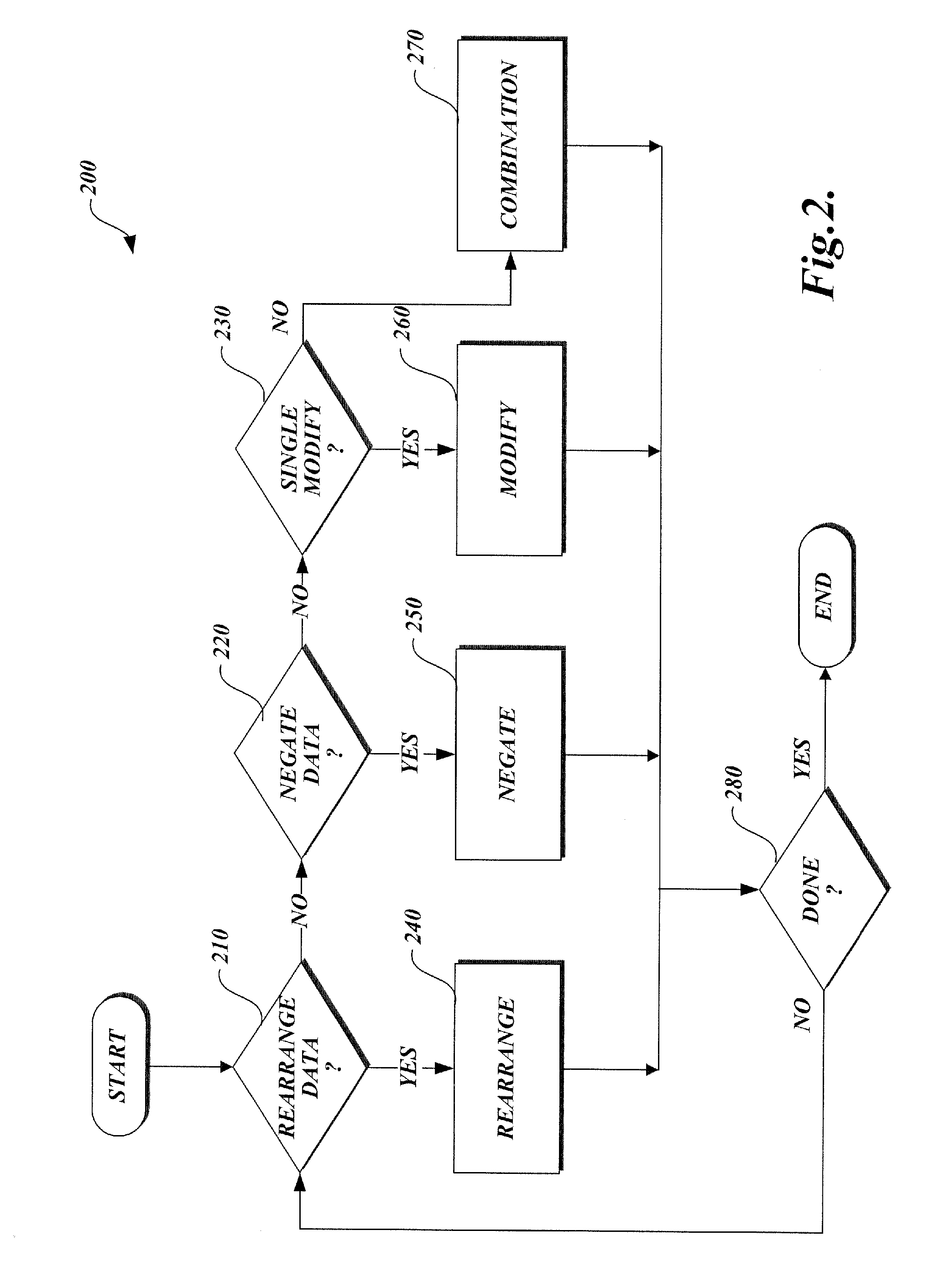
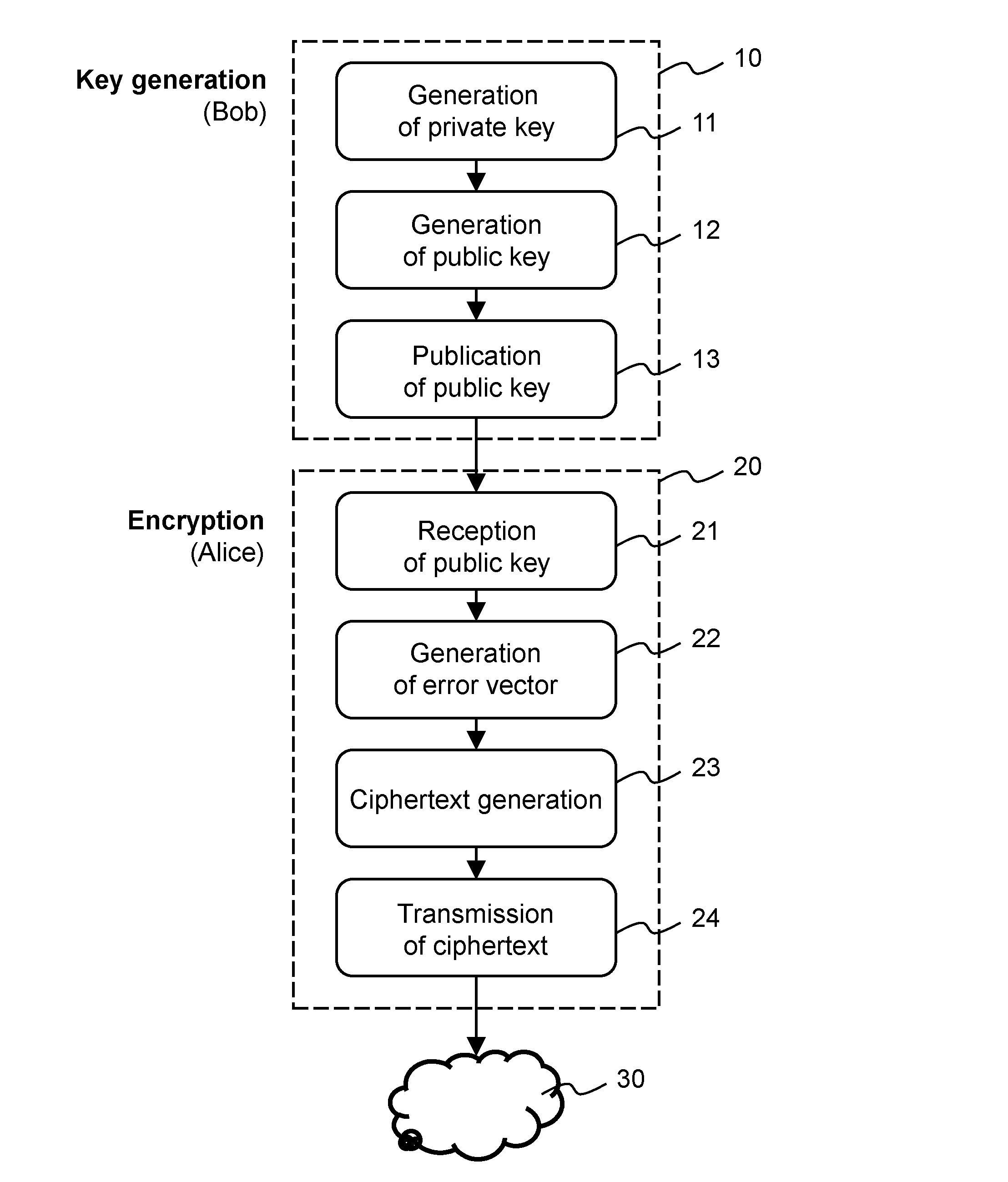
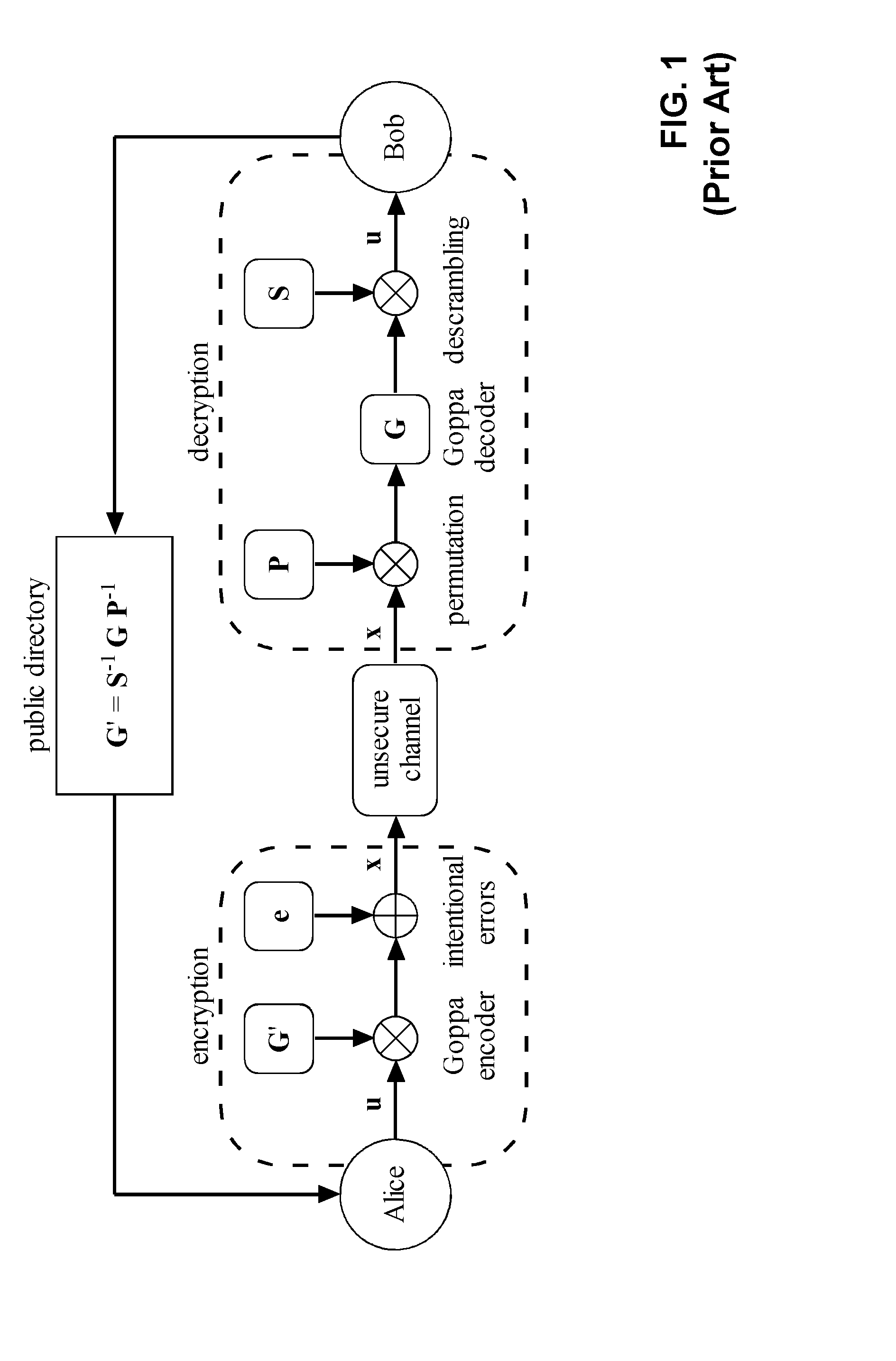
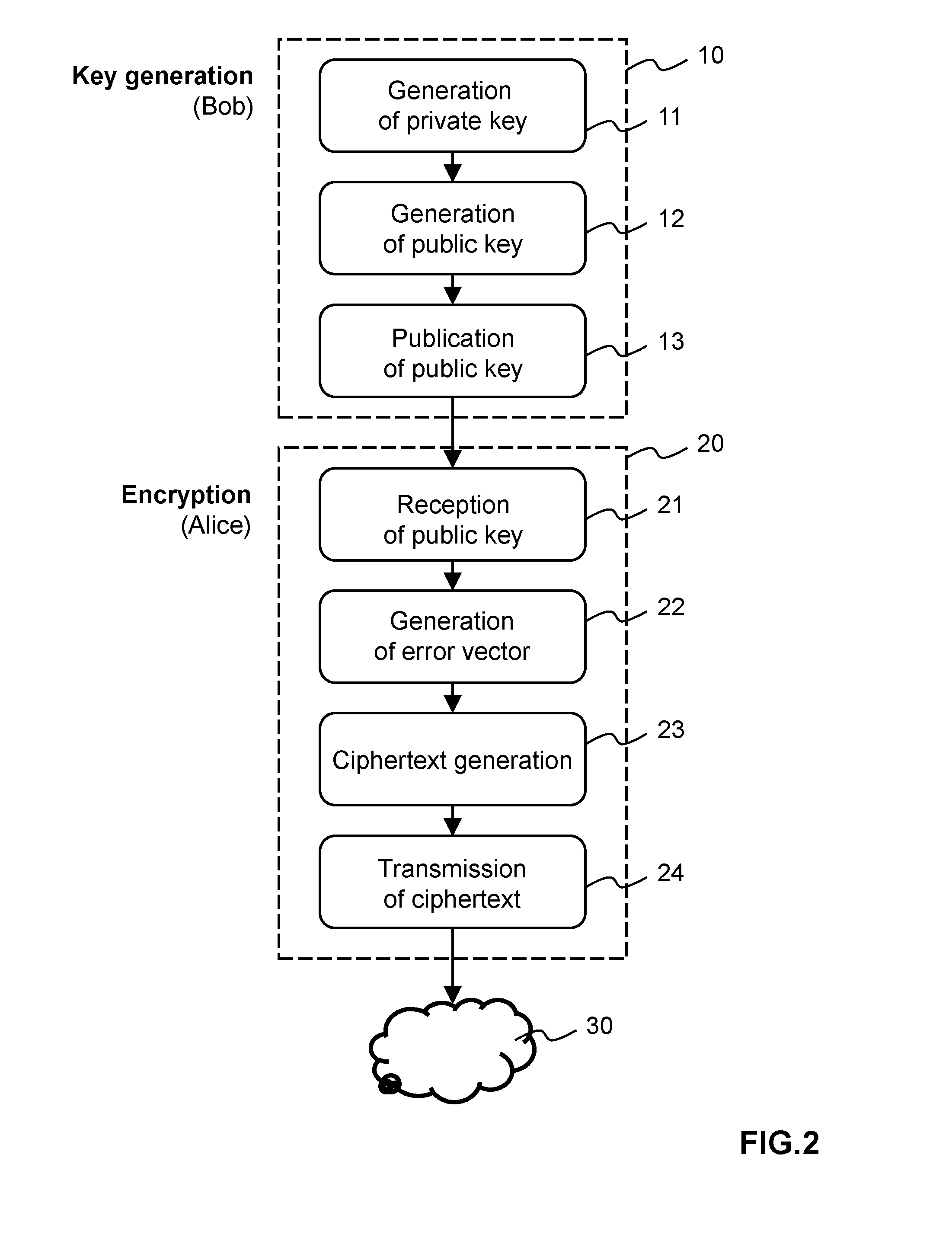
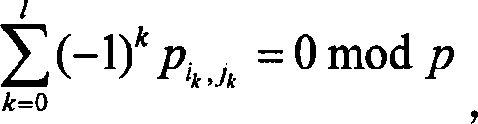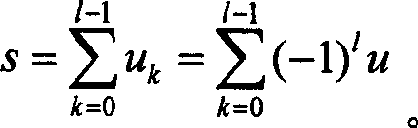Patents
Literature
181 results about "Permutation matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
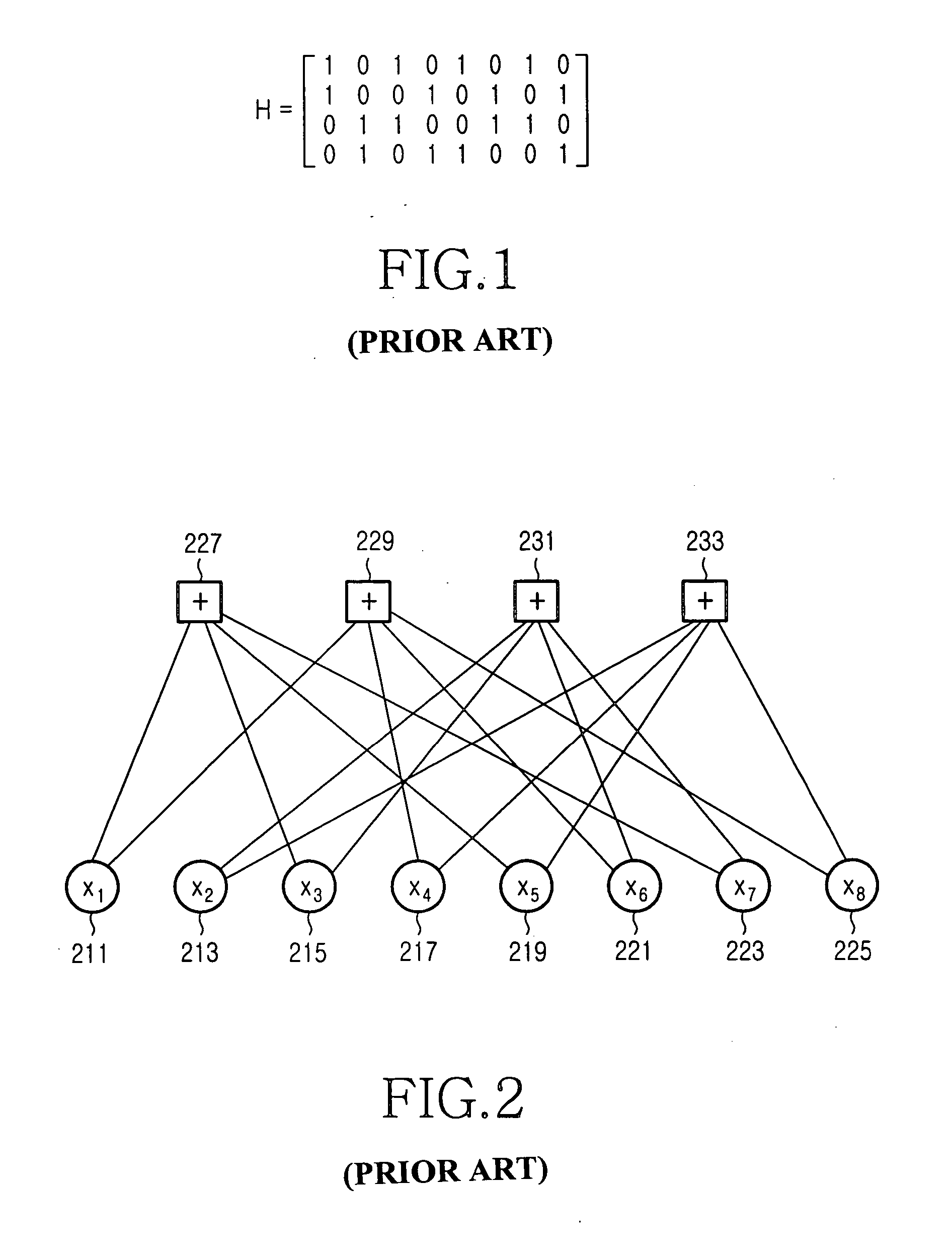
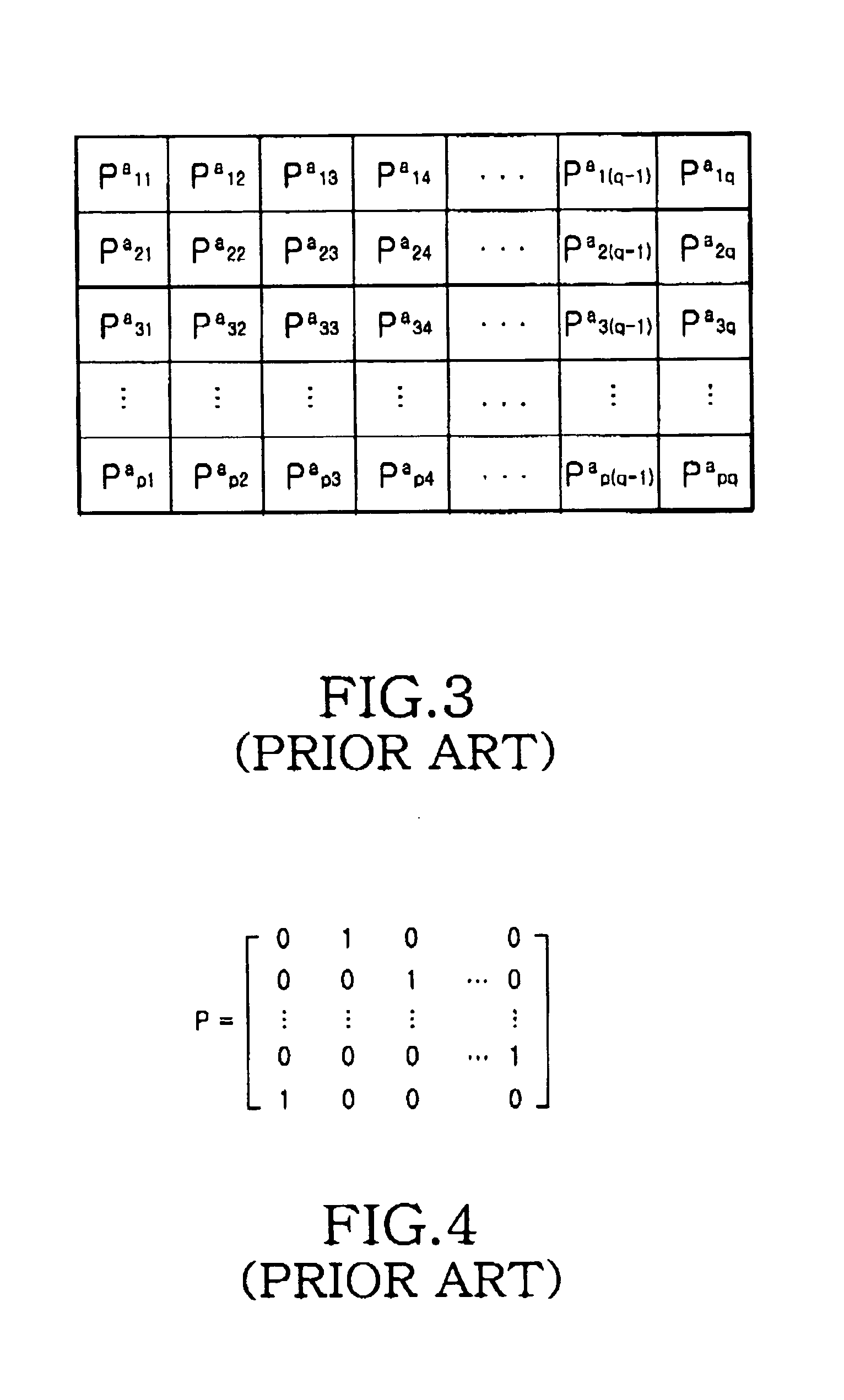
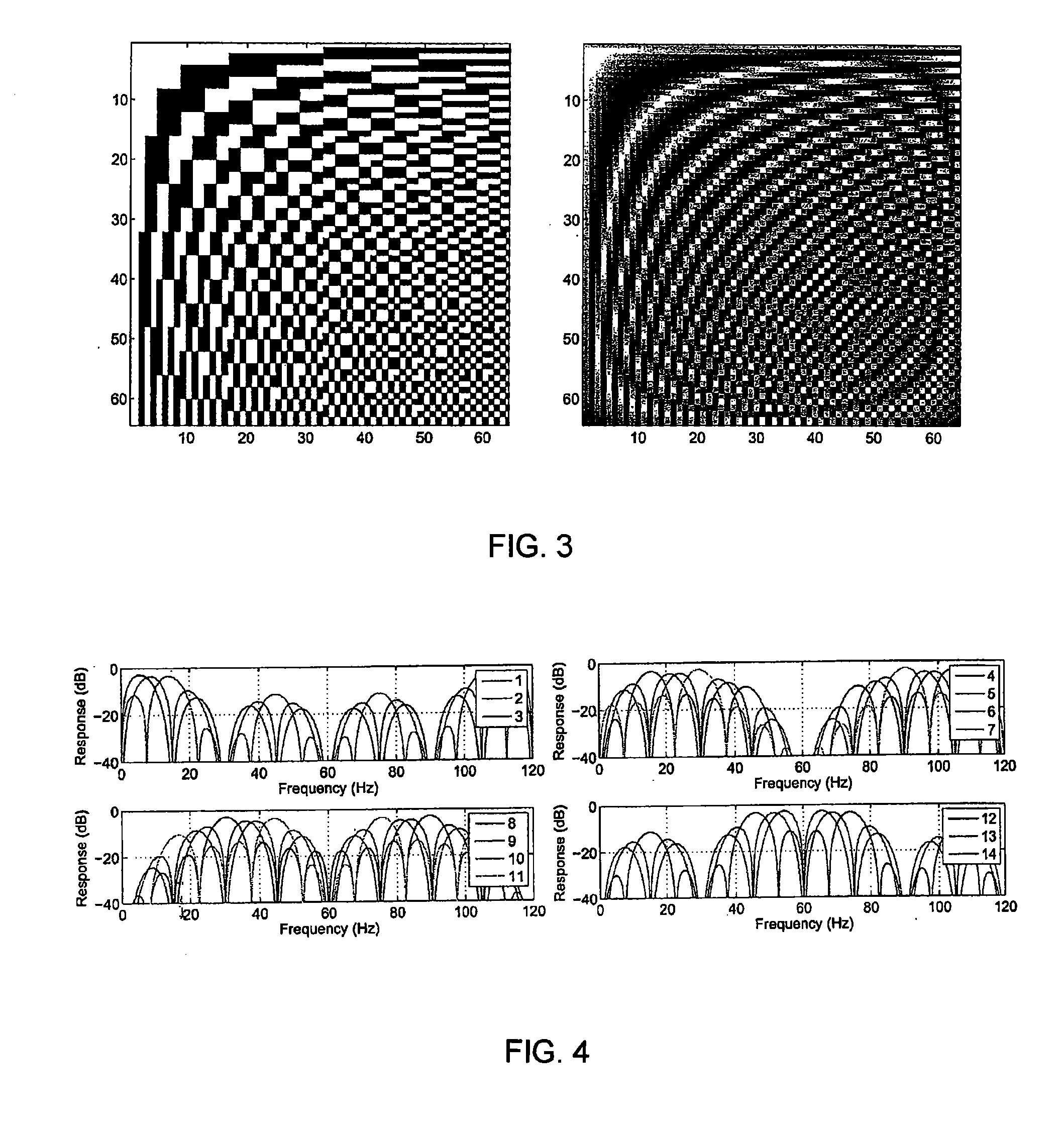
In mathematics, particularly in matrix theory, a permutation matrix is a square binary matrix that has exactly one entry of 1 in each row and each column and 0s elsewhere. Each such matrix, say P, represents a permutation of m elements and, when used to multiply another matrix, say A, results in permuting the rows (when pre-multiplying, to form PA) or columns (when post-multiplying, to form AP) of the matrix A.
