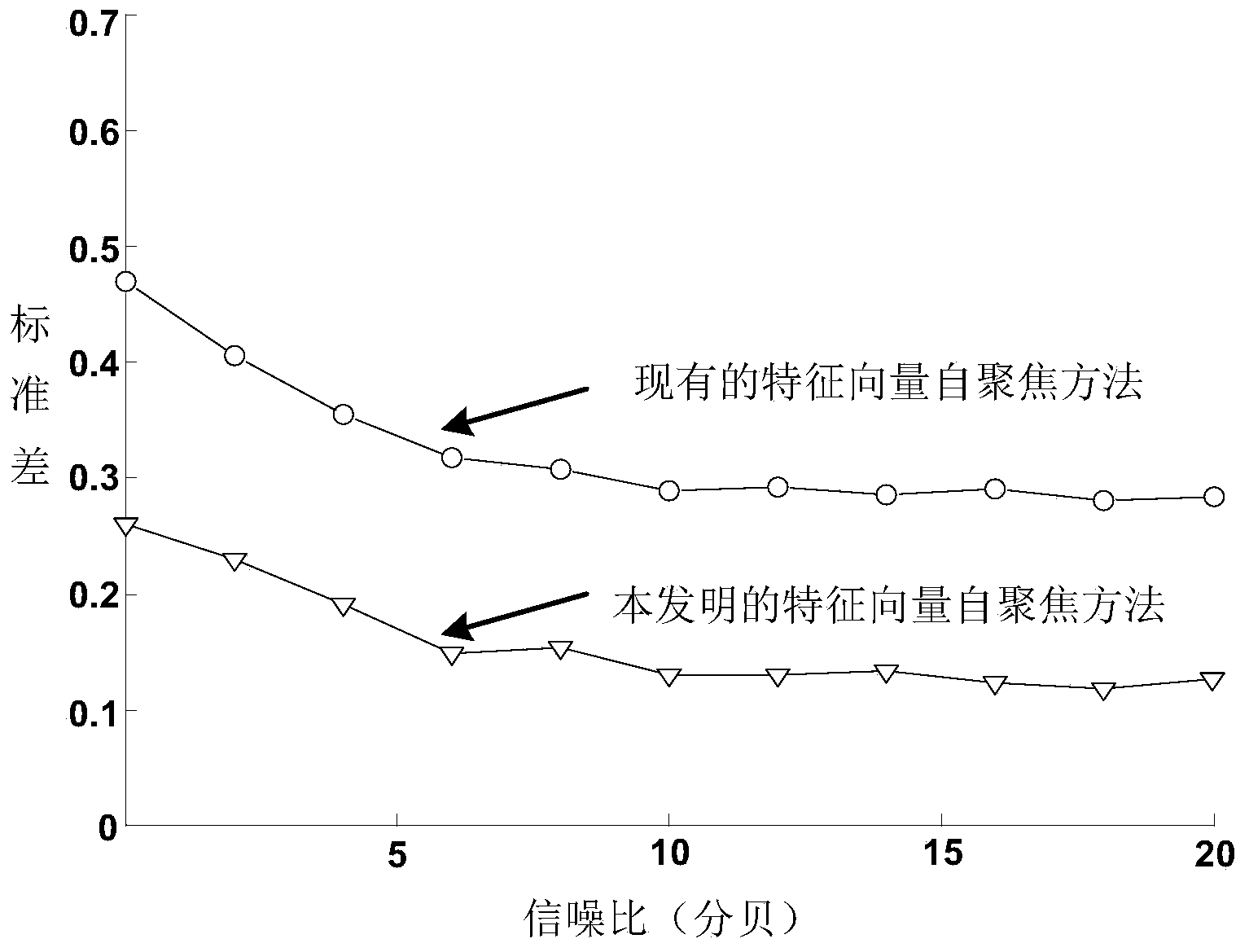
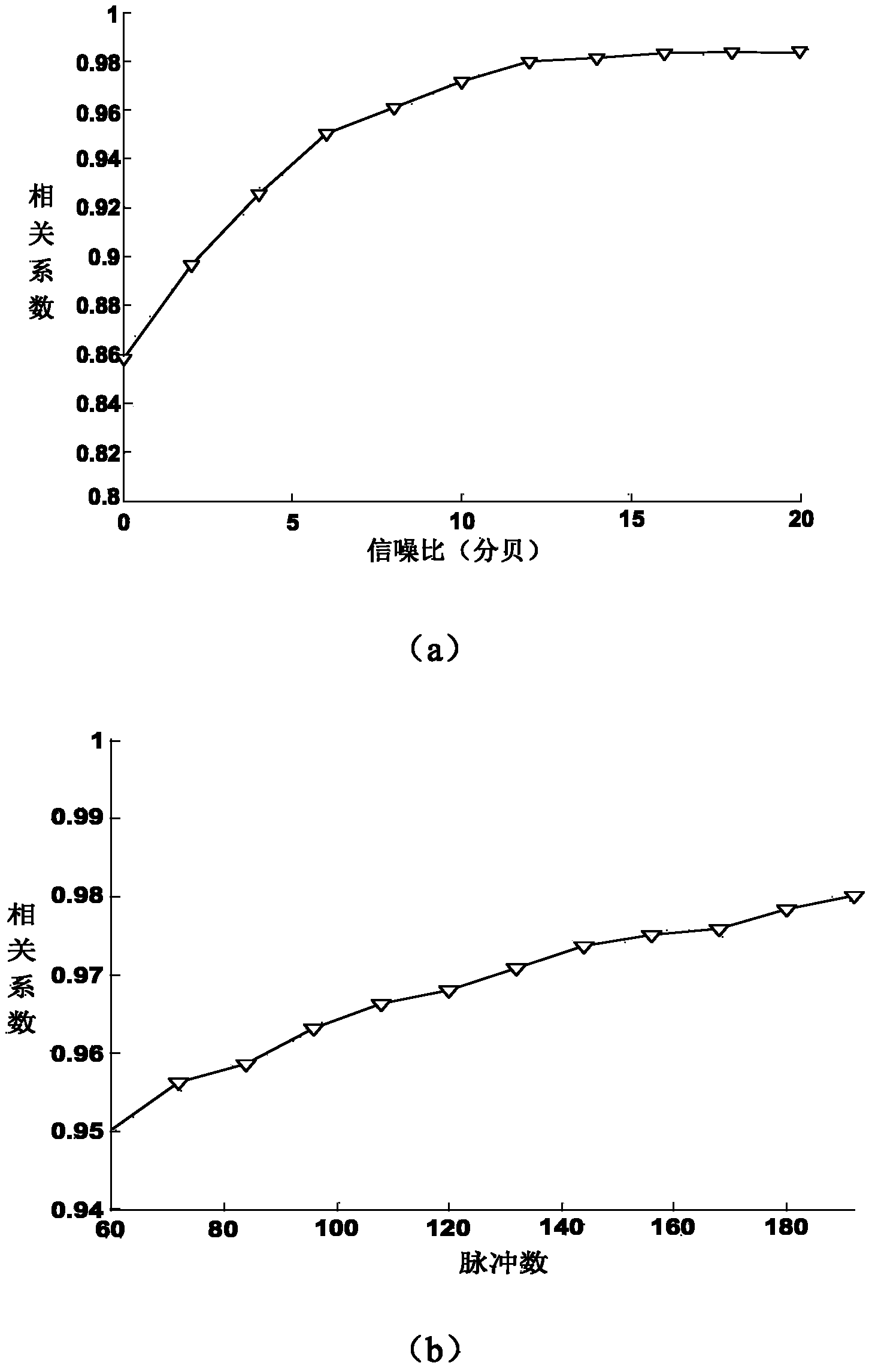
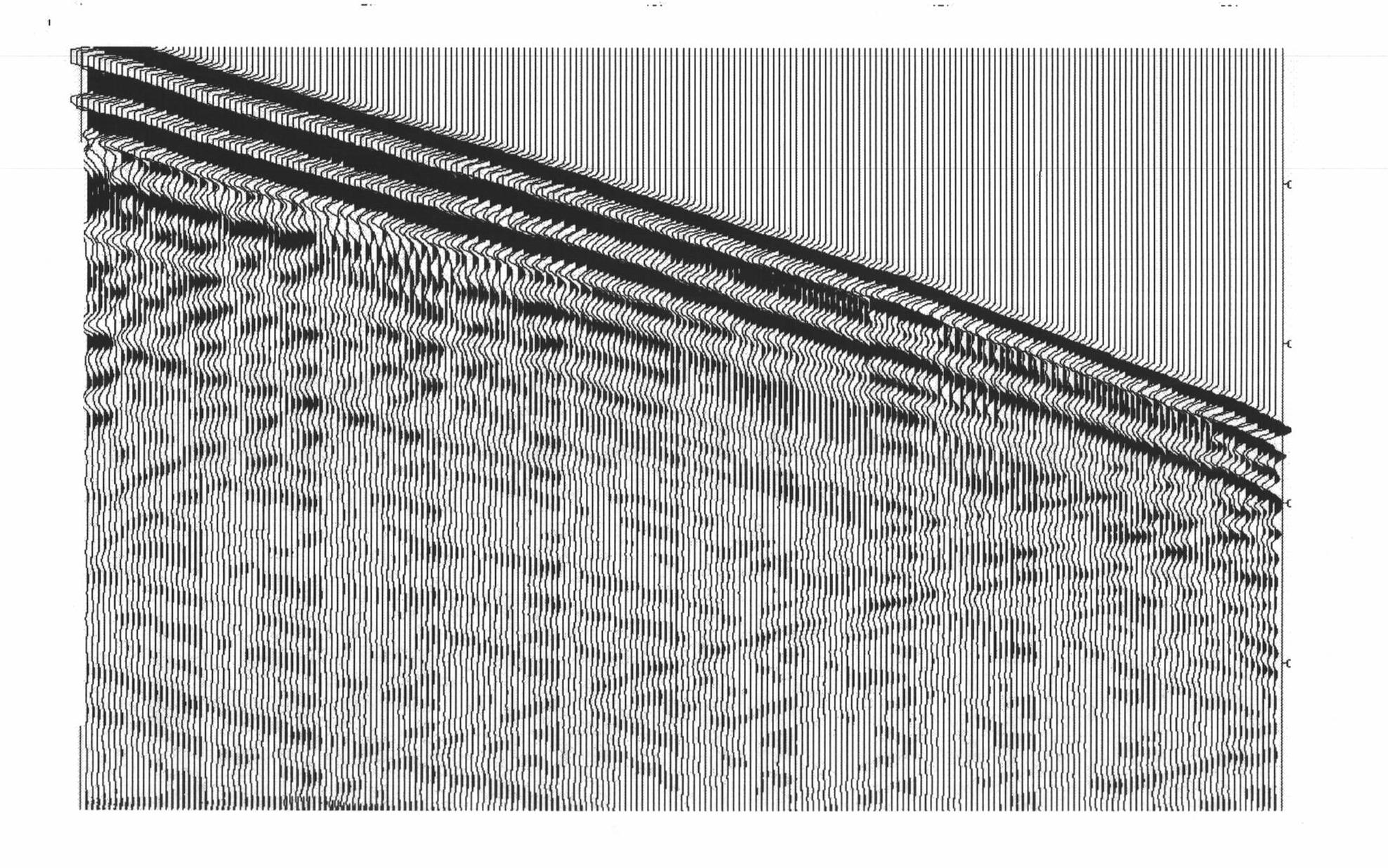
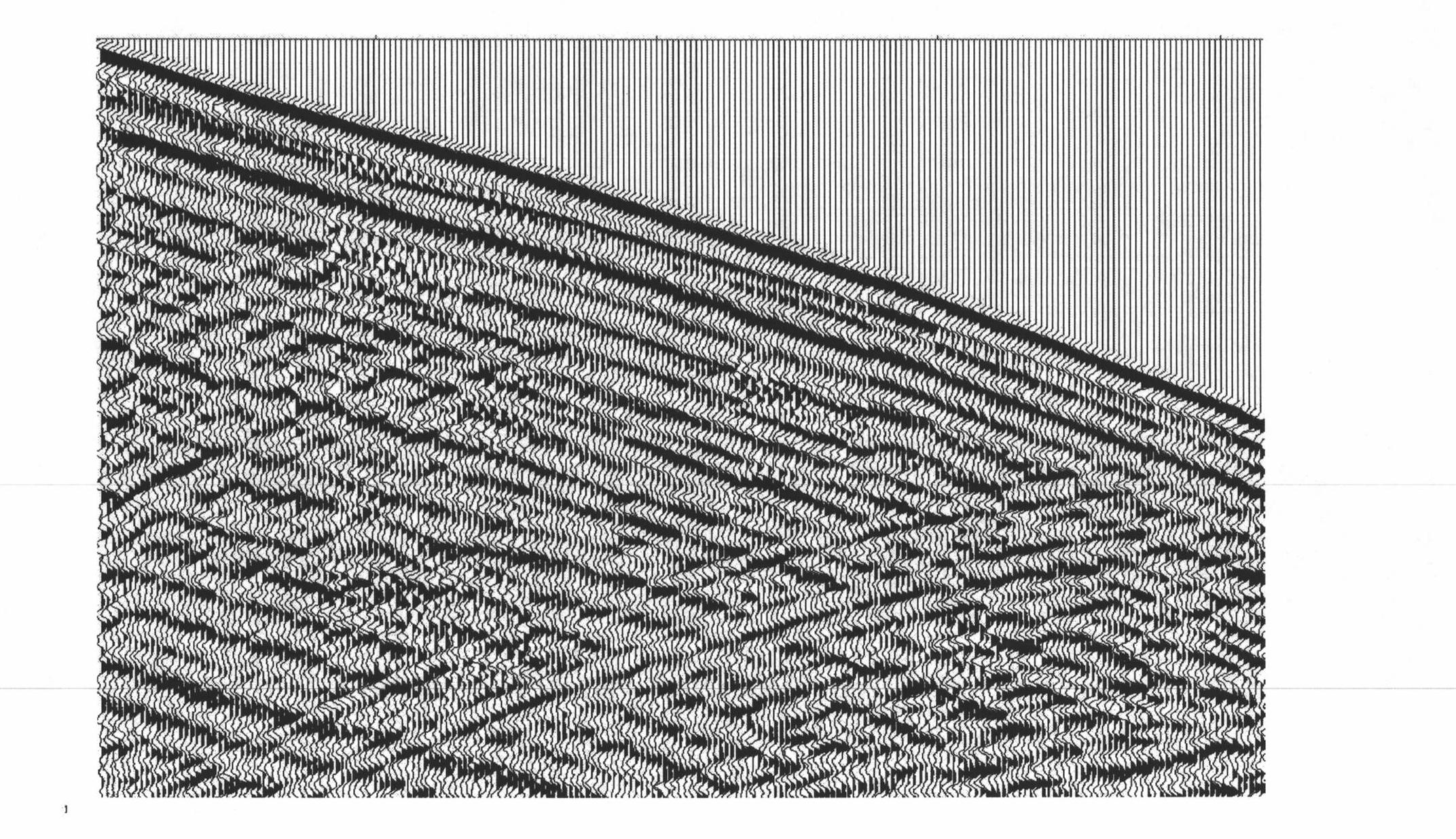
Patents
Literature
2401 results about "Phase compensation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
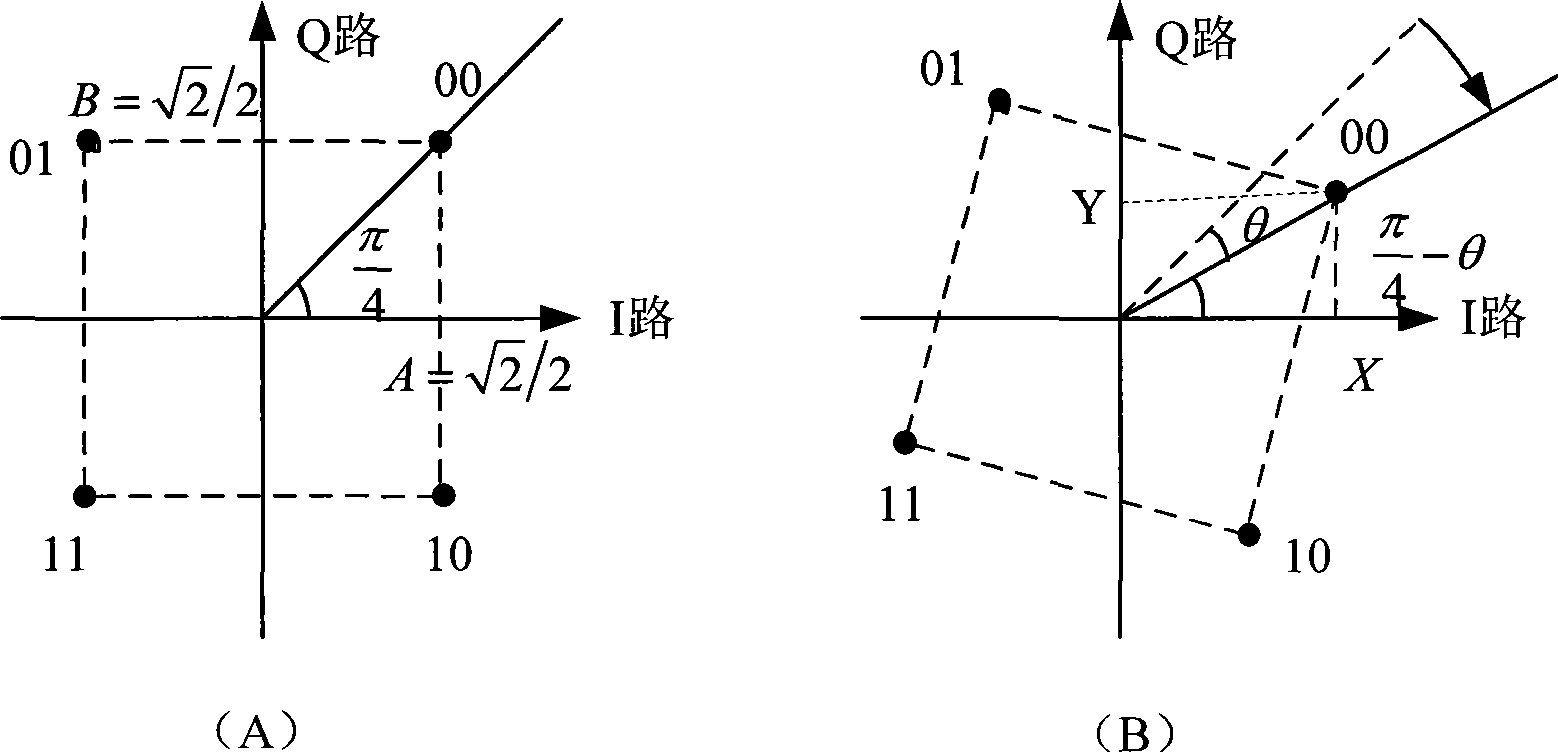
Phase Lead Compensation. A system which has one pole and one dominating zero (the zero which is closer to the origin than all over zeros is known as dominating zero.) is known as lead network. If we want to add a dominating zero for compensation in control system then we have to select lead compensation network.
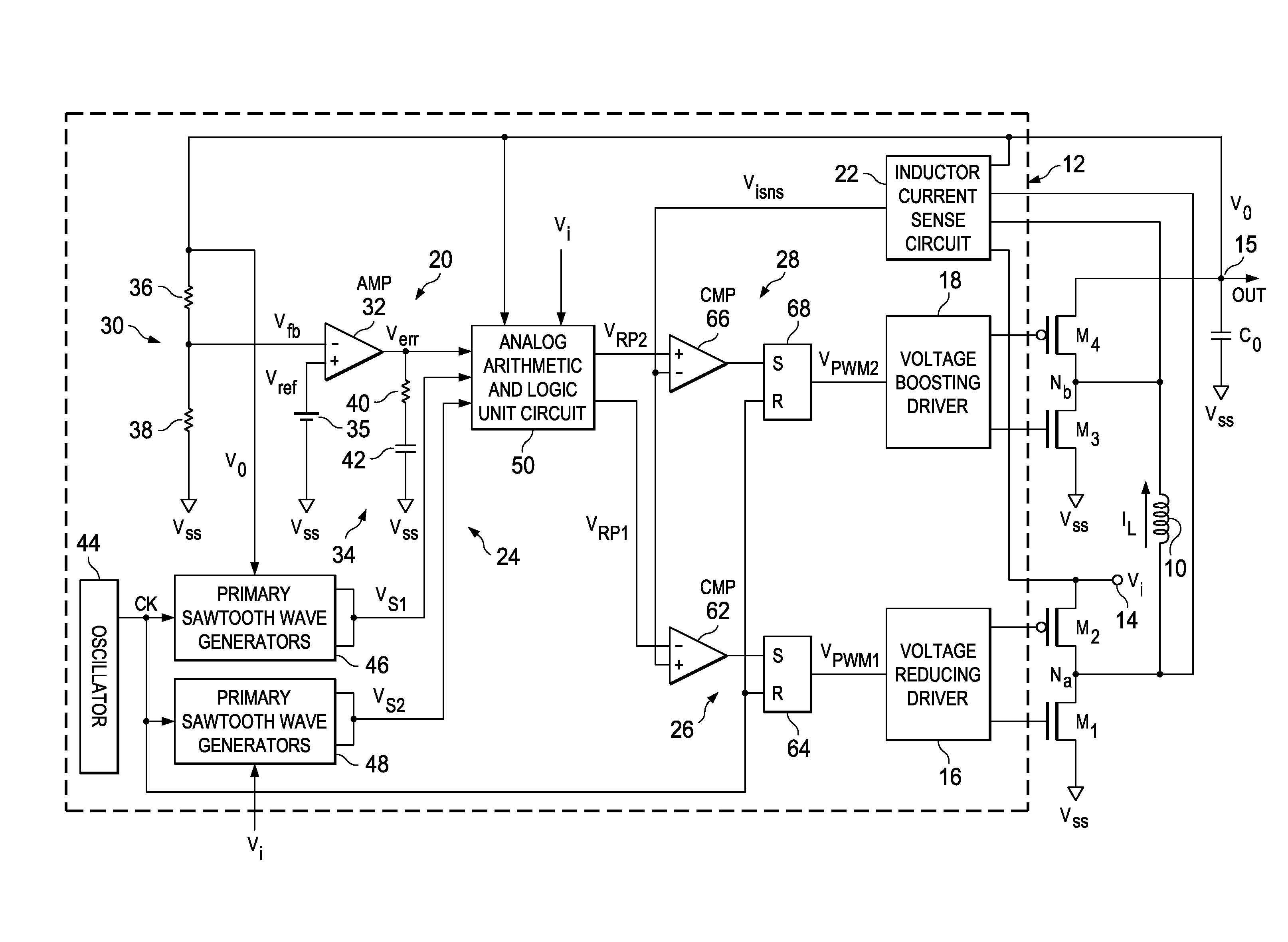
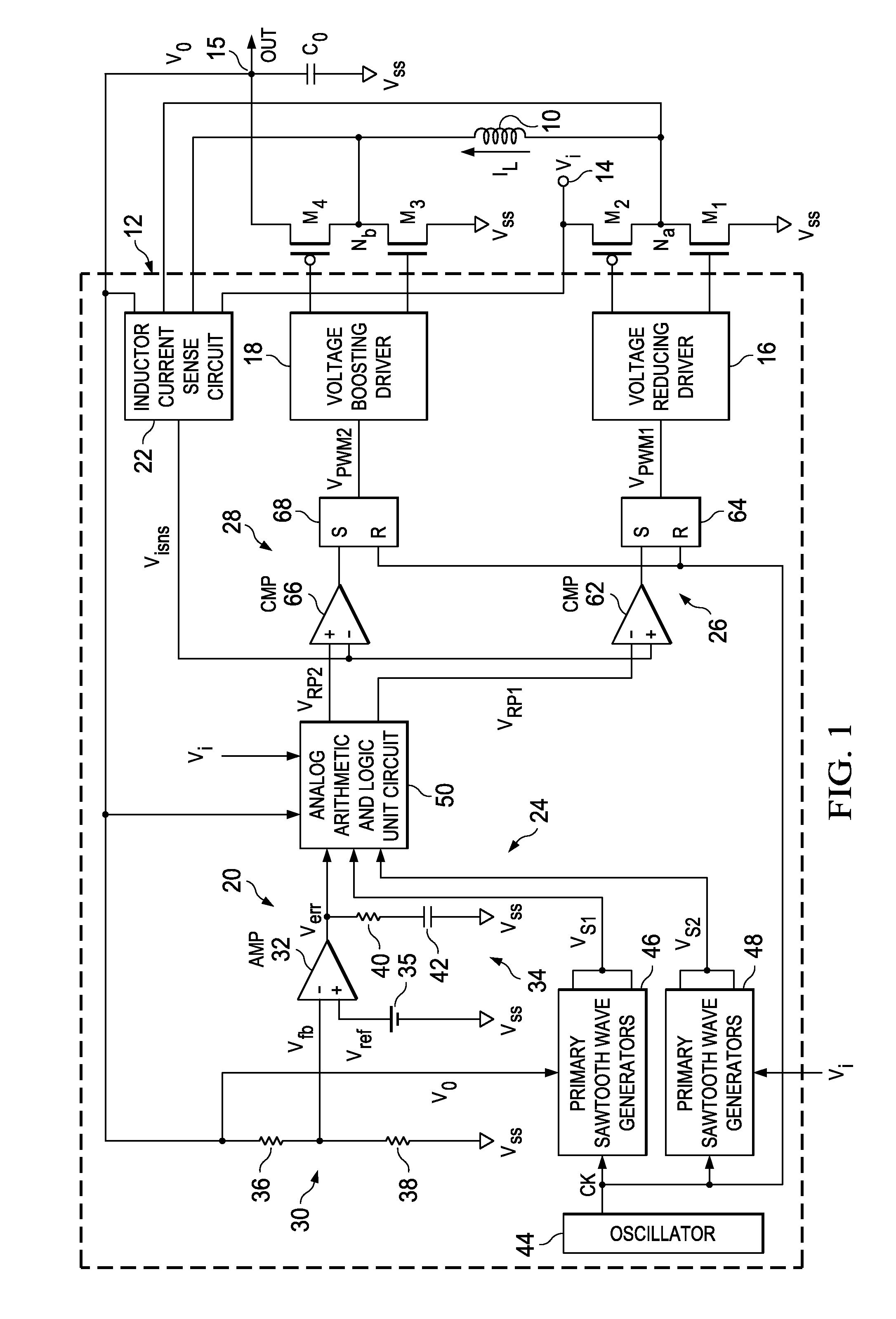
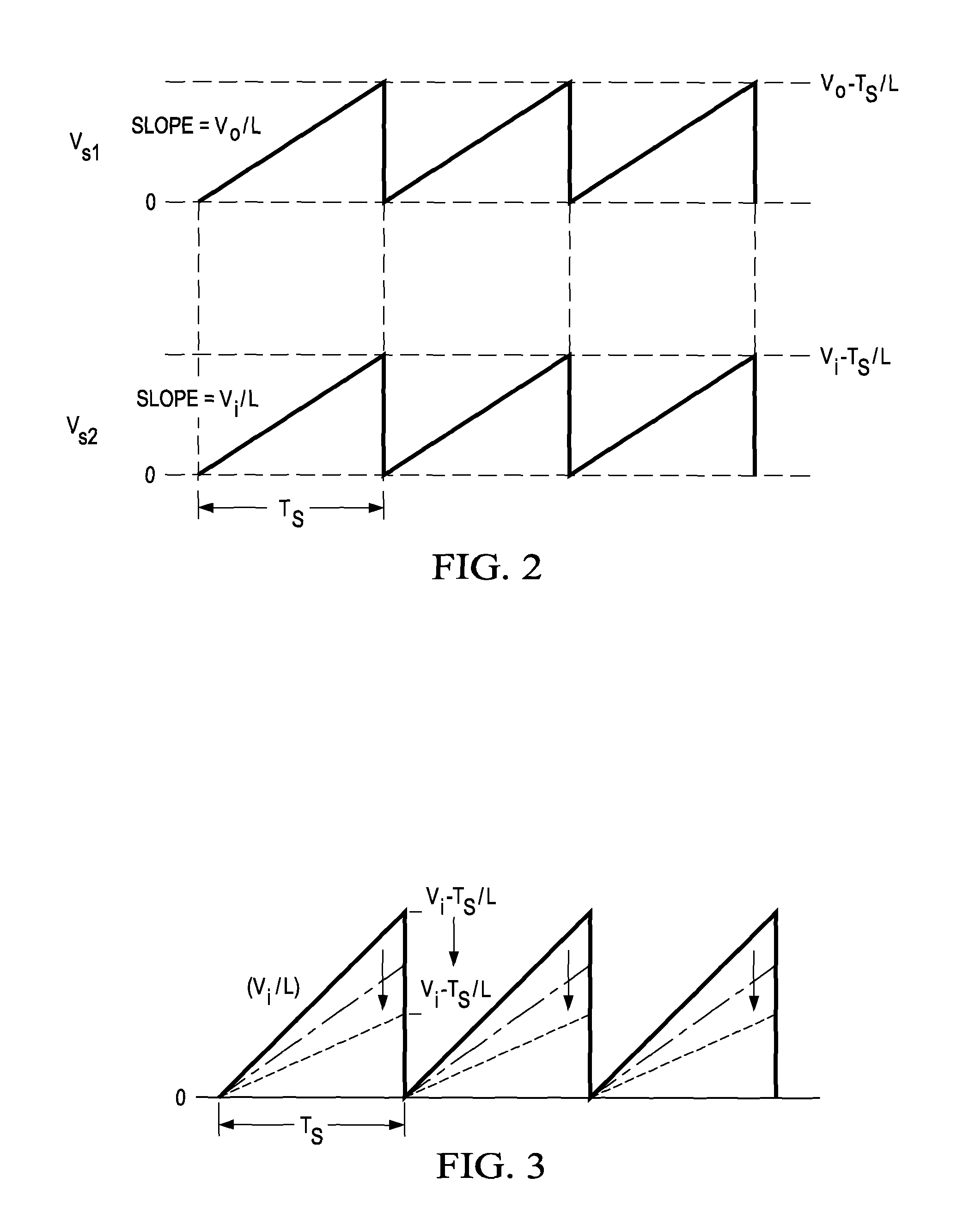
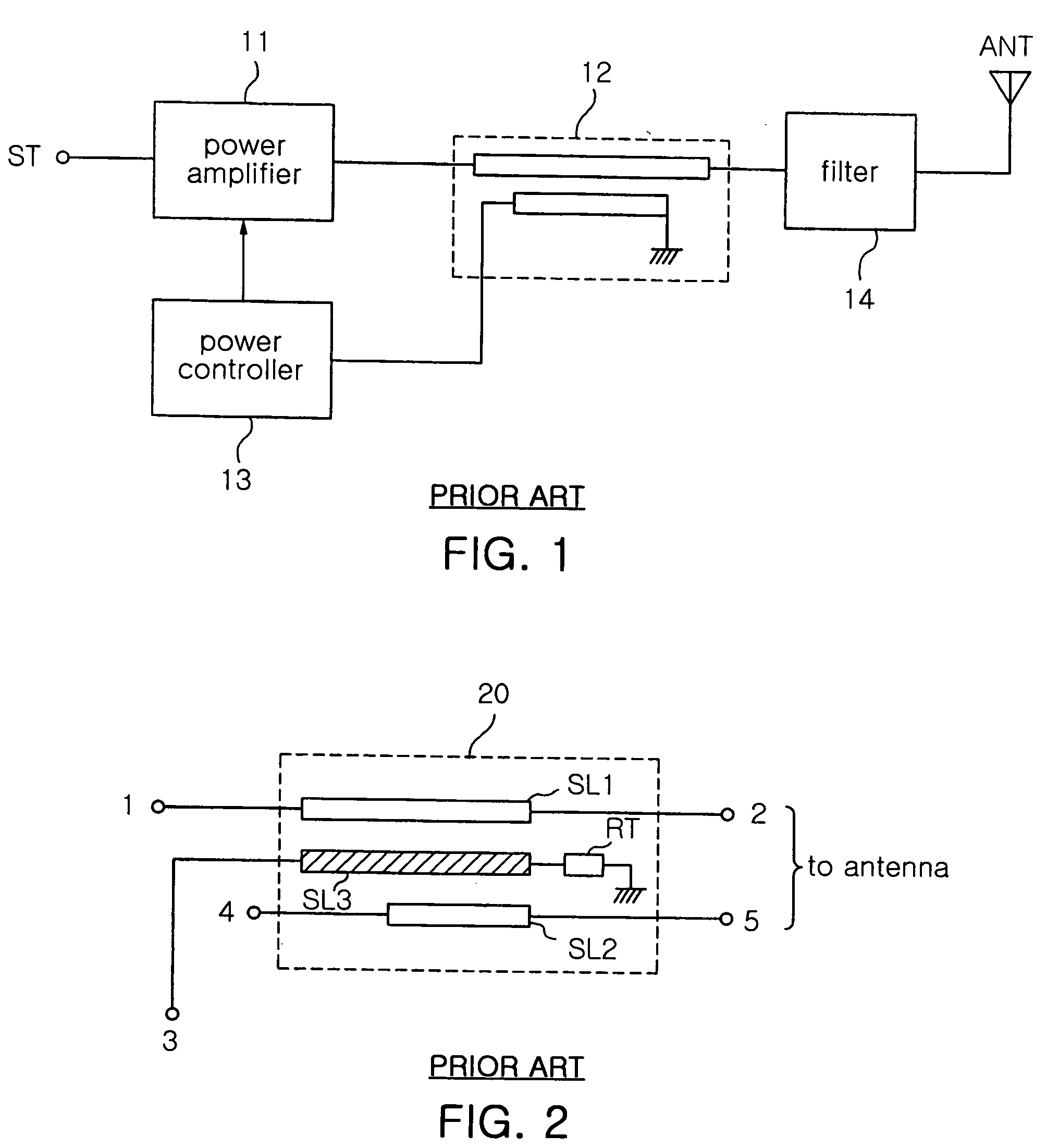
Voltage buck-boost switching regulator
ActiveUS8436592B2Stable, high-speed, high-efficiency constant-voltage output operationStop operationDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCapacitanceEngineering
A stable, high-speed, high-efficiency constant voltage is provided without a complicated, large-scale, high-cost phase compensation circuit over a wide range of operating conditions. This voltage buck-boost switching regulator consists of a pair of voltage reducing transistors, a pair of voltage boosting transistors, inductance coil, output capacitor and controller. The controller has the following parts for performing PWM control of constant voltage for voltage reducing transistors and voltage boosting transistors: an output voltage feedback circuit, an inductor current sense circuit, a variable sawtooth wave signal generator, switching controllers, and a voltage boosting driver.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
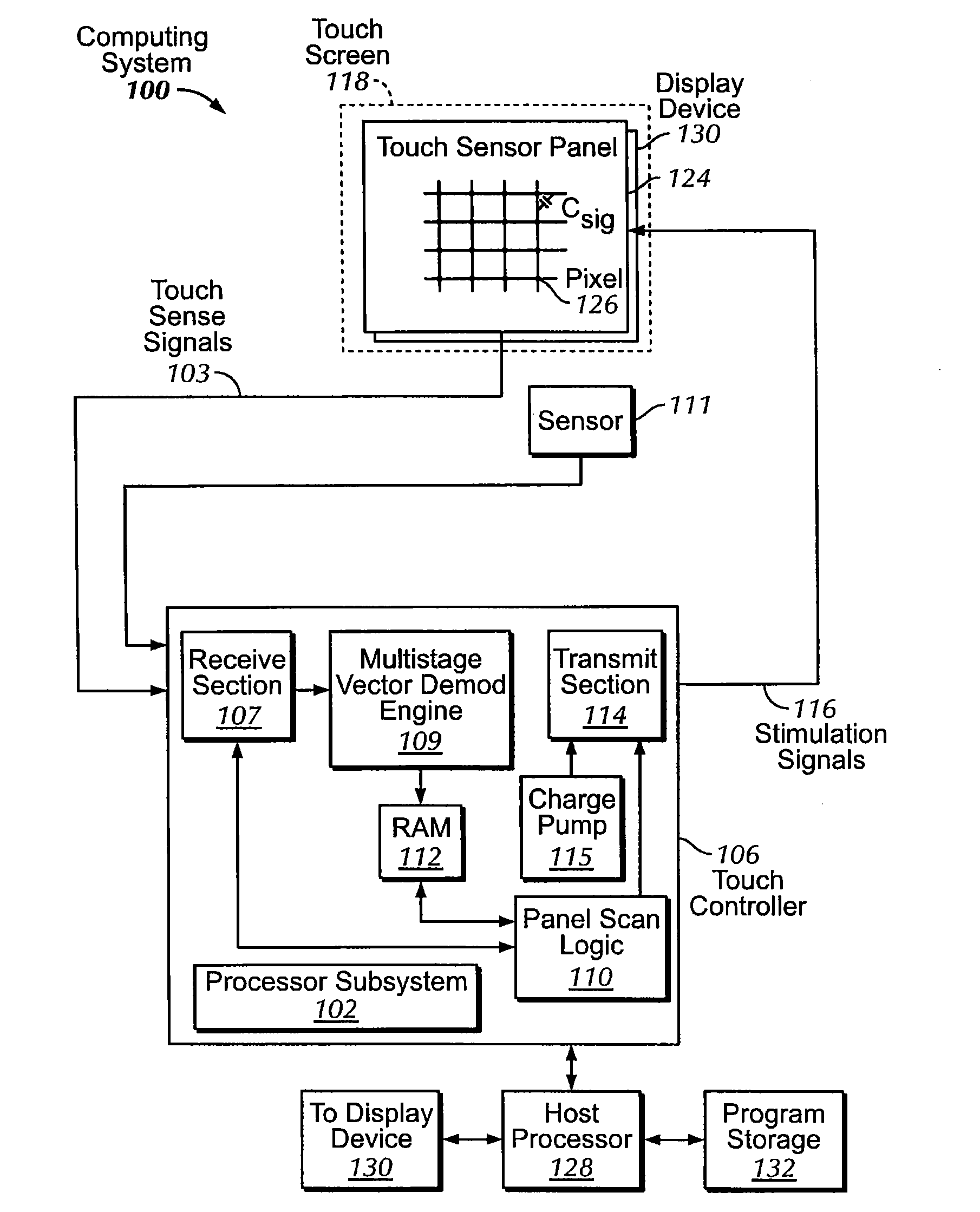
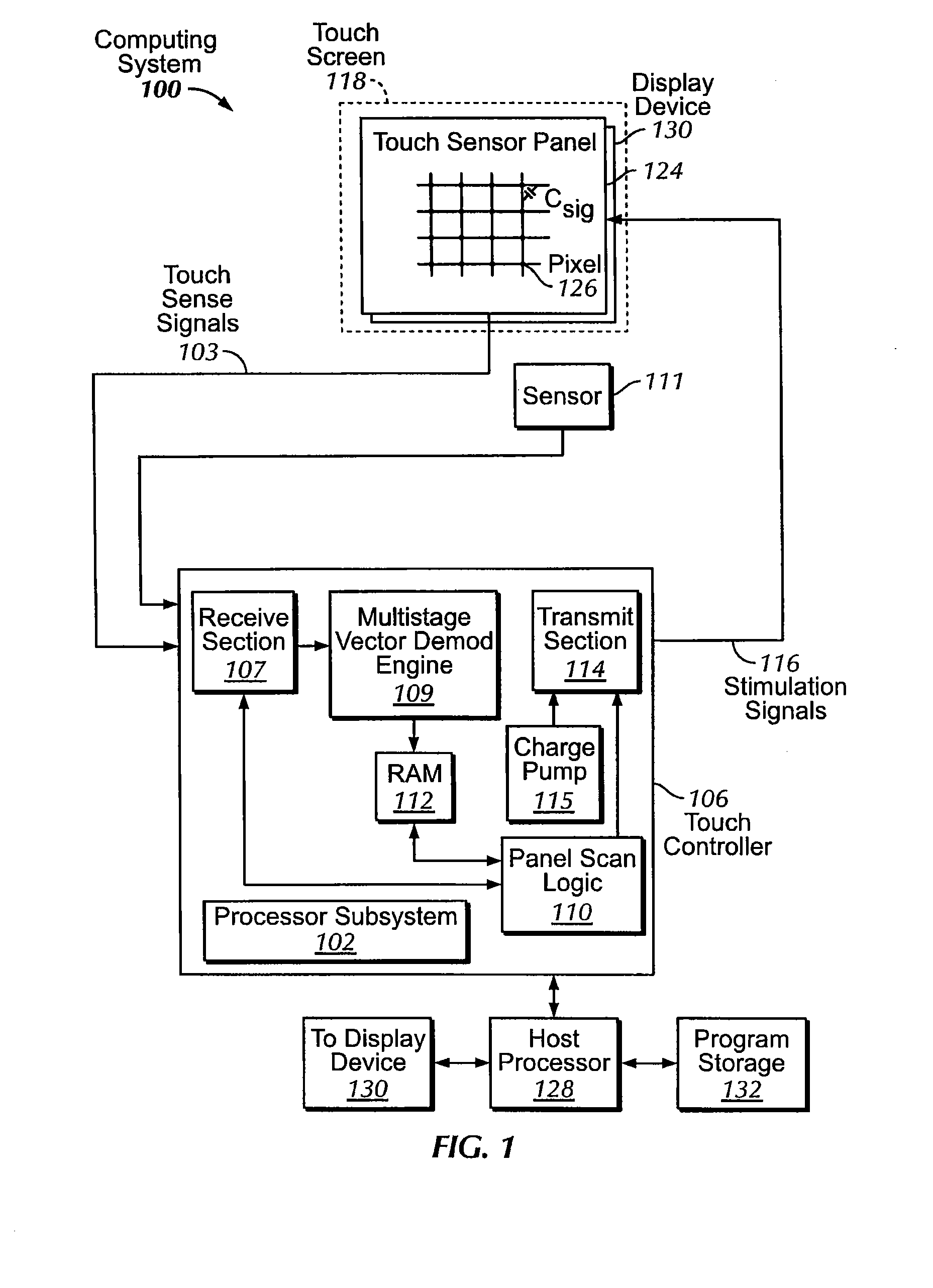
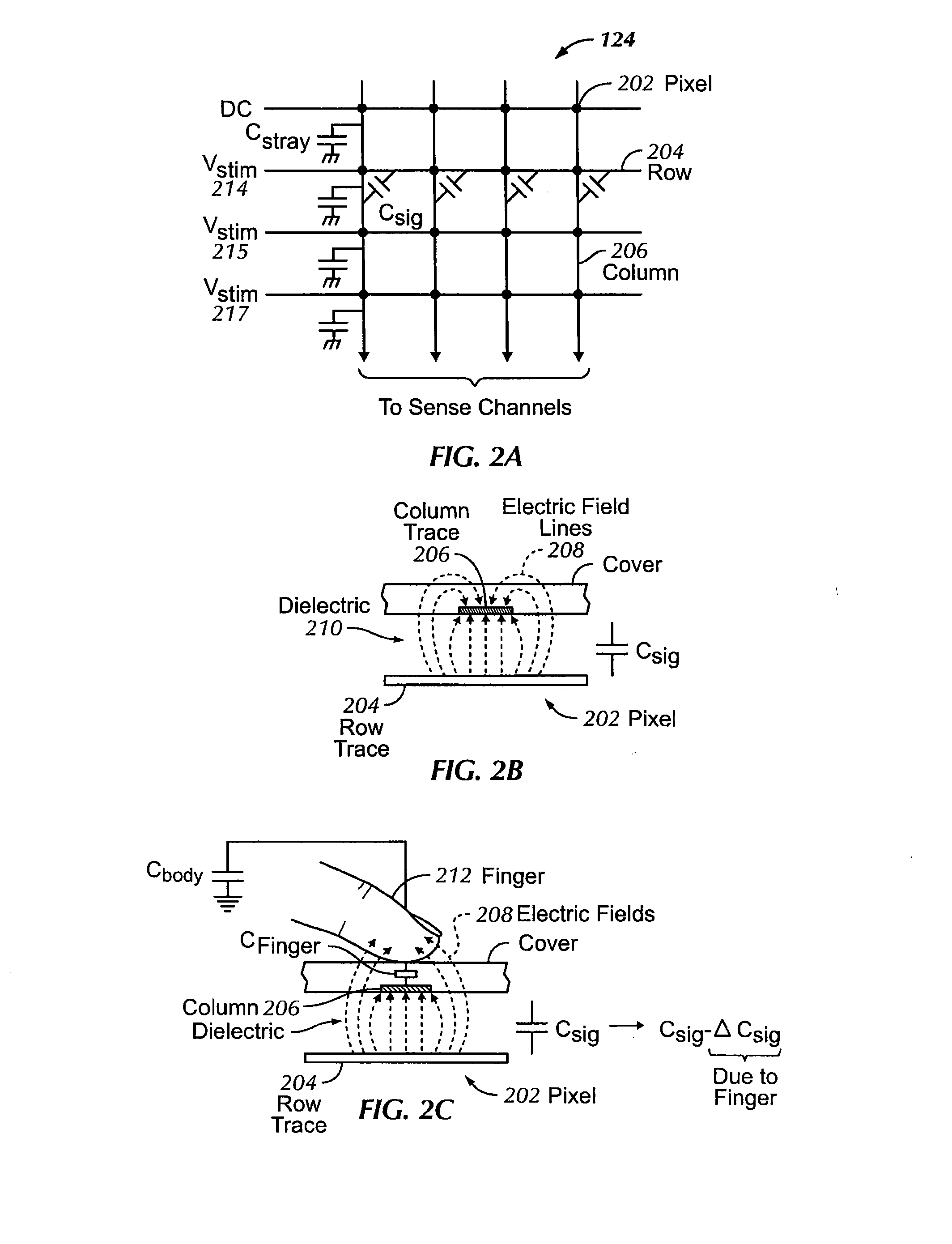
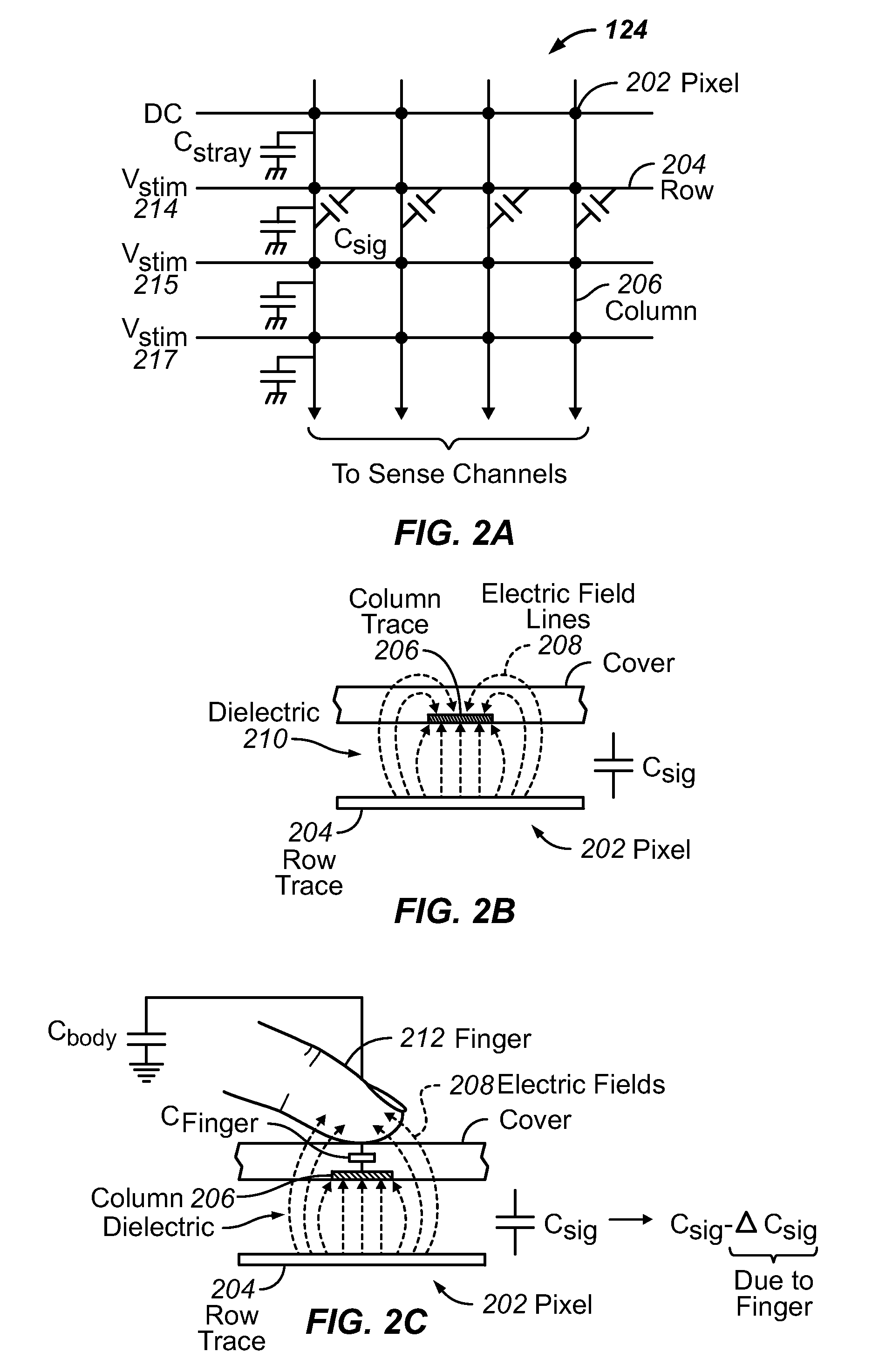
Phase compensation for multi-stimulus controller
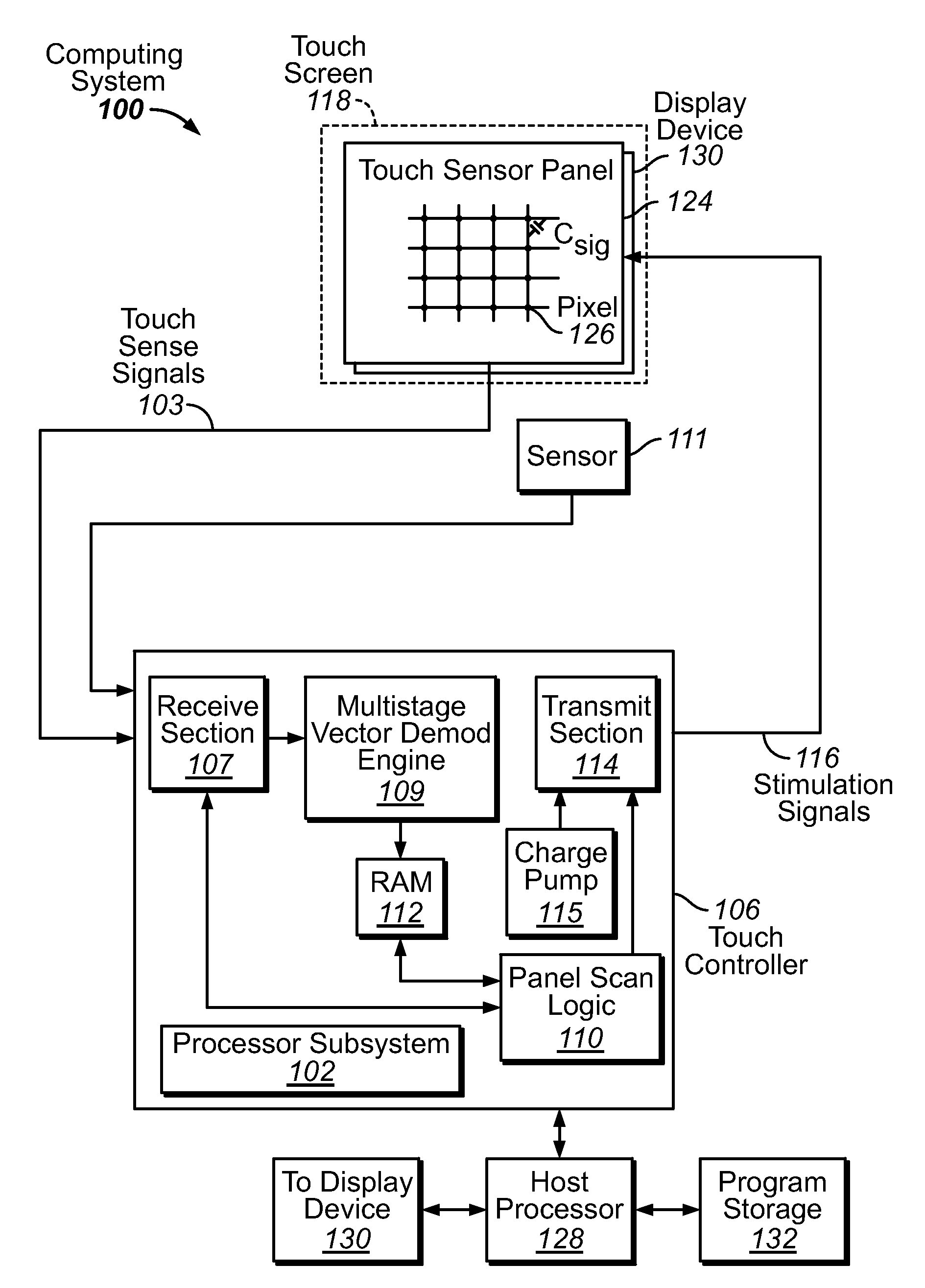
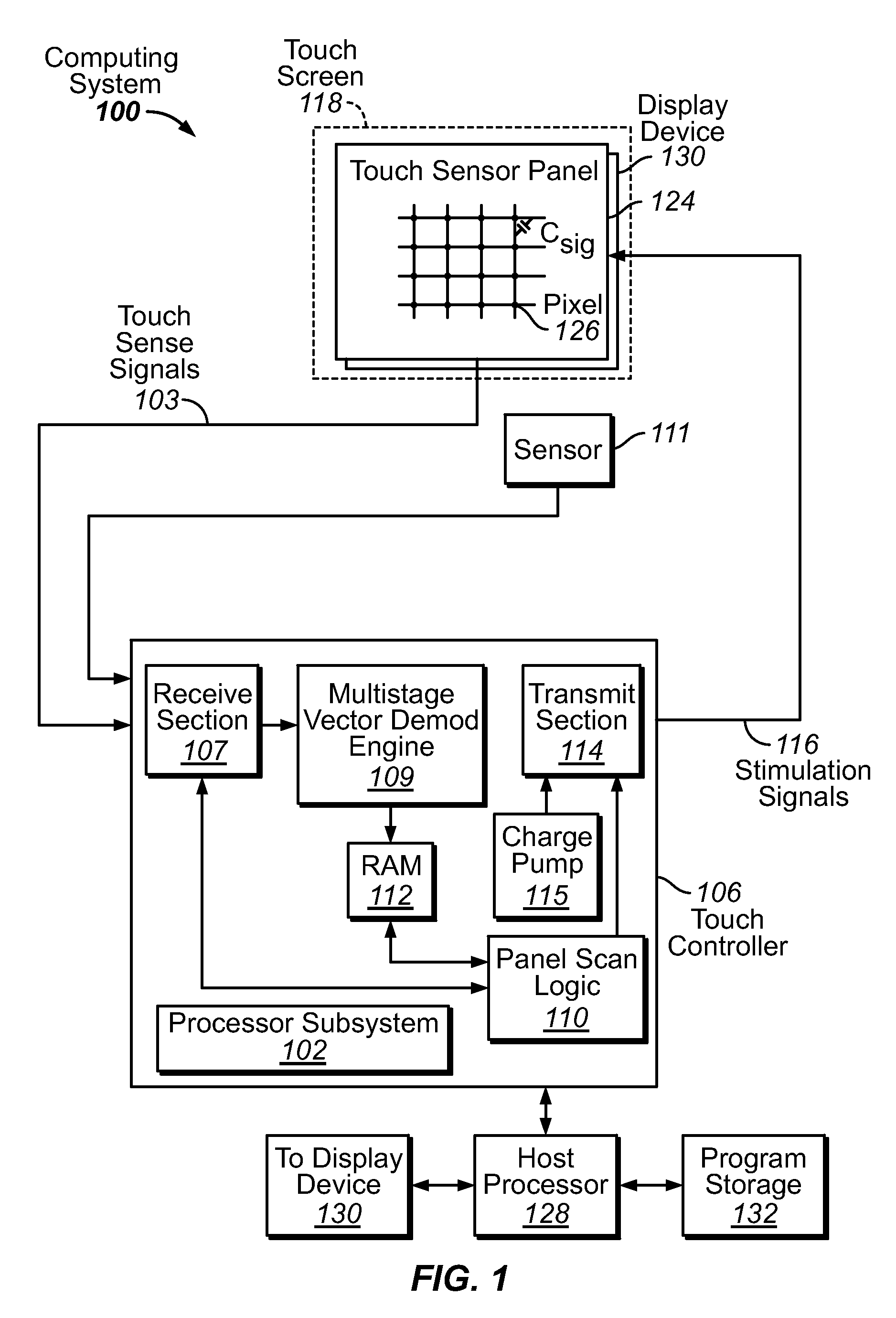
