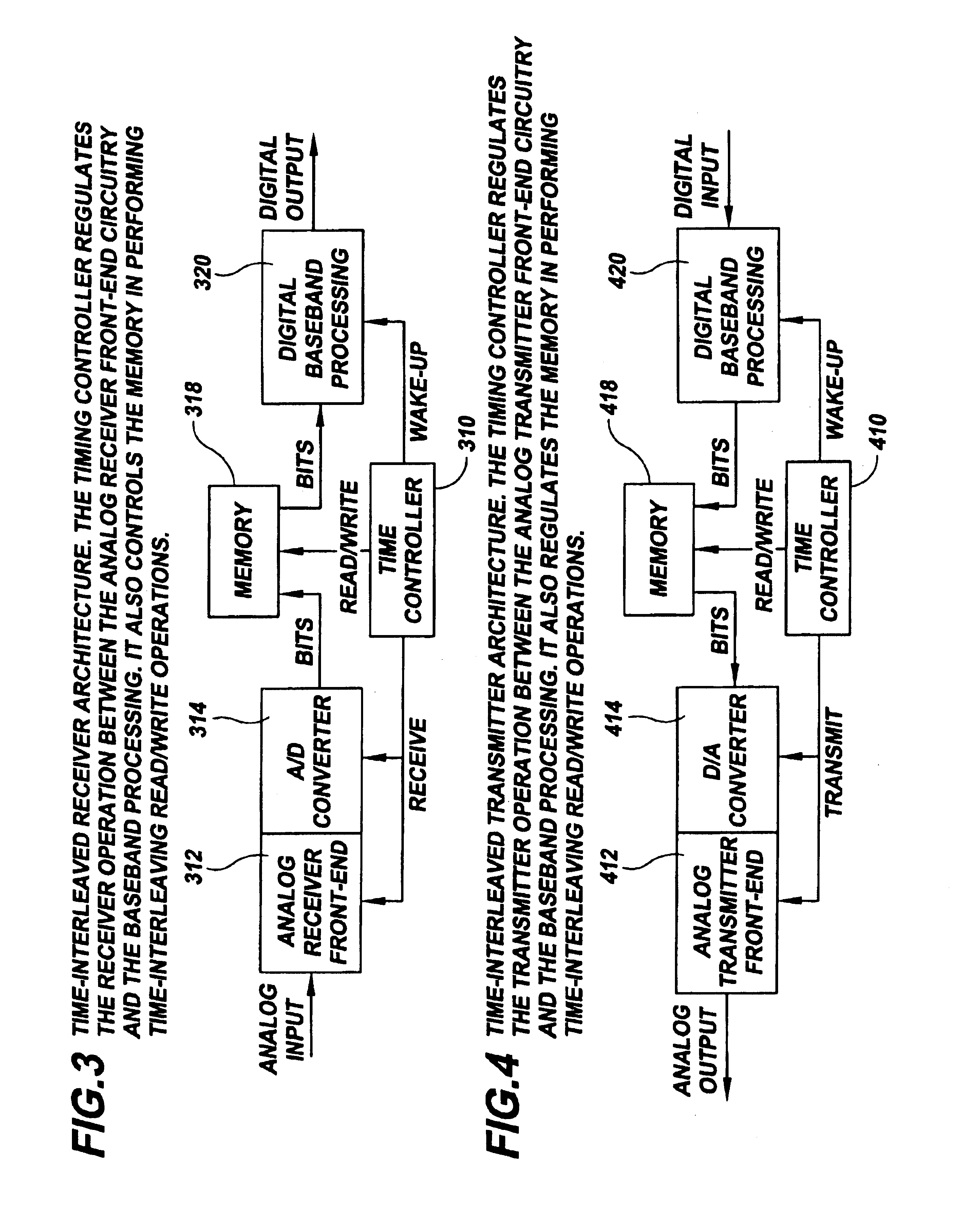
Patents
Literature
4073results about "Line-faulsts/interference reduction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
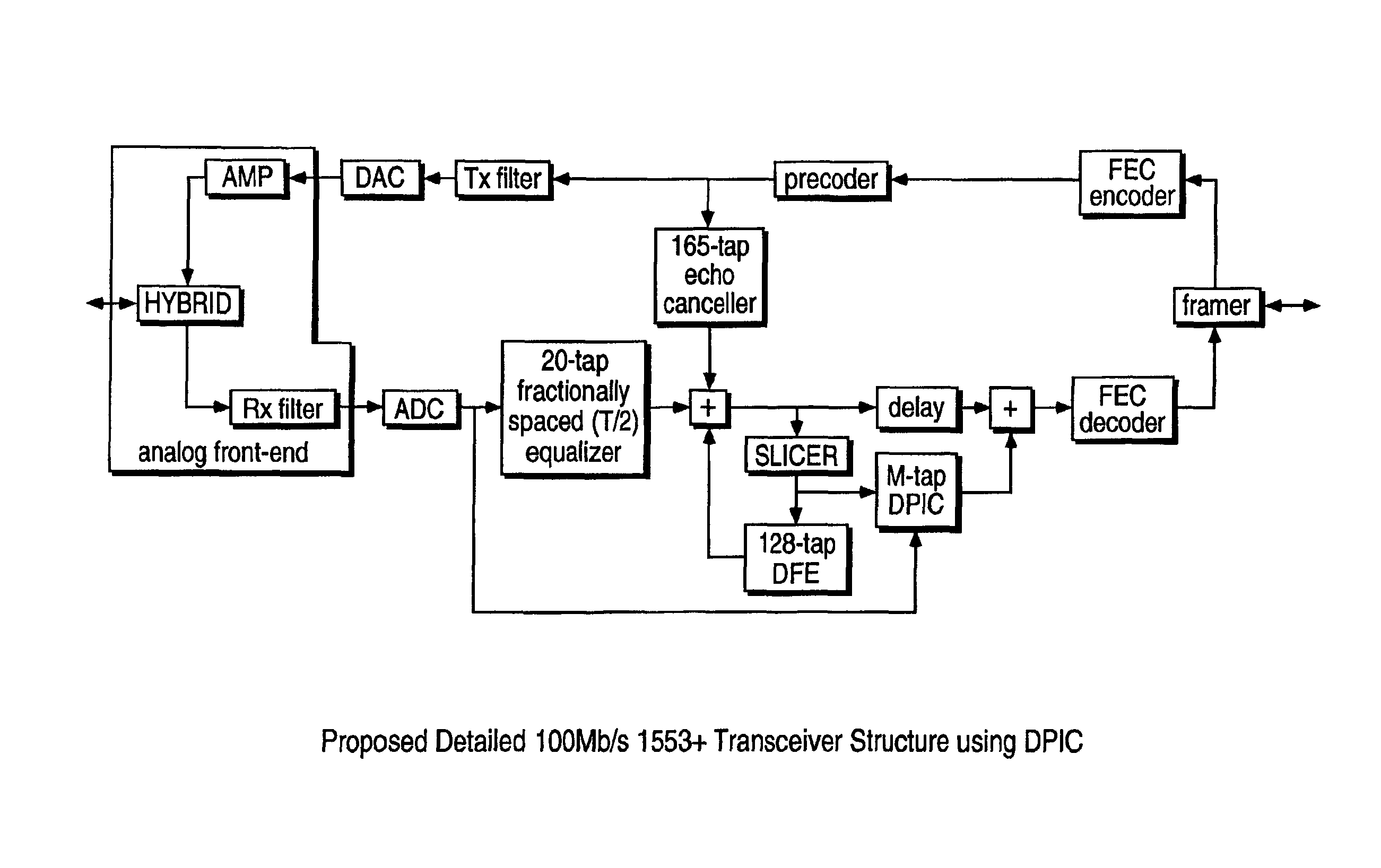
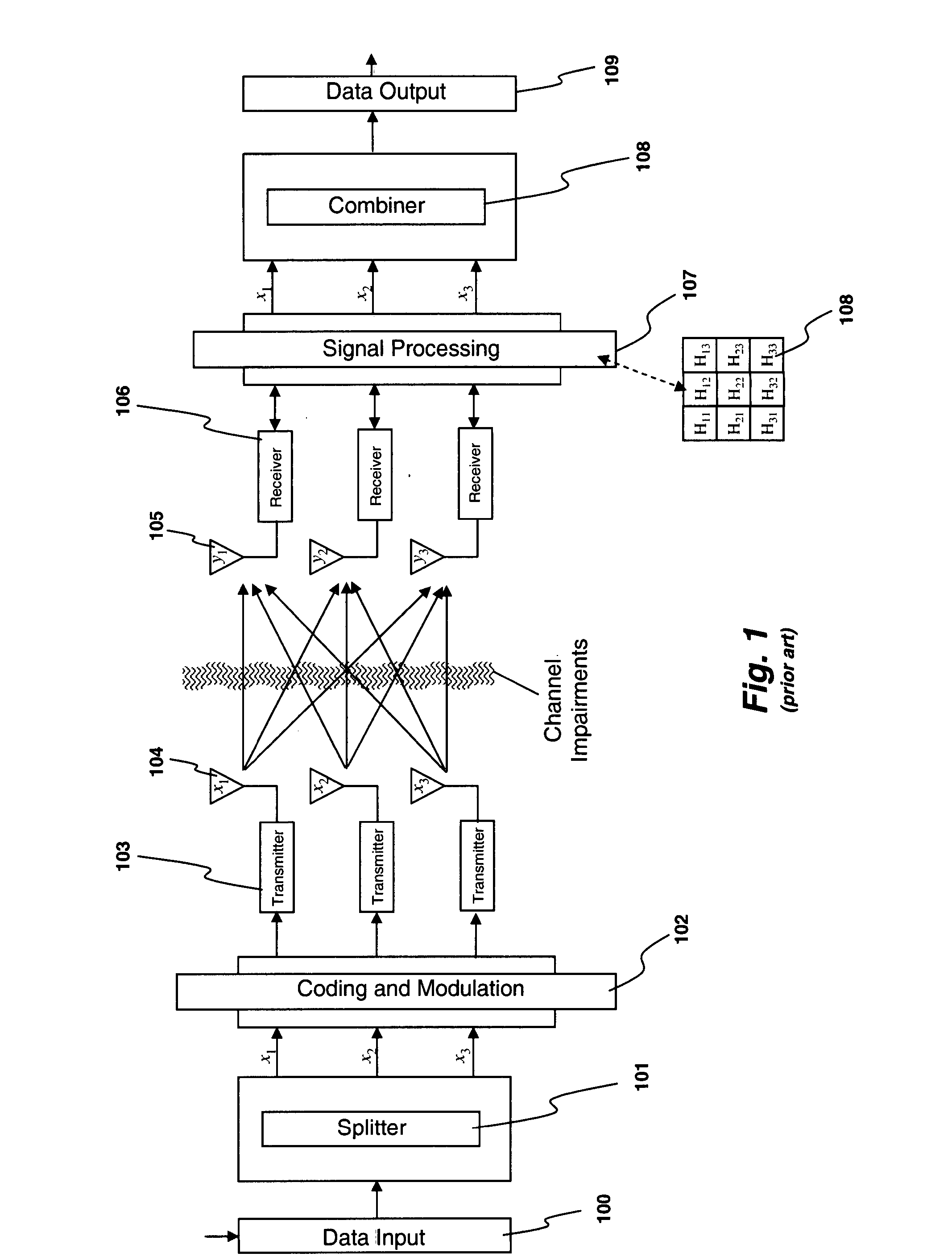
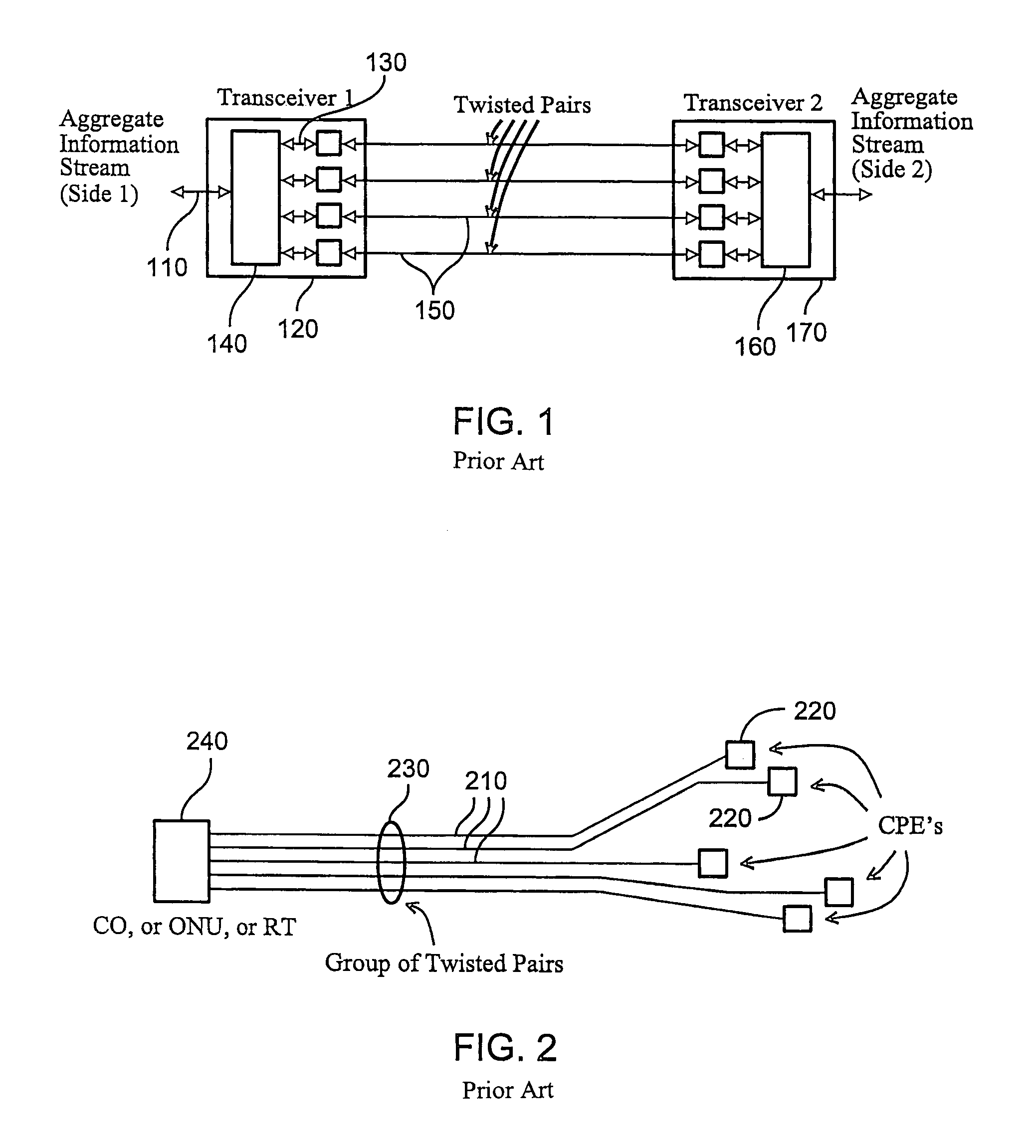
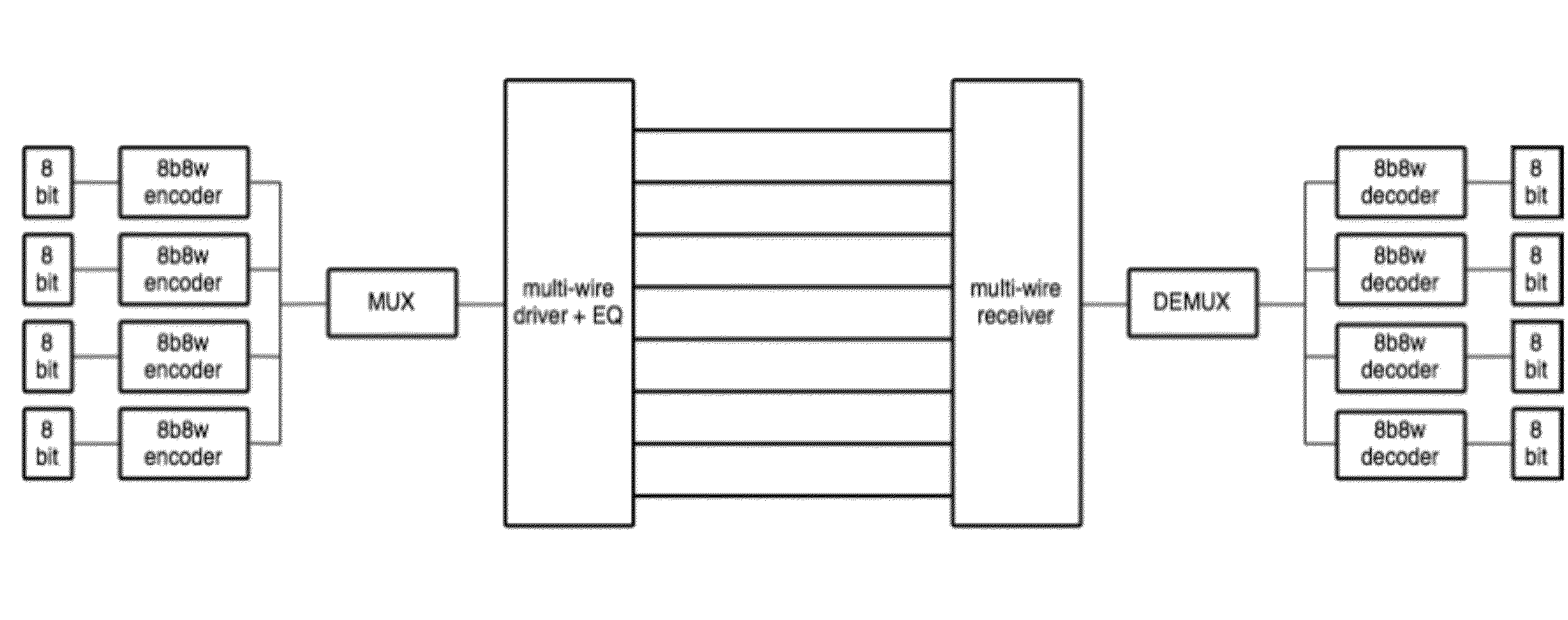
Channel equalization system and method
InactiveUS6904110B2Increase high performance and data rate capacityLow costMultiple-port networksChannel dividing arrangementsFiberEngineering
A system and method for delivering increases speed, security, and intelligence to wireline and wireless systems. The present invention increases channel capacity by using a parallel or multi-channel structure in such wireless and wireline at the edge or the core of. This new architecture of the present invention uses parallel bitstreams in a flexible way and distributed switching / routing technique, is not only to avoid the potential bottlenet of centralized switches, but also to increase speed with intelligence that is seamlessly integrating into the Fiber Optic Backbone such as WDM and SONET of the MAN / WAN network with a Real-time guarantees, different types of traffic (such as Stringent synchronous, isochronous, and asynchronous data messages) with different demands, and privacy & security of multi access and integrated services environment.
Owner:B C LEOW
Channel adaptive equalization precoding system and method
InactiveUS20030086515A1Increase high performance and data rate capacityLow costChannel dividing arrangementsError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorPrecodingOperational system
A system and method for delivering increased speed, security, and intelligence to wireline and wireless systems. The present invention includes a new generation Fast Circuit Switch (packet / circuit) Communication processors and platform which enables a new Internet Exchange Networking Processor Architecture at the edge and core of every communication system, for next generation Web Operating System or Environment (WOE) to operate on with emphasis of a non-local processor or networking processor with remote web computing capabilities.
Owner:TRANS FRANCOIS +1
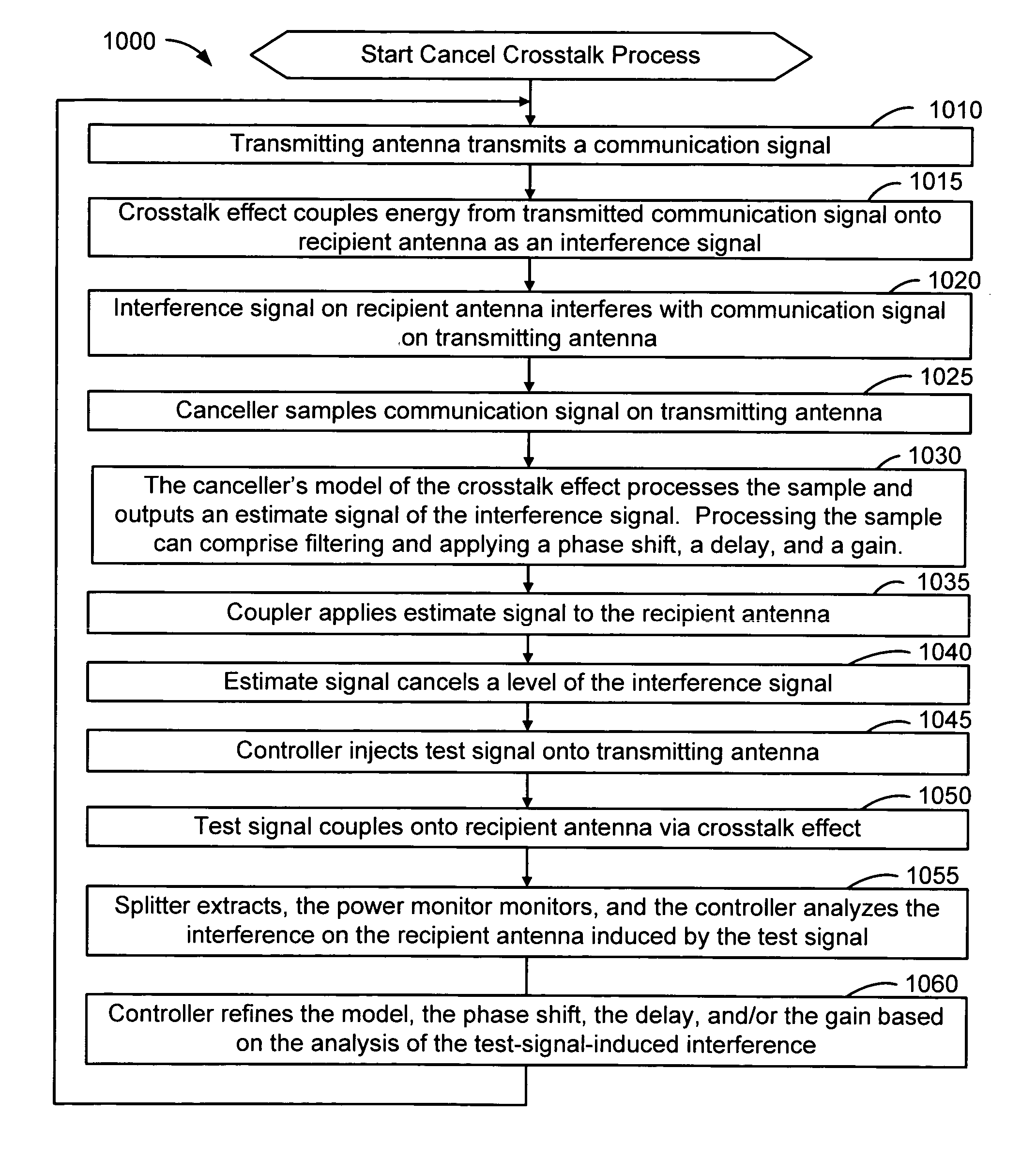
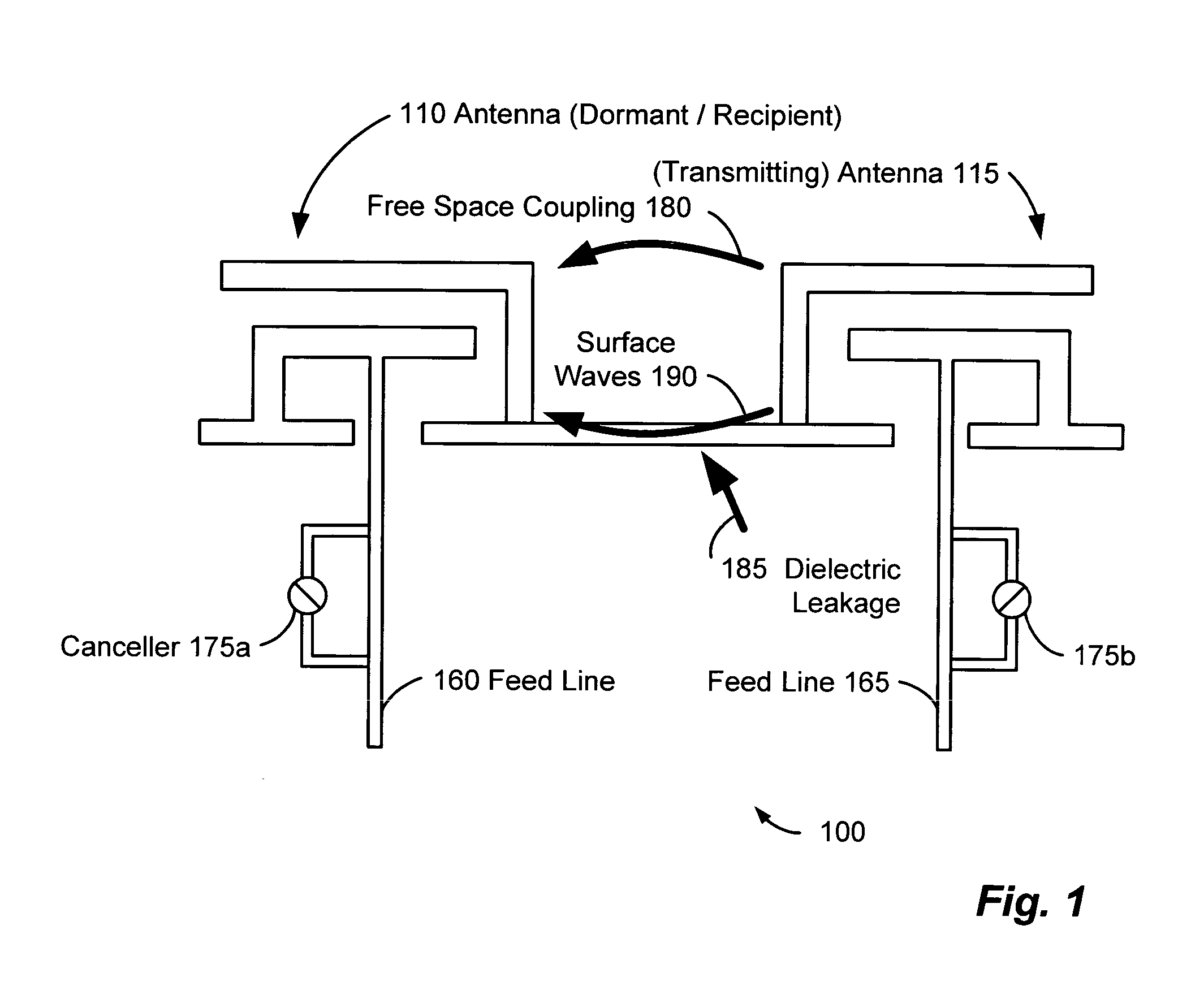
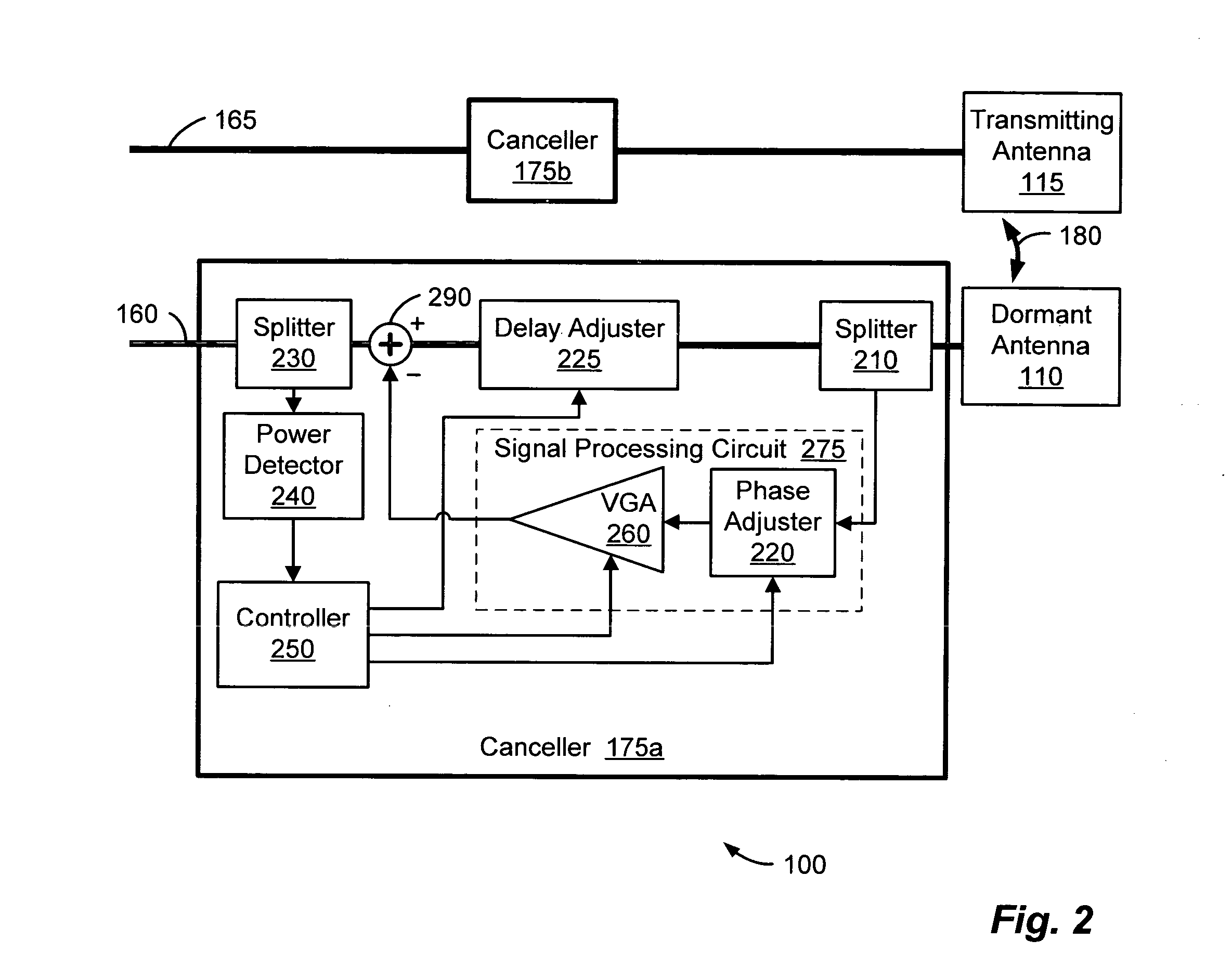
Method and system for antenna interference cancellation
InactiveUS20050226353A1Improve signal qualityHigh bandwidthCorrect operation testingLine-faulsts/interference reductionCommunications systemSignal on
A wireless communication system can comprise two or more antennas that interfere with one another via free space coupling, surface wave crosstalk, dielectric leakage, or other interference effect. The interference effect can produce an interference signal on one of the antennas. A cancellation device can suppress antenna interference by generating an estimate of the interference signal and subtracting the estimate from the interference signal. The cancellation device can generate the estimate based on sampling signals on an antenna that generates the interference or on an antenna that receives the interference. The cancellation device can comprise a model of the crosstalk effect. Transmitting test signals on the communication system can define or refine the model.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
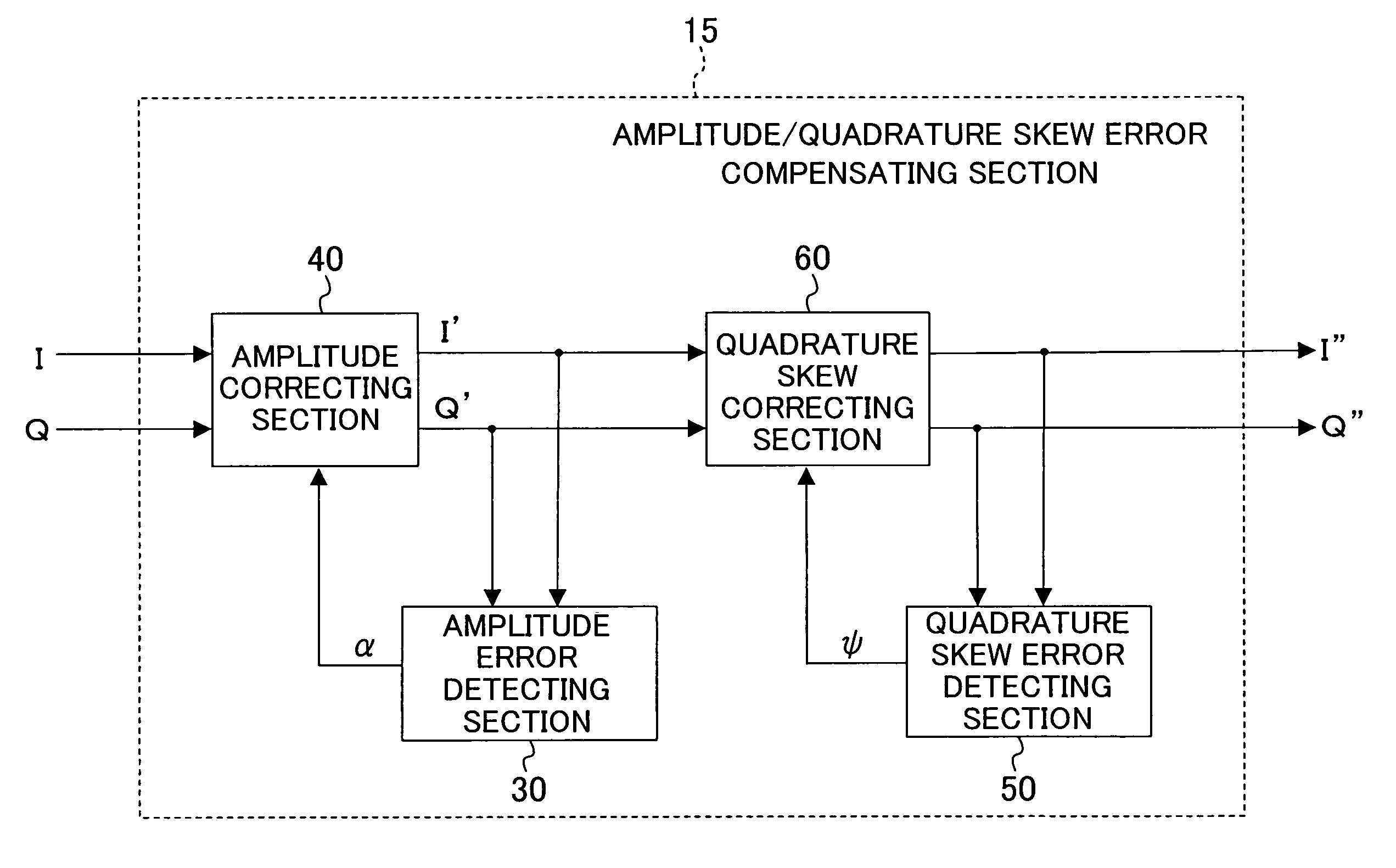
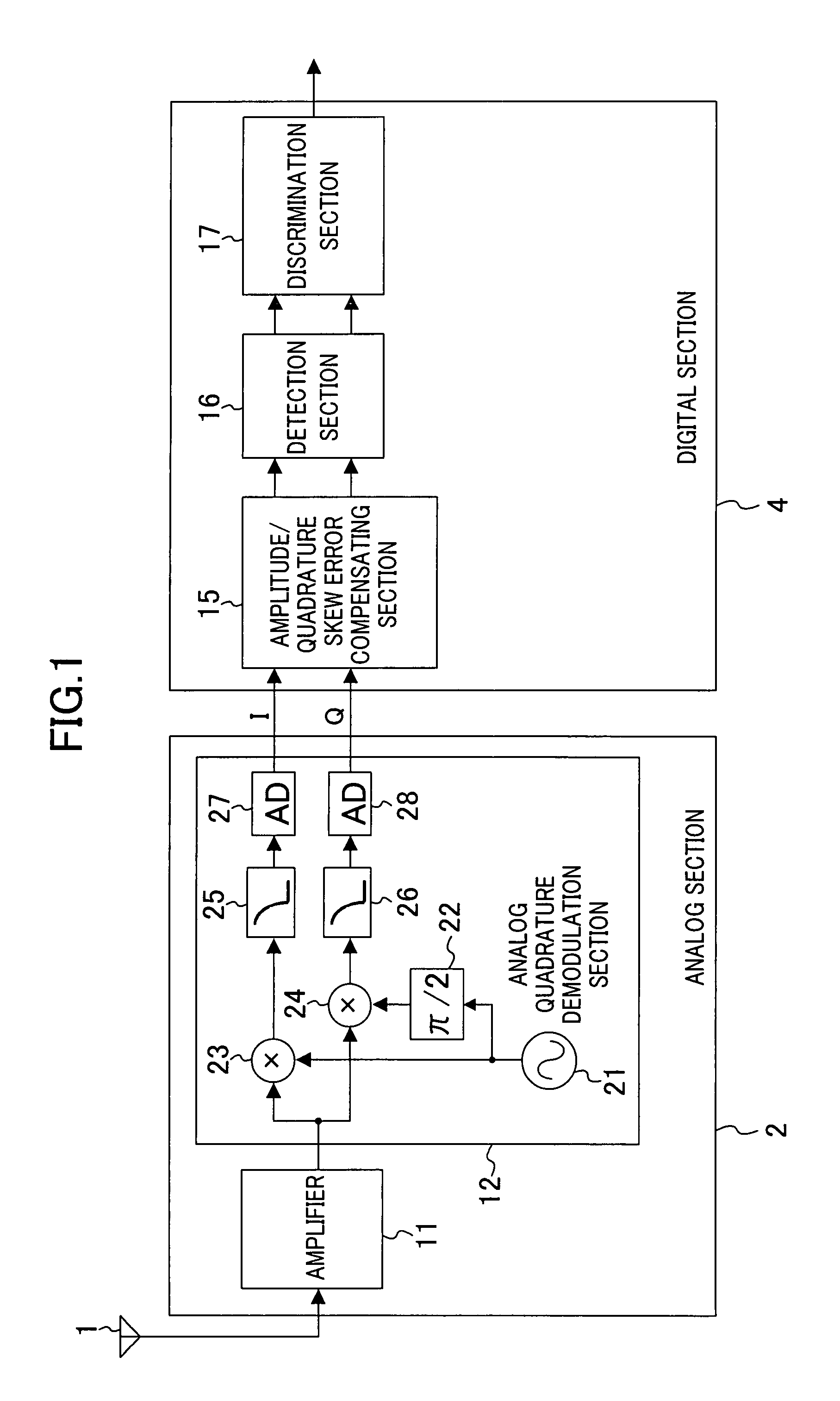
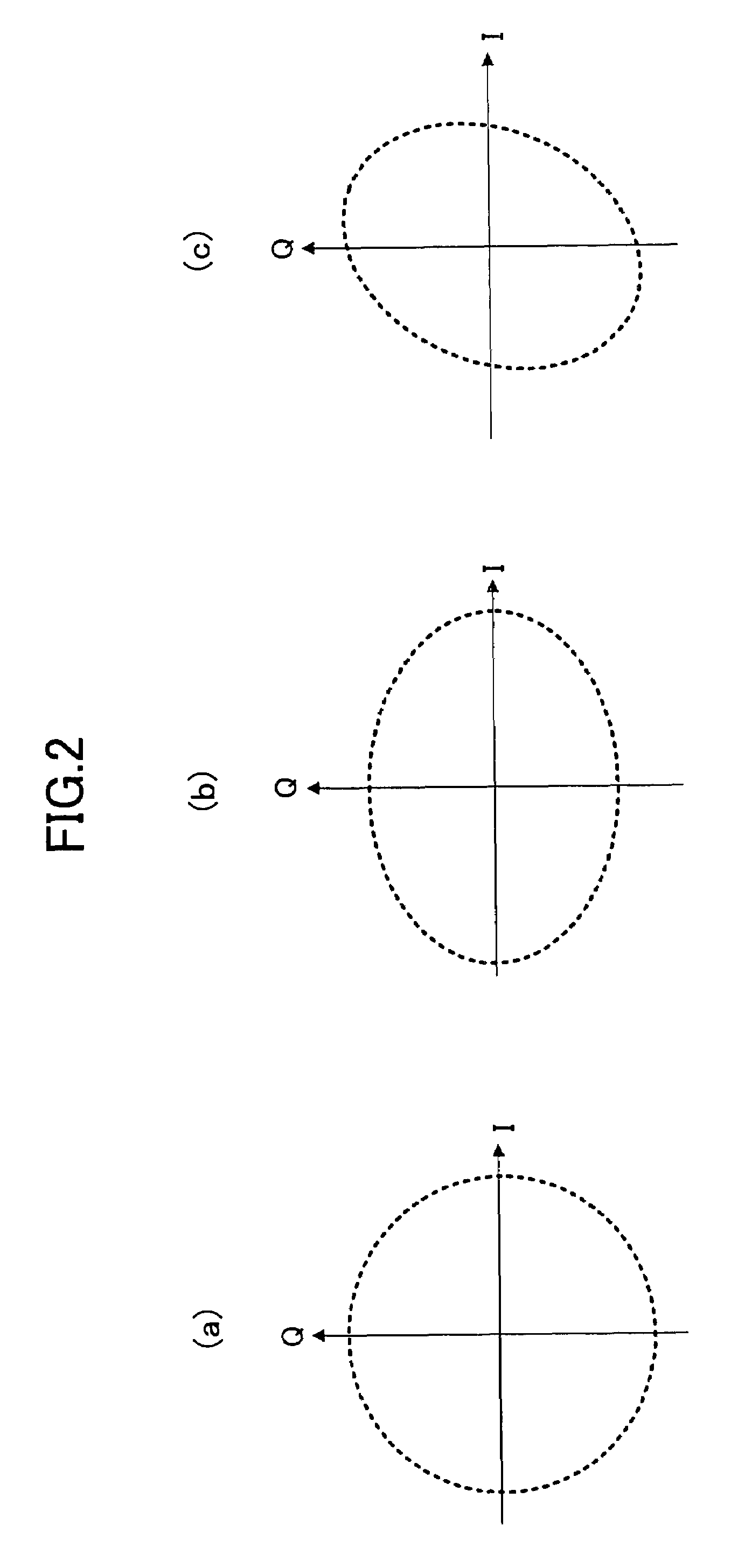
Amplitude error compensating device and quadrature skew error compensating device
InactiveUS7456683B2Error preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionInformation controlQuadrature demodulation
An amplitude error compensating device comprises an amplitude correcting section for performing amplitude correction with respect to an in-phase component and a quadrature component of a complex signal obtained by quadrature demodulation, based on amplitude error information, and outputting a resultant amplitude-corrected complex signal, and an amplitude error detecting section for obtaining the amplitude error information, depending on amplitudes of an in-phase component and a quadrature component of the amplitude-corrected complex signal. The amplitude error detecting section comprises a power difference calculating section for obtaining as a power error a difference in power between the in-phase component and the quadrature component of the amplitude-corrected complex signal, a rotation detecting section for detecting a rotation of a signal point of the amplitude-corrected complex signal, an error information control section for outputting the power error when a rotation of the signal point has been detected, and 0 when a rotation of the signal point has not been detected, and a smoothing section for smoothing an output of the error information control section, and outputting the result as the amplitude error information.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Method and system for down-converting electromagnetic signals
