parallelization mode, and data needed by calculation is transmitted to a GPU; a layered LU decomposition kernel function Sparse LU is calculated in the GPU in the sequence of level progressive increase. The mode of combining program process controlling and basic data processing through the CPU with dense floating-point calculation processing through the GPU is used for improving the efficiency of power flow jacobian matrix LU decomposition, and the problem that flow calculation consumes time greatly in electric system static safety analysis is solved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Ka frequency range deep space communication method and system of q-LDPC-LT cascade fountain code
InactiveCN105162552AReduce dependenceReduce coding complexityCode conversionCoding detailsFountain codeOriginal data
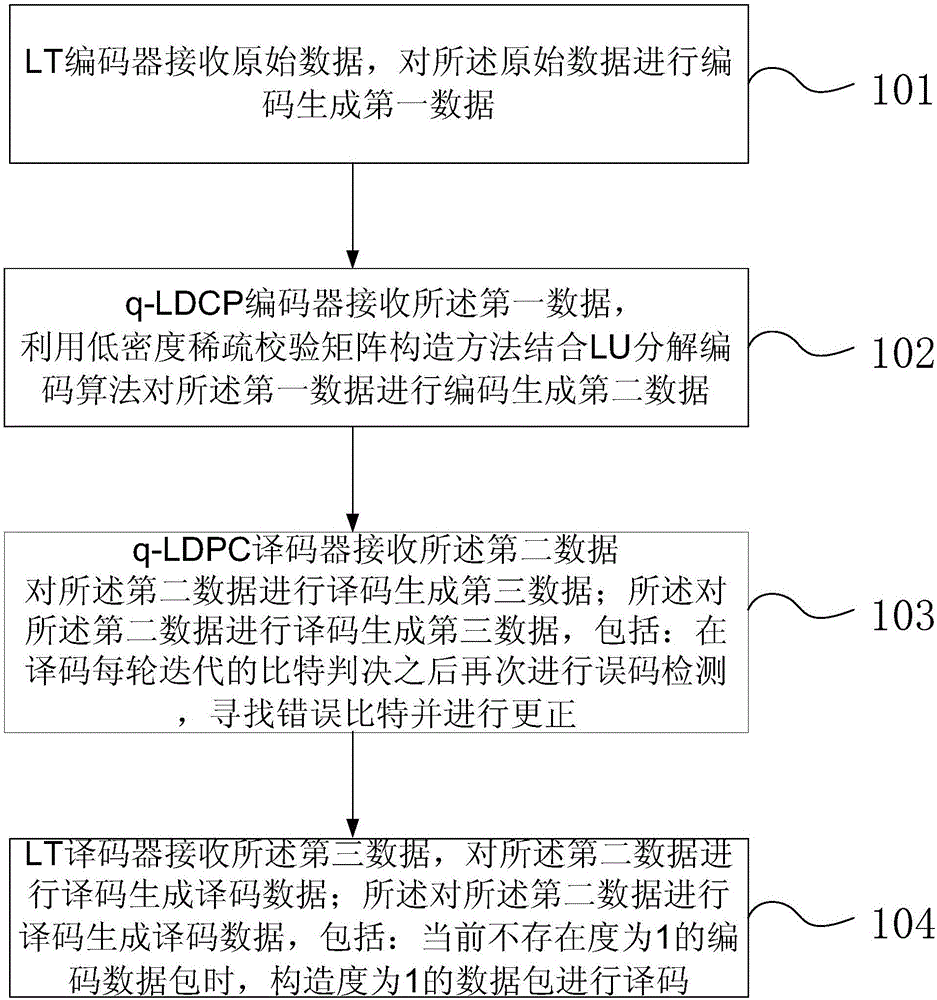
The invention provides a Ka frequency range deep space communication method and system of a q-LDPC-LT cascade fountain code. The method comprises that an LT encoder encodes original data to generate first data; a q-LDPC encoder encodes the first data to generate second data using a low density sparse parity check matrix construction method with an LU decomposition encoding algorithm; a q-LDPC decoder decodes the second data to generate third data; the second data is decoded to generate the third data, wherein error code detection is performed after bit decision of each coding iteration and error