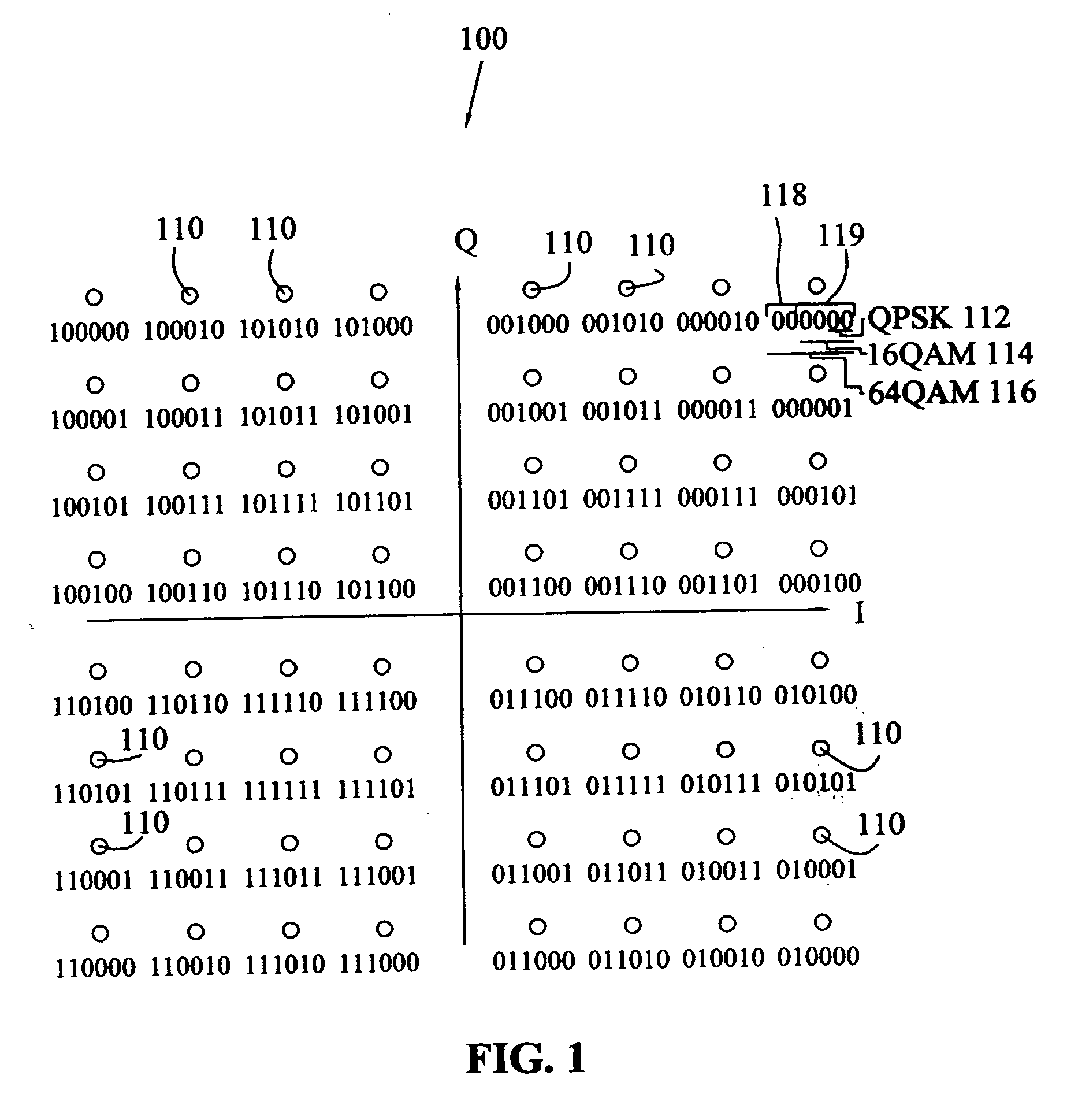
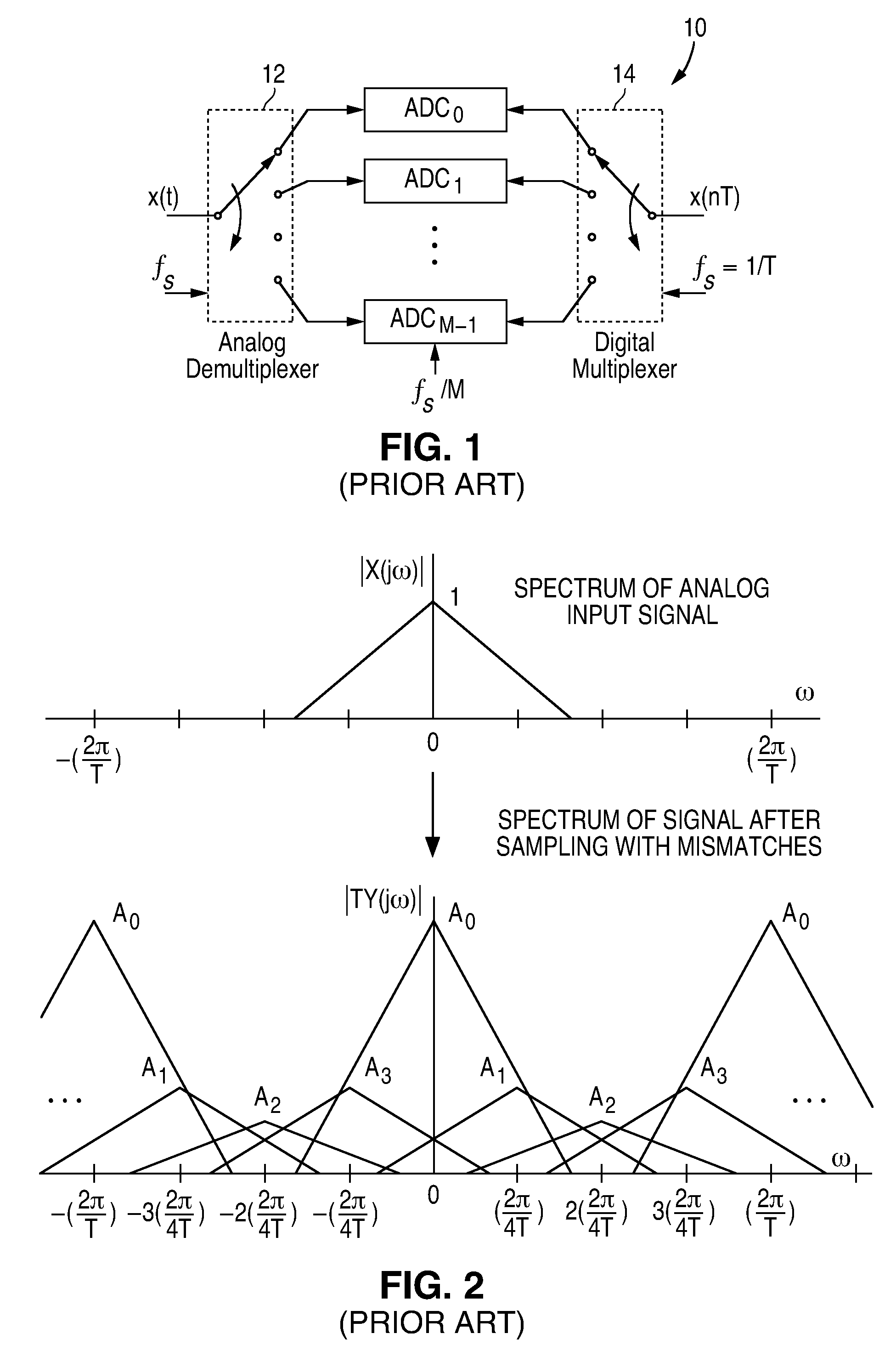
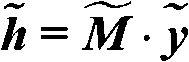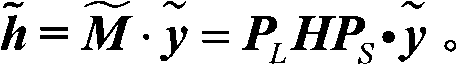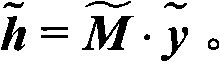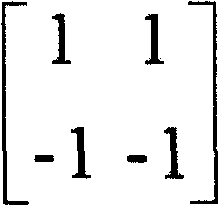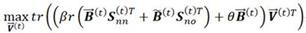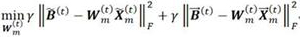Patents
Literature
172 results about "Hadamard matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
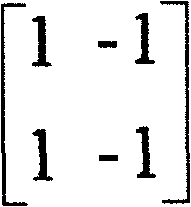
In mathematics, a Hadamard matrix, named after the French mathematician Jacques Hadamard, is a square matrix whose entries are either +1 or −1 and whose rows are mutually orthogonal. In geometric terms, this means that each pair of rows in a Hadamard matrix represents two perpendicular vectors, while in combinatorial terms, it means that each pair of rows has matching entries in exactly half of their columns and mismatched entries in the remaining columns. It is a consequence of this definition that the corresponding properties hold for columns as well as rows. The n-dimensional parallelotope spanned by the rows of an n×n Hadamard matrix has the maximum possible n-dimensional volume among parallelotopes spanned by vectors whose entries are bounded in absolute value by 1. Equivalently, a Hadamard matrix has maximal determinant among matrices with entries of absolute value less than or equal to 1 and so is an extremal solution of Hadamard's maximal determinant problem.
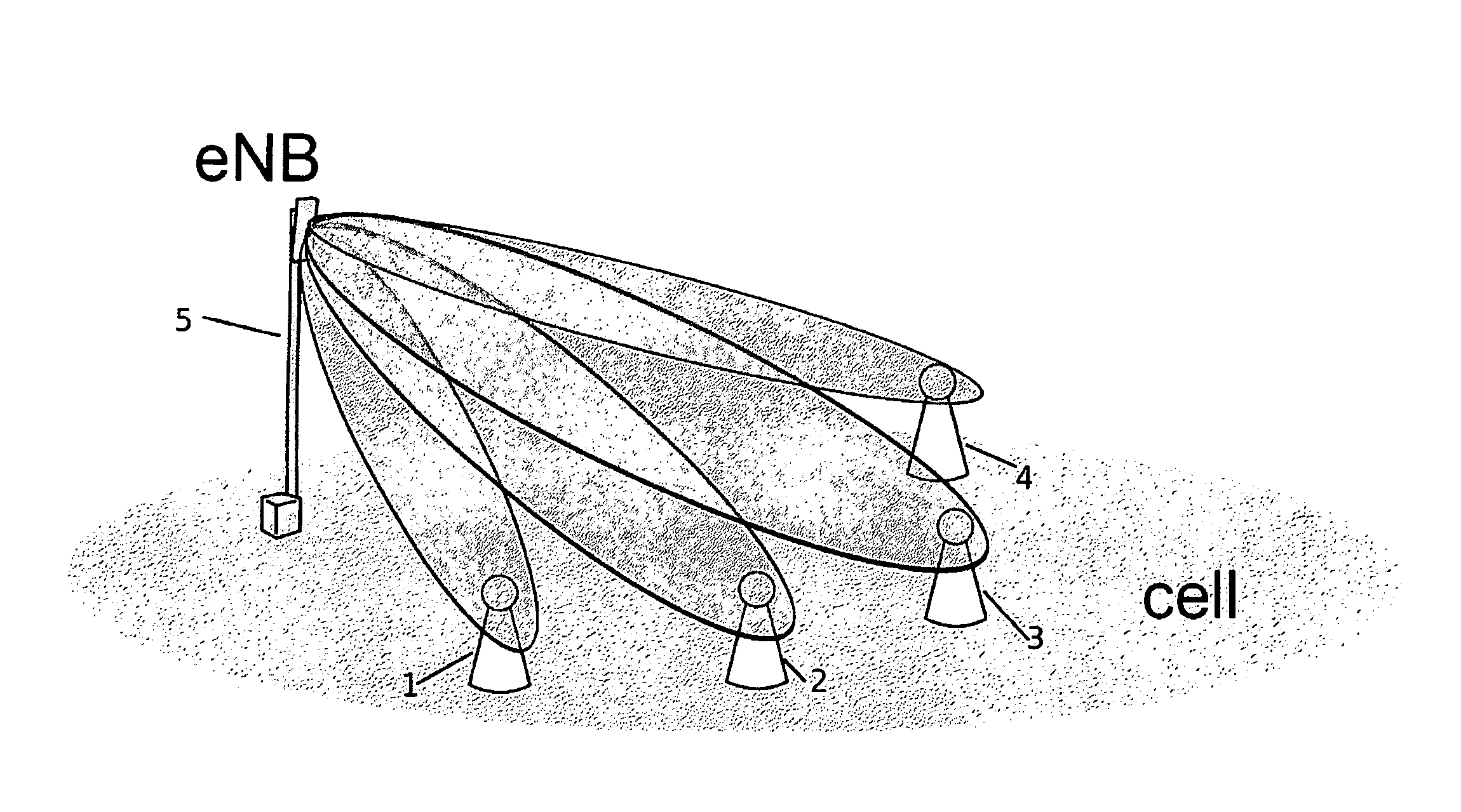
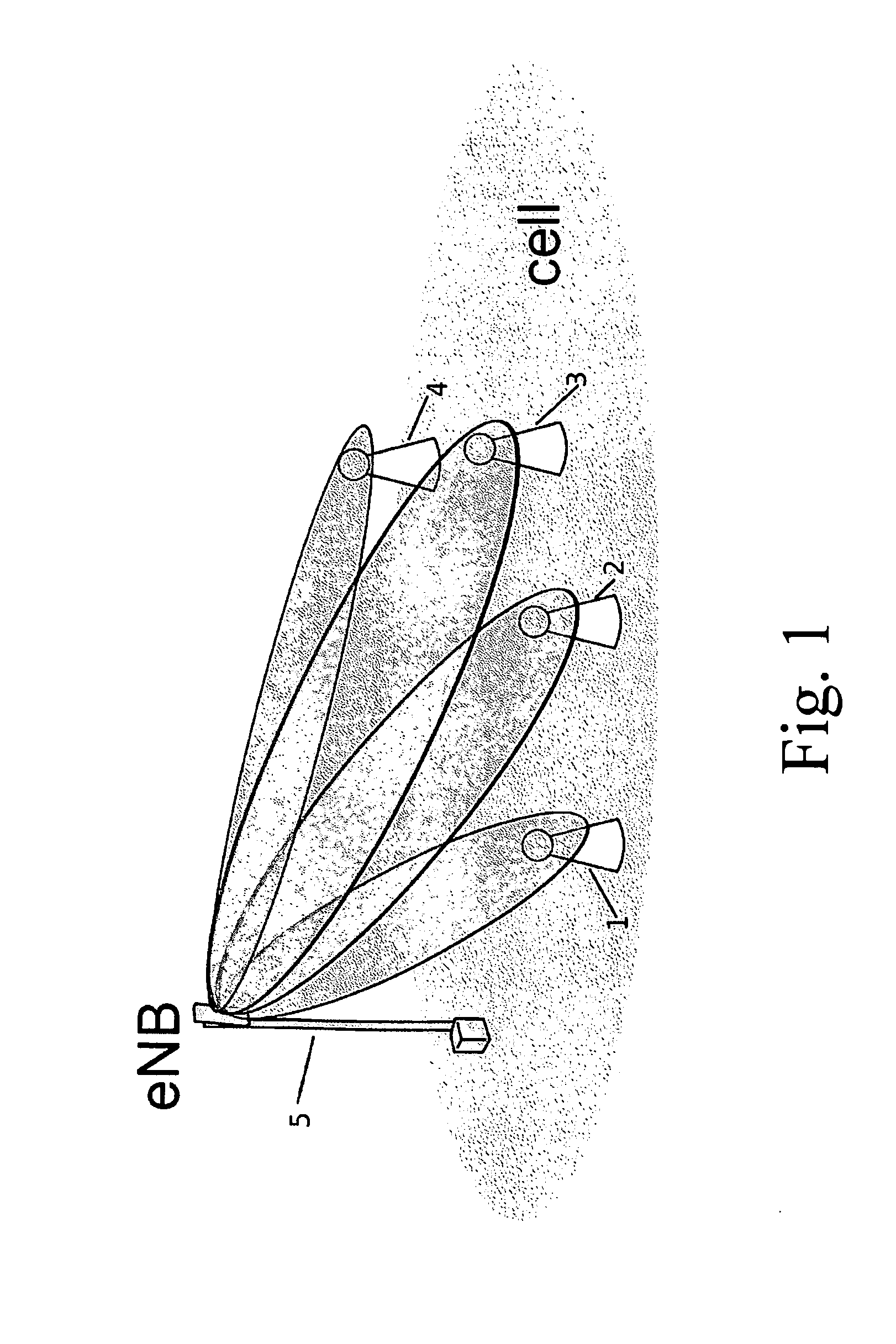
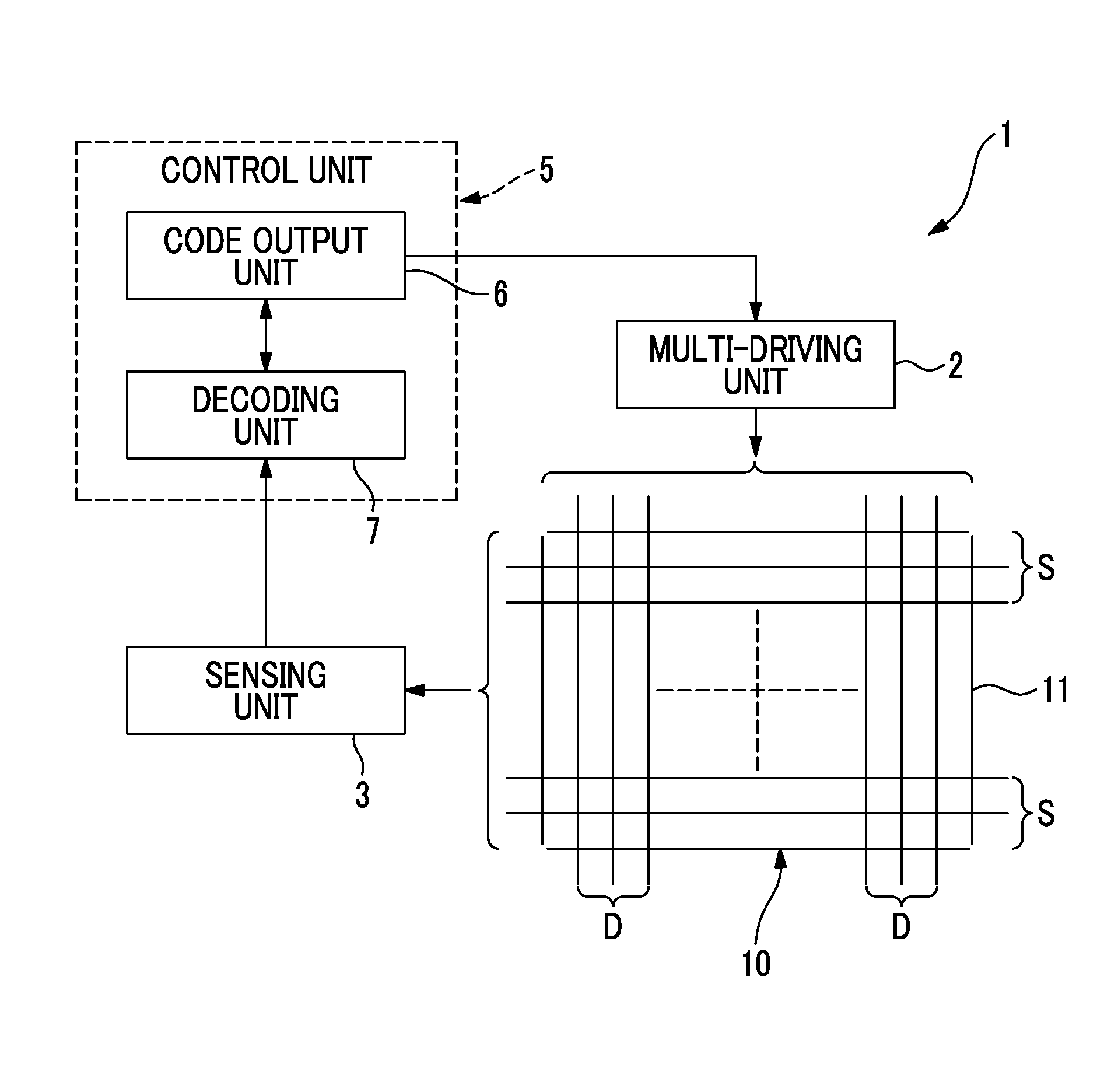
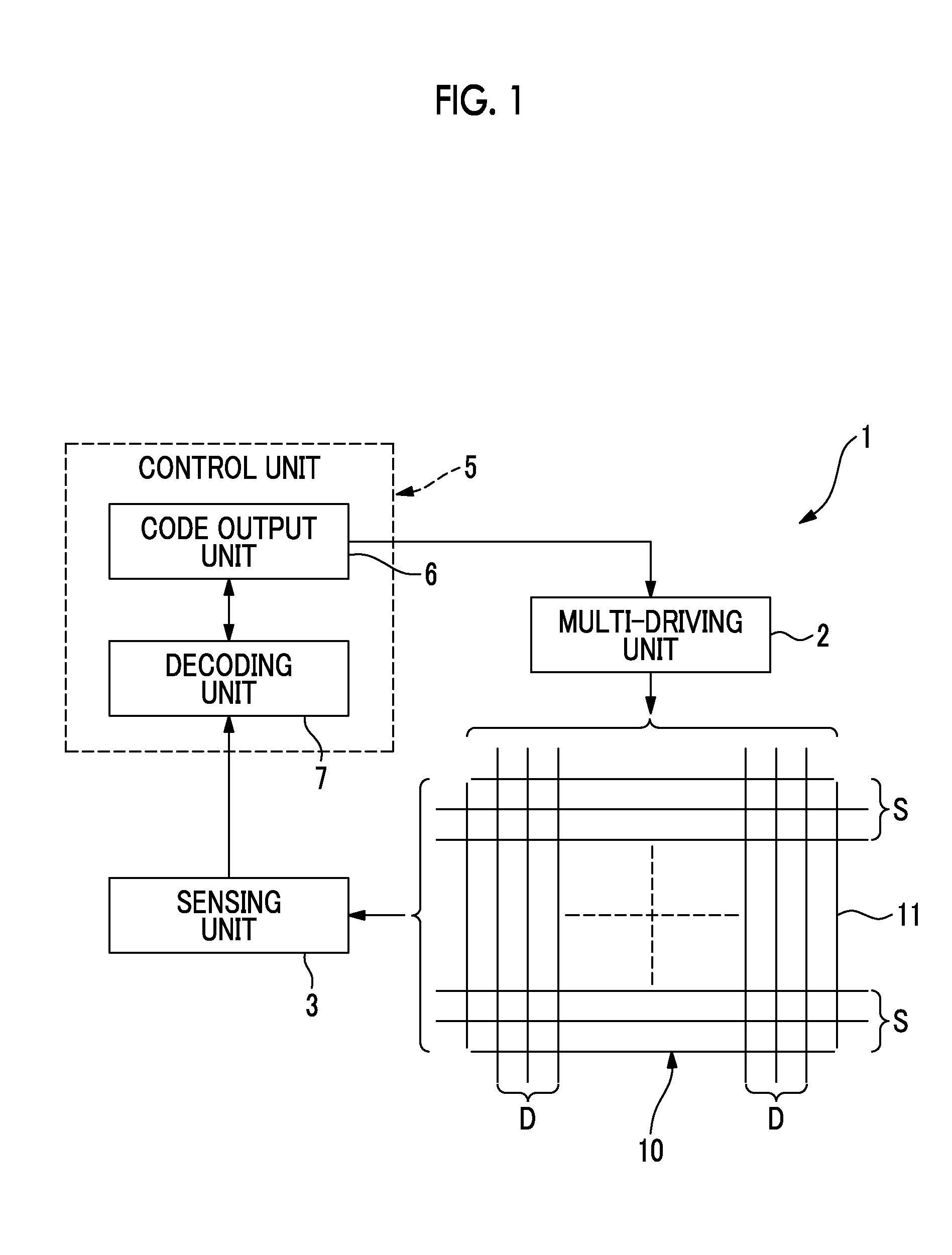
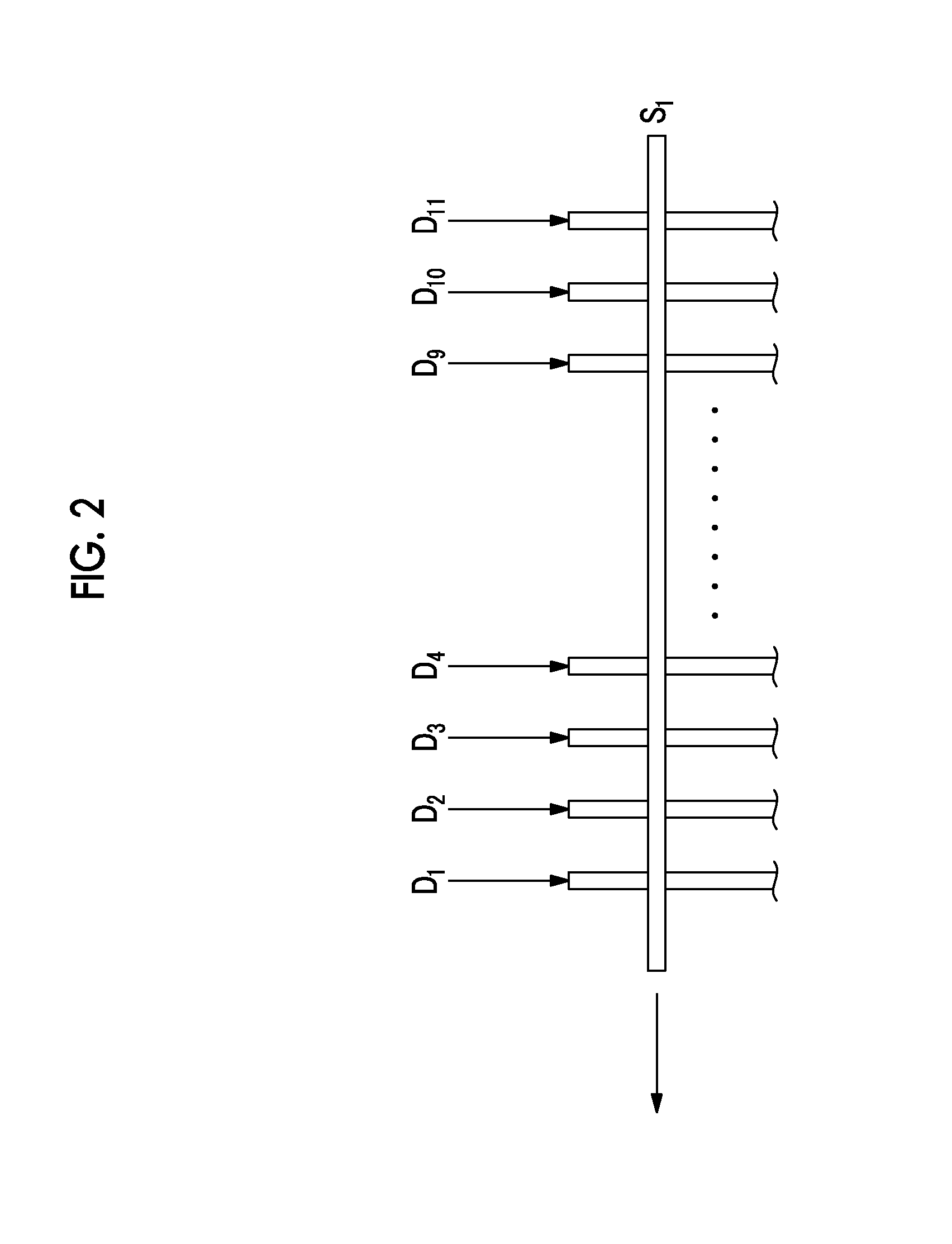
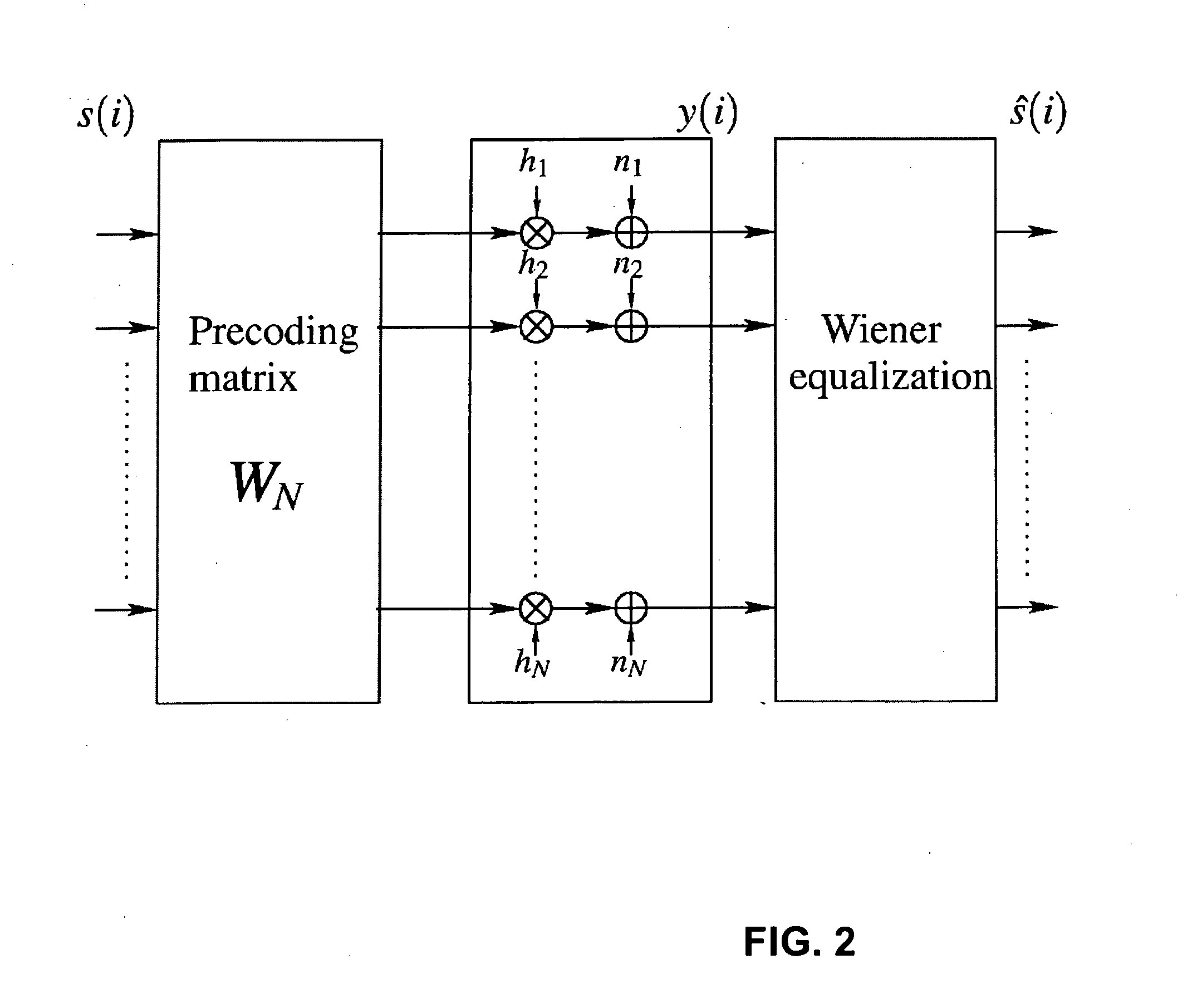
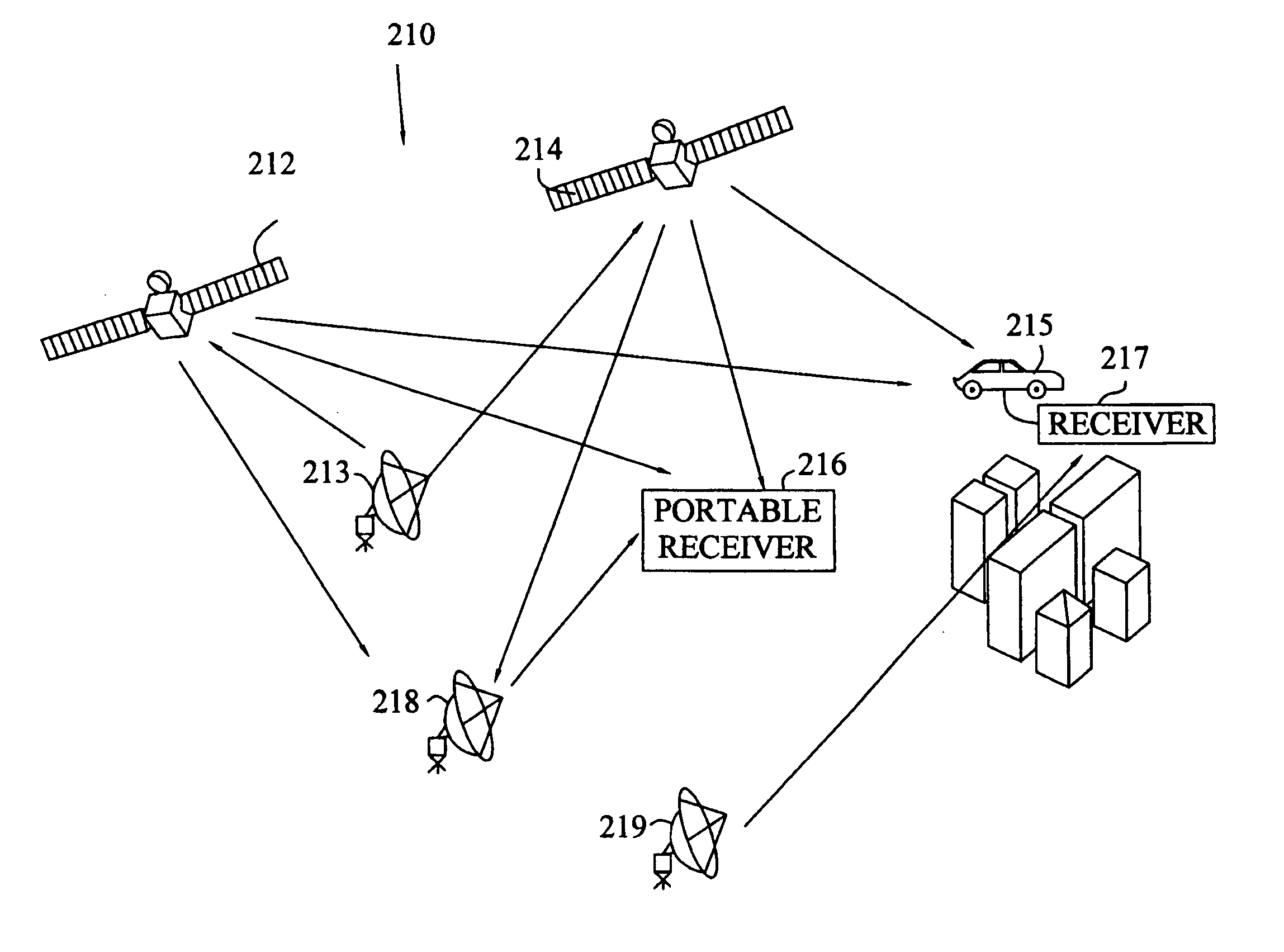
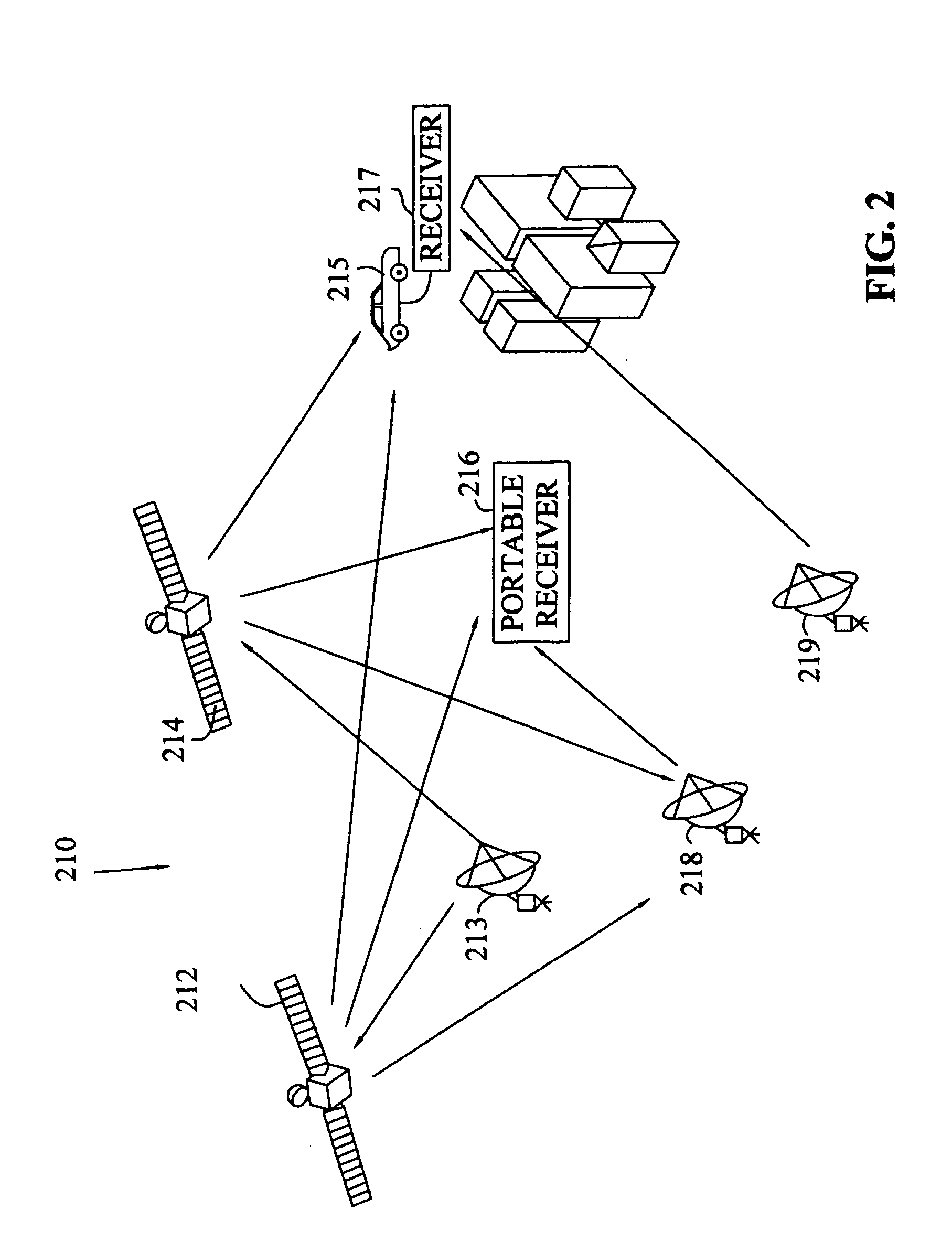
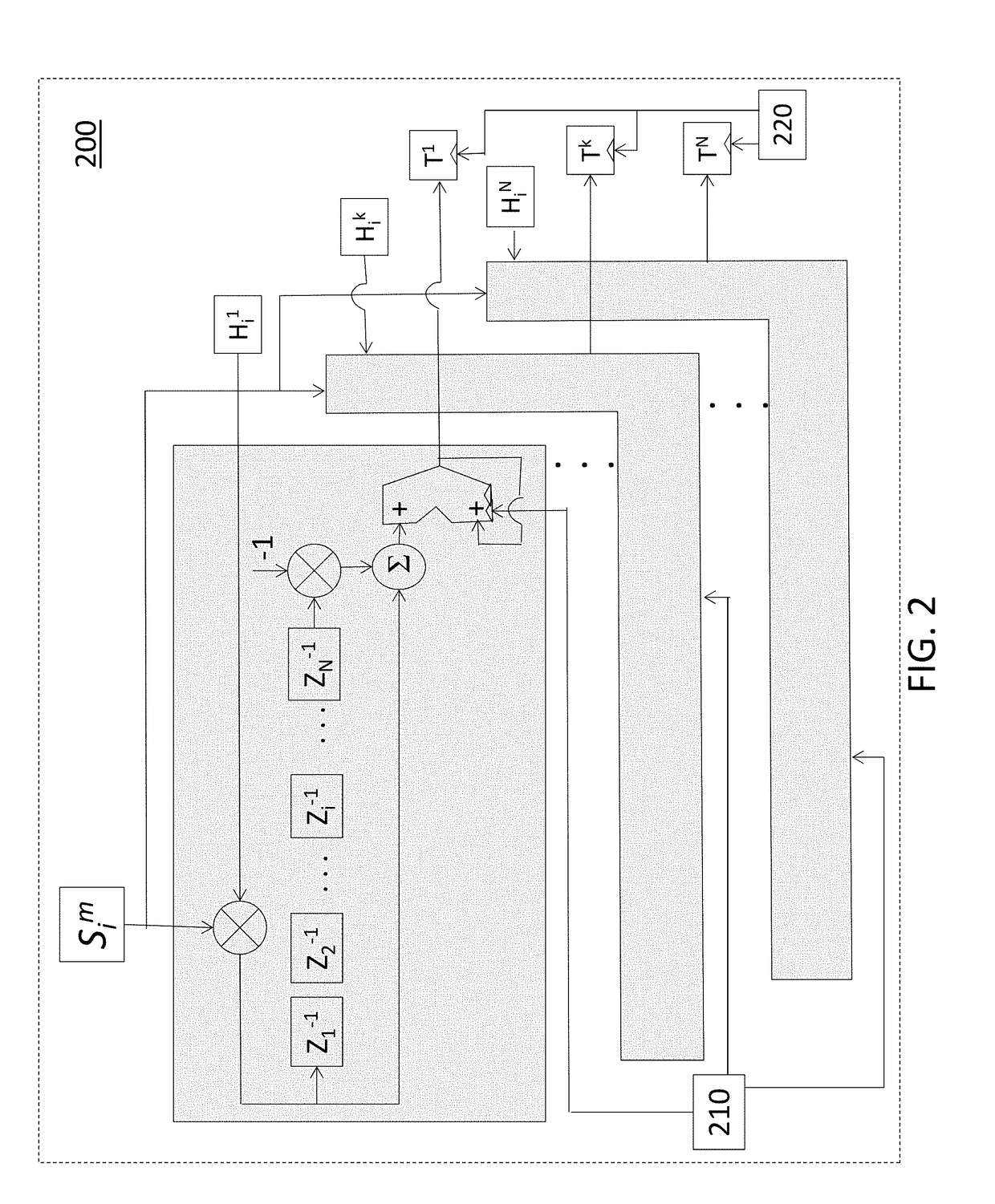
Process for Beamforming Data to be Transmitted by a Base Station in a MU-MIMO System and Apparatus for Performing the Same
InactiveUS20110299379A1Simple structureImprove performanceRadio transmissionOrthogonal multiplexFormation matrixUnitary matrix
A process for beamforming data to be transmitted in a MU-MIMO communication system comprising a base station and a selected set of User Equipments (UE) communicating with said base station; said data being precoded by said base station in accordance with a beamforming matrix complying with a precoding matrix under the form of: (formula 1) Where—M is the number of transmit antennas—D is a diagonal unitary matrix of the form D=diag (formula 2)—P is a permutation matrix interchanging only the last M−1 rows. —A is a general Hadamard matrix. and that the signaling information transmitted by the base station to the UE comprises at least a first and a second index which are representative of D, P and A.
Owner:ST ERICSSON FRANCE +1
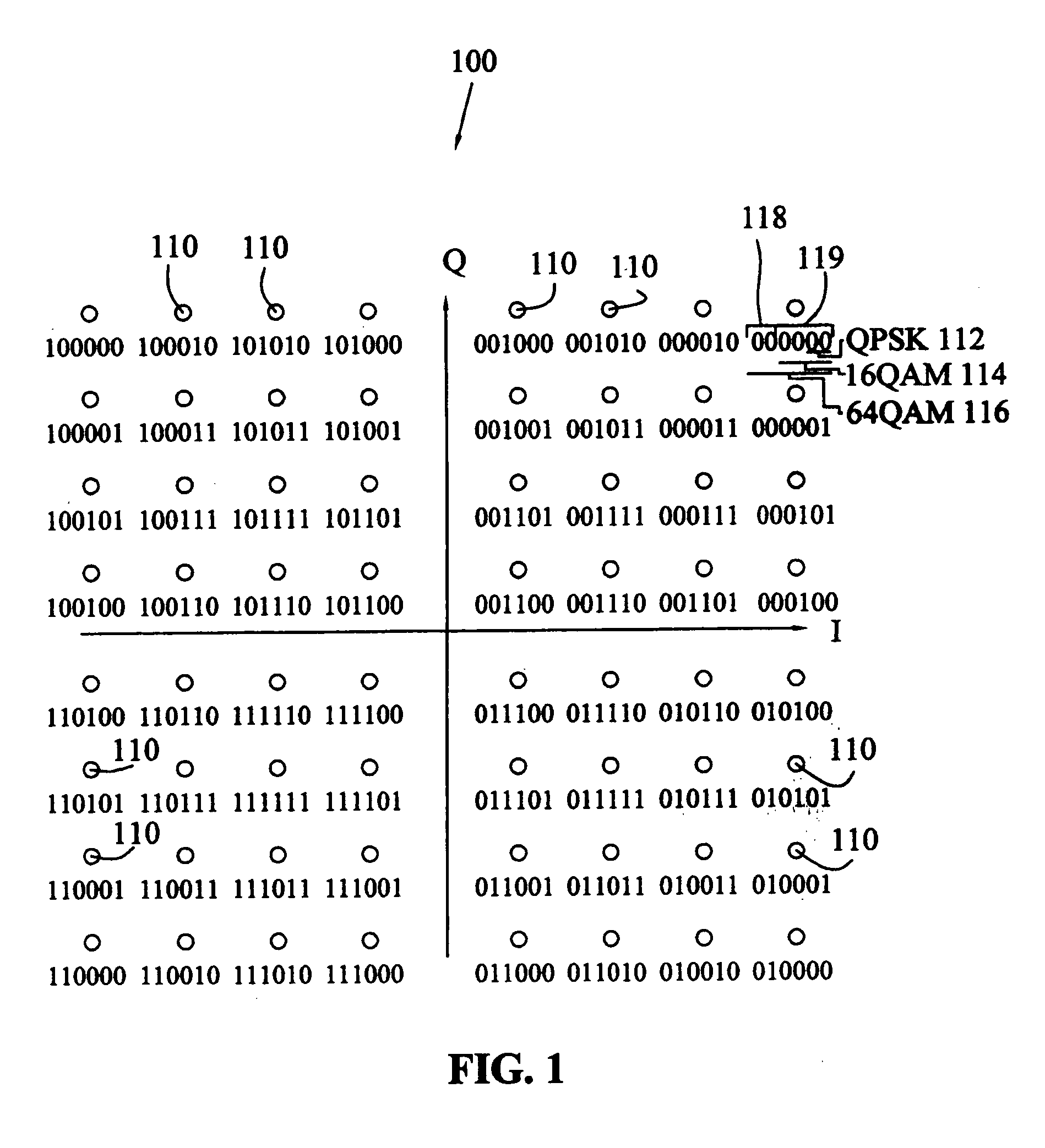
Method to minimize compatibility error in hierarchical modulation using variable phase
InactiveUS20050113040A1Increase volumeIncrease the amount of dataSpatial transmit diversityPhase-modulated carrier systemsDirect-sequence spread spectrumComputer science
The present invention provides a method, receiver and transmitter for use in a SDAR system. The method involves generating a first modulated signal based on first input data. Additional modulation is superimposed on the first modulated signal based on additional input data, being spread across a plurality of symbols in the first modulated signal in a predetermined pattern to generate a modified signal which is then transmitted. The modified signal is decoded by performing a first demodulation of the first modulated signal then additional demodulation is performed to obtain additional input data. The superimposing step uses a plurality of offset sequence values to add the additional modulation to the first modulated signal. The offset sequence may appear as a pseudo-random distribution of offset sequence values, and may include at least one zero offset value. Alternatively, the additional modulated signal may be a fromed as a direct sequence spread spectrum modulation and the offset sequence appearing as a pseudo-noise distribution. A Hadamard matrix sequence may be used as the direct sequence code.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