Determining a compensated phase matrix for a multi-stimulus demodulation process is provided. A first drive line of a multi-stimulus sensing system is selected, and a stimulation signal is transmitted on the selected drive line. A channel gain resulting from the stimulation signal is measured from a received sense signal resulting from the stimulation signal. The measured channel gain is compared with a known channel gain to obtain an individual phase compensation for the selected drive line. A compensated phase matrix is formed of the individual phase compensation values for multiple drive lines.
Owner:APPLE INC
Beam focusing and scanning system using micromirror array lens
ActiveUS20050264867A1Increase speedLarge focal length variationMirrorsMountingsLight beamProjection plane
A beam focusing and scanning system using a micromirror array lens (optical system) includes a light source configured to emit light and a micromirror array lens, including at least one micromirror, optically coupled to the light source, configured to reflect the light onto a projection medium (projection plane). The optical system also includes at least one actuating component coupled to the at least one micromirror, configured to move the at least one micromirror to enable the at least one micromirror to focus the light on the projection medium. The advantages of the present invention include high speed variable focusing and scanning, large focal length variation, phase compensation, high reliability and optical efficiency, low power consumption and low cost.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Liquid Crystal Display Device with Touch Screen Function
ActiveUS20100134448A1Excellent characteristicsImprove visibilityNon-linear opticsInput/output processes for data processingVisibilityLiquid-crystal display
A liquid crystal display (LCD) device with a touch screen function is provided. The LCD device includes a liquid crystal panel layer including a liquid crystal layer filled between first and second substrates, and a touch panel layer which is formed on the first substrate, includes at least one phase compensating means stacked therein, and detects a contact point when an upper electrode and a lower electrode come into contact with each other due to external pressure, wherein the phase compensating means is patterned so that the upper electrode and the lower electrode are able to contact each other, and thus outdoor visibility and viewing angle characteristics can be effectively improved.
