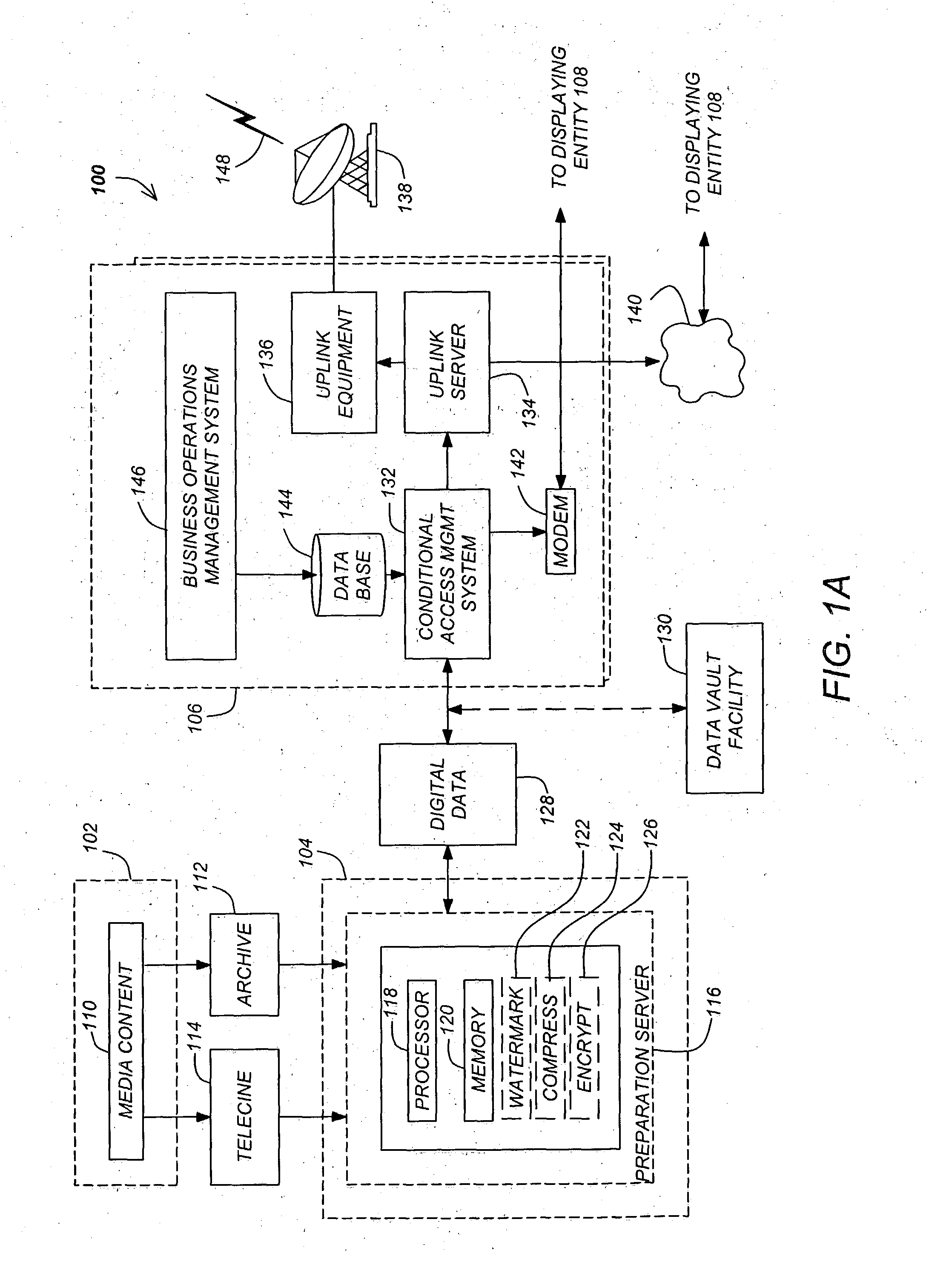
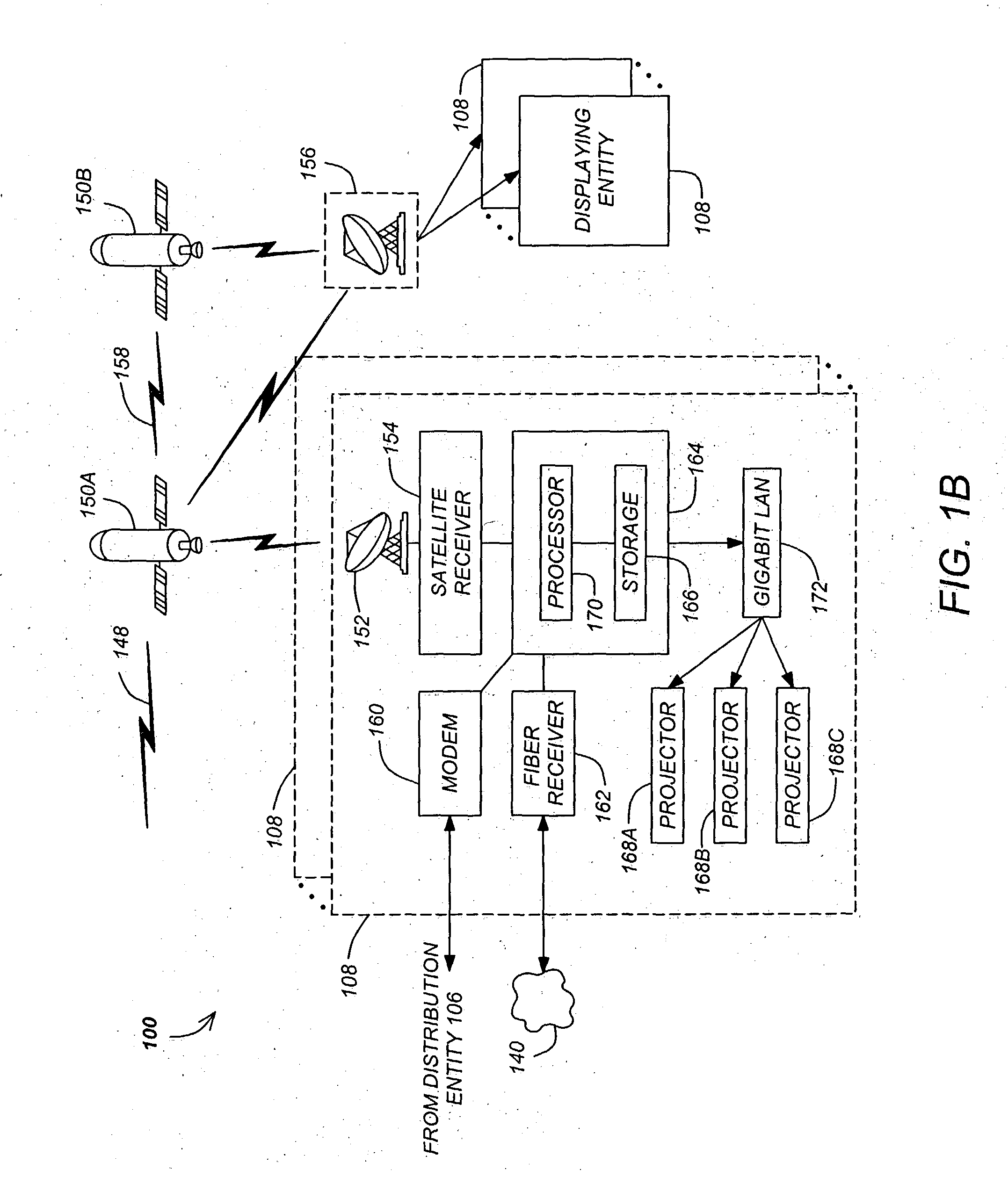
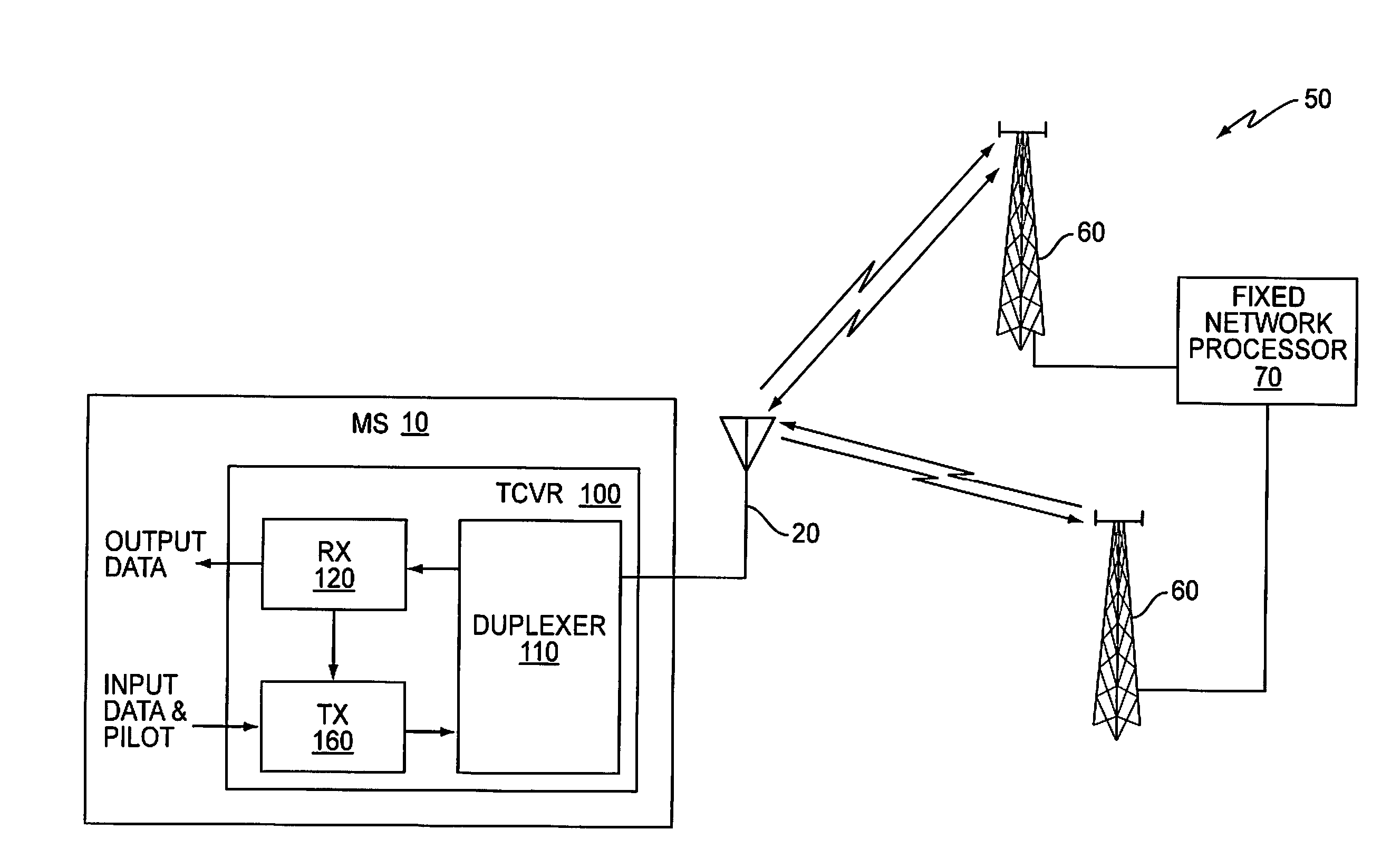
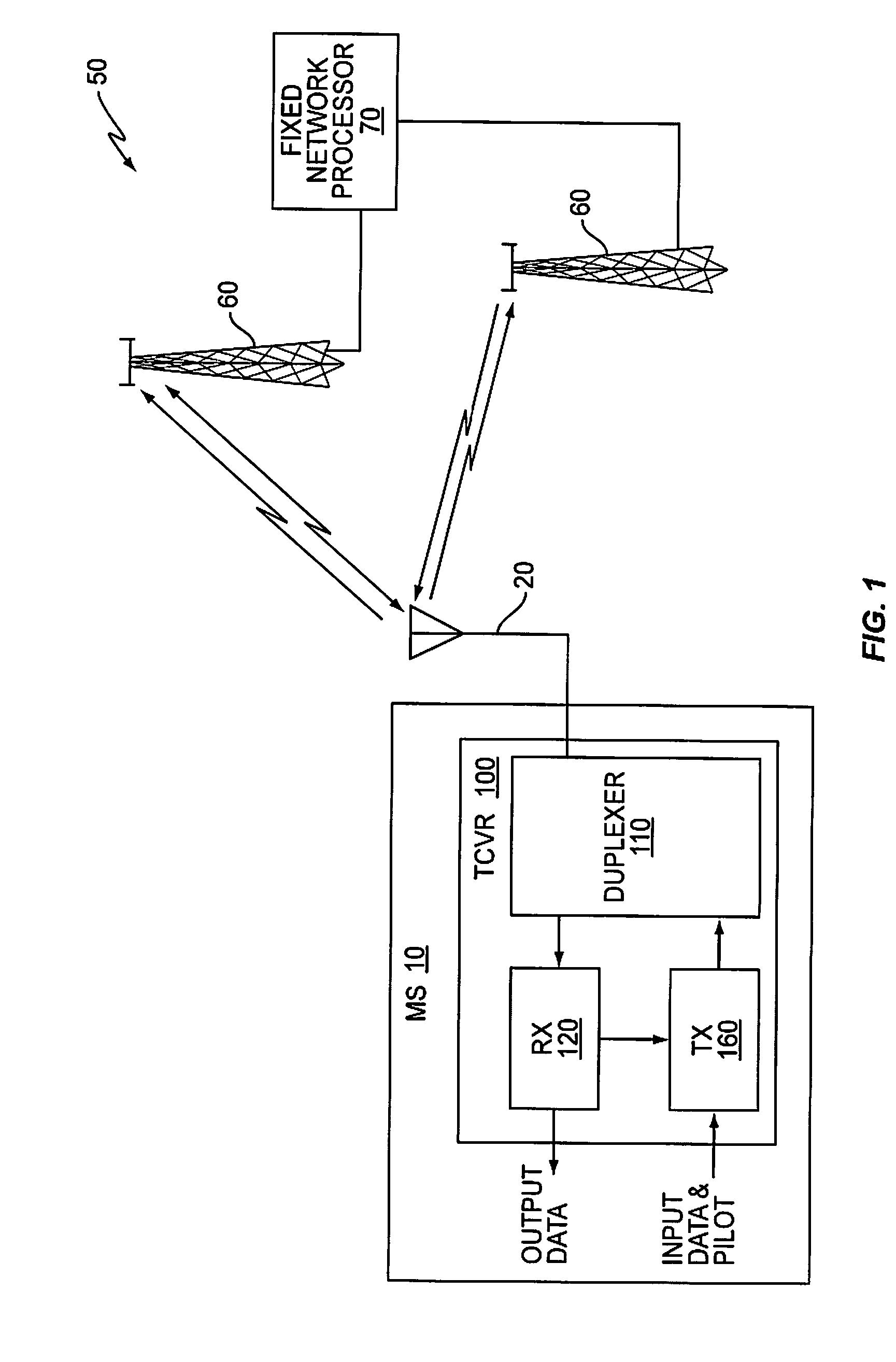
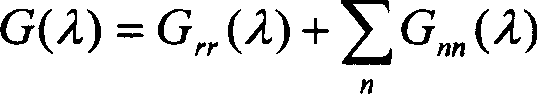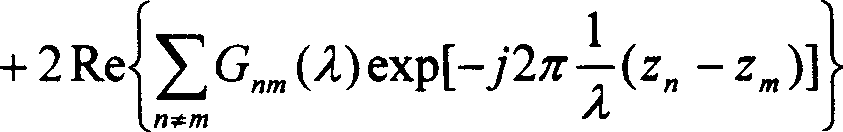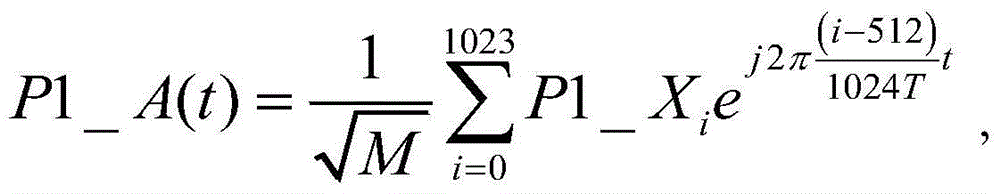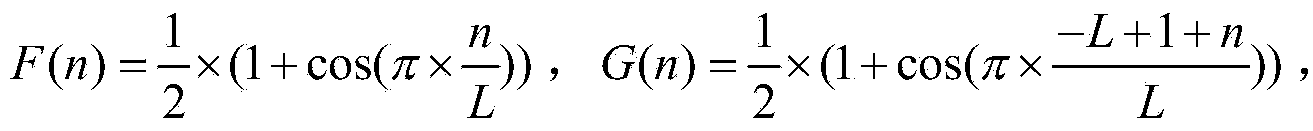Patents
Literature
454 results about "Inverse discrete fourier transform" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
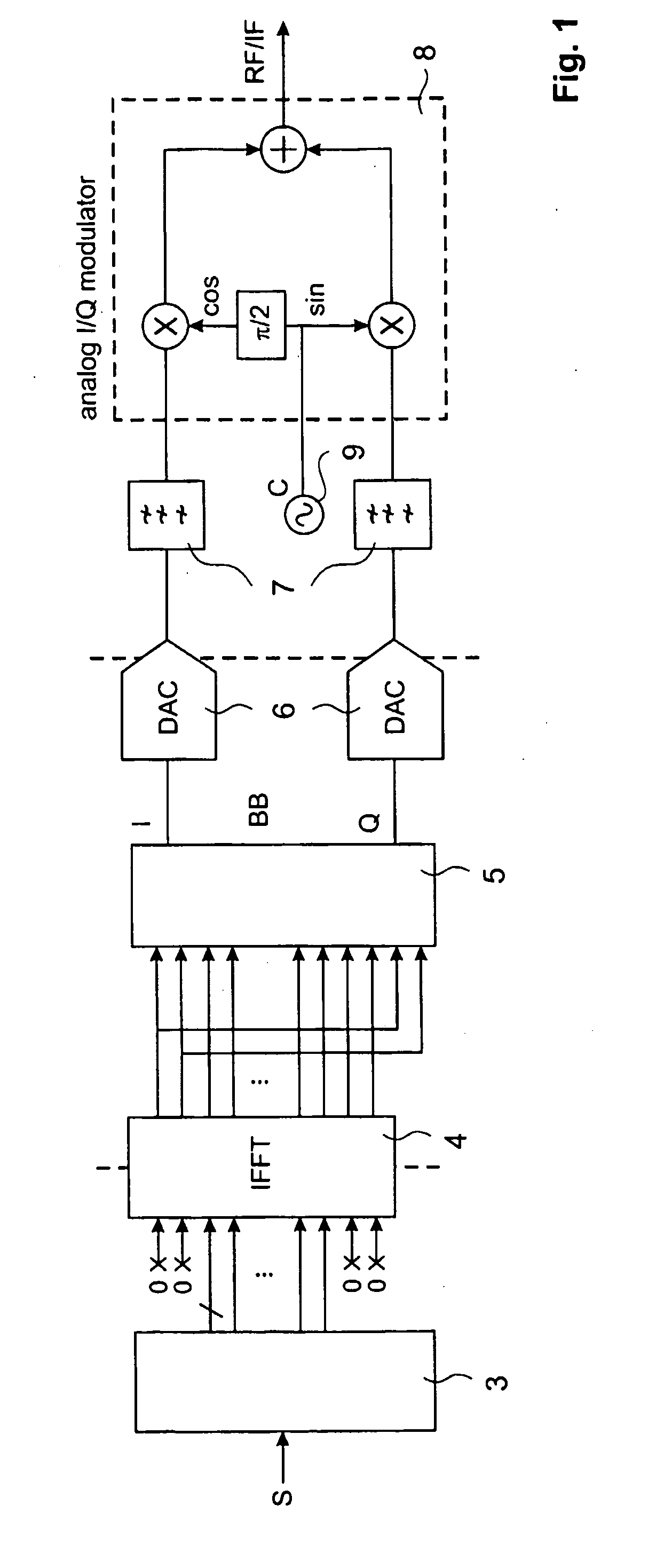
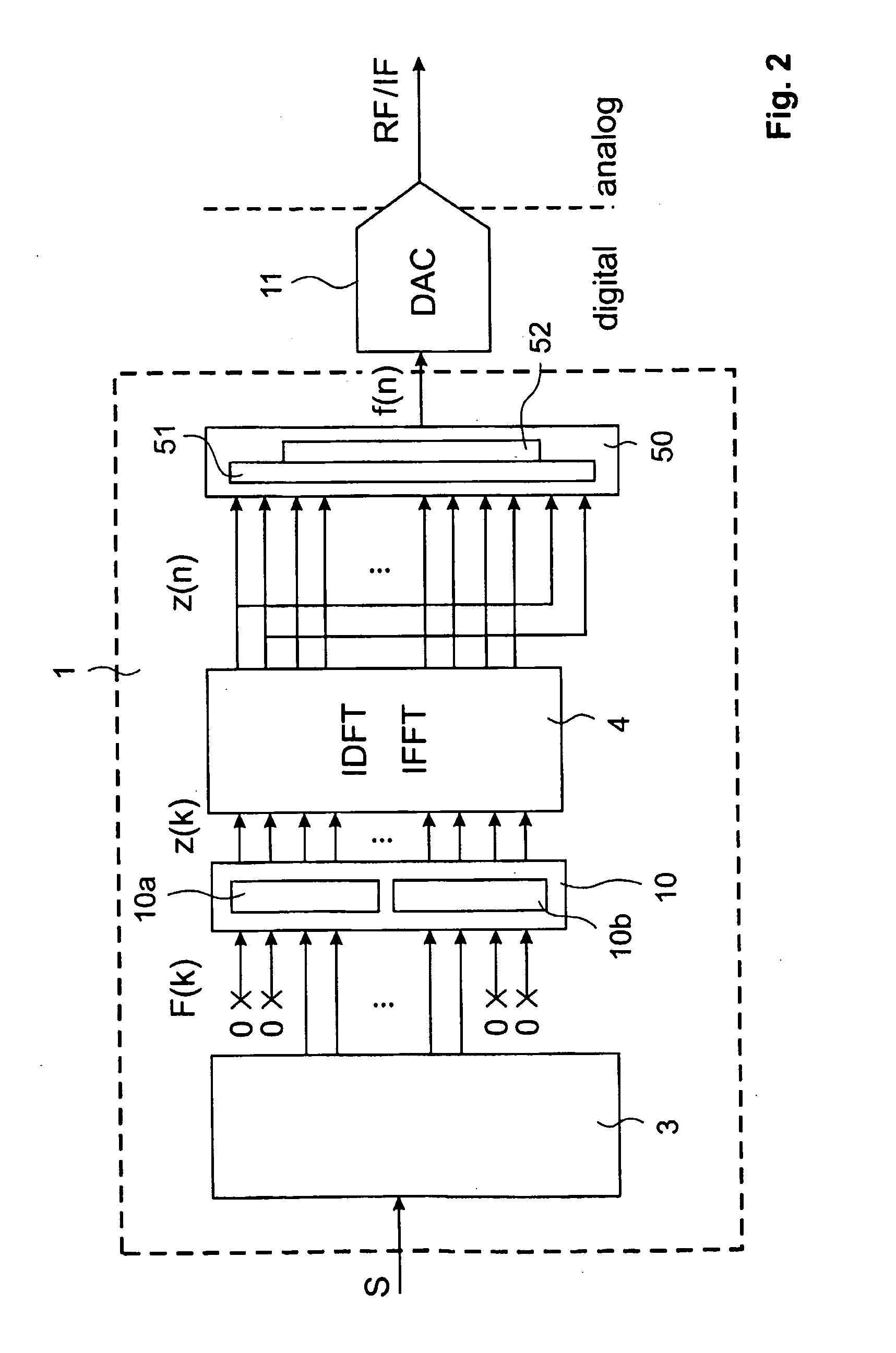
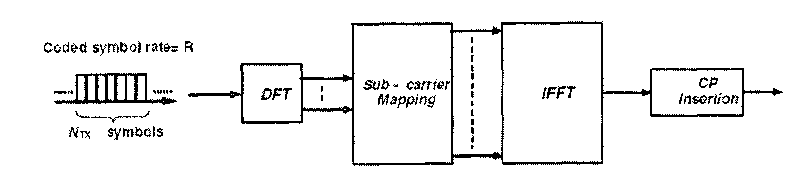
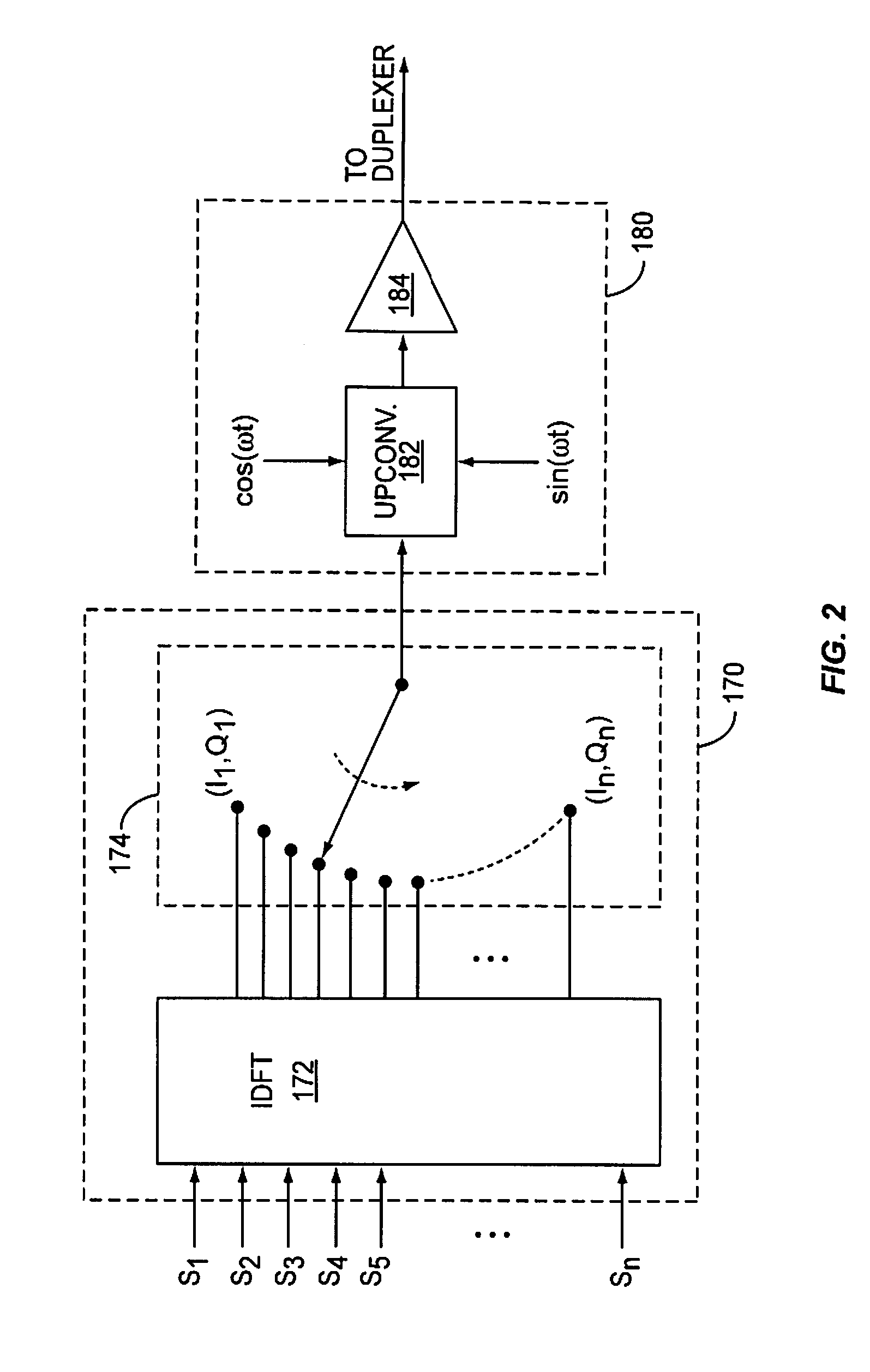
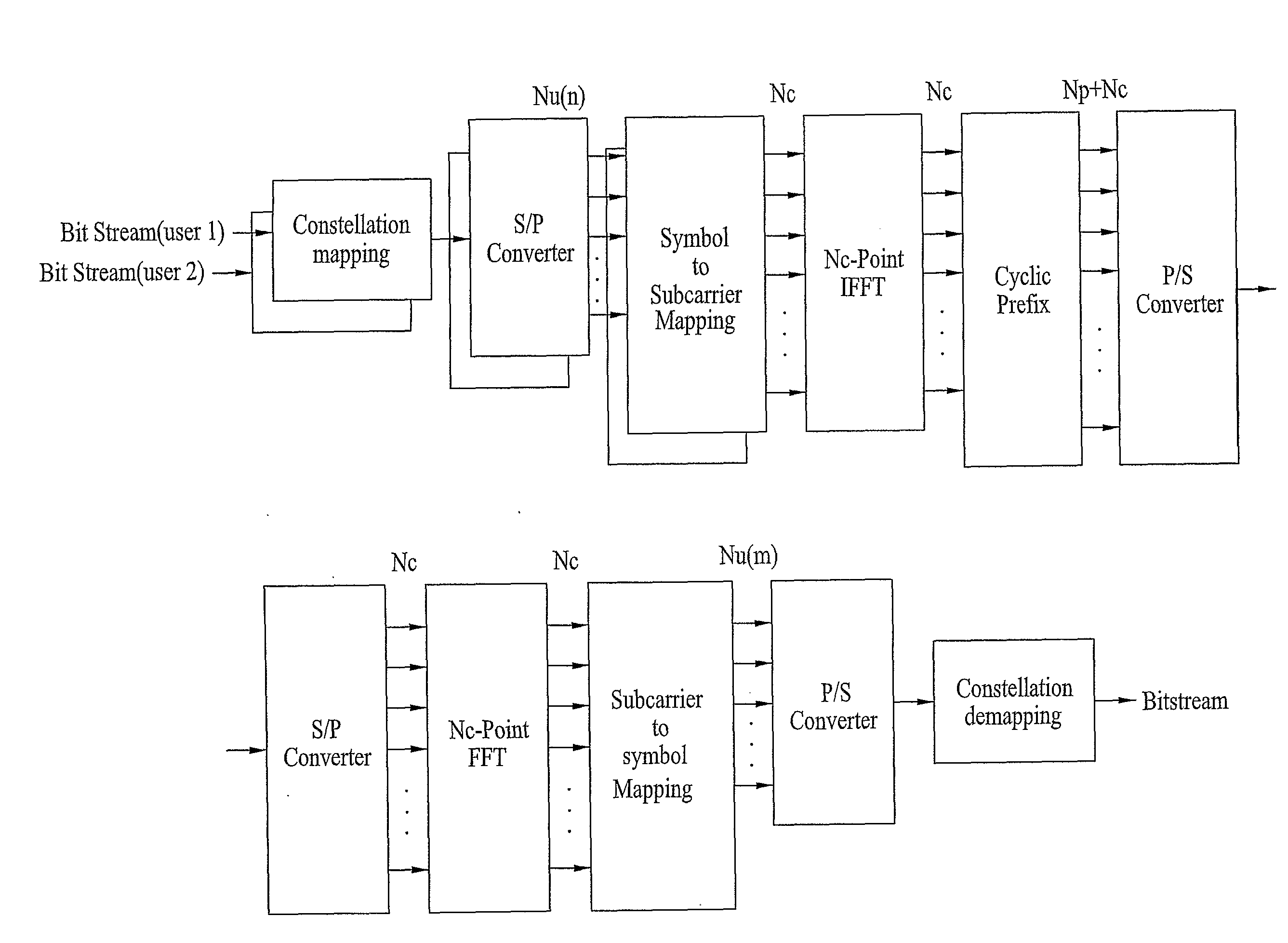
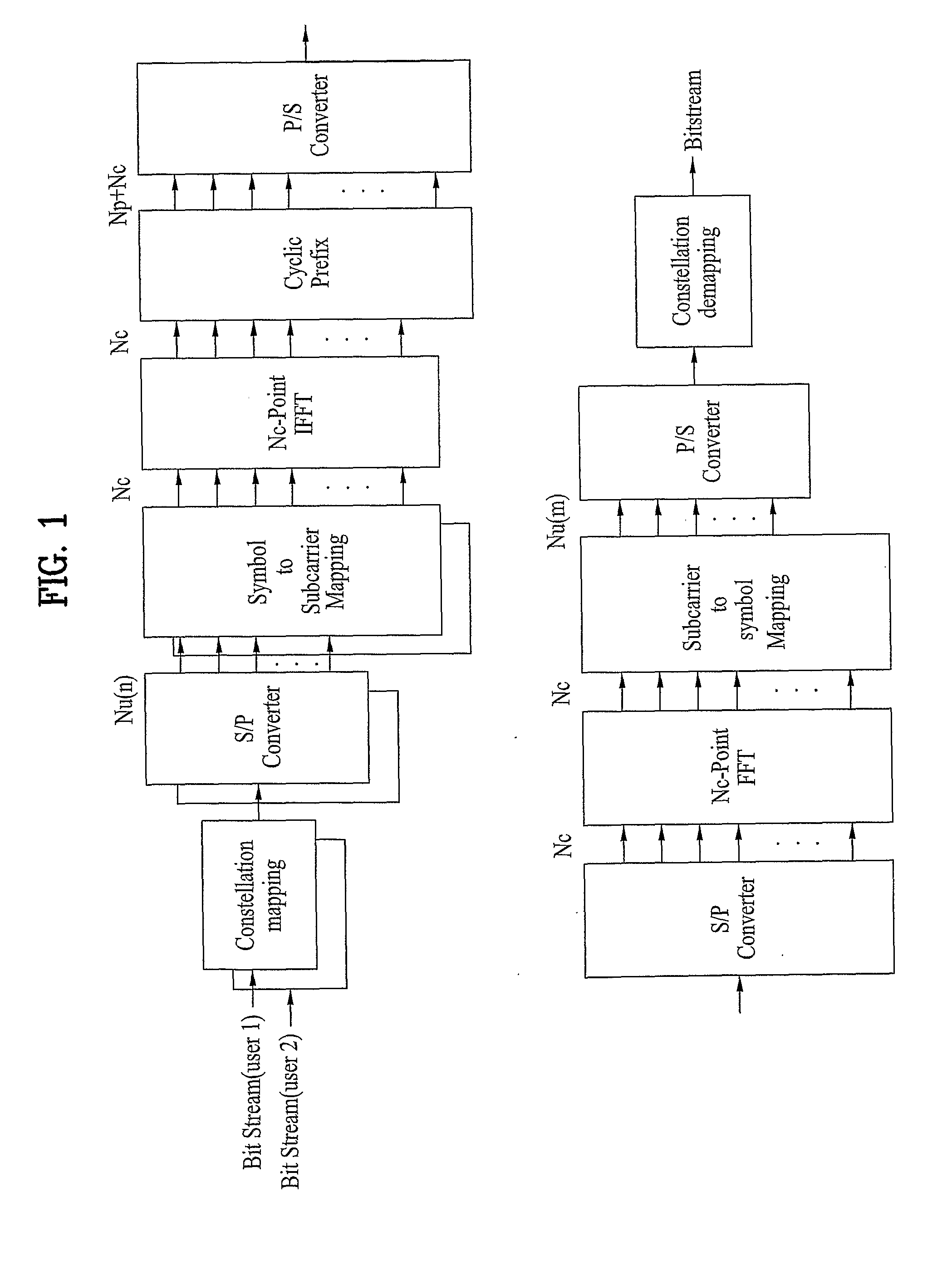
The Inverse Discrete Fourier Transform (IDFT) The Fourier transform takes a signal in the so called time domain (where each sample in the signal is associated with a time) and maps it, without loss of information, into the frequency domain. The frequency domain representation is exactly the same signal, in a different form.