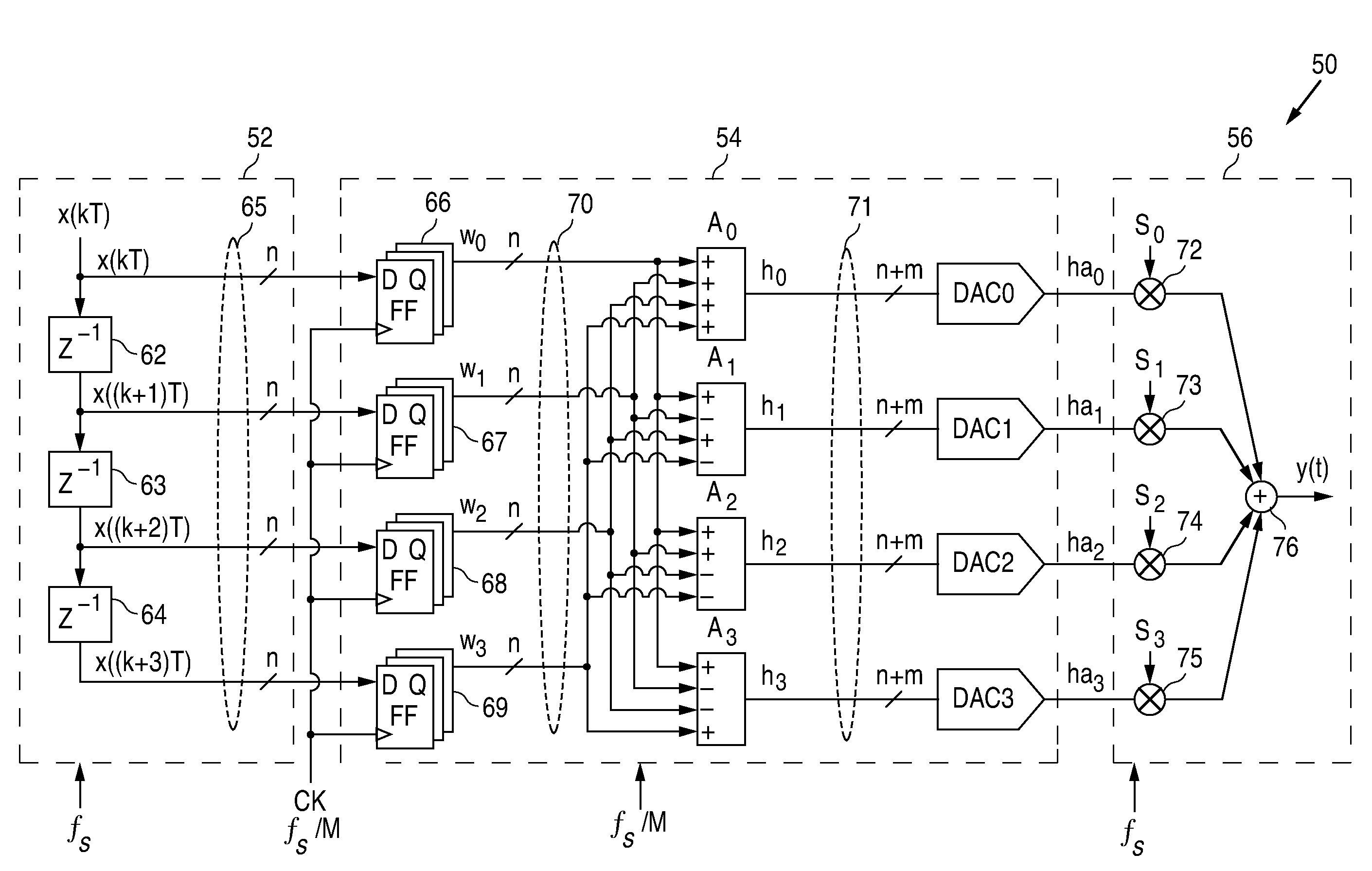
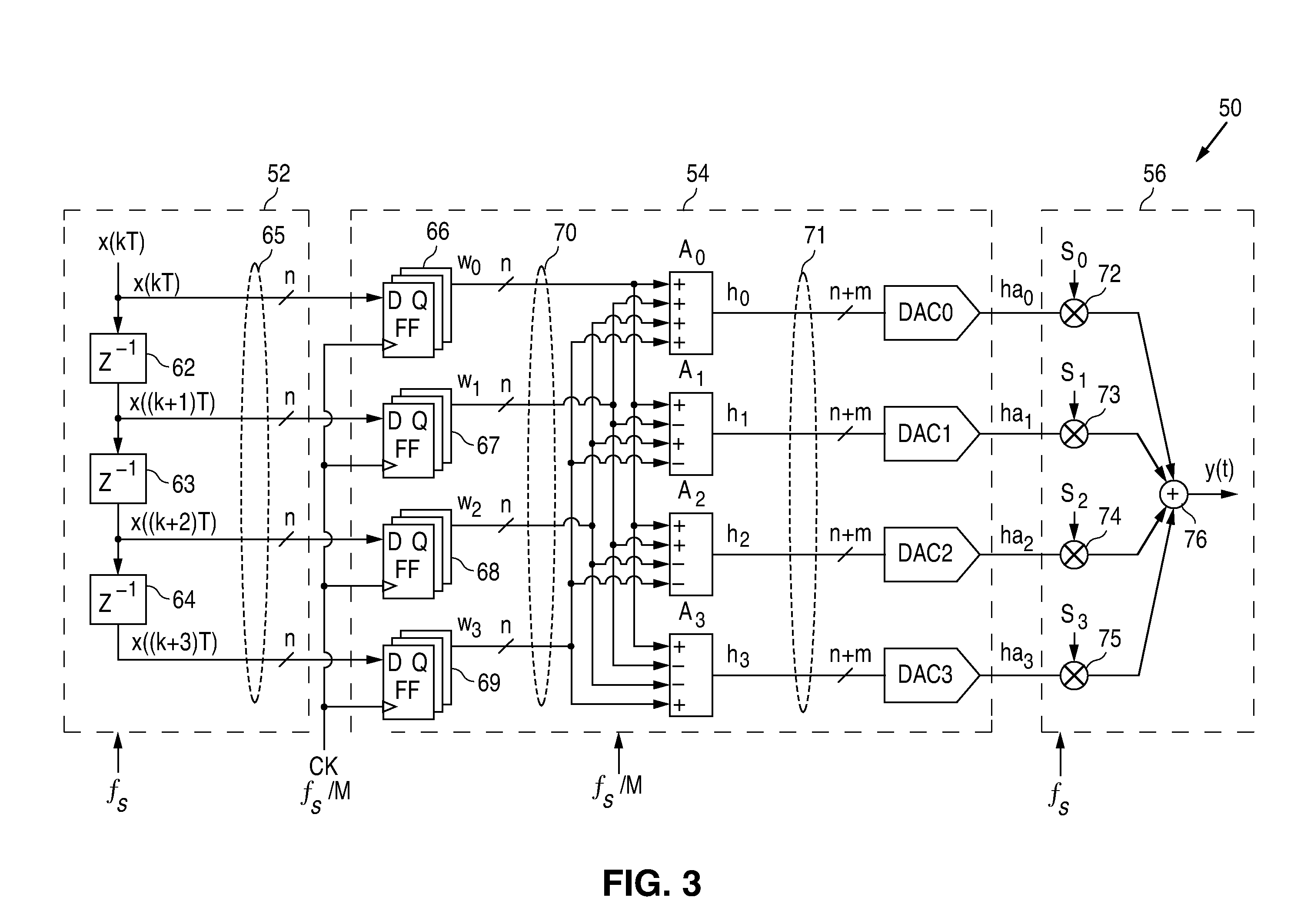
Parallel digital-to-analog-converter
ActiveUS7372386B1Electric signal transmission systemsDigital-analogue convertorsDigital dataData transformation
A method for performing parallel digital-to-analog conversion of an n-bit digital input data signal at a frequency of fs including receiving the n-bit digital input data signal; generating M−1 delayed input data signals, M being the number of parallel conversions channels, the M−1 delayed input data signals having respective increasing amount of unit delay, the digital input data signal and the M−1 delayed input data signals forming M digital signals; holding the M digital signals for a first time period; performing a data transformation of the M digital signals using an M×M Hadamard matrix; generating M (n+m)-bit transformed digital data signals; converting each of the M transformed digital data signals to M analog signals; and performing a reverse data transformation of the M analog signals based on the M×M Hadamard matrix to generate an output analog signal indicative of the n-bit digital input data signal.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Apparatus and method for patient movement tracking
InactiveUS7498811B2Broaden the fieldReal-time correctionOptical detectionElectric/magnetic detectionFourier transform on finite groupsMedical imaging
The present invention relates, in general, to the field of motion tracking, and in particular to join a target in an MRI application. In particular the invention teaches an apparatus and method to track the movement of a target during medical imaging scanning using optical technology. Optical systems record the position and movement of the pattern and are able to perform mathematical analysis of the pattern to determine the positional shift of the patient. Weighted averages, Fourier transforms, Hadamard matrices and cross-correlation of data related to X-Y translation, rotation and scaling of the image of the pattern are used to analyze movement of the subject's head. Feedback related to the movement is provided to the MRI machine which allows for adjustments in focusing coils for real time tracking of the patient's movements during the MRI procedure. As a result, the MRI procedure becomes more accurate as it is adjusted for the patient's movements.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF TEXAS SYST EC32 +1
General method for low-frequency data transmission on a power line
ActiveUS20100054349A1Reduced Power RequirementsIncrease data rateModulated-carrier systemsComponent separationSystems designPulse pattern
A method for producing a set of inbound pulse patterns and detection vectors for lengths longer than 4 cycles in an AC waveform. These are used for generating inbound messages in a two-way automatic communication system (TWACS). The method uses Hadamard matrices adapted to generate a set of detection vectors by permuting rows of a matrix and removing certain columns of the matrix to meet system design requirements. The method can be extended to any length and modified to accommodate multiple pulses per half-cycle to support higher data rates.