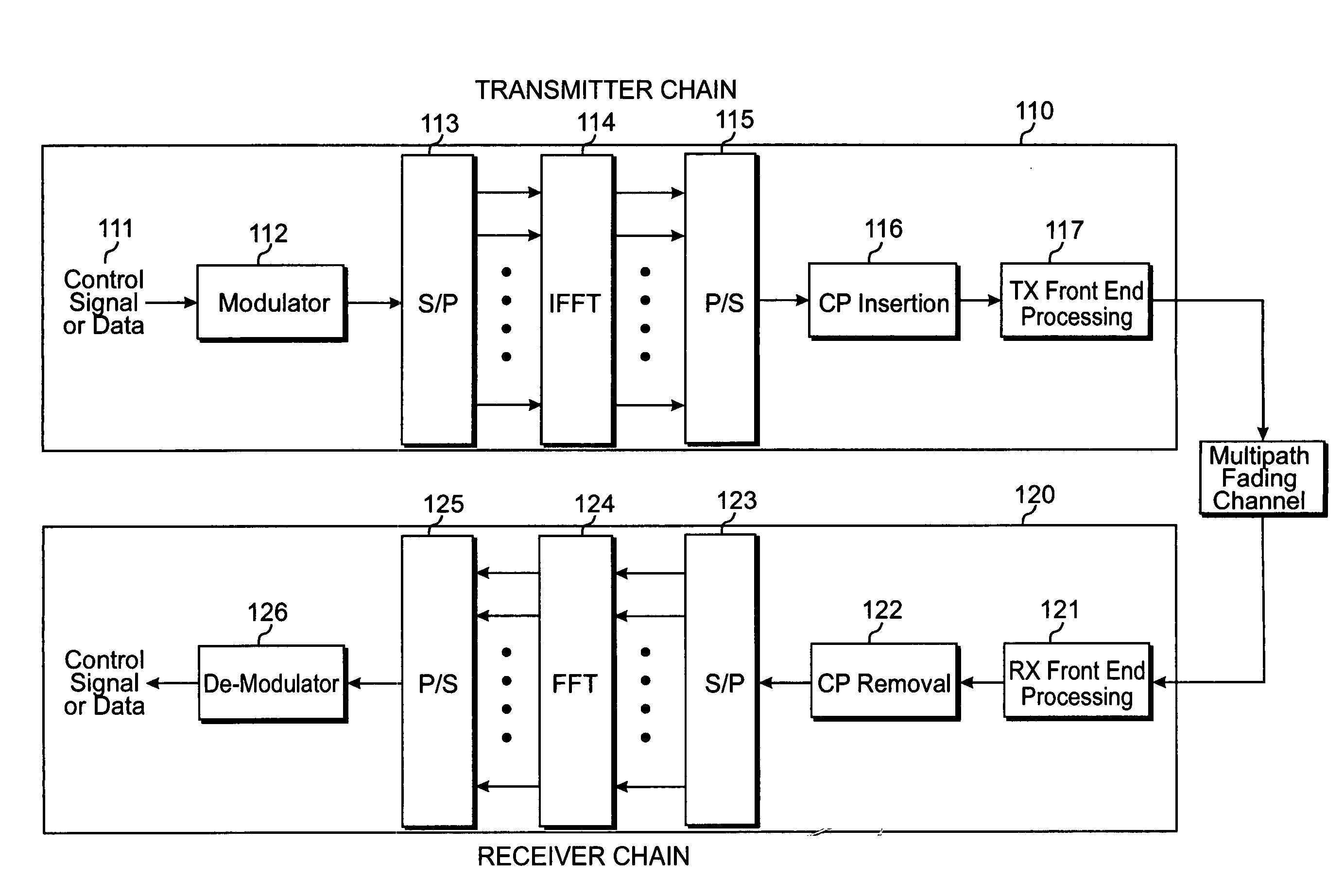
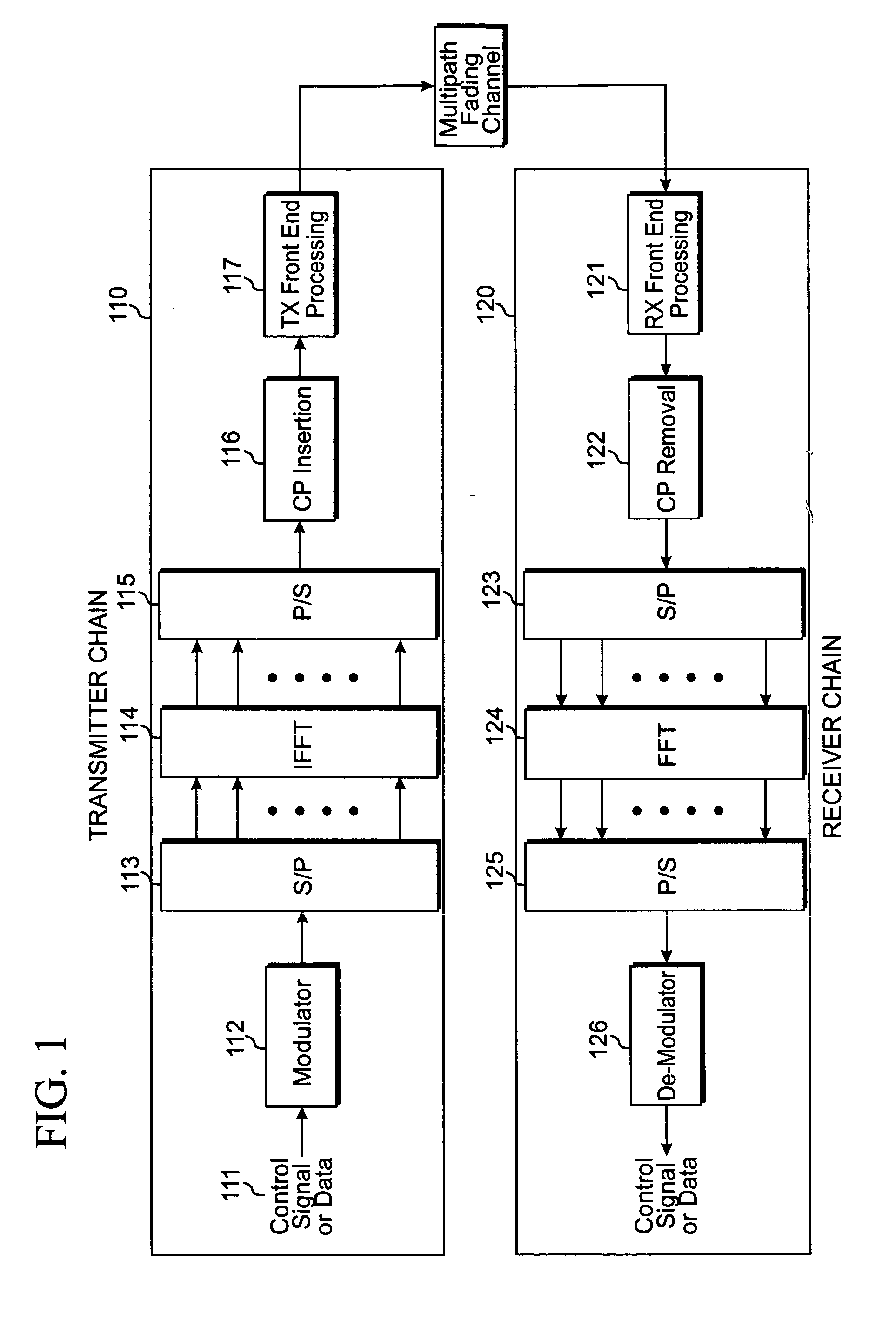
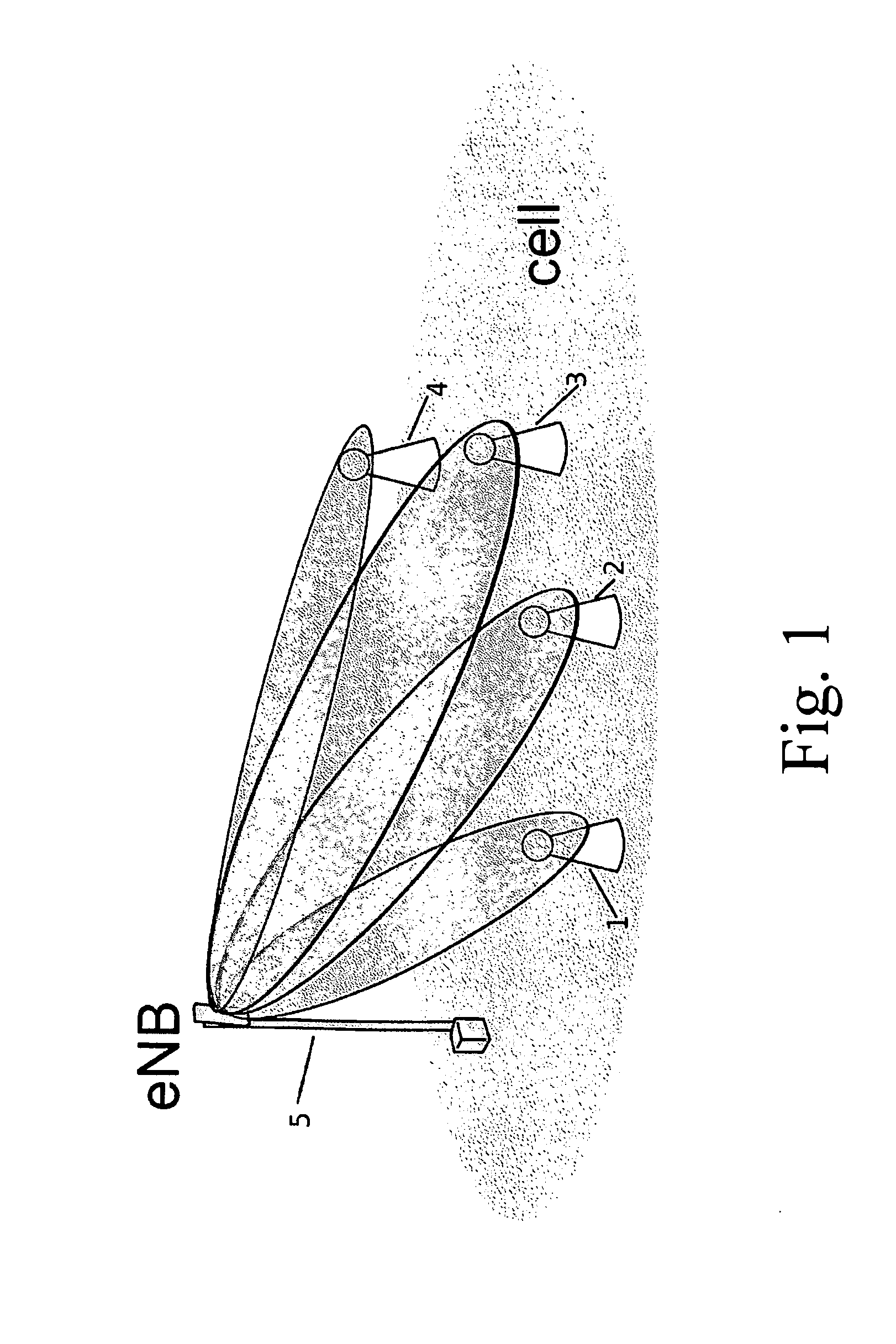
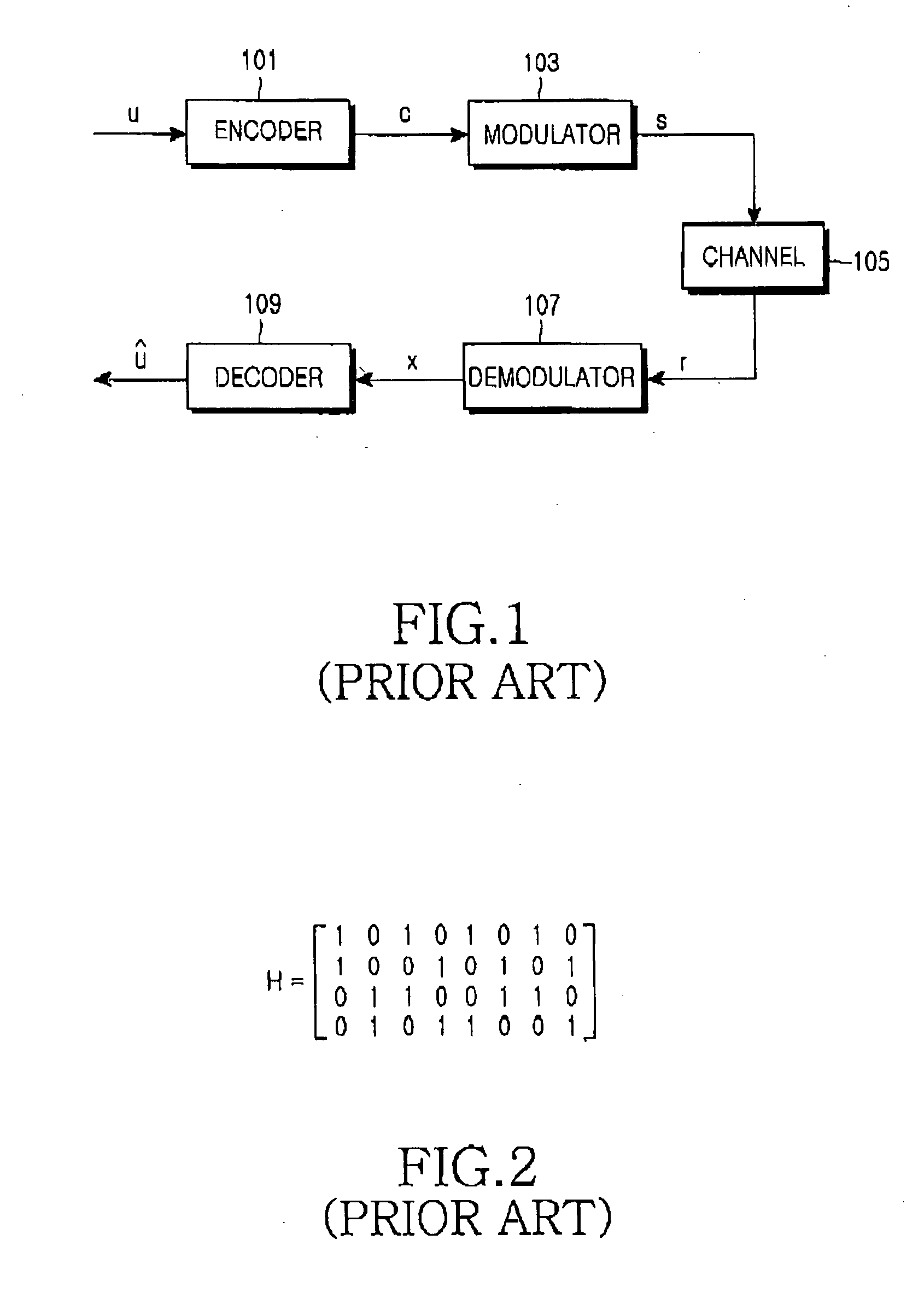
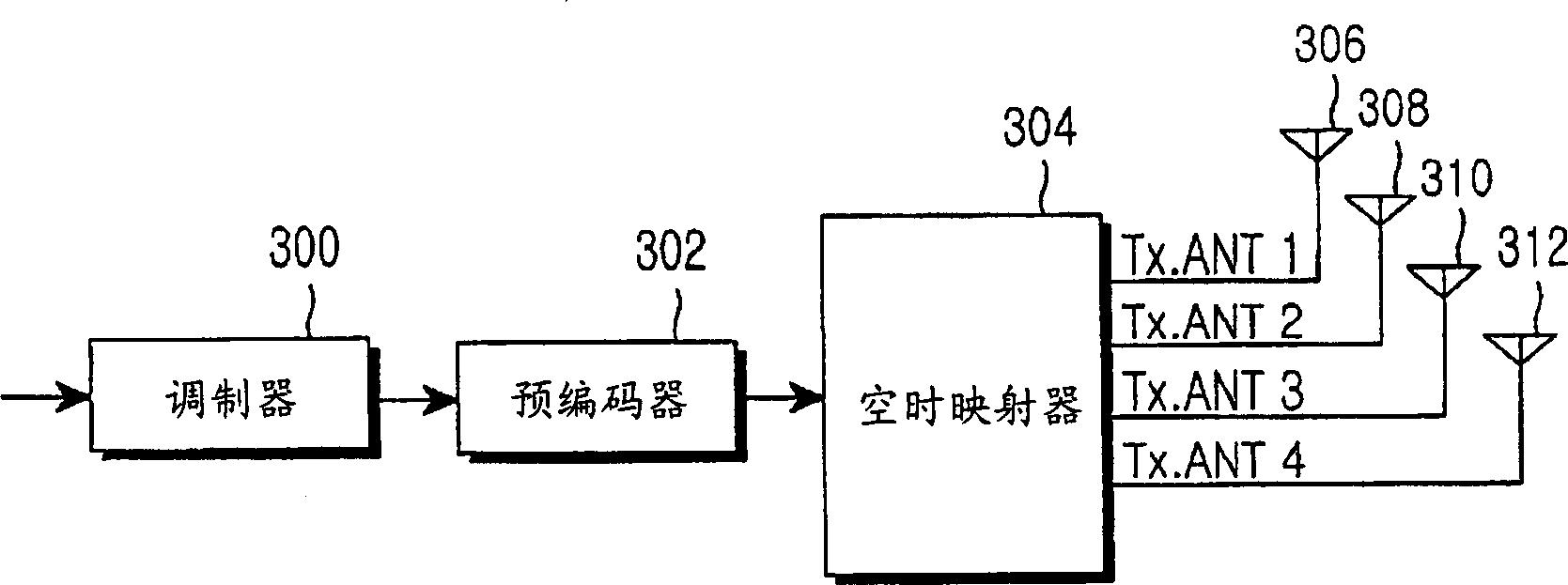
Transmit diversity in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20080267310A1Spatial transmit diversitySecret communicationCommunications systemDiversity scheme
A method for transmitting data via multiple antennas by modulating data to be transmitted into a plurality of modulated symbols, encoding each pair of modulated symbols from among said plurality of symbols in accordance with a transmission diversity scheme to result in a plurality of N by N matrices, with each N by N matrix corresponding to each pair of modulated symbols, generating a M by M code matrix comprised of the plurality of N by N matrices, orthogonally spreading the M by M code matrix to generate an output matrix, generating a plurality of row-permuted matrices by exchanging at least one pair of rows in the output matrix, and transmitting the symbols in the plurality of row-permuted matrices via a plurality of antennas by using either a space time transmission diversity scheme, a space frequency transmission diversity scheme, or a combination of a space time transmission diversity scheme and a space frequency transmission diversity scheme.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
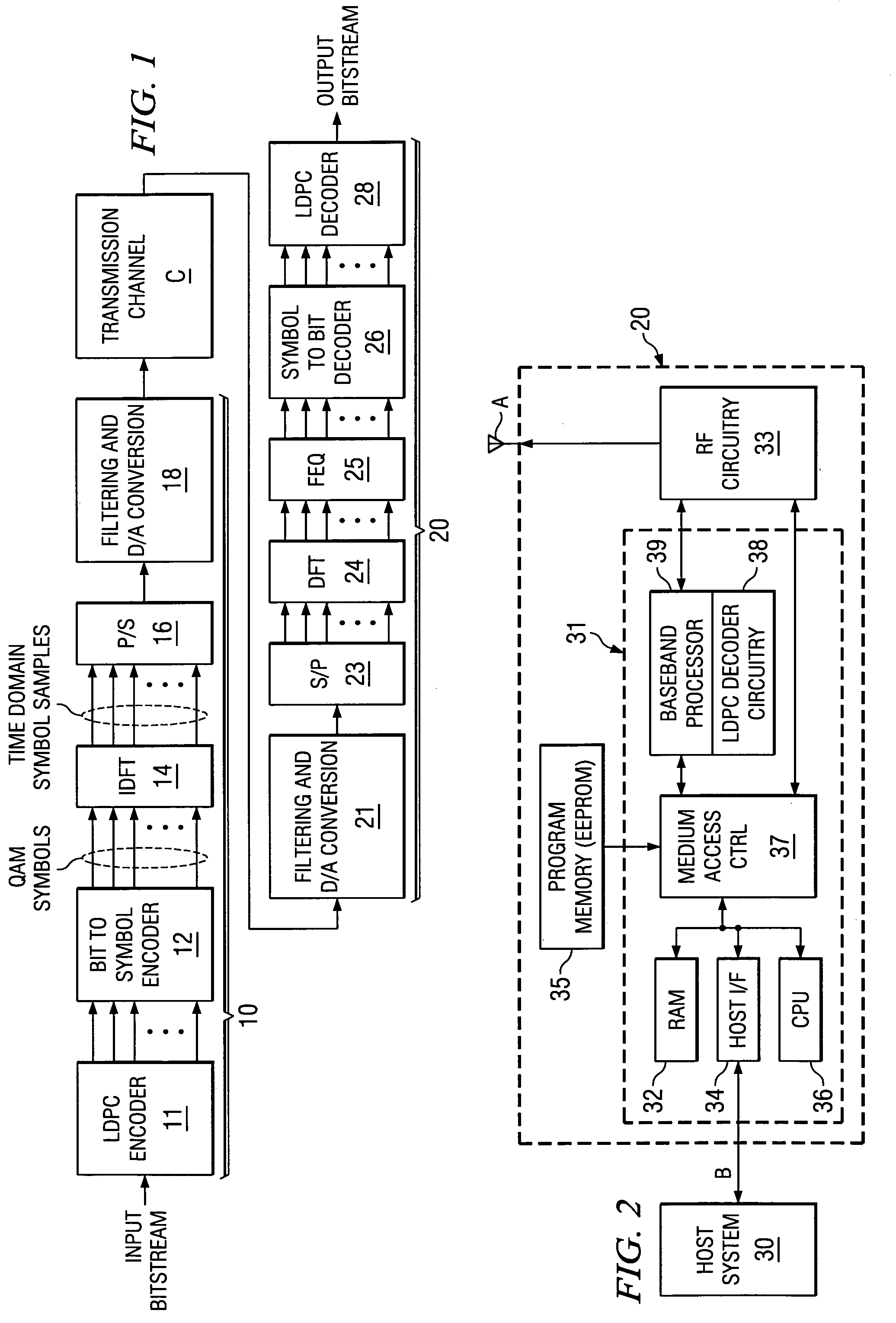
Hardware-efficient low density parity check code for digital communications
ActiveUS7178080B2Efficient implementationEfficient constructionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionMatrix groupParity-check matrix
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
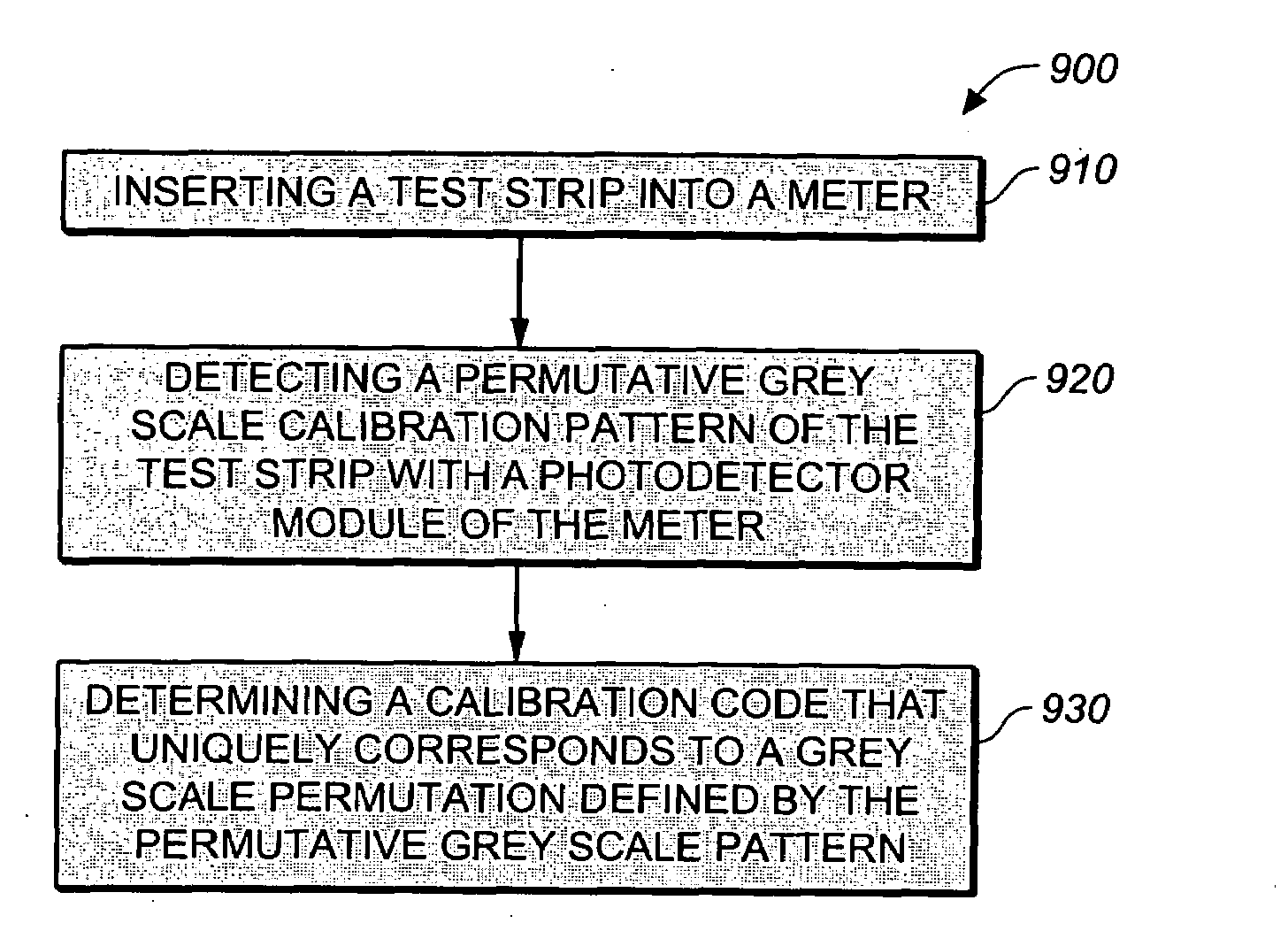
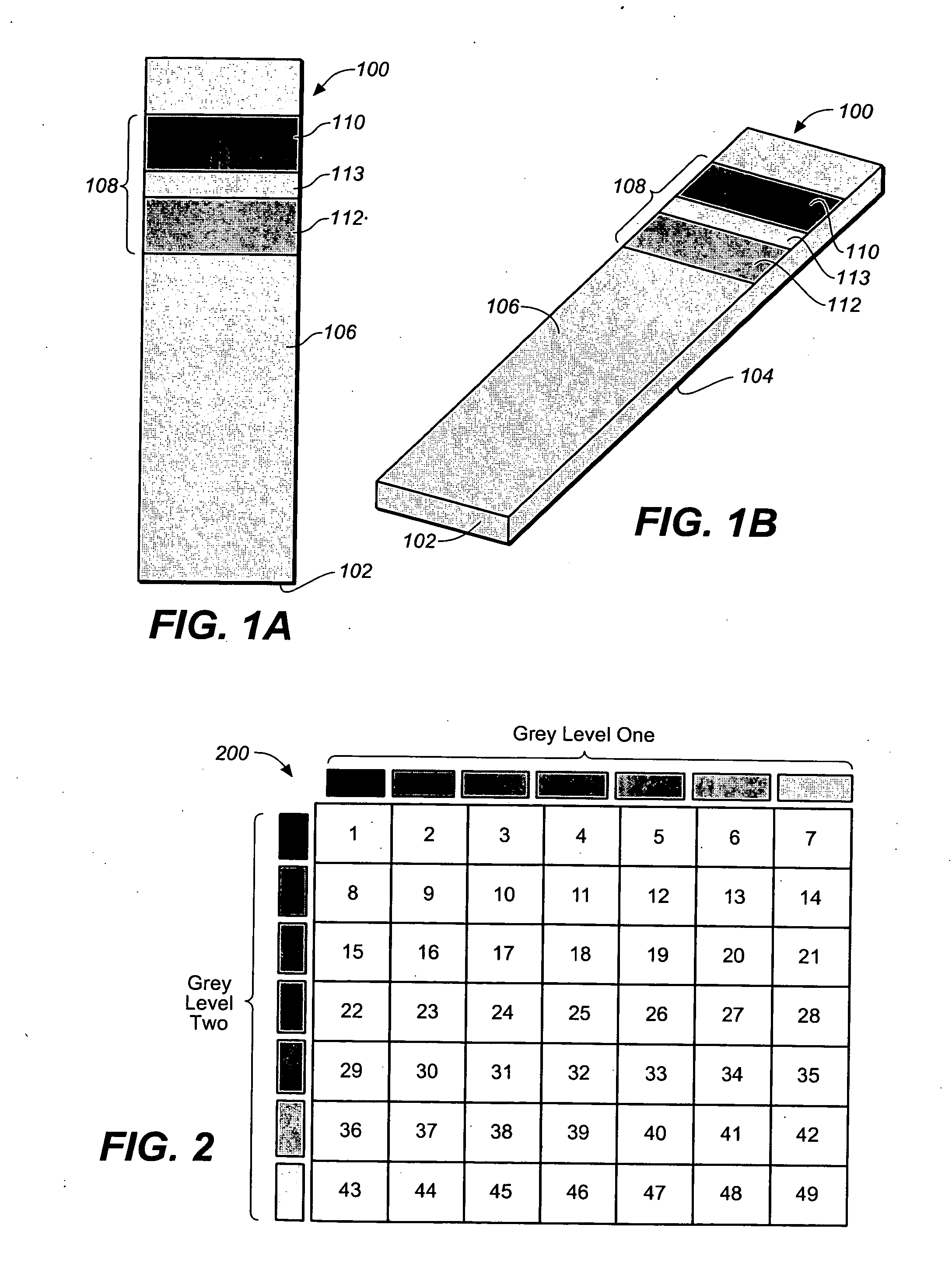
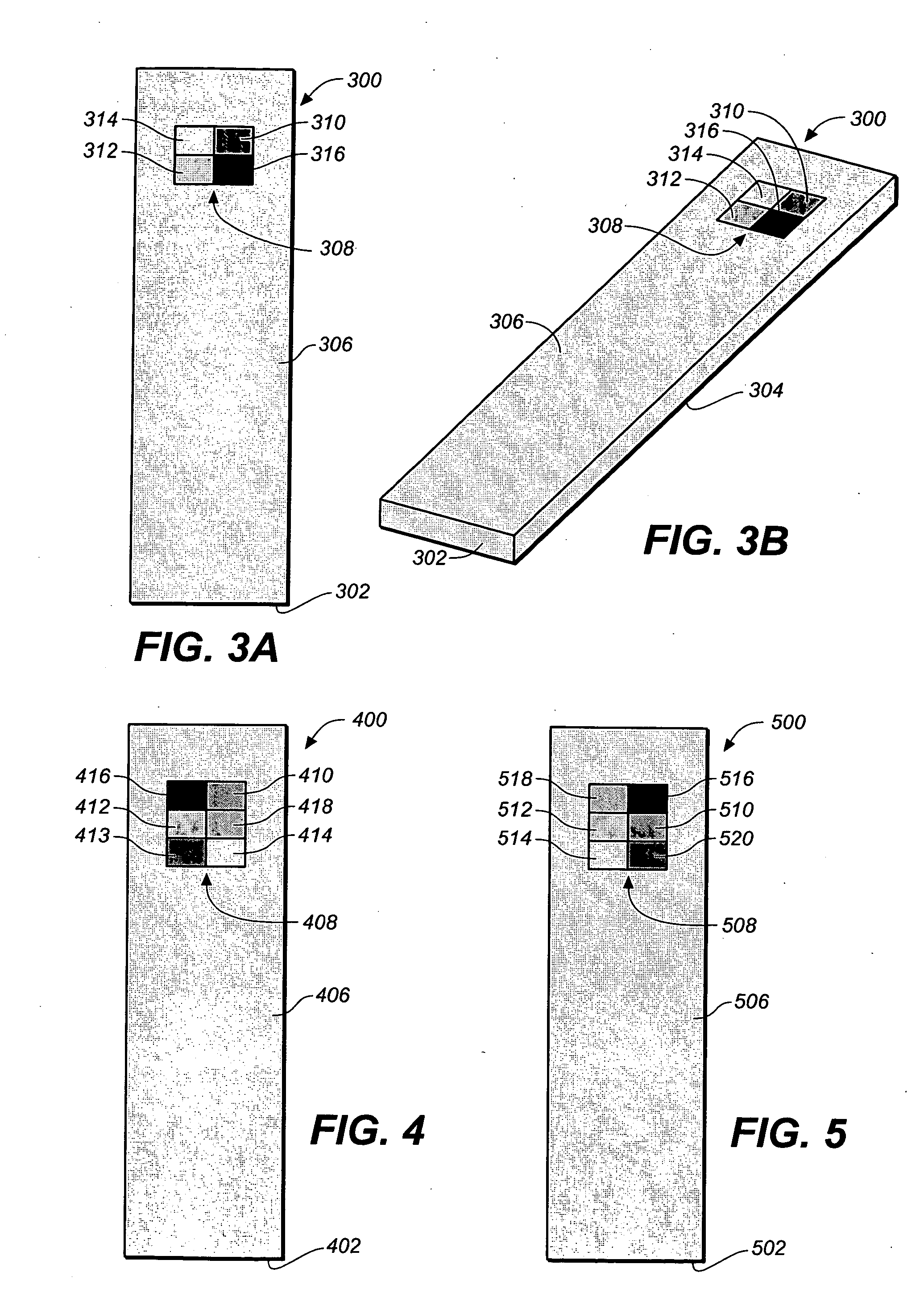
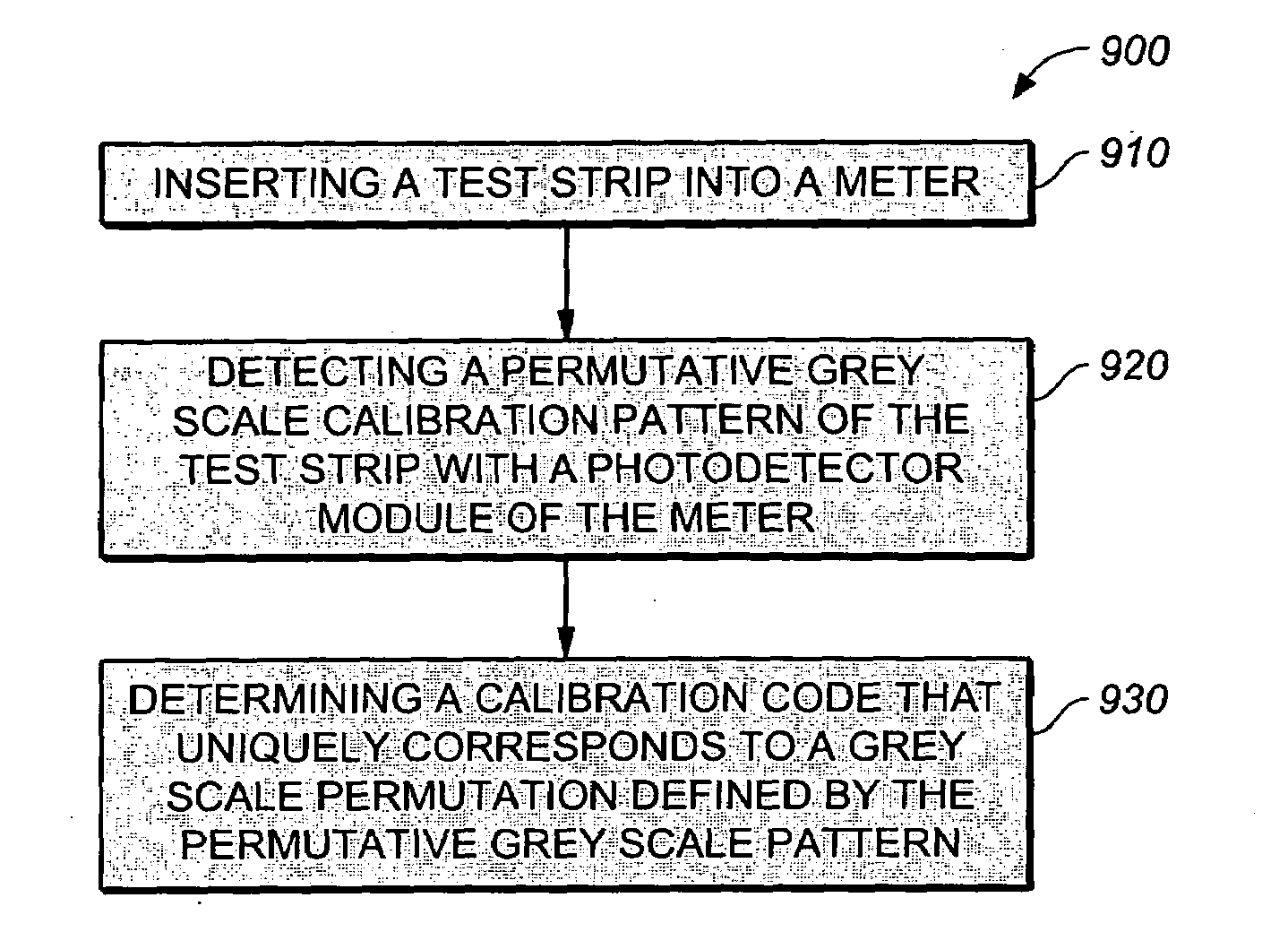
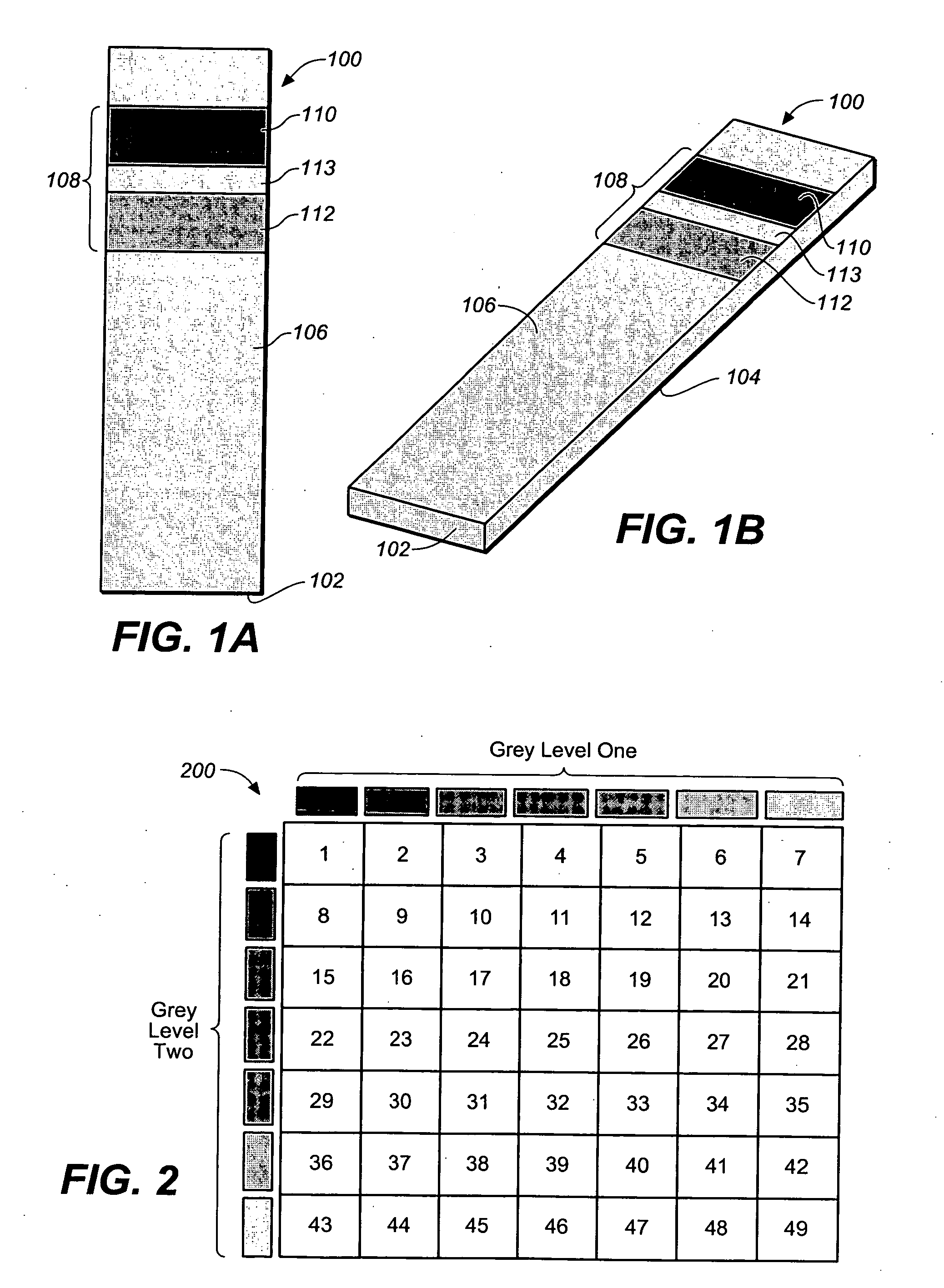
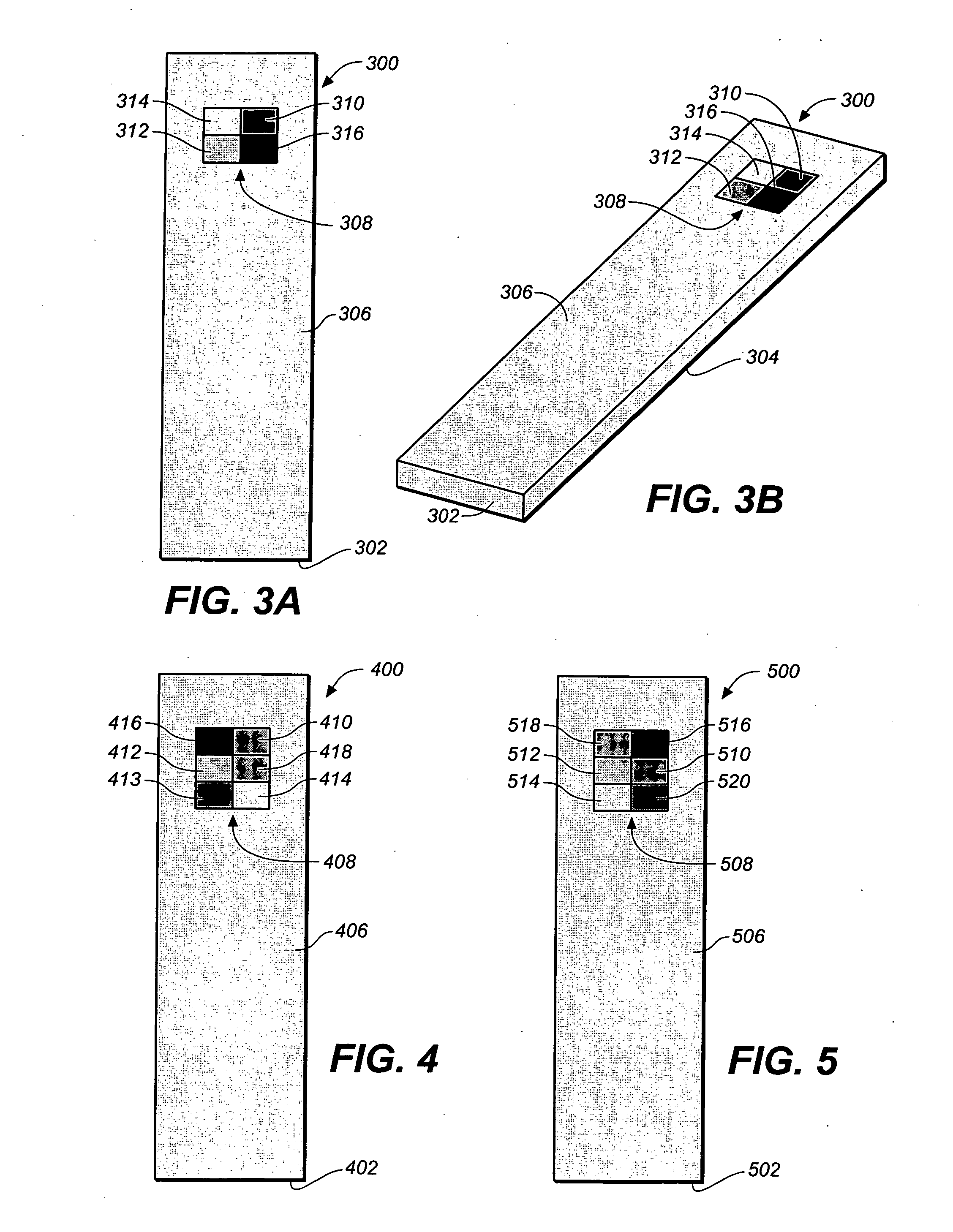
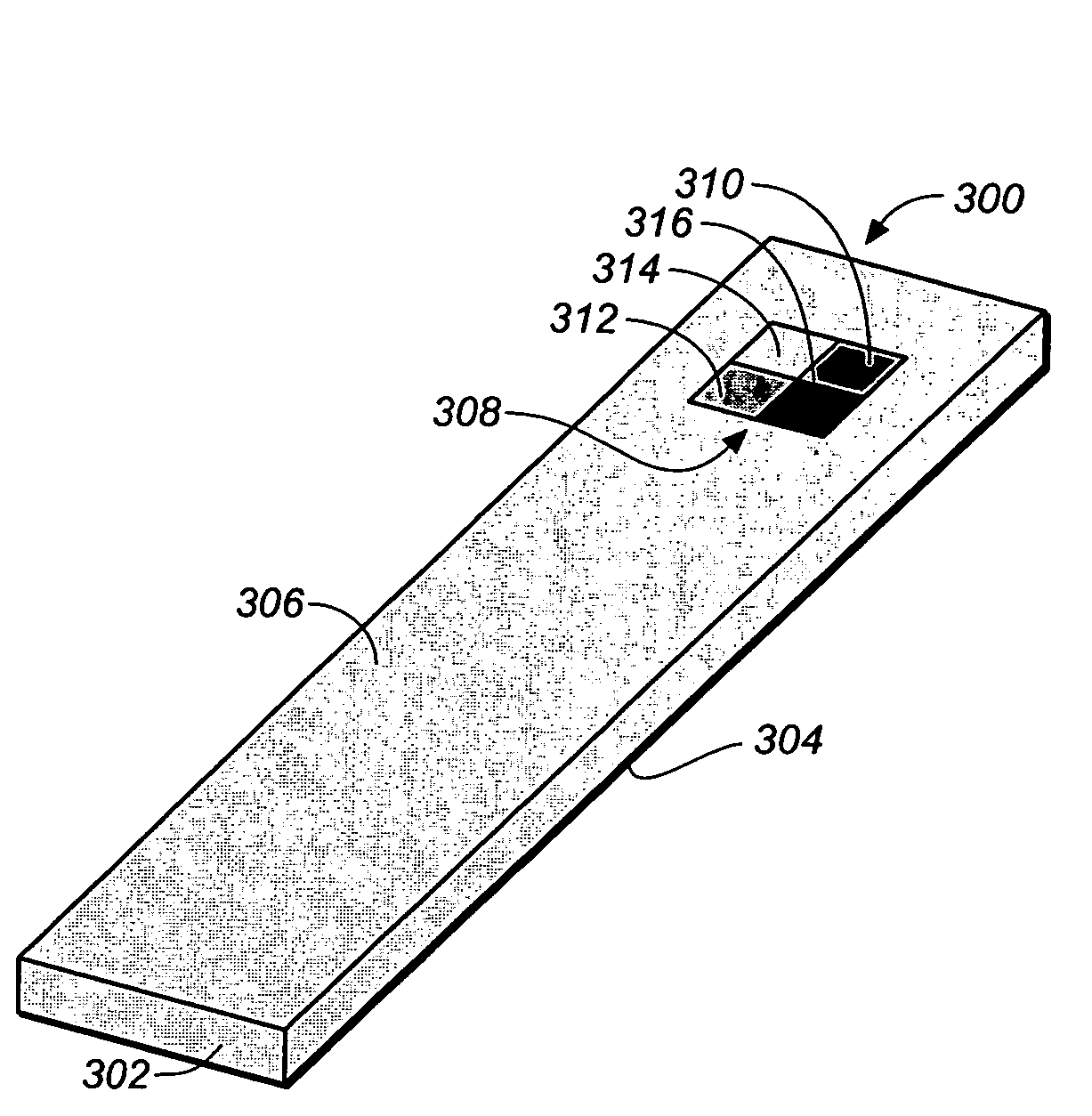
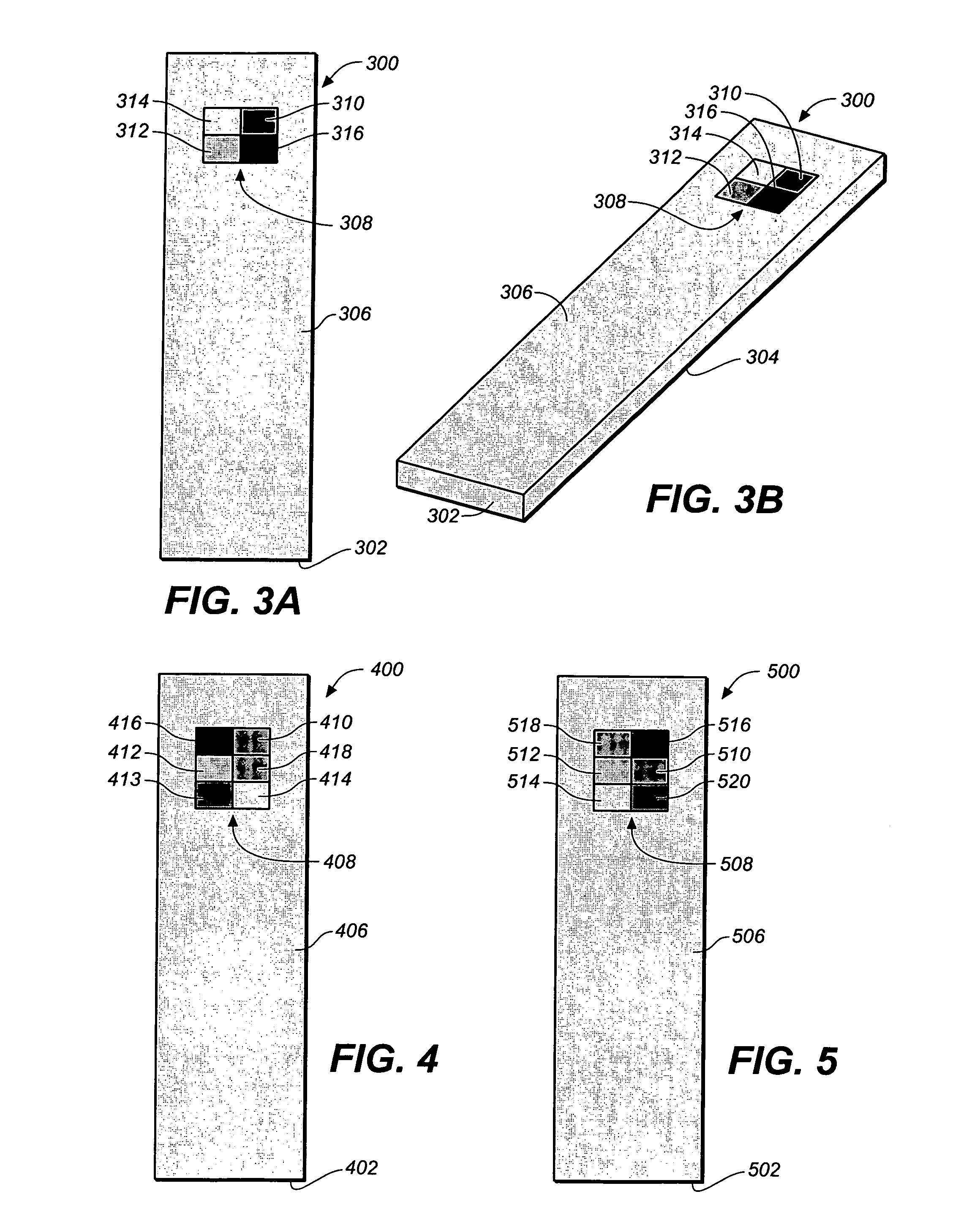
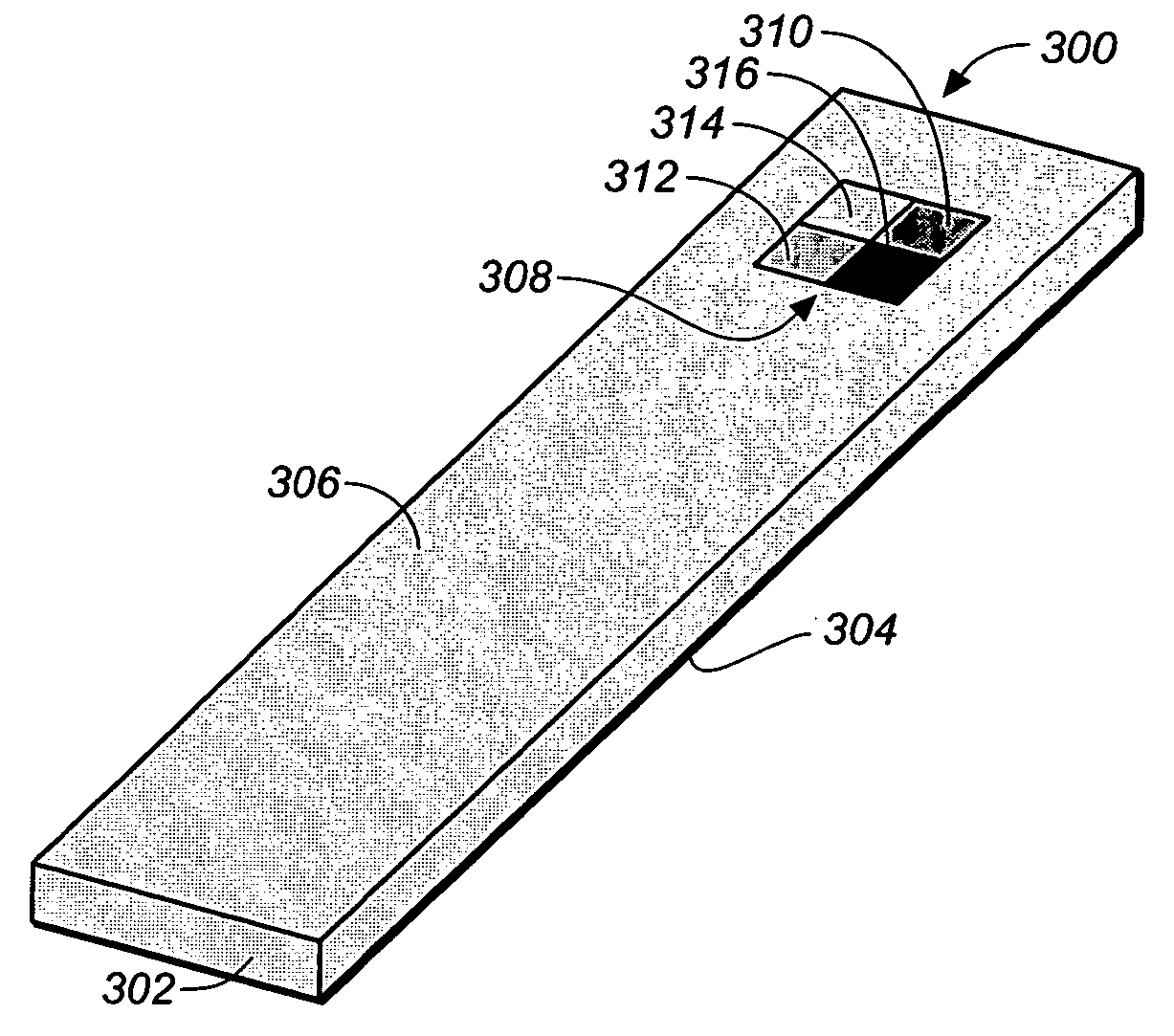
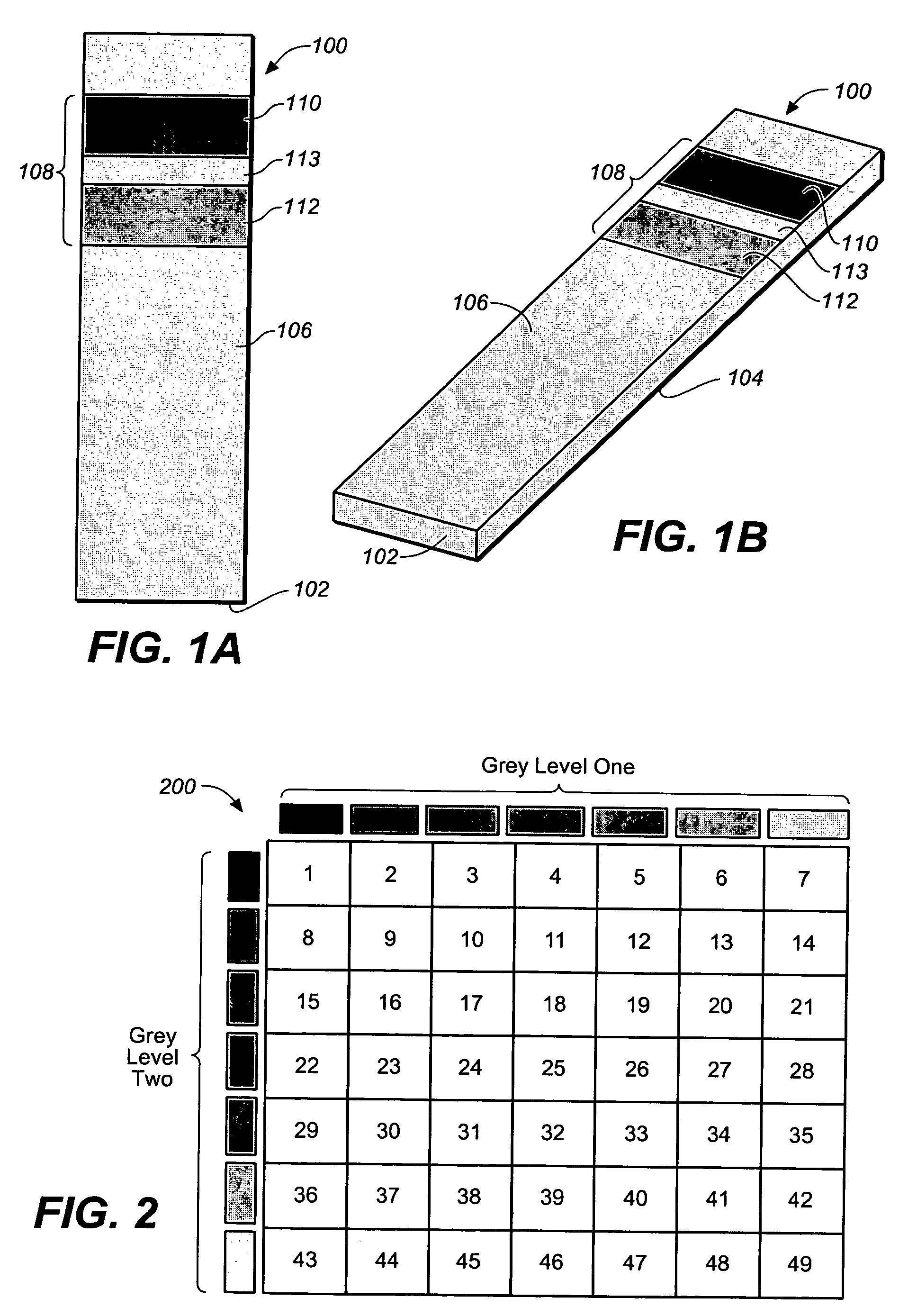
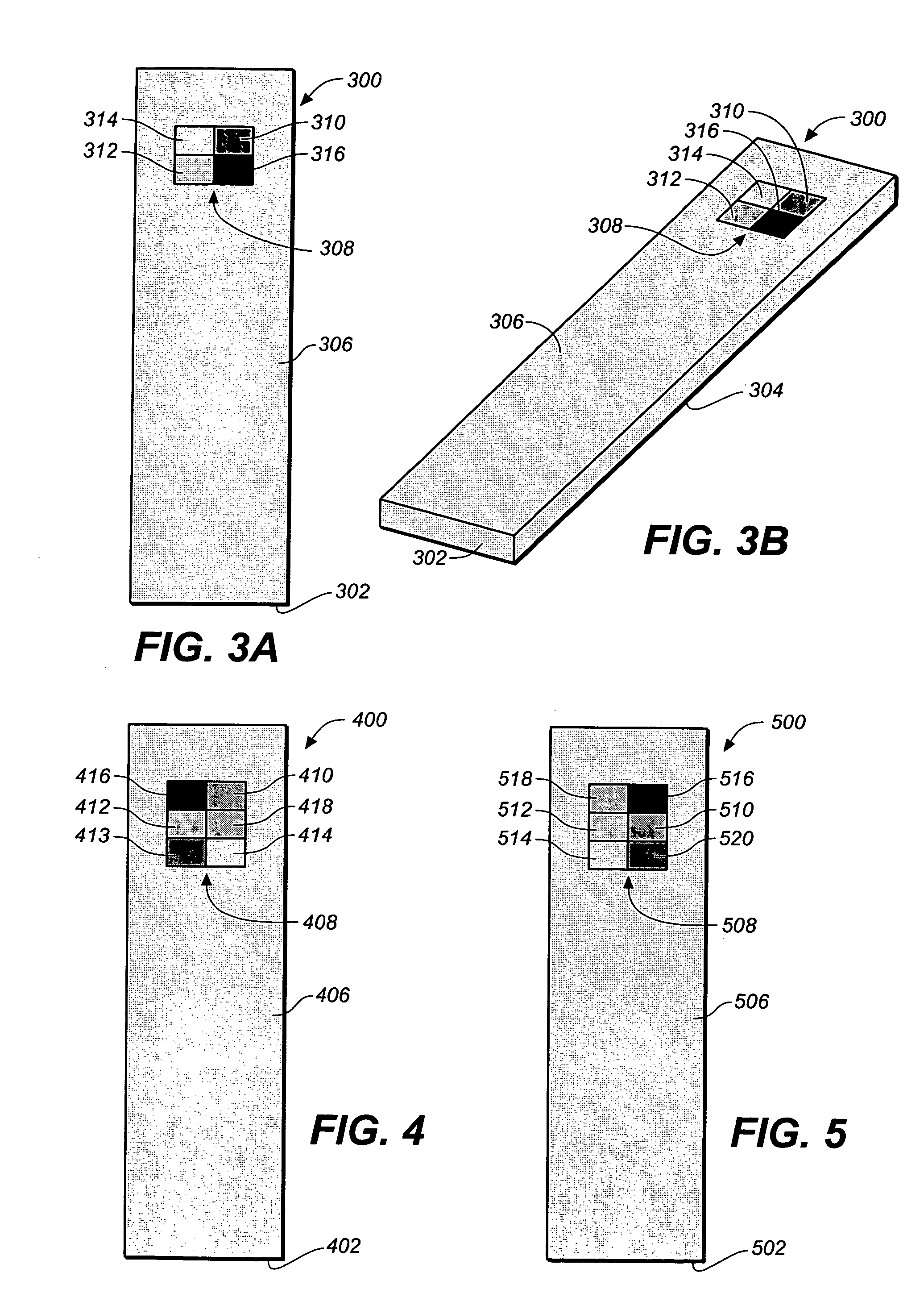
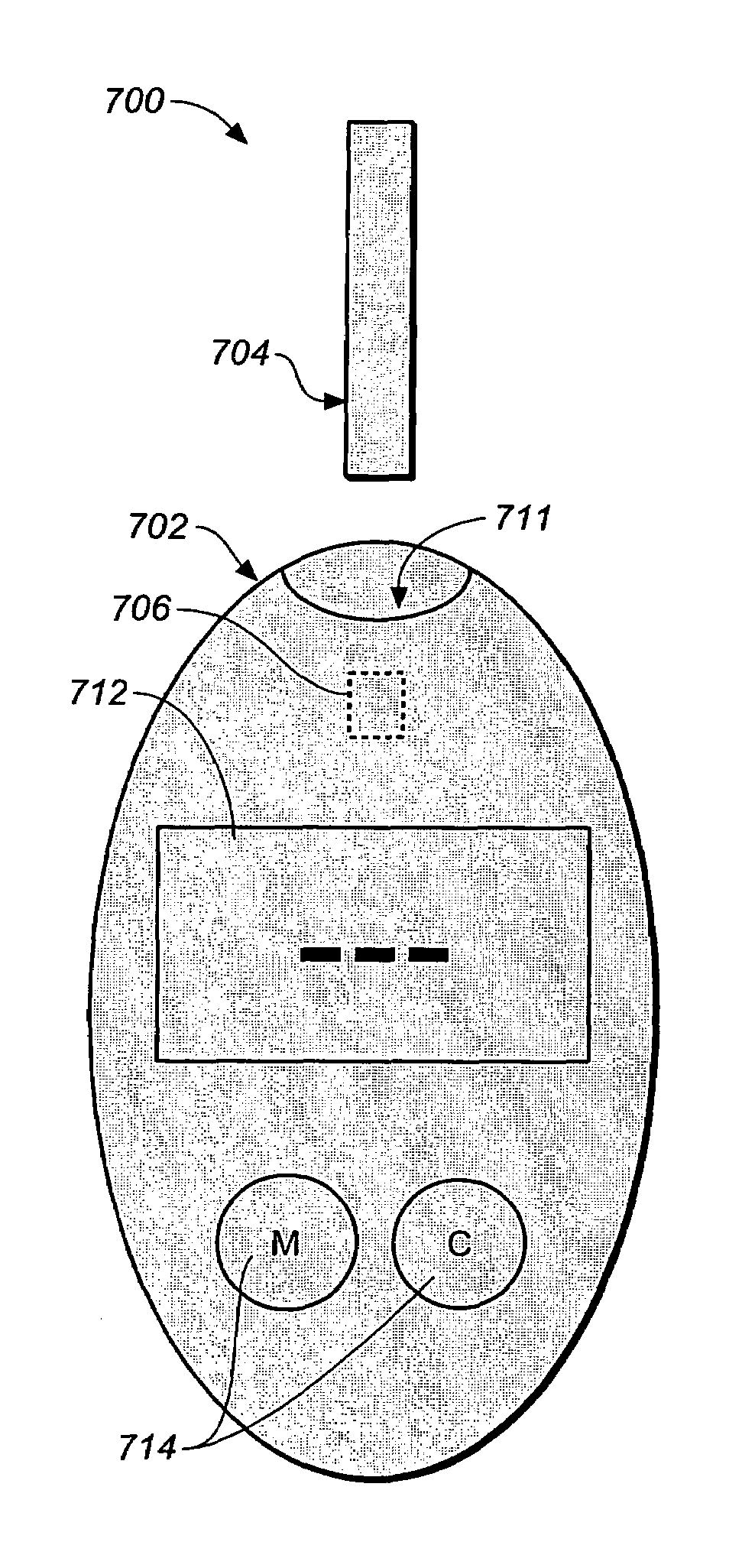
Method for determining a test strip calibration code for use in a meter
ActiveUS20070273904A1Digitally marking record carriersPhotometry using reference valuePhotodetectorEngineering
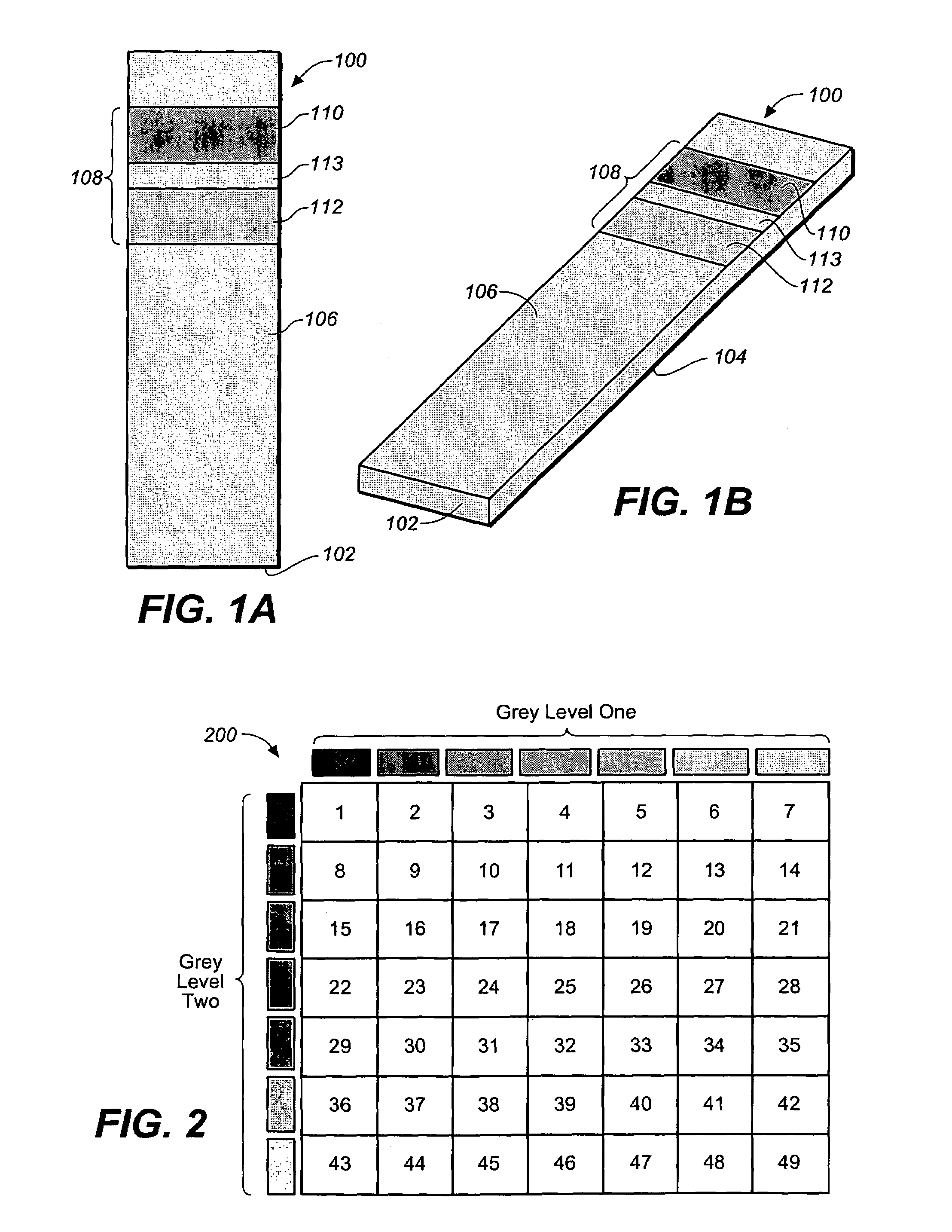
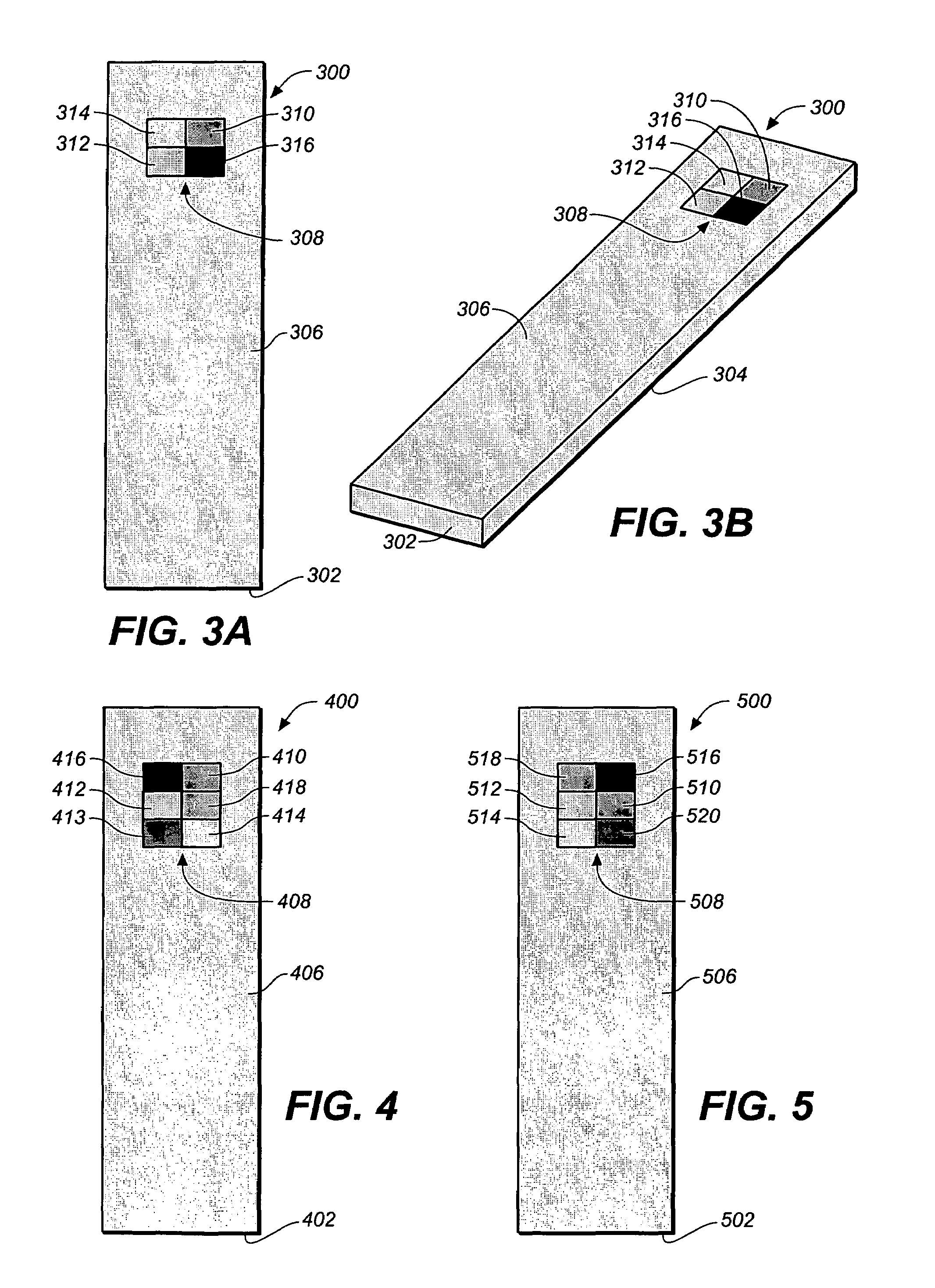
A method for determining a test strip calibration code for use in a meter includes inserting a test strip into the meter. The inserted test strip having a substrate with a working surface for receiving the body fluid sample and a reverse surface that is in opposition to the working surface. The test strip also includes a permutative grey scale calibration pattern disposed on either of the working and reverse surfaces, with the permutative grey scale calibration pattern including more than one grey scale region. Moreover, the scale regions of the test strip define a grey scale permutation that uniquely corresponds to a calibration code of the test strip. The method also includes detecting the permutative grey scale calibration pattern with a grey scale photodetector module of the meter and determining a calibration code that uniquely corresponds to a grey scale permutation defined by the permutative grey scale calibration pattern based on permutation matrix stored in the meter.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Method for determining a test strip calibration code using a calibration strip