bits are searched and corrected; an LT decoder decodes the second data to generate decoding data; and the second data is decoded to generate the decoding data, wherein when there is no encoding data package with the degree of 1, a data package with the degree of 1 is constructed to perform decoding. The invention can reduce the encoding complexity, improve the encoding efficiency, and further improving the decoding reliability, thereby reducing dependence of decoding on the existence of an encoding data package with the degree of 1.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Design method of real-time simulation solver of active power distribution network on basis of FPGA
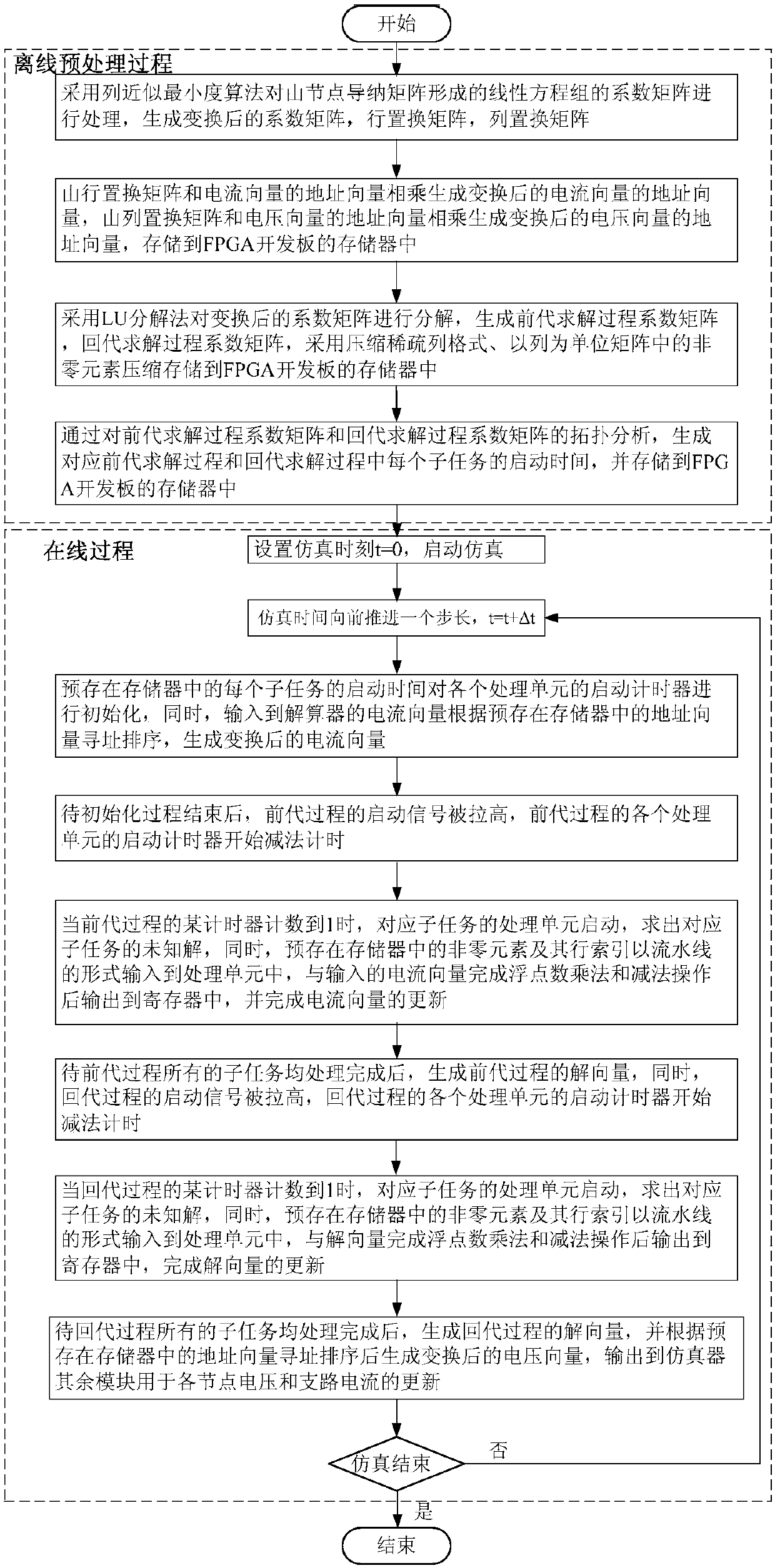
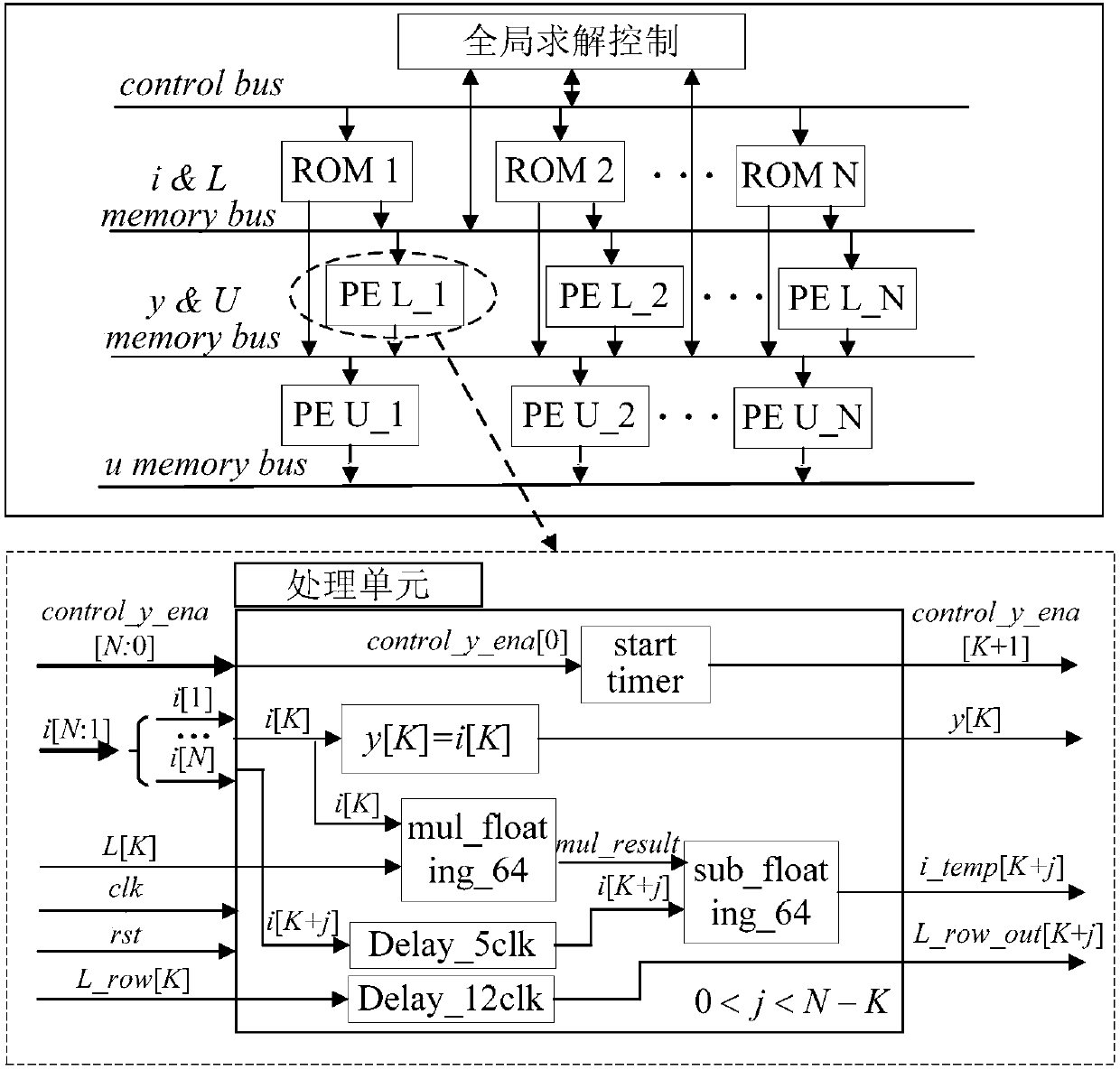
InactiveCN107784158AGuaranteed solution accuracyGuaranteed solution speedDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsStart timeAlgorithm
Disclosed is a design method of a real-time simulation solver of an active power distribution network on basis of an FPGA. The method comprises the steps of offline preprocessing and online solving. During offline preprocessing, a column approximate minimum degree algorithm is adopted for processing a node admittance matrix; the address vectors of current and the address vectors of current voltageare prestored; an LU decomposition method is adopted for decomposing the node admittance matrix; the starting time of each sub-task in the previous