Owner:ACLARA TECH LLC
Apparatus and method for patient movement tracking
InactiveUS20070108978A1Broaden the fieldReal-time correctionOptical detectionElectric/magnetic detectionMedical imagingComputer science
The present invention relates, in general, to the field of motion tracking, and in particular to join a target in an MRI application. In particular the invention teaches an apparatus and method to track the movement of a target during medical imaging scanning using optical technology. Optical systems record the position and movement of the pattern and are able to perform mathematical analysis of the pattern to determine the positional shift of the patient. Weighted averages, Fourier transforms, Hadamard matrices and cross-correlation of data related to X-Y translation, rotation and scaling of the image of the pattern are used to analyze movement of the subject's head. Feedback related to the movement is provided to the MRI machine which allows for adjustments in focusing coils for real time tracking of the patient's movements during the MRI procedure. As a result, the MRI procedure becomes more accurate as it is adjusted for the patient's movements.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF TEXAS SYST EC32 +1
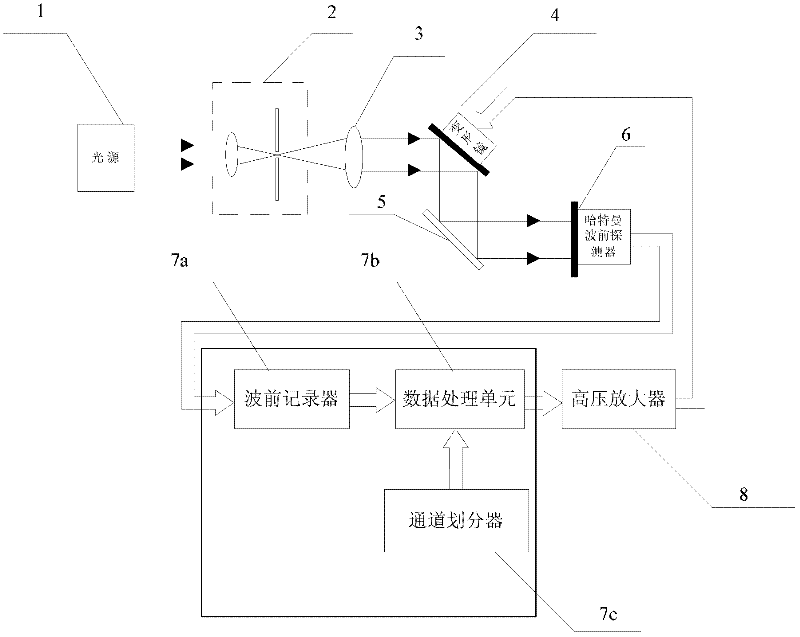
Device and method for measuring transfer matrix of adaptive optics system based on Hadamard matrix multi-channel method
ActiveCN102494785AReduce measurement cycle timeImprove noise immunityOptical measurementsAerodynamic testingWavefrontTransfer matrix
The invention provides a device and a method for measuring a transfer matrix of an adaptive optics system based on a Hadamard matrix multi-channel method. The device comprises an adaptive optics system, a channel divider, a wavefront recorder and a data processing unit, wherein the channel divider divides channels for a driver of a wavefront corrector of the adaptive optics system; the data processing unit applies voltage to the divided channels according to a Hadamard matrix, so that planar waves generate wavefront change after passing through the adaptive optics system; the wavefront recorder calculates and stores a wavefront slope curve; and the data processing unit performs matrix operation on a wavefront slope curve matrix so as to calculate the transfer matrix. The device for measuring the transfer matrix of the adaptive optics system based on the Hadamard matrix multi-channel method has high measuring precision and high speed; and an effective novel method is supplied to measurement of the transfer matrixes of a large adaptive optics system.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Capacitive sensing device
ActiveUS20160117049A1Reduce radiated noiseReduce variationStatic indicating devicesInput/output processes for data processingCapacitanceEngineering
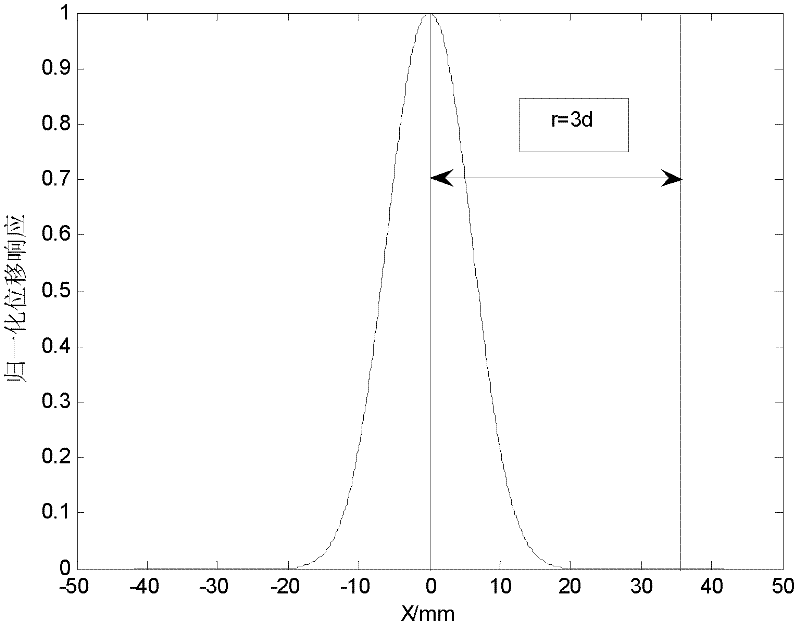
A driving signal is applied to a plurality of driving electrodes using the driving matrix illustrated in FIG. 5A obtained by removing a row in which a sum of codes is greatest and a column having a transposition relationship with the row in a Hadamard matrix. Distribution of capacitance in intersection portions between a sensing electrode and a plurality of driving electrodes can be obtained using an inverse matrix of the driving matrix illustrated in FIG. 5B. Further, when decoding is performed using an extended matrix obtained by replacing “0” with “−1” in FIG. 5B, it is possible to average noise and to improve an S / N ratio.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Compressed sampling matrix decomposition-based infrared small target detection method
InactiveCN103871058AAchieve separationEasy to handleImage analysisMatrix decompositionImaging processing
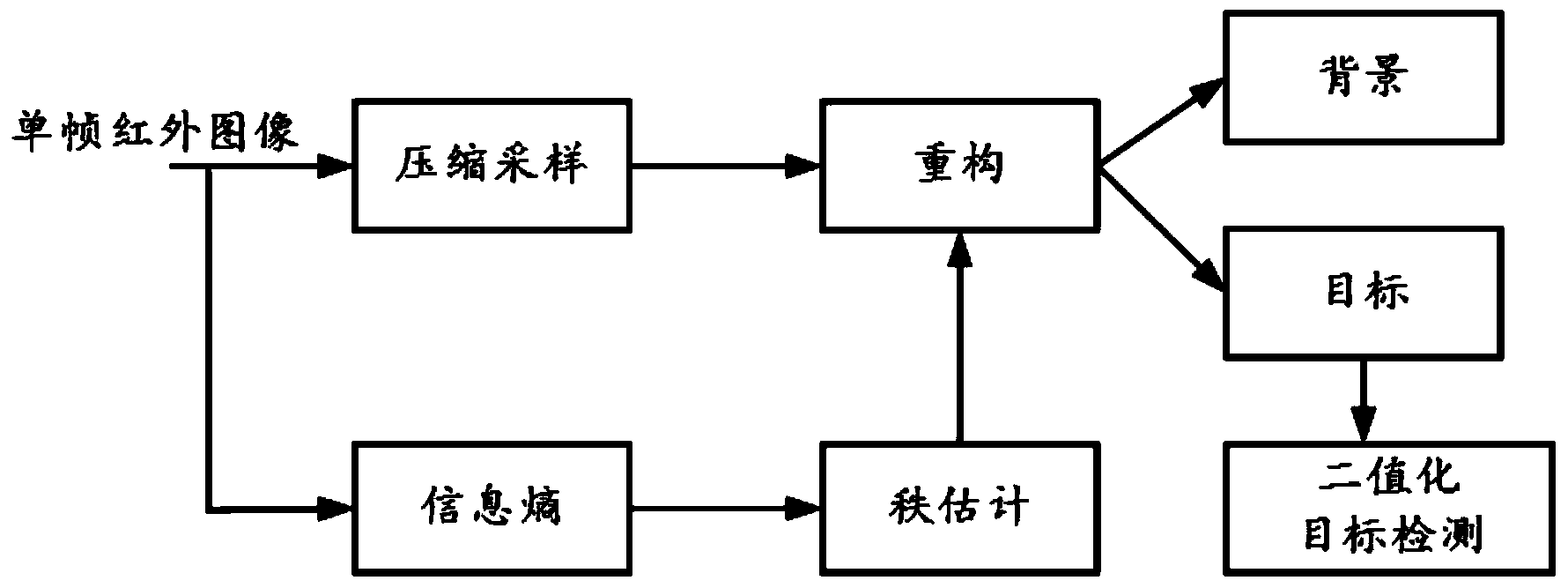
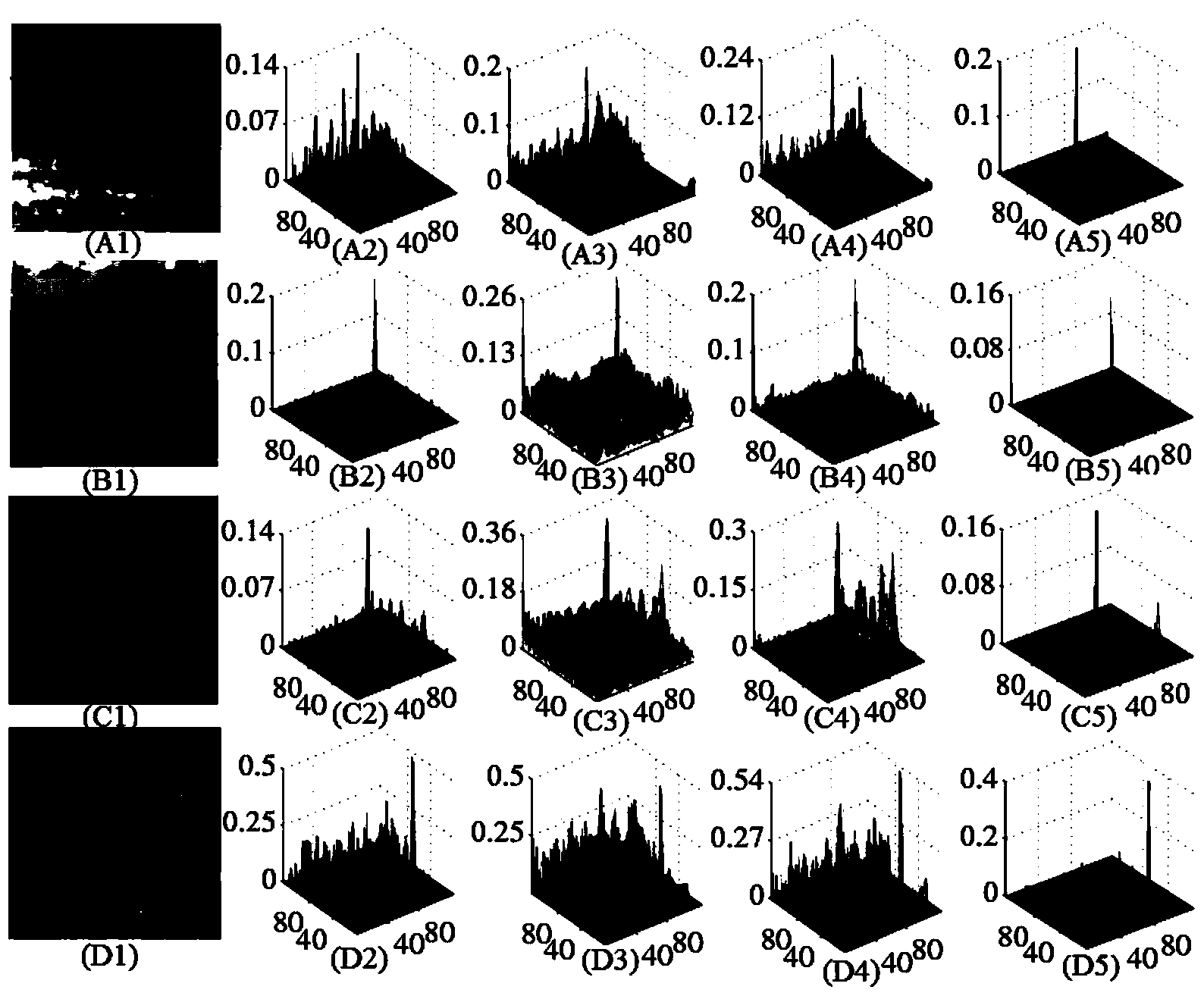
A compressed sampling matrix decomposition-based infrared small target detection method in the technical field of image processing comprises the following steps: 1, inputting an infrared small target image, solving the information entropy of the image and performing rank estimation according to the information entropy of the image; 2, performing column vectorization on the image, and performing compressed sampling by using a Walsh Hadamard matrix to obtain a measured value; 3, performing image reconstruction and meanwhile restoring a background and a target; 4, performing binarization processing on the infrared small target image and detecting the infrared small target. By adopting the method, detecting the infrared small target in a compression domain is realized, data processing capacity and storage capacity are reduced by compressed sampling, the separation of the target from the background is realized after reconstruction, both the target and the background are obtained, the obtained target part has very high gain of signal to noise ratio, the background and noise are effectively restrained, and the infrared small target can be detected only by simple binarization processing in subsequent processing.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Compressed sensing observation matrix constructing method based on sparse Hadamard matrix
ActiveCN102355268AEasy to implementReduce computational complexityCode conversionComputation complexityObservation matrix
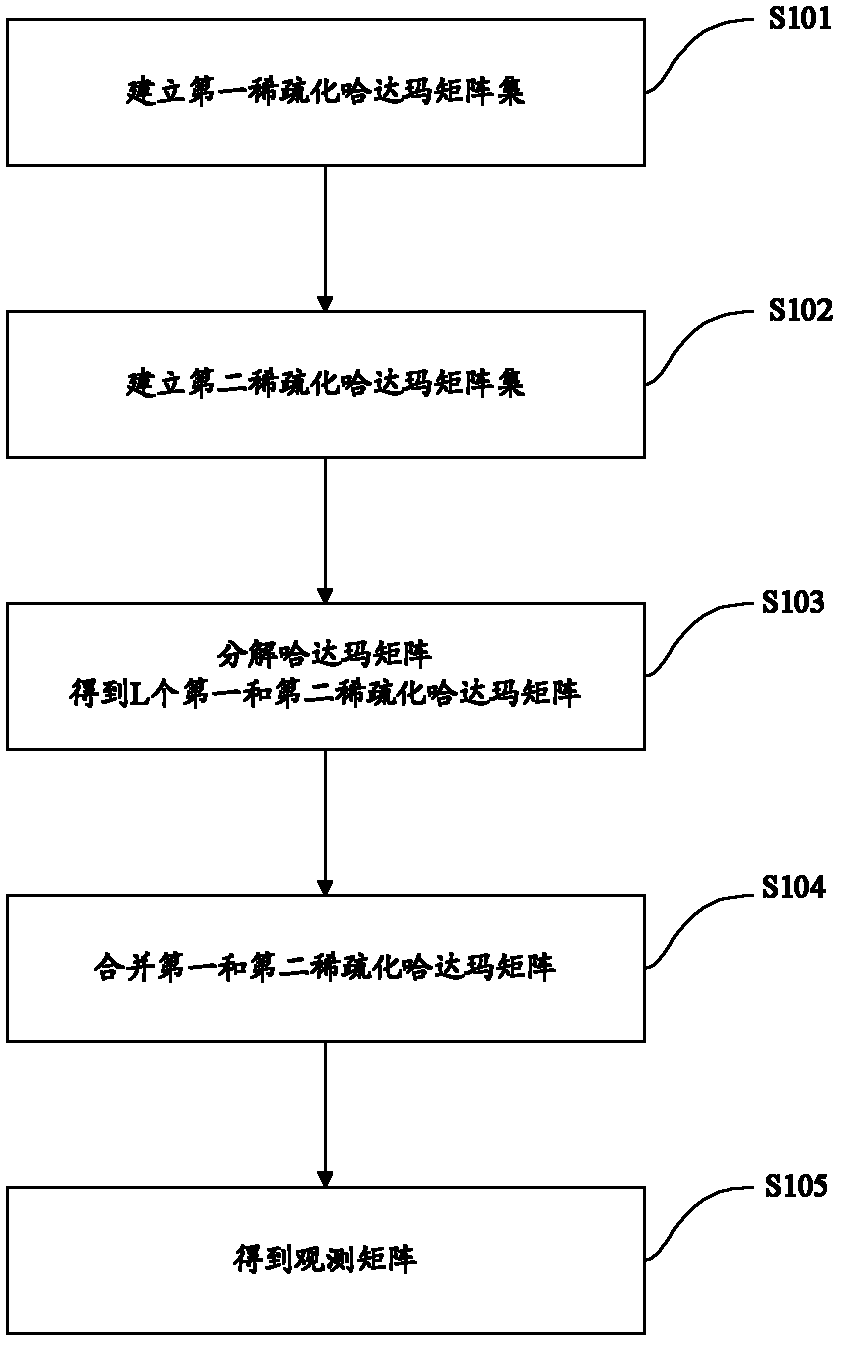
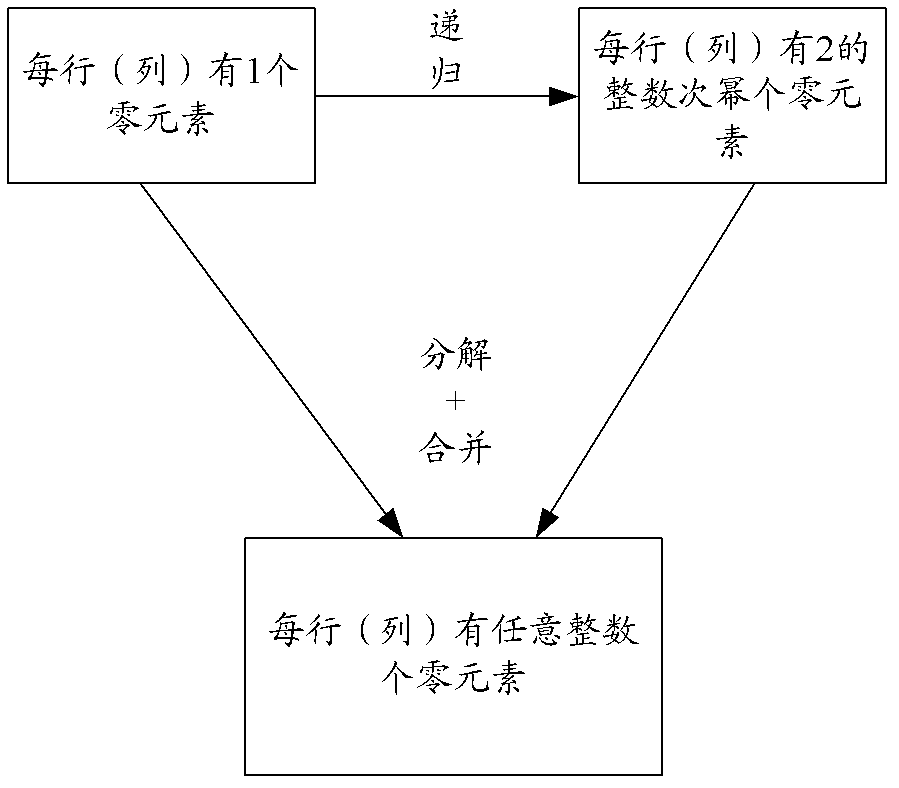
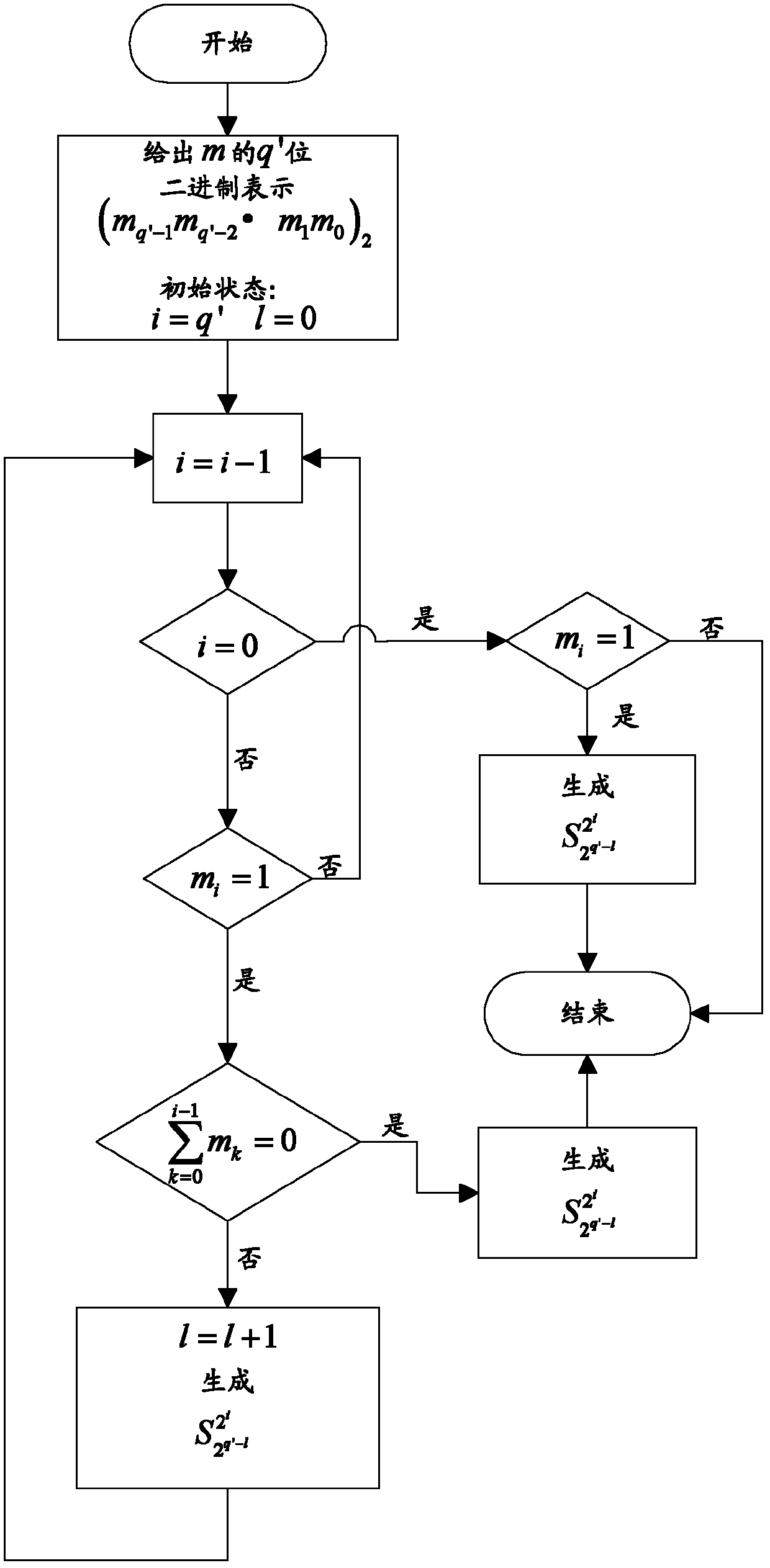
The invention discloses a compressed sensing observation matrix constructing method based on a sparse Hadamard matrix, which comprises the following steps of: A, establishing a first sparse Hadamard matrix set, wherein each first sparse Hadamard matrix in the first sparse Hadamard matrix set is shown in the specficiation; B, obtaining a second sparse Hadamard matrix set according to the first sparse Hadamard matrix set, wherein each second sparse Hadamard matrix in a second sparse Hadamard matrix set is shown in the specification; C, decomposing the sparse Hadamard matrixes to obtain matrixes with forms of the A and the B steps; D merging the matrixes with the forms of the A and the B steps to obtain the sparse Hadamard matrix; and E, extracting preset lines randomly to obtain the observation matrix. The observation matrix obtained through the compressed sensing observation matrix constructing method disclosed by the invention can reduce computation complexity of compressed sensing in compressed sampling and reconfiguration recovery of data. In addition, the observation matrix is more convenient for hardware realization.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Infrared image compressed sensing reconstruction method based on guiding filtering and clipping filtering