ActiveUS20070273903A1Digitally marking record carriersPhotometry using reference valuePhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A method for determining a test strip calibration code for use in a meter includes inserting a calibration strip into the meter, with the calibration strip having a substrate and a permutative grey scale calibration pattern disposed on the substrate. In addition, the permutative grey scale calibration pattern includes more than one grey scale region that define a grey scale permutation uniquely corresponding to a calibration code of test strips in a package associated with the calibration strip. The method also includes: (i) detecting the permutative grey scale calibration pattern with a grey scale photodetector module of the meter, and (ii) determining a calibration code that uniquely corresponds to a grey scale permutation defined by the permutative grey scale calibration pattern based on a permutation matrix stored in the meter.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Method for determining a test strip calibration code using a calibration strip
ActiveUS7474391B2Digitally marking record carriersPhotometry using reference valuePhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A method for determining a test strip calibration code for use in a meter includes inserting a calibration strip into the meter, with the calibration strip having a substrate and a permutative grey scale calibration pattern disposed on the substrate. In addition, the permutative grey scale calibration pattern includes more than one grey scale region that define a grey scale permutation uniquely corresponding to a calibration code of test strips in a package associated with the calibration strip. The method also includes: (i) detecting the permutative grey scale calibration pattern with a grey scale photodetector module of the meter, and (ii) determining a calibration code that uniquely corresponds to a grey scale permutation defined by the permutative grey scale calibration pattern based on a permutation matrix stored in the meter.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
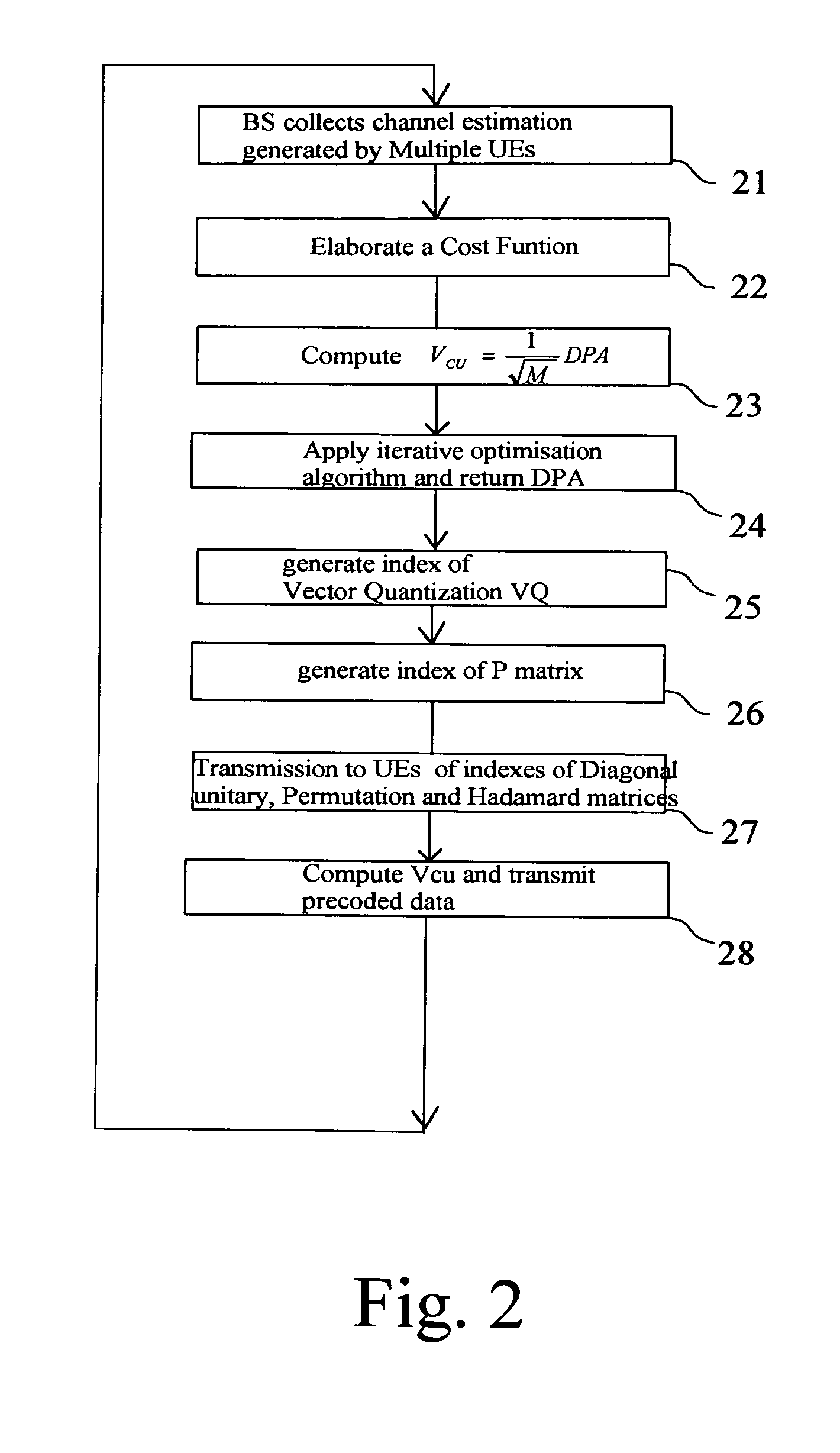
Process for Beamforming Data to be Transmitted by a Base Station in a MU-MIMO System and Apparatus for Performing the Same
InactiveUS20110299379A1Simple structureImprove performanceRadio transmissionOrthogonal multiplexFormation matrixUnitary matrix
A process for beamforming data to be transmitted in a MU-MIMO communication system comprising a base station and a selected set of User Equipments (UE) communicating with said base station; said data being precoded by said base station in accordance with a beamforming matrix complying with a precoding matrix under the form of: (formula 1) Where—M is the number of transmit antennas—D is a diagonal unitary matrix of the form D=diag (formula 2)—P is a permutation matrix interchanging only the last M−1 rows. —A is a general Hadamard matrix. and that the signaling information transmitted by the base station to the UE comprises at least a first and a second index which are representative of D, P and A.
Owner:ST ERICSSON FRANCE +1
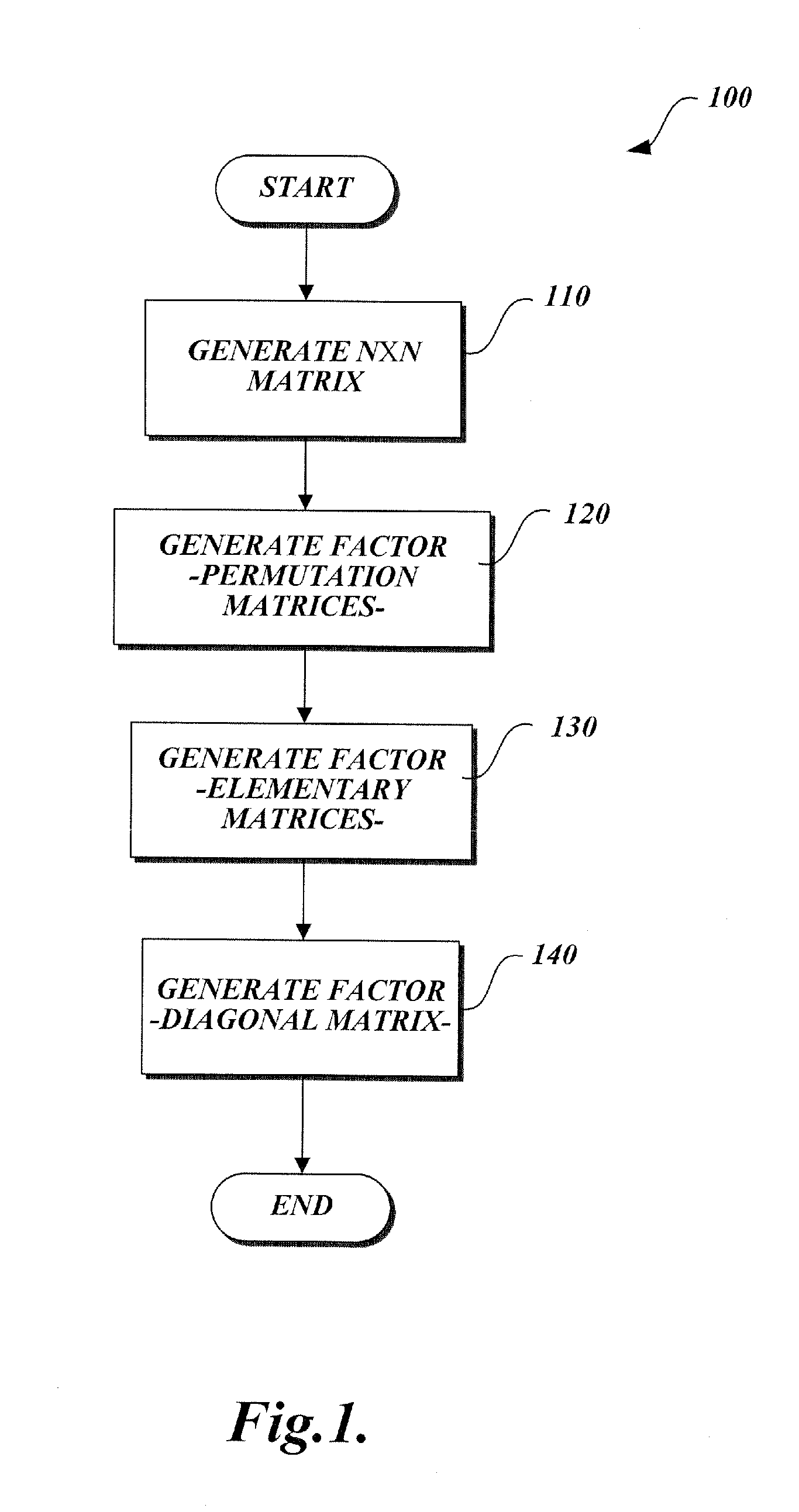
Method of generating matrix factors for a finite-dimensional linear transform
InactiveUS20070211952A1Character and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationPartition of unityLU decomposition
A method of generating matrix factors for a finite-dimensional linear transform using a computer. The linear transform is represented by data values stored in a linear transformation matrix having a nonzero determinant. In one aspect, a first LU-decomposition is applied to the linear transformation matrix. Four matrices are generated from the LU-decomposition, including a first permutation matrix, a second permutation matrix, a lower triangular matrix having a unit diagonal, and a first upper triangular matrix. Additional elements include a third matrix Â, a signed permutation matrix Π such that A=ΠÂ, a permuted linear transformation matrix A′, a second upper triangular matrix U1, wherein the second upper triangular matrix satisfies the relationship Â=U1A′. The permuted linear transformation matrix is factored into a product including a lower triangular matrix L and an upper triangular matrix U. The linear transformation matrix is expressed as a product of the matrix factors.
Owner:CELARTEM