substitution process and the back substitution process is prestored. During online solving, the simulation starting time is set; the simulation time is advanced by one step length; information initialization of each sub-task and addressing sorting ofthe current vectors are completed; when solving begins, a starting timer of each processing unit is initialized according to the prestored starting time of the corresponding sub-task; solving in the previous substitution process is completed, and an intermediate solution vector is generated; solving in the back substitution process is completed, and a final solution vector is generated after addressing sorting; whether or not the simulation time reaches the final simulation moment is determined. By means of the method, while the solving precision and speed are ensured, sparse linear equationsare solved accurately and efficiently.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV +2
Large grid Thevenin equivalent parameter online identification method based on LU decomposition
InactiveCN109494724ACalculation speedVerify correctnessAc network circuit arrangementsLU decompositionPower grid
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV +1
Sparse node positioning algorithm
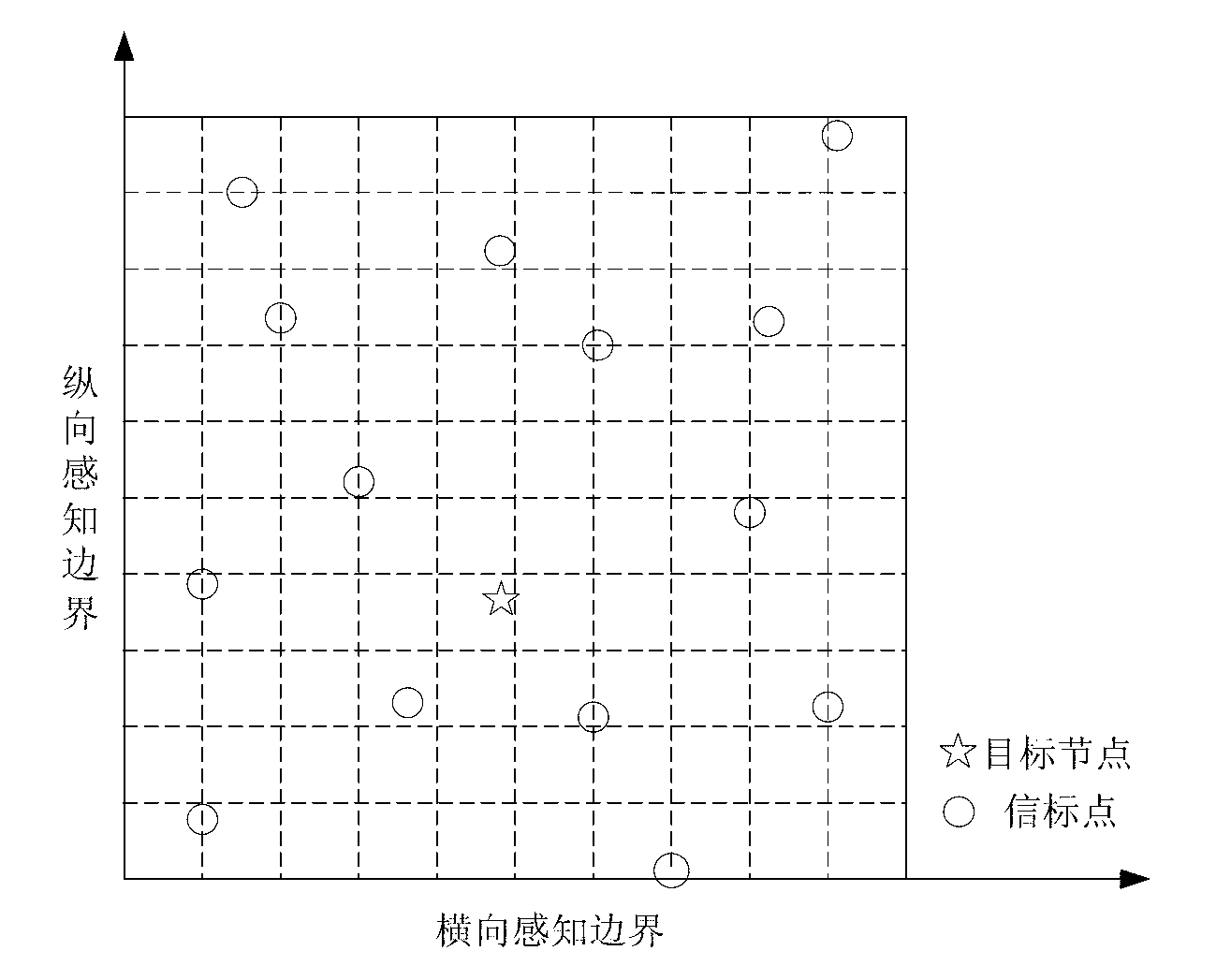
InactiveCN103327608AGuaranteed rebuild performanceEnsure node positioning accuracyPosition fixationTransmission monitoringPretreatment methodLU decomposition