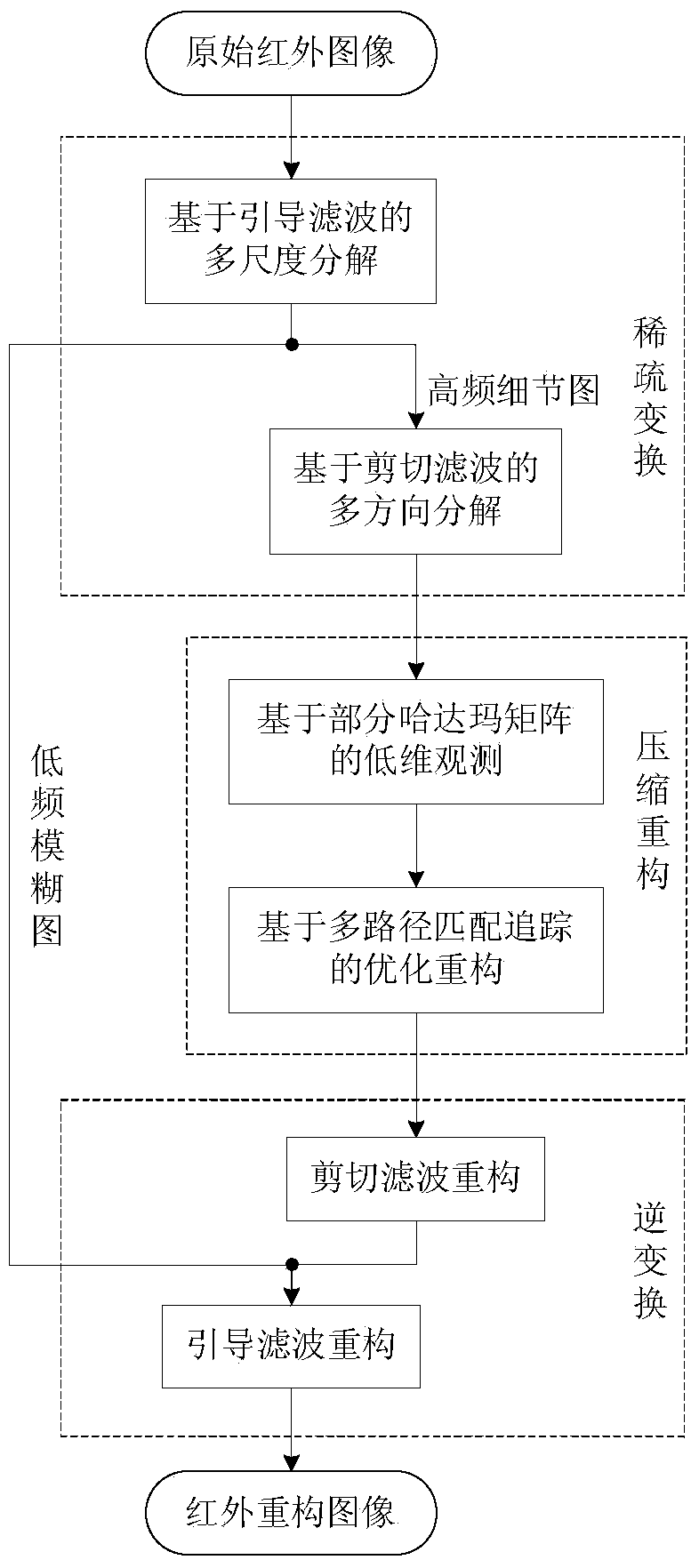
ActiveCN104268907AReduce sparsityCompressed Sensing Refactoring Works WellImage enhancement2D-image generationMultiscale decompositionDecomposition
The invention discloses an infrared image compressed sensing reconstruction method based on guiding filtering and clipping filtering. The method mainly solves the problems that a traditional infrared image is low in quality and an existing compressed sensing reconstruction method is poor in effect. The method comprises the steps of (1) utilizing guiding filtering for conducting multi-scale decomposition on an original infrared image to obtain a low-frequency fuzzy image and a series of high-frequency detailed images, (2) conducting multi-direction decomposition on the high-frequency detailed images by means of the clipping filtering, adopting a partial Hadamard matrix for conducting dimensionality reduction observation for coefficients in different directions, a multi-path matching tracking method is used for optimization and reconstruction, conducting clipping filtering on the reconstructed coefficients in different directions to obtain the reconstructed high-frequency detailed images, and (3) adding the reconstructed high-frequency detailed images with a low-frequency smooth image obtained through traditional linear sampling to obtain an infrared reconstructed image. Compared with an existing compressed sensing technology, the better reconstructed quality is obtained, and the infrared image reconstruction method is effective and feasible.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method of LTE (Long Term Evolution) downlink auxiliary synchronizing channel detection with low complexity
InactiveCN101835184AReduce complexityEasy to implementRadio transmission for post communicationWireless communicationComputation complexityRound complexity
The invention relates to a method of LTE (Long Term Evolution) downlink auxiliary synchronizing signal detection with low complexity, belonging to the technical field of mobile communication. The method comprises the following steps of: separating odd bits and even bits of an auxiliary synchronizing sequence of the received frequency-region signals to acquire an odd sequence and an even sequence; respectively carrying out sequence rearrangement, fast transformation of a Hadamard matrix and sequence rearrangement again on the odd sequence and the even sequence after descrambling to realize serial correlation operation; screening the identification number m0 corresponding to the maximal correlation value from the odd sequence; reducing the serial number range of the even sequence according to the corresponding relation between m0 and m1; screening the identification number m1 corresponding to the maximal correlation value from the even sequence of which the serial number range is reduced; and acquiring the corresponding cell identification mark according to the size relation between m0 and m1, wherein the subframe is a subframe 0 or a subframe 5. The invention simplifies the algorithm complexity of S-SCH signal detection from multiplication of 31*31 times to addition of 5*32 times, thereby greatly reducing the computation complexity in the detection process.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Mutual capacitance large panel phase shift mitigation
ActiveUS9235280B1Reduce areaReduce consumptionInput/output processes for data processingElectrical conductorPhase shifted
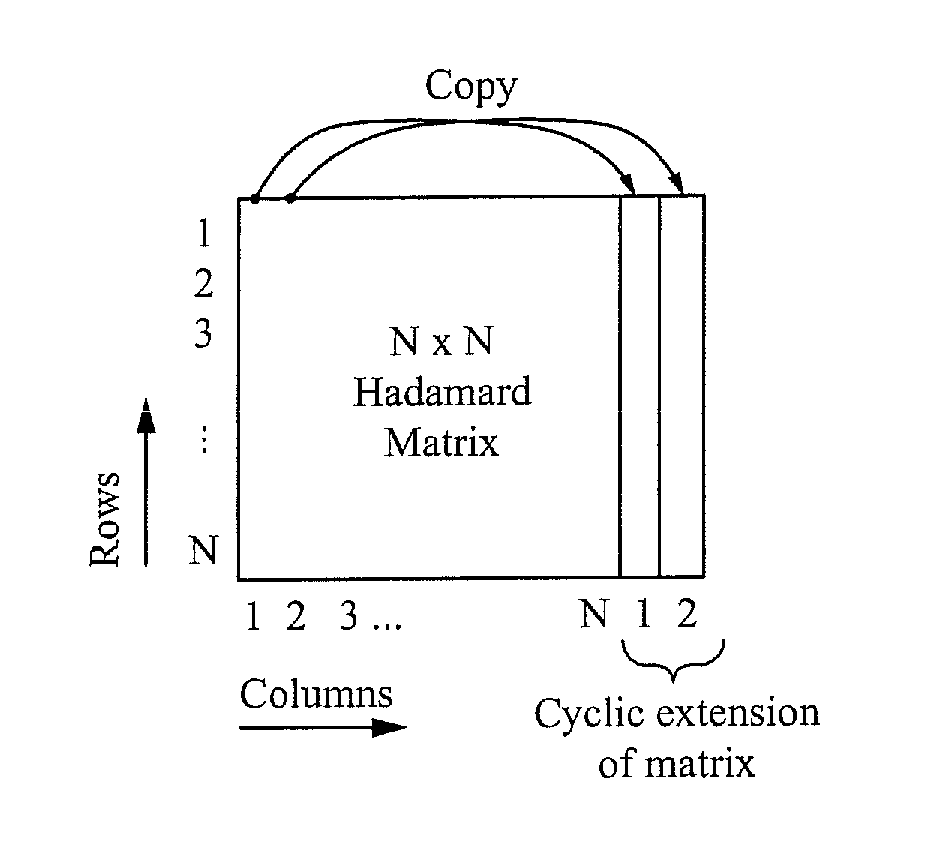
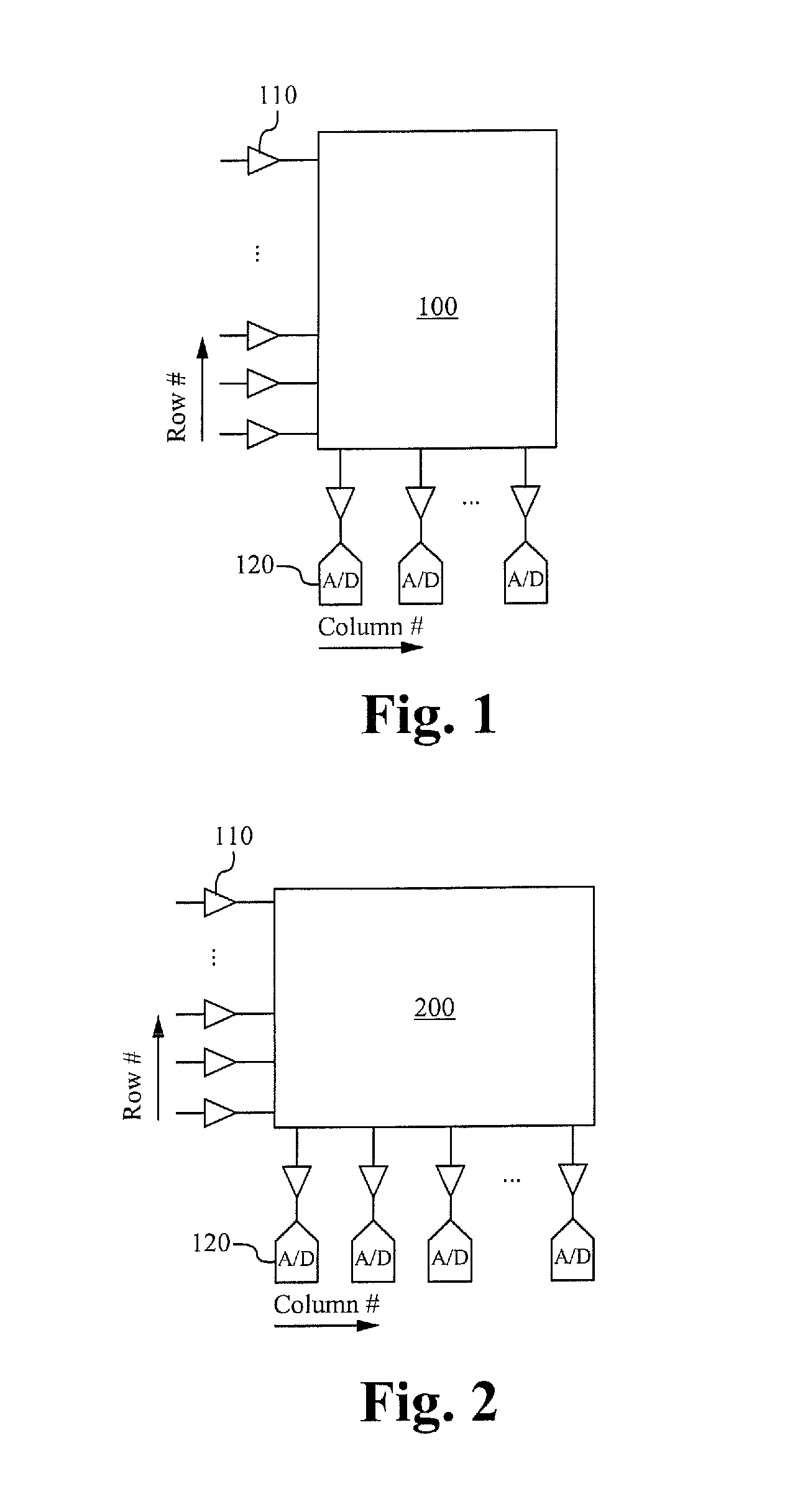
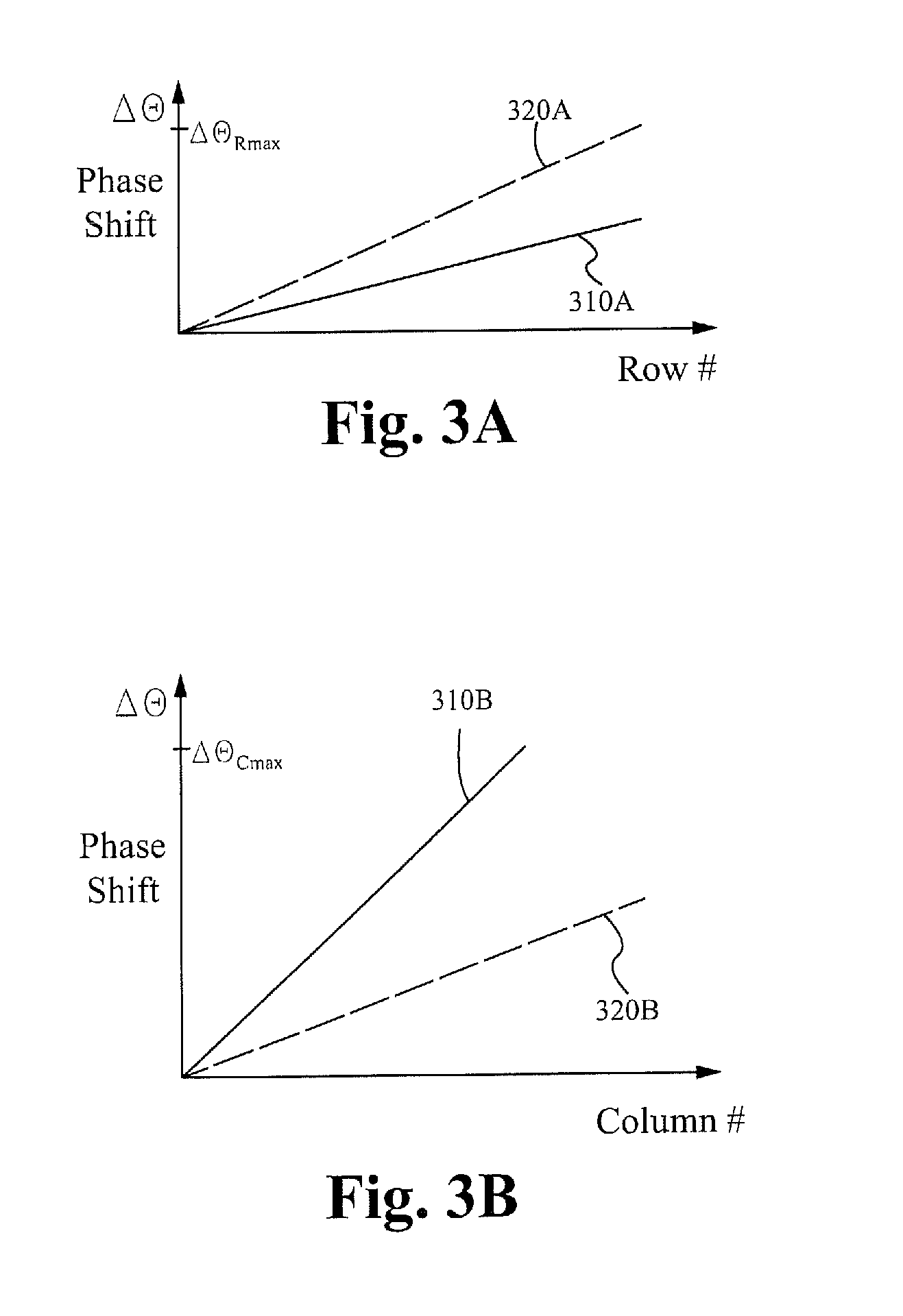
A method of mitigating a phase shift in a mutual capacitance touch screen panel having a plurality of row conductors intersecting with a plurality of column conductors to form a matrix of pixels, the method comprising: driving the row conductors with row drive signals formed from an excitation matrix, wherein each row in the excitation matrix is orthogonal to every other row in the excitation matrix, and the excitation matrix has a dimension larger than the matrix of pixels; sensing signals from the column conductors; and determining the mutual capacitance of the pixels using the sensed signals and an inverse of the excitation matrix. The excitation matrix can be a Hadamard matrix or a modified Hadamard matrix and can comprise a cyclic extension at the end of each row. A different region-specific phase shift can be applied to different clusters of signals.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
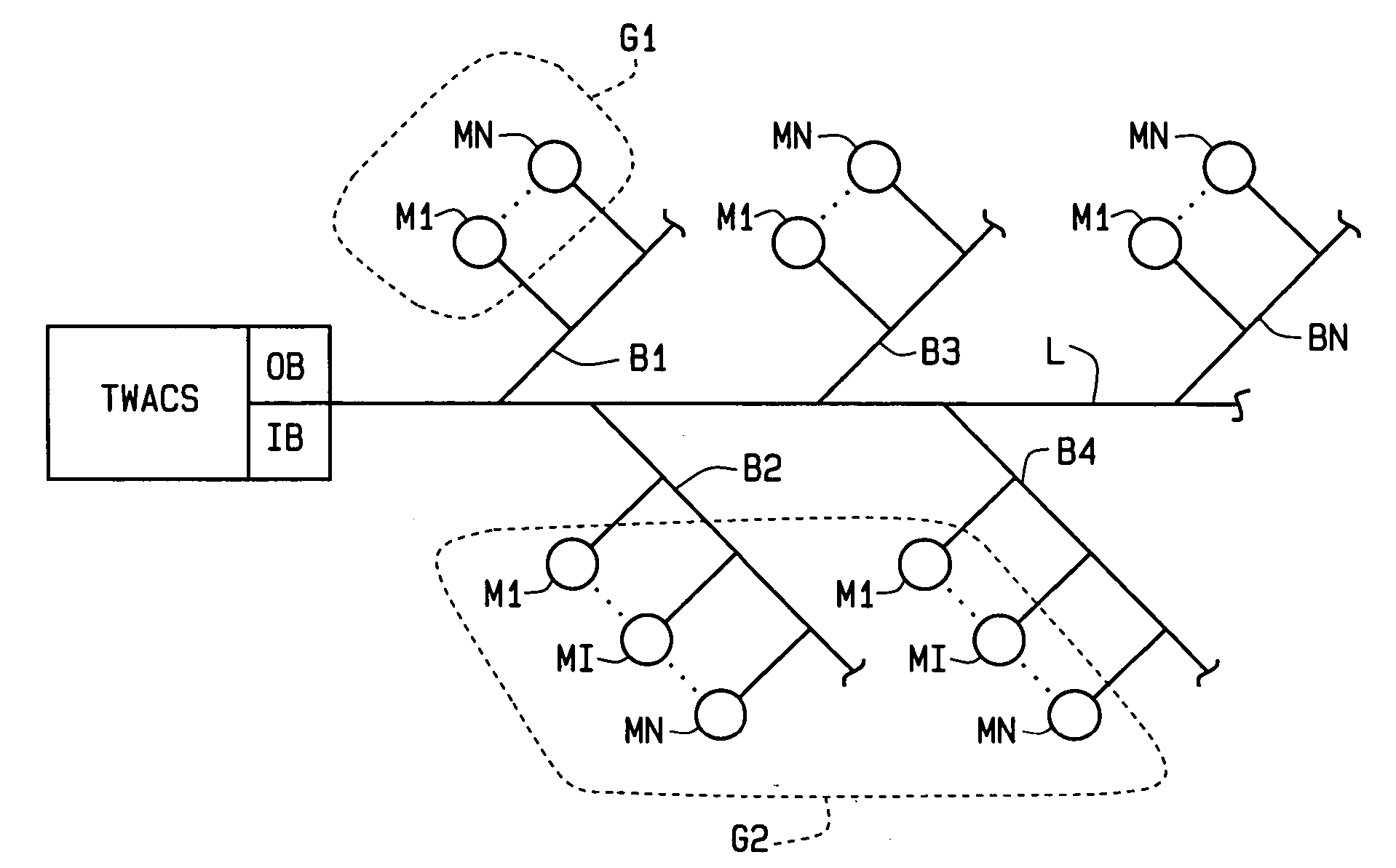
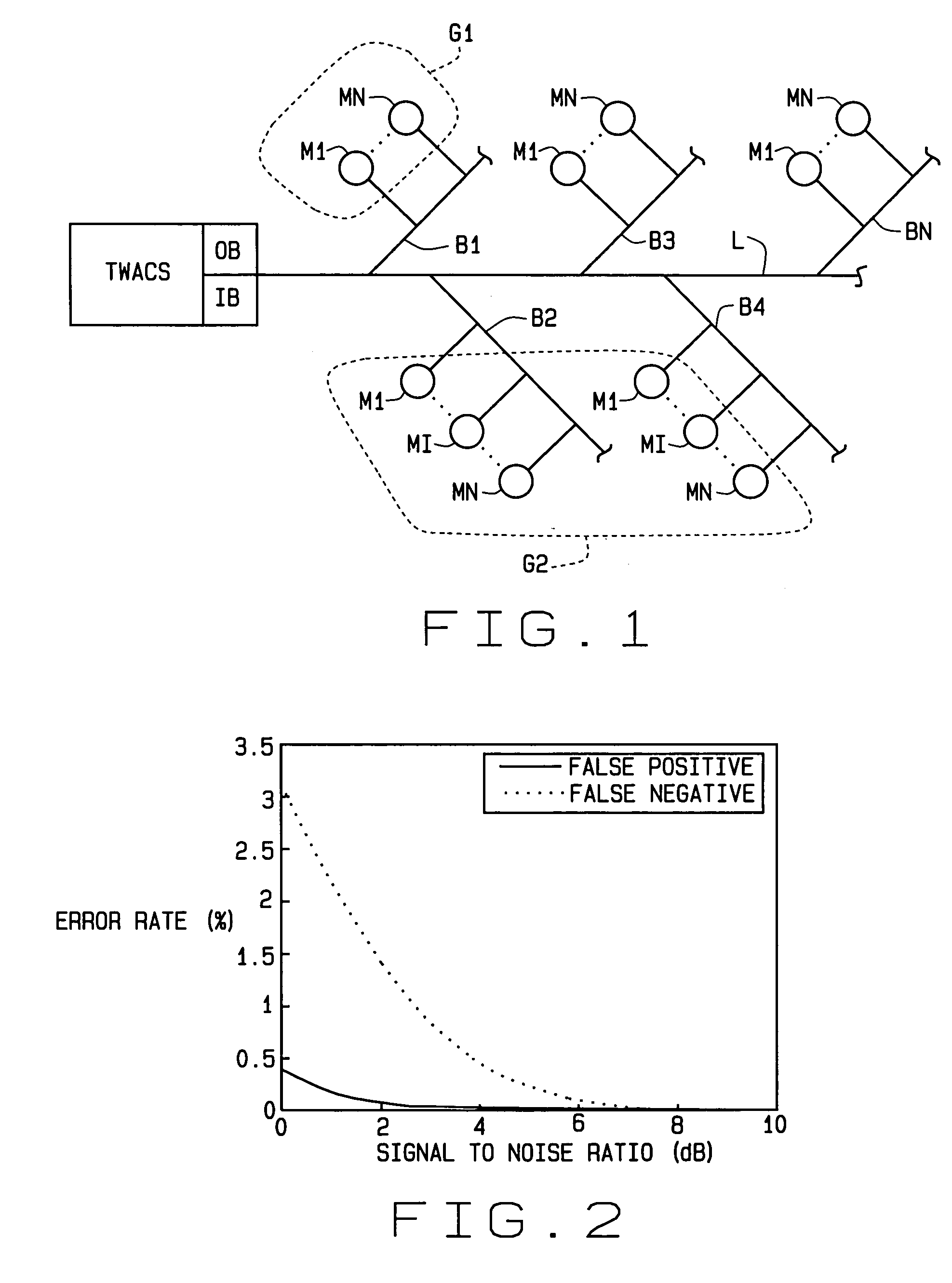
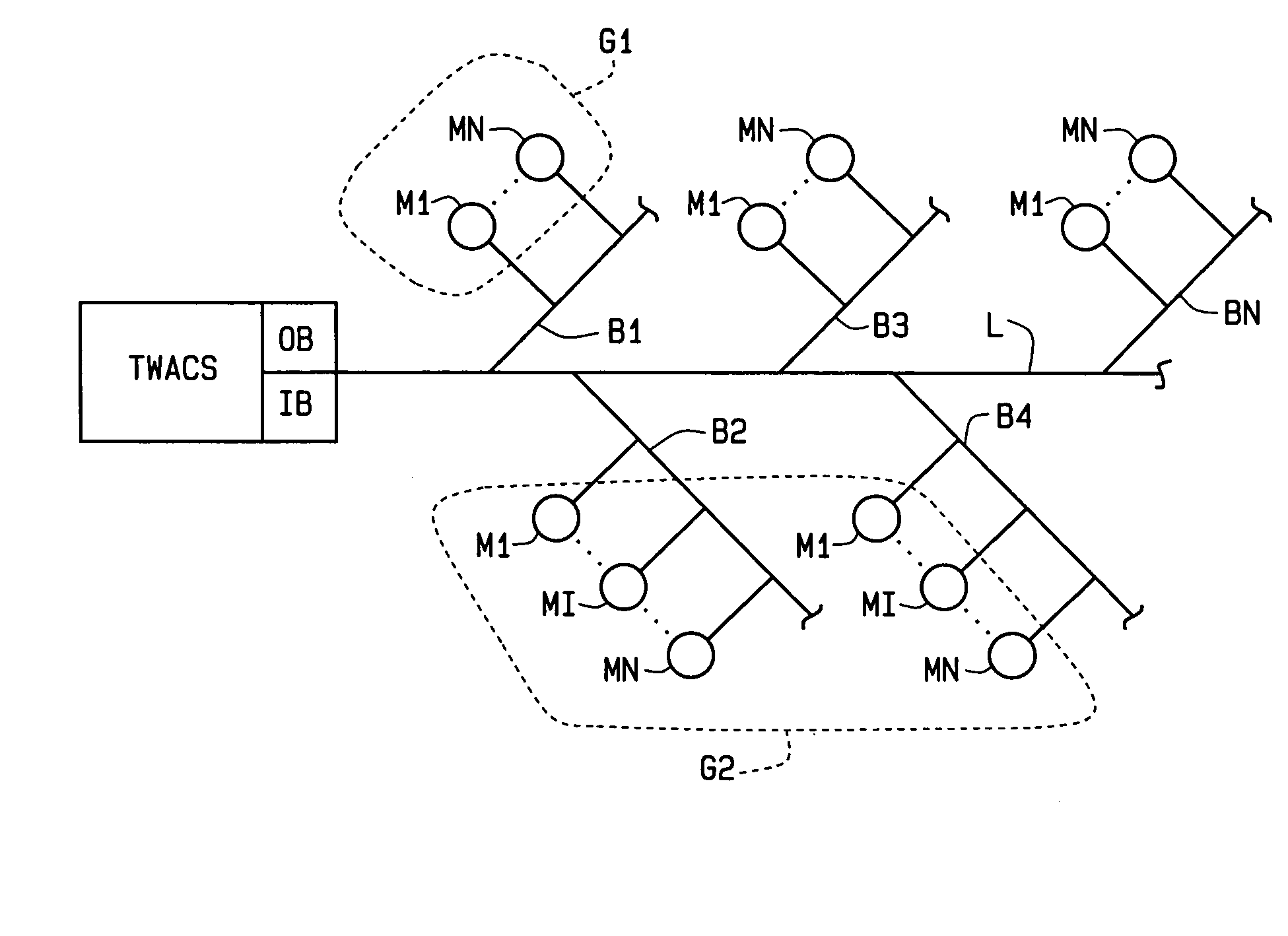
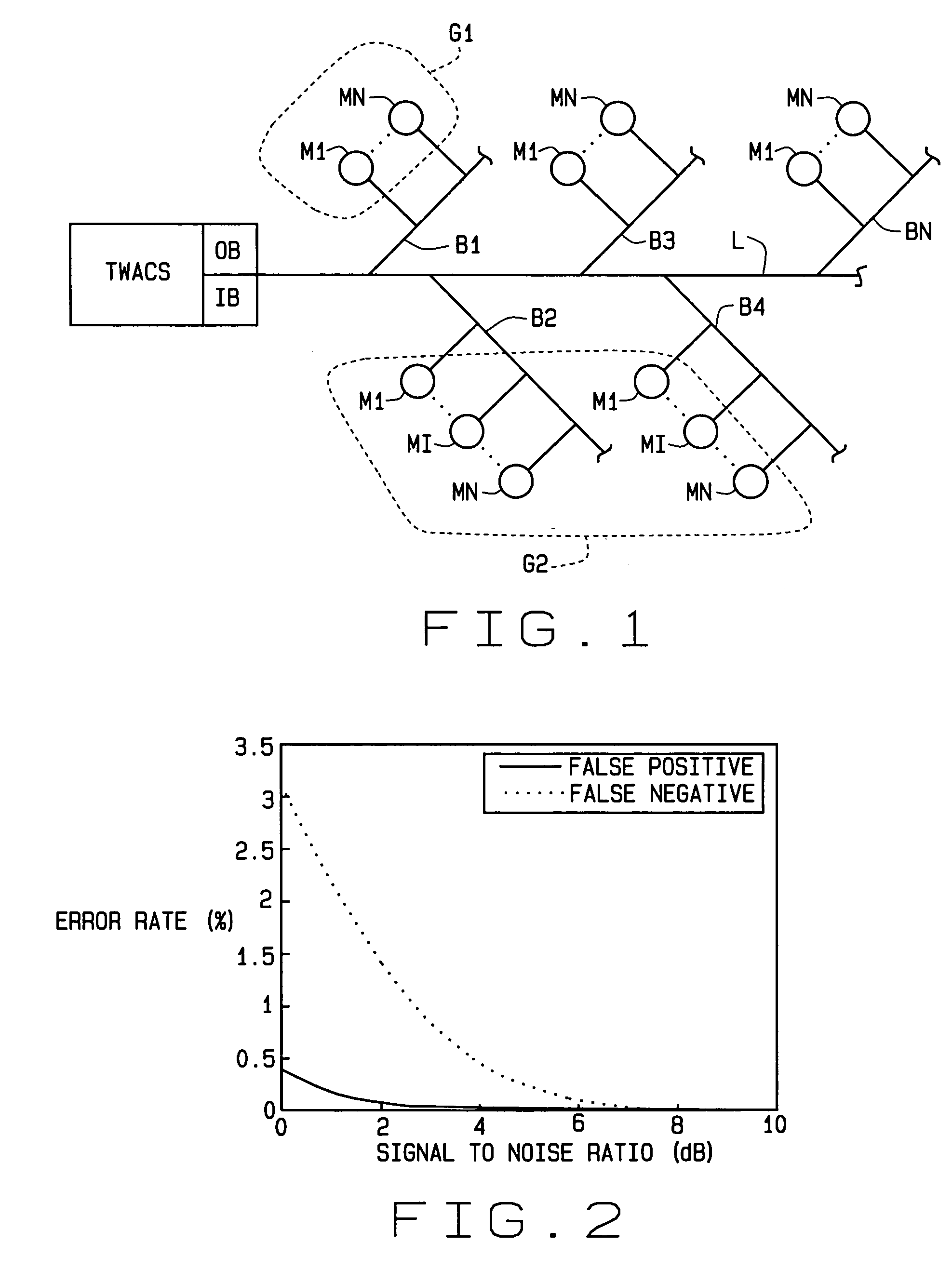
Extremely fast polling method for determining the presence of individual electric meters on a power line
ActiveUS20060202854A1High polling rateHigh rateElectric signal transmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsElectric distribution networkElectric power
A “super-fast” polling method for electrical meters for outage detection. In response to a query, a large group of electric meters (M) all simultaneously transmit reply signals over an electrical distribution network using TWACS®. The signals are separated by an inbound detector (IB) at a receiving end of the network. This allows a very large number of meters to be polled in a very short period of time to determine whether or not an outage has occurred at the location of each meter. Each meter transmits a bit pattern, and bit patterns are designed so a group of meter units can transmit their patterns simultaneously over a power line (L) to the inbound detector. The presence or absence of a bit pattern in the received signal conveys the presence or absence of the associated meter in the system. The ability to transmit multiple bit patterns in parallel requires that they be orthogonal to each other. The Hadamard matrices are a class of matrices whose rows could be used as a set of bit patterns. In addition to super-fast polling for outage detection, the method of the invention can also be used to poll meters for the presence of an alarm condition, as well as for both outage detection and an alarm condition.