Owner:HYDIS TECH
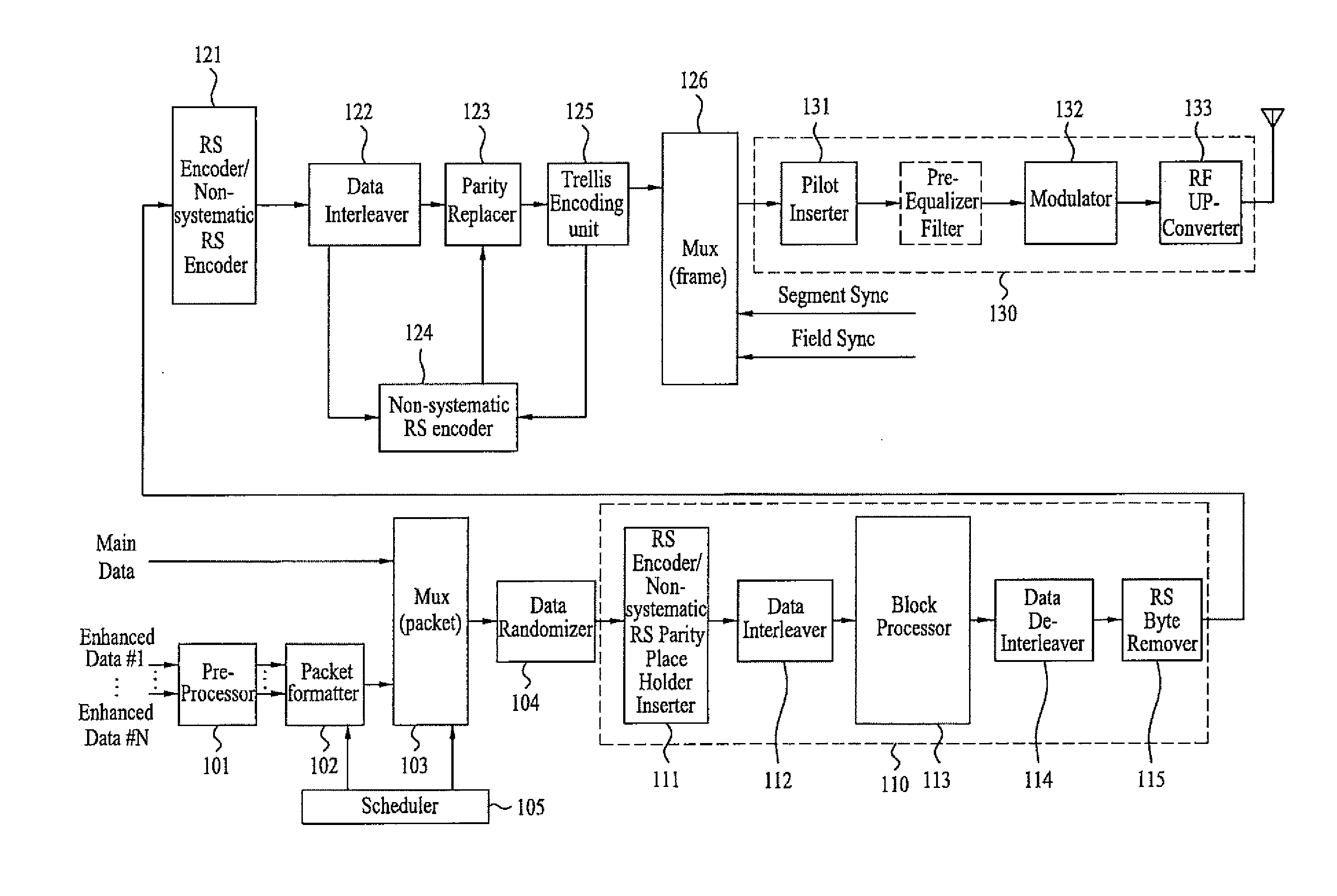
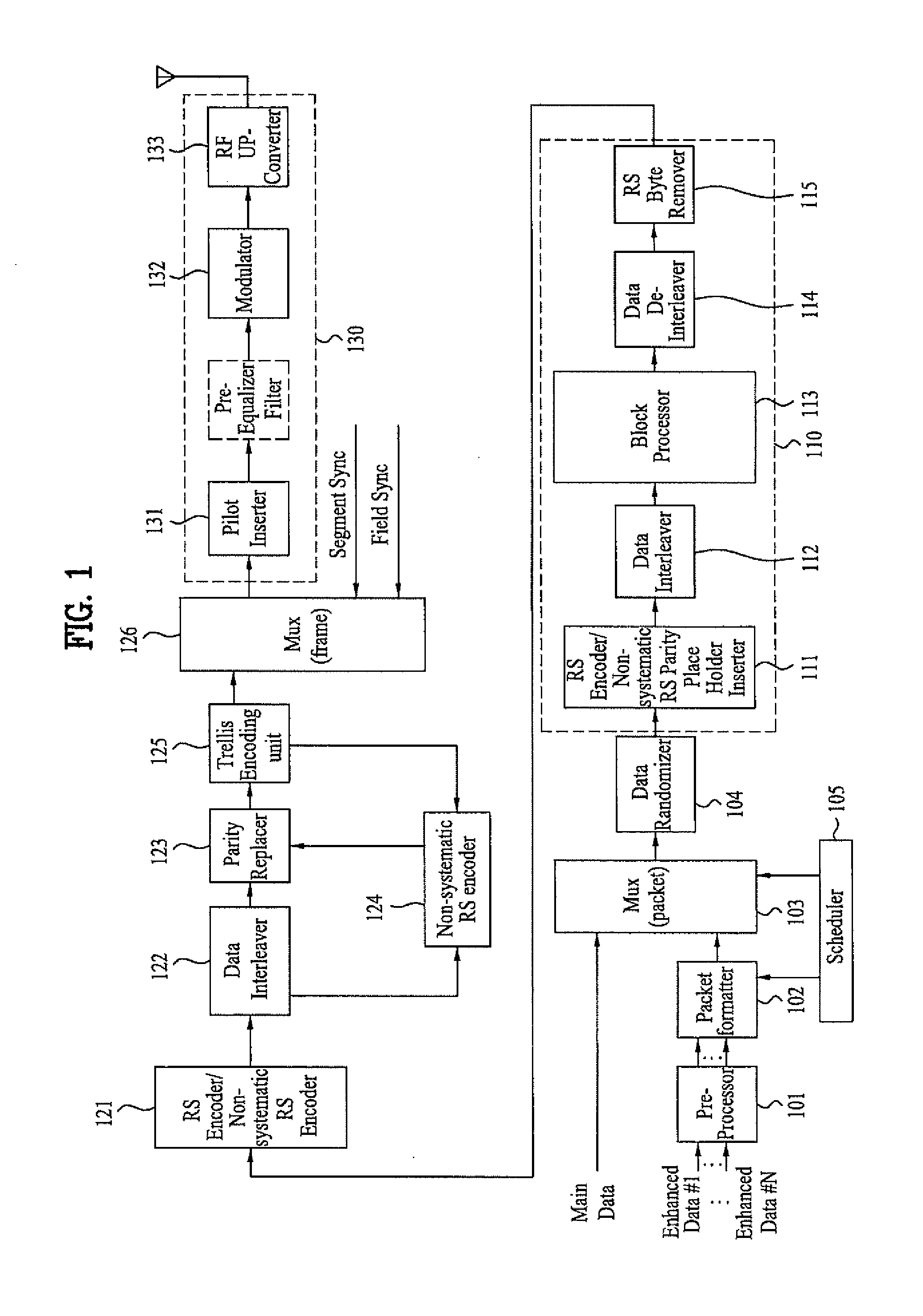
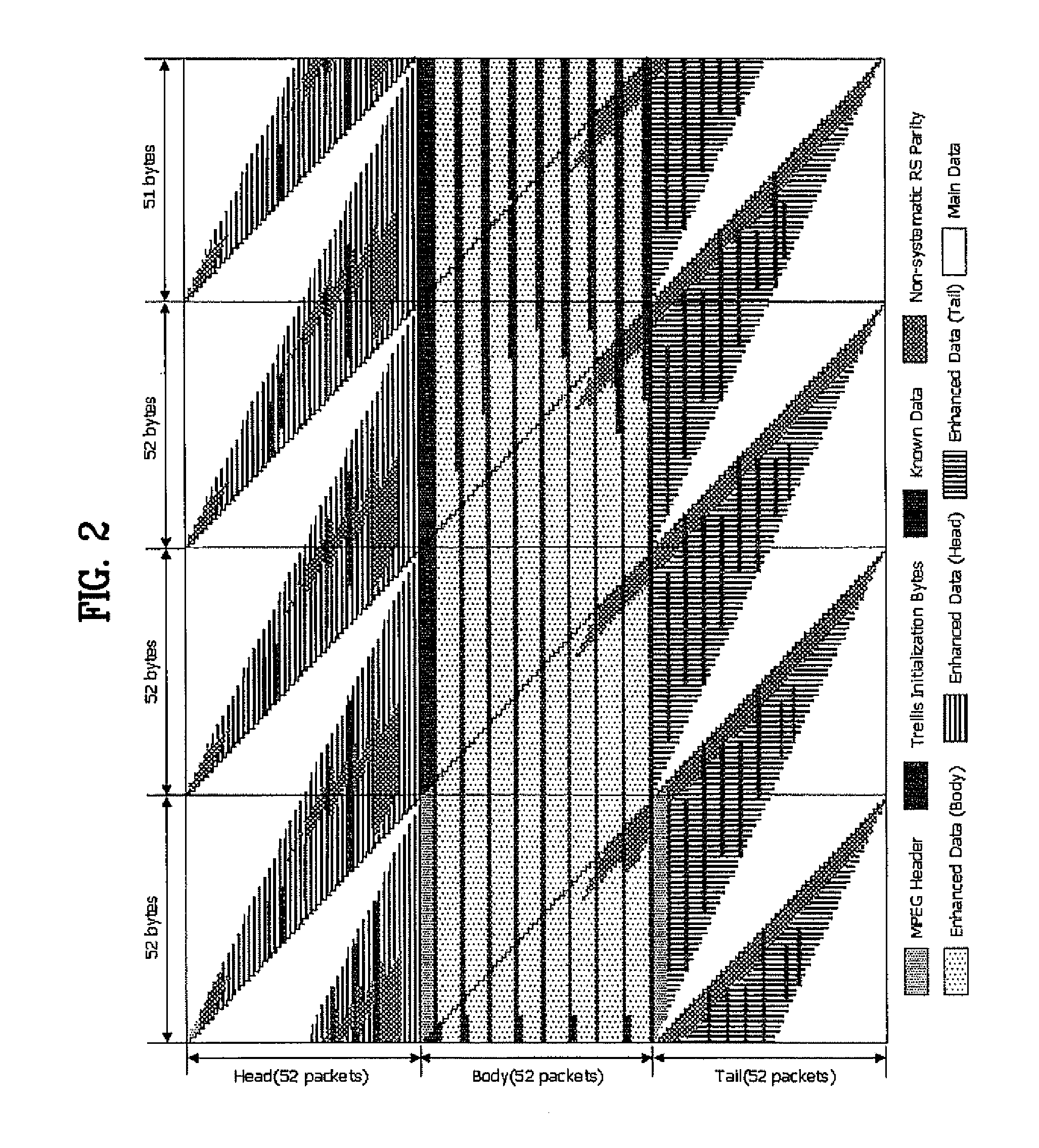
DTV receiving system and method of processing DTV signal
InactiveUS20080170162A1Improve reception performanceTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionComputer scienceData sequences
A digital television (DTV) receiving system includes an information detector, a timing recovery unit, a carrier recovery unit, and a phase compensation unit. The information detector detects position information of a known data sequence periodically repeated in a DTV signal and estimates an initial frequency offset value. The timing recovery unit performs timing recovery on the DTV signal by detecting timing error information from the DTV signal using the position information. The carrier recovery unit performs carrier recovery on the DTV signal using the position information. The phase compensation unit compensates a phase offset of the DTV signal using the position information.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
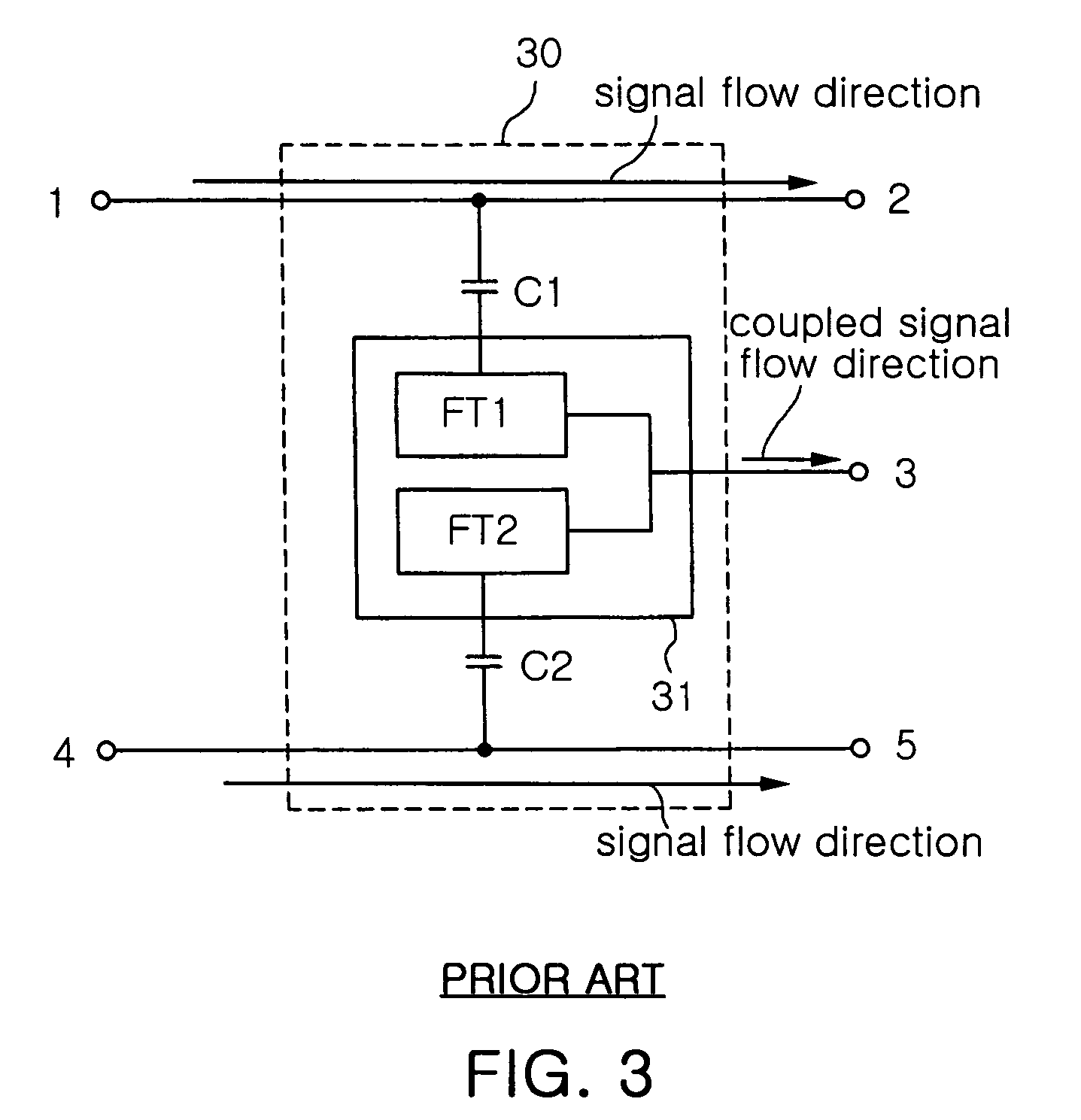
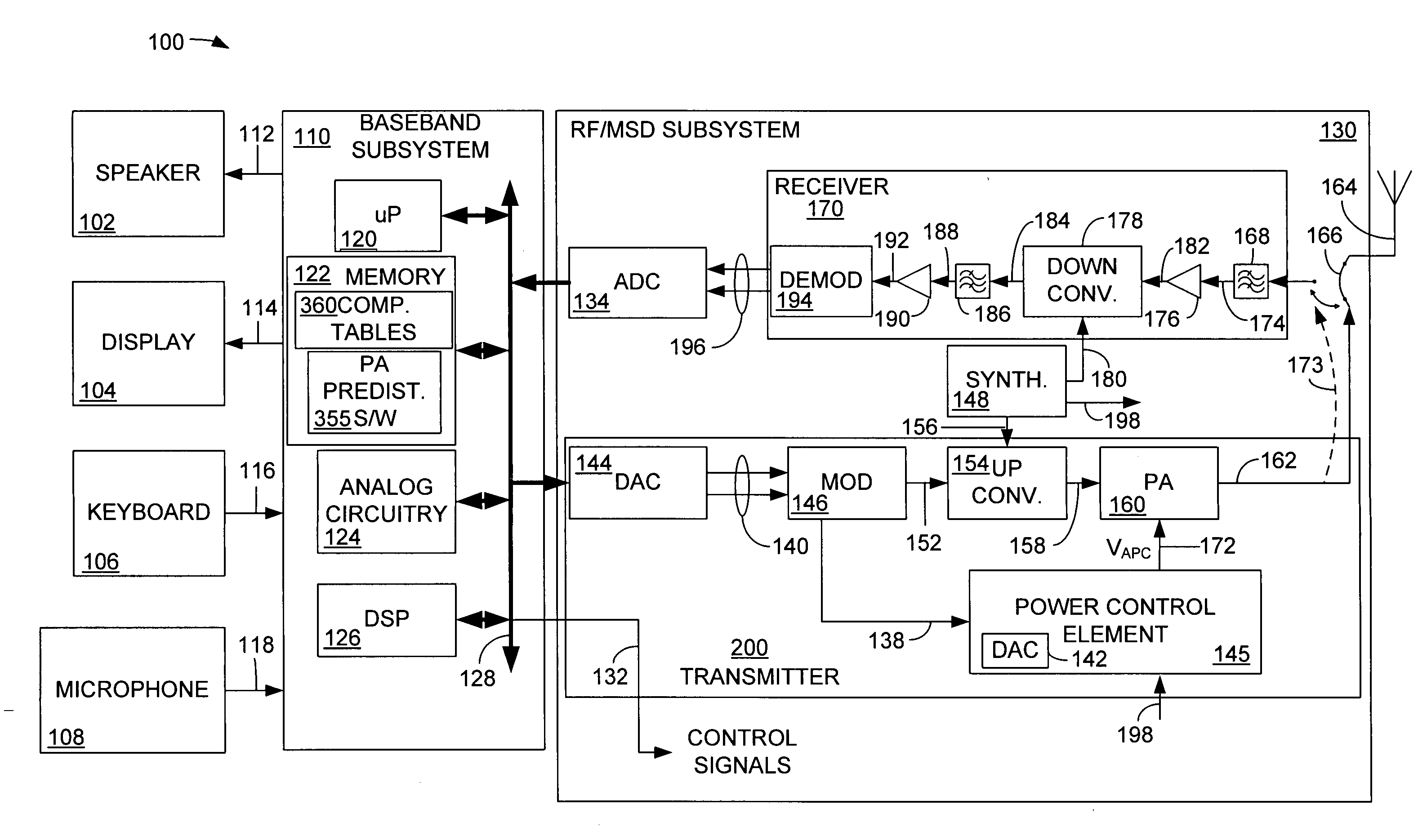
Directional coupler and dual-band transmitter using the same
InactiveUS7187910B2Improve directivityMinimized in process errorResonant long antennasSubstation equipmentCapacitanceCoupling
Disclosed herein are a directional coupler which is implemented with strip lines for signal coupling and inter-digital capacitors for phase compensation, and a dual-band transmitter using the same. The directional coupler includes a first transmission device, a first directional coupling device for coupling a part of a signal from the first transmission device, a first inter-digital capacitor connected between the first transmission device and the first directional coupling device, a second transmission device, a second directional coupling device for coupling a part of a signal from the second transmission device, and a second inter-digital capacitor connected between the second transmission device and the second directional coupling device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
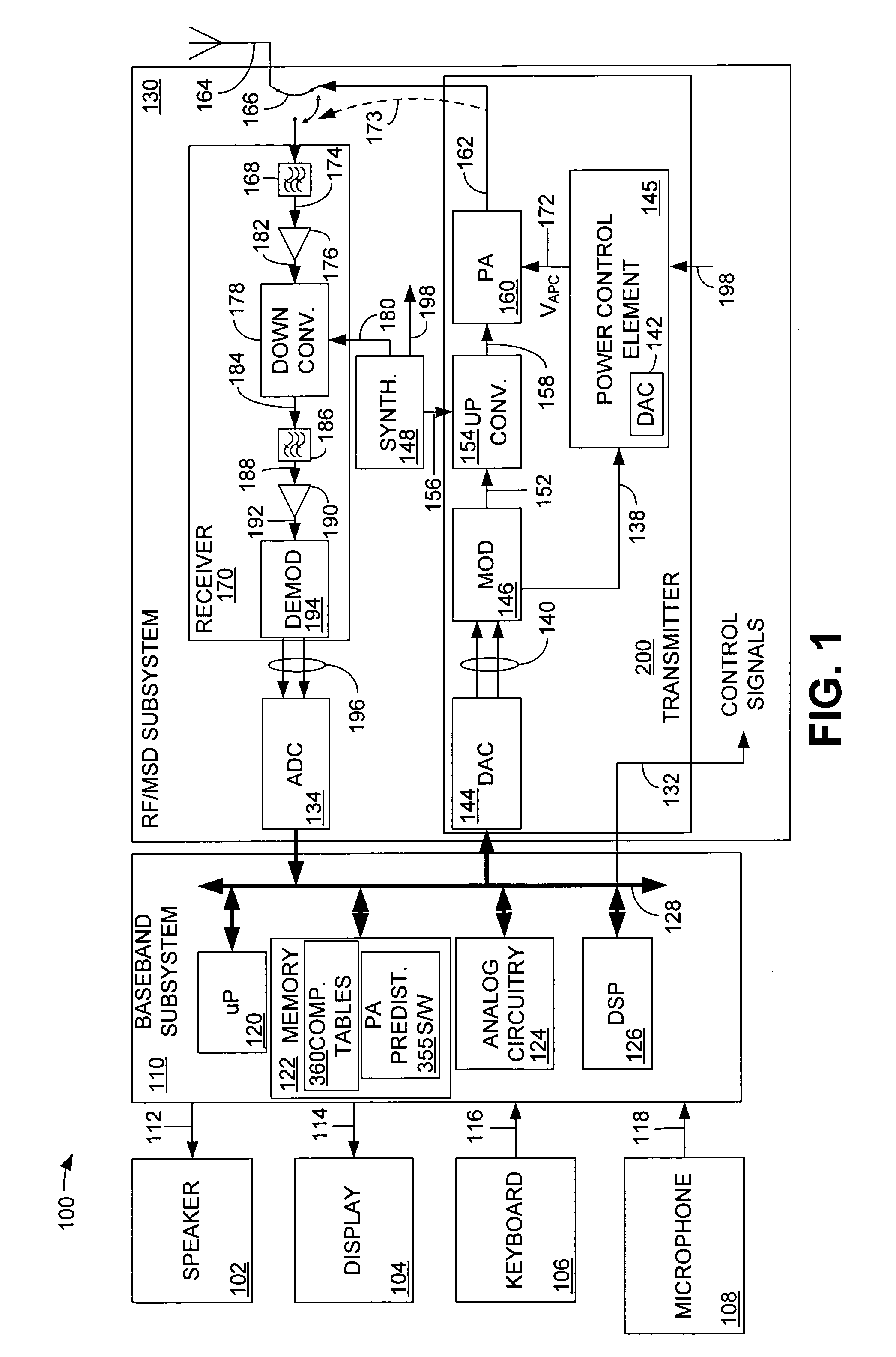
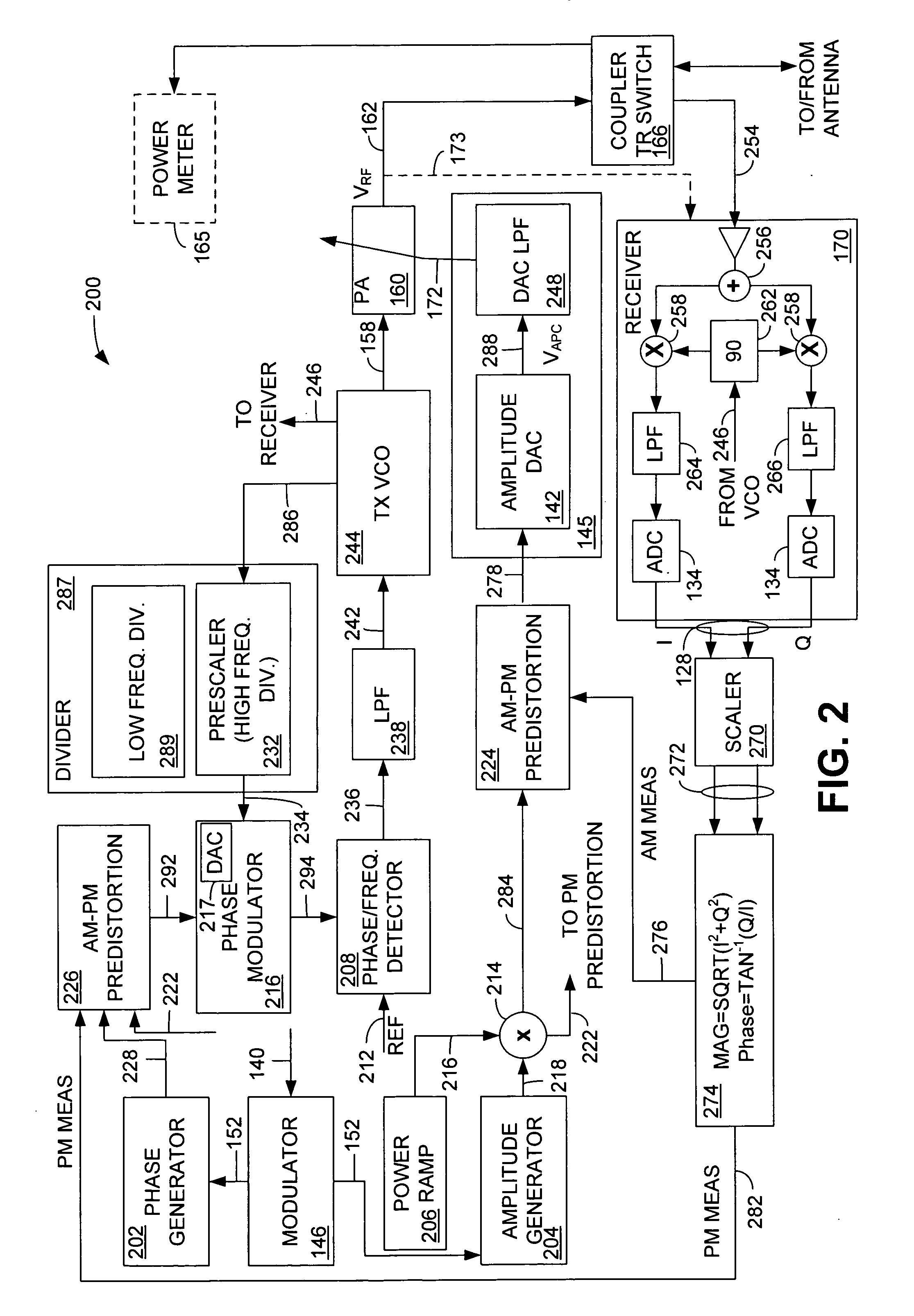
Open loop polar transmitter having on-chip calibration
InactiveUS20070129025A1Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsPower amplifiersPolar transmitterPredistortion
An on-chip calibration system comprises a transmitter, a receiver, a phase and amplitude determination element configured to determine amplitude and phase characteristics of an output signal generated in the transmitter, the signal representing transmitter characteristics, an amplitude comparison element configured to compare the signal representing transmitter characteristics with a desired amplitude signal and generate an amplitude compensation signal, an AM predistortion element configured to modify an ideal AM signal with the amplitude compensation signal, a phase comparison element configured to compare the signal representing transmitter characteristics with a desired phase signal and generate a phase compensation signal, and a PM predistortion element configured to modify an ideal phase signal with the phase compensation signal.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
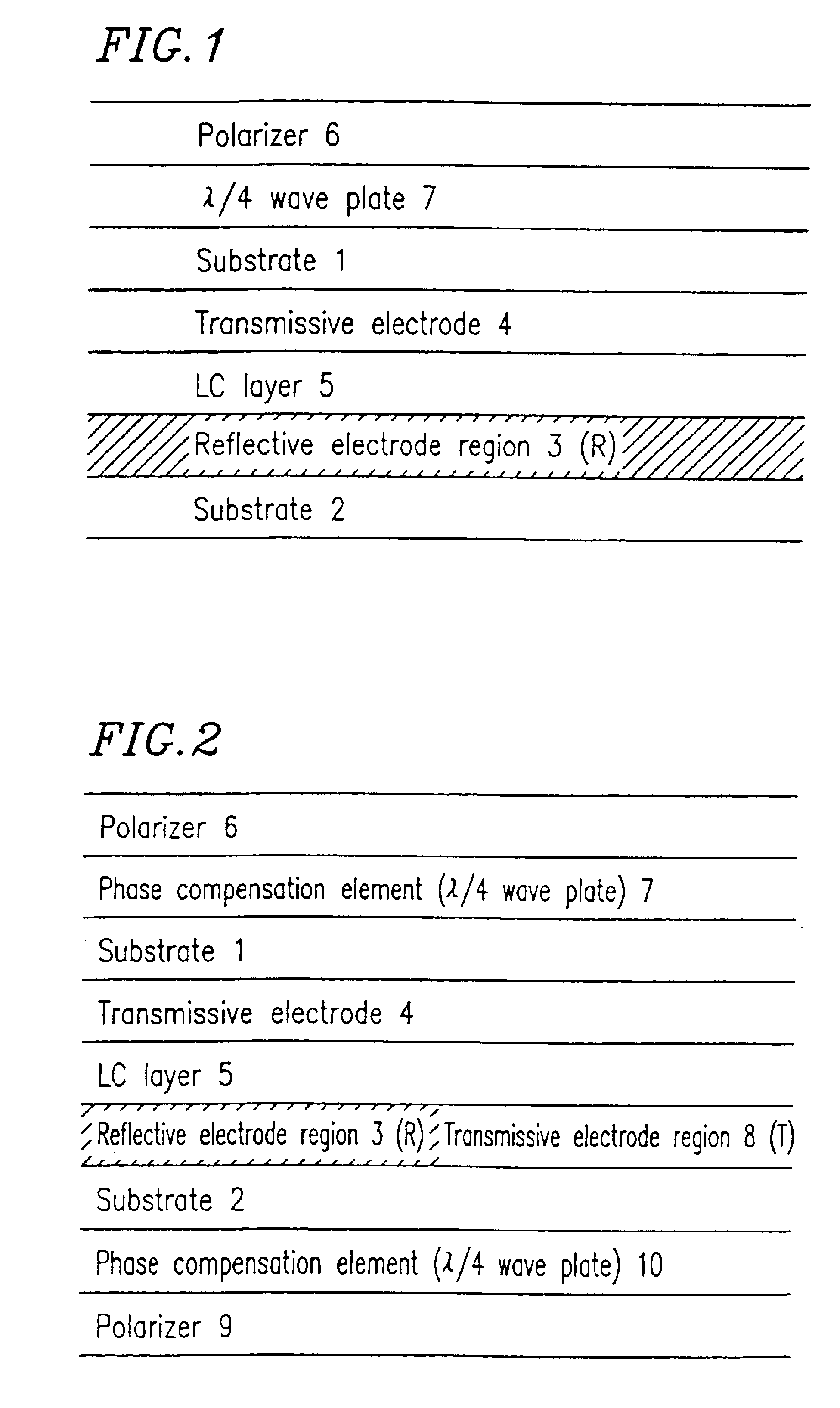
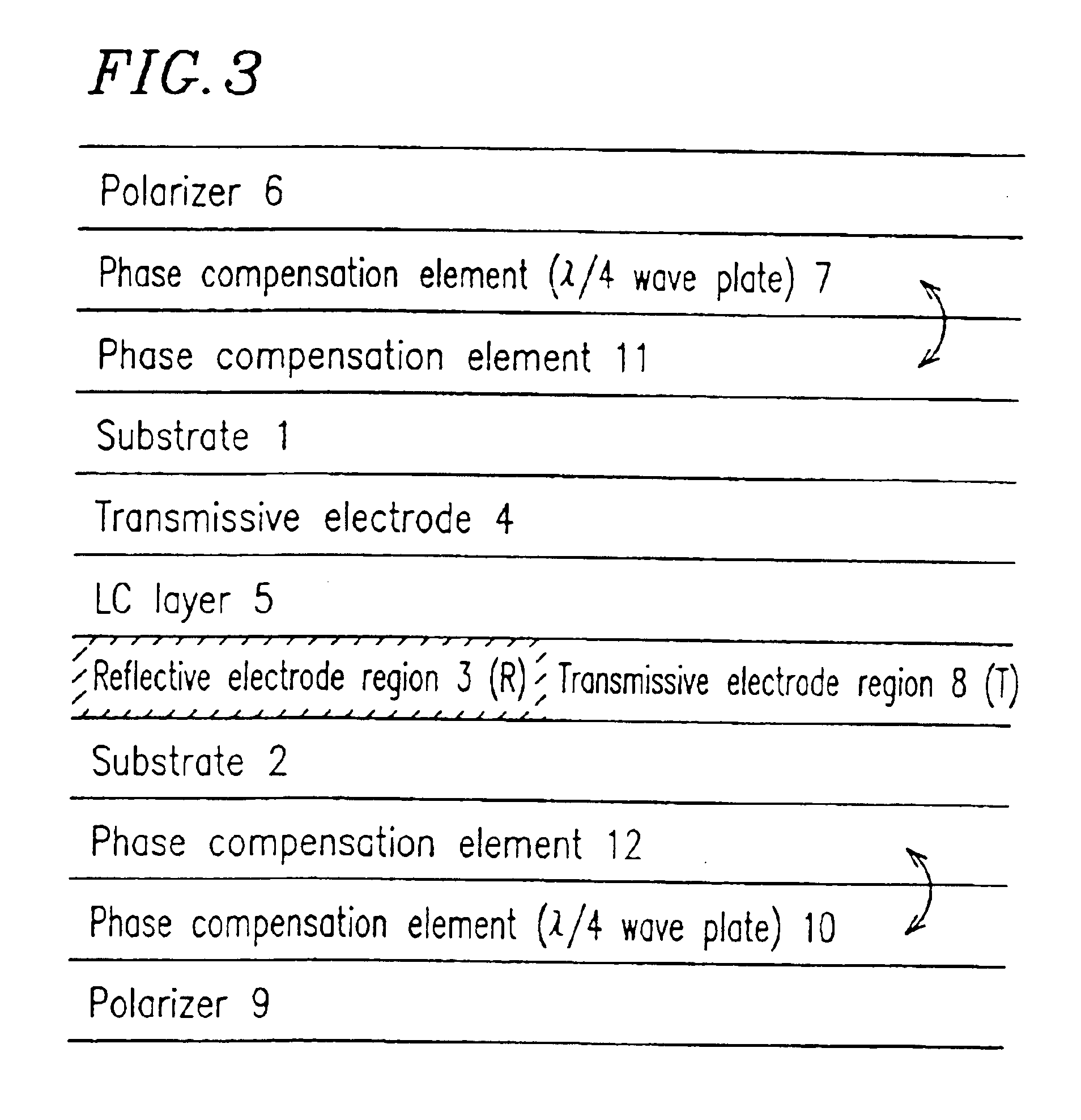
Transflective LCD device having less distance between transmission region and first bus line than transmission region and second bus line
A liquid crystal display device includes a first substrate; a second substrate; a liquid crystal layer interposed between the first substrate and the second substrate; a first polarizer provided on a surface of the first substrate which is on the opposite side to the liquid crystal layer; a second polarizer provided on a surface of the second substrate which is on the opposite side to the liquid crystal layer; a first phase compensation element provided between the first polarizer and the liquid crystal layer; and a second phase compensation element provided between the second polarizer and the liquid crystal layer. A plurality of pixel areas are provided for display. The first substrate includes at least one transmissive electrode, and the second substrate includes a reflective electrode region and a transmissive electrode region in correspondence with each of the plurality of pixel areas.
Owner:SHARP KK
Loop latency compensated PLL filter
InactiveUS6236343B1Minimize jitterReduce sensitivityAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsPhase detectorSquare waveform
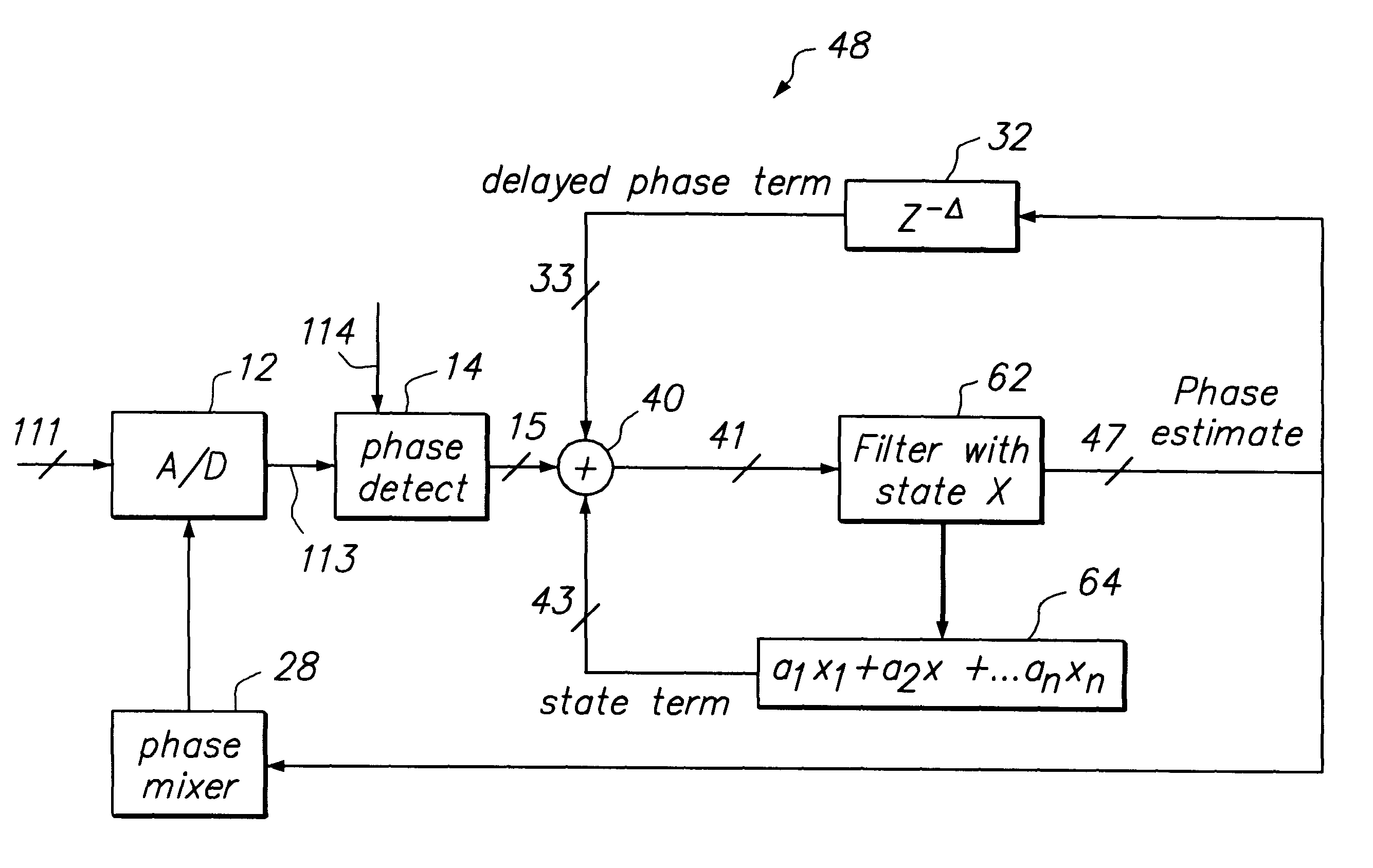
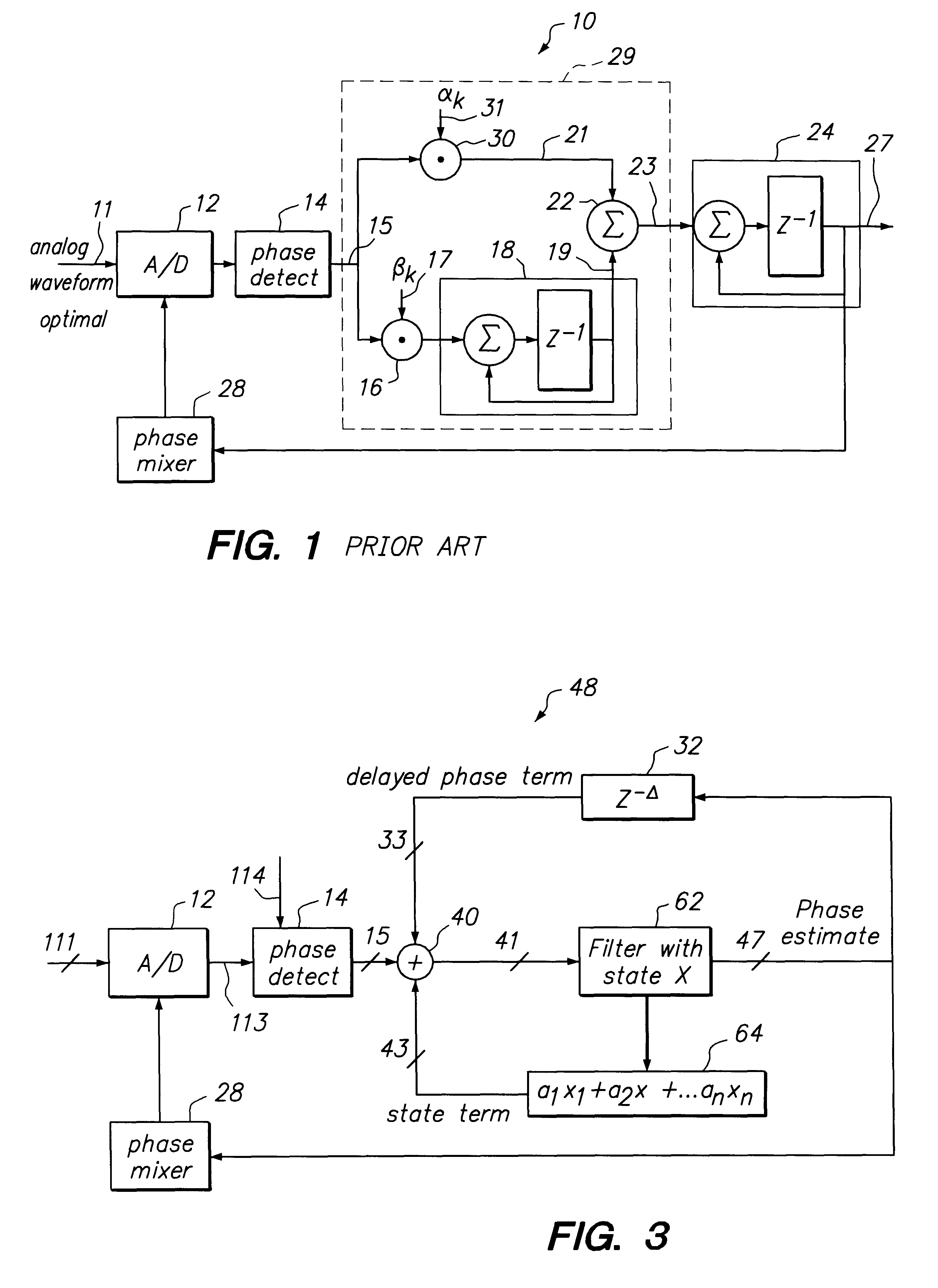
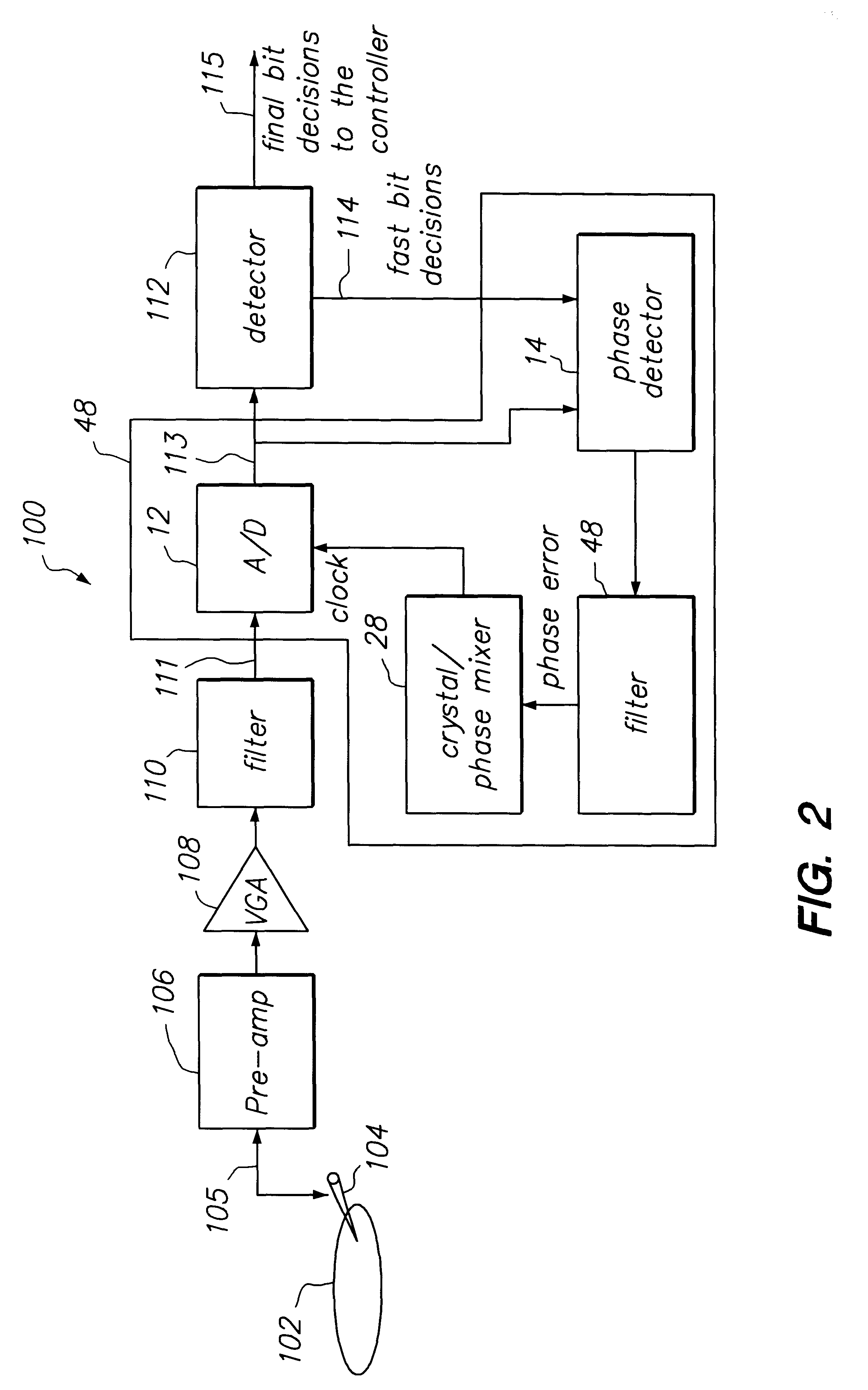
The loop latency compensated PLL filter comprising two additional feedback terms, a delayed phase compensation signal and a state compensation signal, that are provided as input of a PLL filter. Accordingly, the PLL filter input comprises two additional compensation input signals: the delayed phase compensation signal and the state compensation signal in addition to a phase estimated error output from a phase detector that is also coupled to the input of the PLL filter. Consequently, PLL filter thus is able to provide a latency compensated phase error control output that is fedback to control a phase mixer to generate a square waveform used to drive an A / D of the PLL in accordance with the principles of this invention. The loop latency compensated PLL of this invention thus minimizes the jitter of the PLL circuit, provides higher format efficiency, and also has reduced sensitivity to large bursty noises.