InactiveUS6061551AResonant long antennasModulation transferenceIntermediate frequencyElectromagnetic shielding
Methods, systems, and apparatuses for down-converting an electromagnetic (EM) signal by aliasing the EM signal are described herein. Briefly stated, such methods, systems, and apparatuses operate by receiving an EM signal and an aliasing signal having an aliasing rate. The EM signal is aliased according to the aliasing signal to down-convert the EM signal. The term aliasing, as used herein, refers to both down-converting an EM signal by under-sampling the EM signal at an aliasing rate, and down-converting an EM signal by transferring energy from the EM signal at the aliasing rate. In an embodiment, the EM signal is down-converted to an intermediate frequency (IF) signal. In another embodiment, the EM signal is down-converted to a demodulated baseband information signal. In another embodiment, the EM signal is a frequency modulated (FM) signal, which is down-converted to a non-FM signal, such as a phase modulated (PM) signal or an amplitude modulated (AM) signal.
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
Method and system for multiple channel wireless transmitter and receiver phase and amplitude calibration
InactiveUS6862440B2Low costTransmitters monitoringReceivers monitoringTransmission channelEngineering
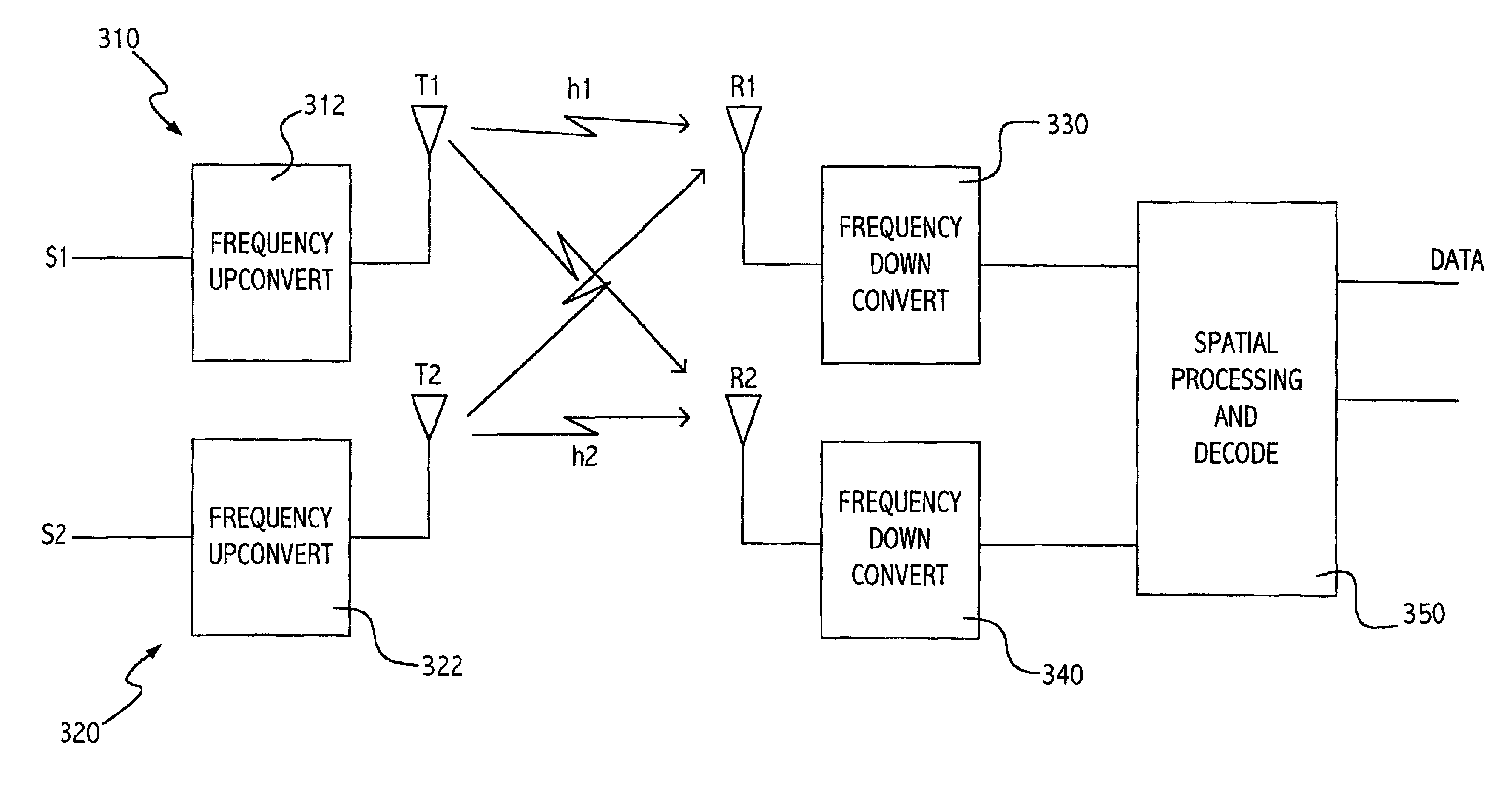
The present invention provides a method and system for estimating common amplitude and phase errors of a multiple channel wireless system. The multiple channel wireless system includes a plurality of transmission channels formed between a plurality of transmission antennas and a plurality of receiver antennas. The method includes estimating transmission channel elements between each transmission antenna and receiver antenna pair of the multiple channel wireless system. Calibration symbols are transmitted from each transmit antenna. Signals are received that correspond to the calibration symbols having traveled through the transmission channels. Received calibration symbols are estimated based upon spatial processing of the received signals and the estimated transmission channel elements. Common amplitude and phase errors are estimated for each transmit and receive antenna pair by comparing the transmitted calibration symbols with the received calibration symbols.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
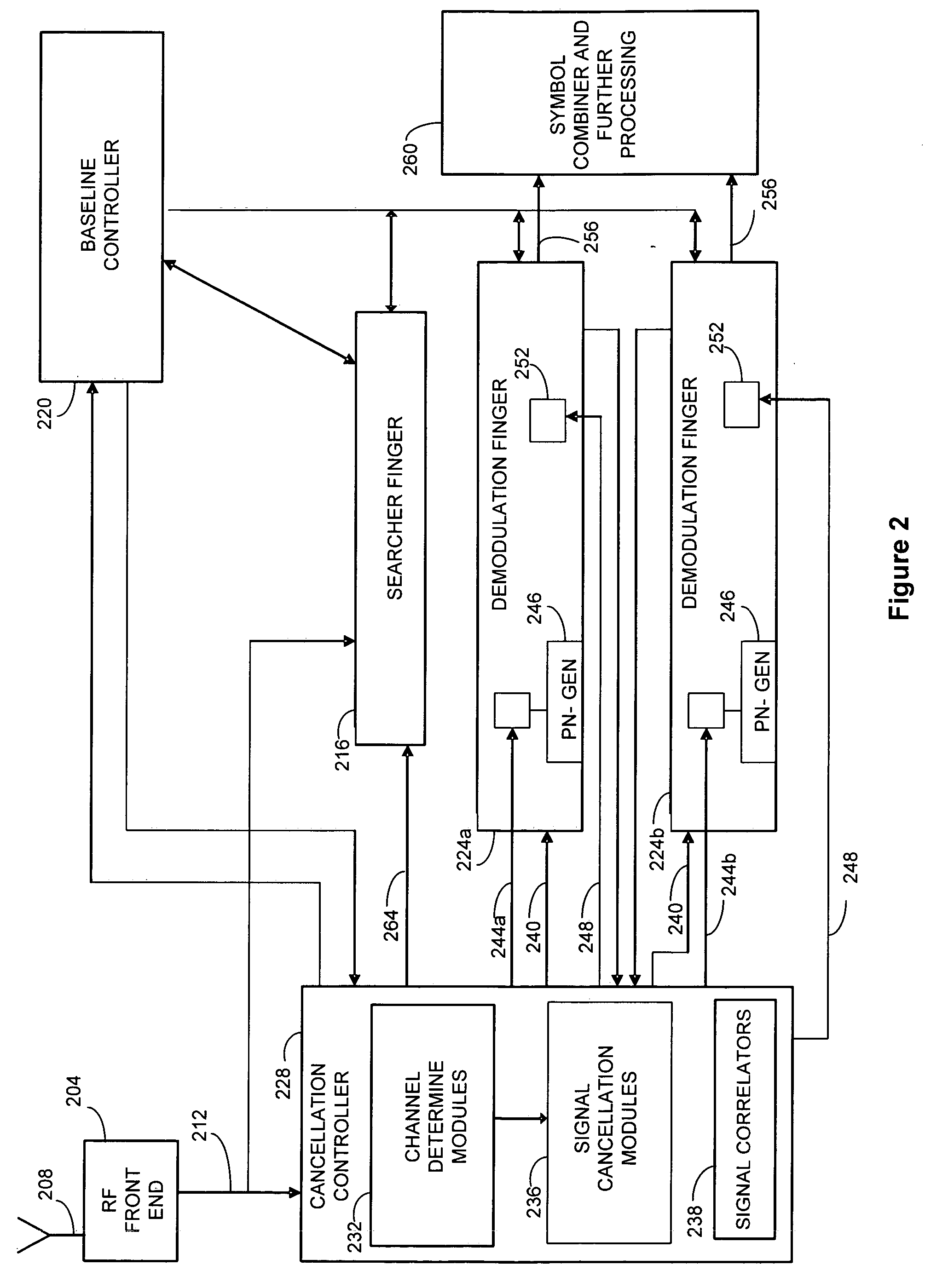
Method and apparatus for selectively applying interference cancellation in spread spectrum systems
ActiveUS20070183483A1High strengthIncrease signal strengthError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionSignal cancellationEngineering
The present invention is directed to the selective provision of interference canceled signal streams to demodulating fingers in a communication receiver. According to the present invention, potential interferer signal paths are identified. Signal streams having one or more potential interferer signals removed or canceled are created, and a correlation is performed to determine whether the strength of a desired signal path increased as a result. If the correlation indicates that the strength of a desired signal path was increased by the signal cancellation, the interference canceled signal stream is provided to the demodulation finger assigned to track the desired signal path. If the correlation determines that the strength of the desired signal path did not increase as a result of performing interference cancellation, the raw or a different interference canceled signal stream is provided to the demodulation finger.
Owner:III HLDG 1
Communication methods and systems for nonlinear multi-user environments
InactiveUS20150207527A1Error preventionModulated-carrier systemsNonlinear distortionMulti user environment
An electronic receiver comprises a nonlinear distortion modeling circuit and a nonlinear distortion compensation circuit. The nonlinear distortion modeling circuit is operable to determine a plurality of sets of nonlinear distortion model parameter values, where each of the sets of nonlinear distortion model parameter values representing nonlinear distortion experienced by signals received by the electronic receiver from a respective one a plurality of communication partners. The nonlinear distortion compensation circuit is operable to use the sets of nonlinear distortion model parameter values for processing of signals from the plurality of communication partners. Each of the sets of nonlinear distortion model parameter values may comprises a plurality of values corresponding to a plurality of signal powers. The sets of nonlinear distortion model parameters may be stored in a lookup table indexed by a signal strength parameter.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
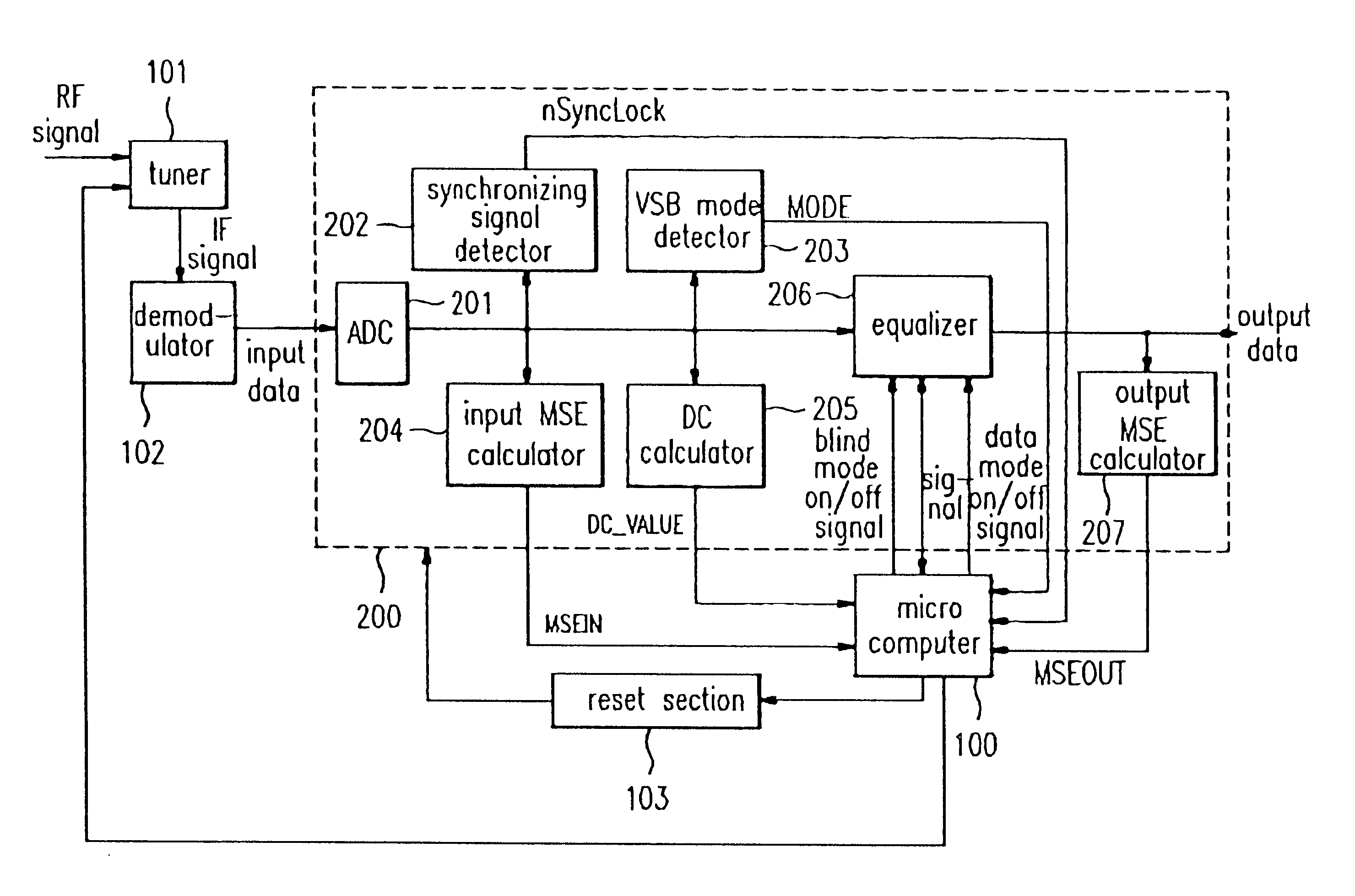