Owner:ACLARA TECH LLC
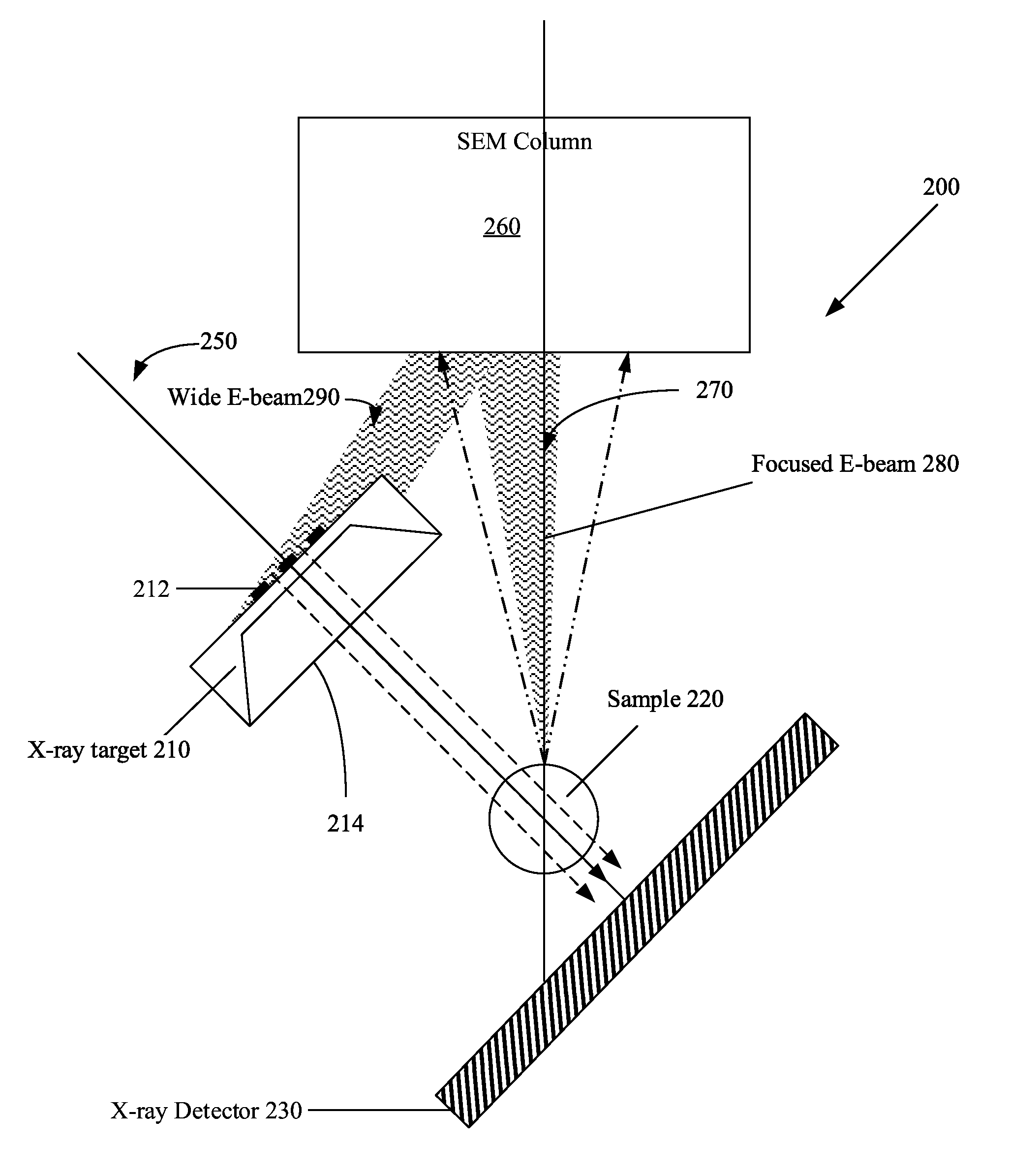
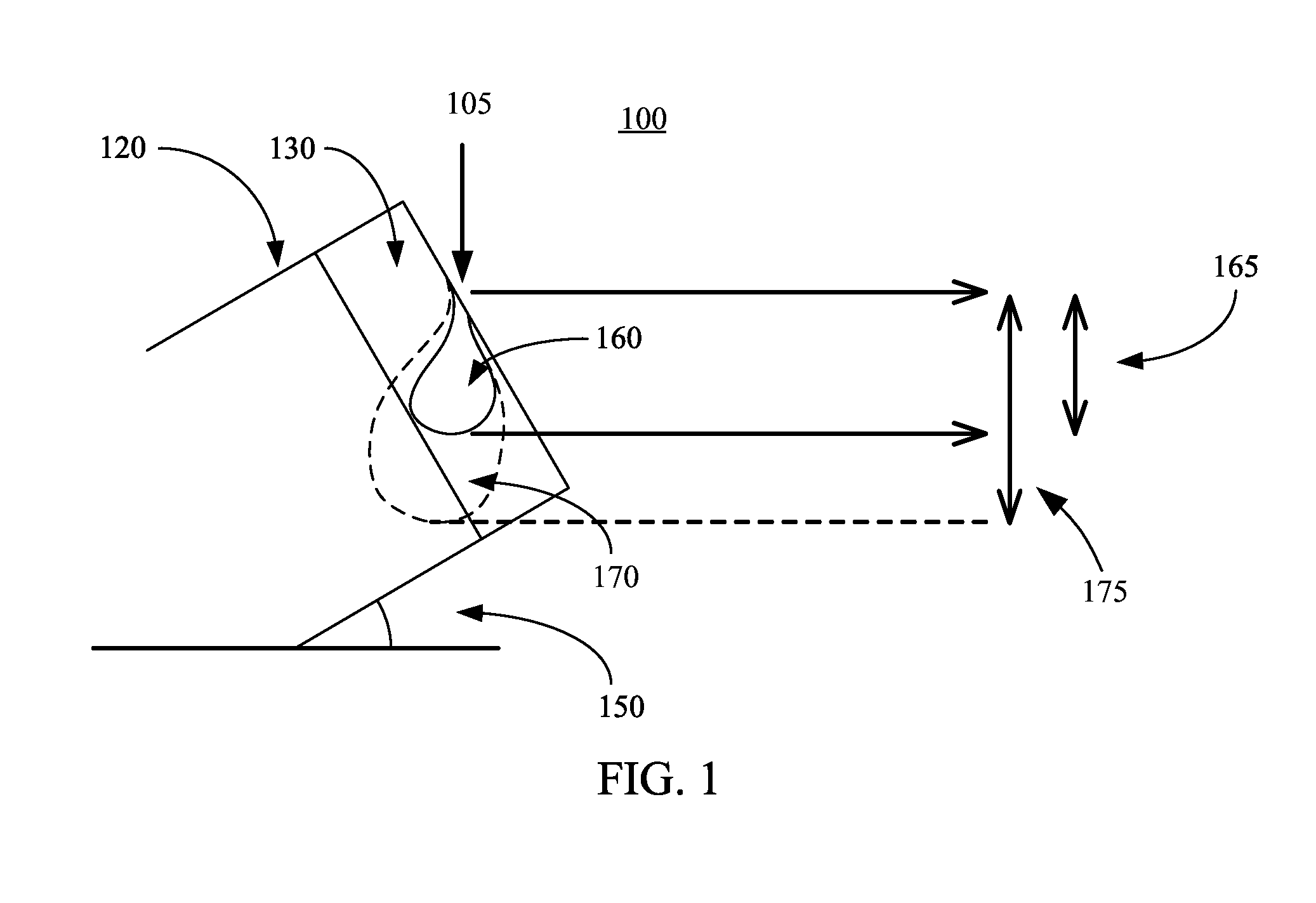
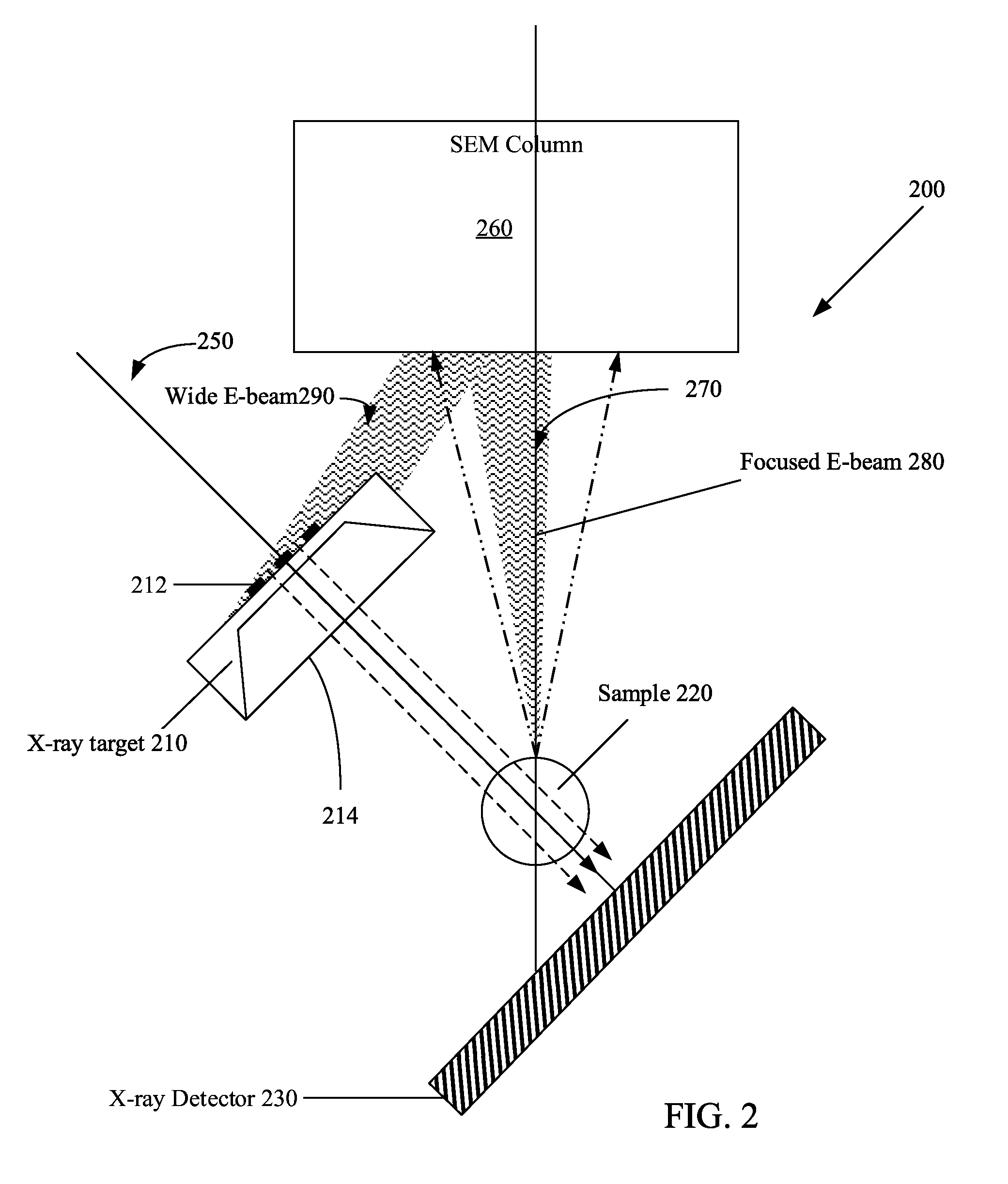
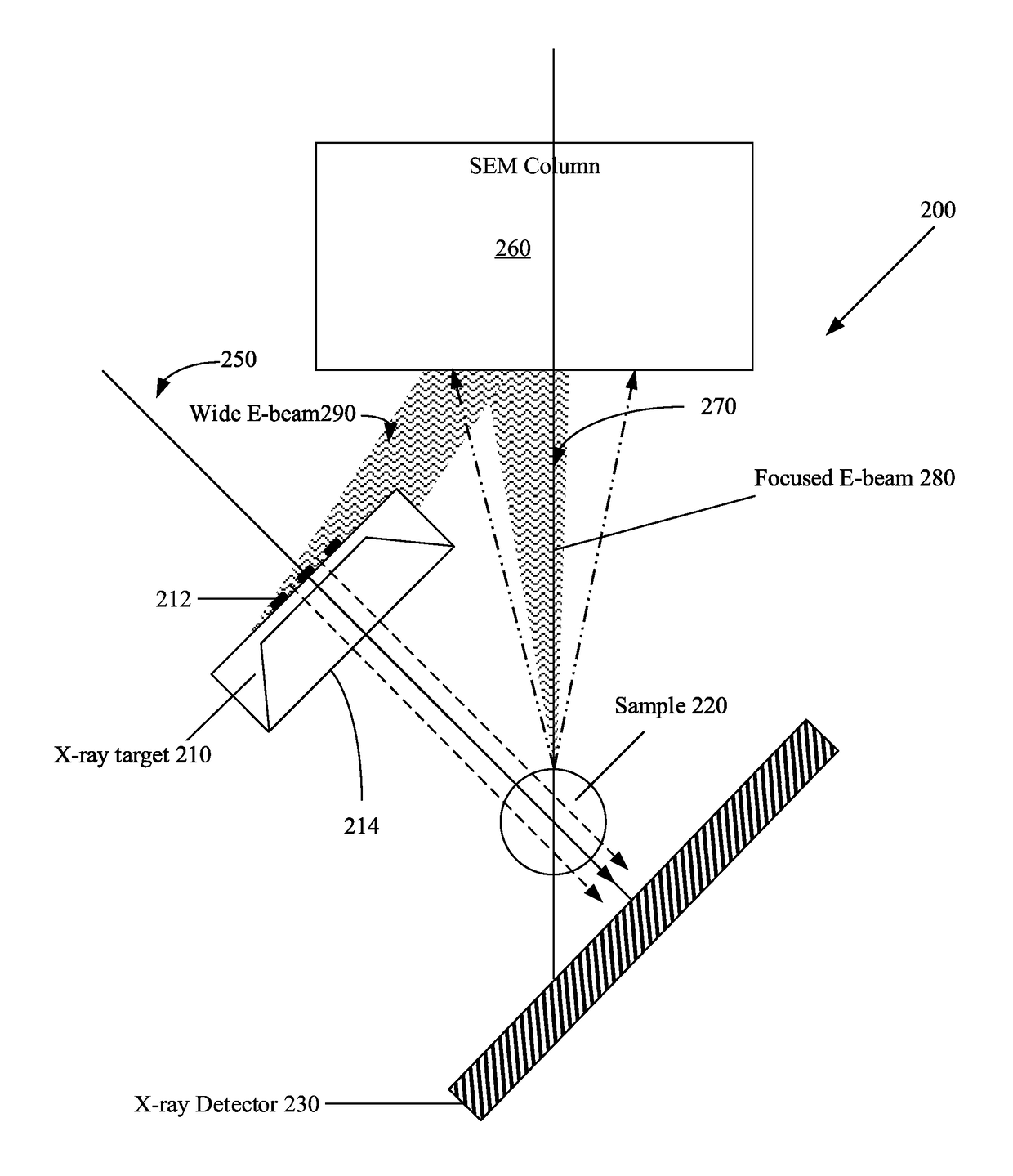
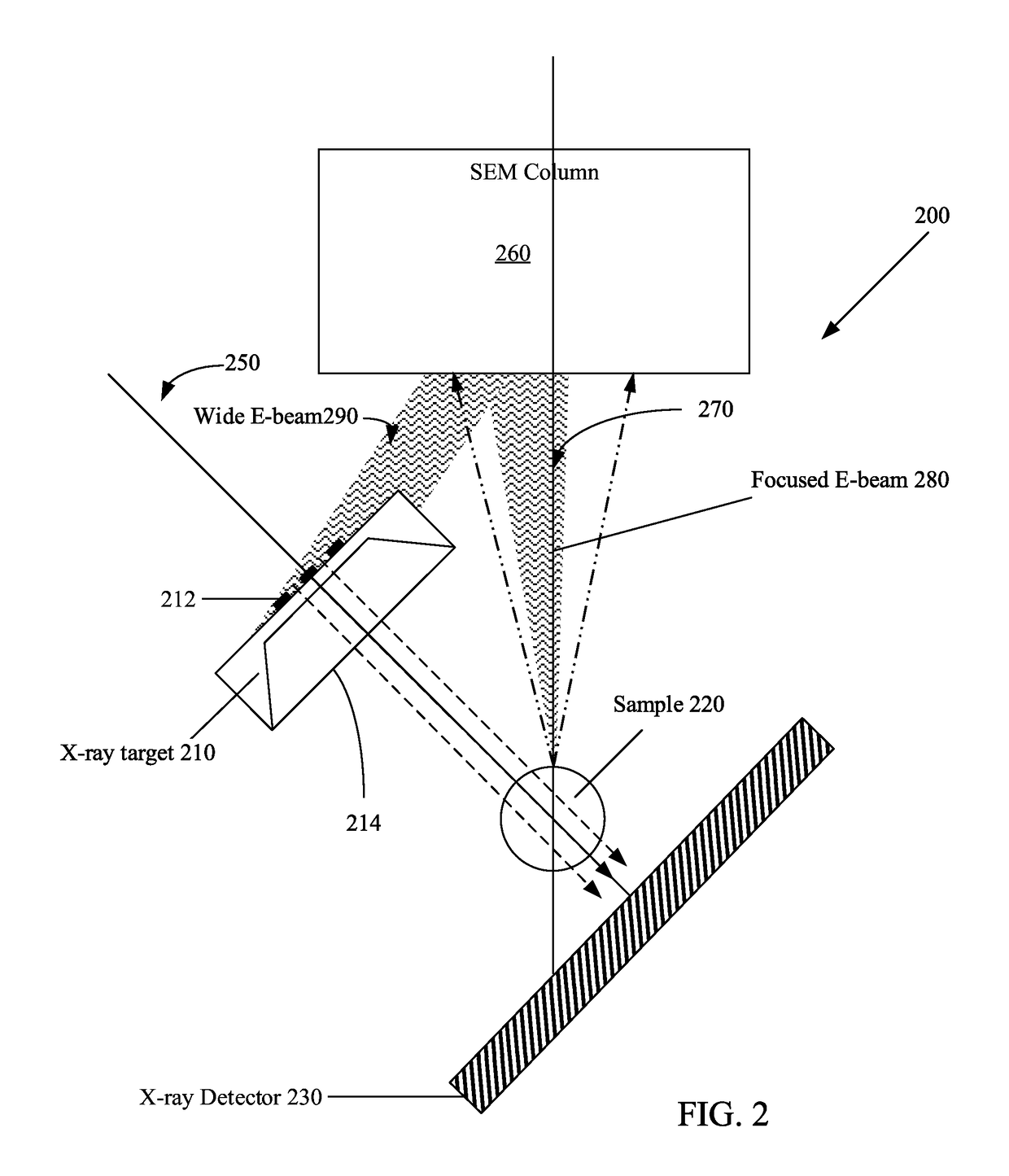
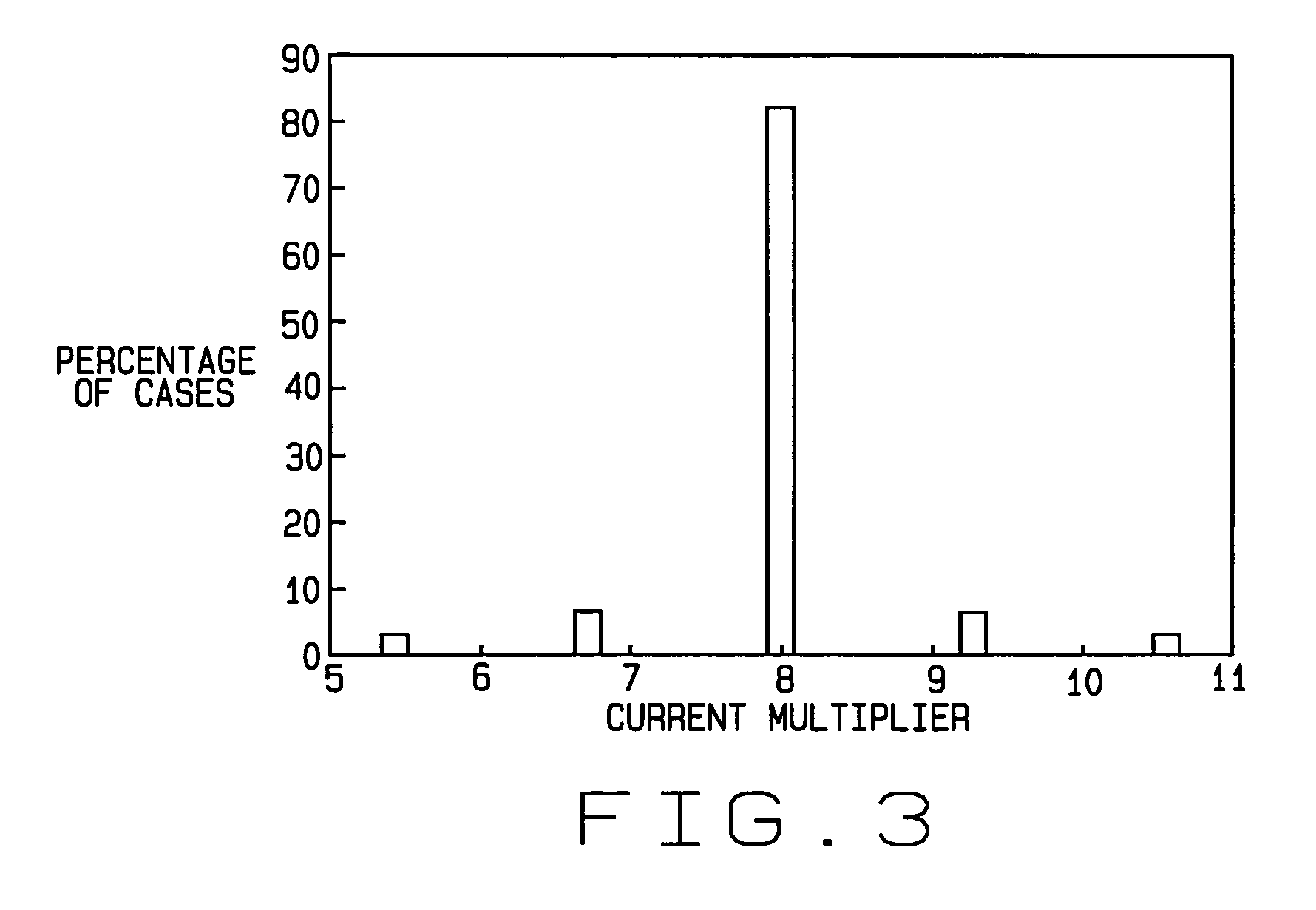
High aspect ratio x-ray targets and uses of same
ActiveUS20150303021A1Simple structureEasy to useX-ray tube laminated targetsRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayHard X-rays
An x-ray target, a method of using the x-ray target, and a computer program product with instructions for carrying out a method of using the x-ray target. The x-ray target includes a substrate made from a soft x-ray producing material and a high aspect ratio structure made from a hard x-ray producing material. The hard x-ray producing material is embedded in the substrate, formed on the substrate, cantilevered out from the edge of the substrate, or any combination thereof. The high aspect ratio structure comprises a plurality of high aspect ratio structures arranged in one or more grids or arrays, and the high aspect ratio structures in one of the one or more grids or arrays are arranged to form a Hadamard matrix structure.