The invention provides a sparse node positioning algorithm. According to the algorithm, through a grid sensing area, a node positioning problem is transformed into a sparse signal reconstruction problem. Then a pretreatment method of LU decomposition is employed, the preprocessing of an observation matrix is carried out, and a restricted isometry condition is effectively satisfied. Finally, aiming at a problem that a determined sparse signal is an approximate sparse signal in a sparse positioning model, a centroid algorithm is employed to improve the positioning performance of the algorithm. According to the algorithm, the compressed sensing theory is introduced, through the grid sensing area, the node positioning problem is effectively converted into an N-dimensional vector reconstruction problem with sparsity of 1, and the characteristics of a node is effectively excavated to complete the node self-positioning.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Full frequency domain sub-band digital watermarking embedding method based on wavelet decomposition
InactiveCN104835106AGuaranteed high volume embeddingApplicable copyright protectionImage data processing detailsArray data structureDecomposition
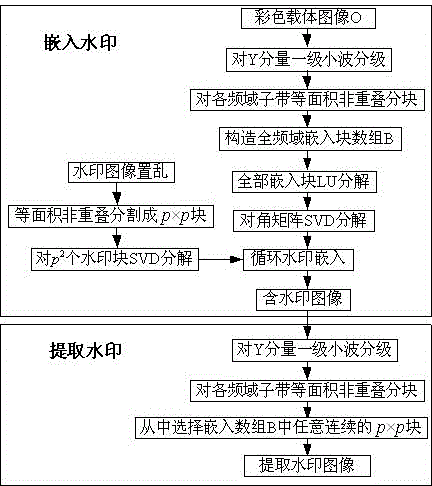
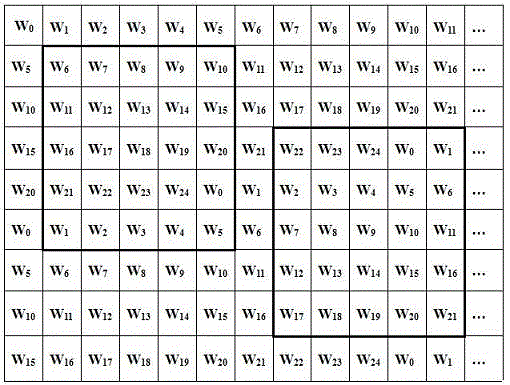
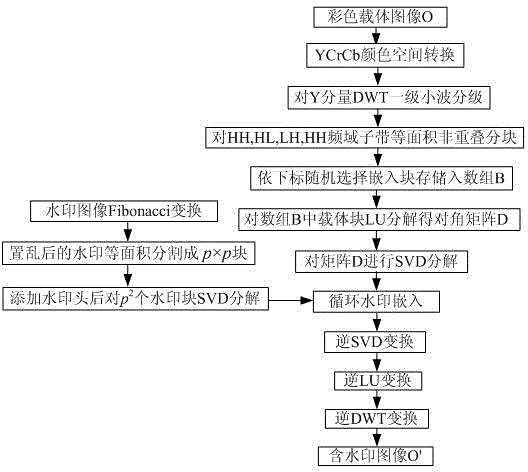
The invention discloses a full frequency domain sub-band digital watermarking embedding method based on wavelet decomposition, comprising the steps of conducting first-level wavelet decomposition on a color host image Y component; conducting equal-area and not-overlapping partition on all the four frequency domain sub bands HH, HL, LH and LL, and selecting embedding blocks from the four frequency domains according to rules at random to form a full frequency domain embedding block array B; conducing LU decomposition on the embedding blocks and selecting diagonal matrix to conduct SVD decomposition; dividing gray-scale watermarking images into p*p blocks after scrambling in a equal-area and non-overlapping manner, and conducting SVD decomposition on each watermarking block; modifying the singular value of the carrier block and completing the circular embedding of watermarks. At the time of extracting watermarks, a complete watermark information can be obtained by selecting any continuous p*p embedding blocks in the embedding array. The full frequency domain sub-band digital watermarking embedding method based on wavelet decomposition is advantageous in that geometric attack like shearing, brightness adjusting, high pass filtering, lossless compression and zooming can be effectively defended; under the prerequisite that high-capacity embedding of watermarks is guaranteed, the relation between the invisibility and robustness can be balanced; the full frequency domain sub-band digital watermarking embedding method is suitable for the copyright protection of color digital images.