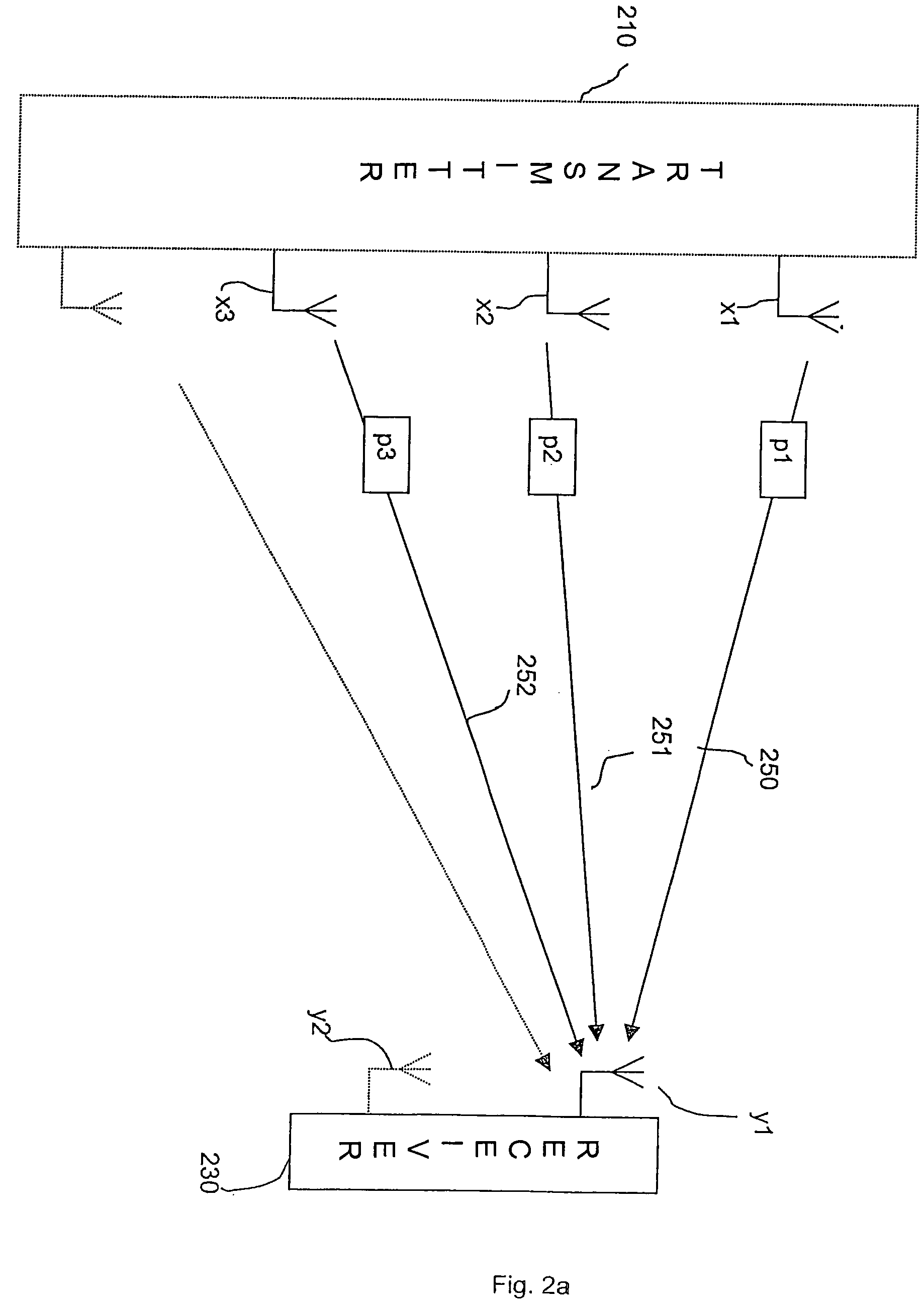
Digital modulation signal receiver with adaptive channel equalization employing discrete fourier transforms
InactiveUS6975689B1Extended durationTelevision system detailsError preventionInverse discrete fourier transformFourier transform on finite groups
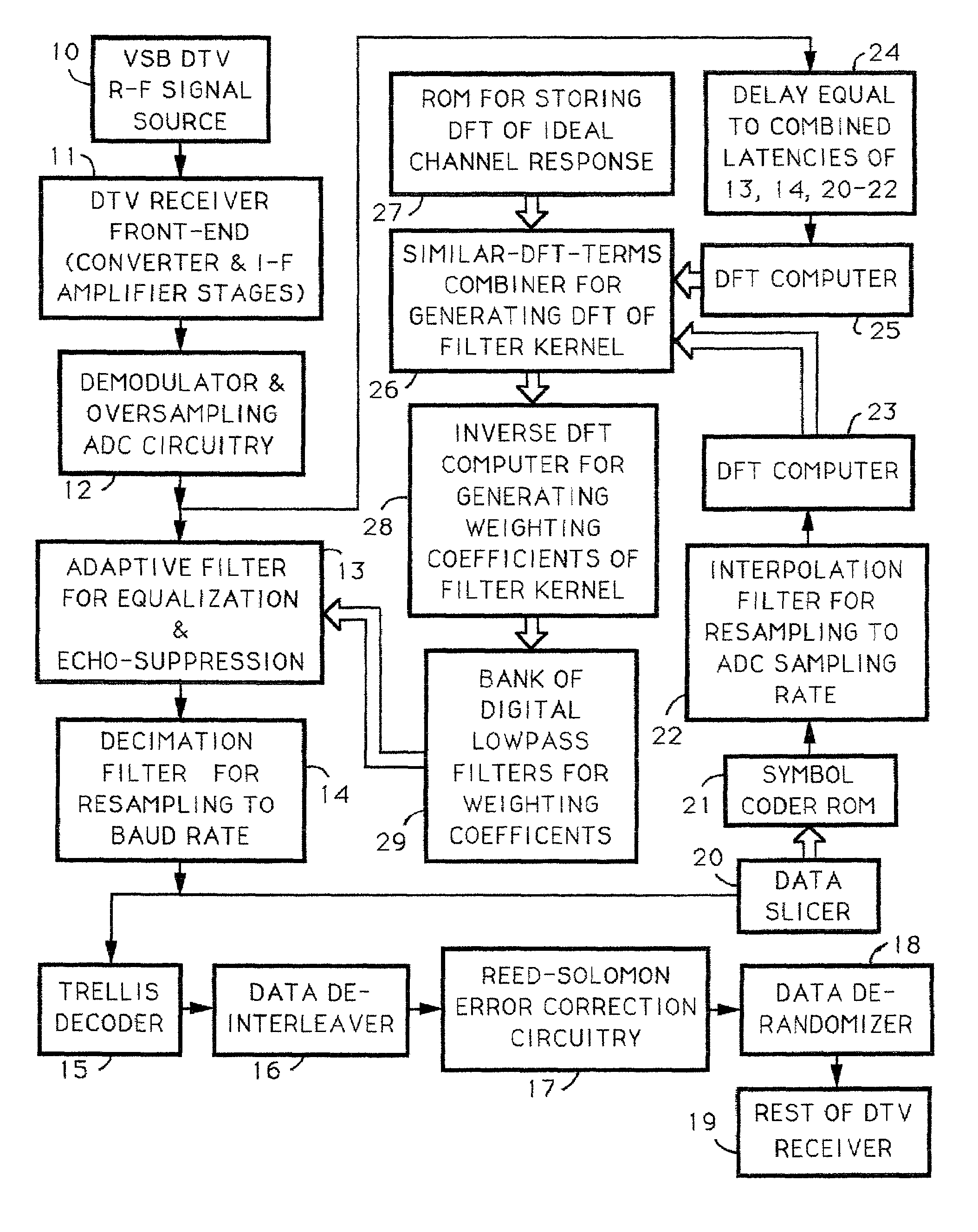
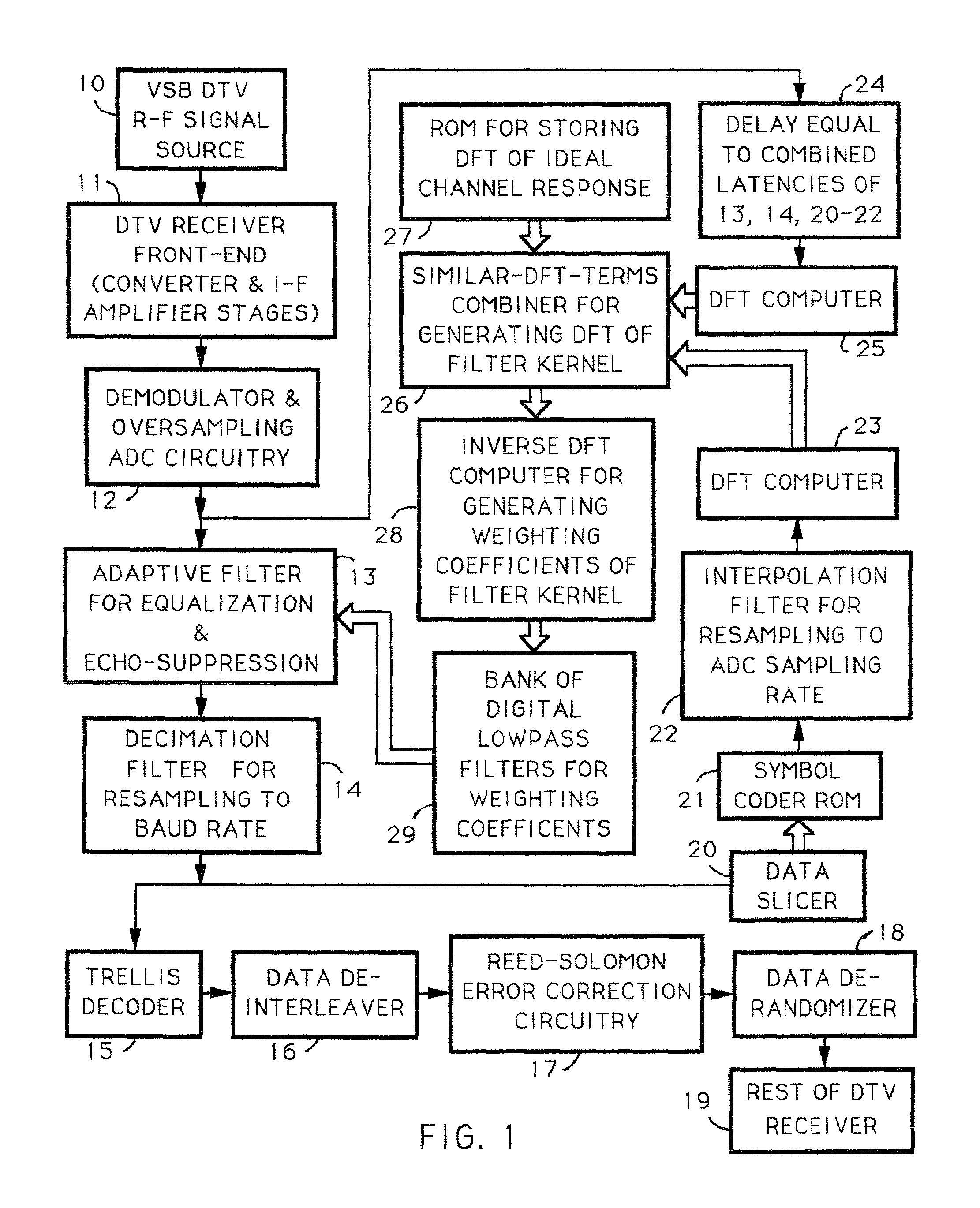
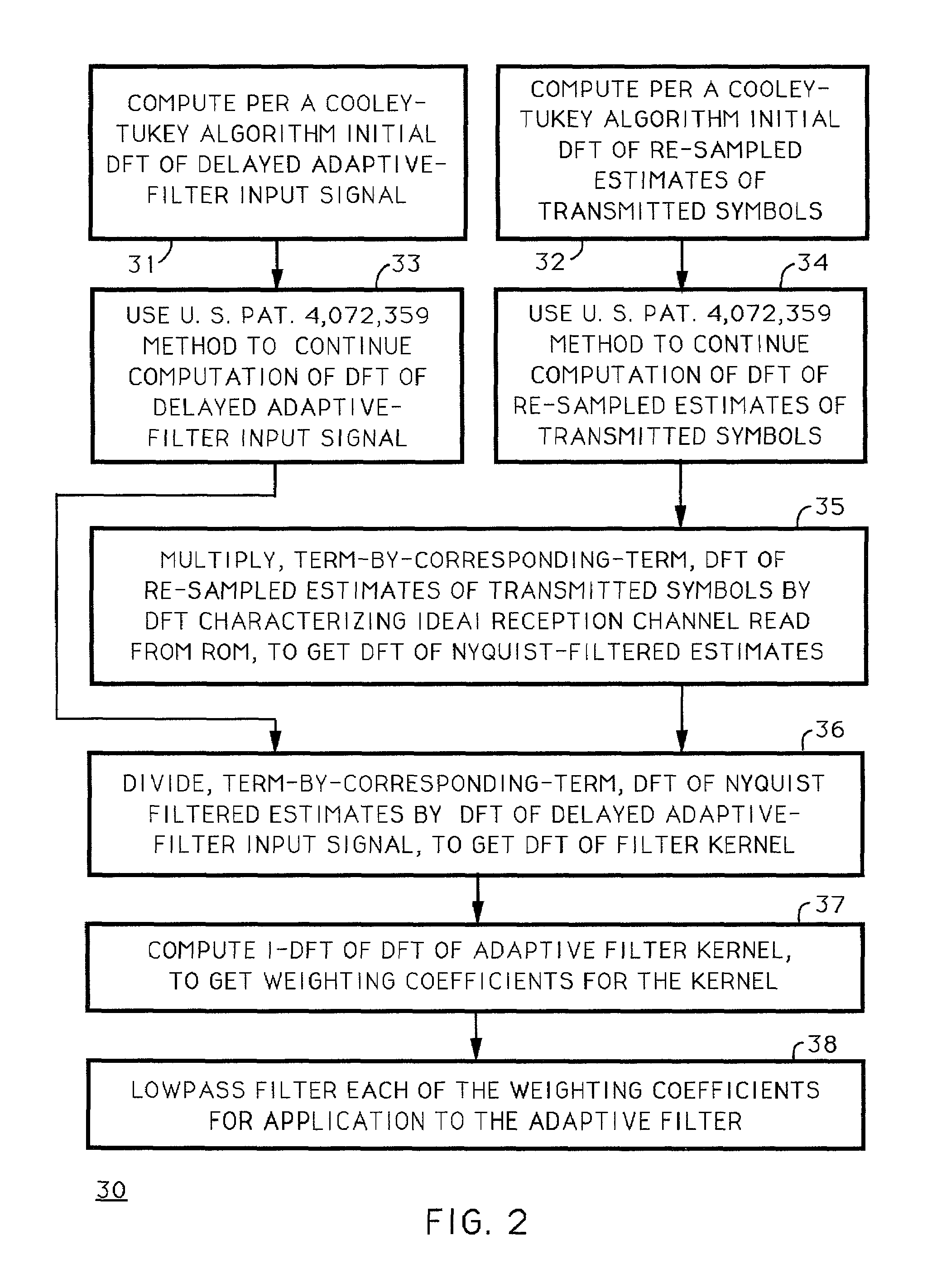
Techniques for calculating the system characteristic of the adaptive filtering used for equalization and echo-suppression in a digital communications receiver, such as one used for receiving over-the-air broadcast digital television signal, are described. In these techniques, the system characteristic of the adaptive filtering is calculated from the discrete Fourier transform of successive portions of the input signal supplied to the adaptive filtering and from the discrete Fourier transform of corresponding portions of the transmitted signal, as estimated in the receiver. Receivers for implementing these techniques in various ways are also disclosed.
Owner:MCDONALD JAMES DOUGLAS +1
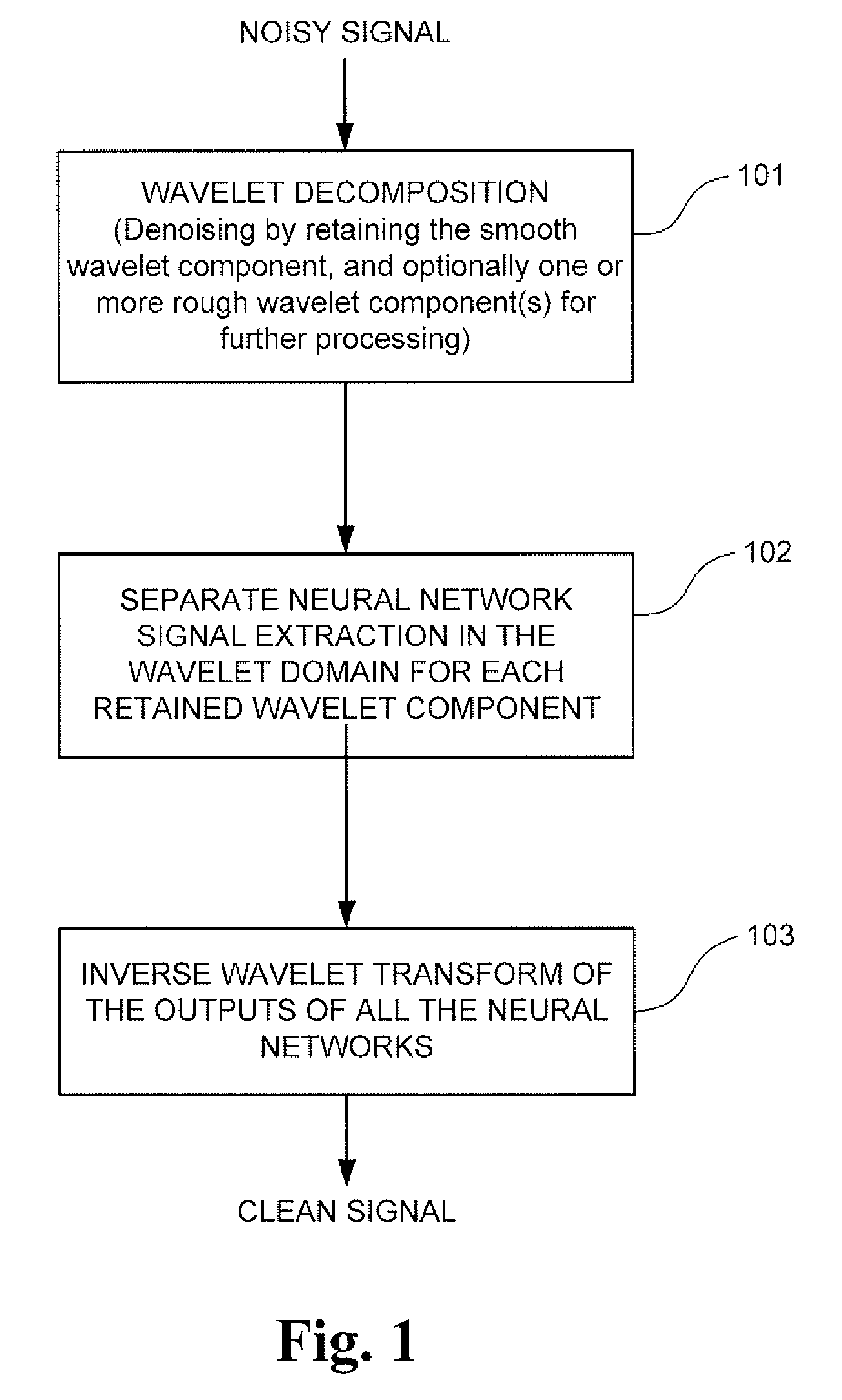
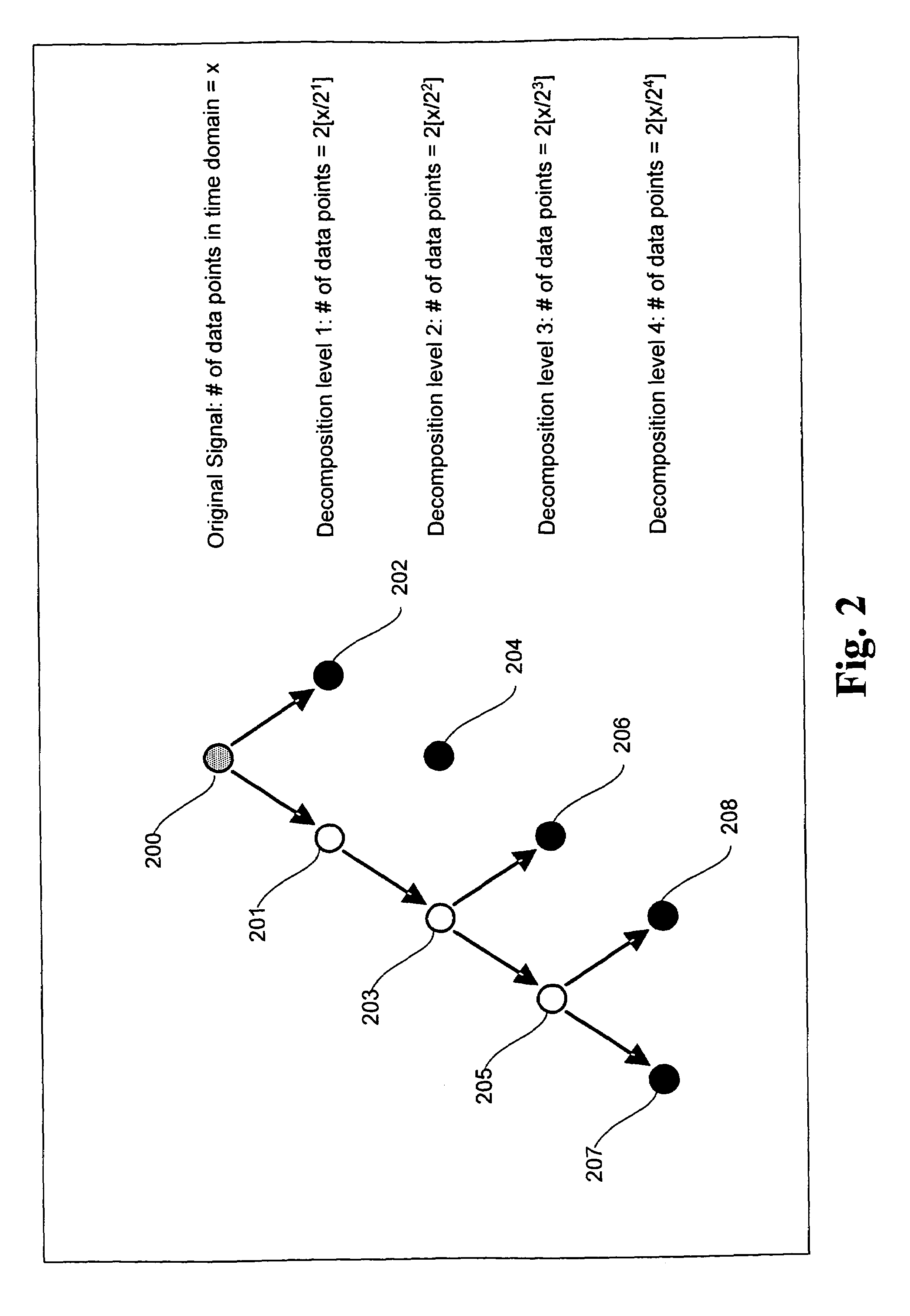
Signal processing method and system for noise removal and signal extraction
InactiveUS7519488B2Noise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionTime domainDecomposition
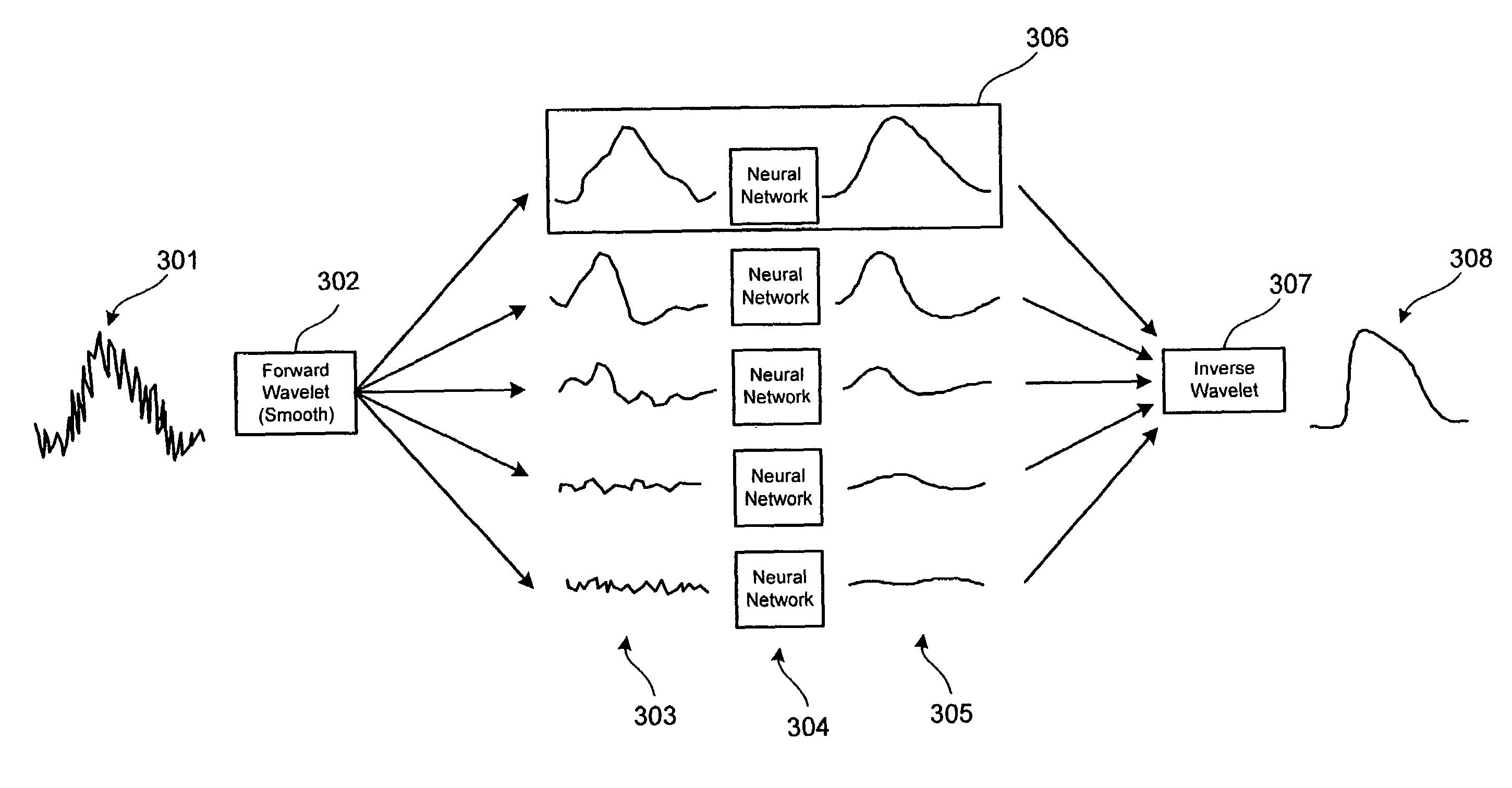
A signal processing method and system combining smooth level wavelet pre-processing together with artificial neural networks all in the wavelet domain for signal denoising and extraction. Upon receiving a signal corrupted with noise, an n-level decomposition of the signal is performed using a discrete wavelet transform to produce a smooth component and a rough component for each decomposition level. The nth level smooth component is then inputted into a corresponding neural network pre-trained to filter out noise in that component by pattern recognition in the wavelet domain. Additional rough components, beginning at the highest level, may also be retained and inputted into corresponding neural networks pre-trained to filter out noise in those components also by pattern recognition in the wavelet domain. In any case, an inverse discrete wavelet transform is performed on the combined output from all the neural networks to recover a clean signal back in the time domain.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
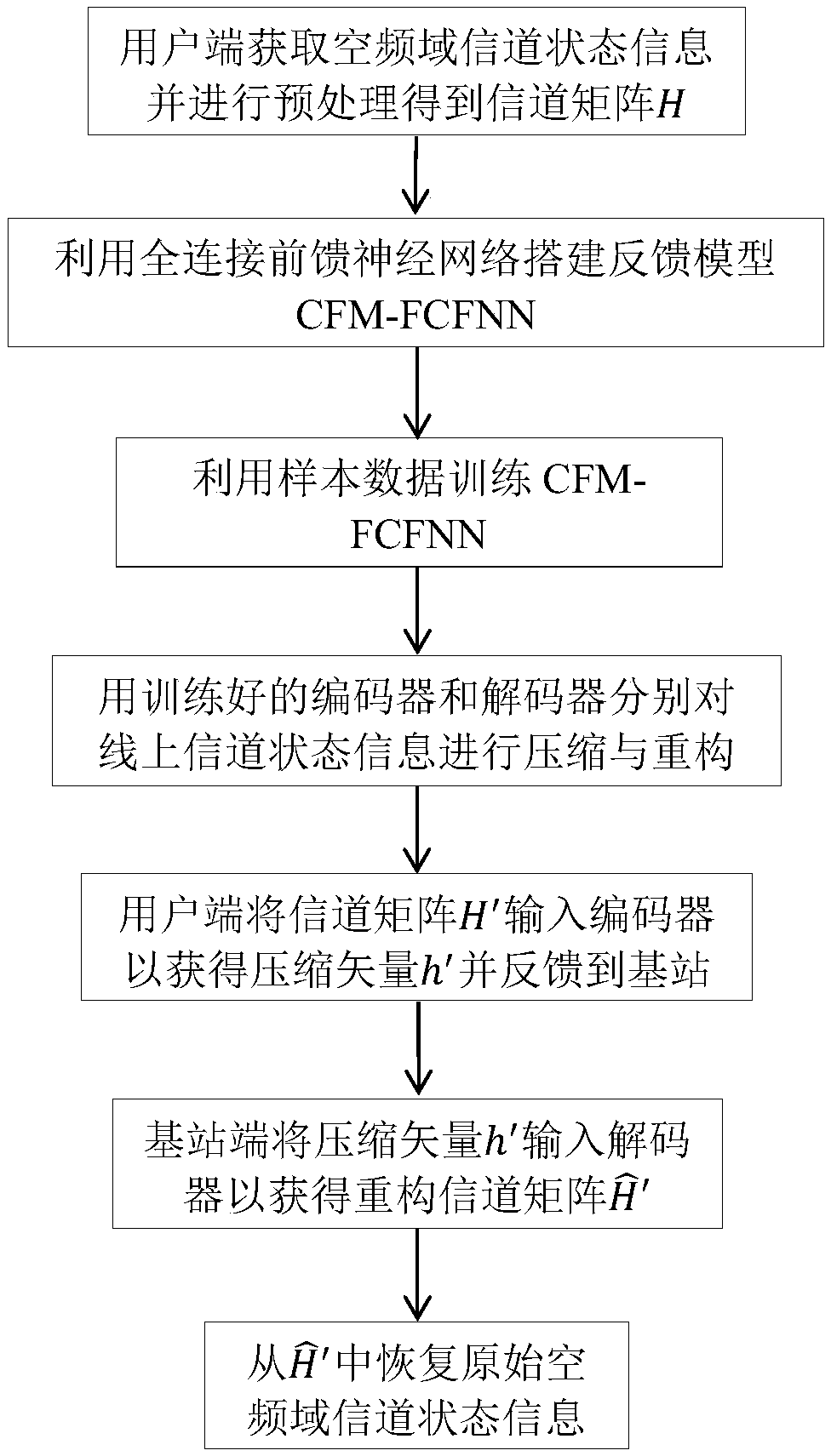
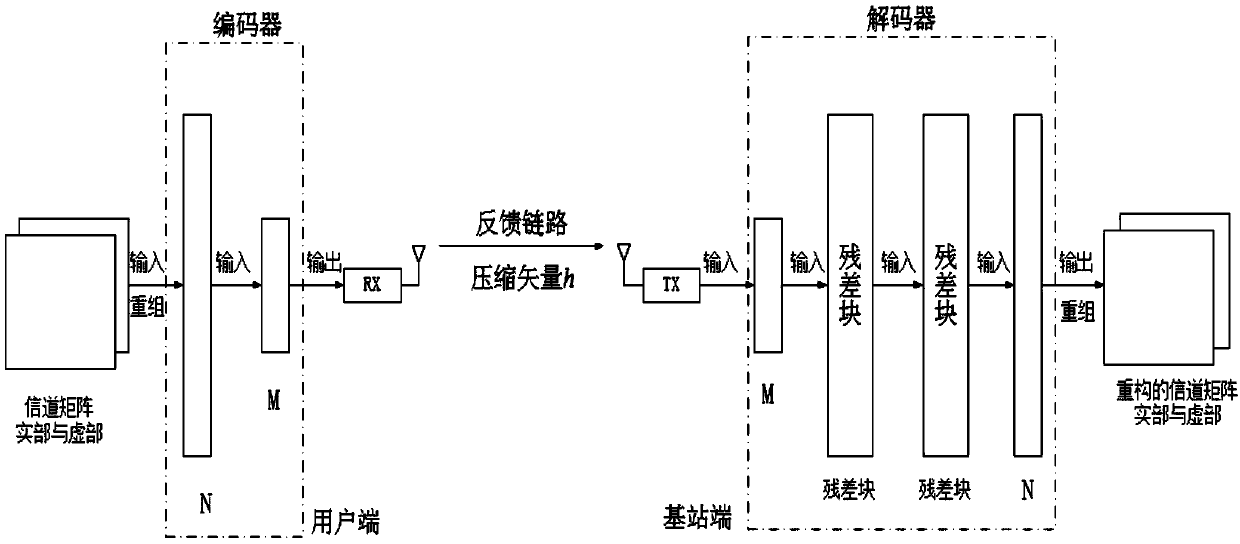
Large-scale MIMO channel state information feedback method based on FCFNN
ActiveCN109672464AQuality improvementFully extractedSpatial transmit diversityNeural architecturesMulti inputInformation feedback