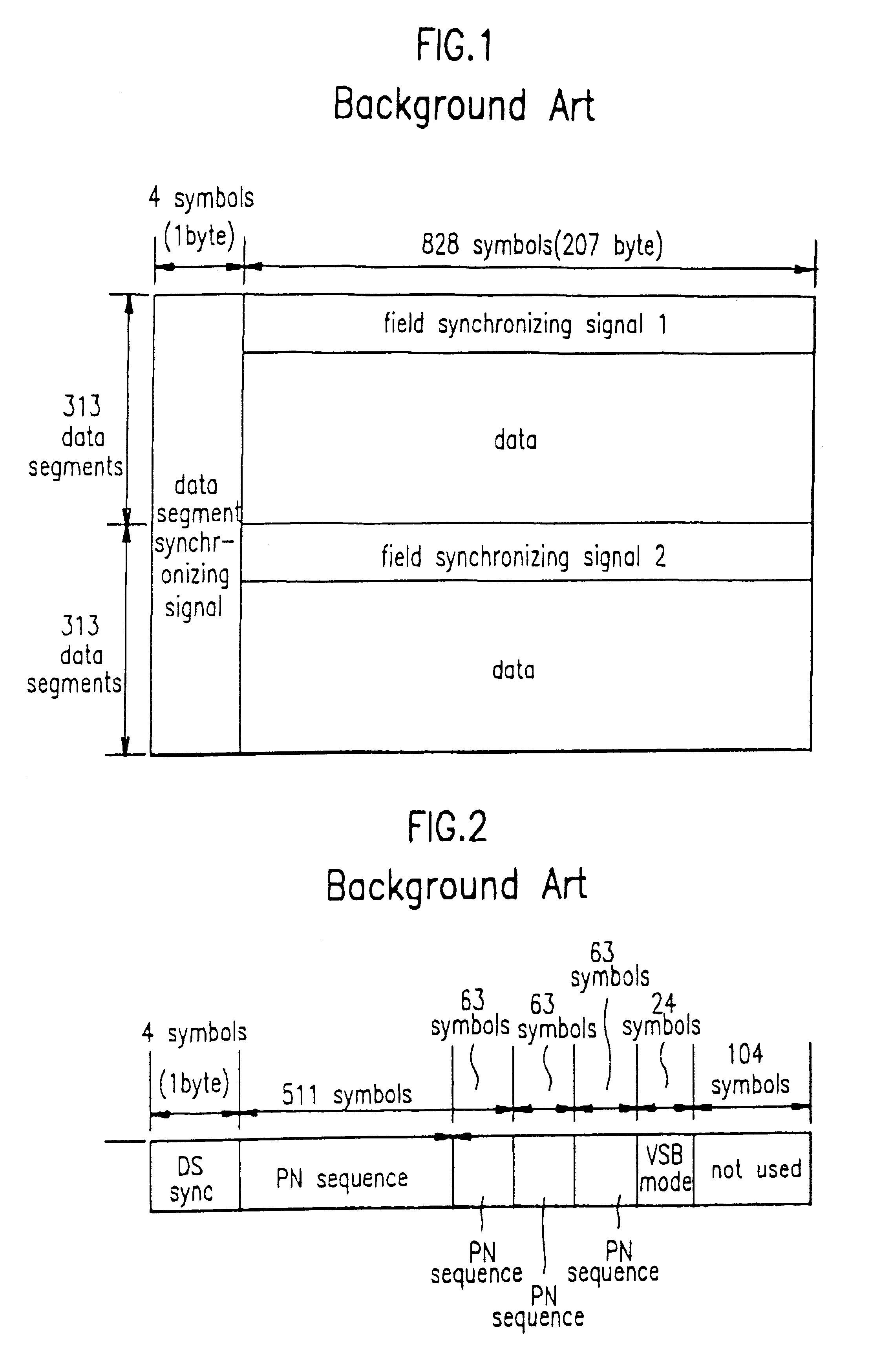
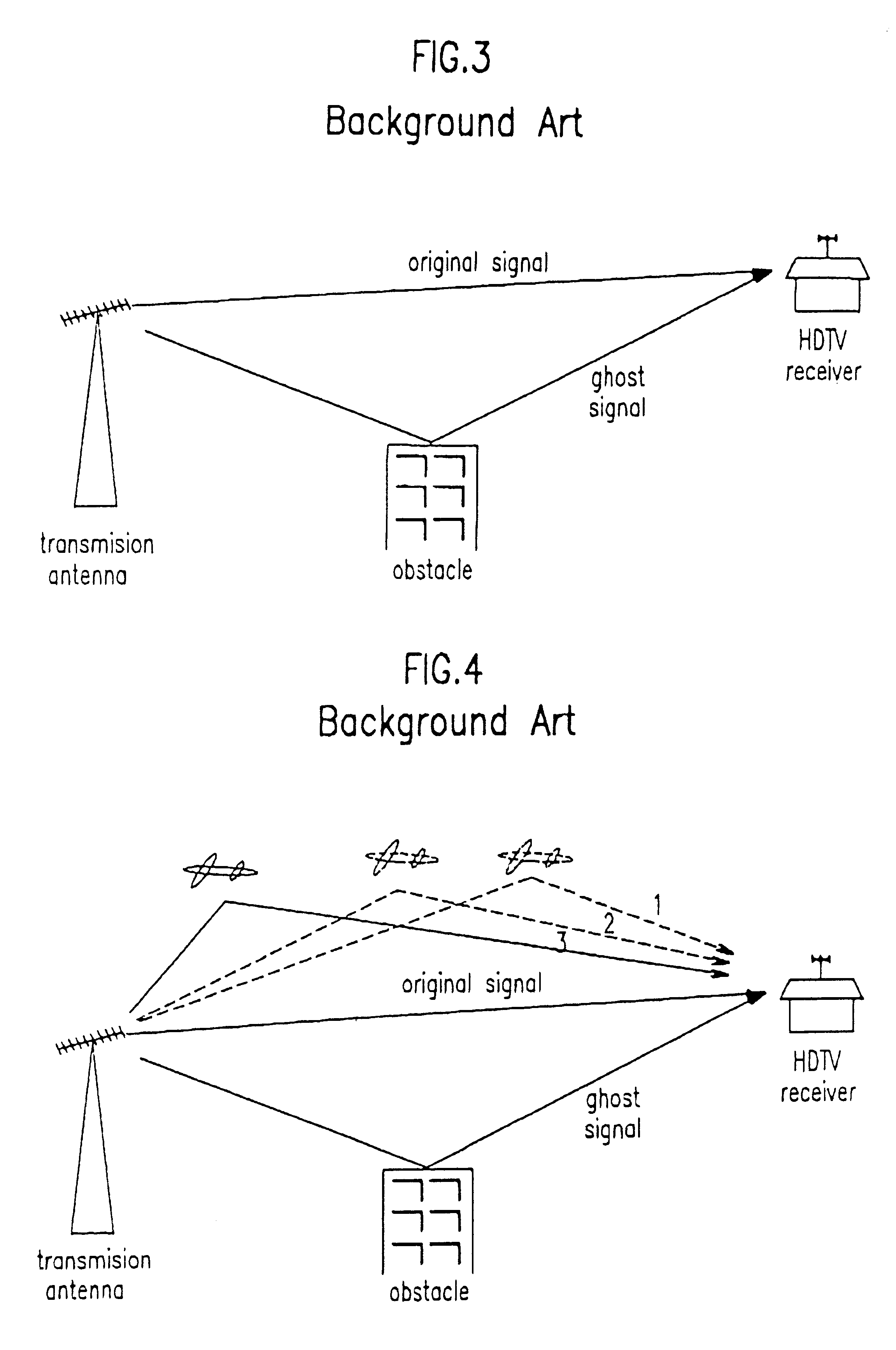
Method and apparatus which compensates for channel distortion
A method and apparatus for compensating for channel distortion is disclosed. In the present invention, equalization is performed in the treating sequence mode when the moving ghost does not exist in the channel and there is no possibility that the equalizer diverges, the data mode is cancelled and the equalization is carried out in the blind mode when the moving ghost does not exist in the channel but there is a possibility that the equalizer diverges, the equalizer is executed in the data mode when there is no possibility that the equalizer diverges but there exists the moving ghost including slowly moving ghosts in the channel, and the equalization is performed in the data mode and blind mode when the moving ghost exists and there is a possibility that the equalizer diverges.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Transmitting and receiving methods
This invention describes a wireless system comprising a plurality of transmitters and receivers, wherein each transmitter has between 1 and n antennas and each receiver has between 1 and m antennas wherein one of said transmitter is arranged to transmit to one of the receivers, said one transmitter is controlled in dependence on at least one of at least one parameter of said transmitters, at least one parameter of said receiver, and at least one parameter of a wireless environment between said transmitter and said receiver.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
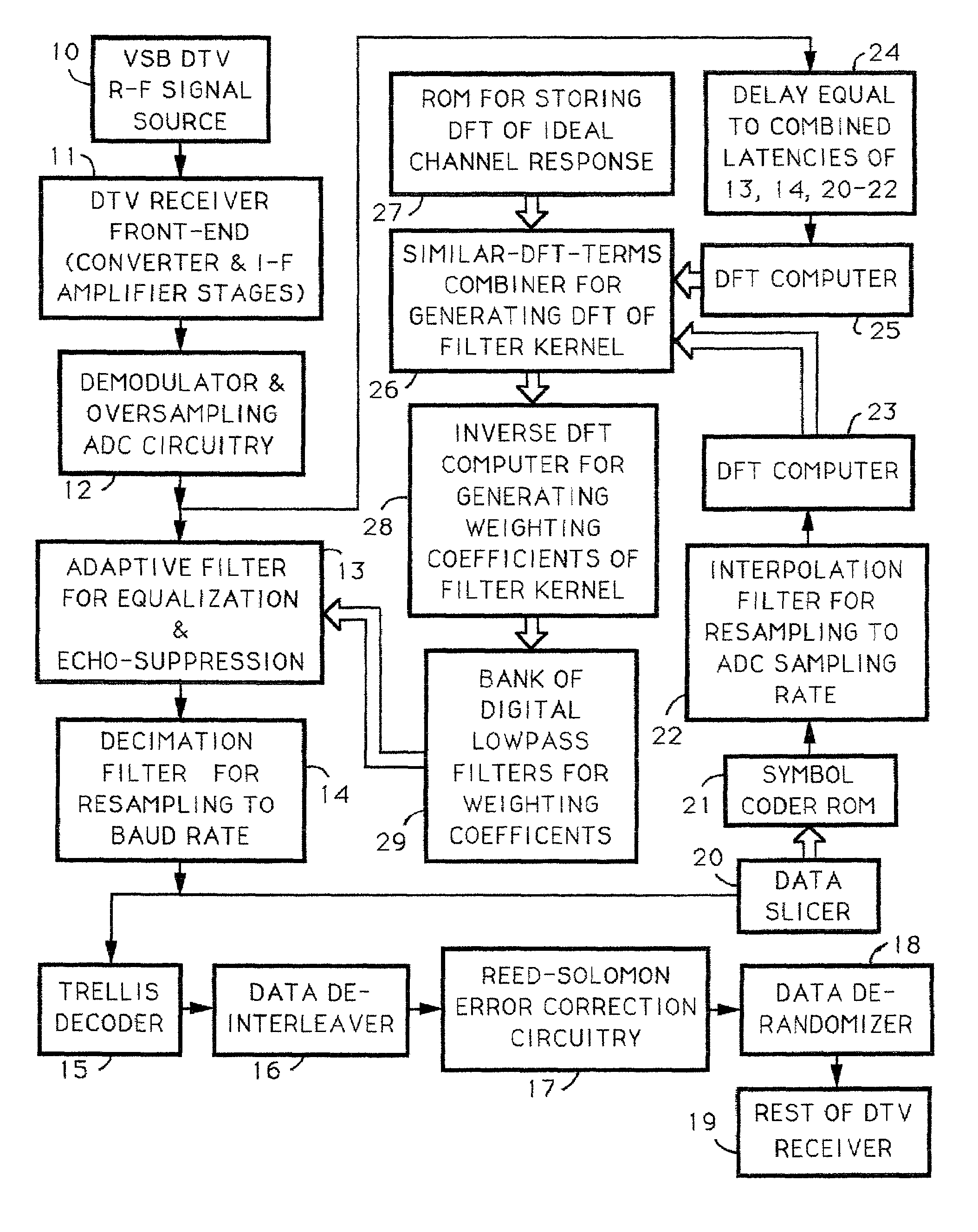
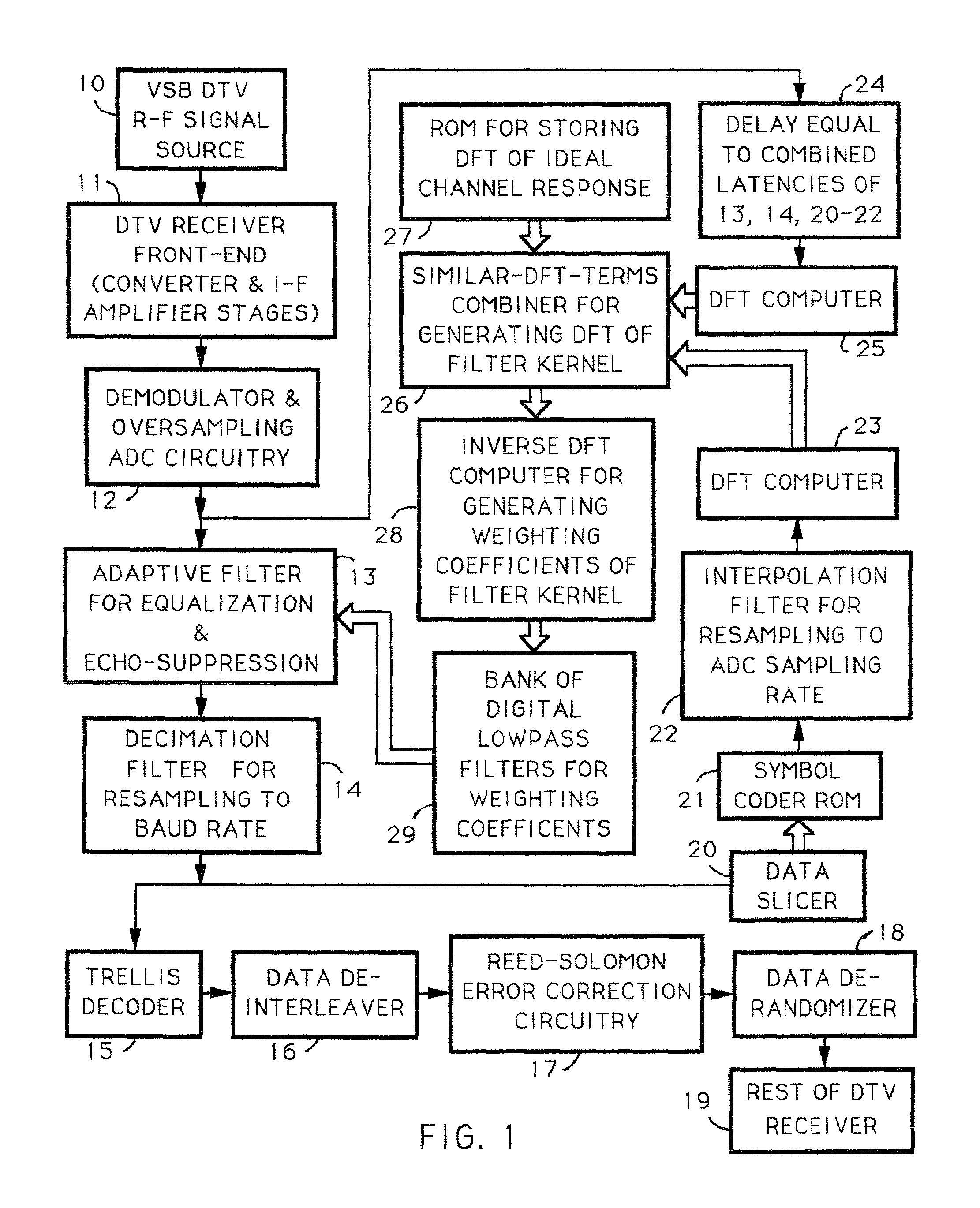
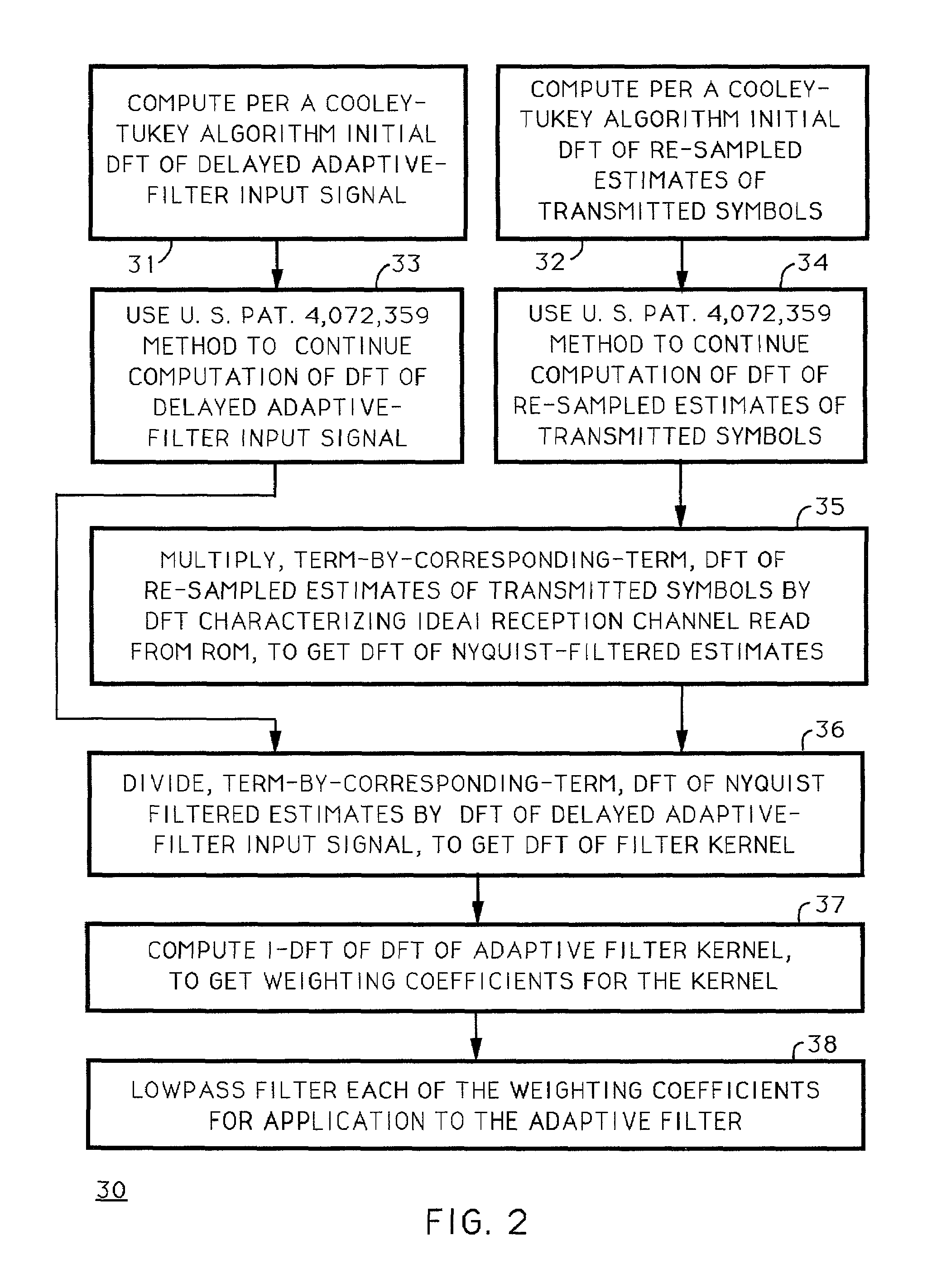
Digital modulation signal receiver with adaptive channel equalization employing discrete fourier transforms
InactiveUS6975689B1Extended durationTelevision system detailsError preventionInverse discrete fourier transformFourier transform on finite groups
Techniques for calculating the system characteristic of the adaptive filtering used for equalization and echo-suppression in a digital communications receiver, such as one used for receiving over-the-air broadcast digital television signal, are described. In these techniques, the system characteristic of the adaptive filtering is calculated from the discrete Fourier transform of successive portions of the input signal supplied to the adaptive filtering and from the discrete Fourier transform of corresponding portions of the transmitted signal, as estimated in the receiver. Receivers for implementing these techniques in various ways are also disclosed.
Owner:MCDONALD JAMES DOUGLAS +1
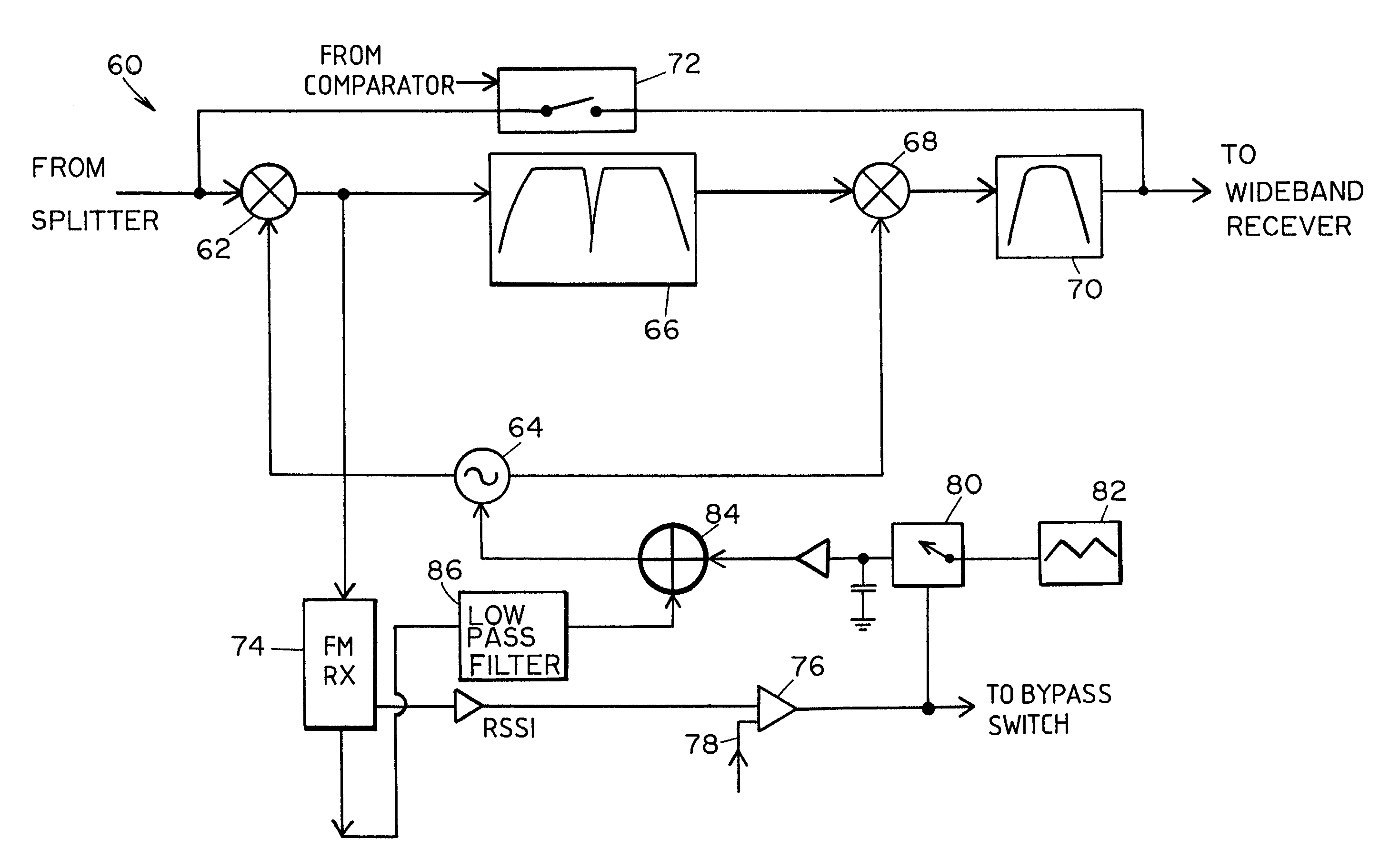
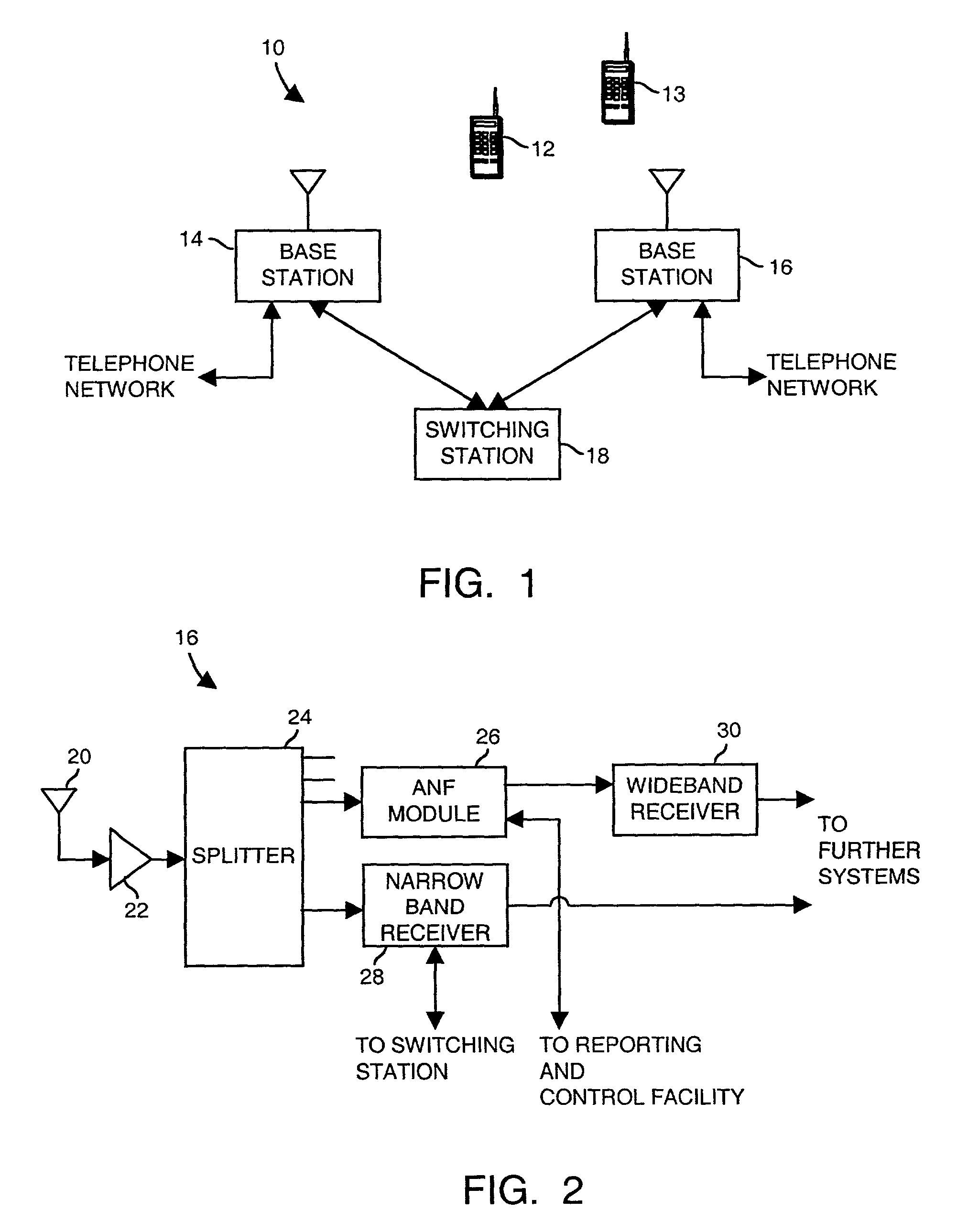
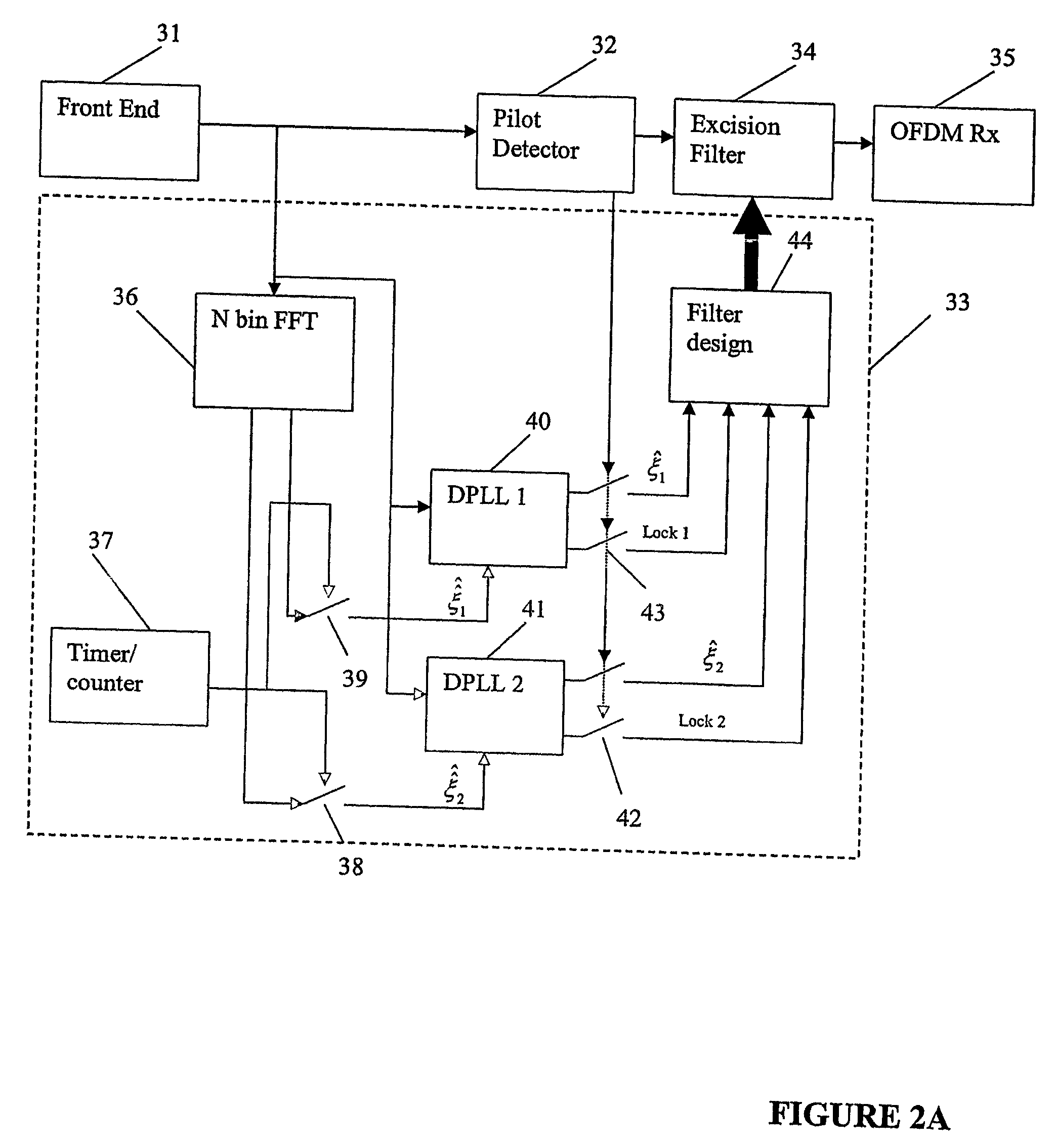
Interference detection, identification, extraction and reporting
An adaptive notch filter (ANF) module selectively filters a received wideband communication signal to eliminate narrowband interference that lies within the frequency spectrum of the wideband communication signal. To determine the presence of narrowband interference, the ANF module scans various known narrowband channels that lie within the frequency spectrum of the wideband communication signal and determines signal strengths for each of the narrowband channels. The signal strengths from the narrowband channels are compared to a threshold that is derived from the narrowband signal strengths. Narrowband channels having signal strengths that are greater than the threshold are determined to have interference.
Owner:ILLINOIS SUPERCONDUCTOR CORP
Method and apparatus for multipath signal compensation in spread-spectrum communications systems
ActiveUS7054396B2Effective multipath signal compensationChange effective lengthMultiple-port networksError preventionCommunications systemImage resolution
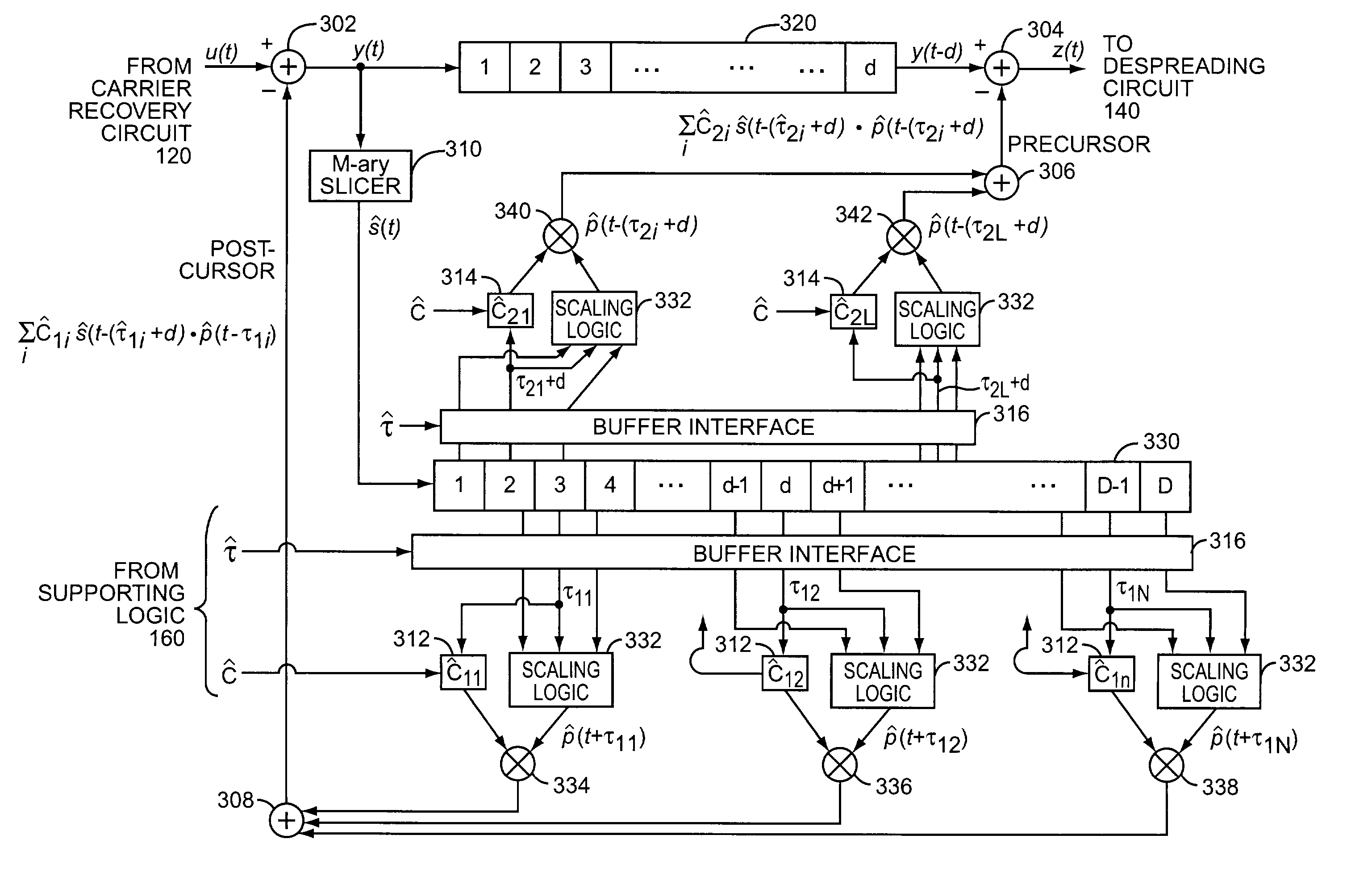
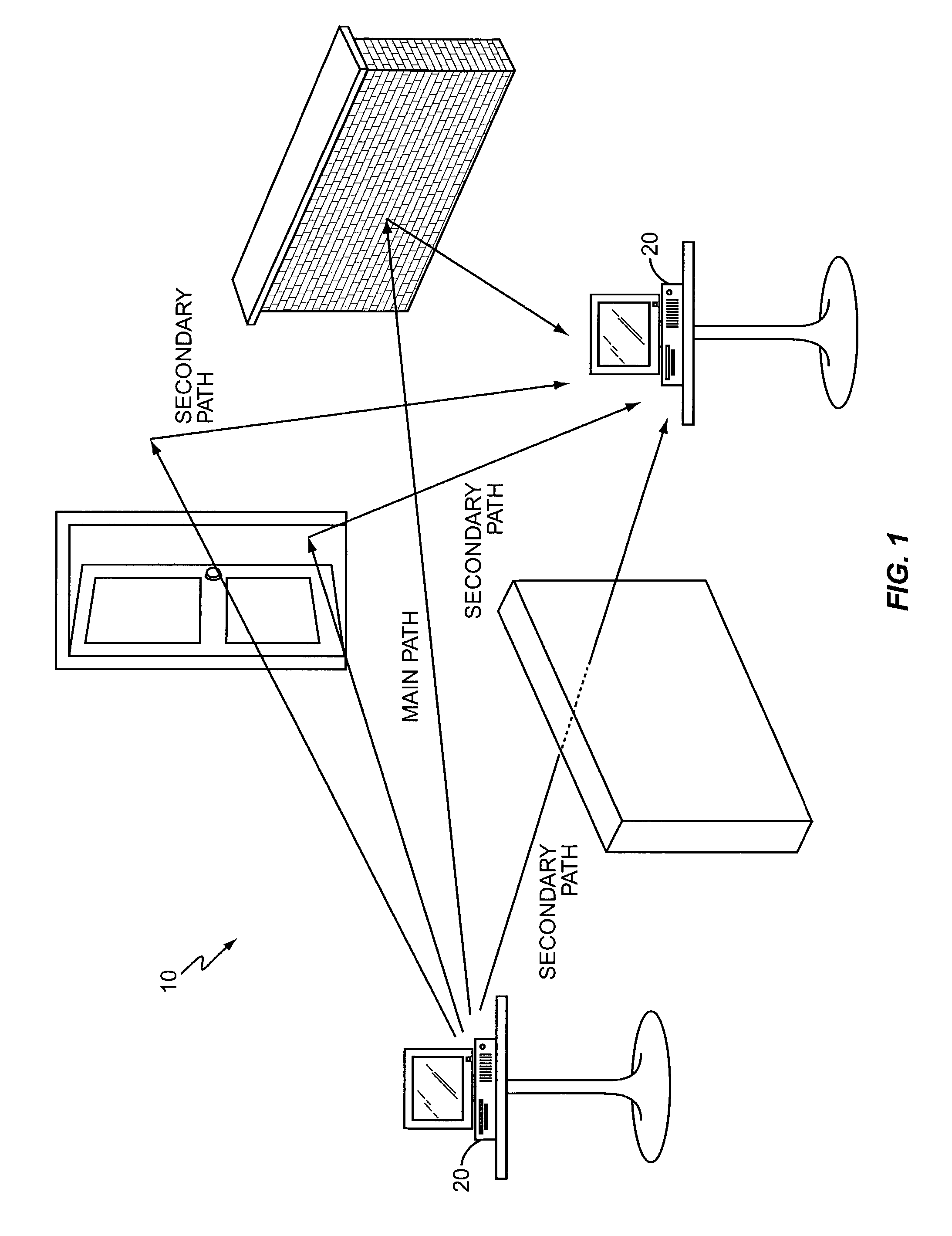
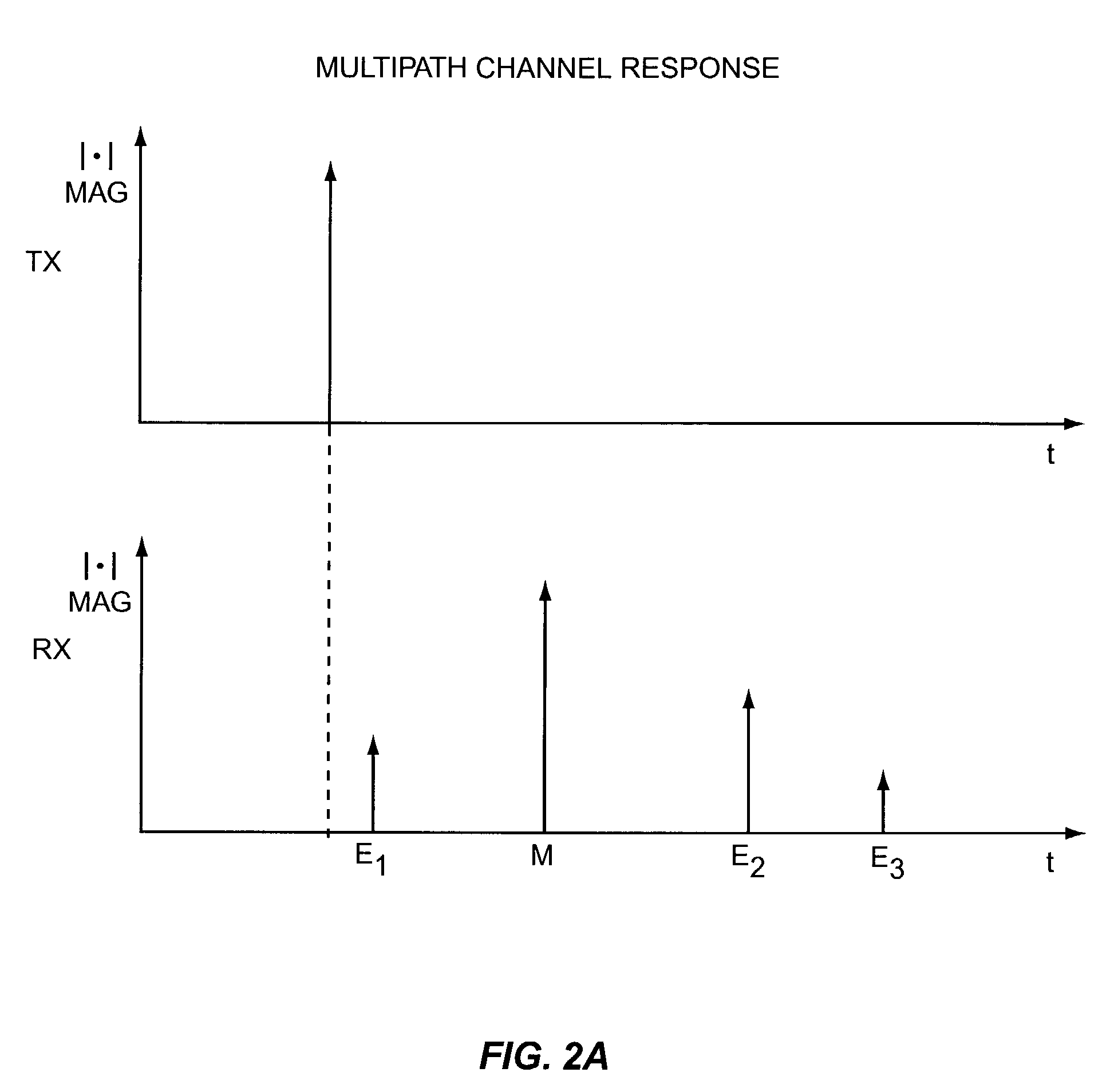
The equalizer of the present invention operates on input multipath signal samples, preferably at chip or sub-chip resolution, to remove or substantially cancel the effects of one or more secondary signals from the main path signal. Using predetermined path information for one or more of the secondary path signals, including magnitude, phase, and time offset relative to the main path signal, the equalizer compensates input multipath signal samples by subtracting estimated secondary signal values from the input samples. For each input sample, the equalizer forms a sliced sample, where the sliced sample represents a nominal phase value defined by the modulation scheme used in the original chip or symbol transmission that is closest in value to the actual phase of the input sample. These sliced samples are held in a running buffer and used, in combination with the predetermined path information and scaling logic, to form the estimated secondary signal values for compensating the input samples.