Owner:FEI CO
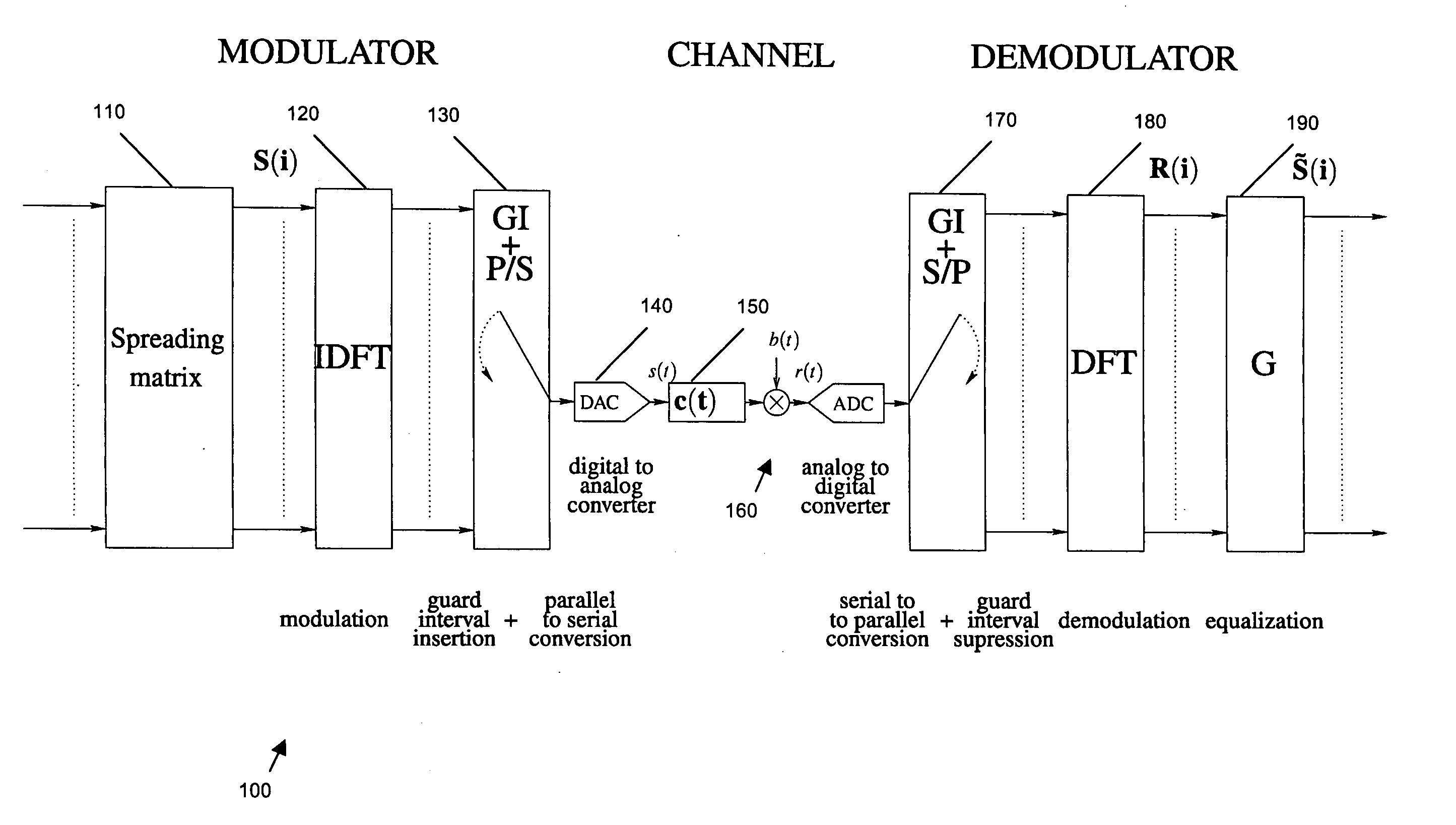
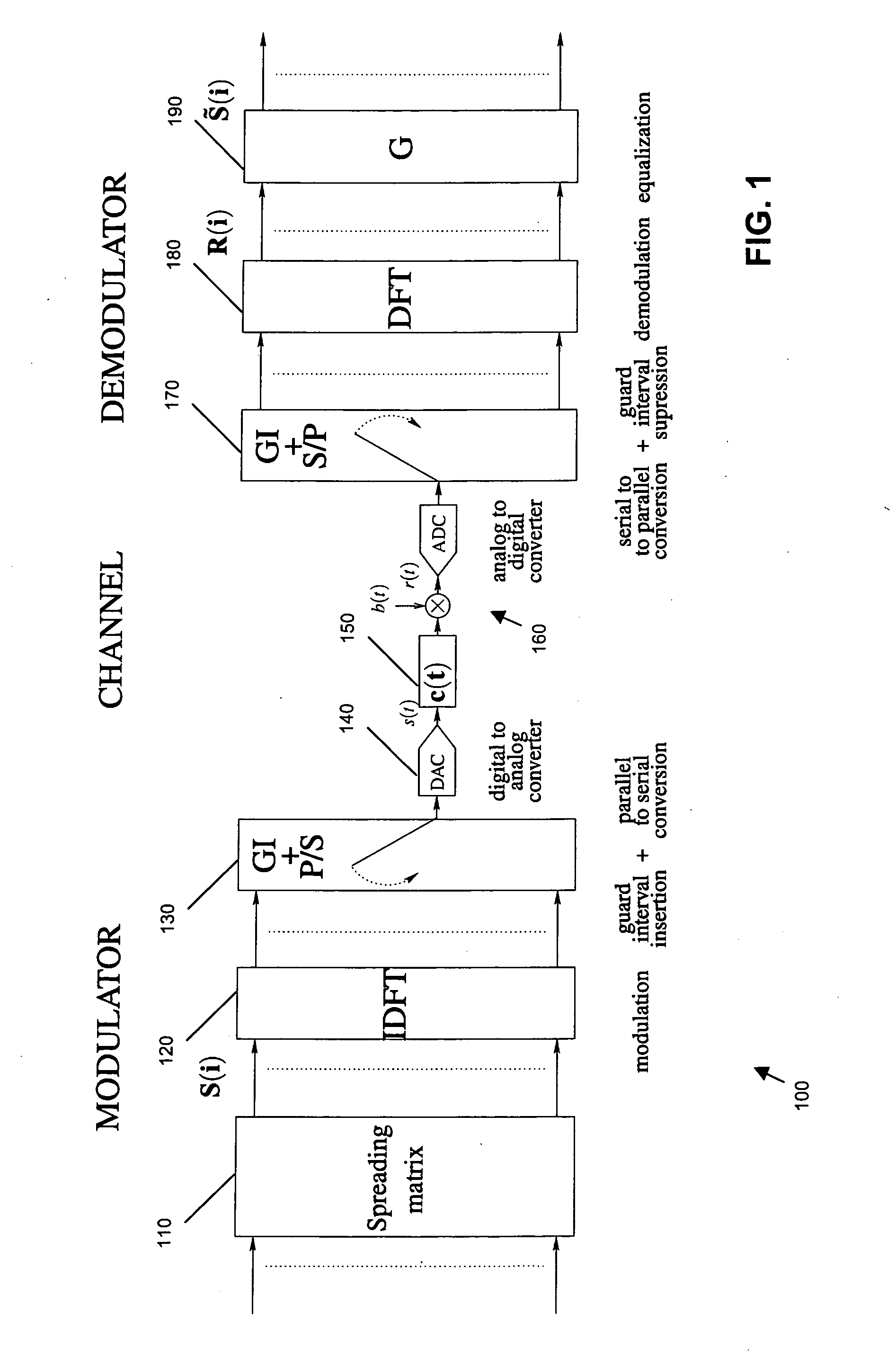
Reception of multicarrier spread-spectrum signals
InactiveUS20050107053A1Reduce complexityEnhanced OFDM modulatorError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionPerformance enhancementCyclic prefix
A system (100), receiver (160-190) and method of operation for spread OFDM wireless communication (single user OFDM-CDMA with cyclic-prefix) by: equalizing the received spread OFDM signal (y) and splitting it into first and second portions (ŝ1, ŝ2); making a decision on the second portion and subtracting the second portion from the received signal to produce a first difference signal; processing the first difference signal to recover the first portion of the received signal in which symbol interfering terms of the second portion are substantially reduced; making a decision on the first portion and subtracting the first portion from the received signal to produce a second difference signal; and processing the second difference signal to recover the second portion of the received signal in which symbol interfering terms of the first portion are substantially reduced. The process may be iterated extensively at this stage. In a second stage, the recovered received signal is split into a greater number of portions (e.g., 4), and processed similarly to further reduce interference. The same mechanisms can be applied to blocks of reduced size (divided into 8, 16 etc.) leading to a higher resolution of the decoding and a tree-like structure. Also, minimum mean square error equalization is performed by multiplying by a first diagonal matrix having elements dependent on channel coefficients; and multiplying by a second matrix which is a subset of a Walsh Hadamard matrix. This provides low arithmetical complexity, it is possible to adjust the number of iterations to be performed based on a performance / complexity tradeoff, it can be viewed as a simple extension of current OFDM systems, and it yields a significant PER performance enhancement (e.g., 3 dB) (FIGS. 1&2 to accompany abstract)
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
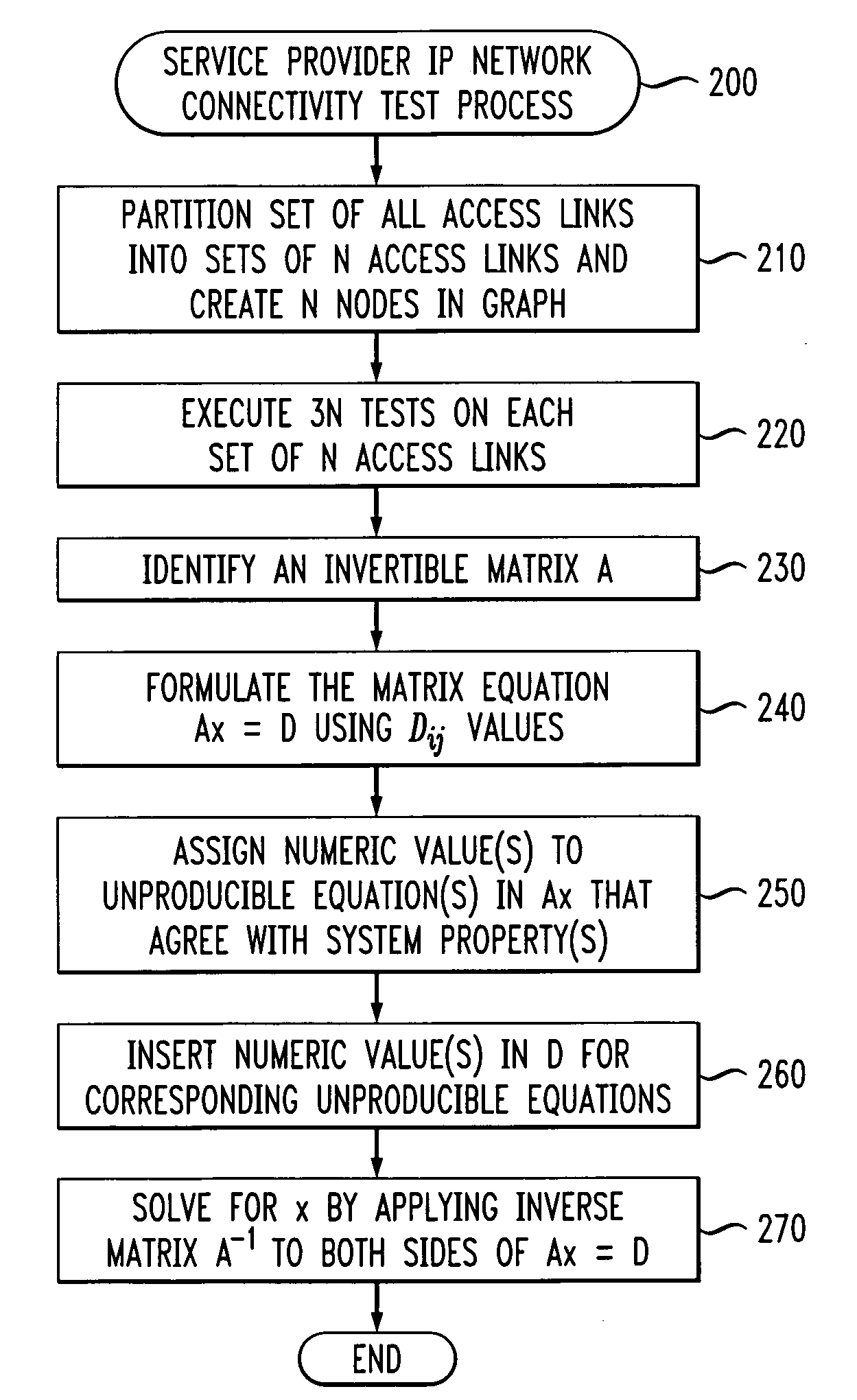
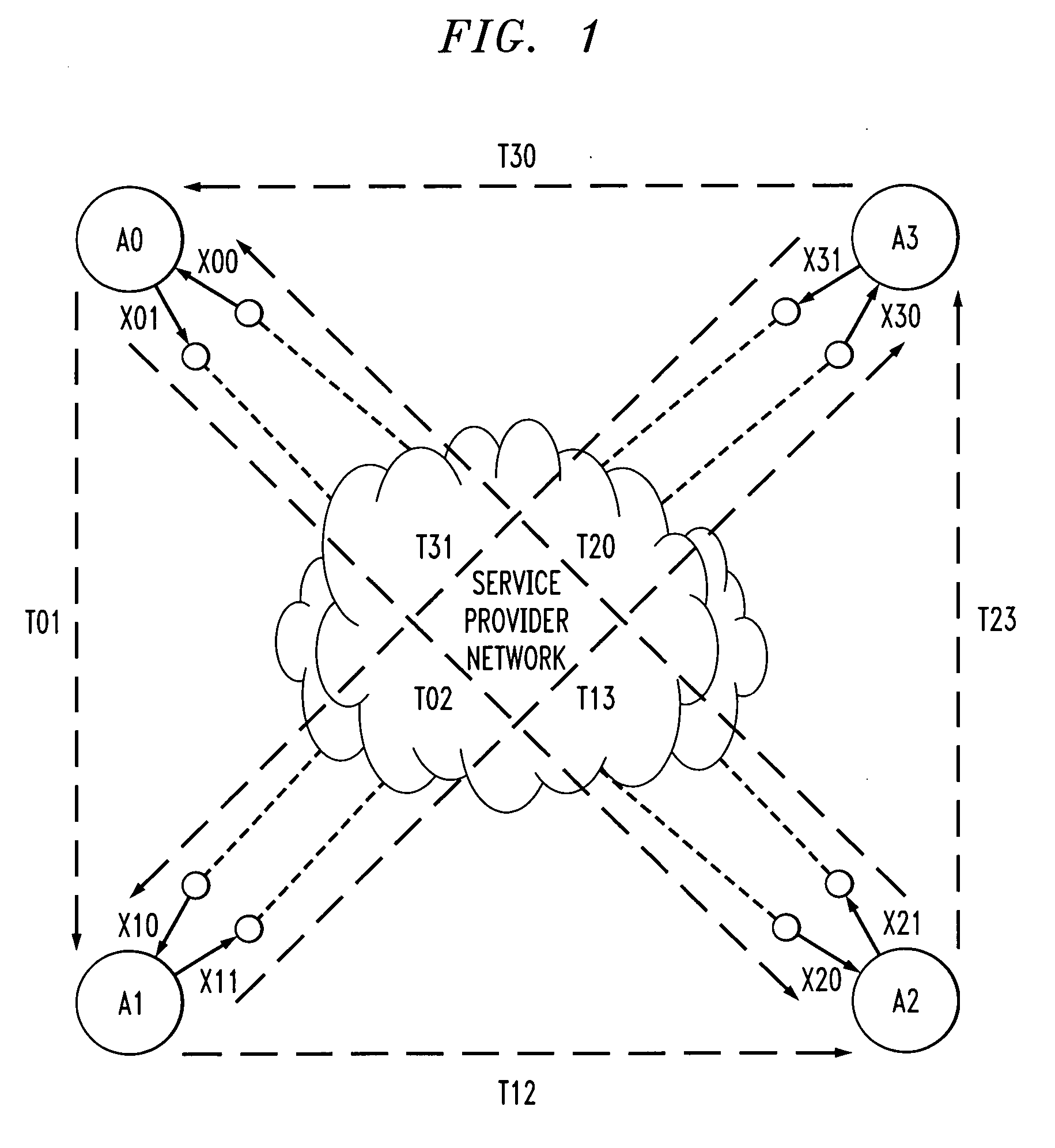
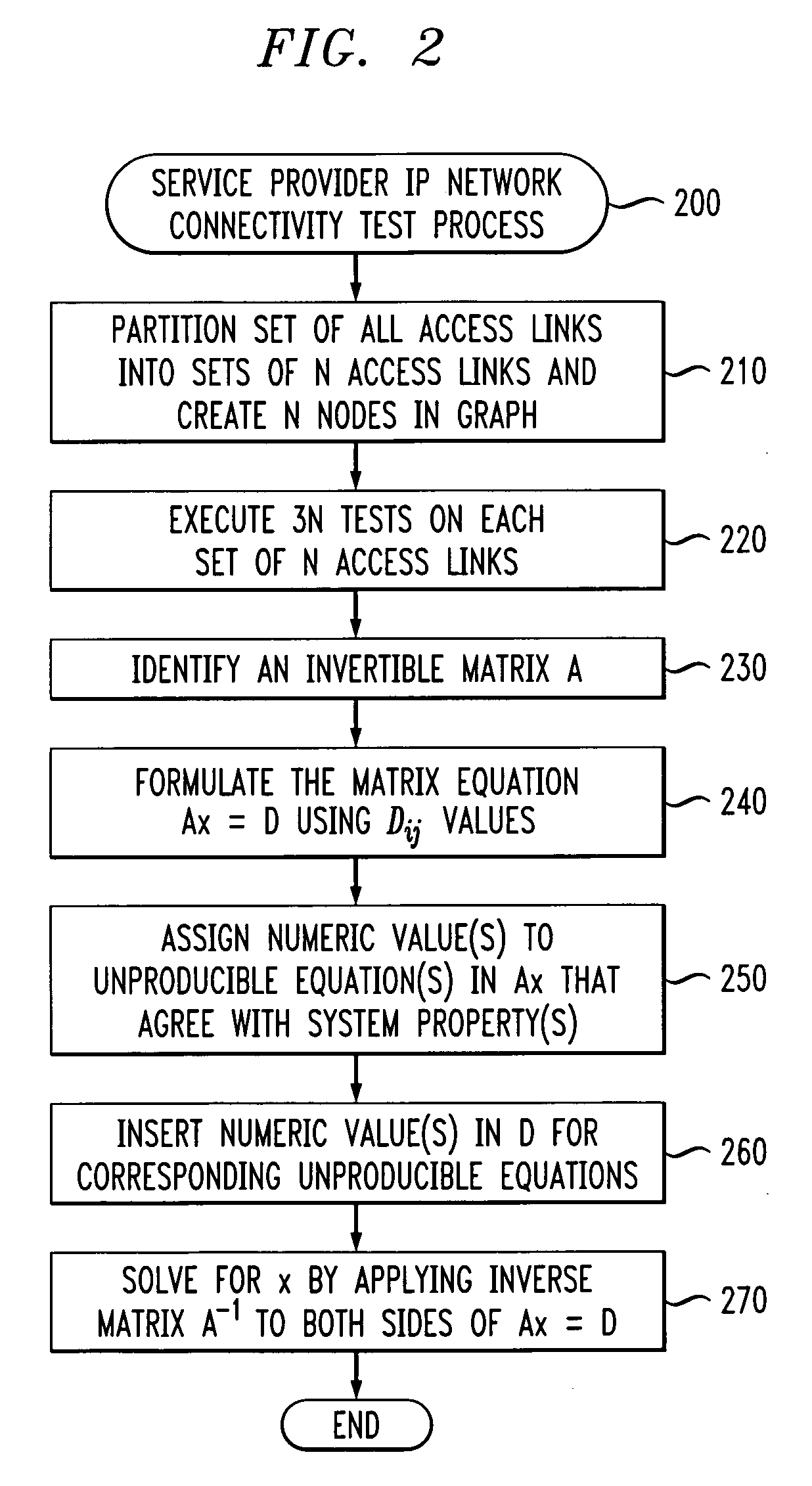
Method and apparatus for link performance measurements in a packet-switched network
InactiveUS20060268731A1Reduce the amount requiredError preventionTransmission systemsAlgorithmTest measurement
Methods and apparatus are provided for measuring and evaluating access link performance in IP networks that reduce the amount of required test traffic. Performance values supported by access links in a packet network that interconnects regions of an enterprise network are evaluated by (i) obtaining a plurality of test measurements for a set of N access links; (ii) formulating a matrix equation (Ax=D), where A is an invertible matrix, such as a Hadamard matrix, x is a vector of unknown access link performance parameters and D is a vector based on the plurality of test measurements; (iii) assigning one or more numeric values to one or more unproducible equations in the matrix equation based on one or more system properties; and (iv) obtaining a performance parameter value on each directed edge for the set by applying an inverse matrix A−1 to each side of of the matrix equation.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Method to minimize compatibility error in hierarchical modulation using variable phase
ActiveUS20060276145A1Increase volumeIncrease the amount of dataRadio transmissionPhase-modulated carrier systemsDigital dataData stream
The present invention provides a method of hierarchically modulating first and second digital data streams in a broadcast system such as an SDAR system that is compatible with legacy receivers. The second digital data stream, but not the first, is provided with a non-binary pseudo-random encoding. A carrier is first modulated, e.g. QPSK, by the first digital data stream; and a second modulation is performed with the encoded second digital data stream. The encoding includes a multiplication of a matrix formed of 2, 3 or 4 consecutive bits of the secondary data stream by a matrix, e.g. a Hadamard matrix to form a product matrix having non-binary values that are used to modify consecutive symbols of the first modulation. The second modulation appears as Gaussian noise to legacy receivers over time.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
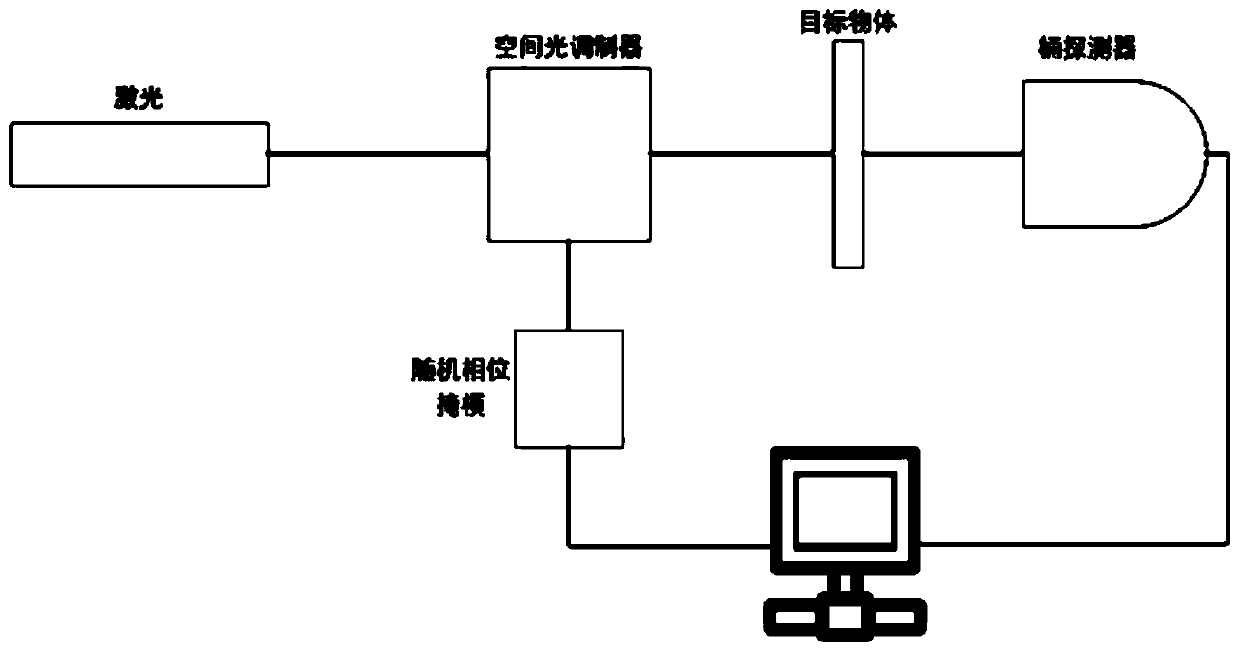
Object positioning method based on single-pixel detector
ActiveCN108895985AAchieve positioningPrecise positioningUsing optical meansSignal responseProjection system
The invention discloses an object positioning method based on a single-pixel detector. The method comprises steps of through a computer, generating a two-dimensional Hadamard matrix; acquiring line-arranged and row-arranged two-dimensional projection patterns; allowing the line-arranged two-dimensional projection patterns and the row-arranged two-dimensional projection patterns to pass a light modulator and a projection system; irradiating the object through a lighting optical field and acquiring a light intensity signal response value, thereby using the light intensity signal response value and line data to carry out calculation; acquiring accumulation distribution curves in the line and row directions of the object image; and carrying out threshold value processing on the curves to acquire the position of the object in the scene. The method is advantageous in that by through fusion single-pixel imaging technology, positioning of the object is achieved; the system is free from a scanning device; by use of a single-pixel detector, cost and complexity of the system can be effectively reduced; and the object positioning ability in case of weak signals can be effectively improved.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High aspect ratio x-ray targets and uses of same
ActiveUS9934930B2Easy to useX-ray tube electrodesCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingSoft x rayHard X-rays
An x-ray target, a method of using the x-ray target, and a computer program product with instructions for carrying out a method of using the x-ray target. The x-ray target includes a substrate made from a soft x-ray producing material and a high aspect ratio structure made from a hard x-ray producing material. The hard x-ray producing material is embedded in the substrate, formed on the substrate, cantilevered out from the edge of the substrate, or any combination thereof. The high aspect ratio structure comprises a plurality of high aspect ratio structures arranged in one or more grids or arrays, and the high aspect ratio structures in one of the one or more grids or arrays are arranged to form a Hadamard matrix structure.