The invention discloses a large-scale MIMO channel state information feedback method based on FCFNN, and mainly aims to solve the problems of overlarge technical feedback overhead and poor channel feedback quality in the prior art. According to the scheme, the method comprises the following steps: on a user side, performing two-dimensional discrete Fourier transform and truncation processing on adownlink channel matrix of a space-frequency domain to obtain a channel matrix H; building a channel feedback model including an encoder and a decoder, and training the channel feedback model; placingthe trained encoder and decoder on the user side and a base station side respectively; inputting the channel matrix H into the encoder to obtain a compressed vector h on the user side, and feeding back the compressed vector to a base station; inputting the h into the decoder to obtain a rebuilt channel matrix by the base station; and performing zero-padding and two-dimension inverse discrete Fourier transform on the rebuilt channel matrix to obtain an original space-frequency domain channel matrix. Through adoption of the large-scale MIMO channel state information feedback method, feedback overhead of the channel state information is lowered, and the channel rebuilding quality is improved remarkably. The large-scale MIMO channel state information feedback method can be applied to a large-scale multi-input and multi-output communication system under a frequency division duplex mode.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
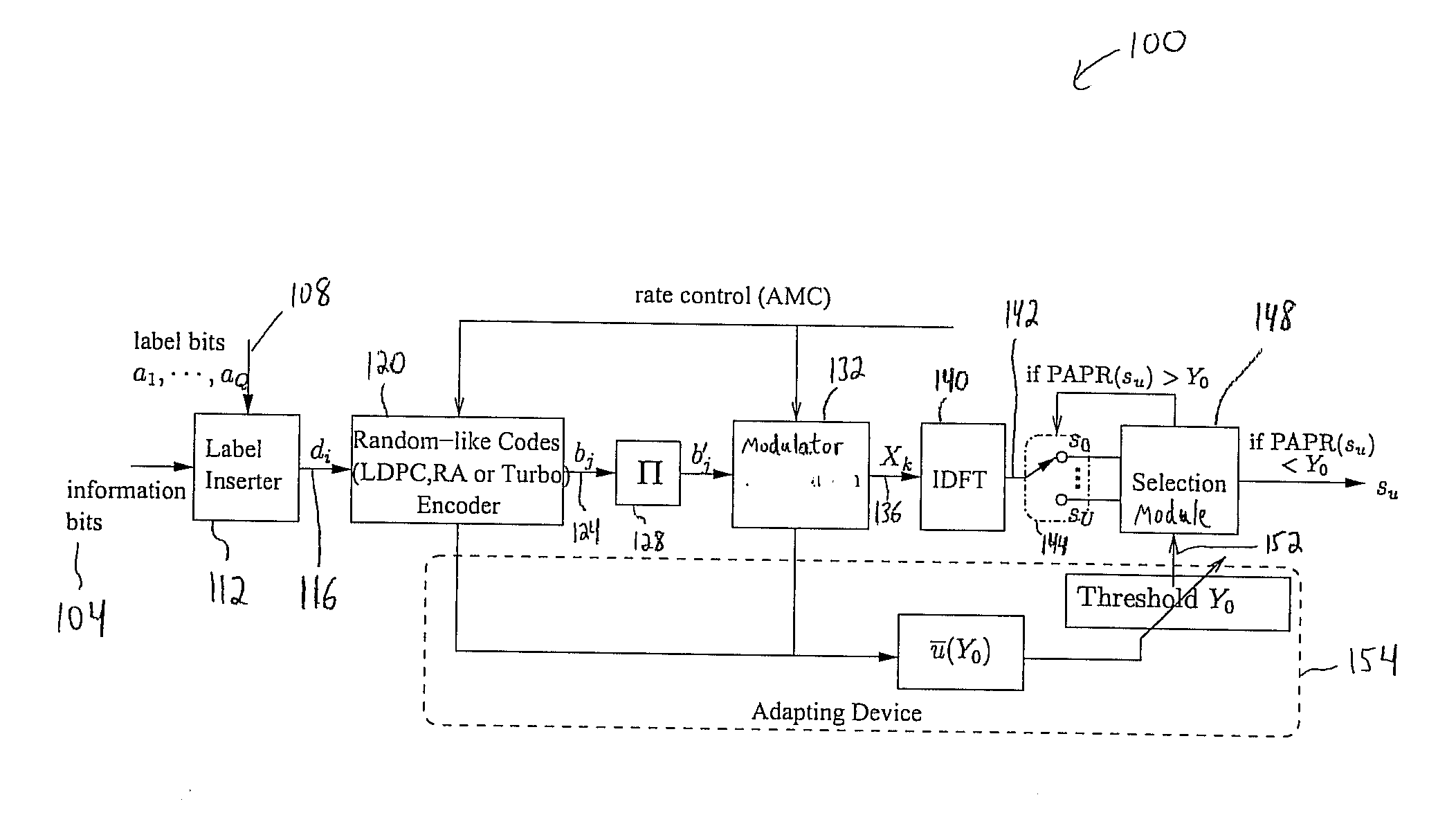
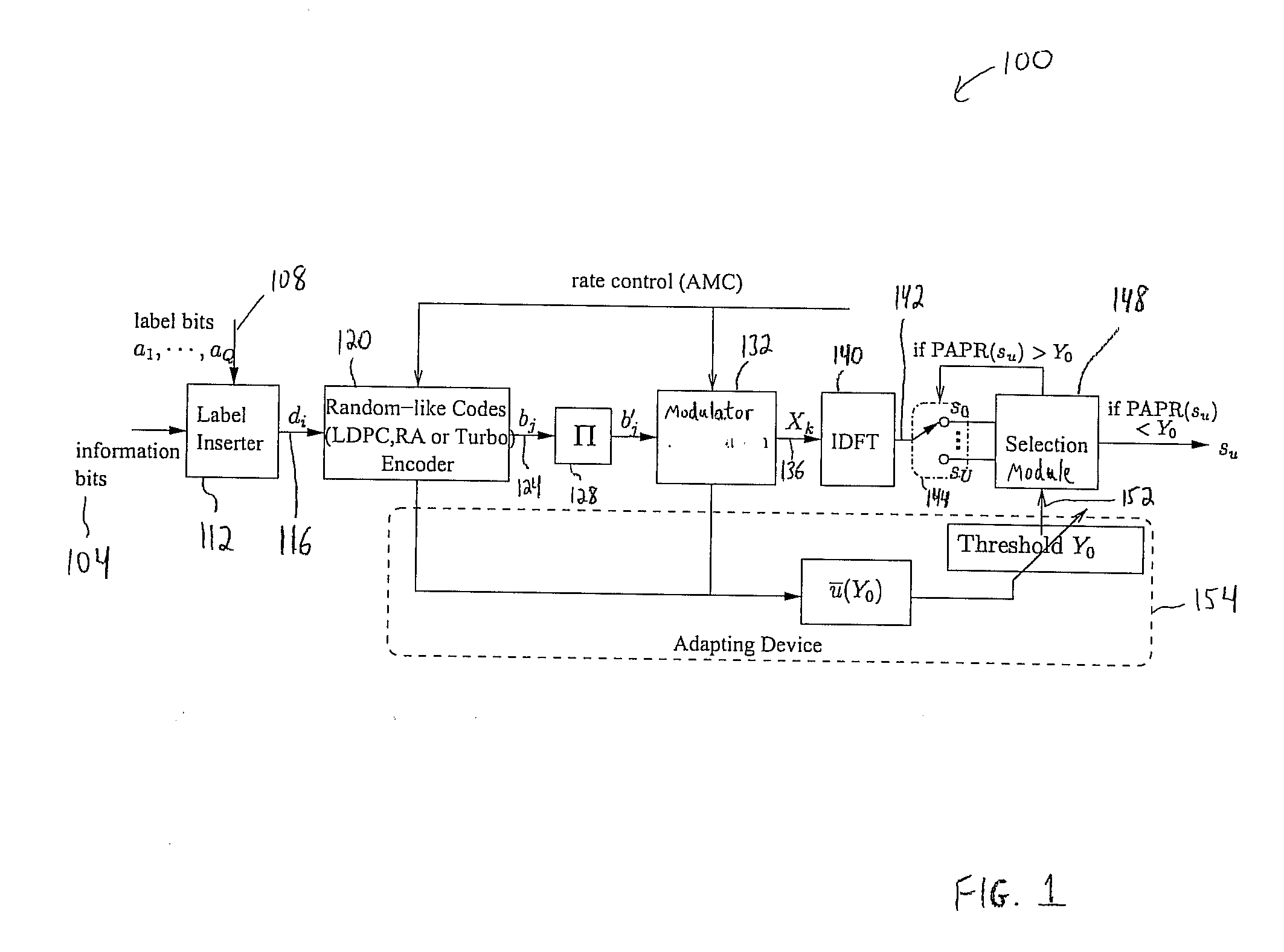
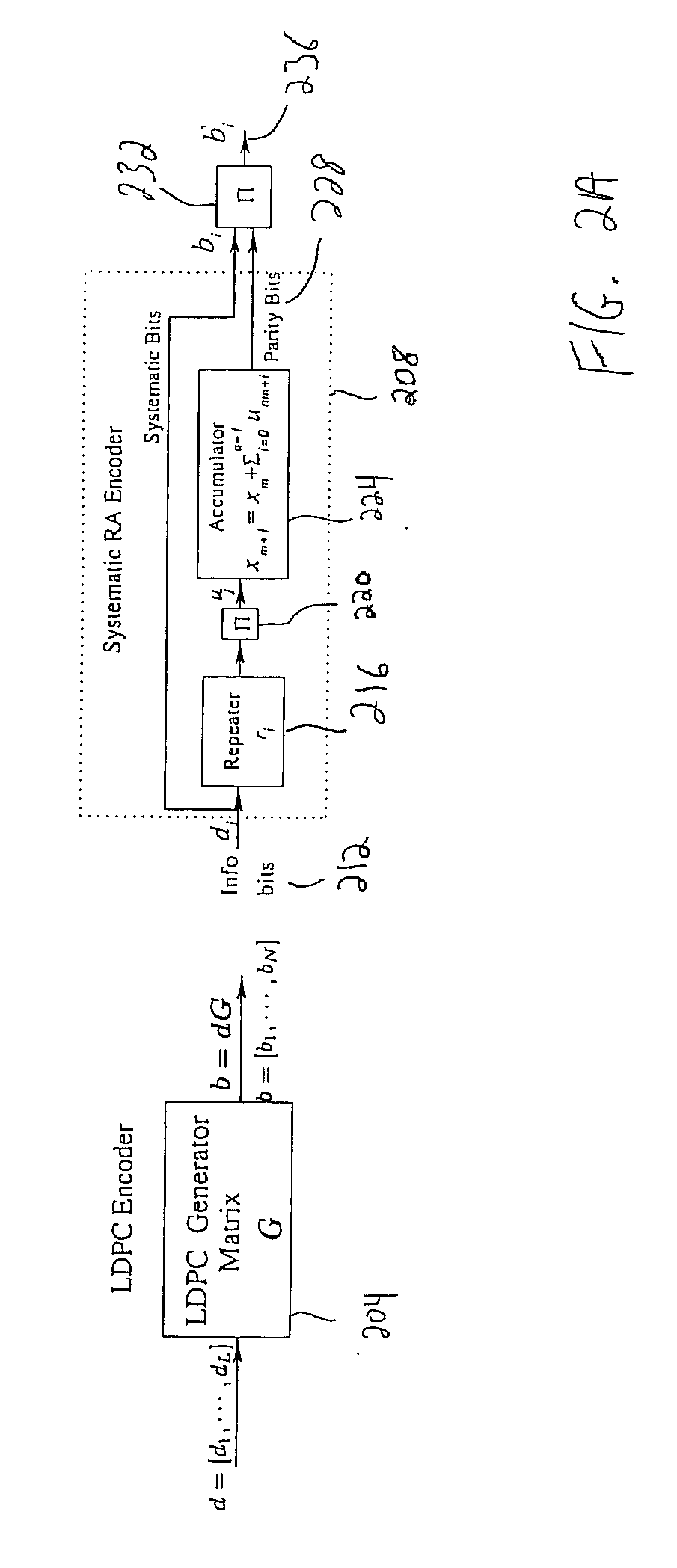
Peak-to-Average Power Ratio Reduction with Threshold Limited Selection for Coded OFDM Systems
InactiveUS20070098094A1Reduce ratio of average powerError preventionSecret communicationInverse discrete fourier transformEngineering
Disclosed is a coded orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) system and method for reducing a peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR). The system and method include a modulator configured to modulate (e.g., using quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM)) coded bits into symbols. The system and method also include an inverse discrete fourier transform (IDFT) module to perform an IDFT on the symbols to produce an OFDM signal. The system and method measure the PAPR of the OFDM signal and transmit the signal to a receiver if the PAPR of the signal is less than a threshold PAPR.
Owner:NEC CORP
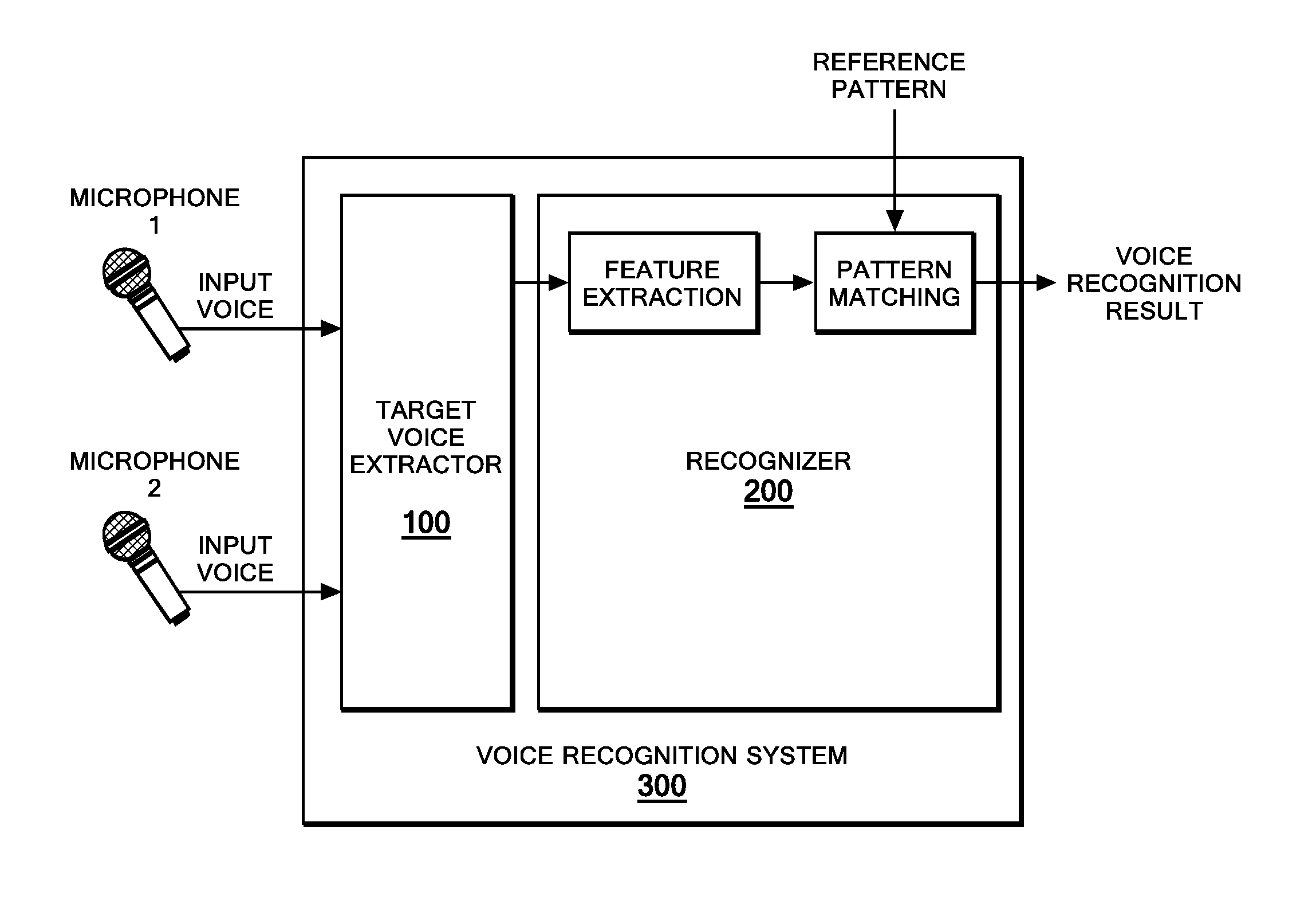
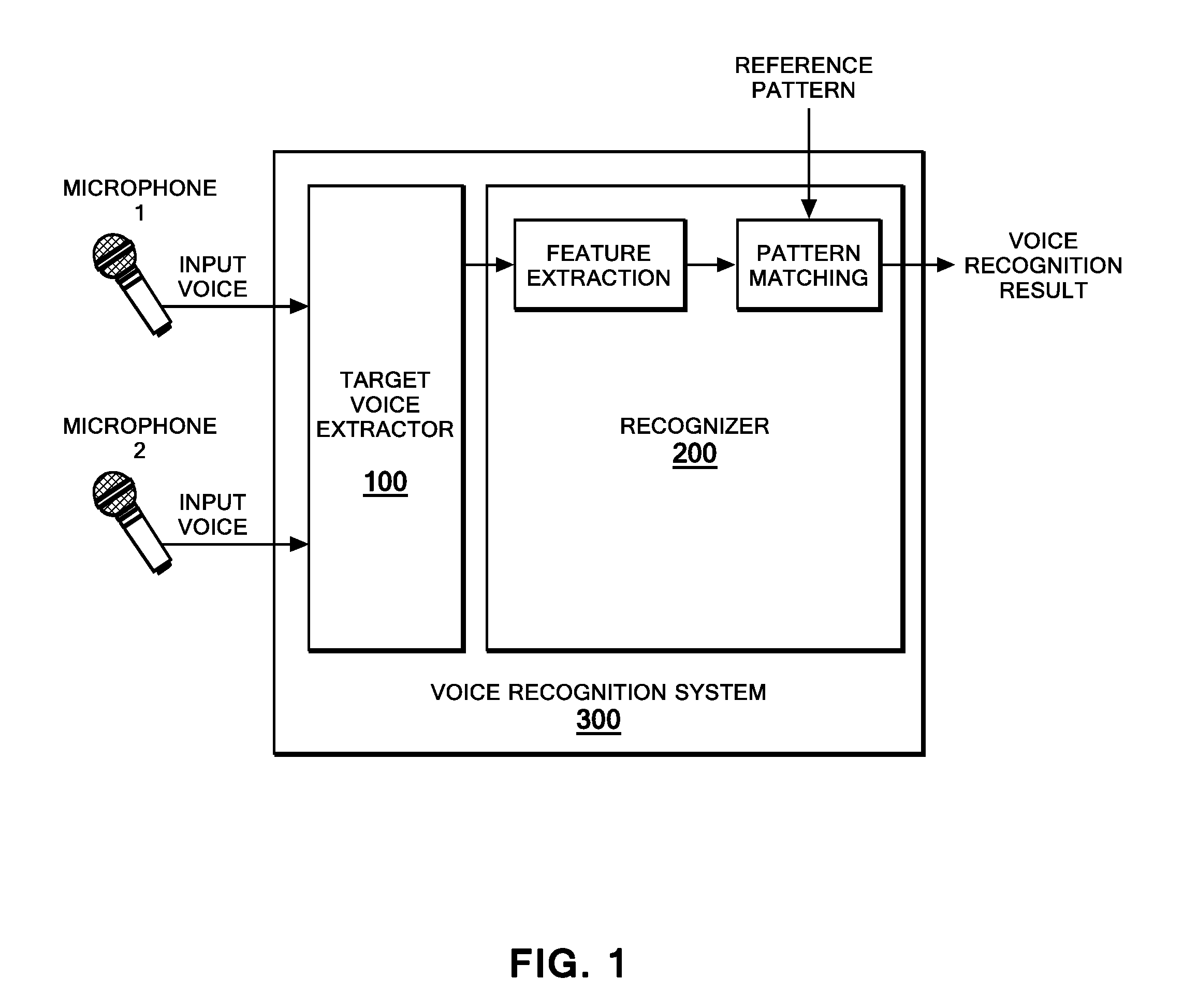
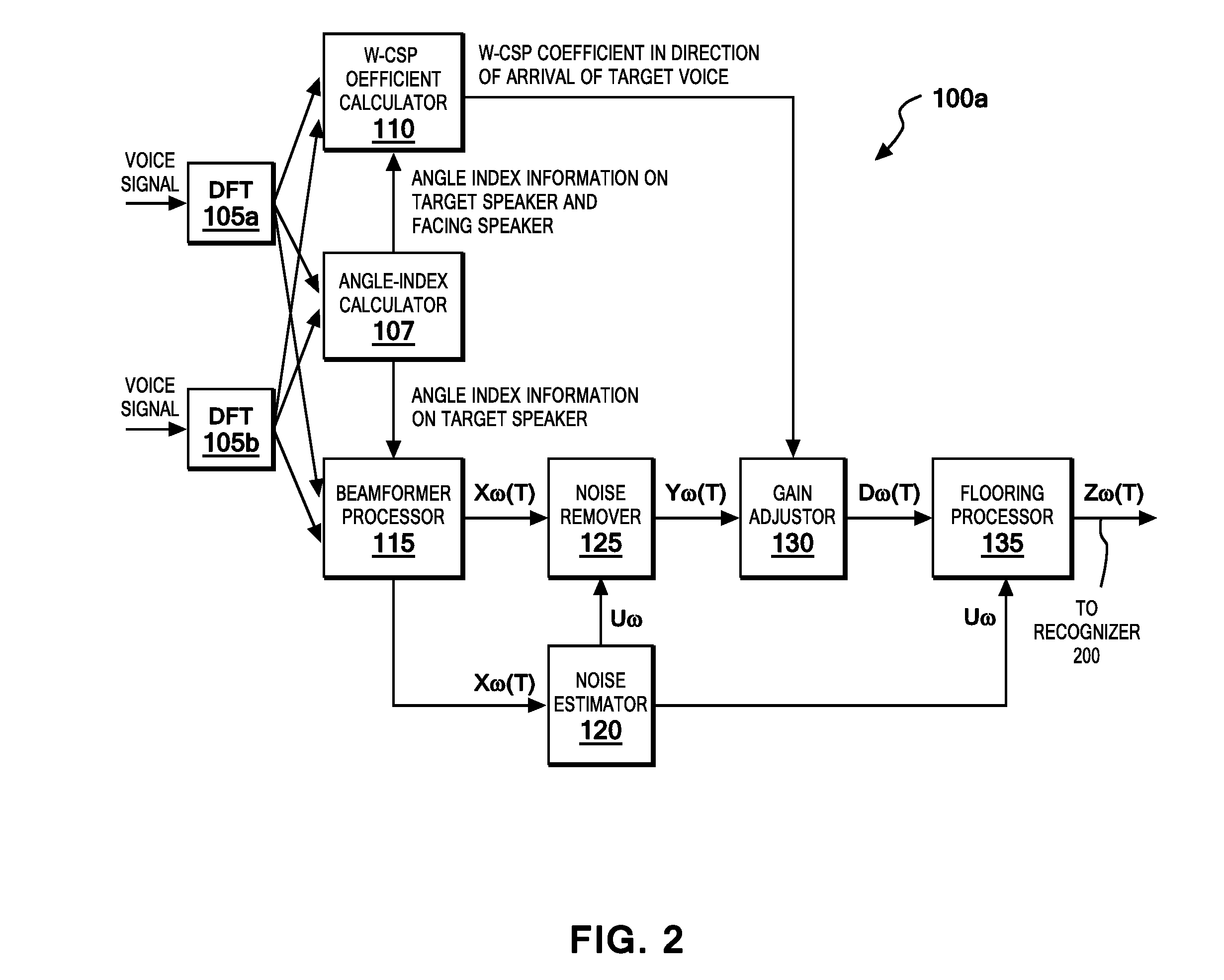
Target voice extraction method, apparatus and program product
An apparatus, program product and method is provided for separating a target voice from a plurality of other voices having different directions of arrival. The method comprises the steps of disposing a first and a second voice input device at a predetermined distance from one another and upon receipt of voice signals at said devices calculating discrete Fourier transforms for the signals and calculating a CSP (cross-power spectrum phase) coefficient by superpositioning multiple frequency-bin components based on correlation of the two spectra signals received and then calculating a weighted CSP coefficient from said two discrete Fourier-transformed speech signals. A target voice is separated when received by said devices from other voice signals in a spectrum by using the calculated weighted CSP coefficient.