Owner:MAXTOR
Signal diversifying method for OFDM system
InactiveCN101394392AImprove performanceEasy to operateMulti-frequency code systemsMultiple carrier systemsZero paddingData information
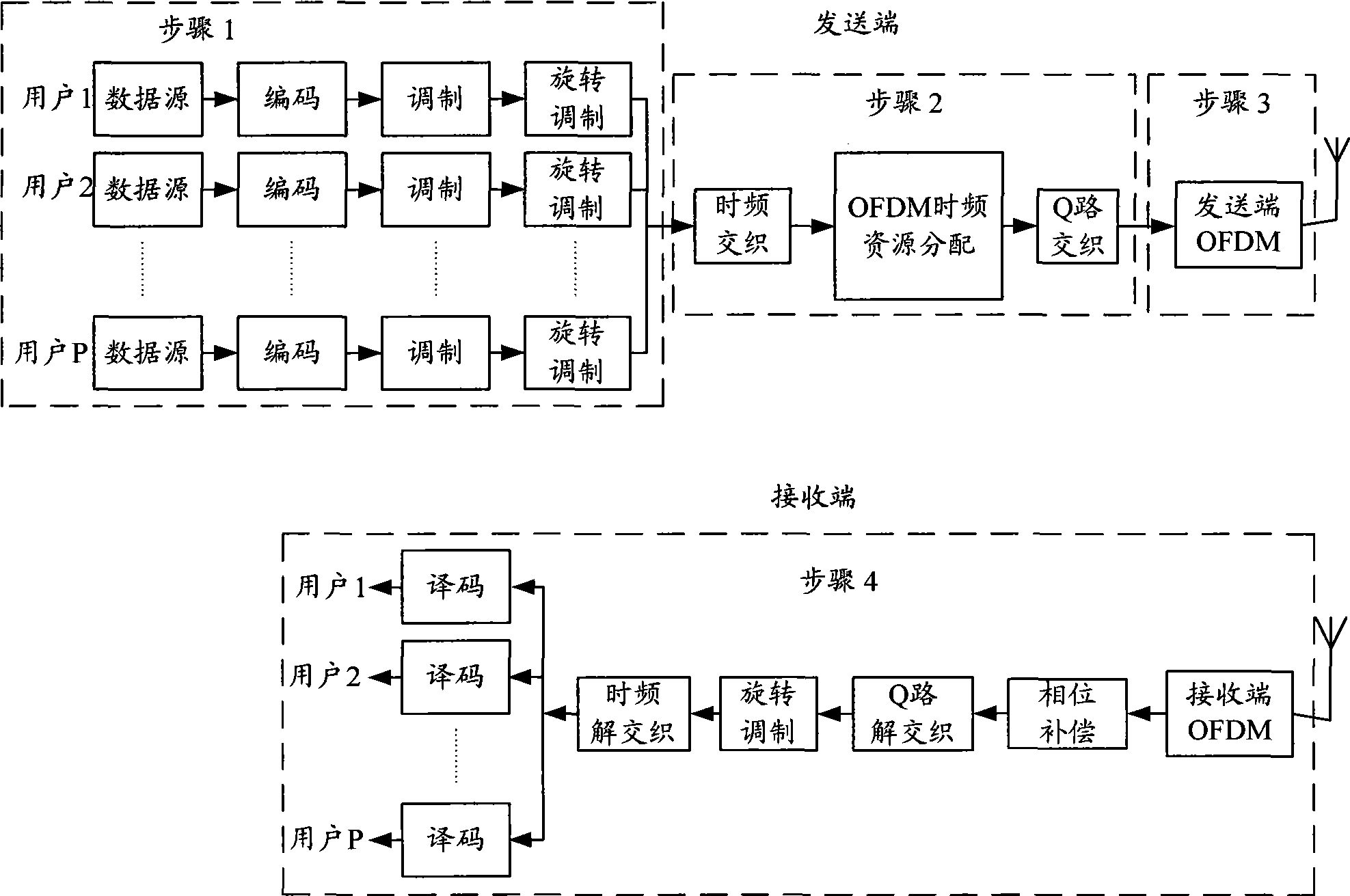
A signal diversity method of an OFDM system comprises the following steps: carrying out data decoding, modulation and rotation-modulation by a transmitting end, and storing the symbols of the processed data blocks; subjecting the symbols of the data blocks of a plurality of users in a memory to grouping and time-frequency interleaving, OFDM time-frequency resource allocation and Q-path interleaving according to the set number of the users, respectively subjecting the symbols of each data block to IFFT operation and CP addition after zero padding according to the OFDM modulation length, then transmitting the data; and subjecting the symbols of the data blocks to de-CP and FFT operations after a receiving end receives the data, carrying out phase compensation and zero removal, and sequentially subjecting the symbols of the obtained data blocks to Q-path de-interleaving, rotation demodulation, time-frequency de-interleaving and coding to obtain the desired data information. By adopting OFDM technique and rotation modulation technique and by selecting an optimal rotation angle, the method can acquire signal diversity gain and maximal performance improvement, thereby improving the system performance.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Composite film and display device
ActiveUS20170343715A1Limited viewing angleReduce large-angle light leakagePolarising elementsNon-linear opticsComposite filmOptical axis
A composite film including a first polarizing film, at least one second polarizing film, and at least one first phase compensation film is provided. The first polarizing film has a first transmission axis. Each second polarizing film has a second transmission axis parallel to the first transmission axis. The at least one first phase compensation film is disposed between the first polarizing film and the at least one second polarizing film. Each first phase compensation film has a first optical axis. An orthographic projection of the first optical axis on the first polarizing film is parallel to an axial direction of the first transmission axis, and a first included angle between the first optical axis and the first polarizing film is greater than 0 degrees and less than 90 degrees. A display device is also provided.
Owner:CORETRONIC
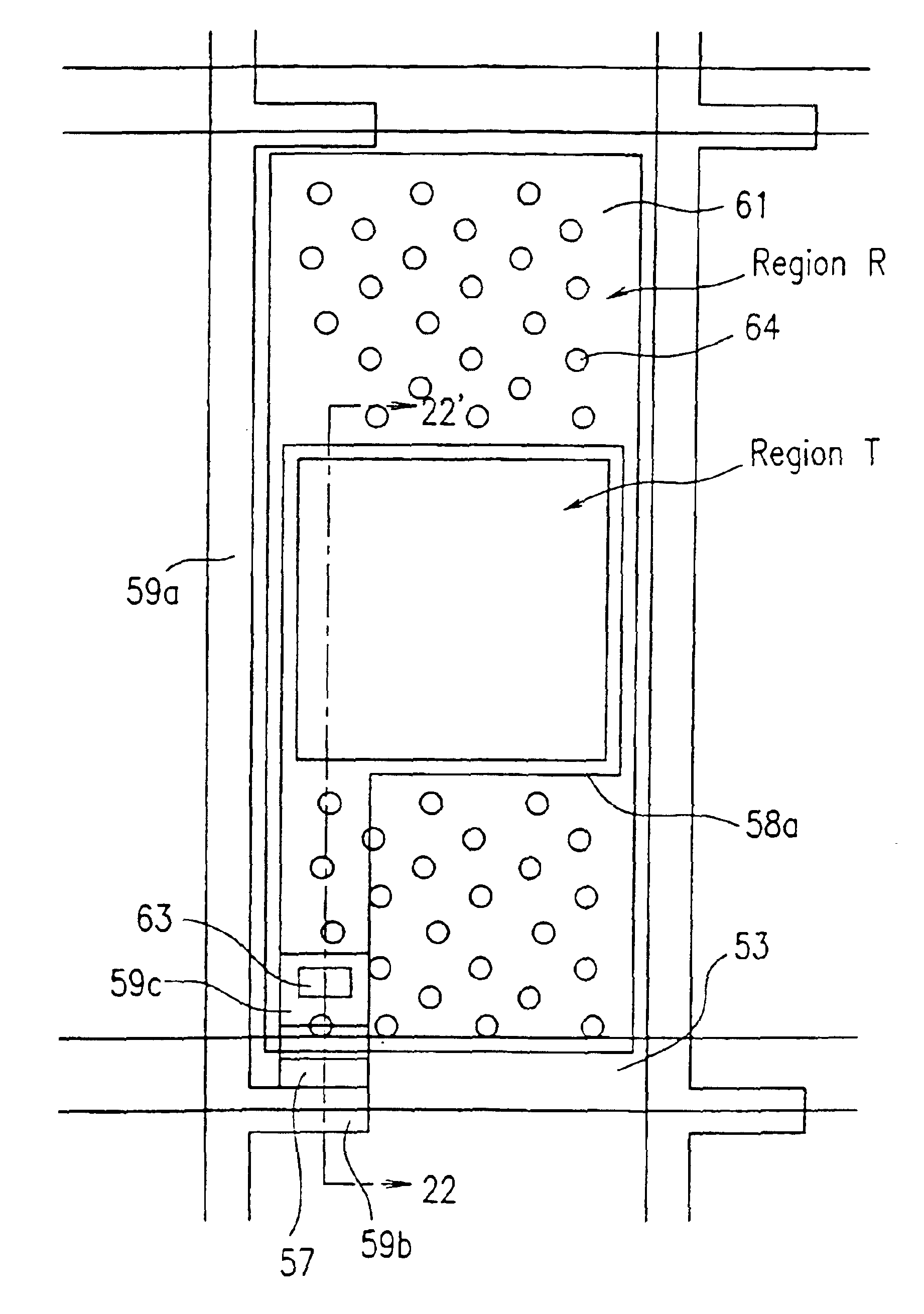
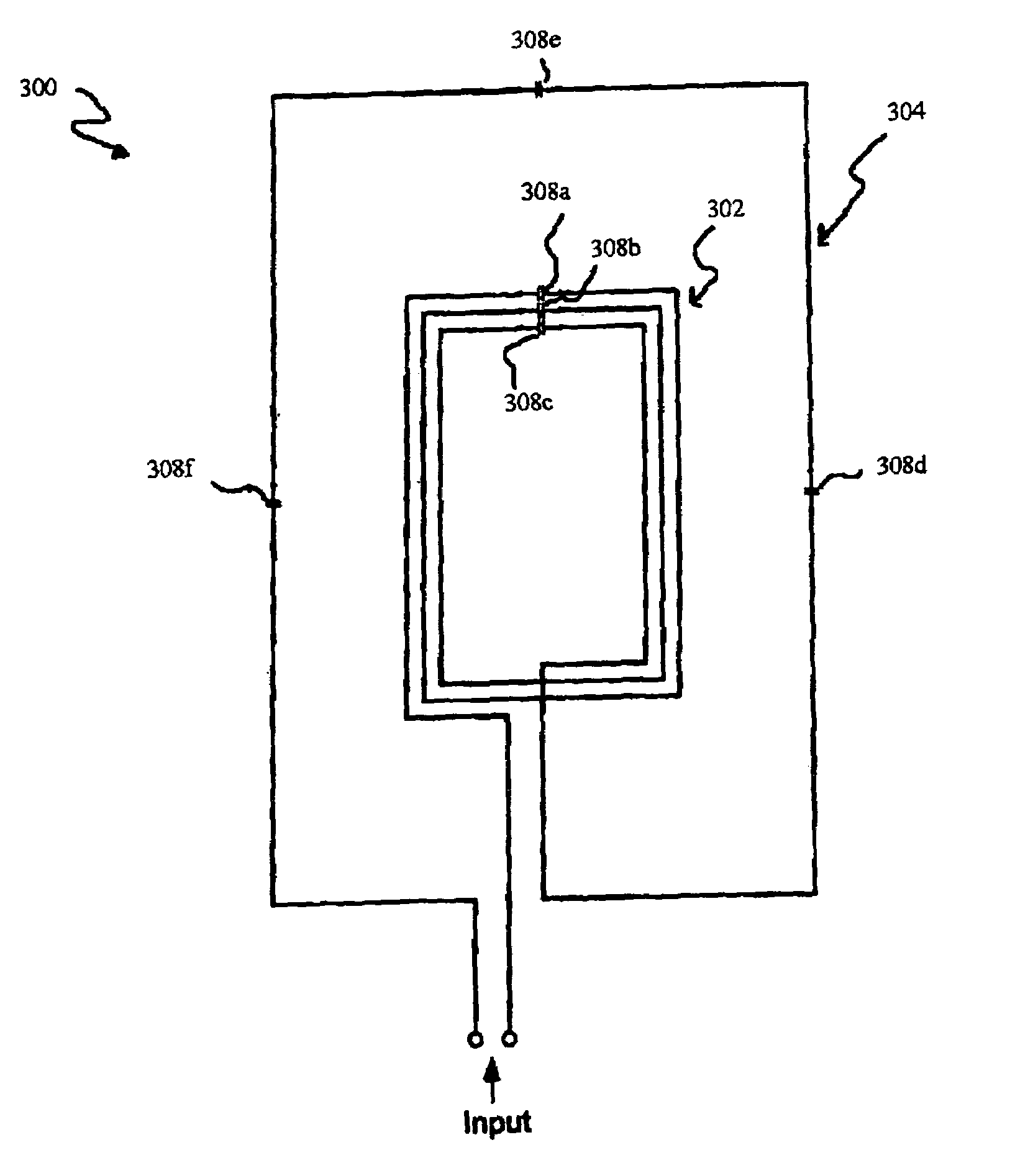
Phase compensated field-cancelling nested loop antenna
InactiveUS6970141B2Reduce variationResonant long antennasCo-operative working arrangementsElectrical currentSlot antenna
A phase compensated loop antenna having phase compensation elements distributed along the length thereof. The phase compensation elements compensate for current variations along the antenna length resulting from increasing the length of the antenna. A nested loop configuration incorporating at least one phase compensated loop antenna is also provided.
Owner:TYCO FIRE & SECURITY GMBH
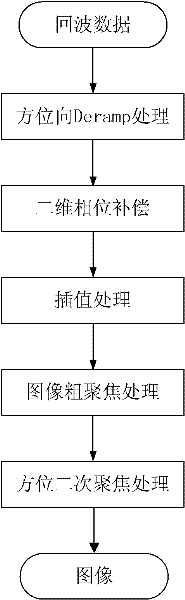
Large squint sliding spotlight SAR (synthetic aperture radar) imaging processing method
InactiveCN102176016AHigh precisionEnables precise focus processingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImaging processingSynthetic aperture sonar
The invention discloses a large squint sliding spotlight SAR(synthetic aperture radar) imaging processing method, which belongs to the signal processing field. The processing method mainly comprises the following five parts, namely directional Deramp processing, two-dimensional phase compensation, interpolation processing, image coarse focusing and directional secondary focusing; the large squintsliding spotlight SAR imaging processing method has high accuracy and can realize accurate focusing in a full scene by using a secondary focus technology for compensating the spare-varying feature ofa Doppler parameter; in addition, the processing method has high efficiency, since distance migration induced by a reference slant distance in an echo signal is removed so as to greatly reduce data volume of the echo signal and improve the processing efficiency; moreover, the processing method has strong practicability and can realize the high-precision imaging process in a large squint angel mode; compared with the traditional imaging processing method, the large squint sliding spotlight SAR imaging processing method has better practicability.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
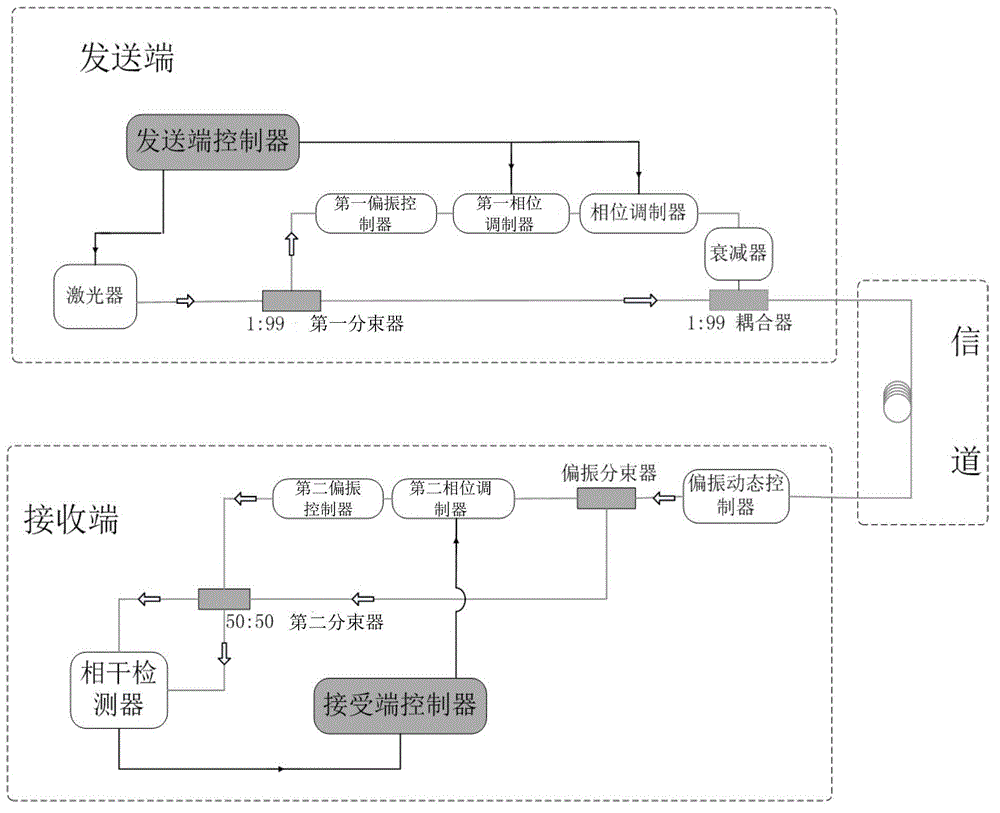
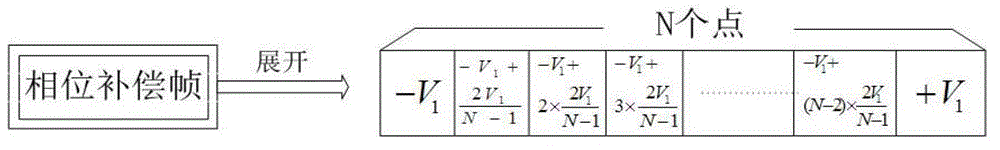
Continuous variable quantum key distribution system and phase compensation method thereof
ActiveCN102868520ACancel noiseEliminate ambient noiseKey distribution for secure communicationEngineeringKey distribution
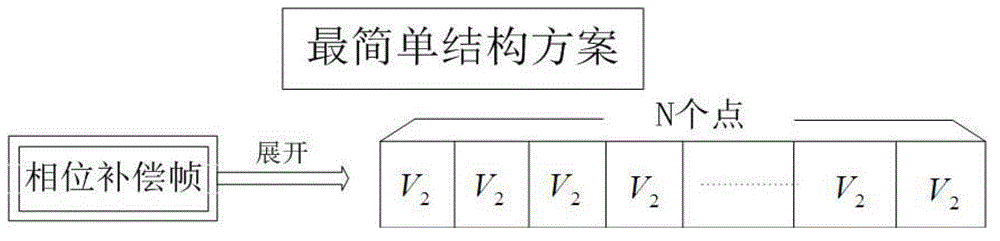
The invention relates to a continuous variable quantum key distribution system and a phase compensation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps that: a sending end determines to send a phase compensation frame and determines a value of frequency A in an insertion signal of the phase compensation frame; the sending end sends the phase compensation frame and receives (A-1) signal frames; a receiving end samples an output signal of a coherent detector and extracts the phase compensation frame; the receiving end calculates a voltage value to be compensated according to the phase compensation frame, compensates the compensated voltage value to (A-1) key frame phases through a second phase modulator to eliminate environment and system noises and stores compensated (A-1) key frames into an original key file; the receiving end receives the subsequent phase compensation frame, extracts the phase compensation frame, and repeatedly performs the operation; and the sending end sends an interrupt transmission signal, and after receiving the interrupt transmission signal, the receiving end stops receiving, so key distribution is finished. The invention has the advantages of low bit error rate and reliable communication.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAODA INTELLECTUAL PORPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD +1
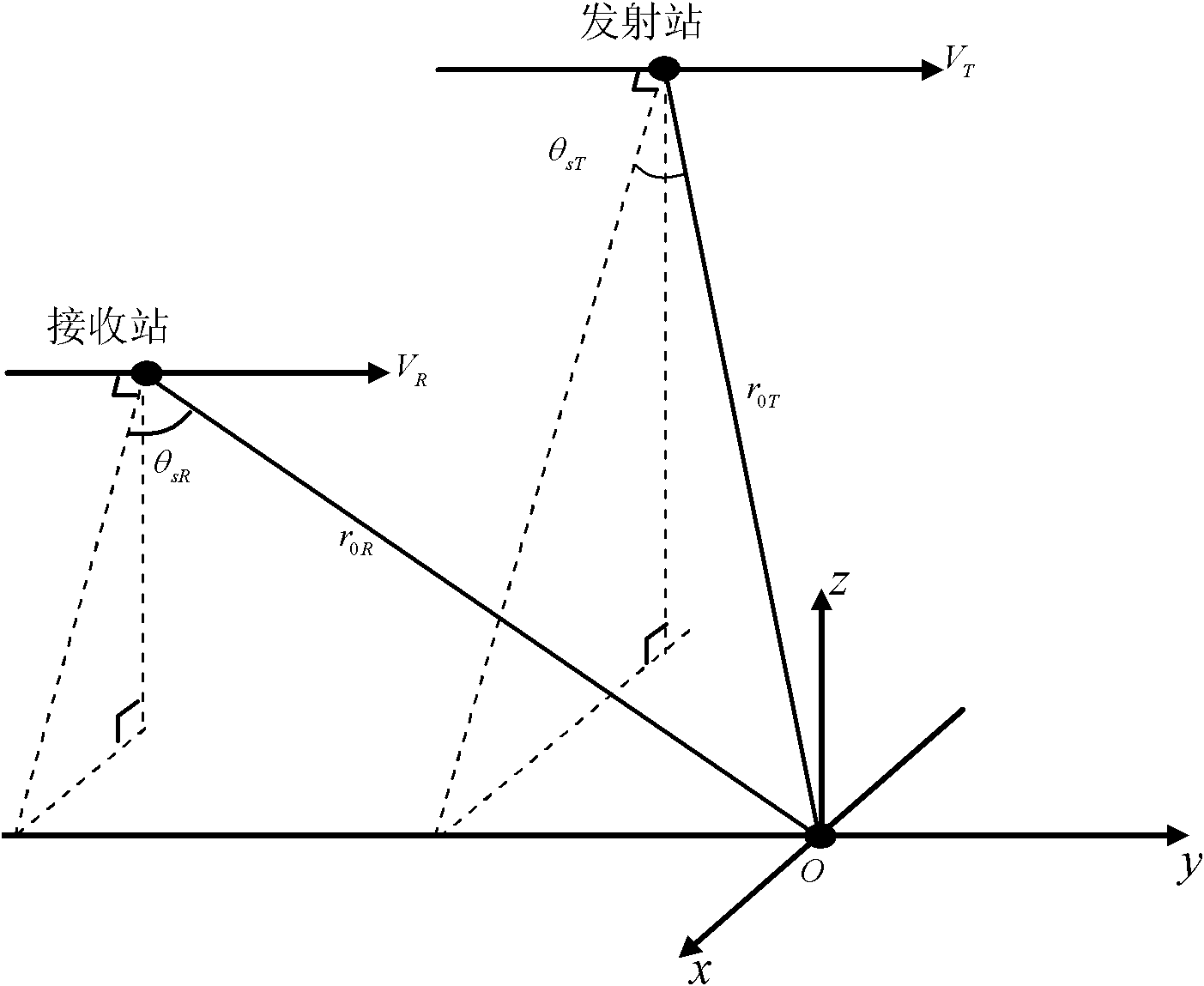
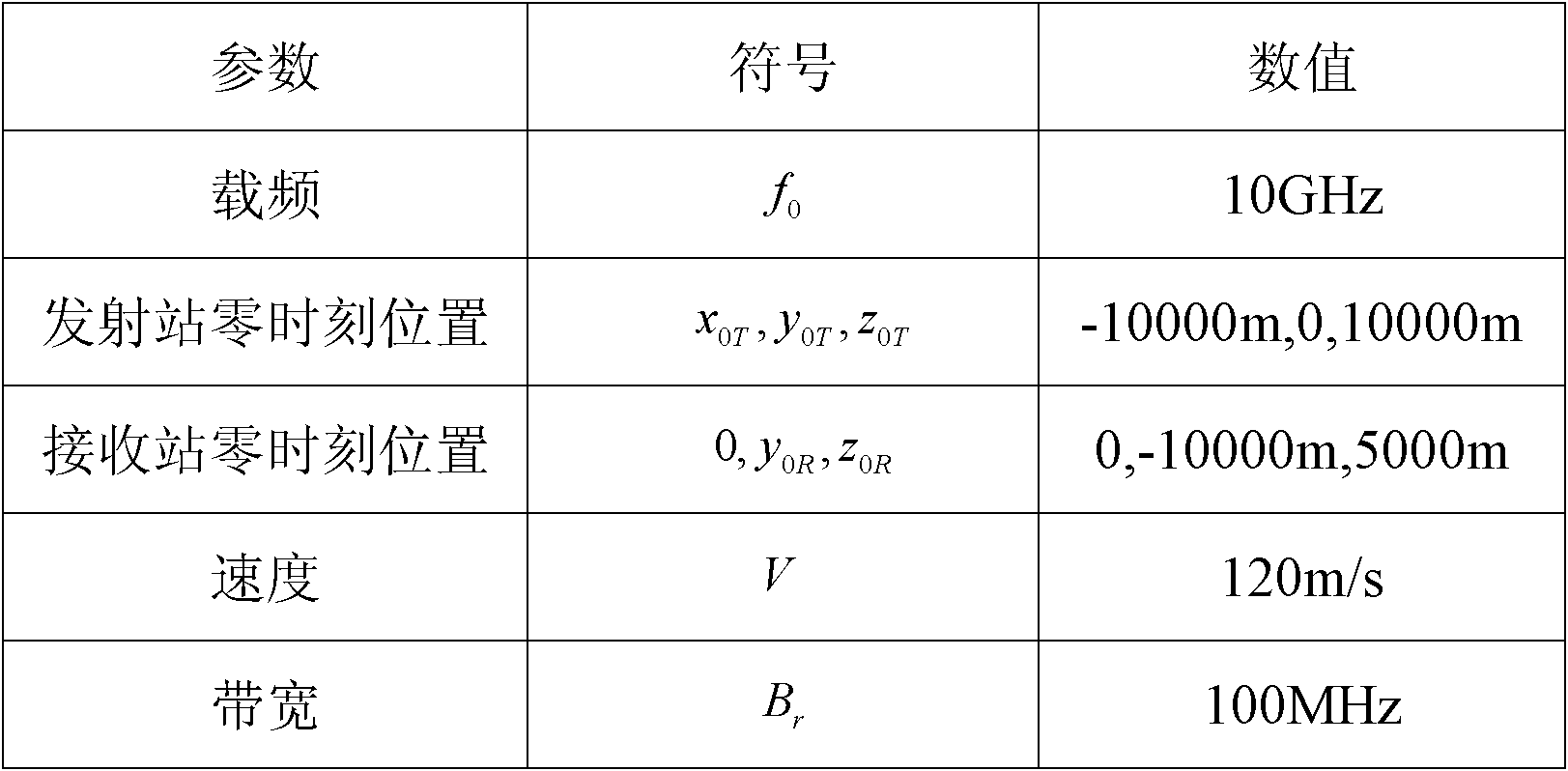
Imaging method for bistatic forward-looking synthetic aperture radar (SAR)
InactiveCN102147469AAchieve precise focusImproving Imaging AccuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDoppler centroidFrequency spectrum
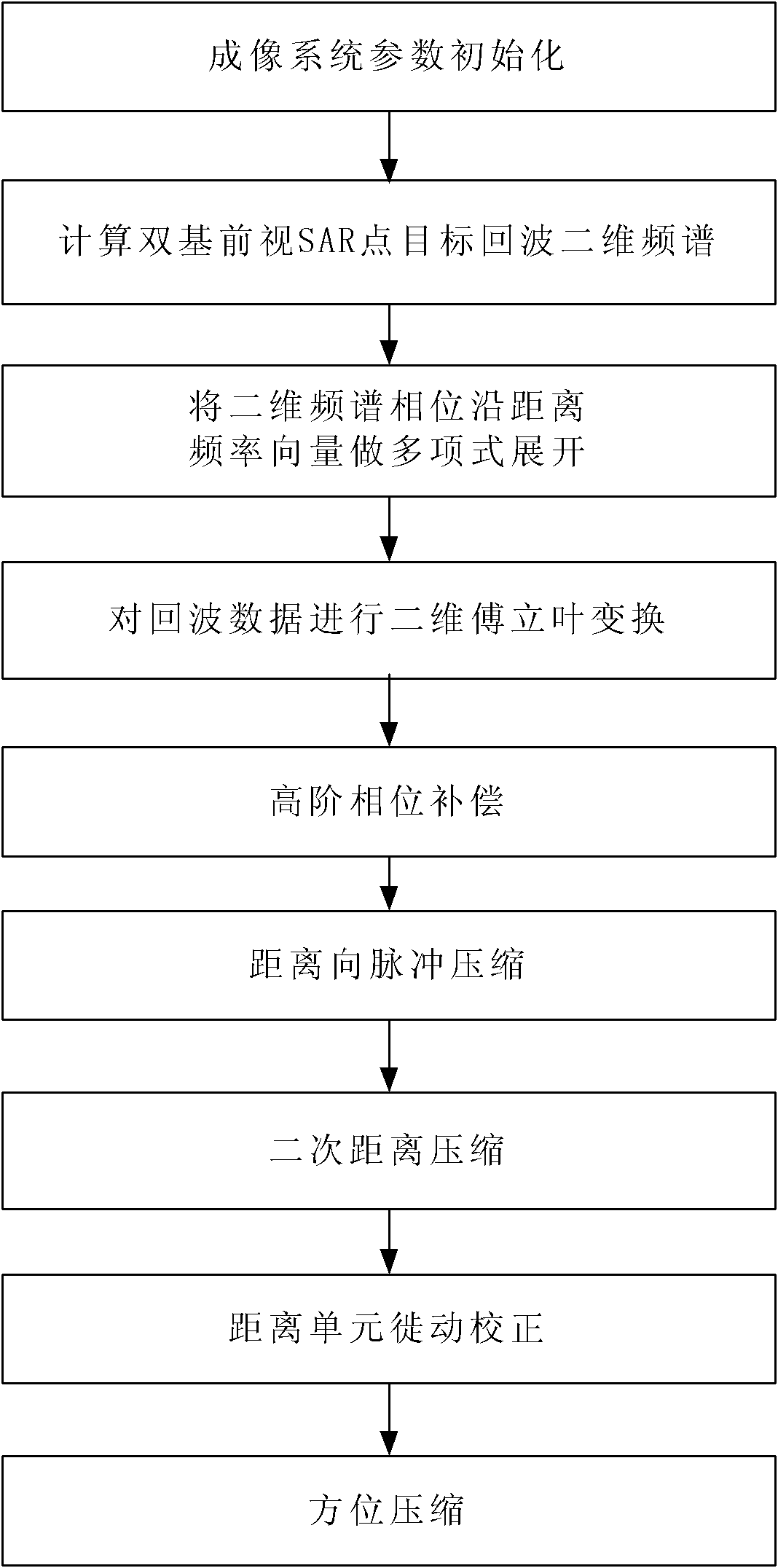