Owner:FEI CO
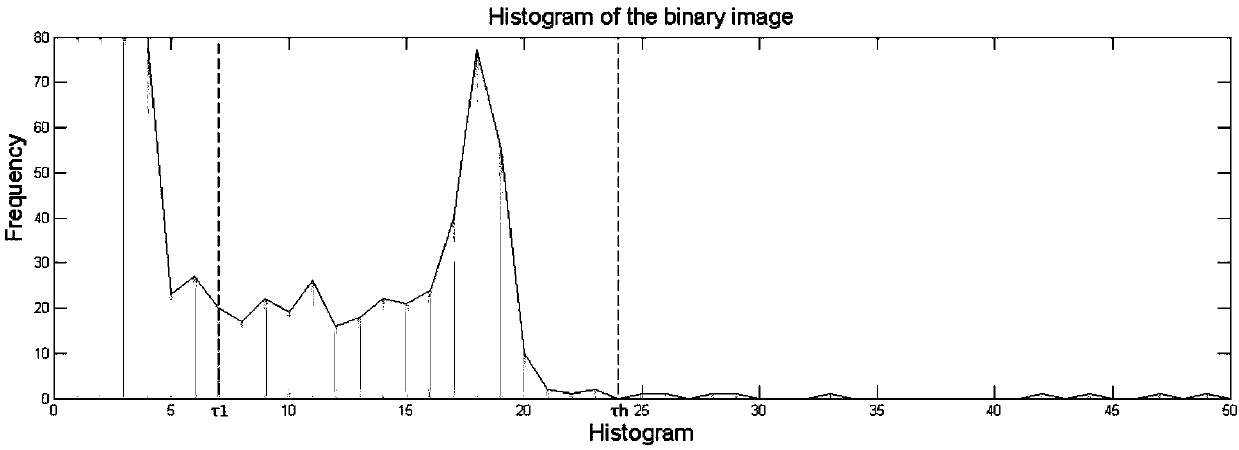
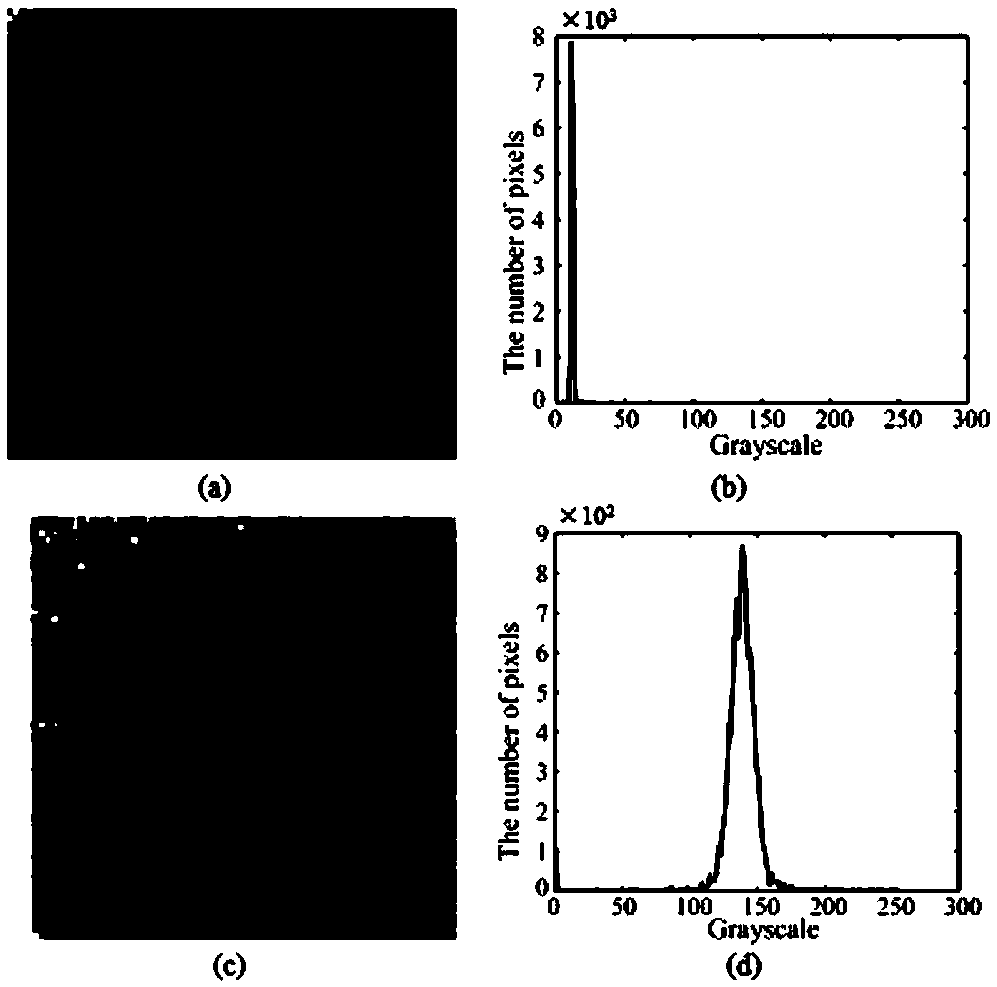
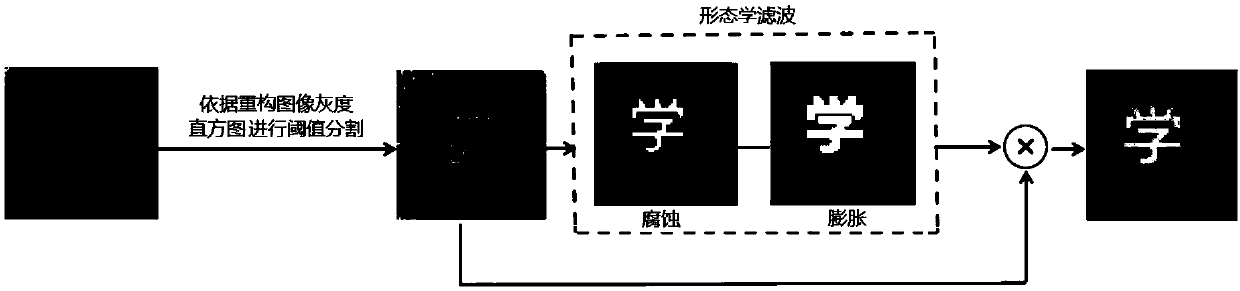
Hadamard coded modulation correlation imaging threshold processing method
ActiveCN109035282AImprove practicalityGood effectImage enhancementImage analysisMorphological filteringImage contour
The invention discloses a threshold value processing method of Hadamard code modulation correlation imaging. The segmentation threshold is determined according to the gray histogram characteristics ofthe reconstructed image obtained by Hadamard matrix modulation correlation imaging, then, the target image is segmented by using the determined segmentation threshold, and the image after the threshold segmentation is subjected to morphological filtering. The morphological filtering comprises the following steps: firstly, the image after the threshold segmentation is subjected to etching operation to eliminate the point noise in the image, and then the binary target image contour is obtained by dilation operation; at last, the outline of the target image is used to enhance the image after thethreshold segmentation, and the point noise around the target image is removed to obtain a clear image. The threshold value processing method of the invention has high feasibility, obtains nearly 8dBoptical image enhancement, has good effect on binary images and gray images, and effectively promotes the practicality of the correlation imaging technology.
Owner:JILIN TEACHERS INST OF ENG & TECH
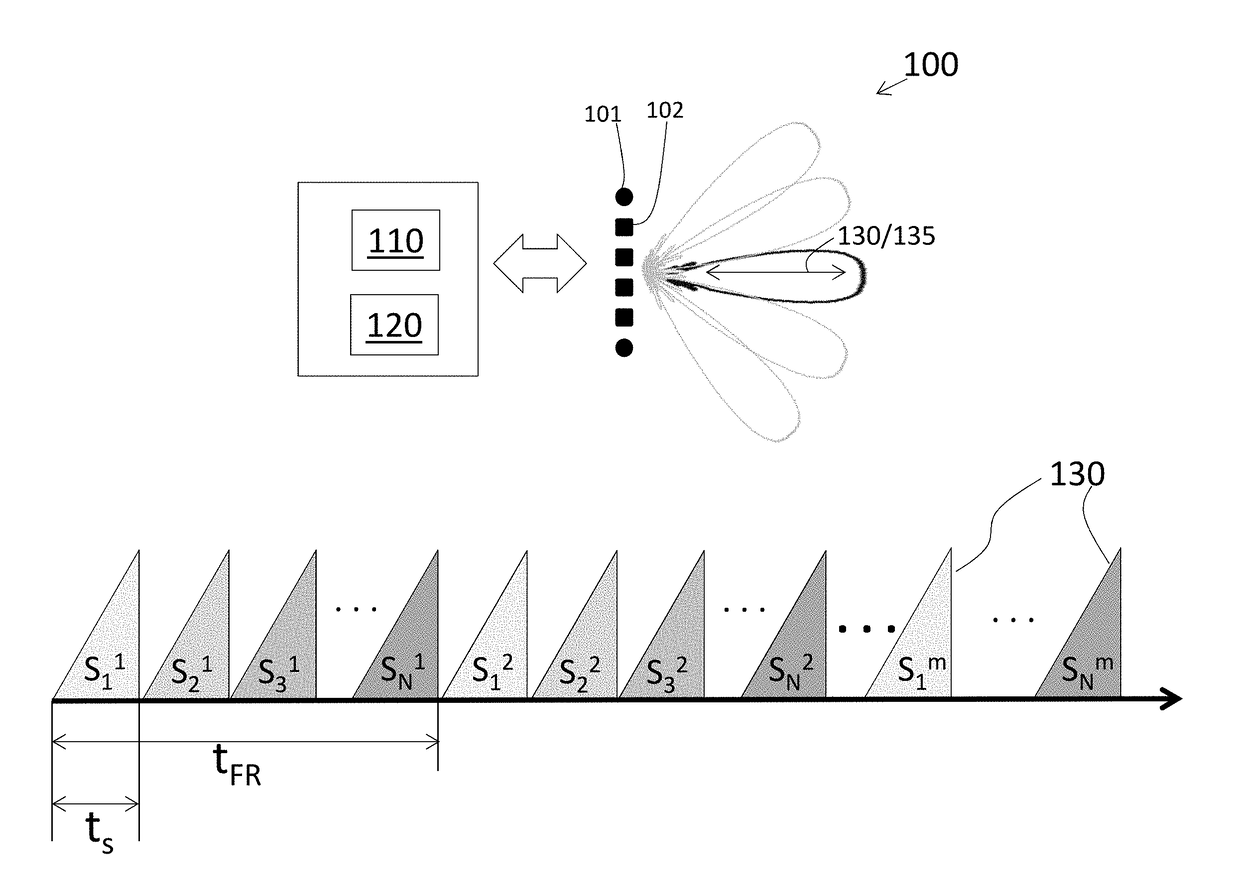
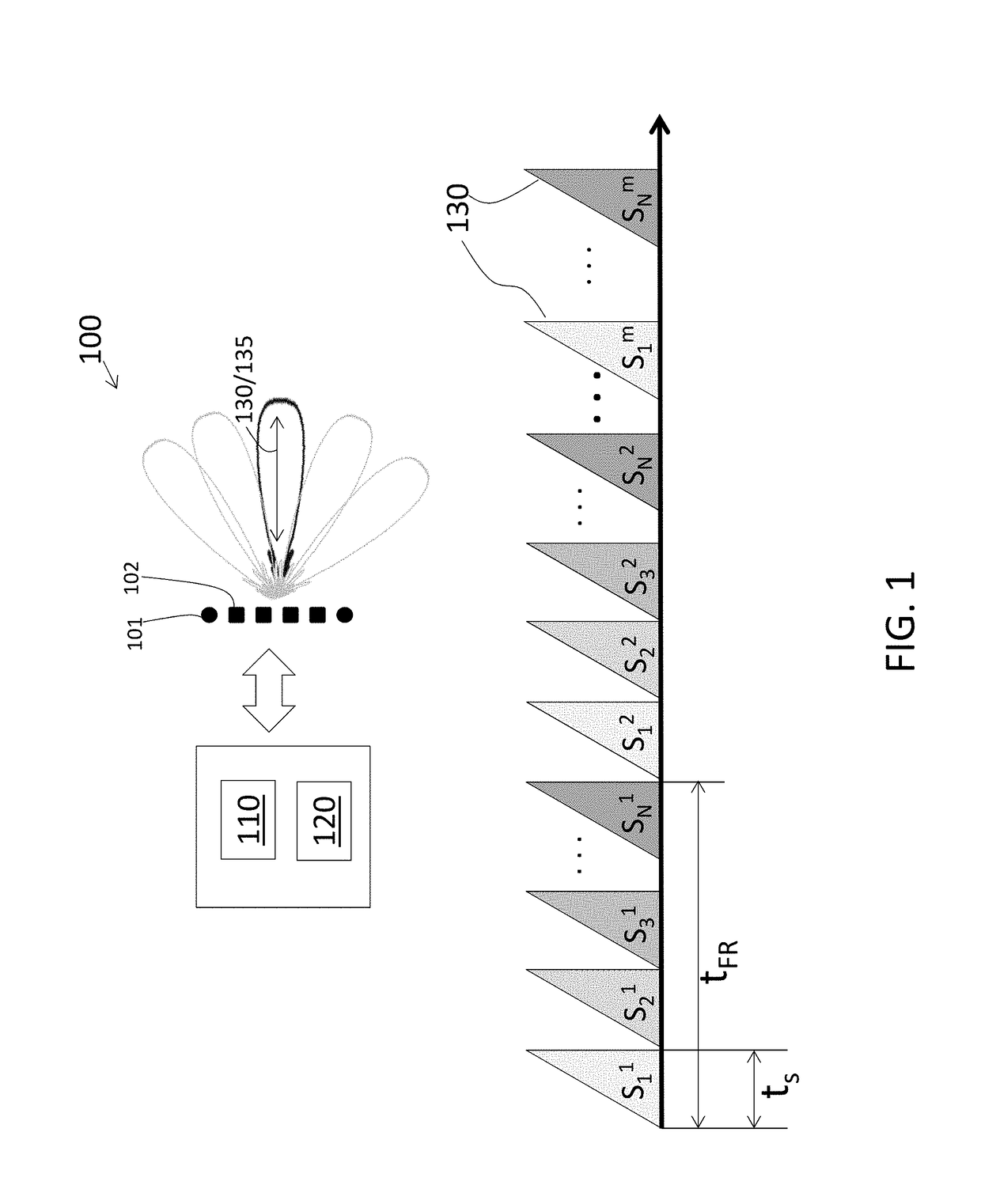
Low latency decoding in multi-input multi-output radar
A multi-input multi-output (MIMO) radar system and method of performing low-latency decoding in a MIMO radar system. The method includes transmitting a different linear frequency-modulated continuous wave (LFM-CW) transmit signal from each of N transmit elements of the MIMO radar system, each transmit signal associated with teach of the N transmit elements including a respective code, and receiving reflections associated with each of the transmit signals from each of the N transmit elements at each receive element of the MIMO radar system. Processing each symbol corresponding with each received reflection on a symbol-by-symbol basis is done to obtain a respective decoded signal prior to receiving all the received reflections associated with all the N transmit elements, wherein the processing includes using a Hadamard matrix with N columns in which each column is associated with the respective code transmitted by each of the N transmit elements.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
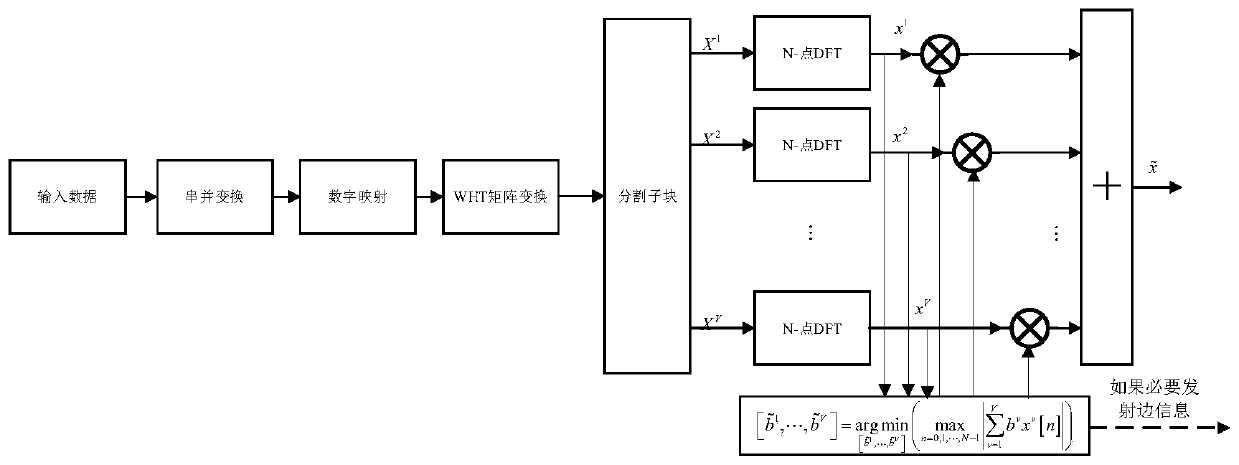
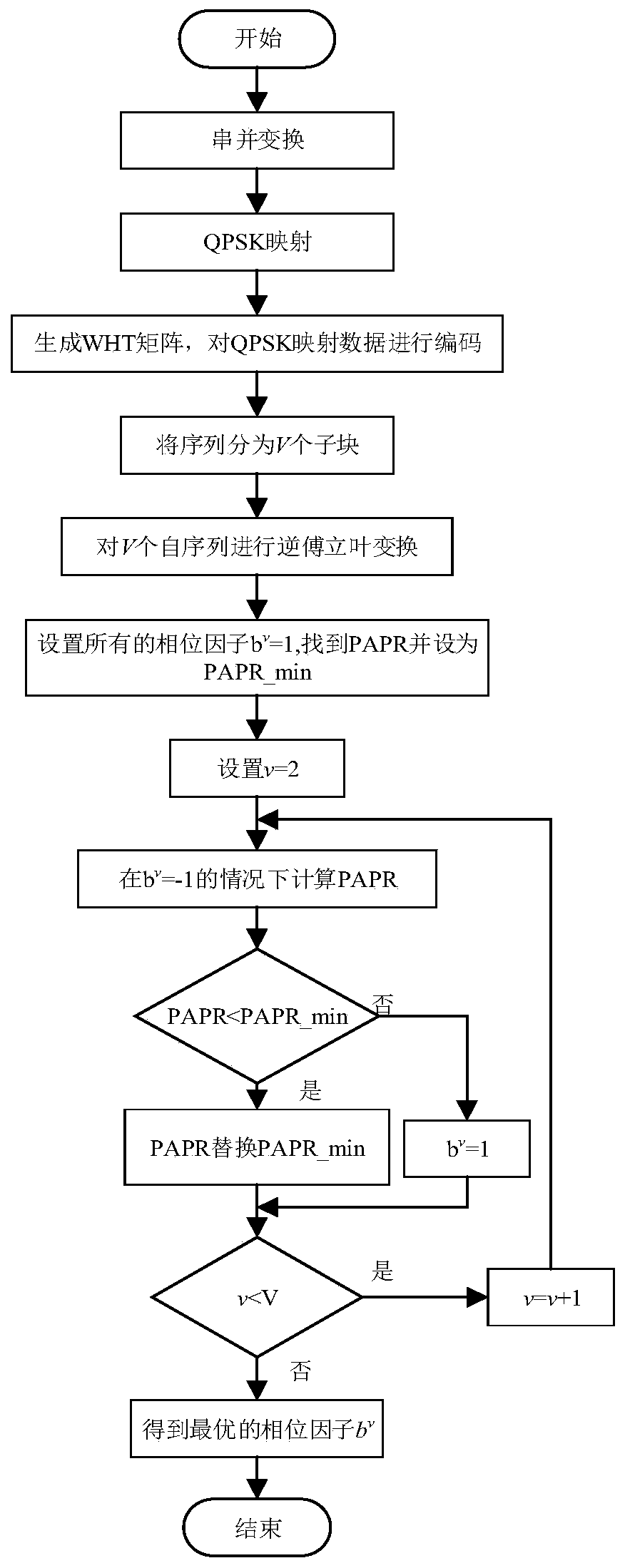
Partial transmission sequence peak-to-average ratio suppression method based on precoding
InactiveCN110351216ATo overcome the shortcomings of insufficient peak-to-average ratio reductionMeet the peak-to-average performance value requirementsMulti-frequency code systemsPrecodingComputer science
The invention belongs to the field of wireless communication, provides a partial transmission sequence peak-to-average ratio inhibition method based on precoding, and aims at solving the problem thatthe inhibition degree of a traditional partial transmission sequence on the peak-to-average ratio is not enough, a coding method is applied to a partial transmission sequence method, and Walsh-Hadamard matrix is used for pre-coding the data after the digital mapping module. As Walsh-Hadamard matrix can reduce the autocorrelation of frequency domain signals, thus the peak-to-average ratio of the system can be reduced. Compared with a traditional peak-to-average ratio suppression algorithm, the improved partial transmission sequence peak-to-average ratio suppression algorithm has better performance.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
High-signal-to-noise ratio quick intensity correlated imaging method
ActiveCN104714258AImprove robustnessOvercoming Severe Weather ImagingOptical based geological detectionImaging qualityControl signal
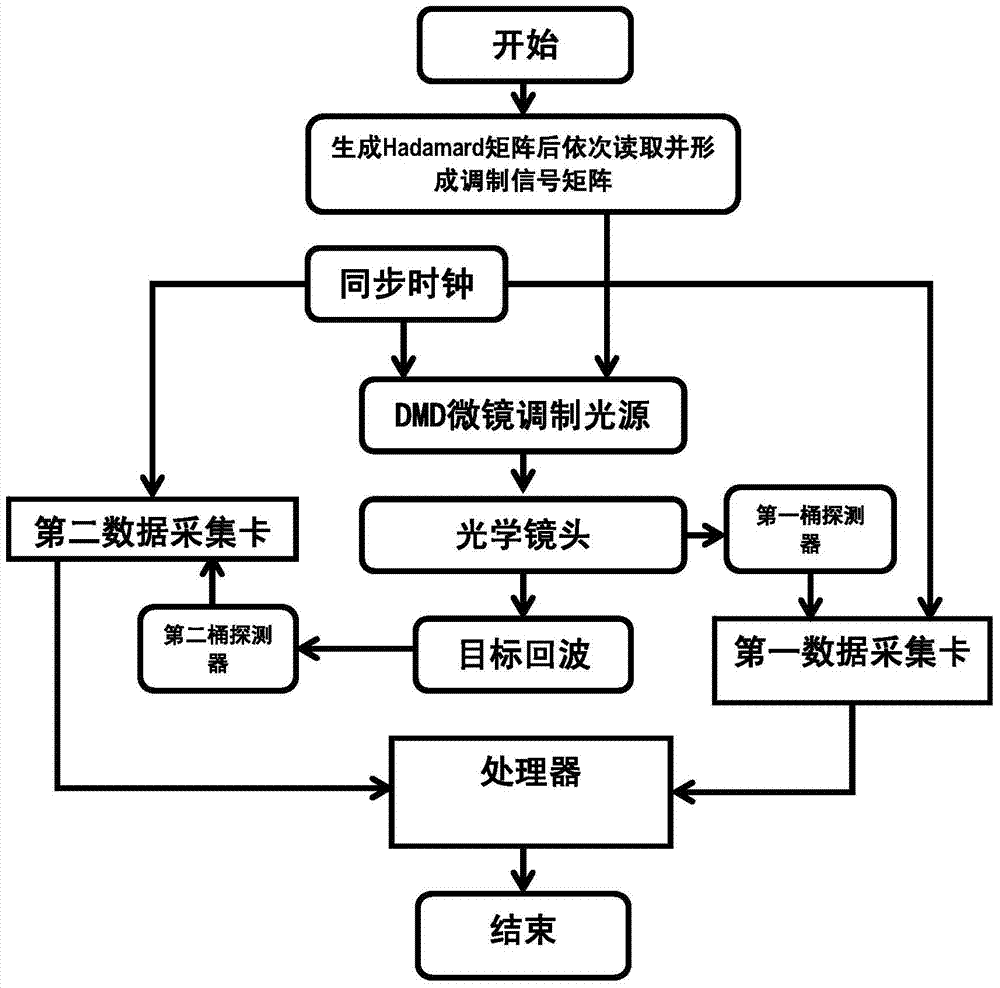
A high-signal-to-noise ratio quick intensity correlated imaging method comprises the steps of extracting lines or rows from a Hadamard matrix with M lines and M rows and conducting normalization, conducting matrix reshaping to obtain a modulating signal matrix, generating a synchronous clock signal, transmitting the modulating signal matrix to a modulated light source light field of a digital micromirror array device according to the synchronous clock signal, transmitting the synchronous clock signal to a first data acquisition card and a second data acquisition card to acquire an electric signal, converting the acquired electric signal into a digital signal to be transmitted to a processor, and obtaining an intensity correlated imaging result after standard image normalization processing is conducted on image matrixes output through measurement conducted M times by means of the processor. By the adoption of the method, imaging can be achieved in severe weather, and imaging robustness is high. Compared with traditional intensity correlated imaging methods, the method has the advantages that signal to noise ratio is high, image quality is high, imaging speed is high, and the requirements for practical application can be met.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF AEROSPACE CONTROL DEVICES
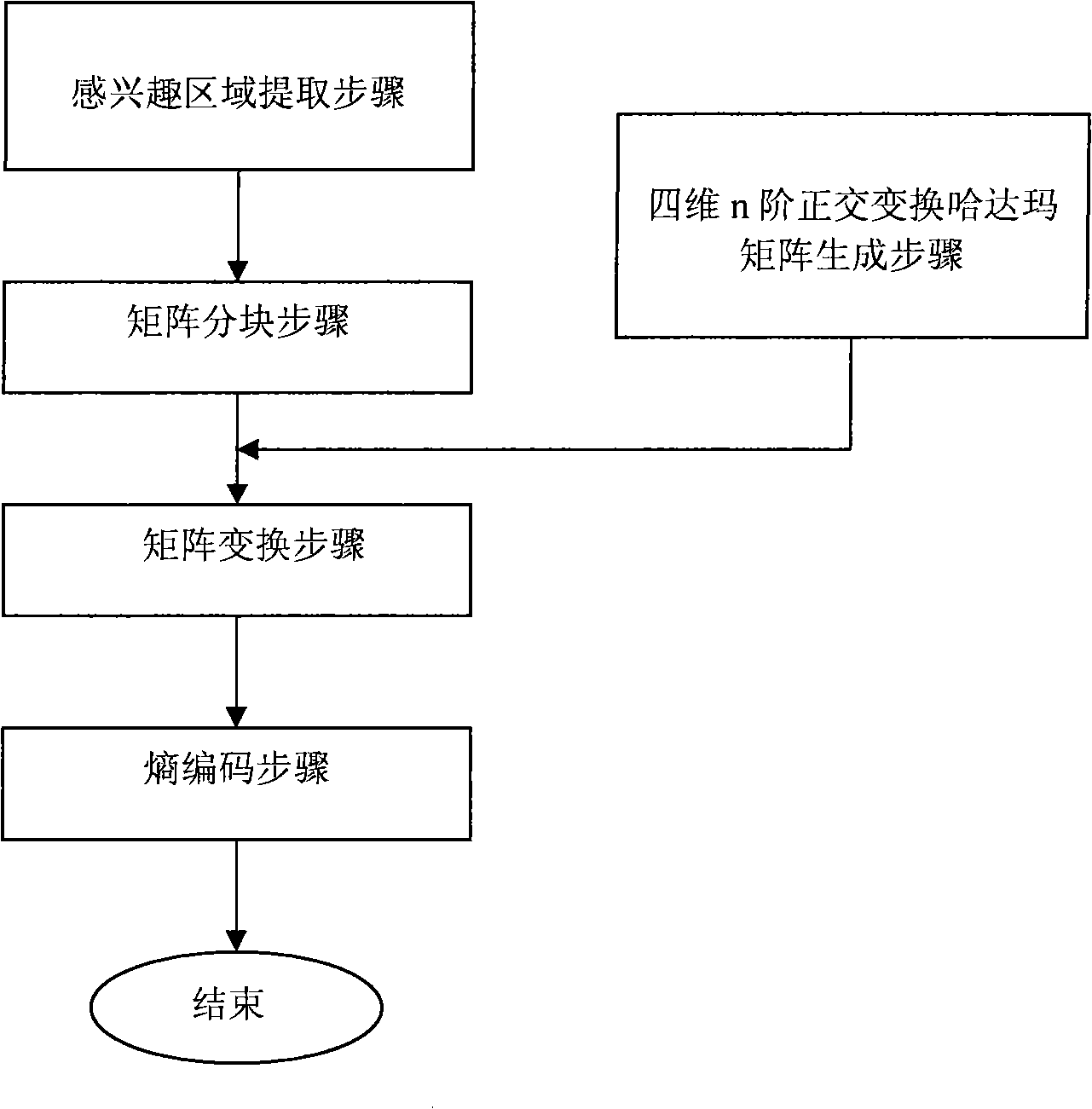
Encoding and decoding method of image sequence nondestructive compression based on interested area
InactiveCN101257629AIncrease the compression ratioTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationMethod of imagesSignal compression
The invention relates to an interesting area based nondestructive compression method, which is mainly used for motion image sequence. The coding / decoding method of nondestructive compression based on motion image sequence of interesting area improves greatly the compression ratio of image on the premise of guaranteeing non-distortion recovery of interesting area image signal. The specific step comprises: step of extracting interesting area; step of dividing blocks; step of transforming matrix; step of coding entropy; step of generating four-dimensional n-order orthogonal transformation Hadamard matrix. The core content of the invention is that the definition of the four-dimensional n-order matrix and the definition of its algorithm are introduced in the image sequence signal compression method, and the corresponding four-dimensional n-order orthogonal transformation are introduced, and Hadamard four-dimensional n-order orthogonal matrix and its Kronic multiplication generation method are provided.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for generating signals of low-interference multi-velocity multi-district quasi-synchronous CDMA communication system
InactiveCN101378294AReduce distractionsChoose flexibleMultiplex code generationOrthogonal sequenceBent function
The invention discloses a signal generation method of a low-interference multispeed multi-cell quasi-synchronous code division multiple access (CDMA) communication system. The method comprises the steps: a spread spectrum sequence code group is an Hadamard matrix set with certain idealized characteristics formed by Bent functions and a Walsh-Hadamard orthogonal sequence set; a sequence set with the characteristic of a similar zero correlation zone (ZCZ) sequence is obtained by calculating with a pair of complementary sequence sets by utilizing the Hadamard matrix set; and a plurality groups of sequence sets with the similar ZCZ sequence characteristics are obtained by carrying out Cartesian convolution operation with the orthogonal sequence set by utilizing the similar ZCZ sequence set. When a system maximum synchronization error and a channel maximum multipath delay spread are in the stated range, the system interference can be reduced greatly. The parameters of the spread spectrum sequence code group and the system efficiency can be adjusted and flexibly selected according to the practical factors. Therefore, the requirements of power control and synchronization by the CDMA communication system are reduced, and the complexity of system realization is lowered.