Owner:IBM CORP
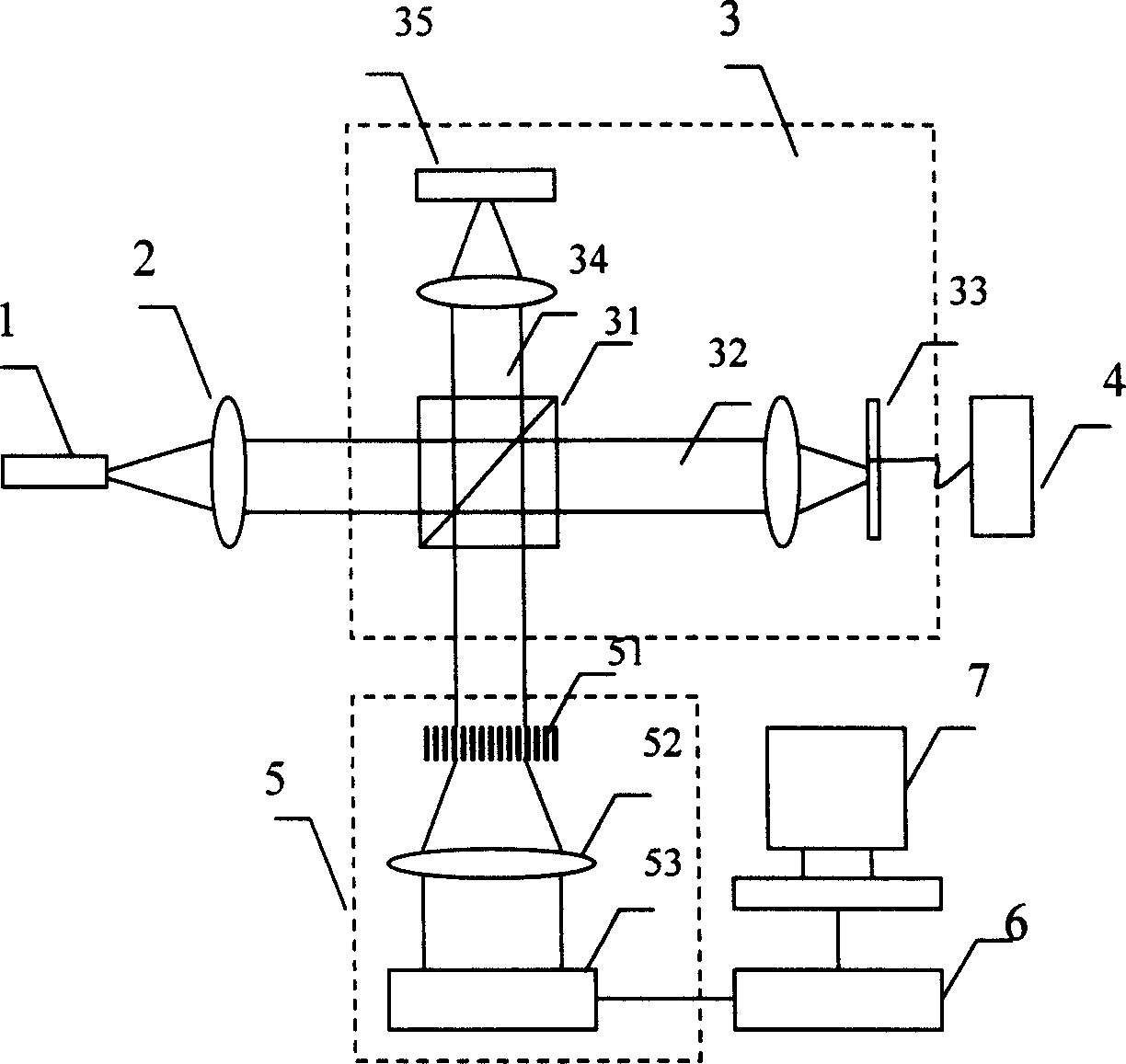
Full-range frequency domain optical coherence tomography method and system thereof
ActiveCN1877305AStrong ability to resist environmental interferenceLight source wavelength independentPhase-affecting property measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringFourier transform on finite groupsWavelength
Disclosed are a method and a system for in frequency domain optical coherent tomography imaging. The method employs sine phase modulation to recreate complex amplitude of the coherent frequency interference signal; and then performs inverse Fourier transform to the complex amplitude to get the tomographic images of the tested objects and eliminate the complex conjugate image, direct current background and self-coherent noise three spurious images, which enlarges the imaging depth of frequency domain optical coherent tomography imaging is two times larger than the original depth and realizes full depth finding of frequency domain optical coherent tomography imaging.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods and arrangements in a telecommunications system
ActiveUS7082159B2Bandwith efficientEffective latencyBaseband system detailsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsCommunications systemChannel impulse response
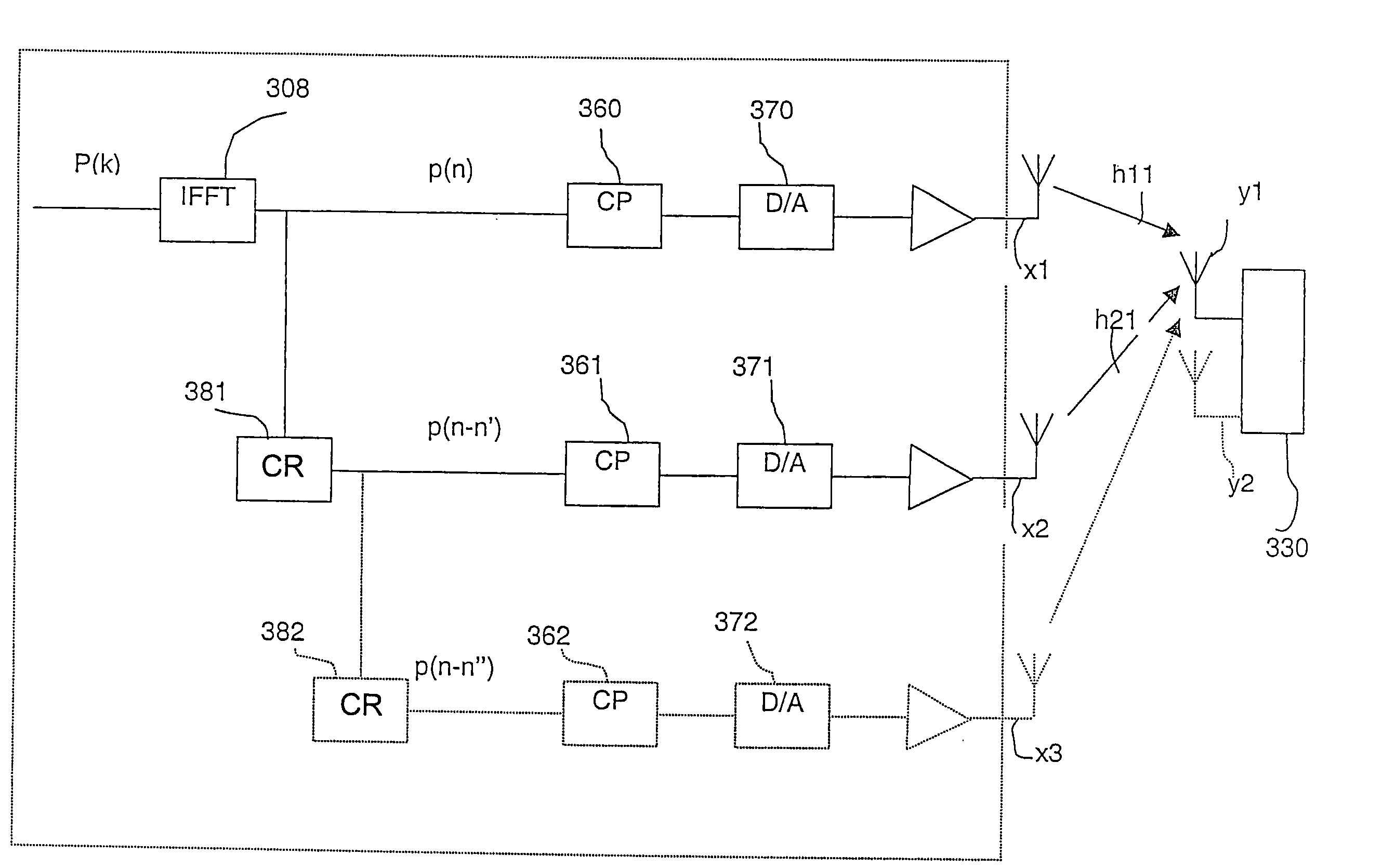
A method and apparatus in a wireless communication system comprising at least one transmitter provided with at least two antennas and at least one receiving unit provided with at least one antenna and wherein training sequences are transmitted from the at least two antennas of the at least one transmitter to the at least one antenna of the at least one receiving unit. Characterized in that first, prior to the transmission, a training sequence P(k) is Inverse Discrete Fourier Transformed to a sequence p(n). Second, for each antenna branch the Inverse Discrete Fourier Transformed sequence p(n) is cyclically rotated by a predetermined step, said predetermined step being p(n) is cyclically rotated by a predetermined step, said predetermined step being different for each antenna branch to generate cyclically rotated training sequences p(n−n1), p(n−n2). Third, the cyclically rotated training sequences p(n−n1), p(n−n2) are transmitted concurrently from said at least two antennas to the receiving unit. Fourth, at the receiving unit receiving the cyclically rotated training sequences, the received sequences being a superposition of transmitted training sequences, each individually affected by the propagation medium, are used to provide channel impulse response estimates for the transmission from respective antenna.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Synchronization techniques using an interpolation filter
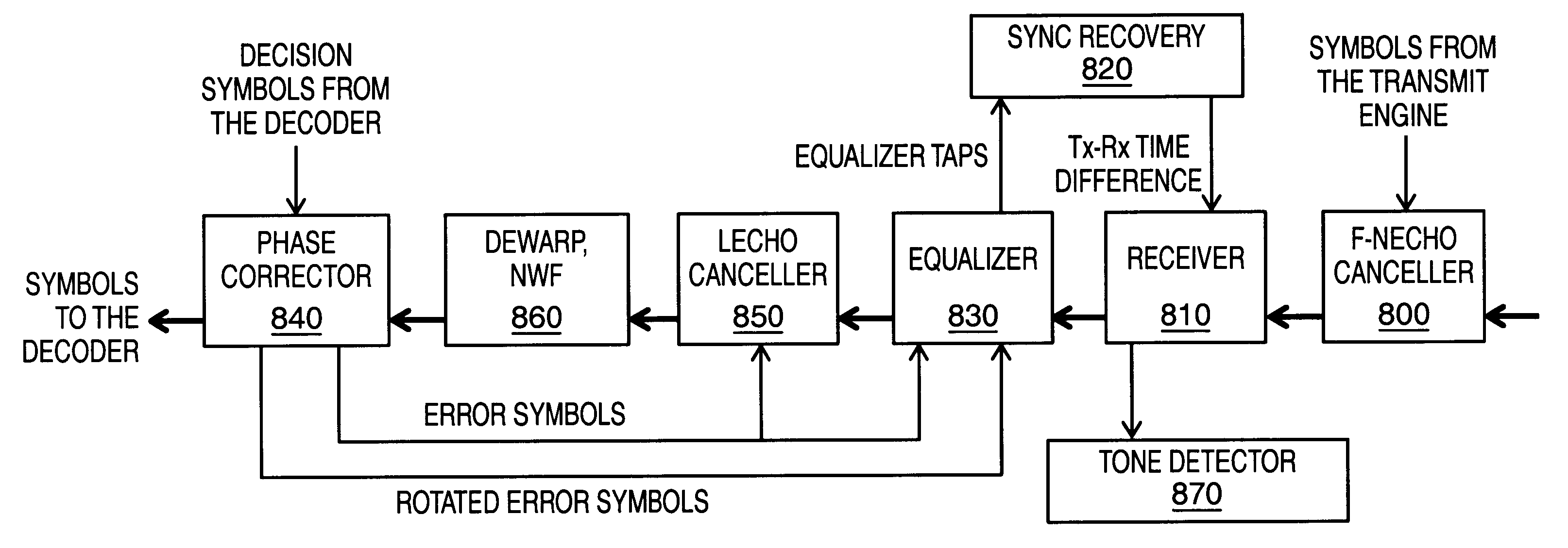
InactiveUS6560276B1Pulse automatic controlTime-division multiplexFrequency spectrumInverse discrete fourier transform
The taps of an equalizer are used as inputs to a discrete Fourier transform (DFT). Certain spectral components are extracted from the DFT and used to estimate the frequency difference. The frequency difference estimate is filtered using a phase locked loop and used to adjust one clock to synchronize the transmit and receive clocks.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Phase difference measuring method based on improved windowing discrete Fourier transform
ActiveCN103454497AEnhanced inhibitory effectAccurate correctionVoltage-current phase angleFrequency spectrumPhase difference
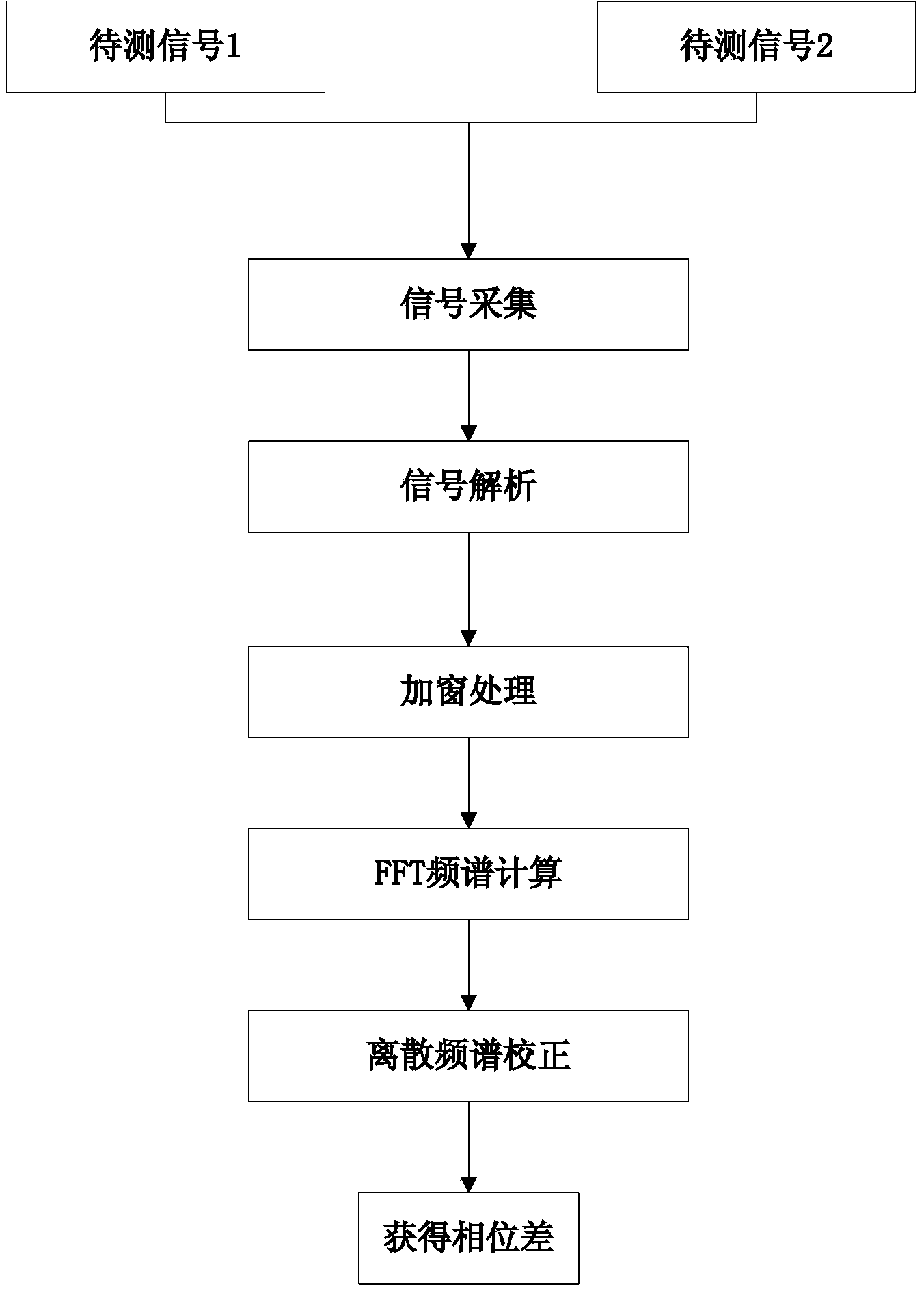
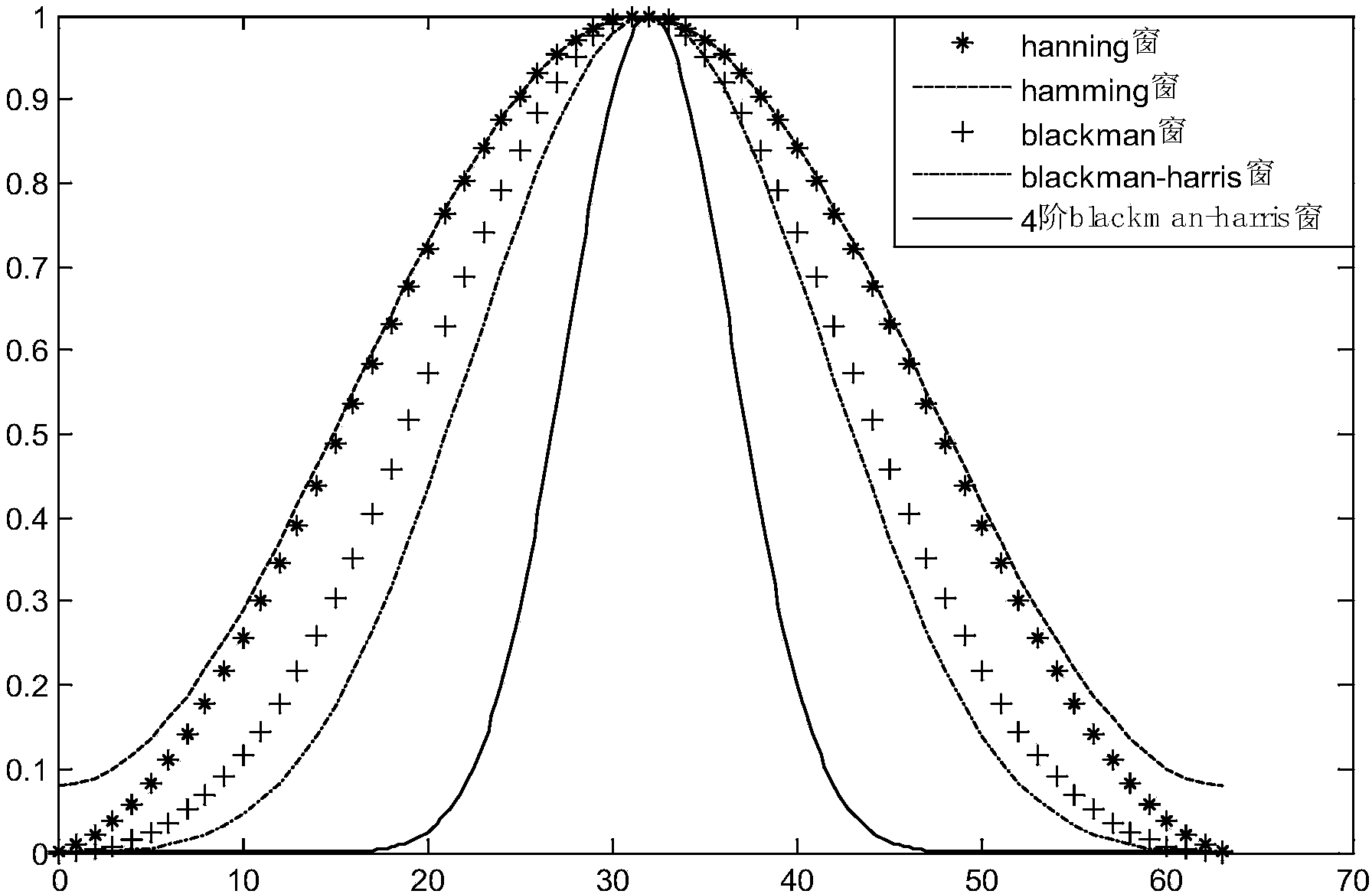
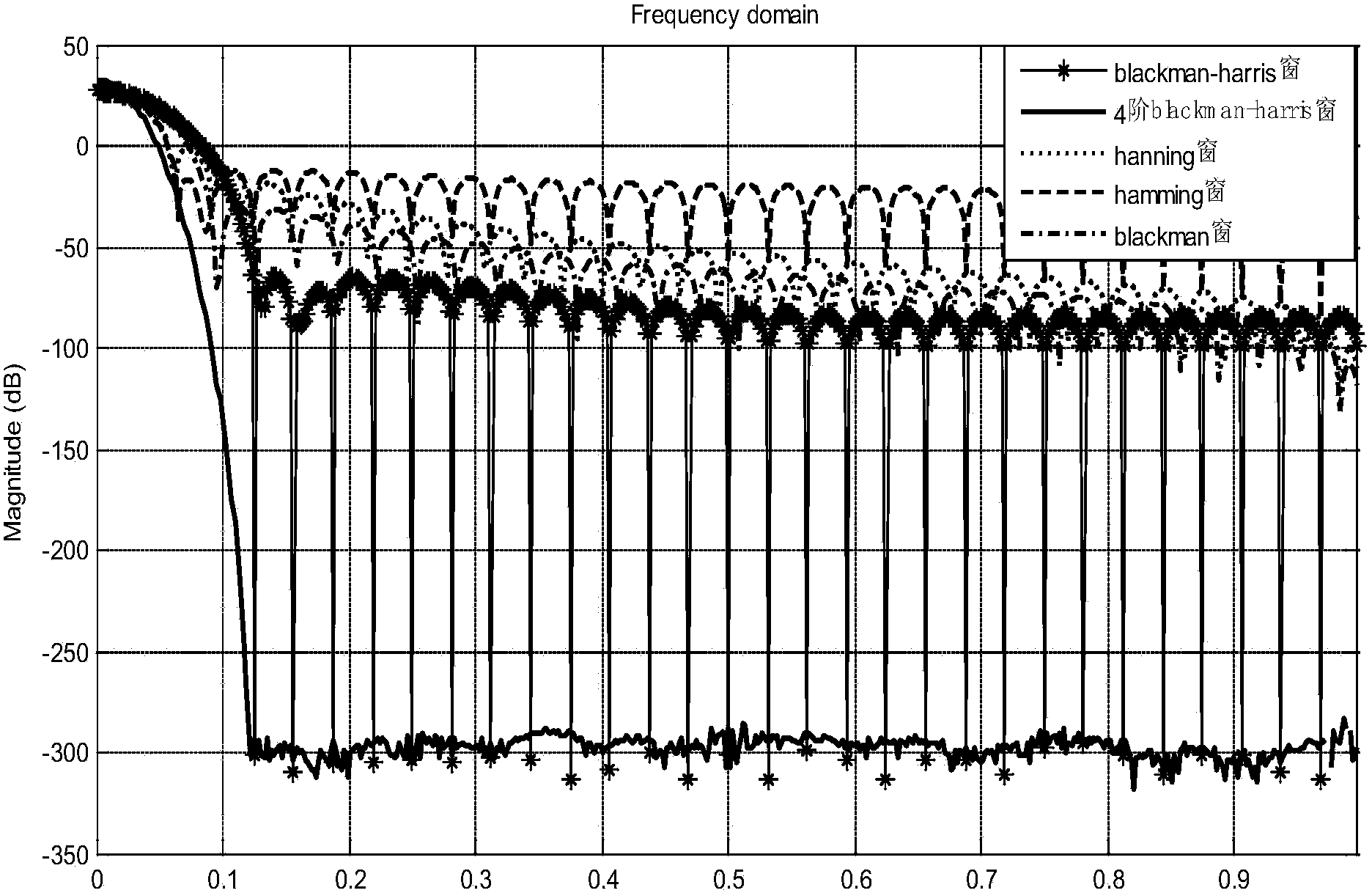
The invention provides a phase difference measuring method based on improved windowing discrete Fourier transform. The phase difference measuring method includes the first step of collecting two periodic signals to be measured, the second step of analyzing the collected periodic signals to digital signals, the third step of carrying out windowing processing on the digital signals by constructing a 4-step Blackman-Harris window, and carrying out FFT spectral analysis on the signals subjected to windowing processing to obtain signal frequency spectrums, extracting fundamental wave parameters and respectively calculating initial phase angles of the periodic signals to be measured, and the fourth step of correcting phase positions of useful frequency spectrums according to a discrete spectrum correction method so as to calculate the phase differences of the periodic signals to be measured. The phase difference measuring method can effectively solve the problems that a time domain of a DFT algorithm is cut off, the introduced spectrums are revealed, and spectral analysis has bigger errors caused by the picket fence effect, overcomes the defects of spectrum leakage and lower frequency resolution in an interpolation method, improves the frequency resolution, and finally achieves the high-precision measurement of the phase differences.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
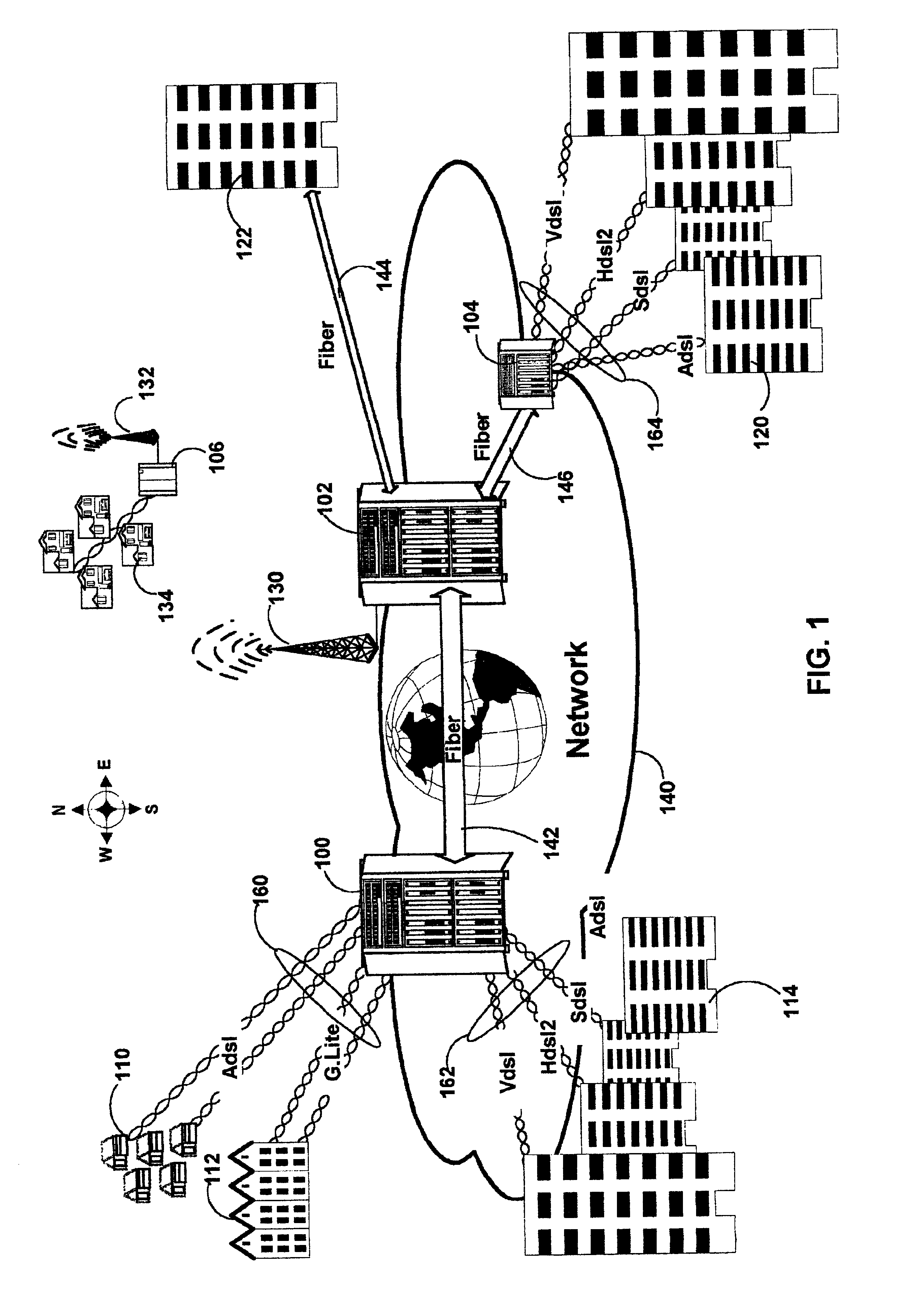
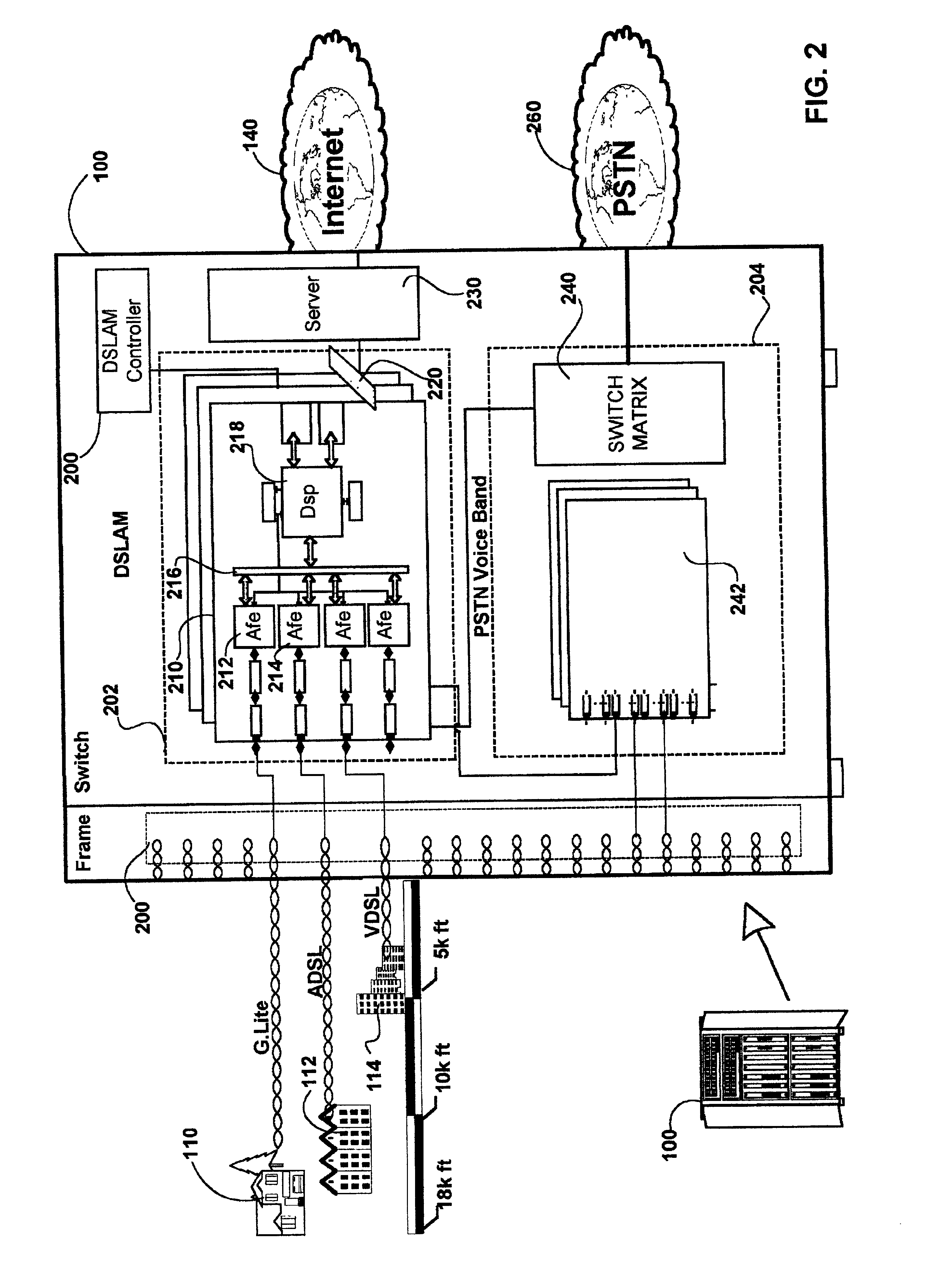
Method and apparatus for a X-DSL communication processor
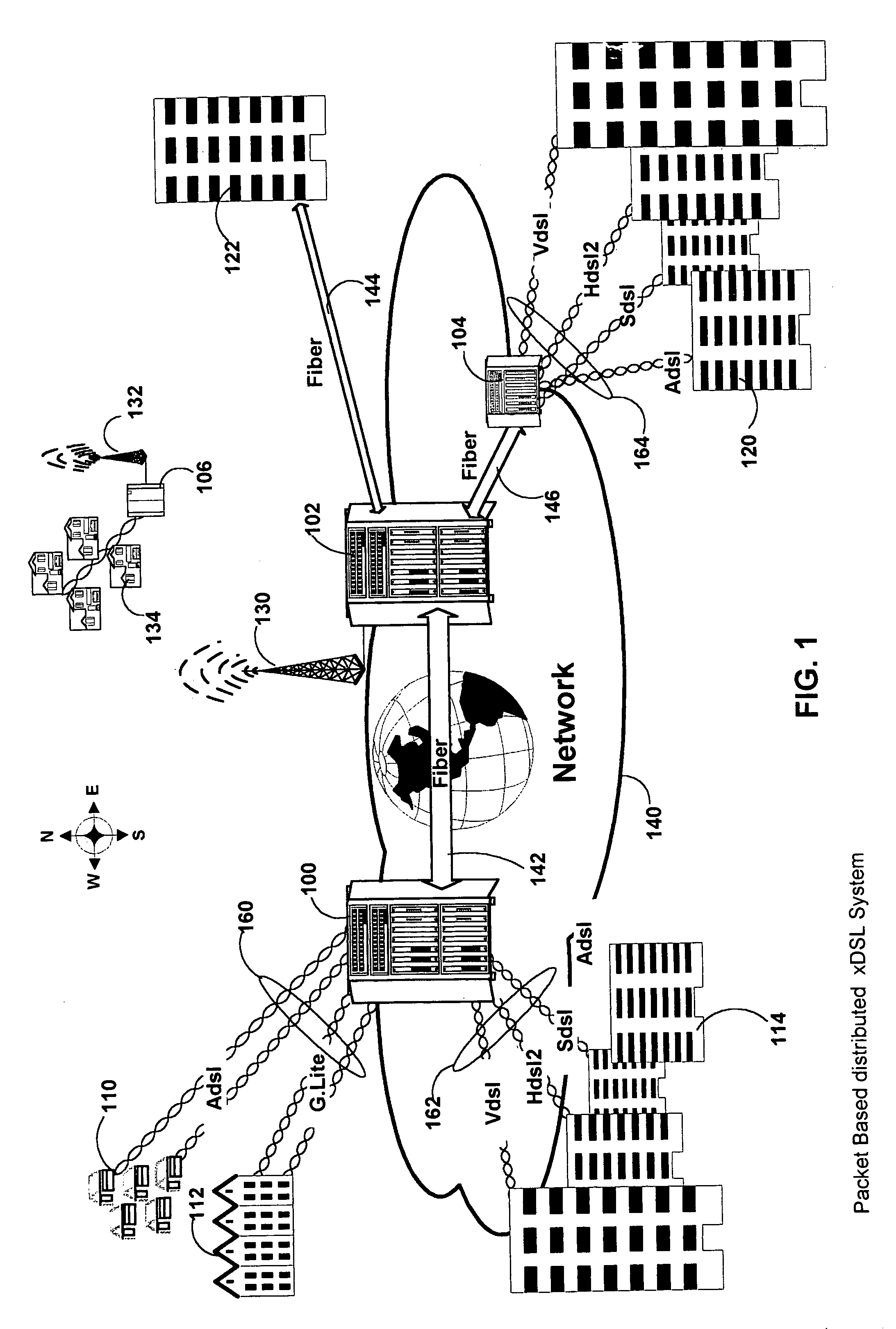
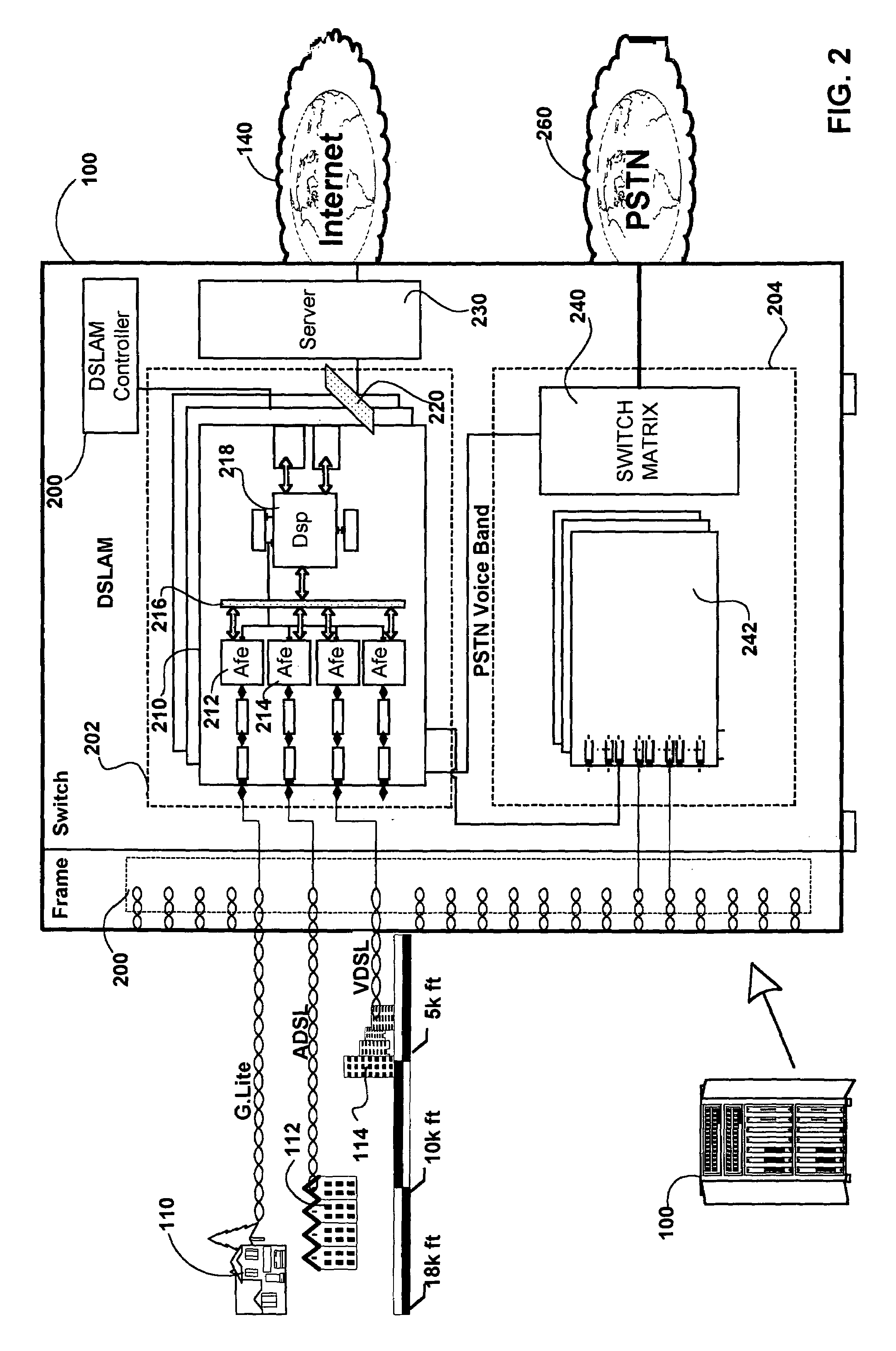
InactiveUS6940807B1Rapid responseModulated-carrier systemsPower distribution line transmissionComputer hardwareExtensibility
The current invention provides a DSP which accommodates multiple current X-DSL protocols and is further configurable to support future protocols. The DSP is implemented with shared and dedicated hardware components on both the transmit and receive paths. The DSP implements both the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) and inverse discrete Fourier transform (IDFT) portions across a wide range of sample sizes and X-DSL protocols. Multiple channels, each with varying ones of the X-DSL protocols can be handled in the same session. The DSP offers the speed associated with hardware implementation of the transforms and the flexibility of a software only implementation. Traffic flow is regulated in the chip using a packet based schema in which each packet is associated with a specific channel of upstream and downstream data. Header and control information in each packet is used to govern the processing of each packet as it moves along either the transmit path or receive path. The DSP of the current invention may advantageously be utilized in fields other than communications, such as: medical and other imaging, seismic analysis, radar and other military applications, pattern recognition, signal processing etc. The present invention provides a signal processing architecture that supports scalability of CO / DLC / ONU resources, and allows a significantly more flexible hardware response to the evolving X-DSL standards without over committing of hardware resources. As standards evolve hardware may be reconfigured to support the new standards.