The invention discloses an imaging method for a bistatic forward-looking synthetic aperture radar (SAR). Aiming at the defect existing when the existing method is used for the imaging process of the bistatic forward-looking synthetic aperture radar, the imaging method adopts a bistatic forward-looking SAR point target response two-dimensional frequency spectrum based on the least square polynomial fitting; the frequency spectrum is the least square approximation of the two-dimensional frequency spectrum with the accurate theory. According to the characteristics of bistatic forward-looking invariant SAR direction, variant range and nonlinear and variant Doppler centroid range of range cell migration in an RD (radar domain) domain, bistatic forward-looking SAR range migration correction, secondary-range compression and high-order phase compensation are realized by the frequency spectrum so as to accurately focus the bistatic forward-looking SAR. Compared with the traditional SAR imaging method and the bistatic forward-looking SAR imaging method, the method disclosed by the invention has higher imaging precision.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Modification of acoustic signals using sinusoidal analysis and synthesis
InactiveUS20050065784A1More realistic modified speechChange shapeSpeech synthesisVocal tractAudio frequency
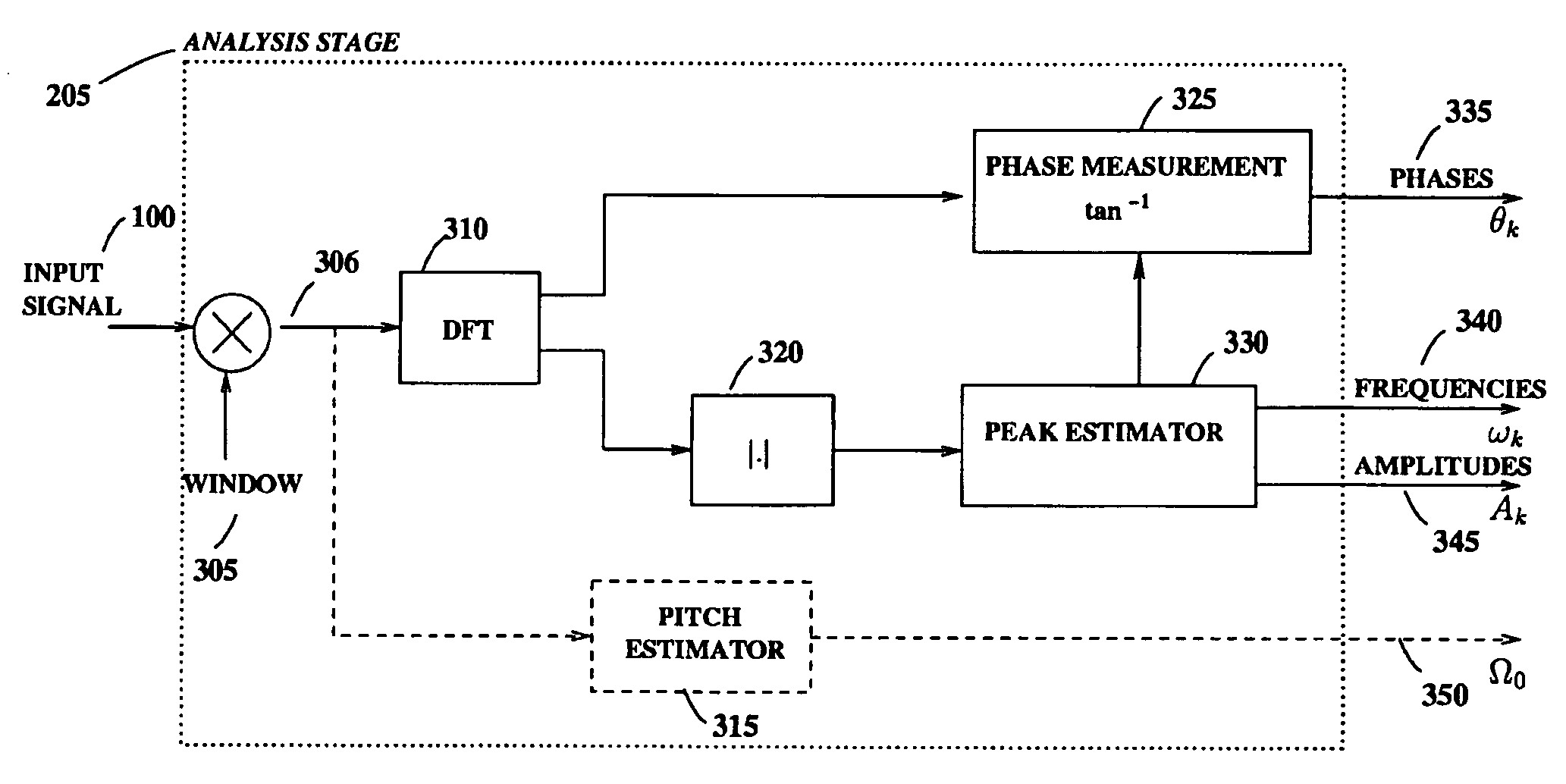
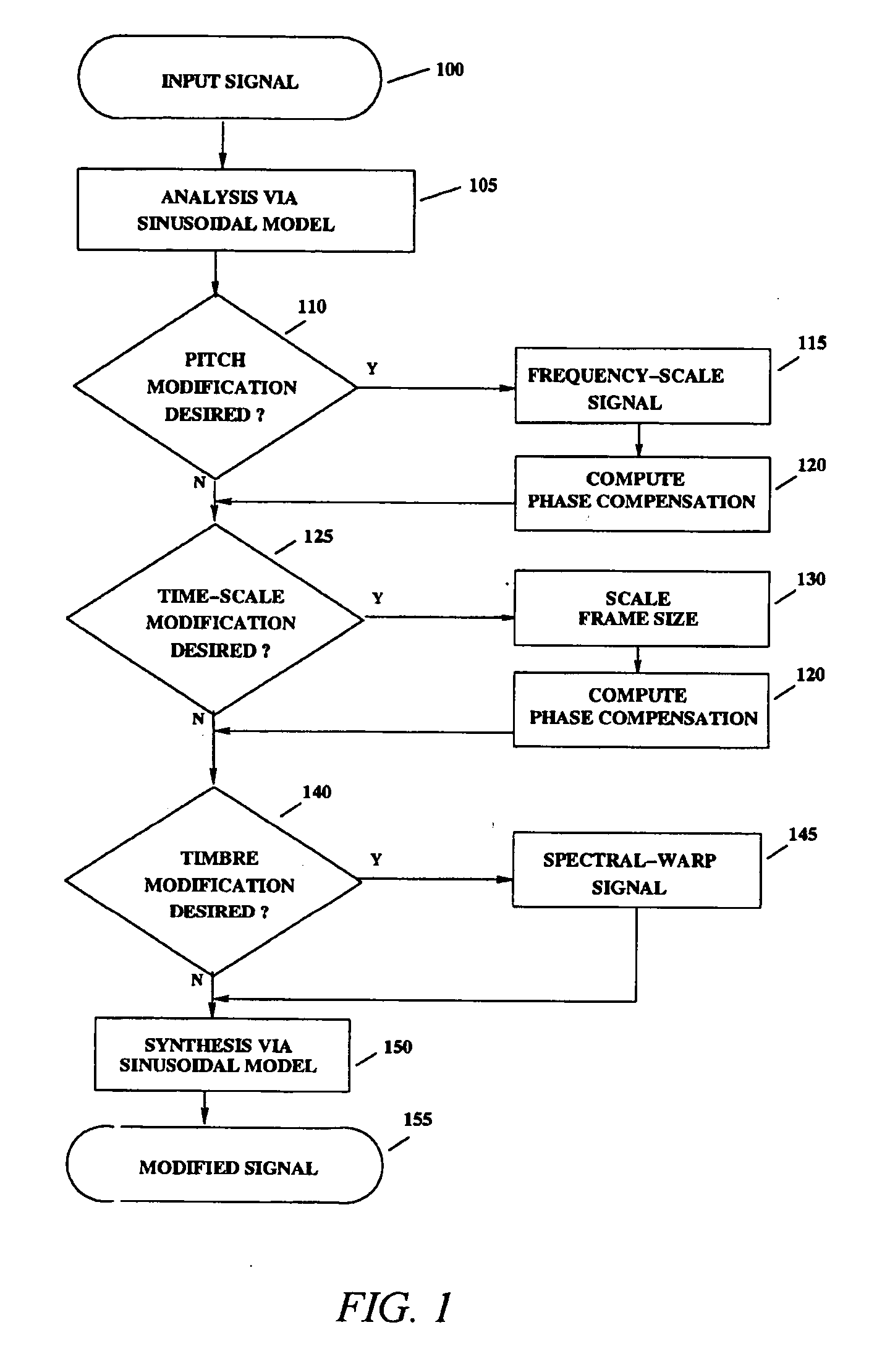
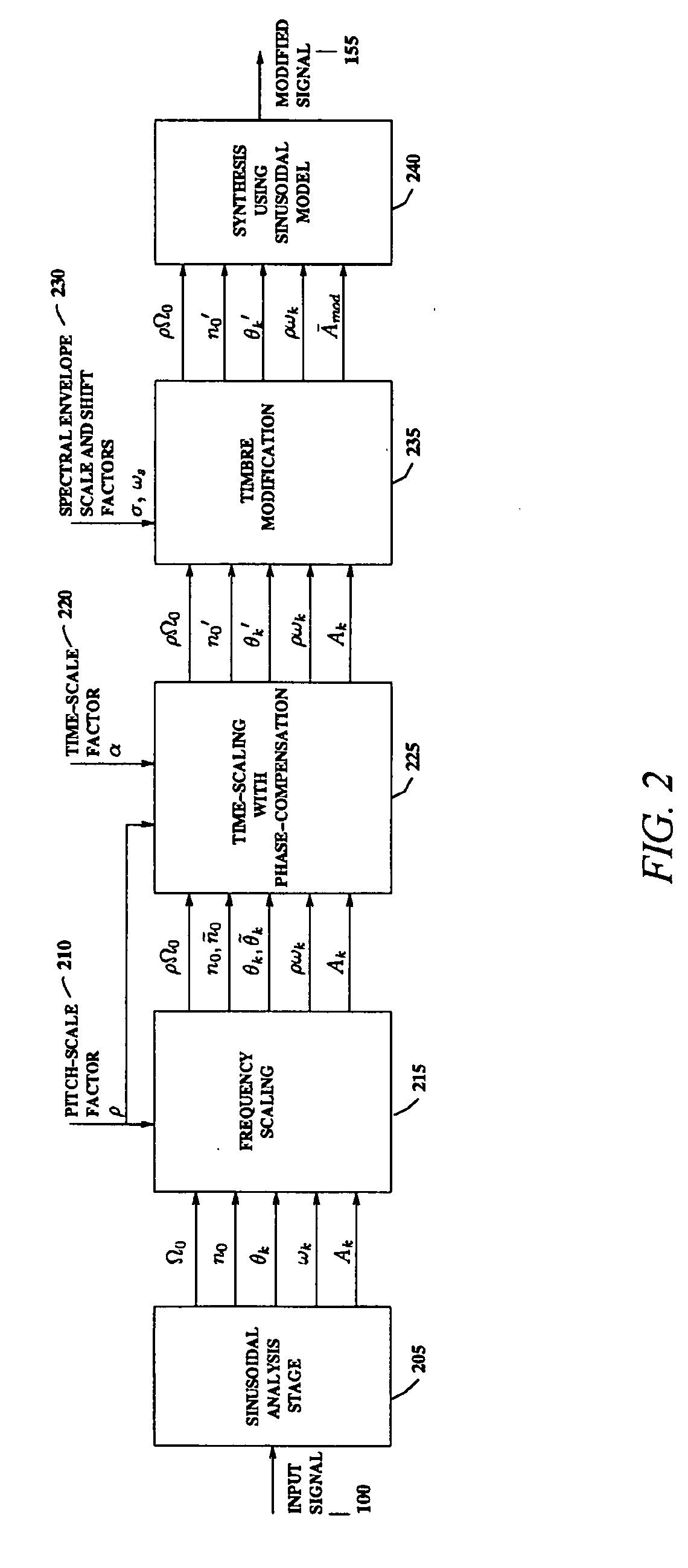
An analysis and synthesis system for sound is provided that can independently modify characteristics of audio signals such as pitch, duration, and timbre. High-quality pitch-scaling and time-scaling are achieved by using a technique for sinusoidal phase compensation adapted to a sinusoidal representation. Such signal modification systems can avoid the usual problems associated with interpolation-based re-sampling so that the pitch-scaling factor and the time-scaling factor can be varied independently, arbitrarily, and continuously. In the context of voice modification, the sinusoidal representation provides a means with which to separate the acoustic contributions of the vocal excitation and the vocal tract, which can enable independent timbre modification of the voice by altering only the vocal tract contributions. The system can be applied to efficiently encode the pitch in sinusoidal models by compensating for pitch quantization errors. The system can also be applied to non-speech signals such as music.
Owner:NELLYMOSER A MASSACHUSETTS CORP
Broadband wireless sensor network transmission scheme based on collaborative communication of amplification forward single node
InactiveCN101237306AReduce processing complexityEffective expansionDiversity/multi-antenna systemsMulti-frequency code systemsLine sensorCyclic prefix
The invention discloses a broadband wireless sensor network transmission scheme based on amplify-and-forward single-node cooperation communication. The scheme is as follows: a source node is firstly used to make an orthogonal space-frequency coding to an original signal, two time slots are respectively used to transmit orthogonal signal frames, then a pilot frequency is inserted and coded signals are subject to IFFT operation to fight against the multi-path attenuation, the coded signals are converted onto a time domain, and the serial data flow is broadcast and sent after the insertion of a cyclic prefix and a training sequence. A first time slot relay node receives signals of the source node, makes frequency deviation and phase compensation, then adopts an amplify-and-forward protocol to synchronously send the processed signals to an information sink node at a second time slot and the source node; an information sink receiver receives a mixed signal from two independent channels, firstly detects a frame head of the signal of the second time slot, then synchronizes with the frame head, then carries out FFT operation to the signal part, converts the signal back to the frequency domain, and performs space-frequency decoding to obtain an original sending symbol. The scheme is simple and easy to operate, can effectively improve the error code rate performance of the system, has strong practicability, and is convenient for the realization of the hardware.
Owner:JIAXING WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS CENT CAS
System and method for programmable polarization-independent phase compensation of optical signals
InactiveUS6879426B1Correcting and reducing and otherwise adjusting chromatic dispersionIncrease speedWavelength-division multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationSpatial light modulatorComputer module
A system and method for programmable phase compensation of optical signals is disclosed. The systems and methods include the use of a polarization-independent spatial light modulator (PI-SLM), so that the state of polarization (SOP) of the incoming optical signal need not be known. The system includes a first dispersive module that spatially separates the optical signal into its frequency components. The frequency components are spread over the active area of the PI-SLM. The active area of the PI-SLM includes an array of independently programmable addressable regions capable of altering the phase of the light incident thereon. An exemplary application of the invention is chromatic dispersion compensation. By knowing the amount of chromatic dispersion in the optical signal, or alternatively, by knowing the amount of chromatic dispersion to be introduced into the optical signal downstream, the appropriate phase adjustments can be made to each frequency component of the signal. The phase-adjusted frequency components are then recombined via a second dispersive module to form a compensated optical signal.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Resonant inverter including feed back circuit having phase compensator and controller
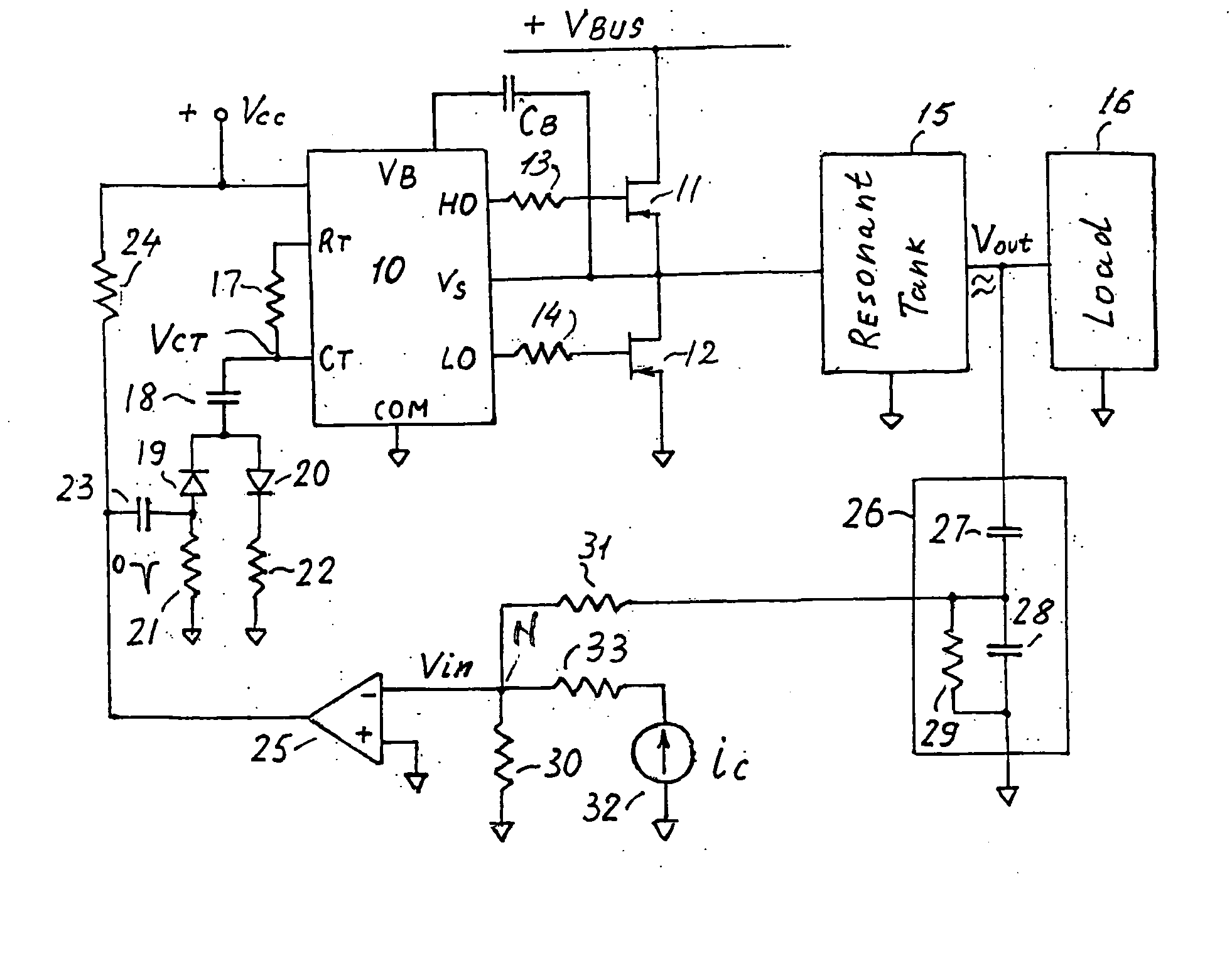
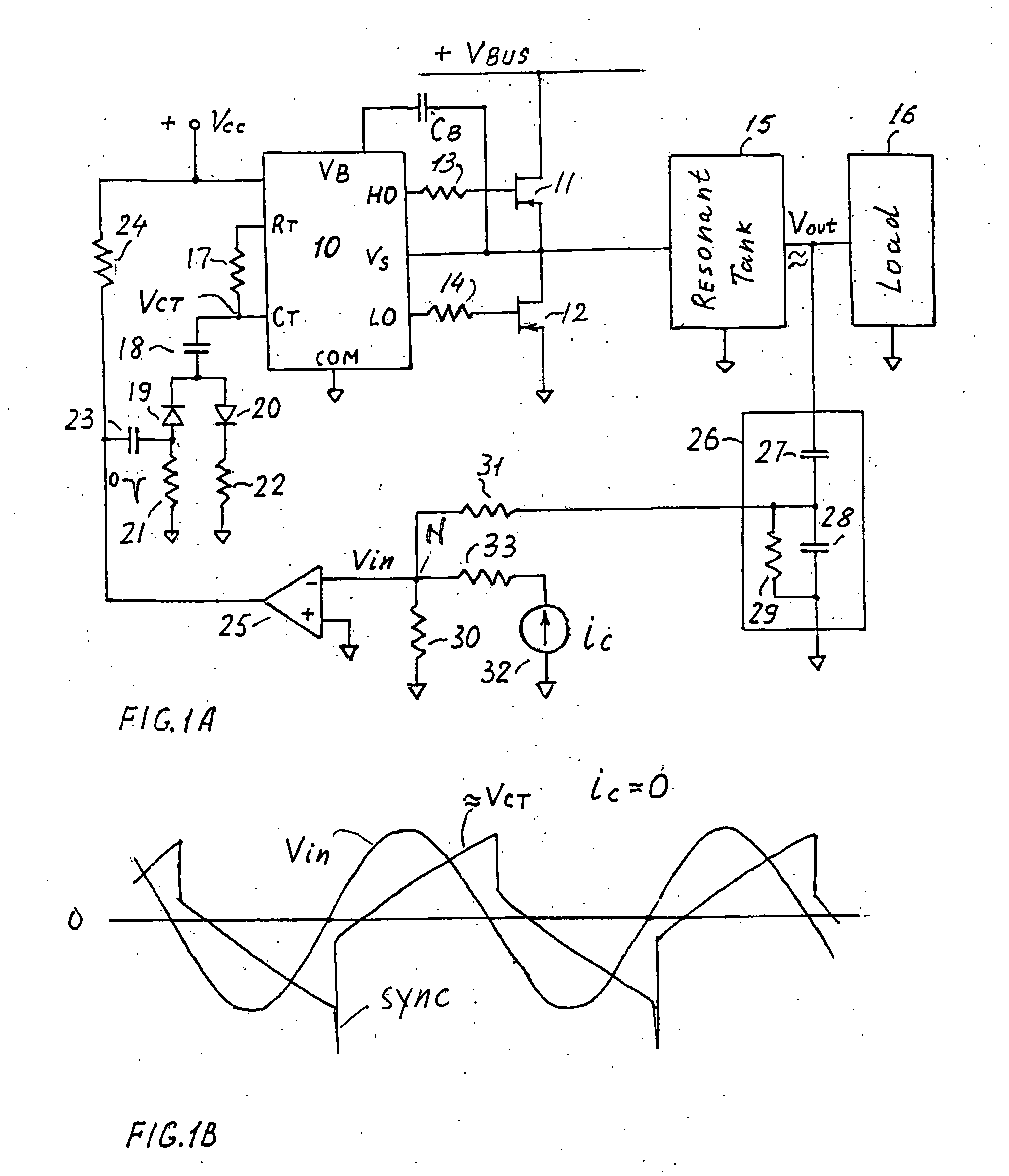
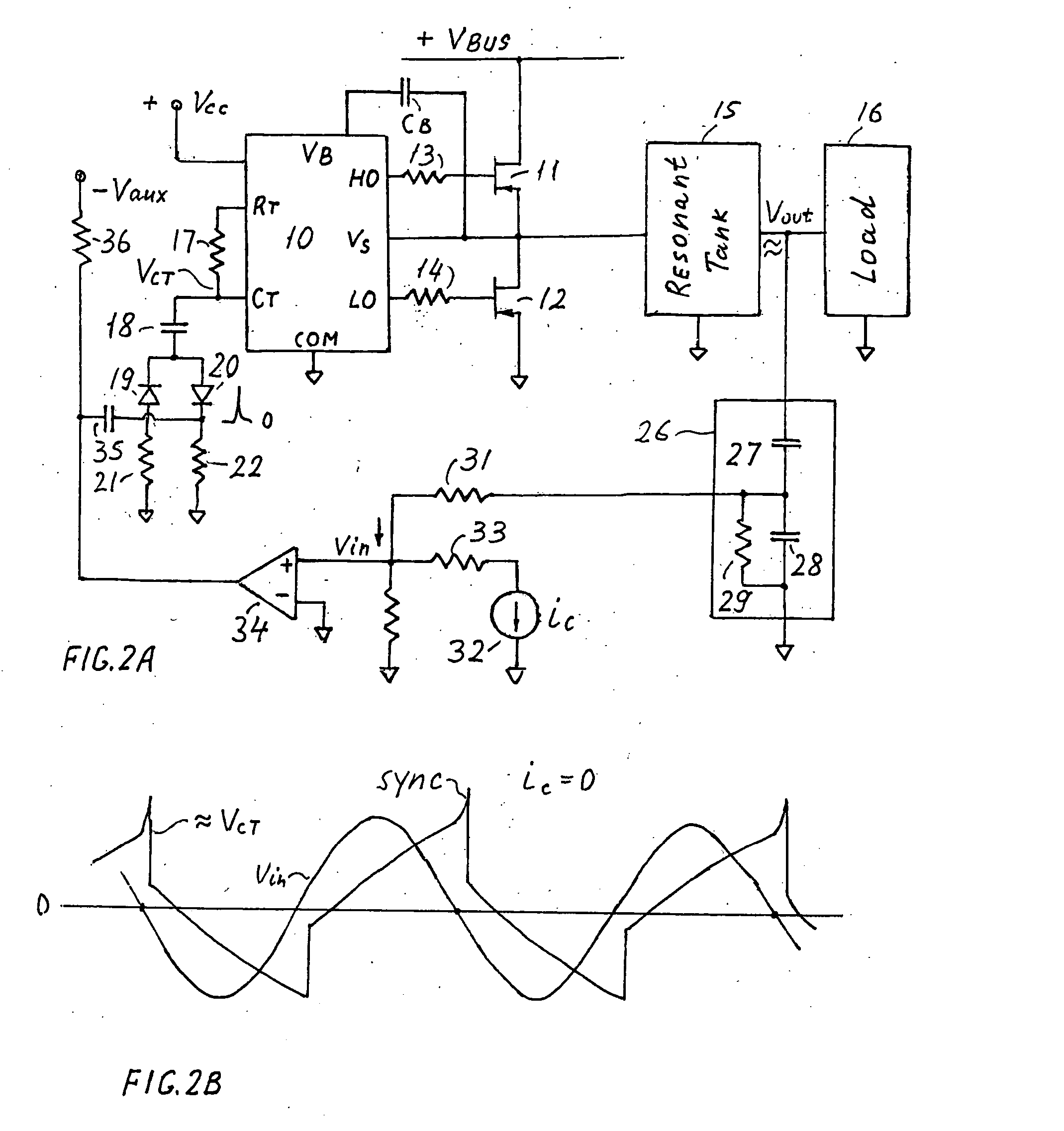
InactiveUS20060006816A1Wide range reliable synchronizationEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionGas-discharge lampResonant inverter
A resonant inverter with a self-oscillating driver IC for powering AC loads, such as gas discharge lamps or regulated DC / DC converters, includes a timing circuit that generates control strobe pulses that are injected into the timing circuit. The timing circuit is coupled to an inverter resonant tank through a feed back circuit providing phase lock for the resonant inverter. The feed back circuit connects the resonant tank circuit to a zero signal detector. The feed back circuit includes a phase compensator and a controller that has a source of a bias current connected to the zero signal detector.