Method for determining a test strip calibration code for use in a meter
ActiveUS7593097B2Digitally marking record carriersPhotometry using reference valuePhotodetectorEngineering
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
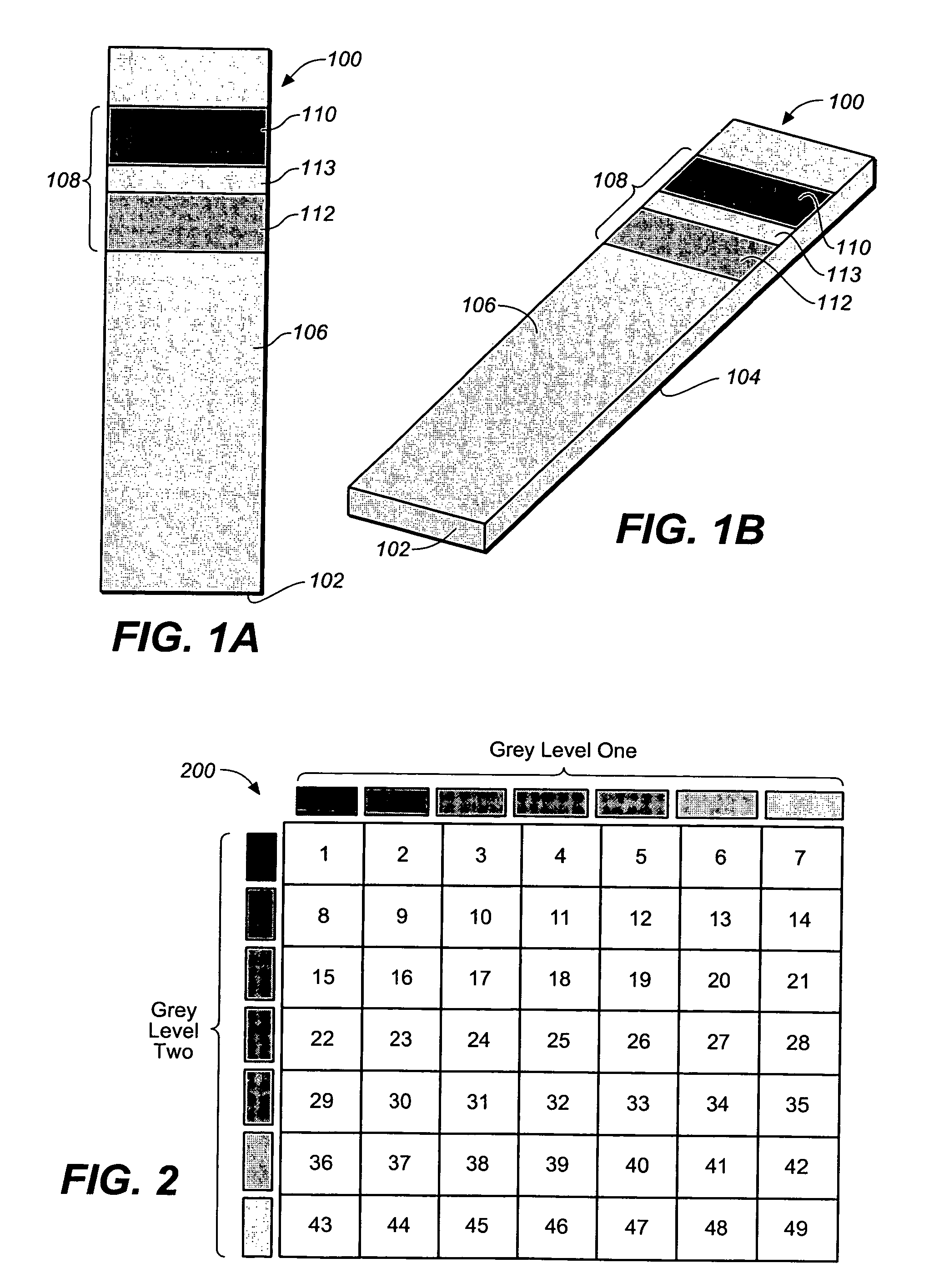
System for analyte determination that includes a permutative grey scale calibration pattern
ActiveUS7589828B2Photometry using reference valueDigitally marking record carriersAnalytePhotovoltaic detectors
A system for measuring an analyte in a body fluid sample includes a meter, with a grey scale photodetector module, and a memory module. The system also includes a test strip. The test strip has a substrate with a working surface for receiving the body fluid sample and a reverse surface that is in opposition to the working surface. The test strip also includes a permutative grey scale calibration pattern disposed on either of the working and reverse surfaces, with the permutative grey scale calibration pattern including more than one grey scale region. Moreover, the scale regions of the test strip define a grey scale permutation that uniquely corresponds to a calibration code of the test strip. The grey scale photodetector module is configured to detect the permutative grey scale calibration pattern of the test strip when the test strip is inserted into the meter. The memory module has stored therein a grey scale permutation matrix with a plurality of calibration codes, each of the calibration codes uniquely corresponding to a grey scale permutation of the permutative grey scale calibration pattern.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
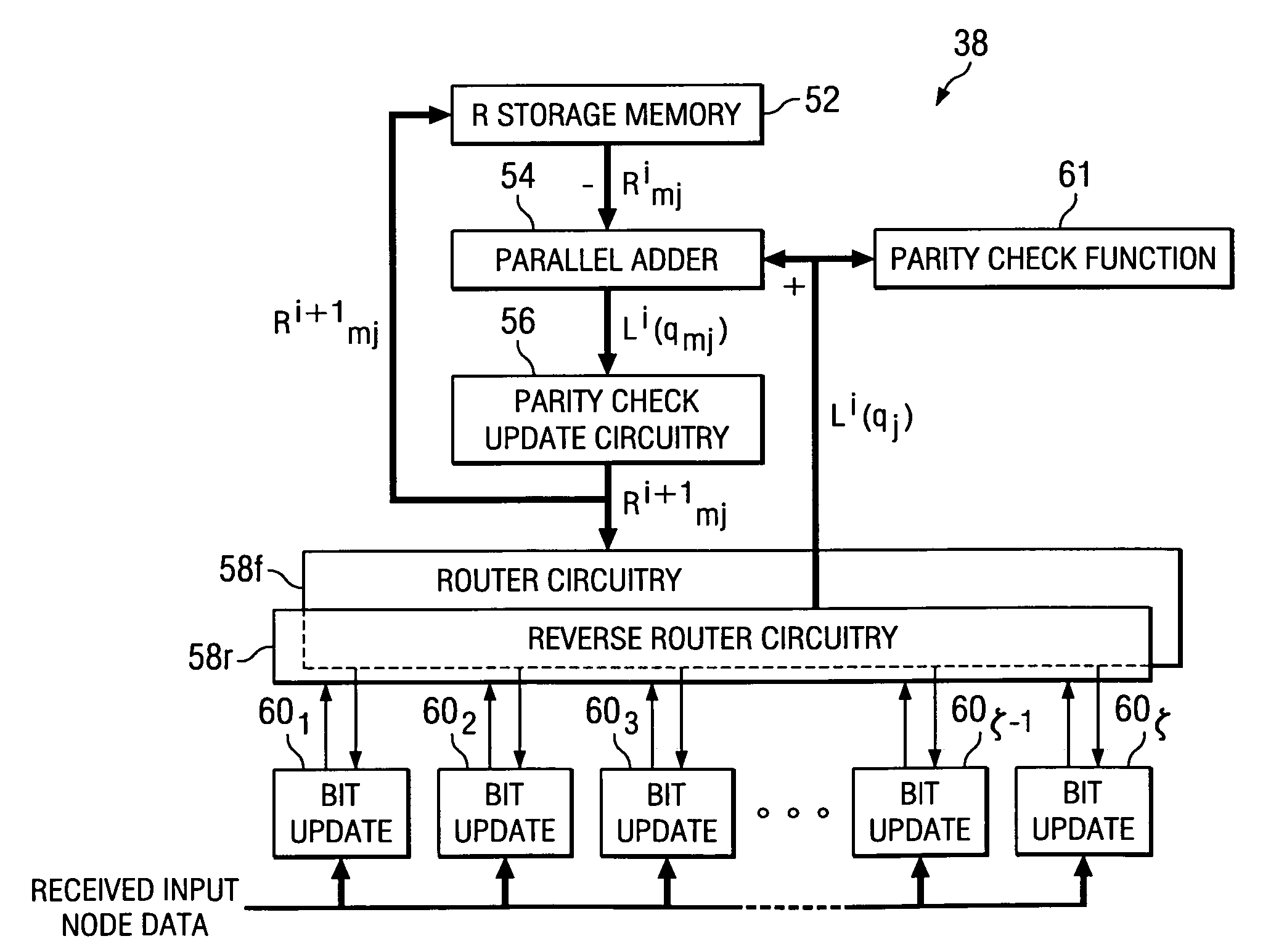
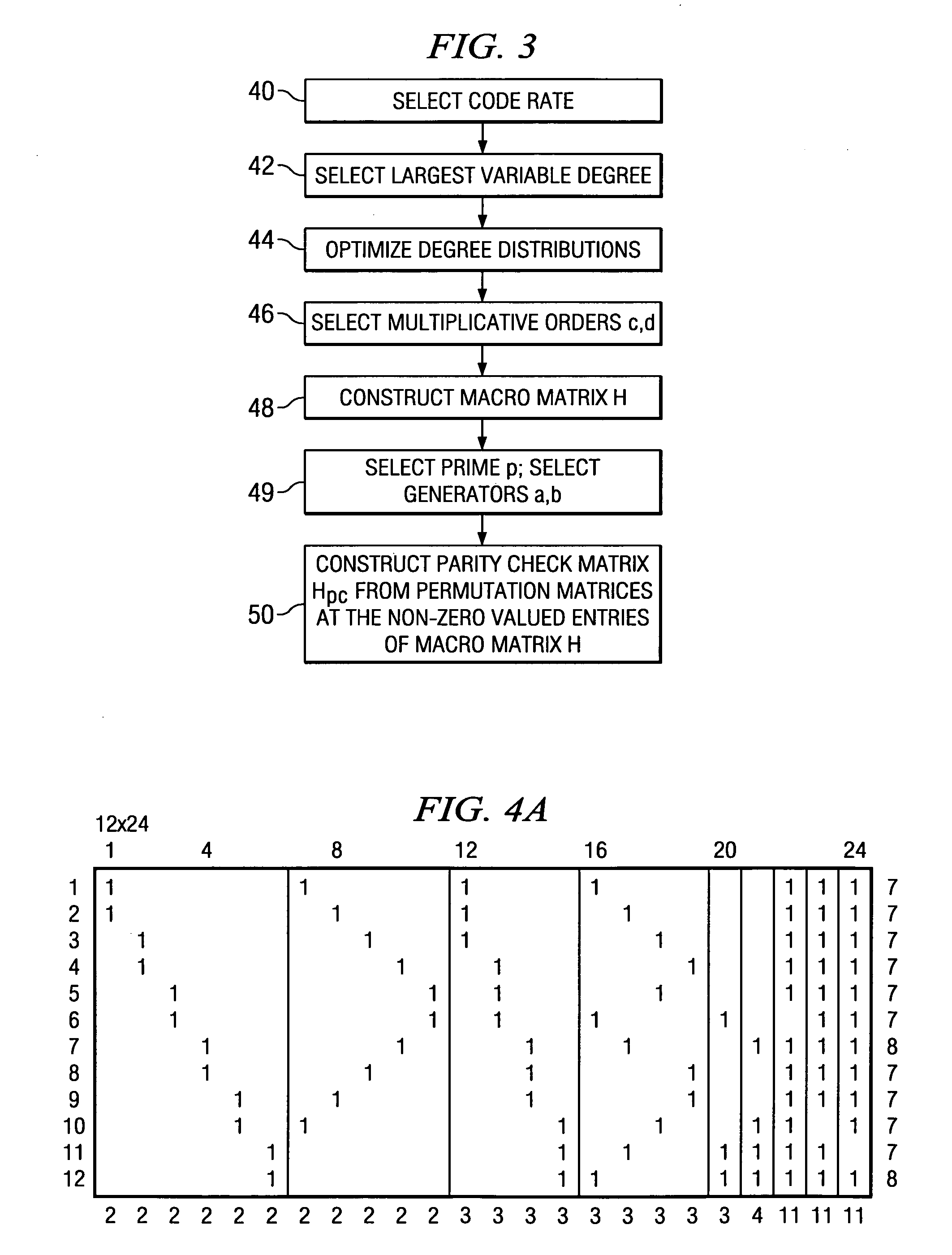
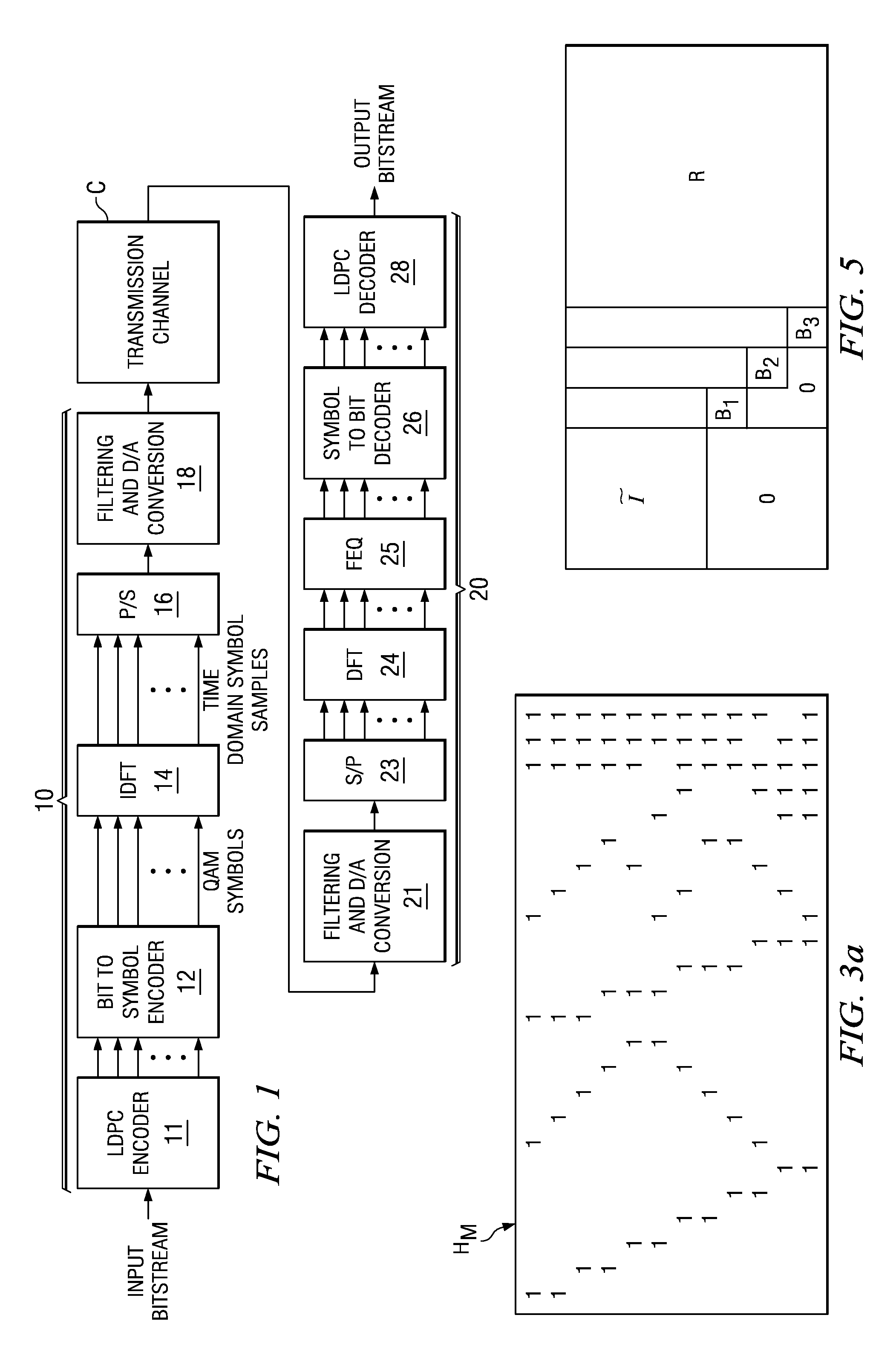
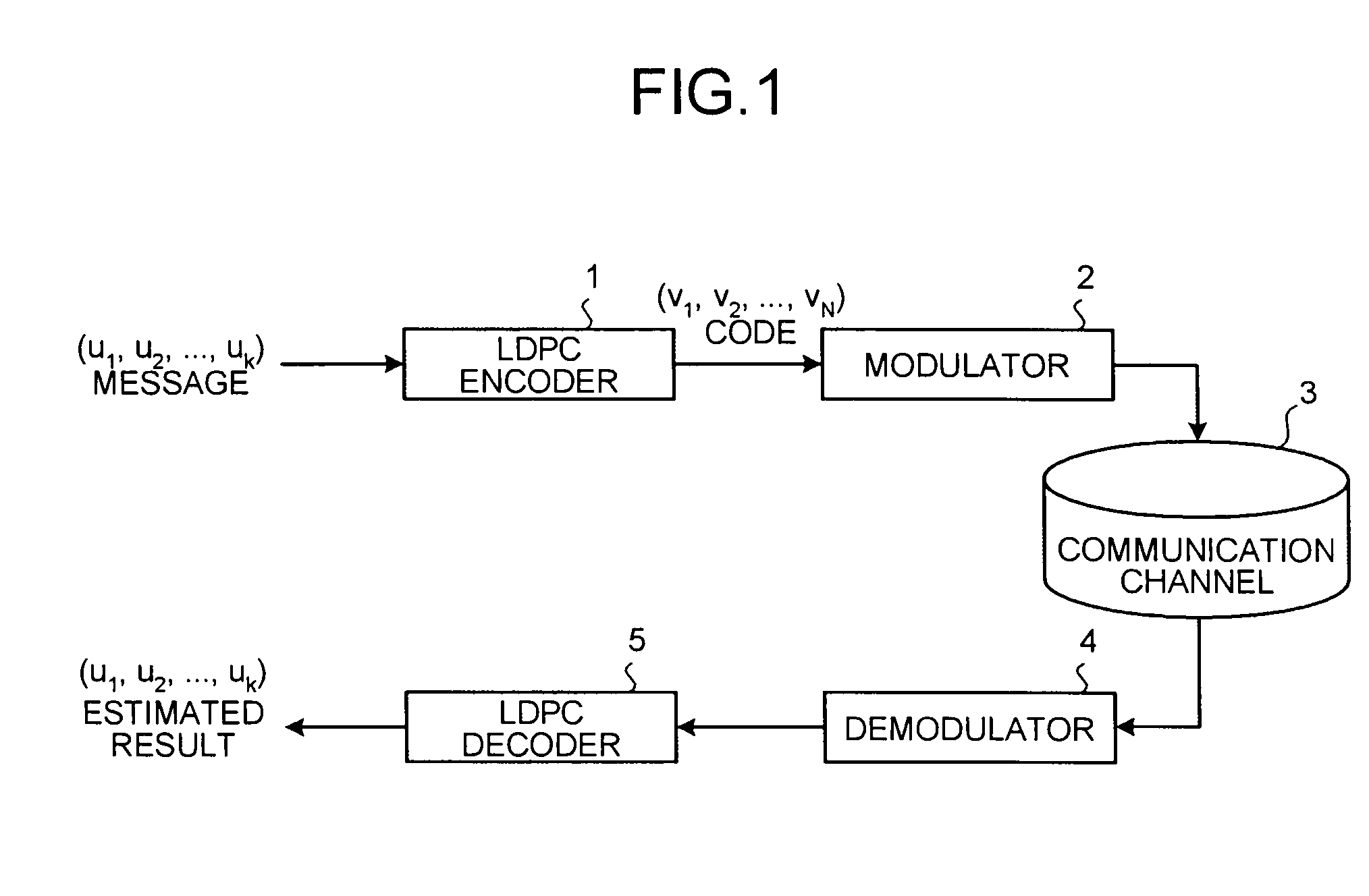
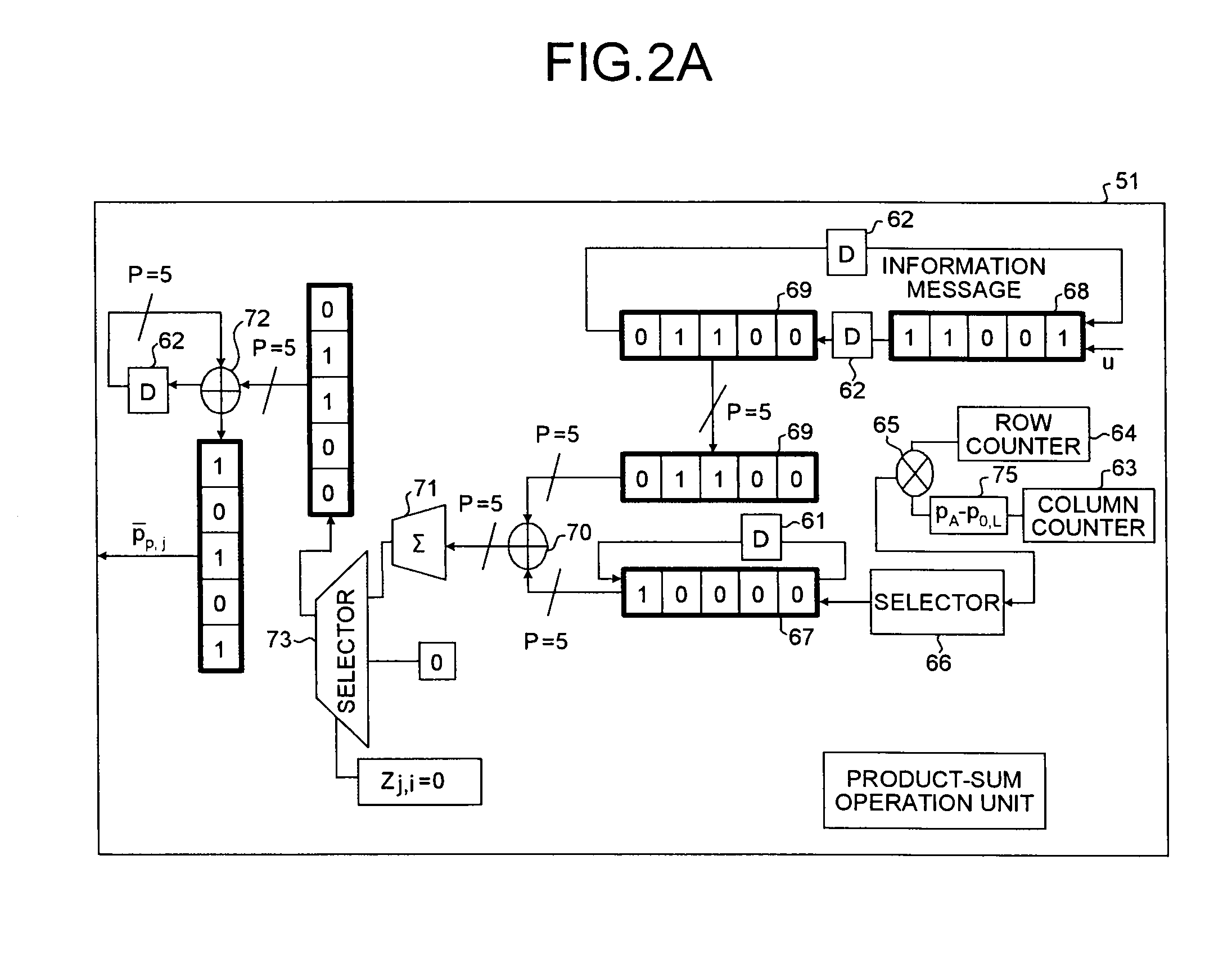
Efficient encoder for low-density-parity-check codes
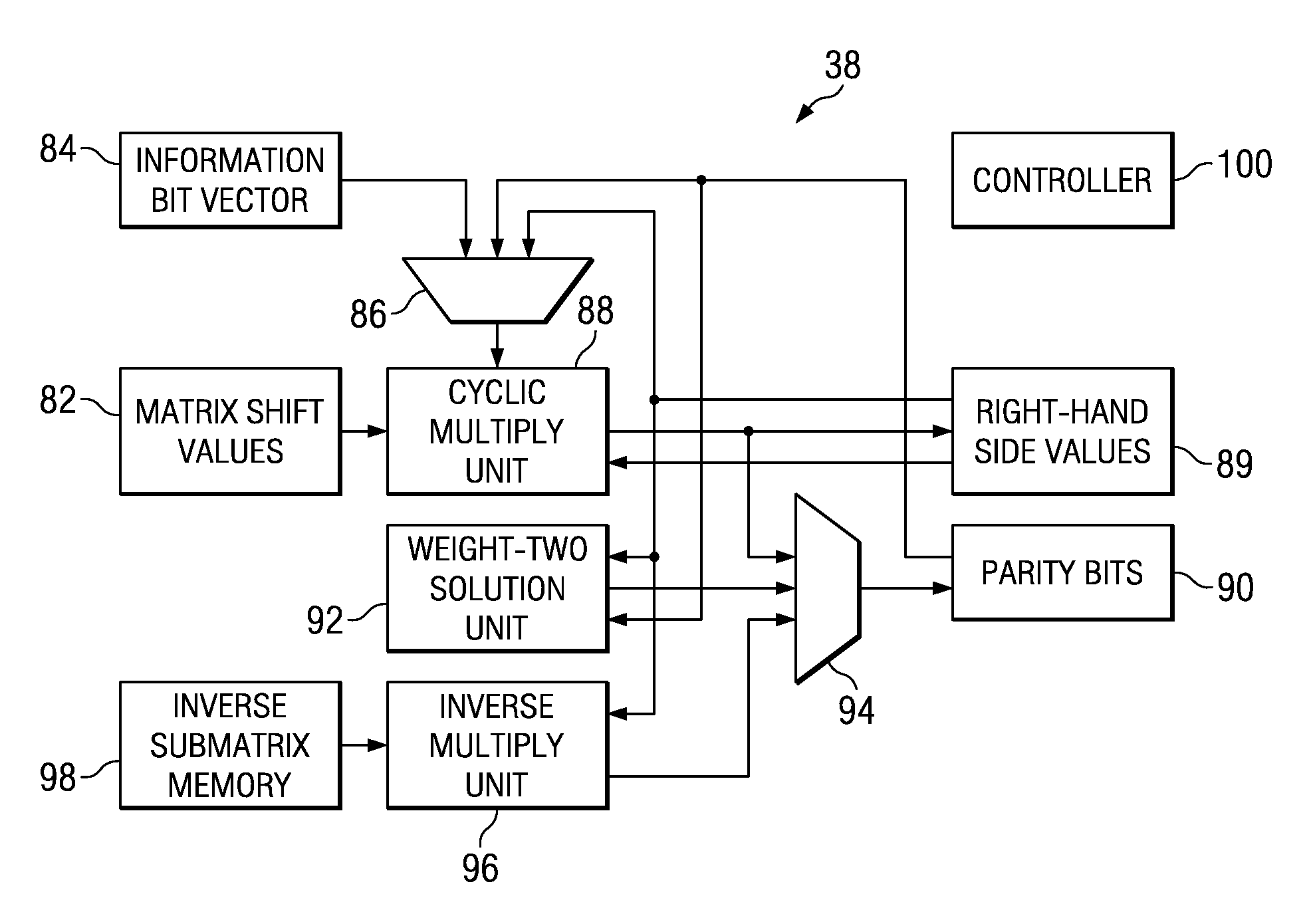
ActiveUS7162684B2Improve efficiencyLow implementation costError detection/correctionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsDiagonalParity-check matrix
Encoder circuitry for applying a low-density parity check (LDPC) code to information words is disclosed. The encoder circuitry takes advantage of a macro matrix arrangement of the LDPC parity check matrix in which a left-hand portion of the parity check matrix is arranged as an identity macro matrix, each entry of the macro matrix corresponding to a permutation matrix having zero or more circularly shifted diagonals. The encoder circuitry includes a cyclic multiply unit, which includes a circular shift unit for shifting a portion of the information word according to shift values stored in a shift value memory for the matrix entry, and a bitwise exclusive-OR function for combining the shifted entry with accumulated previous values for that matrix entry. Circuitry for solving parity bits for row rank deficient portions of the parity check matrix is also included in the encoder circuitry.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
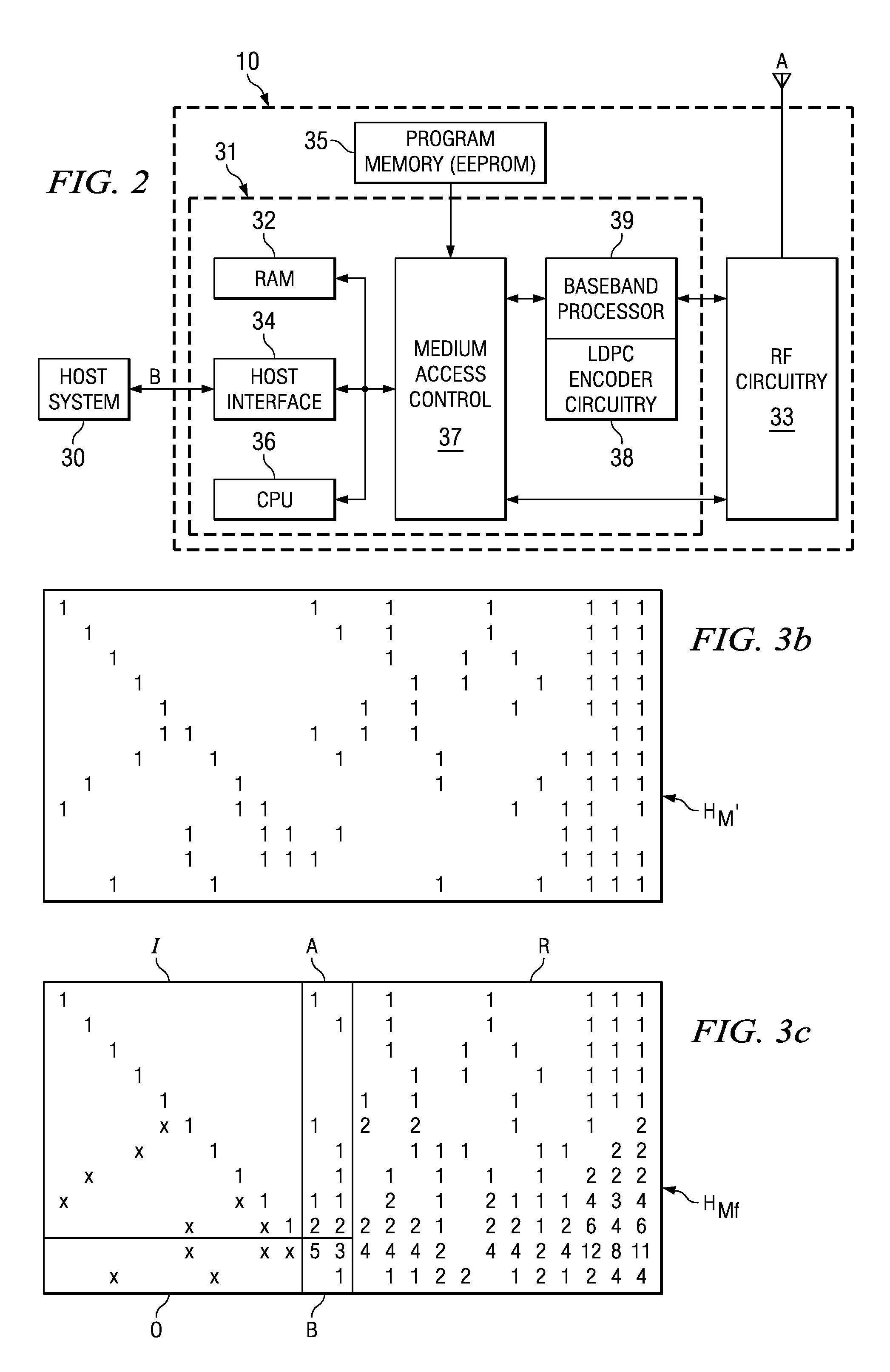
Apparatus and method for coding/decoding block low density parity check code in a mobile communication system
ActiveUS20050050435A1Maximized error correction capabilityMaximized minimum cycle lengthError preventionError detection/correctionTheoretical computer scienceParity-check matrix
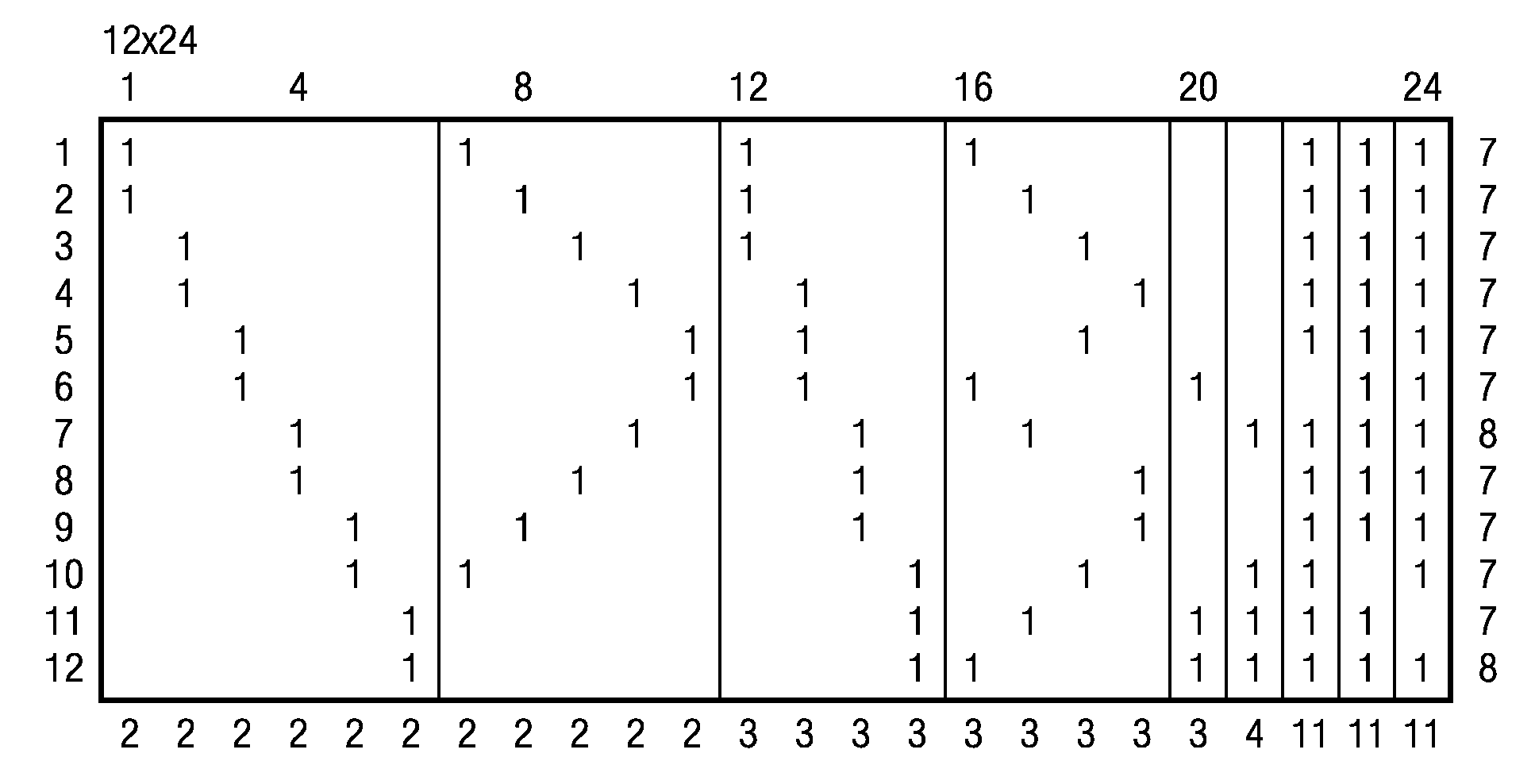
A method for generating a parity check matrix of a block LDPC code is disclosed. The parity check matrix includes an information part corresponding to an information word and a first parity part and a second parity part each corresponding to a parity. The method includes determining a size of the parity check matrix based on a coding rate applied when coding the information word with the block LDPC code, and a codeword length; dividing a parity check matrix with the determined size into a predetermined number of blocks; classifying the blocks into blocks corresponding to the information part, blocks corresponding to the first parity part, and blocks corresponding to the second parity part; arranging permutation matrixes in predetermined blocks from among the blocks classified as the first parity part, and arranging identity matrixes in a full lower triangular form in predetermined blocks from among the blocks classified as the second parity part; and arranging the permutation matrixes in the blocks classified as the information part such that a minimum cycle length is maximized and weight values are irregular on a factor graph of the block LDPC code.