Owner:IKANOS COMMUNICATIONS
Generation method for preamble symbol in physical frame
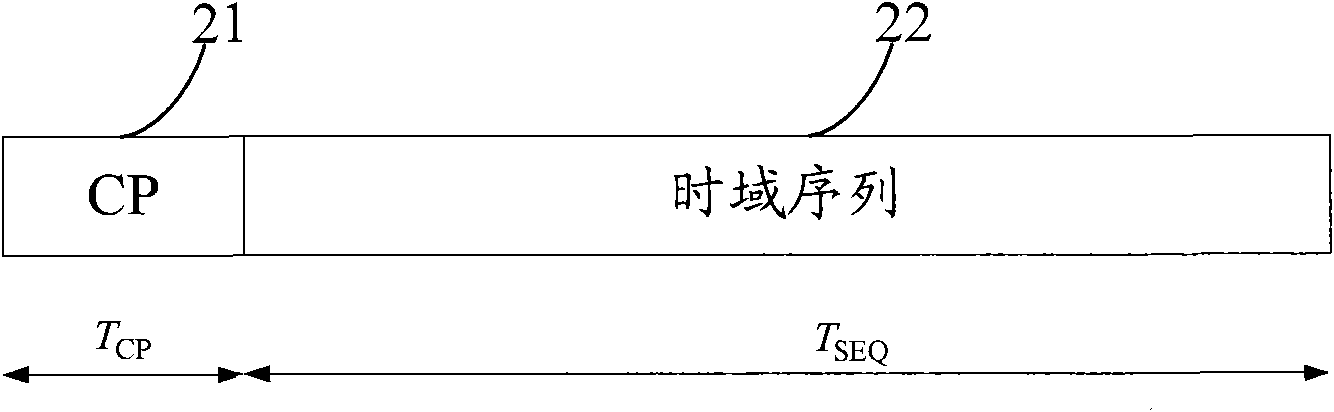
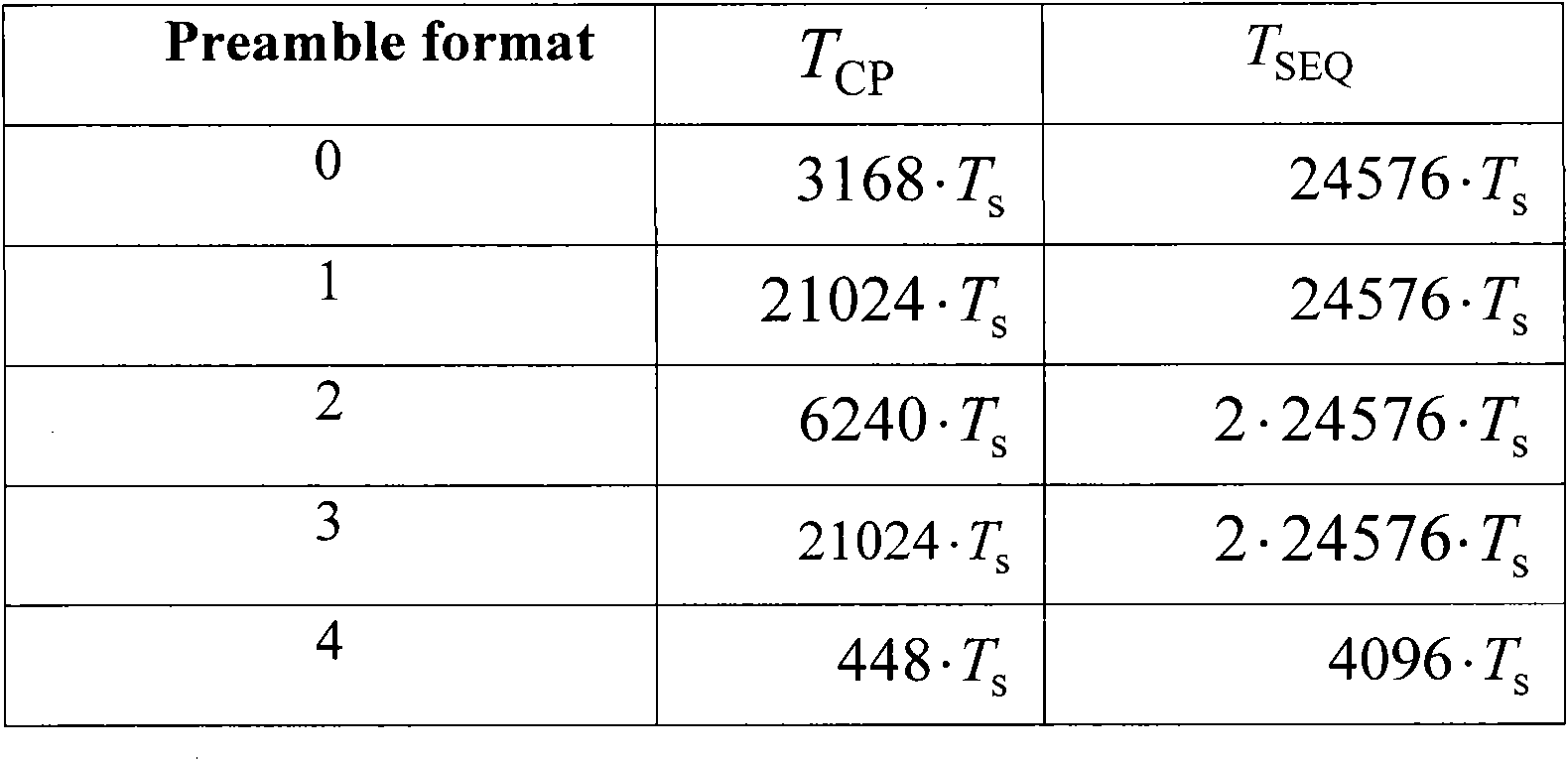
ActiveCN105024791AGood fractional frequency offset estimation performanceGood timing synchronization performanceMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksTime domainInverse discrete fourier transform
The invention discloses a generation method for preamble symbols in a physical frame. The generation method comprises the steps of: carrying out inverse discrete Fourier transform on a frequency domain OFDM symbol with a preset length to obtain a time domain OFDM symbol; determining a cyclic prefix length; intercepting a time domain OFDM symbol with the cyclic prefix length from the time domain OFDM symbol to serve as a cyclic prefix; generating a modulation signal based on the intercepted time domain OFDM symbol with the cyclic prefix length; and generating a preamble symbol based on the cyclic prefix, the time domain OFDM symbol and the modulation signal. The technical scheme provided by the invention solves the problems of the current DVB_T2 standard and other standards that a DVB_T2 time domain structure has no cyclic prefix and is not suitable for coherent detection, and the failure probability of the preamble symbol detected by adopting a low complexity receiving algorithm in a complex frequency selectivity fading channel is high.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT OF DIGITAL TELEVISION
Method and equipment for generating preamble sequence
ActiveCN101860395AAvoid Transformation SituationsFast operationEnergy efficient ICTRadio transmission for post communicationTime domainPhase conversion
The invention discloses a method and equipment for generating a preamble sequence. The method comprises the following steps of: generating a frequency domain ZC sequence; determining a format and a time domain sampling point number of a target preamble sequence; performing inverse discrete Fourier transform of a corresponding preset small point number on the frequency domain ZC sequence according to the time domain sampling point number of the target preamble sequence to obtain a time domain sequence; performing interpolation on the time domain sequence, and converting the length of the time domain sequence into a length corresponding to the time domain sampling point number of the target preamble sequence; acquiring a phase rotation angle according to an initial position of the preset frequency domain resource; multiplying the time domain sequence with the converted length and the phase rotation angle, and performing phase conversion; performing corresponding subsequent processing on the time domain sequence with the converted phase according to the format of the target preamble sequence; and adding a cyclic prefix to the subsequent processed time domain sequence. The preamble sequence generating method disclosed by the embodiment of the invention avoids the occurrence of Fourier transform of a large point number so as to improve the operation speed, reduce the calculation quantity, improve the generating speed and reduce the power consumption and the circuit area at the same time.
Owner:合肥东芯通信股份有限公司
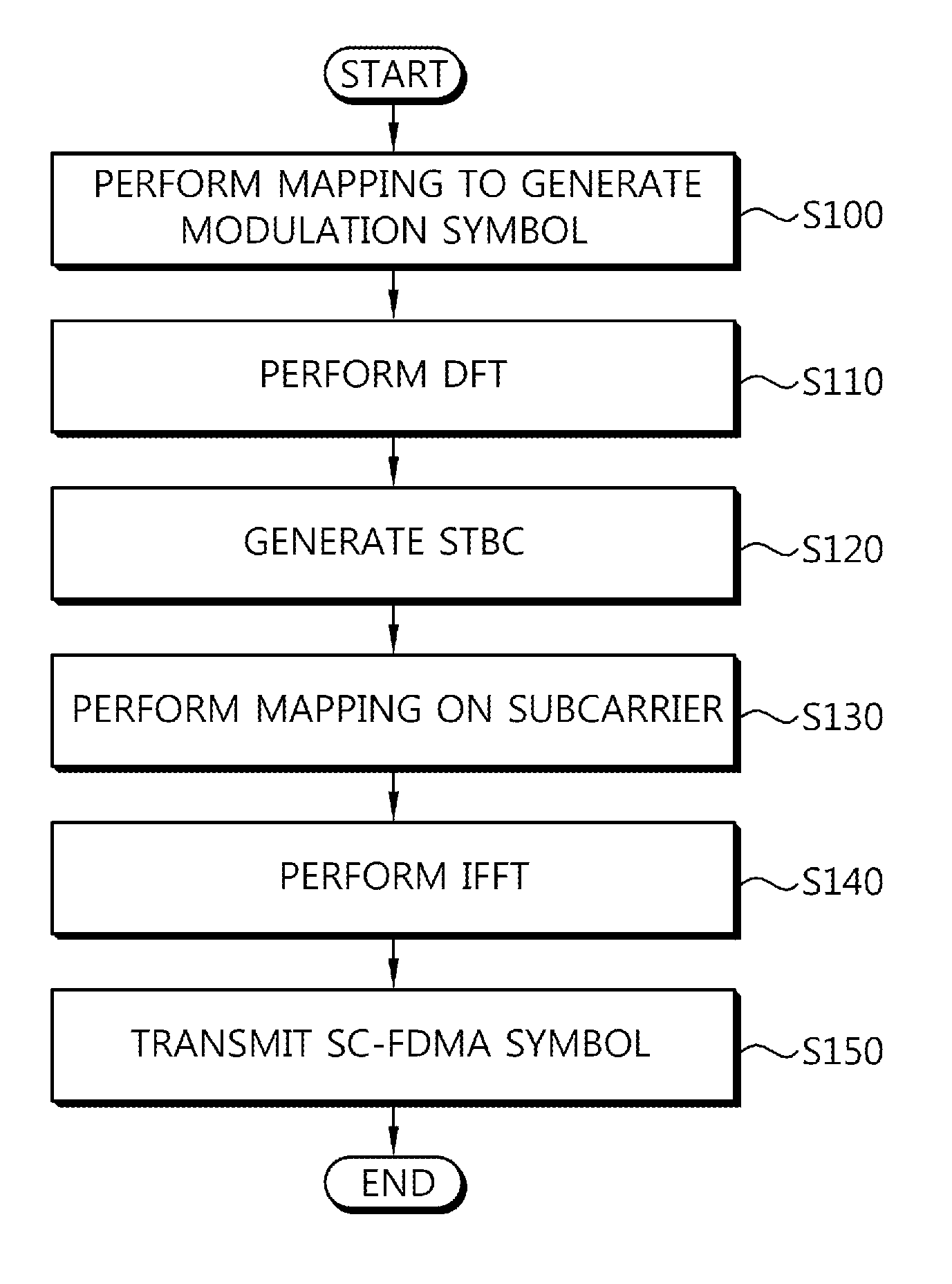
Data transmission method using stbc scheme
InactiveUS20110142076A1Improve robustnessReduce the ratioSpatial transmit diversityError preventionComputer hardwareCode division multiple access
A data transmission method using a space time block code (STBC) scheme is provided. The method includes generating a modulation symbol by performing coding and constellation mapping on an information bit, generating a frequency-domain symbol by performing discrete Fourier transform (DFT) on the modulation symbol, generating a single carrier-frequency division multiple access (SC-FDMA) symbol by performing inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT) after mapping the frequency-domain symbol to a subcarrier, and transmitting the SC-FDMA symbol on a slot basis.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Dft-based channel estimation systems and methods
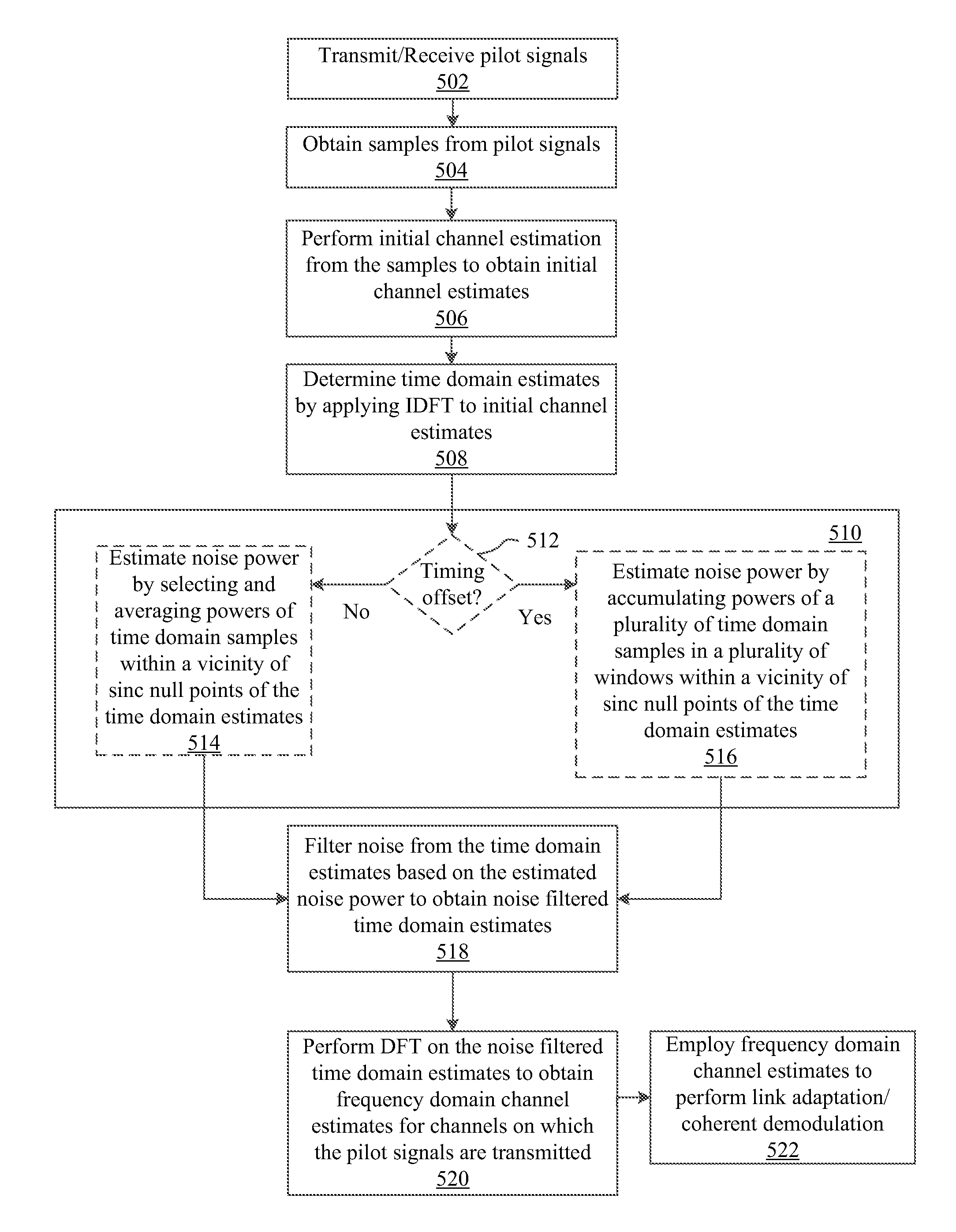
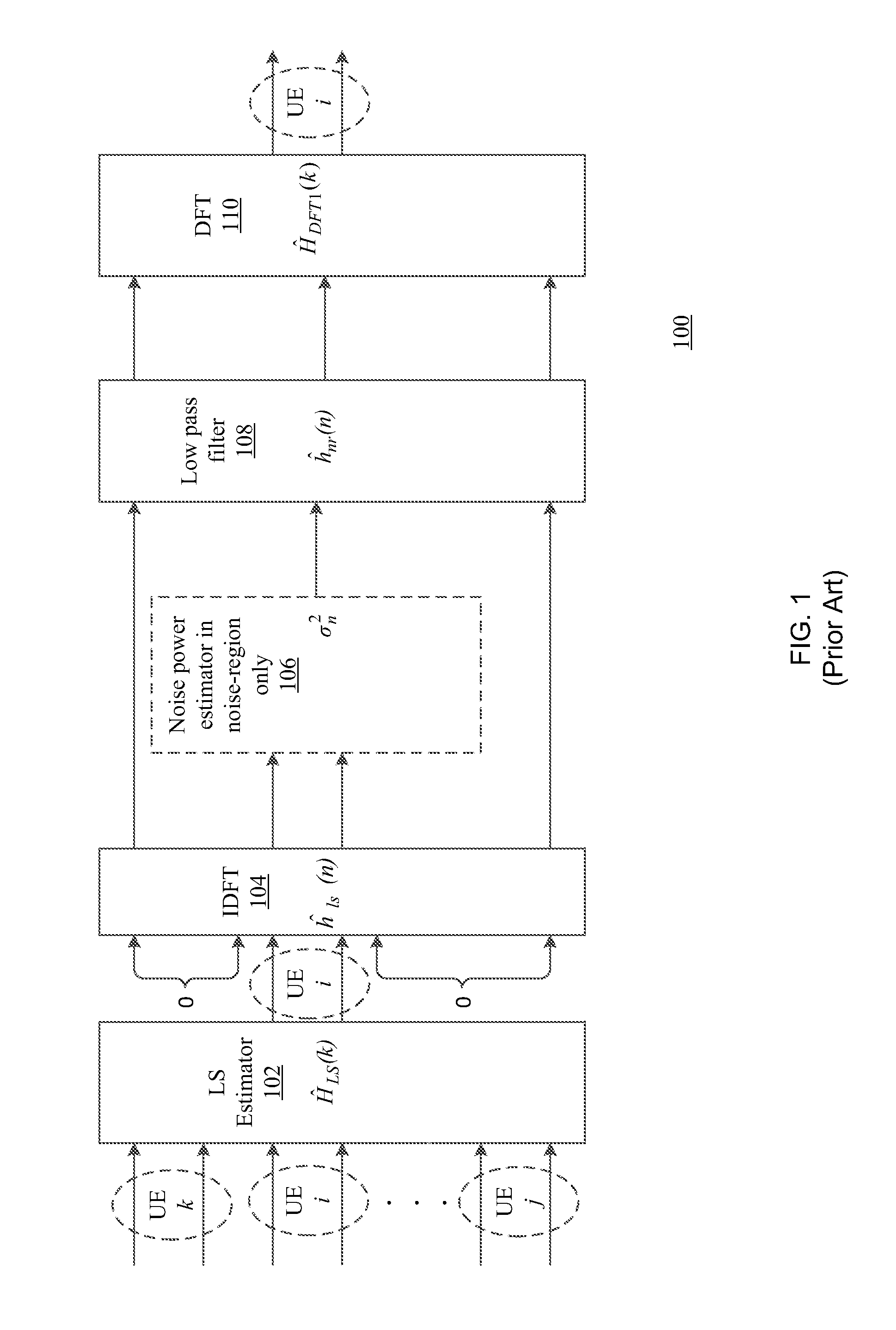
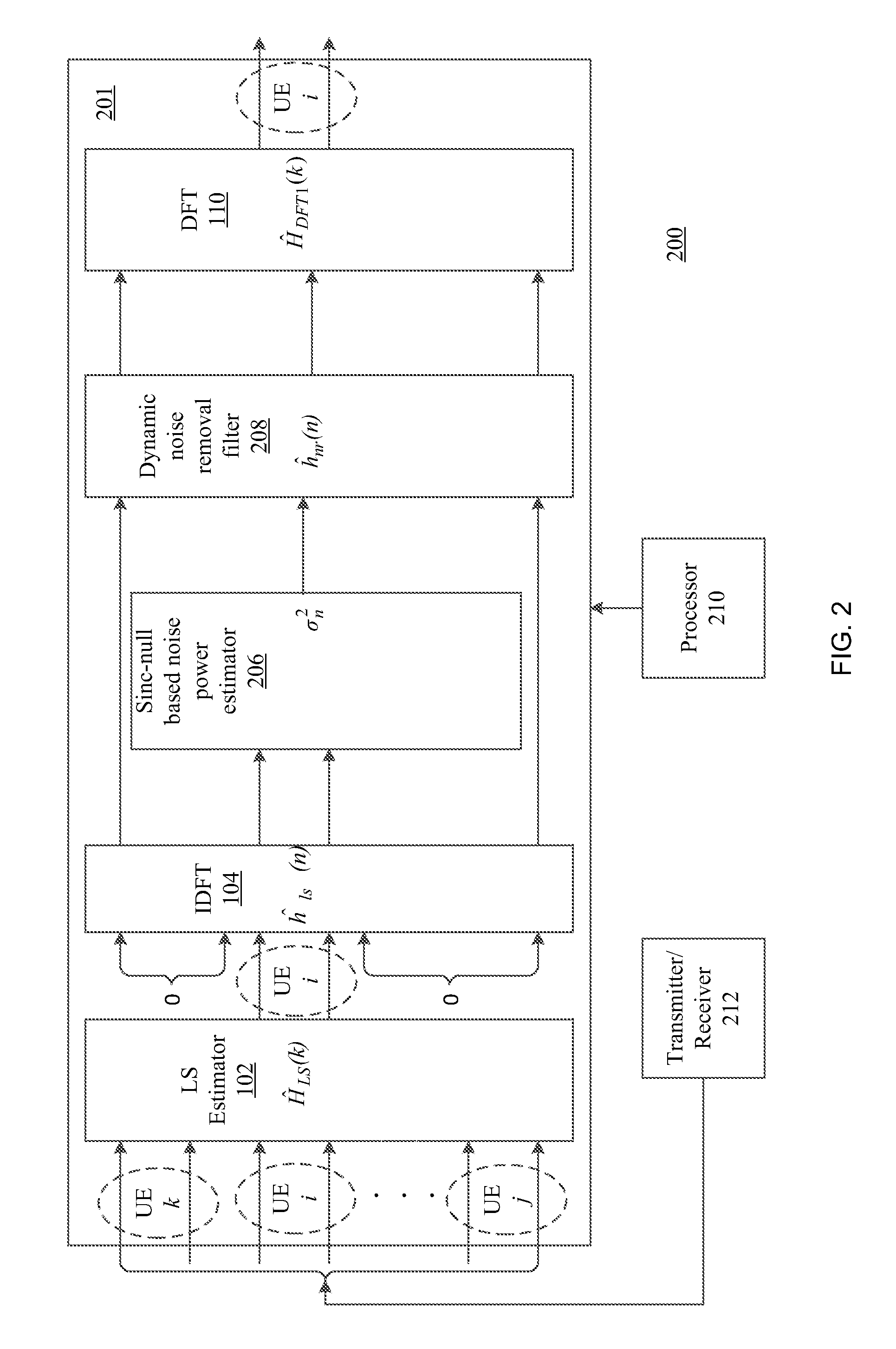
DFT-based channel estimation methods and systems are disclosed. One system includes an inverse discrete Fourier transform module, a noise power estimator, a noise filter and a discrete Fourier transform module. The inverse discrete Fourier transform module is configured to determine time domain estimates by applying an inverse discrete Fourier transform to initial channel estimates computed from pilot signals. Additionally, the noise power estimator is configured to estimate noise power by determining and utilizing time domain samples that are within a vicinity of sinc nulls of the time domain estimates. The noise filter is configured to filter noise from the time domain estimates based on the estimated noise power to obtain noise filtered time domain estimates. Further, the discrete Fourier transform module is configured to perform a discrete Fourier transform on the noise filtered time domain estimates to obtain frequency domain channel estimates for channels on which pilot signals are transmitted.