Owner:CHONGQING WIRELESS OASIS COMM TECHCO +1
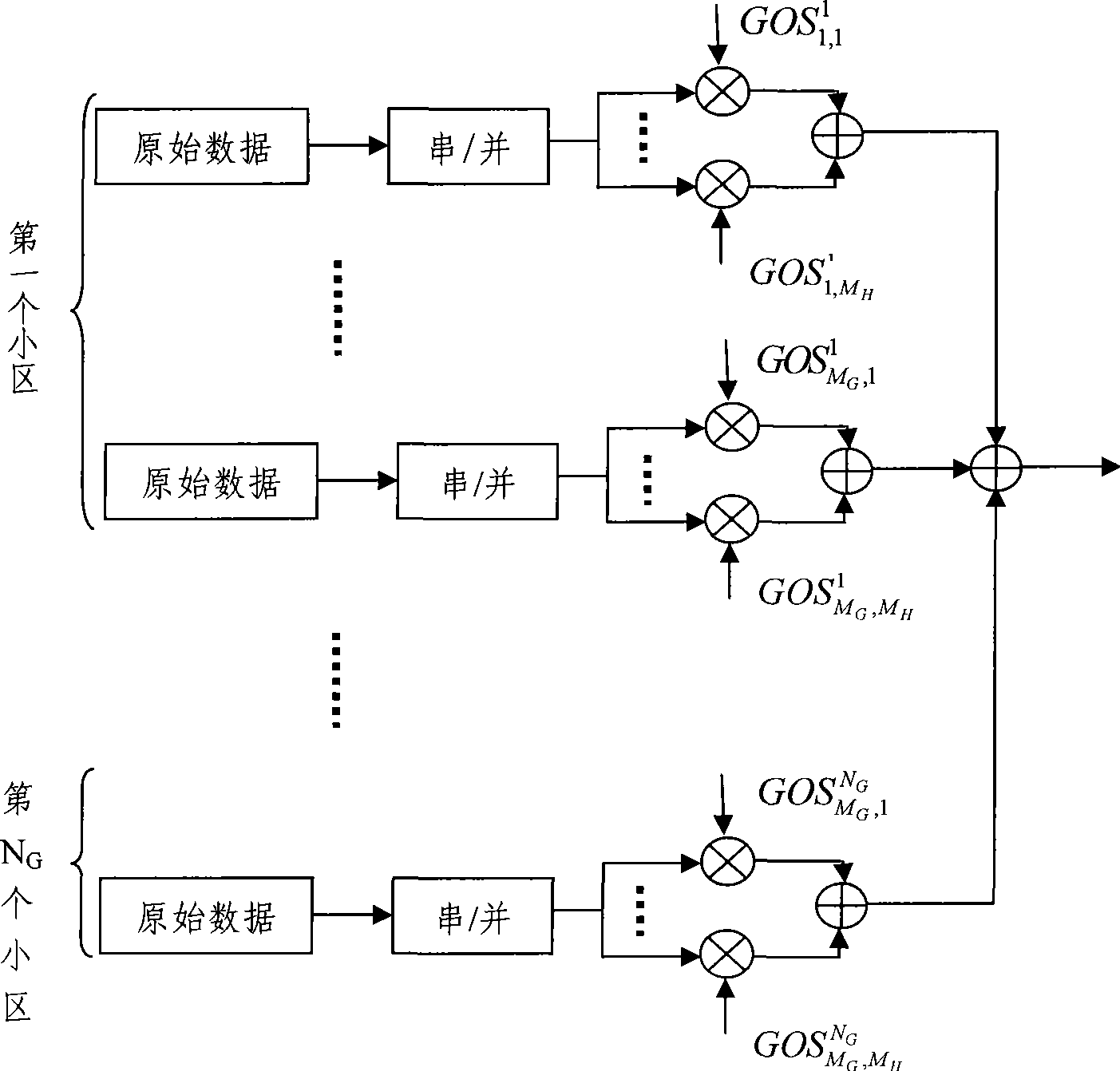
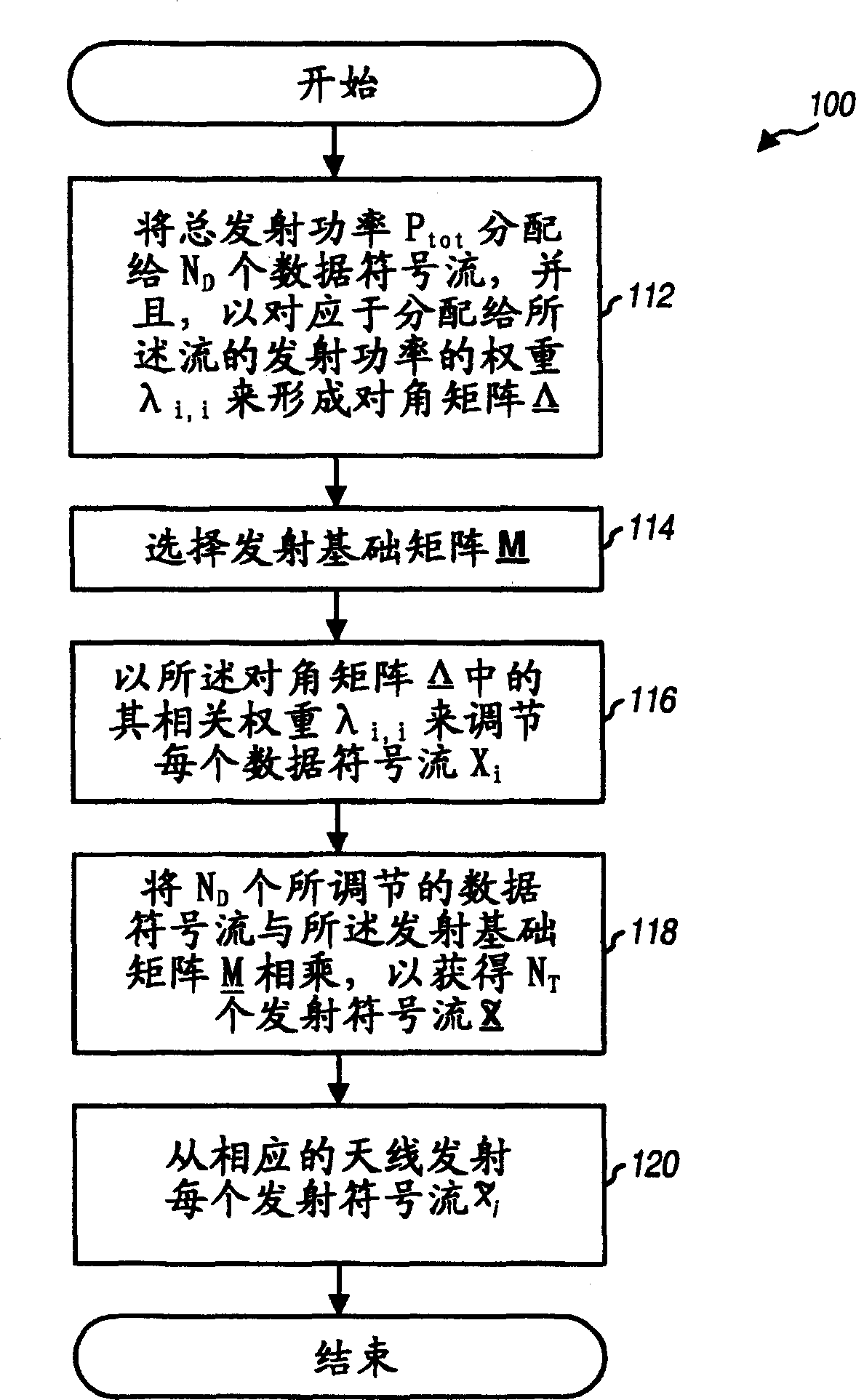
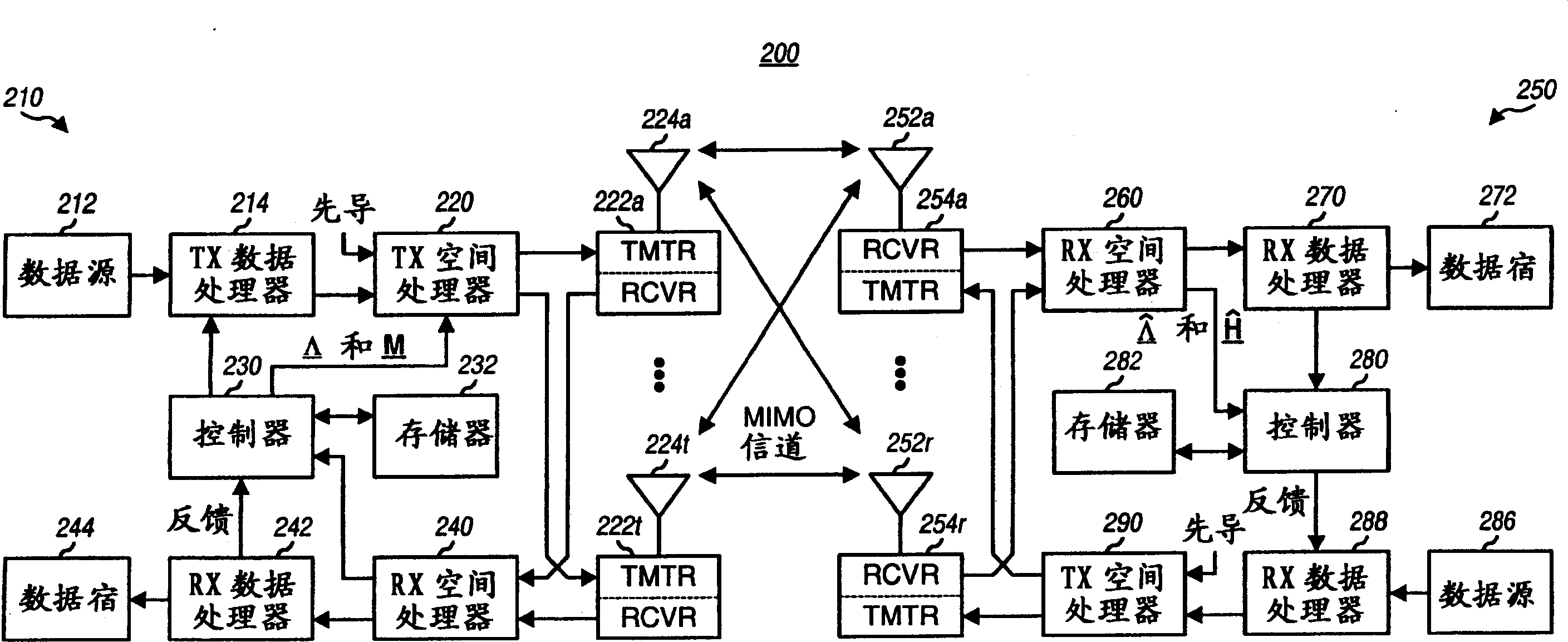
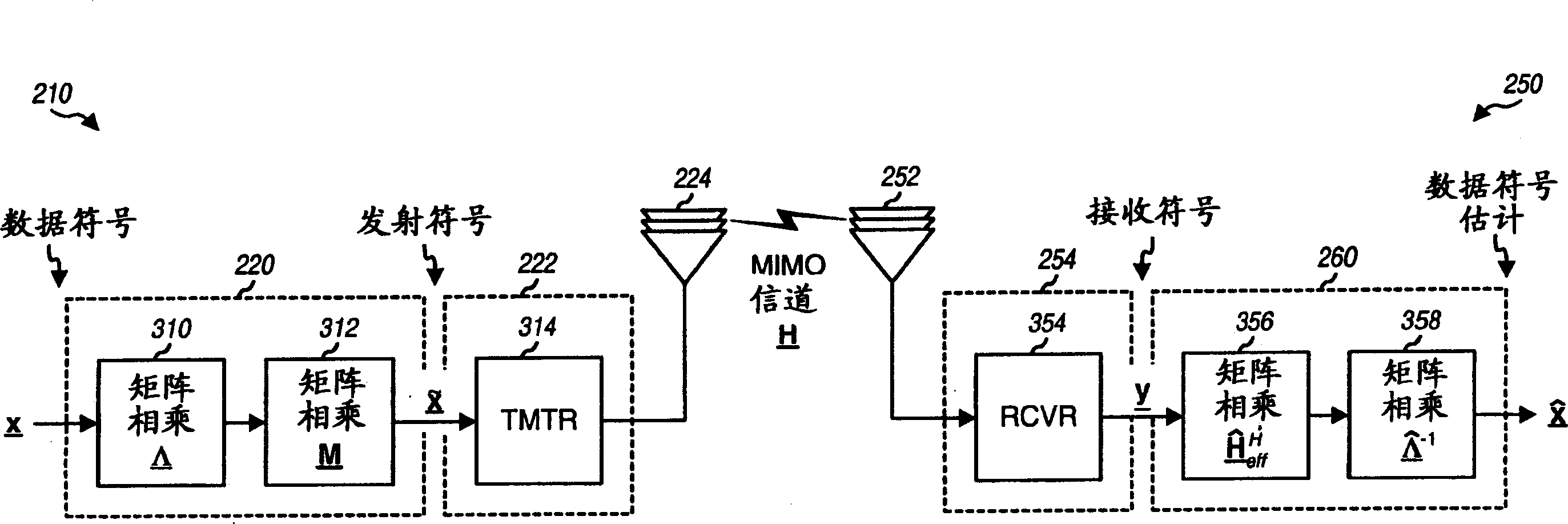
Transmission scheme for multi-carrier MIMO systems
A rate adaptive transmission scheme for MIMO systems, which can transmit a variable number of data symbol streams, provide transmit diversity for each data symbol stream, and fully utilize the total transmit power of the system and the full power of each antenna. In one method, at least one data symbol stream is received for transmission from a plurality of antennas. Each data symbol stream is scaled with a respective weight corresponding to the amount of transmit power allocated to that stream. The scaled data symbol stream(s) are multiplied with a transmit basis matrix to provide a plurality of transmit symbol streams for the plurality of antennas. The transmit basis matrix (e.g., a Walsh-Hadamard matrix or a DFT matrix) is defined such that each data symbol stream is transmitted from all antennas and each transmit symbol stream is transmitted at (or near) the full power for the associated antenna.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Extremely fast polling method for determining the presence of individual electric meters on a power line
ActiveUS7227462B2High rateImprove reliabilityElectric signal transmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsEngineeringOutage detection
A “super-fast” polling method for electrical meters for outage detection. In response to a query, a large group of electric meters (M) all simultaneously transmit reply signals over an electrical distribution network using TWACS®. The signals are separated by an inbound detector (IB) at a receiving end of the network. This allows a very large number of meters to be polled in a very short period of time to determine whether or not an outage has occurred at the location of each meter. Each meter transmits a bit pattern, and bit patterns are designed so a group of meter units can transmit their patterns simultaneously over a power line (L) to the inbound detector. The presence or absence of a bit pattern in the received signal conveys the presence or absence of the associated meter in the system. The ability to transmit multiple bit patterns in parallel requires that they be orthogonal to each other. The Hadamard matrices are a class of matrices whose rows could be used as a set of bit patterns.In addition to super-fast polling for outage detection, the method of the invention can also be used to poll meters for the presence of an alarm condition, as well as for both outage detection and an alarm condition.
Owner:ACLARA TECH LLC
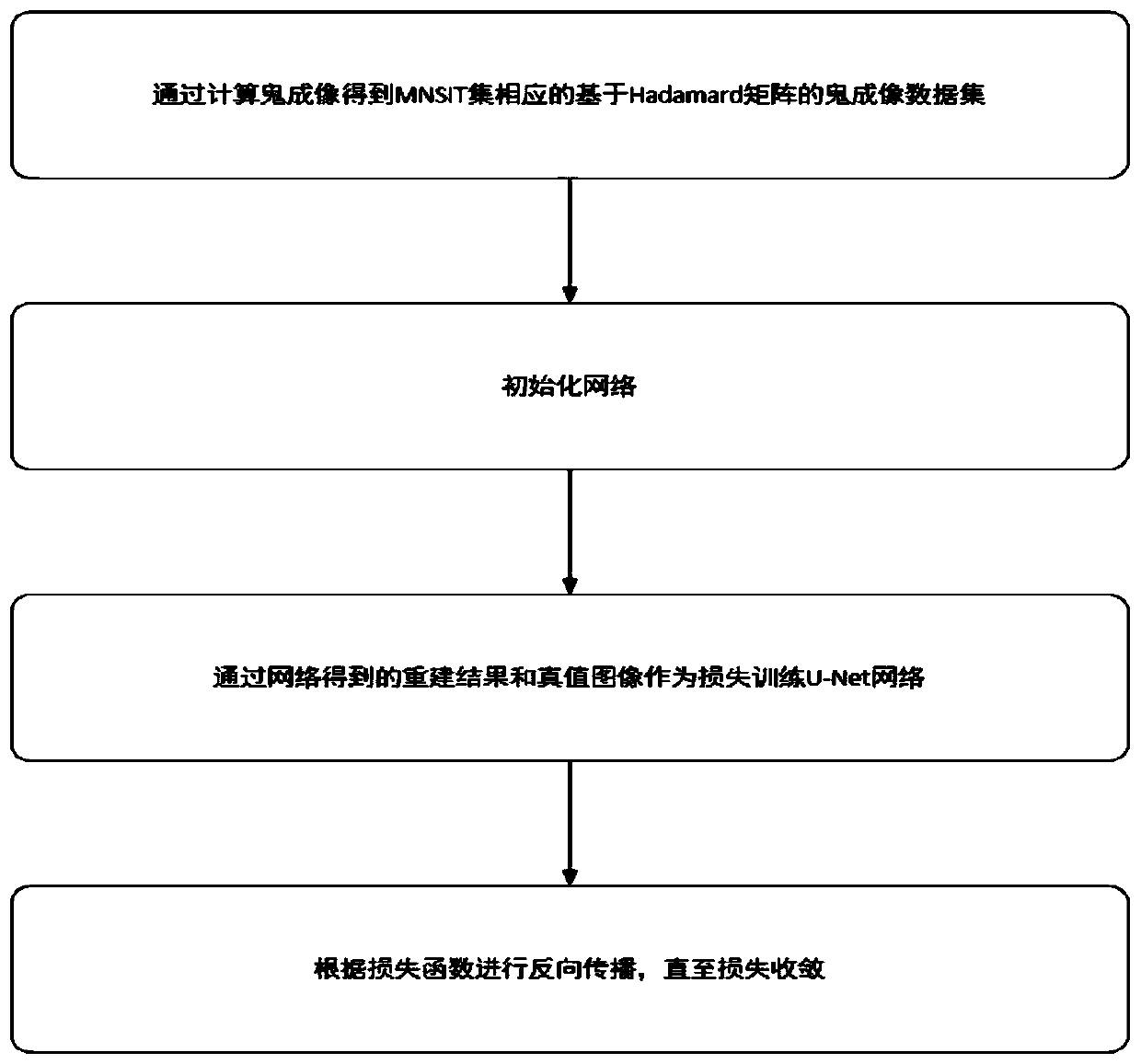
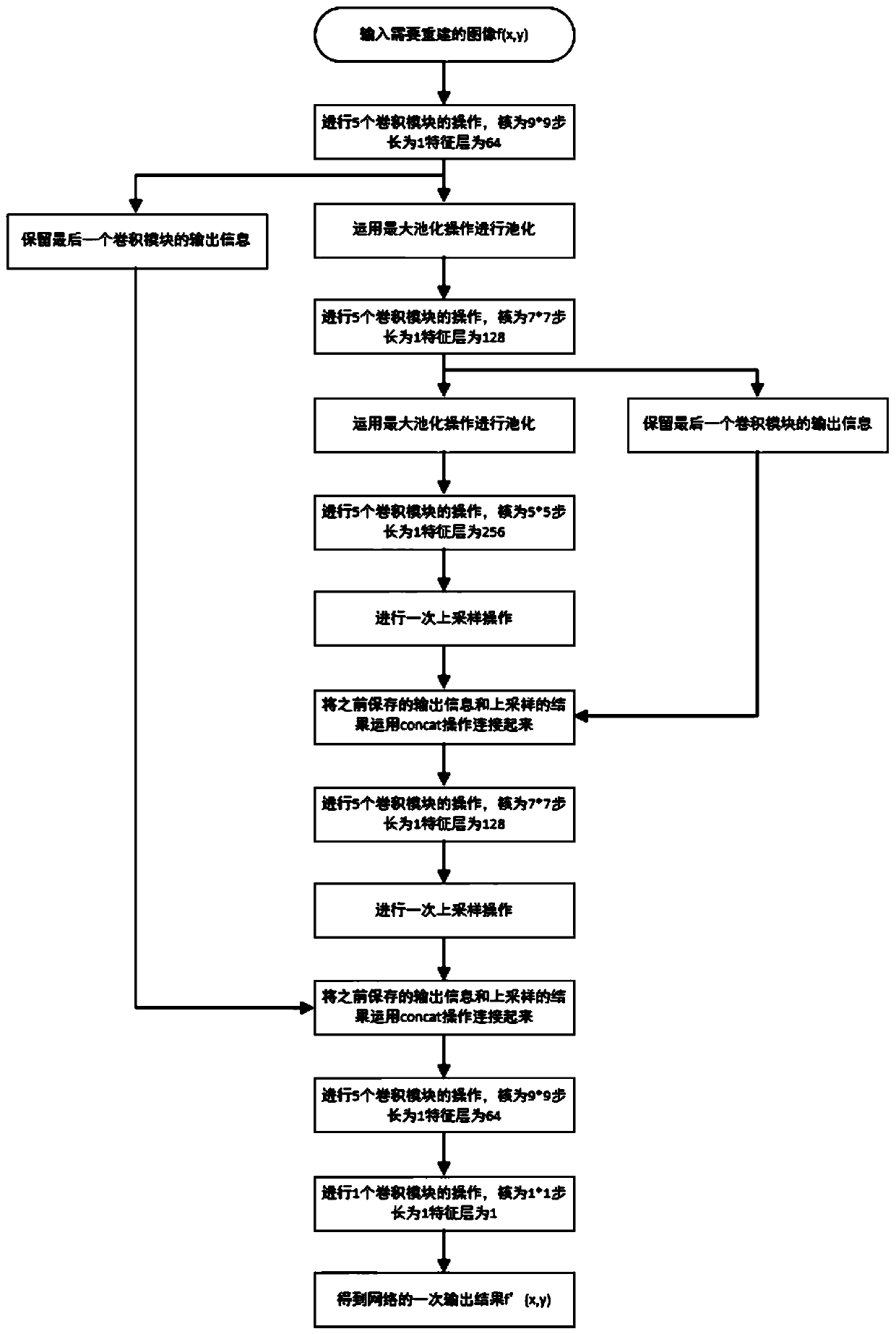
Method for calculating ghost imaging reconstruction recovery based on U-Net network
ActiveCN110675326AAdd depthImprove reconstruction effectImage enhancementImage analysisData setAlgorithm
The invention discloses a method for calculating ghost imaging reconstruction recovery based on a U-Net network. The calculation ghost imaging reconstruction recovery method comprises the steps of firstly obtaining a ghost imaging data set based on a Hadamard matrix corresponding to an MNSIT data set obtained through calculation ghost imaging; then constructing a U-Net network model, dividing theobtained data into a training set and a test set, and training the U-Net network model through training set data; and finally, verifying the trained U-Net network model through a test set and outputting a result to realize calculation ghost imaging reconstruction. According to the method, the number of random phase masks can be reduced to 7%, a good result is obtained, the reconstruction effect ofghost imaging calculation is effectively improved, and the reconstruction speed is increased.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
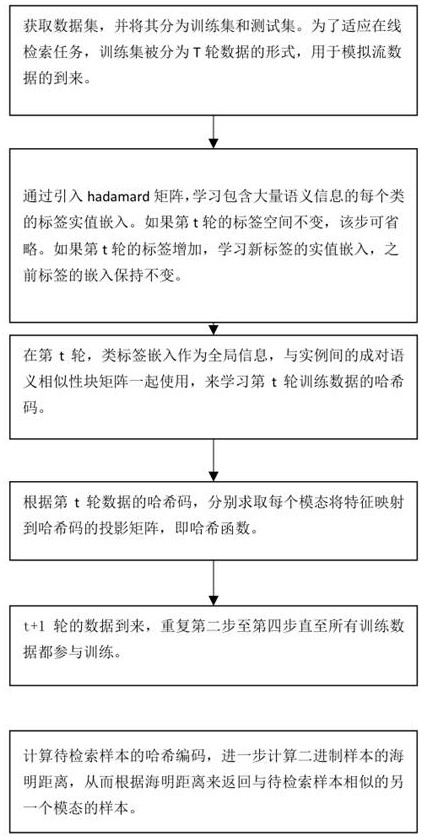
Online cross-modal retrieval method and system using three-step strategy
ActiveCN113326287ALearn accuratelyRich semantic informationDigital data information retrievalSemantic analysisStreaming dataTheoretical computer science
The invention provides an online cross-modal retrieval method and system using a three-step strategy. The online cross-modal retrieval method comprises the following steps: acquiring analog stream data formed by different modals; for analog stream data, generating the representation of each class label by introducing a hadamard matrix, the representation of each class label is used as global information for learning a hash code, and the representation of each class label also keeps local similarity information, using the correlation between newly arrived data in the analog stream data and existing data to learn a Hash code with more discriminative power; updating a hash function by using the learned hash code; and calculating a hash code of the to-be-retrieved sample by using the updated hash function, and calculating a Hamming distance of a binary sample based on the hash code, thereby returning a sample of another modal similar to the to-be-retrieved sample according to the Hamming distance. According to the method, the THOR can reserve more semantic information and learn more accurate hash codes.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com