Owner:OSRAM SYLVANIA INC
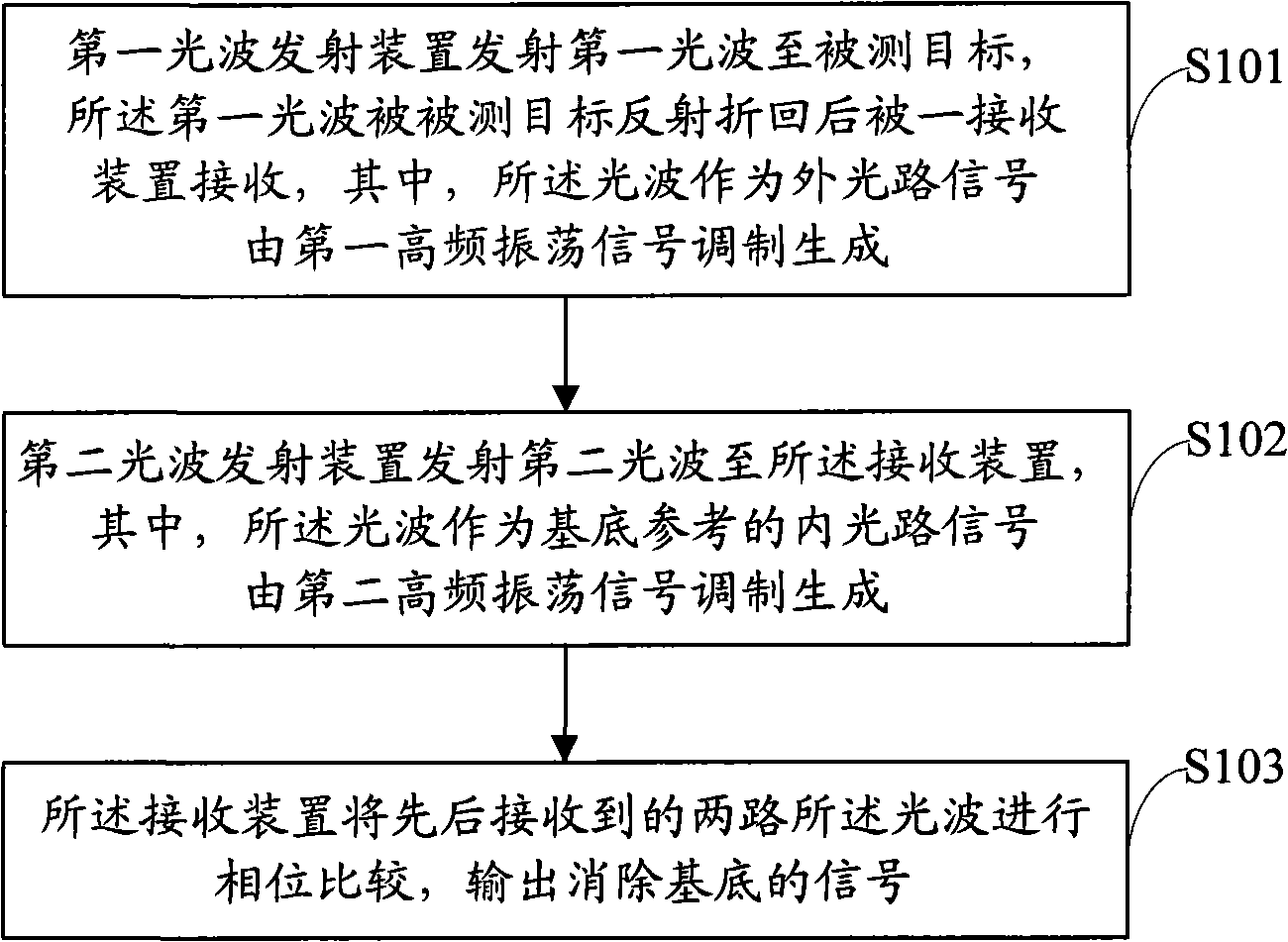
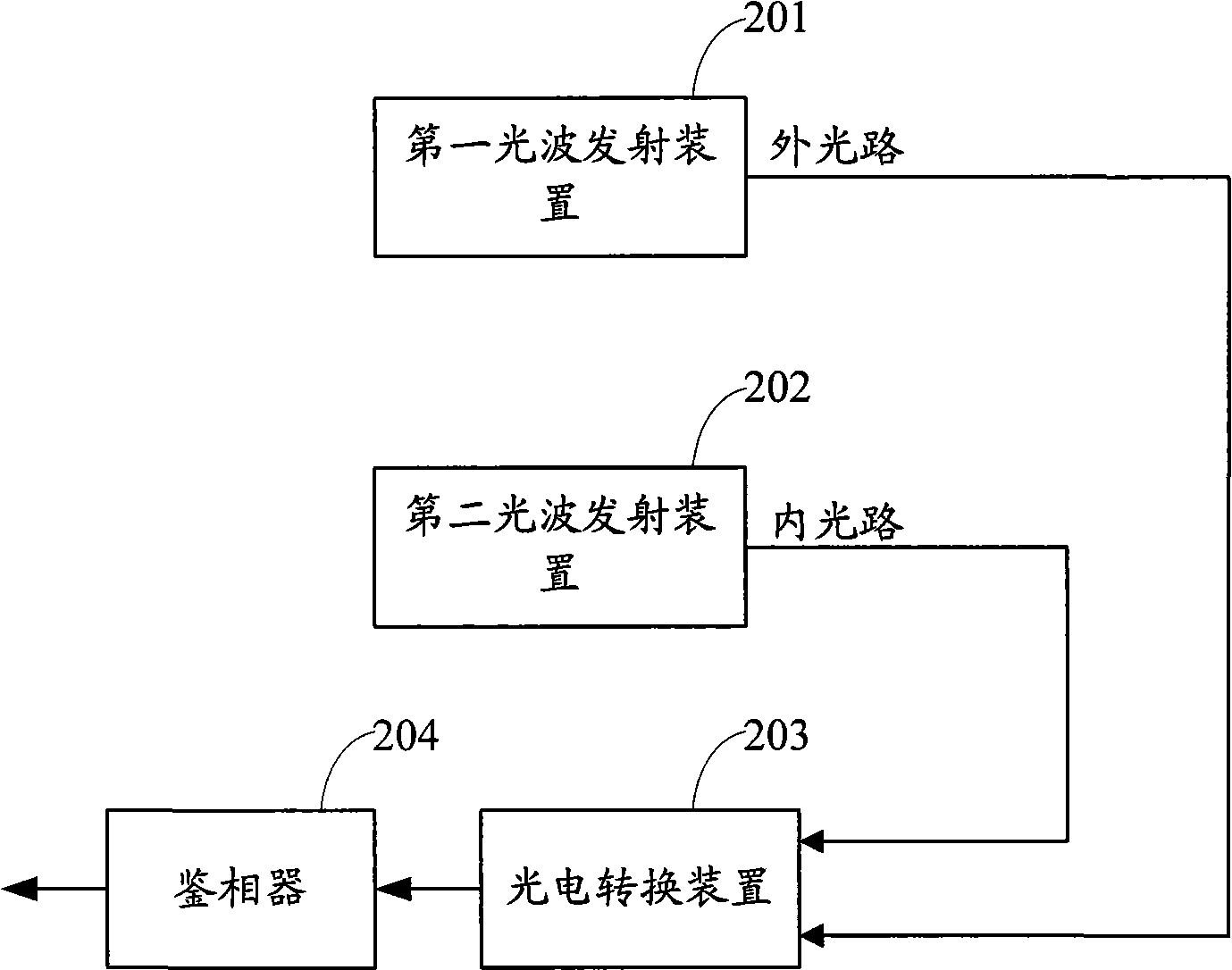
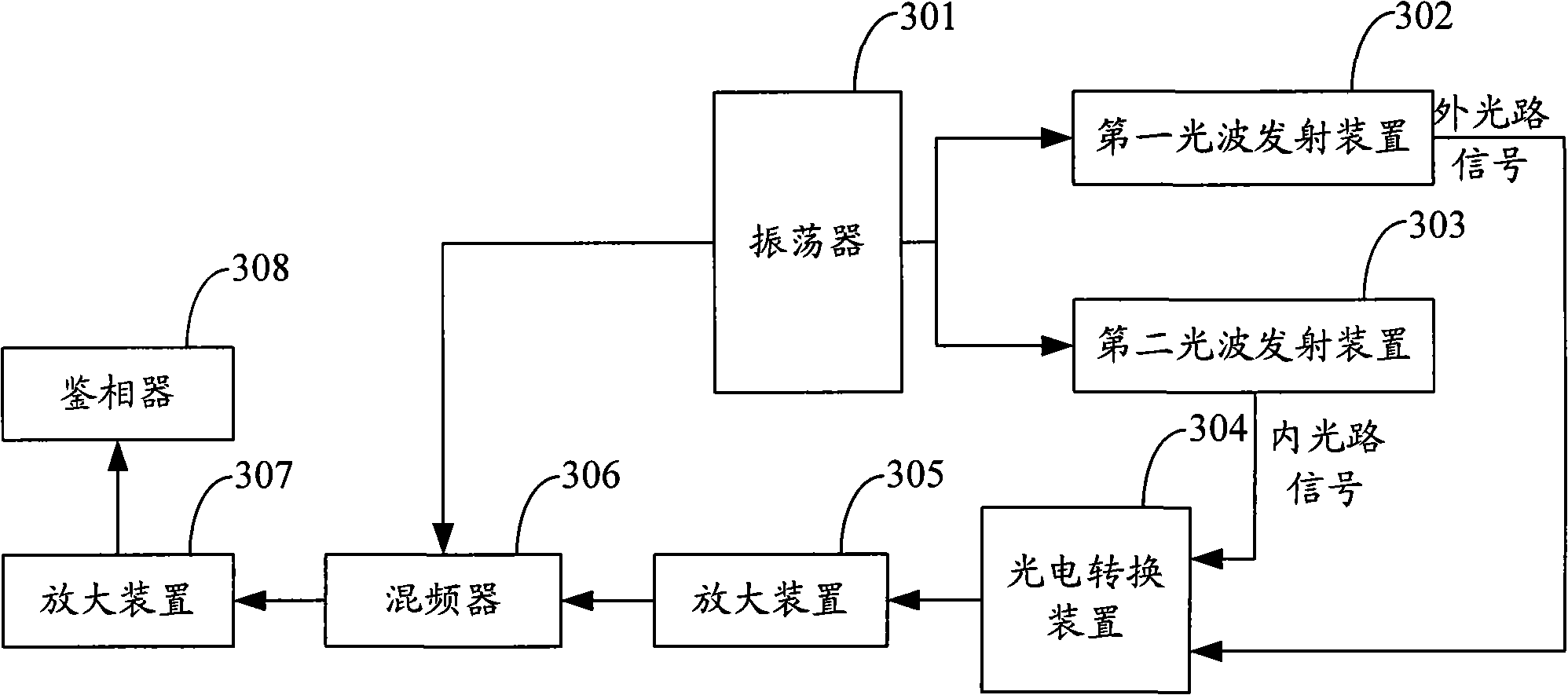
Calibration method for phase measurement, device and distance measuring apparatus
InactiveCN101581783AHigh measurement accuracyLower performance requirementsElectromagnetic wave reradiationLaser rangingPhase noise
The invention is applied to the field of electro optical distance measurement and provides a calibration method for phase measurement, a device and a distance measuring apparatus. The method comprisesthe following steps: a first lightwave emission device emits a first lightwave to a measured object, the first lightwave is reflected by the measured object and received by a receiving device, and the lightwave acting as an outer light path signal is generated by modulating a first high-frequency oscillator signal; a second lightwave emission device emits a second lightwave to the receiving device, and the lightwave acting as a substrate reference of an inner light path signal is generated by modulating a second high-frequency oscillator signal; and the receiving device carries out phase comparison of the two paths of lightwaves received one after the other and outputs signals with substrate elimination. The invention realizes phase compensation and calibration and avoids inducing uncertain phase noise to circuits because of environment variation, thereby improving the measurement precision of laser ranging, reducing the effect of environment factor to ranging error, reducing the costof a system and enhancing the application of laser ranging to various industries.
Owner:SHENZHEN MILESEEY TECH
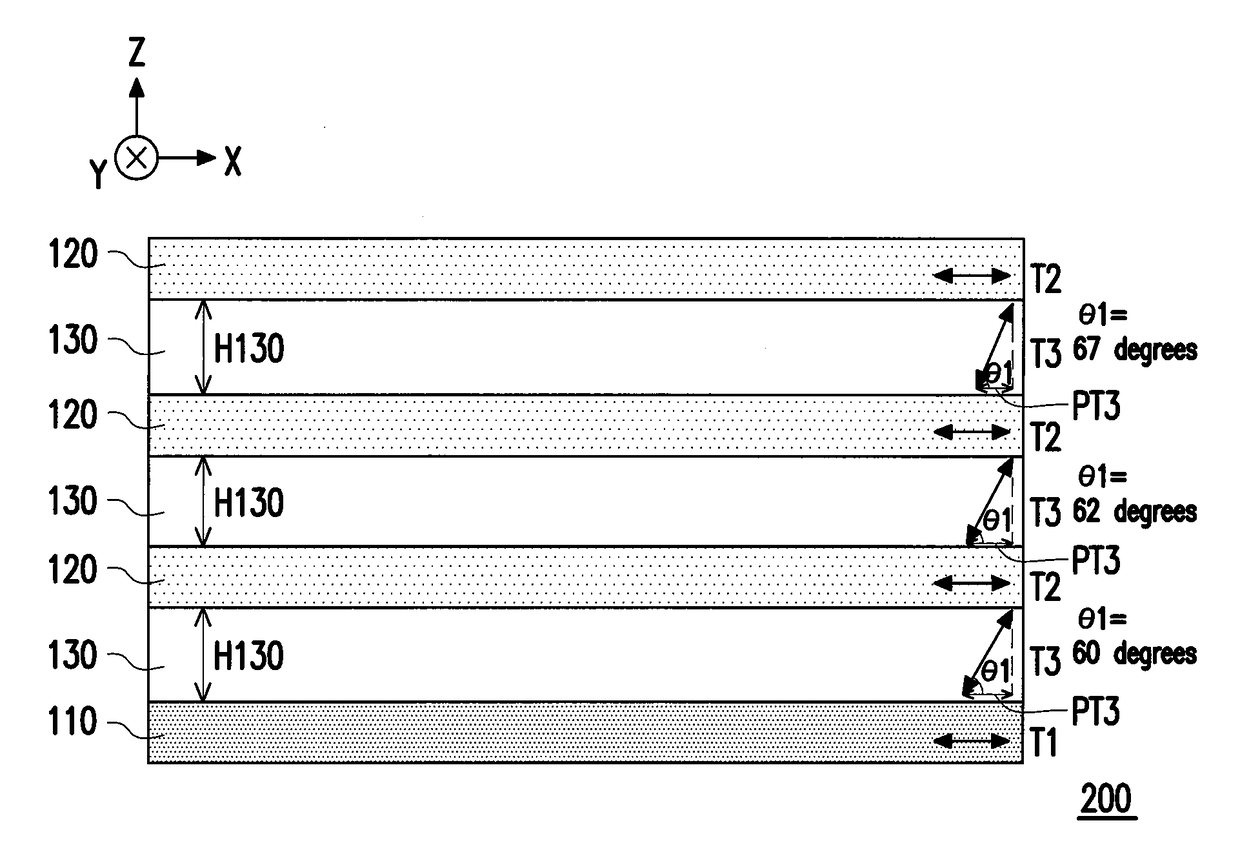
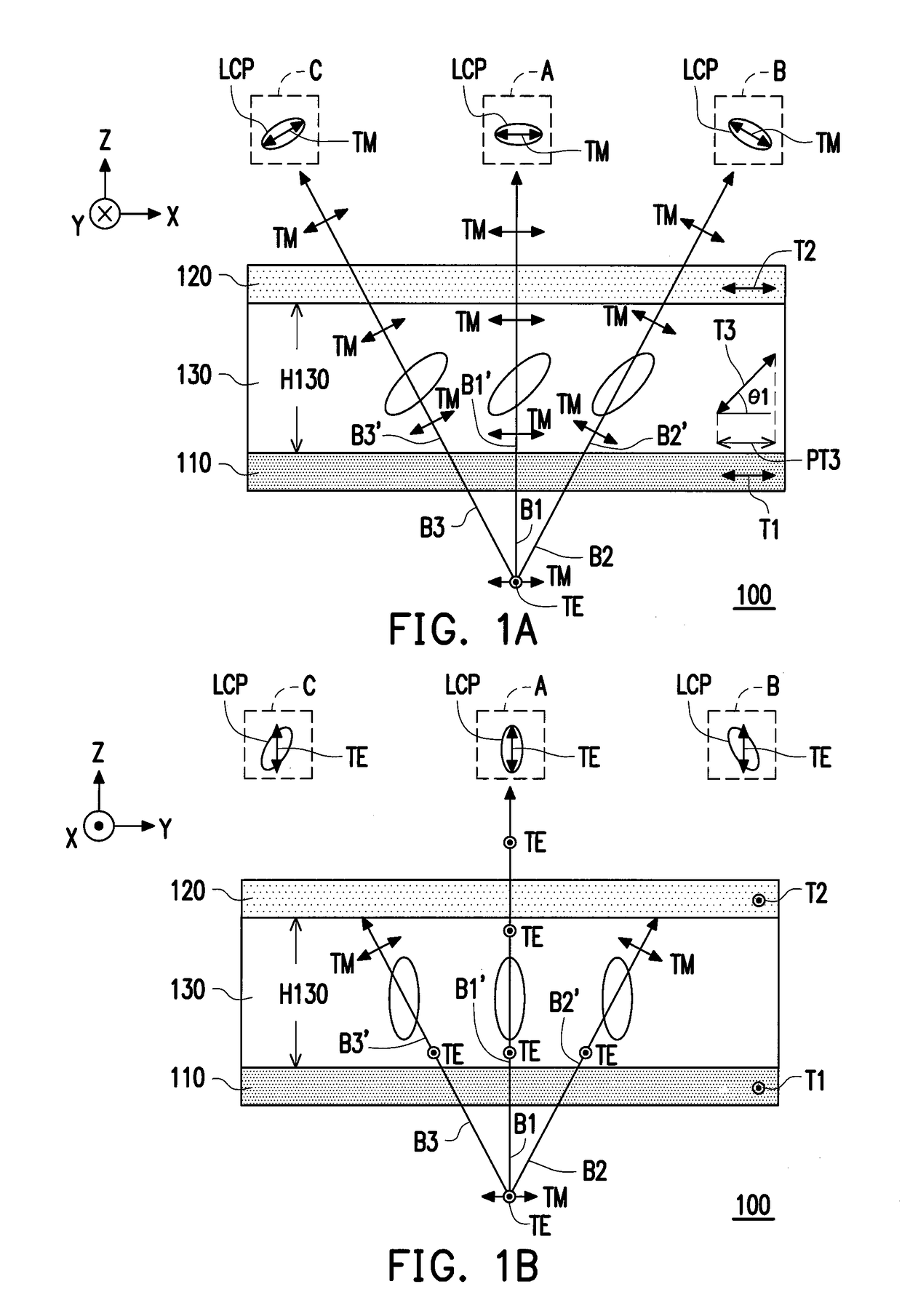
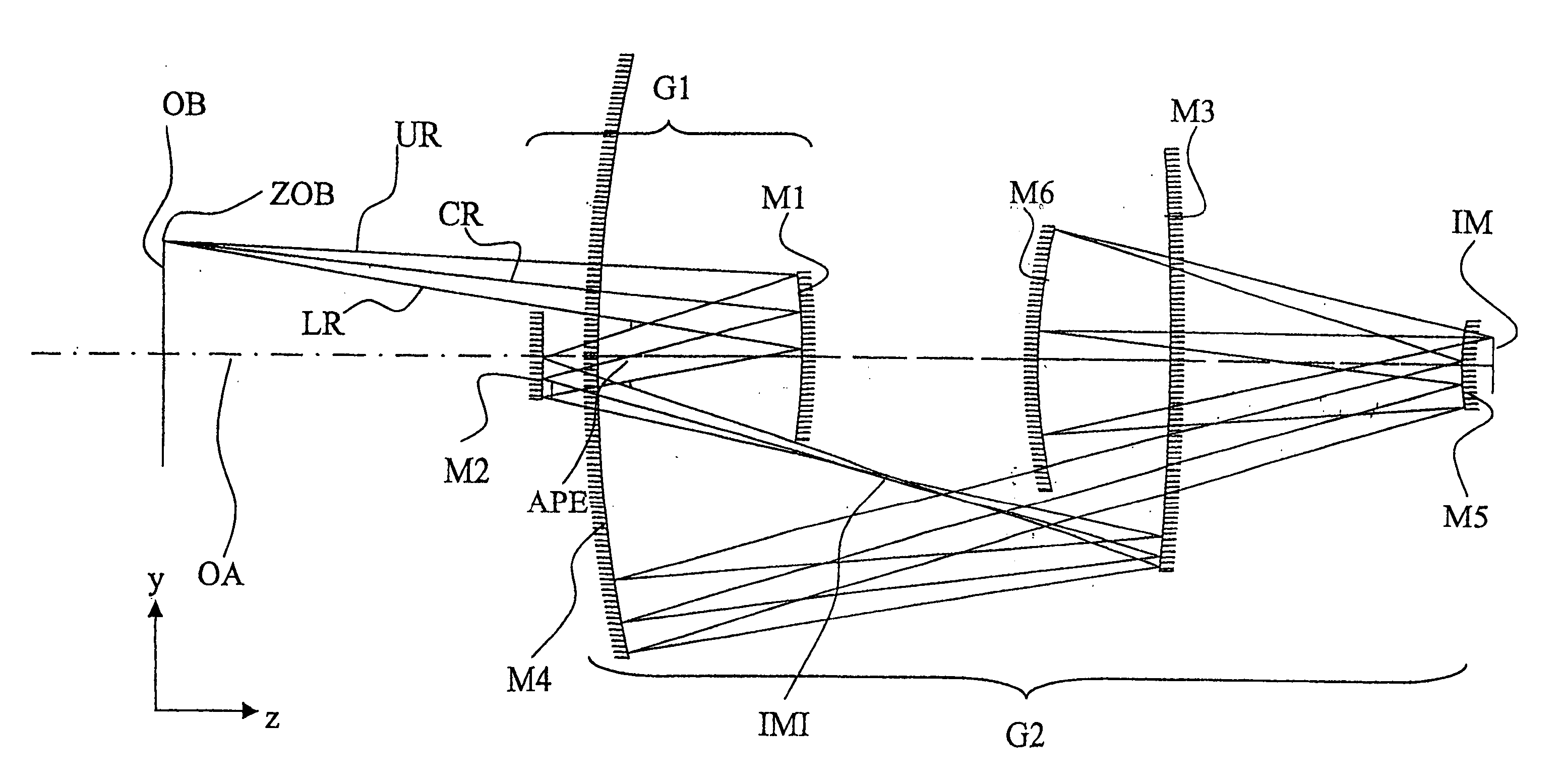
Projection system for EUV lithography
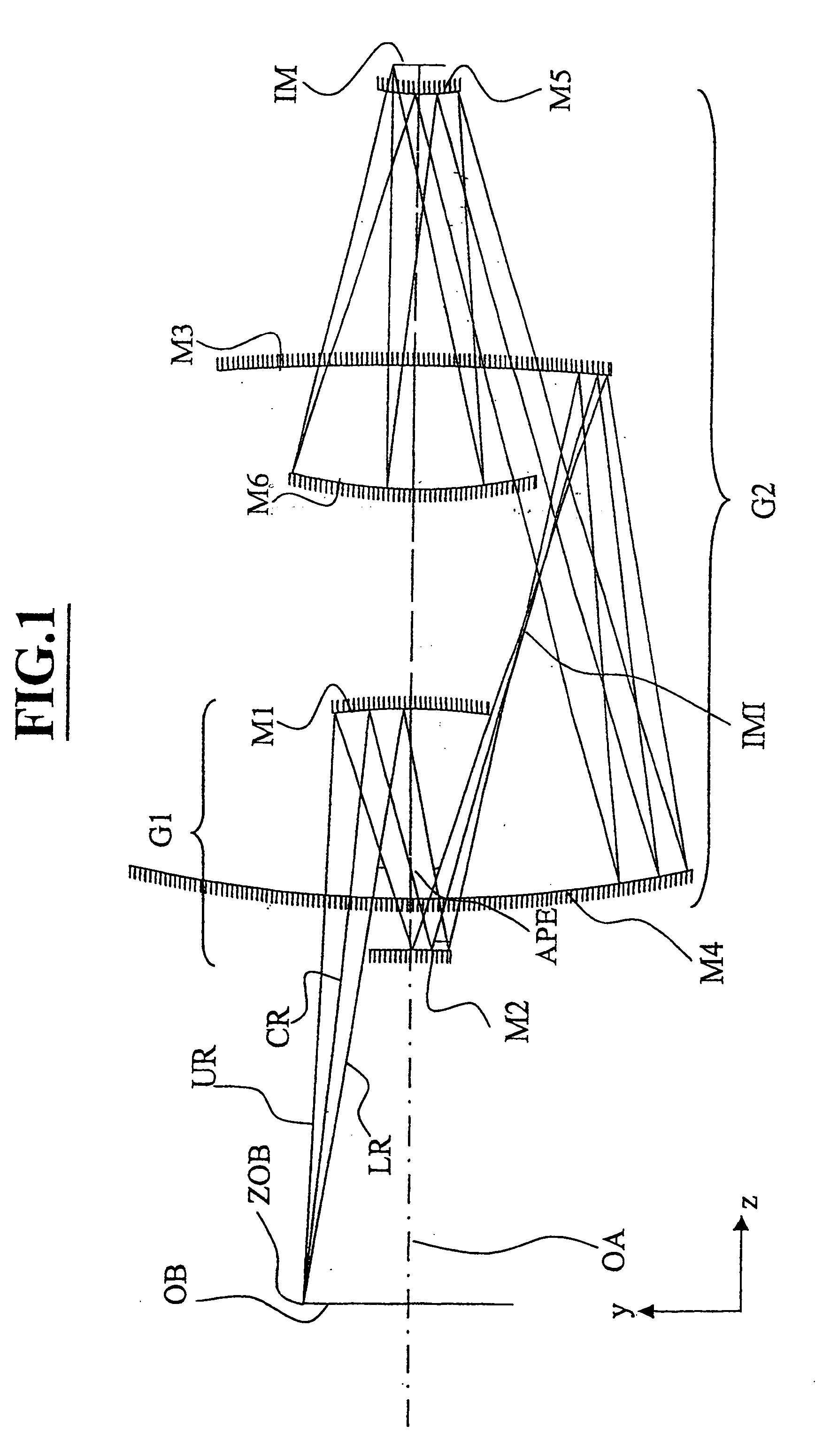
An EUV optical projection system includes at least six mirrors (M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, M6) for imaging an object (OB) to an image (IM). At least one mirror pair is preferably configured as an at least phase compensating mirror pair. The system is preferably configured to form an intermediate image (IMI) along an optical path from the object (OB) to the image (IM) between a second mirror (M2) and a third mirror (M3), such that a first mirror (M1) and the second mirror (M2) form a first optical group (G1) and the third mirror (M3), a fourth mirror (M4), a fifth mirror (M5) and a sixth mirror (M6) form a second optical group (G1). The system also preferably includes an aperture stop (APE) located along the optical path from the object (OB) to the image (IM) between the first mirror (M1) and the second mirror (M2). The second mirror (M2) is preferably convex, and the third mirror (M3) is preferably concave. The system preferably forms an image (IM) with a numerical aperture greater than 0.18.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Phase compensation for multi-stimulus controller
Determining a compensated phase matrix for a multi-stimulus demodulation process is provided. A first drive line of a multi-stimulus sensing system is selected, and a stimulation signal is transmitted on the selected drive line. A channel gain resulting from the stimulation signal is measured from a received sense signal resulting from the stimulation signal. The measured channel gain is compared with a known channel gain to obtain an individual phase compensation for the selected drive line. A compensated phase matrix is formed of the individual phase compensation values for multiple drive lines.