Owner:QORVO US INC
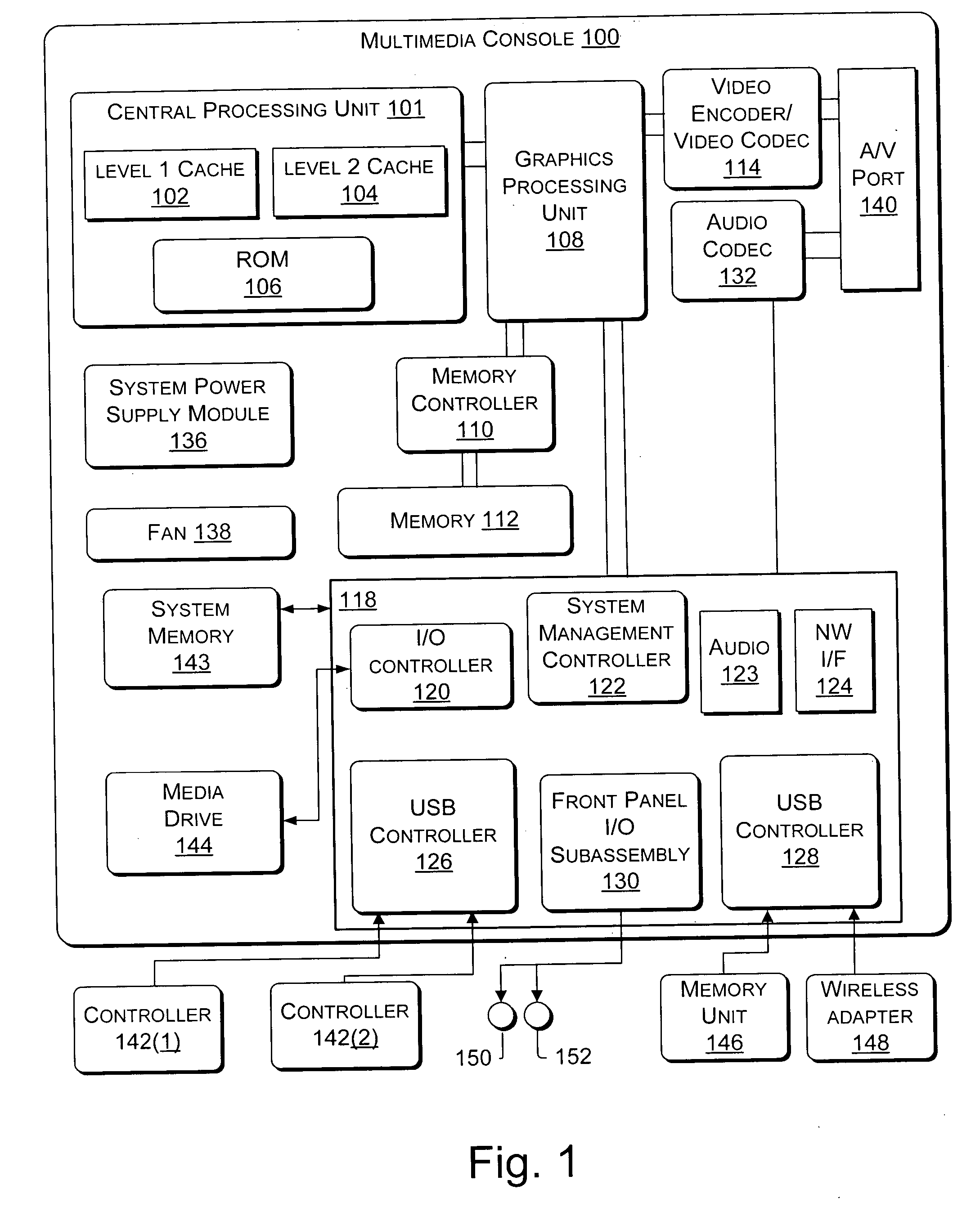
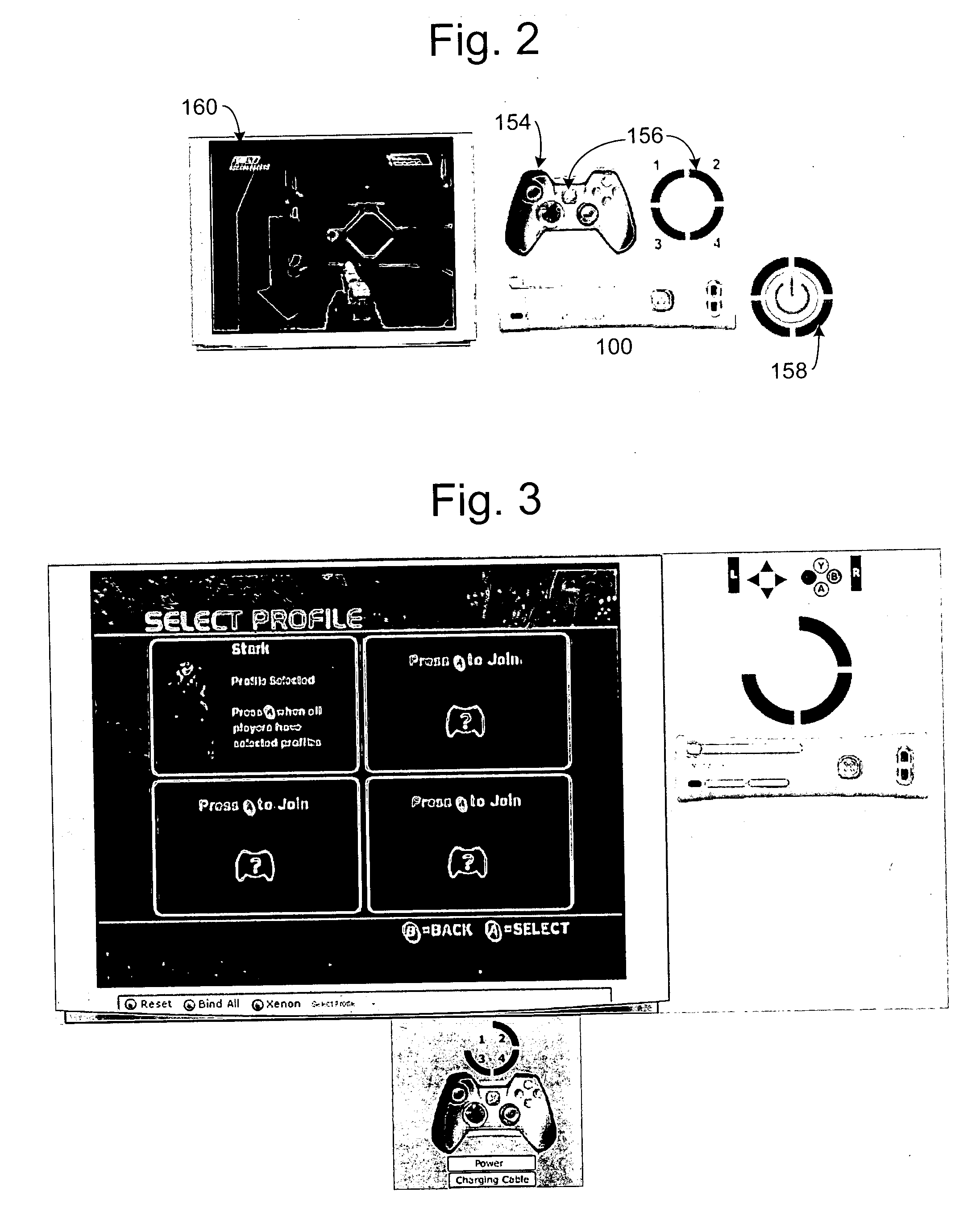
Game console notification system
Systems and methods for providing notifications to players of a gaming console of messages and system notifications. A controller and the gaming console include a four quadrant LED indicator. Each quadrant of the ring may be illuminated individually or together using an LED to indicate the messages and notifications. The quadrants may be illuminated in one of three colors and / or in patterns to indicate different types of notifications. Onscreen displays may be used to supplement the LED indicators to convey information to users. A method of binding and discovering a controller is also provided where the controller may be bound to a gaming console. After a controller is bound to a console, the controller may be discovered by the gaming console where it is assigned a virtual port and enabled for game play.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
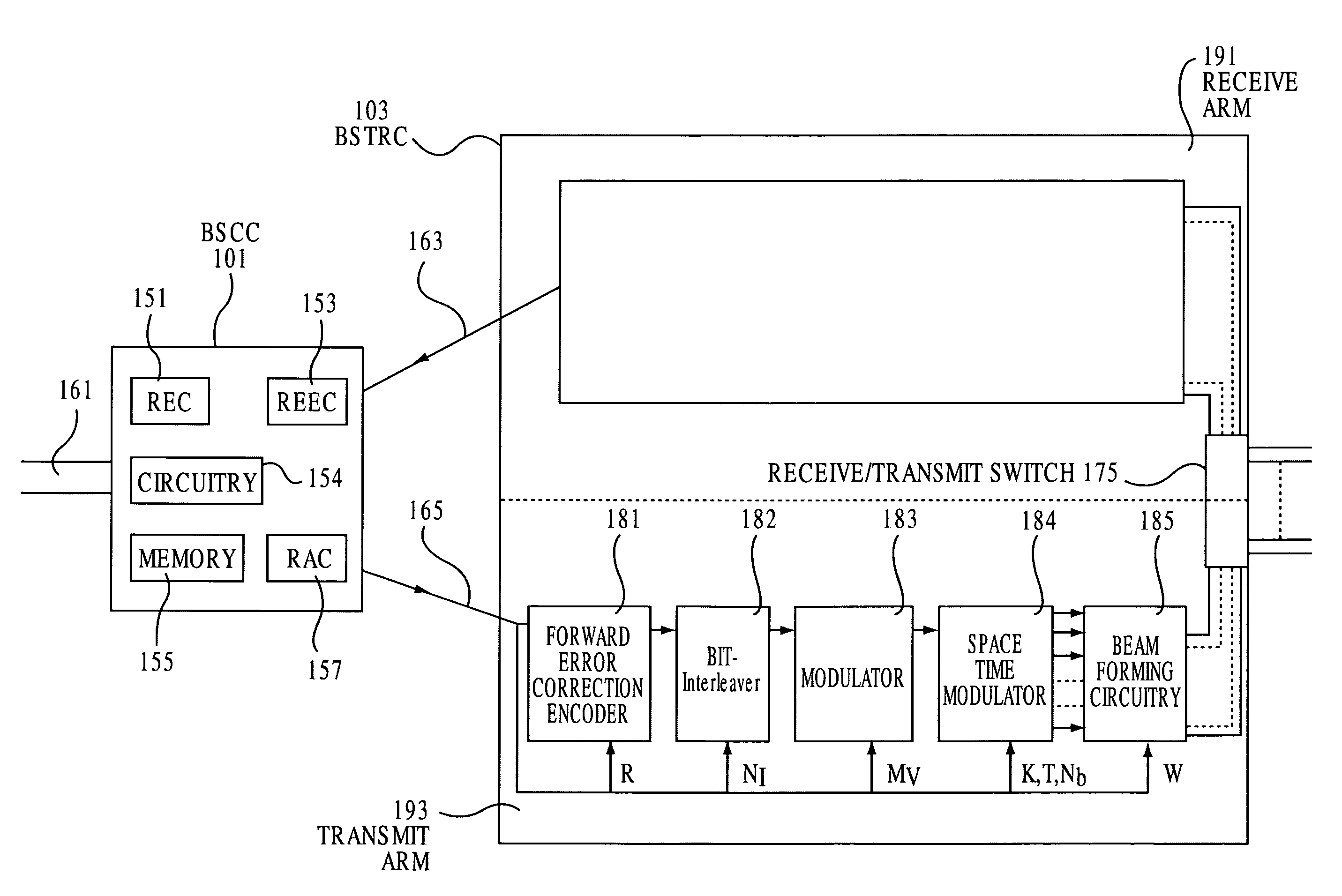
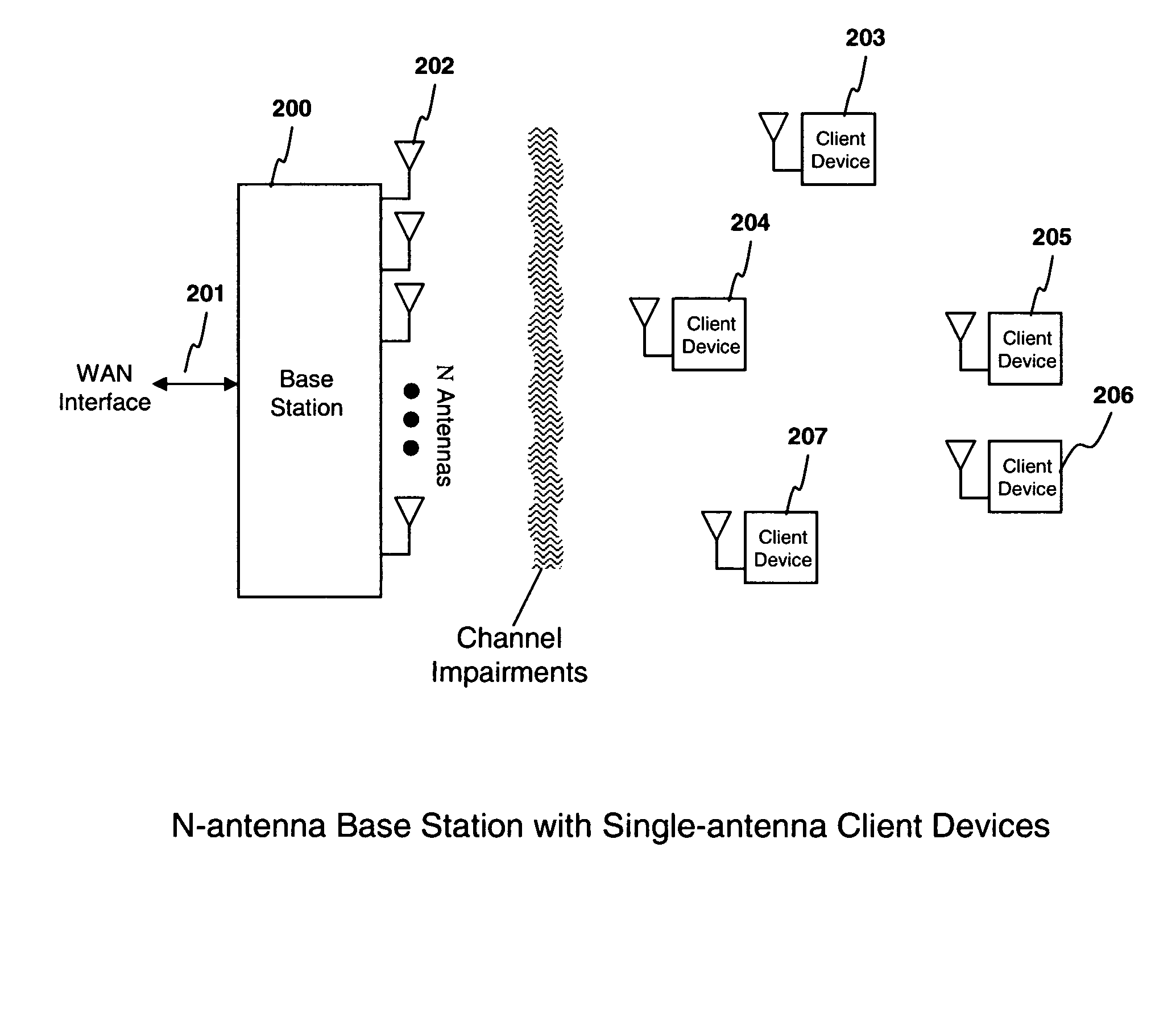
System and method for distributed input distributed output wireless communications
A system and method are described for compensating for frequency and phase offsets in a multiple antenna system (MAS) with multi-user (MU) transmissions (“MU-MAS”). For example, a method according to one embodiment of the invention comprises: transmitting a training signal from each antenna of a base station to one or each of a plurality of wireless client devices, one or each of the client devices analyzing each training signal to generate frequency offset compensation data, and receiving the frequency offset compensation data at the base station; computing MU-MAS precoder weights based on the frequency offset compensation data to pre-cancel the frequency offset at the transmitter; precoding training signal using the MU-MAS precoder weights to generate precoded training signals for each antenna of the base station; transmitting the precoded training signal from each antenna of a base station to each of a plurality of wireless client devices, each of the client devices analyzing each training signal to generate channel characterization data, and receiving the channel characterization data at the base station; computing a plurality of MU-MAS precoder weights based on the channel characterization data, the MU-MAS precoder weights calculated to pre-cancel frequency and phase offset and / or inter-user interference; precoding data using the MU-MAS precoder weights to generate precoded data signals for each antenna of the base station; and transmitting the precoded data signals through each antenna of the base station to each respective client device.
Owner:REARDEN
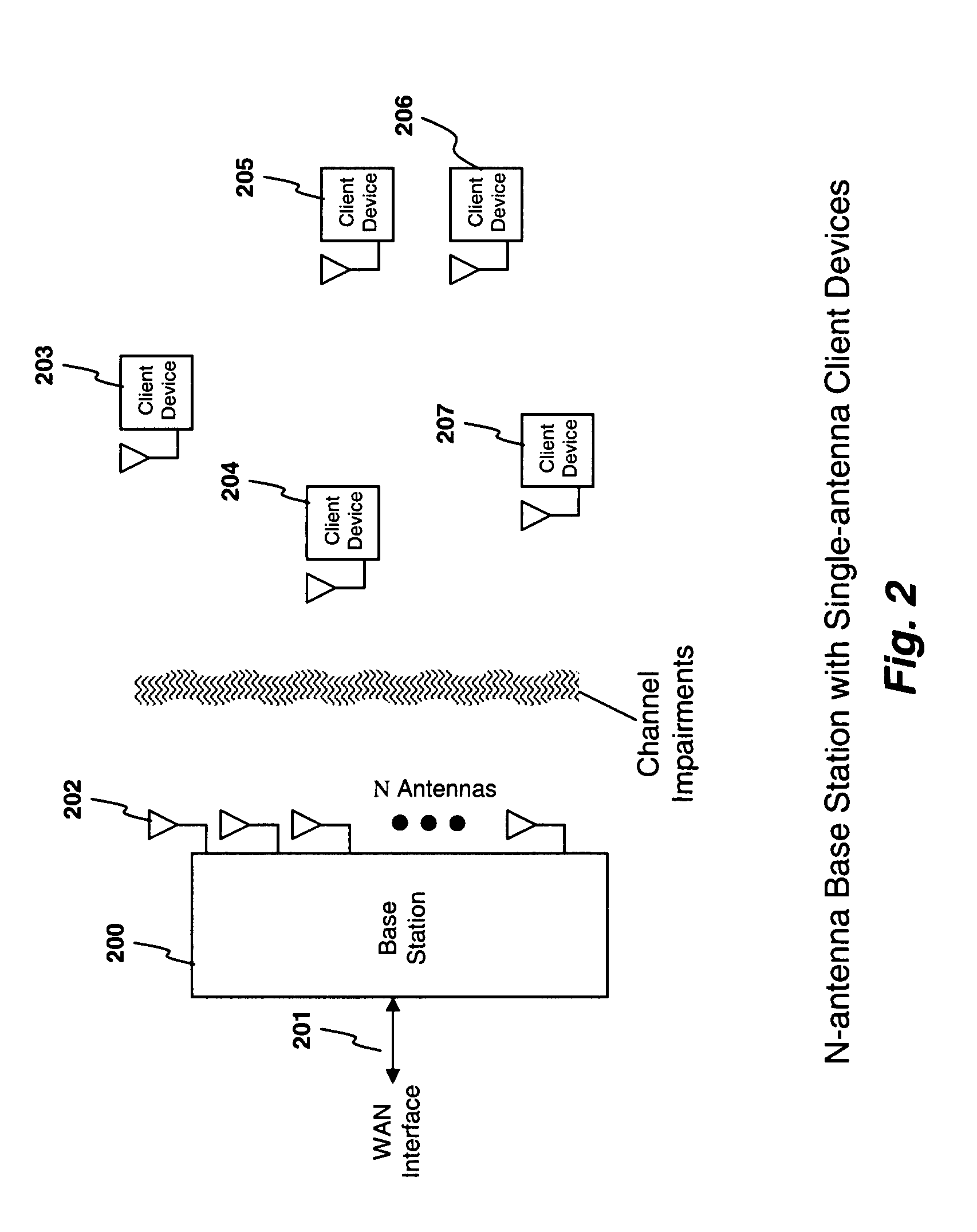
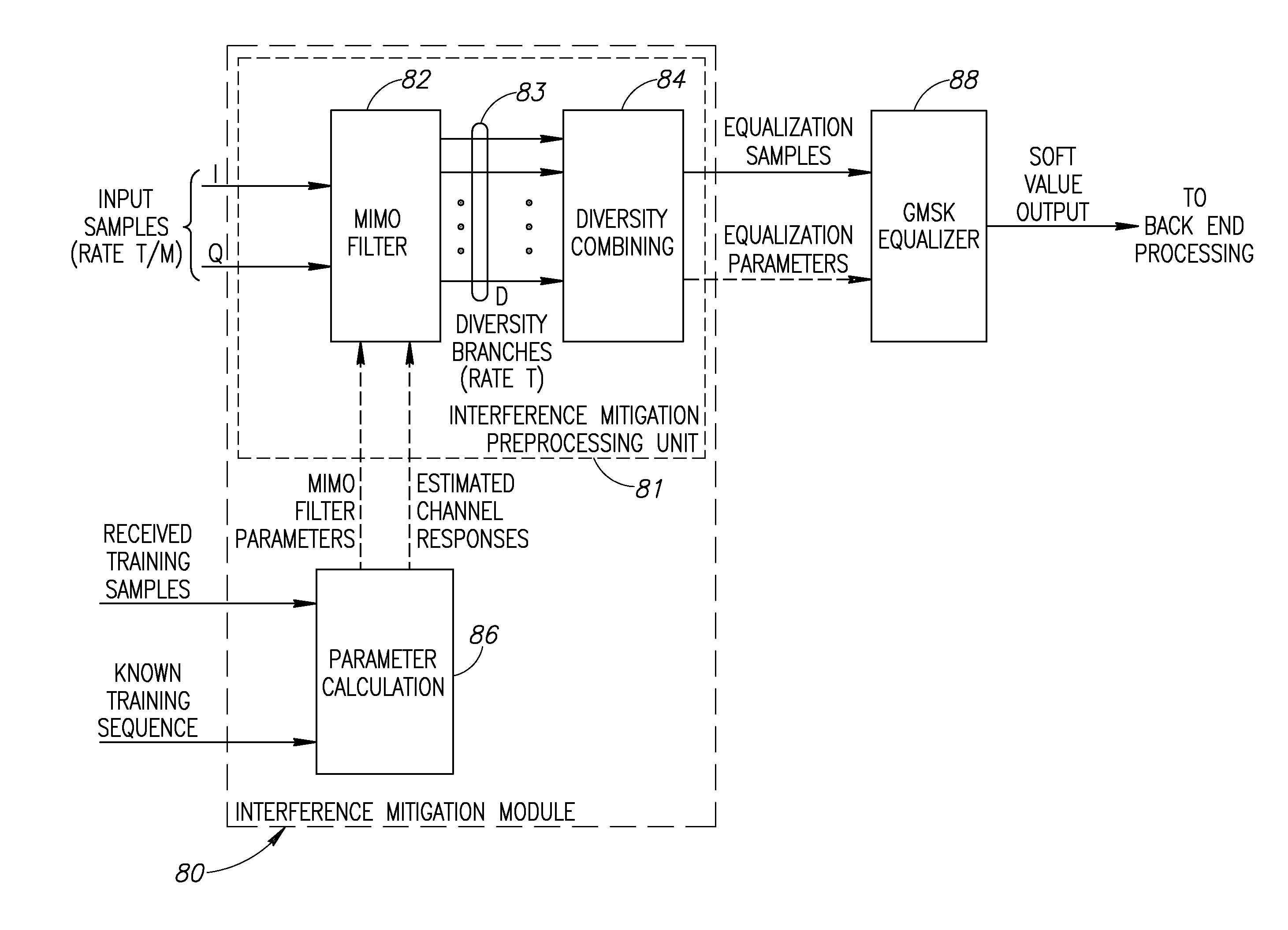
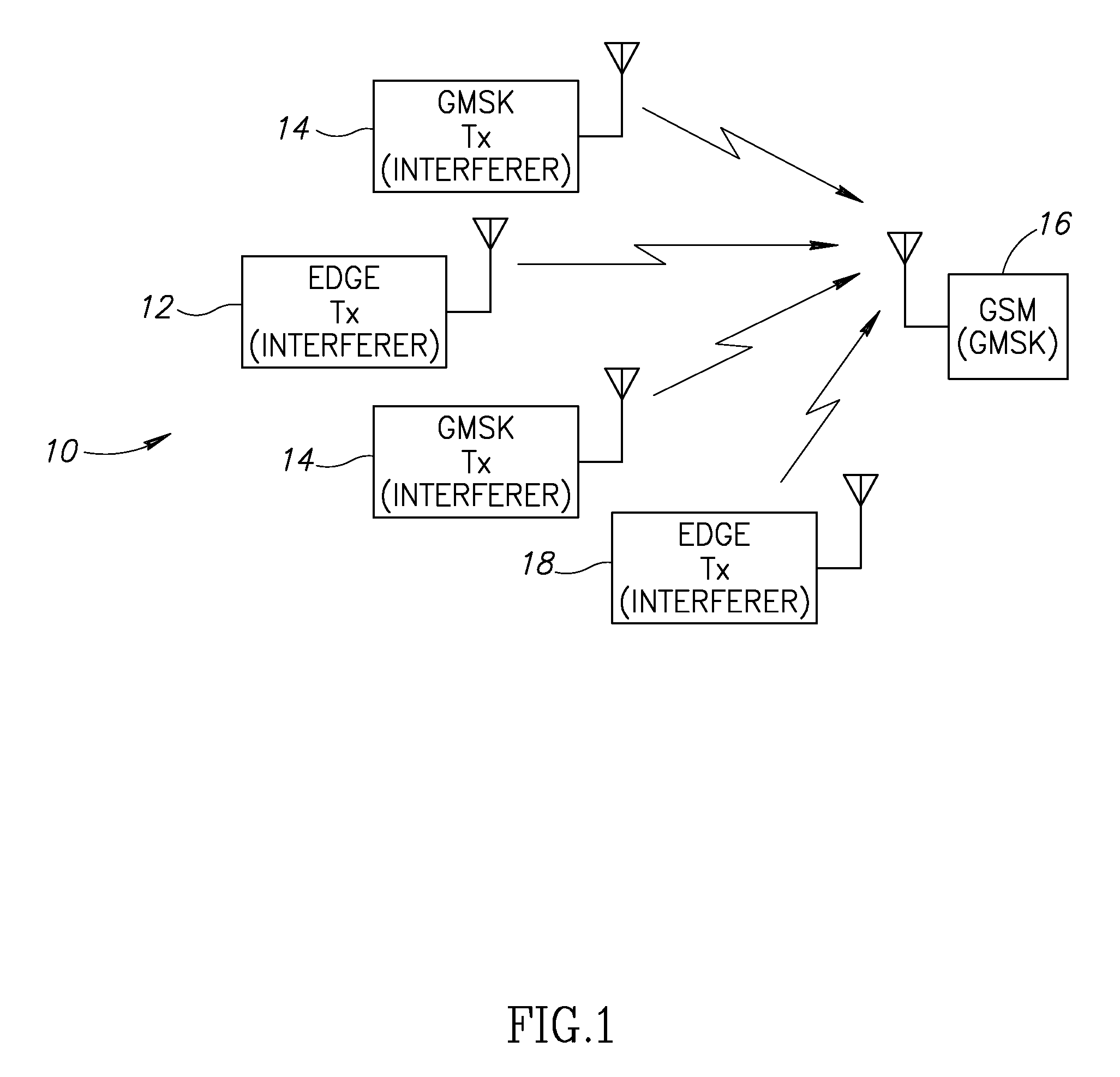
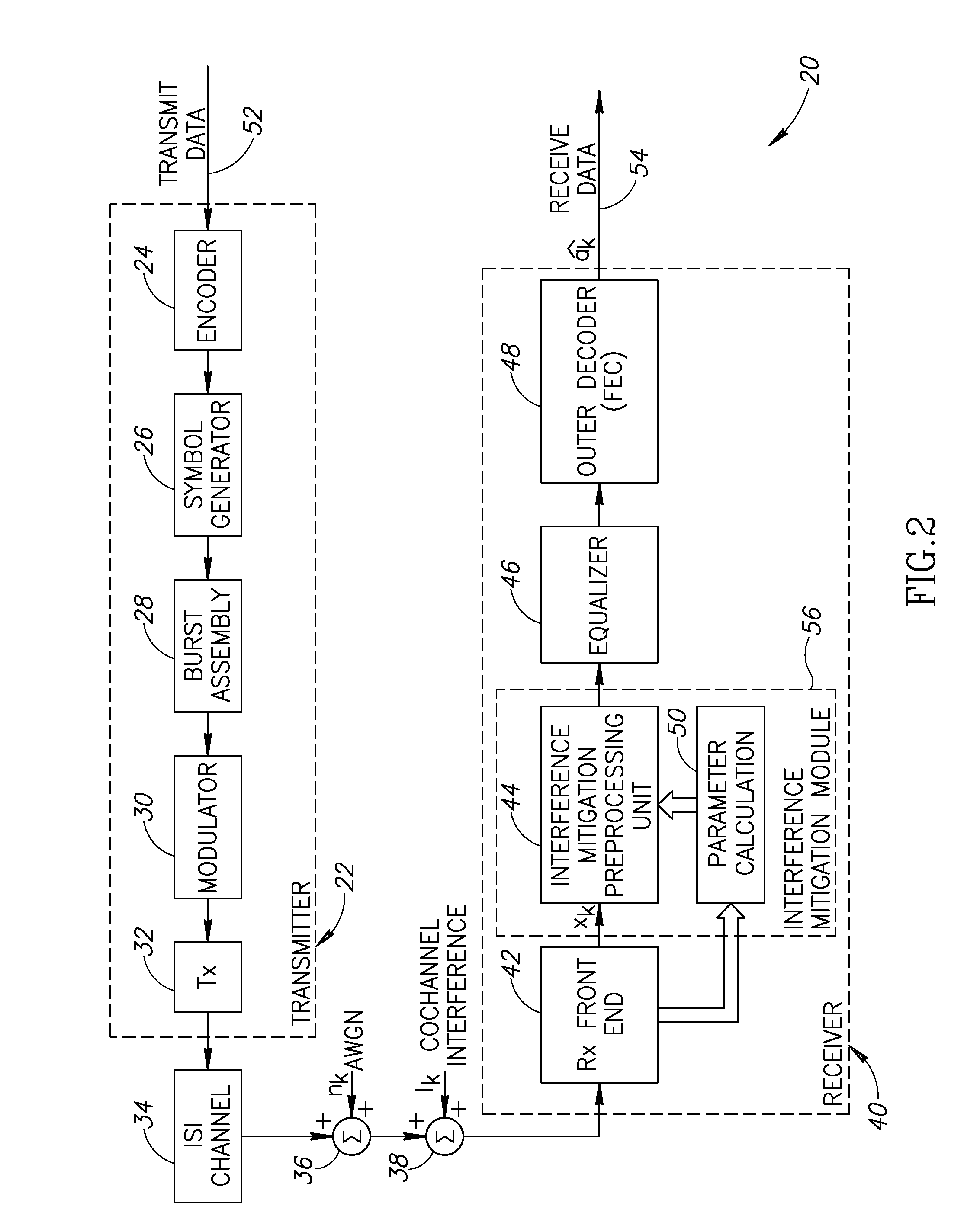
Blind interference mitigation in a digital receiver
InactiveUS20070127608A1Improve acceleration performanceReduce computational complexityError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionEngineeringCo-channel interference
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying (GMSK) single antenna interference cancellation (SAIC) for use in a digital receiver. The invention comprises an interference mitigation module that treats the problem of GMSK SAIC in a blind manner. The interference mitigation mechanism is operative to compensate for the co-channel interference added in the communications channel which is subject to multipath propagation and fading, receiver filter and any pre-channel estimation filtering. The interference mitigation module takes advantage of the spatial diversity making up multiple branches of the received signal. The branches comprise the in-phase and quadrature elements of the received signal, the sampling phases if over sampling is applied (i.e. T / m sampling) and / or multiple antennas. The invention utilizes the spatial diversity of these multiple representations of the received signal and combines (i.e. collapses) the information in the plurality of branches into a single branch that is input to the equalizer.