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Hardware-Efficient Low Density Parity Check Code for Digital Communications
InactiveUS20070011568A1Efficient implementationEfficient constructionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionMatrix groupMemory bank
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
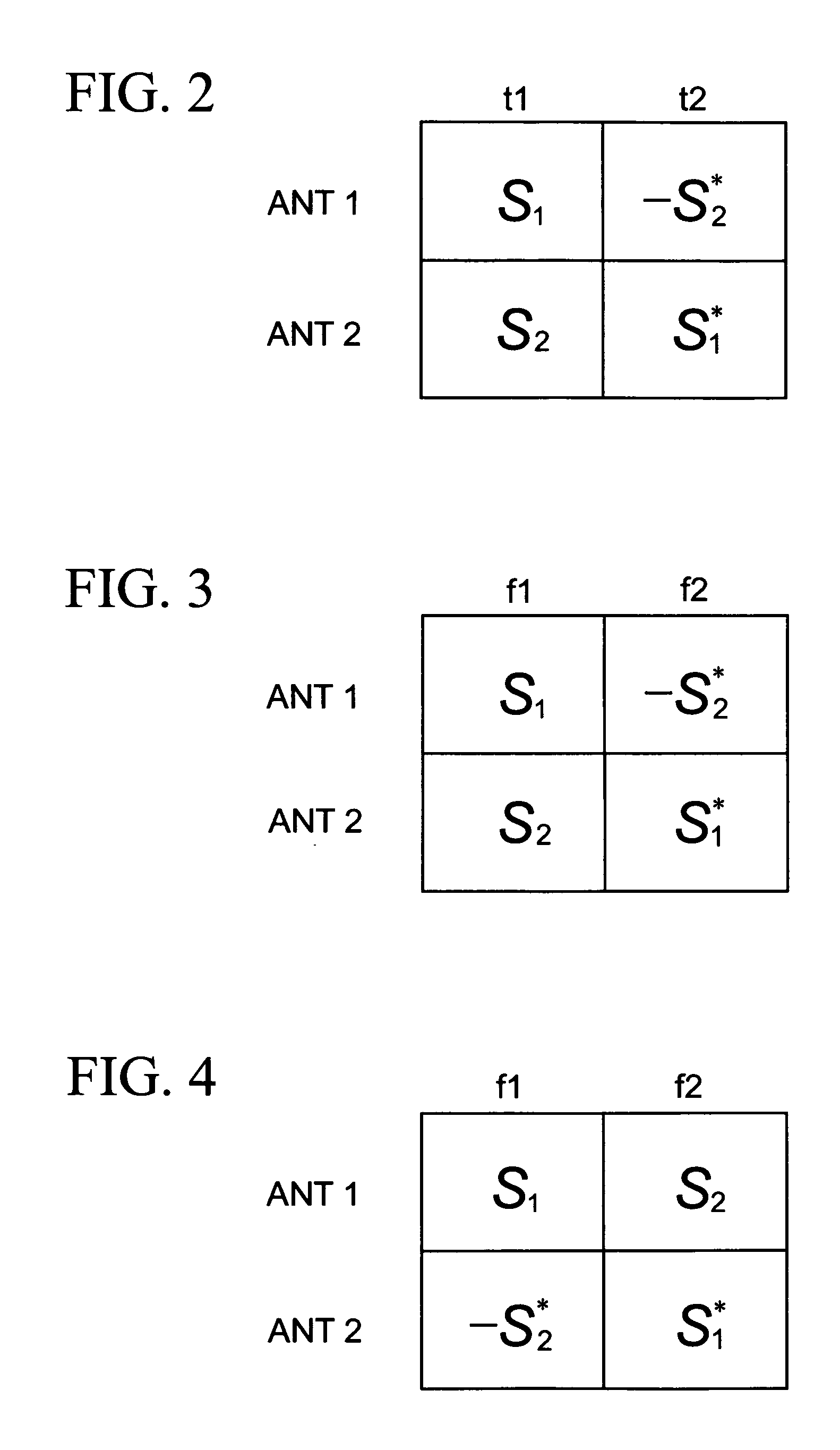
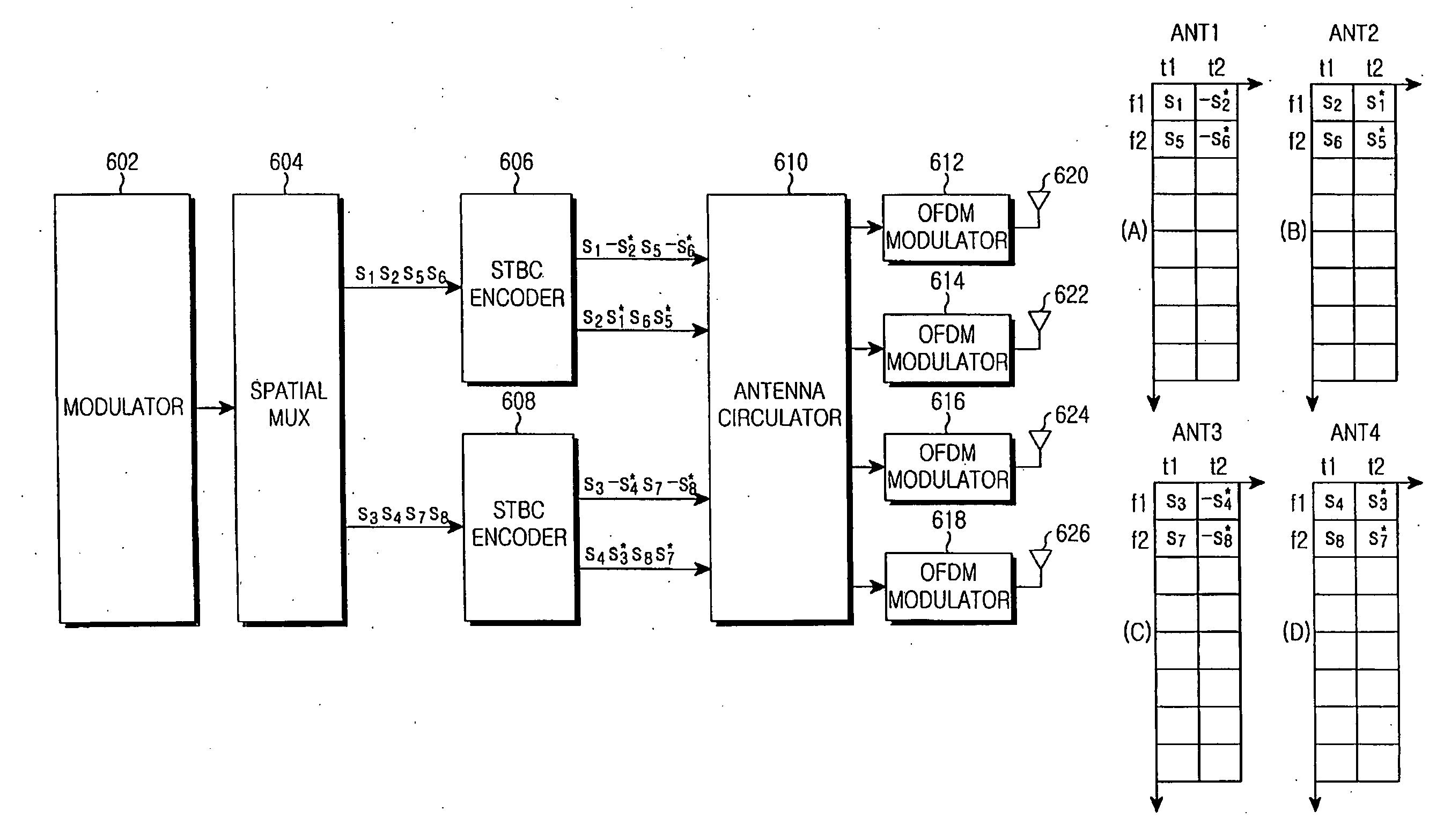
Apparatus and method for space-time frequency block coding in a wireless communication system
InactiveUS20060153312A1Improve rate performanceImprove performanceModulated-carrier systemsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsCommunications systemComputer science
A Space-Time-Frequency Block Coding (STFBC) encoding apparatus and method for a wireless communication system are provided. In a transmitter using a plurality of transmit antennas, an encoder encodes an input symbol sequence according to a predetermined space-time coding matrix. An antenna circulator selects one of predetermined permutation matrices according to a predetermined formula and generates a plurality of symbol vectors by permuting the space-time coded symbols according to the selected permutation matrix.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus and method for coding and decoding irregular repeat accumulate codes
ActiveUS20050132260A1Minimize complexityError prevention/detection by using return channelError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsParity-check matrixDiagonal matrix
An apparatus and method for coding an irregular Repeat Accumulate (RA) code. A repeater repeats a received information word such that the information word corresponds to weights of a first information part and a second information part of a parity check matrix in which permutation matrixes are arranged in the first information part and the second information part corresponding to the information word such that a minimum length of a cycle on a factor graph of the irregular RA code becomes a predetermined length and weights are irregular, and a dual diagonal matrix is arranged in a parity part corresponding to a parity. An interleaver interleaves a signal output from the repeater using an interleaving scheme predefined for the parity check matrix. An accumulator generates the irregular RA code by accumulating a signal output from the interleaver according to a weight of the parity part.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
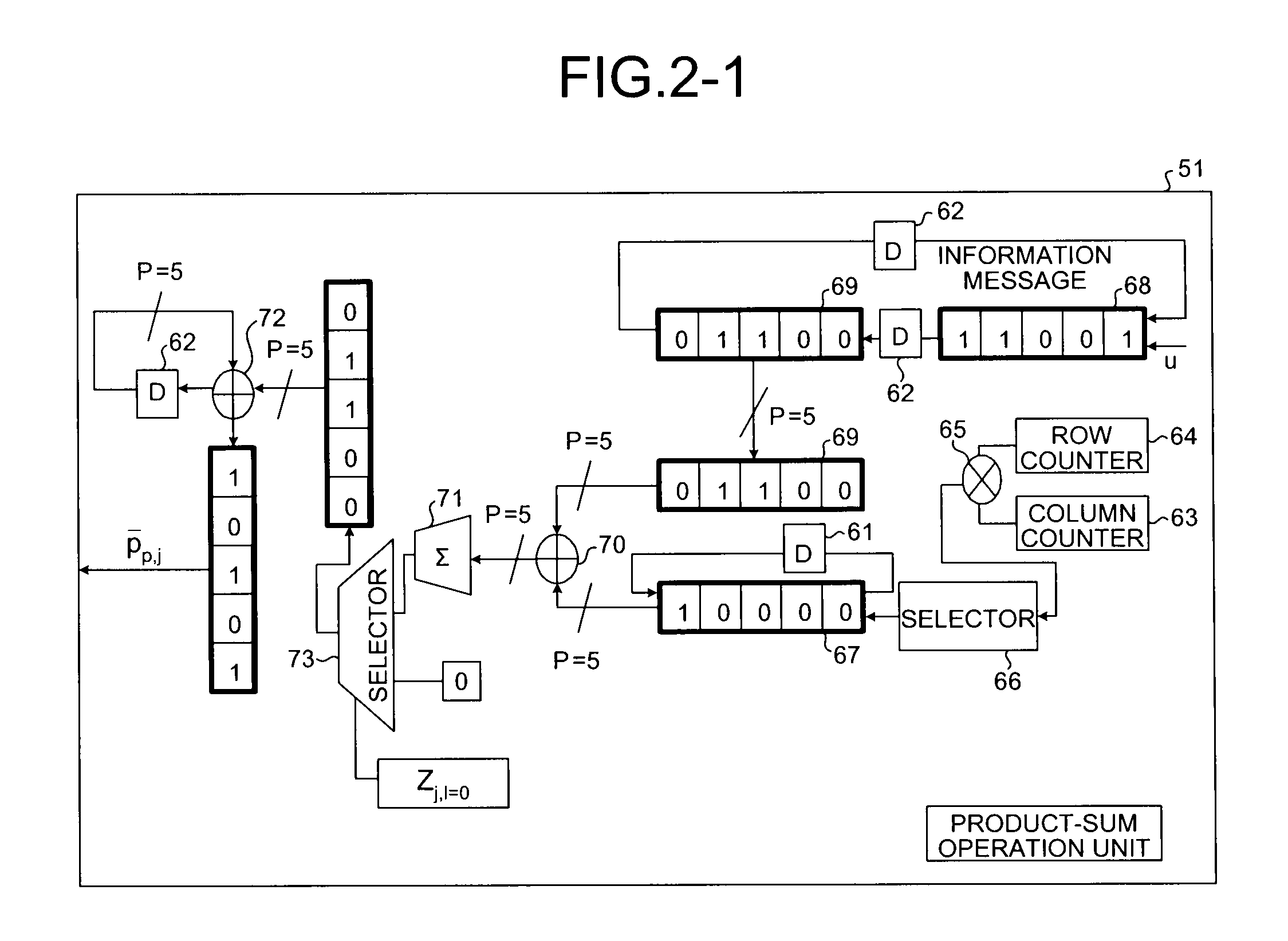
Test matrix generating method, encoding method, decoding method, communication apparatus, communication system, encoder and decoder
ActiveUS20090265600A1Promote generationReduce circuit sizeError preventionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsDecoding methodsCommunications system
A regular quasi-cyclic matrix is prepared, a conditional expression for assuring a predetermined minimum loop in a parity check matrix is derived, and a mask matrix for converting a specific cyclic permutation matrix into a zero-matrix based on the conditional expression and a predetermined weight distribution is generated. The specific cyclic permutation matrix is converted into the zero-matrix to generate an irregular masking quasi-cyclic matrix. An irregular parity check matrix in which the masking quasi-cyclic matrix and a matrix in which the cyclic permutation matrices are arranged in a staircase manner are arranged in a predetermined location.