Owner:EAST CHINA JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
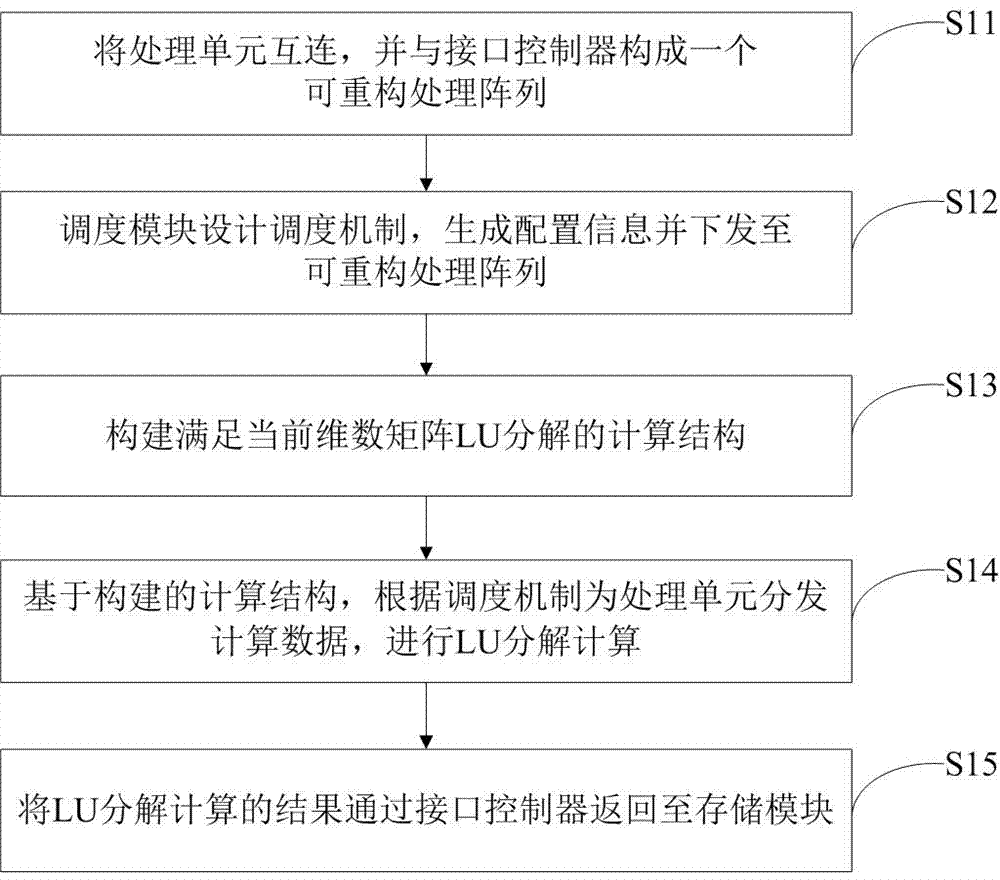
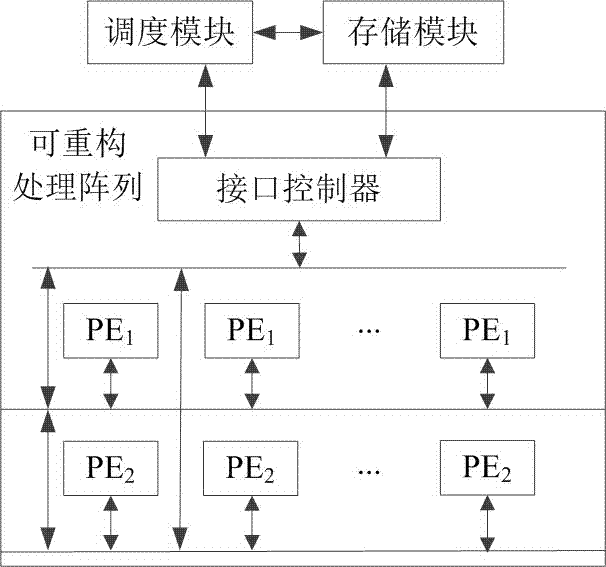
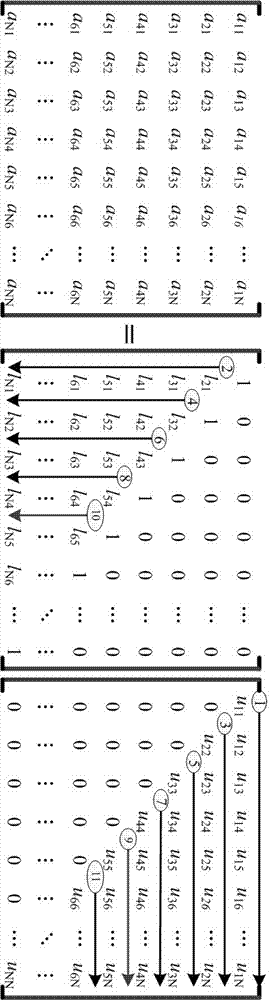
Scheduling method of reconfigurable computing architecture based on LU decomposition of arbitrary dimension matrix
ActiveCN107341133AIncrease flexibilityMeet the needs of decomposition calculationComplex mathematical operationsReconfigurable computing architectureComputer module
The invention belongs to the field of matrix computing technology, and particularly relates to a scheduling method of a reconfigurable computing architecture based on LU decomposition of an arbitrary dimension matrix. The reconfigurable computing architecture based on LU decomposition of the arbitrary dimension matrix consists of processing units, an interface controller, a scheduling module and a storage module. The method comprises the following steps: interconnecting the processing units, and forming a reconfigurable processing array with the interface controller; enabling the scheduling module to design a scheduling