Owner:COMSYS COMM & SIGNAL PROC
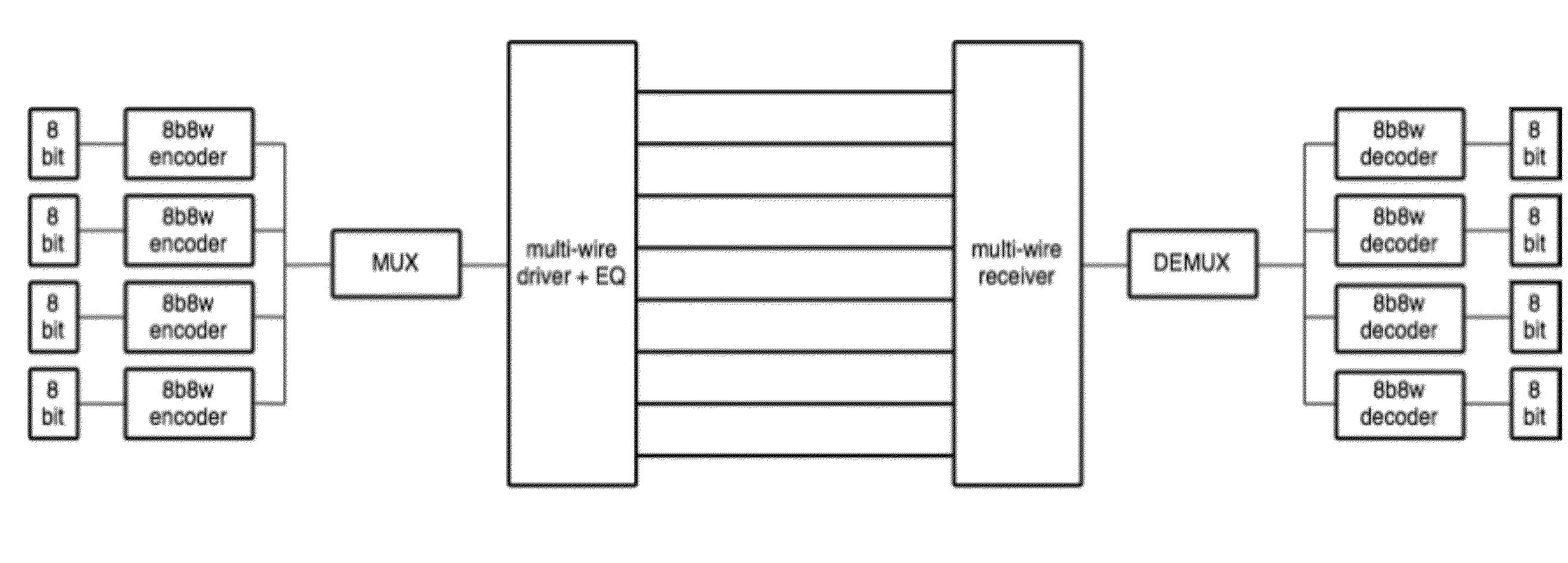
Methods and systems for noise resilient, pin-efficient and low power communications with sparse signaling codes
In bus communications methods and apparatus, a first set of physical signals representing the information to be conveyed over the bus is provided, and mapped to a codeword of a sparse signaling code, wherein a codeword is representable as a vector of a plurality of components, some of which are quiescent components and some of which are non-quiescent components, wherein the number of quiescent components and non-quiescent components meet a sparseness requirement.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
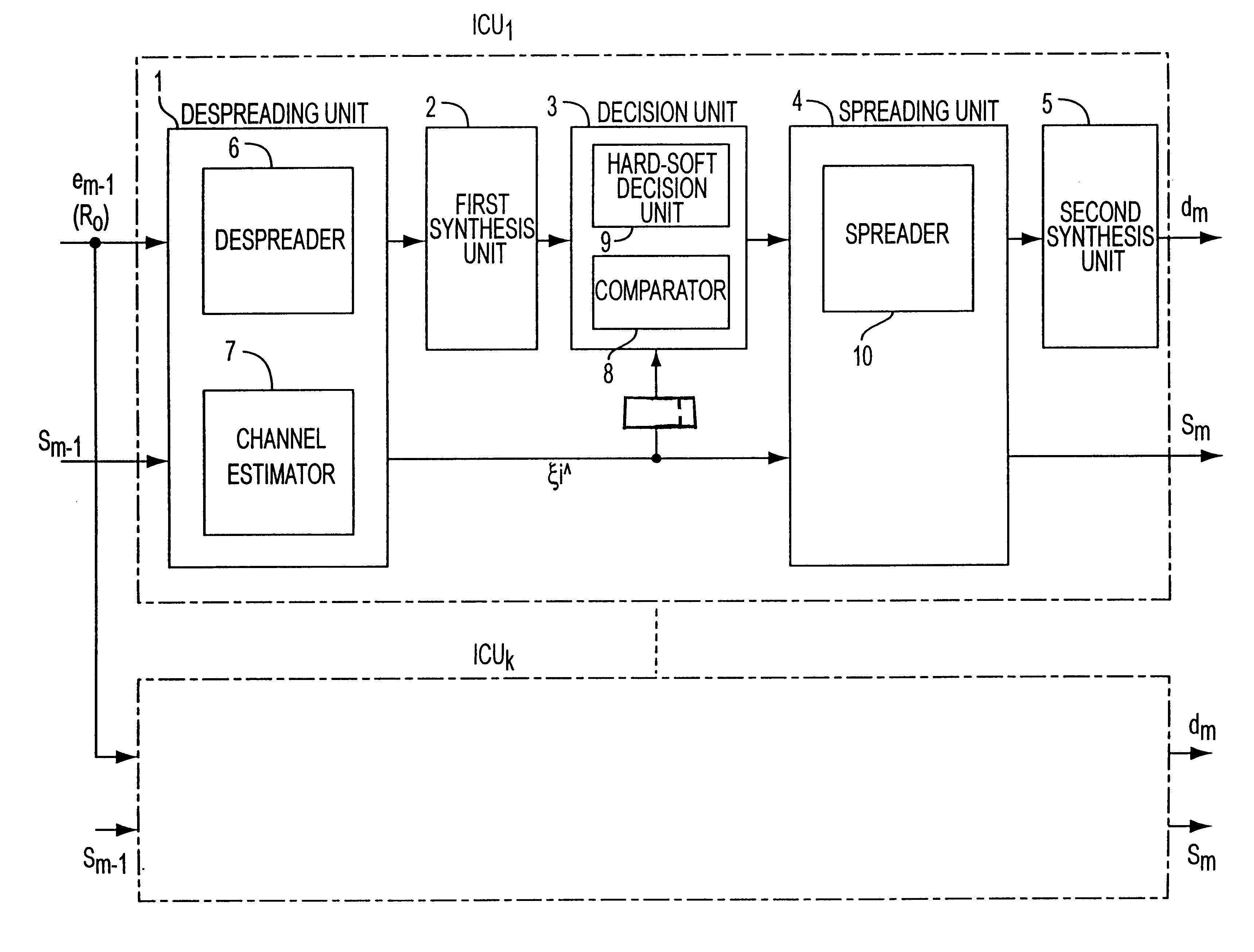
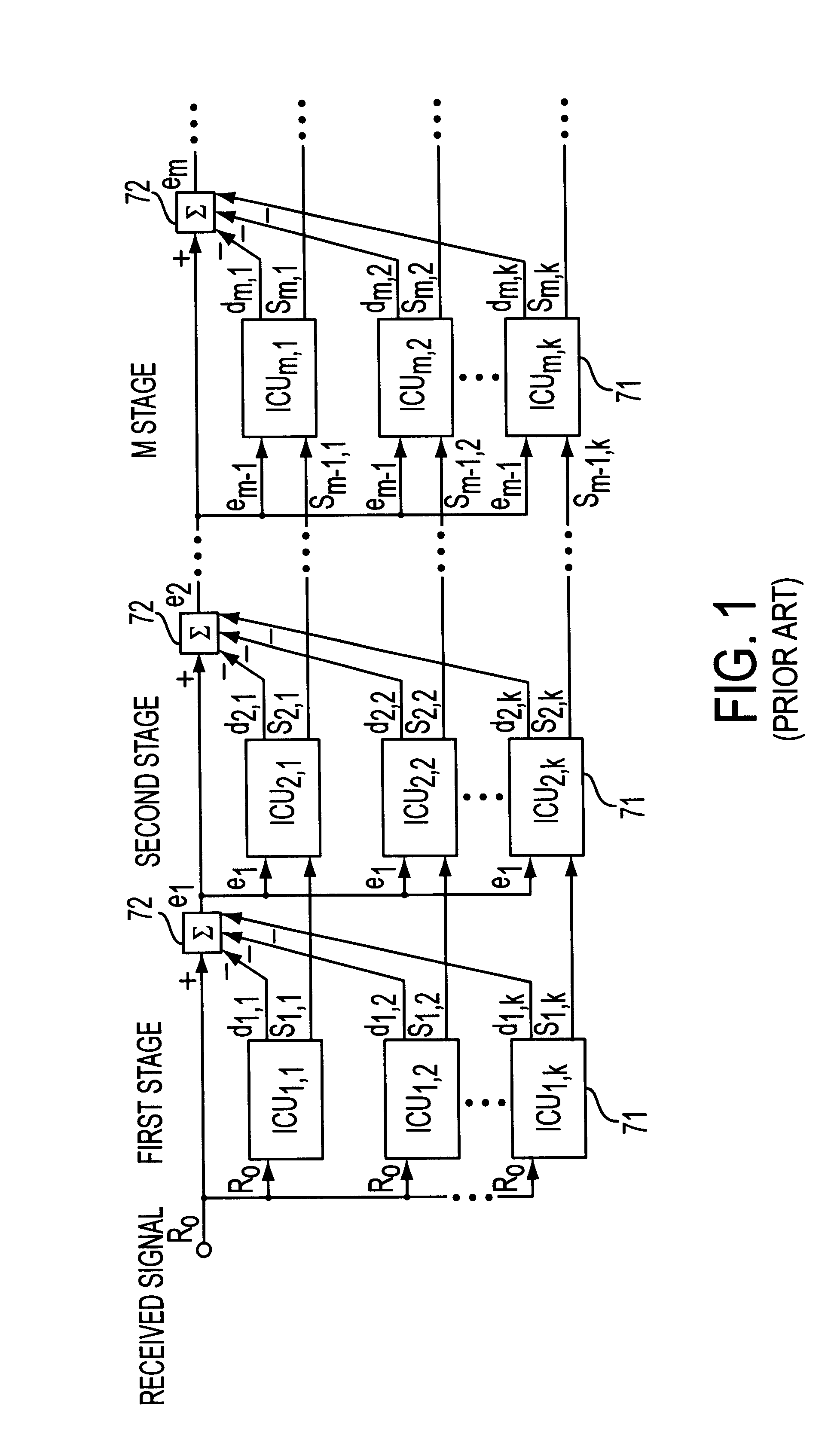
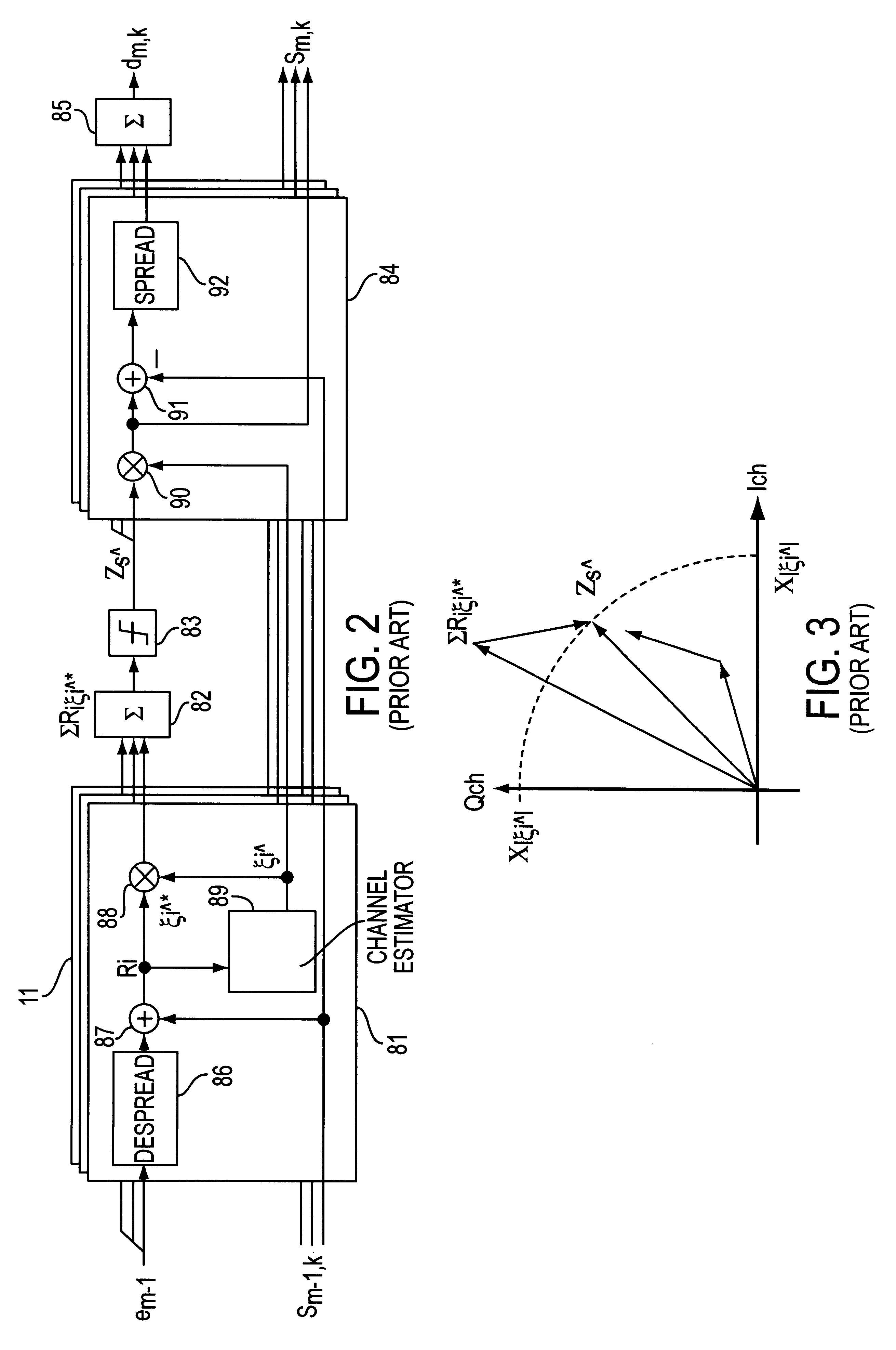
Multistage interference canceller
InactiveUS6192067B1Spatial transmit diversityError preventionInterference cancellerMultipath interference
A multistage interference canceller and method for removing interference between users and multipath interference from received signals in multiple stages includes a plurality of despreading units which produce a received symbol vector and an estimated channel value, a synthesis unit which synthesizes the received symbol vector, an amplitude of the received symbol vector and the amplitude of the estimated value from each reverse spreading unit, and a decision unit which executes a hard decision and a soft decision according to a result of comparing the total amplitude of the received symbol vector and the total amplitude of the estimated channel value.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
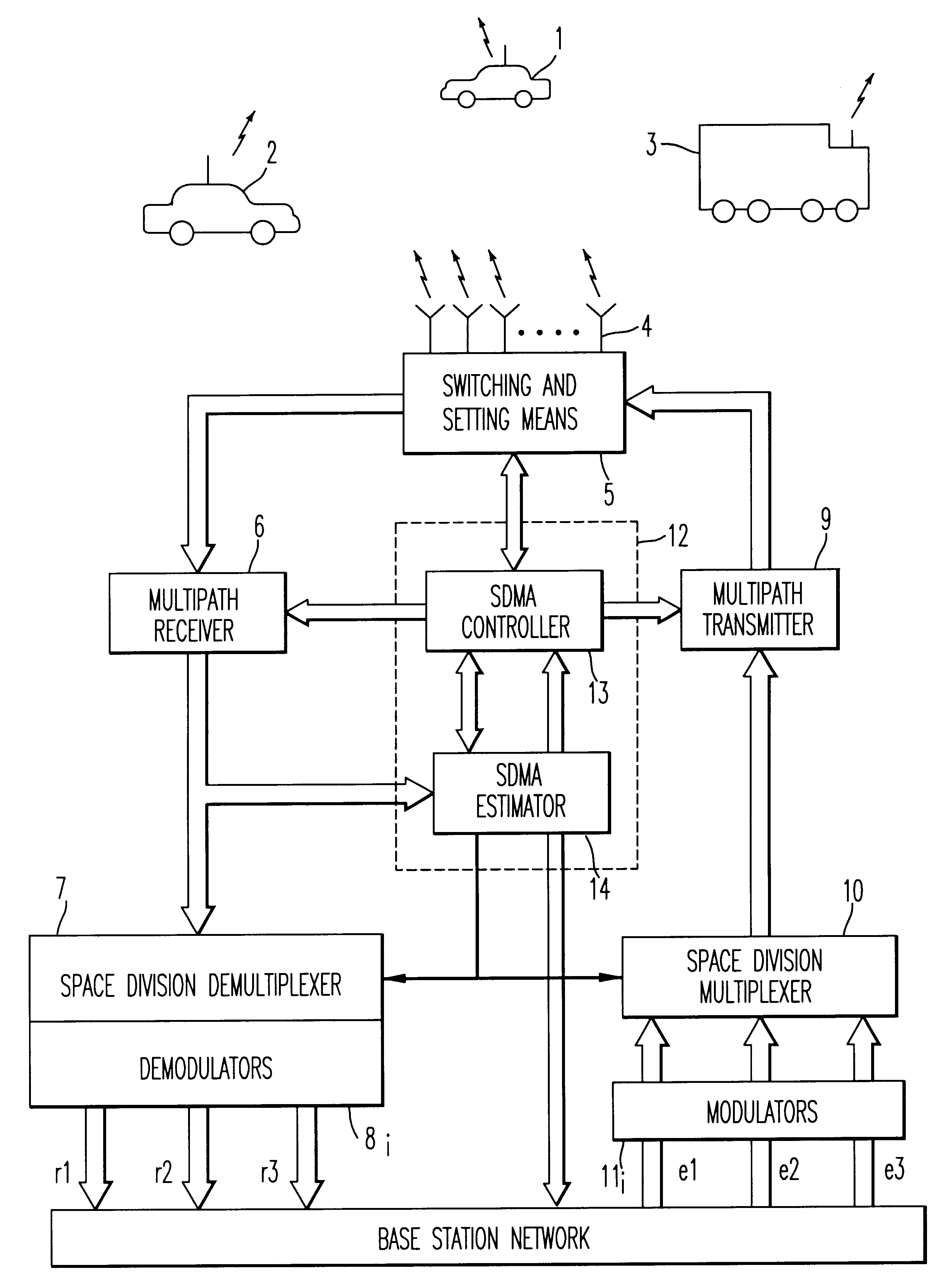
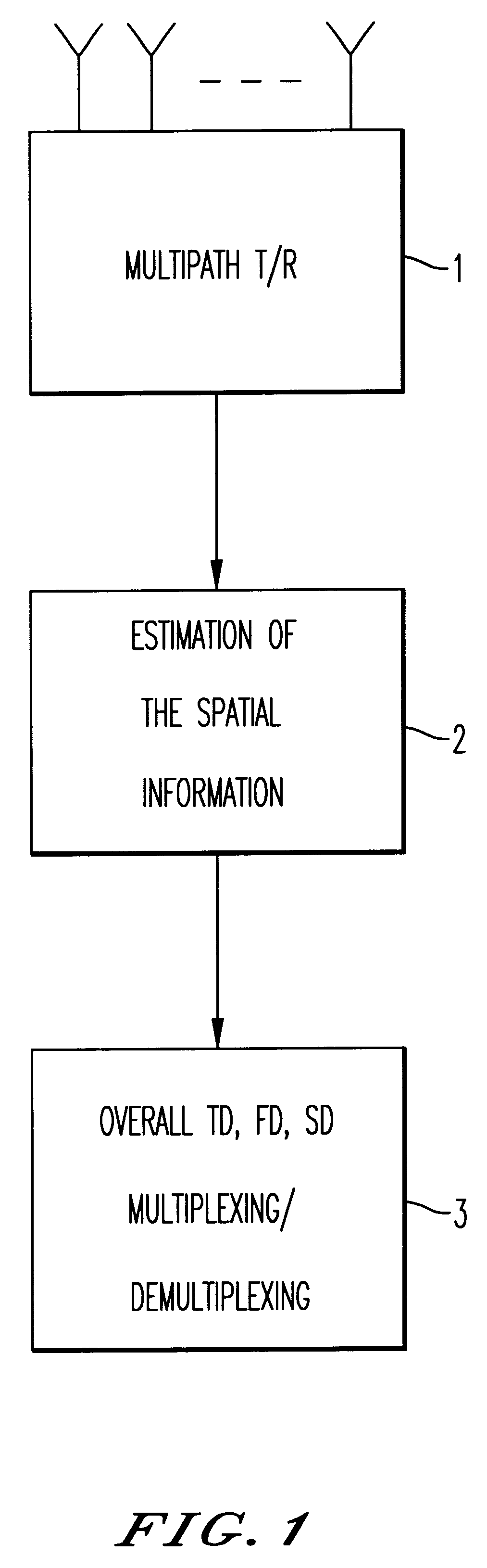
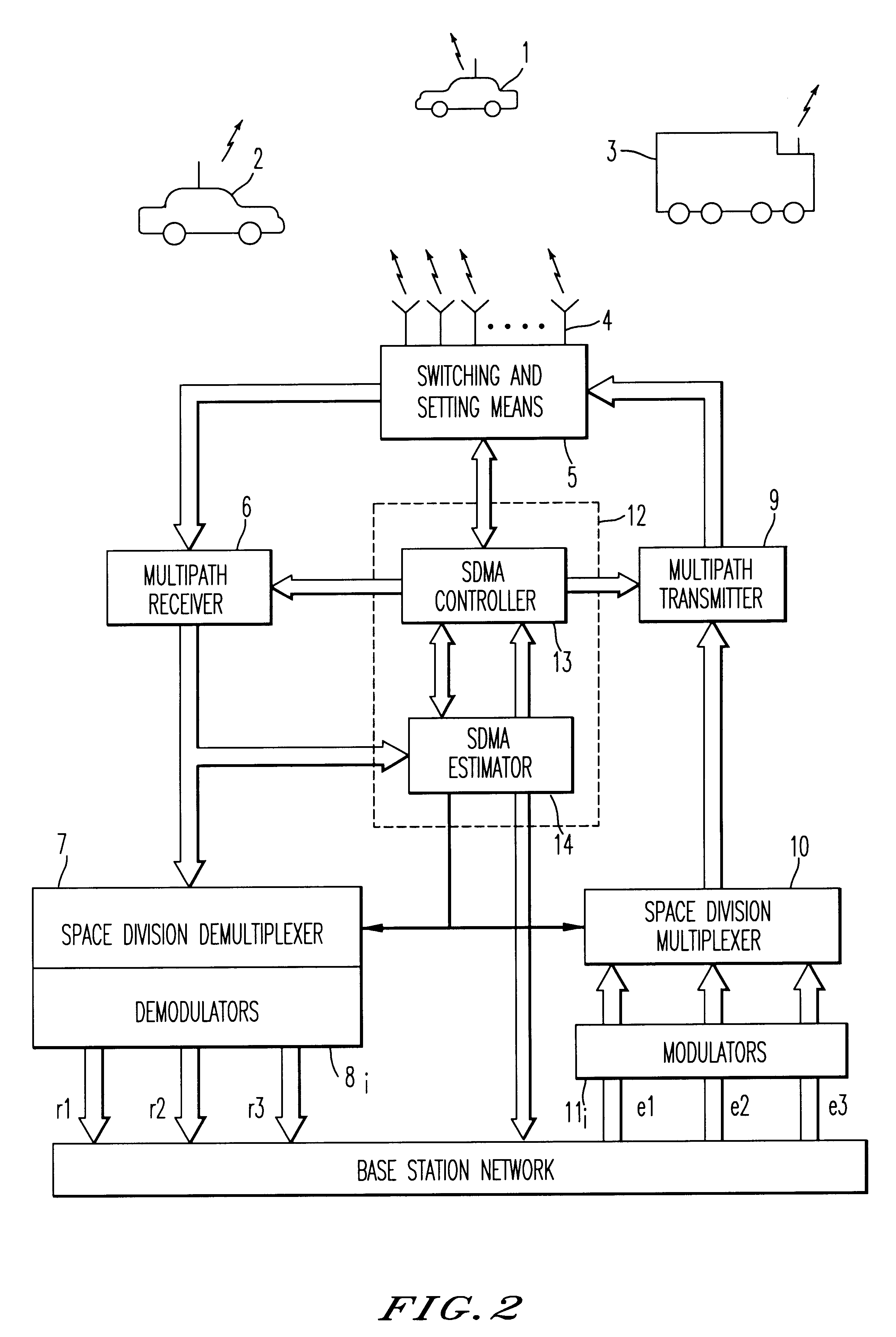
Method and device for space division multiplexing of radio signals transmitted in cellular radio communications
InactiveUS6240098B1Space can be allowedImprove performanceRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsSpatial transmit diversityEngineeringTime-division multiplexing
A method and apparatus for spatial multiplexing and demultiplexing of radio signals. A multichannel transmitter and receiver is integrated in a base station and coupled to an antenna array. Using digital radio signals containing previously known or non-Gaussian sequences and arranged in frames, the spatial information about each mobile unit is estimated on the basis of the signal received by the receiver for the reception and transmission frequencies. This is done by known sequences or by blind source separation methods. The respective paths of each mobile unit with the power above a predetermined threshold is isolated by spatial filtering in the presence of multiple channel paths in order to provide spatial demultiplexing. Simultaneously, the intended signal is transmitted in the direction of the main path of each mobile unit while protecting each mobile unit from signals transmitted in the direction of other mobile units by spatial filtering with cancelling constraints in order to provide spatial multiplexing.
Owner:THOMSON CSF SA
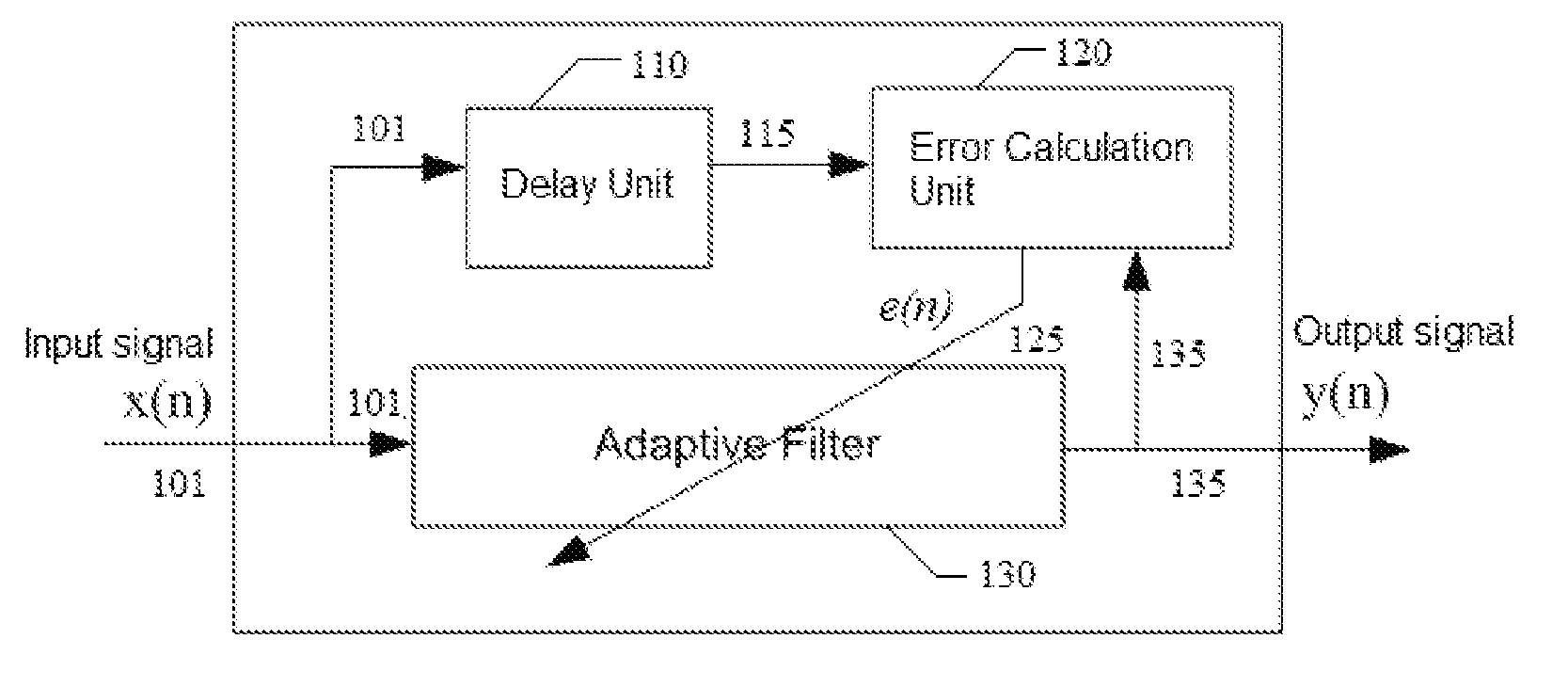
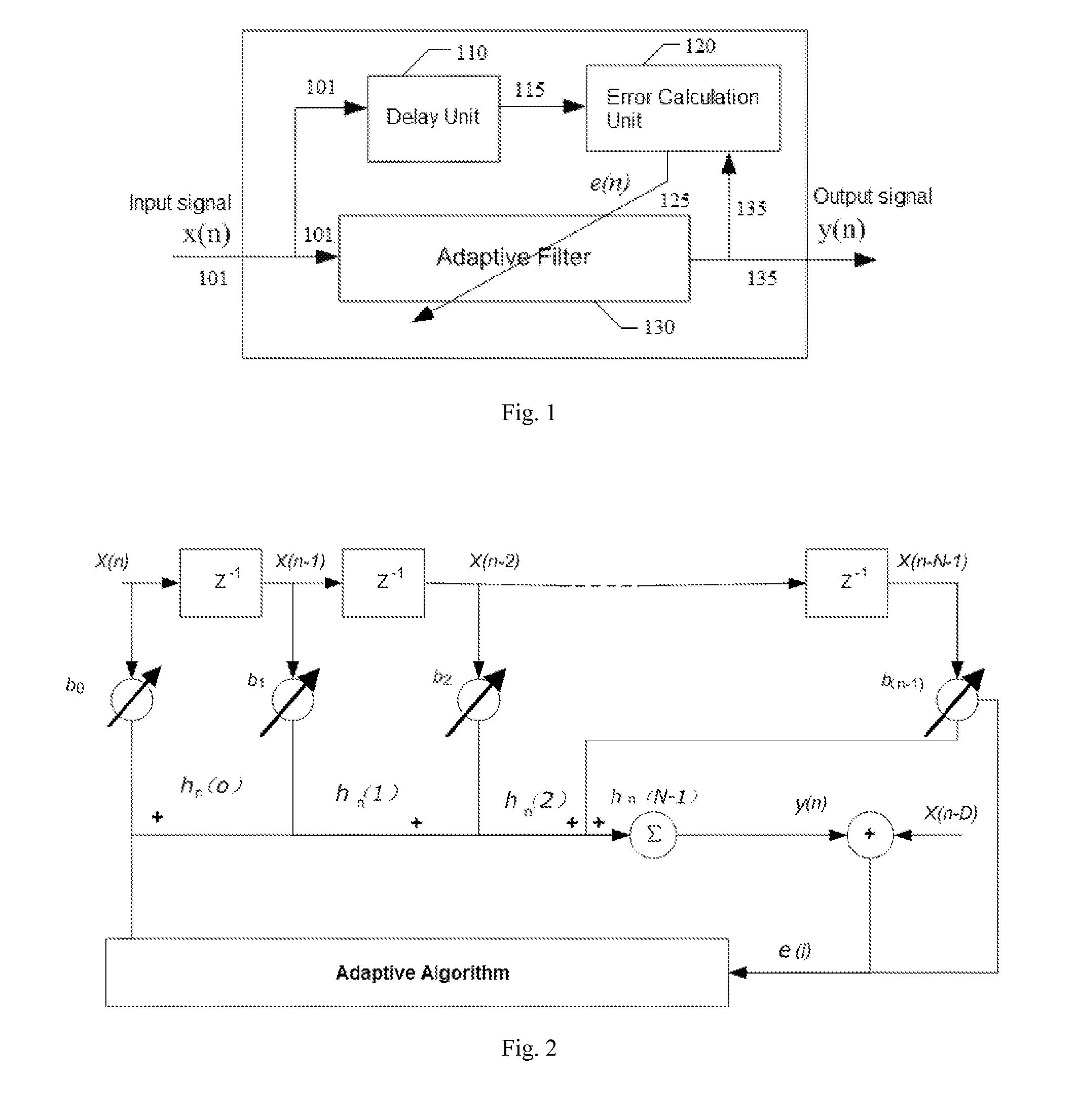
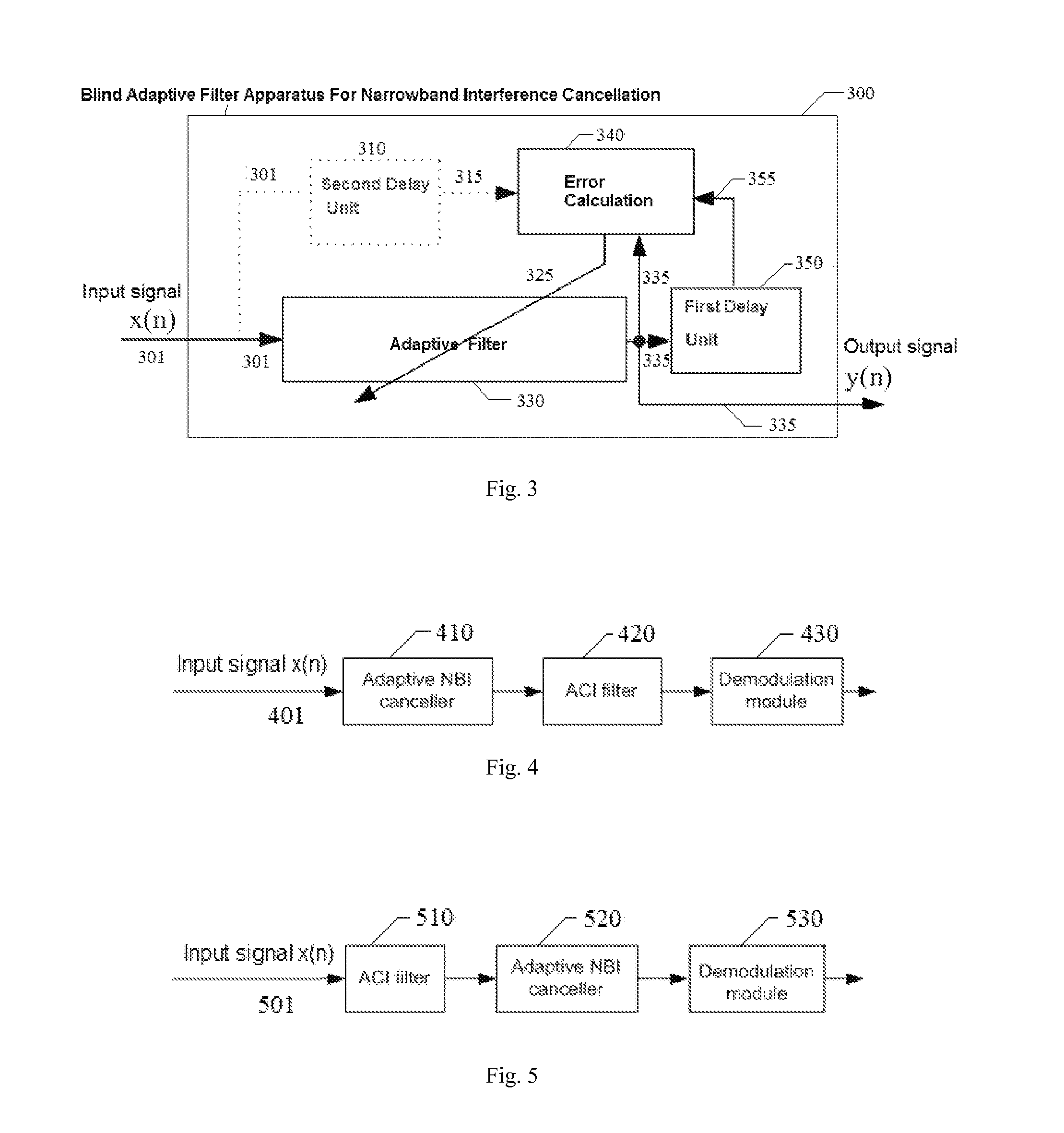
Blind adaptive filter for narrowband interference cancellation
ActiveUS20110305306A1Wide applicationError preventionDigital adaptive filtersSelf adaptiveSweep rate
The present invention relates to a blind adaptive filter for narrowband interference cancellation, which includes an adaptive filter, a delay unit coupled to the adaptive filter for generating a delayed signal with a predetermined delay length from the output signal of the adaptive filter, and an error calculation unit coupled to the adaptive filter and the delay unit. The error calculation unit compares the output signal from the adaptive filter and the delayed signal from the delay unit to extract error information, and feedback the first error information to the adaptive filter. The first error information is formed of a transfer function including a number of coefficients, and used to adjust the adaptive filter and remove interference in the next input signal. The disclosed technique is also applicable in wideband receivers, as well as resisting multiple strong narrowband interferences having a frequency sweep rate of tens of milliseconds.