Owner:RAKUTEN GRP INC
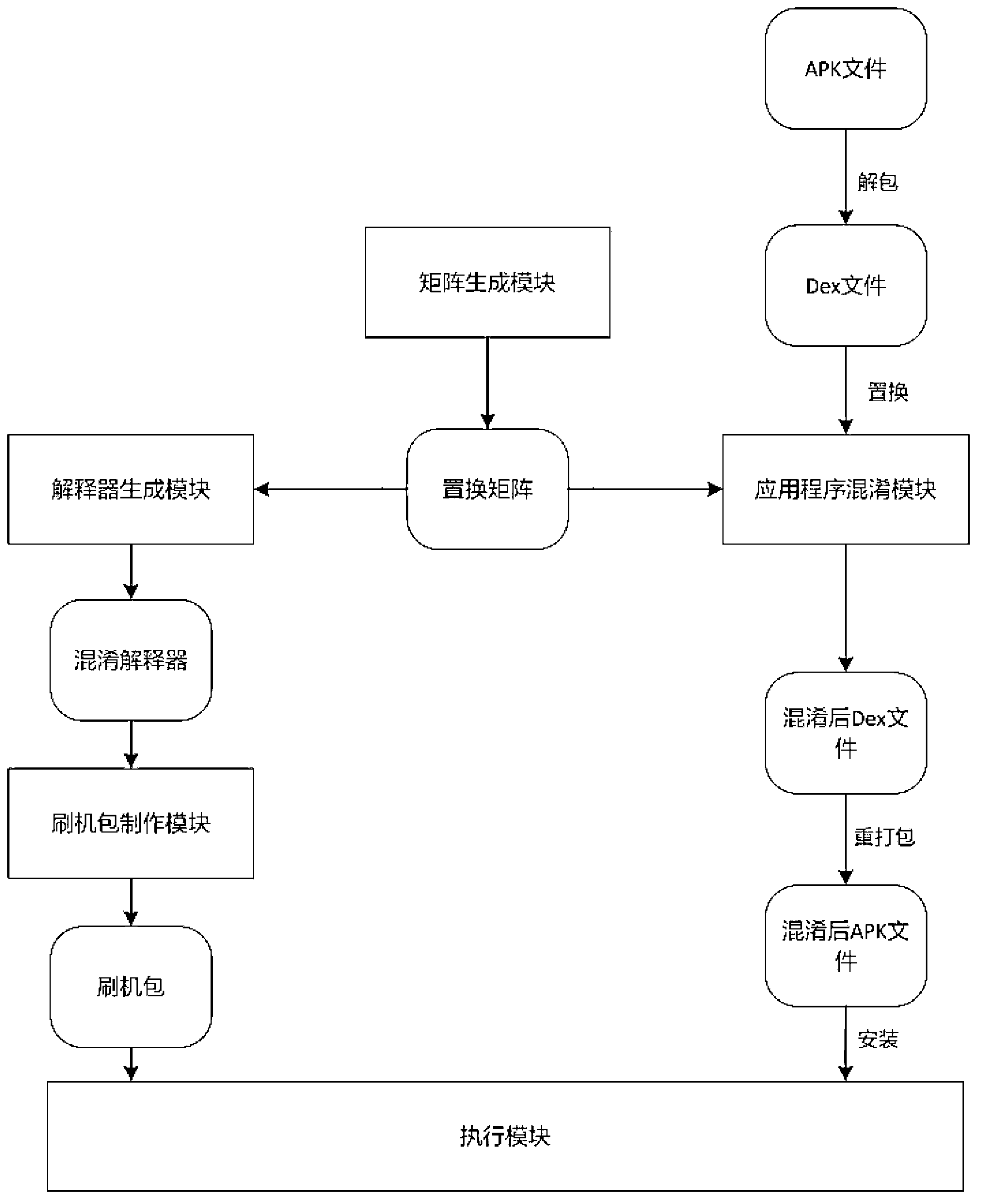
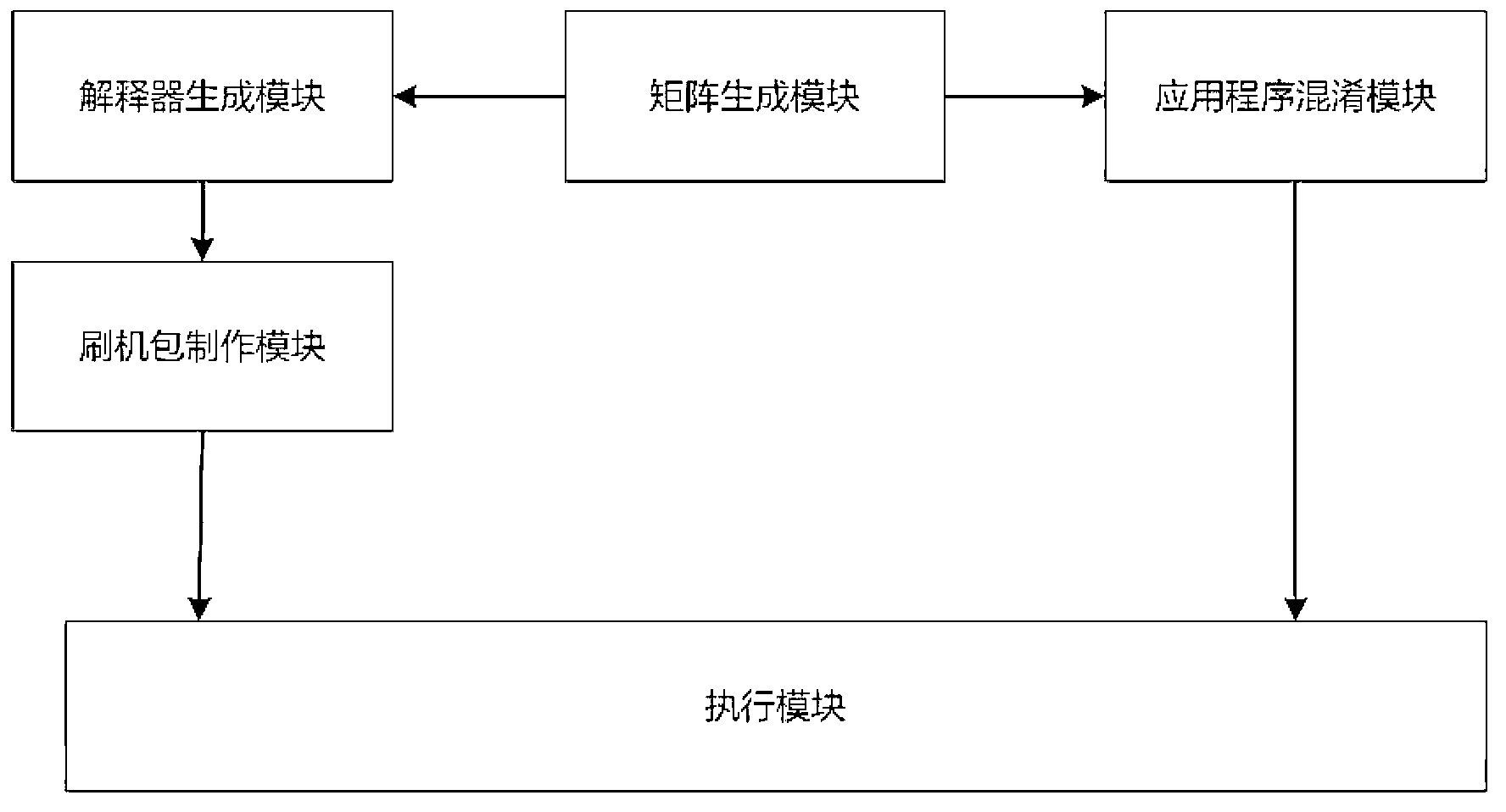
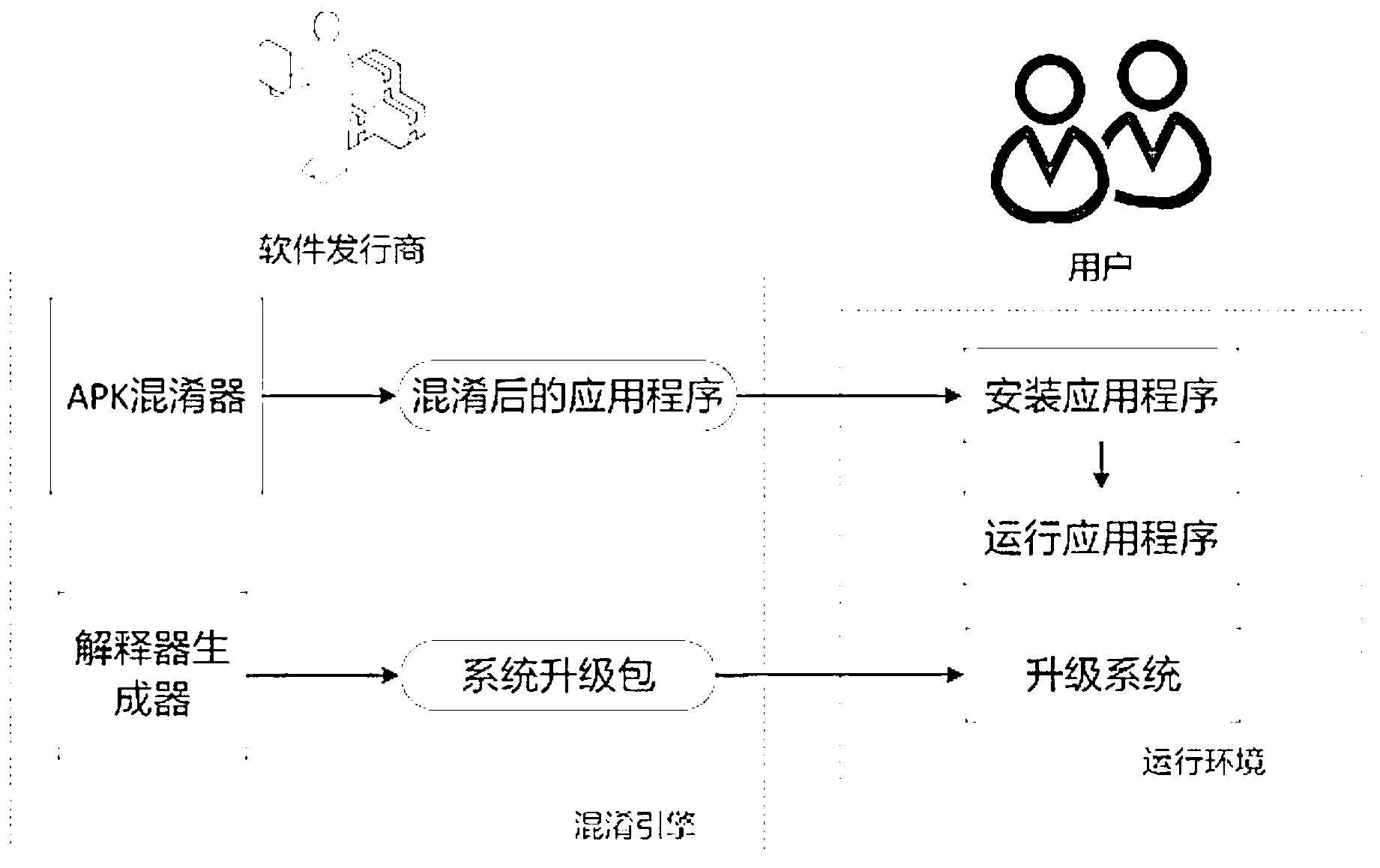
Android application program protective method and system based on order confusion
ActiveCN103324872AResistance to static reverse analysisFully transparent security execution processProgram/content distribution protectionConfusionApplication software
The invention discloses an Android application program protective method and system based on order confusion in the technical field of information safety. A permutation matrix needed when an application program is confused is generated, and binary codes of the Android application program are confused, so that the confused codes can not be reversed. A system mirror image document used for executing the confused application program is generated, a safe executing platform is set up, and the confused application program is executed. The Android application program protective system based on order confusion comprises a matrix generation module, an application program confusion module, an interpreter generating module, a system document generation module and an executing module. The Android application program protective method and system based on order confusion can effectively protect the Android application program from the attack of an attacker suck as reversing and tampering.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Matrix inverse operation method
InactiveCN105426345AImplement the inverse operationMeet performance needsComplex mathematical operationsMatrix inverseLU decomposition
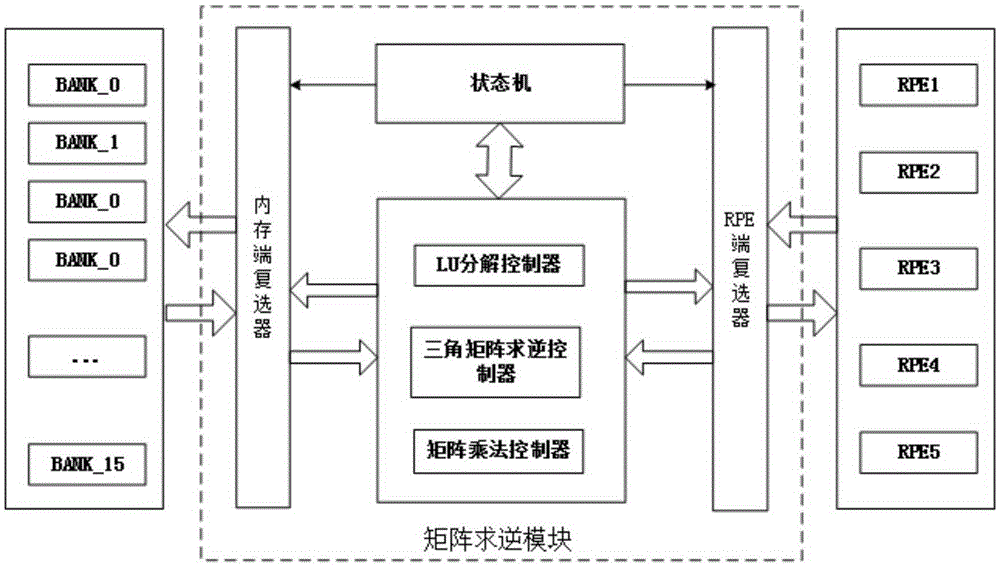
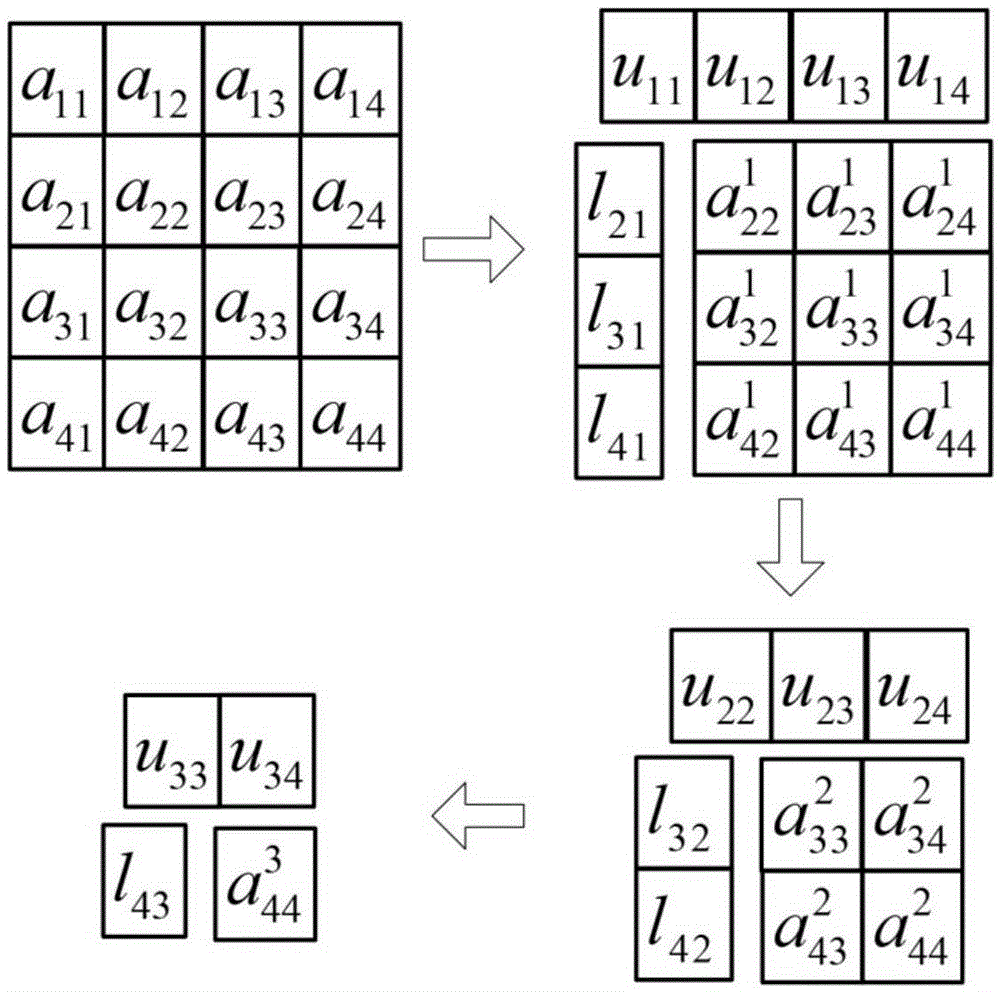
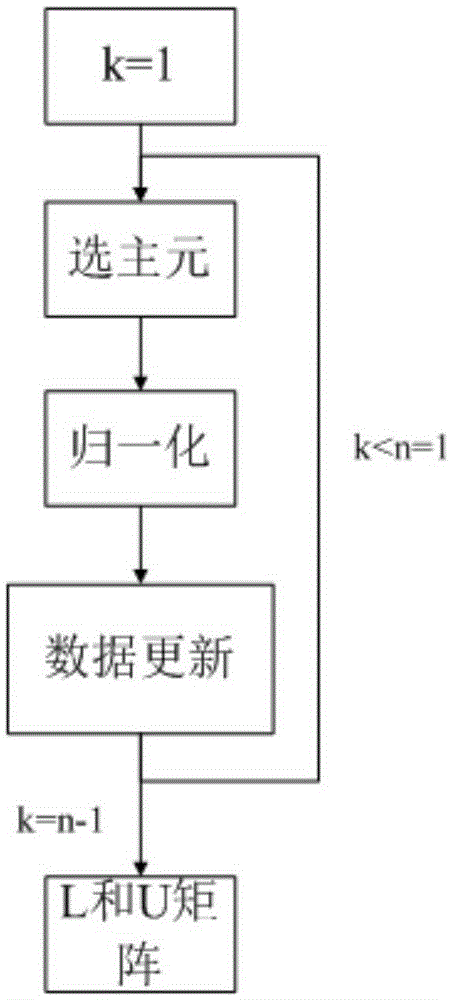
The invention relates to a matrix inverse operation method. The method comprises the steps of 1, conducting column pivoting LU decomposition, wherein a source matrix A is decomposed into a unit lower triangular matrix L, an upper triangular matrix U and a permutation matrix P according to the formula PA=LU; 2, conducting triangular matrix inversion, wherein the inverse matrix L-1 of the matrix L is obtained through matrix inversion, and matrix inversion is conducted on the transposed matrix of the matrix U and then transposition is conducted to obtain U-1; 3, finally conducting matrix multiplication, wherein the matrix U-1 and the matrix L-1 are multiplied, and column transformation is conducted on the matrix multiplication result according to the permutation matrix P to obtain a source matrix A-1. The method has the advantages that by using the column pivoting LU decomposition algorithm, the time complexity of the matrix inversion algorithm is effectively reduced, parallelizability of matrix inversion operation is improved, time for matrix inversion operation is shortened, matrix inversion operation of any order can be conducted, and the number of hardware resources can be increased or reduced according to count requirements of operation so that practical application requirements can be better met.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Check matrix generating method, encoding method, decoding method, communication device, encoder, and decoder
InactiveUS20090063930A1Data representation error detection/correctionCode conversionDecoding methodsParity-check matrix
A regular quasi-cyclic matrix is generated with cyclic permutation matrices and specific regularity given to the cyclic permutation matrices. A mask matrix for making the regular quasi-cyclic matrix into an irregular quasi-cyclic matrix is generated. An irregular masked quasi-cyclic matrix is generated by converting a specific cyclic permutation matrix in the regular quasi-cyclic matrix into a zero-matrix using a mask matrix supporting a specific encoding rate. An irregular parity check matrix with an LDGM structure is generated with a masked quasi-cyclic matrix and a matrix in which the cyclic permutation matrices are arranged in a staircase manner.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
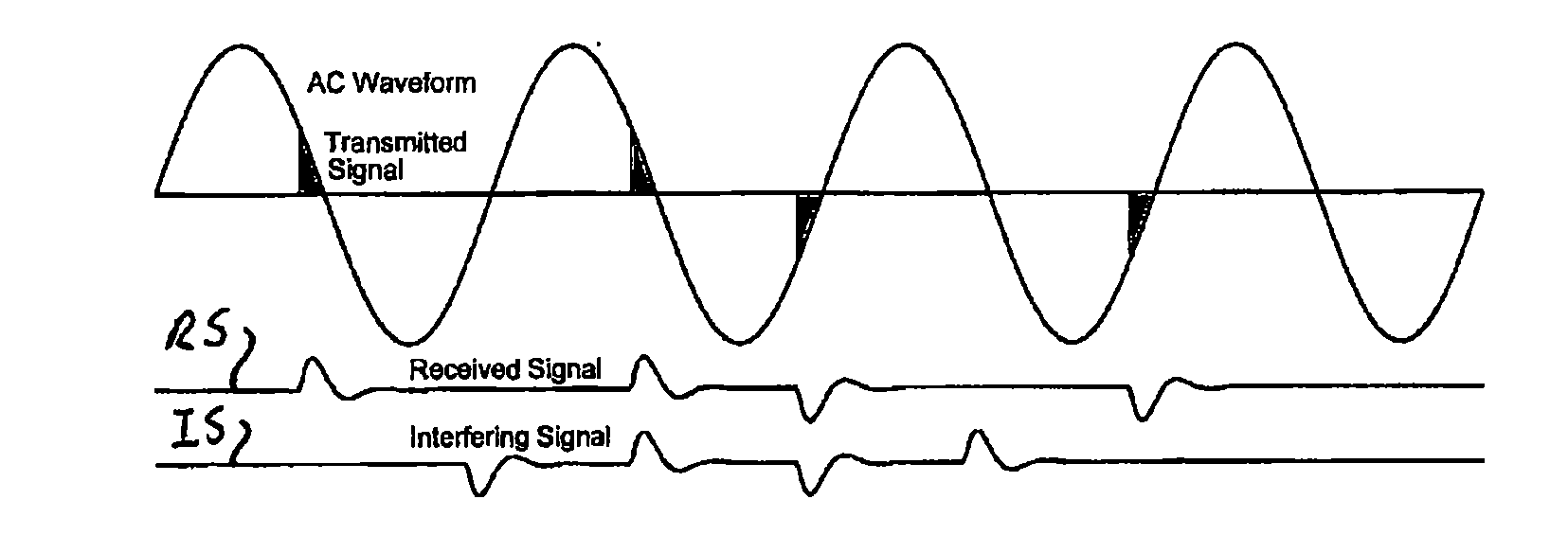
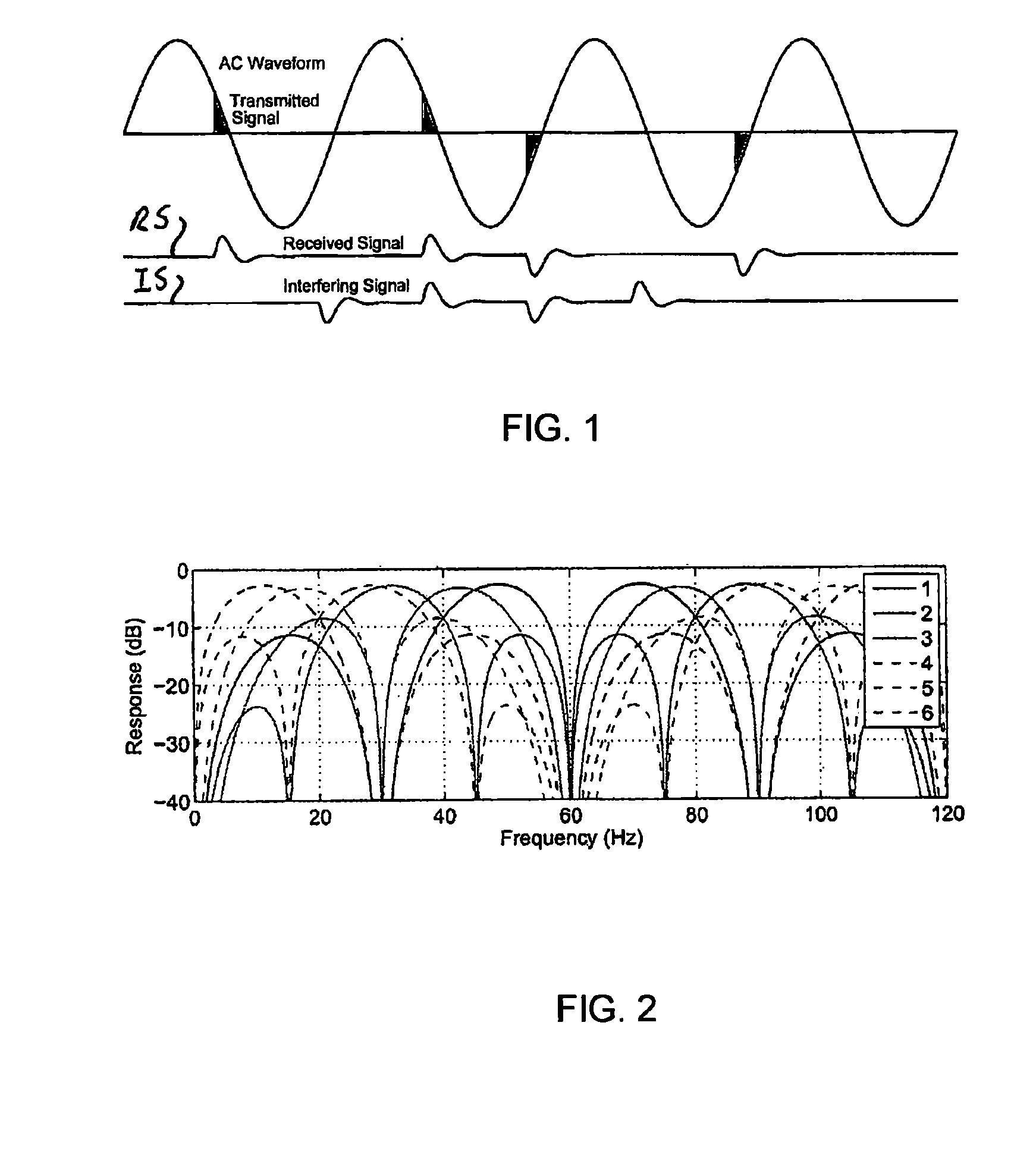
General method for low-frequency data transmission on a power line
ActiveUS20100054349A1Reduced Power RequirementsIncrease data rateModulated-carrier systemsComponent separationSystems designPulse pattern
A method for producing a set of inbound pulse patterns and detection vectors for lengths longer than 4 cycles in an AC waveform. These are used for generating inbound messages in a two-way automatic communication system (TWACS). The method uses Hadamard matrices adapted to generate a set of detection vectors by permuting rows of a matrix and removing certain columns of the matrix to meet system design requirements. The method can be extended to any length and modified to accommodate multiple pulses per half-cycle to support higher data rates.