Owner:NEC LAB AMERICA
Adaptive modulation-demodulation method base on fractional order Fourier transform
InactiveCN101827060AImprove performanceMulti-frequency code systemsError prevention/detection by diversity receptionChannel state informationCurrent channel
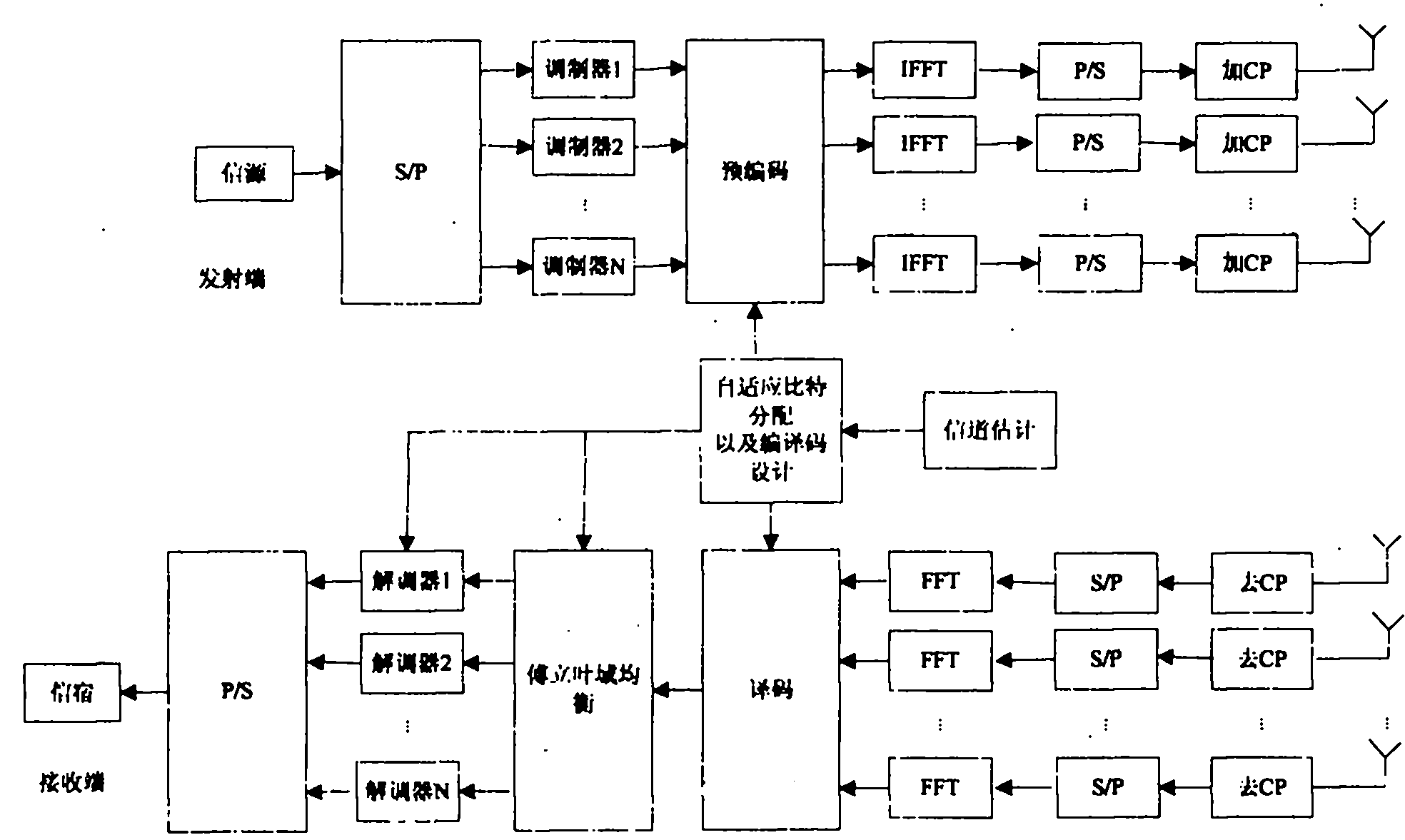
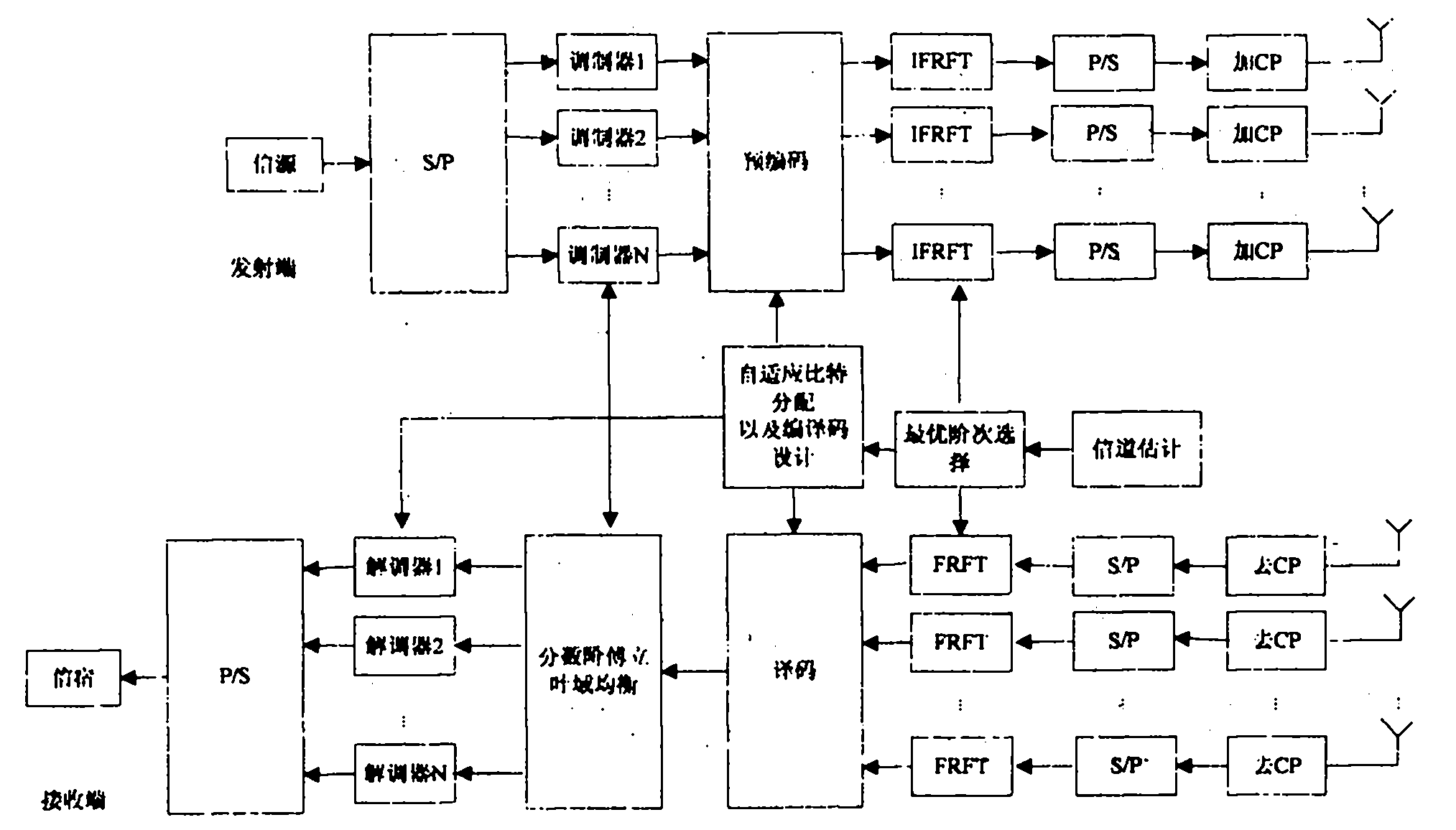
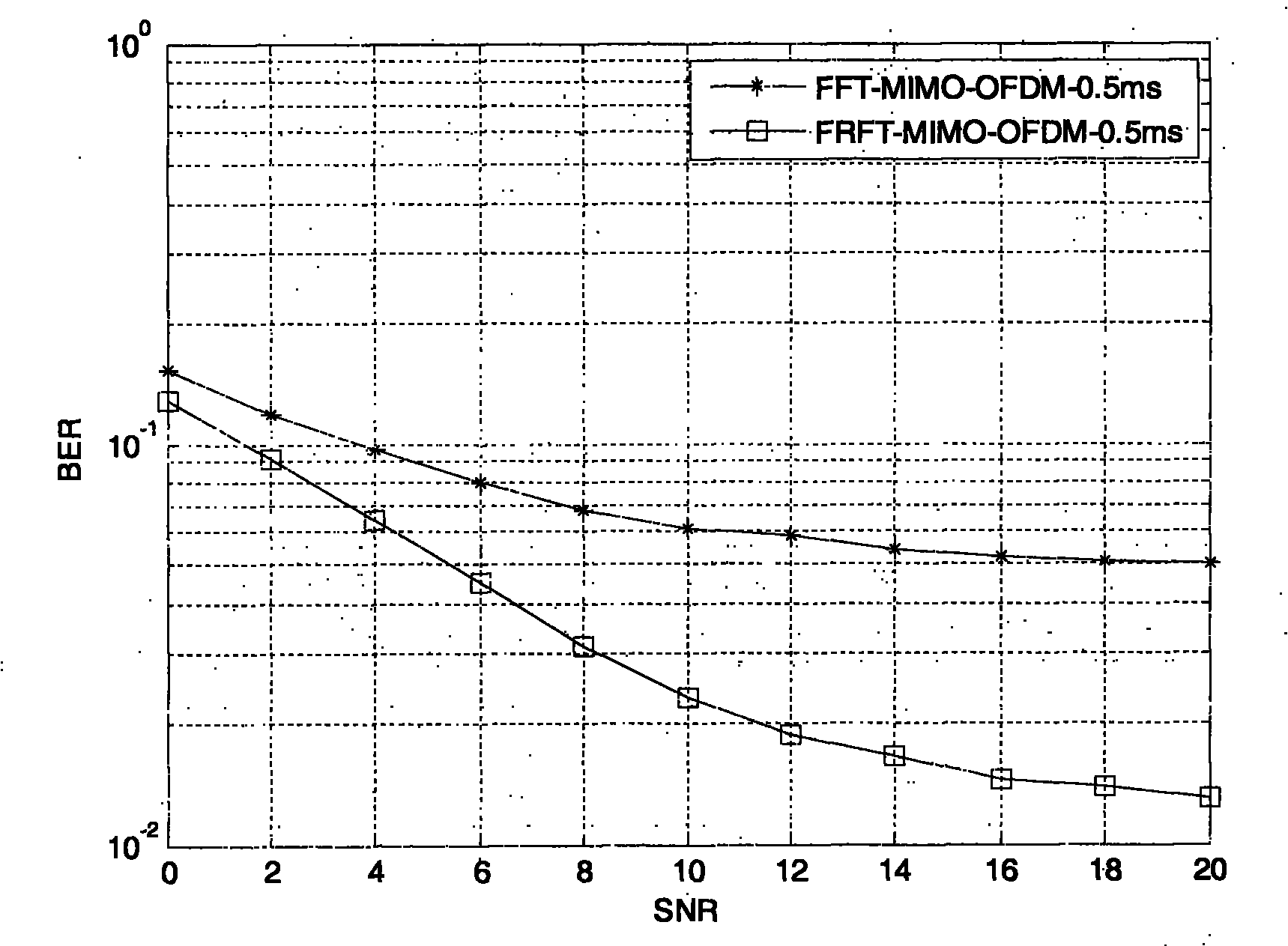
The invention provides an adaptive modulation-demodulation method base on fractional order Fourier transform, aiming at reducing influence caused by feedback time delay specific to an MIMO-OFDM (Multiple Input Multiple Output-Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) adaptive modulation system which has feedback time delay, and enabling the system to have better performance in a fast time-varying channel. The method has the technical scheme that inverse discrete fractional order Fourier transform is used to replace inverse discrete Fourier transform for carrying out subcarrier modulation at a transmitting terminal, discrete fractional order Fourier transform is used to replace discrete Fourier transform for carrying out subcarrier demodulation at a receiving terminal, the optimal fractional order Fourier transform order selection is carried out by channel estimation information fed back to the transmitting terminal by the receiving terminal, the deviation between the current channel state information and the feedback channel state information is reduced and the performance of the system having time delay is enhanced.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Modulation and demodulation of OFDM signals
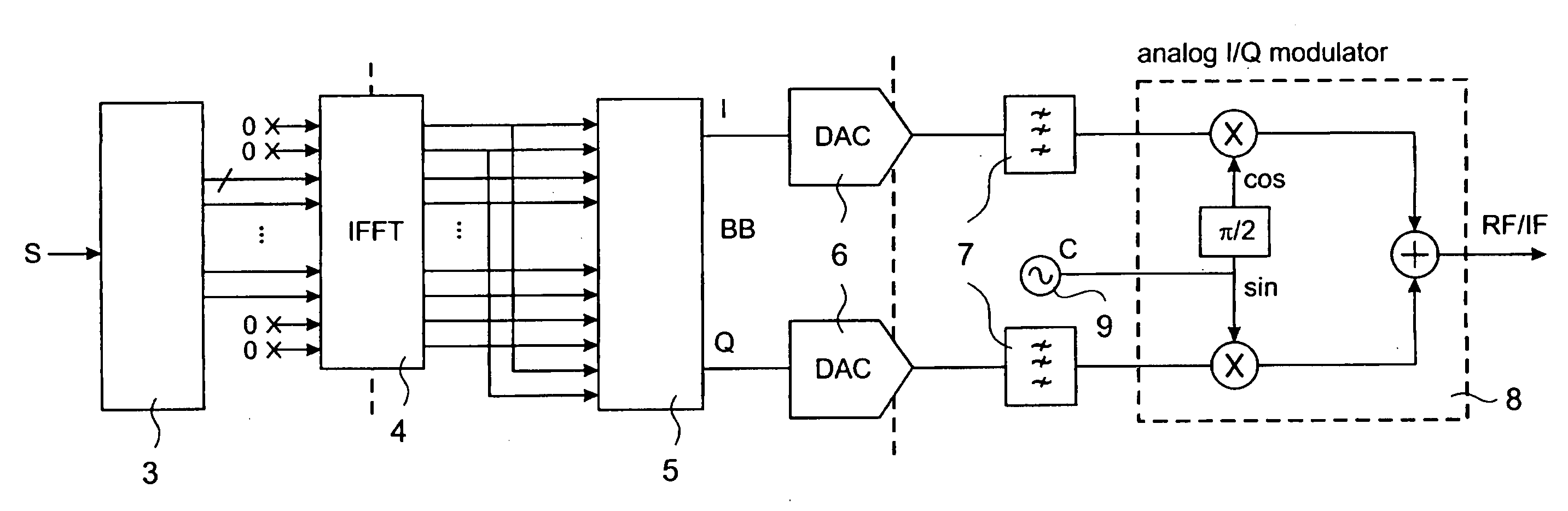
InactiveUS20090323510A1Efficient executionSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsInverse discrete fourier transformCarrier signal
The invention relates to a method for modulating sub-carrier symbols to an intermediate-frequency OFDM signal having even and odd samples, including following steps:transforming a number N of the sub-carrier symbols to pre-processed sub-carrier symbols;performing a complex inverse discrete Fourier transformation (IDFT) on the pre-processed sub-carrier symbols to generate complex output symbols; andtransforming the complex output symbols to the intermediate-frequency OFDM signal,wherein the sub-carrier symbols are transformed so that the even and odd samples of the intermediate-frequency OFDM signal are given by real and imaginary parts of the complex output symbols.
Owner:IBM CORP
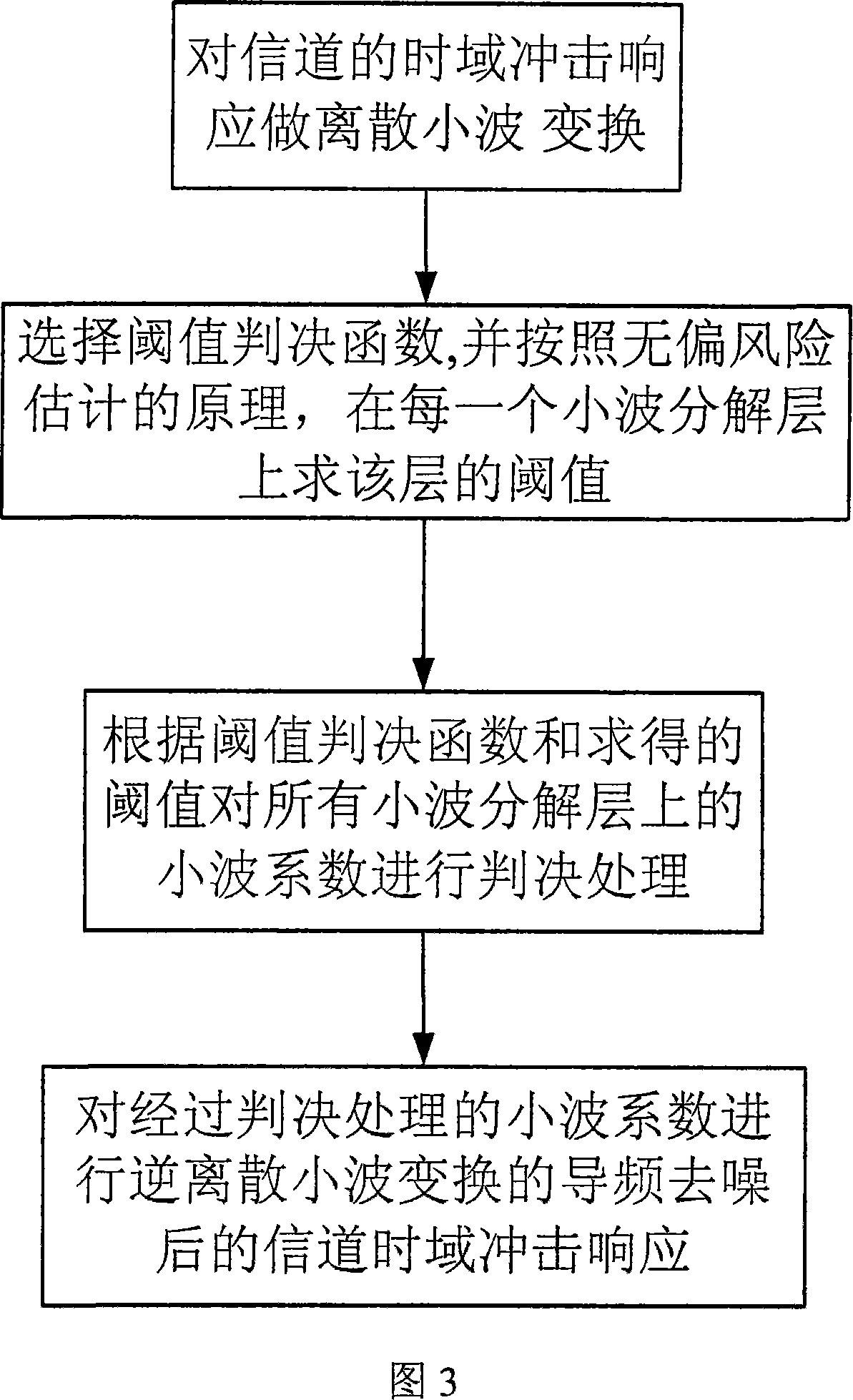
OFDM channel estimating method based on wavelet unbiased risk threshold value noise elimination
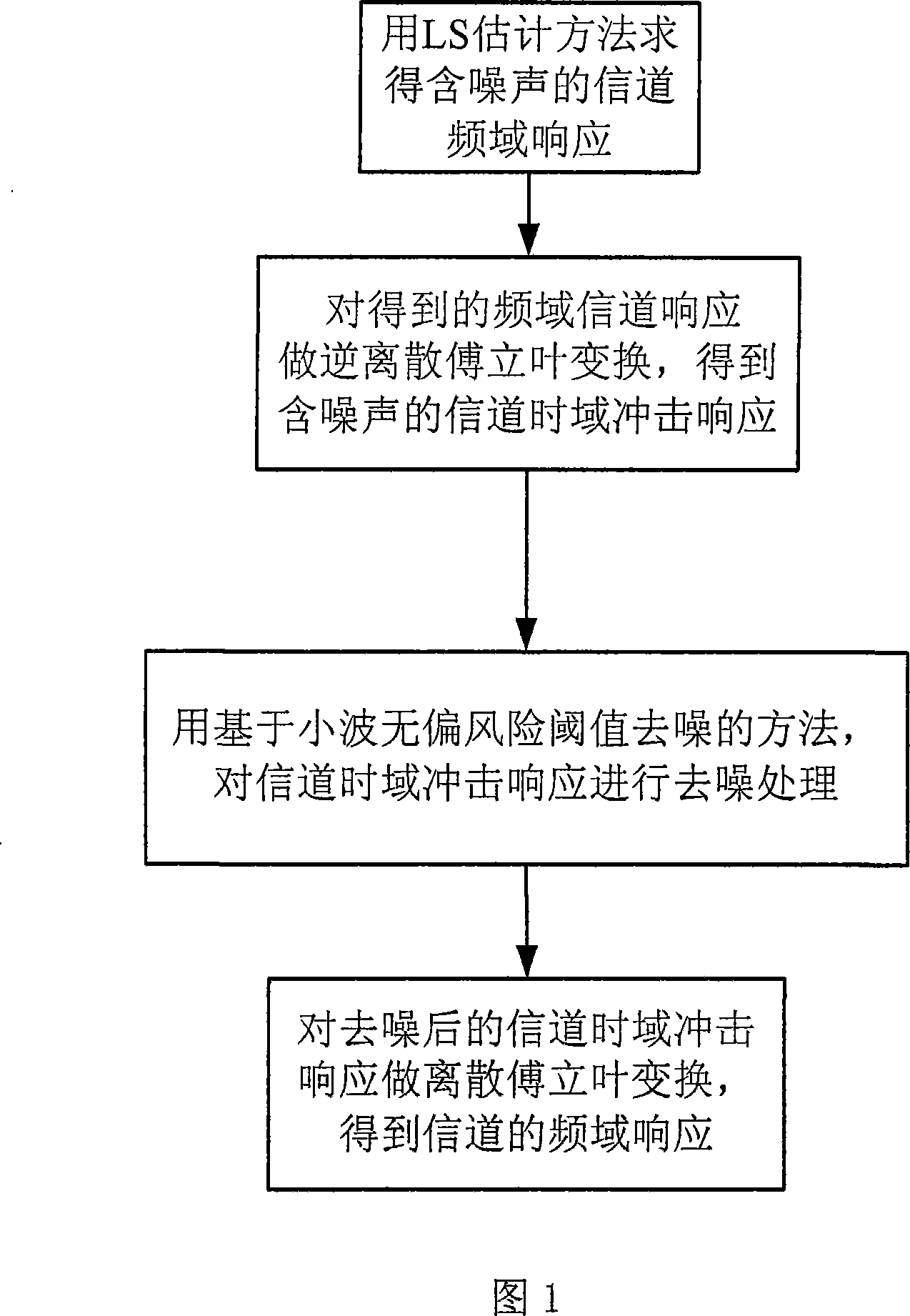
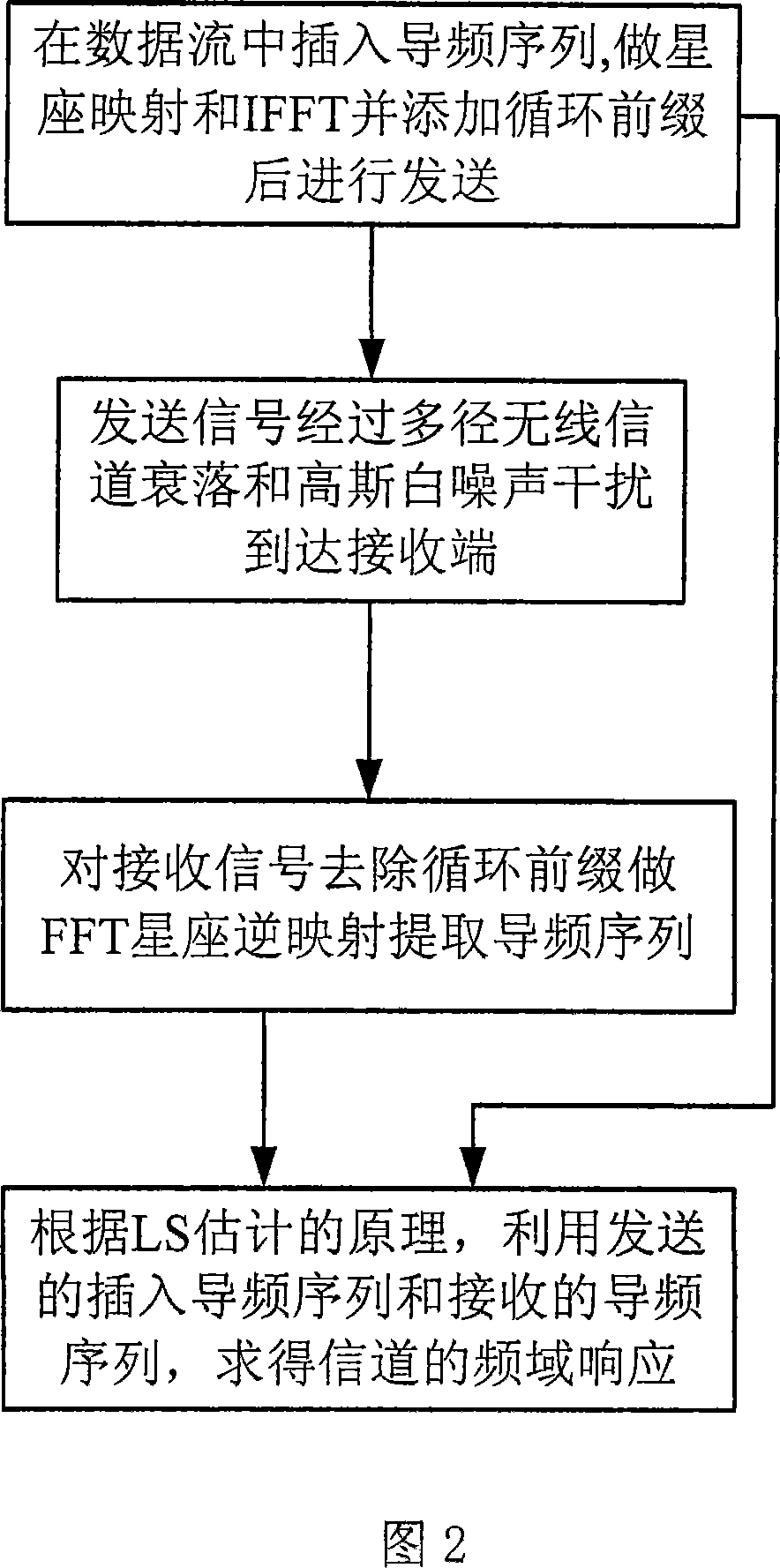
InactiveCN101227438AImprove estimation performanceImprove performanceBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsValue noiseFourier transform on finite groups
The invention discloses an OFDM channel estimation method for de-noising which is based on wavelet unbiased risk threshold value, which relates to the technical field of communication, the purpose of the invention is that the problem that an LS method is easy to be influenced by noise under the condition without channel information is effectively solved. The realizing process of the method comprises first, obtaining channel frequency response which contains noise according to the LS channel estimation method which is on the basis of an OFDM system which is based on pilot frequency, second, doing inverse discrete Fourier transform for the channel frequency response which is obtained and to get channel time-domain impulse response which contains noise, third, de-noising the channel time-domain impulse response the method for de-noising which is based on wavelet unbiased risk threshold value, and getting channel time-domain impulse response after de-noising, fourth, doing inverse discrete Fourier transform for the channel time-domain impulse response after de-noising, and getting frequency domain response of channel, and compensating the received signals by the channel time-domain impulse response after de-noising. The method can be used in OFDM channel estimation techniques under various multi-path channels.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
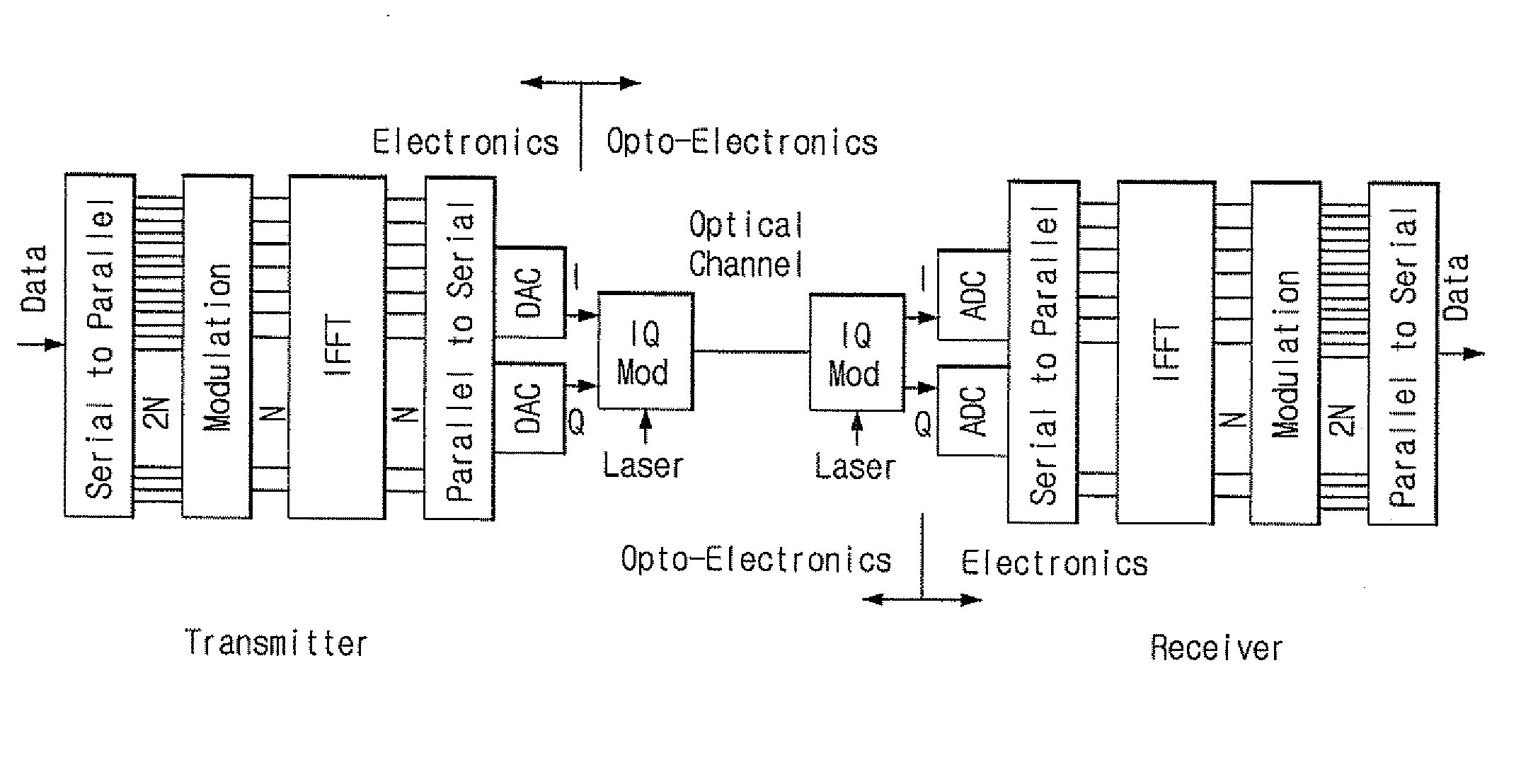
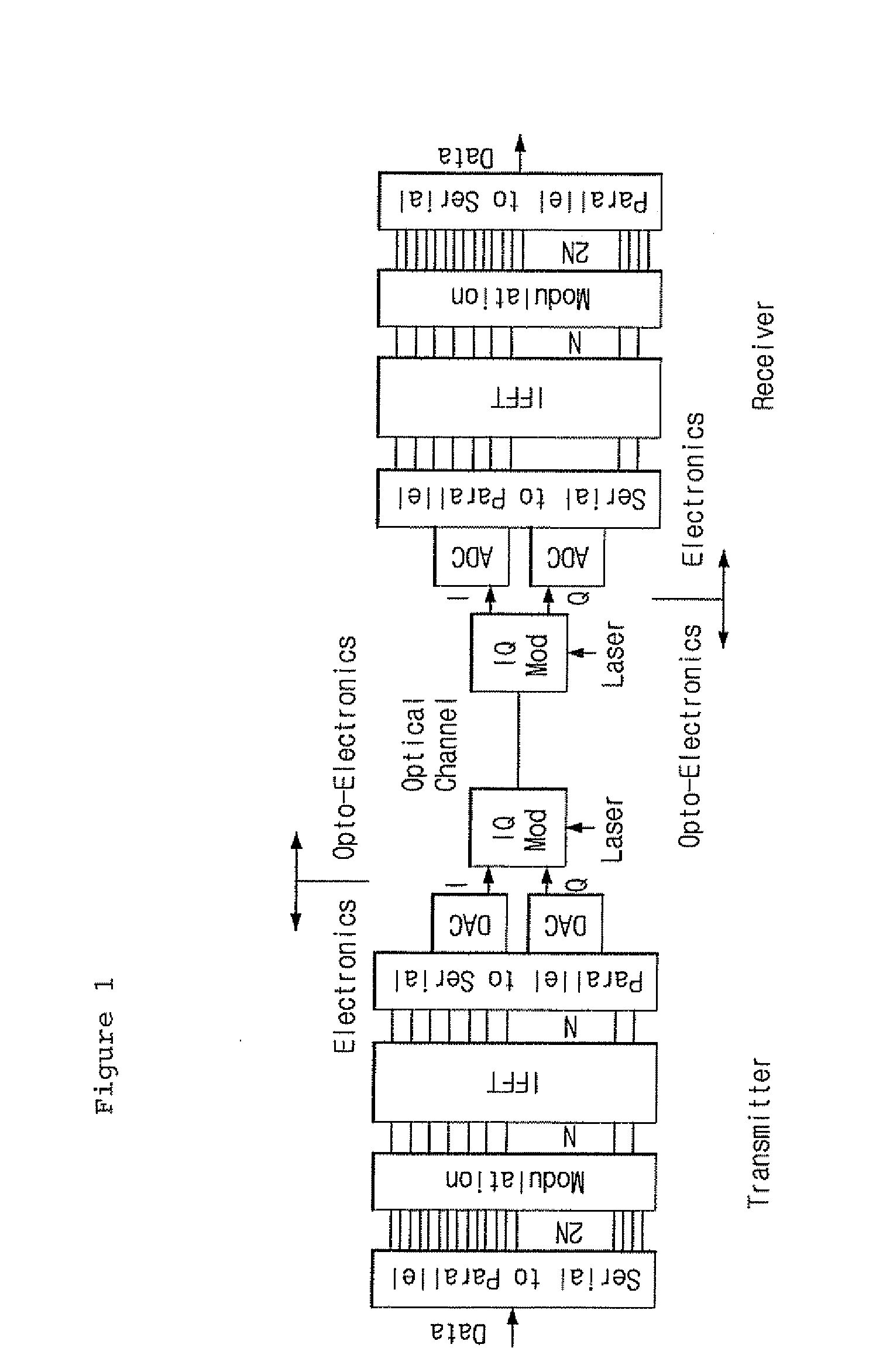
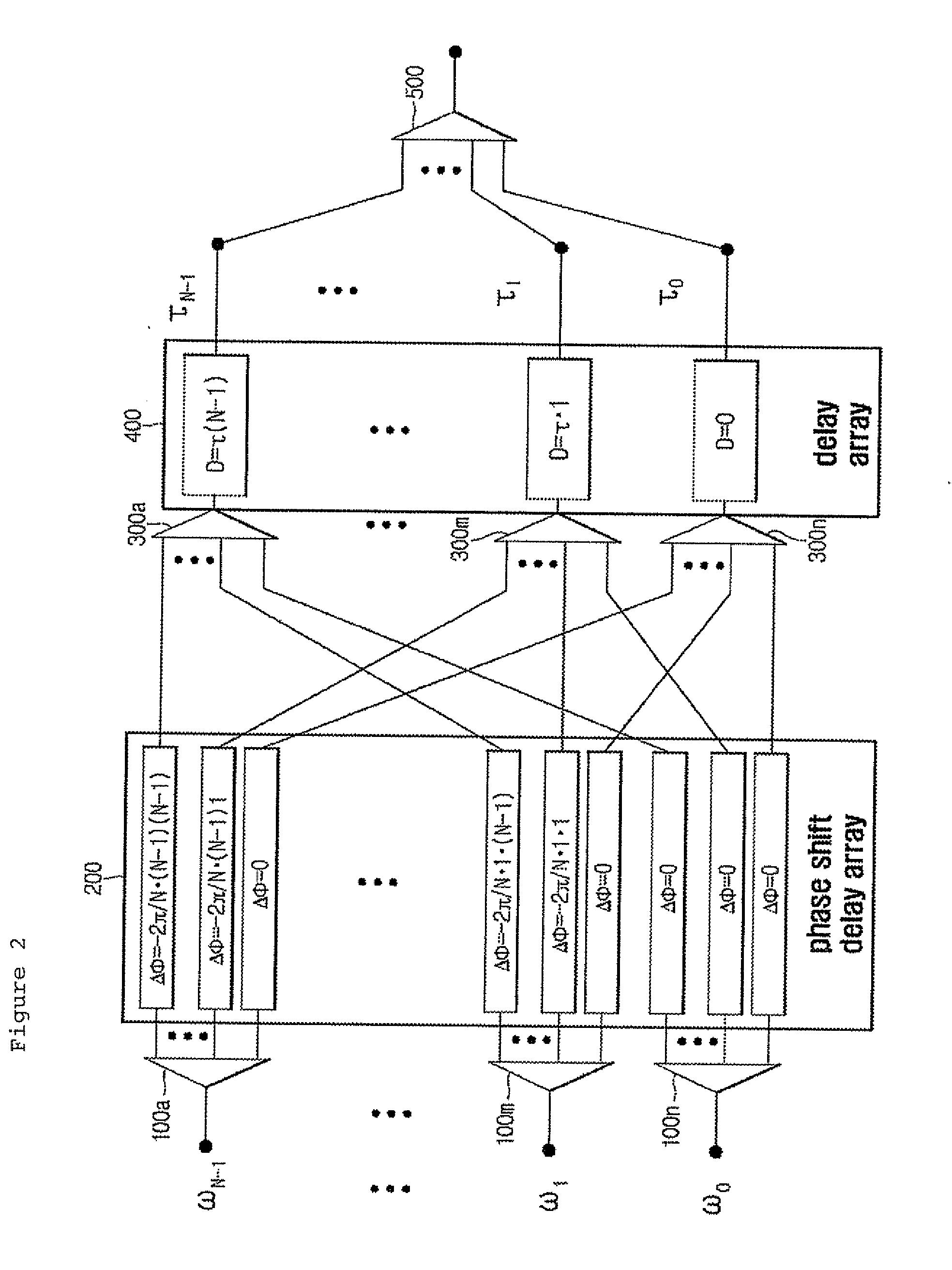
Forward Discrete/Inverse-Discrete Fourier Transform Device and Method for Optical OFDM Communication and Transmitting and Receiving Apparatus Comprising the Device
ActiveUS20090180778A1Modulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionPhase shiftedOptical frequencies
Disclosed are a forward discrete / inverse-discrete Fourier transform device and method for optical orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) communication and a transmitting and receiving apparatus.The forward inverse-discrete Fourier transform device includes N 1:N splitters for splitting subcarrier signals received from N inputs corresponding to the number of optical frequencies of subcarriers, a phase shift delay array module for shifting phases of the split signals from the 1:N splitters, N N:1 power couplers for coupling signals output from the phase shift delay array module, a time delay array module for performing time delay on optical OFDM symbols from the N:1 power couplers, and an N:1 power coupler for coupling signals output from the time delay array module.