Owner:MONTAGE TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Multi-carrier communication systems employing variable symbol rates and number of carriers
ActiveUS20020006167A1Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransmission path divisionCommunications systemClock rate
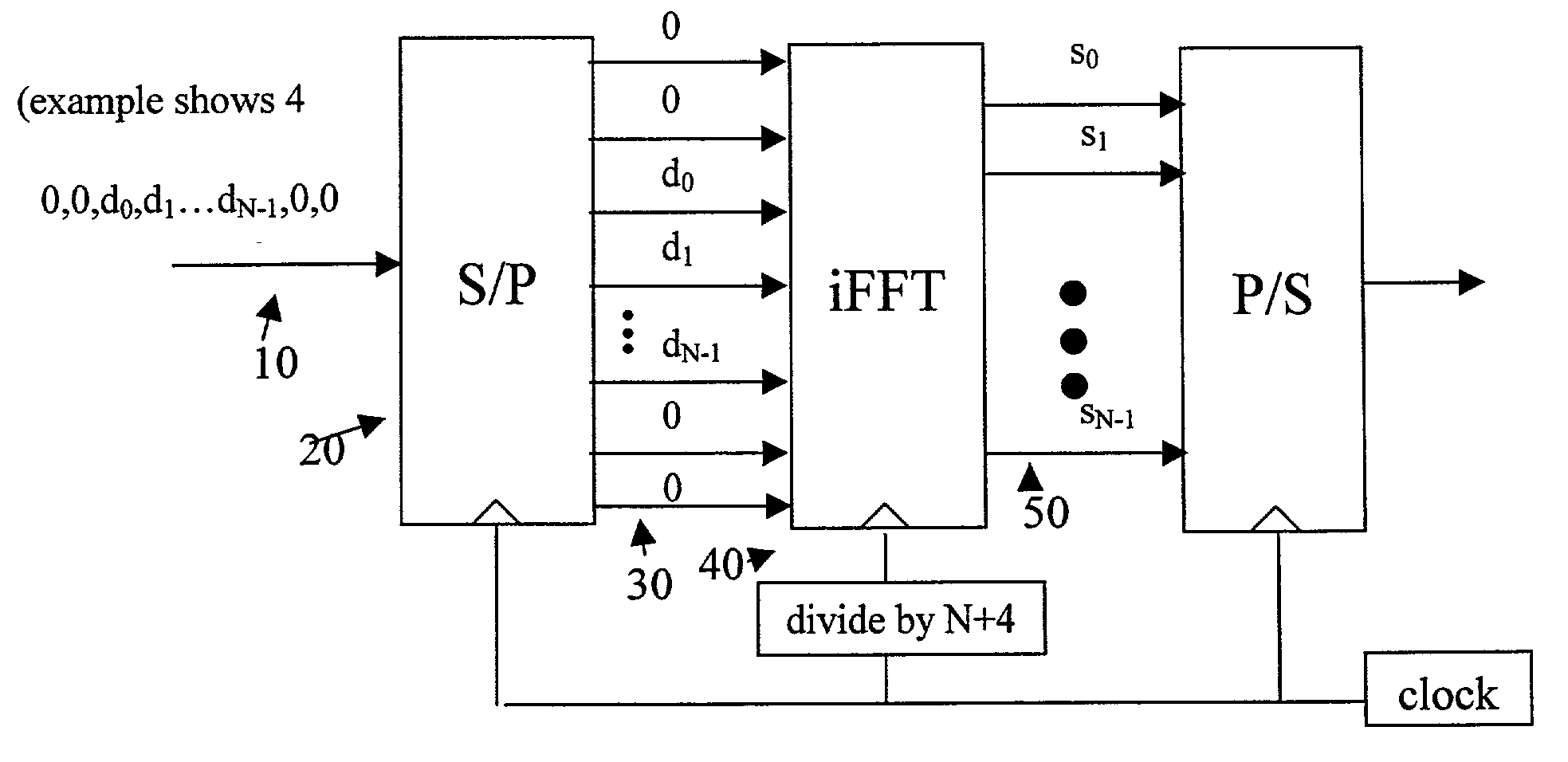
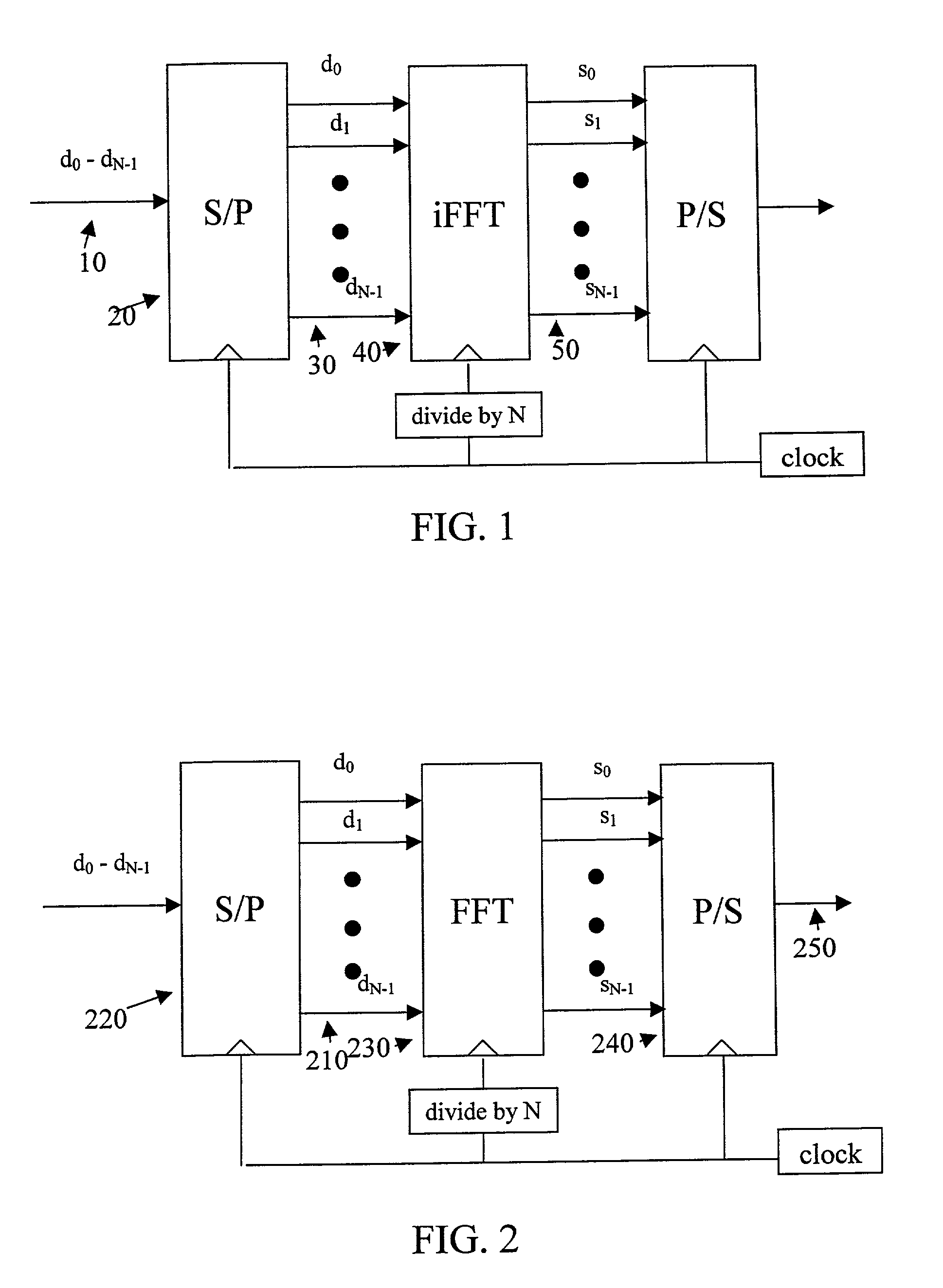
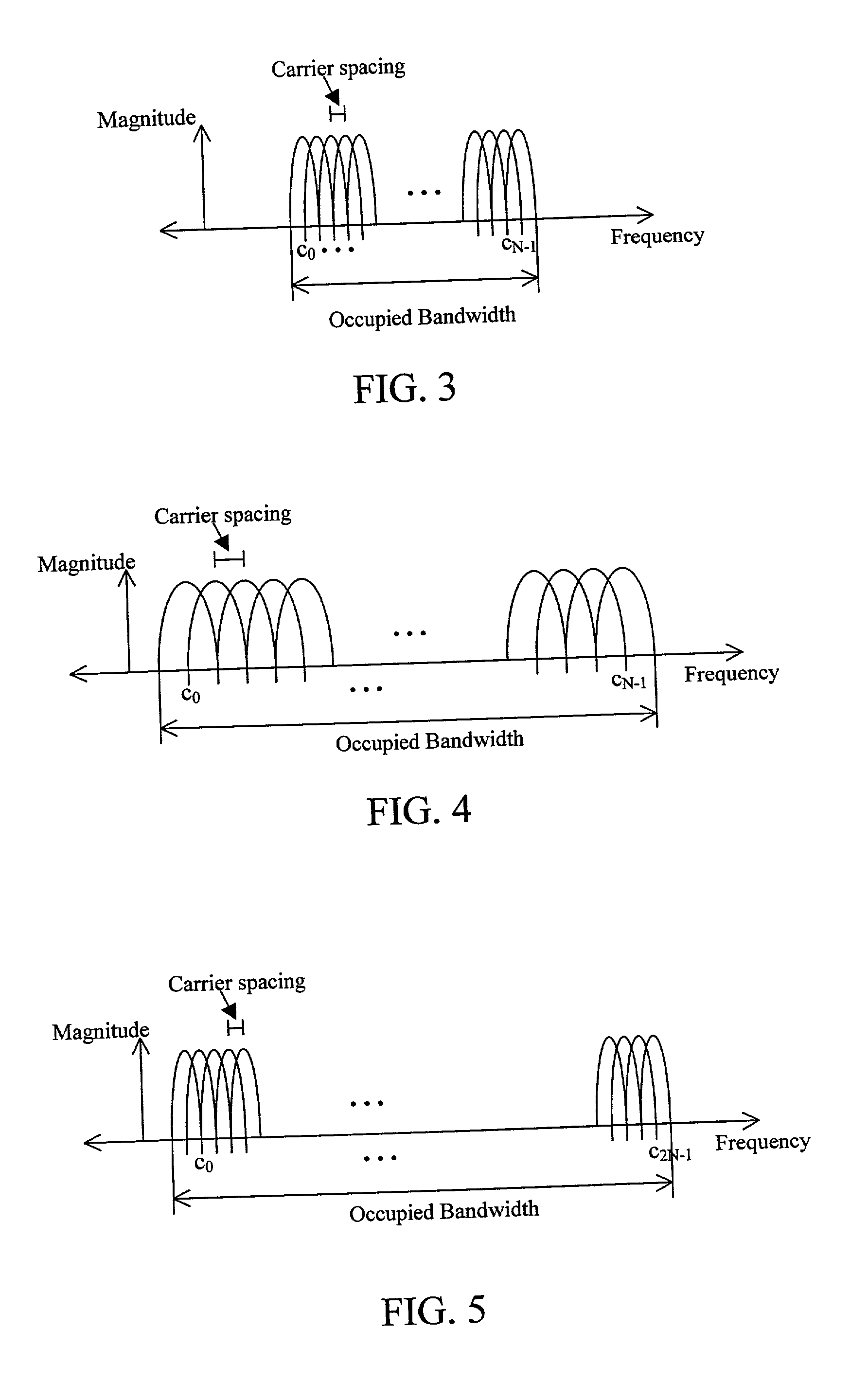
A multi-carrier communication system such as an OFDM or DMT system has nodes which are allowed to dynamically change their receive and transmit symbol rates, and the number of carriers within their signals. Changing of the symbol rate is done by changing the clocking frequency of the nodes' iFFT and FFT processors, as well as their serializers and deserializers. The nodes have several ways of dynamically changing the number of carriers used. The selection of symbol rate and number of carriers can be optimized for a given channel based on explicit channel measurements, a priori knowledge of the channel, or past experience. Provision is made for accommodating legacy nodes that may have constraints in symbol rate or the number of carriers they can support. The receiver can determine the correct symbol rate and number of carriers through a priori knowledge, a first exchange of packets in a base mode that all nodes can understand, or an indication in the header of the data packet which is transmitted in a base mode of operation that all nodes can understand.
Owner:THE CONNECTIVITY PATENT TRUST
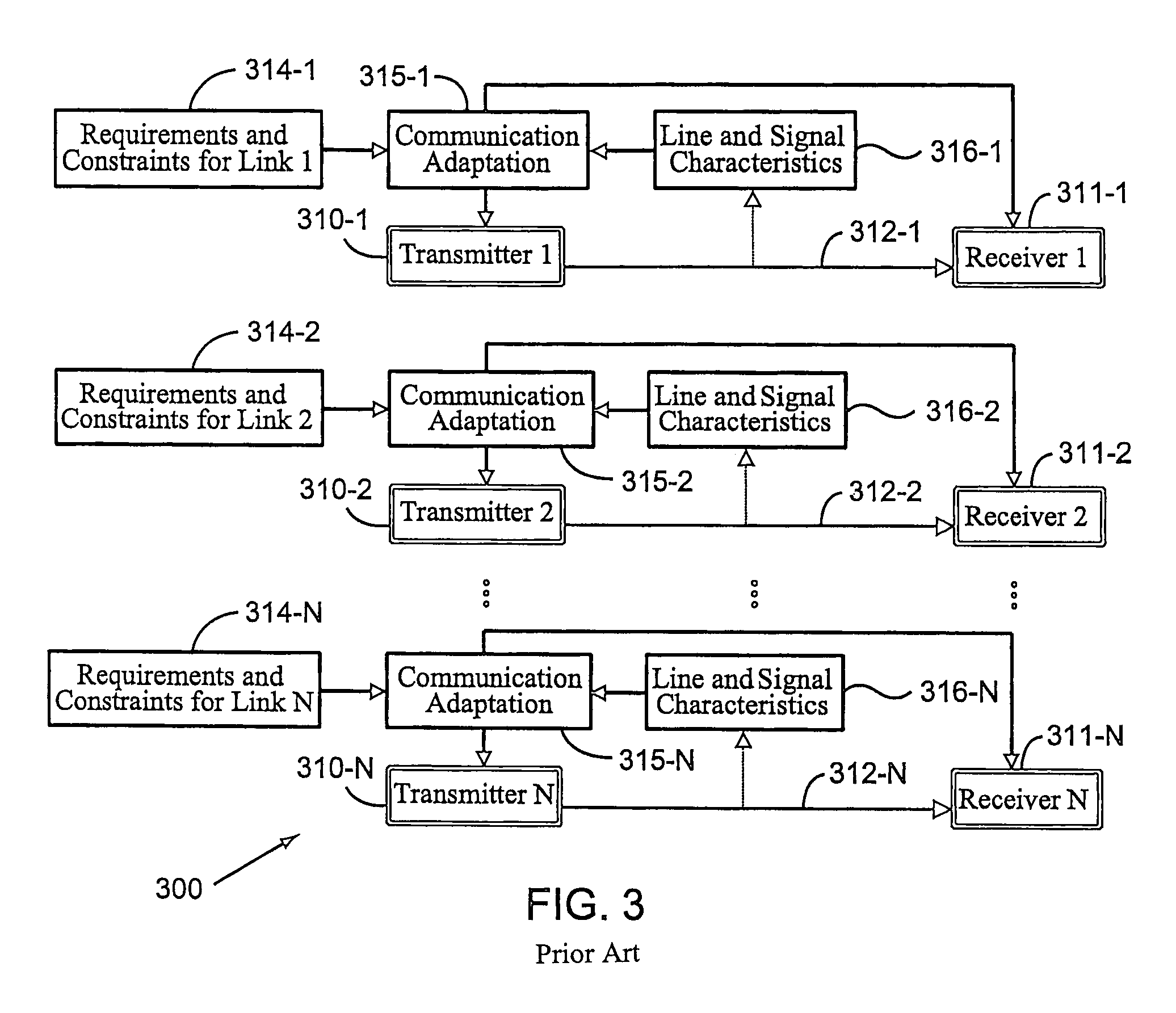
Dynamic digital communication system control
InactiveUS7158563B2Improve performanceMinimize impactError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemControl system
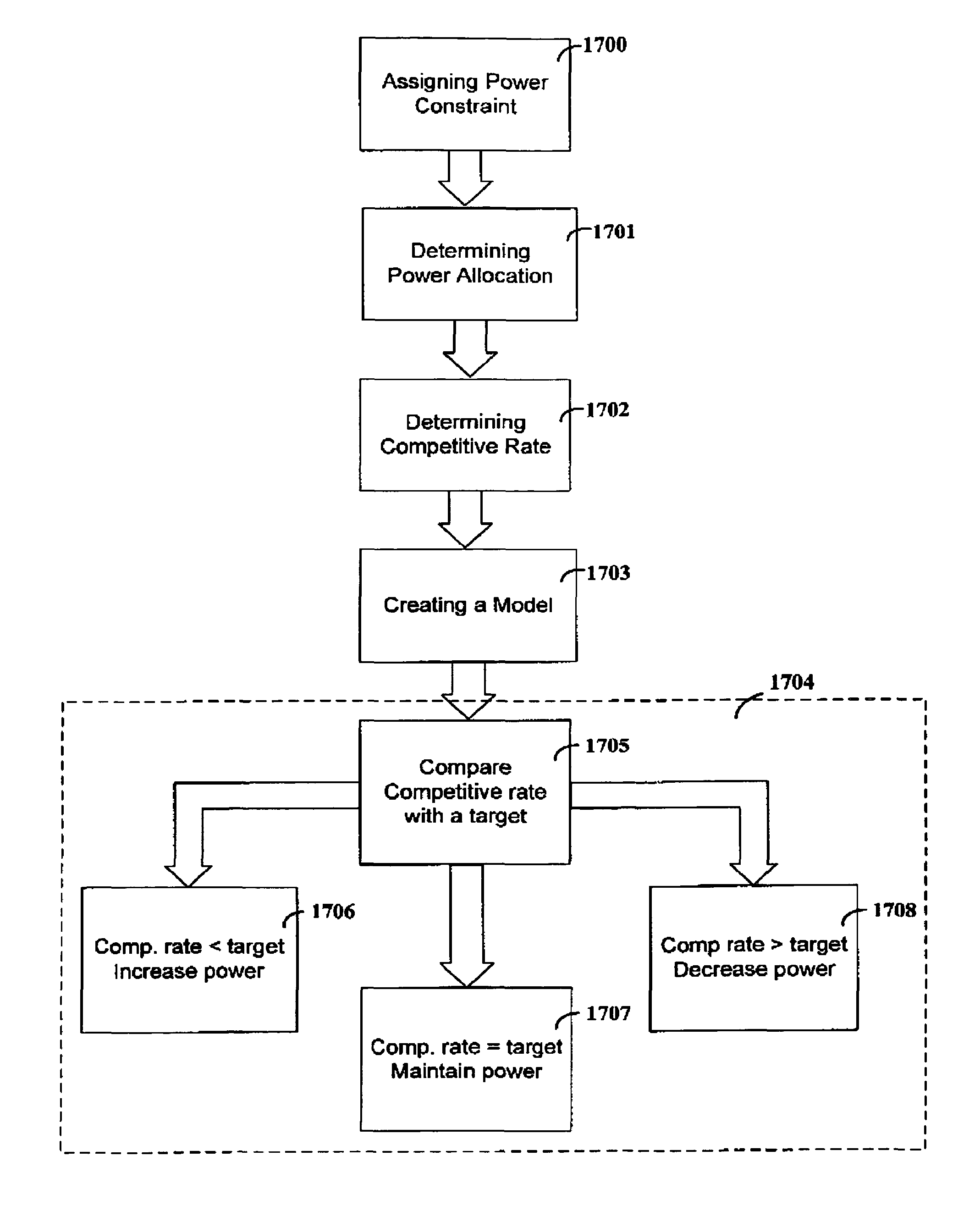
Methods, apparatus and systems for dynamically controlling a digital communication system, such as a DSL system, collect information about digital communication lines in the system and adaptively and / or dynamically determine line and signal characteristics of the digital communication lines, including interference effects. Based on the determined characteristics and the desired performance parameters, operation of the digital communication lines is adjusted to improve or otherwise control the performance of the system. The collection and processing of information may be performed by a party that is not a user in the system. This independent party also may control operational characteristics and parameters of the system. The invention can be used to eliminate or reduce signal interference such as crosstalk that can be induced on communication lines in systems such as DSL systems. Specific iterative power allocation and vectored transmission techniques and apparatus are disclosed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
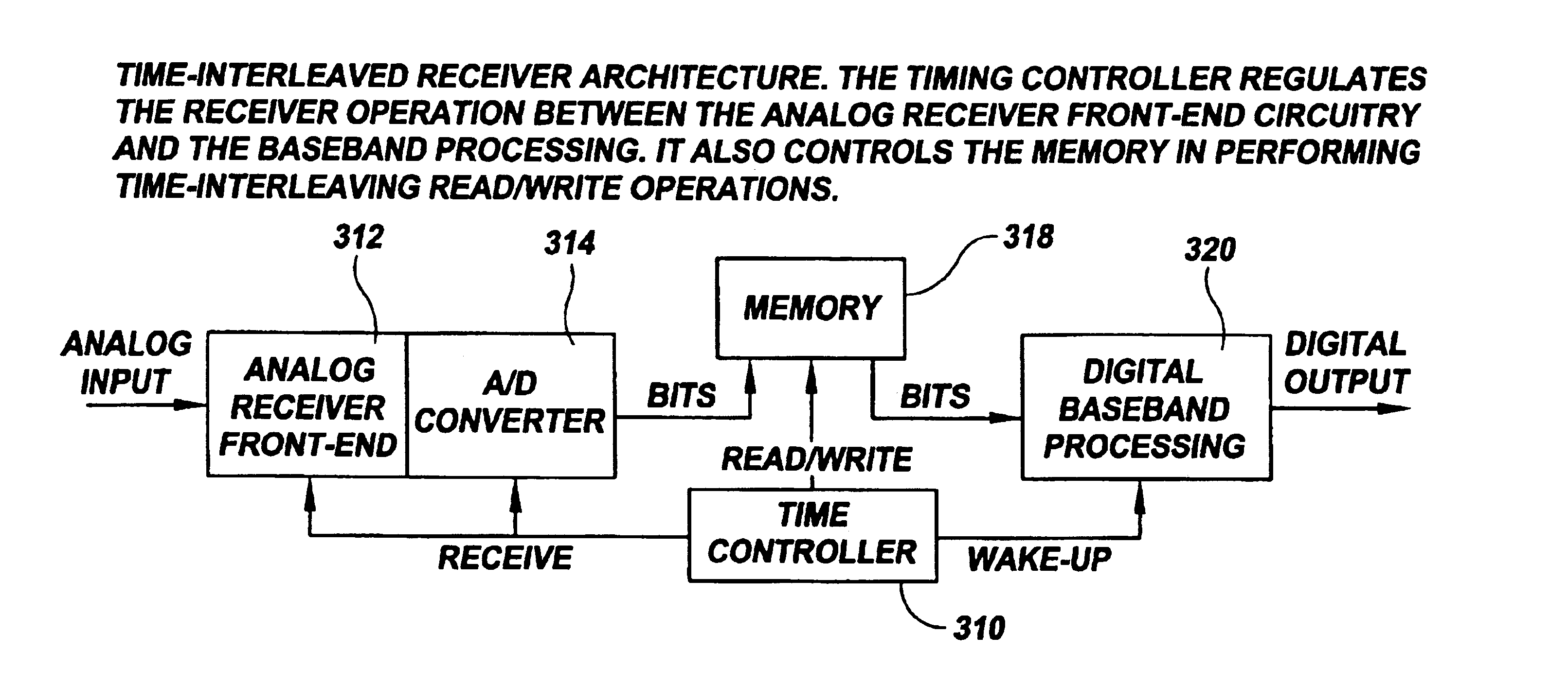
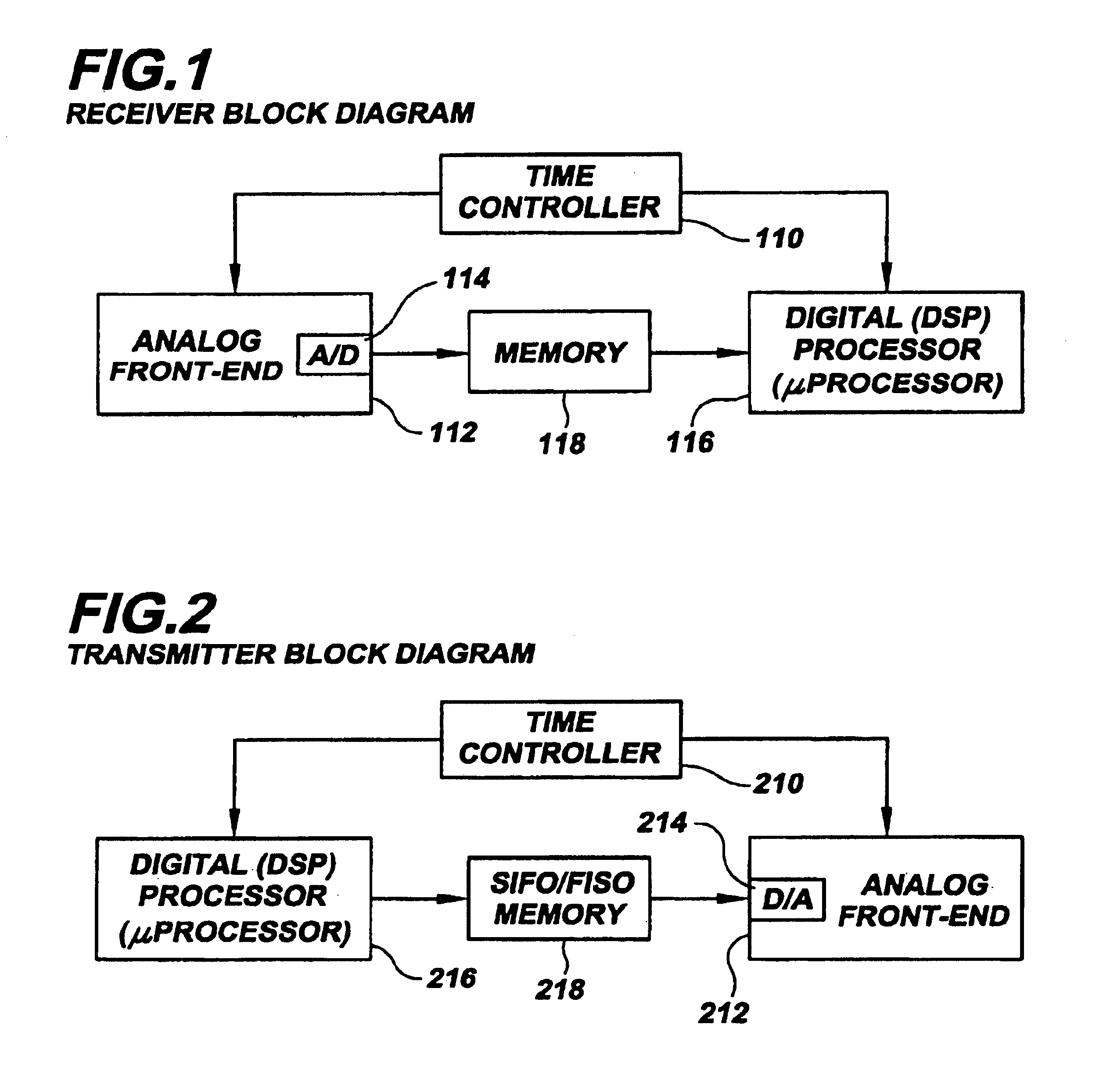
Noise-reducing arrangement and method for signal processing
InactiveUS6963626B1Effective noise reductionImprove noiseError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionCommunications systemDatapath
A communication system uses analog and digital circuits along the same data path in a manner that permits the analog circuitry to avoid adverse affects caused by the digital circuitry. Consistent with one embodiment directed to a signal processing system that detects faint incoming signals, the analog and digital circuits are implemented on a single piece of silicon. In such signal processing systems, noise generated by digital processing blocks can degrade the performance of sensitive analog portions. The effective noise is reduced by causing the analog and digital portions of the system to function during separate time intervals. The noise-generating portions of the system may then be turned off during a first data-communication interval while the analog block operates. The data acquired during this period is stored for subsequent processing by the digital portion during a second shorter data-communication interval. Other aspects are applicable to reception arrangements in which part of the incoming signal may be disregarded without significant degradation in performance of the rest of the system, and other aspects are directed to transmission arrangements in which the inverse of the above reception arrangement is used.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