Owner:ACLARA TECH LLC
Method and device for mapping control channel sources
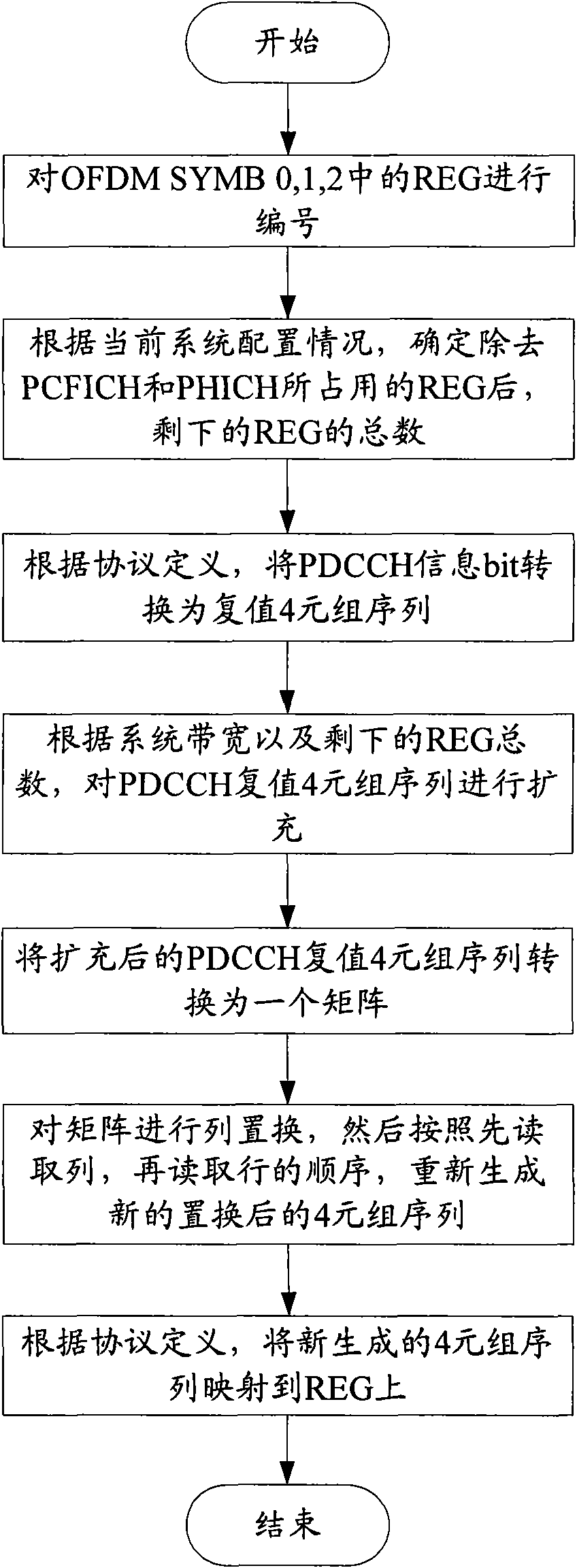
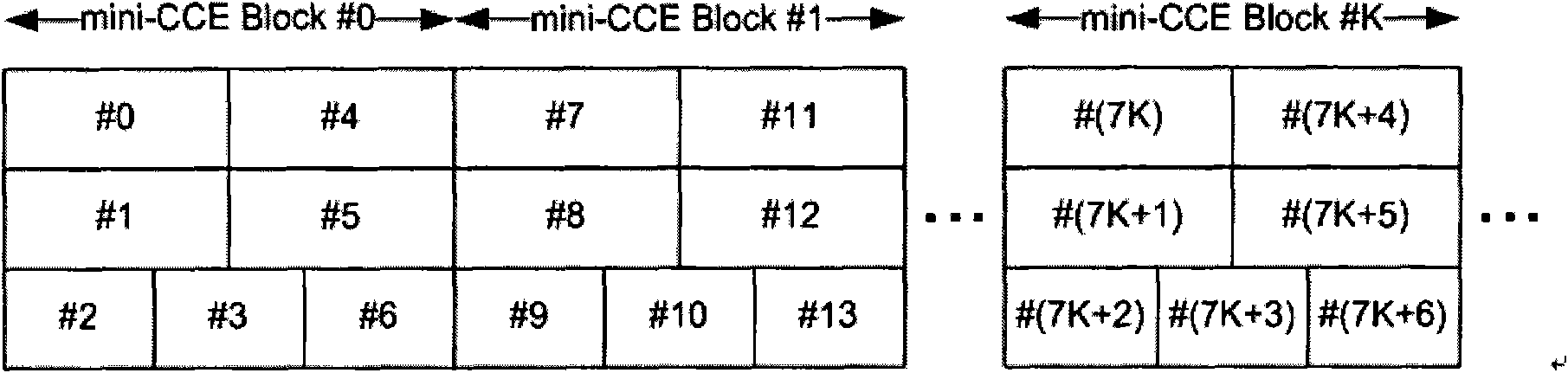
ActiveCN101605023AReduce distractionsIncrease diversity effectError prevention/detection by using return channelMulti-frequency code systemsAutomatic repeat requestResource element
The invention discloses a method for mapping control channel sources. The method comprises the following steps: confirming the number of source element groups occupied by a physical control format indicator channel (PCFICH) and a physical hybrid automatic repeat request indicator channel (PHICH) and the total number of the source element groups supported by a system; confirming a number NREG of the source element groups occupied by a physical downlink control channel (PDCCH) according to the confirmed total number and the number of the source element groups occupied by the PCFICH and the PHICH; expanding a complex value 4-tuple sequence of the PDCCH according to the NREG to obtain an expanded 4-tuple sequence; mapping the expanded 4-tuple sequence into a matrix according to a first preset mode; permuting the columns of the matrix to obtain a permutation matrix; reading the permutation matrix in a second preset mode to obtain a new 4-tuple sequence; and mapping the new 4-tuple sequence to the source element groups by a time priority principle. The invention also discloses a device for mapping the control channel sources. The invention can reduce the mutual interference among the control channels and improve the diversity effect of an OFDM technology.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Construction method of non-regular permutation matrix LDPC code and its device
InactiveCN1794621ASimple designSimplify implementation complexityError preventionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsRing circuitH matrix
This invention relates to a method for constructing new non-standard replacement matrix LDPC codes characterizing that under the principle of optimizing the smallest ring circuit, it takes each sub-block as the smallest unit and utilizes a binary chart with weight to determine the position of the sub-block and the deviation of circulation shift: simplifying the binary chart with bit as the unit of the LDPC code to that with a sub-block as the unit based on the property of the matrix of a replacement unit, then applying the traditional PEG algorithm with the bit as the unit to the new chart with the sub-block as the unit to determine the position of every replacement unit matrix of the H matrix and finally utilizing the ring circuit property of the LDPC code to decide the deviation of circular shift of each replacement unit matrix.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Sub-carrier mapping method
InactiveCN101568128AImprove throughputMeet needsError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency diversityResource blockCarrier signal
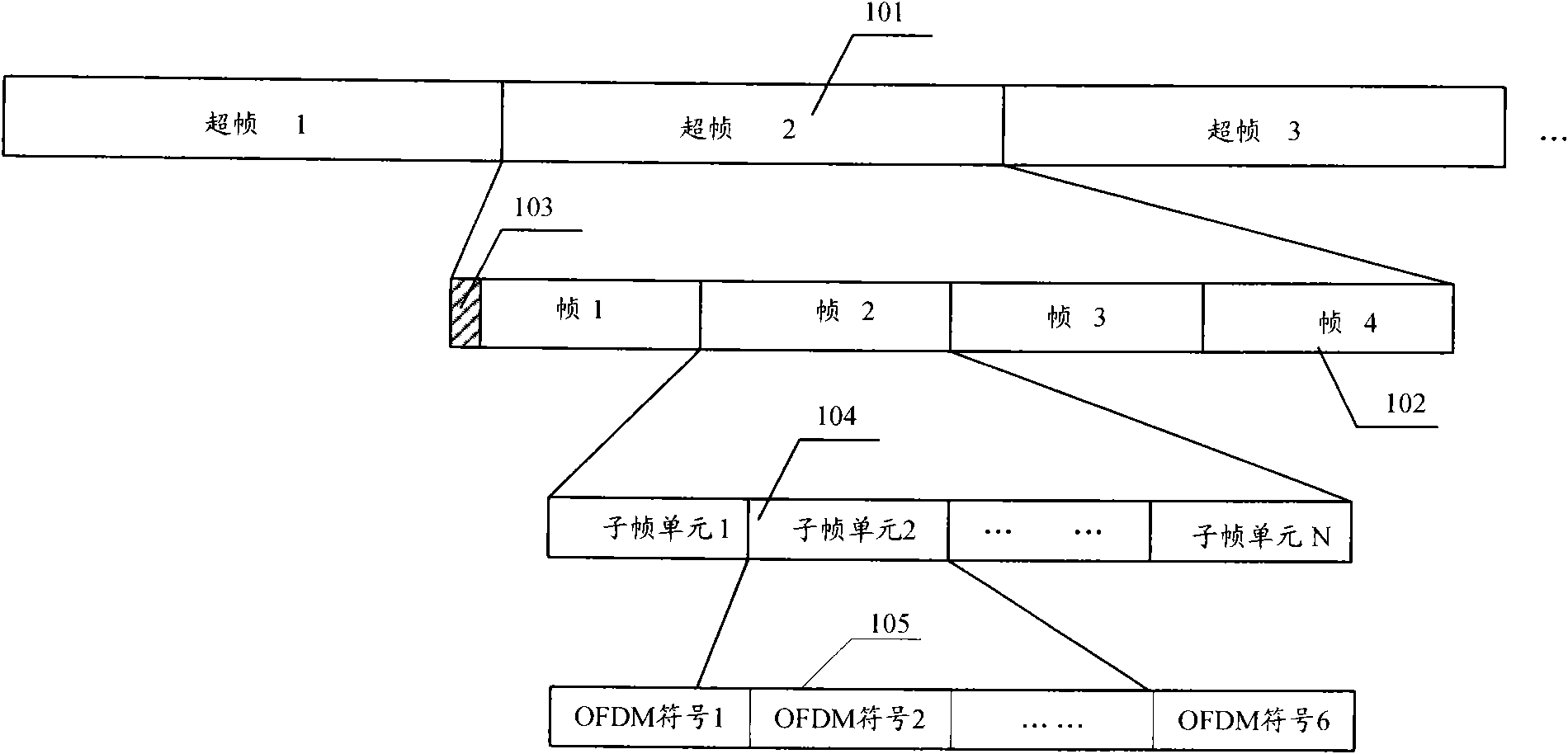
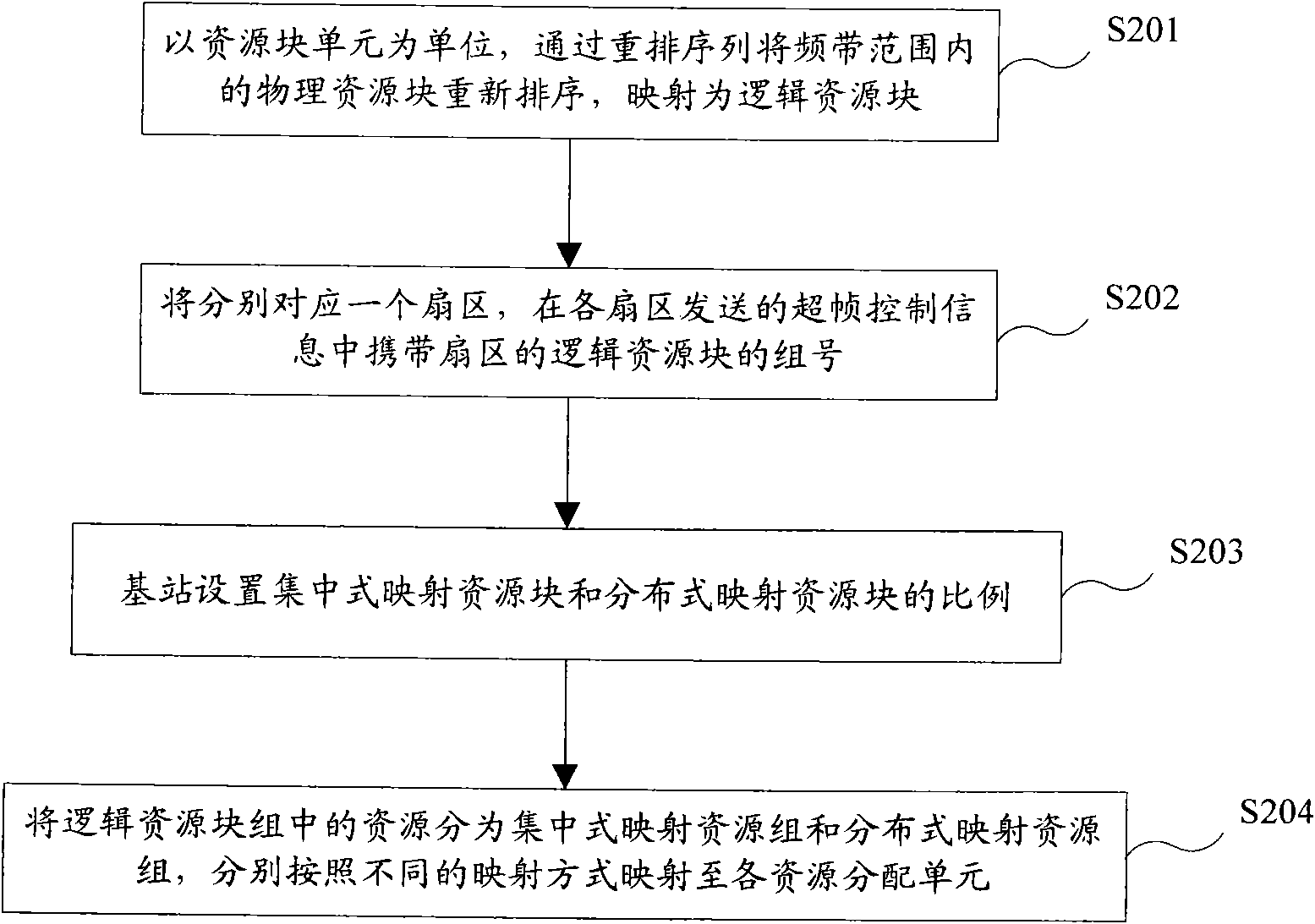
The invention discloses a sub-carrier mapping method which comprises: with the set resource block elements as units, physical resource blocks in the frequency band range are rearranged according to a rearrangement sequence so as to be mapped into logical resource blocks; the mapped logical resource blocks in the frequency band range are grouped by a base station, each grouped logical resource block respectively corresponds to one sector, and the superframe control information sent by each sector carries a logical resource block group number which corresponds to the sector; and in each sector of the base station, the resources in the logical resource block group are divided into a centralized mapping resource group and a distributed mapping resource group according to the set proportion, wherein continuous sub-carriers in each resource block unit in the centralized mapping resource group are directly mapped to each resource allocation unit, and after being rearranged through a permutation matrix, all sub-carriers in the distributed mapping resource group are sequentially mapped to each resource allocation unit. The technical scheme of the invention can ensure that users who move quickly and slowly can obtain high throughput.
Owner:XUZHOU MASTER MECHANICAL TECH CO LTD
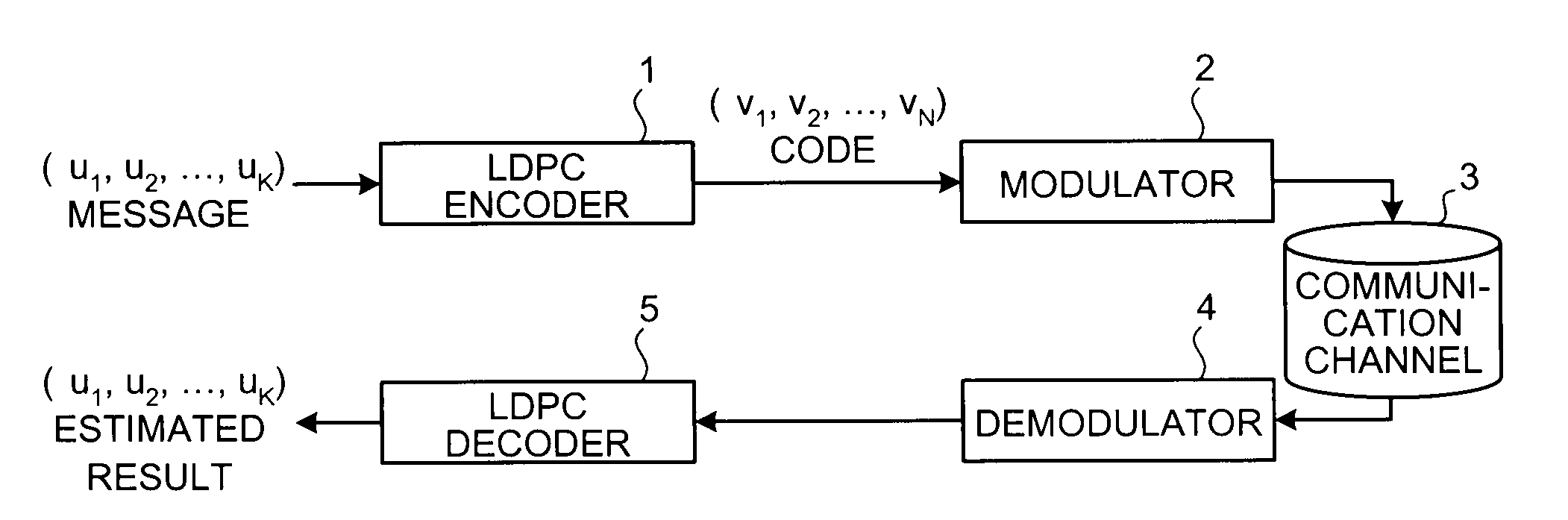
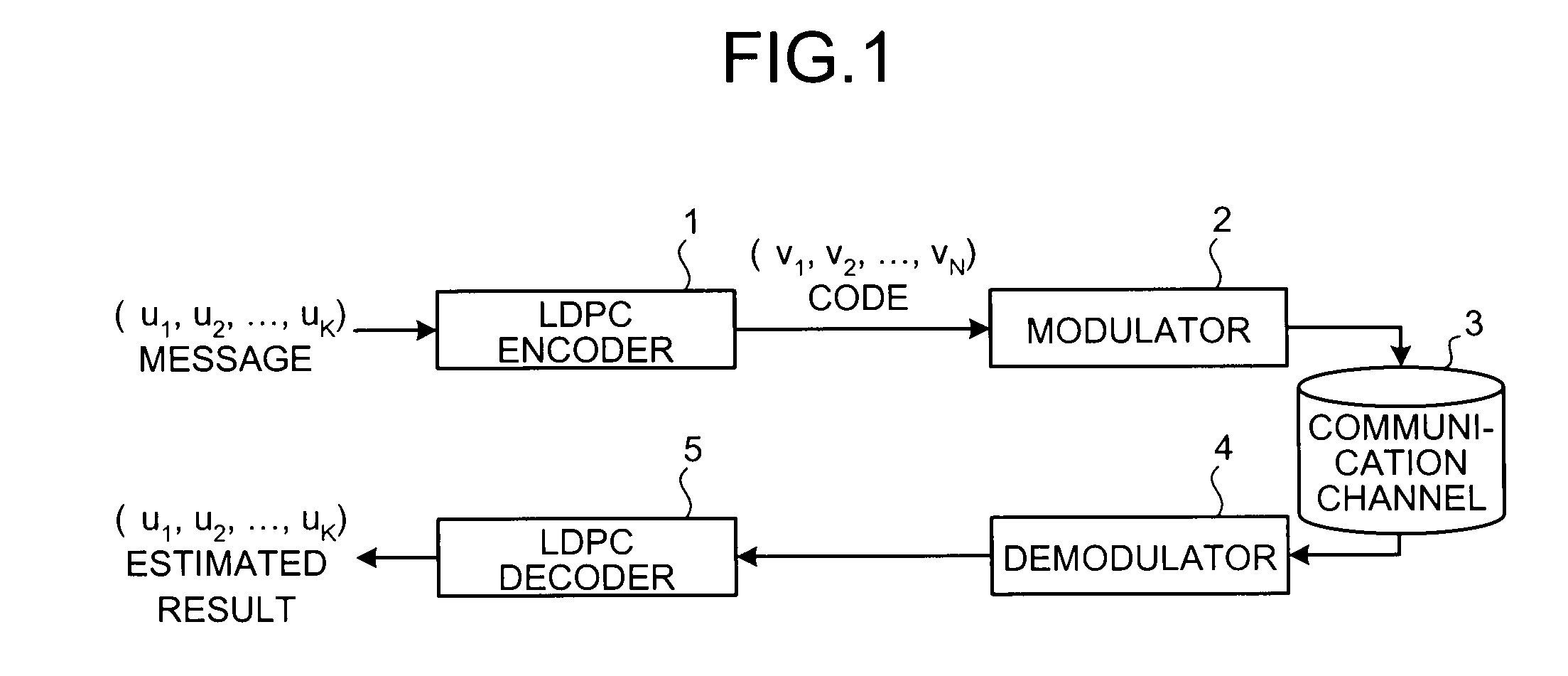
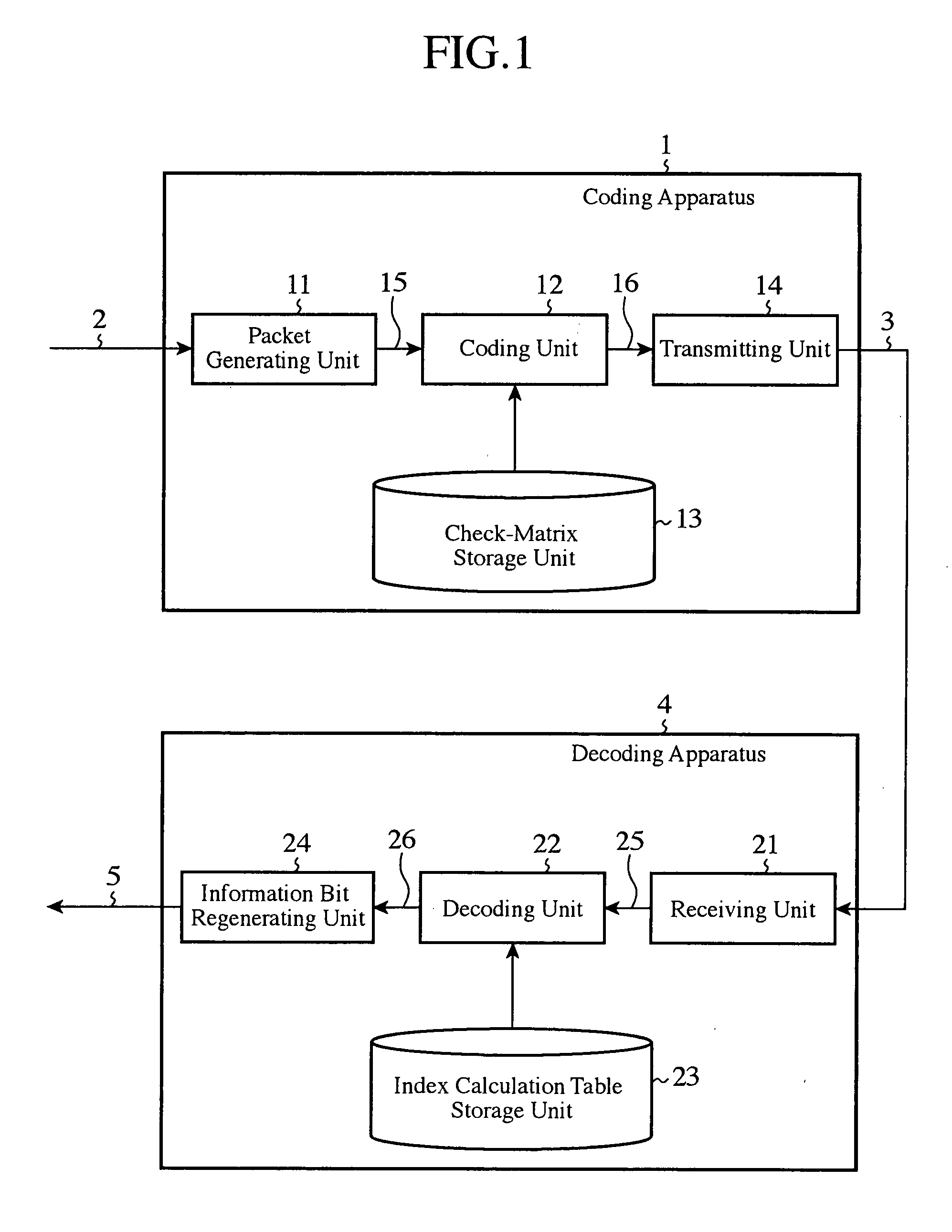
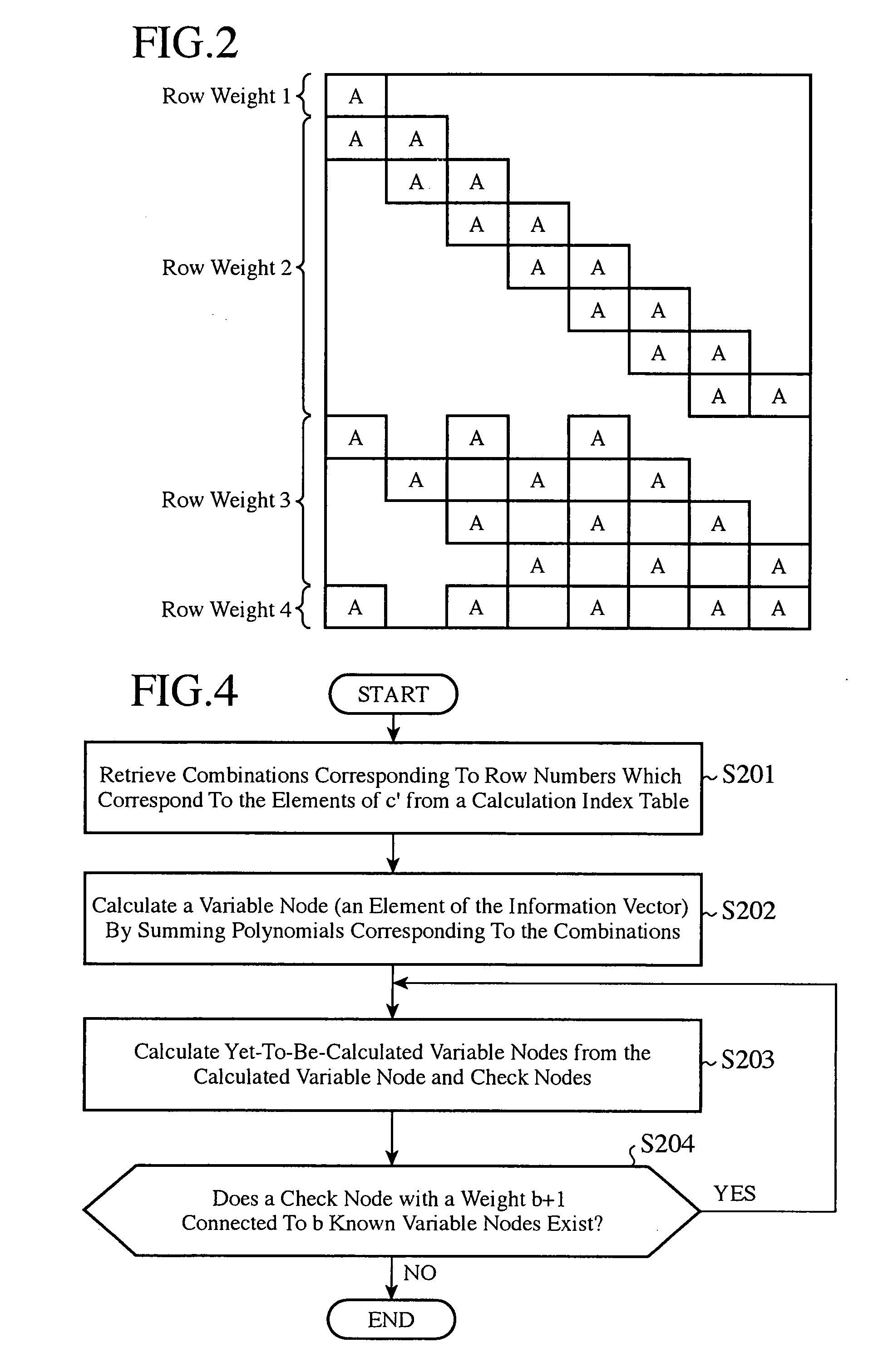
Error correction coding apparatus
InactiveUS20090031186A1Improve efficiencyError preventionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsAlgorithmLow-density parity-check code
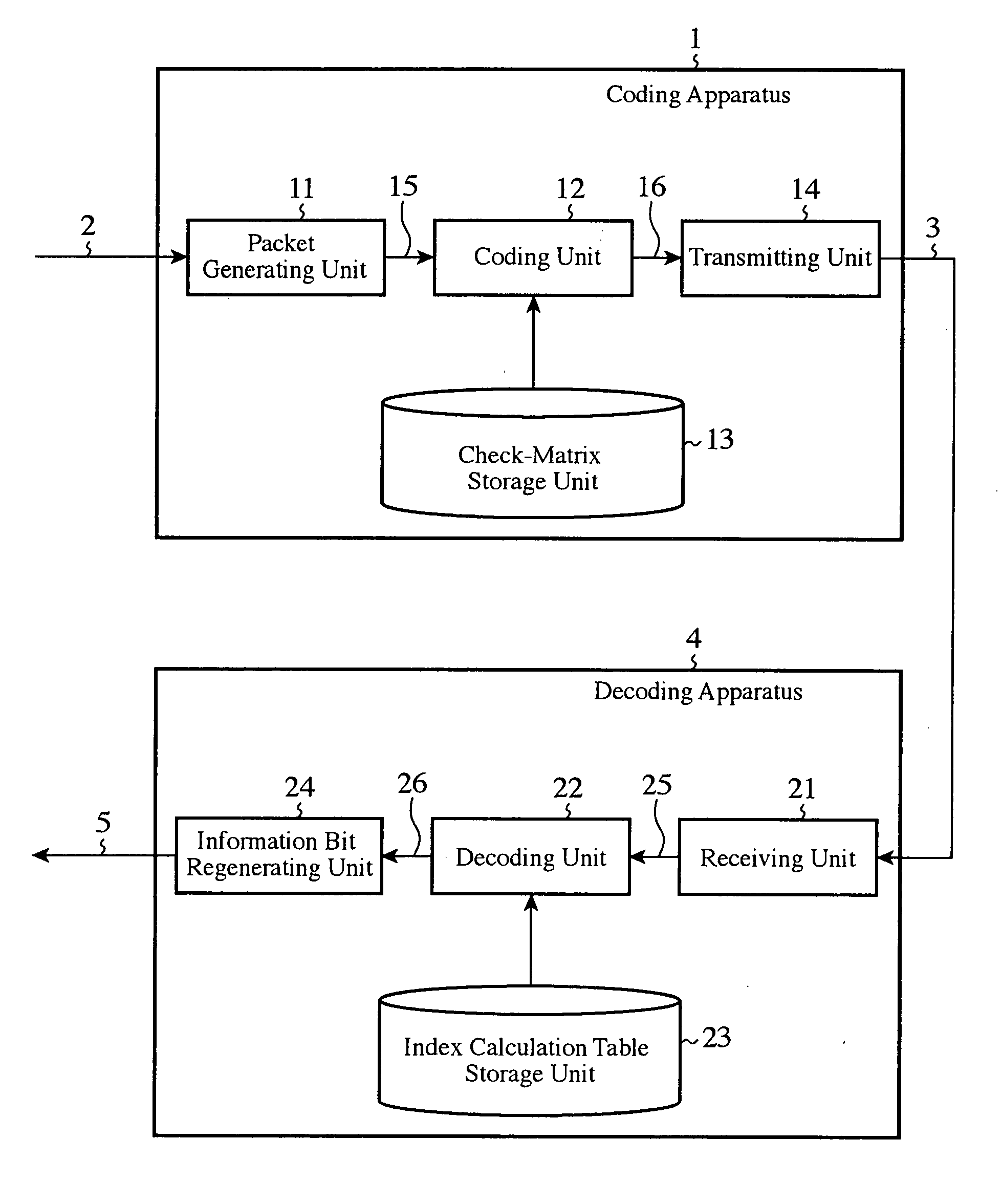
An error correction coding apparatus is disposed to generate a low-density parity-check code 16 from an input information sequence 15 by using a low-density parity-check matrix which satisfies a predetermined weight distribution, and includes a low-density parity-check matrix output means 13 for forming the above-mentioned low-density parity-check matrix by continuously arranging a number of rows in each of which the same number of cyclic-permutation matrices as the row weight are arranged, the number of rows satisfying the above-mentioned predetermined weight distribution, and then gradually increasing or decreasing the row weight, and for outputting the above-mentioned low-density parity-check matrix.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Apparatus and method for space-time-frequency block coding in a wireless communication system
InactiveCN1801665AImprove rate 2 STBC performanceSpatial transmit diversityMulti-frequency code systemsCommunications systemComputer science
A Space-Time-Frequency Block Coding (STFBC) encoding apparatus and method for a wireless communication system are provided. In a transmitter using a plurality of transmit antennas, an encoder encodes an input symbol sequence according to a predetermined space-time coding matrix. An antenna circulator selects one of predetermined permutation matrices according to a predetermined formula and generates a plurality of symbol vectors by permuting the space-time coded symbols according to the selected permutation matrix.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Clash-free irregular-repeat-accumulate code
ActiveUS20070011566A1Error detection/correctionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsTheoretical computer scienceDiagonal matrix
Methods, apparatuses, and systems are presented for performing data encoding involving receiving a sequence of data bits, encoding the sequence of data bits in accordance with a parity check matrix (H-matrix) to generate a sequence of encoded bits, wherein the H-matrix is capable of being partitioned into a first matrix and a second matrix, the first matrix being a dual-diagonal matrix, the second matrix comprising one or more vertically stacked sub-matrices, each sub-matrix consisting of a plurality of columns, each column having a column weight of no more than 1, wherein the second matrix is capable of being expressed as a product of a parity check matrix, an interleaver permutation matrix, and a repeat block matrix, and the interleaver permutation matrix satisfies a clash-free interleaver constraint, and outputting the sequence of encoded bits.