Owner:ICU RES & INDAL COOPERATION GROUP
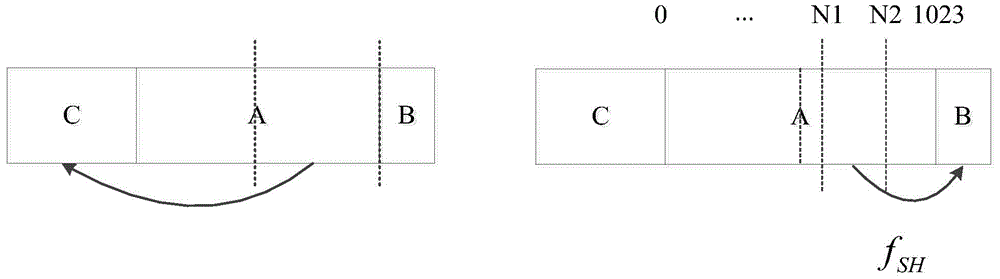
Fast calculation method and device of discrete Fourier transformation (DFT)/inverse discrete Fourier transform (IDFT)
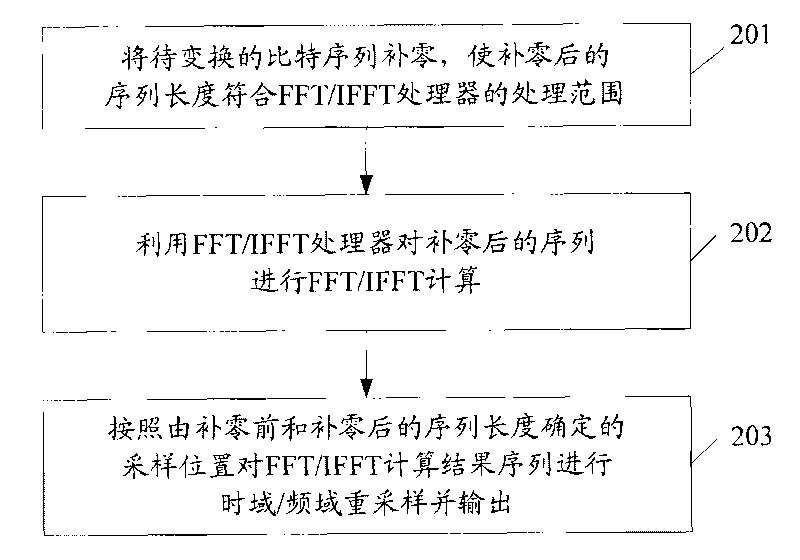
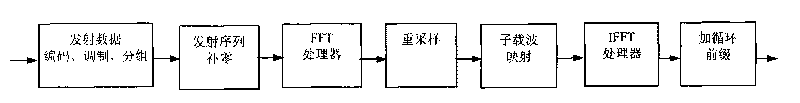
InactiveCN101751375ACalculation speedReduce computational complexityComplex mathematical operationsFinite fourier transformTime domain
The invention discloses a fast calculation method of discrete Fourier transformation (DFT) / inverse discrete Fourier transform (IDFT). The rapid calculation method comprises the following steps of: carrying out zero fill on a bit sequence to be transformed to enable the sequence length after the zero fill to accord with the processing range of a fast Fourier transform (FFT) / inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT) processor; carrying out FFT / IFFT calculation on the sequence after zero fill by utilizing the FFT / IFFT processor, and resampling time domain / frequency domain of an FFT / IFFT calculation result sequence according to a sampling position determined by the sequence lengths before and after the zero fill; and outputting the resampling result as a DFT / IDFT result sequence. The invention also discloses a fast calculation device of DFT / IDFT. By adopting the invention, the calculation complexity of DFT / IDFT can be reduced, and the calculation speed can be improved.
Owner:POTEVIO INFORMATION TECH
Discrete fourier transform (DFT) watermark
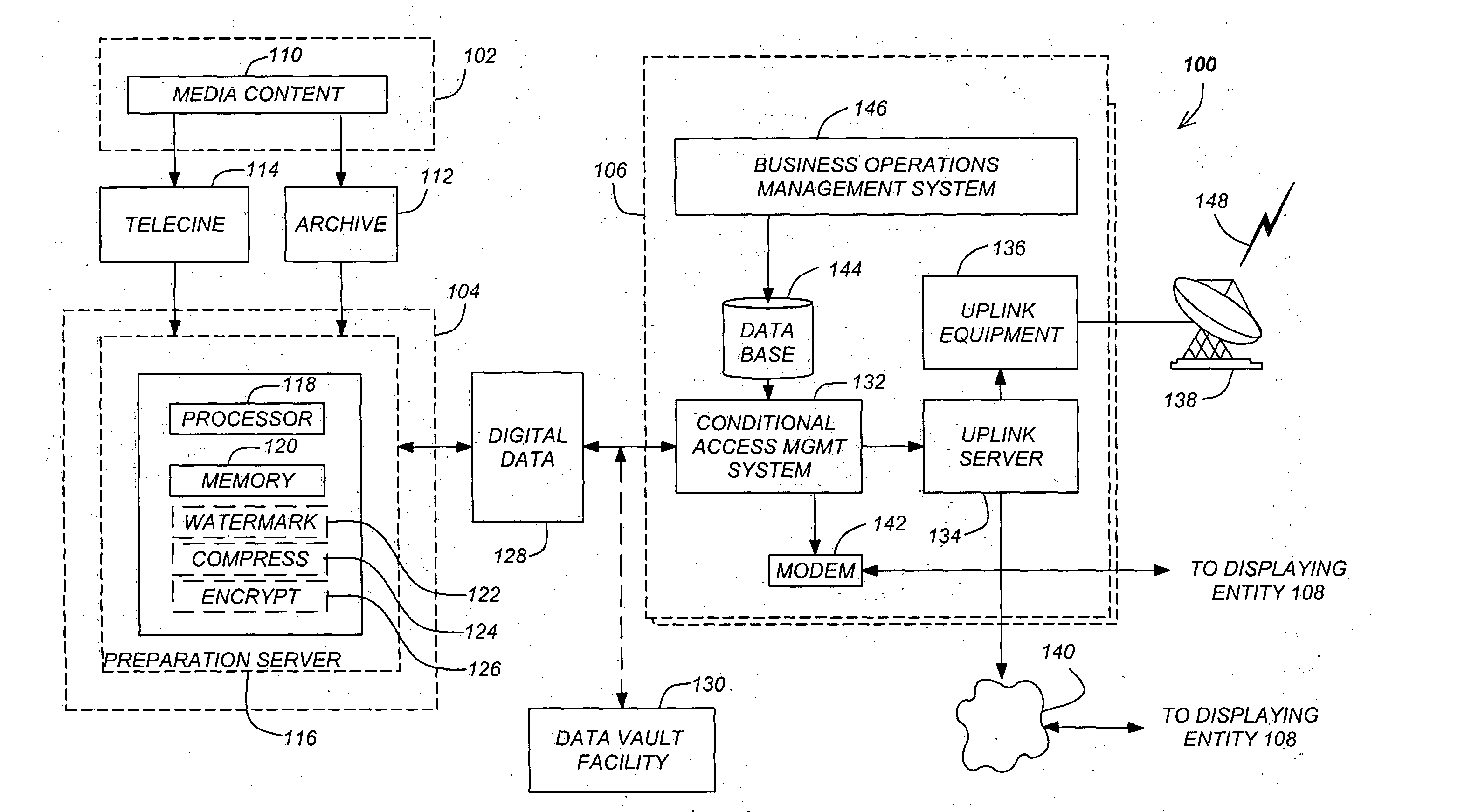
InactiveUS20050036613A1Analogue secracy/subscription systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital dataDigital video
A Discrete Fourier Transform watermark for use with digital images / video. A Y component of a Y, U(Cb), V(Cr) digital data stream representing color components of digital video is extracted as the digital data for embedding the watermark. The digital data is then scaled to a standard size. A Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) is performed on the digital data, and a magnitude domain of the Discrete Fourier Transform is computed. The watermark is embedded into selected frequency bands of the computed magnitude domain of the Discrete Fourier Transform, thereby creating a watermarked magnitude domain. The selected frequency bands comprise one or more middle frequency bands, and the middle frequency bands comprise a band of circular rings of the magnitude domain. An inverse Discrete Fourier Transform is performed on the watermarked magnitude domain to reconstruct the digital data with the embedded watermark.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
MIMO channel loopback
InactiveUS20110150049A1Signal allocationSecret communicationTransceiverInverse discrete fourier transform
A method and apparatus for efficiently providing a large volume of channel feedback, e.g., for OFDM MISO and MIMO systems, is described herein. To that end, a mapping unit in an OFDM transceiver maps channel feedback values, e.g., received reference signal values or channel estimates derived therefrom, on a one-to-one basis to individual transmission subchannels. More particularly, the mapping unit maps a feedback value, e.g., the received reference value or a channel estimate derived therefrom, to a single transmission subchannel of an outgoing OFDM signal. For example, the mapping unit may map the feedback value to an input of a frequency transform unit, such as an inverse discrete Fourier transform unit, to map the feedback value to a single transmission subchannel comprising an OFDM transmission subcarrier. The OFDM transceiver transmits the outgoing OFDM signal to the remote transceiver to provide the feedback value to the remote transceiver.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Constant envelope orthogonal frequency division multiplexing modulation method
ActiveCN103297373AEasy to useMeet high-speed processing needsMulti-frequency code systemsBroadband transmissionTransmitted power
The invention provides a constant envelope orthogonal frequency division multiplexing modulation method which is based on sine / cosine mapping and which is applied in the field of broadband wireless communication. During signal modulation, the method includes performing inverse discrete Fourier transform (IDFT) for a group of complex signals; arraying transformed data to be two groups of sequences of real numbers and performing linear amplitude-limited mapping; after being subjected to linear amplitude limiting, mapping sequences of the real numbers into sine or cosine values of unit circle signals, and allowing a signal receiving end to recover to send messages through linear calculation of two groups of discrete Fourier transform (DFT). During signal demodulation, the method includes performing two groups of discrete Fourier transform, combining two groups of data processed through discrete Fourier transform, and obtaining complex signals for bit demodulation. According to the constant envelope orthogonal frequency division multiplexing modulation method, transmitting power of an amplifier can be utilized completely against frequency selective fading influence of broadband transmission channels, and the problem of the need to reduce system complexity in broadband communication is solved.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
CHIRP-OFDM system frequency domain diversity receiving method
InactiveCN102664687AInhibition effectEfficient use ofMulti-frequency code systemsFrequency spectrumFourier transform on finite groups
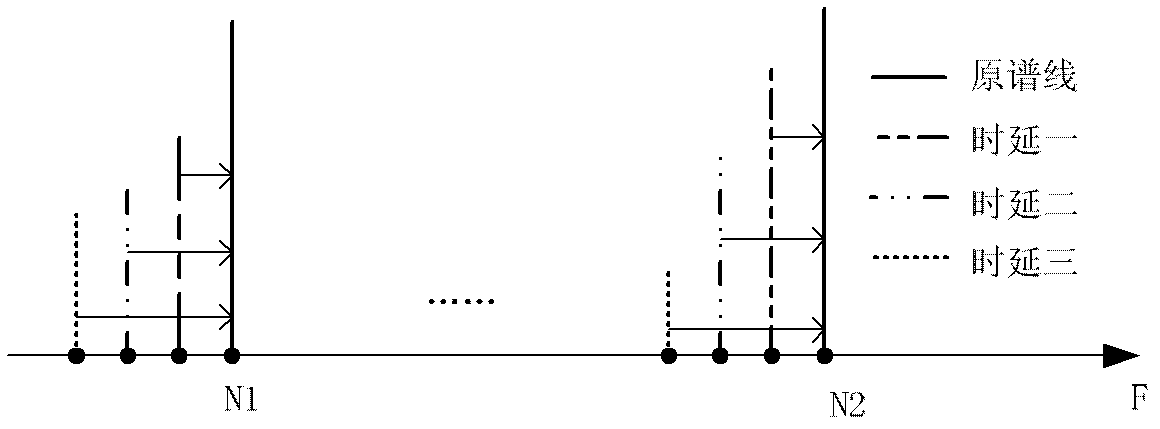
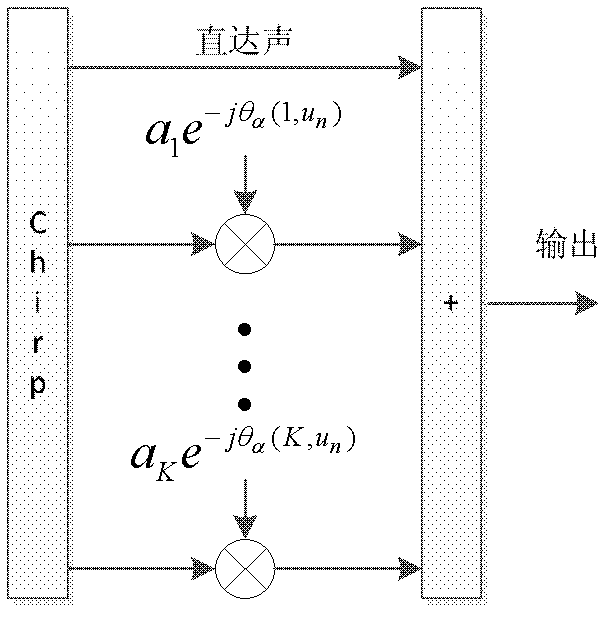
The invention discloses a CHIRP-OFDM (orthogonal frequency division multiplexing) system frequency domain diversity receiving method which comprises the following steps; at an emitting end, modulating data after serial-parallel conversion to a frequency spectrum, carrying out inverse discrete Fourier transform so as to obtain a group of time domain signals, carrying out spread spectrum modulation on the time domain signals by taking chirp signals as carrier waves, and determining a frequency modulation slope; at a receiving end, removing cyclic prefixes of received serial signals, carrying out despread modulation on the signals, and conjugating the frequency modulation slope and the emitting end in a same way of taking determined chirp signals as carrier waves; carrying out the inverse discrete Fourier transform to obtain a frequency domain frequency spectrum, carrying out phase compensation on each spectrum line of multi-path signals, and overlying with each direct signal spectrum line, so as to enable all spectrum lines to be added in a same-phase way, and realize diversity reception and further recover signal sending; and carrying out digital demodulation so as to obtain data output. The method can effectively overcome frequency selective fading in channels and improves the system performance.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
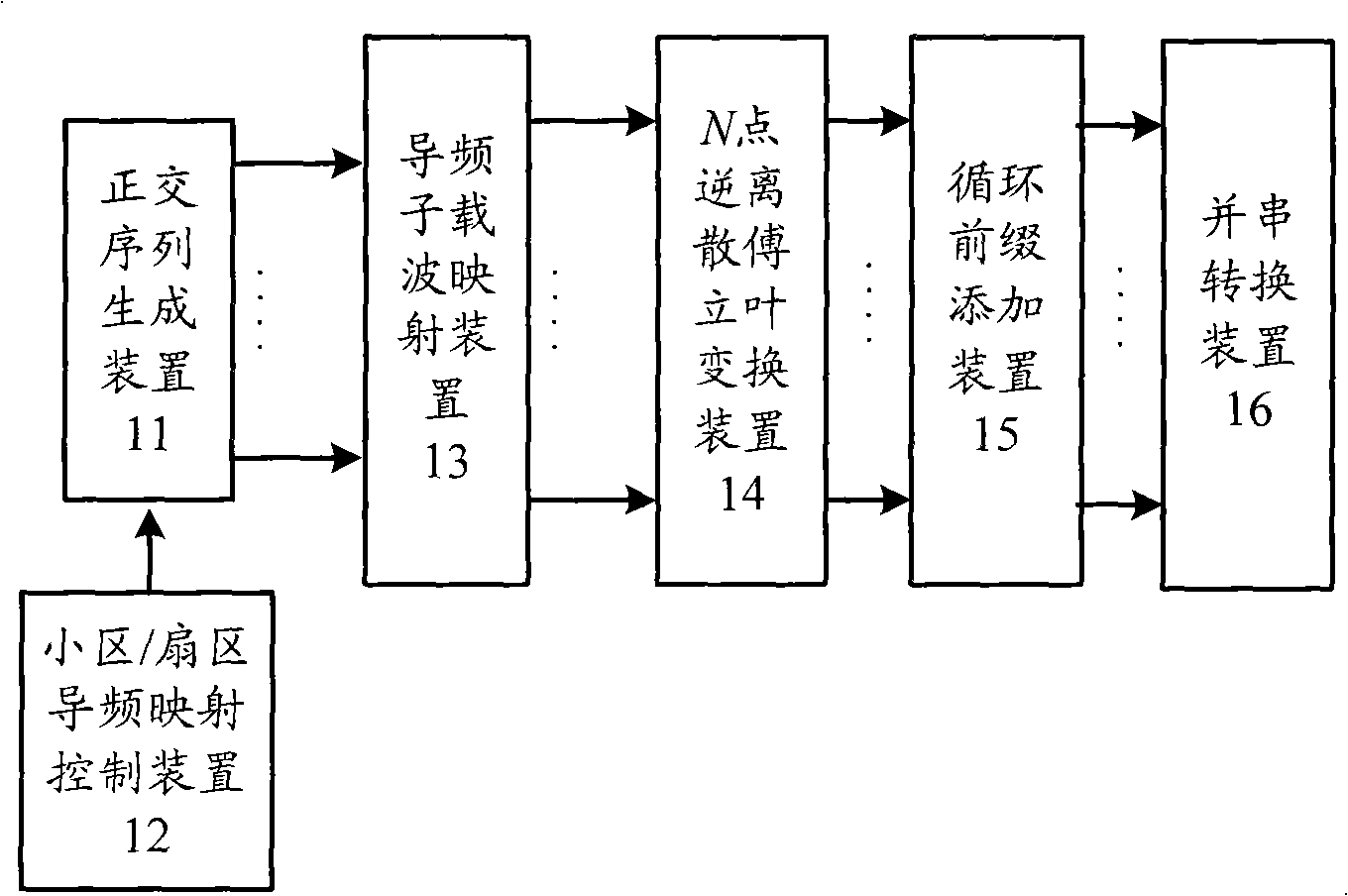
Pilot frequency design method and transmitting/receiving device for idem frequency interference suppression of OFDM system
InactiveCN101304397AReduce the influence of the carrierImprove estimation performanceMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainPhase shifted
The invention provides a pilot design method and a trans-receiving device for preventing the co-frequency interference suppression of an OFDM (orthogonal frequency division multiplexing) system. The different subdistricts adopt pilot sequences generated by different basic orthogonal sequences, and different sectors respectively adopt the pilot sequences obtained by the same basic orthogonal sequence by different phase shifts in the same subdistrict; an emission end sequentially inserts the generated pilot sequences into pilot positions which are distributed bi-dimensionally and discretely with time frequency according to serial numbers of sub-carrier frequency domains to transmit; a receiving terminal firstly carries out relative treatment of the received frequency domain pilot signals and the local orthogonal pilot sequences and then eliminates the co-frequency interferences at time domains by making use of the shift orthogonal performance between the pilots after going through the IDFT (Inverse Discrete Fourier Transform). The device can effectively prevent the affects of pilots on the co-frequency interferences and can improve the channel estimation performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES CENT FOR WIRELESS TECH