mechanism, generating configuration information, and issuing the configuration information to the reconfigurable processing array; constructing a computing architecture that meets the LU decomposition of a current dimension matrix; based on the constructed computing architecture, distributing computing data to the processing units according to the scheduling mechanism, and performing LU decomposition computation; and returning an LU decomposition computation result to the storage module through the interface controller. According to the scheduling method disclosed by the invention, the LU decomposition computation of the arbitrary dimension matrix can be achieved through the mode that the fixed processing units can be reconfigured, and the flexibility of LU decomposition can be improved.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV +1
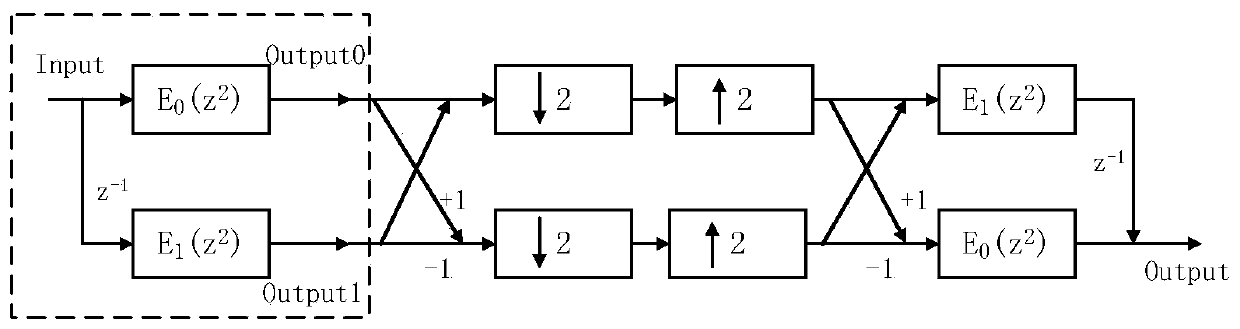
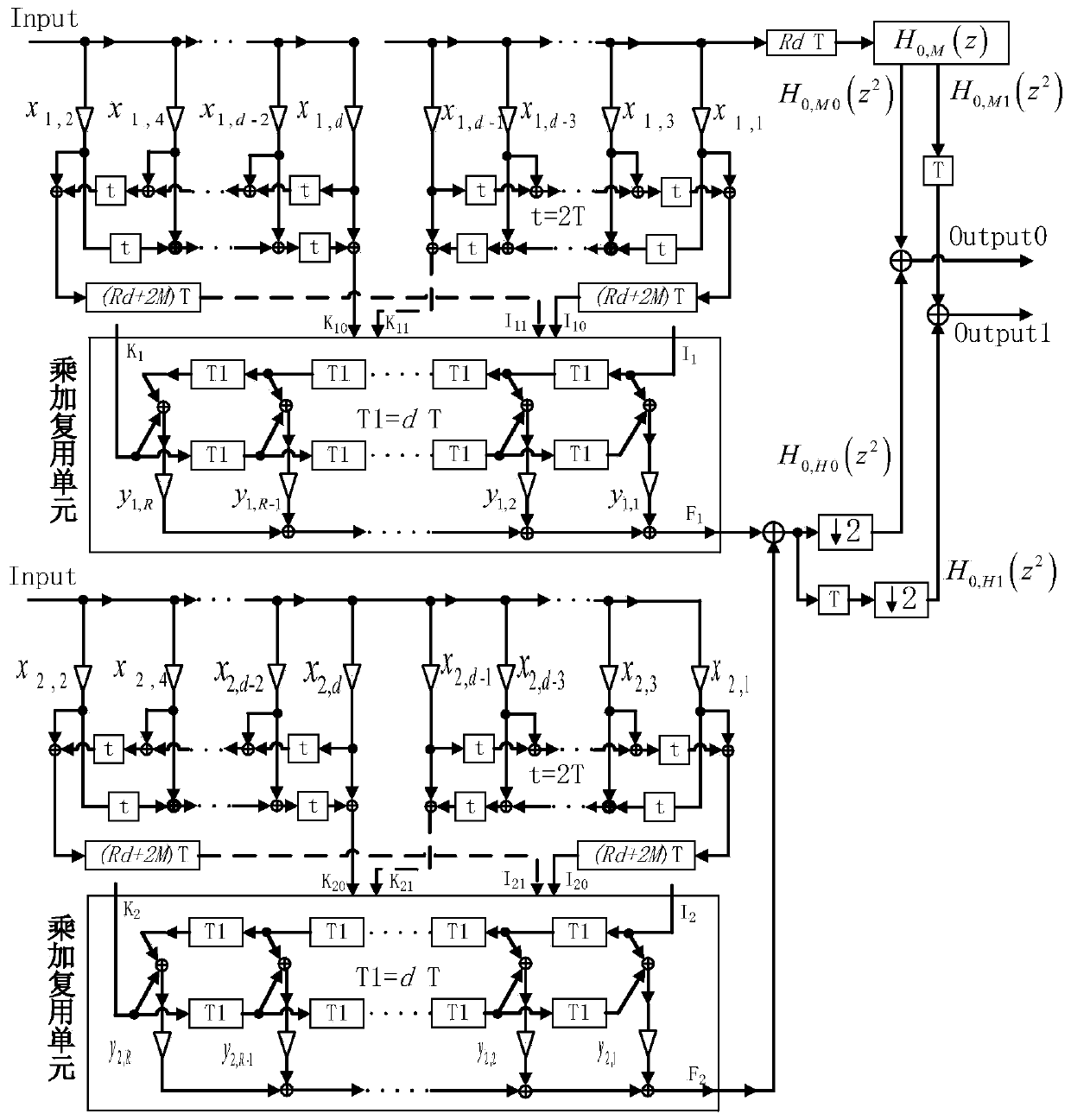
Multi-phase structure of two-channel orthogonal mirror image filter bank and coefficient design method thereof
ActiveCN110365312ASave resourcesReduce execution complexityDigital technique networkBinary multiplierLU decomposition