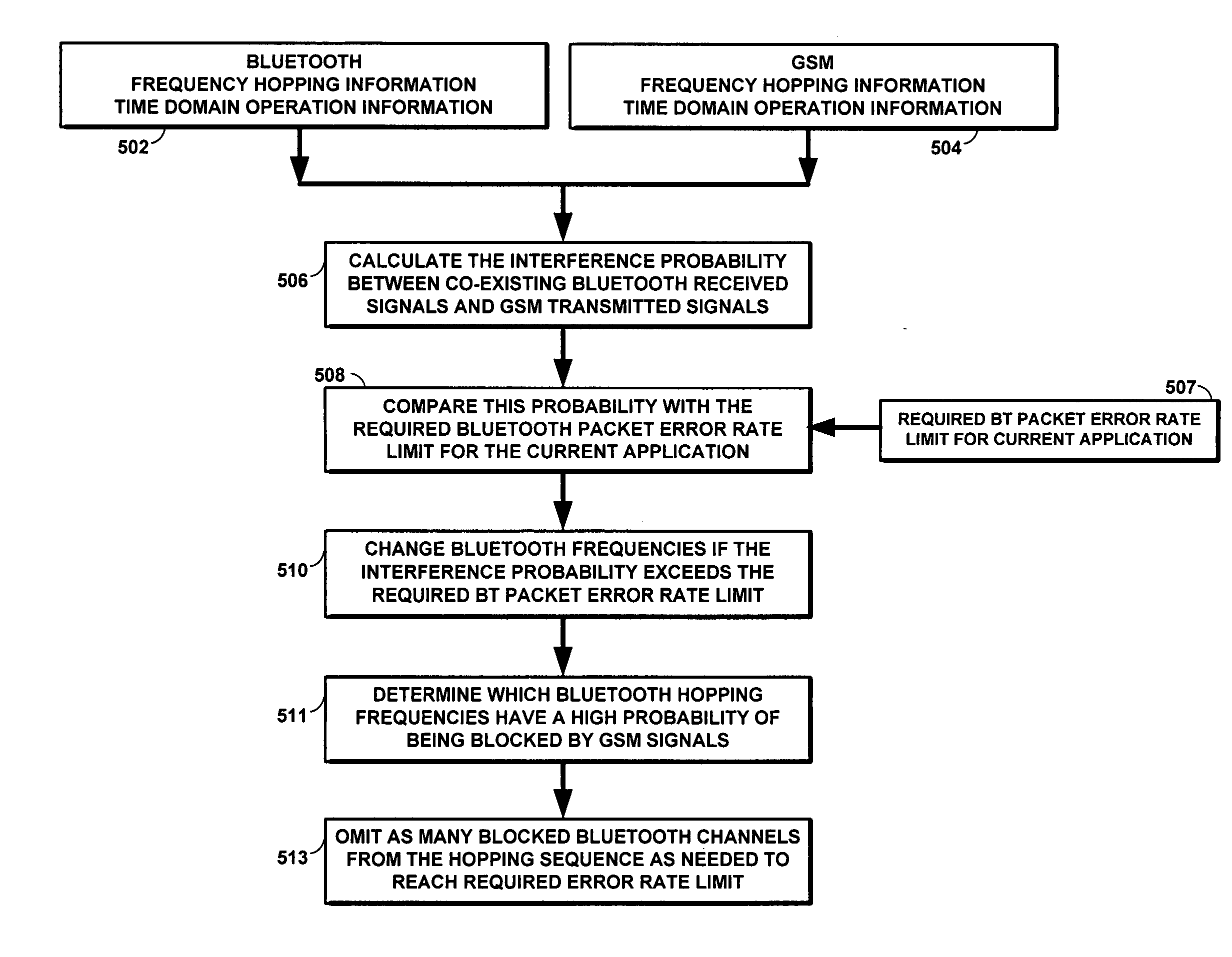
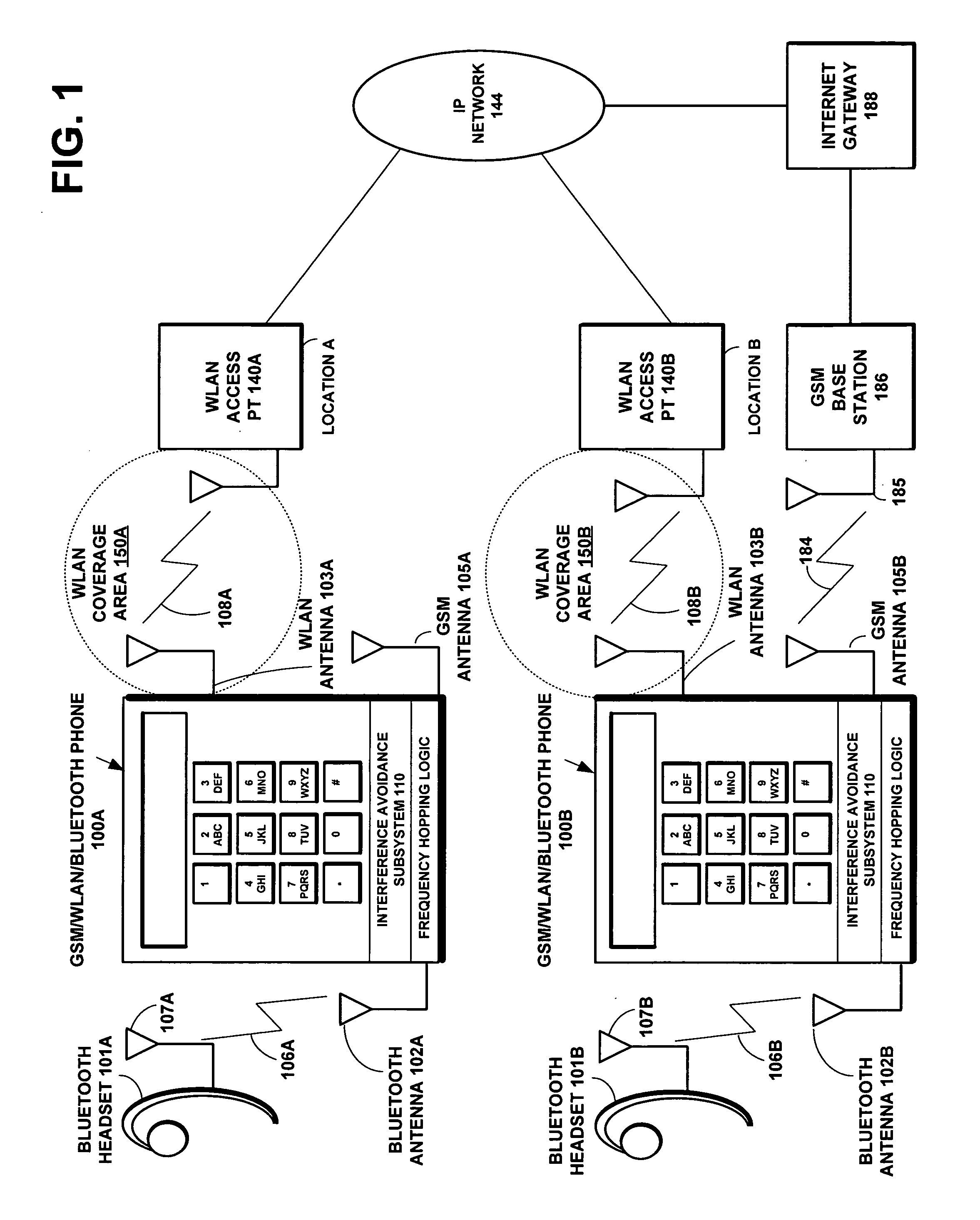
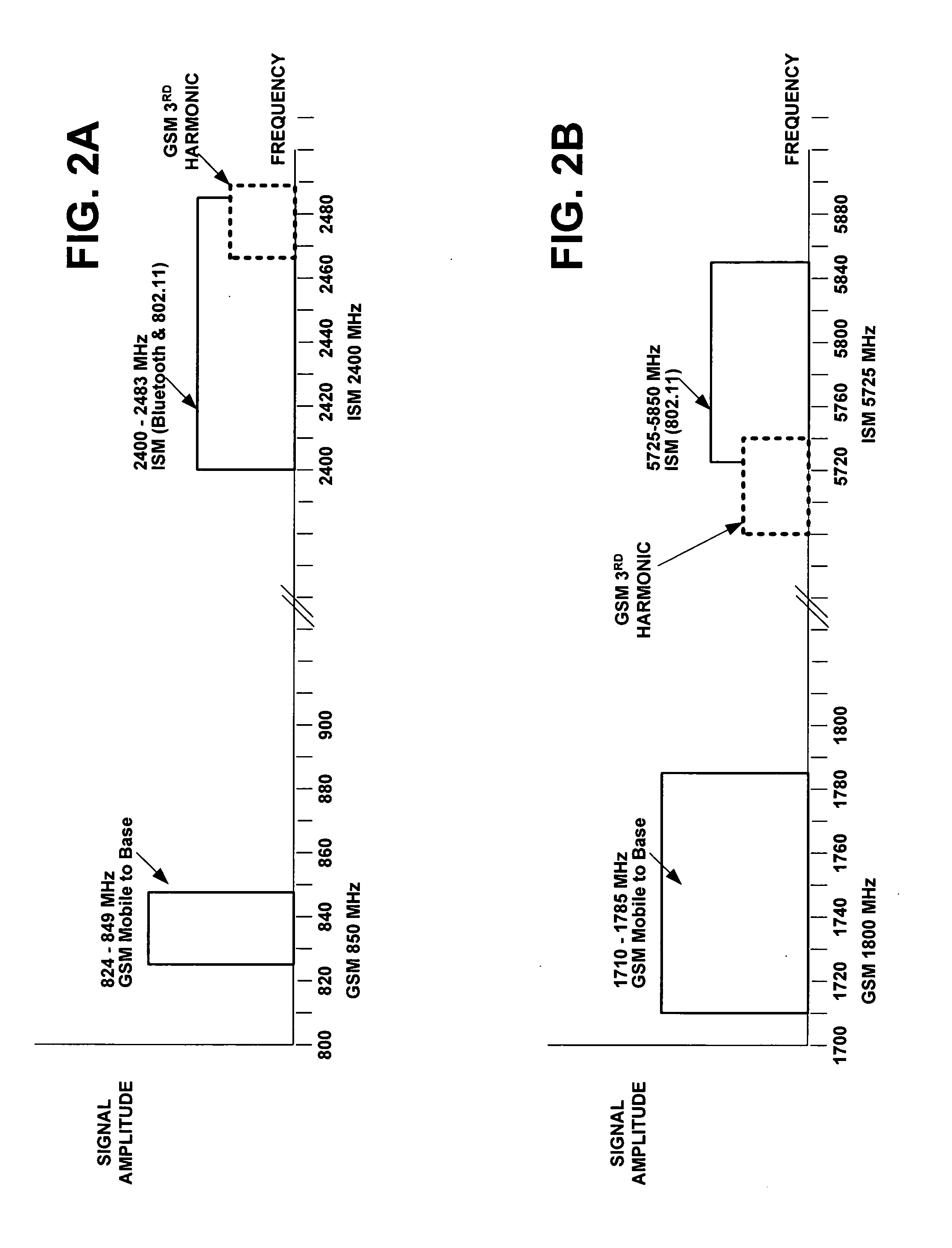
Method for avoiding interference from a cellular transmitter to the 2.4/5GHz ISM band
InactiveUS20070165754A1Avoid interferenceLine-faulsts/interference reductionAmplitude demodulation detailsTime domainCommunication unit
A method, terminal, and computer program are disclosed to reduce radio interference in a wireless communications device having a combination of a wireless telephone unit, such as a GSM cellular phone, and a short range wireless communications unit, such as a WLAN communications unit or a Bluetooth communications unit. An interference avoidance subsystem in the wireless communications device is connected between the GSM frequency hopping logic and the Bluetooth frequency hopping logic. Bluetooth frequency hopping information and time domain operation information are input from the Bluetooth frequency hopping logic to the interference avoidance subsystem. GSM frequency hopping information and time domain operation information are input from the GSM frequency hopping logic to the interference avoidance subsystem. The interference avoidance subsystem then uses this input data to calculate the interference probability between co-existing Bluetooth received signals and GSM transmitted signals. The interference avoidance subsystem then compares the calculated interference probability with the required Bluetooth packet error rate limit for the current application. If the interference probability exceeds the required Bluetooth packet error rate limit, the interference avoidance subsystem sends a signal to the Bluetooth frequency hopping logic to change the Bluetooth frequencies.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Equalization strategy for dual-polarization optical transport system
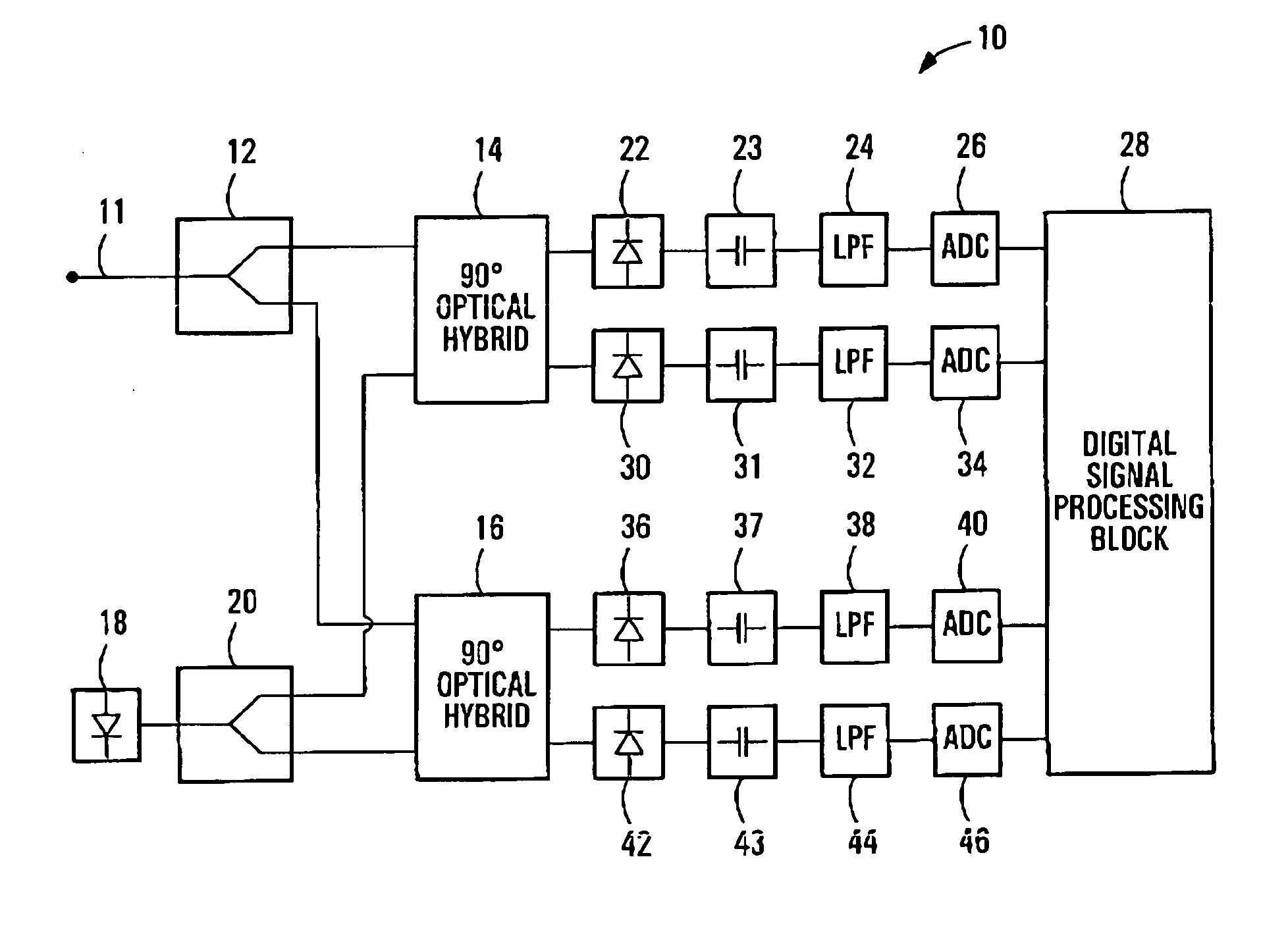
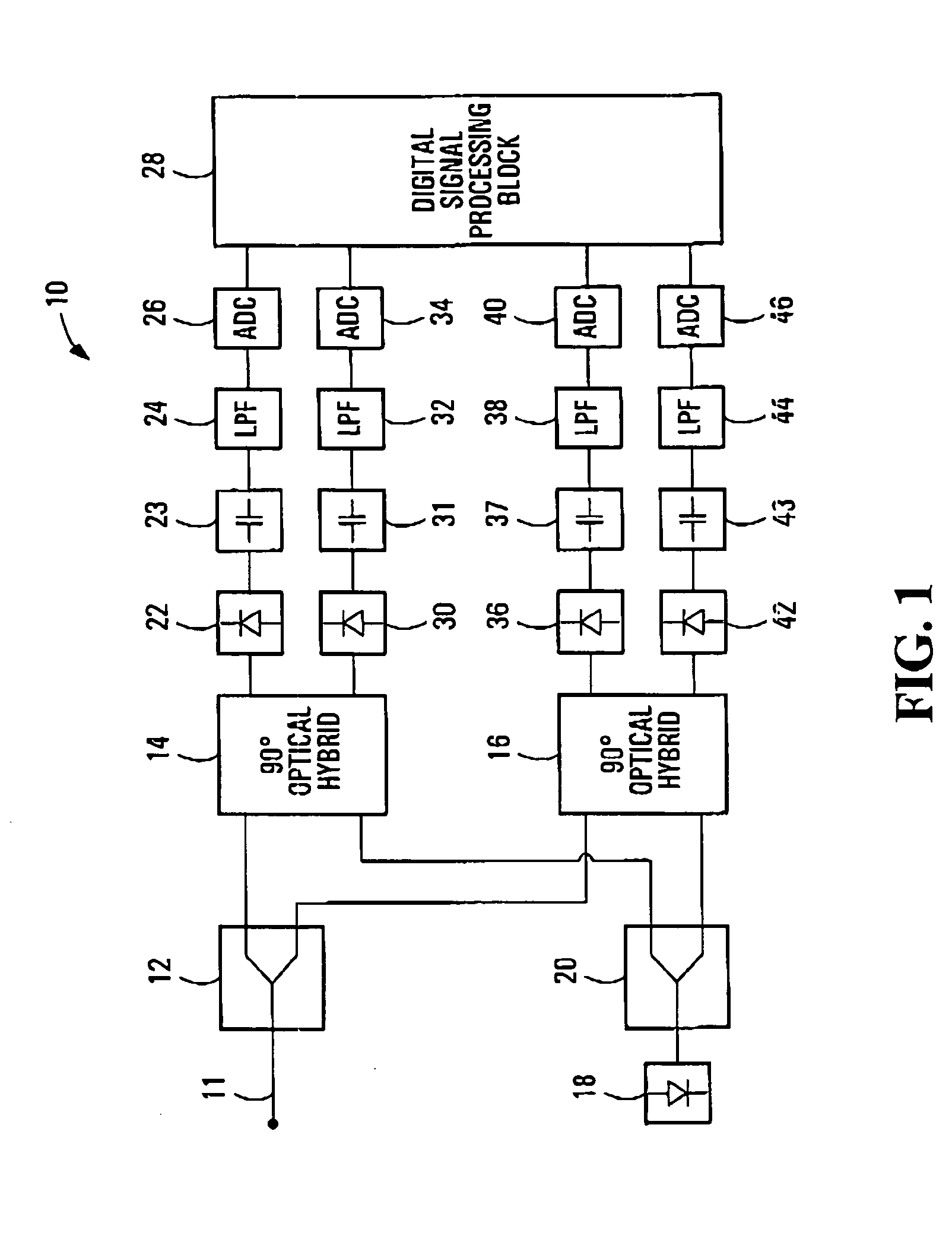
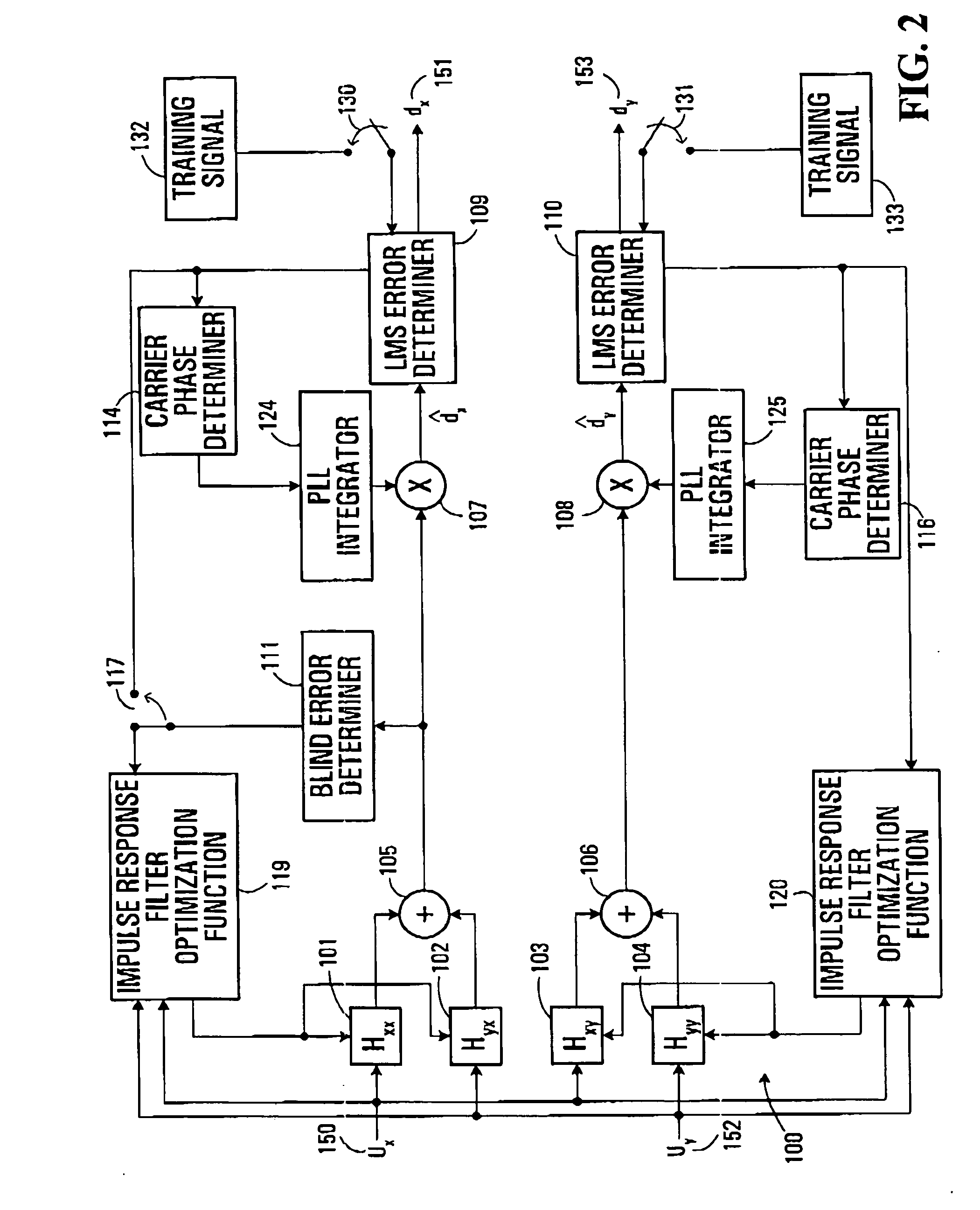
ActiveUS20050196176A1Avoid convergencePrevent degradationMultiple-port networksError preventionDigital signal processingSelf recovery
A method is provided for an equalization strategy for compensating channel distortions in a dual-polarization optical transport system wherein the received signal includes a complex signal of a first transmitted polarization component and a complex signal of a second transmitted polarization component. In a first step, a blind self-recovery mode used a blind adaptation algorithm in calculating and modifying multiple complex equalizer transfer function coefficients to enable recovery of only the complex signal of the first transmitted polarization component. By recovering only a single polarization component in the first step the degenerate case of recovering only a single transmitted signal at both polarization component outputs of an equalizer is prevented. In a second step, equalization is performed in a training mode for calculating and modifying the multiple complex equalizer transfer function coefficients to enable recovery of the complex signals of the first and second transmitted polarization components. In a third step, equalization is performed in a data directed mode for continuing to calculate and modify the multiple complex equalizer transfer function coefficients to ensure continued recovery of the complex signals of the first and second transmitted polarization components. The method is suited for a digital signal processing implementation in a coherent receiver when a modulation scheme used on a transmitted signal is quadriphase-shift keying (QPSK). In other embodiments, the method can be used with modulation schemes such as binary PSK, M-ary PSK where M>4, or Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM).
Owner:CIENA
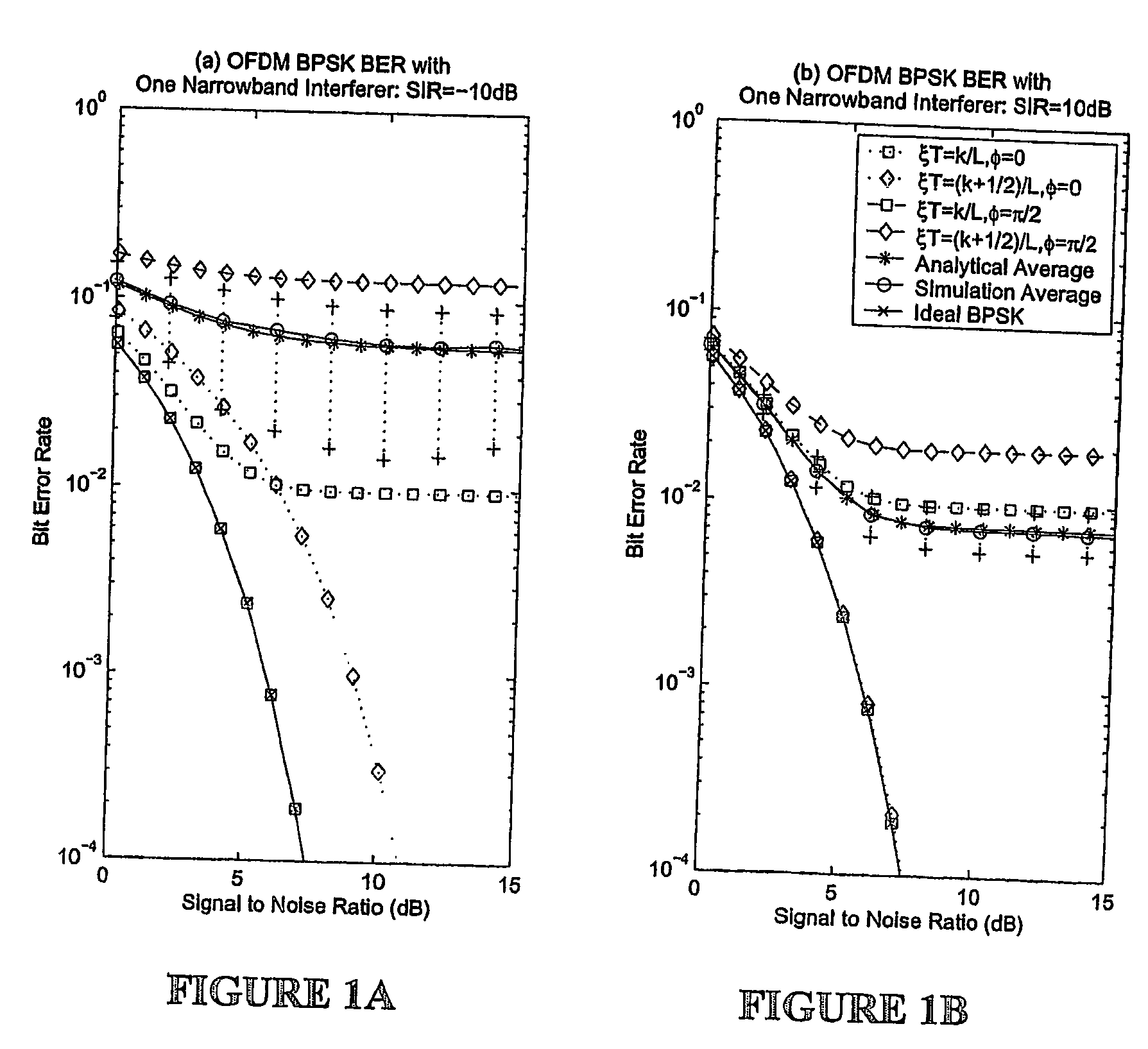
Narrowband interference suppression for ofdm system
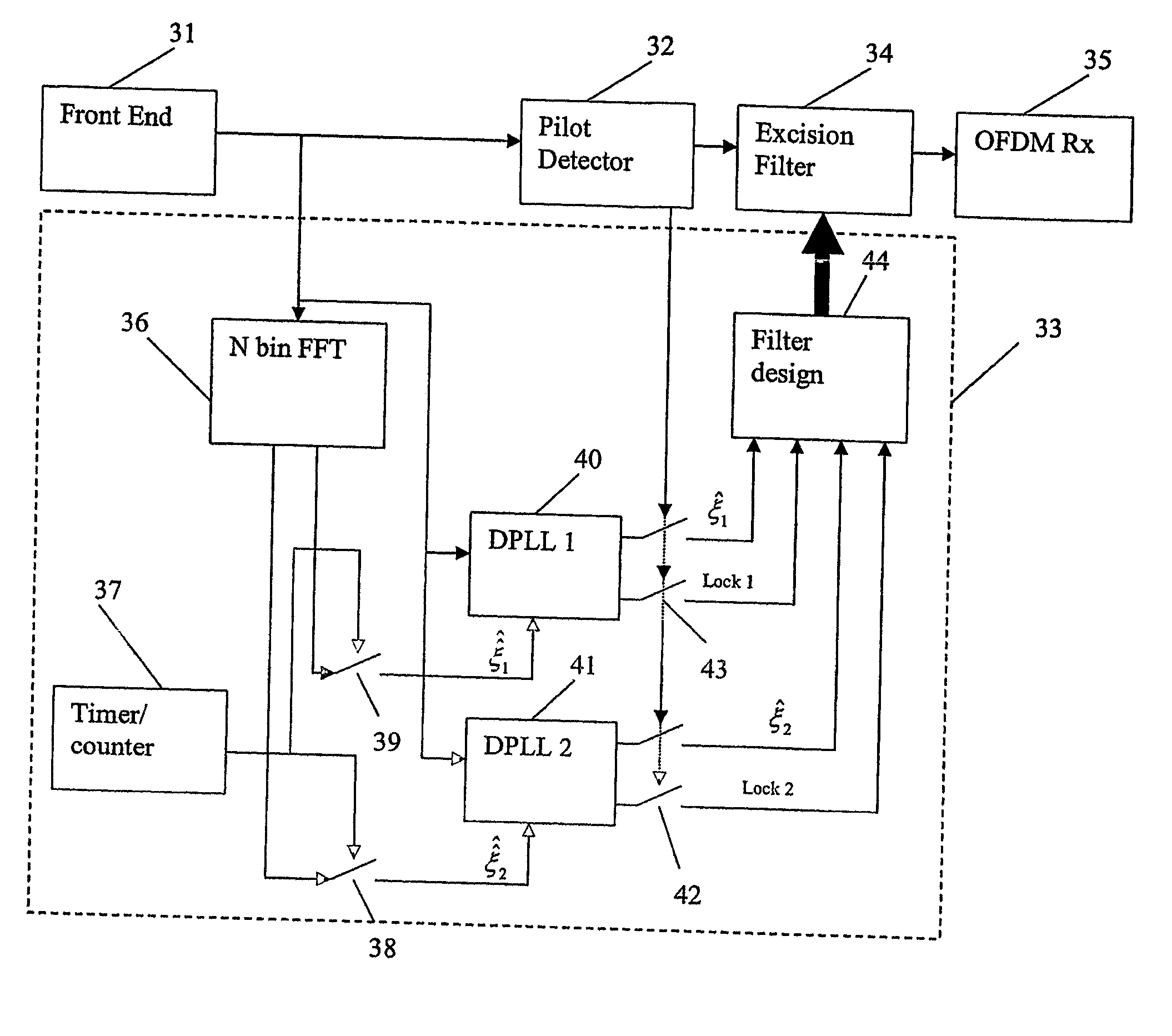
ActiveUS20070009011A1Reduce noiseError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionEngineeringNarrowband interference
A method for suppressing narrowband interference in OFDM receivers is provided including the steps of acquiring a sample of received data, estimating parameters of each of a number of narrowband interferers from the acquired sample of data, forming an excision filter using the estimated parameters and inserting the excision filter into an OFDM receiver.