Owner:TRELLIS WARE TECH
Method and apparatus for public-key cryptography based on error correcting codes
ActiveUS20140105403A1Improve security levelShort processKey distribution for secure communicationQ-matrixComputer hardware
Methods and apparatus for generating a private-public key pair, for encrypting a message for transmission through an unsecure communication medium (30), and for decrypting the message are disclosed. The methods are based on the well-known McEliece cryptosystem or on its Niederreiter variant. More general transformation matrices Q are used in place of permutation matrices, possibly together with an appropriate selection of the intentional error vectors. The transformation matrices Q are non-singular n×n matrices having the form Q=R+T, where the matrix R is a rank-z matrix and the matrix T is some other matrix rendering Q non-singular. The new Q matrices, though at least potentially being dense, have a limited propagation effect on the intentional error vectors for the authorized receiver. The use of this kind of matrices allows to better disguise the private key into the public one, without yielding any further error propagation effect. Based on this family of Q matrices, the presently proposed cryptosystem enables the use of different families of codes than Goppa codes, such as RS codes, by ensuring increased public key security.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH
Structured low-density parity-check (LDPC) code
InactiveUS20100211847A1Error preventionCode conversionParity-check matrixTheoretical computer science
A method for constructing a low-density parity-check (LDPC) code using a structured base parity check matrix with permutation matrix, pseudo-permutation matrix, or zero matrix as constituent sub-matrices; and expanding the structured base parity check matrix into an expanded parity check matrix. A method for constructing a LDPC code using a structured base parity check matrix H=[Hd|Hp], Hd is the data portion, and Hp is the parity portion of the parity check matrix; the parity portion of the structured base parity check matrix is such so that when expanded, an inverse of the parity portion of the expanded parity check matrix is sparse; and expanding the structured base parity check matrix into an expanded parity check matrix. A method for encoding variable sized data by using the expanded LDPC code; and applying shortening, puncturing.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Apparatus and method for coding/decoding block low density parity check code in a mobile communication system
ActiveUS20070283221A1Maximized error correction capabilityMaximized minimum cycle lengthError preventionError detection/correctionTheoretical computer scienceParity-check matrix
A method for generating a parity check matrix of a block LDPC code. The parity check matrix includes an information part corresponding to an information word and a first parity part and a second parity part each corresponding to a parity. The method includes determining a size of the parity check matrix based on a coding rate applied when coding the information word with the block LDPC code, and a codeword length; dividing a parity check matrix with the determined size into a predetermined number of blocks; classifying the blocks into blocks corresponding to the information part, blocks corresponding to the first parity part, and blocks corresponding to the second parity part; arranging permutation matrixes in predetermined blocks from among the blocks classified as the first parity part, and arranging identity matrixes in a full lower triangular form in predetermined blocks from among the blocks classified as the second parity part; and arranging the permutation matrixes in the blocks classified as the information part such that a minimum cycle length is maximized and weight values are irregular on a factor graph of the block LDPC code.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Encoder, decoder, methods of encoding and decoding
InactiveUS20070143657A1Solve problemsElectronic circuit testingError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsTheoretical computer sciencePermutation matrix
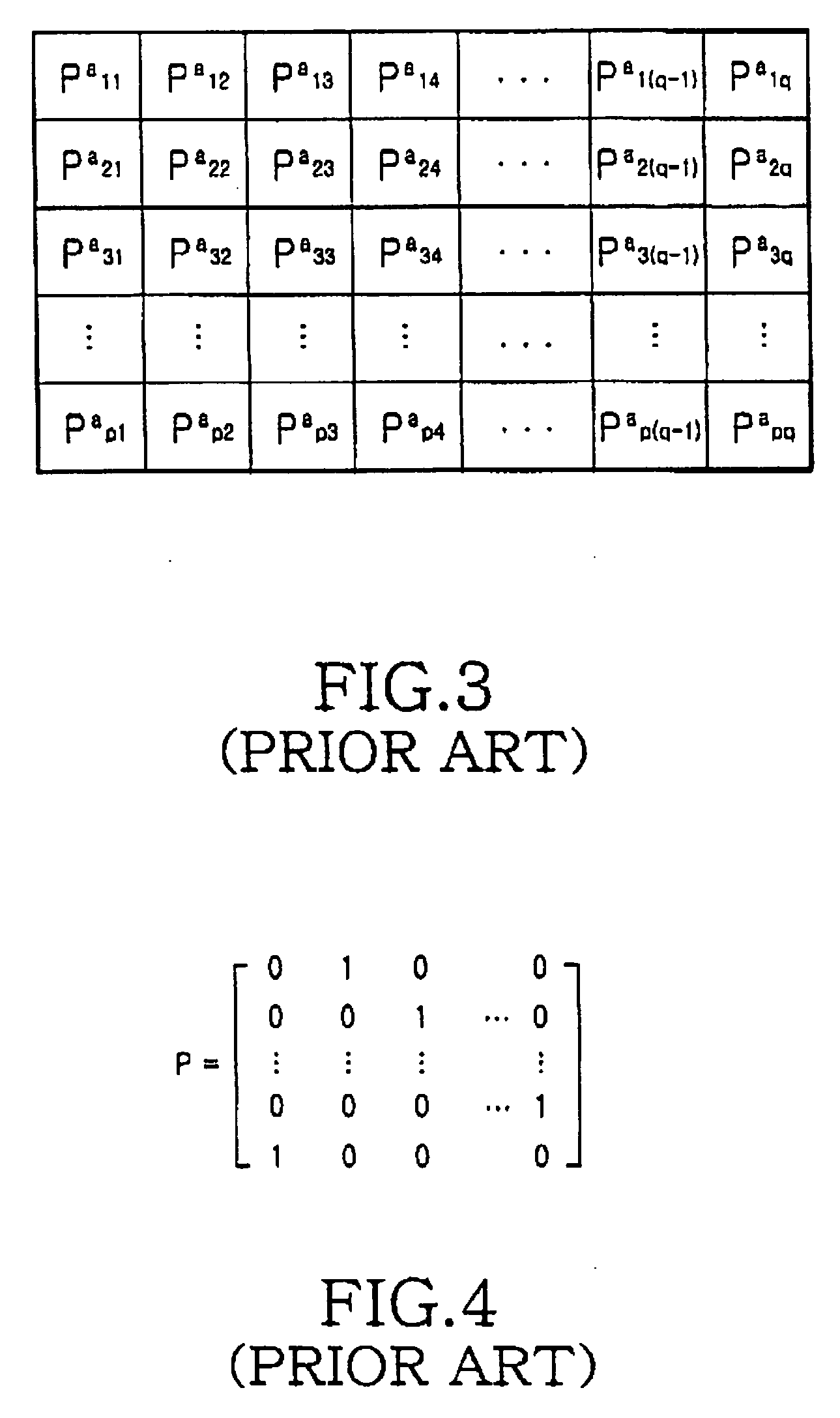
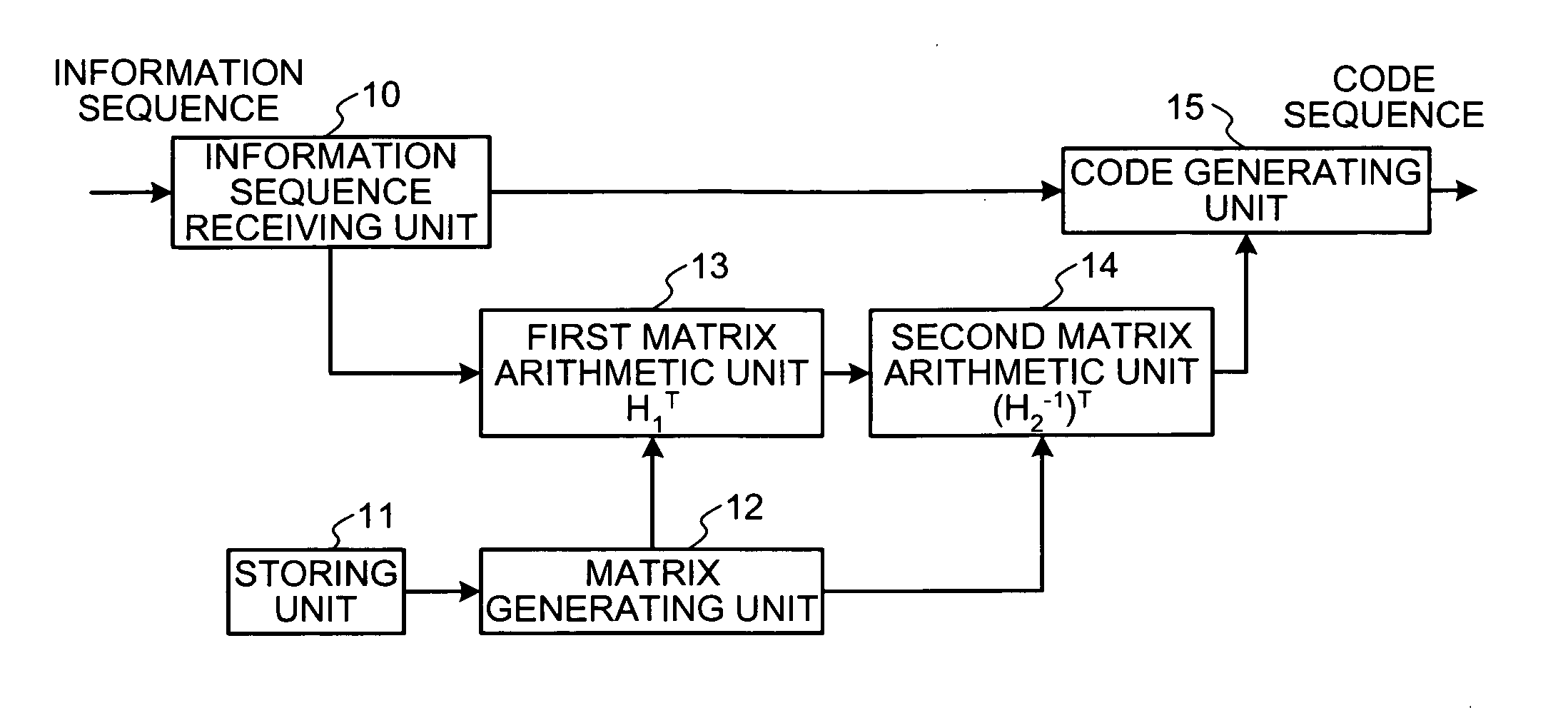
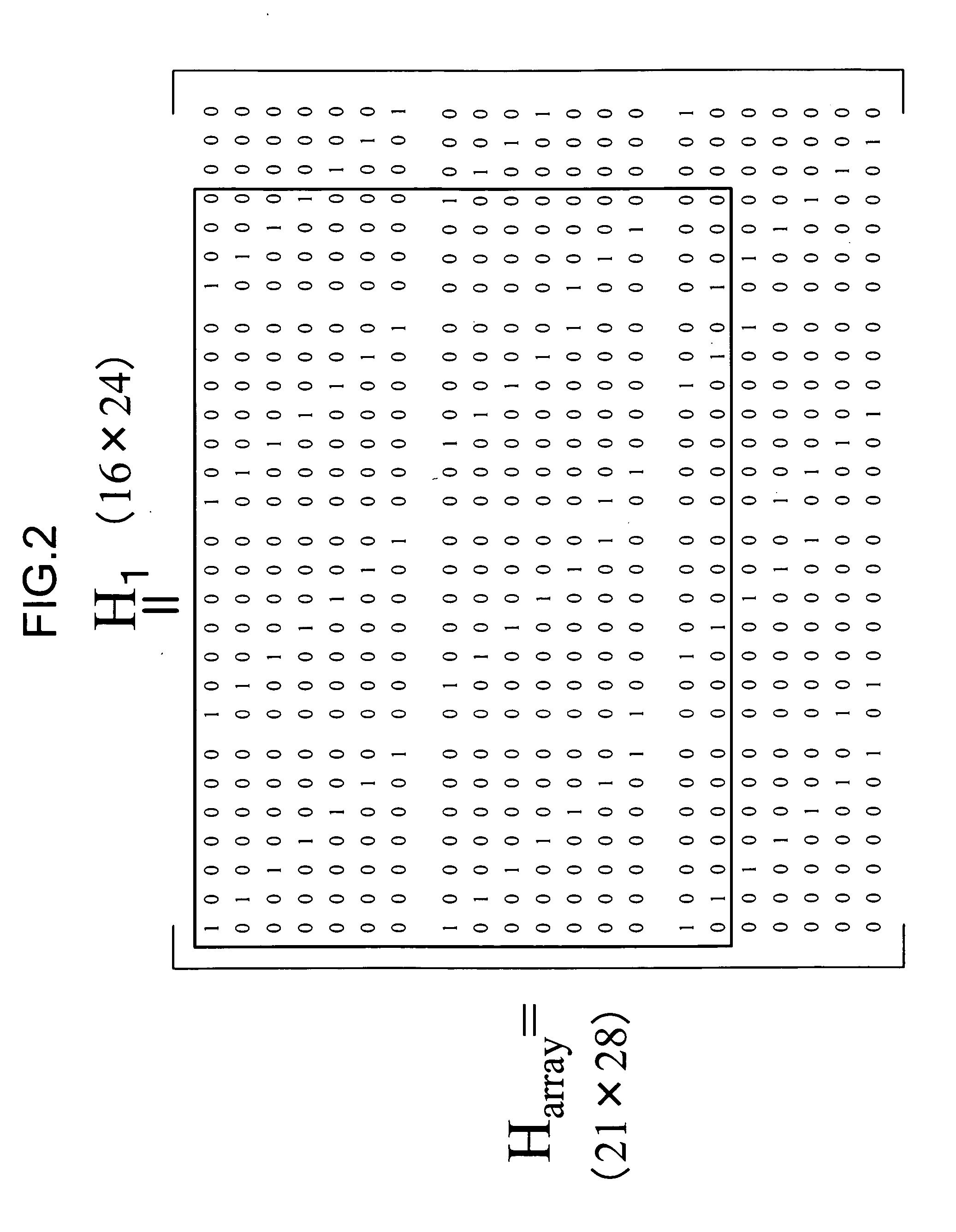
An information sequence having a code length of N (N=K+M), where K is information length and M is parity length, is encoded into a code sequence by using an LDPC code. The LDPC code is generated based on a matrix H, with M rows and N columns. The matrix H includes a check matrix H2 and a check matrix H1. The check matrix H2 has M rows and M columns, it is a cyclic permutation matrix, and an inverse matrix exists for the check matrix H2, and its column weight is 3. The check matrix H1 has M rows and K columns.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
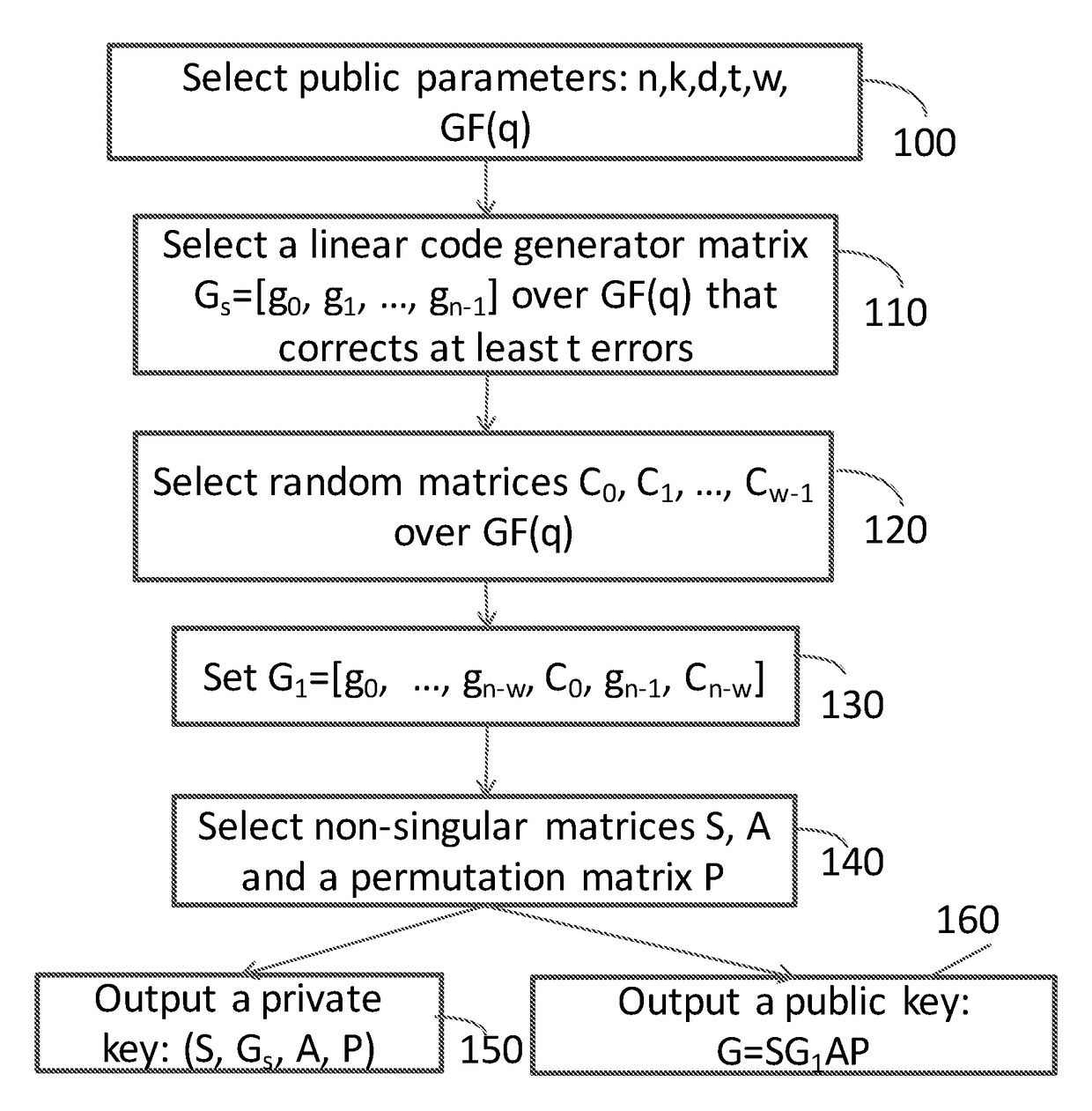
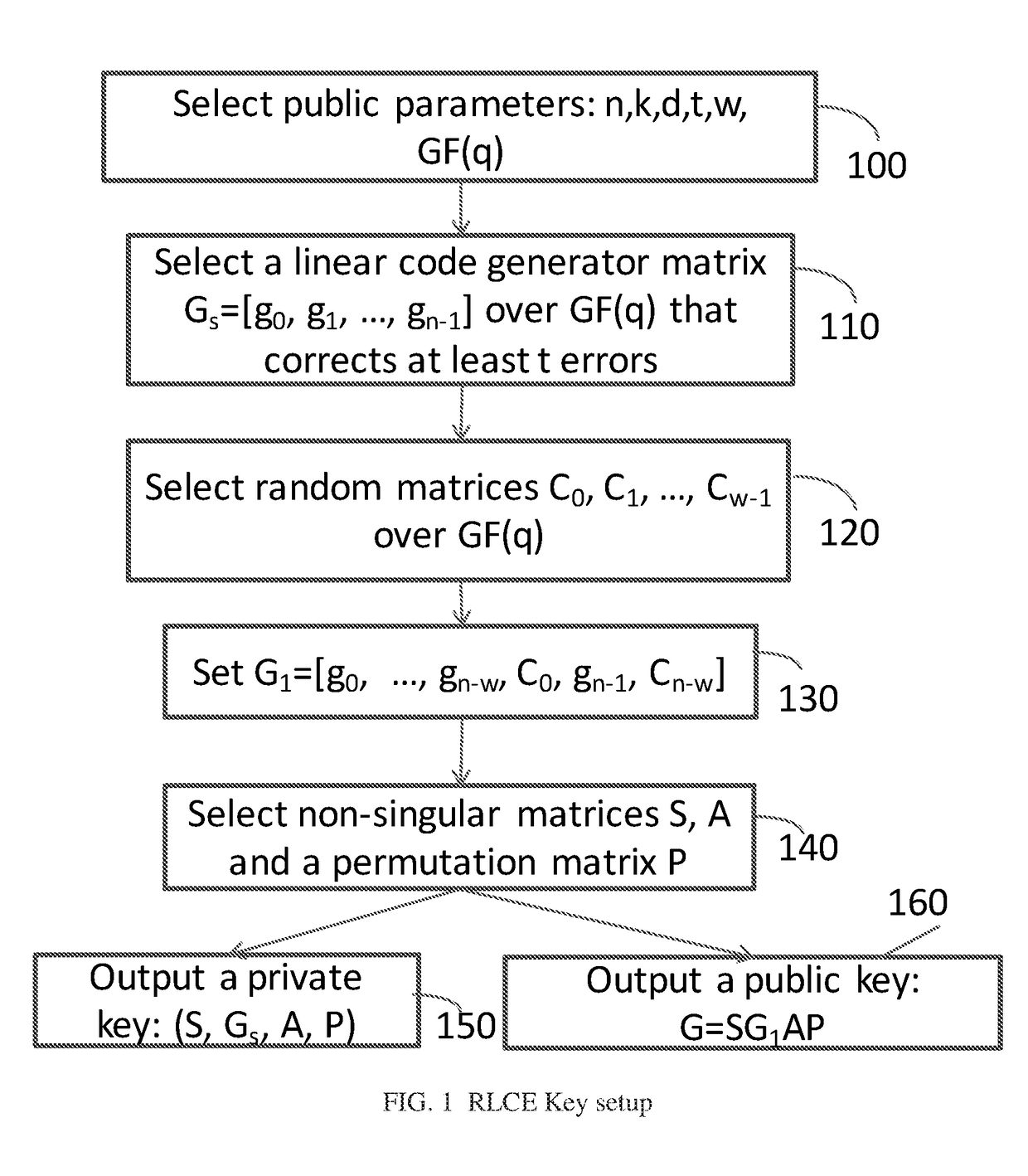
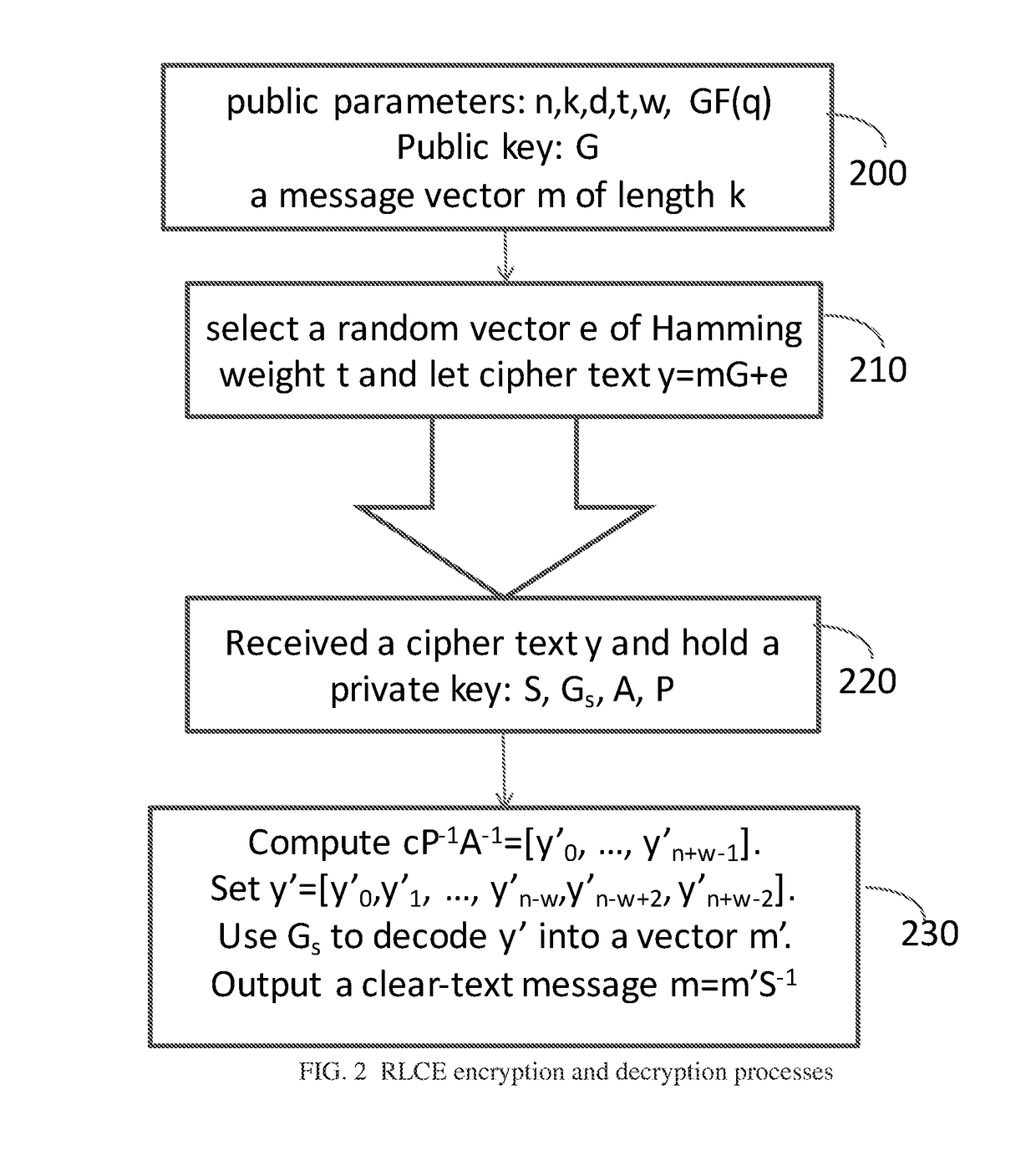
Method and Apparatus for Public Key Encryption Scheme RLCE and IND-CCA2 Security
InactiveUS20180176015A1Improve security levelKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationPlaintextMcEliece cryptosystem
Owner:WANG YONGGE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com