Method for eliminating phase noise using continuous transmission parameter signalling
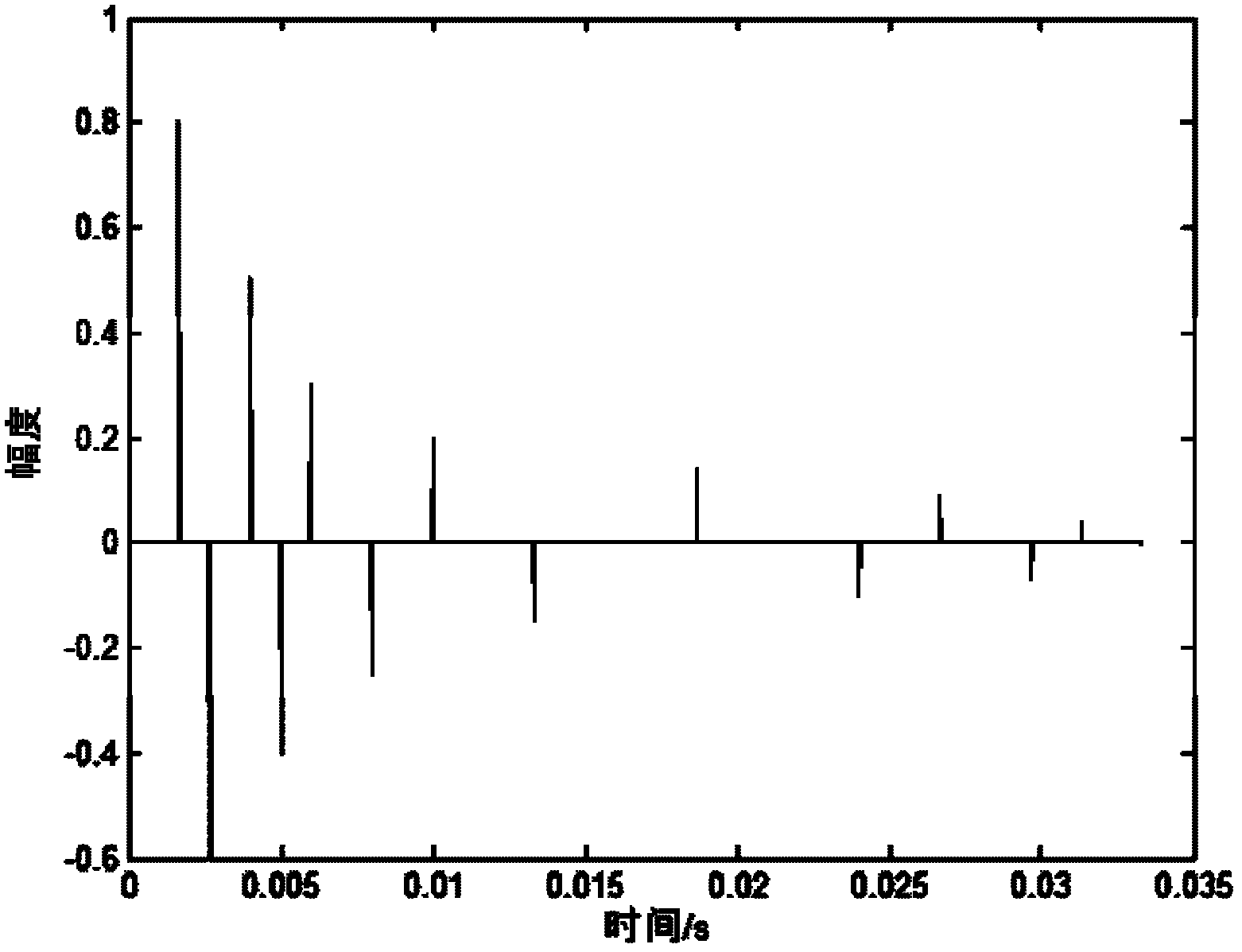
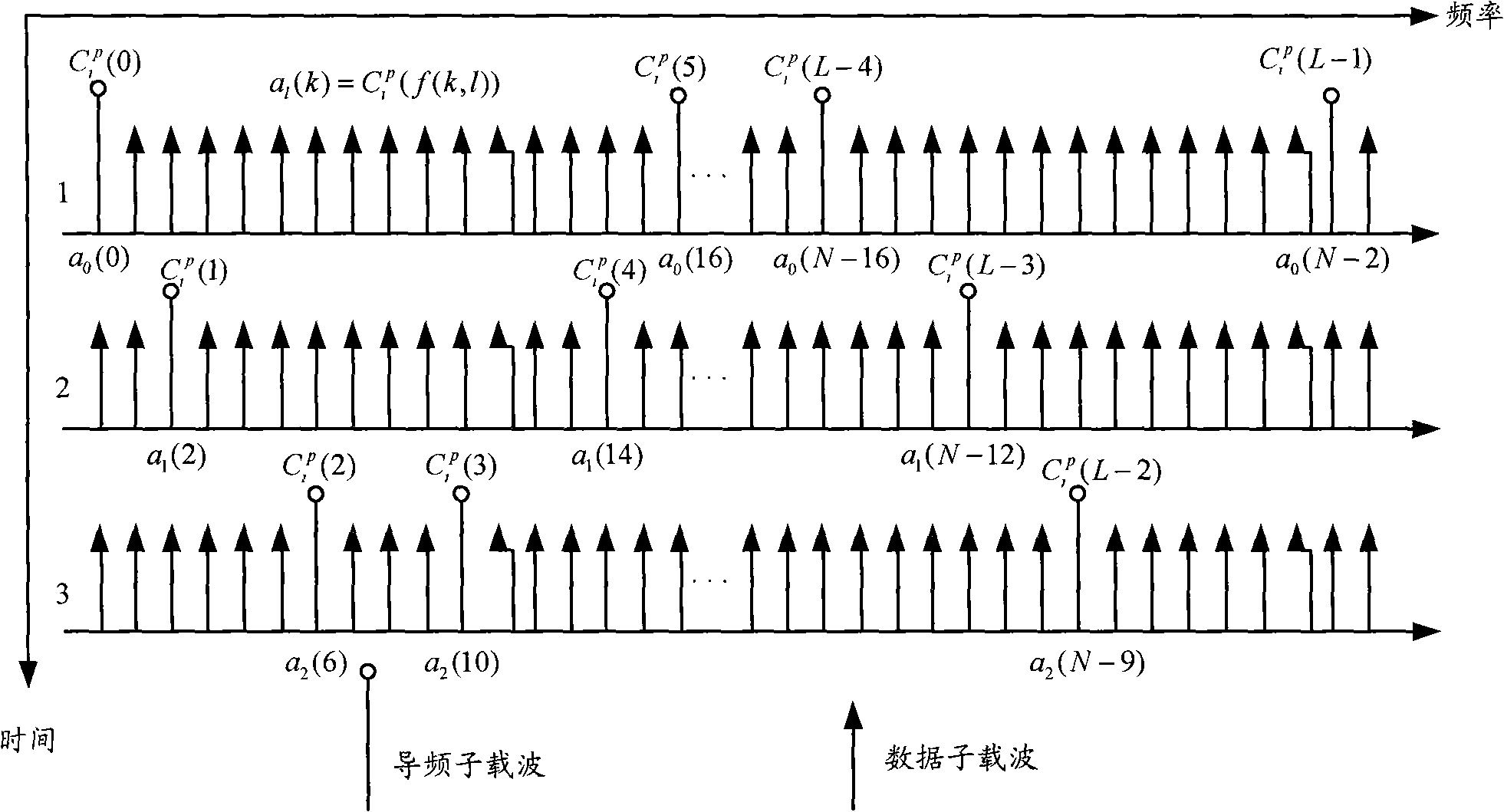
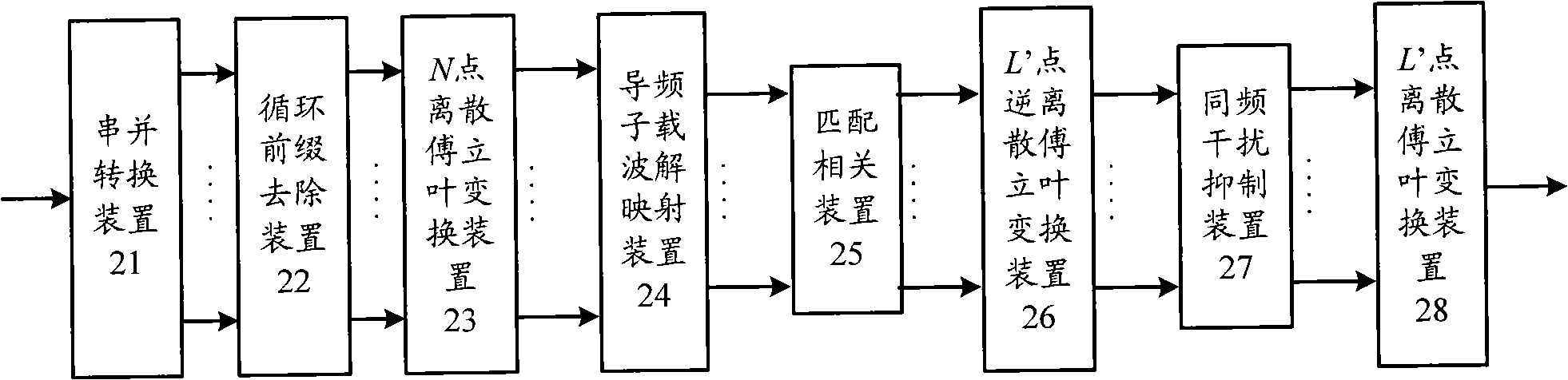
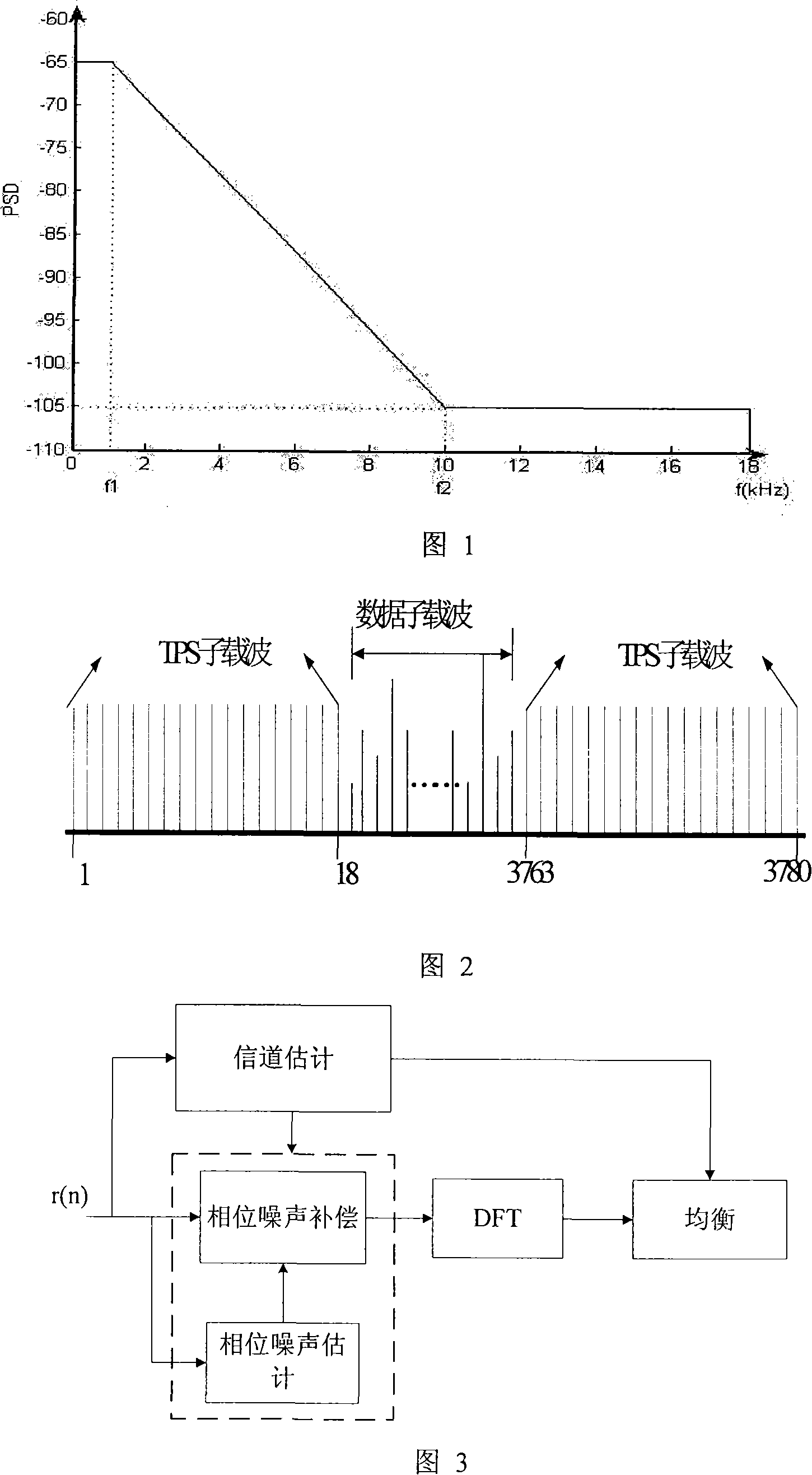
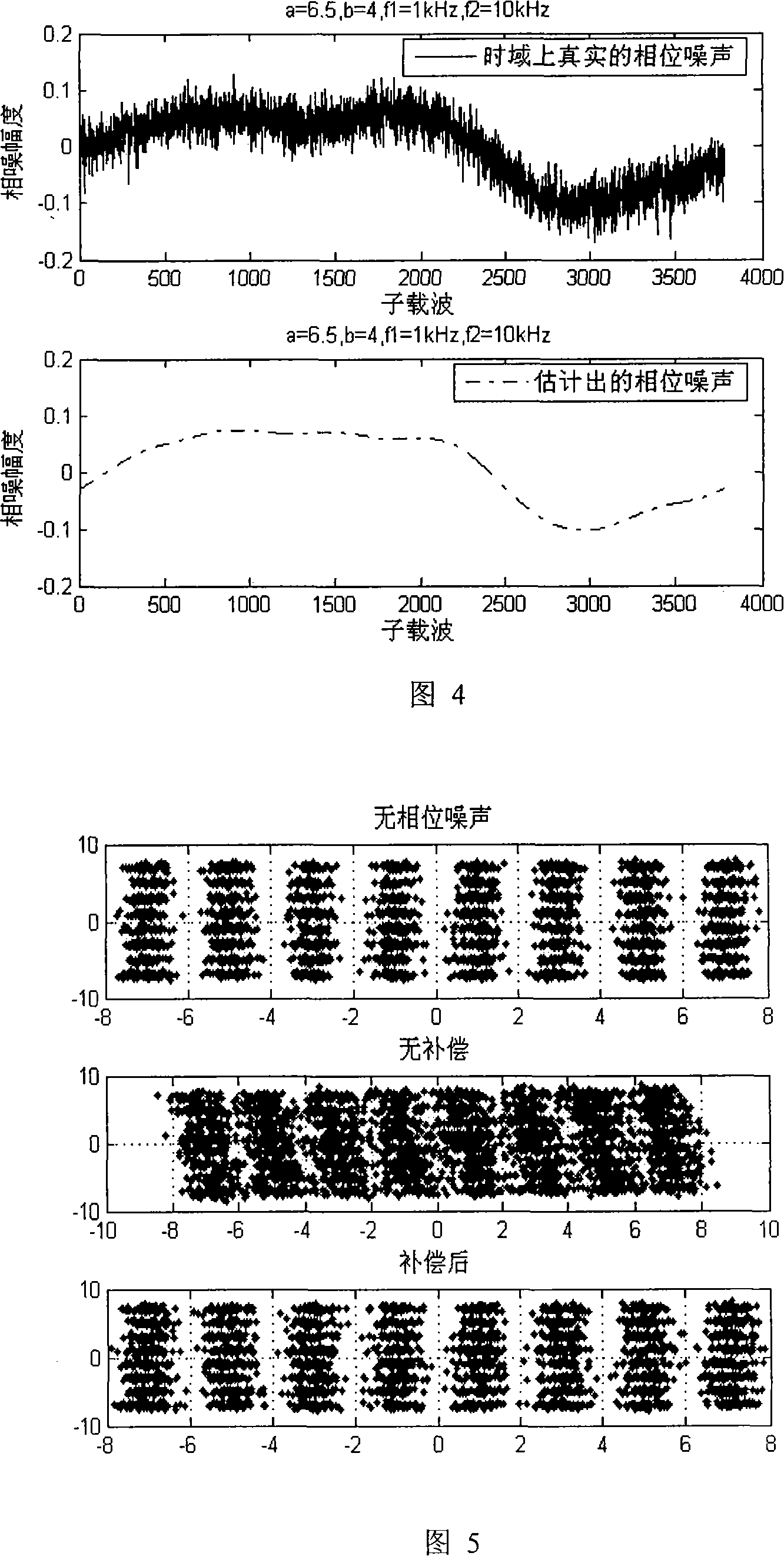
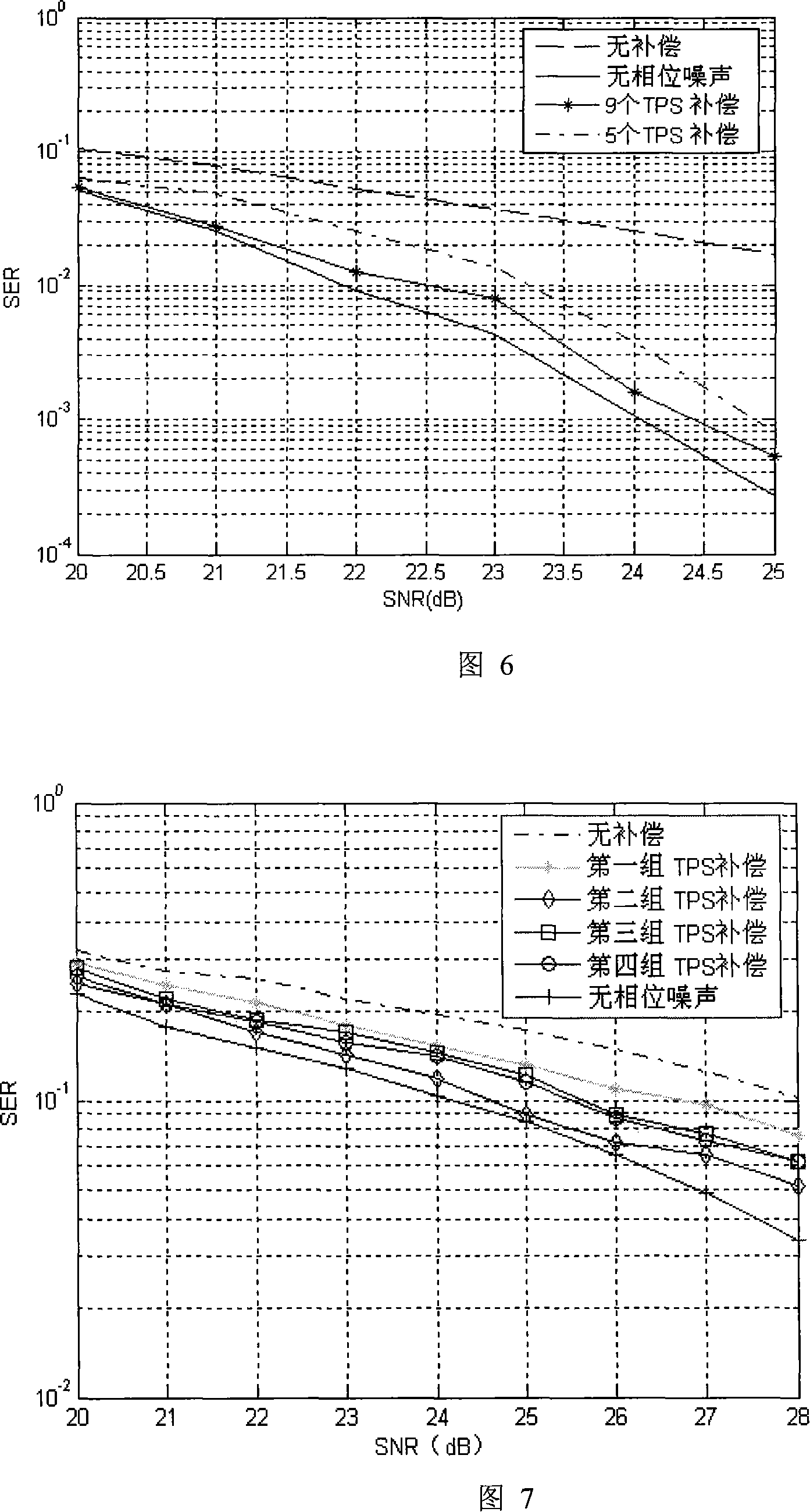
InactiveCN101136731ALittle overheadLow costSignal channelsPhase noiseFourier transform on finite groups
Using a set of consecutive transmission parameter signaling (TPS), the method eliminates phase noise in national standard system about digital TV ground transmission. The method includes steps: estimating phase noise for received TPS sub carrier; solving a set of equation and inverse discrete Fourier transform (IDFT) to obtain estimation of phase noise in time domain; using the estimation of phase noise in time domain to carry out phase compensation for corresponding data not done discrete Fourier transform (DFT); through DFT, the compensated signals are converted to frequency domain, and using equilibrium process to obtain needed result. Theoretical analysis and simulation result shows that the method based on TPS to estimate phase noise can raise performance of symbol error rate (SER) markedly under additivity white Gaussian noise (AWGN) and under multipath channels.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
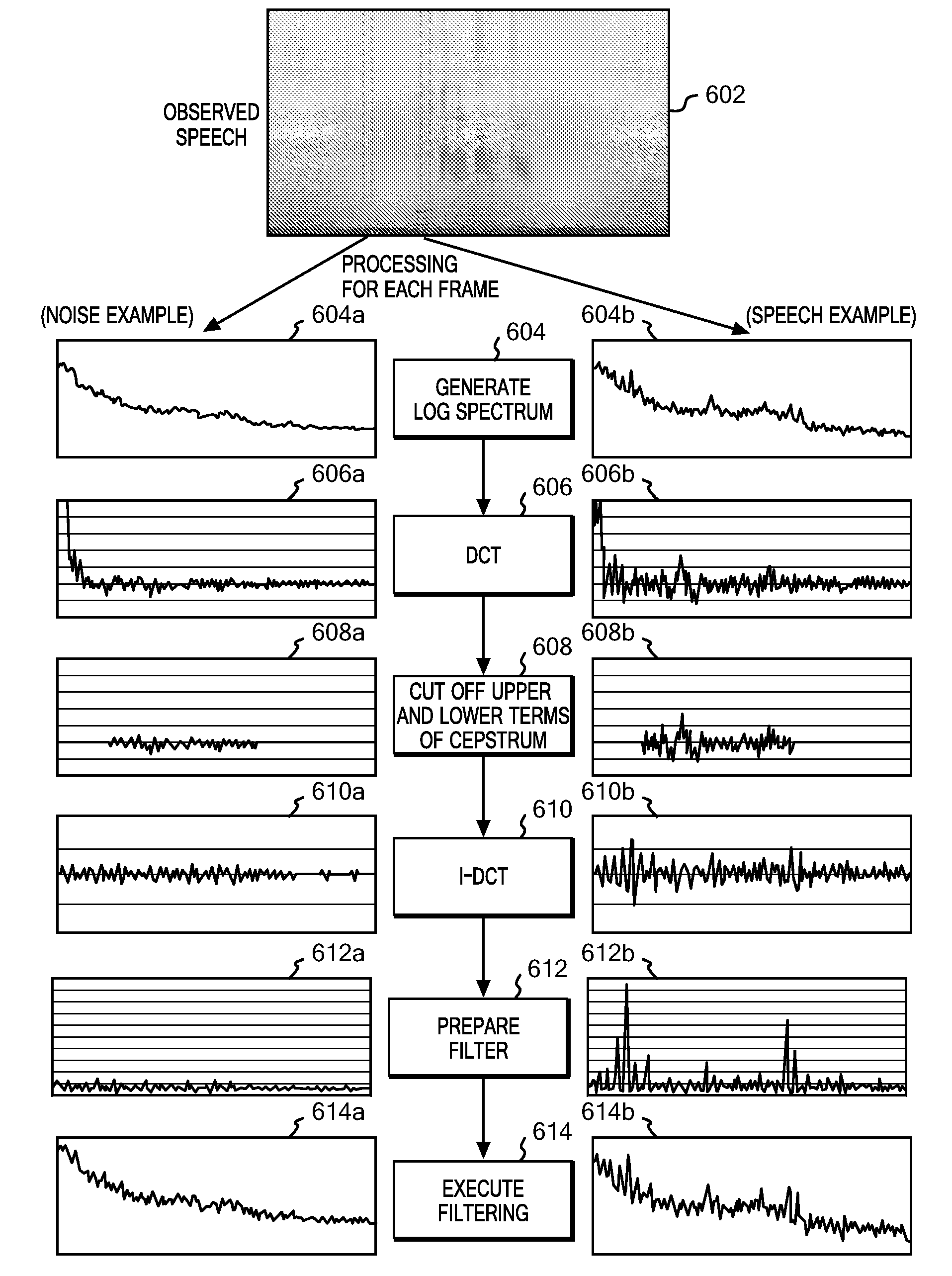
System, method and program for speech processing
The present invention relates to a system, method and program for speech recognition. In an embodiment of the invention a method for processing a speech signal consists of receiving a power spectrum of a speech signal and generating a log power spectrum signal of the power spectrum. The method further consists of performing discrete cosine transformation on the log power spectrum signal and cutting off cepstrum upper and lower terms of the discrete cosine transformed signal. The method further consists of performing inverse discrete cosine transformation on the signal from which the cepstrum upper and lower terms are cut off. The method further consists of converting the inverse discrete cosine transformed signal so as to bring the signal back to a power spectrum domain and filtering the power spectrum of the speech signal by using, as a filter, the signal which is brought back to the power spectrum domain.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for transmitting and receiving data in a multi-carrier system
InactiveUS20090041092A1Eliminate the problemTransmission path divisionInter user/terminal allocationCommunications systemInverse discrete fourier transform
A method of transmitting data in a multi-carrier communication system is disclosed. More specifically, the method includes mapping at least one data symbol to at least one subcarrier of a first frequency domain and at least one data symbol to at least one subcarrier of a second frequency domain, wherein the first frequency domain and the second frequency domain are mutually exclusive and the at least one data symbol mapped to the at least one subcarrier of the second frequency domain is multiplied by a spreading code, transforming the at least one data symbol mapped to the first frequency domain and the at least one data symbol mapped to the second frequency domain by an inverse discrete Fourier transform (IDFT) module, and transmitting the transformed data symbols to a receiving end.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC +1
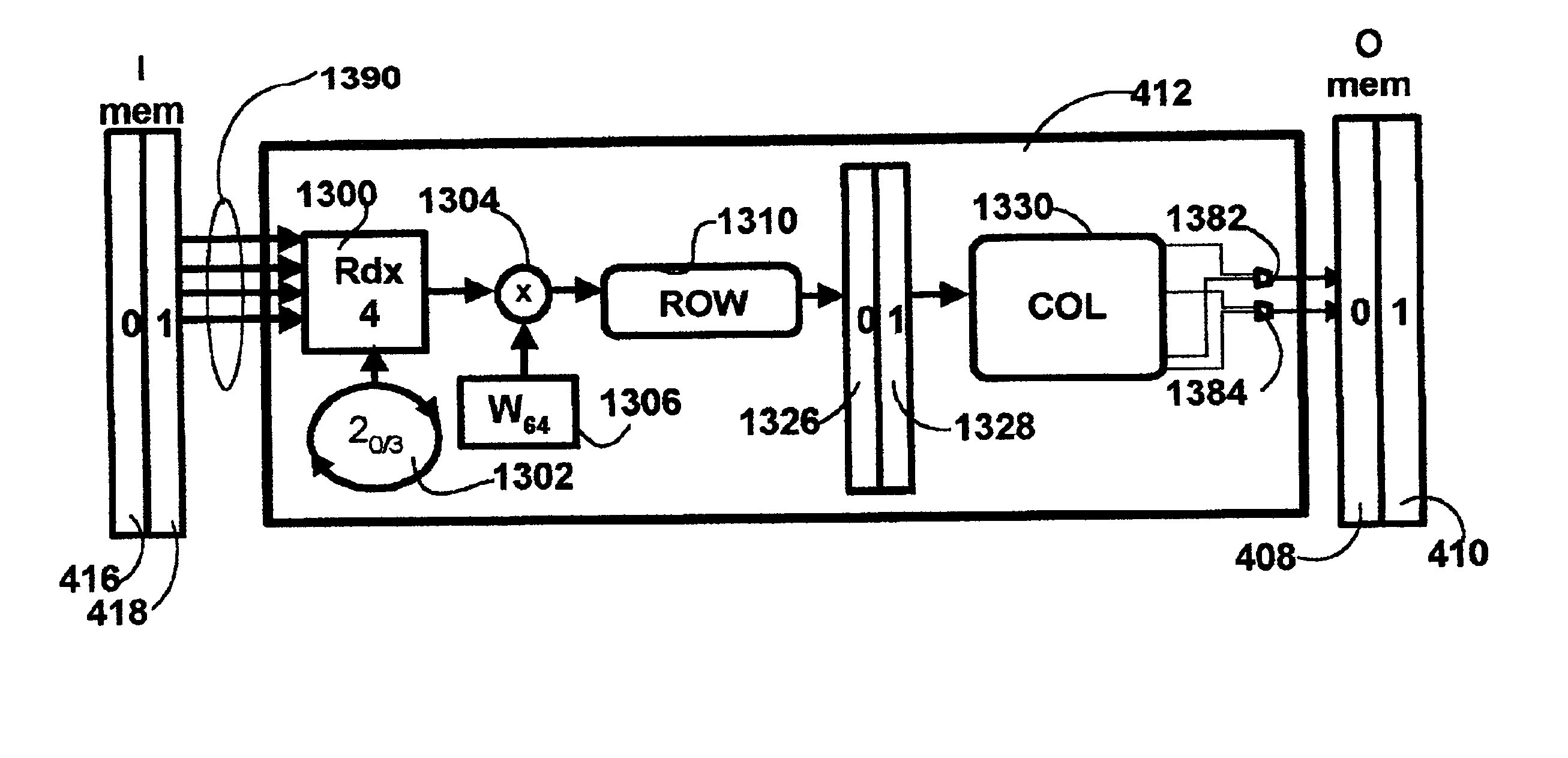
Method and apparatus for a DFT/IDFT engine supporting multiple X-DSL protocols
InactiveUS7028063B1Modulated-carrier systemsDigital computer detailsTime domainInverse discrete fourier transform
A Fourier transform processor utilizing discrete circuits each of which is configurable for processing a wide range of sample sizes. A single pipeline supports multiplexed bi-directional transformations between for example the time and frequency domains. In an embodiment of the invention the Fourier Transform processor may be implemented as part of a digital signal processor (DSP). In this embodiment the DSP may implement both the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) and inverse discrete Fourier transform (IDFT) across a wide range of sample sizes and X-DSL protocols. Multiple channels, each with varying ones of the X-DSL protocols can be handled in the same session.
Owner:IKANOS COMMUNICATIONS
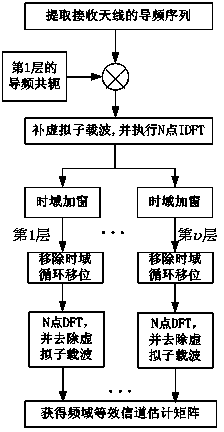
Upstream channel estimation method and upstream channel estimation system suitable for LTE (Long Term Evolution)-Advanced system
InactiveCN103825850AImprove accuracyImprove processing efficiencyBaseband system detailsTime domainTransport layer
The invention relates to an upstream channel estimation method and an upstream channel estimation system suitable for an LTE (Long Term Evolution)-Advanced system. The upstream channel estimation method comprises the steps of extracting pilot frequency subcarrier information on a receiving antenna, and carrying out conjugate multiplying on the pilot frequency subcarrier information and a local pilot frequency of a first layer to obtain a frequency domain channel coefficient of all transport layers subjected to aliasing; according to the length of a subcarrier, adding a virtual subcarrier with a corresponding length at the tail of a primary channel coefficient; carrying out IDFT (Inverse Discrete Fourier Transform) calculation, and transforming to a time domain; adding a window in the time domain, because dislocation of a time domain impulse response of each transport layer occurs on the time domain, separating time domain impulse responses of different transport layers, and carrying out time domain cyclic shift to obtain a time domain impulse response corresponding to each transport layer; and carrying out DFT (Discrete Fourier Transformation) calculation on the time domain impulse response of each transport layer, transforming to the frequency domain, and removing the virtual subcarrier at the tail to obtain a frequency domain equivalent channel estimation matrix of each transport layer corresponding to the receiving antenna. With the adoption of the upstream channel estimation method and the upstream channel estimation system, the channel estimation problem after MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) is introduced into the LTE-A upstream can be effectively solved, and the channel estimation accuracy is also improved; and the method is also suitable for an LTE system.
Owner:WUHAN POST & TELECOMM RES INST CO LTD
Three-dimensional orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing data modulation method and data demodulation method
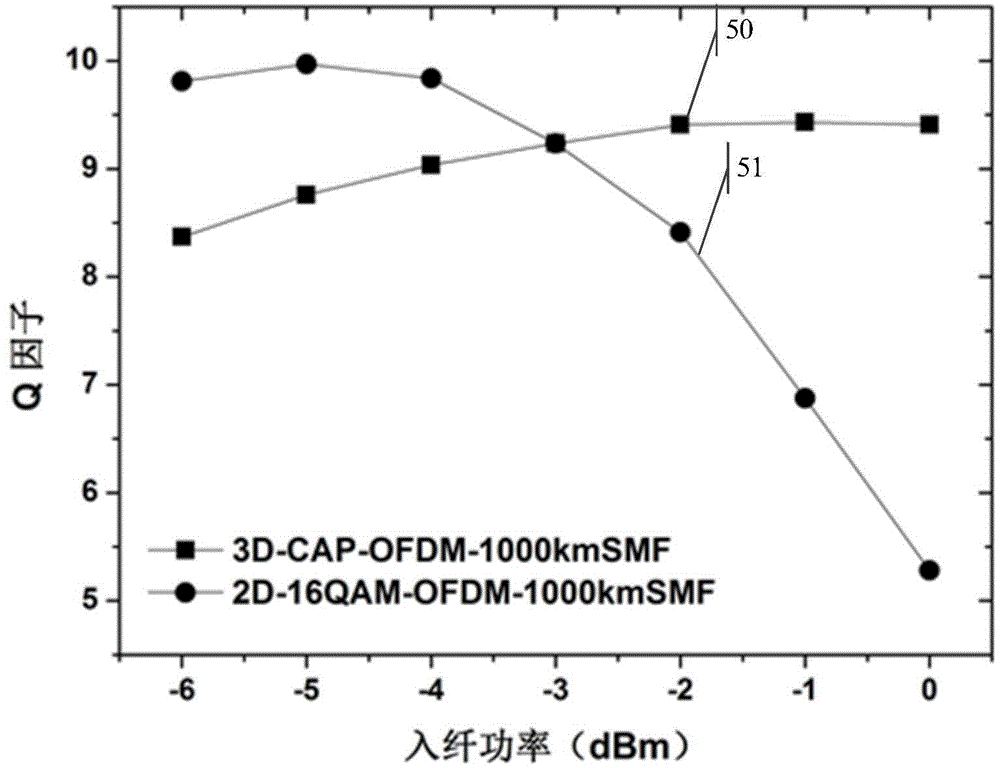
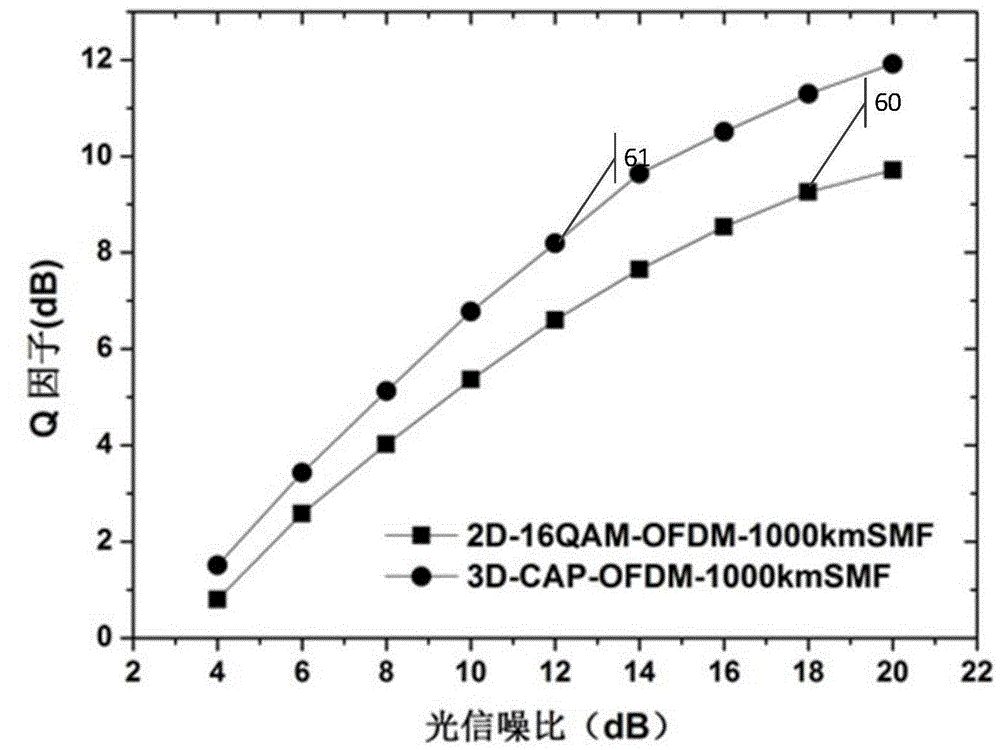
ActiveCN104639254ASave time and efficiencyTime and efficiency are not affectedMulti-frequency code systemsElectromagnetic transmissionConstellationVIT signals
The invention relates to the field of optical fiber communication, discloses a three-dimensional orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing data modulation method and a data demodulation method, and aims to solve the technical problem of incapability of lowering signal PAPR (Peak to Average Power Ratio) under the condition of not influencing other performances of a system in the prior art. The method comprises the following specific steps: performing three-dimensional data constellation points mapping on a bit sequence to be transmitted to obtain an orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) signal based on three-dimensional mapping; performing three-path overlapping on the real parts and imaginary parts of a plurality of time domain signals obtained after performing three-dimensional inverse discrete Fourier transform (3D-IDFT) on a three-dimensional OFDM symbol respectively through a three-dimensional CAP orthogonal filter, and combining to obtain final transmission time domain data; acquiring data to be transmitted through the time domain signal of a 3D-CAP-OFDM system and transmitting the data to be transmitted. By adopting the methods, the technical effect of effectively lowering the signal PAPR under the condition of no influencing the other performance of the communication system is achieved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com