Owner:CALLAGHAN INNOVATION
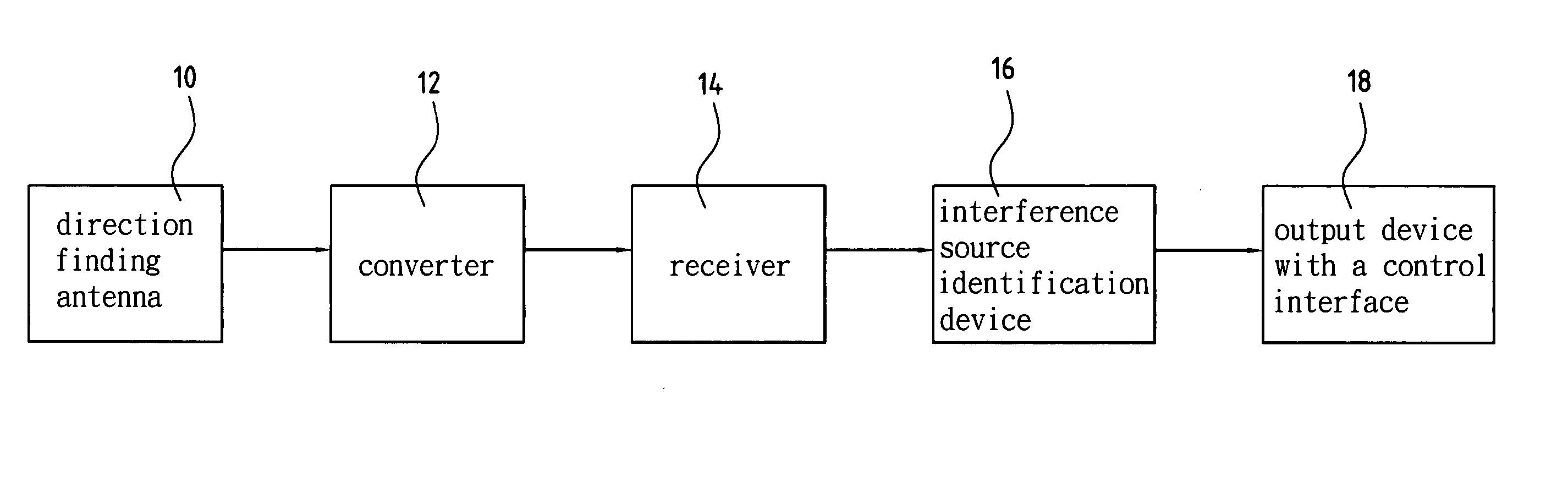
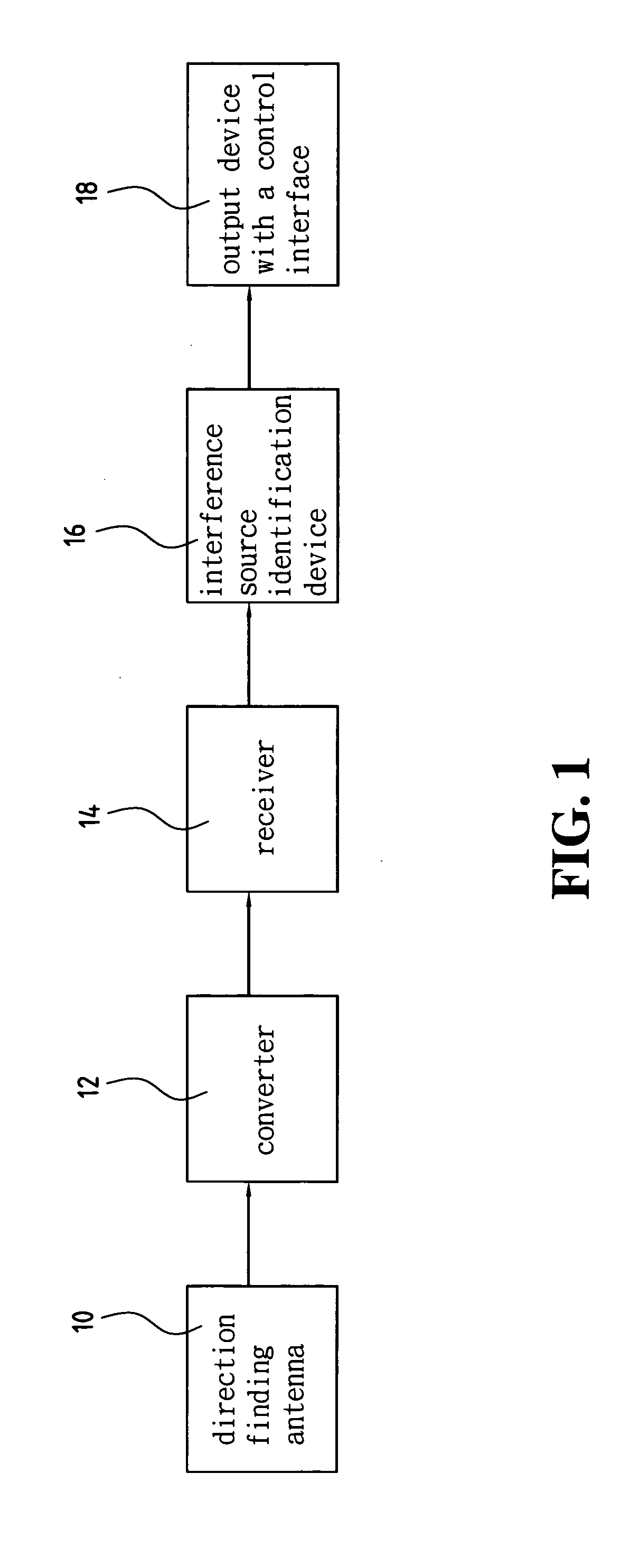
Device and method for identifying interference source in wireless communications
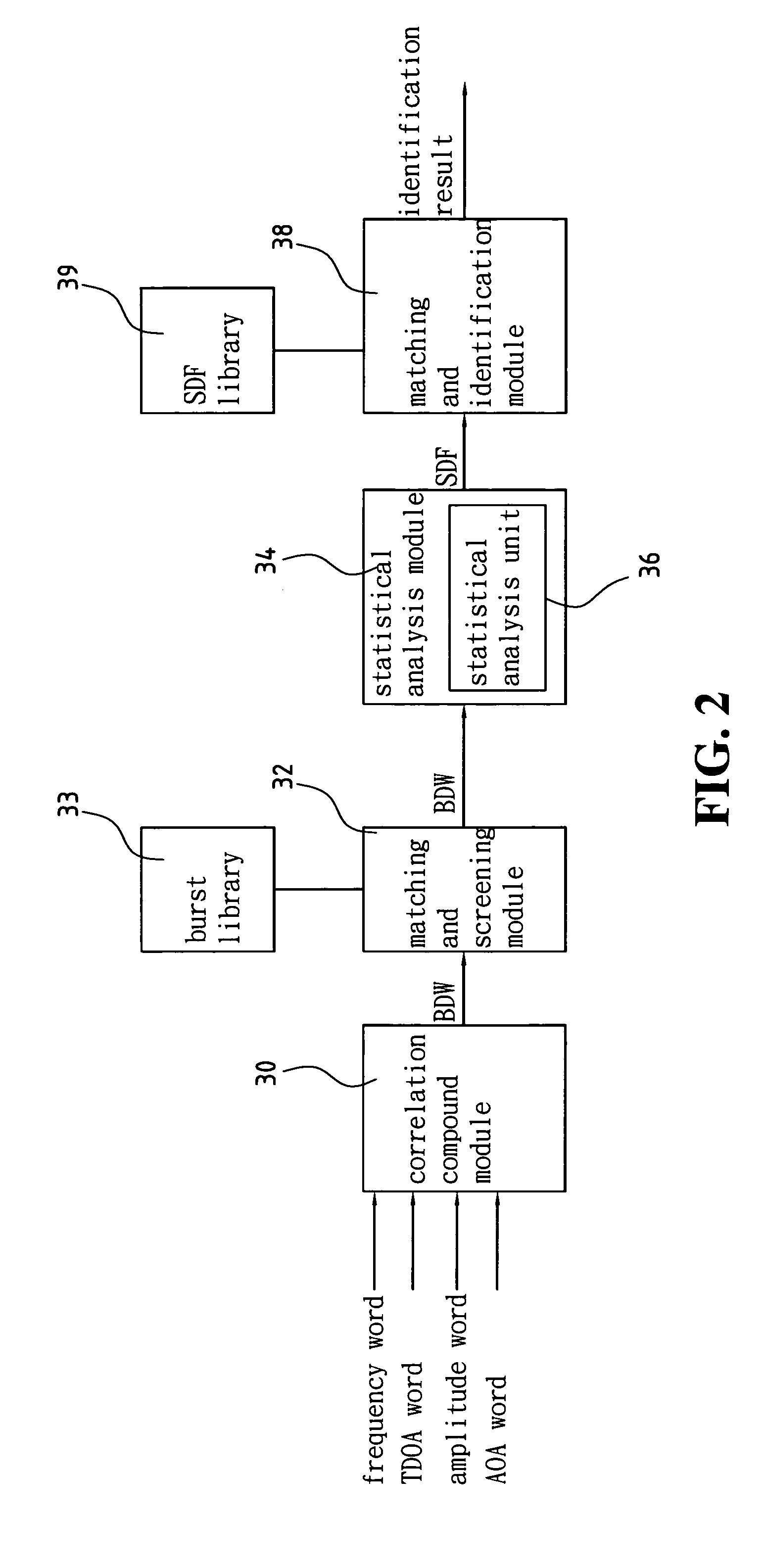
InactiveUS20050117676A1Improve transmission performanceError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorLine-faulsts/interference reductionDiscriminatorMultilateration
A device for identifying interference source in wireless communications is provided, including a correlation compound module, a matching and screening module, a statistical analysis module, and a match identification module. The correlation compound module uses the time of arrival (TOA) of the burst as the synchronization basis to compound the correlated frequency word, time difference of arrival (TDOA) word, amplitude word and angle of arrival (AOA) word to form a burst descriptor word (BDW). The matching and screening module uses the BWD to match the burst library to screen out the non-interference sources. The statistic analysis module uses the screened outcome for statistical analysis, and obtains a source discriminator file (SDF). The matching and identification module uses the SDF to search the interference source library for matching and obtains an identification result.
Owner:ACCTON TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
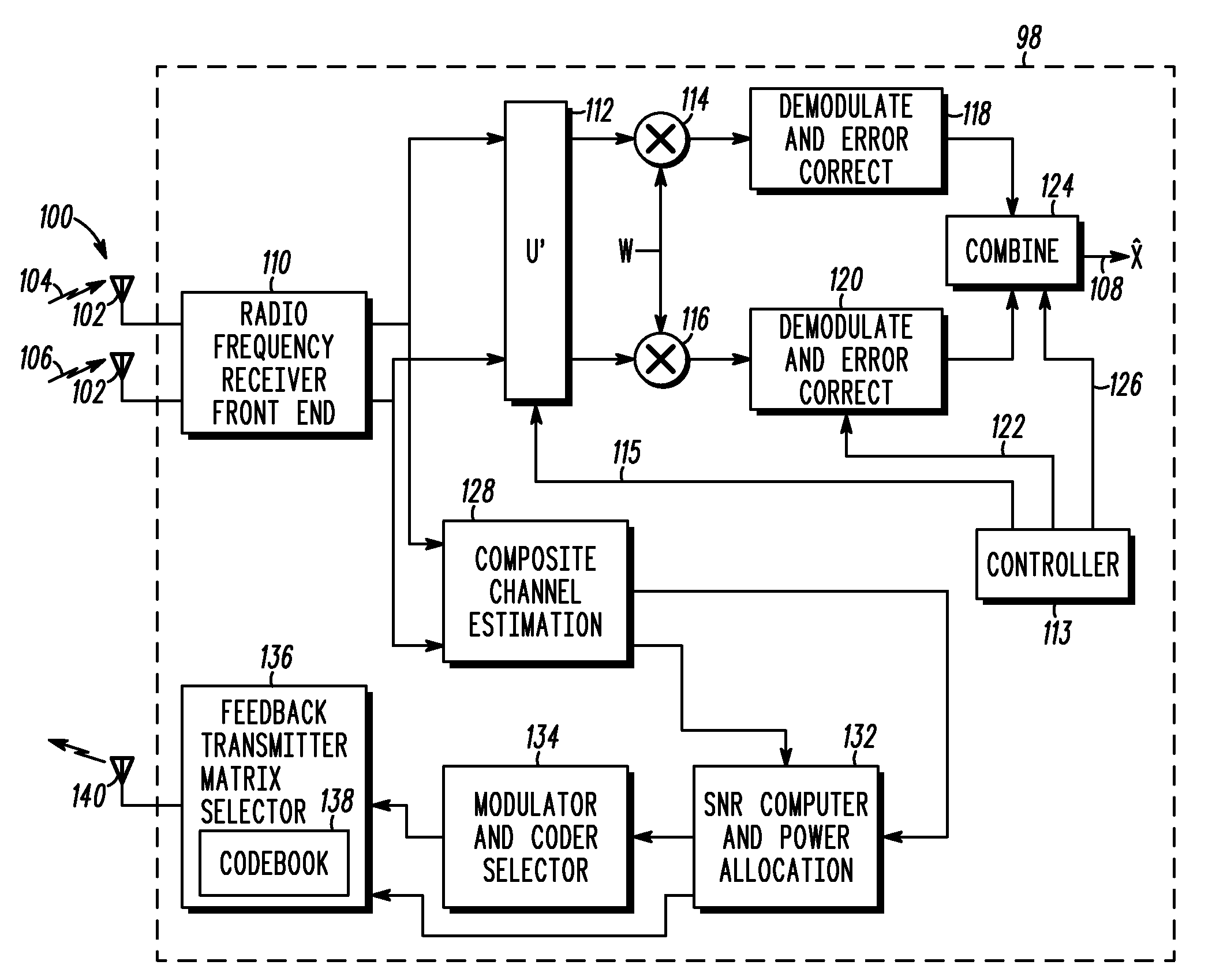
Method and apparatus for feedback in closed loop transmitting
InactiveUS20080285667A1Polarisation/directional diversityLine-faulsts/interference reductionData streamComposite channel
A method an apparatus is described for providing feedback for closed-loop transmitting with multiple transmit and receive antennas. The method includes a first step 900 of providing a codebook containing sets of weightings for each data stream of the multiple transmit antennas with each set identified by an index known to a transmitter and a receiver. The same codebook is utilized for any number of data streams up to the number of transmit antennas. A next step 902 includes measuring a composite channel between the transmitter and receiver. A next step 904 includes determining at least one performance metric for each set of weightings in the codebook. A next step 906 includes selecting preferred weightings for each data stream in response to the performance metrics. A next step 908 includes feeding back an index of the preferred weightings to the transmitter for use in subsequent transmissions.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Methods and systems for noise resilient, pin-efficient and low power communications with sparse signaling codes
ActiveUS8649445B2Weaken energyFrequency-division multiplex detailsModulated-carrier systemsComputer science
In bus communications methods and apparatus, a first set of physical signals representing the information to be conveyed over the bus is provided, and mapped to a codeword of a sparse signaling code, wherein a codeword is representable as a vector of a plurality of components, some of which are quiescent components and some of which are non-quiescent components, wherein the number of quiescent components and non-quiescent components meet a sparseness requirement.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
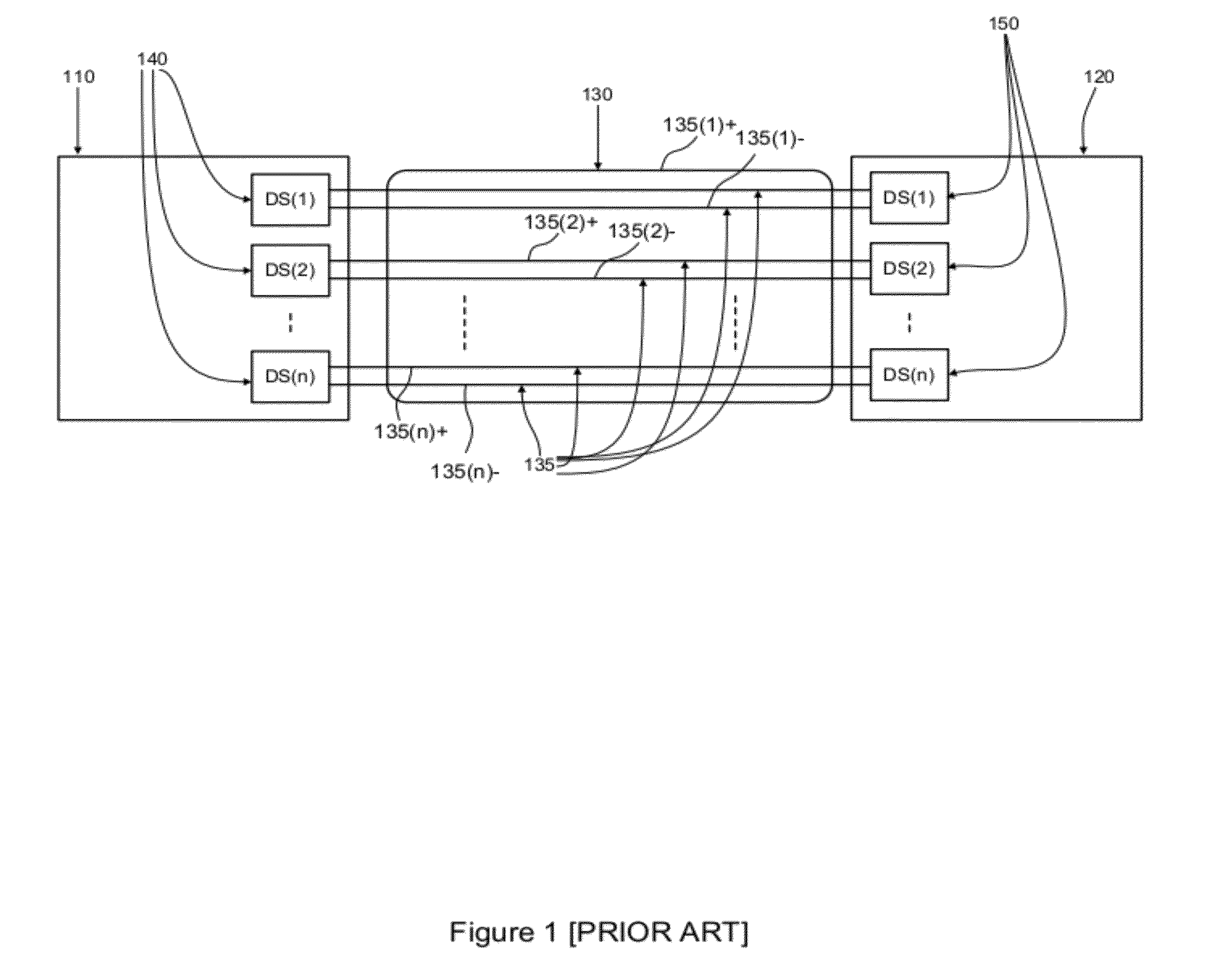
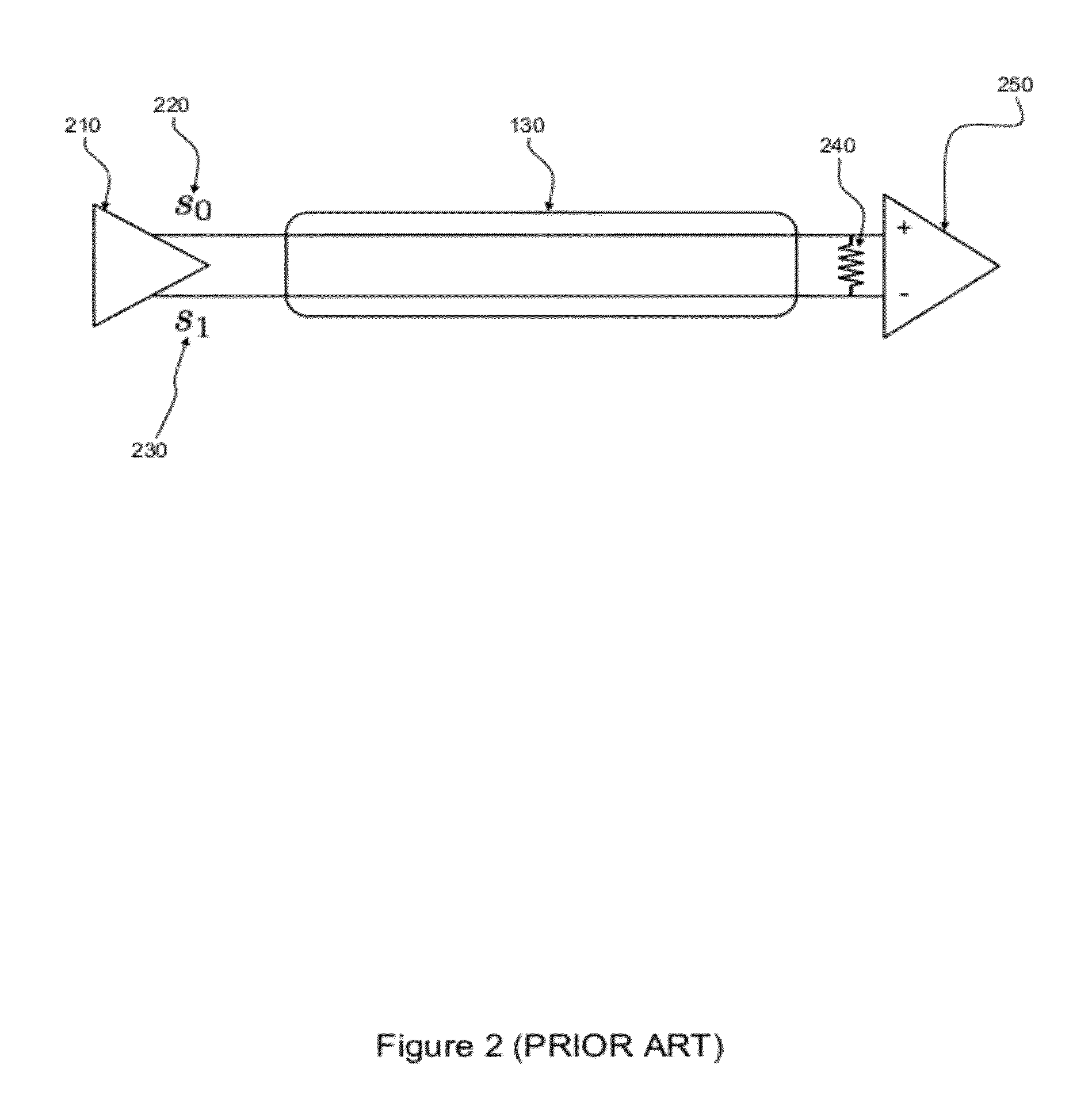
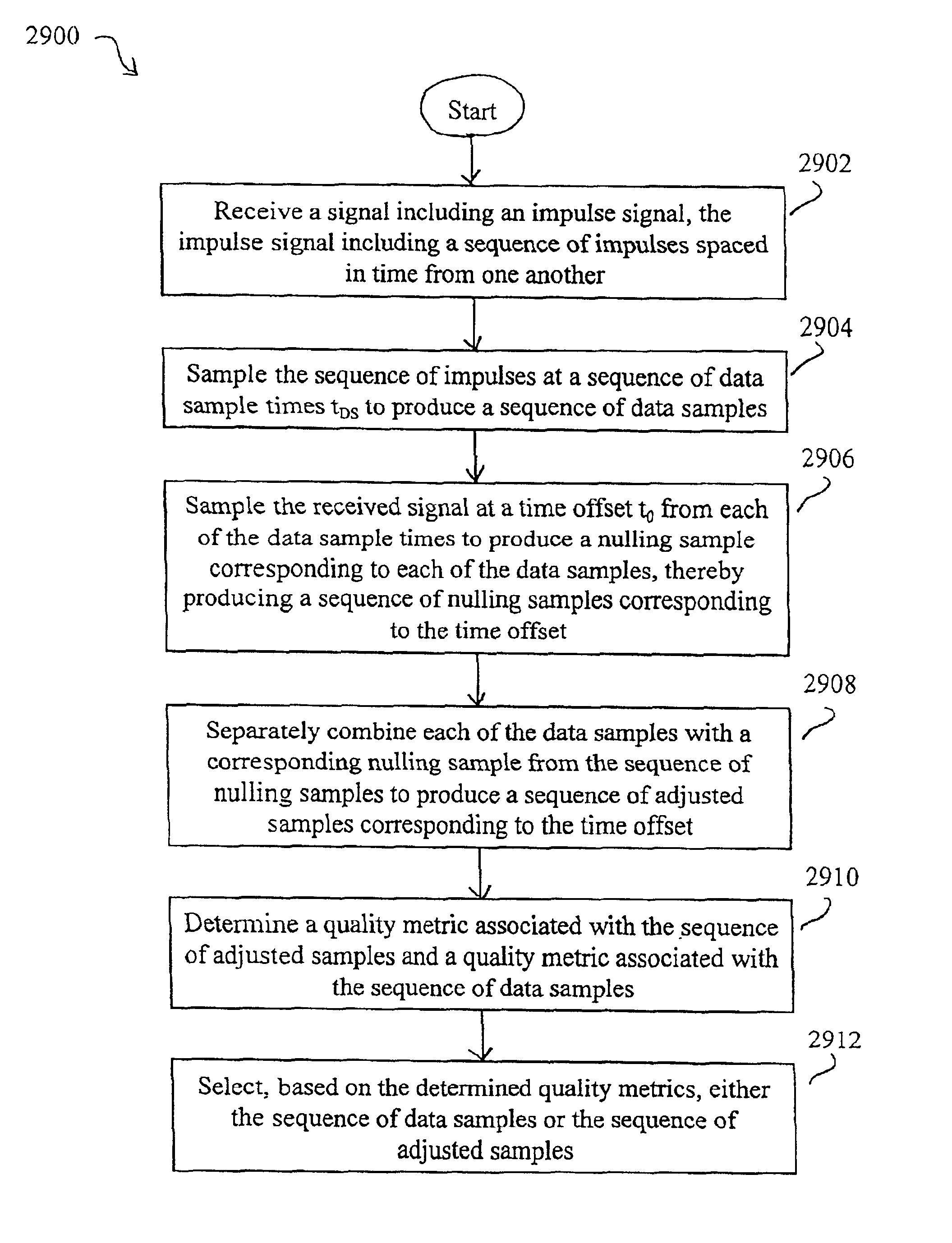
Method and system for reducing potential interference in an impulse radio
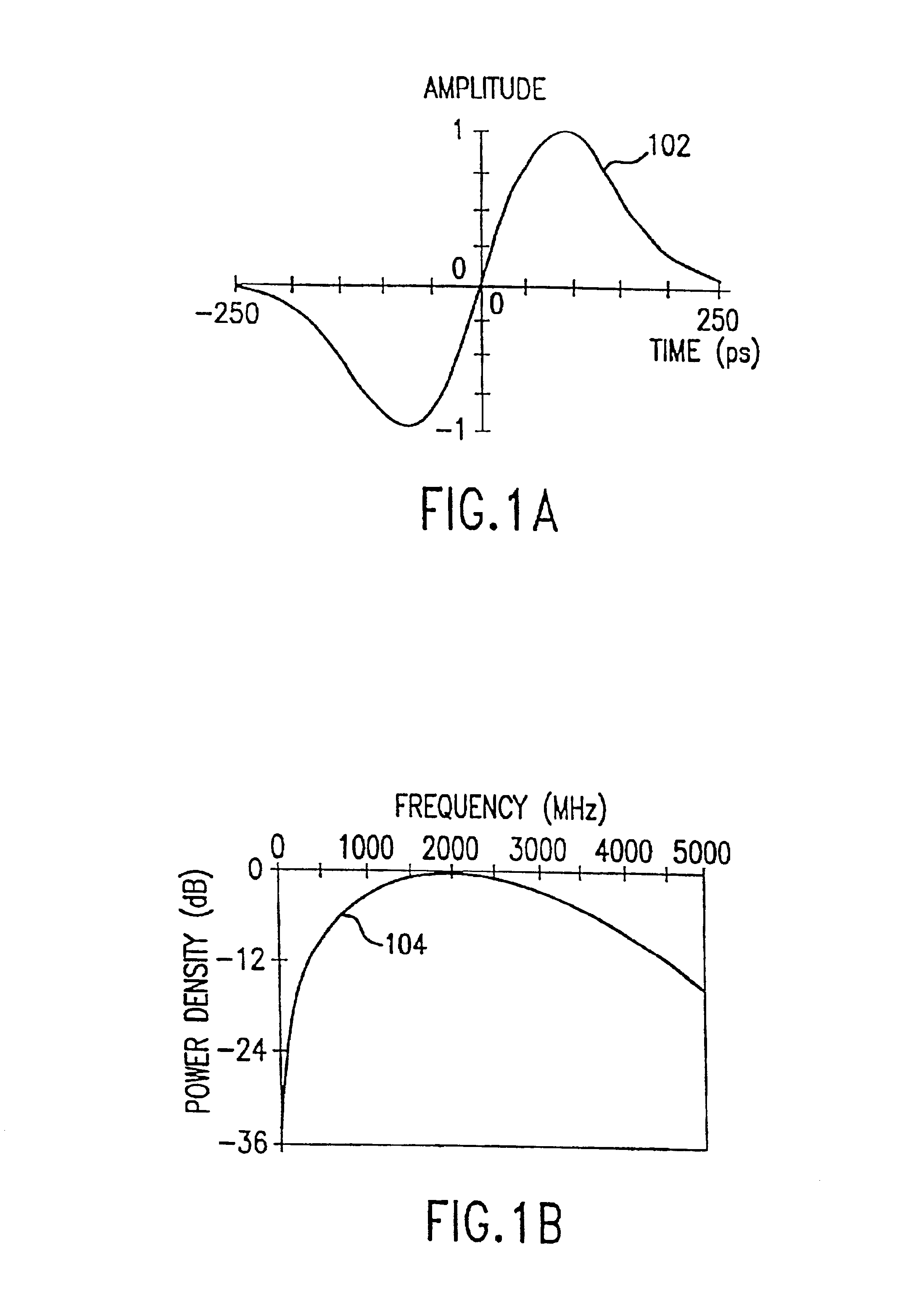
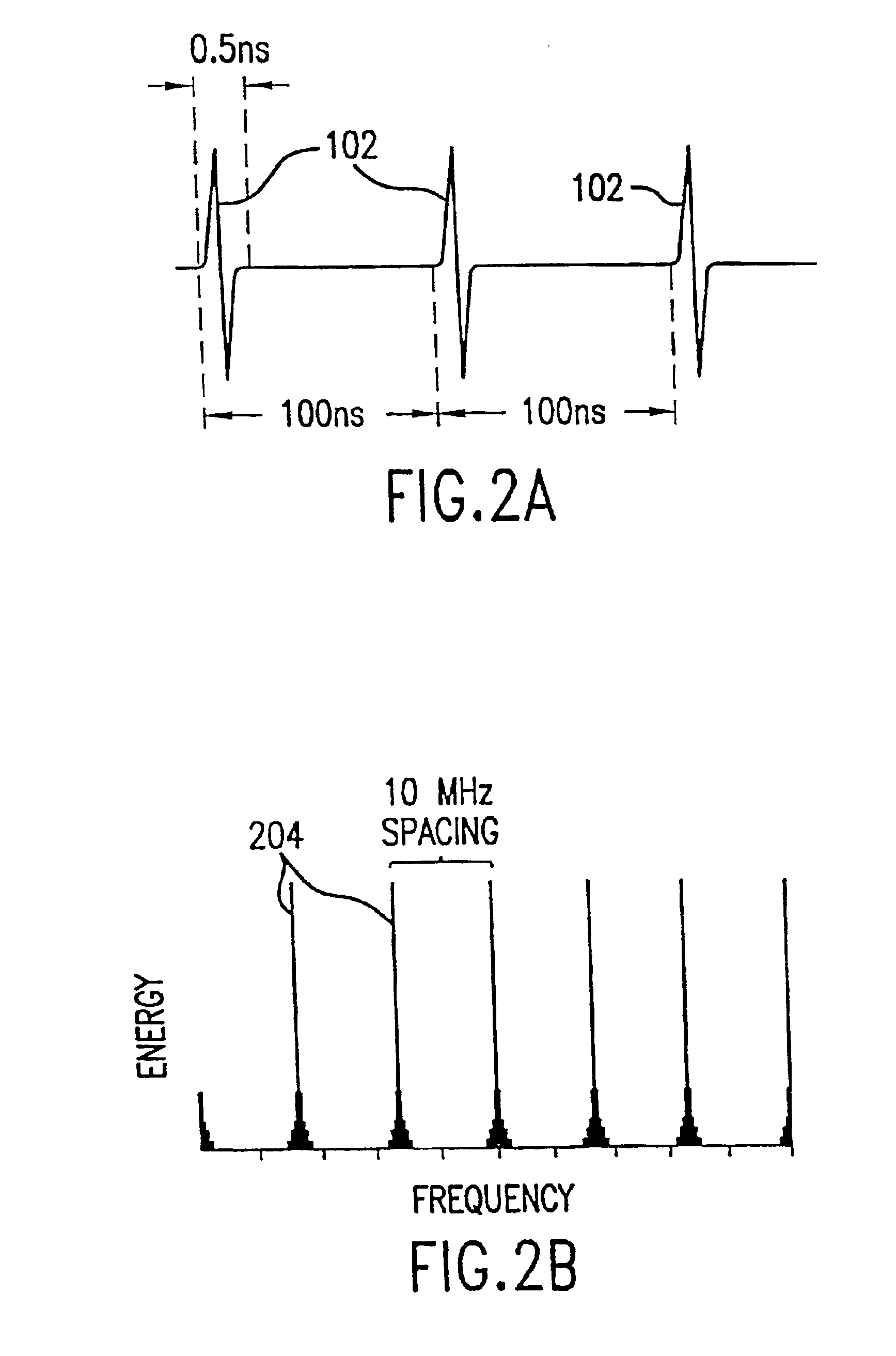
InactiveUS6914949B2Reduce distractionsReduce broadband noiseError preventionTransmission systemsInterference ratioRadio reception
Potential interference is reduced in an impulse radio. A signal including an impulse signal and potential interference is received by the impulse radio. The impulse signal includes a sequence of impulses. The sequence of impulses of the received signal is sampled at a sequence of data sample times to produce a sequence of data samples. The received signal is also sampled at a plurality of time offsets from each of the data sample times to produce a plurality of nulling samples corresponding to each of the data samples. A separate sequence of nulling samples for each of the time offsets is thereby produced. Each of the data samples is then separately combined with a corresponding nulling sample from each of the separate sequences of nulling samples to produce a separate sequence of adjusted samples corresponding to each of the time offsets. A separate quality metric, representative of a signal-to-interference level, is then determined for each of the separate sequences of adjusted samples. A preferred sequence of samples is selected for further signal processing based on the determined quality metrics. Alternatively or additionally, one of the plurality of time offsets is selected as the preferred time offset based on the determined quality metrics.
Owner:ALEREON
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com