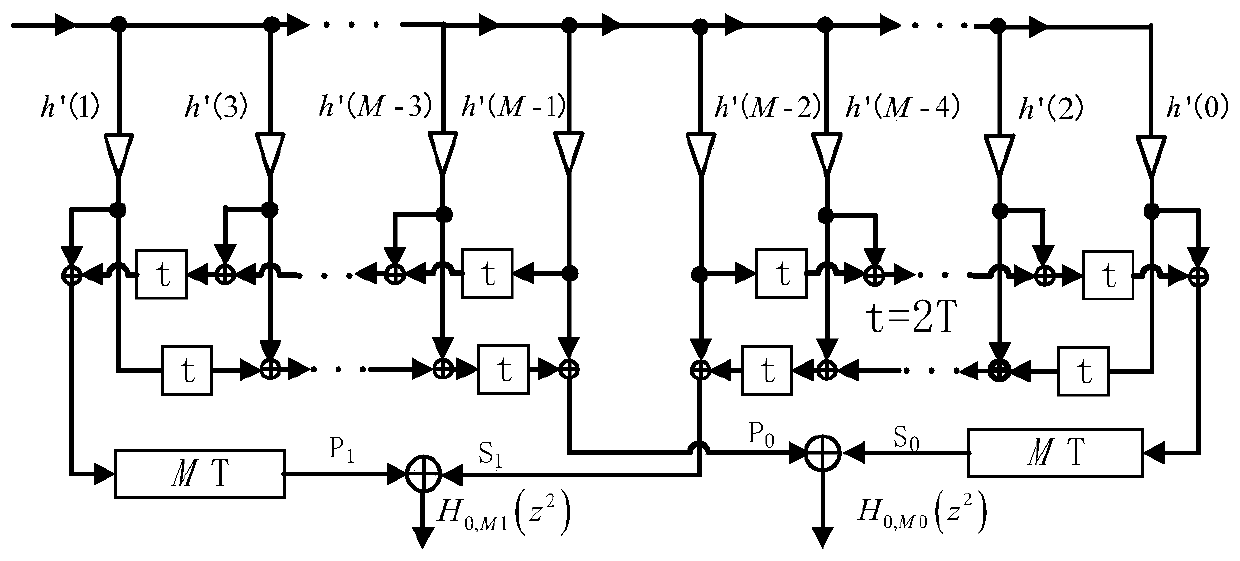
The invention discloses a multi-phase structure of a two-channel orthogonal mirror image filter bank and a coefficient design method of thereof. At present, most known two-channel QFMB design methodsare optimization design of prototype filter coefficients, and do not pay much attention to reduction of hardware implementation complexity of a QMFB structure. The multi-phase structure of the two-channel orthogonal mirror image filter bank comprises an H0 module, an M (z) module, q modules, a module connecting part, a main input port Input, a main output port Output0 and a main output port Output1. According to the multi-phase structure of the two-channel QMFB analysis filter bank part provided by the invention, a traditional QMFB prototype filter coefficient is converted into a form of an extrapolation pulse response filter, and LU decomposition is adopted, so that more 0 and 1 exist in the coefficient, and multiplier and adder resources are saved.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com