Owner:APPLE INC
Micro movement pulsed radar system and method of phase noise compensation
ActiveUS20070171119A1Reduce noiseReduce the noise floorRadio wave reradiation/reflectionLow noiseRadar systems
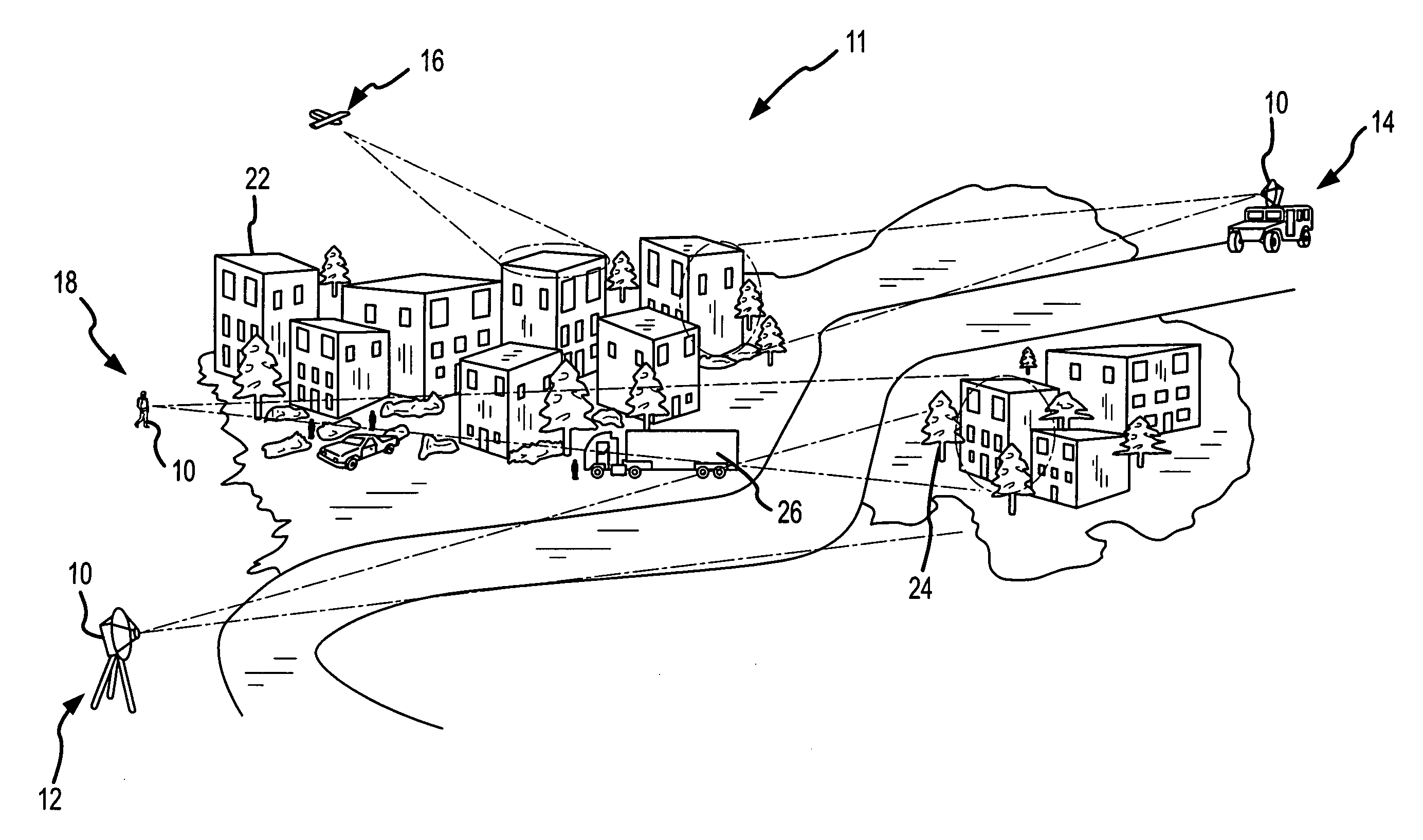
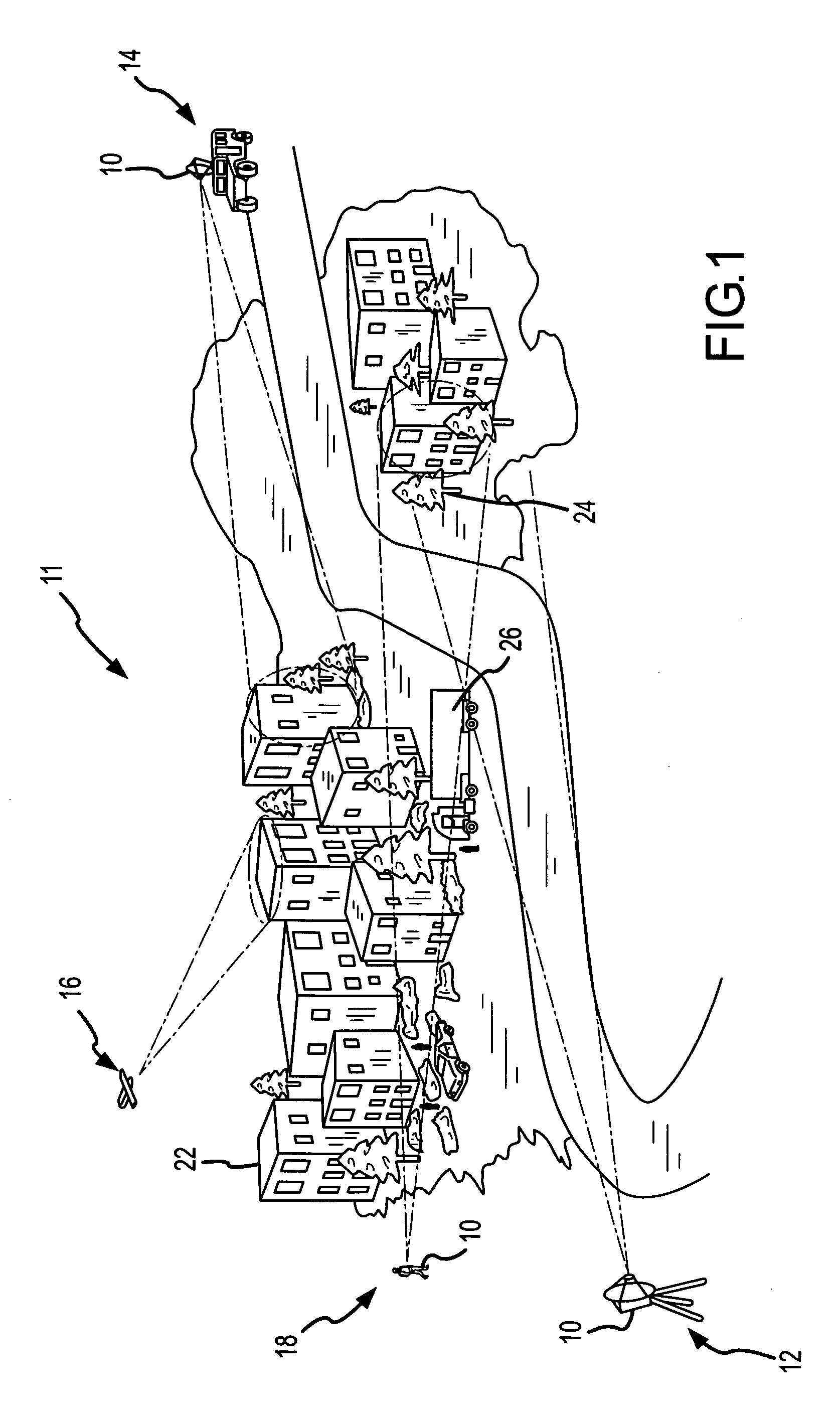
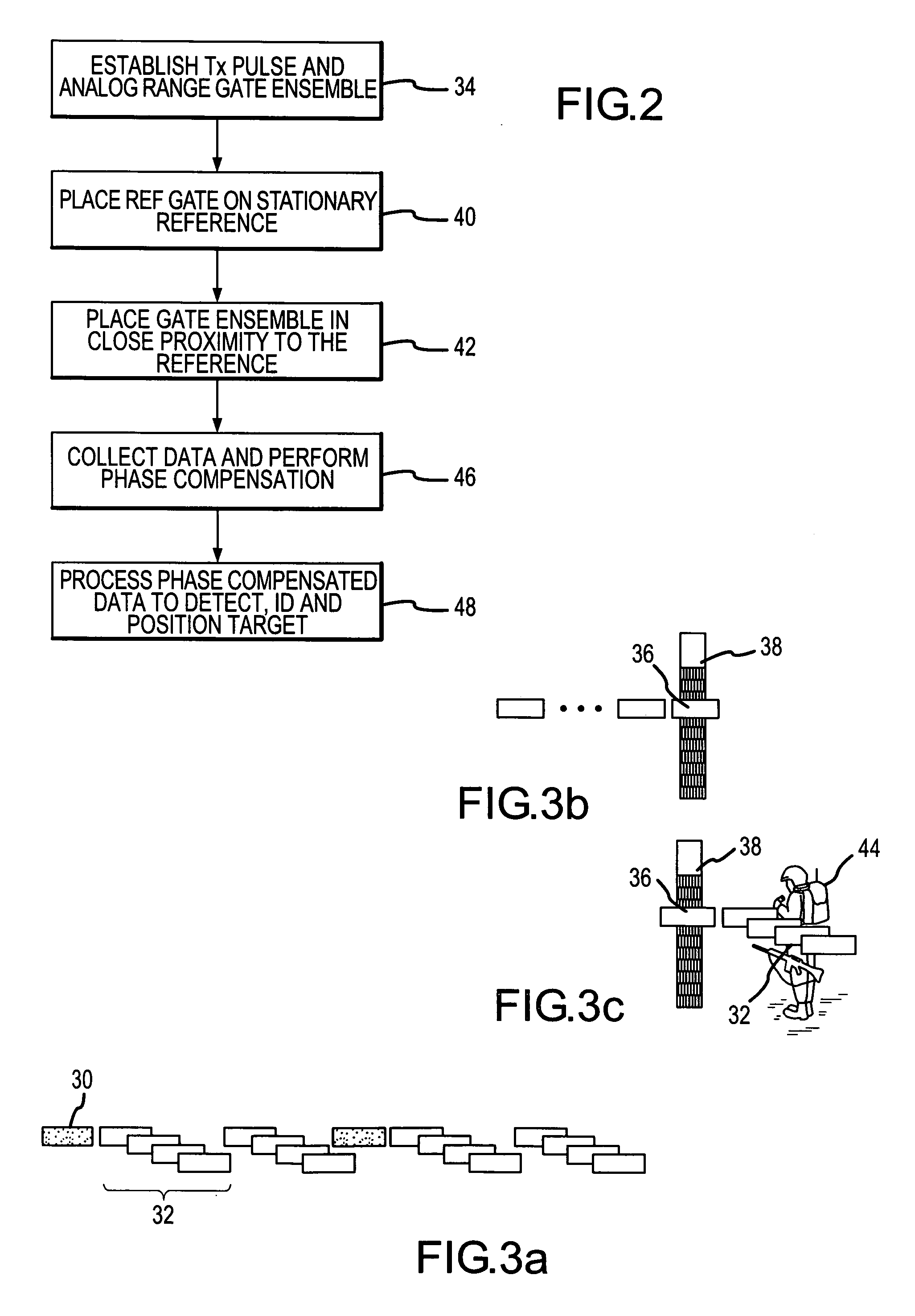
A pulsed radar system uses phase noise compensation to reduce phase noise due to drift of the reference oscillator to enable detection of micro movements and particularly human motion such as walking, breathing or heartbeat. The noise level due to A / D sampling must be sufficiently low for the phase noise compensation to be effective. As this is currently beyond state-of-the-art for high bandwidth A / D converters used in traditional receiver design, the receiver is suitably reconfigured to use analog range gates and narrowband A / D sampling having sufficiently low noise level. As technology continues to improve, the phase compensation techniques may be directly applicable to the high bandwidth A / D samples in traditional receiver designs. Whether phase compensation is applied to traditional receiver designs or a receiver configured with analog range gates, the steps are essentially the same: data is processed to position a reference range bin (either an analog range gate or a particular time sample) on a stationary reference and the phase variation of that reference range bin is used to compensate the phase of target data in range bins (either an ensemble of range gates or other time samples) near the stationary reference. This effectively moves the radar system and particularly the reference oscillator to the stationary reference thereby greatly reducing oscillator drift and phase noise and decoupling the stand-off range from the level of phase noise.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
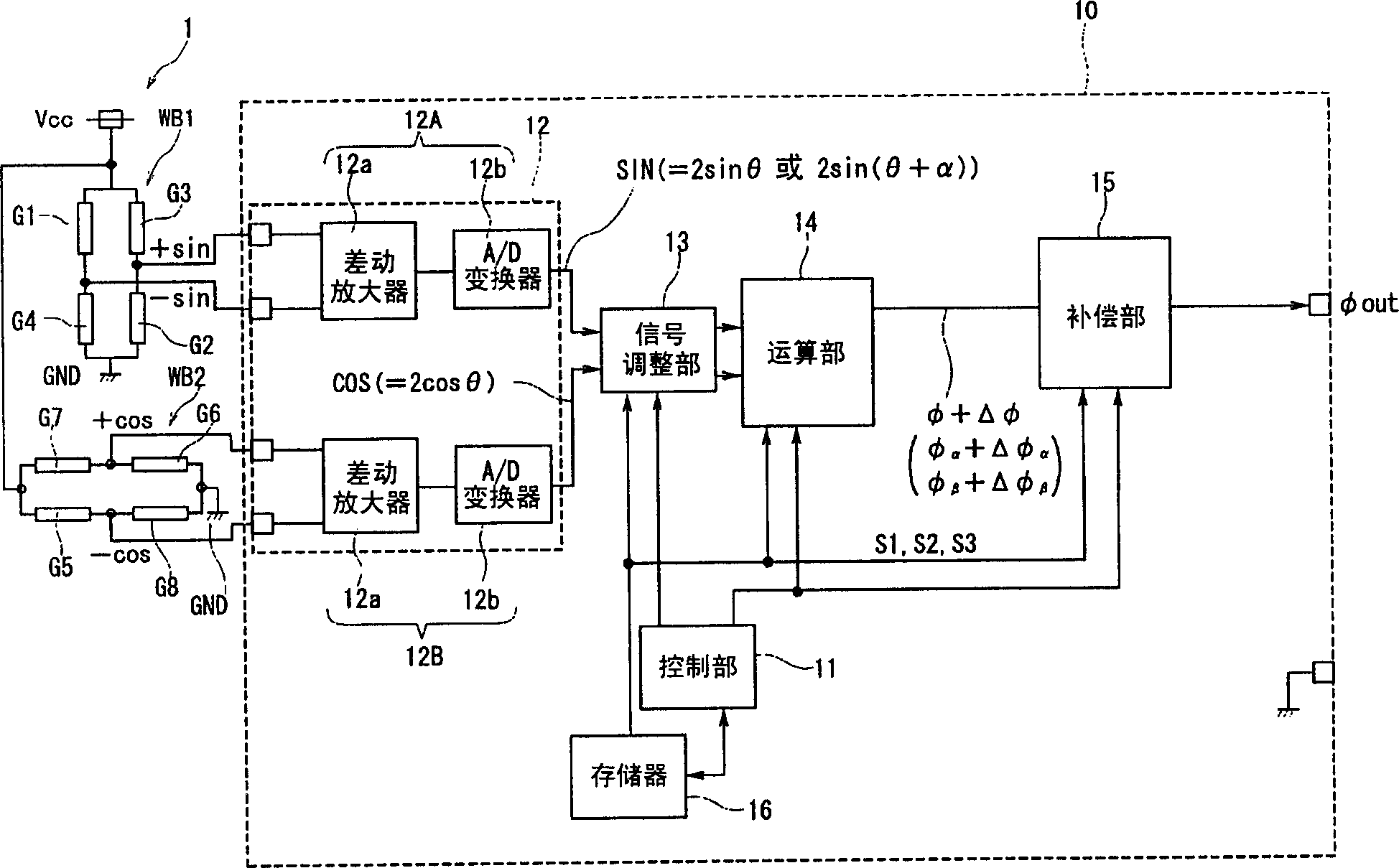
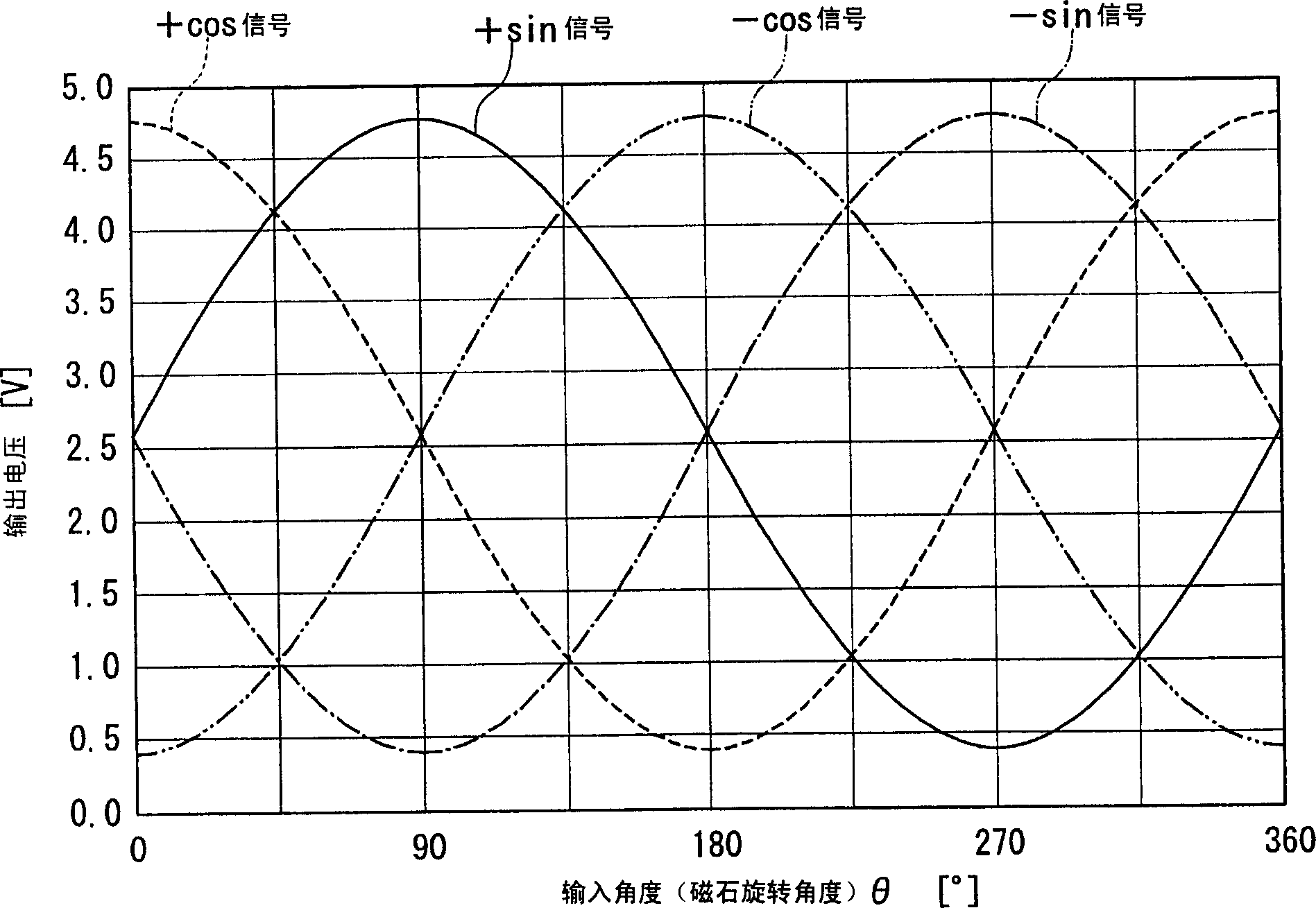
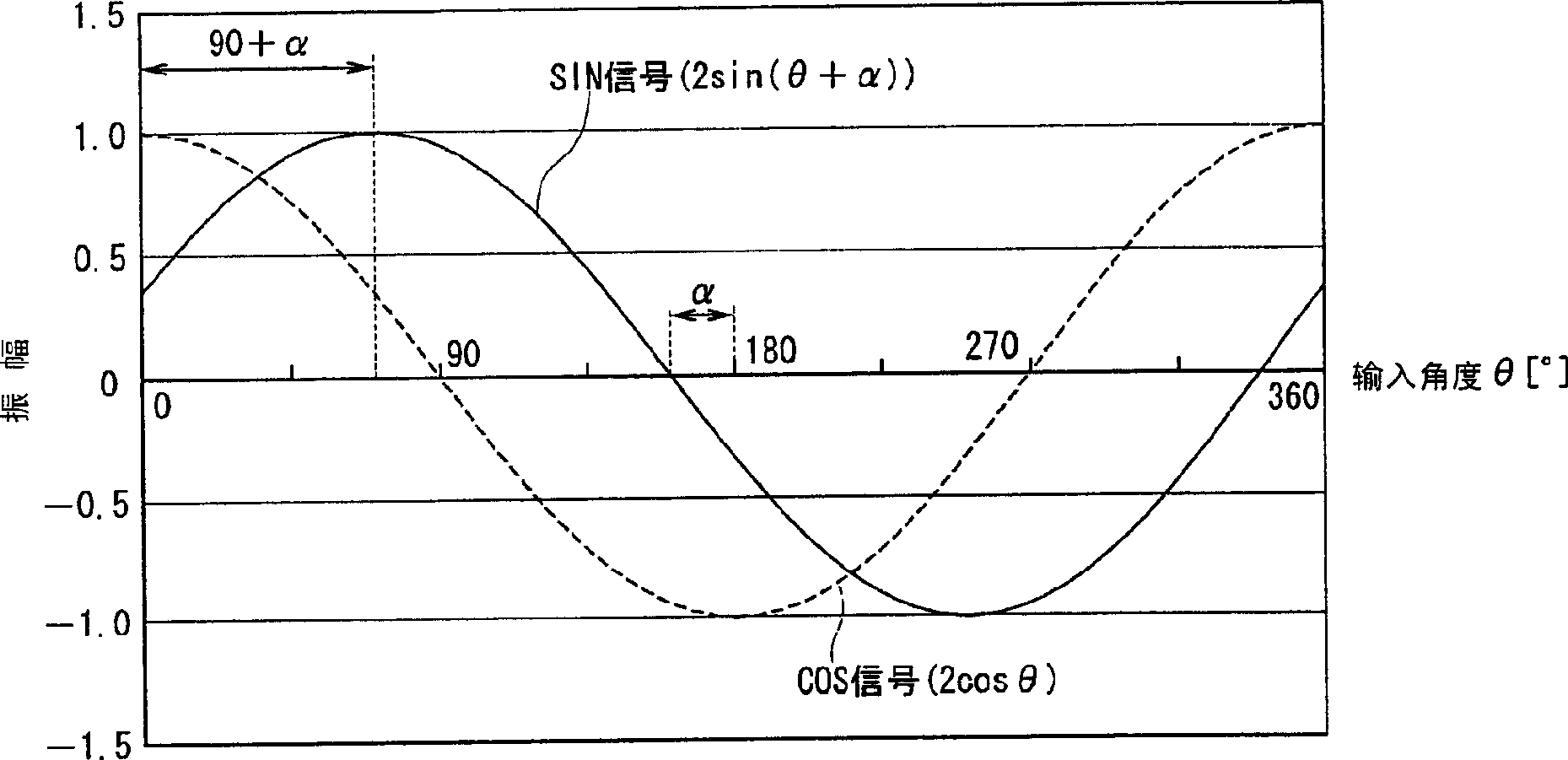
Method of calculating compensation value for angle detecting sensor and angle detecting sensor using the method
InactiveCN1789920AHigh precisionMagnetic measurementsUsing electrical meansCalculation methodsTotal error
The present invention provides a compensation value calculation method of an angle detection sensor capable of obtaining a high-precision angle output even when an output signal from a sensor includes an error signal, and an angle detection sensor using the same. The computing unit (14) calculates the uncorrected rotation angle (φ) of the object to be measured including the total error signal (Δφ) based on the SIN signal and the COS signal output from the sensor module (1) and the signal conversion unit (12) . A control unit (11) extracts, as a phase compensation value (Sα), a signal having a minimum residual energy (E) from first candidate signals (S1) stored in a memory unit (16). In addition, the strain compensation value (Sβ) and the gain compensation value (Sγ) are extracted in the same manner. And by removing the above-mentioned (Sα), (Sβ), and (Sγ) from the total error signal (Δφ), the angle output can be detected with high accuracy.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
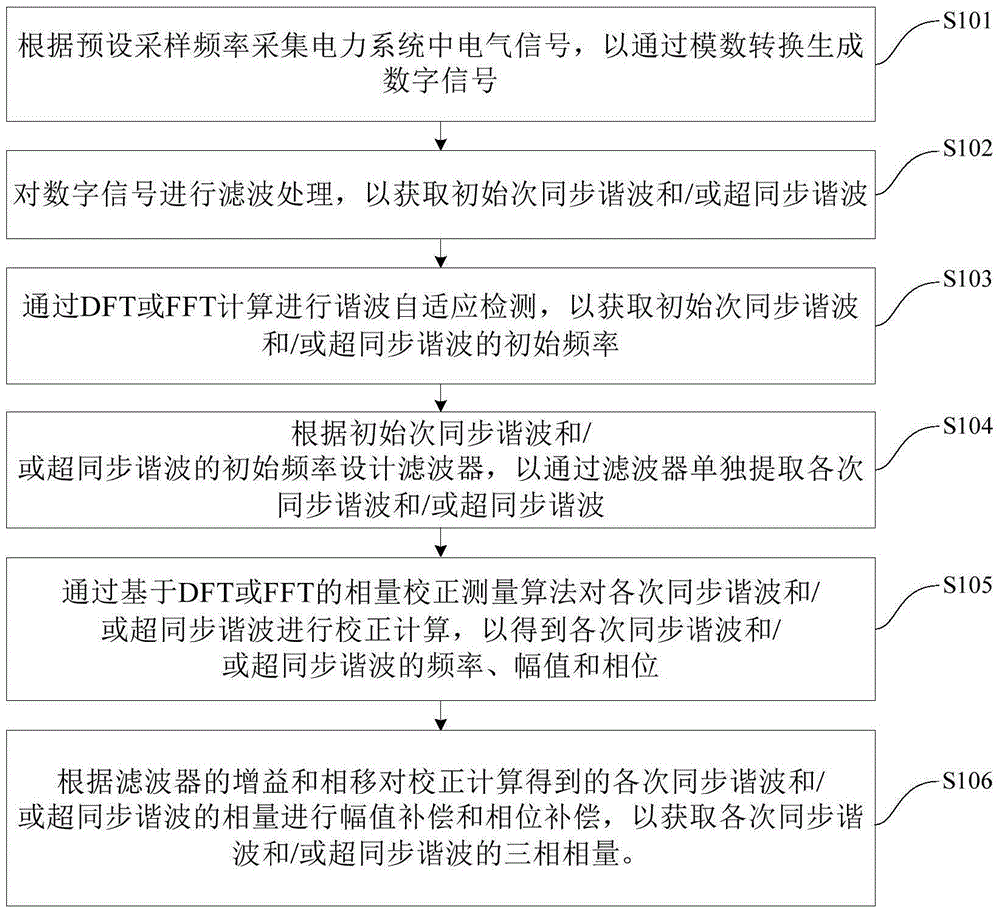
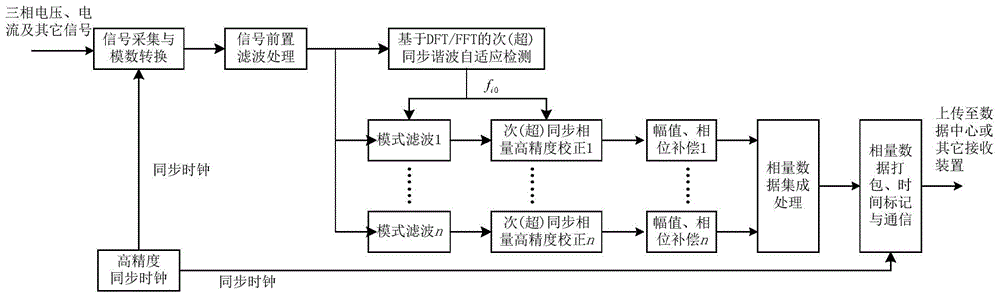
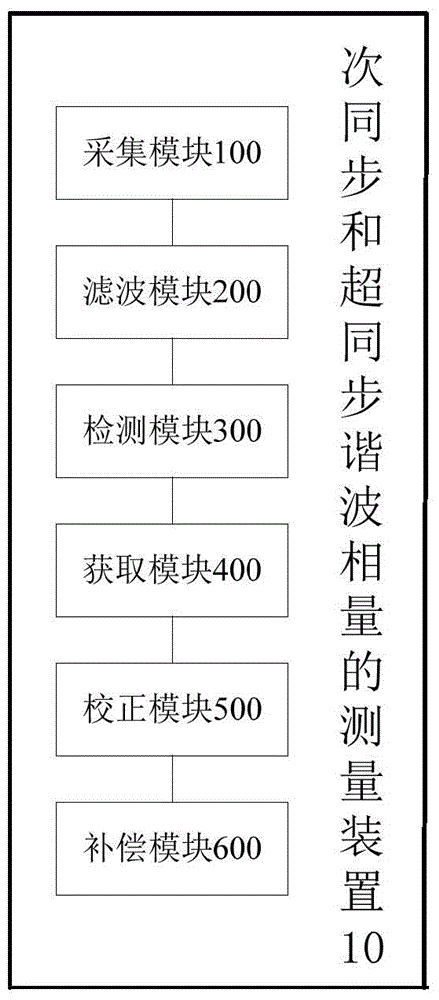
Measuring method and measuring apparatus of subsynchronous and supersynchronous harmonic phasors
The invention discloses a measuring method and measuring apparatus of subsynchronous and supersynchronous harmonic phasors. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring electrical signals so as to generate digital signals; performing filtering processing on the digital signals so as to obtain initial subsynchronous harmonic waves and / or supersynchronous harmonic waves; performing harmonic wave adaptive detection through DFT or FFT so as to obtain an initial frequency; according to the initial frequency, designing a filter so as to extract each subsynchronous harmonic wave and / or each supersynchronous harmonic wave; carrying out correction calculation by use of the phasor correction measuring algorithm so as to obtain the frequency, the amplitude and the phase of corresponding harmonic waves; and according to the gain and phase shift of the filter, performing amplitude compensation and phase compensation on the phasors so as to obtain a three-phase phasor of each subsynchronous harmonic wave and / or each supersynchronous harmonic wave. The measuring method provided by one embodiment of the invention can accurately measure the phasors of the subsynchronous and supersynchronous harmonic waves, thereby being applied to wide-area dynamic monitoring, analyzing, control and protection of subsynchrono resonance / oscillation of a power system.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
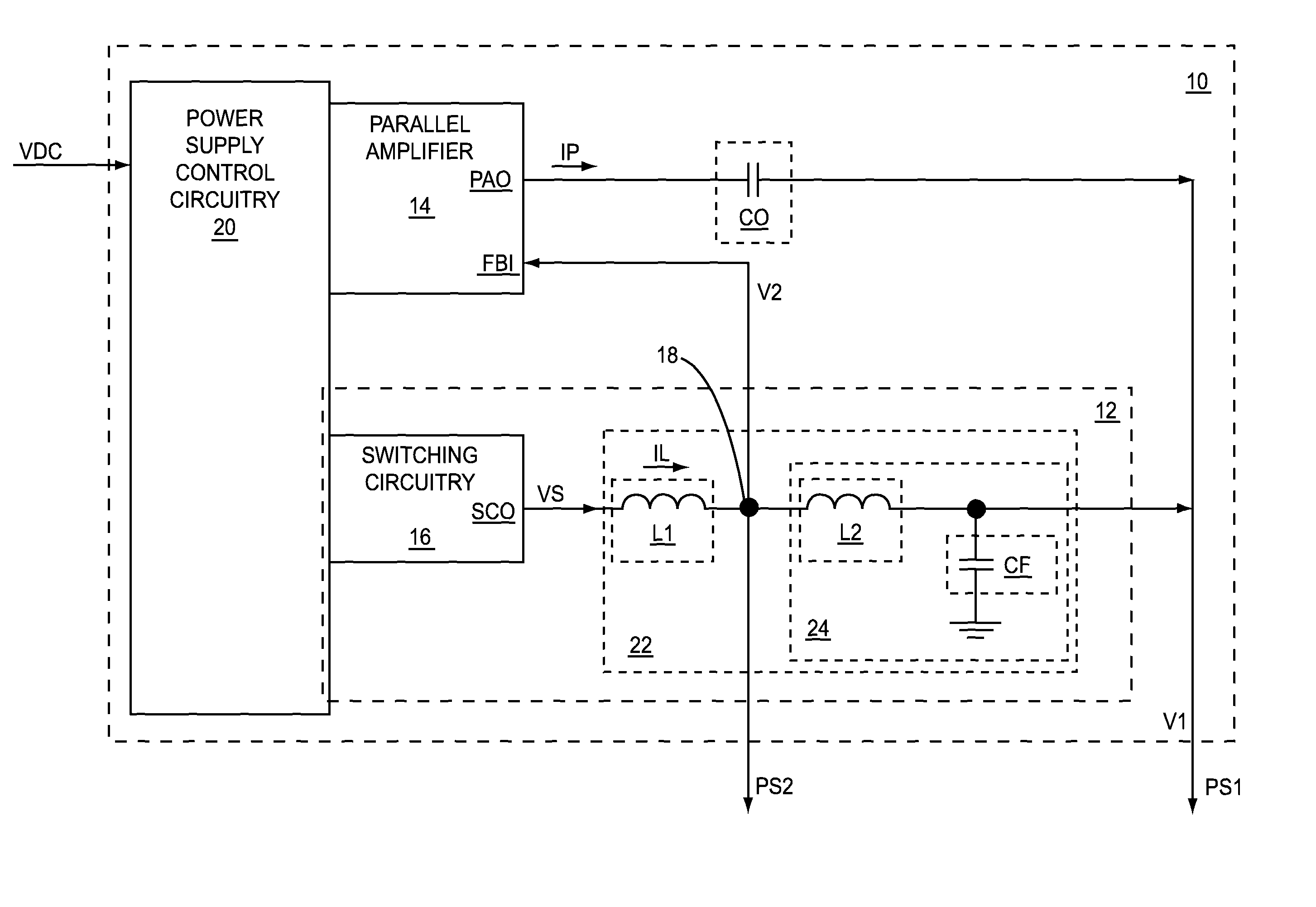
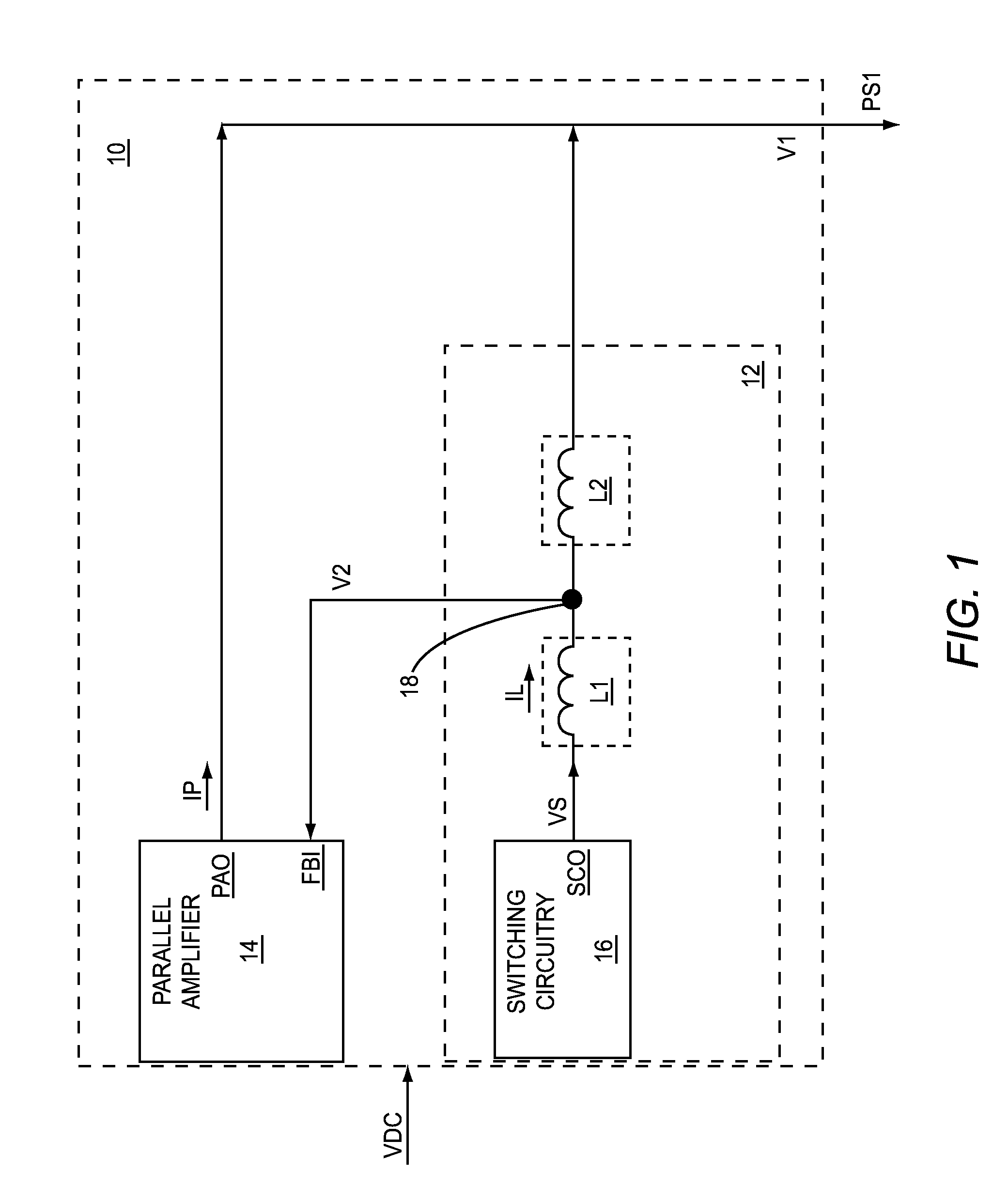
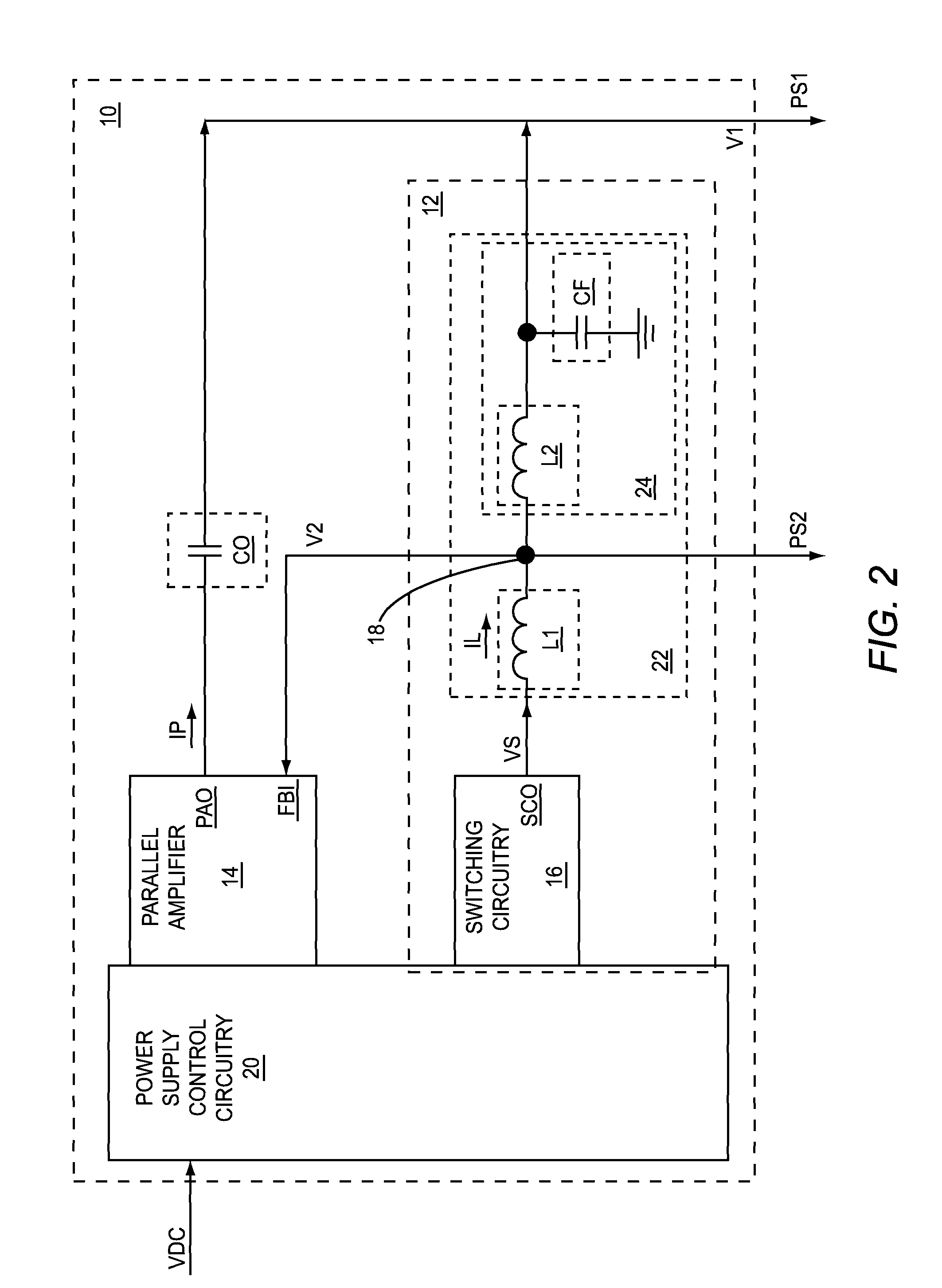
Inductance based parallel amplifier phase compensation
ActiveUS8878606B2Minimize output currentMaximize efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionGain controlAudio power amplifierEngineering
A direct current (DC)-DC converter, which includes a parallel amplifier and a switching supply, is disclosed. The switching supply includes switching circuitry, a first inductive element, and a second inductive element. The parallel amplifier has a feedback input and a parallel amplifier output. The switching circuitry has a switching circuitry output. The first inductive element is coupled between the switching circuitry output and the feedback input. The second inductive element is coupled between the feedback input and the parallel amplifier output.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Method and apparatus for suppressing power frequency common mode interference
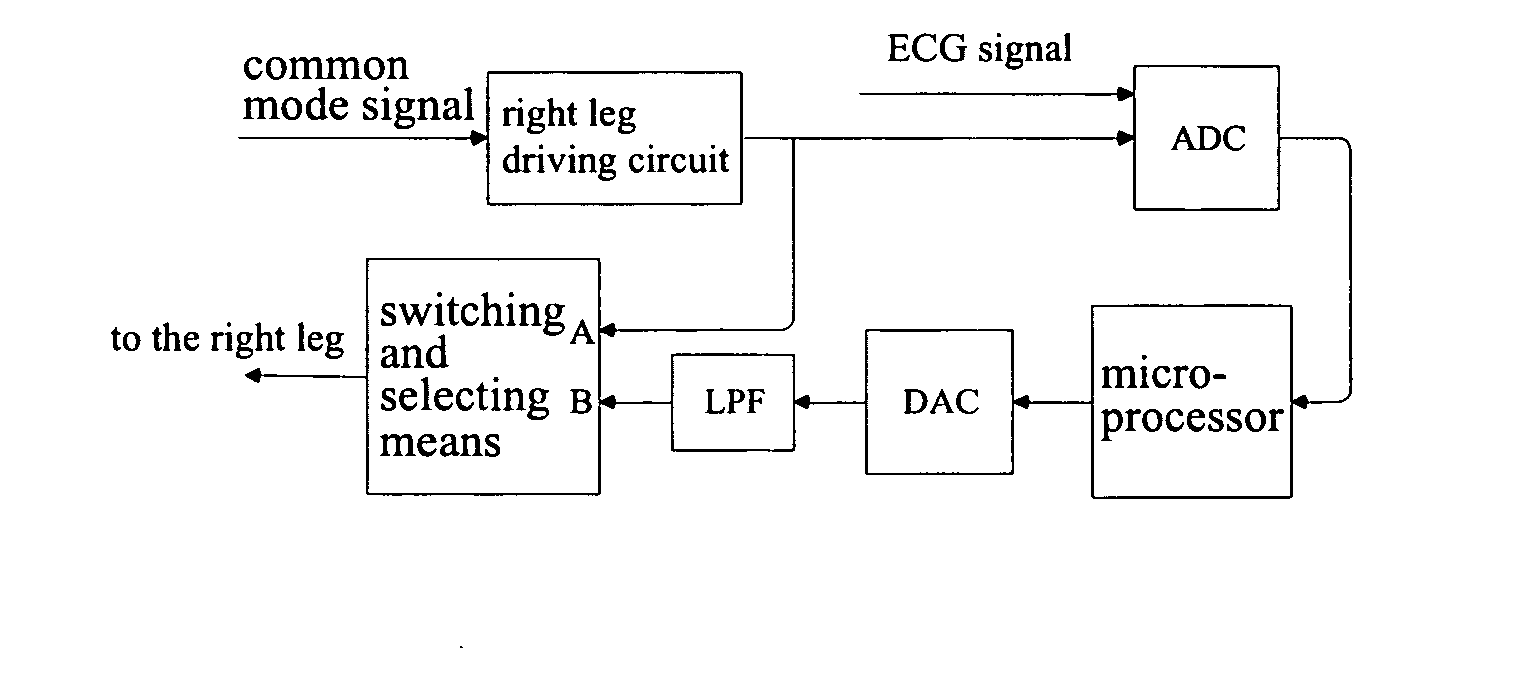
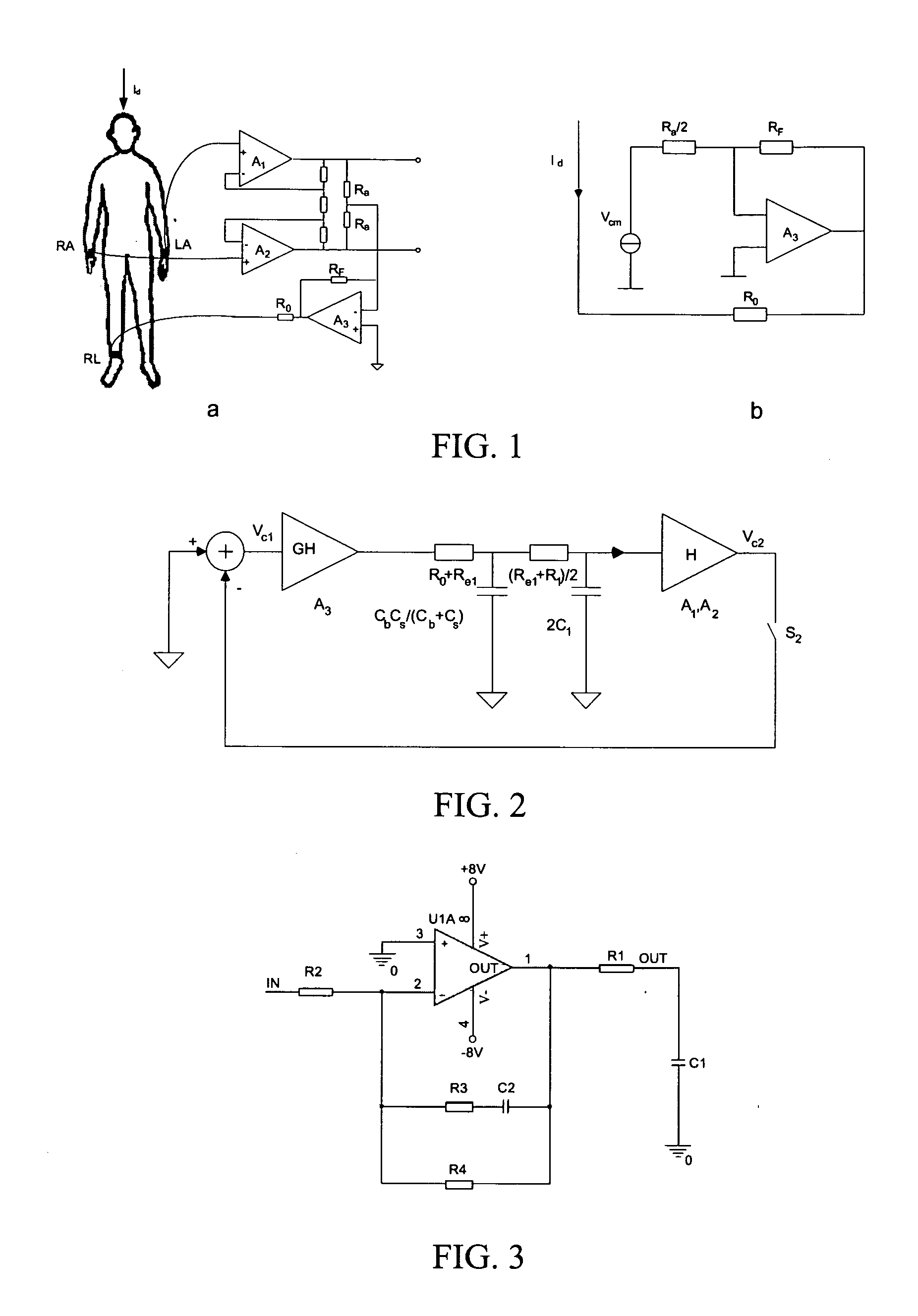
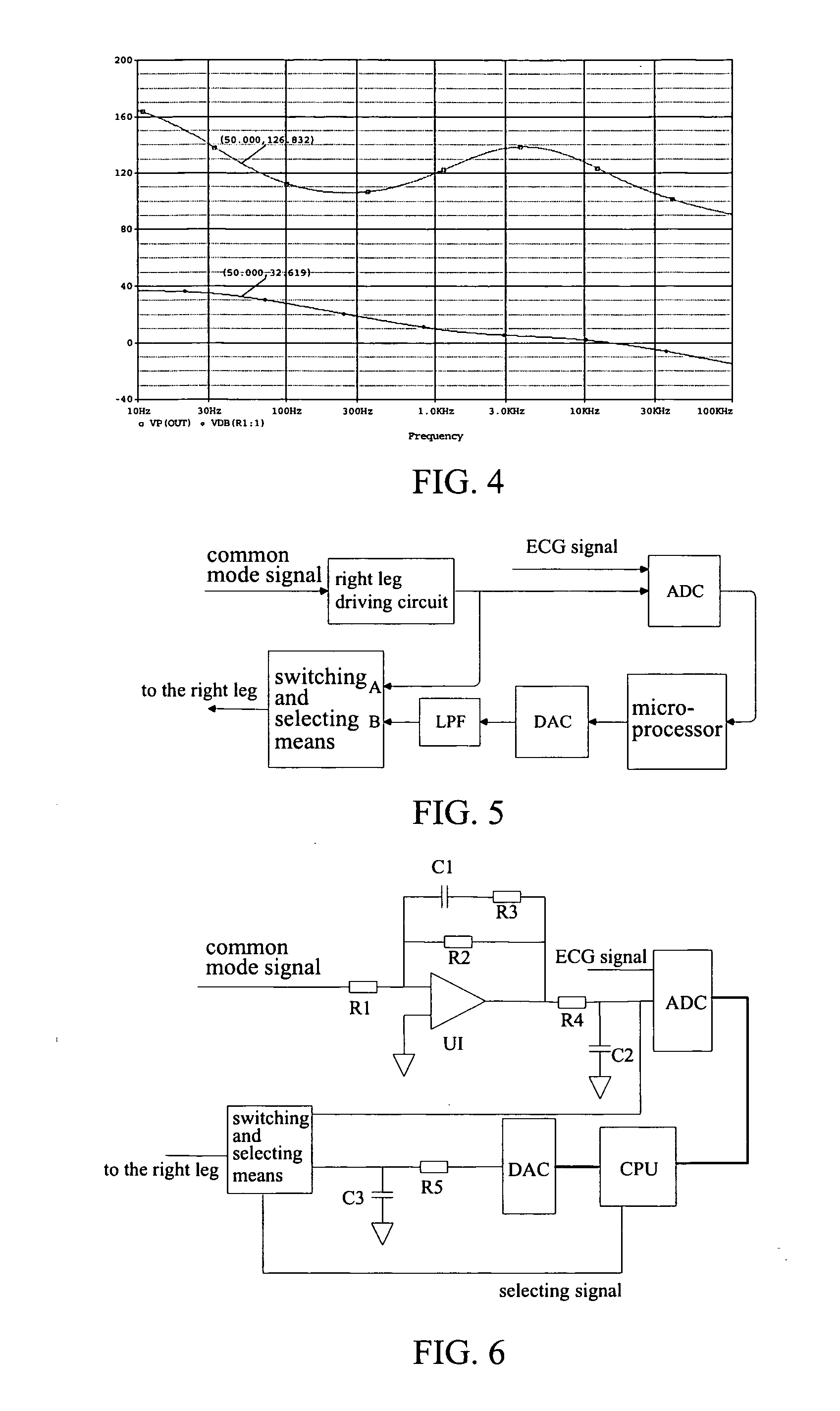
ActiveUS20070087703A1Improve system performanceFacilitates measuring systemDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBiological bodyTime delays
A method and an apparatus for suppressing power frequency common mode interference which are used in a bioelectrical signal measuring system comprising a common mode interference signal extracting circuit and a driving circuit connected to the extracting circuit are provided. The driving circuit changes a phase of a common mode interference signal and amplifies the common mode interference signal, so as to output two-way amplified signals, wherein one amplified signal is selectively outputted to a living body on examination. In particular, the apparatus further includes phase compensating and processing means for receiving both a bioelectrical signal from the living body on examination and the other amplified signal outputted from the driving circuit, determining a phase compensation amount of the other amplified signal outputted from the driving circuit according to a characteristic value of the power frequency interference in the bioelectrical signal so as to phase-compensate the other amplified signal outputted from the driving circuit, and selectively outputting the phase-compensated amplified signal to the living body on examination. The method for suppressing power frequency common mode interference comprises the following steps of: receiving a bioelectrical signal from a living body on examination by phase compensating and processing means; analyzing the characteristic of the bioelectrical signal and determining a phase compensation amount by the phase compensating and processing means; performing a corresponding time delay processing on an amplified signal outputted by the driving circuit; and providing the delay signal to the living body on examination. According to this invention, the capability of the circuit for suppressing power frequency common mode interference is getting improved, and the stability of the analog circuit system and the phase-frequency characteristic of the circuit are maintained. This contributes to the improvement of the quality of the sampled bioelectrical signals.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
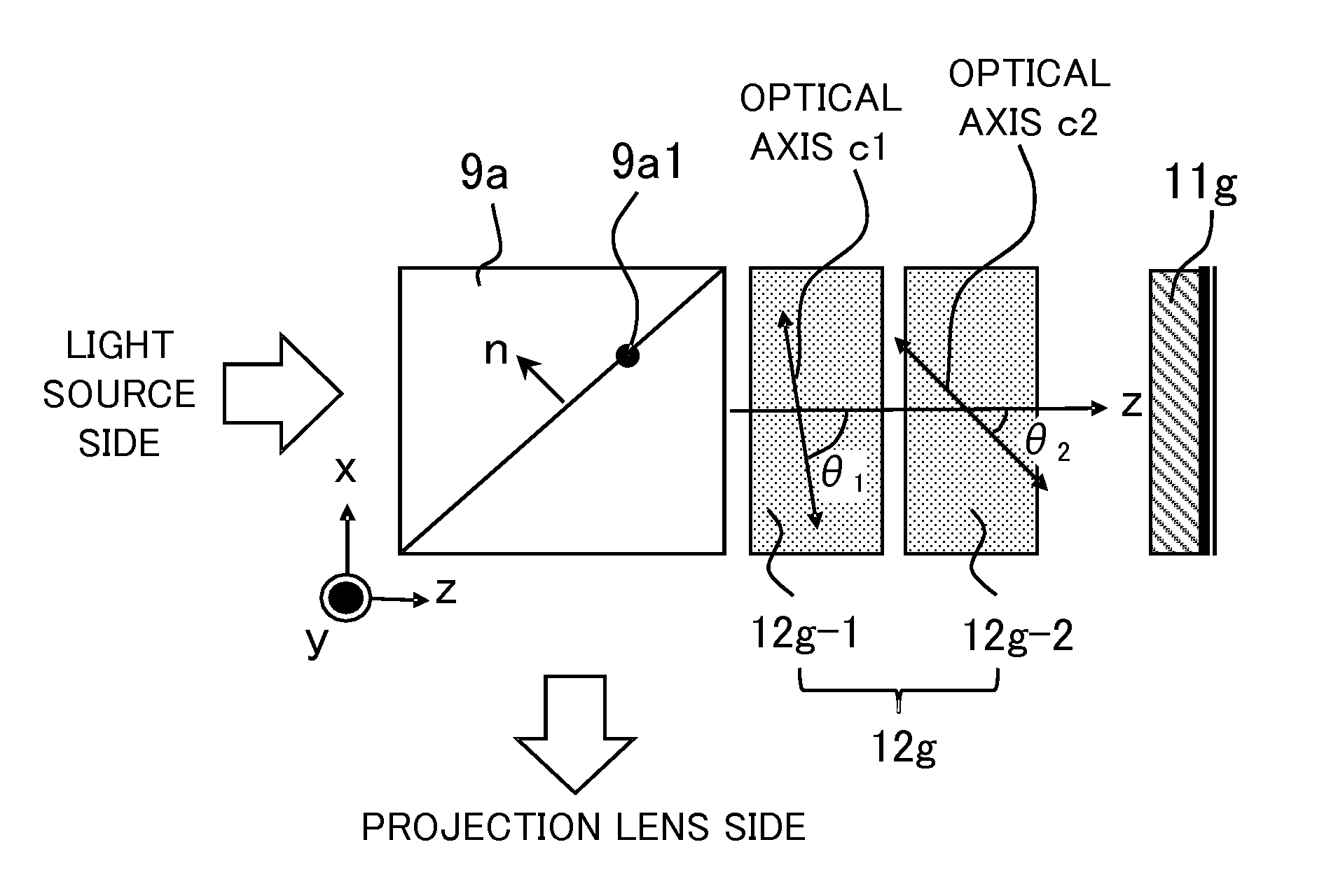
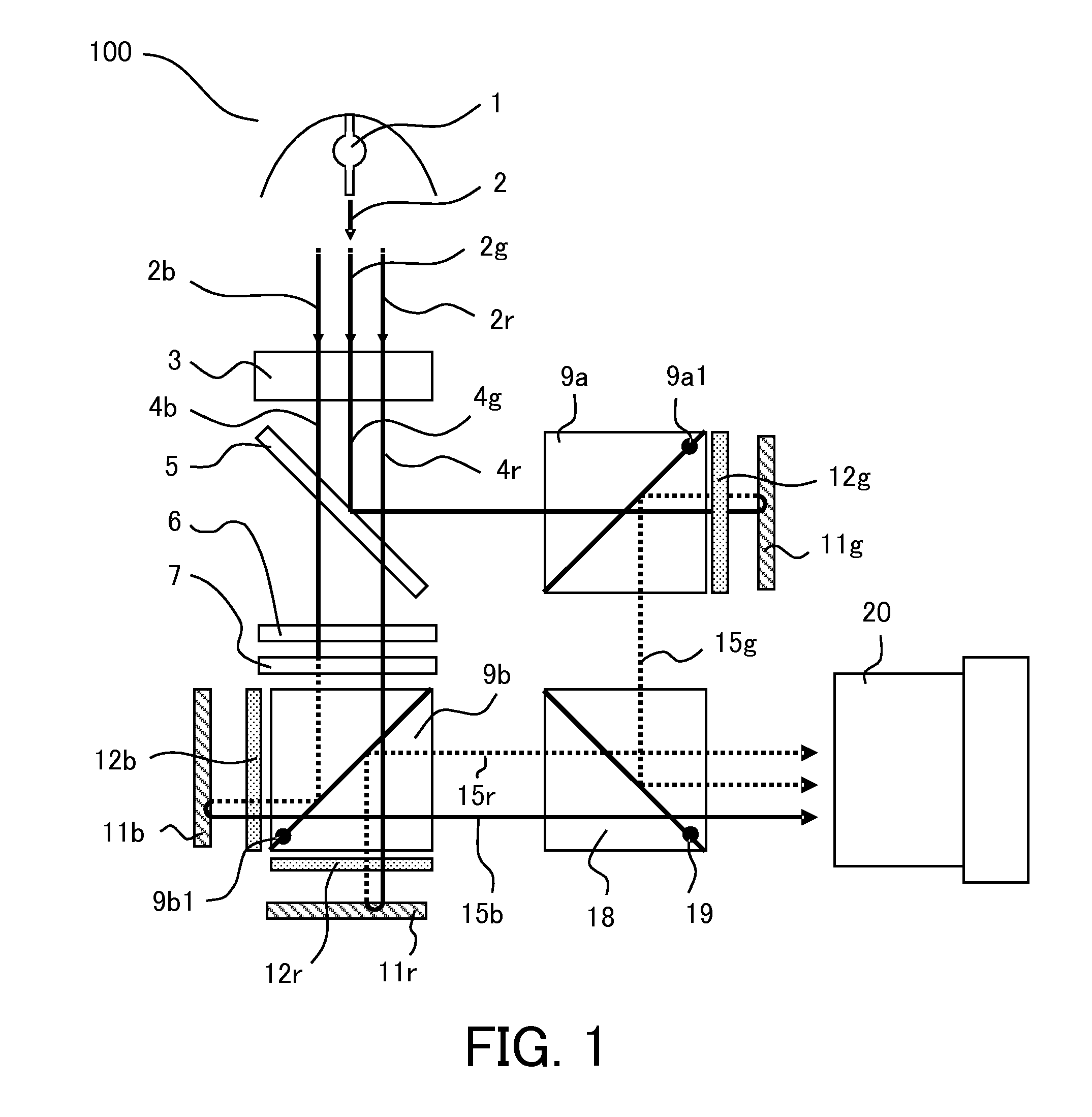
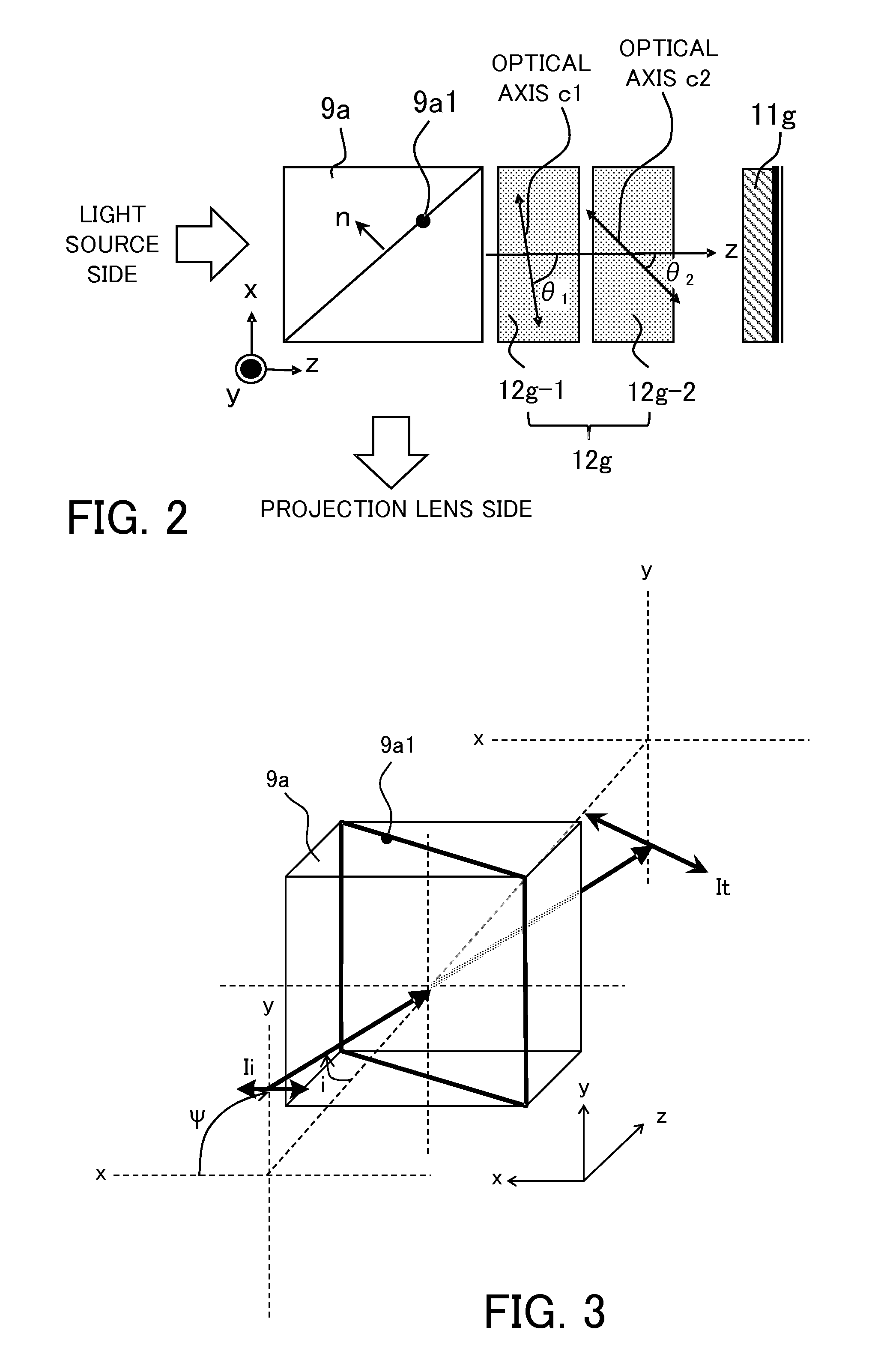
Projection display apparatus
InactiveUS9235111B2Increase contrastProjectorsColor photographyAxis–angle representationOptical axis
A projection display apparatus includes a polarization beam splitter, a first phase compensation plate including two layers, and a light modulator. Each layer has a constant axial angle, and an optical axis of each layer inclines with respect to the x axis in an xz plane. The axial angle of the layer closer to the polarization beam splitter among the two layers is larger than the axial angle of the layer farther from the polarization beam splitter. 20°≦θmax−θmin≦80° is satisfied where θmax is a maximum value of the axial angle and θmin is a minimum value of the axial angle. 40°≦θave≦70° is satisfied where θave is an average value of axial angles of the two layers.
Owner:CANON KK
Inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging method for maneuvering targets on basis of sparse aperture
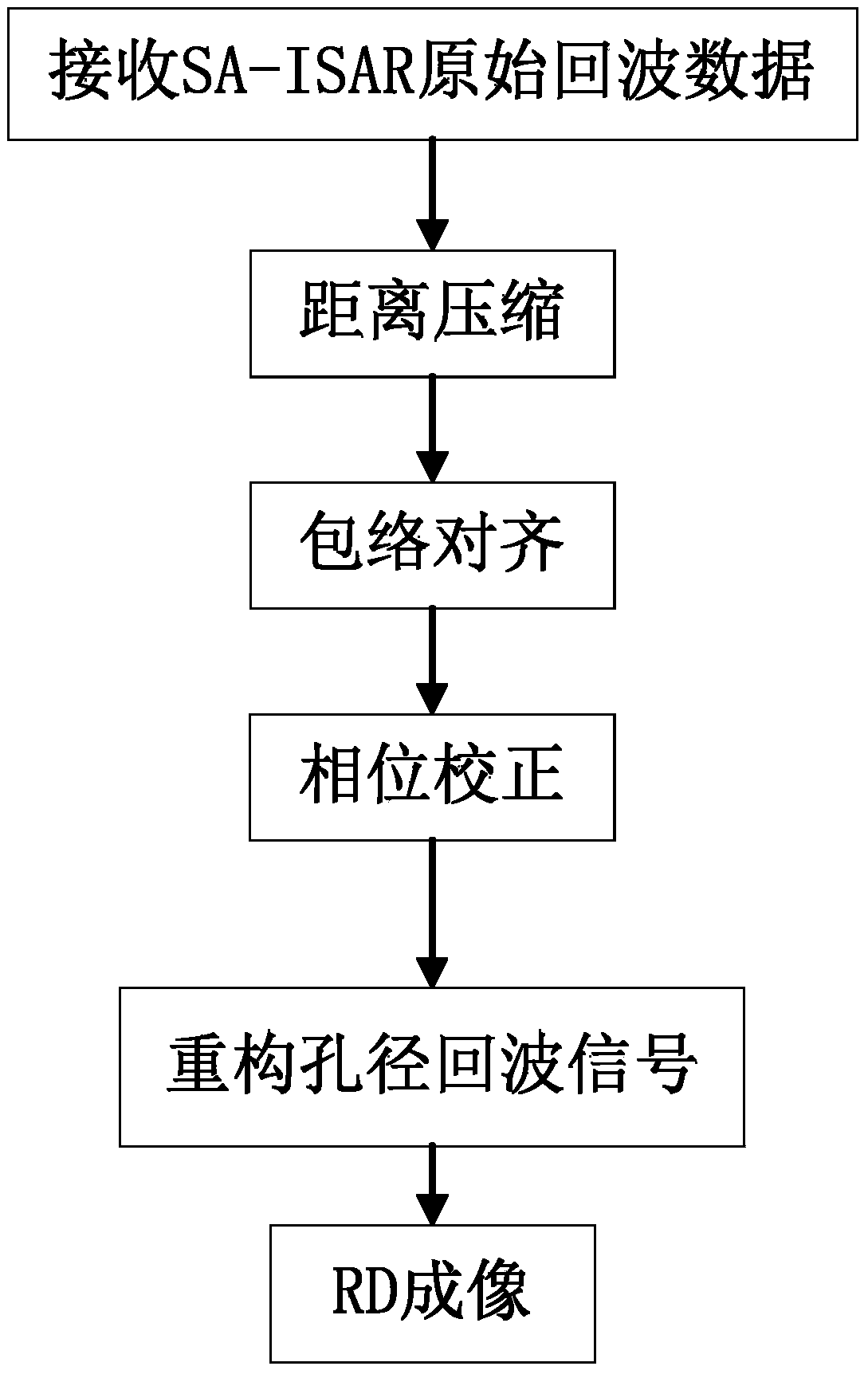
InactiveCN103901429AFocusOvercoming the drawbacks of phase compensation resultsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPhase correctionImaging processing
The invention discloses an inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging method for maneuvering targets on the basis of the sparse aperture. The inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging method for the maneuvering targets on the basis of the sparse aperture comprises the implementation steps that (1) original echo data, with the sparse aperture, of an inverse synthetic aperture radar are received; (2) distance compression and envelope alignment processing are carried out; (3) phase correction is accurately carried out; (4) sparse aperture echo signals are reconstructed; (5) fast Fourier transform is carried out to achieve distance-Doppler imaging. According to the inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging method for the maneuvering targets on the basis of the sparse aperture, accurate phase compensation and accurate data reconstruction can be carried out on ISAR imaging processing under the conditions of the maneuvering targets and the sparse aperture, and a more focused high-quality ISAR imaging result is obtained.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
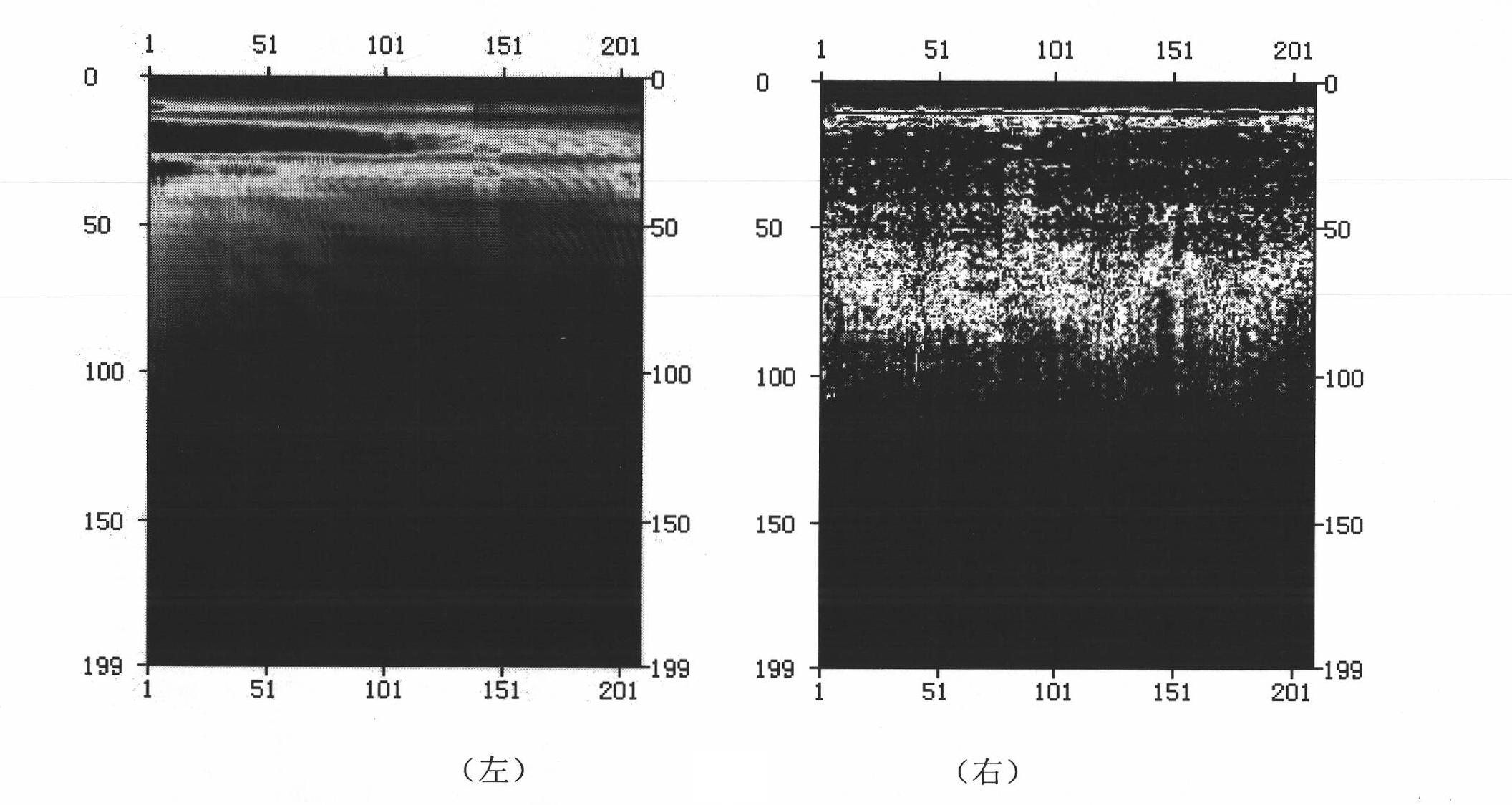
Seismic wave absorption and attenuation compensation method
ActiveCN102109612AImprove signal-to-noise ratioHigh resolutionSeismic signal processingFrequency spectrumCurve fitting
The invention relates to a seismic wave absorption and attenuation compensation method, and belongs to the geophysical exploration data processing technology. The method comprises the following steps: selecting one of VSP (vertical seismic profiling) initial data as reference data, carrying out generalized S-transform on the reference data, selecting sampling points as reference points, and recording the time and time-frequency spectrums of the sampling points; carrying out generalized S-transform on data of each sampling point, and dividing the time-frequency spectrum of corresponding frequency in the time-frequency spectrums of the reference points by the time-frequency spectrum of each sampling point so as to obtain an absorption and attenuation curve; determining a natural logarithm to figure out a phase compensation operator according to a formula of frequency difference of absorption and attenuation signals in a time frequency domain; and carrying out absorption and attenuation compensation and phase compensation in the time frequency domain to obtain a fine VSP wave field profile. The method has the advantages that noise can be eliminated during the process of fitting the absorption and attenuation curve; generalized S-inverse transform without energy loss is realized; signal-to-noise ratio and resolution of the data are improved after compensation; log resolution control is realized; the reference points are selected flexibly; and algorithm is simple and efficient.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com